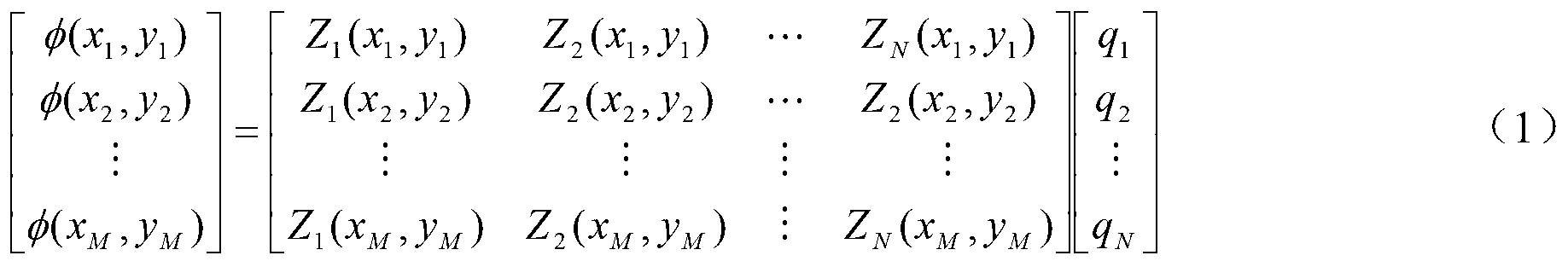Patents
Literature
555 results about "Structural analysis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Structural analysis is the determination of the effects of loads on physical structures and their components. Structures subject to this type of analysis include all that must withstand loads, such as buildings, bridges, vehicles, furniture, attire, soil strata, prostheses and biological tissue. Structural analysis employs the fields of applied mechanics, materials science and applied mathematics to compute a structure's deformations, internal forces, stresses, support reactions, accelerations, and stability. The results of the analysis are used to verify a structure's fitness for use, often precluding physical tests. Structural analysis is thus a key part of the engineering design of structures.
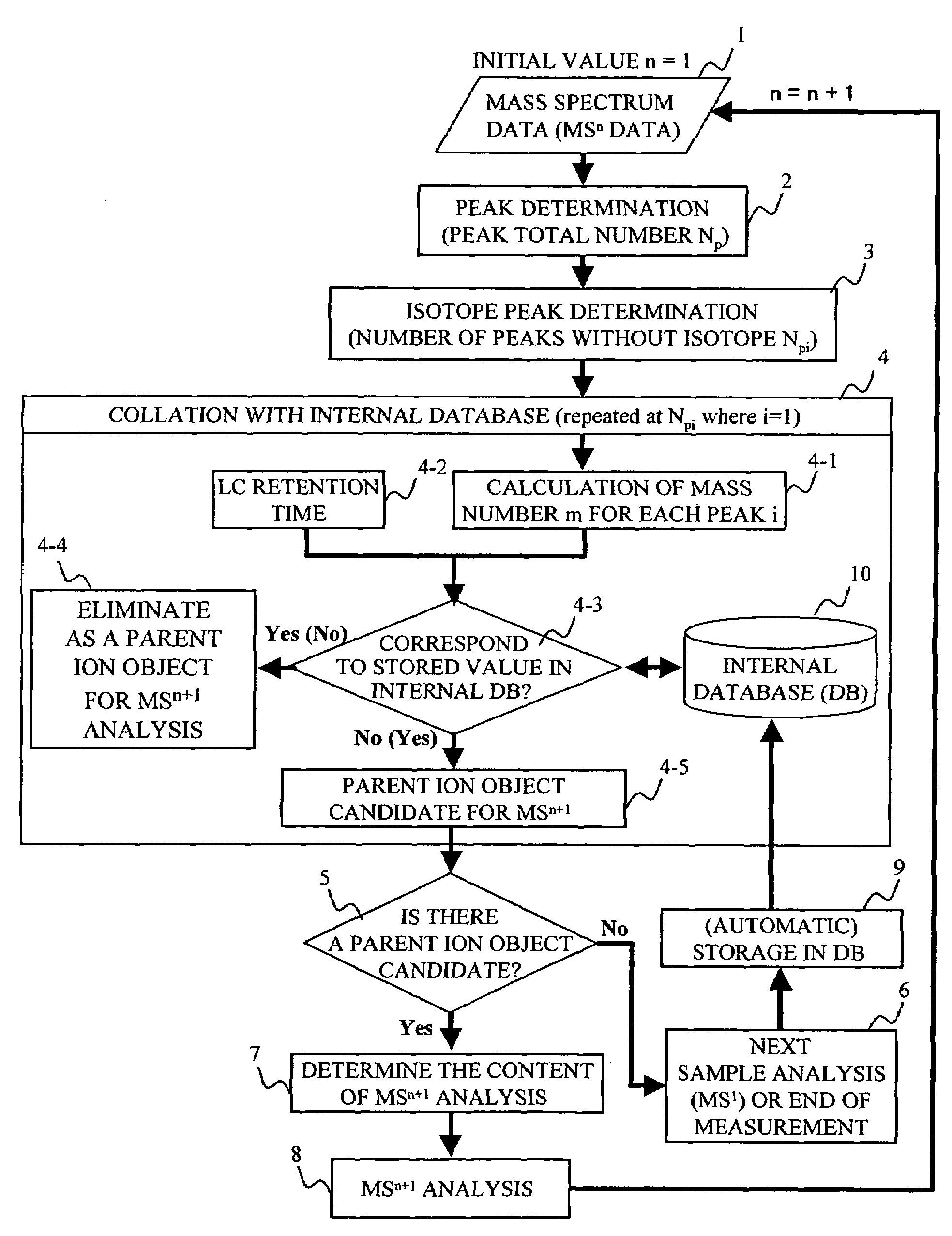
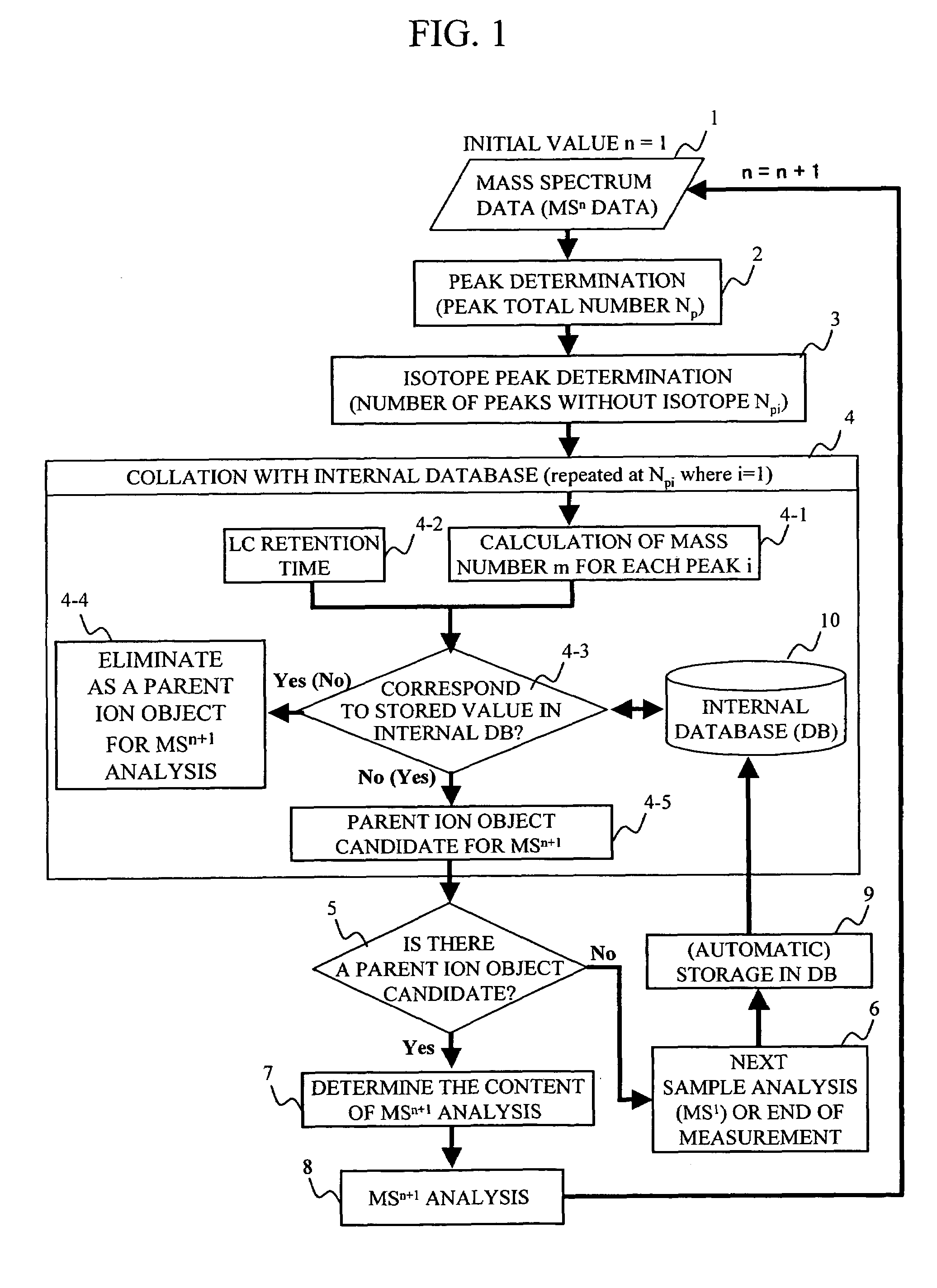
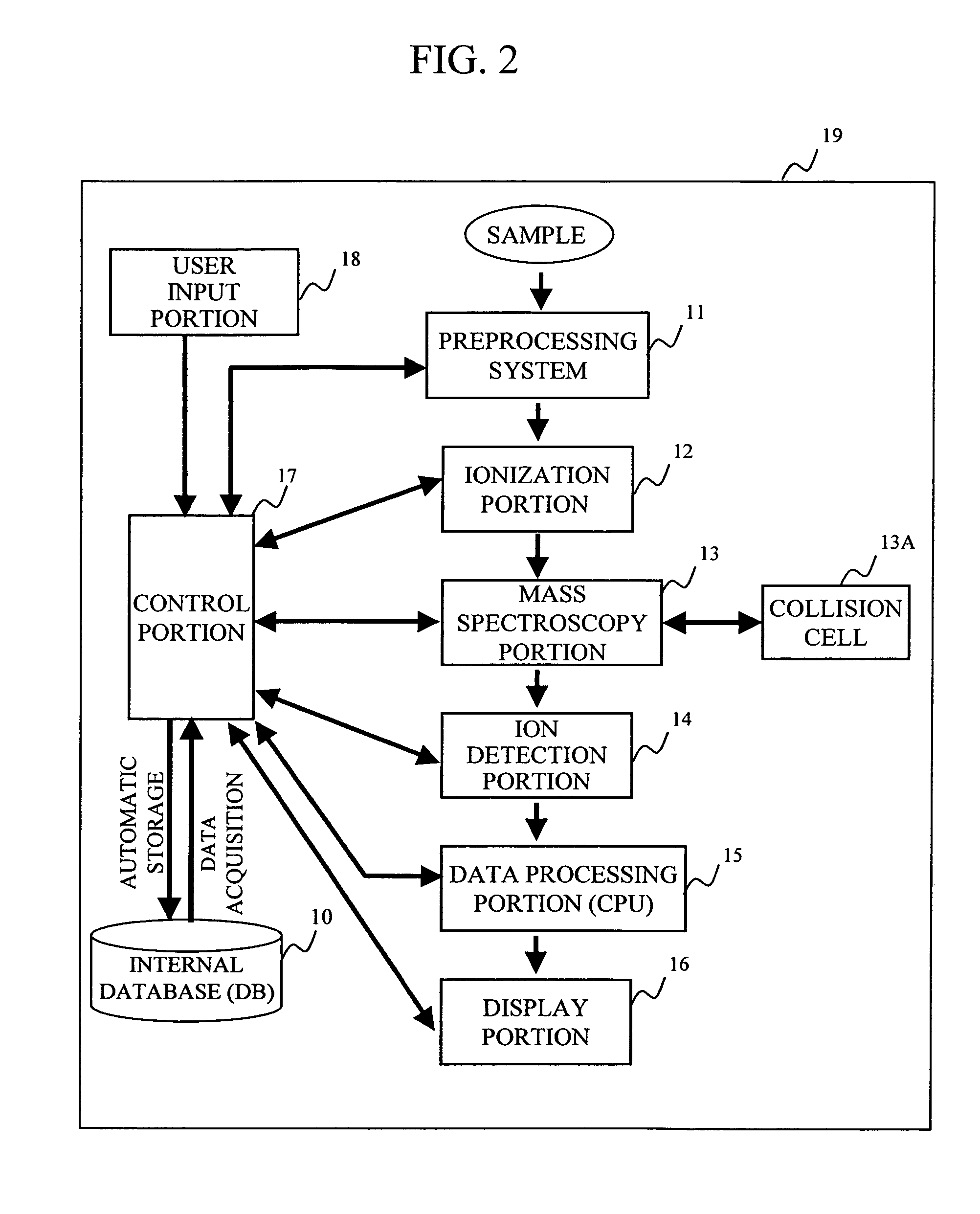
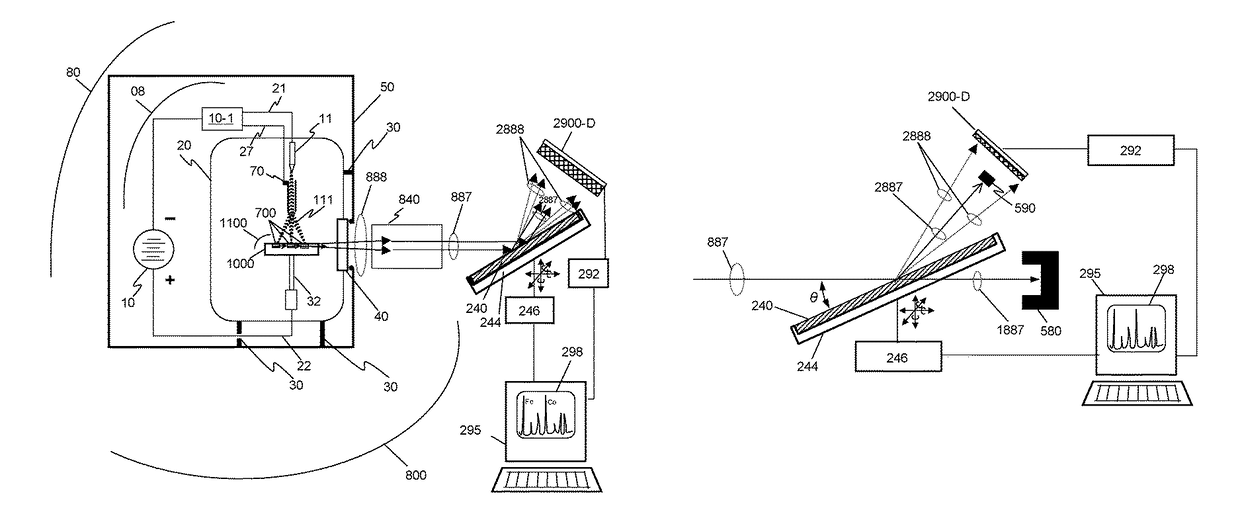
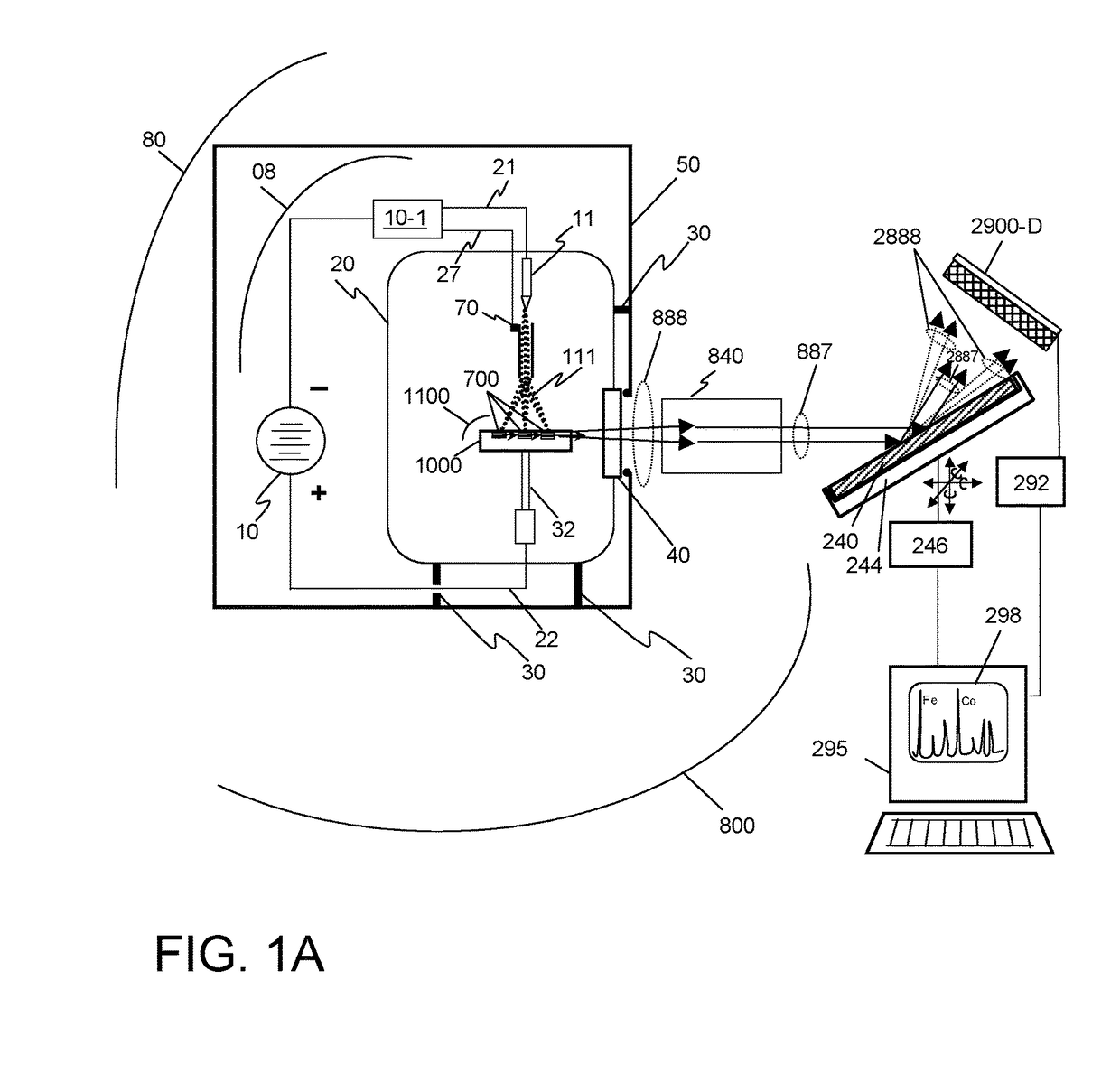
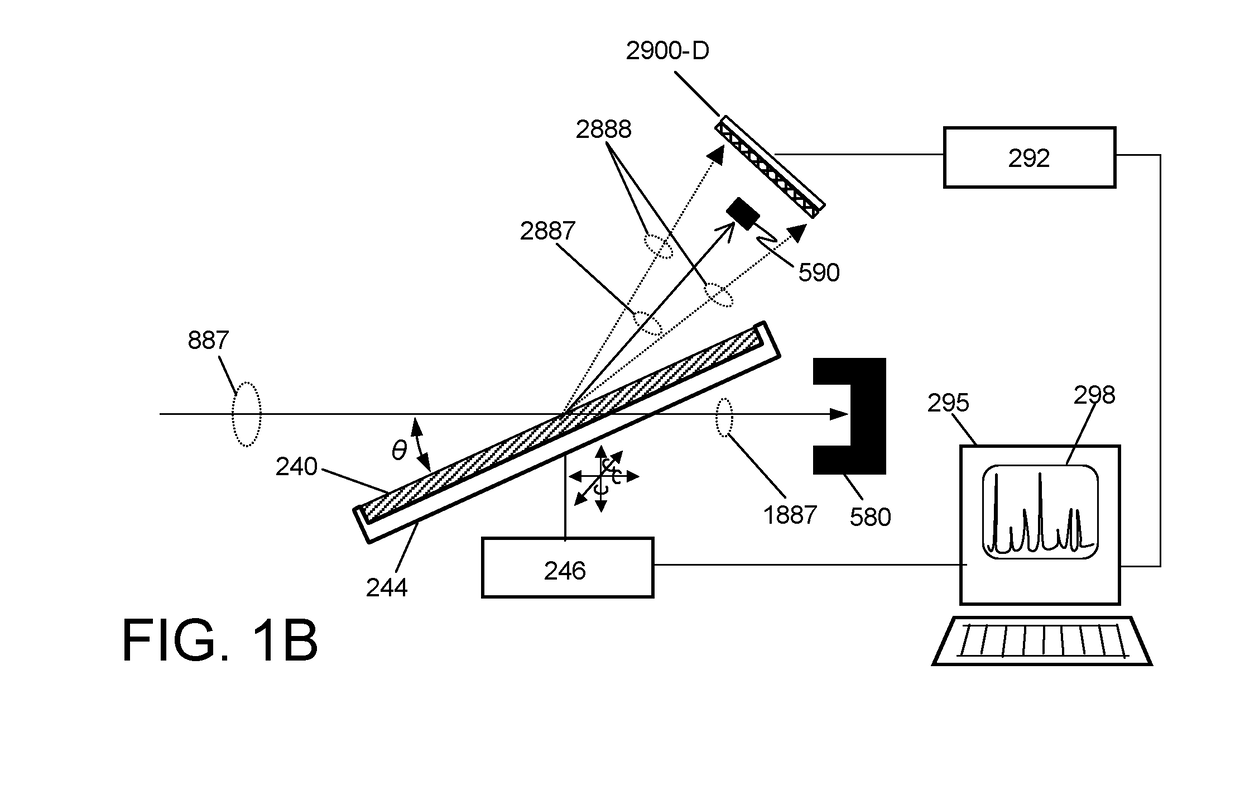
Mass spectrometer system
ActiveUS7473892B2Reduce adverse effectsSamples introduction/extractionIsotope separationPeptide ionsSpectroscopy
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
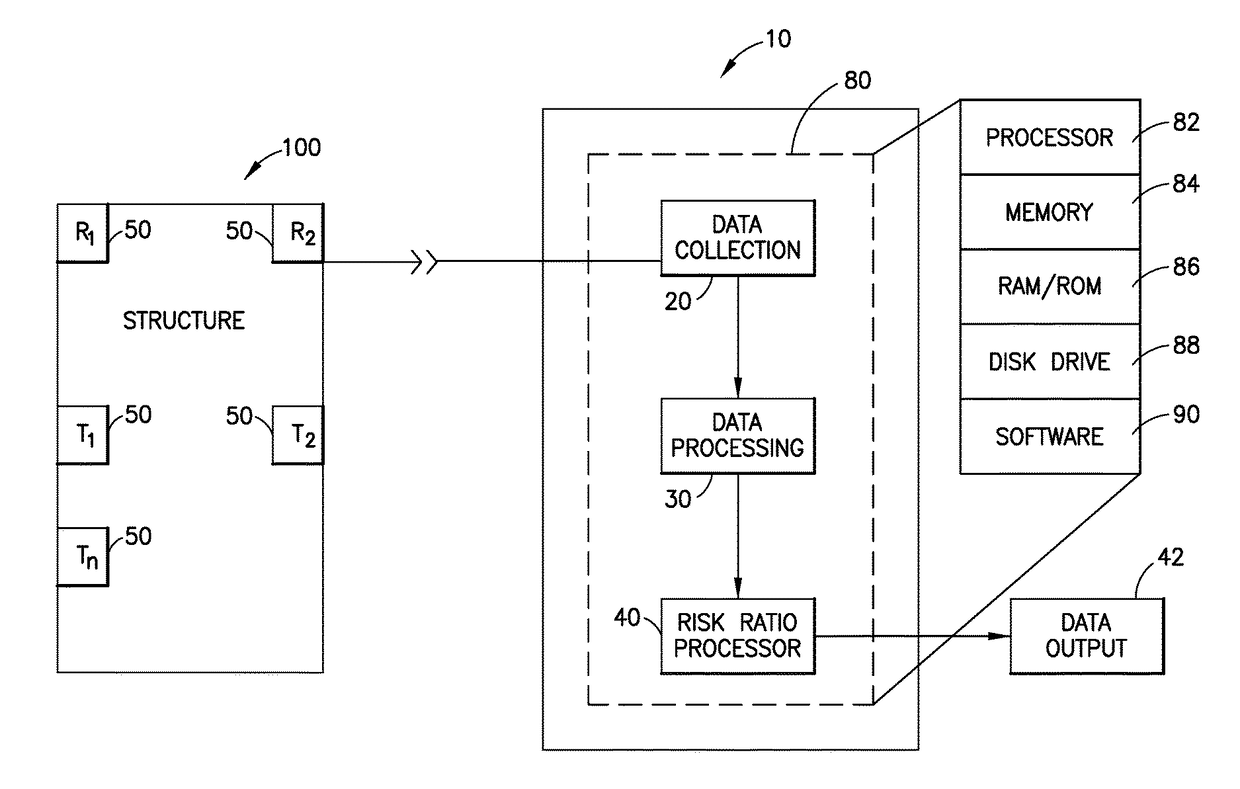
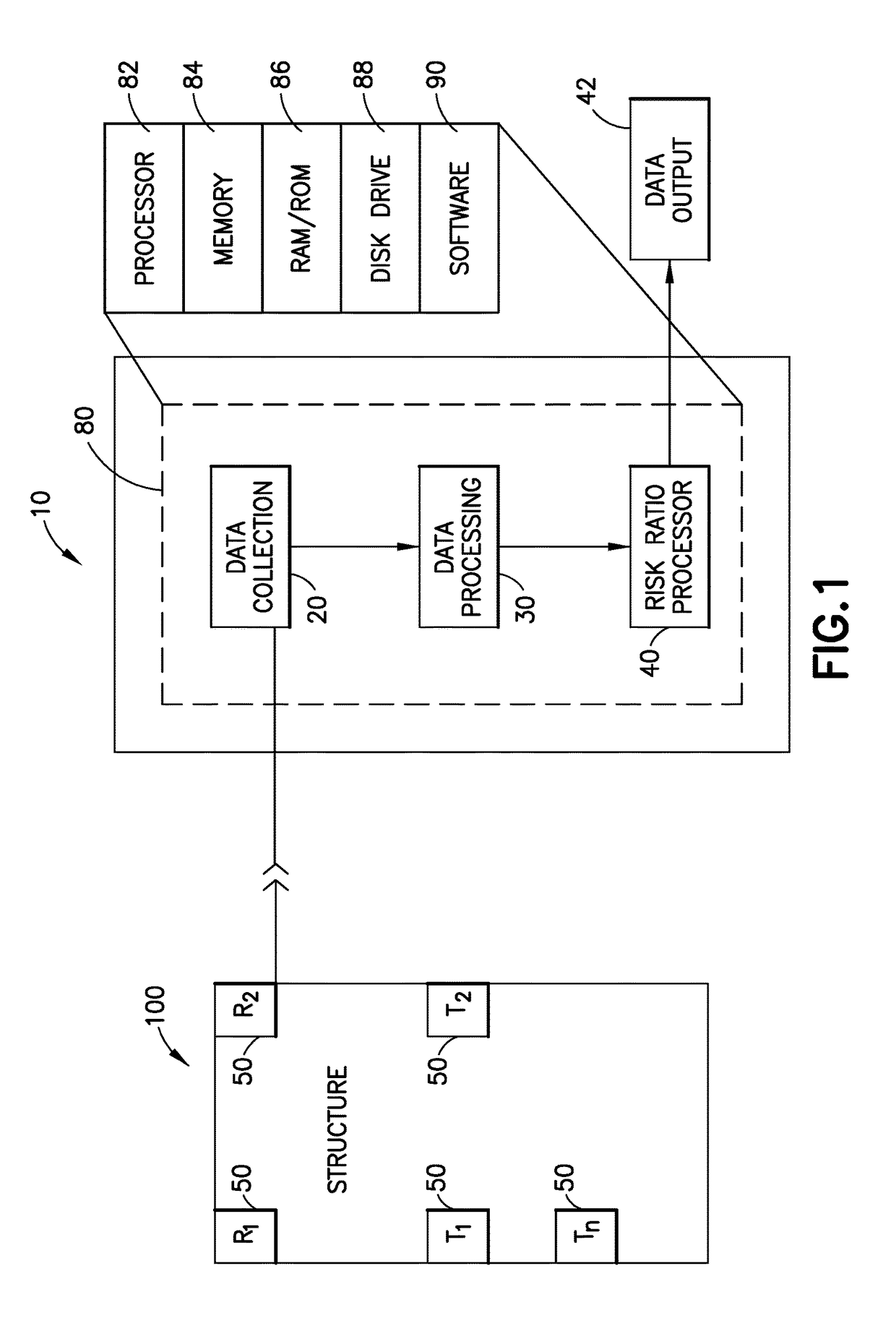
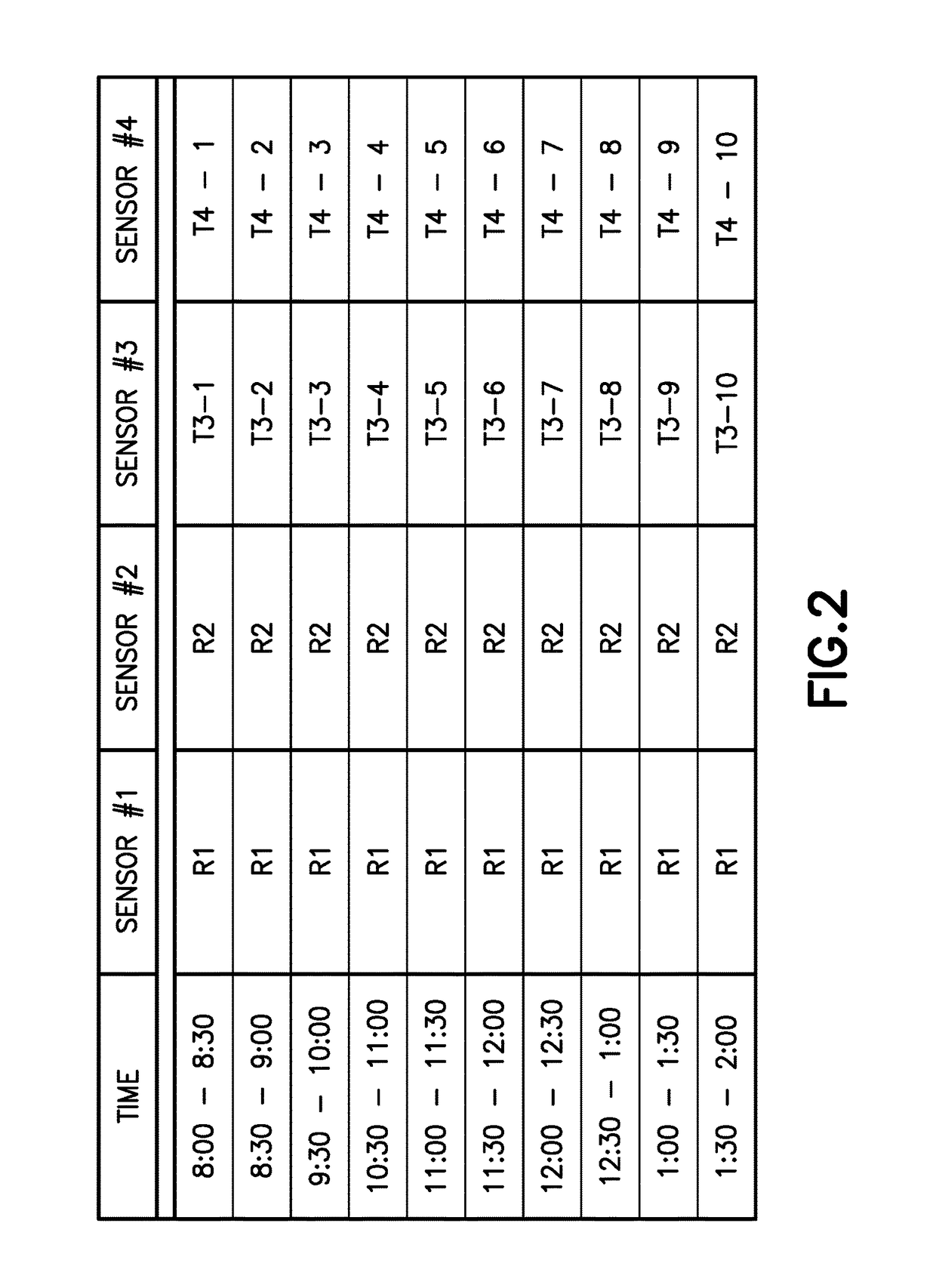
System and method for determining the risk of failure of a structure
ActiveUS20170363504A1Quantifies risk of failureDetermine a risk ratio for the structureElasticity measurementResonanceStructural analysis
A system and method for measuring dynamic properties of a structure, and for using the measured dynamic properties to assess the dynamic performance of the structure. The system and method measures dynamic properties of the structure such as frequencies of resonance, mode shapes, and non-linear damping, and uses them in an analysis of the structure to compare the dynamic response of the structure with the anticipated properties of a structure built according to applicable building code requirements. The system and method thus quantifies a risk of failure of the structure by determining a risk ratio that compares an as-is condition of the structure with an as-designed condition of the structure.
