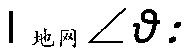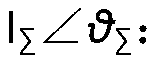Patents
Literature
828 results about "Current vector" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The current density vector is defined as a vector whose magnitude is the electric current per cross-sectional area at a given point in space, its direction being that of the motion of the charges at this point. In SI base units, the electric current density is measured in amperes per square metre.
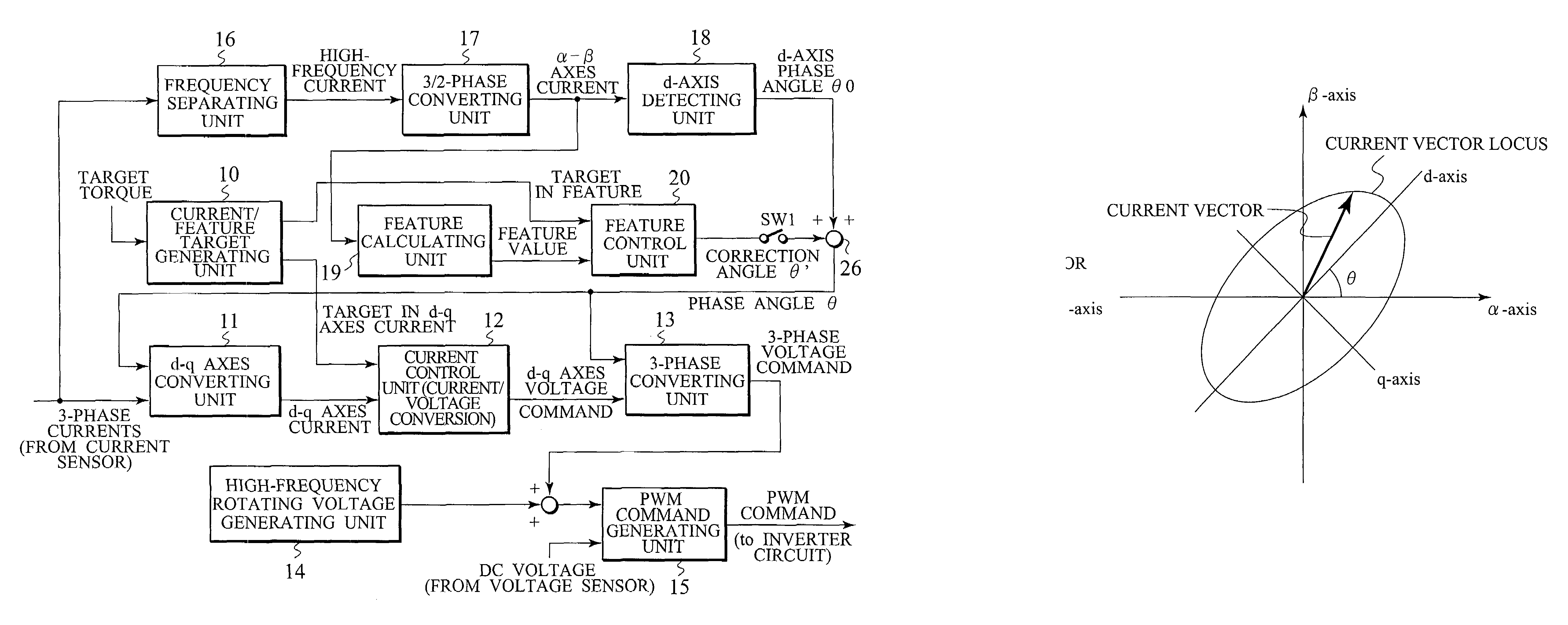
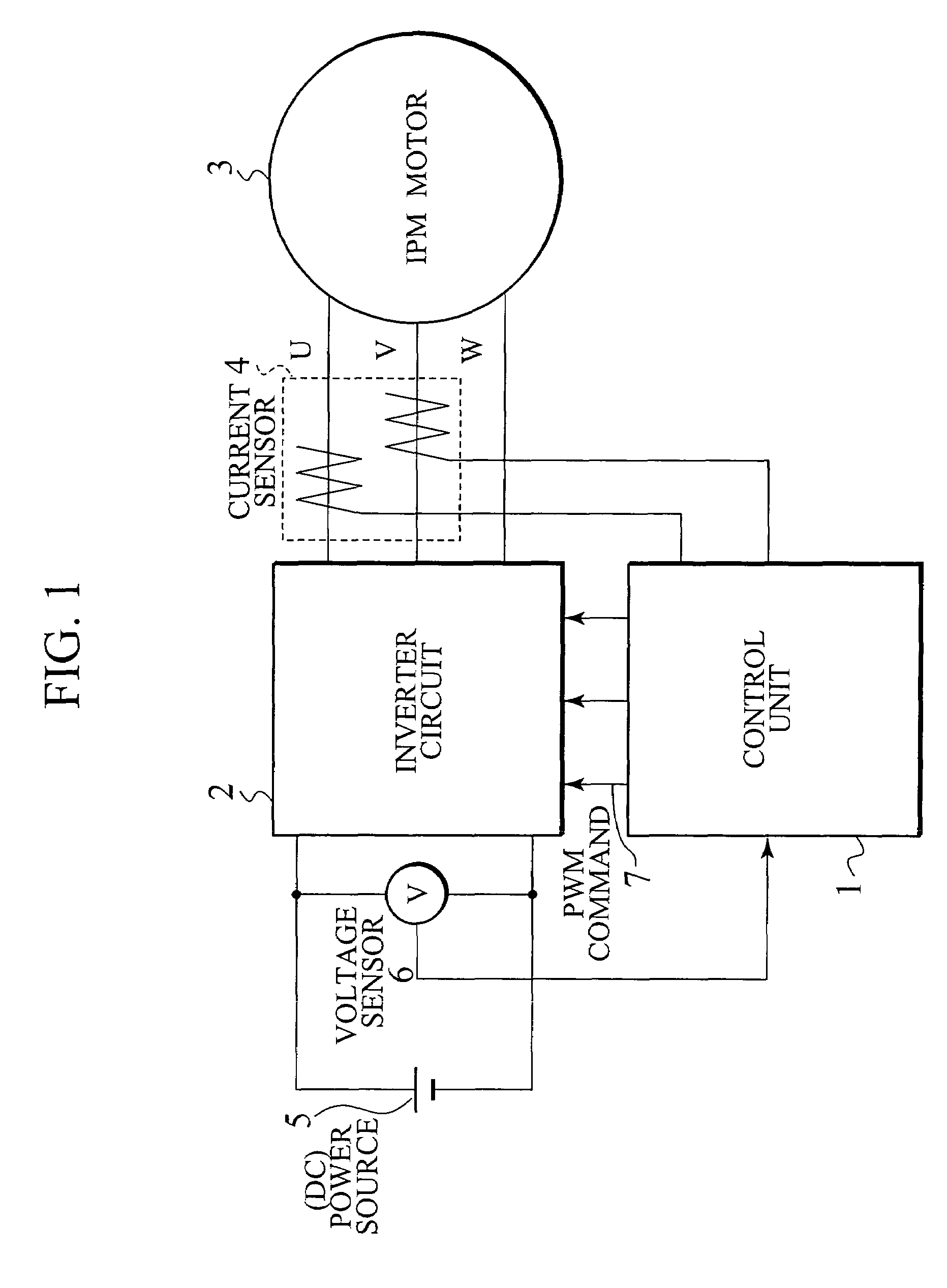
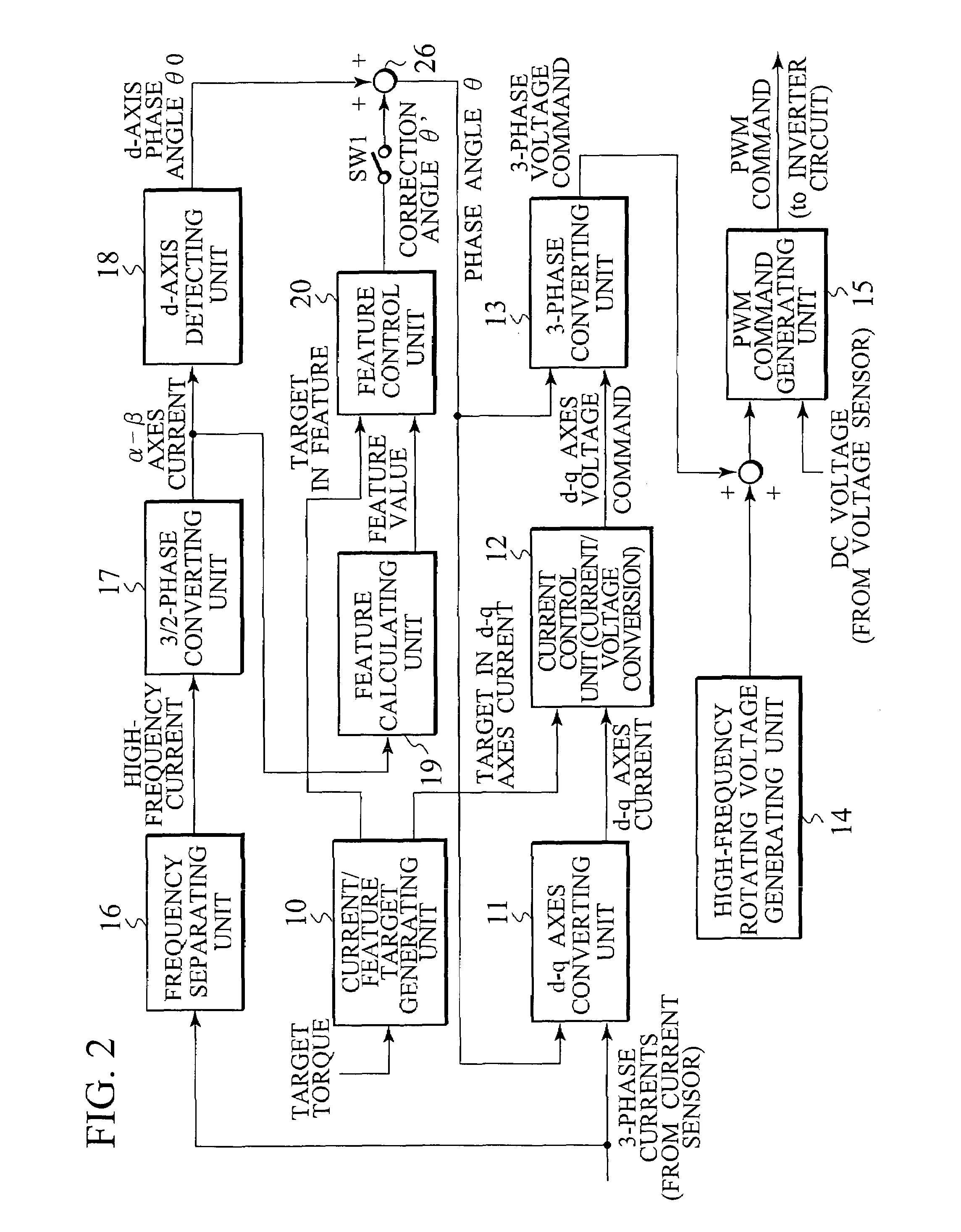
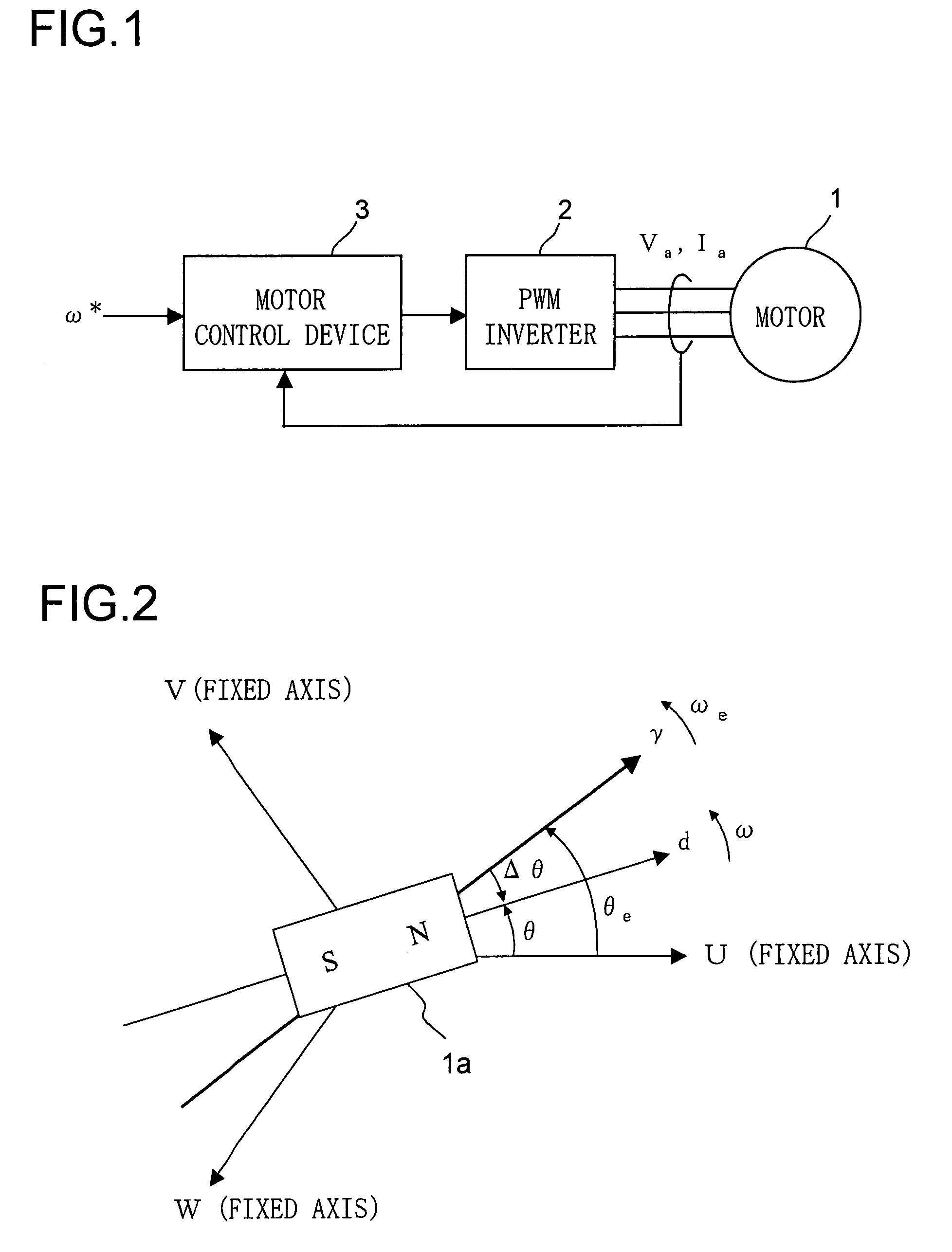
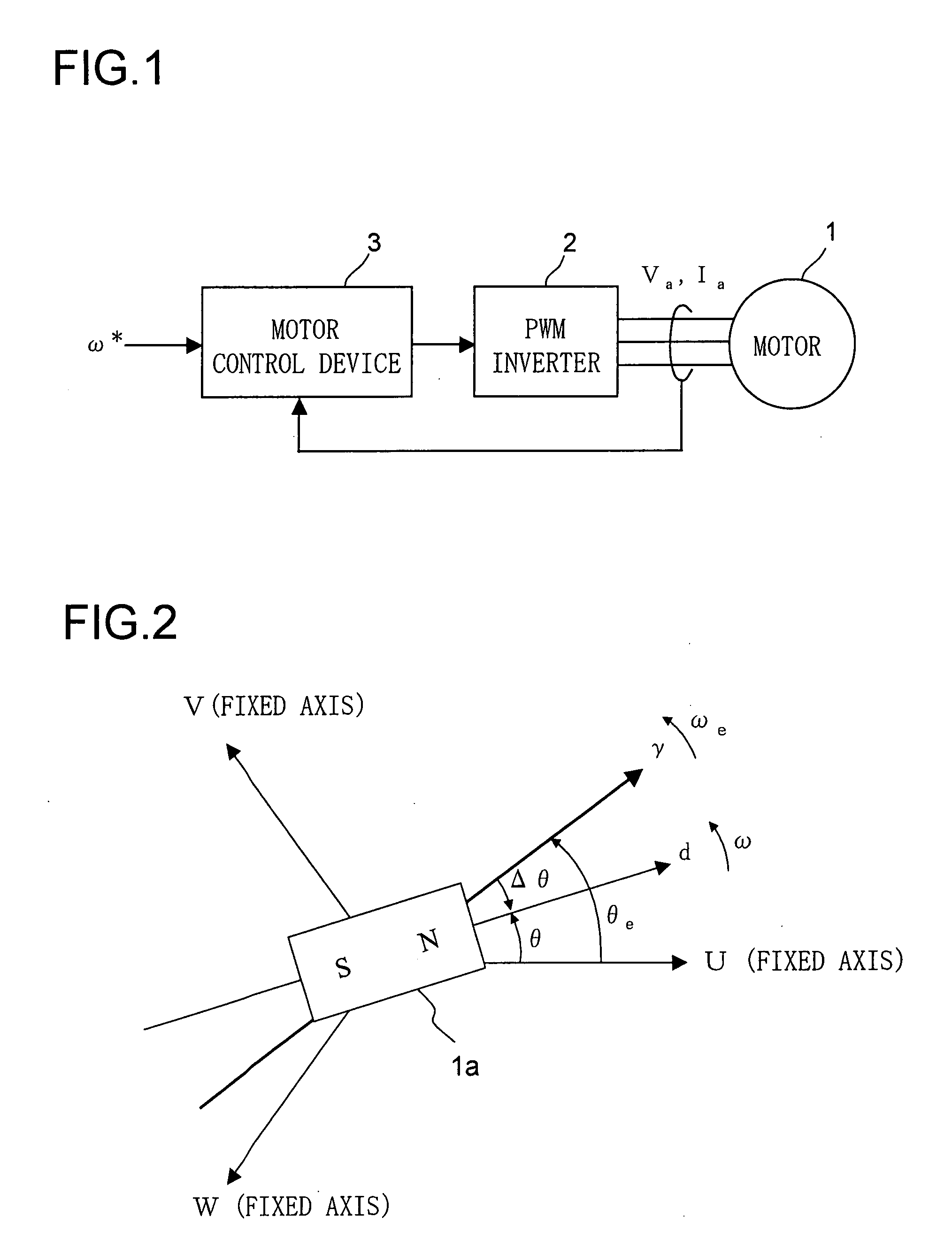
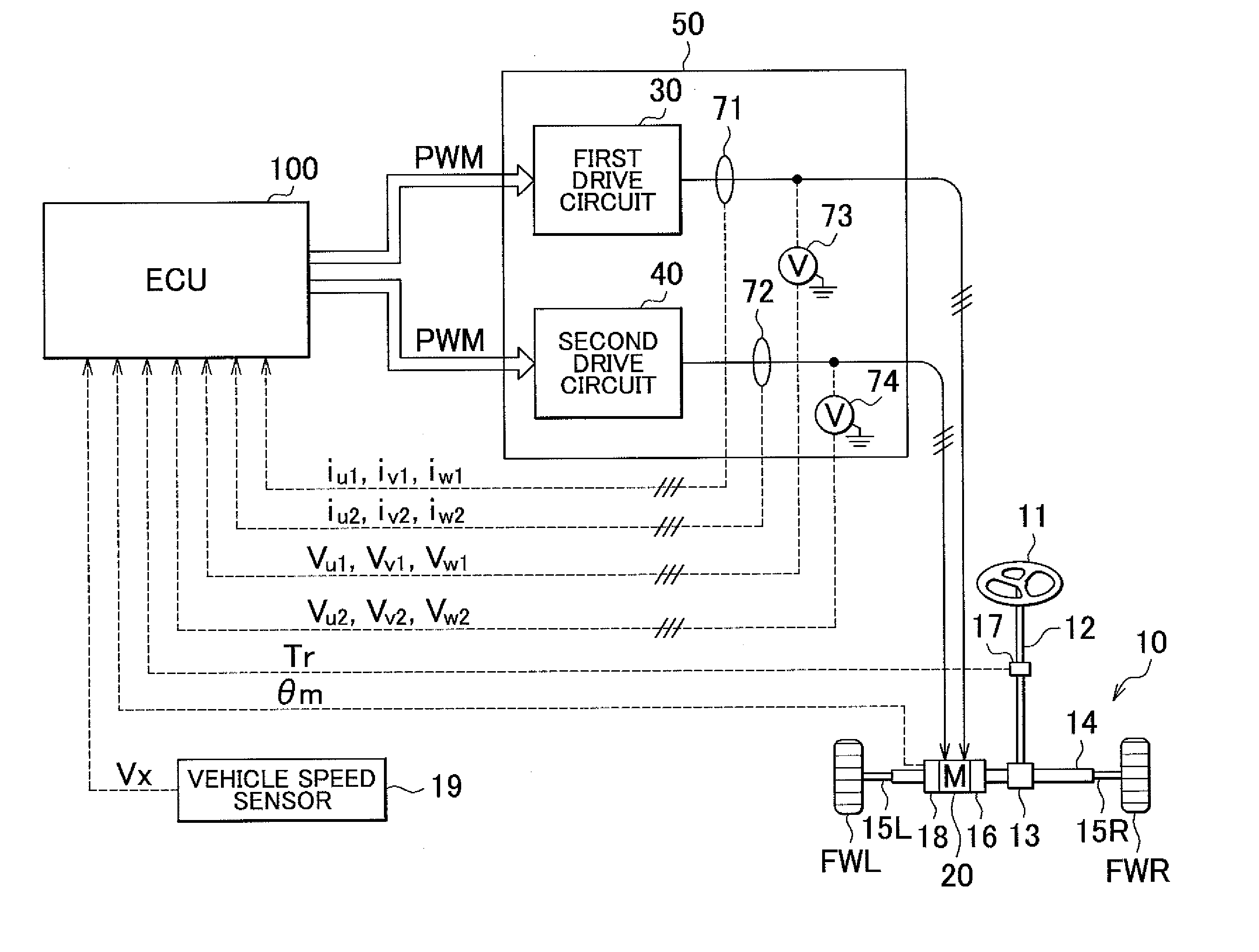
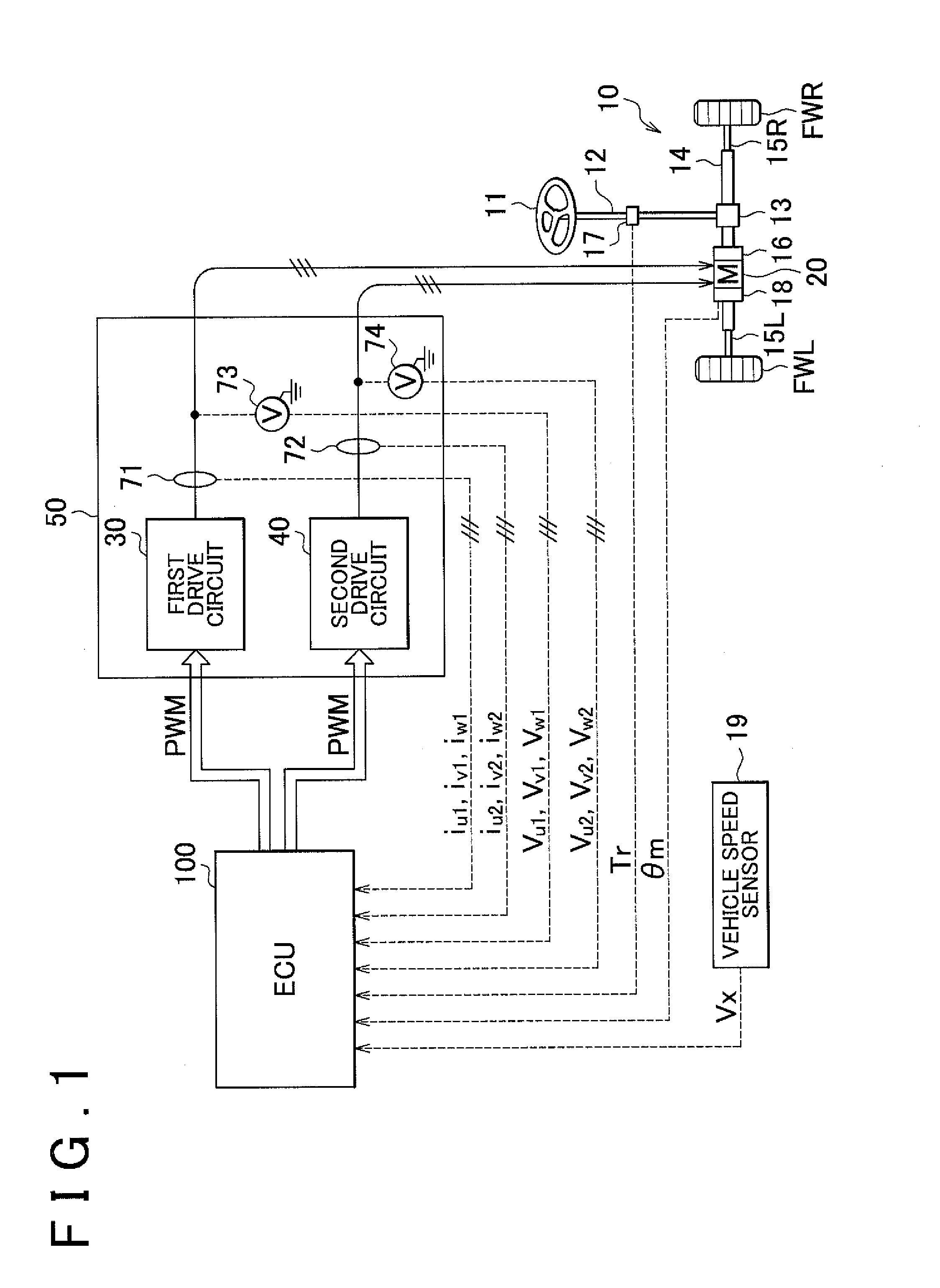
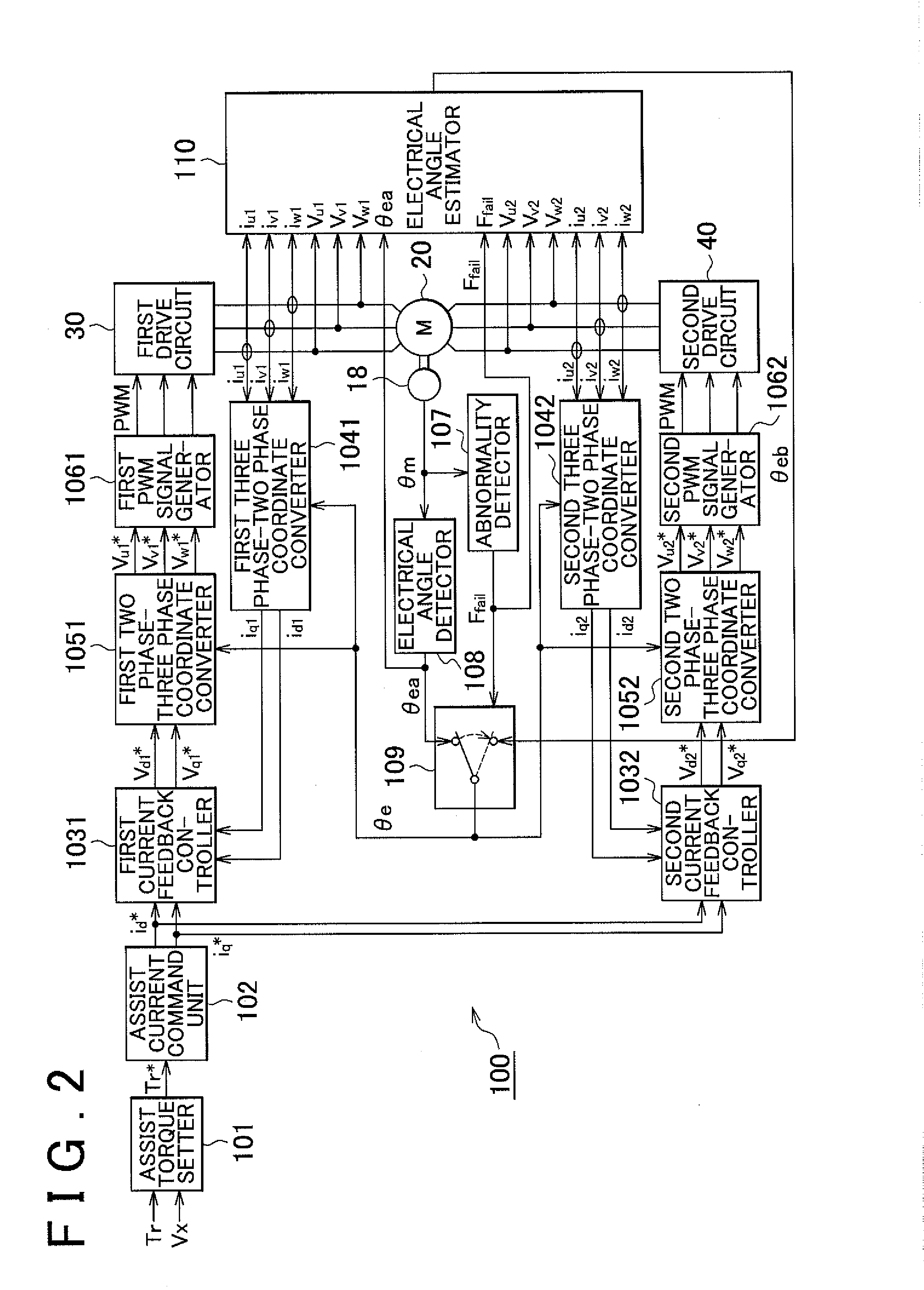
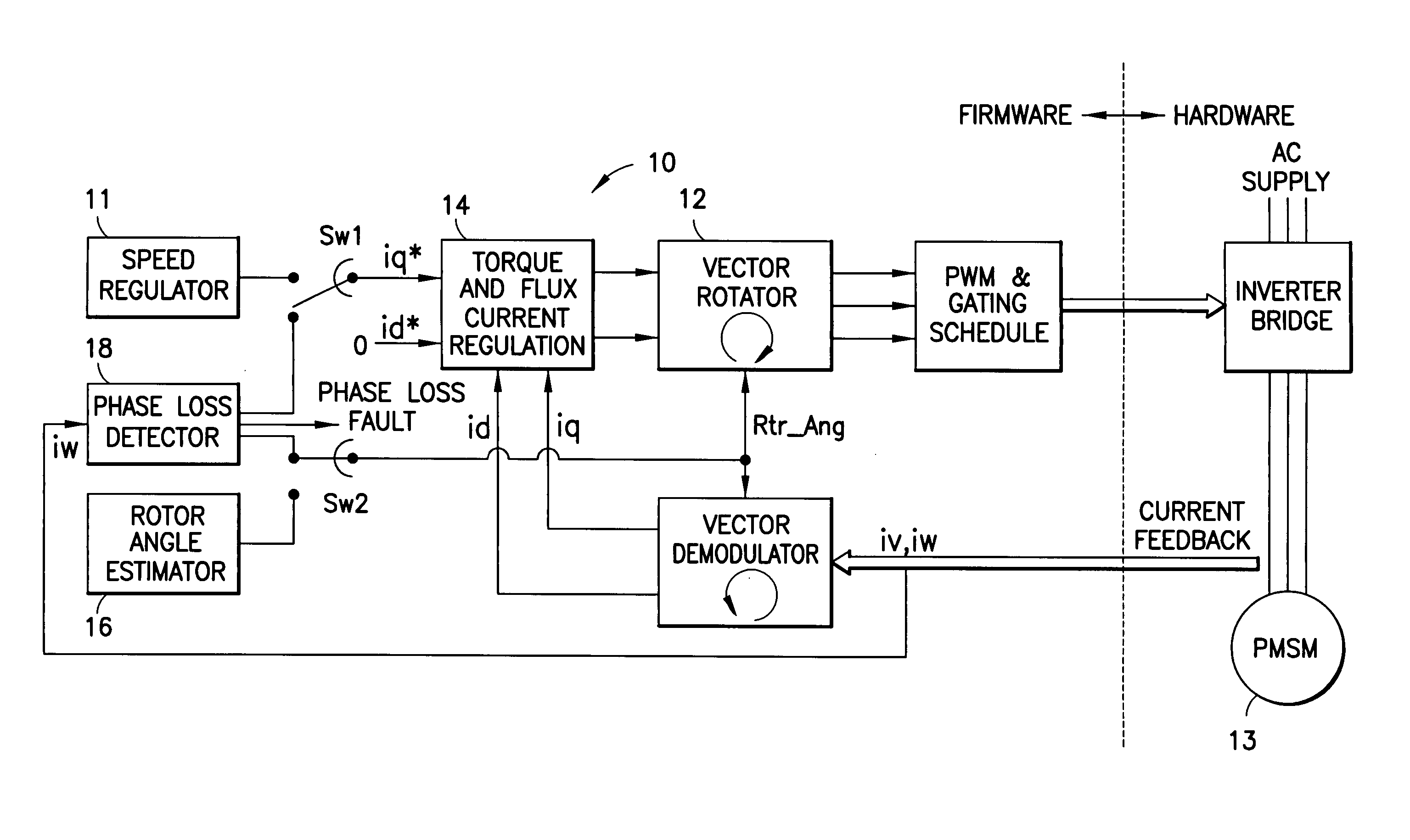
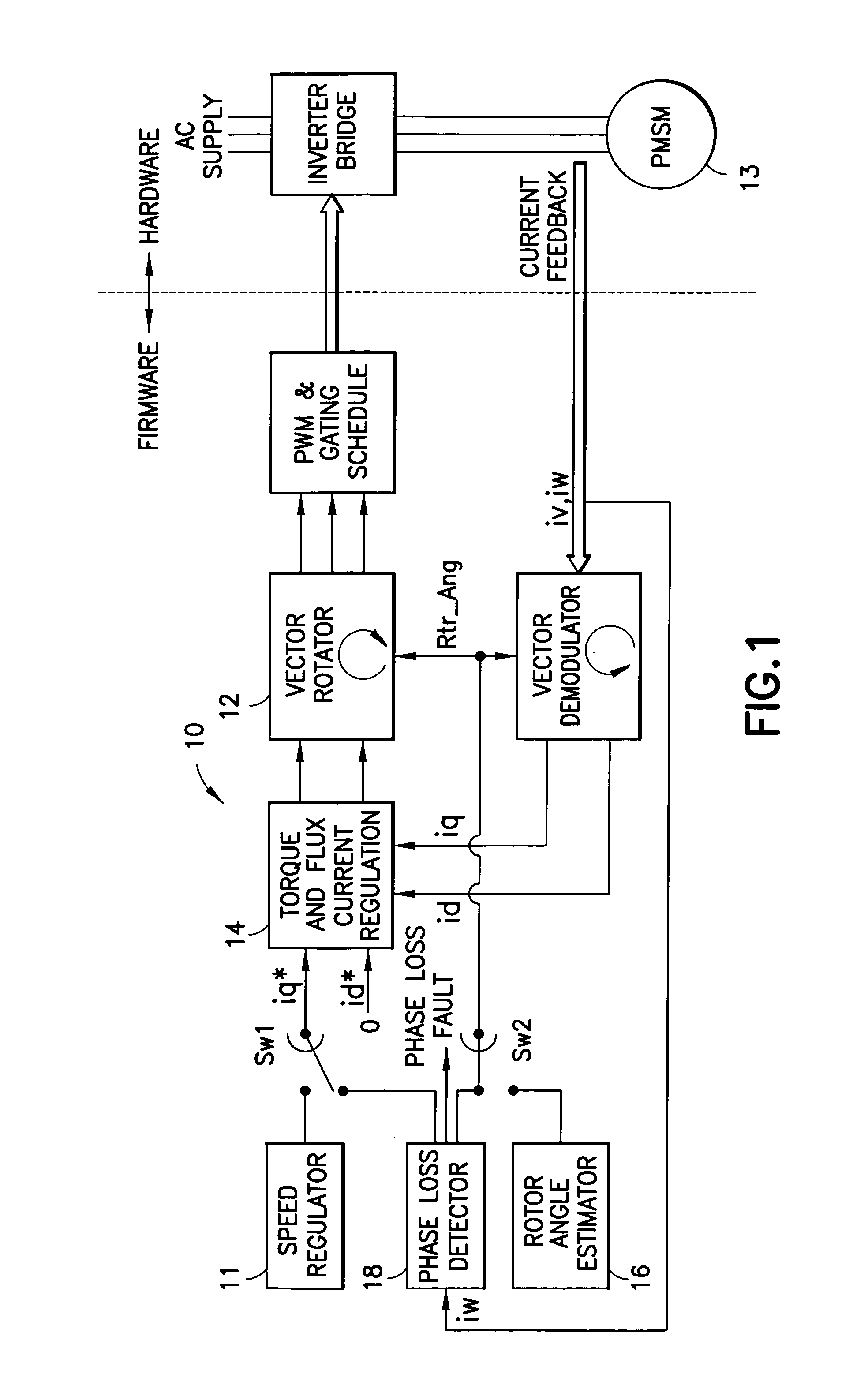
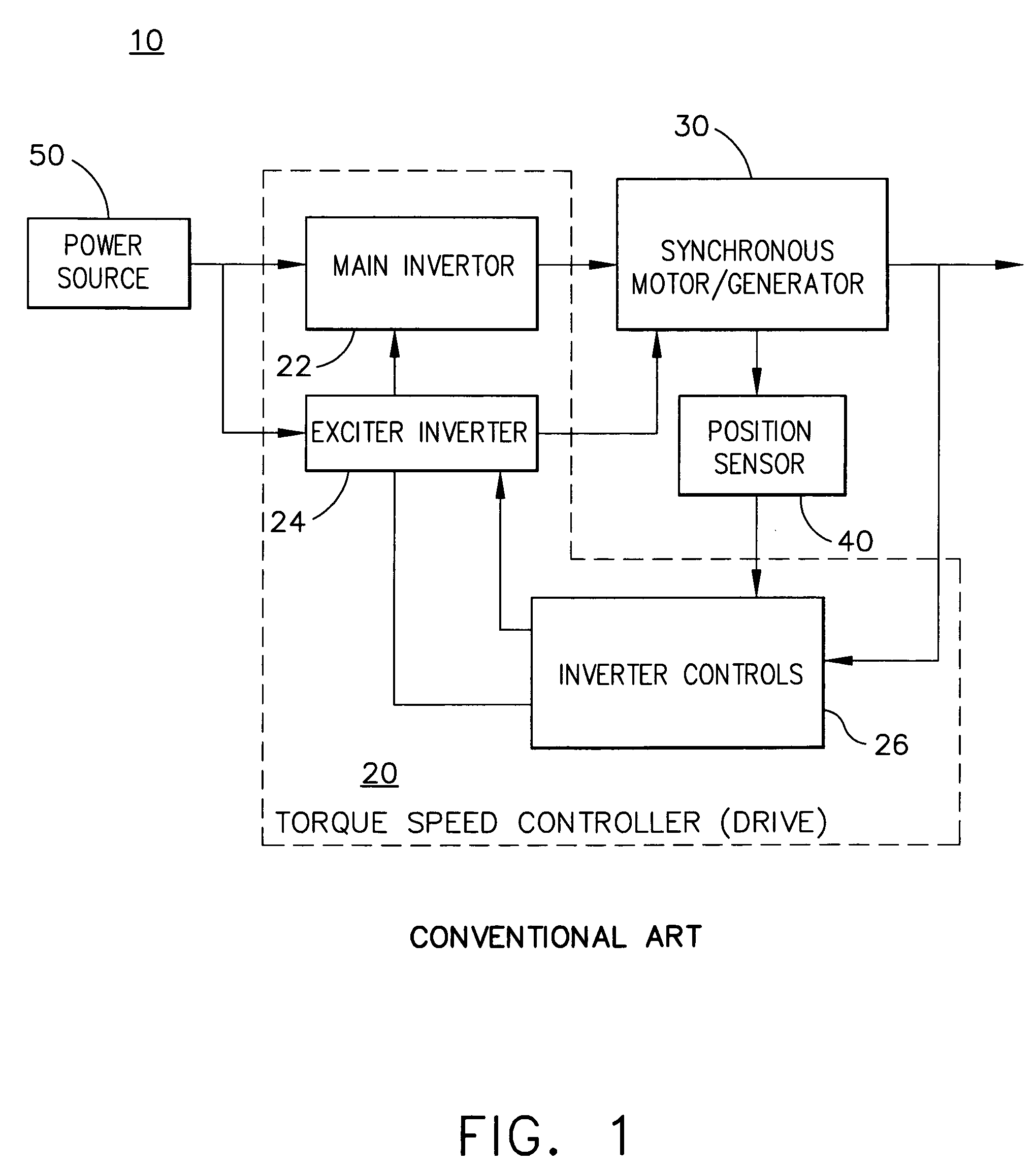
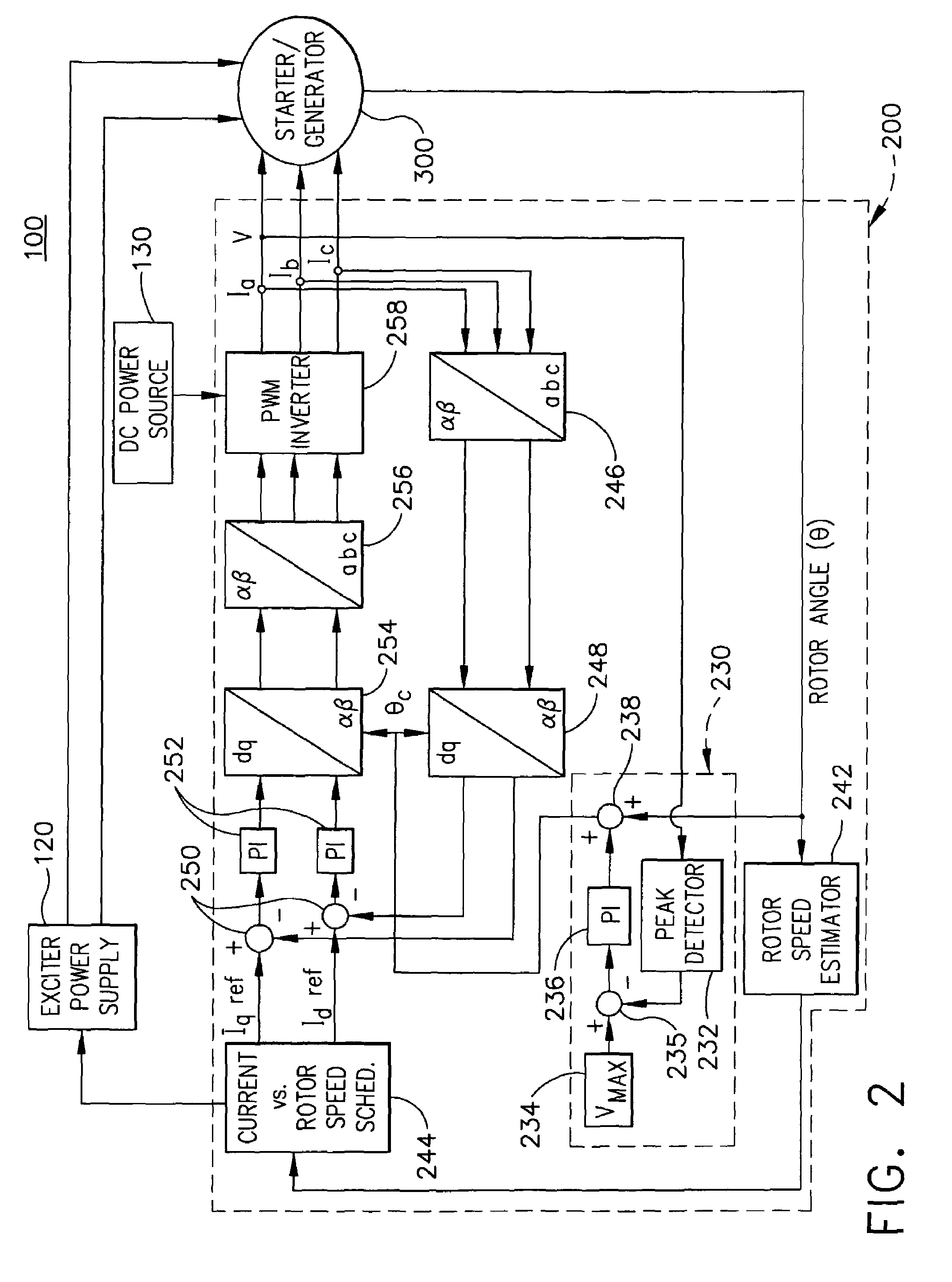
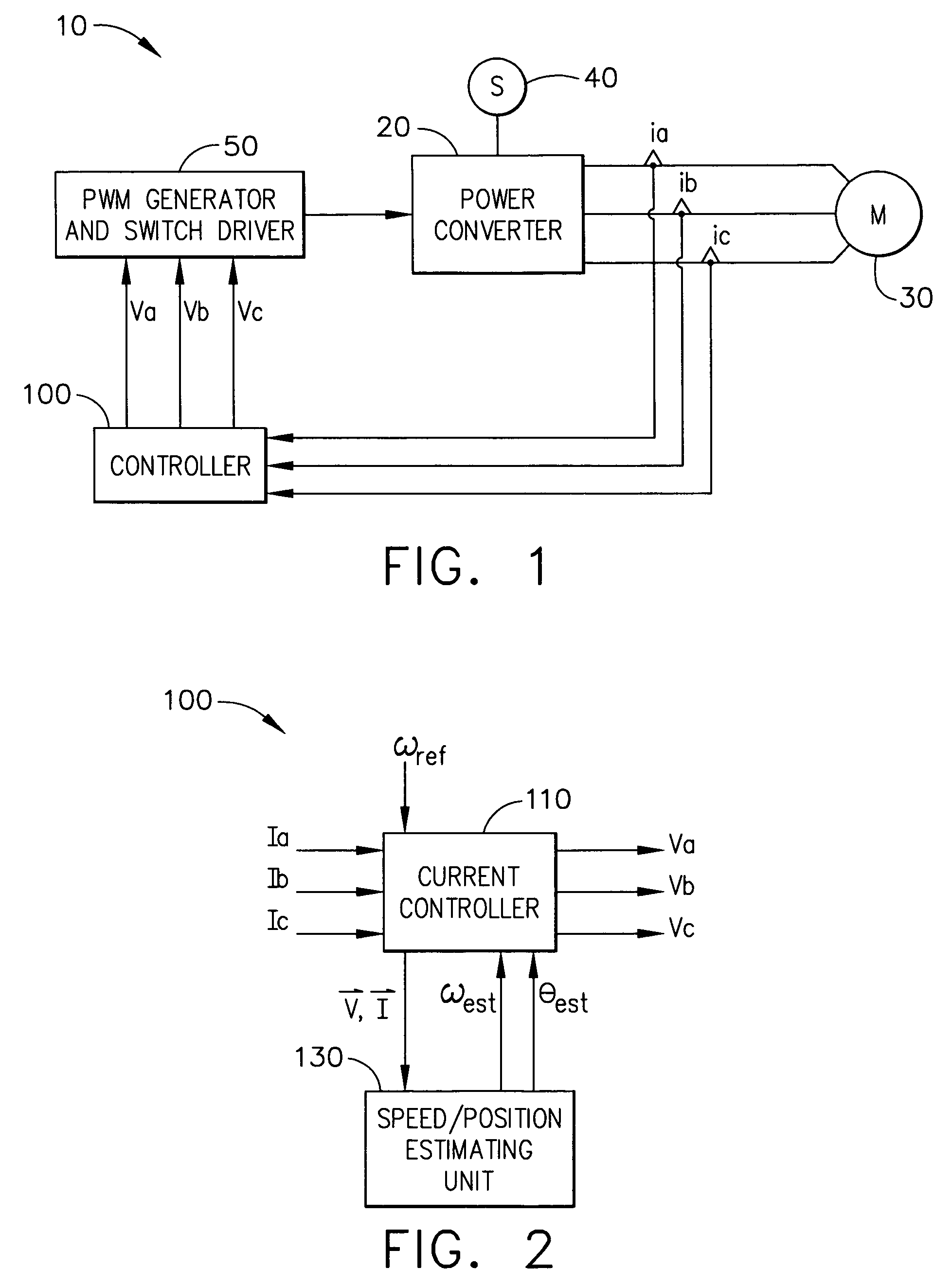
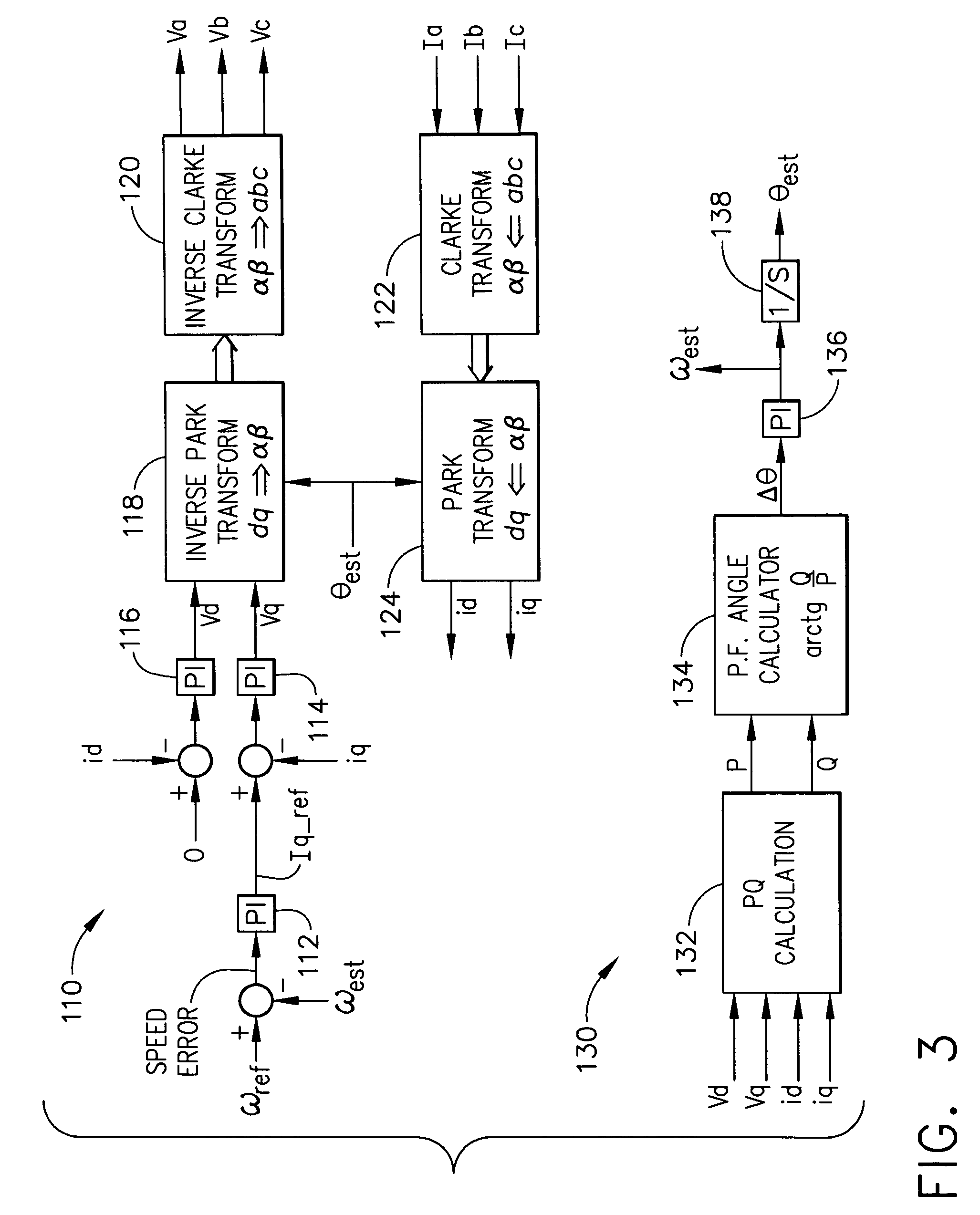
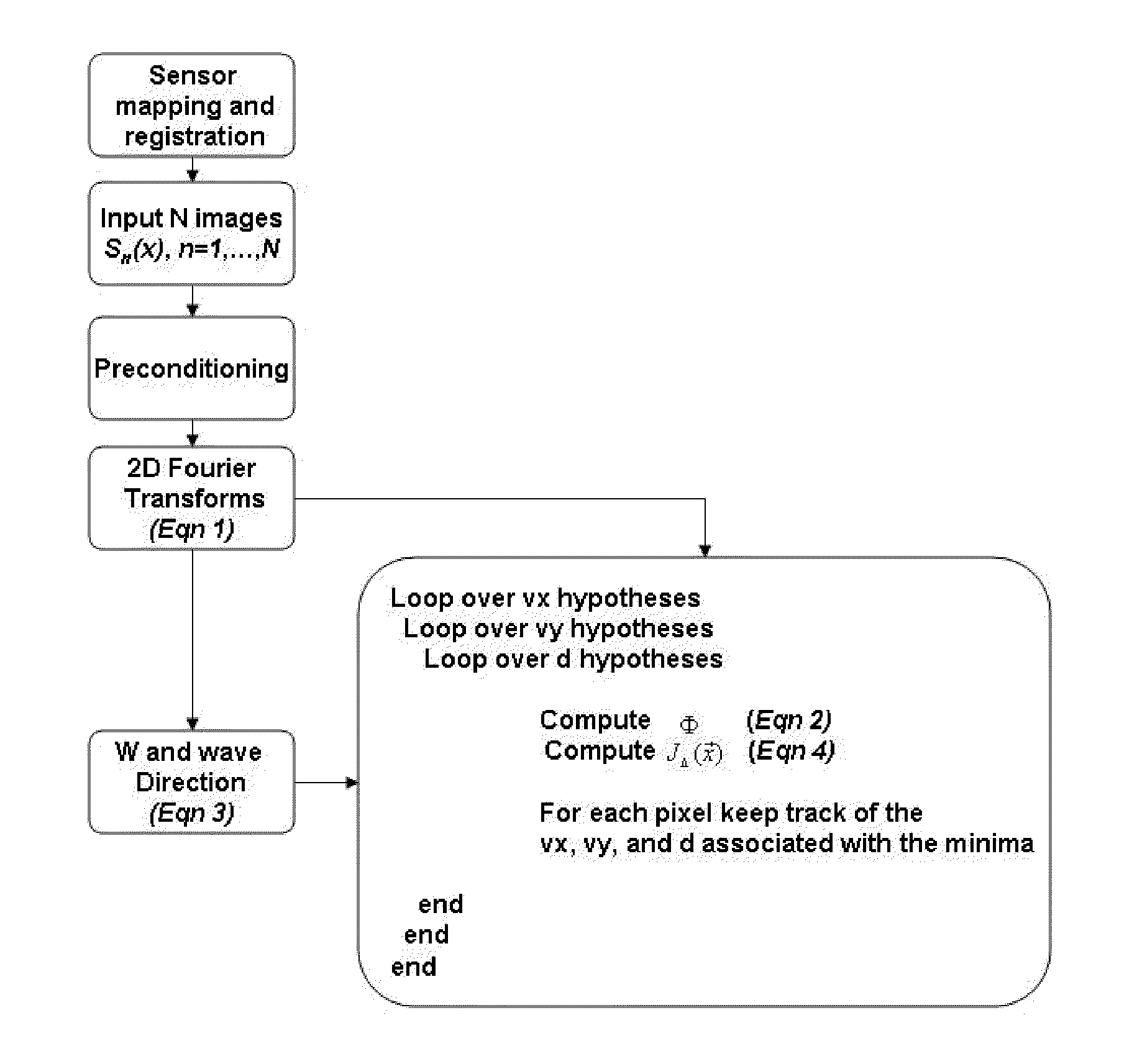
Control device for electric motor
ActiveUS7005828B2Improve artSingle-phase induction motor startersAC motor controlDriving currentAcquired characteristic
Corresponding to a target torque, the control device calculates a target value of a feature based on at least one of the length of a long axis of a current vector locus and the length of the short axis and further superimposes a superimposed current on a drive current for the motor, the superimposed current having a frequency different from the frequency of the drive current. Further, the control device detects an actual value of the feature based on at least one of the length of a long axis of a current vector locus of the superimposed current and the length of the short axis of the same and finally detects a