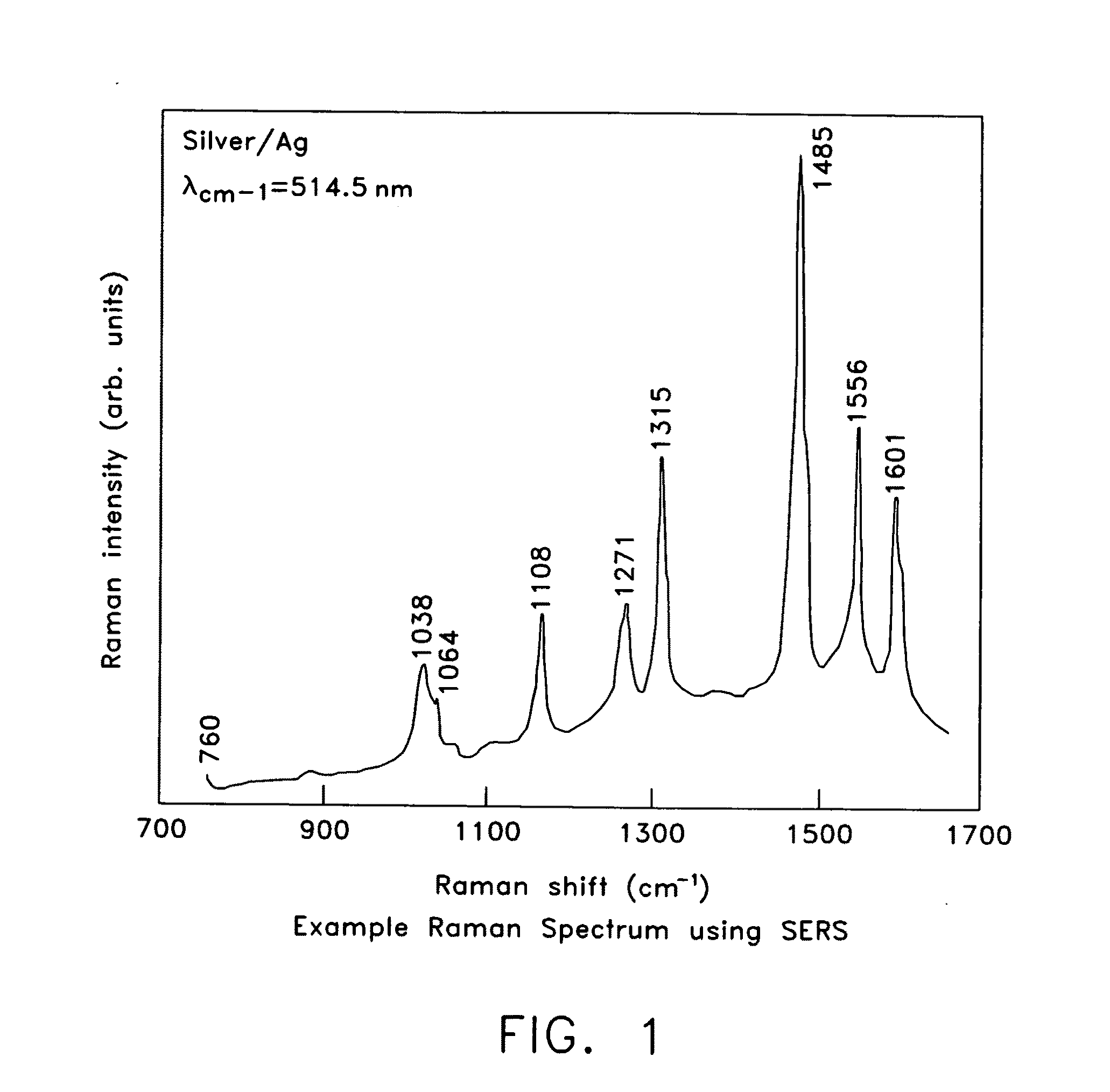
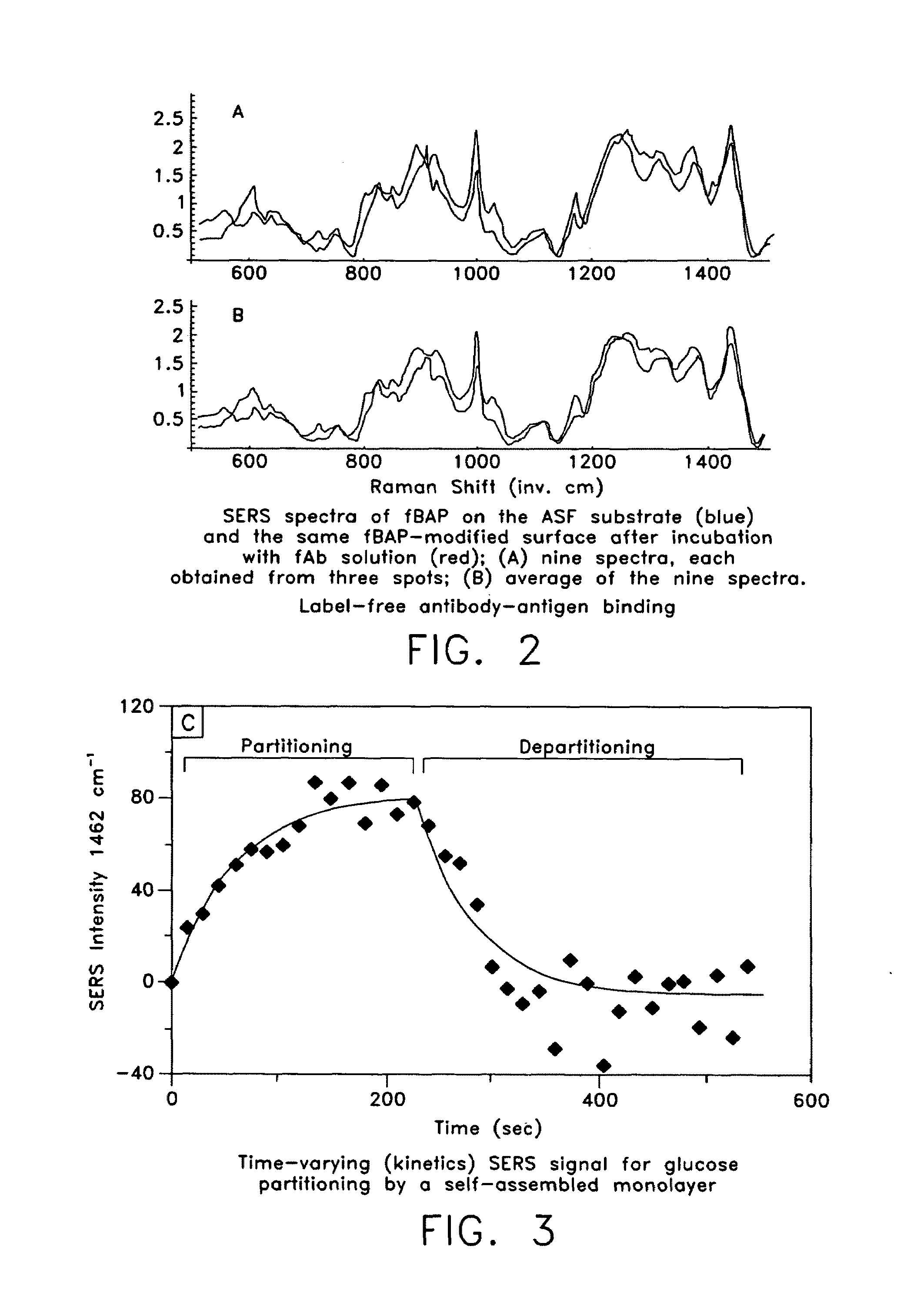
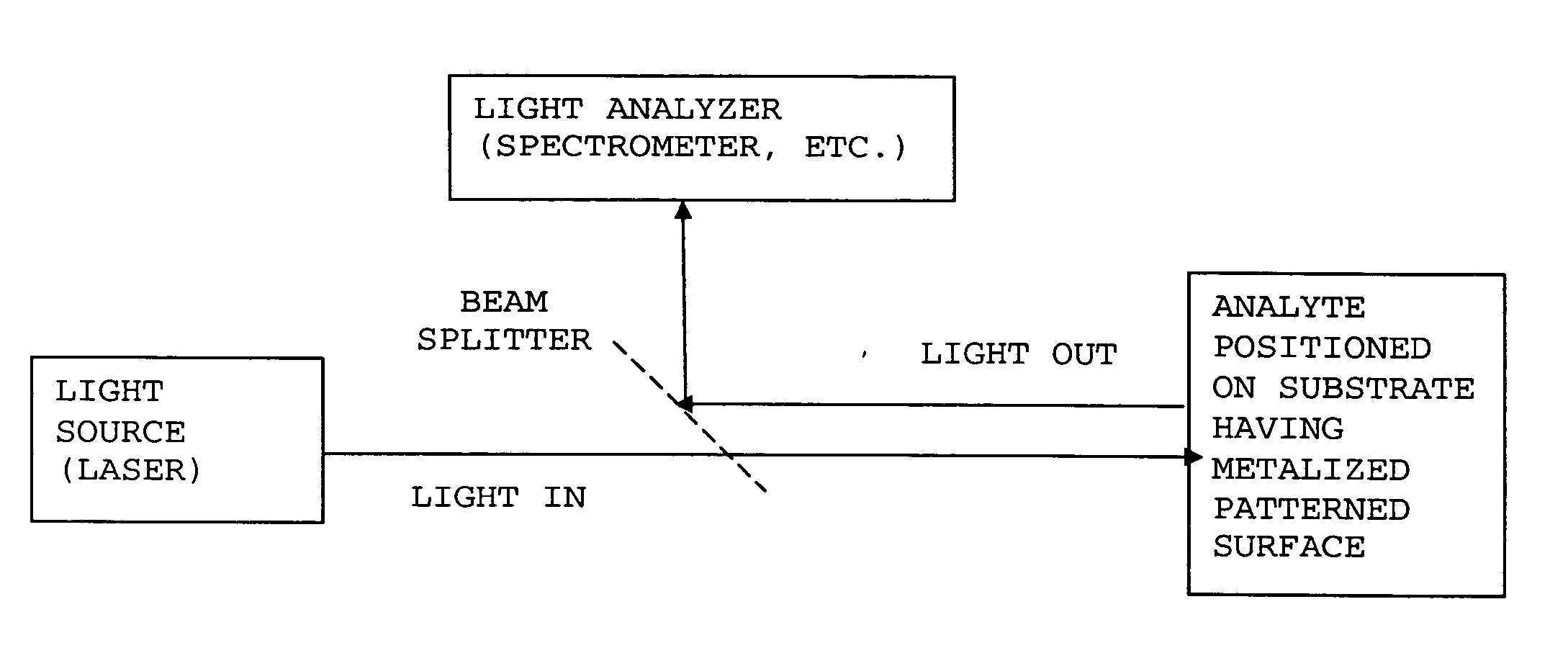
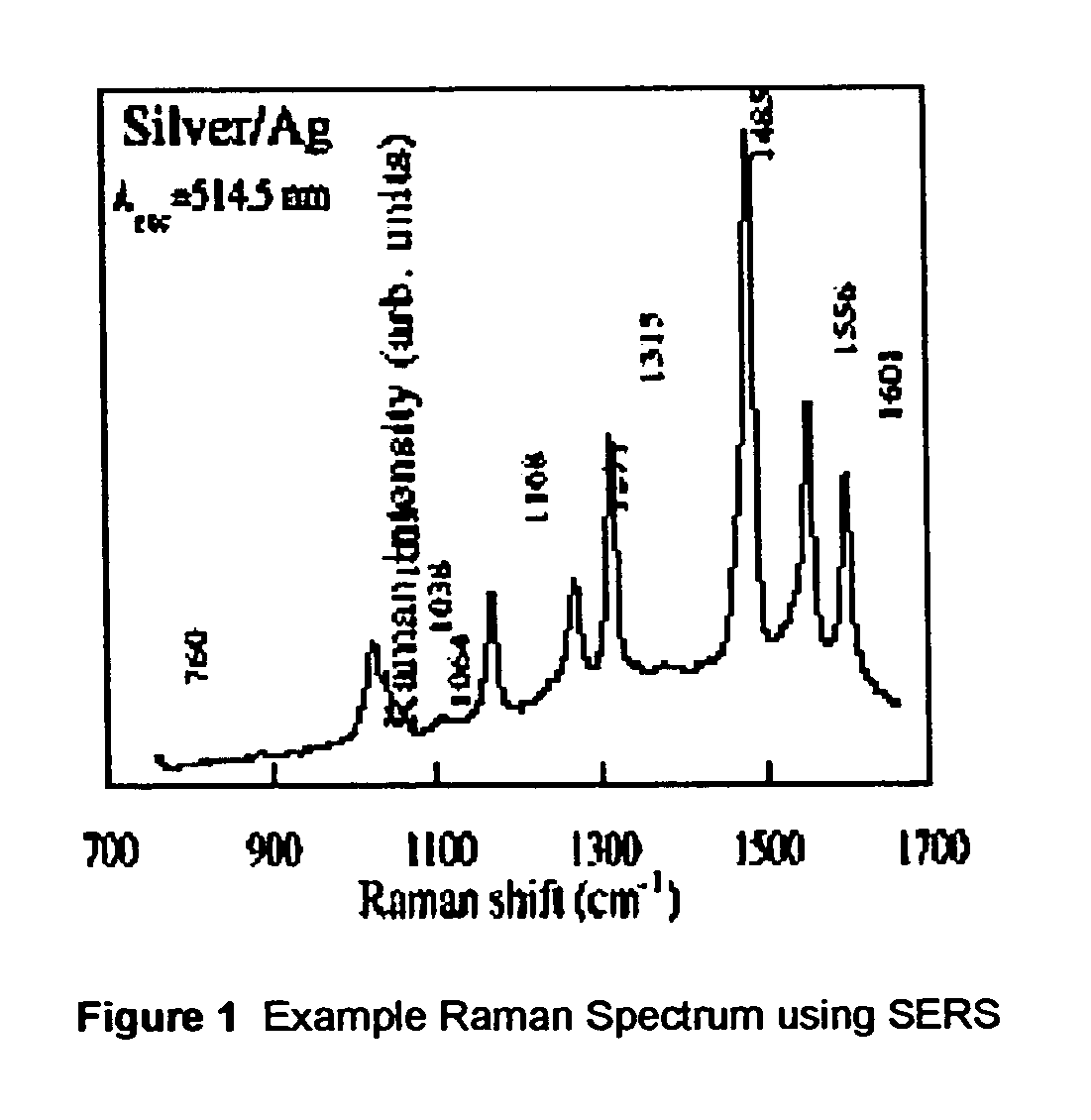
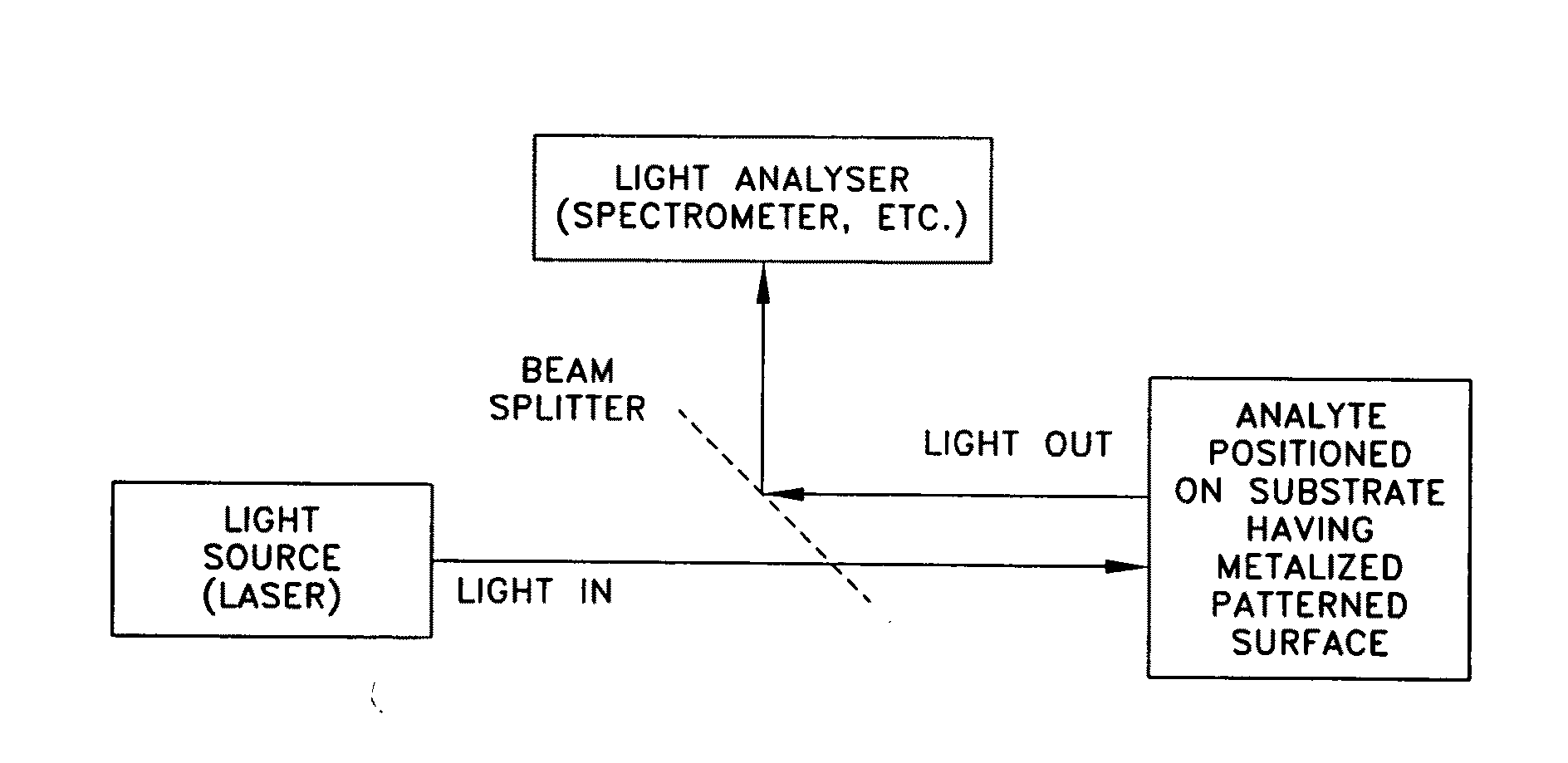
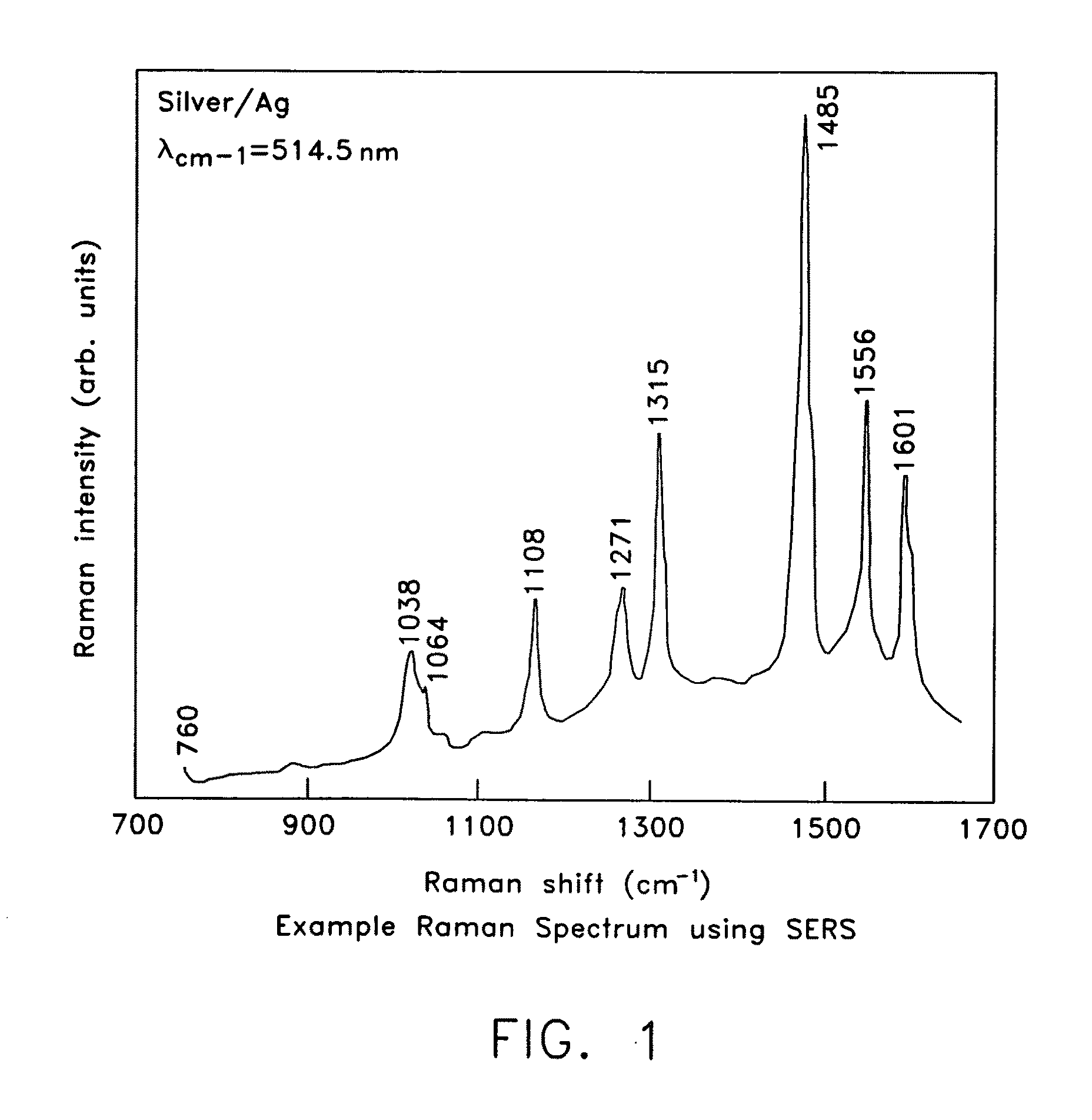
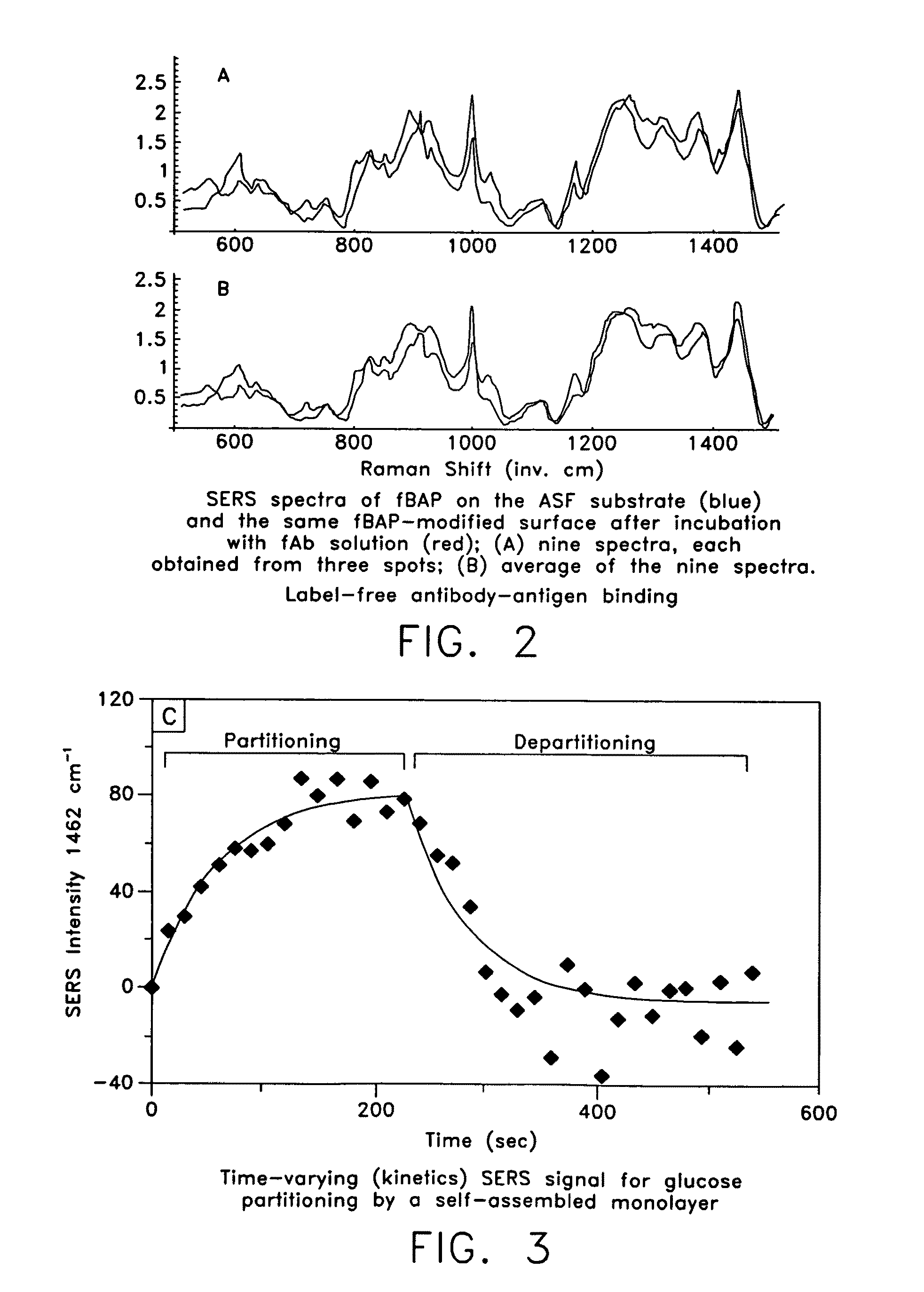
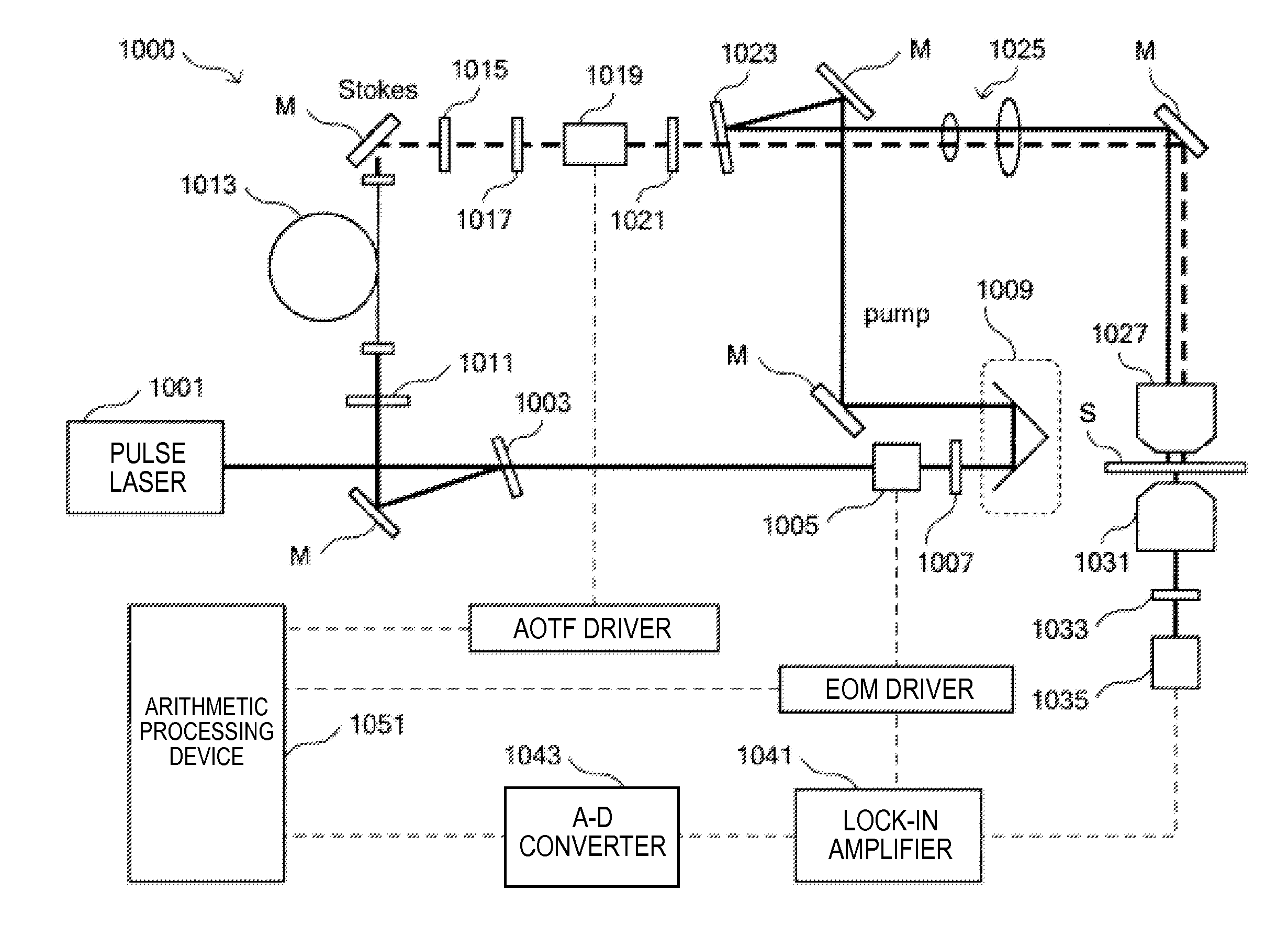
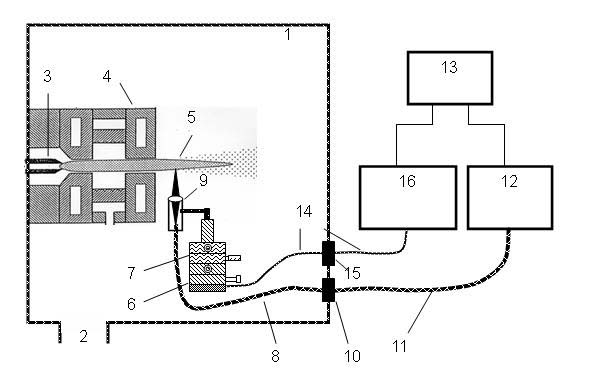
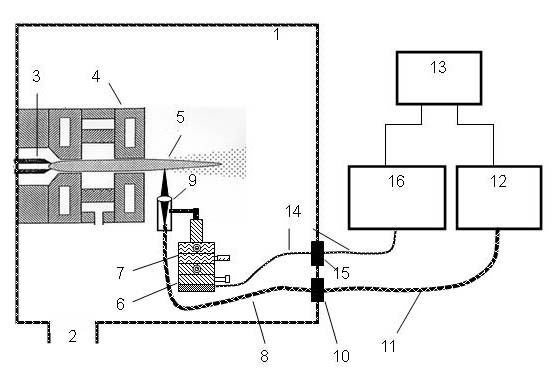
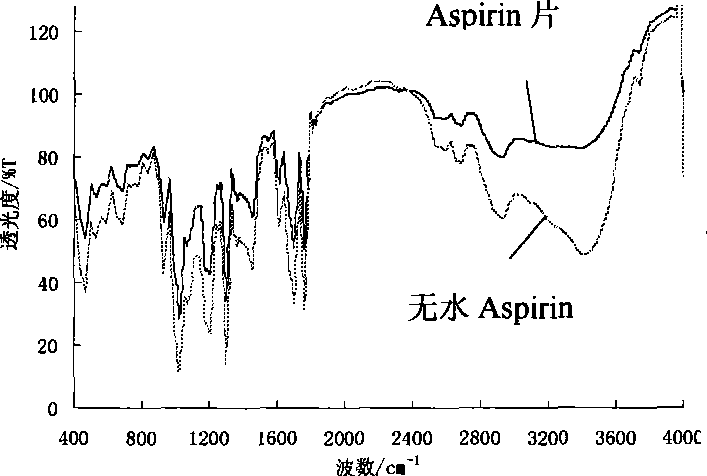
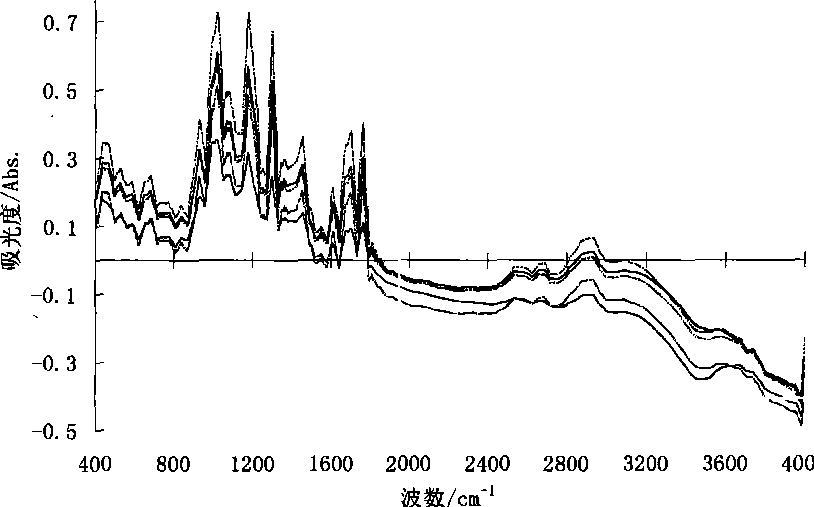
Patents
Literature
98 results about "Molecular vibration" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
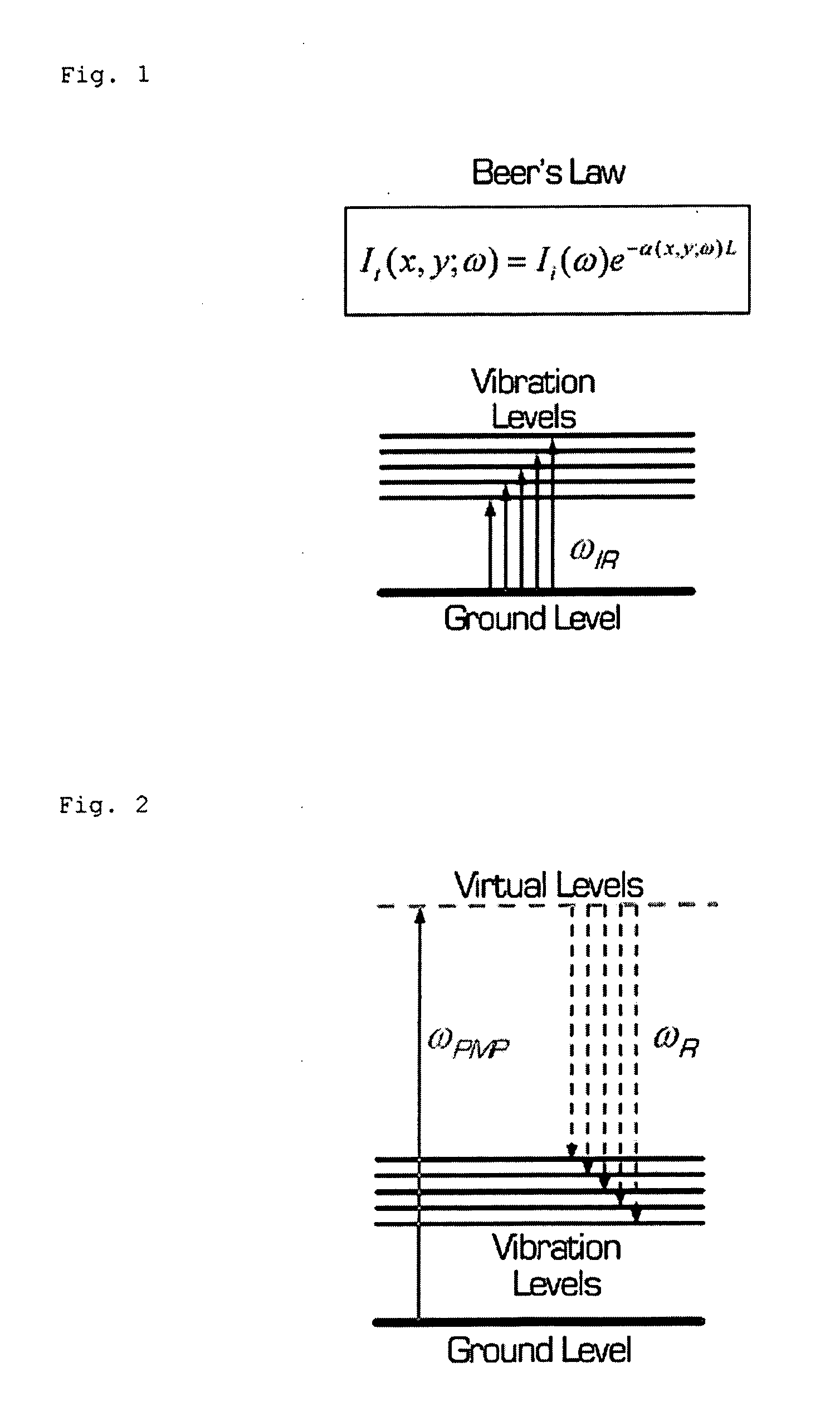
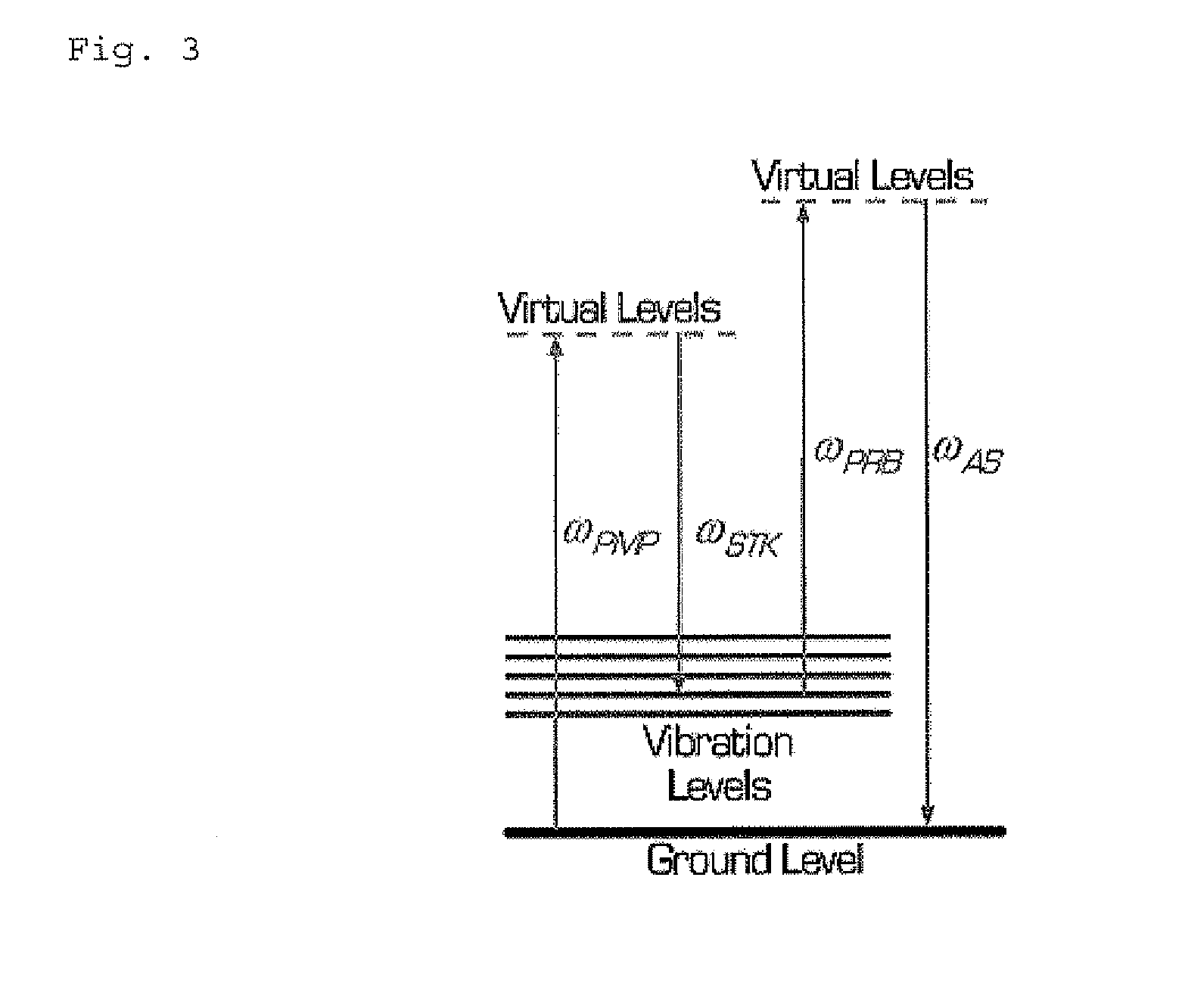
