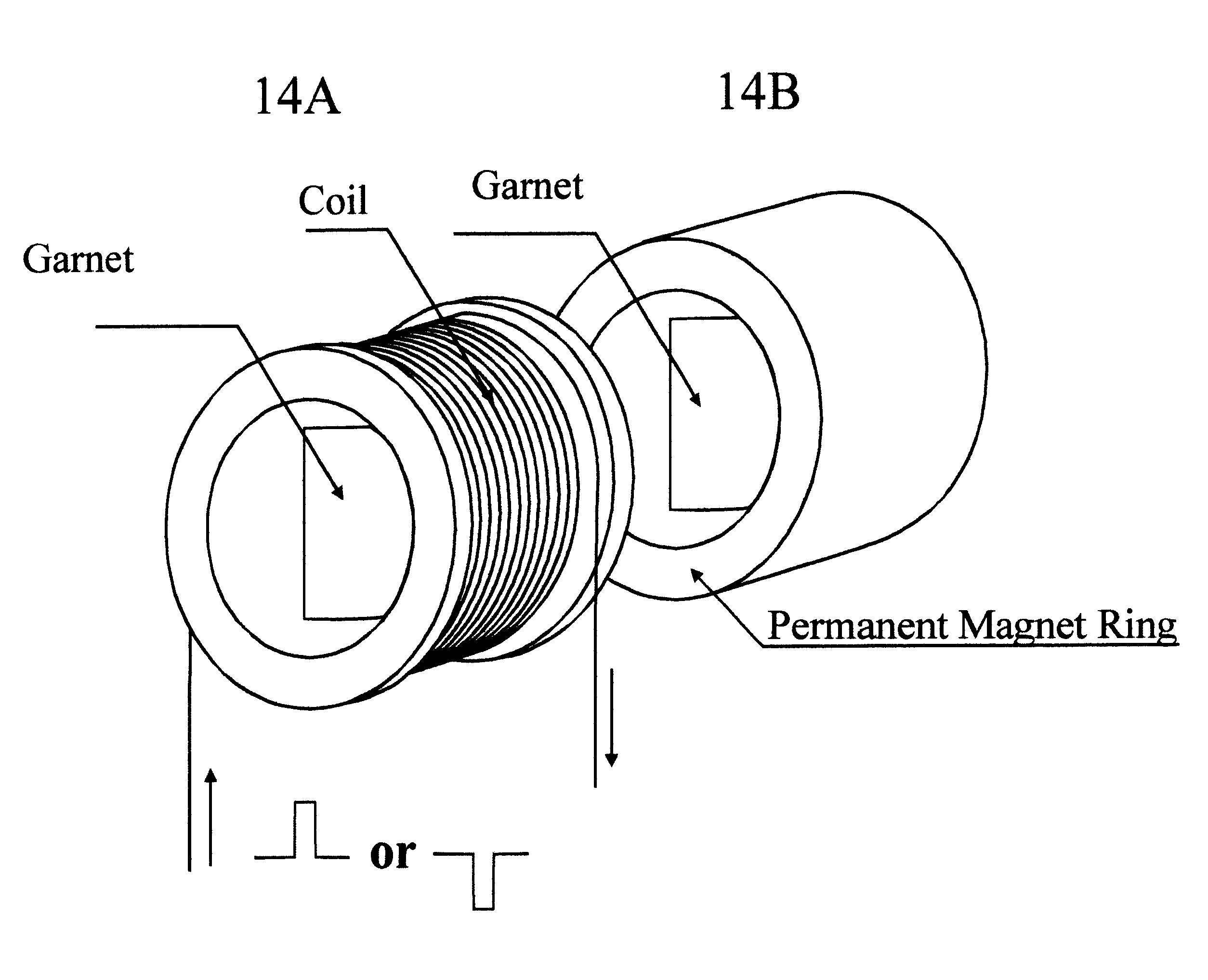
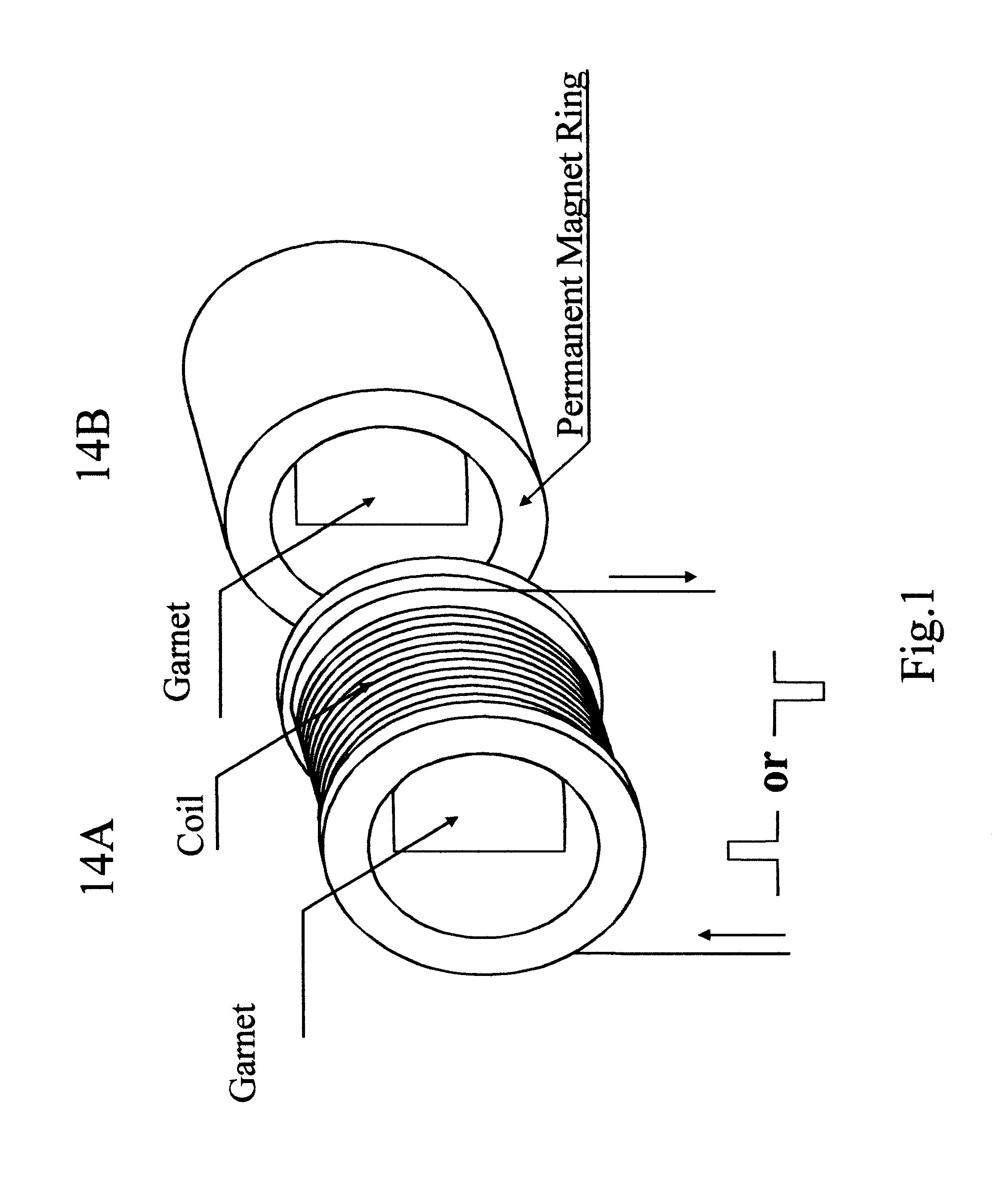
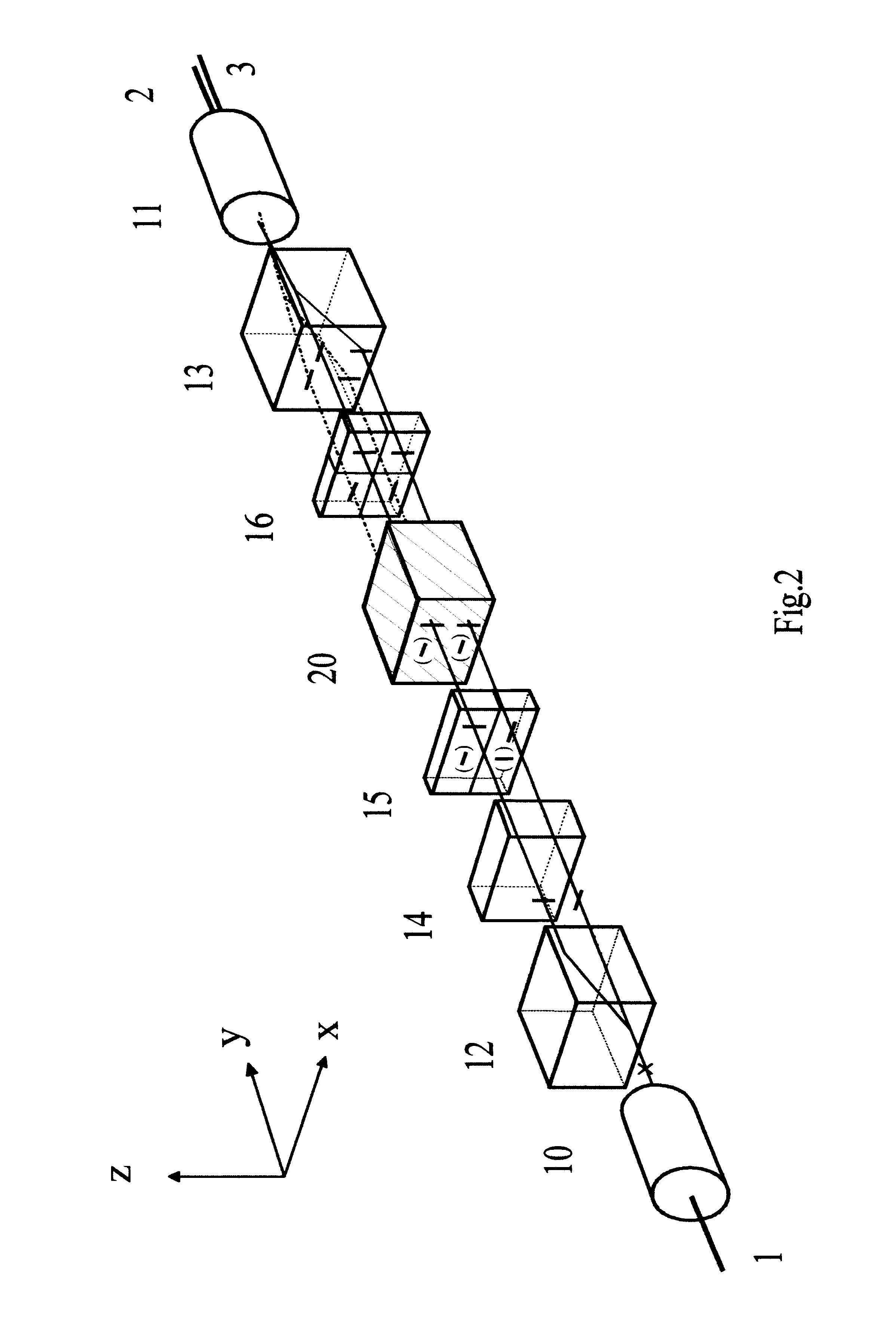
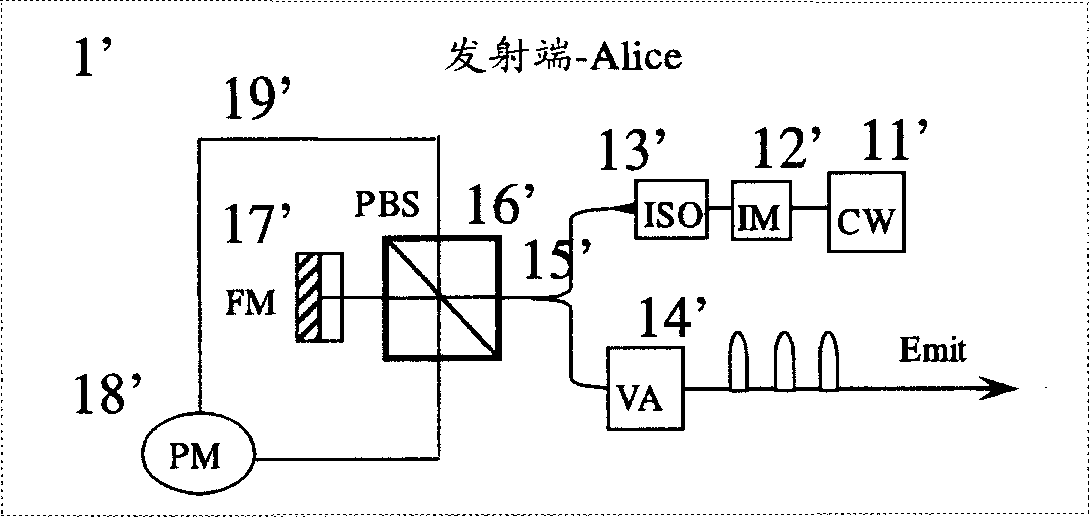
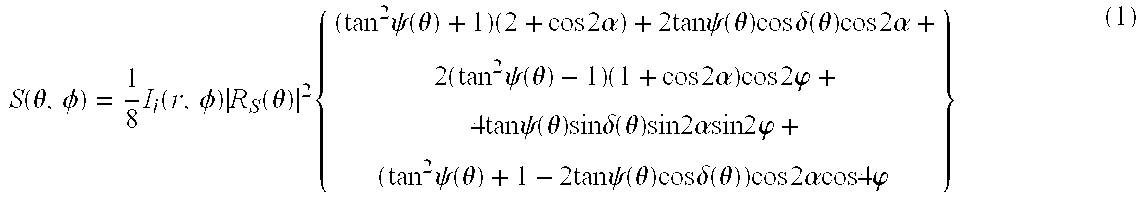Patents
Literature
209 results about "Beam polarization" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A light beam is called unpolarized when the analysis with a polarizer results in 50% of the power to be in each polarization state, regardless of the rotational orientation. Microscopically, this usually means that the polarization state is randomly fluctuating, so that on average no polarization is detected.
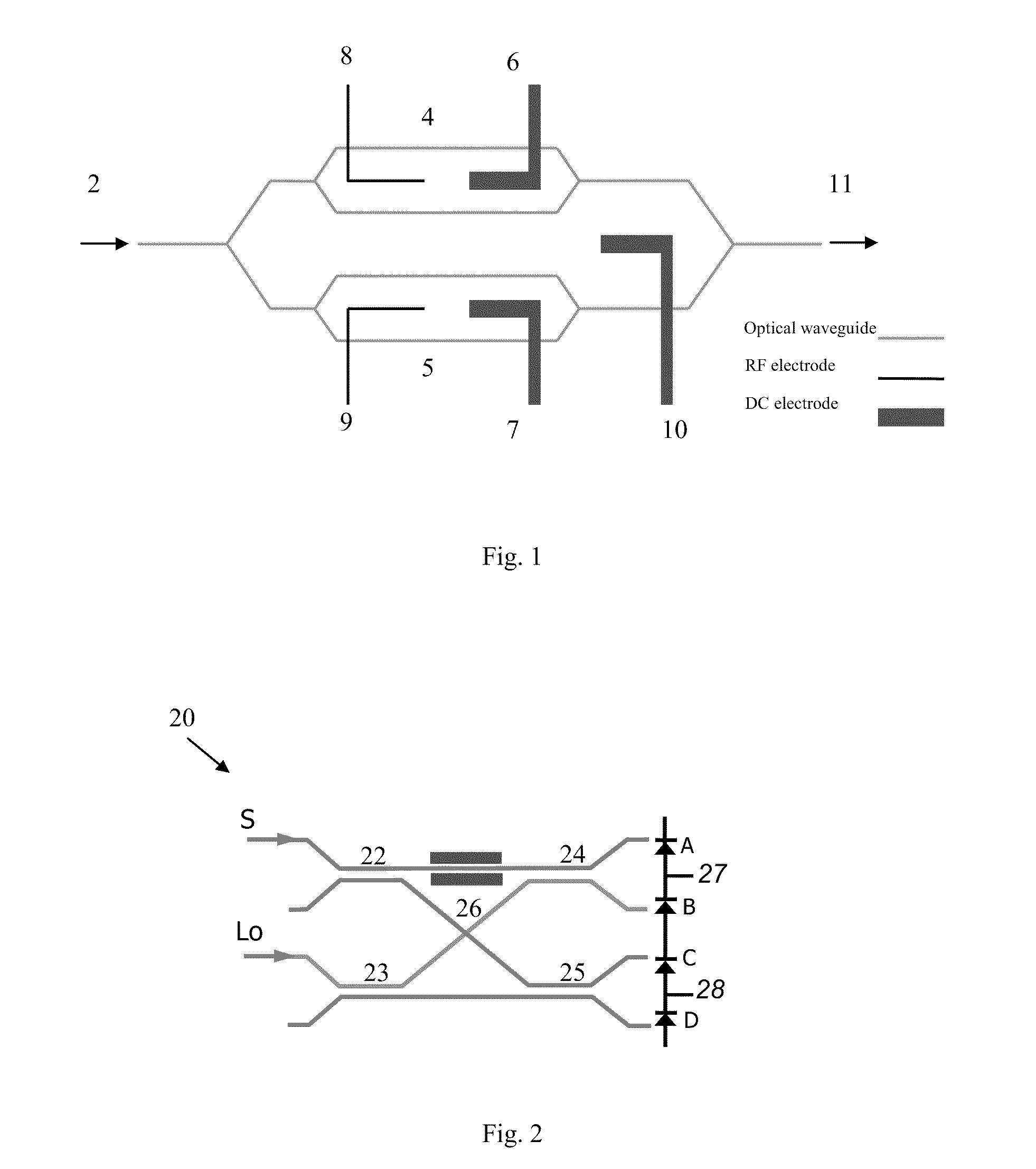
Device capable of switching between an image display status and a mirror status, and an instrument disposed therewith
InactiveUS7495719B2Efficient processImprove usabilityNon-linear opticsBeam polarizationComputer science
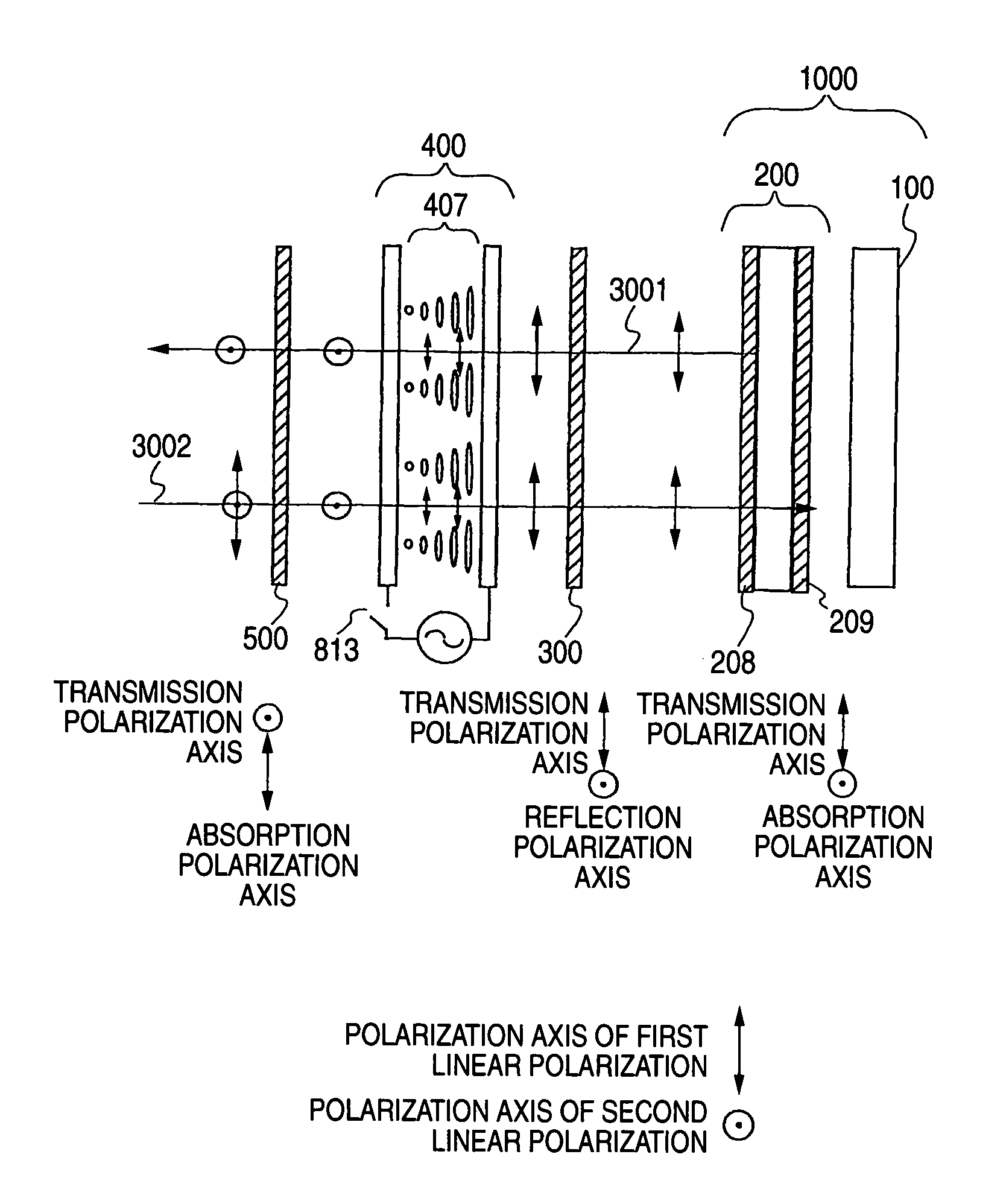
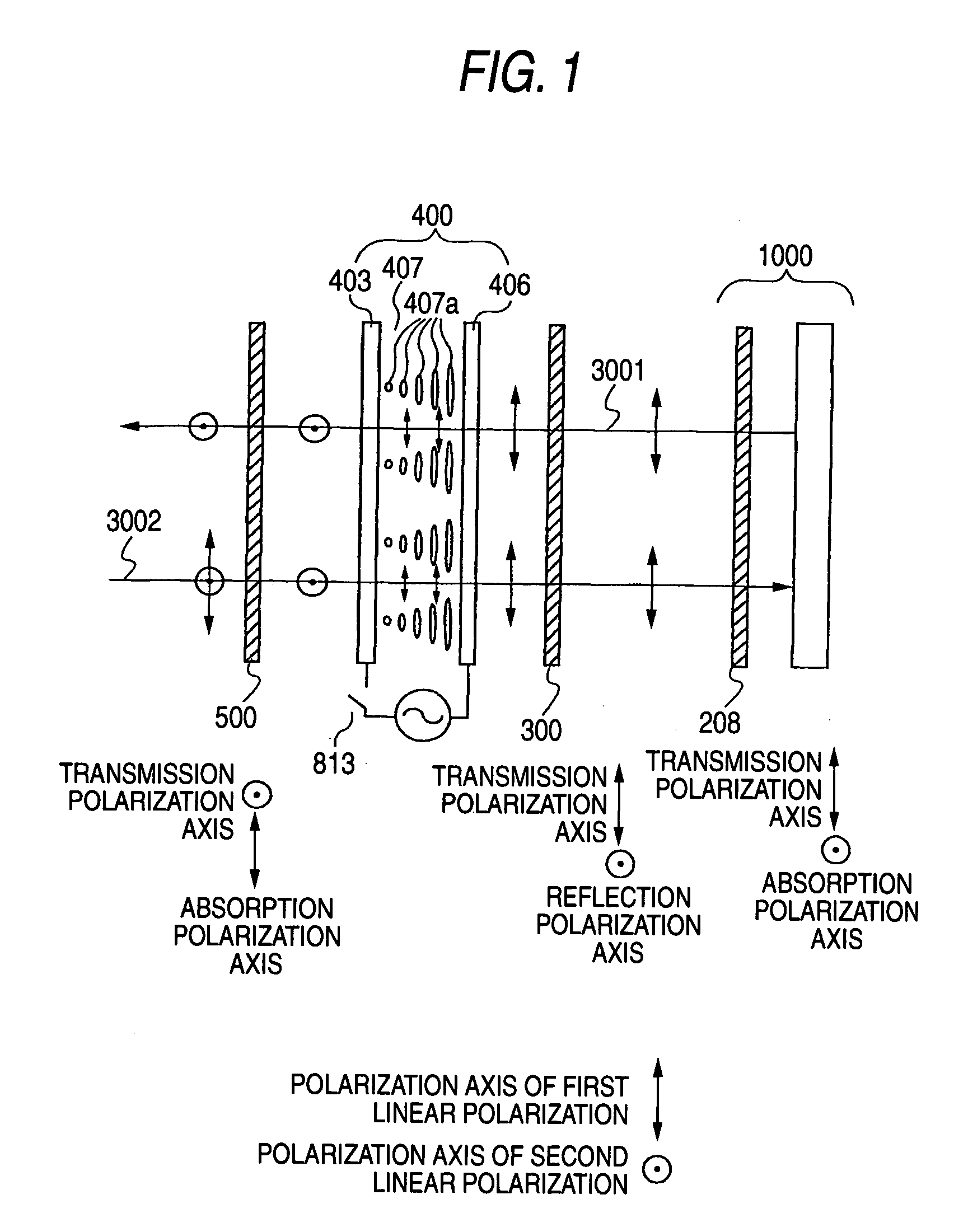
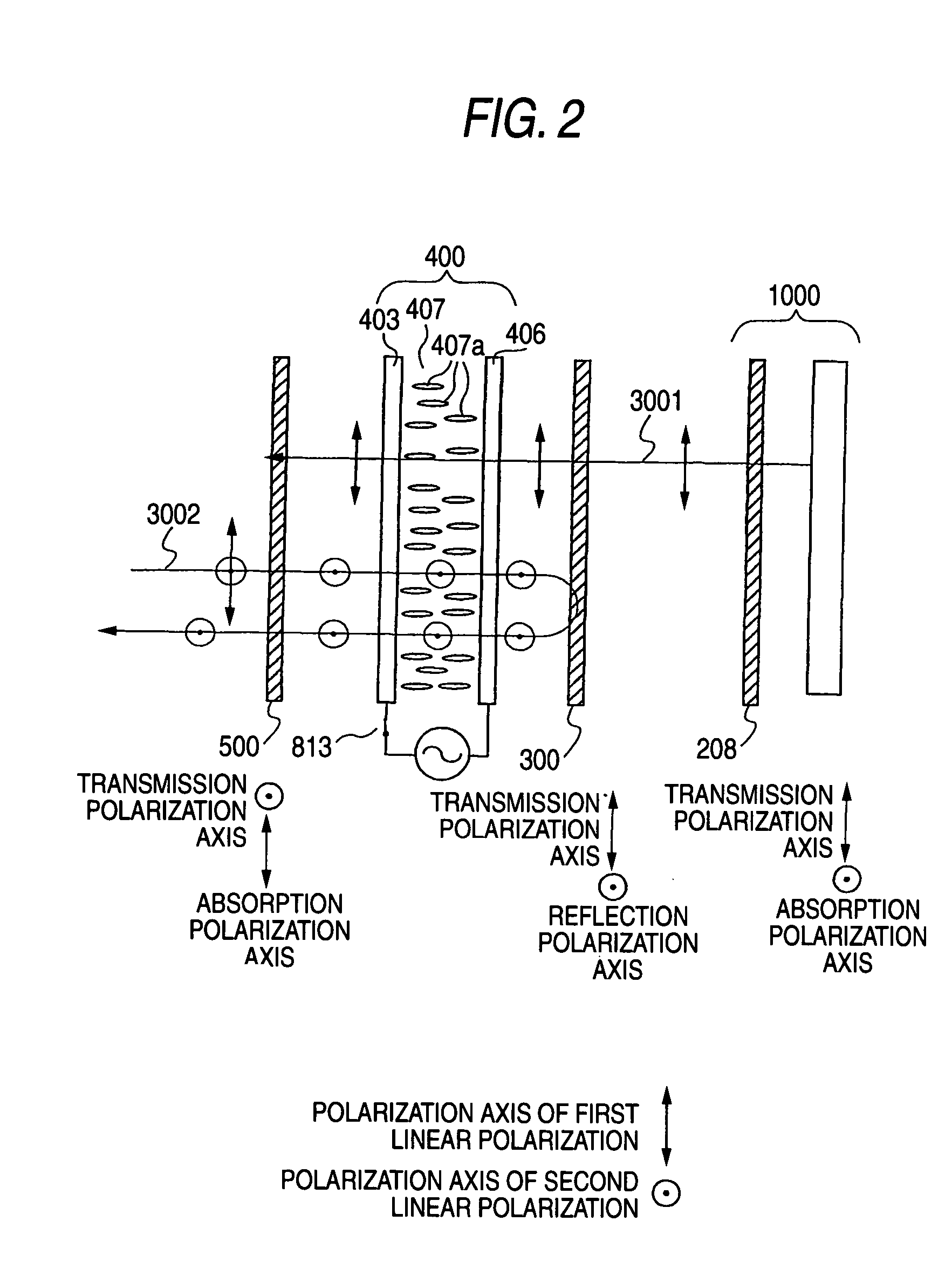
There is provided a device capable of switching between a state that displays a high-quality image and a mirror status in which is obtained an easy-to-view reflection image suitable for a person to view his / her own face or figure. An image display portion 1000 that emits image light 3001, reflective polarization selection means 300 that transmits a first linear polarization component emitted from the image display portion 1000 and reflects a second linear polarization component, whose polarization axis is orthogonal to that of the first linear polarization component, a transmission polarization axis variable portion 400 capable of selecting between one of a state that changes the polarization axis of incident linearly polarized light and a state that does not change the polarization axis of incident linearly polarized light, and a polarization selection member 500 which, of the incident light, absorbs the first linear polarization component and transmits the second linear polarization component, whose polarization axis is orthogonal to that of the first linear polarization component, are disposed in this order. In this case, absorbing polarization selection means 208 is disposed at the image display portion 1000, and the first linear polarization is emitted as the image light.
Owner:PANASONIC LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY CO LTD +1
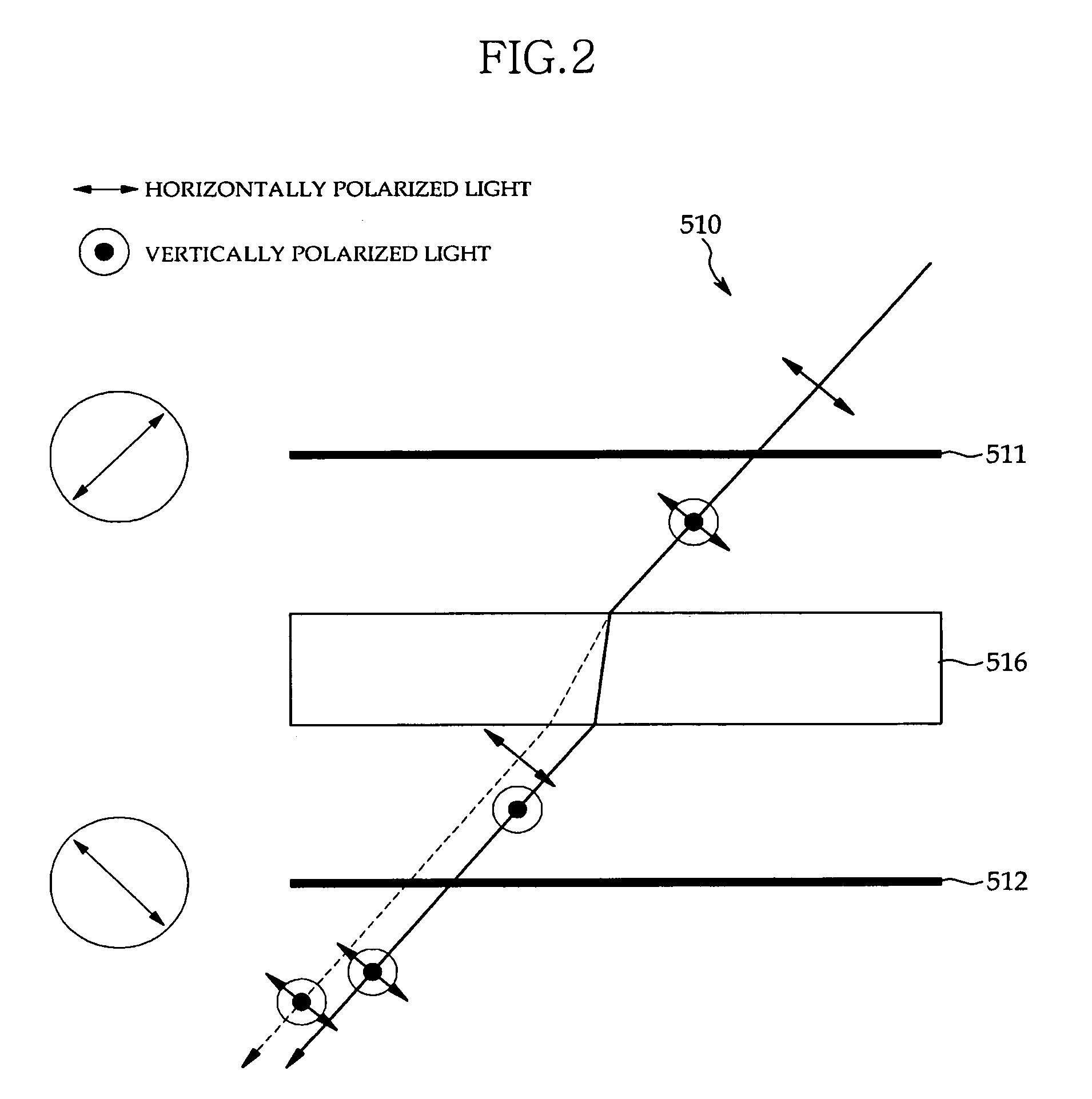
Confocal self-interference microscopy from which side lobe has been removed
