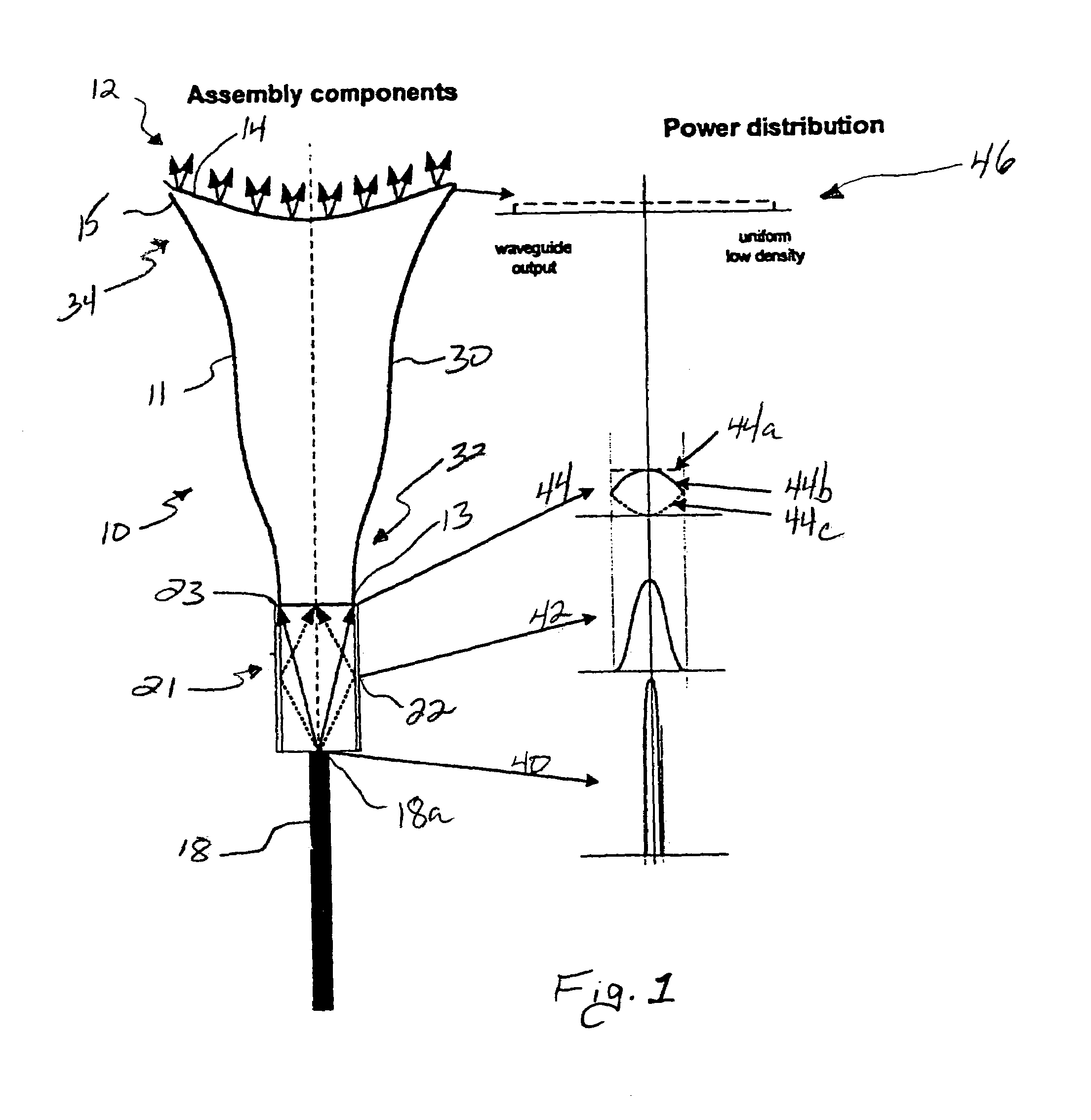
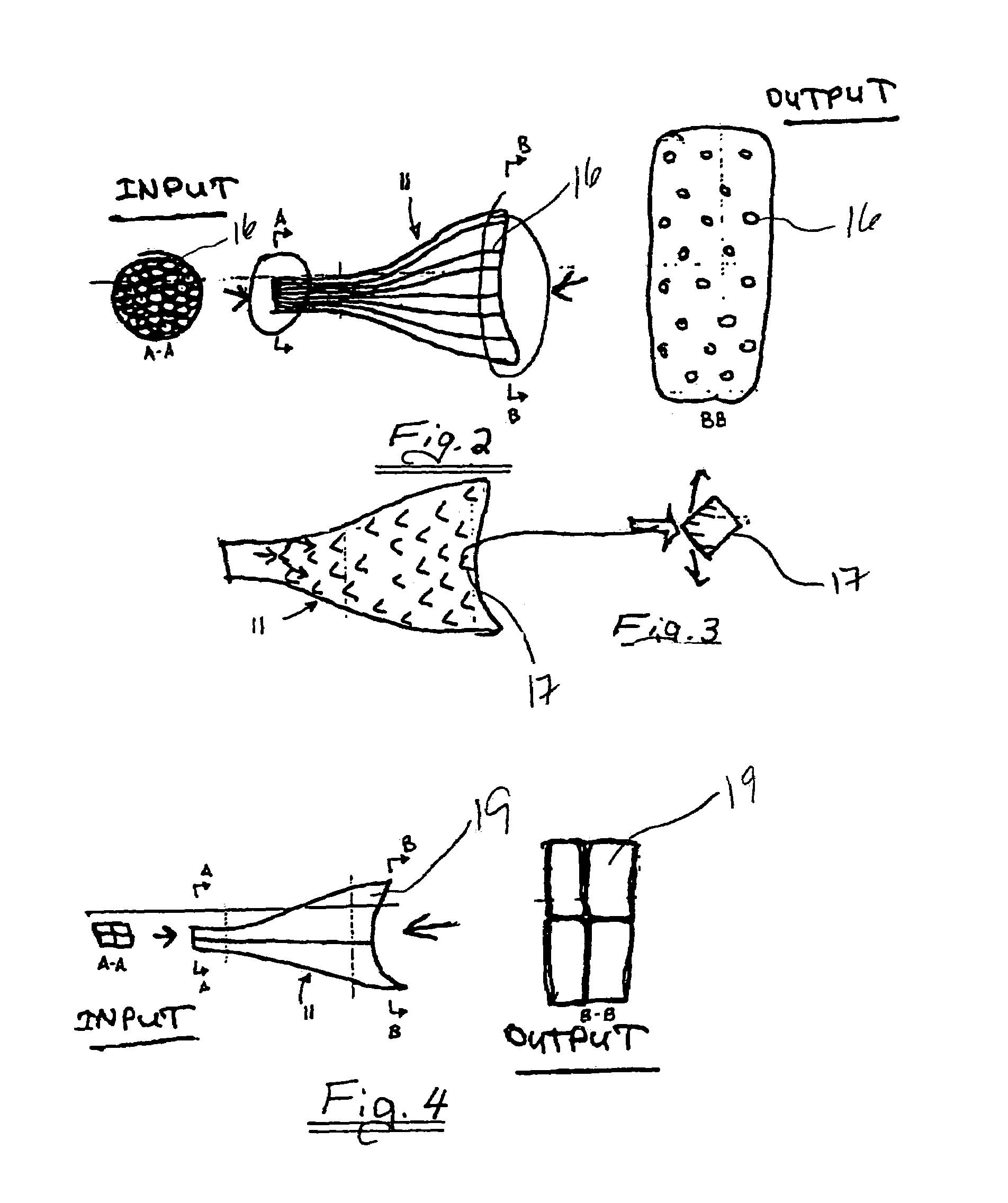
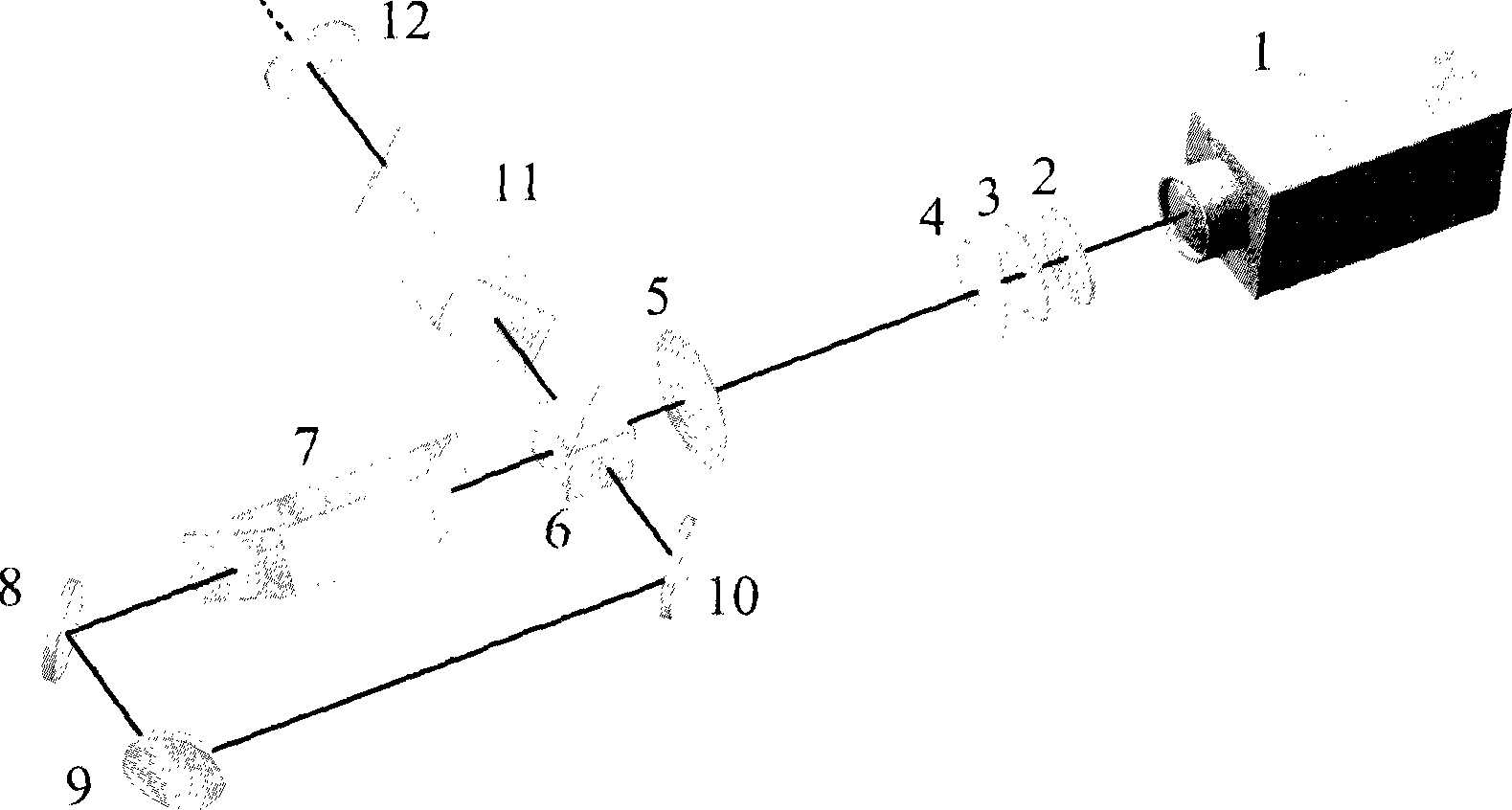
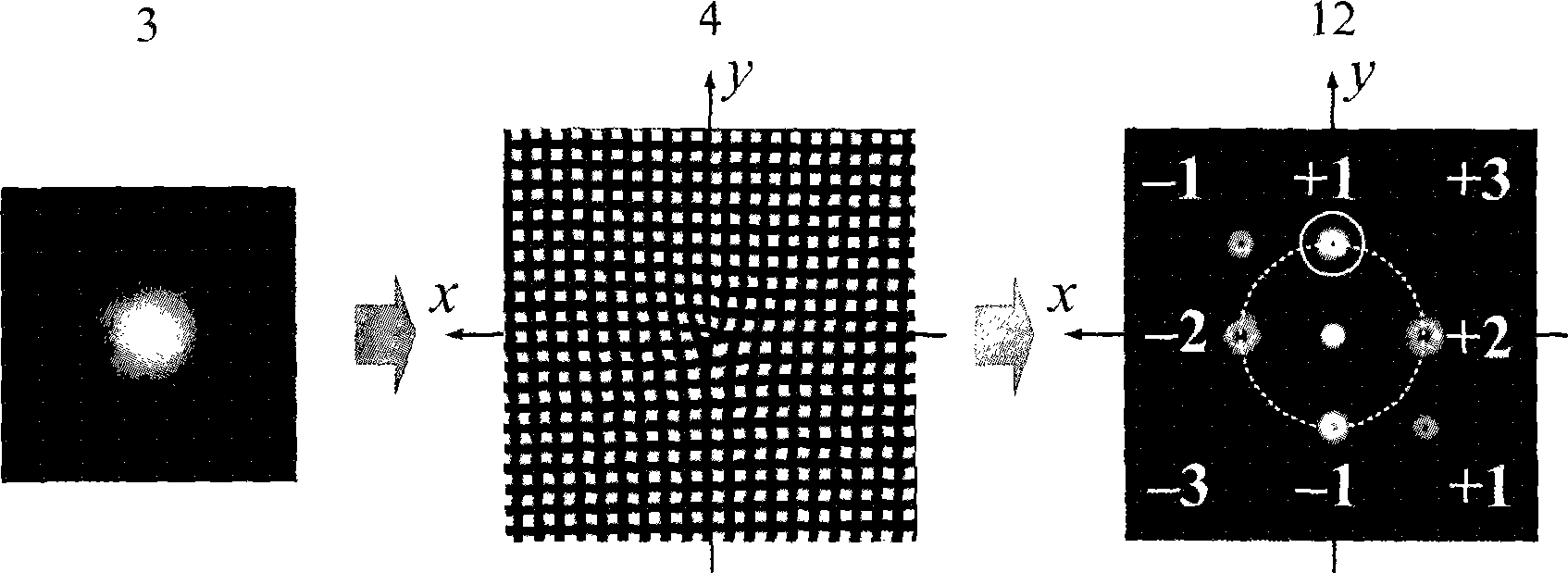
Patents
Literature
3467 results about "Beam splitting" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
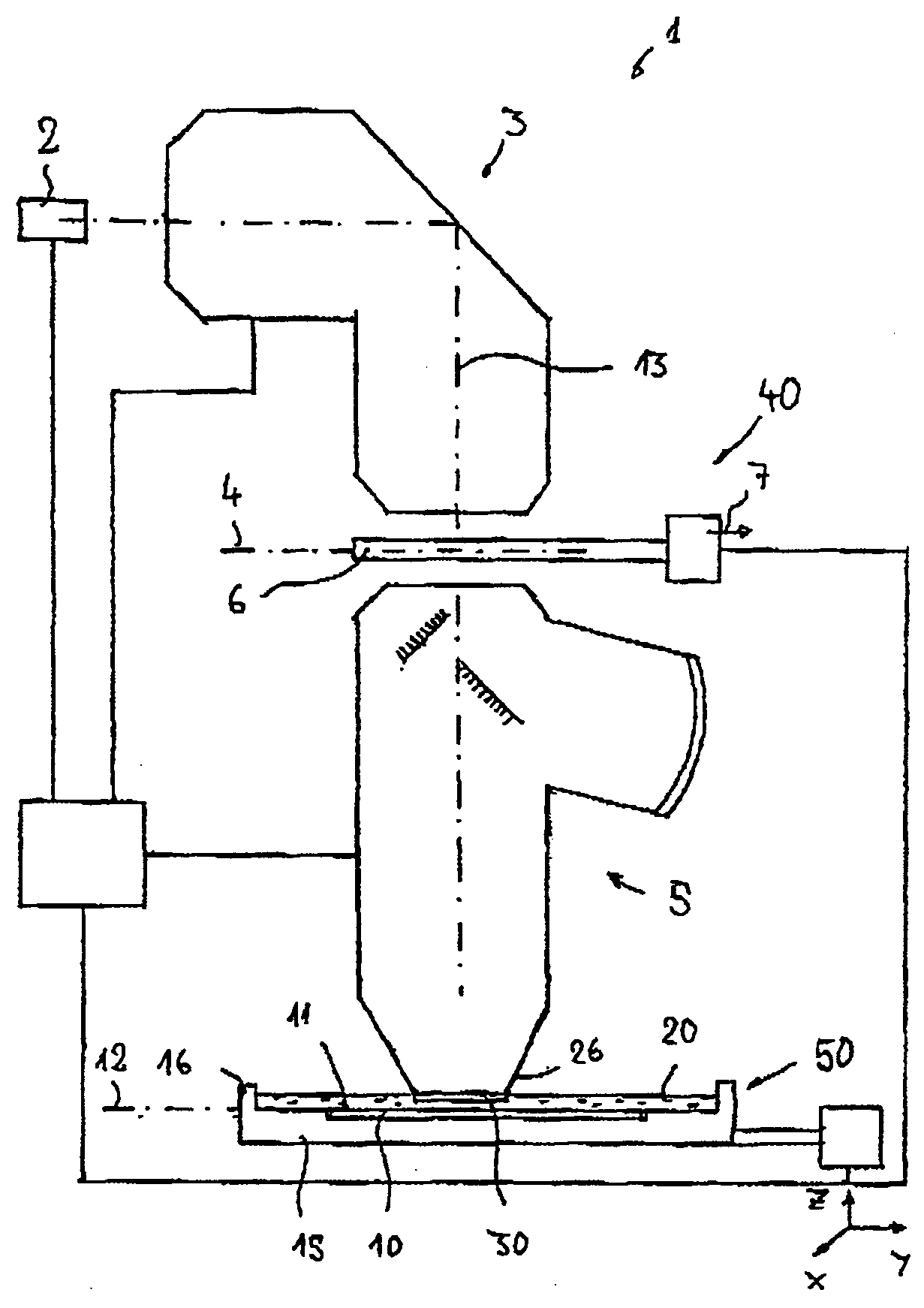
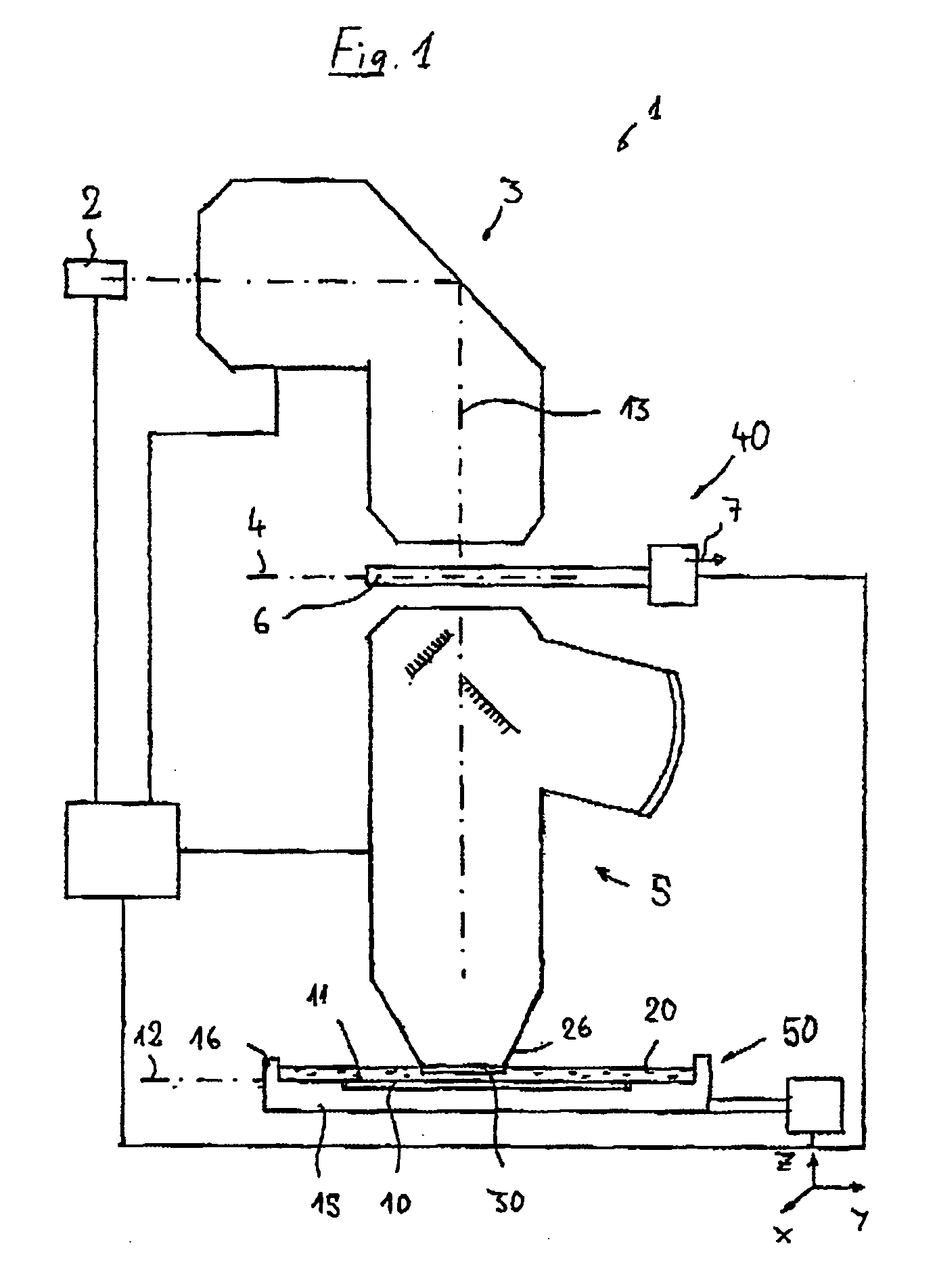
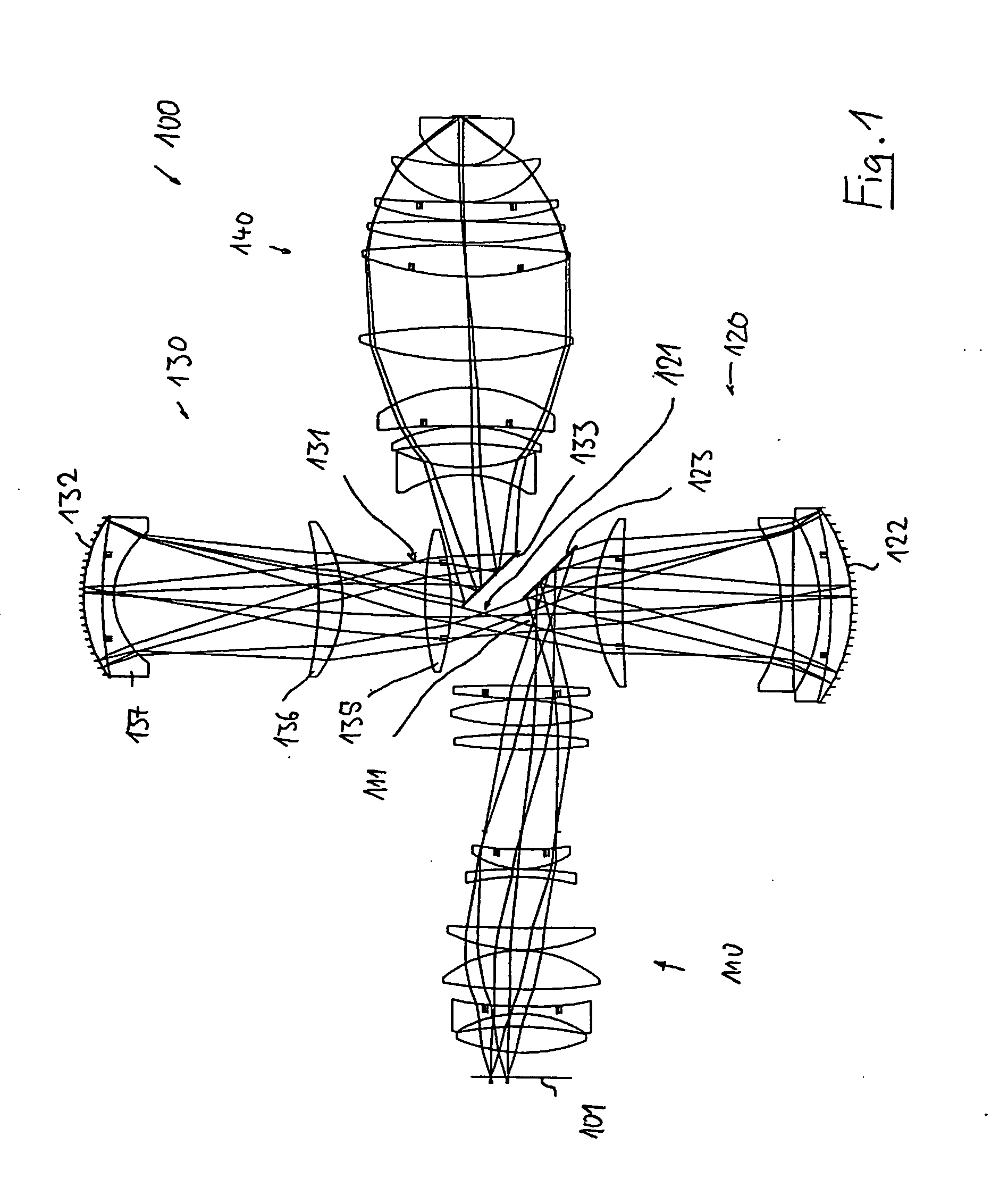
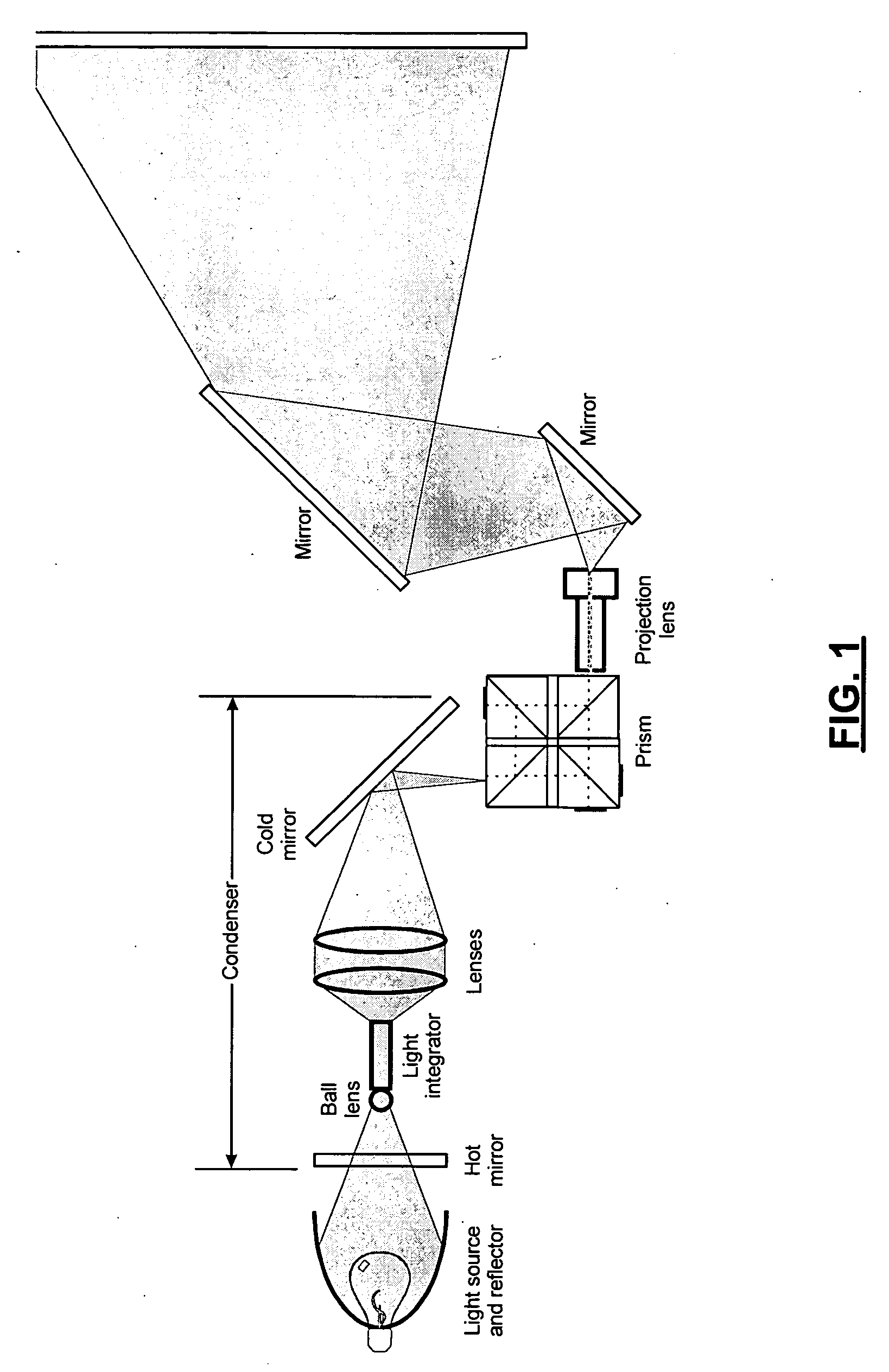
Catadioptric projection objective with geometric beam splitting
InactiveUS20050117224A1Good engineering qualityEasy to installMicroscopesPhotomechanical exposure apparatusIntermediate imageOptical axis
A catadioptric projection objective is used to project a pattern arranged in an object plane of the projection objective into an image plane of the projection objective with the formation of at least one real intermediate image and has an image-side numerical aperture NA>0.7. The projection objective comprises an optical axis and at least one catadioptric objective part that comprises a concave mirror and a first folding mirror. There are a first beam section running from the object plane to the concave mirror and a second beam section running from the concave mirror to the image plane. The first folding mirror is arranged with reference to the concave mirror in such a way that one of the beam sections is folded at the first folding mirror and the other beam section passes the first folding mirror without vignetting, the first beam section and the second beam section crossing one another in a cross-over region.