phase angle of the motor based on the target value and the actual value for the feature. The manipulation of a detecting phase is performed by feedback of a feature obtained by the magnitude of the superimposed current. That is, when the actual feature is more than the target value, the detecting phase is advanced. Conversely, when the actual feature is less than the target value, the detecting phase is delayed.
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD
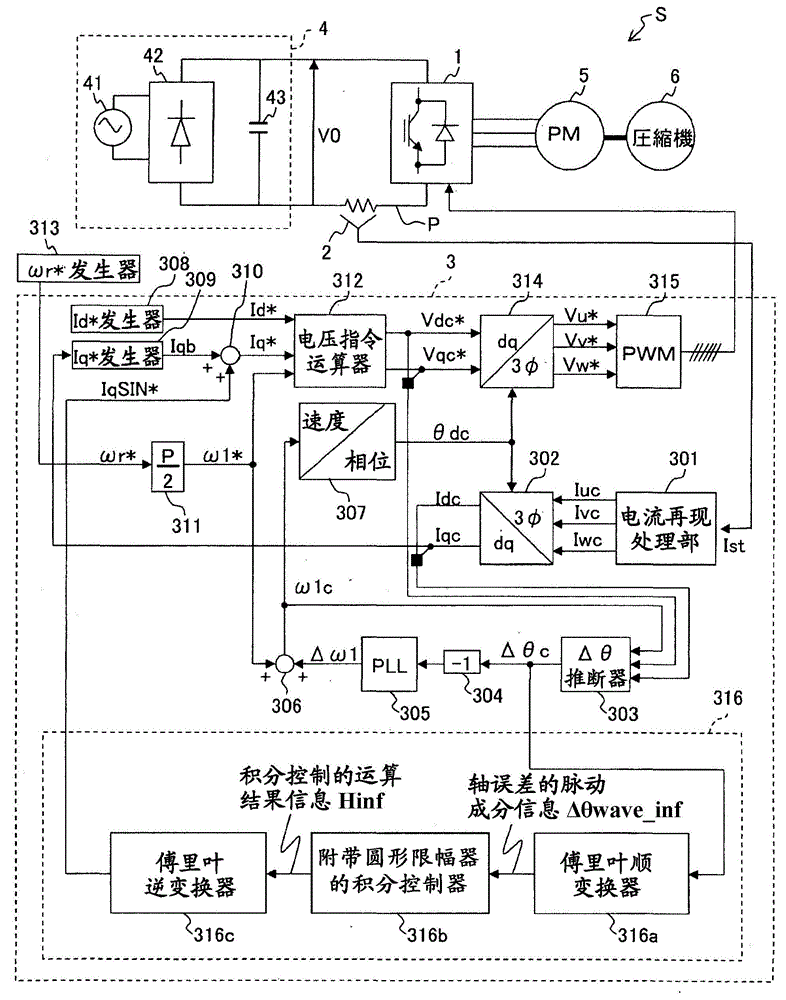
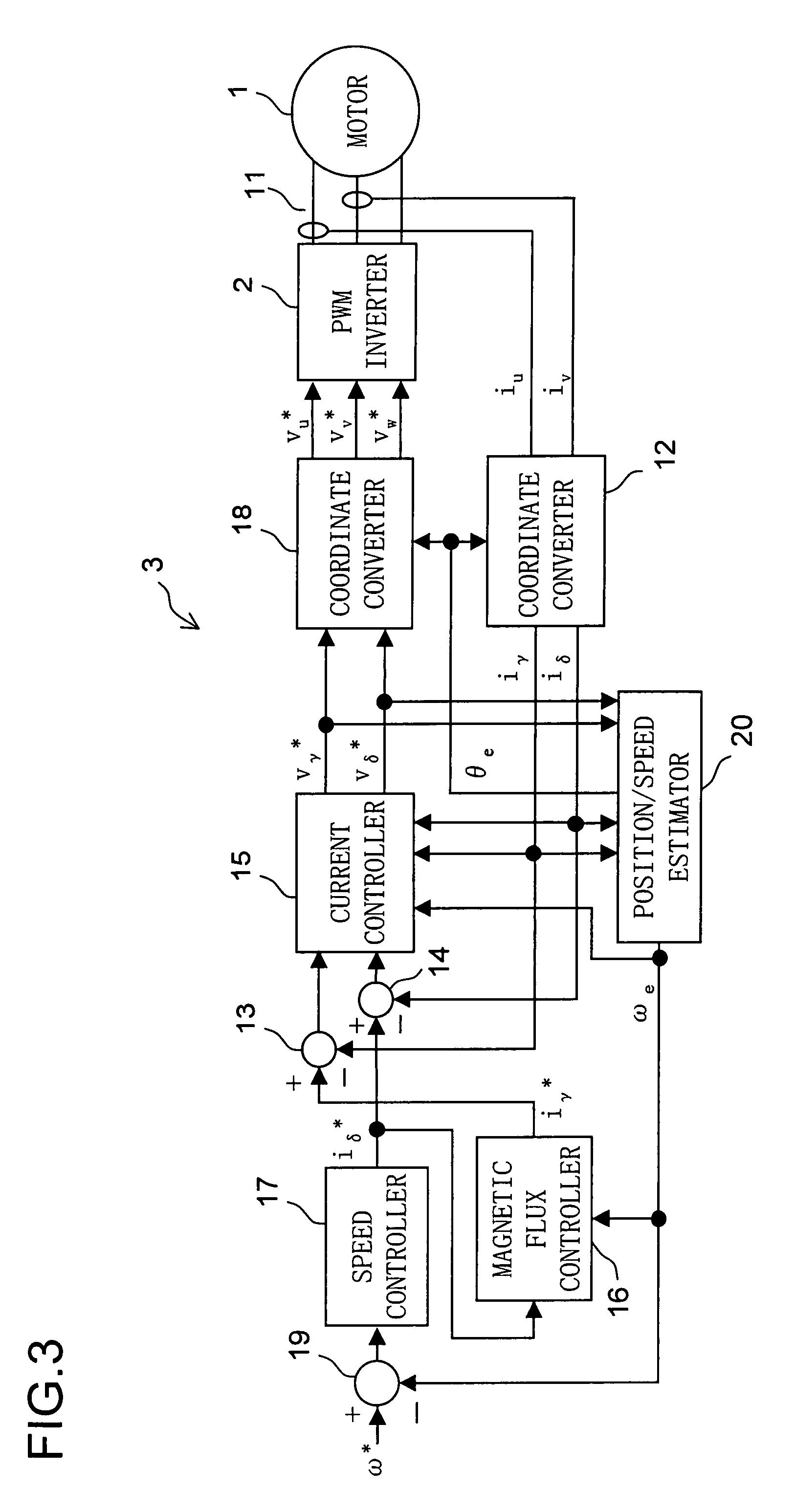
Motor control device
ActiveCN104038127ASuppression of pulsating torqueVector control systemsDynamo-electric converter controlCurrent sensorIntegral controller
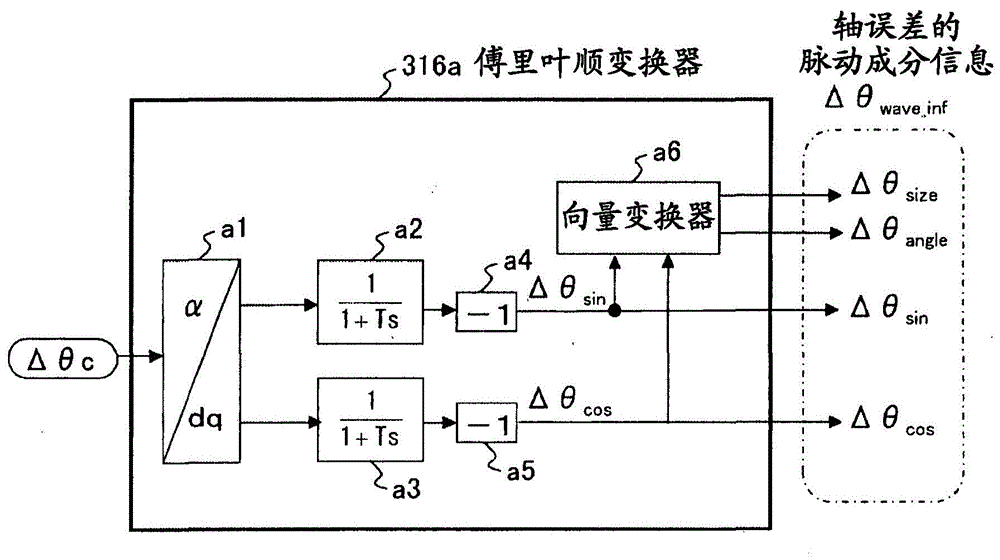
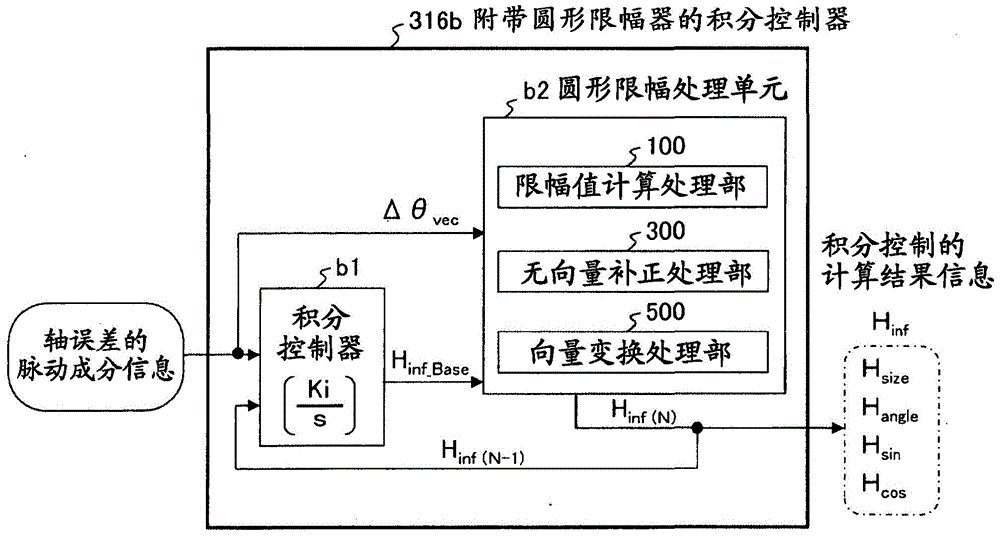
A motor control device capable of suitably inhibiting the pulsating torque of an alternating-current motor is provided. The motor control device comprises an axis error inference machine (30) which infers an axis error based on a current value of an inverter, detected by a current sensor (2); a Fourier rectification machine (316a) which extracts an axis error vector from the time-base changes of the axis error; an integral control machine (316b) additionally provided with a circular amplitude limiter, which is used to calculate a correction current vector for offsetting the pulsating torque, wherein a circle with a set amplitude limiting value serving as the radius is used as the base for limiting the movement of the correction current vector, and the integral control machine (316b) additionally provided with the circular amplitude limiter performs the circular amplitude limiting for limiting the movement of the correction current vector so as to enable the deflection angle of the correction current vector to be close to the deflection angle of the axis error vector.
