Patents
Literature
135results about How to "Achieve resolution" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
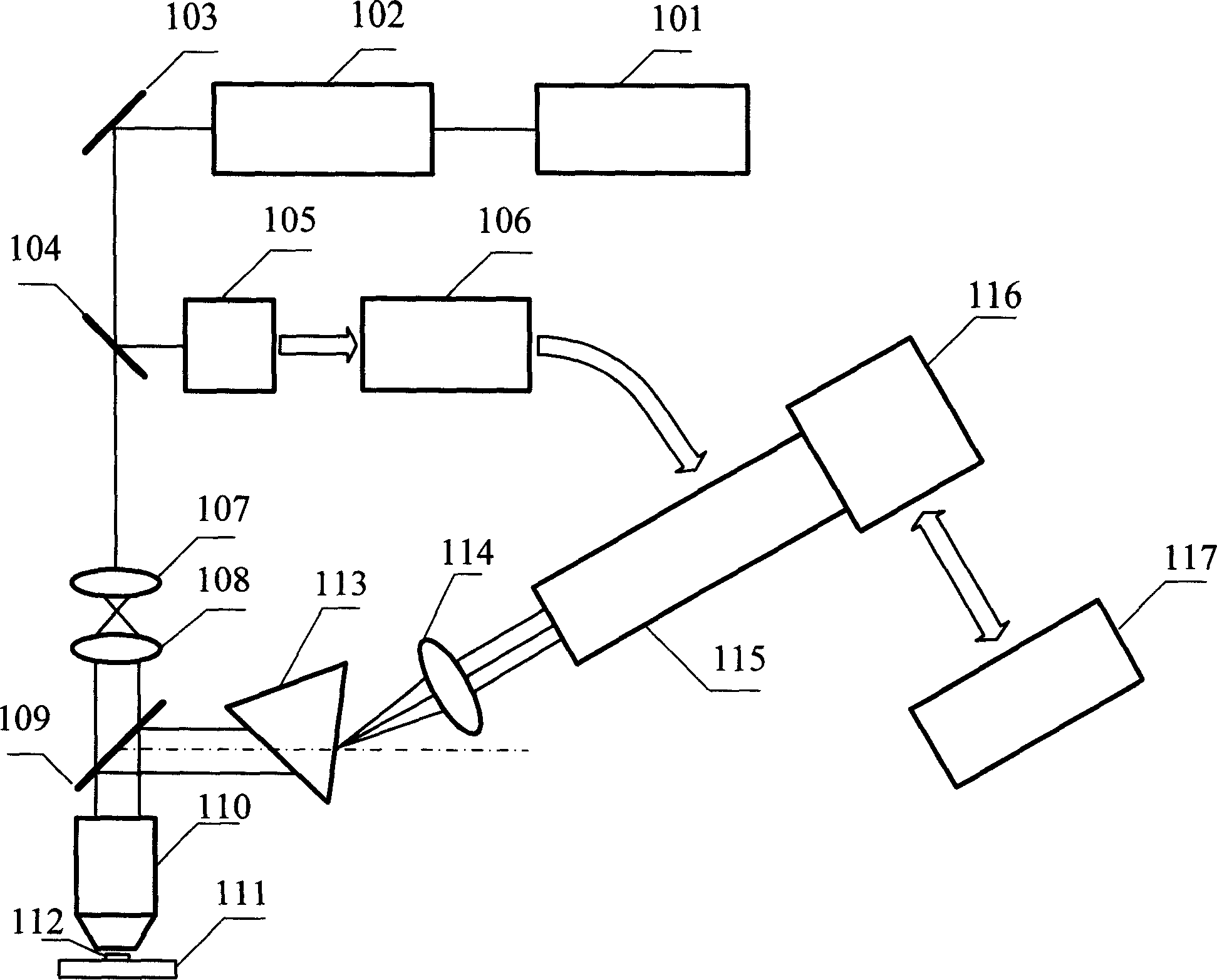
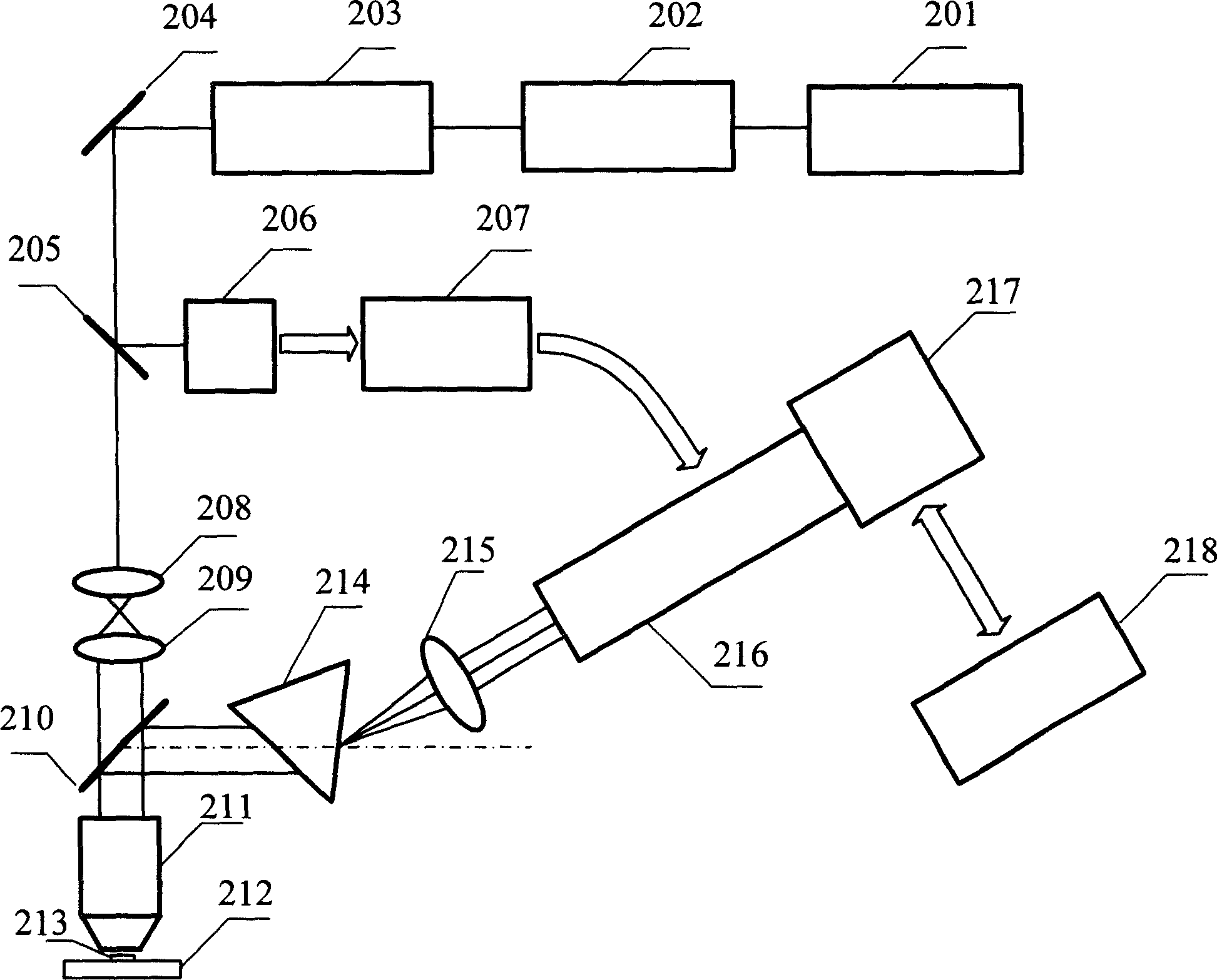
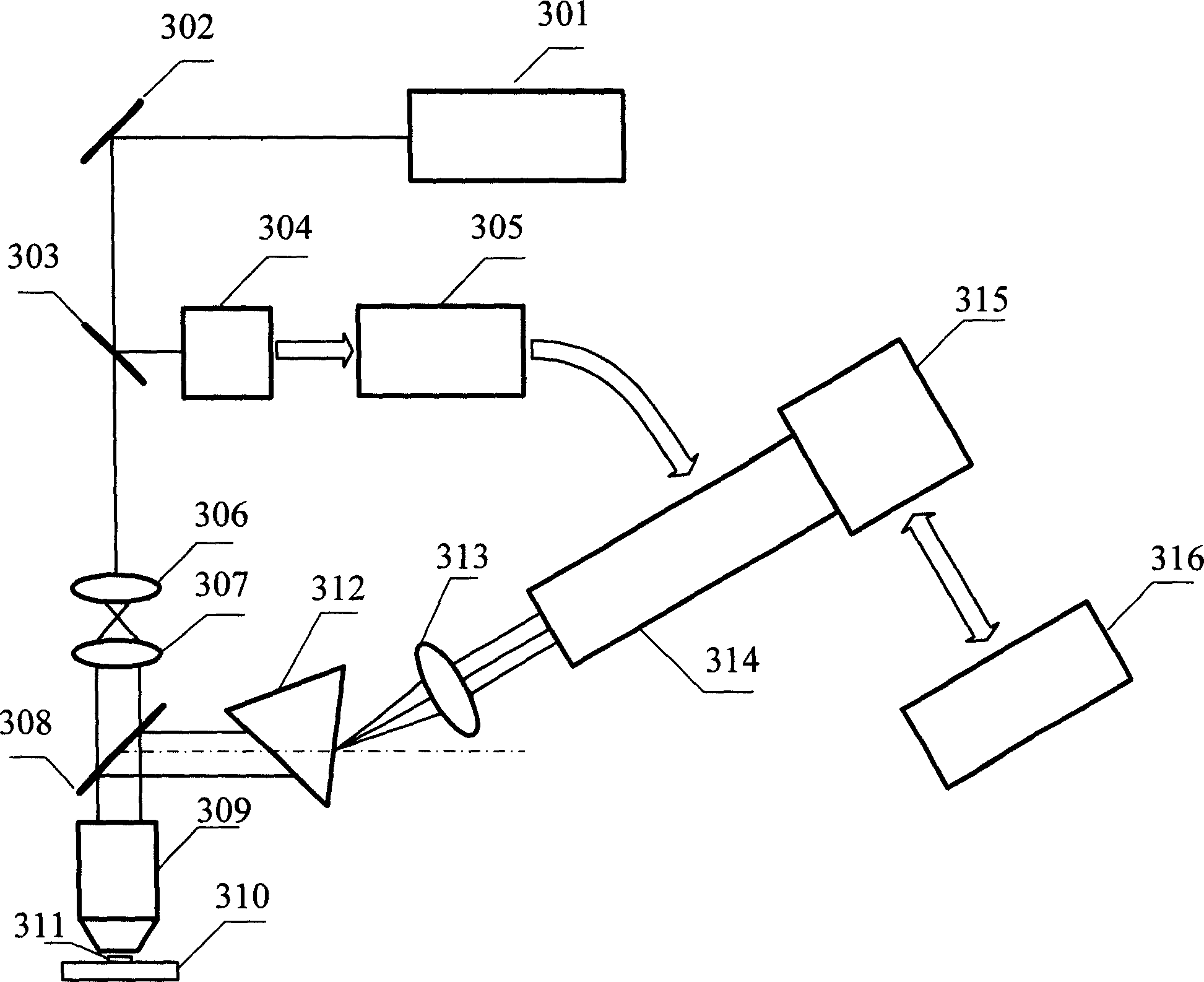
Time resolution fluorescence spectral measuring and image forming method and its device
InactiveCN1912587ADifferent temporal resolutionsAchieving high-sensitivity detectionFluorescence/phosphorescencePhotocathodePicosecond
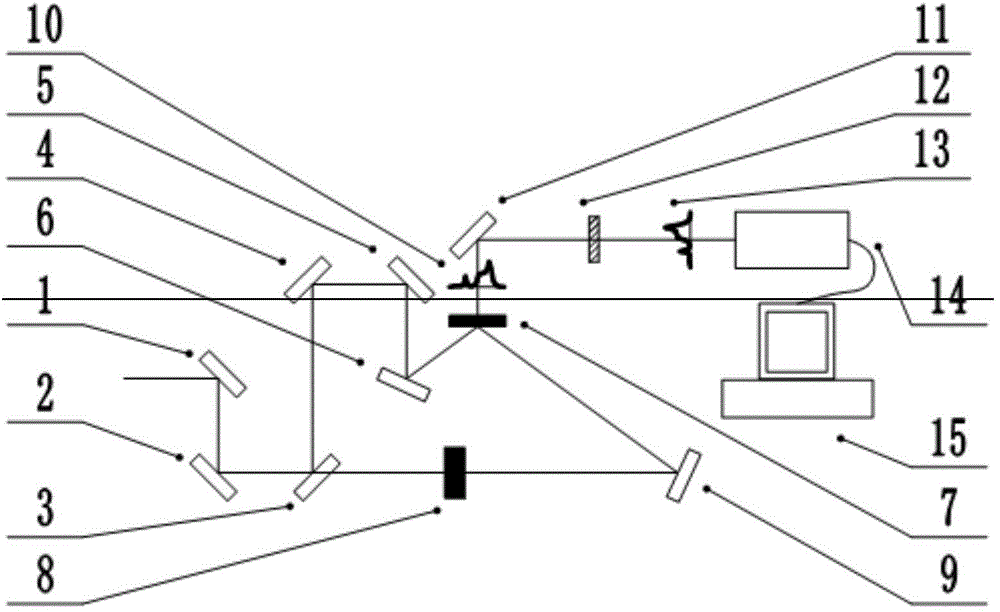
A method of using picosecond scan camera to simultaneously obtain fluorescent light spectrum and fluorescent lifetime of sample includes focusing blue violet light emitted by laser on sample by objective to excite sample single photon, collecting fluorescent from sample then splitting it and focusing it to be image on photoelectric cathode of picosecond scan camera, setting dispersion direction of fluorescent to be the same as slit direction of said camera but to be vertical to scan direction in order to measure out fluorescent lifetime of different light spectrum simultaneously under coaction of scan circuit and image intensifier deflection system.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
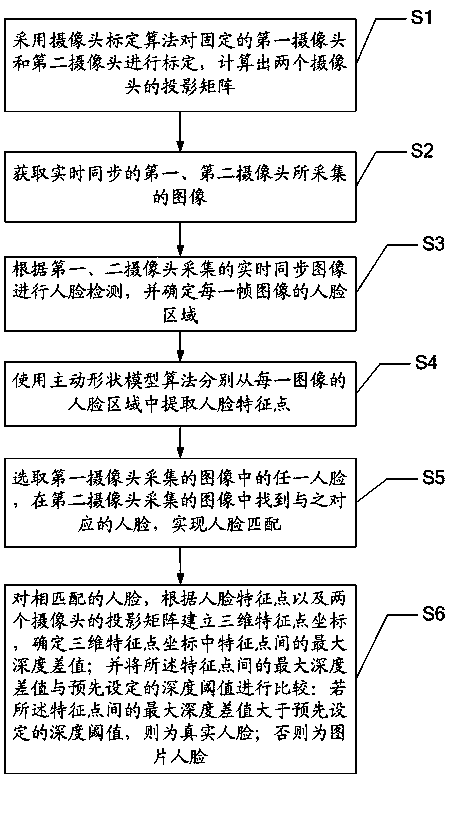
Method and system for distinguishing real face and picture face
InactiveCN103530599AHigh speedAchieve resolutionImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionComputer graphics (images)Computation process
The invention discloses a method and a system for distinguishing a real face and a picture face. Two cameras are adopted to acquire images. Partial depth information of the acquired images is reestablished via the two cameras so that an objective of distinguishing the picture face and the real face by using the cameras is realized. Meanwhile, a mode (i.e. the two cameras are adopted to acquire the images) based on binocular vision is adopted to realize matching of the face, extracting of characteristic points and reestablishing of three-dimensional coordinates of the characteristic points so that the method and the system for distinguishing the real face and the picture face are high is precision. Besides, a small amount of face characteristic points are used in the calculation process so that an algorithm has a relatively high speed as a whole.
