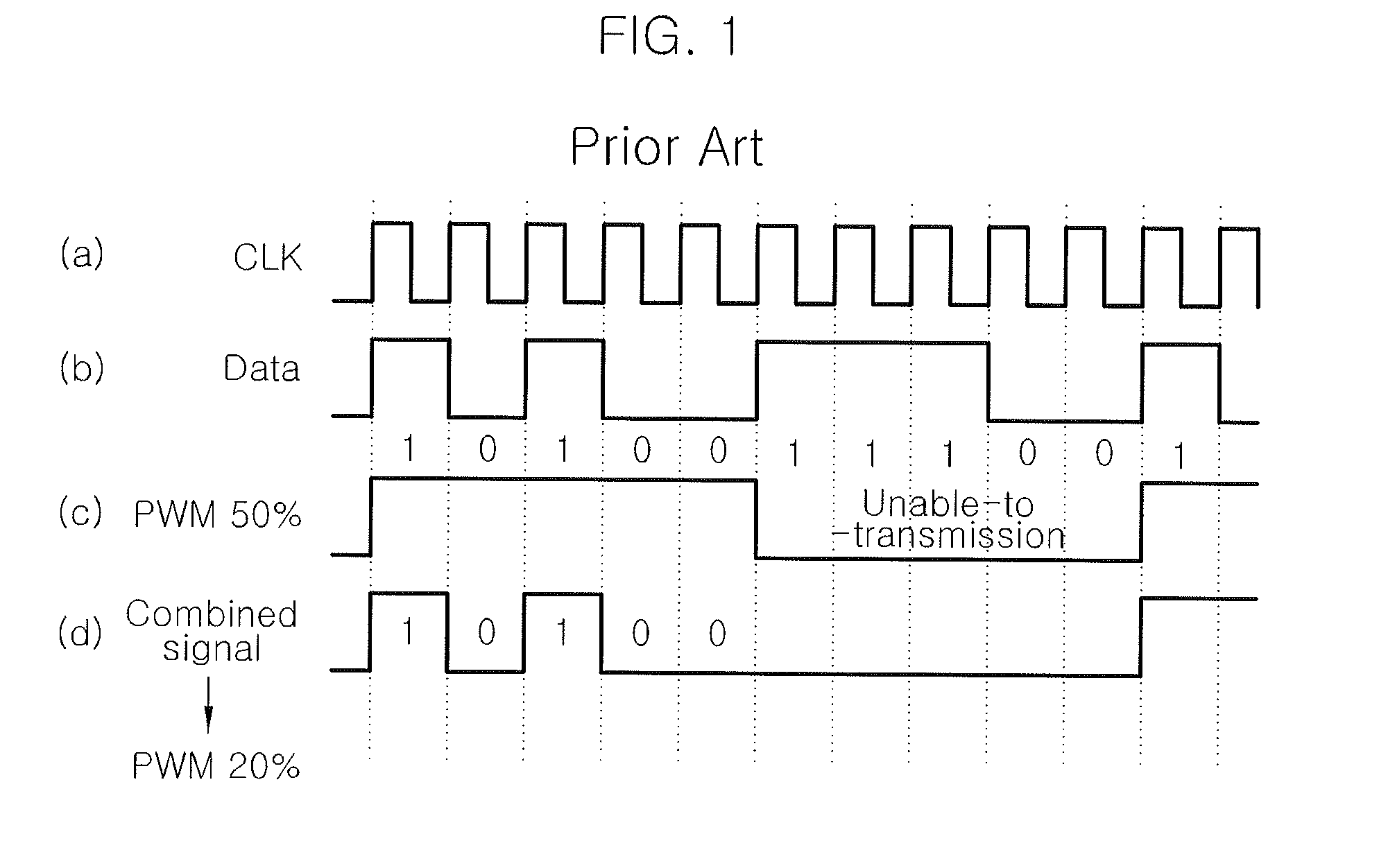
Patents
Literature
1429 results about "Pulse waveform" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
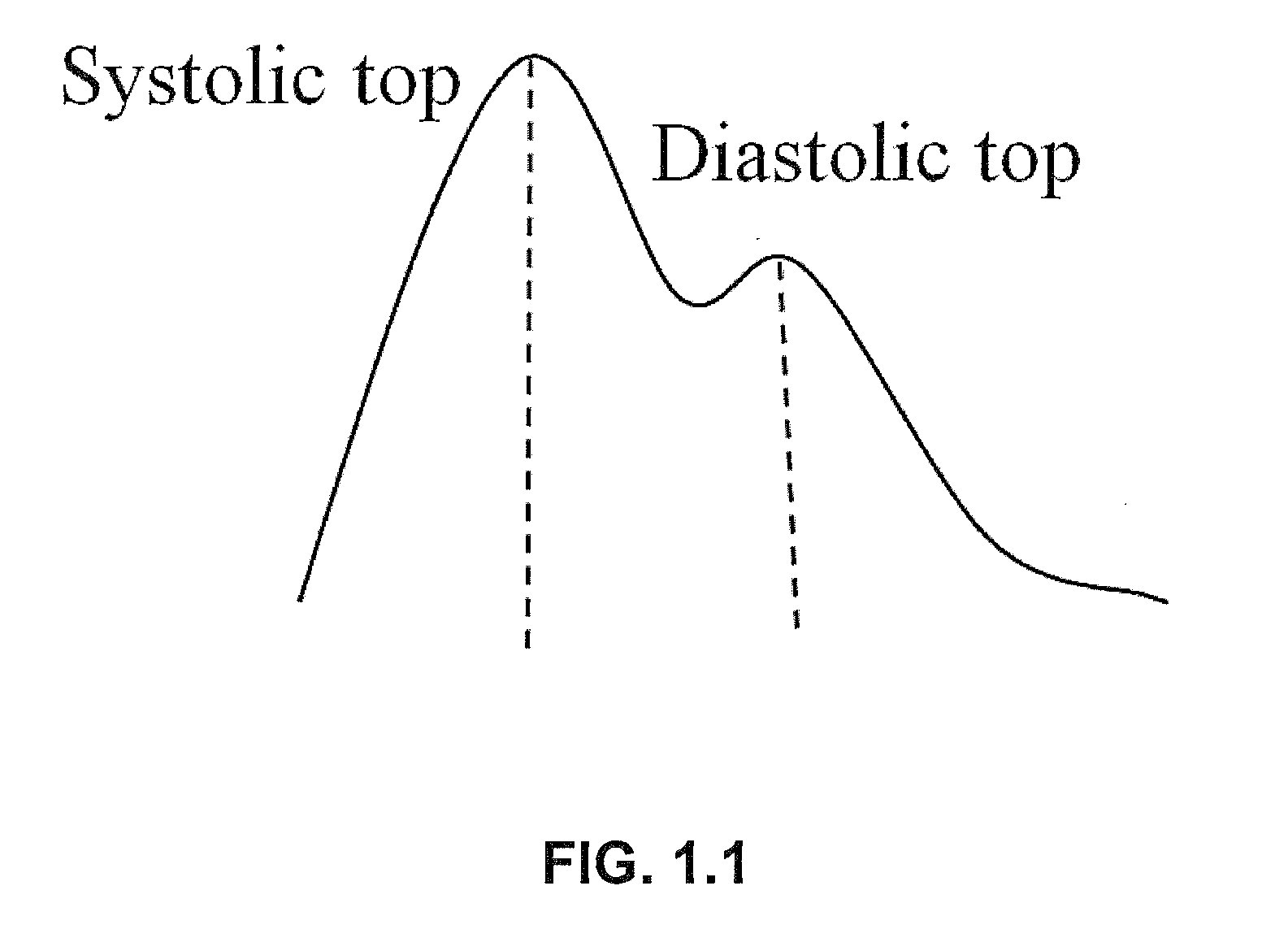
Features of the Pulse Waveform. The arterial pulse waveform is a contour wave generated by the heart when it contracts, and it travels along the arterial walls of the arterial tree. Generally, there are 2 main components of this wave: forward moving wave and a reflected wave.
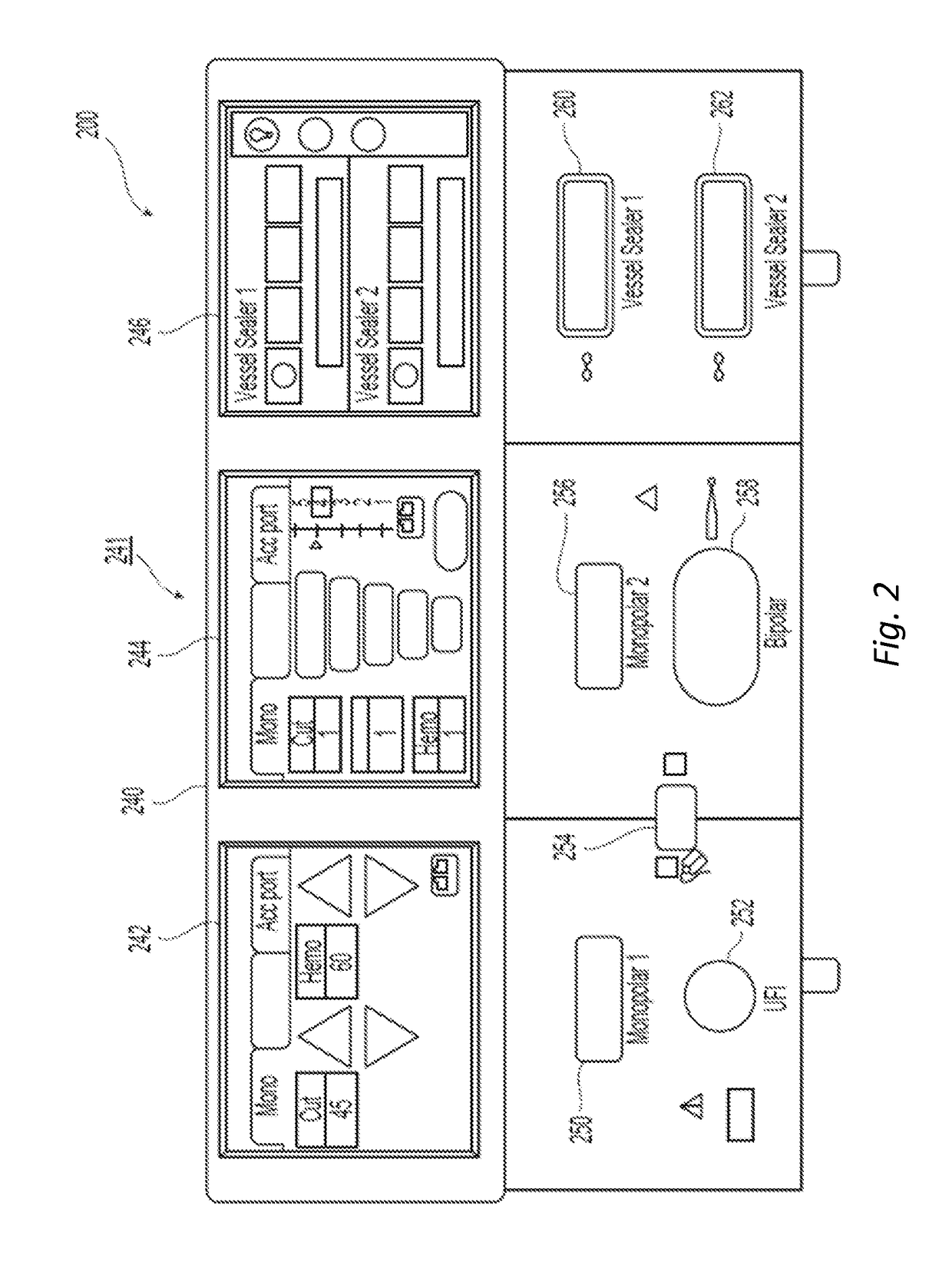
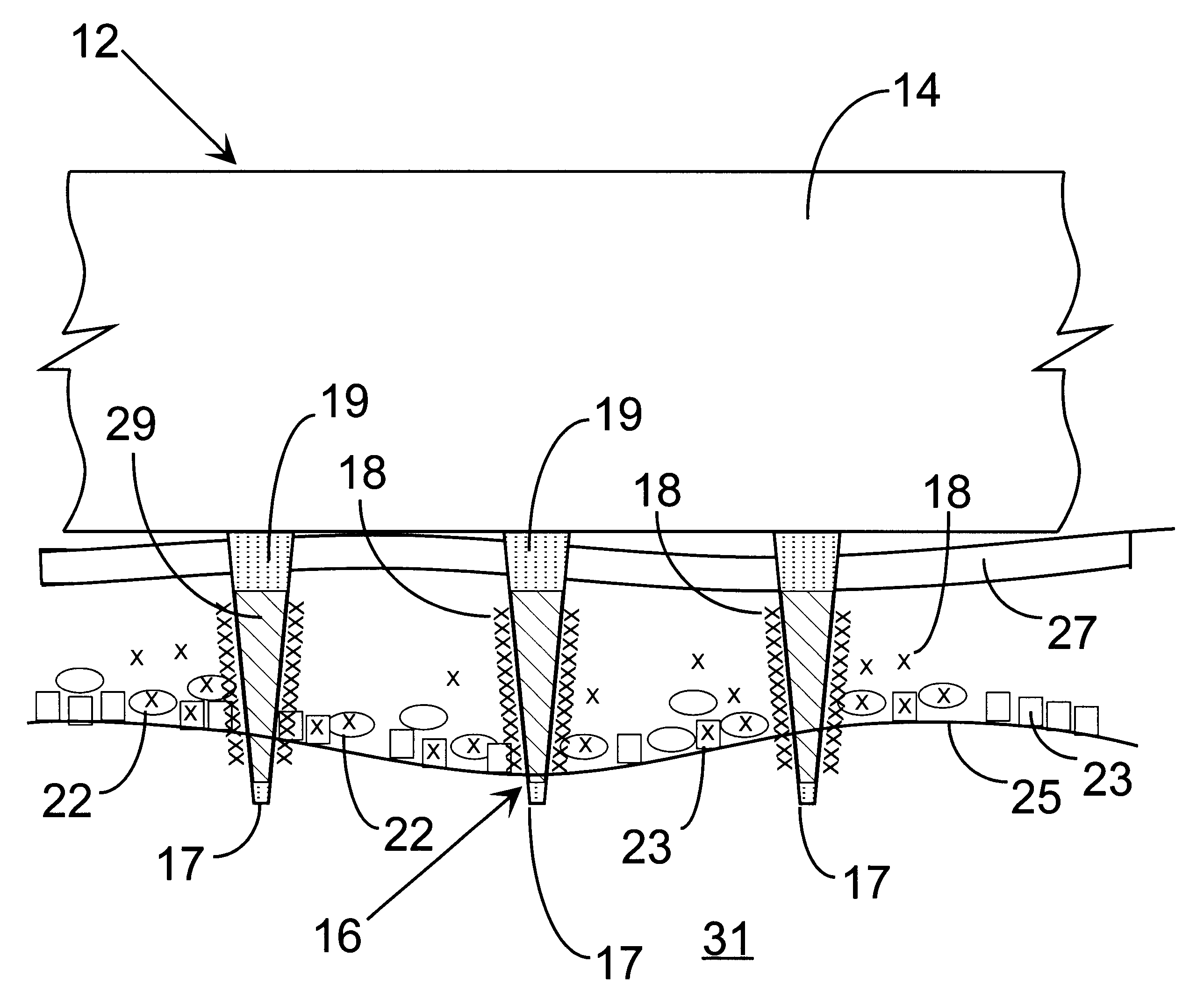
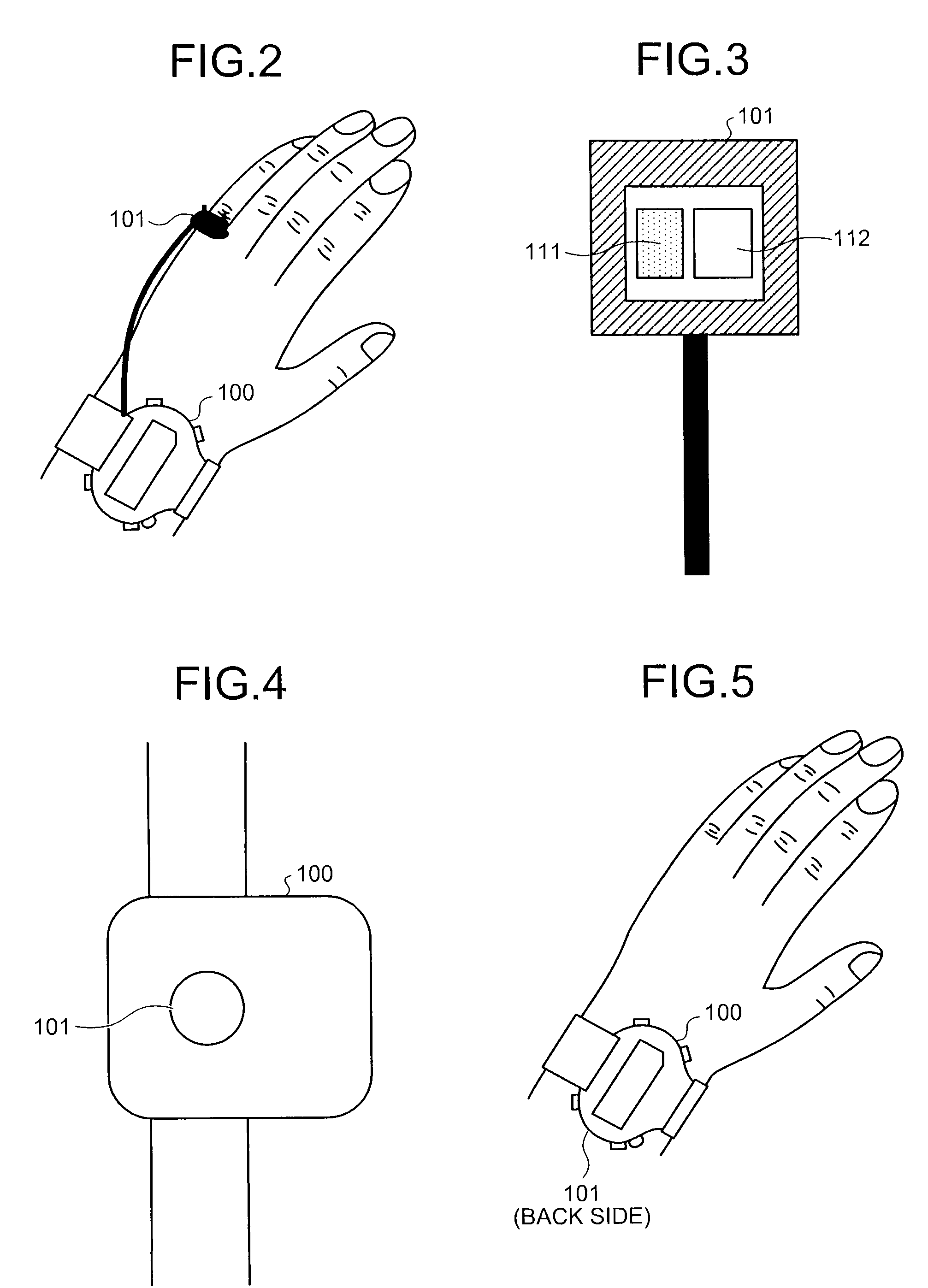
Pulse wave diagnosing device
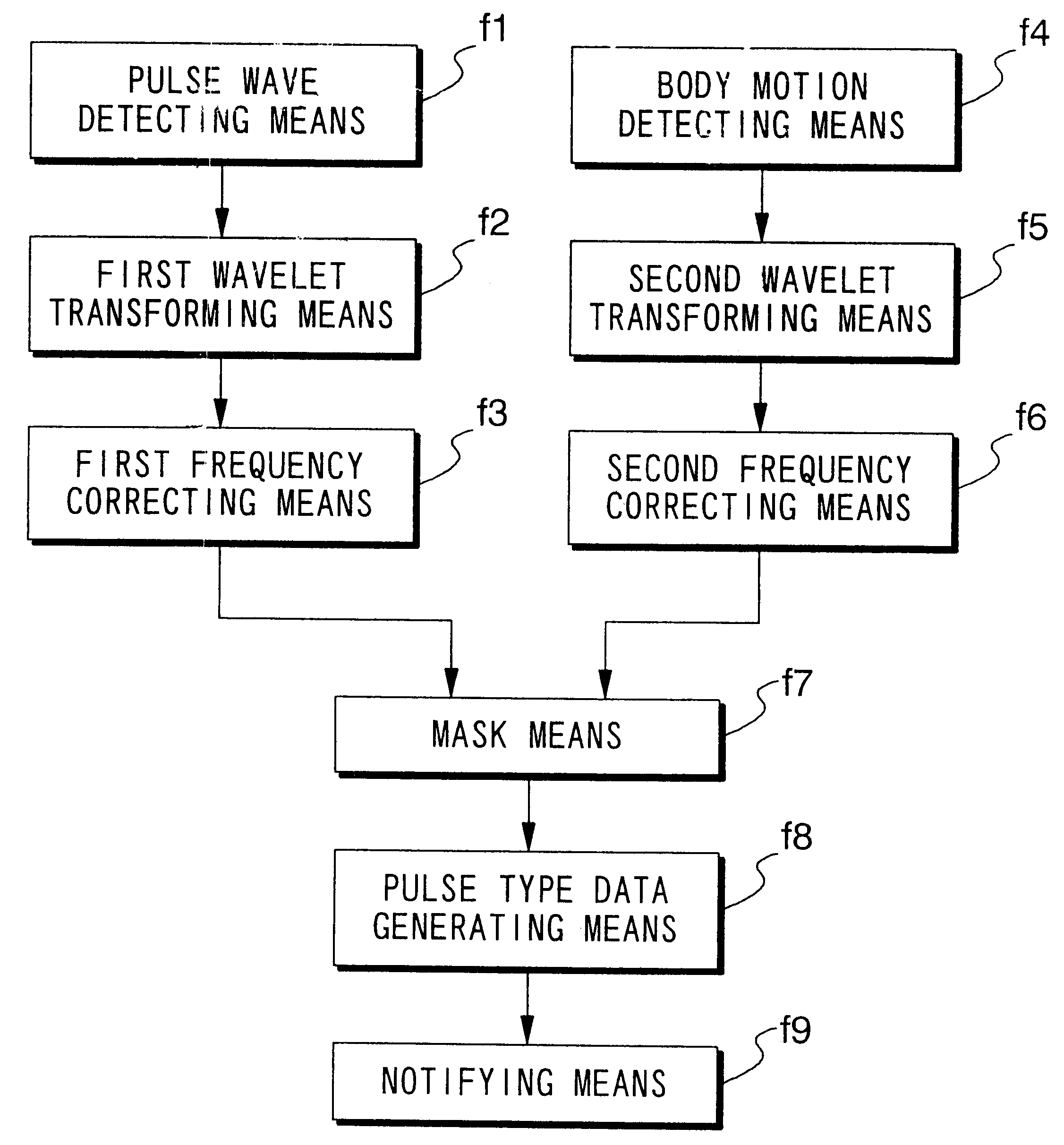
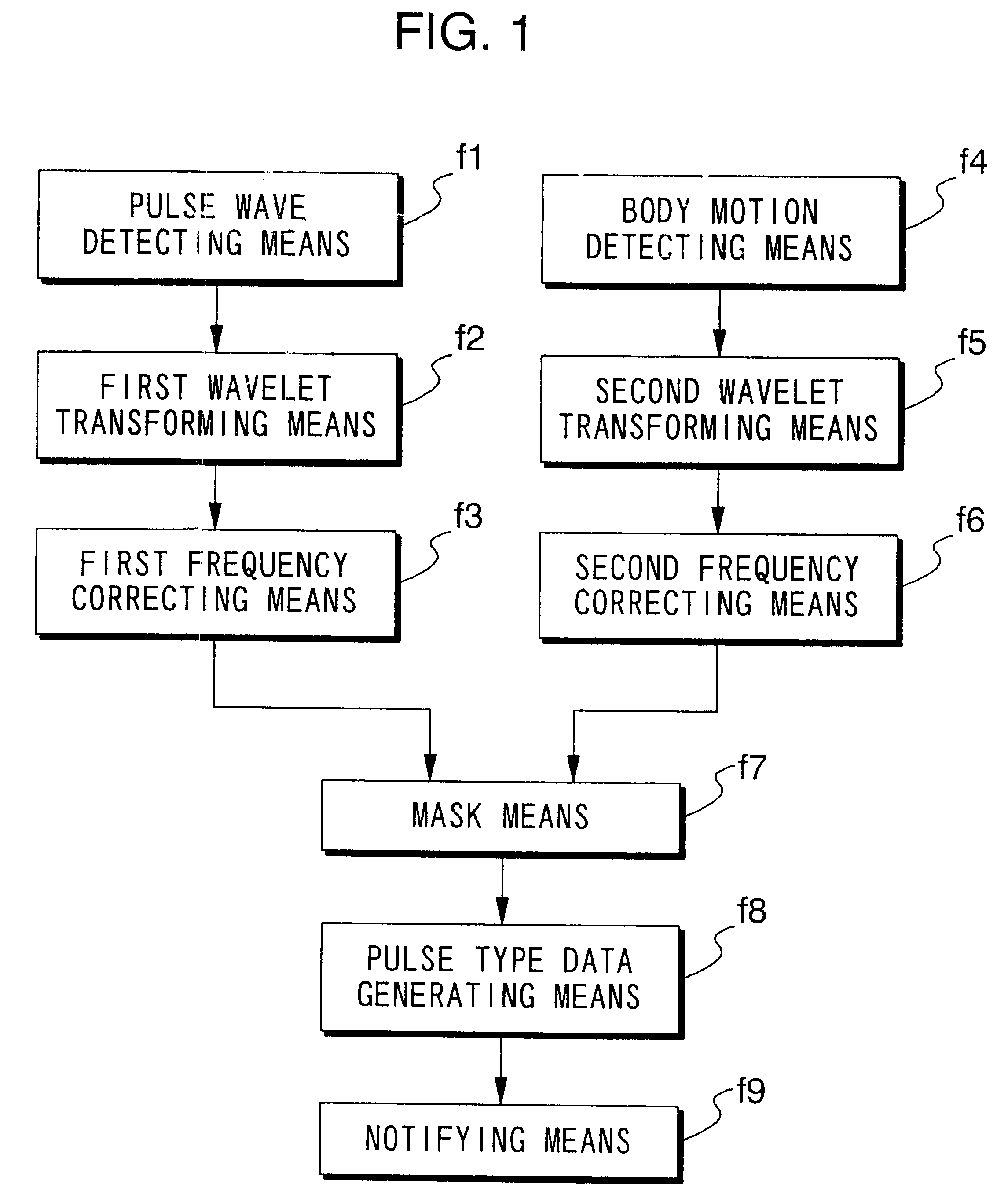
When pulse waveform MH is detected by pulse wave detection sensor unit 130, wavelet transformer 10 performs wavelet transformation on pulse waveform MH and generates analyzed pulse wave data MKD. This analyzed pulse wave data MKD consists of a time region in which one heartbeat is divided into eighths, and the frequency region of 0-4 Hz which has been divided into eighths. Frequency corrector 11 generates corrected pulse wave data MKD' by performing frequency correction on analyzed pulse wave data MKD. Pulse type data generator 12 compares corrected pulse wave data MKD' over each frequency-time region, and generates pulse type data ZD indicating the type of pulse. Display 13 displays the pulse type for pulse waveform MH based on pulse type data ZD.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Signal transmission apparatus and interconnection structure
ActiveUS7446567B2Sufficient capabilitySimple and scalableReliability increasing modificationsBatteries circuit arrangementsLine pairHarmonic
Apparatus for transmitting a digital signal within, for example, an integrated circuit includes a signal transmission line with a directional coupler at one or both ends. The directional coupler blocks the direct-current component of the digital signal while transmitting the alternating-current component, including enough higher harmonics to transmit a well-defined pulse waveform. A suitable directional coupler consists of two adjacent line pairs in materials with different dielectric constants. The apparatus may also include a driver of the inverter type, a receiver of the differential amplifier type, a terminating resistor, and a power-ground transmission line pair for supplying power to the driver. An all-metallic transmission-line structure is preferably maintained from the output interconnections in the driver to the input interconnections in the receiver.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP +11
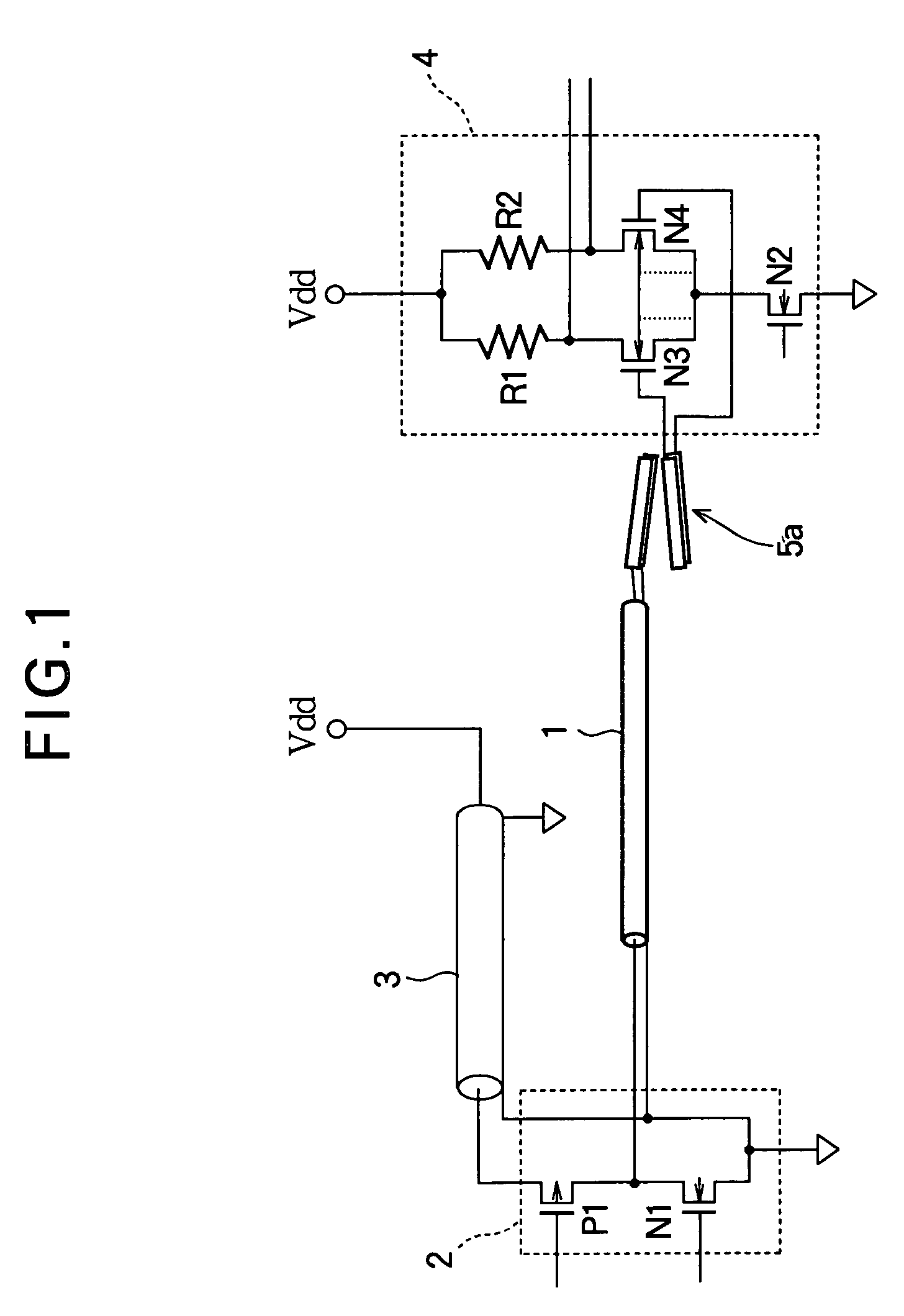
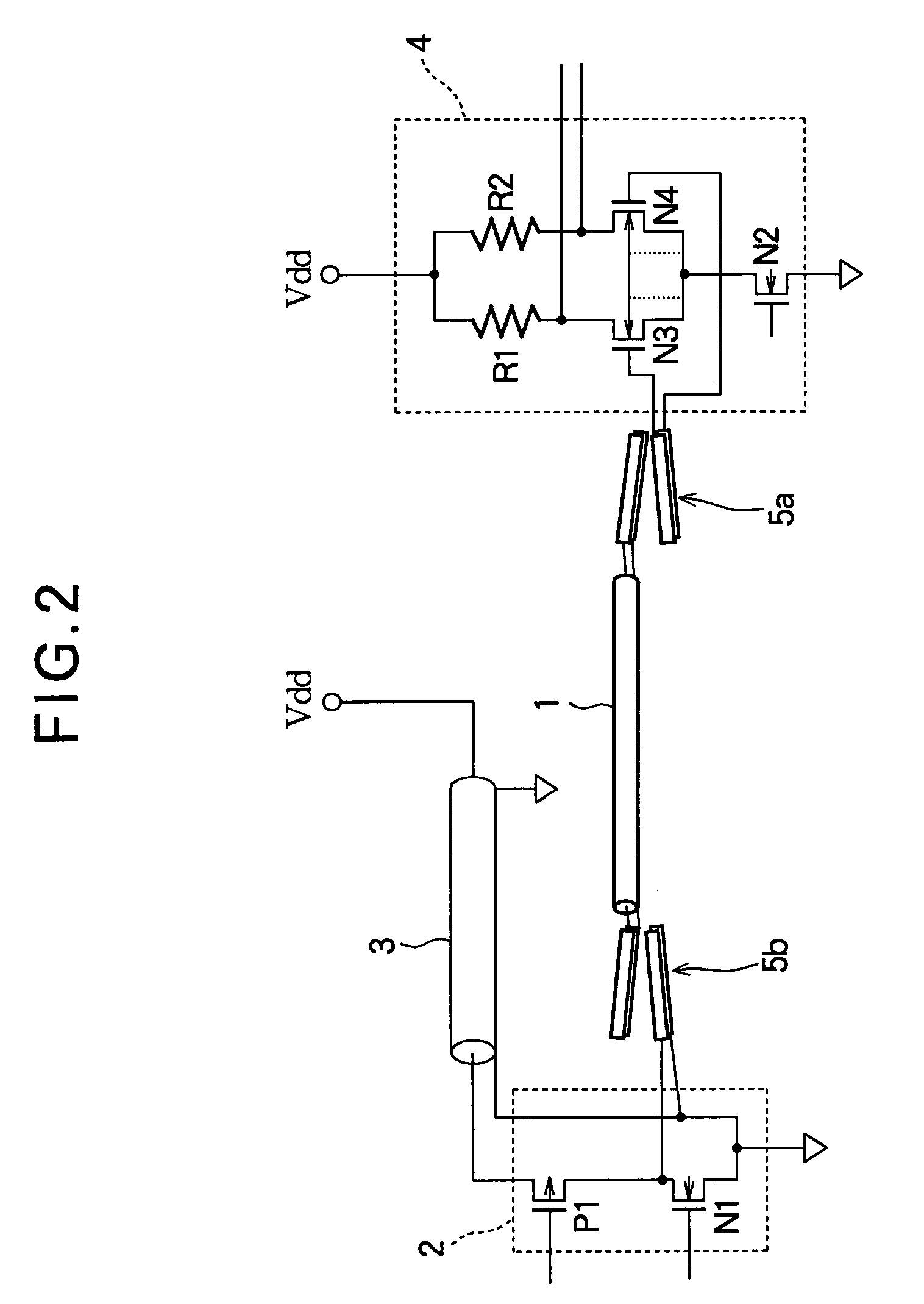
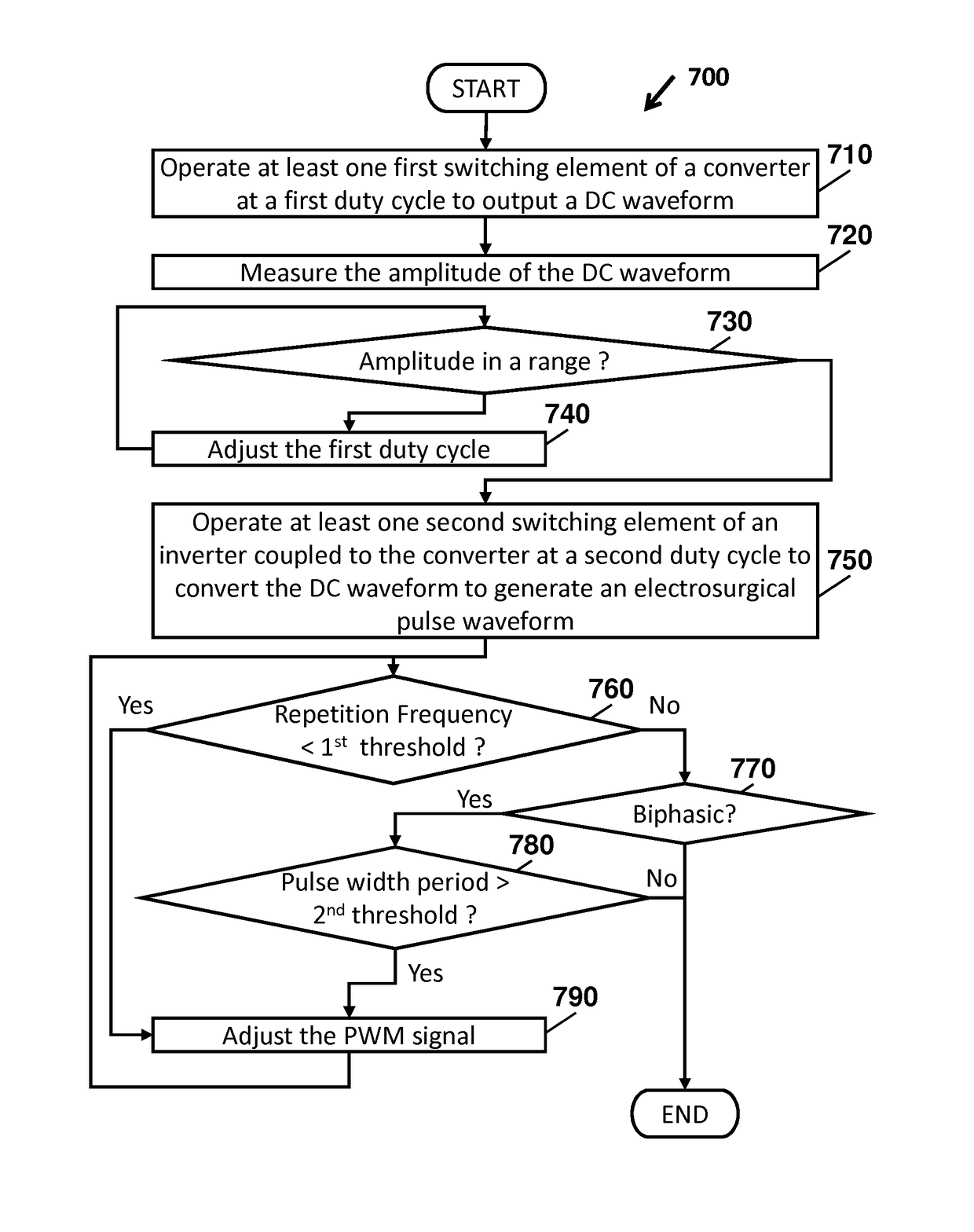
Electrosurgical generator for minimizing neuromuscular stimulation
ActiveUS9839470B2Reduce needAc-dc conversionSurgical instruments for heatingEngineeringNeuromuscular stimulation
A system for minimizing neuromuscular stimulation includes a converter, an inverter, and a controller. The converter is configured to output a dc waveform and includes at least one first switching element operated at a first duty cycle. The inverter is coupled to the converter and includes at least one second switching element operated at a second duty cycle. The inverter is configured to invert the DC waveform to generate an electrosurgical pulse waveform. The controller is coupled to the converter and the inverter, and is configured to control the first duty cycle to adjust a magnitude of the electrosurgical pulse waveform and the second duty cycle to adjust at least one property of the electrosurgical pulse waveform to minimize neuromuscular stimulation.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
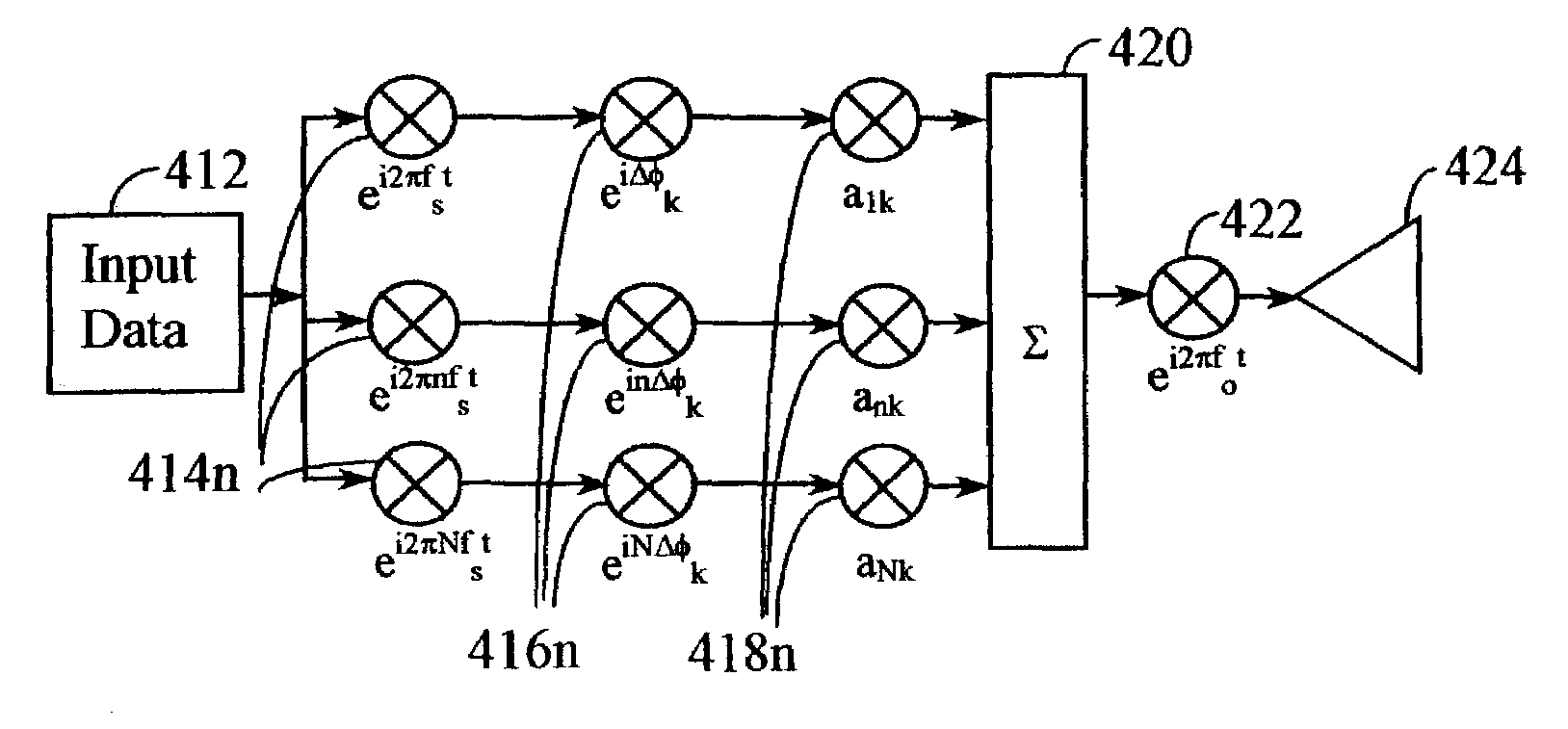
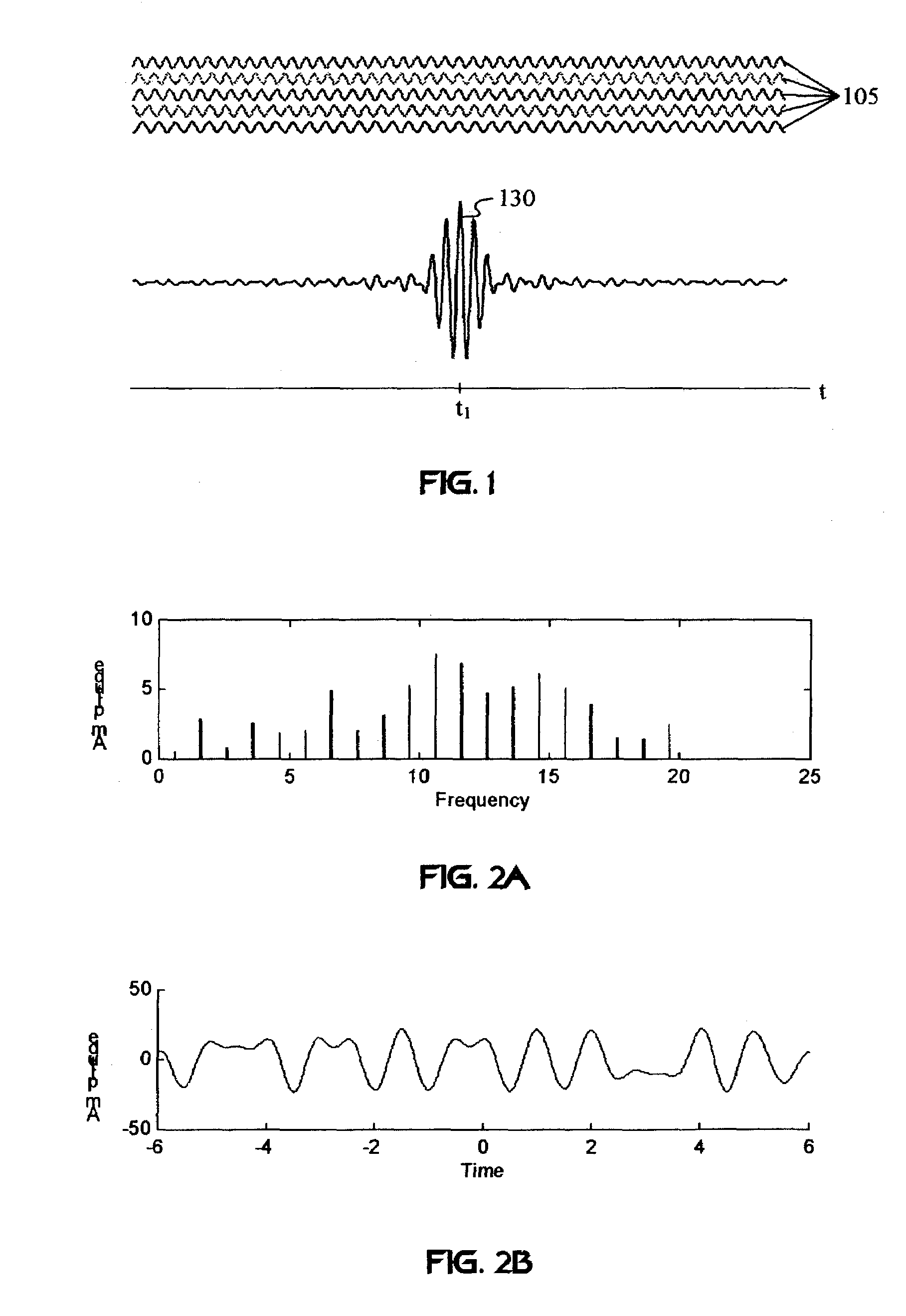
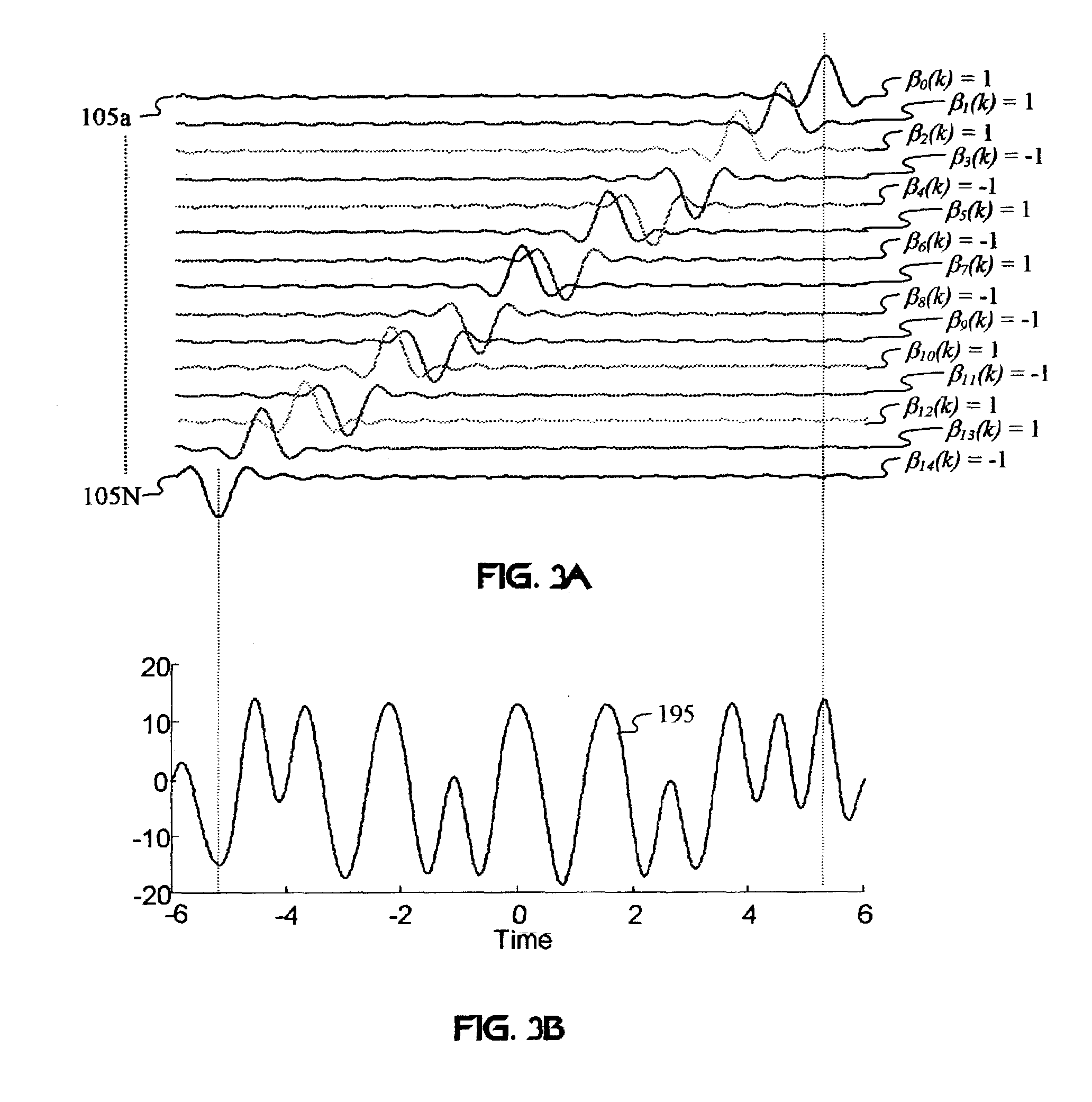