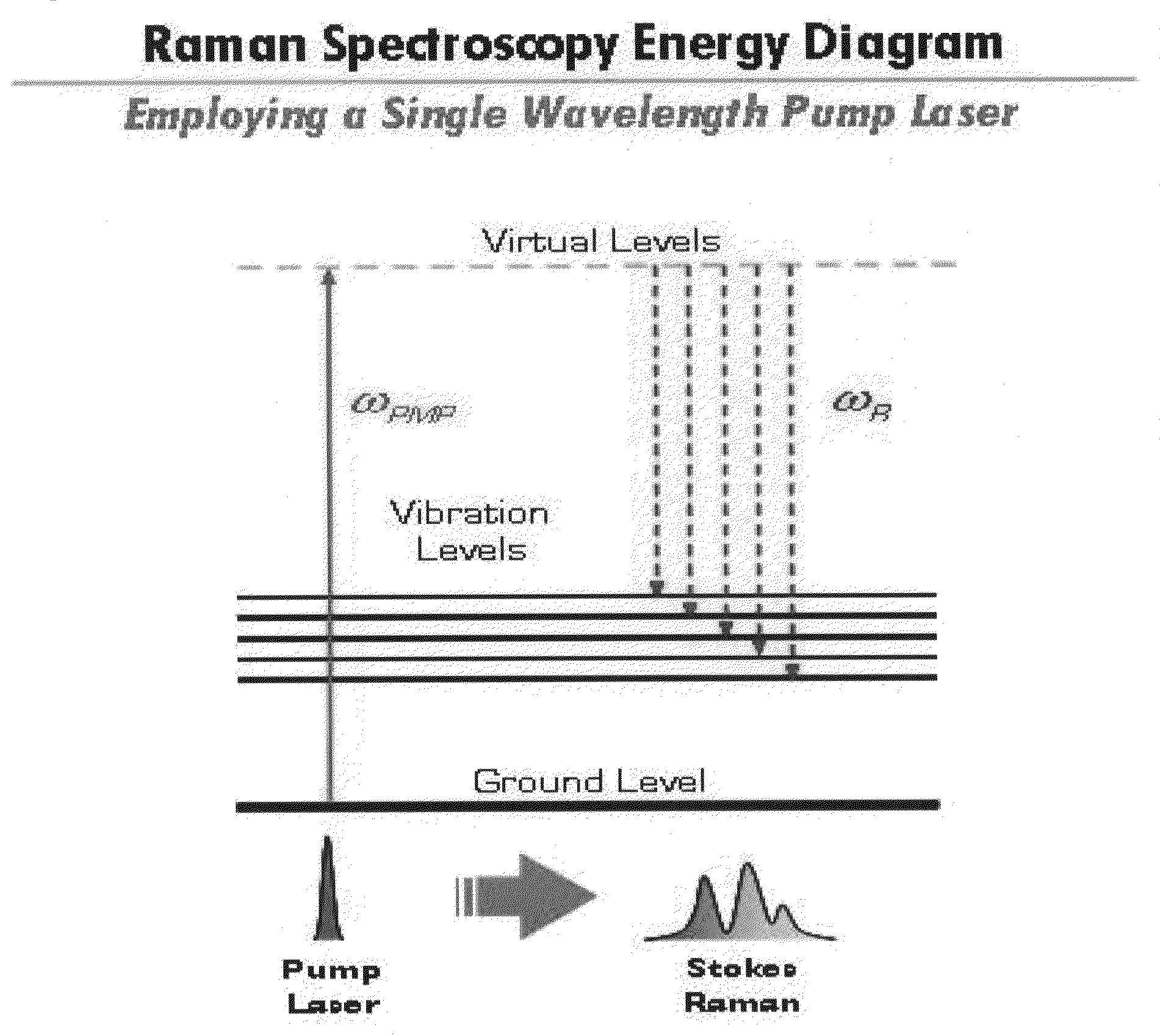
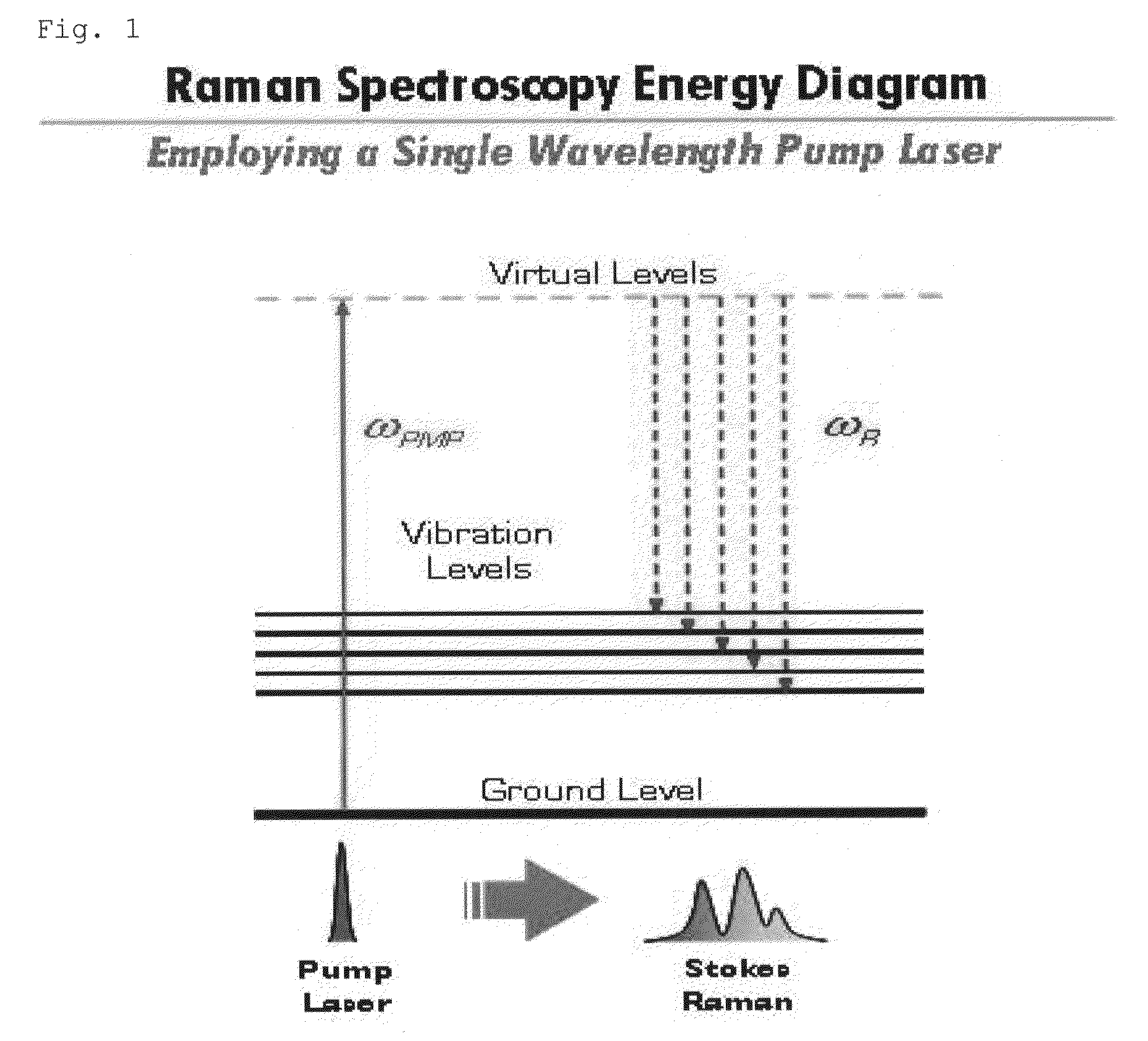
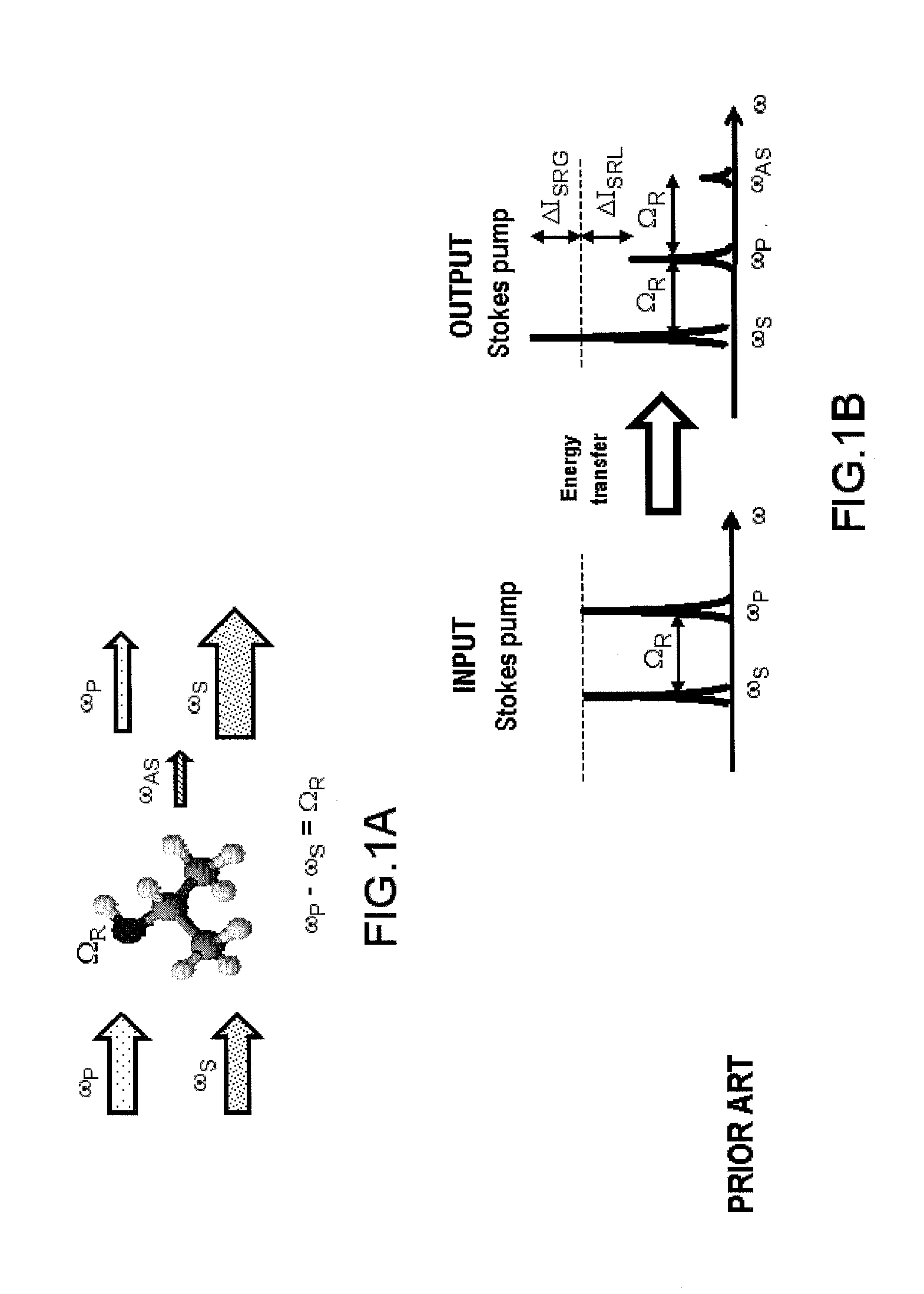
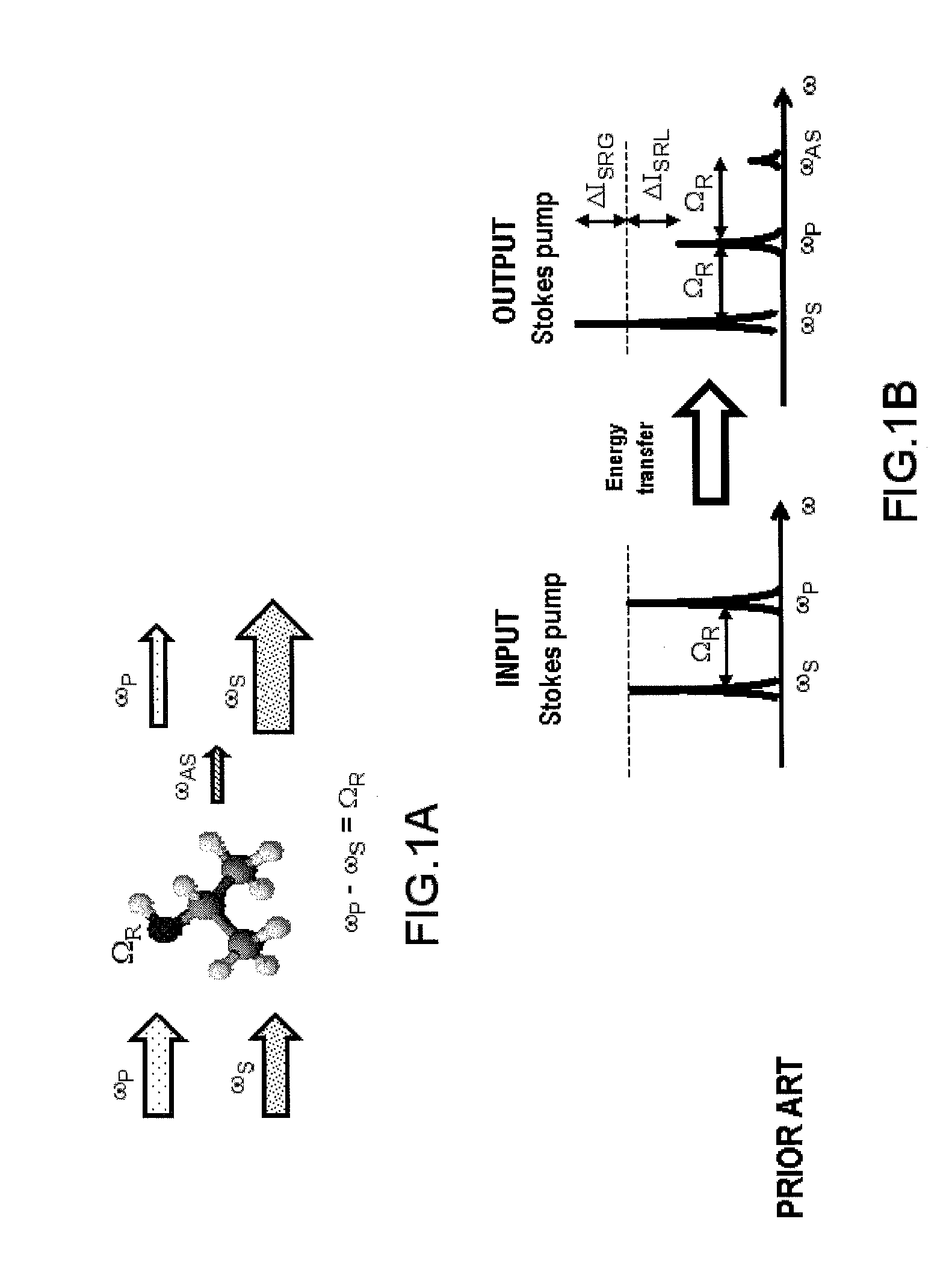
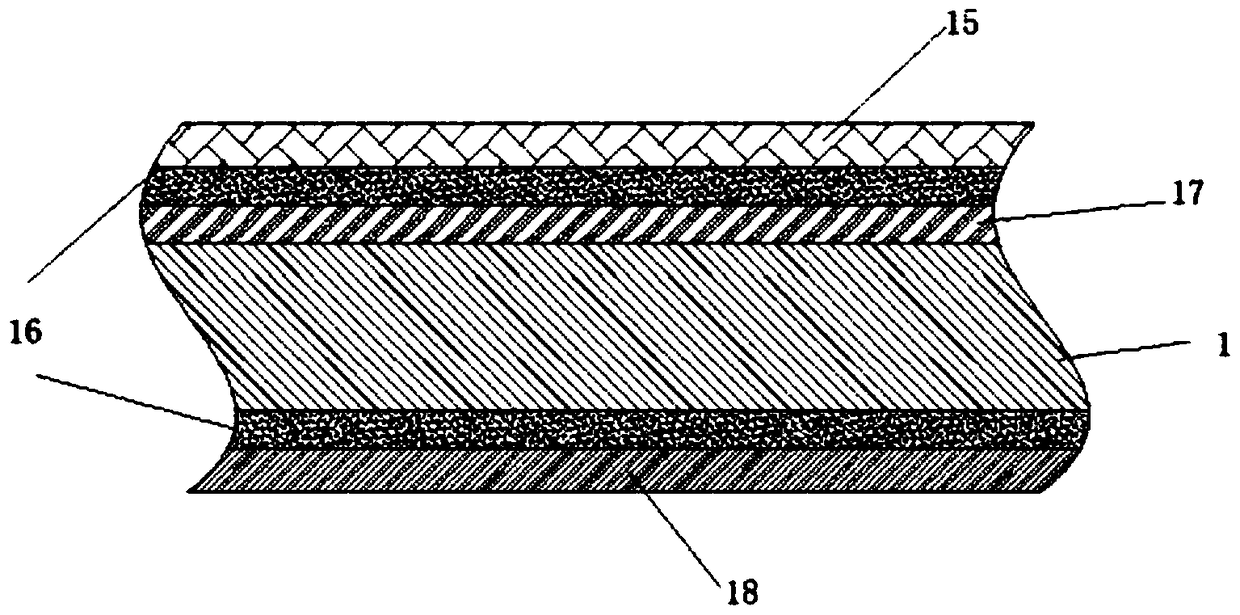
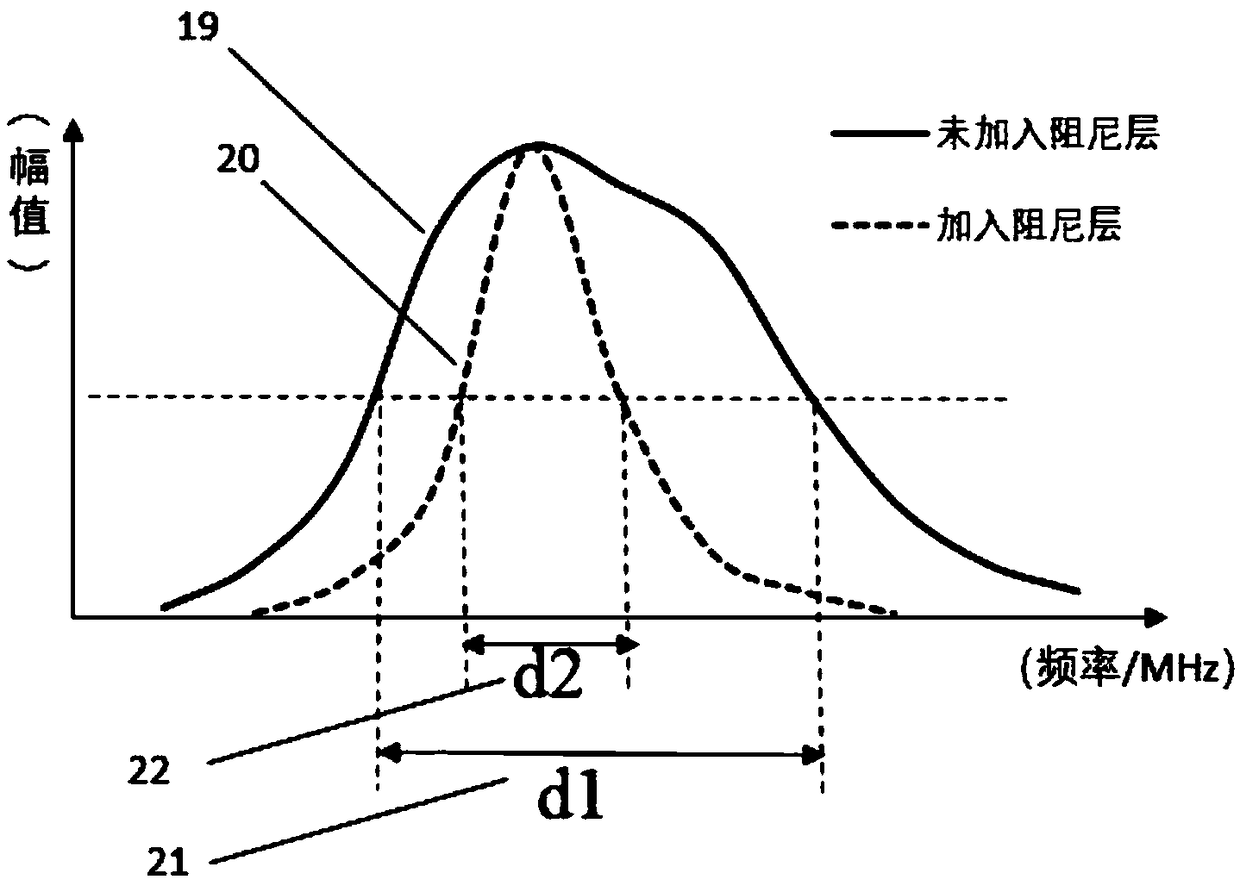
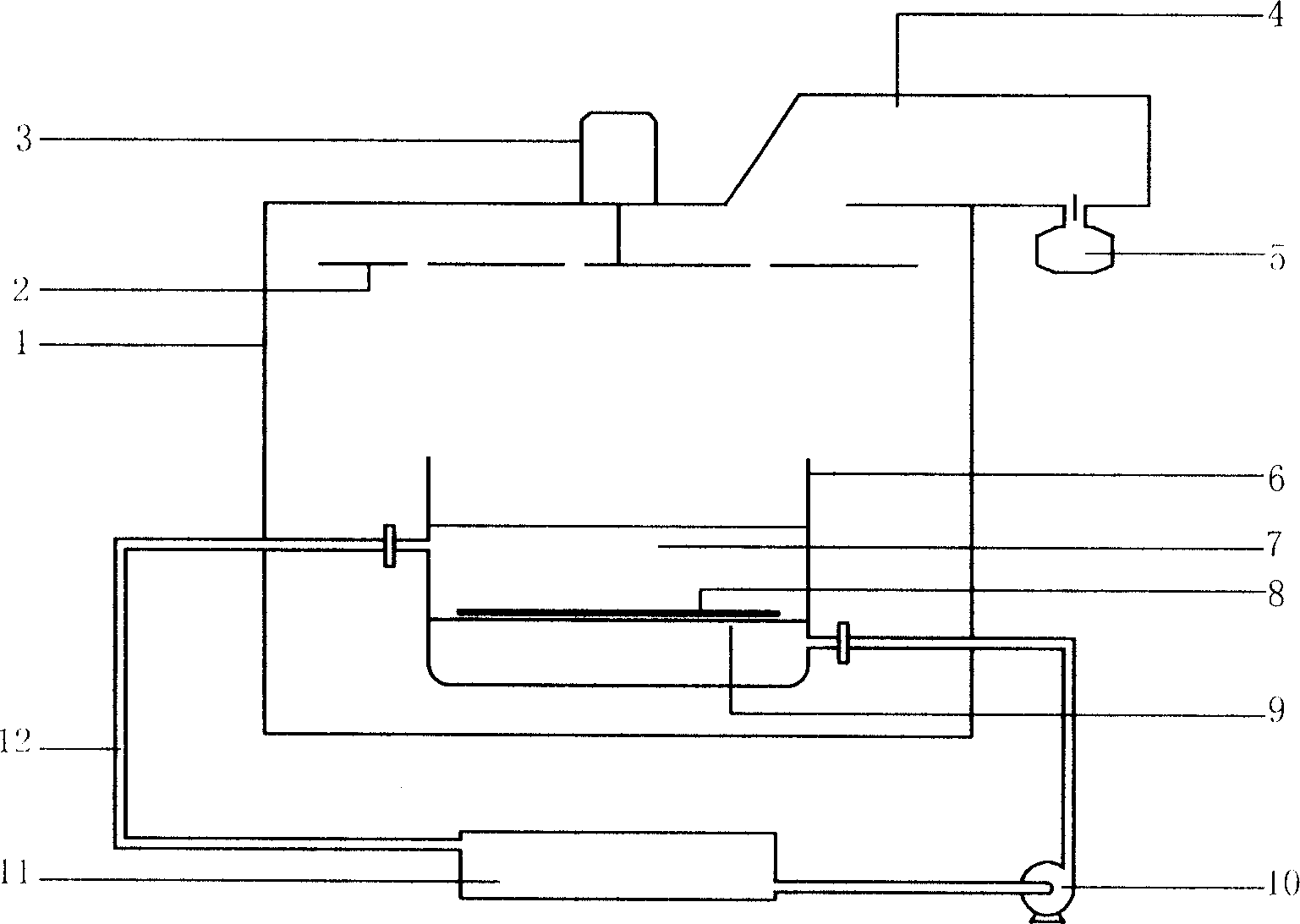
A molecular vibration occurs when atoms in a molecule are in periodic motion while the molecule as a whole has constant translational and rotational motion. The frequency of the periodic motion is known as a vibration frequency, and the typical frequencies of molecular vibrations range from less than 10¹³ to approximately 10¹⁴ Hz, corresponding to wavenumbers of approximately 300 to 3000 cm⁻¹.