Owner:HITACHI JOHNSON CONTROLS AIR CONDITIONING INC
Distribution line breakage monitoring method and device based on voltage and current vectors
The invention discloses a distribution line breakage monitoring method and device based on voltage and current vectors. The method and device are applied in a three-phase three-wire power grid system with a neutral point not grounded or not directly grounded. The line breakage monitoring device is installed on a monitoring point of a line. The line leakage monitoring device works out the effective value and the phase angle of the three-phase line voltage and three-phase current at the same moment through the three-phase line voltage waveform and three-phase current waveform of a periodic three-phase synchronous sampling distribution line; whether a single-phase line breakage fault occurs on an upper-side line of the monitoring point or not is judged by computing and comparing the proportional relation of the sum of the largest voltage, the smallest voltage and the second smallest voltage in the effective value of the three-phase line voltage and the phase difference value relation of the smallest voltage and the second smallest voltage; whether a single-phase line breakage fault occurs on an upper-side or lower-side line of the monitoring point by comparing the proportional relation between the negative-sequence current and the positive-sequence current; whether a single-phase ground fault occurs on a lower-side line of the monitoring point by calculating the zero sequence current value.
Owner:福建省银邦电力工程有限公司
Control method of alternating voltage sensorless high voltage direct current transmission converter
InactiveCN101882799AReduce the numberAvoid structural formsSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsReactive power adjustment/elimination/compensationControl signalReactive power theory
The invention discloses a control method of an alternating voltage sensorless high voltage direct current transmission converter, belonging to the technical field of electrical equipment and comprising the following steps: establishing a stator resistor and an inductor for a virtual motor; building relative position relationships among a current vector, a voltage vector and a flux linkage vector, and analyzing a vectorgram; establishing a converter and flux linkage mathematic model, and calculating a virtual flux linkage vector of a system to obtain a power feedback quantity of the system; acquiring an active control signal and a reactive control signal of the system through a direct power control algorithm, and generating a PWM trigger converter for respectively and independently controlling the active power and reactive power of the system; and utilizing MATLAB simulation software to set up a system model for verifying, and obtaining a systematic selection device when the verification is successful. By utilizing Matlab / Simulink to set up a corresponding simulation model, the designed method is verified to have rapid response speed, the voltage and power after startup can still reach stable values after about 2 power frequency periods and have high steady state precision.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Motor control device
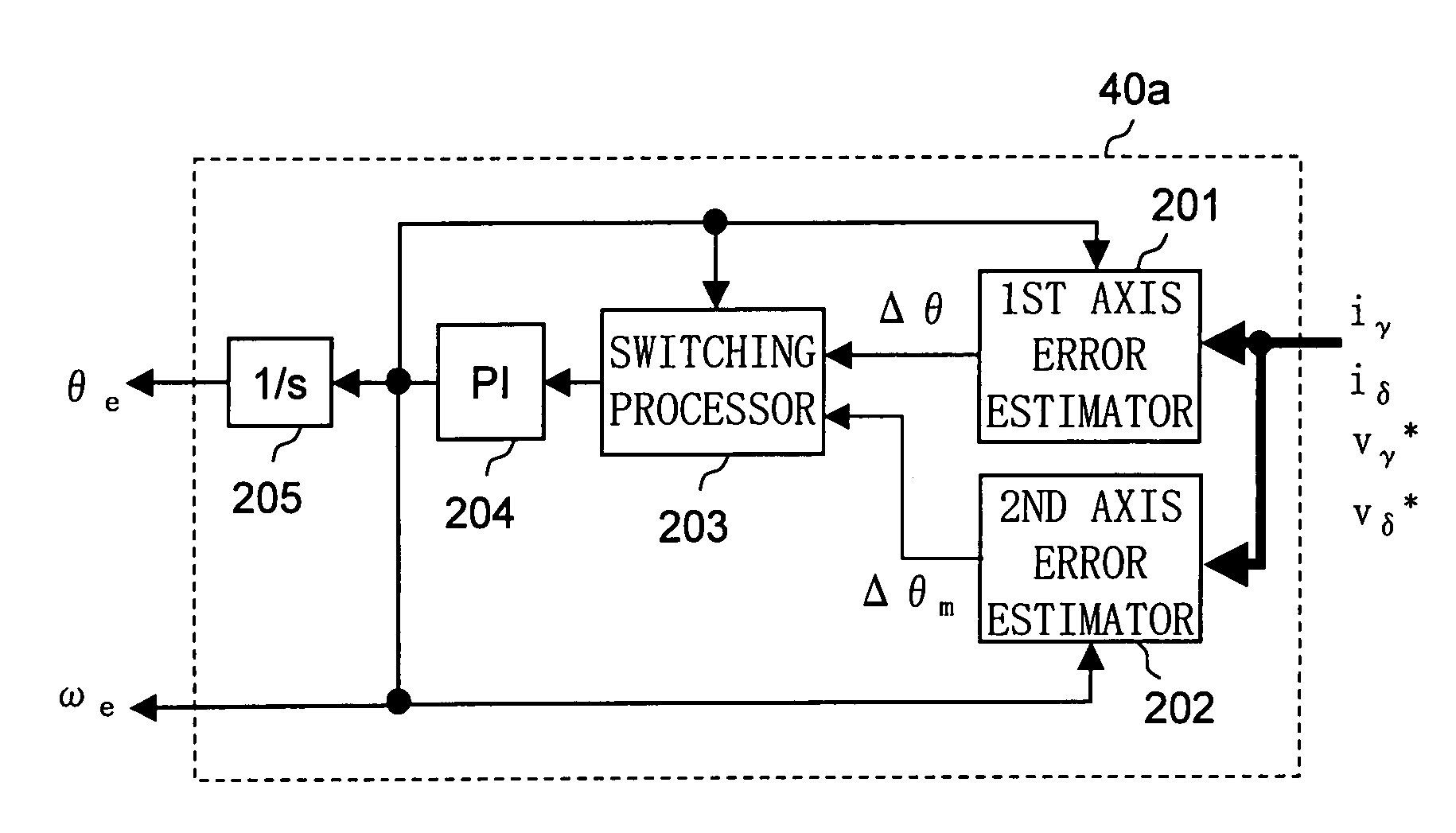
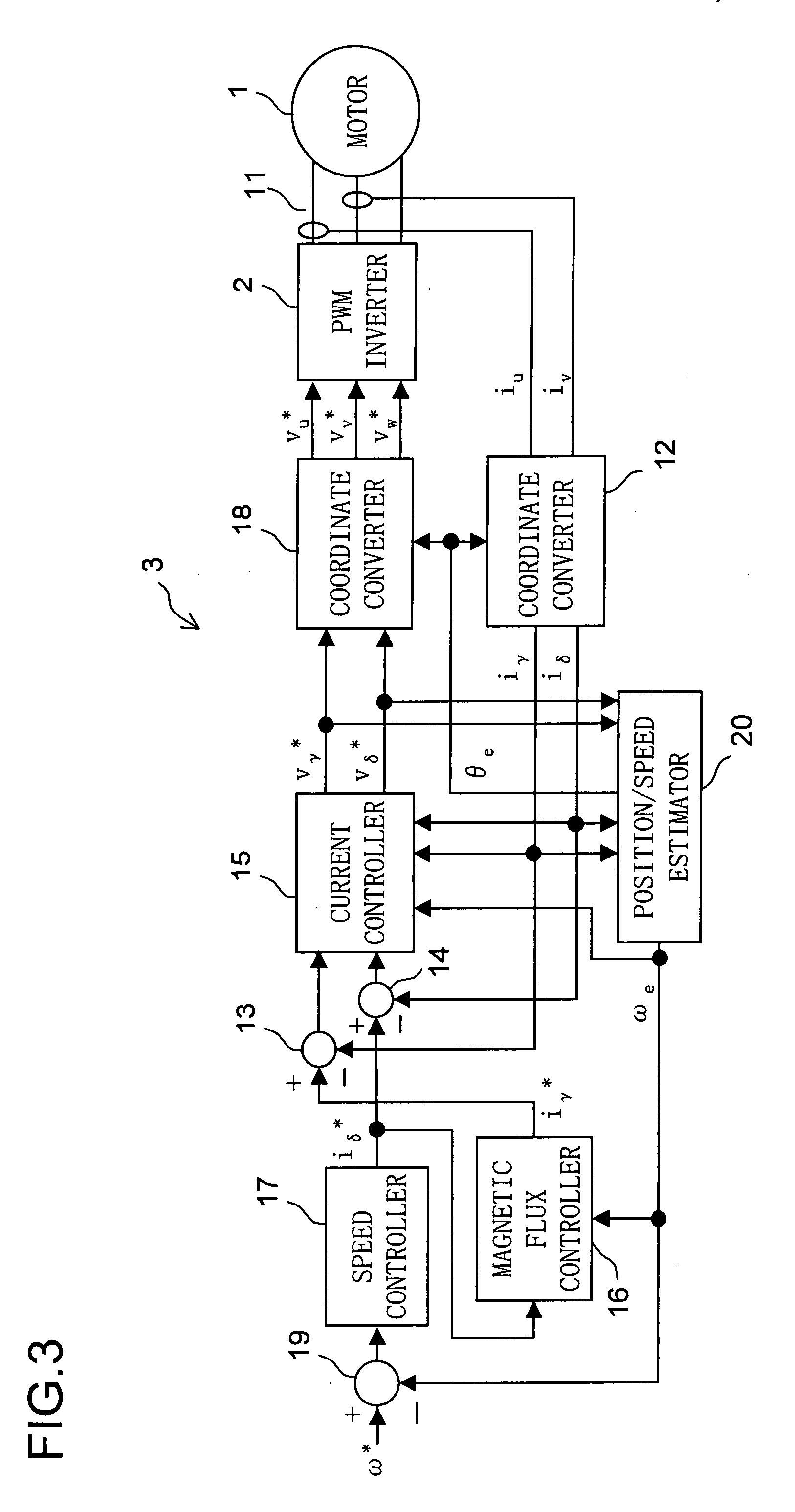
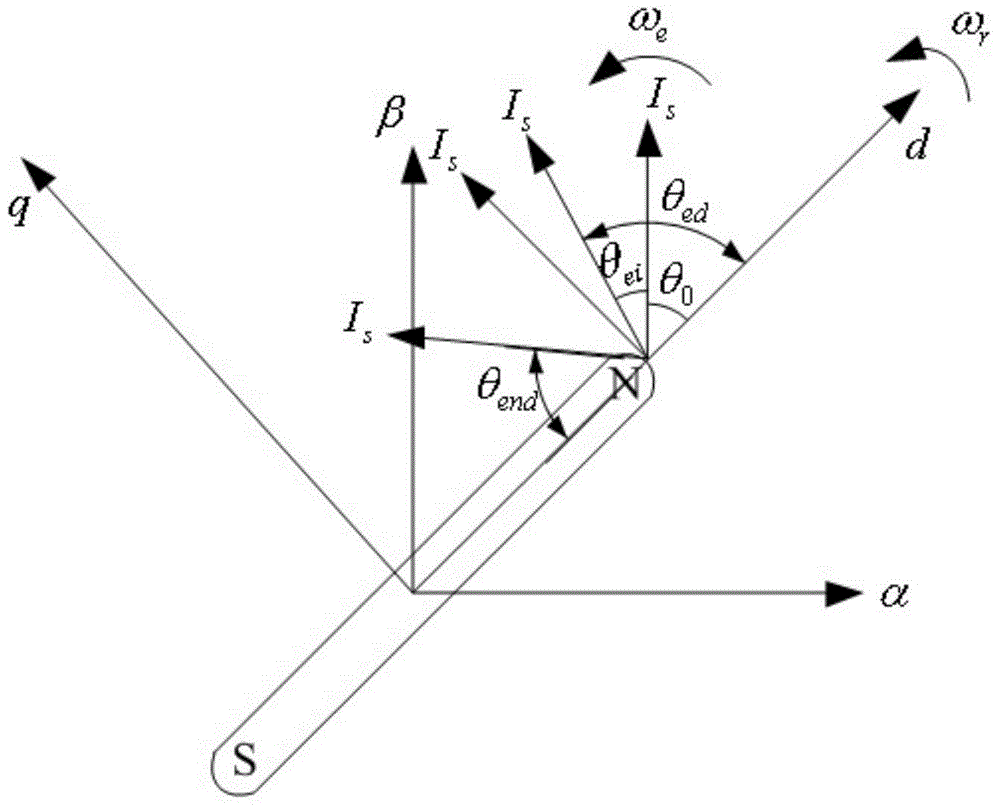
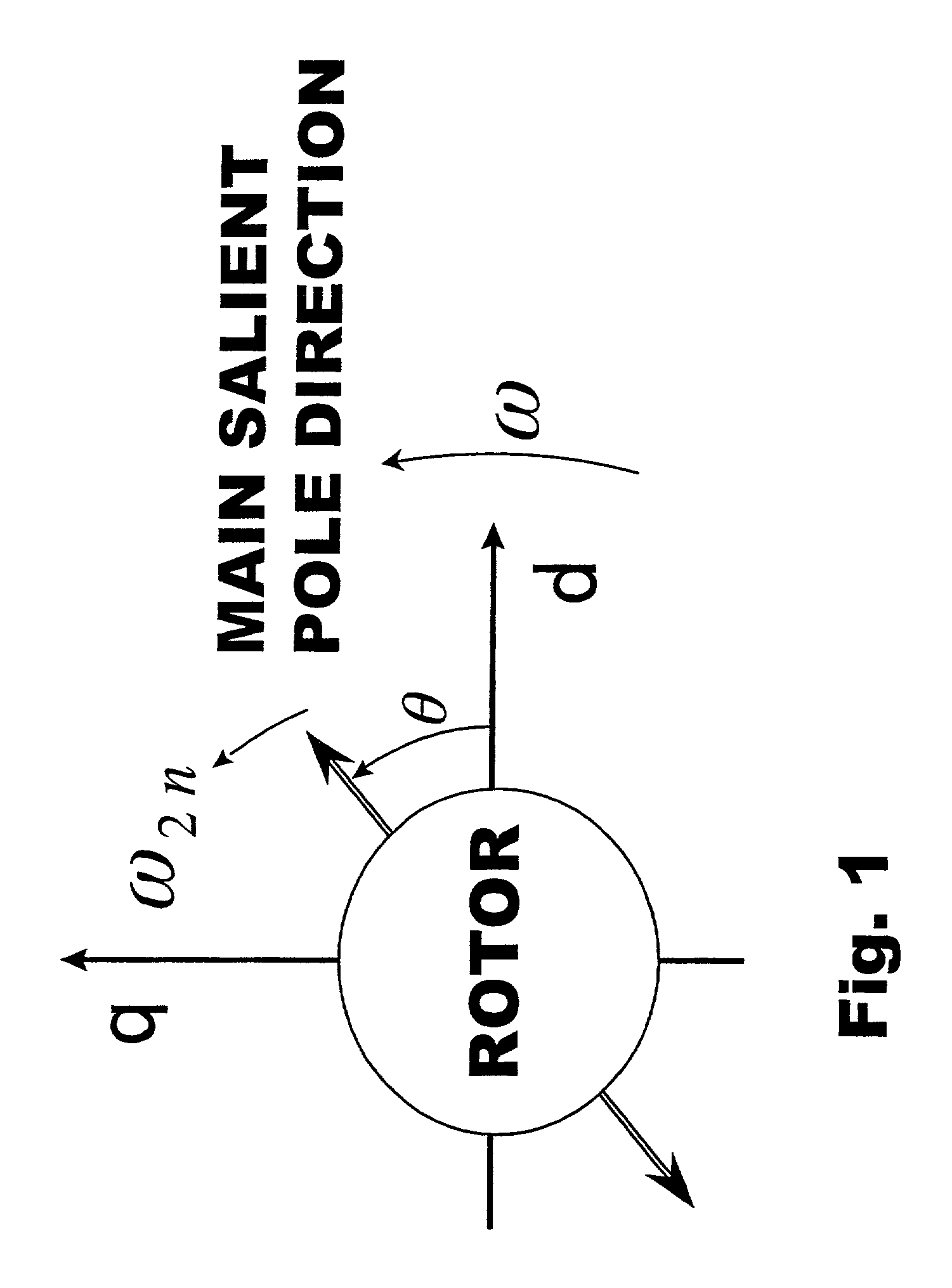
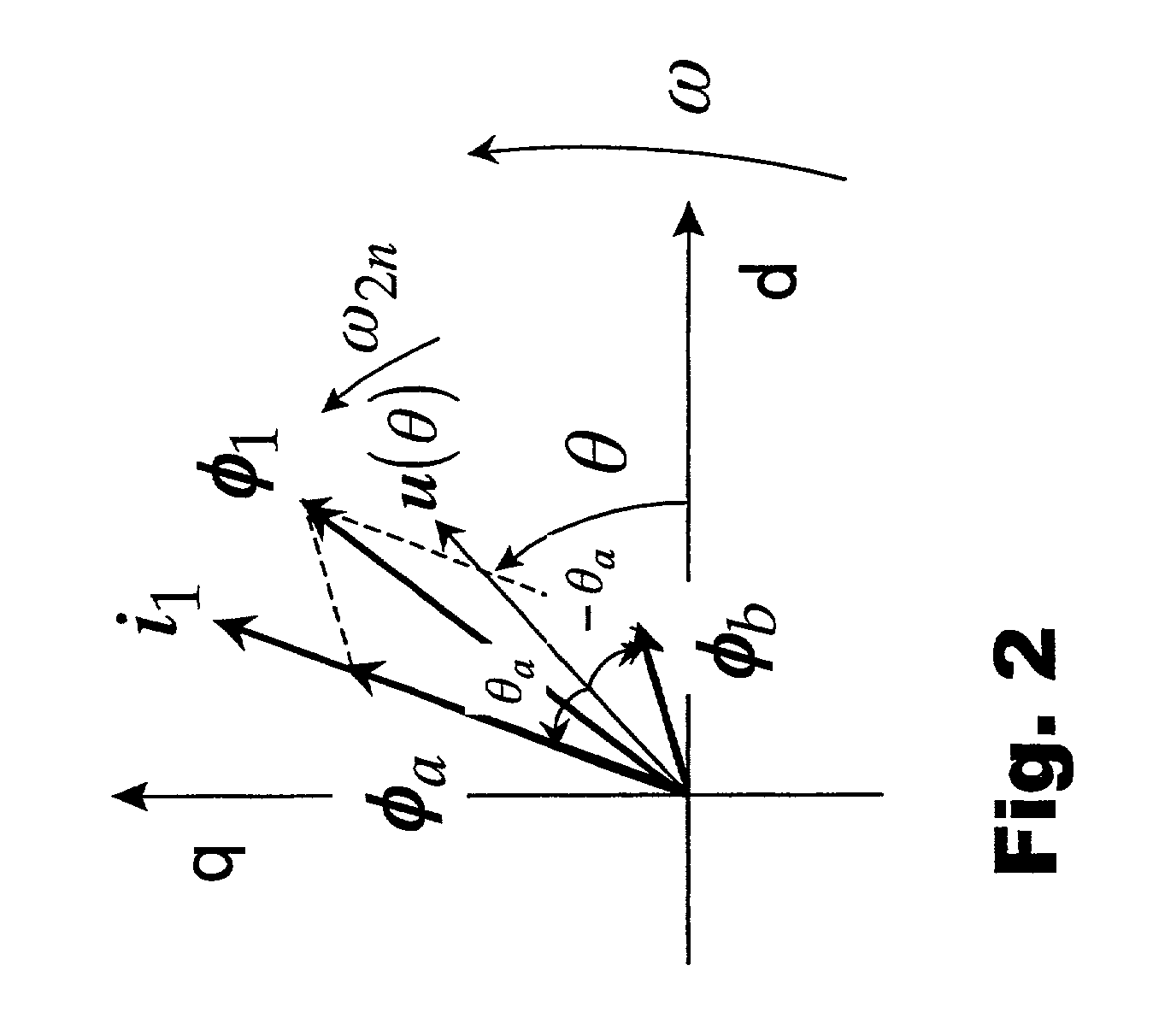
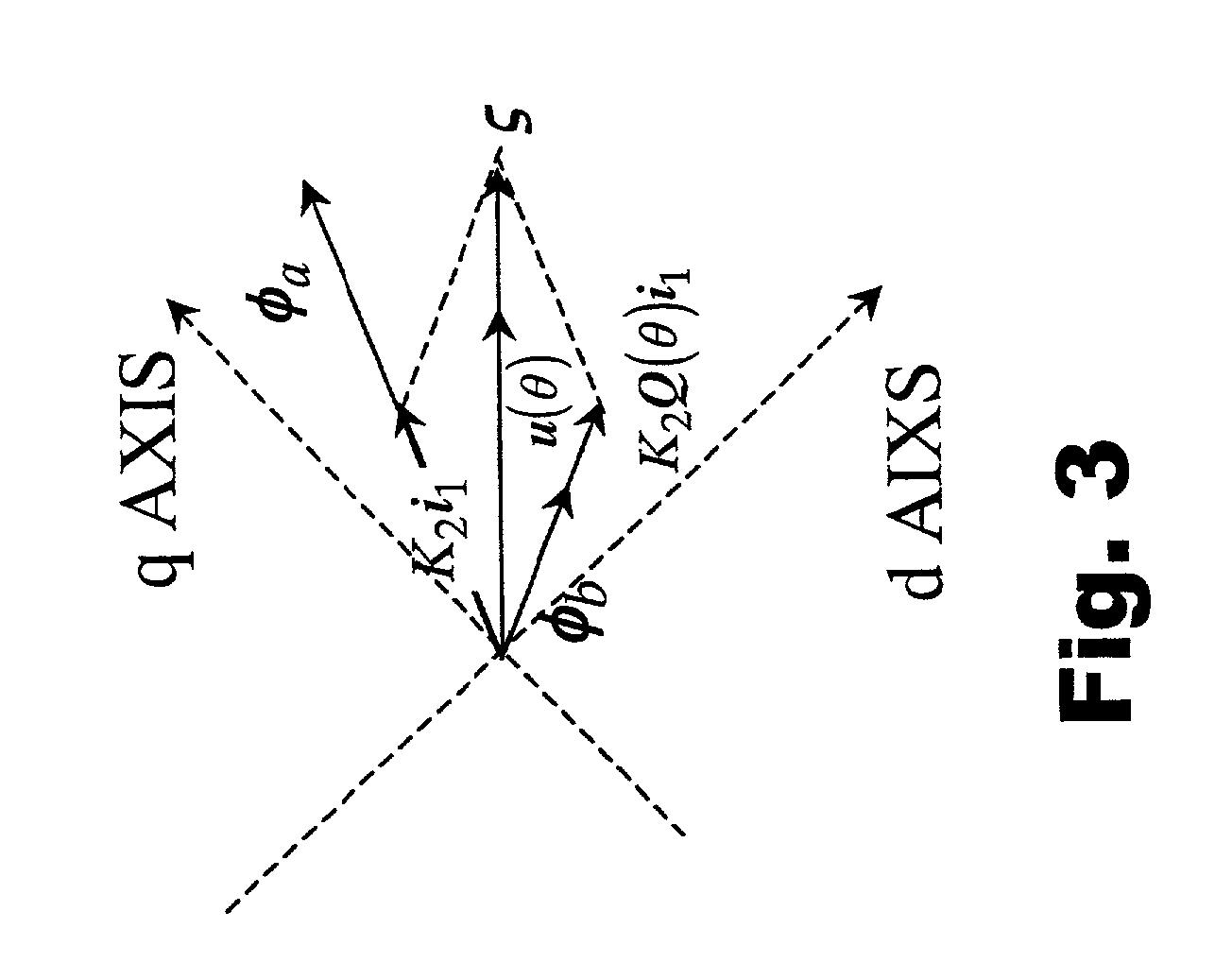
Let the rotating axis whose direction coincides with the direction of the current vector that achieves maximum torque control be called the qm-axis, and the rotating axis perpendicular to the qm-axis be called the dm-axis. A motor control device switches its operation between low-speed sensorless control and high-speed sensorless control according to the rotation speed of the rotor. In low-speed sensorless control, the magnetic salient pole of the motor is exploited, and the d-q axes are estimated by, for example, injection of a high-frequency rotating voltage. In high-speed sensorless control, the dm-qm axes are estimated based on, for example, the induction voltage produced by the rotation of the rotor. During high-speed sensorless control, the γ(dm)-axis current is kept at zero irrespective of the δ(qm)-axis current.
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD
Motor control device
Let the rotating axis whose direction coincides with the direction of the current vector that achieves maximum torque control be called the qm-axis, and the rotating axis perpendicular to the qm-axis be called the dm-axis. A motor control device switches its operation between low-speed sensorless control and high-speed sensorless control according to the rotation speed of the rotor. In low-speed sensorless control, the magnetic salient pole of the motor is exploited, and the d-q axes are estimated by, for example, injection of a high-frequency rotating voltage. In high-speed sensorless control, the dm-qm axes are estimated based on, for example, the induction voltage produced by the rotation of the rotor. During high-speed sensorless control, the γ(dm)-axis current is kept at zero irrespective of the δ(qm)-axis current.
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD
Controllable flux permanent magnetic synchronous motor of multiple pole number built-in mixed rotor magnetic path structure
InactiveCN1617422AChange the magnetizationMemoryMagnetic circuit rotating partsPermanent magnet rotorSynchronous motor
This invention provides a multiple integral hybrid rotor magnetic circuit structure controlled flux magnet synchronous motor including motor spindle, a stator winding, a stator iron core, AlNiCo magnet, A Nd FeB magent, a rotor iron core, a position sensor, a sensor cable, a motor cable and a converter. The permanent rotor is in an integral hybrid rotor magnetic circuit structure, the magnet in the rotor iron cover is set in U shape, the NdFeB is placed tangentially and the AlNiCo magnet is in radial position characterizing in being called a memory motor since it can apply an amplitude controlled d-axis current vector to change the magnetization intensity of the rotor magnet and remember the changed flux intensity.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Electric power steering system
ActiveUS20140207335A1Reduce computing loadSingle motor speed/torque controlDigital data processing detailsElectric power steeringDriver circuit
There is provided a drive control method for a motor including multiple sets of coils and drive circuits in an electric power steering system. In order to reduce computational load when sensorless control is executed, an electrical angle estimator includes an α-axis voltage component adder and a β-axis voltage component adder that add together voltage vectors of a first coil and a second coil expressed in a two-phase fixed coordinate system, an α-axis current component adder and a β-axis current component adder that add together current vectors of the first coil and the second coil expressed in a two-phase fixed coordinate system, and an induced voltage computing unit that computes an induced voltage based on an added voltage vector and an added current vector.
