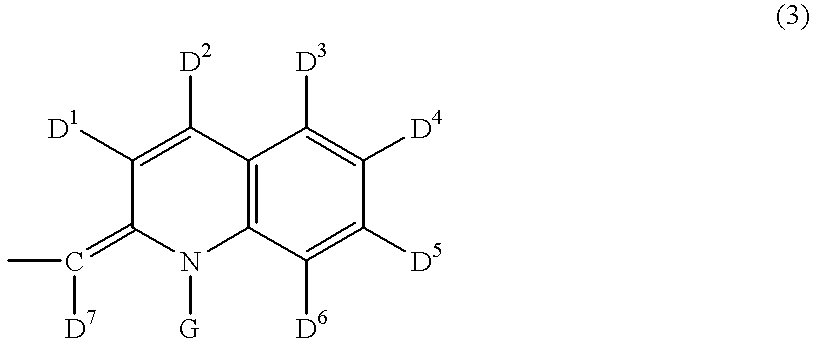
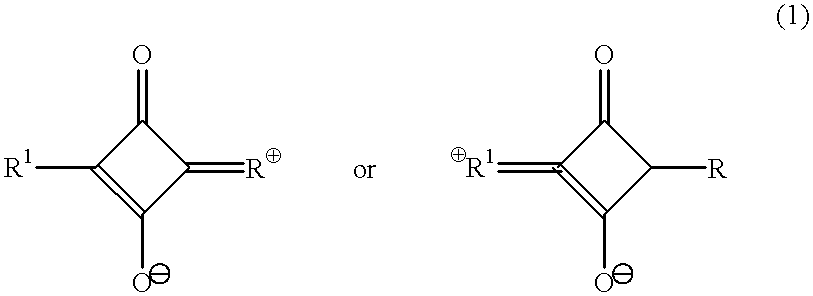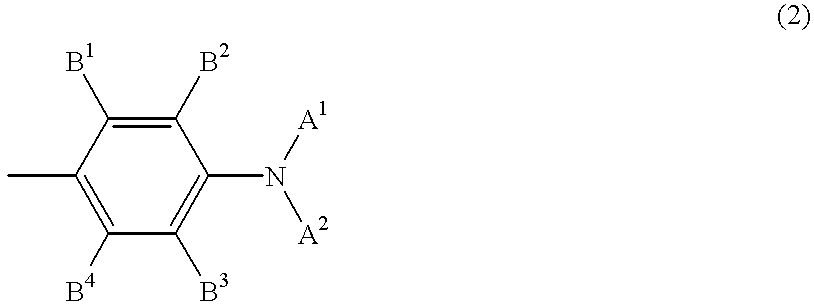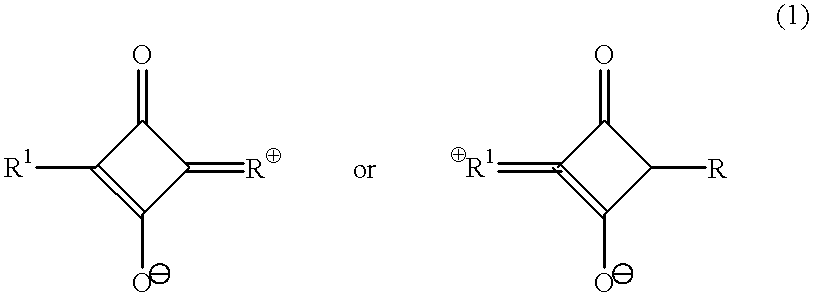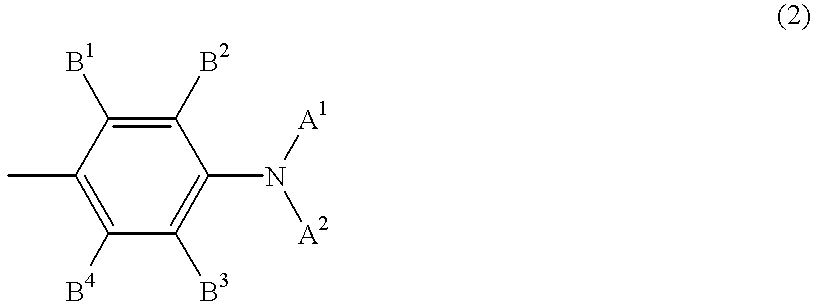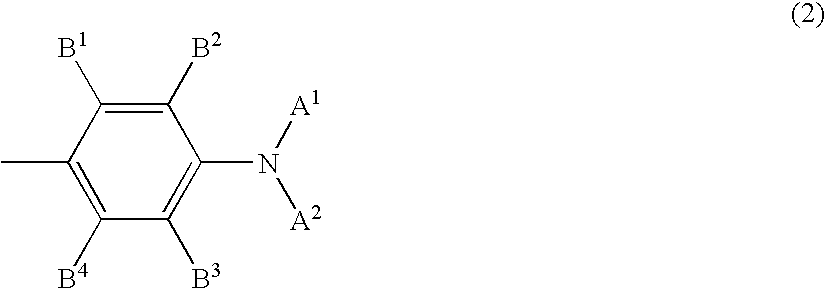Patents
Literature
2482 results about "Raman scattering" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
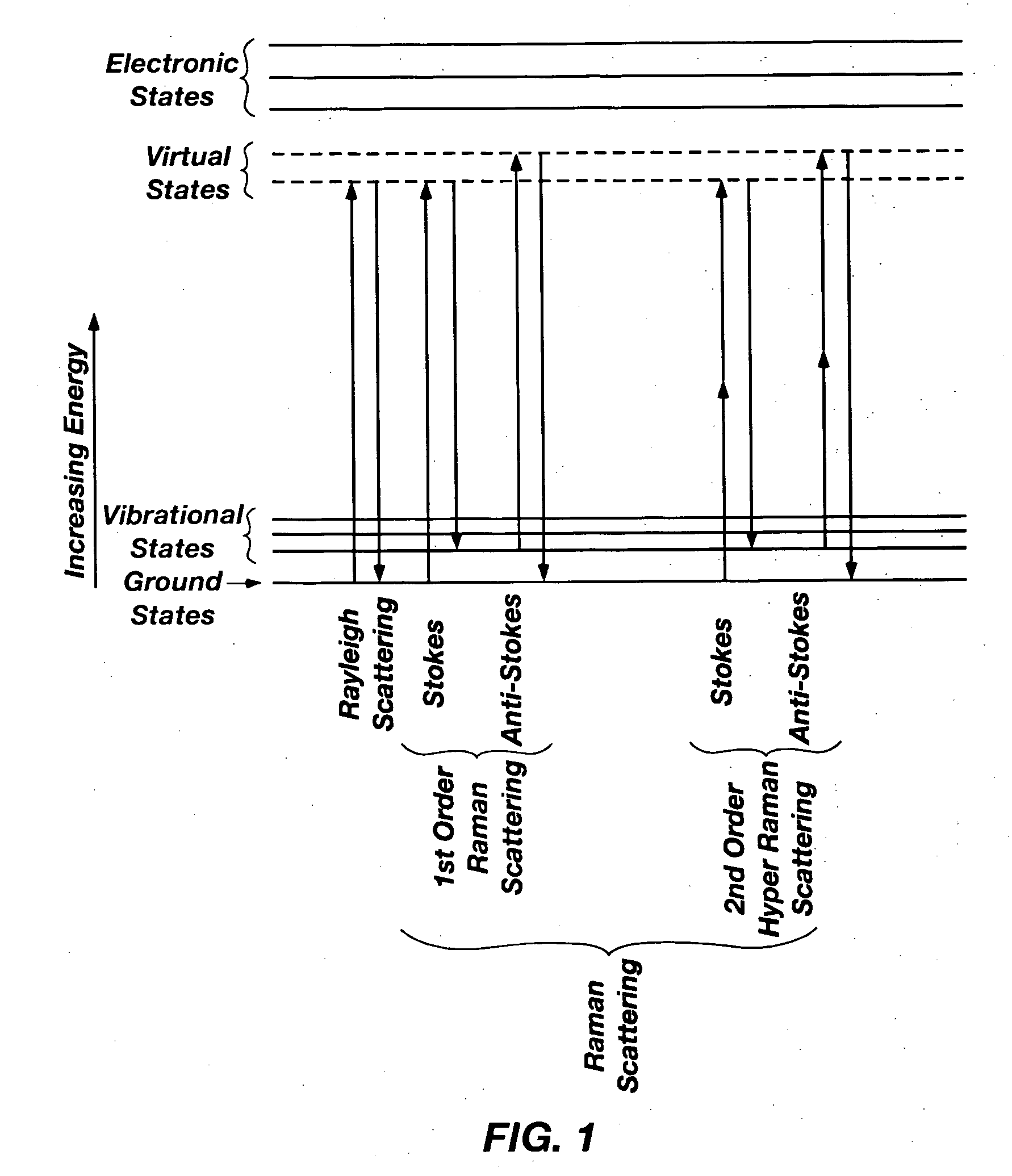
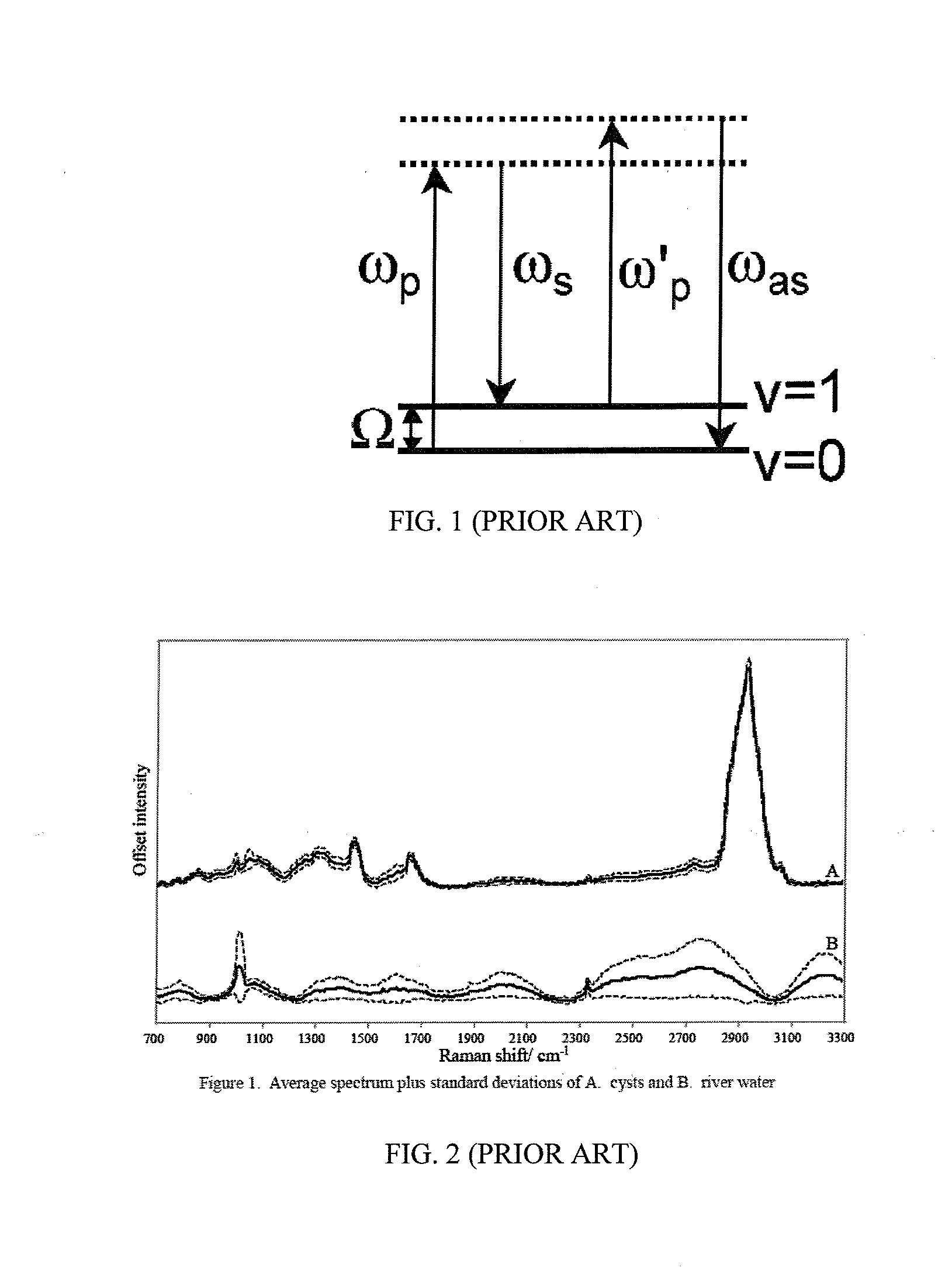
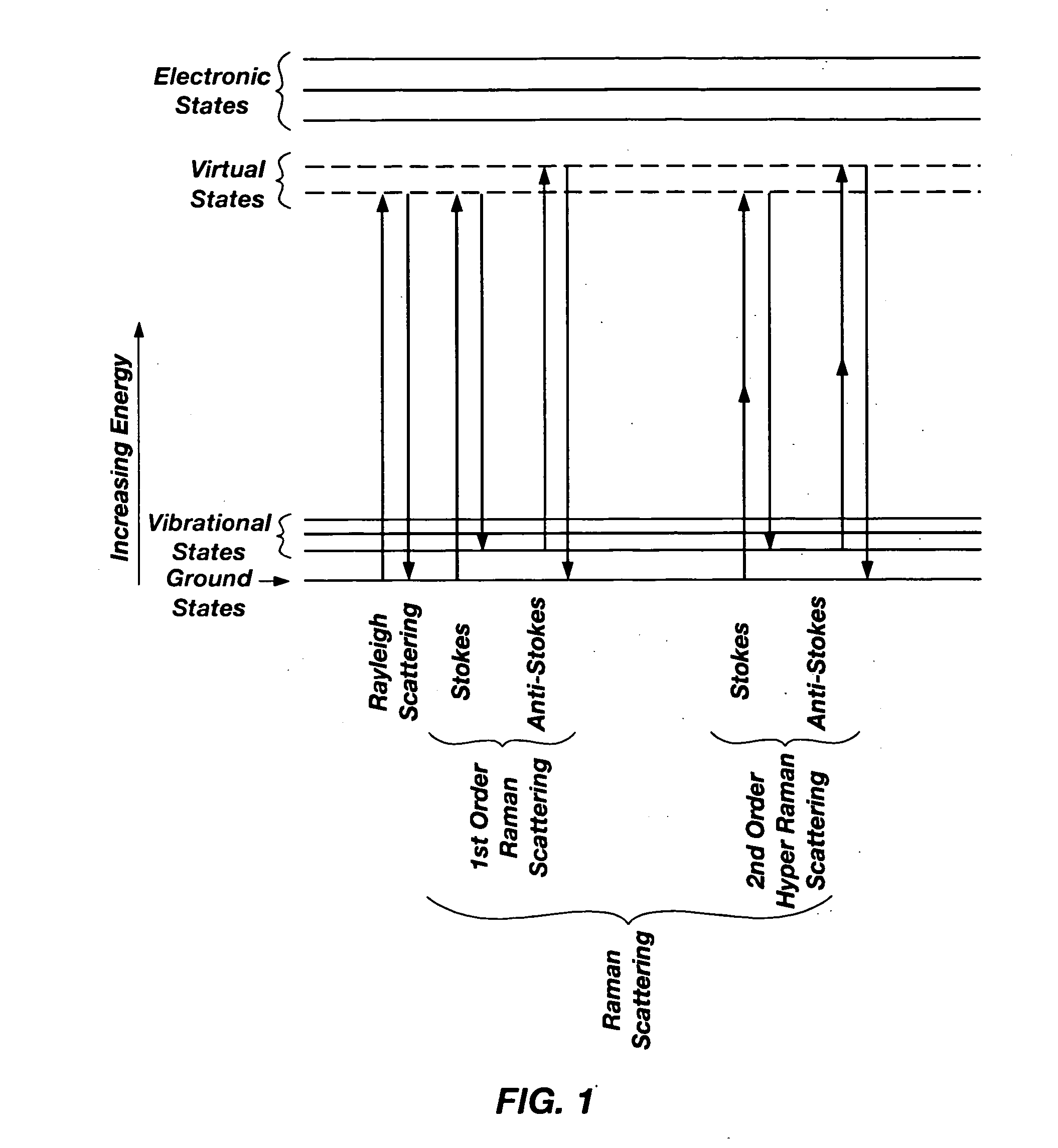
Raman scattering or the Raman effect /ˈrɑːmən/ is the inelastic scattering of photons by matter, meaning that there is an exchange of energy and a change in the light's direction. Typically this involves vibrational energy being gained by a molecule as incident photons from a visible laser are shifted to lower energy. This is called normal Stokes Raman scattering. The effect is exploited by chemists and physicists to gain information about materials for a variety of purposes by performing various forms of Raman spectroscopy. Many other variants of Raman spectroscopy allow Rotational energy to be examined (if gas samples are used) and electronic energy levels may be examined if an X-ray source is used in addition to other possibilities. More complex techniques involving pulsed lasers, multiple laser beams and so on are known.
Raman-active taggants and their recognition
InactiveUS6610351B2Easy to useQuality improvementMaterial nanotechnologyRadiation applicationsMaximum dimensionActive component
An organic or organoelement, linear or branched, monomeric or polymeric composition of matter having a Raman-active component in the form of particles. The particles having a maximum dimension of 50 mum. The Raman-active compound is applied to a substrate. When the Raman-active compound is exposed to a laser light wavelength which is batochromically well beyond a spectral region of maximum absorbance of said Raman-active compound, Raman scattering can be detected.
Owner:QUANTAG SYST
Raman-active taggants and their recognition
InactiveUS20020025490A1Easy to useQuality improvementOptical radiation measurementMaterial nanotechnologyLaser lightLasing wavelength
An organic or organoelement, linear or branched, monomeric or polymeric composition of matter having a Raman-active component in the form of particles. The particles having a maximum dimension of 50 mum. The Raman-active compound is applied to a substrate. When the Raman-active compound is exposed to a laser light wavelength which is batochromically well beyond a spectral region of maximum absorbance of said Raman-active compound, Raman scattering can be detected.
Owner:QUANTAG SYST
Raman-active taggants and thier recognition
InactiveUS20040058058A1Easy to useQuality improvementMaterial nanotechnologyRadiation pyrometryLasing wavelengthLaser light
An organic or organoelement, linear or branched, monomeric or polymeric composition of matter having a Raman-active component in the form of particles. The particles having a maximum dimension of 50 mum. The Raman-active compound is applied to a substrate. When the Raman-active compound is exposed to a laser light wavelength which is batochromically well beyond a spectral region of maximum absorbance of said Raman-active compound, Raman scattering can be detected.
Owner:SHCHEGOLIKHIN ALEXANDER NIKITOVICH +4
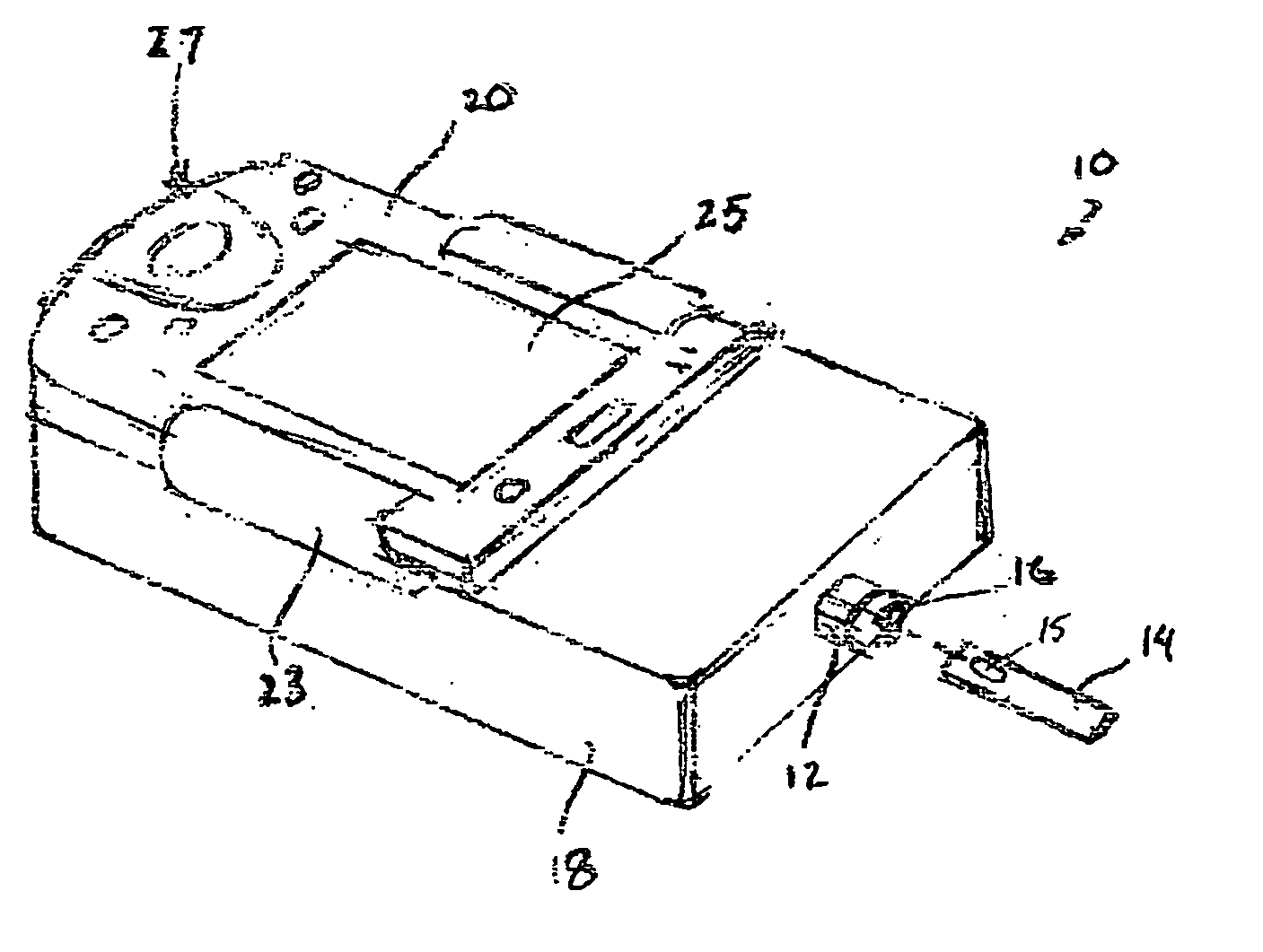
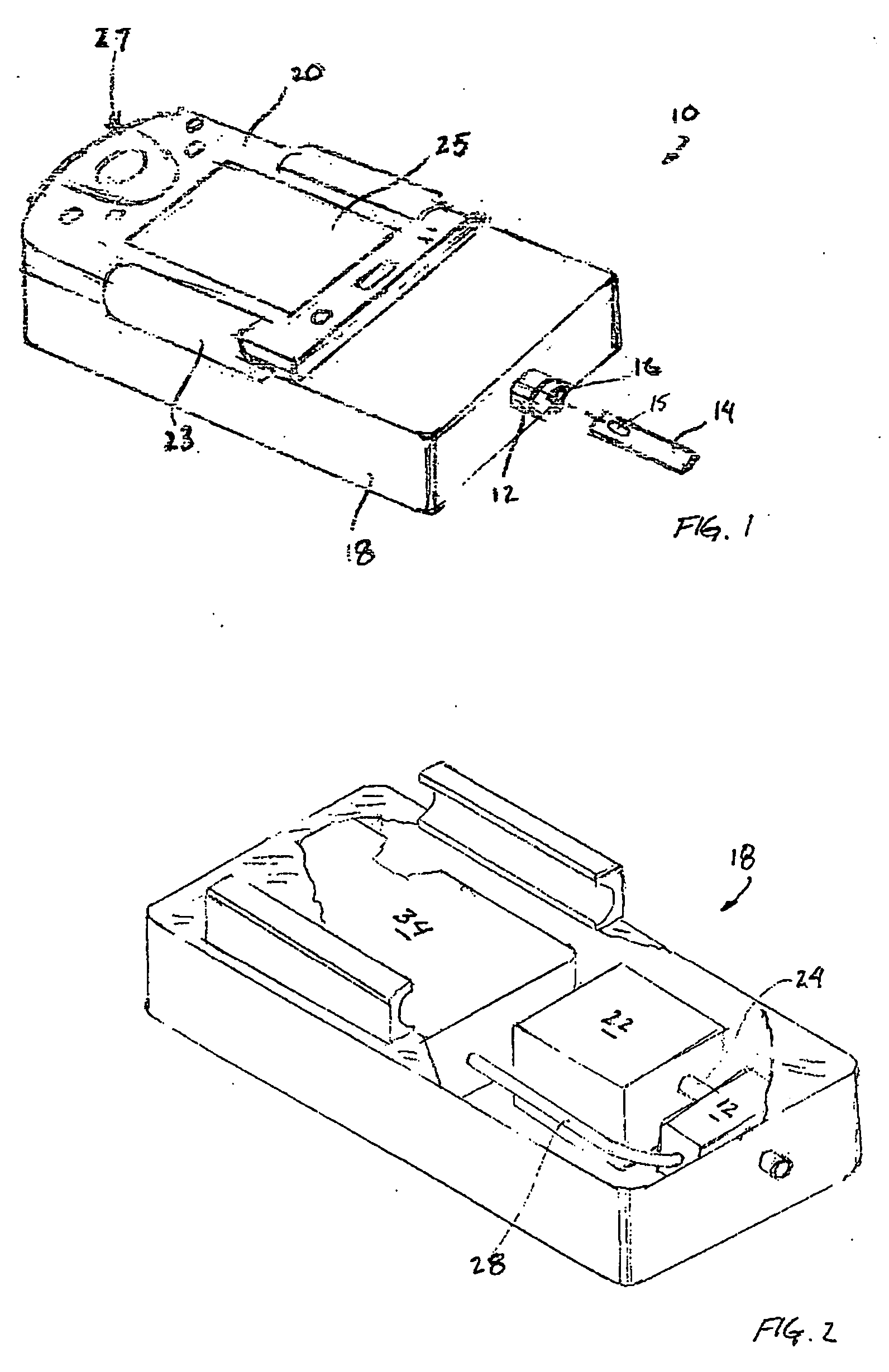
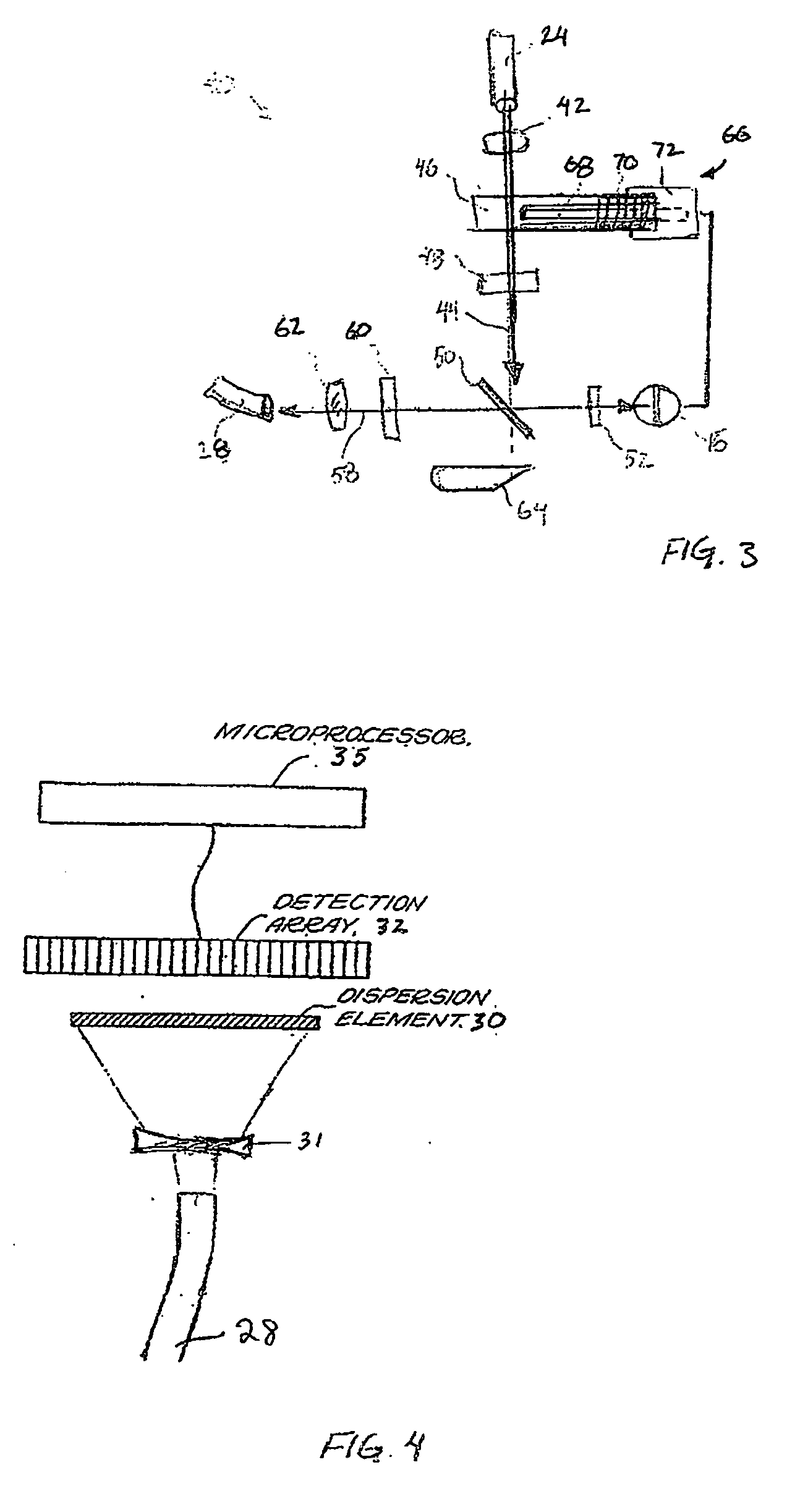
Handheld raman blood analyzer
InactiveUS20060166302A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAnalyteImage resolution
Methods and apparatus for in vitro detection of an analyte in a blood sample using low resolution Raman spectroscopy are disclosed. The blood analyzer includes a disposable strip for receiving a sample of blood on a target region, the target region including gold sol-gel to provide surface enhanced Raman scattering. A light source irradiates the target region to produce a Raman spectrum consisting of scattered electromagnetic radiation that is separated into different wavelength components by a dispersion element. A detection array detects a least some of the wavelength components of the scattered light and provides data to a processor for processing the data. The results of the processed data are displayed on a screen to inform a user about an analyte within the blood sample.