Owner:CARL ZEISS SMT GMBH
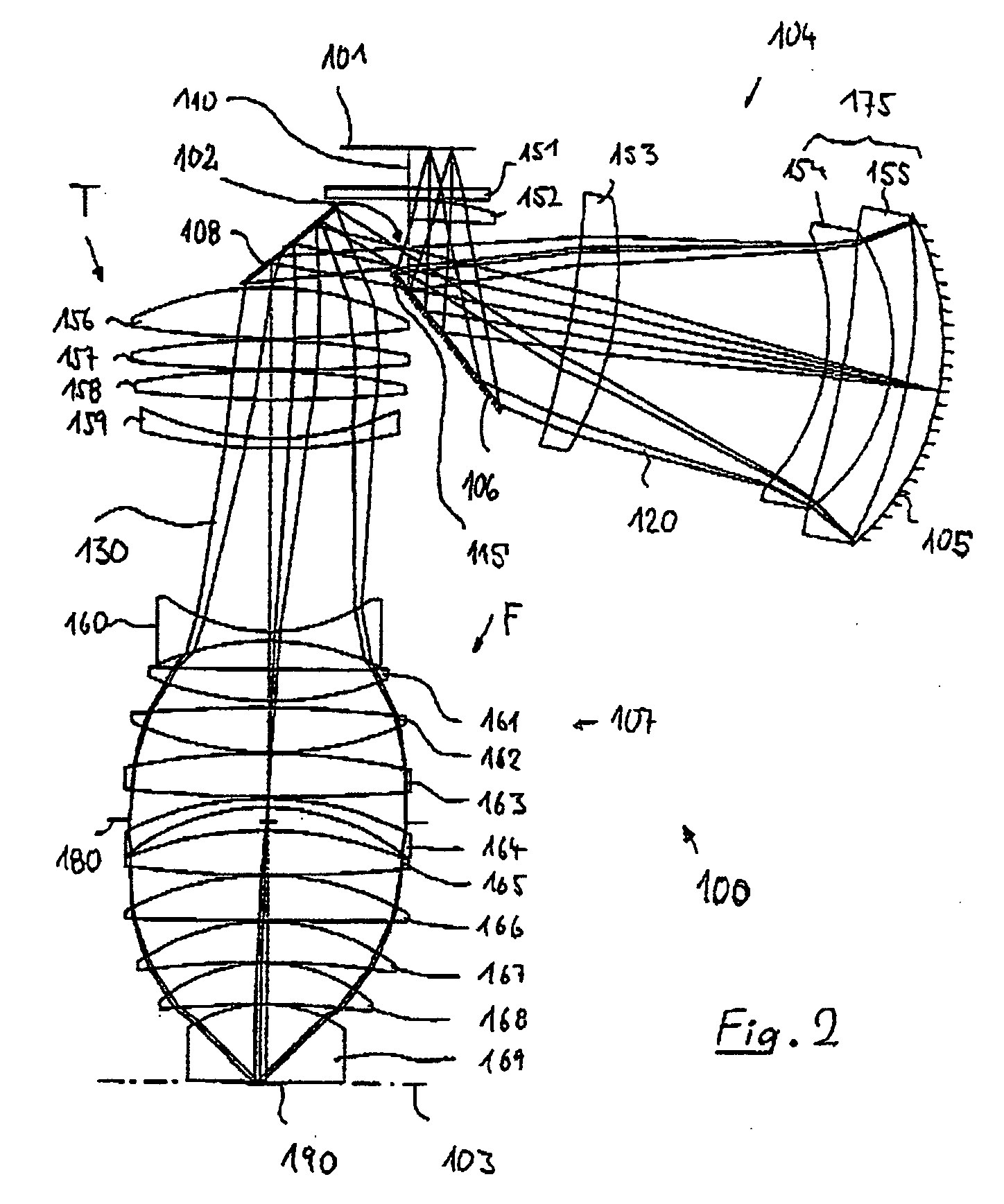
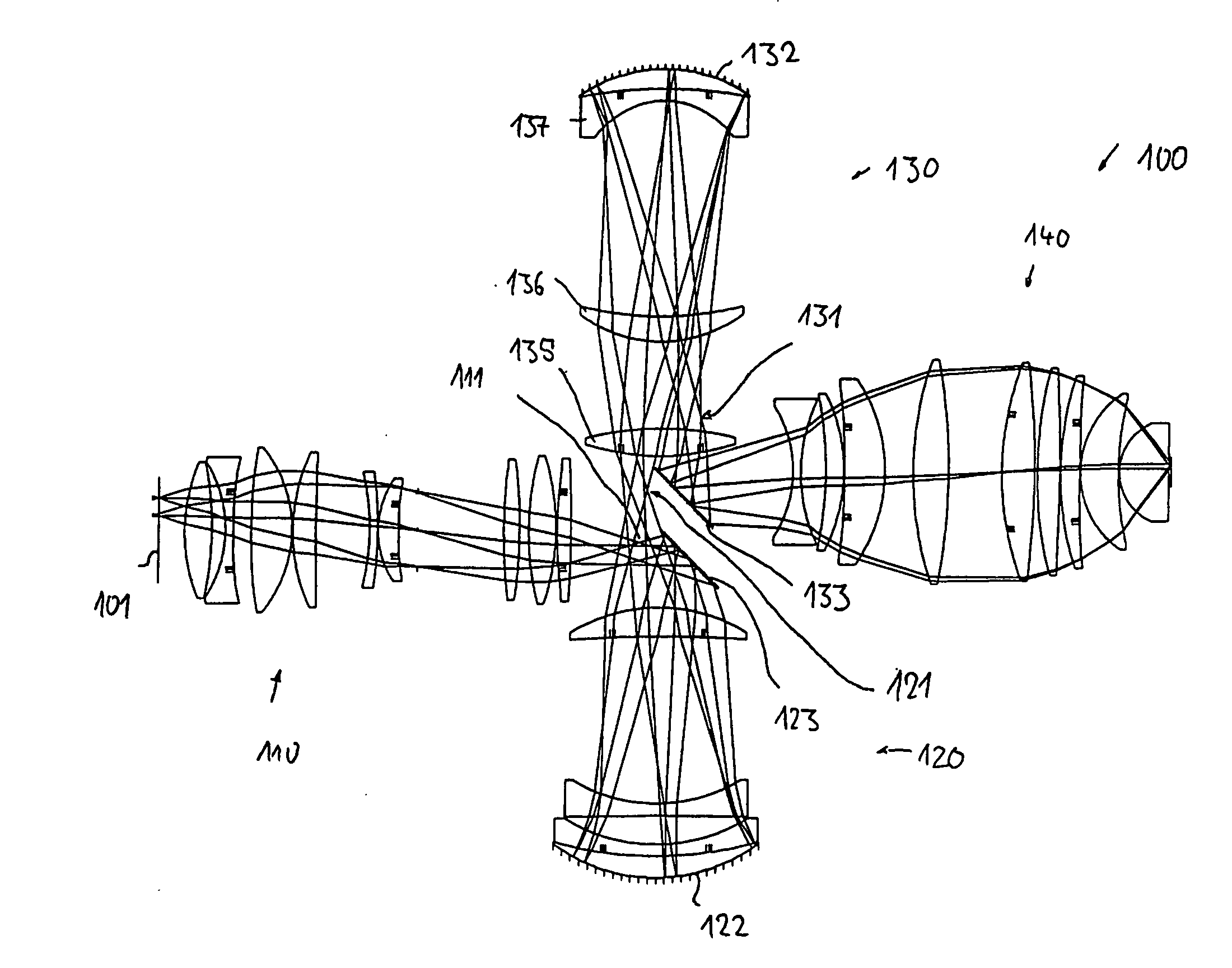
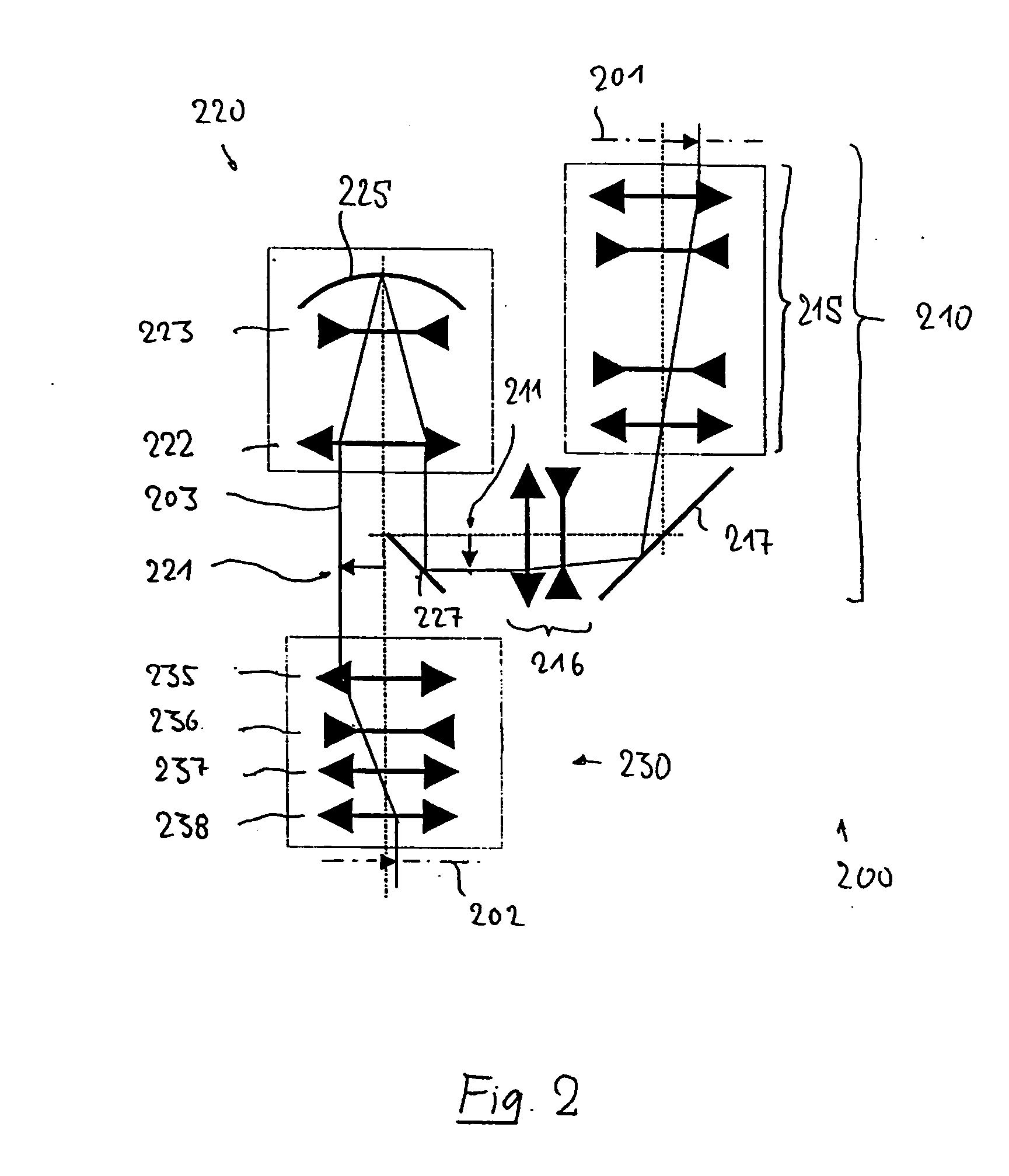
Catadioptric projection objective with geometric beam splitting
InactiveUS20050185269A1Easy to correctCorrect chromatic aberrationMicroscopesPhotomechanical exposure apparatusIntermediate imageBeam splitting
A catadioptric projection objective for imaging a pattern arranged on the object plane of the projection objective, on the image plane of the projection objective, comprising: a first objective part for imaging an object field in a first real intermediate image; a second objective part for producing a second real intermediate image with the radiation coming from the first objective part; and a third objective part for imaging the second real intermediate image on the image plane; wherein at least one of the objective parts is a catadioptric objective part with a concave mirror, and at least one of the objective parts is a refractive objective part and a folding mirror is arranged within this refractive objective part in such a way that a field lens is arranged between the folding mirror and an intermediate image which is closest to the folding mirror.
Owner:CARL ZEISS SMT GMBH
Collimating optical member for real world simulation
A collimating image-forming apparatus comprising a first linear polarizer is disclosed. A first quarter-wave plate is disposed adjacent the first polarizer and has its fast and slow axes at substantially 45° to the plane of polarization of the first polarizer. The apparatus further comprises a beam-splitting curved mirror having a convex surface adjacent the first polarizer and facing towards the first quarter-wave plate, a second quarter-wave plate adjacent the concave side of the curved mirror, the second quarter-wave plate having its having its fast and slow axes oriented with respect to the corresponding axes of the first quarter-wave plate at angles substantially equal to a first integral multiple of 90°, and a reflective-transmissive polarizing member adjacent the second quarter-wave plate. A second linear polarizer is adjacent the reflective-transmissive polarizing member, the second linear polarizer having its plane of polarization oriented with respect to the plane of polarization of the first linear polarizer at an angle substantially equal to a second integral multiple of 90°, both of the multiples being even or both being odd.
Owner:OPTICAL RESOLUTIONS +1
Endoscope system
InactiveUS6790175B1Accurate diagnosisShort timeSurgeryMaterial analysis by optical meansLight guideBeam splitting
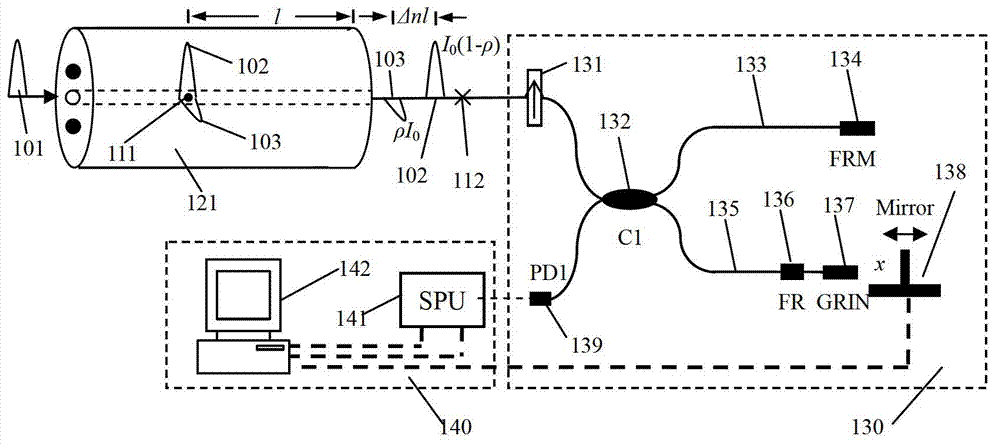
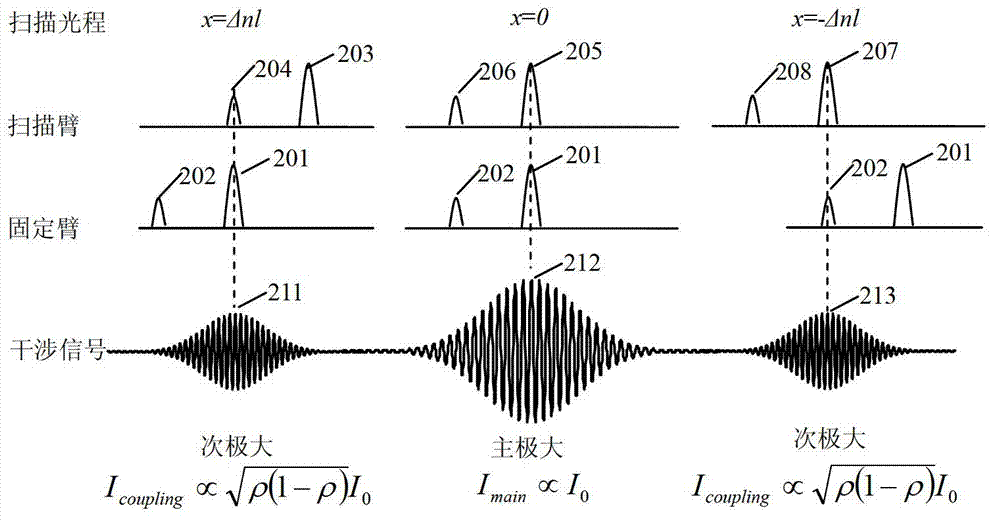
An endoscope system is provided with a light guide including a plurality of optical paths, and a low-coherent light source that emits a low-coherent light beams. The low-coherent light source is provided at a proximal end side of the light guide. The light beams emitted by the low-coherent light source are incident on the plurality of optical paths, respectively. The endoscope system is further provided with an interferometer unit. The interferometer unit includes a beam splitting element that splits each of the low-coherent beams emitted from the distal end of the light guide and emits split one of each of the beams to an object, a reference optical system that guides the other split beam of each of the beams, a reflector unit that reflects the beams guided by the reference optical system toward the beam splitting element, and a light detecting device that detects an interfered beam generated by interference, at the beam splitting element, between the beam reflected by the object and the beam reflected by the reflector unit. The endoscope system is further provided with a driving unit that moves the interferometer unit toward / away from the object, and a signal processing system that generates a tomogram based on signals detected by the light detecting device.
Owner:ASAHI KOGAKU KOGYO KK
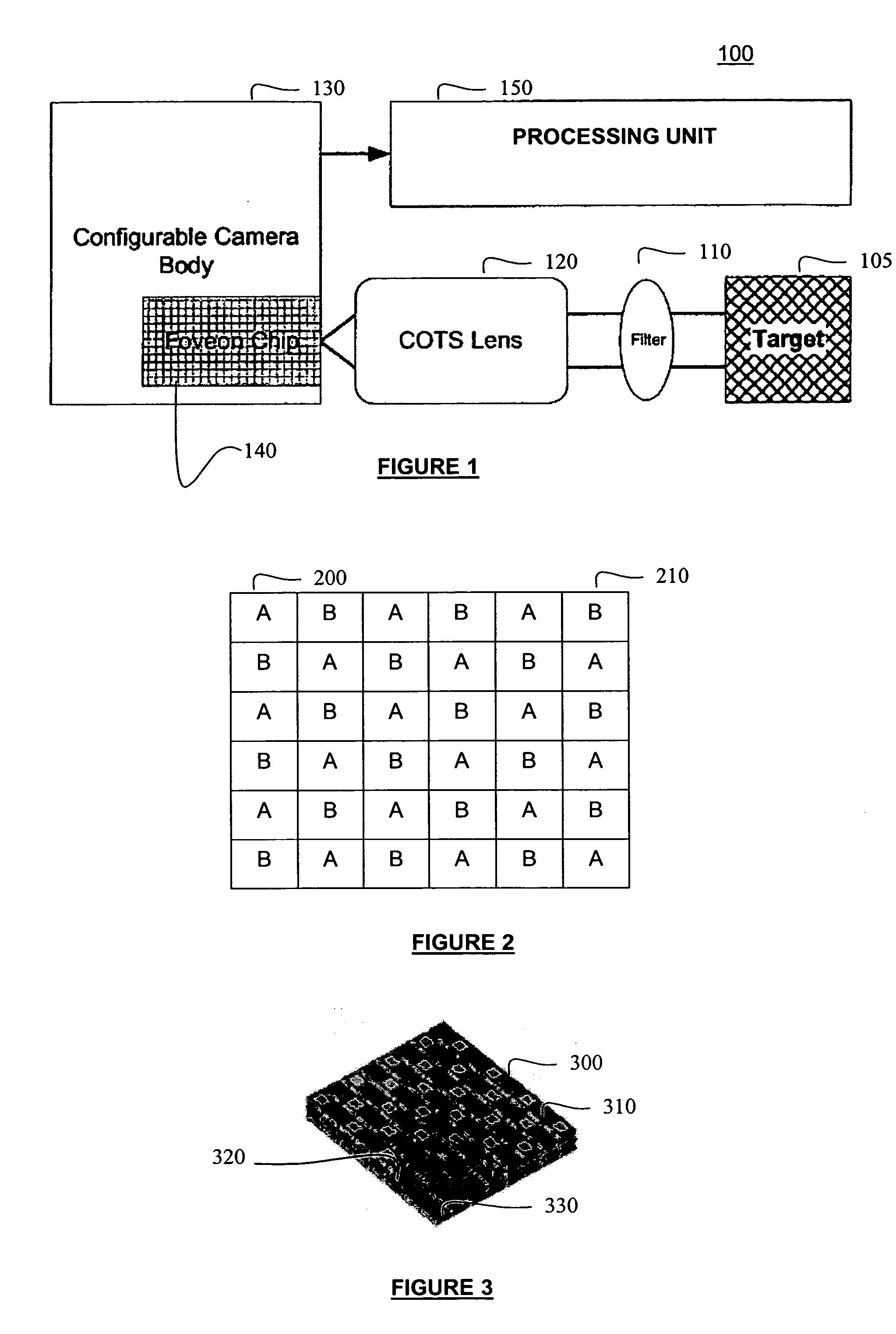
Single camera multi-spectral imager
ActiveUS20070159541A1Improve discriminationTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsMulti bandSpectral bands
An imaging system has a single focal plane array that does not require the precise alignment of multiple cameras relative to one another. It incorporates a multi-band, band pass filter that includes filter elements corresponding to pixel regions of a detector within a camera. The imaging system may further incorporate a detector that vertically discriminates among radiation in different spectral bands incident on an image plane of the detector. In this manner, spectral content may be determined in each spatial region without the need for beam splitting or multiple cameras. The filter itself may further comprise different filter elements, for example, filter elements A and B arranged in a checkerboard pattern, where filter element A passes different spectral bands than filter element B. In this manner, multi-spectral, high resolution images may be generated using a single camera that significantly improves upon image discrimination as compared to, for example, the Bayer color filter array pattern. The single camera implementation is well suited for incorporation into marine, land and air vehicles.