The present invention relates to confocal self-interference microscopy. The confocal self-interference microscopy further includes a first polarizer for polarizing reflected or fluorescent light from a specimen, a first birefringence wave plate for separating the light from the first polarizer into two beams along a polarizing direction, a second polarizer for polarizing the two beams from the first birefringence wave plate, a second birefringence wave plate for separating the two beams from the second polarizer into four beams along the polarizing direction, and a third polarizer for polarizing the four beams from the second birefringence wave plate, in the existing confocal microscopy. Optic-axes of the first and second birefringence wave plates exist on the same plane, optic-axes of the first and second birefringence wave plates are inclined from an optical axis of the entire optical system at a predetermined angle, and self-interference spatial periods of the first and second birefringence wave plates are different from each other.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
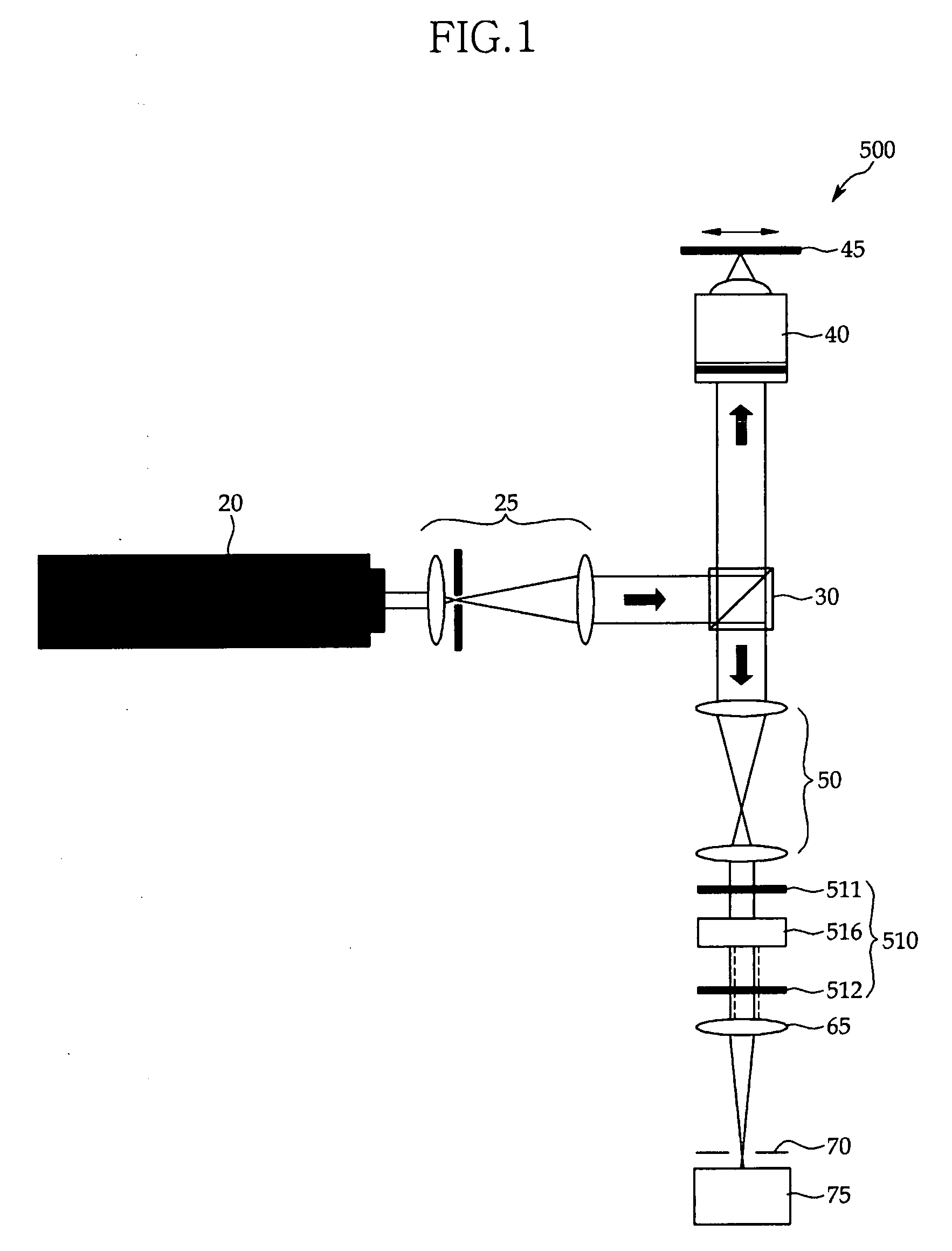
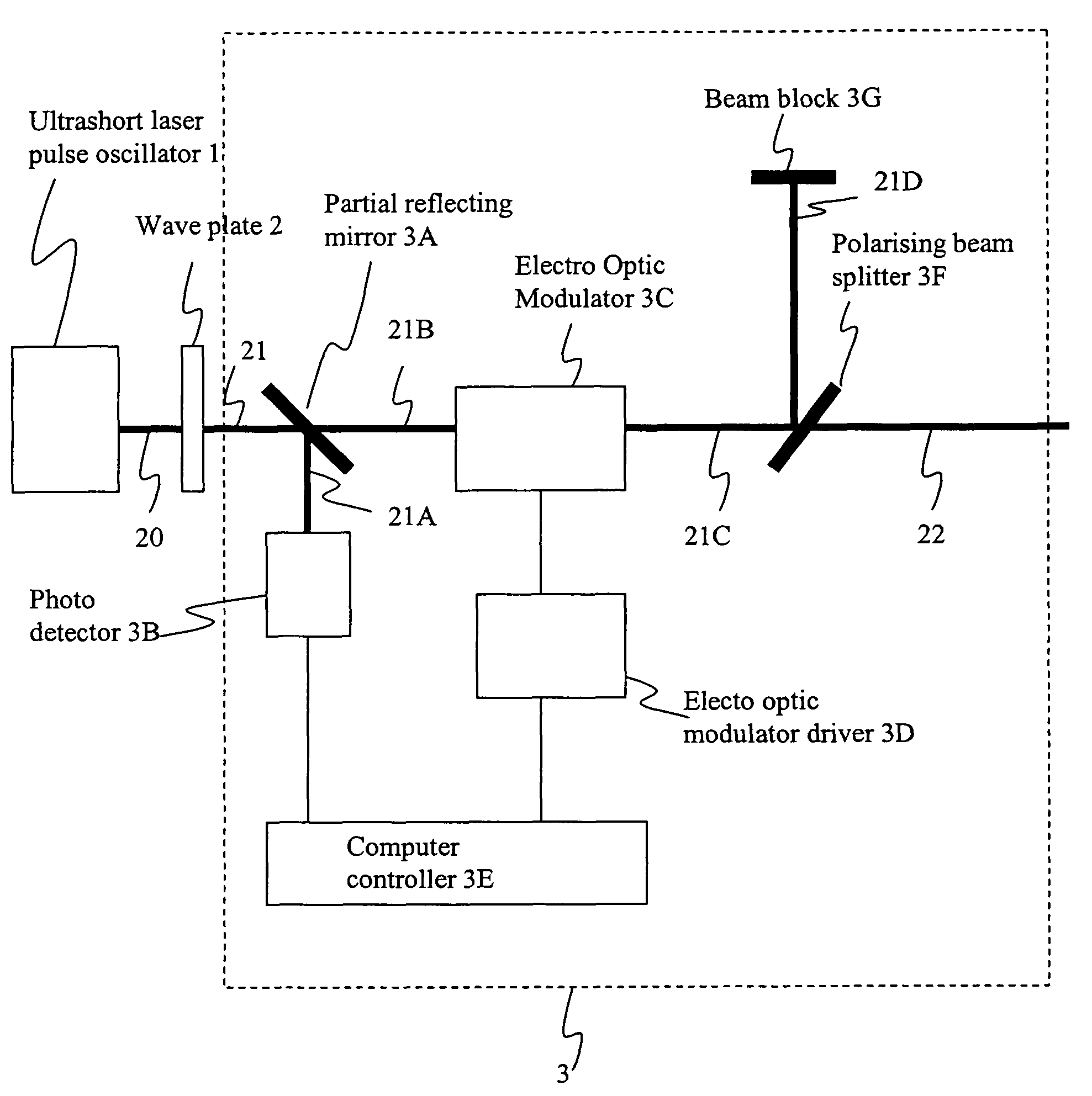
Method and apparatus for dicing of thin and ultra thin semiconductor wafer using ultrafast pulse laser
InactiveUS7804043B2Minimize heating effectImprove machine qualityWelding/soldering/cutting articlesMetal working apparatusPicosecond laserBeam polarization
The present invention relates to the apparatus, system and method for dicing of semiconductor wafers using an ultrafast laser pulse of femtosecond and picosecond pulse widths directly from the ultrafast laser oscillator without an amplifier. Thin and ultrathin semiconductor wafers below 250 micrometer thickness, are diced using diode pumped, solid state mode locked ultrafast laser pulses from oscillator without amplification. The invention disclosed has means to avoid / reduce the cumulative heating effect and to avoid machine quality degrading in multi shot ablation. Also the disclosed invention provides means to change the polarization state of the laser beam to reduce the focused spot size, and improve the machining efficiency and quality. The disclosed invention provides a cost effective and stable system for high volume manufacturing applications. An ultrafast laser oscillator can be a called as femtosecond laser oscillator or a picosecond laser oscillator depending on the pulse width of the laser beam generated.