Owner:STRAAM GRP INC
Automatic Repair Planning and Part Archival System (ARPPAS)
InactiveUS20090234616A1Easy accessGuaranteed maximum utilizationNuclear monitoringDigital computer detailsResidual strengthStructural analysis
An automated repair structural analysis processing system for aircraft composite parts is disclosed, combining a method for digitally describing damage on composite components with a system that evaluates composite aircraft repair options for a given part design, damage set, and repair history, and provides automatic calculation of the residual strength of damaged metal and composite parts. In addition, this invention provides a system that automatically informs maintenance specialists when they will not be allowed to repair a part based on an automatic structural analysis of that part, and automatically generates an assessment of conformity with engineering acceptance standards that can be used to generate a request for engineering disposition automatically sent to the appropriate engineering or executive authority.
Owner:SYNCRETEK
High resolution chromosomal mapping
ActiveUS20070238105A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsStructural analysisGenome
The present invention generally relates to spatial and structural genomic analysis compositions, which can be used for the mapping of chromosomes and structural analyses of chromosomal rearrangements, including the entire chromosome, as well as specific portions or regions of interest of the chromosomes. In some embodiments, multiple portions of the genome can be distinguished, for instance, using a first detection entity and a second detection entity different from the first detection entity. The detection entities may be immobilized relative to oligonucleotides, which may be selected to bind to different locations within the chromosome. For instance, the oligonucleotides may be at least substantially complementary to the chromosome, e.g., substantially complementary to a specific location of the chromosome.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
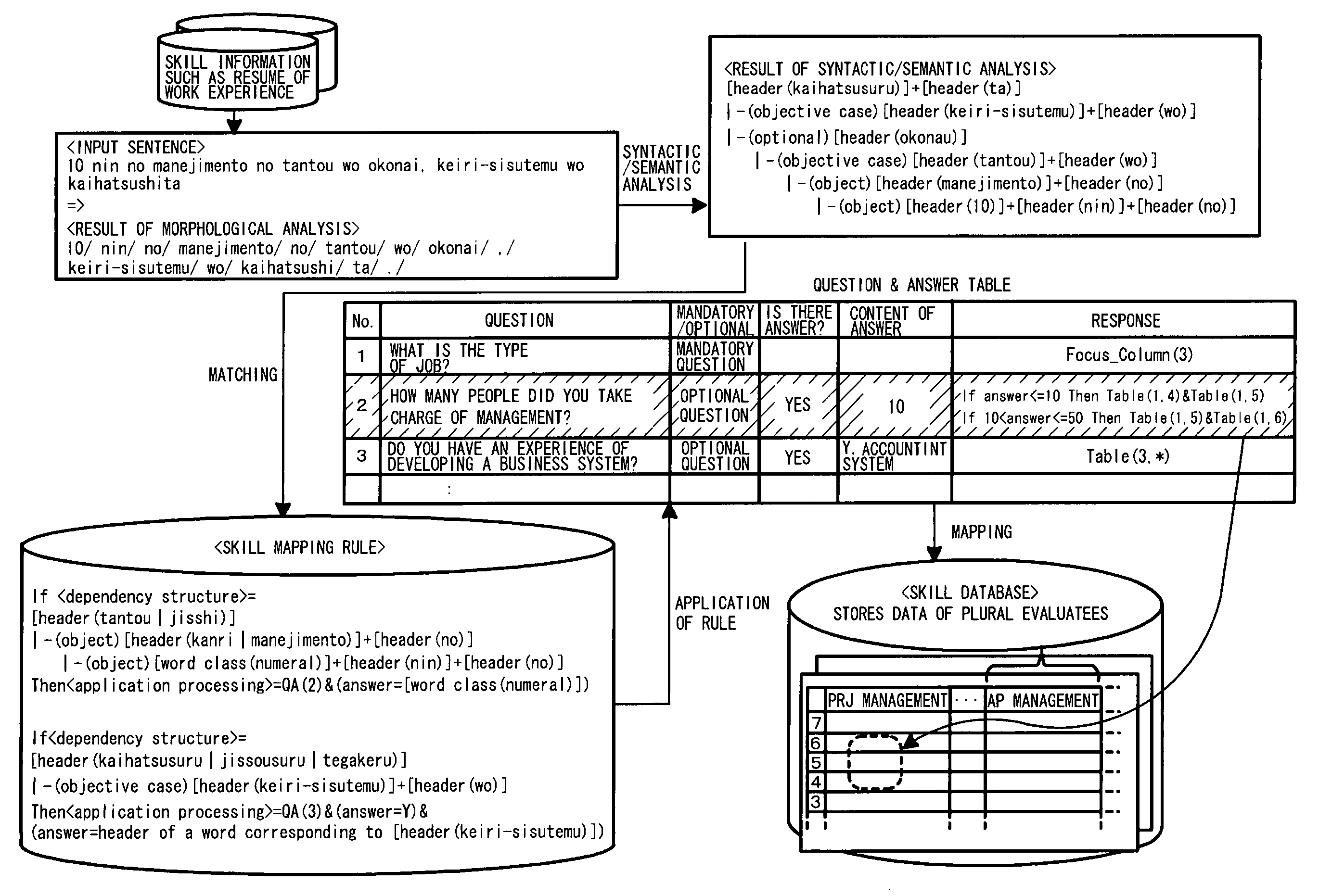
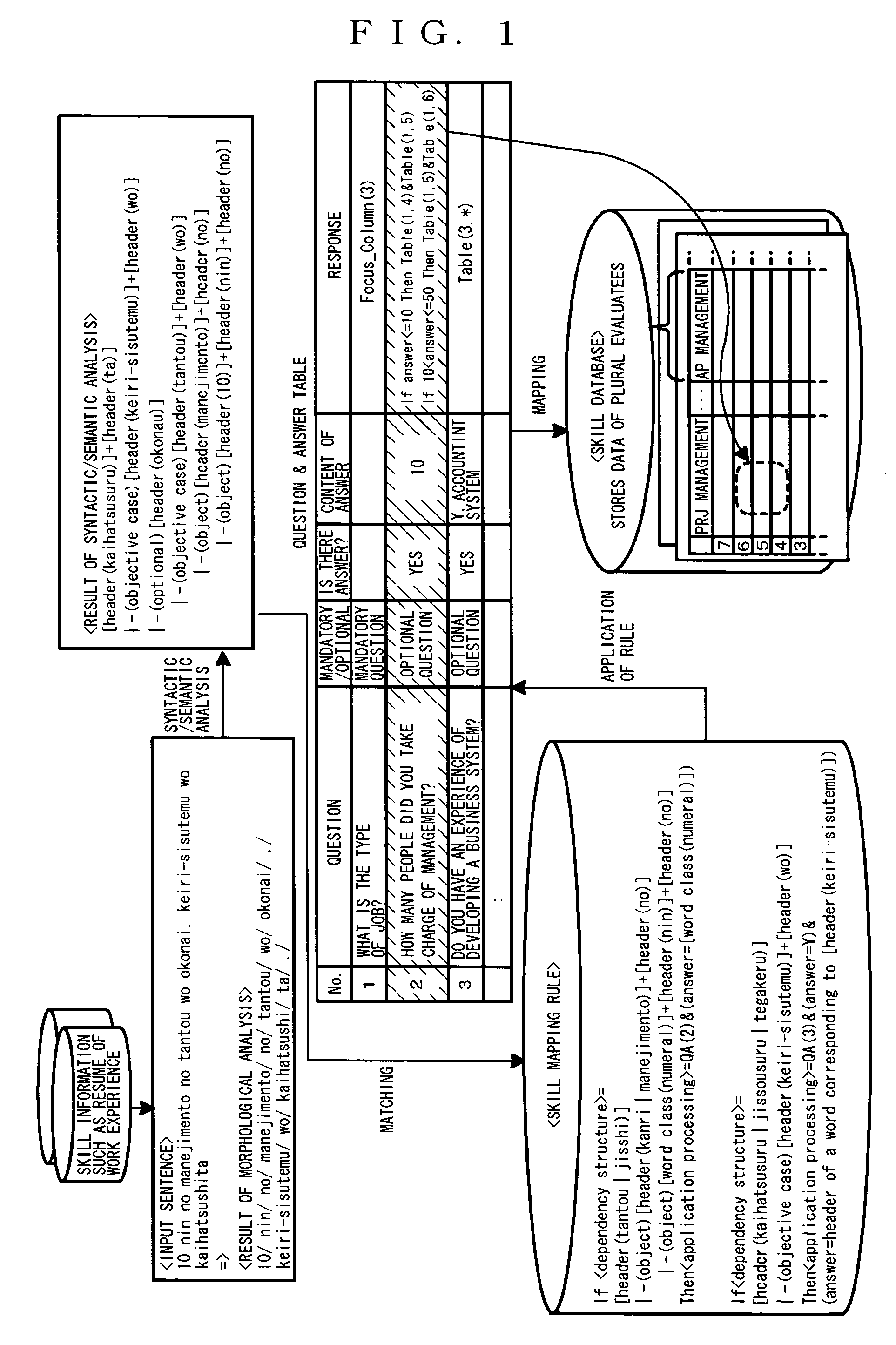
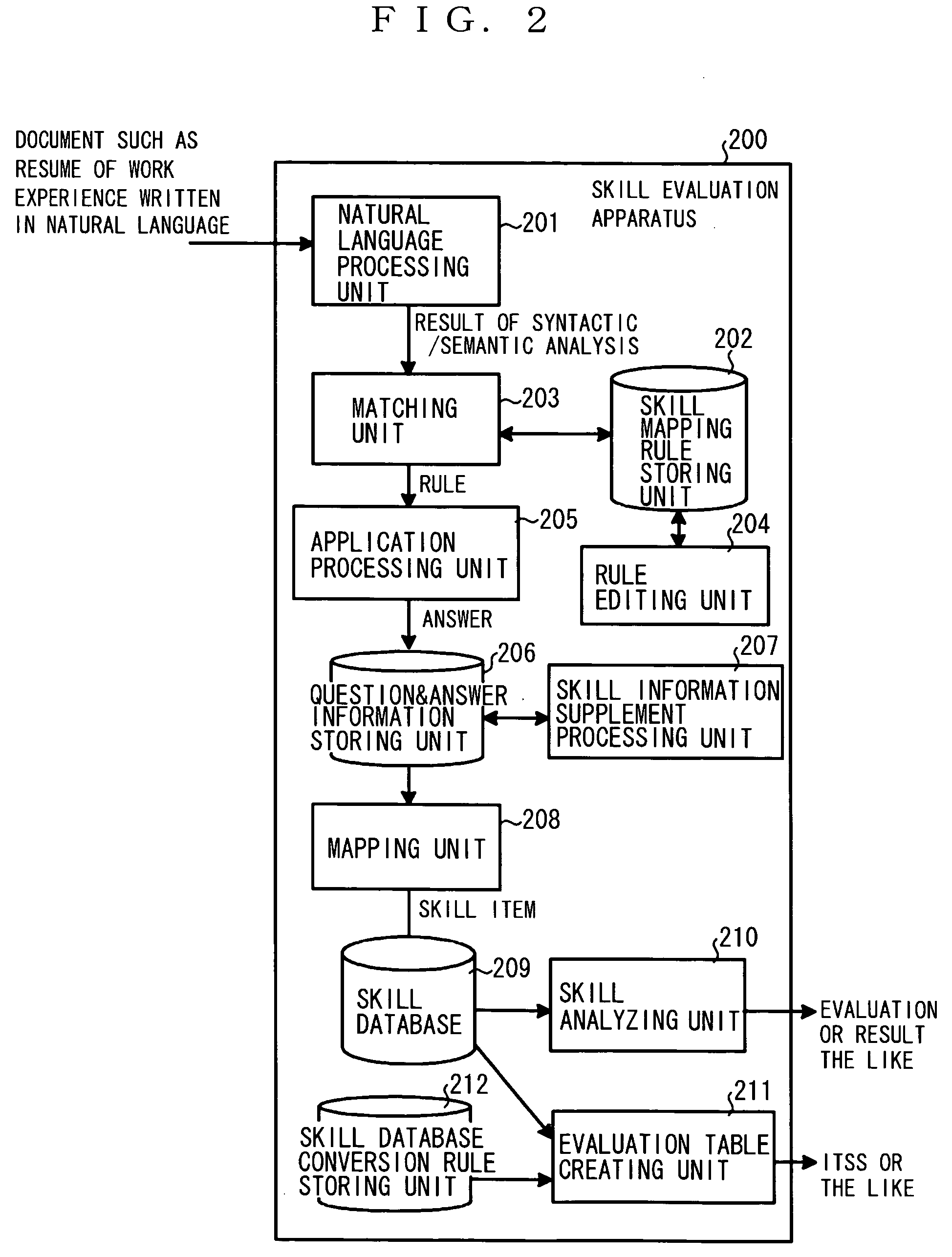
Apparatus for ability evaluation, method of evaluating ability, and computer program product for ability evaluation
An ability evaluation apparatus which evaluates an individual ability and stores a result of evaluation in an ability database, includes an ability mapping rule storing unit that stores an ability mapping rule which associates an ability item extracted from an ability sentence written in a natural language about an individual ability with a data item in the ability database using a structure of the ability sentence, a natural language processing unit that analyzes each sentence in a document written in the natural language about the individual ability to output a result of structural analysis, and an ability item storing unit that extracts the ability item from the result of structural analysis output from the natural language processing unit using the ability mapping rule stored in the ability mapping rule storing unit, and stores the extracted ability item in the ability database.
Owner:CSK CORP
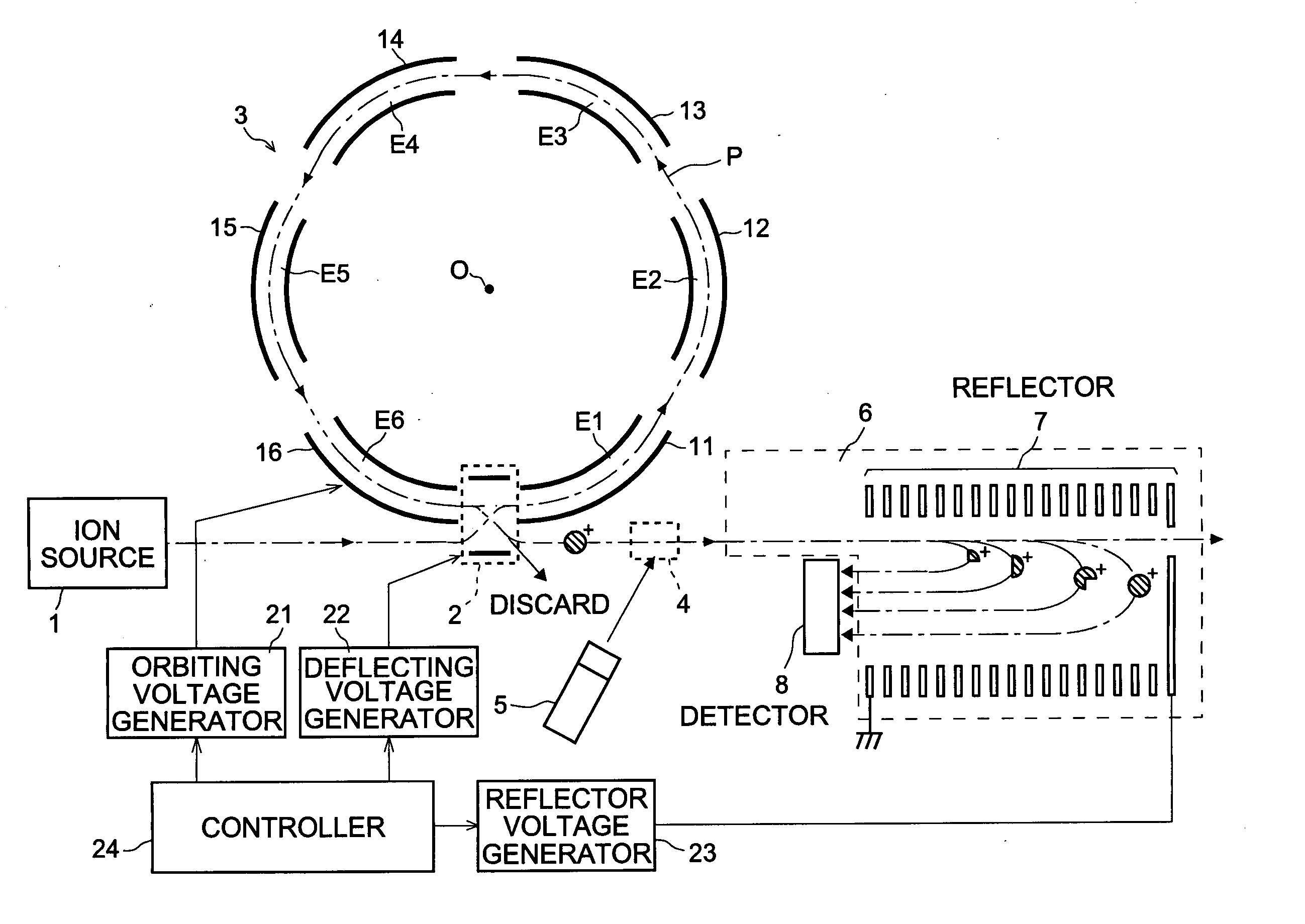
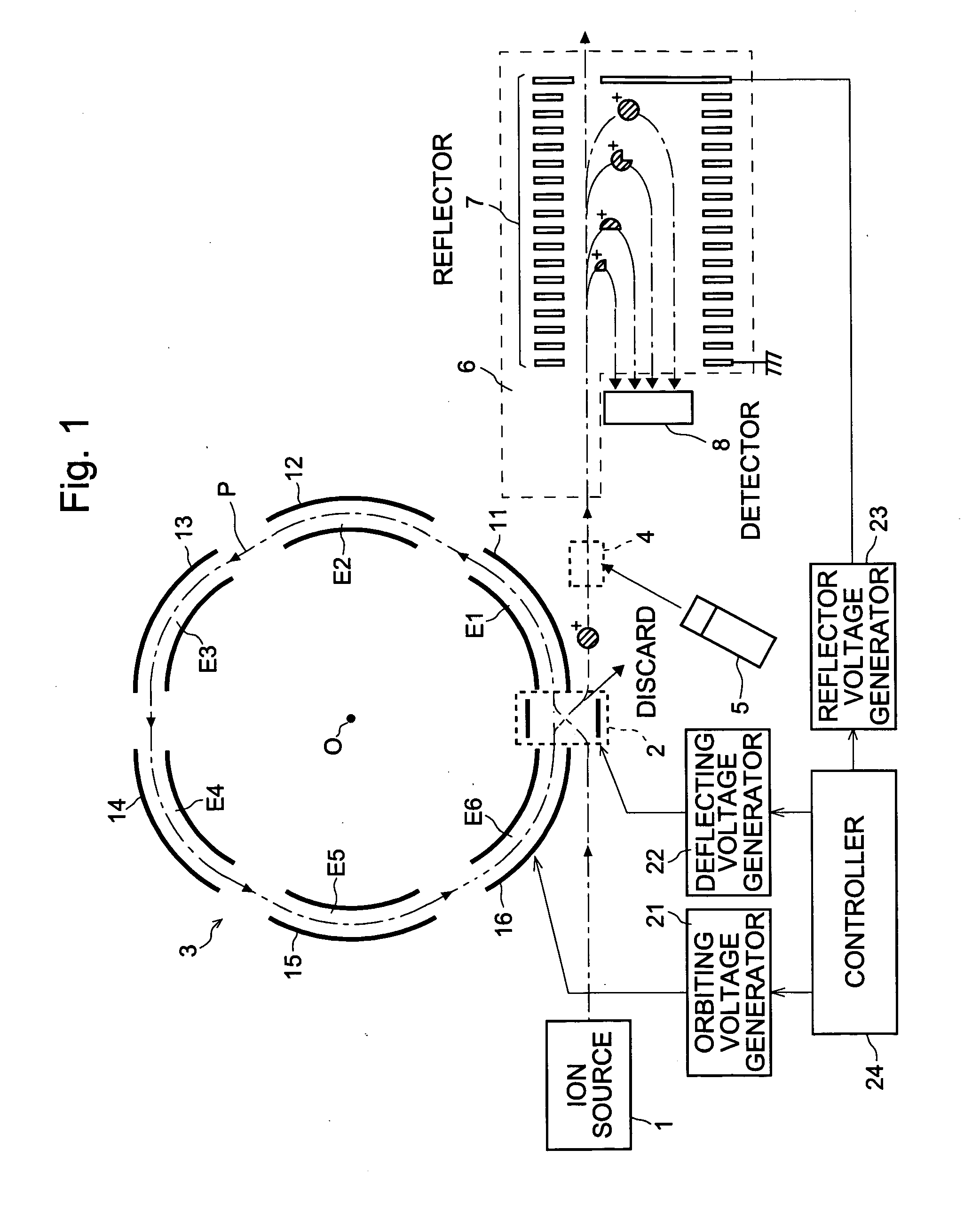
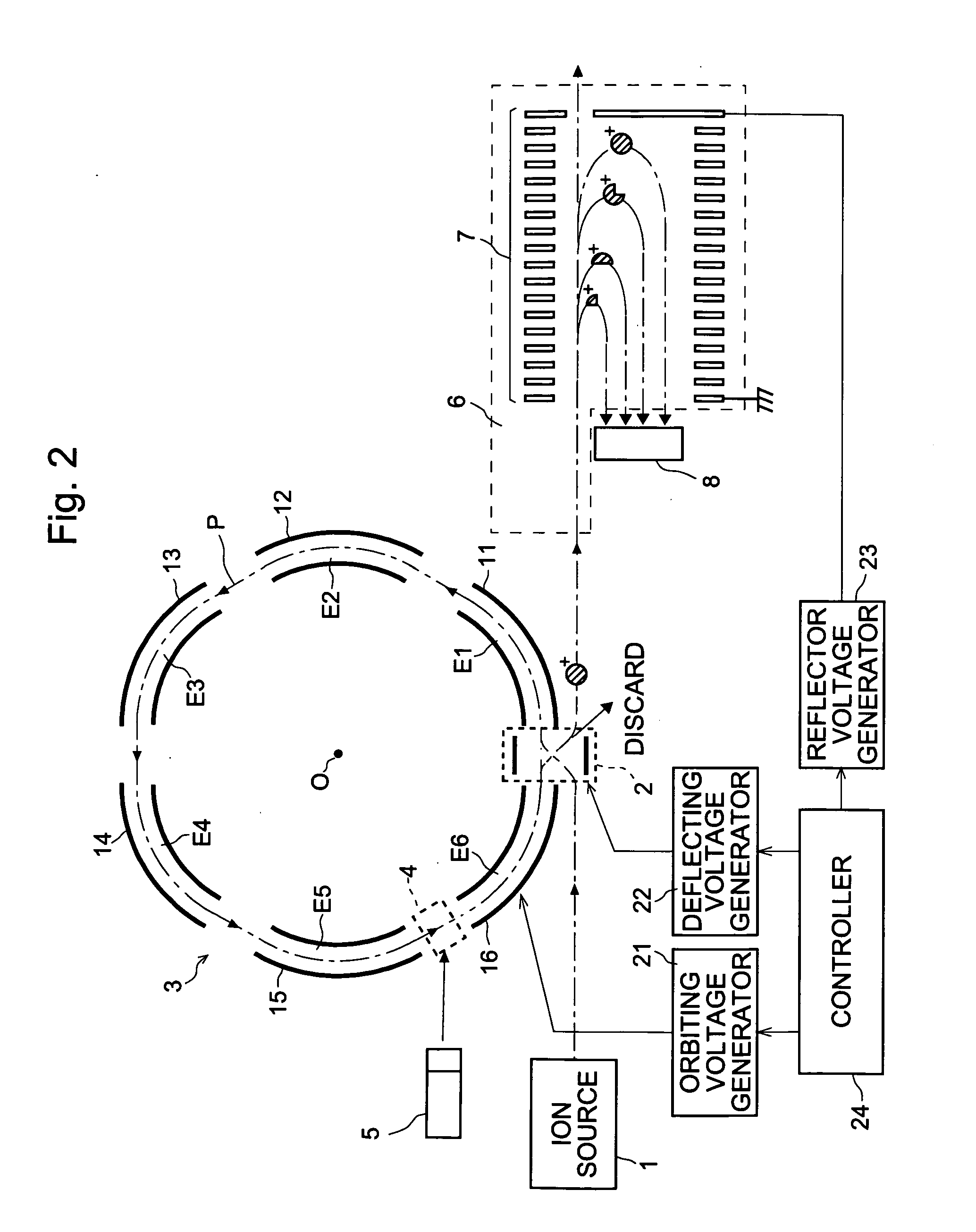
Mass spectrometer
ActiveUS20050151076A1Quality improvementMass resolutionTime-of-flight spectrometersElectron/ion optical arrangementsMass analyzerStructural analysis
In the mass spectrometer of the present invention, a flight space is provided before the mass analyzer, and the flight space includes a loop orbit on which ions fly repeatedly. While ions fly on the loop orbit repeatedly, ion selecting electrodes placed on the loop orbit selects object ions having a specific mass to charge ratio in such a manner that, for a limited time period when the object ions are flying through the ion selecting electrodes, an appropriate voltage is applied to the ion selecting electrodes to make them continue to fly on the loop orbit, but otherwise to make or let other ions deflect from the loop orbit. If ions having various mass to charge ratios are introduced in the loop orbit almost at the same time, the object ions having the same mass to charge ratio continue to fly on the loop orbit in a band, but ions having mass to charge ratios different from that are separated from the object ions while flying on the loop orbit repeatedly. Even if the difference in the mass to charge ratio is small, the separation becomes large when the number of turns of the flight becomes large. After such a separation is adequately achieved, the ion selecting electrodes can select the object ions with high selectivity, or at high mass resolution. By adding dissociating means, fragment ions originated only from the selected object ions can be analyzed, which enables the identification and structural analysis of the sample at high accuracy.