Owner:JTEKT CORP
Permanent-magnet synchronous-motor position-free-sensor control method based on rotating-current vectors
ActiveCN103607155ARun perfectlyGuaranteed stabilityElectronic commutation motor controlAC motor controlLoad torquePosition angle
The invention relates to the field of electrical transmission and aims at providing a permanent-magnet synchronous-motor position-free-sensor control method based on rotating-current vectors. The method includes: setting the amplitude of the rotating-current vectors; setting the angle frequency of the rotating-current vectors; setting the position angle of a permanent-magnet synchronous-motor rotor; carrying out coordinate transformation on stator output current of a three-phase permanent-magnet synchronous motor; simulating PI operations of a d-p coordinate system; carrying out inverse transformation on coordinates and realizing whole driving via an inverter; and observing the power angle of the permanent-magnet synchronous motor. Starting of the permanent-magnet synchronous motor is completed after the above-mentioned seven steps are finished. The permanent-magnet synchronous-motor position-free-sensor control method based on the rotating-current vectors makes use of an inherent characteristic that under a condition that the permanent-magnet synchronous motor does not step out, the rotating speed of the rotor is capable of synchronously tracking of given frequency of a stator rotating magnetic field. The operation state of the permanent-magnet synchronous motor is observed through a load torque angle and controlled so that system stability is ensured. The method is low in cost, simple in control algorithm and capable of realizing full-speed-section operation of the permanent-magnet synchronous-motor position-free sensor perfectly.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
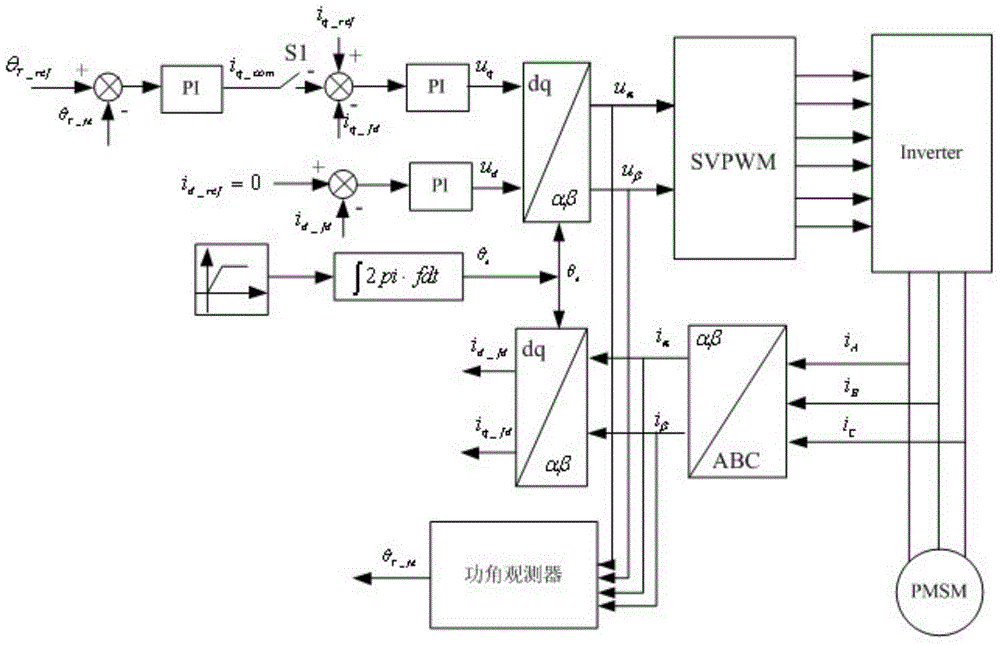
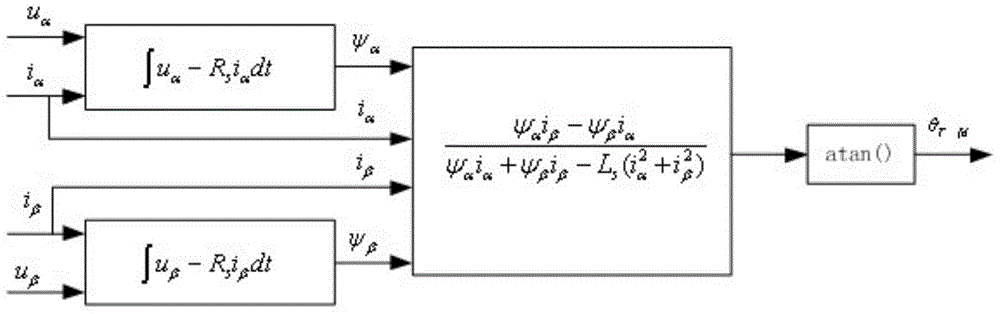
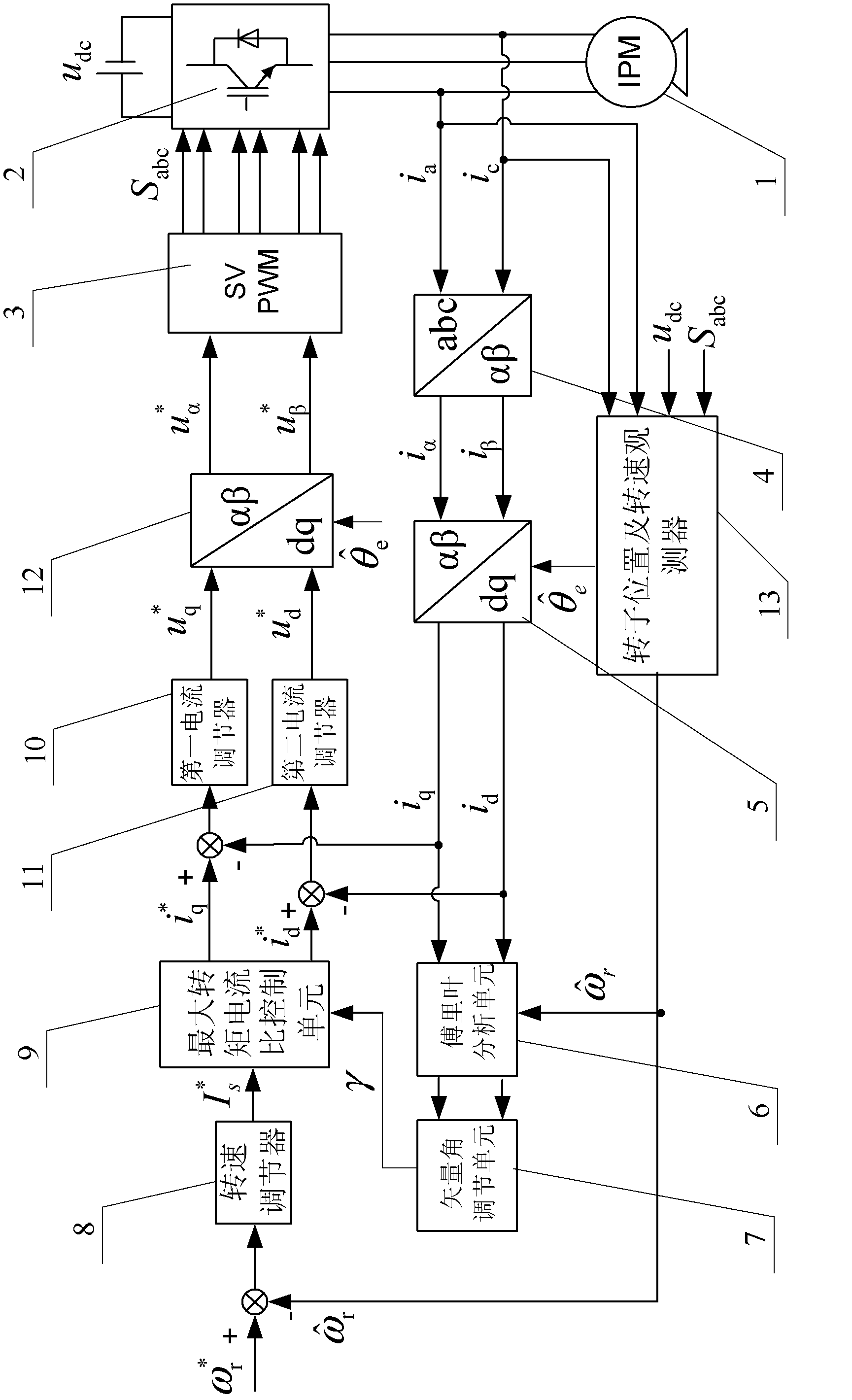
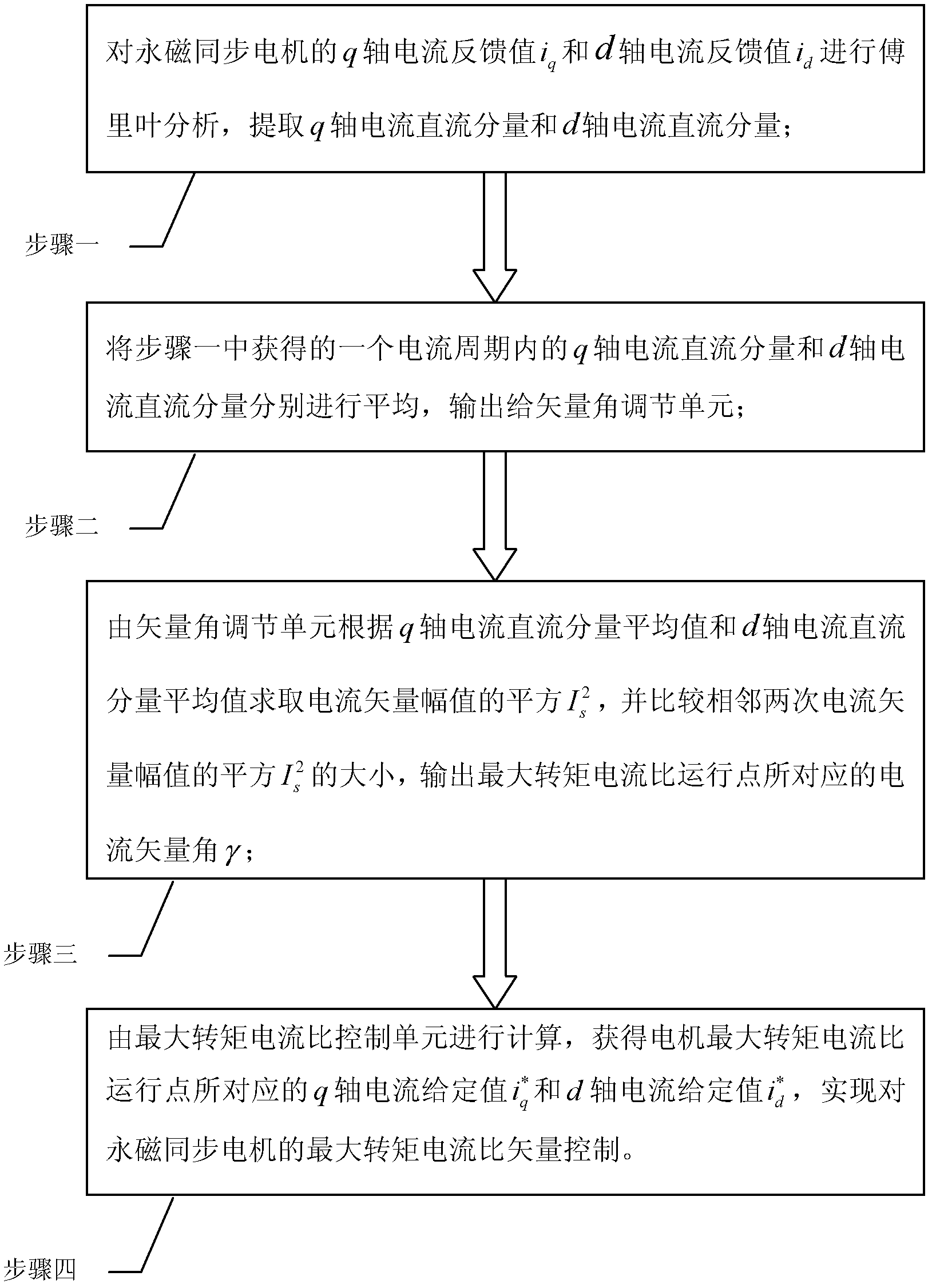
Maximum torque per ampere vector control system and control method for position sensor-free internal permanent magnet synchronous motor
InactiveCN102594250AImprove overload capacityImprove power densityElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsOperating pointAmpere
The invention discloses a control method of a maximum torque per ampere vector control system for a position sensor-free internal permanent magnet synchronous motor, and belongs to the field of motor control. The problems of complexity of a computing method and low accuracy of an obtained current set value in the conventional maximum torque per ampere control strategy are solved. The control system comprises a permanent magnet synchronous motor, an inverter, a space vector pulse width modulation unit, a three-phase-two-phase coordinate conversion unit, a static-rotational coordinate conversion unit, a Fourier analysis unit, a vector angle regulation unit, a rotating speed regulator, a maximum torque per ampere control unit, a first current regulator, a second current regulator, a rotational-static coordinate conversion unit and a rotor position and rotating speed observer. According to the control method, the magnitude of current amplitude is automatically regulated and compared on the basis of a current vector angle gamma, and an operating point with maximum torque per ampere is automatically searched. The system and the method are applied to maximum torque per ampere vector control over the motor.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
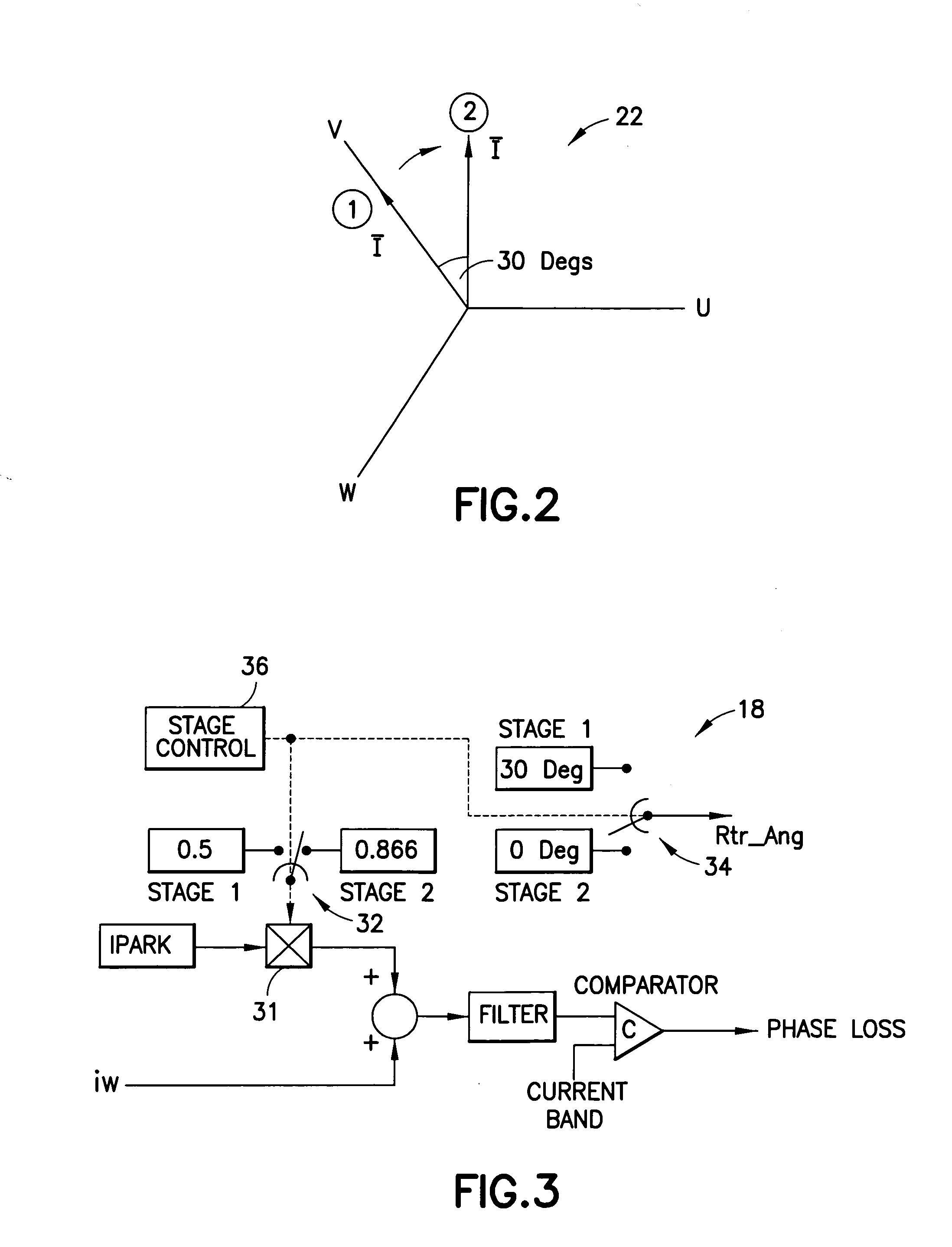
Phase-loss detection for rotating field machine
ActiveUS20060186914A1Avoid mechanical damageExtended boot timeEmergency protective circuit arrangementsDynamo-electric machine testingConductor CoilElectrical current
A method for detecting a loss of a phase in a multiphase rotating field machine, the method comprising providing a first electrical current into the machine windings to cause the current vector to assume a first current vector position, sensing a first current in at least one selected phase winding of the machine, comparing the sensed first current in the at least one selected phase winding with a first calculated current for the selected phase winding, and detecting that a first phase fault has occurred if the first calculated and sensed first currents differ by more than a predetermined value.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AMERICAS CORP
PMSM rotary transformer zero position initial angle calibration method and calibration system
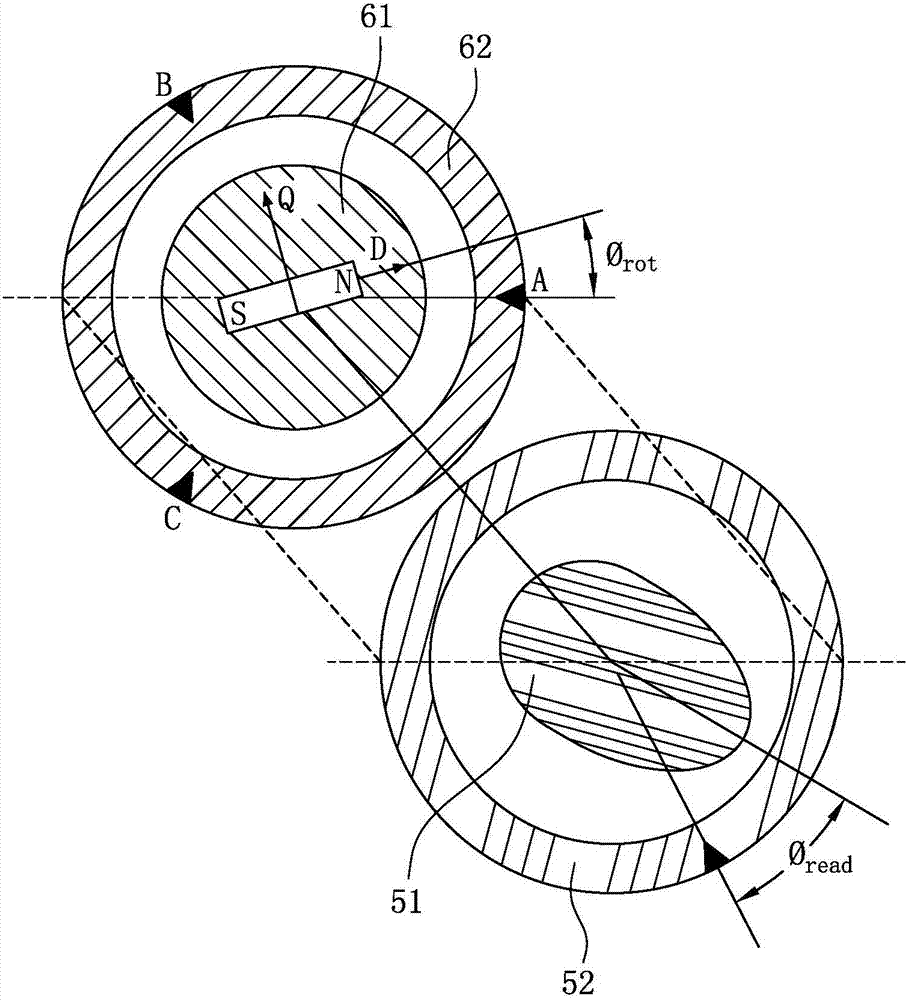
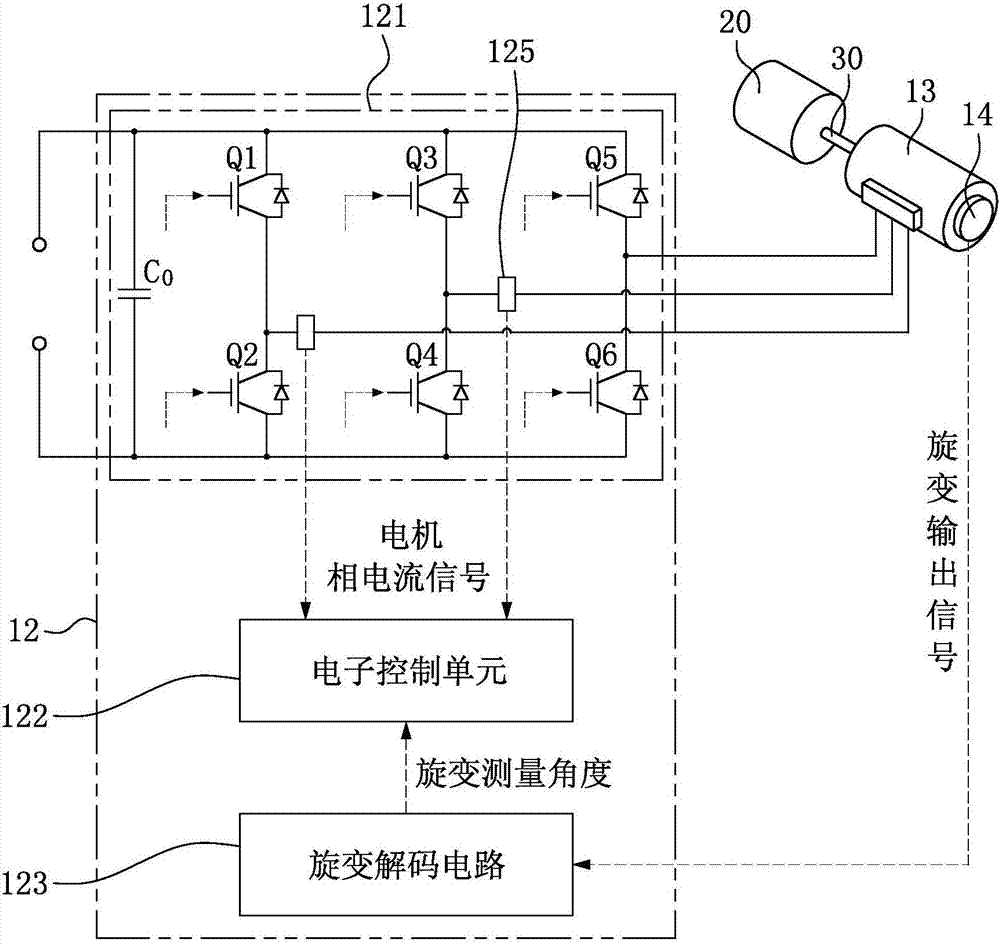
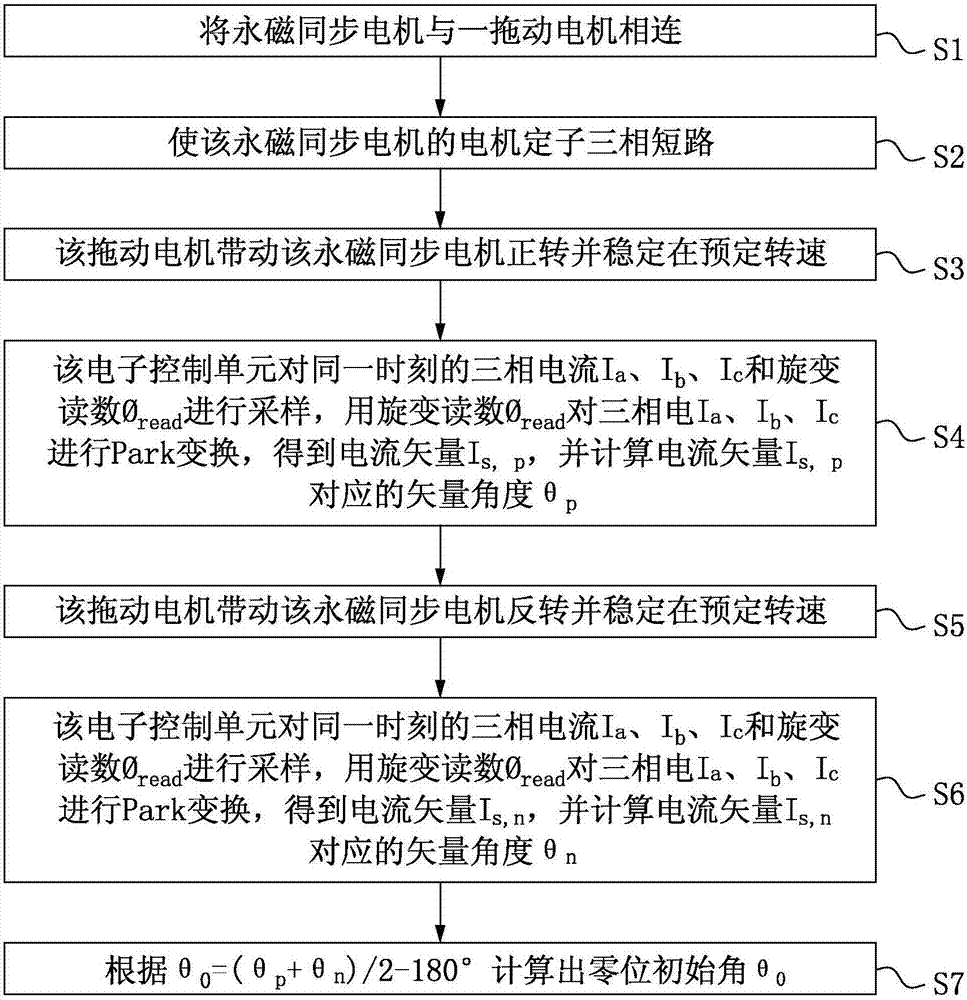
ActiveCN107404272ACalibration is easy to operateCalculation method is simpleAC motor controlVector control systemsThree-phaseDrive motor
The invention discloses a PMSM rotary transformer zero position initial angle calibration method and calibration system. The PMSM rotary transformer zero position initial angle calibration method comprises steps of connecting an PMSM, on which a rotary transformer is installed, to a driving motor, enabling a motor stator of the PMSM to perform three-phase short circuit, using the driving motor to drive the PMSM to rotate forward and maintain at a preset rotation speed, using an electronic control unit to perform sampling on three phase current Ia, Ib and I c and a rotary transformer reading phi read at a same moment, using the rotary transformer reading phi read to perform Park conversion on three phase current Ia, Ib and Ic to obtain current vectors Is,p, calculating a vector angle theta p corresponding the current vector Is,p, using the driving motor to drive the PMSM to rotate backwards and maintaining the rotation at a preset rotation speed, using the electronic control unit to record a vector angle theta n corresponding to a current vector Is,n when the motor is rotated backwards, and calculating that a practical electric rotation angle theta 0 corresponding to the rotary transformer reading zero point angle is a zero position initial angle according to a formula theta 0=(thetap+thetan) / 2-180 degree.
