Patents
Literature
235 results about "Roll-off" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
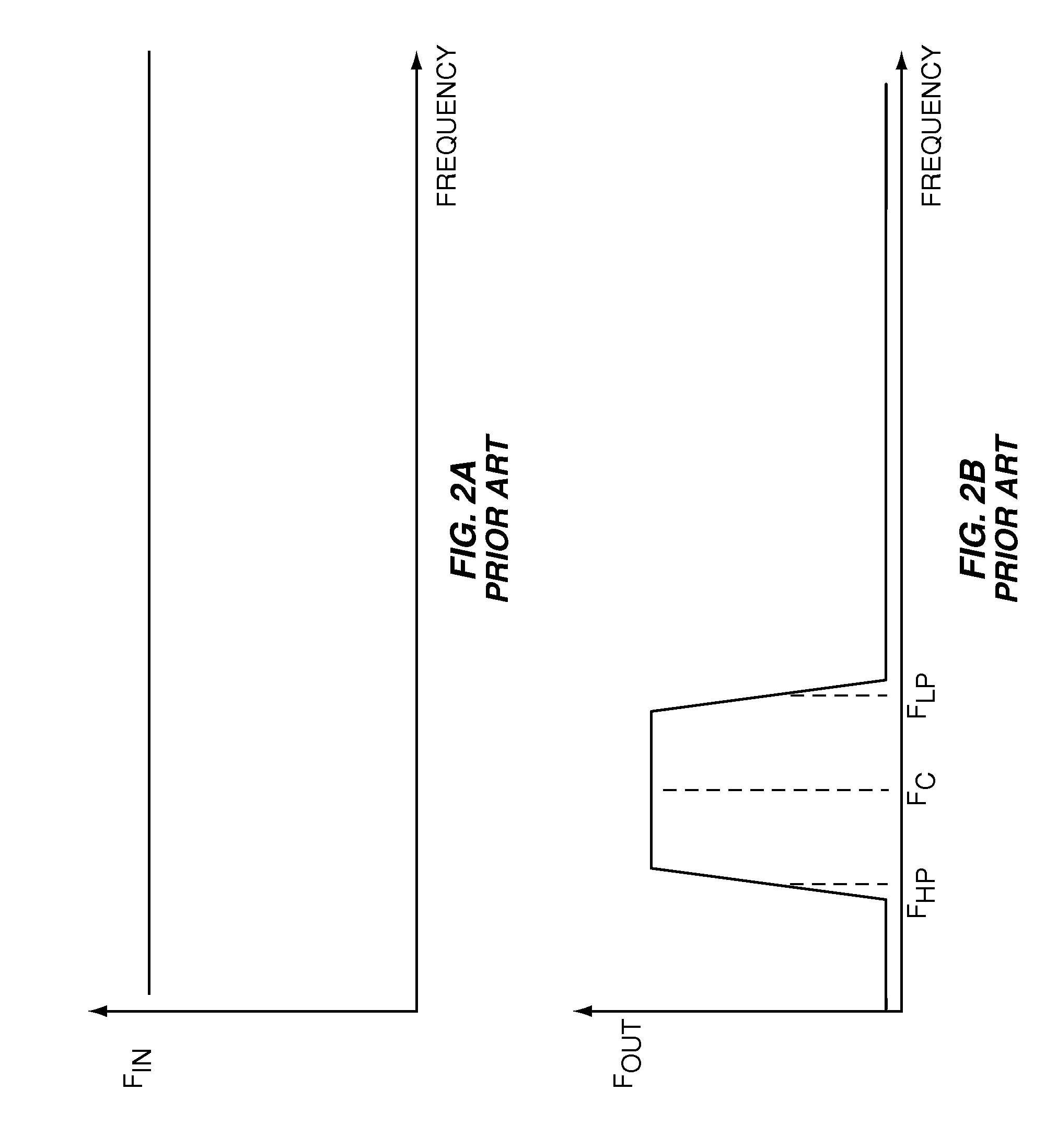
Roll-off is the steepness of a transfer function with frequency, particularly in electrical network analysis, and most especially in connection with filter circuits in the transition between a passband and a stopband. It is most typically applied to the insertion loss of the network, but can, in principle, be applied to any relevant function of frequency, and any technology, not just electronics. It is usual to measure roll-off as a function of logarithmic frequency; consequently, the units of roll-off are either decibels per decade (dB/decade), where a decade is a tenfold increase in frequency, or decibels per octave (dB/8ve), where an octave is a twofold increase in frequency.
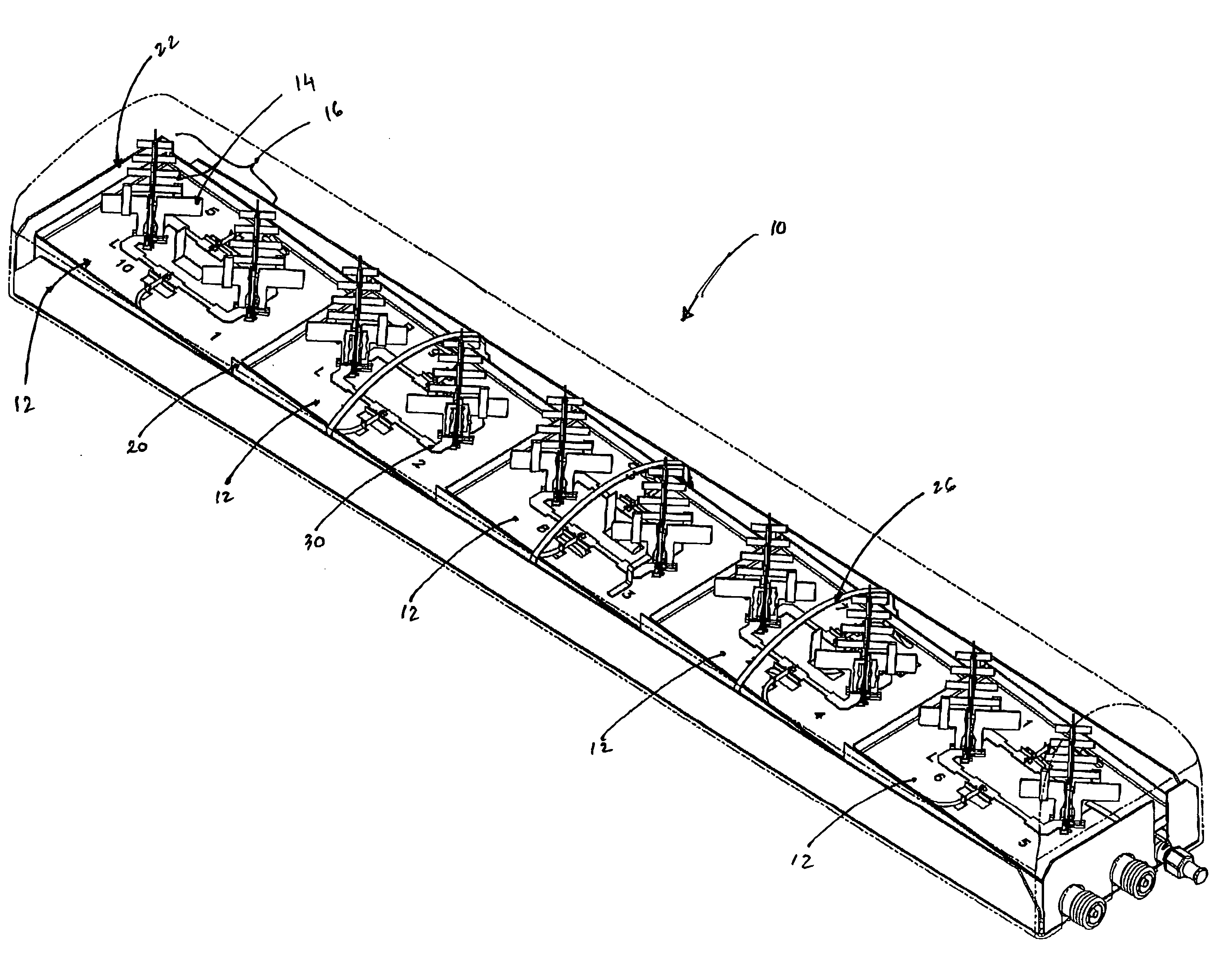
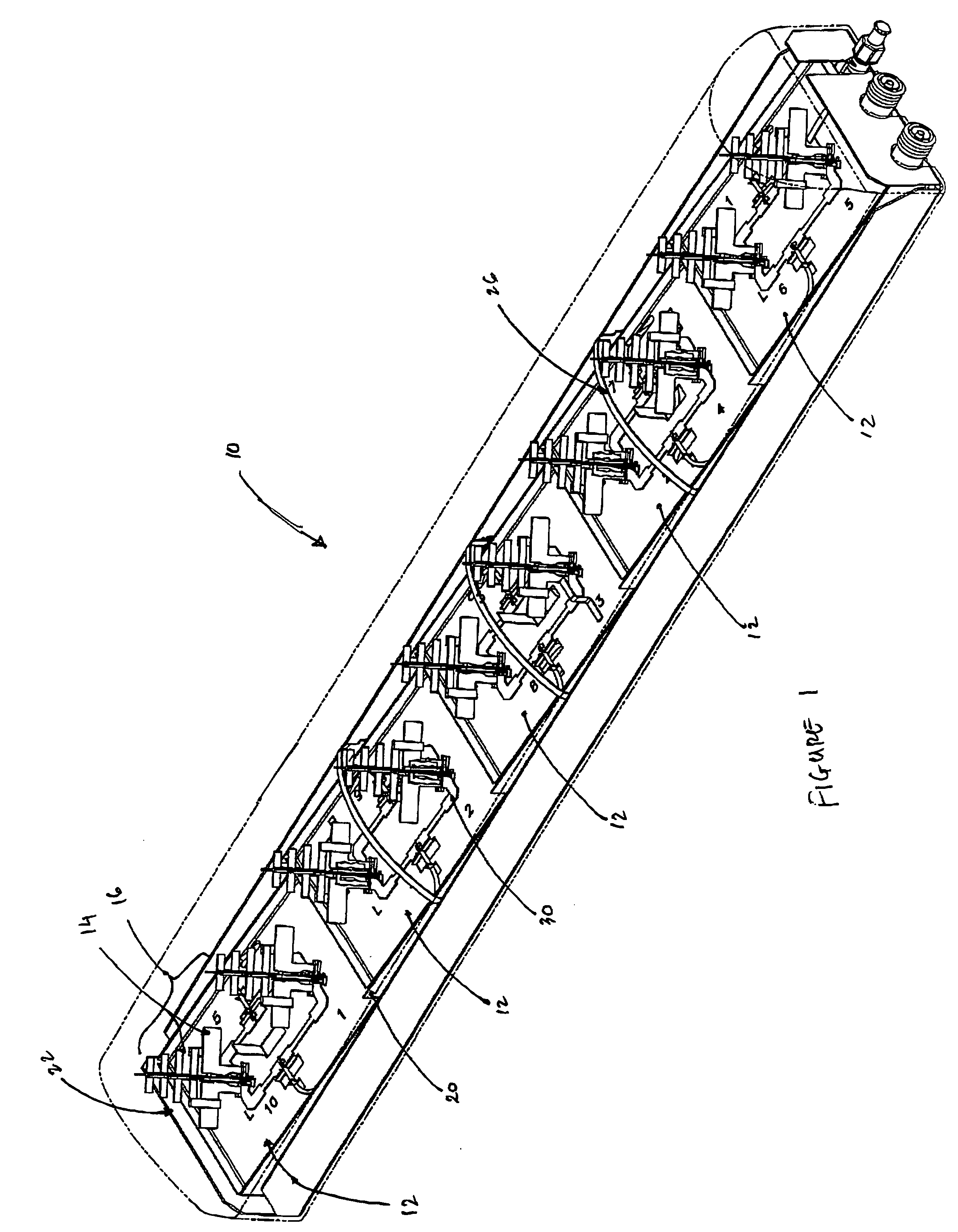
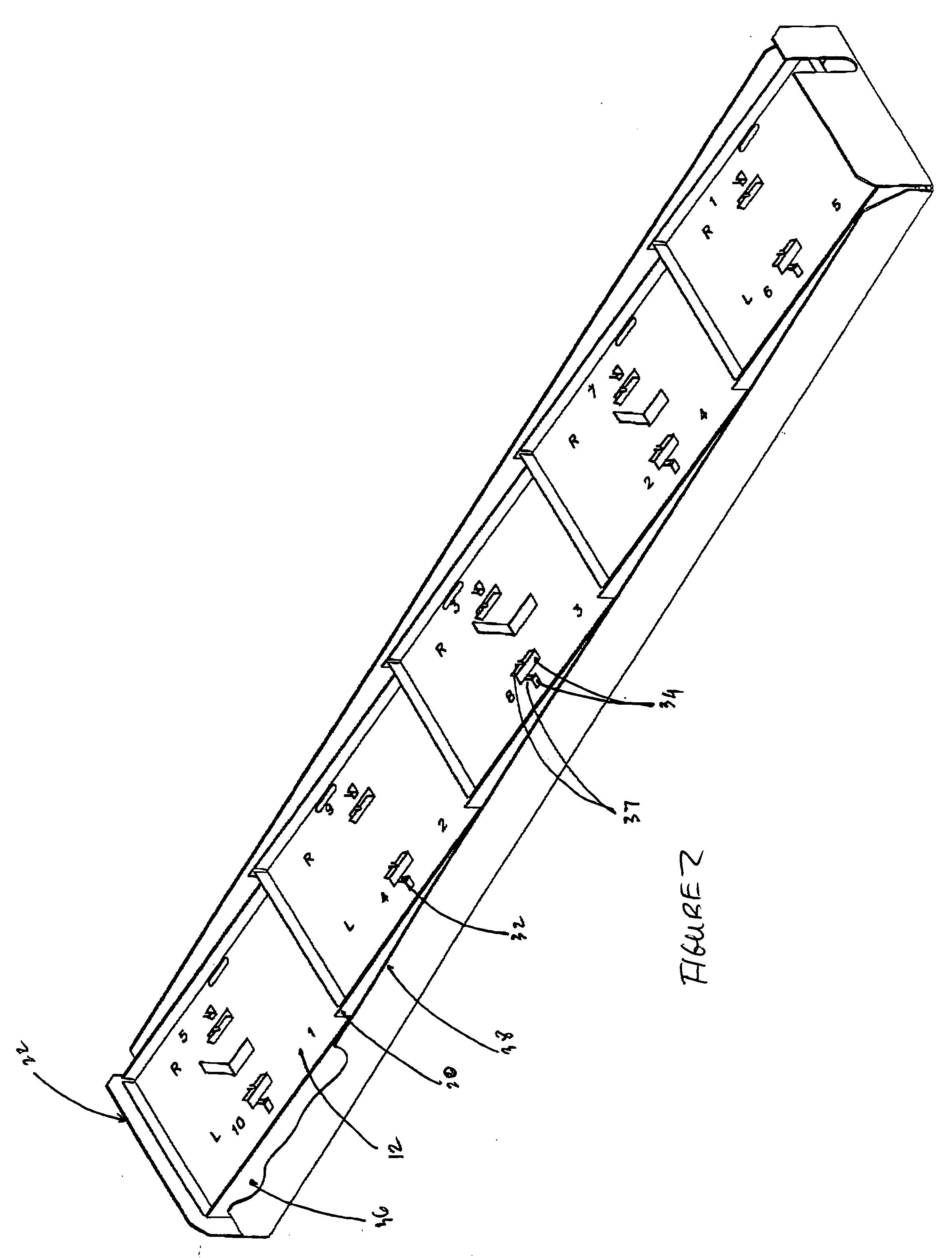
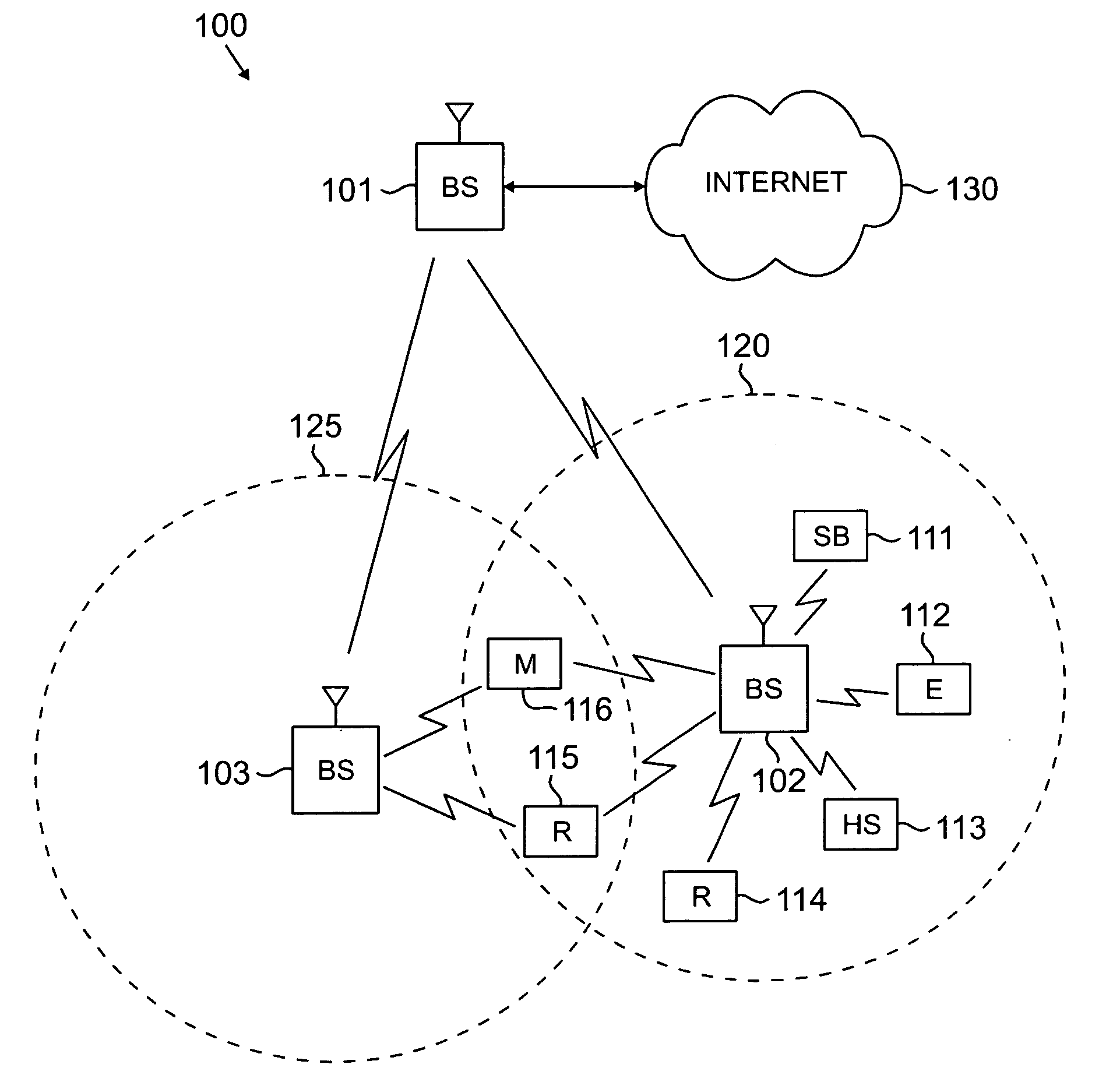
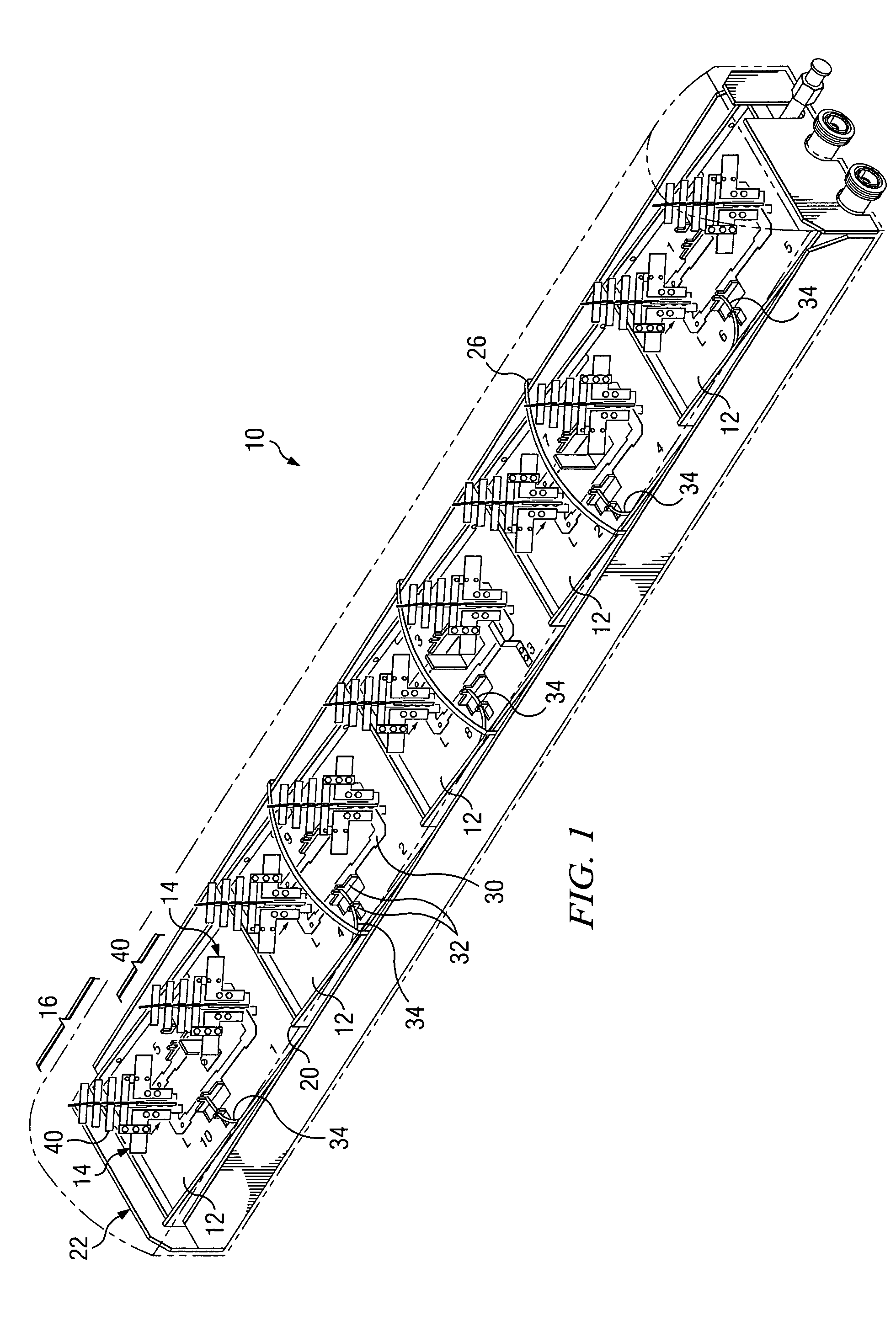
