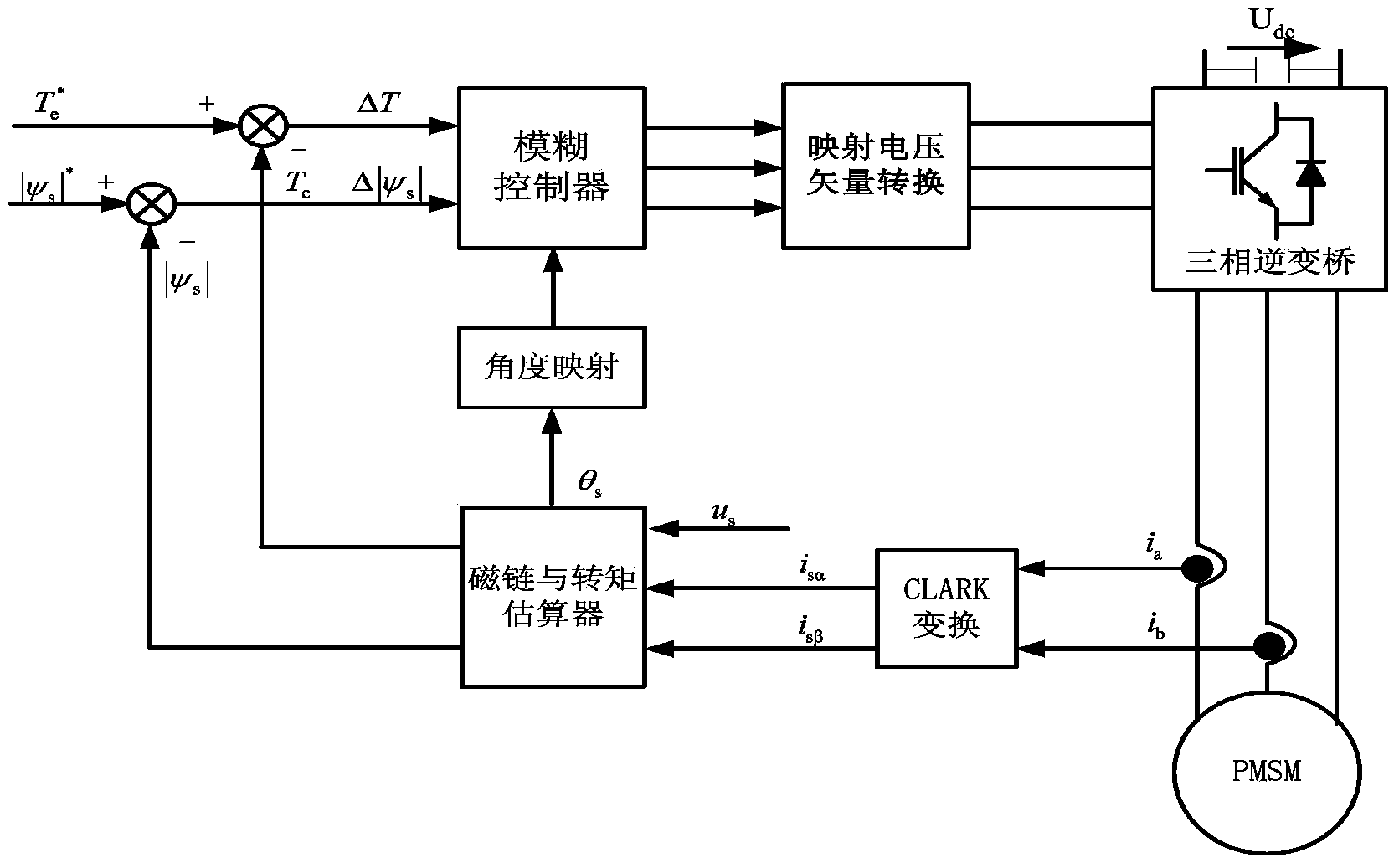
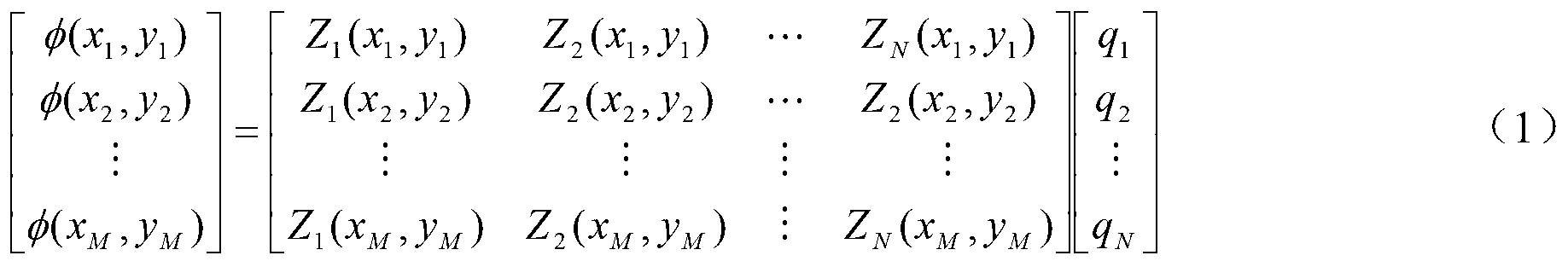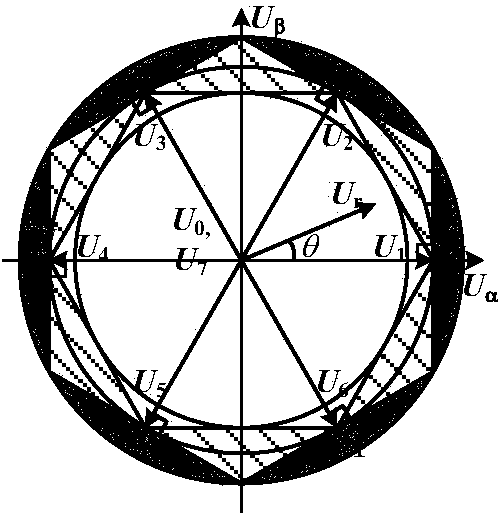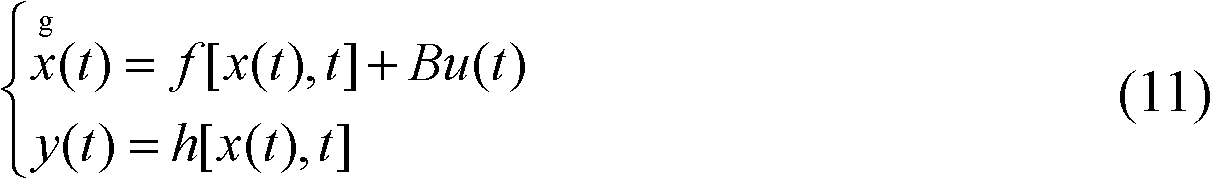Patents
Literature
2431 results about "Voltage vector" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
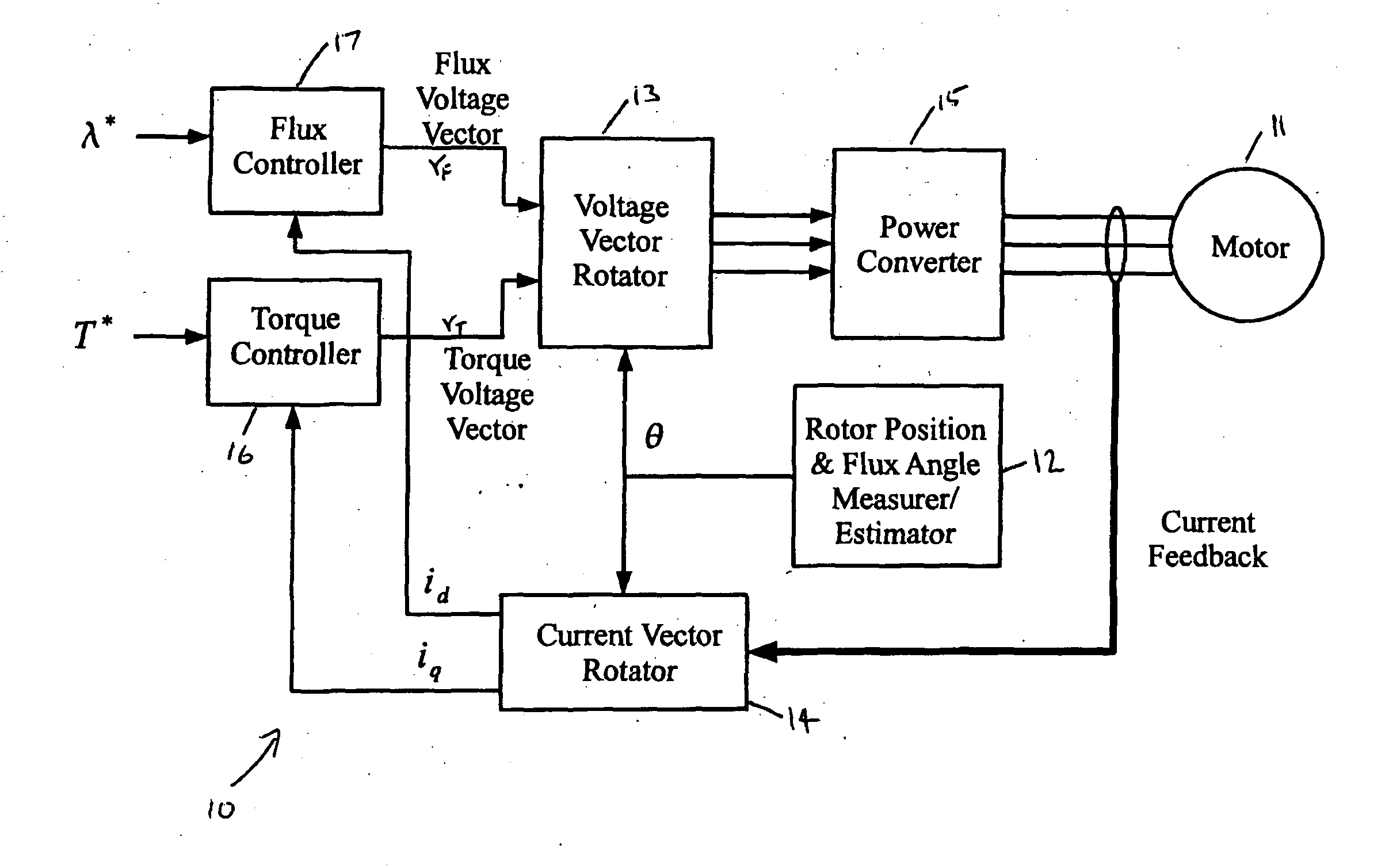
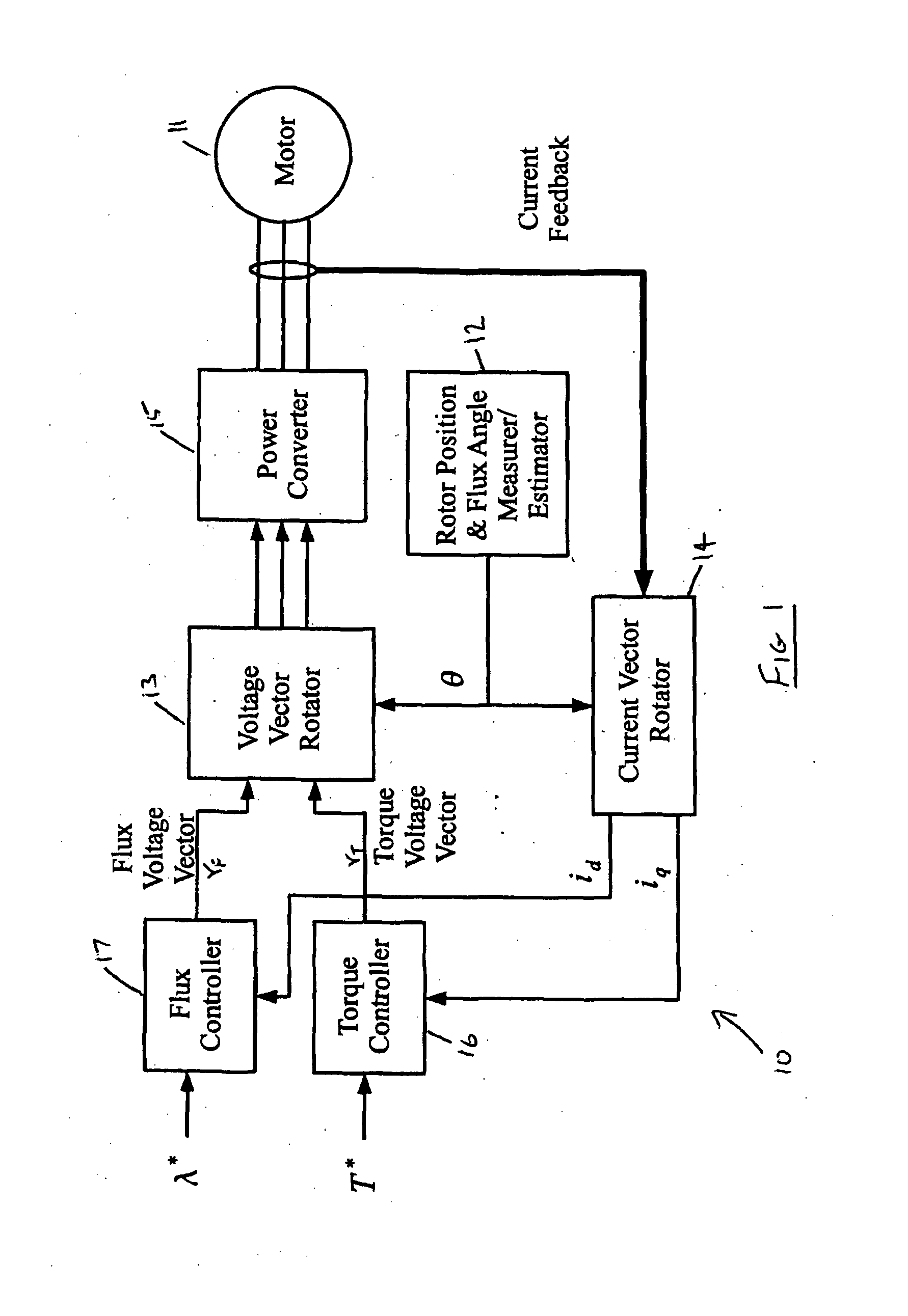
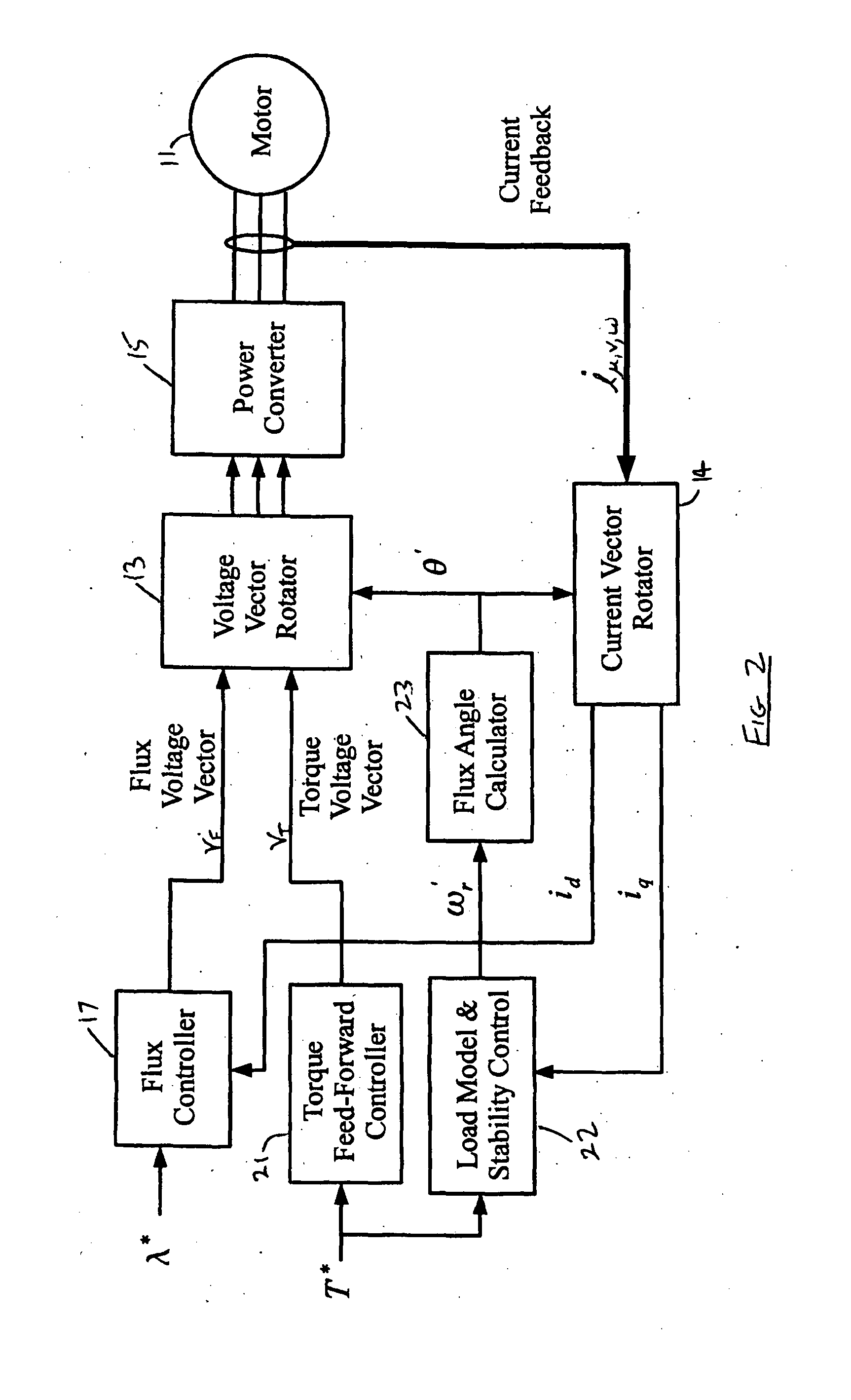
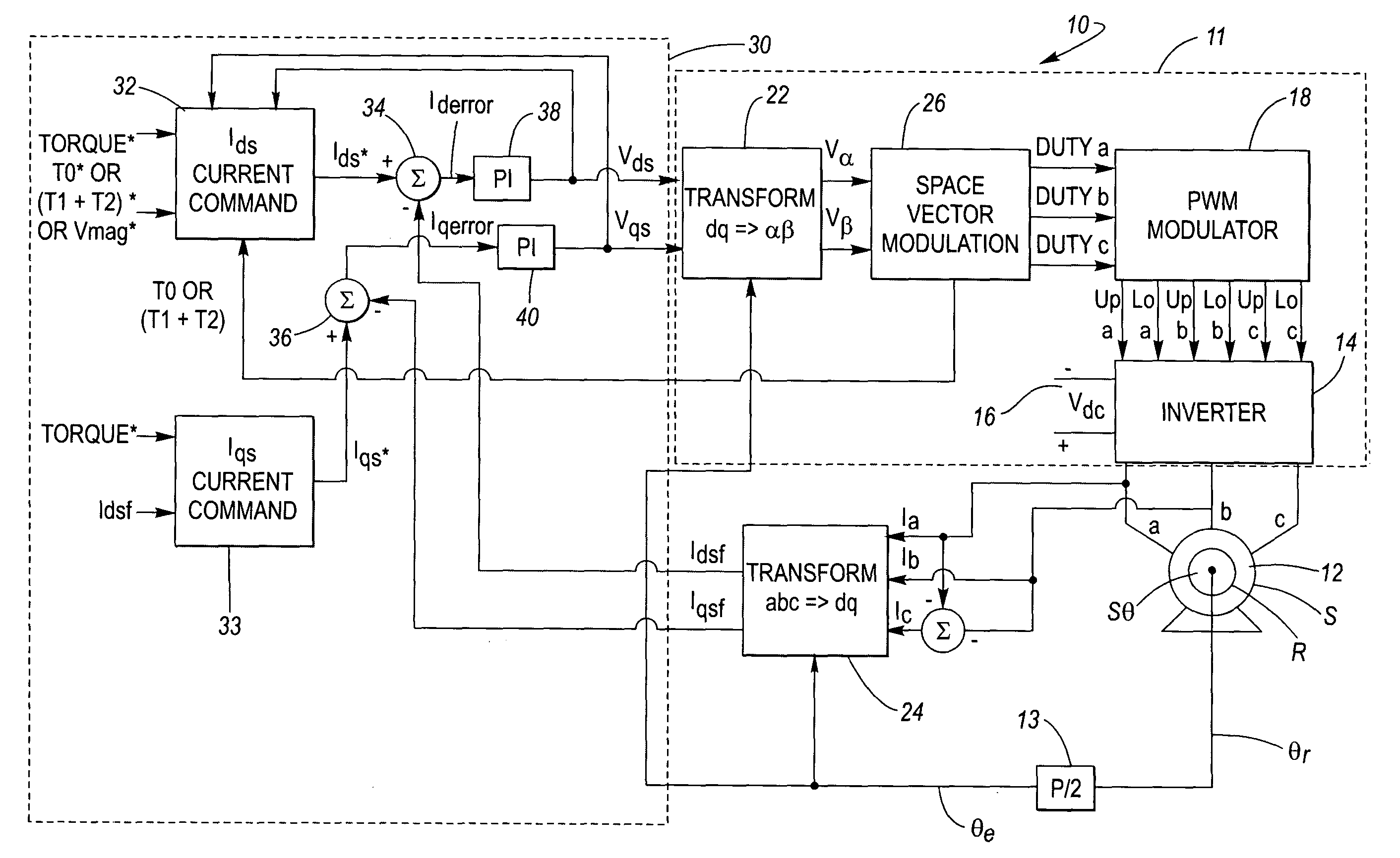
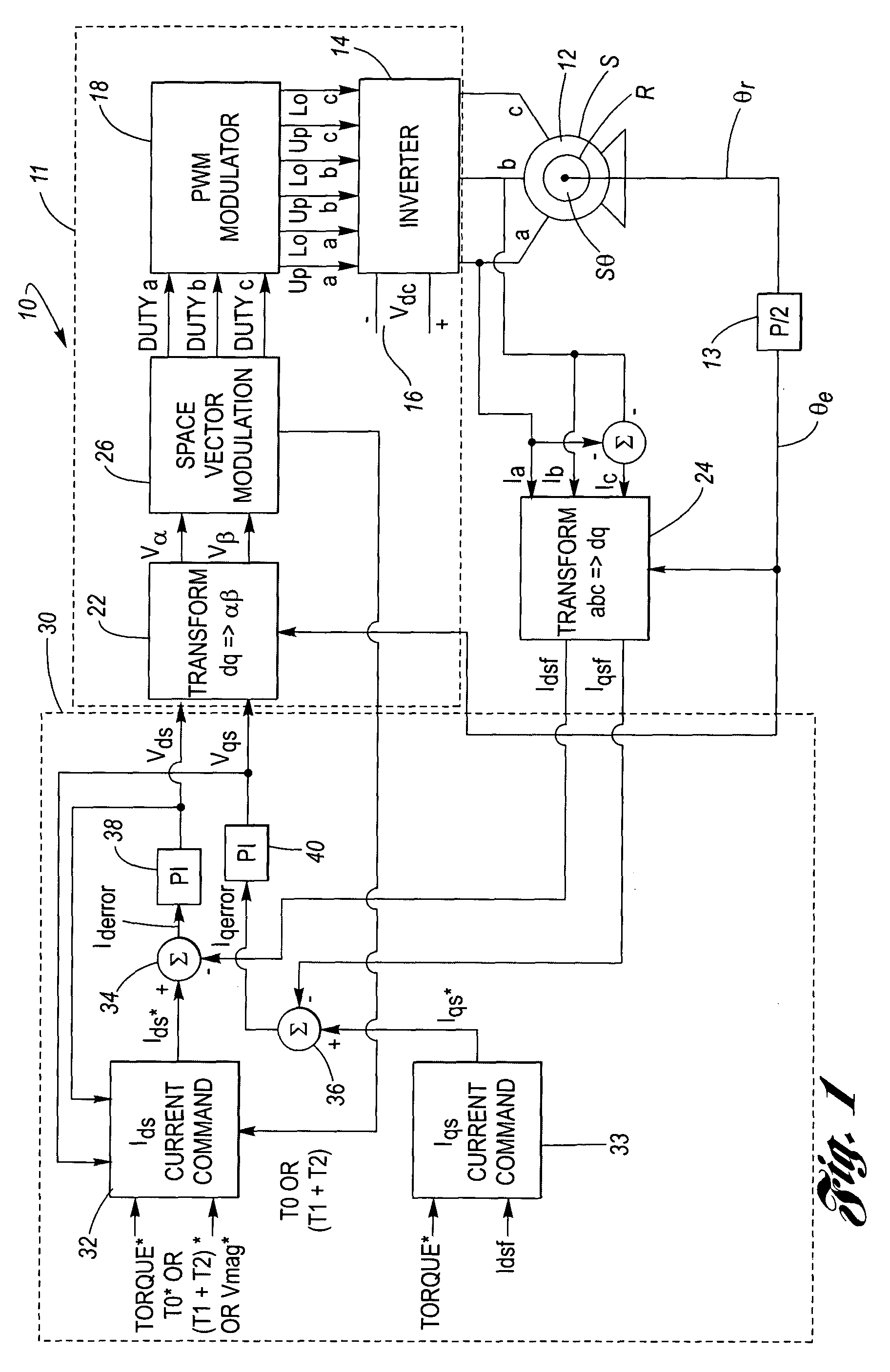
Sensorless ac motor controller
ActiveUS20130221885A1Control changesImprove stabilityCommutation monitoringMotor/generator/converter stoppersMotor speedVoltage vector
A controller for an AC electric motor, includes a Feed Forward Torque Controller and a load model. The Torque controller directly derives a torque related component of applied motor voltages from a signal representing a torque command input T* and at least one motor parameter. The load model derives a motor speed value including a model of motor speed behaviour of the AC electric motor to provide an output signal which represents the motor speed of the AC electric motor. This motor speed output signal is used in determining a frequency of rotation of an applied motor voltage vector. Where an input to the load model is the signal representing the torque command input T*, the load model uses the signal representing the torque command T*, at least over a part of an operating speed range of the AC motor which includes zero speed, to determine the motor speed output signal.