Owner:PRESCIENT MEDICAL
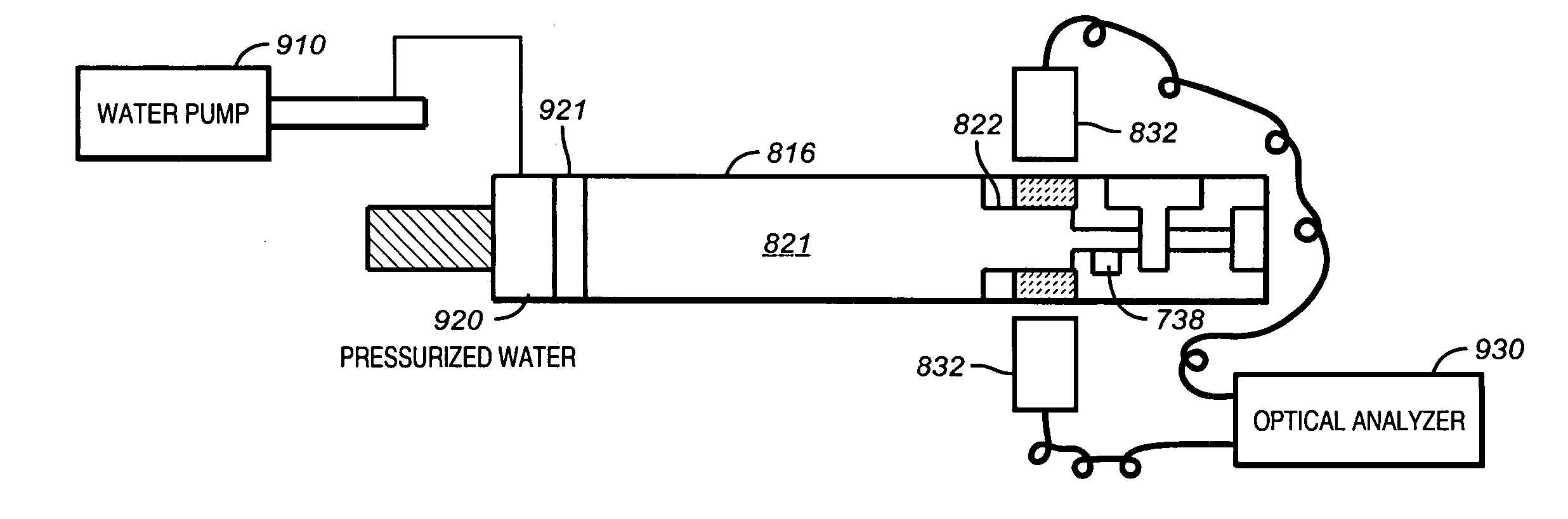
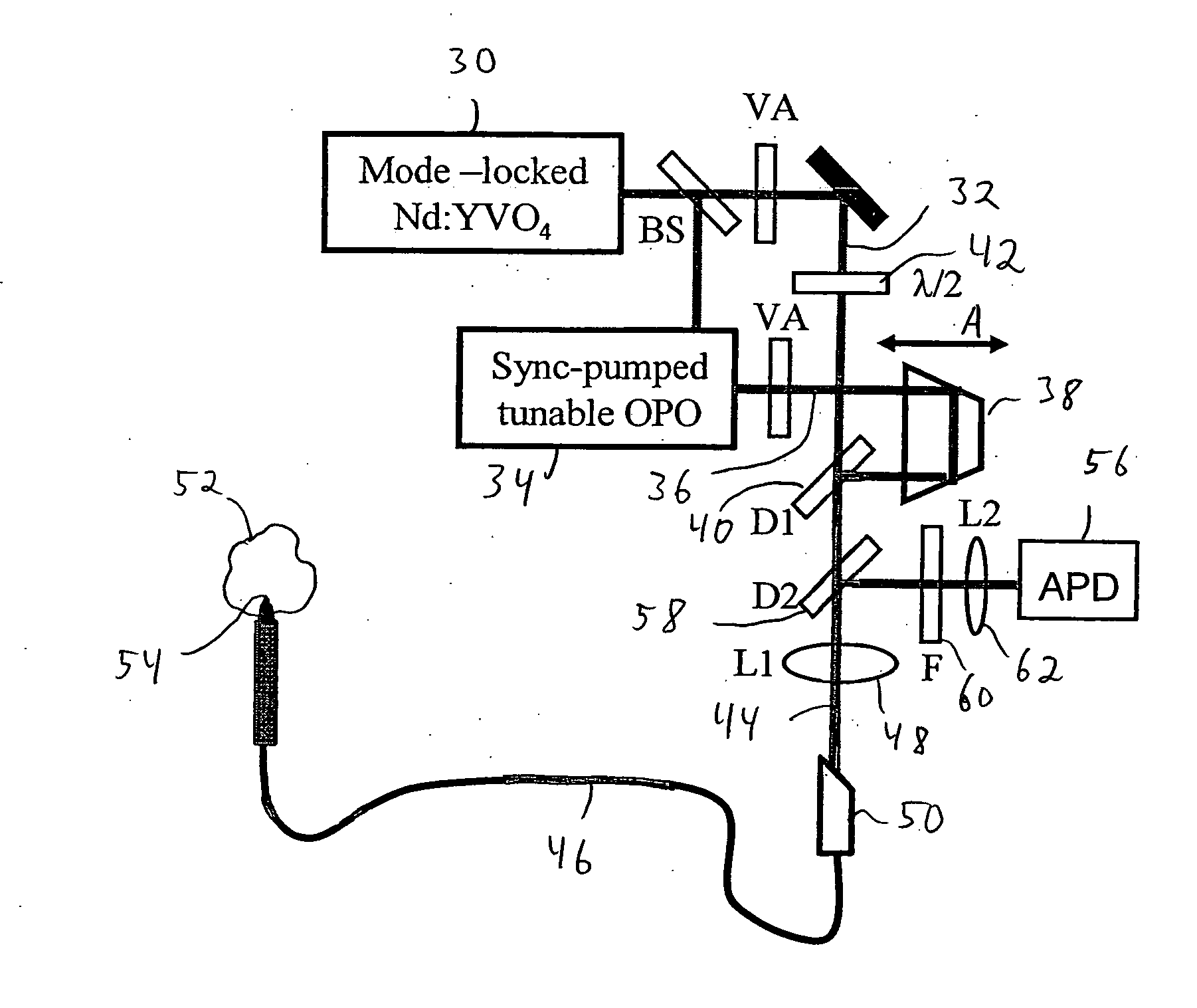
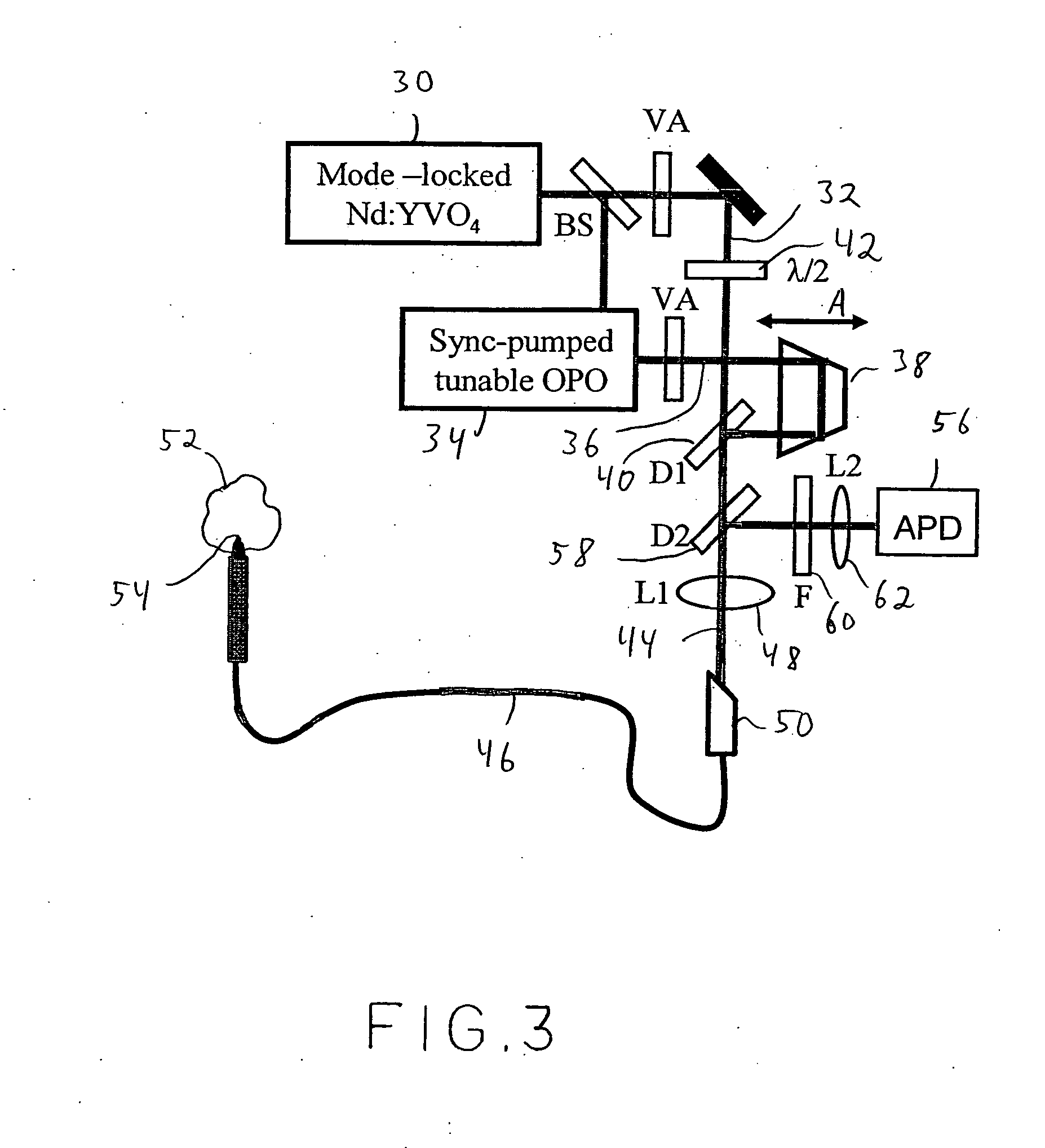
Method and apparatus for a tunable diode laser spectrometer for analysis of hydrocarbon samples
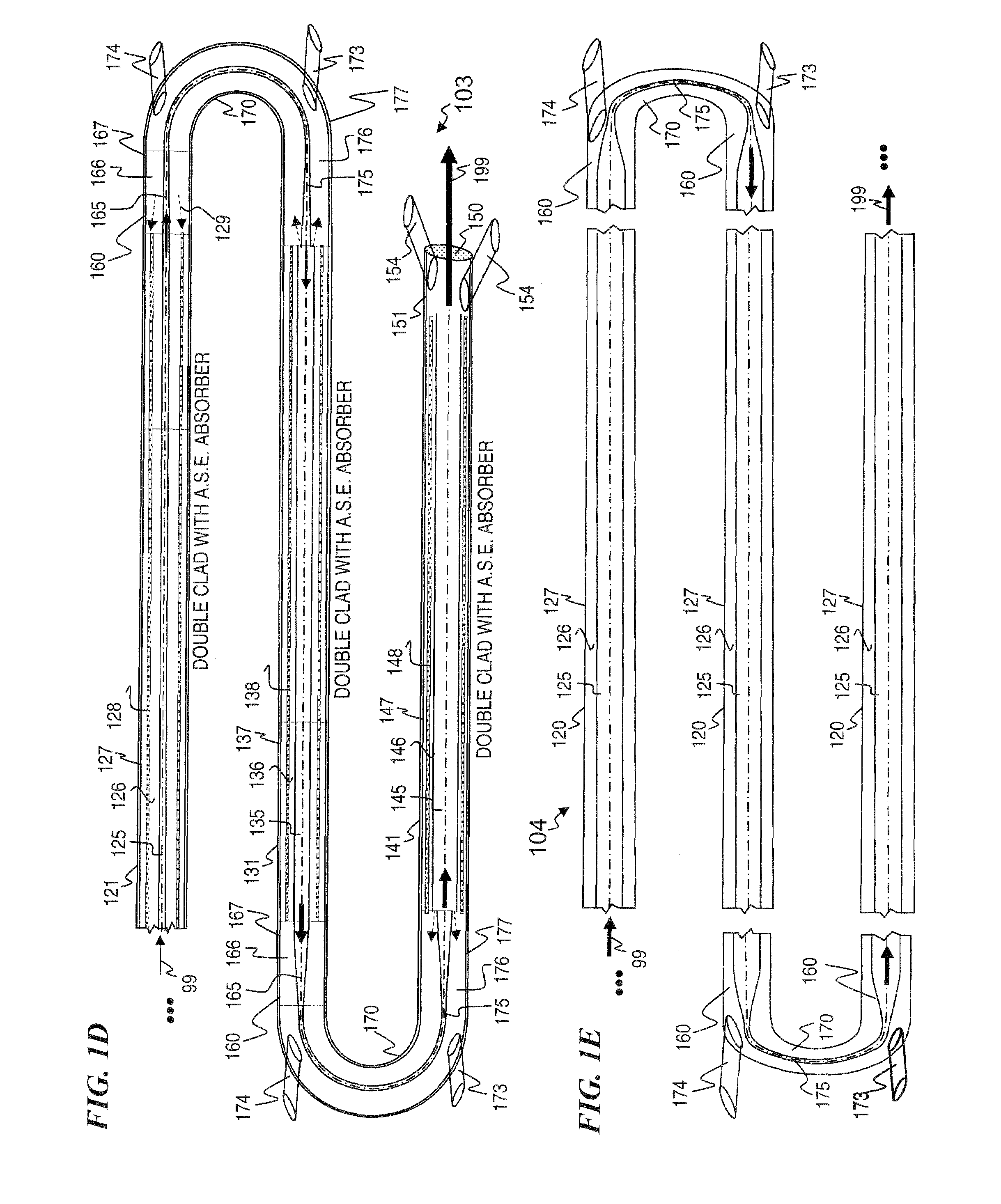
The present invention provides an down hole apparatus and method for ultrahigh resolution spectroscopy using a tunable diode laser (TDL) for analyzing a formation fluid sample downhole or at the surface to determine formation fluid parameters. In addition to absorption spectroscopy, the present invention can perform Raman spectroscopy on the fluid, by sweeping the wavelength of the TDL and detecting the Raman-scattered light using a narrow-band detector at a fixed wavelength. The spectrometer analyzes a pressurized well bore fluid sample that is collected downhole. The analysis is performed either downhole or at the surface onsite. Near infrared, mid-infrared and visible light analysis is also performed on the sample to provide an onsite surface or downhole analysis of sample properties and contamination level. The onsite and downhole analysis comprises determination of aromatics, olefins, saturates, gas oil ratio, API gravity and various other parameters which can be estimated by correlation, a trained neural network or a chemometric equation.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
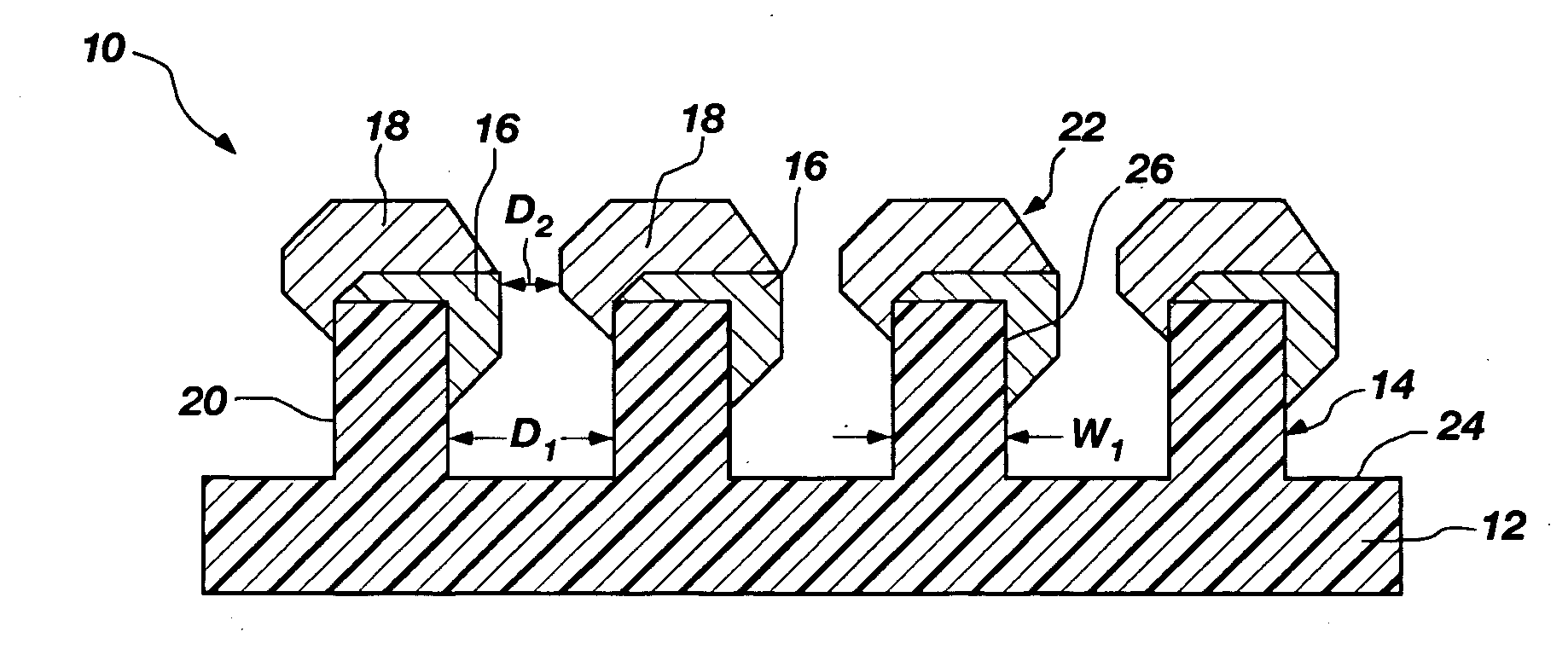
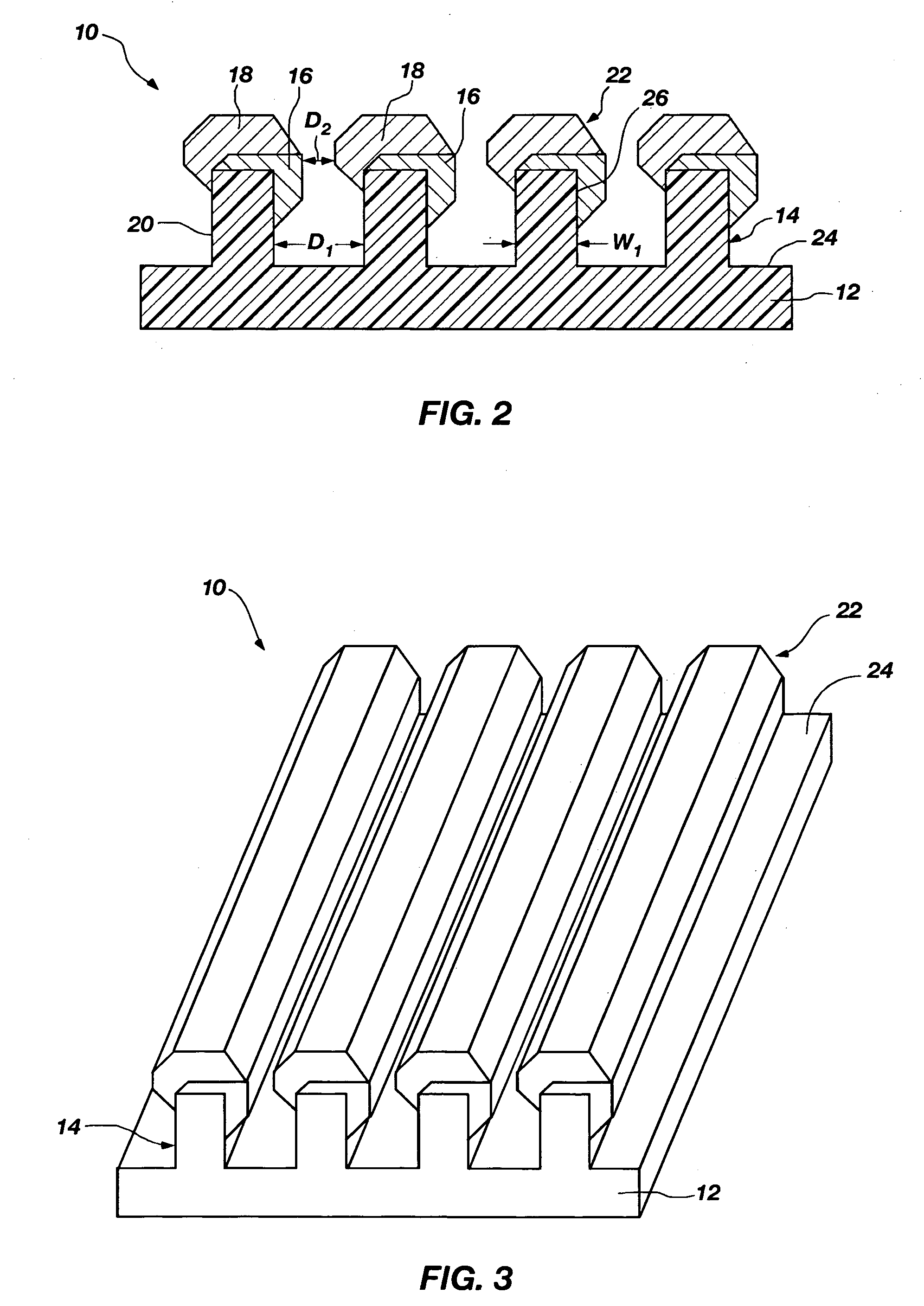
Nanoscale structures, systems, and methods for use in nano-enhanced raman spectroscopy (NERS)
NERS-active structures for use in Raman spectroscopy include protrusions extending from a surface of a substrate. A Raman signal-enhancing material is disposed on at least one surface of a first protrusion and at least one surface of a second protrusion. The Raman signal-enhancing material disposed on the first protrusion projects laterally in a direction generally towards the second protrusion, and the Raman signal-enhancing material disposed on the second protrusion projects laterally in a direction generally towards the first protrusion. At least a portion of the Raman signal-enhancing projecting from the first protrusion and at least a portion of the Raman signal-enhancing material projecting from the second protrusion may be separated by a distance of less than about 10 nanometers. Raman spectroscopy systems include such NERS-active structures, and methods for performing Raman spectroscopy include irradiating an analyte proximate such a NERS-active structure and detecting Raman-scattered radiation scattered by the analyte.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Optical terahertz generator / receiver
InactiveUS20050242287A1Increase output powerIncrease emitted bandwidthColor/spectral properties measurementsX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentFiberTerahertz radiation
A method for the high power generation and detection of terahertz radiation is presented. It comprises of an optical waveguide with a core, and a mostly hollow cladding or terahertz wave transparent material surrounding the core. The cladding region is a terahertz waveguide. A pump light source is coupled to the core to promote nonlinear optical process, such as Raman scattering, in the core which in turn leads to terahertz radiation being emanated or received through fiber cladding.