Wideband dual polarized base station antenna offering optimized horizontal beam radiation patterns and variable vertical beam tilt
ActiveUS6924776B2Improved radiation patternImprove front-to-back ratioLogperiodic antennasAntenna supports/mountingsRadiation patternPhysics
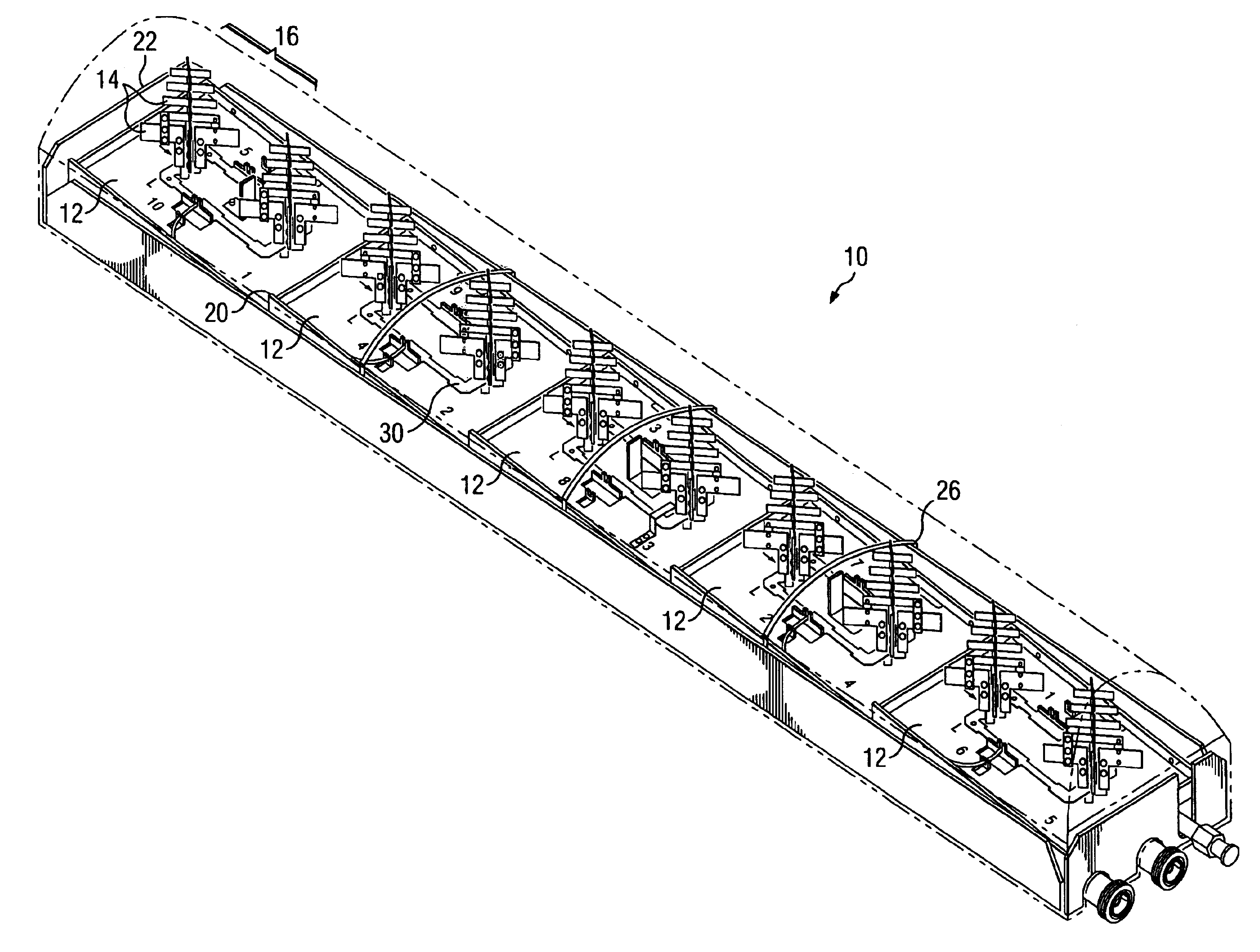
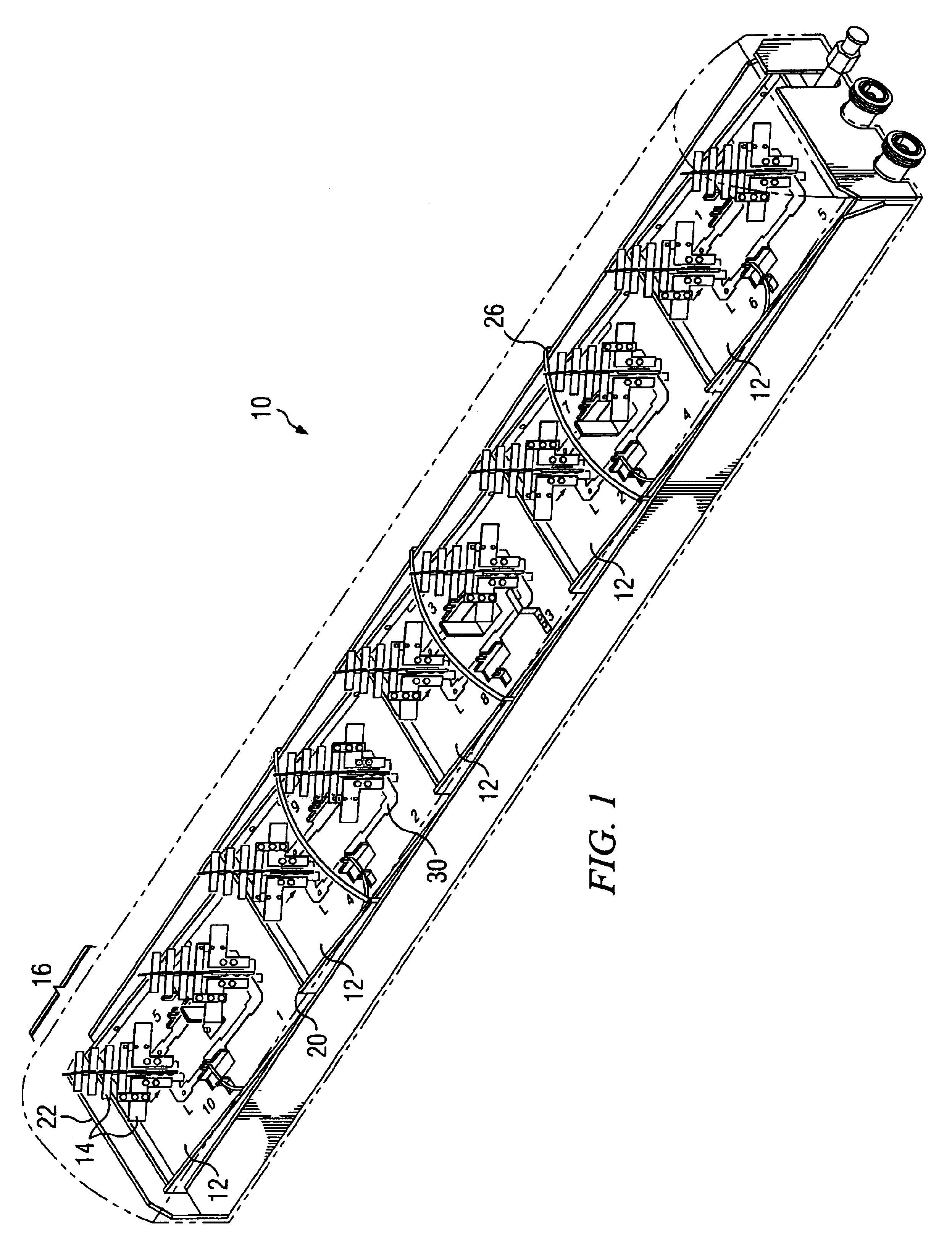
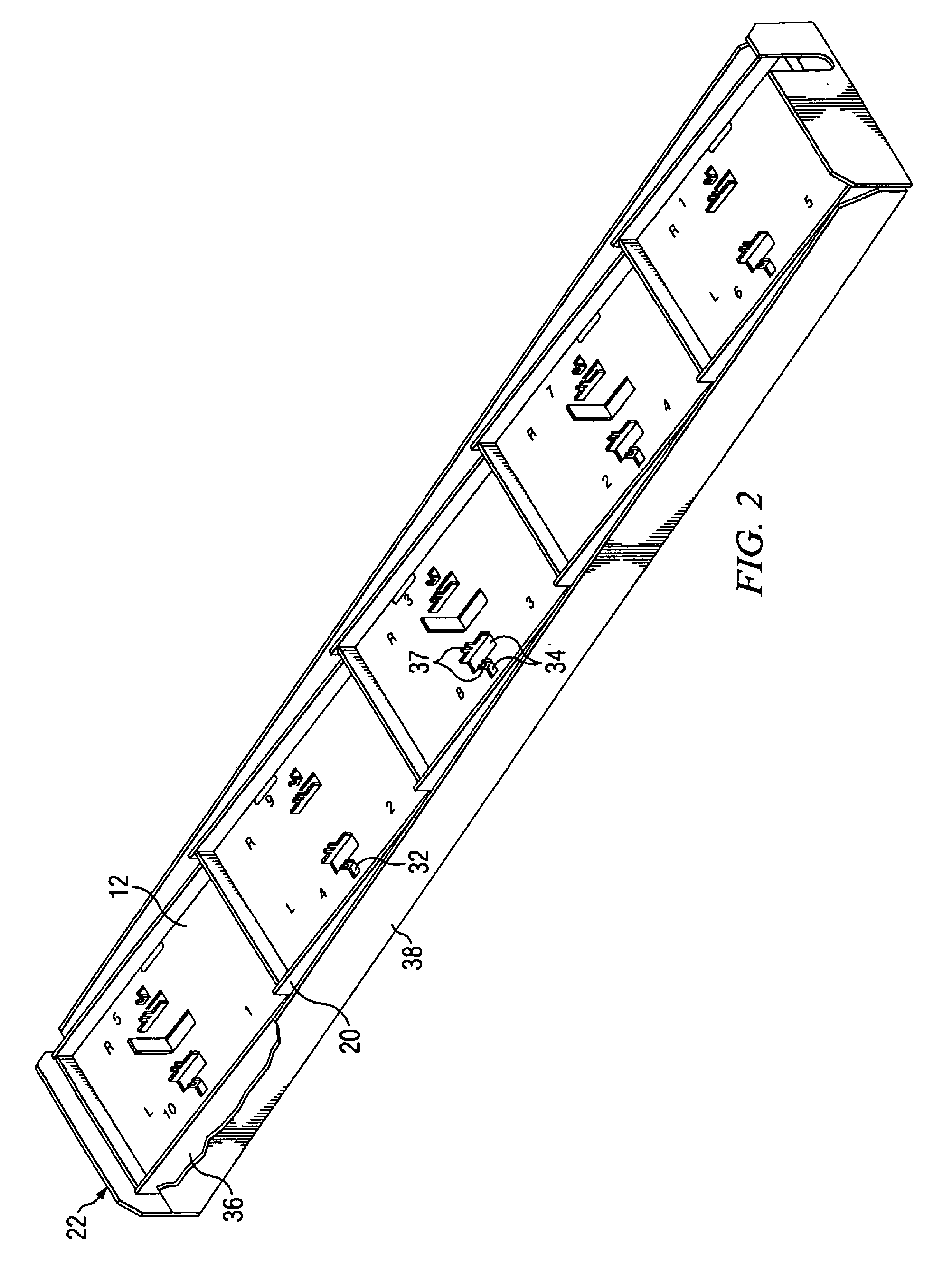
A dual polarized variable beam tilt antenna (10) having a plurality of offset element trays (12) each supporting pairs of dipole elements (14) to orient the dipole element pattern boresight at a downtilt. The maximum squint level of the antenna is a consistent downtilt off of boresight and which is at the midpoint of the antenna tilt range. The antenna provides a high roll-off radiation pattern through the use of Yagi dipole elements configured in this arrangement, having a beam front-to-side ratio exceeding 20 dB, a horizontal beam front-to-back ratio exceeding 40 dB, and is operable over an expanded frequency range.
