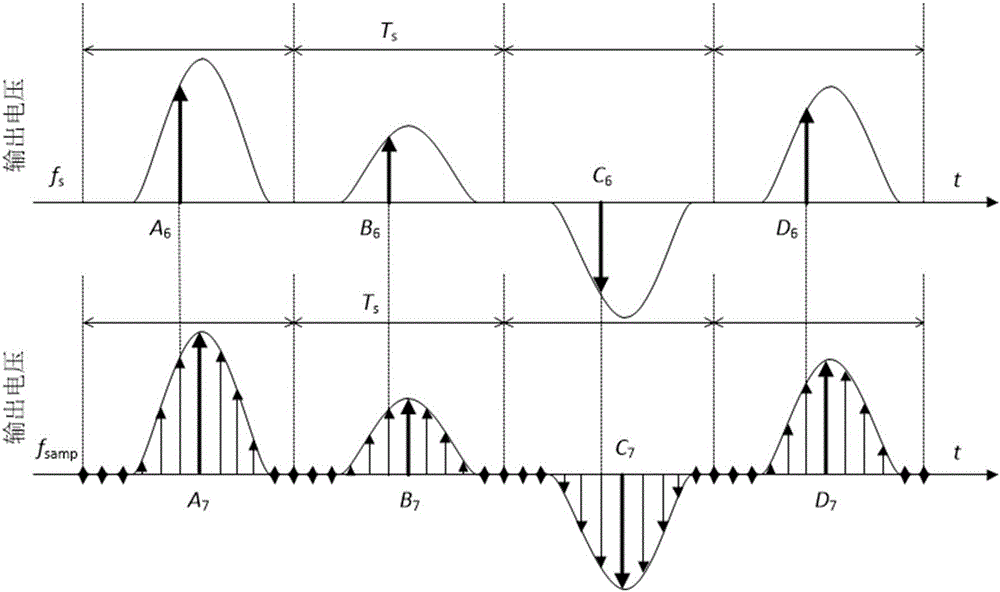
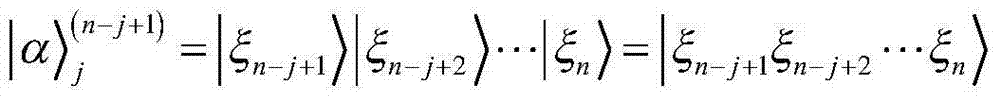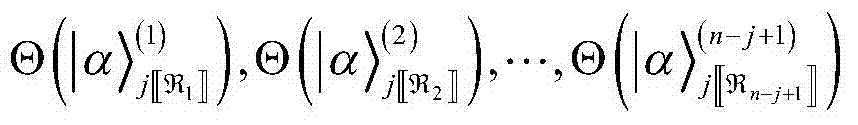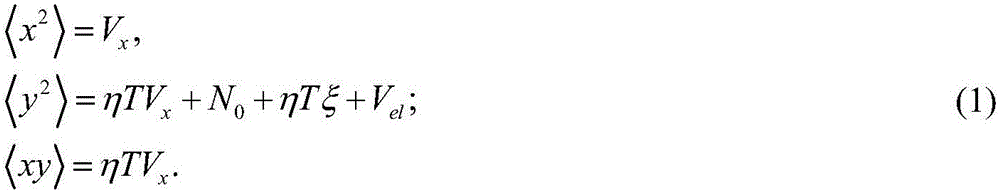Patents
Literature
255 results about "Quantum information" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In physics and computer science, quantum information is the information of the state of a quantum system. It is the basic entity of study in quantum information theory, and can be manipulated using quantum information processing techniques. Quantum information refers to both the technical definition in terms of Von Neumann entropy and the general computational term.
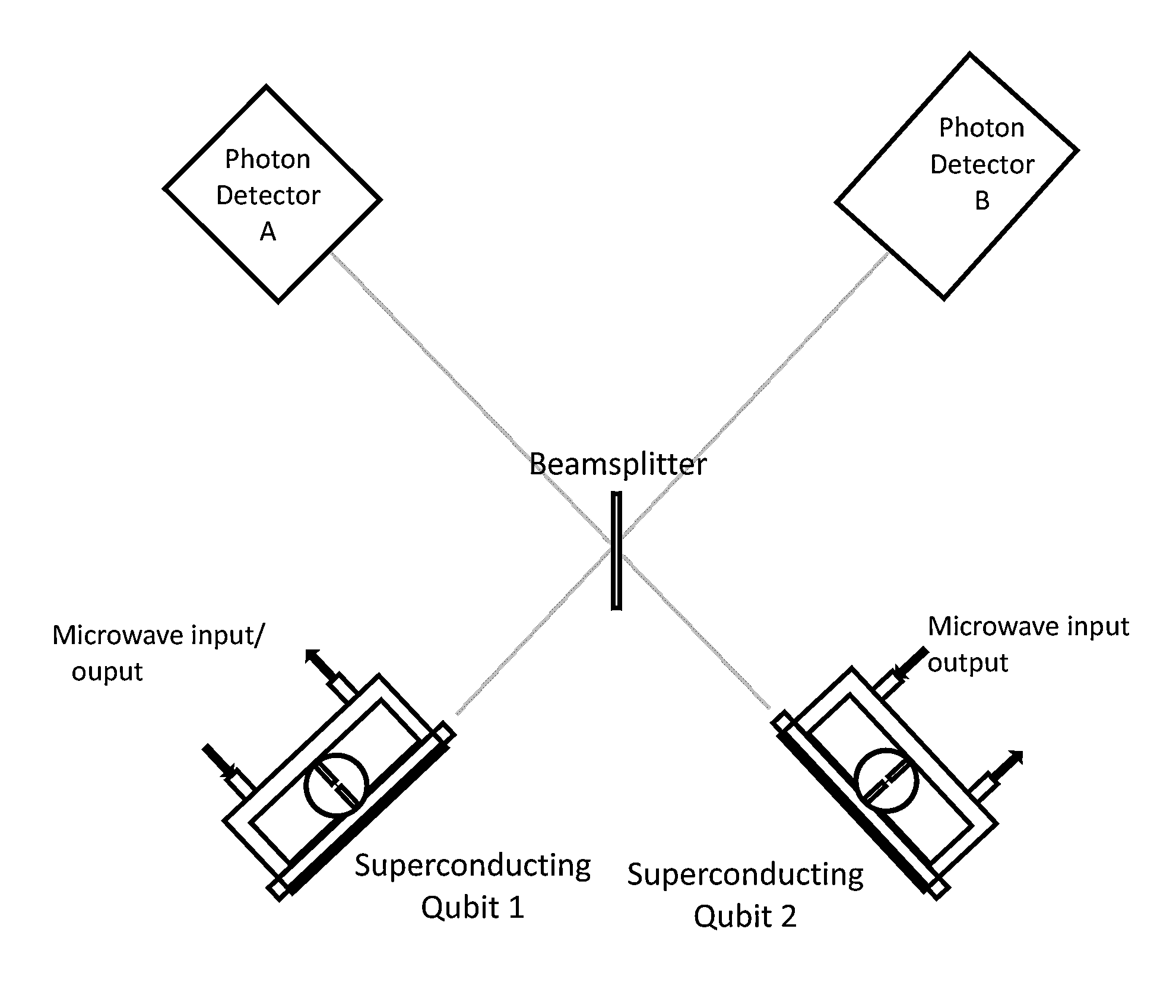
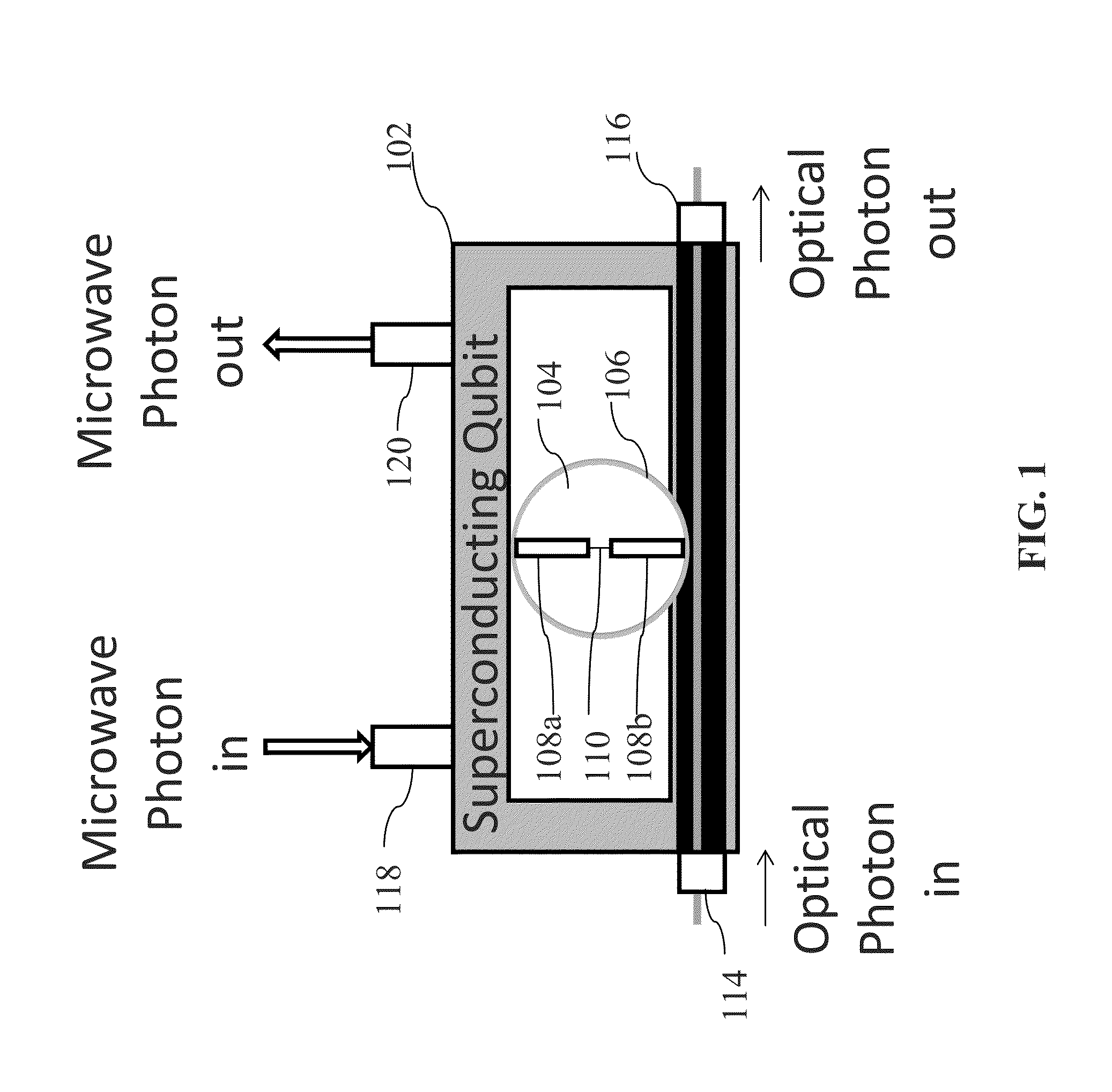
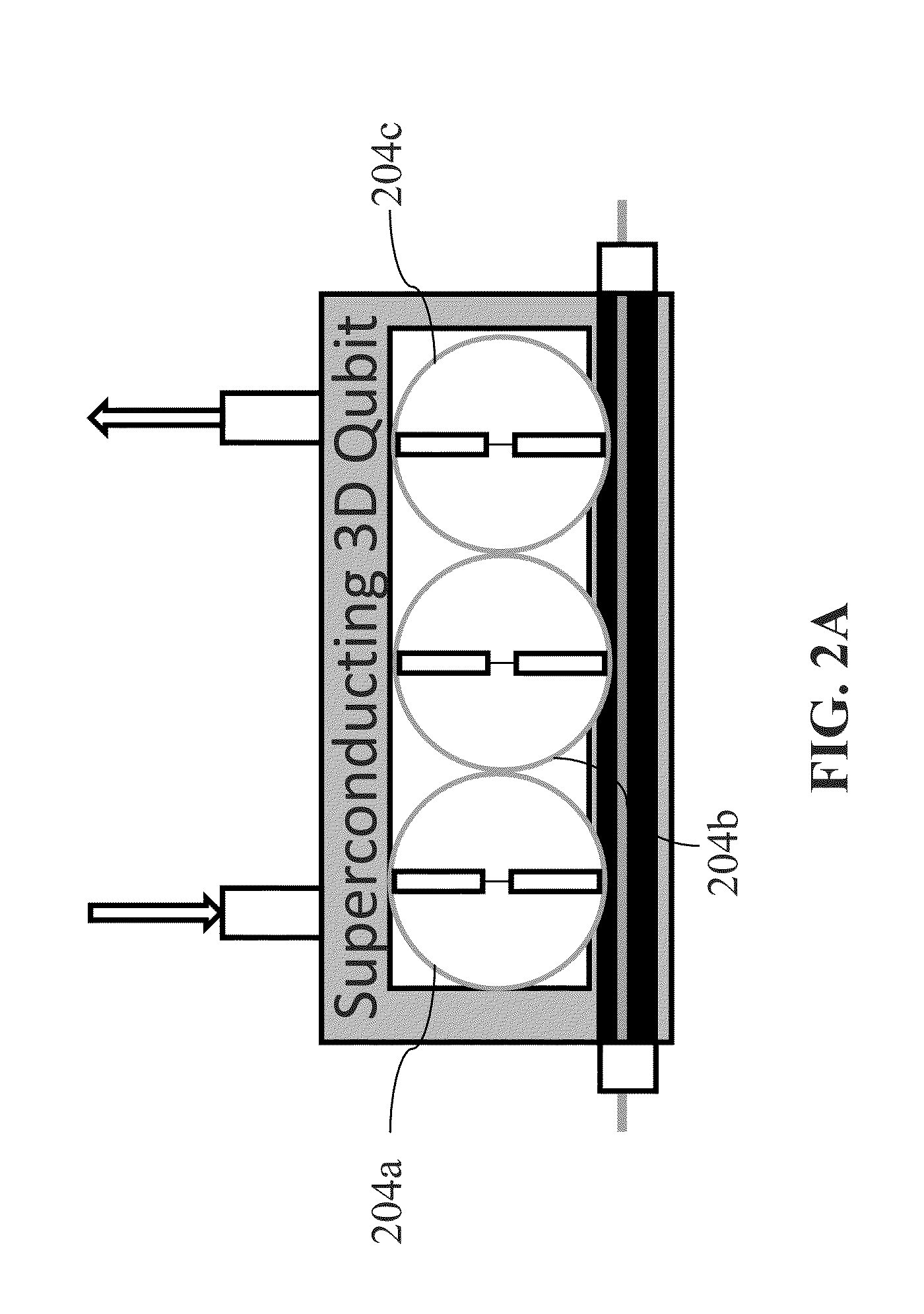
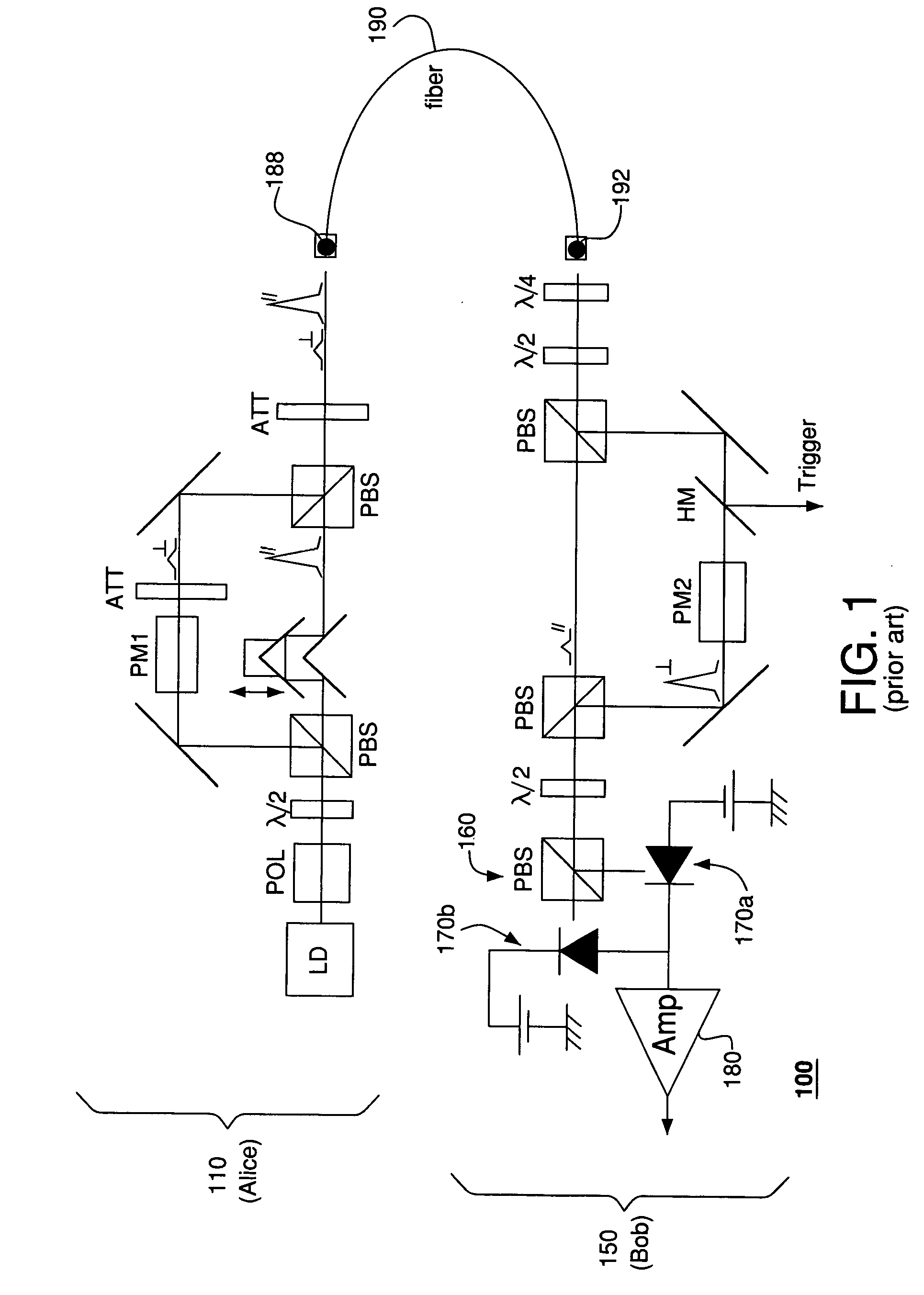
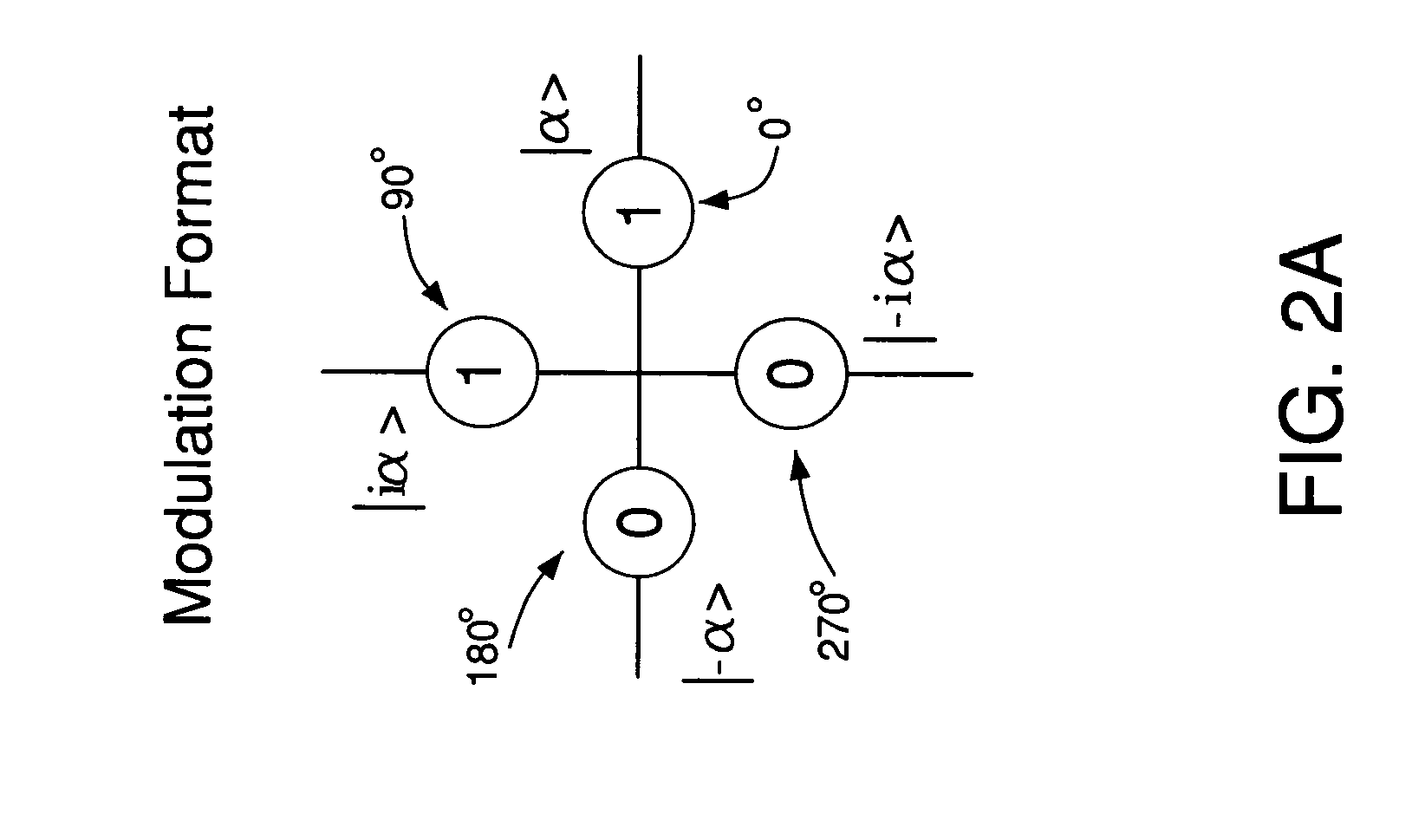
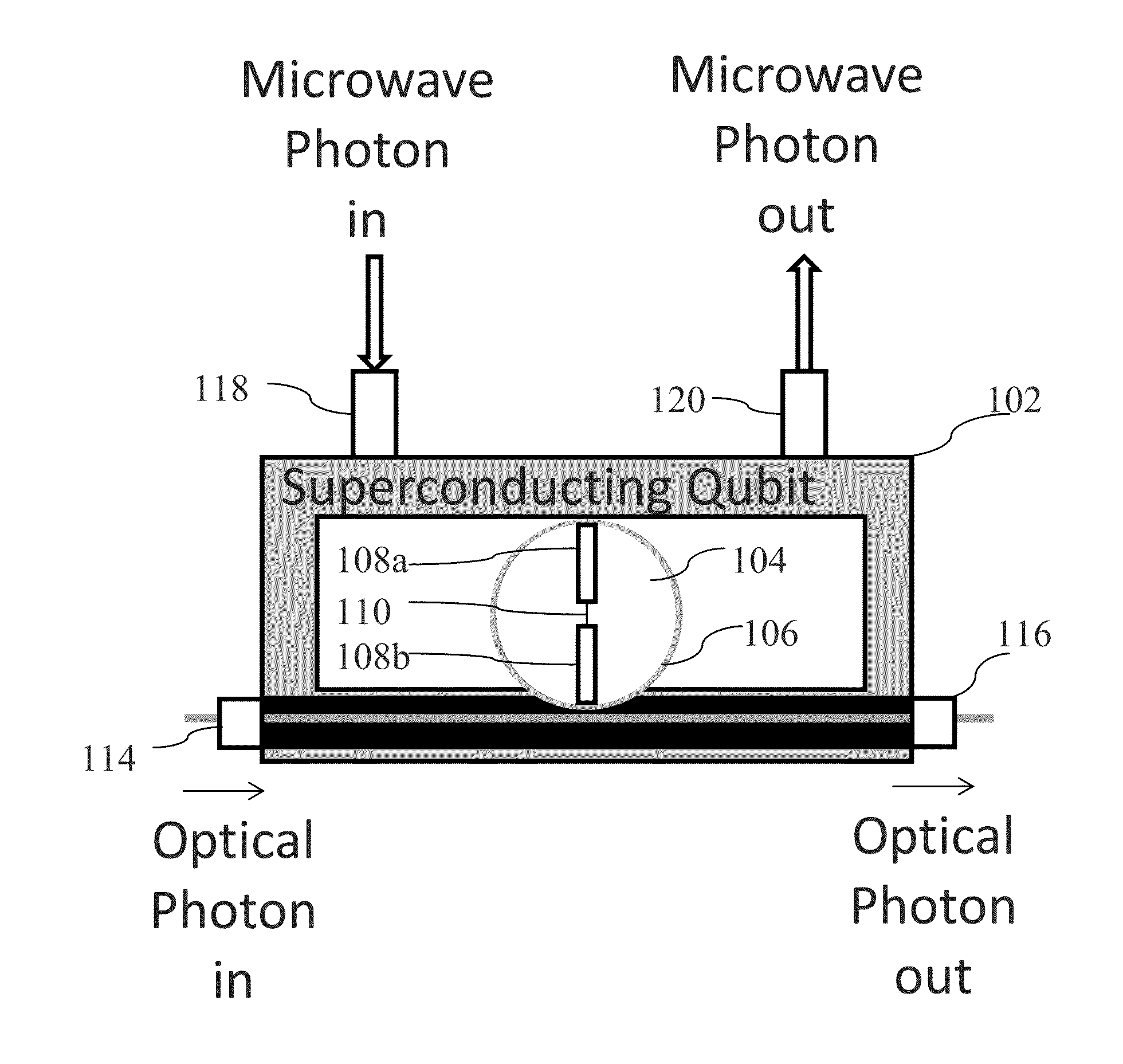
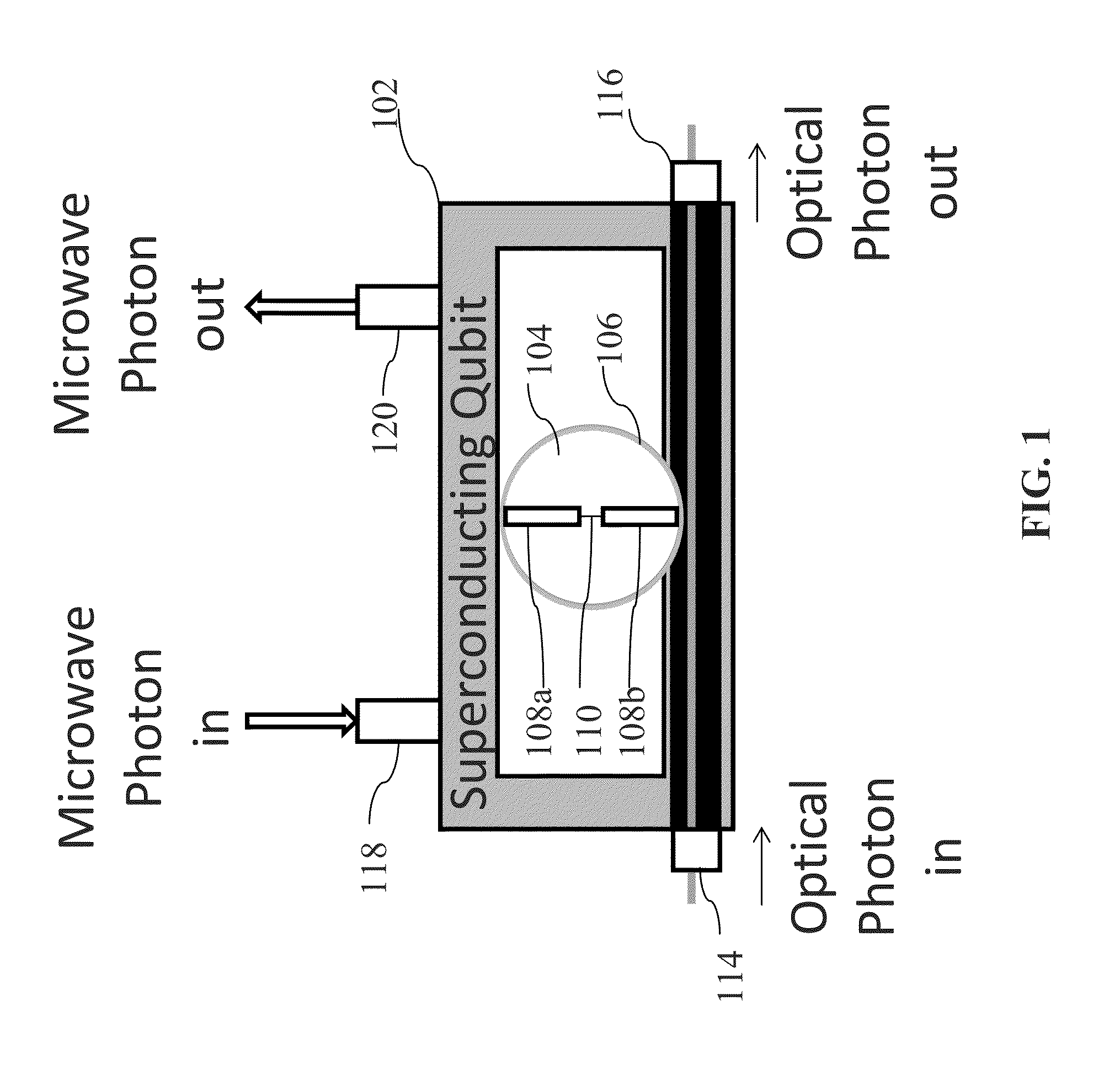
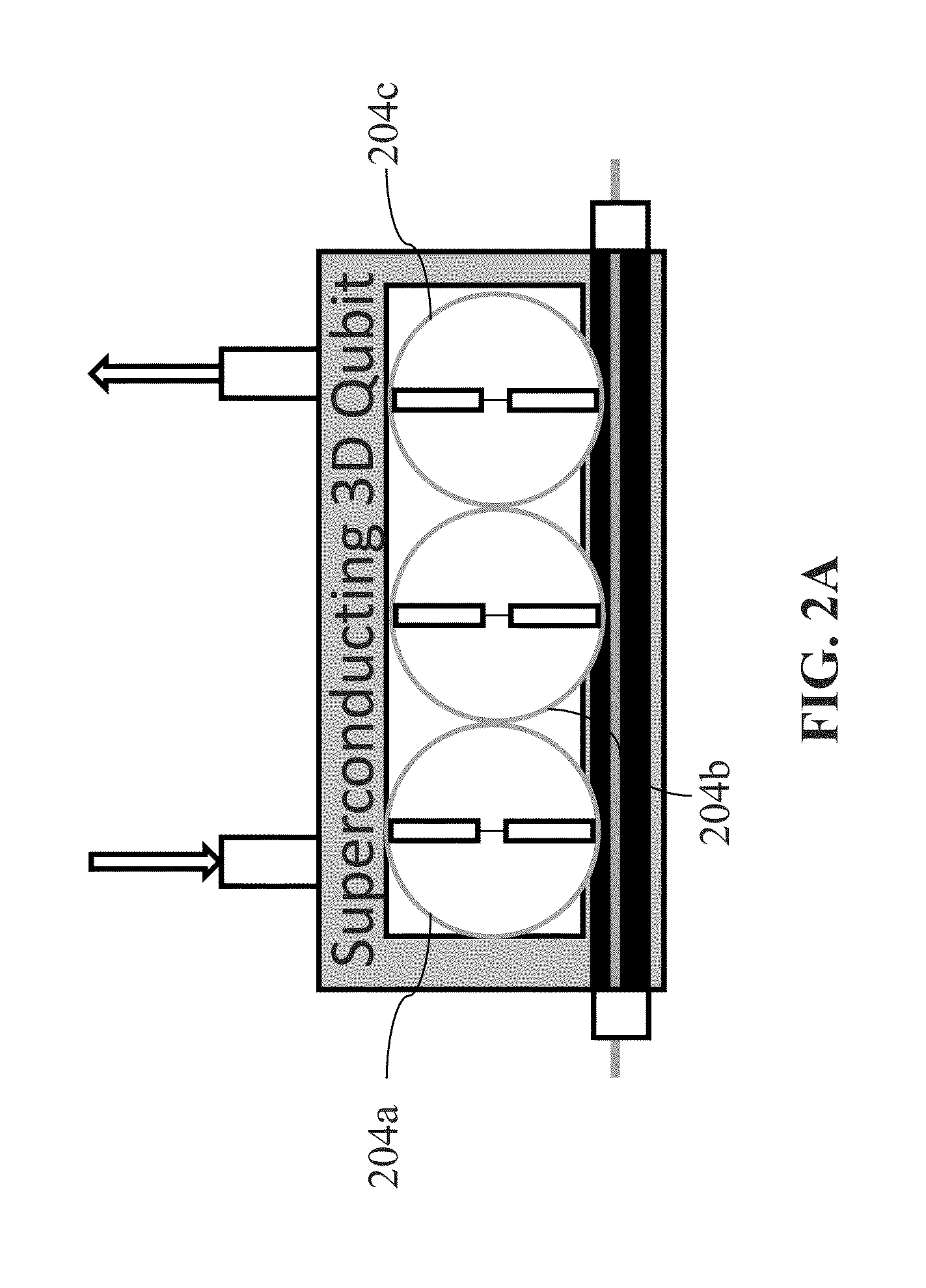
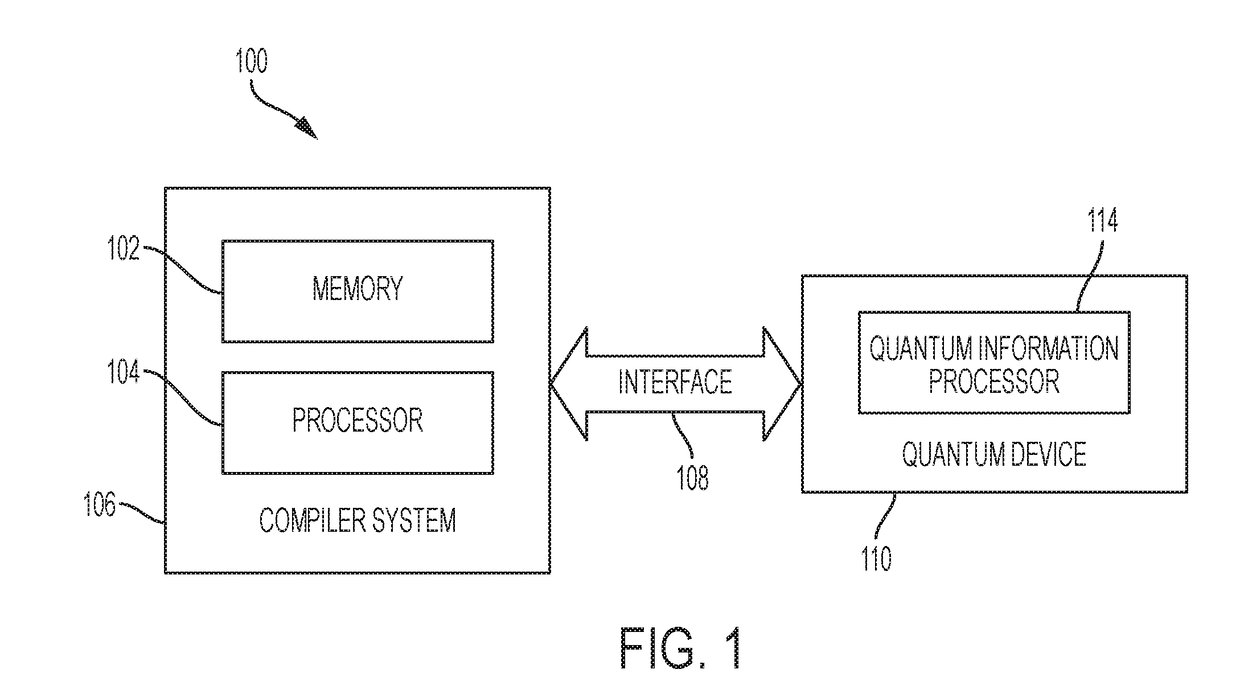
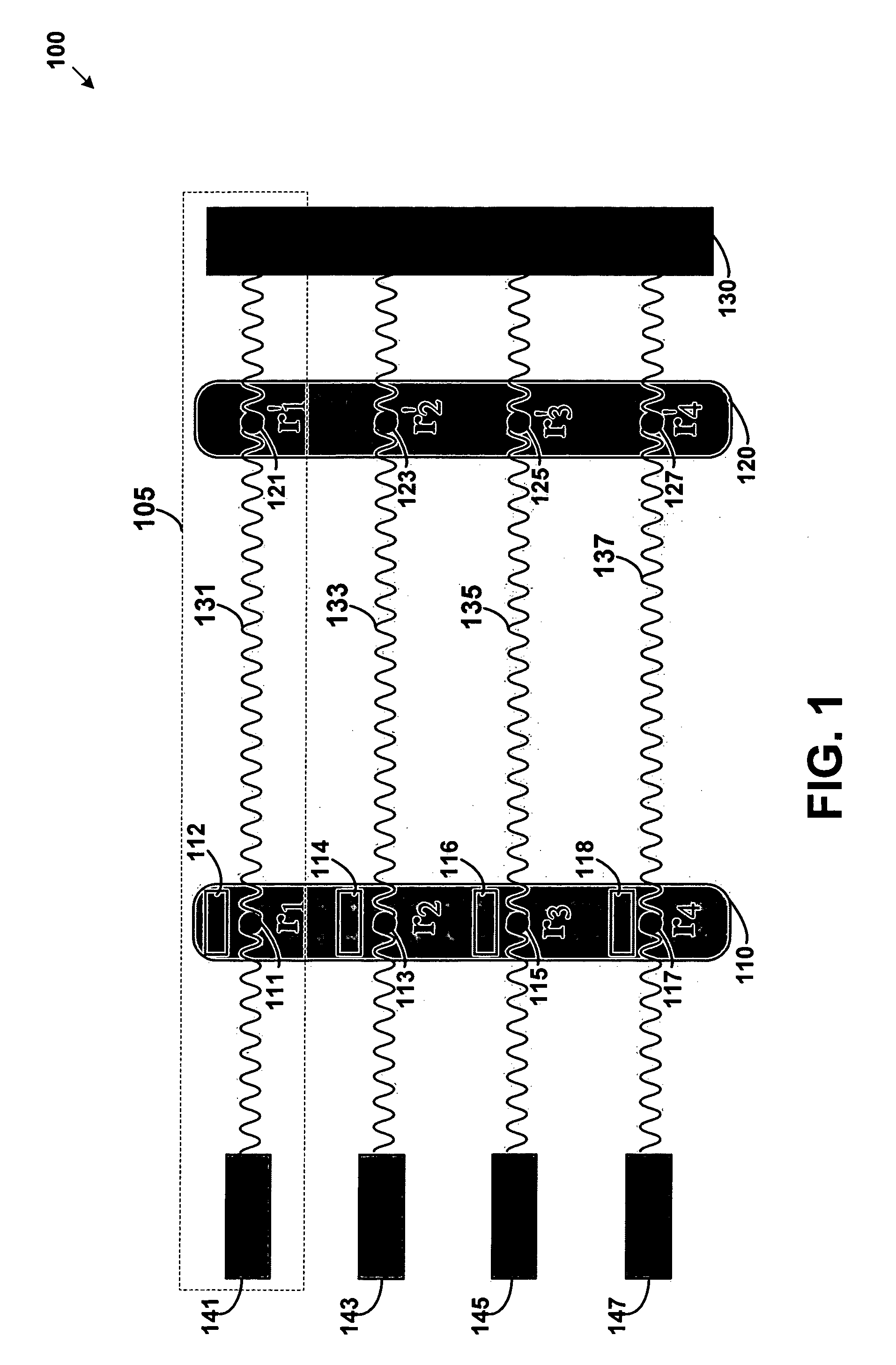