Owner:TCL CORPORATION
Active matrix device and method of driving
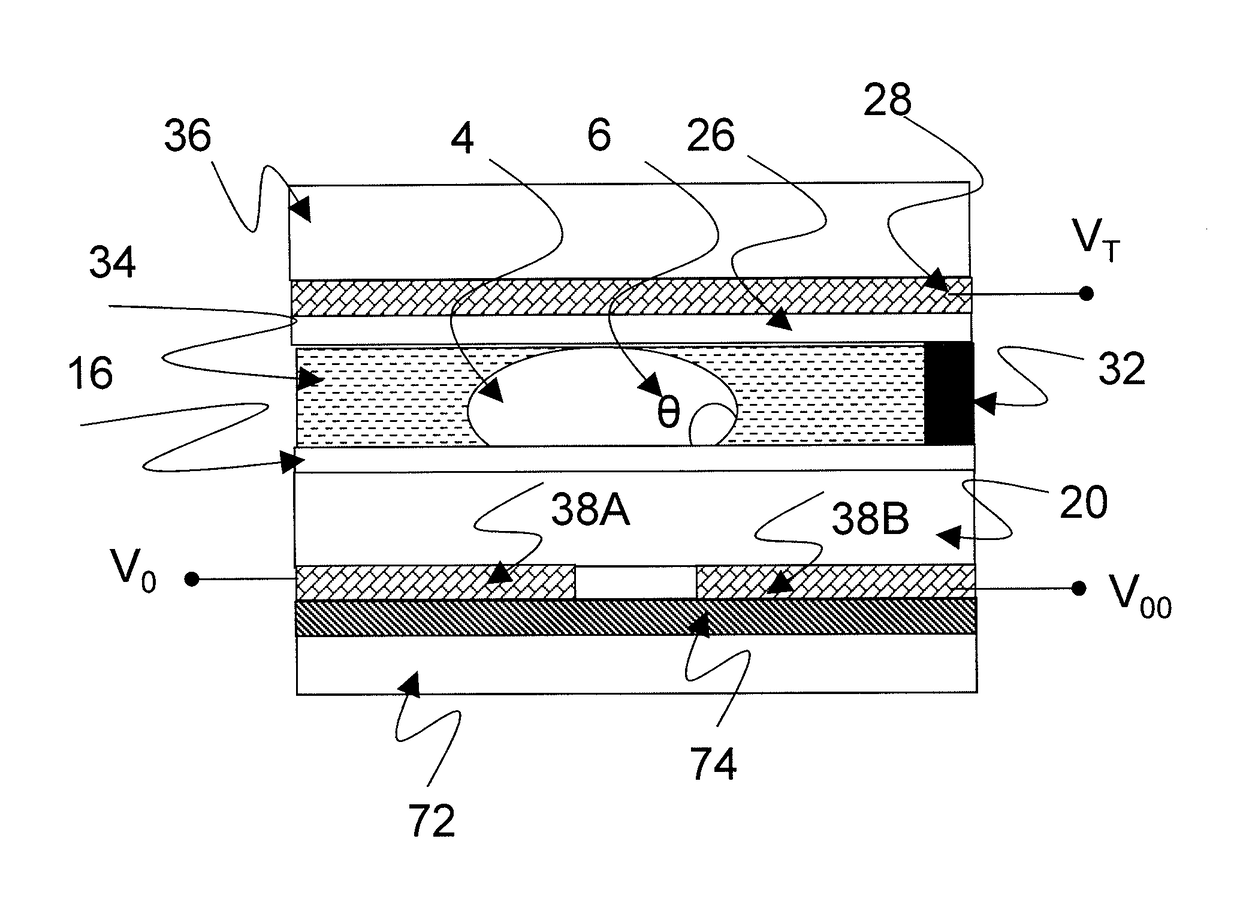
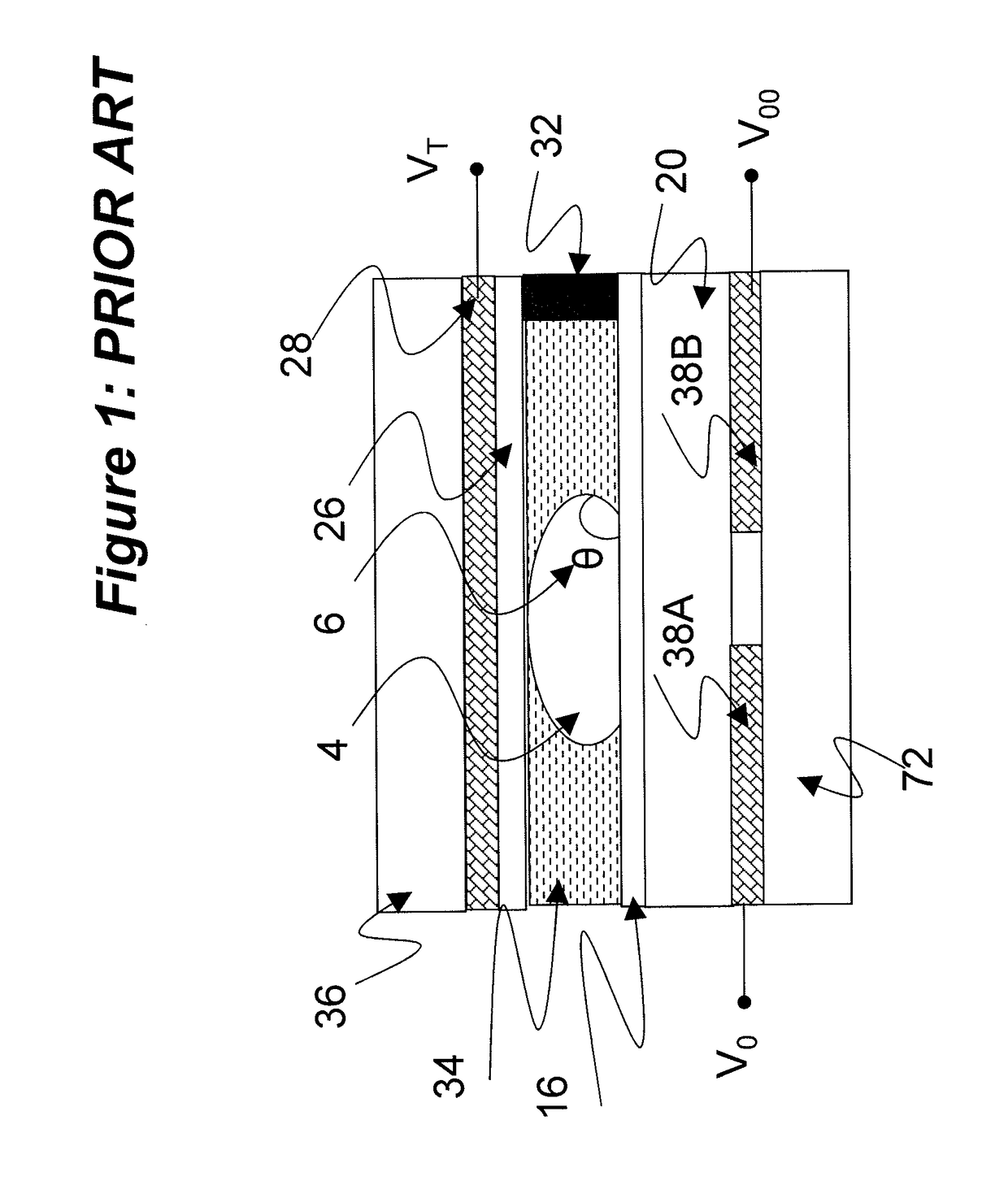
ActiveUS20170076676A1Improve linearityReducing complexity and number of transistorStatic indicating devicesLaboratory glasswaresDielectricActive matrix
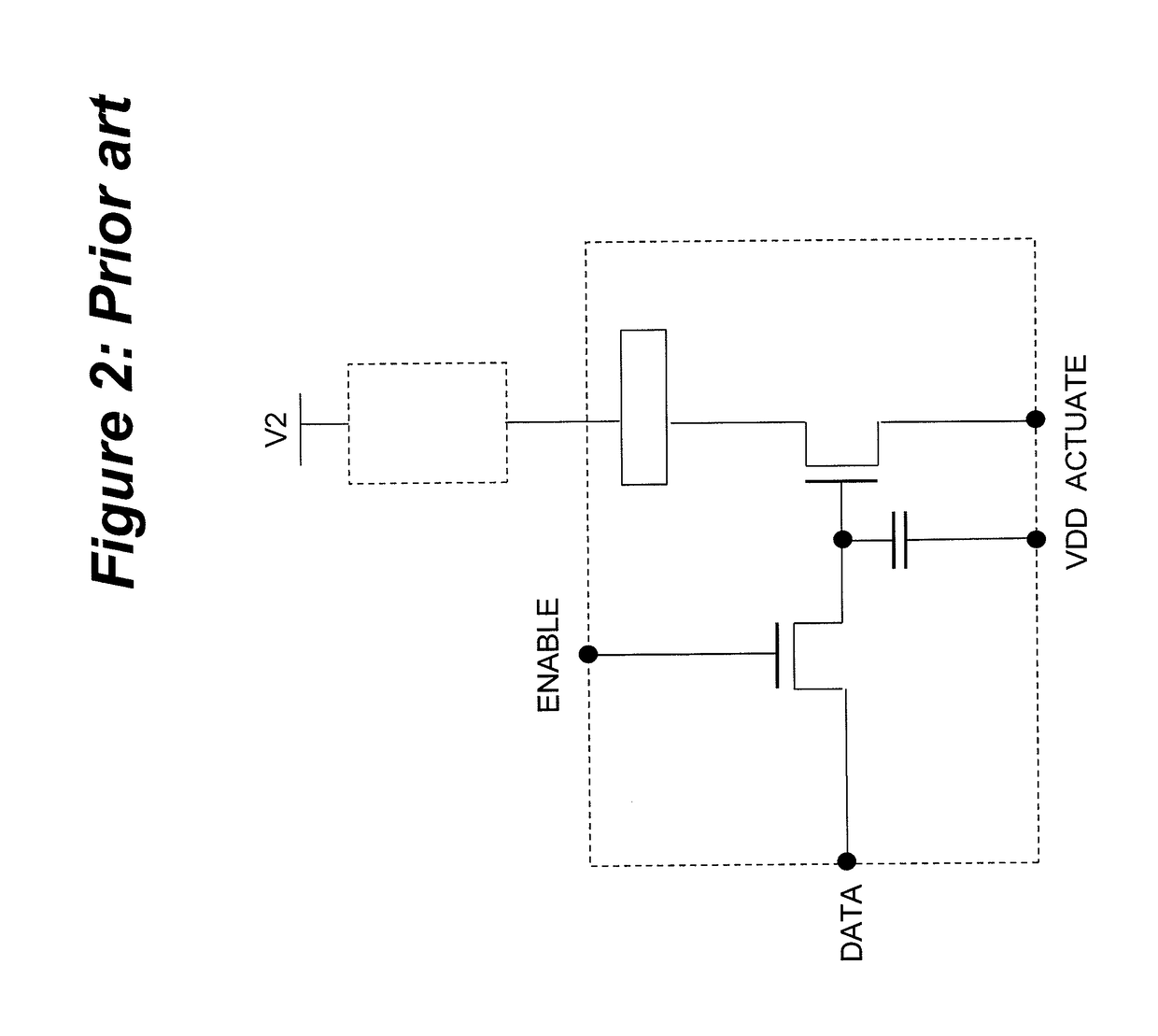
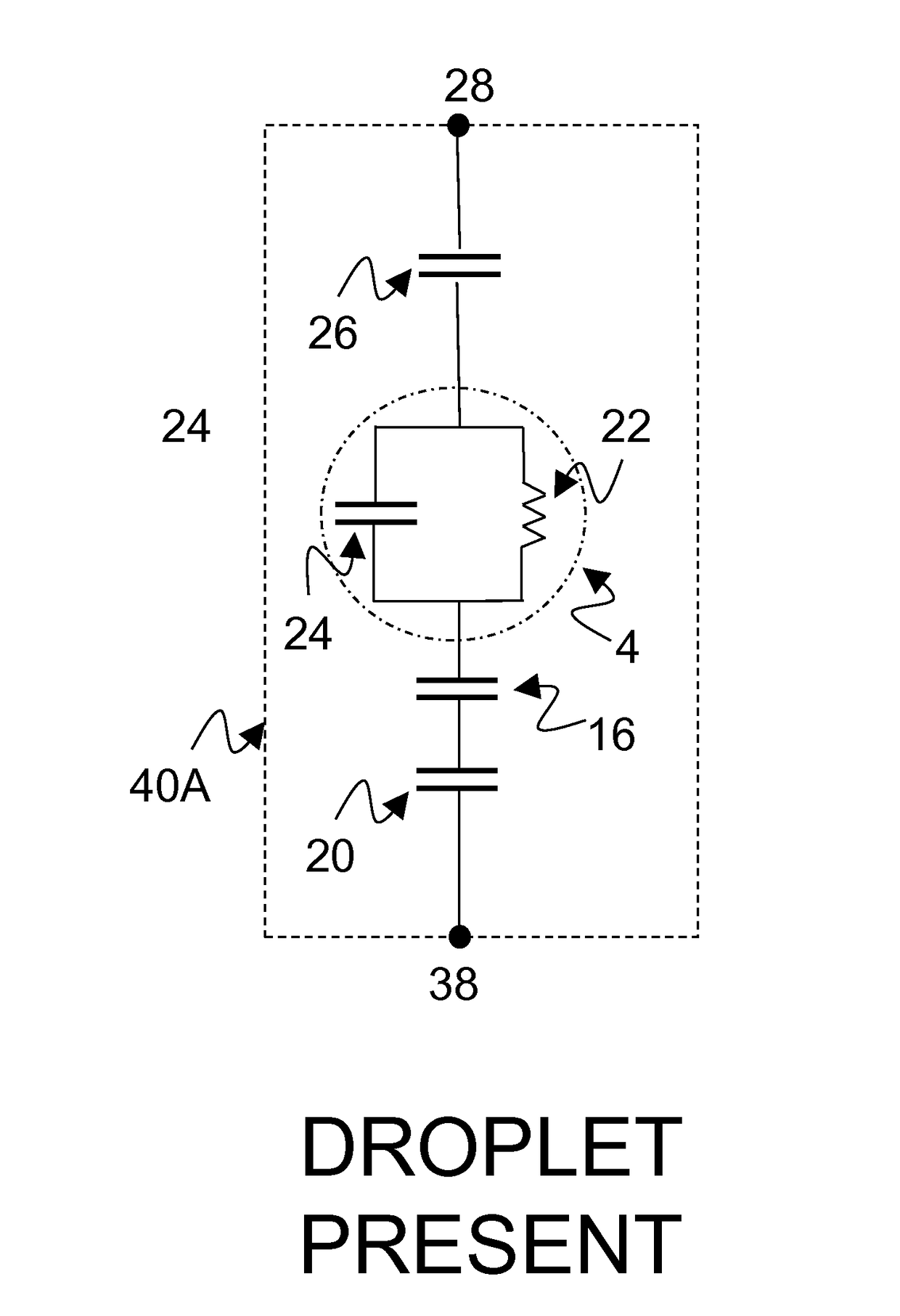
An active matrix electro-wetting on dielectric (AM-EWOD) device includes a plurality of array elements arranged in an array, each of the array elements including array element circuitry, an element electrode, and a reference electrode. The array element circuitry includes an actuation circuit configured to apply actuation voltages to the electrodes, and an impedance sensor circuit configured to sense impedance at the array element electrode to determine a droplet property at the array element. The impedance sensor circuit is operated by perturbing a potential applied to the reference electrode. The AM-EWOD device includes a common row addressing line. The impedance sensor circuit further is operated by supplying voltage signals over the common addressing line to effect both a reset operation and an operation for selecting a row in the array to be sensed. The circuitry isolates the array element from the actuation voltage during operating the impedance sensor circuit.
Owner:SHARP LIFE SCI EU LTD
Apparatus capable of simultaneously measuring diesel spray structure and combustion characteristic and method thereof
ActiveCN106404410AReduce radiation interferenceAchieve resolutionInternal-combustion engine testingDiesel sprayDiesel combustion
The invention belongs to the diesel spray and combustion visualization research field and discloses a measurement apparatus capable of simultaneously measuring a diesel spray structure and a combustion characteristic based on a laser diagnosis technology and a method thereof. In the past, test researches of a diesel spray characteristic and the combustion characteristic can not be performed simultaneously. In the invention, through using a Mie scattering technology of a laser and a laser induced fluorescence technology (OH-PLIF), the spray structure and the combustion characteristic during diesel combustion can be simultaneously measured and researched. The corresponding apparatus comprises a laser system, a constant volume combustion bomb system, a fuel oil supply system, a signal synchronization system and a signal acquisition system. The test apparatus can simultaneously carry out test researches of a liquid phase length of diesel spray and OH-PLIF distribution under a combustion condition, simultaneously can indicate a liquid phase area in a diesel combustion OH-PLIF distribution map and solves an interference problem of a liquid phase signal to a laser-induced fluorescence signal.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
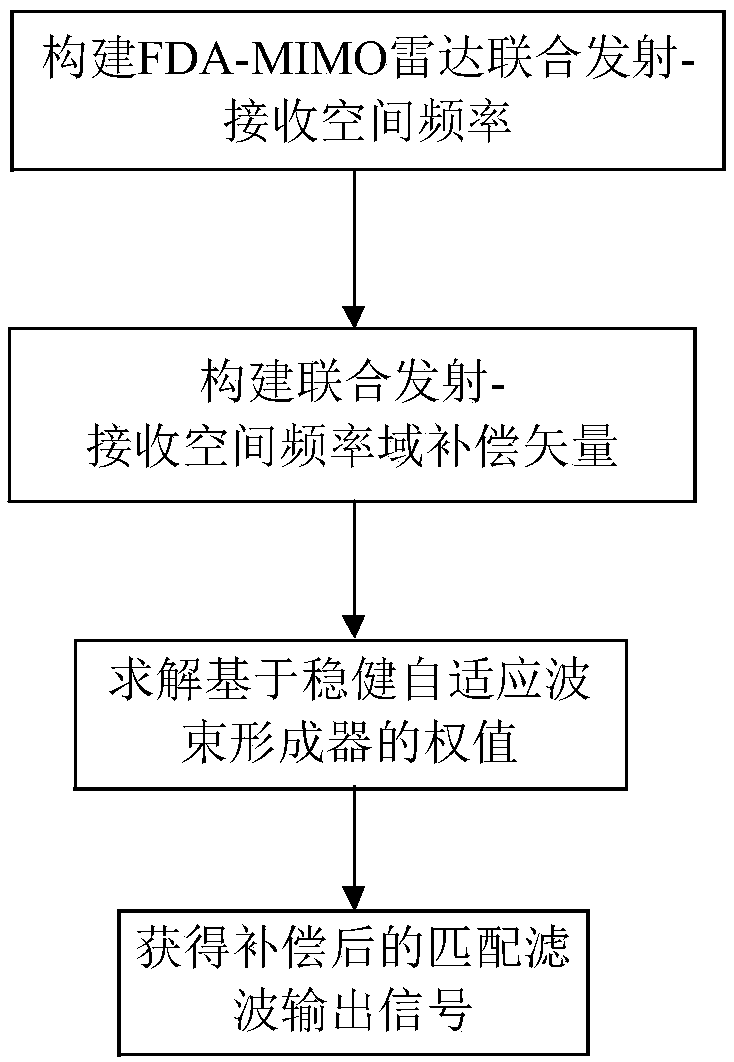
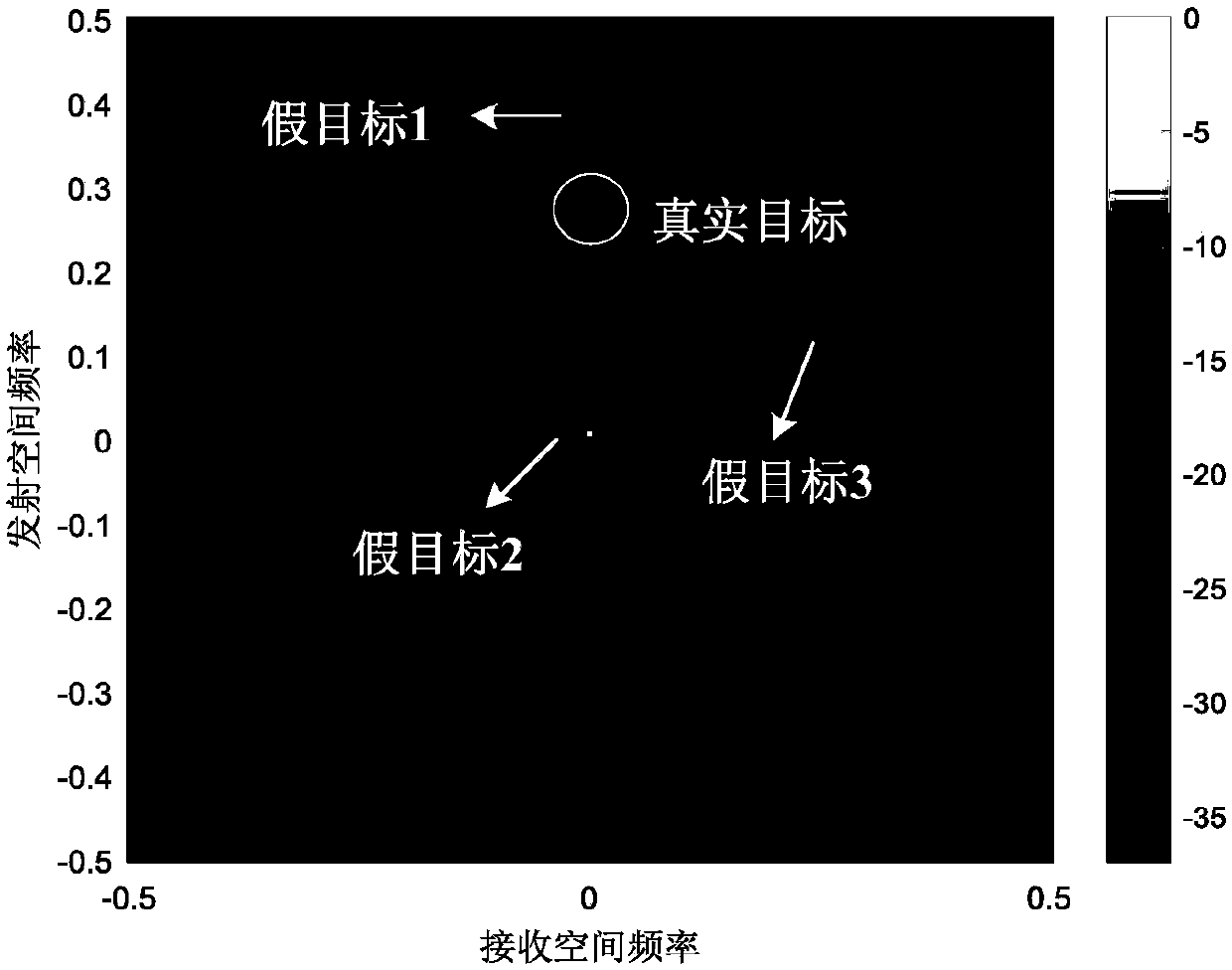
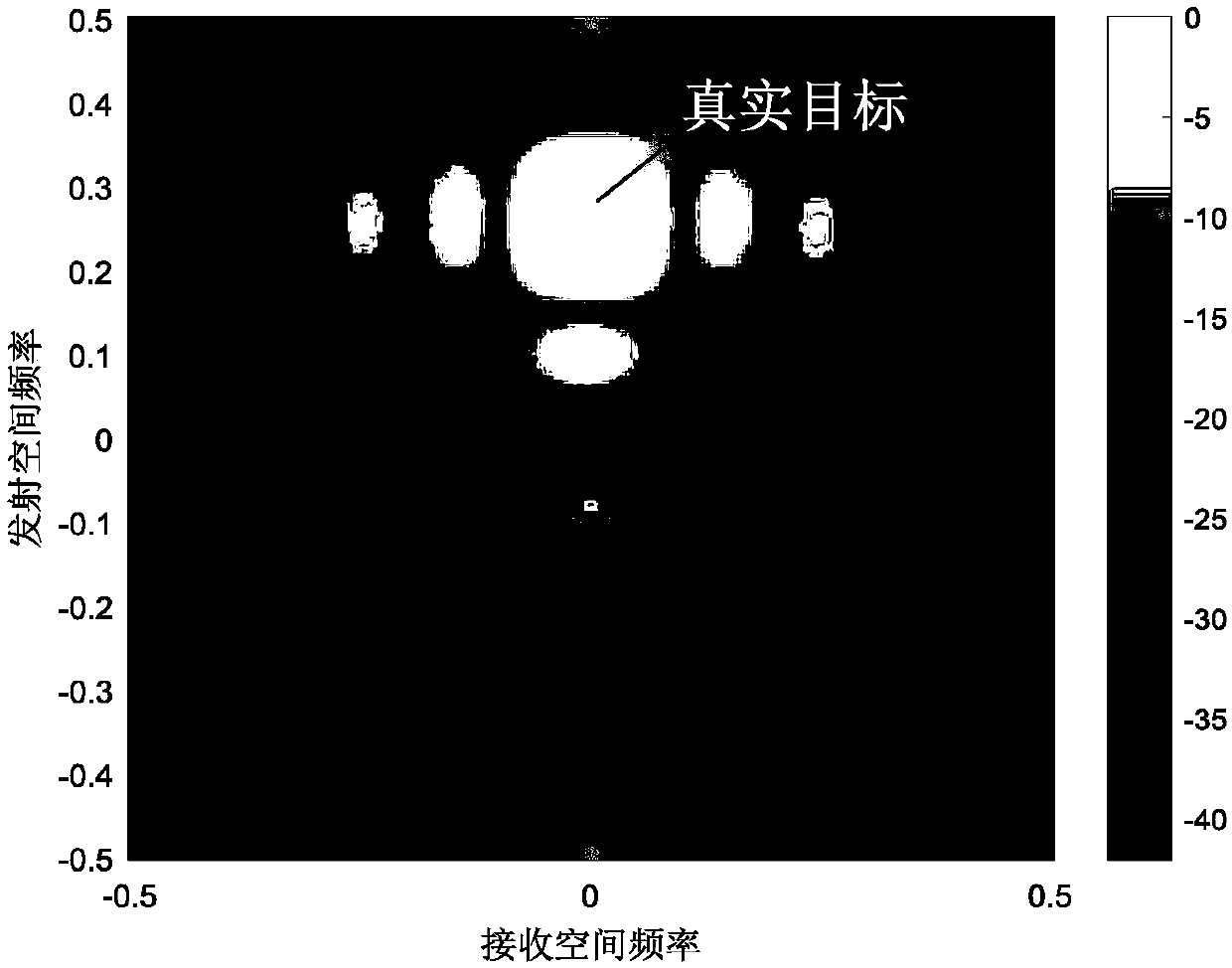
Method for FDA-MIMO (Frequency Diverse Array-Multiple-Input and Multiple-Output) radar to suppress mainlobe deceptive interference
ActiveCN108594186AOvercoming dense false target interference suppressionAchieve inhibitionWave based measurement systemsSelf adaptiveAdaptive beamformer
The invention provides a method for an FDA-MIMO (Frequency Diverse Array-Multiple-Input and Multiple-Output) radar to suppress mainlobe deceptive interference. The invention mainly aims to solve a problem that an existing radar system has little possibility of suppressing deceptive interference from a mainlobe direction. The method includes the following steps that: 1, the joint transmission-receiving spatial frequency of the FDA-MIMO radar is constructed; 2, a transmission-receiving spatial frequency domain compensation vector is constructed to compensate a transmission spatial frequency domain; 3, a weight obtained according to the constraint conditions of a robust adaptive beamformer is solved; and 4, compensated matched filtered output signals are obtained. With the method of the invention adopted, the extra distance dimension controllable degree of freedom of a frequency diversity array (FDA) is fully utilized. The method can be used for suppressing mainlobe deceptive interference.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Method for assessing biofilms
InactiveUS20060275847A1Larger effective field-of-viewResolution is sacrificedMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroscopesFluorescenceElectromagnetic radiation
An automated method for measuring the development of a biofilm, containing one or more fluorescent moieties, on a plurality of surfaces using a confocal imaging system including: a) a radiation source system for forming a beam of electromagnetic radiation including one or more wavelengths; b) an optical system for directing and focusing said beam onto one or more planes of the object; c) a detection system for detecting electromagnetic radiation emitted from the object and producing image data; and d) a scanning system for scanning the object in a plurality of planes with the electromagnetic radiation, the method comprising the steps of: i) growing said biofilm on said plurality of surfaces; ii) detecting the presence of said one or more fluorescent moieties within the biofilm by scanning the biofilm with electromagnetic radiation in a plurality of planes and collecting fluorescent emissions to produce a plurality of images; and iii) analysing said images by means of a data processing system under the control of computer software to determine the structure of the biofilm.