Owner:SHIMADZU CORP
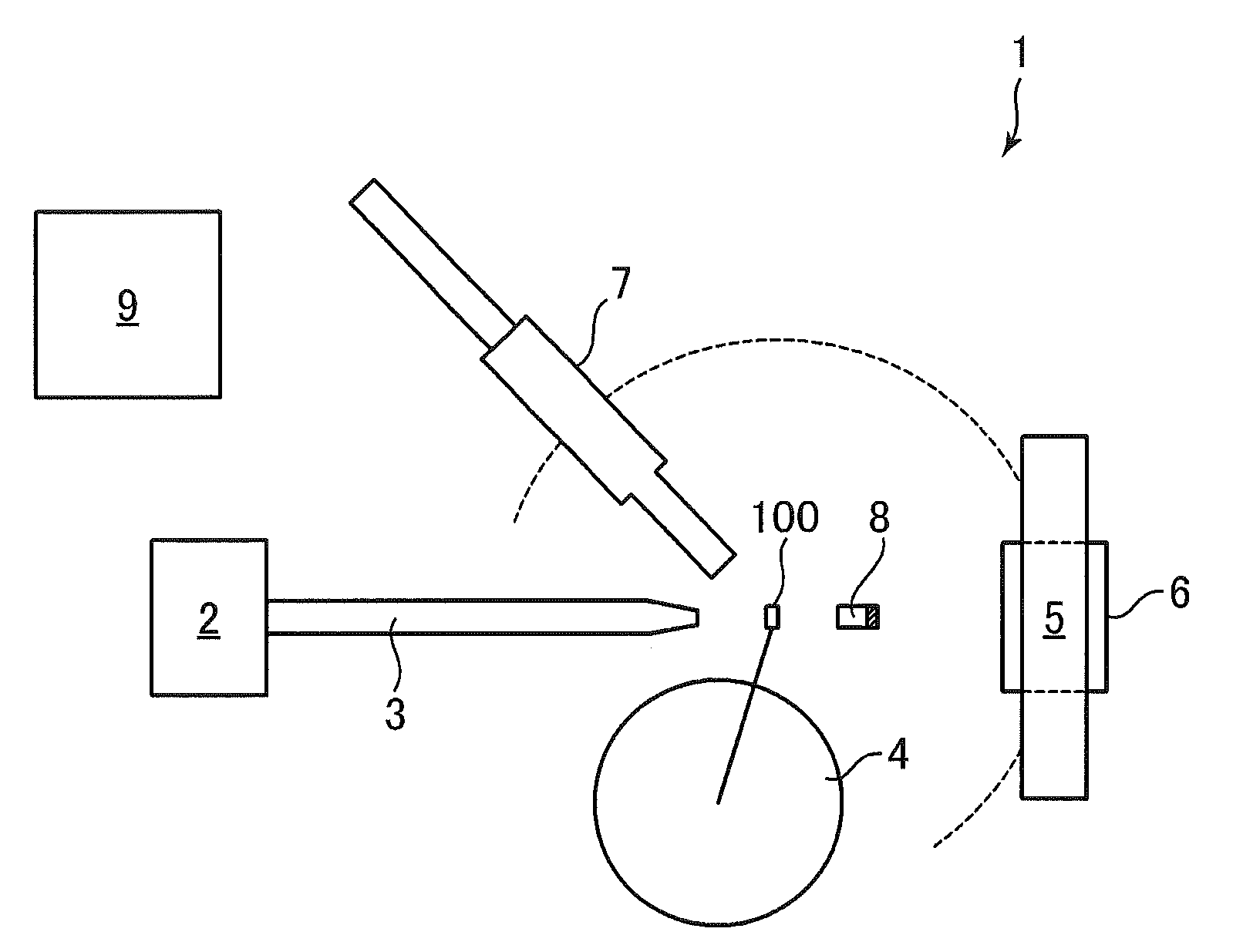
X-ray surface analysis and measurement apparatus
InactiveUS9823203B2Wide choiceIncrease brightnessMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationX-ray tube electrodesHigh energyDesign for X
Systems for x-ray diffraction / scattering measurements having greater x-ray flux and x-ray flux density are disclosed. These are useful for applications such as material structural analysis and crystallography. The higher flux is achieved by using designs for x-ray targets comprising a number of microstructures of one or more selected x-ray generating materials fabricated in close thermal contact with a substrate having high thermal conductivity. This allows for bombardment of the targets with higher electron density or higher energy electrons, which leads to greater x-ray flux. The high brightness / high flux source may then be coupled to an x-ray reflecting optical system, which can focus the high flux x-rays to a spots that can be as small as one micron, leading to high flux density, and used to illuminate materials for the analysis based on their scattering / diffractive effects.
Owner:SIGRAY INC
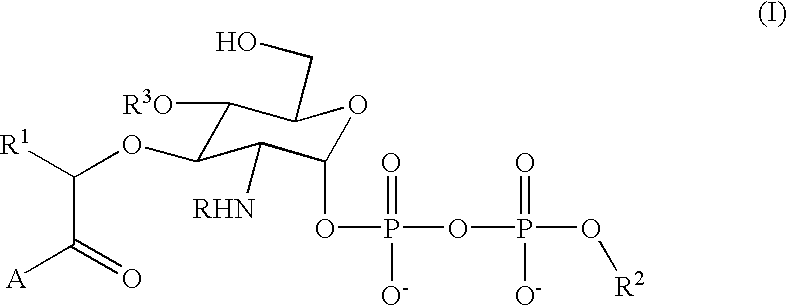
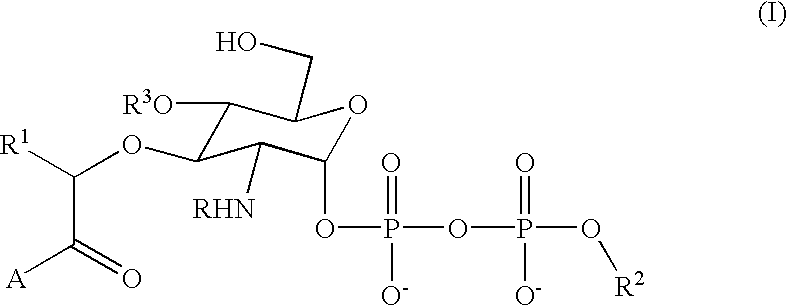
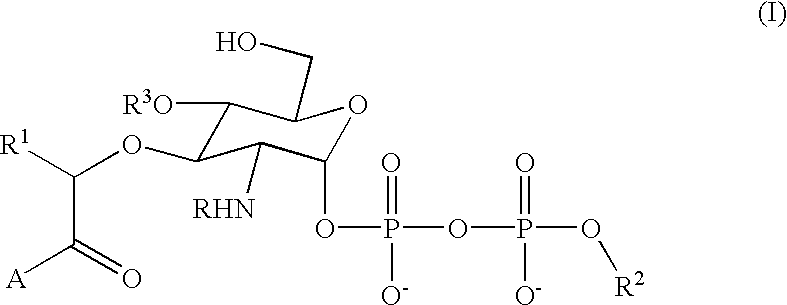
Bacterial transglycosylases: assays for monitoring the activity using Lipid II substrate analogs and methods for discovering new antibiotics
InactiveUS6461829B1Easy to detectEasy to measureMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisEnzymatic synthesisSubstrate analog
This invention provides a direct method for monitoring bacterial transglycosylase activity using labeled substrates produced by chemo-enzymatic synthesis wherein the labels are selected to permit the detection of both polymeric and non-polymeric products simultaneously, either directly or following the separation of product from starting material. The invention promotes the discovery of new antibiotics with activity against bacterial transglycosylases by a) laying the groundwork for structural analysis of purified, active transglycosylase (which permits structure-based design); and b) providing an assay that can be used to screen for inhibitors.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES FOR PRINCETON UNIV
High resolution chromosomal mapping
ActiveUS8058055B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsStructural analysisGenome
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
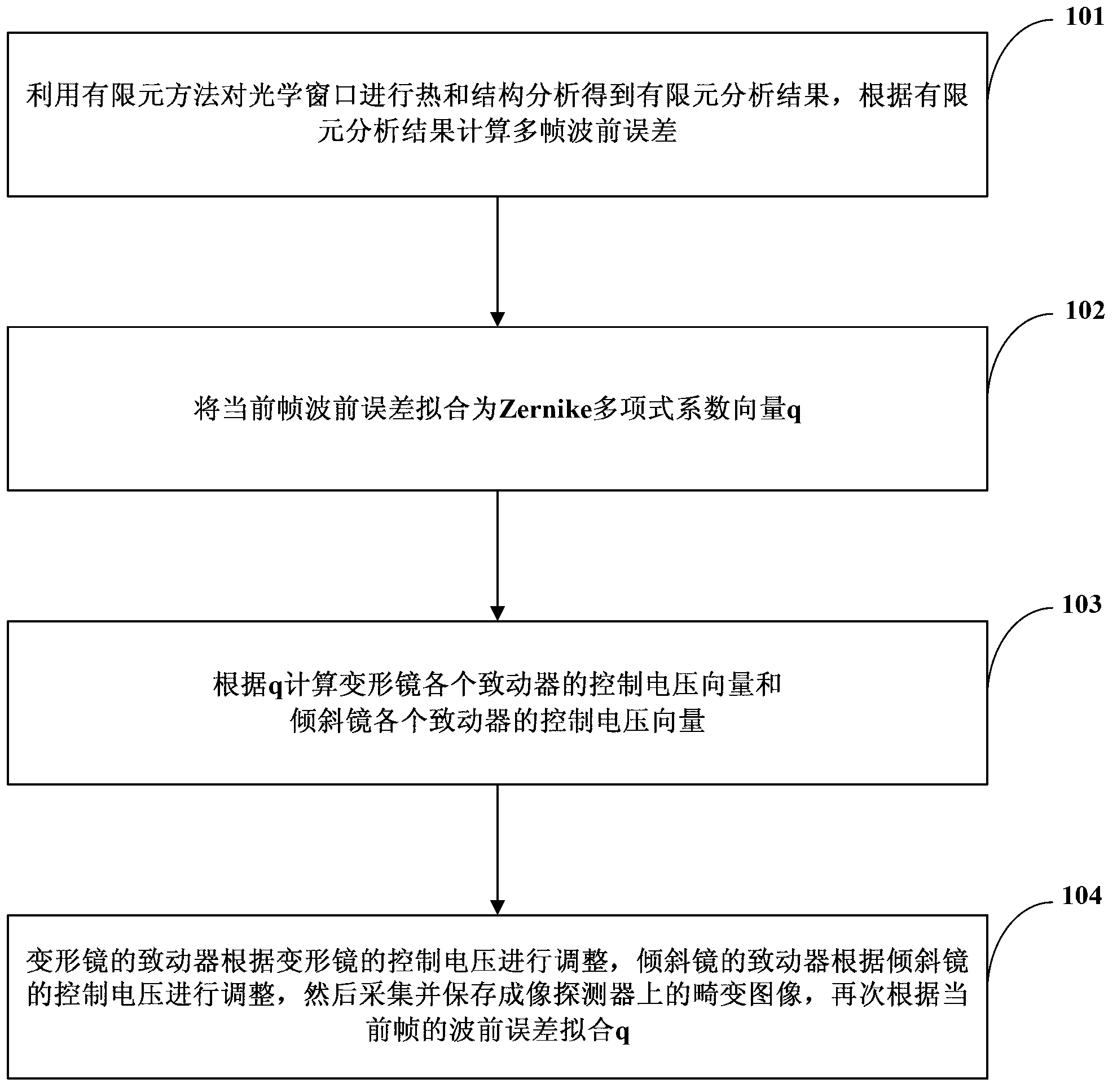
Method and system for simulating aero-optical effect
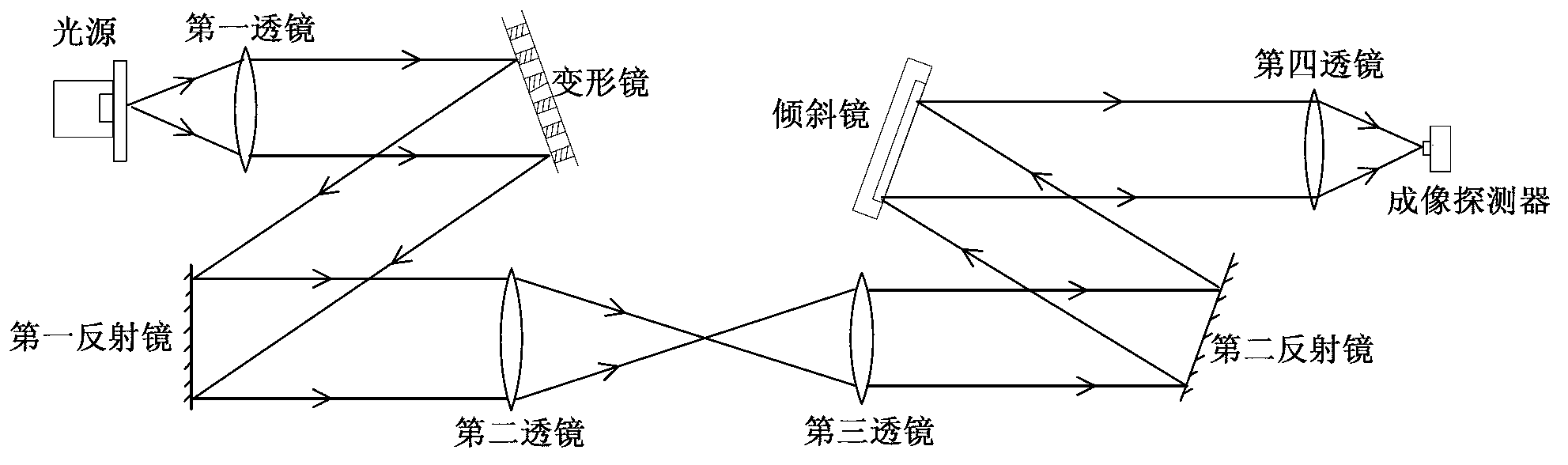
The invention relates to a method for simulating an aero-optical effect. The method comprises the steps of conducting thermal and structural analysis to an optical window by adopting a finite element analysis method to obtain a finite element analysis result, and calculating multi-frame wave-front errors according to the finite element analysis result; fitting the current frame wave-front error to be a Zernike polynomial coefficient vector q; calculating control voltage vectors of all actuators of a deformable mirror and control voltage vectors of all actuators of a tilting mirror according to the q; and adjusting the actuators of the deformable mirror according to the control voltage of the deformable mirror, adjusting the actuators of the tiling mirror according to the control voltage of the tiling mirror, acquiring and saving distorted images on an imaging detector and again fitting the q according to the current frame wave-front error. The invention additionally discloses a system for simulating the aero-optical effect. By using the method and the system provided by the embodiment of the invention, dynamic distorted image data under the influence of the aero-optical effect can be obtained and experimental conditions are provided for researches on the correction of the aero-optical effect.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY +1
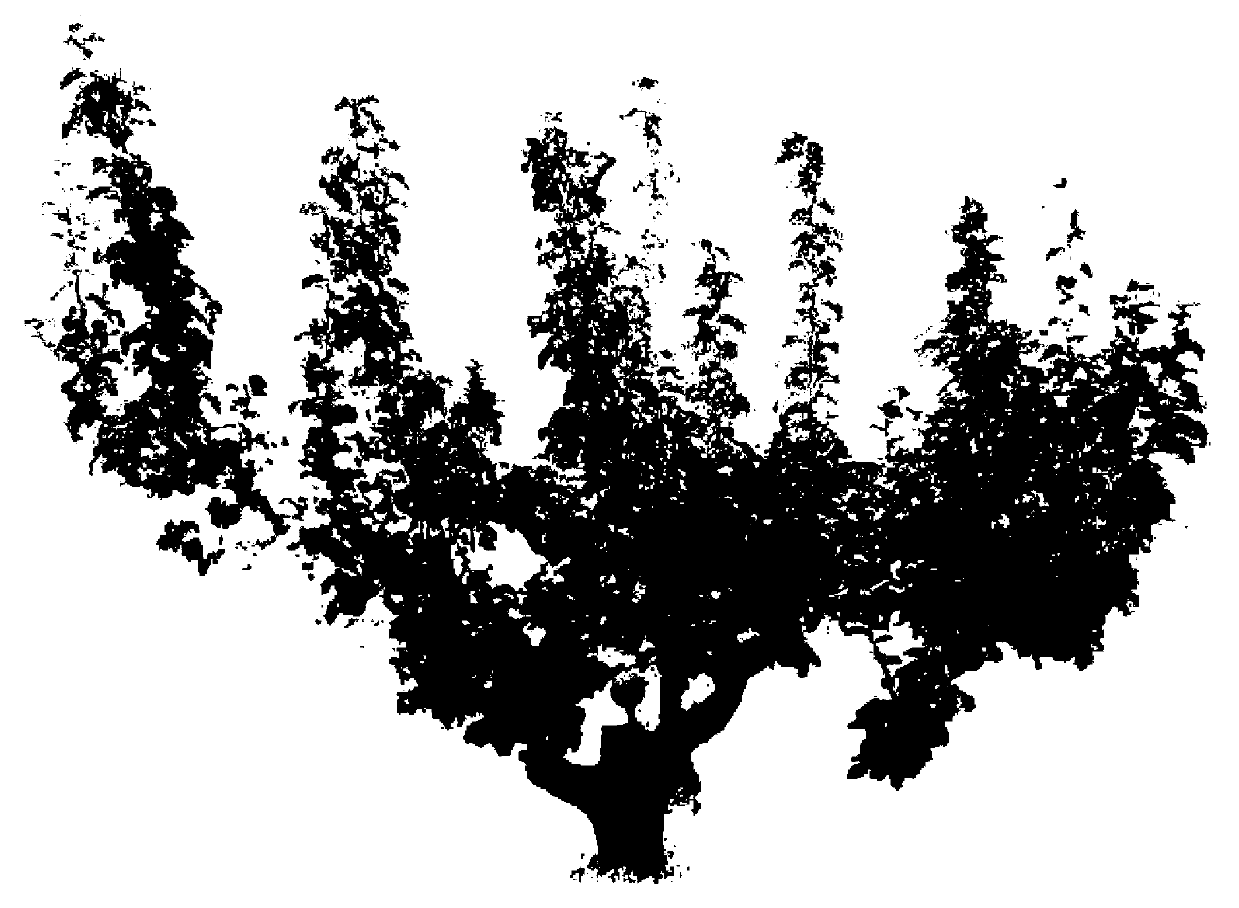
Method and system of three-dimensional reconstruction of shape structure of trees in leaved state
ActiveCN103106684AFast 3D reconstructionAccurate 3D reconstructionImage enhancement3D modellingData setAlgorithm
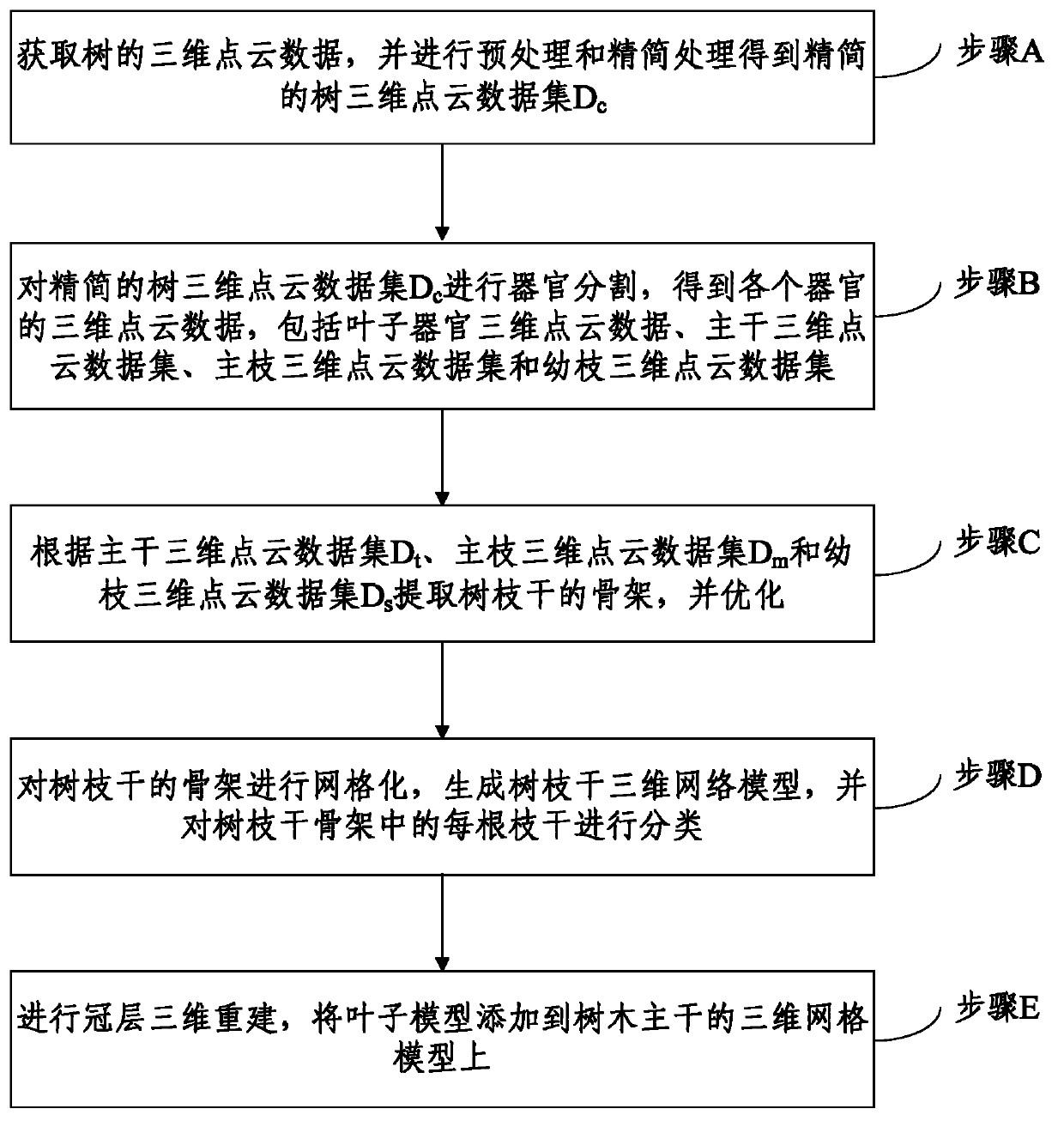
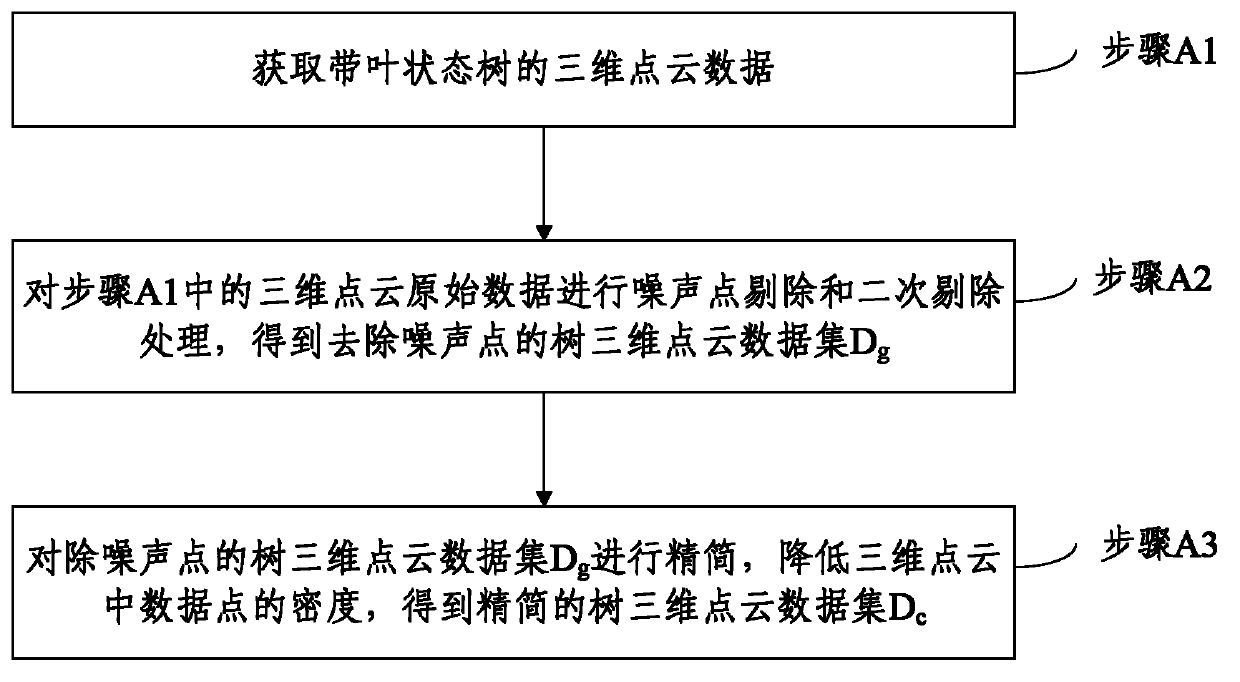
The invention discloses a method and a system of three-dimensional reconstruction of a shape structure of trees in a leaved state. The method comprises acquiring three-dimensional point cloud data of trees and carrying out preprocessing and simplifying processing to obtain simplified three-dimensional cloud data set of the trees, carrying out organ segmentation to the simplified three-dimensional point cloud data set of the trees to obtain the three-dimensional point cloud data of each organ, wherein the three-dimensional point cloud data of each organ comprise the three-dimensional point cloud data of a leaf organ, the three-dimensional point cloud data set of a main trunk, the three-dimensional point cloud data set of a main branch and the three-dimensional point cloud data set of a sprout, extracting the frameworks of limbs of the trees according to the three-dimensional point cloud data set of the main trunk, the three-dimensional point cloud data set of the main branch and the three-dimensional point cloud data set of the sprout and optimizing the frameworks of the limbs of the trees, carrying out meshing to the frameworks of the limbs of the trees to generate a three-dimensional mesh model of the limbs of the trees, classifying each limb of the frameworks of the limbs of the trees, and carrying out canopy three-dimensional reconstruction. The fast three-dimensional reconstruction of the shape structure of the trees in the leaved state is achieved, and therefore a method and a high-precision basic model support are provided for the structural analysis of the canopies of the trees, the evaluation of the physiological and ecological characteristics and the like.