Unified multi-carrier framework for multiple-access technologies
InactiveUS7406261B2Reduce the impactReduce transmit powerModulated-carrier systemsOptical multiplexTransmission protocolCarrier signal
A wireless communication system transmits data on multiple carriers simultaneously to provide frequency diversity. Orthogonality is provided by carrier interference, which causes a narrow pulse in the time domain corresponding to each transmitted data symbol. Selection of the frequency separation and phases of the carriers controls the timing of the pulses. Equivalently, pulse waveforms may be generated from an appropriate selection of polyphase sub-carrier codes. Time division of the pulses and frequency division of the carriers may be employed for multiple access. Received signals are processed by combining frequency-domain components corresponding to a desired user's allocated carriers. Individual data symbols are processed by providing polyphase decoding, matched filtering, or time-domain shifting the received carriers. Carrier Interferometry components may be used to build various signals corresponding to other transmission protocols.
Owner:DEPARTMENT 13 INC
Delivery of macromolecules into cells
InactiveUS6603998B1Raise the threshold voltageReducing pulse widthBioreactor/fermenter combinationsElectrotherapyLangerhan cellA-DNA
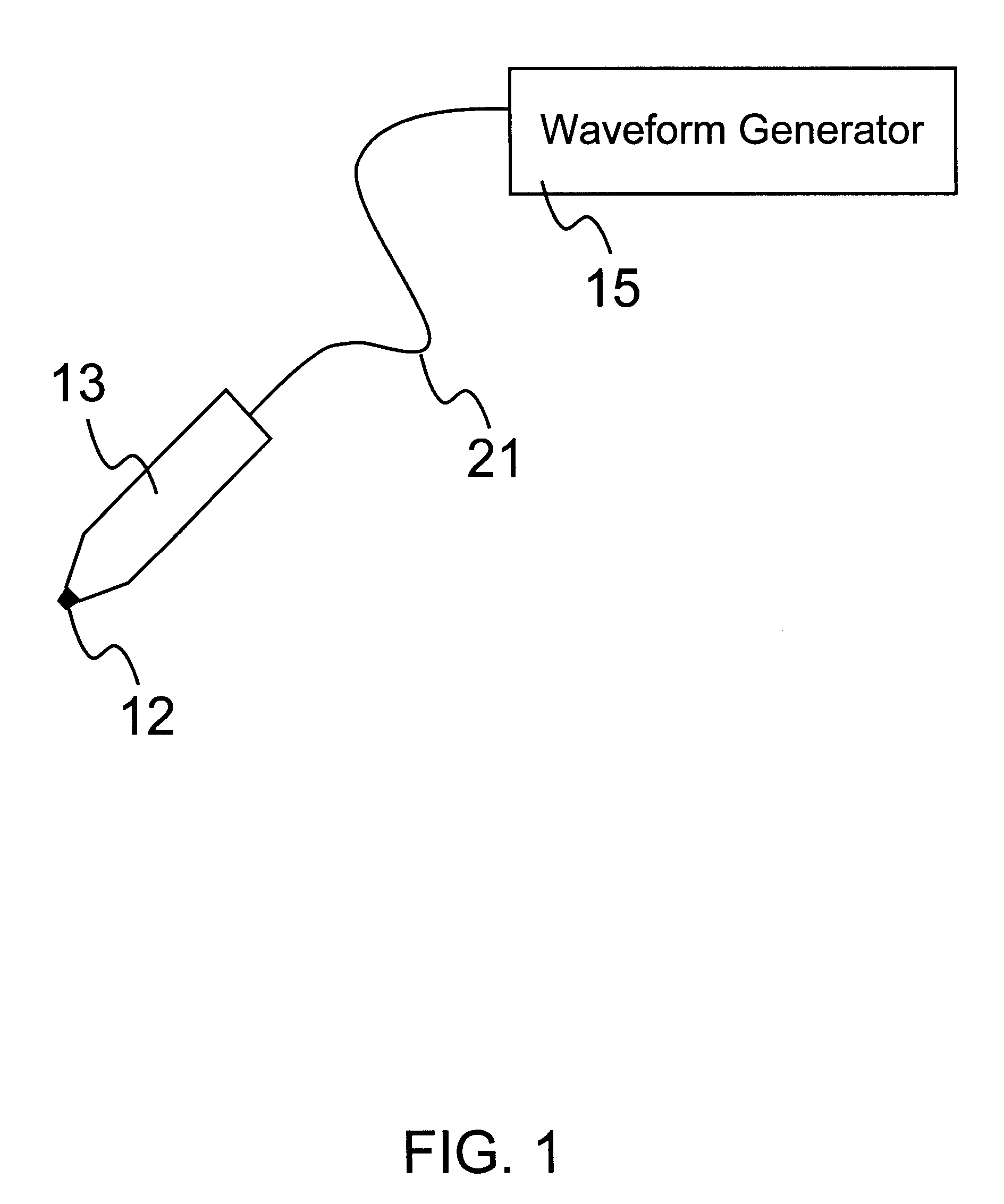
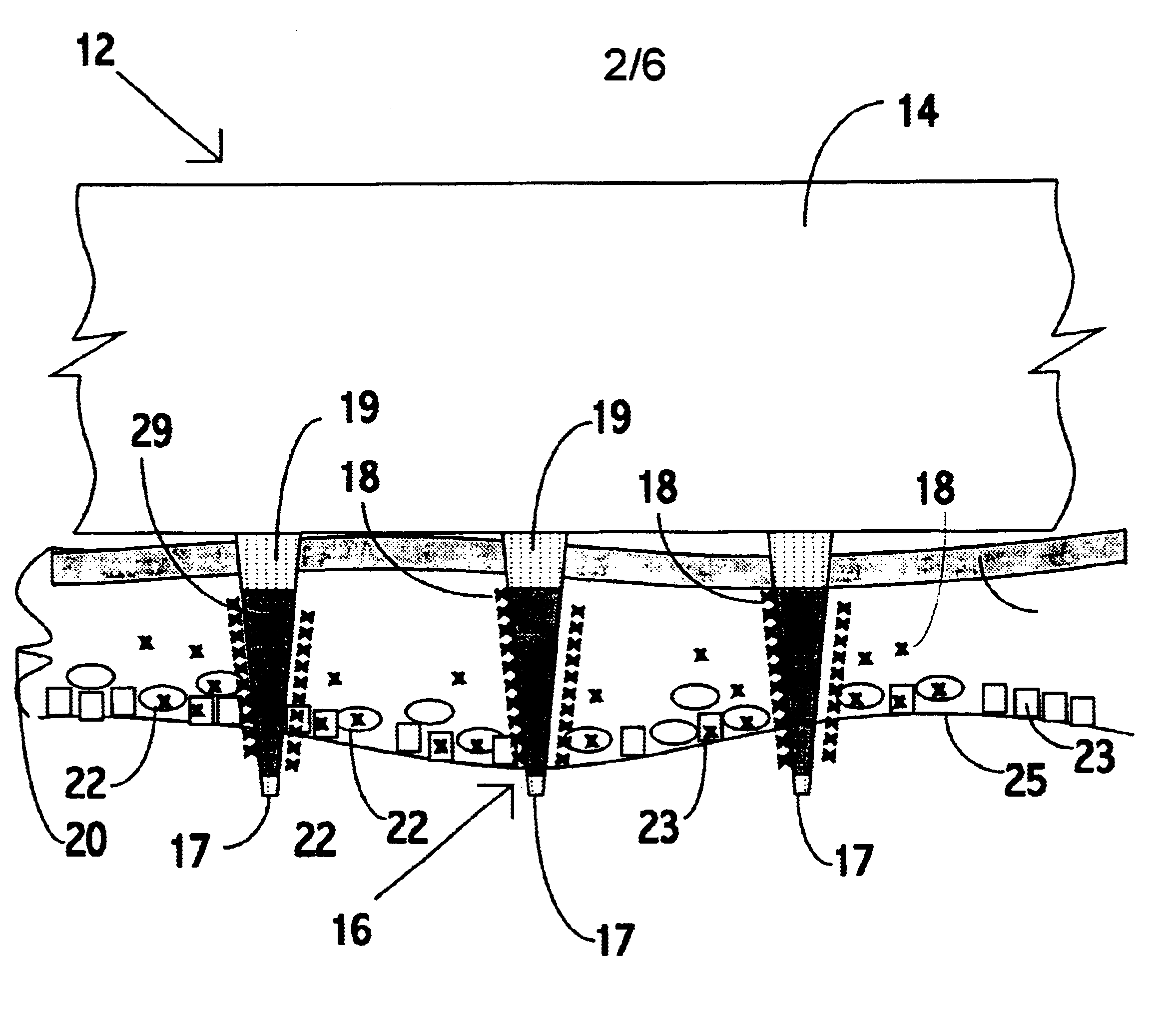
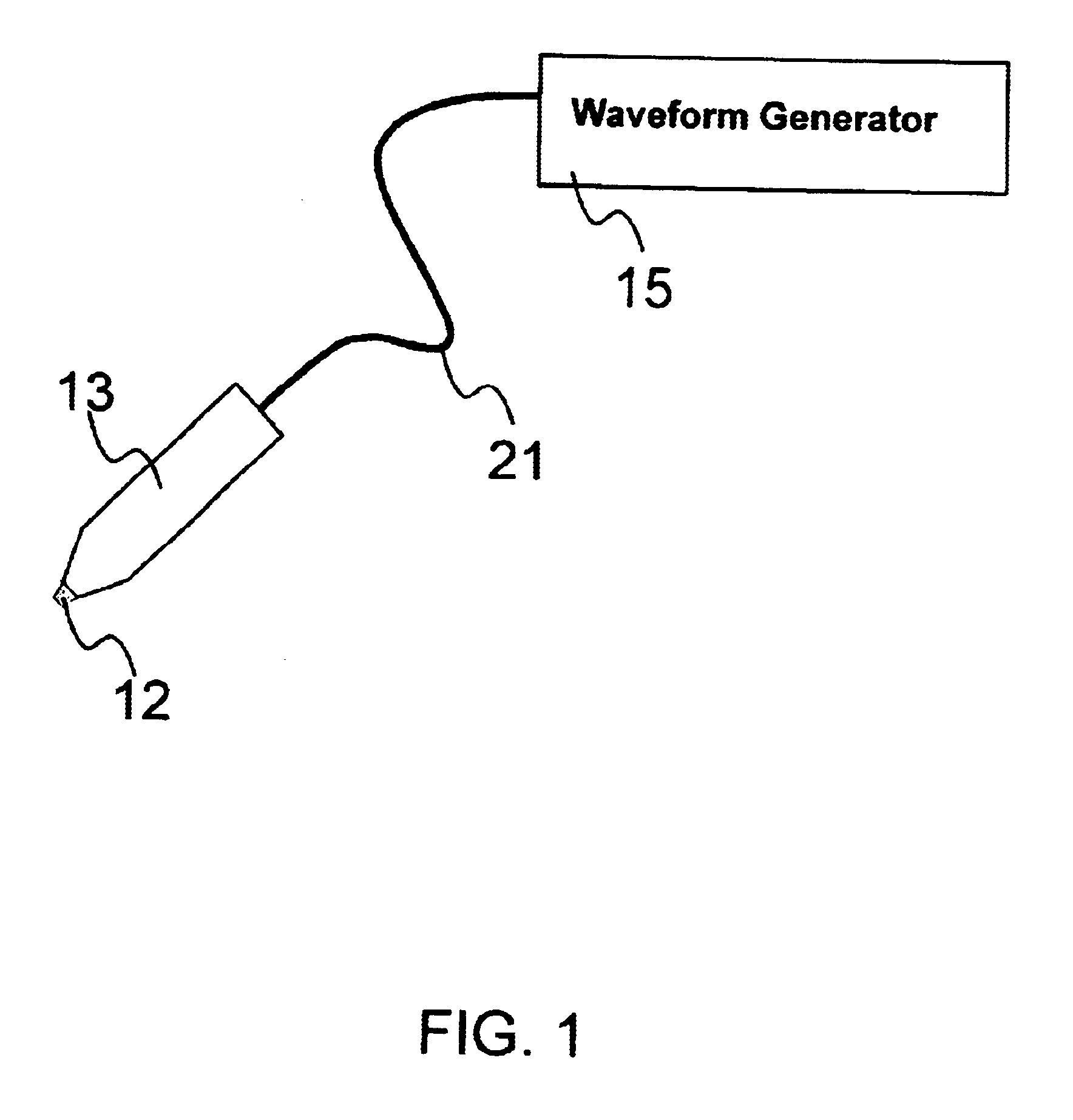
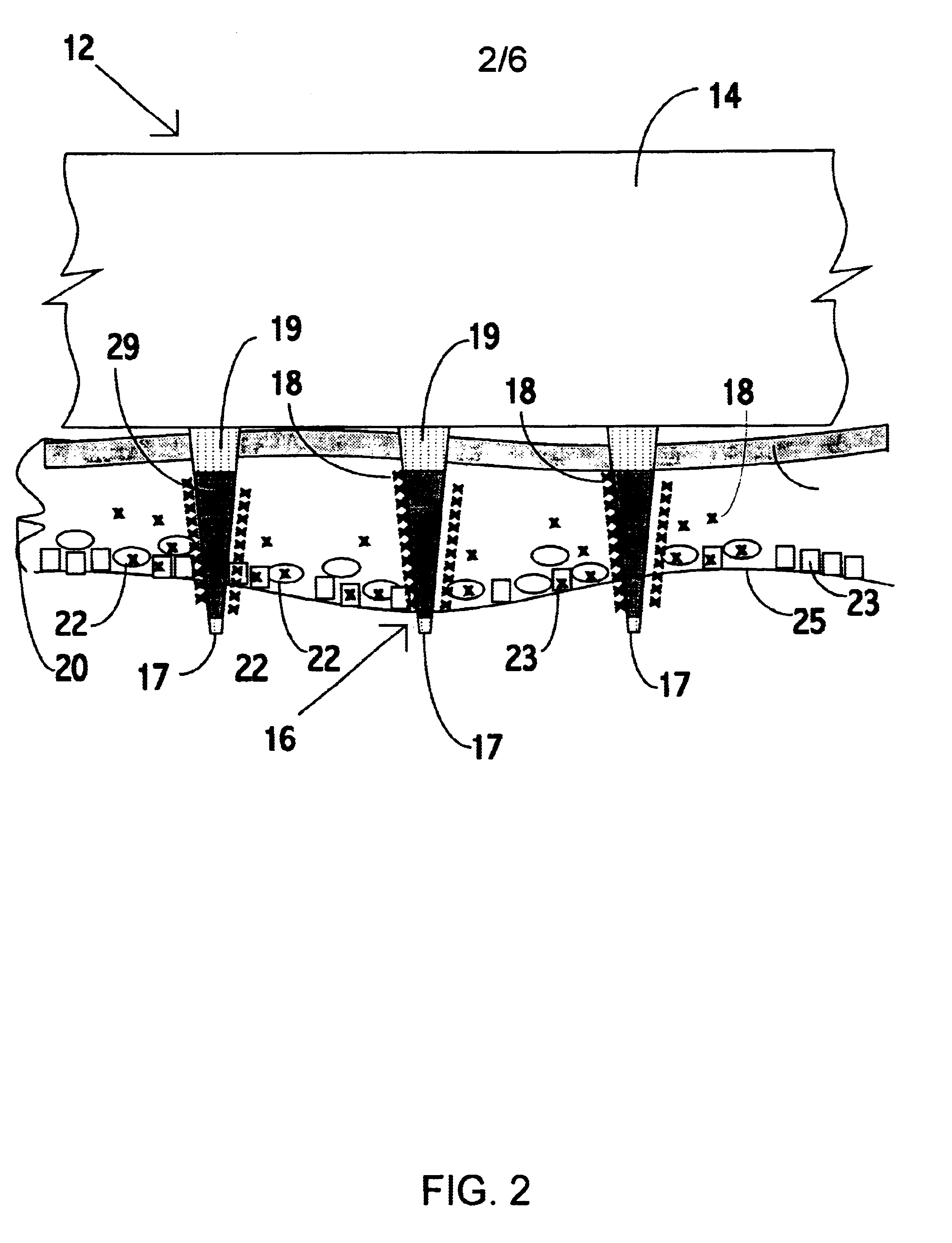
An object of the invention is to provide a method for delivery of macromolecules into biological cells, such as Langerhans cells (22) in the epidermis (20) of a patient, which includes the steps of coating electodes (16) in an electrode assembly (12) with solid phase macromolecules to be delivered, such as a DNA, and / or RNA vaccine or a protein-based vaccine, attaching the electrode assembly (12) having the coated electrodes (16) to an electrode assembly holder (13), providing a waveform generator (15), establishing electrically conductive pathways between the electrodes (16), and the waveform generator (15), locating the electrodes (16) such that the biological cells are situated therebetween, such as by penetrating the needle electrode (16) into the epidermis (20) above the epidermal basal lamina, and providing pulse waveform from the waveform generator (15) to the electrodes (16), such that macromolecule on the electrodes (16) is driven off of the electrodes (16), and delivered into the biological cells, such as the Langerhans cells (22).
Owner:CELLECTIS SA
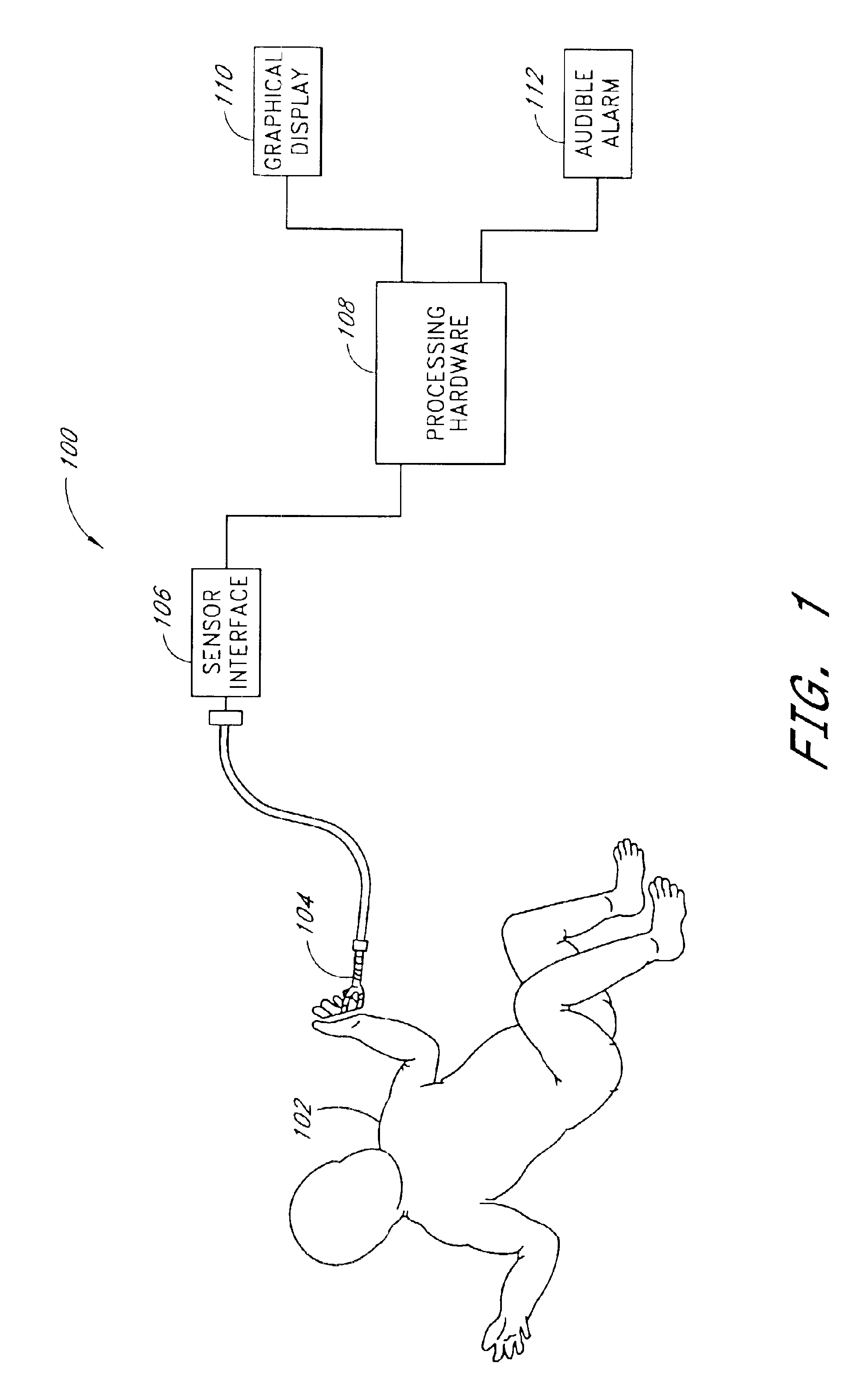
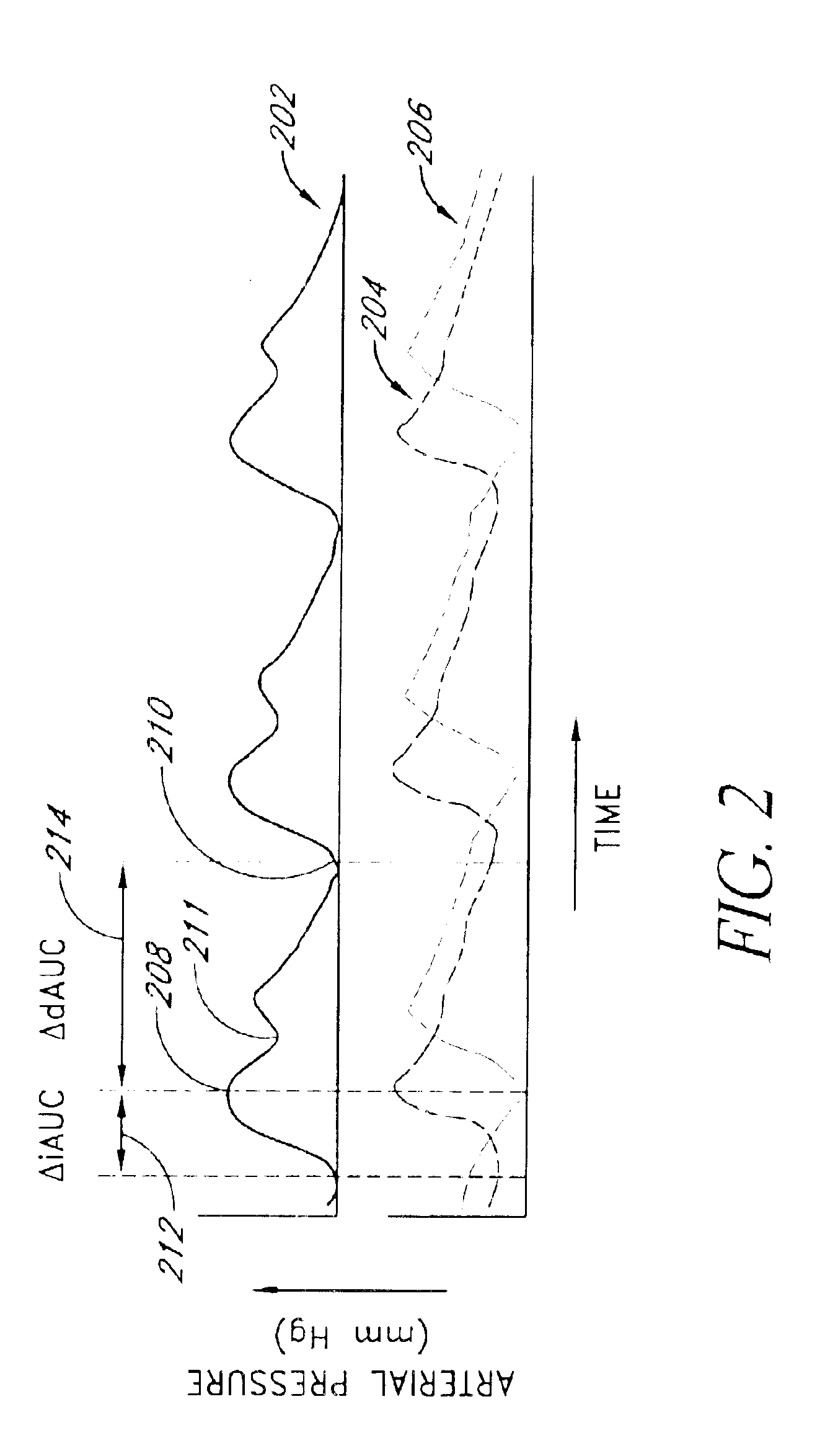
Method and apparatus for measuring pulsus paradoxus
InactiveUS6869402B2Accurate measurementReliable measurementCatheterDiagnostic recording/measuringTime domainPulsus paradoxus
A method and apparatus are disclosed of utilizing a source of arterial and / or arteriolar pulse waveform data from a patient for the purpose of measuring pulsus paradoxus. The arterial pulse waveform data source described is a pulse oximeter plethysmograph but can be any similar waveform data source, including intra-arterial transducer, blood pressure transducer, or plethysmograph. Through incorporation of the measurements of values, such as the area under the pulse waveform curve, that are time-domain functions of a change in height of the pulse waveform over at least a partial duration of the waveform, embodiments of the present invention represent a significant improvement upon previously described methods of measuring pulsus paradoxus and, further, produce improved accuracy in measurement of the multiple contributing variables generating pulsus paradoxus, in particular the contribution of diastolic events, to the extent that the physical signs so measured can be regarded as “Revised Pulsus Paradoxus.”