Owner:HAKIMI HOSAIN
Thermoplastic resin composition, molding material, and molded article thereof
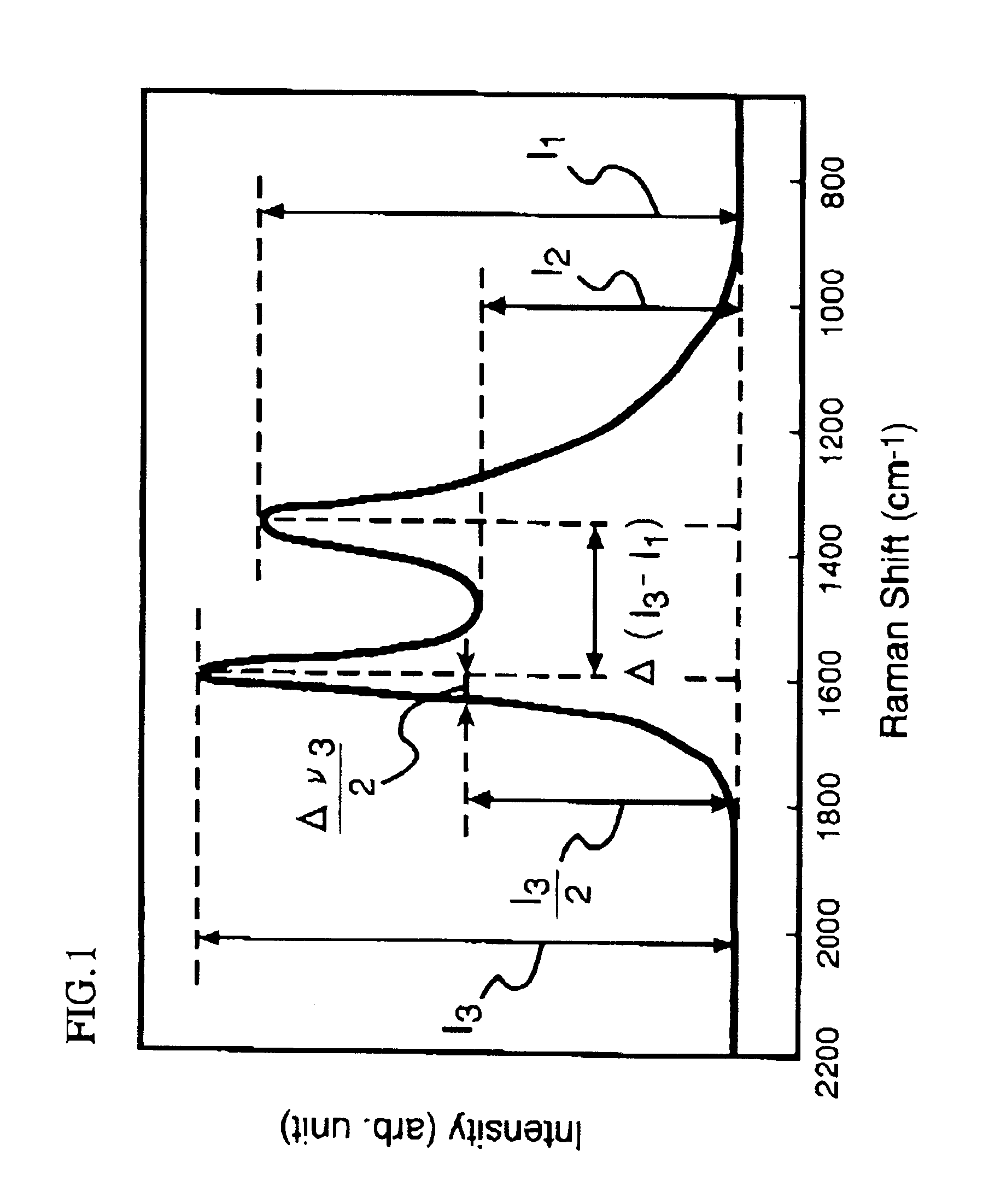
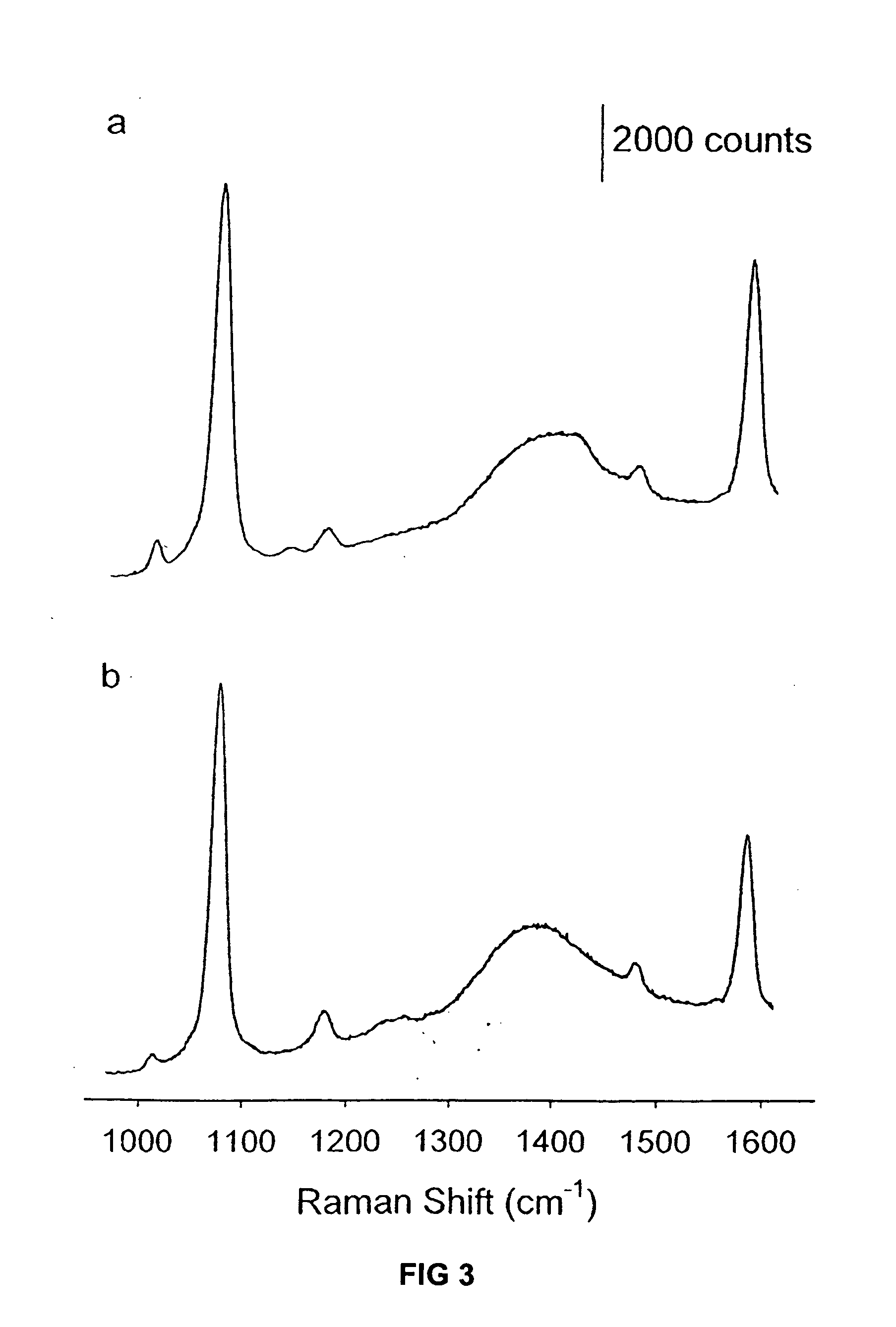
A thermoplastic resin composition capable of providing a thin walled molded article whose flame retardancy with a thickness of 1.6 mm ({fraction (1 / 16)} inch) in accordance with an UL 94 standard is V-0 or better, and which comprises the following components [A], [B] and [C], wherein the component [B] satisfies the following conditions (B1) and / or (B2):[A]: an electrically conductive fiber;[B]: a carbon powder;[C]: a thermoplastic resin;(B1): Raman scattering intensity ratio I2 / I1 is 0.55-0.8;(B2): Raman scattering intensity ratio I2 / I3 is 0.54-0.8; whereI1: local maximum value of Raman scattering intensity appearing near a Raman shift of 1360 cm-1;I2: local minimum value of the Raman scattering intensity appearing near a Raman shift of 1480 cm-1;I3: local maximum value of the Raman scattering intensity appearing neat a Raman shift of 1600 cm-1.
Owner:TORAY IND INC
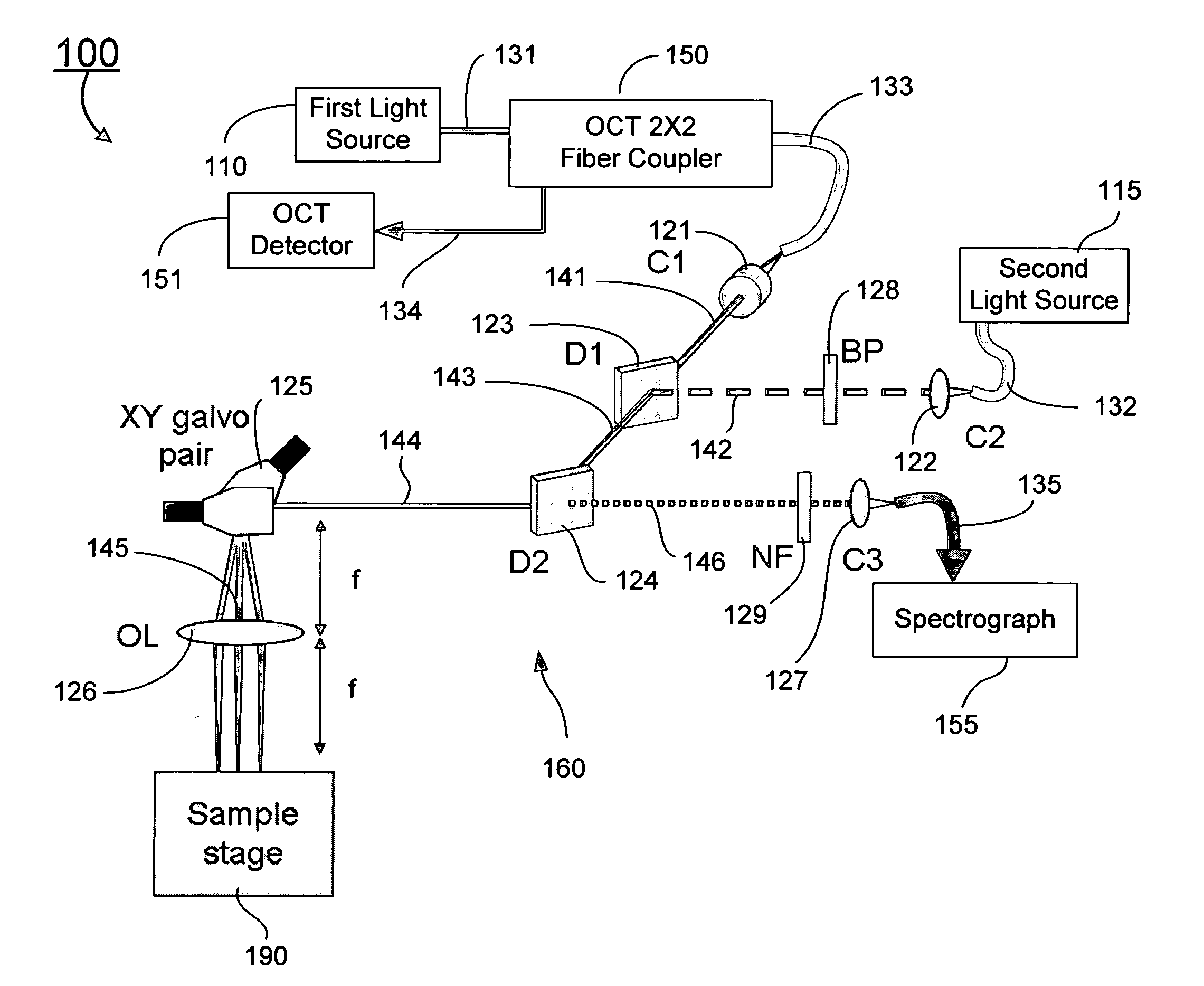
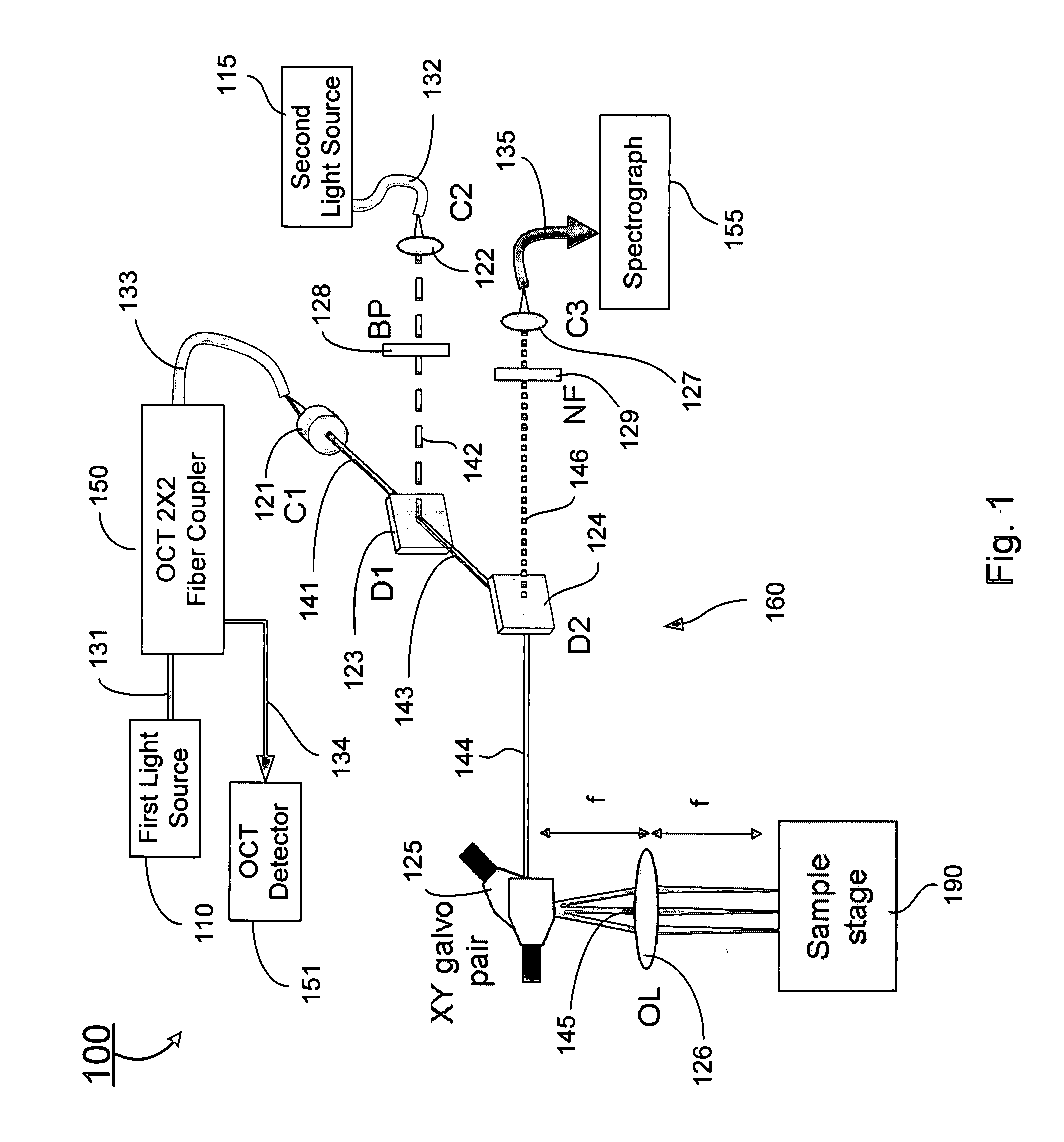
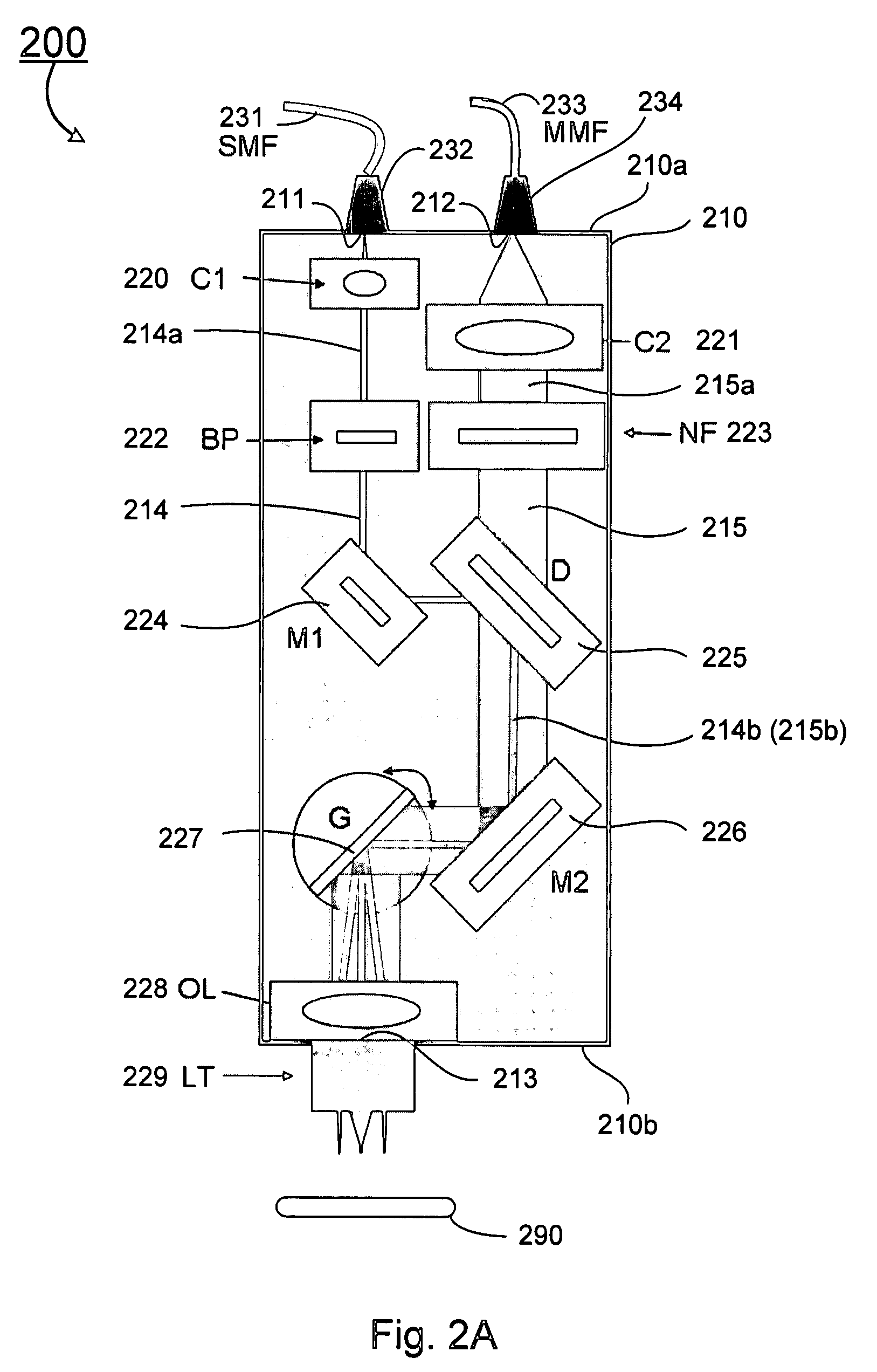
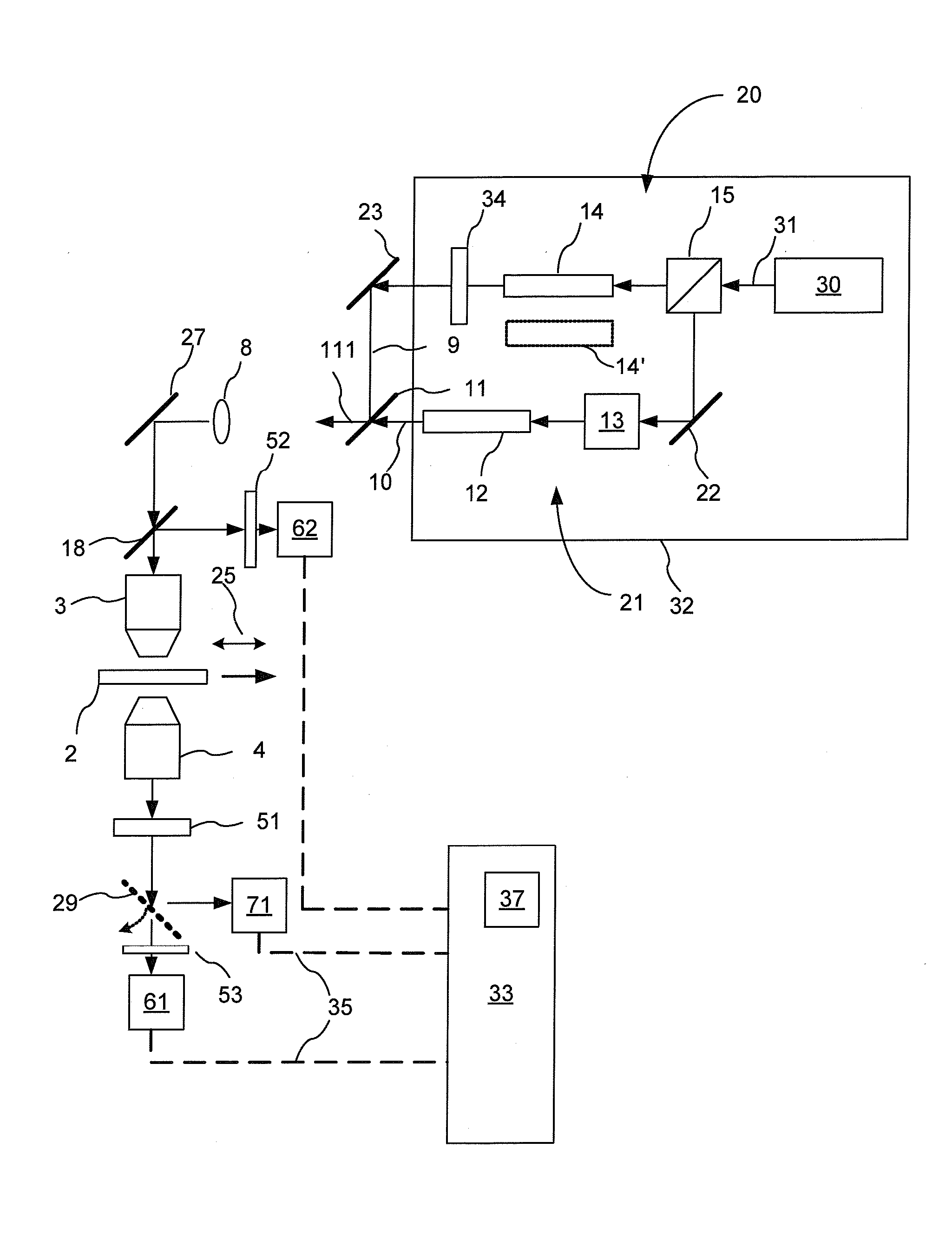
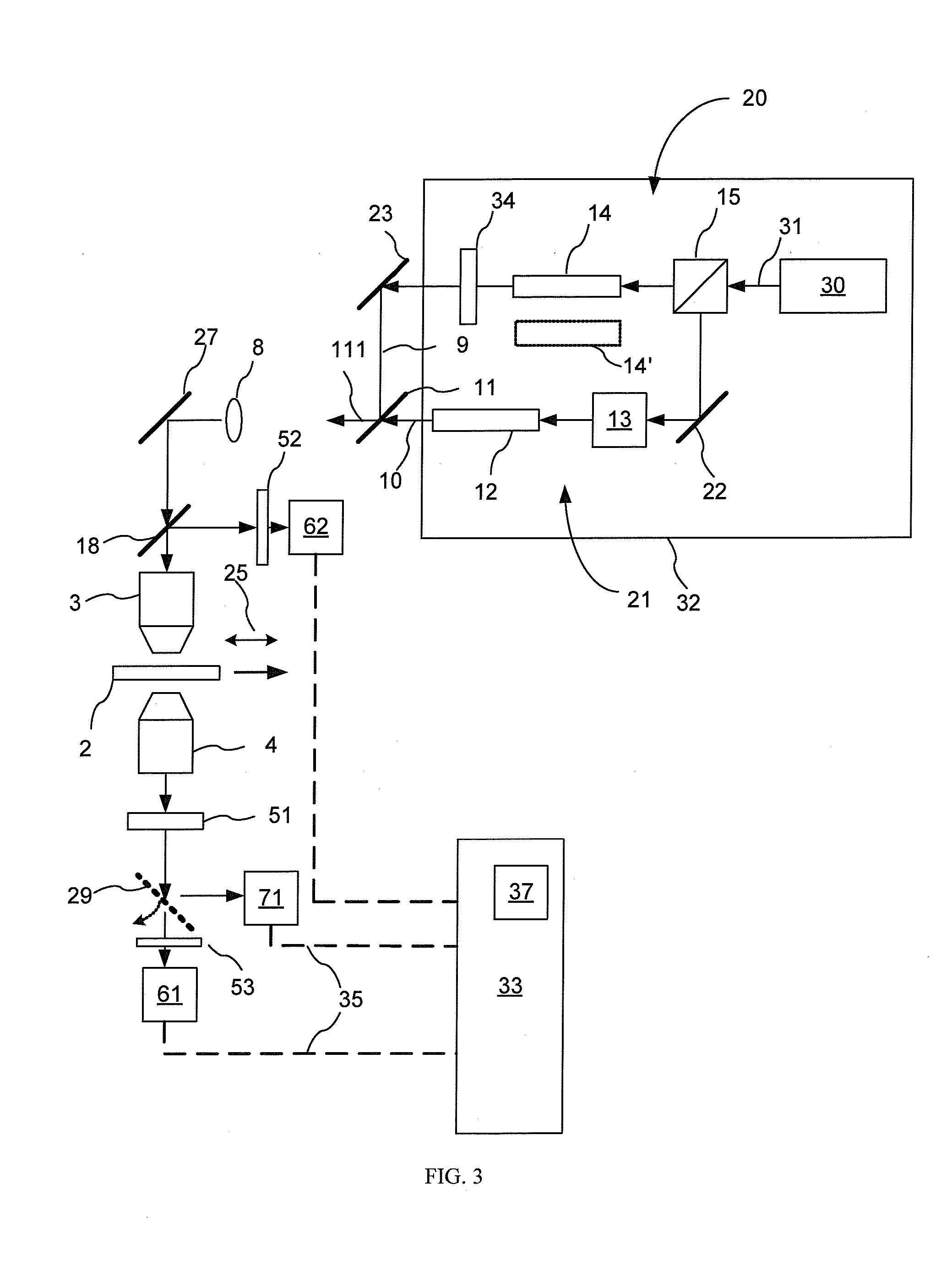
Combined raman spectroscopy-optical coherence tomography (rs-oct) system and applications of the same
ActiveUS20090021724A1Eliminate the problemRadiation pyrometryInterferometersBiological bodyMonochromatic color
An apparatus for evaluating a target of interest of a living subject. In one embodiment, the apparatus has a first light source for generating a broadband light, a second light source for generating a monochromatic light, a beamsplitter optically coupled to the first light source for receiving the broadband light and splitting it into a reference light and a sample light, a reference arm optically coupled to the beamsplitter for receiving the reference light and returning it into the beamsplitter, and a probe having a working end placed proximal to a target of interest of a living subject, optically coupled to the beamsplitter and the second light source for receiving the sample light and the monochromatic light, delivering them from the working end to the target of interest, collecting from the working end a backscattering light and a Raman scattering light that are obtained from interaction of the sample light and the monochromatic light with the target of interest, respectively, and returning the backscattering light into the beamsplitter so as to generate an interference signal between the returned backscattering light and the returned reference light in the beamsplitter.
Owner:VANDERBILT UNIV
Arrays of Nano Structures for Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering
InactiveUS20070153267A1Maximizing numberImprove binding efficiencyRadiation pyrometryMaterial analysis by optical meansNanostructureNanometre
Owner:OPTOTRACE TECH
Raman-active reagents and the use thereof
InactiveUS20050089901A1Minimizes separationMaximizing numberHybrid immunoglobulinsSugar derivativesAntigenBiological materials
The present invention provides a new class of Raman-active reagents for use in biological and other applications, as well as methods and kits for their use and manufacture. Each reagent includes a Raman-active reporter molecule, a binding molecule, and a surface enhancing particle capable of causing surface enhanced Raman scattering (SERS). The Raman-active reporter molecule and the binding molecule are affixed to the particle to give both a strong SERS signal and to provide biological functionality, i.e. antigen or drug recognition. The Raman-active reagents can function as an alternative to fluorescence-labeled reagents, with advantages in detection including signal stability, sensitivity, and the ability to simultaneously detect several biological materials. The Raman-active reagents also have a wide range of applications, especially in clinical fields (e.g., immunoassays, imaging, and drug screening).