Owner:HUNTER GREGORY PETER
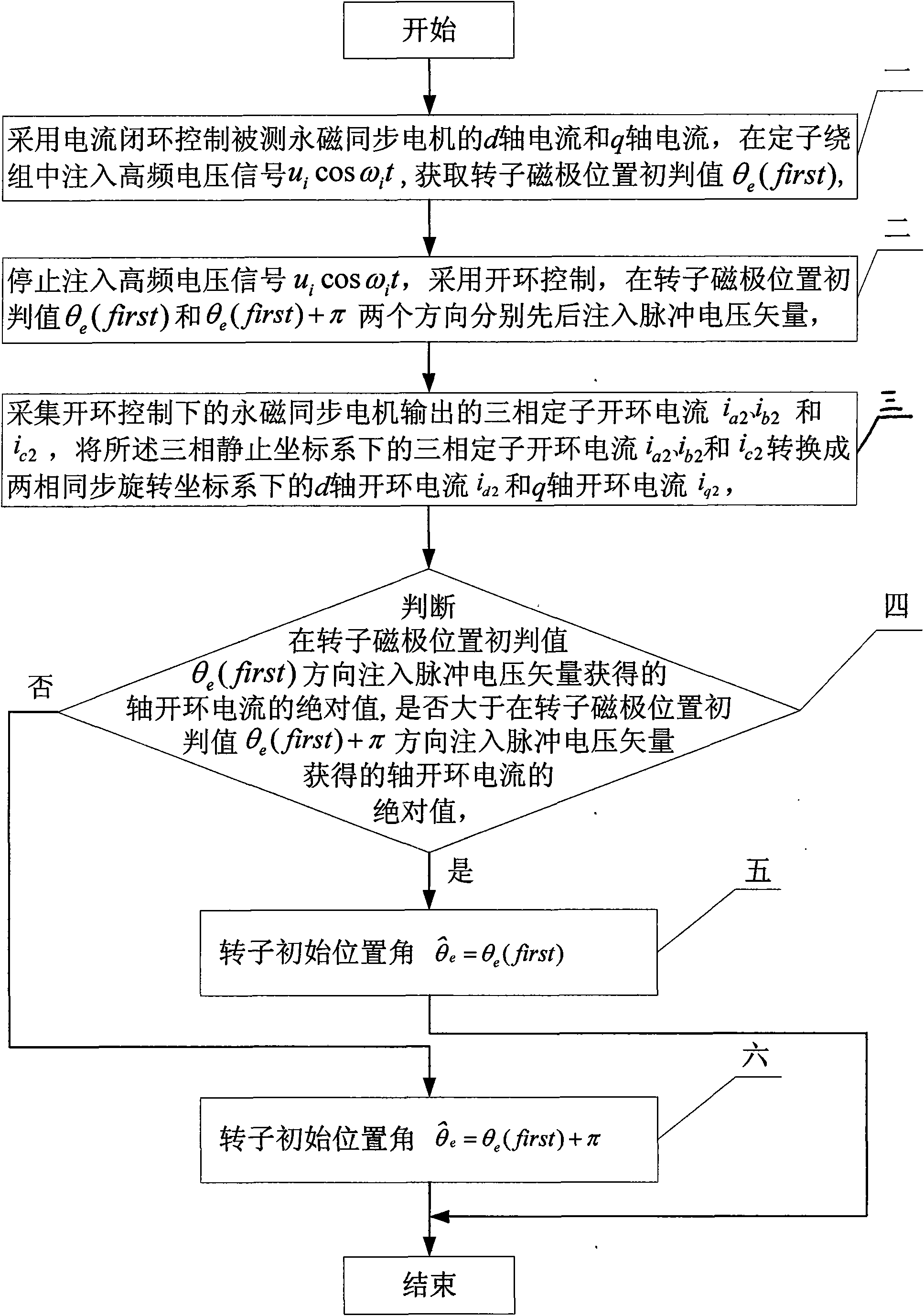
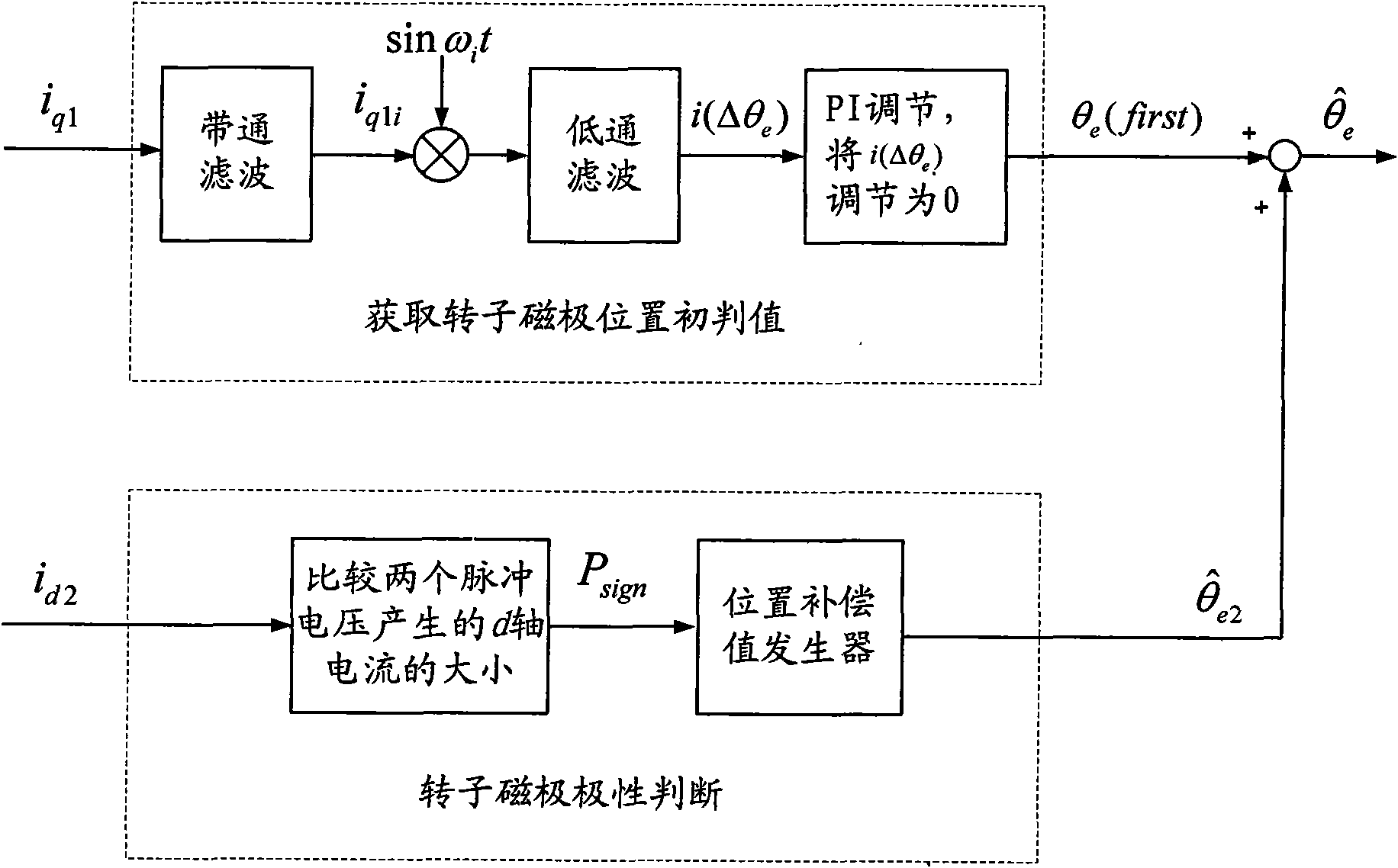
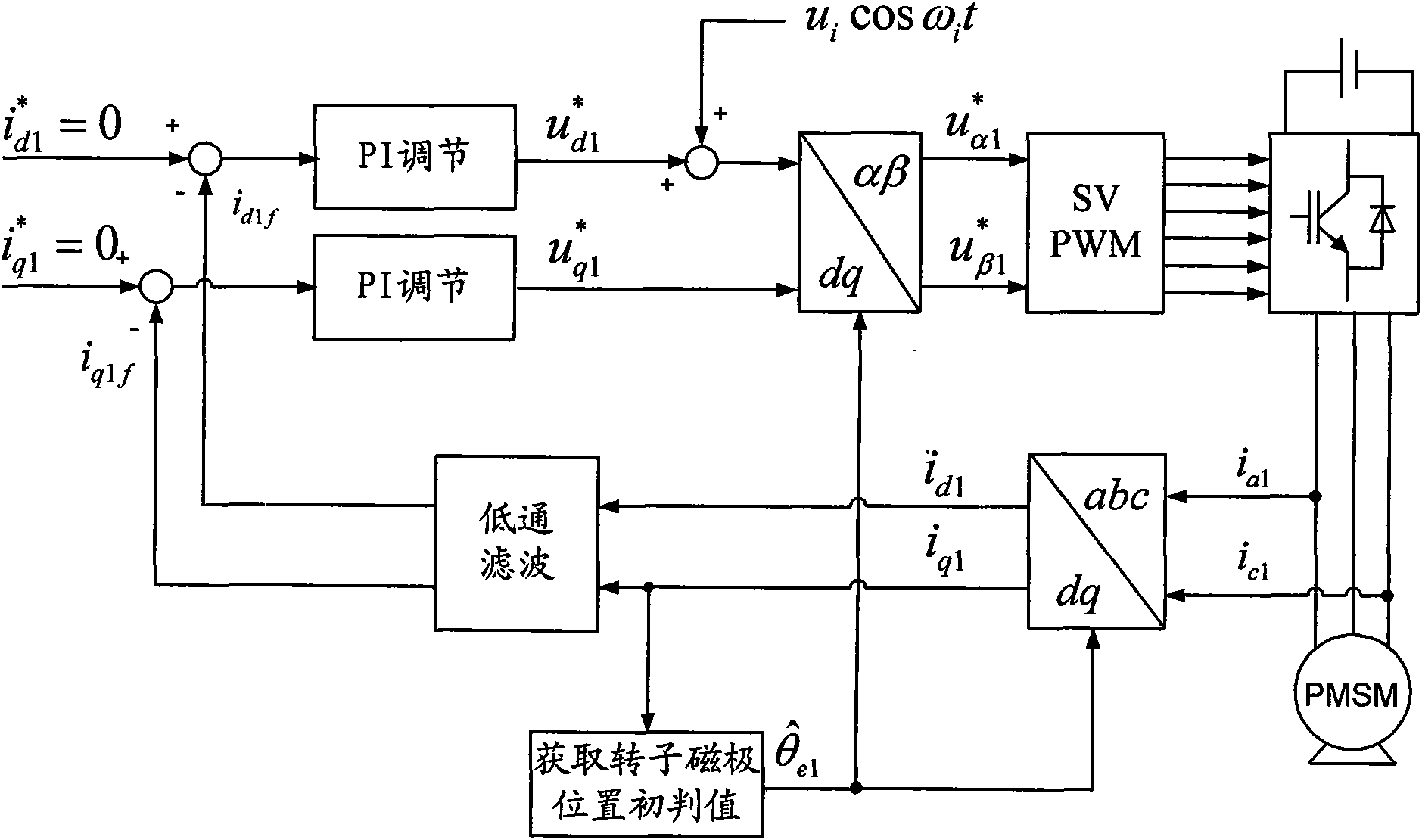
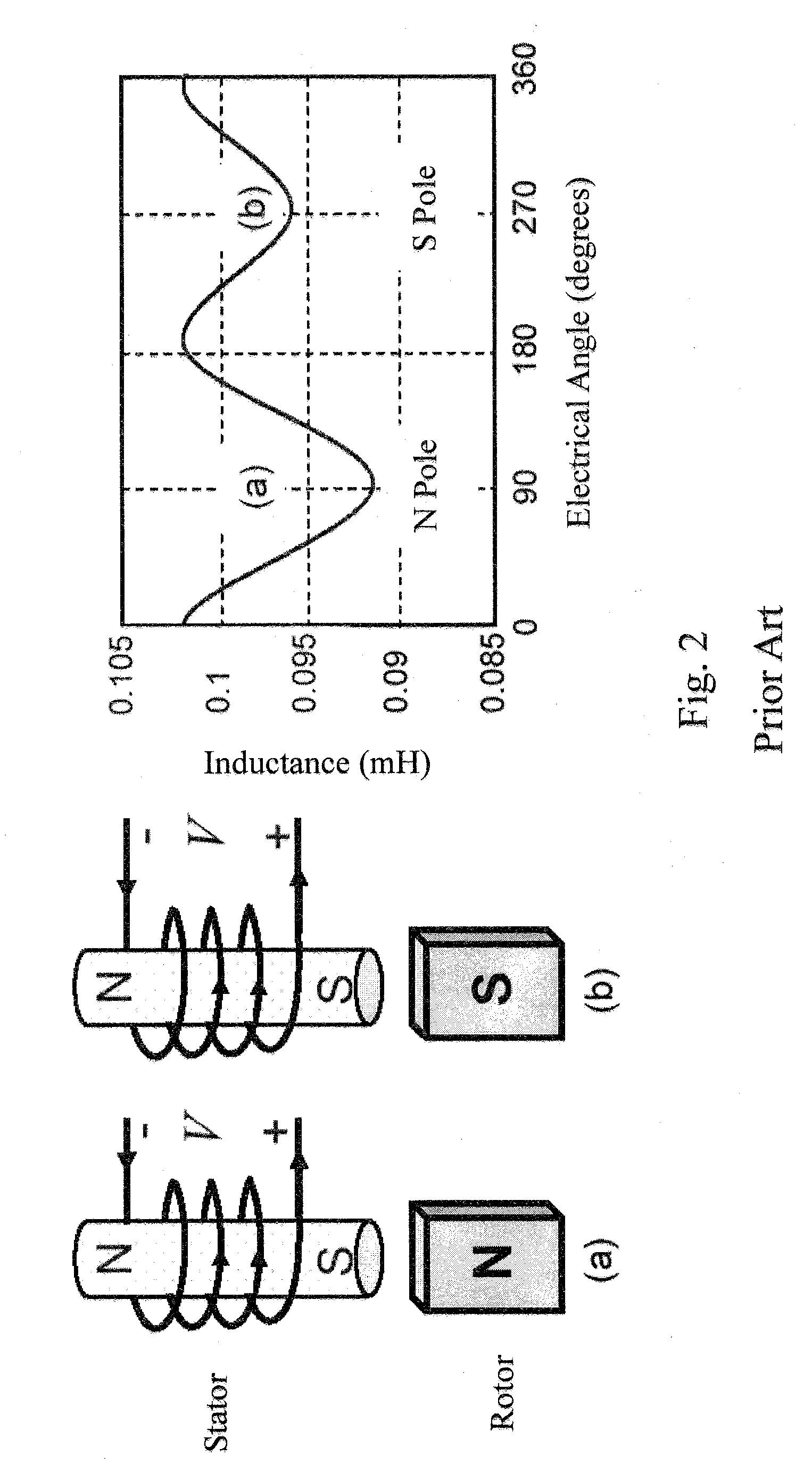
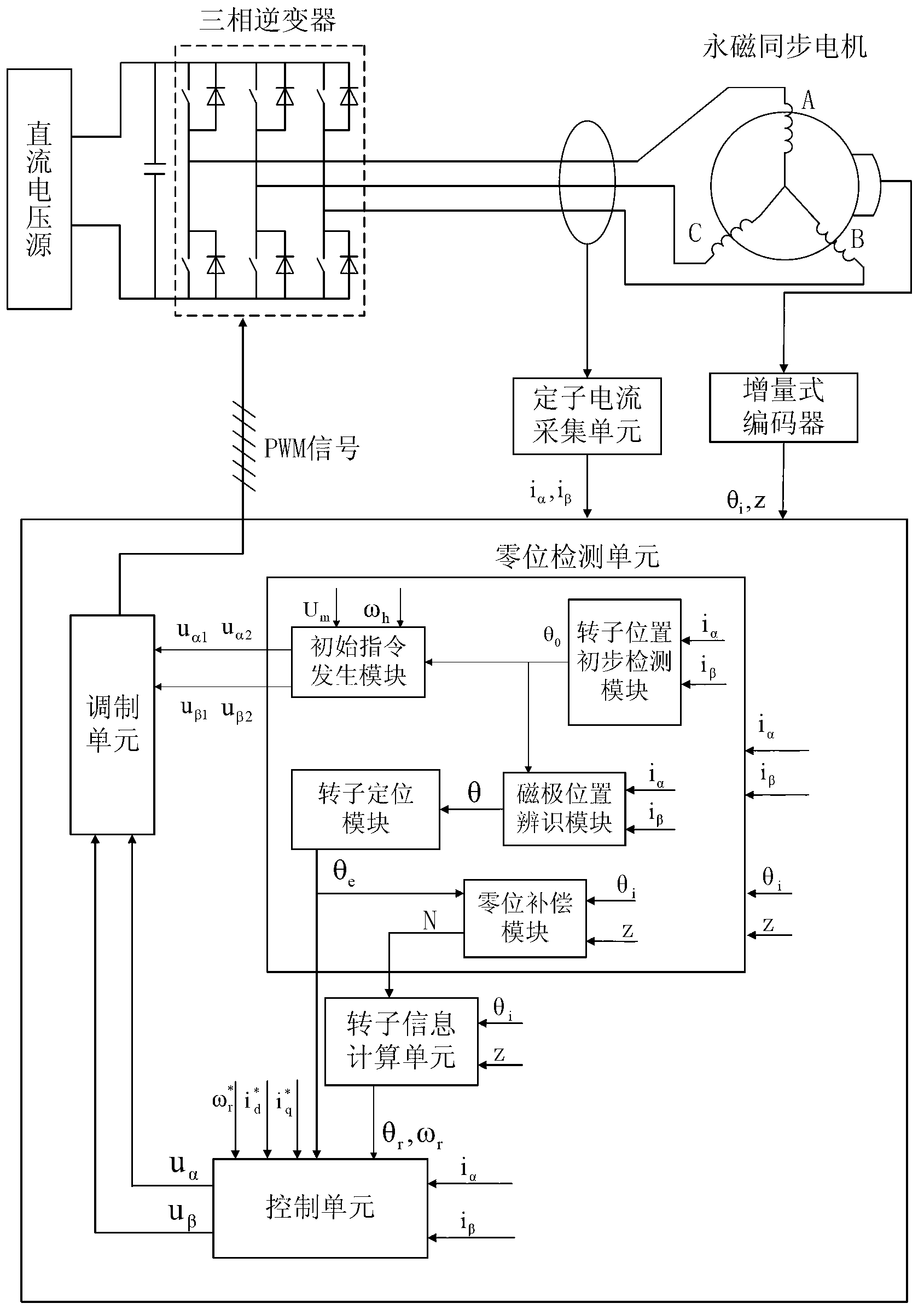
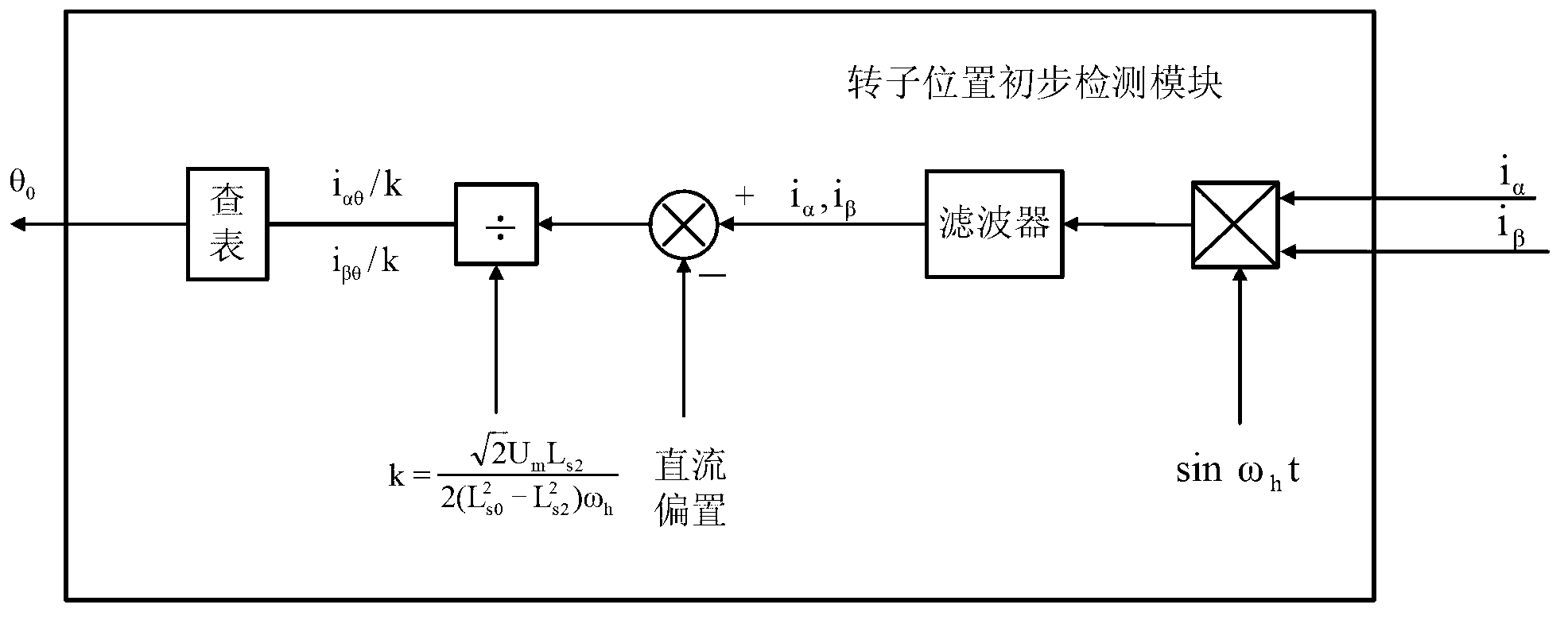
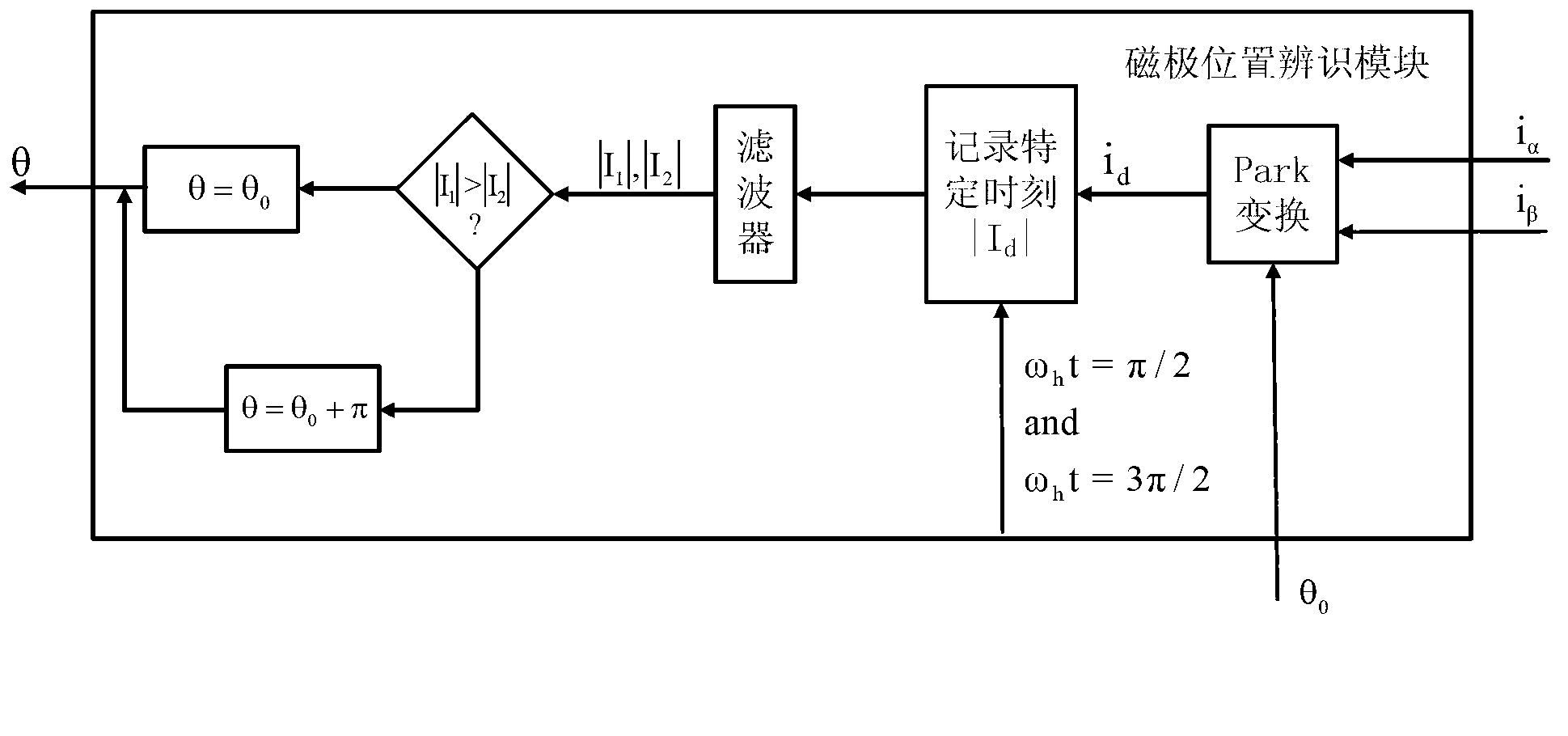
Method for identifying initial position of rotor of permanent magnet synchronous motor of non-position sensor
InactiveCN101630938AEfficient identificationSatisfied with the initial position identification accuracyAC motor controlVector control systemsVoltage vectorPosition angle
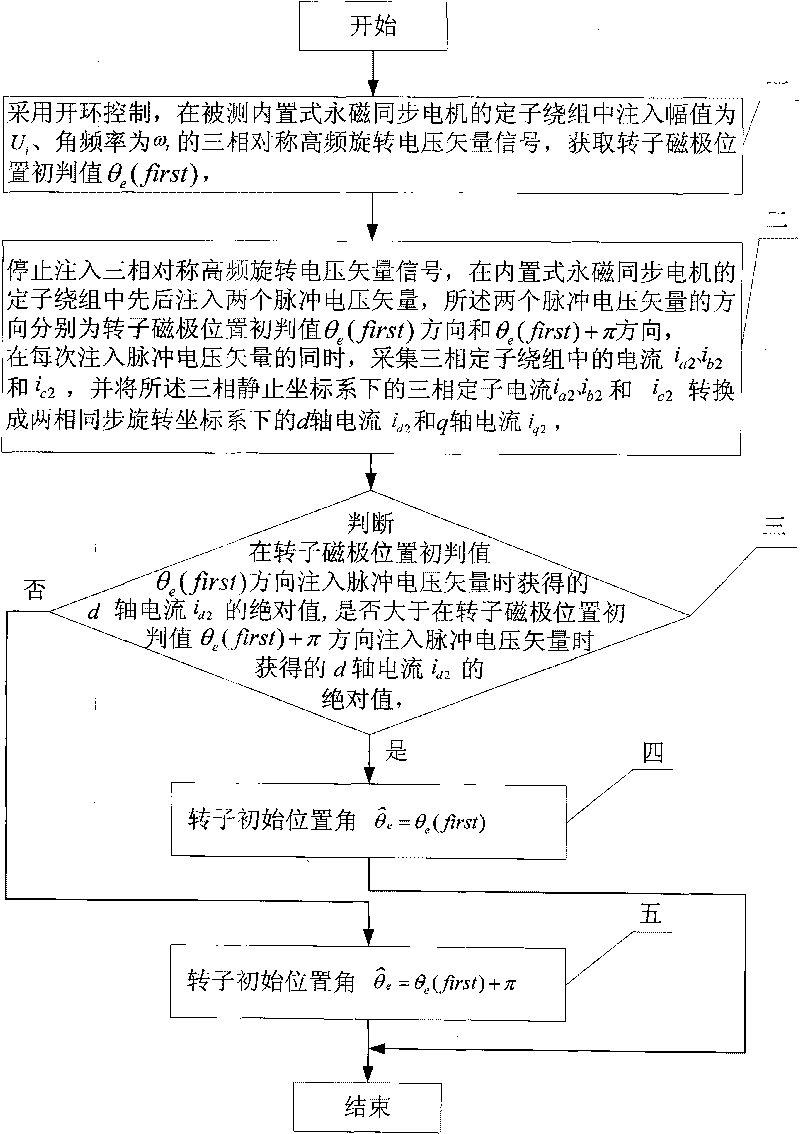
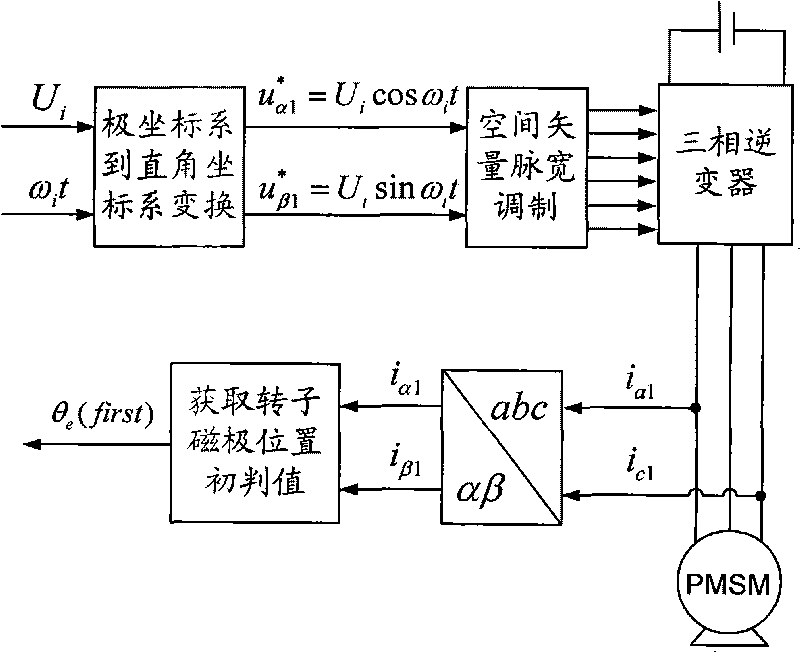
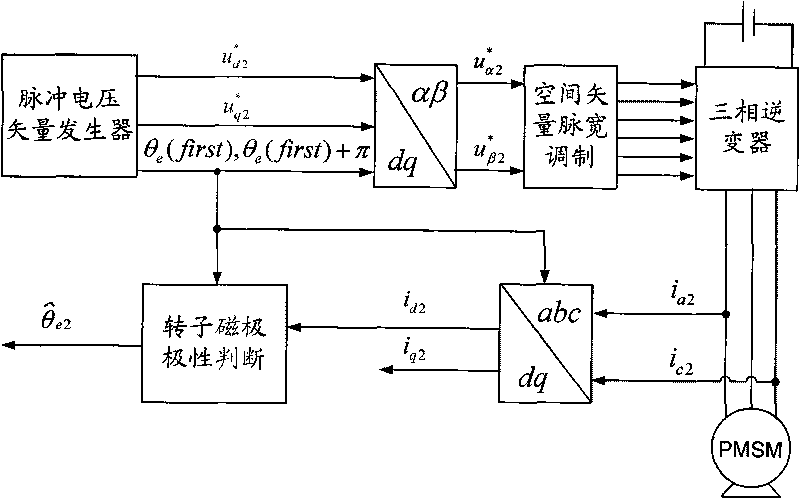
A method for identifying an initial position of a rotor of a permanent magnet synchronous motor of a non-position sensor belongs to the motor control field, and aims at solving the problems of the traditional method for identifying the initial position of magnetic poles of the rotor such as position change of the rotor, low identification precision or complex algorithm. The method comprises the following steps: maintaining the rotor under a static state during the identification process of the initial position of the rotor, injecting a high-frequency voltage signal to a stator winding, carrying out rotational coordinate conversion on three-phase stator current, and acquiring position information of the magnetic poles of the rotor by current components at q axis to obtain an initial judgment value of the magnetic pole position of the rotor; and then injecting two impulse voltage vectors in opposite directions to the stator winding, judging the polarity of the magnetic poles by comparing size of current components at d axis, and correcting the initial judgment value of the magnetic pole position obtained formerly by the judged polarity information of the magnetic poles to finally obtain an initial position angle of the rotor.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