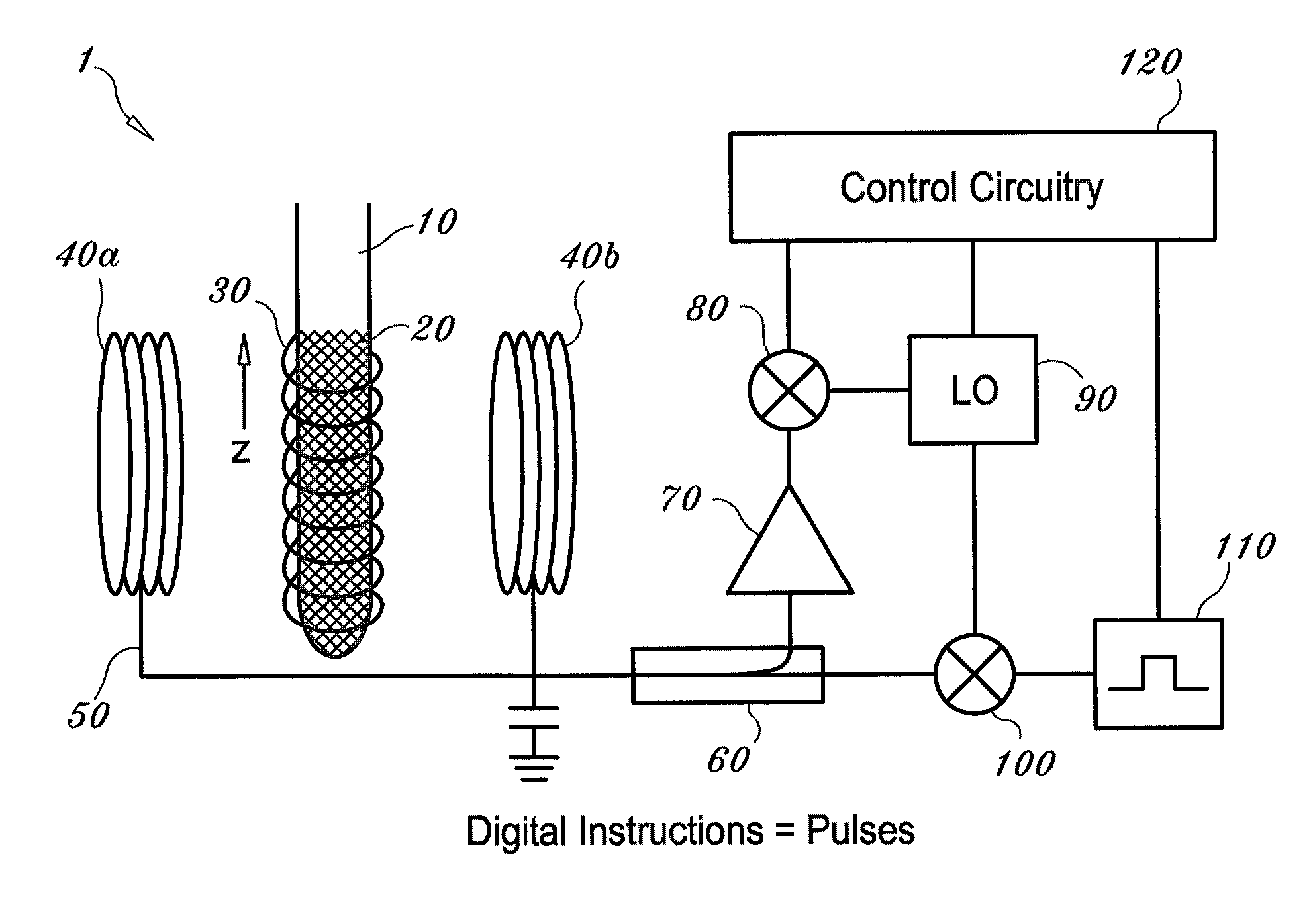
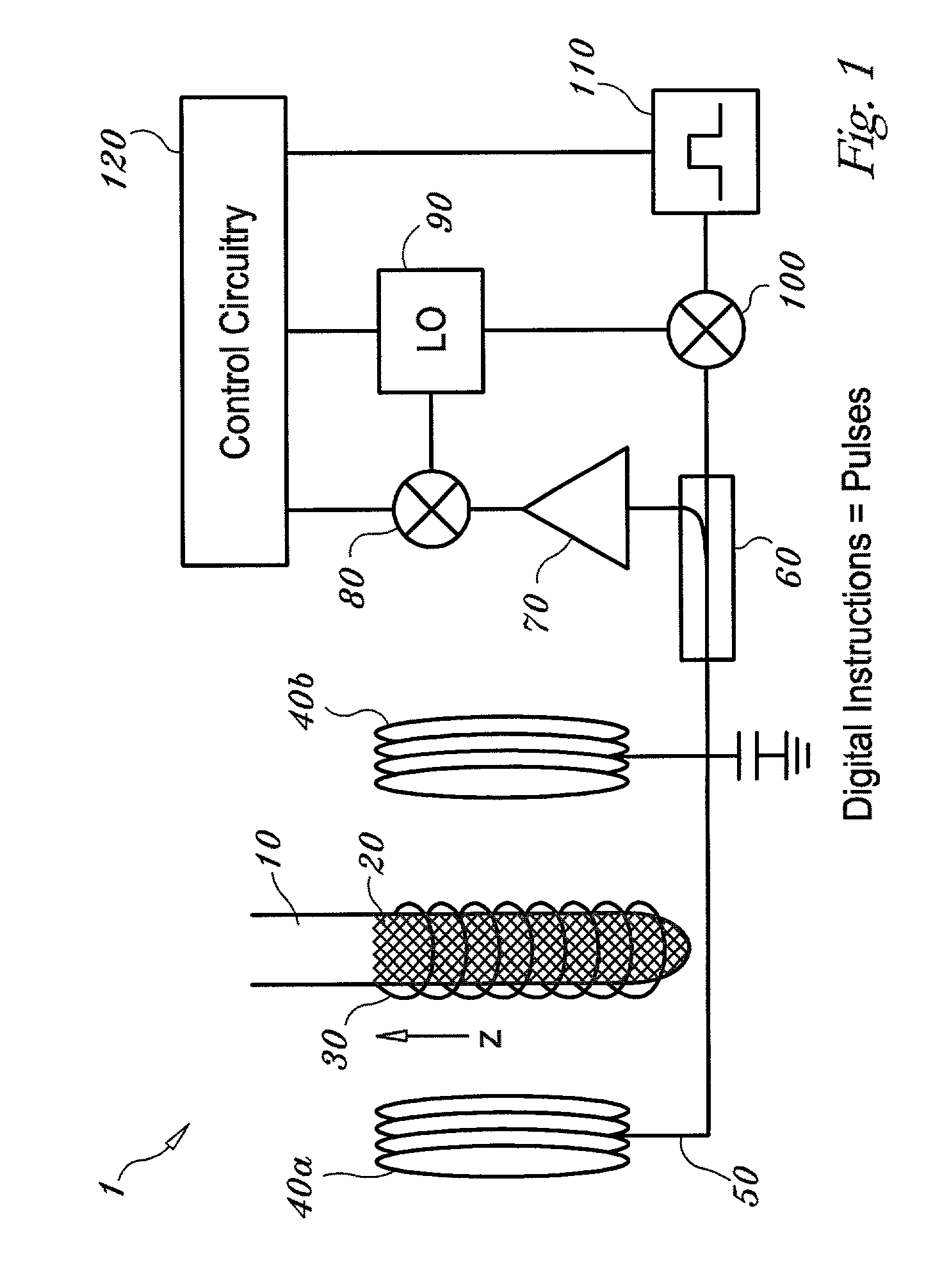
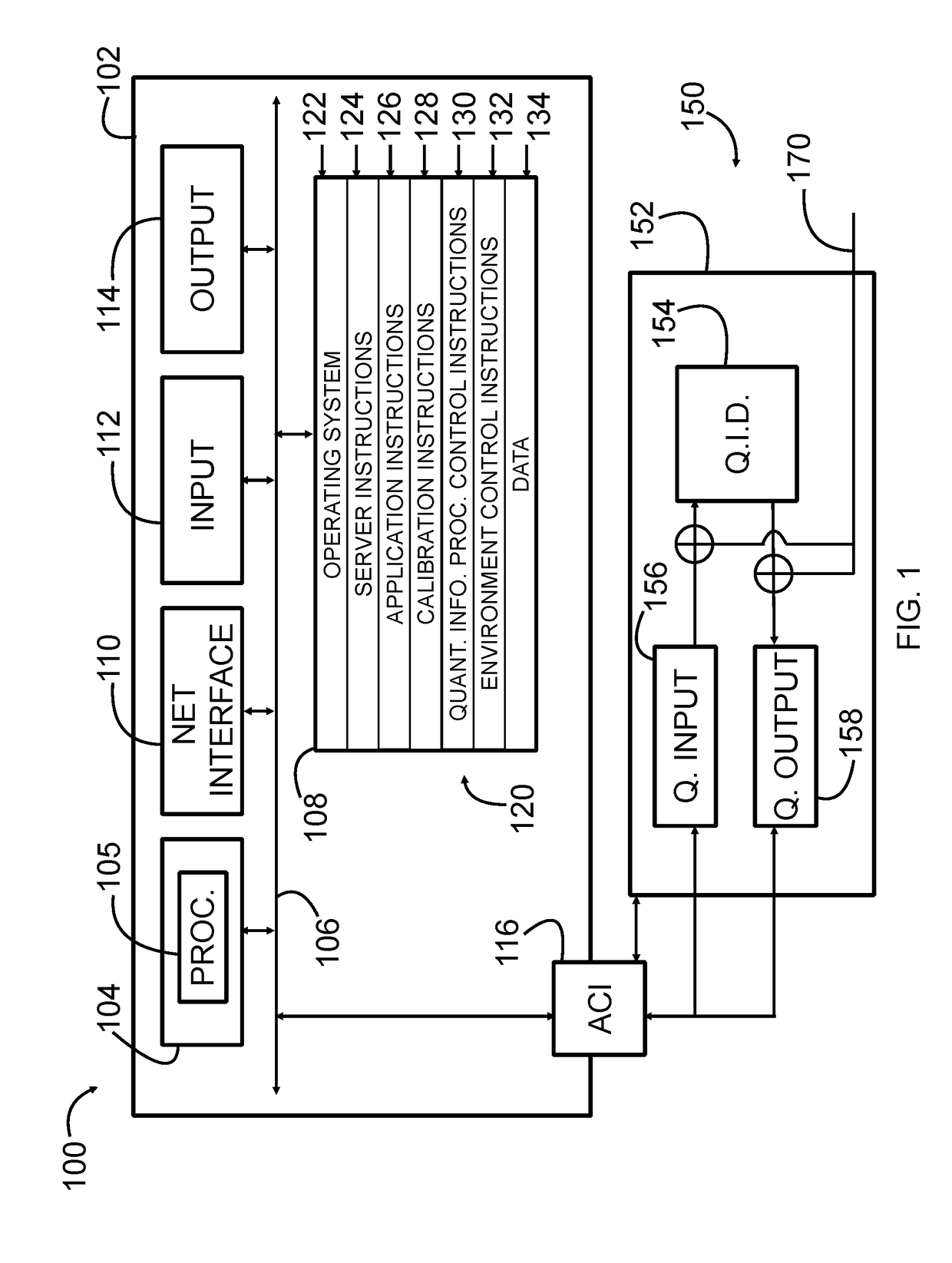
System and method for quantum information transfer between optical photons and superconductive qubits
ActiveUS20140314419A1Modulation frequencyQuantum computersNanoinformaticsMicrowave cavityDirect coupling
An electro-optical system for exchanging quantum information between optical qubits and including a superconductive microwave cavity; an electro-optical material: a superconductive qubit circuit formed on the electro-optical material including a superconductive qubit; a dipole antenna, formed on the electro-optical material for directly coupling the superconductive qubit to the superconductive microwave cavity; an optical input for receiving input optical photons; a microwave input for receiving input microwave photons; and an optical output for outputting modulated optical photons, wherein a frequency and a phase of the optical photon is modulated with a state of the superconducting qubit by the dipole antenna.