Owner:GUANGZHOU AUTOMOBILE GROUP CO LTD
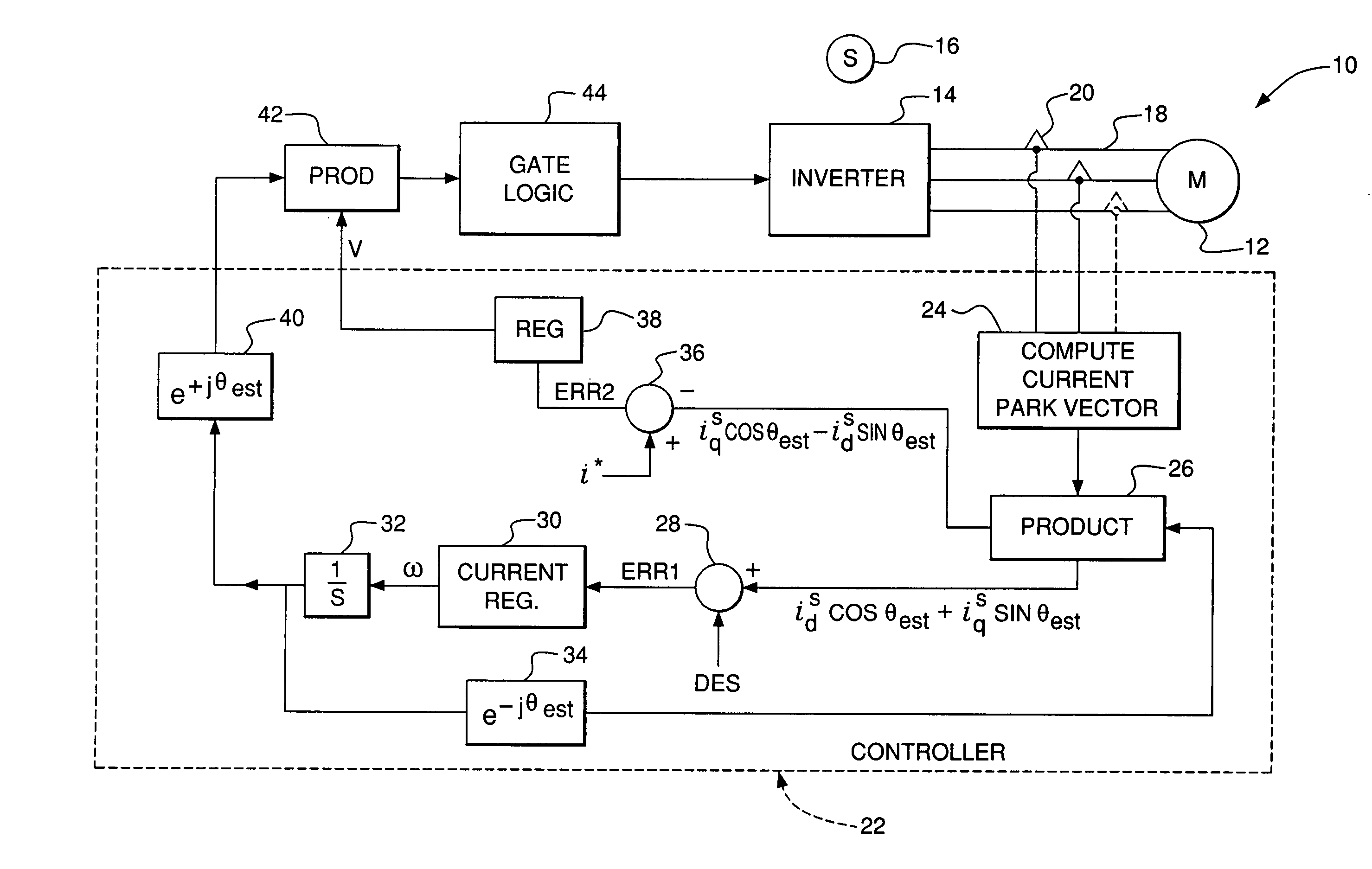
Decoupling of cross coupling for floating reference frame controllers for sensorless control of synchronous machines
ActiveUS6940251B1Avoid disadvantagesMotor/generator/converter stoppersAC motor controlPhase currentsSynchronous motor
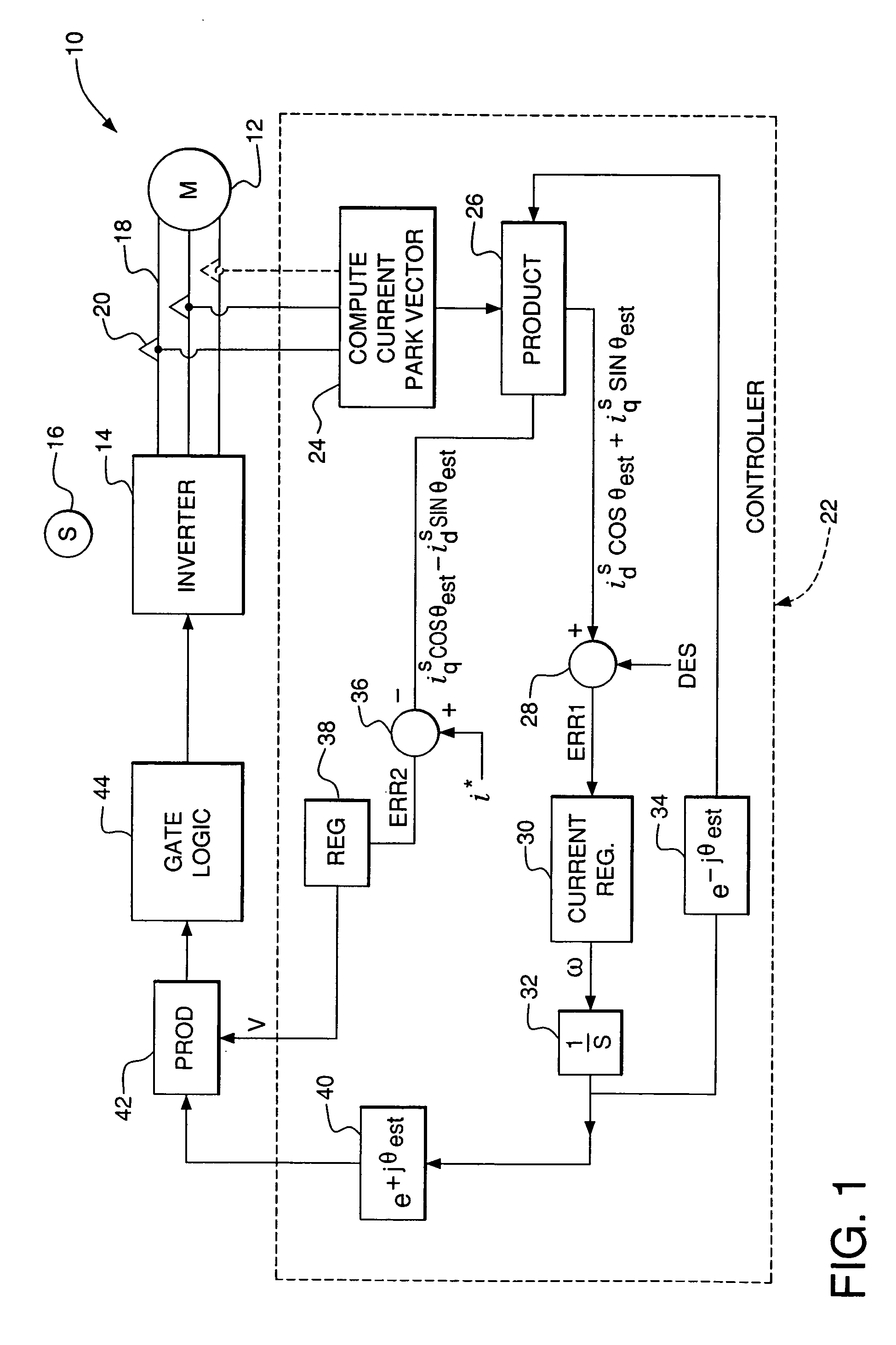
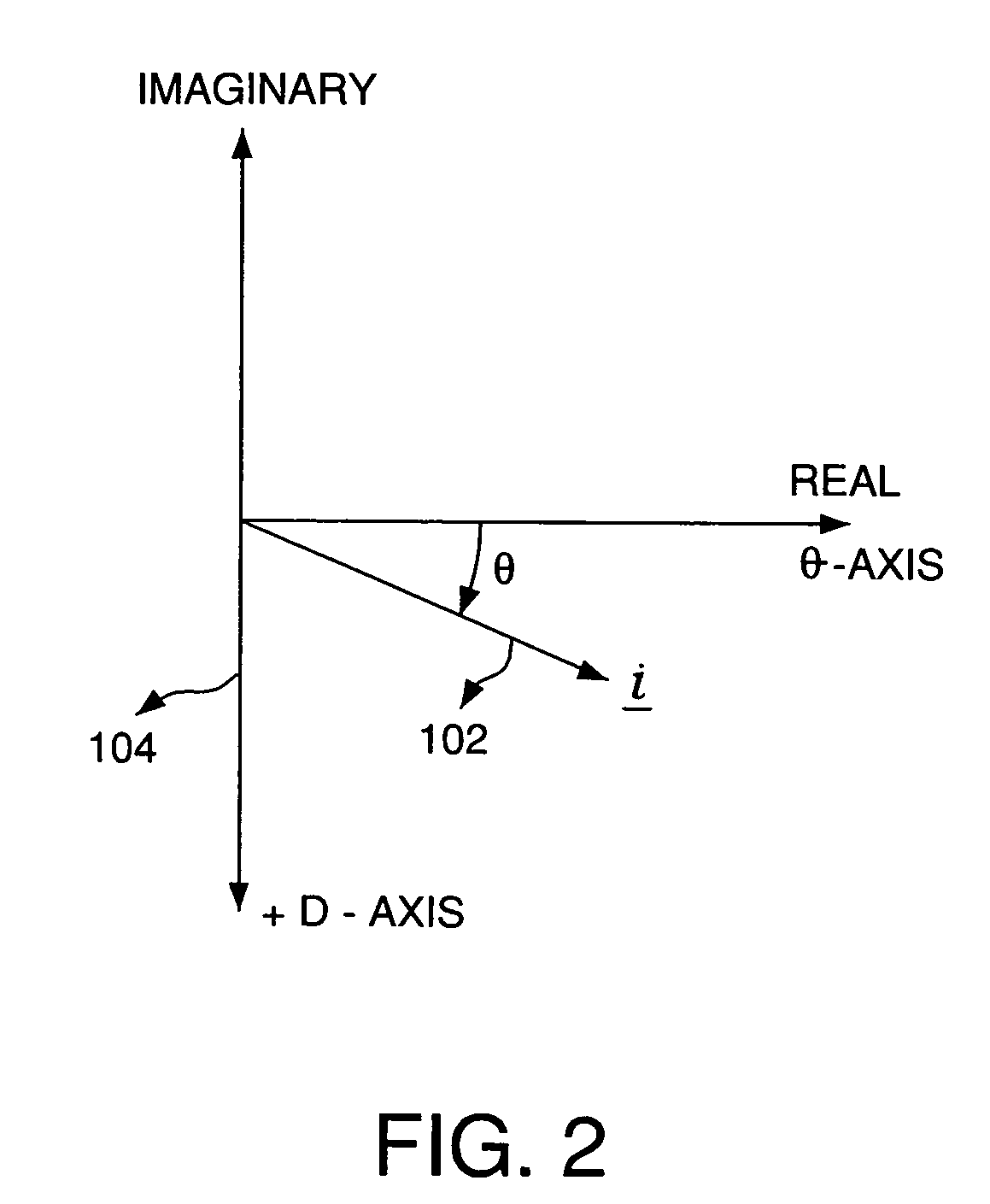
A synchronous motor controller and method of controlling a synchronous motor without using rotor position sensors are provided. In a floating synchronous reference frame controller, phase currents are measured and a current Park vector is determined. The error between an initially arbitrary floating reference frame is reduced with a control loop. Decoupling terms based on the estimated speed of the rotor and the stator winding inductance are used to generate decoupled voltage terms in the v- and u-axis of the floating synchronous reference frame. The decoupled voltage command is converted back to a stator reference frame and applied to the synchronous motor via a power electronic converter. As a result u-axis current is minimized during transients, and a robust and accurate estimation of the current vector to be used in coordinate transformation for controlling the machine are achieved and the need for overrating of motor and inverter components is avoided.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
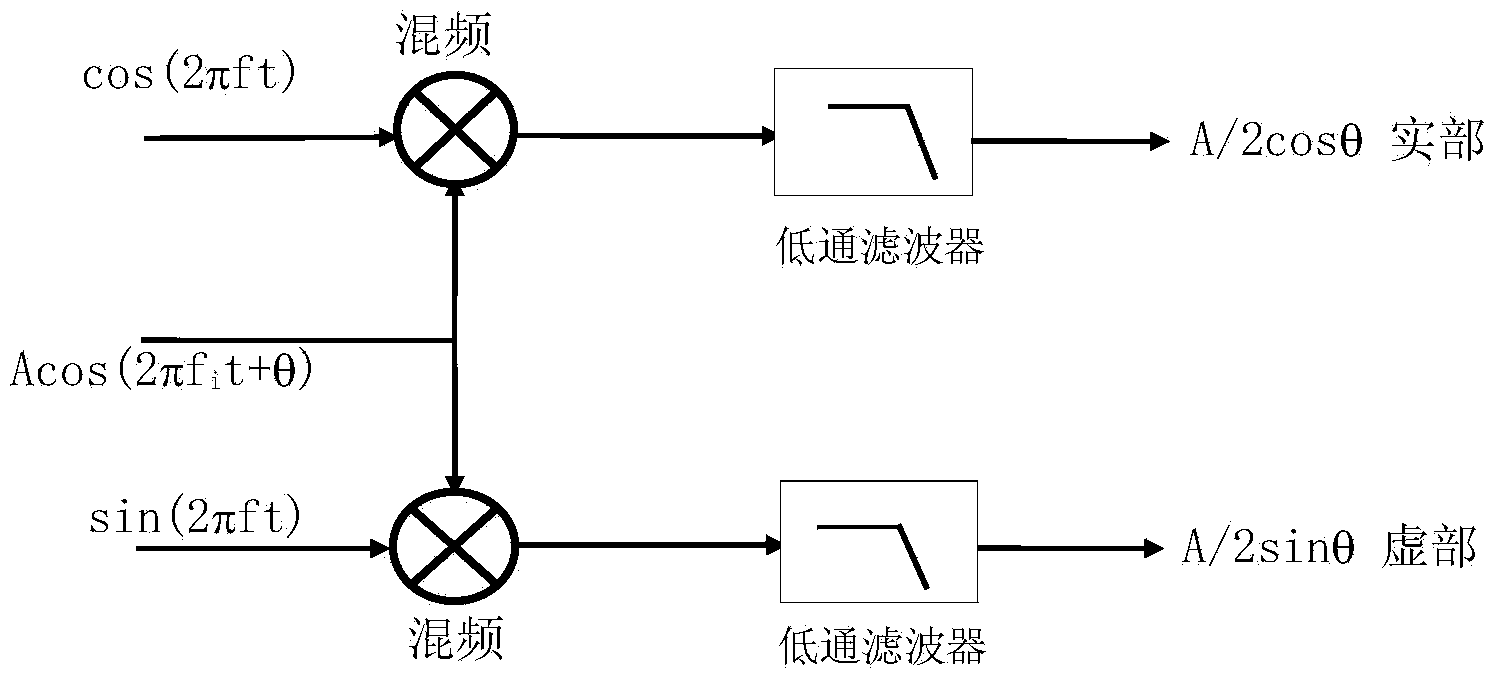
Method for detecting harmonic wave and reactive current based on spatial transformation of voltage vectors
InactiveCN101893652AReduce adverse effectsPhysical concepts are clearFrequency analysisReactive/real component measurementsVoltage vectorActive component
Aiming at a problem that an ip-iq algorithm cannot precisely acquire fundamental wave positive sequence active currents under the conditions of non-ideal power network voltages, the invention provides a method for detecting a harmonic wave and a reactive current based on spatial transformation of voltage vectors. The method comprises the steps of performing coordinate transformation on currents and voltages on an ip-iq algorithm channel to acquire phase information of three-phase fundamental wave positive sequence voltages; defining a p-q coordinate system; defining correct positive sequence active components and positive sequence reactive components by using the projection of a current vector on a voltage vector and a normal line thereof under the coordinate system; then accurately solving fundamental wave positive sequence active components, fundamental wave positive sequence reactive components, fundamental wave negative sequence active components and fundamental wave negative sequence reactive components in a load current by taking the correct positive sequence active components and the positive sequence reactive components as reference volumes and using an improved ip-iq algorithm; and popularizing the detection of the four fundamental wave current magnitudes into the detection of any sub-harmonic current magnitude to form a current detection system under the conditions of non-ideal voltages so as to provide reasonable reference instruction currents for various compensation requirements.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
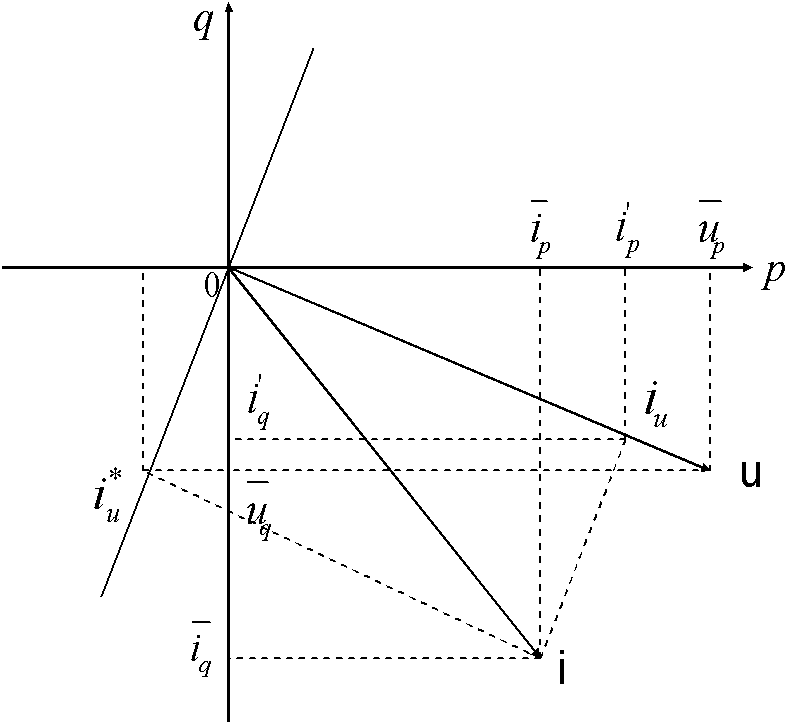
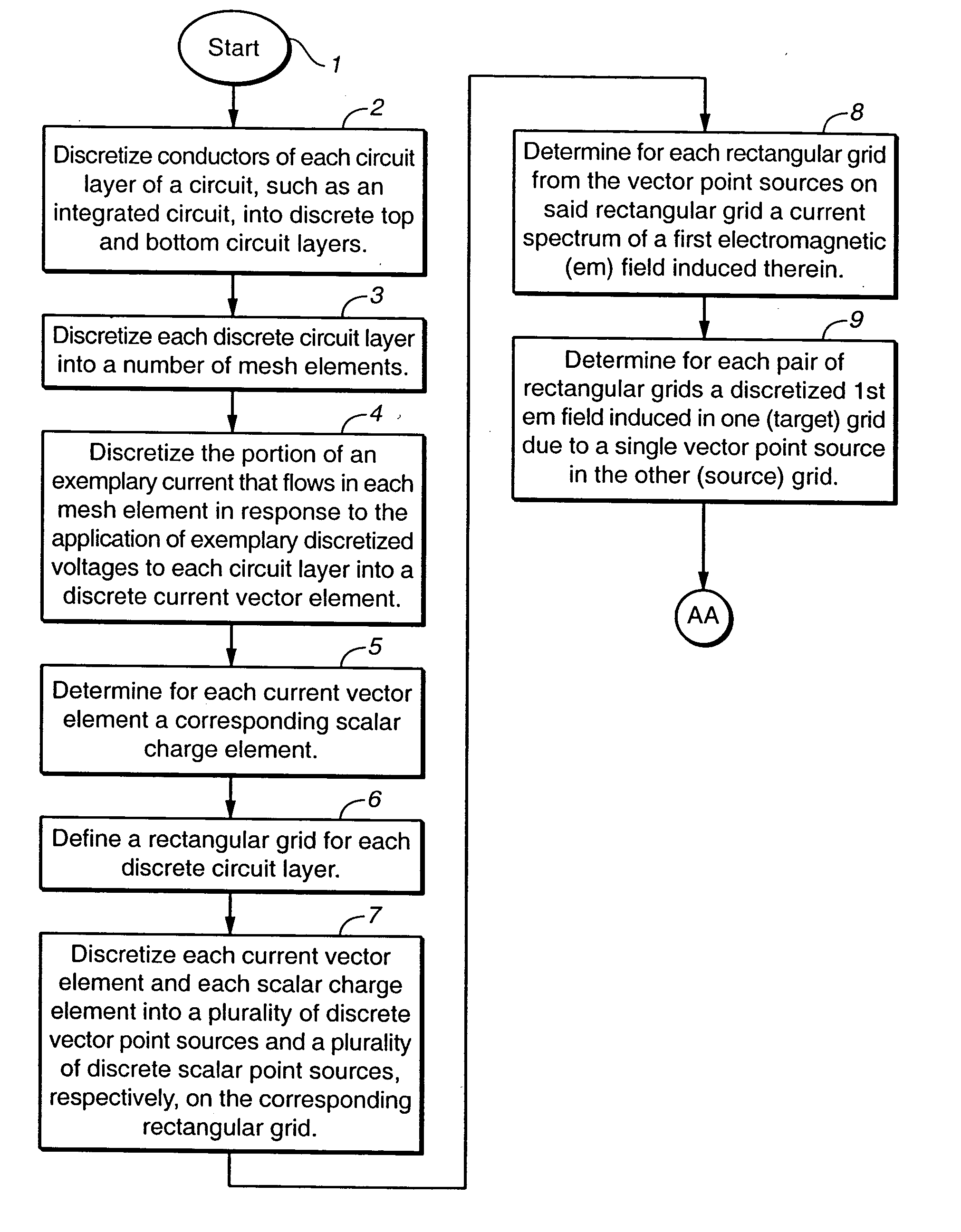
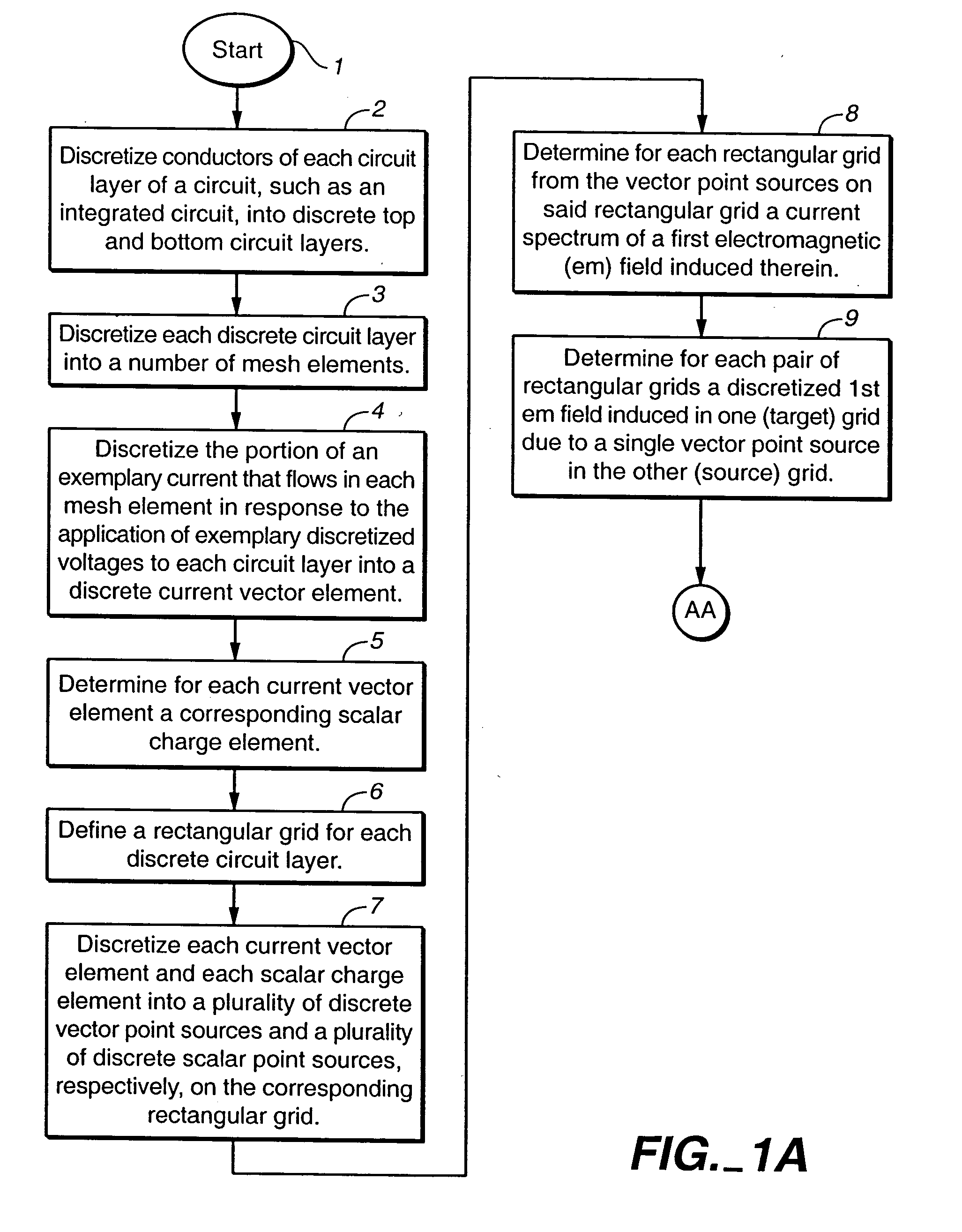
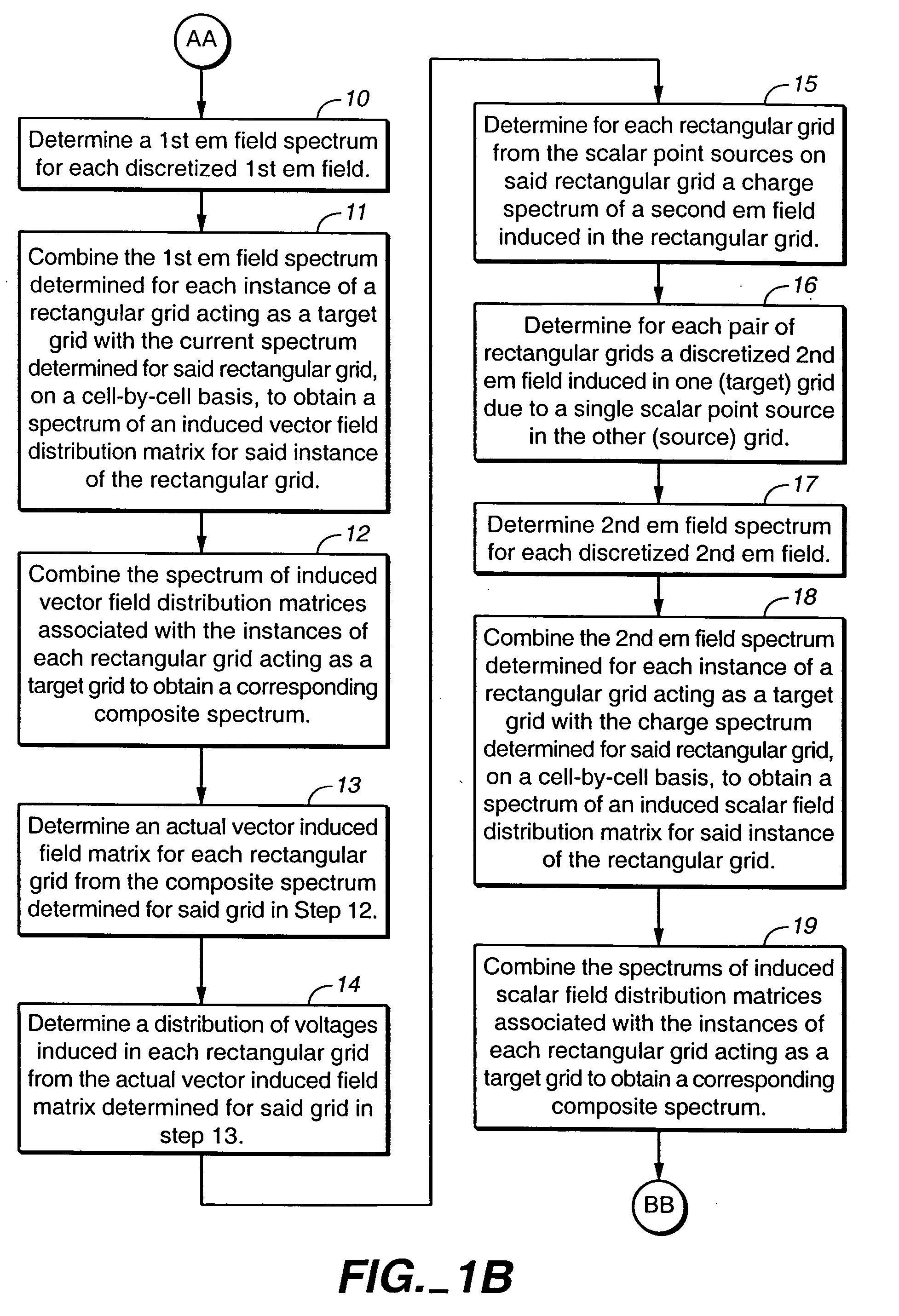
Method and apparatus for determining interactive electromagnetic effects among conductors of a multi-layer circuit
ActiveUS20050076317A1Current/voltage measurementComputation using non-denominational number representationElectrical conductorEngineering
To estimate a distribution of voltages or currents in the layers of a multi-layer circuit, an exemplary current flow in each layer is discretized into a number of current vector elements and at least one scalar charge element related to the charge associated with each current vector element. A first distribution of voltages induced in each circuit layer is determined from current vector elements in all of the circuit layers. A second distribution of voltages induced in each circuit layer is determined from the scalar charge elements in all of the circuit layers. For each circuit layer, the first and second distributions of voltages induced therein are combined to determine an actual distribution of voltages in the circuit layer.
Owner:CADENCE DESIGN SYST INC
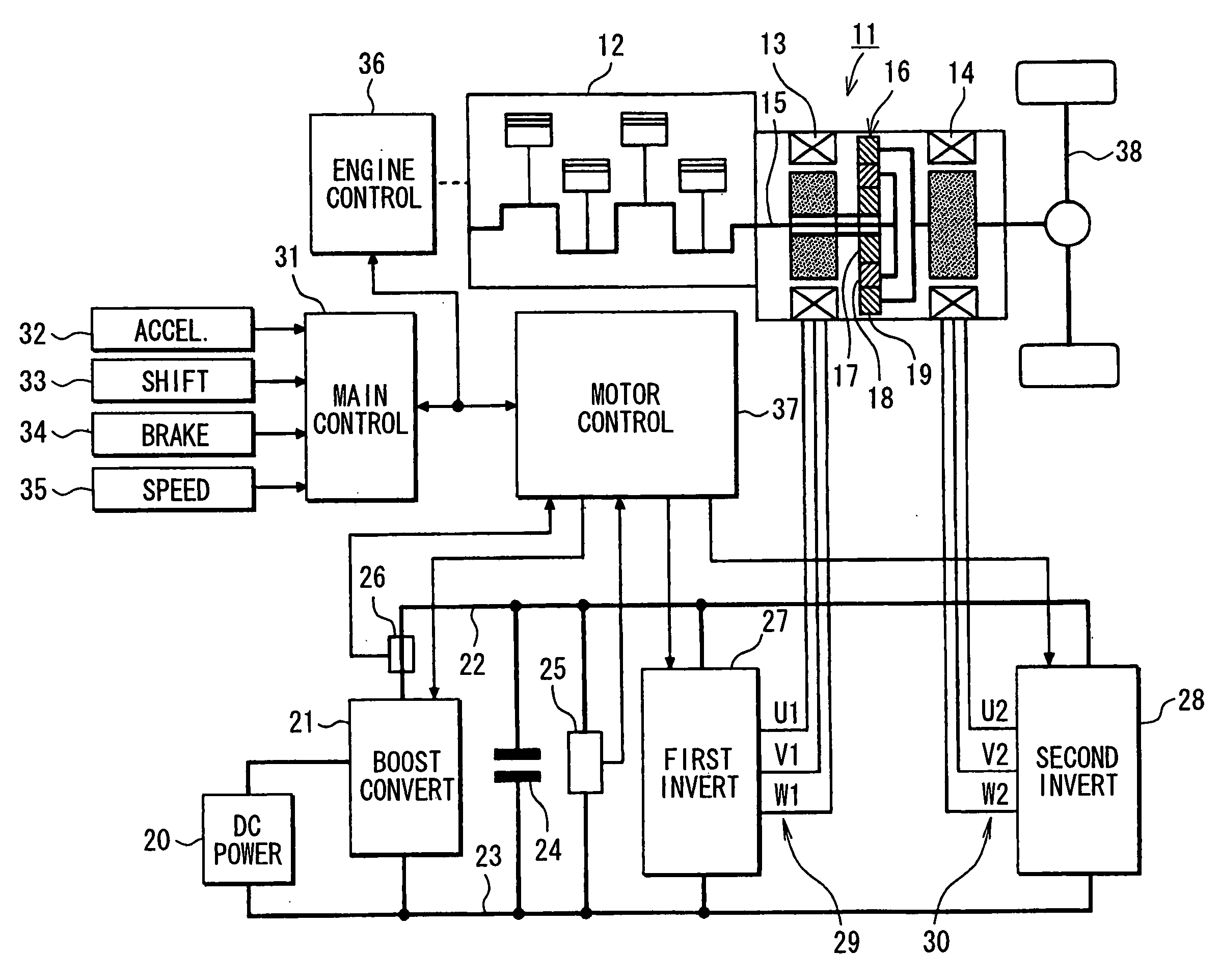
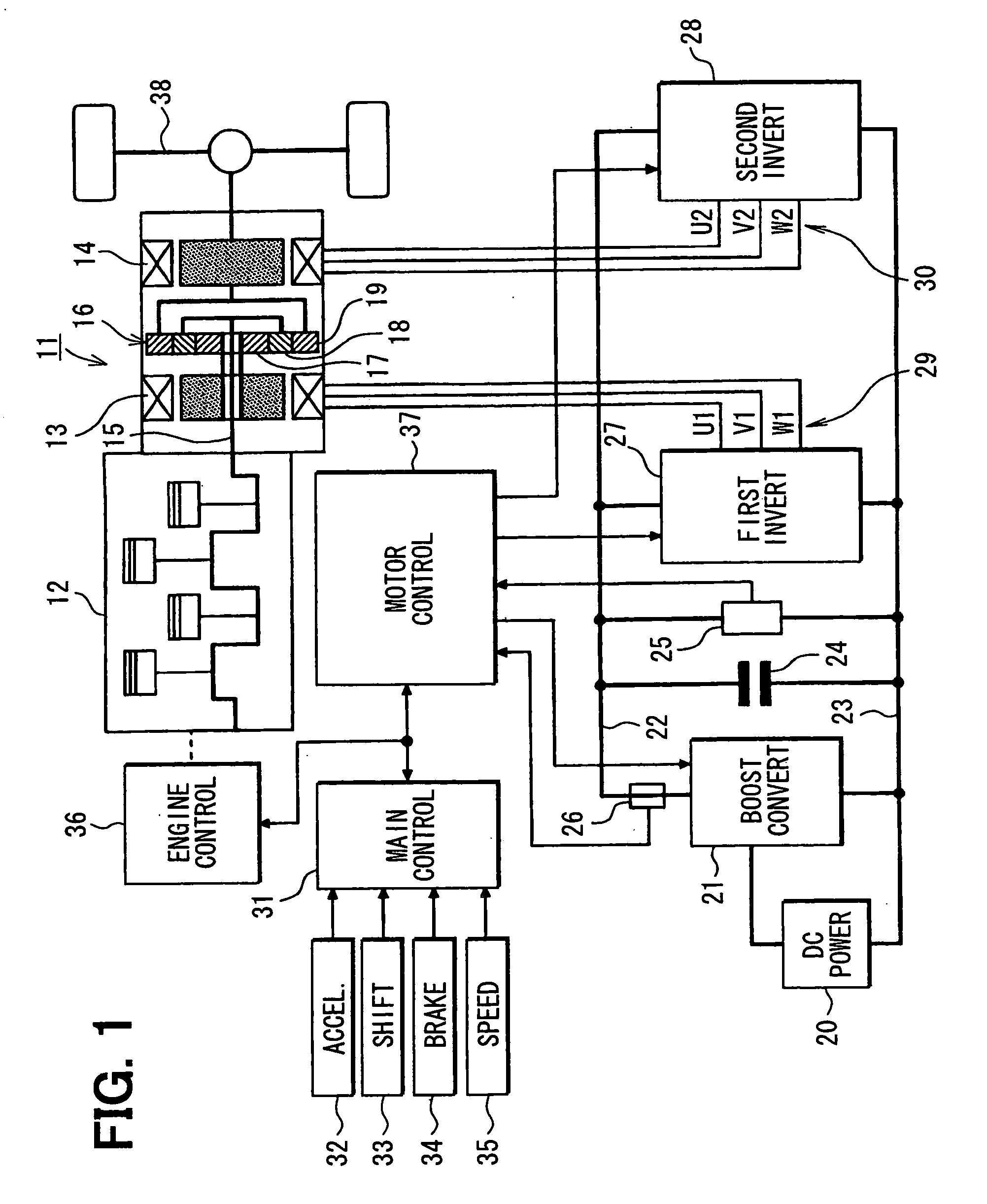
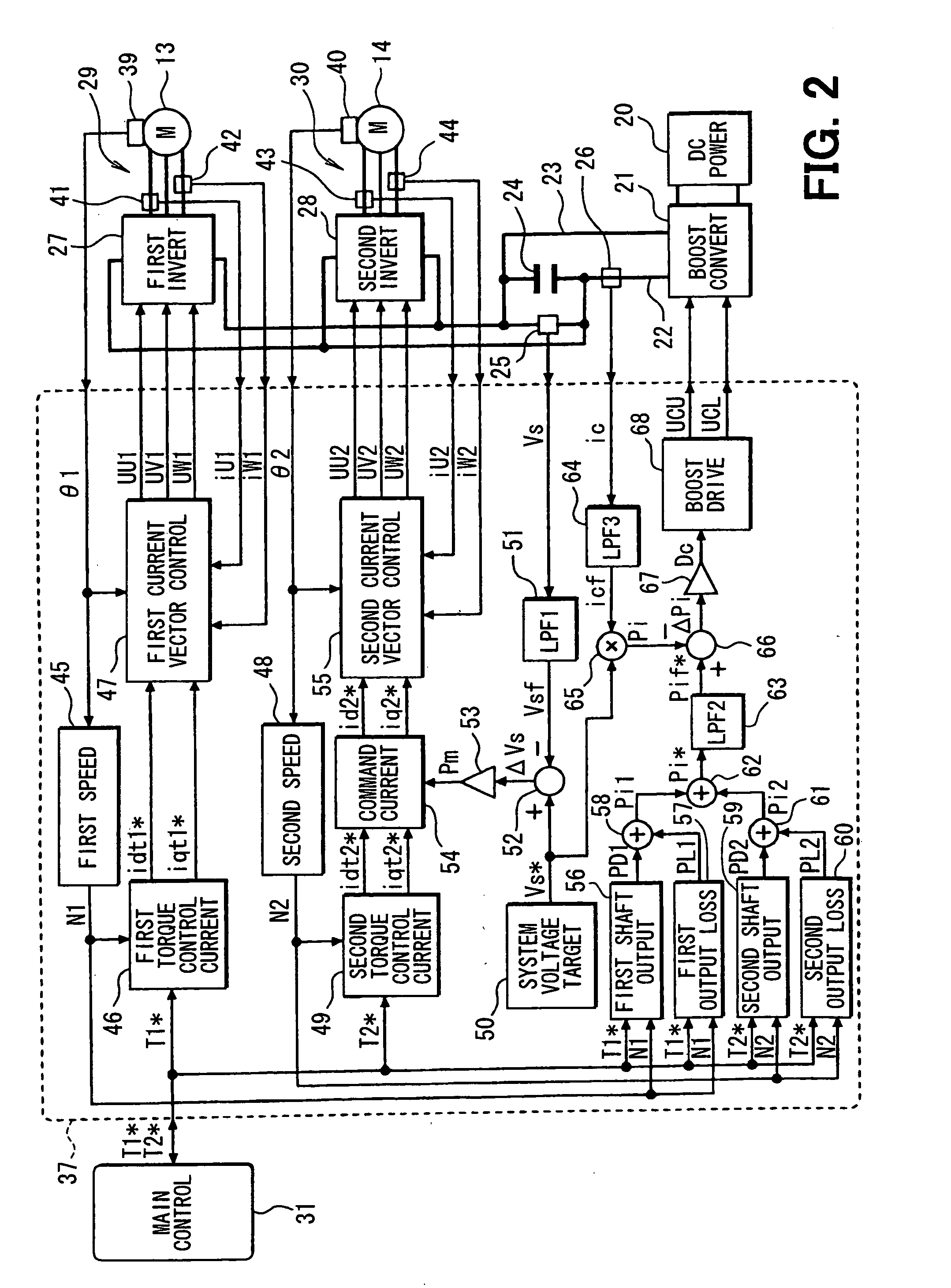
Control apparatus for electric vehicles
Owner:DENSO CORP
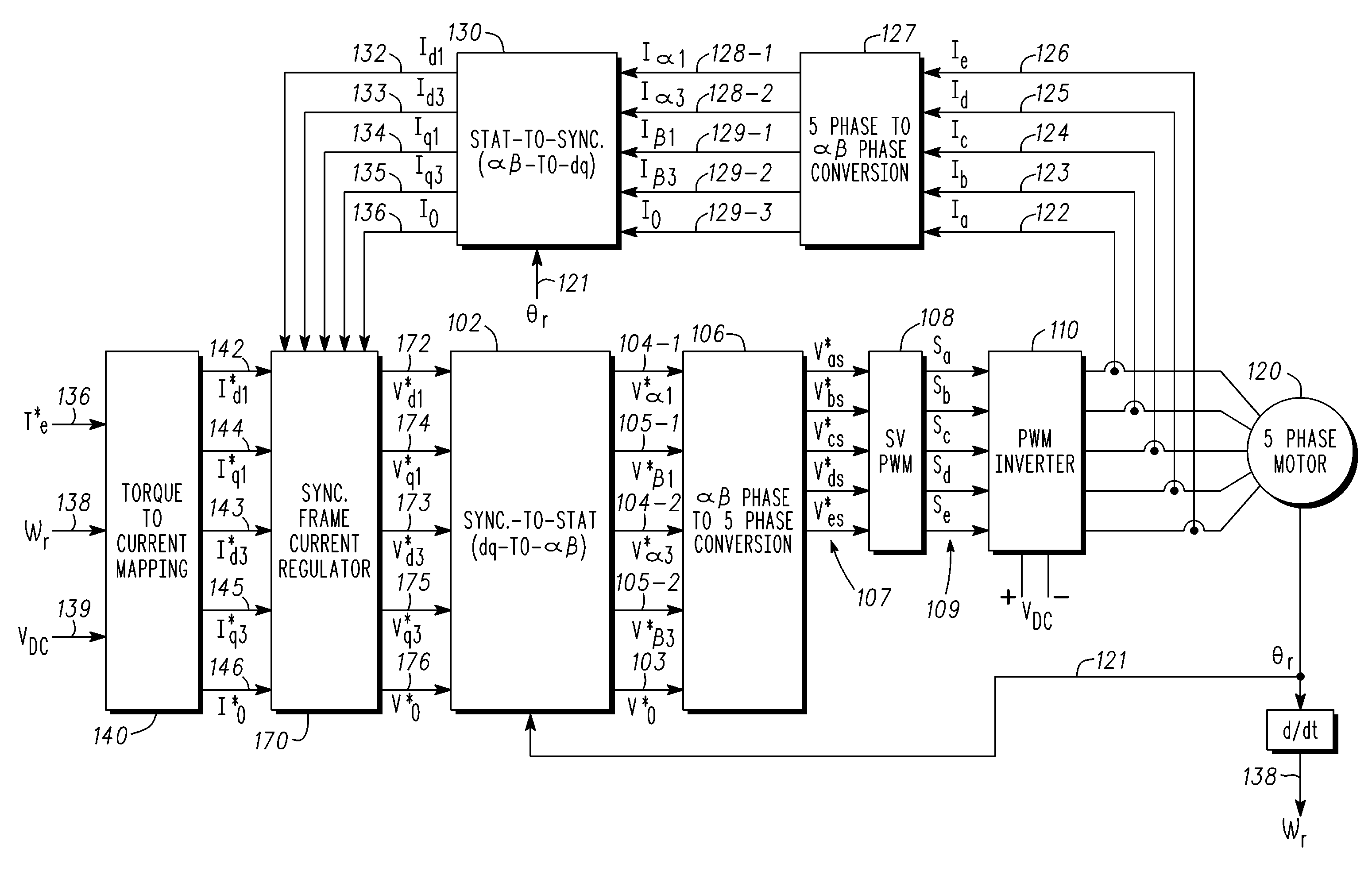
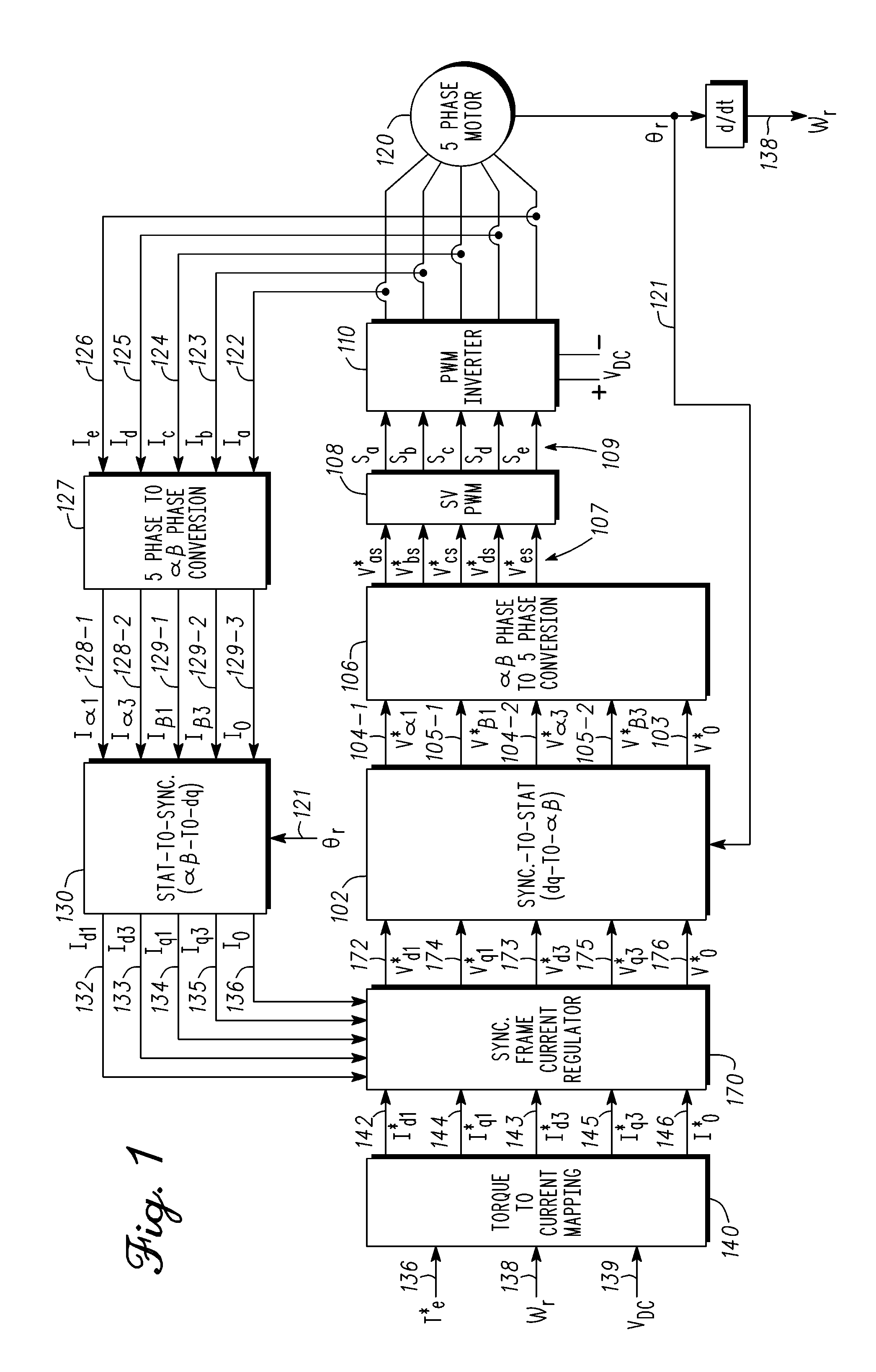
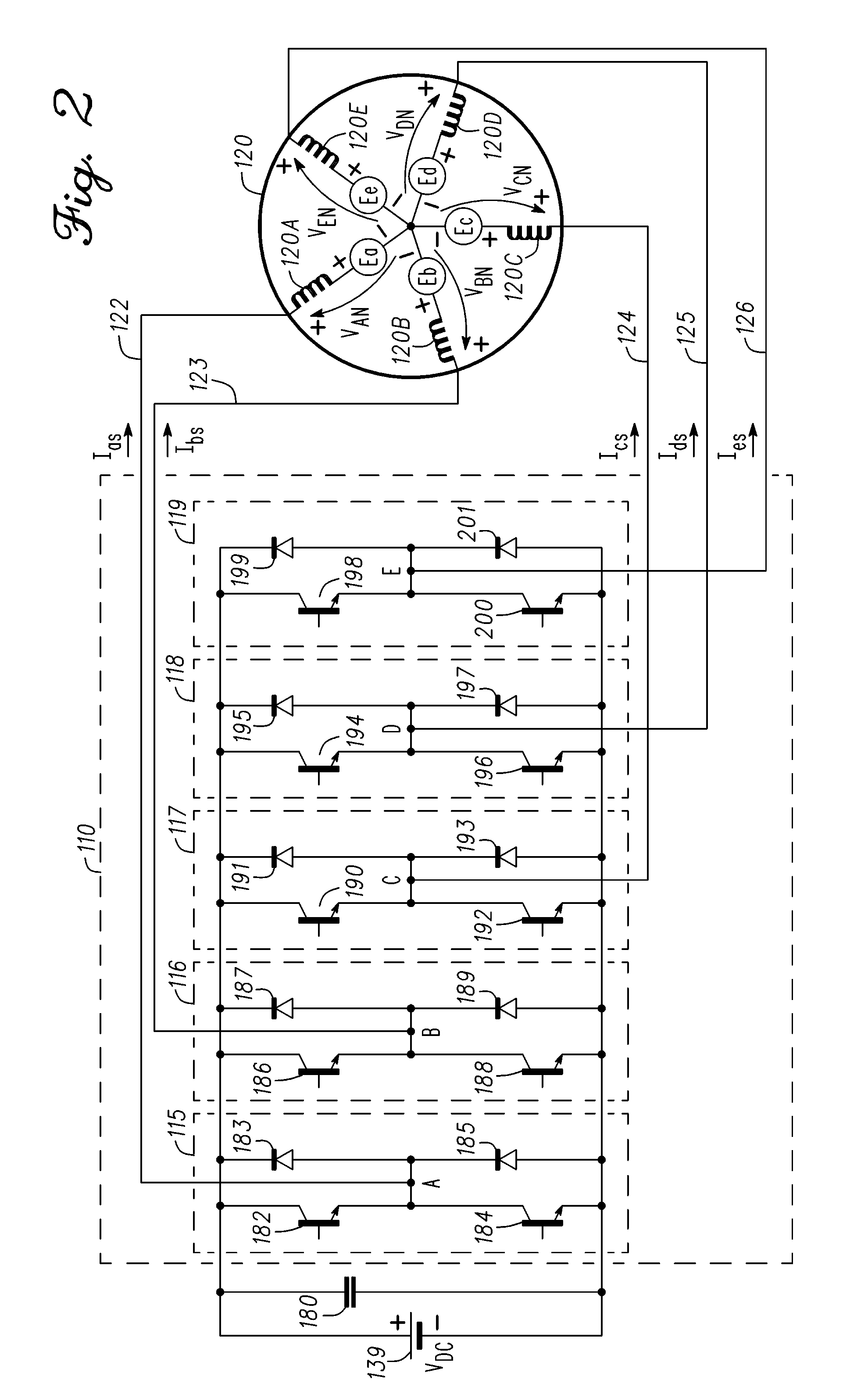
Methods, systems and apparatus for optimization of third harmonic current injection in a multi-phase machine
InactiveUS20110221365A1Improves phase voltage utilizationSynchronous motors startersAC motor controlControl vectorOperating point
Methods, system and apparatus are provided for increasing voltage utilization in a five-phase vector controlled machine drive system that employs third harmonic current injection to increase torque and power output by a five-phase machine. To do so, a fundamental current angle of a fundamental current vector is optimized for each particular torque-speed of operating point of the five-phase machine.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
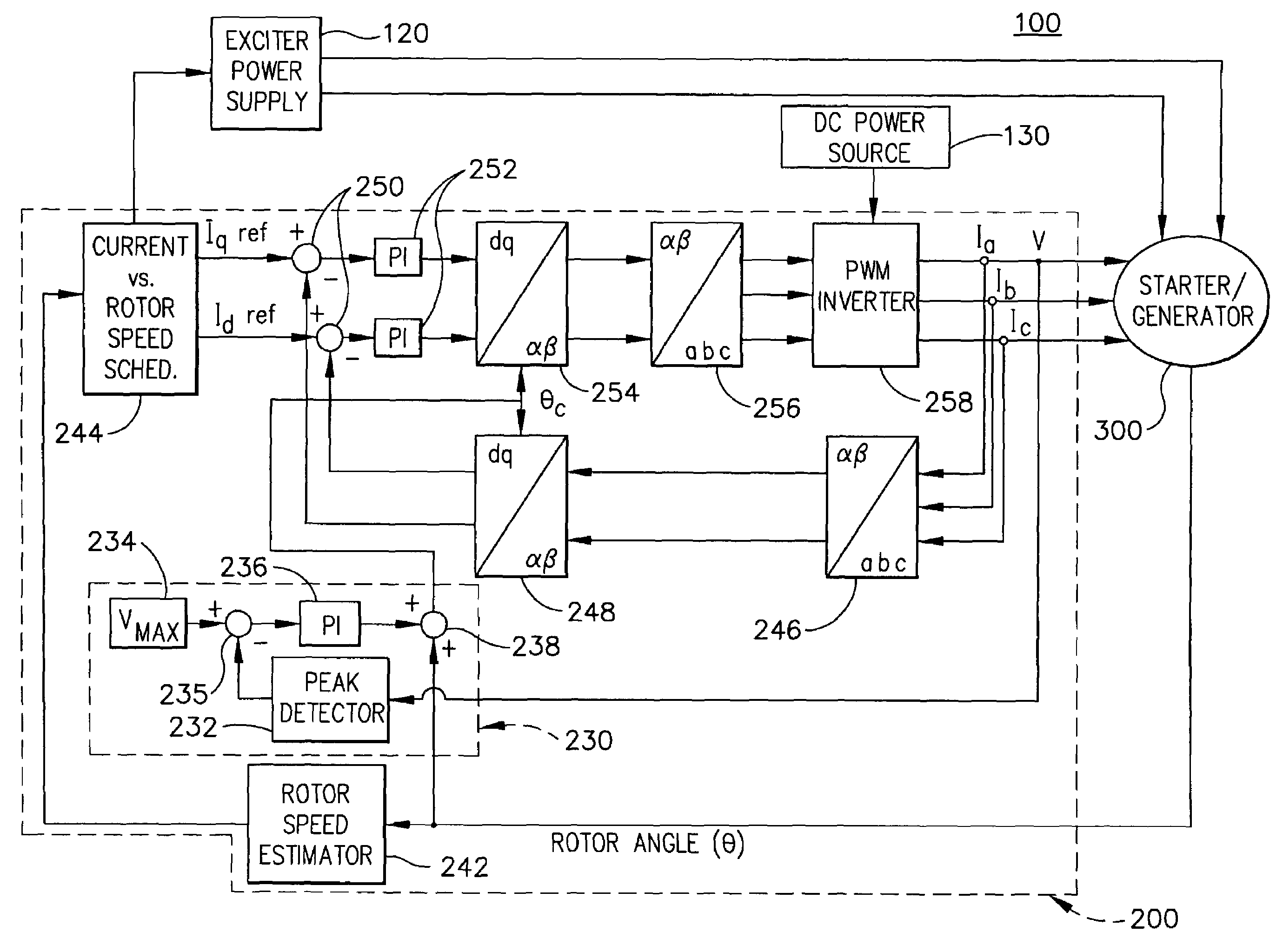
Apparatus and method to control torque and voltage of an AC machine
ActiveUS7208908B2Electronic commutation motor controlMotor/generator/converter stoppersMaximum levelEngineering