Owner:PRECISION PULSUS
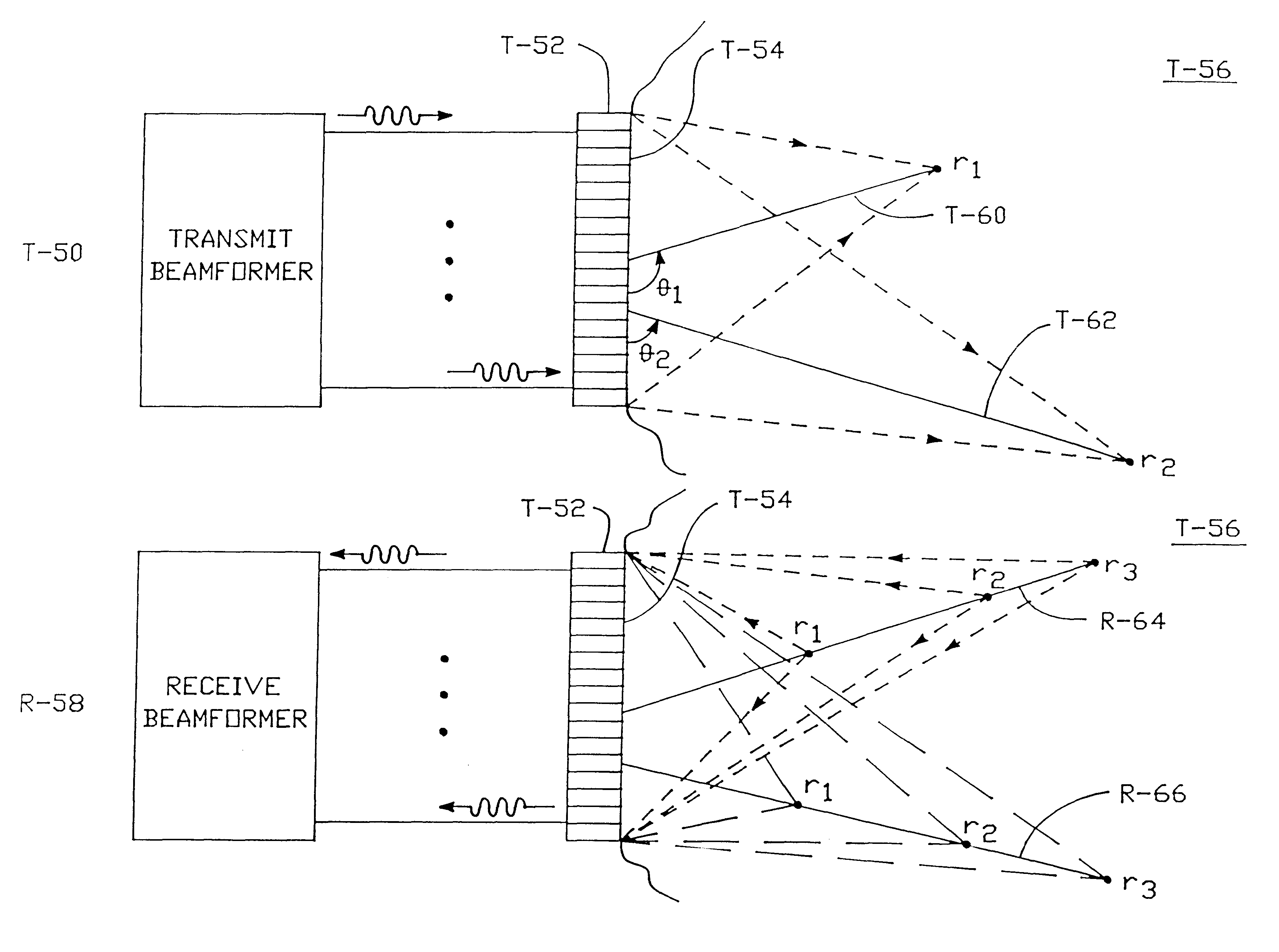
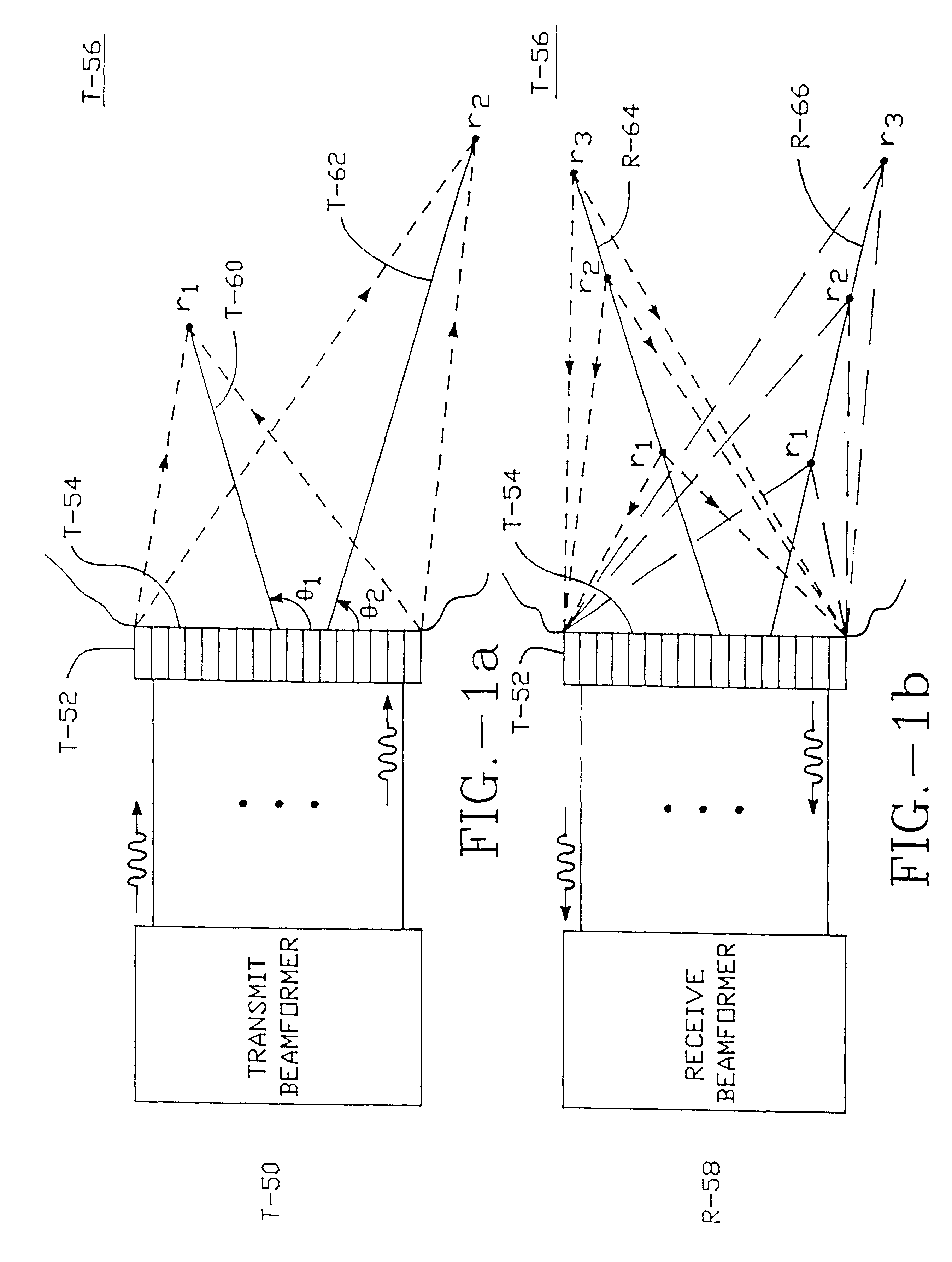
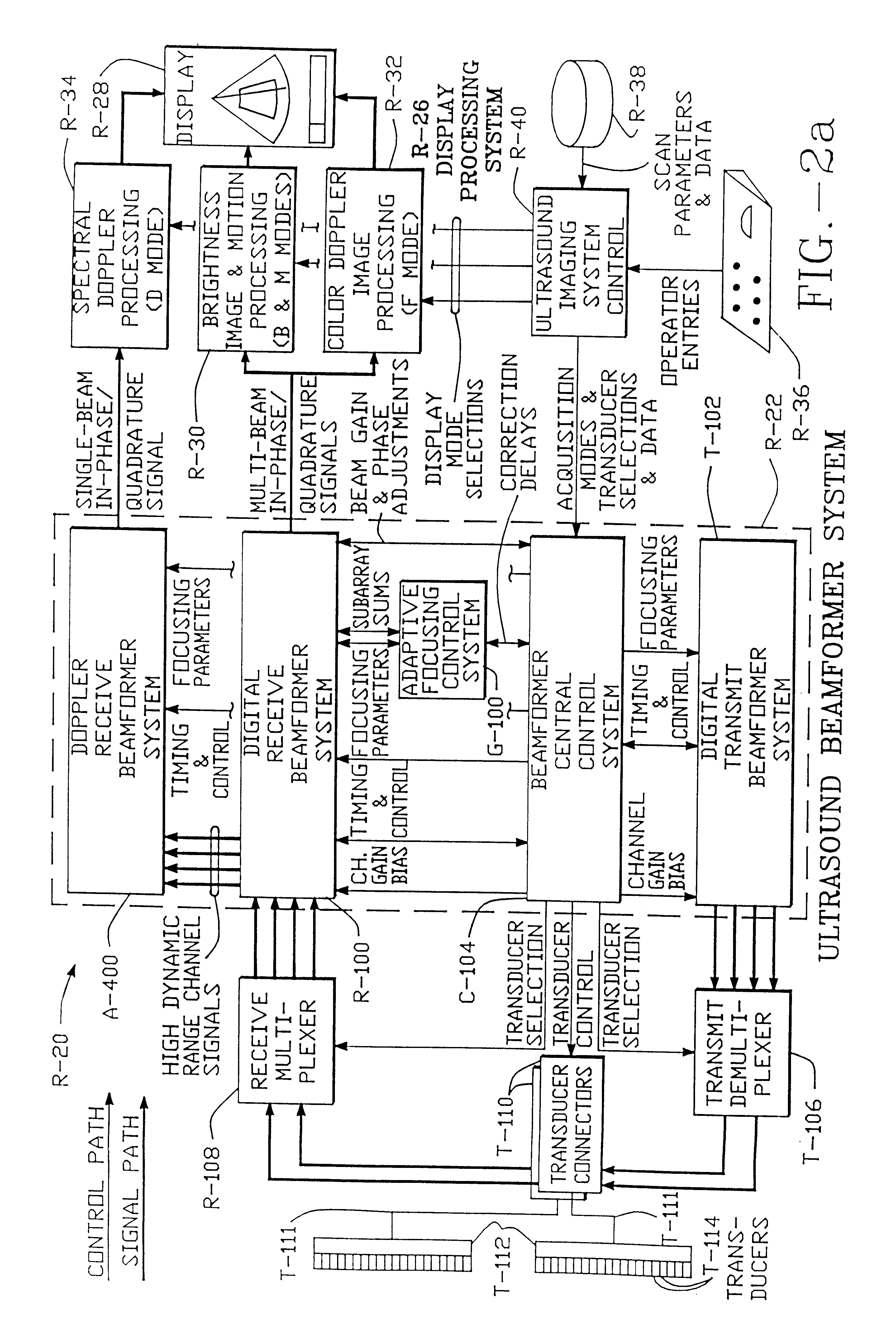
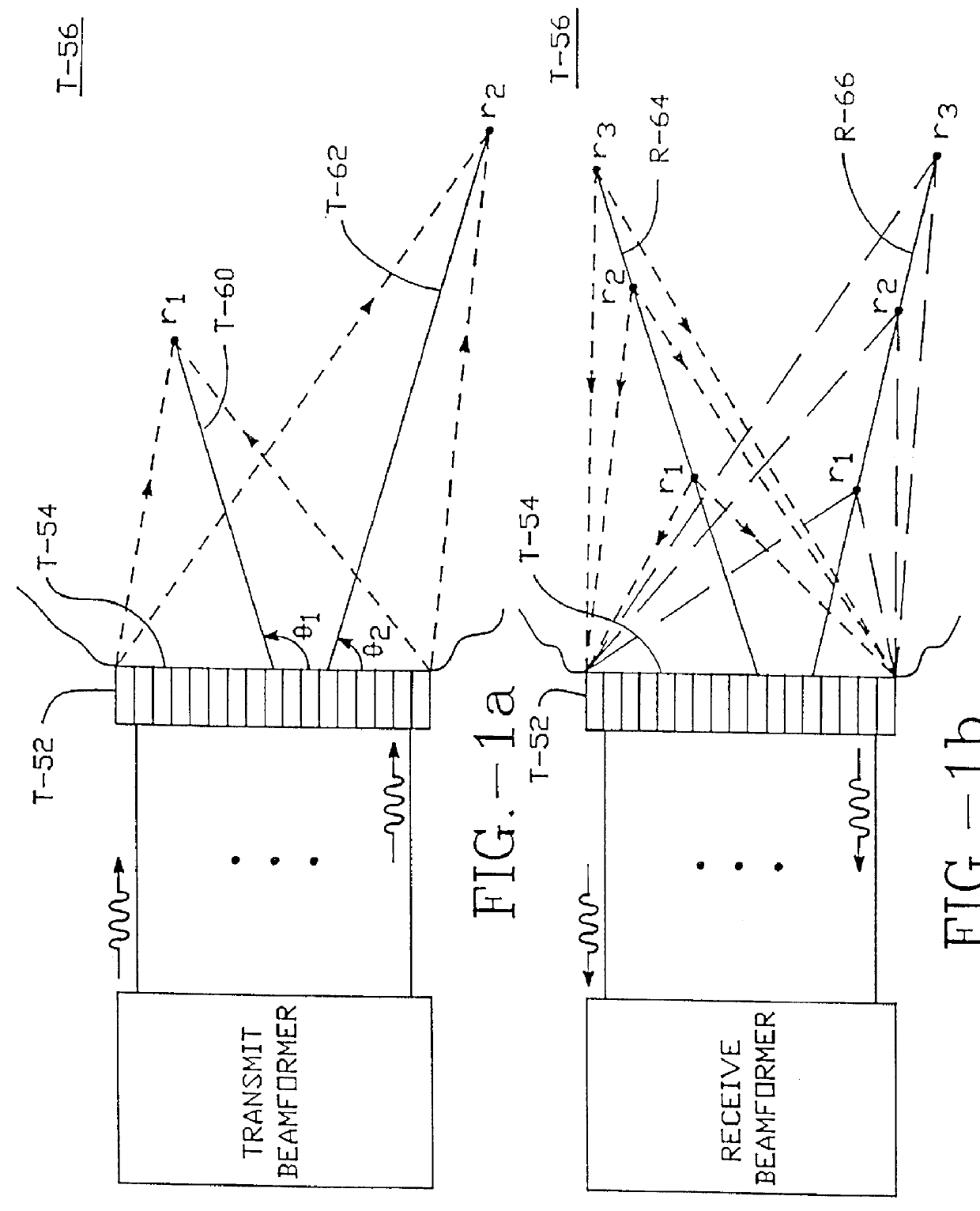
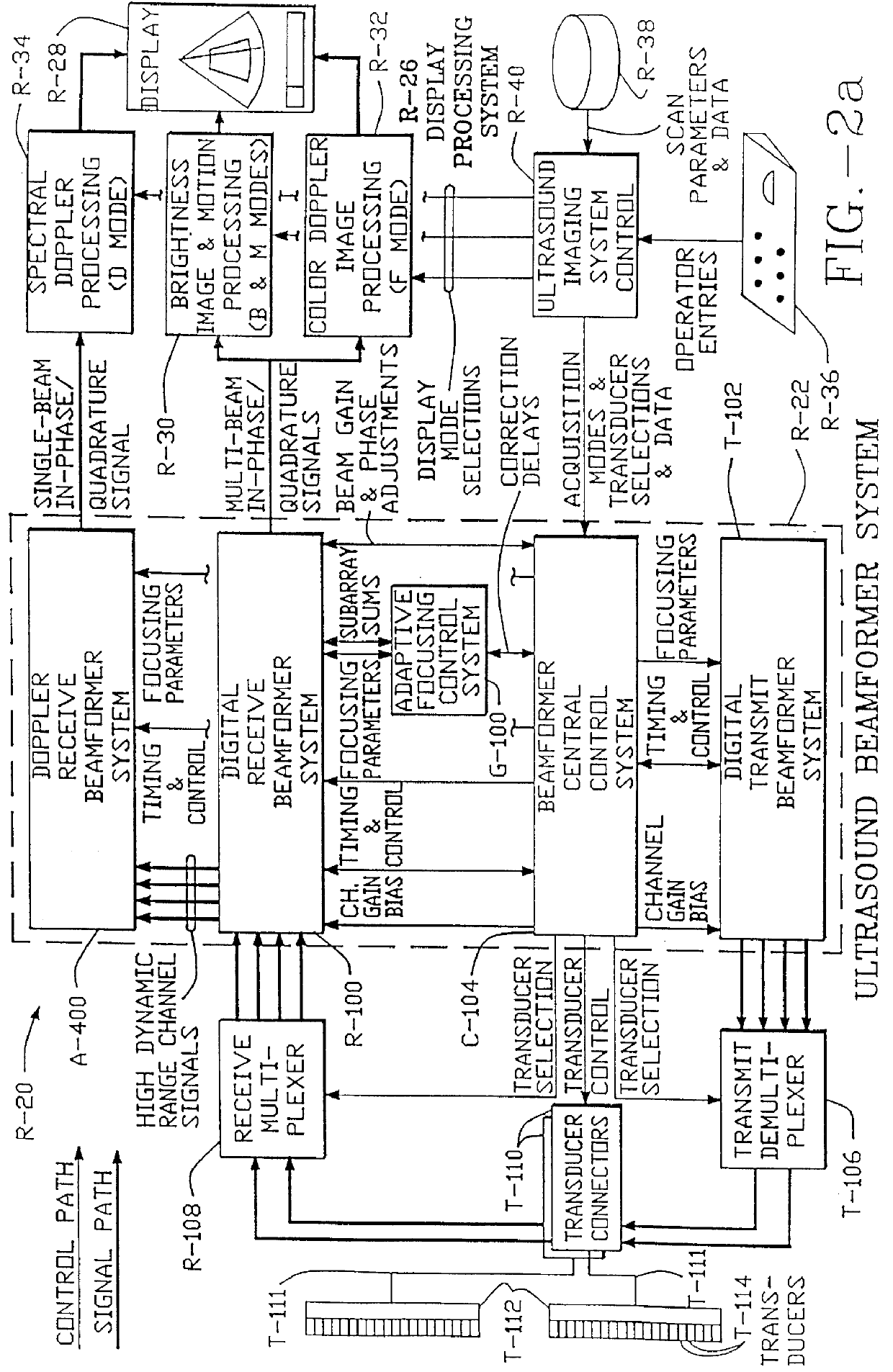
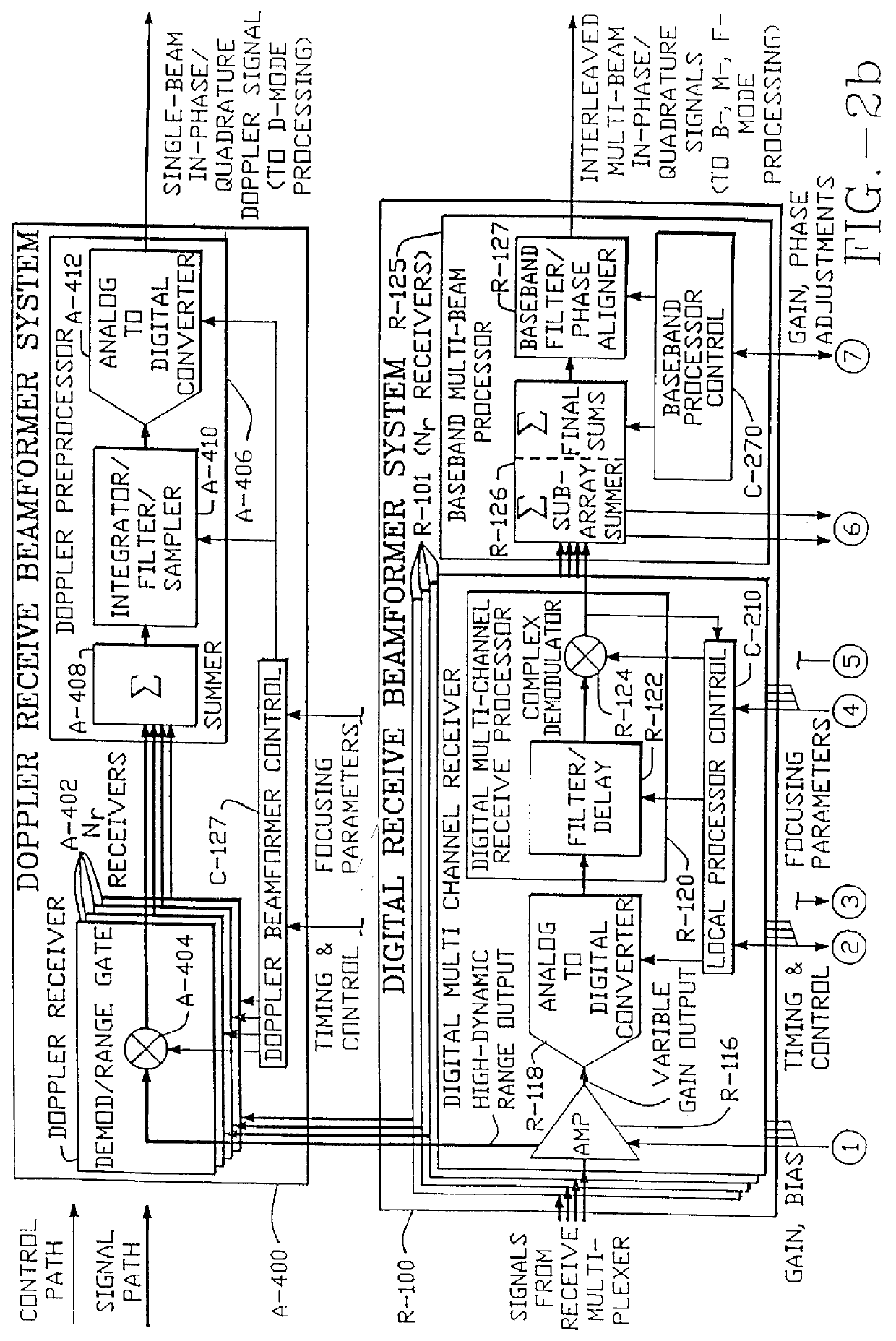
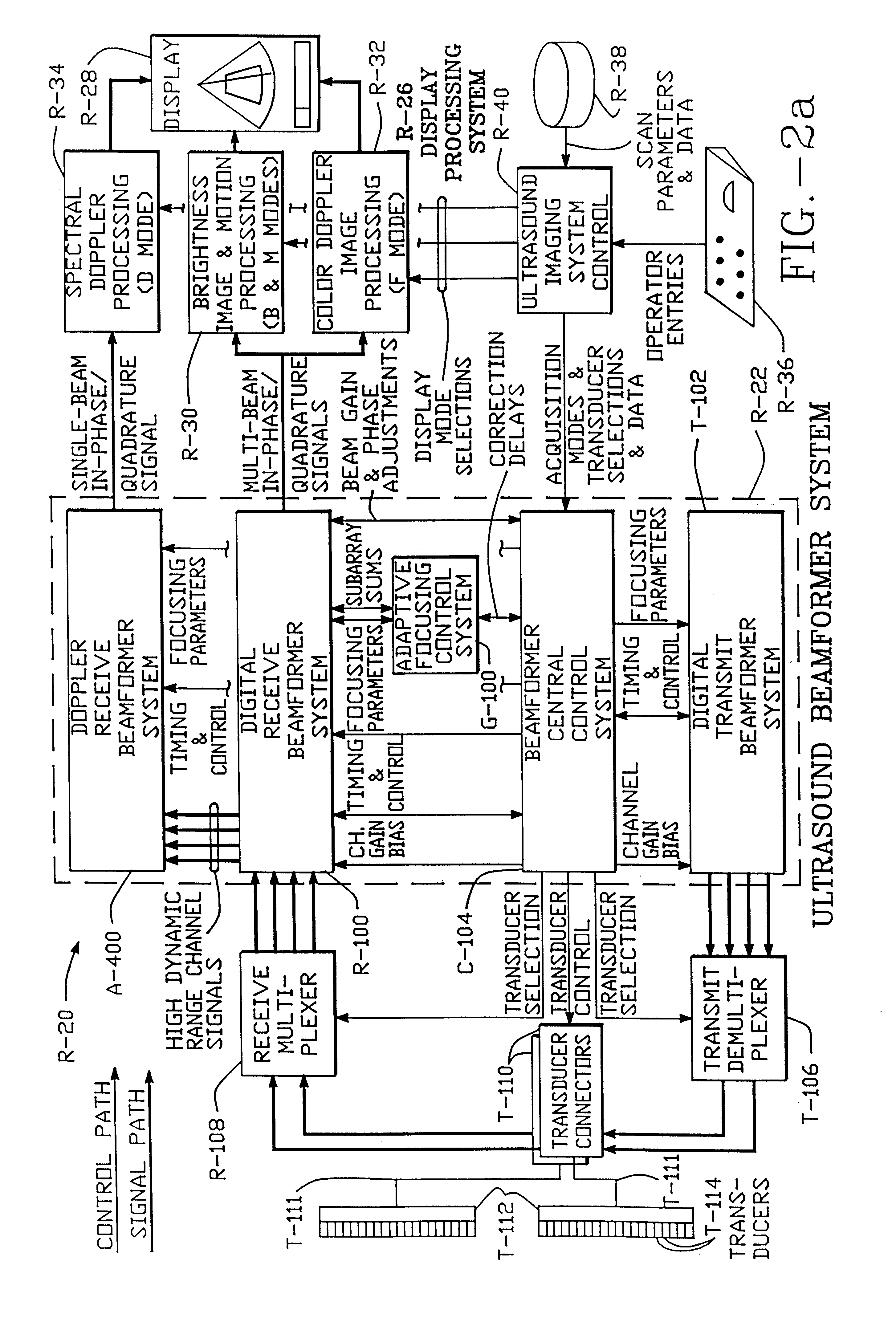
Method and apparatus for transmit beamformer system
InactiveUS6363033B1Improve programmabilityMaximum flexibilityUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsProcessing detected response signalTrade offsApodization
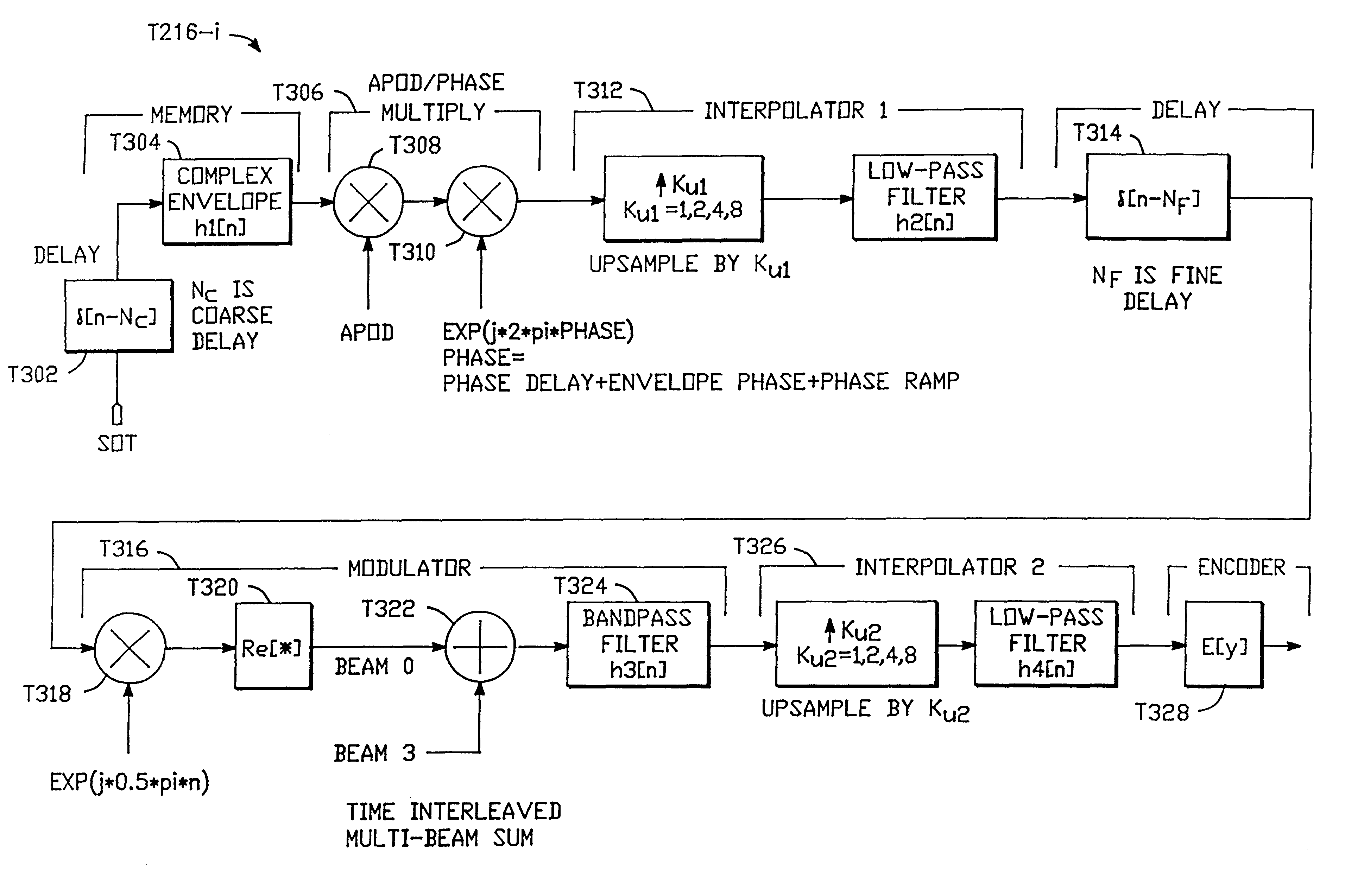
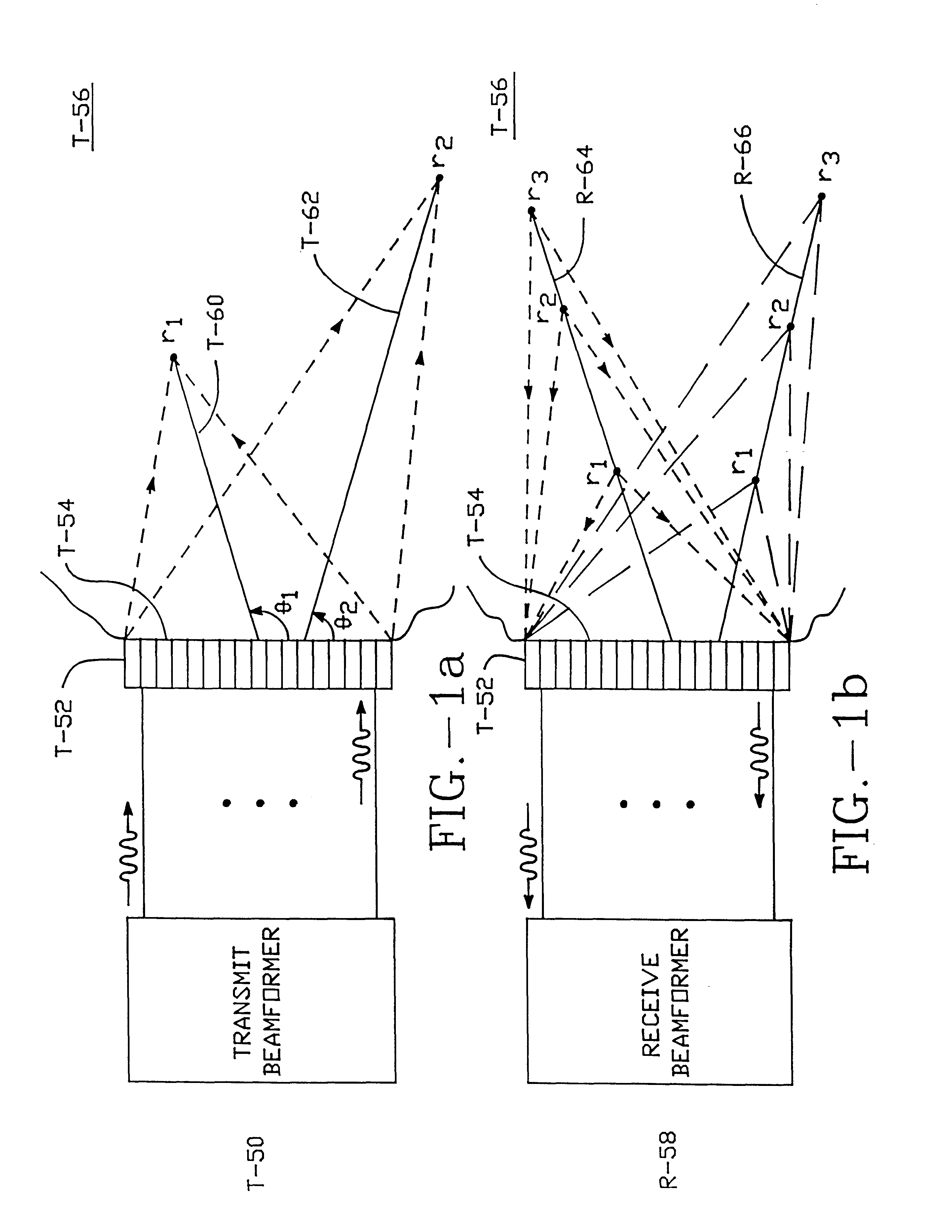
A digital transmit beamformer system with multiple beam transmit capability has a plurality of multi-channel transmitters, each channel with a source of sampled, complex-valued initial waveform information representative of the ultimate desired waveform to be applied to one or more corresponding transducer elements for each beam. Each multi-channel transmitter applies beamformation delays and apodization to each channel's respective initial waveform information digitally, digitally modulates the information by a carrier frequency, and interpolates the information to the DAC sample rate for conversion to an analog signal and application to the associated transducer element(s). The beamformer transmitters can be programmed per channel and per beam with carrier frequency, delay, apodization and calibration values, For pulsed wave operation, pulse waveform parameters can be specified to the beamformer transmitters on a per firing basis, without degrading the scan frame rate to non-useful diagnostic levels. Waveform parameters can be specified to the transmitters by an external central control system which is responsible for higher level flexibility, such as scan formats, focusing depths and fields of view. The transmit pulse delay specified per-channel to each transmitter is applied in at least two components: a focusing time delay component and a focusing phase component. The carrier frequency can be specified for each transmit beam, to any desired frequency within a substantially continuous predefined range of frequencies, and a beam-interleaved signal processing path permits operation in any of several predefined processing modes, which define different parameter sets in a trade-off among (1) the number of beams produced; (2) per-beam initial waveform sample interval; and (3) transmit frequency.
Owner:ACUSON
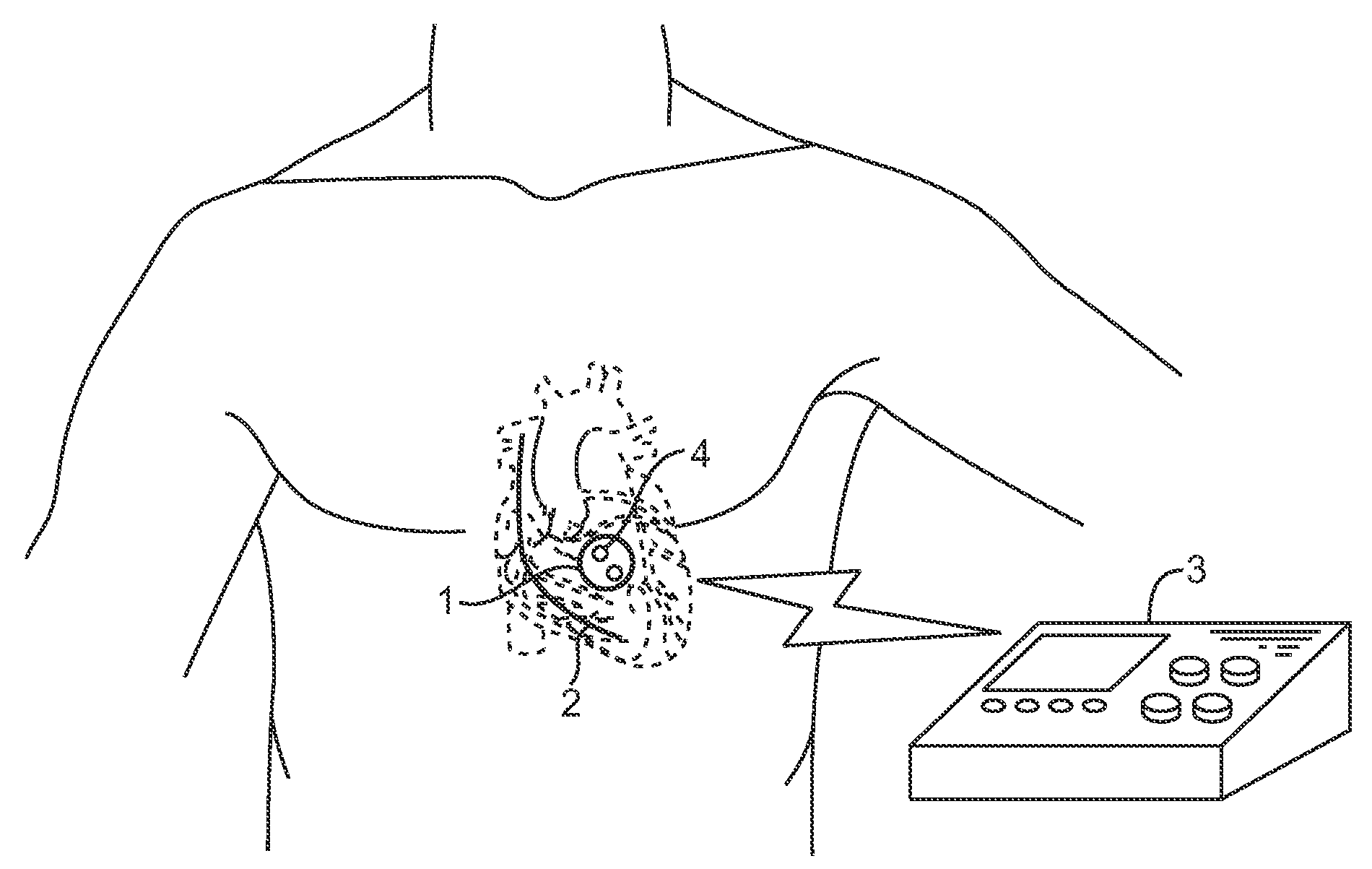
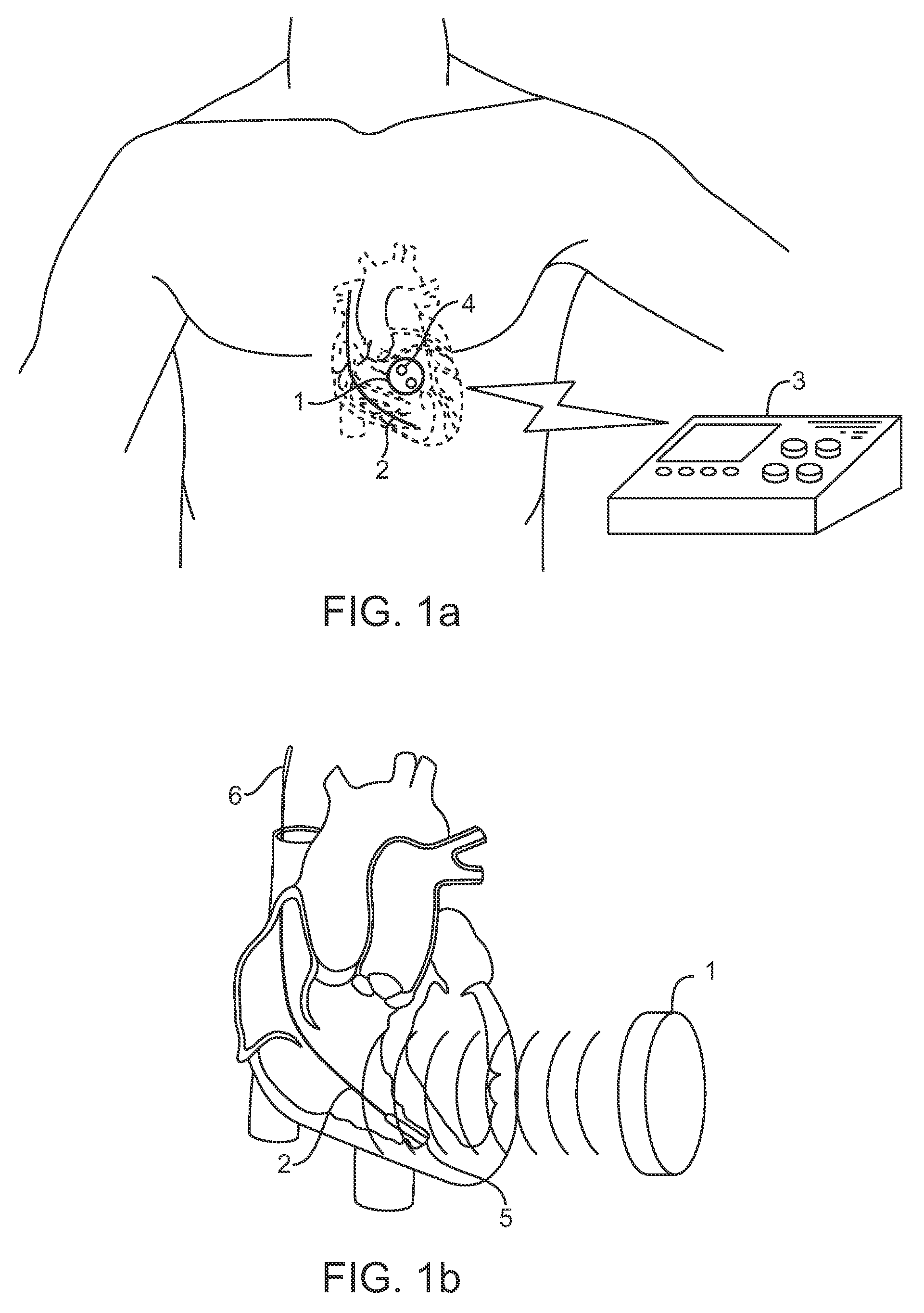
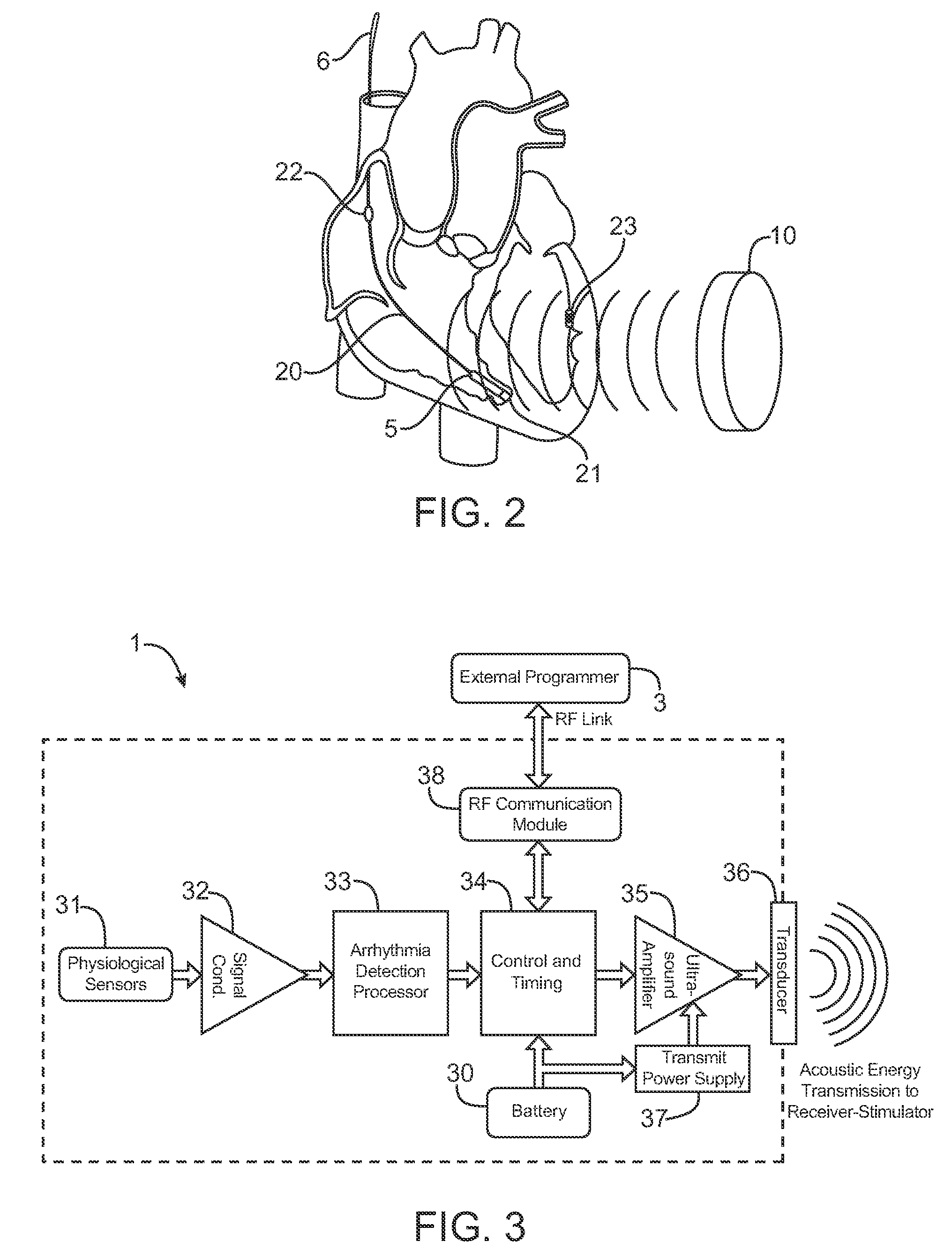
Acoustically-powered wireless defibrillator
An acoustic transmitter produces a pulsed ultrasound waveform which is transmitted through body tissues to an implanted receiver-stimulator device. The waveform has an acoustic amplitude, pulse width, and pulse repetition period, which corresponds to a pacing pulse electrical amplitude, pacing pulse width, and pacing cycle length, respectively. The receiver-stimulator device intercepts at least a portion of the transmitted acoustic energy and coverts that acoustic energy into electrical energy using piezoelectric or other devices. This electrical energy is applied to circuitry, which produces a desired stimulating pulse waveform, which is then applied to tissue-contacting electrodes.