Owner:COMMSCOPE TECH LLC
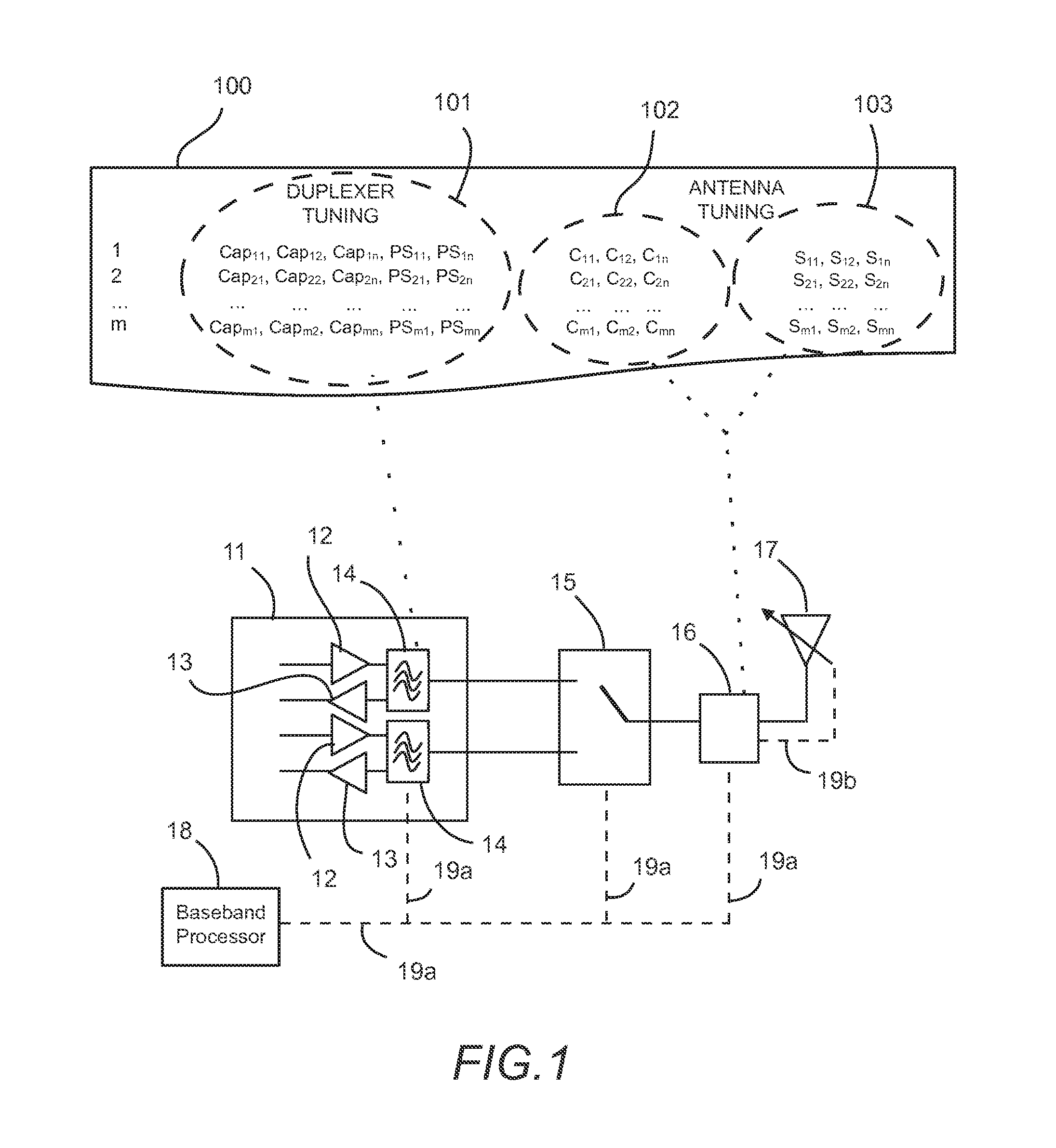
Tunable duplexing circuit
ActiveUS20150303892A1Improve performanceImprove out-of-band rejection performanceMultiple-port networksDigital technique networkRF front endTransceiver
A tunable duplexer circuit is described, wherein the frequency response as well as bandwidth and transmission loss characteristics can be dynamically altered, providing improved performance for transceiver front-end applications. The rate of roll-off of the frequency response can be adjusted to improve performance when used in duplexer applications. A method is described where the duplexer circuit characteristics are optimized in conjunction with a specific antenna frequency response to provide additional out-of-band rejection in a communication system. Dynamic optimization of both the duplexer circuit and an active antenna system is described to provide improved out-of-band rejection when implemented in RF front-end circuits of communication systems. Other features and embodiments are described in the following detailed descriptions.
Owner:KYOCERA AVX COMPONENTS (SAN DIEGO) INC
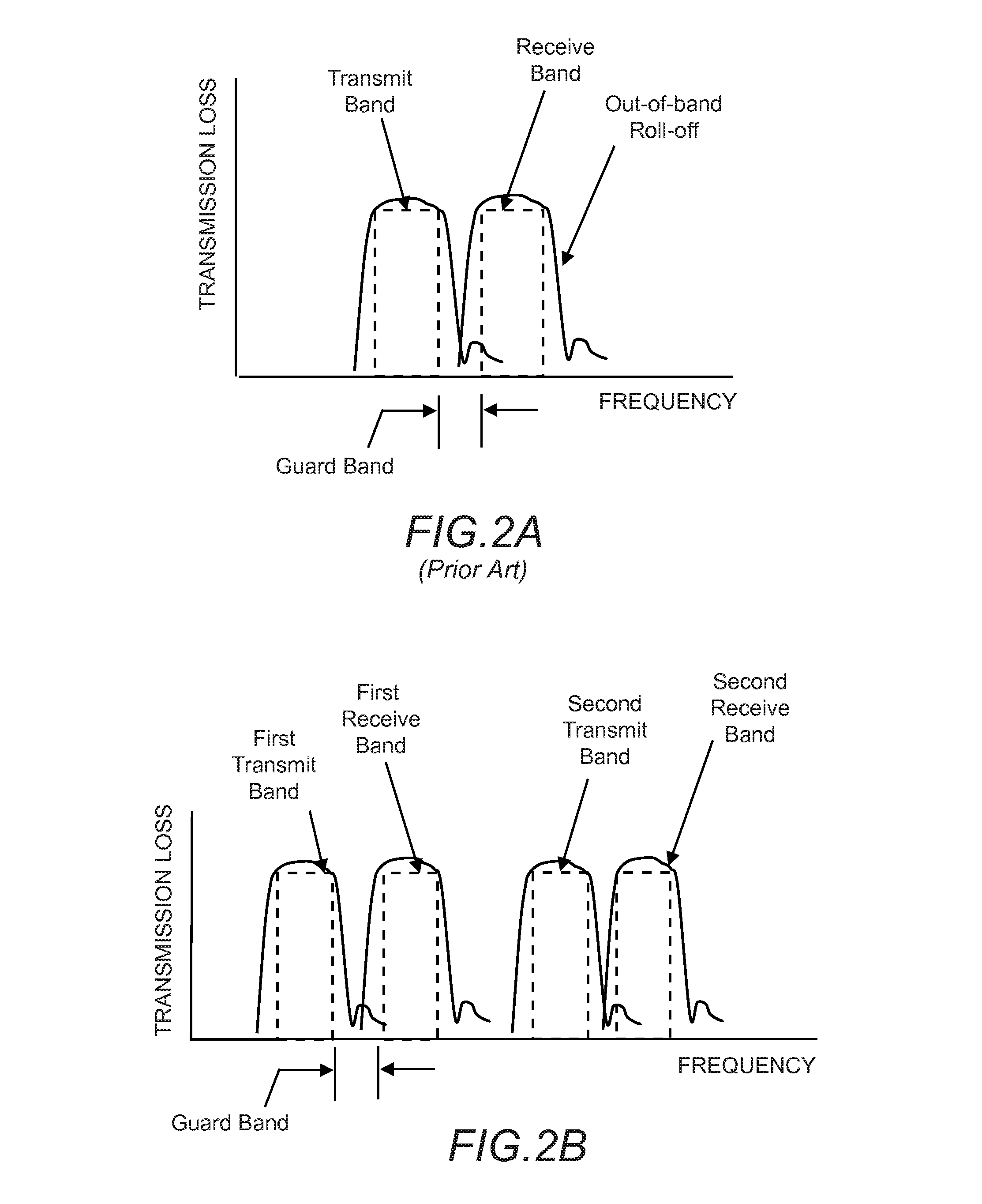
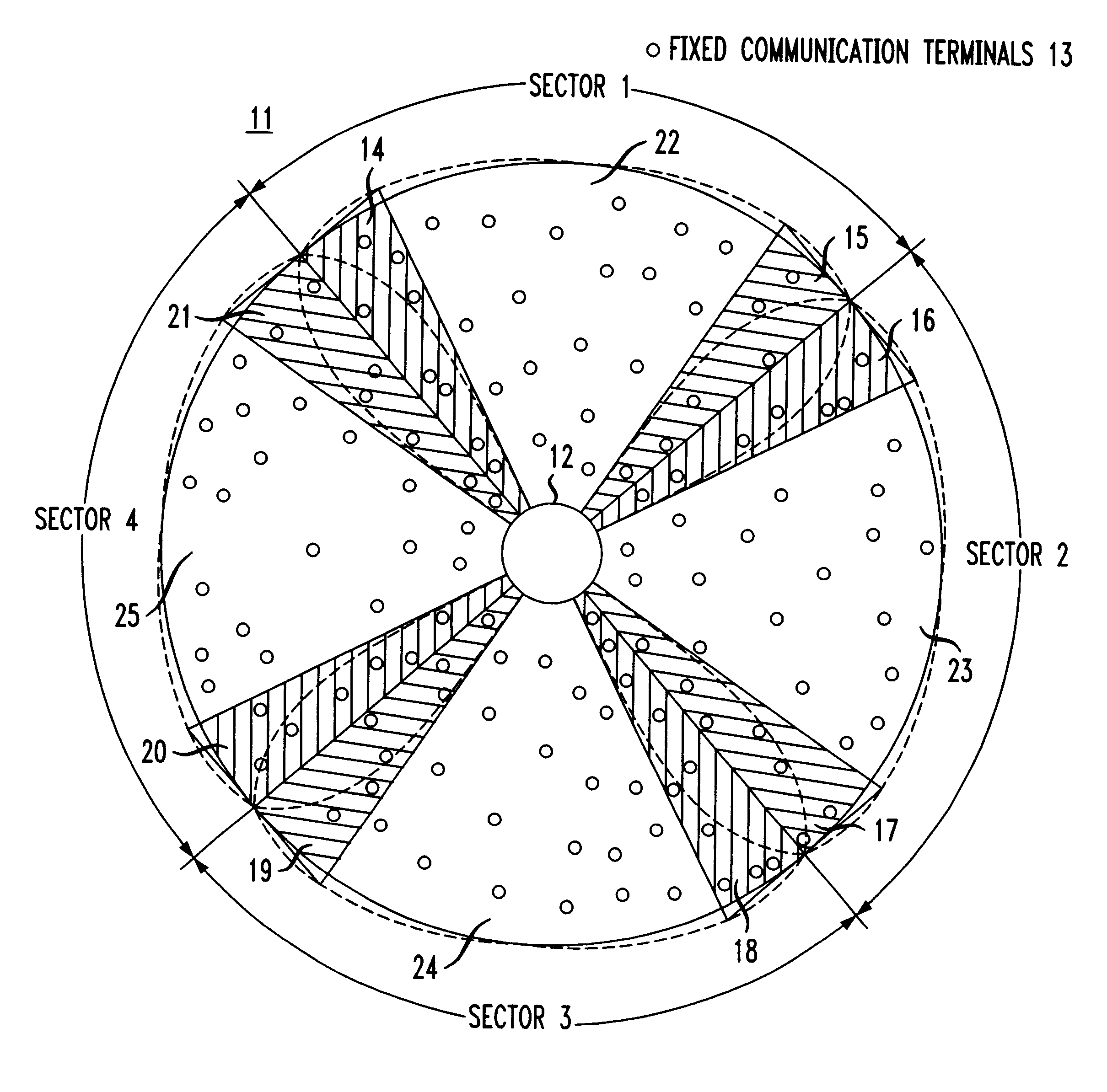
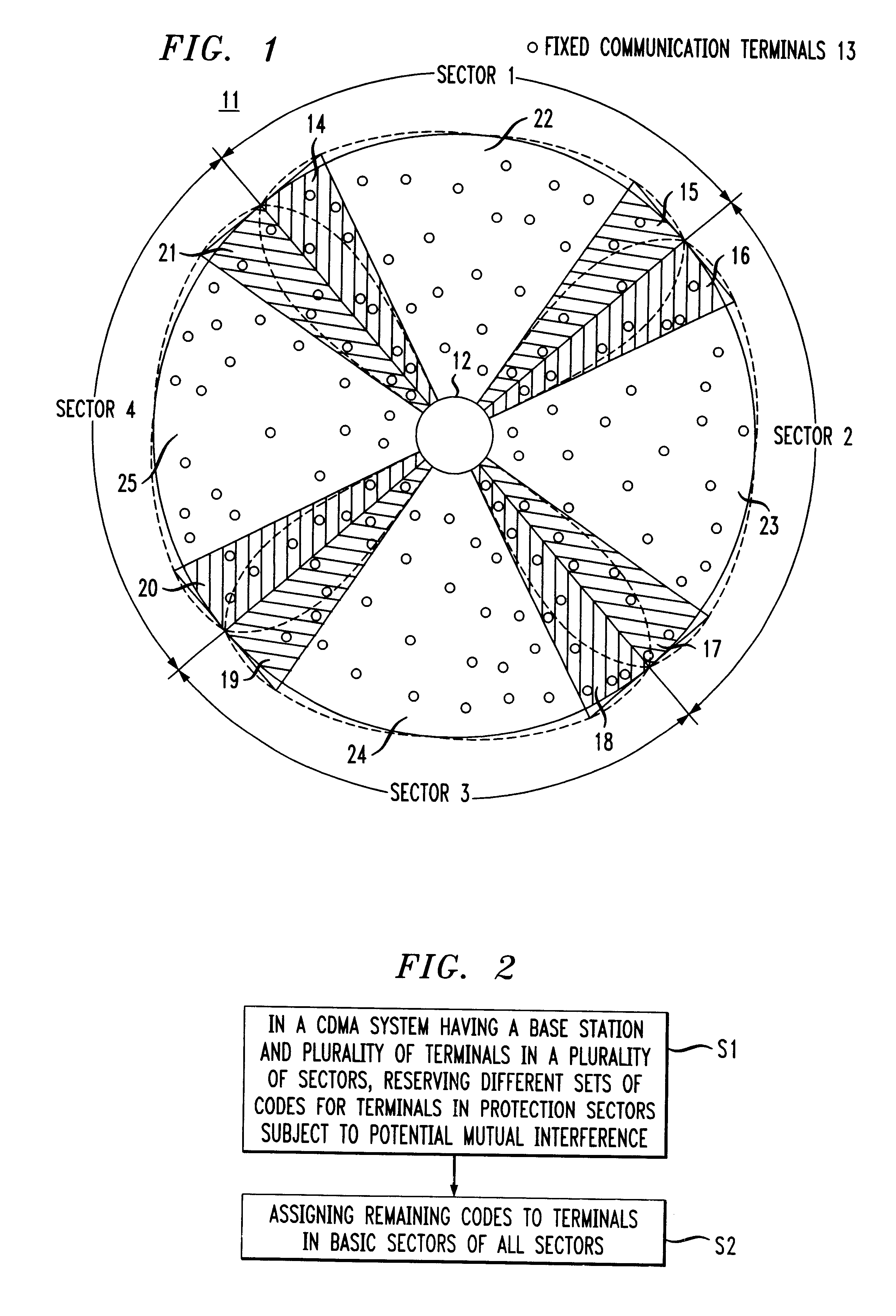
Reuse of codes and spectrum in a CDMA system with multiple-sector cells
InactiveUS6388998B1Avoid mutual interferenceRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsSubstation equipmentFrequency spectrumAntenna radiation patterns