A method of controlling a power converter (258) of a synchronous machine drive system (100) determines position and speed of a rotor (350) of the synchronous machine (300); regulates a current vector relative to a reference frame, having a direct-axis component and a quadrature-axis component, the regulating step selectively causing the current vector to lag a quadrature axis of the machine (300); and outputs a command signal to the power converter (258) as a function of the regulating step. According to one implementation, this process creates higher total torque and maintains supply voltage within a maximum level during a high speed range of the machine.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
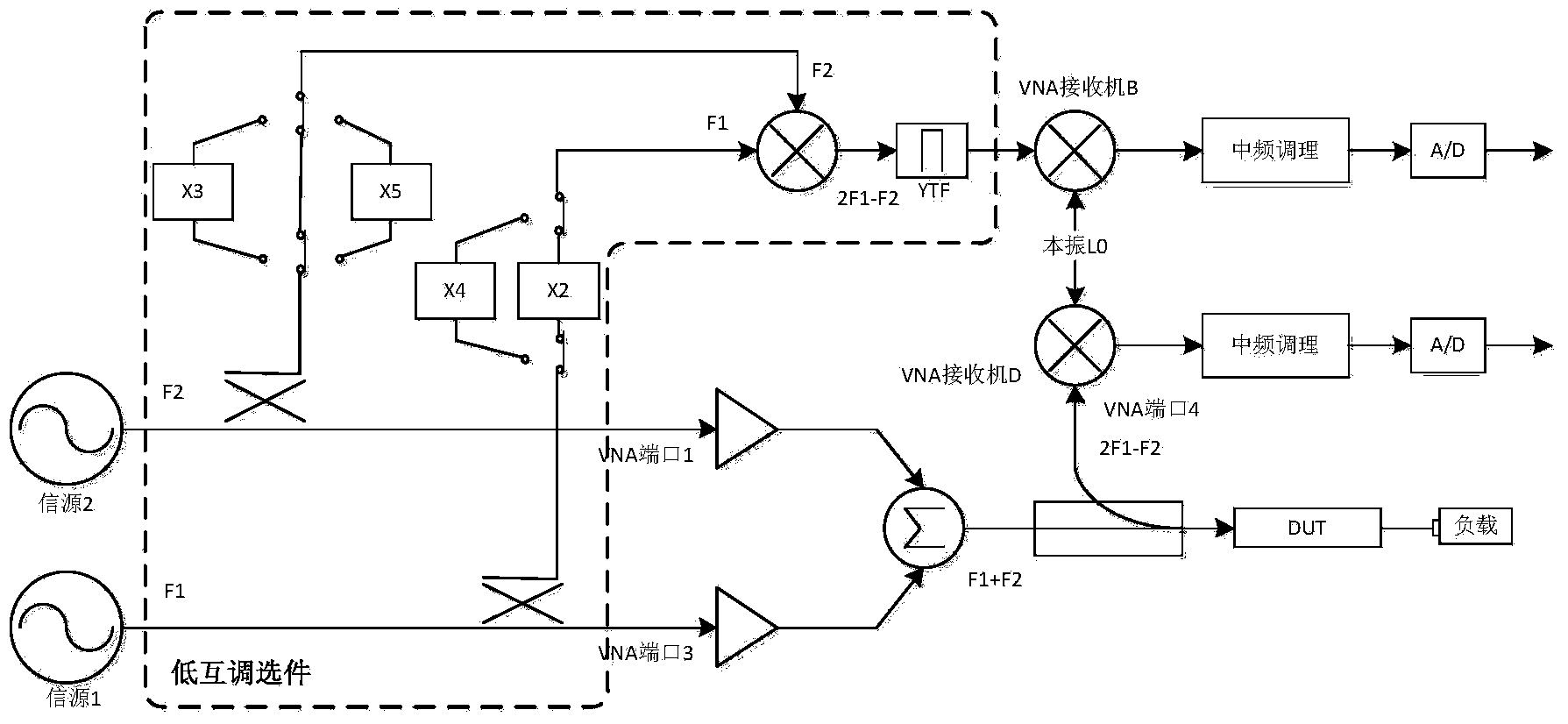
Passive intermodulation outlier quick locating method based on vector network analyzer
InactiveCN103684490AImprove product added valueImprove accuracyTransmission monitoringFrequency spectrumCommunications system
The invention provides a passive intermodulation outlier quick locating method based on a vector network analyzer. The vector network analyzer is used as two-path signal sources and a receiver (spectrum analyzer), two paths of testing signals enter a power amplifier module respectively, after amplification, a testing device is connected in to carry out combining, and 2 * 43dBm double-tone signals are formed and are loaded on a tested device. Reflection PIM signals pass through a filtering channel of the testing device, after filtering, PIM interference enters the network analyzer for measuring, and the amplitude and the phase are measured. According to the scheme, the quick locating function on a passive intermodulation outlier of the vector network analyzer can be achieved, the product added value of the current vector network analyzer is increased, locating can be carried out on an abnormal device according to a higher-order PIM product, and better adaptability is achieved on a system in which only a high-order PIM product falls into a receiving belt to form interference, such as a signal satellite communication system.
Owner:THE 41ST INST OF CHINA ELECTRONICS TECH GRP
Vector control method for synchronous reluctance motor
InactiveUS6339308B2Accurate and Efficient EstimationImprove accuracyElectronic commutation motor controlMotor/generator/converter stoppersSynchronous reluctance motorControl vector
In a driving control method for a synchronous reluctance motor, a novel vector control method is employed which does not need the salient pole position angle detector. More particularly, the present invention provides a vector control method which can accurately and efficiently estimate cosine and sine signals, being rotation signals for the vector rotators.A flux vector estimator 12a uses voltage and current information of a stator to estimate a stator flux vector by dividing it into an in-phase flux vector having the same direction as a current vector and a mirror-phase flux vector determined as a difference between the stator flux vector and the in-phase flux vector. A cosine and sine generator 12b uses the estimated in-phase and mirror-phase flux vectors to generate the cosine and sine values of an intermediate angle of the angles of such flux vectors and outputs a rotation signal of the vector rotators. Thus, vector control is established.
Owner:OKUMA CORP
Instantaneous power floating frame controller
The present invention relates to a method of controlling a power converter (20) of a synchronous machine system (10), the method comprising sampling phase-current values between the power converter (20) and the synchronous machine (30); selecting a reference frame; regulating a current vector to align with the selected reference frame, the selected reference frame having a direct-axis component and a quadrature-axis component; estimating rotor speed and position as a function of instantaneous power; adjusting the selected reference frame, based on estimated rotor position, to synchronize the selected reference frame with a magnetic axis of the rotor, thereby generating a synchronized floating frame; and applying the synchronized floating frame to control the power converter (20). The present invention also related to a power converter controlling apparatus (100) for controlling a power converter (20) of a synchronous machine system (10) without use of a machine position sensor.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
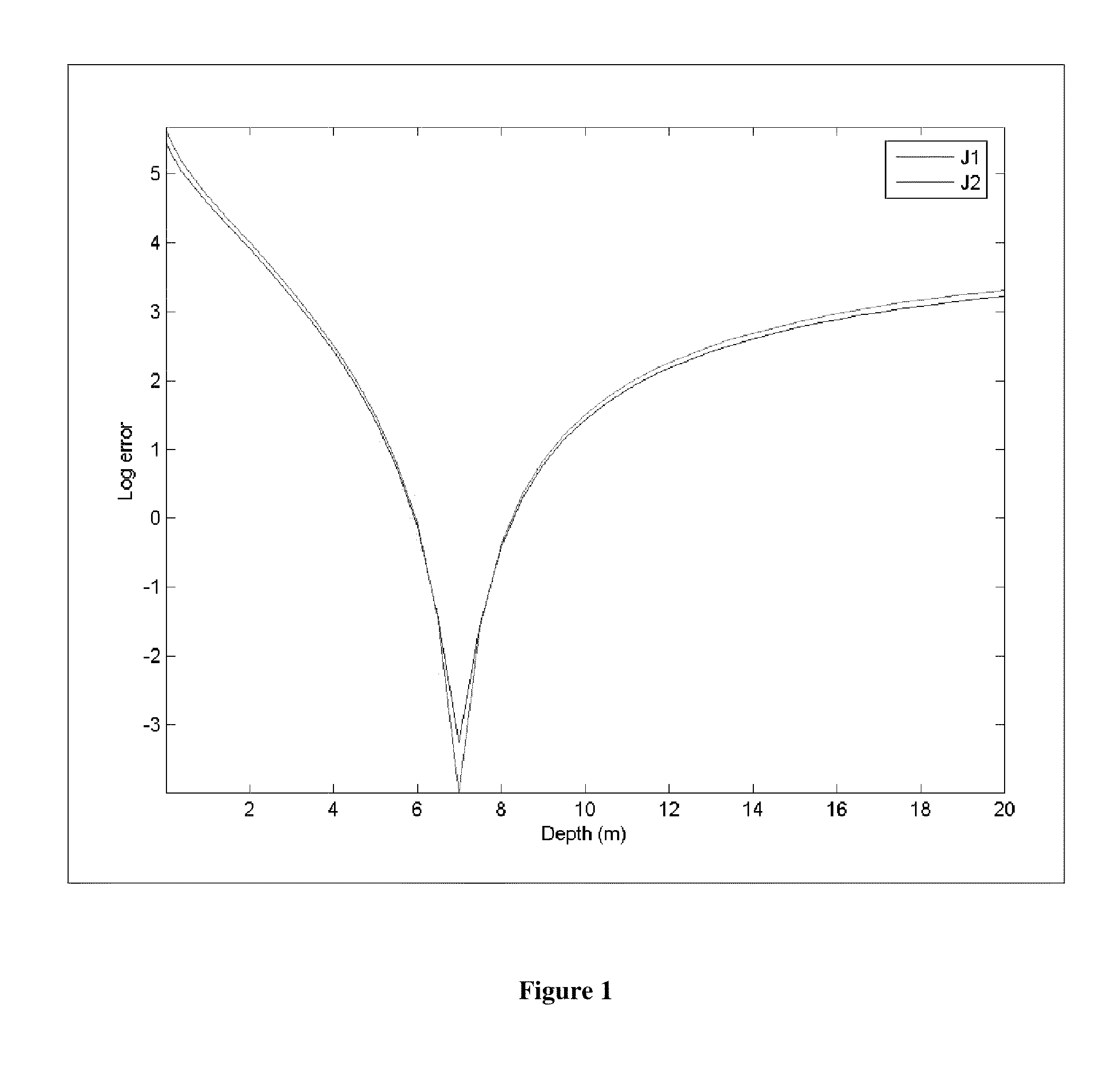
Methods for mapping depth and surface current
ActiveUS20120020527A1Easy to identifyEasy to trackScene recognitionDiagnostic Radiology ModalityFourier transform on finite groups
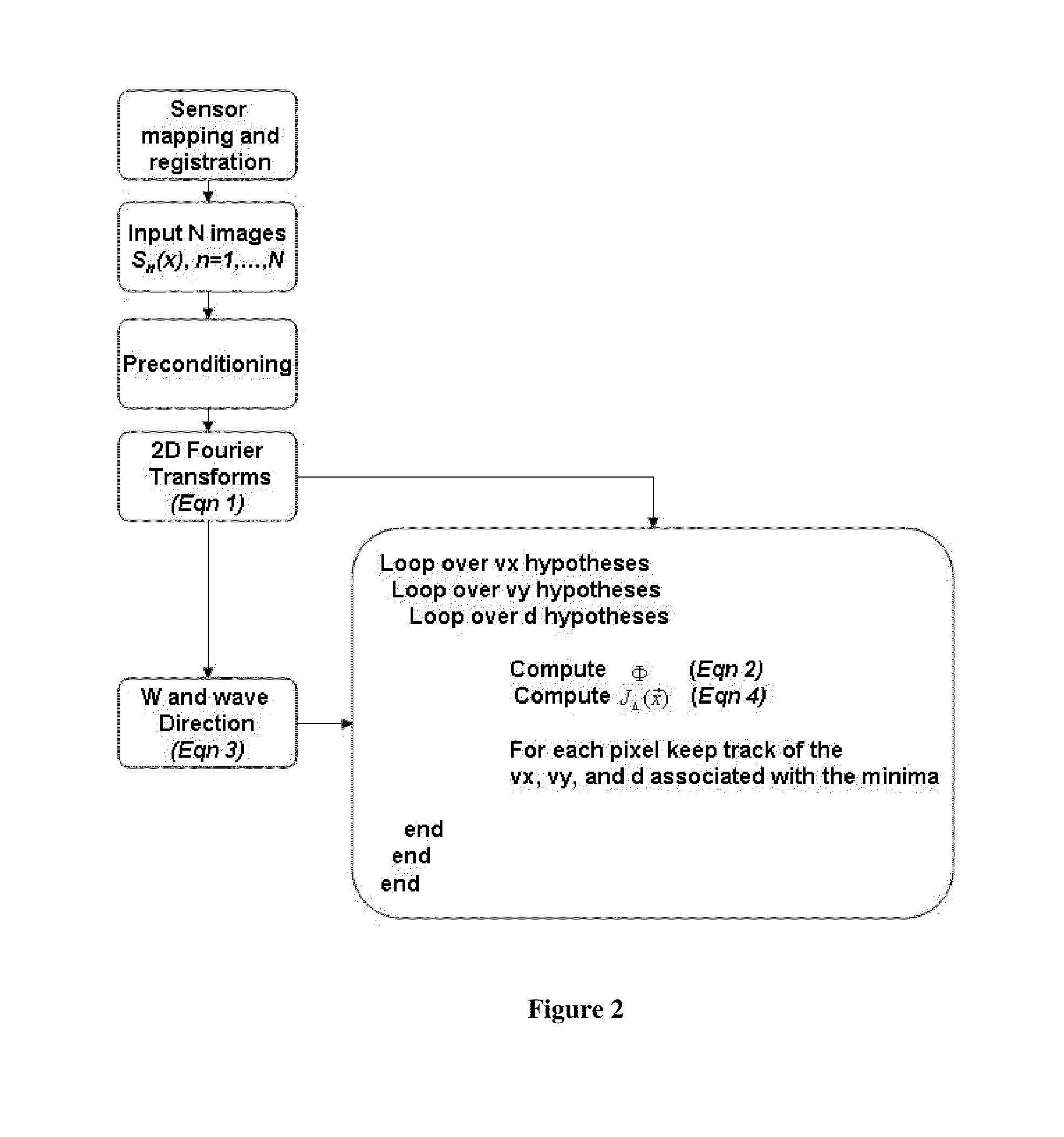
Systems and methods for acquiring accurate maps of near-shore depth and surface currents are disclosed. An imaging platform is provided which is able to obtain a time series of overhead images of an area of a body of water having pixel intensity correlated with wave height. The platform may be on a tower, or may be airborne, space-borne, or ship-borne. The imaging modality may be optical, radar, or LIDAR. Image processing corrects the images, as and if needed, such they are mapped onto a grid of fixed coordinates, and the pixel intensities have a near linear relationship to wave height. A two-dimensional Fourier transform of each image is obtained, then the extremum of an objective function is found, wherein the objective function is a function of the depth and surface current (velocity) vector at each pixel location, and the extremum is sharply peaked at a particular set of depth and a particular set of surface current vector values. A pixel-by-pixel map of depths and or currents can be produced.