Owner:EBR SYST
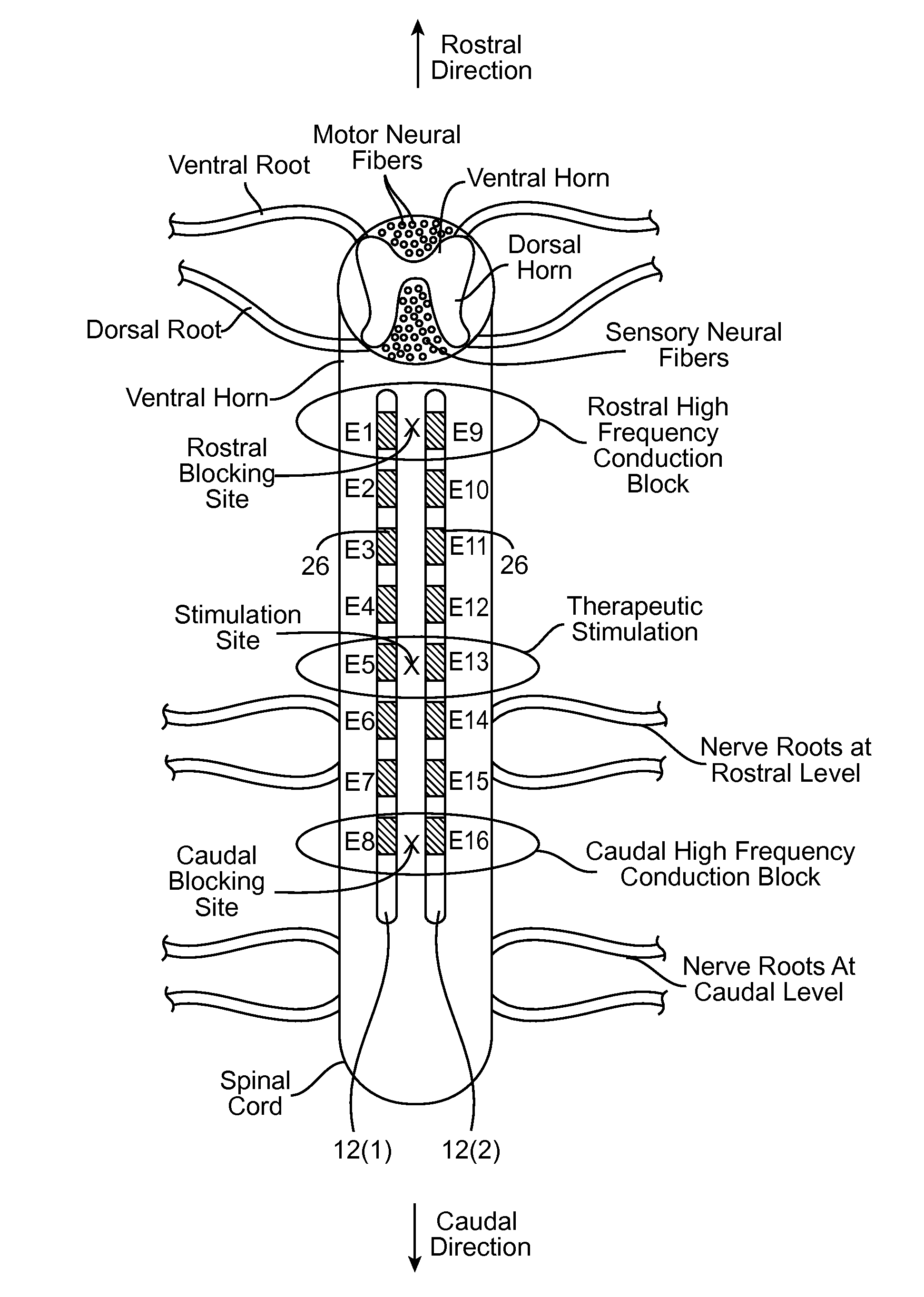
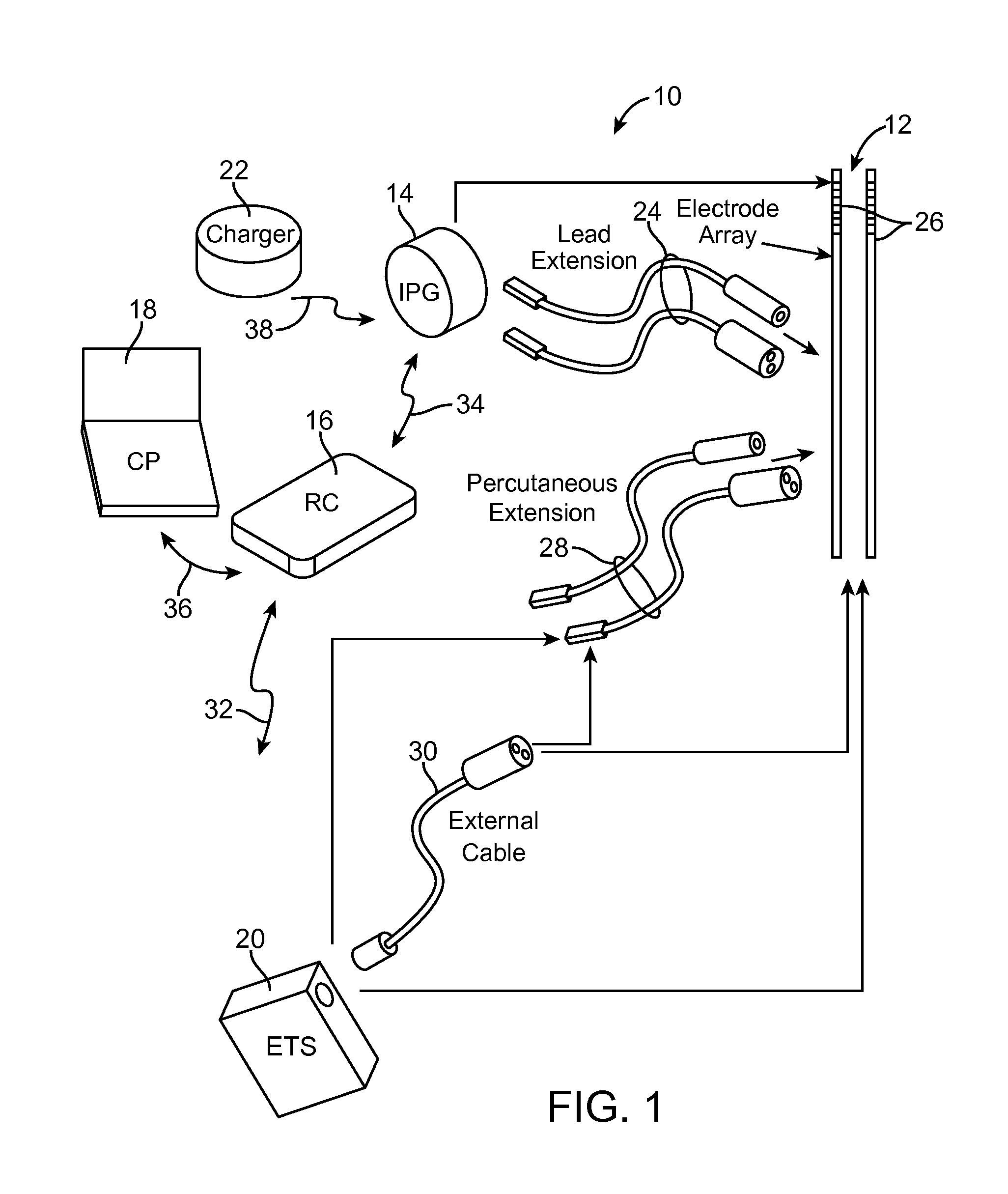
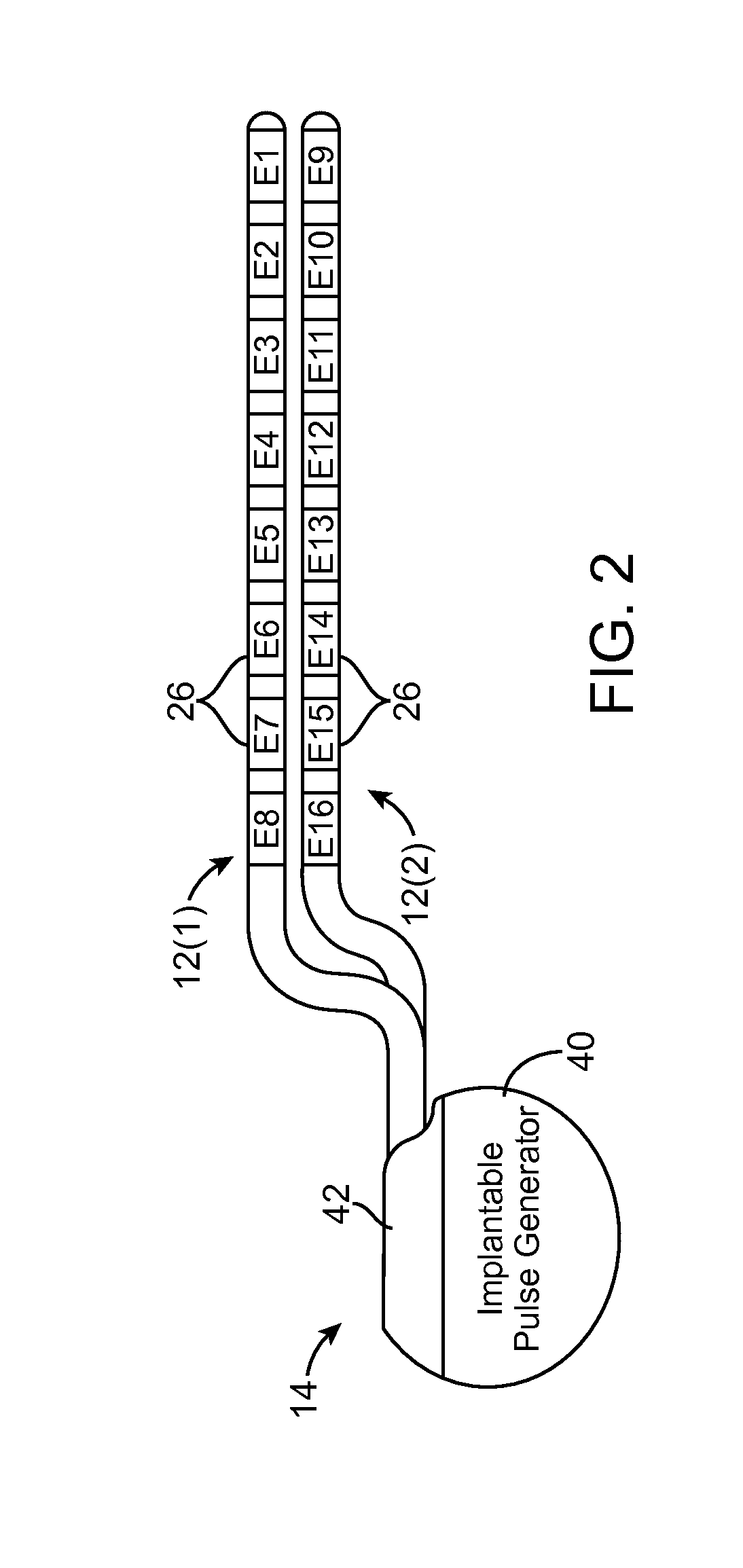
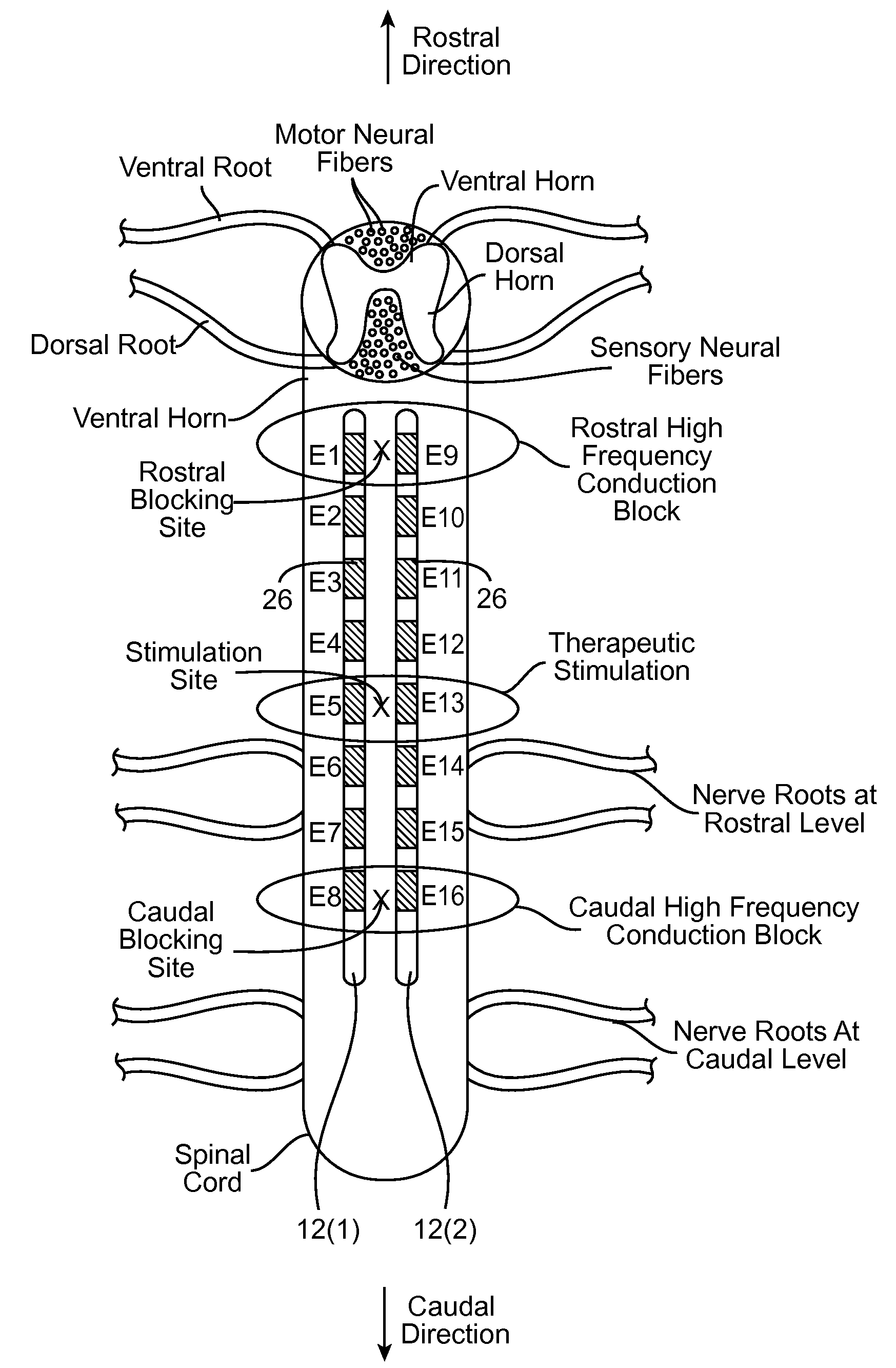
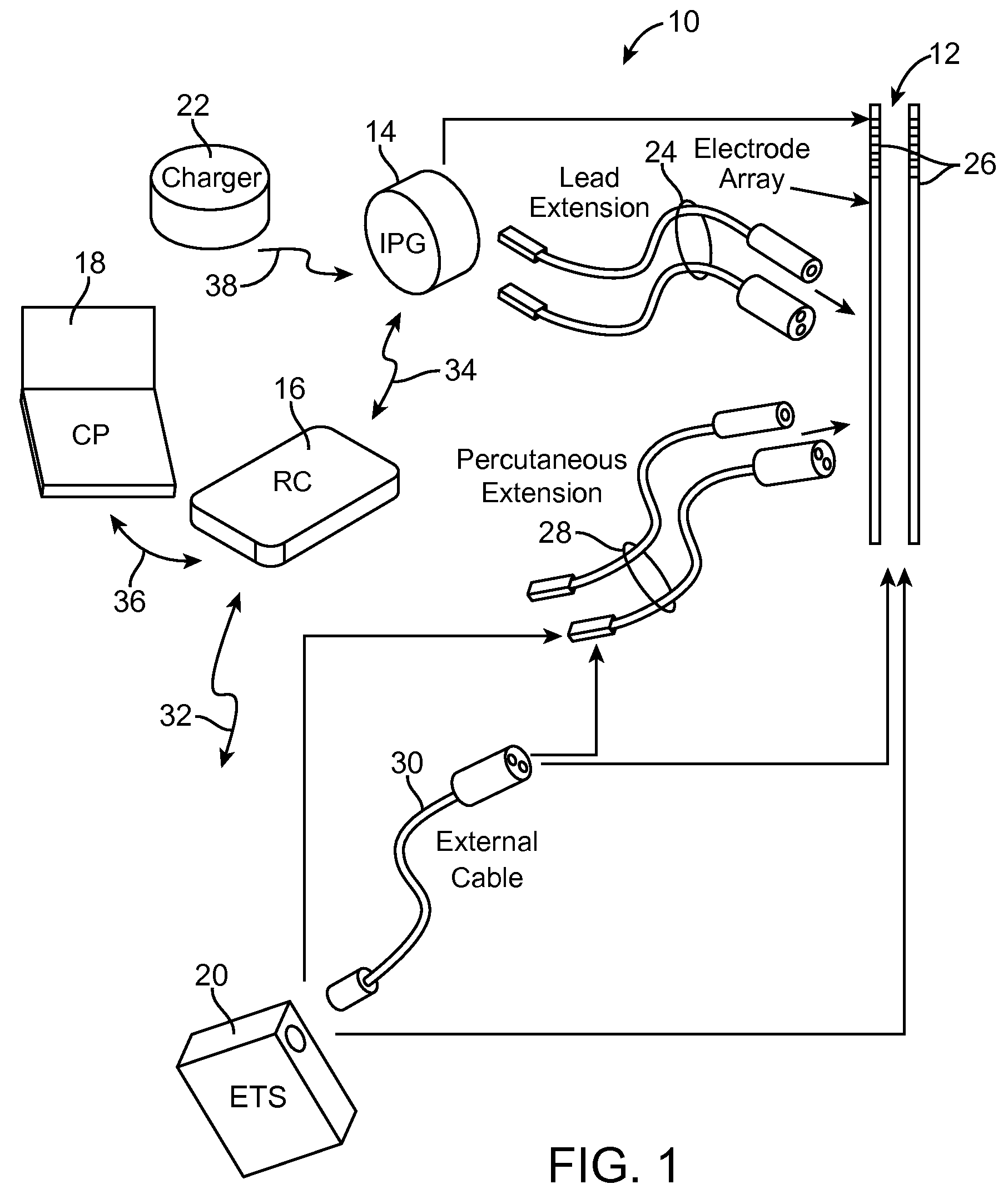
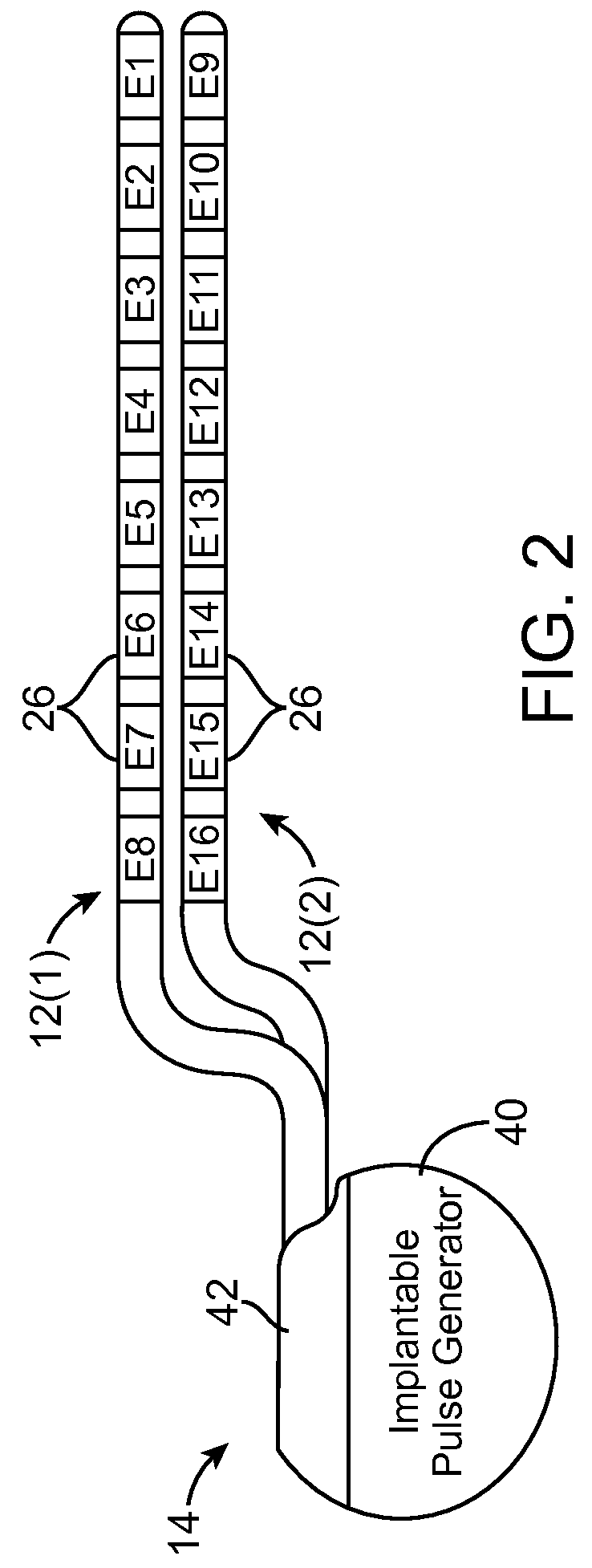
Neurostimulation system and method for providing therapy to patient with minimal side effects
ActiveUS20120089200A1Decrease their propagationEliminate side effectsSpinal electrodesArtificial respirationSide effectMedicine
A method comprises conveying a pulsed waveform between an electrode and a stimulation site of a spinal cord, thereby evoking the antidromic propagation of action potentials along a first sensory neural fiber creating a therapeutic effect in the tissue region, evoking the orthodromic propagation of action potentials along the first sensory neural fiber potentially creating paresthesia corresponding to the tissue region, and evoking the antidromic propagation of action potentials along a second sensory neural fiber potentially creating a side-effect in another tissue region. The method further comprises conveying electrical energy between an electrode and a blocking site rostral to the stimulation site, thereby blocking the action potentials propagated along the first sensory neural fiber and reducing the paresthesia, and conveying electrical energy between an electrode and a blocking site caudal to the stimulation site, thereby blocking the action potentials propagated along the second sensory neural fiber and reducing the side-effect.
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP
Method and apparatus for transmit beamformer system
InactiveUS6104673AImprove abilitiesImprove programmabilityUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsProcessing detected response signalSoftware engineeringCarrier signal
A digital transmit beamformer system with multiple beam transmit capability has a plurality of multi-channel transmitters, each channel with a source of sampled, complex-valued initial waveform information representative of the ultimate desired waveform to be applied to one or more corresponding transducer elements for each beam. Each multi-channel transmitter applies beamformation delays and apodization to each channel's respective initial waveform information digitally, digitally modulates the information by a carrier frequency, and interpolates the information to the DAC sample rate for conversion to an analog signal and application to the associated transducer element(s). The beamformer transmitters can be programmed per channel and per beam with carrier frequency, delay, apodization and calibration values. For pulsed wave operation, pulse waveform parameters can be specified to the beamformer transmitters on a per firing basis, without degrading the scan frame rate to non-useful diagnostic levels. Waveform parameters can be specified to the transmitters by an external central control system which is responsible for higher level flexibility, such as scan formats, focusing depths and fields of view. The transmit pulse delay specified per-channel to each transmitter is applied in at least two components: a focusing time delay component and a focusing phase component. The carrier frequency can be specified for each transmit beam, to any desired frequency within a substantially continuous predefined range of frequencies, and a beam-interleaved signal processing path permits operation in any of several predefined processing modes, which define different parameter sets in a trade-off among (1) the number of beams produced; (2) per-beam initial waveform sample interval; and (3) transmit frequency.
Owner:ACUSON
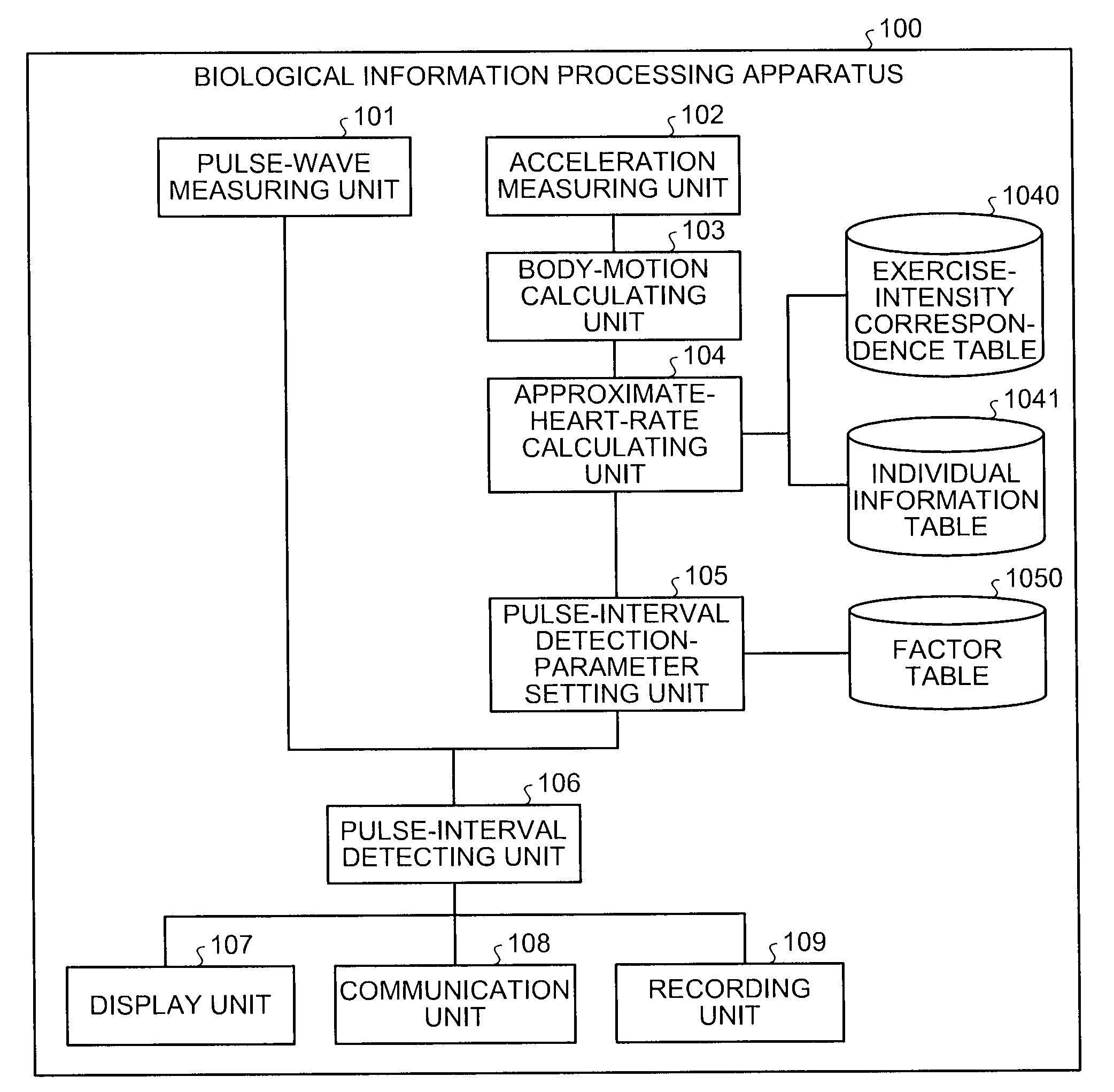
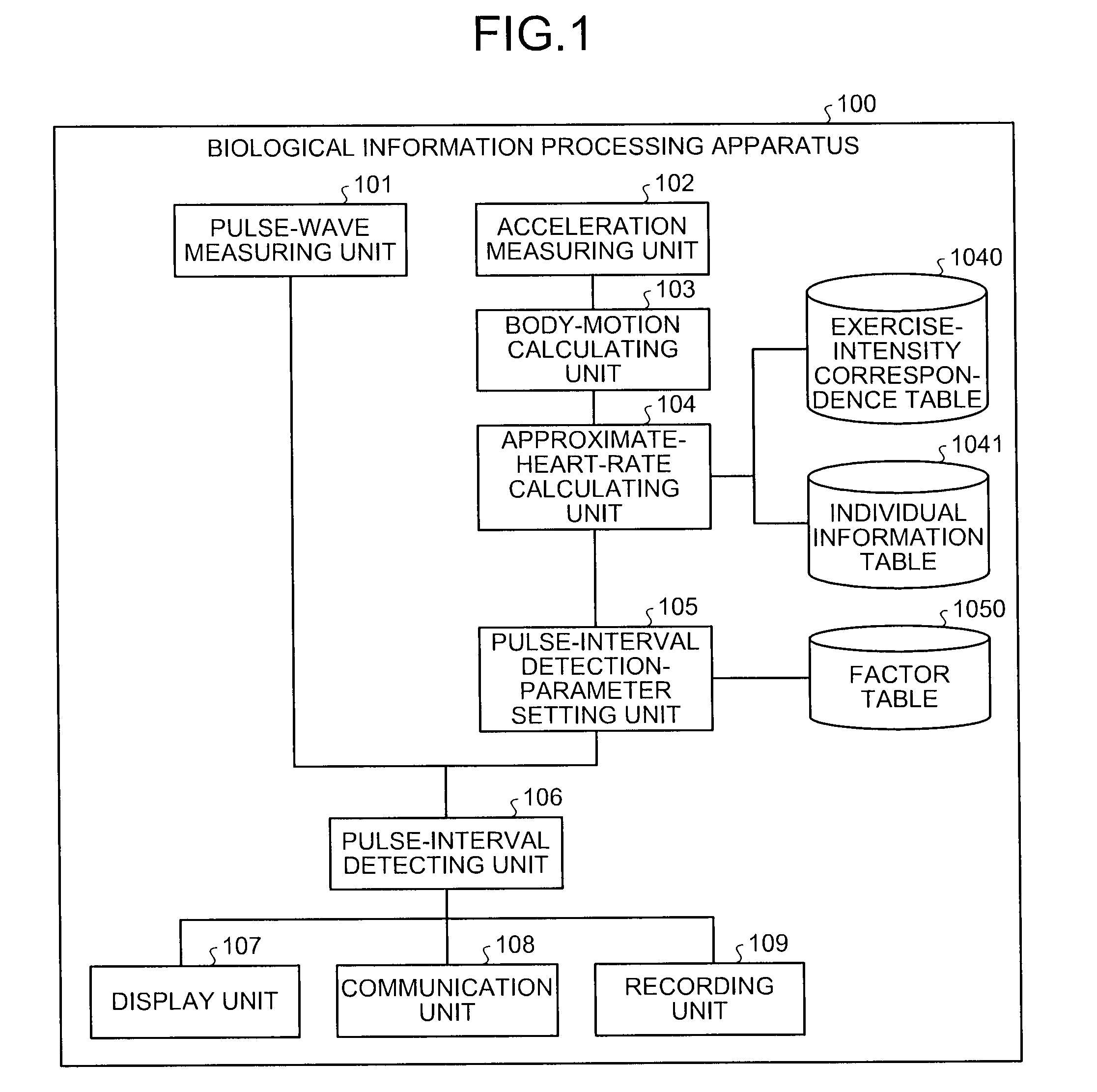
Biological information processing apparatus and biological information processing method
A biological information processing apparatus obtains a pulse wave signal indicating a pulse wave of a subject, and acceleration measured according to body motion of the subject and calculates an amount of body motion of the subject using the acceleration. By using at least one of the body motion amount and the acceleration, the apparatus approximates a heart rate of the subject and sets a parameter to be used for detection of a pulse interval using the heart rate. Then, the apparatus detects each pulse interval using a pulse waveform indicated by the pulse wave signal and the parameter.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
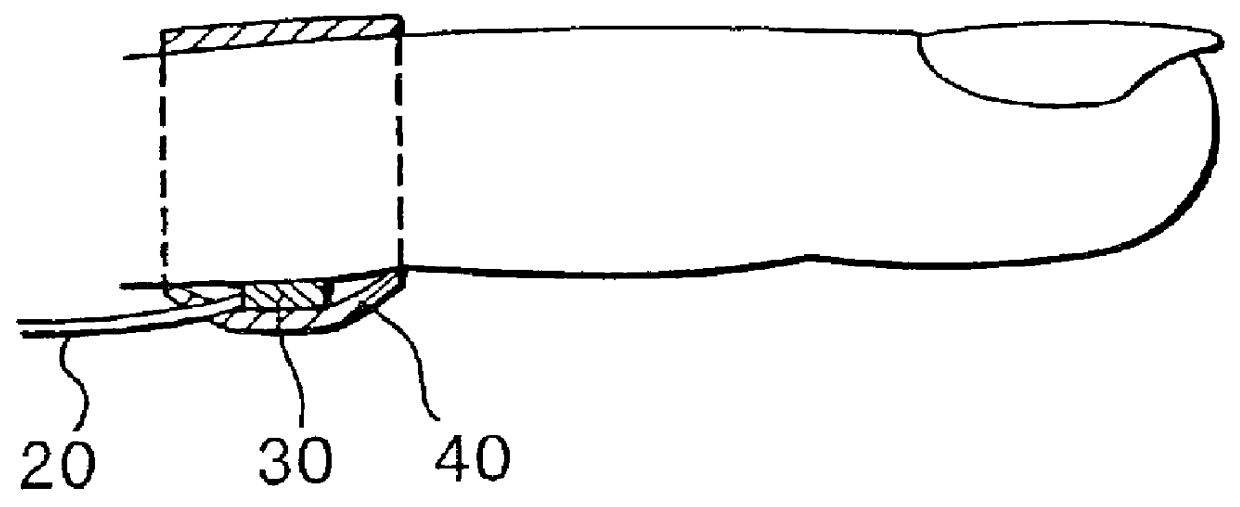
Electrodes coated with treating agent and uses thereof
InactiveUS6713291B2Rapidly ready for useShort pulse widthBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBiological cellCoated electrodes
An object of the invention is to provide a method for delivery of macromolecules into biological cells in the tissues of a patient and includes the steps of: (a) providing electrodes (16) in an electrode assembly (12), wherein the electrodes have fixed electrode surfaces (42) which are coated with at least one static layer of electrode releasable molecules (44) to be delivered; (b) providing a waveform generator (15) for generating electric fields; (c) establishing electrically conductive pathways between the electrodes (16) and the waveform generator (15); (d) locating the electrodes (16) such that the biological cells are situated therebetween, and (g) providing electric fields in the form of pulse waveforms from the waveform generator (15) to the electrodes (16), such that molecules in the at least one static layer of the electrode releasable molecules (44) on the electrodes (16) are delivered into the biological cells. The electrode releasable molecules (44) can be either electric field separable molecules and / or solvent separable material. Another object of the invention is to provide an apparatus for carrying out the method of the invention. The static-coated electrode assembly (12) can be provided in a sterile package (24), from which the electrode assembly (12) is removed prior to use. The statically-coated electrode assembly (12) can be in a form of a disposable assembly (12) which is removable and replaceable from an electrode assembly holder (13).