Owner:BEIJING RES CENT FOR INFORMATION TECH & AGRI
Method and equipment for inspecting reinforced concrete pipe
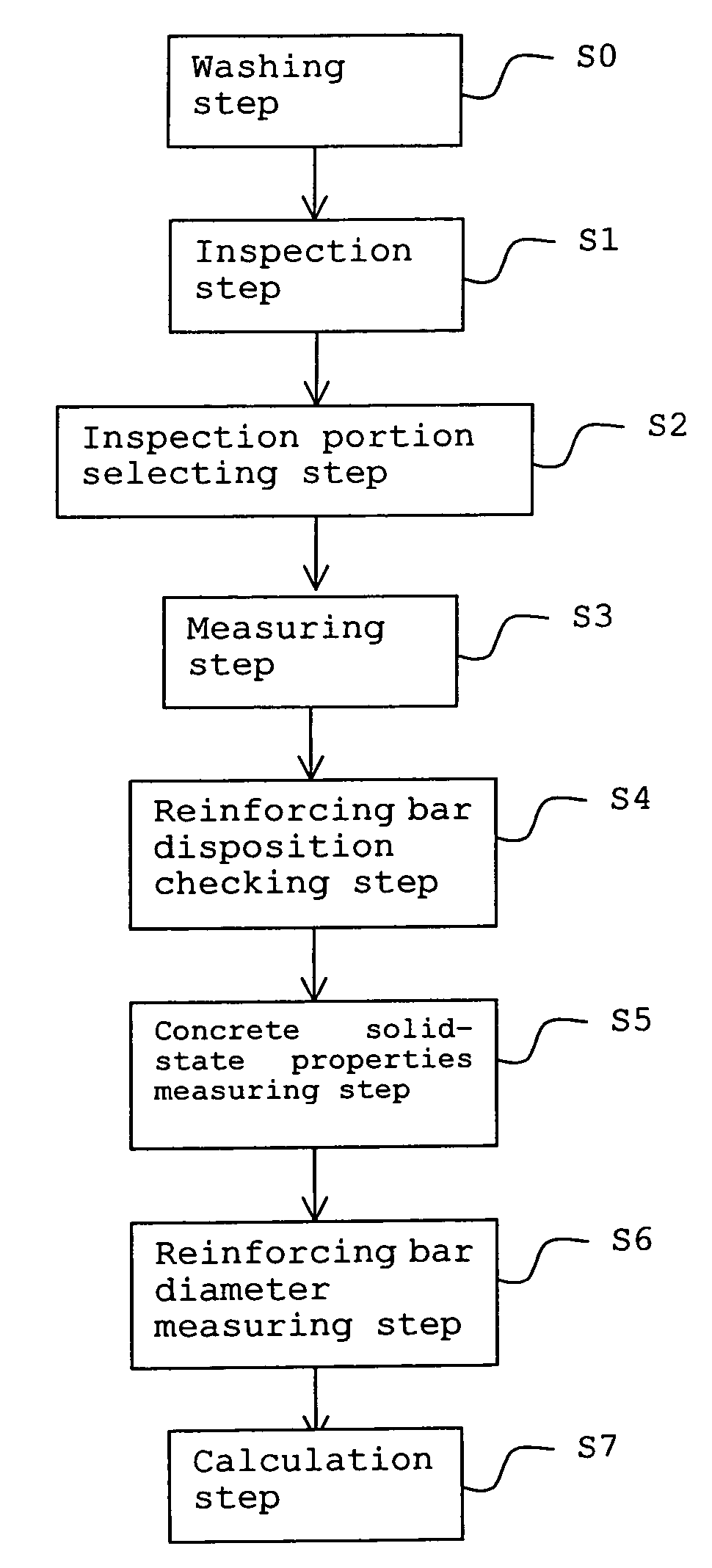
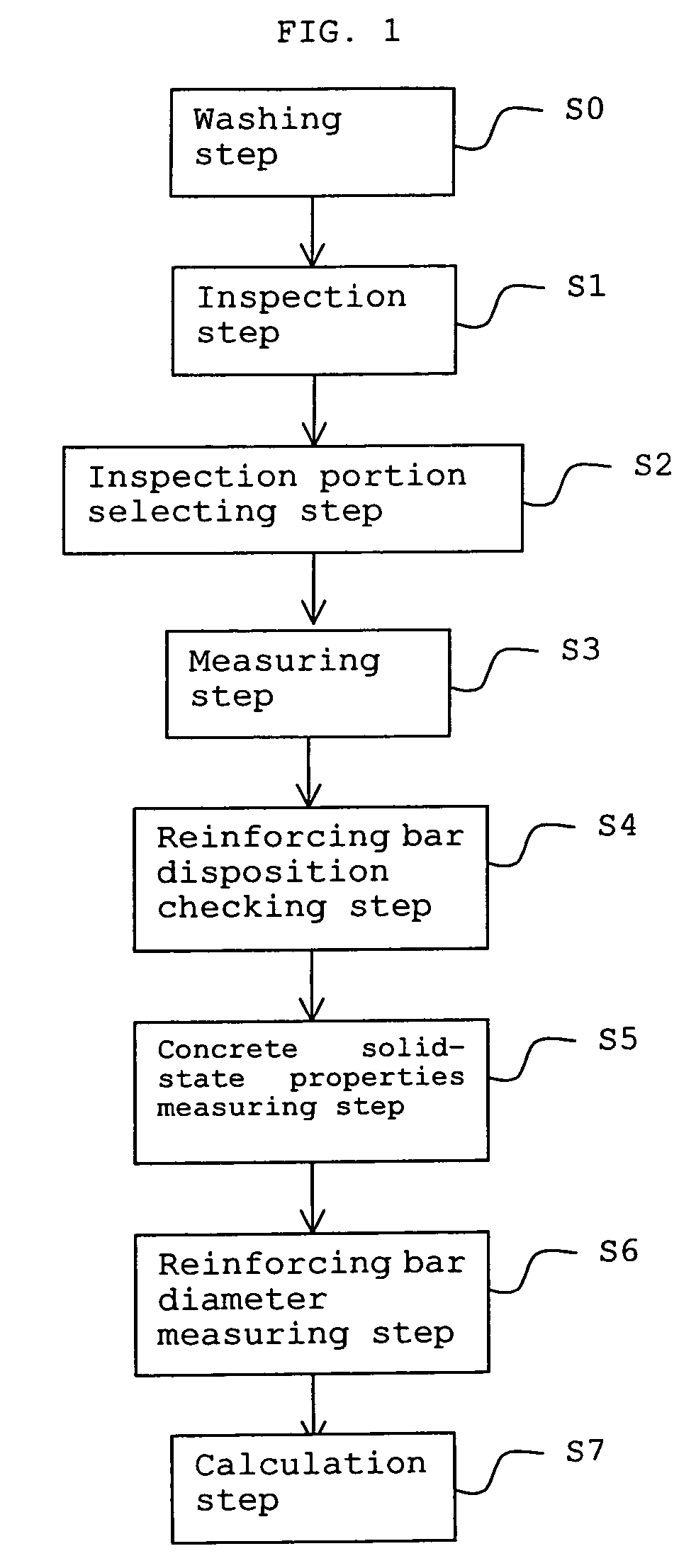
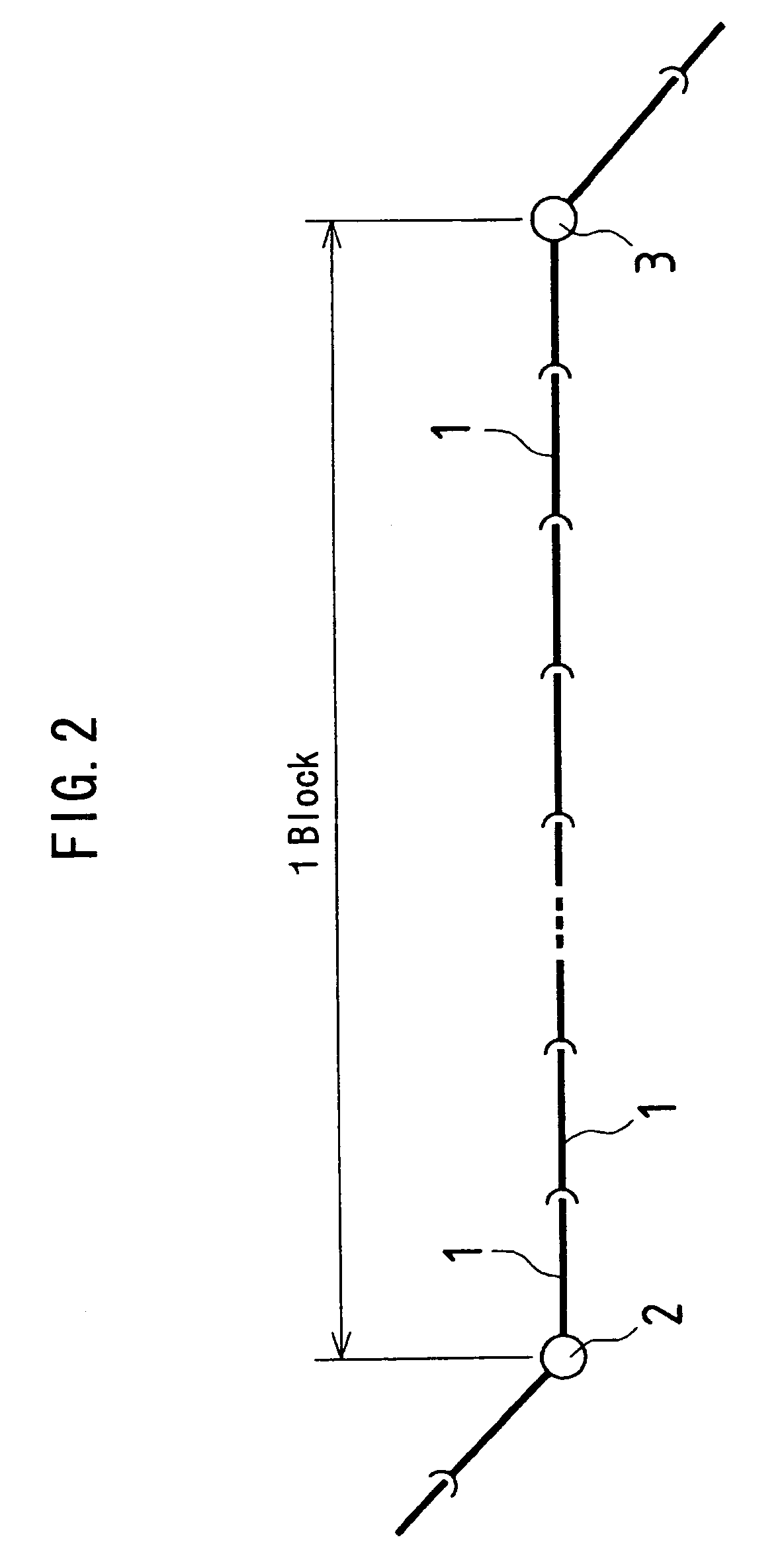
InactiveUS7360462B2Shorten operation timeImprove accuracyVibration measurement in solidsDetection of fluid at leakage pointReinforced concreteStructural analysis
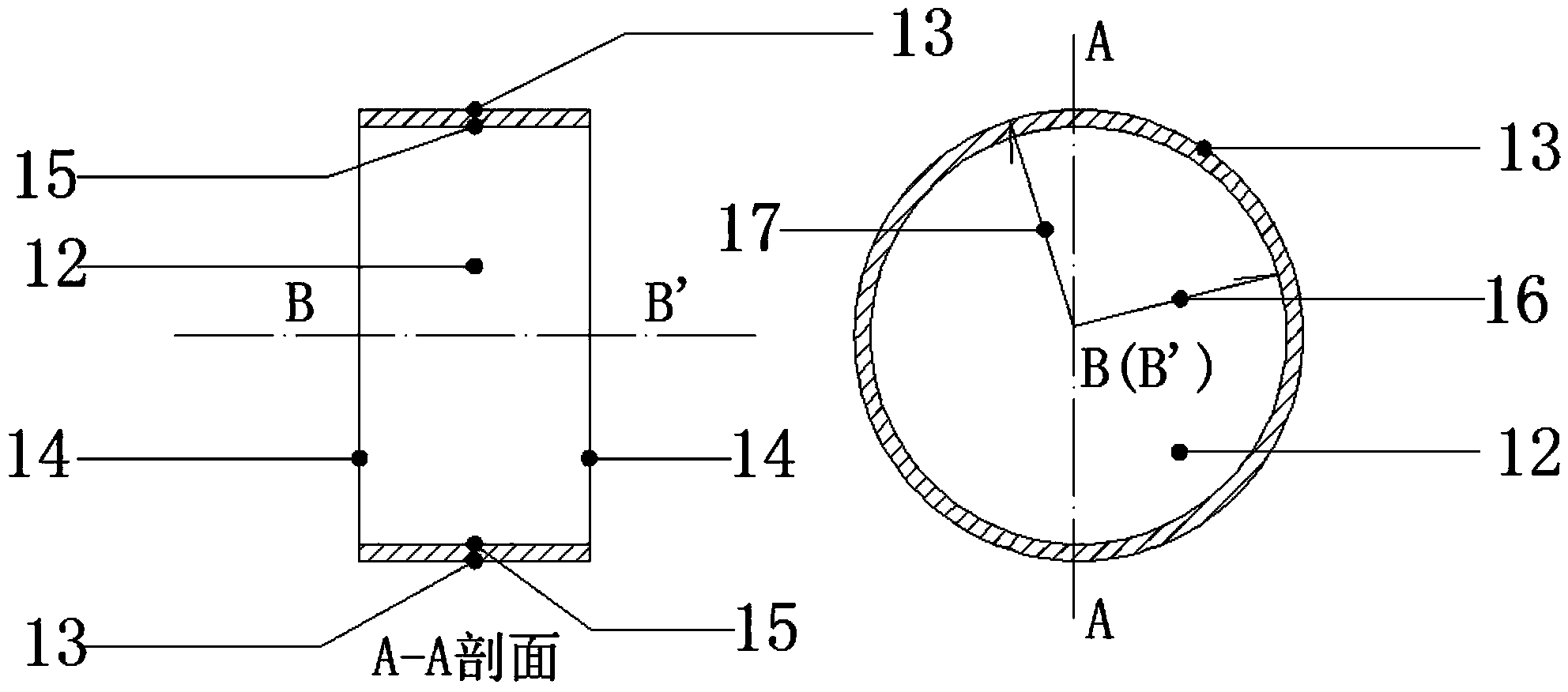
Deterioration of reinforced concrete pipes is checked and the deterioration progress level is classified. Based on the inspection result, a portion to be inspected in detail in an inspection area is selected. With respect to the selected portion to be inspected in detail, the pipe thickness and the diameter of reinforcing bars are measured and the location of reinforcing bars in the portion to be inspected in detail are checked. Using the data of the thickness of a pipe, the diameter of the reinforcing bar and disposition of the reinforcing bars, structural analysis is carried out and the strength of the reinforced concrete pipe is calculated. The calculation result is used as information for evaluating the deterioration state of the reinforced concrete pipe.
Owner:SEKISUI CHEM CO LTD
Experiment-numerical analysis combined determination method for relative permeability coefficient of unsaturated soil
ActiveCN103760089AHigh standardTroubleshoot testing difficultiesPermeability/surface area analysisOsmotic coefficientStructural analysis
The invention relates to an experiment-numerical analysis combined determination method for the relative permeability coefficient of unsaturated soil. The method comprises simple experiment tests and numerical analyses, the relative permeability coefficient equation of soil under unsaturated state is obtained via simple laboratory experiments and numerical optimization fitting analyses, therefore, the relative permeability coefficient of the unsaturated soil is obtained by calculation. The method is mainly suitable for cohesive soil with a small permeability coefficient. At the same time, the invention provides a numerical analysis procedure which comprises a basic analysis module and an optimization back analysis module, wherein the basic analysis module simulates the dehydration process of test specimens under the condition of a given boundary; the optimization back analysis module takes a determined dehydration mass-time curve as basic input to confirm two parameters Pr and m describing the changes of the relative permeability coefficient of the unsaturated soil along with saturation via an orthogonal optimization method in the numerical analyses. The method is simple in experiments, convenient to operate, wide in usable ranges and good in accuracy; the determined relative permeability coefficient equation can be directly applied to soil engineering structure analyses.
Owner:SHANDONG AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
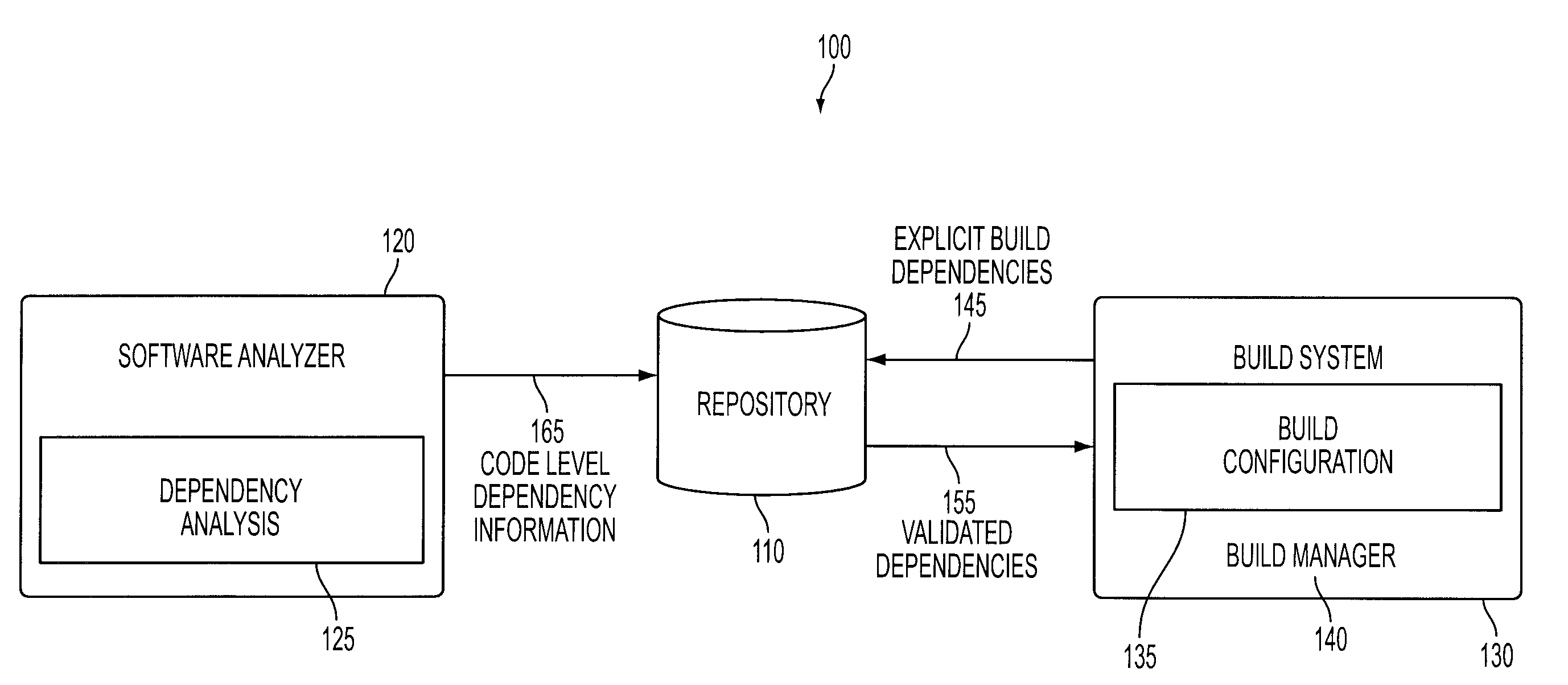
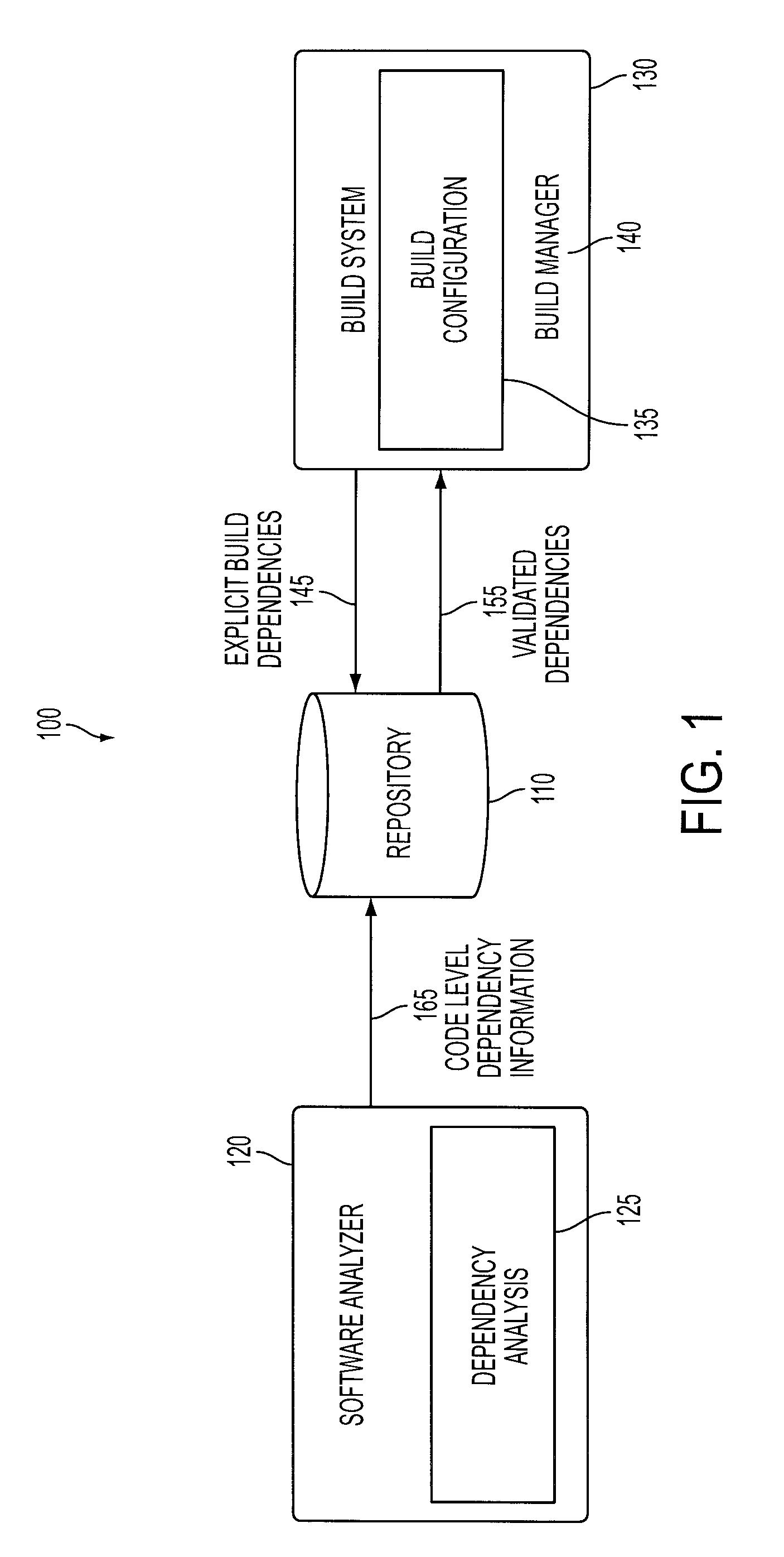
Build optimization with applied static analysis
InactiveUS20100042974A1Version controlSpecific program execution arrangementsAnti-patternSoftware analytics
A method of constructing a software build using a static structural analysis system is disclosed. A software build configuration may be run and analyzed by a software analyzer to detect dependencies among code classes and components. A code dependency map is constructed identifying code level dependencies. The code dependency map may be referenced for code classes and components selected for modification. Identified dependency relationships with the selected code classes and components enable a builder to rebuild those code classes and components affected by the modification. Additionally, the software analyzer may identify undesirable dependencies and anti-patterns in potential need of deletion or modification.