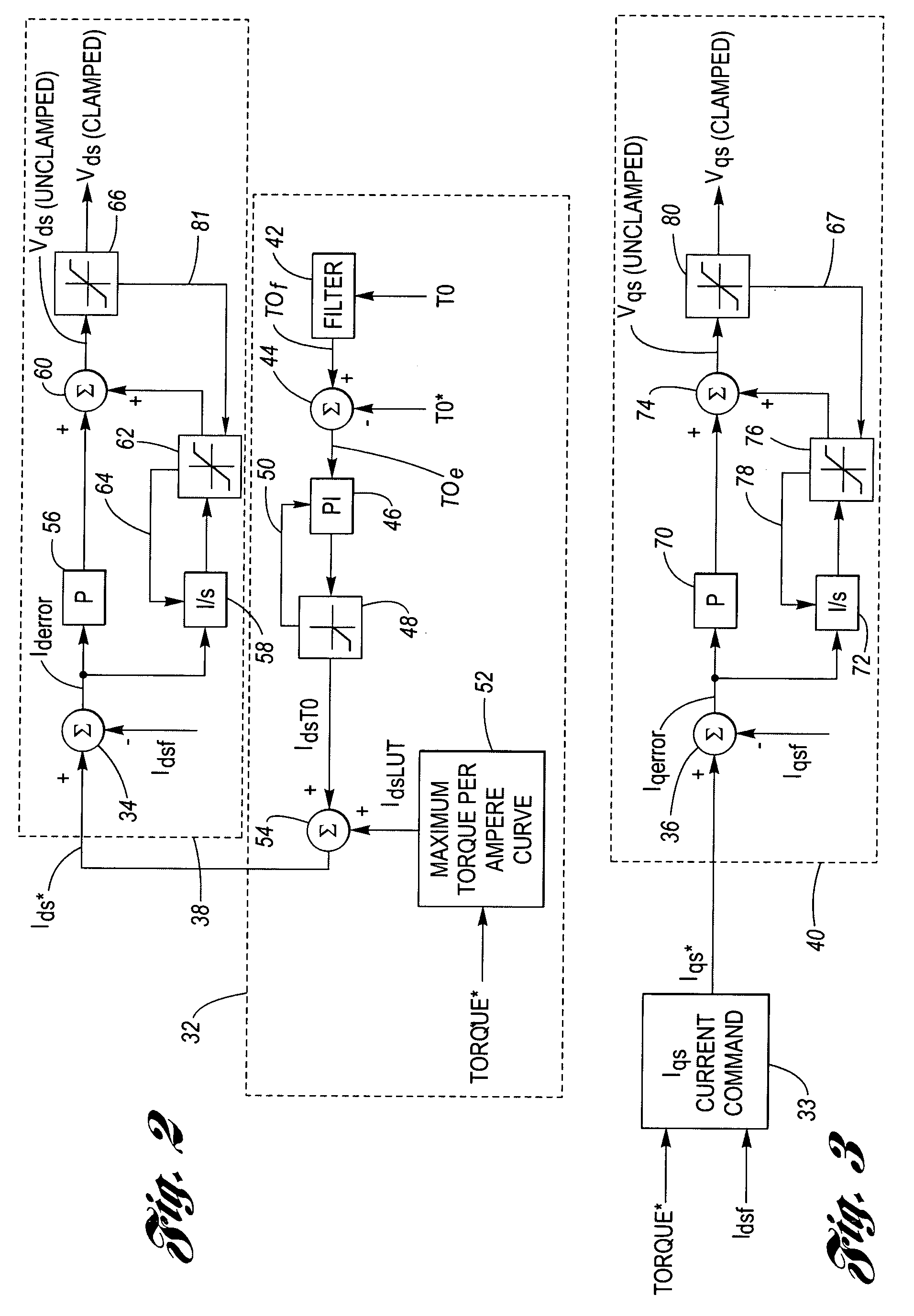
System and method for clamp current regulation in field-weakening operation of permanent magnet (PM) machines
ActiveUS20050046370A1Maximize processing efficiencyMaximum possible torqueAC motor controlDC motor speed/torque controlPhase currentsIntegrator
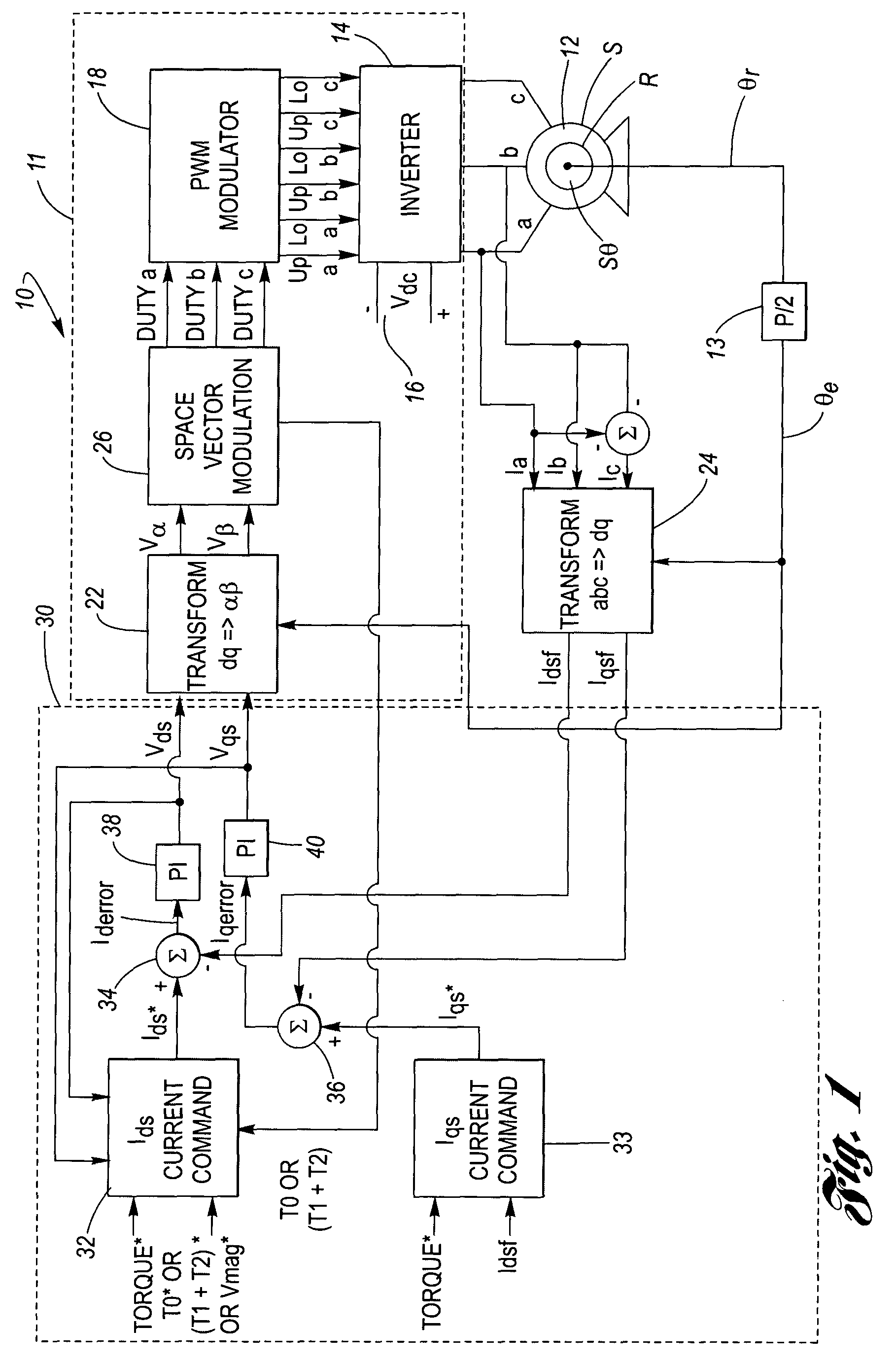
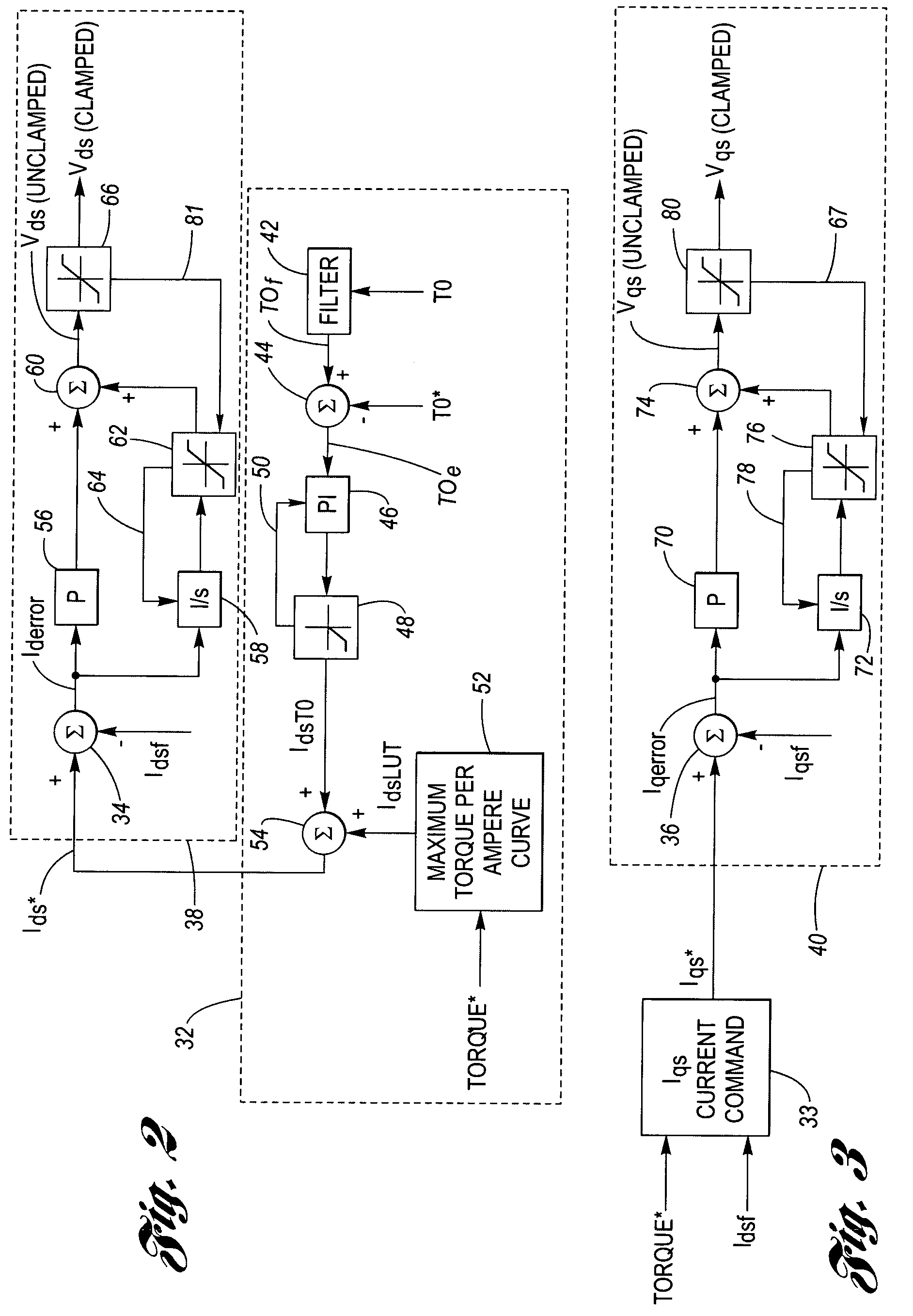
A device to regulate current produced by a permanent magnet machine responsive to a plurality of phase current signals. The motor produces torque for application on a shaft. A processing and drive circuit responsive to a direct current command signal and a quadrature current command signal produces phase current signals for input to the motor. A command circuit responsive to the phase current signals, an angular position of said shaft, and a voltage input command signal to produce a direct current error signal and a quadrature current error signal. A control circuit responsive to the direct and quadrature current error signals produces the direct voltage signal command and the quadrature voltage signal command. The control circuit has a direct and quadrature proportional gain, integrator and clamp circuits. An algorithm produces limited or clamped voltage modulation index signals to obtain maximum efficiency and maximum torque per ampere in the speed range. The algorithm ensures that the current regulator does not run out of voltage by limiting the voltage vector to the achievable voltage vector range that provides maximum torque per ampere and maximum efficiency.