Owner:BAE SYST INFORMATION & ELECTRONICS SYST INTERGRATION INC
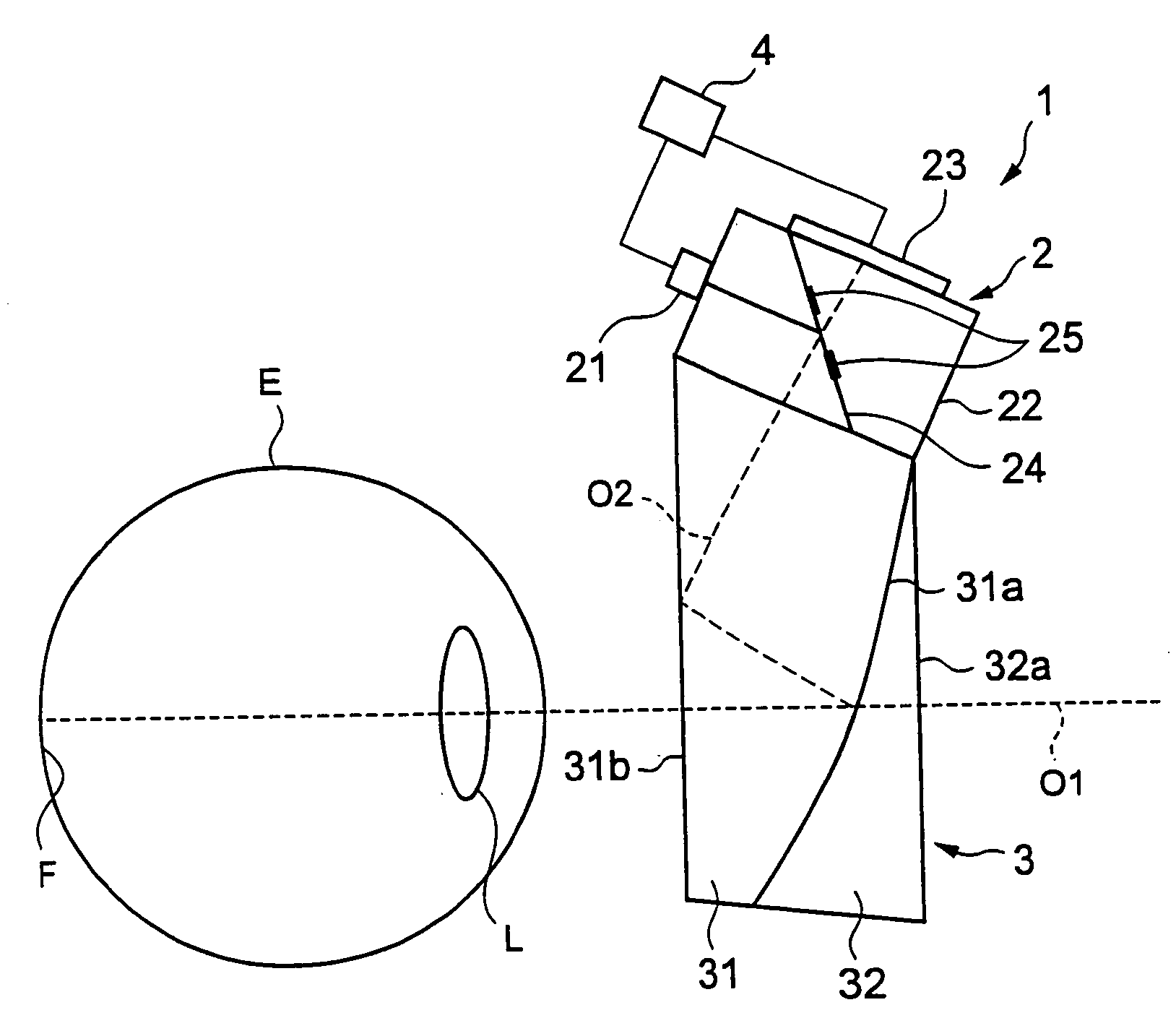
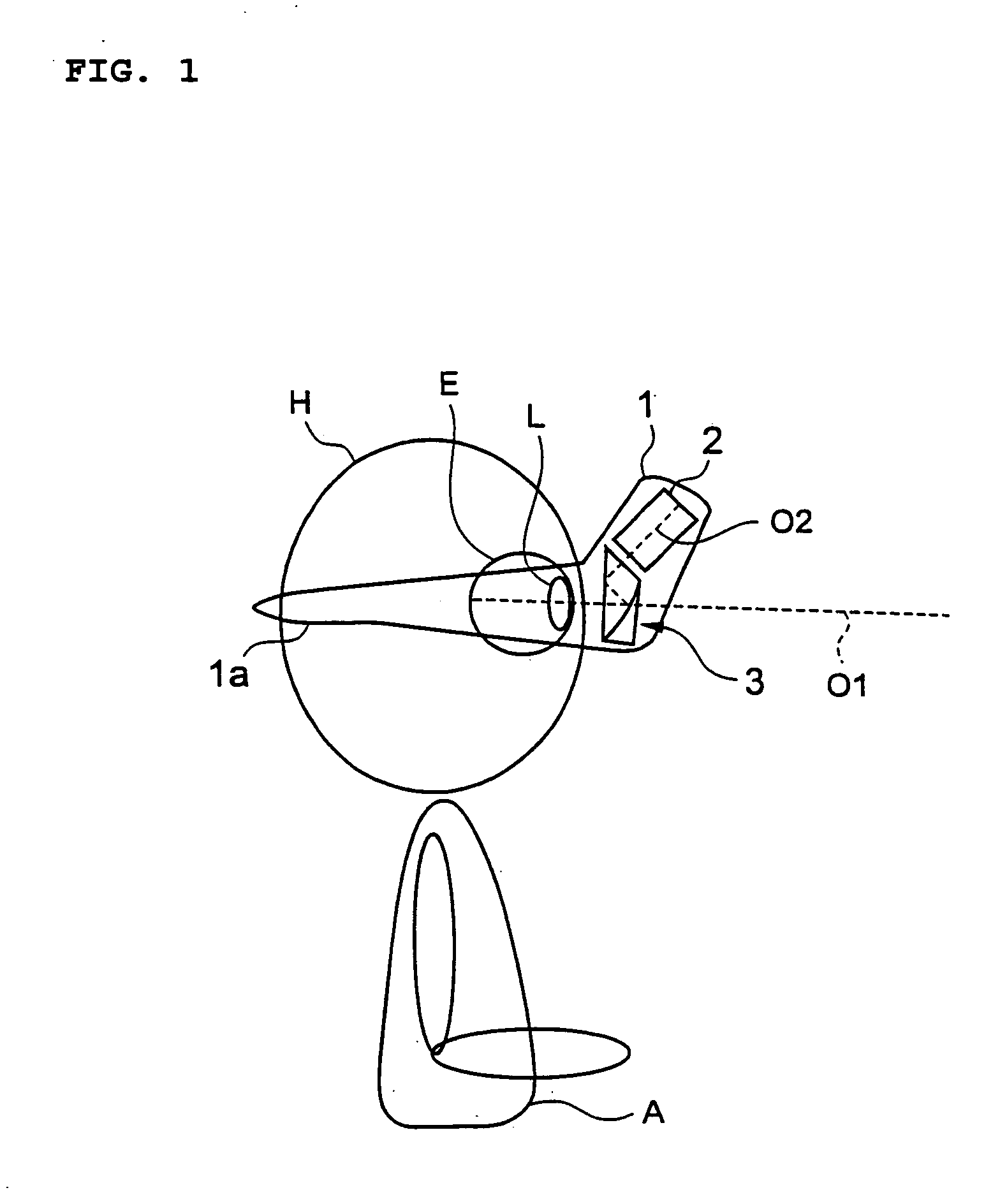
Refraction measuring instrument
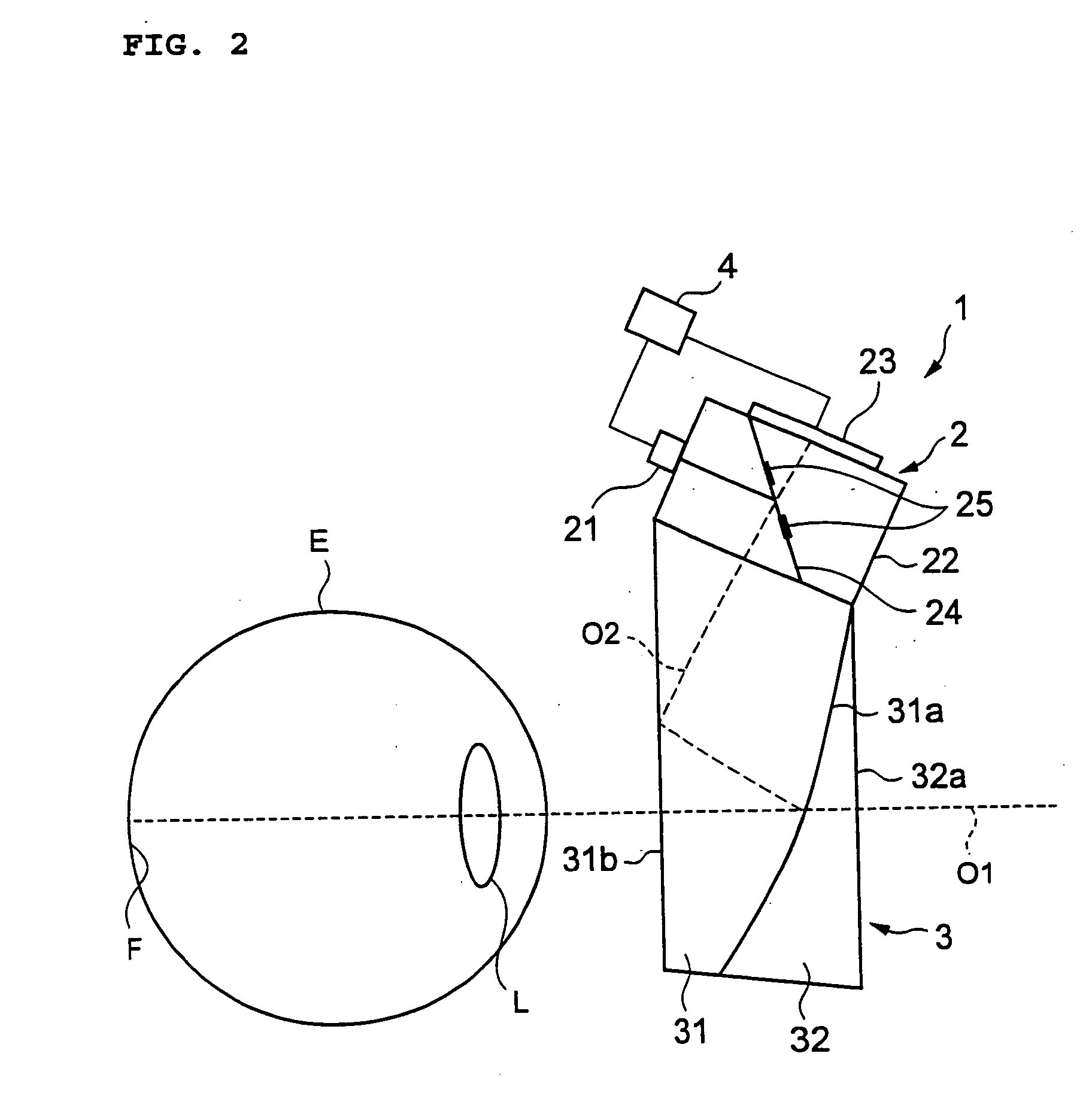
InactiveUS20060215111A1Small sizeReduce weightRefractometersSkiascopesMeasuring instrumentBeam splitting
A refraction measuring instrument for measuring the refraction of an eye to be examined while the subject is viewing an external object in a more natural posture. A measuring light beam from a light source 21 is reflected from a mirror 25, shaped into a beam with a ring cross section, directed to a free curved surface prism 31 along an optical axis O2, reflected from a surface 31b and a beam splitting surface 31a, guided to an eye E along an optical axis O1 together with the visible light from outside the instrument, and form a ring pattern on the fundus F. The measurement beam reflected from the fundus F is received by a CCD 23 through the free curved surface prism 31 and a prism 22, and a ring pattern is imaged. A calculation control device 4 analyzes the imaged ring pattern and calculates the sphericity, the degree of astigmatism, and the astigmatic axis angle. For measurement, the subject A wears the refraction measuring instrument 1 on the head H through a wearing section 1a.
Owner:KK TOPCON
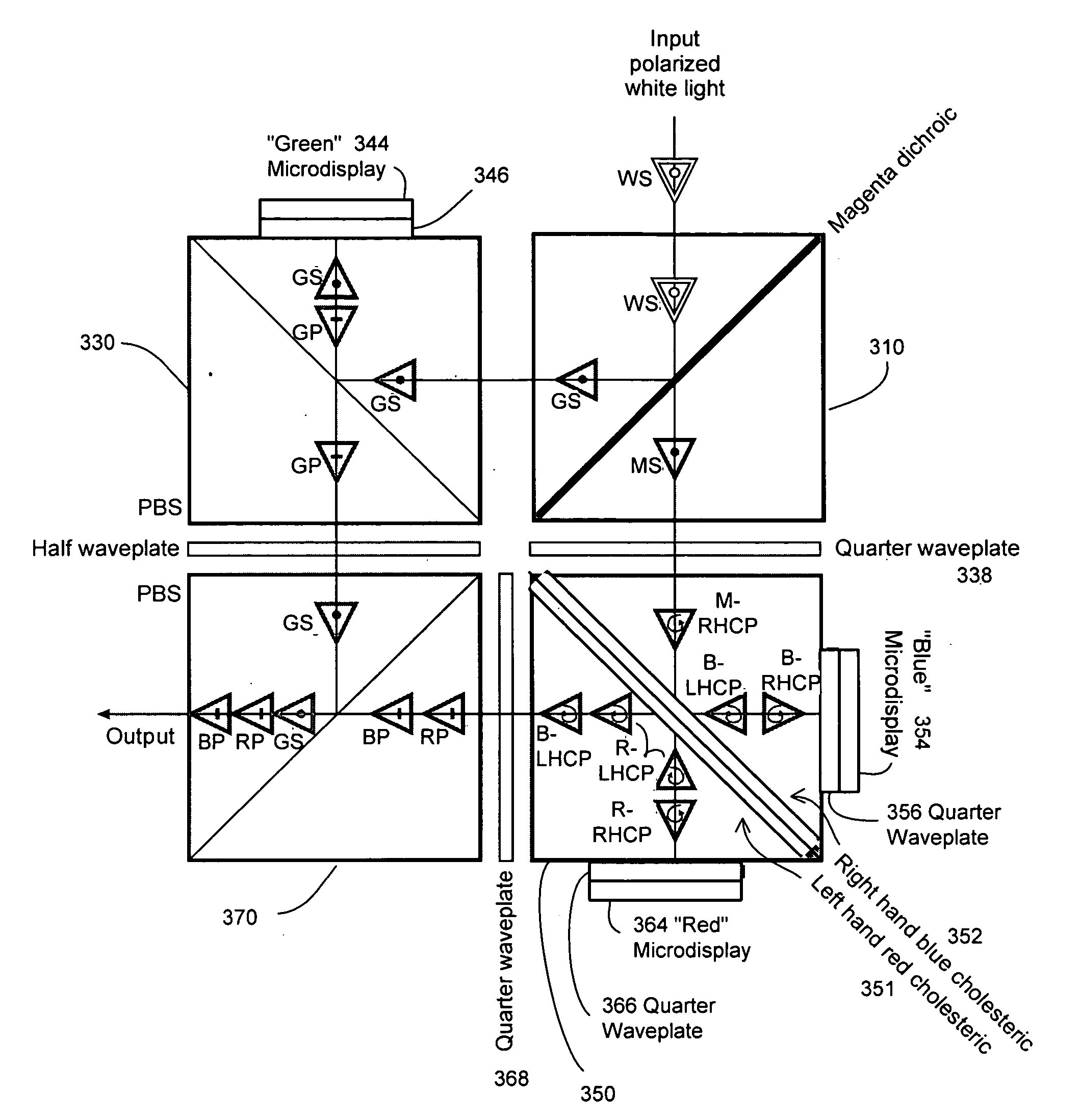
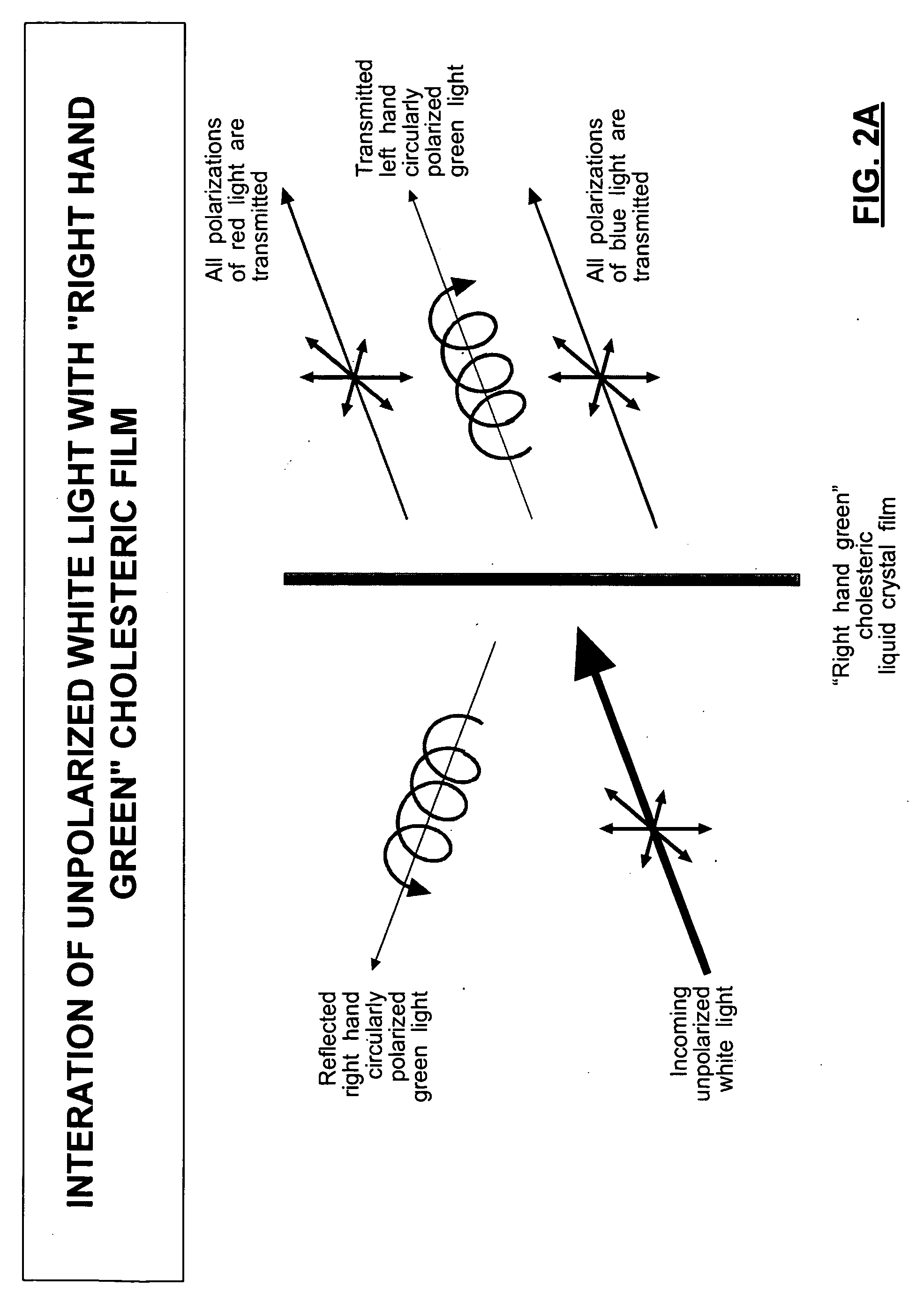
Advanced prism assemblies and prism assemblies using cholesteric reflectors
A prism assembly using only cholesteric layers for splitting input light into component light beams and individually directing the component light beams to modulating devices. Liquid coupling prism assembly components to produce reduced stress index and pathlength matched prism assemblies from low tolerance components. Pathlength matching in beam splitting devices using a variety of optical component shapes and beam splitting layer materials. Various prism assembly designs using cholesteric layers supported on planar and / or on optical component diagonals.