Owner:RAYTHEON BBN TECH CORP
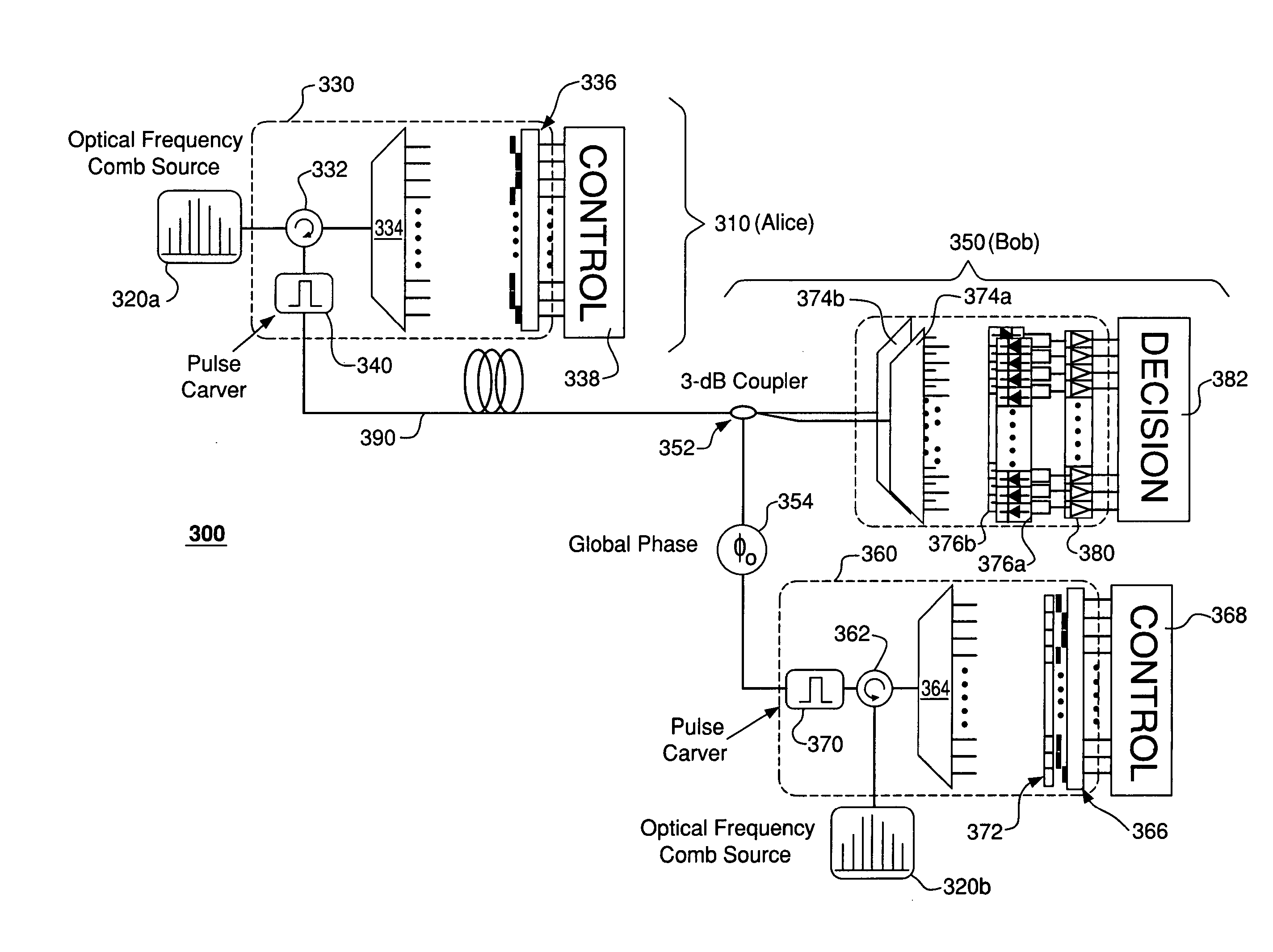
Multi-channel transmission of quantum information
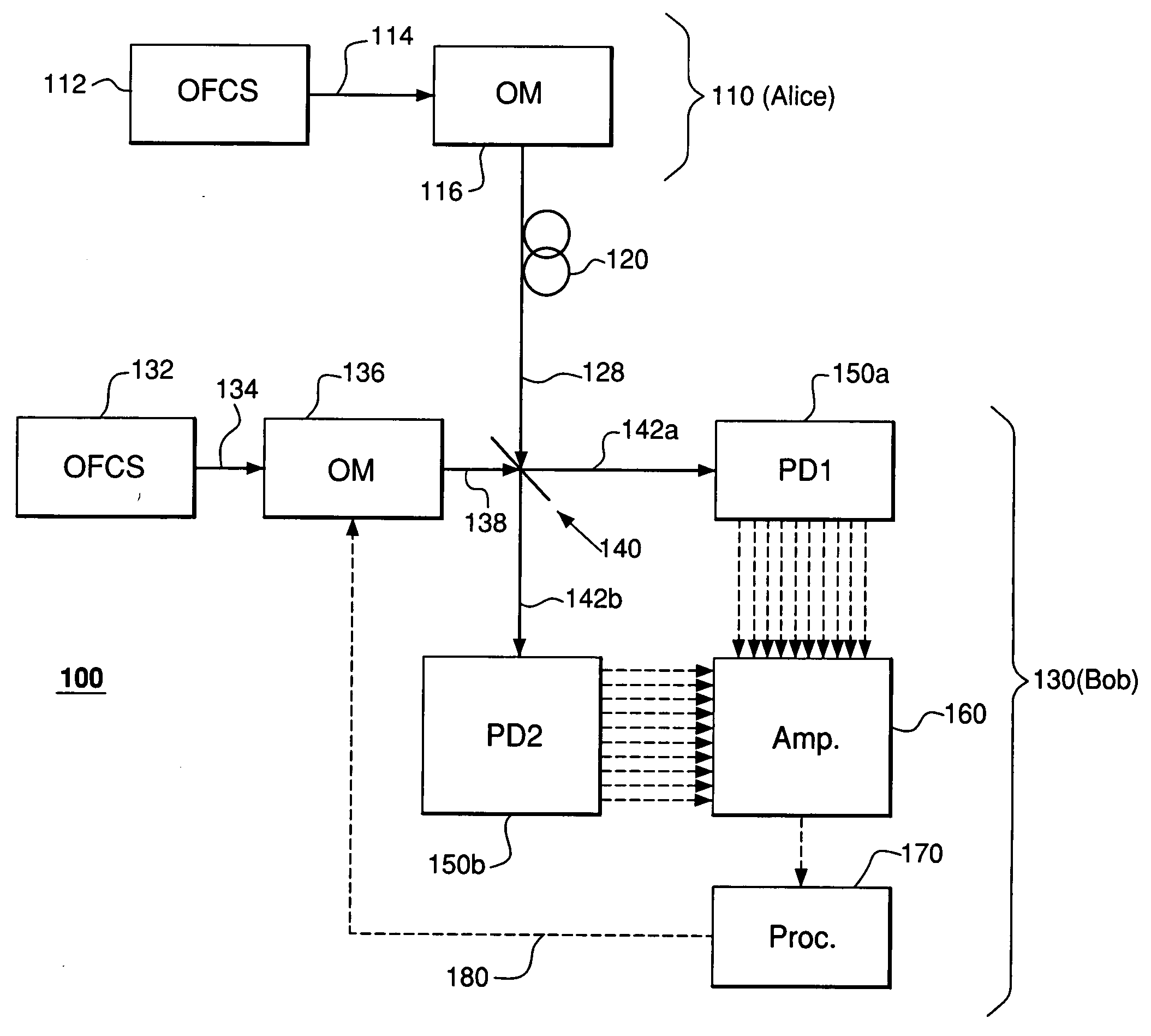
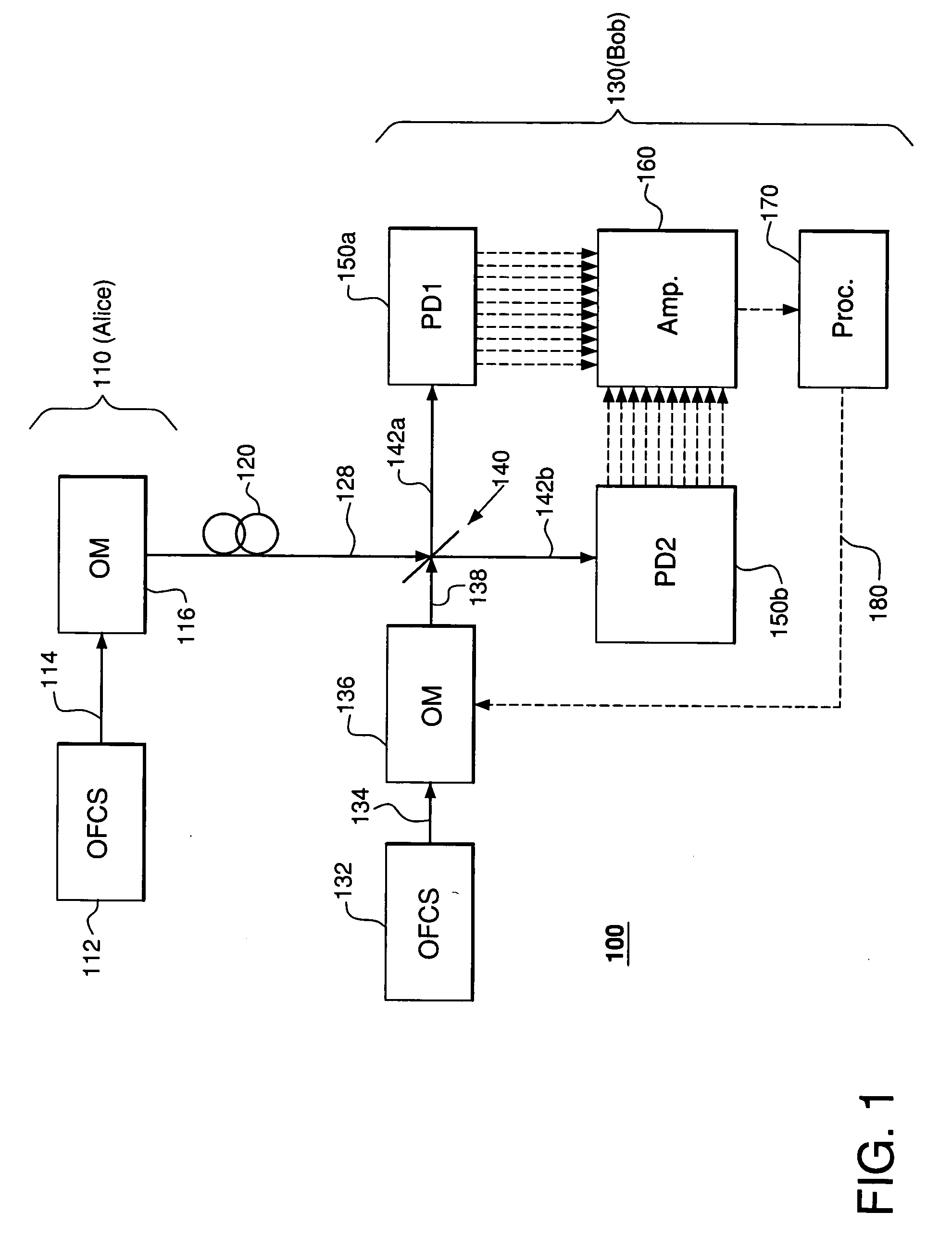
InactiveUS20060263096A1Optical multiplexElectromagnetic transmittersFrequency standardQuantum information
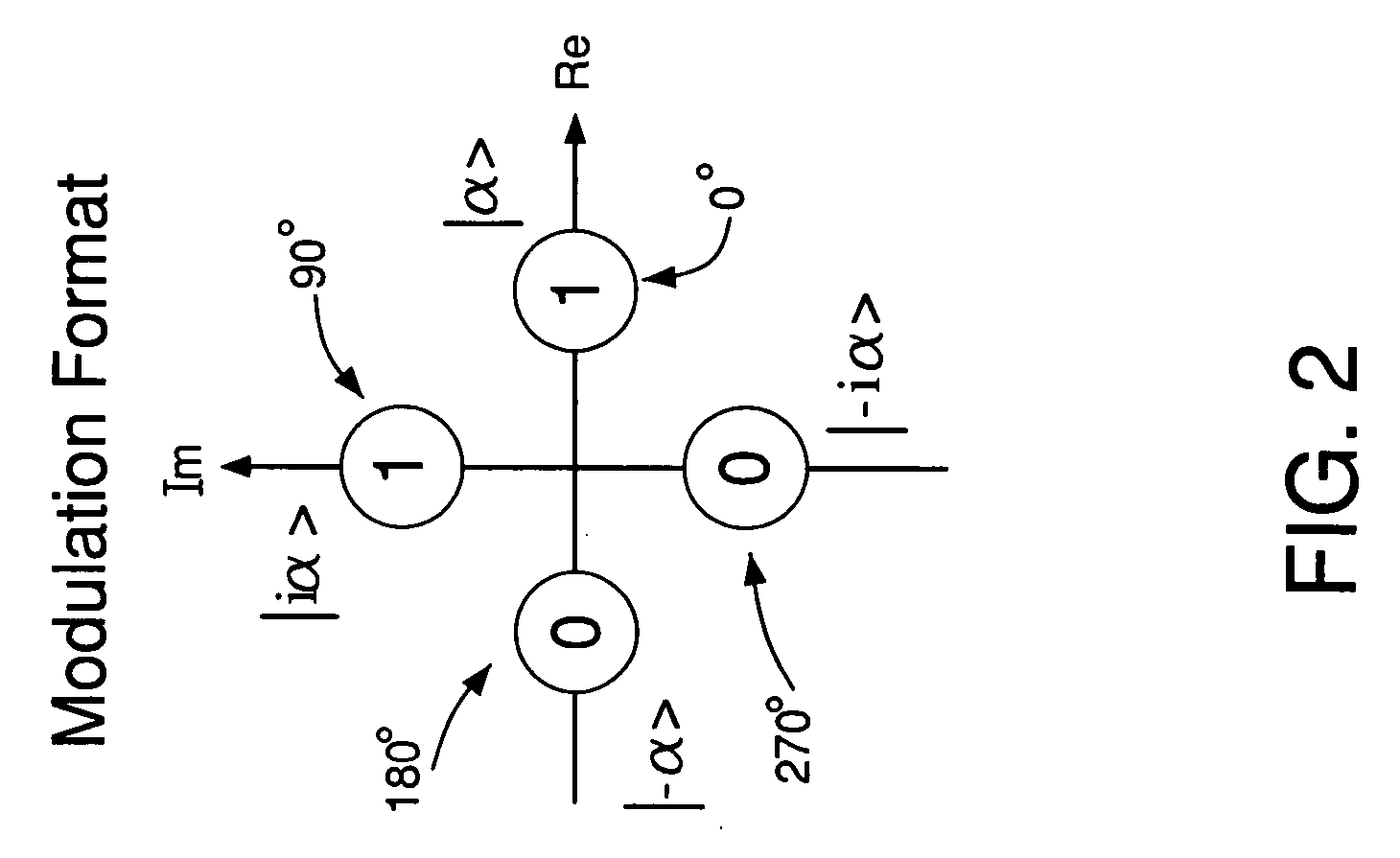
A communication system adapted to use wavelength (frequency) division multiplexing for quantum-key distribution (QKD). In one embodiment, a communication system of the invention has a transmitter coupled to a receiver via a transmission link. The transmitter has (i) a first optical-frequency comb source (OFCS) adapted to generate a first plurality of uniformly spaced frequency components and (ii) a first multi-channel optical modulator adapted to independently modulate each component of the first plurality to produce a quantum-information (QI) signal applied to the transmission link. The receiver has (i) a second OFCS adapted to generate a second plurality of uniformly spaced frequency components and (ii) a second multi-channel optical modulator adapted to independently modulate each component of the second plurality to produce a local-oscillator (LO) signal. Each of the first and second optical-frequency comb sources is referenced to a frequency standard such that the frequency components generated by these comb sources have substantially the same frequencies. The receiver employs a multi-channel homodyne detector adapted to process interference signals produced by combining the LO signal with the QI signal to ascertain quantum information carried by the QI signal.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
System and method for quantum information transfer between optical photons and superconductive qubits
An electro-optical system for exchanging quantum information between optical qubits and including a superconductive microwave cavity; an electro-optical material; a superconductive qubit circuit formed on the electro-optical material including a superconductive qubit; a dipole antenna, formed on the electro-optical material for directly coupling the superconductive qubit to the superconductive microwave cavity; an optical input for receiving input optical photons; a microwave input for receiving input microwave photons; and an optical output for outputting modulated optical photons, wherein a frequency and a phase of the optical photon is modulated with a state of the superconducting qubit by the dipole antenna.
Owner:RAYTHEON BBN TECH CORP
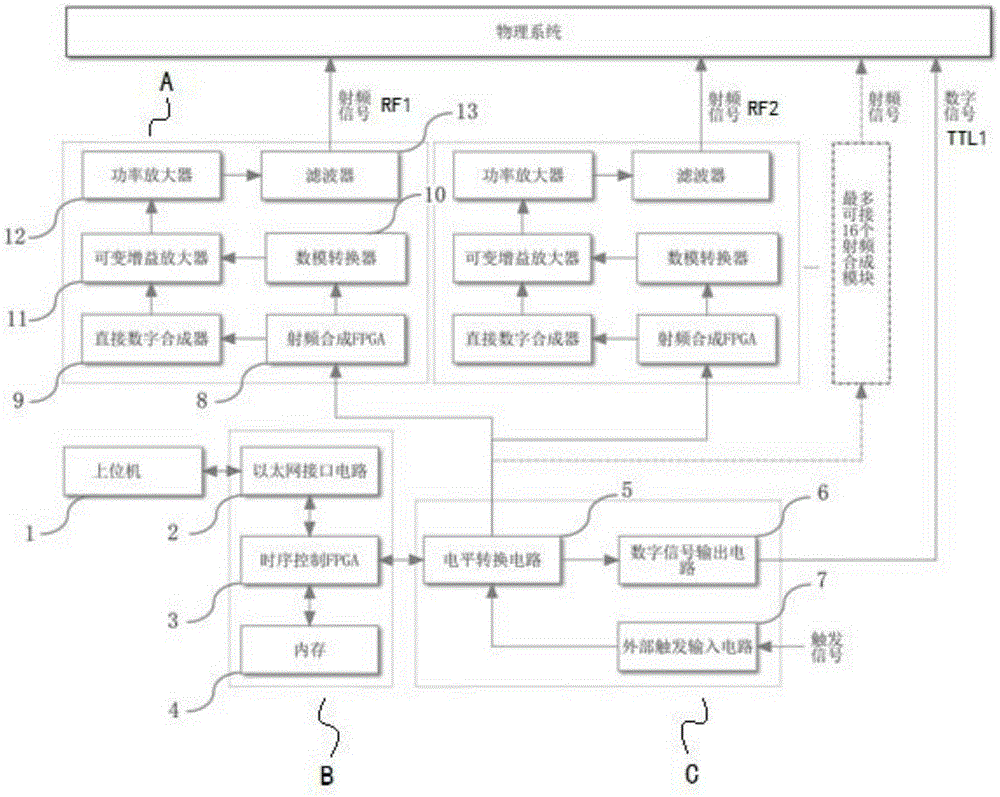
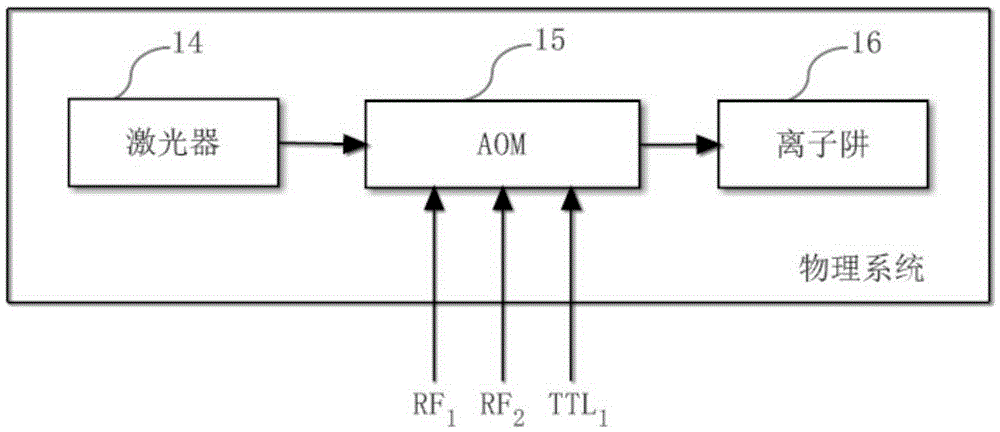
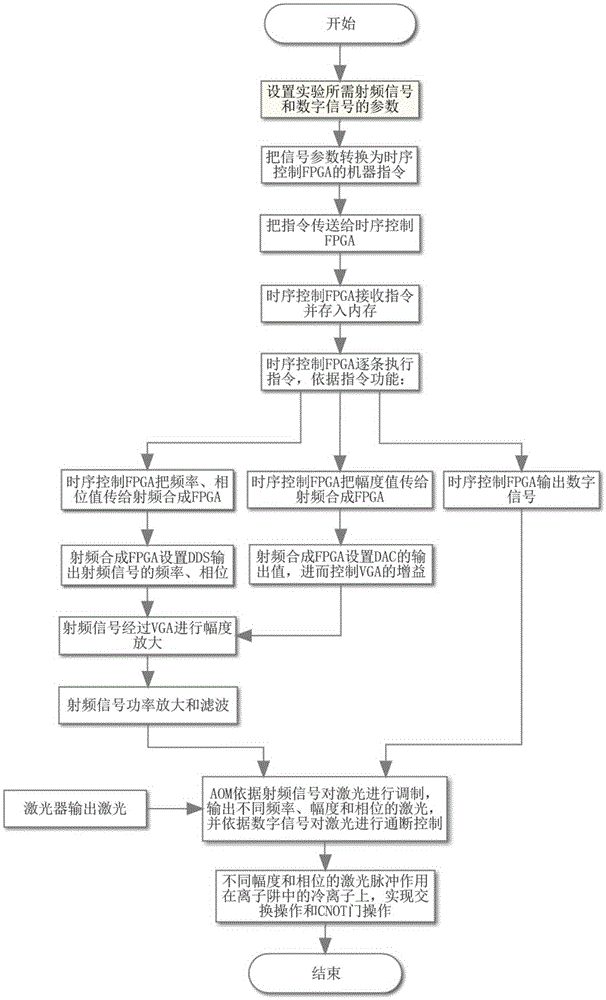
Sequential control signal generation method and device of cold ion quantum information processor
ActiveCN105281886ARealize intuitive descriptionAvoid duplication of workSynchronising arrangementControl signalRadio frequency signal
The invention provides a sequential control signal generation method of a cold ion quantum information processor. Radio frequency signal and digital signal parameters are set through a principal computer command on a principal computer; the principal computer command is converted into a machine command which is transmitted to a sequential control FPGA; the sequential control FPGA executes the machine command and digital signals and radio frequency signals are output through a conversion module and a radio frequency synthesis module. The invention also provides a sequential control signal generation device of a cold ion quantum information processor. The device comprises a principal computer, a sequential control module, a radio frequency synthesis module and a conversion module. According to the invention, sequential control signals for experiments are described intuitively; programmed principal computer commands can be used repeatedly, so that repeated work is prevented and improvement can be made according to experiment results conveniently; the parameters such as the frequency, the phase and the amplitude of radio frequency signals can be changed conveniently; multiple paths of control signals can be controlled accurately to work cooperatively; the extendibility is great.