Owner:LASERFACTURING
Reflective LCD projection system using wide-angle Cartesian polarizing beam splitter and color separation and recombination prisms
InactiveUS7023602B2Increase contrastImprove light outputProjectorsPolarising elementsBeam splitterBeam polarization
An optical imaging system including an illumination system, a Cartesian PBS, and a prism assembly. The illumination system provides a beam of light, the illumination system having an f / # less than or equal to 2.5. The Cartesian polarizing beam-splitter has a first tilt axis, oriented to receive the beam of light. A first polarized beam of light having one polarization direction is folded by the Cartesian polarizing beam splitter and a second polarized beam of light having a second polarization direction is transmitted by the Cartesian polarizing beam splitter. The Cartesian polarizing beam splitter nominally polarizes the beam of light with respect to the Cartesian beam-splitter to yield the first polarized beam in the first polarization direction. The color separation and recombination prism is optically aligned to receive the first polarized beam. The prism has a second tilt axis, a plurality of color separating surfaces, and a plurality of exit surfaces. The second tilt axis maybe oriented perpendicularly to the first tilt axis of the Cartesian polarizing beam-splitter so that the polarized beam is nominally polarization rotated into the second polarization direction with respect to the color separating surfaces and a respective beam of colored light exits through each of the exit surfaces. Each imager is placed at one of the exit surface of the color separating and recombining prism to receive one of the respective beams of colored light, wherein each imager can separately modulate the polarization state of the beam of colored light.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Improved free space optical bus
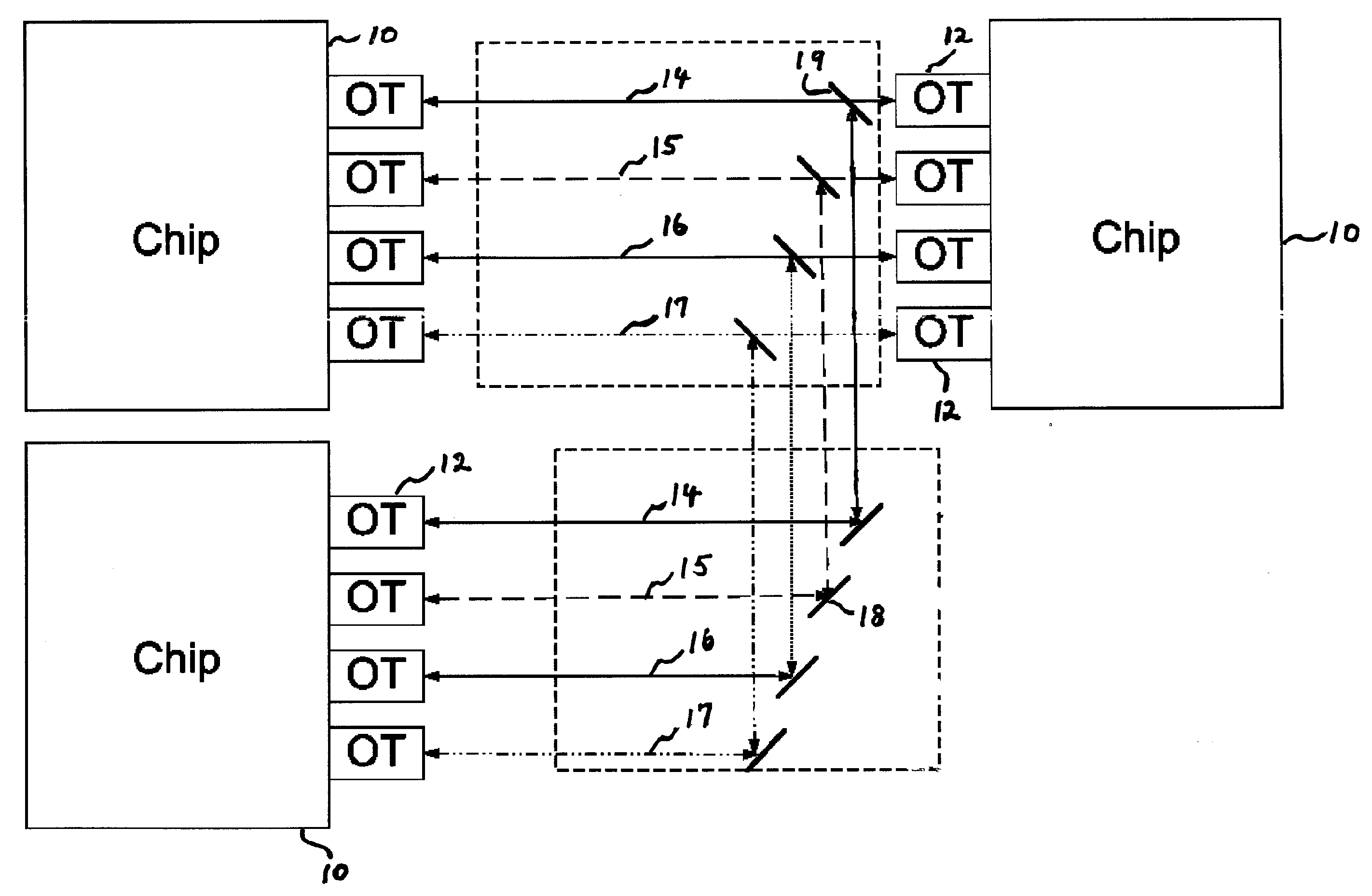
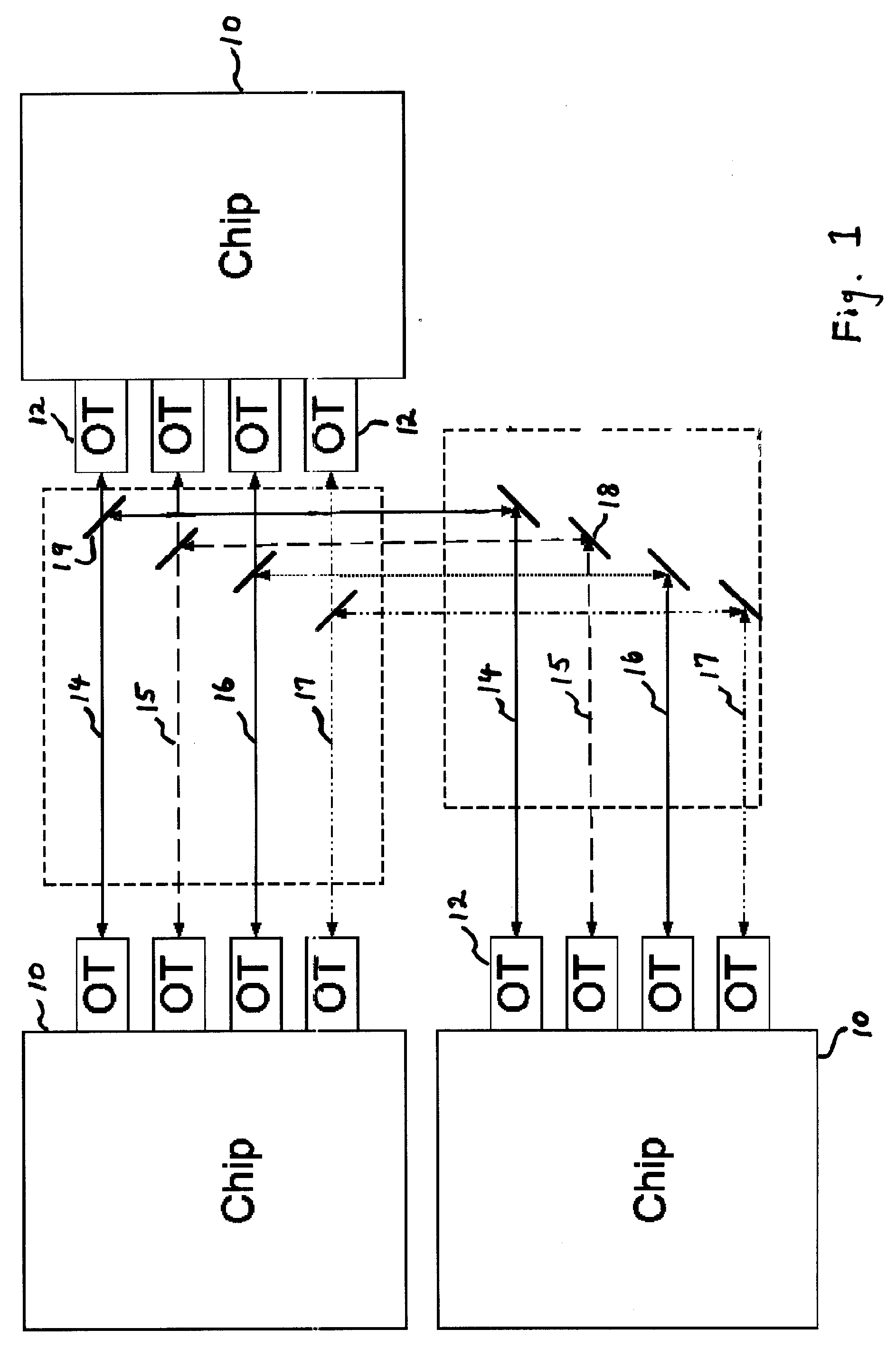
InactiveUS20060251421A1Quality improvementImprove transmission qualityNetwork traffic/resource managementPolarisation/directional diversityCross-linkAntenna gain
A method and apparatus for improving the transmission quality of a free space optical bus between circuitry elements in high speed computing, communication and signal processing systems. Use is made of an adaptive algorithm that learns the transmission properties of the bus, and selects or adjusts transmission paths or characteristics to provide optimum bus performance. Each transmitter on the bus transmits a signal which is generally measured by all of the receivers on the bus, and the measured signals are used to generate a matrix which maps desired transmission along information links, and cross-link interference. Transmission quality is optimized by adjusting one or more characteristics associated with transmission along the bus, including emitted power, beam divergence, wavelength, beam polarization, antenna gain and antenna polar diagram of the transmitters, and power sensitivity, gain, equalizer coefficients, field of view, polarization sensitivity, antenna gain and antenna polar diagram of the receivers. Novel bus configurations are described, including use of different wavelengths for different bus functions.
Owner:BEN GURION UNIVERSITY OF THE NEGEV
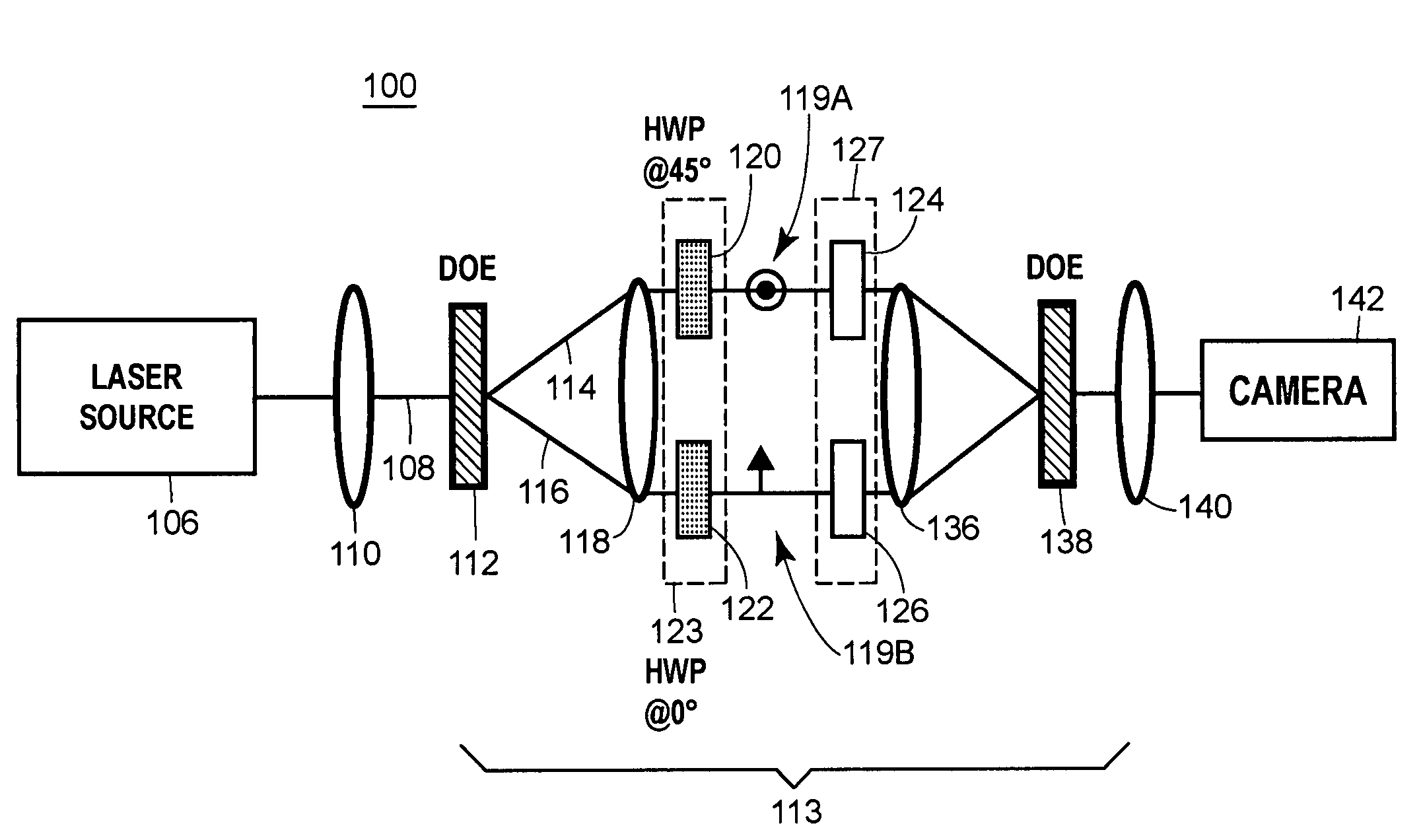
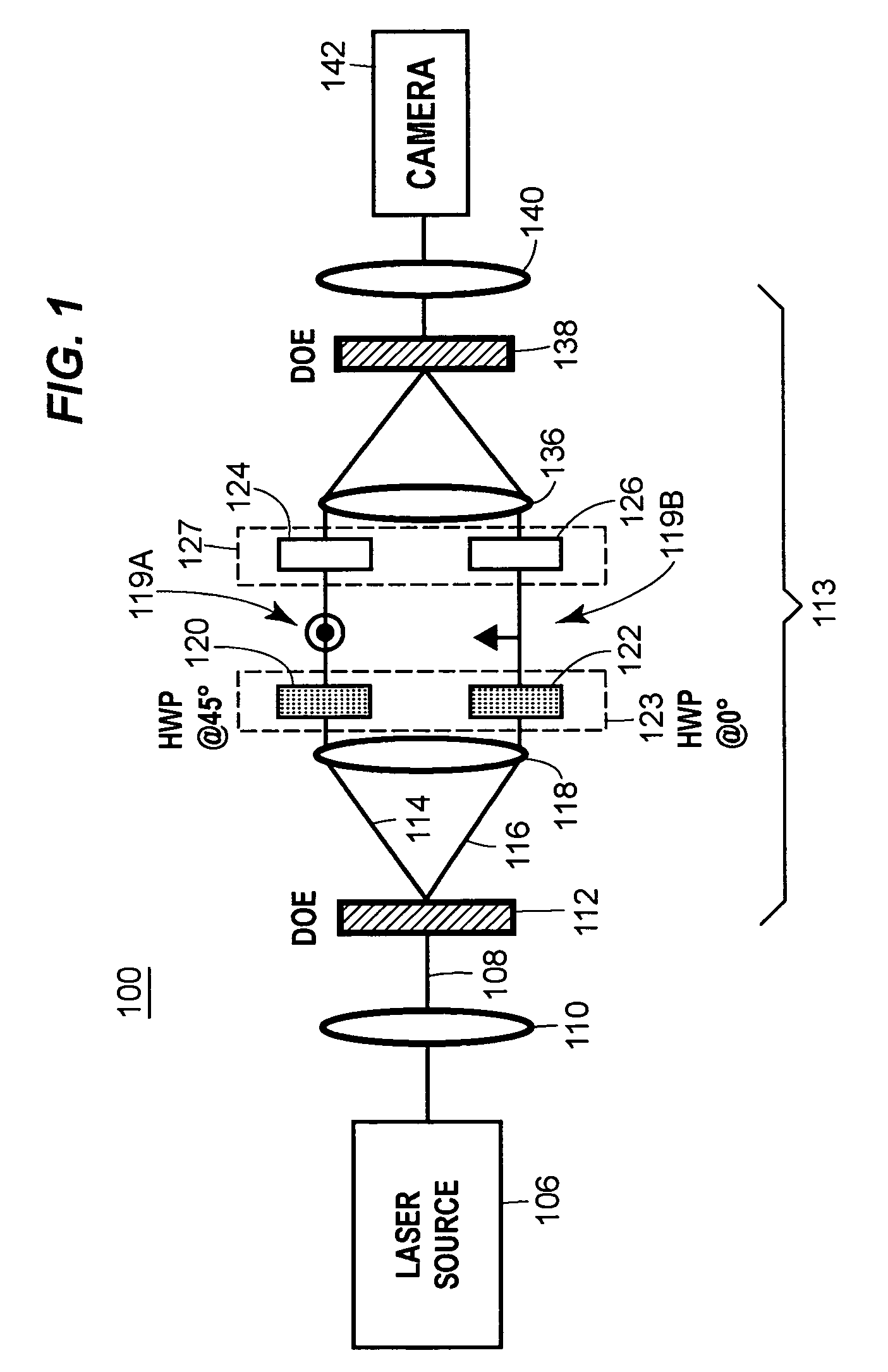
Vector beam generator using a passively phase stable optical interferometer
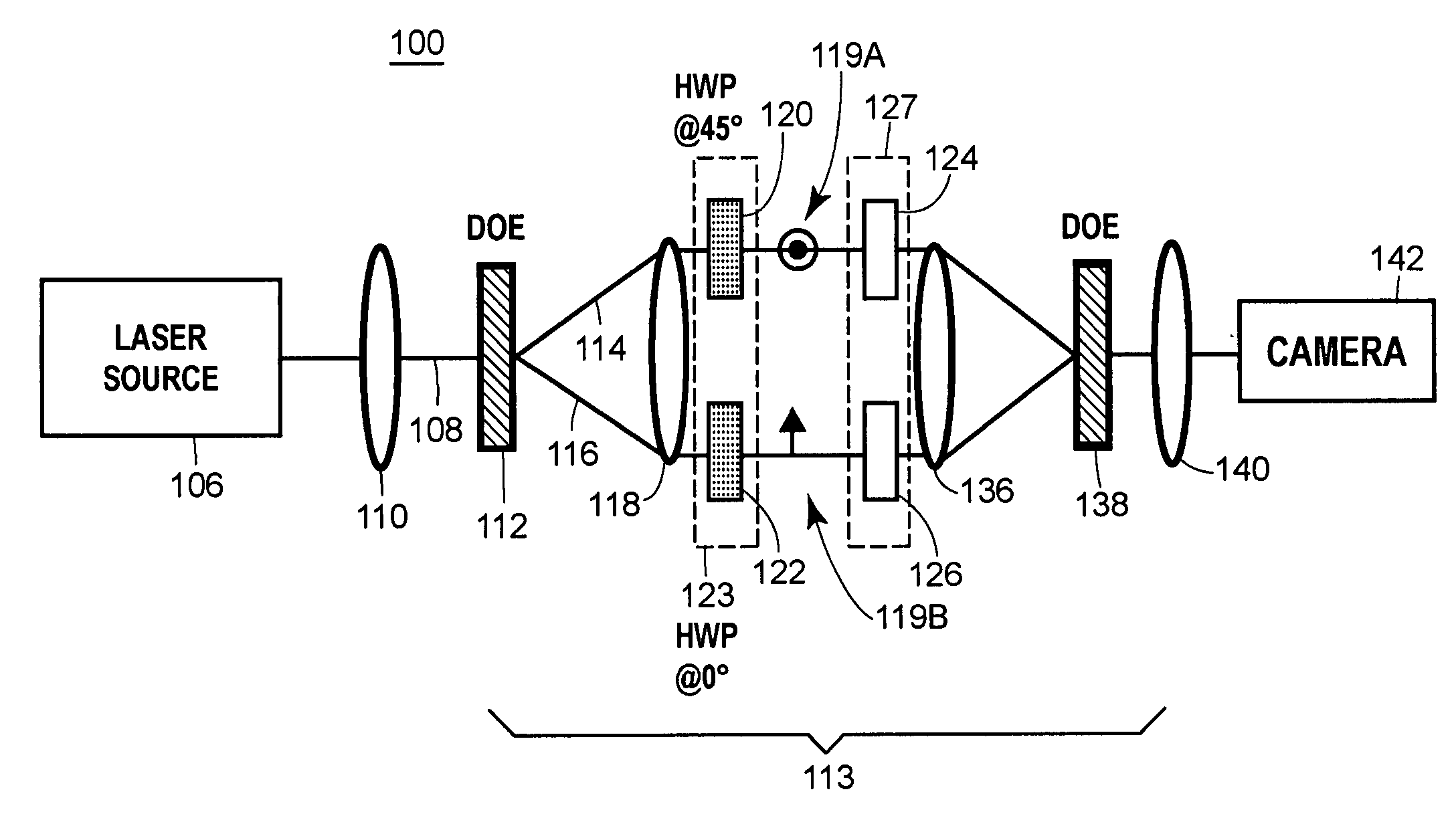
InactiveUS20060268408A1Improvement in point spread functionIncrease pointsProjectorsPhotomechanical apparatusWavefrontBeam splitting
Provided are techniques for generating optical vector beams (e.g., radially and azimuthally polarized light) using passive or active phase stable optical interferometry. Techniques may split an input optical beam into at least two output beams, and then couple those beams simultaneously into a passively phase stable optical interferometer. Beam splitting may be achieved by a diffractive optical element and coupling may be achieved by a single refractive optical device (lenses) or by a single mirror device (e.g., parabolic and spherical). The interferometer may provide the ability to manipulate (or transform) the polarization of part of the wavefront of each beam, as well as the ability to manipulate (or transform) the phase of part of the wavefront of each beam, such that the beams when combined have a vector beam polarization state.