Owner:LIGHTMASTER SYST
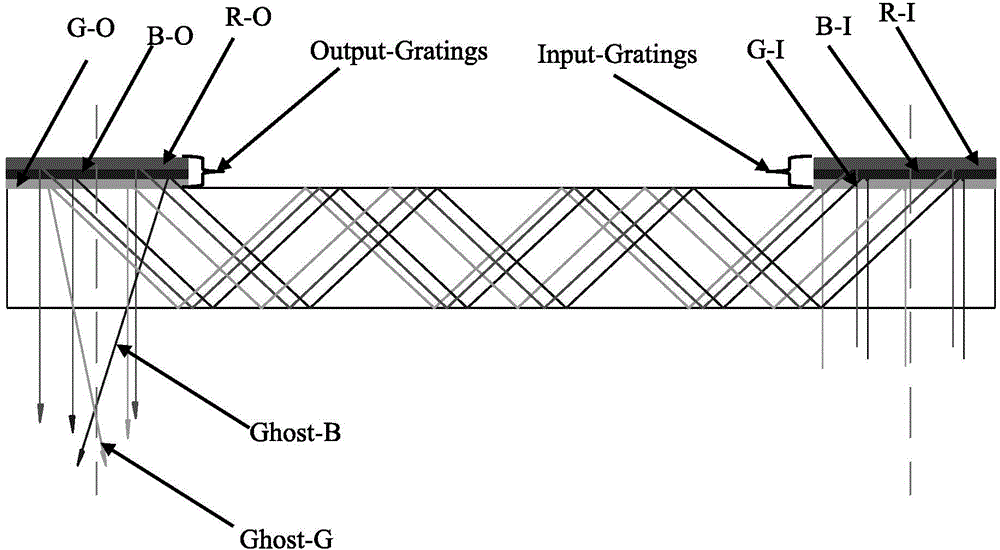
One camera stereo system
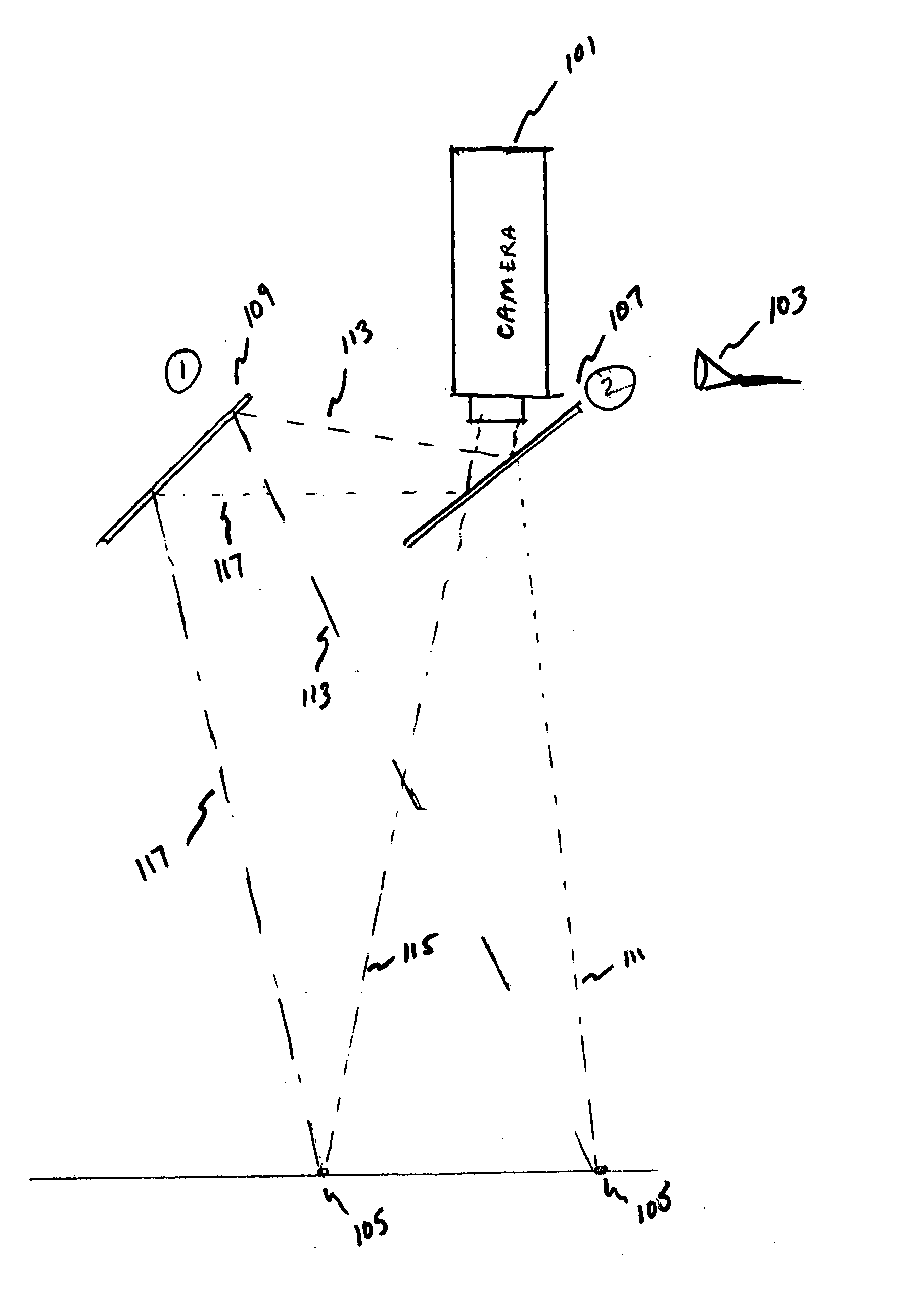
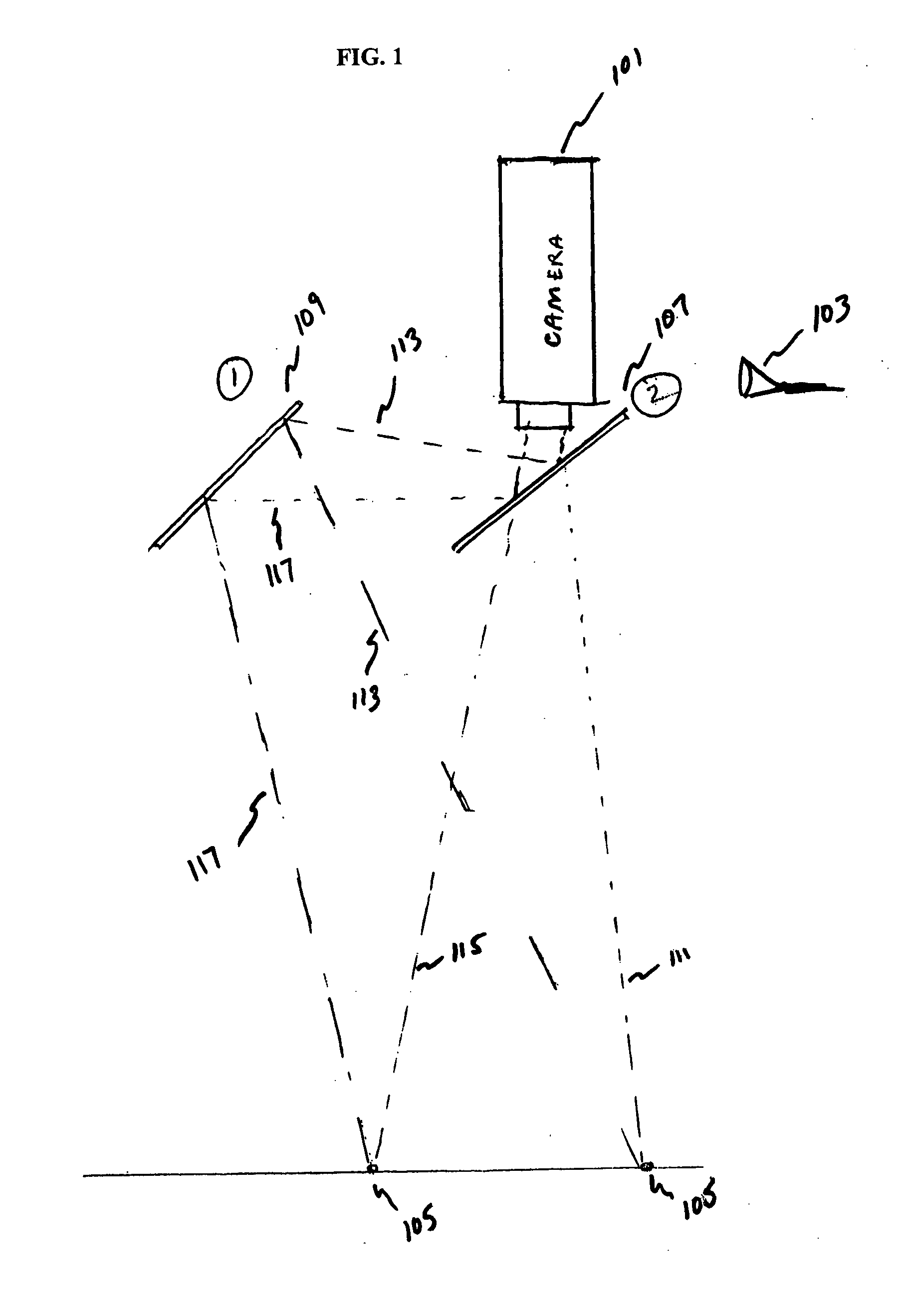
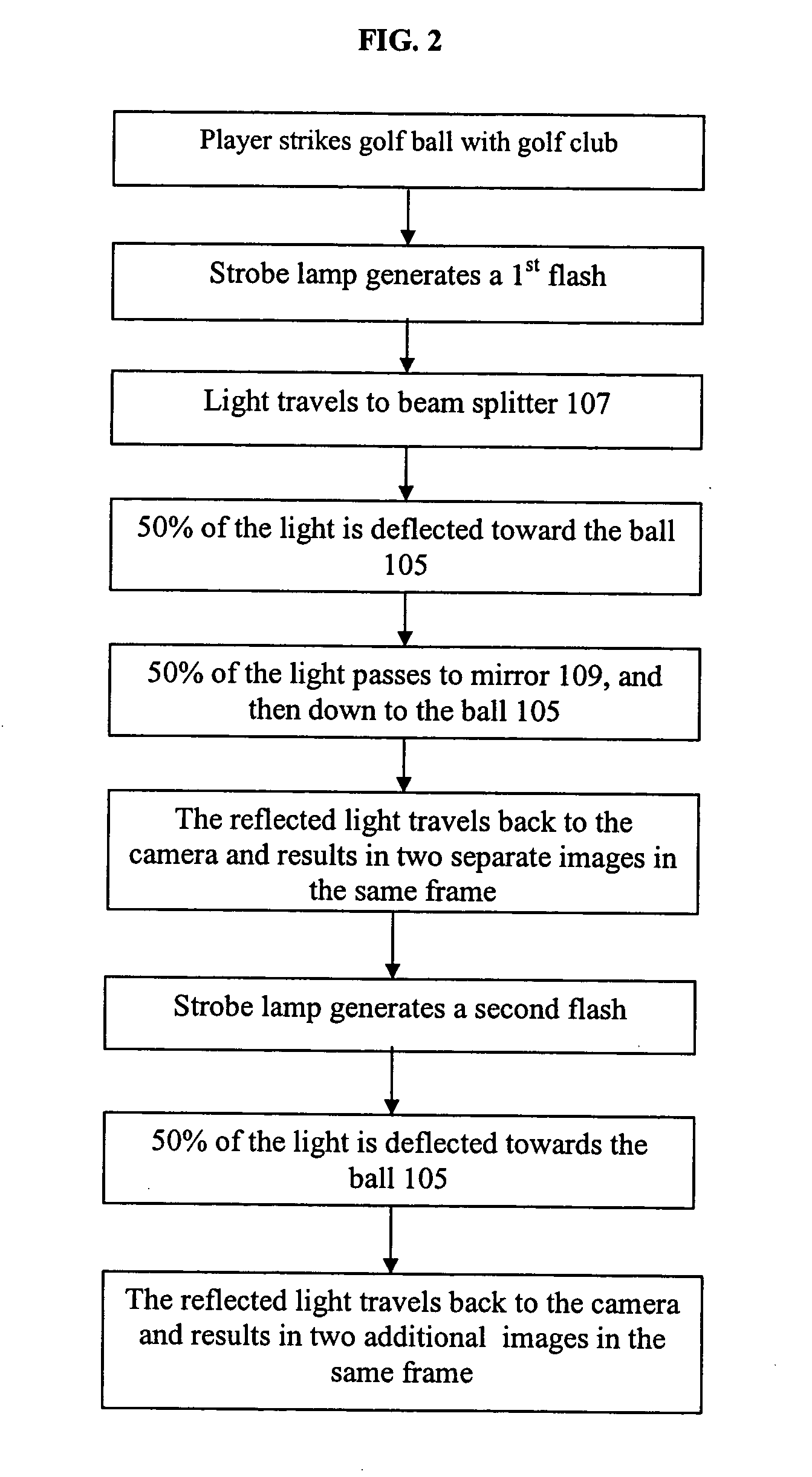
ActiveUS20050168578A1Accurate three dimensional informationTelevision system detailsGymnastic exercisingKinematicsBeam splitting
Owner:ACUSHNET CO
Apparatus and method for stimulating hair growth
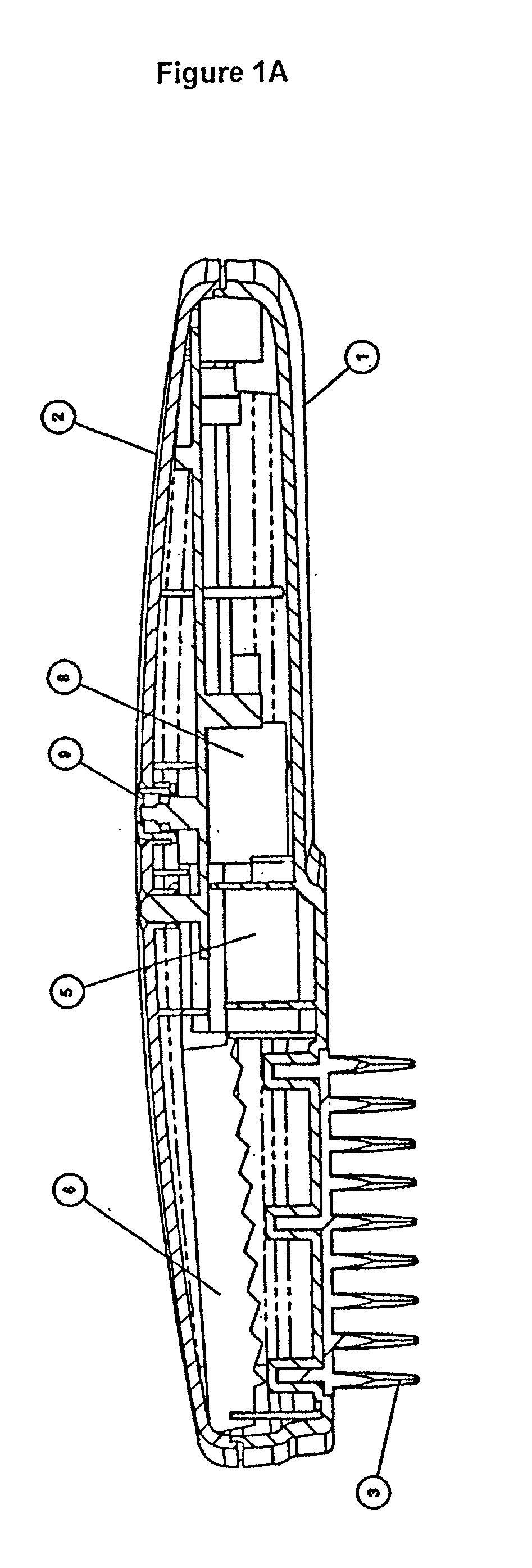
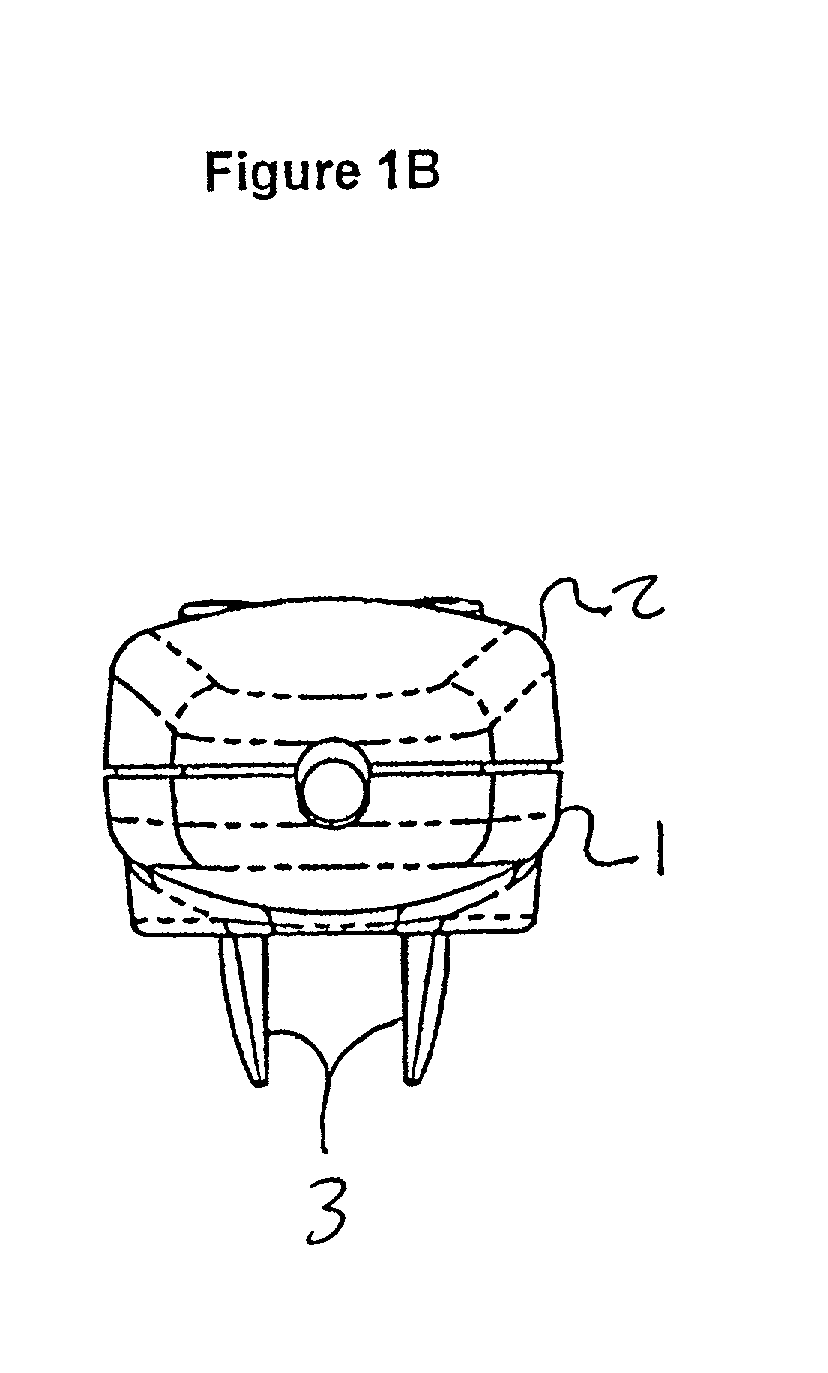
A hand-held laser device that stimulates hair growth. The device provides distributed laser light to the scalp while simultaneously parting the user's hair to ensure that the laser light contacts the user's scalp. A unique beam splitting reflector splits a single laser beam to ensure that energy from the laser beam is evenly distributed. The reflector is mechanically aligned with the laser source and has a zigzag structure which mechanically deflects portions of the beam as it passes over the peaks of the reflector. The portions of the laser beam form a line of laser beams that project toward the user's scalp. Parallel rows of teeth are aligned with a central row of individual laser beams and part the user's hair to form furrows in the user's hair as the device is combed through the user's hair. The furrows create an unobstructed path for the laser beam to reach the scalp of the user.
Owner:LEXINGTON INT LLC
Dual-wavelength dipulse non-fuzzy laser ranging device
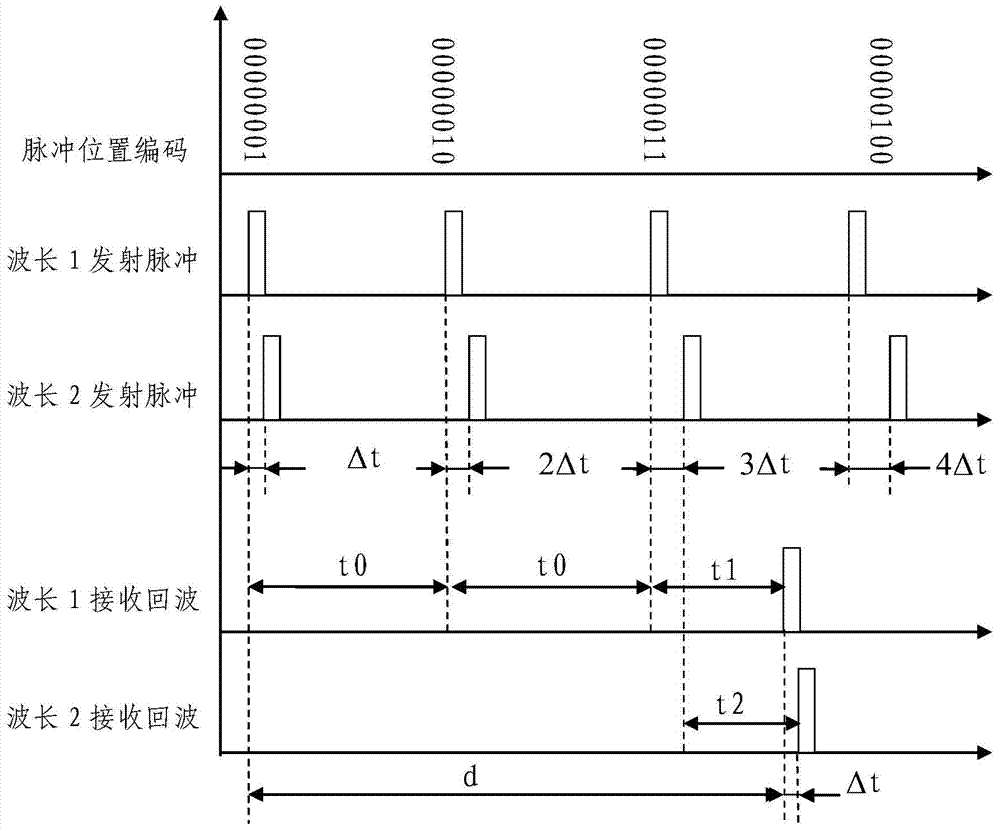
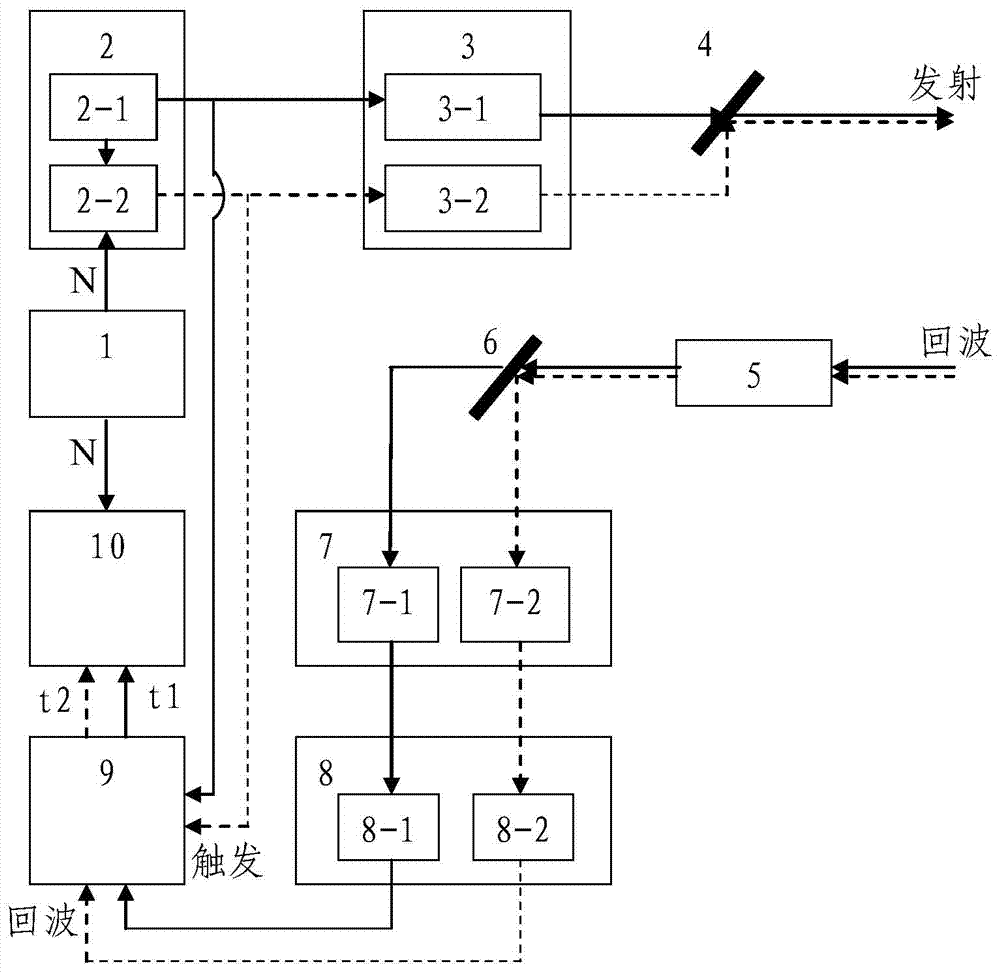
ActiveCN103885065AOvercoming distance ambiguityNo modulation misalignmentElectromagnetic wave reradiationLaser rangingBeam splitting
The invention discloses a dual-wavelength dipulse non-fuzzy laser ranging device. According to the basic principle, two laser pulses with two wavelengths are emitted, time intervals of the two laser pulses are sequentially encoded, a receiving channel receives laser back waves with two wavelengths with a wavelength beam splitting method and transmits the laser back waves to two detectors respectively, and time measurement is conducted on the laser back waves; back wave time difference between the pulses with the two wavelengths is calculated, the time difference of the starting pulse corresponding to the current laser back wave is accurately decoded, and the distance of a target is calculated. The dual-wavelength dipulse non-fuzzy laser ranging device has the advantages that the two pulses with the two wavelengths and encoded time intervals are adopted for ranging, and remote high-repetition-frequency non-fuzzy laser ranging can be achieved.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
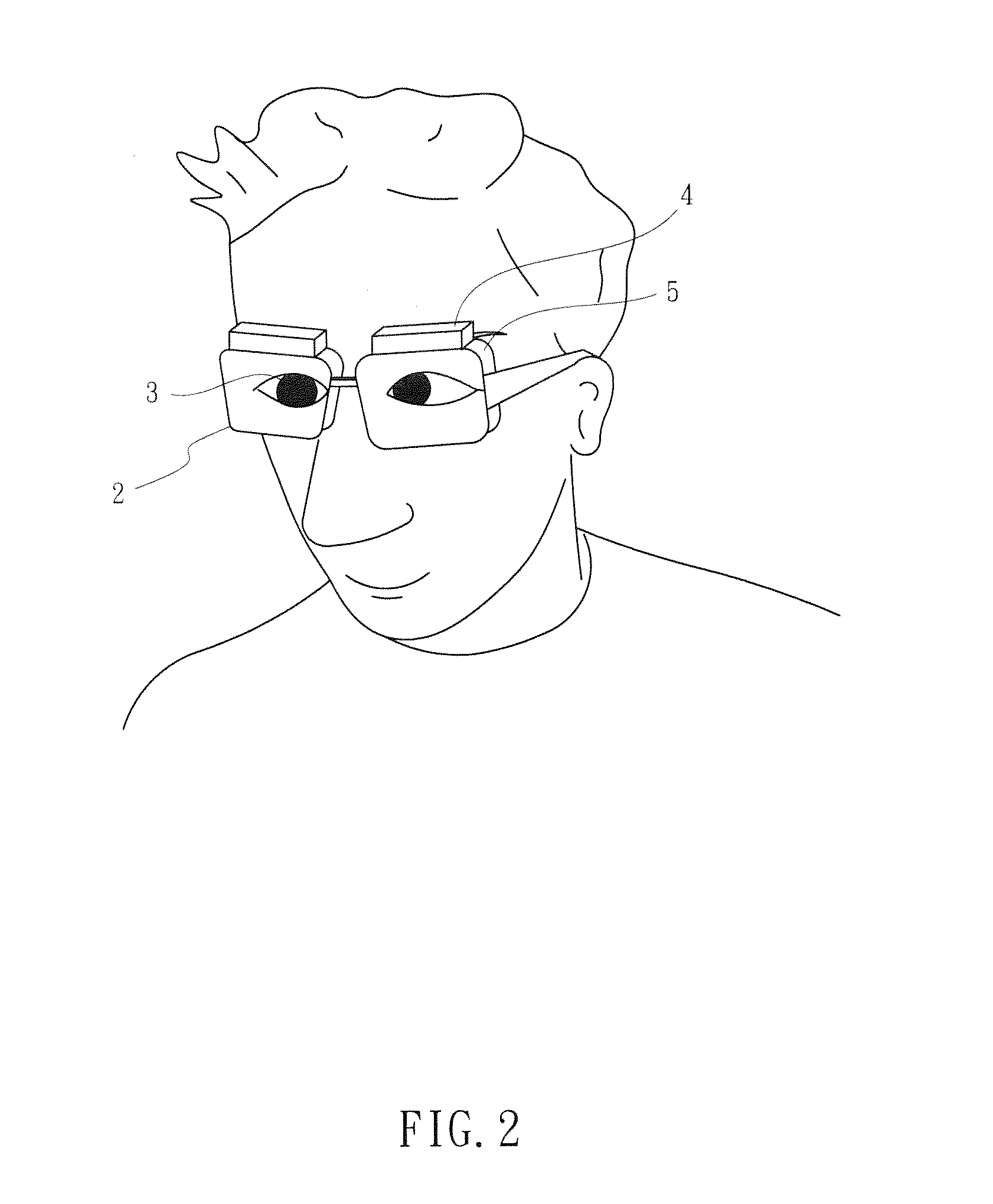
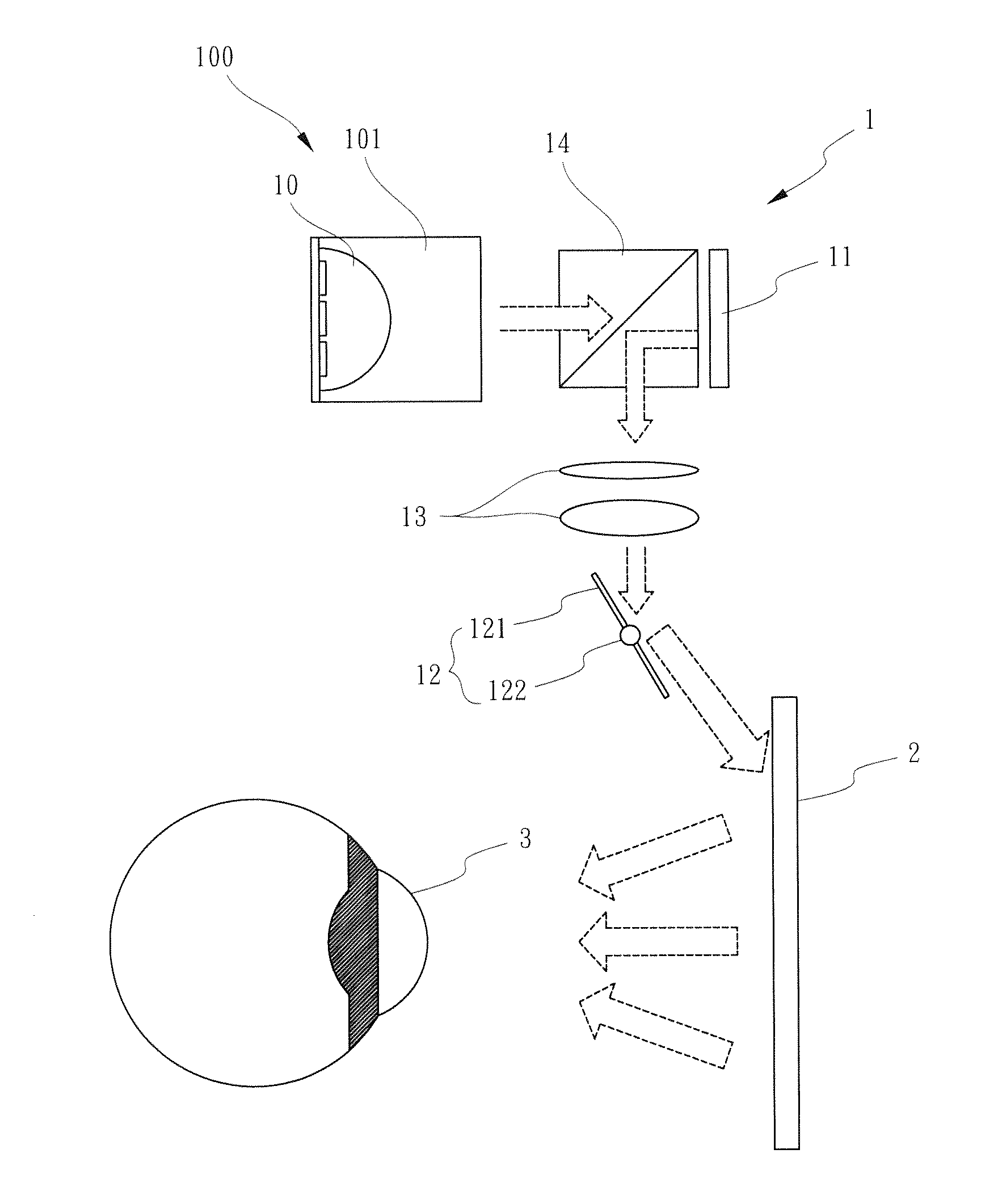
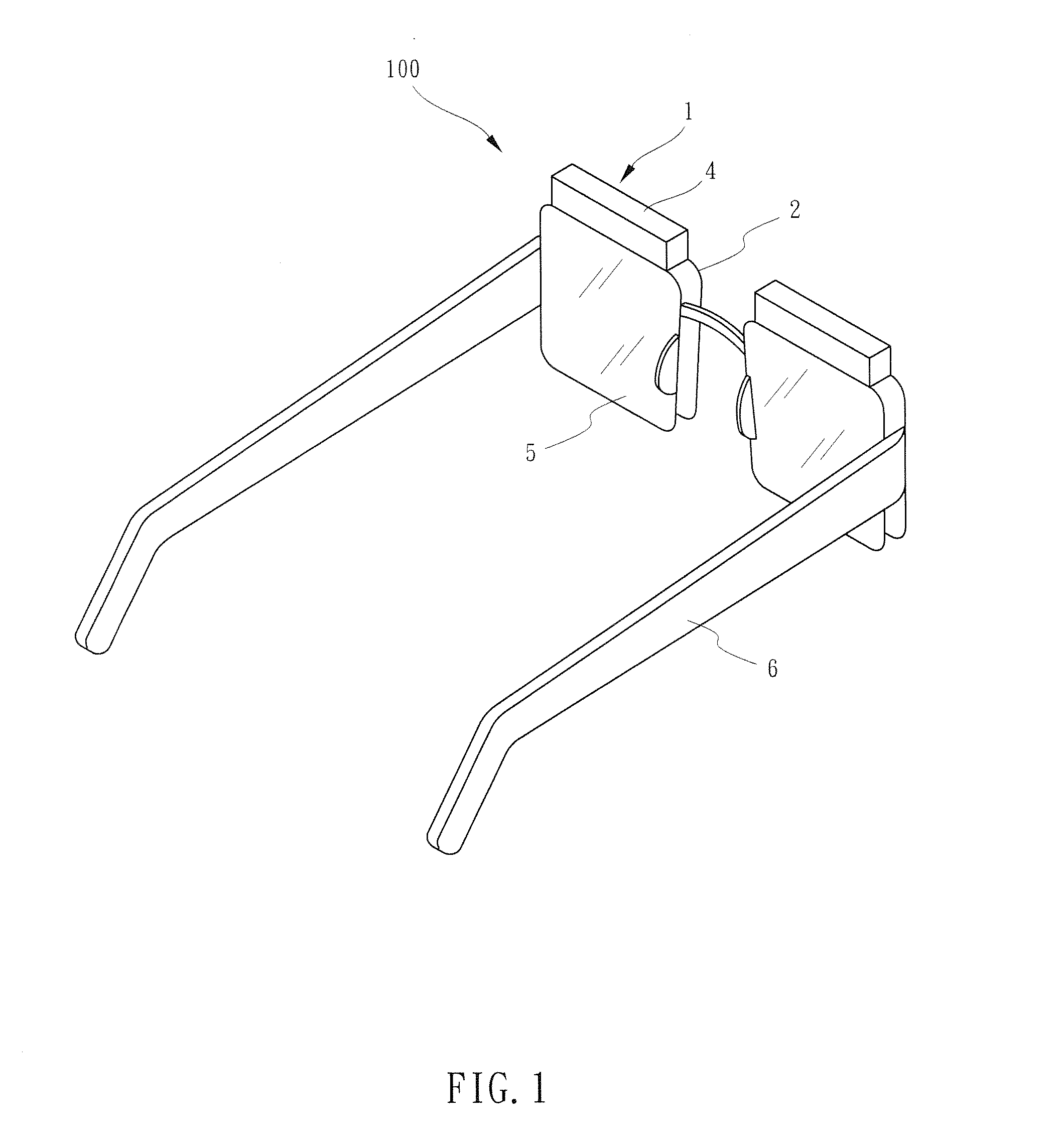
Optical head-mounted display with mechanical one-dimensional scanner
ActiveUS20140226193A1Optical enhancementLess energy lossOptical elementsSpatial light modulatorPersistence of vision