Owner:IBM CORP
Device for testing thin specimens in pure bending
An improved test fixture to evaluate thin composite laminates commonly used in deployable space structures. The fixture is designed to impart a pure moment into the coupon, a necessary improvement to prior test methods where results are obtained by fitting material properties in a nonlinear structural analysis of the test. Fixture mechanics allow for direct calculation of the coupon flexural modulus and allowable flexural strain based on two key measurements, fixture displacement and applied load.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESETNED BY THE SEC OF THE AIR FORCE
Methods and Systems for Automatically Assessing and Reporting Structural Health
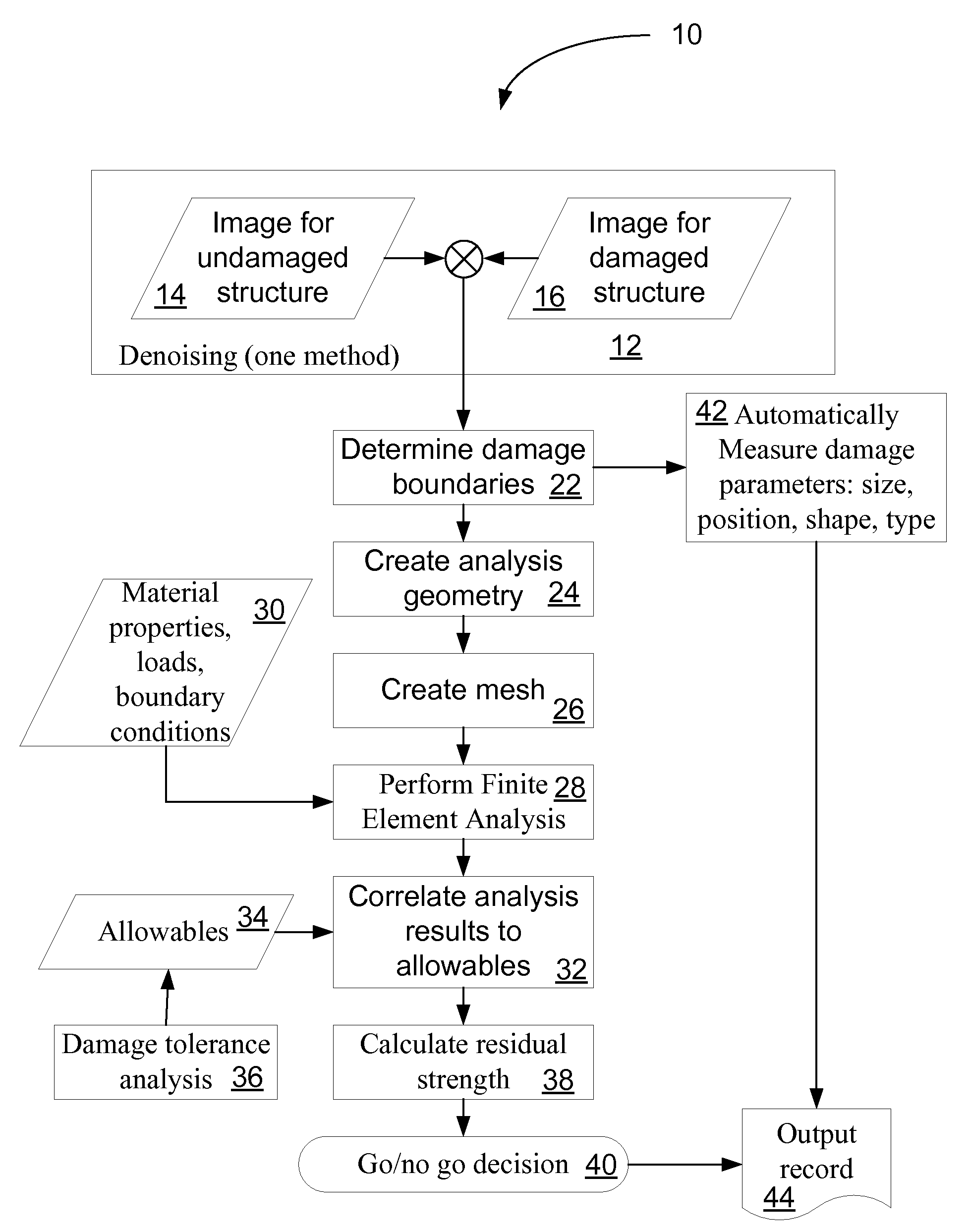
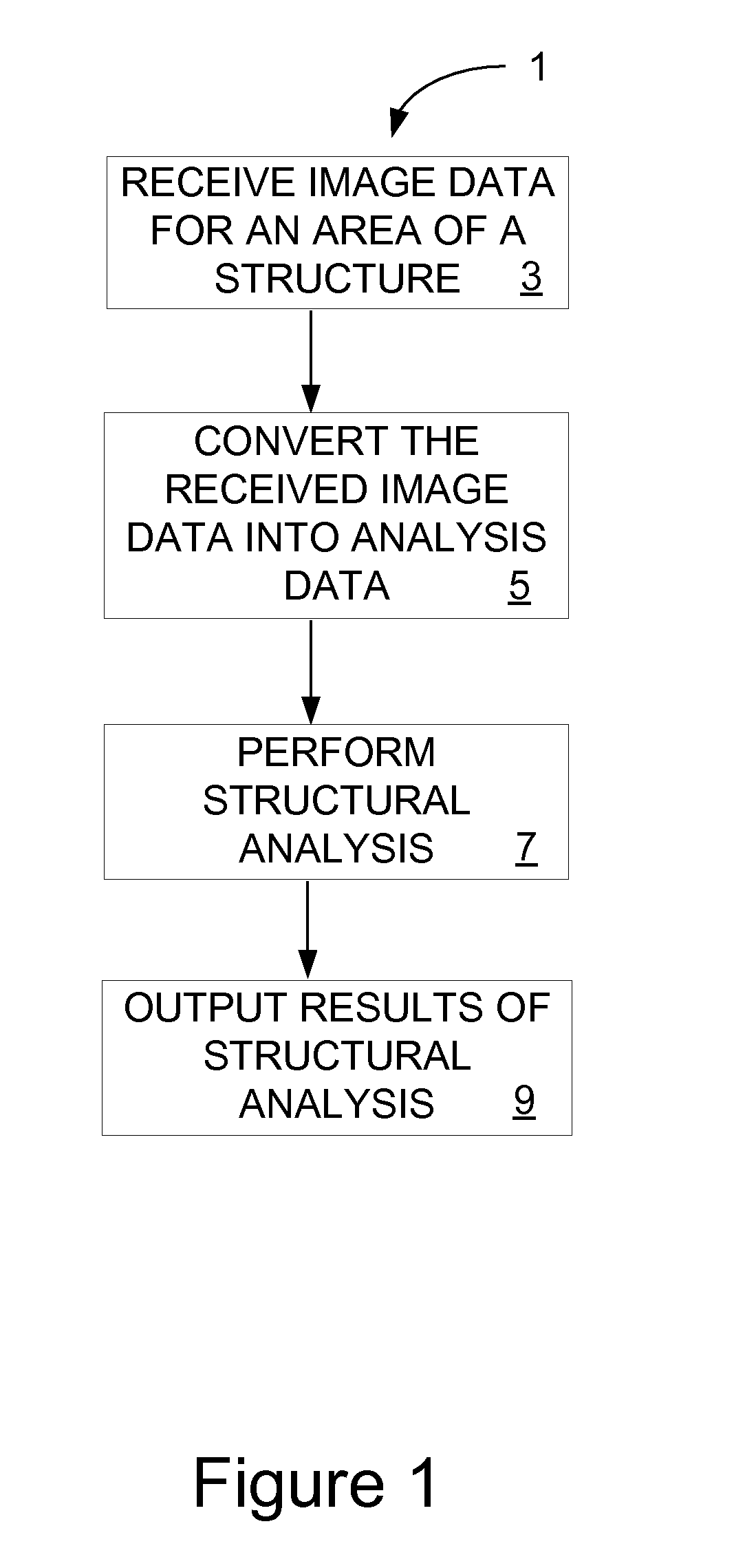
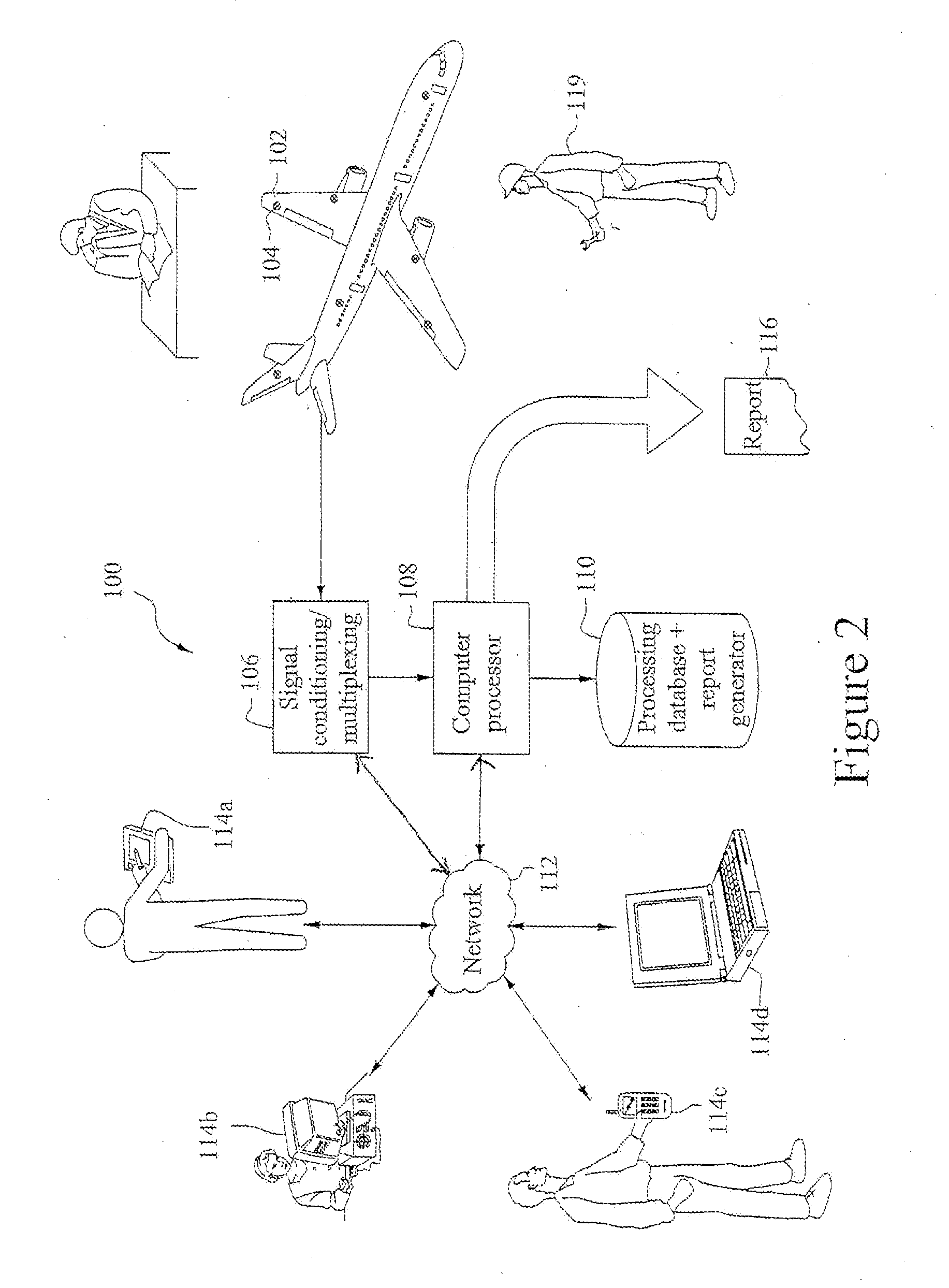
ActiveUS20080183402A1Low costImprove accuracyPlug gaugesAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceAnalysis dataStructural analysis
Structural analysis systems and methods are disclosed. One embodiment provides a method for analyzing a structure includes receiving damage image data; converting the received image data into analysis data in an analyzable format; performing a structural analysis on the analysis data; and outputting the results of the structural analysis. The system includes a computer or other processing device that is capable of analyzing a structure. The system receives damage image data; converts the received image data into analysis data in an analyzable format; performs a structural analysis on the analysis data; and outputs the results of the structural analysis.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Integration of direct binding label-free biosensors with mass spectrometry for functional and structural characterization of molecules
InactiveUS20060003372A1Microbiological testing/measurementColor/spectral properties measurementsCombined methodMass Spectrometry-Mass Spectrometry
The invention provides methods for the detection, quantification, identification and structural analysis of one or more molecules. Mass spectrometry (MS) is not a universal detector as all molecules do not ionize equally well leading to poor signal to quantity information. MS can be optimized to identify the specific mass of a binding component when the presence of a material is known. Colorimetric resonant reflectance optical sensors provide a universal mass detector in that nearly all biological masses give equally proportional signals. The combined methods allow selection and or detection with quantification of all masses binding to the sensor with the ability to identify specific molecules by their individual masses and structure analyses.
Owner:SRU BIOSYST
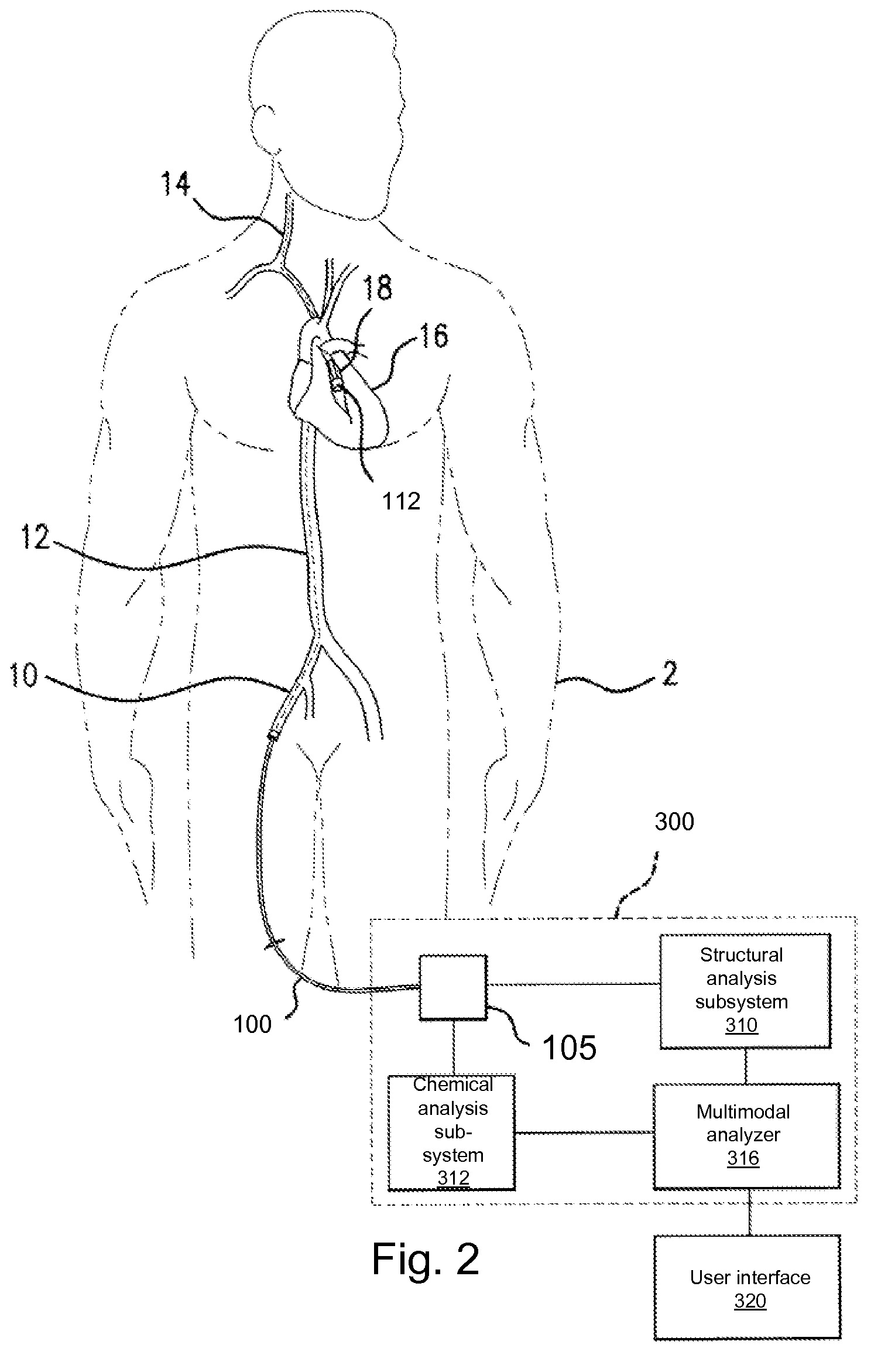
System and Method for Intravascular Structural Analysis Compensation of Chemical Analysis Modality
ActiveUS20090253989A1Improve accuracyUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsDiagnostics using spectroscopyHead vesselsDiagnostic Radiology Modality
A multimodal intravascular analysis uses a structural intravascular analysis modality to compensate for a chemical analysis modality. Examples of structural analysis are IVUS, OCT, including optical coherence domain Reflectometry (OCDR) and optical frequency domain imaging (OFDI), and / or sonar range finding. Examples of chemical or functional analysis are optical, NIR, Raman, fluorescence and spectroscopy, thermography and reflectometry. In one example, the structural analysis is used to characterize the environment structurally, such as catheter head-vessel wall distance. This information is then used to select from two or more algorithms which are depth specific (e.g. shallow vs. deep), to achieve improved accuracy in the chemical or functional analysis.
Owner:INFRAREDX INC
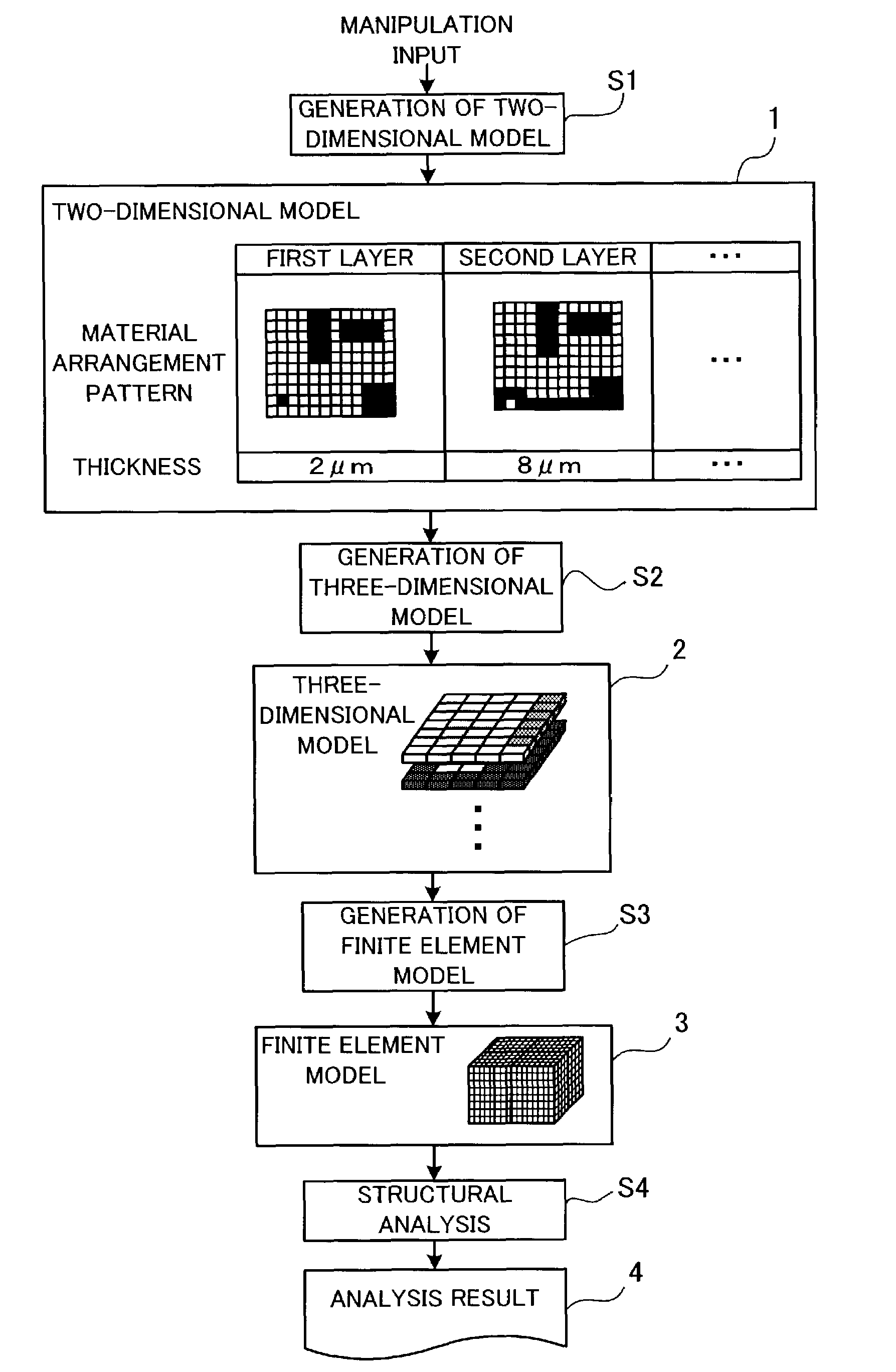
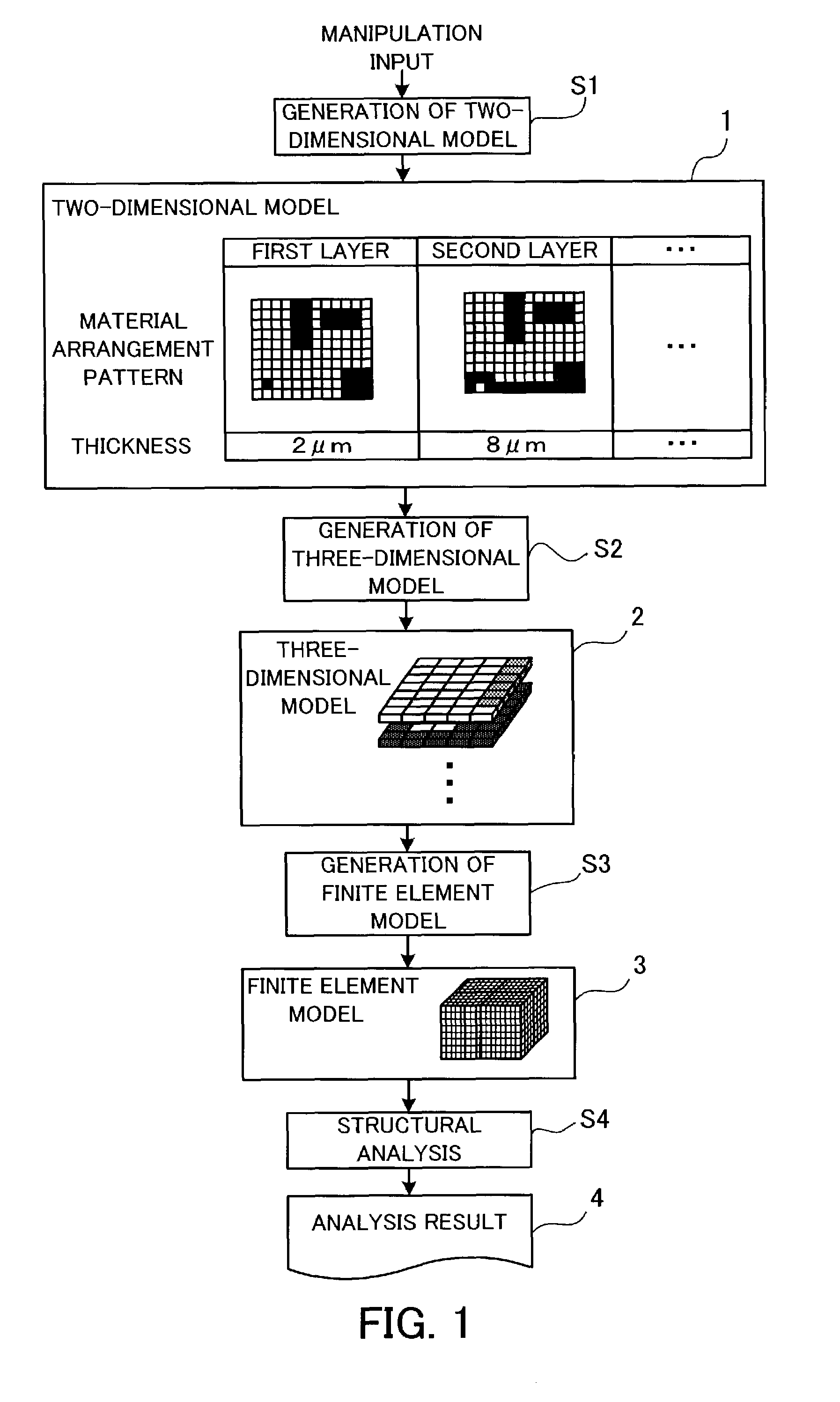
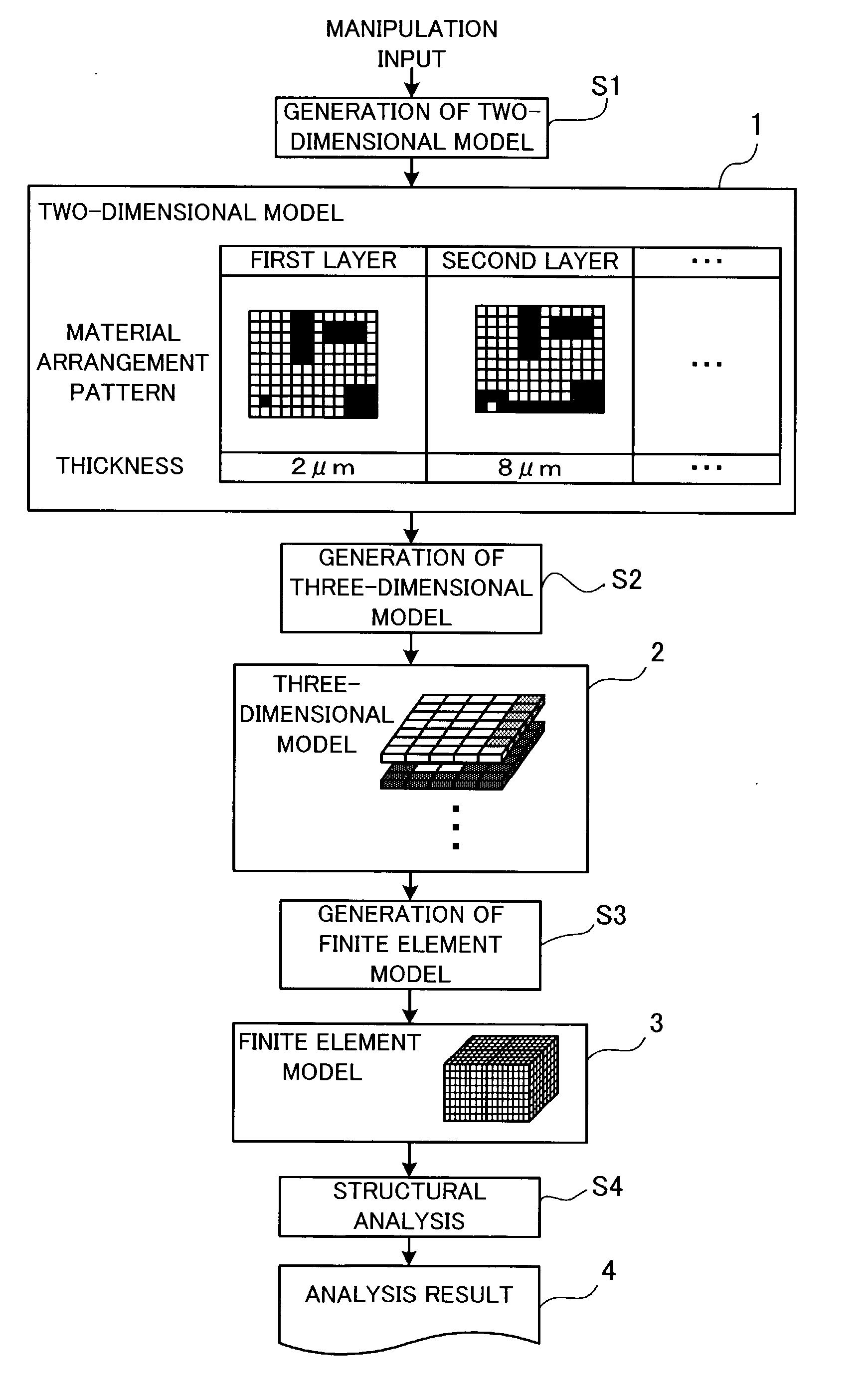
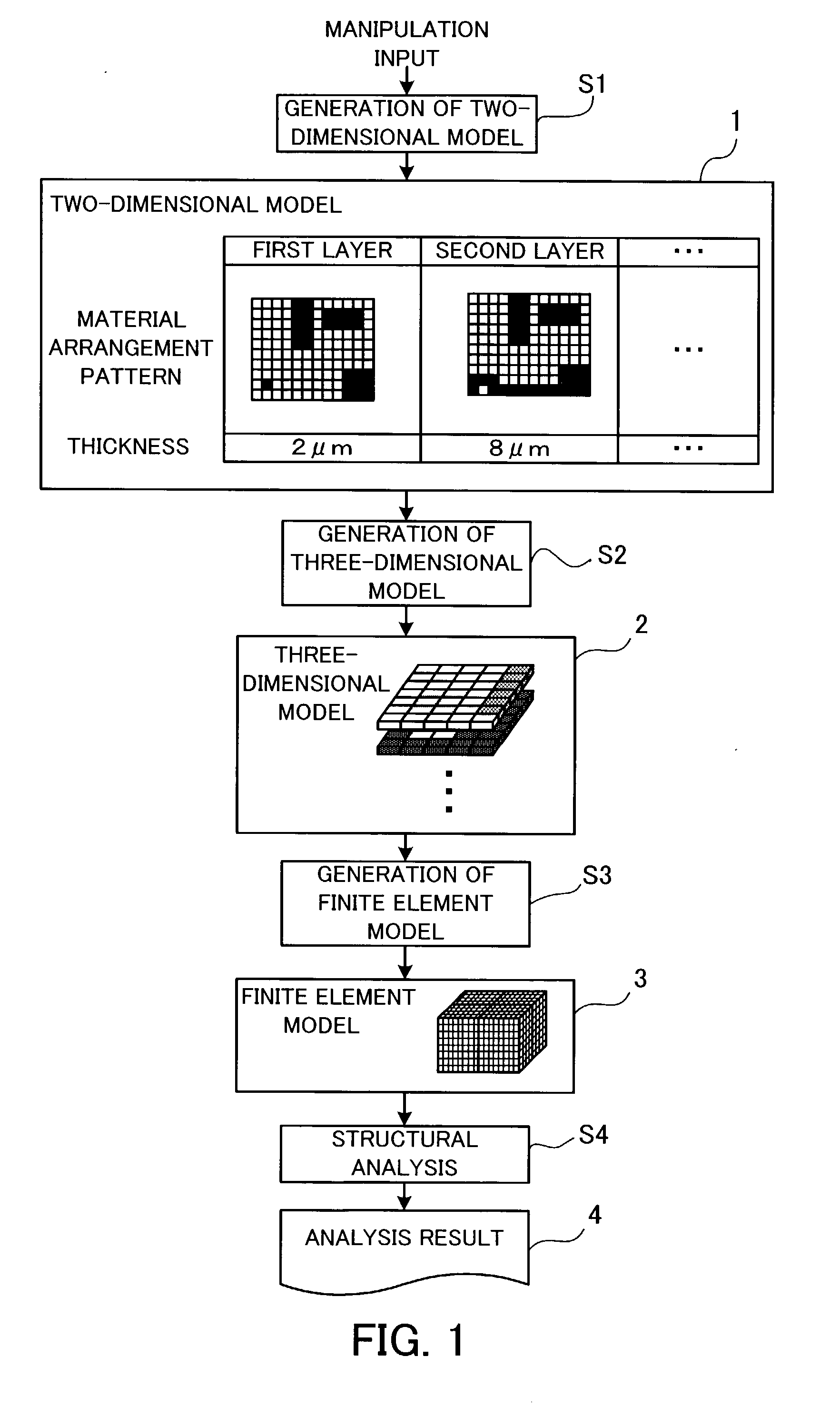
Structural analysis program, a structural analysis method, a structural analysis apparatus, and a production process of a semiconductor integrated circuit
InactiveUS7483818B2Easy to implementHigh strengthDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsElement modelVoxel
A structural analysis program which enables easy structural analysis in accordance with a finite element method based on data representing a two-dimensional shape. A two-dimensional model of a structure is produced in response to a manipulation input which designates a material arrangement pattern and a thickness of each layer of the structure. A three-dimensional model is produced by adding the designated thickness of each layer to the material arrangement pattern of the layer so as to make the material arrangement pattern three-dimensional and stacking the three-dimensionalized material arrangement pattern of each layer. A finite element model is produced by dividing the three-dimensional model into a plurality of voxels. The computer performs structural analysis based on the produced finite element model. Thereby, an analysis result of a multilayer structure defined by the two-dimensional model is obtained.