A system and a method for code division multiple access (CDMA) communication. The system includes fixed terminals communicating with a central base station. The terminals in protection sectors of each sector are configured to employ codes from different sets of codes to overcome potential mutual interference between sectors on account of antenna radiation pattern roll-off. The remaining codes, preferably the majority of the available codes, are used in any one of a plurality of basic sectors, each of which separates the protection sectors of a respective sector. For an even number of sectors in a cell, the available codes are partitioned into three groups, two for the protection sectors and one for the basic sectors. For an odd number of sectors in a cell, the available codes are partitioned into four groups, three for the protection sectors and one for the basic sectors. Protection sectors are relatively narrow but broad enough to counteract the potential mutual interference between sectors.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC +1
Digital broadcasting transmission/reception capable of improving a receiving performance and a signal processing method thereof
InactiveUS20050013380A1Improve reception performanceImprove compatibilityPulse modulation television signal transmissionError preventionTransmission channelEngineering
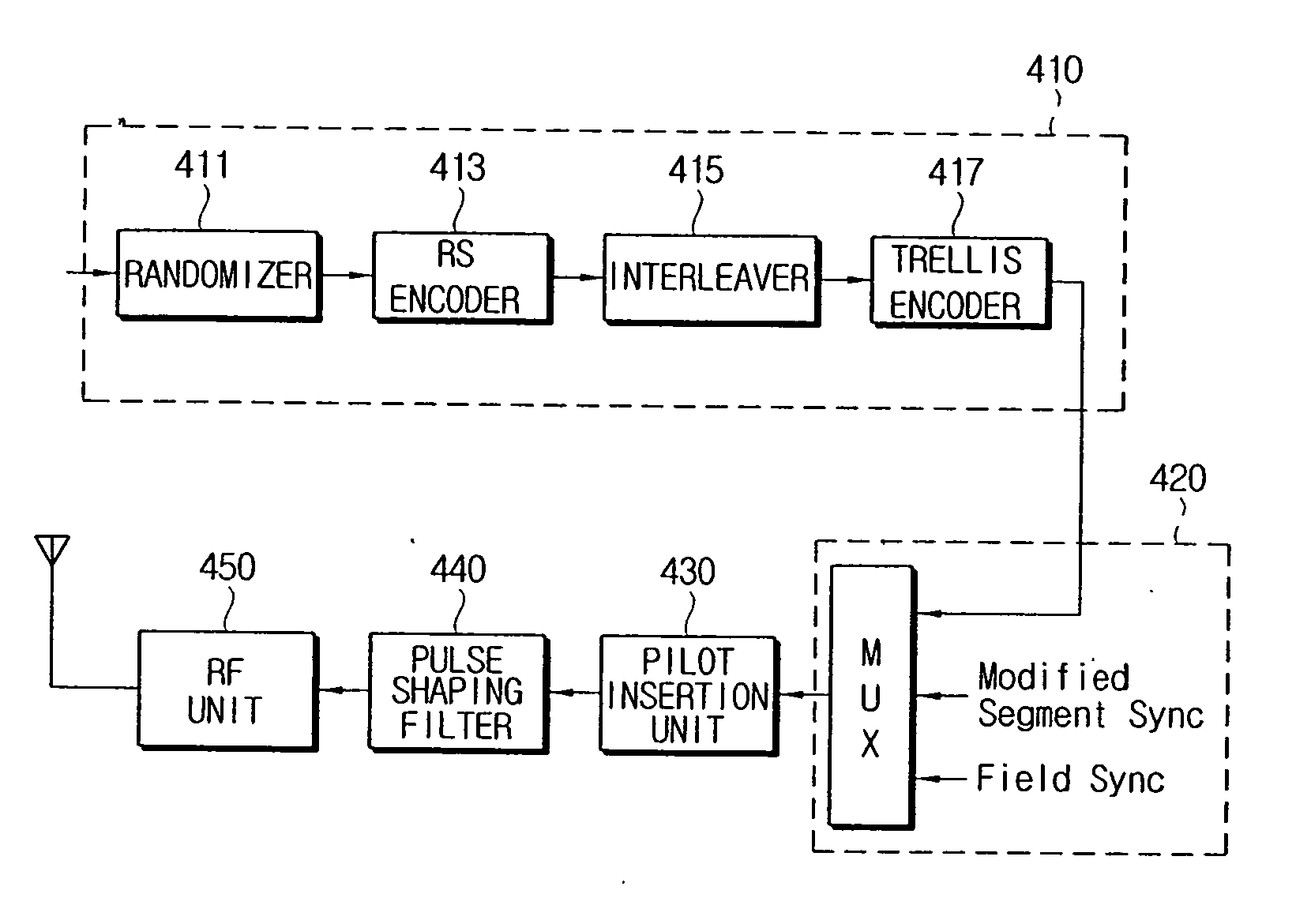
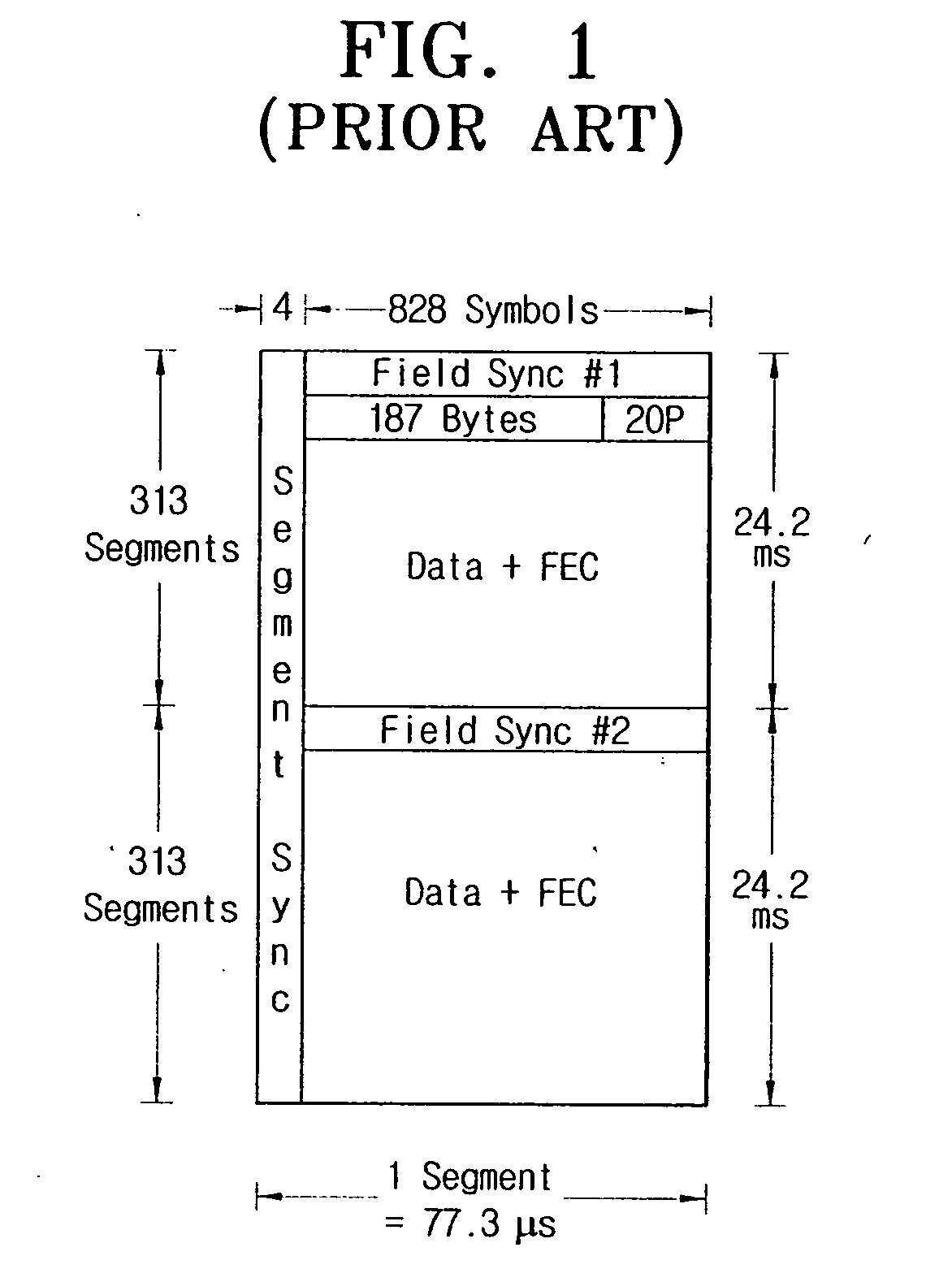
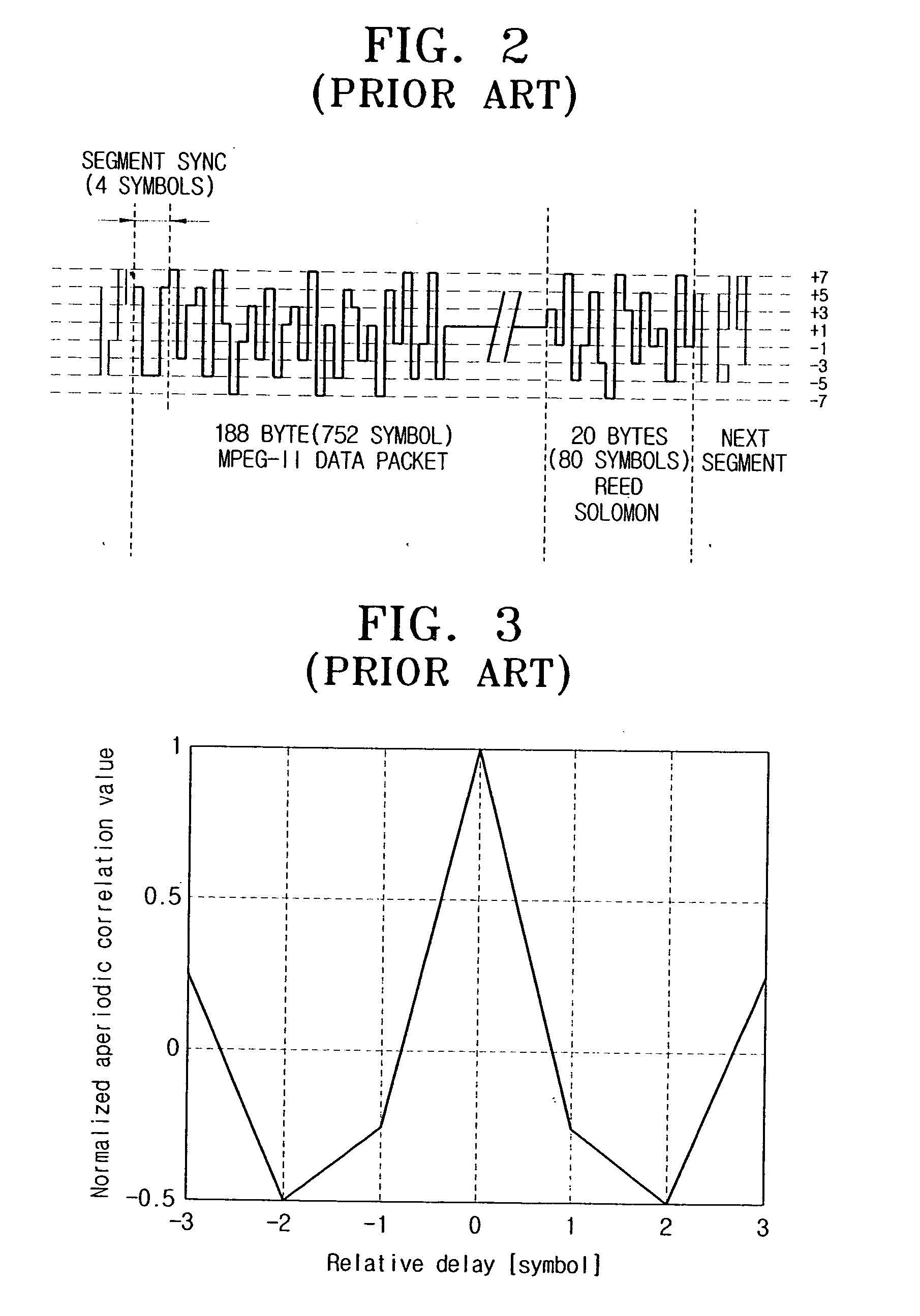
Digital broadcasting transmission / reception systems capable of improving the synchronization acquisition and the equalization performance, and signal processing methods thereof. The digital broadcasting transmission / reception systems include a FEC encoder encoding an incoming signal according to a FEC scheme, a sync signal insertion unit inserting into the encoded signal a segment sync signal including modified segment syncs, a pilot insertion unit inserting a pilot signal into the