Owner:WUHAN INST OF PHYSICS & MATHEMATICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Encryption method and apparatus encrypting and adding signature information to qubits
InactiveUS7035411B2Quantum computersKey distribution for secure communicationQuantum informationEncryption
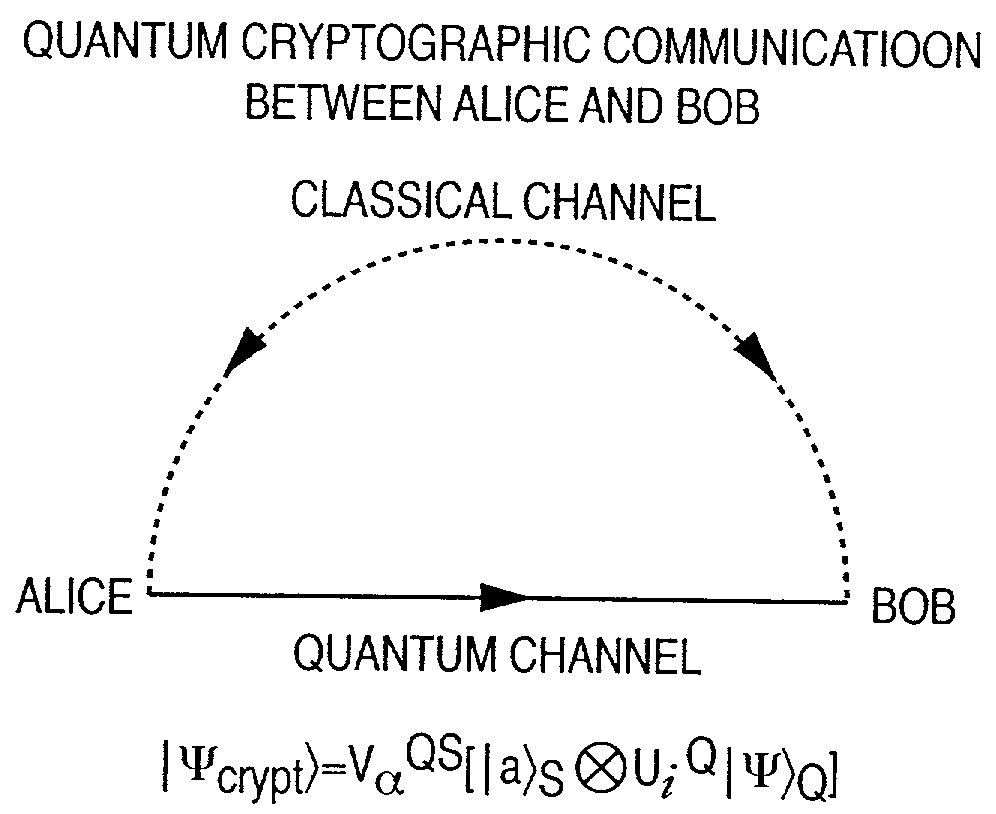
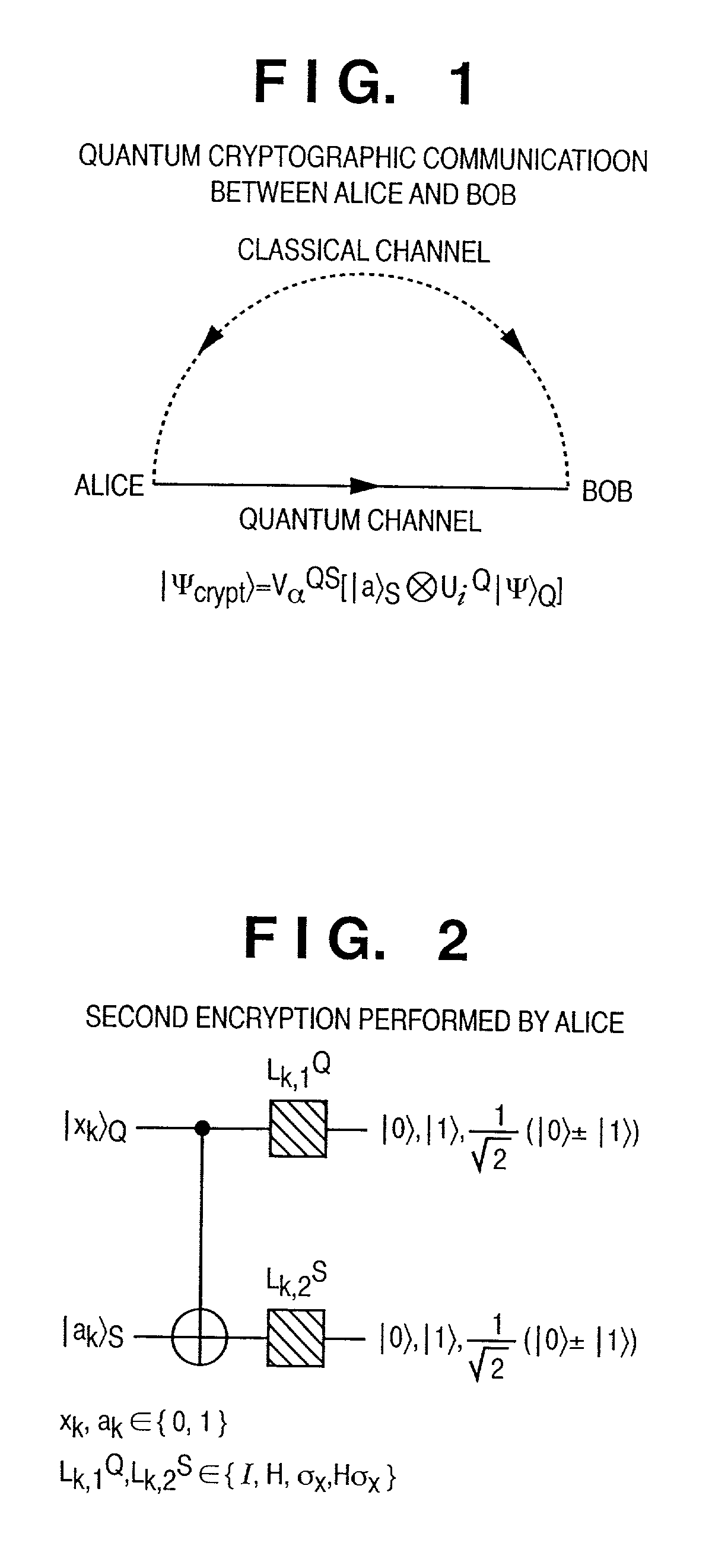
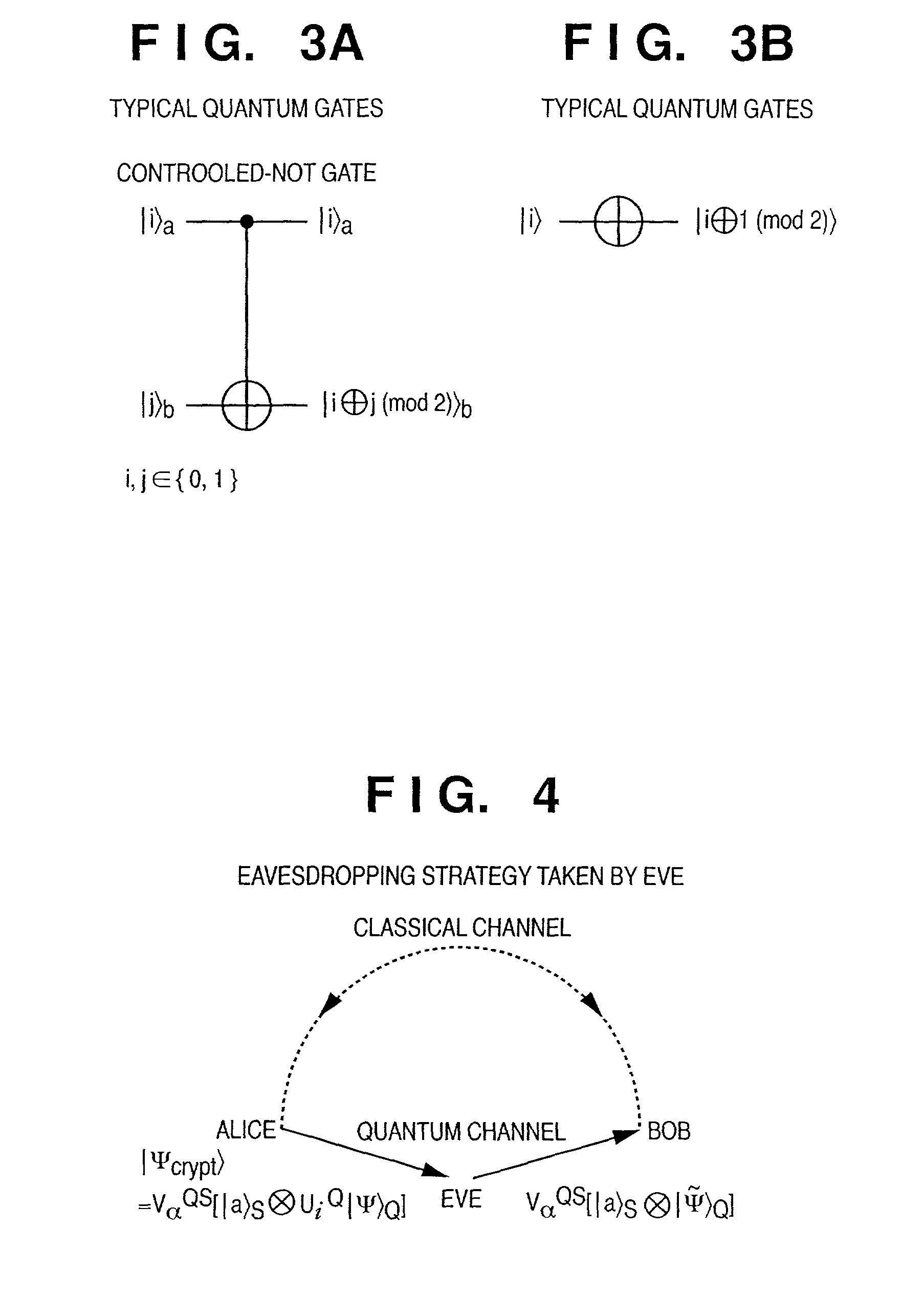
Arbitrary quantum information is input. The information of a quantum two-state system is acquired as a qubit by performing a computation in consideration of a physical system. The acquired qubit is encrypted. A quantum system having signature information for guaranteeing that the qubit is really transferred from a sender to a recipient is added to the encrypted qubit. The qubit to which the quantum system having the signature information is added is further encrypted. In this manner, an arbitrary quantum state can be encrypted and transmitted without letting the sender and recipient share an entangled pair of qubits in advance.
Owner:CANON KK +1
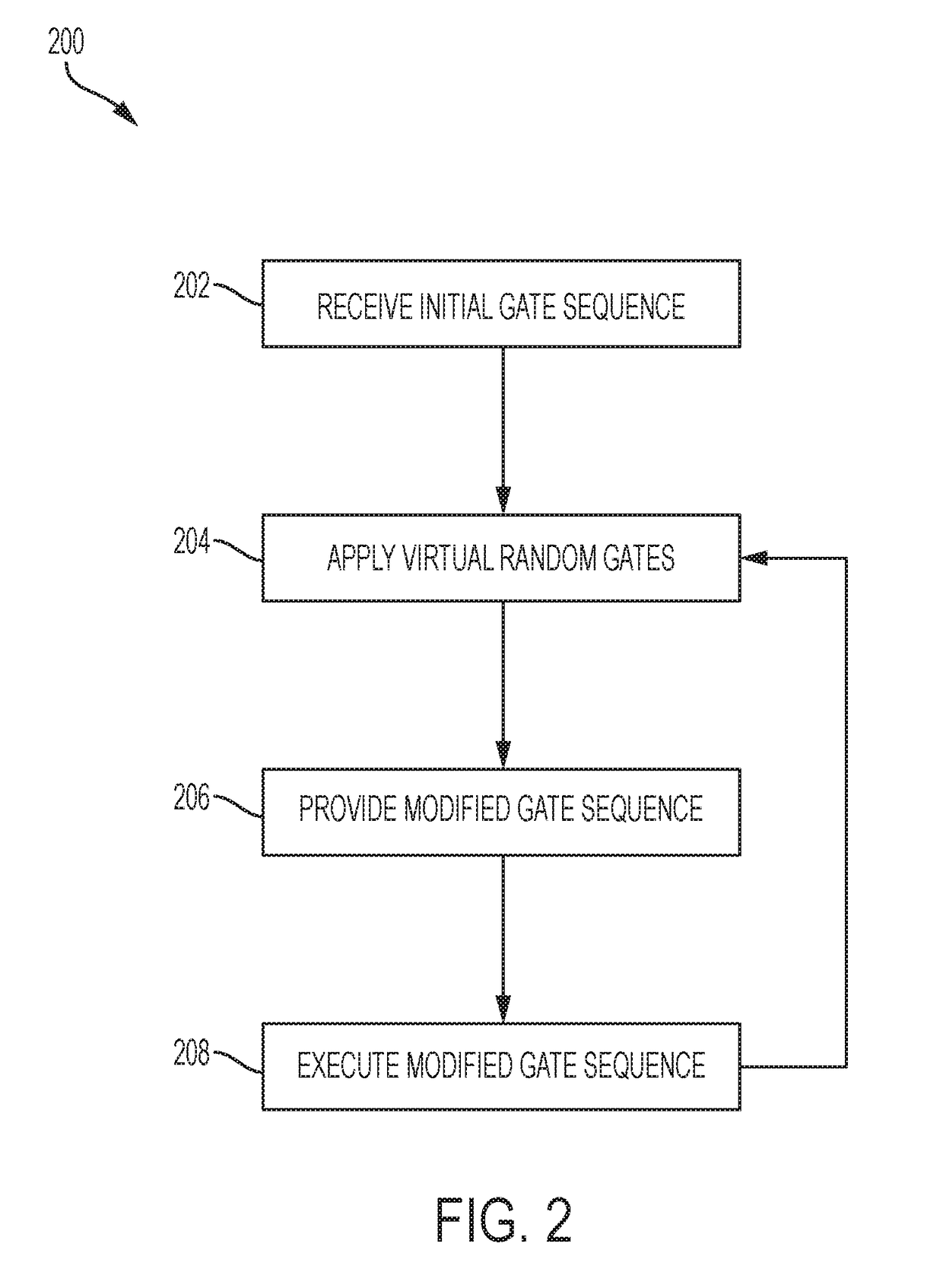
Randomized Compiling for Quantum Computation
In a general aspect, randomized compiling techniques for quantum computing are described. In some aspects, an initial quantum-logic gate sequence is received. A modified quantum-logic gate sequence is generated by applying virtual random gates to the initial quantum-logic gate sequence, such that the initial quantum-logic gate sequence is logically equivalent to the modified quantum-logic gate sequence. The modified quantum-logic gate sequence can be provided to a quantum information processor for execution.
Owner:KEYSIGHT TECH CANADA INC
Phase-differential quantum key allocation and allocating system
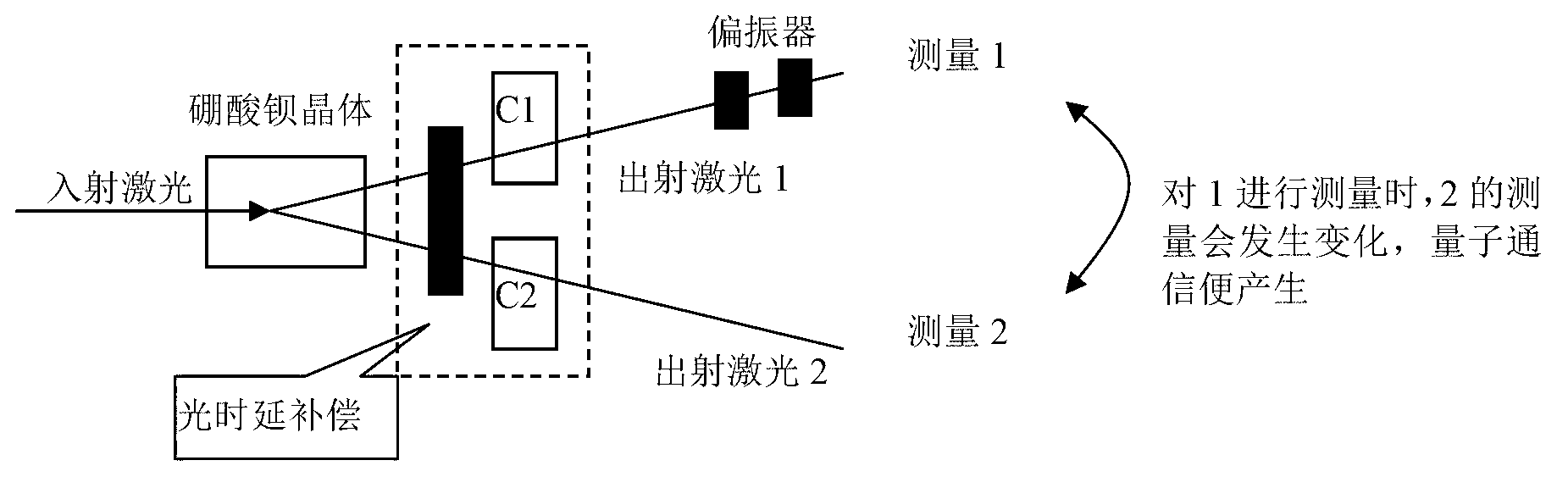
InactiveCN1897519AHighlight substantiveSignificant progressKey distribution for secure communicationDifferential phaseBeam splitting
The invention manages to provide a stable and fast differential quantum key distribution method and system thereof. At transmitting end, with a continuous laser source, the quantum codes are prepared using two approaches: 1) using the beam-splitting, polarization-independent and phase-stabilizing approach to prepare the stable quantum code; 2) using polarization approach to directly prepare stable quantum code. At receiving end,differential phase-Faraday-Micheal test approach is used to directly receive the quantum information.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY
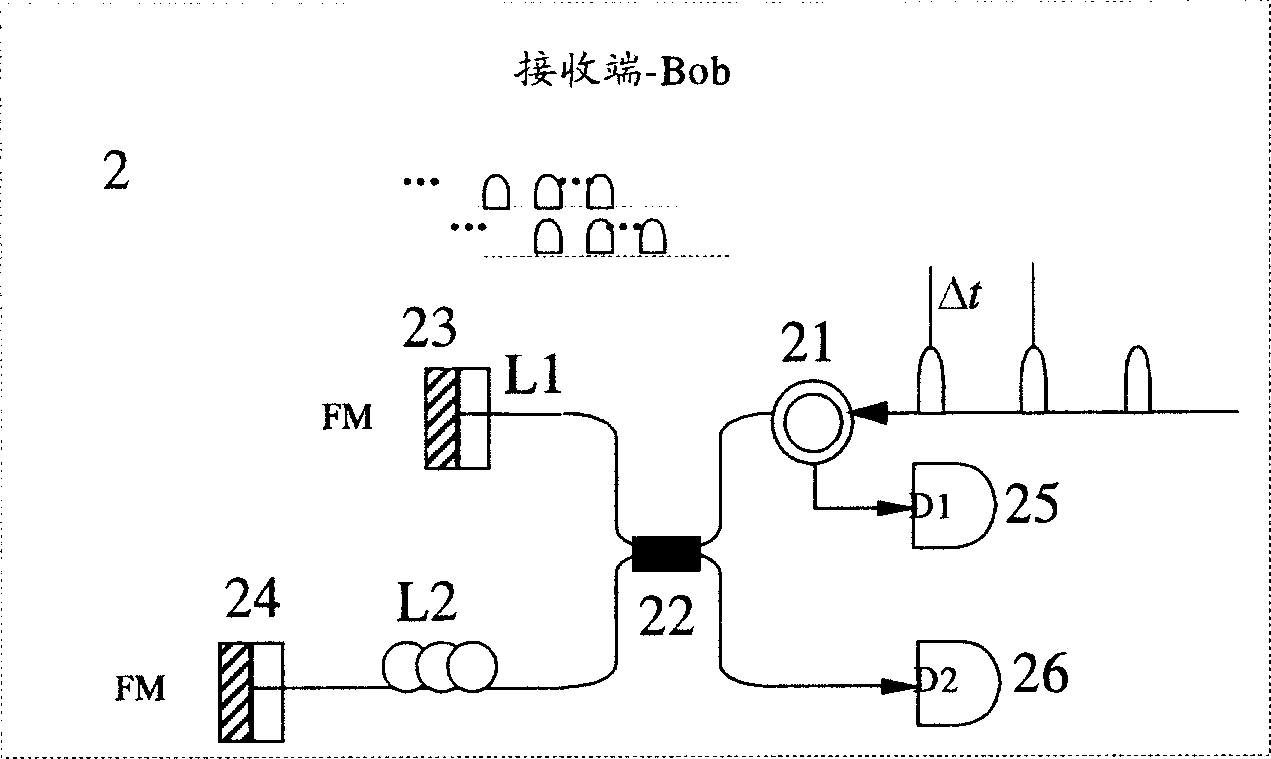
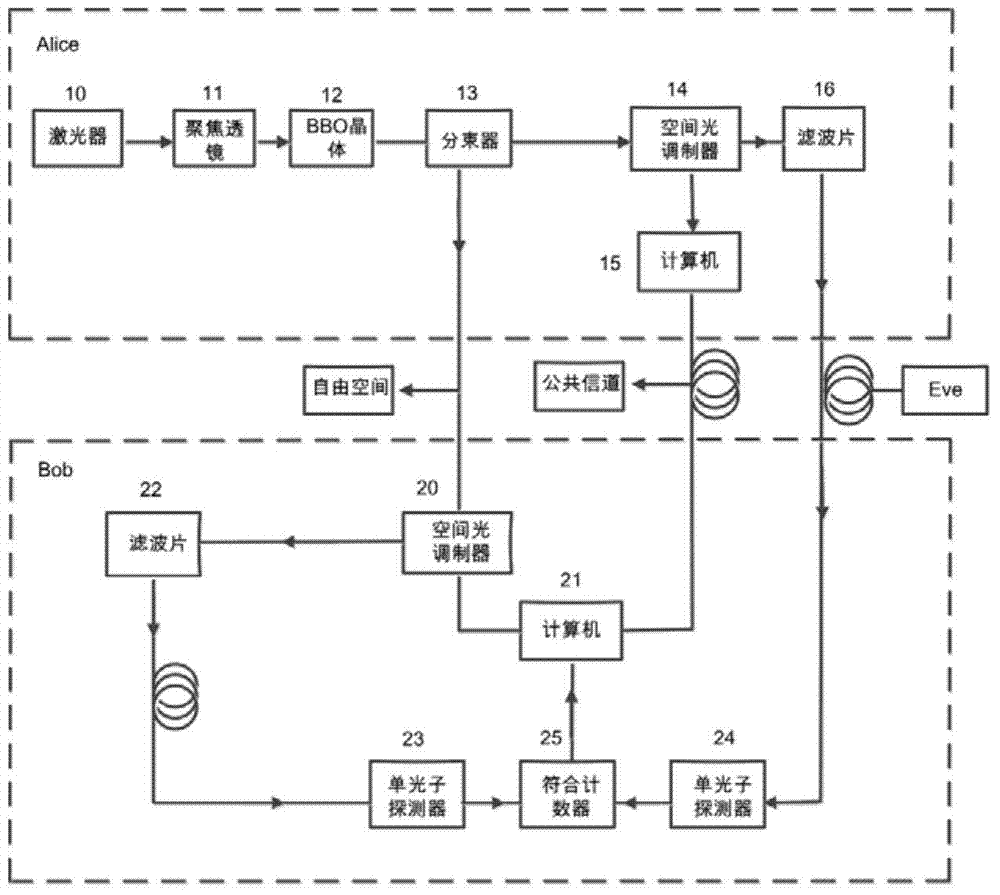
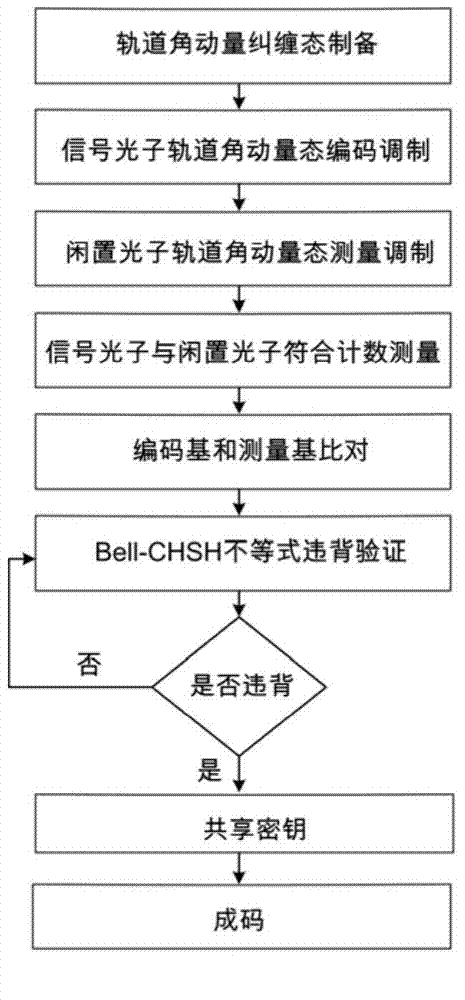
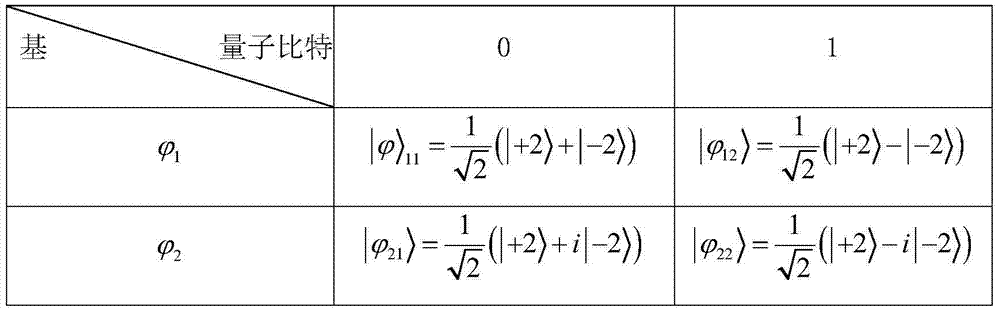
Quantum key distribution method and system based on orbital angular momentum encoding
ActiveCN104506309AEvenly distributedHigh bit rateKey distribution for secure communicationSpatial light modulatorQuantum codes
The invention provides a quantum key distribution method and system based on orbital angular momentum encoding. An orbital angular momentum entangled state is used as an information encoding carrier at a quantum key encoding transmitting terminal; orbital angular momentum is dynamically modulated through a spatial light modulator, and stable quantum codes are output; received quantum information can be stably and quickly measured at a receiving terminal through the spatial light modulator and a coincidence counting measurer, and by comparing encoding bases and measuring bases on a public channel, quantum bit code information is accurately decoded. The quantum key modulating and demodulating process is highly functionally integrated, information can be conveniently transmitted and received in real time, the system is efficient and stable, tapping behaviors of tappers can be judged in real time by violation verification of a Bell-CHSH inequation, and high-security quantum key distribution is guaranteed.