An optical head-mounted display includes an eyeglass frame, a holographic optical element supported by the eyeglass frame to be confronted by an eye of a wearer, and a projector mounted on the eyeglass frame to project image information on the holographic optical element. The projector includes a LED light source, a beam-splitting polarizer, a spatial light modulator, a lens set and a mechanical one-dimensional scanner. The mechanical one-dimensional scanner reflects the transformed light beam from the lens set onto the holographic optical element in one dimension at a time. When the reflective sheet is rotated at a range of angle in a brief moment of time, the holographic optical element receives from the rotating reflective sheet an array of one-dimensional modulated light beams and reflects the latter to form a two-dimensional image in the eye because of persistence of vision.
Owner:NAT CENT UNIV
Detector for optically detecting at least one object
InactiveUS20170074652A1Avoid disadvantagesImprove long-term stabilityMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationOptical rangefindersBeam splittingLight beam
A detector for determining a position of at least one object, where the detector includes: at least one optical sensor, where the optical sensor has at least one sensor region, where the optical sensor is designed to generate at least one sensor signal in a manner dependent on an illumination of the sensor region by illumination light traveling from the object to the detector; at least one beam-splitting device, where the beam-splitting device is adapted to split the illumination light in at least two separate light beams, where each light beam travels on a light path to the optical sensor; at least one modulation device for modulating the illumination light, where the at least one modulation device is arranged on one of the at least two light paths; and at least one evaluation device, where the evaluation device is designed to generate at least one item of information from the at least one sensor signal.
Owner:BASF AG
Method and apparatus for modifying the spread of a laser beam
InactiveUS20070153293A1Input/output for user-computer interactionLaser detailsBeam splittingLight beam
An apparatus and method for modifying the spread of a laser beam. The apparatus comprises a laser source operable to generate a laser beam having a flux that exceeds a predetermined value and an optical train operable to modify the beam such that the flux of the beam through a predetermined aperture does not exceed the predetermined value. The optical train may include a focusing lens, a diffractive focusing vortex lens, a beam splitting device, or a two-dimensional diffraction grating.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
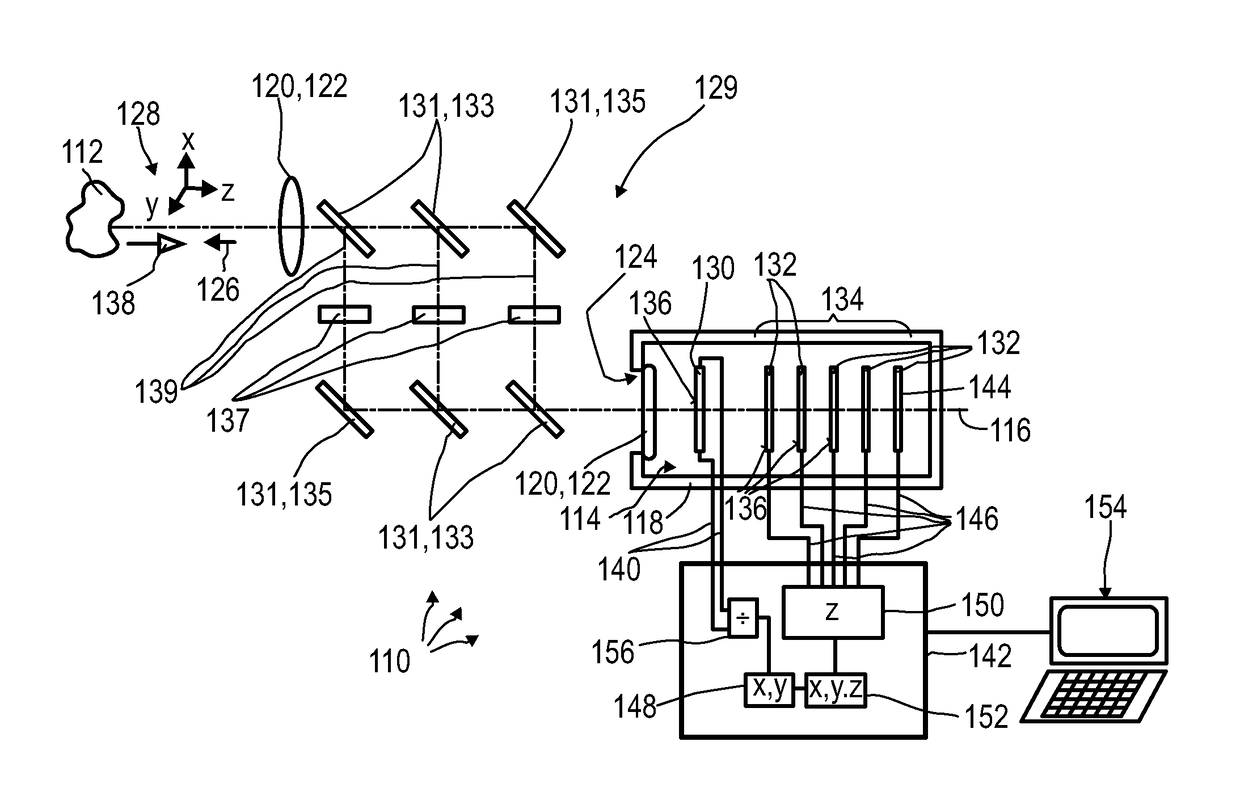
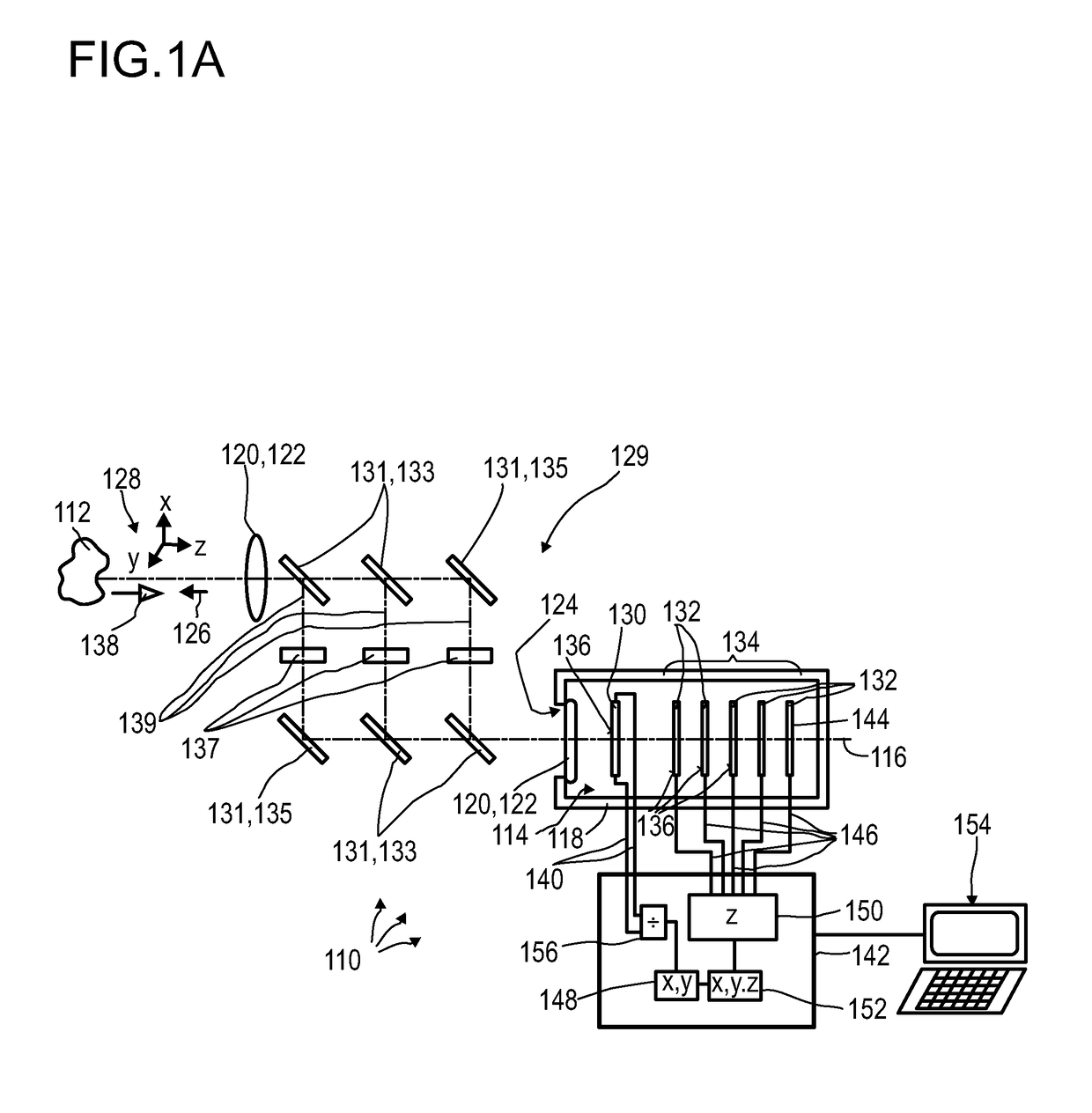
3D Biplane Microscopy
A microscopy system is configured for creating 3D images from individually localized probe molecules. The microscopy system includes a sample stage, an activation light source, a readout light source, a beam splitting device, at least one camera, and a controller. The activation light source activates probes of at least one probe subset of photo-sensitive luminescent probes, and the readout light source causes luminescence light from the activated probes. The beam splitting device splits the luminescence light into at least two paths to create at least two detection planes that correspond to the same or different number of object planes of the sample. The camera detects simultaneously the at least two detection planes, the number of object planes being represented in the camera by the same number of recorded regions of interest. The controller is programmable to combine a signal from the regions of interest into a 3D data.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MAINE +1