sync-inserted signal, a pulse shaping filter pulse-shaping the pilot-inserted signal with a roll-off factor, and a RF unit transmitting the pulse-shaped signal through a transmission channel band. The modified segment sync includes a predetermined number of sync signals, and an average of correlation values with respect to the predetermined number of the sync signals has an auto-correlation property. The transmission scheme utilizing the modified segment syncs promotes compatibility with the conventional reception system, minimizes hardware complexity, and enhances synchronization acquisition and equalization performance.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Audio frequency amplifier
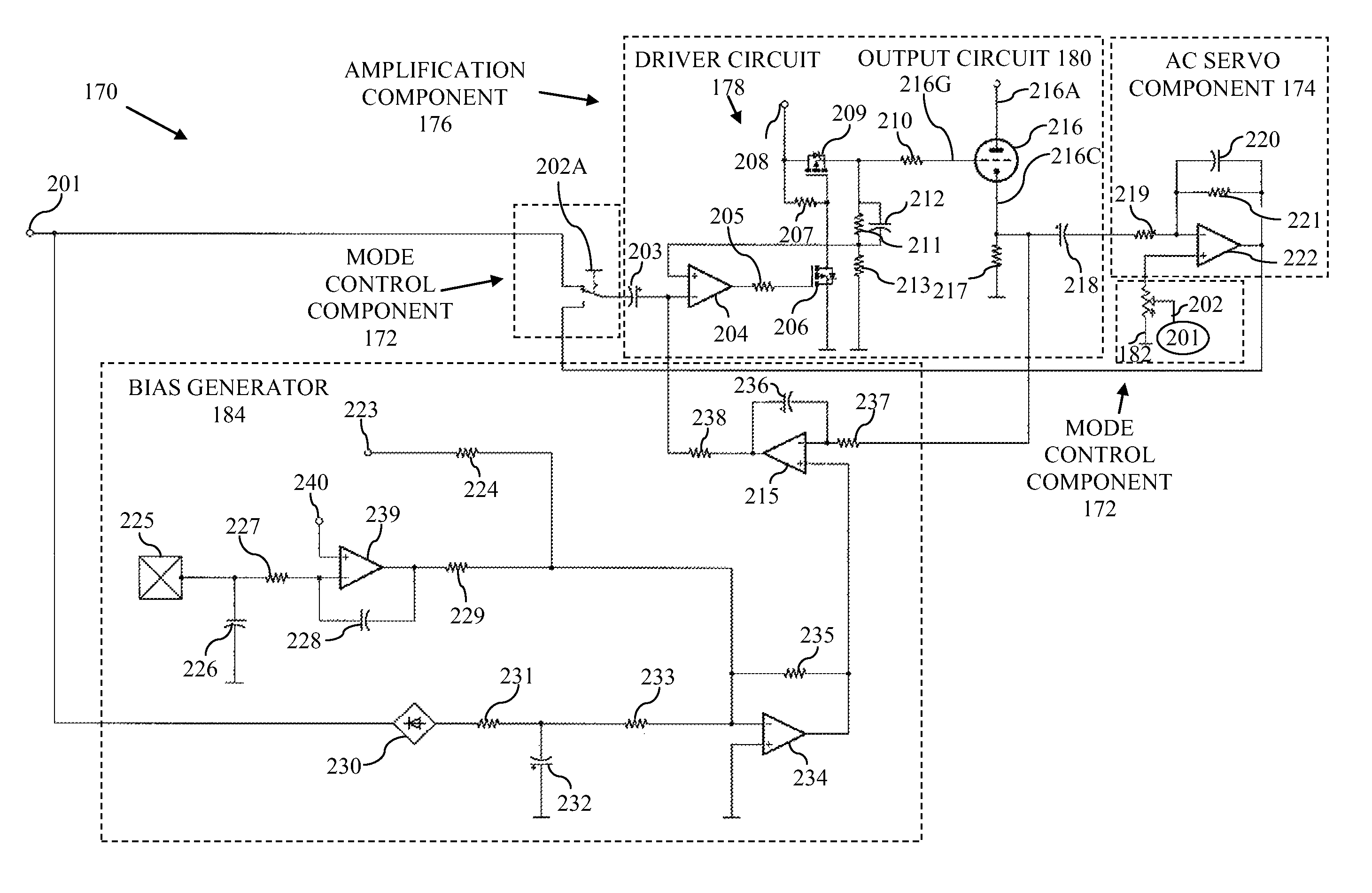
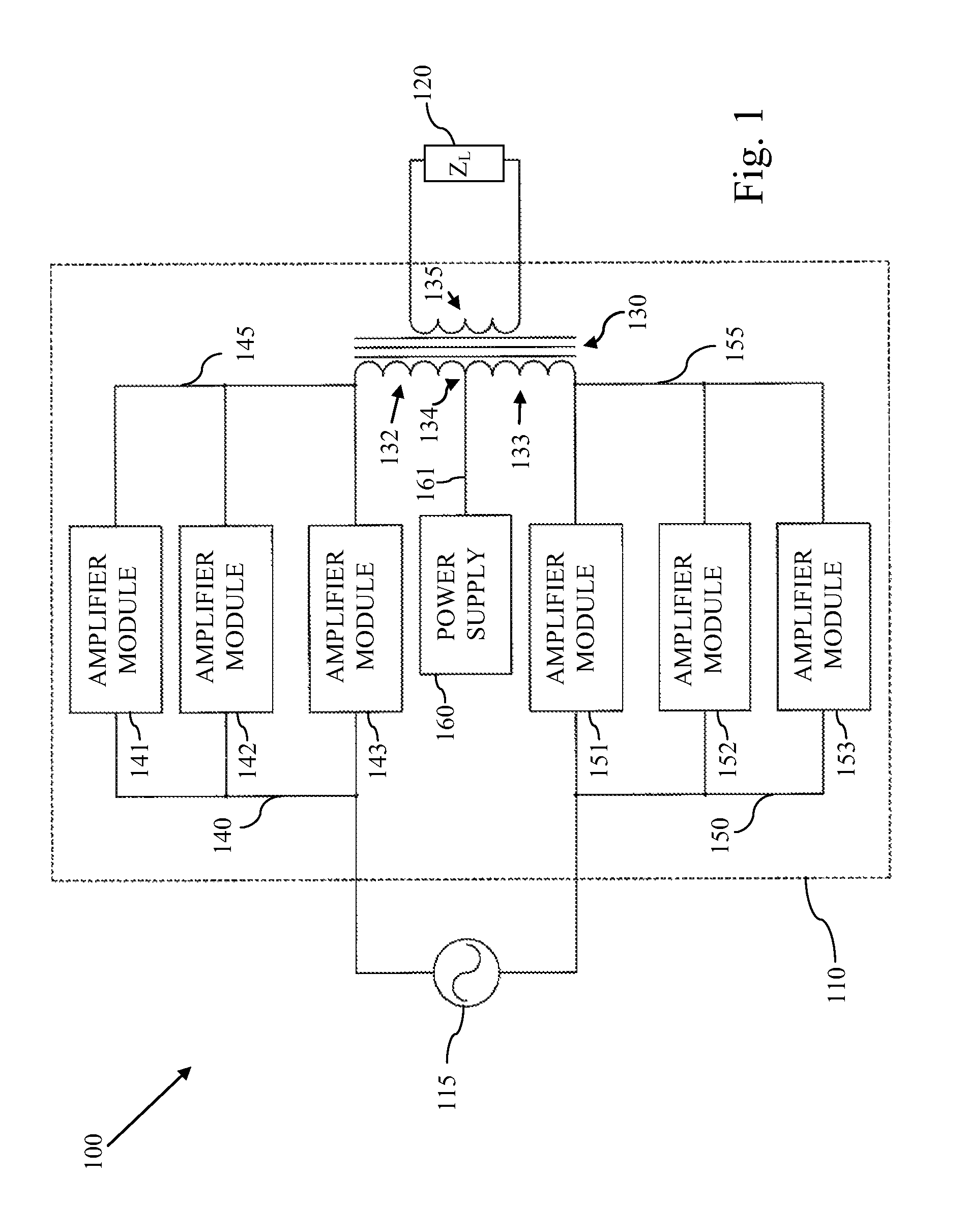
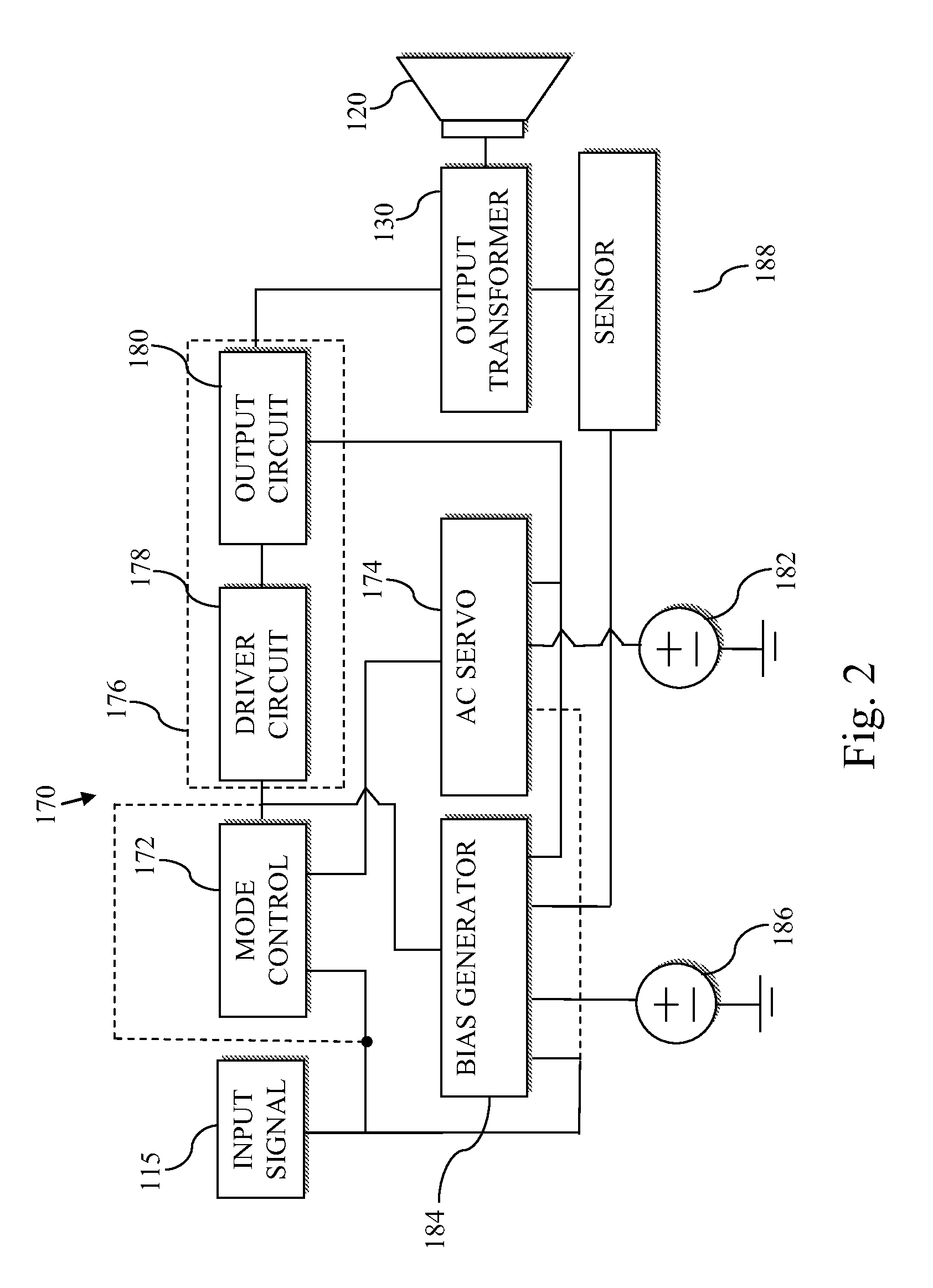
An amplifier is operable in push-pull mode, single-ended mode, or a composite mode that is an intermediate between single-ended and Push-pull modes. Moreover, at least one output device may be configured to operate using a high performance AC servo loop that functions the output device as a current source. Still further, a control input driver stage is provided that is capable of supplying sufficient AC current to overcome Miller capacitance induced roll off within the intended frequency spectrum of triode vacuum tubes. Additionally, methods are provided to substantially null or selectively introduce DC magnetic bias within the output transformer core. Still further, a solid state power supply stage provides substantial AC hum reduction during single-ended operation and simultaneously provides output voltage load regulation attributes similar to traditional vacuum tube rectifier circuits.