Owner:ABILEAH RON
Power converter with current vector controlled dead time
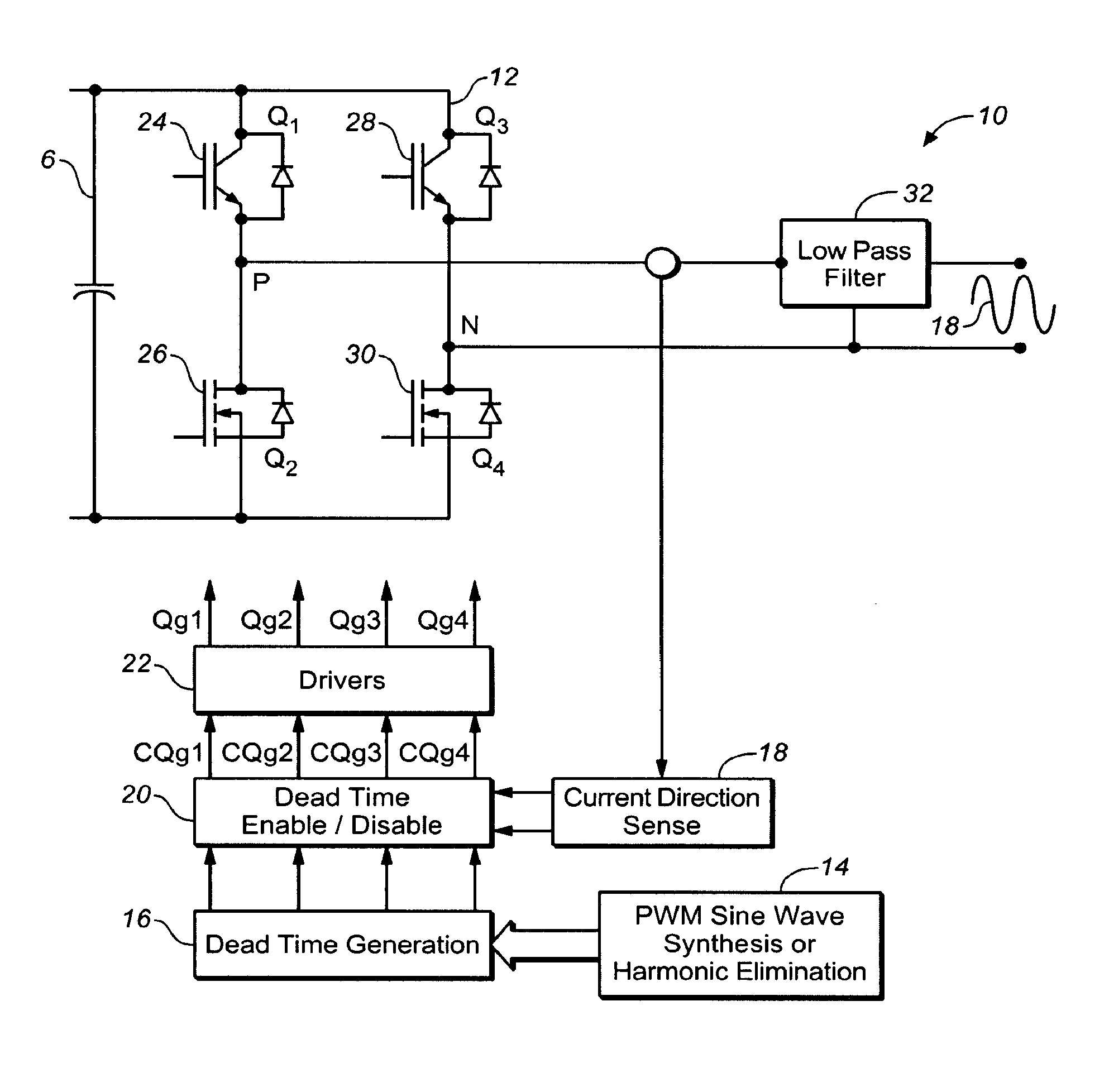
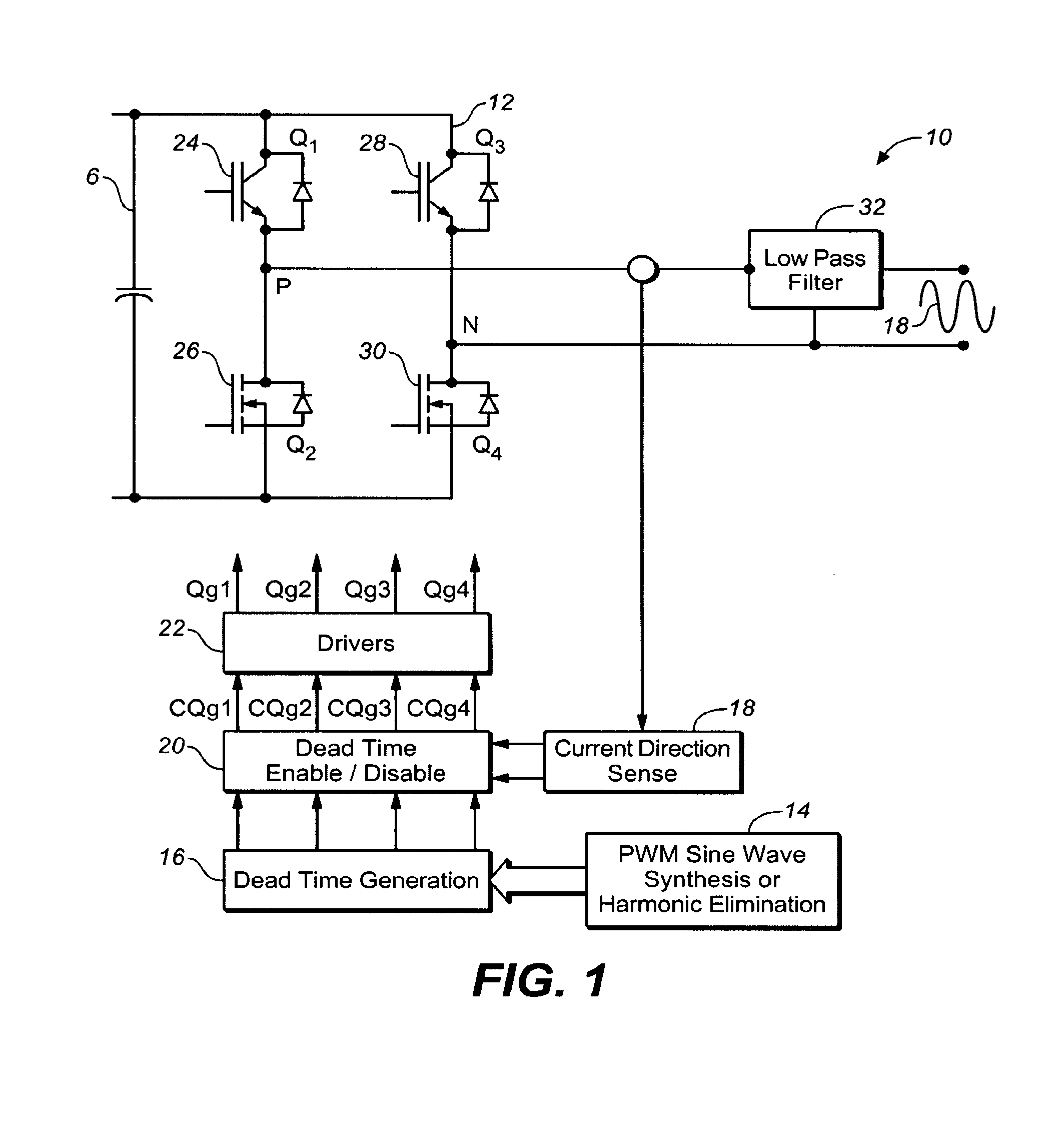
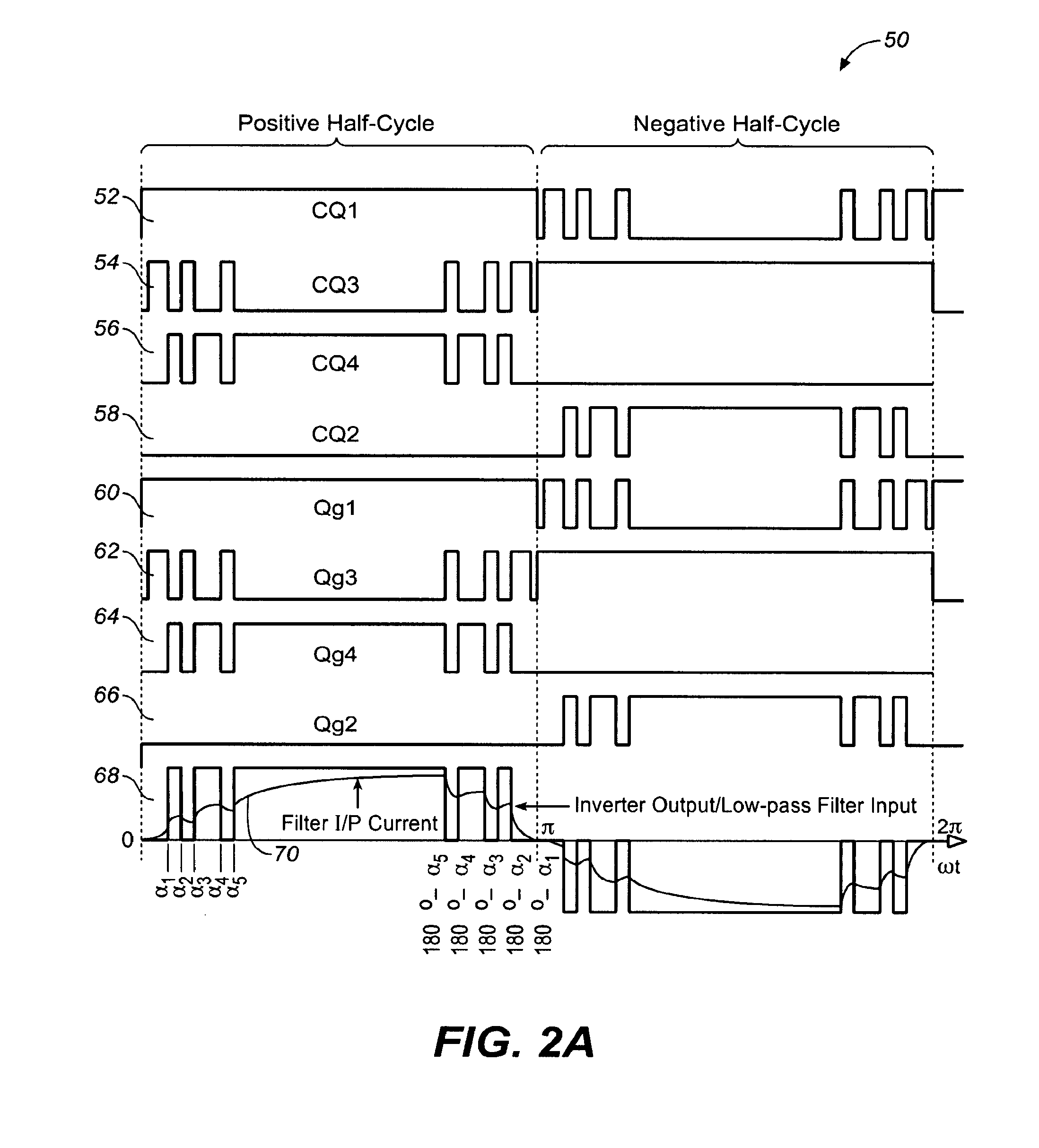
ActiveUS8385092B1Small sizeEnabling and disabling of dead timeEmergency protective circuit arrangementsAc-dc conversionPower flowTransverter
In one embodiment, a method is provided for a power converter system comprising a switching circuit having a plurality of switches operable to be turned on and off to cause current to flow to deliver power to a load. The method includes the following: generating PWM control signals for turning on and off the switches in the switching circuit; sensing the direction of current flow, wherein the direction of current flow is related to a likelihood of shoot-through in the switching circuit; providing a current vector signal indicative of the direction of current flow; and enabling or disabling introduction of a dead time into the PWM control signals for the switches in the switching circuit in response the current vector signal.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
Circuit protection order component phase selectiing method using both end information
ActiveCN101038316AThe principle is simple and reliableHigh sensitivityFault locationPhase currentsElectrical current
The present invention relates to a circuit protecting order component phase selecting method adopting two-end information. First, synchronous samplings of the phase current of the own side and the opposite side of the circuit are performed in a preset sampling speed, and the sampling value of the phase current of the opposite side is transmitted to the own side; then, the differential current vectors of each phase of said sampling result is calculated and the positive-sequence vector, the negative-sequence vector and the zero- sequence vector I1d, I2d, I3d are extracted using the A phase as the standard phase; the negative-sequence vector and the zero- sequence vector of the differential current are compared: -90 DEG 1.5*[1d] , it is the single-phase groud fault; or, it is the two-phase ground fualt. The method adopts a differential current to performe judging, and the principle is simple and reliable and is not influenced by the running mode of the system. The device has a high sensitivity and can select phase correctly when a conversion fault occurs.
Owner:NANJING GUODIAN NANZI POWER GRID AUTOMATION CO LTD
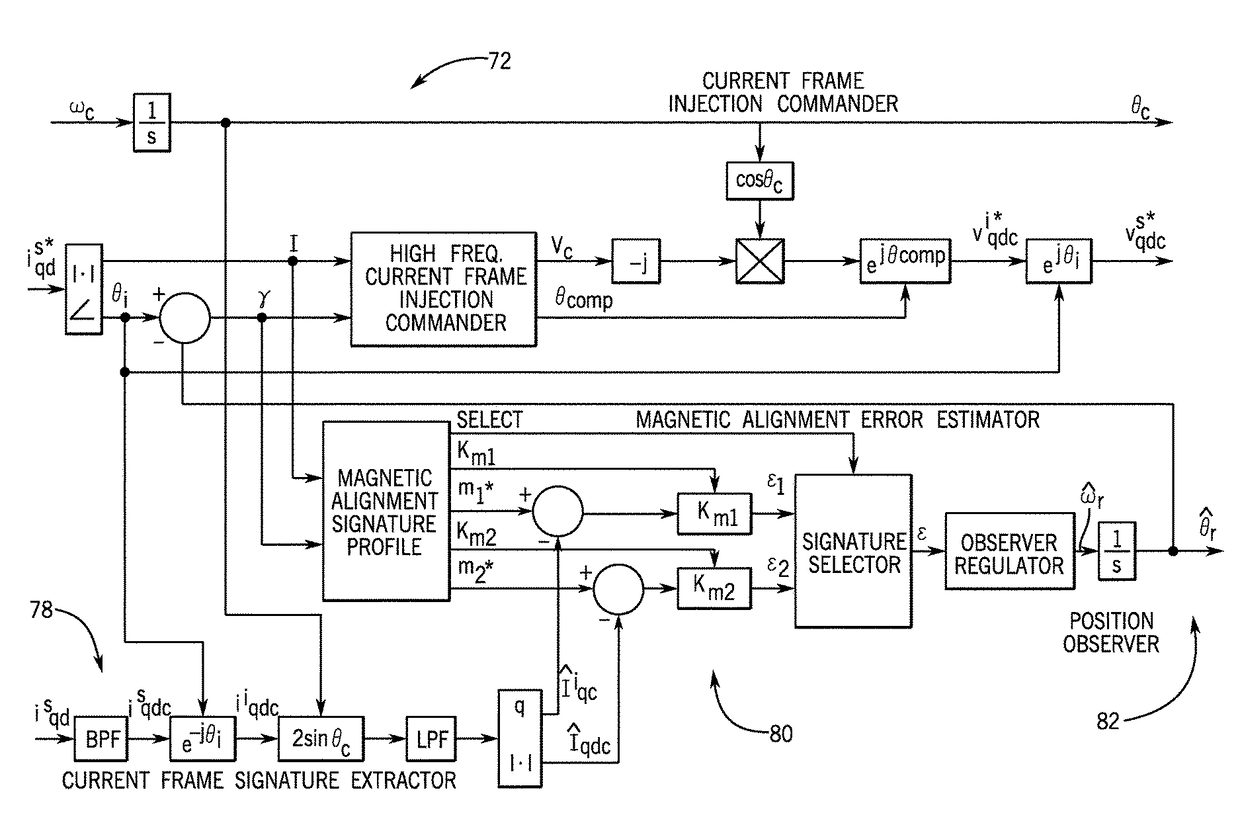
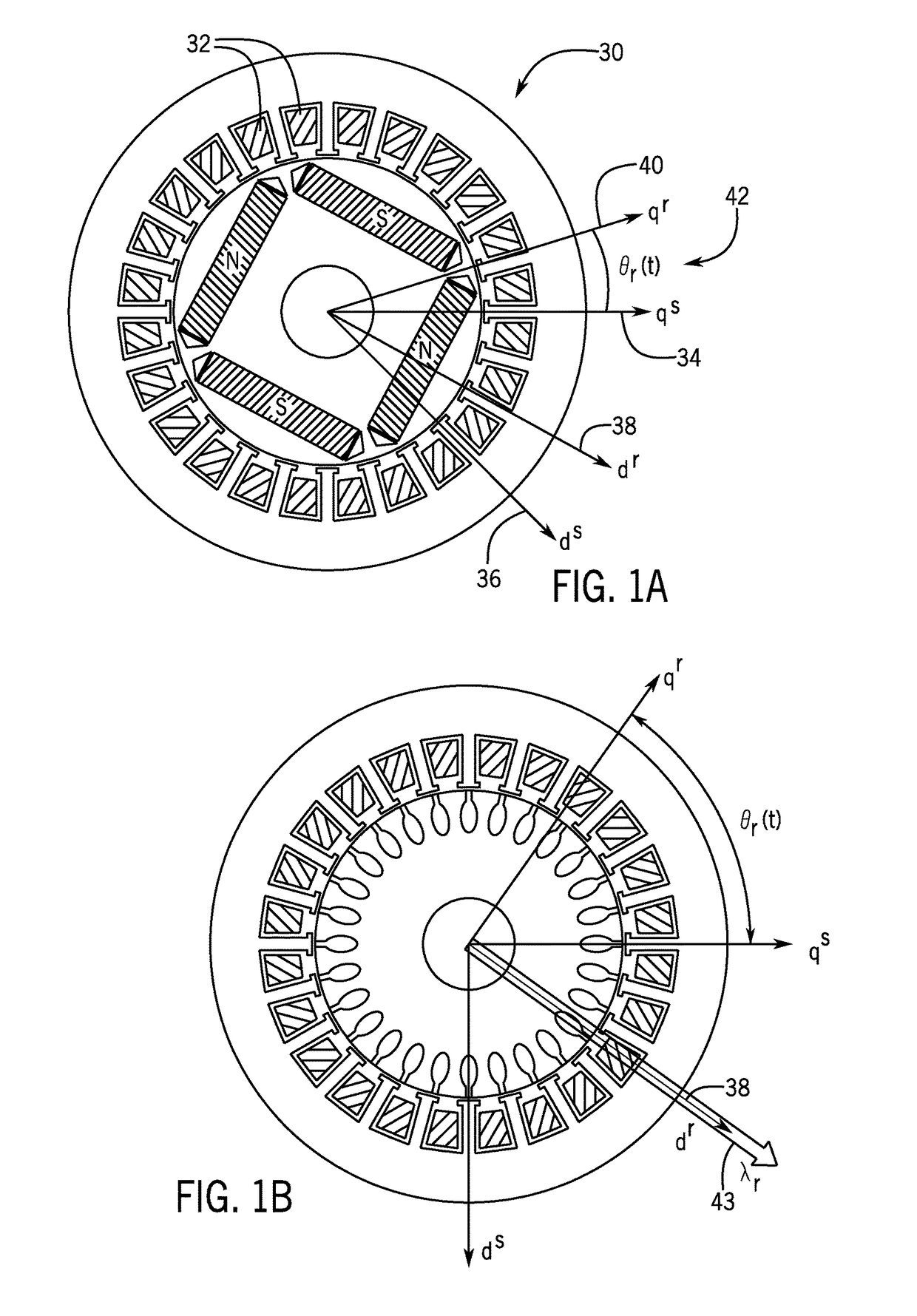
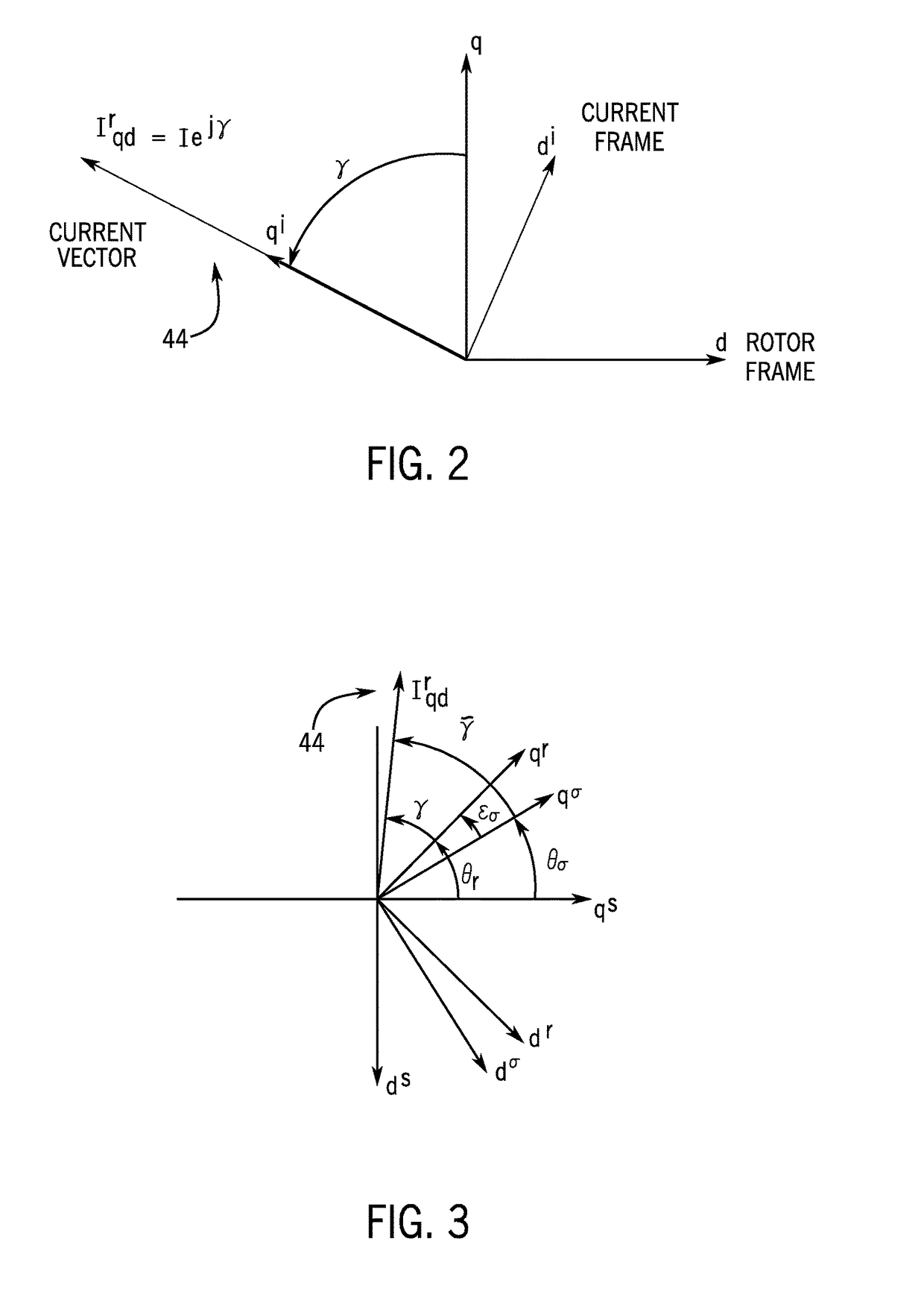
System and method for sensorless control of electric machines using magnetic alignment signatures
A system and method for position sensorless control of an AC electric machine is disclosed. A drive system for driving an AC electric machine provides a primary current excitation to drive the AC electric machine, the primary current excitation comprising a current vector having a magnitude and angle. The drive system injects a carrier signal to the AC electric machine that is superimposed onto the current vector, with the carrier signal being selected to generate a carrier response signal that has sensitivity to magnetic alignment information of the AC electric machine at its operating point. The drive system measures at least one magnetic alignment signature of the AC electric machine from the generated carrier response signal and controls an orientation of the current vector using the measured at least one magnetic alignment signature, so as to achieve a desired magnetic operation of the AC electric machine.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
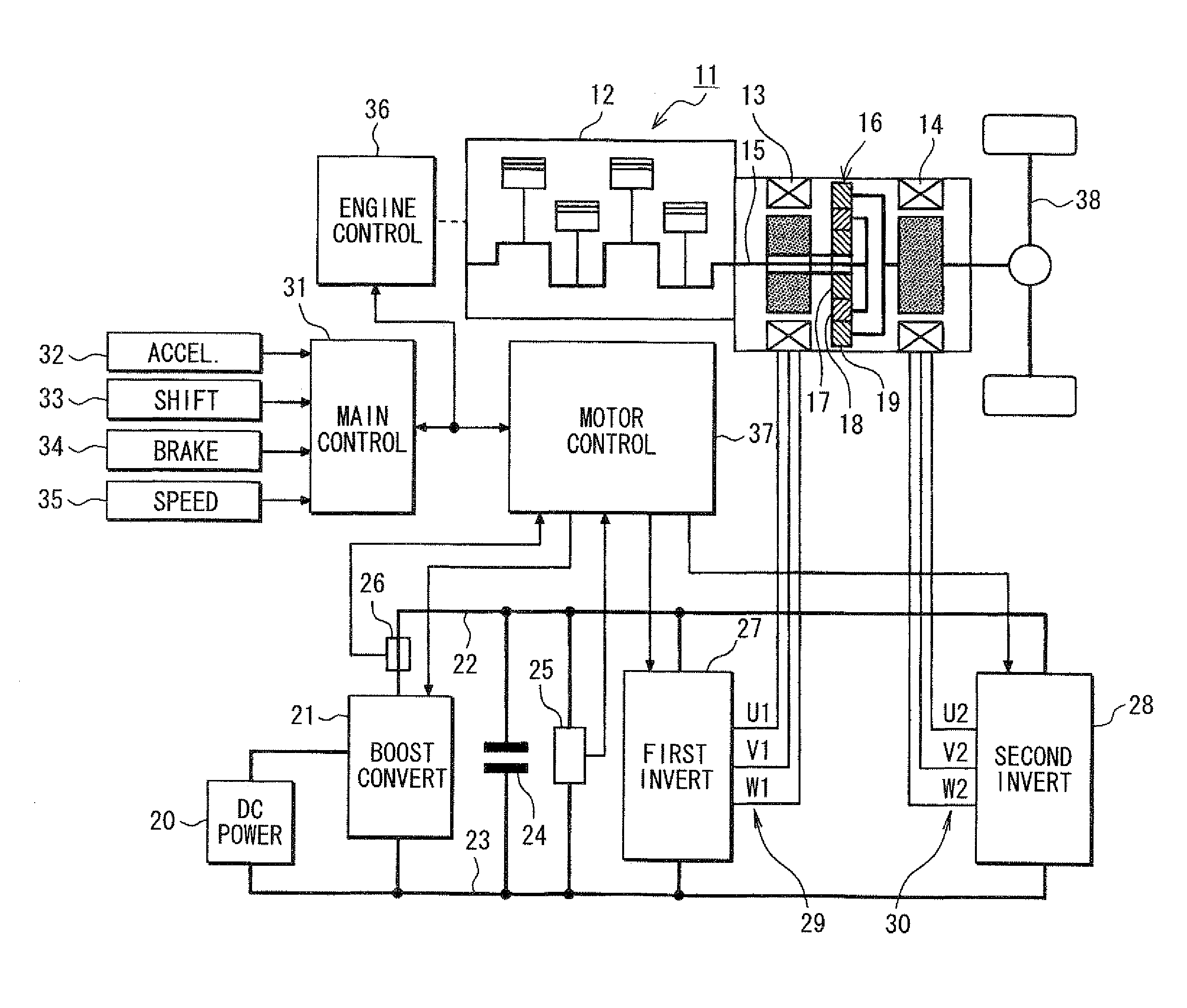
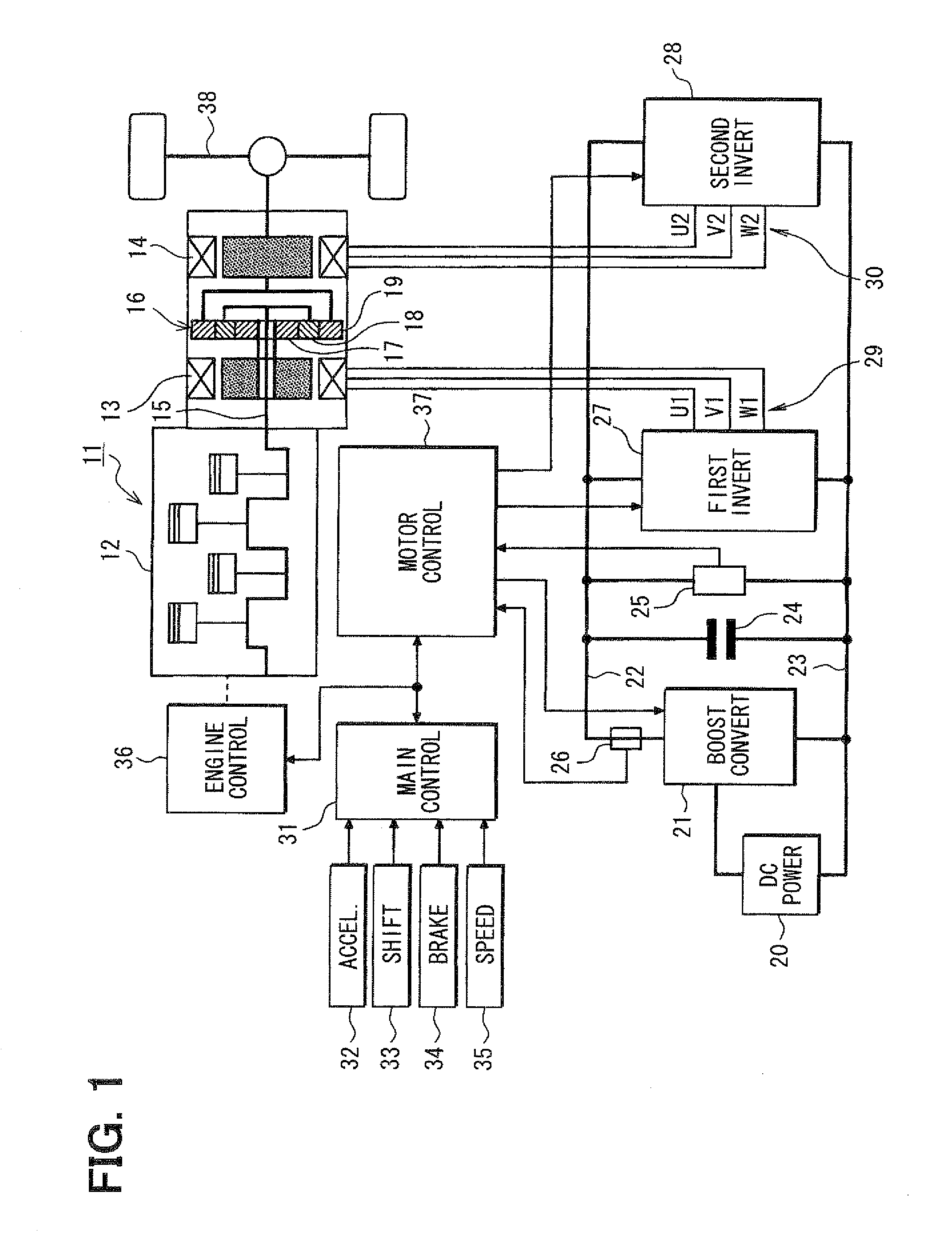
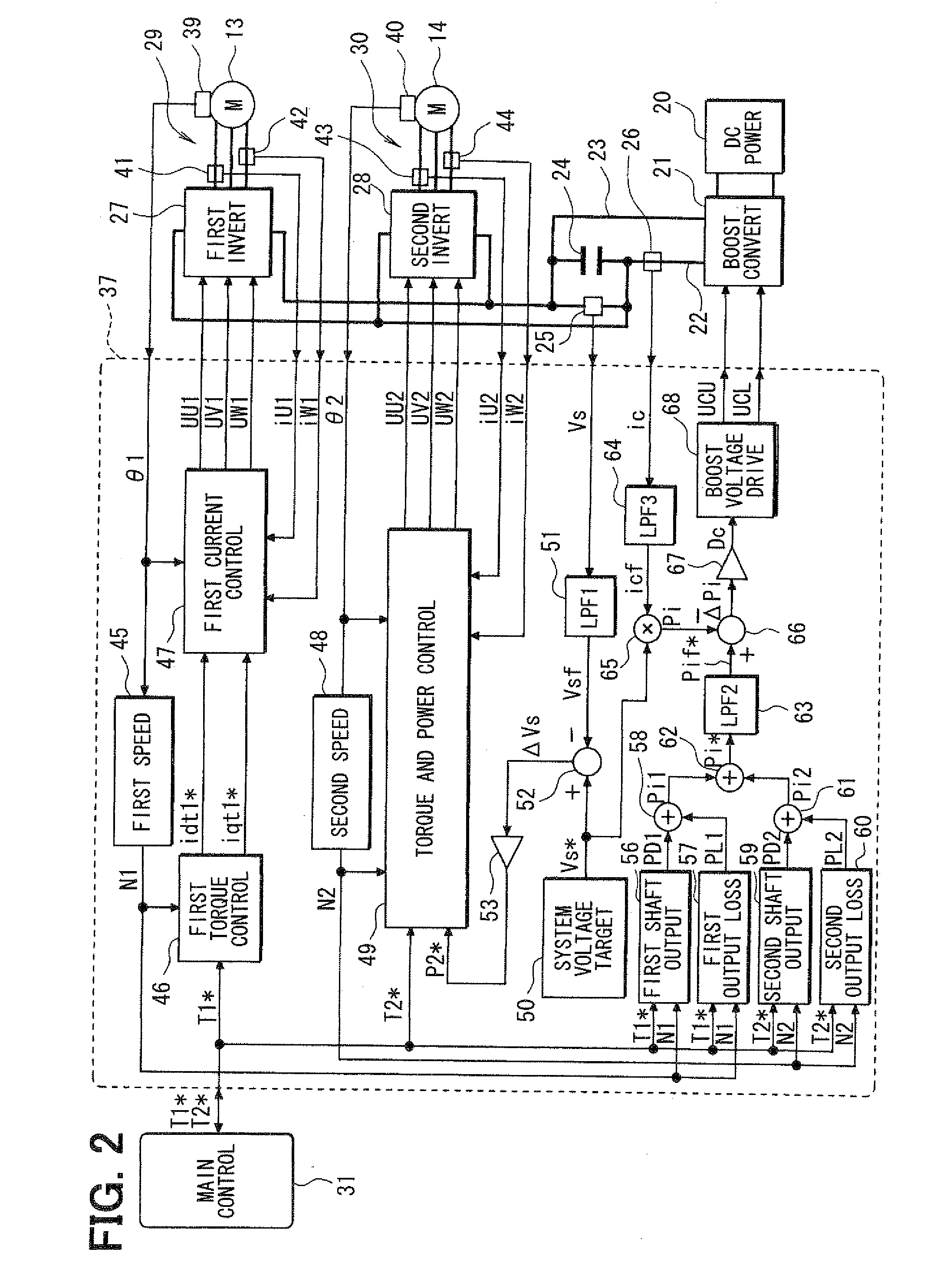
Control apparatus for electric vehicles
ActiveUS20080281480A1Small sizeLow costAuxillary drivesDigital data processing detailsWave shapeElectric vehicle
A motor control unit controls the input electric power of a MG unit to thereby suppress variations of a system voltage and stabilize the system voltage. The torque control of an AC motor and the input electric power control of the MG unit are executed independently from each other, so that the torque control and the input electric power control are stabilized. Further, torque variation zeroing control for correcting a phase of a pulse waveform voltage is executed so that a difference between a first estimated torque computed based on a torque control detection current vector of the AC motor and a second estimated torque computed based on a detection motor current vector is reduced to zero. Thus, uncomfortable torque variation is suppressed in a transient condition of the input electric power control of the MG unit.