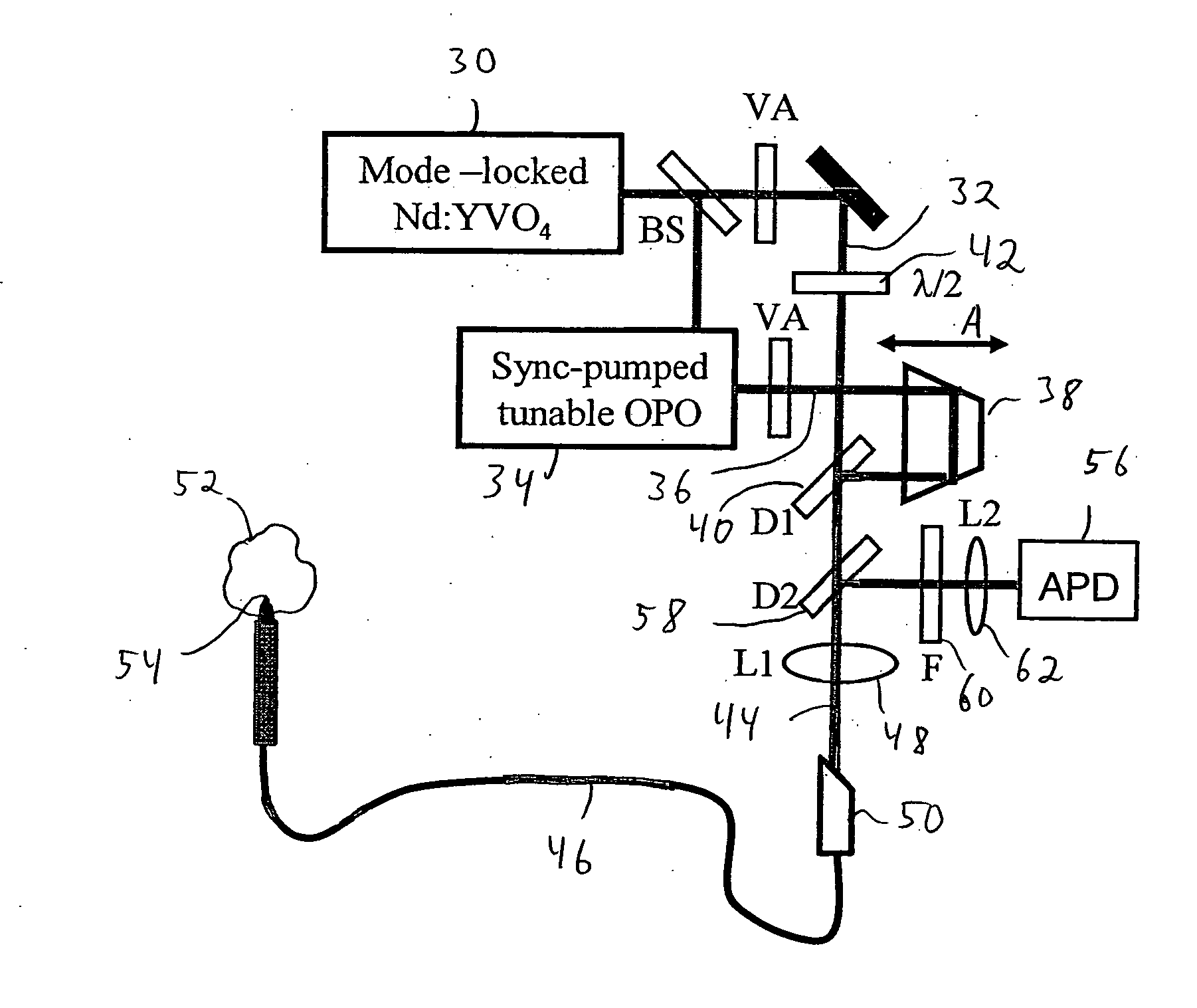
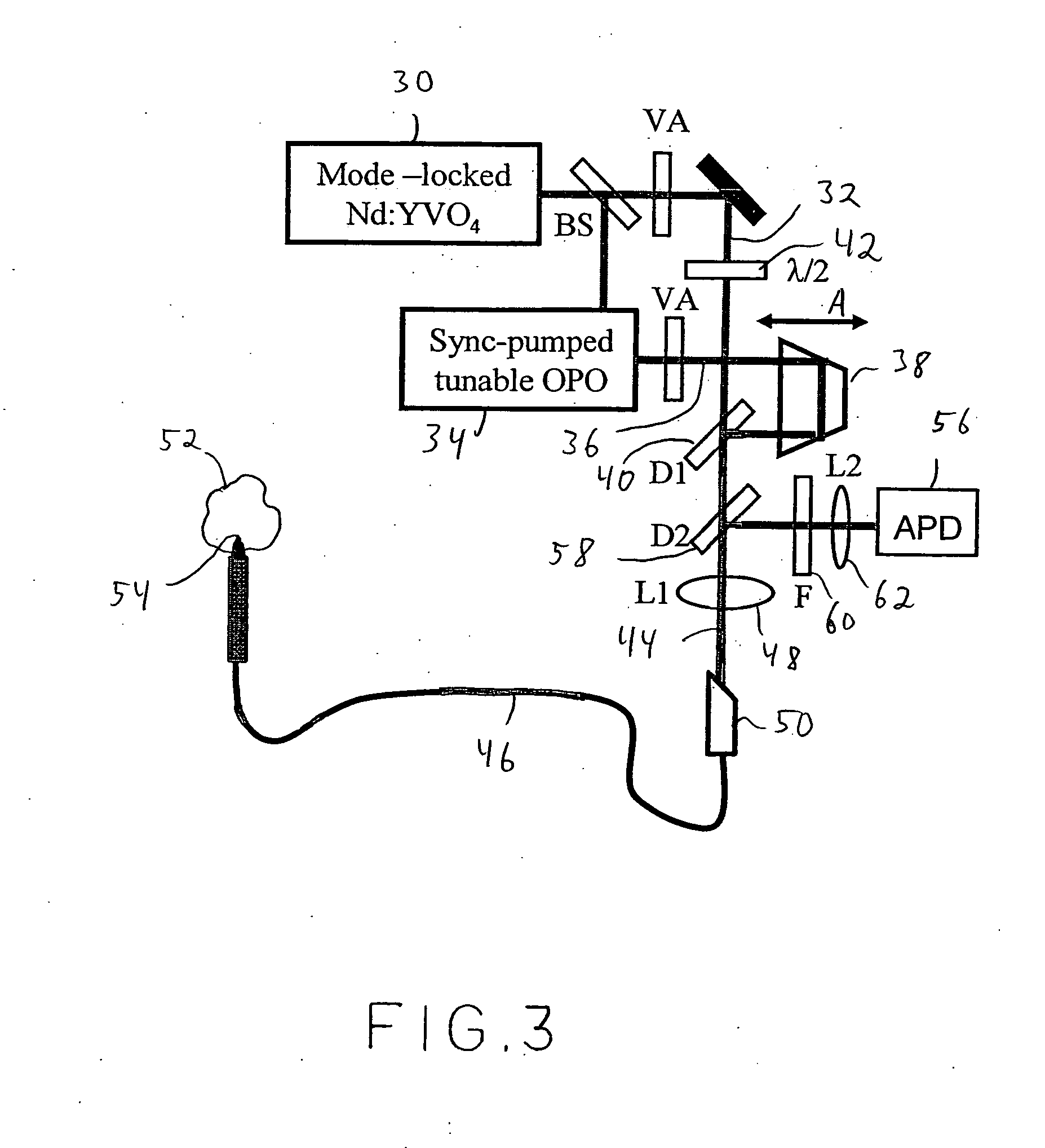
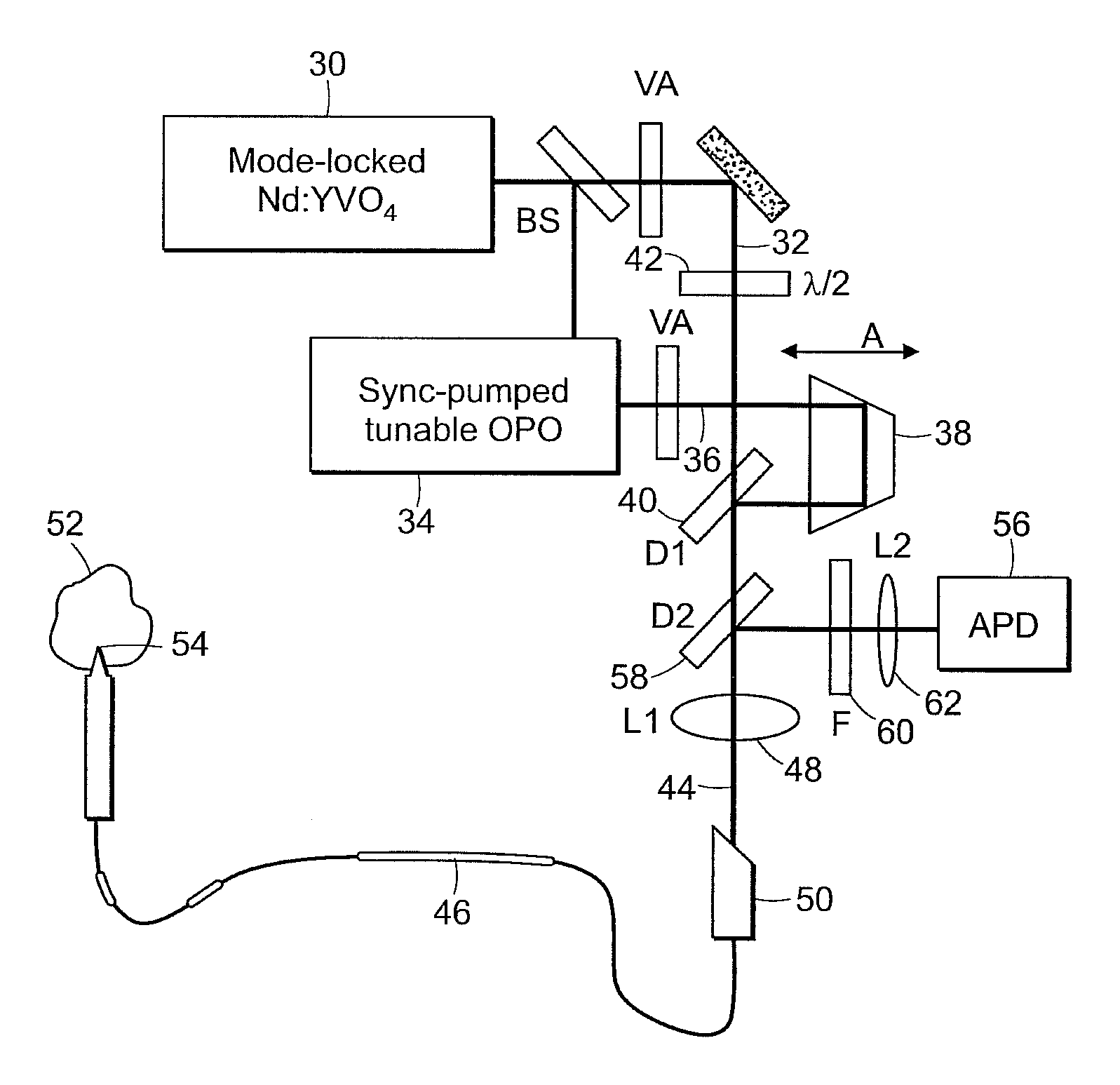
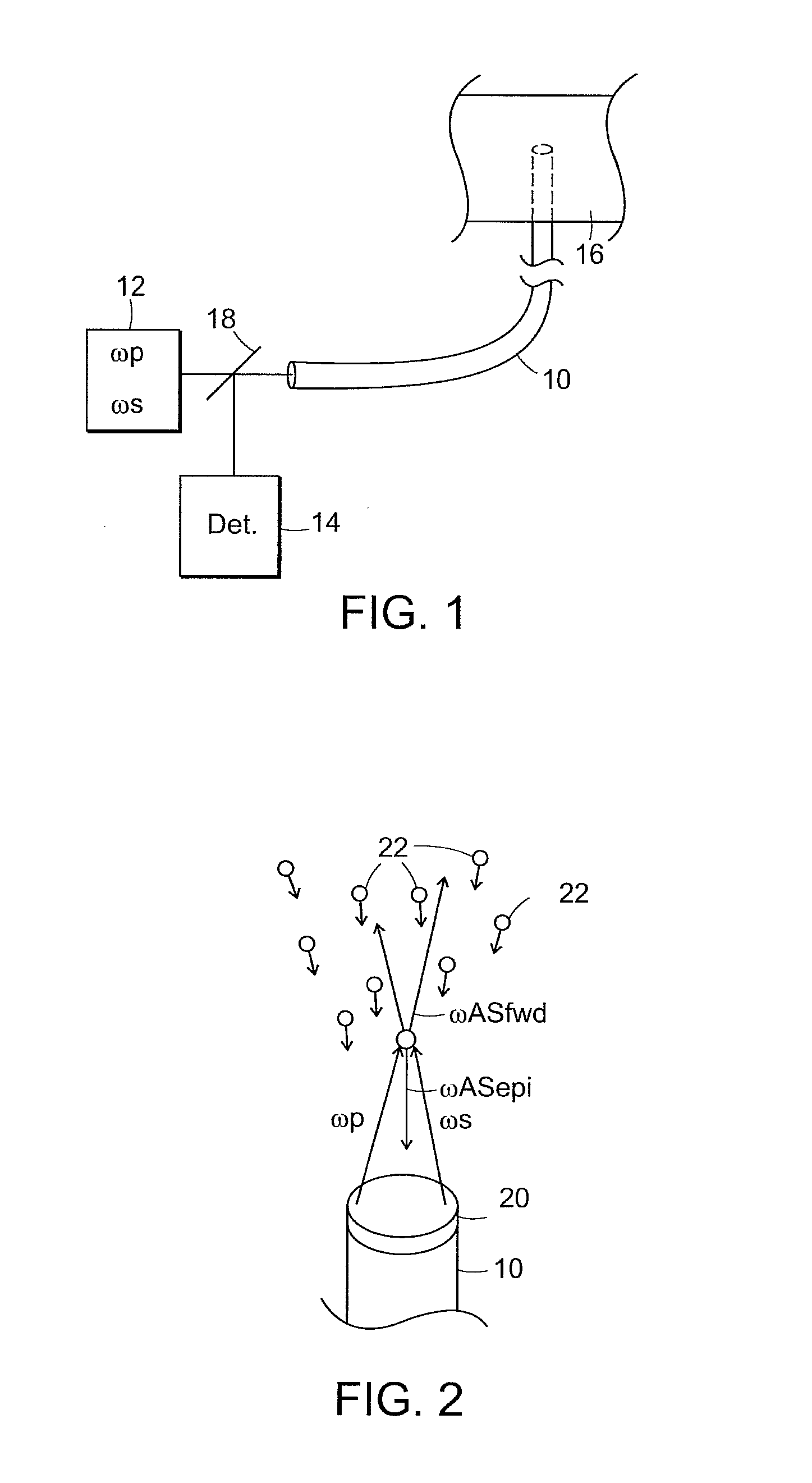
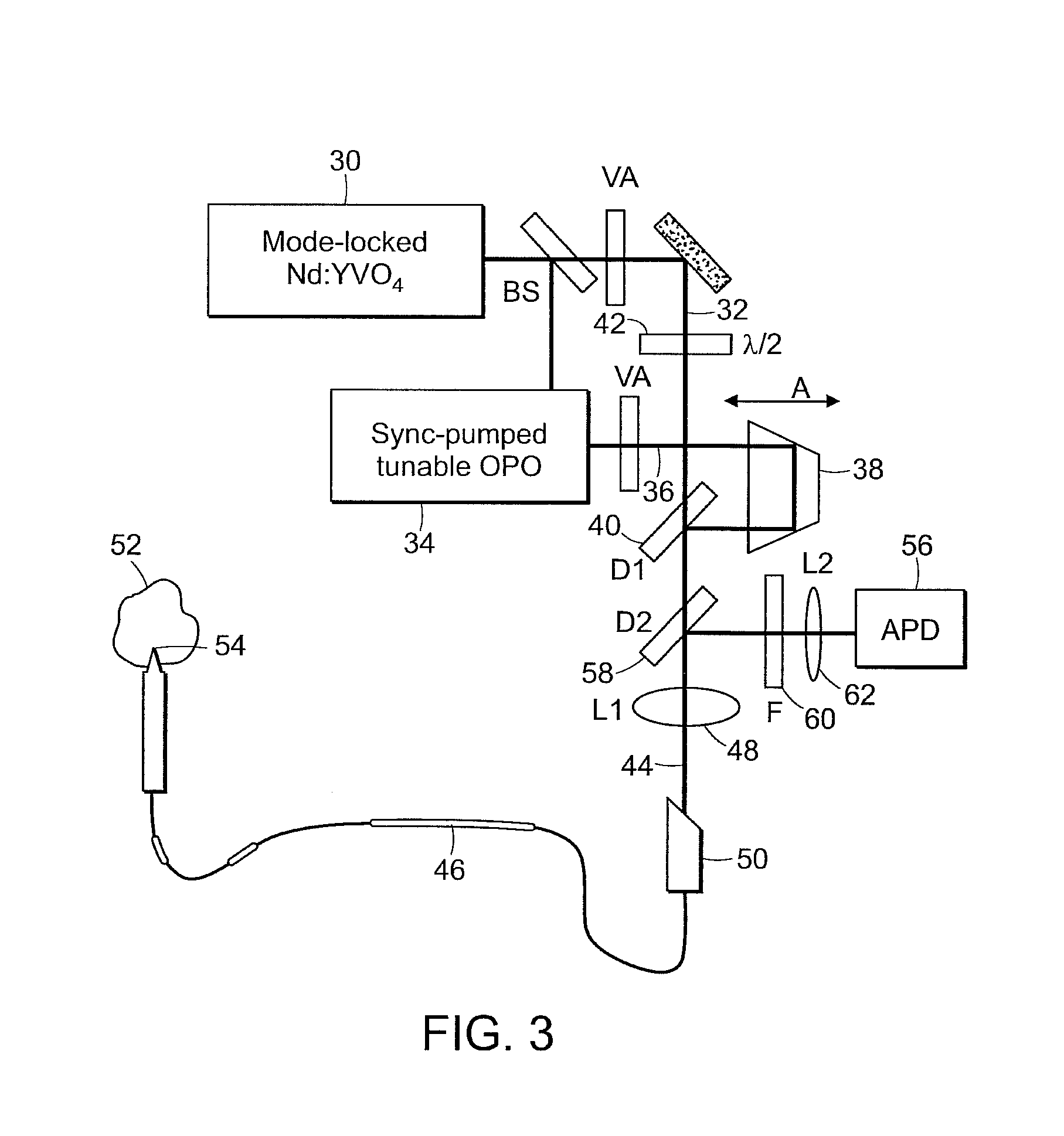
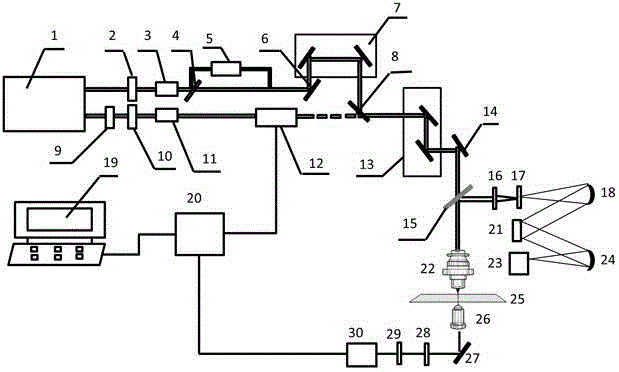
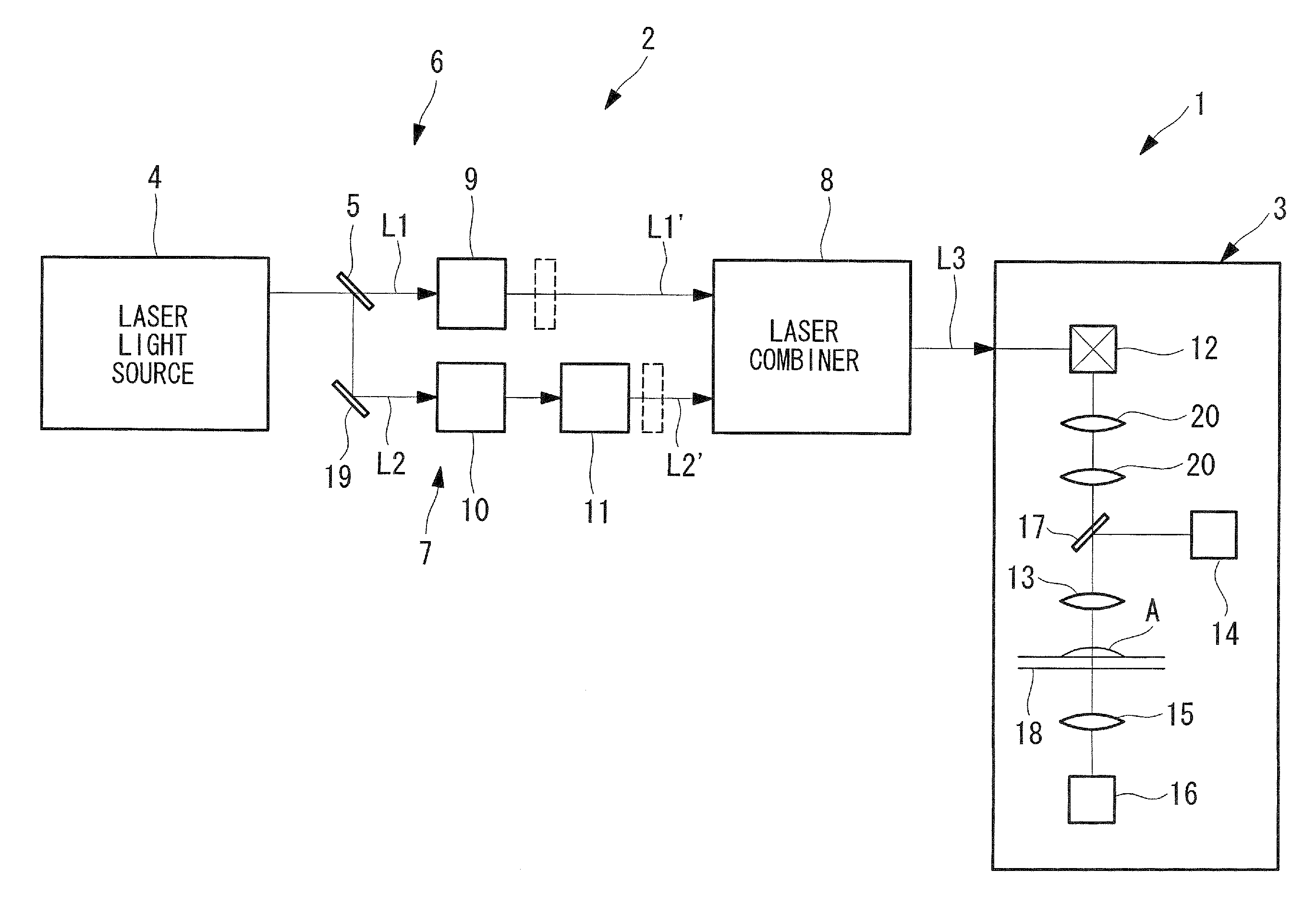
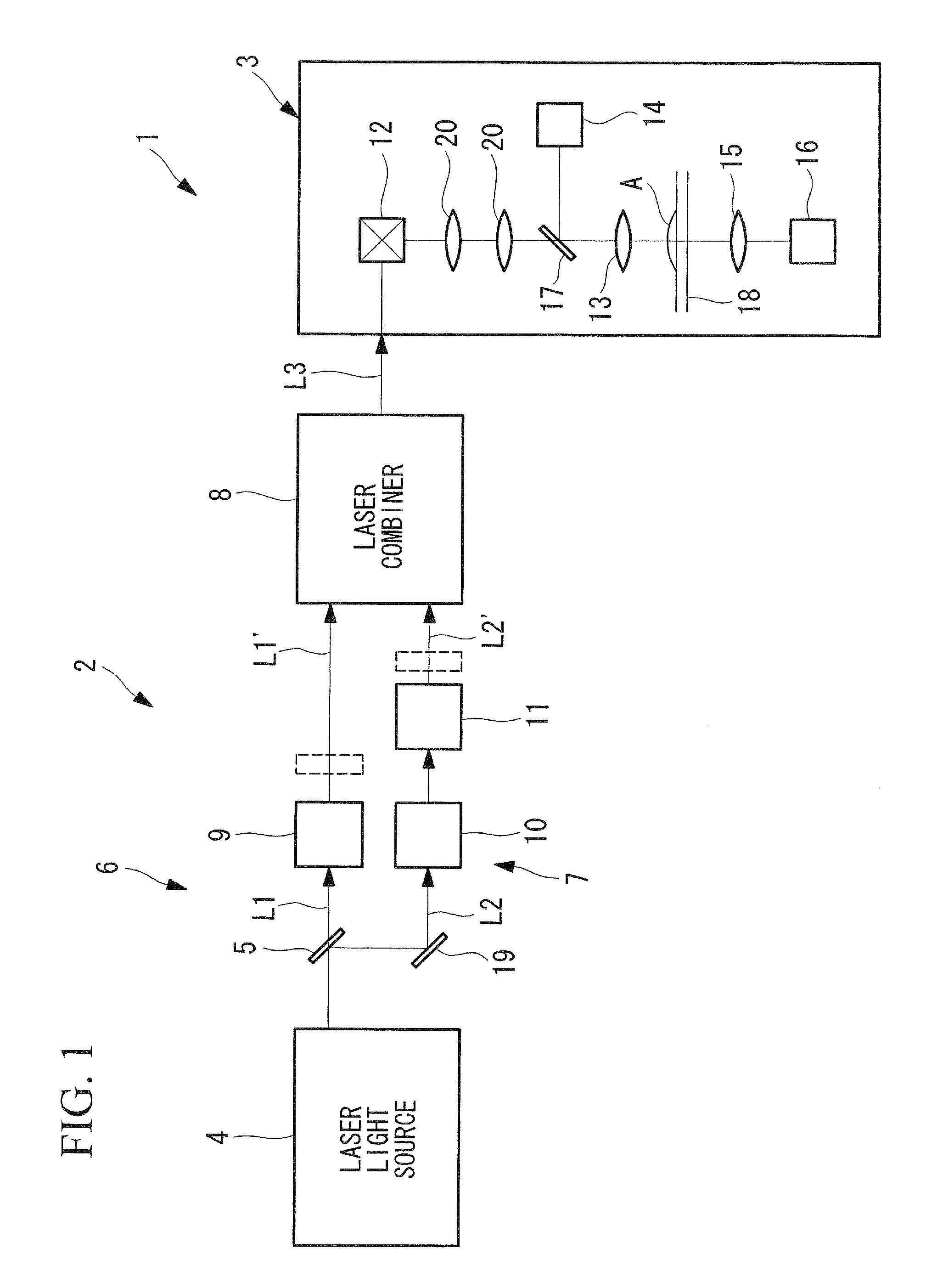
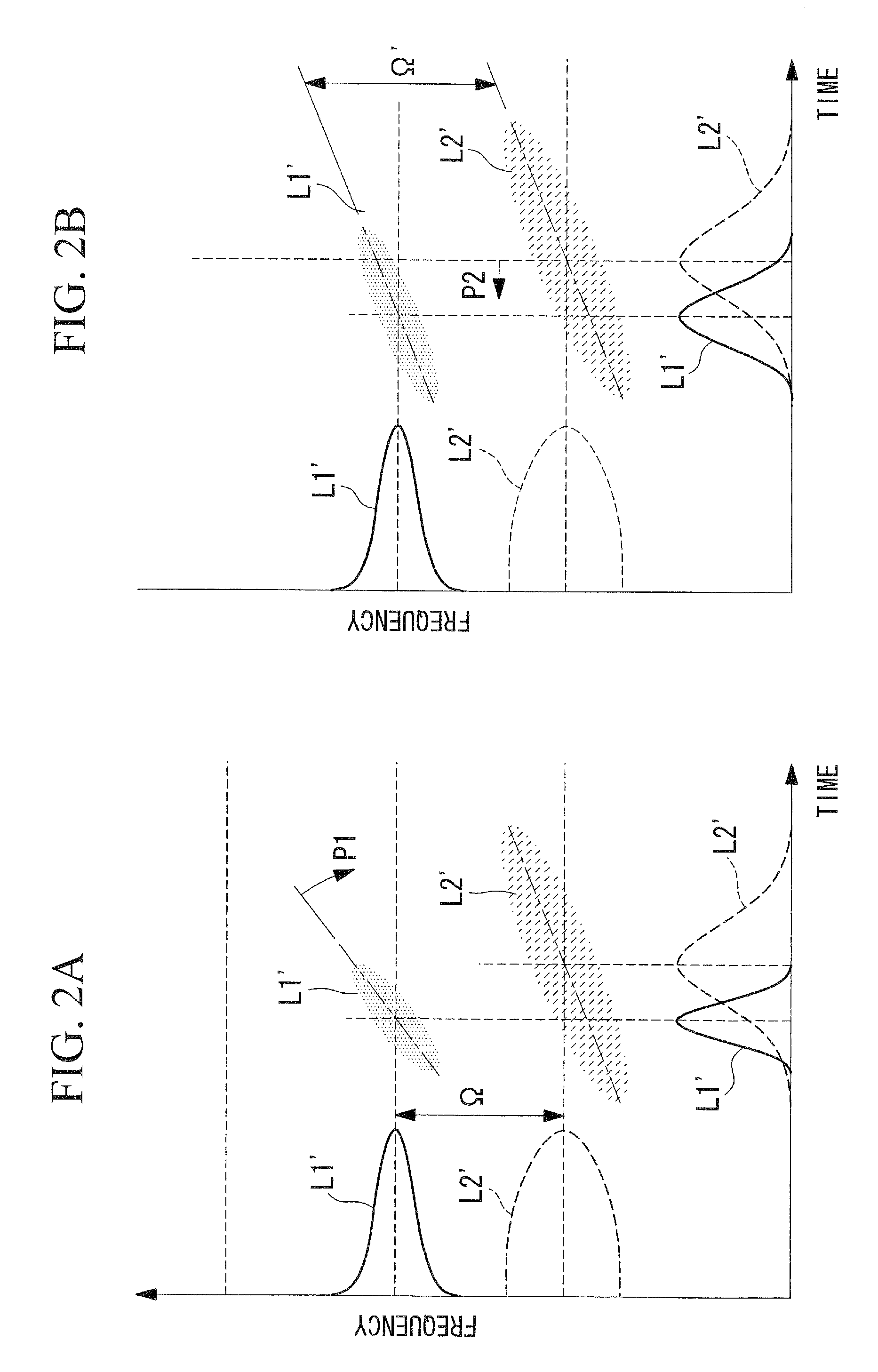
System and method for coherent anti-stokes raman scattering endoscopy
A system is disclosed for detecting a signal field from a sample volume. The system includes a source system and an optical fiber system. The source system provides a first electromagnetic field at a first frequency and a second electromagnetic field at a second frequency that is different from the first frequency. The optical fiber system includes at least one optical fiber for guiding the first and second electromagnetic fields to the sample volume to generate coherent radiation characteristic of molecular vibrations by non-linear interaction of the first and second fields with the sample volume. The optical fiber system also receives the signal field resulting from the coherent radiation, and guides the signal field to a detector.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
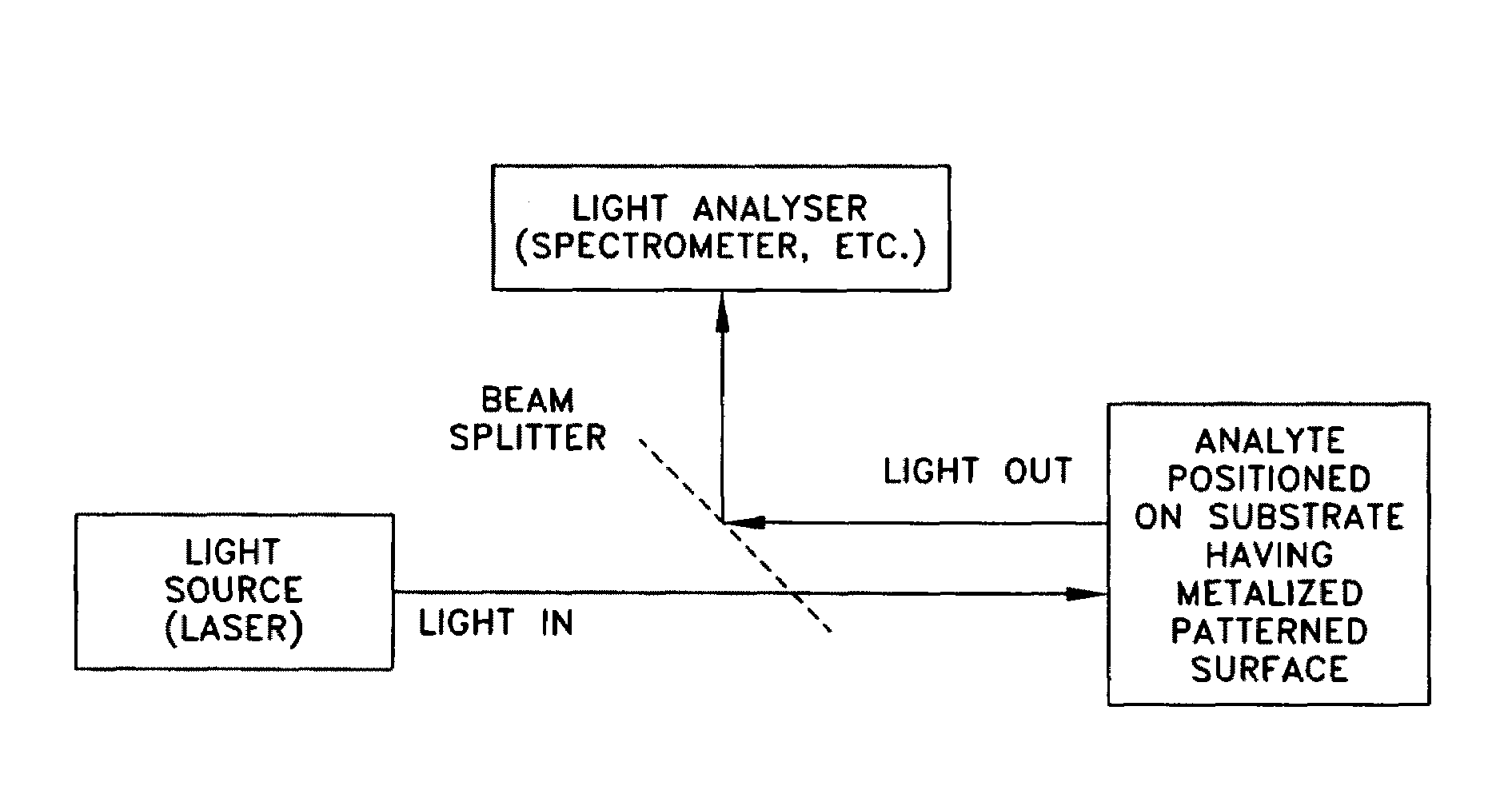
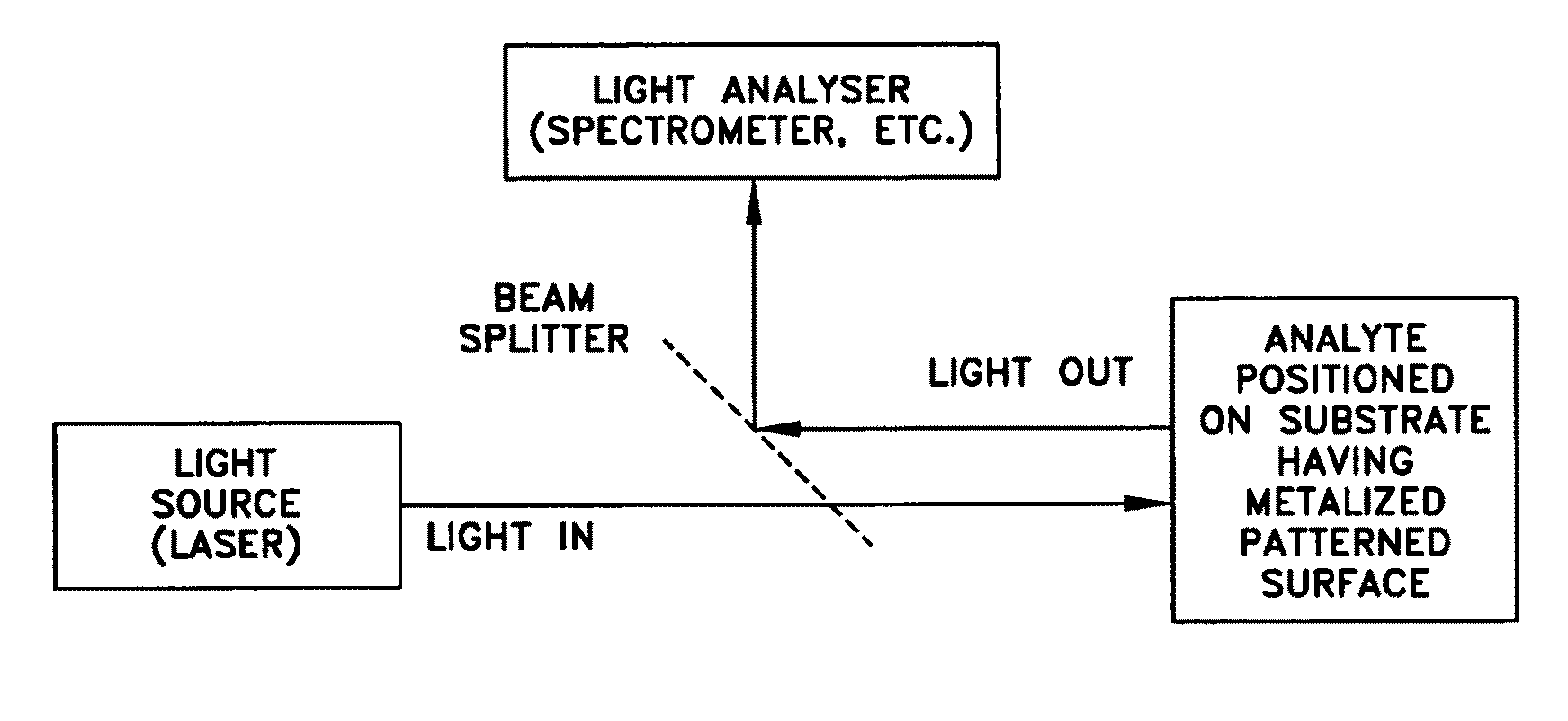
Applications of laser-processed substrate for molecular diagnostics
Owner:EBSTEIN STEVEN M
Applications of laser-processed substrate for molecular diagnostics
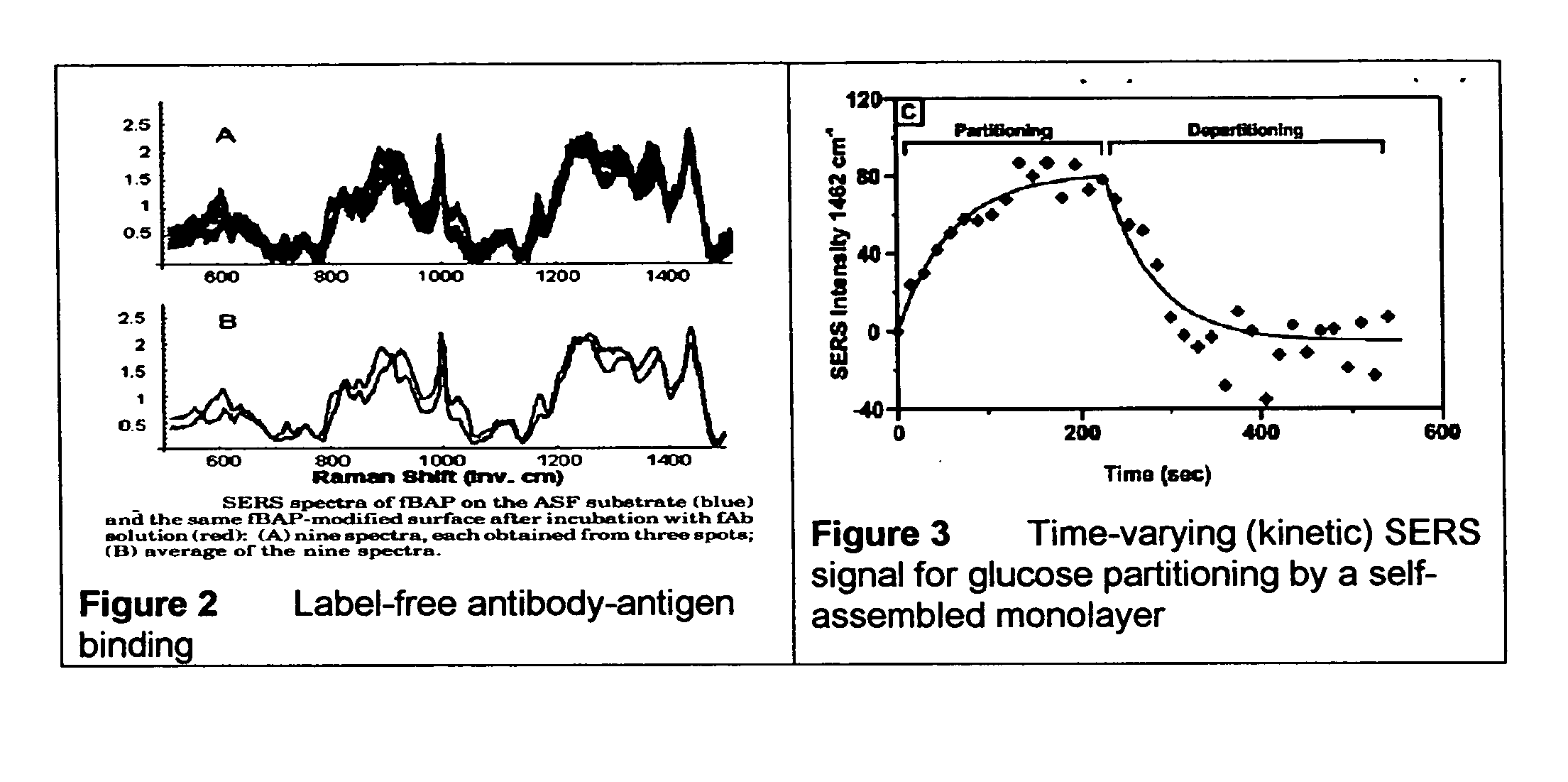
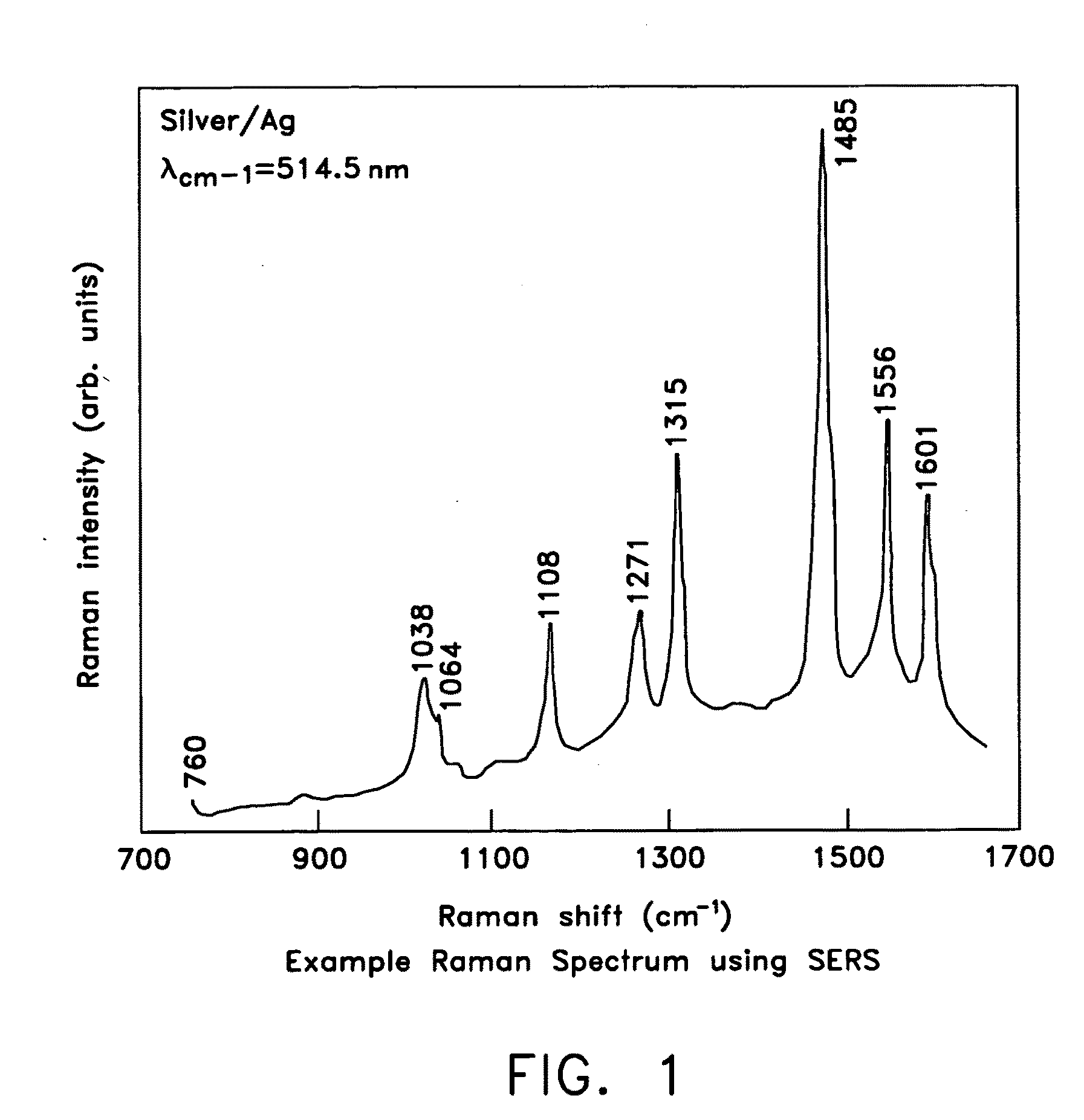
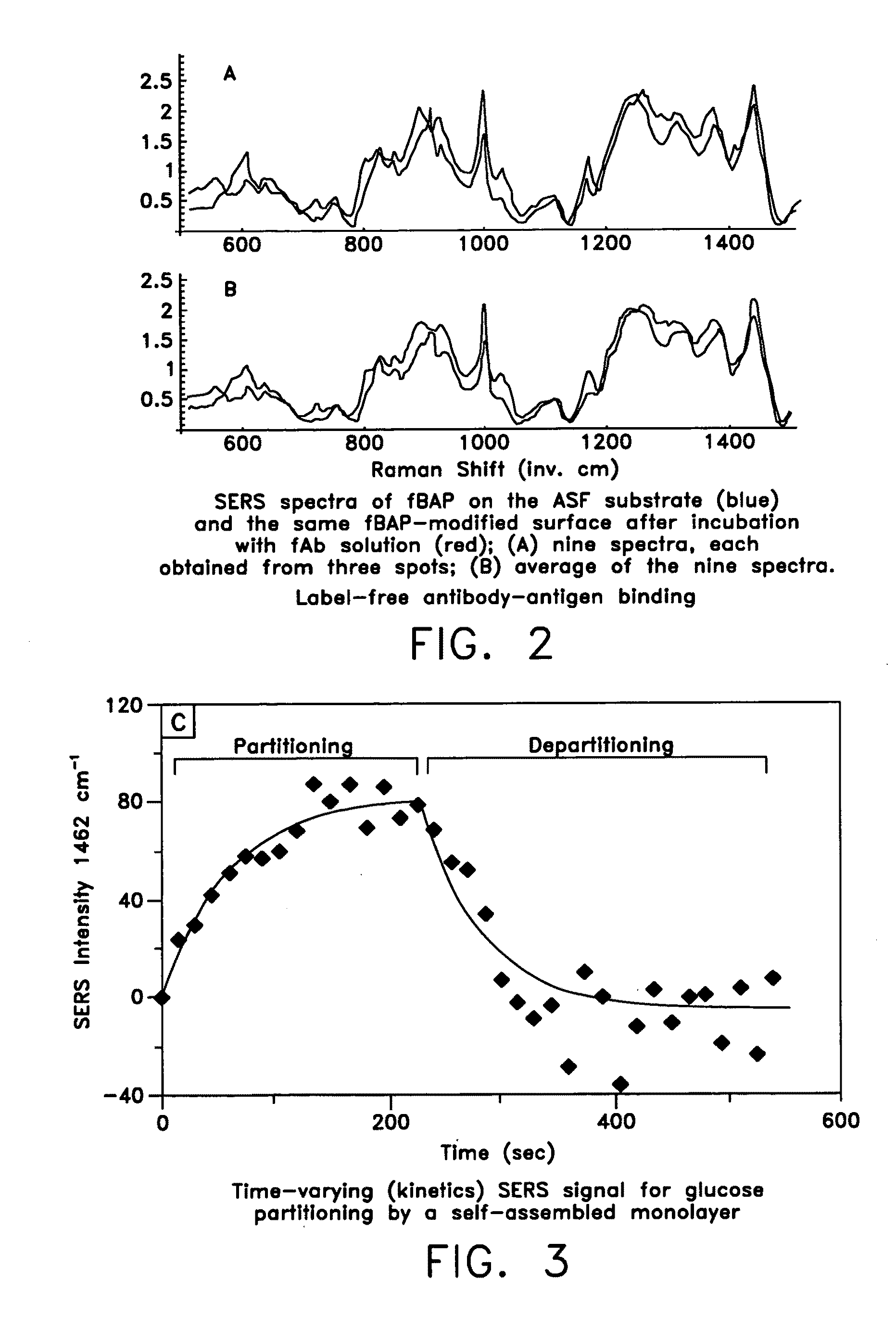
ActiveUS20070115469A1Facilitate SERS analysisMaterial nanotechnologyRadiation pyrometryChemical reactionPhotonics
Surface enhanced Raman Scattering (SERS) and related modalities offer greatly enhanced sensitivity and selectivity for detection of molecular species through the excitation of plasmon modes and their coupling to molecular vibrational modes. One of the chief obstacles to widespread application is the availability of suitable nanostructured materials that exhibit strong enhancement of Raman scattering, are inexpensive to fabricate, and are reproducible. I describe nanostructured surfaces for SERS and other photonic sensing that use semiconductor and metal surfaces fabricated using femtosecond laser processing. A noble metal film (e.g., silver or gold) is evaporated onto the resulting nanostructured surfaces for use as a substrate for SERS. These surfaces are inexpensive to produce and can have their statistical properties precisely tailored by varying the laser processing. Surfaces can be readily micropatterned and both stochastic and