Owner:PORTER MARC D
Apparatus and method for estimating filtrate contamination in a formation fluid
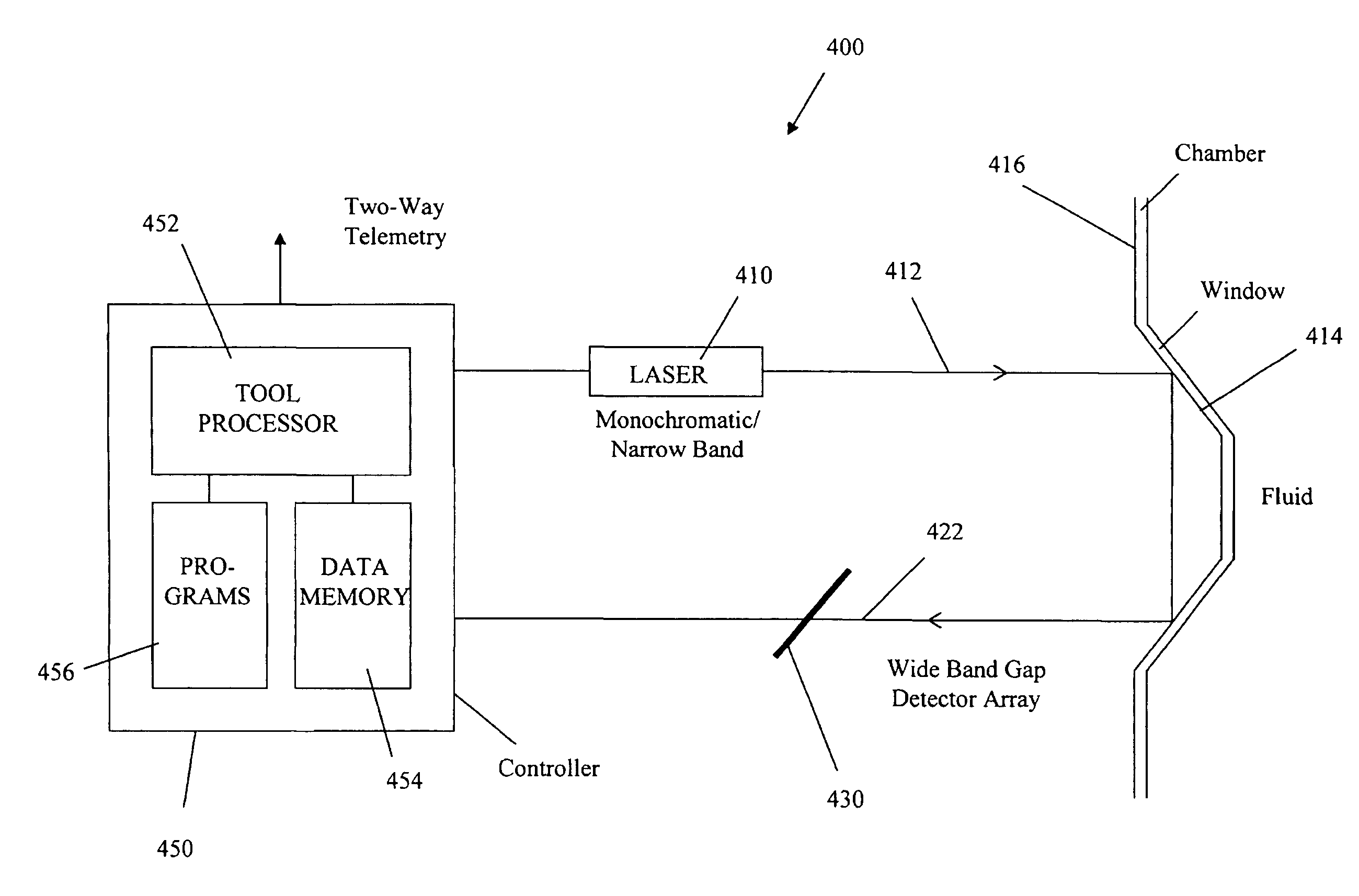
InactiveUS20070081157A1Enhanced Raman effectSurface-enhancing Raman effectRadiation pyrometryOptical prospectingUltravioletEffect light
The disclosure, in one aspect, provides a method for estimating a property of a fluid that includes: pumping an ultraviolet (UV) light into a fluid withdrawn from a formation downhole at a wavelength that produces light due to the Raman effect at wavelengths that are shorter than the substantial wavelengths of fluorescent light produced from the fluid; detecting a spectrum corresponding to the Raman effect light (“Raman spectrum”); and processing the detected Raman spectrum at one or more selected wavelengths to estimate a property of the fluid. In another aspect, the disclosure provides an apparatus that includes a laser that induces UV light at a selected wavelength into a fluid in a chamber, a detector that detects Raman scattered light at wavelengths shorter than the wavelengths of the fluorescent light scattered by the fluid, and a processor that analyzes a spectrum corresponding the Raman scattered light at a selected wavelength to estimate a property of the fluid.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
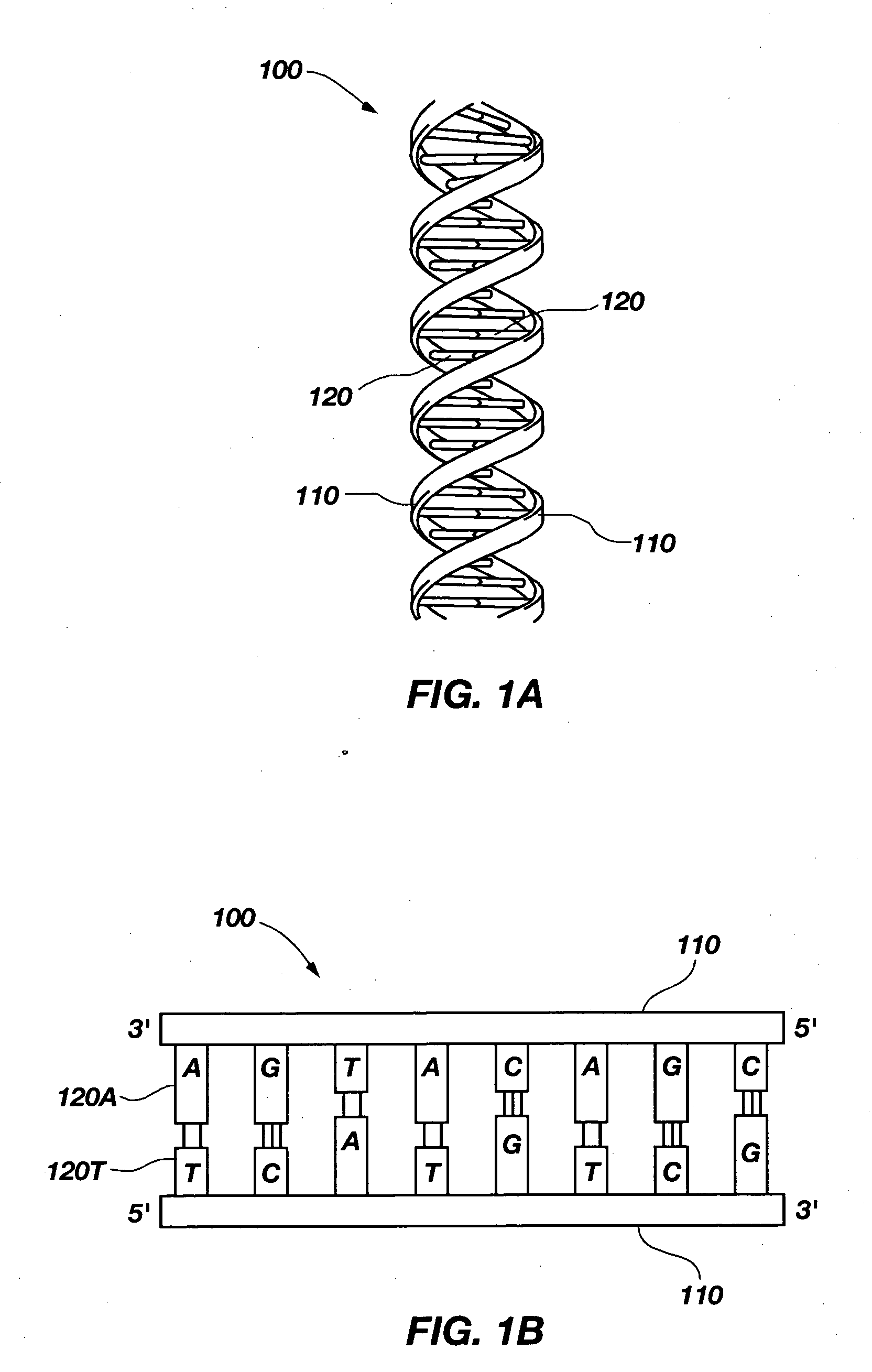
Apparatus and method for analysis of nucleic acids hybridization on high density NA chips.
InactiveUS20020123050A1High sensitivityUseful in detectionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsRadiation pyrometryHigh densityNucleic acid hybridisation
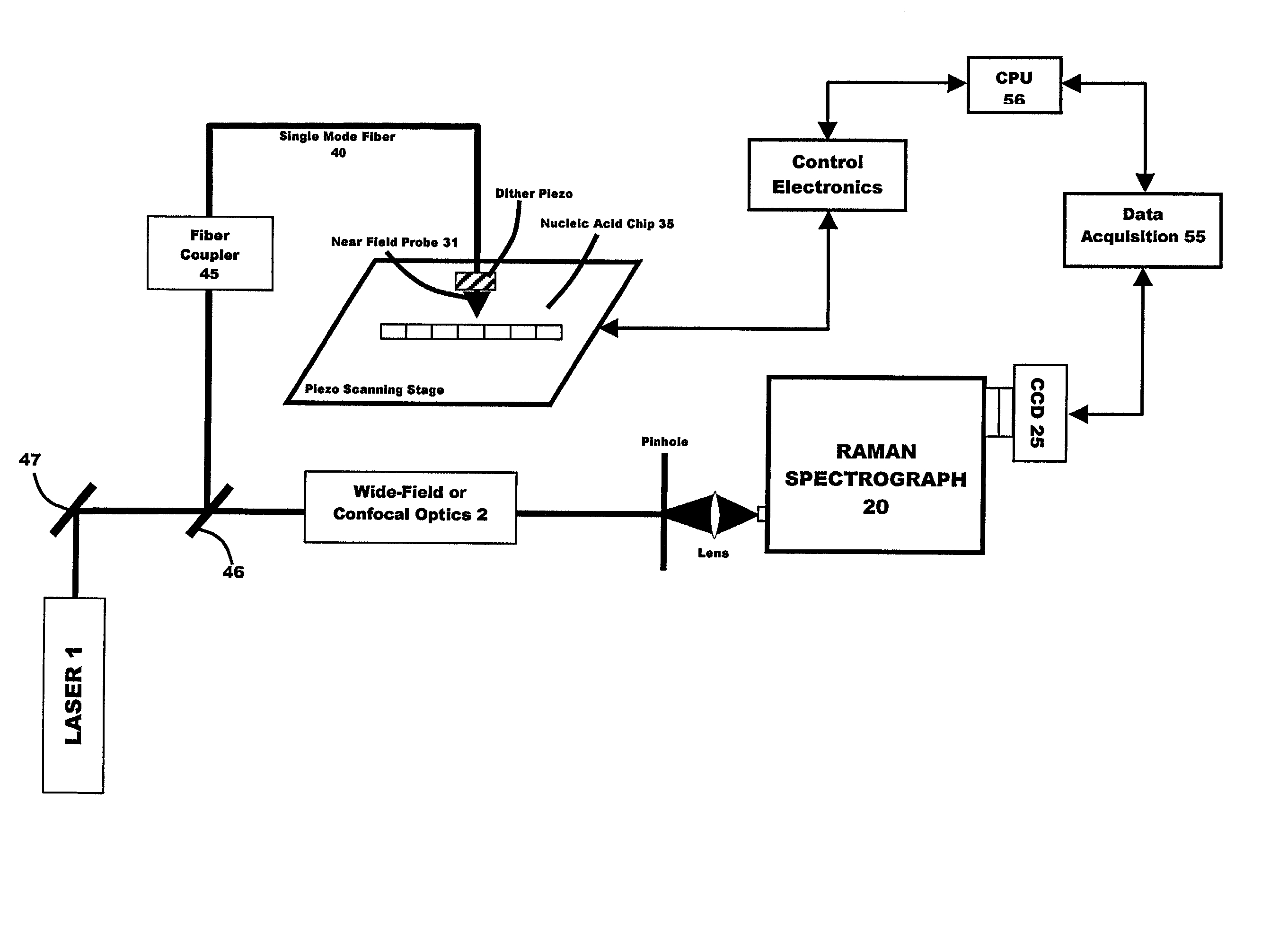
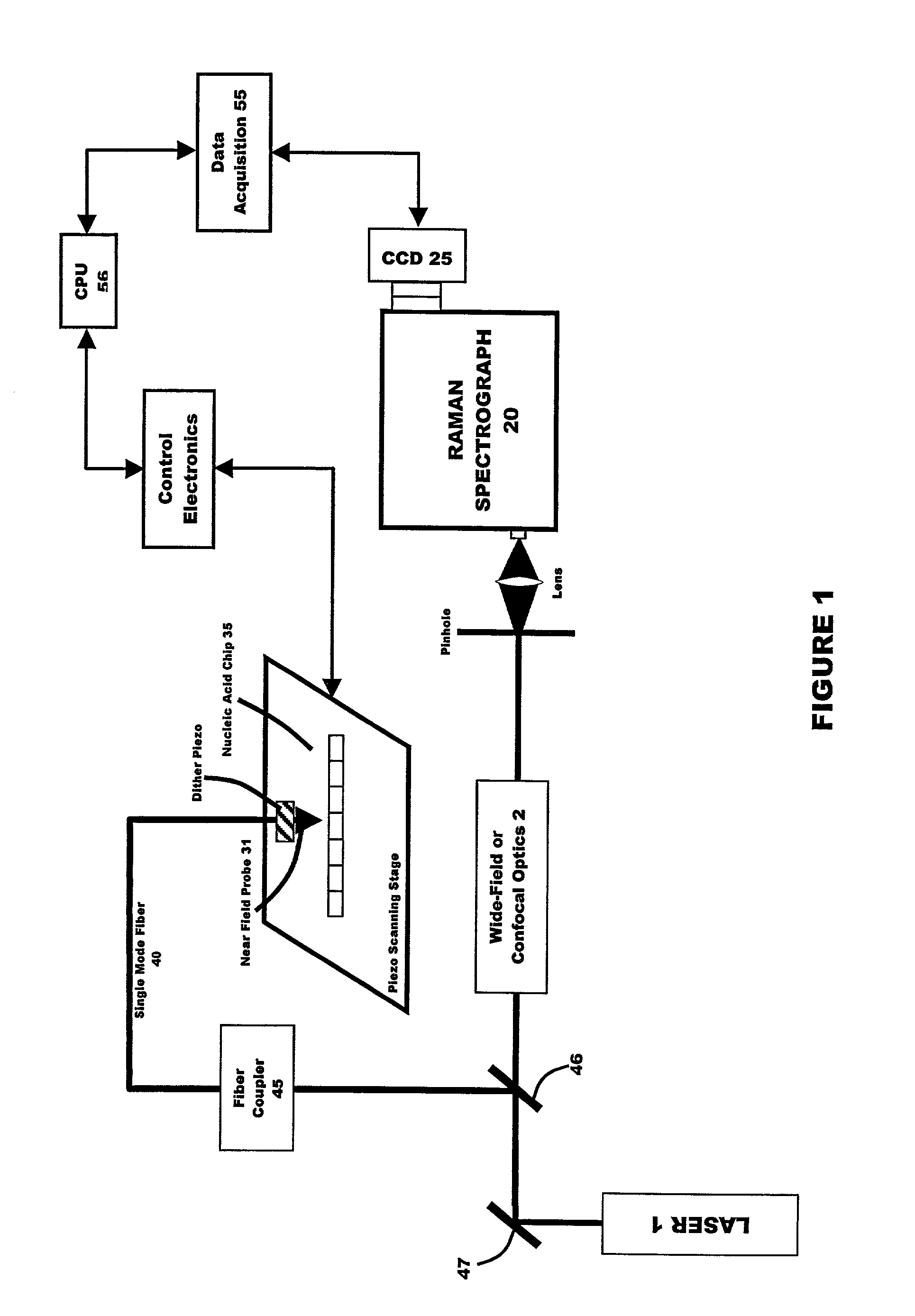
The invention generally relates to a new gene probe biosensor employing near field surface enhanced Raman scattering (NFSERS) for direct spectroscopic detection of hybridized molecules (such as hybridized DNA) without the need for labels, and the invention also relates to methods for using the biosensor.
Owner:POPONIN VLADIMIR
Systems and methods for spectroscopy of biological tissue
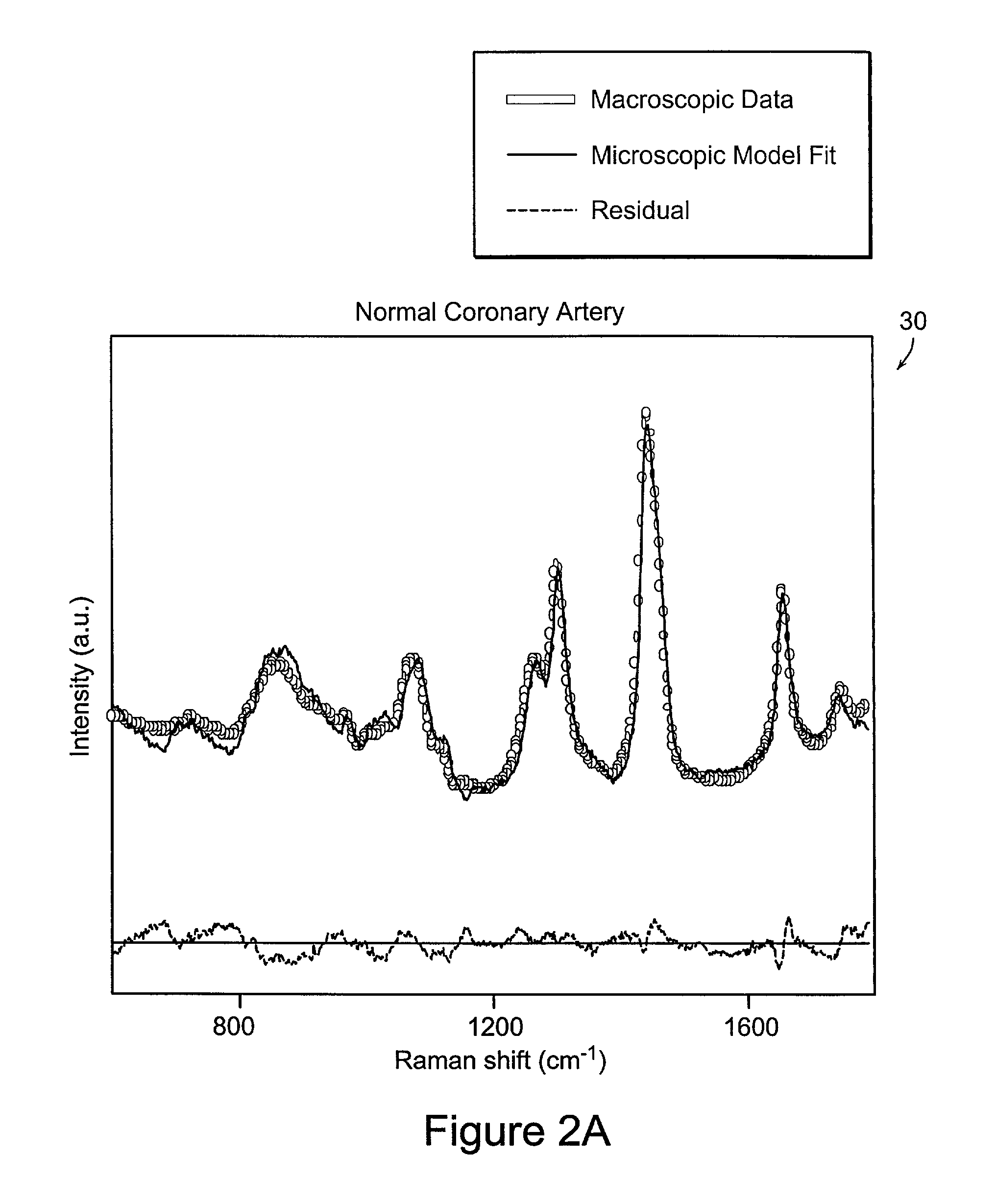
InactiveUS7647092B2Rapid and natureAccurate assessmentSurgeryScattering properties measurementsCoronary artery diseaseSpectroscopy
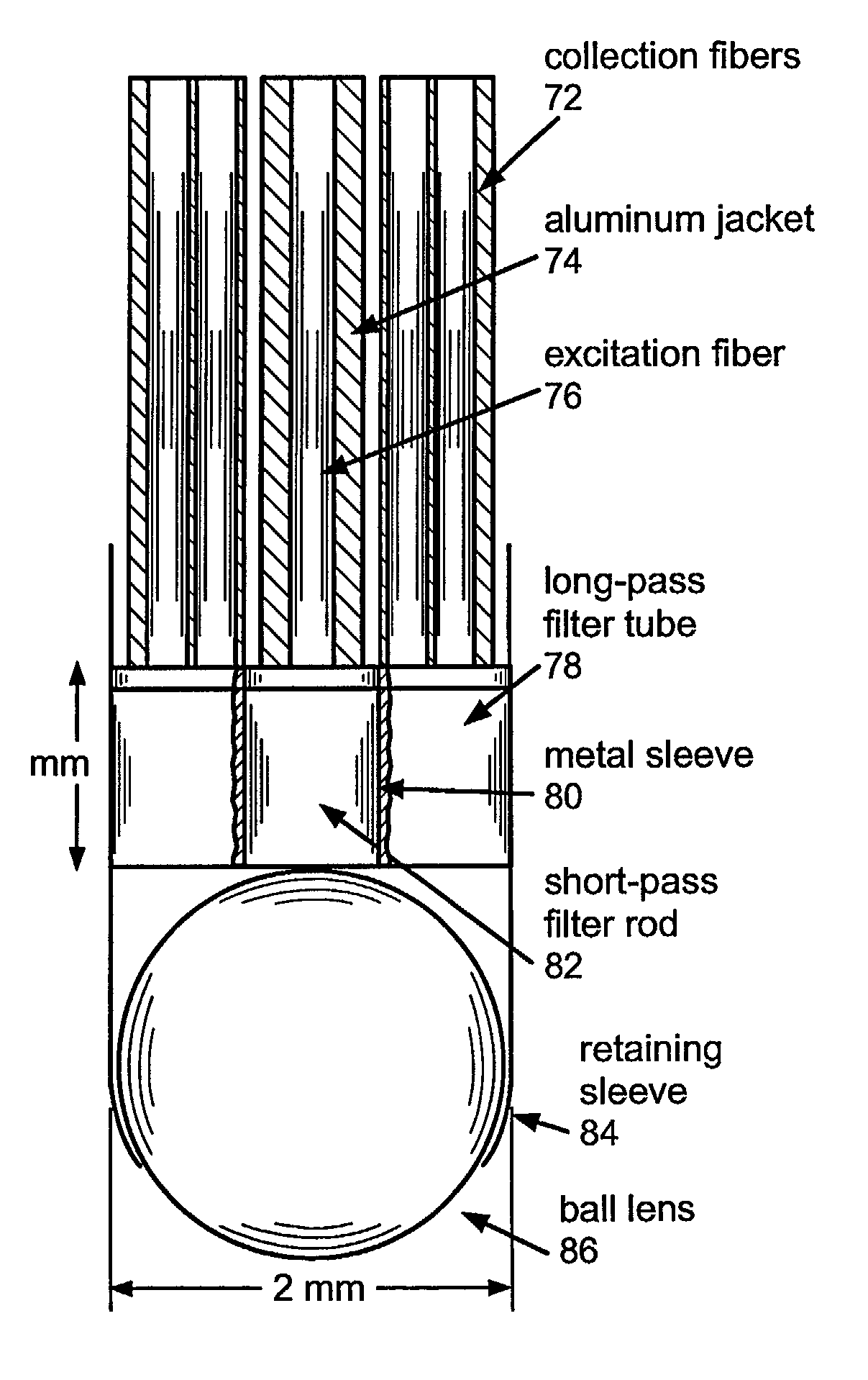
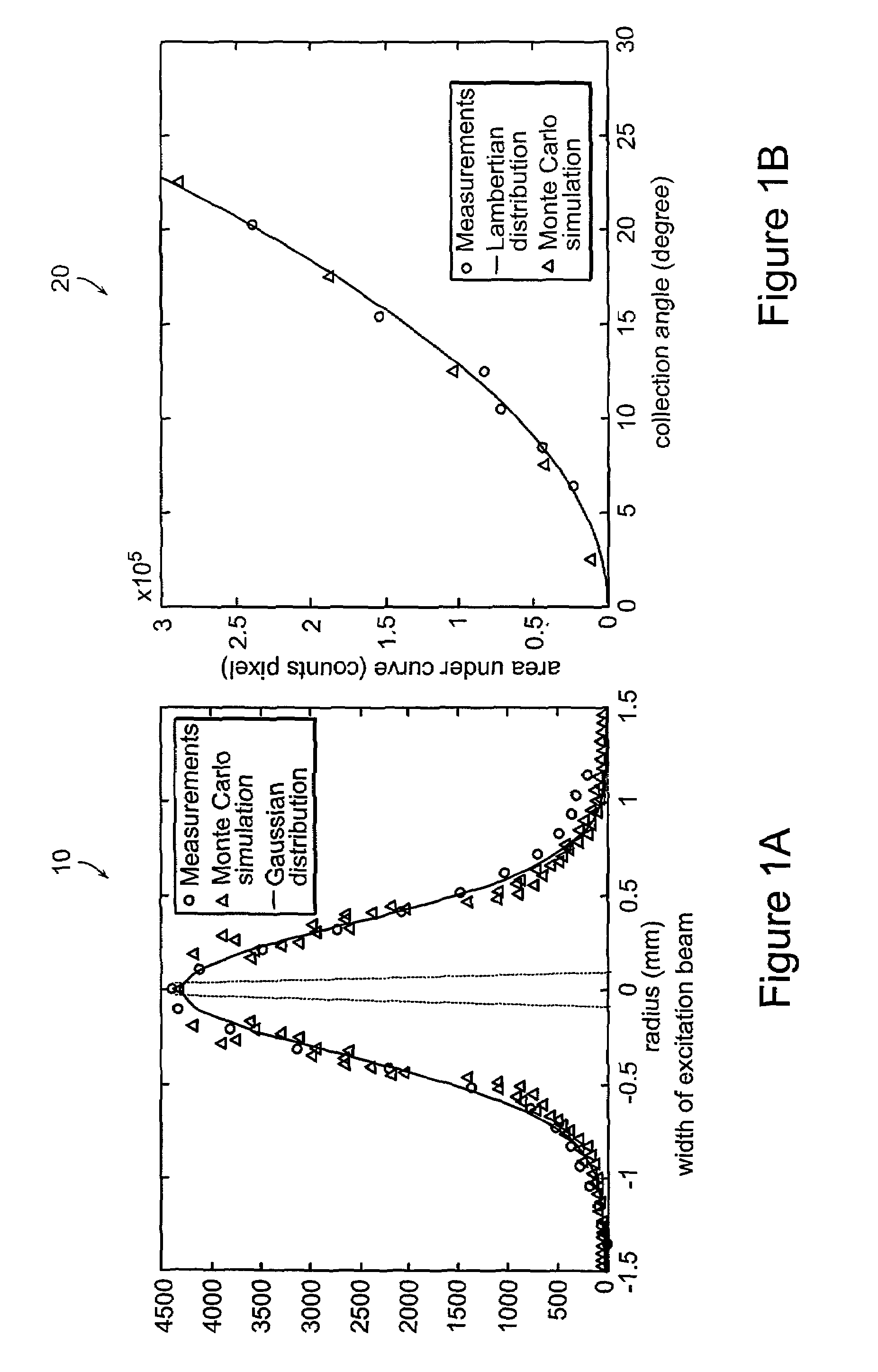
The system and method of the present invention relates to using spectroscopy, for example, Raman spectroscopic methods for diagnosis of tissue conditions such as vascular disease or cancer. In accordance with a preferred embodiment of the present invention, a system for measuring tissue includes a fiber optic probe having a proximal end, a distal end, and a diameter of 2 mm or less. This small diameter allows the system to be used for the diagnosis of coronary artery disease or other small lumens or soft tissue with minimal trauma. A delivery optical fiber is included in the probe coupled at the proximal end to a light source. A filter for the delivery fibers is included at the distal end. The system includes a collection optical fiber (or fibers) in the probe that collects Raman scattered radiation from tissue, the collection optical fiber is coupled at the proximal end to a detector. A second filter is disposed at the distal end of the collection fibers. An optical lens system is disposed at the distal end of the probe including a delivery waveguide coupled to the delivery fiber, a collection waveguide coupled to the collection fiber and a lens.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Cytological methods for detecting a disease condition such as malignancy by Raman spectroscopic imaging
InactiveUS20060281068A1Superior resolution and intensitySensitive assessmentRadiation pyrometryMicrobiological testing/measurementEpitheliumCancer cell
Raman molecular imaging (RMI) is used to detect mammalian cells of a particular phenotype. For example the disclosure includes the use of RMI to differentiate between normal and diseased cells or tissues, e.g., cancer cells as well as in determining the grade of said cancer cells. In a preferred embodiment benign and malignant lesions of bladder and other tissues can be distinguished, including epithelial tissues such as lung, prostate, kidney, breast, and colon, and non-epithelial tissues, such as bone marrow and brain. Raman scattering data relevant to the disease state of cells or tissue can be combined with visual image data to produce hybrid images which depict both a magnified view of the cellular structures and information relating to the disease state of the individual cells in the field of view. Also, RMI techniques may be combined with visual image data and validated with other detection methods to produce confirm the matter obtained by RMI.