Owner:GUANGDONG INCUBATOR TECH DEV CO LTD
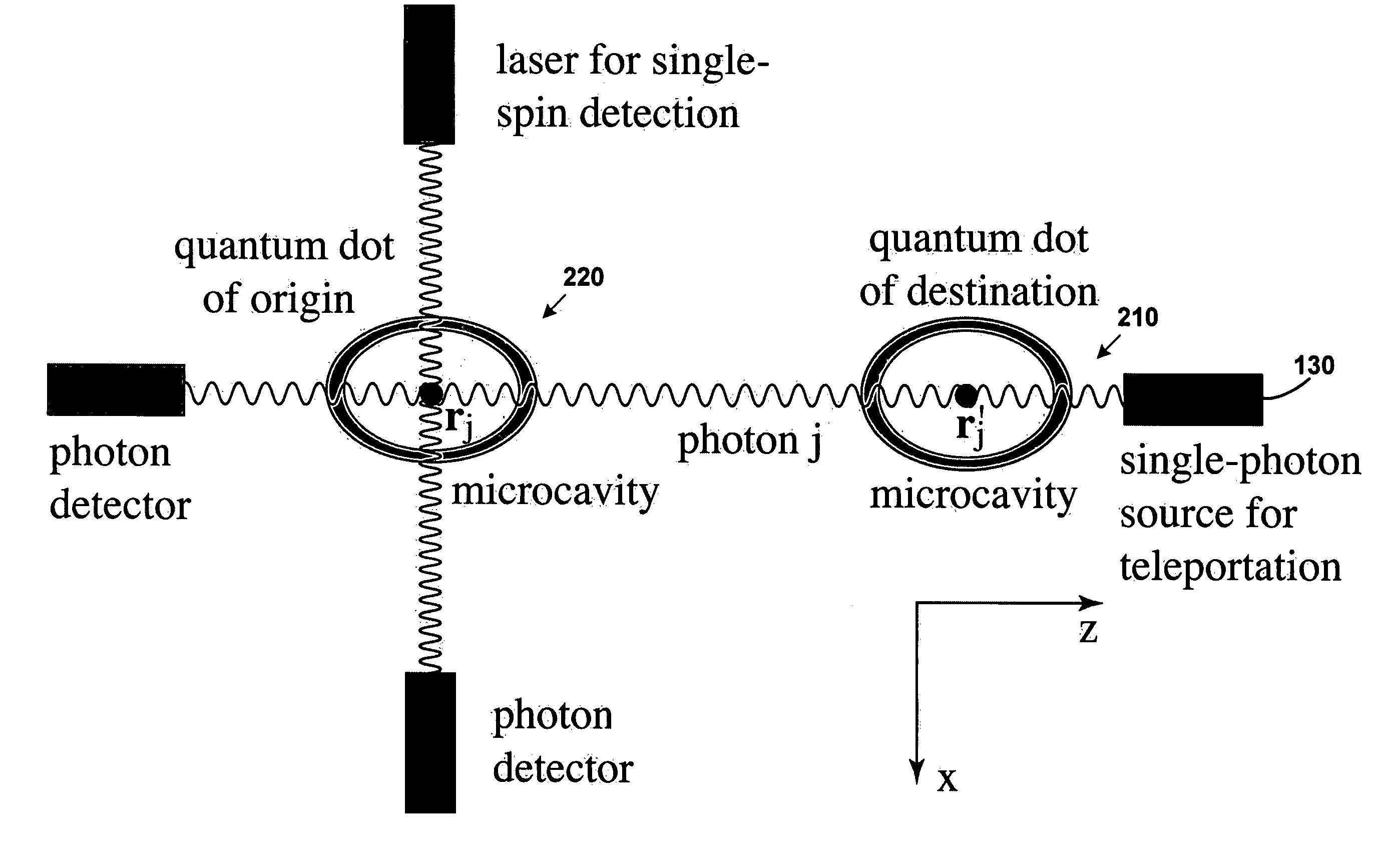
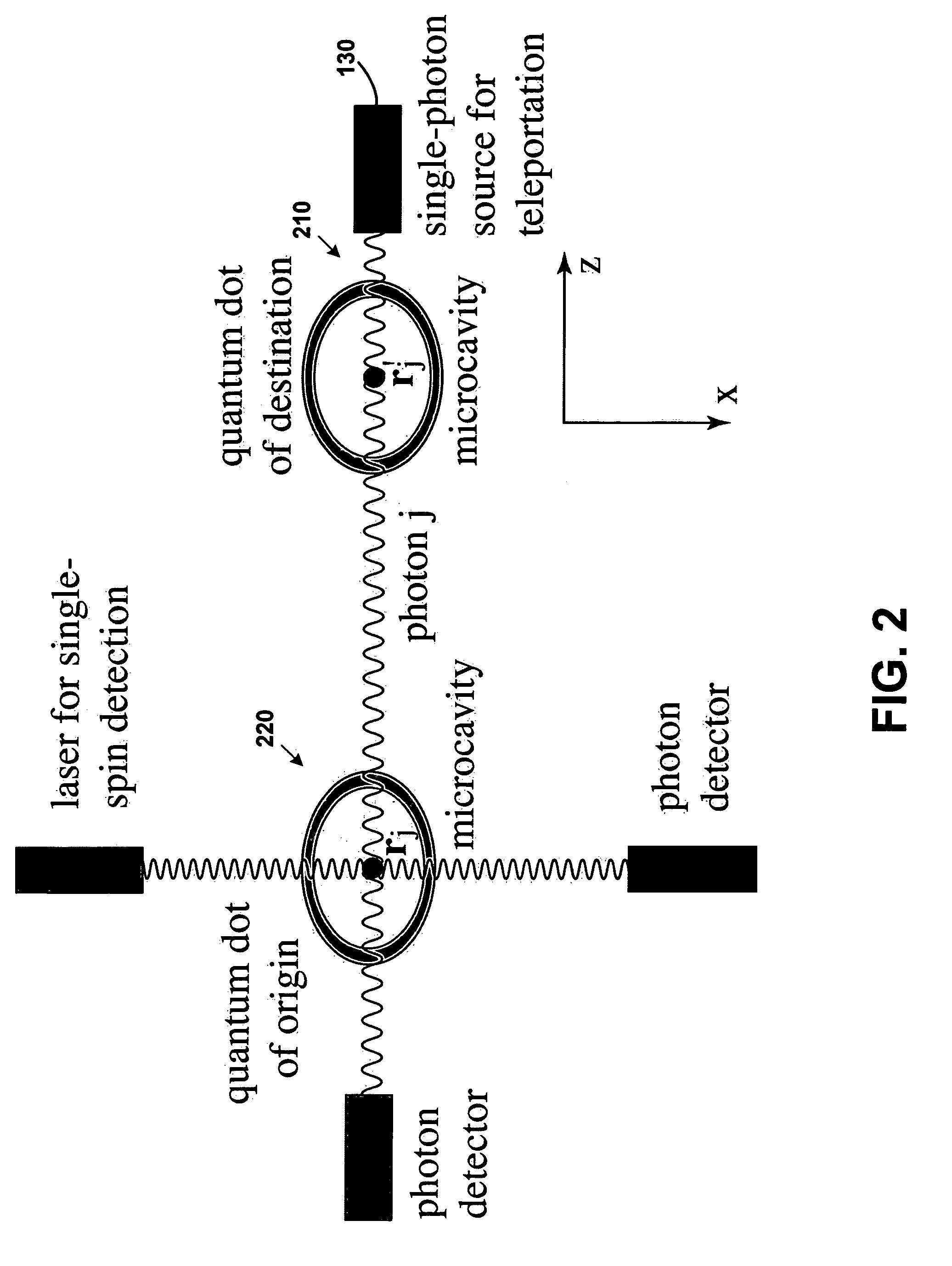
Teleportation system for electronic many-qubit states using individual photons
A method for creating a logic state for teleporting quantum information using a single photon is described. The method includes receiving a photon with an initial polarization and causing a first semiconductor crystal to have a first spin orientation. The photon interacts with the first semiconductor crystal for producing a resulting polarization dependent upon the first spin orientation. Causing the photon to interact with the first semiconductor crystal generates a maximally entangled state.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +1
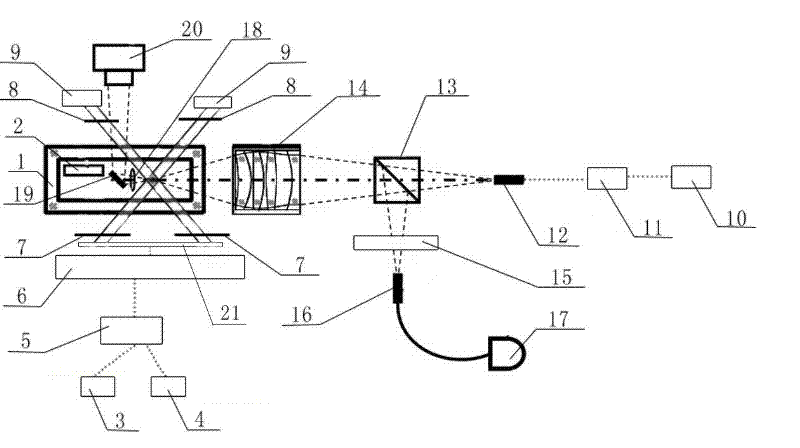
Detection method capable of realizing direct acquirement of image of single atom
The invention relates to a method for acquirement an image of a single atom and especially relates to a detection method capable of realizing direct acquirement of an image of a single atom. The detection method capable of realizing direct acquirement of an image of a single atom solves the problem that during single atom imaging, detection is difficult because of strong background signals. The detection method capable of realizing direct acquirement of an image of a single atom comprises the following steps that 1, a quadrate quartz-made glass vacuum room is treated; 2, a light field part and a magnetic field part of a magneto-optical trap system are constructed; 3, a far red-detuned micro-optical dipolar trap is constructed; 4, after an exciting light is superposed with one of three light beams which are orthogonal, fluorescent lights produced by caesium atoms are collected by a lens unit, are reflected to an interference filter by a polarization beam splitter and enter into multimode fibers; and 5, the fluorescent lights produced by caesium atoms are collected by an aspherical mirror and are reflected to a camera of a charge-coupled device by a total reflective mirror forming an angle of 45 degrees with the horizontal plane; and an image of a single atom is obtained by adjustment of an imaging zone of the camera of the charge-coupled device. The detection method provided bythe invention can realize direct acquirement of an image of a single atom and can be widely utilized for the fields of control and measurement of a single atom, and quantum information.
Owner:SHANXI UNIV
Hyperbolic metamaterial composite grating-enhanced high-frequency quantum-dot single photon source
ActiveCN107452844AIncrease spawn rateImprove production efficiencySemiconductor devicesGratingParticle physics
The invention discloses a hyperbolic metamaterial composite grating-enhanced high-frequency quantum-dot single photon source. The hyperbolic metamaterial composite grating-enhanced high-frequency quantum-dot single photon source comprises a substrate, a hyperbolic metamaterial and quantum dots, wherein a grating microstructure is arranged on a surface of the hyperbolic metamaterial or in the hyperbolic metamaterial, the hyperbolic metamaterial is of a one-dimensional periodic structure formed by alternatively arranging dielectric thin films and metal thin films or the dielectric thin films and metal-like thin films, and the quantum dots are arranged in the one-dimensional periodic structure or a near field of the hyperbolic metamaterial. Spontaneous radiation enhancement of wideband of the quantum dots is achieved by the hyperbolic metamaterial, the light emergent efficiency is improved by simultaneously combining directional coupling output characteristic of the grating, the photon generation ratio and the collection and utilization ratio of the quantum-dot single photon source are greatly improved, and the high-frequency, high-brightness and directional-emission quantum-dot single photon source of GHz or above can be achieved; and meanwhile, two excitation modes of optical pumping and electric pumping are compatible, and the quantum-dot single photon source is suitable for various wave bands to an infrared band from an ultraviolet band and can be widely applied to related fields of quantum information, quantum computation, quantum imaging, quantum authentication and quantum precision measurement.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRONICS ENG CHINA ACAD OF ENG PHYSICS
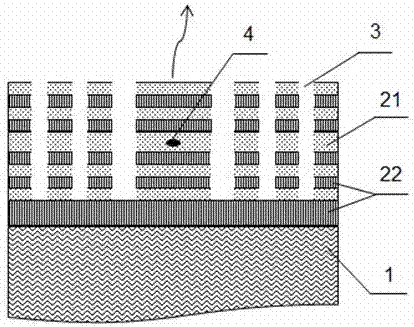
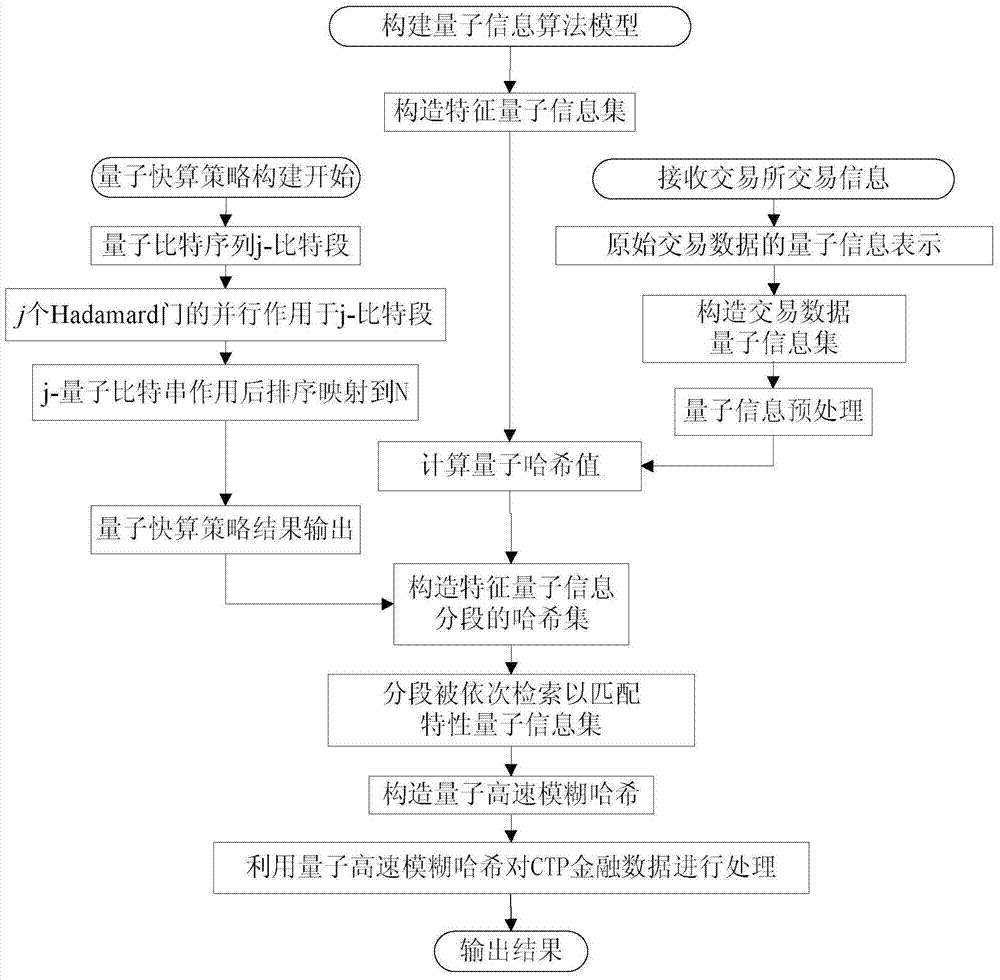
Quantum information feature extraction method based on CTP financial data
ActiveCN104504601AImplement featuresReduce computational complexityFinanceComputation complexityFeature extraction
The invention discloses a quantum information feature extraction method based on CTP financial data. Data issued by an exchange is processed by means of a quantum information algorithm model, a superposed-state quantum information presentation mode is firstly adopted to effectively describe the diversity of transaction data, description and processing by means of a quantum algorithm are facilitated on the basis, the data processing capacity of a quantum information algorithm model established on the basis of a quantum quick-calculation strategy and a quantum high-speed fuzzy hash method is improved remarkably, the calculation complex of the model is reduced remarkably, response delay is effectively reduced, the calculation complex of the algorithm is reduced, the response delay is reduced, and feature extraction and feature classification of the CTP financial data are achieved on the basis of the quantum information algorithm model.
Owner:上海卡方信息科技有限公司
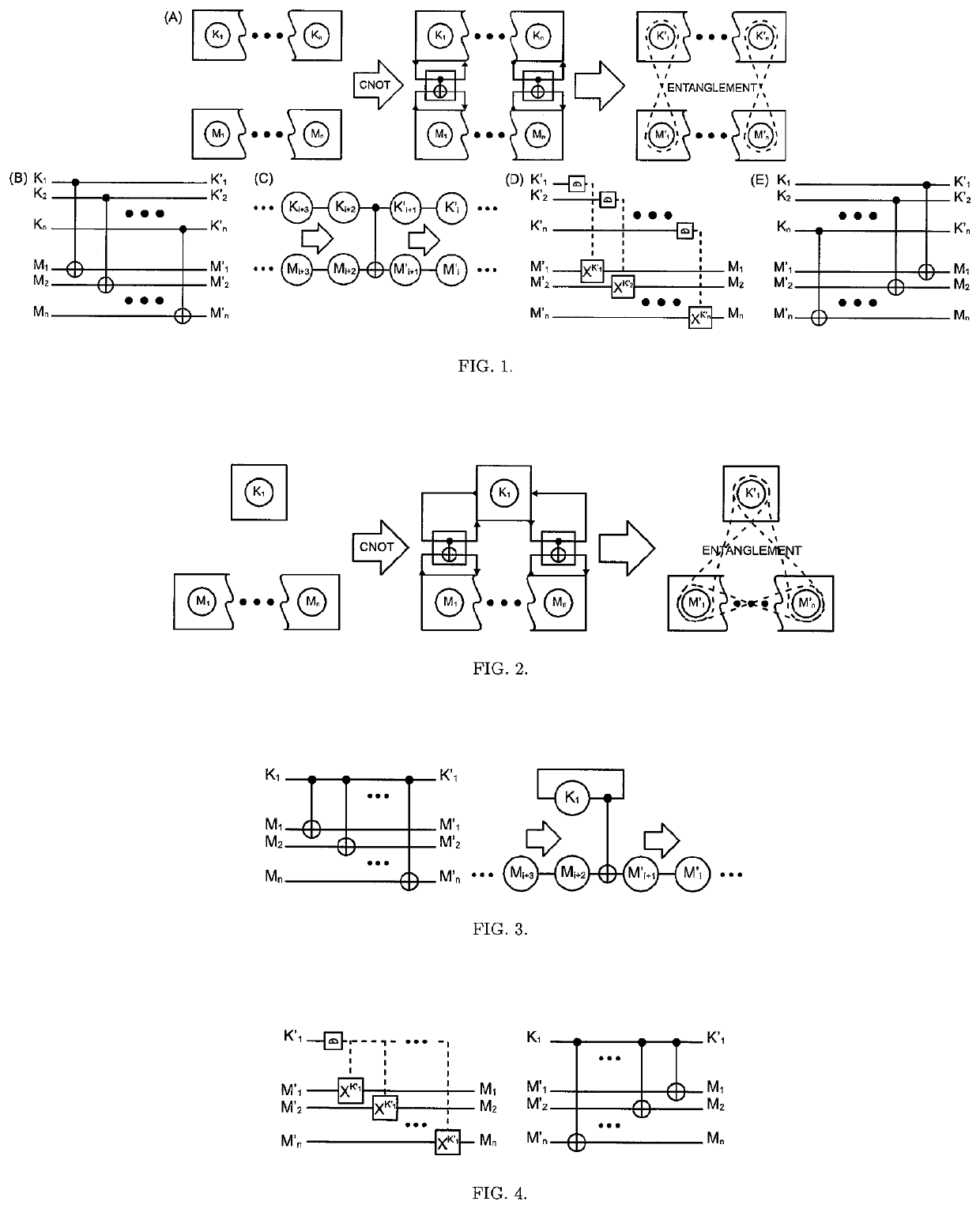
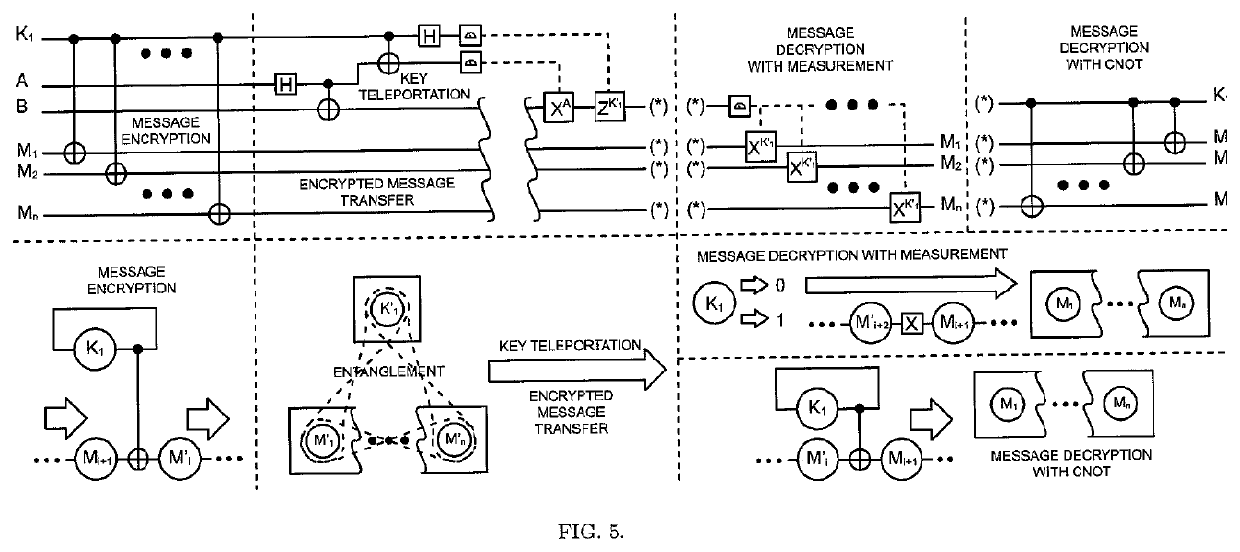
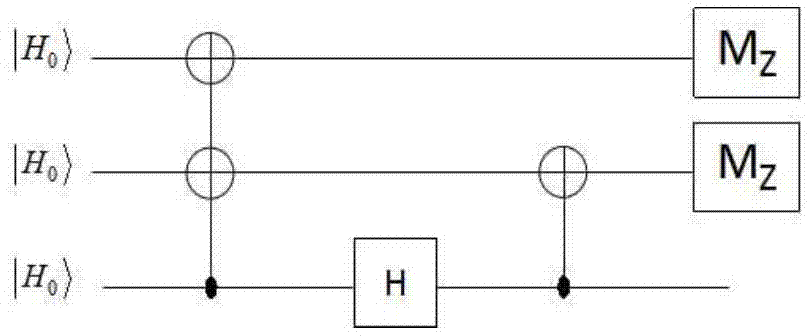
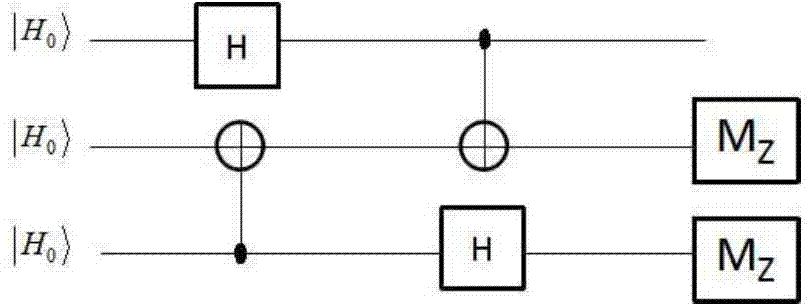
The One-Qubit Pad (OQP) for entanglement encryption of quantum information
InactiveUS20210058244A1Quantum computersKey distribution for secure communicationInformation processingQuantum teleportation
The One-Qubit Pad (OQP) protocol and its generic implementing device constitute a novel, maximally efficient scheme for encryption of quantum information with a quantum key of just a single qubit in an arbitrary unknown quantum state. The OQP enables encryption of the quantum information of n qubits register with a single qubit key upon provision of a multi-qubit entanglement between the single qubit key and the n qubits of the quantum message by the iterative application of the CNOT gate on the same key qubit (control input) and subsequent qubits of the message (target input). This results in an entanglement of all n+1 qubits, which locks original quantum information qubits and the single qubit of the key in a jointly entangled state that cannot be disentangled without the single qubit key. In order to decrypt the quantum message (by its disentanglement) one needs to have the qubit key and either reverse the protocol (applying CNOT operations in the reversed order) or simply measure the entangled key qubit and then depending on the outcome either straightforwardly obtain the decrypted quantum message or its quantum negation (dealt with by again applying quantum negation on all of the message qubits thus restoring their original states). The OQP protocol and its implementing device is proposed one hundred years after the classical One-Time Pad (Vernam cipher) was invented in 1917. The main differences between two schemes show how much quantum and clasical information differ. It is of course impossible to unconditionally securely encrypt classical sequence of n bits with just 1 bit of a key or guarantee that the random key that can be used for this purpose of n bits length (same as of the message) could not be copied. In contrast both these features are possible for the quantum information as described upon the proposed invention. The main characteristic of the OQP protocol to use only a single qubit as the key to enable information-theoretic security of n qubits quantum information encryption follows from the introduction in the invention of the multi-qubit entanglement, which is a non-local, topological and non-classical phenomenon giving quantum information significant edge over its classical counterpart. The main application of the OQP protocol and its implementing generic device is to lock quantum information with the single key qubit in order to prevent any unauthorized access to it (not only a classical access upon a measurement, but more importantly a quantum access by a quantum information processing device). This application can be also extended to communication scenario jointly with the Quantum Teleportation, which without OQP requires pre-sharing of n pairs of Bell states between Alice and Bob to securely communicate n qubits long quantum message, whereas in contrast with the OQP protocol just one pair of Bell state is required to securely teleport only the single qubit key for the OQP encrypted quantum message sent through an insecure quantum channel and still be access-protected from Eve (an adversary).