Owner:DELPHI TECH IP LTD
Optimizing PWM modulation method capable of restraining harmonic wave
InactiveCN101295935AAvoid solving problemsSolve capacity problemsAC motor controlConversion with intermediate conversion to dcVoltage vectorHarmonic
The invention discloses a modulating method for the optimized PWM of restrainable harmonic waves, which utilizes the combination of space voltage vectors (SVPWM) to realize the elimination of 'm' ('m' equals to 6 multiplied 'j' and plus or minus1; 'j' equals to 1, 2, ellipsis) times of harmonic wave, wherein, 'm' refers to a certain odd number which is not divisible by 3 and comprises 5, 7, 11, 13, etc. The method of the invention is characterized in that the method can be realized by programming, thereby not only solving the problem of calculated amount or look-up table memory capacity existing in a SHEPWM method, using the combined voltage vector to approach the circular trace of a flux linkage, and helping to reduce torque pulsation, but also fulfilling the task of selectively eliminating the harmonic wave.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Space vector PWM modulator for permanent magnet motor drive
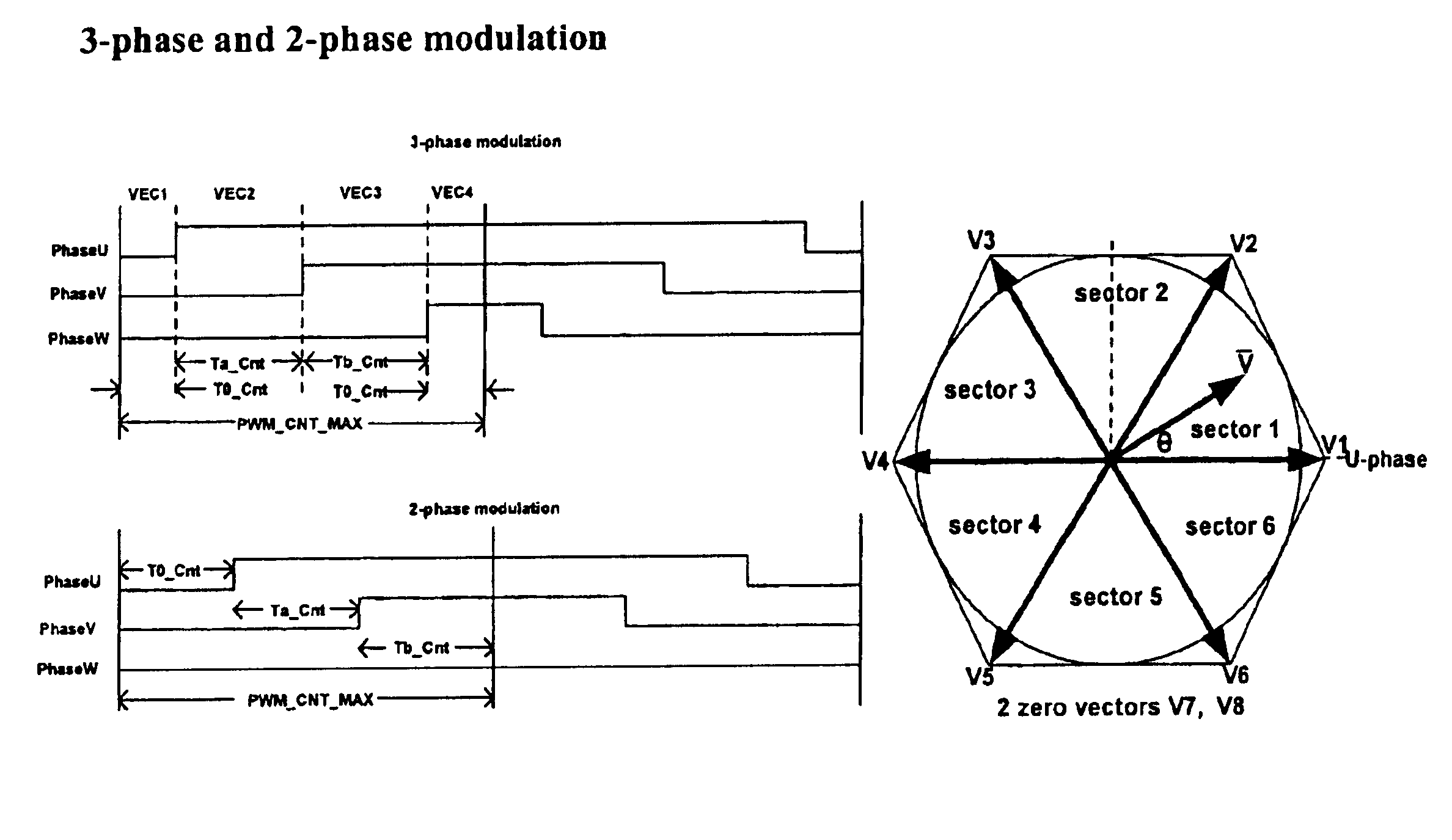
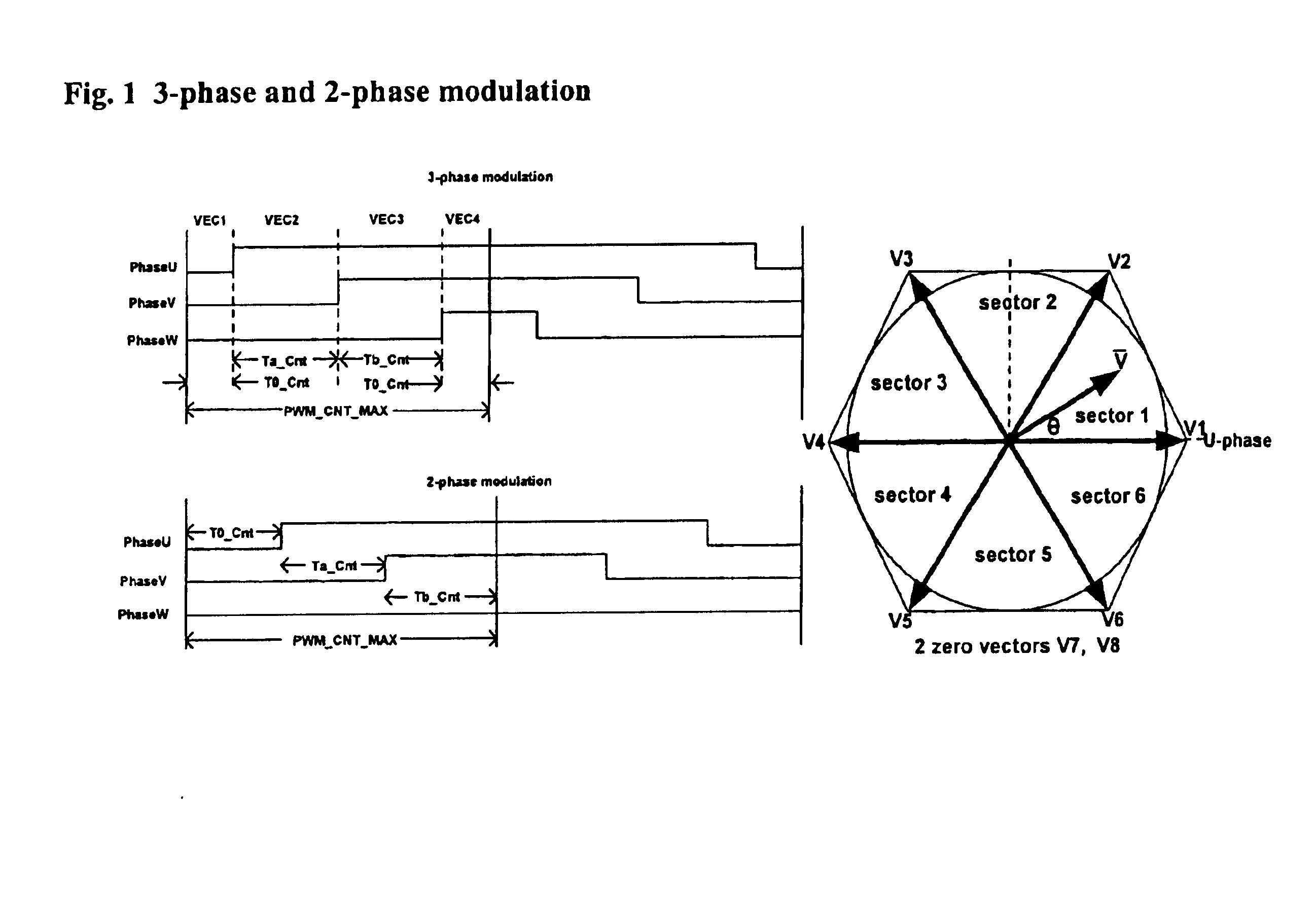
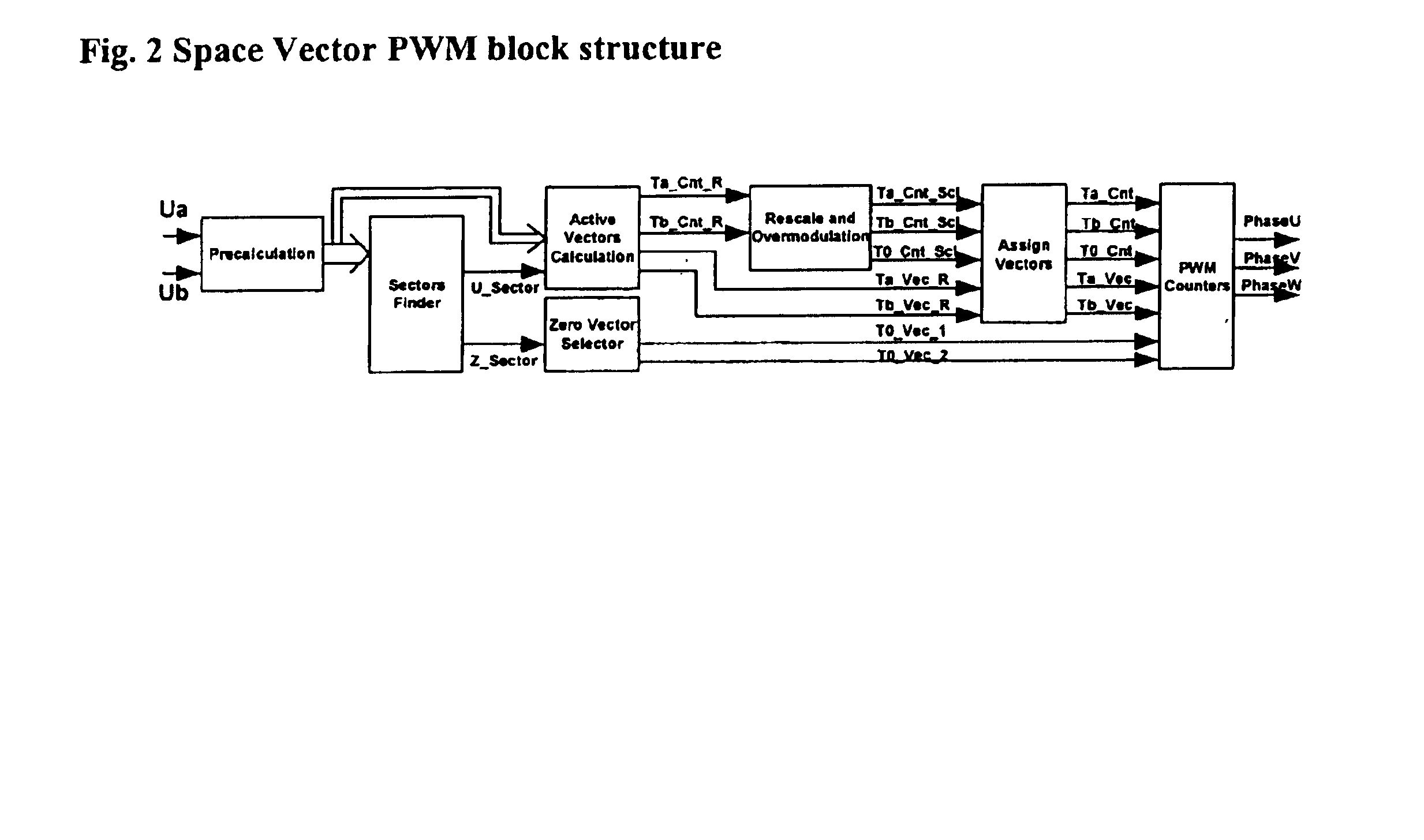
A space vector pulse-width modulator (SVPWM) and a method implemented by the modulator. A precalculation module accepts Ua and Ub modulation indexes and in response thereto, outputs modified Ua and Ub information; a sector finder has a U module which receives the modified Ua information and outputs a U sector; and a Z module which receives the U sector and the modified Ub information and outputs a Z sector. The U sector and the Z sector are 2-phase control signals for implementing 2-phase modulation. For 3-phase modulation, the SVPWM and method further possess an active vectors calculation module and an assign vectors module which receive the modified Ua and Ub information and the U sector, and which calculate active vectors for 3-phase modulation; a zero vector selector which receives the Z sector and calculates zero vectors for 3-phase modulation; and a PWM counter block which receives the active vectors and zero vectors and outputs 3-phase control signals for implementing 3-phase modulation. The SVPWM and method may have a symmetrical PWM mode, an asymmetrical PWM mode, or both. Advantageously there may also be a rescale and overmodulation module which receives duration information corresponding to the vectors and in response thereto, detects the occurrence of overmodulation. Overmodulation may be detected in response to a negative zero vector time. The module may respond to overmodulation by clamping the zero vector time to zero and rescaling the active vector times to fit within the PWM cycle. The rescaling may restrict a voltage vector to stay within hexagonal boundaries on the space vector plane, while preserving voltage phase.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AMERICAS CORP
Control system for distributed power generation, conversion, and storage system
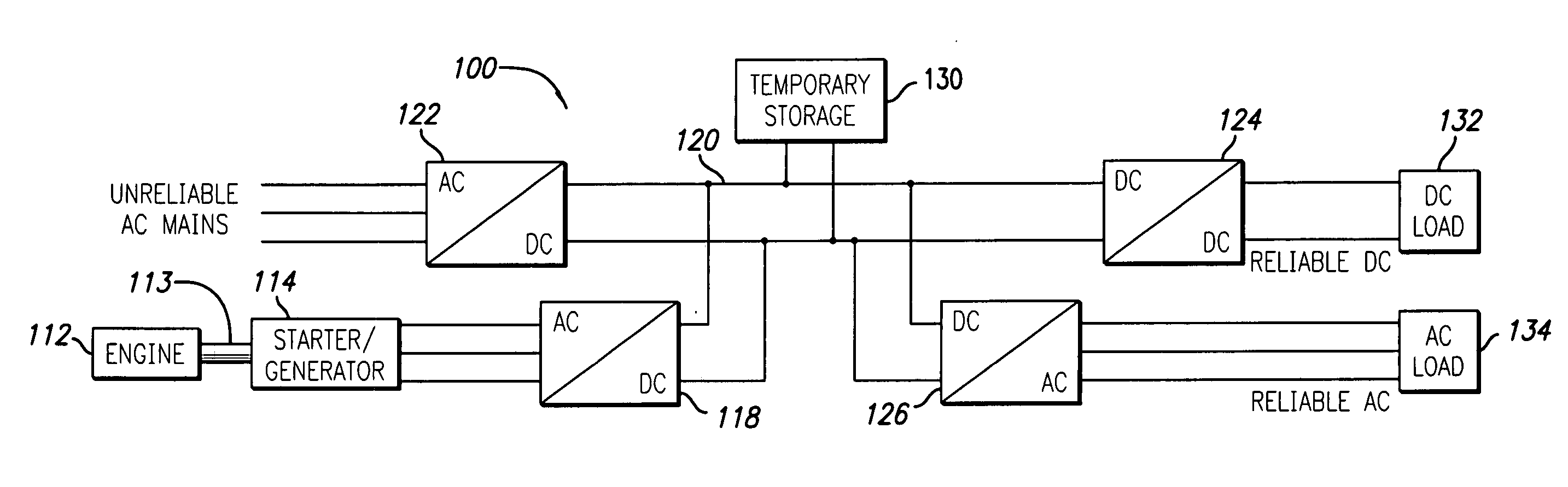
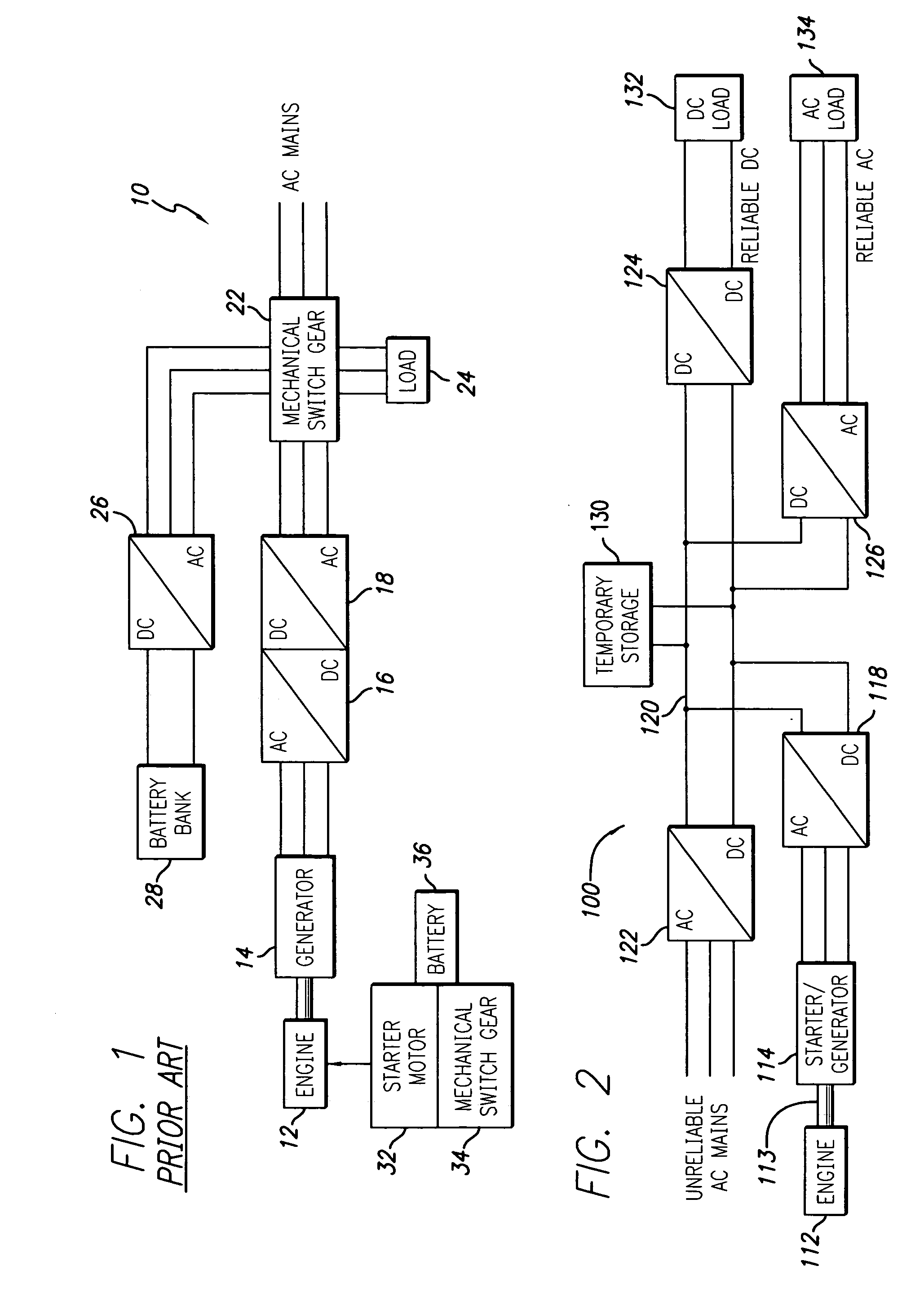
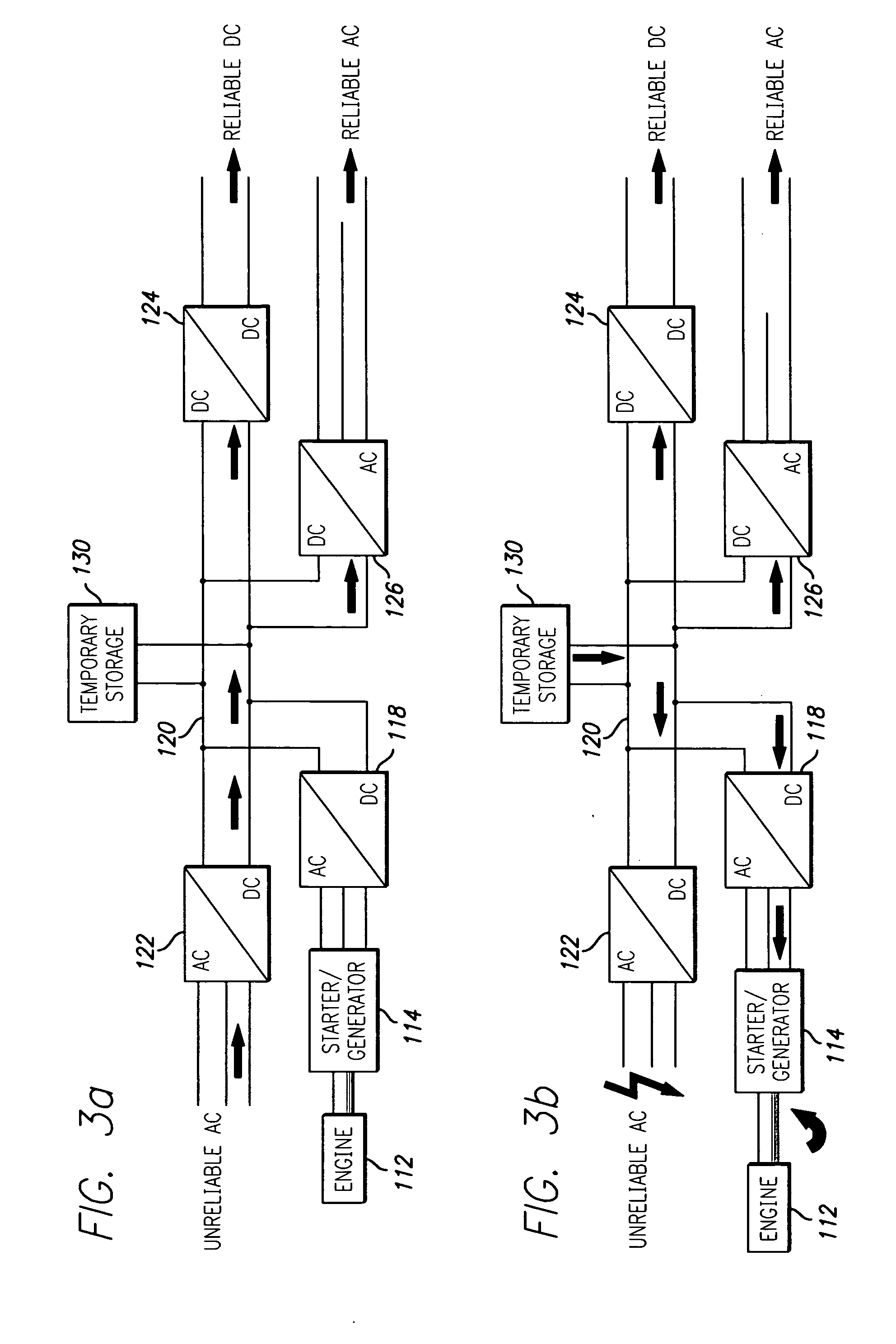
InactiveUS20060017328A1Rapid and reliable start-upReduce needBatteries circuit arrangementsElectric powerVoltage vectorDistributed power generation
A distributed power generating system enables very rapid and reliable start-up of an engine used to generate back-up power, thereby substantially reducing the need for stored power. More particularly, the distributed power generating system comprises a power bus electrically coupled to commercial power and to a load, an engine comprising a rotatable shaft, a starter / generator operatively coupled to the shaft of the engine and electrically coupled to the power bus, and a temporary storage device electrically coupled to the power bus. The distributed power generating system further comprises a control system adapted to detect a failure of the commercial power and cause the starter / generator to start the engine from a standstill condition. The control system provides the starter / generator with an initial voltage vector selected to rapidly bring the engine to an operational speed sustainable by the engine alone. The temporary storage device supplies electrical power to the power bus for delivery to the load and for powering the starter / generator until the engine reaches the operational speed, whereupon the control system causes the starter / generator to take over supply of electrical power to the power bus for delivery to the load. The control system starts the engine upon detection of a voltage on the power bus below a predetermined lower limit. After the engine has started, the control system monitors speed of the engine to determine whether the operational speed is reached. The control system terminates operation of the engine upon detection of a voltage on the power bus above a predetermined upper limit.