Owner:FUJITSU SYST EAST
System and method for remote and automatic assessment of structural damage and repair
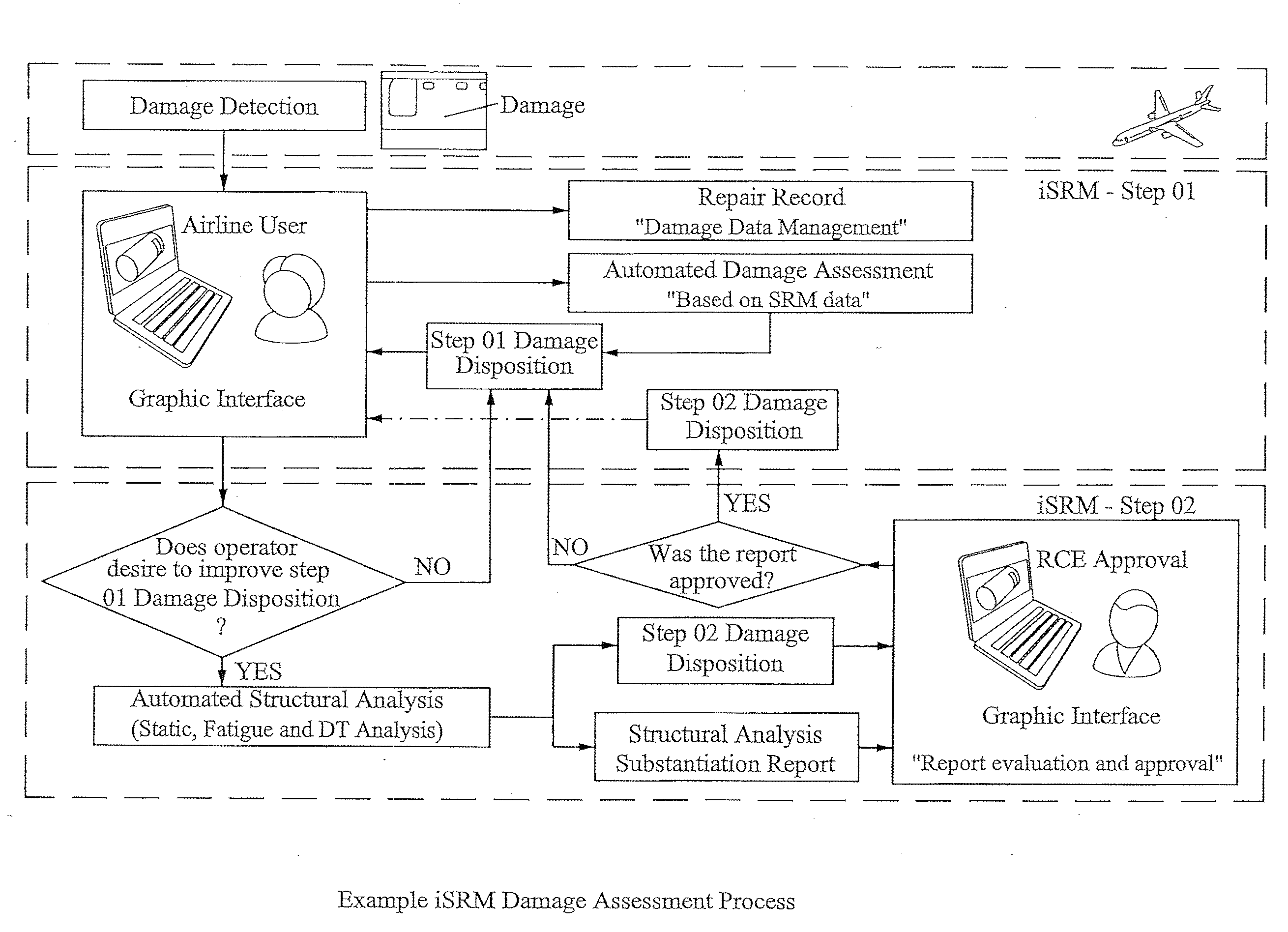
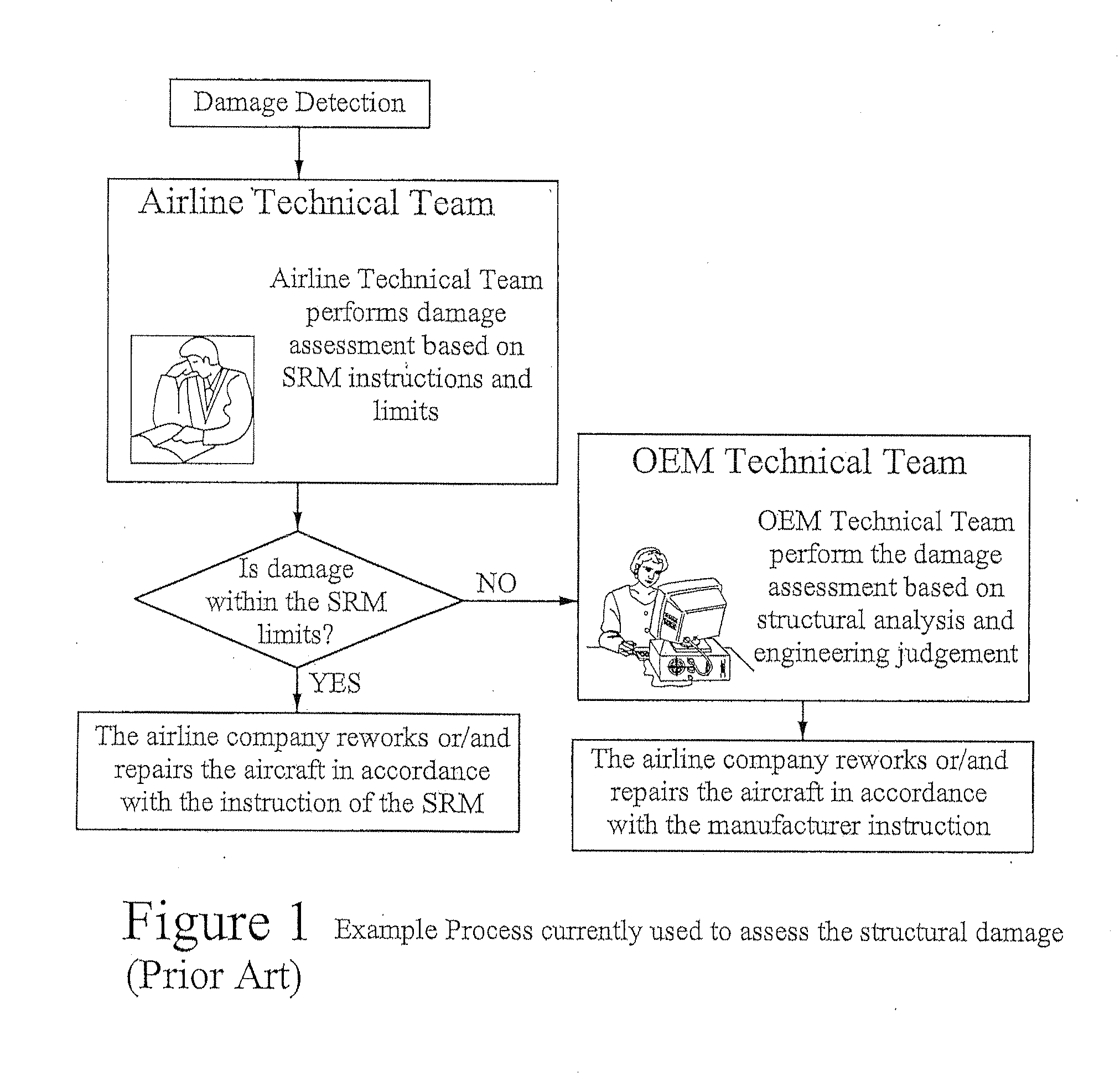
InactiveUS20130166458A1Reduce errorsReduce maintenance costsTesting/monitoring control systemsAircraft maintainanceStructural analysisAnalysis method
Structural analysis automation allows the implementation of more detailed or accurate analysis methodology that reflects the actual behavior of the damaged or repaired structure and consequently improves the resulting damage disposition for example by Increasing the allowable damages and structural repairs applicability, increasing the allowable damage limits causing the reduction of unnecessary installation of structural repairs, optimizing repairs and increasing fly-by periods and inspection intervals.
Owner:EMBRAER SA
Ultra-short wavelength x-ray system
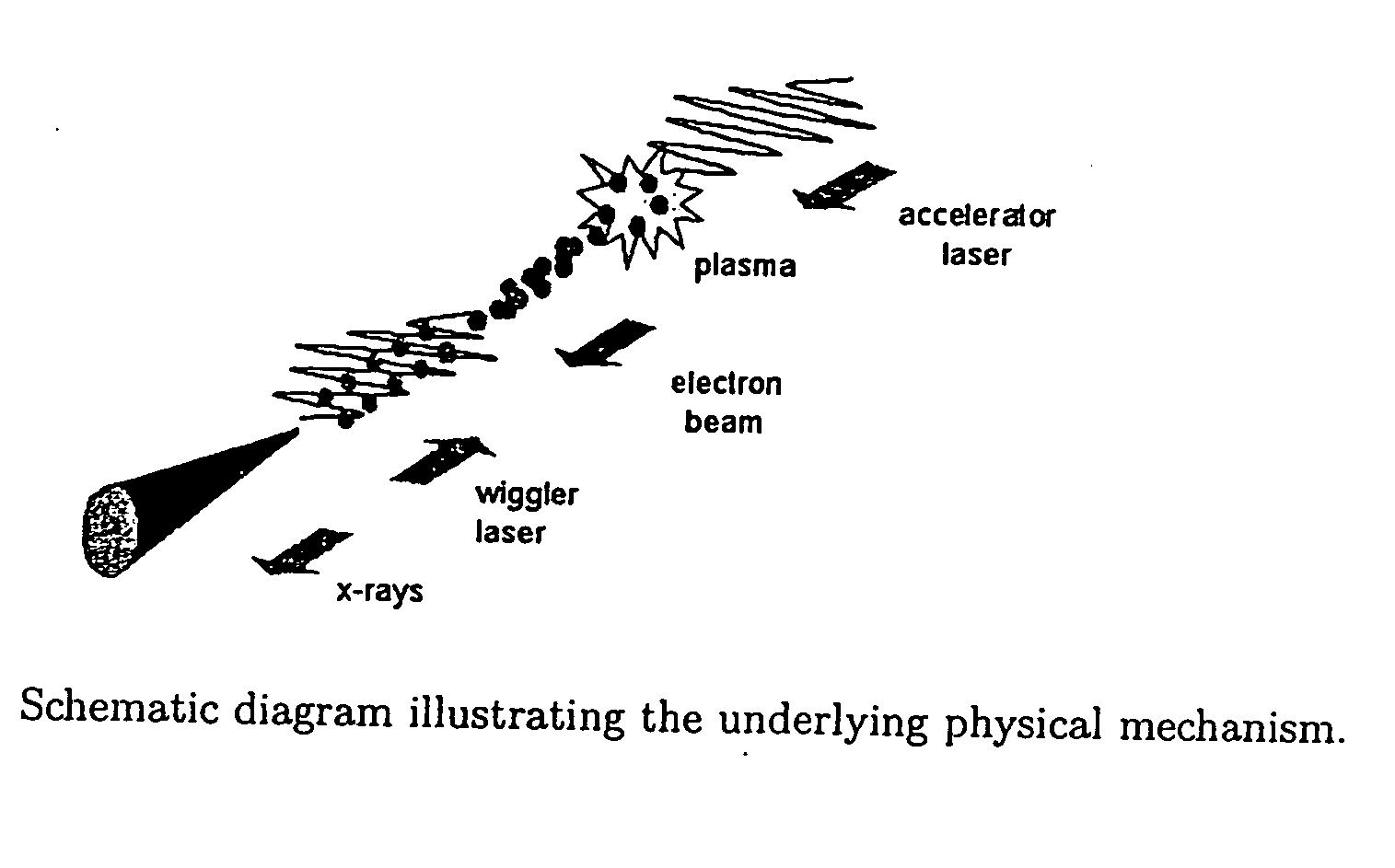
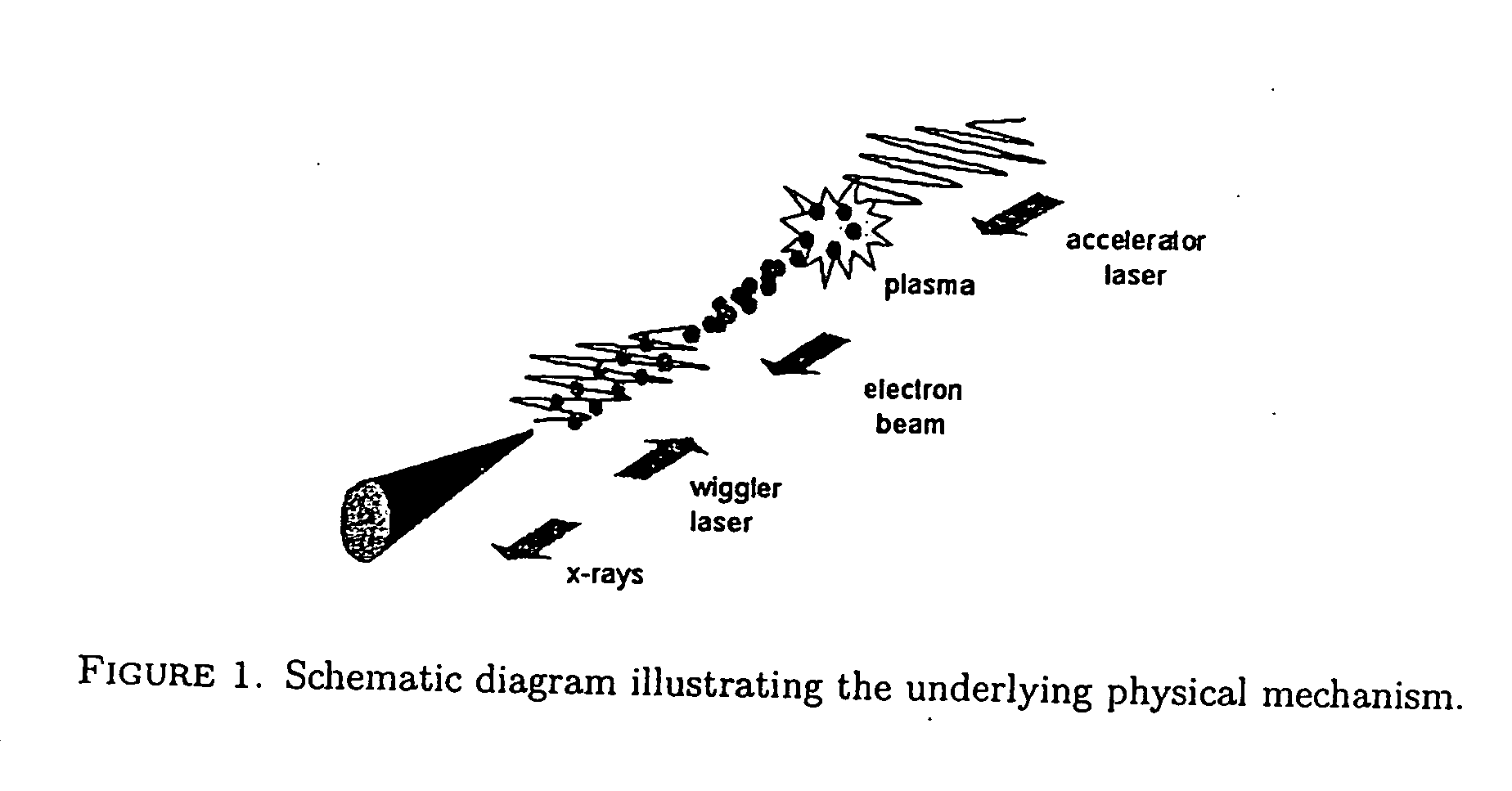
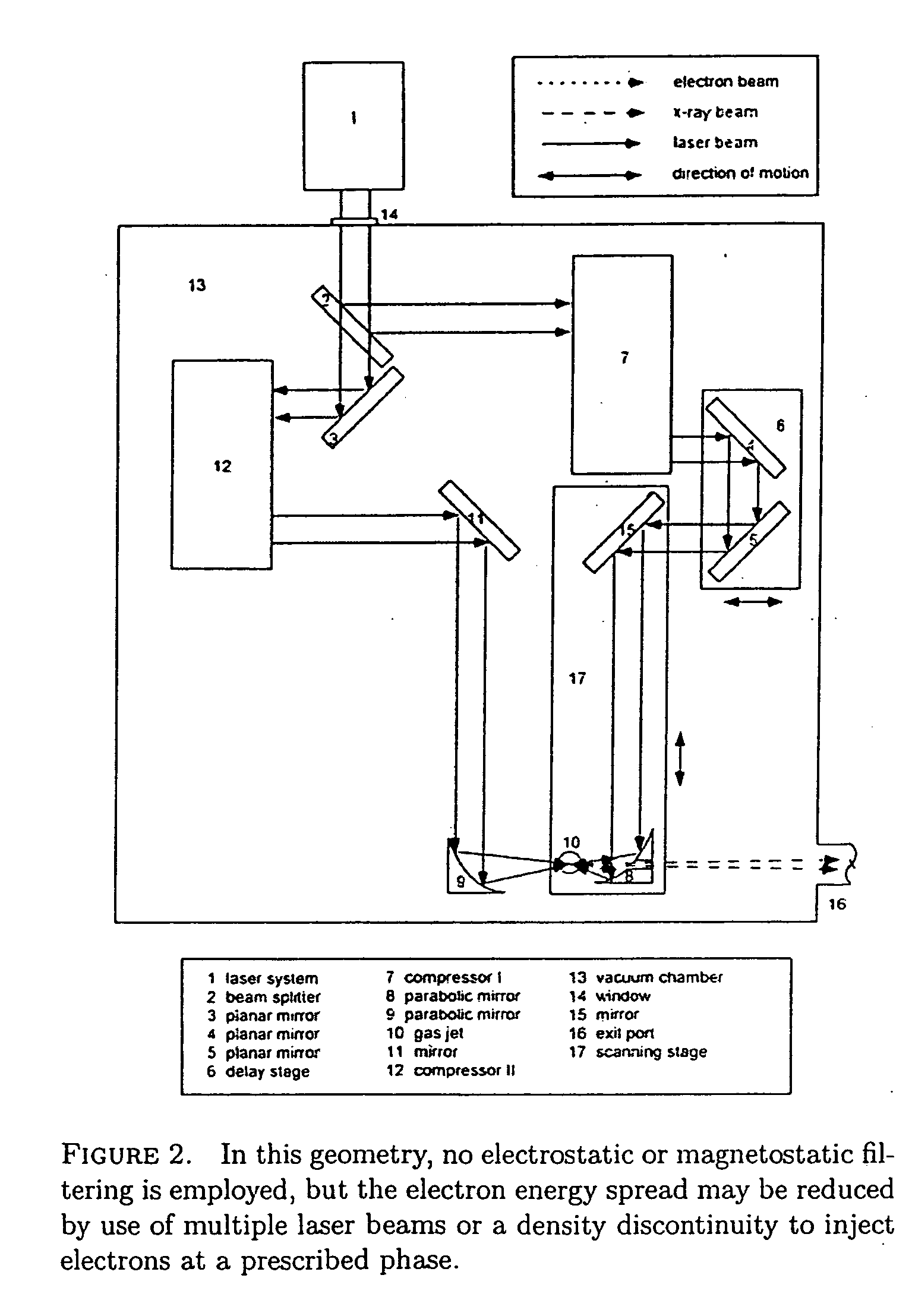
ActiveUS20050147147A1Improve fluencyEnergy spread can be reducedLaser using scattering effectsExcitation process/apparatusX-rayStructural analysis
A method and apparatus to generate a beam of coherent light including x-rays or XUV by colliding a high-intensity laser pulse with an electron beam that is accelerated by a synchronized laser pulse. Applications include x-ray and EUV lithography, protein structural analysis, plasma diagnostics, x-ray diffraction, crack analysis, non-destructive testing, surface science and ultrafast science.