Owner:CHEMIMAGE CORP
Pathogen Detection Using Coherent Anti-Stokes Raman Scattering Microscopy
The invention provides a system and method for automatic real-time monitoring for the presence of a pathogen in water using coherent anti-stokes Raman scattering (CARS) microscopy. Water sample trapped in a trapping medium is provided to a CARS imager. CARS images are provided to a processor for automatic analyzing for the presence of image artifacts having pre-determined features characteristic to the pathogen. If a match is found, a CARS spectrum is taken and compared to a stored library of reference pathogen-specific spectra for pathogen identification. The system enables automatic pathogen detection in flowing water in real time.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE +1
Method and apparatus for moleclular analysis using nanostructure-enhanced Raman spectroscopy
InactiveUS20060275911A1Microbiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by optical meansMolecular analysisBiopolymer
Devices and methods for detecting the constituent parts of biological polymers are disclosed. A molecular analysis device includes a molecule sensor and a molecule guide. The molecule sensor comprises a nanostructure, which is configured for producing a nanostructure-enhanced Raman scattered radiation when an excitation radiation irradiates at least a portion of a molecule disposed near the NERS structure.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Analyte stages including tunable resonant cavities and Raman signal-enhancing structures
An analyte stage for use in a spectroscopy system includes a tunable resonant cavity that is capable of resonating electromagnetic radiation having wavelengths less than about 10,000 nanometers, a substrate at least partially disposed within the cavity, and a Raman signal-enhancing structure at least partially disposed within the tunable resonant cavity. A spectroscopy system includes such an analyte stage, a radiation source, and a radiation detector. Methods for performing Raman spectroscopy include using such analyte stages and systems to tune a resonant cavity to resonate Raman scattered radiation that is scattered by an analyte.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Distributed optical fibre measurements
InactiveUS7284903B2Not distort measurementHigh measurement accuracyRadiation pyrometryMaterial analysis by optical meansRayleigh scatteringRayleigh Light Scattering
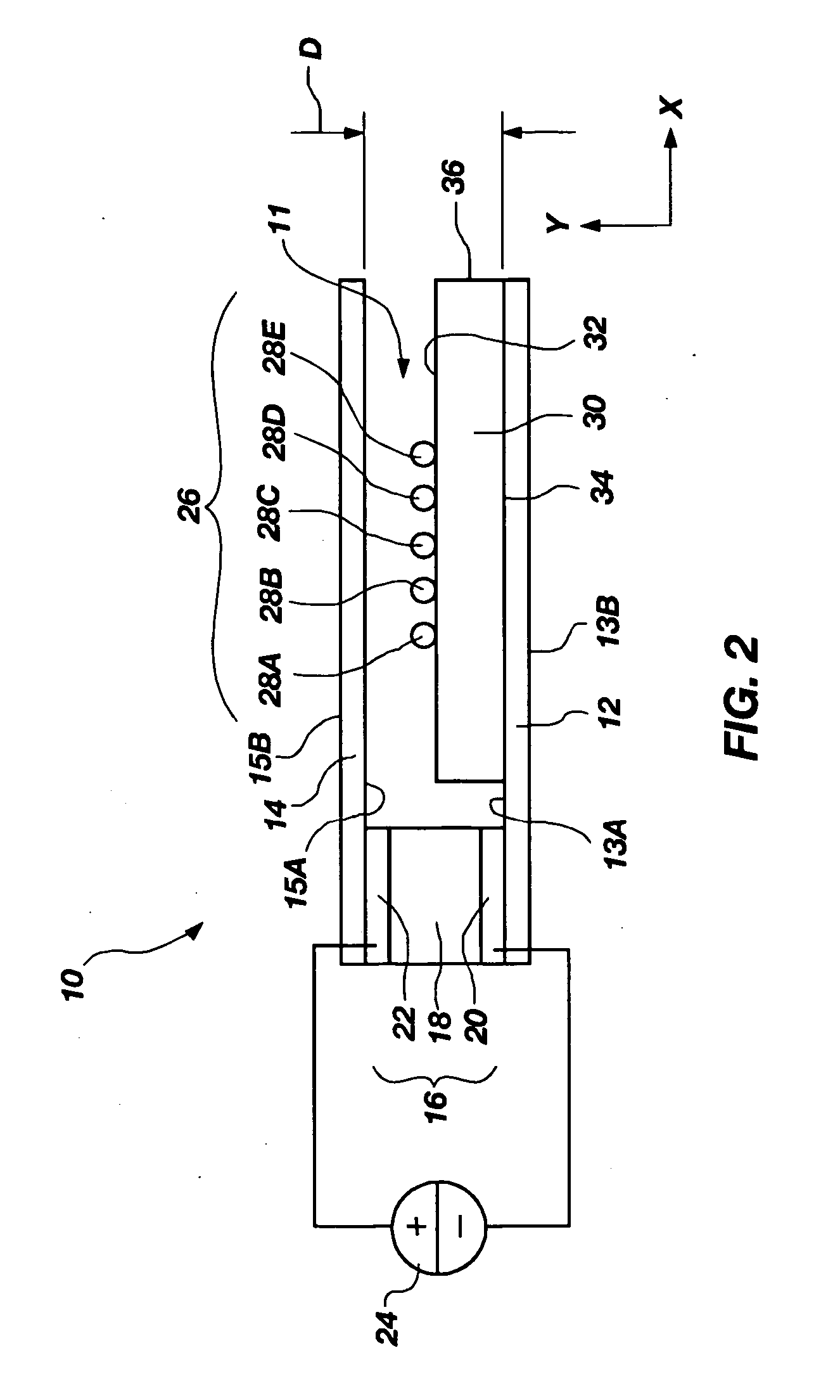
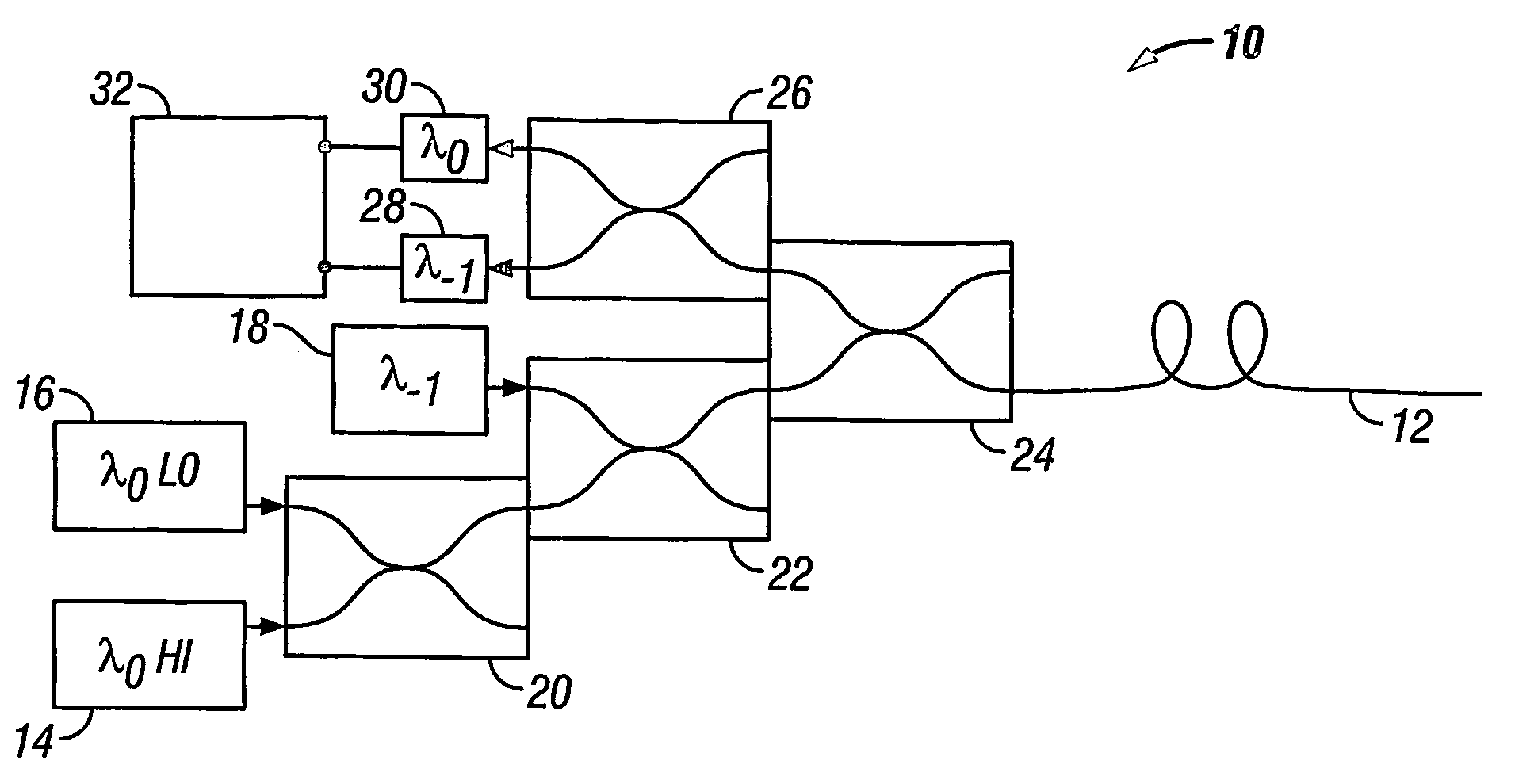
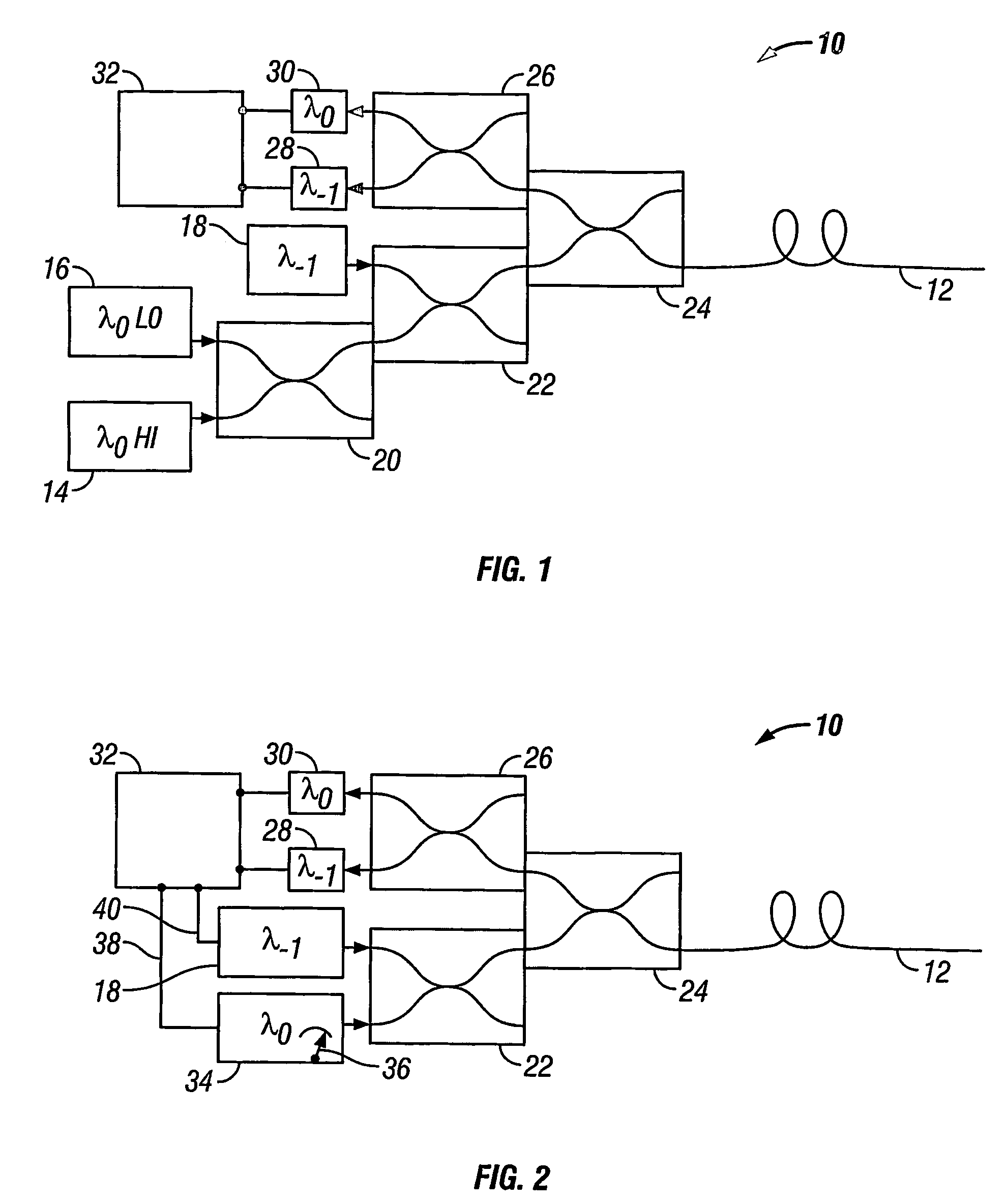
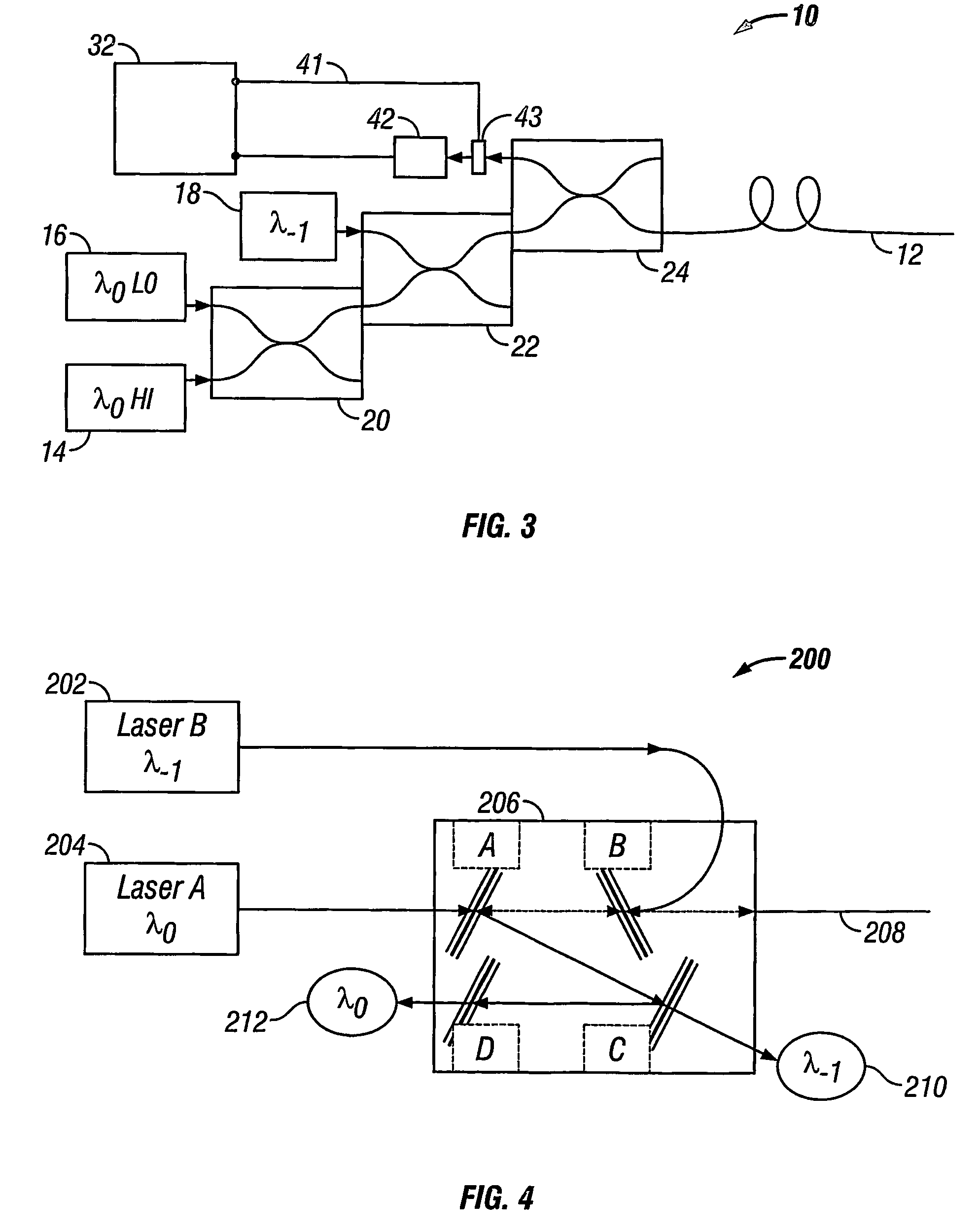
A method of obtaining a distributed measurement comprises deploying an optical fibre in a measurement region of interest, and launching into it a first optical signal at a first wavelength λ0 and a high power level, a second optical signal at a second wavelength λ−1, and a third optical signal at the first wavelength λ0 and a low power level. These optical signals generate backscattered light at the second wavelength λ−1 arising from Raman scattering of the first optical signal which is indicative of a parameter to be measured, at the first wavelength λ0 arising from Rayleigh scattering of the first optical signal, at the second wavelength λ—1 arising from Rayleigh scattering of the second optical signal, and at the first wavelength λ0 arising from Rayleigh scattering of the third optical signal. The backscattered light is detected to generate four output signals, and a final output signal is derived by normalising the Raman scattering signal to a function derived from the three Rayleigh scattering signals, which removes the effects of wavelength-dependent and nonlinear loss.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
System and method for coherent anti-stokes raman scattering endoscopy
A system is disclosed for detecting a signal field from a sample volume. The system includes a source system and an optical fiber system. The source system provides a first electromagnetic field at a first frequency and a second electromagnetic field at a second frequency that is different from the first frequency. The optical fiber system includes at least one optical fiber for guiding the first and second electromagnetic fields to the sample volume to generate coherent radiation characteristic of molecular vibrations by non-linear interaction of the first and second fields with the sample volume. The optical fiber system also receives the signal field resulting from the coherent radiation, and guides the signal field to a detector.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