Owner:COMPSECUR SP ZOO
Method for achieving common quantum computation through fault tolerance
InactiveCN103942460AGuaranteed reliabilityEnsuring the reliability of quantum computingSpecial data processing applicationsFault toleranceHandling system
The invention relates to the field of quantum information, and particularly discloses a method for achieving common quantum computation through fault tolerance. The method comprises the steps that firstly, a large number of unsteady substates (please see the formula in the specification) are obtained; the unsteady substates (please see the formula in the specification) are used as auxiliary states, a Non-Clifford door is achieved through the fault tolerance and operations in a Clifford cluster, and therefore the common quantum computation is achieved. The method is used for guaranteeing that a reliable processing system is arranged in the quantum computation, and the operating rate is improved. According to the method, the Non-Clifford door is achieved in a fault tolerance mode to solve the quantum decoherence problem so as to achieve the common quantum computation; the Non-Clifford door in a fault tolerance common door set is denser, time needing to be consumed by achieving the quantum computation aim is shorter, and the resources needing to be consumed by achieving the quantum computation aim are fewer.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Quantum circuit for quantum state discrimination
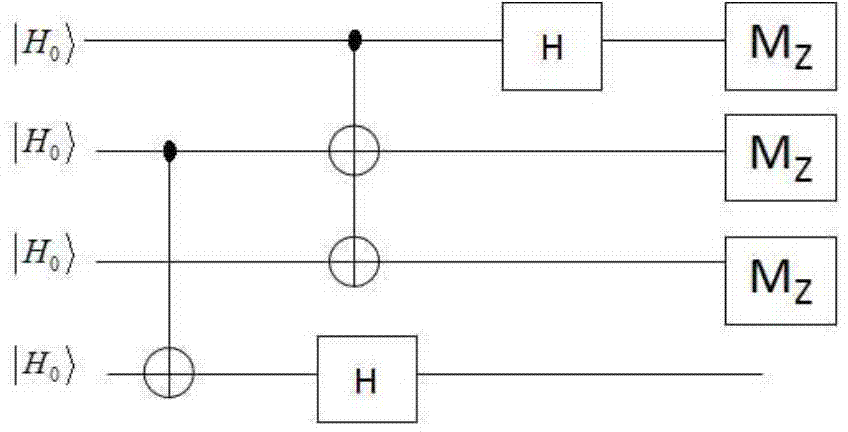
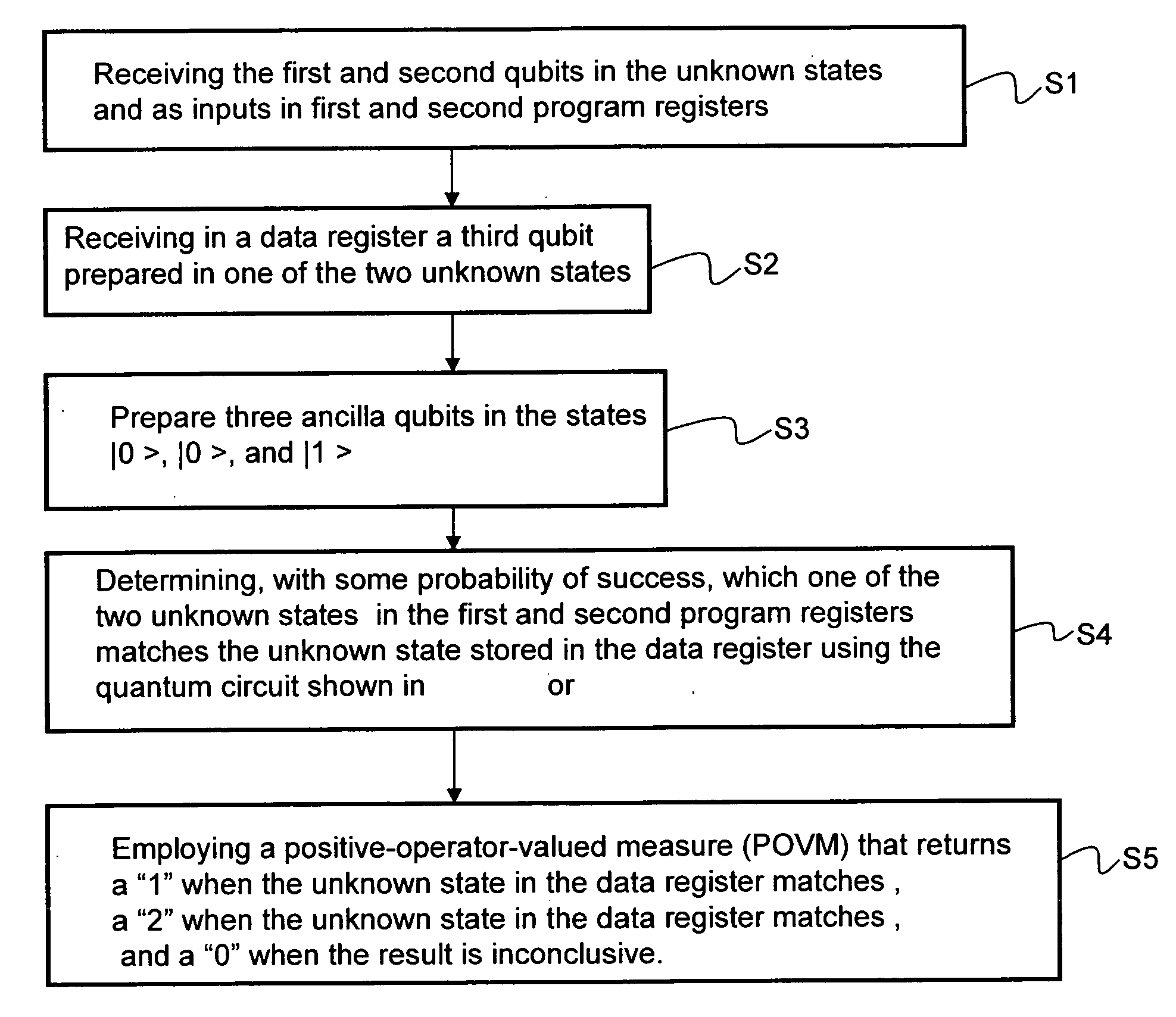
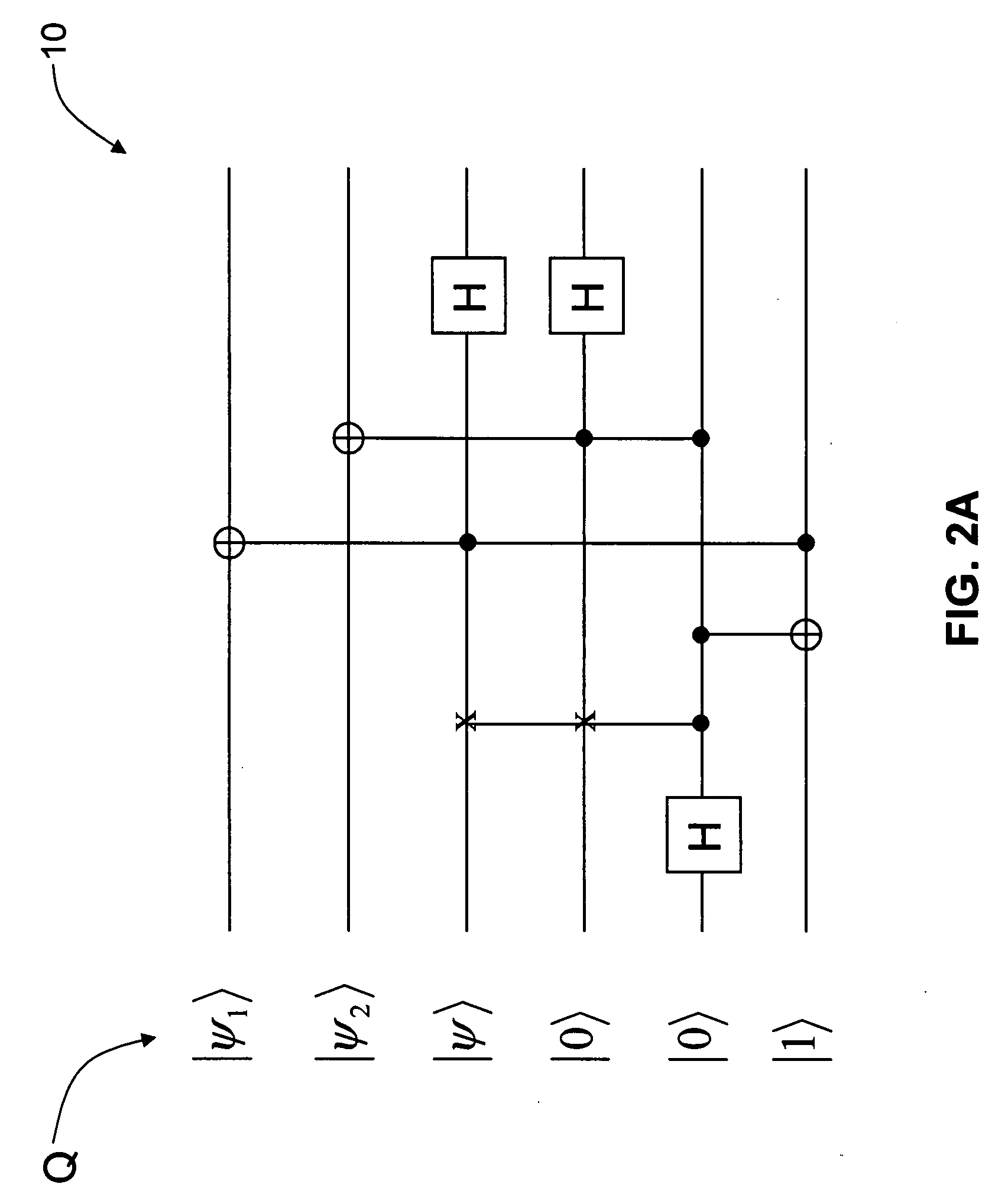
The invention is a quantum circuit that unambiguously discriminates between two unknown quantum states of qubits. The circuit receives the qubits in the unknown states as inputs, or programs, in first and second program registers. A data register also receive a third qubit prepared in one of the two states stored in the program registers. The circuit, with some probability of success, determines which unknown state of the qubit in the data register matches the state stored in the first or second program registers. The optimal circuit, i.e., one that maximizes the probability of success, is universal because it does not depend on the actual unknown states to be discriminated. The quantum circuit has industrial applicability to quantum information, and in particular to quantum computing.
Owner:MAGIQ TECH INC
Quantum computation
ActiveUS7184555B2Improved quantum computationQuantum computersKey distribution for secure communicationFree stateQuantum computer
The invention includes systems for and methods of performing quantum computation. The method of quantum computation includes preparing a set of one or more qubits capable of storing quantum information in 2n possible states, wherein the number of qubits n≧1. The qubit set is subject to a decoherence mechanism that could cause a loss of quantum information stored in some but not all of the qubit states. The method also includes determining, via a quantum measurement of the qubit system or just by analyzing the decoherence of the qubit states, which of the 2n states or their superposition is / are not susceptible to decoherence. The method further includes encoding and processing quantum information in one or more of the decoherence-free states by controlling qubit-qubit interactions or via an electromagnetic interaction with the set of qubits.
Owner:MAGIQ TECH INC
Systems, devices, and methods to interact with quantum information stored in spins
A quantum information processing device including a semiconductor substrate. An optical resonator is coupled to the substrate. The optical resonator supports a first photonic mode with a first resonator frequency. The quantum information processing device includes a non-gaseous chalcogen donor atom disposed within the semiconductor substrate and optically coupled to the optical resonator. The donor atom has a transition frequency in resonance with the resonator frequency. Also disclosed herein are systems, devices, articles and methods with practical application in quantum information processing including or associated with one or more deep impurities in a silicon substrate optically coupled to an optical structure.
Owner:PHOTONIC INC
Self-excited spinning single-electron electromagnetic field effect transistor, preparation method and application
ActiveCN104779275ASmall blocking voltageReflect the entanglement effectGalvano-magnetic hall-effect devicesSemiconductor devicesNanowireSelf excited
The invention discloses a self-excited spinning single-electron electromagnetic field effect transistor, a preparation method and the application. The electromagnetic field effect transistor comprises a base plate, a source electrode, a drain electrode, a gate electrode and a nanowire active area. The source electrode, the drain electrode and the gate electrode are arranged on the base plate. The nanowire active area is a current channel between the source electrode and the drain electrode, and the nanowire active area is polymorphic silicon carbide nanowires mingling with magnetic metals. According to the self-excited spinning single-electron electromagnetic field effect transistor, the preparation method and the application, and the indoor temperature can realize a single-electron coulomb block effect and a single-electron tunneling effect; at the same time, when the single-electron coulomb block effect and the single-electron tunneling effect are achieved, the single electron oscillation generates a variable electric field, and the variable electric field generates a magnetic field; under the condition that drain voltage replenishes energy, multi-structure electromagnetic oscillation can be presented, and pA-grade single-electron spinning current is generated. The self-excited spinning single-electron electromagnetic field effect transistor can be used as component for generating, converting, transferring and storing of quantum information.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV OF TECH
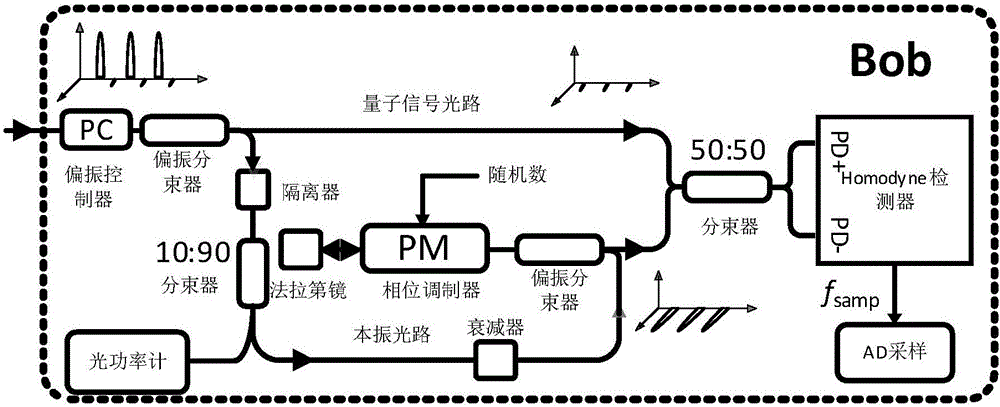
Continuous variable quantum key distribution method capable of resisting actual attack
ActiveCN106788706ASimplify actual costsReduce complexityKey distribution for secure communicationElectromagnetic transmissionHardware structureGaussian process
The invention provides a continuous variable quantum key distribution (CVQKD) method capable of resisting actual attack. The method comprises the following steps: step A, performing continuous variable quantum information transmission; step B, performing a data post-processing step containing a pre-processing operation, namely, the Bob acquires an original key according to the peak-valley value searching and the Gaussian post-selecting, and acquires the accurate parameter evaluation in combination with the local oscillation light intensity evaluation in real time monitoring, and finally acquires the final key after performing the data post-processing; the existing all actual attacks aiming at the Gaussian modulation CVQKD are resisted on the basis of unchanging the traditional Gaussian modulation CVQDK hardware structure, the actual cost of resisting the actual attack is greatly simplified, and the system complexity is lowered. The attenuation on a signal path by the traditional resisting method is avoided, thereby guaranteeing that the Gaussian-modulation CVQKD system has higher key output rate; furthermore, the potential security flaws of the system are eliminated, and the robustness of the system is improved.
Owner:上海循态量子科技有限公司
Generating device for continuous variable polychrome entangled optical field
InactiveCN103091933ACompact structureImprove performanceNon-linear opticsQuantum memoryOptical field
The invention provides a generating device for a continuous variable polychrome entangled optical field. The generating device for the continuous variable polychrome entangled optical field comprises a laser device, two non-degenerate optical parametric oscillation cavities and three to five unequal-arm Mach-Zehnder interference measuring systems. Due to the fact that the two cascading non-degenerate optical parametric oscillation cavities are utilized to generate the continuous variable polychrome entangled optical field, the generating device for the continuous variable polychrome entangled optical field has the advantages of being compact in structure, convenient to adjust, good in reliability and the like. The generated continuous variable polychrome entangled optical field can be applicable to both quantum memory and quantum communication and has important application values in quantum information networks.
Owner:SHANXI UNIV
Transmission cavity frequency regulator capable of carrying out frequency stabilization on multiple beams of laser
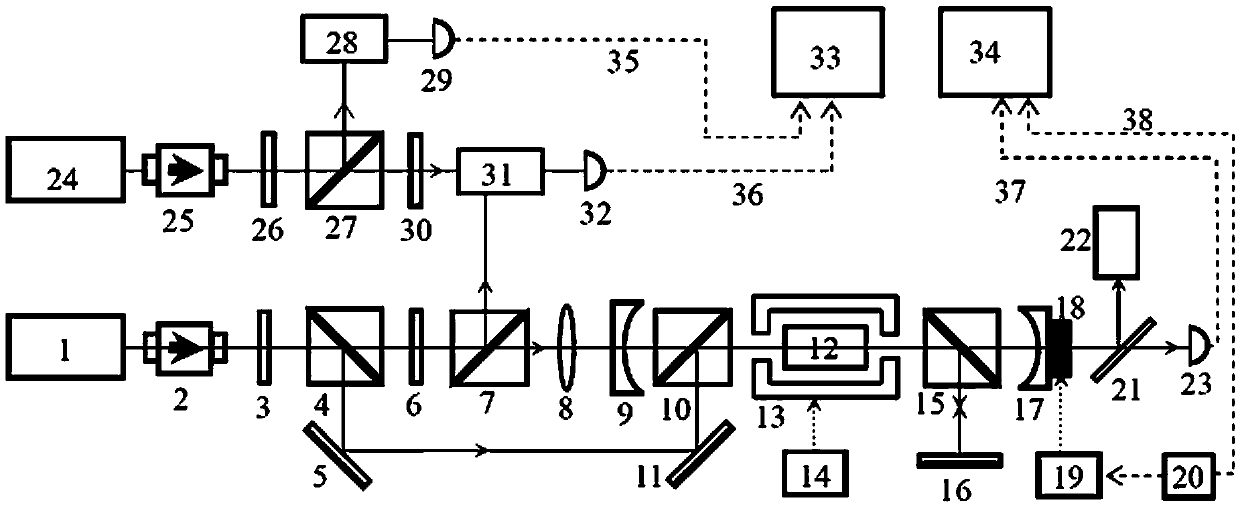
ActiveCN103887700AInhibition of long-term driftEasy to useLaser detailsFrequency stabilizationTemperature control
The invention discloses a transmission cavity frequency regulator capable of carrying out frequency stabilization on multiple beams of laser, and relates to the field of laser frequency stabilization. The abstract attached diagram is a structure diagram of the transmission cavity frequency regulator capable of carrying out frequency stabilization on four beams of laser. The frequency regulator is composed of a transmission cavity (11), a reference laser (1), four lasers to be stabilized with different wave lengths (2, 3, 16 and 17), lenses (4, 5, 6, 18 and 19), reflector mirrors (7, 10, 20 and 21), spectroscopes (8, 9, 22 and 23), a piezoelectric controller (12), a calculation controller (13), a temperature controller (14) and a photoelectric detector (15). The transmission cavity frequency regulator capable of carrying out frequency stabilization on the multiple beams of laser has the advantages of being capable of simultaneously locking the frequencies of the multiple beams of laser, restraining long-time drifting of the frequencies of the multiple beams of laser, being convenient to use, saving space and lowering cost, and can be widely applied to the fields needing laser frequency stabilization such as laser physics, frequency standards and quantum information.