Owner:GE HEALTHCARE LTD
Grating heterodyne interference auto-collimation measuring device
A grating heterodyne interference auto-collimation measuring device mainly comprises a two-frequency laser, a 1 / 4 wave plate, a beam splitting system, a photoelectric conversion system, a polarization beam splitter, a reflector and a grating. The two-frequency laser emits two-frequency laser which passes the 1 / 4 wave plate and which then turns into two mutually-perpendicular linearly-polarized beams. The beams entering the beam splitting system are divided into three beams; one beam enters a reference light path photoelectric conversion system; last two enter a positive-negative gage beam polarization beam splitter. In the laser entering the polarization beam splitter, a reflected beam S is reflected to the grating by the reflector, and an incident angle is set into an auto-collimation angle of the corresponding diffraction order; through reference light information, horizontal and vertical displacements of the grating can be known. The auto-collimation right angle is set not depending on grating displacements. Therefore, the grating heterodyne interference auto-collimation measuring device is applicable to measuring horizontal large-travel displacement and vertical displacement.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
Bionic super-resolution imaging sensor and imaging method
ActiveCN107105147AHigh image resolutionAchieve a large field of viewTelevision system detailsColor television detailsImaging processingFoveated imaging
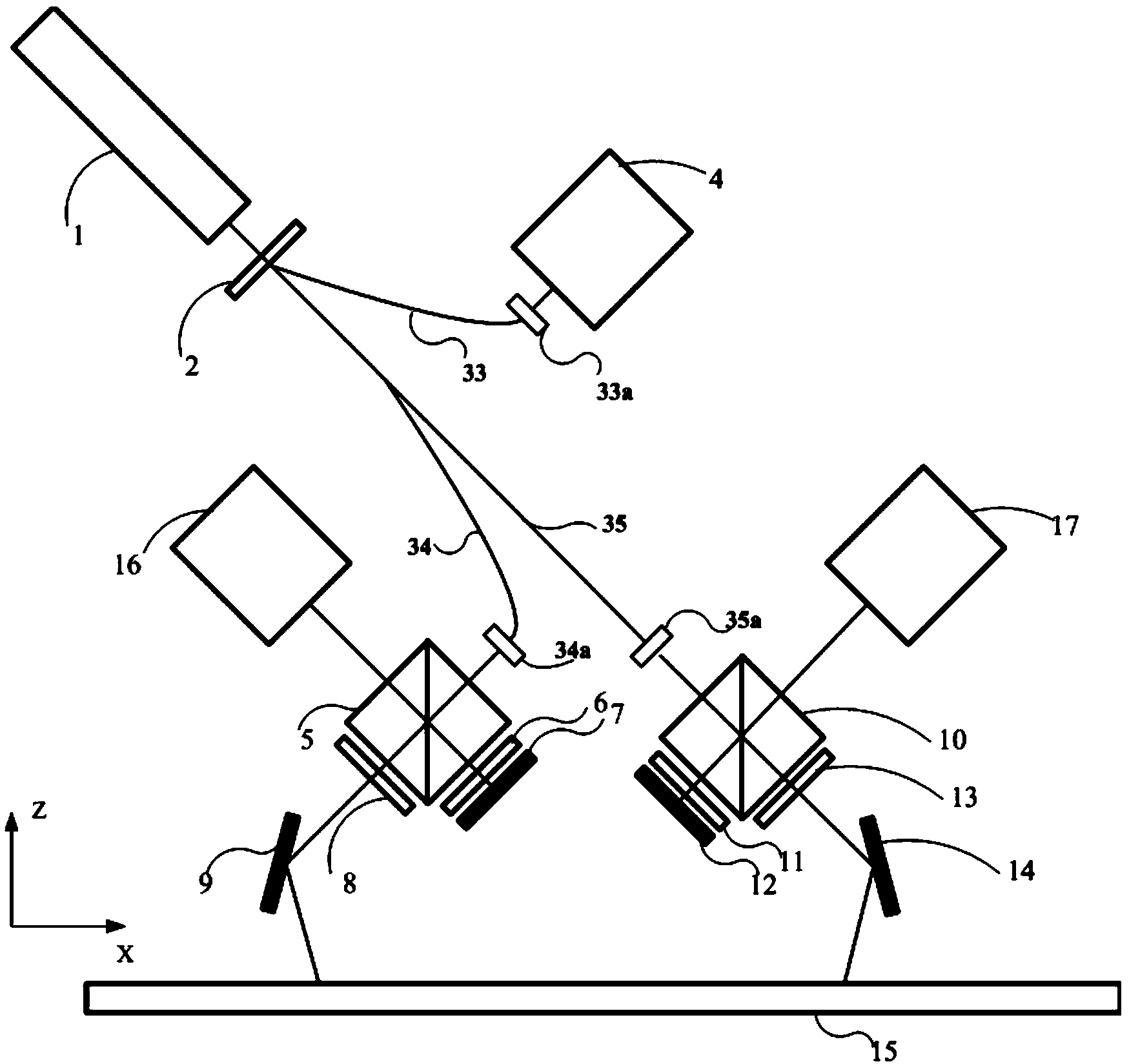
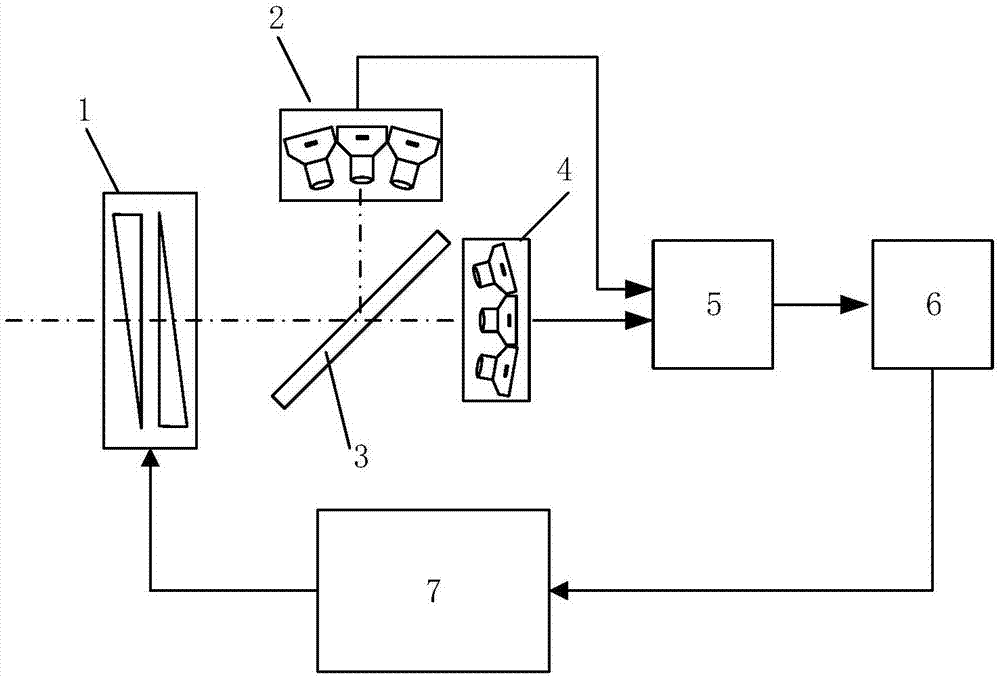
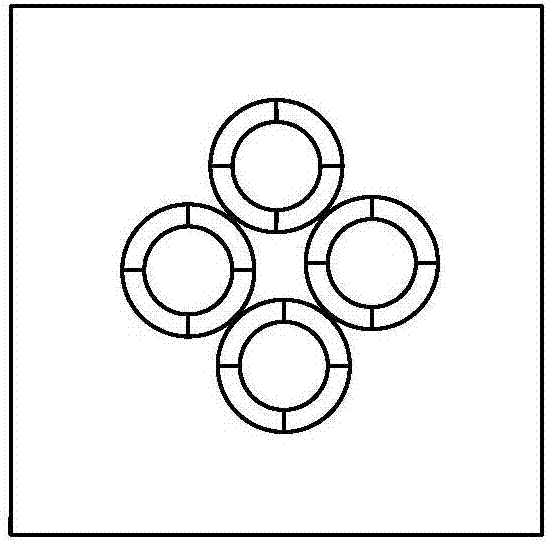
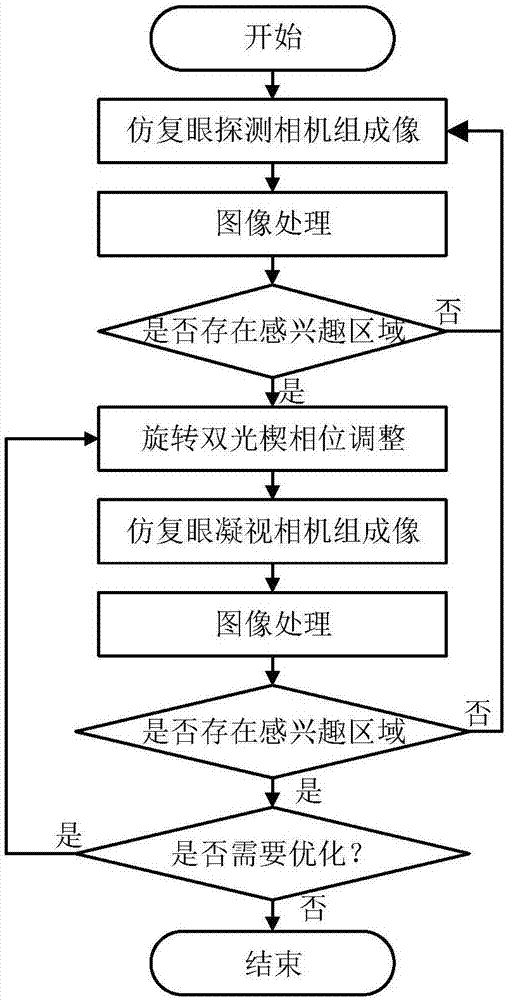
The invention discloses a bionic super-resolution imaging sensor and imaging method, relates to the imaging sensor and imaging method and belongs to the technical field of optical imaging. The bionic super-resolution imaging sensor disclosed by the invention comprises rotary double optical wedges, a bionic compound eye detection camera group, a spectroscope, a bionic compound eye staring camera group, an imaging processing module, a central control unit and a servo motor. The rotary double optical wedges are used for adjusting positions of areas of interest in a scene within a field of vision. The bionic compound eye detection camera group is used for simulating insect compound eyes to realize large field of view imaging and carrying out large field of view detection on areas in which targets may exist. The invention also discloses the imaging method realized based on the bionic super-resolution imaging sensor. According to the imaging sensor and imaging method with a large field of view imaging and foveated imaging mode switching function, two times of detection and judgment can be carried out on the areas of interest, and the accuracy is relatively high.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Focusing of microscopes and reading of microarrays
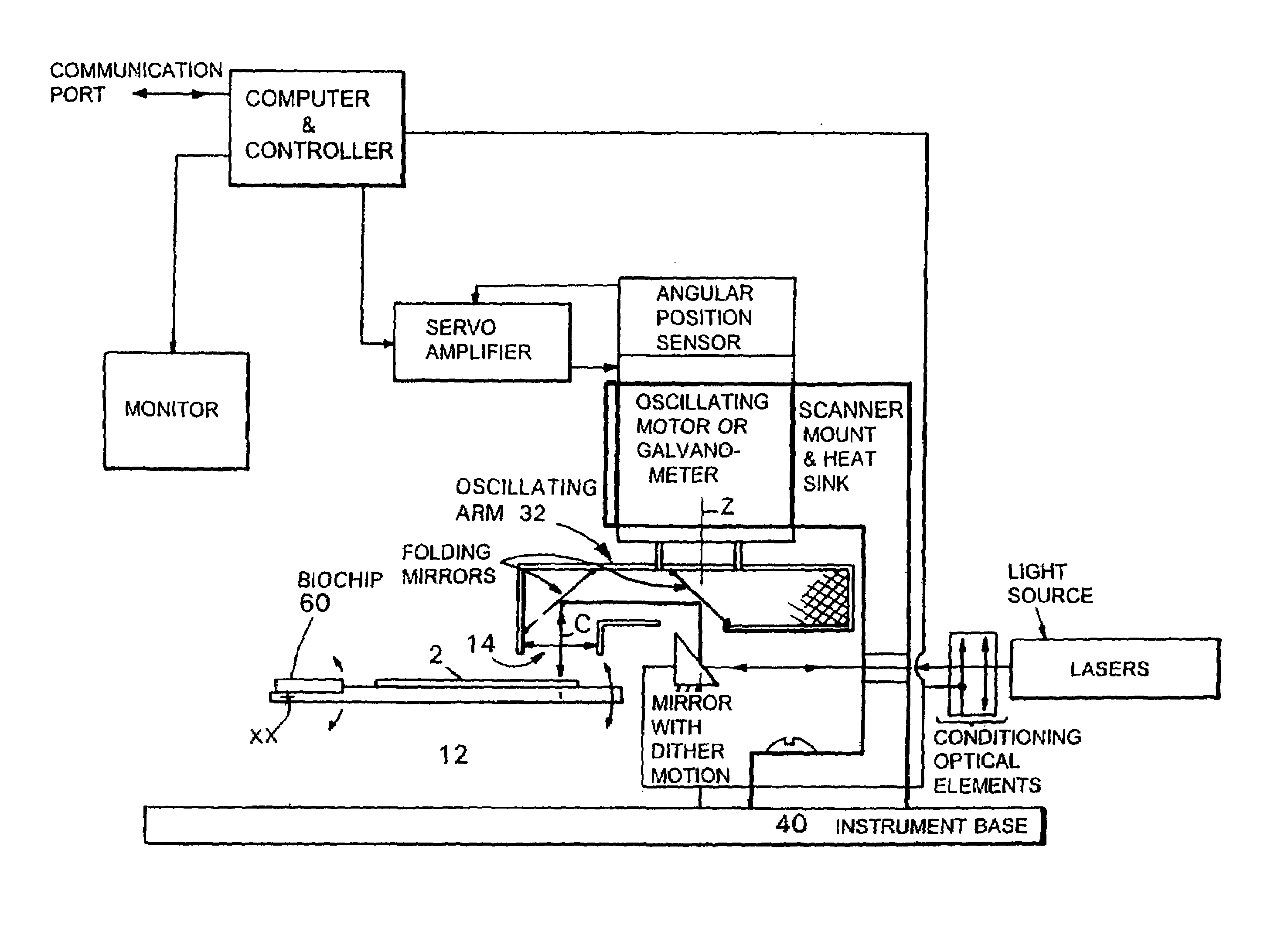
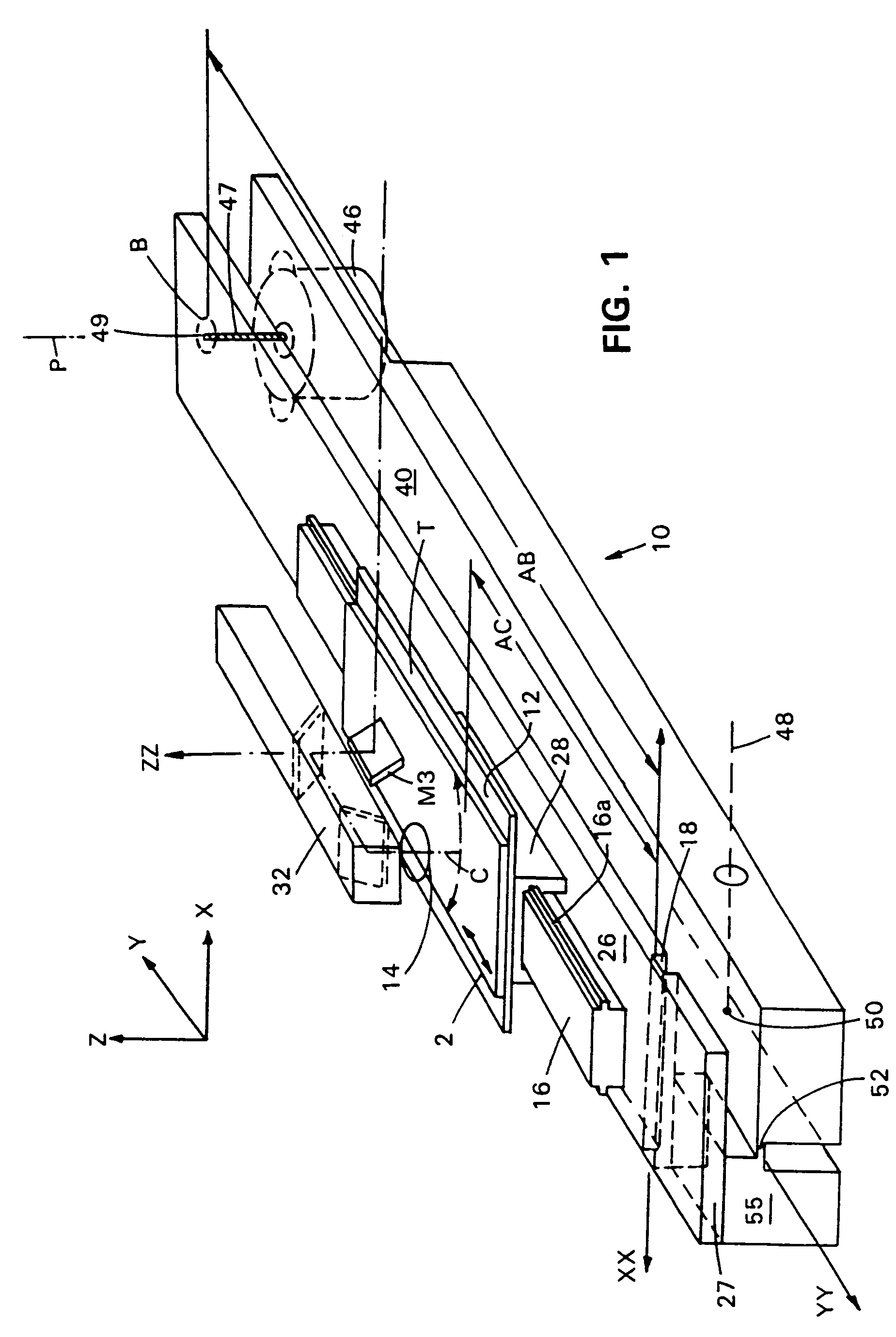
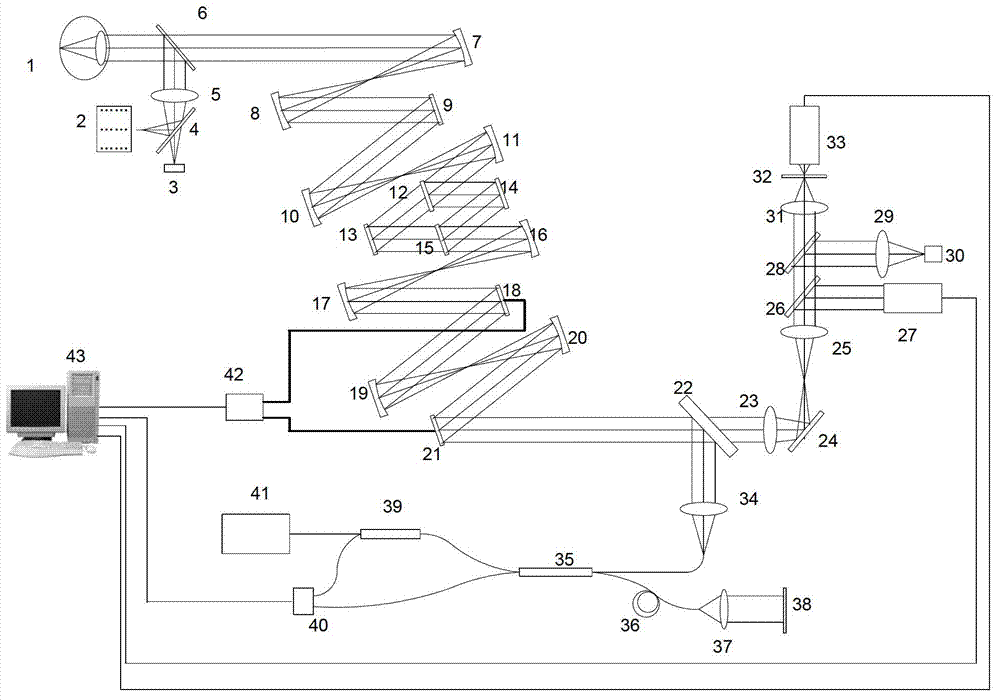
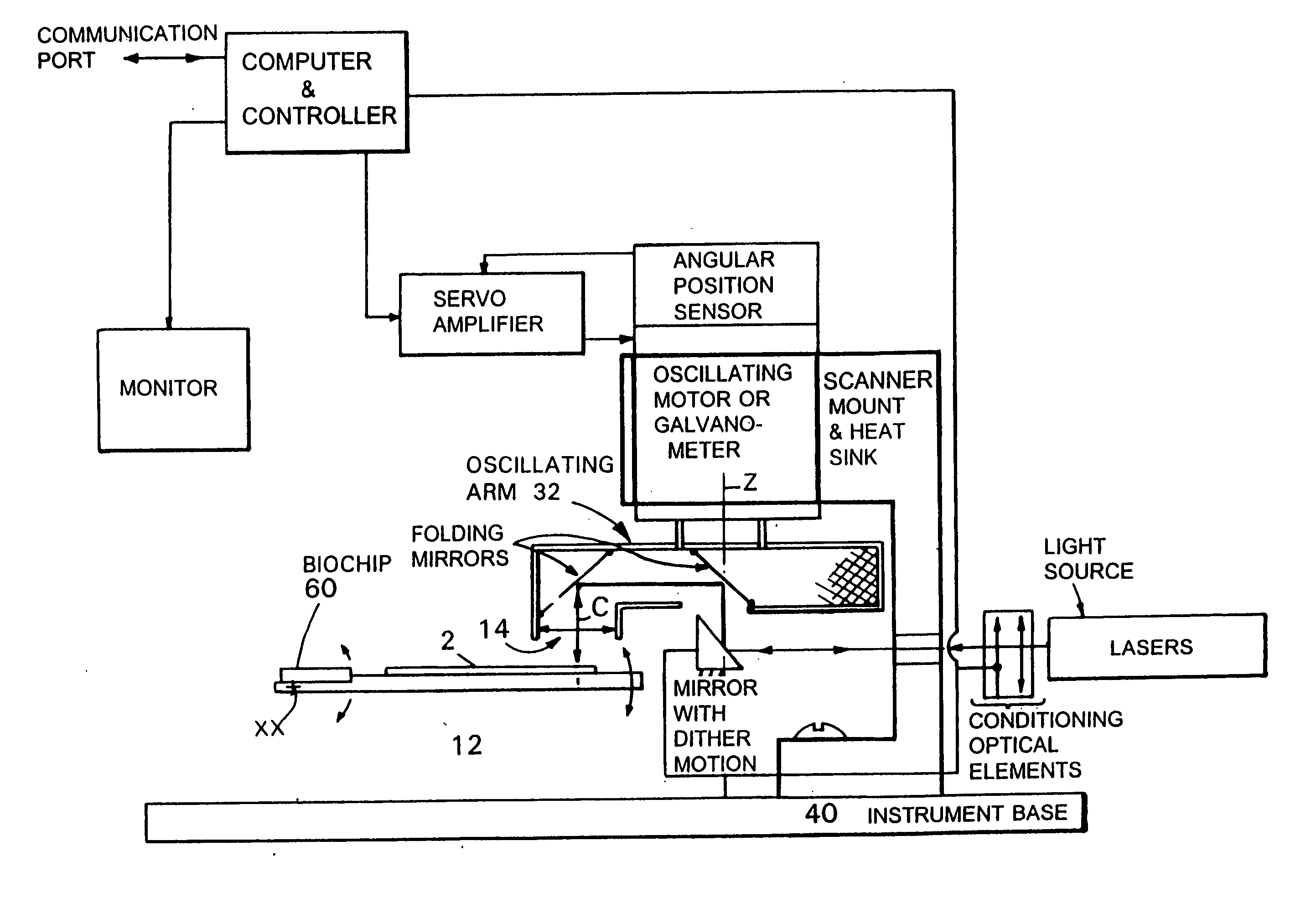
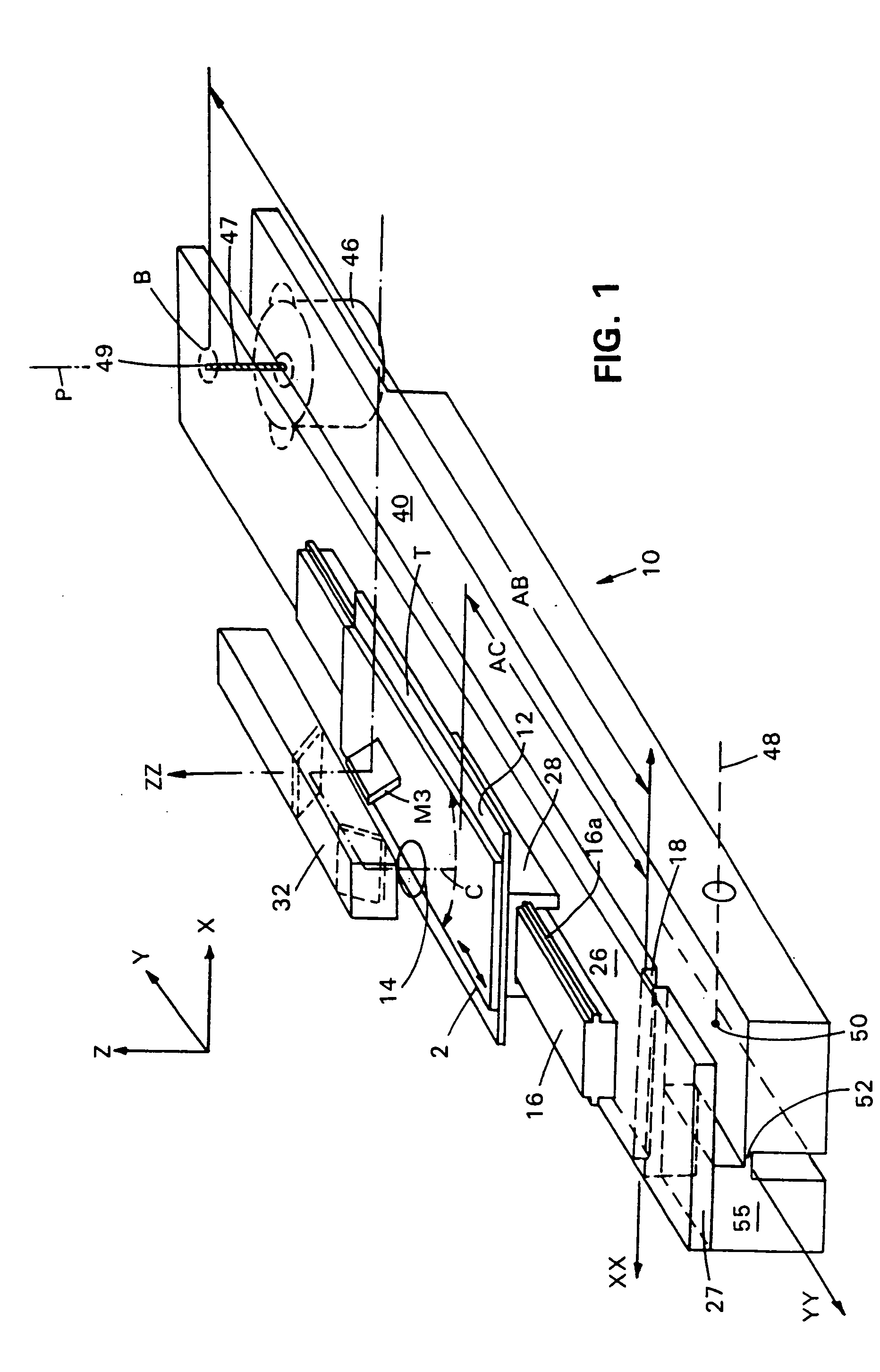
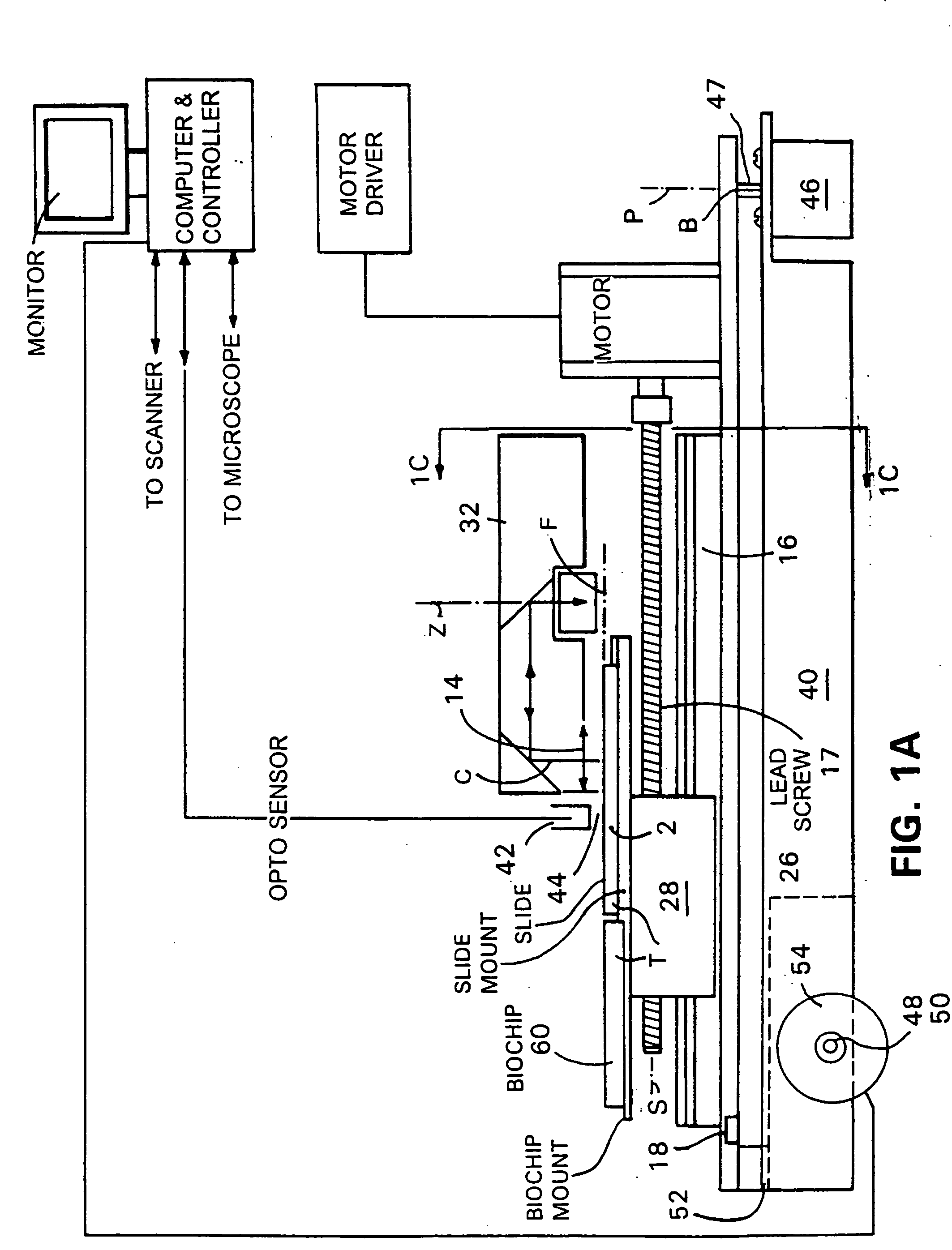
InactiveUS7095032B2Low costAchieve resolutionPhotometryLuminescent dosimetersMicroscope slideMicroscopic scale
Microscopes, including viewing and other microscopic systems, employ a hinged, tiltable plate to adjust focus on a flat object such as a microscope slide or biochip by motion, achieved by tilting, which is substantially normal to the focus point on the plane of the object. By employing two such tiltable arrangements, relatively long scan lines of e.g., flying objective, single pixel on-axis scanning can be accommodated. The tilting support plate is specifically constructed to provide tailored locations for different objects in series along the Y axis of the plate. The plate can accommodate beaters and cooled plates and / or the flat object being examined. In a fluorescence scanning microscope, locations are specifically adapted to receive microscope slides and biochip cartridges such as Affymetrix's “Gene Chip®”. A scanning microscope under computer control, employing such a focusing action, enables unattended scanning of biochips with a simple and economical instrument. Also shown are flexure-mounting of a support plate to define the hinge axis, techniques for automatically determining position and focus, and a rotatably oscillating flying micro-objective scanner combined with the tilting plane focus system. Construction and control techniques are shown that realize simple and accurate focusing. Methods of examination of biological materials are disclosed. Simple and efficient focused scanning with a flying micro-objective of ordered arrays of nucleotides and nucleic acid fragments carried upon a microscope slide or other substrate is disclosed. Quantified fluorescence imaging is economically achieved by combined use of the described scanning and focusing arrangement and use of simple and accurate calibration modules respectively for example for Affymetrix's “Gene Chip” microarray modules and for microscope slides.
Owner:AFFYMETRIX INC
Nanometer positioning device and system