self-organized structures can be fabricated. This material has application to a variety of genomic, proteomic, and biosensing applications including label free applications including binding detection. Using this material, monolithic or arrayed substrates can be designed. Substrates for cell culture and microlabs incorporating microfluidics and electrochemical processing can be fabricated as well. Laser processing can be used to form channels in the substrate or a material sandwiched onto it in order to introduce reagents and drive chemical reactions. The substrate can be fabricated so application of an electric potential enables separation of materials by electrophoresis or electro-osmosis.
Owner:EBSTEIN STEVEN M
Imaging Apparatus for IR Four-Wave Mixing Polarization Microscopy
InactiveUS20080304047A1Reduce spatial resolutionReduce spacingRadiation pyrometryPolarisation-affecting propertiesBeam splitterPhotodetector
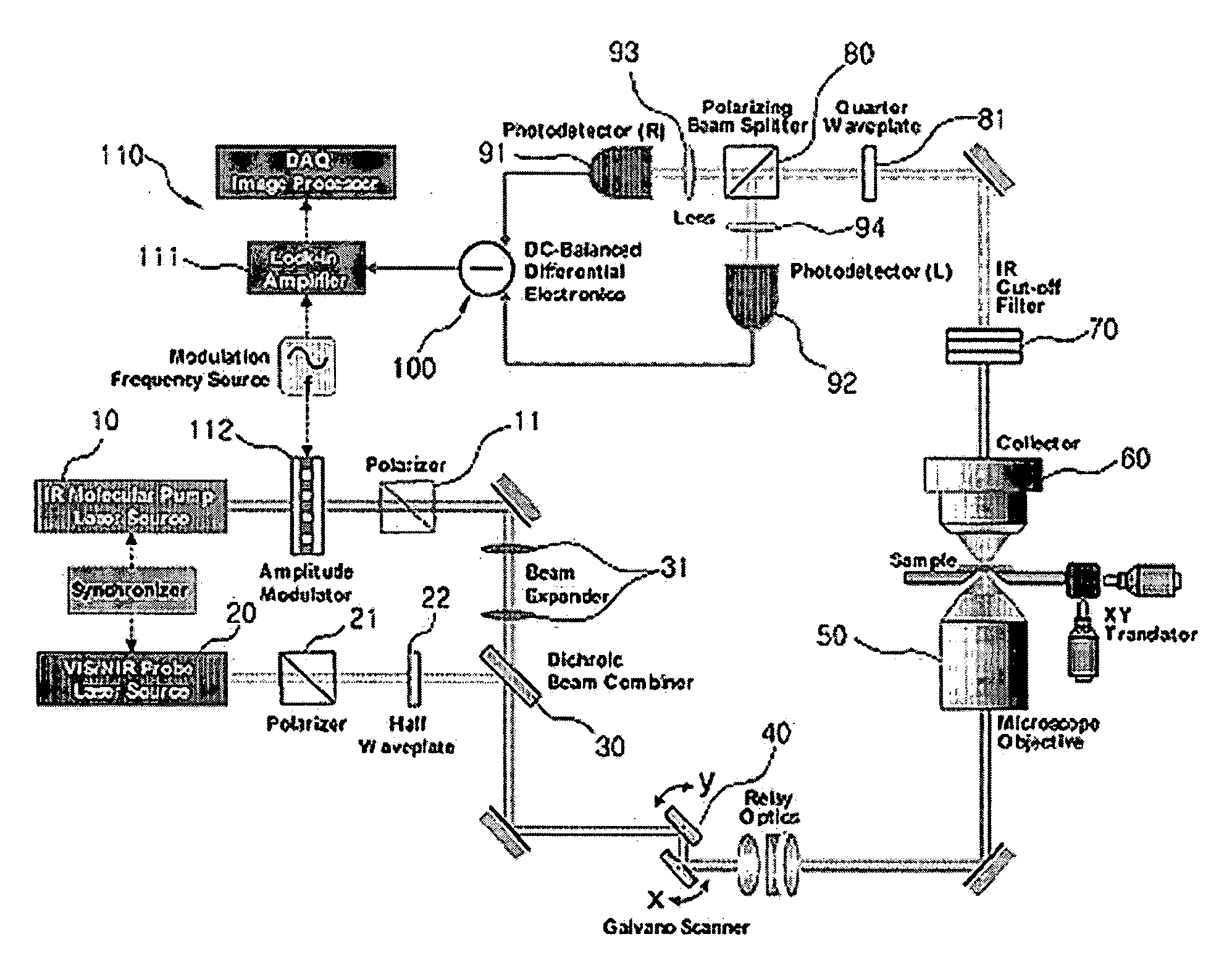
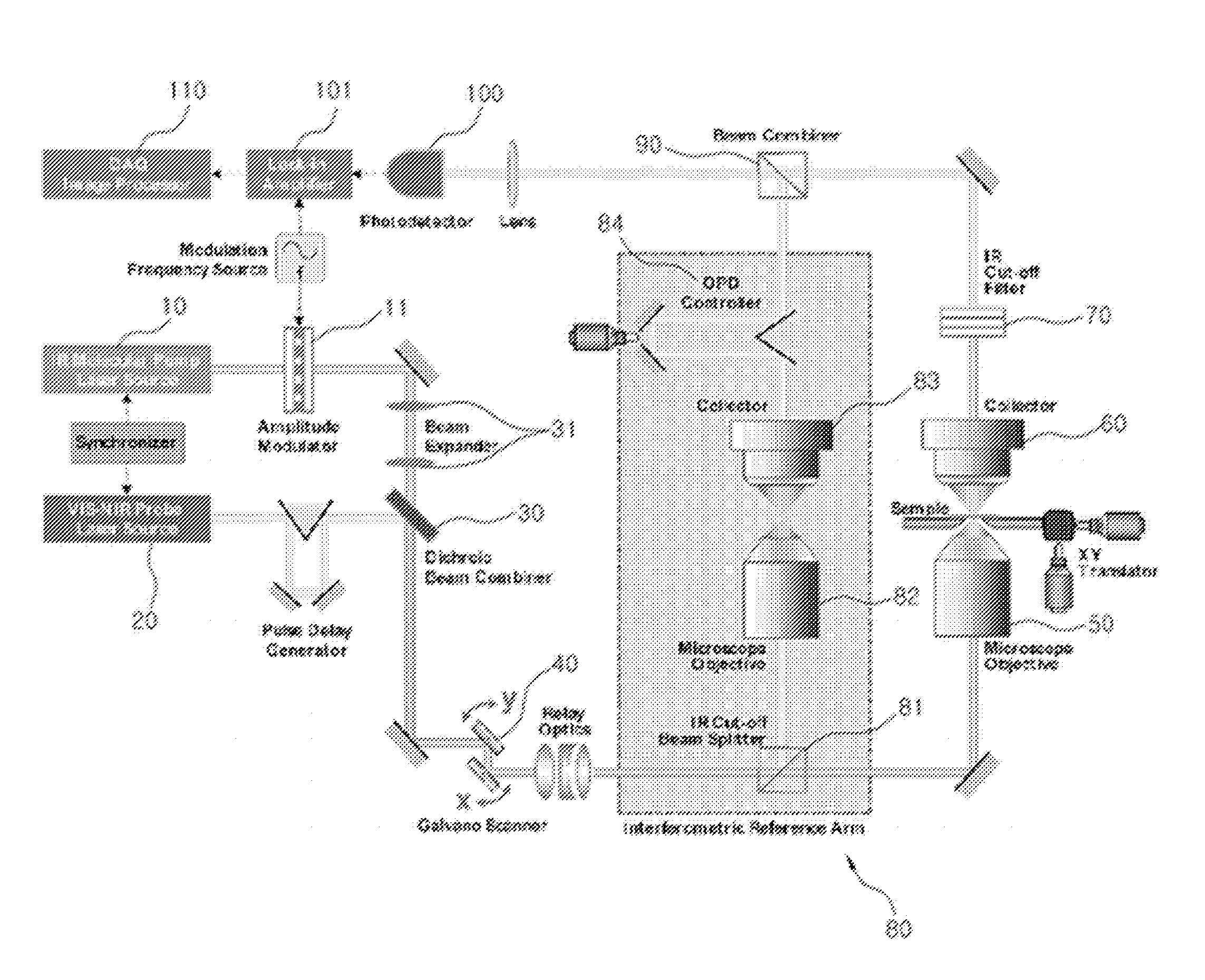
The present invention relates to an imaging apparatus for IR four-wave mixing polarization microscopy. The imaging apparatus comprises a pump beam source for generating an infrared pump beam; a probe beam source for generating a probe beam (search beam); a polarizer for linearly polarizing the pump beam and probe beam; a beam combiner which synchronizes temporally and overlaps spatially the polarized pump beam and probe beam on the same axis; a scanner for two-dimensionally scanning the combined pump beam and probe beam; an optical focusing system for focusing the scanned pump beam and probe beam on a local point of the sample; a collecting optical system for collecting the beam which is formed by that the focused beams are interacted with the sample and of which phase is anisotropically retarded by nonlinear birefringence of the sample and forming a parallel beam; a dichroic beam splitter for removing the infrared pump beam out of the parallel beam and splitting the probe beam of which phase is anisotropically retarded; a polarizing beam splitter for converting the split and ansotripically phase-retarded probe beam into linerly polarized beams having their axes perpendicular to each other; a photodetector for detecting an intensity of each of the converted linerly polarized beams; a polarization differential detector for detecting a polarization difference based on the detected intensities of the linerly polarized beams; and a data analyzer for acquiring the detected polarization difference signal and extracting a spectrospcopic information corresponding to the strength of molecular vibrational coherence of the sample.