Owner:BRYDE JAN HENRIK
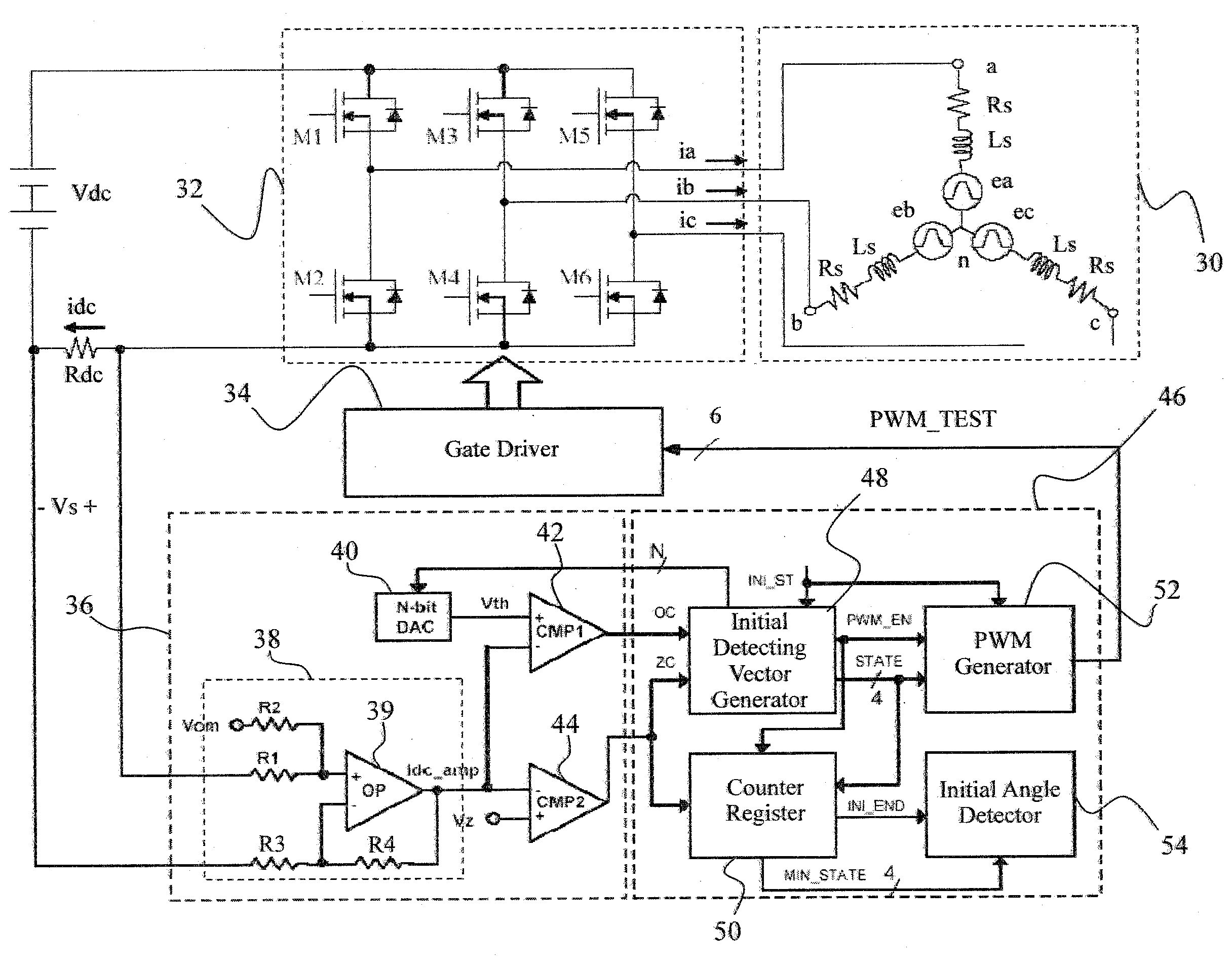
Initial rotor position detection for permanent magnet synchronous motors
ActiveUS20100181952A1High sensitivityAvoid uneven performanceMotor/generator/converter stoppersSynchronous motors startersFall timeVoltage vector
Owner:RICHTEK TECH
Method for detecting initial position of magnetic pole of rotor of built-in permanent magnetic synchronous motor
InactiveCN101714844AKeep stillEfficient detectionVector control systemsDynamo-electric converter controlSynchronous motorVoltage vector
The invention provides a method for detecting the initial position of a magnetic pole of a rotor of a built-in permanent magnetic synchronous motor, belongs to the field of motor control, and solves the problems of over-complicated processing, easy occurrence of polarity misjudging, poor practicality and the like existing in the conventional method based on high-frequency signal injection for detecting the initial position of the rotor. The method comprises the following steps: constantly maintaining the stationary state of the rotor; injecting a rotating high-frequency voltage signal into a stator winding; detecting three-phase stator current and converting the three-phase stator current into two-phase static coordinates; acquiring an error signal capable of reflecting position information of the magnetic pole of the rotor through signal processing; adjusting the error signal by using a PI tracker so as to acquire an initial judging value of the position of the magnetic pole of the rotor; and injecting two impulse voltage vectors in opposite directions into the stator winding, comparing values of direct axis current components by detecting the three phase current and converting the rotating coordinates so as to determine the polarity of the magnetic pole, and finally acquiring the initial position angle of the magnetic pole of the rotor of the built-in permanent magnetic synchronous motor.
Owner:哈尔滨同为电气股份有限公司 +1
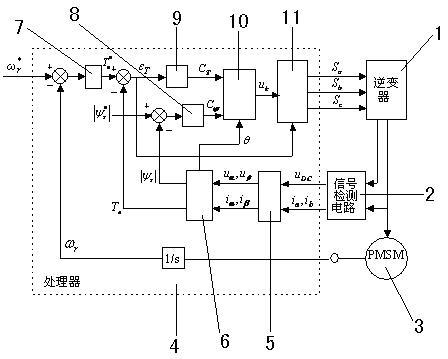
Permanent magnet synchronous motor control method and system based on encoder automatic zero set
ActiveCN103269198AClarify initial positioningPrevent inversionElectronic commutation motor controlAC motor controlVoltage vectorControl system
The invention discloses a permanent magnet synchronous motor control method based on encoder automatic zero set. An improved high-frequency voltage injection method is used for detecting the initial position of a rotor, the initial position of the rotor is clear, voltage vectors can be applied conveniently, and a motor rotor reverse rotating phenomenon is avoided. Meanwhile, encoder zero compensation is carried out automatically, a compensation value is stored, direct calling in the future is convenient, and trouble of manual zero set is removed. Once calibration or zero reset is needed, operation through the method is carried out for one time, an encoder is subjected to accurate zero set again, a process is simple, and accuracy is high. The invention further discloses a control system which achieves the control method. After the initial position of the rotor is obtained through a rotor locating module, a voltage vector closest to the position is chosen to be applied, so that a rotor back-and-forth vibration phenomenon during locating is avoided, a high-frequency voltage signal is injected only before the rotor is located initially, phase lag and time lag cannot be brought to system operation, and noise cannot be introduced during operation.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
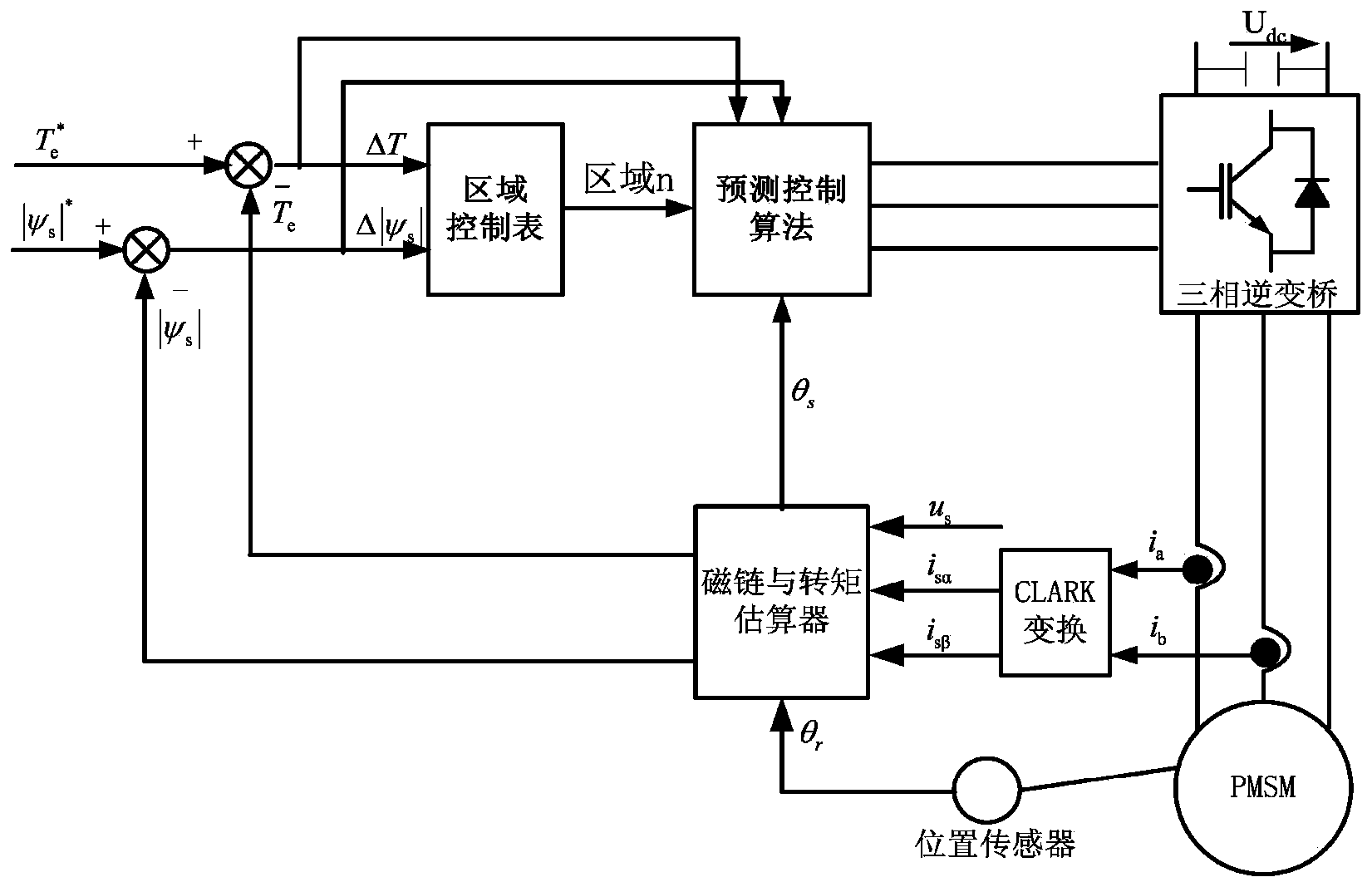
Direct torque control device and method for permanent magnet synchronous motor
InactiveCN101931362AIncrease the number of optional vectorsReduce torque rippleTorque ripple controlVector control systemsVoltage vectorPermanent magnet synchronous motor
The invention discloses a direct torque control device and a direct torque control method for a permanent magnet synchronous motor. The DC bus voltage of an inverter and a current signal of the permanent magnet synchronous motor are output to a signal detection circuit; the signal detection circuit outputs the DC bus voltage and the current signal to a processor; meanwhile, a rotating speed pulse signal of the permanent magnet synchronous motor is output to the processor and is processed by the processor to form a proper switch signal which is then output to the inverter so as to control the motor. A proper voltage vector is selected from twelve synthesized voltage vectors according to a flux linkage error and a torque error and the position of the flux linkage in twelve sectors, and the duty ratio of the selected voltage vector is determined in real time according to the torque error so as to generate a proper inverter switch signal for controlling the permanent magnet synchronous motor. The number of the selectable voltage vectors in the traditional direct torque control is increased, the duty ratio of an acting vector is adjusted in real time according to the torque error, and the torque pulsation in the traditional direct torque control can be effectively reduced.
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF TECH
Dead-beat based direct torque control method for permanent magnet synchronous motor
InactiveCN103684169ASimple structureImprove performanceElectronic commutation motor controlAC motor controlVoltage vectorFlux linkage
The invention discloses a dead-beat based direct torque control method for a permanent magnet synchronous motor. Errors between given magnetic linkage amplitude and actual magnetic linkage amplitude as well as between given torque amplitude and actual torque amplitude are compensated accurately and simultaneously within a control cycle, and dead-beat control of magnetic linkage and torque is realized. Meanwhile, a space voltage vector modulation method is introduced into a control system to enable switching frequency to be constant. By the control method, system performance can be well improved, magnetic linkage and torque pulsation can be lowered obviously, dynamic response speed of the torque is equivalent to that of a conventional direct torque control scheme, and the direct torque control method basically keeps the advantages of simple structure and fast dynamic torque response.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
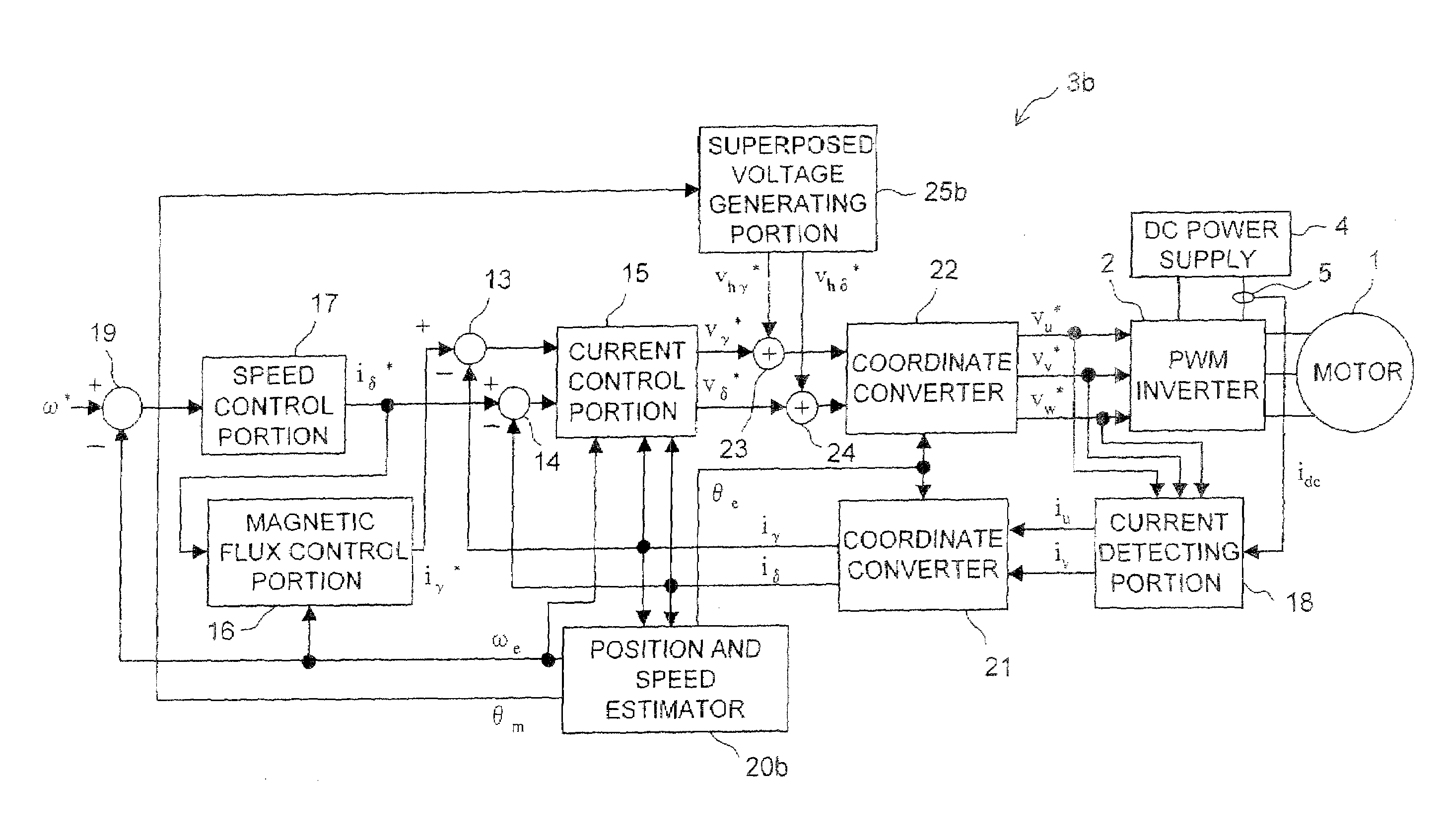
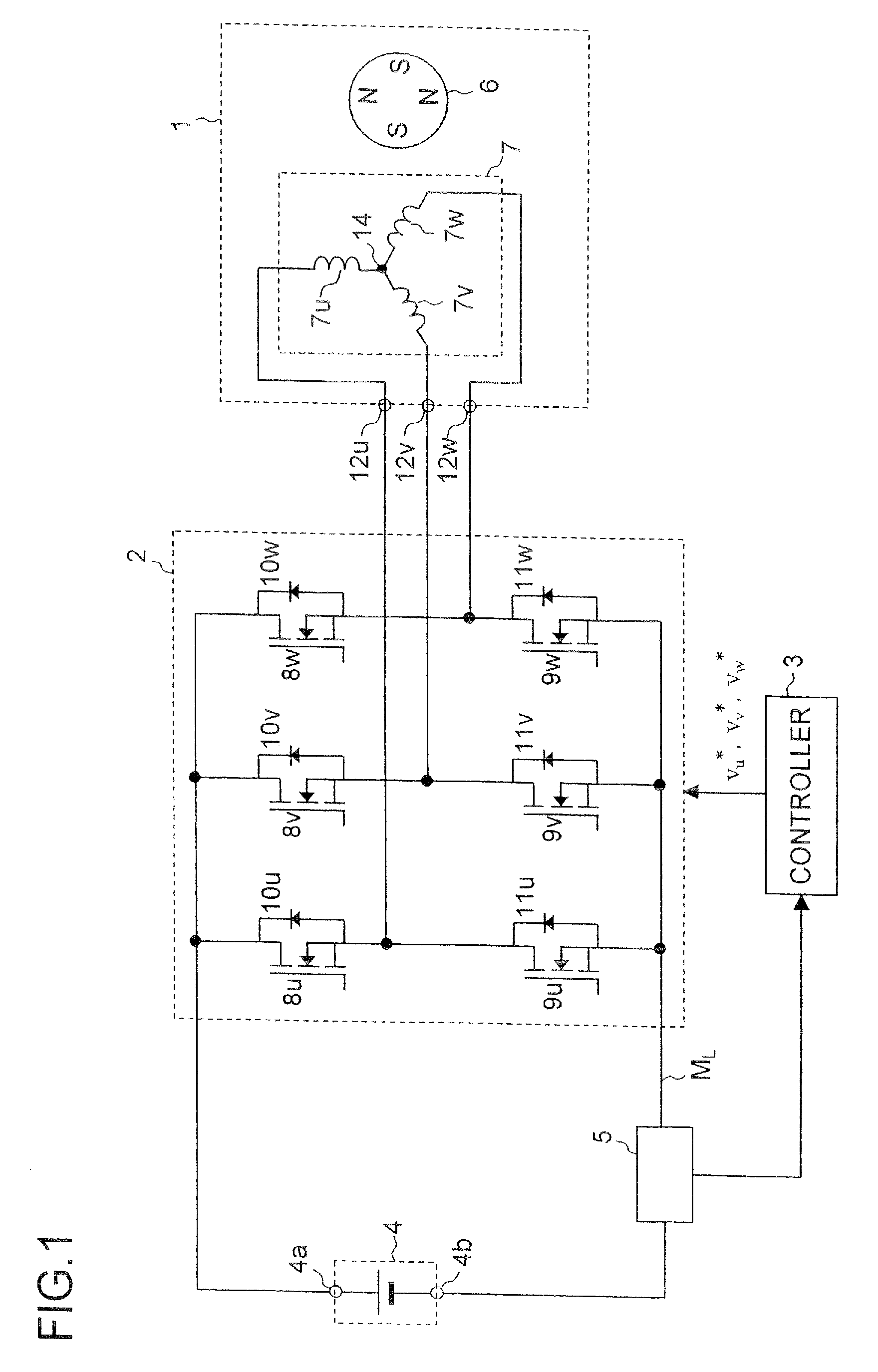
Motor control device
ActiveUS7482777B2Small sizeSynchronous motors startersVector control systemsPhase currentsPhase conversion
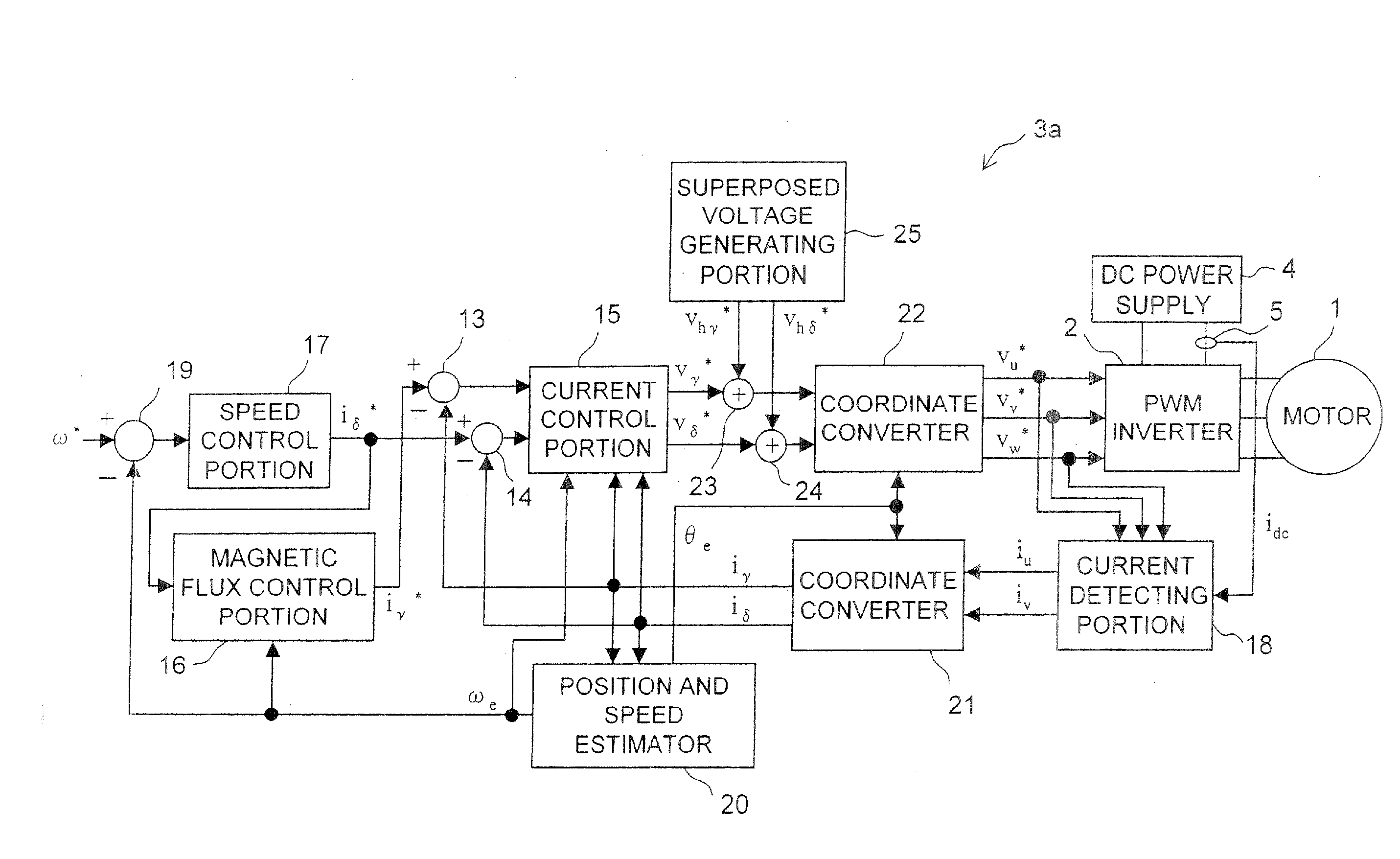
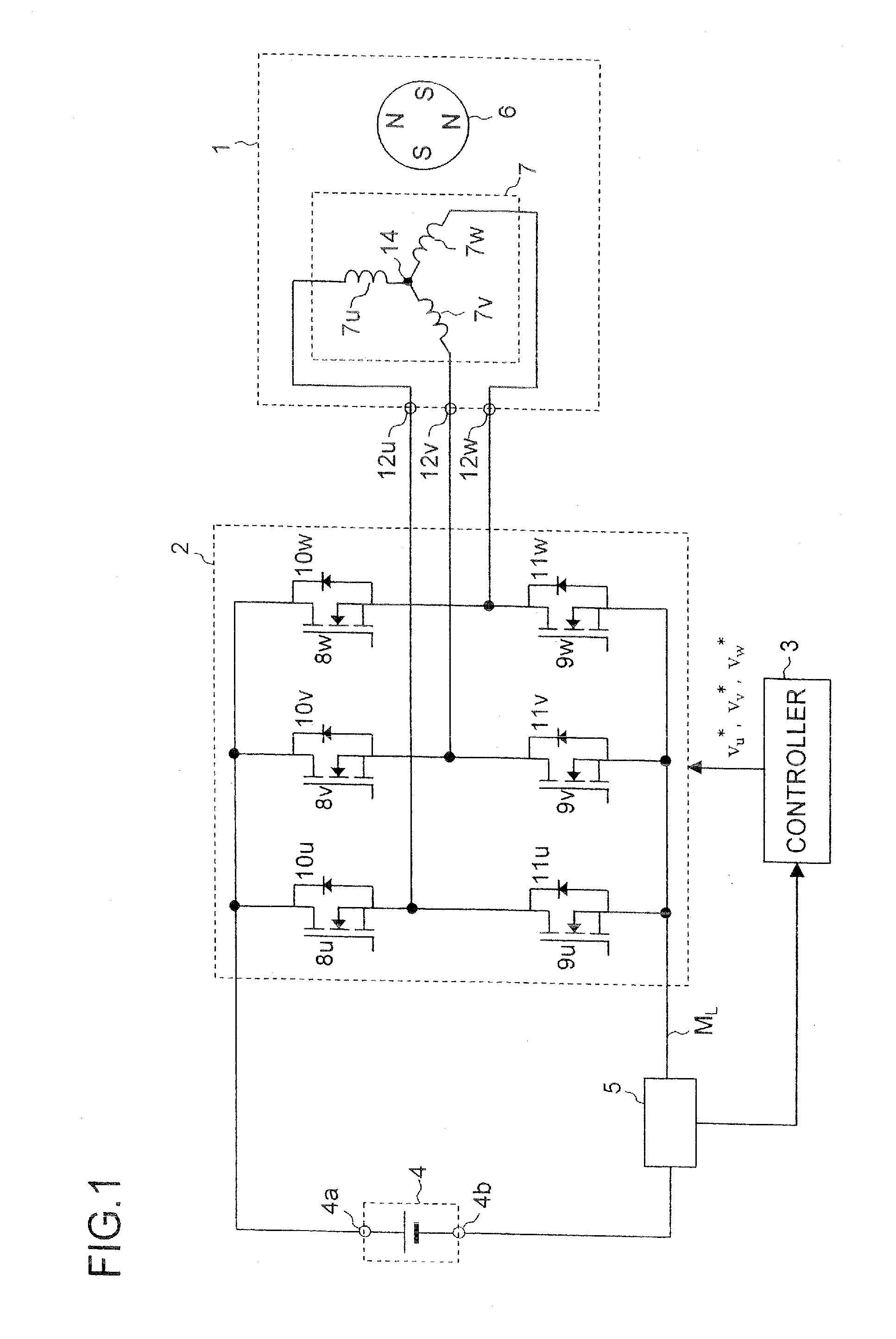
The motor control device includes a current detecting portion for detecting a phase current that flows in an armature winding of a stator of a three-phase motor based on current that flows between an inverter for driving the motor and a DC power supply. The motor control device performs a position sensorless vector control for the motor based on a control current that is obtained by a three-phase to two-phase conversion of the phase current based on an estimated rotor position of the motor. The motor control device farther includes a superposing portion for superposing a superposed voltage having a predetermined frequency on a drive voltage for driving the motor and an estimating portion for deriving the estimated rotor position based on the superposed current that is extracted from the control current and flows in the motor in accordance with the superposed voltage. A voltage vector locus of the superposed voltage from the superposing portion presents an ellipse.