Owner:CHICAGO UNIV OF
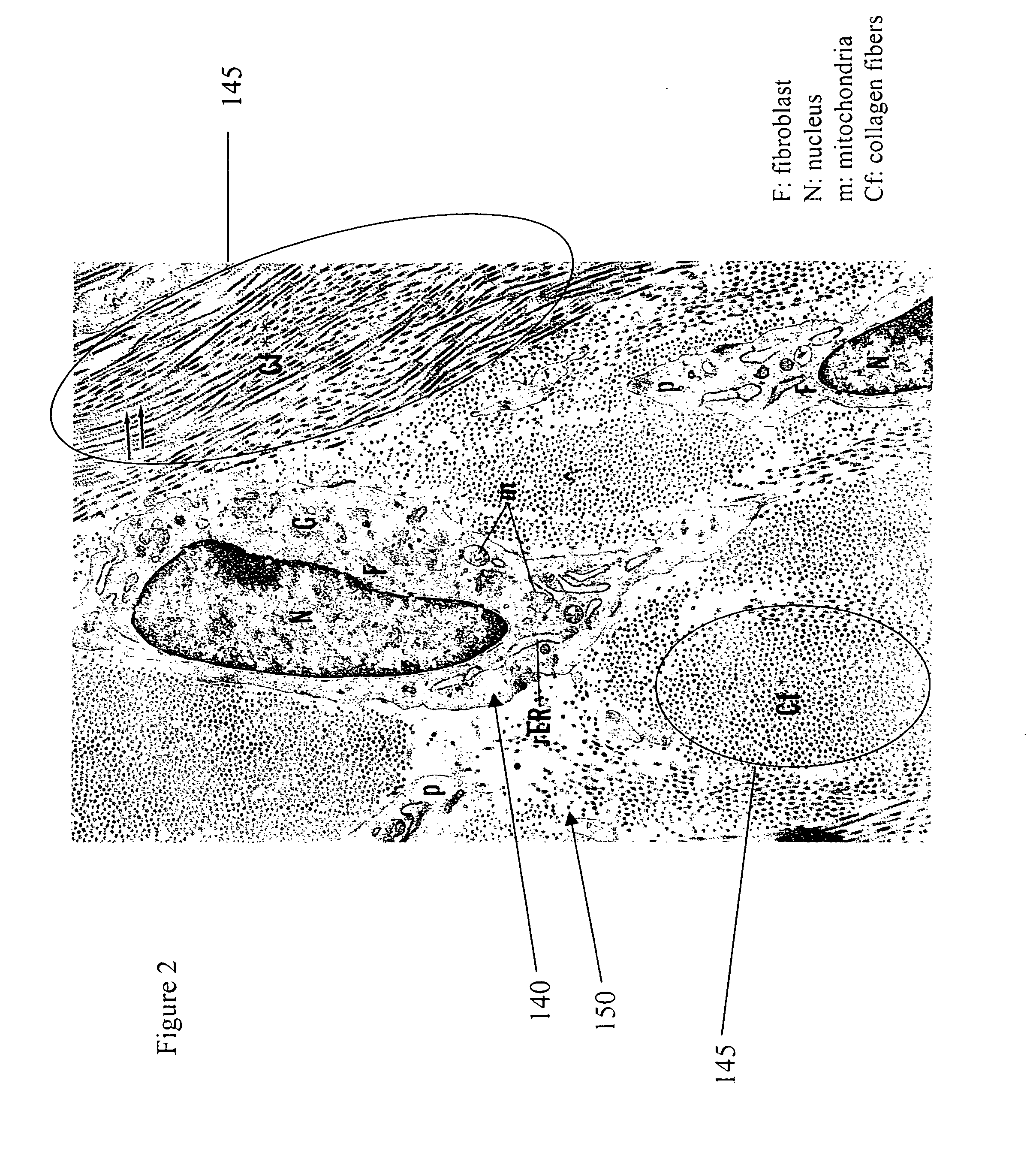
Device for optically stimulating collagen formation in tissue
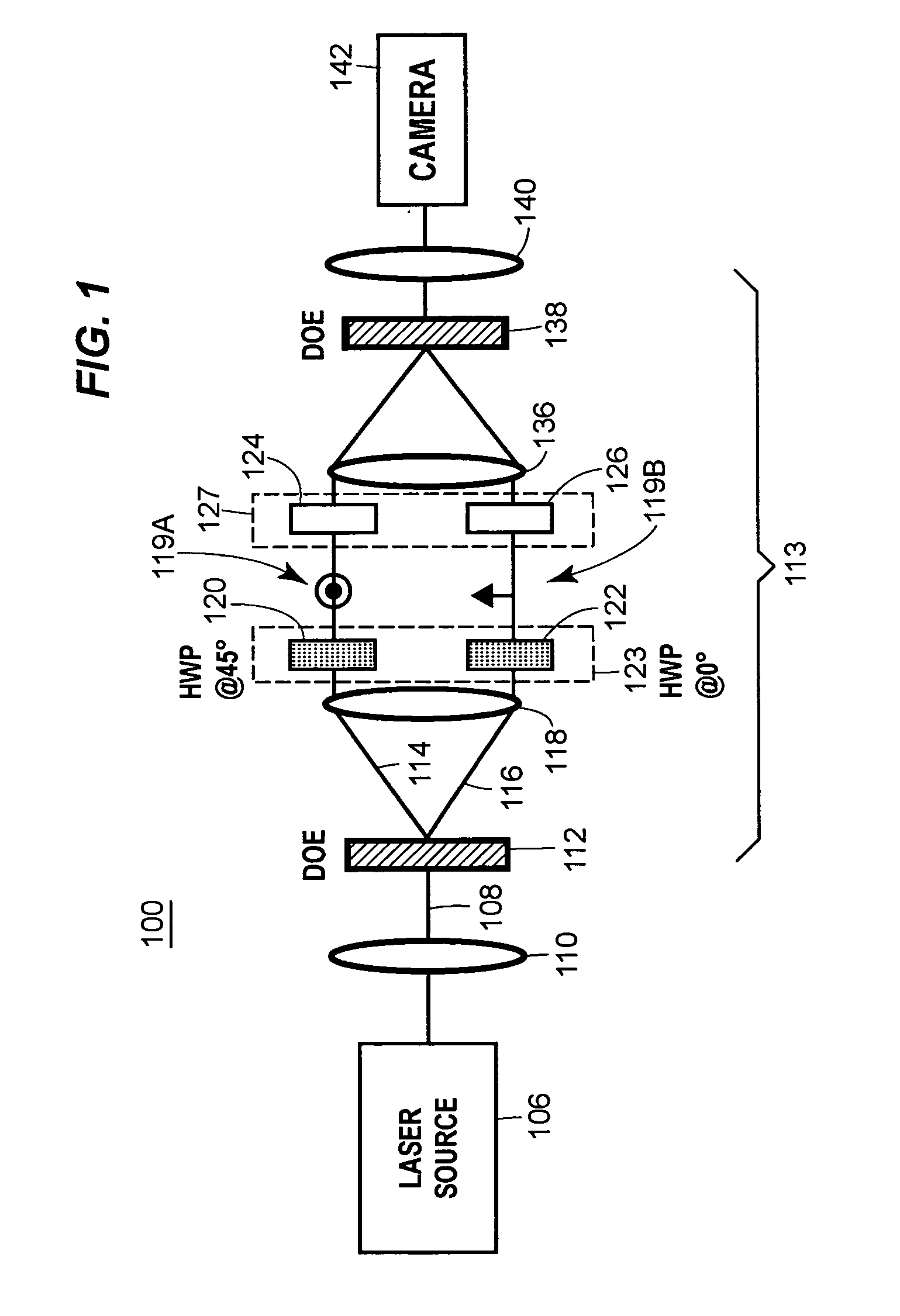
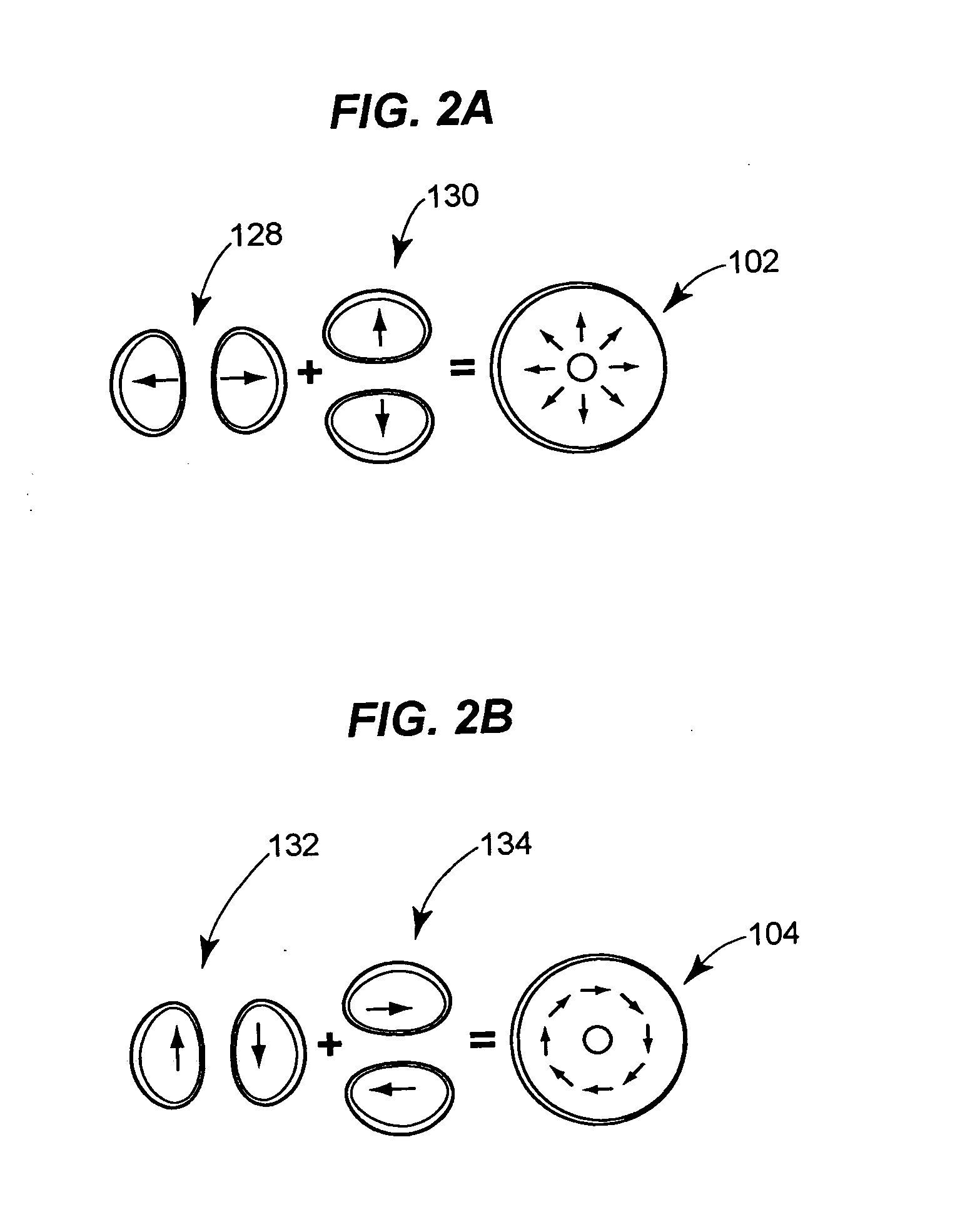
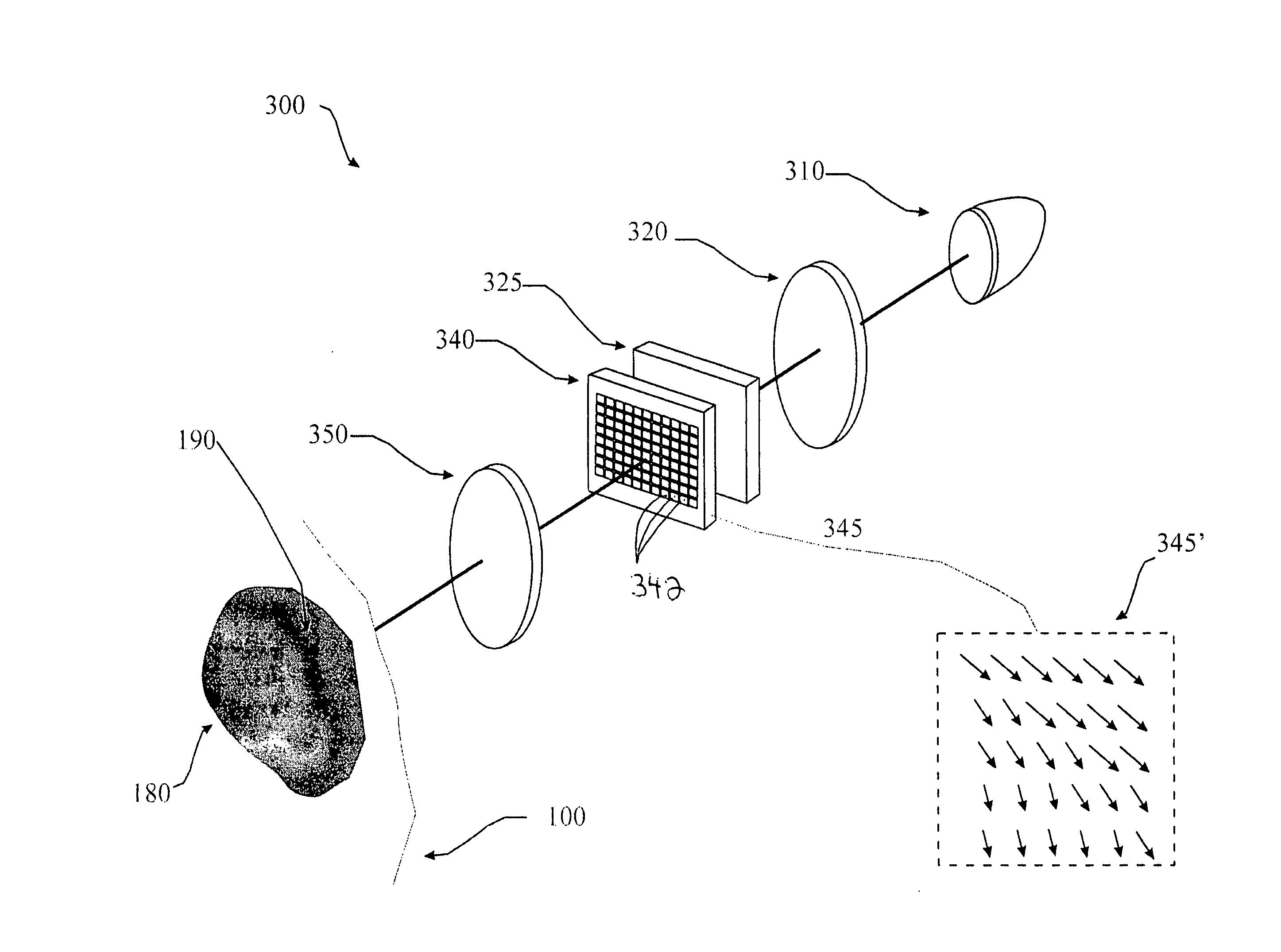
A polarization based medical device (300) for optically stimulating the formation of collagen in tissue (100) comprises a light source (310) for providing a beam of light. A polarizer polarizes the beam of light. A first beam shaping optics (320) directs the polarized beam of light to a spatial light modulator (340). A second beam shaping optics (350) directs the polarized beam from the spatial light modulator to an area of interest within the tissue. A spatially controlled pattern of polarized light is directed onto the tissue, thereby affecting the orientation of formation of collagen within the tissue.