Owner:GIOVANNOTTO ROBERTO MICHELE
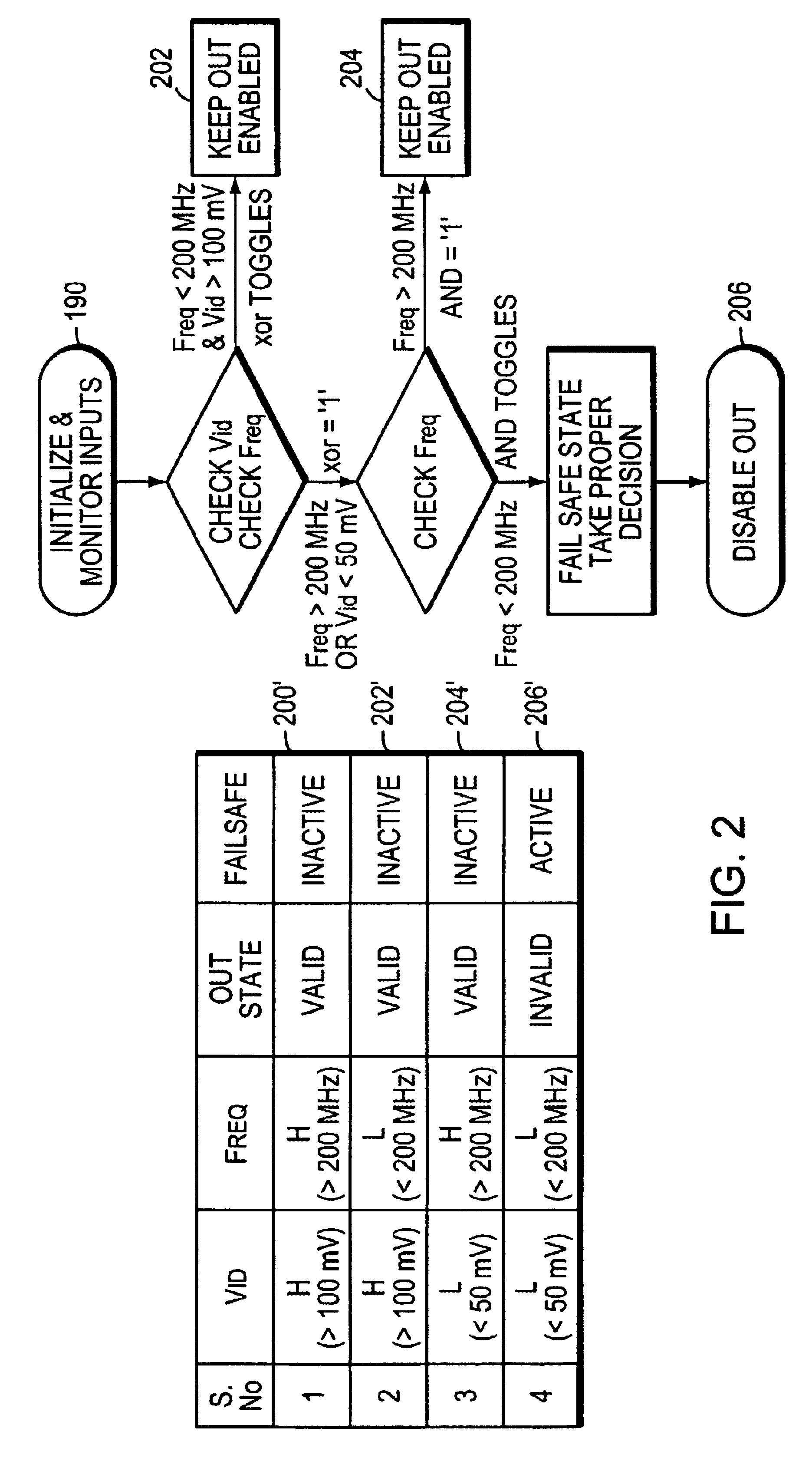
Failsafe differential amplifier circuit
InactiveUS6781456B2Not affect high-frequency performance of receiverFail-safe circuitsAmplifier combinationsAudio power amplifierSafety status
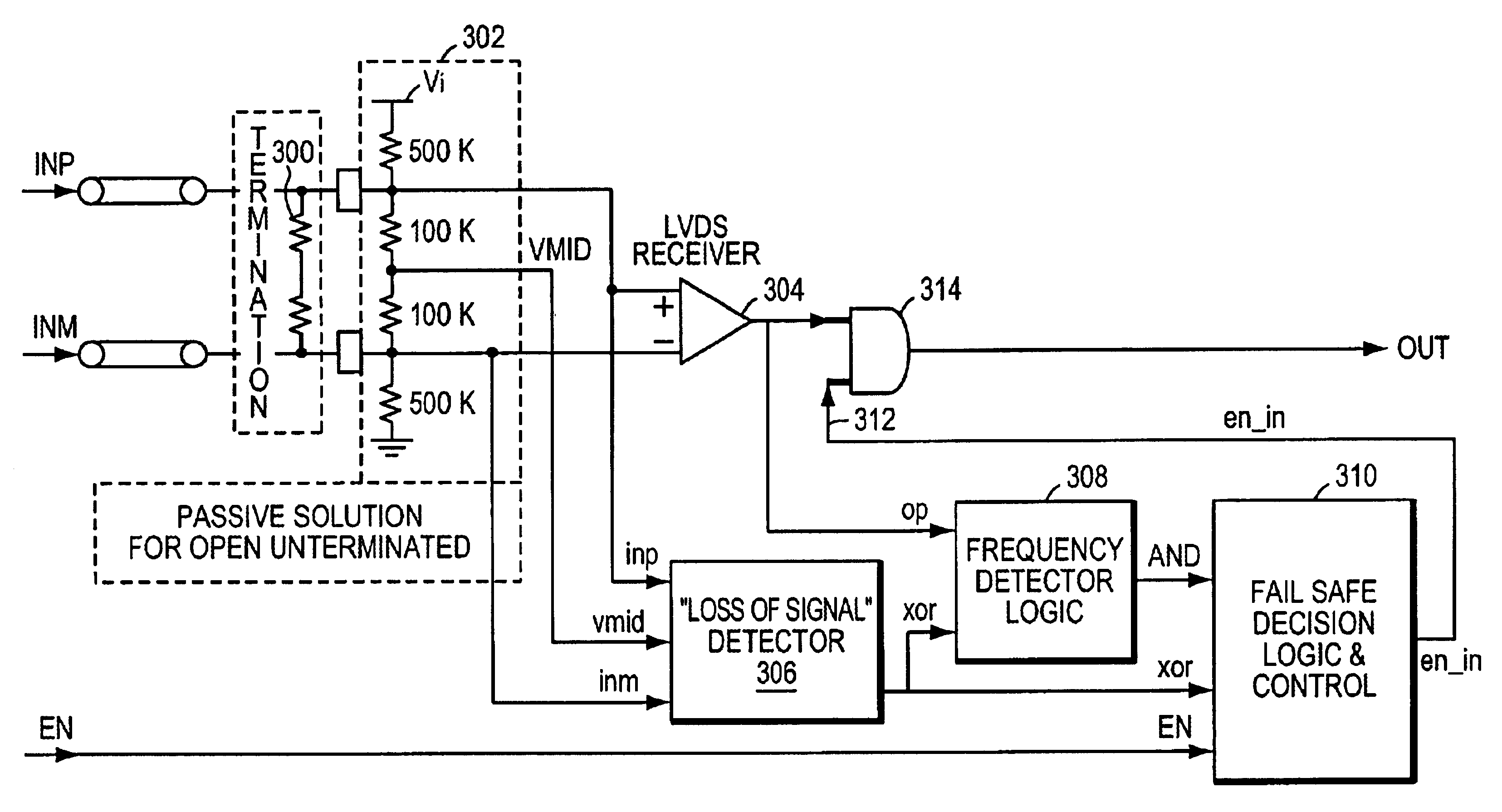
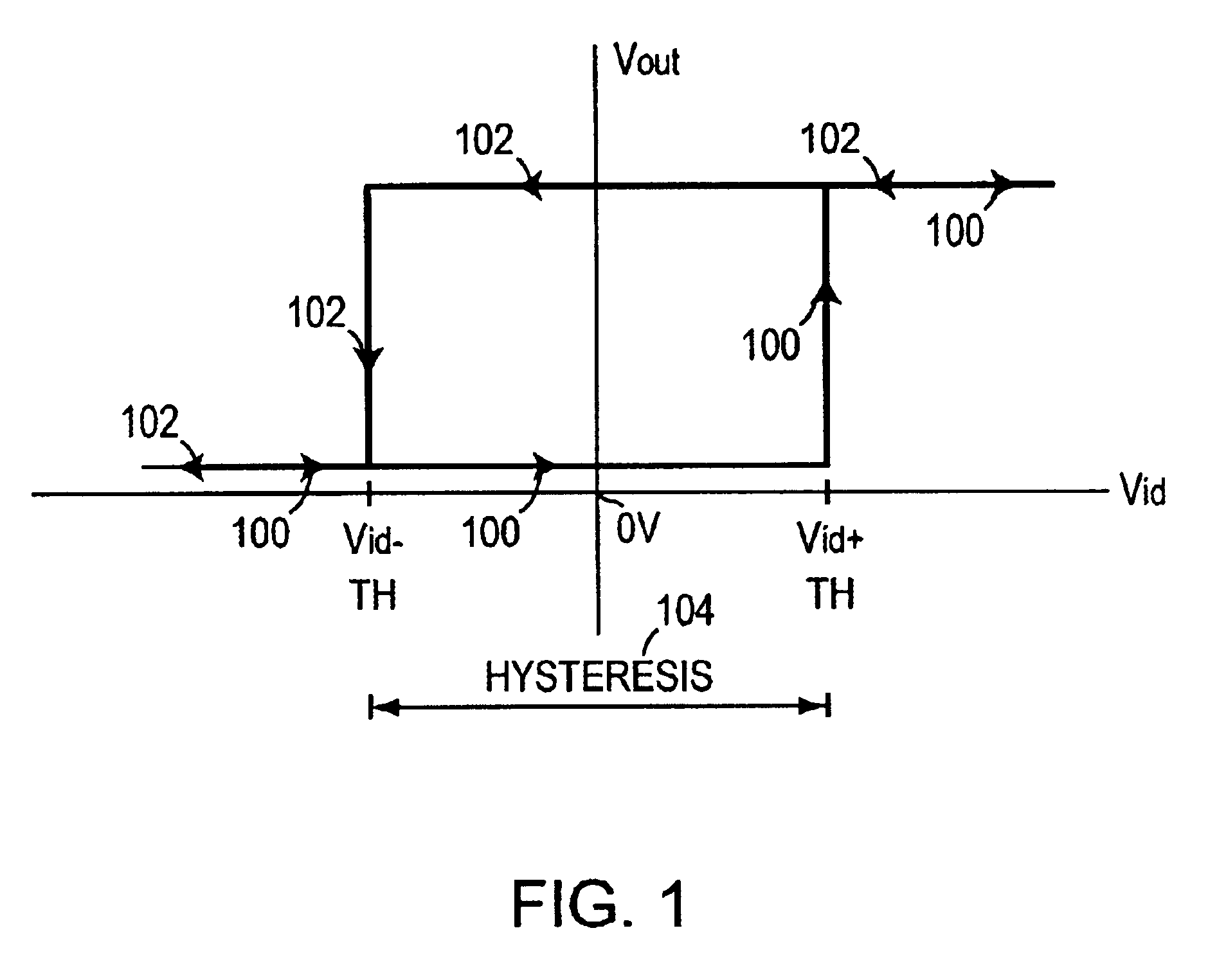
Differential input fail safe circuitry is disclosed that detects missing or too low differential signals combined with a frequency lower than a frequency limit where a final safe condition is detected and signaled. The output signal form the fail safe circuitry is held in a given state that is an invalid representation of the differential input signal. A frequency detector, complementary offsetting auxiliary amplifiers with limit frequency roll offs are used to detect the fail safe condition. In addition a delay circuit is used that requires the fail safe condition to exist for some time before the fail safe circuit is active. Initialization circuitry ensures a proper power up conditions where the circuitry is enabled to detect the fail safe conditions and guarantees a reliable fail safe irrespective of the previous state of the signal.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
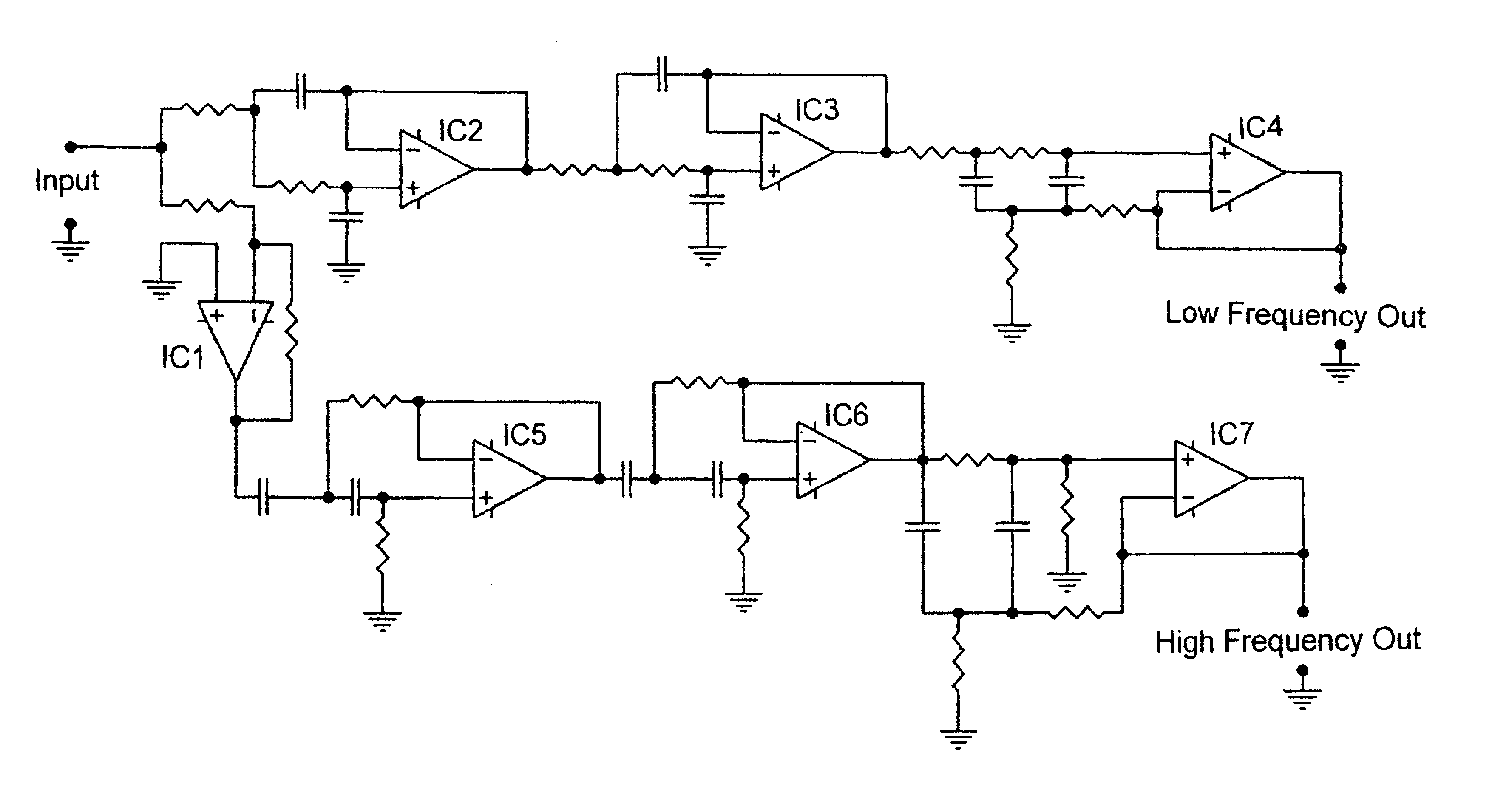
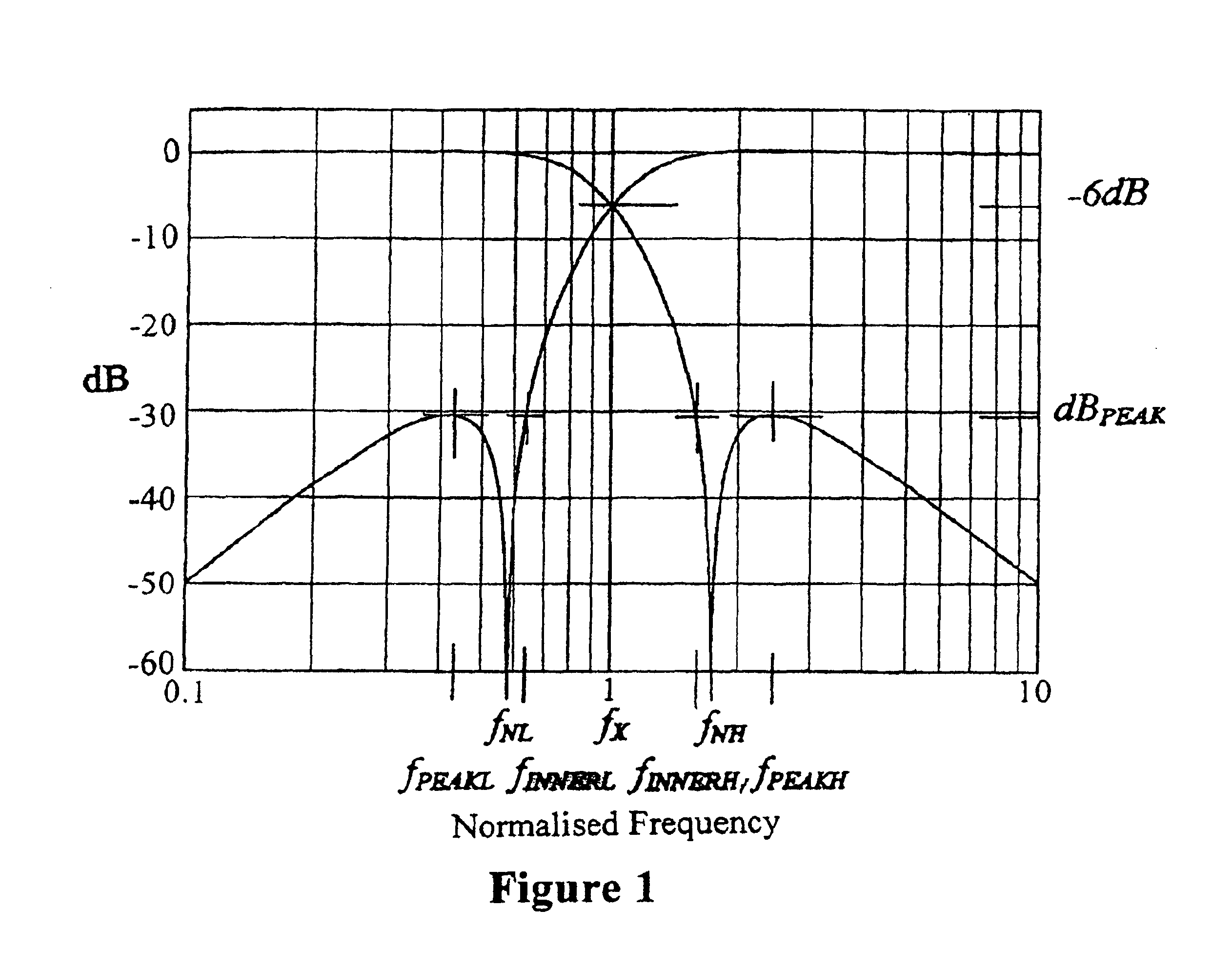
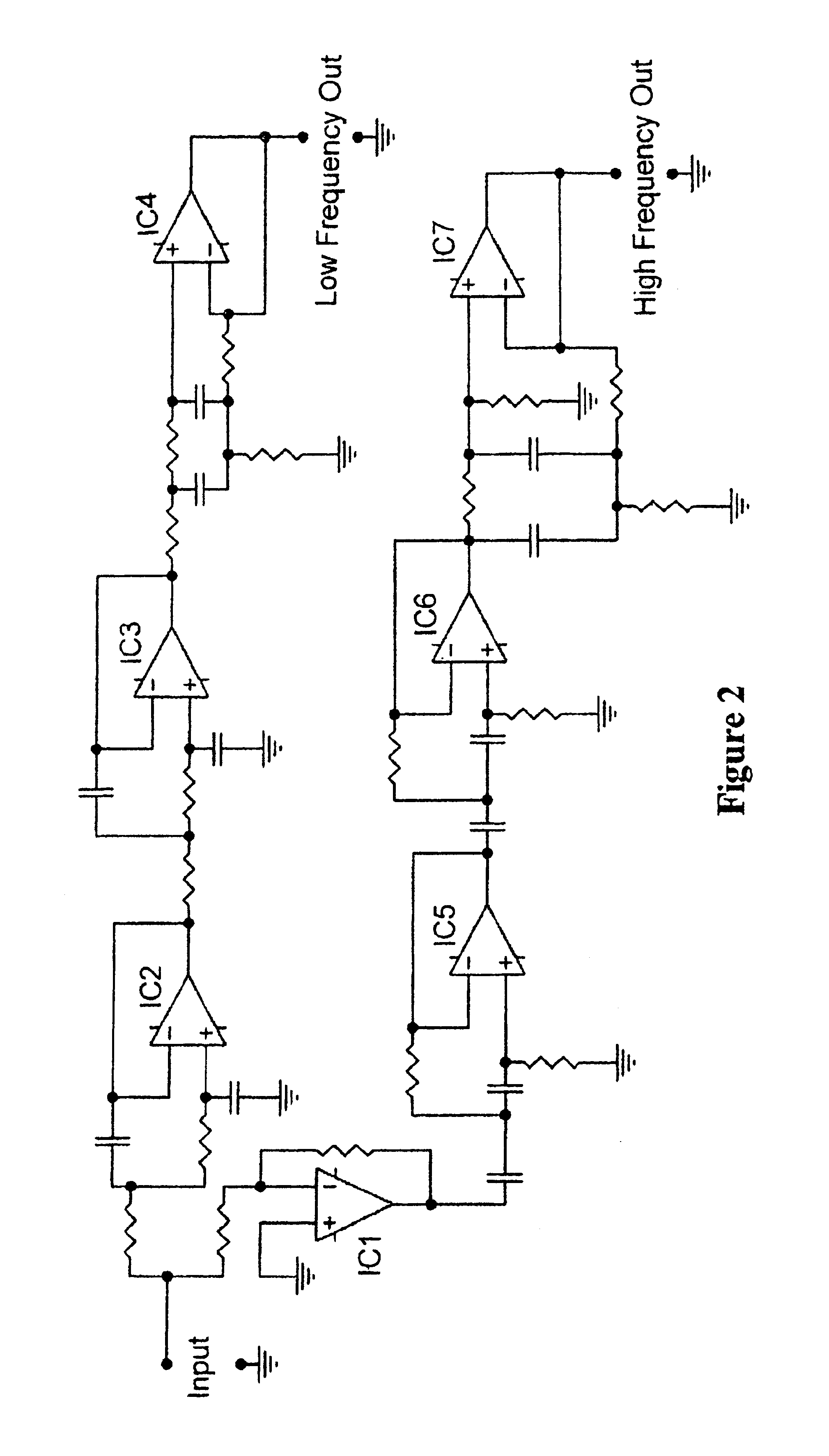
Crossover filter system and method
InactiveUS6854005B2Increased and steep roll offImproved amplitude responseElectric/magnetic computingLoudspeaker signals distributionFilter systemEngineering
A filter system including a low pass filter having a response which rolls off towards a crossover frequency and a high pass filter having a complementary response which rolls off towards the crossover frequency. The responses are arranged such that the combined response of the filters is substantially constant in amplitude at least in the region of the crossover frequency. The response of the low pass filter is defined by a low pass complex transfer function having a first numerator and a first denominator. The response of the high pass filter is defined by a high pass complex transfer function having a second numerator and a second denominator. The desired response is obtained when the second denominator is substantially the same as the first denominator and the sum of the first and second numerators has substantially the same squared modulus as the first or second denominator.