Owner:CELLECTIS SA
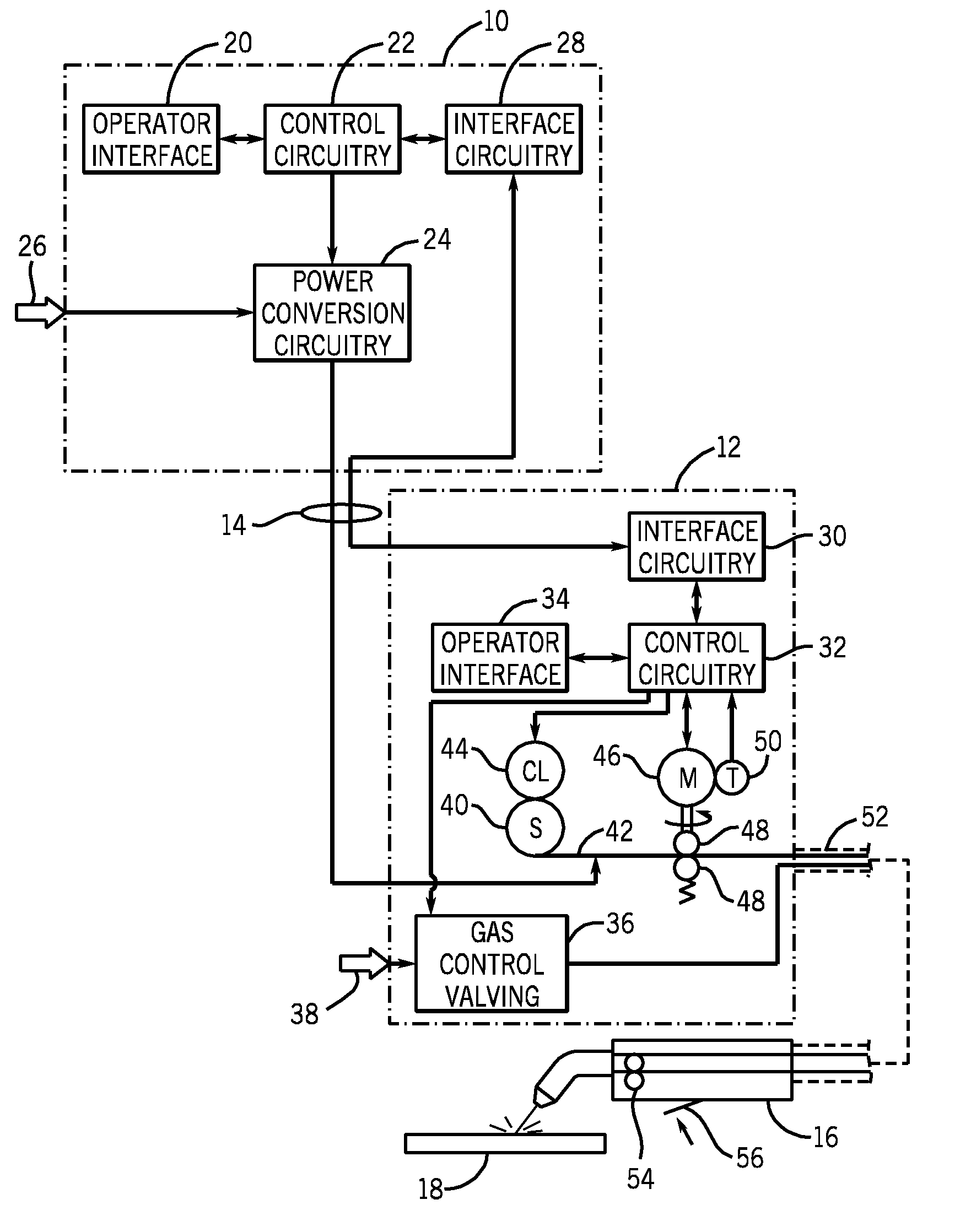
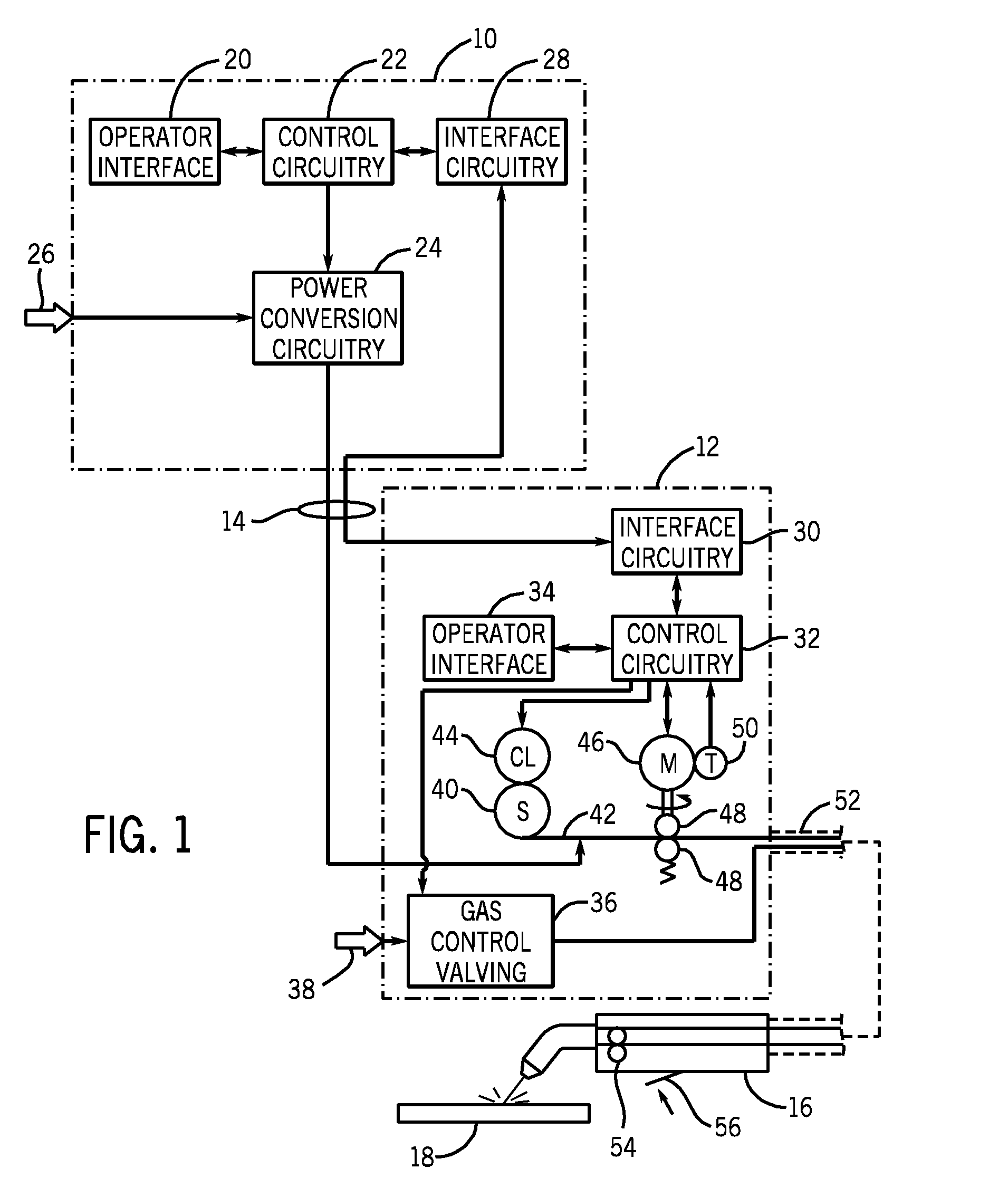
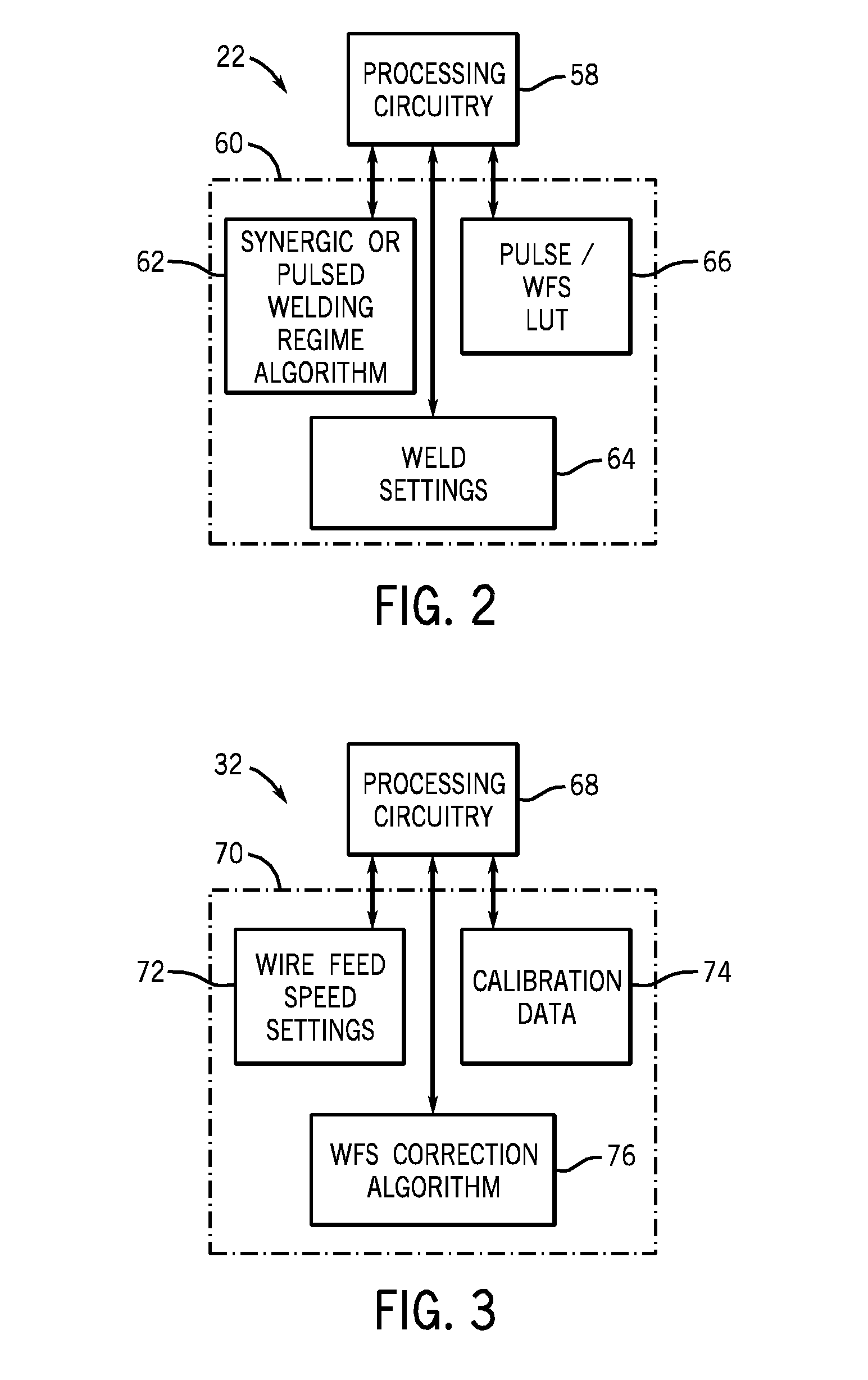
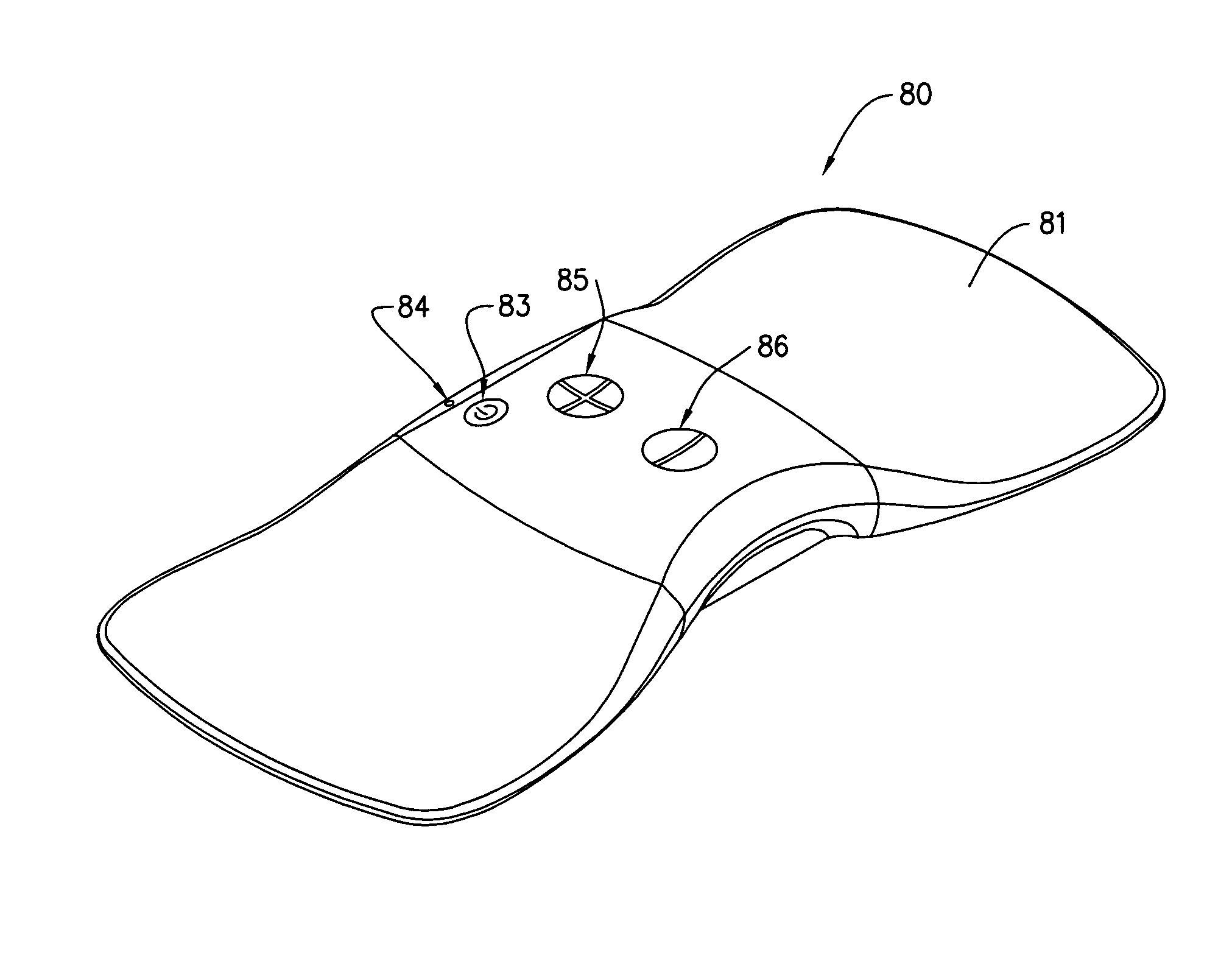
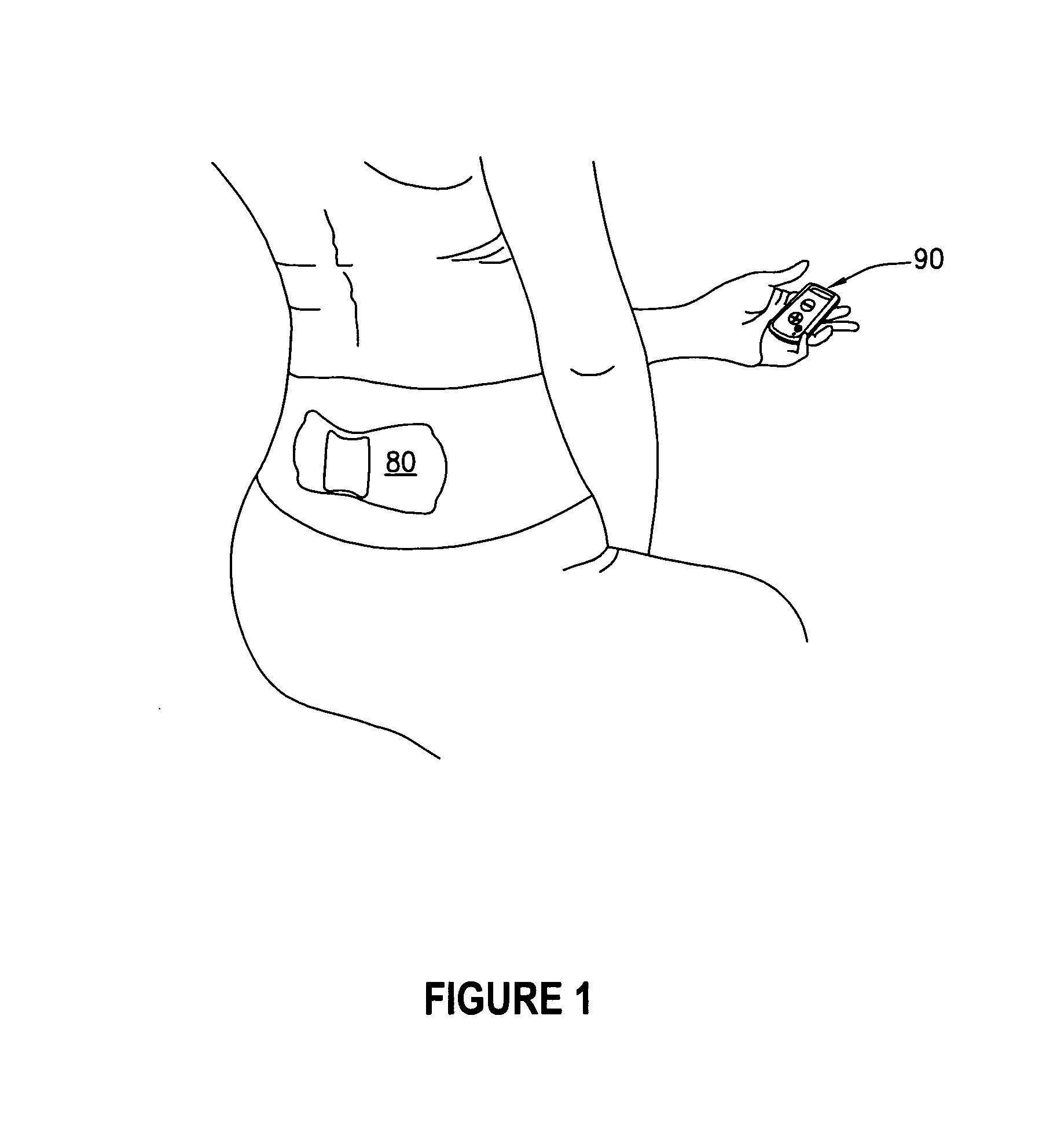
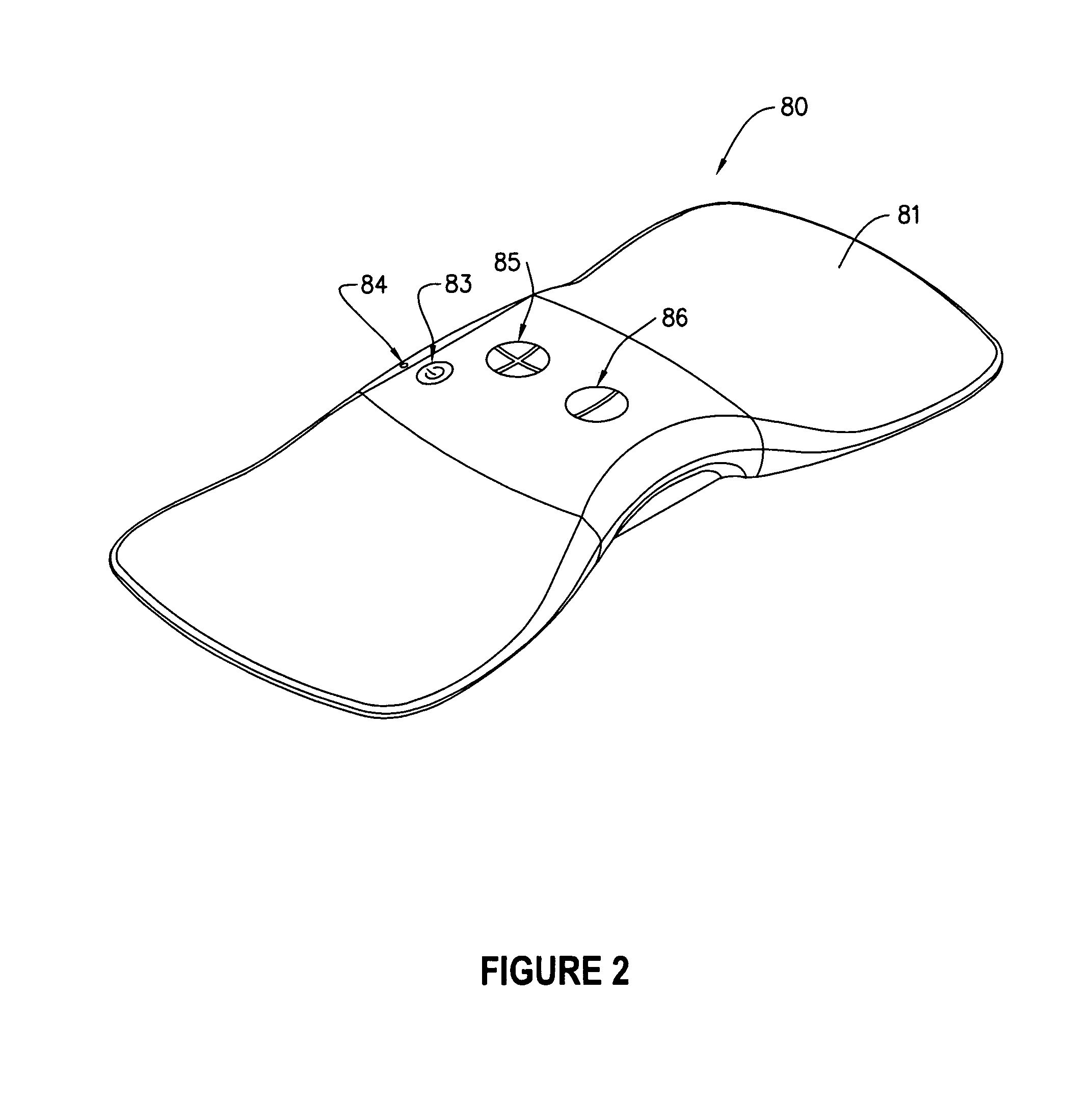
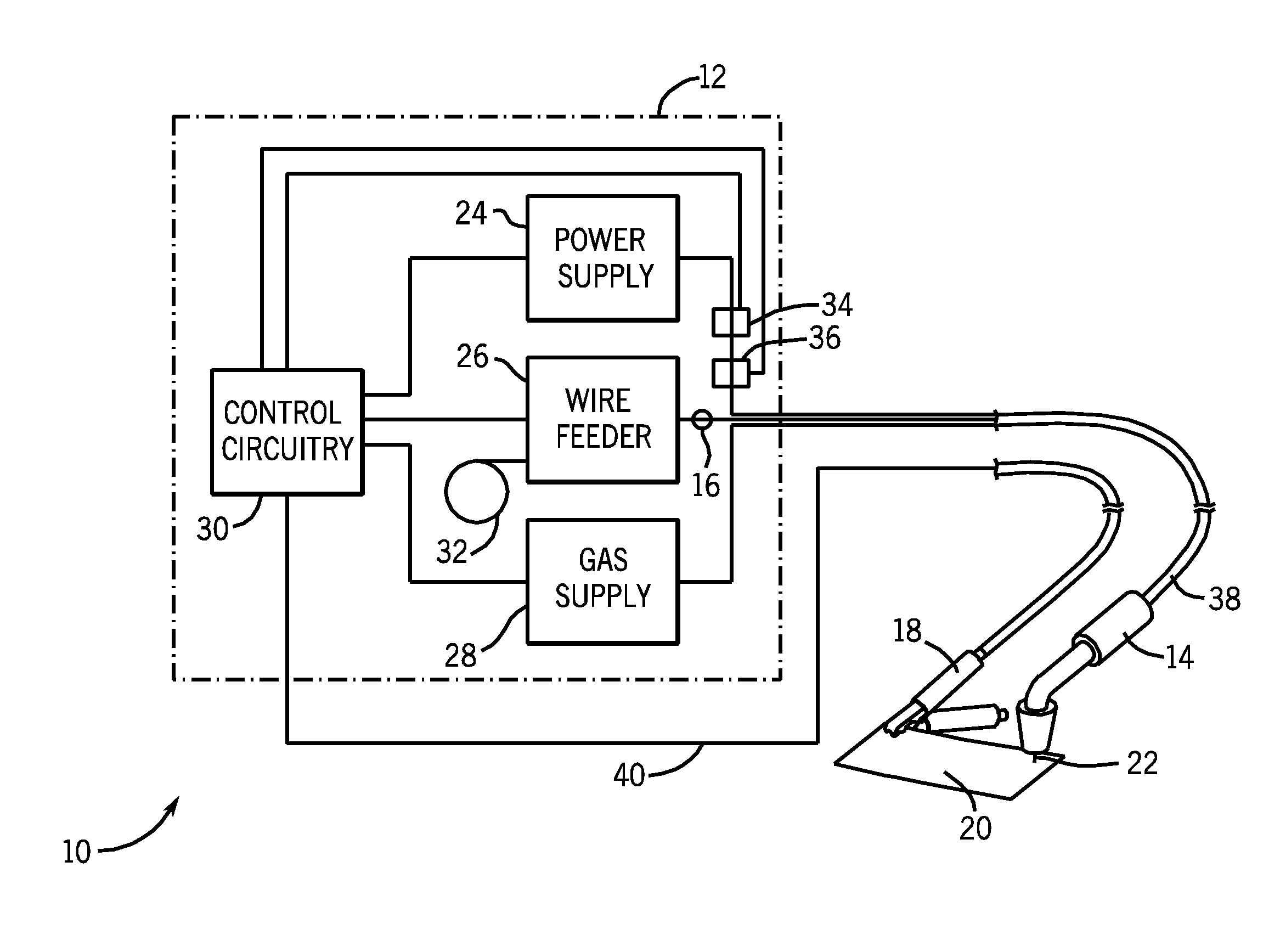
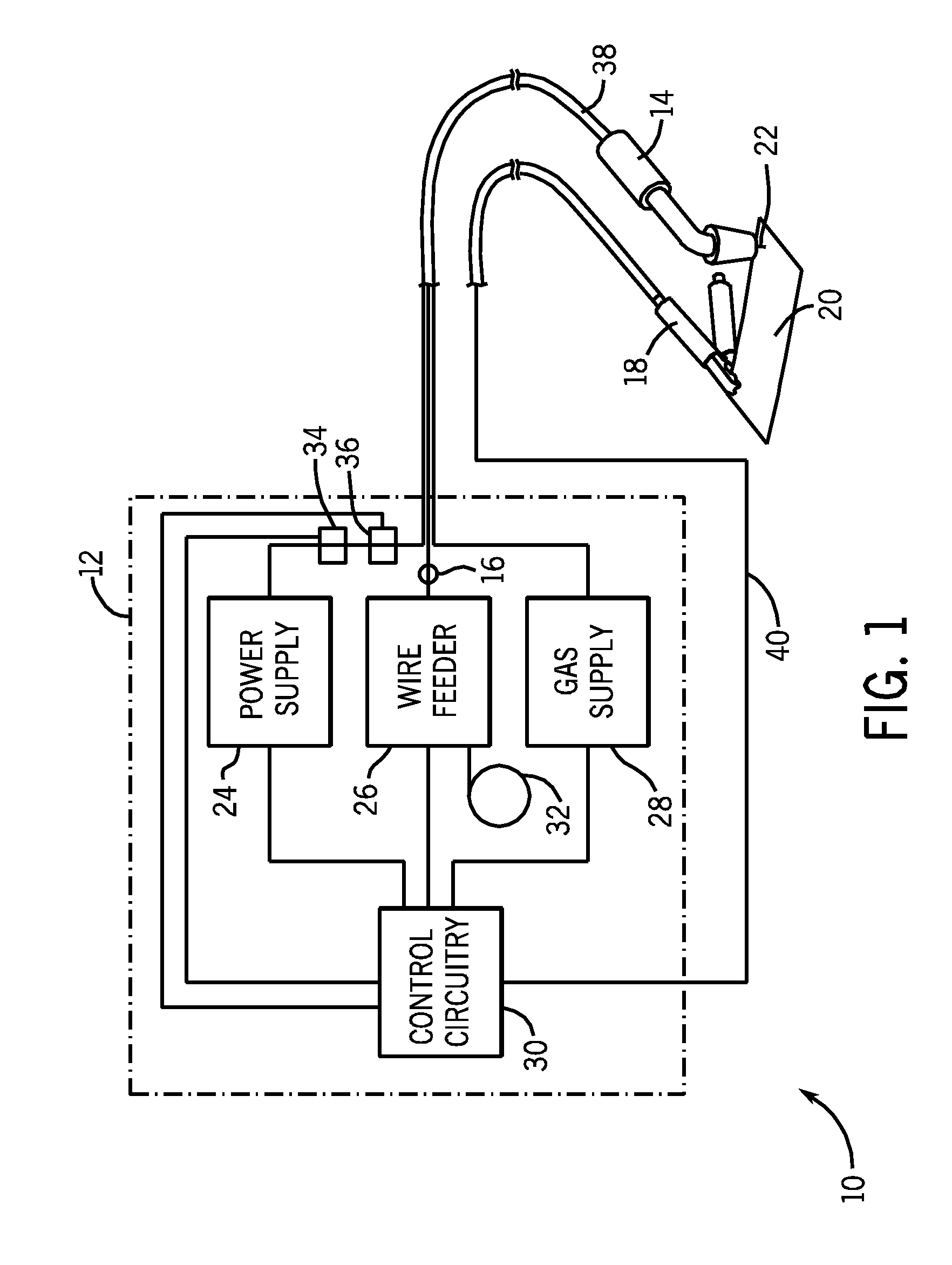
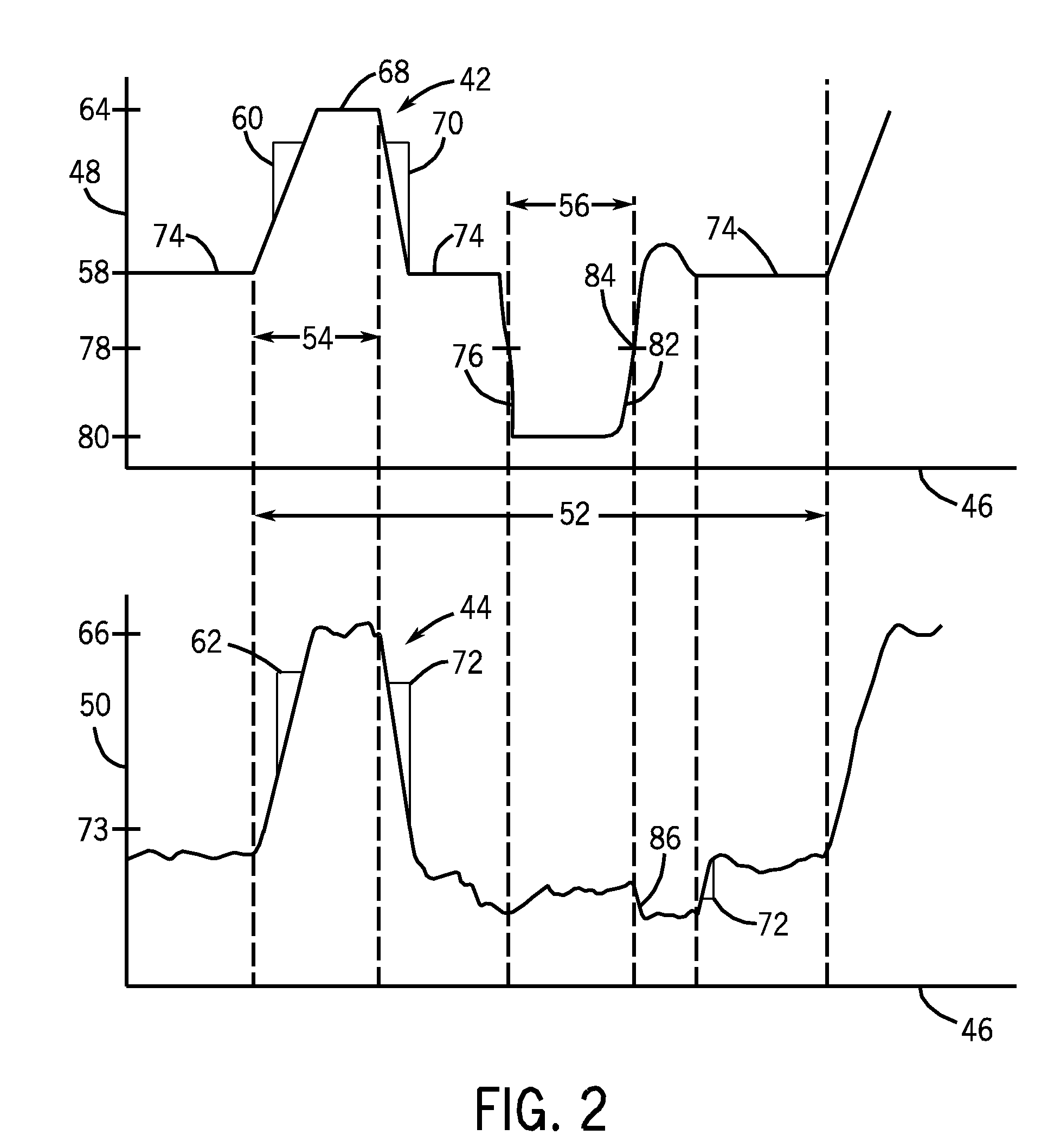
Wire feed speed referenced variable frequency pulse welding system
A pulsed waveform welding operation is implemented by reference to a commanded wire feed speed set by an operator. The wire feed speed is set on a wire feeder, and a signal representative of the commanded wire feed speed is applied to a power supply. The power supply control circuitry references a look-up table in which pulsed waveform parameters are provided based upon wire feed speed. The parameters may include multiple parameters such as pulse frequency, peak current, background current, and current ramp rates. The control circuitry commands power conversion circuitry to generate the commanded waveform as a function of the commanded wire feed speed.
Owner:ILLINOIS TOOL WORKS INC
Neurostimulation system and method for providing therapy to patient with minimal side effects
ActiveUS8731675B2Decrease their propagationReducing (and preferably eliminating) the paresthesiaSpinal electrodesFiberSide effect
A method comprises conveying a pulsed waveform between an electrode and a stimulation site of a spinal cord, thereby evoking the antidromic propagation of action potentials along a first sensory neural fiber creating a therapeutic effect in the tissue region, evoking the orthodromic propagation of action potentials along the first sensory neural fiber potentially creating paresthesia corresponding to the tissue region, and evoking the antidromic propagation of action potentials along a second sensory neural fiber potentially creating a side-effect in another tissue region. The method further comprises conveying electrical energy between an electrode and a blocking site rostral to the stimulation site, thereby blocking the action potentials propagated along the first sensory neural fiber and reducing the paresthesia, and conveying electrical energy between an electrode and a blocking site caudal to the stimulation site, thereby blocking the action potentials propagated along the second sensory neural fiber and reducing the side-effect.