Owner:CARESTREAM HEALTH INC
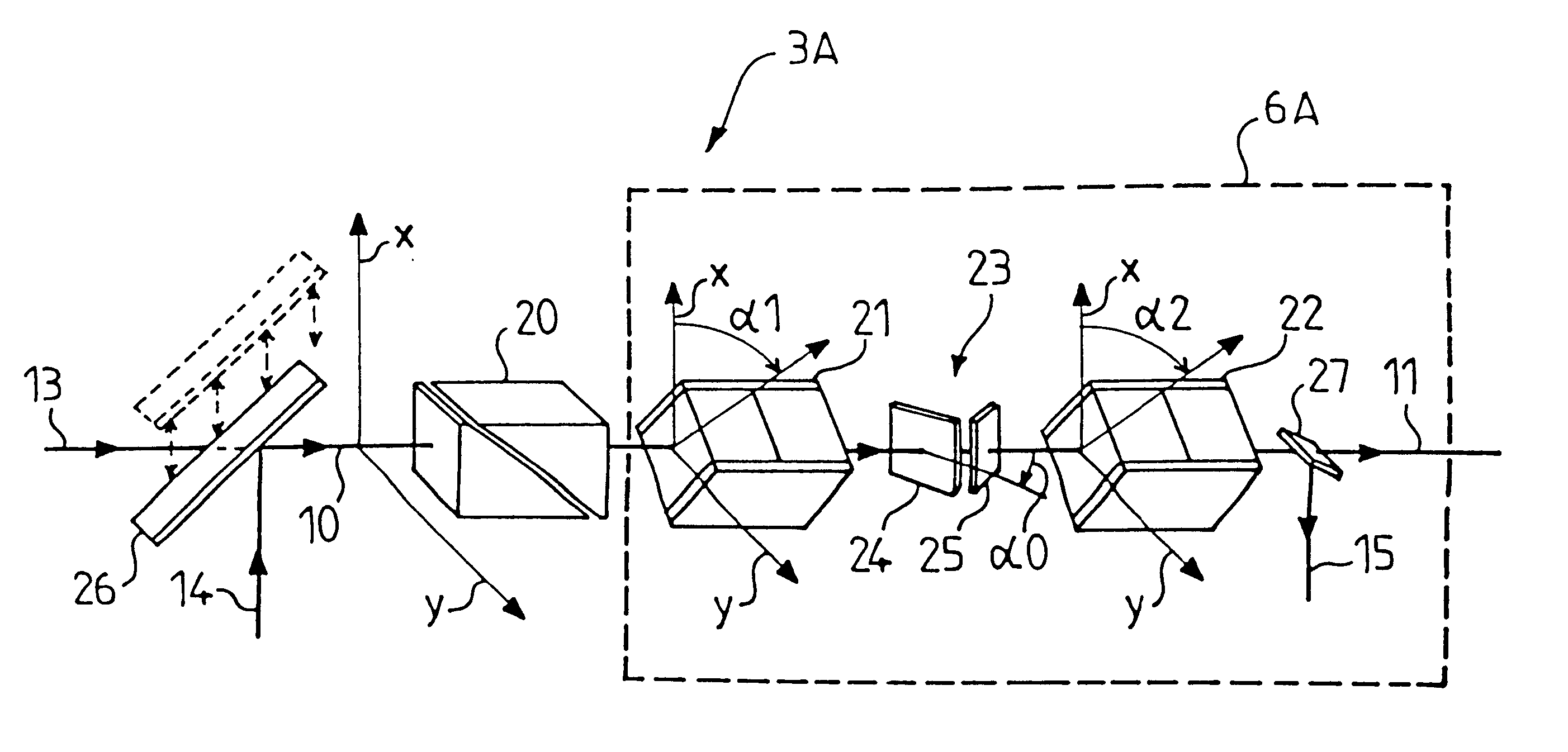
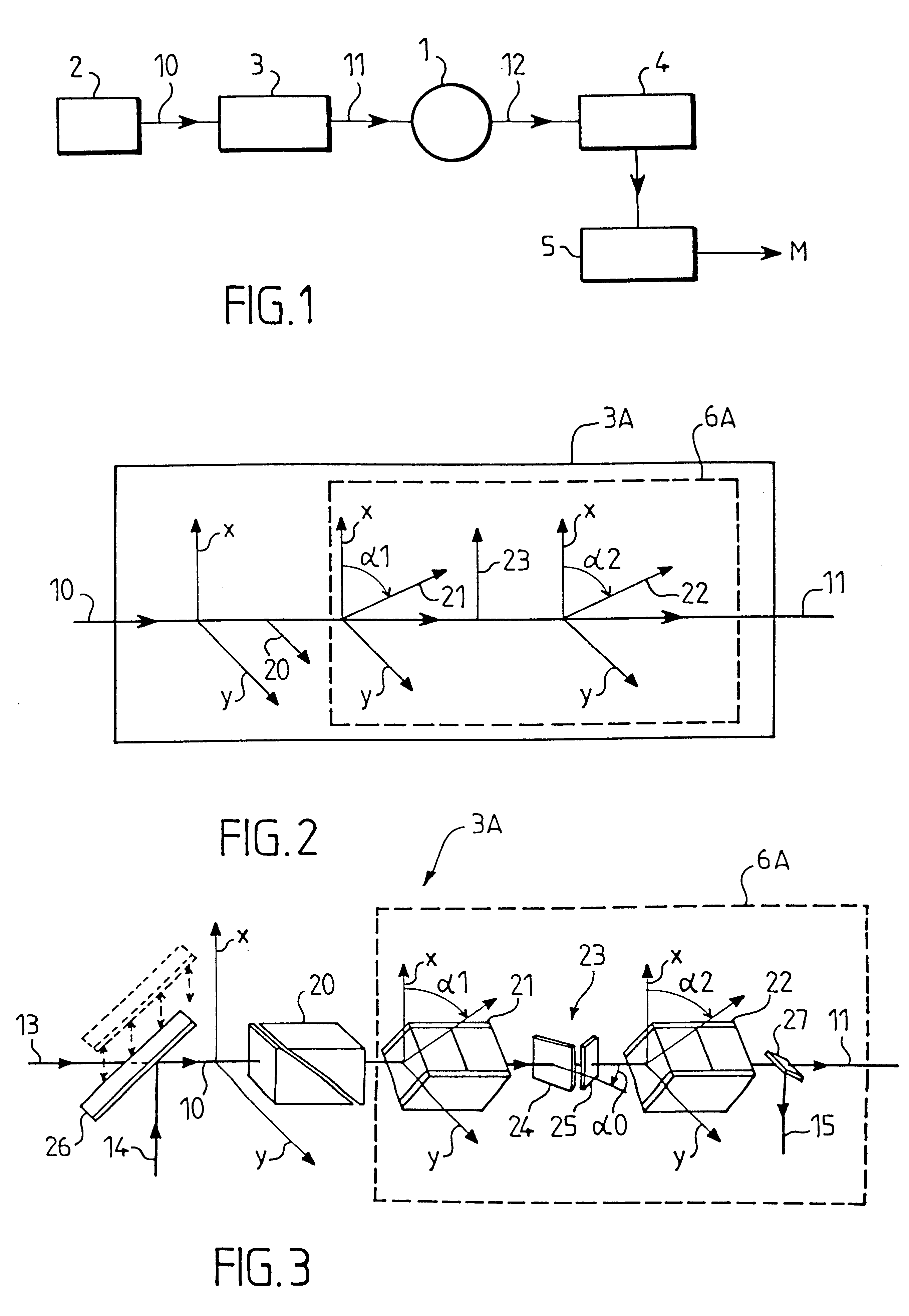
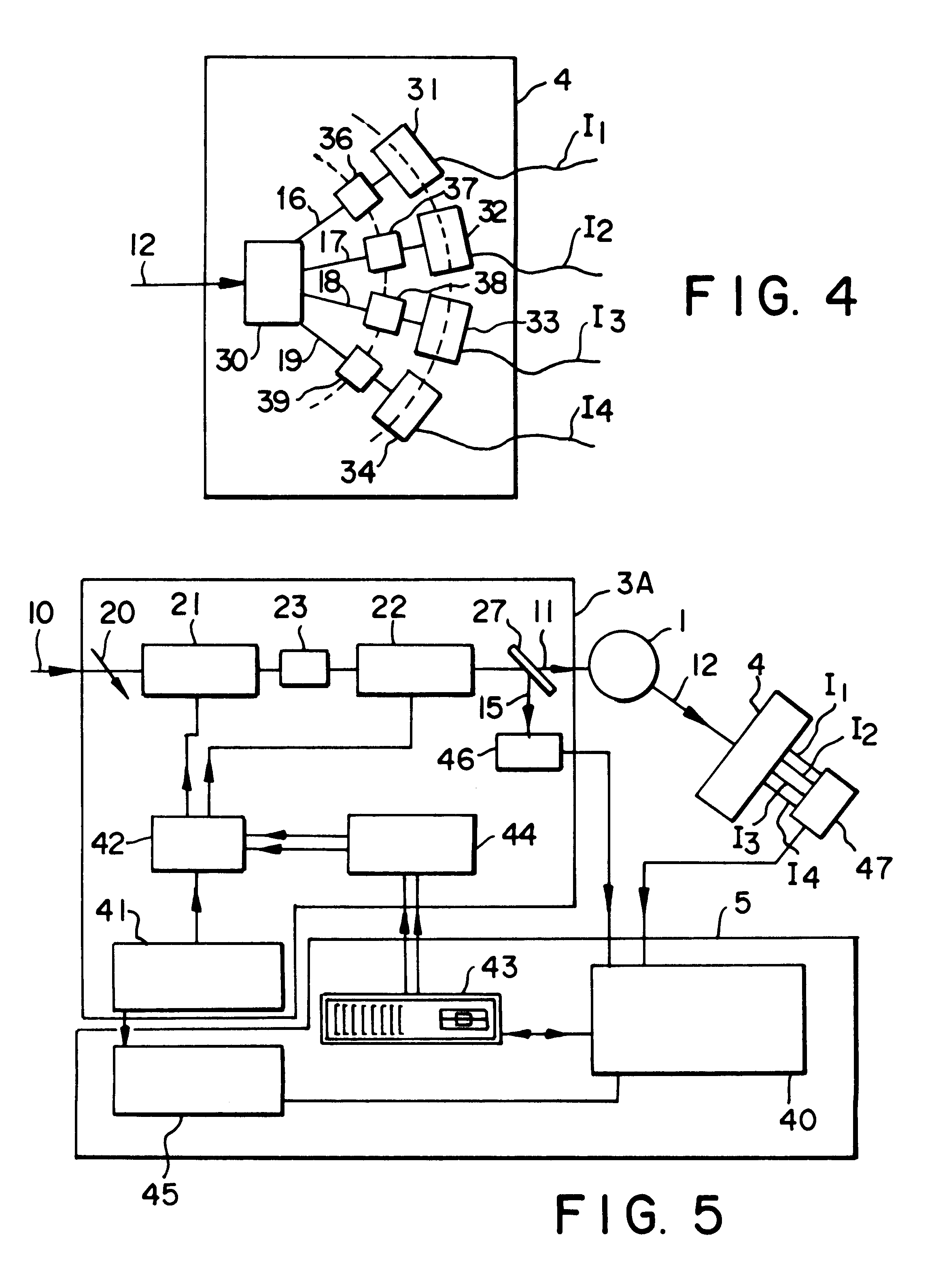
Optical component for polarization modulation, a mueller polarimeter and ellipsometer containing such an optical component, a process for the calibration of this ellipsometer, and an ellipsometric measurement process
InactiveUS6175412B1Easy to implementImprove accuracyOptical measurementsPolarisation-affecting propertiesBeam polarizationFourier transform on finite groups
An optical component for modulation of polarization, a Mueller polarimeter and ellipsometer containing such an optical component. The optical component modulates a linearly polarized incident beam and returns a modulated beam. It includes a coupled phase modulator which modulates the incident beam twice in succession, the two modulations having the same frequency of omega / 2pi, and a coupling system modifying the polarization state of the light between the two modulations. The ellipsometer includes the means for detection of a measurement beam returned by a sample, which receives the modulated beam, in addition to a processing unit. The means of detection include a polarimeter producing n measured quantities representing the polarization states of the beam, and the processing unit produces m values for each of these quantities by Fourier transform, with nxm>=16 and m>=4, providing simultaneous access to the sixteen components of the Mueller matrix of the sample.
Owner:CENT NAT DE LA RECHERCHE SCI
Multi-channel vector holographic polarization multiplexing method based on birefringent medium metasurface
ActiveCN109459870AArbitrary regulationIncrease information capacityNon-linear opticsMicro nanoEtching
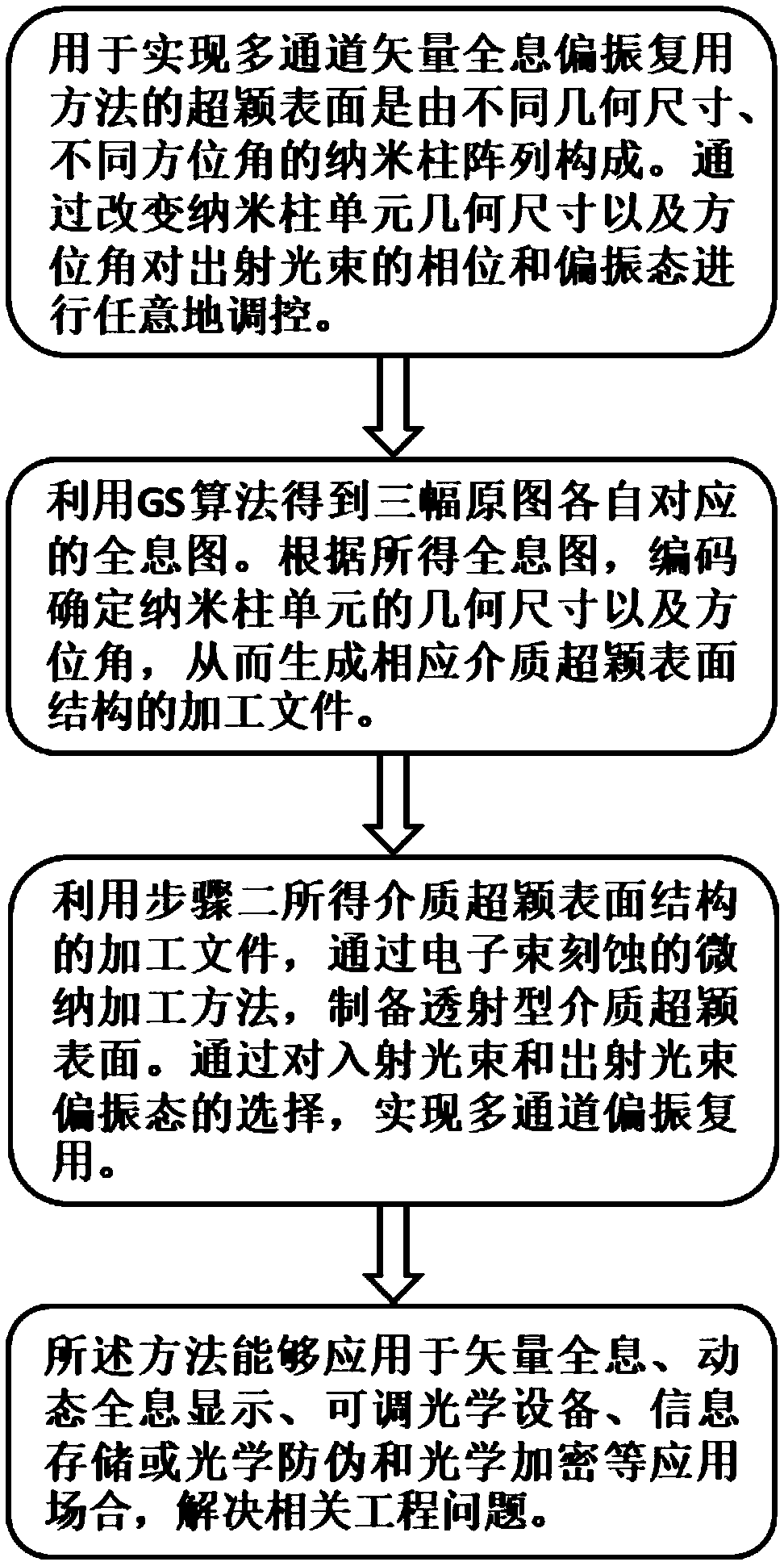
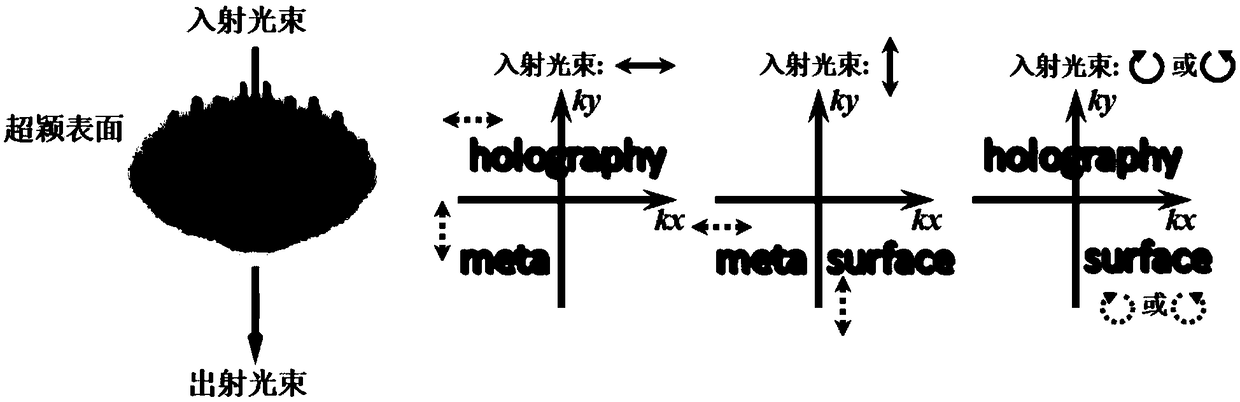
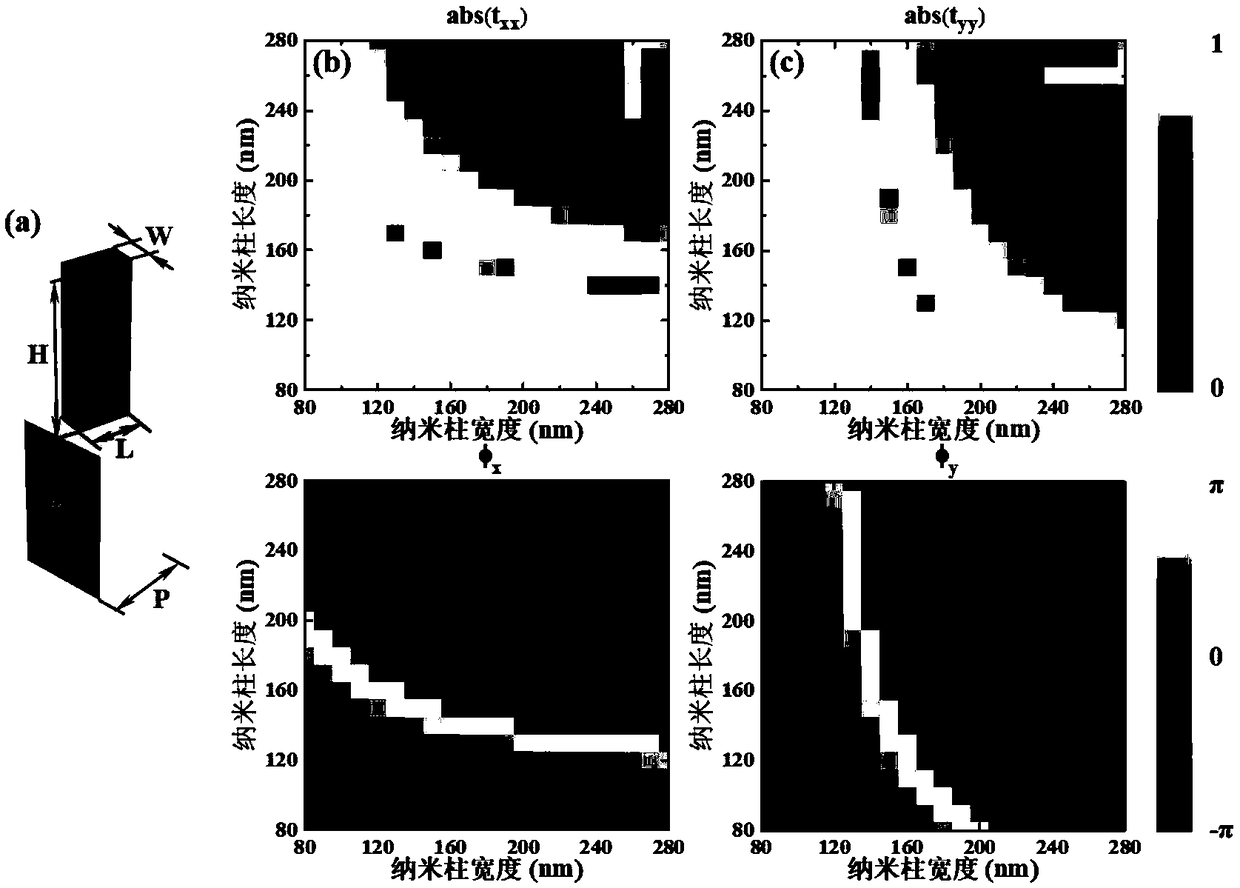
The invention discloses a multi-channel vector holographic polarization multiplexing method based on a birefringent medium metasurface, and belongs to the technical field of micro-nano optics and holographic multiplexing application. The method comprises the following steps that: the metasurface for achieving the holographic polarization multiplexing is composed of nano column arrays with rectangular cross sections and different geometric dimensions and different azimuth angles; by changing the geometric size and azimuth angles of the nano column unit, the phase and polarization state of the emergent light beam are randomly regulated and controlled by the metasurface; holograms corresponding to different mutually independent original images are obtained by using a GS algorithm; according to the obtained holograms, the geometric size and azimuth angles of the nano column unit are determined by coding so as to generate a processing file of a corresponding medium metasurface structure; the metasurface of the transmission-type medium is processed by adopting a micro-nano processing process of electron beam etching; through the selection of the polarization states of the incident lightbeam and emergent light beam, the combination and multiplexing of seven different polarization images of twelve different polarization channels are achieved.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY +1
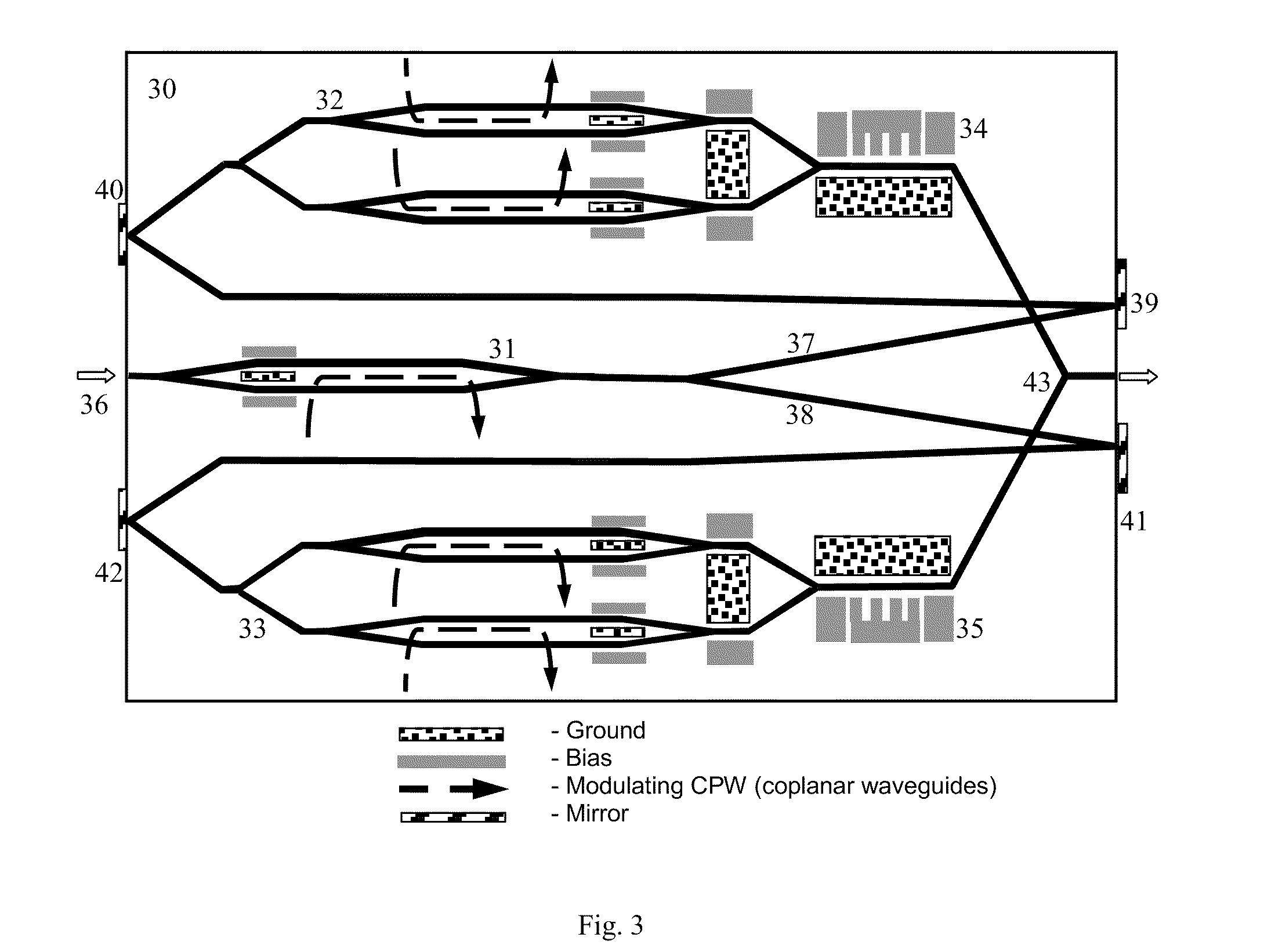
Single chip two-polarization quadrature synthesizer, analyser and optical communications system using the same
InactiveUS20090185810A1Improve communication performanceElectromagnetic transmittersElectromagnetic receiversBeam polarizationOptical communication
An optical beam synthesizer formed on a single chip is provided. It allows M-PSK modulation for both beam polarizations. The synthesizer comprises an optical pulse shaper and two M-PSK modulators for each polarization. A single-chip-integrated analyzer is provided to receive a modulated data. Analyzer comprises a pulse shaper operating as an optical sampler and a pair of 90-degrees optical hybrids for each polarization. Each optical hybrids mix incoming portions of the modulated beams with portions of the local oscillator beams. Both the synthesizer and the analyzer include a set of mirrors located on the back and front surfaces of the chips to create compact designs. The output beams from the analyzer are detected by a set of balanced photodiodes, and the data is recovered. It is another object of the invention to provide a communication system for data transmission having the synthesizer and the analyzer.