Owner:IMMERSION TECH PROPERTY
Techniques for accurately deriving physiologic parameters of a subject from photoplethysmographic measurements
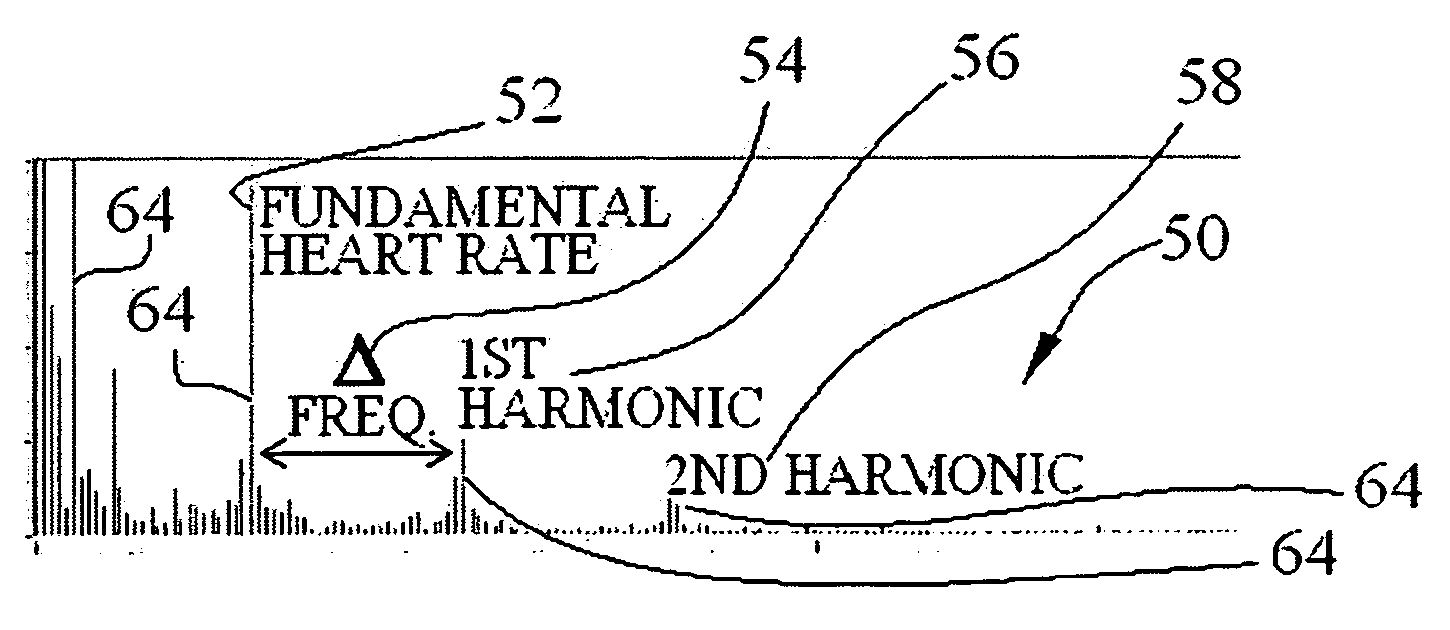
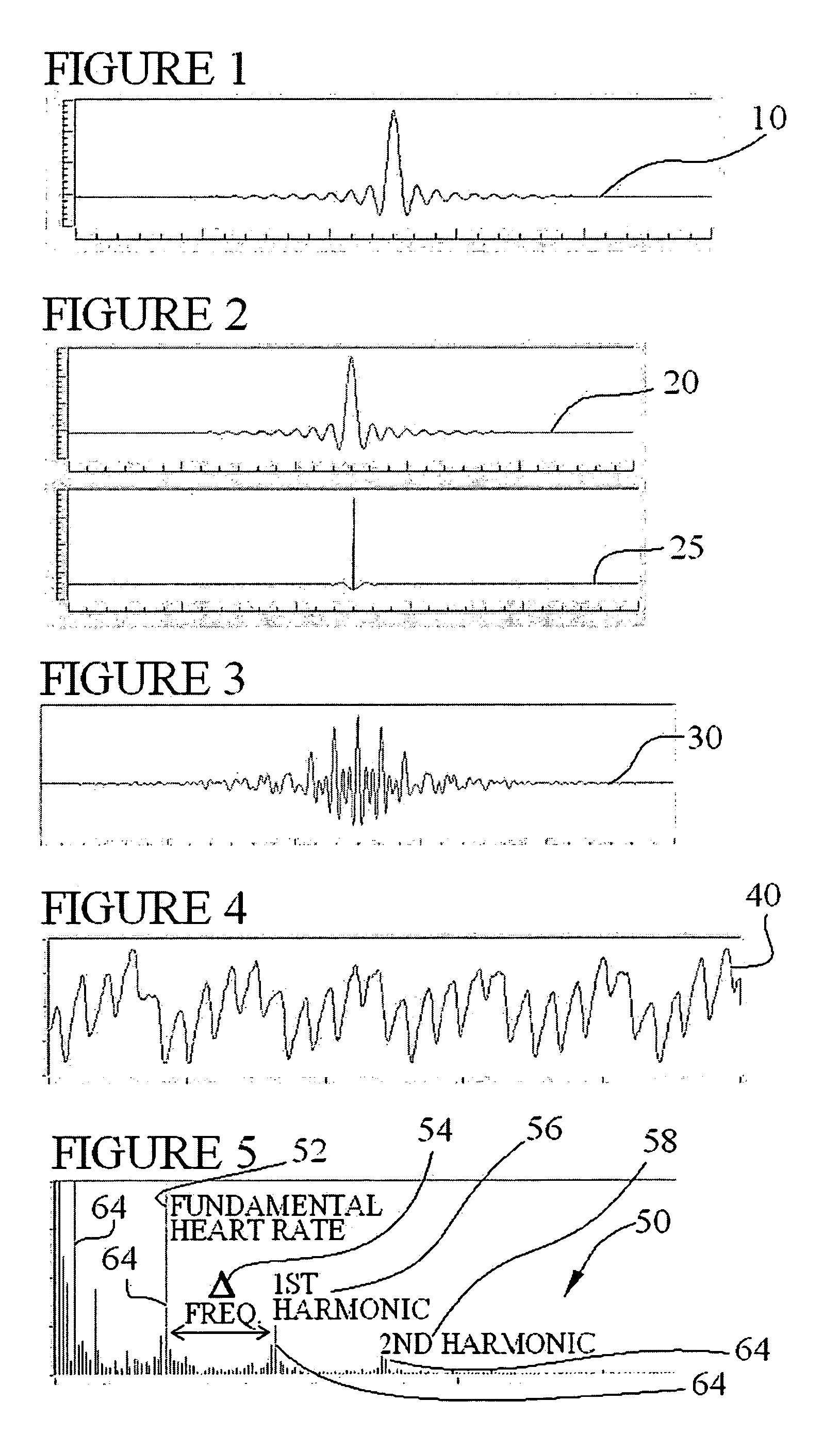
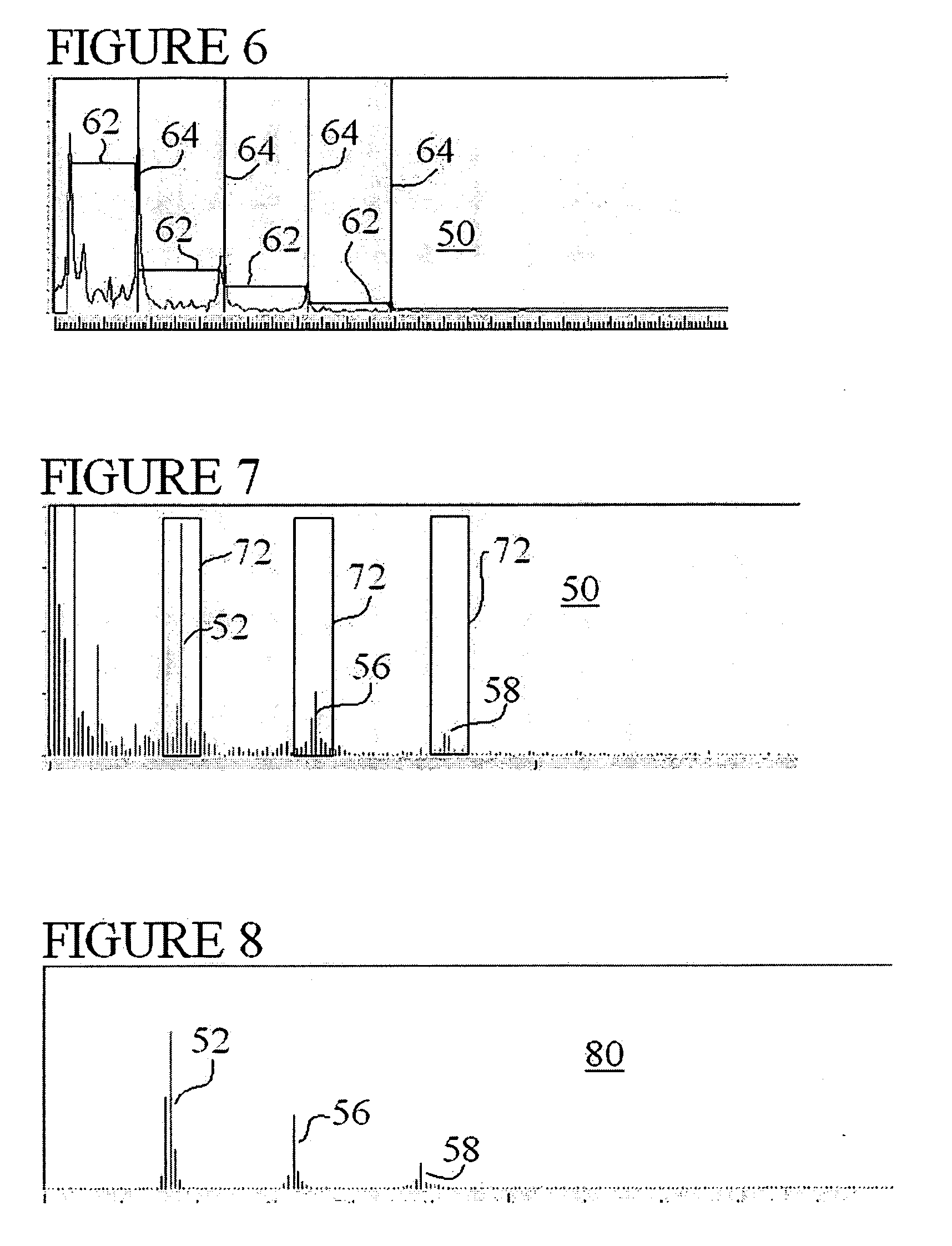
ActiveUS20080167564A1Good for scrollingUndesirable frequency content eliminated and reducedCatheterRespiratory organ evaluationData setPulse oximeters
Several techniques are disclosed for isolating either heart or breath rate data from a photoplethysmograph, which is a time domain signal such as from a pulse oximeter. The techniques involve the use of filtering in the frequency domain, after a Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) has been conducted on a given photoplethysmograph also references as a given set of discrete time-domain data. The filtering may be applied to an identified fundamental frequency and one or more harmonics for heart related parameters. The filter may be truncated to the frequency data set and further applied multiple times to improve roll off. After filtering, an Inverse FFT (IFFT) is used to reconstruct the time-domain signal, except with undesirable frequency content eliminated or reduced. Calculation or measurement of parameters is then conducted on this reconstructed time-domain signal.