InactiveCN103481321AReduced Effects of Nanopositioning AccuracyEliminate positioning errorsMetal working apparatusElectricityAutomatic control
The invention relates to a nanometer positioning device and a nanometer positioning system, belongs to the technical field of automatic control of grating ruling machinery and solves the technical problems that in the prior art, the upper limit of the adjusting amplitude of a tilt angle and the adjusting precision of a nanometer positioning device are limited by the performance parameters, and the data collecting control module of a nanometer positioning system is large in developing difficulty. The nanometer positioning device comprises a substrate, a macro positioning platform, a first guiding guide track, a second guiding guide track, a micro-positioning platform, piezoelectric ceramic, a first laser interference displacement detection mechanism and a second laser interference displacement detection mechanism; one end of the piezoelectric ceramic is fixed on the macro positioning platform while the other end is contacted with the micro-positioning platform; the macro positioning platform slides along the first and second guiding guide tracks; the piezoelectric ceramic drives the micro-positioning platform to generate displacement. The invention also provides the nanometer positioning system applying the nanometer positioning device. The nanometer positioning device and the nanometer positioning system have a larger upper limit of the adjusting amplitude of the tilt angle and adjusting flexibility.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Multifunctional wide-range ultra-short pulsed laser autocorrelator
InactiveCN101900608AAchieve resolutionRealization of resolutionInstrumentsBeam splitterOptoelectronics
The invention relates to a multifunctional wide-range ultra-short pulsed laser autocorrelator which comprises a precision mobile platform, a first right-angle reflector, a chopper, a second right-angle reflector, a parabolic mirror, a two-photon detector and a signal acquisition system, wherein the first right-angle reflector is fixed on the precision mobile platform and comprises two reflectors; the chopper is positioned at the front end of one reflector in the first right-angle reflector, a first light path is formed between the chopper and one reflector in the first right-angle reflector, and a first beam splitter is placed on the first light path; the second right-angle reflector comprises two reflectors, the second right-angle reflector is positioned at one side of the first light path, and a second light path is formed between the first beam splitter and one reflector in the second right-angle reflector; the parabolic mirror is positioned at the other side of the first light path, a third light path is formed between the parabolic mirror and the other reflector in the second right-angle reflector, a second beam splitter is placed on the third light path, and a fourth light path is formed between the second beam splitter and the other reflector in the first right-angle reflector; the two-photon detector is positioned at one side of the parabolic mirror; and the signal acquisition system is electrically connected with the two-photon detector.
Owner:NAT INST OF METROLOGY CHINA
Active matrix device and method of driving
ActiveUS20170074814A1Design and fabrication is facilitatedAchieve resolutionLaboratory glasswaresMaterial impedanceDielectricActive matrix
An active matrix electro-wetting on dielectric (AM-EWOD) device includes a plurality of array elements arranged in an array, each array element including array element circuitry, an element electrode, and a reference electrode. The array element circuitry includes an actuation circuit configured to apply actuation voltages to the electrodes, and an impedance sensor circuit configured to sense impedance at the array element electrode to determine a droplet property. The actuation circuitry includes a memory capacitor for storing voltage data corresponding to either an actuated state or an unactuated state of the array element, and an input applied to the memory capacitor operates to effect an operation of the impedance sensor circuit. Such input may isolate the array element from the actuation voltage during operation of the impedance sensor circuit, and the memory capacitor may operate as part of the impedance sensor circuit as a reference capacitor for determining the droplet property.
Owner:SHARP LIFE SCI EU LTD
Method for panoramic imaging ophthalmology protomerite detected by ultrasound biological microscopes
ActiveCN101288585ASmall geometric distortionHigh resolutionImage enhancementImage analysisSonificationLongitude
The invention discloses a panoramic view imaging method for realizing ophthalmonogy prosthomere by UBM. Firstly, at least four continuous pictures with two adjacent pictures mutually overlapped are obtained along the cornea longitude direction by linear UBM; then a whole eyeball prosthomere picture is spliced with the pictures by image filtering, binarization, lines clustering, joint location searching and image fusion. The method has the image precision of linear UBM, at the same time, the eyeball prosthomere panoramic view imaging is realized.