Owner:WUHAN INST OF PHYSICS & MATHEMATICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Information coordination method easily implemented by hardware in quantum key distribution
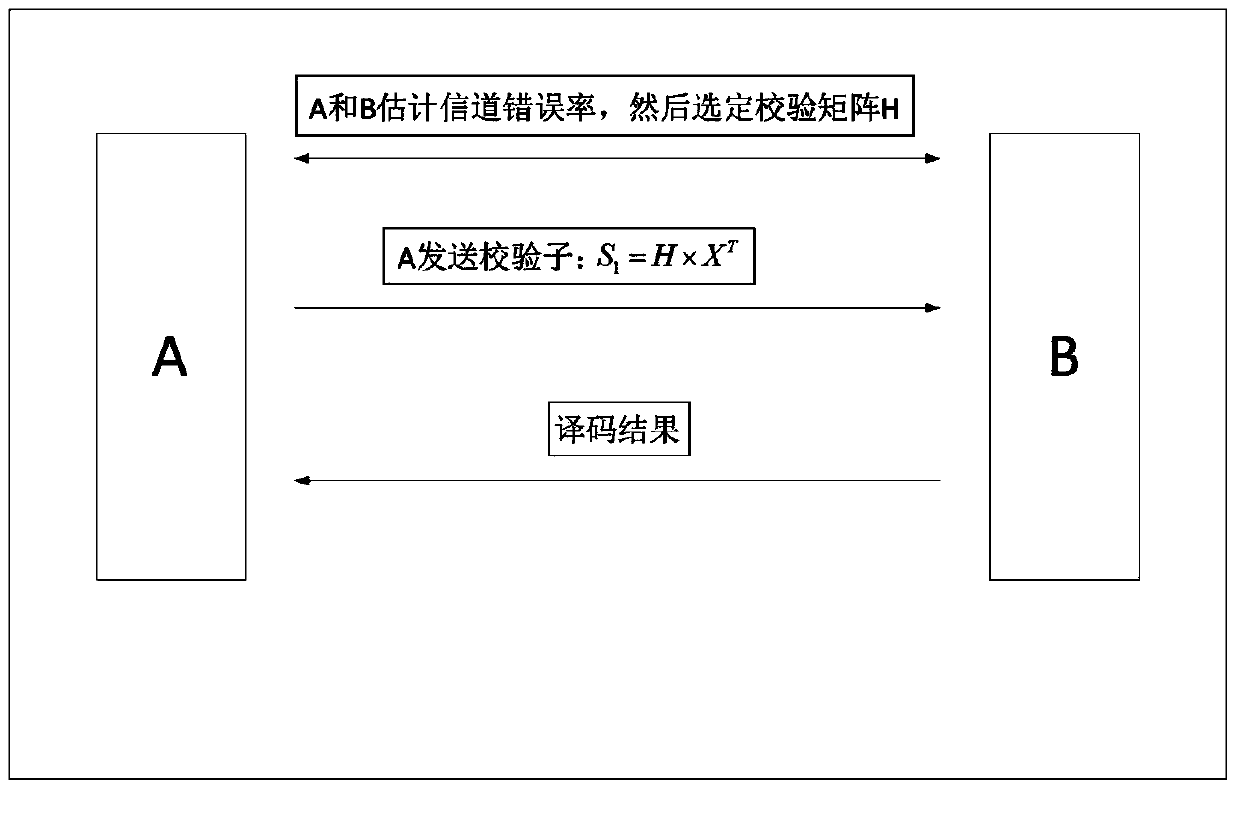
ActiveCN104092536AReduce storageDecoding speed is fastKey distribution for secure communicationComputer hardwareLow-density parity-check code
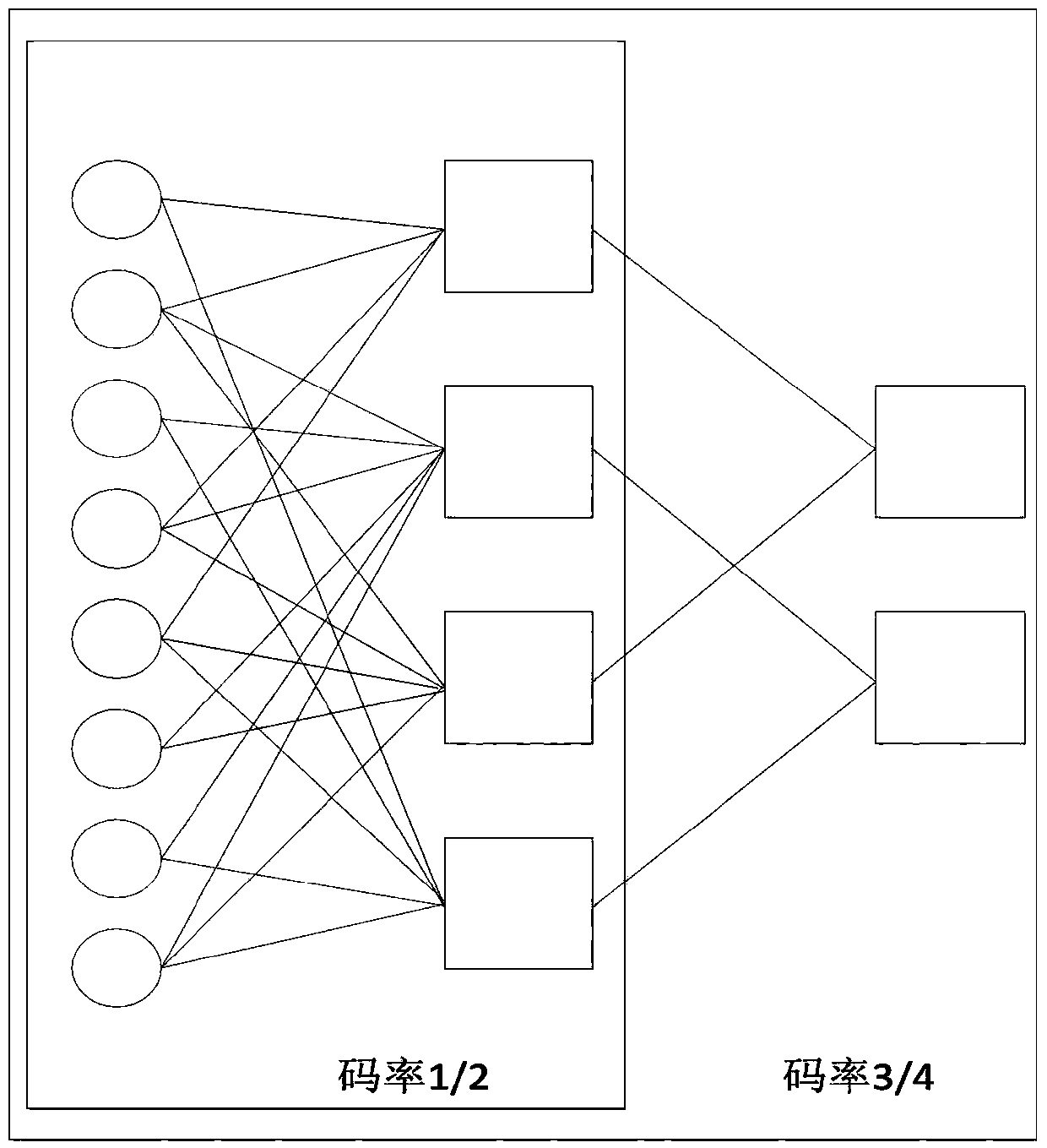
The invention relates to the technical field of quantum information, and particularly relates to an information coordination method easily implemented by hardware in quantum key distribution. The two parties of information coordination are set as A and B, and after A and B pre-generate a mother code and a son code, a strategy for basis matrix and row combination of the mother code is stored. (1) A and B estimate the error rate of a channel through random sampling; (2) A and B select an appropriate low-density parity check code through a row combination method, A sends a solved syndrome S1=H*X<T> to B, wherein X refers to a key string of A; and (3) after receiving S1, B works out a syndrome S2=H*Y<T> corresponding to a key string Y of B. If S1 and S2 are the same, A and B have the same key string. If S1 and S2 are different, B performs decoding correction according to S1 and returns a decoding result to A. A protocol ends if decoding succeeds, and a section of data is abandoned if decoding fails. The low-density parity check (LDPC) code adopted in the invention has a quasi cyclic structure, is easily implemented by hardware and is high in decoding speed.
Owner:THE PLA INFORMATION ENG UNIV
Superconducting dot/anti-dot flux qubit based on time-reversal symmetry breaking effects
InactiveUS20020130313A1Overcome effectSuppresses decoherence processQuantum computersNanoinformaticsMagnetic force microscopeSuperconductor classification
A solid-state quantum computing structure includes a dot of superconductive material, where the superconductor possesses a dominant order parameter with a non-zero angular momentum and a sub-dominant order parameter that can have any pairing symmetry. Alternately a solid-state quantum computing structure includes an anti-dot, which is a region in a superconductor where the order parameter is suppressed. In either embodiment of the invention, circulating persistent currents are generated via time-reversal symmetry breaking effects in the boundaries between superconducting and insulating materials. These effects cause the ground state for the supercurrent circulating near the qubit to be doubly degenerate, with two supercurrent ground states having distinct magnetic moments. These quantum states of the supercurrents store quantum information, which creates the basis of qubits for quantum computing. Writing to the qubits and universal single qubit operations may be performed via the application of magnetic fields. Read-out of the information may be performed using a SQUID microscope or a magnetic force microscope.
Owner:D WAVE SYSTEMS INC
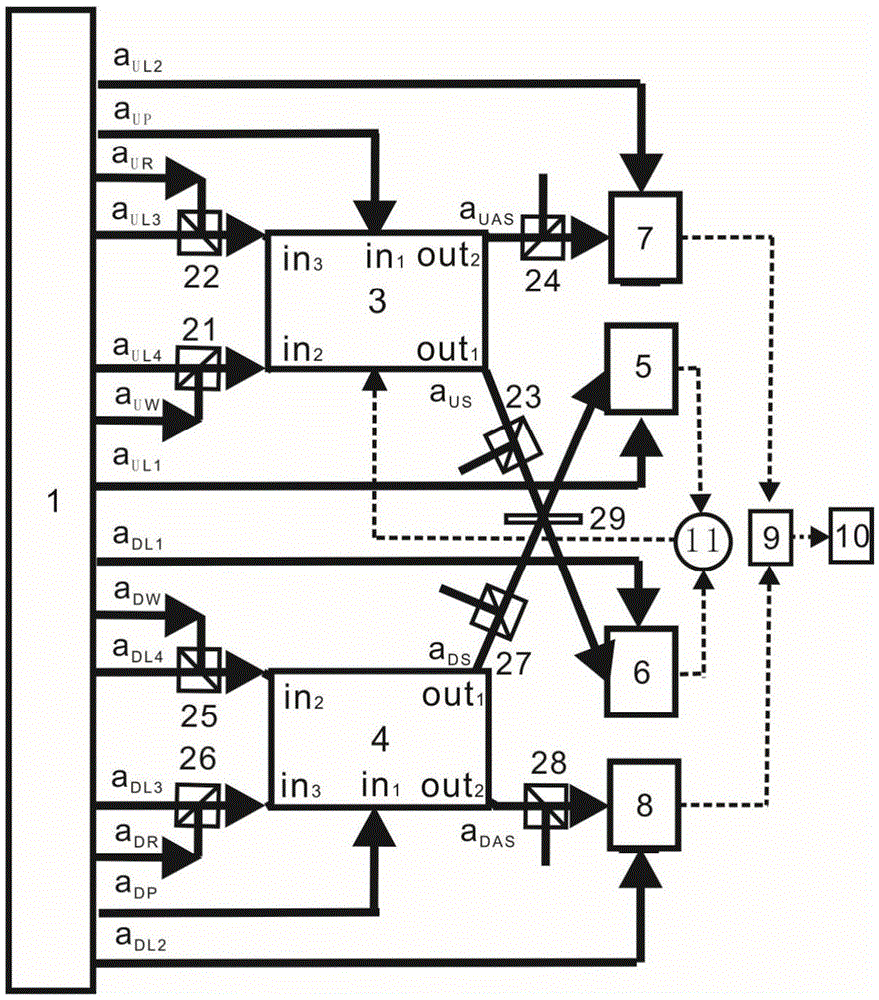
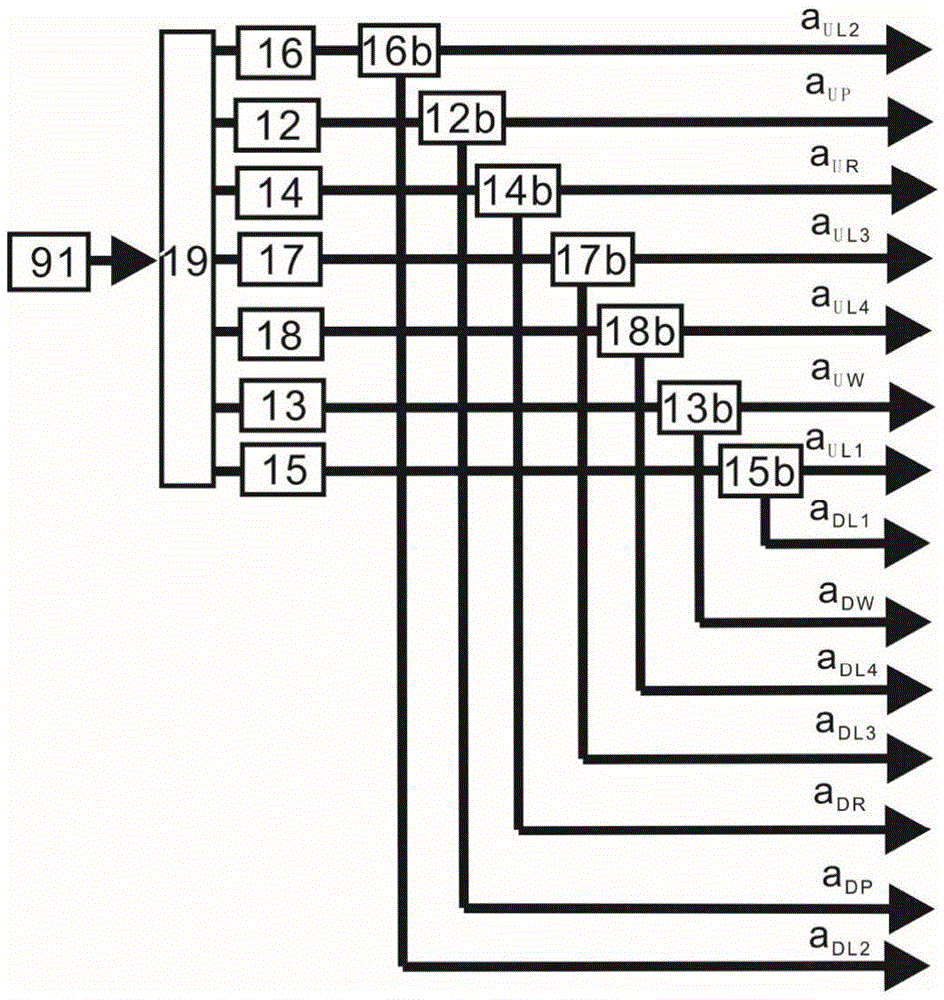
Continuous variable light and atom ensemble entanglement production device
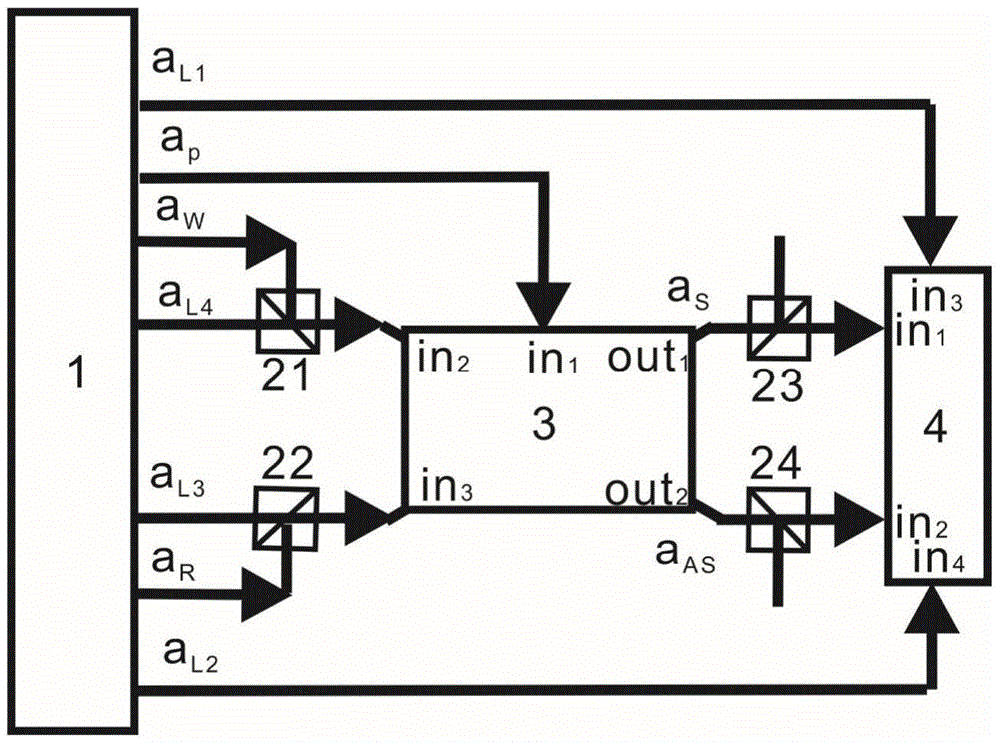
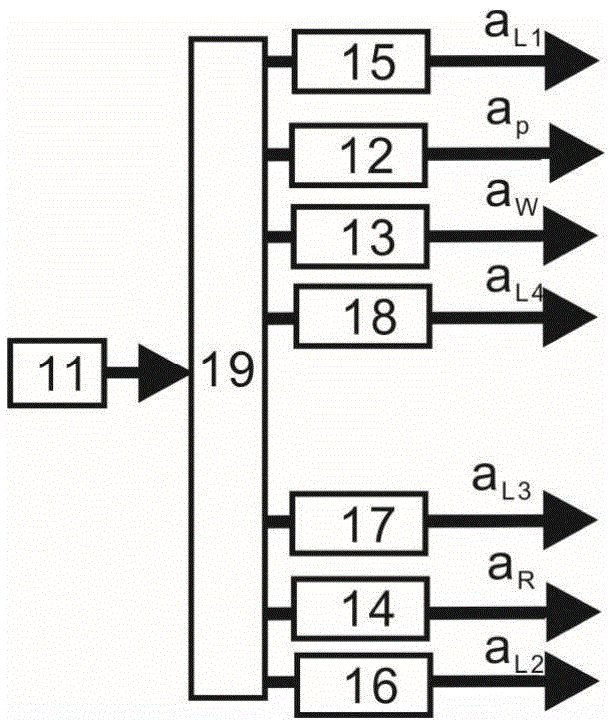
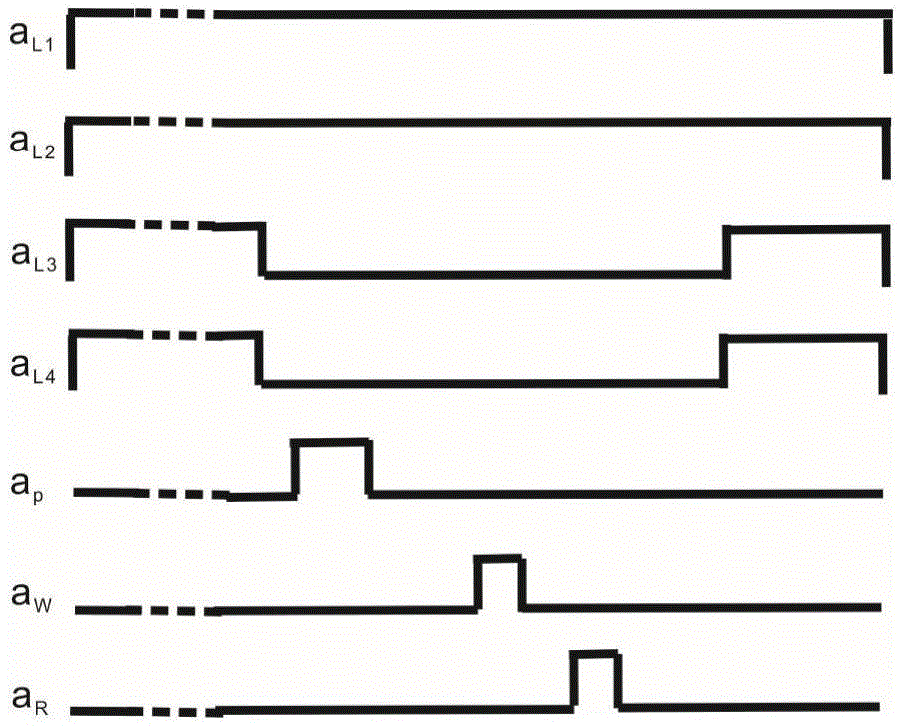
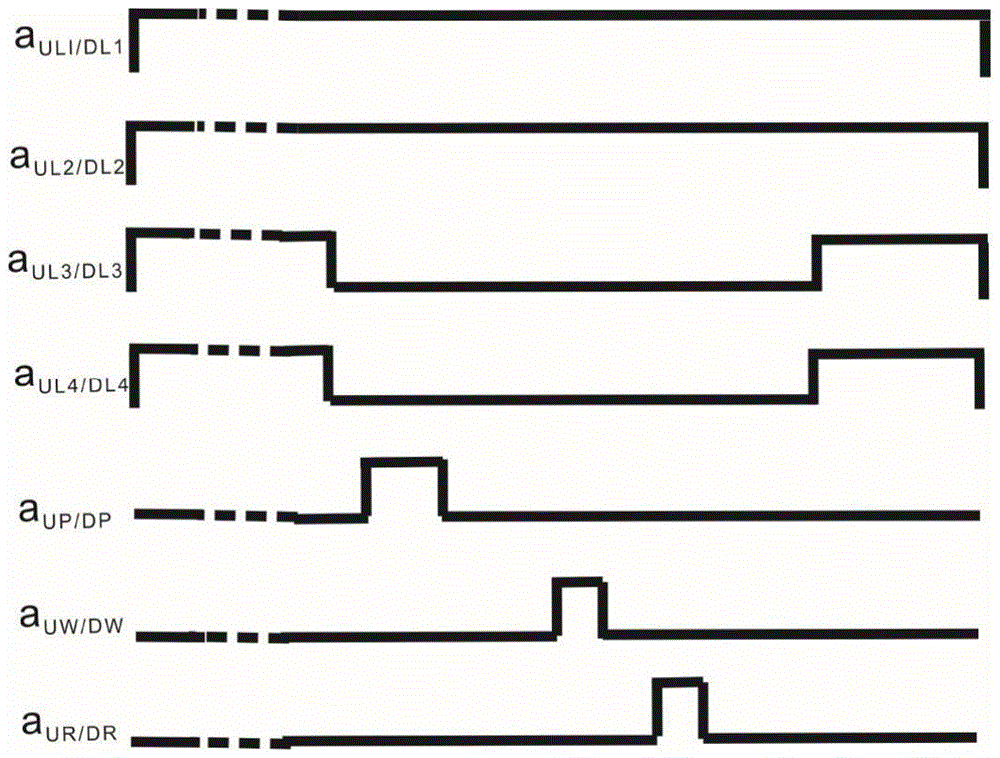
ActiveCN105652555AVerification entanglementDeterministic preparationNon-linear opticsLight beamSpins
The invention relates to a continuous variable light and atom ensemble entanglement production device and mainly aims at solving the technical problem of existing probable production of separated variable light and atom ensemble entanglement. According to the technical scheme, the continuous variable light and atom ensemble entanglement production device comprises a light source unit, a plurality of light beam coupling systems, an atom system and a measurement system. The light source unit is provided with a pump light pulse signal aP output end, a writing light pulse signal aW output end, a reading light pulse signal aR output end, an output end for two local oscillation light signals aL1 and aL2 and an output end for two simulation light pulse signals aL3 and aL4. The device utilizes orthogonal components of light fields in continuous variable quantum information and collective spin waves of atom ensembles to definitely produce Stokes light and atom ensemble entanglement through spontaneous Raman scattering process and conducts measurement and analysis on the light and atom ensemble entanglement through anti-Stokes light produced in the spontaneous Raman scattering process.