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP
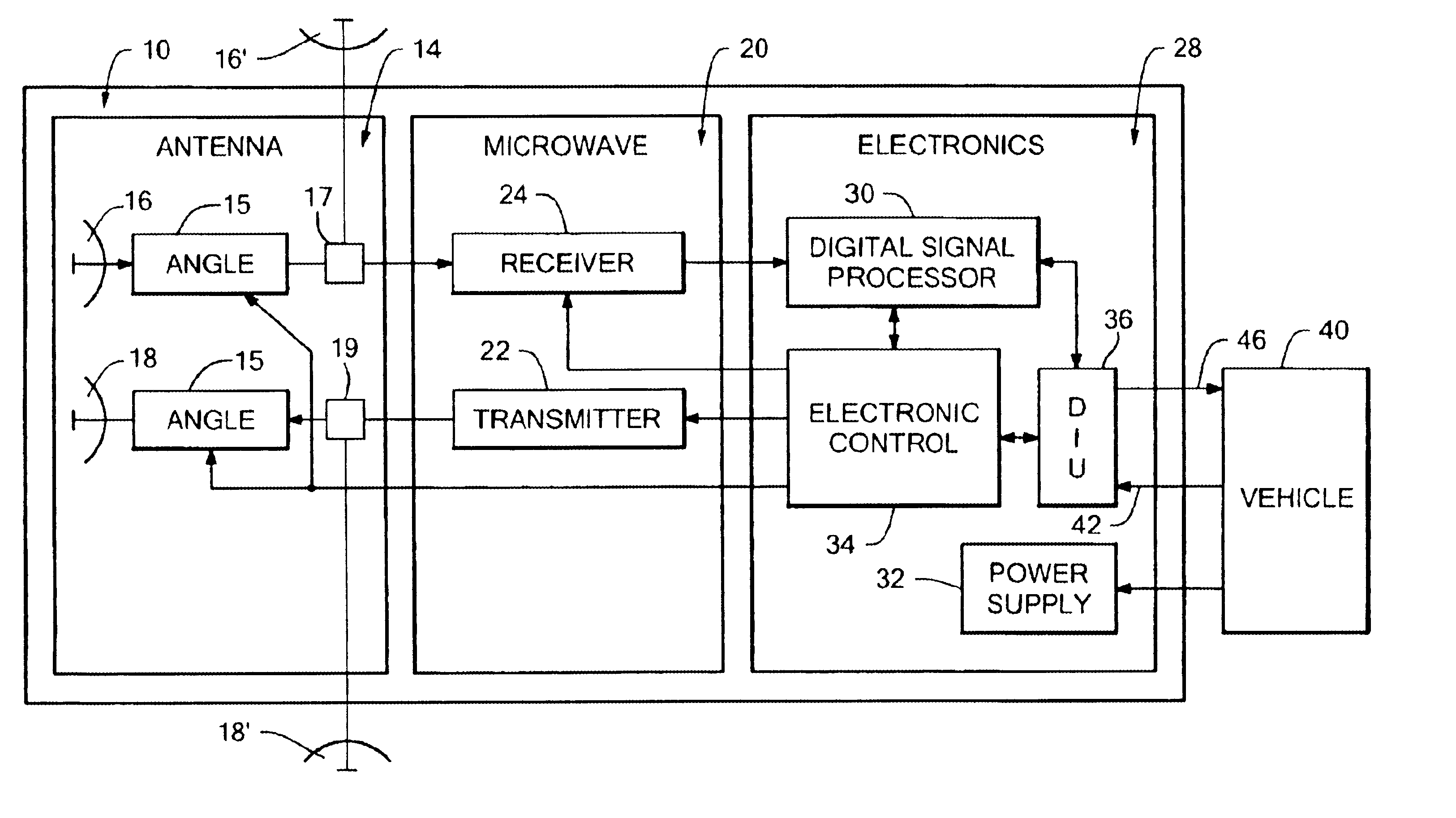
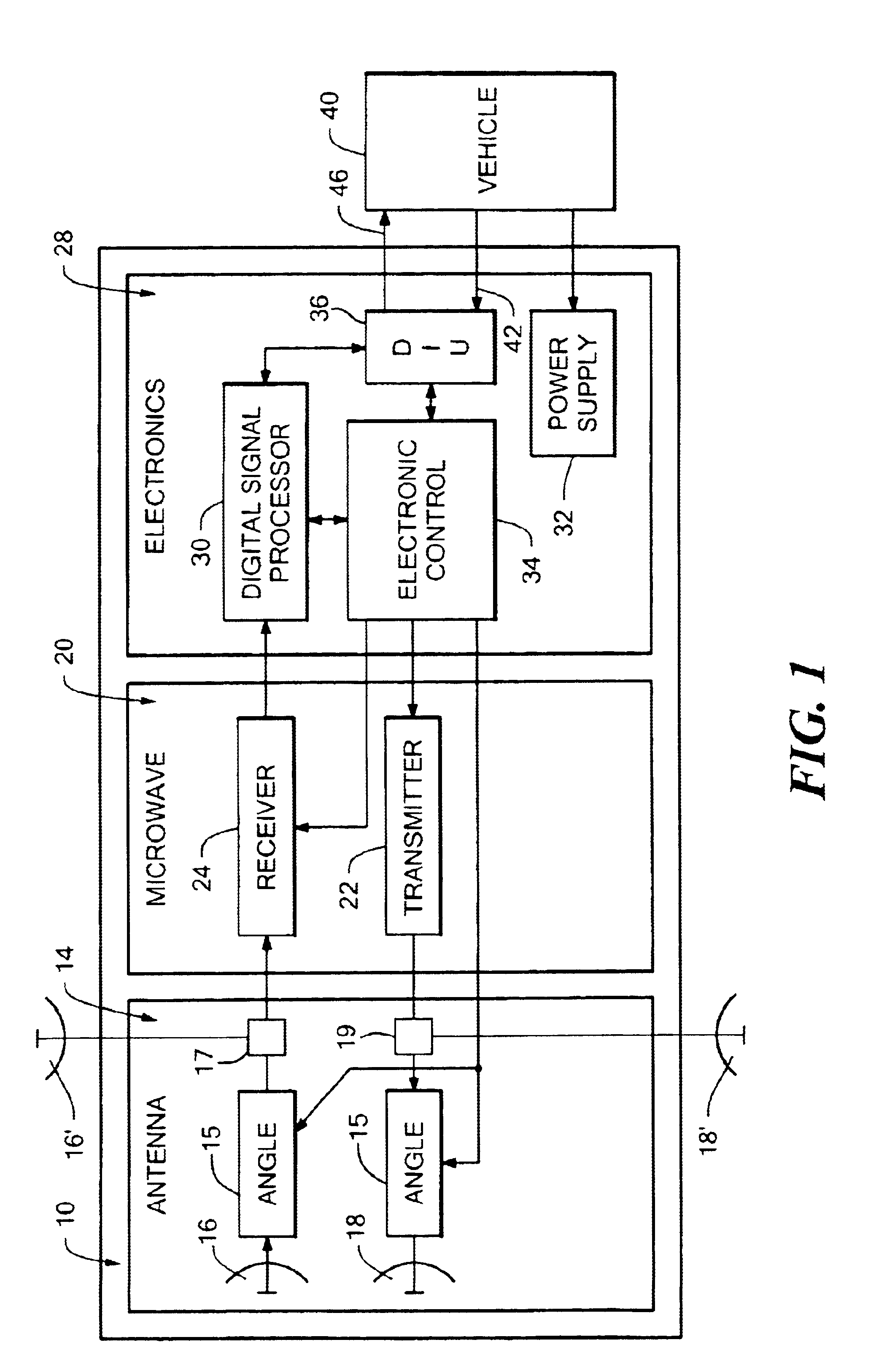
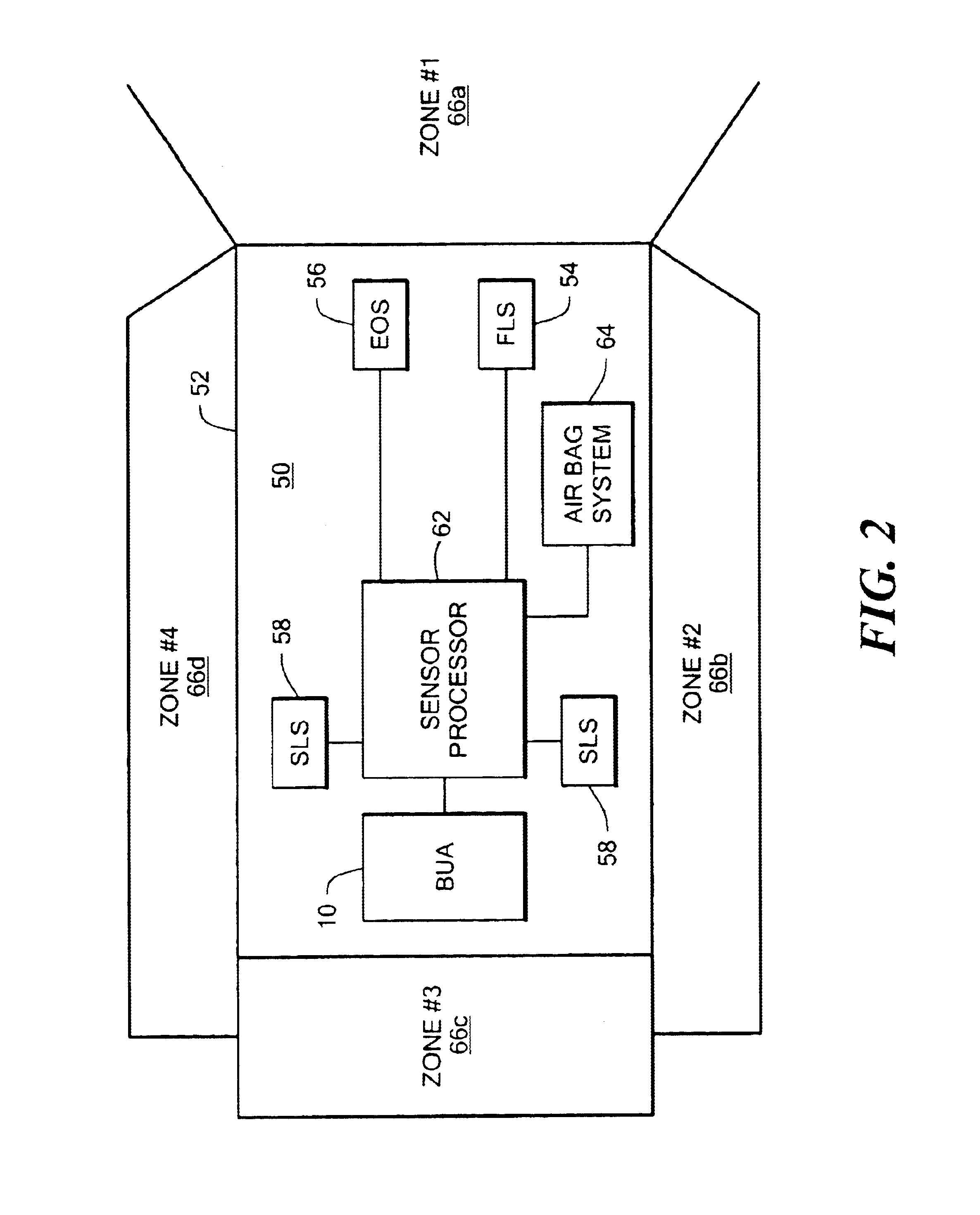
Back-up aid indicator using FMCW chirp signal or a time domain pulse signal
InactiveUS6873250B2Reduce leakageHigh energyAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesAnti-collision systemsTime domainContinuous wave
A back-up aid indication system includes a sensor for providing detection coverage in a predetermined coverage zone behind a vehicle. The sensor includes a transmit antenna adapted for transmitting an RF signal having a quasi-collimated antenna pattern in a near field. The system further includes a waveform generator which selectively provides one of a frequency modulated continuous wave FMCW Chirp signal and a pulse waveform signal as the transmitted RF signal.
Owner:VALEO RADAR SYST
Pulsed radar level gauging with relative phase detection
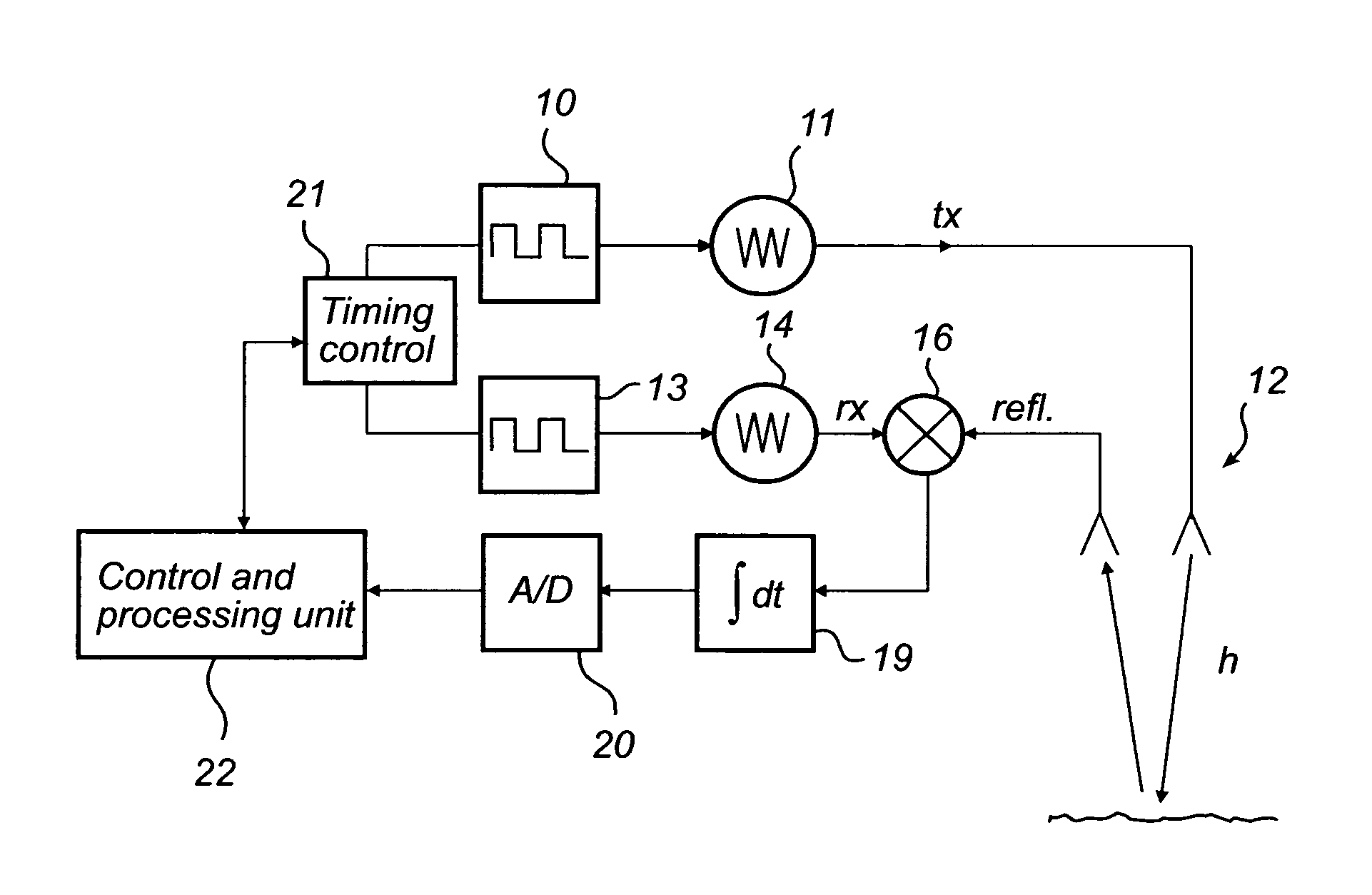
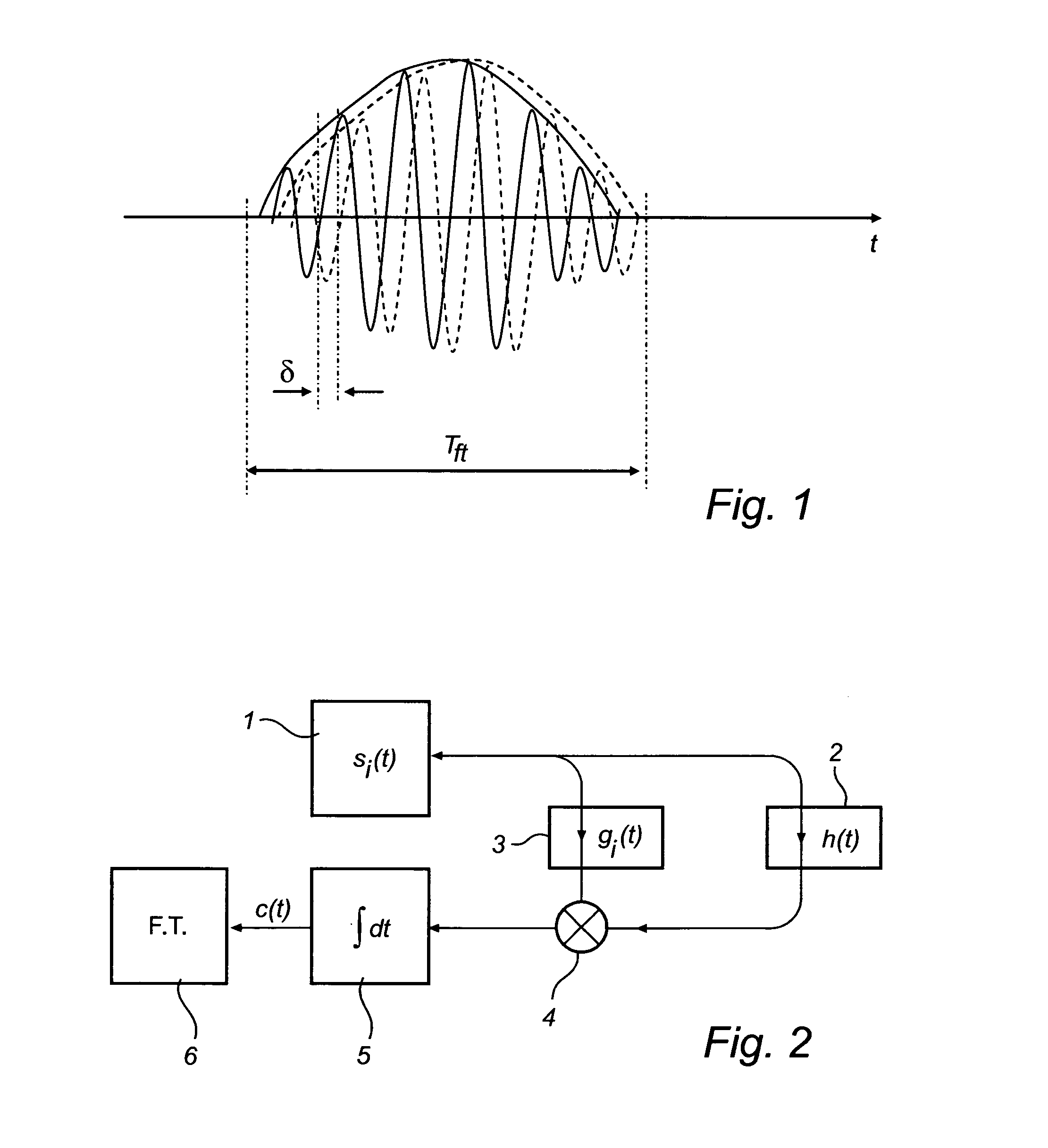
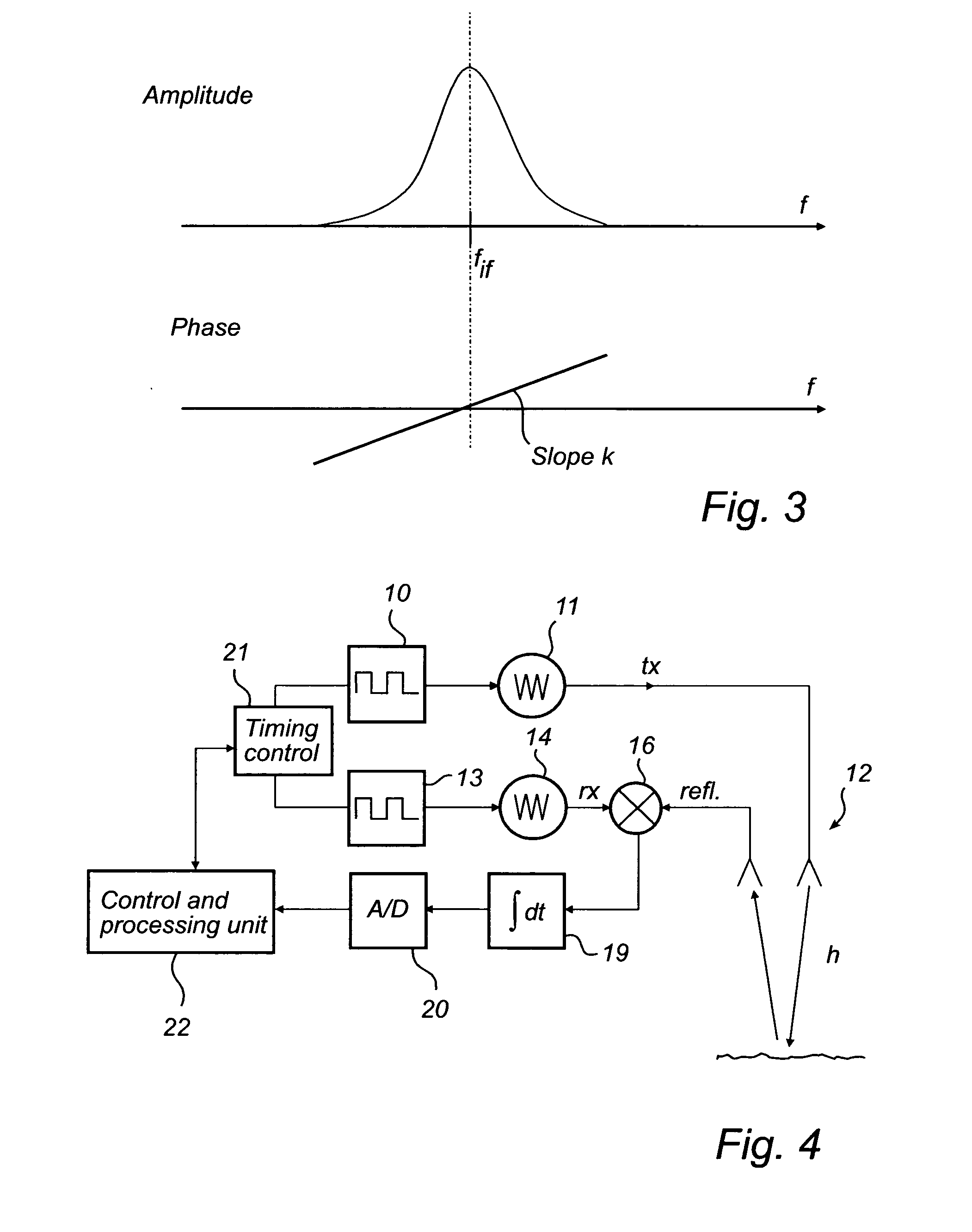
InactiveUS20080105048A1Accurate detectionLower requirementMachines/enginesLubrication indication devicesFrequency spectrumTime correlation
A method for determining a process variable of a product in a tank based on a time delay of electromagnetic waves. The method further comprises forming a measurement signal comprising a sequence of values, each value representing a time correlation between a pulse of a reference signal and a reflected signal, sampling and digitizing this measurement signal to form a digital signal, identifying a time window of the digital signal including the surface echo peak, determining a relative time period between a reference time corresponding to the predefined reference and a beginning of the time window, time-to-frequency transforming the digital signal in the time window to obtain a phase spectrum, determining a relative phase shift of the spectrum and using the relative phase shift to calculate a corresponding time shift, and determining the time delay by adding the relative time period and the time shift.The invention is based on the realization that major improvement of measurement performance, compared to amplitude detection only, can be achieved by discrimination of the phase difference between the reflected signal and a reference. The detection is further independent of the pulse waveform and modulation, significantly reducing the requirements on pulse modulation.
Owner:ROSEMOUNT TANK RADAR
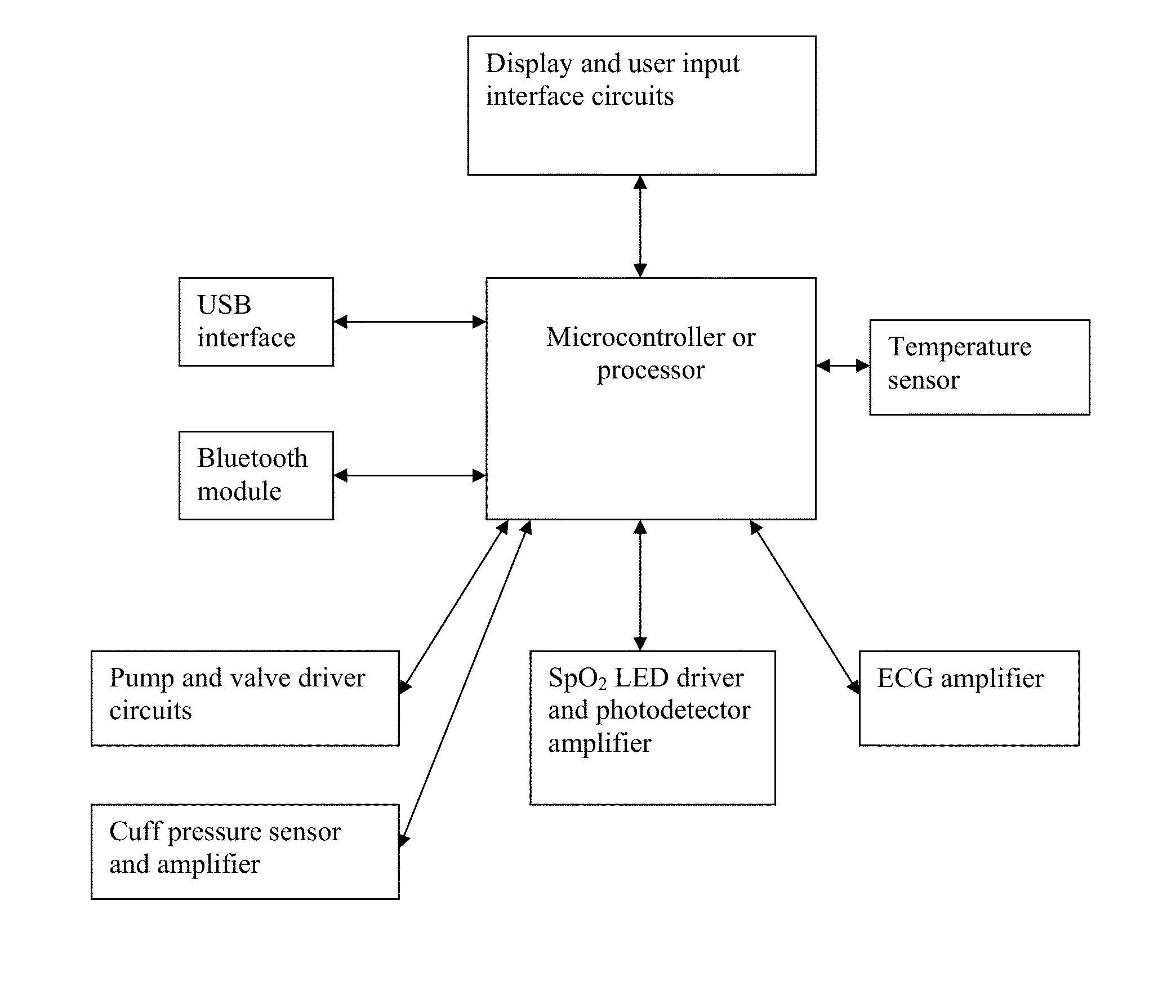
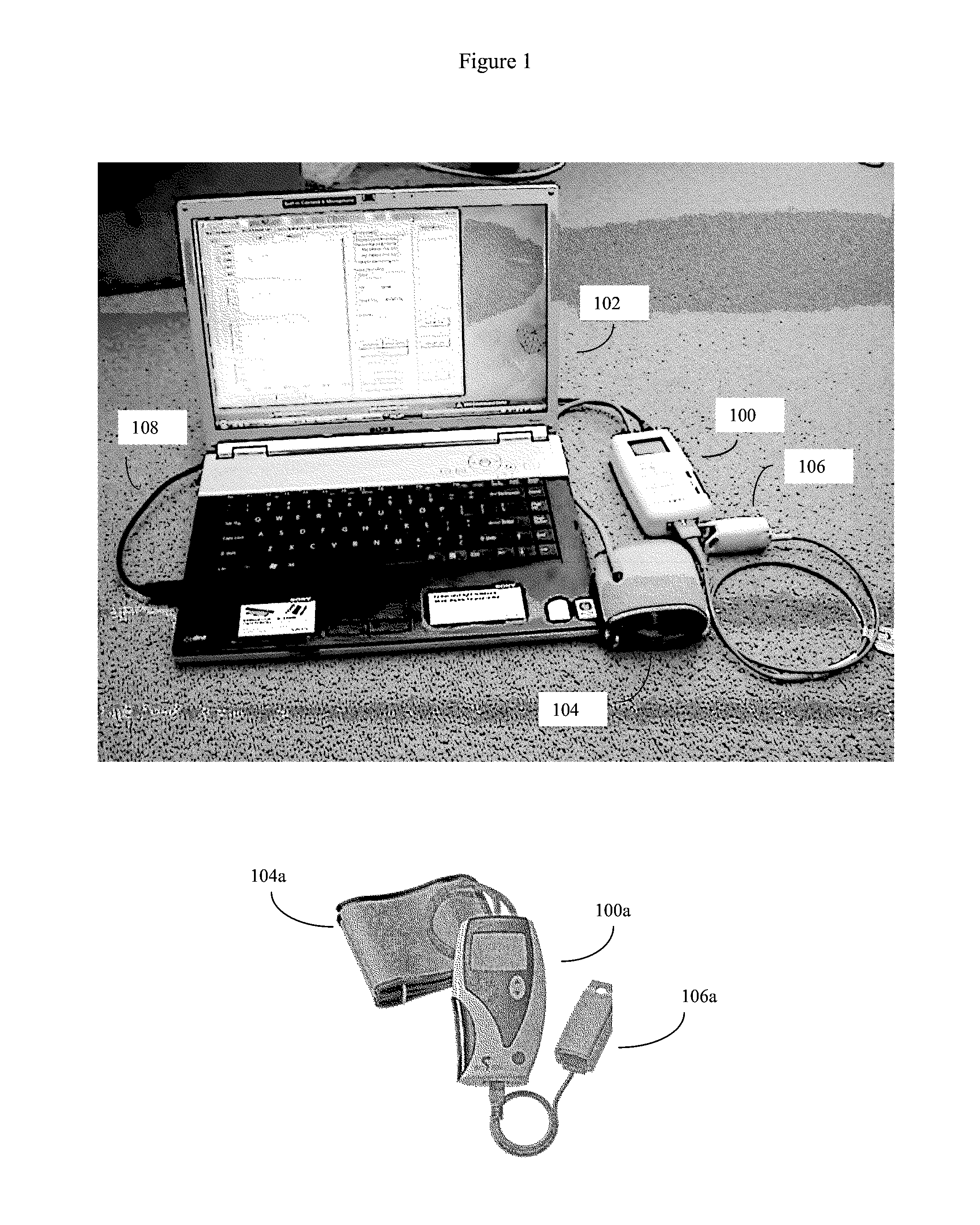
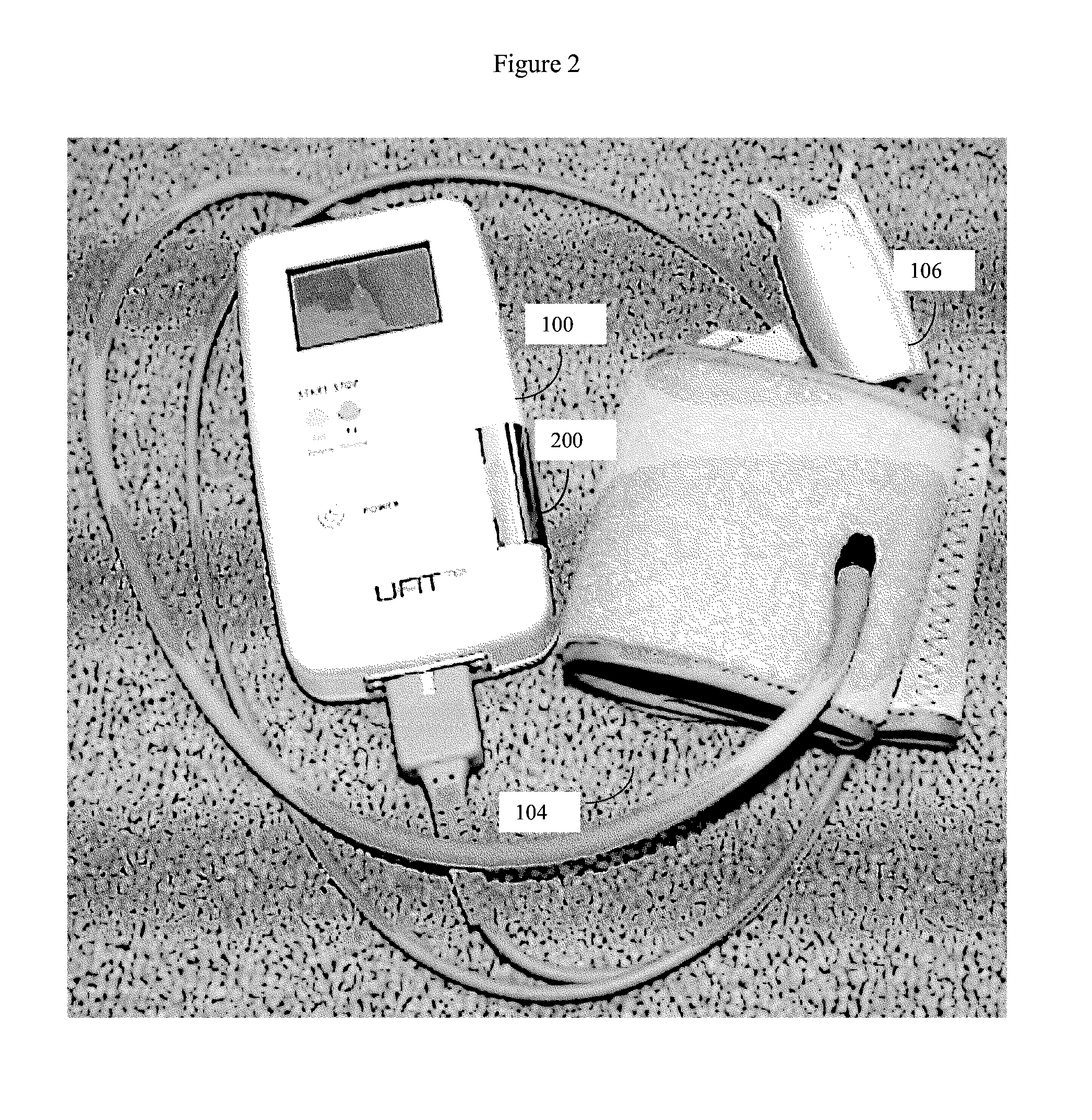
Simultanious multi-parameter physiological monitoring device with local and remote analytical capability
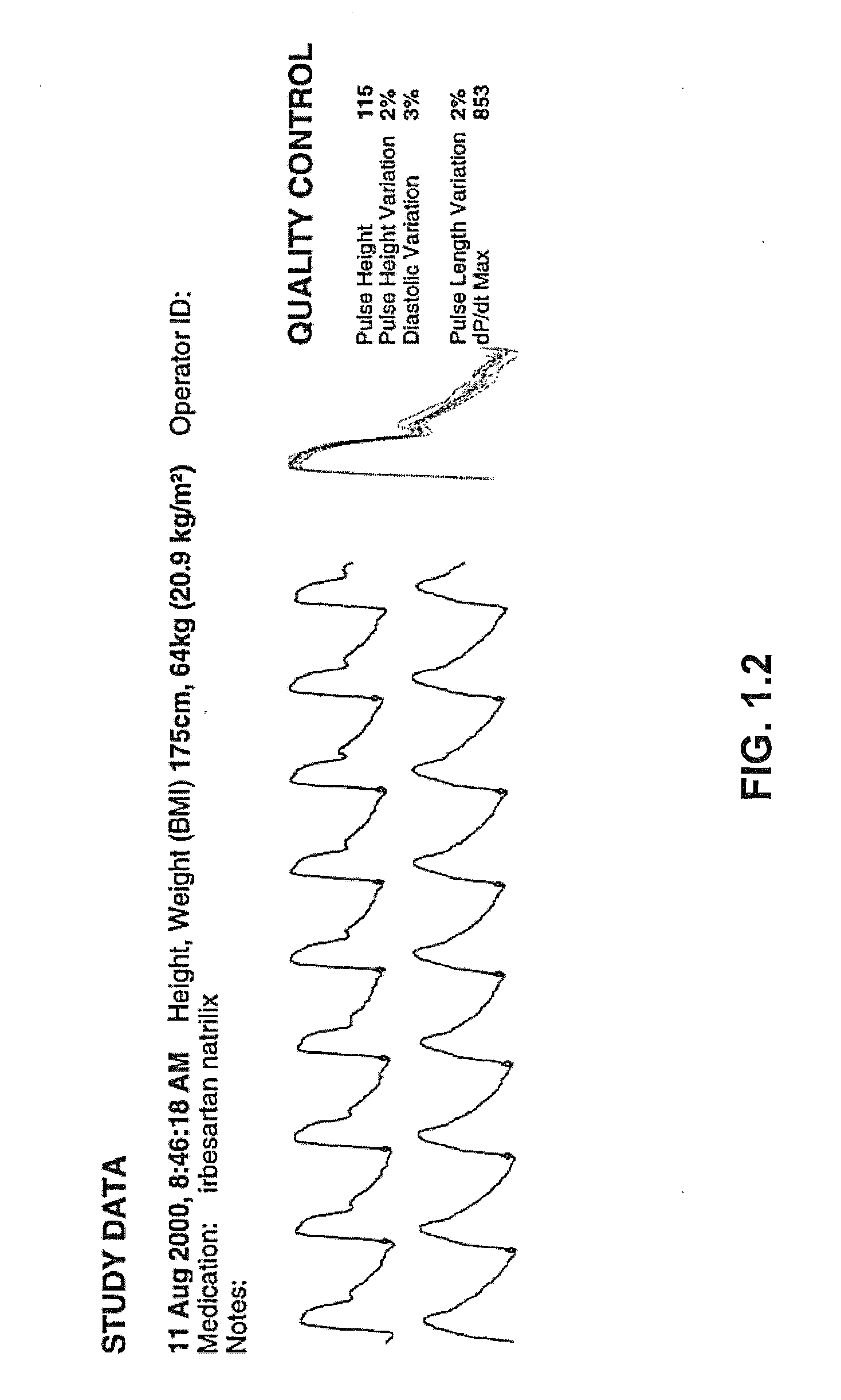
ActiveUS20140243612A1High level of quality controlEnhanced authenticationElectrocardiographyEvaluation of blood vesselsHome environmentHand held
Handheld medical diagnostic instrument that provides high time-resolution pulse waveforms associated with multiple parameters including blood pressure measurements, blood oxygen saturation levels, electrocardiograph (ECG) measurements, and temperature measurements. The device stores and analyzes the pulse waveforms simultaneously obtained from all tests, and thereby allows an unusually detailed view into the functioning of the user's cardiovascular heart-lung system. The device is designed for use by unskilled or semi-skilled users, thus enabling sophisticated cardiovascular measurements to be obtained in a home environment. Data from the device can be analyzed onboard, with local computerized devices, and with remote server based systems. The remote server may be configured to analyze this data according to various algorithms chosen by the physician to be most appropriate to that patient's particular medical condition (e.g. COPD patient algorithms). The server may be further configured to automatically provide alerts and drug recommendations.