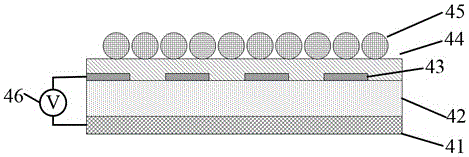
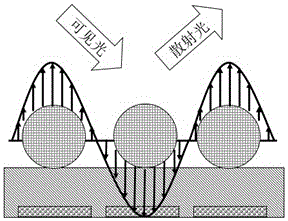
Micro fluid control detection device based on surface-enhanced Raman scattering active substrate
ActiveCN101792112AIncrease productivityHighly integratedNanostructure manufactureDecorative surface effectsFiberFluid control
The invention discloses a micro fluid control detection device based on surface-enhanced Raman scattering active substrate. The micro fluid control detection device is obtained by the method including the following steps: photoresist is coated on substrate in spinning way, prebaking, exposure, developing and fixing are sequentially carried out on the photoresist, so as to form photoresist graph in micro fluid shape; plasma dry etching is carried out on the photoresist, thus forming nano granular structure or nano fiber upright structure in vertical distribution on the substrate; the nano granular structure is a mask, anisotropic etching is carried out on the substrate, thus forming nano column on the substrate; metal nano granular layer is sputtered on the silicon nano column or nano fiber upright structure, so as to obtain surface-enhanced Raman scattering active substrate; and a silicon-PDMS double-layer structure SERS micro fluid control detection device which has no impurity interference and can be monitored in real time is formed by combining micro fluid device and processing technology thereof. The micro fluid control device not only can be used for detection of liquid analyte to be analyzed but also can be used for detection of colloid and gas analyte to be analyzed.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Method and apparatus for optical gain fiber having segments of differing core sizes
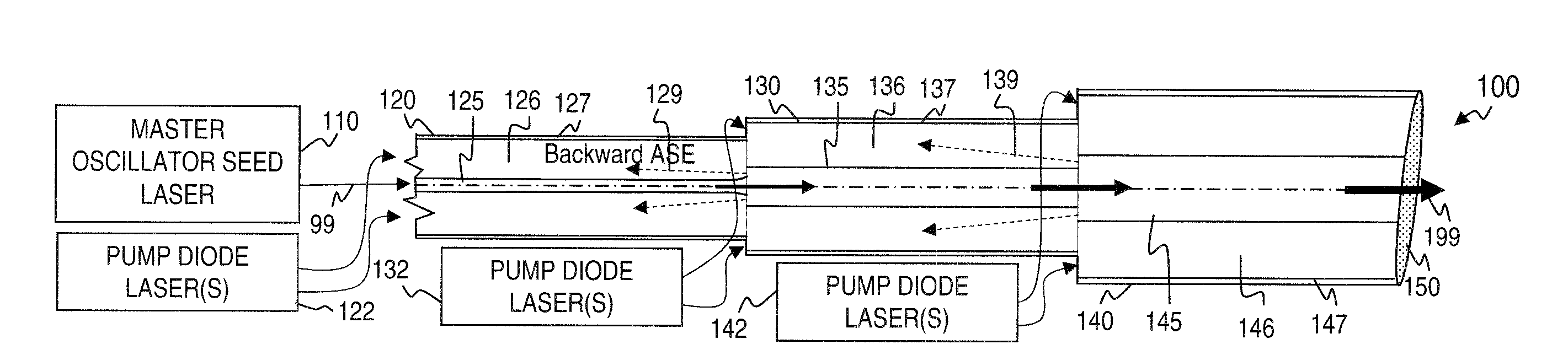
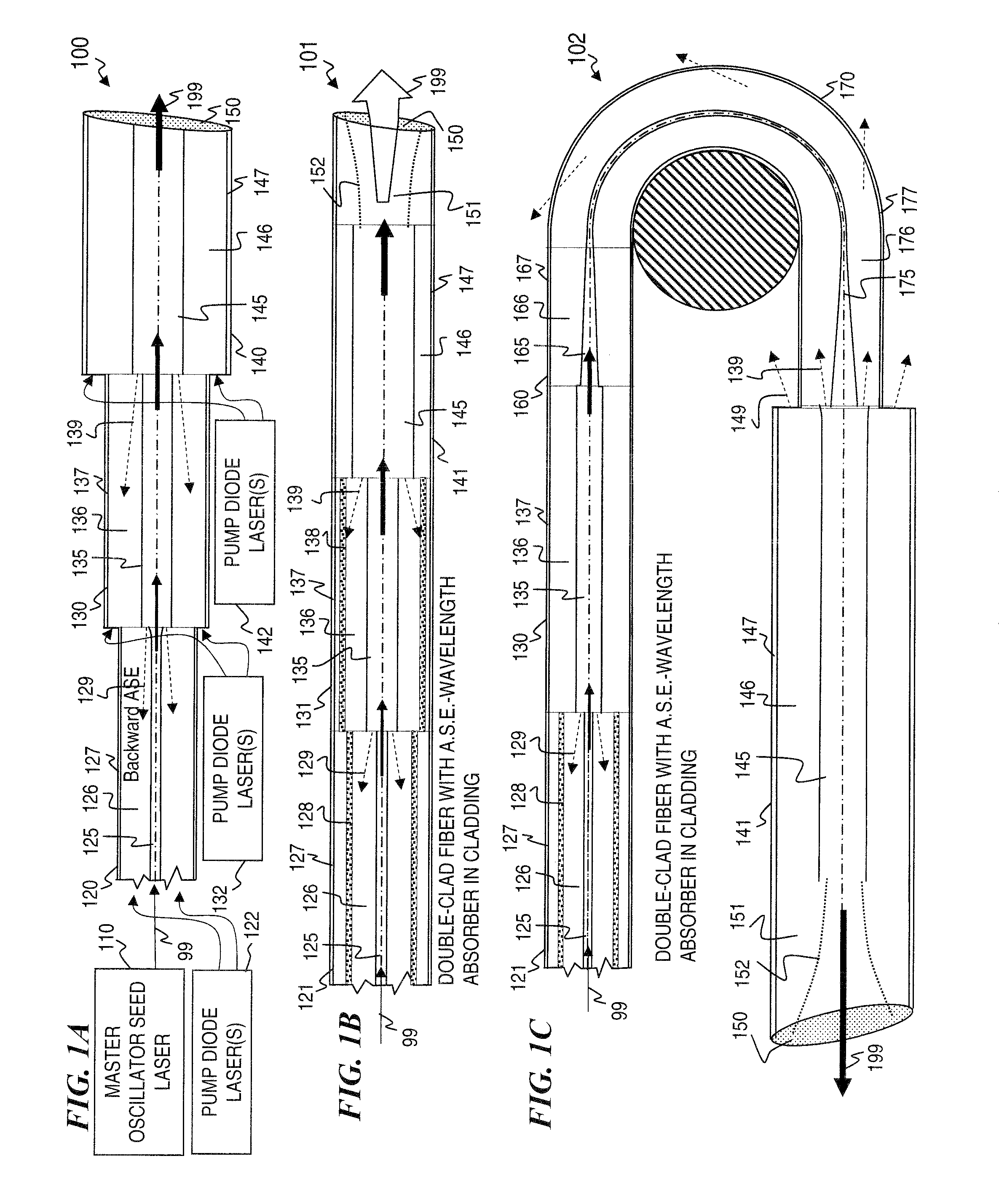
ActiveUS7768700B1Enhanced energy extractionReduce the amount requiredLaser using scattering effectsFibre transmissionFiberBandpass filtering
Apparatus and method for amplifying laser signals using segments of fibers of differing core diameters and / or differing cladding diameters to suppress amplified spontaneous emission and non-linear effects such as four-wave mixing (FWM), self-phase modulation, and stimulated Brillouin and / or Raman scattering (SBS / SRS). In some embodiments, different core sizes have different sideband spacings (spacing between the desired signal and wavelength-shifted lobes). Changing core sizes and providing phase mismatches prevent buildup of non-linear effects. Some embodiments further include a bandpass filter to remove signal other than the desired signal wavelength and / or a time gate to remove signal at times other than during the desired signal pulse. Some embodiments include photonic-crystal structures to define the core for the signal and / or the inner cladding for the pump. Some embodiments include an inner glass cladding to confine the signal in the core and an outer glass cladding to confine pump light in the inner cladding.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
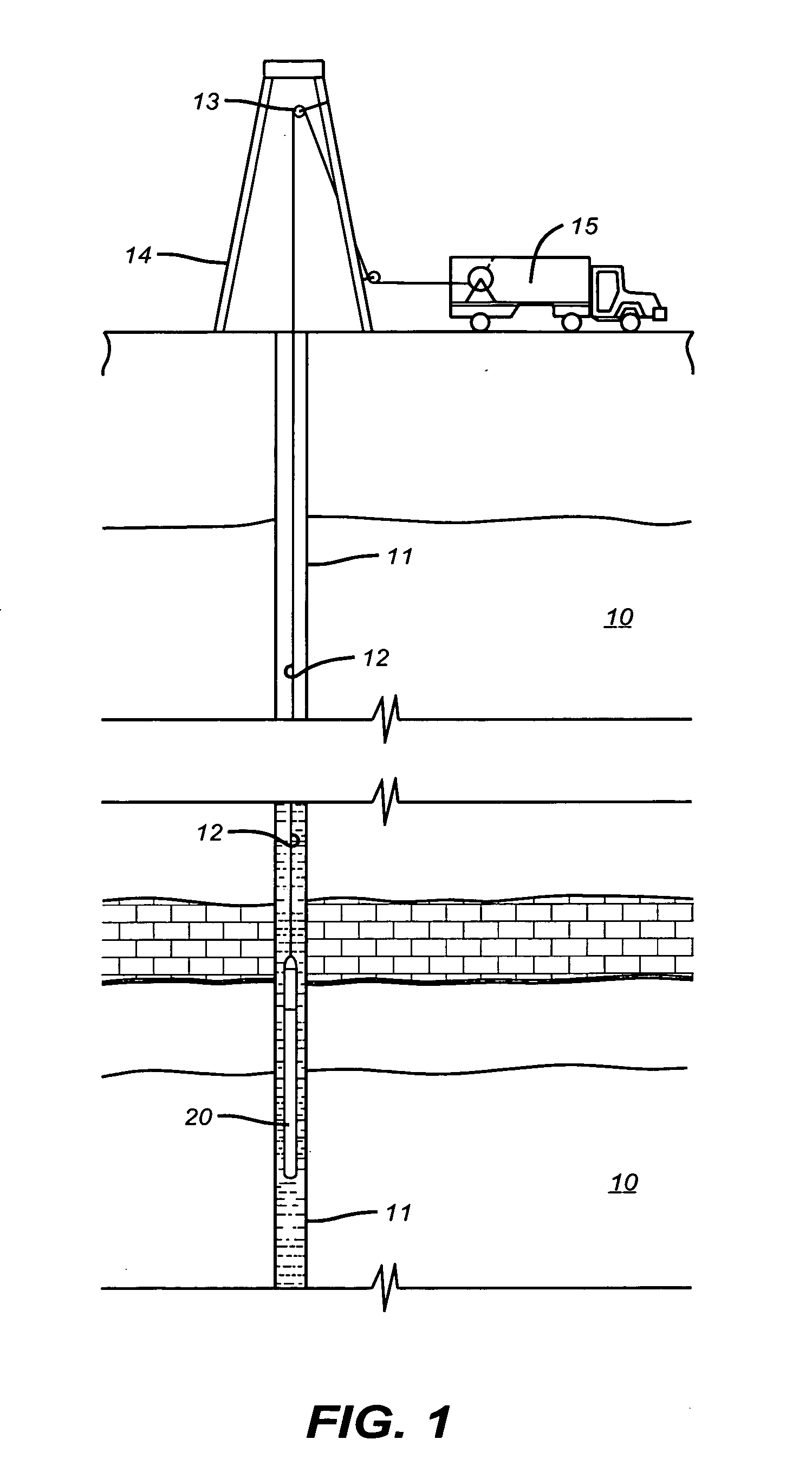
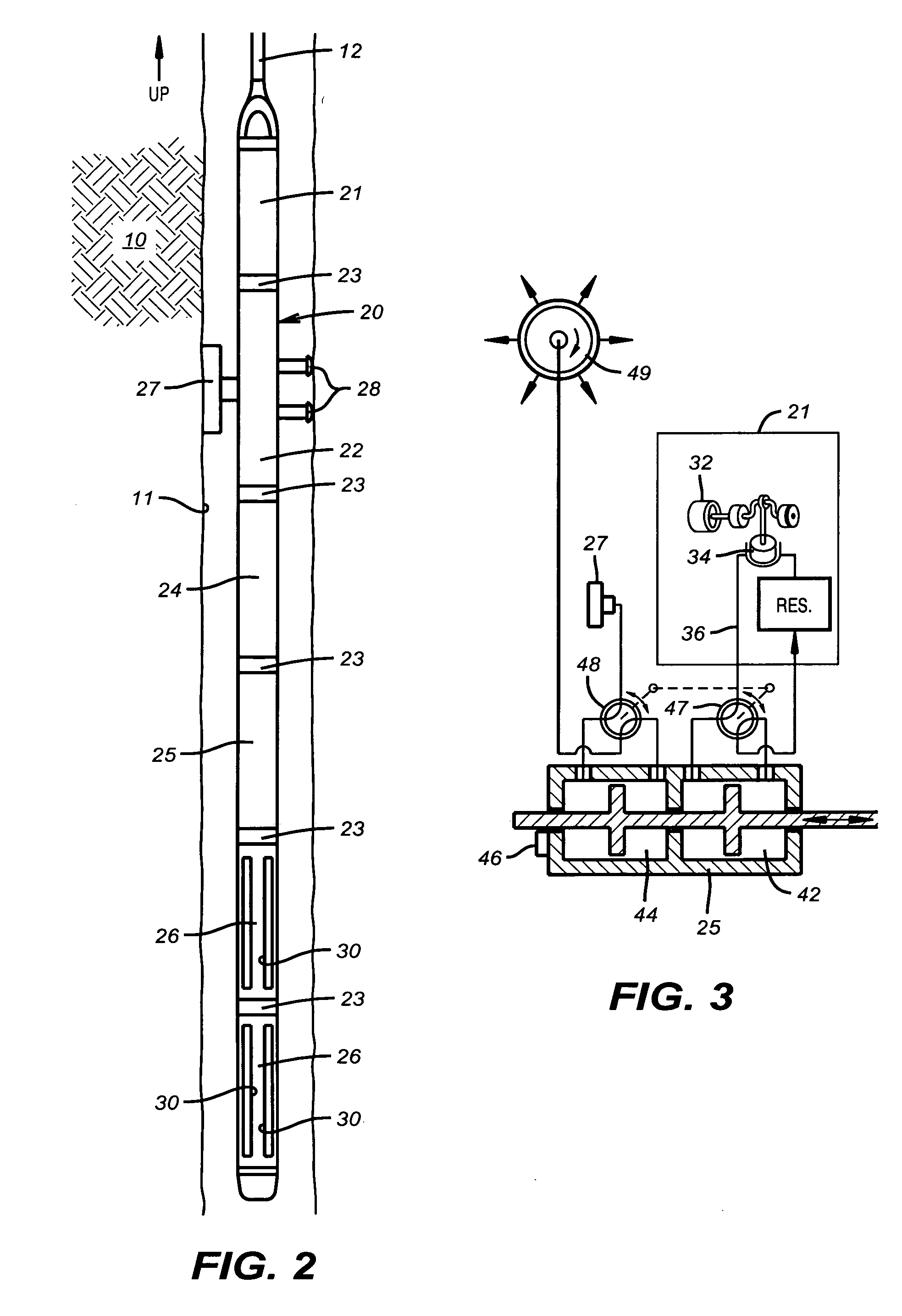
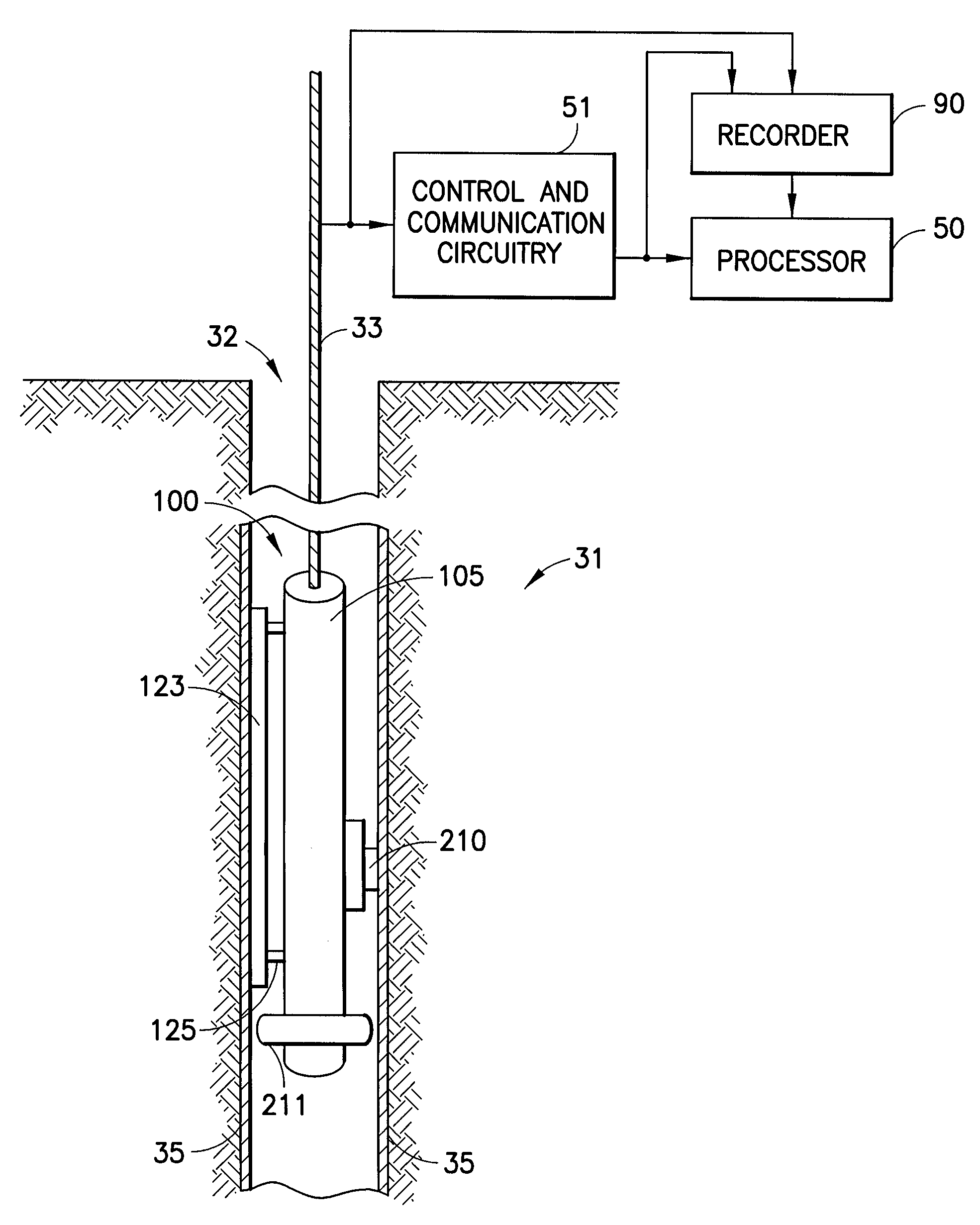
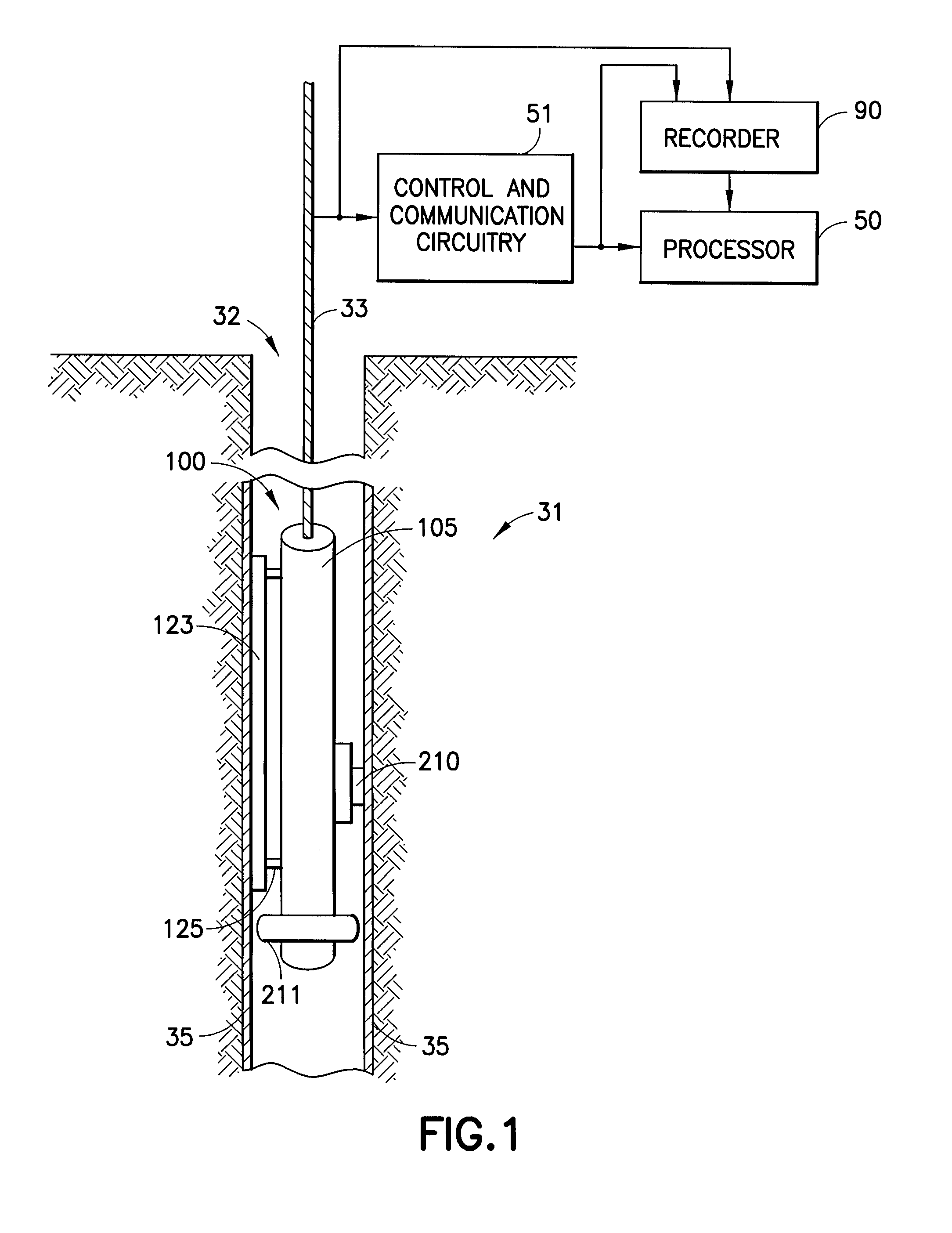
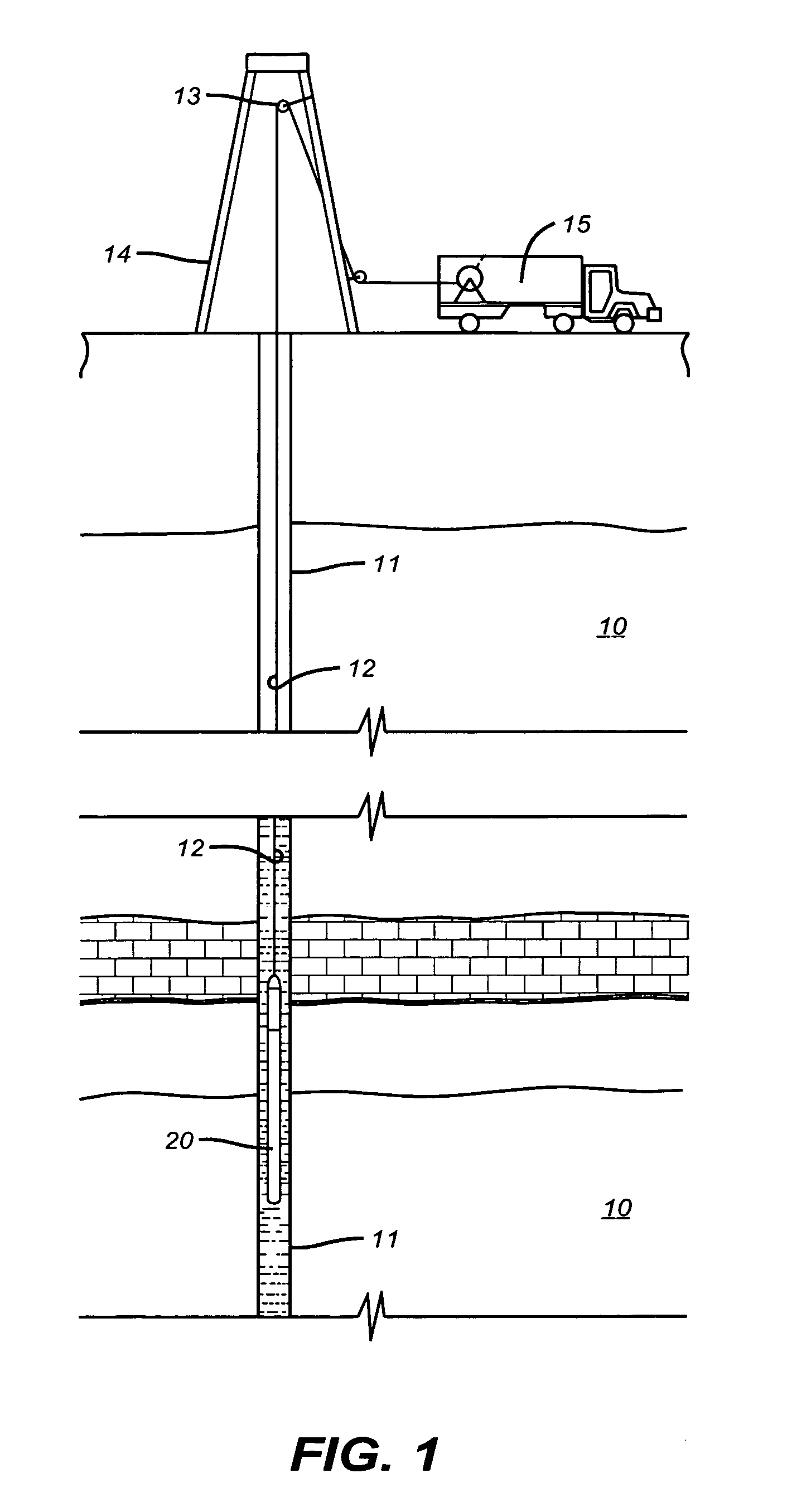
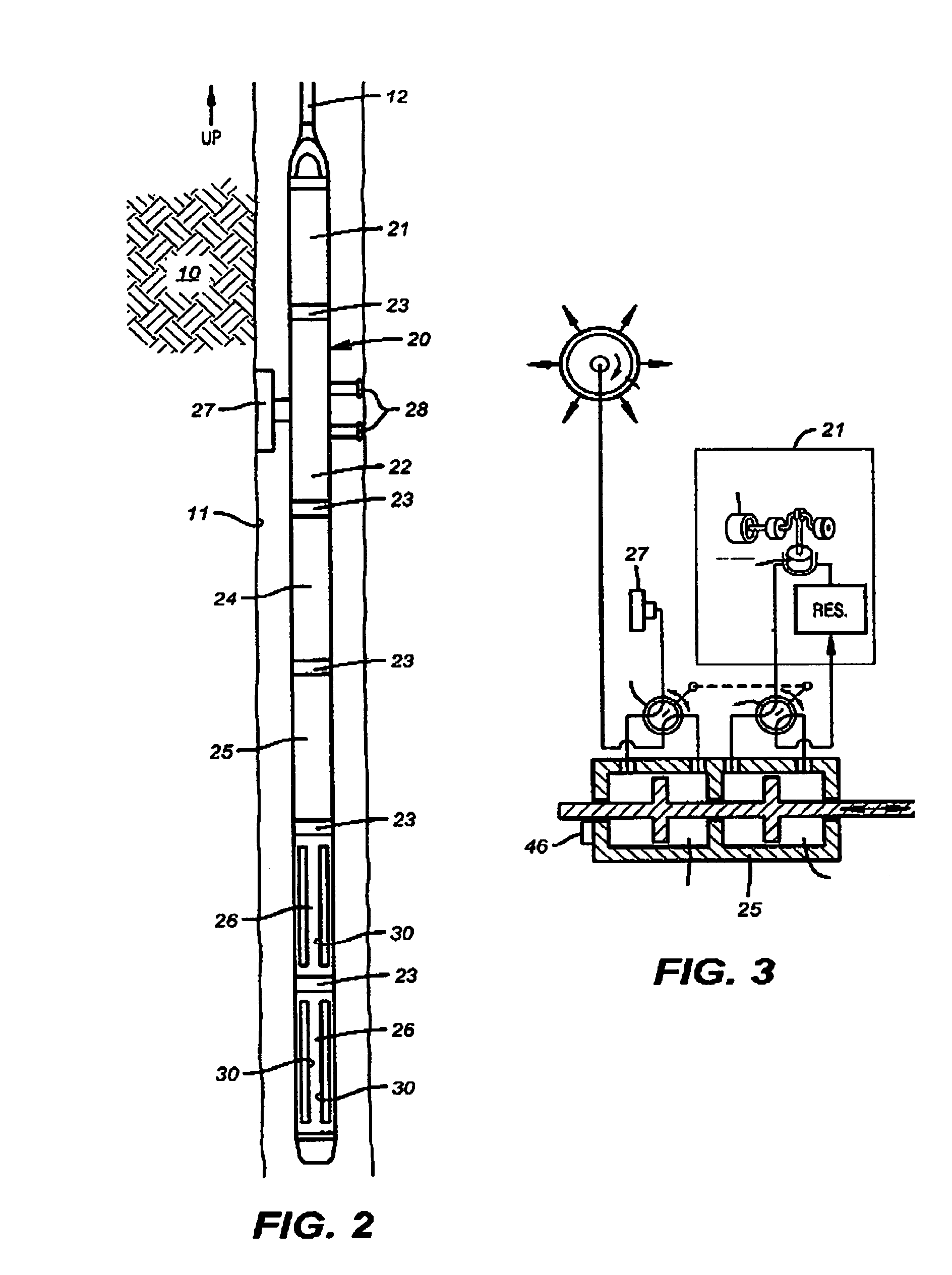
Downhole measurement of substances in earth formations
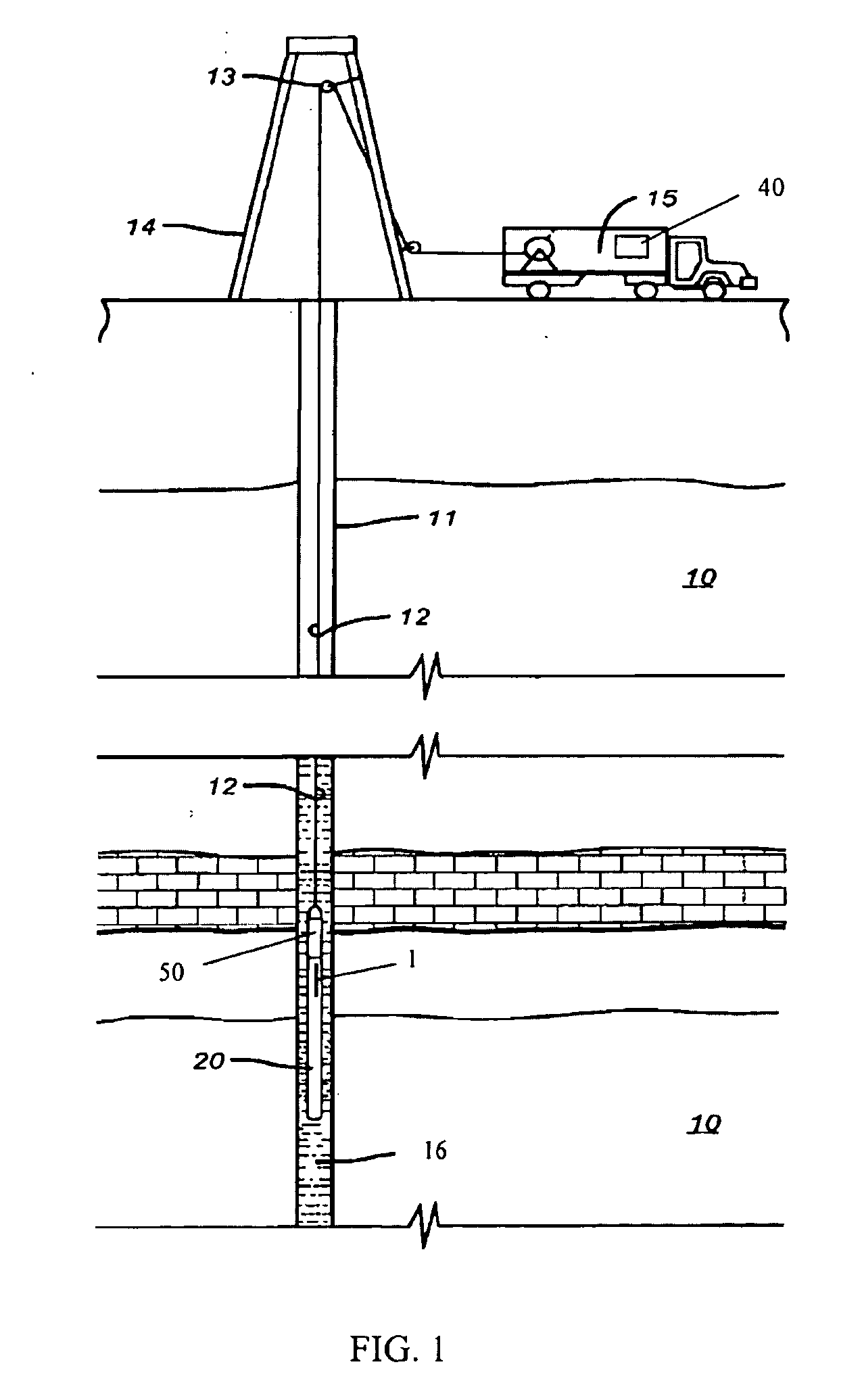
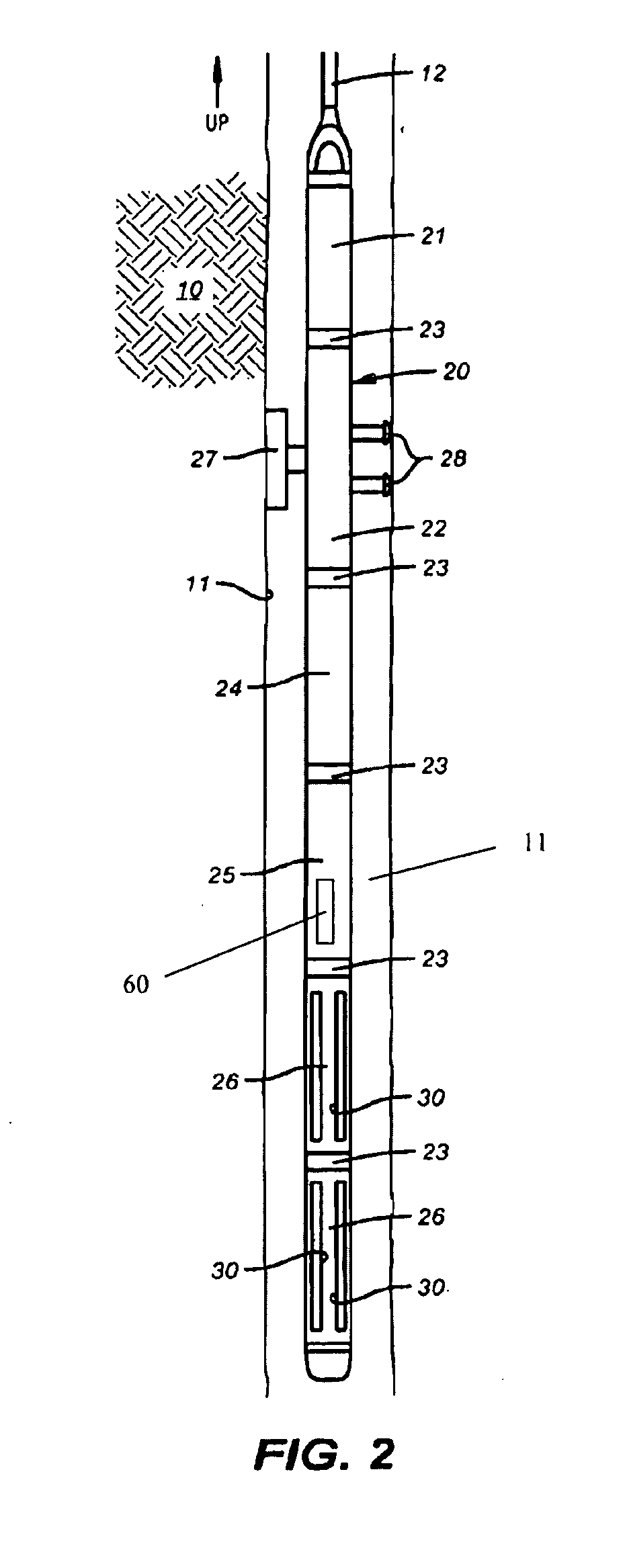
A method for determining a property of earth formations surrounding a borehole, including the following steps: isolating a region of the borehole, and obtaining a sample of borehole fluid from the isolated region; and implementing measurements, dowhole, of the Raman scattering of electromagnetic energy directed at the fluid sample; the property of the earth formations being determinable from the measurements. In a disclosed embodiment, the steps of isolating a region of the borehole and obtaining a sample of borehole fluid from the isolated region include: providing a logging device in the borehole in sealing engagement with the isolated region, causing formation fluid from the isolated region to flow in a flow line of the logging device, and providing a measurement cell in the logging device which receives the sample of formation fluid via the flow line.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