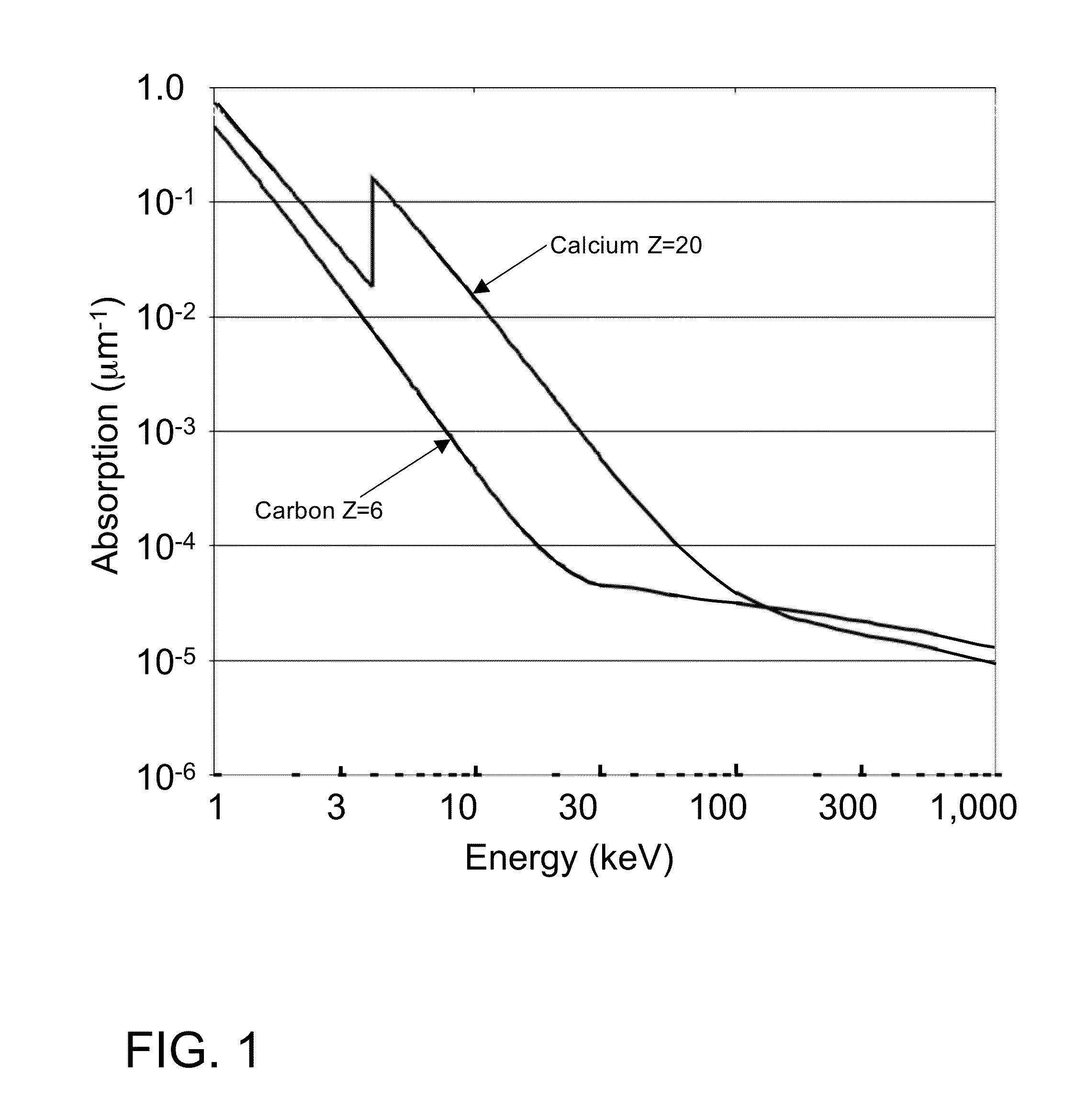
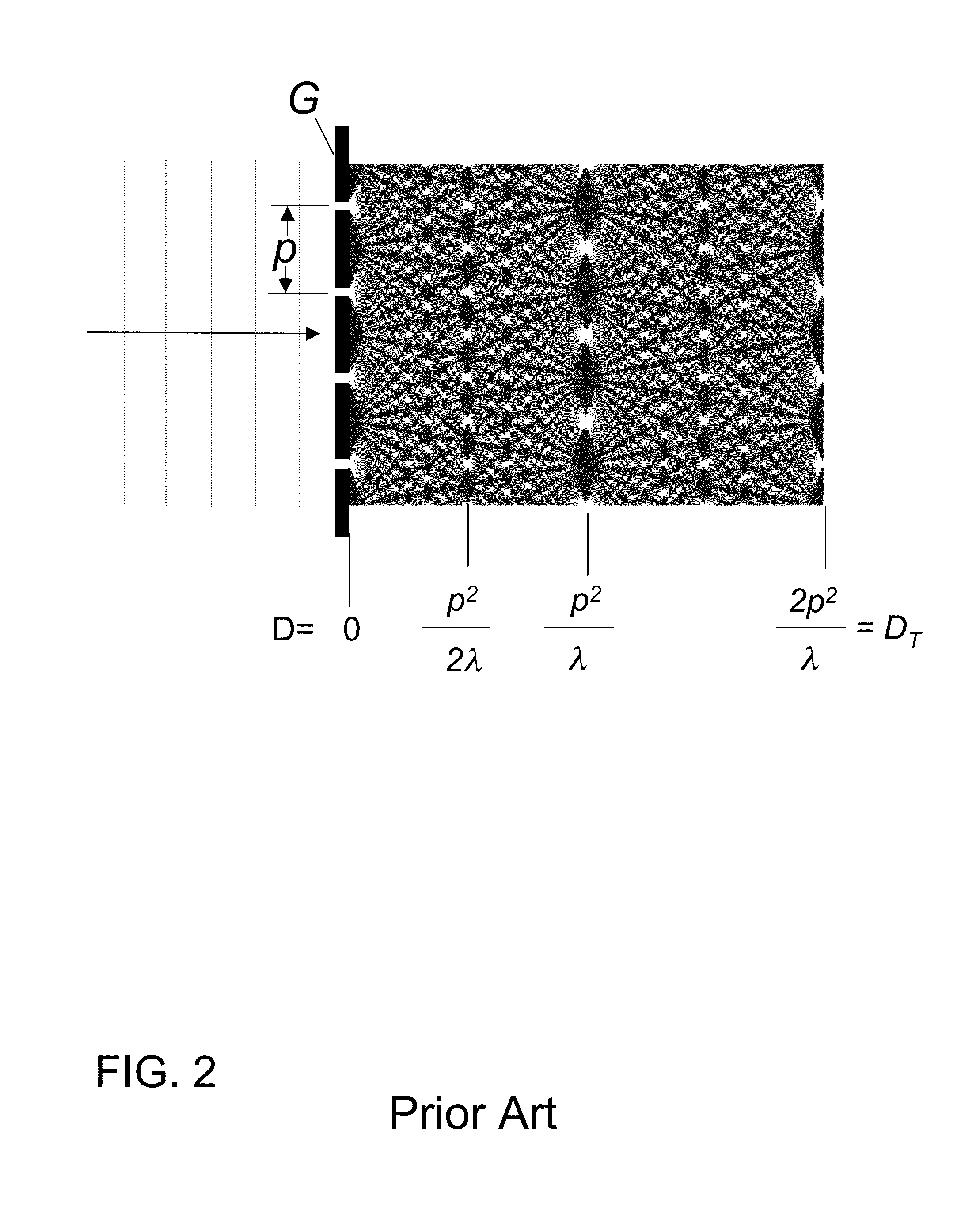
X-ray interferometric imaging system
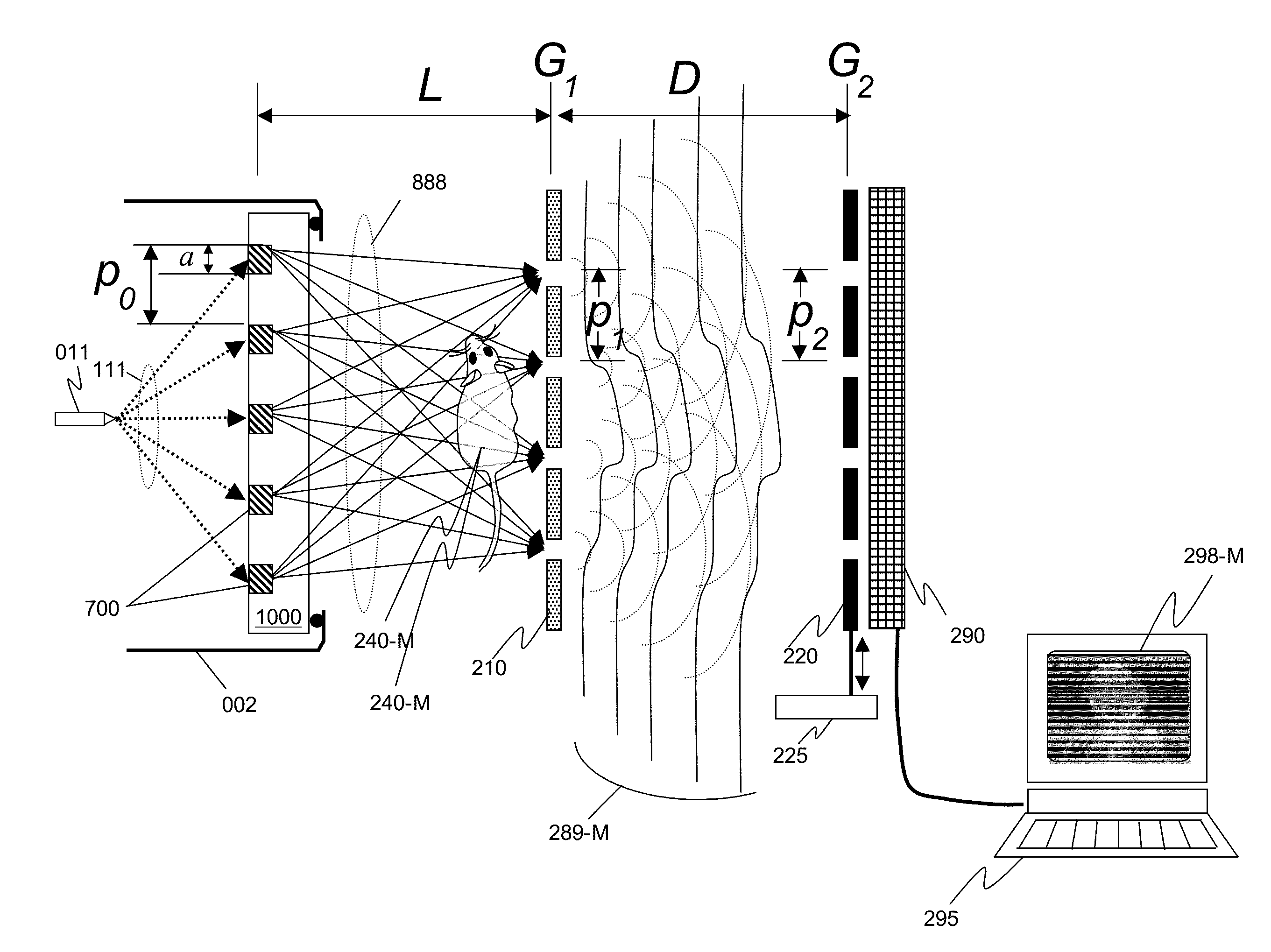
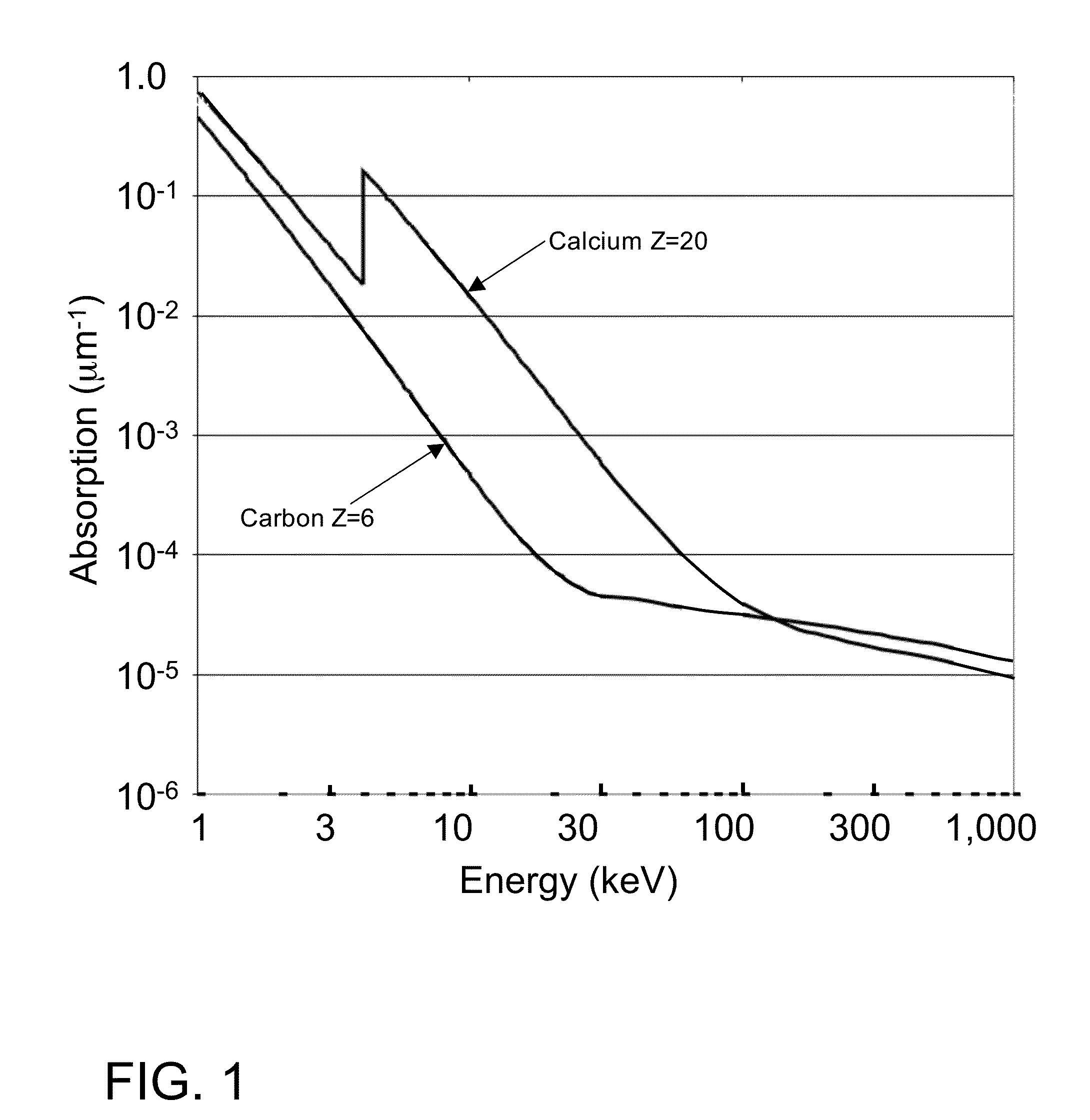
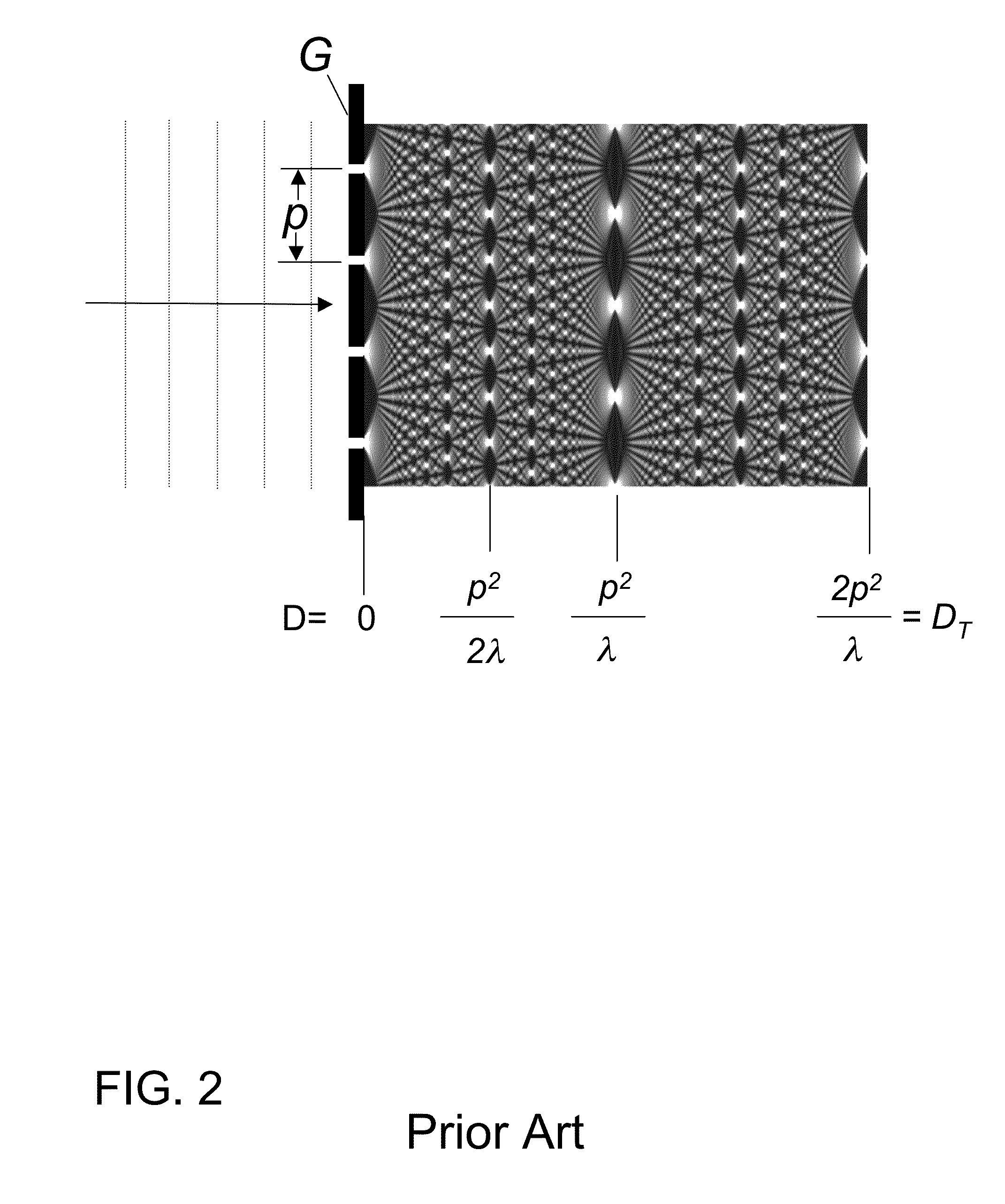
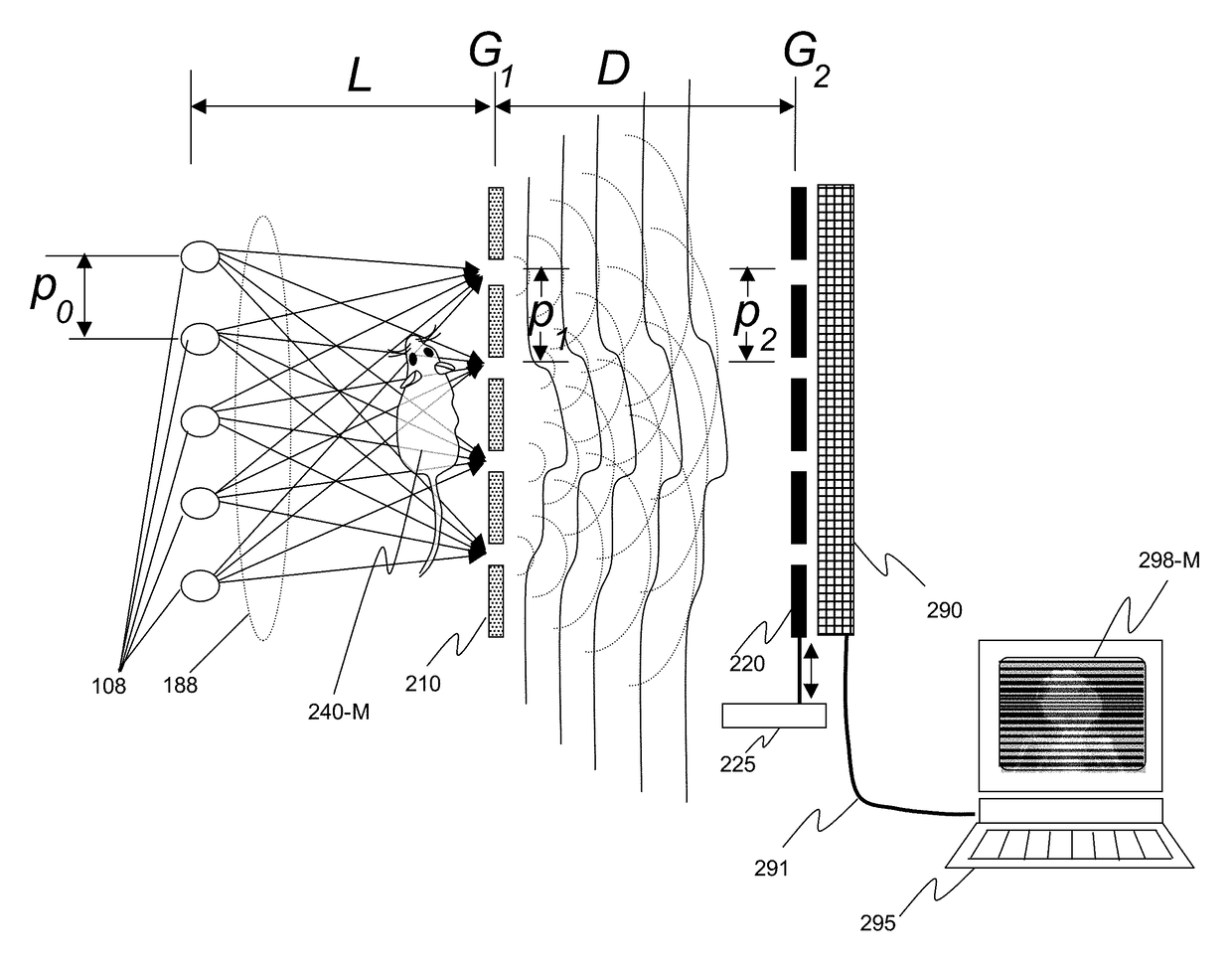
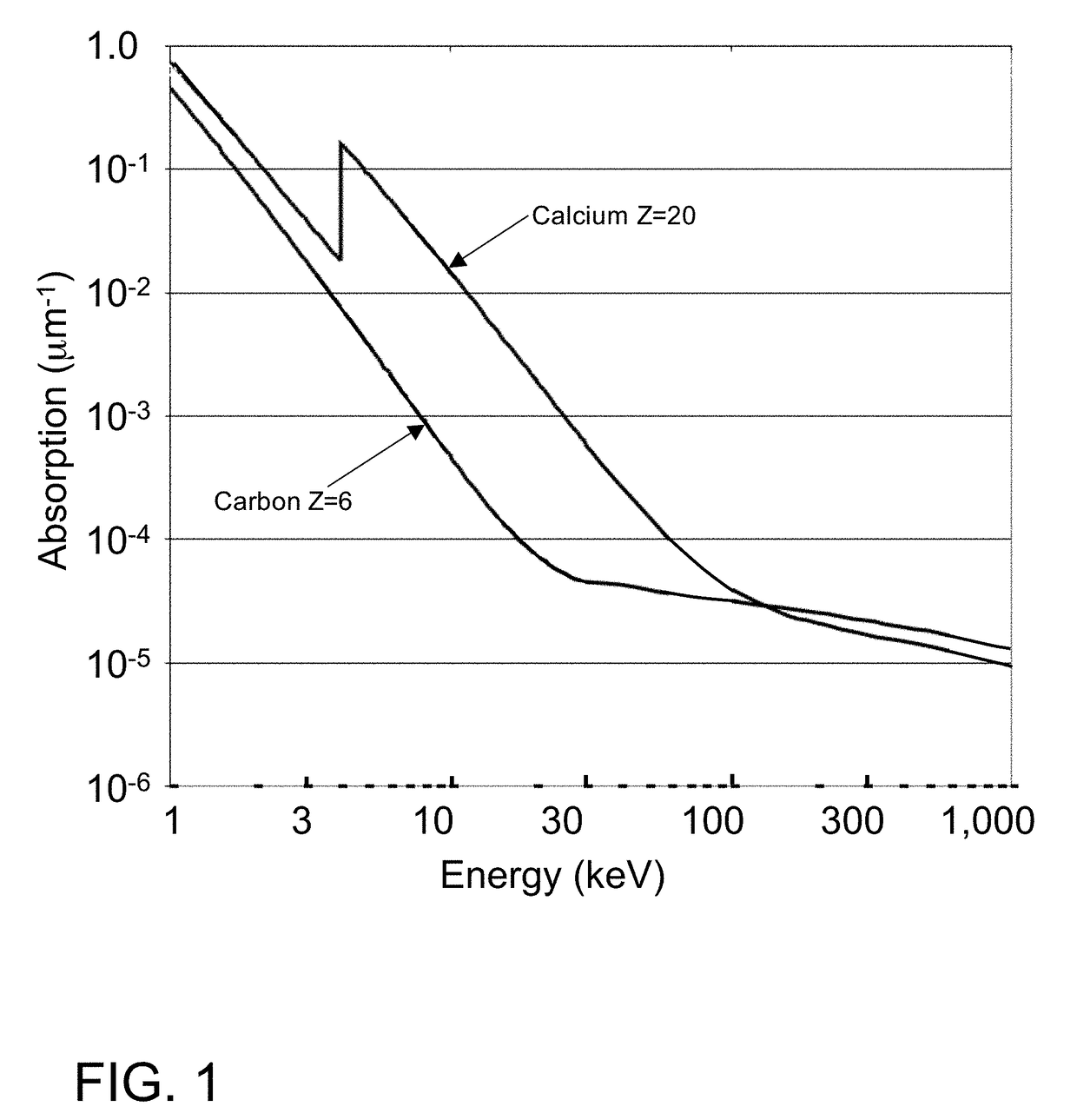
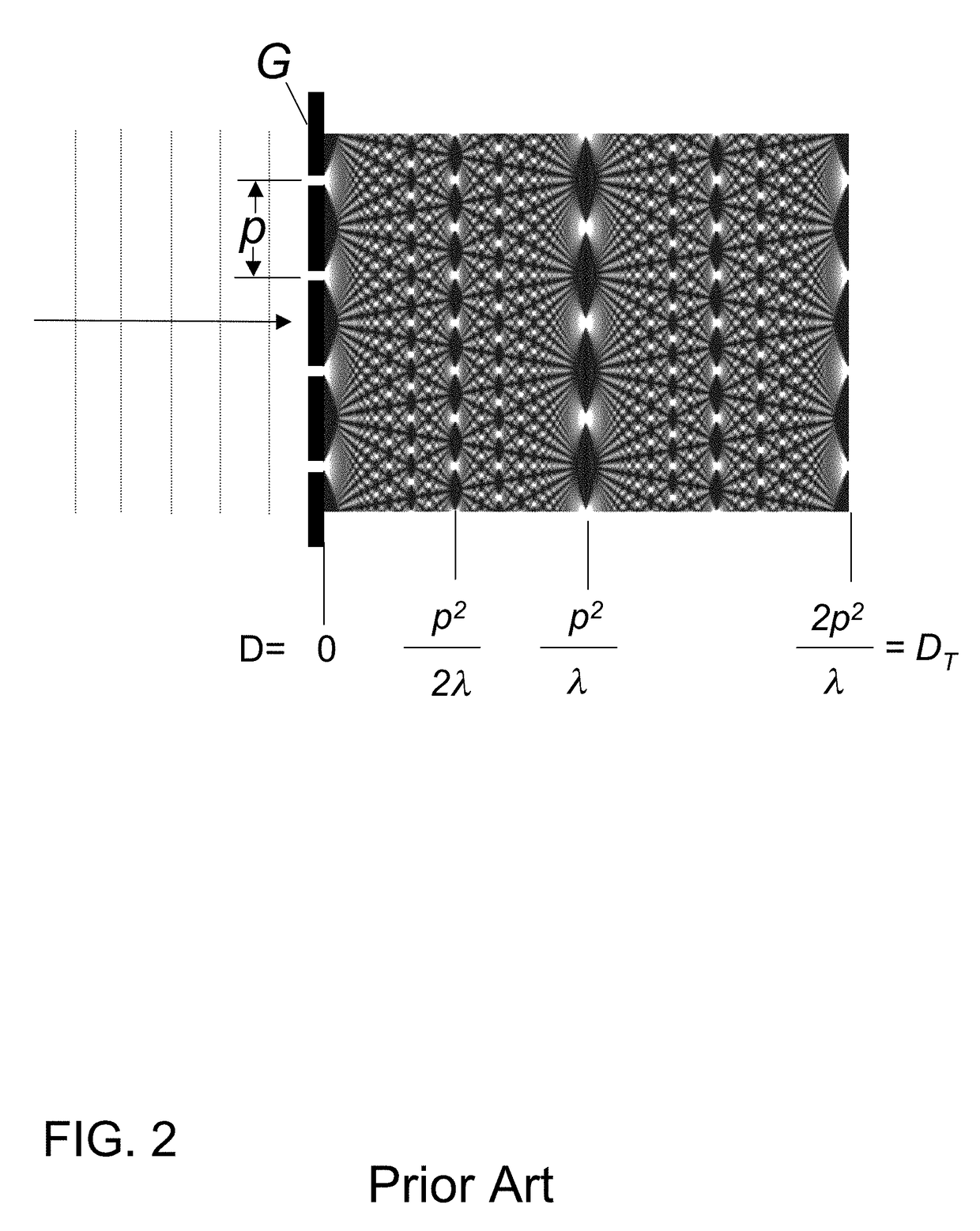
InactiveUS20150117599A1Increase brightnessLarge x-ray powerImaging devicesMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationSoft x rayGrating
We disclose an x-ray interferometric imaging system in which the x-ray source comprises a target having a plurality of structured coherent sub-sources of x-rays embedded in a thermally conducting substrate. The system additionally comprises a beam-splitting grating G1 that establishes a Talbot interference pattern, which may be a π phase-shifting grating, and an x-ray detector to convert two-dimensional x-ray intensities into electronic signals. The system may also comprise a second analyzer grating G2 that may be placed in front of the detector to form additional interference fringes, and a means to translate the second grating G2 relative to the detector.In some embodiments, the structures are microstructures with lateral dimensions measured on the order of microns, and with a thickness on the order of one half of the electron penetration depth within the substrate. In some embodiments, the structures are formed within a regular array.
Owner:SIGRAY INC
Conjugated narrow-band tri-phosphor staggered volume holographic grating waveguide near-to-eye optical display device
The invention provides a conjugated narrow-band tri-phosphor staggered volume holographic grating waveguide near-to-eye optical display device. The device comprises an image display light source which is used for providing image information to be viewed, a P&S photo-conversion component which is used for converting P light and S light, a collimating lens group which is used for collimating light wave, a PBS component which is used for the polarizing beam-splitting of light wave, a beam-splitting selecting component which is used for uniformly spreading the light wave on a coupling input surface; a conjugated tri-phosphor staggered coupling input volume holographic grating which is used for dispersing incident ray and totally reflecting and transmitting the ray inside the substrate, a light-guide transmitting substrate which is used for totally reflecting and transmitting the light wave, and a conjugated tri-phosphor staggered coupling output volume holographic grating which is used for coupling the dispersed incident ray in sequence and outputting the ray to the outside of the substrate. The device has the advantages of full color, ultra-thinness, large field angle and simplicity in process and implementation, and can be applied to the damage-free display of a mobile screen, the display of a terminal, the scene teaching instruction for a doctor, the real-time information positioning for fire fighting, 3D game and other fields.