Owner:CLOUD DS INC CORP
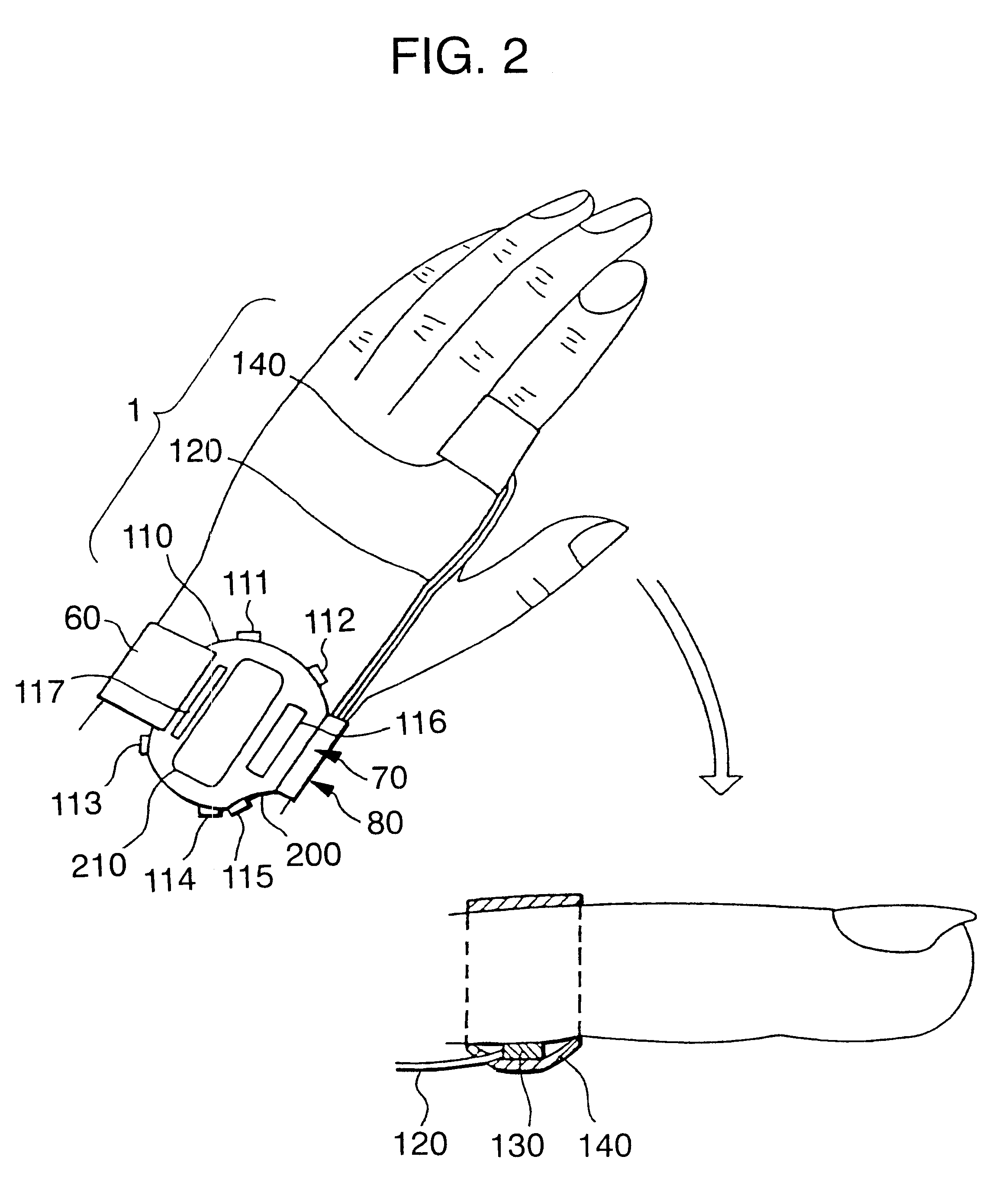
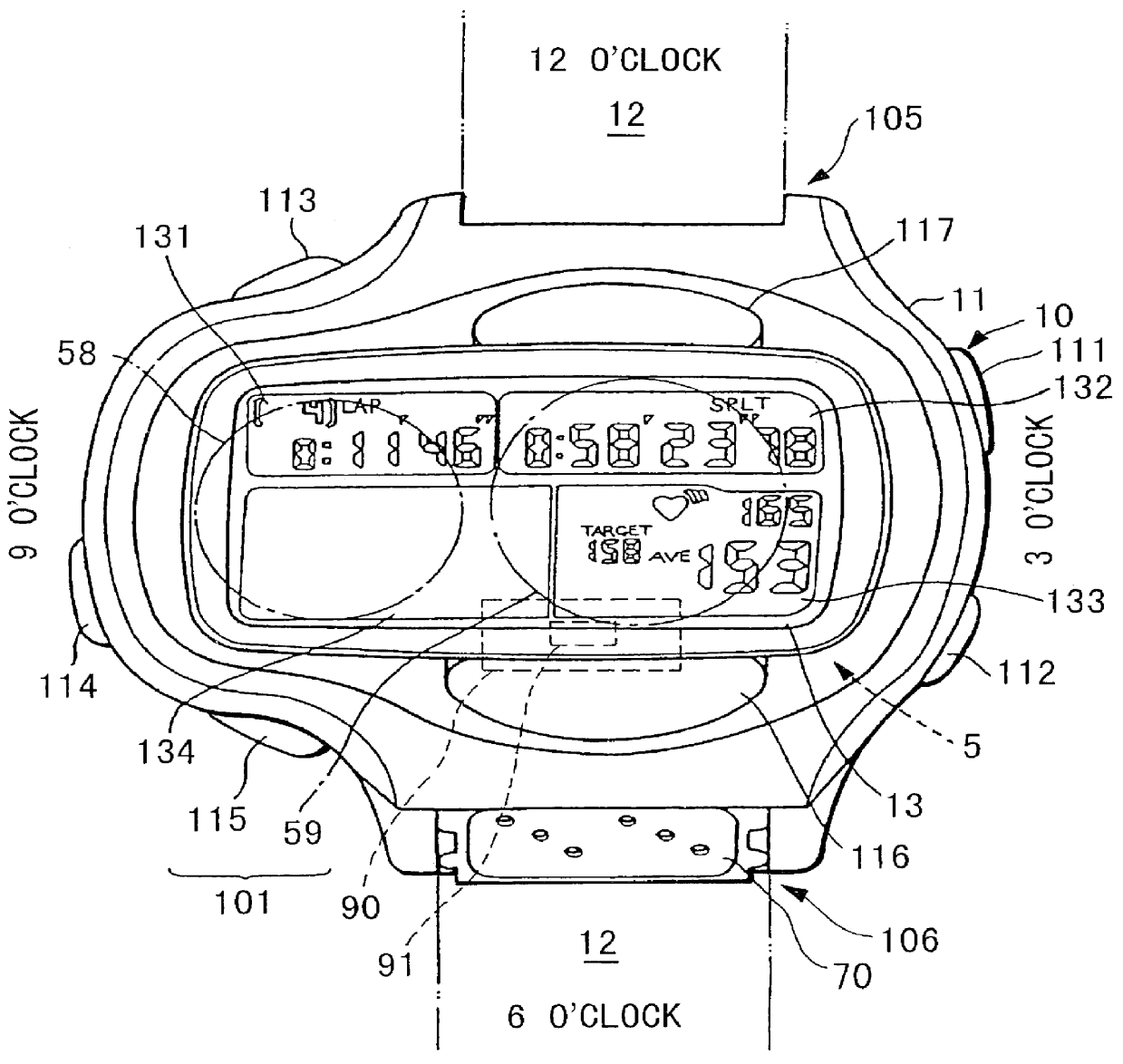
Pulse wave detecting device and pulse measurer
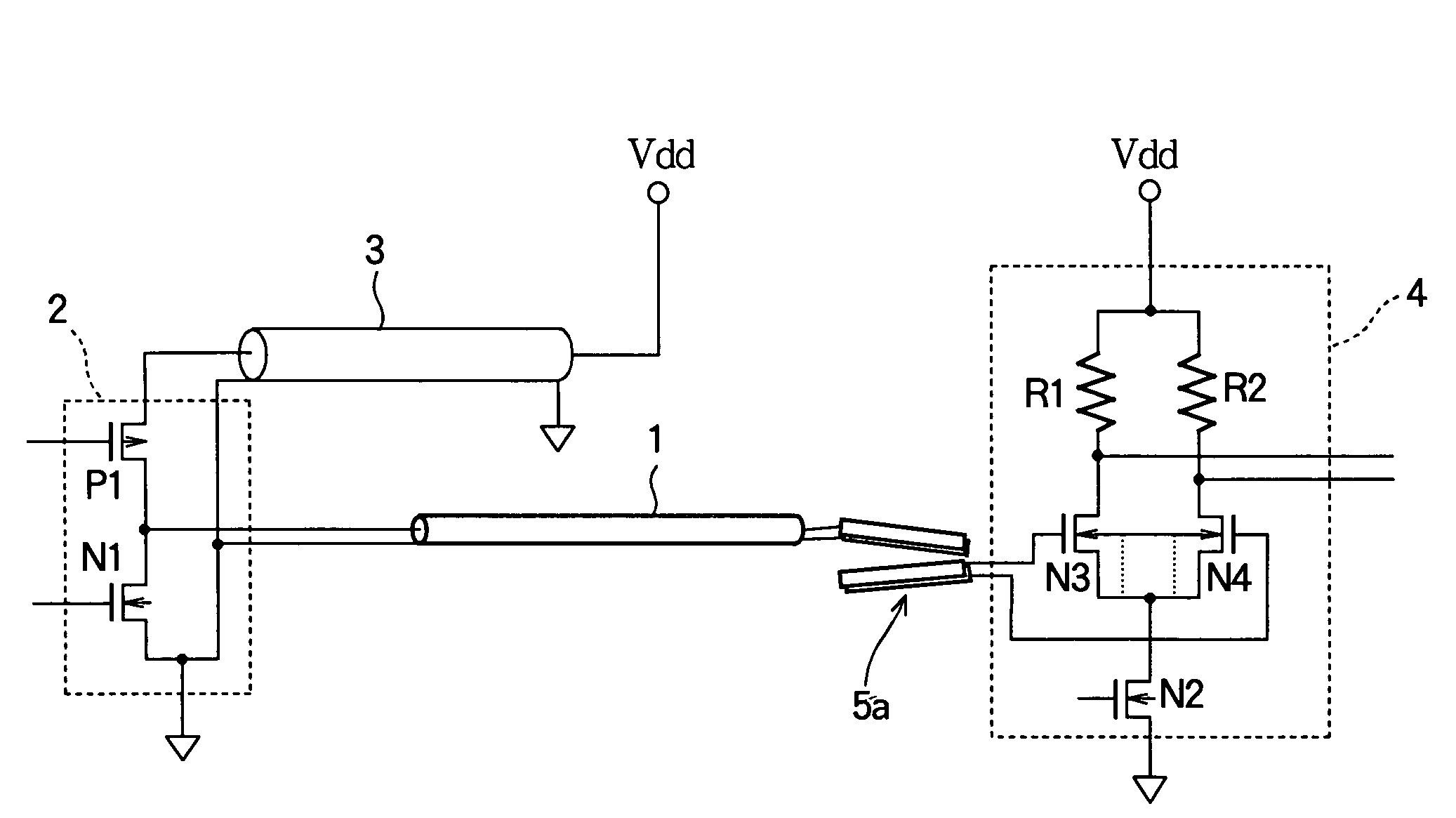
PCT No. PCT / JP98 / 01128 Sec. 371 Date Nov. 4, 1998 Sec. 102(e) Date Nov. 4, 1998 PCT Filed Mar. 17, 1998 PCT Pub. No. WO98 / 41143 PCT Pub. Date Sep. 24, 1998The present invention relates to a pulse wave detecting device for detecting pulse waves, and to a pulse measurer employing this pulse wave detecting device. The present invention addresses the problem of obtaining a pulse wave signal in which the noise components have been suitably removed from a pulse waveform, and of determining the pulse rate with high accuracy based on this pulse wave signal. The method for deriving the pulse wave signal and pulse rate is as follows. The pulse wave signal from pulse wave detecting sensor unit (30) is temporarily stored in buffer (503). When impulse noise is detected in the pulse wave signal in buffer (503) by impulse noise detecting means (505), the band pass for first digital filter (506) becomes a hill-shaped curve centered on the frequency corresponding to the preceding pulse rate, and impulse noise in the pulse wave signal output from buffer (503) is decreased. Thereafter, overall noise and body movement components are decreased in the pulse wave signal by means of second digital filter (507) and third digital filter (508). The signal is then subjected to frequency analysis by frequency analyzer (509), and the pulse rate is calculated from the results of this analysis.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP +1
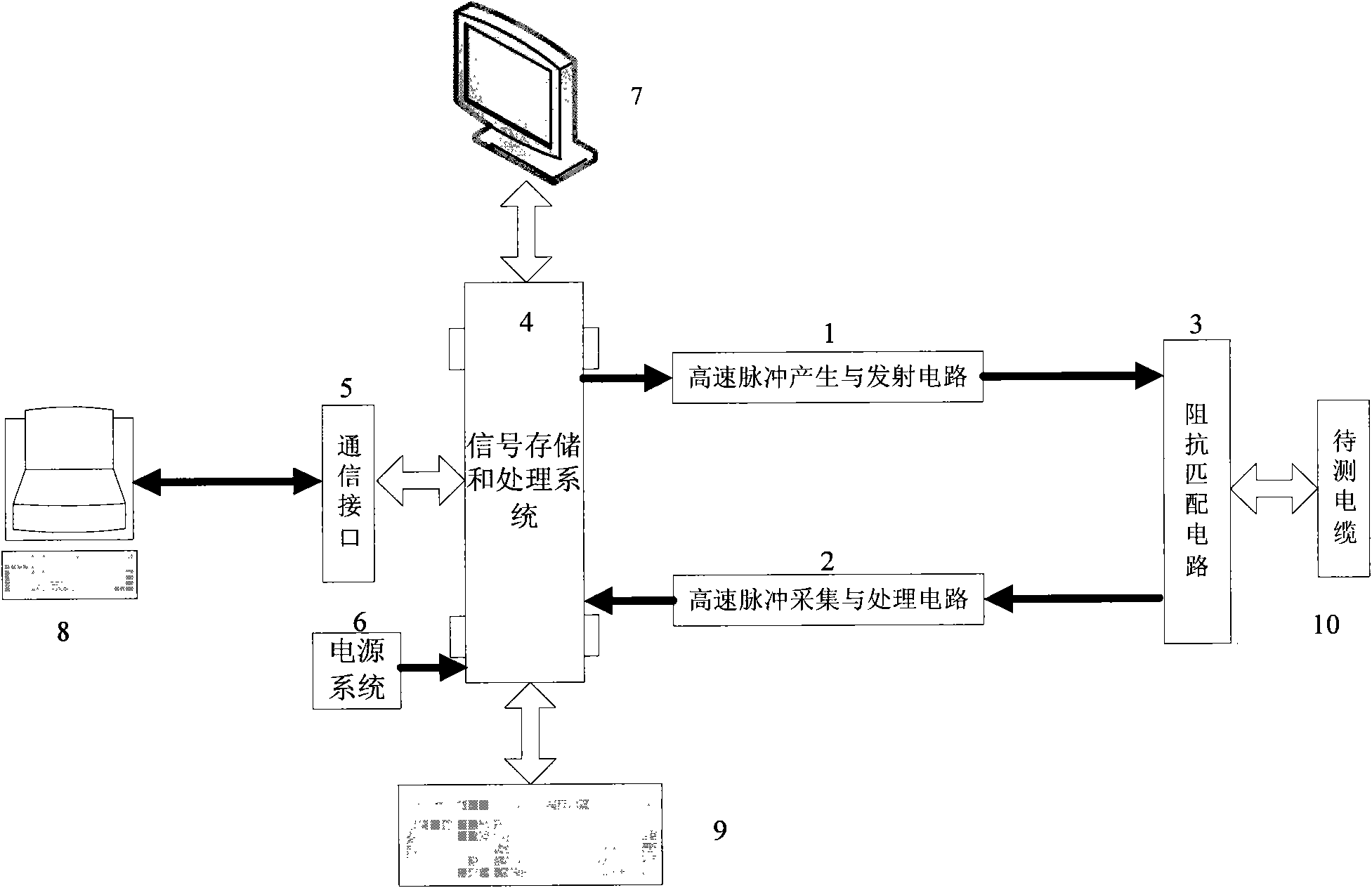
Plane cable fault locator based on time domain reflection
InactiveCN101566665AImprove maintenance efficiencyEnsure flight safetyFault location by pulse reflection methodsIn planeTime domain
A plane cable fault locator based on time domain reflection includes a high speed pulse generating and transmitting circuit, a high speed pulse acquisition and treatment circuit, an impedance matching circuit, a signal storing and treating system, a communication interface, a power supply system, an information display system, an external connection computer system and an information input system. The plane cable fault locator based on time domain reflection adopts a low pressure high speed pulse reflection method to diagnose the types of plane cable short circuit and open circuit and other faults through observing fault point reflection pulse waveform according to a time domain reflection principle, and subsequently calibrates the position of a fault point by measuring the time difference of transmitted pulse and the reflected pulse of the fault point. As the rising edge time of the pulse transmitted by the locator is short and reaches nanosecond level, the locating precision is high. In addition, the locator can accurately calibrate the plane cable fault position so as to avoid taking a plurality of clamping plates apart when looking for faults in plane cable maintenance, thus improving the maintenance efficiency of planes and ensuring the flying safety of planes.
Owner:CIVIL AVIATION UNIV OF CHINA
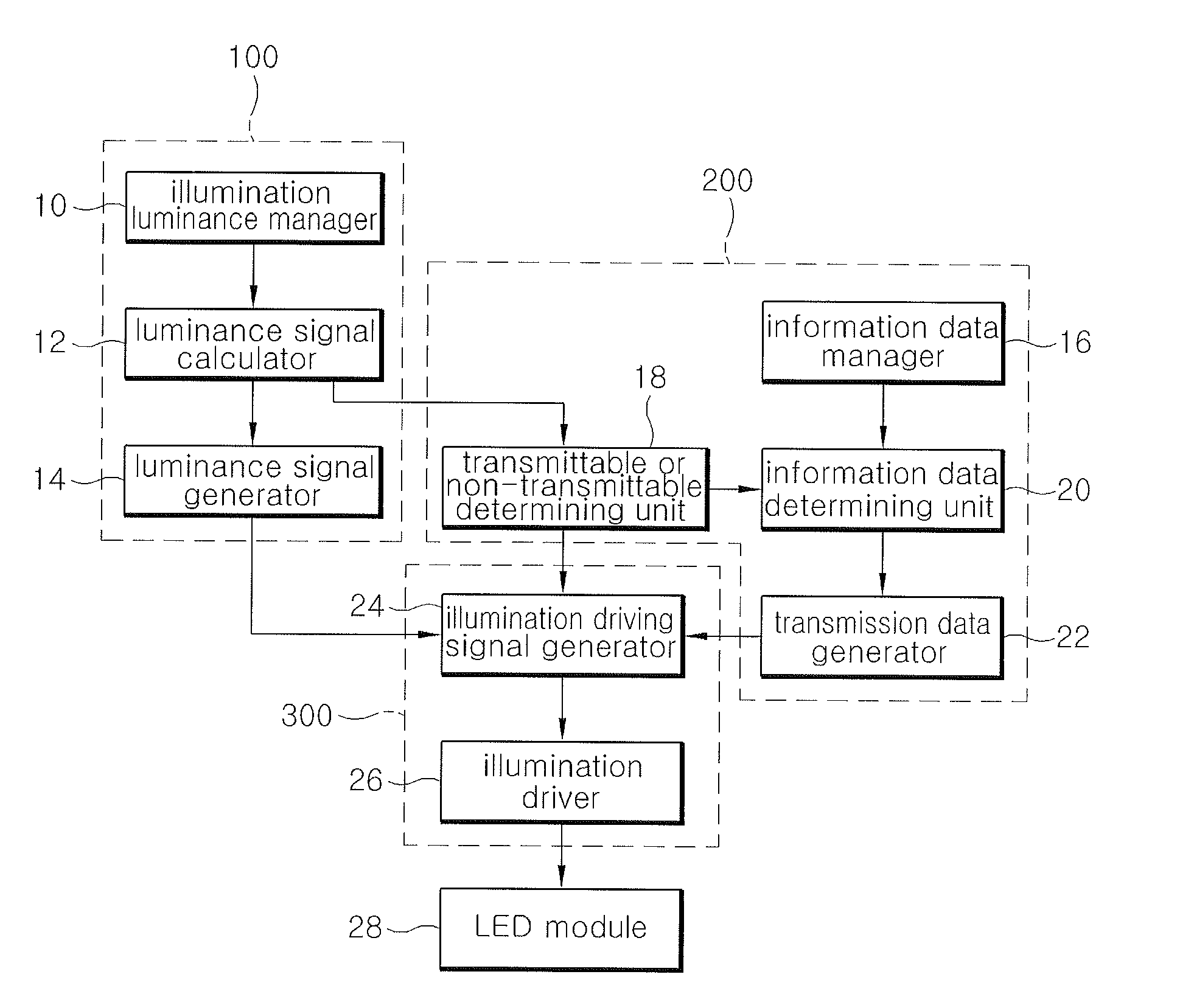
Visible light communication apparatus and visible light communciation method
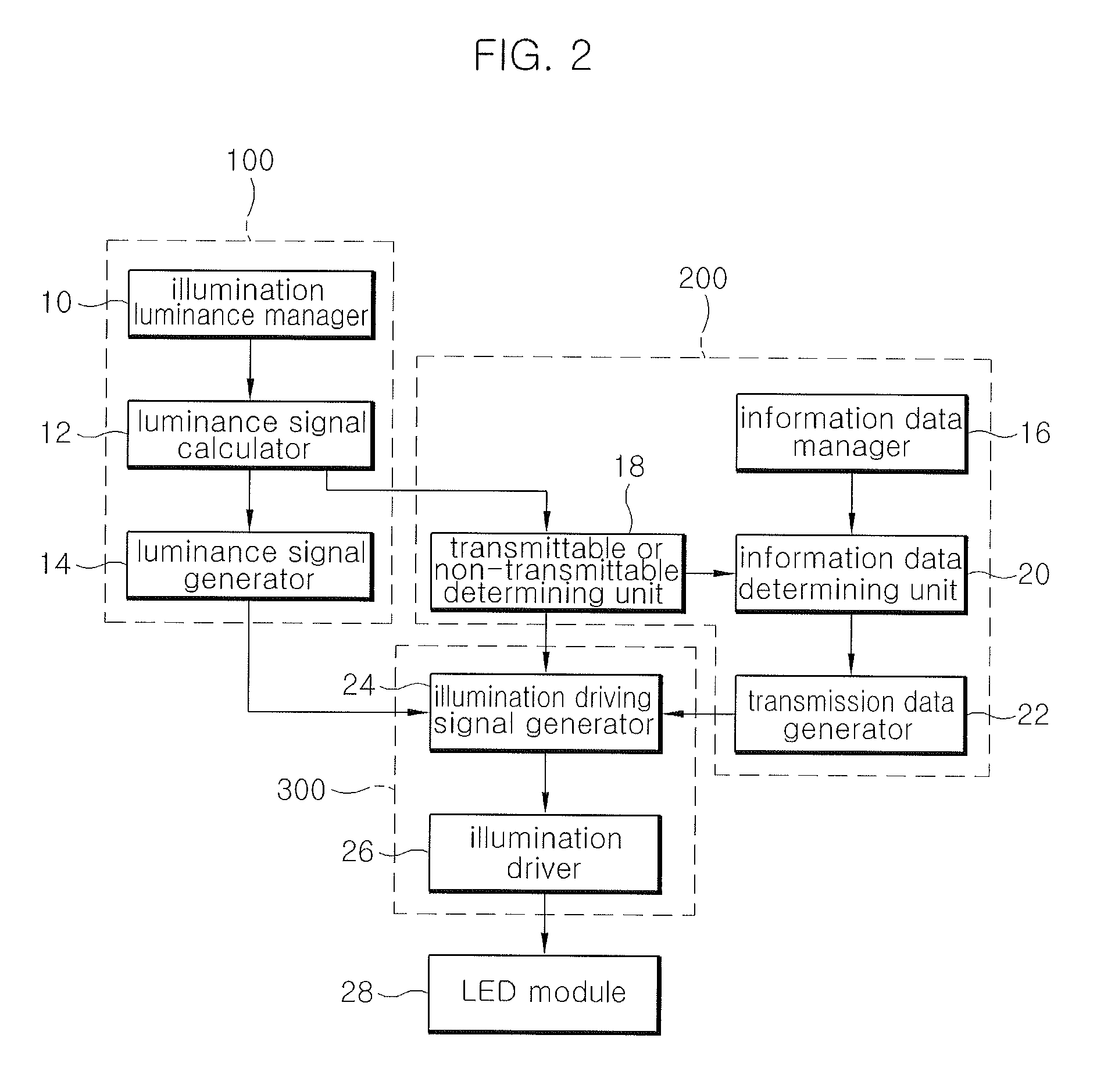
ActiveUS20100135669A1Without hindering a luminance control function of illuminationClose-range type systemsClock rateSignal generator
The visible light communication apparatus includes: a luminance signal generator that calculates a duty cycle of an illumination driving signal corresponding to input luminance request information and generates clock frequency information on luminance signals based on the calculated duty cycle; a transmission data generator that generates transmission data; an illumination driver that generates and outputs an illumination driving signal in a pulse waveform based on the clock frequency information of the luminance signals and the transmission data and controls a pulse position of a turn on section for each bit unit time in the waveform of the illumination driving signal based on the transmission data; and an illumination that is operated according to the illumination driving signal from the illumination driver.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Method and apparatus for transmit beamformer system
InactiveUS6172939B1Improve abilitiesImprove programmabilityUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsProcessing detected response signalEngineeringTrade offs
A digital transmit beamformer system with multiple beam transmit capability has a plurality of multi-channel transmitters, each channel with a source of sampled, complex-valued initial waveform information representative of the ultimate desired waveform to be applied to one or more corresponding transducer elements for each beam. Each multi-channel transmitter applies beamformation delays and apodization to each channel's respective initial waveform information digitally, digitally modulates the information by a carrier frequency, and interpolates the information to the DAC sample rate for conversion to an analog signal and application to the associated transducer element(s). The beamformer transmitters can be programmed per channel and per beam with carrier frequency, delay, apodization and calibration values. For pulsed wave operation, pulse waveform parameters can be specified to the beamformer transmitters on a per firing basis, without degrading the scan frame rate to non-useful diagnostic levels. Waveform parameters can be specified to the transmitters by an external central control system which is responsible for higher level flexibility, such as scan formats, focusing depths and fields of view. The transmit pulse delay specified per-channel to each transmitter is applied in at least two components: a focusing time delay component and a focusing phase component. The carrier frequency can be specified for each transmit beam, to any desired frequency within a substantially continuous predefined range of frequencies, and a beam-interleaved signal processing path permits operation in any of several predefined processing modes, which define different parameter sets in a trade-off among (1) the number of beams produced; (2) per-beam initial waveform sample interval; and (3) transmit frequency.
Owner:ACUSON
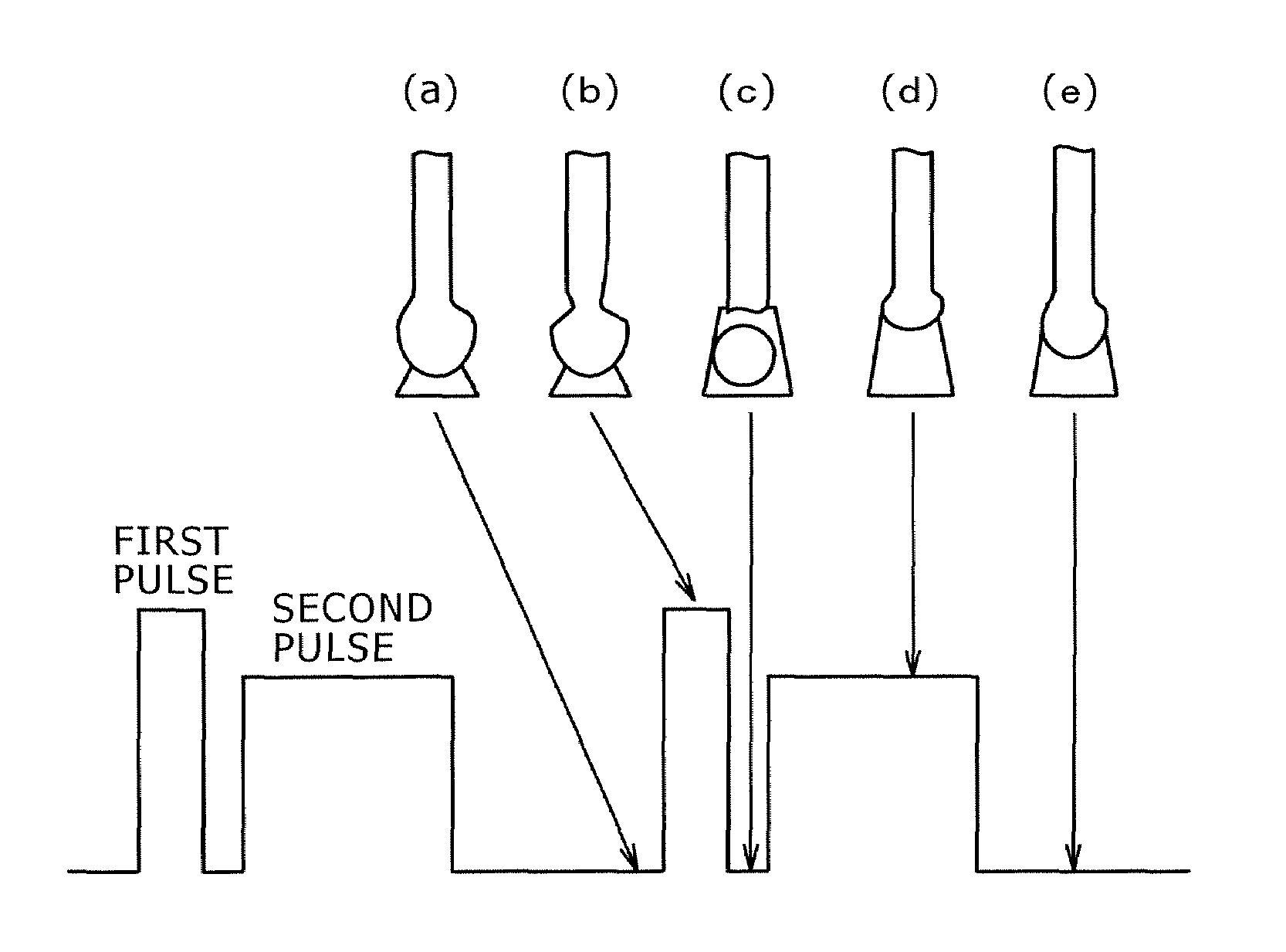
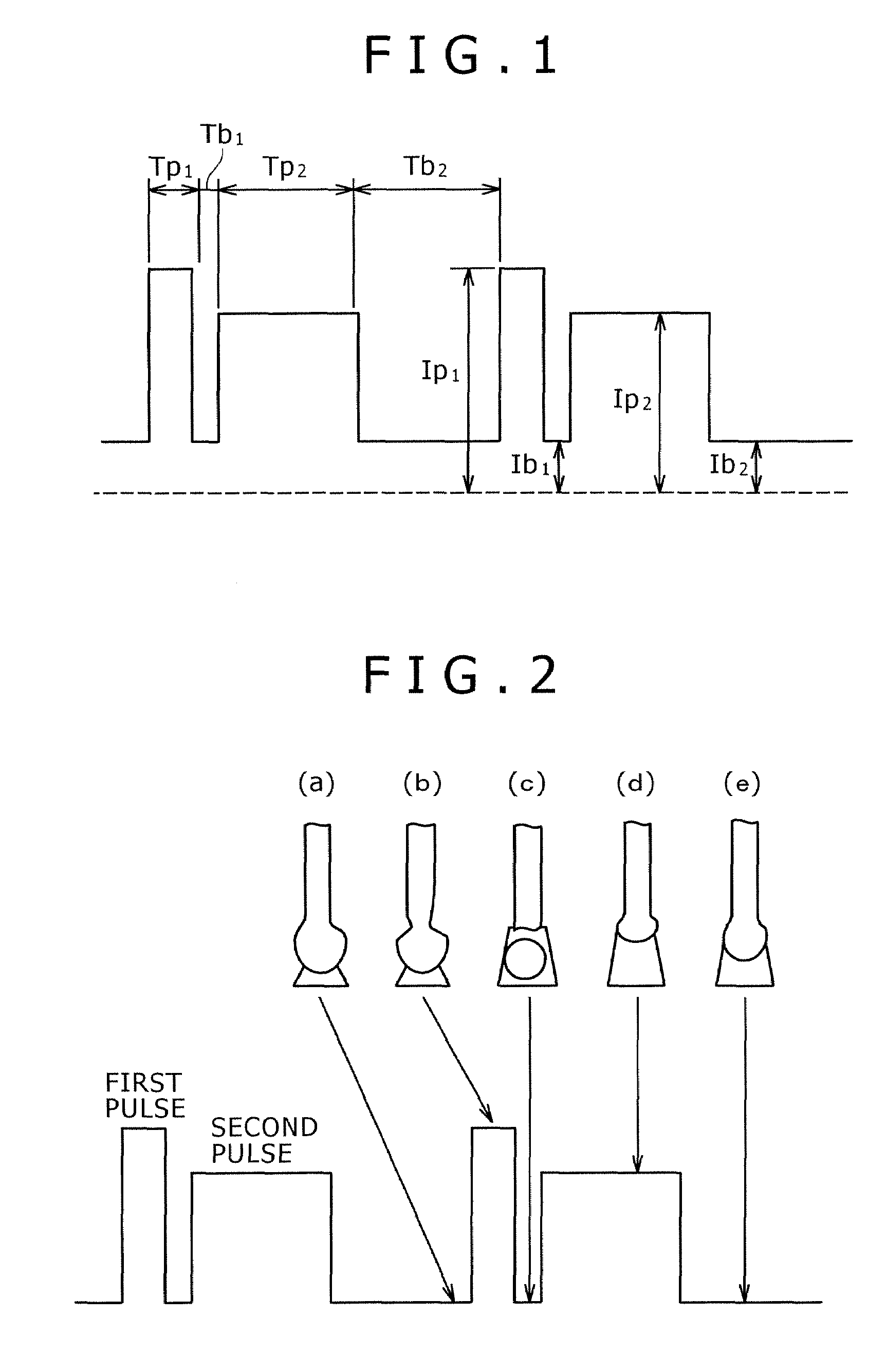
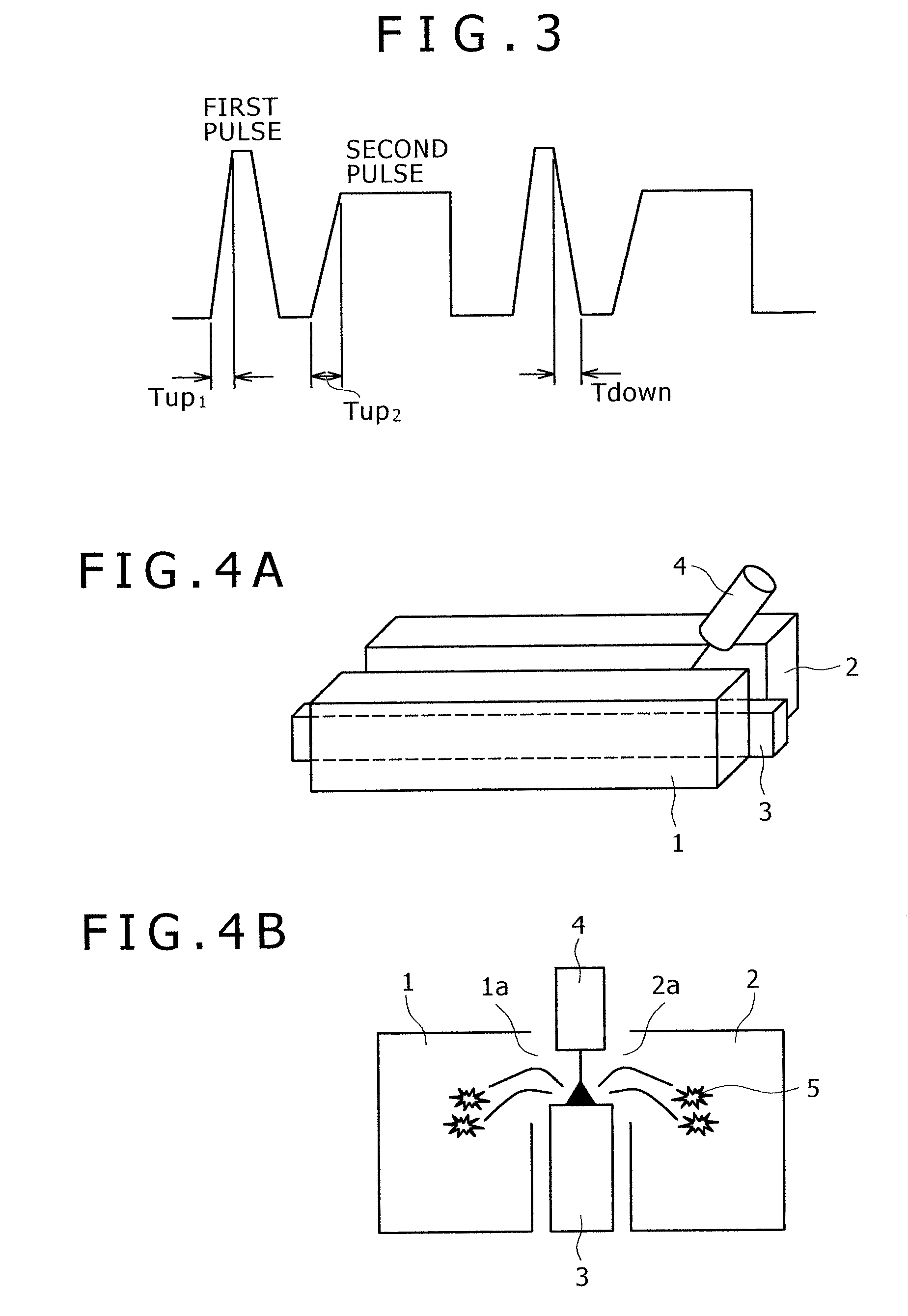
Pulsed arc welding method
ActiveUS20070210048A1Good saveImprove stabilityArc welding apparatusShielding gasCarbon Dioxide / Helium
Disclosed is a pulsed arc welding method using a pulse current of alternately repeating first and second pulses as a weld current, wherein the first pulse and the second pulse have a pulse waveform of a different pulse peak current level and a different pulse width, respectively, and the following conditions are satisfied: peak current of the first pulse (Ip1)=300 to 700A; peak period (Tp1)=0.3 to 5.0 ms; base current Ib1=30 to 200A, base period (Tb1)=0.3 to 10 ms; peak current of the second pulse (Ip2)=200 to 600A; peak period (Tp2)=1.0 to 15 ms; base current (Ib2)=30 to 200A; and base period (Tb2)=3.0 to 20 ms. In this manner, the consumable electrode arc welding using carbon dioxide gas alone or a mixed gas made mainly of carbon dioxide gas as a shield gas can benefit from stabilized welding arc, improved regularity of droplet transfer, and significantly reduced generation rates of spatters and fumes.
Owner:KOBE STEEL LTD
Portable TENS Apparatus And Method Of Use Thereof
ActiveUS20140194946A1Reduction of acute painReduce chronic painElectrotherapyArtificial respirationSquare waveformEngineering
A TENS apparatus includes a portable TENS device having a housing with a lower surface, a pair of integral electrodes that are incorporated in the lower surface of the housing, and a pulse driver that is located within the housing and adapted to generate a program of pulse waveforms, each of which is an asymmetrical biphasic square waveform.
Owner:MODULAR THERAPEUTX
Metal core welding wire pulsed welding system and method
InactiveUS20080264917A1Avoid damageImprove waveformArc welding apparatusWelding/cutting media/materialsThin metalNuclear engineering
Provided is a welding system and method for controlling a welding system with an improved pulsed waveform suitable for use with metal core welding wires. The waveform includes peak pulses (of voltage, current, power, energy or a combination thereof) that aid in transfer of molten metal from the wire to the weld pool. The pulse duration is sufficiently short to avoid damage to the metal core welding wire. The waveform enables welding of thin metals and reduces spatter.
Owner:ILLINOIS TOOL WORKS INC
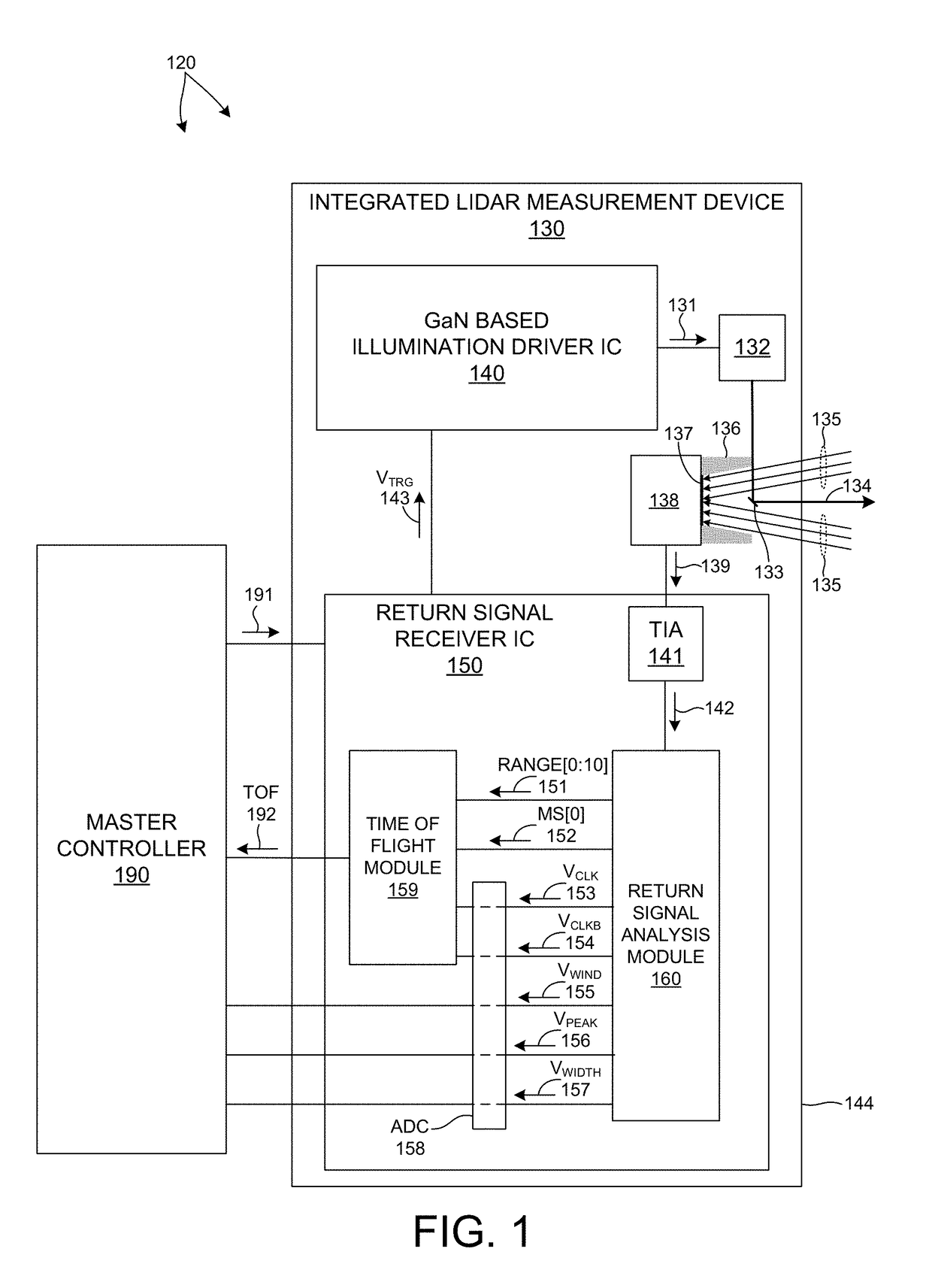
LIDAR Data Acquisition And Control
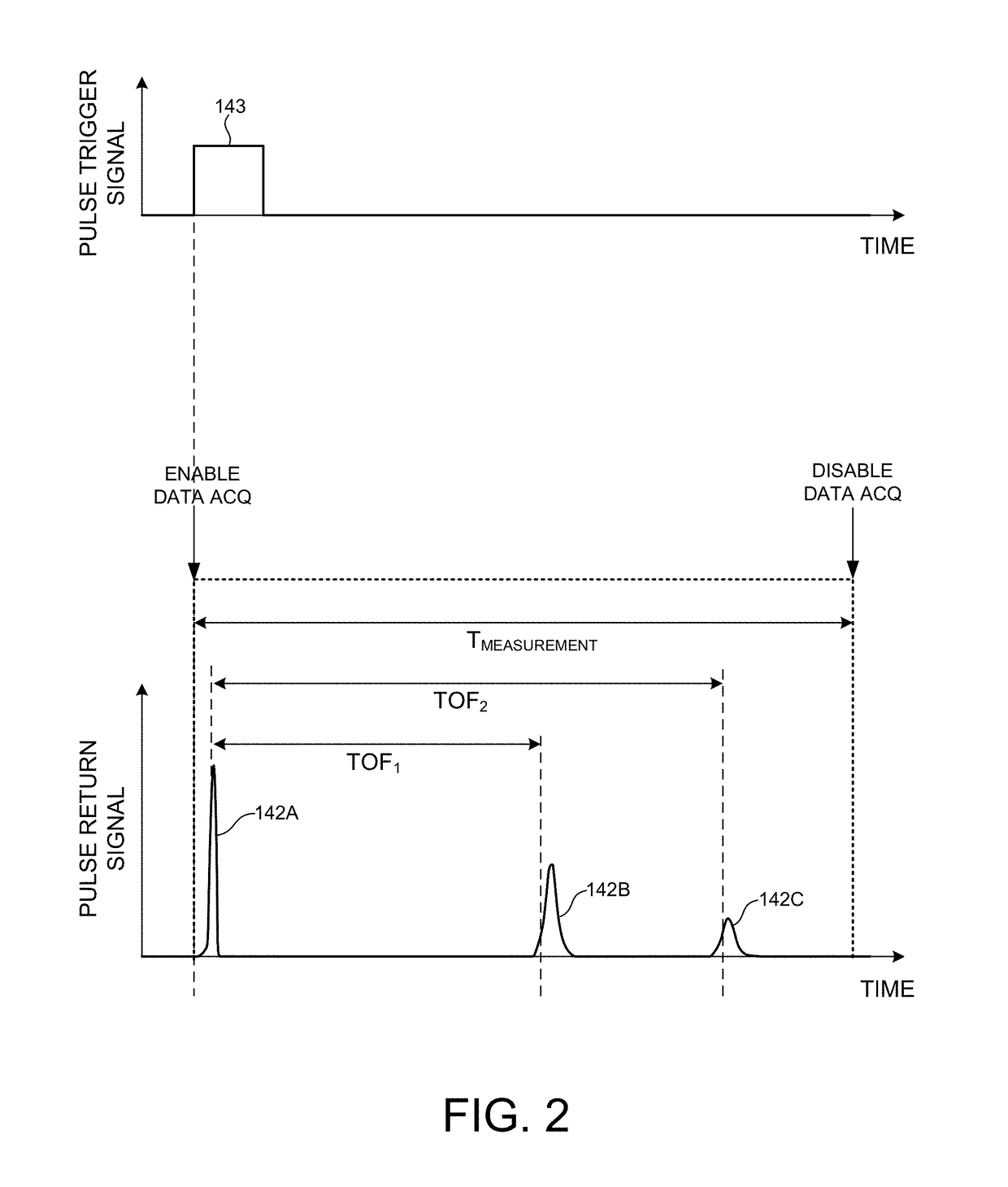
ActiveUS20180321360A1Accurate synchronizationAccurate timingElectromagnetic wave reradiationMeasurement deviceData acquisition
Methods and systems for performing three dimensional LIDAR measurements with an integrated LIDAR measurement device are described herein. In one aspect, a return signal receiver generates a pulse trigger signal that triggers the generation of a pulse of illumination light and data acquisition of a return signal, and also triggers the time of flight calculation by time to digital conversion. In addition, the return signal receiver also estimates the width and peak amplitude of each return pulse, and samples each return pulse waveform individually over a sampling window that includes the peak amplitude of each return pulse waveform. In a further aspect, the time of flight associated with each return pulse is estimated based on a coarse timing estimate and a fine timing estimate. In another aspect, the time of flight is measured from the measured pulse due to internal optical crosstalk and a valid return pulse.