Owner:DENSO CORP
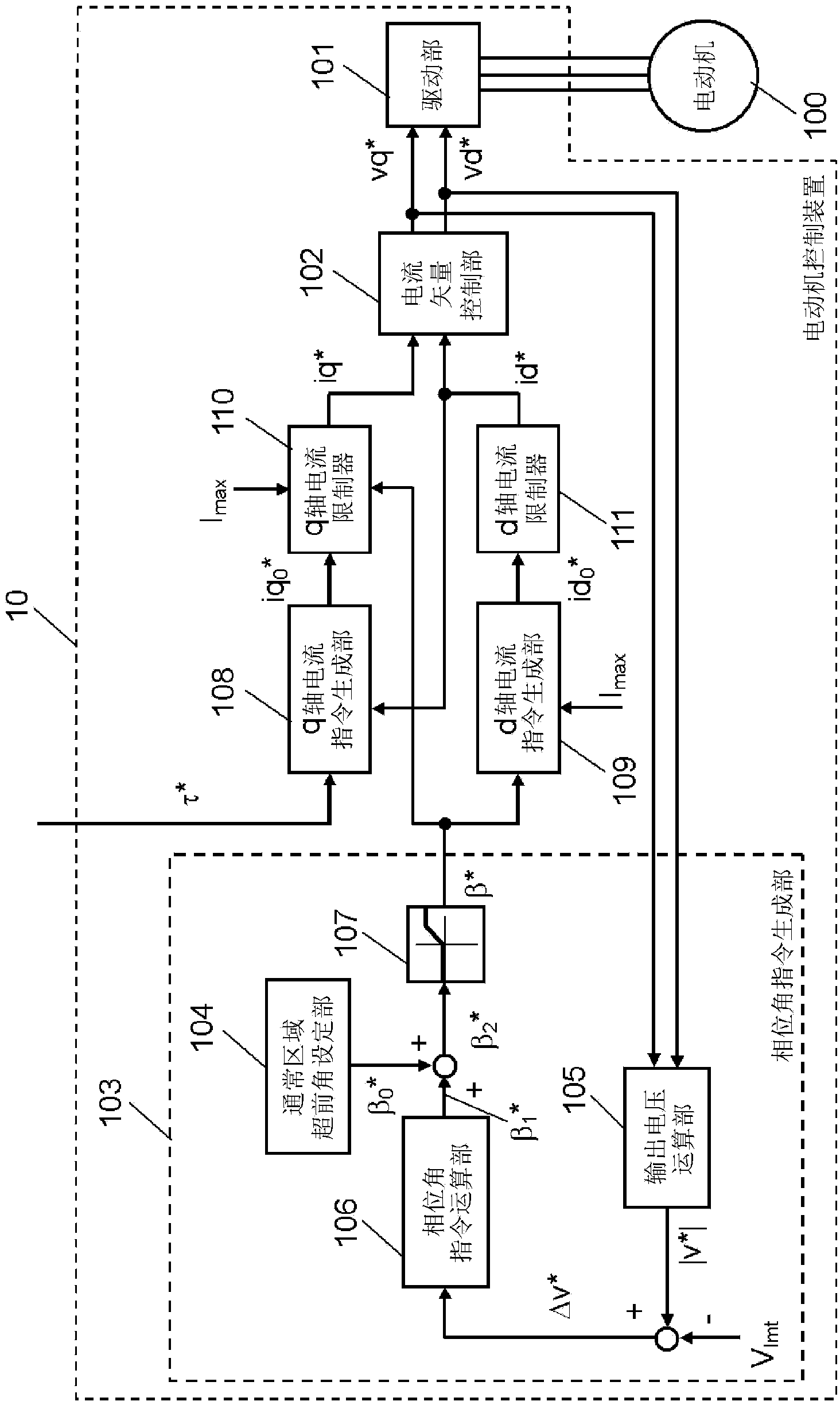
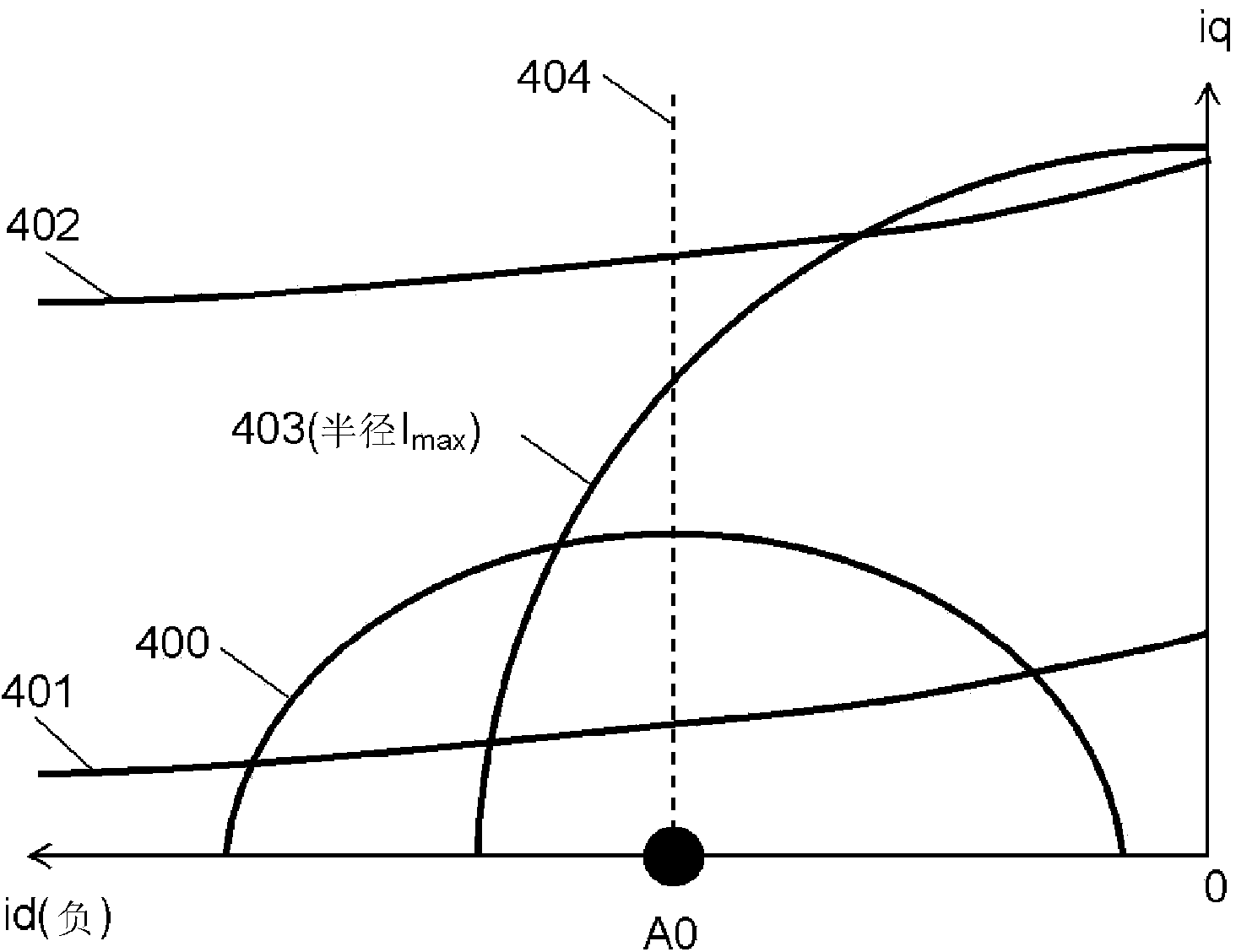
Electric motor control device
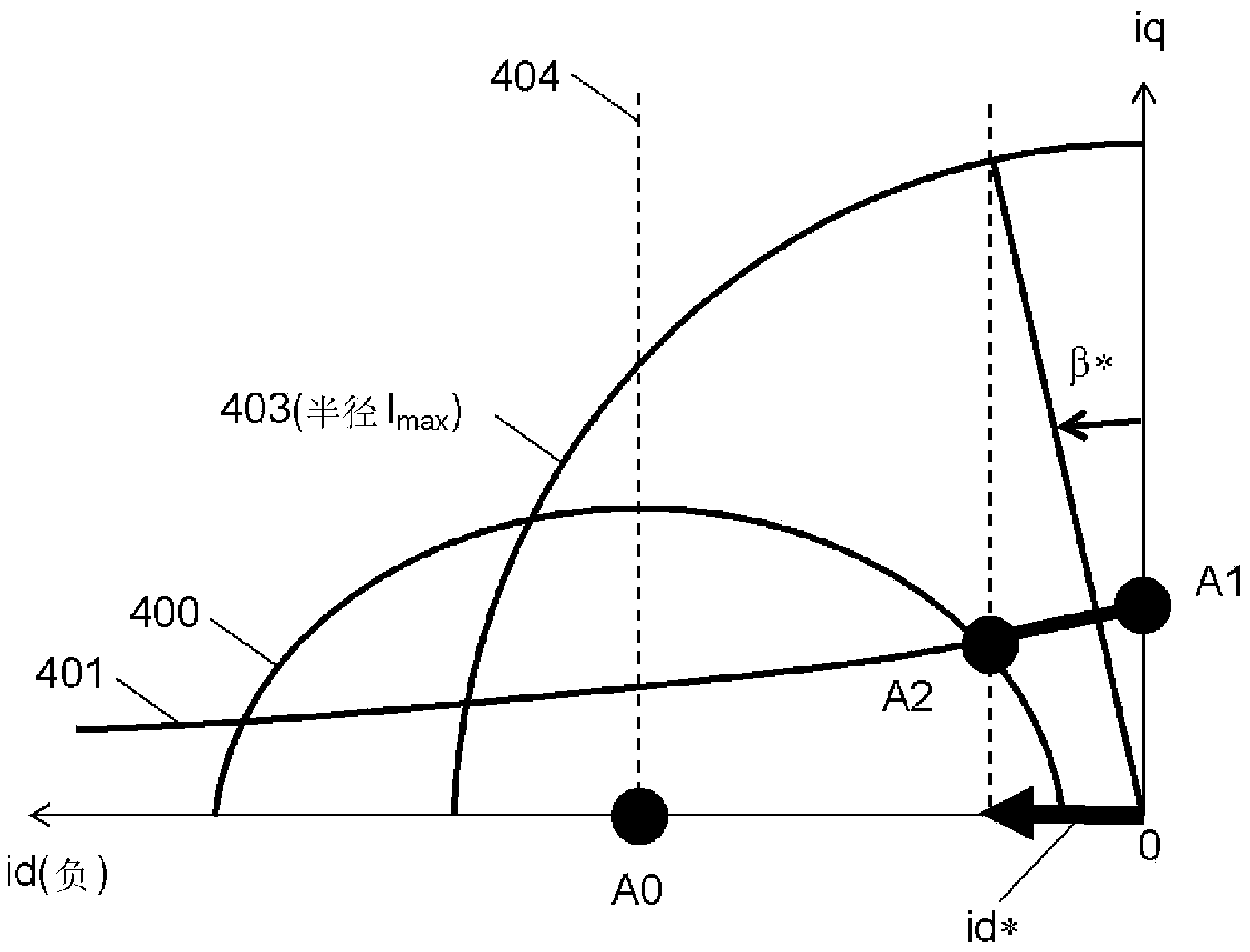
ActiveCN103988419AHighly stable regenerative actionPrevent overcurrentElectronic commutation motor controlAC motor controlCurrent limitingFault current limiter
In the present invention, a current vector control unit, which separately controls a d-axis current and a q-axis current that are obtained from a current of an electric motor by means of orthogonal transformation according to a target command value, is provided, and a drive unit drives the electric motor. Furthermore, a phase angle command generation unit generates a phase angle command ([beta]*) on the basis of the difference ([increment]v*) between the absolute value (|v*|) of a voltage command from the current vector control unit to the drive unit and a predetermined reference value (Vlmt). A d-axis current command generation unit generates a d-axis current command (id*) on the basis of the sine value of the phase angle command ([beta]*). A q-axis current limiter sets a limit value for a q-axis current command (iq*) on the basis of the cosine value of the phase angle command ([beta]*). Due to this configuration, voltage saturation is eliminated, and the electric motor is highly stably driven while producing a high output even when a target command value in access of the possible output limit of the electric motor is input when the voltage is nearly saturated.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
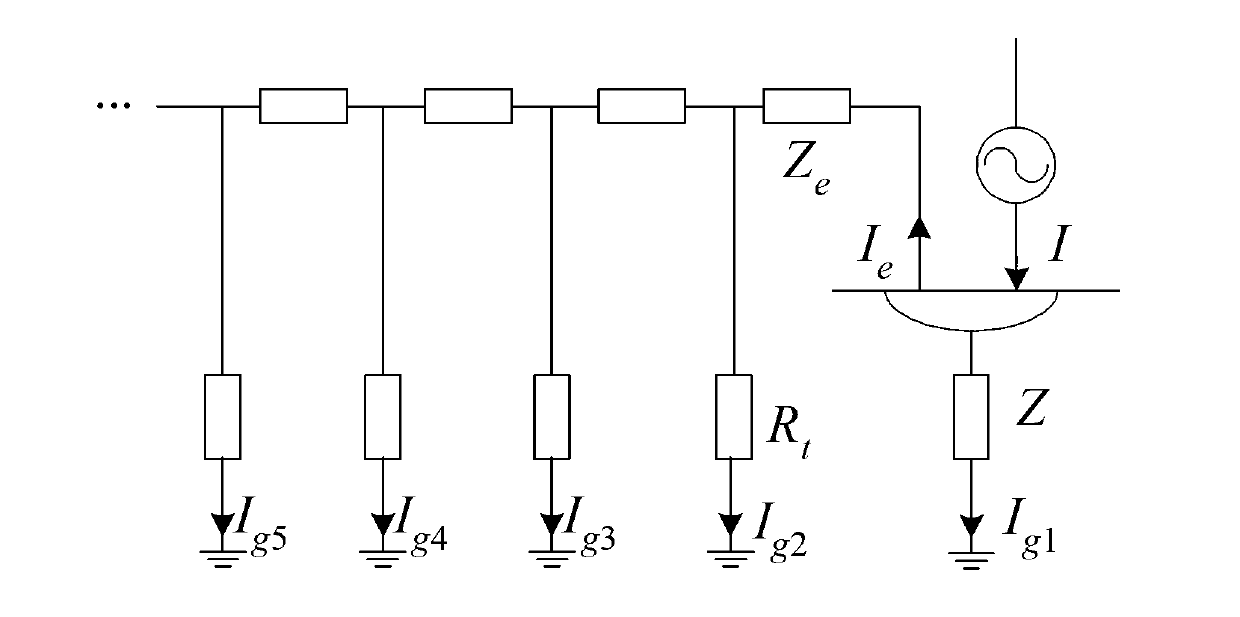
Method for measuring ground impedance of large grounding grid
ActiveCN103217584AAccurate and accurate evaluationAchieve accurate evaluationEarth resistance measurementsGrounding gridReference vector
The invention discloses a method for measuring the ground impedance of a large grounding grid, and relates to the technical field of the measurement of grounding characteristics of large grounding grids such as grounding grids in power stations or transformer substations. Based on the phase difference measurement of a reference vector of test current, module values and phase difference of an outlet overhead ground wire and a power cable outer sheath of a power station or a transformer substation to shunts of the test current are obtained; and through a vector of each shunt and calculation, the actual diffused current vector of the test current passing the grounding grid is accurately solved, so that the ground impedance of the grounding grid is accurately measured. According to the conventional method for measuring the ground impedance of the grounding grid under the condition that the running power station or transformer substation is provided with an outlet ground wire, the shunts of the overhead ground wire and the cable outer sheath are not measured, or the vector of each shunt is only measured, the phase difference from the vector of the test current is not measured, a result that the shunt module value is subtracted from the test current is only obtained, and the simple treatment method is changed. The accuracy for measuring the ground impedance is improved, serious systematic errors are avoided, and the state of the grounding grid is accurately evaluated.
Owner:ELECTRIC POWER RES INST OF GUANGDONG POWER GRID +1
Vector control method for synchronous reluctance motor
InactiveUS20010024100A1Improve accuracyReduce the amount of calculationElectronic commutation motor controlMotor/generator/converter stoppersControl vectorSynchronous reluctance motor
In a driving control method for a synchronous reluctance motor, a novel vector control method is employed which does not need the salient pole position angle detector. More particularly, the present invention provides a vector control method which can accurately and efficiently estimate cosine and sine signals, being rotation signals for the vector rotators. A flux vector estimator 12a uses voltage and current information of a stator to estimate a stator flux vector by dividing it into an in-phase flux vector having the same direction as a current vector and a mirror-phase flux vector determined as a difference between the stator flux vector and the in-phase flux vector. A cosine and sine generator 12b uses the estimated in-phase and mirror-phase flux vectors to generate the cosine and sine values of an intermediate angle of the angles of such flux vectors and outputs a rotation signal of the vector rotators. Thus, vector control is established.
Owner:OKUMA CORP
Power network analyzer for an integrated circuit design
ActiveUS20060095870A1Improve calculation accuracyImprove accuracyCAD circuit designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationElectrical connectionHemt circuits
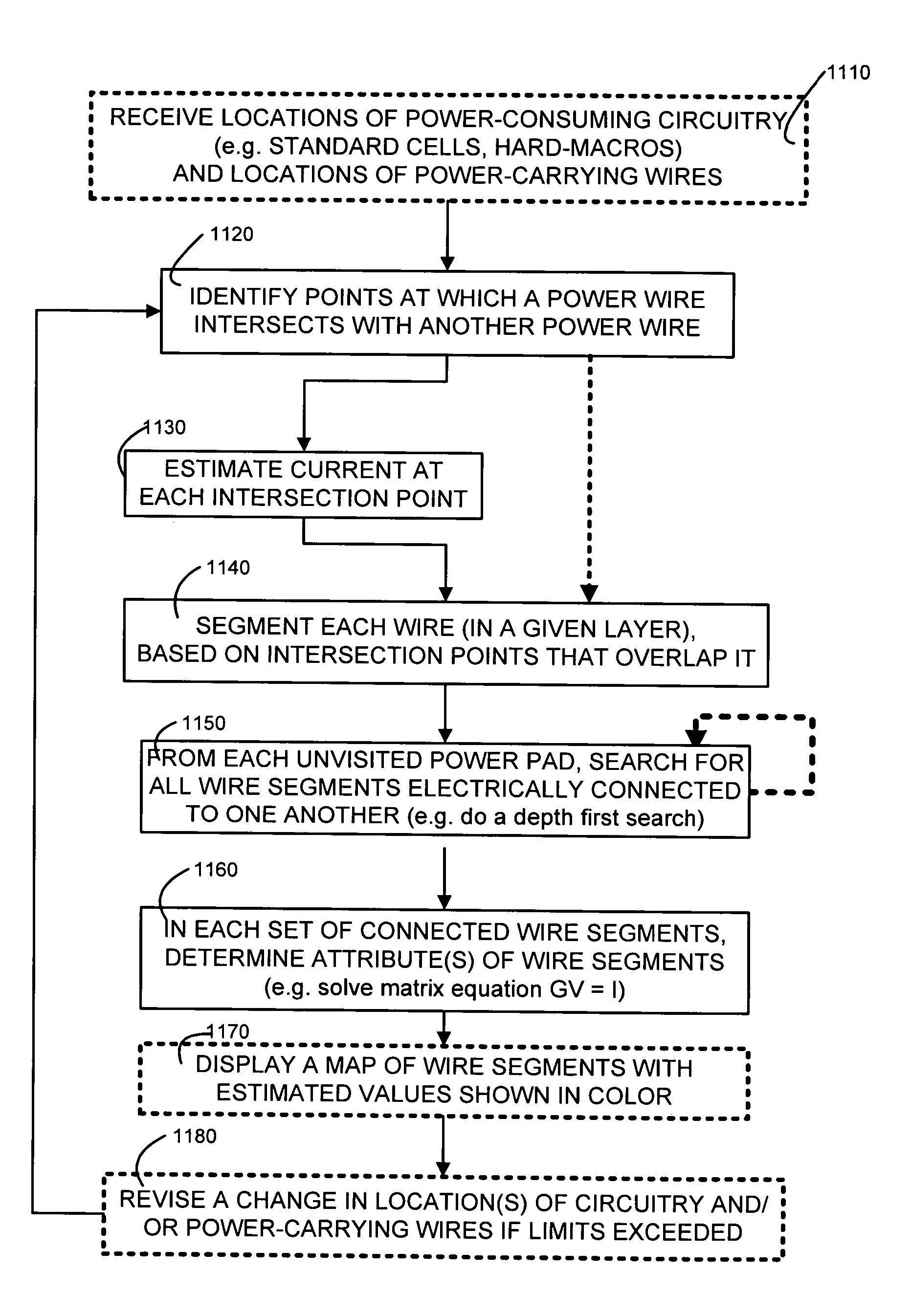
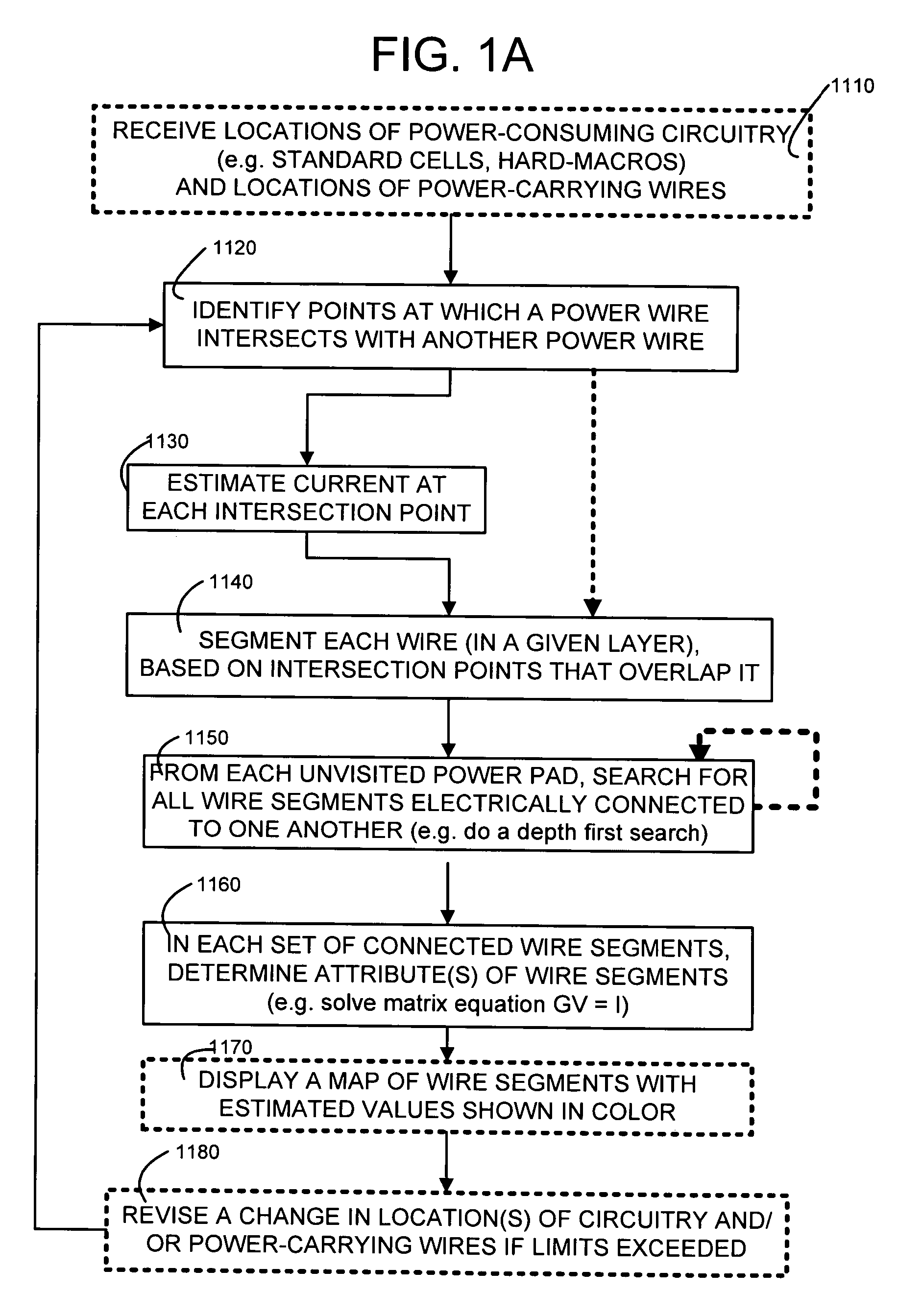
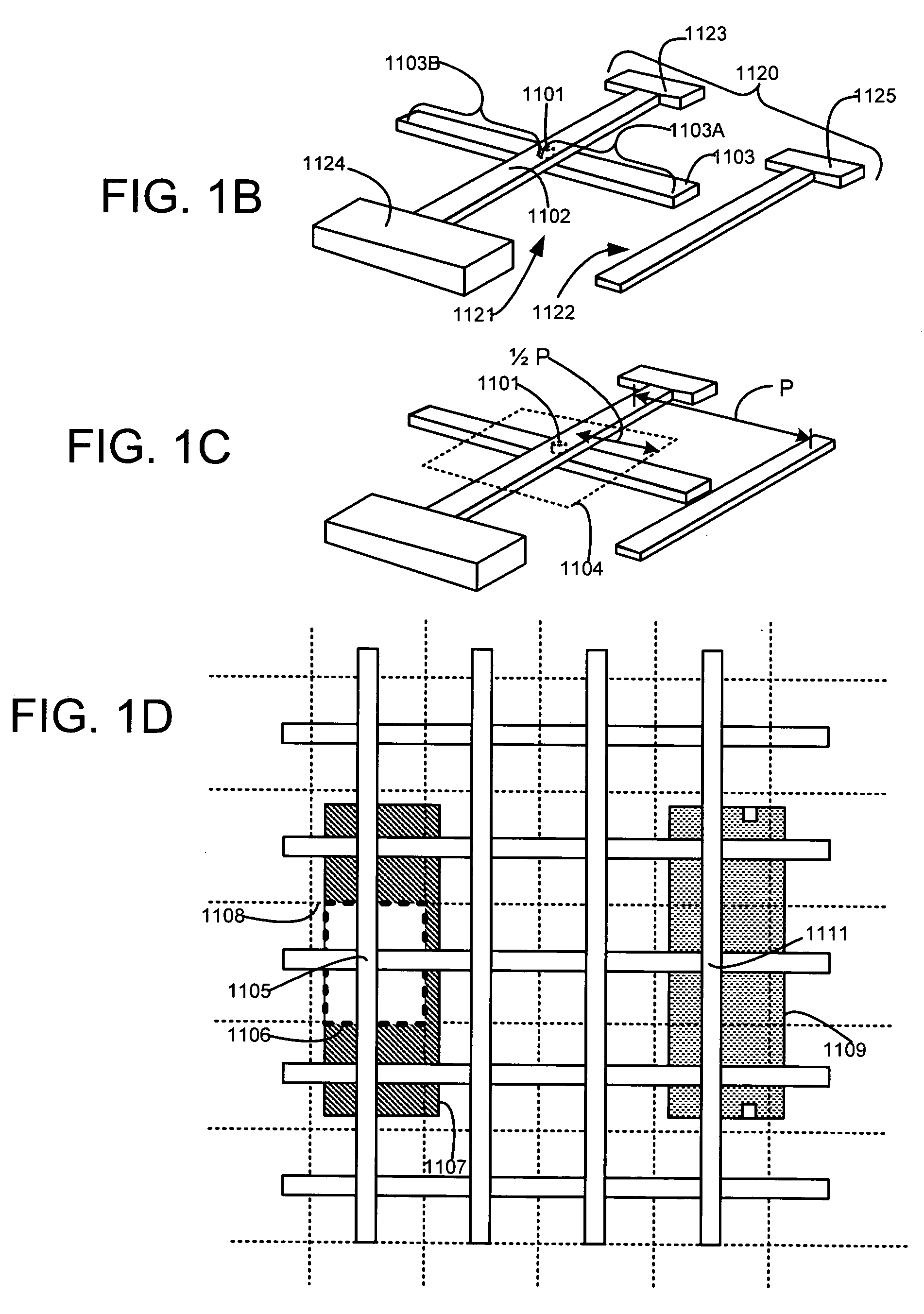
A design of an integrated circuit device, in which locations of power wires and memory / logic circuitry are known, is analyzed by at least: identifying intersections of power wires with one another, for power wires that are electrically connected to one another through vias; segmenting power wires, at their intersections; preparing estimates of conductance of vias and wire segments in the form of conductance matrix G; and preparing estimates of current I at each intersection based on power consumed by surrounding circuitry, and current vector “I” and conductance matrix “G” are used to solve for voltage drop ΔV, in a matrix equation GΔV=I, and the voltage drop is displayed, to allow a human to make changes in the design. Pins of unconnected hard macros are temporarily connected to their closest wires, and current therethrough is included in the estimates.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com