Owner:MICHIGAN UNIVERISTY OF
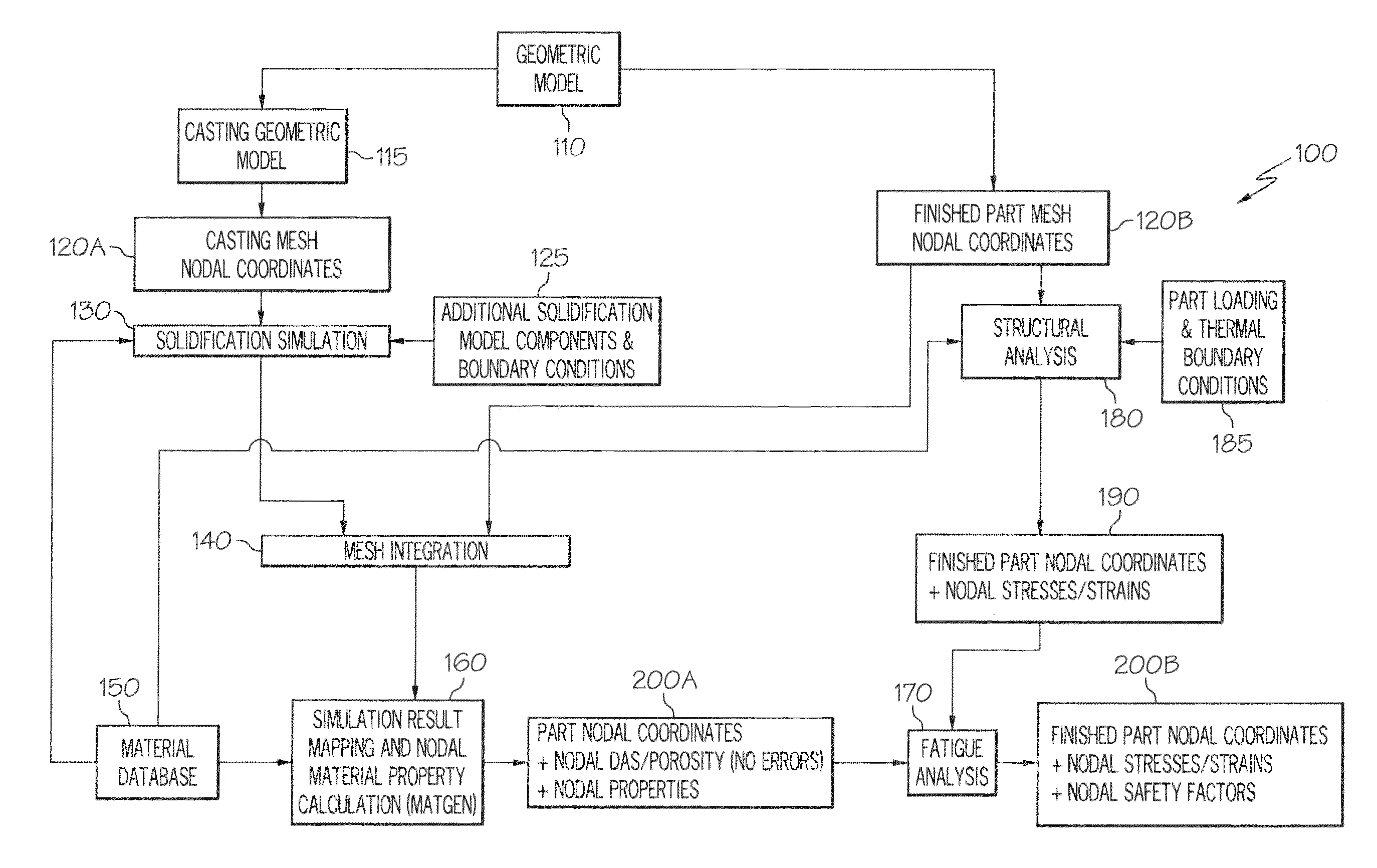
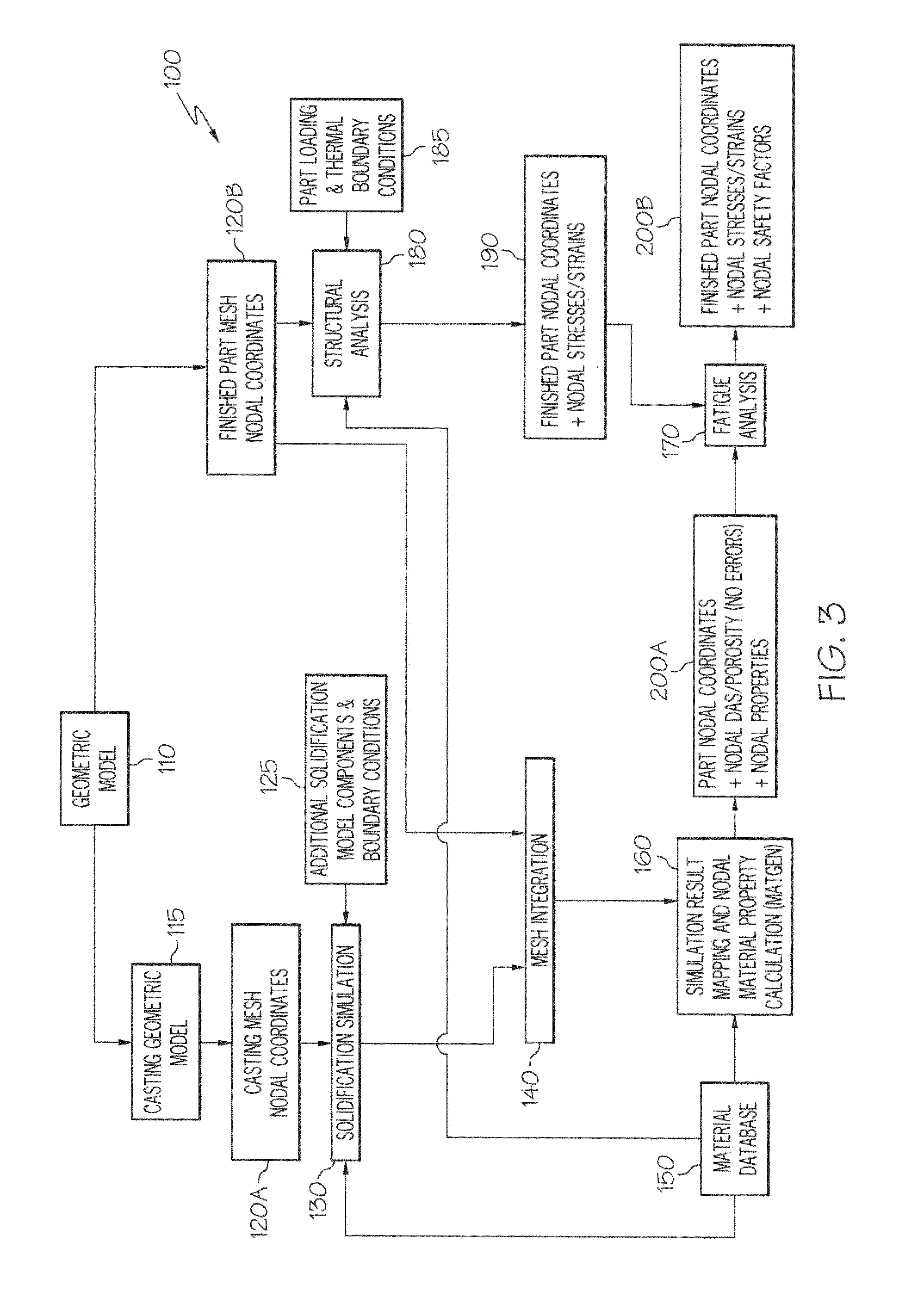
Material property distribution determination for fatigue life calculation using dendrite arm spacing and porosity-based models
ActiveUS20120232858A1Accurate prediction of durability and performanceComputation using non-denominational number representationDesign optimisation/simulationPorosityStructural analysis
A method to predict a distribution of material properties of a cast component. In one form, the method includes accepting at least one of dendrite arm spacing data and porosity data that have been previously determined, as well as accepting casting geometry data and structural analysis geometric data, calculating material properties of the casting based on one or both of dendrite arm spacing data and porosity data at each of the various nodes within the casting FEA or FD mesh and mapping the calculated material properties to the various nodes of the finished part FEA mesh. The method may be used as a basis for conducting fatigue or a related durability analysis on the component.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
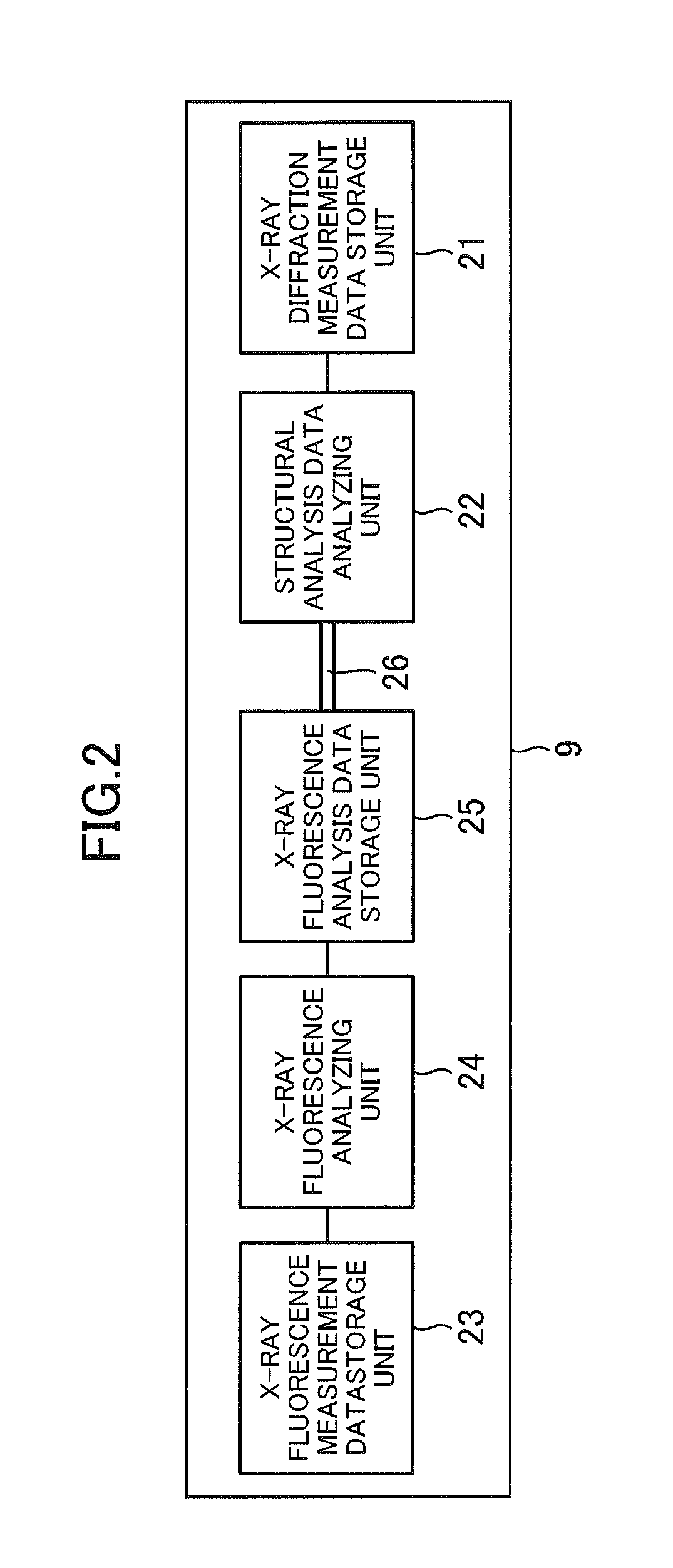
X-ray multiple spectroscopic analyzer
InactiveUS20120288058A1Material analysis using wave/particle radiationX-ray spectral distribution measurementSoft x rayAnalysis data
Owner:RIGAKU CORP
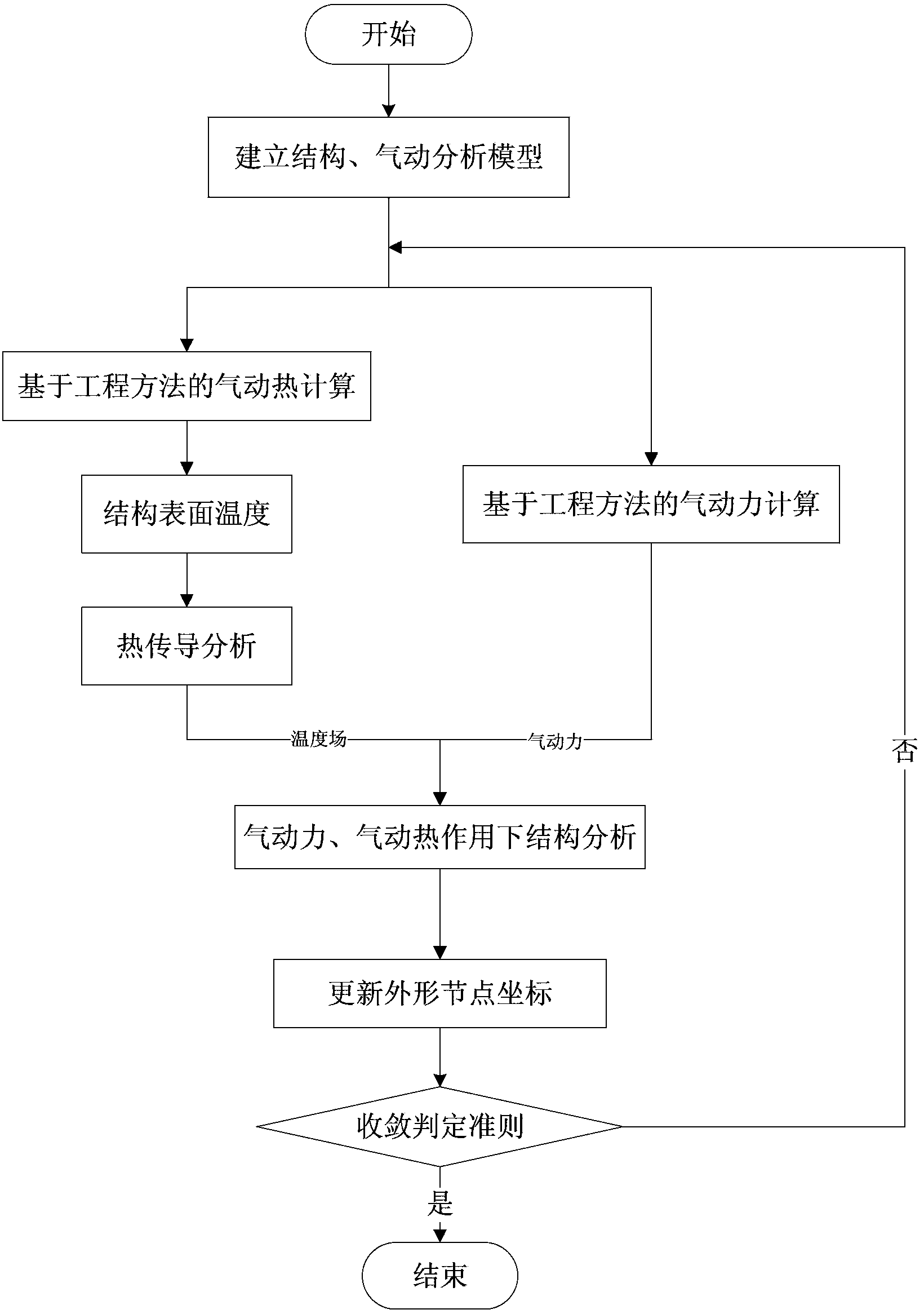
Method for analyzing hot pneumostatic elasticity of hypersonic aerocraft
ActiveCN103366052AThe result is accurateImprove calculation accuracySustainable transportationSpecial data processing applicationsHeat flowHeat flux
The invention discloses a method for analyzing hot pneumostatic elasticity of a hypersonic aerocraft, which comprises the following steps: (1) according to the original outline of the hypersonic aerocraft, building a structural and pneumatic analytical model of the hypersonic aerocraft; (2) calculating the aerodynamic force and aerodynamic heat of the hypersonic aerocraft by utilizing the engineering approach; (3) according to the heat flux on the surface of the hypersonic aerocraft, calculating the surface temperature and the temperature field of the structure of the hypersonic aerocraft through heat conduction analysis; (4) loading the aerodynamic force load and the temperature field calculated in the step (3) into the structural analytical model built in the step (1), and calculating the elastic deformation of the hypersonic aerocraft; (5) updating the outline node coordinates in the structural and pneumatic analytical model of the hypersonic aerocraft by utilizing the calculated elastic deformation of the hypersonic aerocraft, determining the maximum displacement point of the deformation, judging whether the deformation rate of the maximum displacement point is less than the preset threshold value or not, if yes, regarding the aerodynamic force, aerodynamic heat and elastic deformation of the hypersonic aerocraft currently calculated as the final analysis result, otherwise, moving to the step (2) for loop execution.
Owner:CHINA ACAD OF AEROSPACE AERODYNAMICS
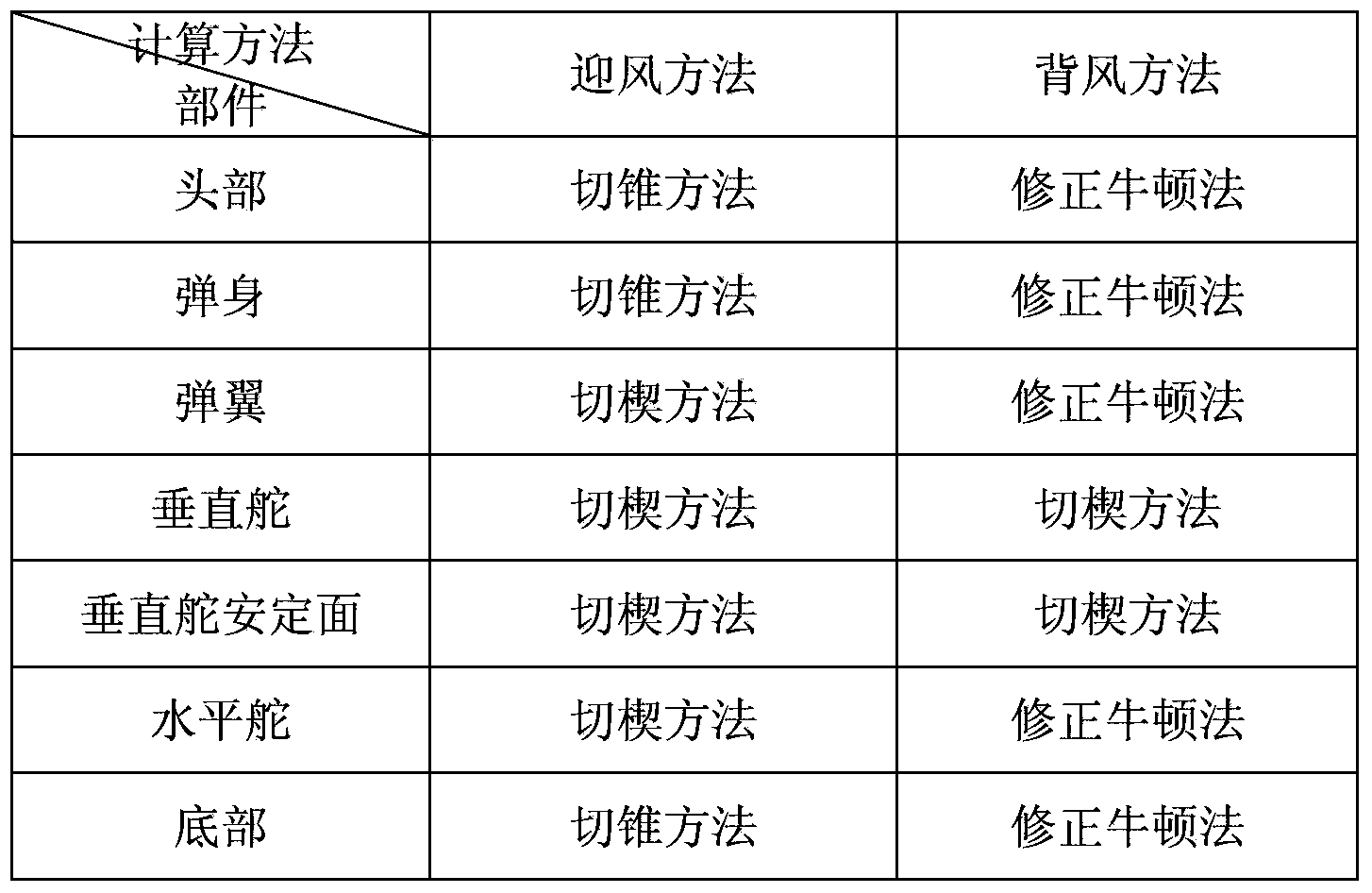
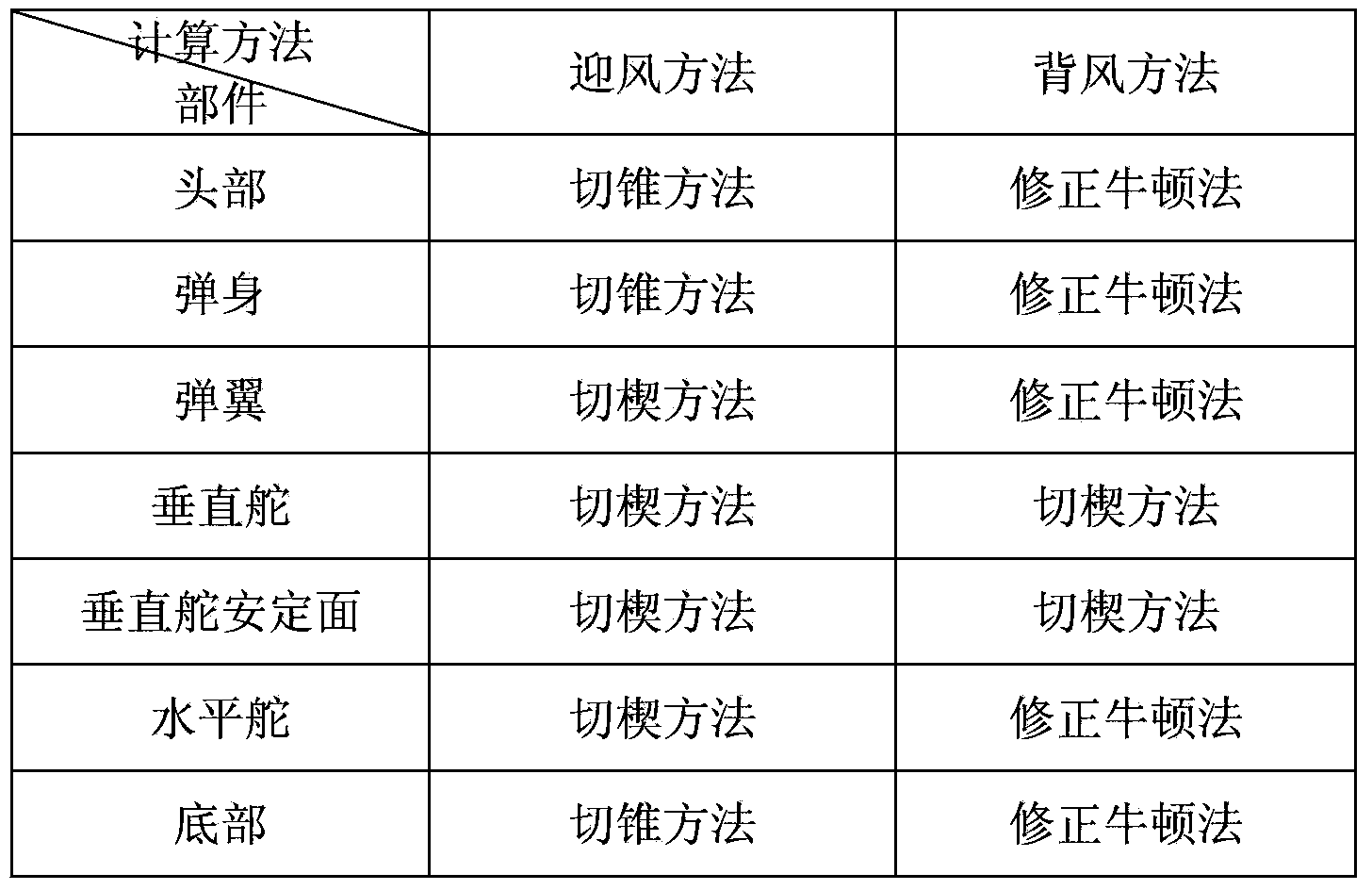
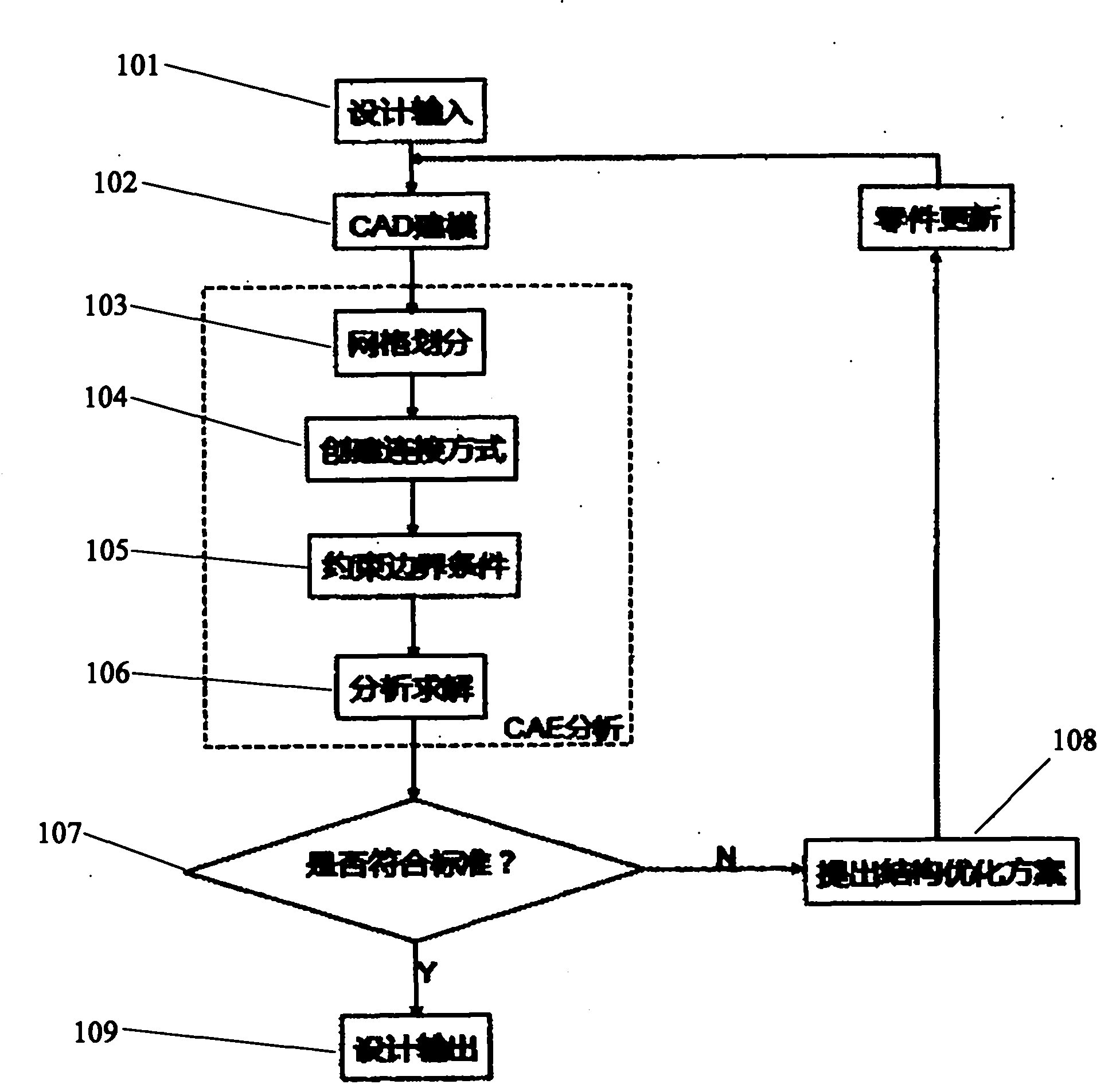
Optimization design method for sagging problem of car door based on CAE (Computer Aided Engineering) structural analysis
InactiveCN101916322AShort cycleShorten the timeSpecial data processing applicationsComputer Aided DesignElement model
The invention discloses an optimization design method for the sagging problem of a car door based on CAE structural analysis, which comprises the steps of: obtaining a design input condition from total arrangement and configuration of a car body; creating a CAD (Computer Aided Design) model by modeling software; dividing grids of the CAD model; simulating actual conditions to create a connection relationship; simulating a boundary constraint condition during an actual test of a car door assembly; carrying out solution analysis on a finite element model generated finally; comparing a result obtained by finite element simulation operation with an industry standard; if an obtained conclusion is lower than the industry standard, providing a structural optimization design; and if the obtained conclusion is higher than the industry standard, completing final design output. The method not only enhances the inspection accuracy, but also greatly reduces the period of a whole repair part so as to shorten the time of developing the whole car. Structural errors can be corrected in time by CAE analysis in early design, thereby reducing the cost of developing the whole car.