Owner:TIANJIN SUOWEI ELECTRONICS TECH
Substrate processing apparatus and method
ActiveUS20090028683A1The effect is accurateSpin easilyElectric discharge tubesNanoinformaticsRotary stageEngineering
Substrate processing methods and apparatus are disclosed. In some embodiments a substrate processing apparatus may comprise a support structure and a moveable stage including first and second stages. The moveable stage has one or more maglev units attached to the first stage and / or second stage proximate an edge of the first stage. The first stage retains one or more substrates and moves with respect to a first axis that is substantially fixed with respect to the second stage. The second stage translates along a second axis with respect to the support structure. In other embodiments, a primary motor may maintain a rotary stage at an angular speed and / or accelerate or decelerate the stage from a first angular speed to a second angular speed. A secondary motor may accelerate the stage from rest to the first angular speed and / or decelerate the stage from a non-zero angular speed.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
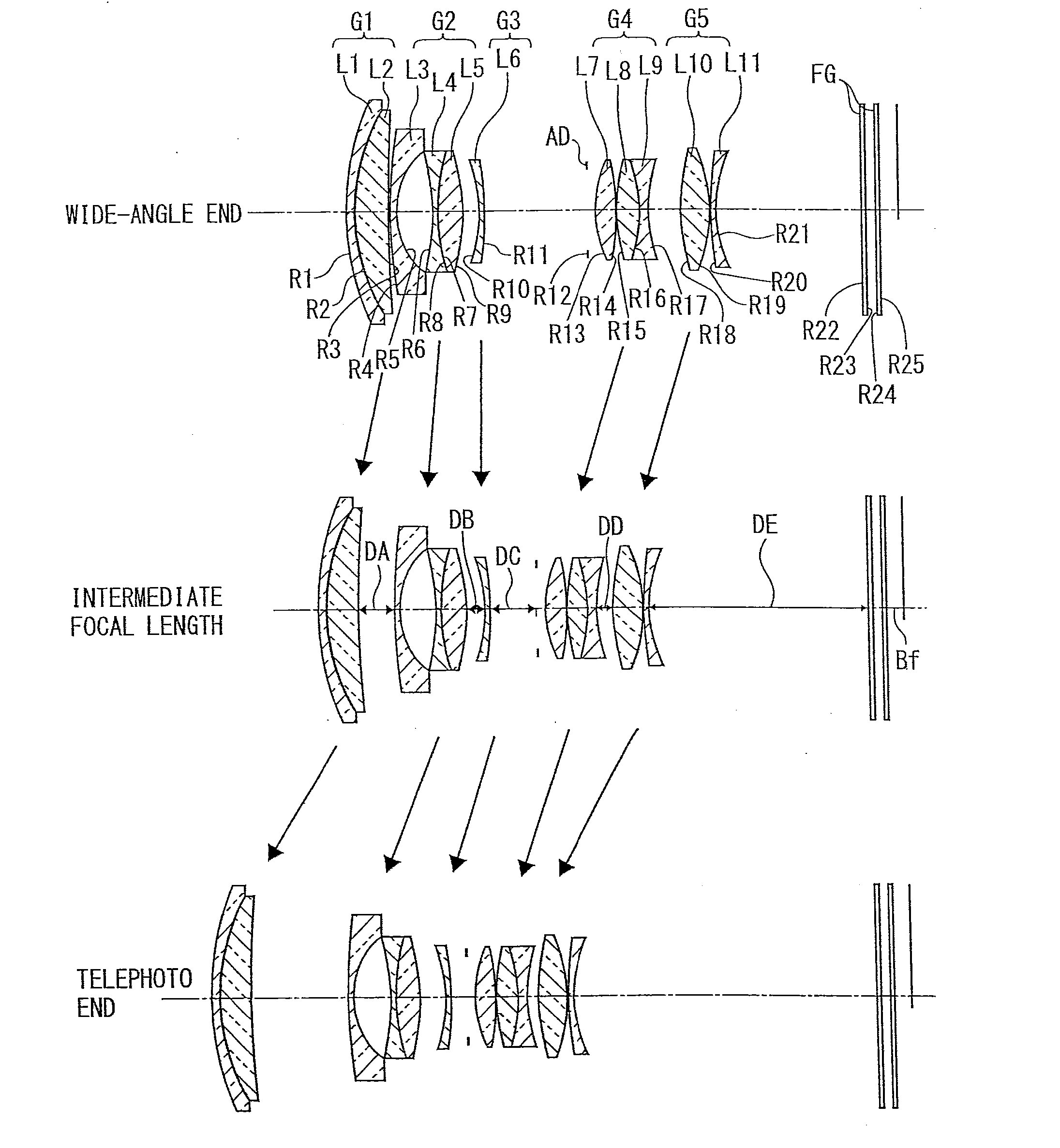
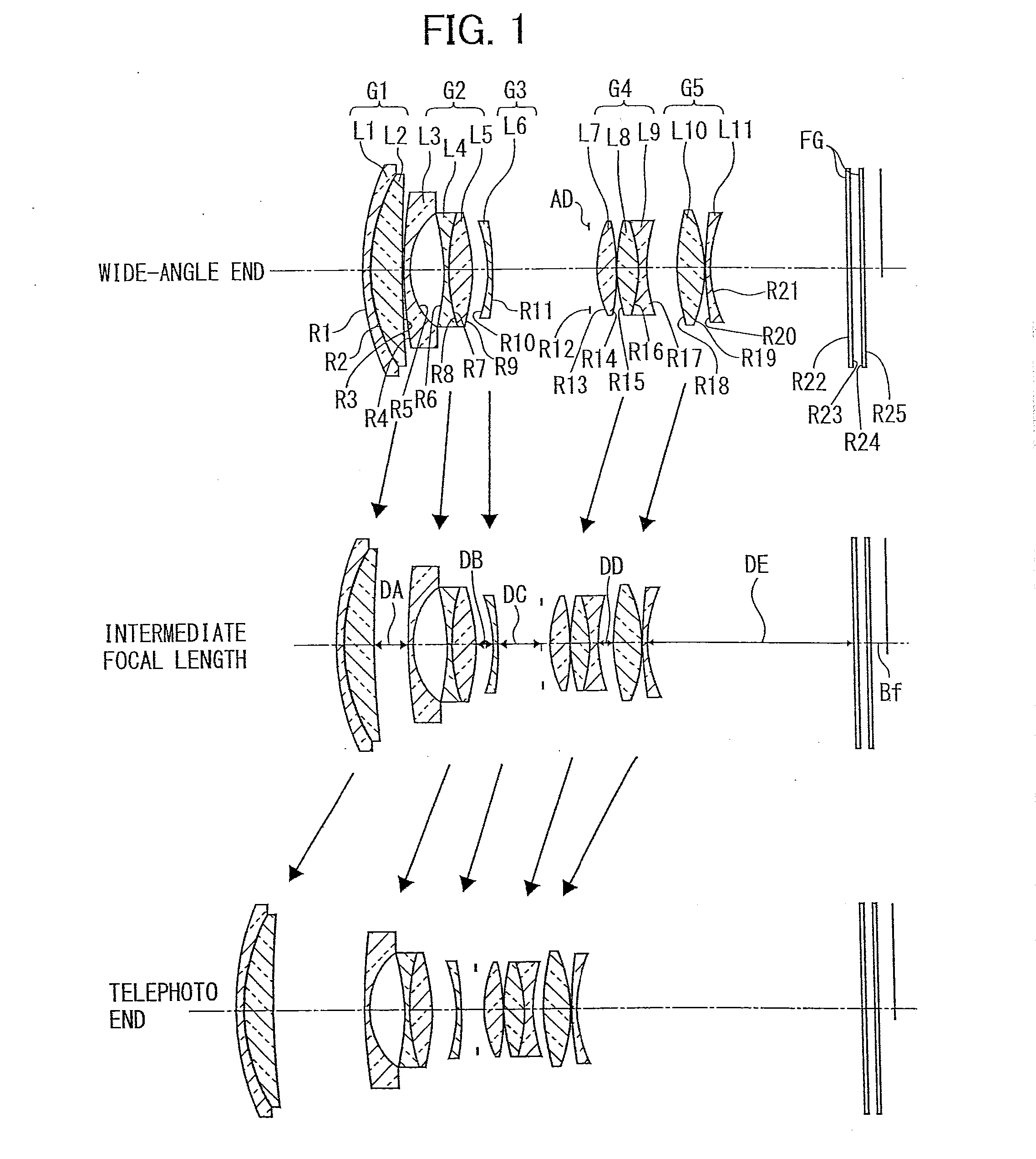
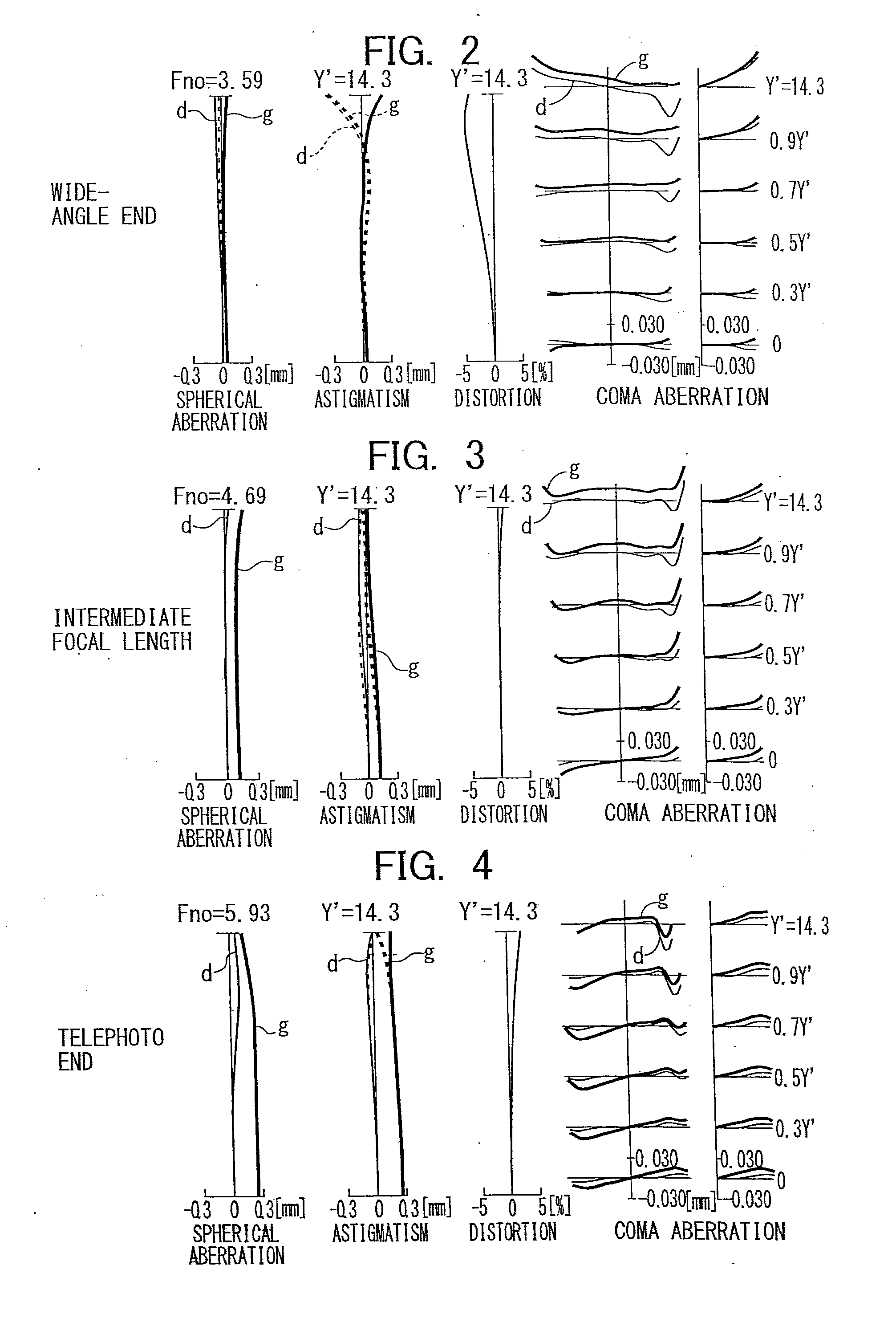
Zoom lens, imaging device, and portable digital device
A zoom lens includes, in order from an object side along an optical axis, a first lens group having a positive refractive power, a second lens group having a negative refractive power, a third lens group having a negative refractive power, a fourth lens group having a positive refractive power, and a fifth lens group having a positive refractive power, wherein with a change in a magnification from a wide-angle end to a telephoto end, an interval between the first lens group and the second lens group is increased, the interval between the second lens group and the third lens group is changed, the interval between the third lens group and the fourth lens group is decreased, the interval between the fourth lens group and the fifth lens group is decreased, and focusing is performed by the third lens group.
Owner:RICOH KK
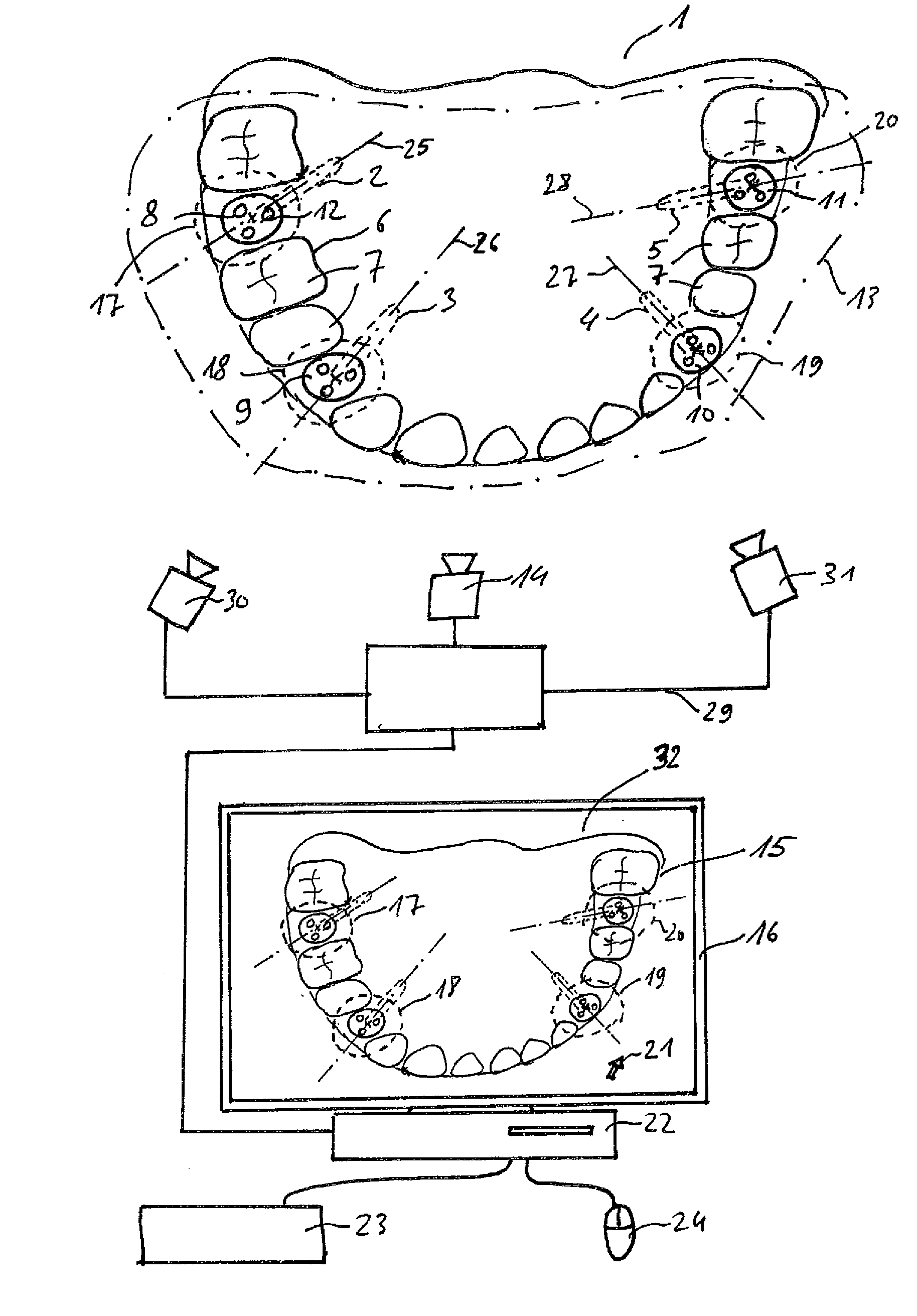
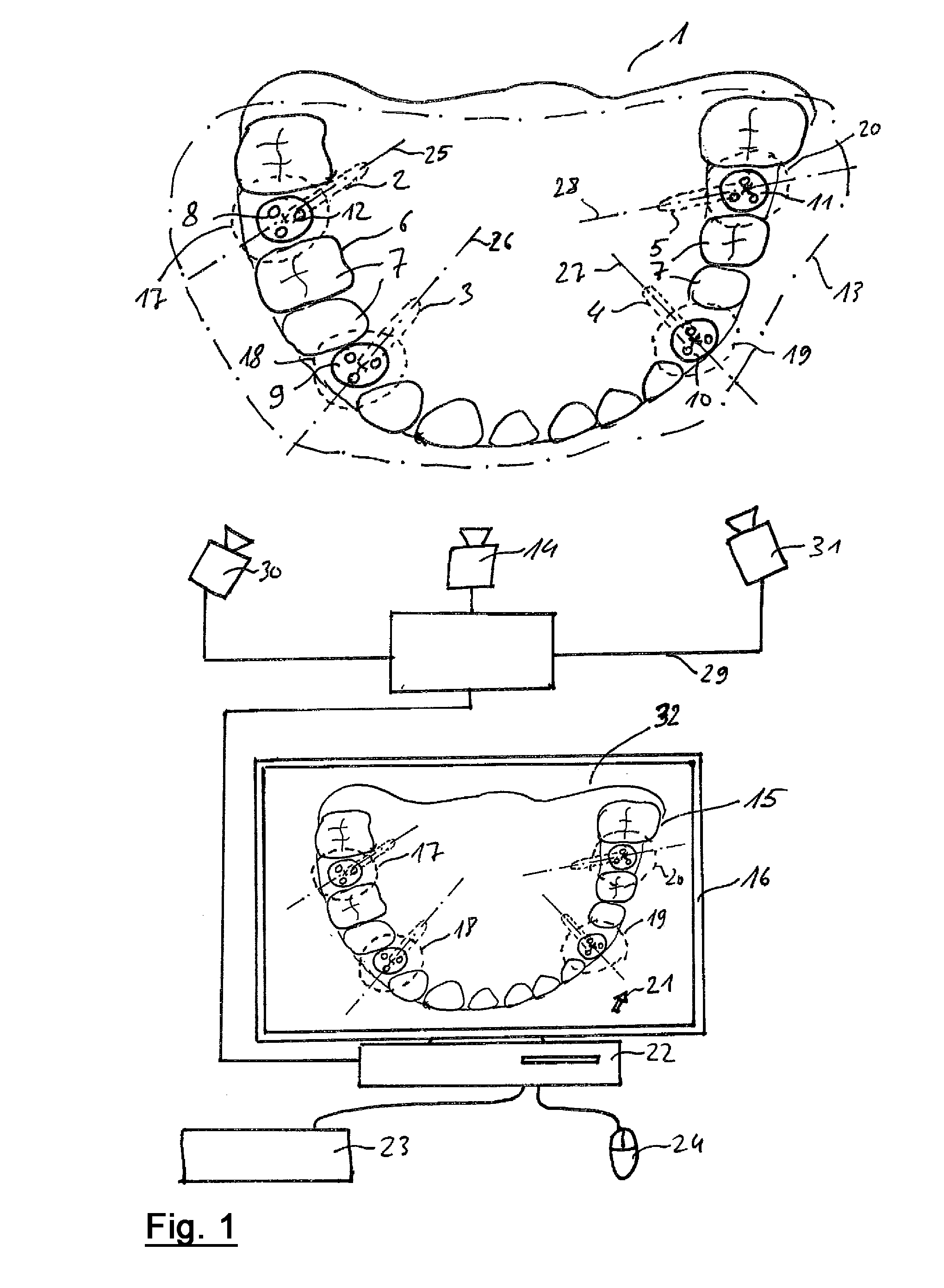
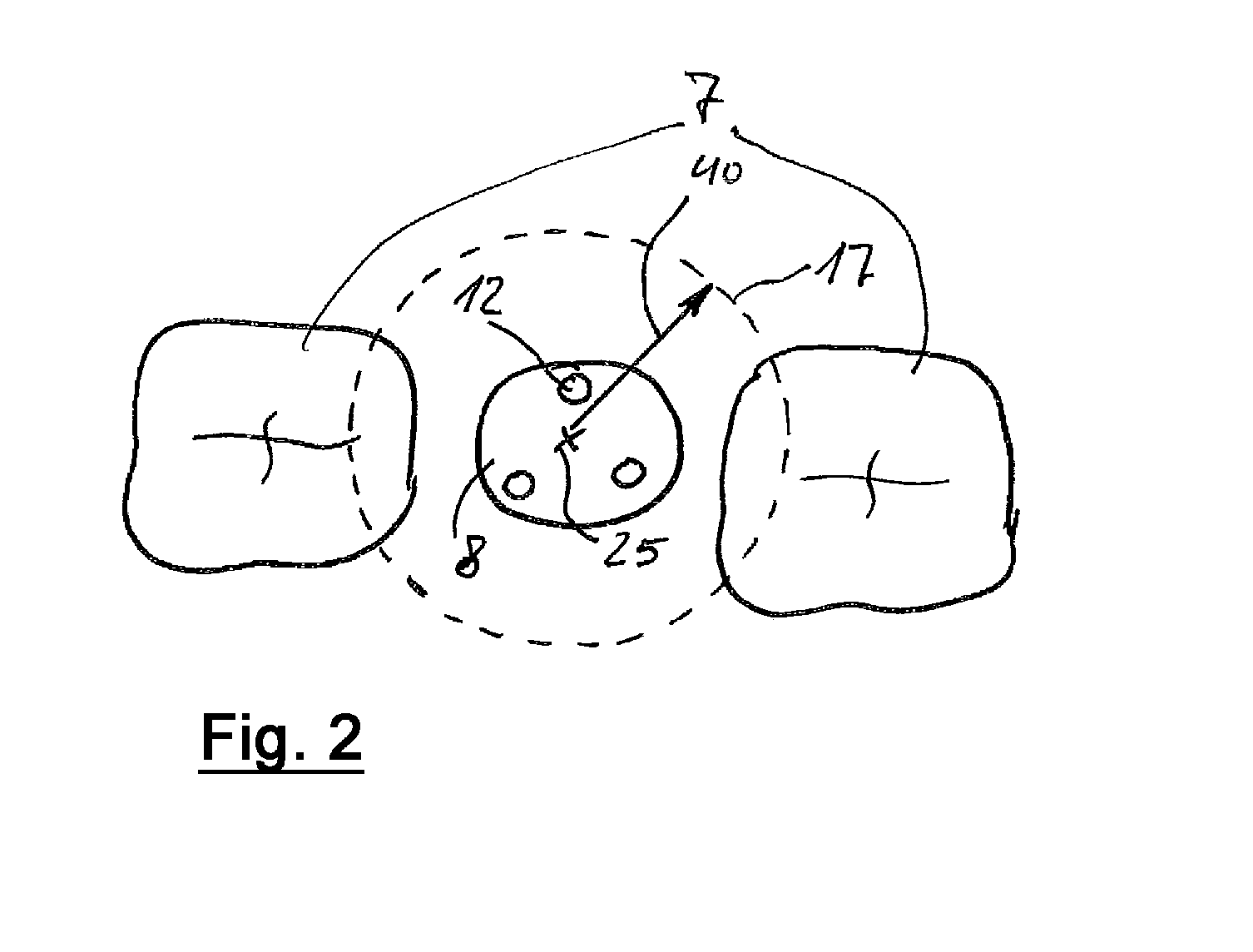
Method for measuring a dental situation
ActiveUS20150072313A1Increase exposureAchieve resolutionImpression capsRadiation diagnostics for dentistryBiomedical engineeringZones of the lung
Owner:SIRONA DENTAL SYSTEMS
Self-adaptive optical retina imaging device and method
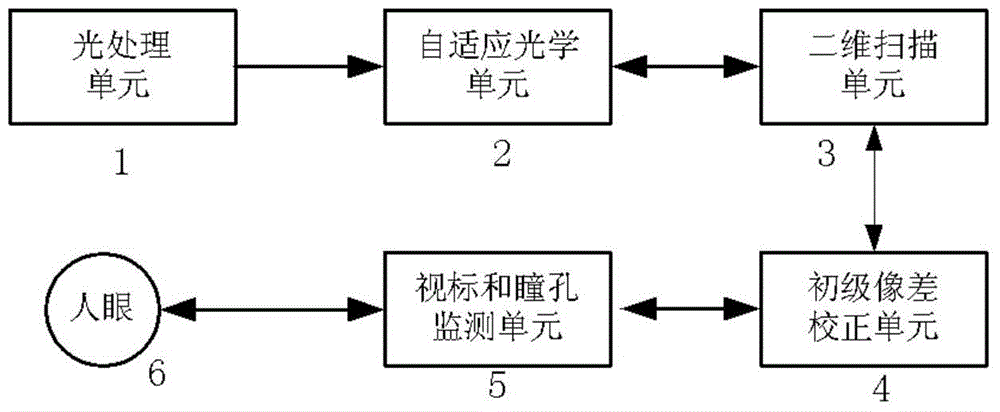
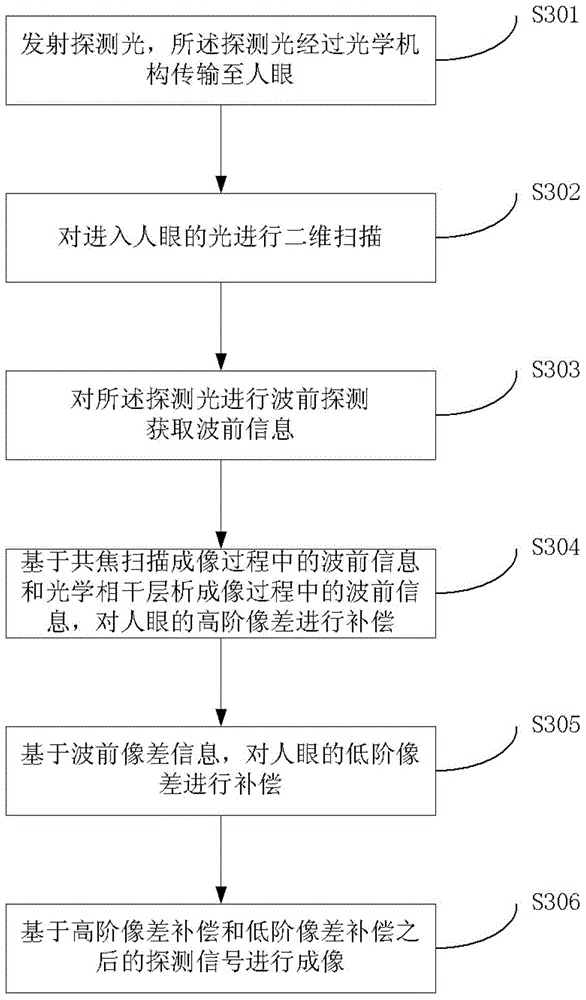
InactiveCN104783755AAchieve resolutionImprove practicalityMicroscopesOthalmoscopesWavefront sensorHigh resolution imaging
The invention discloses a self-adaptive optical retina imaging device and method. The self-adaptive optical retina imaging device comprises an optical processing unit, a self-adaptive optical unit, a two-dimensional scanning unit and a primary aberration correcting unit. An imaging unit included in the optical processing unit is used for imaging based on signals after high-order aberration compensation and low-order aberration compensation. The self-adaptive optical technology, the confocal scanning imaging technology and the optical coherence tomography are combined, two wavefront sensors are used for detecting wavefront aberration of a confocal scanning light path and an optical coherence tomography light path, meanwhile, two wavefront correctors are used for correcting low-order aberration and high-order aberration of human eyes, low-order aberration and high-order aberration can be conducted on the two light paths, and transverse high resolution imaging and longitudinal high resolution imaging of the human eyes can be achieved at the same time.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Point cloud and grid partitioning method in aerial photography terrain three-dimensional reconstruction system
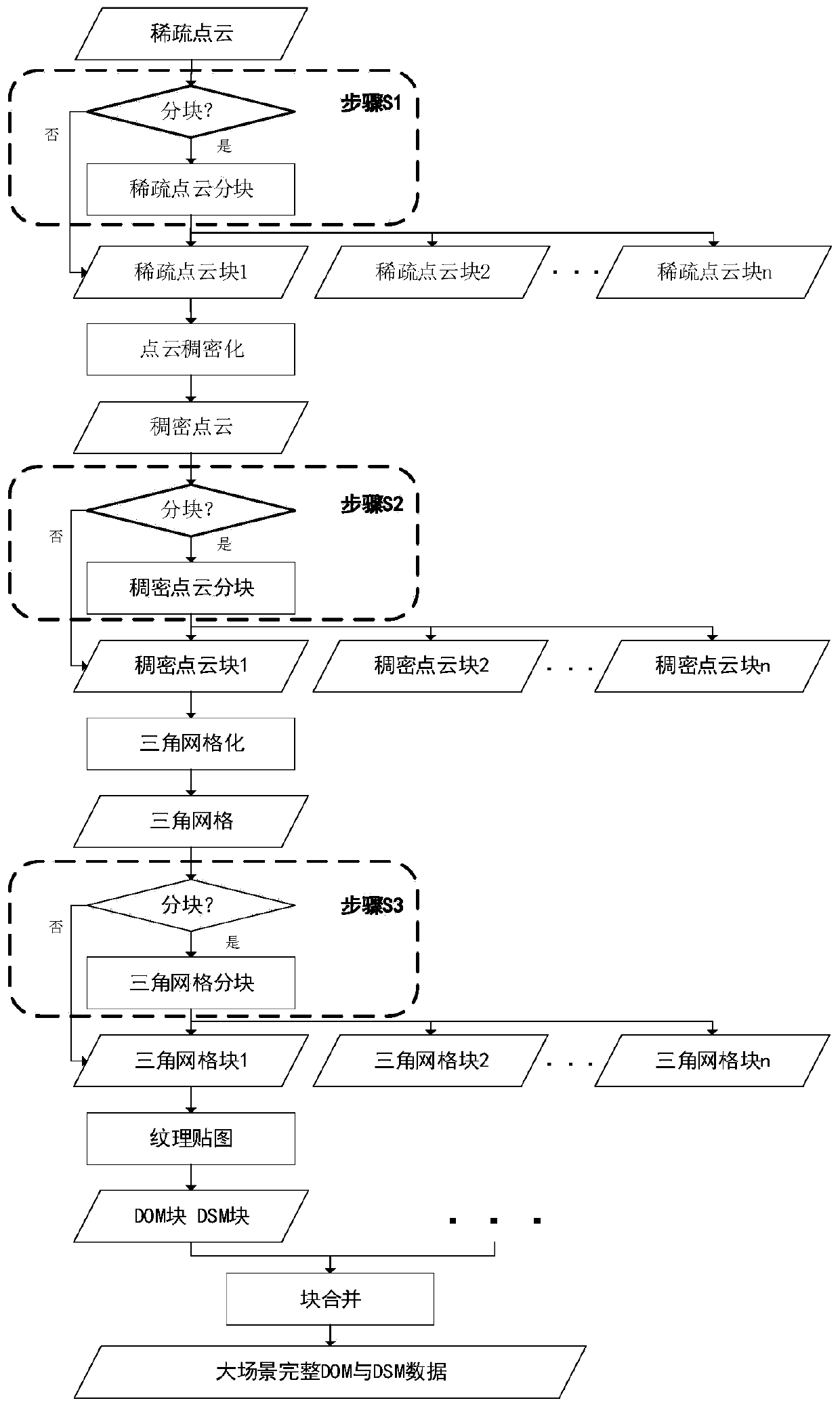
PendingCN110379022AHandle flexible implementationReduce merge error3D-image renderingTerrainPoint cloud
The invention discloses a point cloud and grid partitioning method in an aerial photography terrain three-dimensional reconstruction system. According to the method, the problem that important modulessuch as point cloud densification, triangular gridding and texture mapping in a three-dimensional reconstruction system cannot be processed due to large data volume of point cloud is solved by partitioning three-dimensional data generated by aerial photography of large-scale scene terrain. According to the method, layer-by-layer segmentation is carried out on three-dimensional data in stages according to the memory use condition in a module, point cloud is partitioned before point cloud densification and triangular meshing, and then triangular meshes are partitioned before texture mapping processing. The hardware threshold of operation of a three-dimensional reconstruction system is reduced, the intra-block and inter-block relationship after partitioning can be well reserved, and a solidfoundation is laid for generating a large-scene high-resolution digital orthoimage (DOM) and a digital surface model (DSM).
Owner:西安因诺航空科技有限公司
Retina three-dimensional imaging device based on double wavefront correctors for human eyes
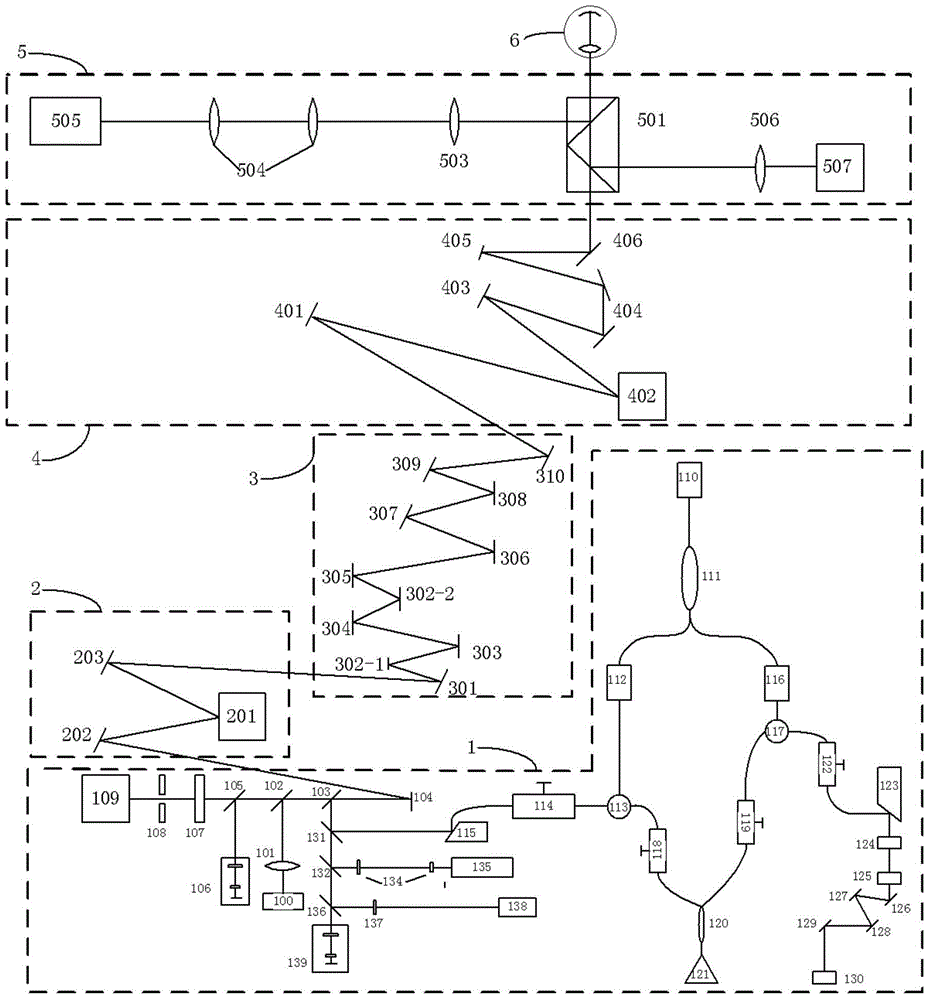
ActiveCN102860816AImprove the correction effectMeet the needs of aberration correctionOthalmoscopesWavefront sensorAudio power amplifier