Owner:III HLDG 7
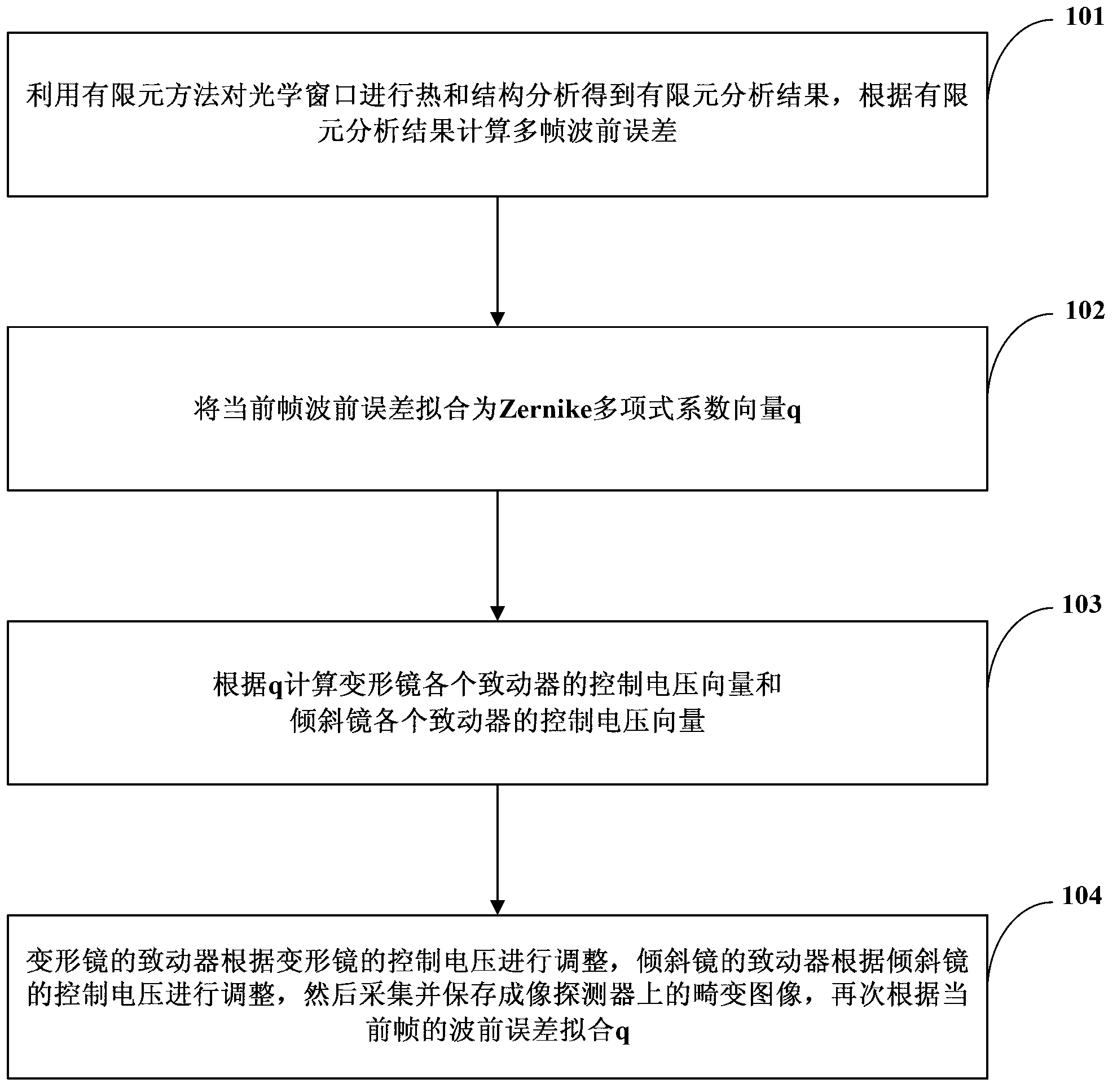
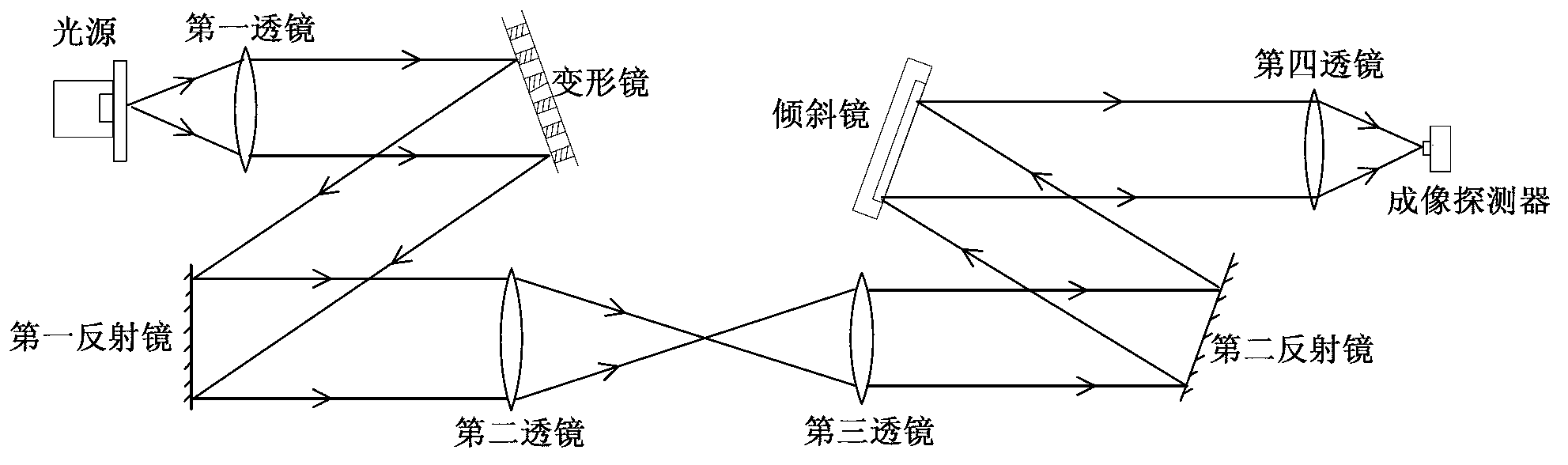
Method and system for simulating aero-optical effect
The invention relates to a method for simulating an aero-optical effect. The method comprises the steps of conducting thermal and structural analysis to an optical window by adopting a finite element analysis method to obtain a finite element analysis result, and calculating multi-frame wave-front errors according to the finite element analysis result; fitting the current frame wave-front error to be a Zernike polynomial coefficient vector q; calculating control voltage vectors of all actuators of a deformable mirror and control voltage vectors of all actuators of a tilting mirror according to the q; and adjusting the actuators of the deformable mirror according to the control voltage of the deformable mirror, adjusting the actuators of the tiling mirror according to the control voltage of the tiling mirror, acquiring and saving distorted images on an imaging detector and again fitting the q according to the current frame wave-front error. The invention additionally discloses a system for simulating the aero-optical effect. By using the method and the system provided by the embodiment of the invention, dynamic distorted image data under the influence of the aero-optical effect can be obtained and experimental conditions are provided for researches on the correction of the aero-optical effect.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY +1
Control method of alternating voltage sensorless high voltage direct current transmission converter
InactiveCN101882799AReduce the numberAvoid structural formsSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsReactive power adjustment/elimination/compensationControl signalReactive power theory
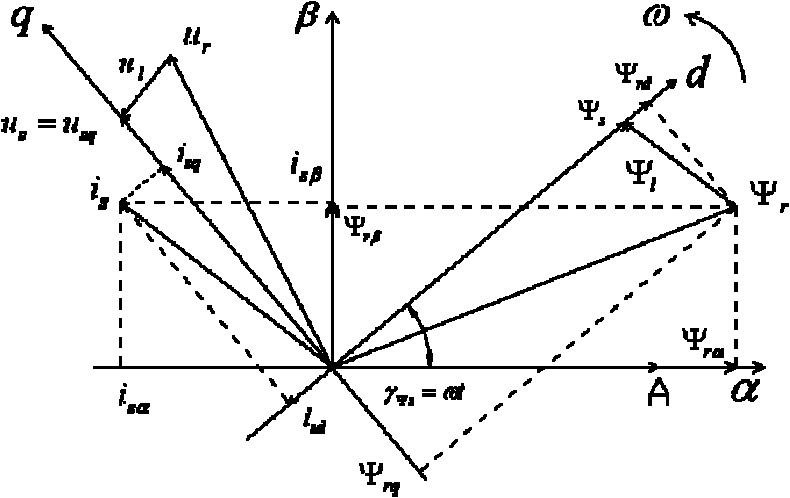
The invention discloses a control method of an alternating voltage sensorless high voltage direct current transmission converter, belonging to the technical field of electrical equipment and comprising the following steps: establishing a stator resistor and an inductor for a virtual motor; building relative position relationships among a current vector, a voltage vector and a flux linkage vector, and analyzing a vectorgram; establishing a converter and flux linkage mathematic model, and calculating a virtual flux linkage vector of a system to obtain a power feedback quantity of the system; acquiring an active control signal and a reactive control signal of the system through a direct power control algorithm, and generating a PWM trigger converter for respectively and independently controlling the active power and reactive power of the system; and utilizing MATLAB simulation software to set up a system model for verifying, and obtaining a systematic selection device when the verification is successful. By utilizing Matlab / Simulink to set up a corresponding simulation model, the designed method is verified to have rapid response speed, the voltage and power after startup can still reach stable values after about 2 power frequency periods and have high steady state precision.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Motor control device
ActiveUS20080197799A1Small sizeSynchronous motors startersVector control systemsPhase currentsPhase conversion
The motor control device includes a current detecting portion for detecting a phase current that flows in an armature winding of a stator of a three-phase motor based on current that flows between an inverter for driving the motor and a DC power supply. The motor control device performs a position sensorless vector control for the motor based on a control current that is obtained by a three-phase to two-phase conversion of the phase current based on an estimated rotor position of the motor. The motor control device farther includes a superposing portion for superposing a superposed voltage having a predetermined frequency on a drive voltage for driving the motor and an estimating portion for deriving the estimated rotor position based on the superposed current that is extracted from the control current and flows in the motor in accordance with the superposed voltage. A voltage vector locus of the superposed voltage from the superposing portion presents an ellipse.
Owner:III HLDG 7
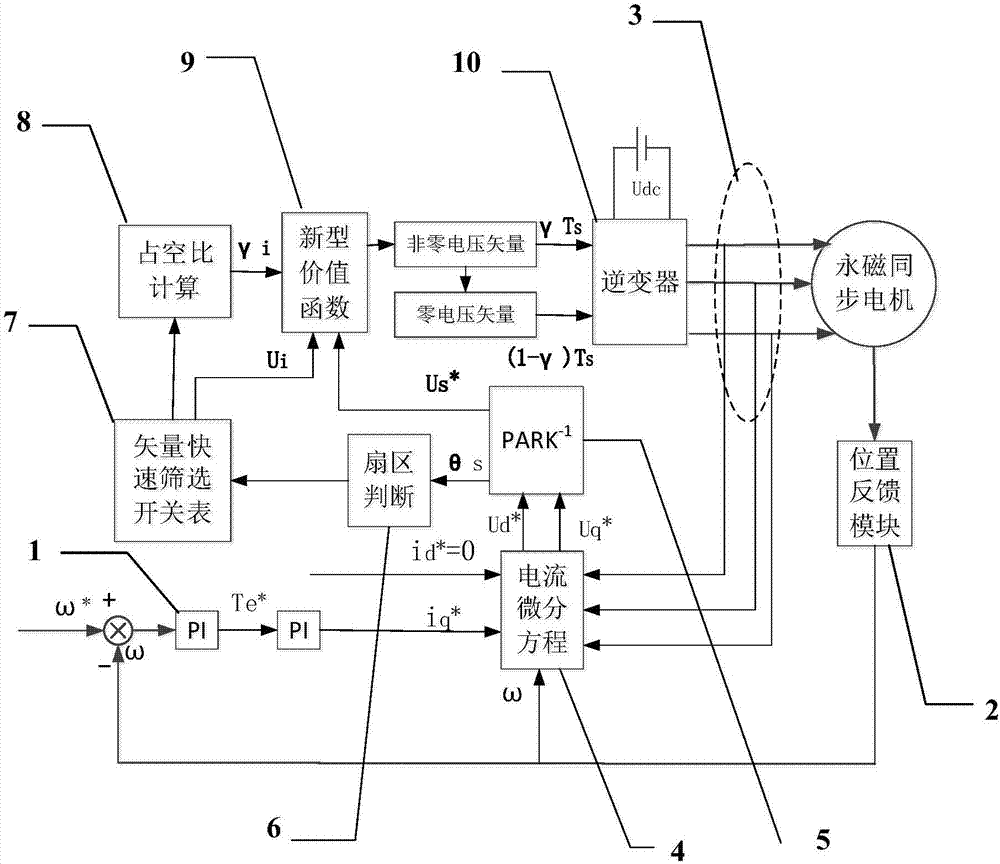
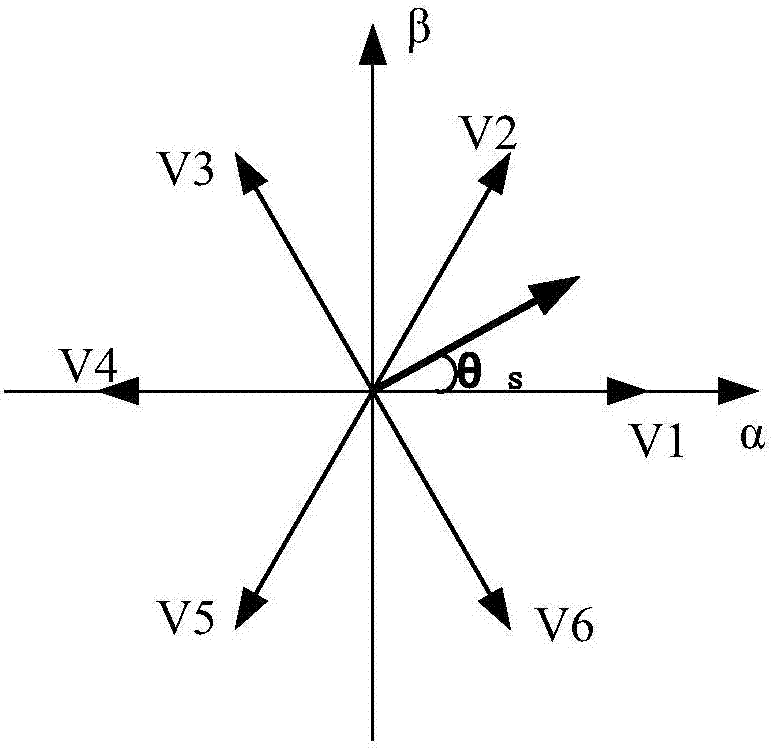
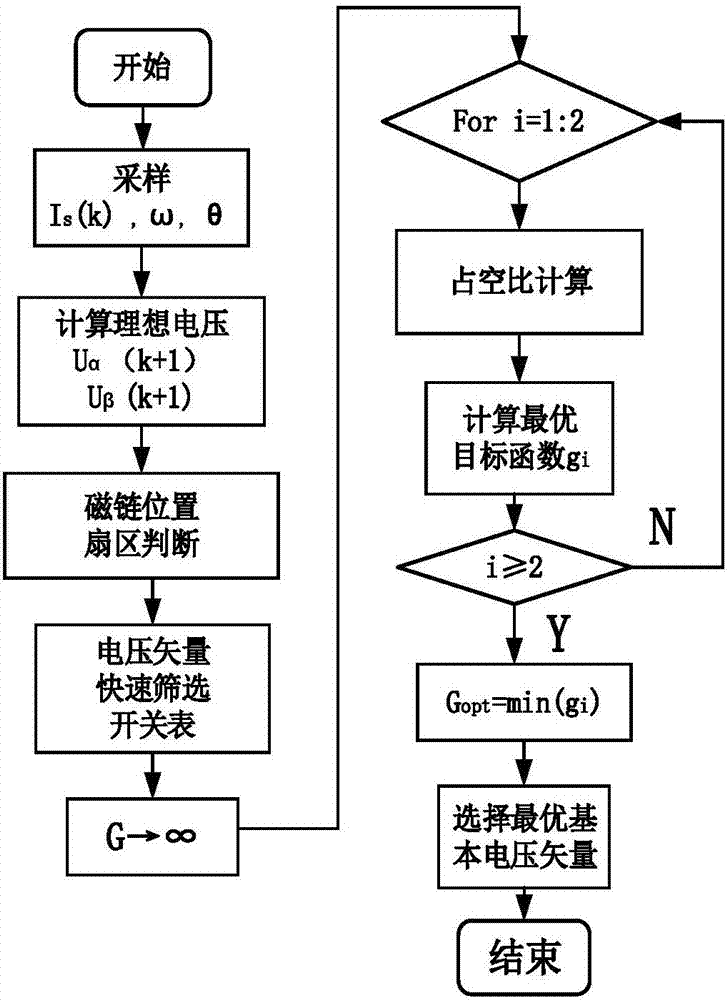
Vector screening and duty cycle combined motor model prediction control system and method
ActiveCN106936356AAvoid control performance impactReduce the burden onTorque ripple controlAC motor controlVoltage vectorPosition angle
The invention discloses a vector screening and duty cycle combined motor model prediction control system and method. The method comprises the steps that a reference voltage vector is acquired according to the idea of no-beat control; the sector of the reference voltage vector is judged through the position angle of the reference voltage vector, and at the same time two effective non-zero voltage vectors are quickly selected; the comparison between the reference voltage vector and two quickly selected effective non-zero voltage vectors is used as a value function; a new value function is provided, and a duty cycle control method is used to calculate the action time of the non-zero voltage vectors; and based on the principle of switching loss minimization, the appropriate zero voltage vector is selected according to the non-zero voltage vectors, and the action time of the zero voltage vector is calculated. The switching state and action time of the non-zero voltage vectors and the switching state and action time of the zero voltage vector are applied on an inverter in turn. The inverter converts the switching state into voltage and outputs the voltage to a permanent magnet synchronous motor to drive a motor to run.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
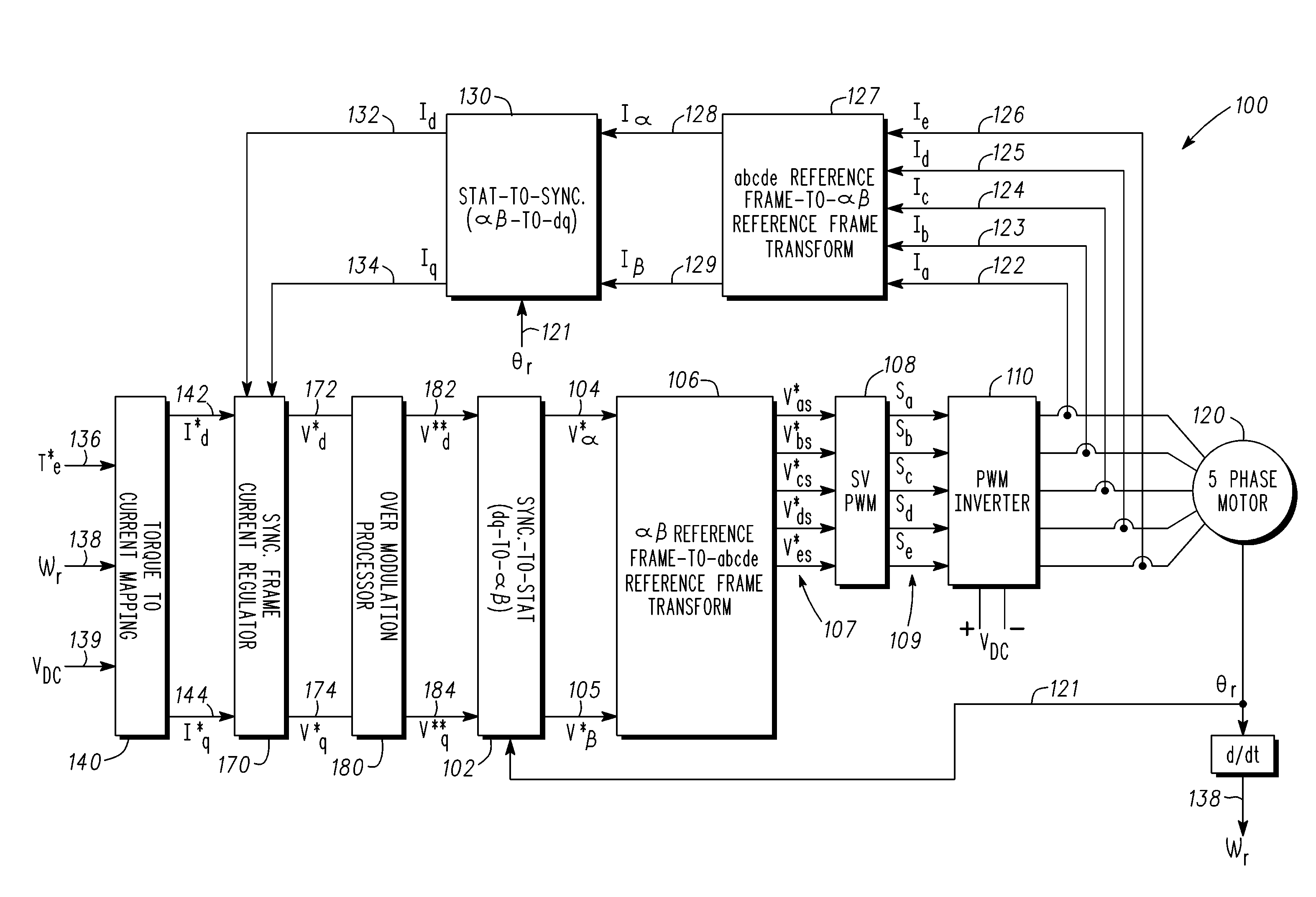
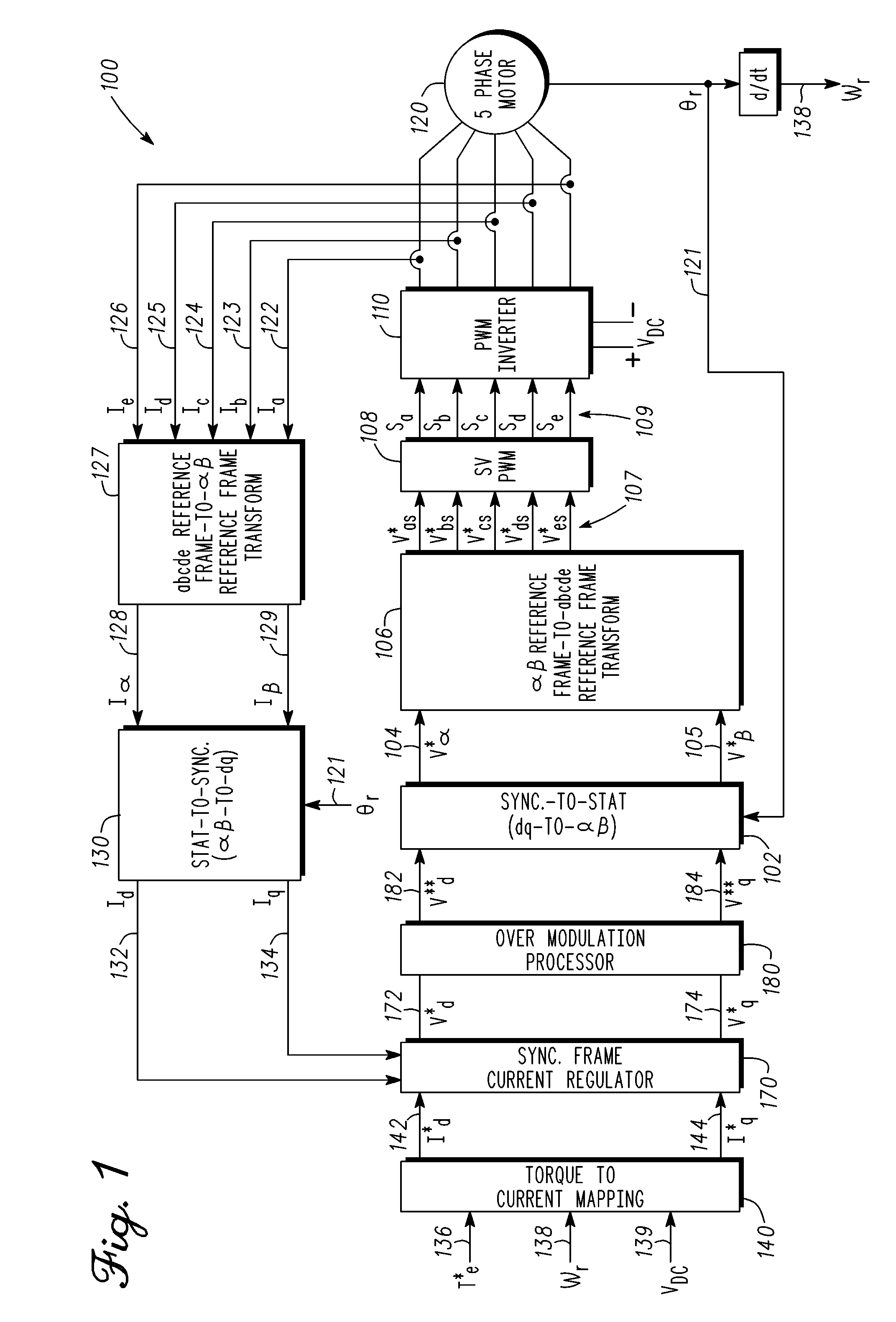
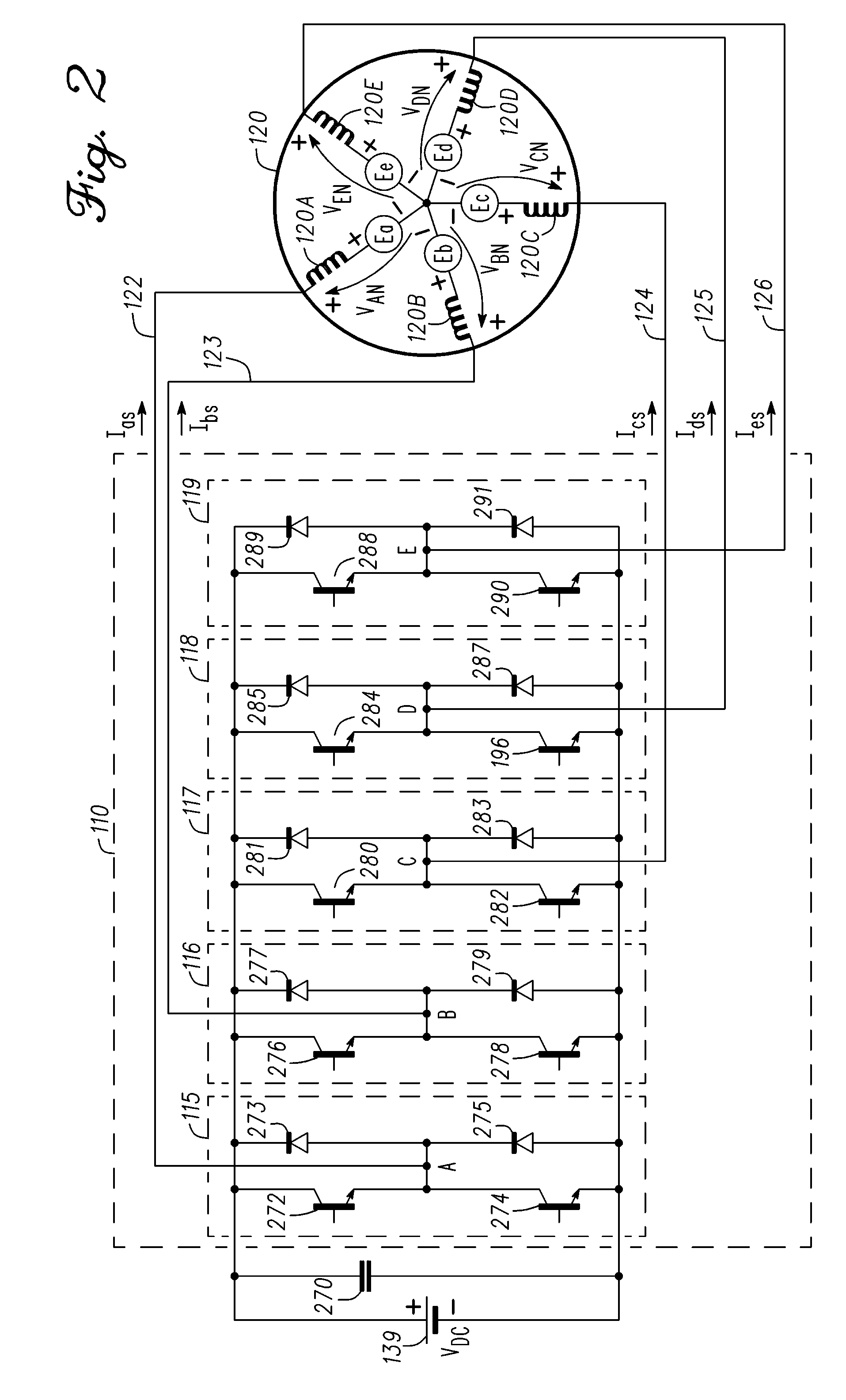
Methods, systems and apparatus for overmodulation of a five-phase machine
InactiveUS20110221367A1Increase the output voltageElectronic commutation motor controlMotor/generator/converter stoppersVoltage vectorComputer module
Methods, system and apparatus are provided for overmodulation of a five-phase machine in a vector controlled motor drive system that includes a five-phase PWM controlled inverter module that drives the five-phase machine. Techniques for overmodulating a reference voltage vector are provided to optimize voltage command signals that control a five-phase inverter module to increase output voltages generated by the five-phase inverter module.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
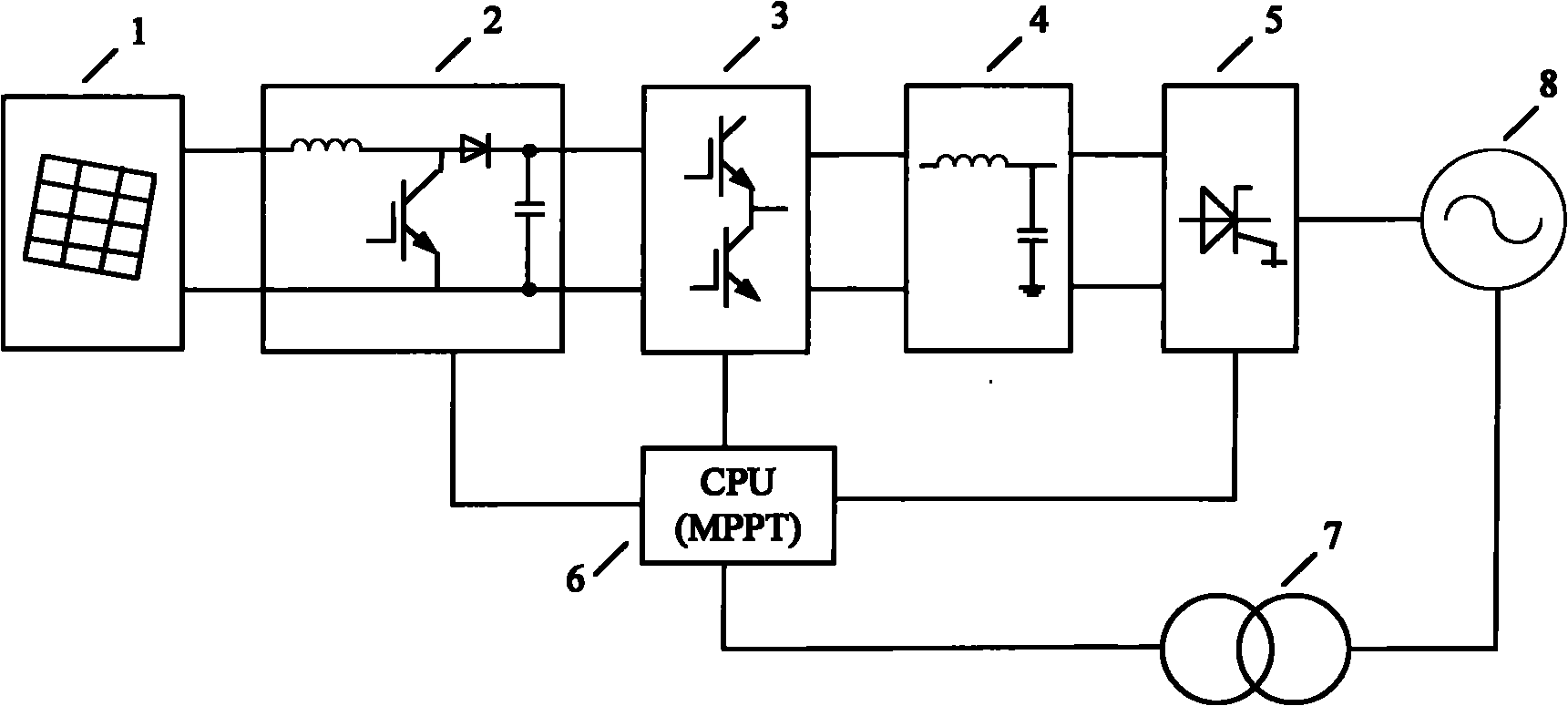
Grid-connection control method for solar photovoltaic power generation
InactiveCN101841160AReduce misjudgment and misoperationFast and stable operationSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsPhotovoltaic energy generationVoltage amplitudeVoltage vector