Owner:SHANXI UNIV
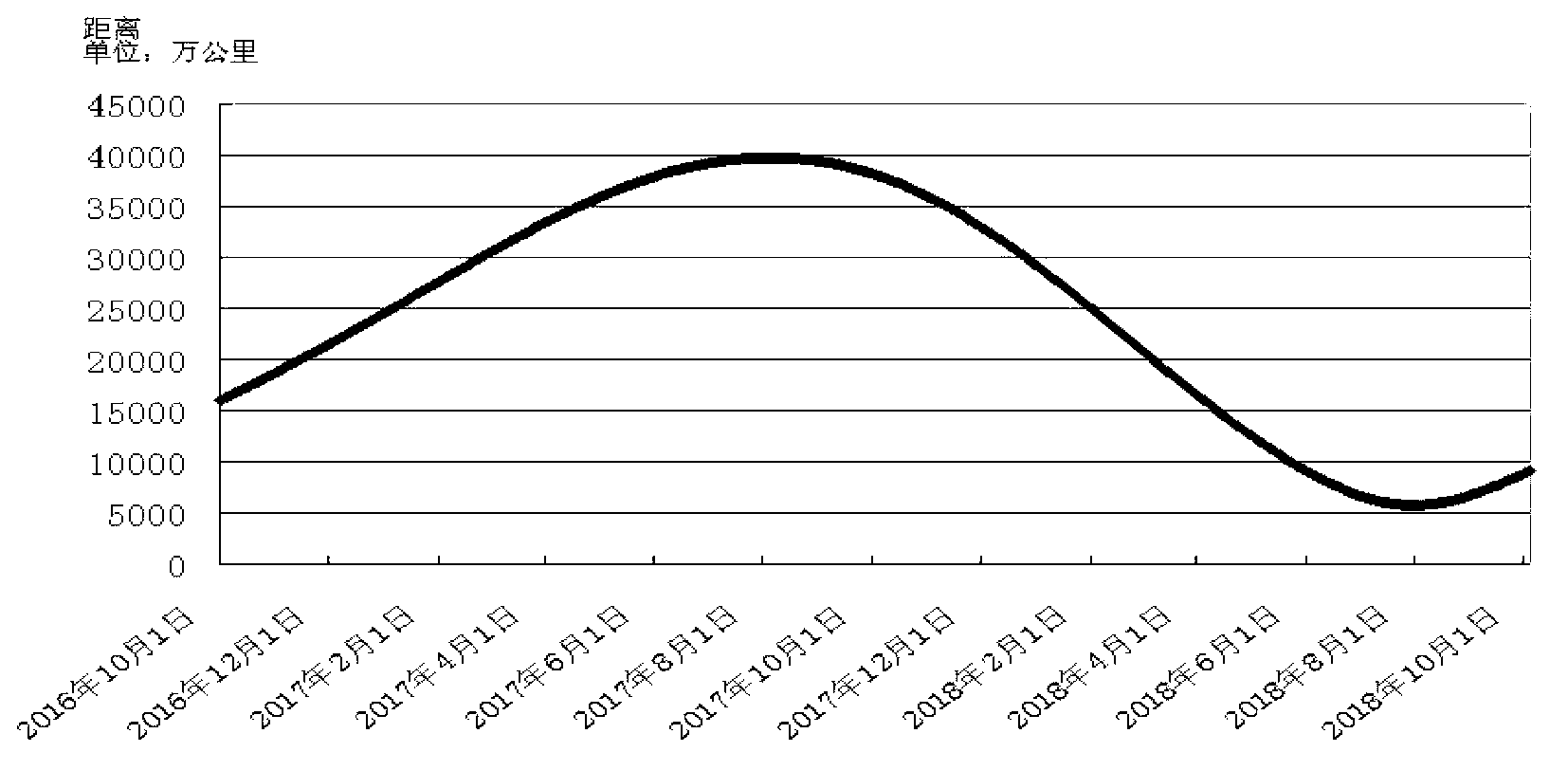
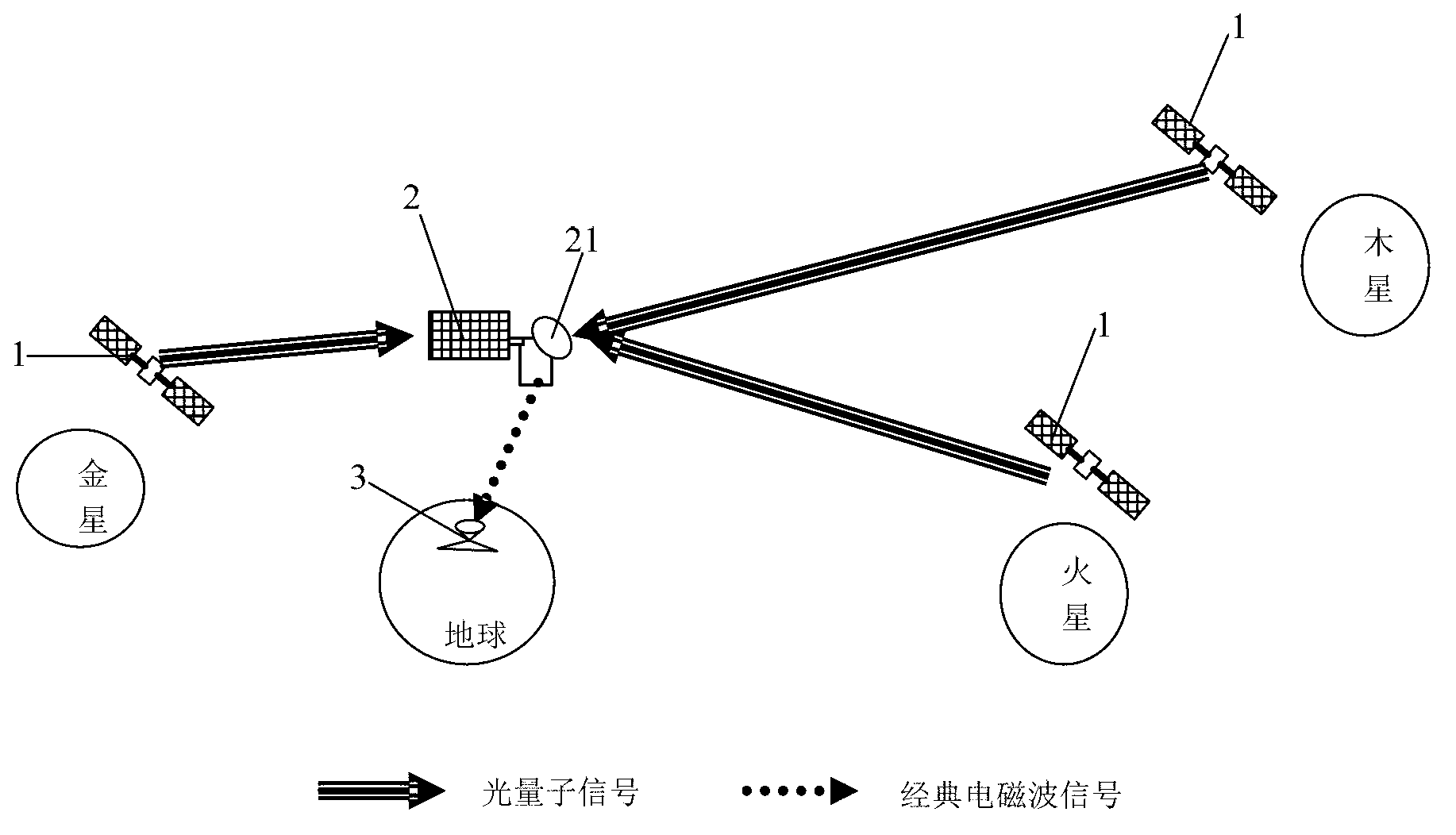
Deep space exploration communication system based on light quantum communication technology
ActiveCN103023578ASolve lossSolve the speed problemPhotonic quantum communicationTelecommunications linkGround station
The invention provides a deep space exploration communication system based on light quantum communication technology. The deep space exploration communication system comprises a plurality of deep space probes, an earth track satellite and a ground station. The deep space probes are provided with quantum information sending sub-systems, the earth track satellite is provided with a quantum communication receiving station, and the quantum communication receiving station is respectively in communication connection with the quantum information sending sub-systems and the ground station. Quantum communication is conducted among the quantum information sending sub-systems and the quantum communication receiving station, and scientific probing data explored by the deep space probes is converted into light quantum signals to be sent to the quantum communication receiving station. The quantum communication receiving station receives the light quantum signals, conducts information decoding on the light quantum signals, and restores the light quantum signals into digital signals, and the digital signals are sent to the ground station through a radio frequency communication method. By means of the deep space exploration communication system, an energy consumption problem of a traditional classic communication scheme is solved fundamentally, and an effective method for building a high-speed broadband communication link for deep space exploration tasks is provided.
Owner:SHANGHAI SATELLITE ENG INST
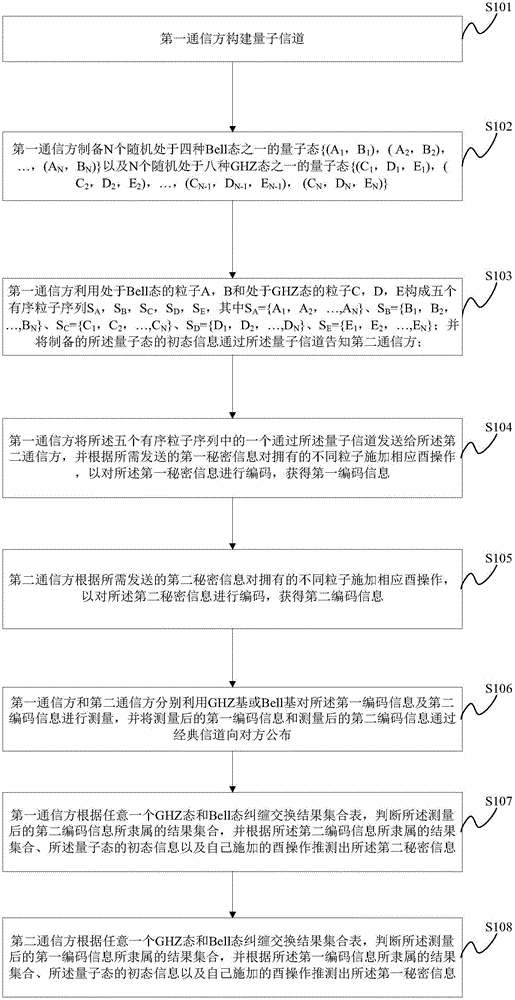
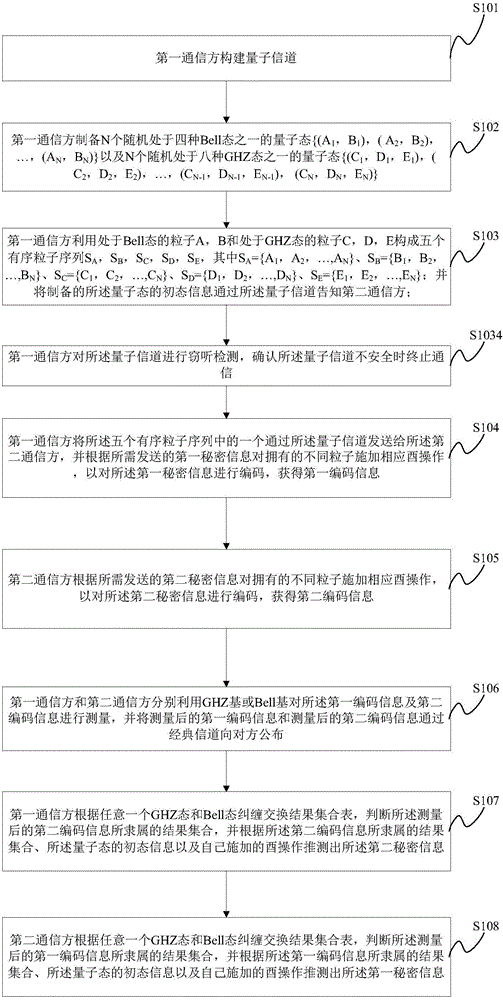
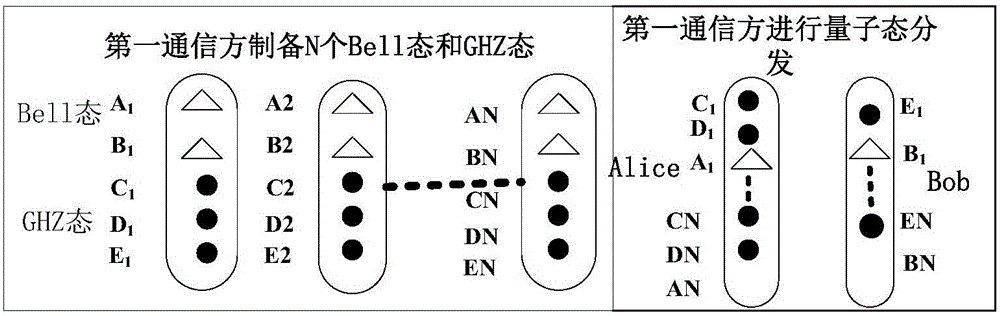
Quantum dialogue method for asymmetric capacity based on GHZ state and Bell state
ActiveCN105933114AReduce leakageImprove confidentialityKey distribution for secure communicationBell stateConfidentiality
The invention discloses a quantum dialogue method for an asymmetric capacity based on a GHZ state and a Bell state. The quantum dialogue method for the asymmetric capacity based on the GHZ state and the Bell state uses the Bell state and the GHZ state to perform quantum communication simultaneously, so that a quantum communication process with the asymmetric capacity with three-bit secrete information in one party and two-bit secrete information in the other party in a round of quantum communication process can be realized. Besides, in a whole communication process, only first measured encoding information and second measured encoding information need to be published once through a classical channel, so that the possibility of information leakage in the communication process is reduced. Further, a first communication party and a second communication party in the communication process do not need to truly transfer first secrete information and second secrete information to the other party through quantum information, so that the confidentiality of the quantum dialogue method for the asymmetric capacity based on the GHZ state and the Bell state can be greatly improved.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Phase locking in a multi-channel quantum communication system
InactiveUS20060262930A1Problem be addressSecret communicationSecuring communicationMultiplexingCommunications system
A communication system adapted to use wavelength (frequency) division multiplexing for quantum-key distribution (QKD) and having a transmitter coupled to a receiver via a transmission link. In one embodiment, the receiver is adapted to (i) phase-shift a local oscillator (LO) signal generated at the receiver, (ii) combine the LO signal with a quantum-information (QI) signal received via the transmission link from the transmitter to produce interference signals, (iii) measure an intensity difference for these interference signals, and (iv) phase-lock the LO signal to the QI signal based on the measurement result. In one configuration, the QI signal has a plurality of pilot frequency components, each carrying a training signal, and a plurality of QKD frequency components, each carrying quantum key data. Advantageously, the system can maintain a phase lock for the QKD frequency components of the QI and LO signals, while the QKD frequency components of the QI signal continuously carry quantum key data.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC +2
Method and device for generation of higher-order transverse modes on the basis of atom-cavity coupling
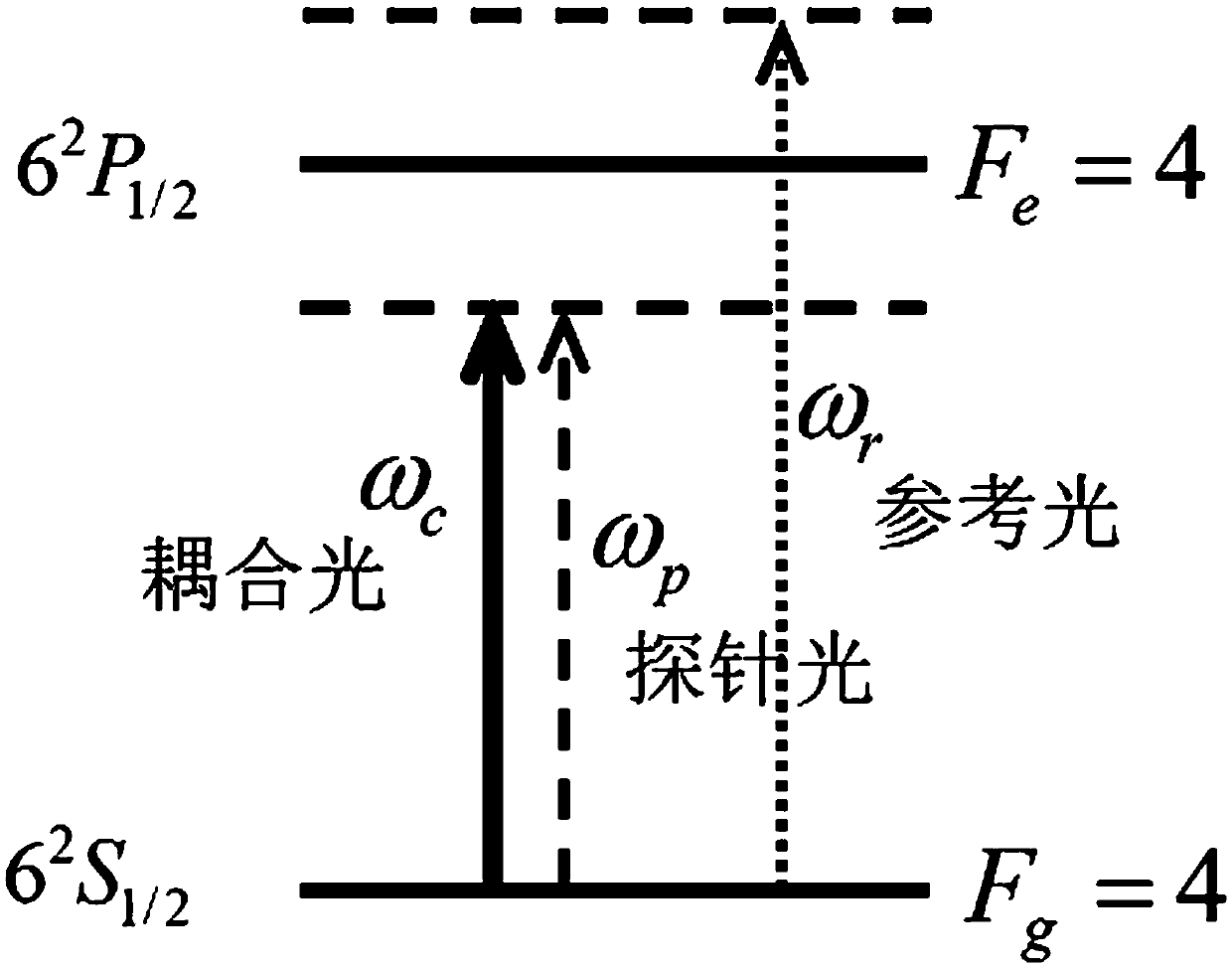
ActiveCN105375250APromote conversionEasy to operateOptical resonator shape and constructionTrappingRefractive index
The present invention provides a method and device for generation of higher-order transverse modes on the basis of atom-cavity coupling. The problem is solved that higher-order transverse modes are generated through traditional modes such as inclination of a resonant cavity mirror or a light propagation direction. In a system of coupling of an atom steam chamber and a standing wave cavity, when a pair of strong coherent coupling fields performs bi-directional radiation and passes through the atomic medium in the cavity, the refractive index of a weak cavity mode field is modulated through the medium in the cavity so as to induce the generation of the higher-order transverse modes. A higher-order transverse mode laser generation system is composed of a semiconductor laser, an optical isolator, a half wave plate, a polarization splitting prism, a total reflective mirror and a convex lens, a concave lens and a cesium atom air chamber. The method and device for generation of higher-order transverse modes on the basis of an atom-cavity coupling may be applicable to the research fields such as the preparation of seed light source on the basis of a space higher-order transverse mode correlated light field near an alkali-metal atom absorption line, accurate measurement of a small displacement through adoption of higher-order transverse modes, laser cooling and optical trapping, quantum information storage, and the like.
Owner:SHANXI UNIV
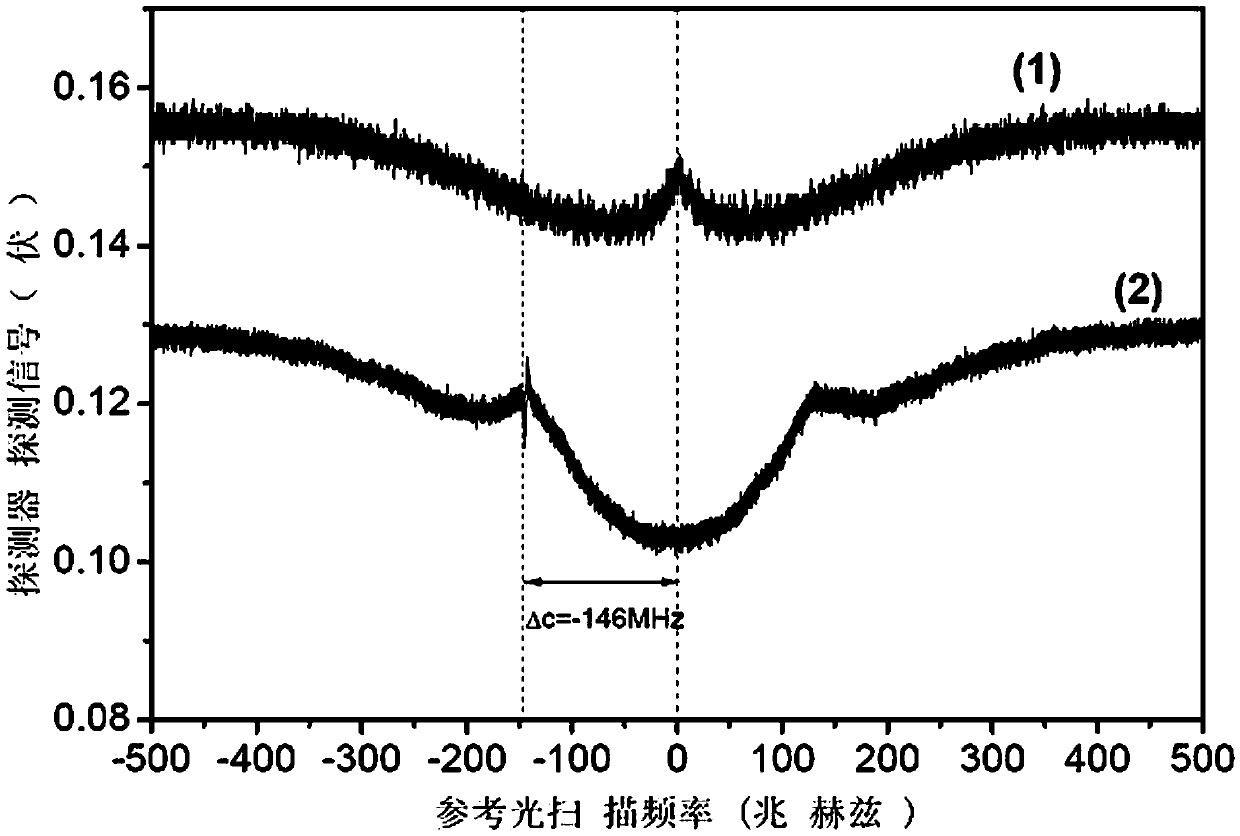
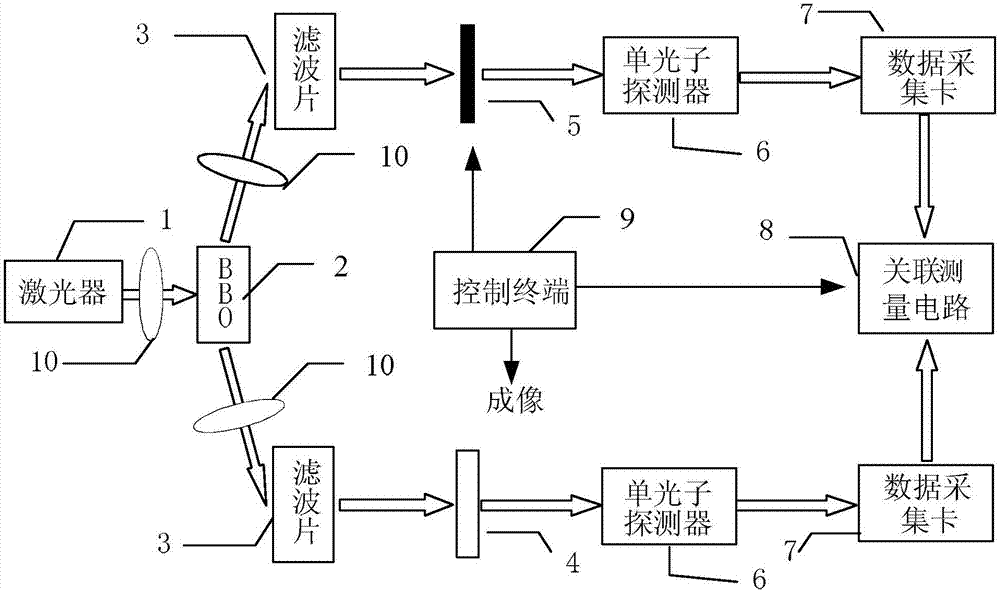
Pure phase object imaging system based on photon orbit angular momentum
Provided is a pure phase object imaging system based on photon orbit angular momentum, belonging to the technical field of quantum information and solving the problem of difficult imaging of pure phase objects in a conventional imaging system. The pure phase object imaging system includes a laser, a BBO crystal, two lenses, two filters, a spiral phase plate, a spatial light modulator, two single photon detectors, two data acquisition cards, an associated measurement circuit and a control terminal. The system analyzes the imaging process of the pure phase object on the basis of the photon orbit angular momentum entangled state, divides the generated entangled photon pair into two paths, places an all-phase object in one path which is the signal optical path and the other is an idle optical path, and can recover the intelligible image of the pure phase object by means of the correlation algorithm by recording the correlation count of the two optical paths. The system is suitable to be applied to the non-localized pure phase object imaging in the military, medical, astronomy and search and rescue fields.
Owner:黑龙江省工研院资产经营管理有限公司
Generating device for entanglement of continuous variable atom ensemble
ActiveCN105676559AVerification entanglementEntanglement goodNon-linear opticsQuantum entanglementLight beam
The invention relates to a generating device for entanglement of continuous variable atom ensemble and belongs to the generating device for the entanglement of atom ensemble applied to a quantum information network. The generating device is used for solving the technical problem that probability preparation exists in the present preparation for the entanglement of atom ensemble of variables separation. According to the technical scheme provided by the invention, the generating device for entanglement of continuous variable atom ensemble comprises a light source unit, a plurality of beam coupling systems, two sets of atom ensembles, an entanglement measuring system and a feedback unit. The orthogonal component of a light field in the continuous variable quantum information and the collective spin wave of the atom ensemble are utilized to generate the entanglement of two sets of stokes light and spin wave of atom ensemble in a spontaneous raman scattering process, and then interference signals of the two beams of stokes light are fed back to a first atom ensemble through the quantum entanglement exchange, the entanglements of the first atom ensemble and the second atom ensemble are certainly prepared, and the generated stokes light is utilized to measure and analyze the entanglement of the atom ensemble.
Owner:SHANXI UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com