Owner:CELIGHT
Vector beam generator using a passively phase stable optical interferometer
Provided are techniques for generating optical vector beams (e.g., radially and azimuthally polarized light) using passive or active phase stable optical interferometry. Techniques may split an input optical beam into at least two output beams, and then couple those beams simultaneously into a passively phase stable optical interferometer. Beam splitting may be achieved by a diffractive optical element and coupling may be achieved by a single refractive optical device (lenses) or by a single mirror device (e.g., parabolic and spherical). The interferometer may provide the ability to manipulate (or transform) the polarization of part of the wavefront of each beam, as well as the ability to manipulate (or transform) the phase of part of the wavefront of each beam, such that the beams when combined have a vector beam polarization state.
Owner:CHICAGO UNIV OF
Method and device for high-accuracy and small-angle measurement
InactiveCN102226690AHigh resolutionLarge measuring rangeUsing optical meansLight beamOptoelectronics
The invention discloses a method and device for high-accuracy and small-angle measurement, wherein the method comprises the following steps: polarizing and splitting the reference light beam which is obtained after the collimation processing to obtain the first linearly polarized light; converting into the circularly polarized light and radiating to a measuring target mirror after the beam expansion; detecting the reverse return of the light beam which is reflected by the target mirror; carrying out the beam contraction and the secondary conversion to obtain the second linearly polarized light; polarizing and splitting the second linearly polarized light again and dividing the second linearly polarized light into the reflected light and the transmission light which have the light intensity ratio of 1 to 1; respectively radiating the two beams of light to two prisms to be reflected; and respectively receiving and processing the reflected light signals through two detectors. The device disclosed by the invention comprises a laser emitting unit, a beam expansion lens unit, a measuring target mirror unit and a differential detection unit, wherein the laser emitting unit comprises a light source, a single mode fiber, a collimation lens, a polarization splitter and a lambda / 4 wave plate; and the differential detection unit comprises the splitter, the two prisms and the two detectors. The method and device disclosed by the invention have the advantages of ultrahigh accuracy and large measuring range.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Bi-directional optical switch
The present invention provides improved optical switches in which no mechanical movement is required to direct optical pathways between plural fiber ports and light transmission is bi-directional. Advantageously, the inventive switches permit bi-directional light transmission. The inventive switches also incorporate light bending devices to allow two fibers to be coupled to the light beams using a single lens for compactness. In the inventive switch, an optical signal is spatially split into two polarized beams by a birefringent element, which passes through a polarization rotation device that comprises waveplates, walk-off elements, and an electrically controllable polarization rotator, and recombine into an output fiber, achieving polarization independent operation. The switches of the present invention rely on electro-magnetically or electro-optically switching the beam polarizations from one state to another to rapidly direct the light path.
Owner:AGILTRON
Phase-differential quantum key allocation and allocating system
InactiveCN1897519AHighlight substantiveSignificant progressKey distribution for secure communicationDifferential phaseBeam splitting
The invention manages to provide a stable and fast differential quantum key distribution method and system thereof. At transmitting end, with a continuous laser source, the quantum codes are prepared using two approaches: 1) using the beam-splitting, polarization-independent and phase-stabilizing approach to prepare the stable quantum code; 2) using polarization approach to directly prepare stable quantum code. At receiving end,differential phase-Faraday-Micheal test approach is used to directly receive the quantum information.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Fast polarization detector and detecting method
ActiveCN104457995AImprove compatibilityQuick fixLight polarisation measurementBeam polarizationLight beam
The invention discloses a fast polarization detector and a detecting method adopting the detector. The fast polarization detector comprises a polarization detecting module, a light intensity detector and a signal processing device connected with the output end of the light intensity detector, the polarization detecting module, the light intensity detector and the signal processing device are sequentially arranged on a light path, the polarization detecting module comprises at least three polarization detecting channels, and the polarization detecting channels carry out simultaneous split beam polarization detection on the same polarization light beam to be detected, so that emergent light split beams passing through the polarization detecting channels comprise different polarization information. The light intensity detector can detect the light beams with the number not smaller than that of the polarization detecting channels, the light intensity detector records the light intensity information of the emergent light beams and outputs the light intensity information of the emergent light beams to the signal processing device, and the signal processing device determines the polarization state of the polarization light beam to be detected according to the light intensity information of the emergent light beams and the polarization character of the polarization detecting channels. The fast polarization detector can measure the polarization state of light simultaneously, fast and accurately, and is simple in structure and low in cost.
Owner:SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL TSINGHUA UNIV
Adjustable ring vector light beam producing system
InactiveCN101363964AChange horizontal sizeLow incident beam requirementsMirrorsPolarising elementsBeam polarizationCircular cone
The invention relates to an adjustable ring-shaped vector beam generating system. The prior art has high incident beam requirements, and cannot realize the ring-shaped vector beam and the beam size adjustment. In the invention, the incident beam sequentially passes through a beam expanding shaper, an external reflection circular conical surface reflector, a cylindrical curved polarizer, an internal reflection circular conical surface reflector, and two halfwave plates positioned in parallel; after a light source emergent beam passes through the beam expanding shaper and the external reflection circular conical surface reflector, a radial propagating beam is formed; a ring-shaped rotation vector polarized beam is formed by the reflection of the internal reflection circular conical surface reflector after the radial propagating beam passes through the cylindrical curved polarizer; the polarization state is changed by adjusting the optical axis angle of the two halfwave plates through a rotary motion part; and the transverse size of the beam is changed by adjusting the space between the external reflection circular conical surface reflector and the internal reflection circular conical surface reflector through an axial motion part. The invention has the advantages of low incident beam requirements, ring-shaped vector beam output, convenient beam polarization state and transverse size adjustment, etc.
Owner:高秀敏
Grating heterodyne interference auto-collimation measuring device
A grating heterodyne interference auto-collimation measuring device mainly comprises a two-frequency laser, a 1 / 4 wave plate, a beam splitting system, a photoelectric conversion system, a polarization beam splitter, a reflector and a grating. The two-frequency laser emits two-frequency laser which passes the 1 / 4 wave plate and which then turns into two mutually-perpendicular linearly-polarized beams. The beams entering the beam splitting system are divided into three beams; one beam enters a reference light path photoelectric conversion system; last two enter a positive-negative gage beam polarization beam splitter. In the laser entering the polarization beam splitter, a reflected beam S is reflected to the grating by the reflector, and an incident angle is set into an auto-collimation angle of the corresponding diffraction order; through reference light information, horizontal and vertical displacements of the grating can be known. The auto-collimation right angle is set not depending on grating displacements. Therefore, the grating heterodyne interference auto-collimation measuring device is applicable to measuring horizontal large-travel displacement and vertical displacement.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