Owner:KOREA RES INST OF STANDARDS & SCI
System and method for coherent anti-Stokes Raman scattering endoscopy
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Laser-processed substrate for molecular diagnostics
ActiveUS20090279085A1Facilitate SERS analysisMaterial nanotechnologyRadiation pyrometryChemical reactionPhotonics
Surface enhanced Raman Scattering (SERS) and related modalities offer greatly enhanced sensitivity and selectivity for detection of molecular species through the excitation of plasmon modes and their coupling to molecular vibrational modes. One of the chief obstacles to widespread application is the availability of suitable nanostructured materials that exhibit strong enhancement of Raman scattering, are inexpensive to fabricate, and are reproducible. I describe nanostructured surfaces for SERS and other photonic sensing that use semiconductor and metal surfaces fabricated using femtosecond laser processing. A noble metal film (e.g., silver or gold) is evaporated onto the resulting nanostructured surfaces for use as a substrate for SERS. These surfaces are inexpensive to produce and can have their statistical properties precisely tailored by varying the laser processing. Surfaces can be readily micropatterned and both stochastic and self-organized structures can be fabricated. This material has application to a variety of genomic, proteomic, and biosensing applications including label free applications including binding detection. Using this material, monolithic or arrayed substrates can be designed. Substrates for cell culture and microlabs incorporating microfluidics and electrochemical processing can be fabricated as well. Laser processing can be used to form channels in the substrate or a material sandwiched onto it in order to introduce reagents and drive chemical reactions. The substrate can be fabricated so application of an electric potential enables separation of materials by electrophoresis or electro-osmosis.
Owner:EBSTEIN STEVEN M
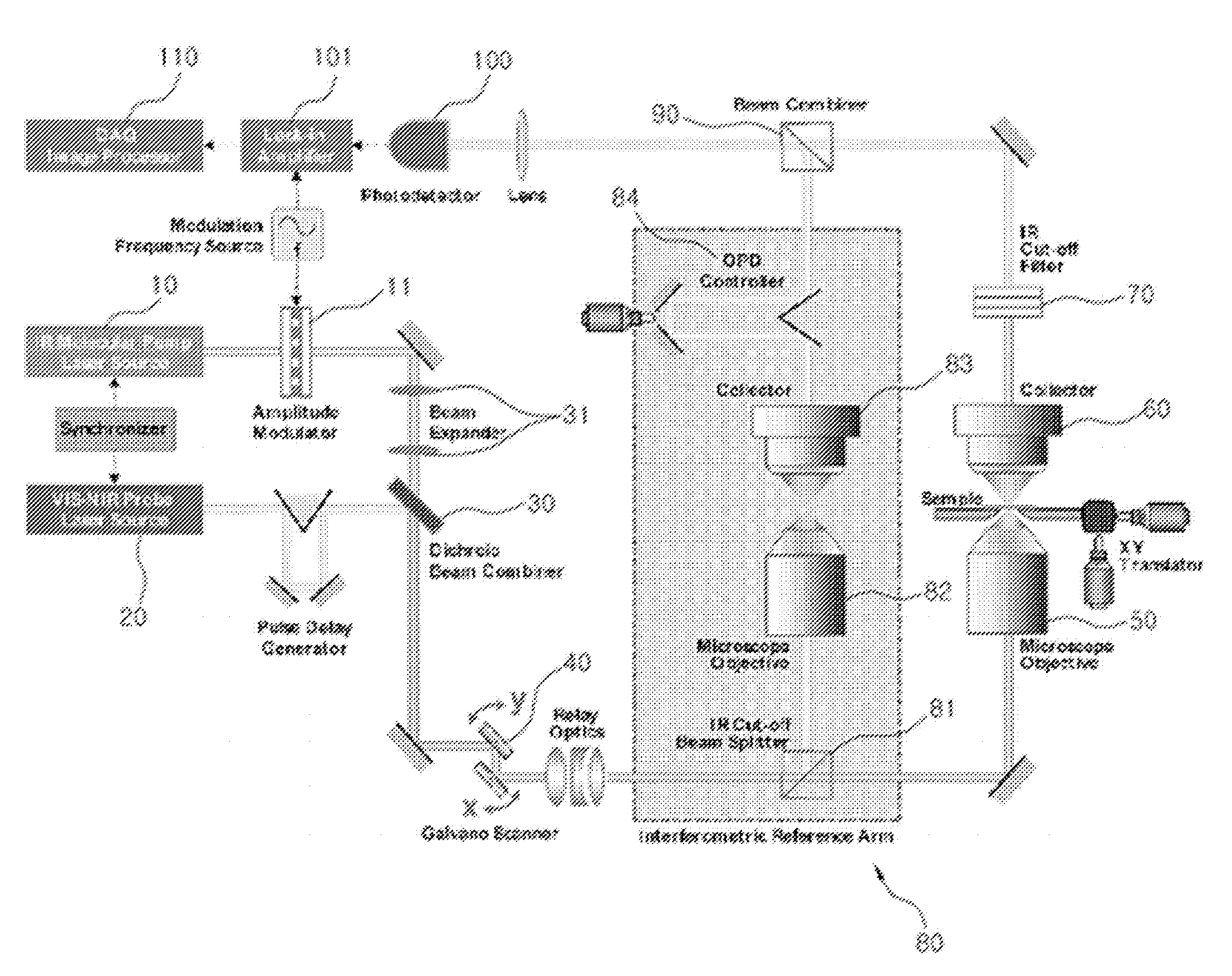
Imaging Apparatus for Infrared Rays Nonlinear Molecular Vibrational Microscopy
InactiveUS20080304046A1Reduce spatial resolutionReduce spacingRadiation pyrometryInterferometric spectrometryBeam splitterBeam source
The present invention relates to an imaging apparatus for infrared rays nonlinear molecular vibrational microscopy. The imaging apparatus comprises a pump beam source for generating an infrared pump beam; a probe beam source for generating a probe beam; a beam combiner which synchronizes temporally and overlaps spatially the pump beam and probe beam on the same axis; a scanner for two-dimensionally scanning the combined pump beam and probe beam; a first optical focusing system for focusing the scanned pump beam and probe beam on a local point of the sample; a first collecting optical system for collecting the beam of which phase is shifted by interaction with the sample and forming a parallel beam; a first dichroic beam splitter for removing the infrared pump beam out of the parallel beam and splitting the probe beam of which phase is shifted; a reference interferometer for splitting a part of the probe beam out of the beams scanned by the scanner and generating a reference probel beam; an interferometric beam combiner for combining the probe beam having the shifted phase and the reference probe beam; a photodetector for detecting an intensity of a molecular vibrational beam signal from the combined probe beam; and a data analyzer for acquiring the detected signals and extracting a spectrospcopic information corresponding to the strength of molecular vibrational coherence of the sample.
Owner:KOREA RES INST OF STANDARDS & SCI
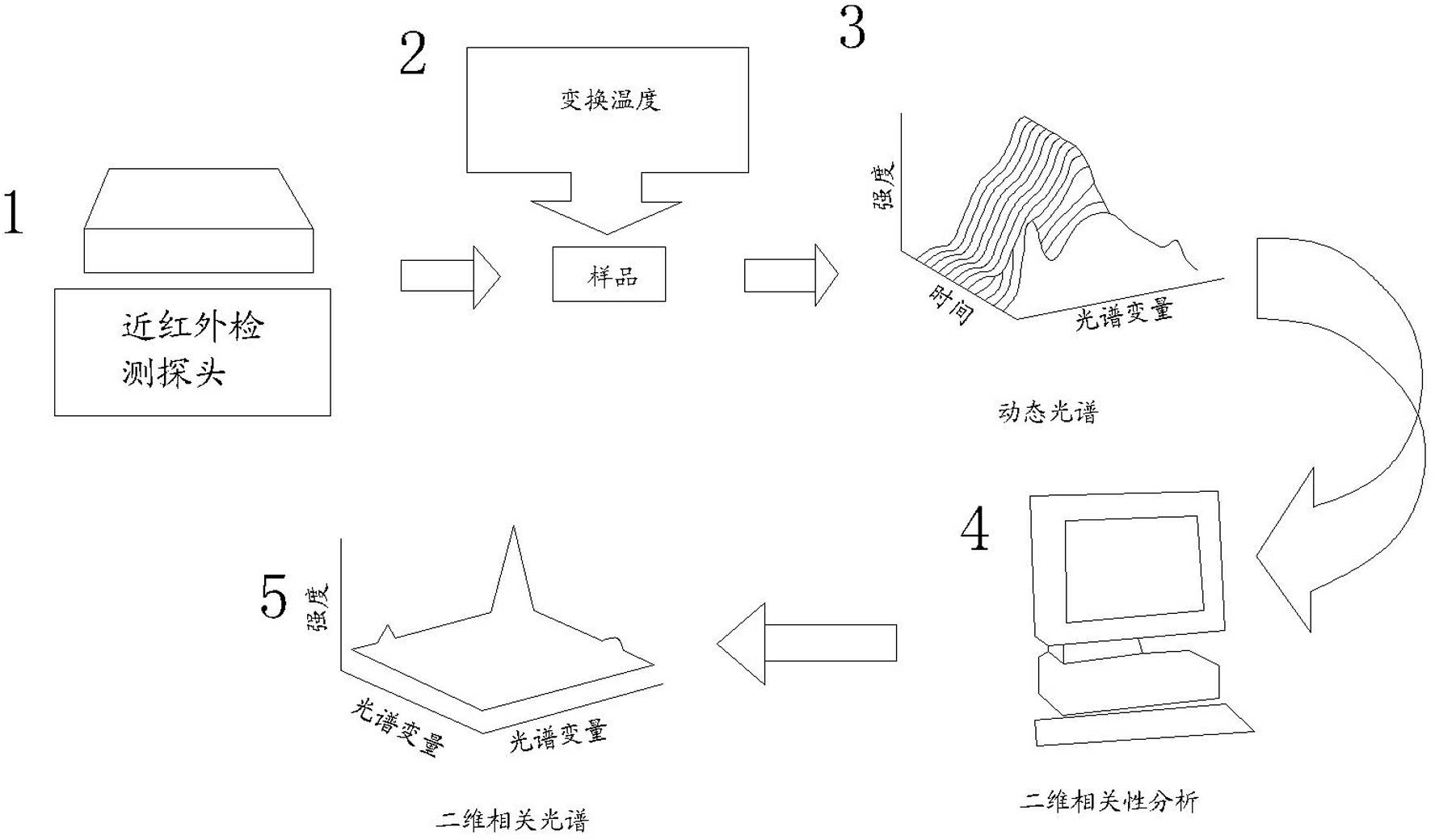
Method for detecting near-infrared two-dimensional correlation spectra
InactiveCN102435575AHigh-resolutionEfficient separationColor/spectral properties measurementsChemical reactionMolecular vibration
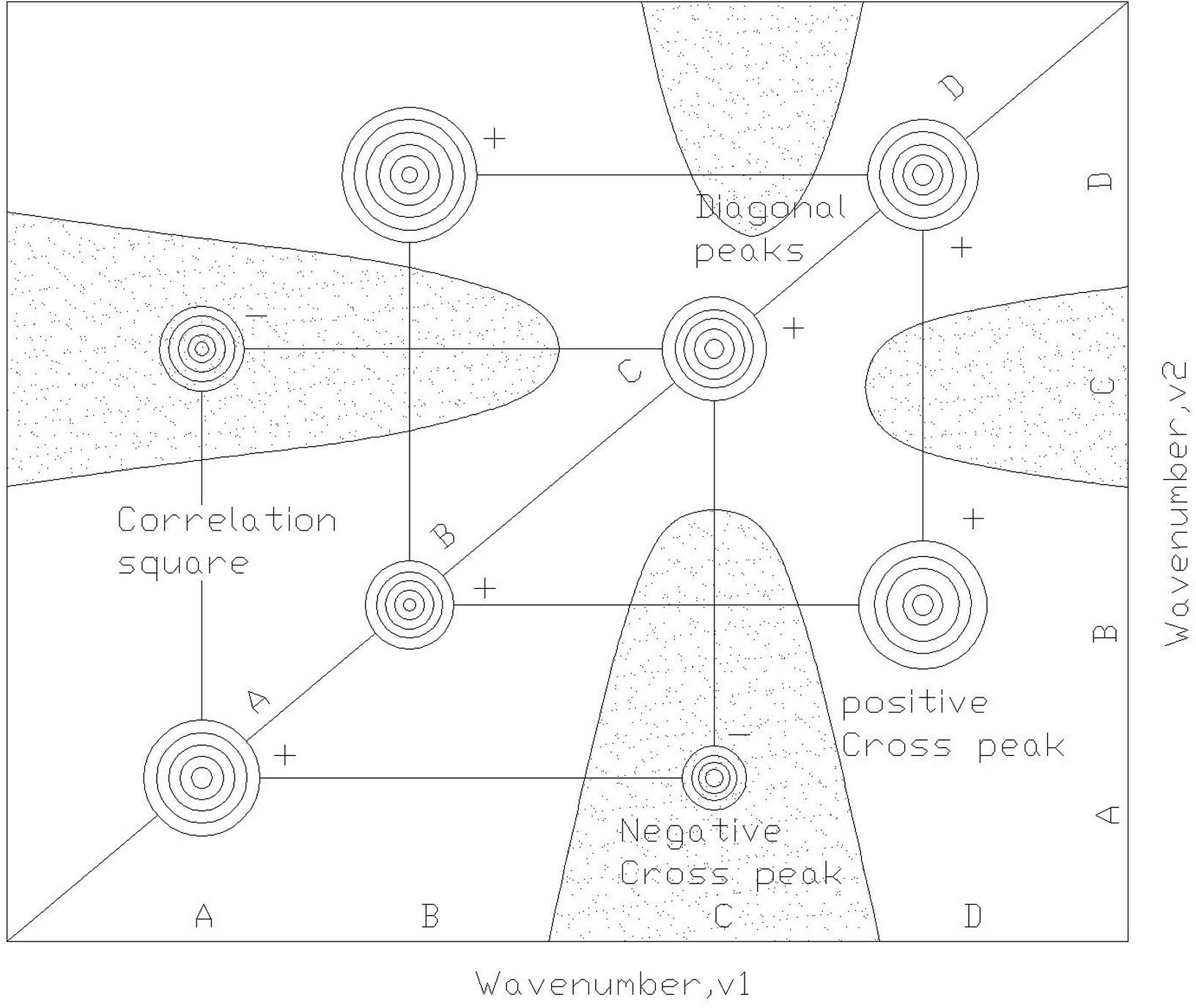
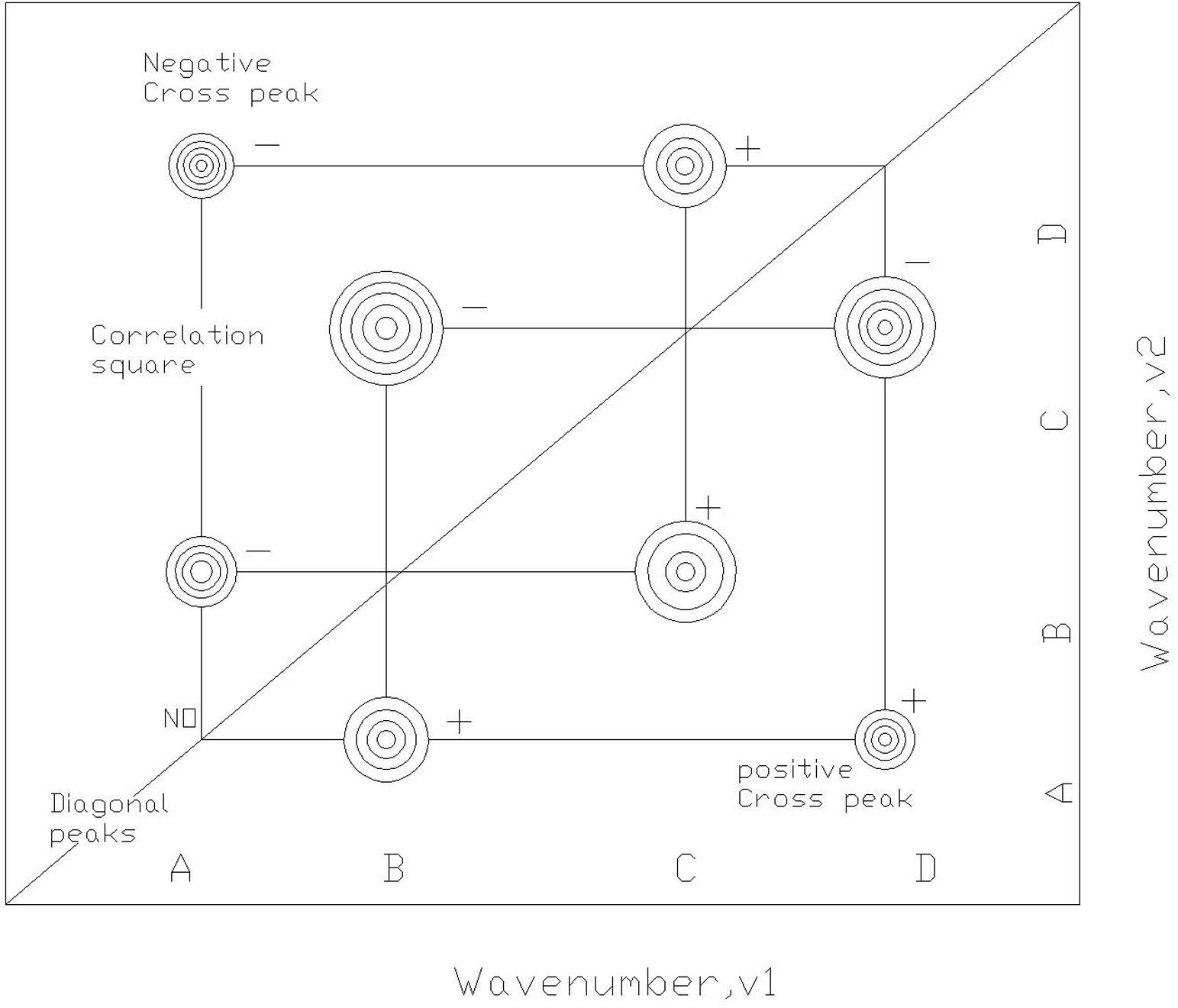
A method for detecting near-infrared two-dimensional correlation spectra includes the following steps: a near-infrared spectroscopy detector is first set into an operating state, and after being prepared, a sample placed into a temperature-controlling accessory and positioned under a near-infrared detection probe; the temperature-controlling accessory is then utilized to control the temperature; afterwards, variable-temperature detection is carried out to obtain a series of spectrograms, and the spectrograms are digitalized; matlab software is run, and a calculation program is started to work out a dynamic spectrum; a band is selected according to a prompt to work out the synchronous diagrams and asynchronous diagrams of the two-dimensional correlation spectrum; and finally, according to the spectral characteristics in the synchronous diagrams and the asynchronous diagrams, identification or other qualitative analyses are carried out on the sample. The method spreads the absorption peaks of the spectrum on the second dimension, so that the spectral peaks of the near-infrared spectrum are more convenient to assign; by means of an analysis on the correlation between spectral lines, the interaction between different molecules or in molecules can be studied in detail; and by detecting the sequence of spectral intensity change, the process of chemical reaction and the kinetic process of molecular vibration can be effectively studied in detail.
Owner:中山市中健药业有限公司
Different modal molecular vibration spectrum detection and imaging device and method
ActiveCN104359892AEnabling Quantitative MicroscopyEnabling Qualitative Spectral AnalysisRaman scatteringStimulate raman scatteringMolecular vibration
The invention relates to a different modal molecular vibration spectrum detection and imaging device and a method. The device mainly consists of related apparatuses of functional units such as a laser unit, an optical scanning microscopic unit, a stimulated Raman scattering signal probing and acquiring unit and a spontaneous Raman spectrum detection member and the like. In light of implementation by the method, two different modal molecular vibration scattered signals are quickly acquired in situ on a living cell, an isolated biological tissue and a living small animal: spontaneous Raman spectrum detection under a single laser beam working mode and stimulated Raman scattering microimaging under a double laser beam working mode to achieve quantitative microimaging and qualitative spectral analysis on a target so as to obtain characteristic information of target components, thereby providing important data for optical analysis and deep analysis of a sample.
Owner:FUJIAN NORMAL UNIV
Measurement device and measurement method
InactiveCN103959045AHigh Sensitivity Relaxation TimeRaman scatteringSpectrometry/spectrophotometry/monochromatorsMeasurement deviceSpectroscopy
Owner:SONY CORP
Applications of laser-processed substrate for molecular diagnostics
Surface enhanced Raman Scattering (SERS) and related modalities offer greatly enhanced sensitivity and selectivity for detection of molecular species through the excitation of plasmon modes and their coupling to molecular vibrational modes. One of the chief obstacles to widespread application is the availability of suitable nanostructured materials that exhibit strong enhancement of Raman scattering, are inexpensive to fabricate, and are reproducible. I describe nanostructured surfaces for SERS and other photonic sensing that use semiconductor and metal surfaces fabricated using femtosecond laser processing. A noble metal film (e.g., silver or gold) is evaporated onto the resulting nanostructured surfaces for use as a substrate for SERS. These surfaces are inexpensive to produce and can have their statistical properties precisely tailored by varying the laser processing. Surfaces can be readily micropatterned and both stochastic and self-organized structures can be fabricated. This material has application to a variety of genomic, proteomic, and biosensing applications including label free applications including binding detection. Using this material, monolithic or arrayed substrates can be designed. Substrates for cell culture and microlabs incorporating microfluidics and electrochemical processing can be fabricated as well. Laser processing can be used to form channels in the substrate or a material sandwiched onto it in order to introduce reagents and drive chemical reactions. The substrate can be fabricated so application of an electric potential enables separation of materials by electrophoresis or electro-osmosis.