The invention provides a retina three-dimensional imaging device based on double wavefront correctors for human eyes. The device comprises an adaptive optical assembly, an eye ground monitoring imaging and sighting mark assembly, a confocal scanning assembly and an optical coherent chromatography assembly. The adaptive optical assembly comprises a wavefront sensor (27), the double wavefront correctors and a series of spherical reflectors. The double wavefront correctors are respectively a wavefront corrector (18) and a wavefront corrector (21). The wavefront sensor (27) receives reflected light reflected by the human eyes to conduct wavefront detecting to obtain low-order aberration and high-order aberration of the human eyes. After a computer (43) calculates the low-order aberration and the high-order aberration, and a high-voltage amplifier (42) is controlled to output voltage to control the double wavefront correctors to correct the low-order aberration and the high-order aberration of the human eyes. The retina three-dimensional imaging device adopts the double wavefront correctors to improve correcting capacity of the adaptive optical system on the aberrations of the human eyes. Simultaneously, high-resolution three-dimensional imaging of retinas of the human eyes is achieved.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Focusing of microscopes and reading of microarrays
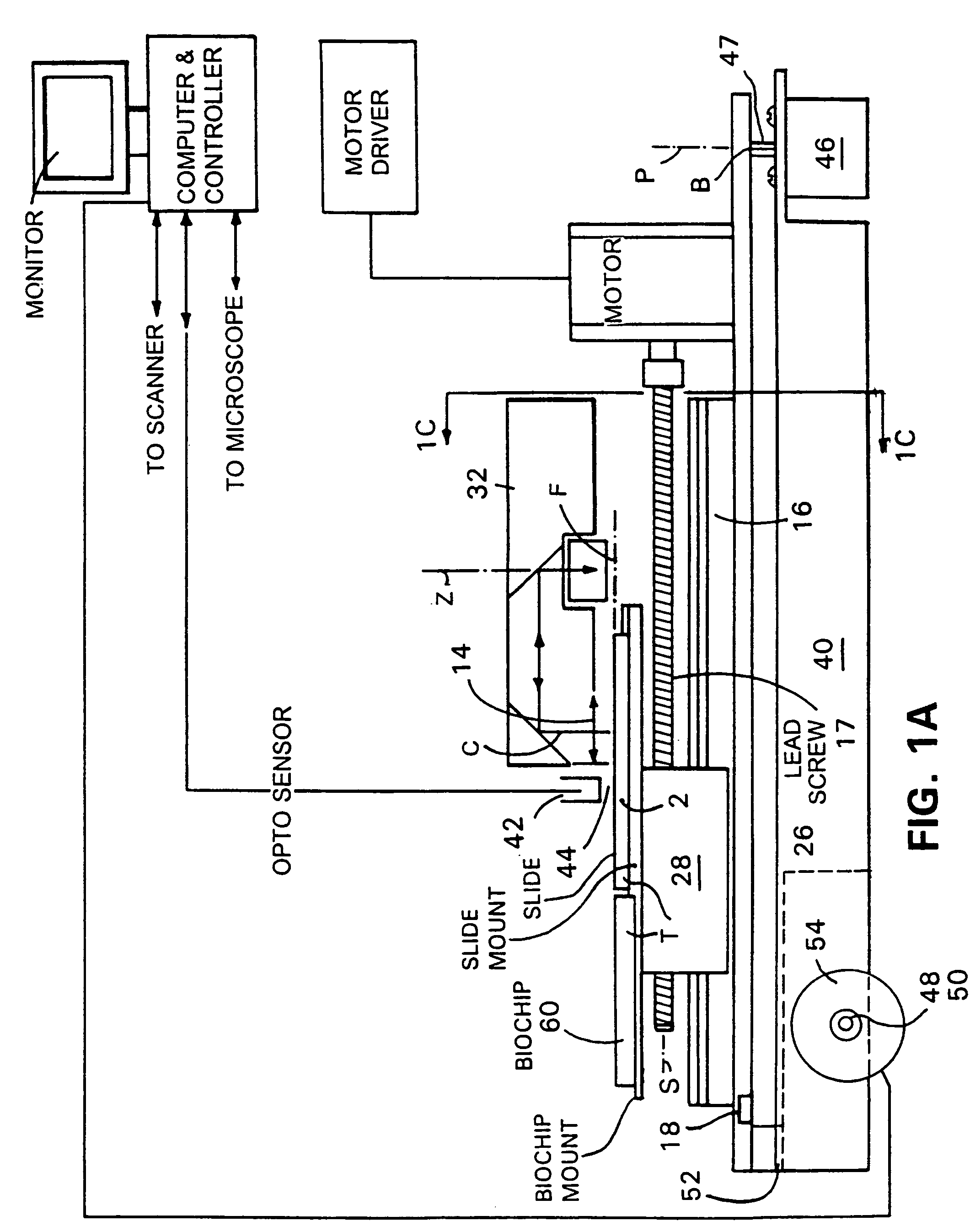
InactiveUS20050285049A1Low costAchieve resolutionPhotometryLuminescent dosimetersMicroscope slideBiological materials
Microscopes, including viewing and other microscopic systems, employ a hinged, tiltable plate to adjust focus on a flat object such as a microscope slide or biochip by motion, achieved by tilting, which is substantially normal to the focus point on the plane of the object. By employing two such tiltable arrangements, relatively long scan lines of e.g., flying objective, single pixel on-axis scanning can be accommodated. The tilting support plate is specifically constructed to provide tailored locations for different objects in series along the Y axis of the plate. The plate can accommodate heaters and cooled plates and / or the flat object being examined. In a fluorescence scanning microscope, locations are specifically adapted to receive microscope slides and biochip cartridges such as Affymetrix's “Gene Chip®”. A scanning microscope under computer control, employing such a focusing action, enables unattended scanning of biochips with a simple and economical instrument. Also shown are flexure-mounting of a support plate to define the hinge axis, techniques for automatically determining position and focus, and a rotatably oscillating flying micro-objective scanner combined with the tilting plane focus system. Construction and control techniques are shown that realize simple and accurate focusing. Methods of examination of biological materials are disclosed. Simple and efficient focused scanning with a flying micro-objective of ordered arrays of nucleotides and nucleic acid fragments carried upon a microscope slide or other substrate is disclosed. Quantified fluorescence imaging is economically achieved by combined use of the described scanning and focusing arrangement and use of simple and accurate calibration modules respectively for example for Affymetrix's “Gene Chip” microarray modules and for microscope slides.
Owner:AFFYMETRIX INC
Ultra-short pulse time waveform and chirp rate measuring device and method
ActiveCN104697647AAchieve resolutionRealize analysisInstrumentsMeasurement devicePhotovoltaic detectors
An ultra-short pulse time waveform and chirp rate measuring device comprises a first coupling mirror, a second coupling mirror, a spectroscope, a first reflecting mirror, a second reflecting mirror, a third reflecting mirror, a cross-correlation crystal, a frequency doubling crystal, a fourth reflecting mirror, a fifth reflecting mirror, a diffraction element, a photoelectric detector and a computer. Front-edge and rear-edge high-resolution ratio measuring of ultra-short pulses is achieved through a cross-correlation method to obtain time waveforms and pulse widths. Ultra-short pulse spectrum measuring is achieved through diffraction elements orthogonal to the time axis to obtain the spectrum width, and accordingly, the chirp rate of measured pulses can be obtained based on the pulse width and the spectrum width, the requirement of physical experiments for the time waveform measuring and the requirement of an Ultra-short pulse laser system for measuring of the chirp rate are met conveniently.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Active matrix device and method of driving
ActiveUS10078986B2Reducing complexity and number of transistorImprove device performanceStatic indicating devicesLaboratory glasswaresDielectricActive matrix
An active matrix electro-wetting on dielectric (AM-EWOD) device includes a plurality of array elements arranged in an array, each of the array elements including array element circuitry, an element electrode, and a reference electrode. The array element circuitry includes an actuation circuit configured to apply actuation voltages to the electrodes, and an impedance sensor circuit configured to sense impedance at the array element electrode to determine a droplet property at the array element. The impedance sensor circuit is operated by perturbing a potential applied to the reference electrode. The AM-EWOD device includes a common row addressing line. The impedance sensor circuit further is operated by supplying voltage signals over the common addressing line to effect both a reset operation and an operation for selecting a row in the array to be sensed. The circuitry isolates the array element from the actuation voltage during operating the impedance sensor circuit.