The invention discloses a grid-connection control method for solar photovoltaic power generation and belongs to the field of solar photovoltaic power generation. The method is characterized in that: constant voltage control of a direct-current bus is taken as a basic starting point and the output voltage and current of a photovoltaic cell are adjusted by adjusting the pulse-width modulation (PWM) duty ratio of a DC / DC converter so as to realize the tracking control of the maximum output power point of the photovoltaic cell; and in addition, stable and grid-connection running of a photovoltaic generating system is realized and the constant voltage of the direct-current bus is maintained by adjusting the output current of a DC / AC grid-connected inverter. The tracking control of the maximum power point of the photovoltaic cell is characterized in that: the variation track of a power-voltage vector is obtained by sampling the output voltage and current of the photovoltaic cell at three or more points and is matched with a preset variation mode so as to determine the adjusting direction of the output current. During grid-connection running, the PWM duty ratio of the inverter is adjusted by using the measured voltage amplitude, phase position and frequency information of a power grid so as to synchronize the voltage generated by the system and the power grid. Moreover, the voltage of the direct-current bus is kept constant by using high-speed feedback of the output current of the inverter, so that the power of the system fed in the power grid is close to the power generated by a solar cell to the maximum.
Owner:孔小明 +2
Current control method for improving output torque of permanent magnet synchronous motor overmodulation area
ActiveCN103595323AIncrease open loop gainInhibit currentElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsVoltage vectorDrive motor
The invention belongs to the technical field of controlling of power converters of driving motors, and relates to a current control method for improving the output torque of a permanent magnet synchronous motor overmodulation area. The method includes the steps that a PI controller is adopted to a rotating speed loop; a current controller based on resonance control is used for a dq shaft electric current loop, and parameter setting is carried out on the current controller; the PI controller is adopted in a field-weakening control link, and output of the PI controller serves as a d shaft current set value through an amplitude limiting link; according to set voltage vector dq shaft components output by the current controller, the duty ratio is calculated through an SVPWM overmodulation link, and a PWM signal driving motor is produced. The method suppresses current harmonics caused by flux weakening overmodulation, open-loop gains of the current loop are increased, and current, harmonic and torque fluctuation caused by overmodulation can be effectively suppressed.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
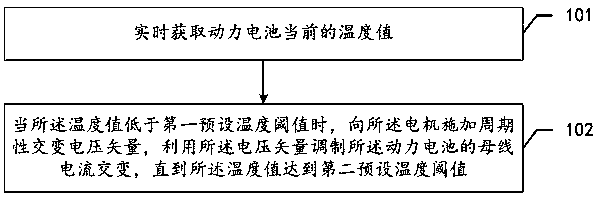
Control method of drive system, drive system and new energy vehicle
ActiveCN109823234AGet temperature value in real timeIncrease temperatureElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsPeriodic alternatingVoltage vector
The invention discloses a control method of a drive system, the drive system, and a new energy vehicle. The method obtains a current temperature value of a power battery in real time; when the temperature value is lower than a first preset temperature threshold, the temperature is raised to restore the drive capability of the drive system. A motor controller applies a periodic alternating voltagevector to a motor, the voltage vector is utilized to modulate bus current of a power battery to alternate, and during the process, the battery is driven to be repeatedly charged and discharged periodically to increase the temperature of the battery. Until the temperature value reaches a second preset temperature threshold, the battery is warmed to a desired operating temperature and the motor controller stops applying the voltage vector. Three-phase winding of the motor and three sets of bridge arms are used during the heating of the power battery. The recovery of the drive capability of the drive system is more economical without the need for additional external heating equipment. During the entire process of applying the voltage vector, the power battery is continuously and uniformly heated, the battery heating efficiency is very high, and rapid recovery of the drive capability is achieved.
Owner:SAIC MOTOR
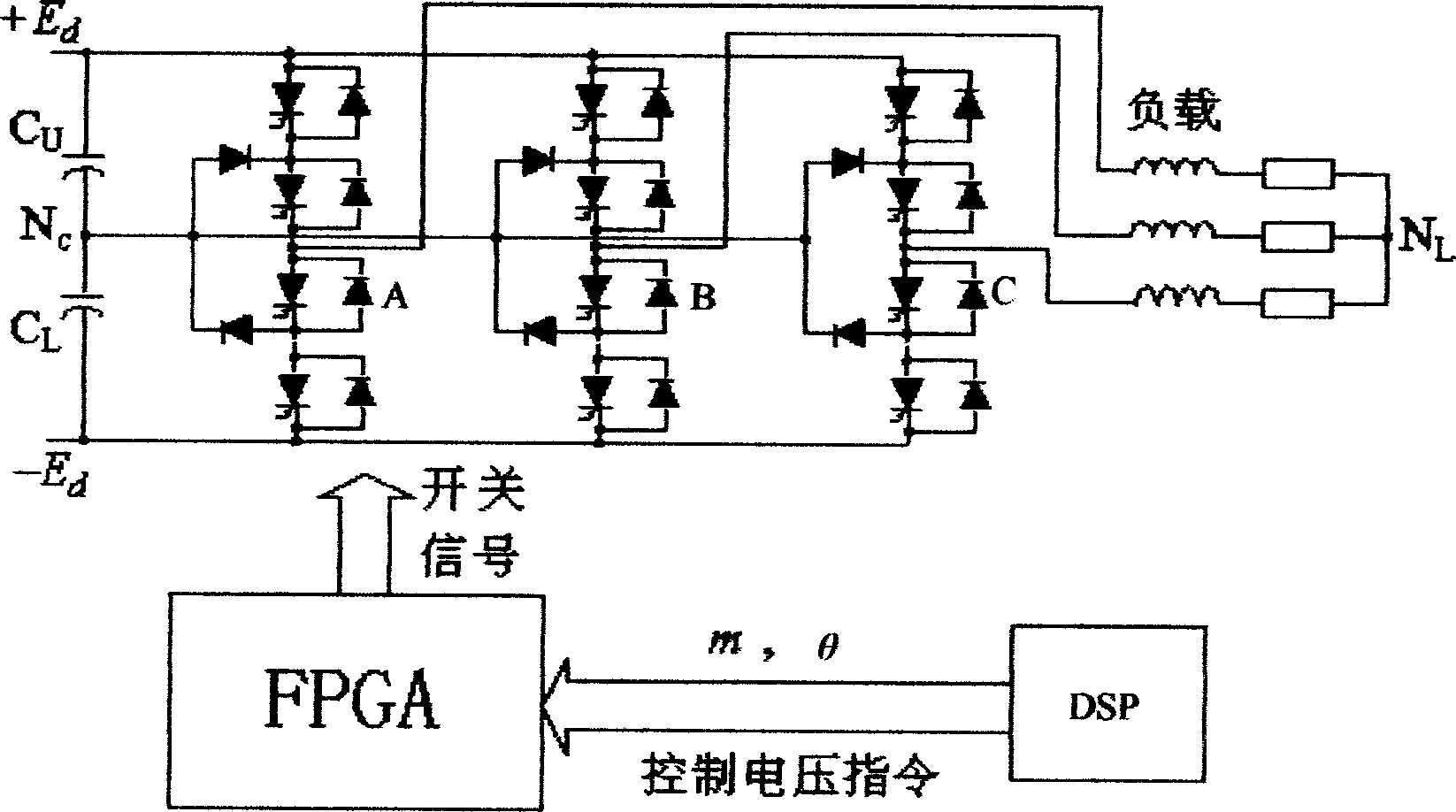
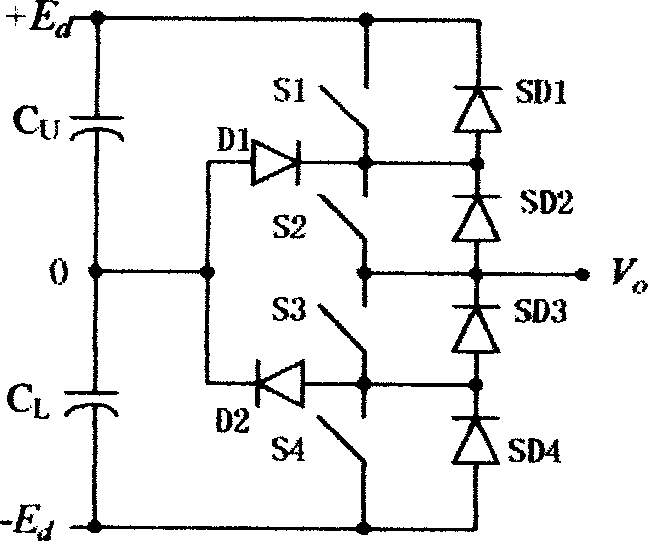
Three level inverter control system and method
InactiveCN1829061AFulfil requirementsImprove real-time performanceDc-ac conversion without reversalFpga field programmable gate arrayVoltage vector
The present invention discloses a three electric level inverter control system. It contains three electric level voltage source inverter (NPC), field programmable gate array (FPGA), digital signal processor (DSP), wherein FPGA field programmable gate array (FPGA) receiving digital signal processor (DSP) sent control voltage instruction generating three electric level voltage source inverter (NPC) control signal. The present invention also discloses three level inverter control method, featuring 1, digital signal processor (DSP) transmitting space voltage vector amplitude value m and argument for controlling three level inverter triphase reference voltage, 2, field programmable gate array (FPGA) receiving DSP sent space voltage vector amplitude value m and argument, generating signal Vca, Vcb, Vcc, through direct current biasing and dead zone compensation techniques processing to generate three-phase voltage modulation signal Vca **, Vcb **, Vcc **, 3, finally respectively comparing with positive triangular wave, negative triangular wave to generate control pulse. The present invention overcomes the insufficiency of current pulse width modulation method (SVPWM) and special harmonic cancellation method (SHE-PWM), provides a fine rapidity, simple controlling, and practical three level inverter control system and method.
Owner:GUANGDONG MINGYANG LONGYUAN POWER ELECTRONICS
Method and system for measuring position compensation angles of permanent magnet synchronous motor rotor
ActiveCN102097988ALow costImprove reliabilityVector control systemsDynamo-electric converter controlVoltage vectorPermanent magnet synchronous motor
The invention provides a method and device for measuring position compensation angles of a permanent magnet synchronous motor rotor, wherein the method comprises the following steps: setting a forcible magnetic field directional angle Theta Force; setting component instruction value of a d shaft voltage as u*d=0; inputting the component instruction value u*q of a q shaft voltage which can enable the permanent magnet synchronous motor to enter into a zero speed shaft locking state; according to the forcible magnetic field directional angle Theta Force, obtaining voltage vectors by virtue of PARK inverse transformation of u*d and u*q; generating a power device pulse-width signal needed by a voltage source inverter by a space vector pulse width modulation (SVPWM) algorithm; driving the permanent magnet synchronous motor to rote to a position of ThetaForcee+90 DEG by the voltage source inverter; obtaining the angle Theta xr read by an absolute encoder mounted on the rotor; and calculating the compensation angle that Theta c= Theta Force+ 90 DEG-Theta xr. The method provided by the invention can be simply, conveniently and easily realized; a current sensor is unnecessary to work, and the flitter is not existed during initial location.