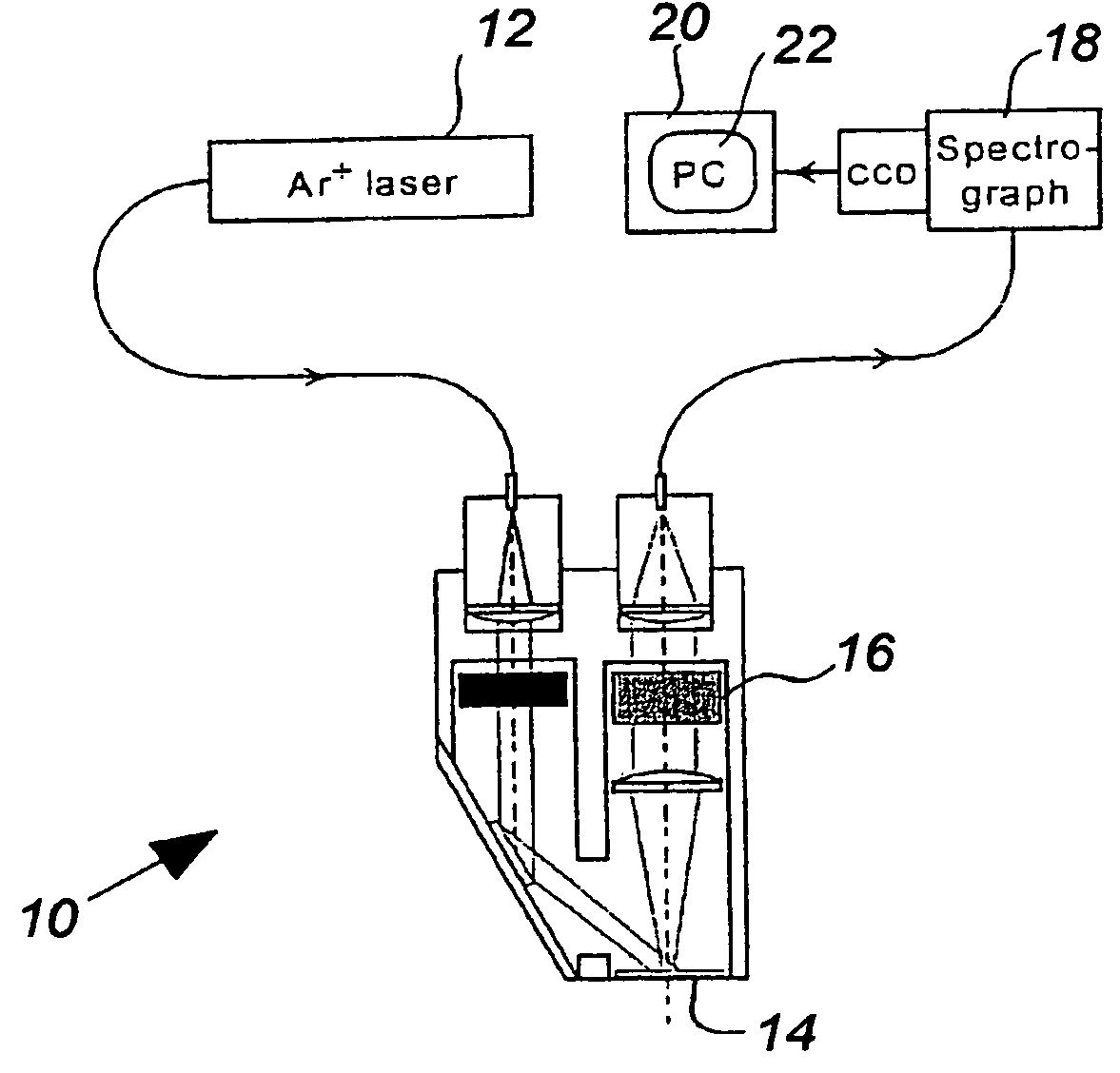
Raman spectroscopic system with integrating cavity
InactiveUS6975891B2Efficient collectionImprove power densityRadiation pyrometryRaman scatteringSpectral widthSpectrum analyzer
The present invention provides an apparatus for measurement of Raman scattered radiation comprising. The apparatus comprises at least one source of electromagnetic radiation for producing an electromagnetic radiation beam characterized by a narrow spectral width, an integrating cavity having an interior and an exterior, wherein a sample is placed in said interior. The integrating cavity further having at least one port for insertion of the sample in the interior and for transmission of the electromagnetic radiation into and out from the interior, the at least one port extending from the exterior to said interior of said integrating cavity. The integrating cavity also comprises a first optical element for transmitting the electromagnetic radiation into the interior of the integrating cavity through the at least one port, and a second optical element for collecting Raman scattered electromagnetic radiation from the sample through the at least one port. The apparatus also comprises a spectrum analyzer for determining spectral composition of the Raman scattered electromagnetic radiation, a detector for measuring the Raman scattered electromagnetic radiation; and a system for determining concentration of at least one chemical compound from the measured Raman scattered electromagnetic radiation. The apparatus may also comprise a radiation expanding element. A method for measuring the concentration of one or more chemical compounds in a sample using Raman scattering is also provided.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Method and apparatus for a tunable diode laser spectrometer for analysis of hydrocarbon samples
The present invention provides an down hole apparatus and method for ultrahigh resolution spectroscopy using a tunable diode laser (TDL) for analyzing a formation fluid sample downhole or at the surface to determine formation fluid parameters. In addition to absorption spectroscopy, the present invention can perform Raman spectroscopy on the fluid, by sweeping the wavelength of the TDL and detecting the Raman-scattered light using a narrow-band detector at a fixed wavelength. The spectrometer analyzes a pressurized well bore fluid sample that is collected downhole. The analysis is performed either downhole or at the surface onsite. Near infrared, mid-infrared and visible light analysis is also performed on the sample to provide an onsite surface or downhole analysis of sample properties and contamination level. The onsite and downhole analysis comprises determination of aromatics, olefins, saturates, gas oil ratio, API gravity and various other parameters which can be estimated by correlation, a trained neural network or a chemometric equation.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Applications of Raman scattering probes
InactiveUS20050206892A1Wide applicationExpected can be lowRadiation pyrometryRaman scatteringHomeland securityNanostructure
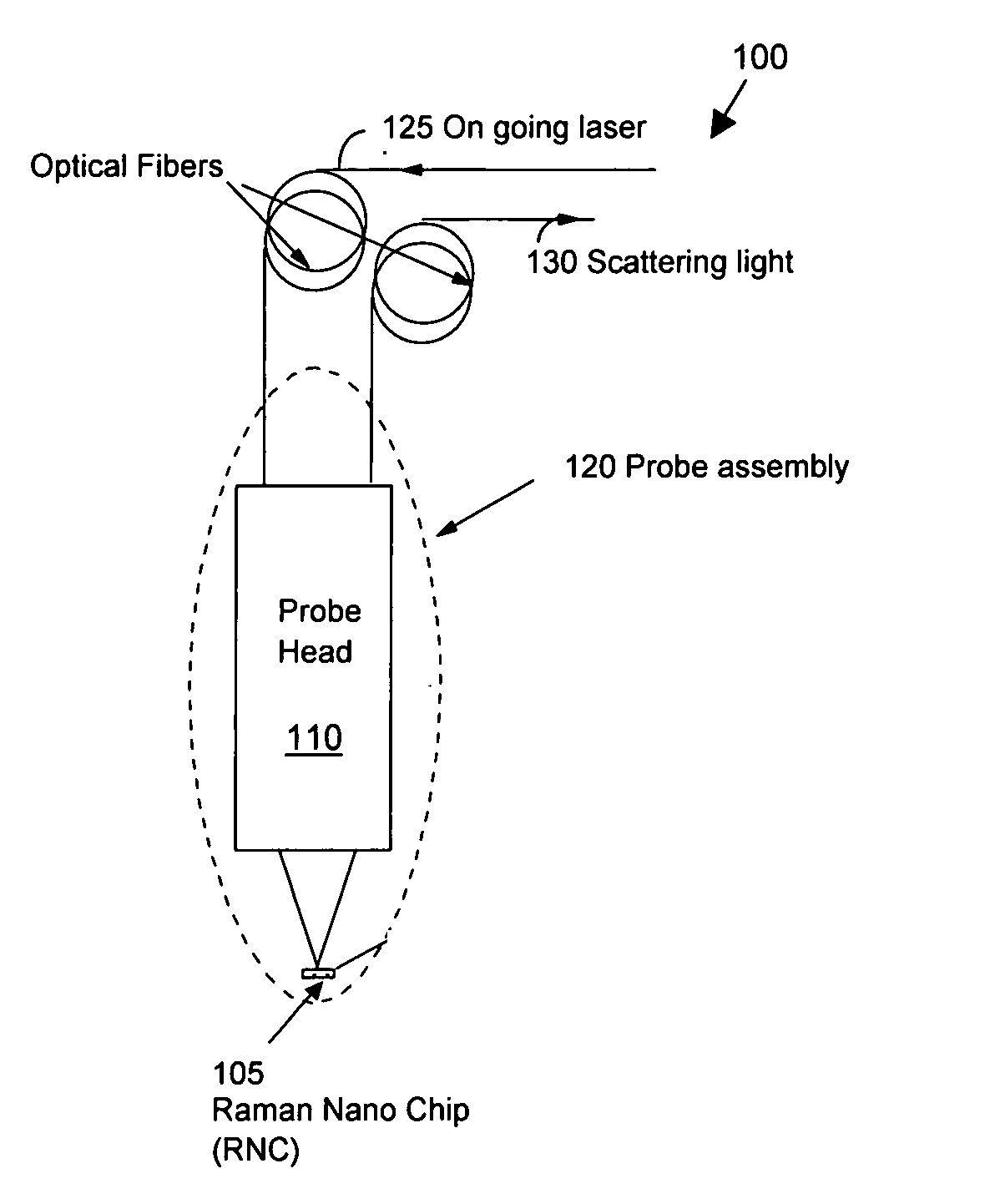
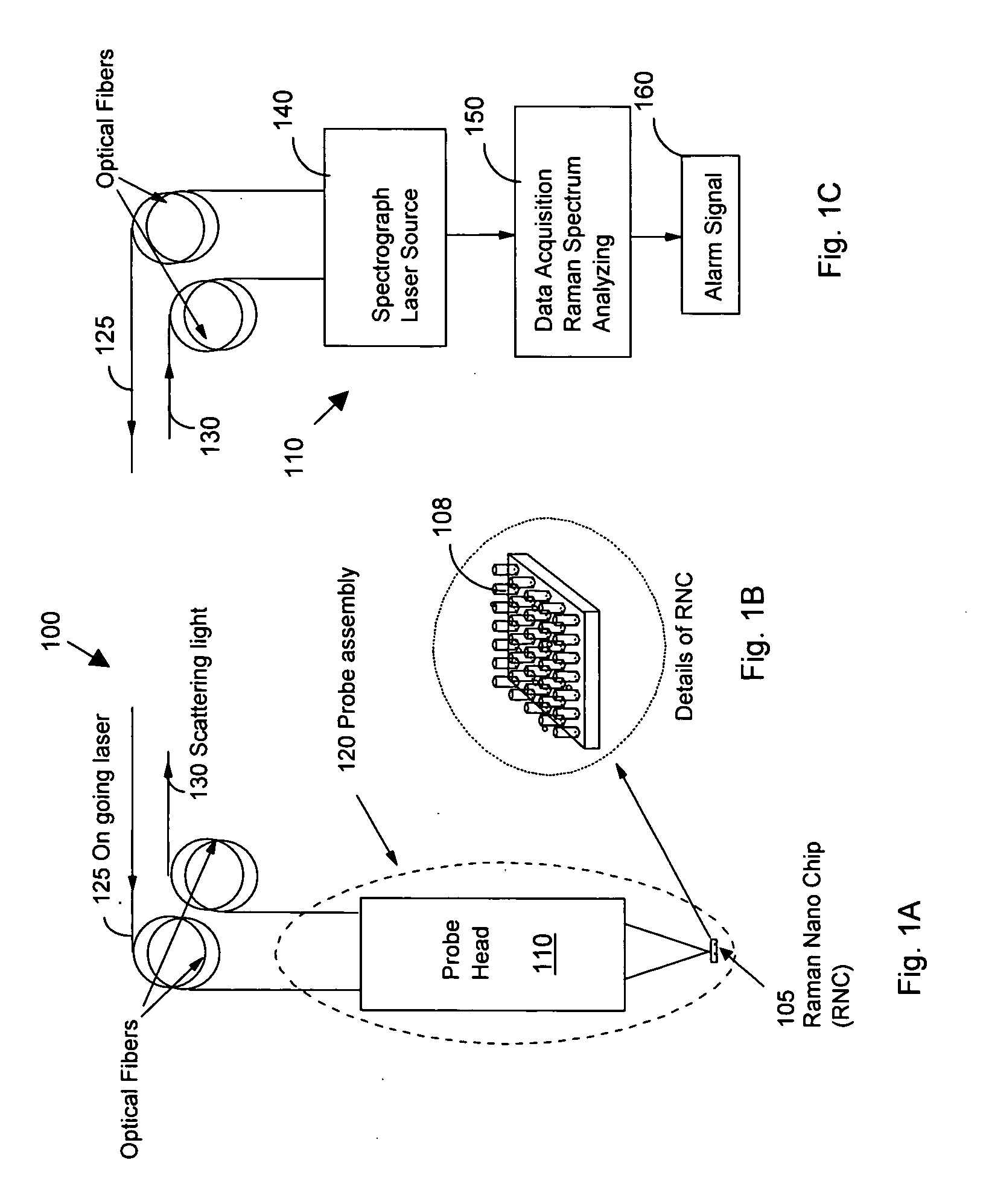
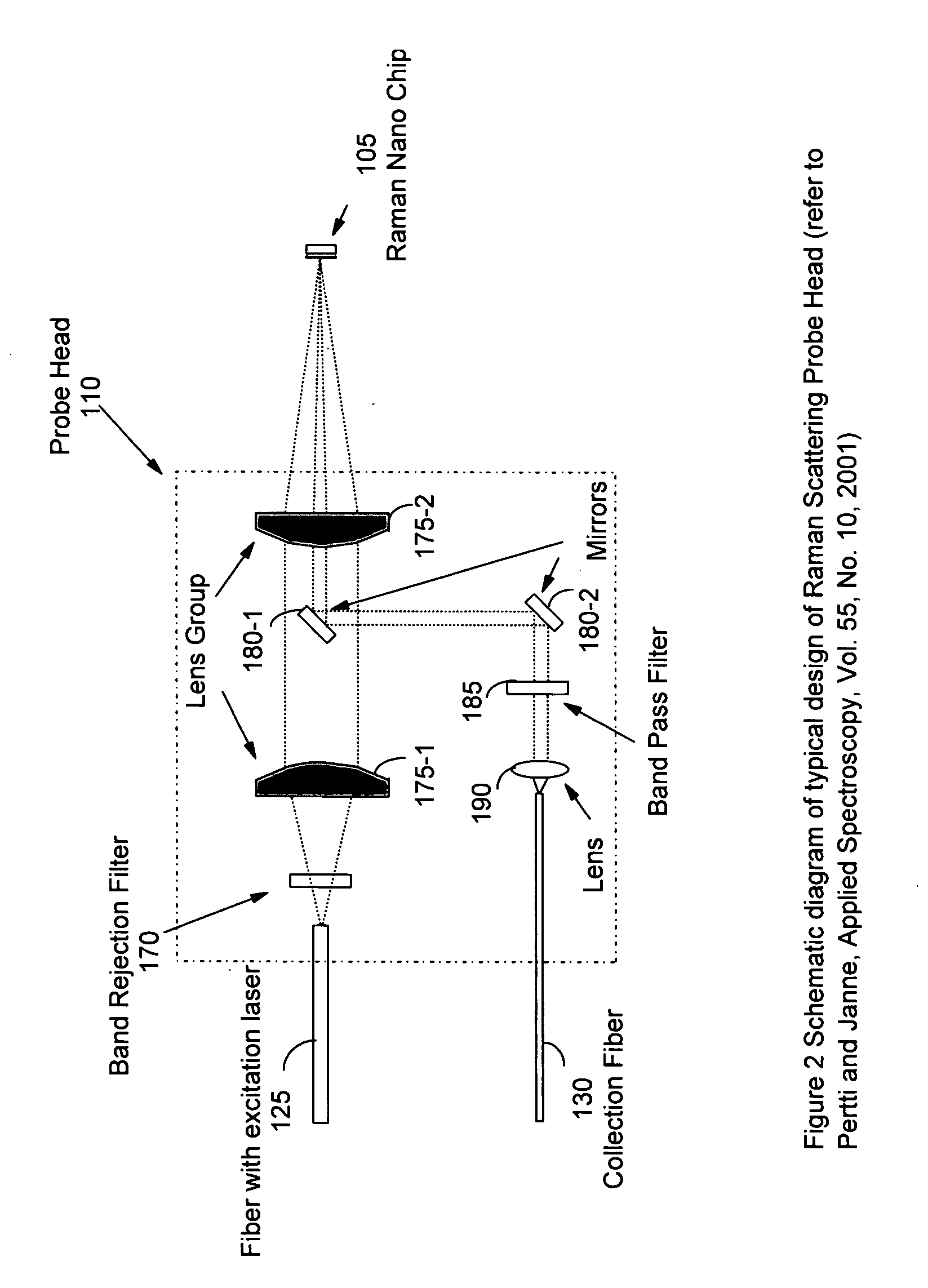
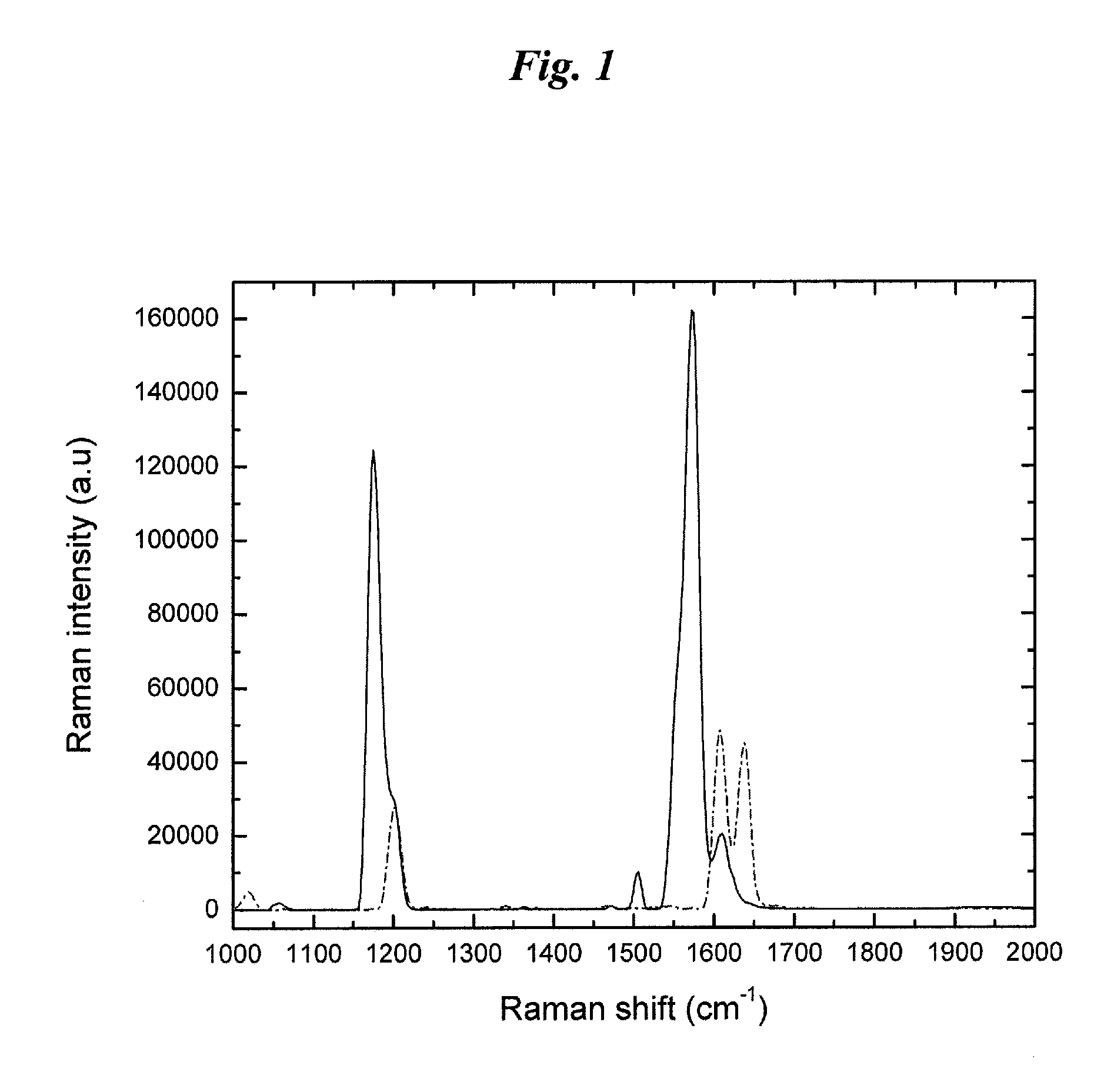
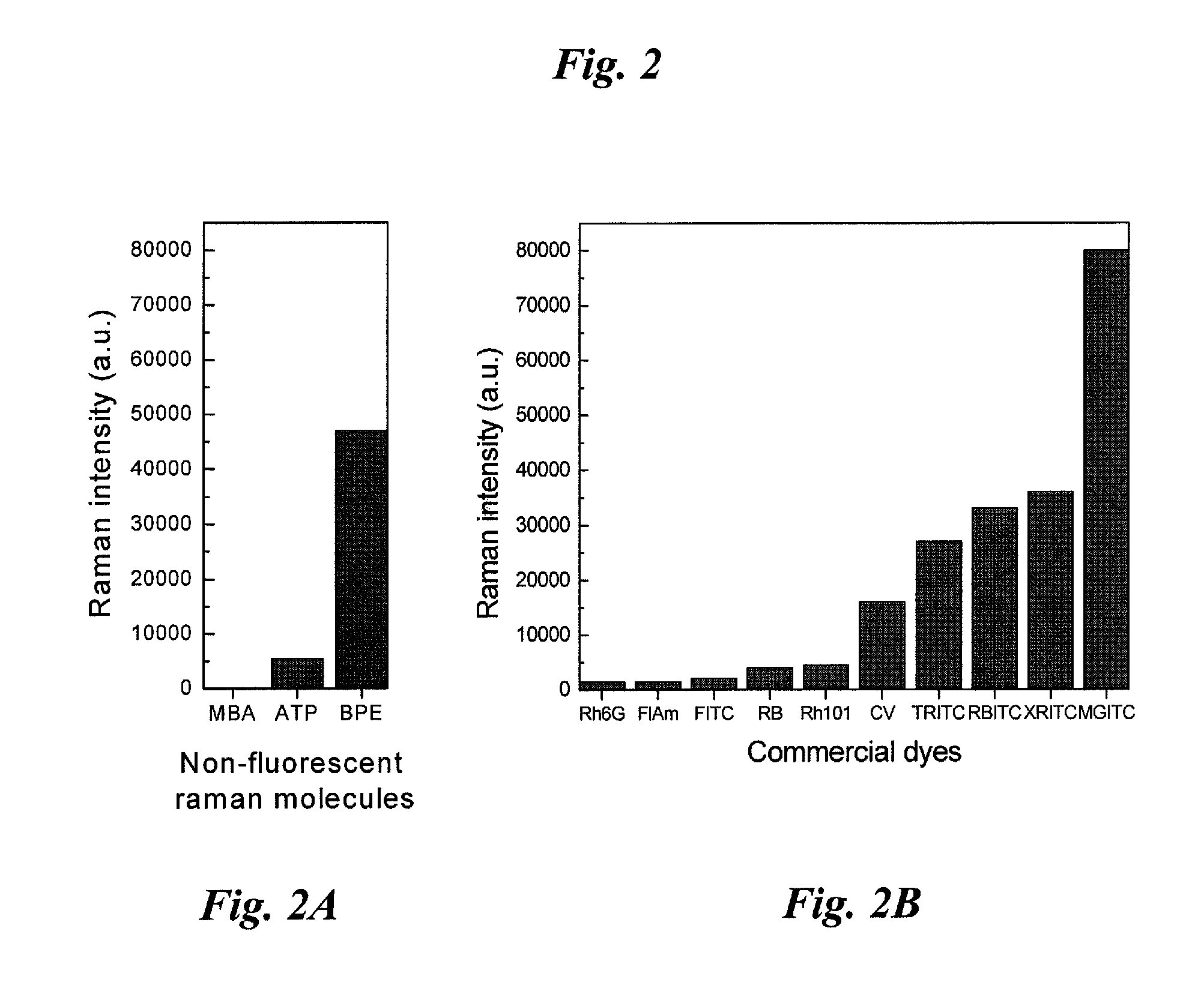
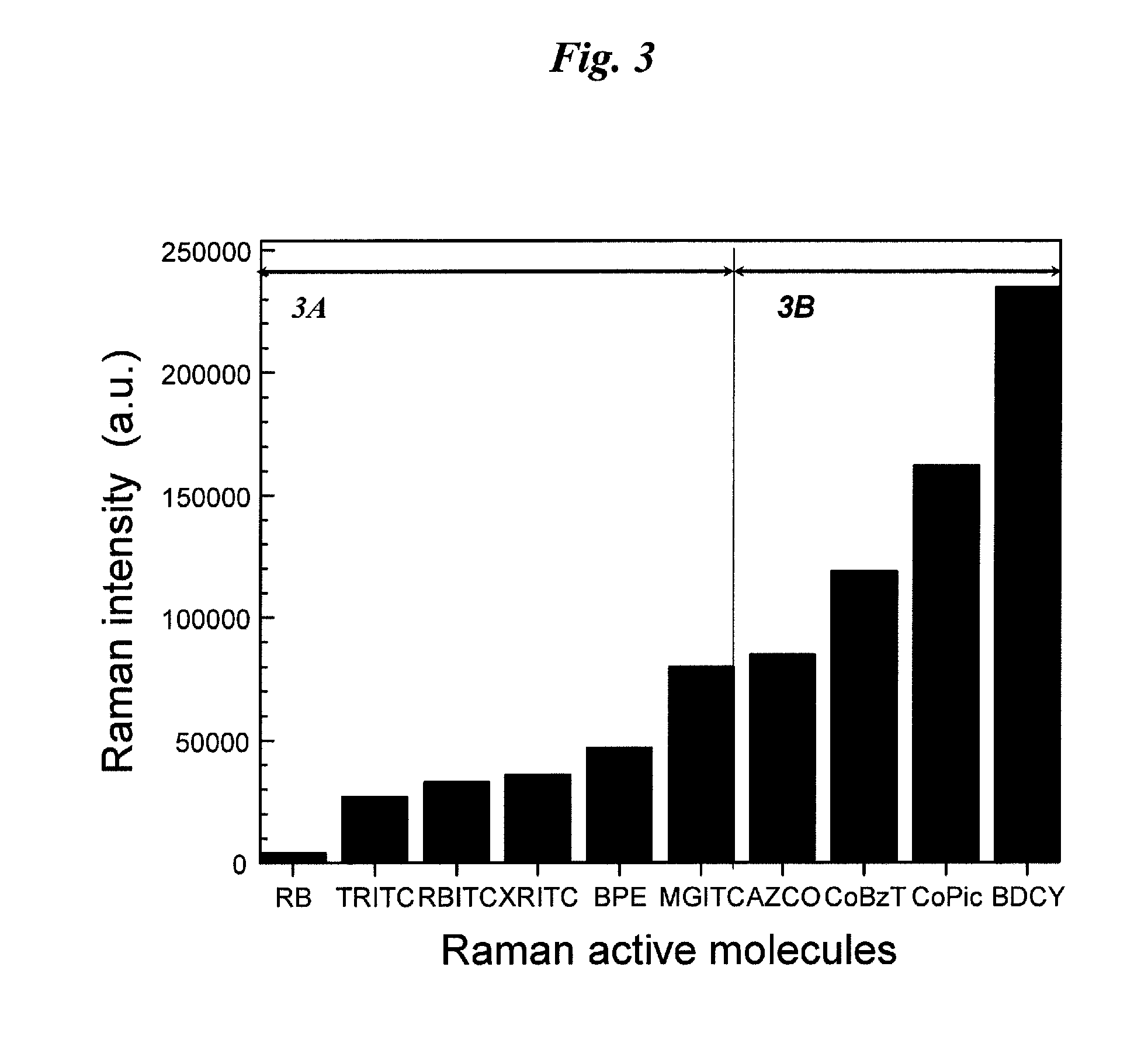
New and improved applications of Raman Scattering are disclosed. These applications may be implemented with or without using an enhanced nano-structured surface that is trademarked as the RamanNanoChip™ disclosed in a pending patent. As a RamanNanoChip™ provides much higher sensitivity in SERS compared with conventional enhance surface, broader scopes of applications are now enabled and can be practically implemented as now disclosed in this application. Furthermore, a wide range of applications is achievable as new and improved Raman sensing applications. By applying the analysis of Raman scattering spectrum, applications can be carried out to identify unknown chemical compositions to perform the tasks of homeland security; food, drug and drinking materials safety; early disease diagnosis; environmental monitoring; industrial process monitoring, precious metal and gem authentications, etc.