Owner:VELODYNE LIDAR USA INC
Cardiovascular pulse wave analysis method and system
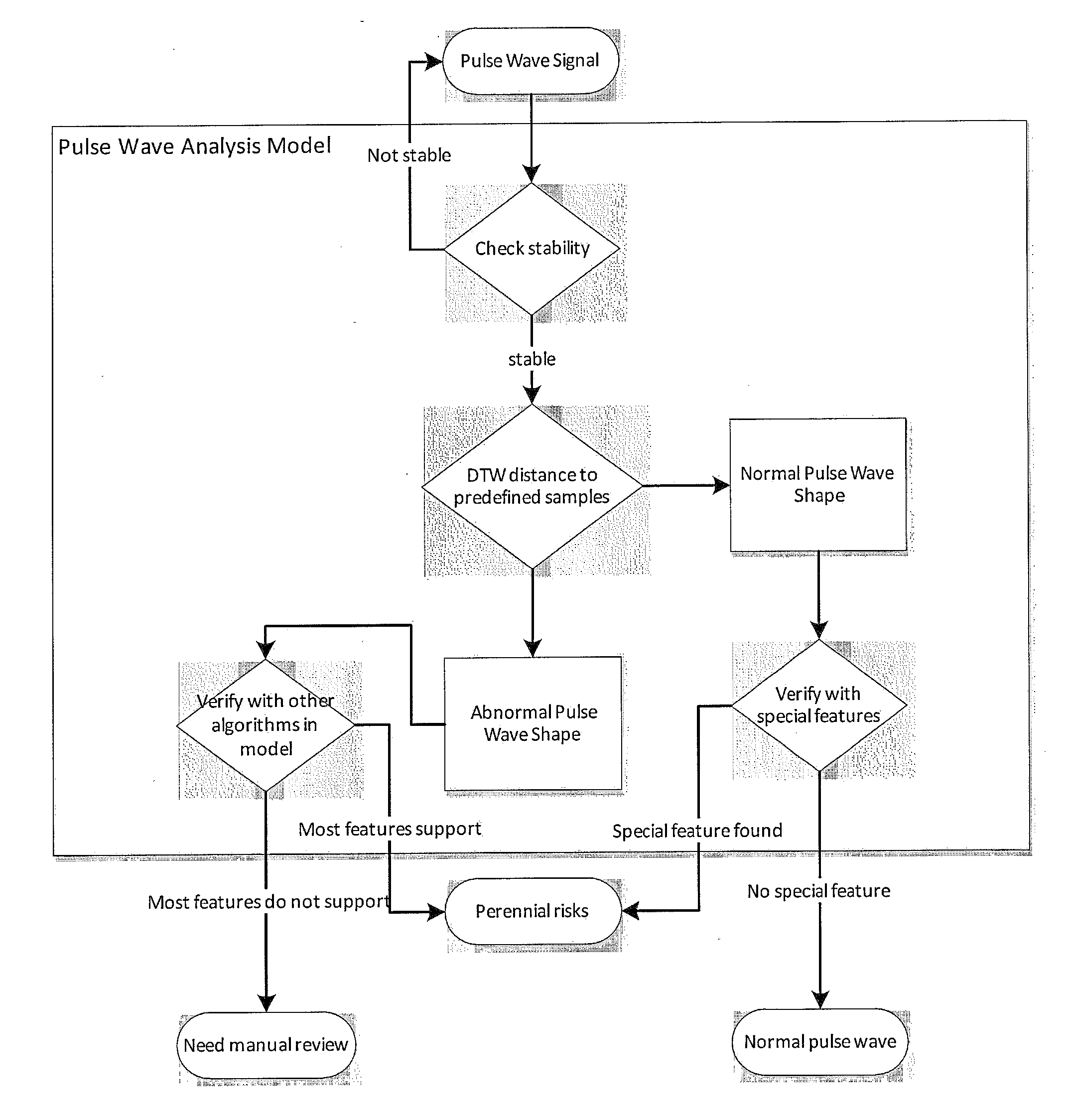
InactiveUS20140249424A1Easy to useComputing time to provide the pulse analysis results is negligibleHealth-index calculationCatheterDiseaseFactor base
Factor retrieving is a major approach for pulse wave analysis. Stiffness index and cardiac output are widely used factors for cardiac risk detection. Research has been done on clinical pulse wave data which are collected by pulse oximeter. The result shows that collected factors have a positive correlation with certain cardiac risks. Some adjustments have been applied on the algorithms that increase the significance. In addition to the factor based analysis, other signal processing techniques for pulse waveforms are included such as bispectrum estimation, Wavelet transform, and weighted dynamic time warping. Bispectrum estimation and Wavelet transform have meaningful features of pulse waveforms with some special shapes. Weighted dynamic time warping compares the similarity of waveforms. It also includes medical significance into the calculation by adjusting the weight vector. This algorithm has higher accuracy when providing more samples to compare. The factor based analysis and waveform analysis compose an analytic model which can be used for risk evaluation, classification and disease detection.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF WINNIPEG
System and method for a non-invasive medical sensor
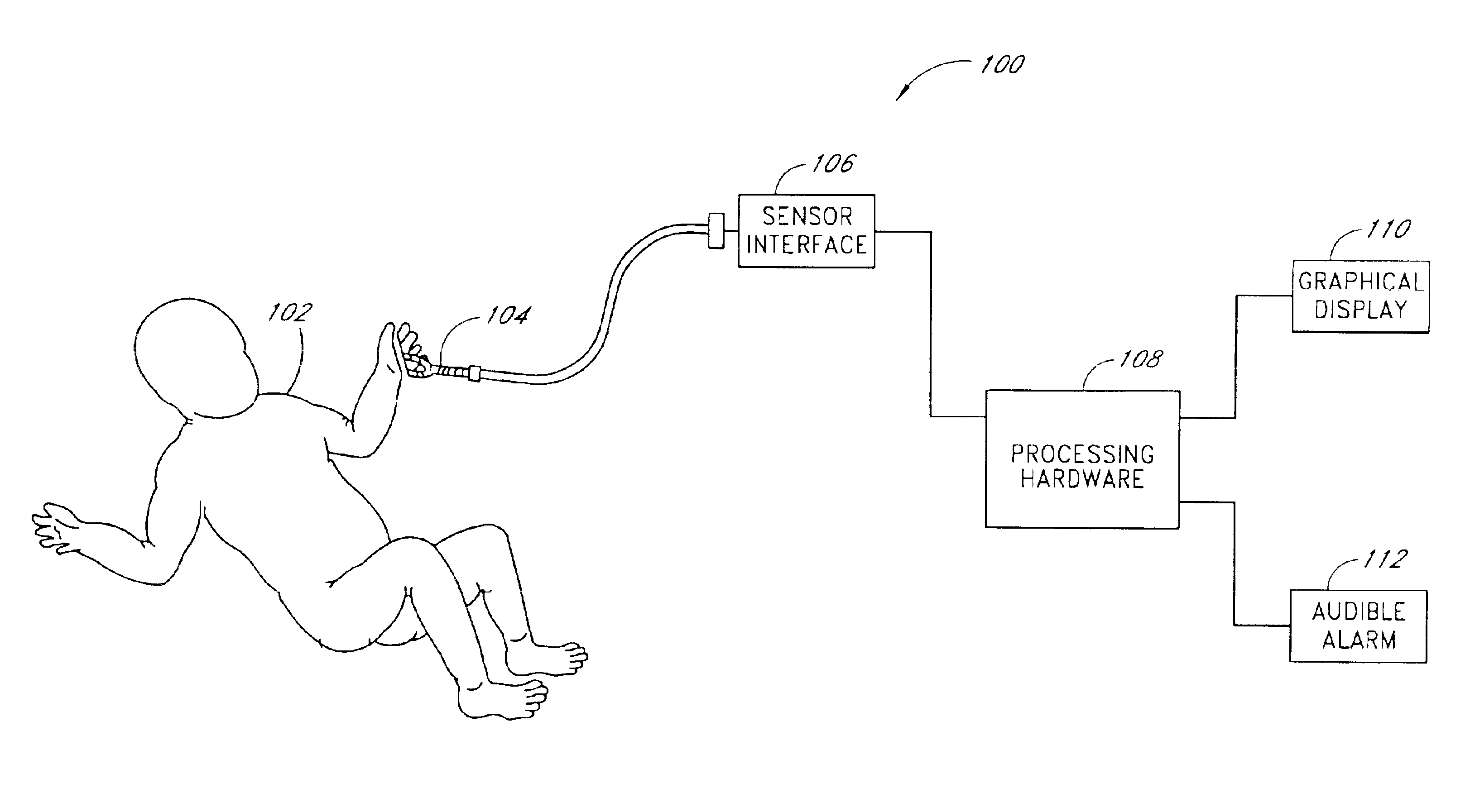
A sensor is disclosed having one or more light sources, and one or more light detectors. At least one of the detectors produces an output in response to received light. Also, electrical circuitry in response to the output generates a pulse waveform proportional to the arterial and venous pulse of a human body, wherein the pulse waveform is used to synchronize an arterial-pulse measurement of the absorption or reflectance of one or more coherent light sources.
Owner:BIOINTELLISENSE INC
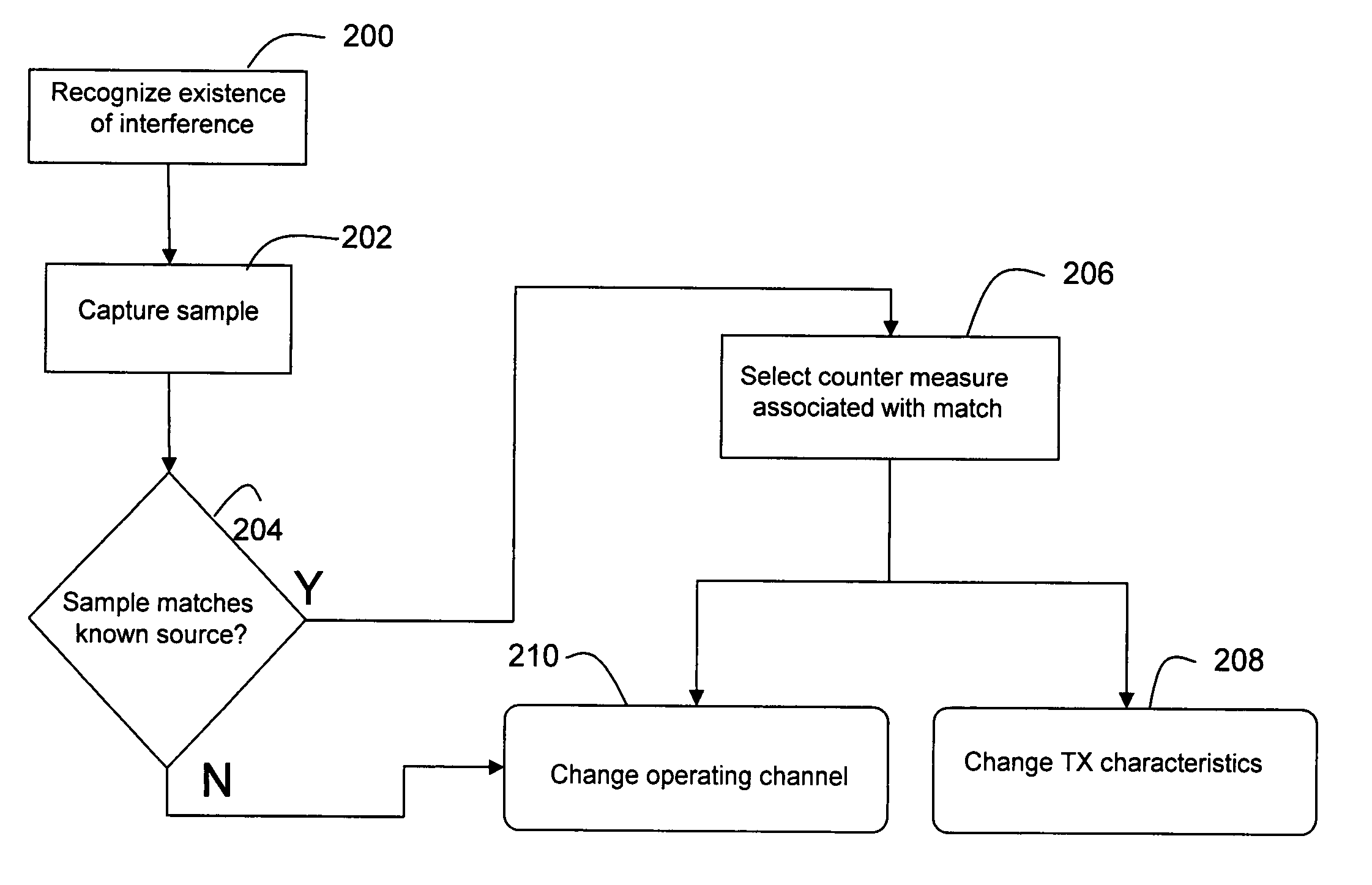
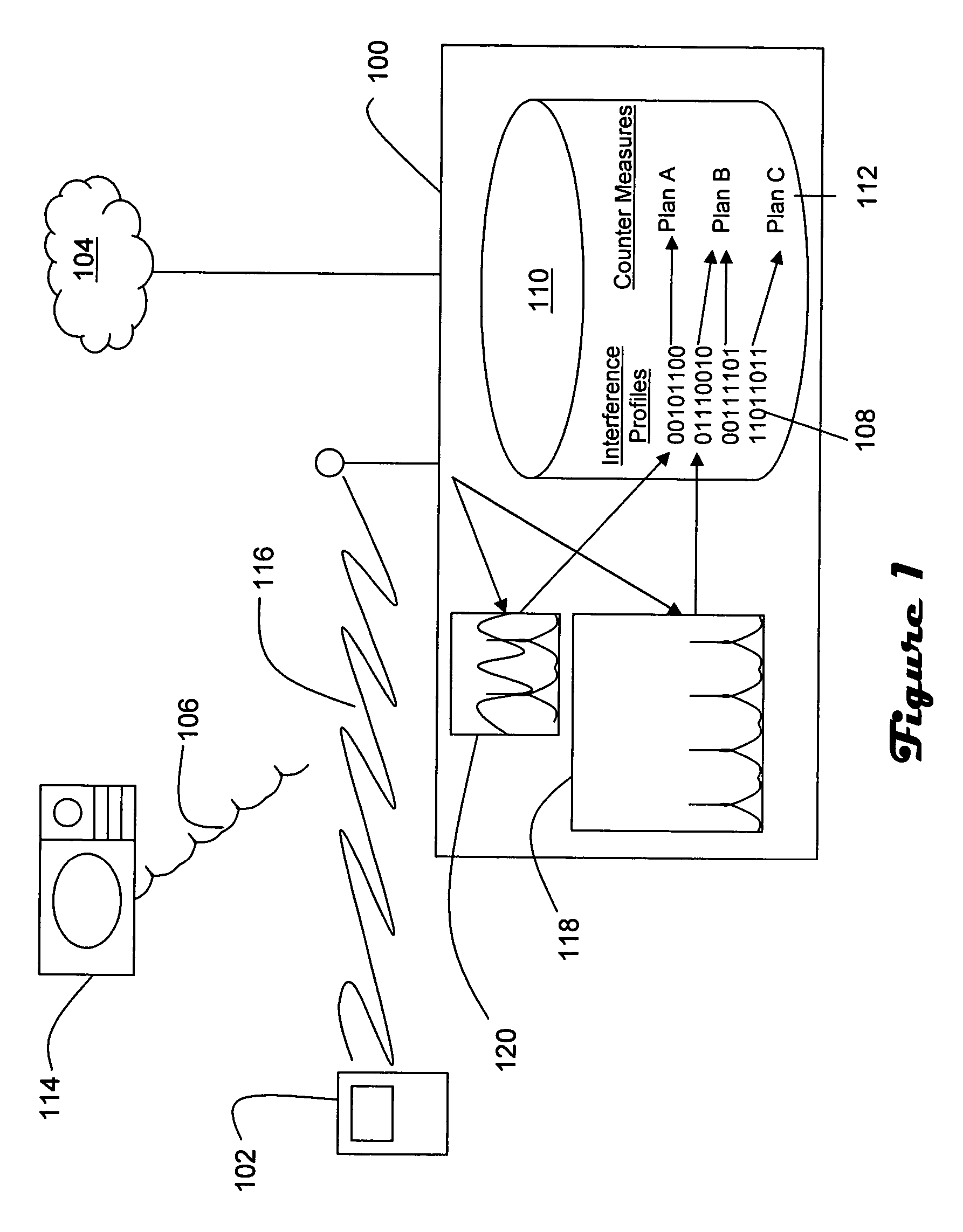
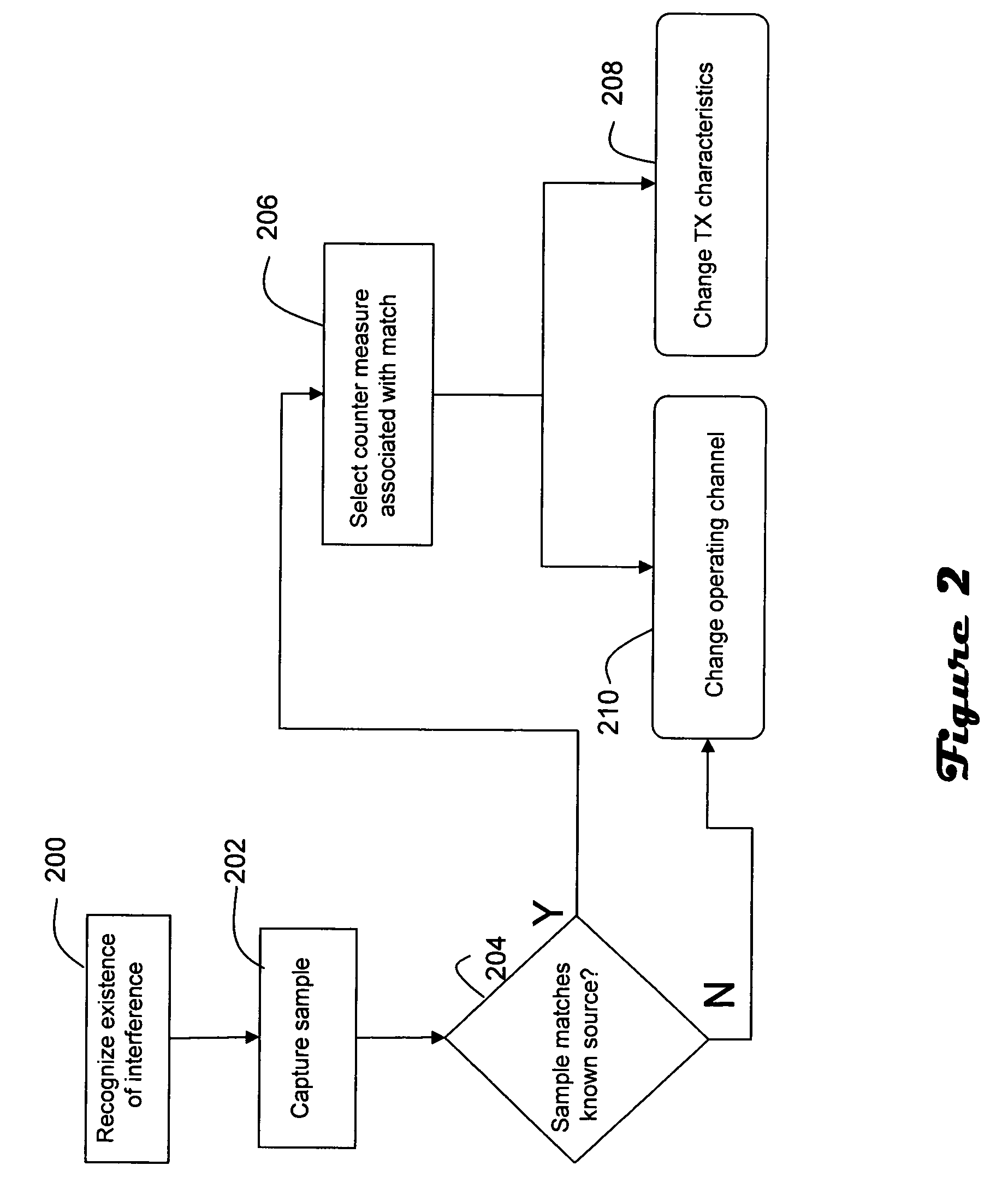
Remedial actions for interference in wireless LANs
InactiveUS20060171326A1Facilitate communicationIncrease powerPower managementFrequency-division multiplex detailsPulse periodTime duration
In a wireless network having an access point and at least one wireless end device, the access point is operable to differentiate between normal communications and interference from another device in order to capture a sample of the interference, determine whether the interference originates from a known type of device, and prompt remedial actions such as moving communications to a distant channel, increasing transmission power, changing data rate, and packet fragmentation based on whether the interference originates from a known type of device. Interference pulse duration may be used to at least initially narrow the possible sources of interference. Pulse period may be employed to differentiate between interference sources which exhibit similar pulse duration. If pulse duration and period are not sufficient to identify the interference source then other characteristics may be examined, such as pulse waveform, roll off and period in relation to local power frequency. In the case of microwave interference it is generally best to move to a distant channel. Increased transmission power and packet fragmentation can be used to maintain communications while scanning for a new channel.
Owner:PICCATA FUND LIABILITY
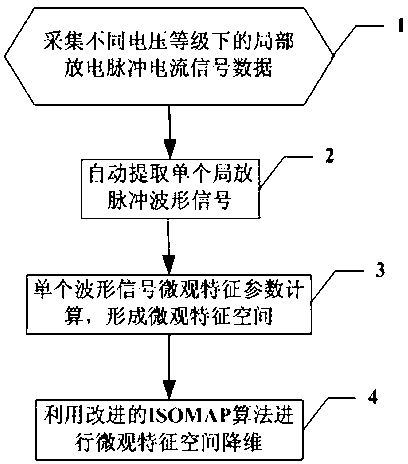
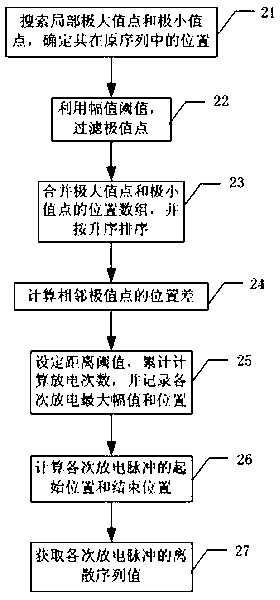
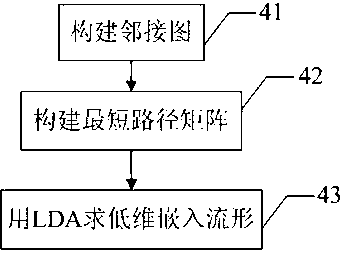
Method for extracting waveform feature of local discharge pulse current
ActiveCN102854445AEffective Dimensionality ReductionCalculation speedTesting dielectric strengthPulse characteristics measurementsTransformerStatistical analysis
The invention relates to a method for extracting the waveform feature of a local discharge pulse current, comprising the following steps of: acquiring data of a local discharge signal of a transformer; automatically extracting a pulse waveform signal of the local discharge signal; calculating each microcosmic characteristic parameter of the extracted single discharge pulse waveform; and carrying out characteristic space dimension reduction on the microcosmic characteristic parameter of the local pulse waveform. By using the method, the microcosmic characteristics can be effectively extracted from continuous sampled waveform signals; the defect that the obtained local discharge data cannot be sufficiently utilized because most of current digital local discharge instruments carry out statistic analysis treatment by only utilizing the microcosmic characteristic of local discharge data is overcome; single discharge pulse waveforms of various discharge types can be adaptively extracted from the acquired data, and effective dimension reduction of the waveform microcosmic characteristic can be carried out through an improved manifold learning algorithm, so that the low-dimension and effective discharge pulse waveform characteristic can be extracted.
Owner:SHANGHAI MUNICIPAL ELECTRIC POWER CO +2
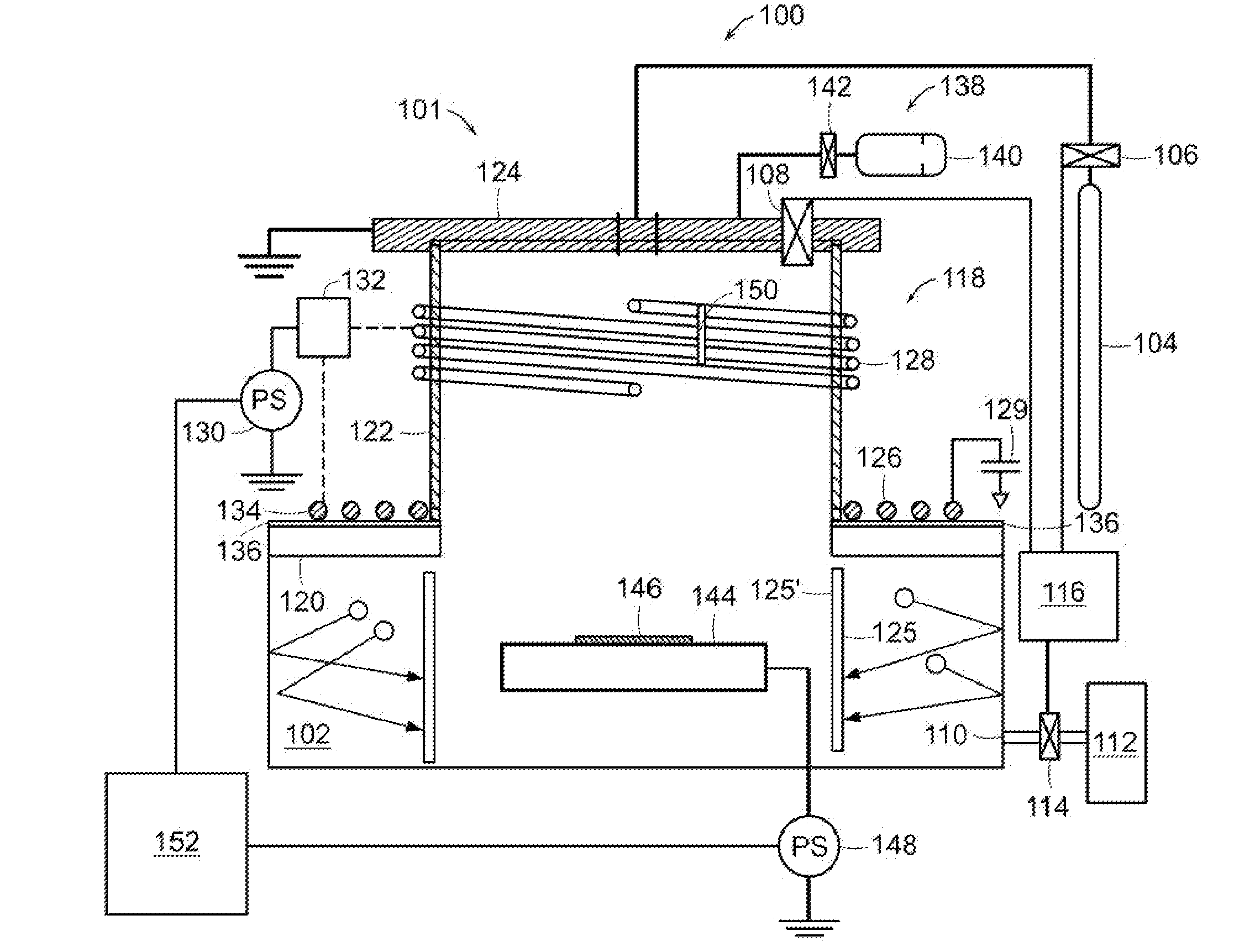
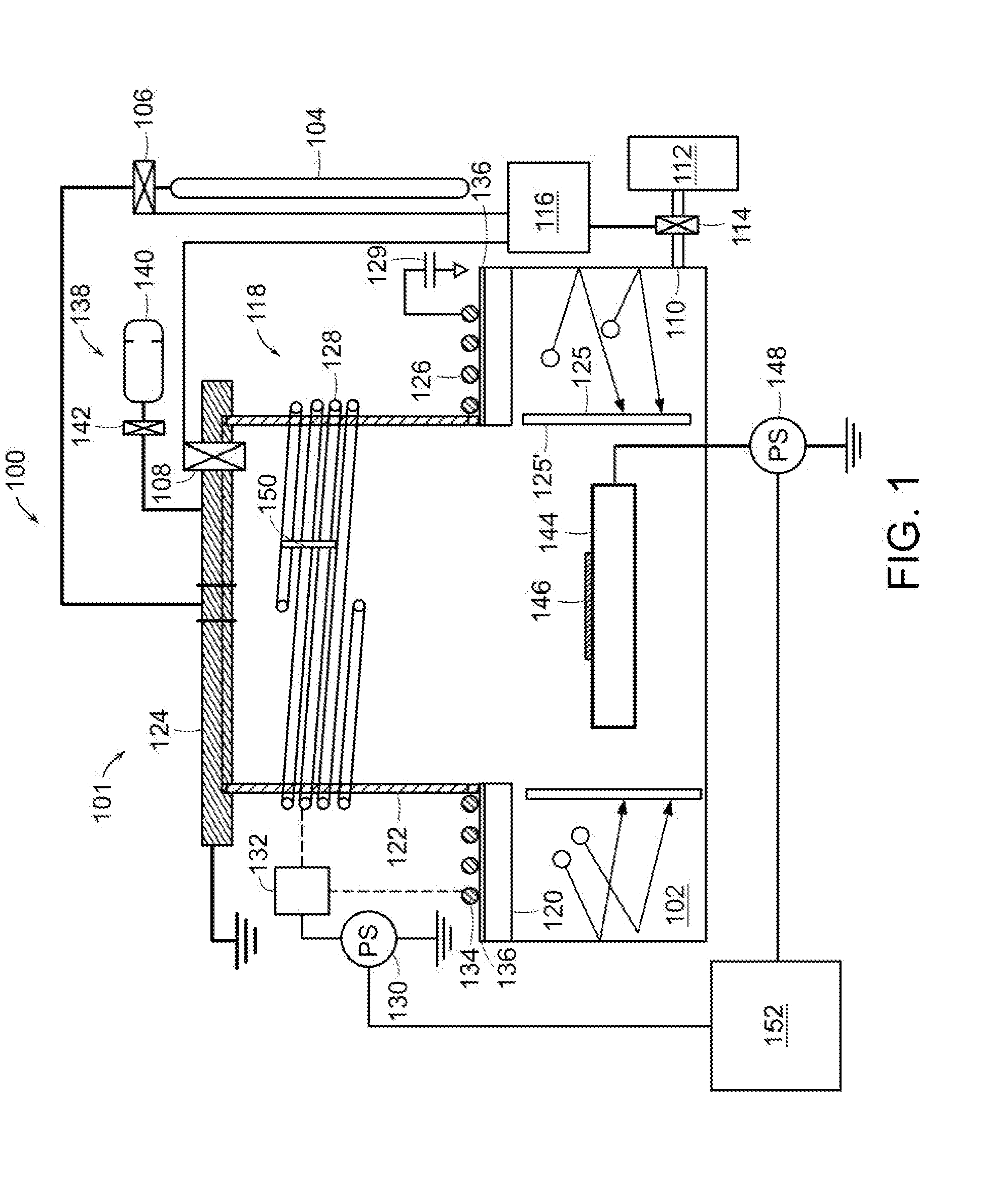
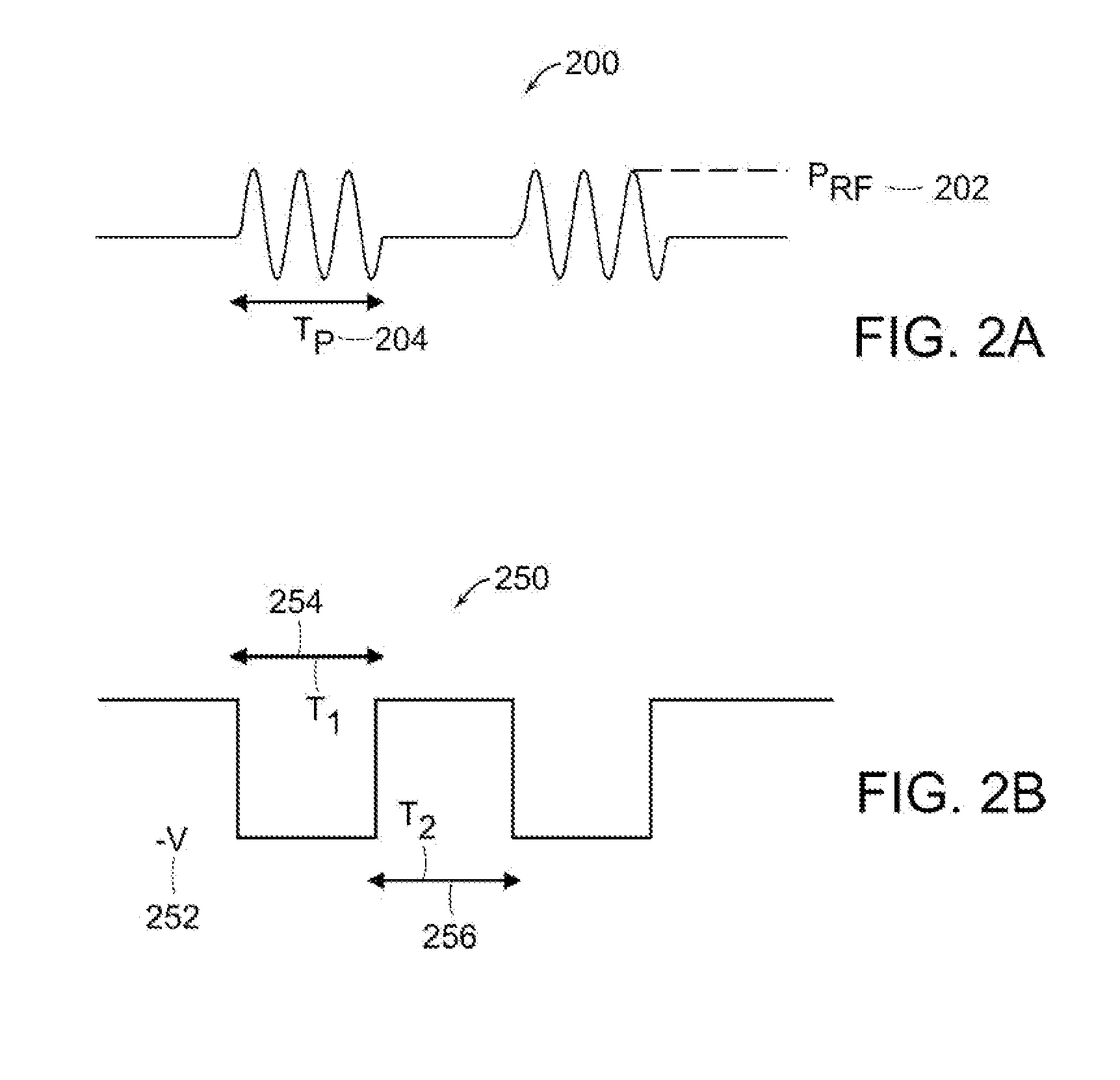
Plasma doping with enhanced charge neutralization
A plasma doping apparatus includes a pulsed power supply that generates a pulsed waveform having a first period with a first power level and a second period with a second power level. A plasma source generates a pulsed plasma with the first power level during the first period and with the second power level during the second period. A bias voltage power supply generates a bias voltage waveform at an output that is electrically connected to a platen which supports a substrate. The bias voltage waveform having a first voltage during a first period and second voltage with a negative potential that attract ions in the plasma to the substrate for plasma doping during a second period. At least one of the first and second power levels of the RF waveform is chosen to at least partially neutralize charge accumulating on the substrate.
Owner:VARIAN SEMICON EQUIP ASSOC INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com