Owner:SHANGHAI RAYPAI PHOTONIC CRYSTAL LTD
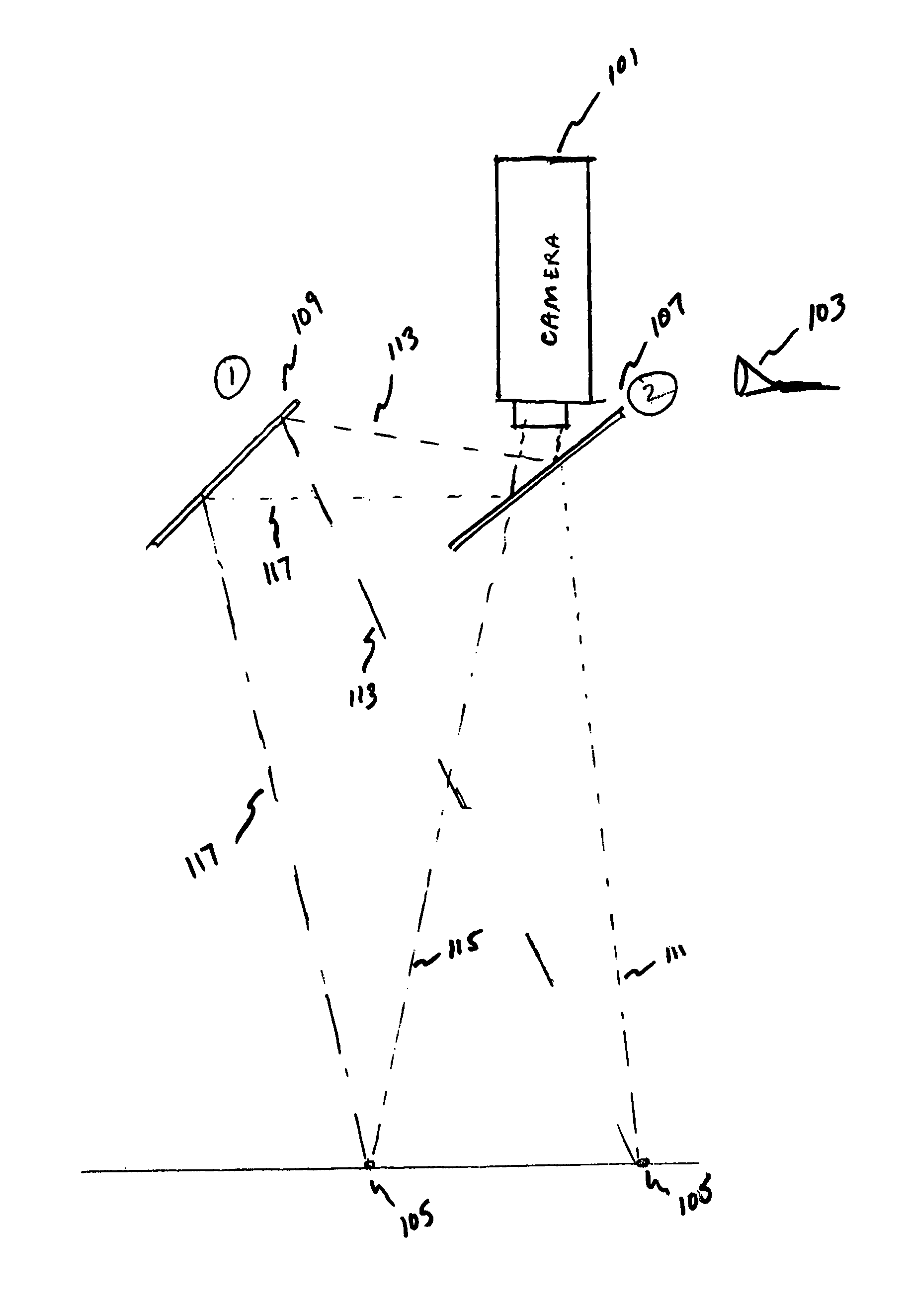
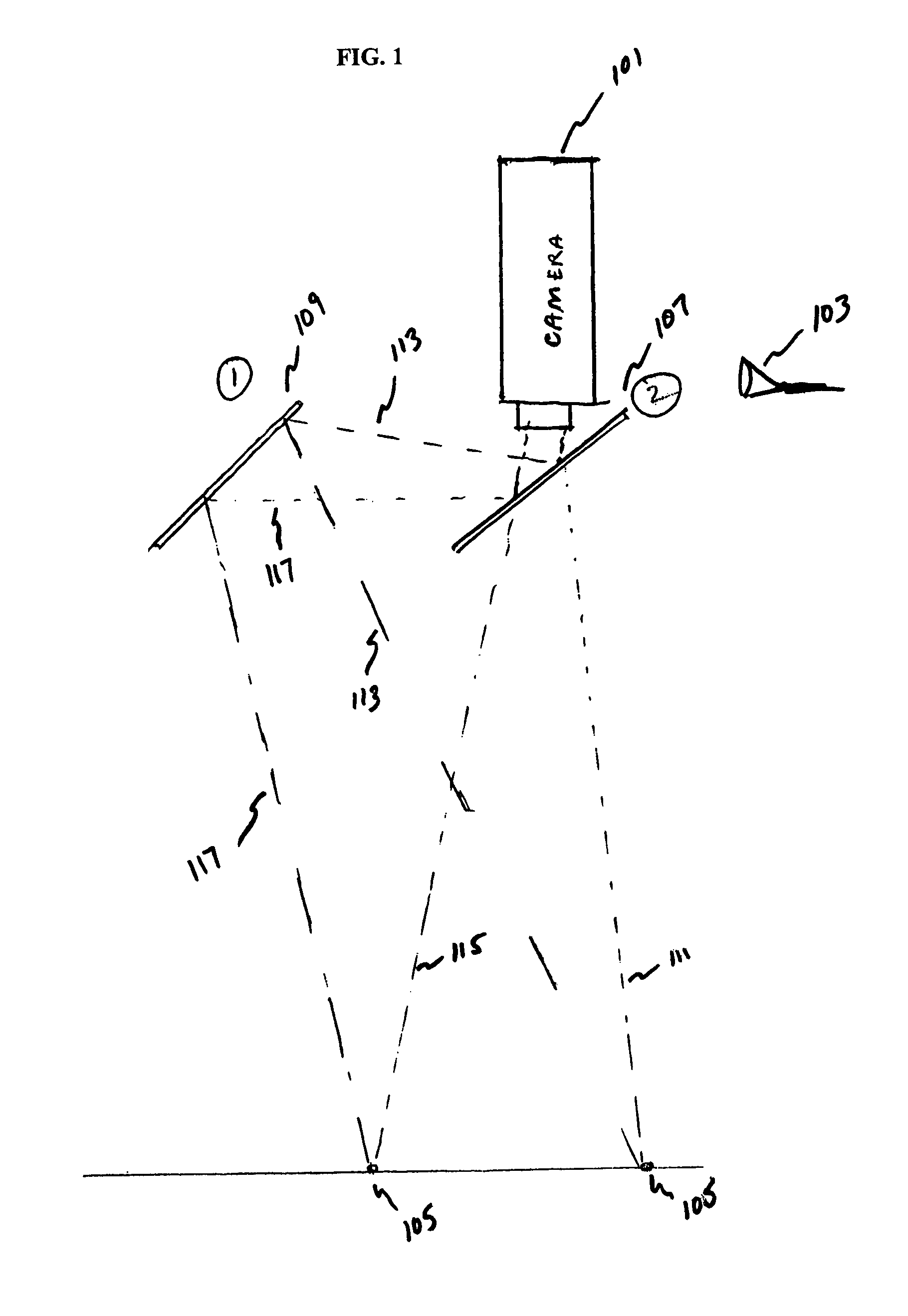
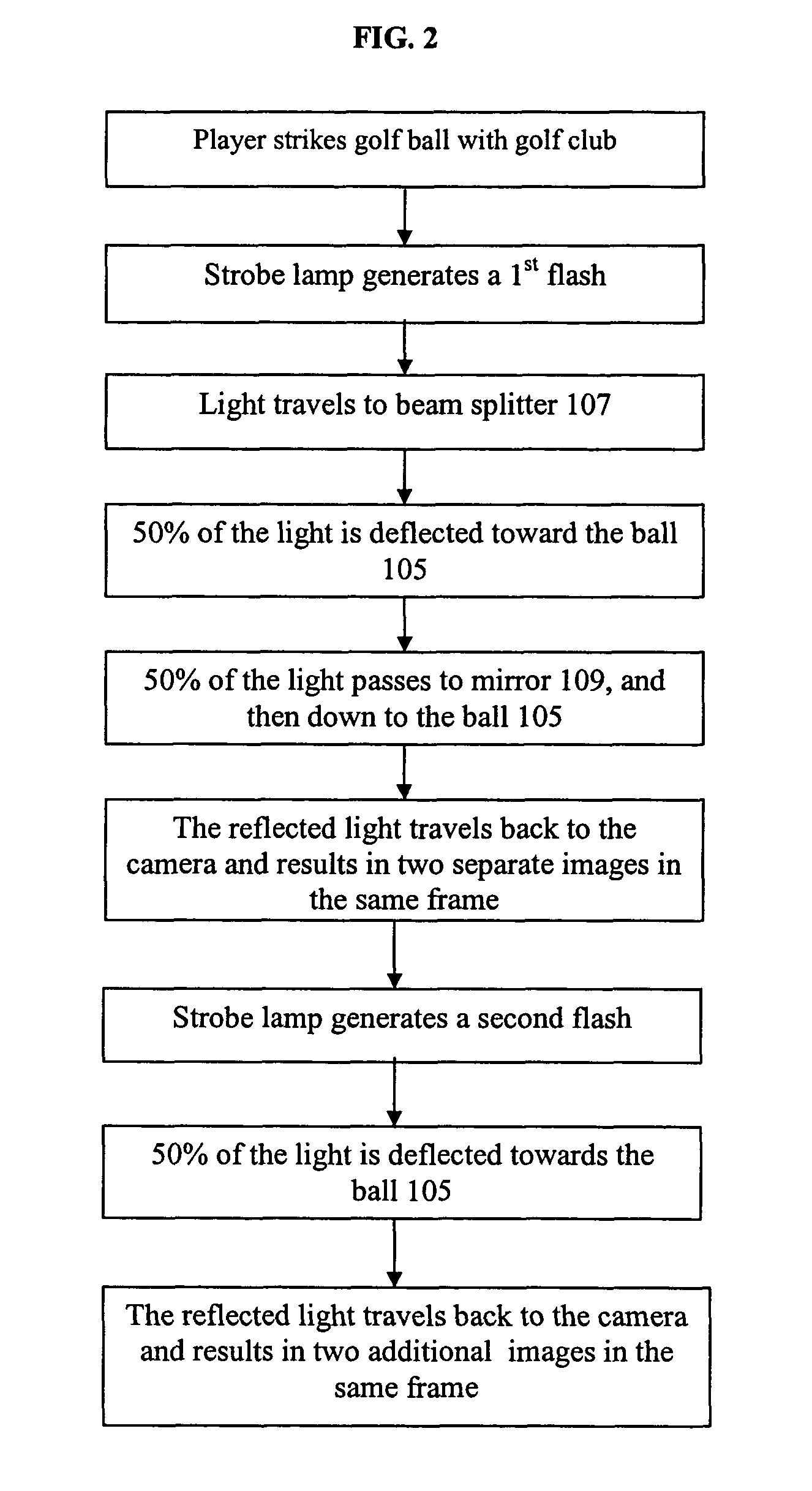
One camera stereo system
ActiveUS8872914B2Accurate three dimensional informationImprove accuracyTelevision system detailsGymnastic exercisingKinematicsBeam splitting
A one camera system that measures golf club and golf ball kinematics is disclosed. Preferably, a plurality of retroreflective or fluorescent markers are placed on the surface of a golf ball. Using a single strobe lamps, images of a golf ball at two points in motion are acquired. The output of each of the strobe lamps is preferably filtered to pass predetermined colors of light. The input to each of the cameras is also preferably filtered. The output from the strobe lamp passes through at least one of a beam splitting mirror and reflective front surface mirror. Based on the filtered light outputs generated by the strobe lamp and the filtered camera input, at least two images of the golf ball, taken from two different angles, may be acquired. The acquired images may be used to analyze the kinematics of the golf ball.
Owner:ACUSHNET CO
X-ray method for the measurement, characterization, and analysis of periodic structures
ActiveUS20150260663A1Lightweight productionIncrease brightnessImaging devicesX-ray tube electrodesSoft x rayGrating
Periodic spatial patterns of x-ray illumination are used to gather information about periodic objects. The structured illumination may be created using the interaction of a coherent or partially coherent x-ray source with a beam splitting grating to create a Talbot interference pattern with periodic structure. The object having periodic structures to be measured is then placed into the structured illumination, and the ensemble of signals from the multiple illumination spots is analyzed to determine various properties of the object and its structures. Applications to x-ray absorption / transmission, small angle x-ray scattering, x-ray fluorescence, x-ray reflectance, and x-ray diffraction are all possible using the method of the invention.
Owner:SIGRAY INC
X-ray interferometric imaging system
ActiveUS9719947B2Lightweight productionIncrease brightnessImaging devicesX-ray tube electrodesSoft x rayGrating
Owner:SIGRAY INC
All-fiber testing device for testing polarization crosstalk of optical device
ActiveCN102928198AImprove stabilityEliminate back lightTesting optical propertiesBeam splittingPolarizer
The invention provides an all-fiber testing device for testing the polarization crosstalk of an optical device. The all-fiber testing device comprises a wide-spectrum light source (501), a polarizer (511), a to-be-tested polarizing device (522), an optical path correlator (530), a difference detector (550) and a photoelectric signal conversion and signal recording device (560), wherein the wide-spectrum light source (501) is connected with the to-be-tested optical fiber device (522) through the polarizer (511) and a first rotary connector (521) and is connected with the optical path correlator (530) with a polarization beam splitting Michelson structure through a second rotary connector (523); and the optical path correlator (530) is connected with the polarization difference detector (550) through a third rotary connector (541) and is connected with an interference signal detecting and processing device (560). The all-fiber testing device has the advantages of small size, high measurement accuracy, high temperature and vibration stability and the like, so that the all-fiber testing device is widely applied to high-accuracy measurement and analysis of the polarization performance of the optical device.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Vector beam generator using a passively phase stable optical interferometer
InactiveUS20060268408A1Improvement in point spread functionIncrease pointsProjectorsPhotomechanical apparatusWavefrontBeam splitting
Provided are techniques for generating optical vector beams (e.g., radially and azimuthally polarized light) using passive or active phase stable optical interferometry. Techniques may split an input optical beam into at least two output beams, and then couple those beams simultaneously into a passively phase stable optical interferometer. Beam splitting may be achieved by a diffractive optical element and coupling may be achieved by a single refractive optical device (lenses) or by a single mirror device (e.g., parabolic and spherical). The interferometer may provide the ability to manipulate (or transform) the polarization of part of the wavefront of each beam, as well as the ability to manipulate (or transform) the phase of part of the wavefront of each beam, such that the beams when combined have a vector beam polarization state.
Owner:CHICAGO UNIV OF
Polarization beam splitter and optical system using the same, and image displaying apparatus, using the same
In a conventional polarization beam splitter, it has been difficult to improve the angle-dependence characteristic of polarized beam splitting efficiency even if the number of layers is increased. The polarization beam splitter of the present invention is a polarization beam splitter having a polarized beam splitting layer having structure in which a plurality of gratings parallel to a first direction are periodically disposed in a second direction orthogonal to the first direction, and of light incident on the polarization beam splitter, chiefly light of a polarized component parallel to the first direction is transmitted therethrough, and chiefly light of a polarized component parallel to the second direction is reflected.
Owner:CANON KK
Imaging spectrometer absolute radiation calibration method
ActiveCN102829868ARealize full-band absolute radiometric calibrationSolving the challenge of absolute radiometric calibrationSpectrum investigationIlluminanceRadiometer
The invention discloses an imaging spectrometer absolute radiation calibration method and belongs to the field of optical metrological testing. The method utilizes a high-stability radiation source combination imaging system, a beam-splitting system and an integrating sphere to generate uniform monocolor radiation through a heavy-caliber parallel collimator to form collimated radiation to be received by a standard radiometer with a precise diaphragm and a measured imaging spectrometer, spectral radiant luminance on an entrance pupil face of the measured imaging spectrometer is calibrated by the standard radiometer, and full wavelength absolute radiation calibration of the imaging spectrometer can be realized. The imaging spectrometer absolute radiation calibration method solves the problem of absolute radiation calibration of current imaging spectrometers, measuring of responsivity uniformity of the imaging spectrometer can also be realized, and the imaging spectrometer absolute radiation calibration method has the advantages of high calibration accuracy and wide application prospect.
Owner:中国兵器工业第二0五研究所
Diopter-adjustable curved surface waveguide near-to-eye optical display device
ActiveCN104656258ALarge field of viewImprove energy utilizationOptical elementsBeam splittingHigh energy
The invention provides a diopter-adjustable curved surface waveguide near-to-eye optical display device which comprises an image display light source used for providing image information used for observation, a collimating lens set used for collimating optical waves, a PBS (polarization beam-splitting) assembly used for performing polarization beam-splitting on the optical waves, a P&S photo-conversion assembly used for realizing conversion of P light and S light, a P&S beam-splitting selection assembly capable of enabling the optical waves to uniformly cover a coupling input surface, a micro-curved surface waveguide substrate used for performing total-reflection propagation on the optical waves, and a micro-local curvature coupling output surface used for enabling the transmitted optical waves to be coupled and output out of the substrate, expanding a view field angle and adjusting the diopter. The diopter-adjustable curved surface waveguide near-to-eye optical display device has the advantages of adjustable diopter, lightweight, thinness, large view field angle, simplicity for processing and design, easiness for realization, compact structure and high energy utilization rate of an image source, can be used in various fields of remote medical information teaching, virtual reality simulation training, fire rescue information positioning guidance, road enhancement display and the like, and can be used as a display of a terminal.
Owner:SHANGHAI RAYPAI PHOTONIC CRYSTAL LTD
Display unit, display method and equipment using thereof
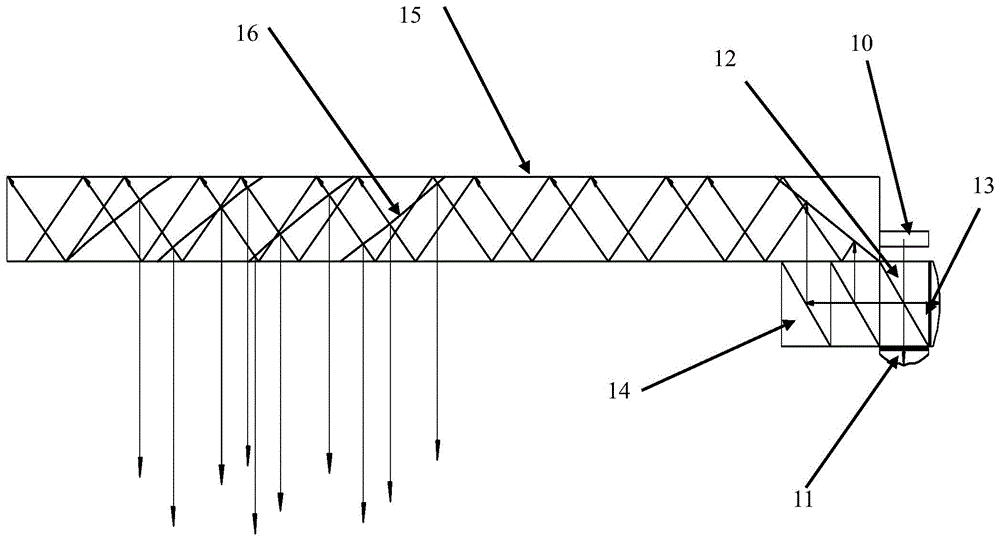
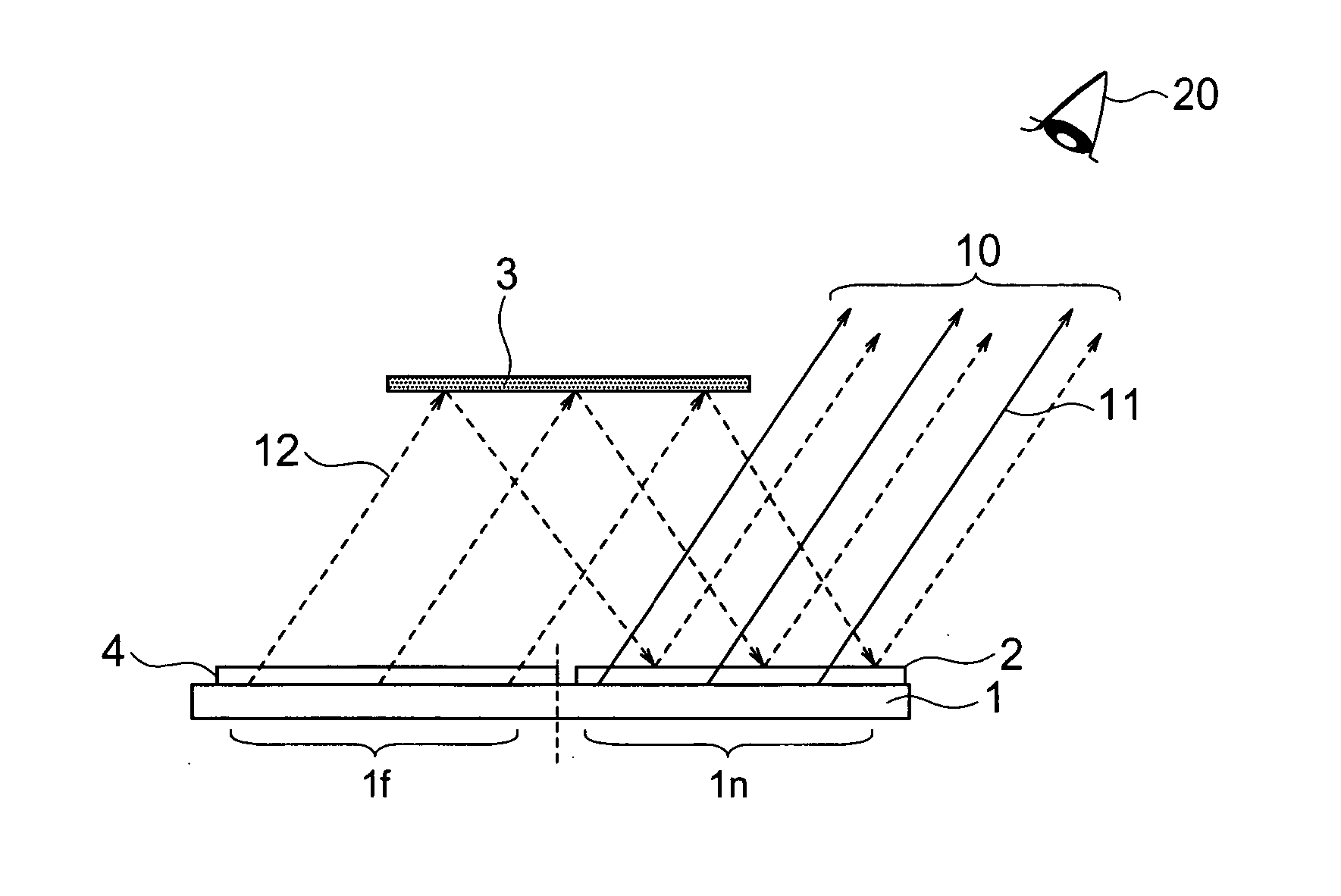
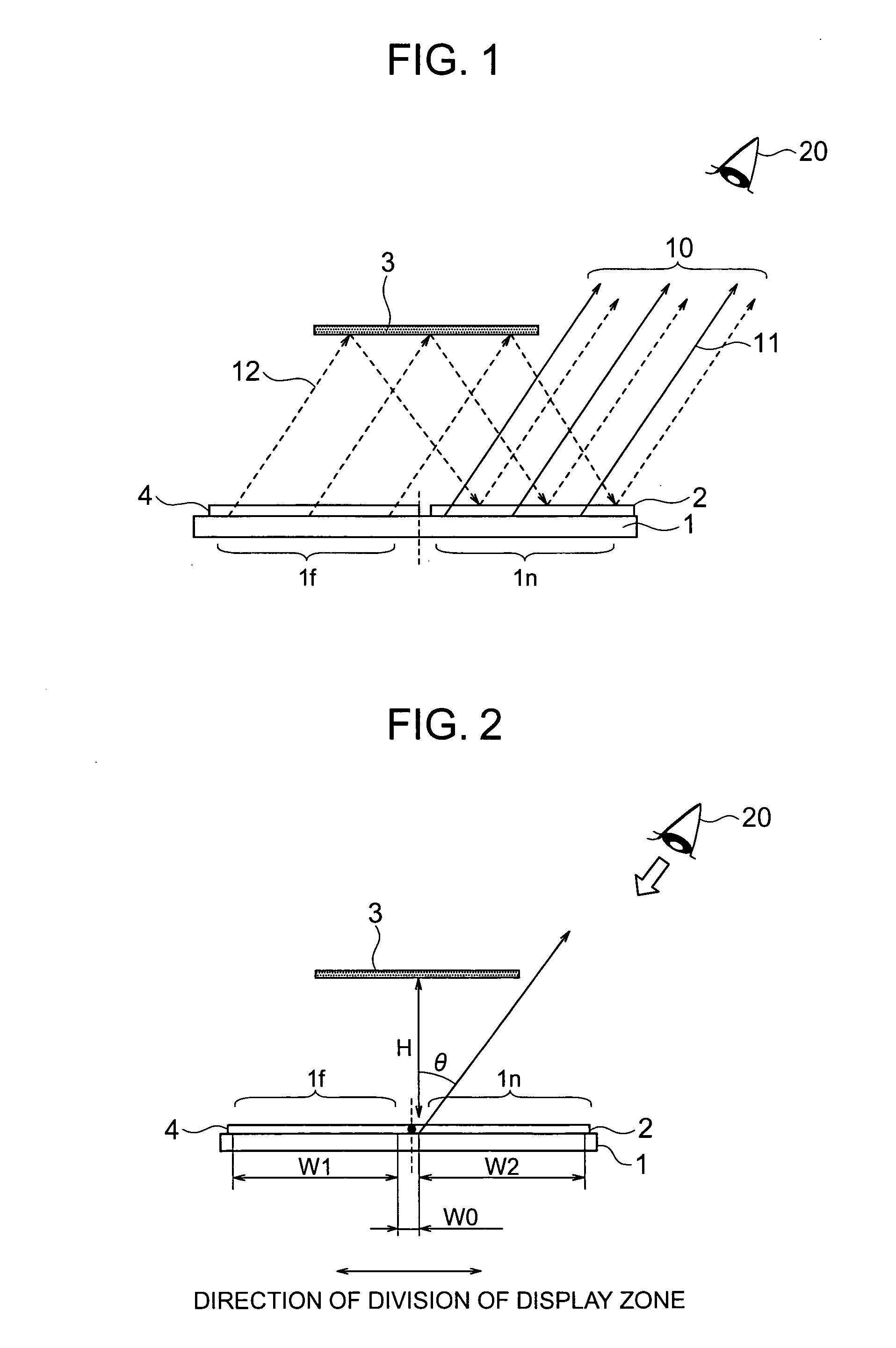
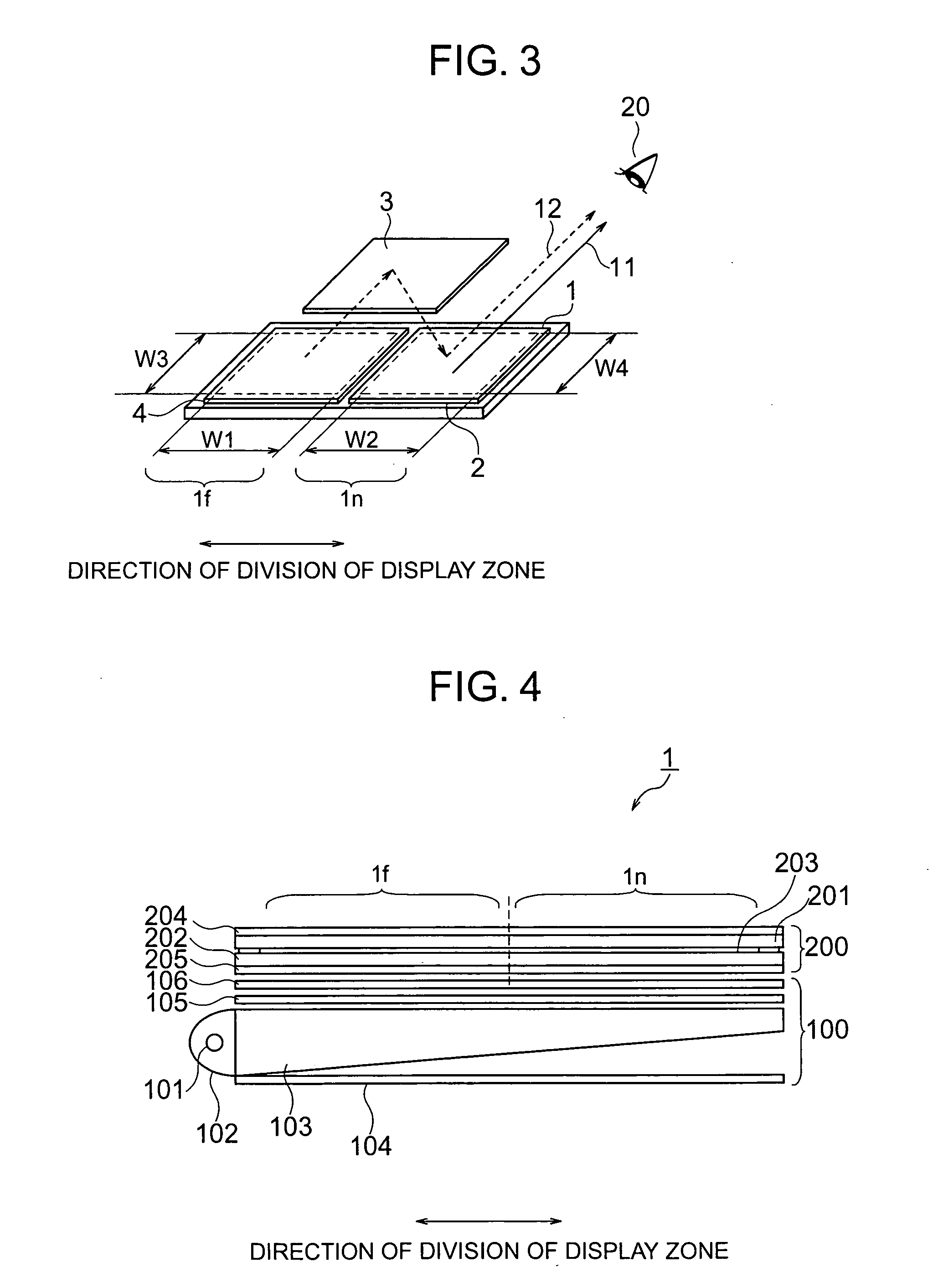
ActiveUS20050156813A1Reduce in quantityPrevent number of componentCathode-ray tube indicatorsSteroscopic systemsBeam splittingDisplay device
A thin display unit which display a plurality of objects to be viewed located at different depthwise positions viewed from the viewer so as to exhibit an image with depthwise feeling, comprising: a single display portion having a screen which is divided into a far-distant display zone and a near-distant display zone, a polarized beam splitting element located in front of the near-distant display zone, a polarized beam changing element located in front of the far-distant display zone, and a total reflection mirror for reflecting an image beam emitted from the far-distant display zone, onto the polarized beam splitting element, wherein an image beam emitted from the near-distant display zone is transmitted through the polarized beam splitting element and then viewed by the viewer, and an image beam emitted from the far-distant display zone is transmitted through the polarized beam changing element, then is reflected at the total reflection mirror, and thereafter is reflected by the polarized beam splitting element before it is viewed by the viewer.