Owner:OPTOTRACE TECH
Near-infrared dyes as surface enhanced raman scattering reporters
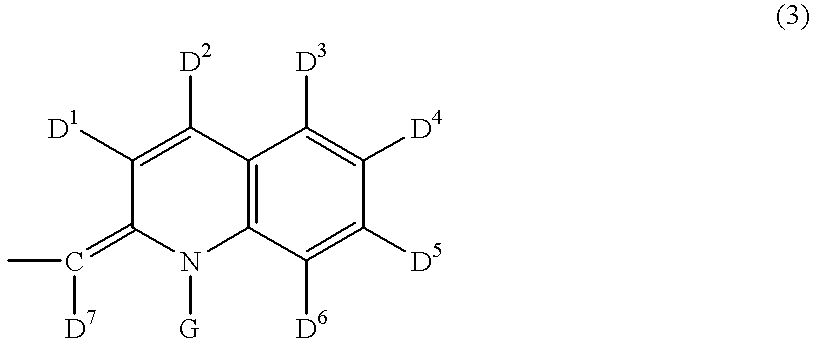
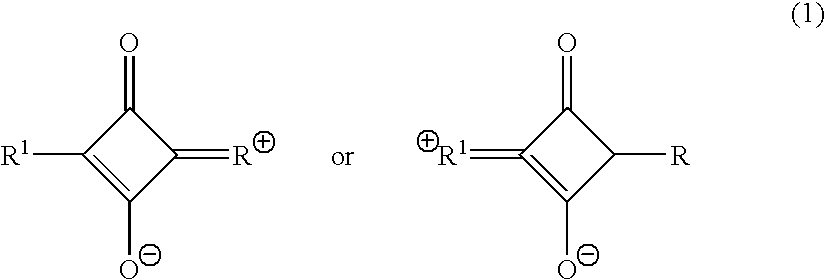
Nanoparticles comprising surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) reporter molecules of the formula A-Y and methods of their use are disclosed, wherein A is selected from the group consisting of:wherein X1 is CR4 or N; and Y is selected from the group consisting of:
Owner:BECTON DICKINSON & CO
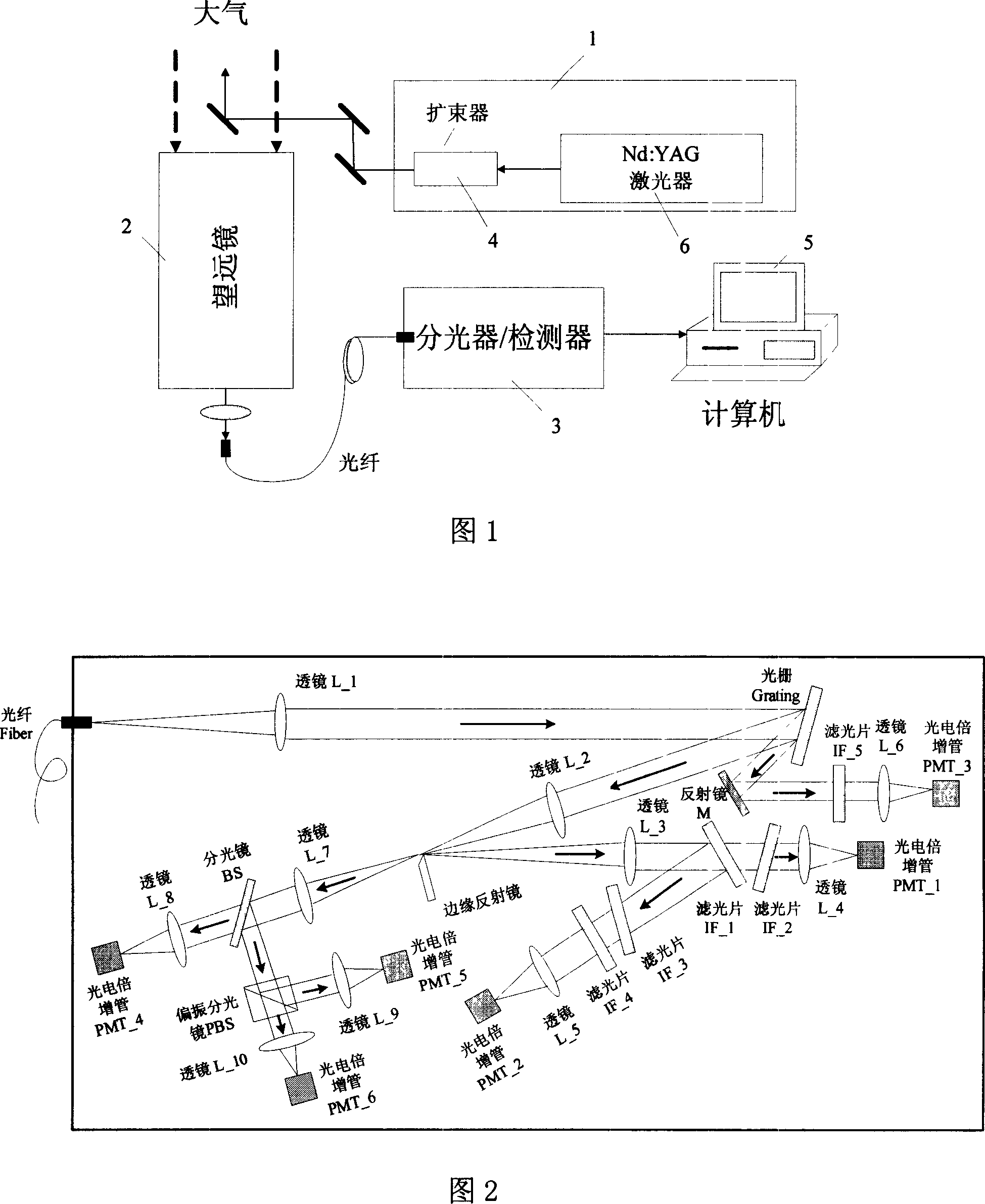
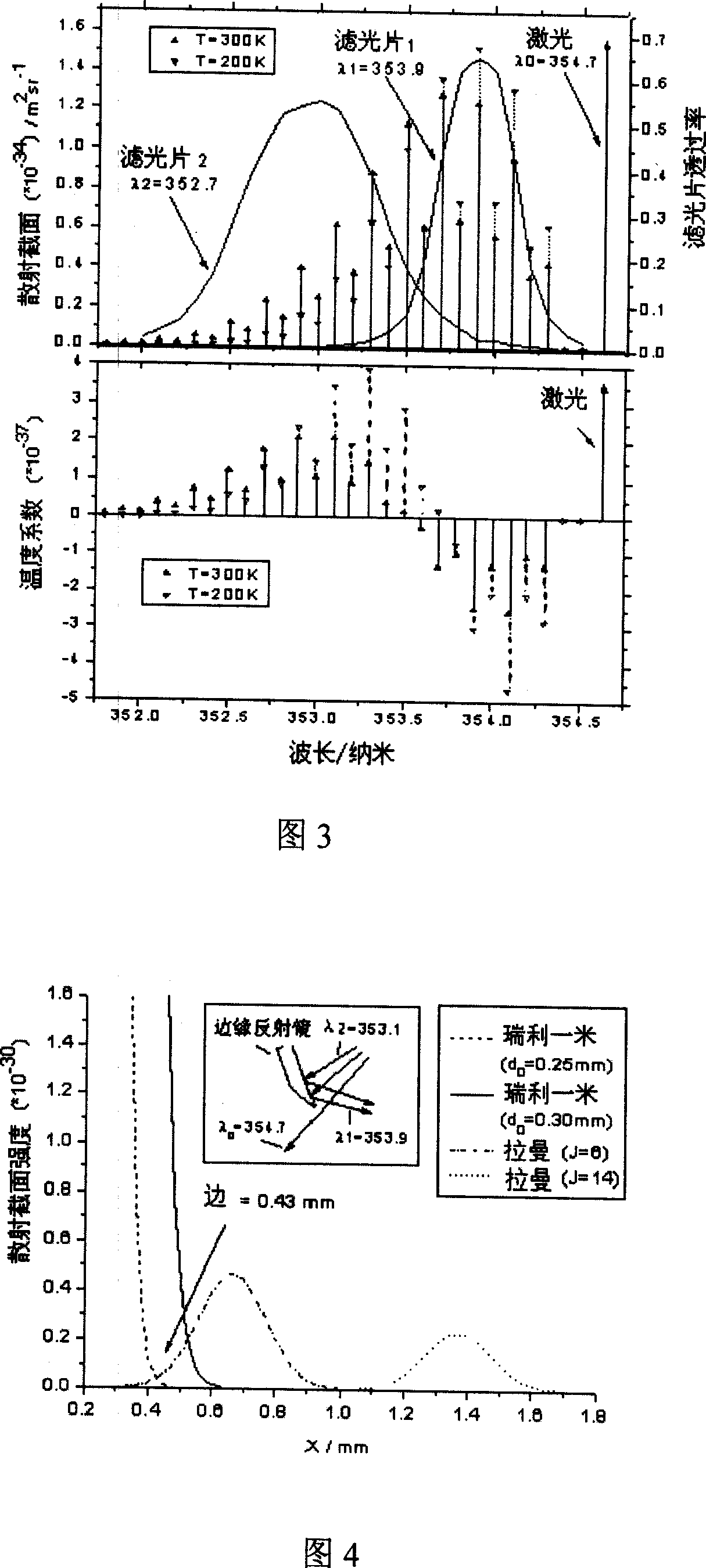
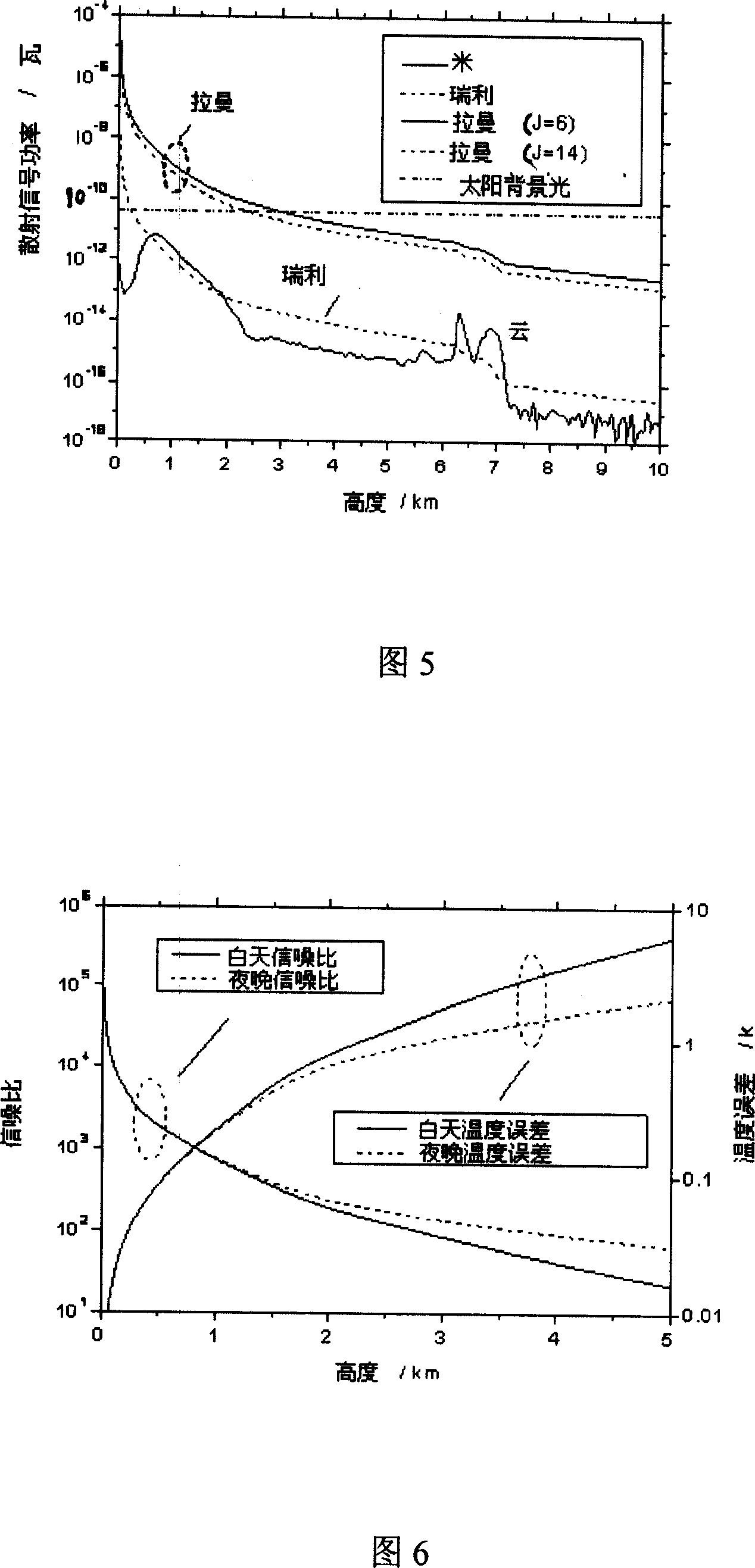
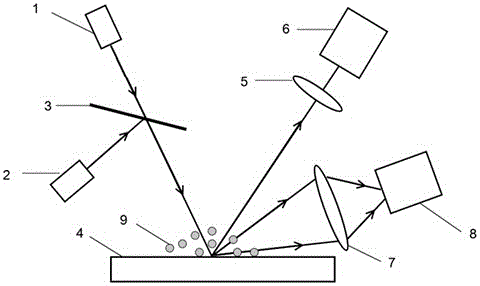
Raman scattering laser radar system for meterological and atmospheric environment observation
InactiveCN1987520ARealize measurementRealize functionIndication of weather conditions using multiple variablesElectromagnetic wave reradiationProcess systemsRadar systems
The laser radar system includes transmission system, receiving system, spectrum and photoelectric detection system, and data process system. After collimation, light sent from the pulse laser is sent to atmosphere vertically. The receiving system of the laser radar receives backscattering light generated after interaction between laser and molecules, particles in atmosphere. The received atmosphere echo signal of the laser radar is sent to spectrum system to carry out spectrum. Detected by the photoelectric detection system the spectrum is sent to the data process system to carry out analysis and process. Based on preloaded program, the invention obtains temperature value of atmosphere, density of vapor, optical character parameters of atmospheric aerosol, and depolarization ratio of backscattering light of not spheroidal particle.
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF TECH
Surface Raman and infrared spectroscopy double-enhanced detecting method based on graphene and nanogold compounding
ActiveCN105699358ARealize measurementComplete measurementMaterial nanotechnologyRaman scatteringPlasma effectComposite substrate
Provided is a surface Raman and infrared spectroscopy double-enhanced detecting method based on graphene and nanogold compounding.According to the method, light sources, a lens, a graphene nanobelt and gold nanoparticle composite substrate, an infrared Fourier spectrograph and a Raman spectrometer are included.Infrared light waves and visible light waves emitted by the infrared light source and the laser light source respectively pass through a beam combiner and then irradiate the graphene nanobelt and gold nanoparticle composite substrate, after the light waves and trace molecules adsorbed on the substrate interact, reflected light is gathered by the focusing lens to enter the infrared Fourier spectrograph, and meanwhile scattered light is gathered into the Raman spectrometer.Raman scattering signals of the trace molecules can be enhanced through the local area plasma effect of the gold nanoparticles, and meanwhile infrared absorption spectrum signals of the trace molecules can be dynamically enhanced through the graphene surface plasma effect within the broadband range.According to the method, double enhancement of surface Raman and broadband infrared spectroscopy signals is achieved on the same substrate, and the advantages of being wide in enhancement wave band, high in detecting sensitivity, wide in detected matter variety range, good in stability and the like are achieved.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Optical method and apparatus for determining status of agricultural products
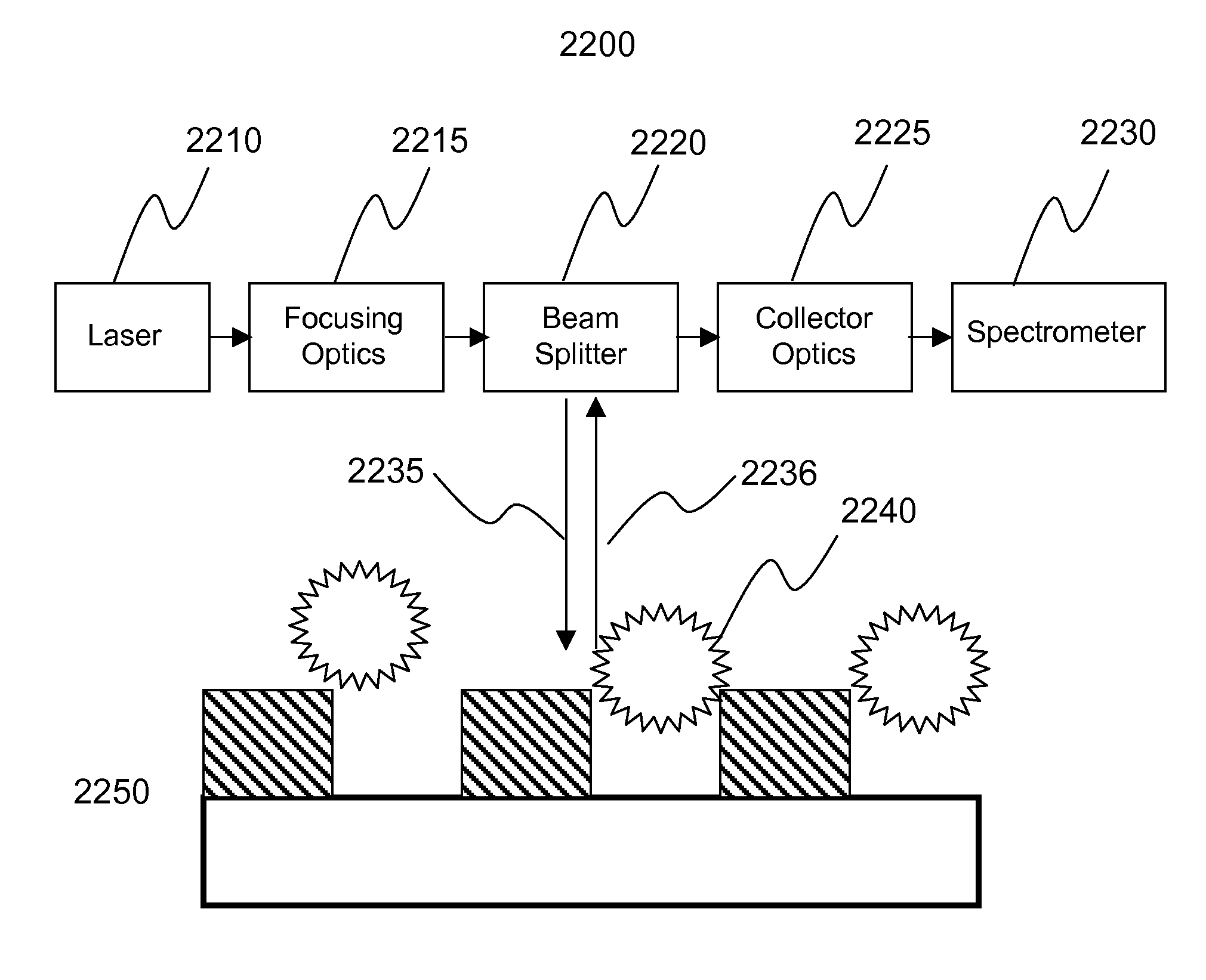
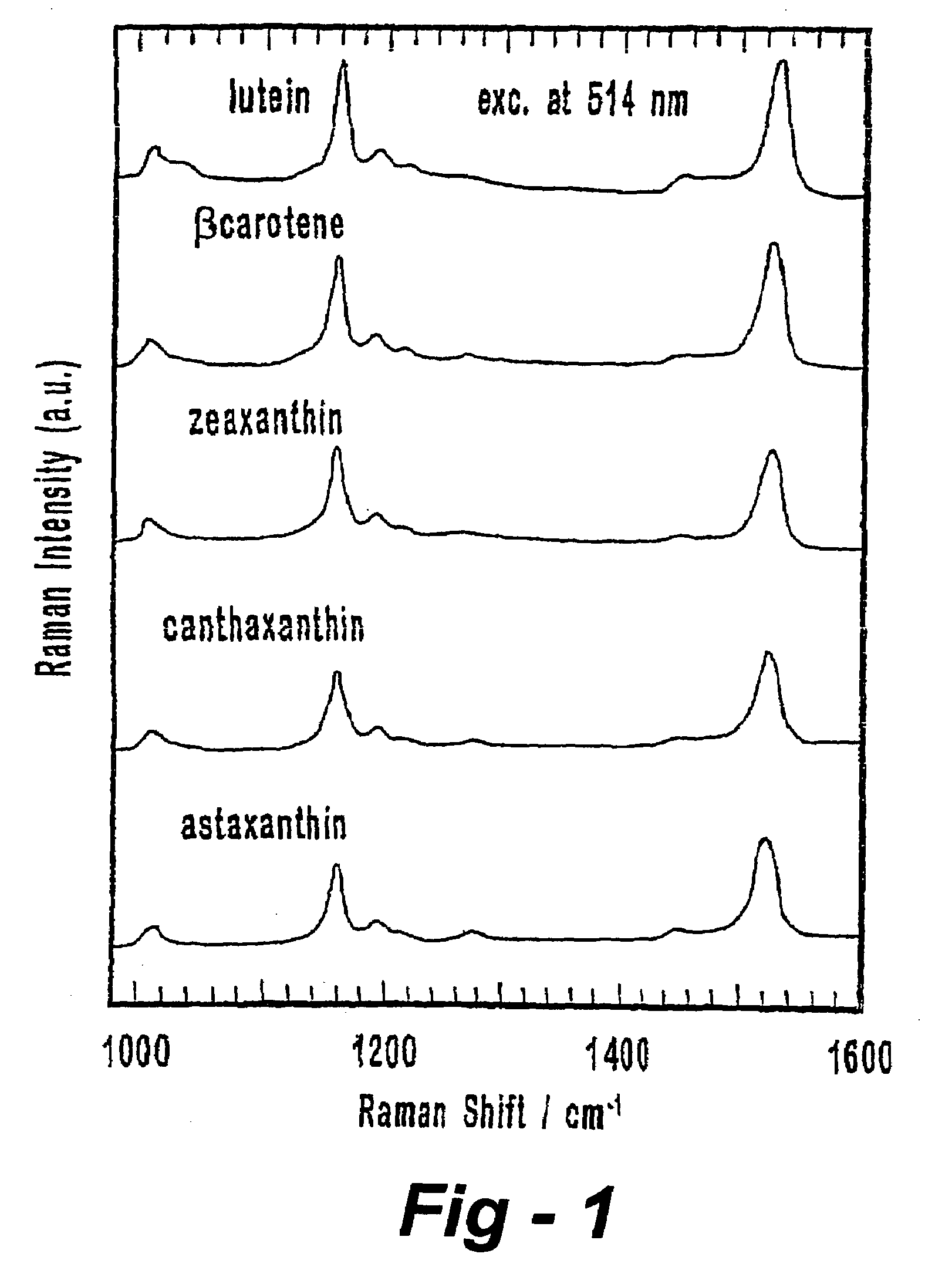
InactiveUS7215420B2Improve efficiencyAutomation of quality controlRadiation pyrometryComponent separationBeta-CaroteneLycopene
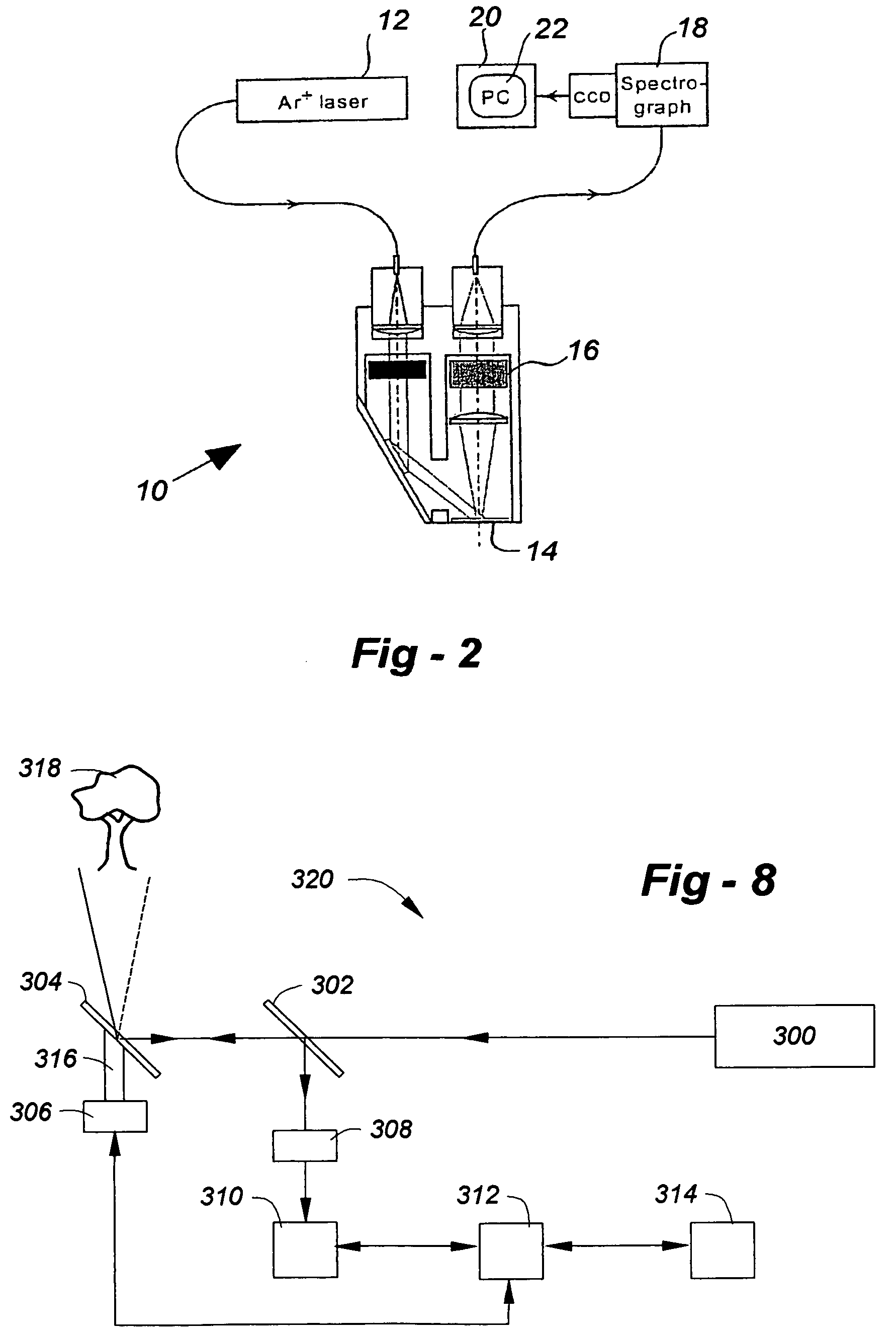
A spectroscopic method, preferably Raman scattering, is used to rapidly determine the general health or stress status of living plants and plant products, including agricultural crops, forests, and harvested fruits and vegetables. In the preferred embodiments, carotenoid levels are used to provide an indication of oxidative deterioration. Based upon the results of the analysis, further action may or may not be taken, for example, in terms of choosing, picking, harvesting or sorting the agricultural product in accordance with the carotenoid level. Concentration levels of an analyte substance can be determined relative to an external standard, to each other, or relative to another substance in the item being analyzed. Carotenoids such as lycopene, beta-carotene, lutein, violaxanthin, neoxanthin, antheraxanthin, and zeaxanthin are determined according to the invention, through other plant components may be analyzed such as other terpenes, polyenes, chlorophyll, proteins, starches, sugars, overall nitrogen levels, flavonoids, and vitamins. The hardware associated with the invention may be field portable or mounted on a piece of equipment such as a harvester or sorter.
Owner:UNIV OF UTAH RES FOUND
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com