Owner:EBSTEIN STEVEN M
Measurement apparatus and measurement method
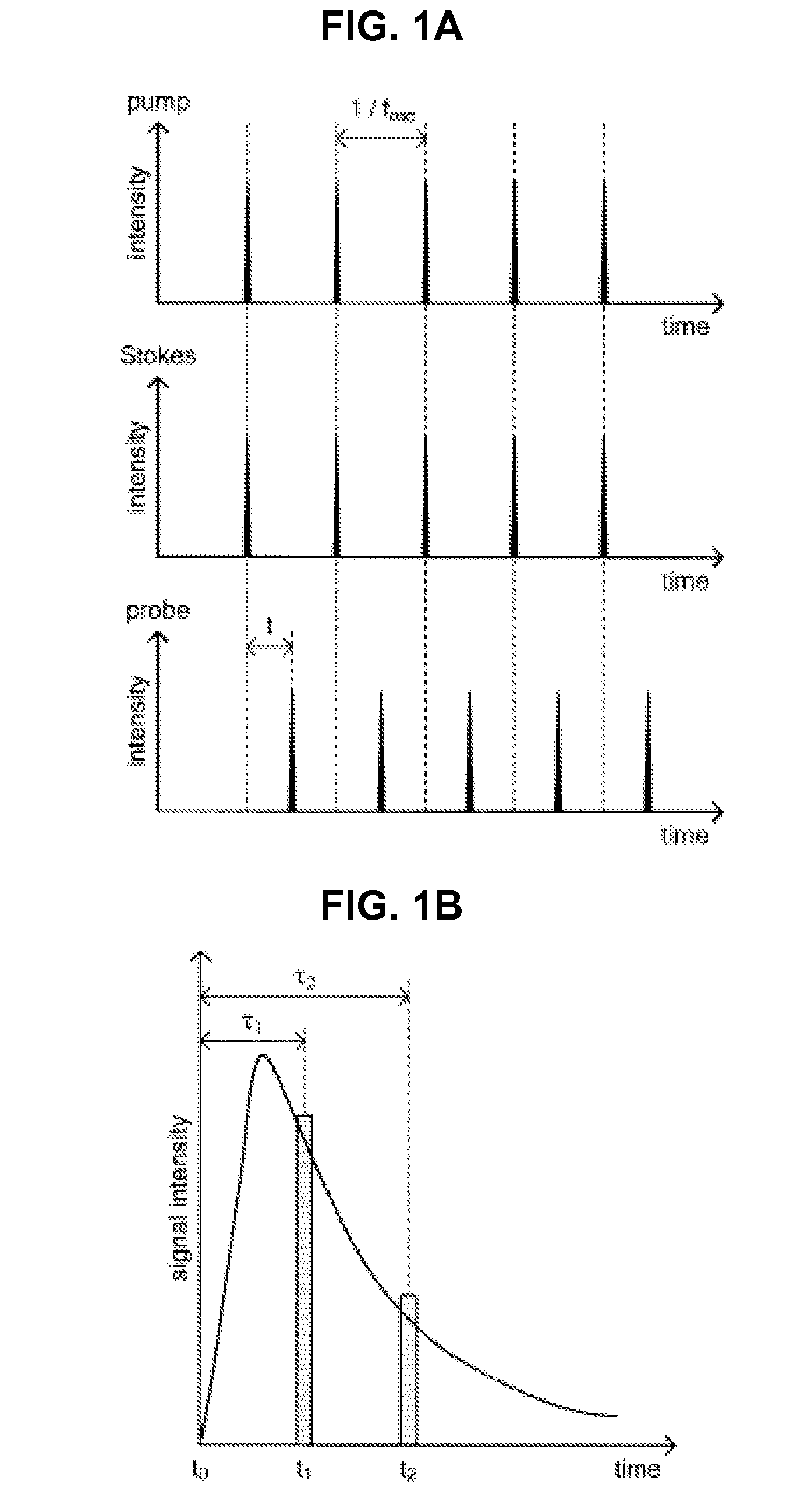
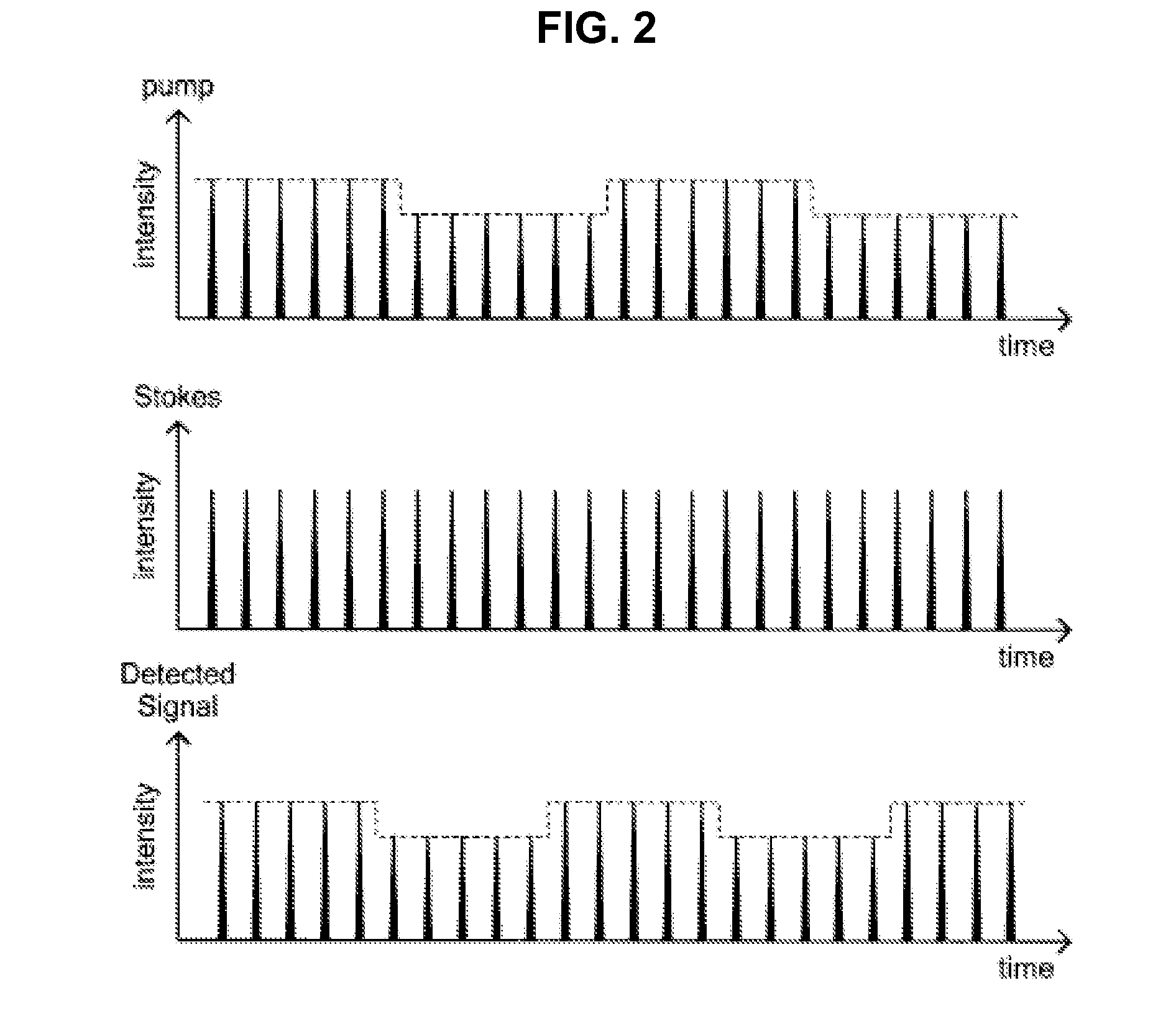
InactiveUS20140268131A1High sensitivityRadiation pyrometryRaman scatteringMeasuring instrumentMolecular vibration
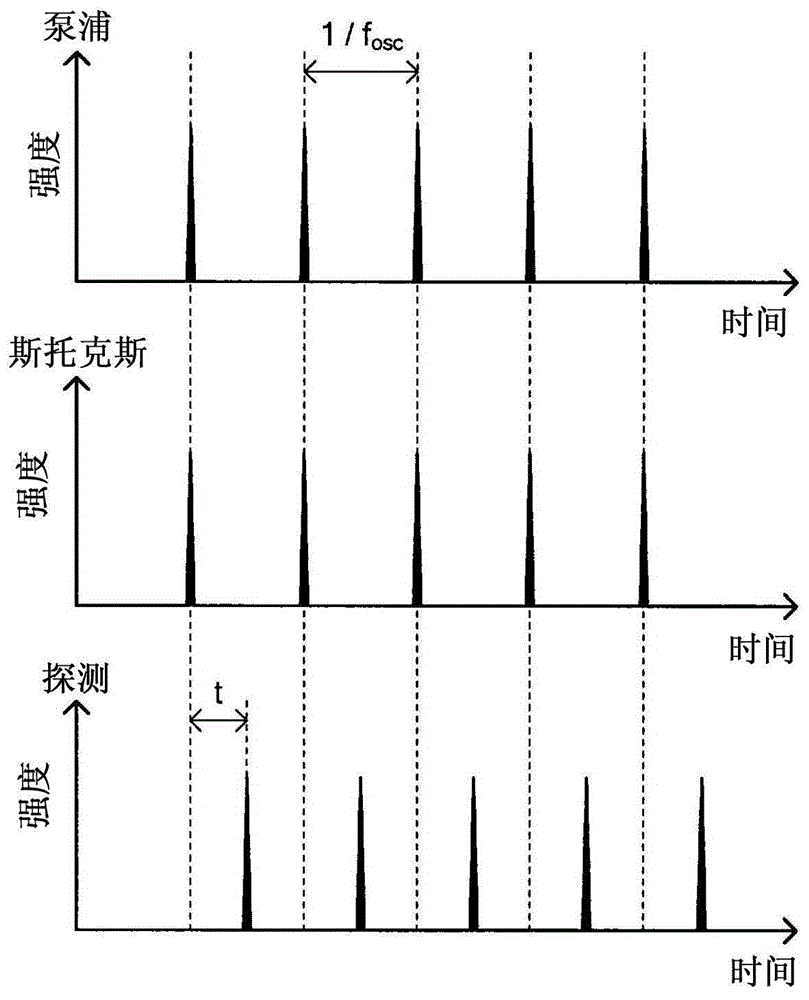
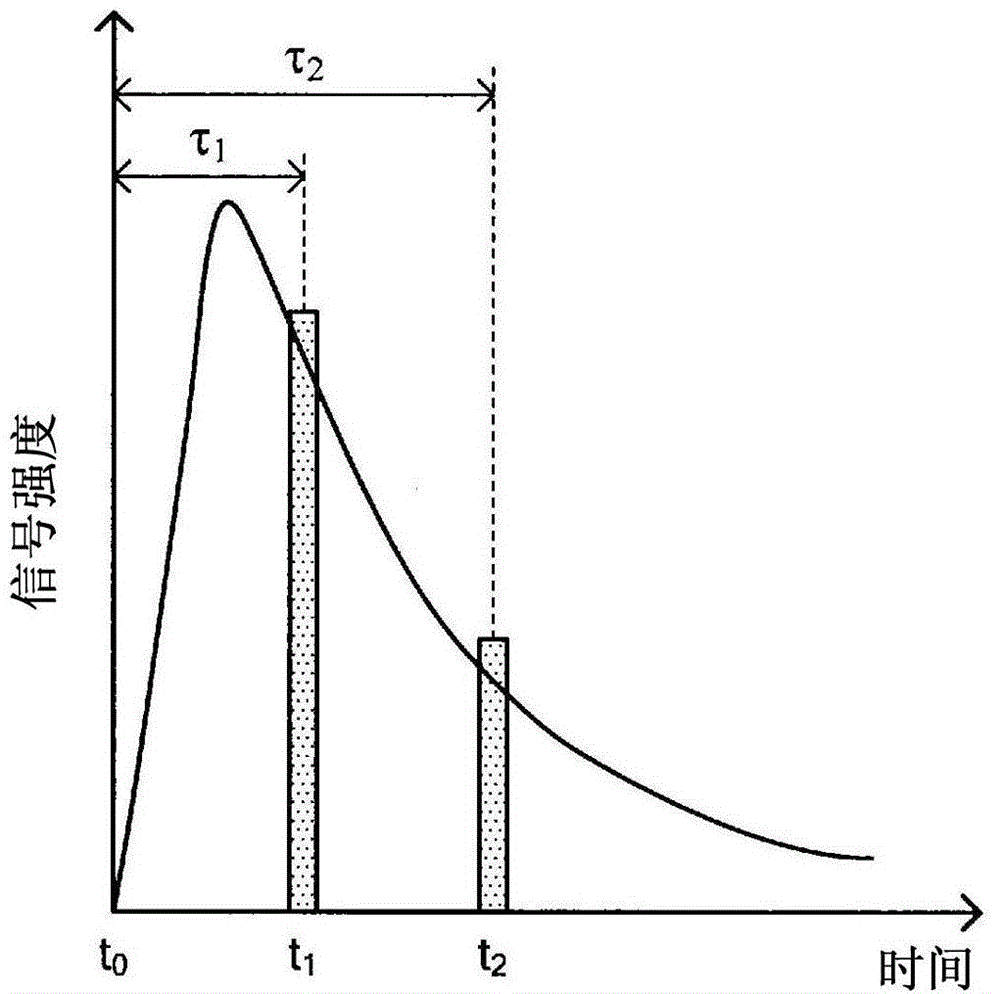
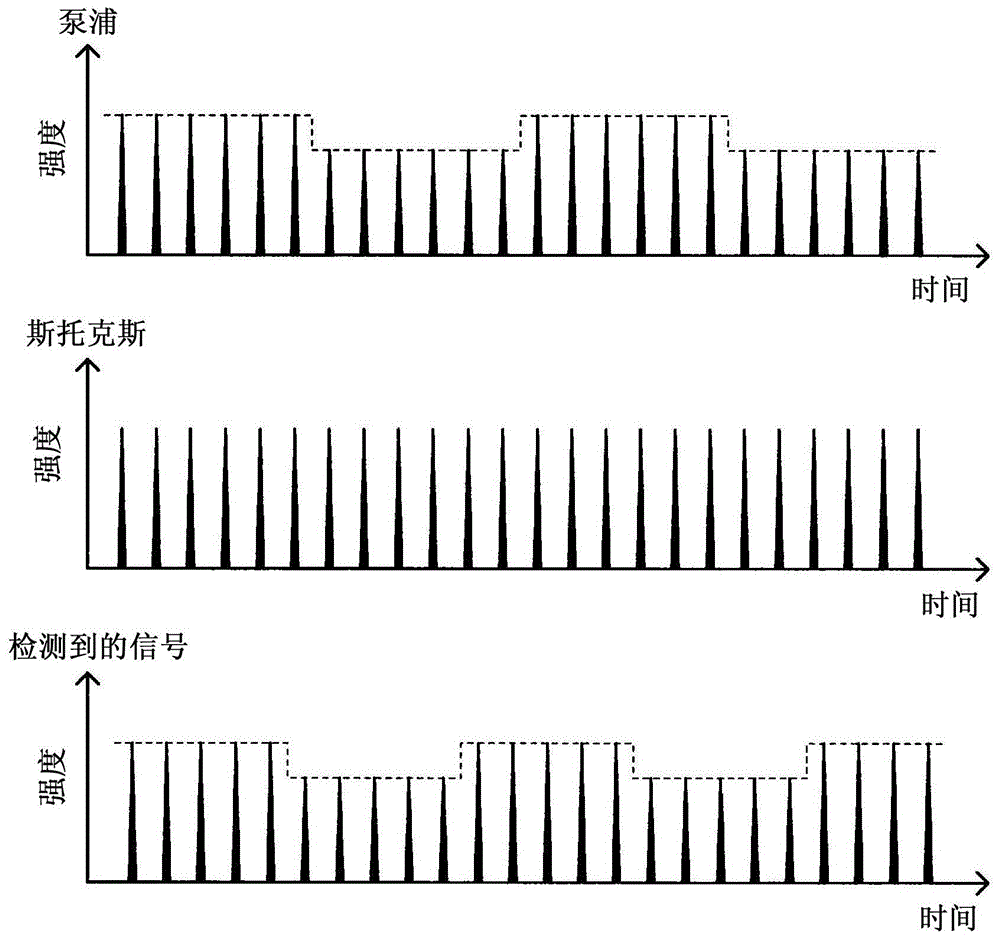
There is provided a measurement apparatus including a light source unit configured to emit pulsed laser light used for pump light and Stokes light that excite predetermined molecular vibration of a measurement sample and for probe light that is intensity-modulated with a predetermined reference frequency and that has a same wavelength as the pump light or the Stokes light, a pulse control unit configured to cause time delay of the probe light generated by the light source unit and then to guide the pump light, the Stokes light, and the time-delayed probe light to the measurement sample, and a detection unit configured to detect transmitted light transmitted through the measurement sample or reflected light from the measurement sample. A relaxation time of the molecular vibration of the measurement sample is measured using time-resolved stimulated Raman gain spectroscopic measurement or time-resolved stimulated Raman loss spectroscopic measurement of the measurement sample.
Owner:SONY CORP
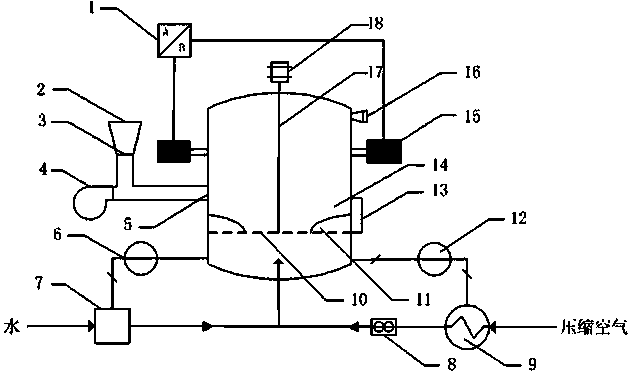
Microwave-hot air combined fluidized bed drying experiment device
ActiveCN104034127AEvenly distributedHeating evenlyDrying solid materials with heatDrying gas arrangementsFluidized bed dryingEnergy absorption
A microwave-hot air combined fluidized bed drying experiment device is characterized by comprising a tower type fluidized bed, a microwave drying device disposed on the lateral wall of the tower type fluidized bed and a hot air drying system connected to the bottom of the tower type fluidized bed. The microwave drying device comprises a microwave generator and a microwave controller. The hot air drying system comprises a hot air heater, a temperature controller, a steam generator, a humidity detector and a compressed air source. By the microwave-hot air combined fluidized bed drying experiment device which is high in automation level, small in floor space and simple and safe to operate, fast temperature rise of materials can be achieved in a short time, even heating is achieved, and evenness of microwave energy absorption is increased; during drying, microwaves can stimulate polar molecules to change orientations constantly to generate a non-thermal effect by high-speed molecule vibration so as to accelerate drying, materials (such as tobacco) with the effective components mostly being glycoside, terpene lactone and volatile oil can be well protected, and quality of dried materials is guaranteed.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU TOBACCO RES INST OF CNTC
3-Color multiplex cars spectrometer
InactiveUS20100020318A1Solve the real problemStable and sufficient outputRaman/scattering spectroscopyRadiation pyrometryLine widthSpectrograph
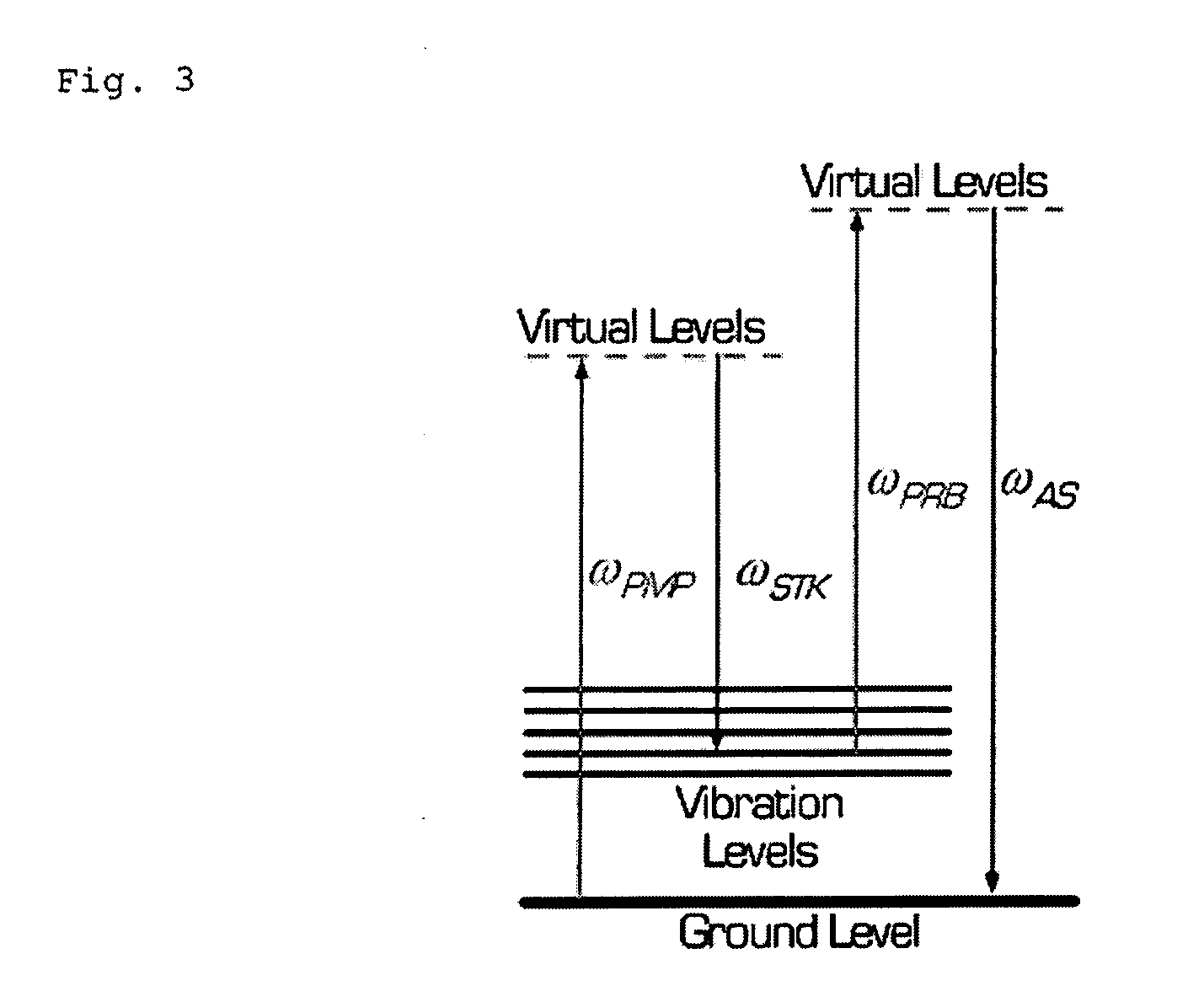
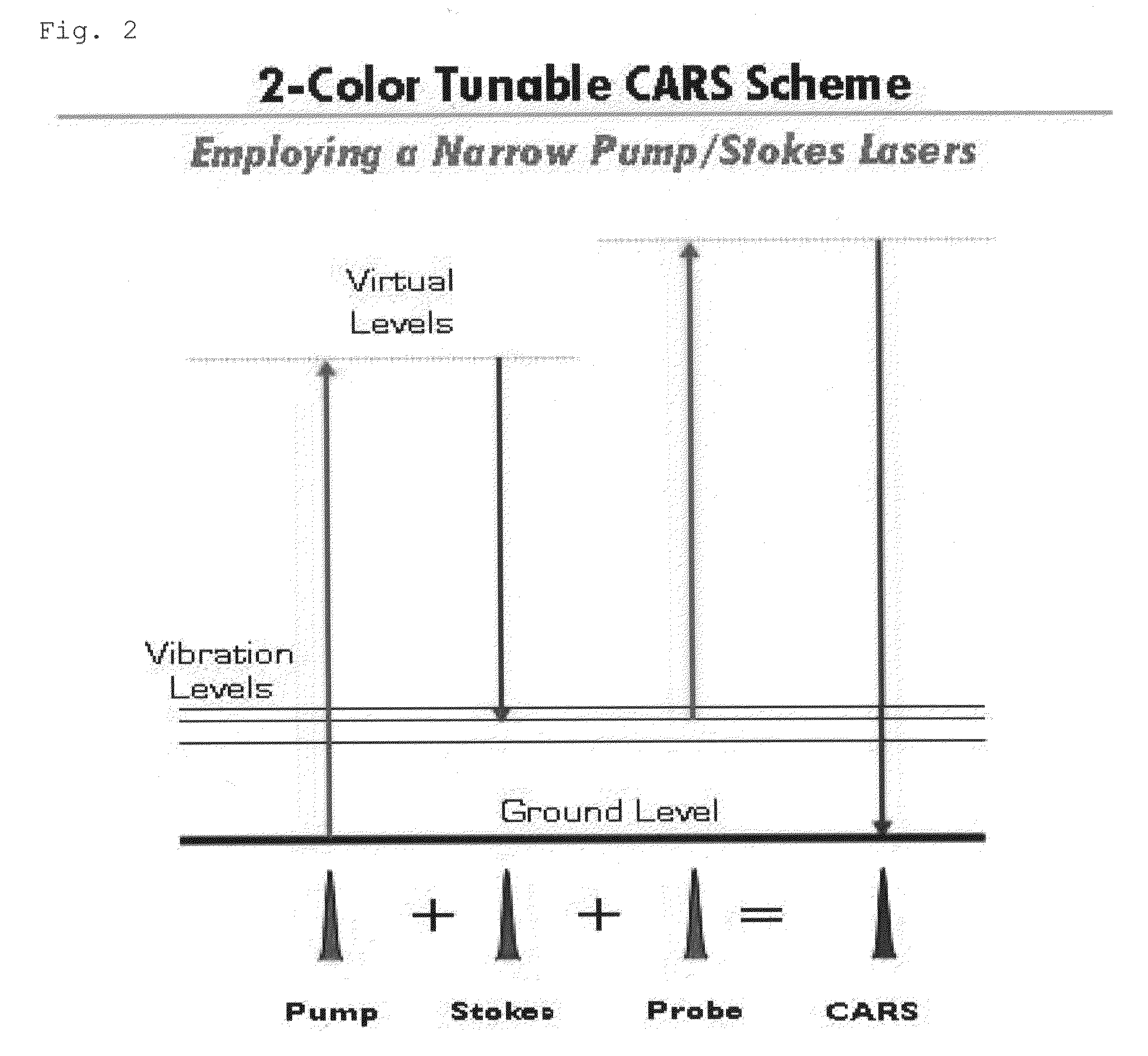
The present invention relates to a 3-color multiplex CARS spectrometer. In the 3-color multiplex CARS spectrometer, Raman resonance is achieved for multiple molecular vibrations of a sample by the combination of a short-wavelength pump beam generated by a broadband laser light source and a long-wavelength Stokes beam generated by a stable laser light source, and another short-wavelength laser beam having a narrow linewidth is then introduced separately to serve as a probe beam that interacts with the laser-driven sample, thereby generating CARS spectral signals whose wavelength components can be resolved. Accordingly, the 3-color multiplex CARS spectrometer solves problem of the conventional 2-color multiplex CARS spectroscopy in which the wavelength decomposition of CARS signals, necessary for high spectral resolution, is not possible with broadband pump light causing the CARS spectrum distortion.
Owner:KOREA RES INST OF STANDARDS & SCI
Laser microscope apparatus
ActiveUS20090290150A1Generate efficientlyLow priceRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationFluorescenceMolecular vibration
To enable both observations of coherent anti-Stokes Raman scattering light and multiphoton fluorescence in a same apparatus so as to observe a specimen by various observation methods. There is provided a laser microscope apparatus comprising: two optical paths for guiding pulsed laser beams having two different frequencies whose frequency difference is approximately equal to a specific molecular vibration frequency in a specimen; a multiplexer for combining the pulsed laser beams guided through these two optical paths; and a frequency dispersion adjuster which is provided on at least one of these two optical paths, and is capable of adjustment to approximately equalize frequency dispersion quantities of the pulsed laser beams guided through the two optical paths.