Owner:北京和利时电机技术有限公司
Direct torque control system of permanent-magnet synchronous motor
InactiveCN102611381AEmbody practicalityBroaden the field of studyElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsVoltage vectorSynchronous motor
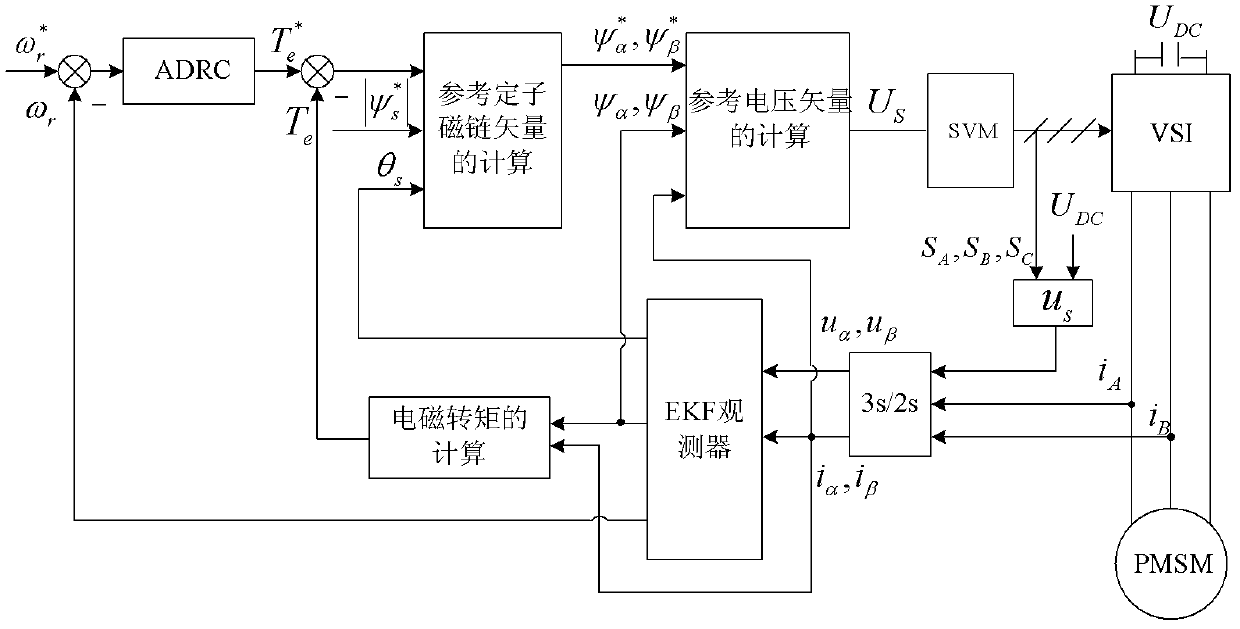
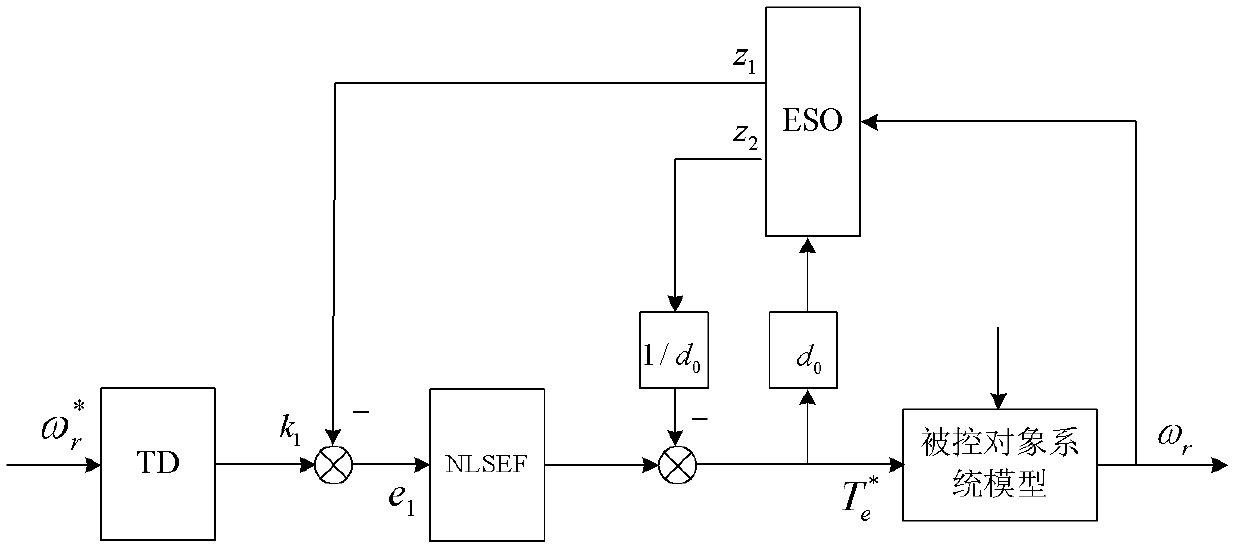
The invention relates to a direct torque control system of a permanent-magnet synchronous motor. According to the control system, an extended kalman filter (EKF) observer is adopted for stator magnetic linkage and rotation speed estimation, according to a mathematical model of the permanent-magnet synchronous motor, the state variable x of the system equals to [Psi alpha, Psi beta, Omega gamma, Theta gamma] T, the input variable mu equals to [mu alpha, mu beta] T, the output variable y equals to [Iota alpha, Iota beta ] T, and state equations and output equations (11) of the system are obtained. The motor rotating speed is used as the input of an automatic data rate changer (ADRC) speed controller, the measurement value Te of the electromagnetic torque is calculated through the obtained stator magnetic linkage, in addition, the measurement value Te and electromagnetic torque given signals are compared, comparison results are used as the input of a space voltage vector pulse generator, and the output of the space voltage vector pulse generator is connected with a voltage source inverter of the permanent-magnet synchronous motor. The direct torque control system has the advantages of good dynamic performance, better stability performance, high robustness and high anti-interference capability.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Distribution line single-phase break line judgment and positioning method based on line voltage vector criterion
ActiveCN104777397AThree-phase load changes have little influenceLittle influence of voltage fluctuationElectrical testingVoltage vectorTransformer
The invention discloses a distribution line single-phase break line judgment and positioning method based on a line voltage vector criterion. The distribution line single-phase break line judgment and positioning method comprises the following steps: step A, acquiring and counting three-phase line voltage; step B, verifying the three-phase line voltage vector; step C, judging a break line fault; step D, outputting the judgment result; step E, positioning the break line fault section. The distribution line single-phase break line judgment and positioning method disclosed by the invention has the following benefits: 1. the voltage vector is used as the parameter for judging the break line fault and is a little influenced by the three-phase load change situation, so that the break line fault can be normally recognized under the situations of no-load, light load, heavy load and three-phase load imbalance of the line; 2. the three-phase mains voltage fluctuation is low in influence; 3. the range of surveillance is wide, and a break line monitoring device can accurately judge and recognize the single-phase break line of the line from the mounting position to a line power supply; 4. the break line monitoring device is convenient to mount and implement and is mounted by a parallel connection method, and the existing three-phase voltage transformer on the line can be directly used as a voltage measurement input device.
Owner:福建省银邦电力工程有限公司
Control method of open winding permanent magnet synchronous motor system of hybrid inverter
ActiveCN103281026AImprove active voltage utilizationGuaranteed uptimeElectronic commutation motor controlAC motor controlConstant powerVoltage vector
The invention discloses a control method of an open winding permanent magnet synchronous motor system of a hybrid inverter. The control method comprises the following steps: after acquiring voltage and current of a three-phase stator of a motor, performing three-phase / two-phase static coordinate transformation to obtain voltage and current under a two-phase static coordinate system, thereby obtaining actual feedback values of electromagnetic torque and stator flux linkage; obtaining an initial given value of the electromagnetic torque through a PI (Proportional Integral) controller so as to obtain given values of the electromagnetic torque and the stator flux linkage; then combining output of a capacitor voltage PI controller to obtain final given voltage vectors of two inverters; finally generating a switching signal of the inverters through space vector pulse width modulation; and triggering a switching device of the hybrid inverter to realize direct torque control of the open winding permanent magnet synchronous motor. According to the control method, wide-range operation of low, medium and high speed of the open winding permanent magnet synchronous motor is realized, the electromagnetic torque in a motor acceleration process is increased, the voltage utilization rate of a direct current voltage source is improved, and high-speed constant-power operation of the permanent magnet synchronous motor is guaranteed.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Phase current detection method, inverter control method, motor control method, and apparatuses used in these methods
InactiveUS7173393B2Suppression of distortionRemoving affectionMotor/generator/converter stoppersDC motor speed/torque controlPhase currentsVoltage vector
Apparatus and methods for phase current detection used for driving a motor by supplying outputs from a pulse width modulation (PWM) converter to the motor. One method presented provides detecting a DC link current and a vector pattern, determining whether a voltage vector lengths exceeds a predetermined value, and adjusting the voltage vector by adding a positive or reversed voltage based upon the above determination and an integrated error value.
Owner:DAIKIN IND LTD
Controller of exciting power-supply net sided converter for double-feedback speed-variable frequency-constant wind-driven generator
InactiveCN1983785AHarmonic reductionGuaranteed control accuracyElectronic commutation motor controlAc-dc conversion without reversalWind drivenVoltage vector
The invention is concerned with a controller of side converter to excitation electrical source web of double fed variable speed constant frequency wind generator. It controls current by a deadbeat control based on predicted current control, turns the current command signal of dq coordinate to two-phase immobile coordinate to get positive and negative order current present value of alpha and beta axes. Get present value of current to two-phase immobile coordinate through addition operation and carry immobile coordinate commutation about current of power system to get alpha and beta component of actual current value. Make the difference of command and present value, and get inductance pressure drop according to change ratio of current to count the input voltage, and get impulse signal to control on-off tube through SVPWM (space voltage vector). It keeps the control precision of DC voltage, eliminates influence to rotor side converter of fluctuation to DC side voltage, restrains common-mode voltage and differential-mode voltage output by rotor side converter to reduce burden of processor under lopsided state of power system.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRICAL ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
System and method for clamp current regulation in field-weakening operation of permanent magnet (PM) machines
ActiveUS7242163B2Extended speed rangeFunction increaseAC motor controlDC motor speed/torque controlPhase currentsVoltage vector
A device to regulate current produced by a permanent magnet machine responsive to a plurality of phase current signals. The motor produces torque for application on a shaft. A processing and drive circuit responsive to a direct current command signal and a quadrature current command signal produces phase current signals for input to the motor. A command circuit responsive to the phase current signals, an angular position of said shaft, and a voltage input command signal to produce a direct current error signal and a quadrature current error signal. A control circuit responsive to the direct and quadrature current error signals produces the direct voltage signal command and the quadrature voltage signal command. The control circuit has a direct and quadrature proportional gain, integrator and clamp circuits. An algorithm produces limited or clamped voltage modulation index signals to obtain maximum efficiency and maximum torque per ampere in the speed range. The algorithm ensures that the current regulator does not run out of voltage by limiting the voltage vector to the achievable voltage vector range that provides maximum torque per ampere and maximum efficiency.
Owner:DELPHI TECH IP LTD
Electric power steering system
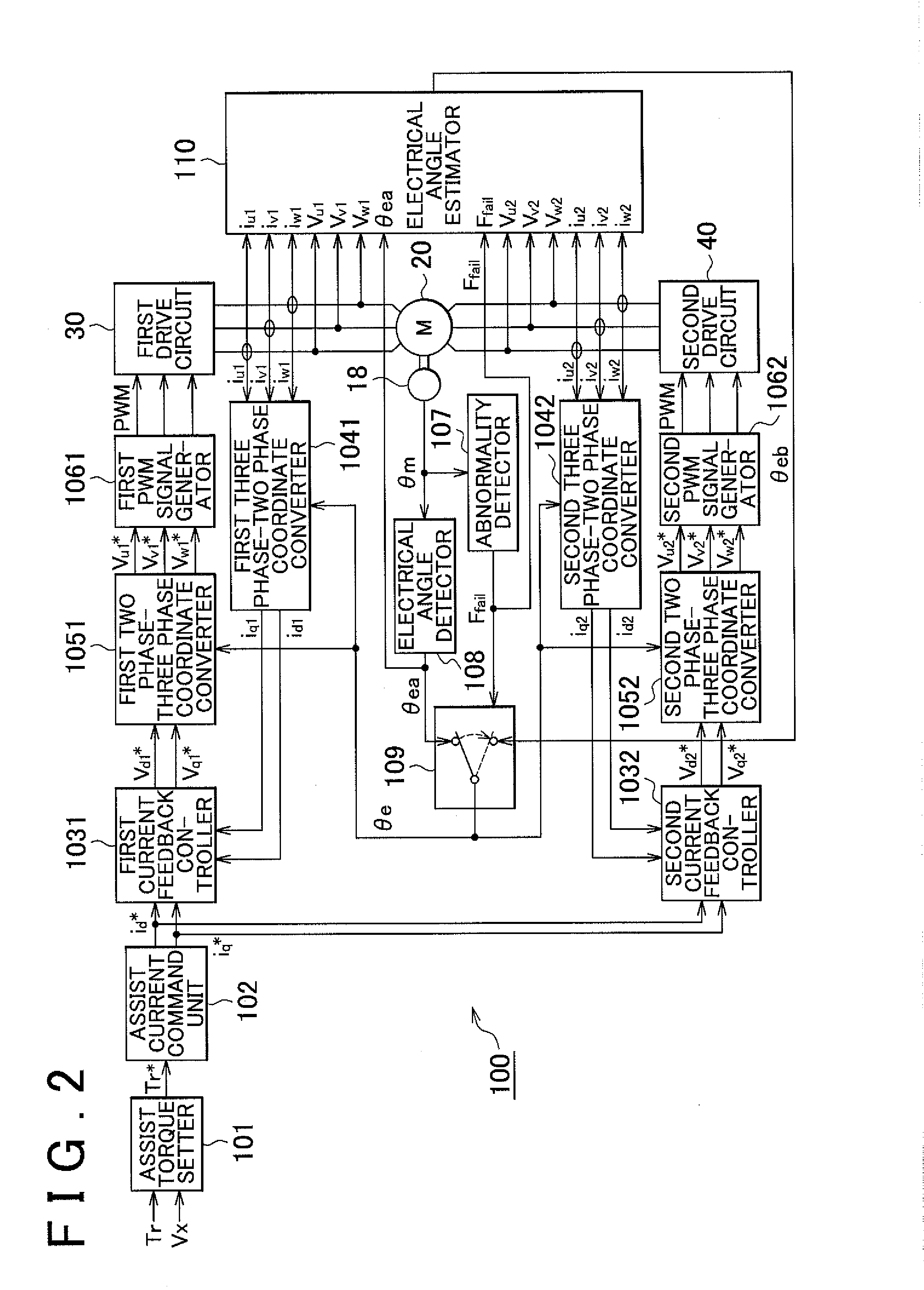
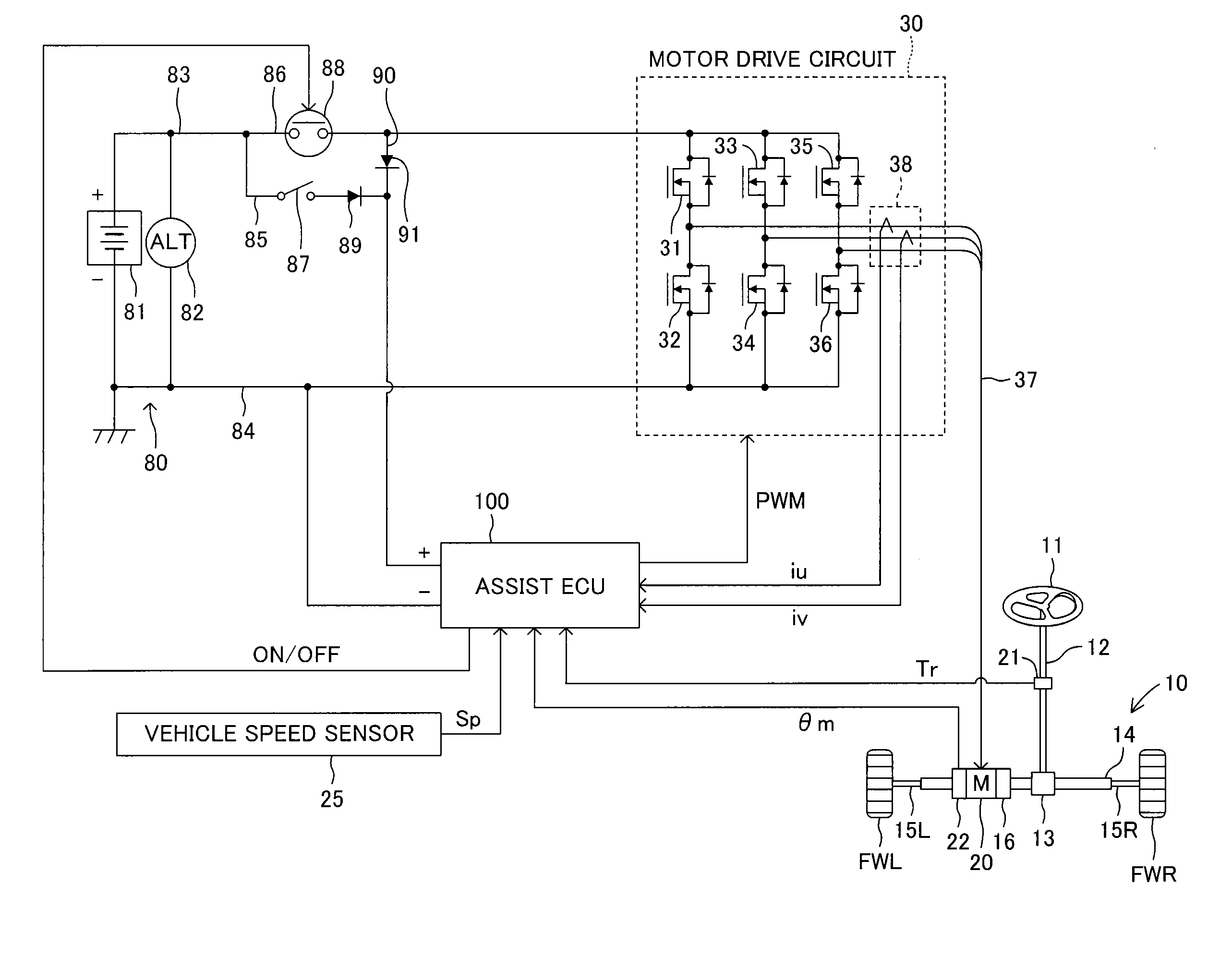
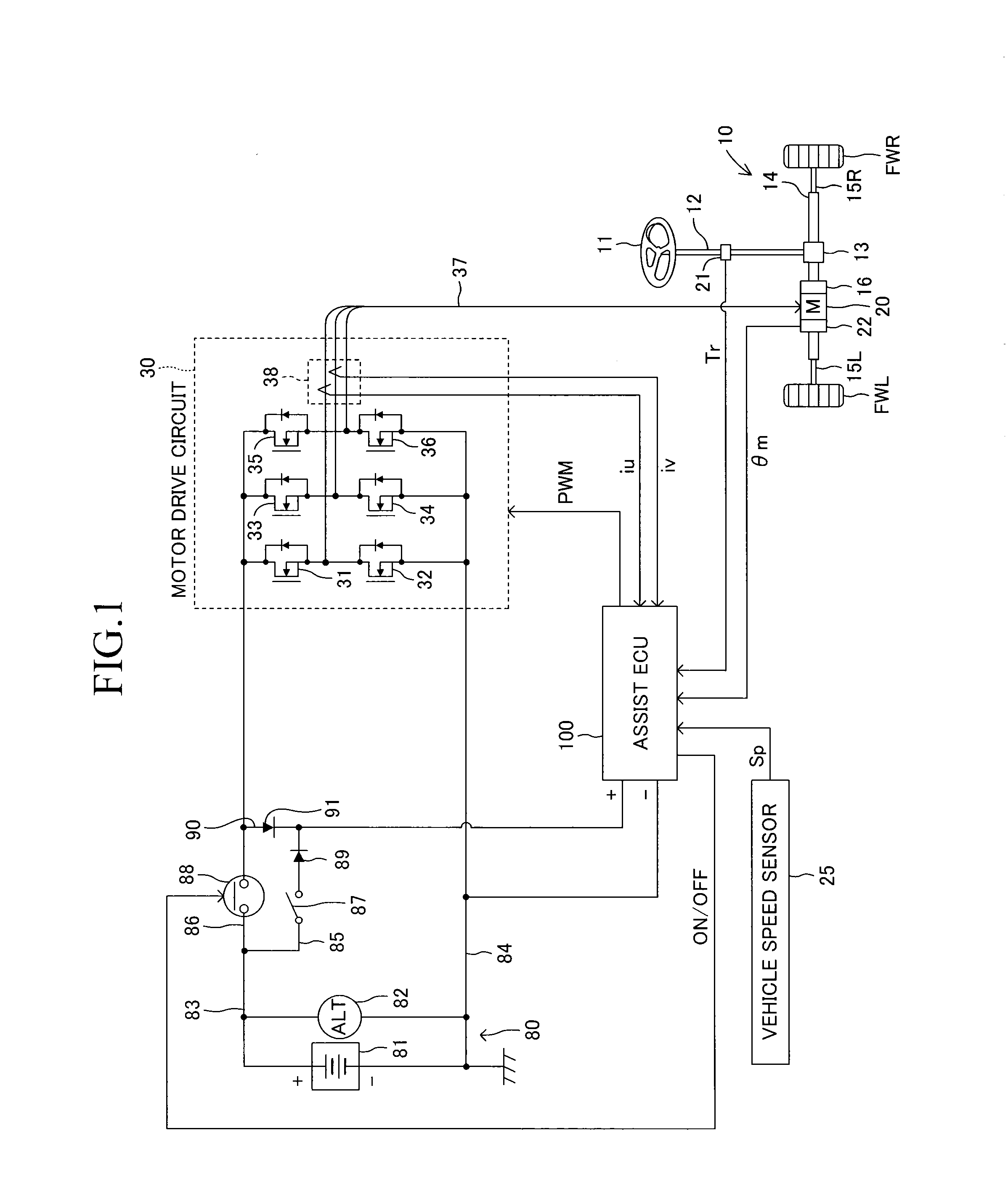
ActiveUS20140207335A1Reduce computing loadSingle motor speed/torque controlDigital data processing detailsElectric power steeringDriver circuit
There is provided a drive control method for a motor including multiple sets of coils and drive circuits in an electric power steering system. In order to reduce computational load when sensorless control is executed, an electrical angle estimator includes an α-axis voltage component adder and a β-axis voltage component adder that add together voltage vectors of a first coil and a second coil expressed in a two-phase fixed coordinate system, an α-axis current component adder and a β-axis current component adder that add together current vectors of the first coil and the second coil expressed in a two-phase fixed coordinate system, and an induced voltage computing unit that computes an induced voltage based on an added voltage vector and an added current vector.
Owner:JTEKT CORP
Electric power steering system
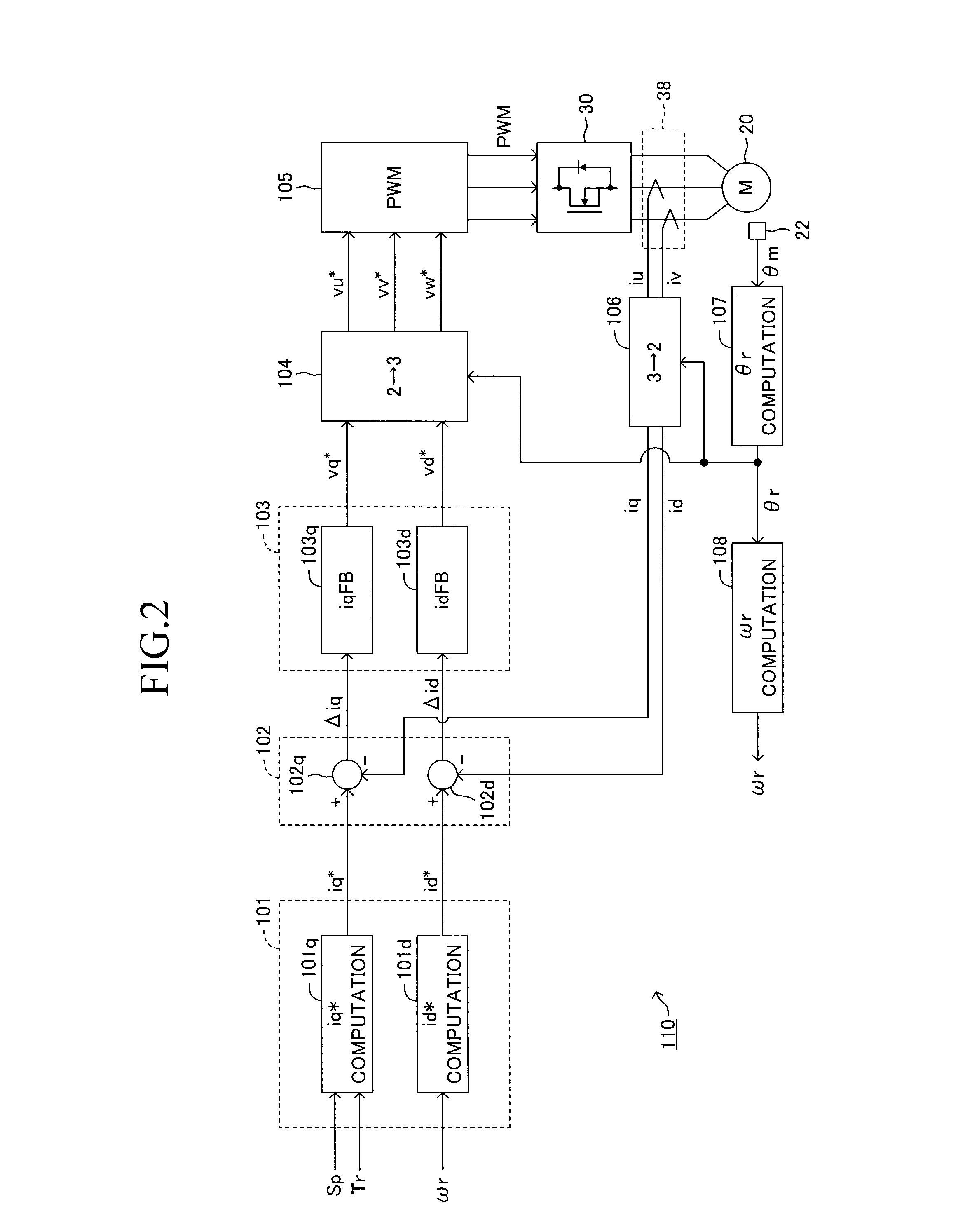
InactiveUS20130013154A1Improve performanceTorque can be increasedAC motor controlVector control systemsElectric power steeringDriver circuit
A feedforward control section computes, on the basis of a target current absolute value, a voltage limit value of a motor drive circuit, and a rotational speed ωr of a motor, a phase angle of a voltage vector which represents the output voltage of the motor drive circuit by a d-q coordinate system, the phase angle being a phase angle in relation to the d-axis of the d-q coordinate system. A feedback control section computes a phase angle based on a deviation between the target current absolute value and the actual current absolute value. A PWM control signal generation section outputs PWM control signals such that the motor drive circuit outputs a three-phase drive voltage whose electrical angle is advanced by a phase angle. Thus, in the case where a large reverse input is applied to a steering mechanism, the motor is caused to generate a large torque to thereby prevent the steering wheel from being rotated.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com