Owner:SHARP LIFE SCI EU LTD
Laser range sensor system optics adapter and method
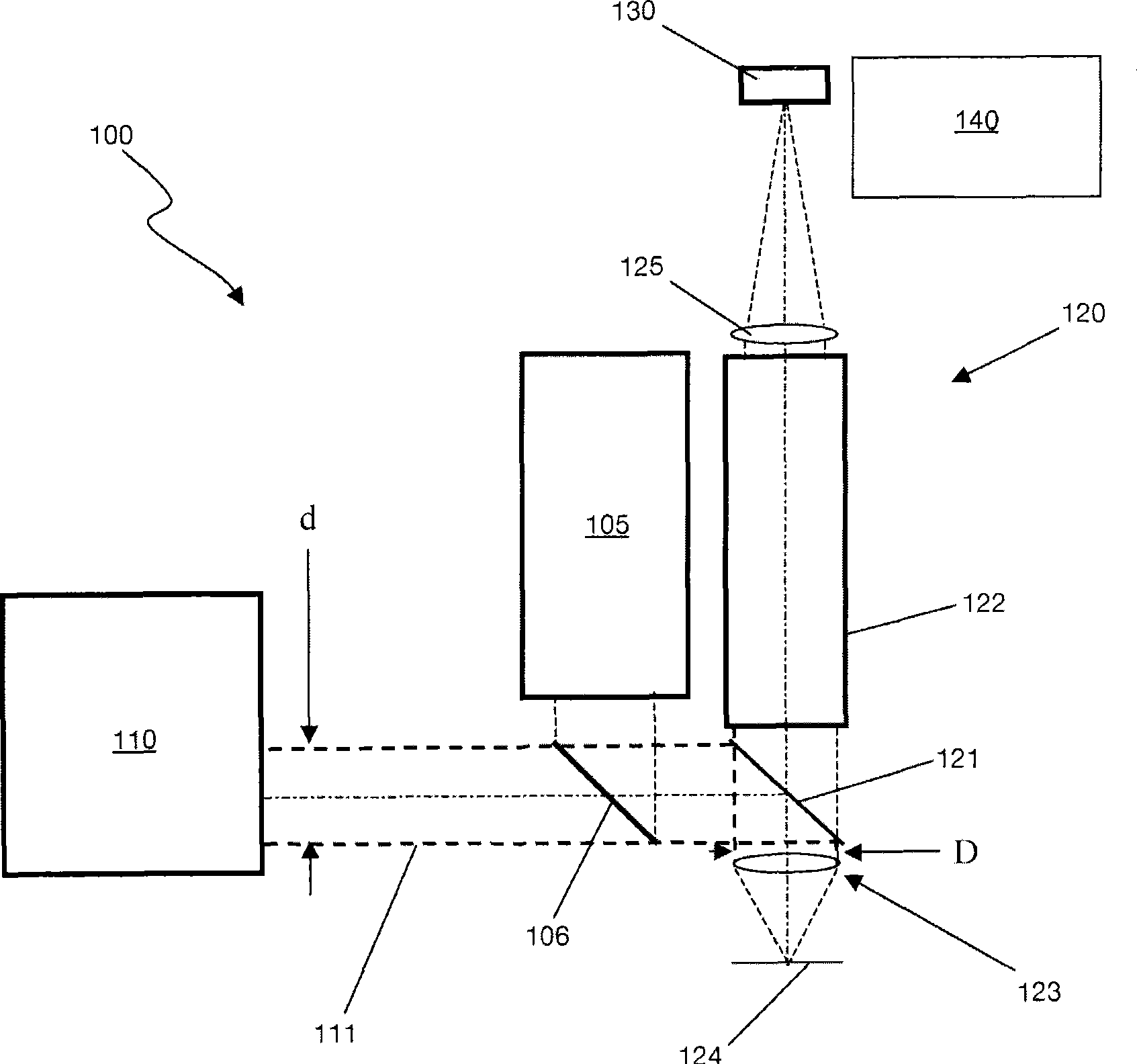
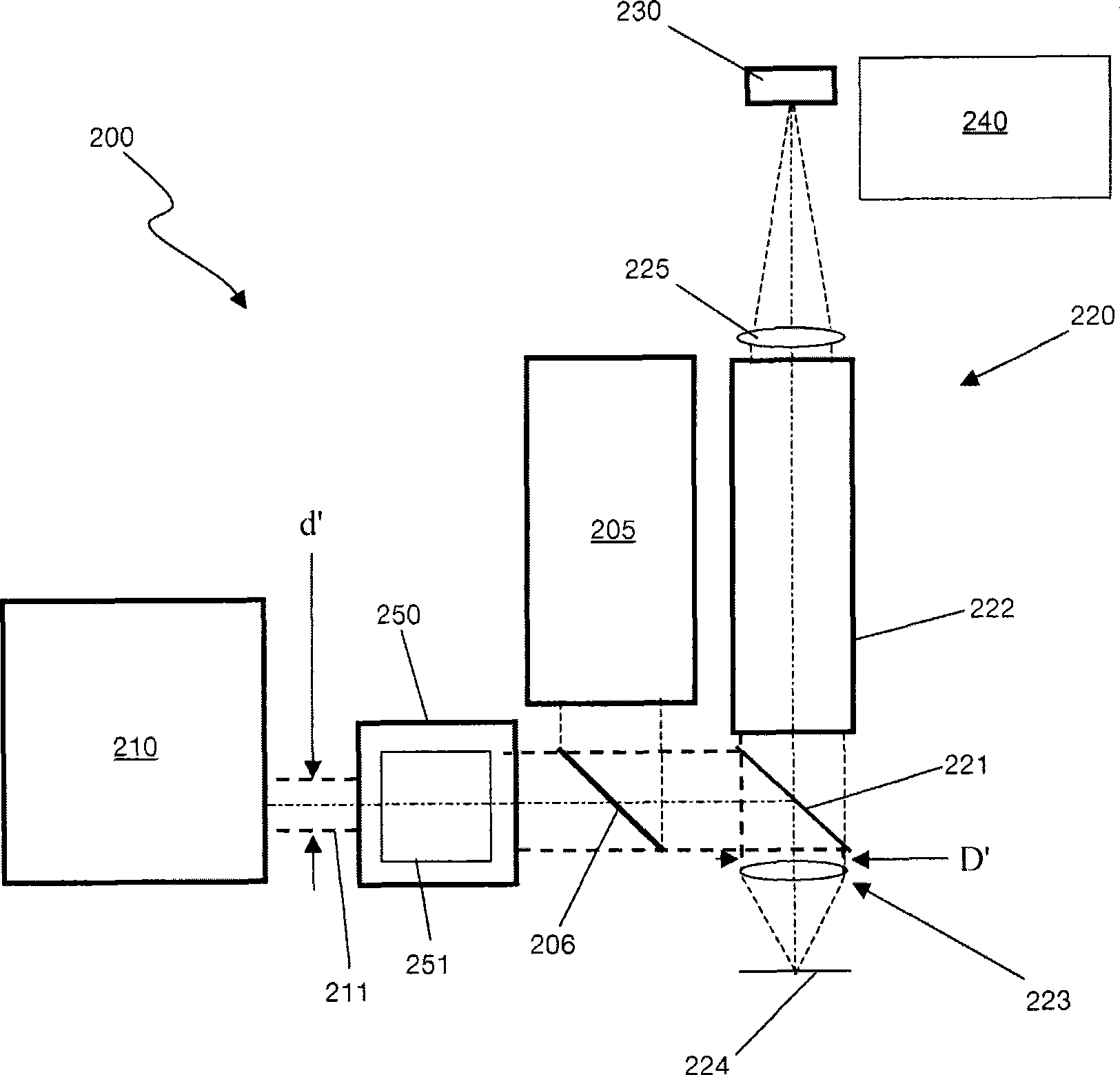
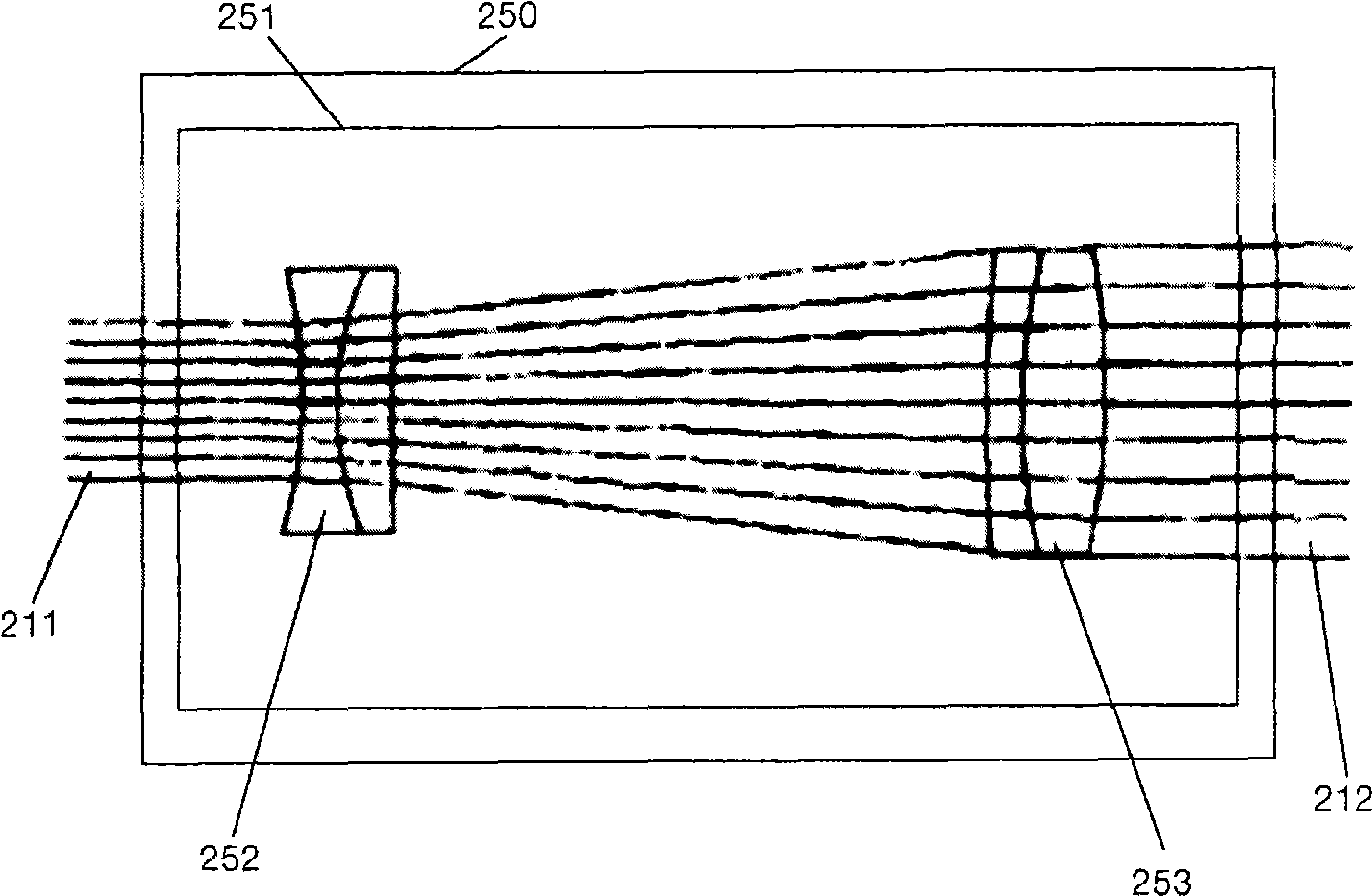
InactiveCN101490504AAchieve high sensitivityAchieve resolutionOptical rangefindersCamera lensLaser ranging
An adapter and a method for through the lens (TTL) laser range sensor probes enable use of a TTL probe of a given exit pupil size to be used with a shared objective lens requiring a entrance pupil size, as entered from the laser range sensor, that is different from the TTL probe exit pupil size. Embodiments of the adapter include optics, such as a first lens and a resolving second lens that expand or contract the TTL laser radiation depending on whether the first lens is a diverging, a negative focal length lens, or a converging, positive focal length lens, and the second lens is converging or diverging, respectively, in a Galilean arrangement. Embodiments also provide a Keplerian arrangement, can function with non-collimated radiation, and can include mirrors to yield a more compact adapter. Additional embodiments include at least one adjustable lens element between the first and second lenses.
Owner:QUALITY VISION INT
Time interpolation flash adc having automatic feedback calibration
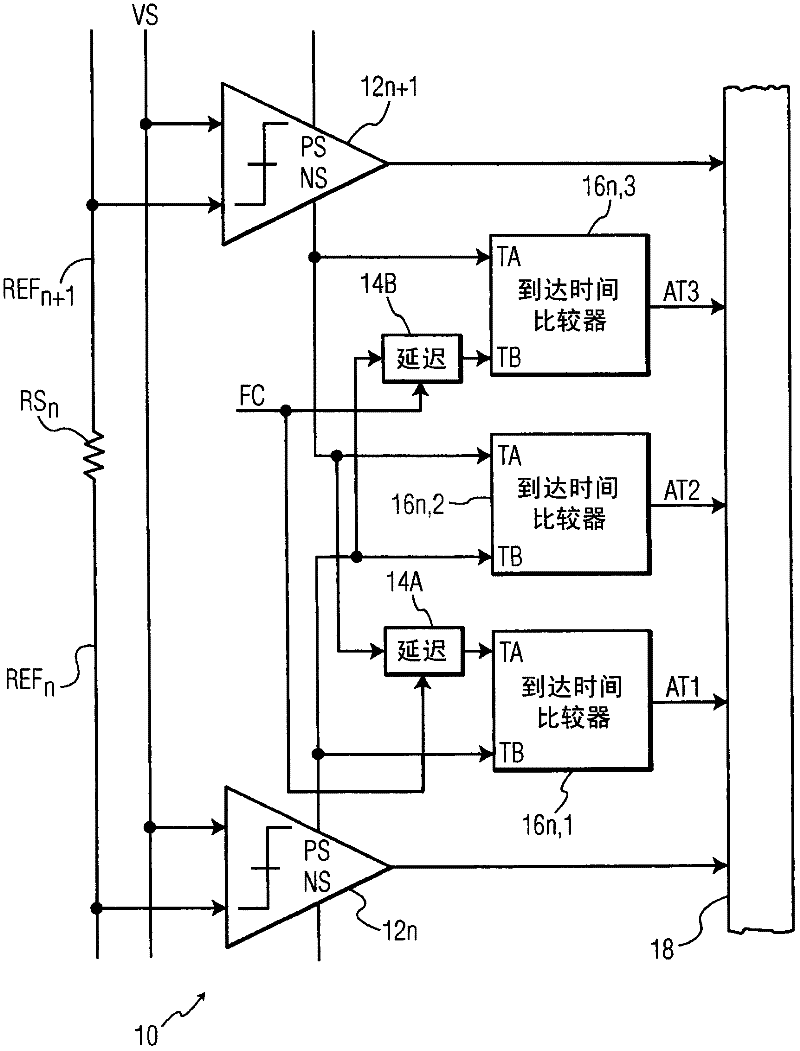
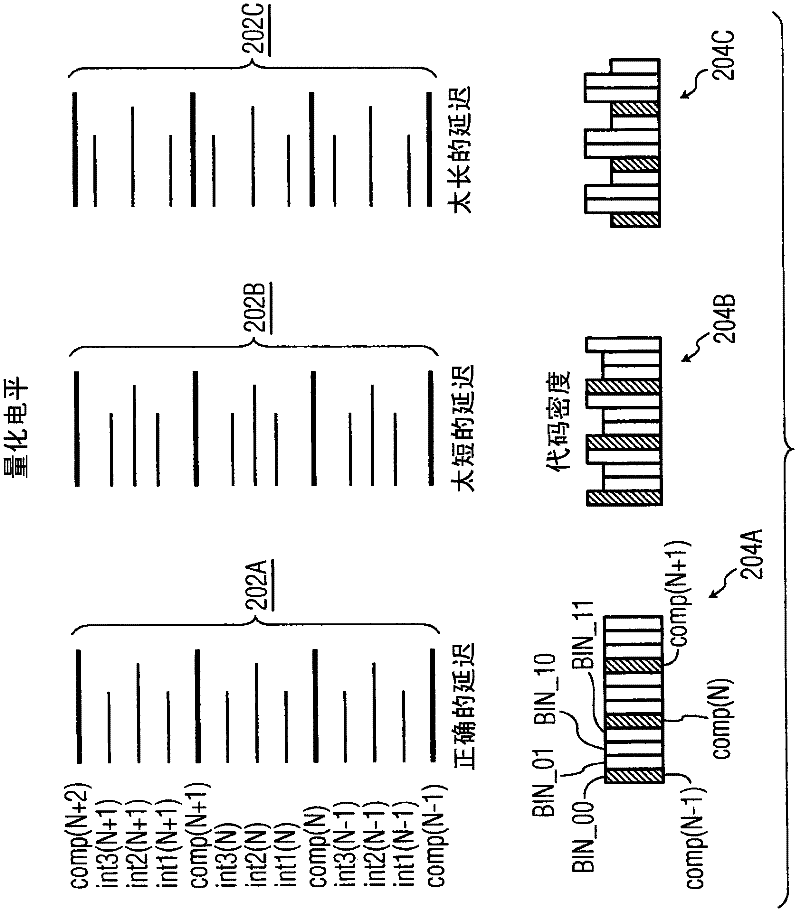
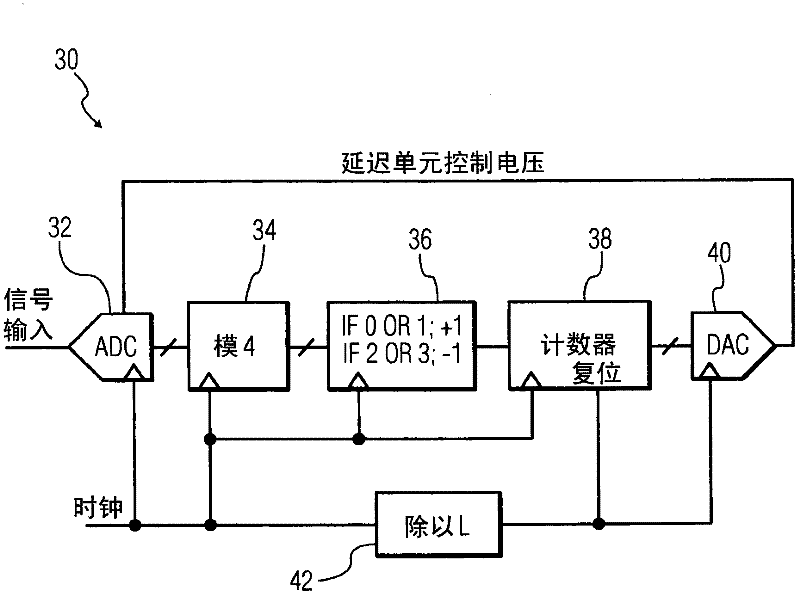
InactiveCN102210104AHigh resolution bitsAchieve resolutionAnalogue-digital convertersLeast significant bitArrival time
An input signal is compared to 2N - 1 reference voltages to generate 2N - 1 corresponding binary valued comparison signals, delaying at least one of the comparison signals by a variable delay and detecting a difference in arrival time between the delayed signal and another comparison signal. A time interpolation signal encoding a plurality of bins within a least significant bit quantization level is generated, based on the detected difference in arrival time. An M-bit output data is generated based on the comparison signals and the time interpolation signal. A non-uniformity of a code density of the M-bit output data is detected, and based on the detecting the delaying is varied.