Owner:EVIDENT CORP
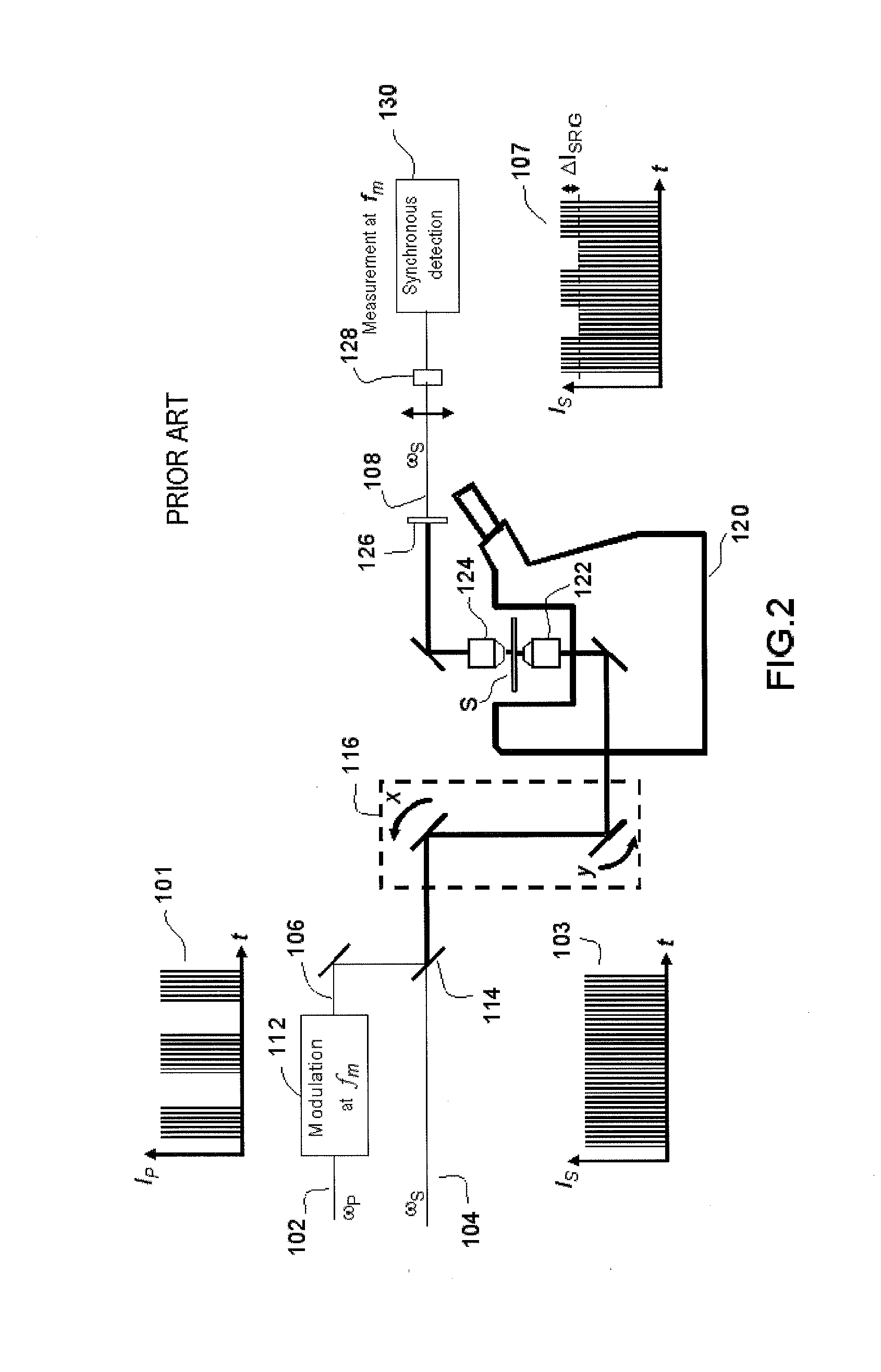
Device and method for stimulated raman detection
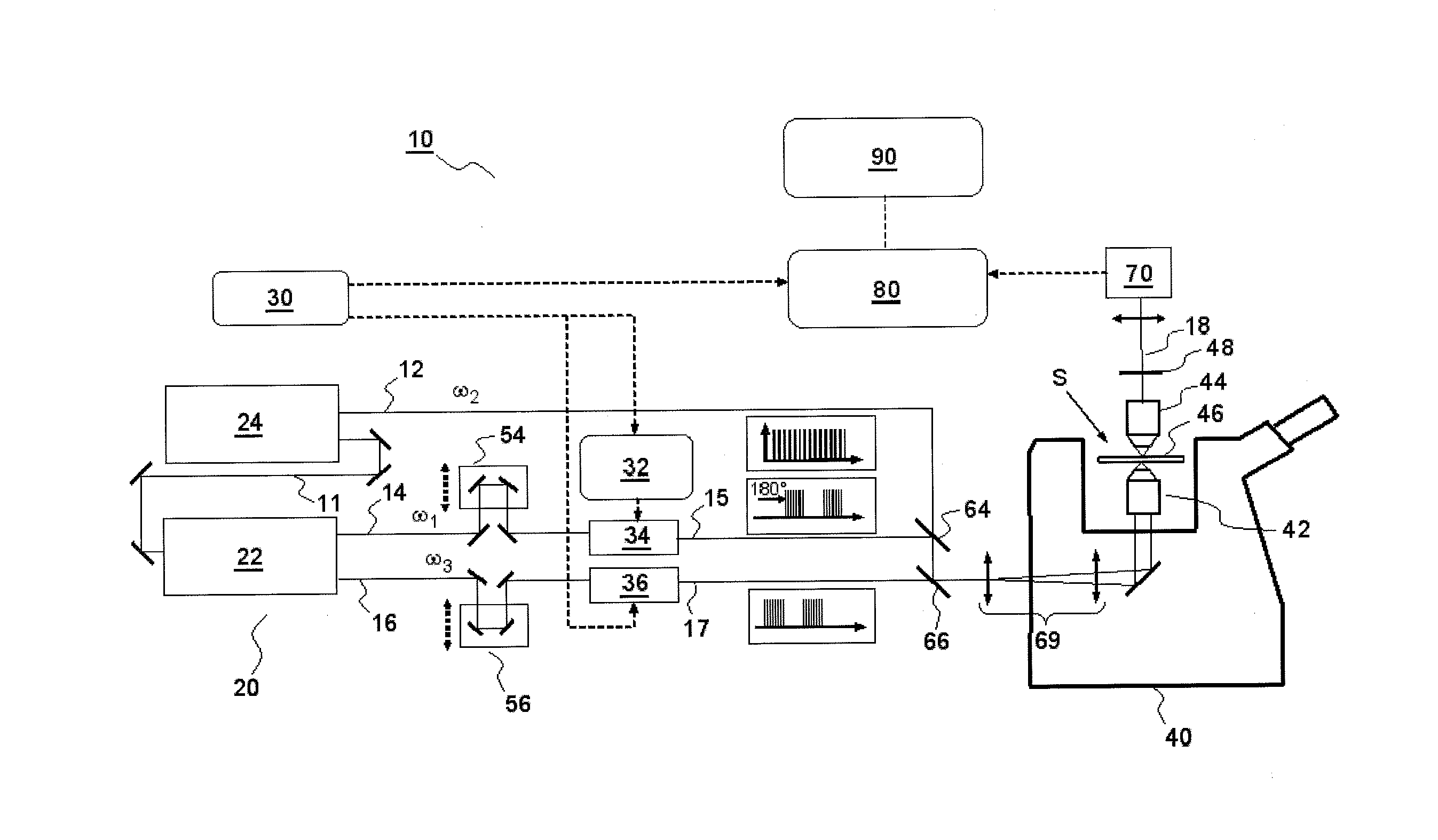
ActiveUS20160047750A1Suppress artifactsArtifact dueRadiation pyrometryRaman scatteringMolecular vibrationSynchronous detection
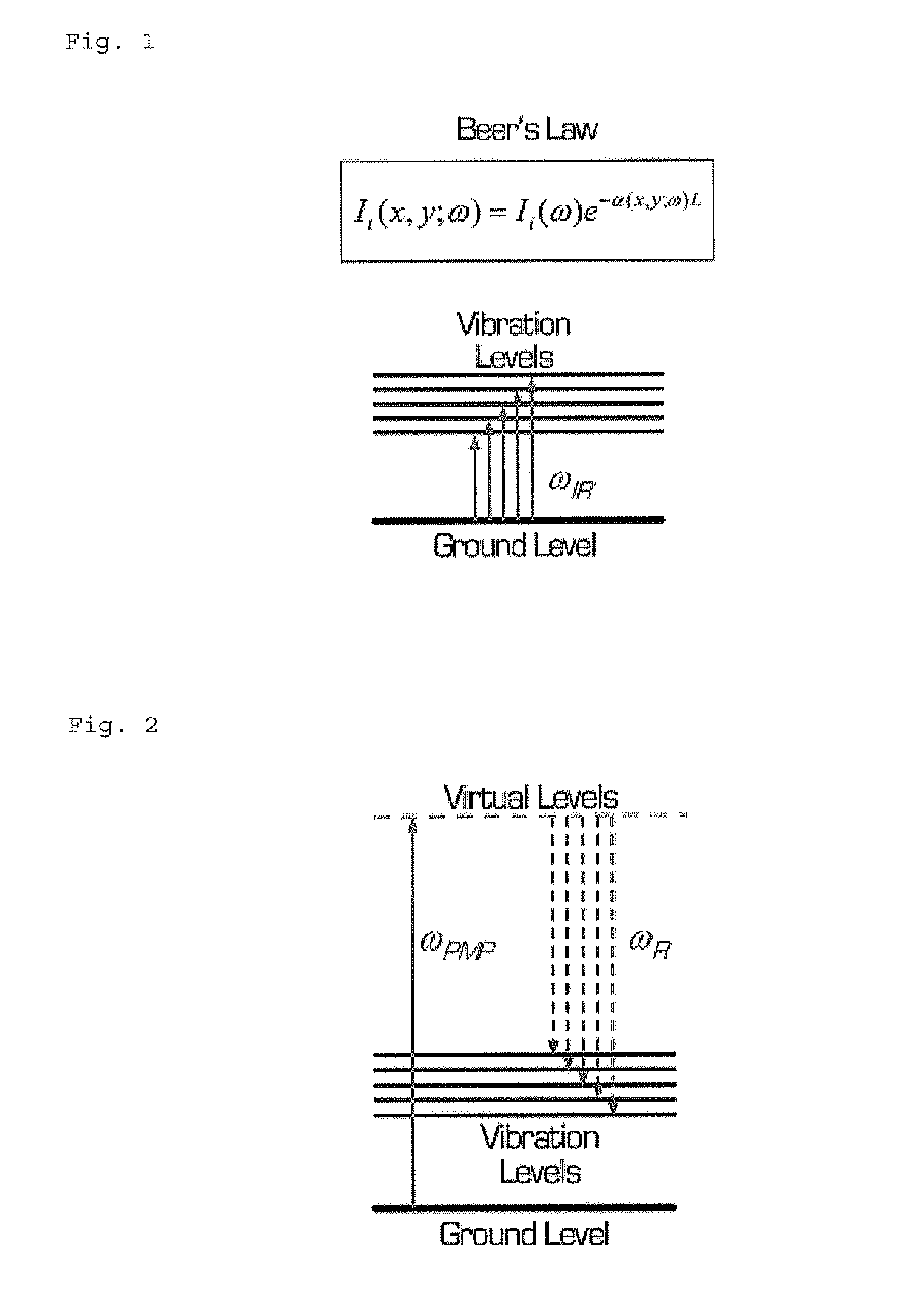
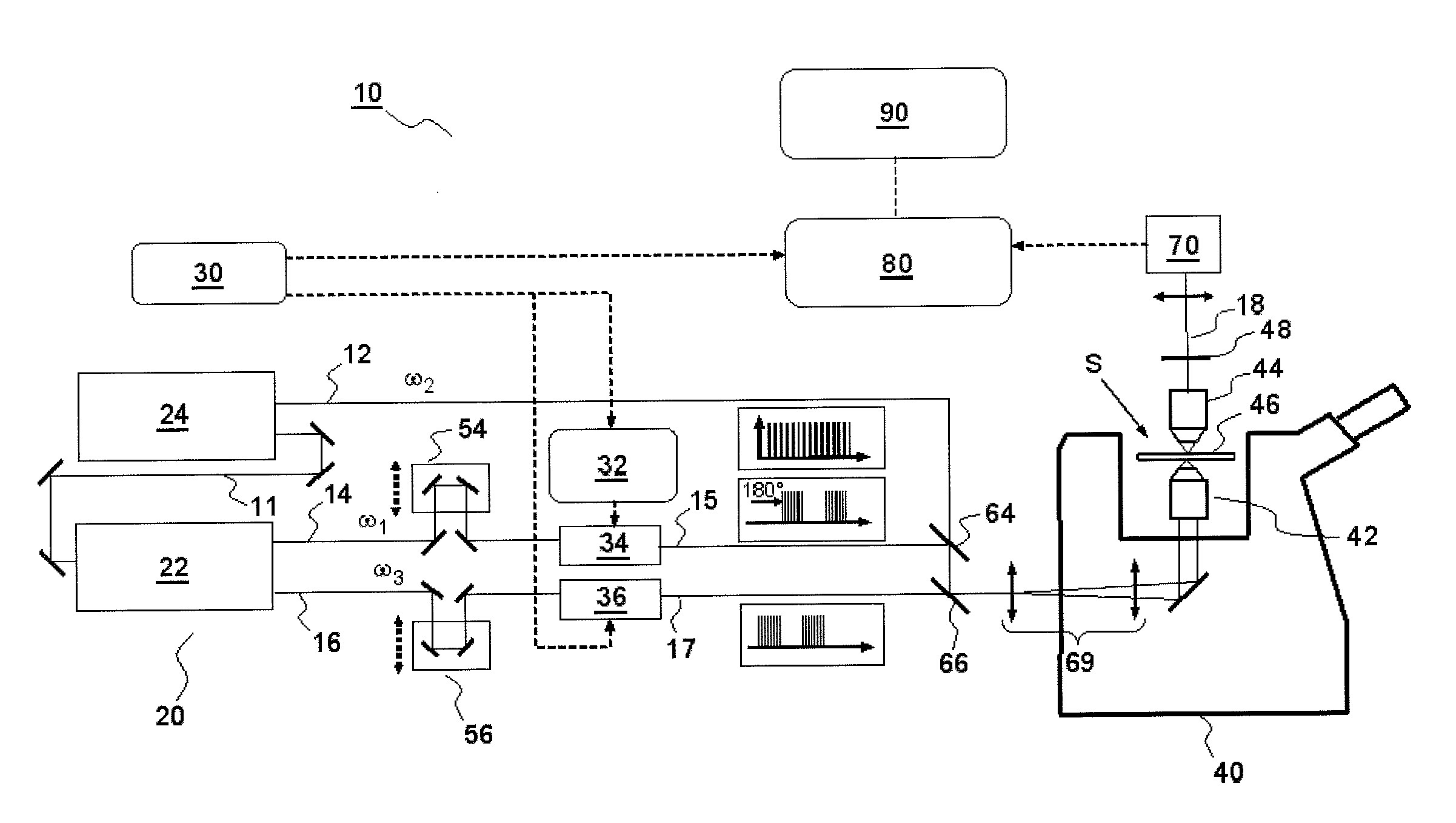
According to one aspect, the invention relates to a device for detecting a resonant non-linear optical signal of Stimulated Raman Scattering (SRS) type induced in a sample. The device comprises electro-optical means for making interact in the sample, at a first modulation frequency, trains of light pulses of angular frequencies ω1 and ω2 and, at a second modulation frequency, trains of light pulses of angular frequencies ω2 and ω3, such that ω2−ω1=ω3−ω2=ΩR where ΩR is a molecular vibrational resonant angular frequency of the sample. Moreover, the device comprises means for synchronous detection at the first and second modulation frequencies of non-linear optical signals resulting from the interaction of the light pulses in the sample, and electronic processing means making it possible to obtain, from electronic signals resulting from the synchronous detection, a signal characterizing the molecular vibrational resonance of the sample.
Owner:UNIV DE PROVENCE D AIX MARSEILLE I +1
Organic light emitting device, carbonyl bridged triarylamine derivative and application of carbonyl bridged triarylamine derivative
InactiveCN109456326AImprove luminous efficiencyImprove luminous performanceOrganic chemistrySolid-state devicesCarbon numberMolecular vibration
The present invention relates to an organic light emitting device, a carbonyl bridged triarylamine derivative and application of the carbonyl bridged triarylamine derivative. The carbonyl bridged triarylamine derivative comprises compounds represented in the following formulas I and II shown in the description. In the formulas I and II, Ar1, Ar2, Ar3, Ar4, Ar5 and Ar6 are each independently selected from one of an aromatic ring or aromatic heterocyclic ring with a carbon number being C6-C60 and substituted or unsubstituted by halogen, a cyano group, an alkyl group of 1-6 carbons, fluorinated alkyl of 1-6 cartons, an aromatic ring with the carbon atom number of C6-C30, an aromatic heterocyclic ring with a carbon atom number of C3-C30, and the like. The carbonyl bridged triarylamine derivative has electron-rich nitrogen atoms and electron-donating carbonyl groups and thus has bipolar transmission property, and meanwhile, since the rigid structure of the compound can effectively suppressvibration relaxation caused by molecular vibration and rotation, the compound has a narrow light emitting peak. The carbonyl bridged triarylamine derivative is applied to the organic light emitting device and is beneficial to balanced transmission of charge carriers, and therefore performance-excellent emitted light with high color purity is obtained.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Method using emission spectrum for diagnosing space distribution character of low-pressure plasma torch
ActiveCN102184831AElectric discharge tubesAnalysis by electrical excitationLuminous intensityMeasurement point
The invention discloses a method using an emission spectrum for diagnosing the space distribution character of a low-pressure plasma torch. The method adopts a computer to control a precise two-dimensional electric platform to control the measuring point to move; for the diagnosis on the space distribution character of the plasma torch, especially the low-pressure plasma torch, the space two-dimensional distribution of the luminous intensity, electron temperature, electron density, molecular rotation temperature and the molecular vibration temperature of the plasma torch can be obtained through analyzing the full spectrum obtained, and the space two-dimensional distribution has high sensitivity and spatial resolution.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Infrared spectrum non-linear modeling quantitative anslysis method
InactiveCN101368905AReduce measurement errorImprove measurement accuracyAbsorption/flicker/reflection spectroscopyColor/spectral properties measurementsObservational errorInfrared
The invention discloses an infrared spectrum non-linear modeling quantitative analysis method based on the molecular vibration theory; the method makes use of Matlab software programming and Statistica software data processing to establish a non-linear model and obtain the final quantitative result through the model. Through the establishment of the non-linear model, the invention realizes quantitative analysis and reduces measurement error to improve the measurement accuracy, precision and feasibility.
Owner:HUAIYIN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
Near infrared spectrum quick detecting technique for E.coli
InactiveCN1900697AShort detection timeNo pollution in the processMicrobiological testing/measurementColor/spectral properties measurementsInfra red spectroscopyMolecular vibration
Based on spectroscopic analysis technique of Fourier transform infrared (FTIR), using near infrared spectral scan obtains near infrared spectroscopic data and spectral graph in range of wave number between 3000cm-1 and 9000cm-1. In detection of near infrared spectrum, seven characteristic absorption peaks are 7144, 3167, 3742, 6712, 3456, 6631, 5339. The invention is rapid analysis method of carrying out quantitative analysis or discrimination for components of matter. Using interaction between infrared radiation and molecular vibration or rotation, recording infrared absorption spectrum of sample, the disclosed method carries out qualitative, quantitative and structural analysis. Features are: not destroying object to be tested, short test time, and no pollution.
Owner:HENAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
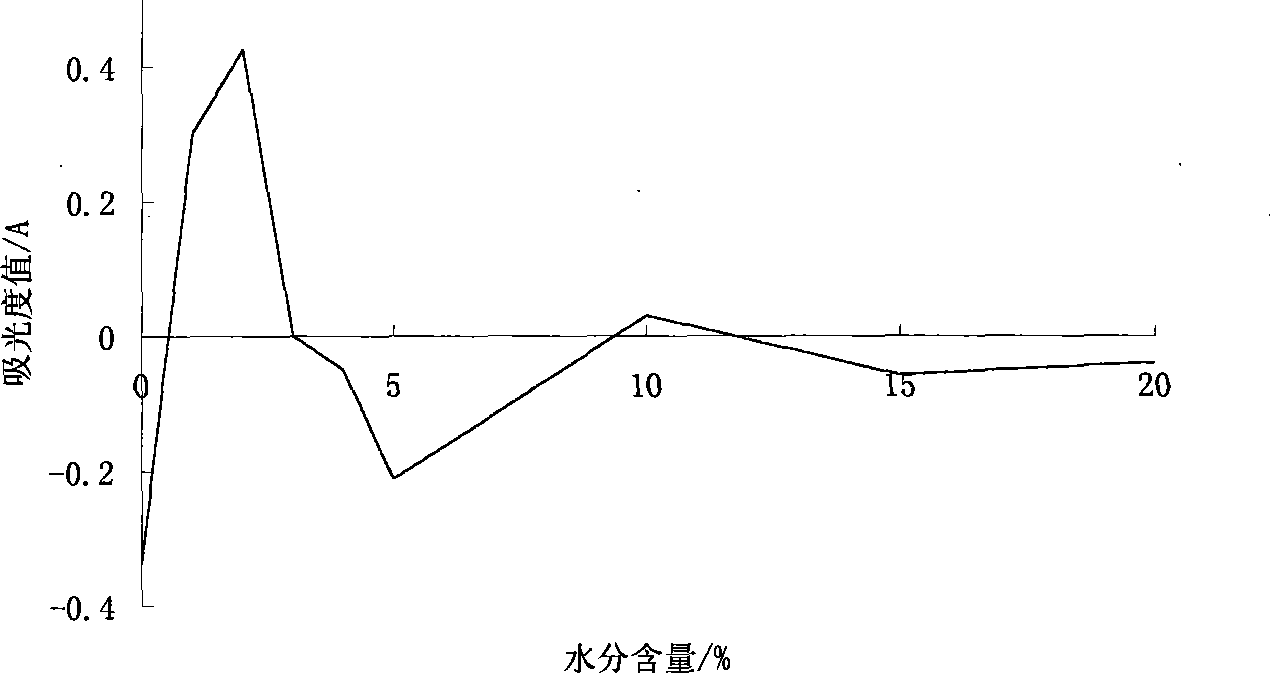
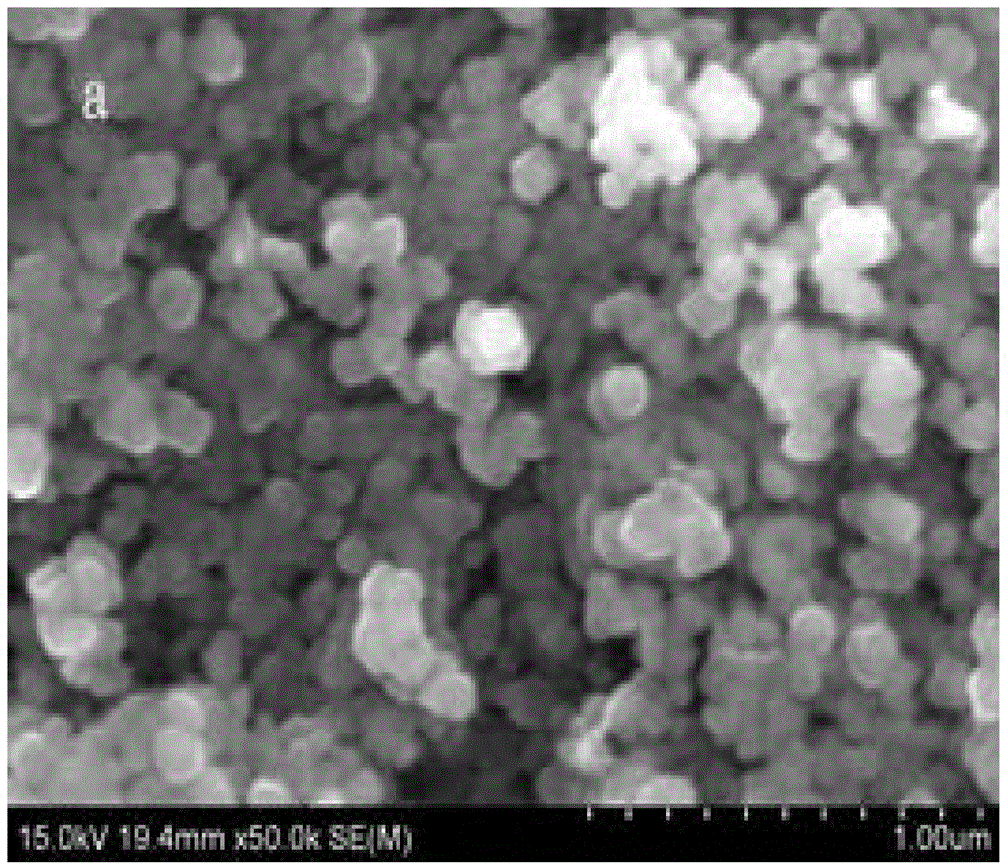
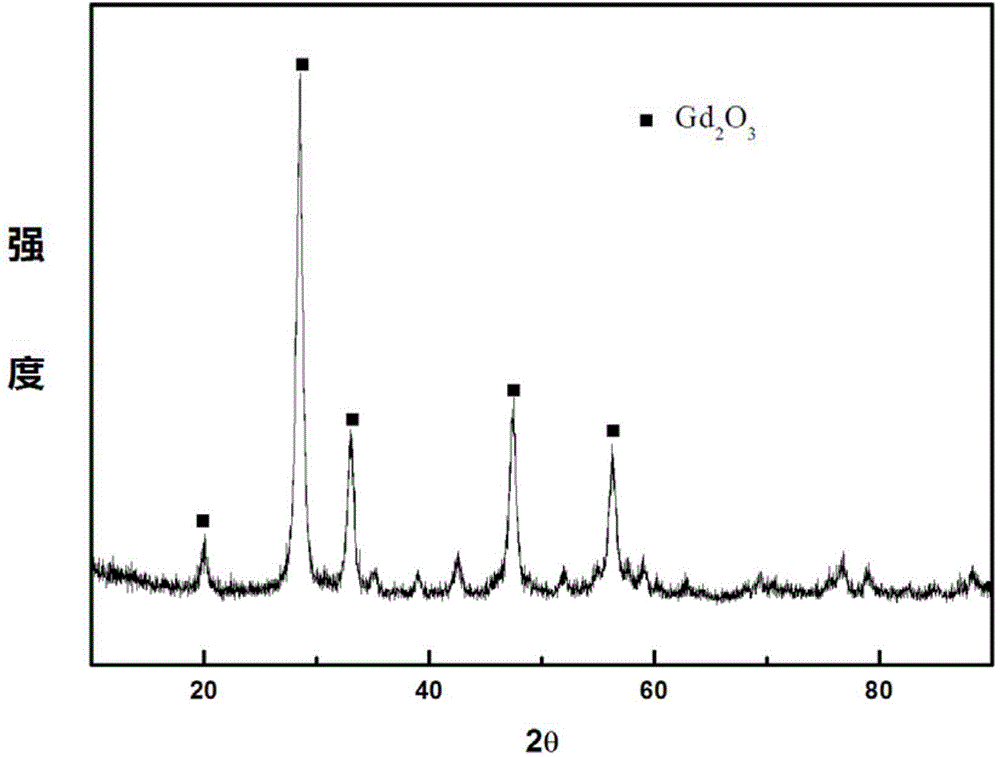
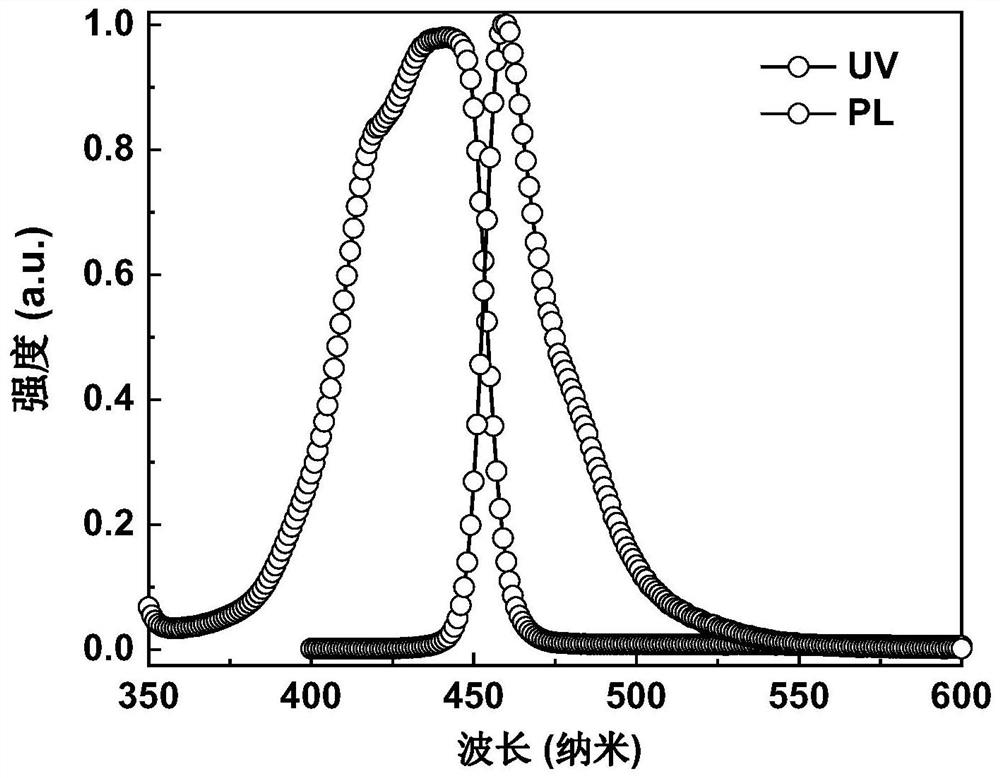
Microwave burning preparation method of nano gadolinium oxide powder
InactiveCN104973615APromote crystallizationNot easy to reuniteMaterial nanotechnologyRare earth metal compoundsMicrowaveSynthesis methods
The invention relates to a microwave burning preparation method of nano gadolinium oxide powder. The preparation method comprises the following steps: (1) mixing gadolinium oxide powder with a nitric acid solution to prepare a gadolinium nitrate solution; (2) evenly mixing the gadolinium nitrate solution with a critic acid solution according to a mole ratio of Gd3+ to citric acid of 4:(1-2) to obtain a precursor solution; (3) adjusting the pH value of the precursor solution to 8-10; (4) burning the precursor solution with an adjusted pH value by microwaves to obtain white powder; (5) burning the white powder for 2 to 5 hours at a constant temperature of 450 to 800 DEG C; (6) ball-grinding the burned white powder, and drying to obtain the target product. The preparation method adopts a microwave burning synthesis method, the microwave energy is utilized to vibrate the inner molecules in the precursor so as to generate heat, and the heat energy is evenly distributed.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Polycyclic boron-containing compound and electronic device thereof
ActiveCN111647010AGood film formingImprove thermal stabilitySilicon organic compoundsSolid-state devicesQuantum yieldCarbazole
The invention relates to a polycyclic boron-containing compound and an electronic device thereof. By introducing the boron element, the compound with rigid structural characteristics is constructed, and the rigid structure can effectively inhibit vibration relaxation caused by molecular vibration and rotation, thereby being beneficial to enhancing the fluorescence quantum yield of the molecules and reducing the half-peak width of the luminescent spectrum. In addition, due to the rigid structure, the molecules have excellent film-forming property and thermal stability, and the stability of thedevice can be further improved; in addition, since the polycyclic boron-containing compound is positioned at the 1 or 4 positions of carbazole and fluorenyl elements, no isomer is generated during preparation, and purification is facilitated. The electroluminescent device prepared from the compound provided by the invention has the advantages of low driving voltage, high luminous efficiency, longservice life, high spectral color purity and the like. In addition, the preparation method of the polycyclic boron-containing compound is simple, raw materials are easy to obtain, the materials are easy to purify, and the industrial development requirement can be met.