Owner:PANASONIC LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY CO LTD +1
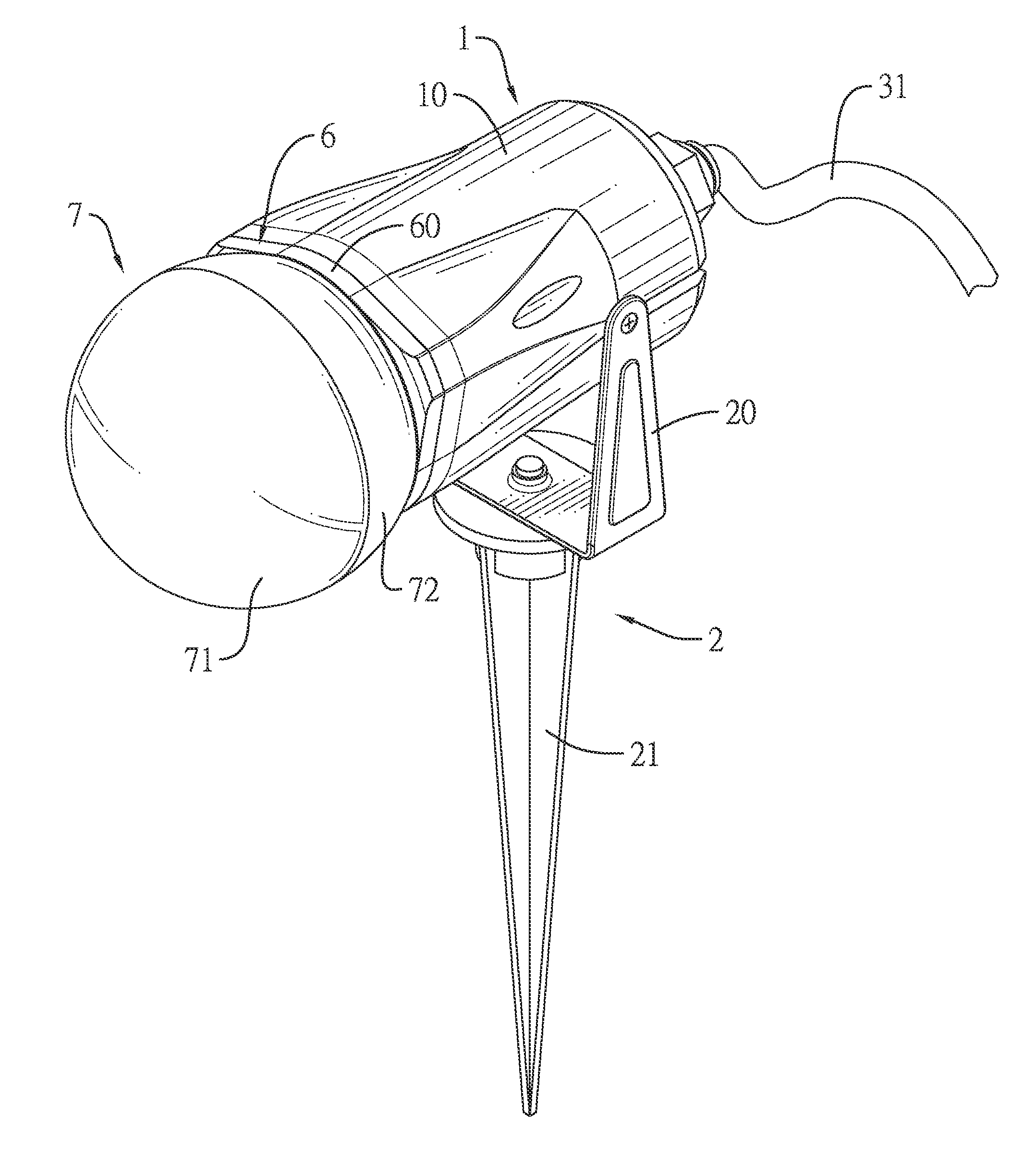
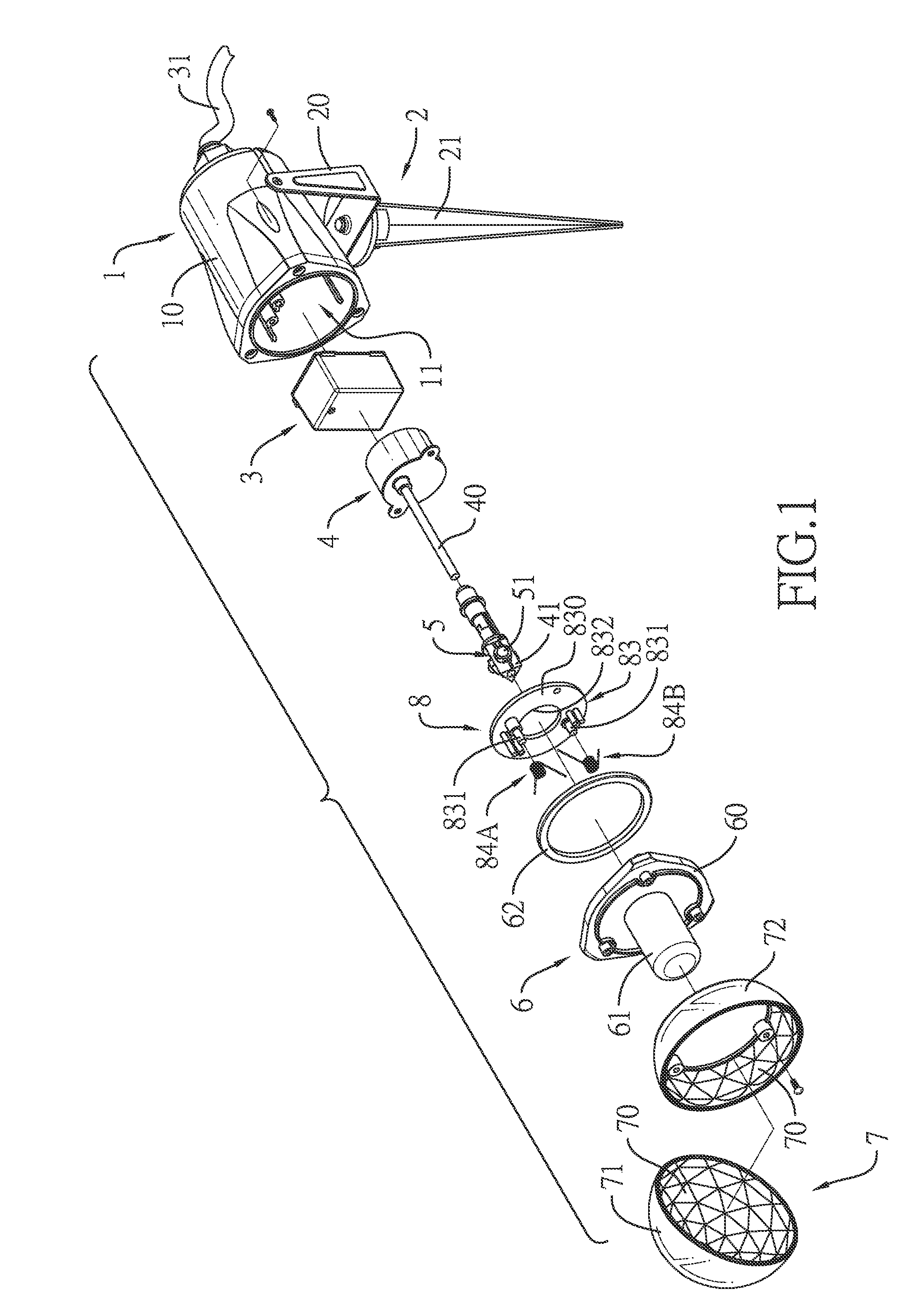
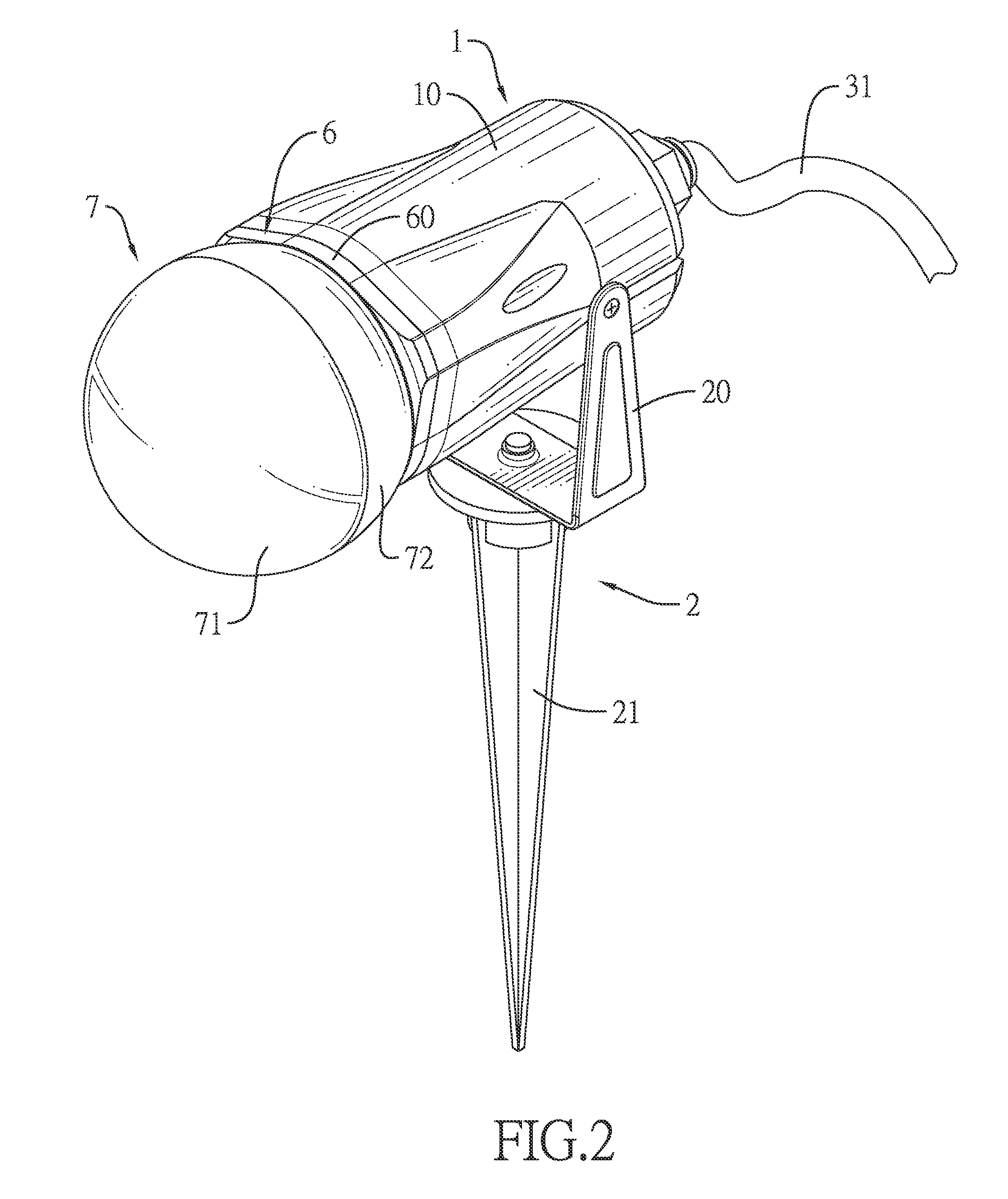
Rotary projector light
A rotary projector light can include a lamp case defining a hollow mounting chamber and having an open front end; a power supply located inside the lamp case, the power supply connected to a power cable adapted to connect to an external power source; a motor located inside the lamp case, the motor electrically connected to the power supply and having a spindle; a positioning seat mounted on the spindle; a plurality of light emitting diode (LED) elements located on the positioning seat, the LED elements electrically connected to the power supply; and a beam-splitting lens cover located on the open front end of the lamp case. The beam-splitting lens cover can have an inner surface with multiple convex lenses directed at multiple refraction angles.
Owner:GEMMY IND CORP
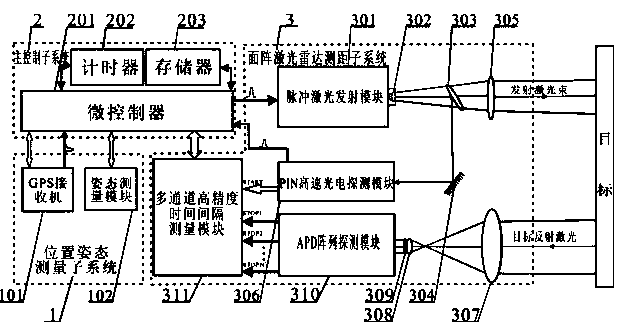
Small low-altitude light area array laser radar measuring system
ActiveCN103412313ASmall sizeReduce weightElectromagnetic wave reradiationBeam splittingOptoelectronics
The invention discloses a small low-altitude light area array laser radar measuring system. The master control sub-system of the measuring system triggers a pulse laser emitting module to emit lasers, the lasers are collimated and generate two paths of laser signals through a beam splitting sheet, one path is used for determining the time of emitting the lasers and generating timing starting signals, the other path irradiates an object through beam expansion, echo signals are received by an APD array detection module and generate N2 paths of stopping pulses, and a multi-channel high-precision time interval measuring module is combined with starting signals to measure the round-trip flight time difference of N2 paths of lasers of a rectangular detection area. The location attitude measuring sub-system, the master control sub-system and the area array laser radar distance-measuring sub-system of the measuring system are integrated, original three-dimensional information can be obtained in real time, and assembling and verification are eliminated. The laser radar measuring system does not need scanning, three-dimensional imaging can be achieved through a single pulse, the imaging speed is high, measuring precision and working efficiency are high, the size is small, the weight is small, and the small low-altitude light area array laser radar measuring system is suitable for being carried small low-altitude light remote sensing platforms.
Owner:GUILIN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Forward Scanning OCT Endoscope
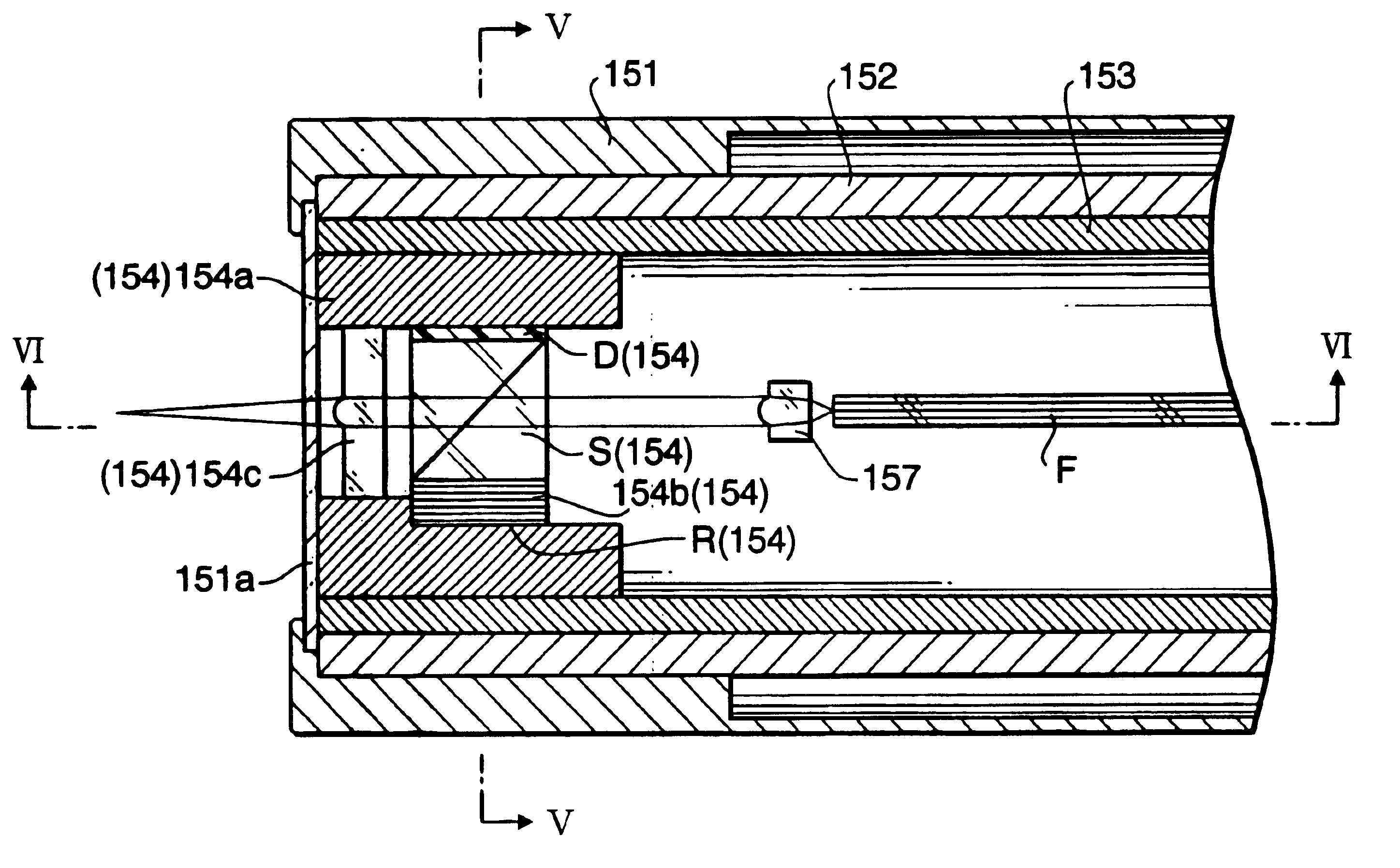
InactiveUS20100292539A1Compact and narrow designLikely can be usedSurgeryEndoscopesBeam splittingRefractive index
An apparatus for optical coherence tomography has a broadband light source with a short coherence length, an optical fiber that guides the light from the light source to a focusing optics, and a graded-index optics arranged between the optical fiber and the focusing optics with two opposite parallel flat sides, that is contacted on its first flat side by the optical fiber forming an irradiation point guiding light to the graded-index optics and having a pitch of N / 8, N being a natural number that cannot be divided by 4. A first structure for light reflection is arranged on the first flat side of the graded-index optics adjacent to the irradiation point, and a second structure for beam splitting is arranged on the second flat side of the graded-index optics. The focusing optics are designed for focusing the light transmitted by the second structure essentially at right angles to the flat sides of the graded-index optics.
Owner:MEDIZINISCHES LASERZENTRUM LUEBECK GMBH
Tapered fused waveguide for delivering treatment electromagnetic radiation toward a target surfaced
Owner:BIOLASE INC
Apparatus for implementing orbit angular momentum state super position and modulation
InactiveCN101251655AAchieve overlayGood for long-distance transmissionDiffraction gratingsNon-linear opticsBeam splittingPolarizer
The invention relates to a device for realizing superposition and modulation of orbital angular momentum states of light beams, belonging to the laser application technical field. The invention consists of a laser, a polarizer, a one-fourth wave plate, a diffraction grating, a Fourier lens, a polarized beam-splitting prism, two Dove prisms, three holophotes and a pinhole diaphragm, wherein, firstly, an optical system which takes the diffraction grating and the Fourier lens as core elements is adopted to generate a plurality of bundles of light beams which are equidistantly distributed on the circumference which takes an optical axis of incident light as the center and are positioned in different orbital angular momentum states; secondly, an optical system which consists of the polarized beam-splitting prism, the holophotes and the rotatable Dove prisms is adopted to decompose an optical field into field components which rotate towards the opposite direction; thirdly, the field components are superposed, and superposition of required orbital angular momentum states is realized and then superposition and modulation of the orbital angular momentum states are realized. The device for realizing superposition and modulation of the orbital angular momentum states of the light beams has application value in the free space optical communication field.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com