Transmission-type metal metamaterial beam polarization distribution transform device
InactiveCN107272216AAvoiding Plasmon ResonanceImprove work efficiencyOptical elementsResonant cavityLight beam
The invention provides a transmission-type metal metamaterial beam polarization distribution transform device. The device comprises a dielectric substrate, a metal metamaterial layer which is arranged on the dielectric substrate and comprises a metal particle periodic array, and a dielectric coating layer which is arranged on the metal metamaterial layer. Each metal particle in the metal particle periodic array at least comprises one pair of parallel smooth planar sidewalls used for forming Fabry-Perot resonant cavities between adjacent metal particles in the direction perpendicular to the smooth planar sidewalls. The metal metamaterial layer comprises the metal particle periodic array with an azimuth angle. The polarization rotation angle of incident light is adjusted by varying the azimuth angle. Alternatively, the metal metamaterial layer comprises a number of metal particle periodic arrays with different azimuth angles. The spatial polarization distribution of incident light is changed by changing the spatial arrangement of a number of metal particle periodic arrays. The device has the characteristics of wide band adaptation, high work efficiency, simple structure and easy preparation.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method of controlling hole shape during ultrafast laser machining by manipulating beam polarization
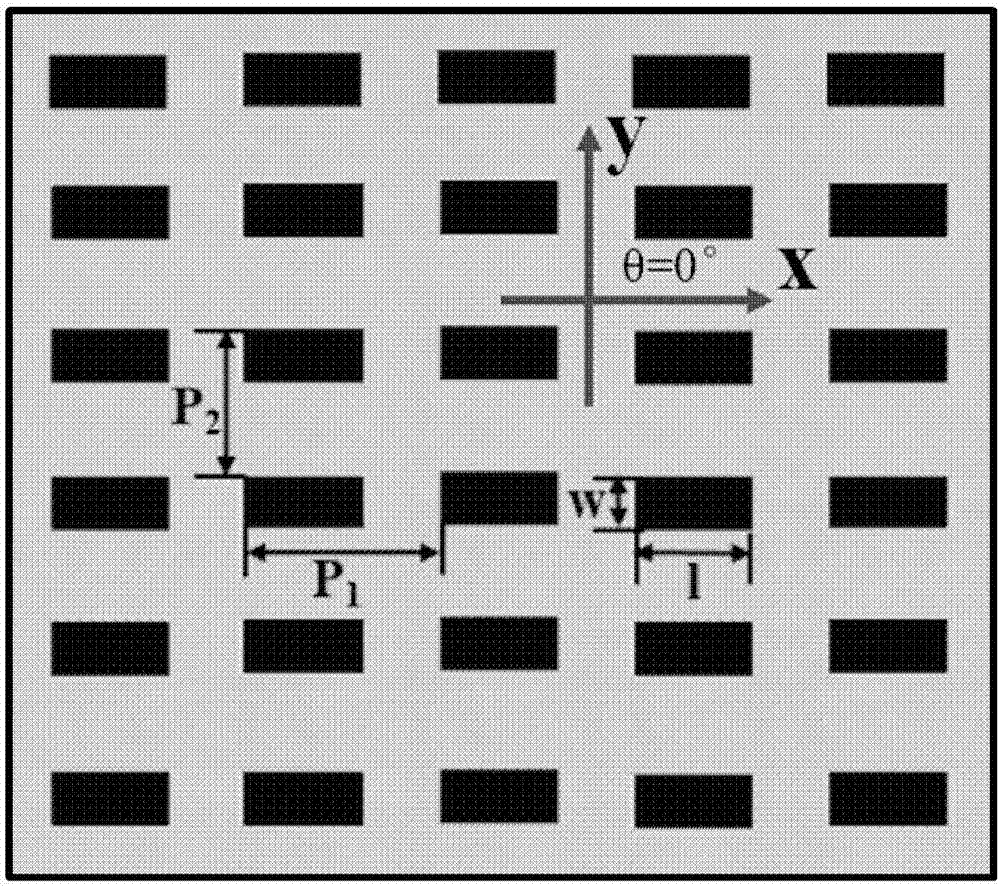
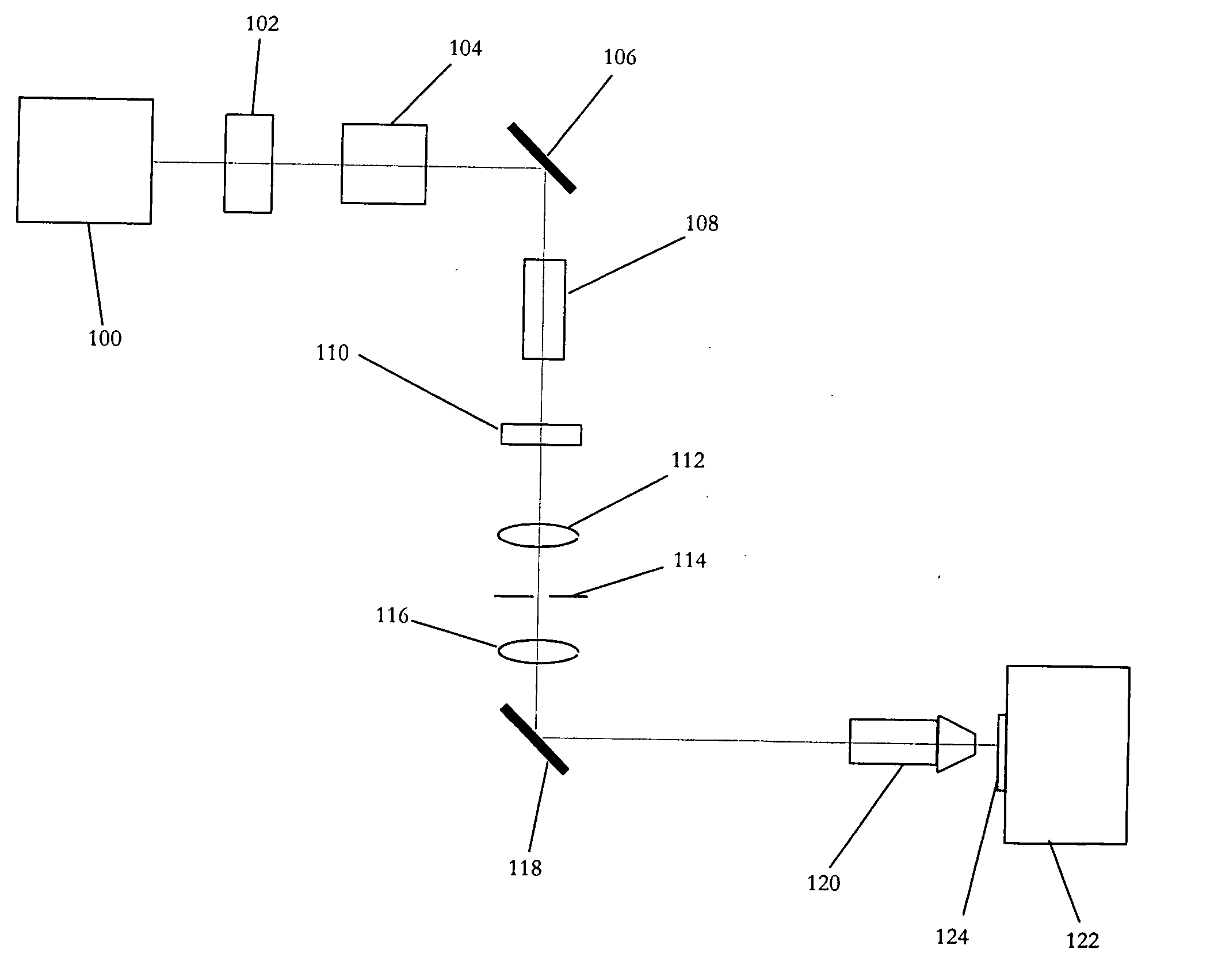
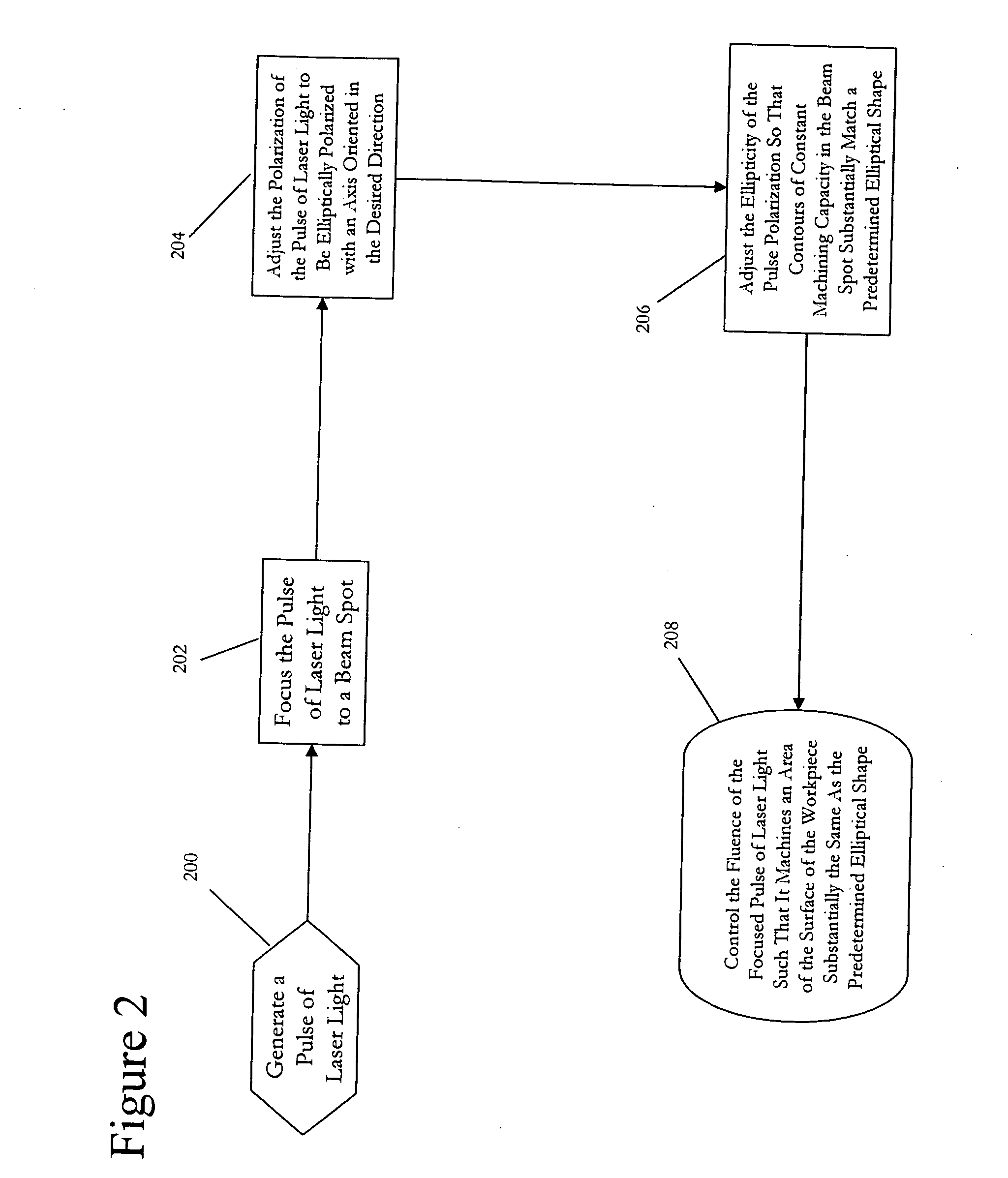
InactiveUS20050205538A1Similar shapeRecording apparatusMaterial nanotechnologyEllipseBeam polarization
A method for controlling the shape of the area machined by a pulse of laser light on a surface, such that the shape has a desired elliptical shape with its major axis aligned in a desired direction and the length of this major axis is less than or equal to a diameter of a beam spot. The pulse is generated and focused to the beam spot within a target area. The polarization of the pulse is adjusted to be elliptically polarized with an axis of the polarization ellipse oriented in the desired direction. The ellipticity of the polarization of the pulse is adjusted such that the pulse of laser light has contours of constant machining capacity on the workpiece surface, which have a similar shape to the desired shape. The fluence of the pulse light is controlled such that the area machined by the pulse is substantially the desired shape.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
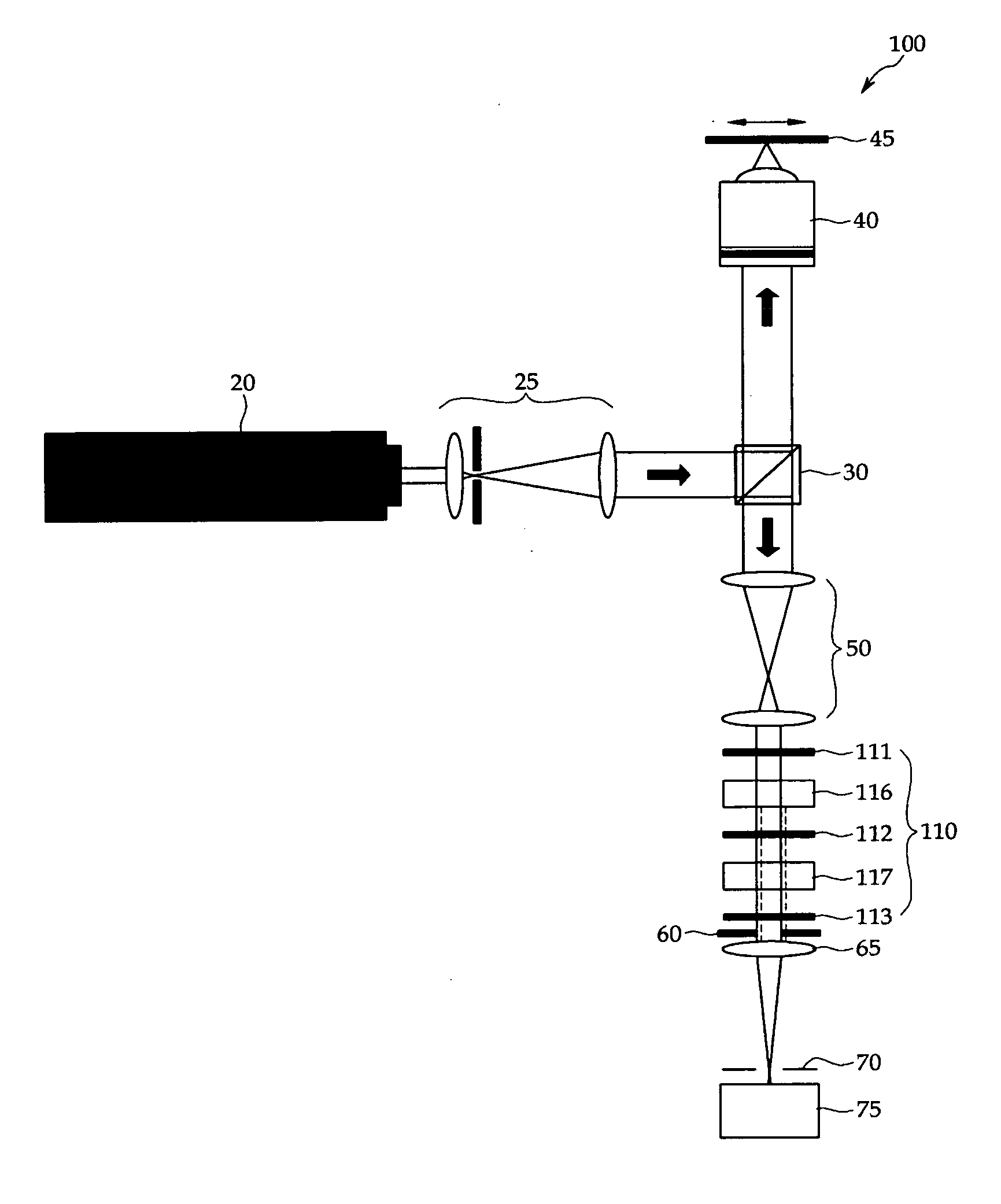
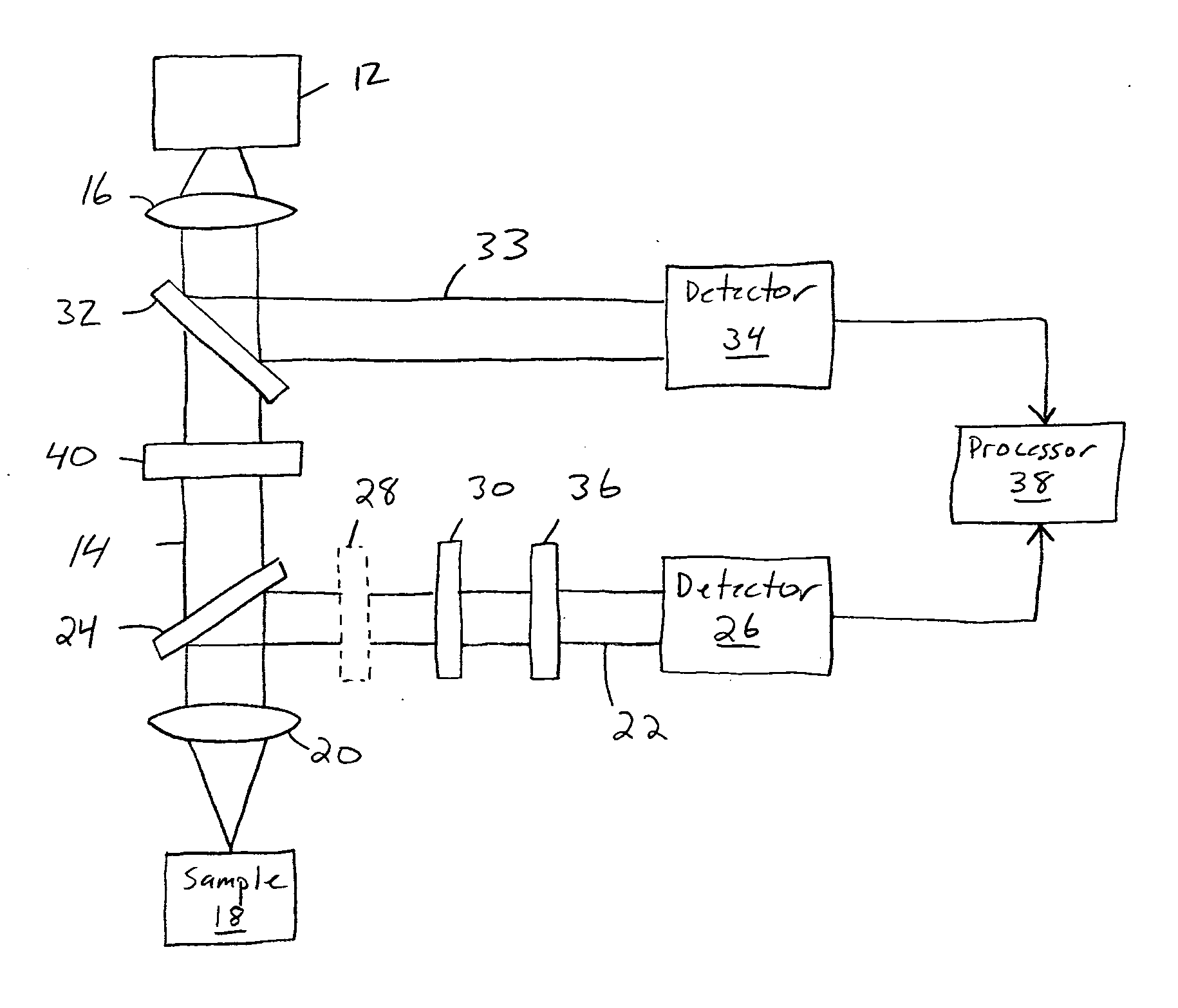
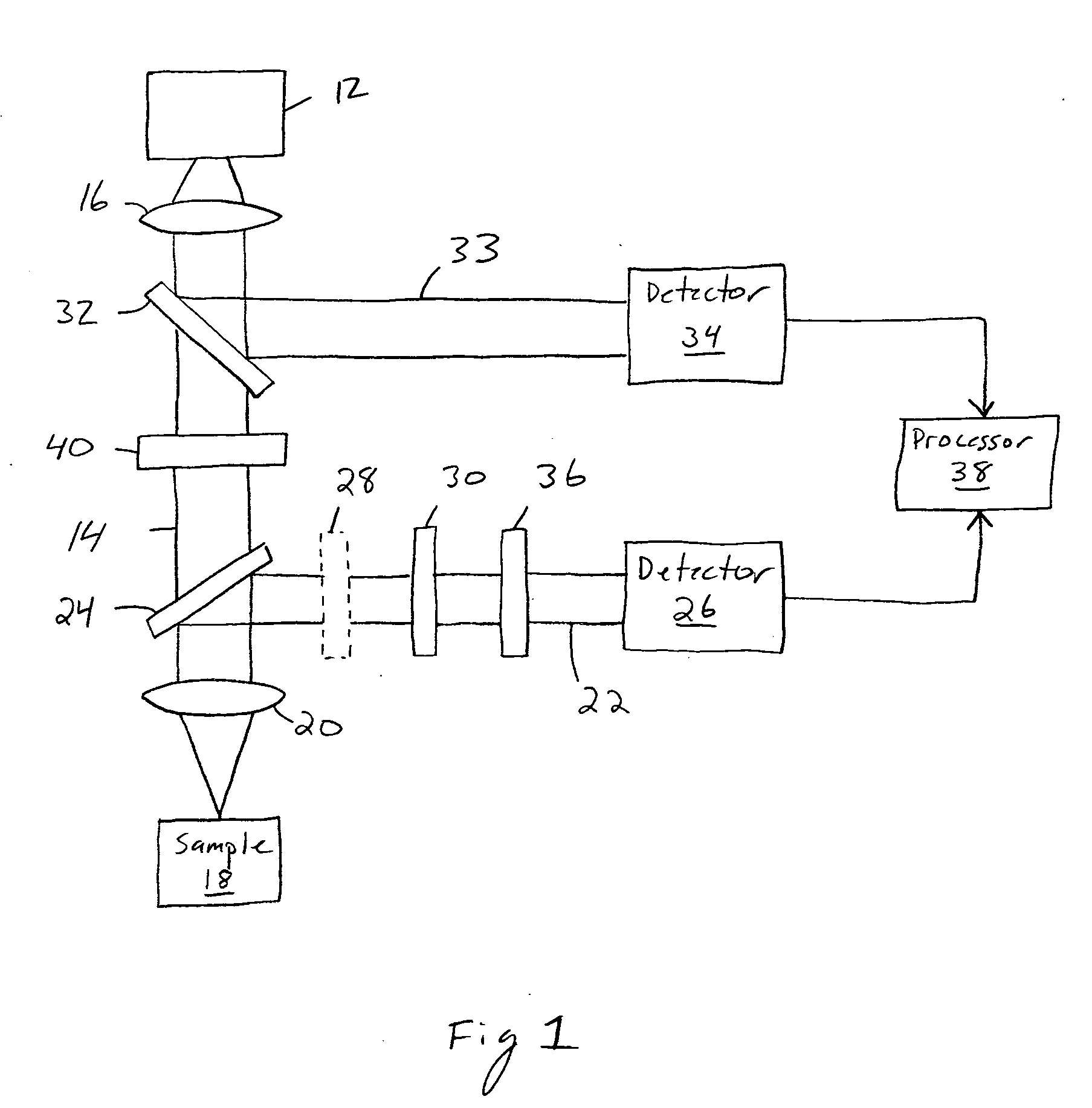
Beam profile complex reflectance system and method for thin film and critical dimension measurements
InactiveUS20050248773A1Polarisation-affecting propertiesPhase-affecting property measurementsAngle of incidenceMeasurement device
Device and method for measuring complex reflectance using a light source for generating a light beam with known polarization state, a lens for focusing the beam onto a sample surface such that various rays within the focused beam create a spread of angles of incidence θ, a waveplate for retarding one polarization state of the beam, a polarizer for generating interference between beam polarization states, and a detector with a two dimensional array of detector elements for generating intensity signals in response to the beam, wherein each detector element corresponds to a unique angle of incidence θ and azimuthal angle φ of the reflected beam. A processor calculates magnitude and phase values for the reflected beam by using the intensity signals corresponding to at least one incident angle θ and a plurality of azimuthal angles φ within the at least one incident angle θ sufficient to enable a meaningful Fourier analysis thereof.
Owner:ROSENCWAIG ALLAN
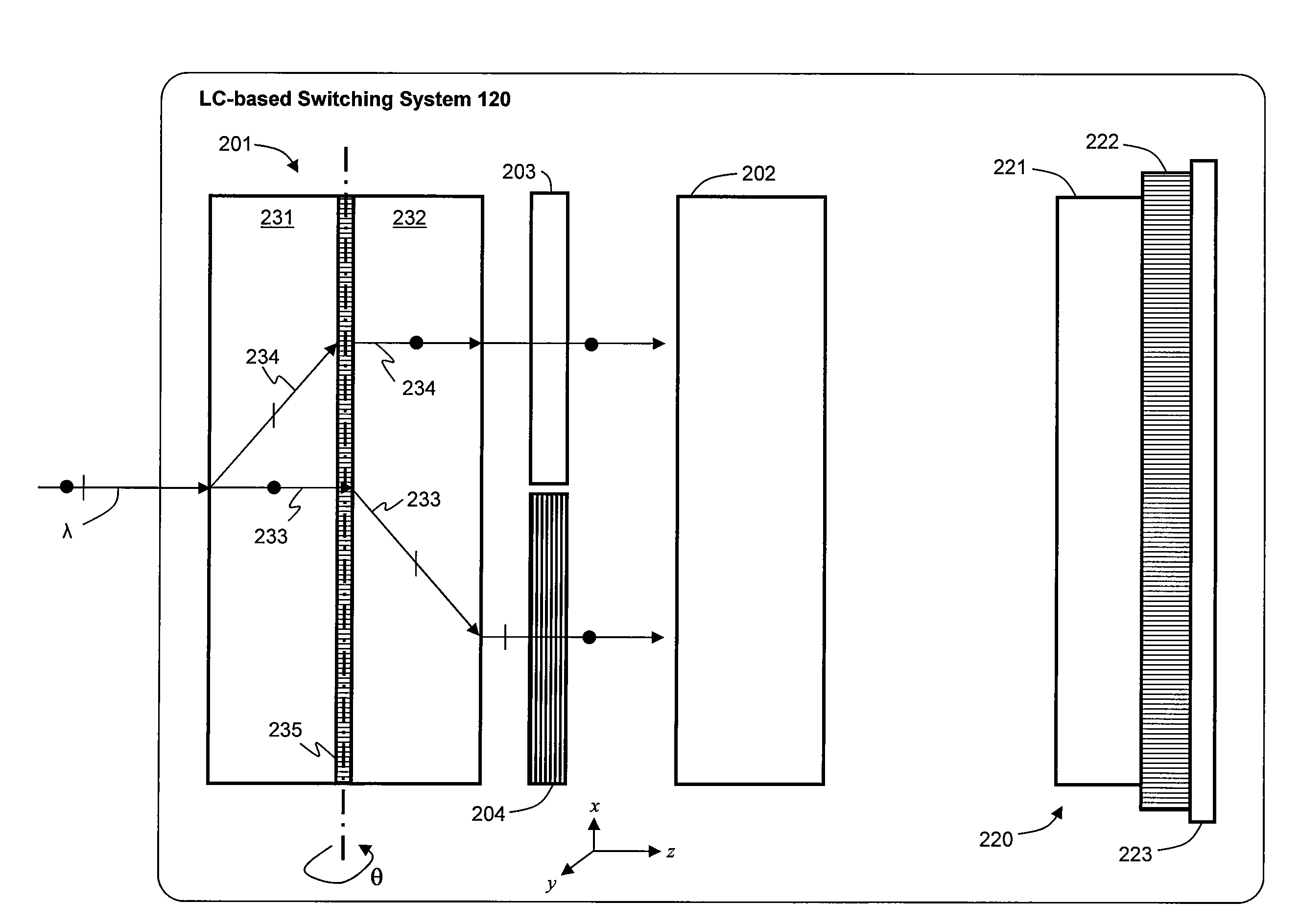
Liquid crystal optical device configured to reduce polarization dependent loss and polarization mode dispersion
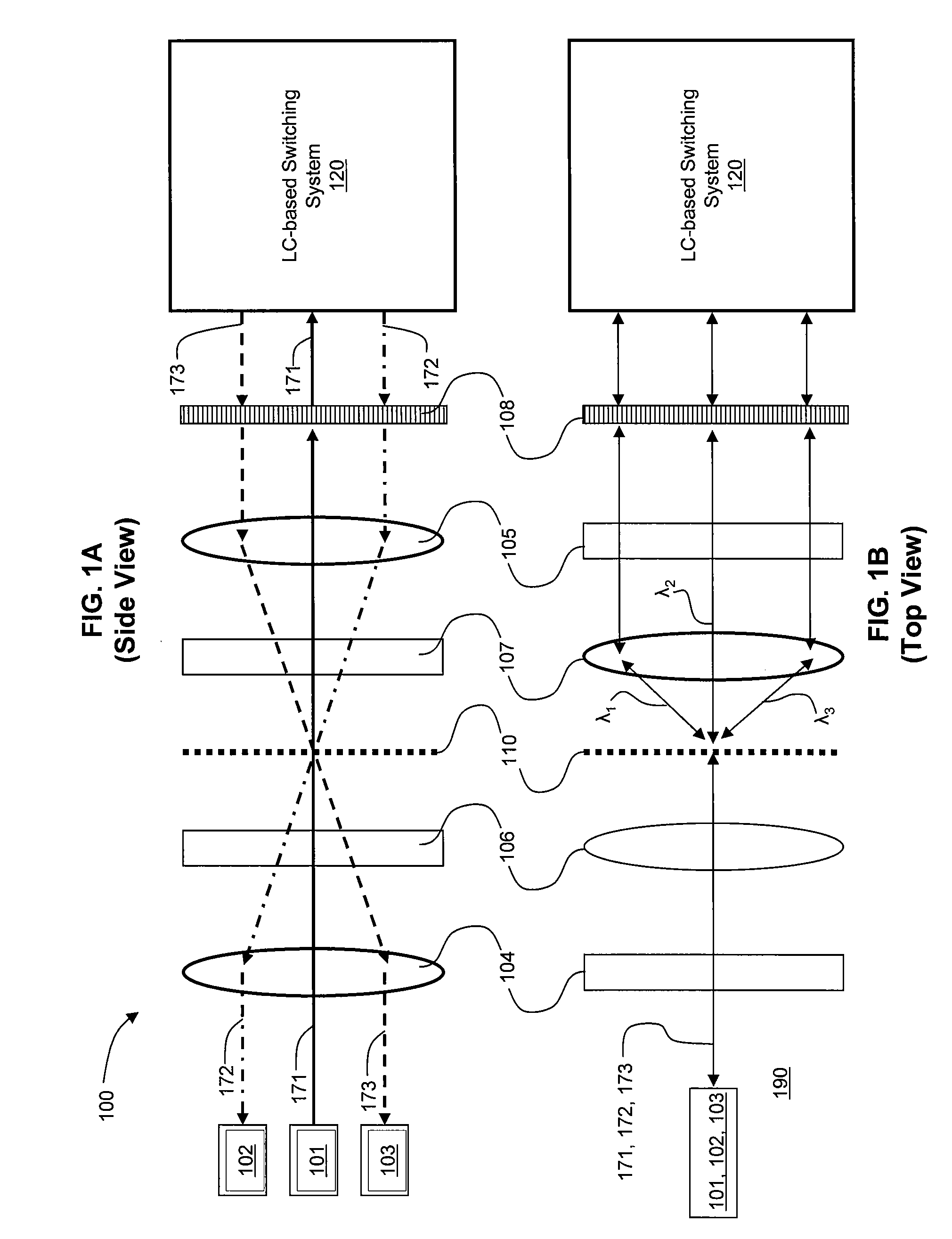
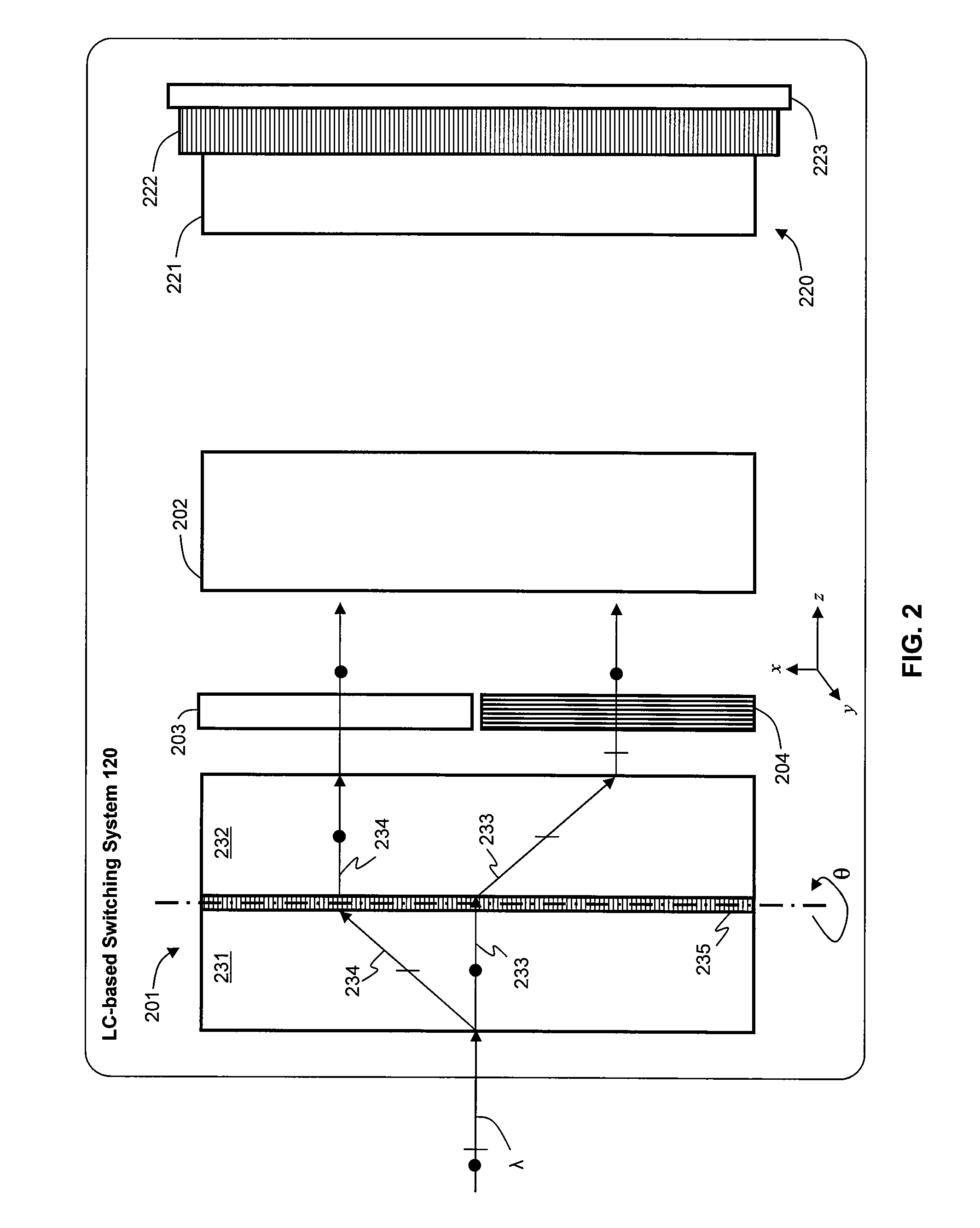
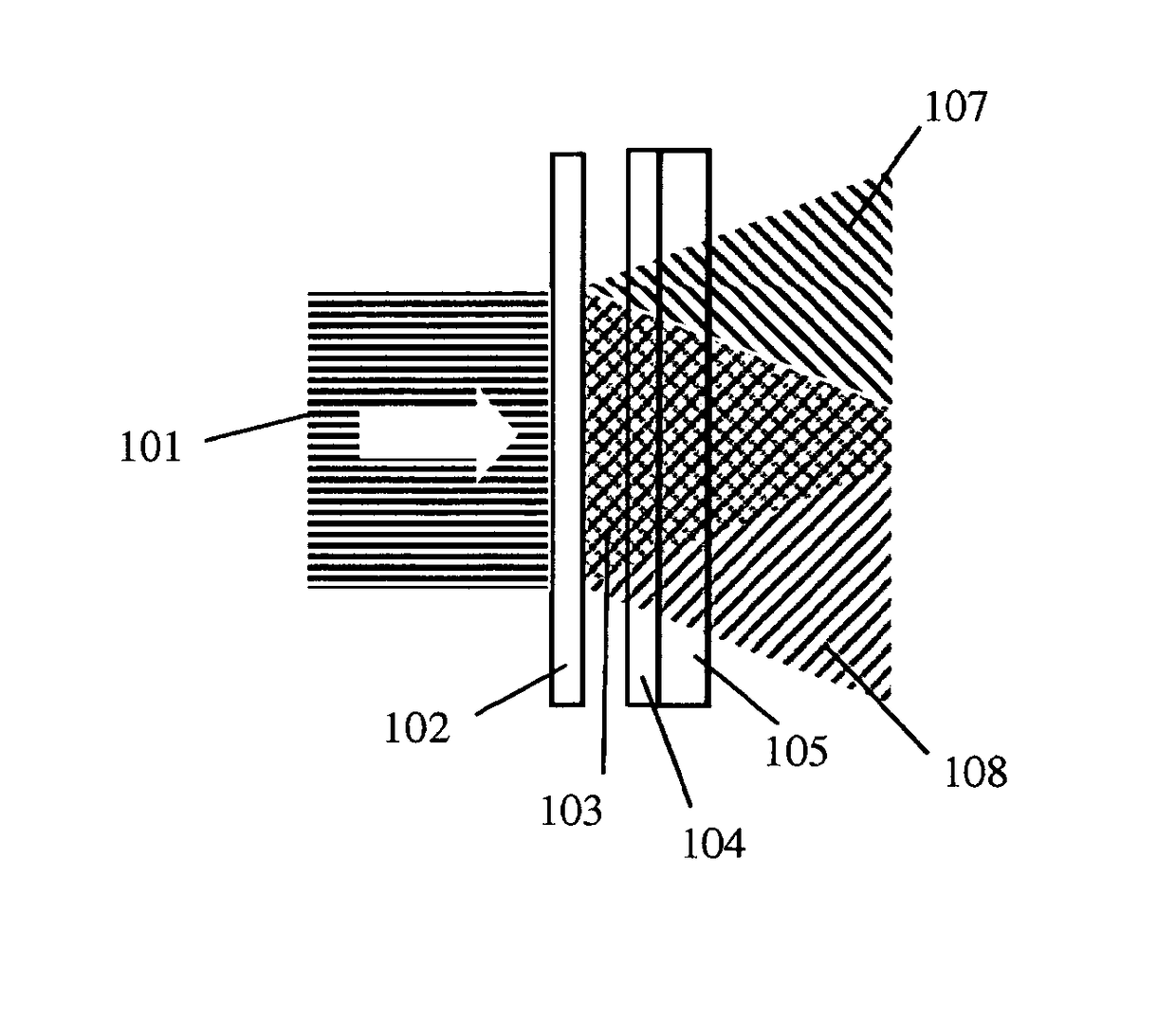
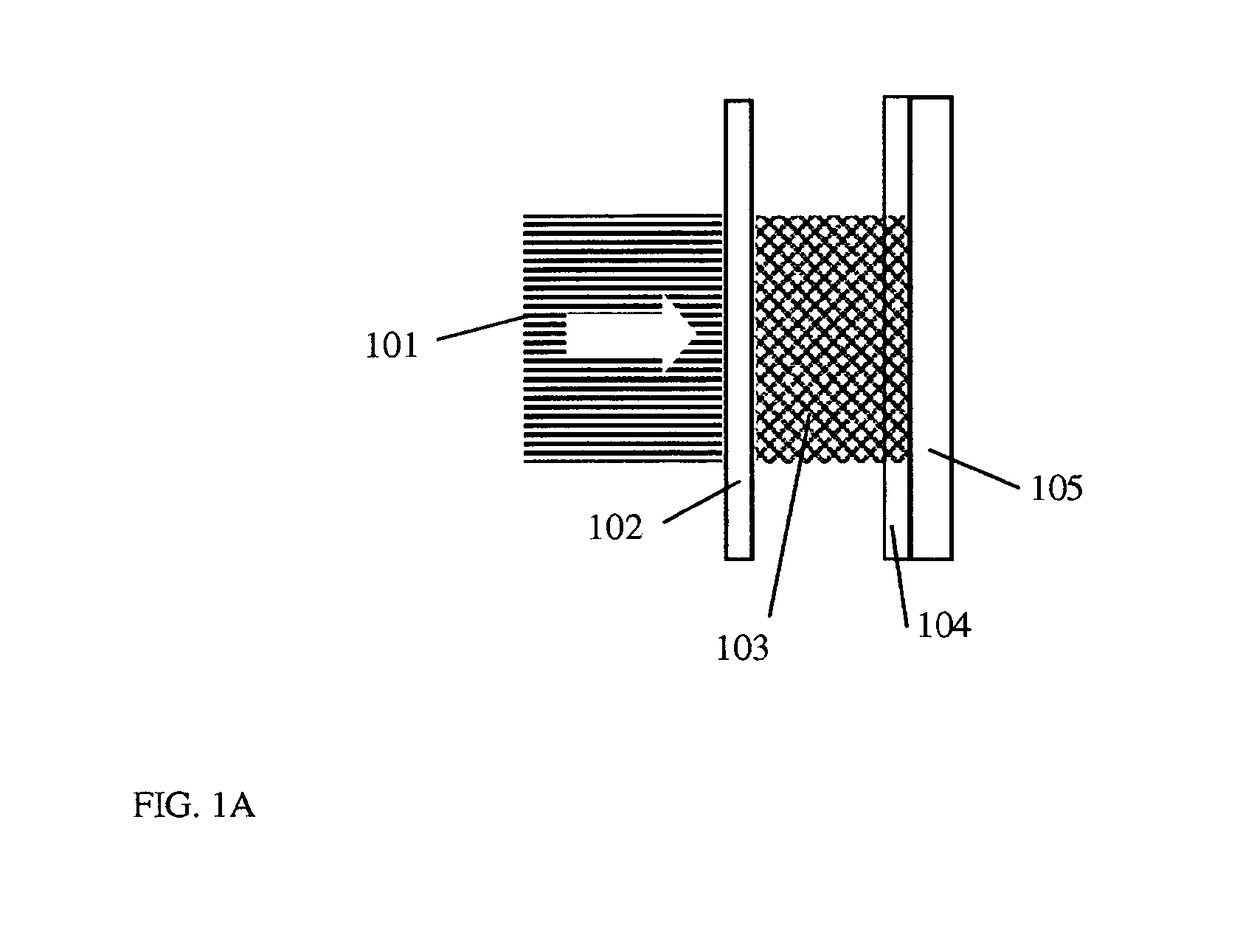
ActiveUS20100302469A1Reduce PDL and PMDMinimize the differenceStatic indicating devicesNon-linear opticsLight beamPolarization mode dispersion
An LC-based optical device compensates for differences in optical path lengths of polarization components of input beam. As a result, PDL and PMD of the optical device are reduced. The compensation mechanism may be a glass plate that is disposed in an optical path of a polarization component so that the optical path length of that polarization component can be made substantially equal to the optical path length of the other polarization component that traverses through a half-wave plate. Another compensation mechanism is a birefringent displacer that has two sections sandwiching a half-wave plate, wherein the two sections are of different widths and the planar front surface of the birefringent displacer can be positioned to be non-orthogonal with respect to the incident input light beam.
Owner:II VI DELAWARE INC
Fabrication of high efficiency, high quality, large area diffractive waveplates and arrays
ActiveUS9983479B2Quality improvementHigh yieldPolarising elementsPhotomechanical exposure apparatusBeam polarizationWavelength
An apparatus and method for fabricating high quality one- or two-dimensional diffractive waveplates and arrays that exhibit high diffraction efficiency and capable of inexpensive large volume production. A generally non-holographic and aperiodic polarization converter for converting the polarization of a coherent input light beam of a visible wavelength into a pattern of continuous spatial modulation at the output of the polarization converter. A photoresponsive material characterized by an anisotropy axis according to polarization of the light beam is exposed to a polarization modulation pattern and coated subsequently with an anisotropic material overlayer with ability of producing an optical axis orientation according to and under the influence of the anisotropy axis of the photoresponsive material layer. The diffractive waveplates are obtained when exposure time of photoresponsive material layer exceeds an order of magnitude the time period that is known to produce spatially homogeneous orientation of the anisotropic overlayer.
Owner:BEAM ENG FOR ADVANCED MEASUREMENTS
Method for improving measurement precision of beam polarization degree
ActiveCN101949734AReduce measurement impactPhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusBeam polarizationData treatment
The invention relates to a method for improving measurement precision of a beam polarization degree. A utilized polarization detection device comprises a phase delay device, an analyzer and a photo detector which are sequentially arranged along an optical axis of a system of the device, wherein the output of the photo detector is connected with a signal processing system, a beam to be measured which is parallel to the optical axis of the system is emitted to the phase delay device and the analyzer and detected by the photo detector, and the electric signal output by the photo detector is sent to the signal processing system for data processing. The method is characterized in that the transmission axis direction of the analyzer and the polarization direction of the beam to be measured are adjusted to be parallel or vertical according to the polarization direction of the beam to be measured, and then the measurement of the polarization degree of the beam to be measured is carried out. A stokes parameter and the polarization degree of the beam to be measured are obtained according to the light intensity detected by the photo detector. The invention can improve the measurement precision of the polarization degree.
Owner:BEIJING GUOWANG OPTICAL TECH CO LTD
Quantum computer and quantum computation method