Owner:NXP BV
Image processing method and apparatus, and image forming apparatus
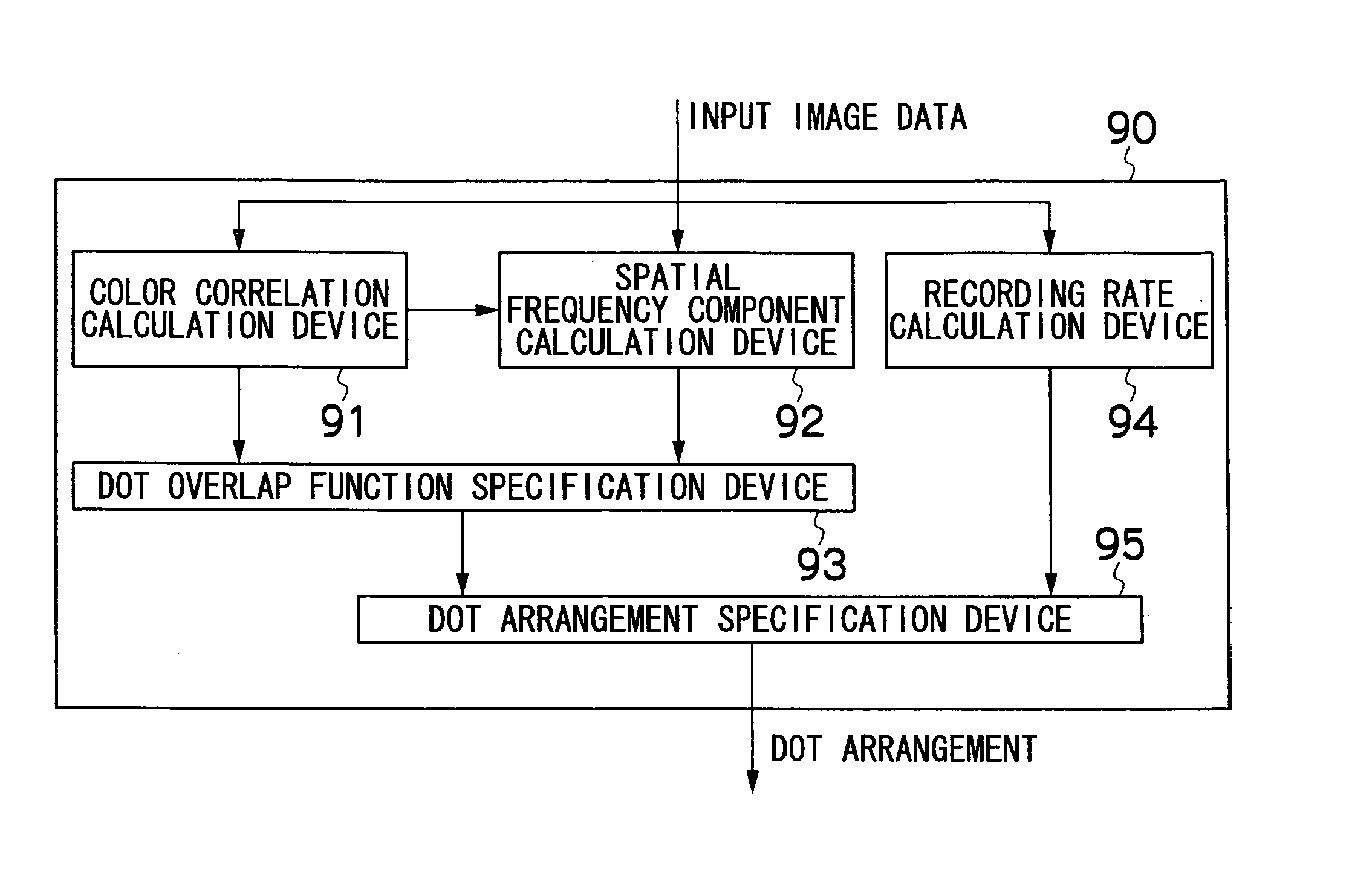
InactiveUS20050219295A1High-quality image recordingStrong visual impactOther printing apparatusPictoral communicationImaging processingComputer science
The image processing method for specifying dot arrangements for respective ink components according to image data, when forming an image on a recording medium by means of dots of inks of n colors, where n is any positive integer, the method comprises the steps of: calculating color correlation and spatial frequency components from the image data; specifying a dot overlap function for controlling overlapping between dots of the ink components, according to the calculated color correlation and spatial frequency components; calculating an ink recording rate of each of the inks from the image data; specifying the dot arrangement of a first ink component by means of a prescribed method, according to the ink recording rate; and determining a dot arrangement for the inks of the n colors, in such a manner that, taking k to be an integer where 2≦k≦n, the dot arrangement of the kth ink component is specified according to the ink recording rate of the kth ink component, and the previously specified dot arrangement and dot overlap function of the first ink component through to the (k−1)th ink component.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Airborne thinned array antenna downward-looking three-dimensional imaging radar system and imaging method
ActiveCN103389497AImplement motion compensationHigh precision motion compensationRadio wave reradiation/reflectionPhysicsThinned array
The invention discloses an airborne thinned array antenna downward-looking three-dimensional imaging radar system and imaging method. The airborne thinned array antenna downward-looking three-dimensional imaging radar system comprises an aerial carrier platform, a thinned array antenna system and a distributed position and orientation system (POS). The aerial carrier platform is used for carrying the thinned array antenna system and the distributed POS, and array antennae can be distributed in the middle and on two sides of an aircraft. The thinned array antenna system is composed of a plurality of densely distributed sub arrays arranged in the middle and one or two sub arrays located on two sides. Accurate measuring of the multi-phase center relative space position of the array antennae can be achieved through the distributed POS. In the direct downward-looking mode, the observation width is broadened through a scanning mode which combines a Scan SAR mode and a Sweep SAR mode. When the aerial carrier operates in the upper air, a cross rail direction equivalent array can be obtained in a thinned re-navigation mode with Barker codes serving as the sampling criterion, and the cross rail direction resolution is improved. The array antennae in space thinned distribution are adopted in the cross rail direction of the aerial carrier and high-resolution wide-width three-dimensional imaging of the observation scenes is achieved.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Time domain-based spectrum detection system
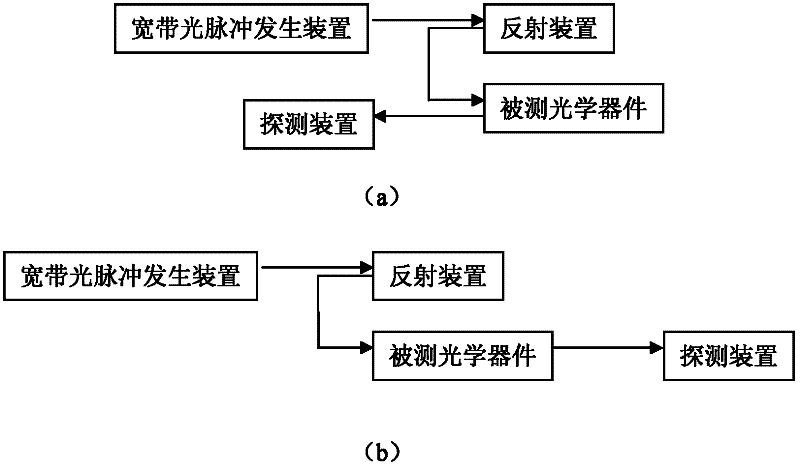
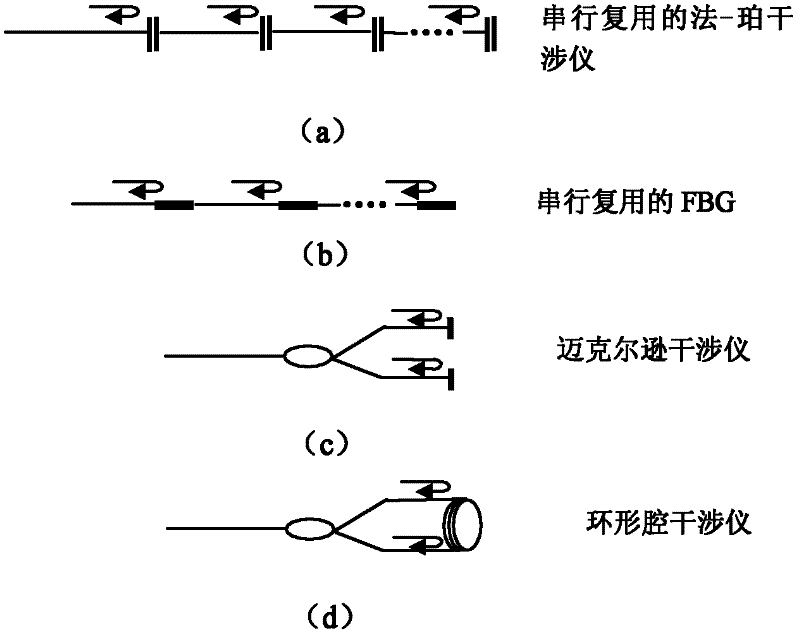
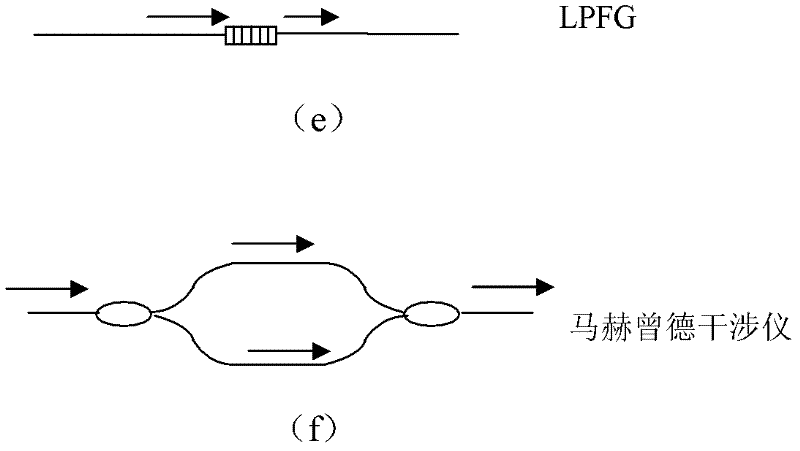
InactiveCN102445326AAchieve resolutionSpectral detection implementationTesting optical propertiesTime domainBroadband
The invention provides a time domain-based spectrum detection system, which can be used for performing spectrum detection on a serial multiplex detected optical device. In the detection system, a reflection device comprises n reflection units at different spatial positions; each reflection unit is used for reflecting optical pulses of different wavelengths; n is an integer of over 2; broadband optical pulses generated by a broadband optical pulse generating device are transmitted to the reflection device; the reflection device is used for reflecting the received broadband optical pulses by using the reflection units at different positions to form optical pulse strings which correspond to the optical intensity of different wavelengths at different positions on a time domain; and a detection device is used for detecting the optical intensity of each pulse in the optical pulse strings which are reflected or transmitted by the detected optical device to obtain a spectrum of the detected optical device. In the system provided by the invention, discrete optical pulse strings on the time domain formed by the broadband optical pulses reflected by the reflection device enter the detected optical device, so that the spectrum information of the detected optical device can be distinguished on the time domain.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Ultrahigh numerical aperture lithography imaging polarization compensation apparatus and method thereof
ActiveCN103869626APrecise Control of Polarization StateImprove photolithographic effectPhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusSilicon chipHigh numerical aperture
The invention discloses an ultrahigh numerical aperture lithography imaging polarization compensation apparatus. The apparatus comprises a light source used for providing an illumination light beam, an illumination unit used for adjusting the illumination light beam to an exposed light beam and irradiating a mask plate, a projection objective used for imaging an imaging light beam transmitting the mask plate to a silicon chip, and a polarization compensation device used for the polarization modulation of the exposed light beam or / and the imaging light beam, and positioned between the illumination unit and the mask plate or between the projection objective and the silicon chip.
Owner:SHANGHAI MICRO ELECTRONICS EQUIP (GRP) CO LTD
Multi-line laser radar
ActiveCN110161512ARealize 3D space scanning detectionAchieve resolutionElectromagnetic wave reradiationLaser transmitterRadar
The invention relates to a multi-line laser radar. The multi-line laser radar comprises a laser emitting device which comprises at least two laser emitters and is used for emitting multiple paths of emergent laser light, a minor reflector used for dividing the emergent laser light into multiple beams of laser light and reflecting the multiple beams of laser light to a galvanometer at a specific angle, the galvanometer used for reflecting the emergent laser light reflected by the minor reflector again to a target object in a detection field of view, a main reflector used for receiving the reflected laser light and reflecting the reflected laser light to a laser detection device, a receiving lens used for collecting the reflected laser light to the laser detection device, and the laser detection device used for receiving the reflected laser light and outputting a detection signal, wherein the reflected laser light is the laser light returned after reflection of the target object; and thegalvanometer and the main reflector rotate synchronously around a central axis. According to the multi-line laser radar, the two-dimensional space scanning detection of the multi-line laser radar canbe realized by only rotating the galvanometer and the main reflector, so that the usage amount of devices is greatly reduced, the structure of the multi-line laser radar is simplified, and the manufacturing cost of a multi-line laser is further reduced.
Owner:SUTENG INNOVATION TECH CO LTD
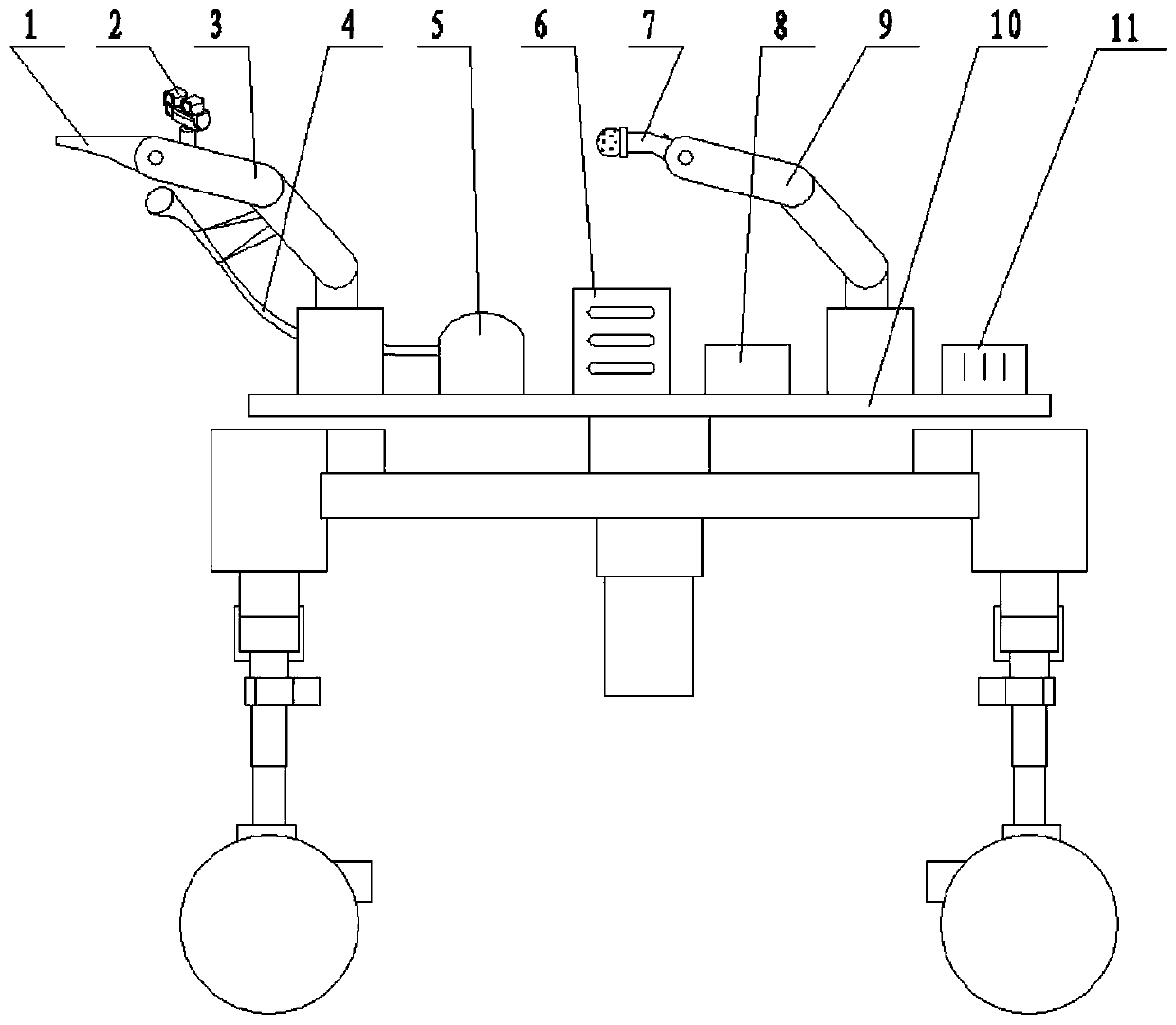
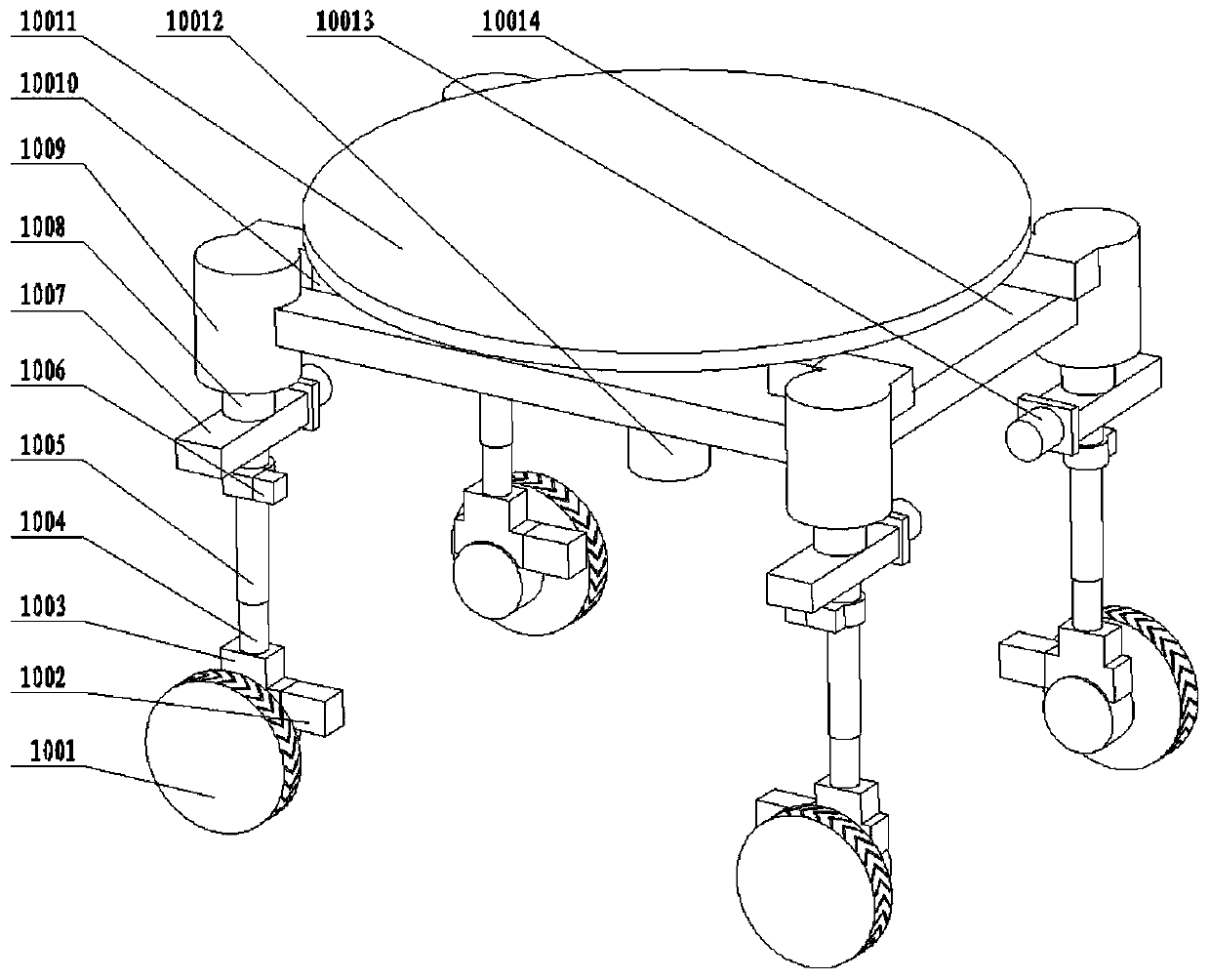
Multifunctional tea picking robot
PendingCN110859087AAchieve resolutionReasonable structureWatering devicesCultivating equipmentsAgricultural engineeringControl engineering
The invention relates to a multifunctional tea picking robot which comprises a picking mechanism, a spraying mechanism, a power device, a dynamic visual recognition system and an omnibearing travelingtrolley. The picking mechanism, the spraying mechanism and the power device are fixed on a top chassis of the omnibearing traveling trolley, the picking mechanism is used for picking tea leaves, thespraying mechanism is used for spraying liquid, and the power device provides compressed air for the picking mechanism; a first rotating shaft motor of the dynamic visual recognition system drives a first rotating shaft to rotate so as to drive a support to rotate around the first rotating shaft, and a second rotating shaft motor drives a second rotating shaft to rotate so as to drive the supportto rotate around the second rotating shaft. The multifunctional tea picking robot has the advantages that the robot is reasonable in integral structure and convenient for operation; the picking mechanism, the spraying mechanism, the dynamic visual recognition system and the omnibearing traveling trolley are adopted for matched running to realize distinguishing and picking of the tea leaves and spraying of liquid like pesticide and water, so that tea picking efficiency is improved; the omnibearing traveling trolley is driven to run by adopting multiple movement mechanisms, thereby being able toadapt to any terrain.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH LIAONING
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com