Owner:SUZHOU JOYSUN ADVANCED MATERIALS CO LTD
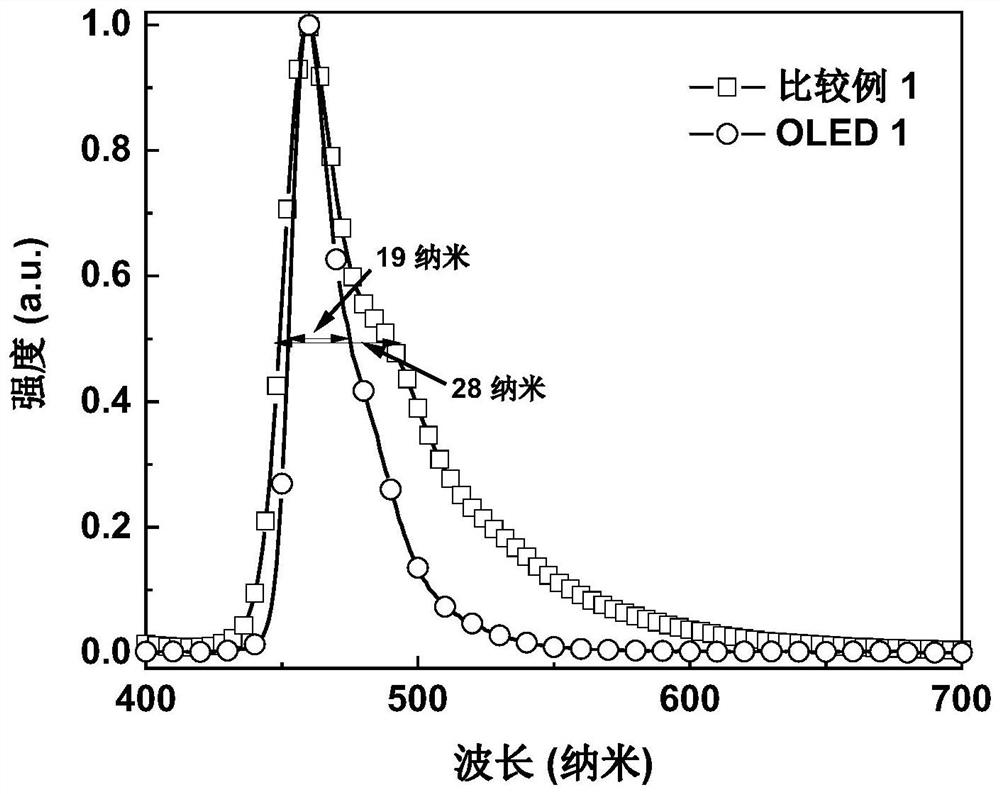
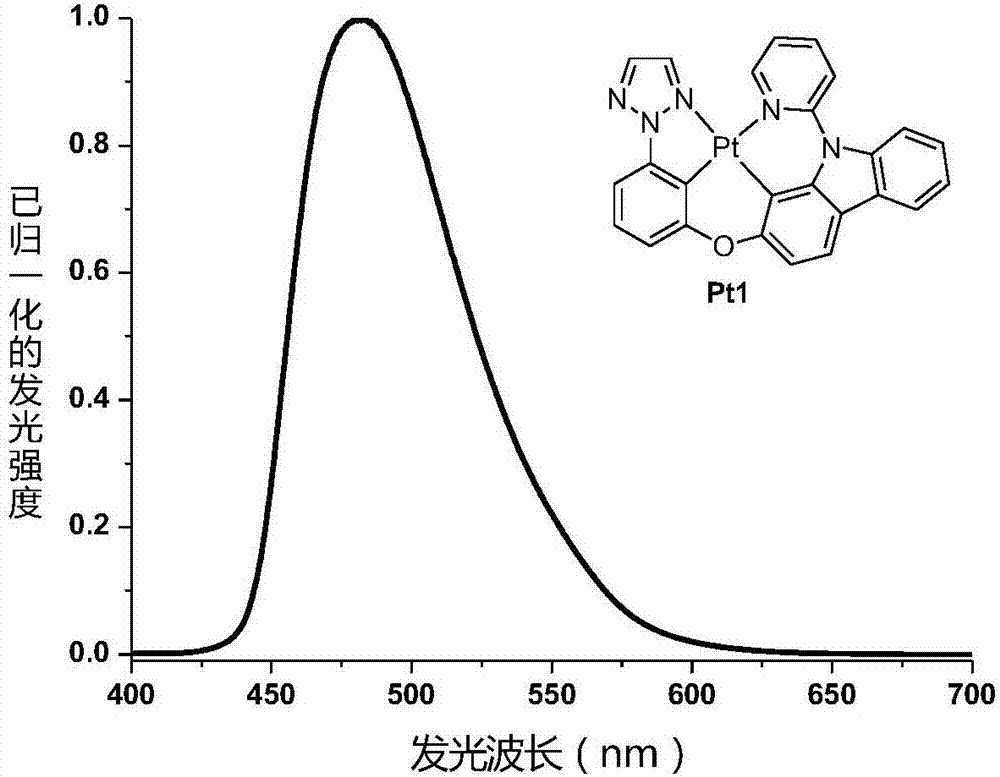
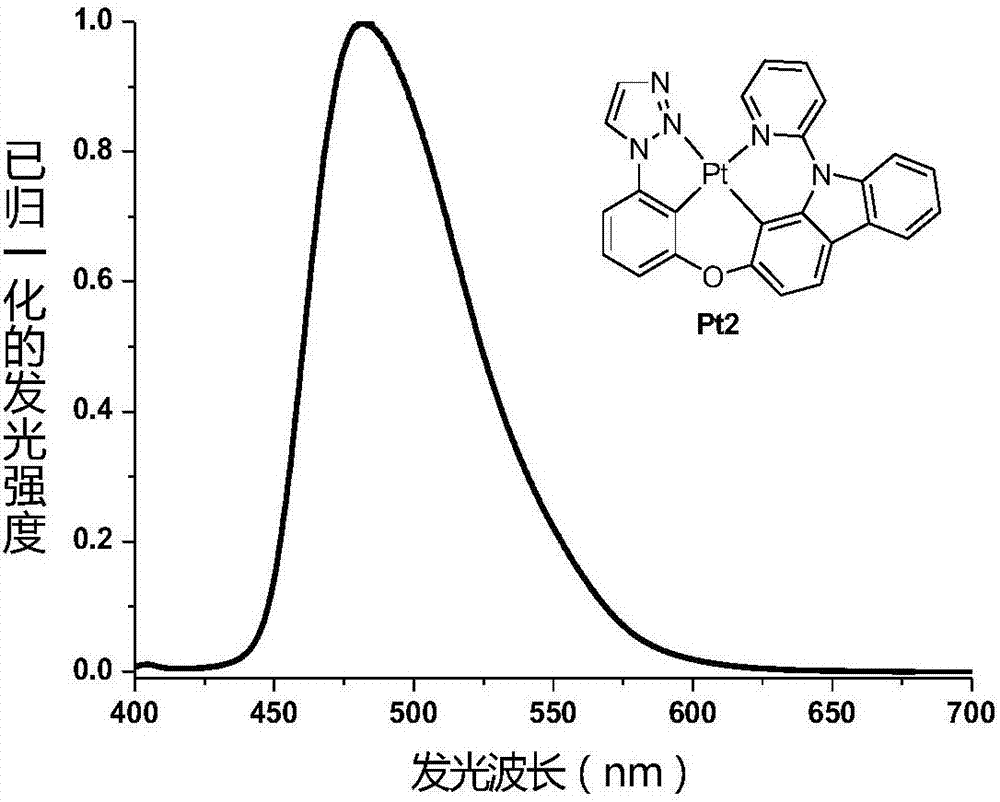
Four-gear ring metal platinum (II) complex phosphorescent luminescent materials
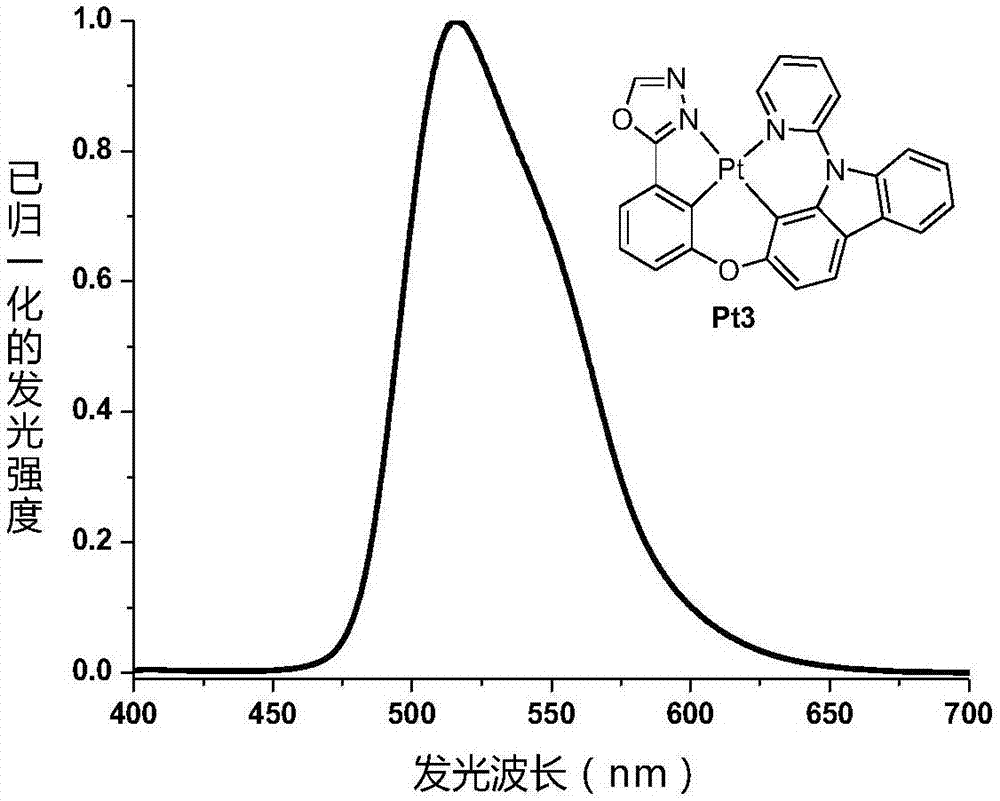
ActiveCN107266505AEasy to purifySingle structureSolid-state devicesPlatinum organic compoundsHeat stabilityMolecular vibration
The invention discloses four-gear ring metal platinum (II) phosphorescent luminescent materials as shown in a formula (I) in the specification, wherein a five-membered heterocyclic aromatic group Ar is as shown in the specification; Ar is selected from one of the following: 2H-1,2,3-triazole, X1=N, X2=N, X3=CH); 1H-1,2,3-triazole, X1=CH, X2=N, X3=N; 1,3,4-oxadiazole, X1=O, X2=C, X3=N; oxazole, X1=O, X2=C, X3=CH; or thiazole, X1=S, X2=C, X3=CH. One or more of the four-gear ring metal platinum (II) phosphorescent luminescent materials disclosed by the invention are applied to a luminescent layer of an organic illuminator. The four-gear ring metal platinum (II) phosphorescent luminescent materials disclosed by the invention have strong molecular rigidity, can effectively reduce energy consumed owing to molecular vibration, and have high phosphorescent quantum efficiency, good chemical stability and good heat stability.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
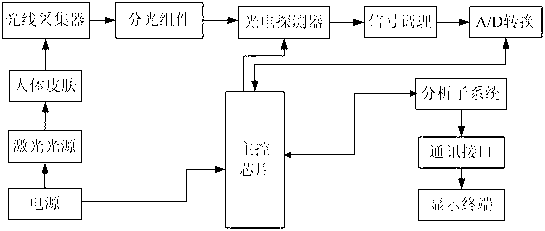
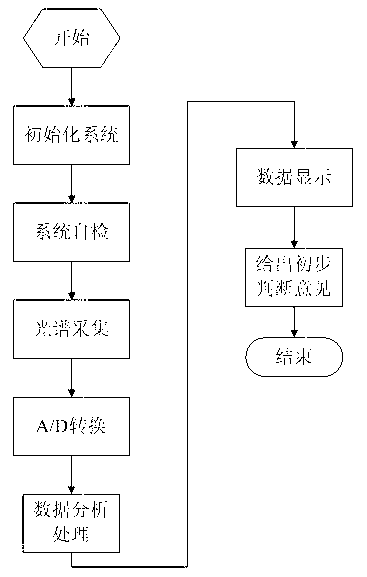
Laser Raman technique-based glucometer
ActiveCN103190917ARapid Qualitative and Quantitative AnalysisSimple Qualitative and Quantitative AnalysisDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsSignal processing circuitsGlucose meter device
The invention relates to a laser Raman technique-based glucometer and relates to the field of medical detecting instruments, biological medical detection and health monitoring. The laser Raman technique-based glucometer comprises a power source, a laser source, a Raman spectral signal acquisition module, a signal processing circuit, a master control chip and a data analysis and display system. Molecular vibration and rotation structural information is obtained by the analysis on Raman scattering generated by mutual action of specific-wavelength laser and a measured object and the analysis by Raman spectral analysis technique, so that qualitative and quantitative analysis is quick, simple, repeatable and lossless. Raman spectrum of glucose molecules is well specific, fundamental frequency spectral lines are clear, and recognition is easy. Raman spectrum is non-sensitive to polar materials such as water, and interference by Raman spectrum of the water in near-infrared areas is avoided effectively. Samples need not be pretreated, and in-situ measurement is available.
Owner:CHONGQING INST OF GREEN & INTELLIGENT TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
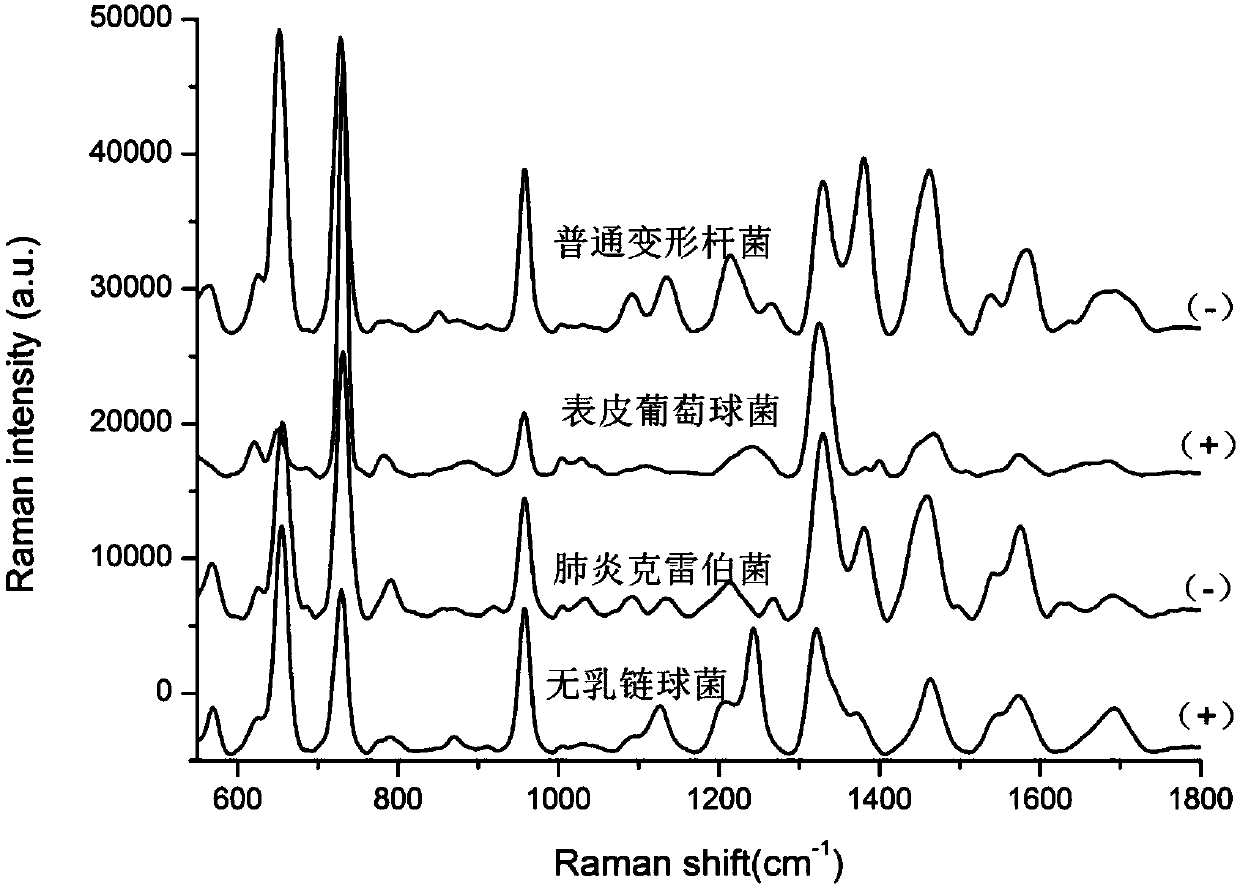
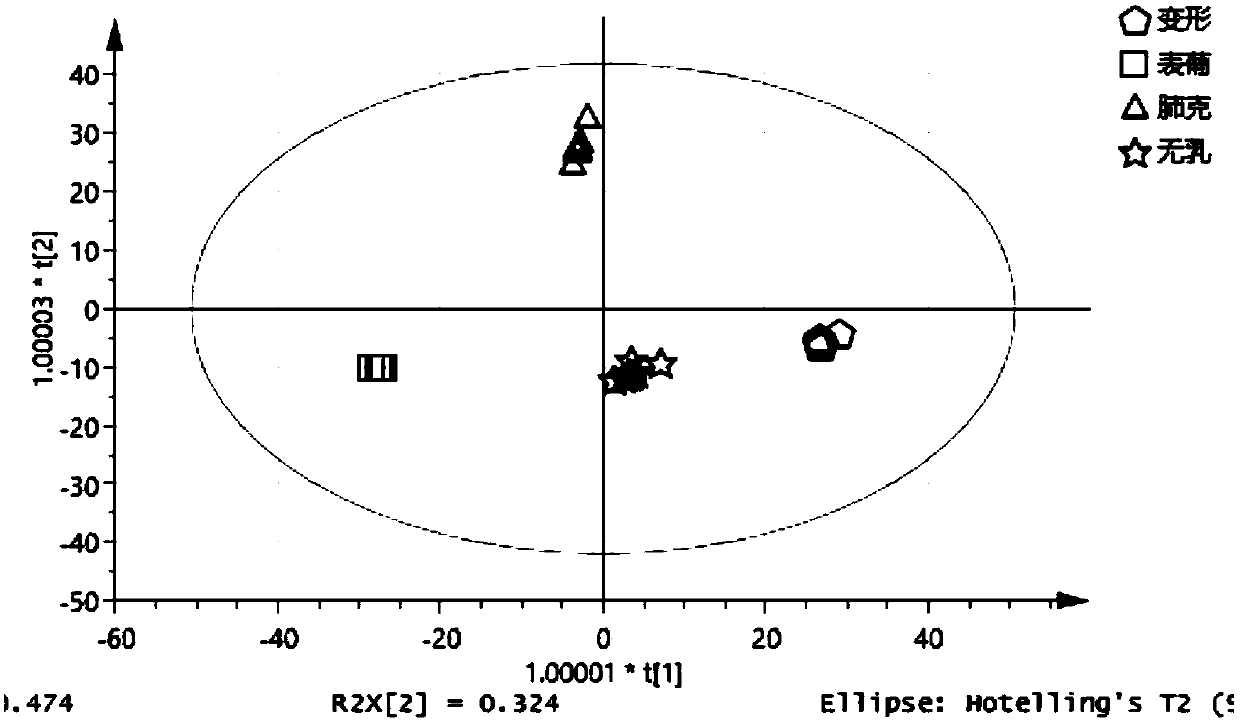
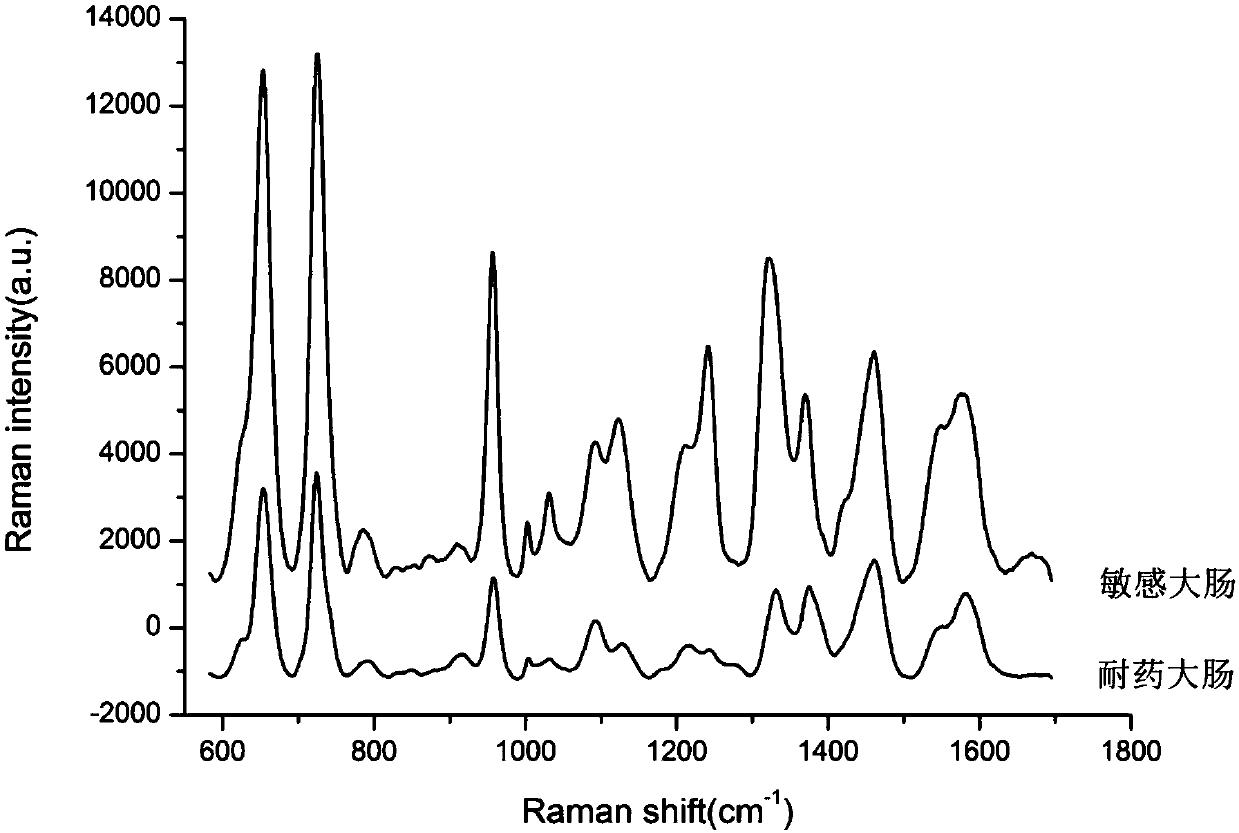
Rapid identification method for carbapenem drug susceptibility, based on Raman spectra technology
InactiveCN107586823AReduce dosageShort detection timeMicrobiological testing/measurementRaman scatteringStructure analysisRapid identification
The invention relates to a rapid identification method for carbapenem drug susceptibility, based on a Raman spectra technology. According to the method, a portable Raman detector is adopted, pathogenic bacteria to be detected is irradiated through laser, different types of nanostructures are taken as detection substrates, and scattered spectrum, the frequency of which is different from the frequency of incident light, is analyzed, so that information, such as molecular vibration, of a sample to be detected is obtained, corresponding molecular structure analysis is performed, obtained spectroscopic data of carbapenem drug sensitive bacteria and drug-resistance bacteria is analyzed through a chemometrics method, so that drug-resistance bacteria and sensitive bacteria are distinguished, and the method becomes an ultrasensitive pathogenic bacteria rapid detection tool. Compared with the clinically traditional drug sensitivity pathogenic microorganism detection method, the detection technology has the advantages that the quantity of samples is less, the detection time is short, the sensitivity is high, the detection time of clinical samples is shortened, and particularly as for detection samples with complex chemical and biochemical components, the detection efficiency is improved on the basis that the detection quality is guaranteed.
Owner:XUZHOU MEDICAL UNIV
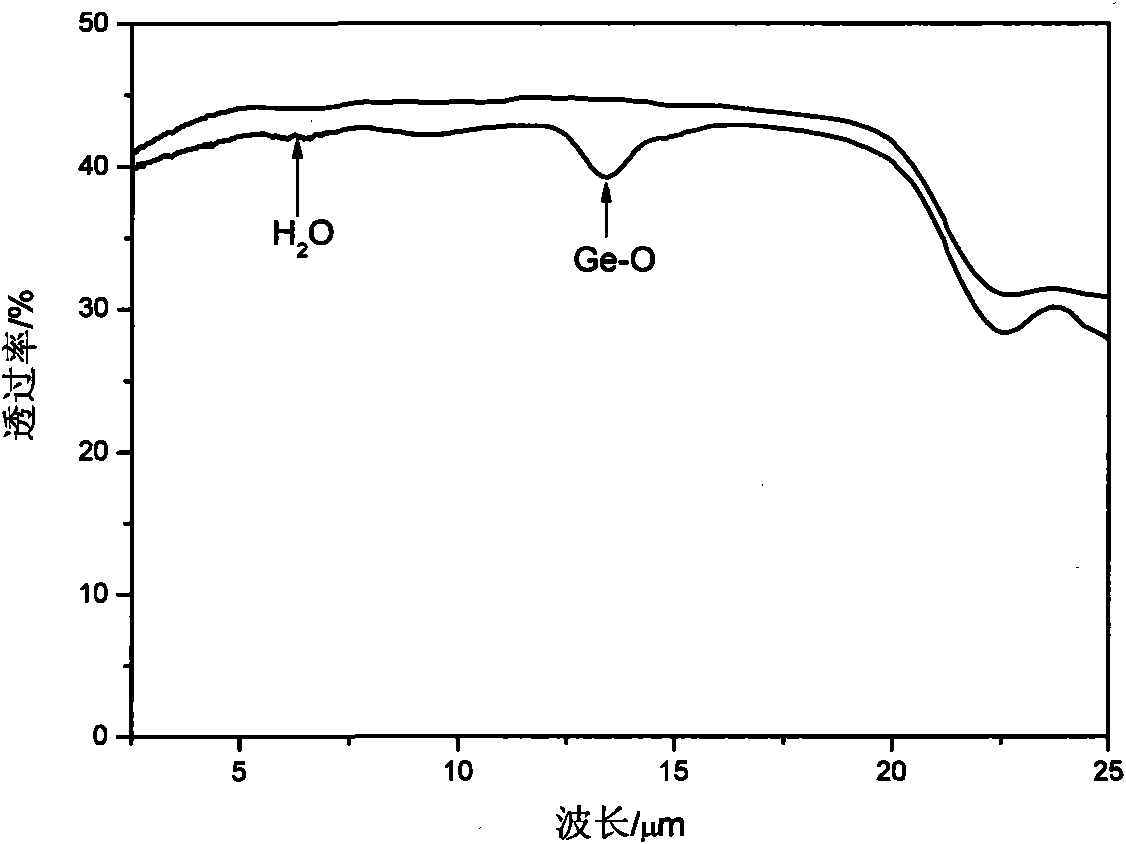
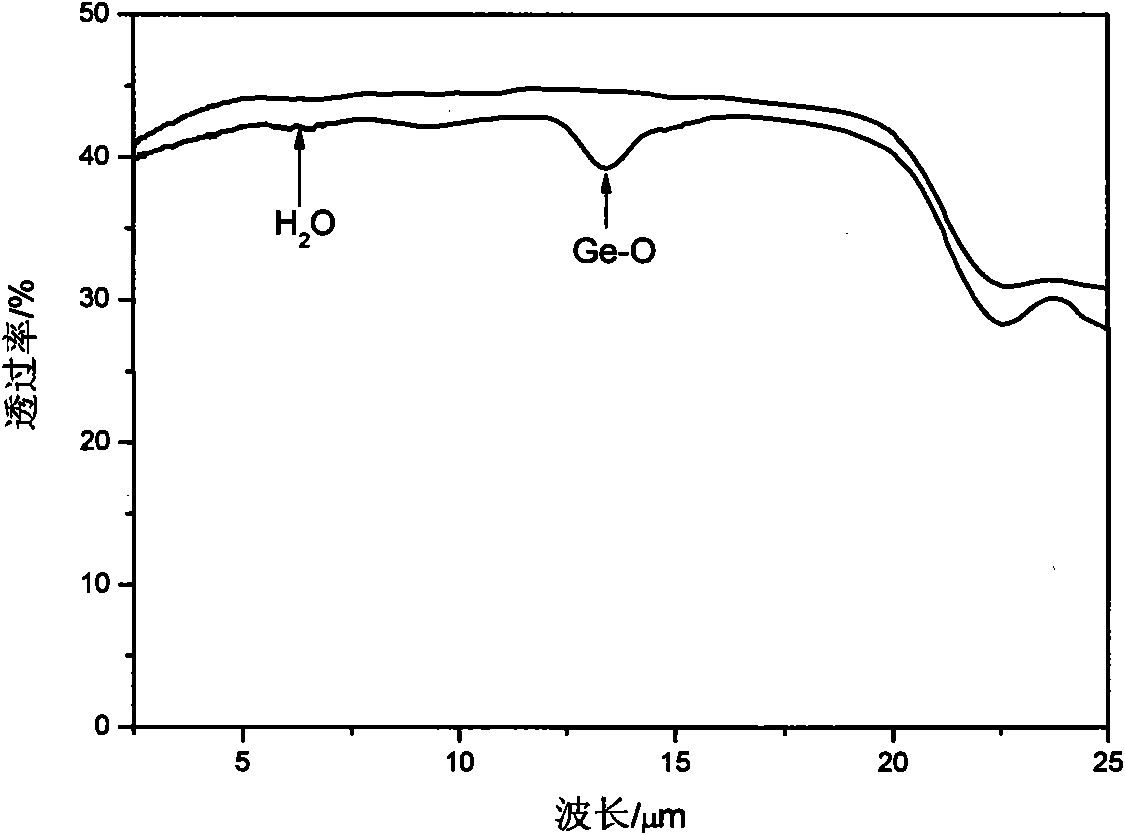
Tellurium-based sulfur series infrared glass and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses tellurium-based sulfur series infrared glass. The glass comprises the following components: 10 to 20 mole percent of In2Te6, 45 to 80 mole percent of GeTe 4 and 5 to 40 mole percent of AgX, wherein the total mole percentage of all components is 100 percent; X is Cl or Br or I; the transition temperature (Tg) of the glass is between 170 and 200 DEG C; the thermal stability temperature (delta T) of the glass is between 100 and 120 DEG C; the thickness of the glass is no more than 1.4 millimeters; and a cut-off edge through which an infrared band can pass is up to 25 mu m. The glass has an appropriate transition temperature, and high thermal stability, reduces the base frequency molecular vibration of the glass due to the adoption of a heaviest element in a sulfur group, namely, tellurium and reduces the phonon energy of the glass. Simultaneously, the thickness of the glass is controlled to be no more than 1.4 millimeters so that the influence of multi-phonon absorption is reduced, the cut-off edge, through which the infrared band can pass, of the tellurium-based sulfur series infrared glass is enhanced and can reach 25 mu m, substances with long far infrared wavelengths can be absorbed and spectrum detection space is expanded. The glass preparation method has the advantages of simple process, high glass forming capability, no corrosion, easy operation, short processing period and high efficiency.
Owner:宁波阳光和谱光电科技有限公司
Imaging apparatus for infrared rays nonlinear molecular vibrational microscopy
InactiveUS7667848B2Reduce spacingEasy to implementRadiation pyrometryInterferometric spectrometryInfraredMolecular vibration
Owner:KOREA RES INST OF STANDARDS & SCI
Device and method for stimulated Raman detection
According to one aspect, the invention relates to a device for detecting a resonant non-linear optical signal of Stimulated Raman Scattering (SRS) type induced in a sample. The device comprises electro-optical means for making interact in the sample, at a first modulation frequency, trains of light pulses of angular frequencies ω1 and ω2 and, at a second modulation frequency, trains of light pulses of angular frequencies ω2 and ω3, such that ω2−ω1=ω3−ω2=ΩR where ΩR is a molecular vibrational resonant angular frequency of the sample. Moreover, the device comprises means for synchronous detection at the first and second modulation frequencies of non-linear optical signals resulting from the interaction of the light pulses in the sample, and electronic processing means making it possible to obtain, from electronic signals resulting from the synchronous detection, a signal characterizing the molecular vibrational resonance of the sample.
Owner:UNIV DAIX MARSEILLE +1
Optical ultrasound imaging device for diagnosing breast cancer
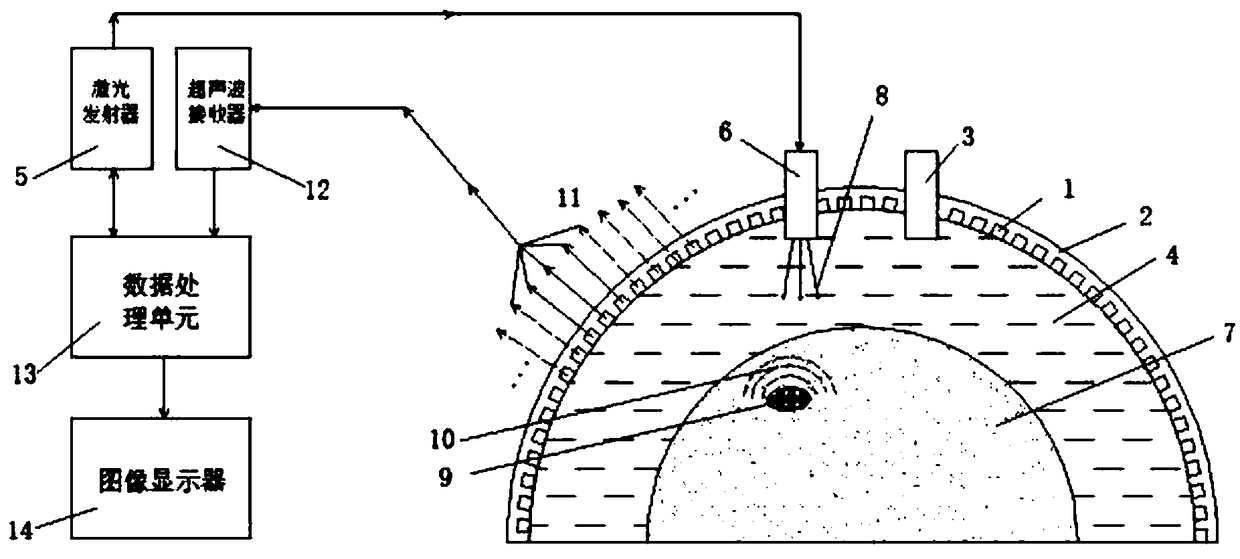
InactiveCN109124589APrecise positioningPrecise imaging of lesion locationDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsUltrasonic sensorLaser probe
The invention discloses an optical ultrasonic imaging device for diagnosing breast cancer, which comprises a bowl-shaped flexible ultrasonic probe, a laser probe, a pulsed laser emitter, an ultrasonicreceiver, a data processing unit and an image display. The device comprises a bowl-shaped flexible ultrasonic probe, a laser probe, a pulsed laser emitter, an ultrasonic receiver, a data processing unit and an image display. The ultrasonic transducer adopts bowl-shaped shell and flexible structure, adopts multi-array array composite wafer structure, utilizes multi-array array composite wafer, andcombines the principle of phased array technology to obtain the signal sources with different initial phases. An ultrasonic transducer is connected to an ultrasonic receiver. A laser probe connectedwith a pulse laser emitter emits a laser beam with a certain frequency to that inside of the tissue, molecules or substances that absorb light at a particular wavelength are called chromophores. The light energy absorbed by the chromophore is converted into heat energy by molecular vibration and thermoelastic expansion to generate ultrasonic wave, which is detected by an ultrasonic sensor in the device, and the waveform signal is synthesized into an image through an ultrasonic receiver and a data processing unit and displayed on an image display.
Owner:NANCHANG HANGKONG UNIVERSITY
Gel electrochromatophoresis band fast dyeing method
InactiveCN1609608APreparing sample for investigationMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansTemperature controlMicrowave
The fast gel electrophoresis belt dyeing method includes the following steps: setting gel plate obtained through electrophoresis into dyeing liquid inside non-metal container, and applying microwave radiation for 2-10 min while maintaining the flow of the dyeing liquid and controlling the temperature in 25-60 deg.c. The microwave radiation to promote molecule vibration and raise the temperature can shorten the dyeing time greatly.
Owner:崔学晨 +2
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com