Owner:上海奕代汽车技术有限公司
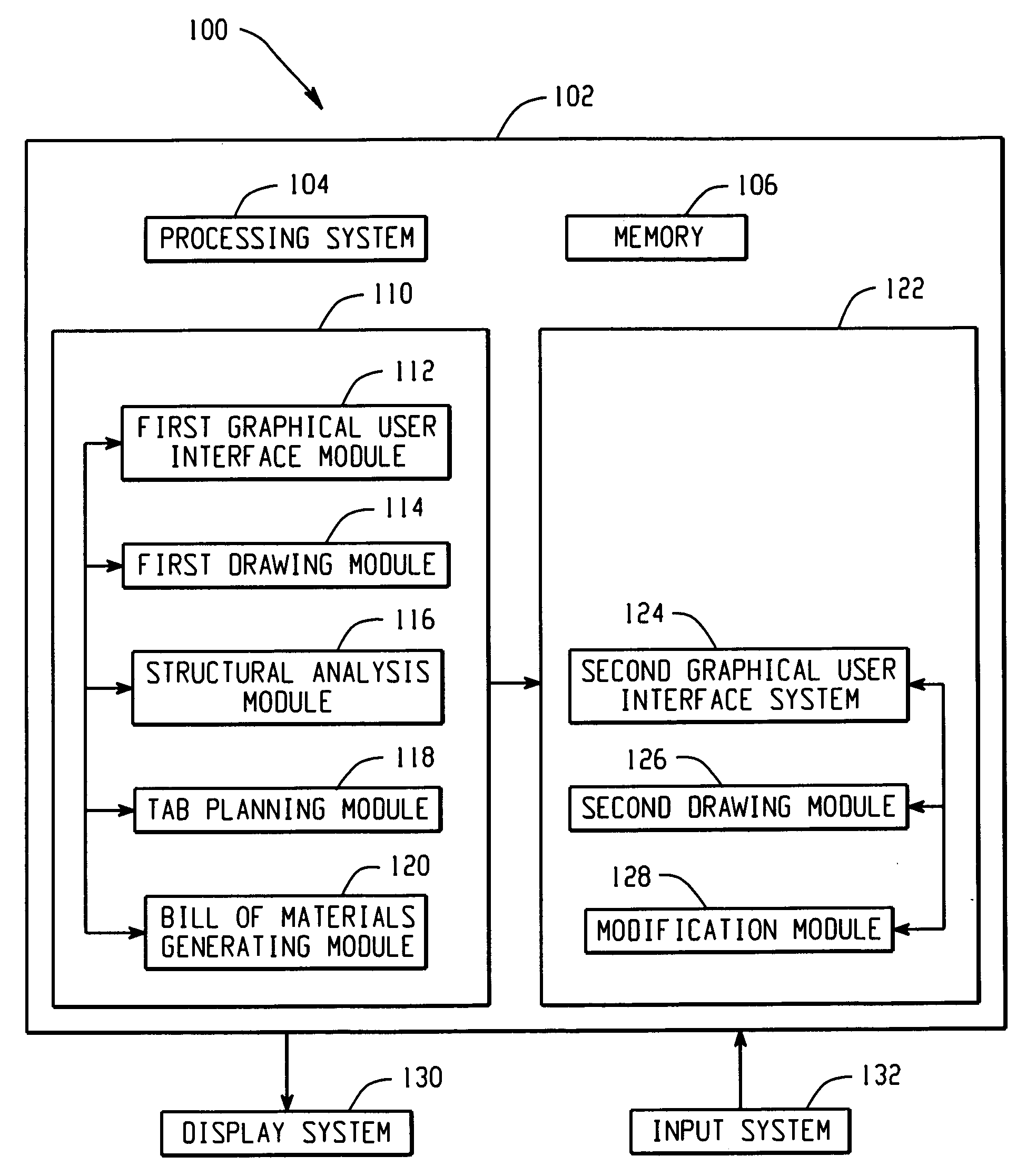
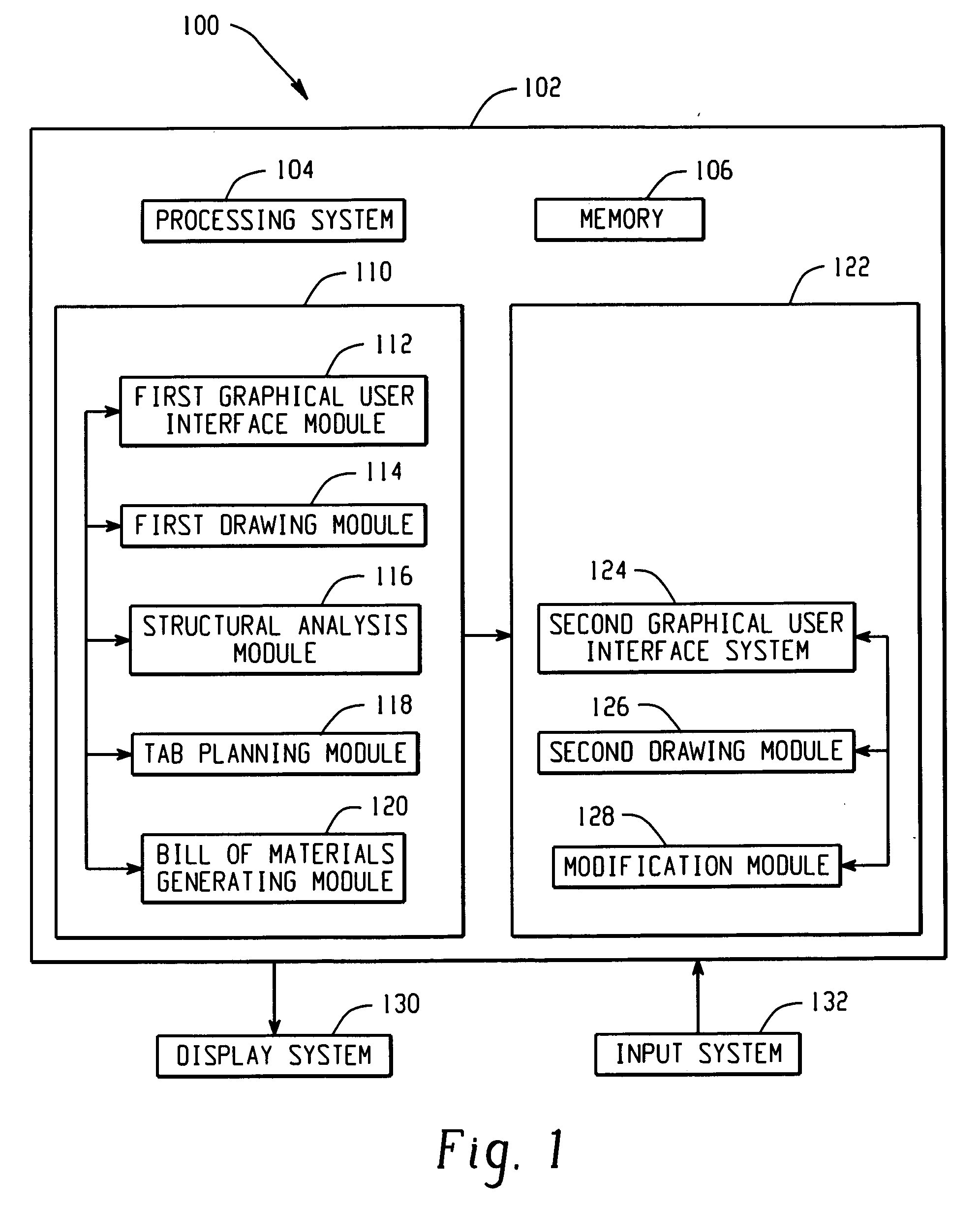
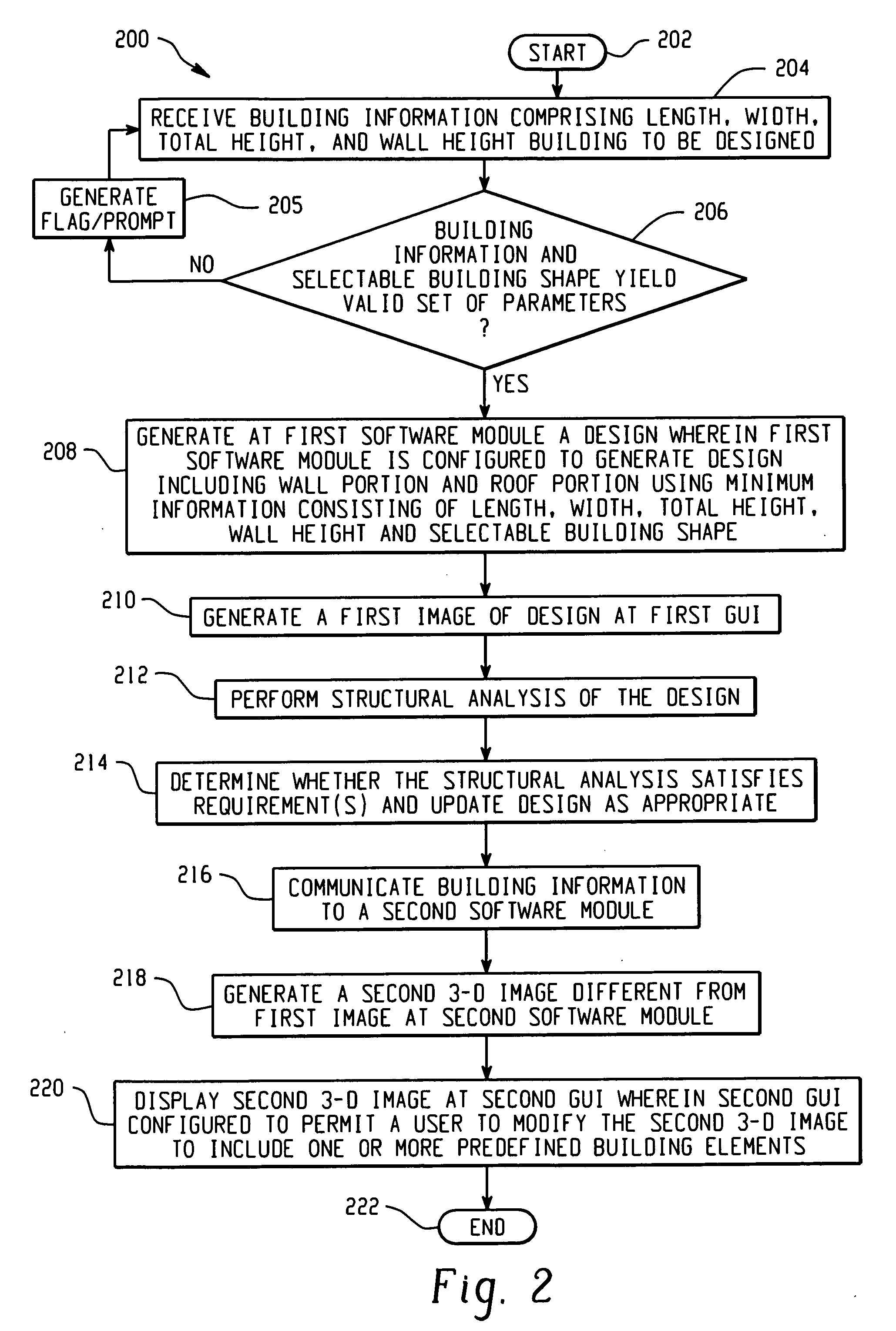
Systems and methods for computational design and modeling of buildings
A method and system generates a building design and a three-dimensional image thereof. First building information comprising a length, width, total height and wall height of a building is received via a first graphical user interface. If the length, width, total height, wall height, and a selectable building shape yield a valid set of building parameters, a design of said building is generated at a first software module, which is configured to generate the design, including wall portions and a roof portion, using minimum information consisting of the length, width, total height, wall height, and selectable building shape. A first image and a structural analysis of the design are generated. A second software module generates a second three-dimensional image of the building, which is different from the first image. A second graphical user interface permits a user to modify the second image to include predefined building elements.
Owner:MIC IND INC
Structural analysis program, a structural analysis method, a structural analysis apparatus, and a production process of a semiconductor integrated circuit
InactiveUS20030055612A1High strengthDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsVoxelElement model
A structural analysis program which enables easy structural analysis in accordance with a finite element method based on data representing a two-dimensional shape. A two-dimensional model of a structure is produced in response to a manipulation input which designates a material arrangement pattern and a thickness of each layer of the structure. A three-dimensional model is produced by adding the designated thickness of each layer to the material arrangement pattern of the layer so as to make the material arrangement pattern three-dimensional and stacking the three-dimensionalized material arrangement pattern of each layer. A finite element model is produced by dividing the three-dimensional model into a plurality of voxels. The computer performs structural analysis based on the produced finite element model. Thereby, an analysis result of a multilayer structure defined by the two-dimensional model is obtained.
Owner:FUJITSU SYST EAST
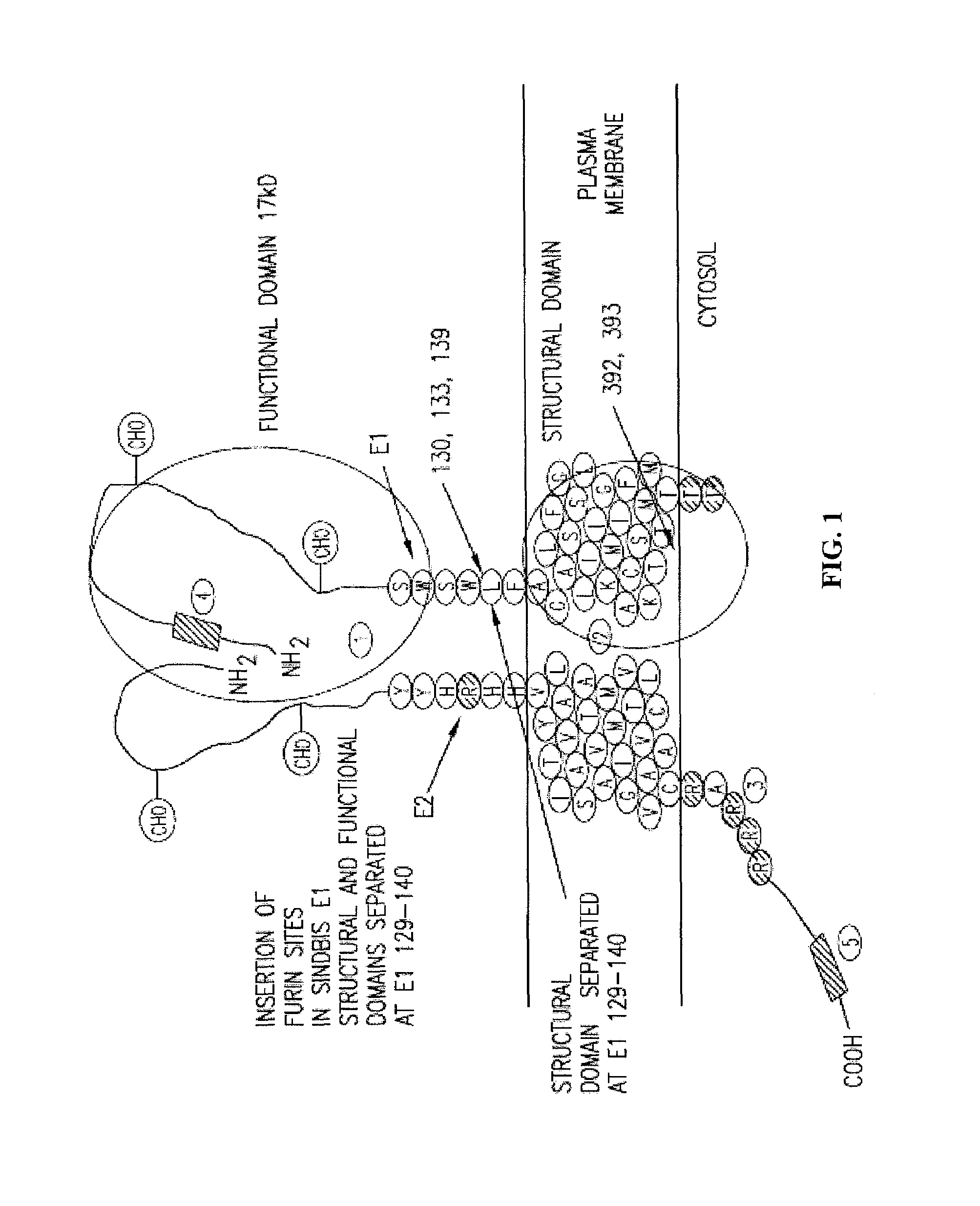
Insertion of furin protease cleavage sites in membrane proteins and uses thereof
Cleavage site for the protease furin is inserted between domains of a membrane glycoprotein. Upon cleavage by furin in the trans-Golgi network, the protein is separated into individual membrane-free domain that retains its native conformation. This protocol can be used to produce virus membrane protein domains for structural analysis and for trials as vaccines.
Owner:RES DEVMENT FOUND
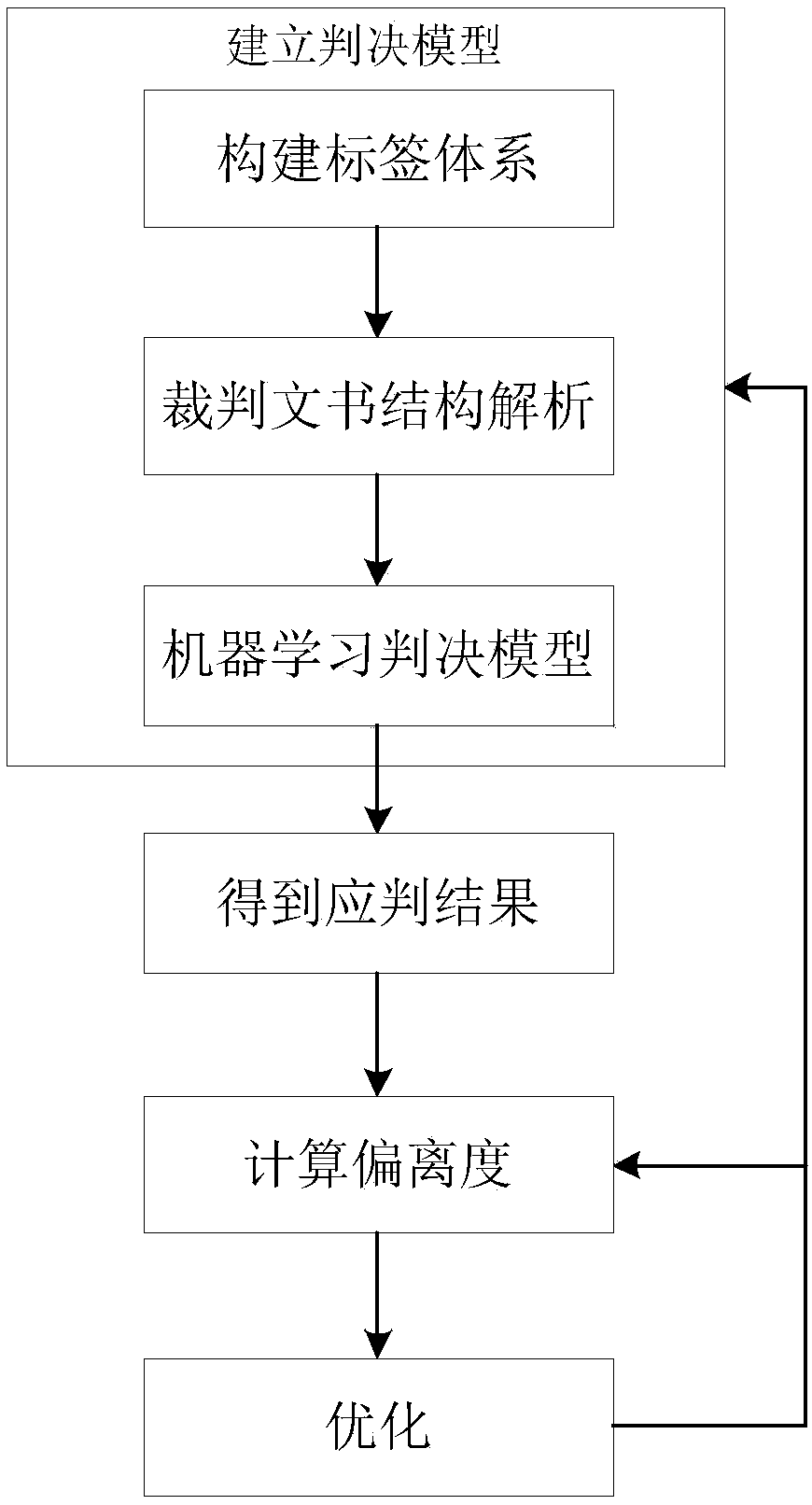
Criminal case judging result measurement method and system
The invention discloses a criminal case judging result measurement method and a system for realizing the method. The method comprises the following steps of: establishing a judging model (constructinga label system and carrying out judging document structural analysis ad machine learning to obtain the judging model); substituting a prediction model which is constructed through a machine learningalgorithm into case data, so as to predict a judging result through the model; calculating a result deviation degree; and optimizing the model or the result. The system comprises a judging model establishment module, a prediction module and a deviation degree calculation module. The criminal case judging result measurement method and a system are capable of carrying out relatively scientific and accurate quantification on quality of cases judged by judges, providing intelligent assistance for the judges, and providing technical support for forming a uniform judging scale.
Owner:南京擎盾信息科技有限公司 +3
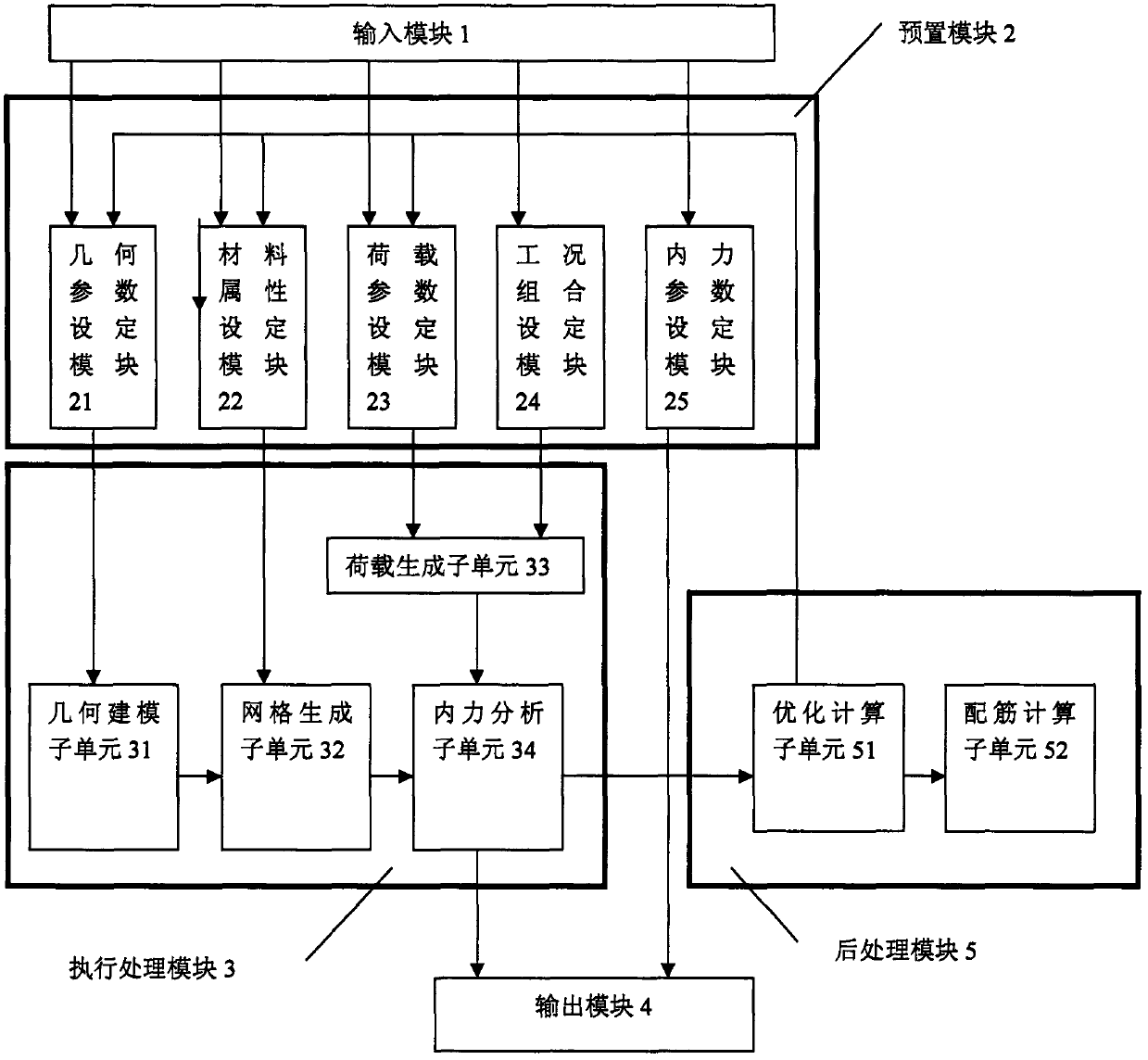
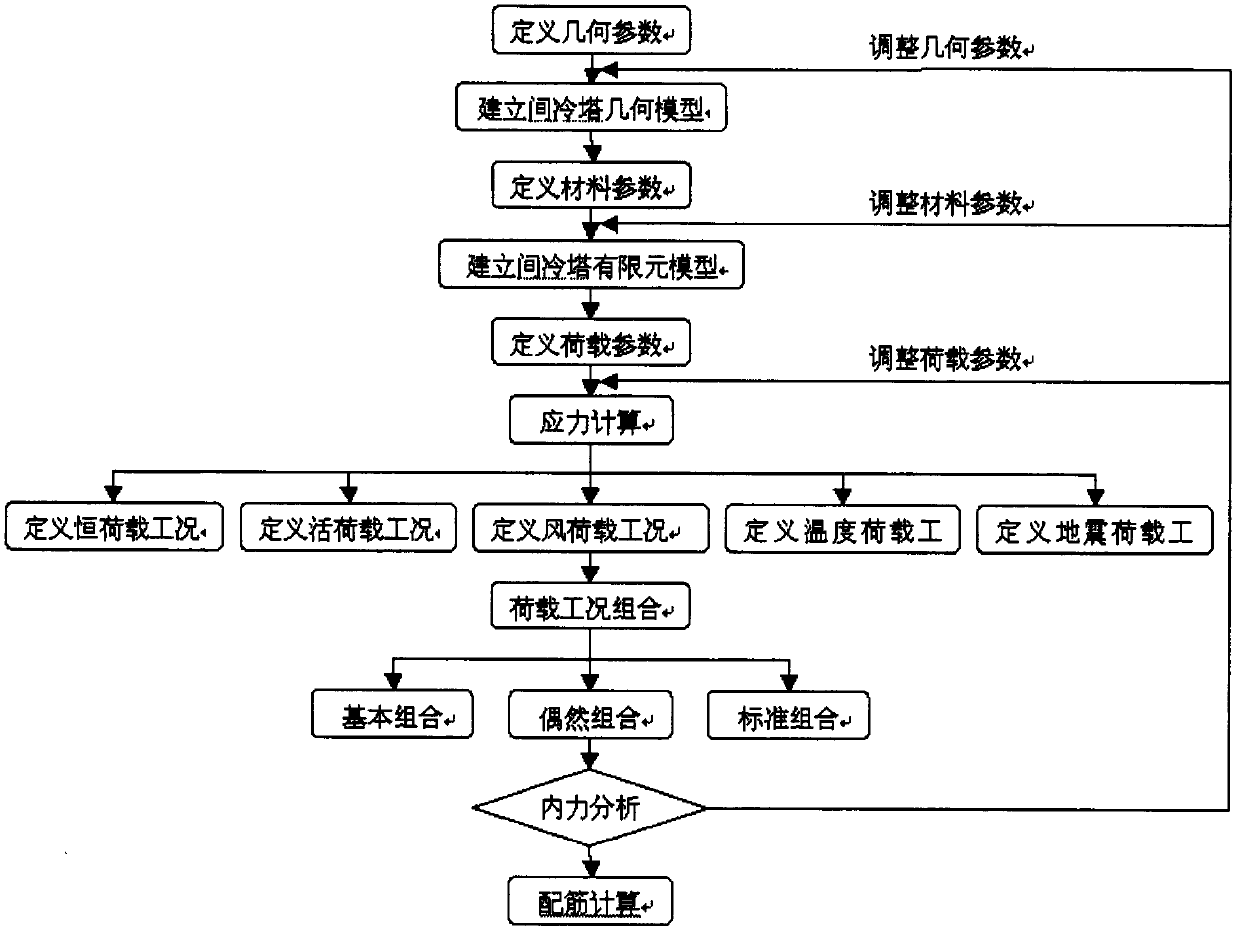
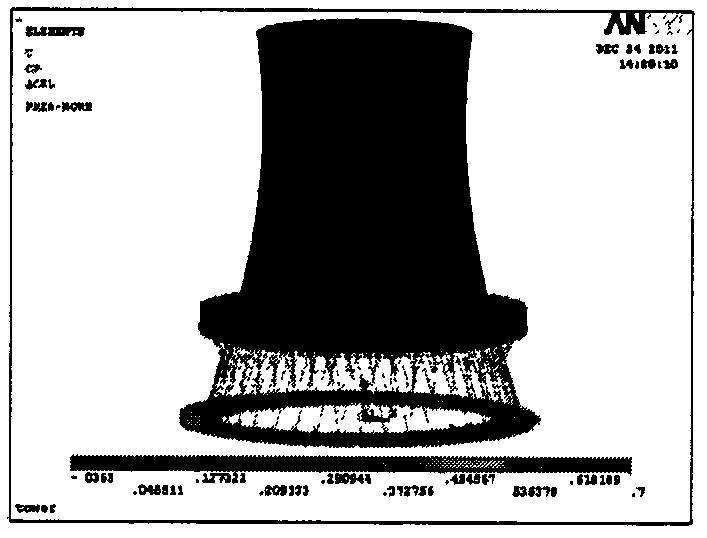
System and method for structural analysis of indirect dry cooling tower
ActiveCN103150460AAvoid duplication of workImprove analysis efficiencySpecial data processing applicationsCooling towerElement model
The invention relates to a power station indirect dry cooling system, and provides a system and a method for structural analysis of an indirect dry cooling tower based on APDL (ANSYS Parametric Design Language). The method comprises the following steps of: 1) according to geometric outside dimension of the indirect cooling tower, defining geometric parameters of the indirect cooling tower, and establishing a parameterized geometric model of the indirect cooling tower; 2) defining the unit type, real constants and material constants of the indirect cooling tower; 3) defining unit meshing size, performing self-adapting meshing division, and establishing a finite element model of the indirect cooling tower; 4) respectively applying parameterized loading for the indirect cooling tower under five loading working conditions (dead load, live load, wind load, temperature load and earthquake load) and performing computational analysis; and 5) performing combination of loading working conditions, and extracting computed results. Through the application of the system, the full process control of the indirect cooling tower from modeling to calculation can be realized. Meanwhile, the indirect cooling tower can be optimally designed by adjusting the value of each parameter. A large amount of repeated work is avoided, and the efficiency of structural analysis and design can be greatly improved.
Owner:DATANG BEIJING ENERGY MANAGEMENT
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com