Quantum computer includes optical systems arranged in series each of the plurality of optical systems includes first half-wave plate, first polarizing beam splitter, first switching mirror, first photodetector, first polarization rotator, optical cavity which contains atom, second switching mirror, second photodetector, second polarization rotator, and high reflection mirror, first polarization beam splitter outputting third light beam received from first switching mirror or second switching mirror to adjacent one of optical systems, third switching mirrors each provided between adjacent two optical systems, each of third switching mirrors reflecting or transmitting light beam output from one of two optical systems, light sources each providing light beam to corresponding optical system, and measurement system which measures polarization of incoming light beam.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Four-wave mixing source of squeezed light for image processing and interferometry
ActiveUS20080212166A1Improve efficiencyLight demodulationNon-linear opticsExcited stateImaging processing
A four-wave mixing squeezed light source includes: a mixing medium having chi(3) non-linear characteristics including two atomic ground states coupled to each other by transitions through optically-excited states; a pump beam having a polarization and a frequency, said frequency being near the ground-to-excited atomic transition but far enough from the atomic transition such that the pump beam is substantially unabsorbed; and a probe beam having a polarization that is orthogonal with respect to the pump beam polarization, the probe beam having a frequency of the pump beam frequency plus or minus a frequency splitting of the two atomic ground states. The mixing medium, the pump beam and the probe beam interact to produce a phase conjugate beam having a polarization that is orthogonal to the pump beam polarization, such that the beams are non-degenerate with the pump beam, and the probe beam is amplified.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE COMMERCE
Spatially resolved spin resonance detection
InactiveUS6946835B1High sensitivityImprove spatial resolutionMagnetic measurementsMaterial analysis by using resonanceBio moleculesBeam polarization
Methods for spatially resolved spin resonance detection in a sample of material, with a resolution as small as 0.5 μ m –1 mm. In one embodiment, a coupler having at least one pair of degenerate orthogonal modes provides an evanescent input signal along one coupler axis to the sample, to which a magnetic field is applied, and senses a spin interaction signal along another coupler axis. In another embodiment, an evanescent input signal is applied to the sample along one of two identical transmission line resonators, and a difference of the two resonator signals provides a spin interaction signal. In another embodiment, a polarized laser beam provides an evanescent input signal to the sample, and the spin interaction signal is sensed according to a second beam polarization direction. Certain ferromagnetic or ferrimagnetic molecules, such as YIG, can be used to tag selected chemical and biological molecules, using spatially resolved spin resonance detection for interrogation.
Owner:INTEMATIX
Discrete polarization state rotatable compensator spectroscopic ellipsometer system, and method of calibration
InactiveUS7075649B1Reduce in quantityMinimize the numberMaterial analysis by optical meansLight polarisation measurementMathematical modelBeam polarization
Disclosed are spectroscopic ellipsometer and combined spectroscopic reflectometer / ellipsometer systems. The spectroscopic ellipsometer system portion includes polarizer and analyzer elements which remain fixed in position during data acquisition, and a step-wise rotatable compensator electromagnetic beam transmitting means, which serves to enable imposing a plurality of sequentially discrete, rather than continuously varying, polarization states on said beam of electromagnetic radiation. Further disclosed is a calibration procedure for said spectroscopic ellipsometer system portion of the invention which involves the gathering of, for each of a plurality of ellipsometrically distinct sample systems, spectroscopic data at a sequential plurality of discrete electromagnetic radiation beam polarization states, combined with providing of a mathematical model of the spectroscopic ellipsometer system and application of a mathematical regression procedure.
Owner:J A WOOLLAM CO
Method and device for measurement of nanometer resolution total reflection differential micrometric displacement
InactiveCN102121818AHigh sensitivityAvoid measurement effectsUsing optical meansBeam splitterBeam polarization
The invention discloses a method and device for measurement of nanometer resolution total reflection differential micrometric displacement. The device comprises a laser device, a single-mode fiber, a collimating lens, a polarizing beam splitter, a lambda / 4 wave plate, a micro objective, a detected target lens, a rhombic prism, a convex lens, a differential detector and a driving and display unit. The method comprises steps as follows: after being filtered, collimated and split by polarization, laser sequentially passes through a fast axis and the lambda / 4 wave plate and micro objective to reach the detected target lens, wherein the included angle between the lambda / 4 wave plate and micro objective and the polarization direction of vertical incidence light beam is 45 degrees; after being reversed, the laser passes through the micro objective and lambda / 4 wave plate, and then vertically enters the polarizing beam splitter again; then, the laser enters the rhombic prism, is subjected to total reflection in the rhombic prism, and exits; and finally, after being collected, the laser enters the differential detector for processing, thus obtaining a signal for reflecting the position change of the detected target lens, and displaying the position change of the detected target lens. The invention can be used for detecting the manometer resolution and can be widely applied to the industrial precision measurement and monitoring fields.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Light beam stokes parameter measuring device and measuring method
InactiveCN102692274AReduced measurement accuracyLight polarisation measurementBeam splitterBeam polarization
The invention discloses a light beam stokes parameter measuring device and a measuring method thereof. The polarization measuring device is composed of a beam splitter prism group, a phase retarder array, a polarization analyzer, a photoelectric detector array and a signal processing system, wherein all units of the photoelectric detector array correspond to all units of the phase retarder array one by one. The measuring method is realized through the following steps: adopting the phase retarder array to replace the rotational phase retarder; according to the polarization direction of a to-be-measured light beam, adjusting the direction of a light-transmitting shaft of the polarization analyzer to be parallel to or vertical to the polarization direction of the to-be-measured light; measuring the polarization parameters of the to-be-measured light beam; processing data as per light intensity signals detected by the photoelectric detector array so as to realize the real-time high accuracy measurement of the light beam stokes parameters. Though adopting the method, the stokes parameters of the light beam can be measured in real time, and furthermore, the influences on the measurement accuracy of the light beam polarization state caused by the phase delay error of phase delaying devices, the fast-shaft direction error, the direction error of the light-transmitting shaft of the polarization analyzer and the extinction ratio error are reduced.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Tunable filter
InactiveUS20020126385A1High diffraction efficiencyPrismsRadiation pyrometryBeam polarizationLight beam
A tunable filter includes a polarizer, a polarization rotator, a diffraction grating and a diffraction grating adjustor. The polarizer polarizes a light beam and splits the light beam into first and second light beams. The polarization rotator rotates a plane of polarization of the first light beam at 90.degree. to generate a rotated light beam. The diffraction grating receives the rotated light beam and the second light beam. The diffraction grating adjustor adjusts the diffraction grating to change incident angles of the rotated light beam and second light beam.
Owner:ANDO ELECTRIC CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com