Owner:STARR LIFE SCI
Electronic components with reactive filters
ActiveCN103477543AIncrease working frequencyAc-dc conversionField or armature current controlElectricitySwitching frequency
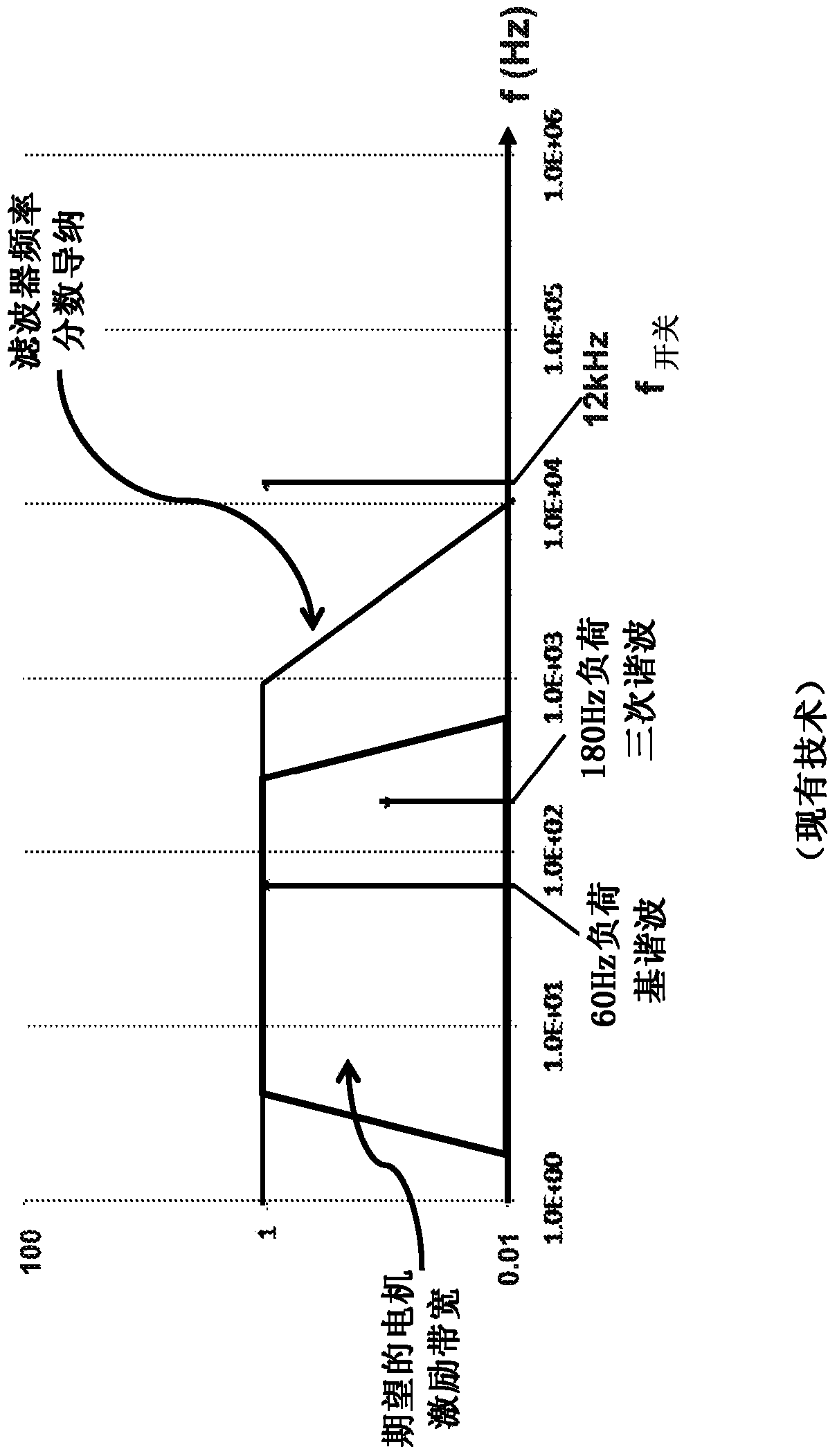
An electronic component comprising a half bridge adapted for operation with an electrical load having an operating frequency is described. The half bridge comprises a first switch and a second switch each having a switching frequency, the first switch and the second switch each including a first terminal, a second terminal, and a control terminal, wherein the first terminal of the first switch and the second terminal of the second switch are both electrically connected to a node. The electronic component further includes a filter having a 3dB roll-off frequency, the 3dB roll-off frequency being less than the switching frequency of the switches but greater than the operating frequency of the electrical load. The first terminal of the filter is electrically coupled to the node, and the 3dB roll-off frequency of the filter is greater than 5 kHz.
Owner:TRANSPHORM INC
Radio frequency filter using intermediate frequency impedance translation
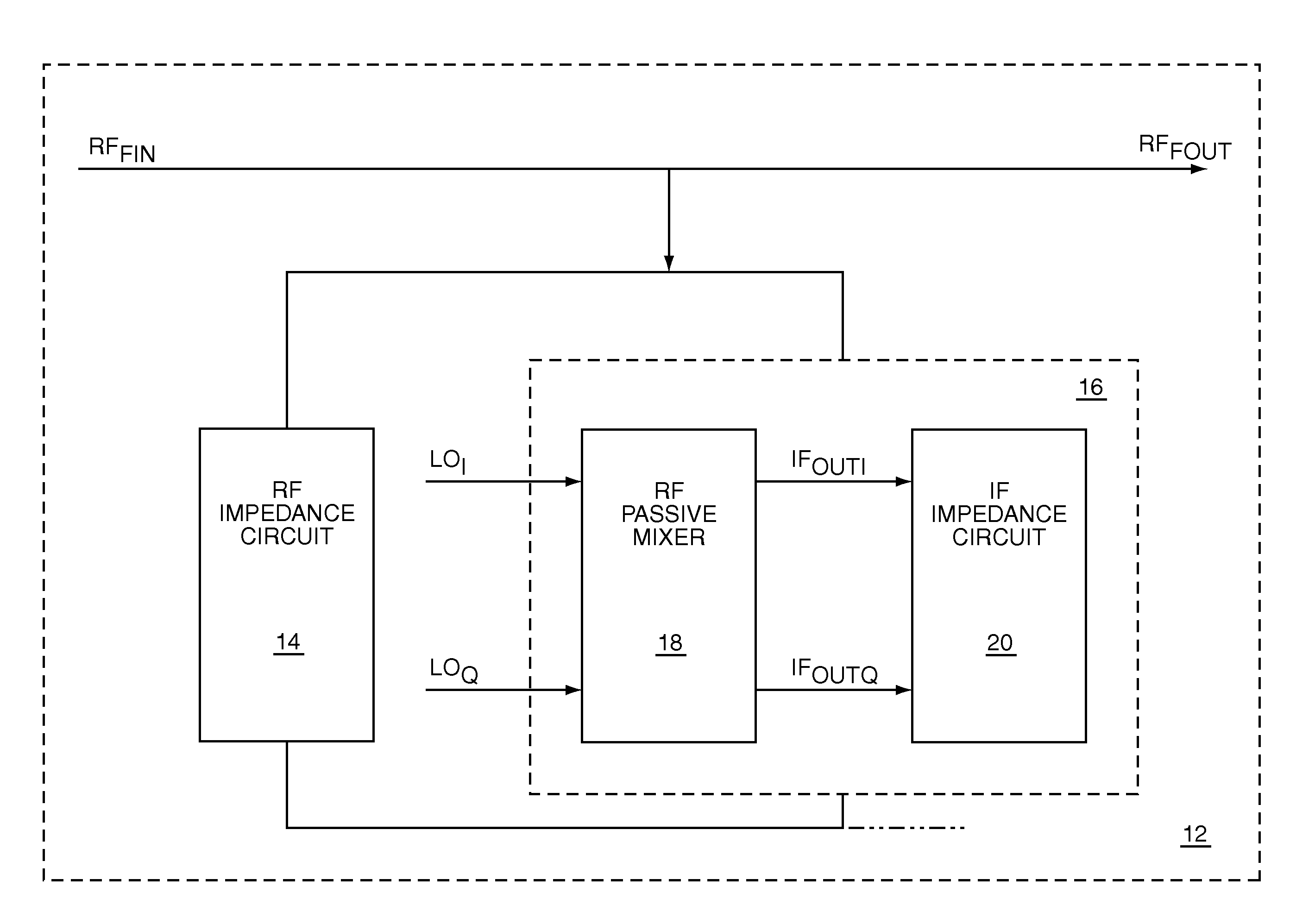
The present invention is an RF filter that translates impedances of an IF circuit to create a filter with an RF center frequency having the high Q roll-off characteristics of an IF filter. The RF filter is self-aligned with the frequency of an RF local oscillator. The RF filter has an impedance divider, which is formed by coupling an RF impedance circuit to a translated IF impedance circuit. The translated IF impedance circuit includes an RF passive mixer and an IF impedance circuit. The mixer translates the impedance of the IF impedance circuit by mixing an RF input signal with an RF local oscillator signal, which determines the RF center frequency. Filtered RF signals may be provided by the impedance divider. Filtered IF signals may be provided by the IF impedance circuit. To effectively translate and preserve the IF impedance characteristics, the IF impedance circuit presents a high impedance at harmonics of the RF local oscillator signal.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
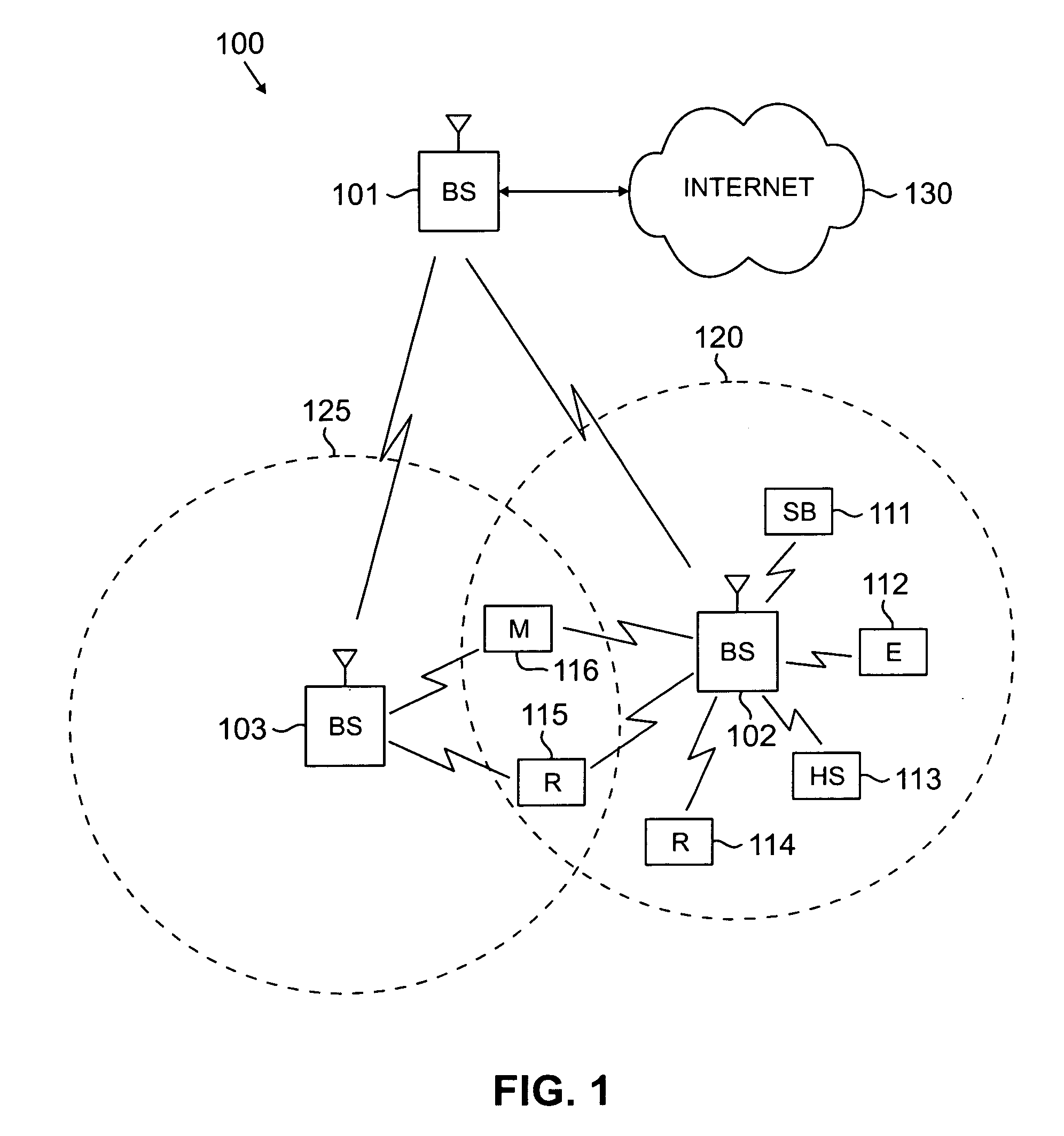
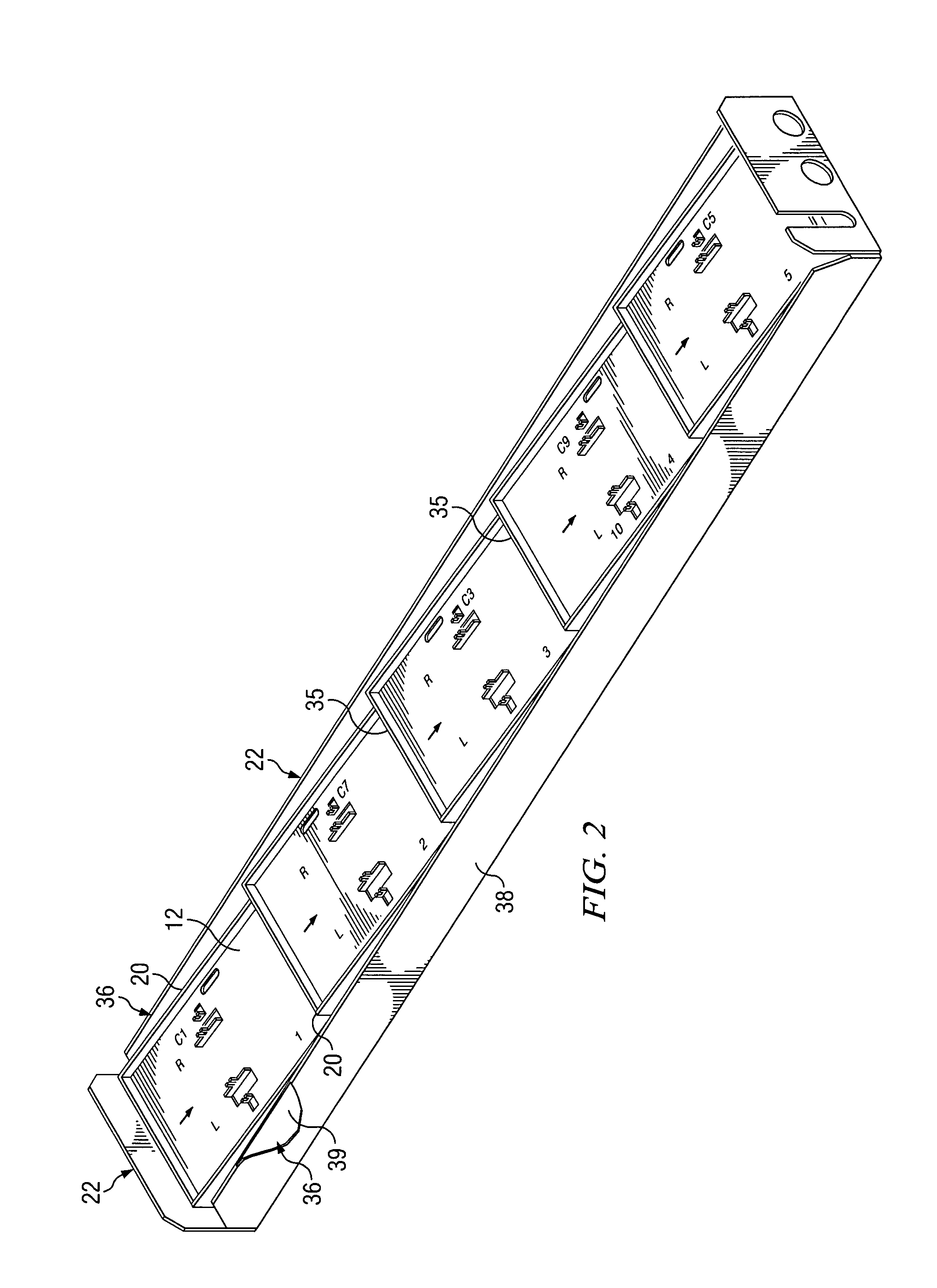
Wideband dual polarized base station antenna offering optimized horizontal beam radiation patterns and variable vertical beam tilt
ActiveUS20050001778A1Improves horizontal plane radiation patternIncreased horizontal pattern front-to-back ratioLogperiodic antennasAntenna supports/mountingsRadiation modeRoll-off
A dual polarized variable beam tilt antenna (10) having a plurality of offset element trays (12) each supporting pairs of dipole elements (14) to orient the dipole element pattern boresight at a downtilt. The maximum squint level of the antenna is a consistent downtilt off of boresight and which is at the midpoint of the antenna tilt range. The antenna provides a high roll-off radiation pattern through the use of Yagi dipole elements configured in this arrangement, having a beam front-to-side ratio exceeding 20 dB, a horizontal beam front-to-back ratio exceeding 40 dB, and is operable over an expanded frequency range.
Owner:COMMSCOPE TECH LLC
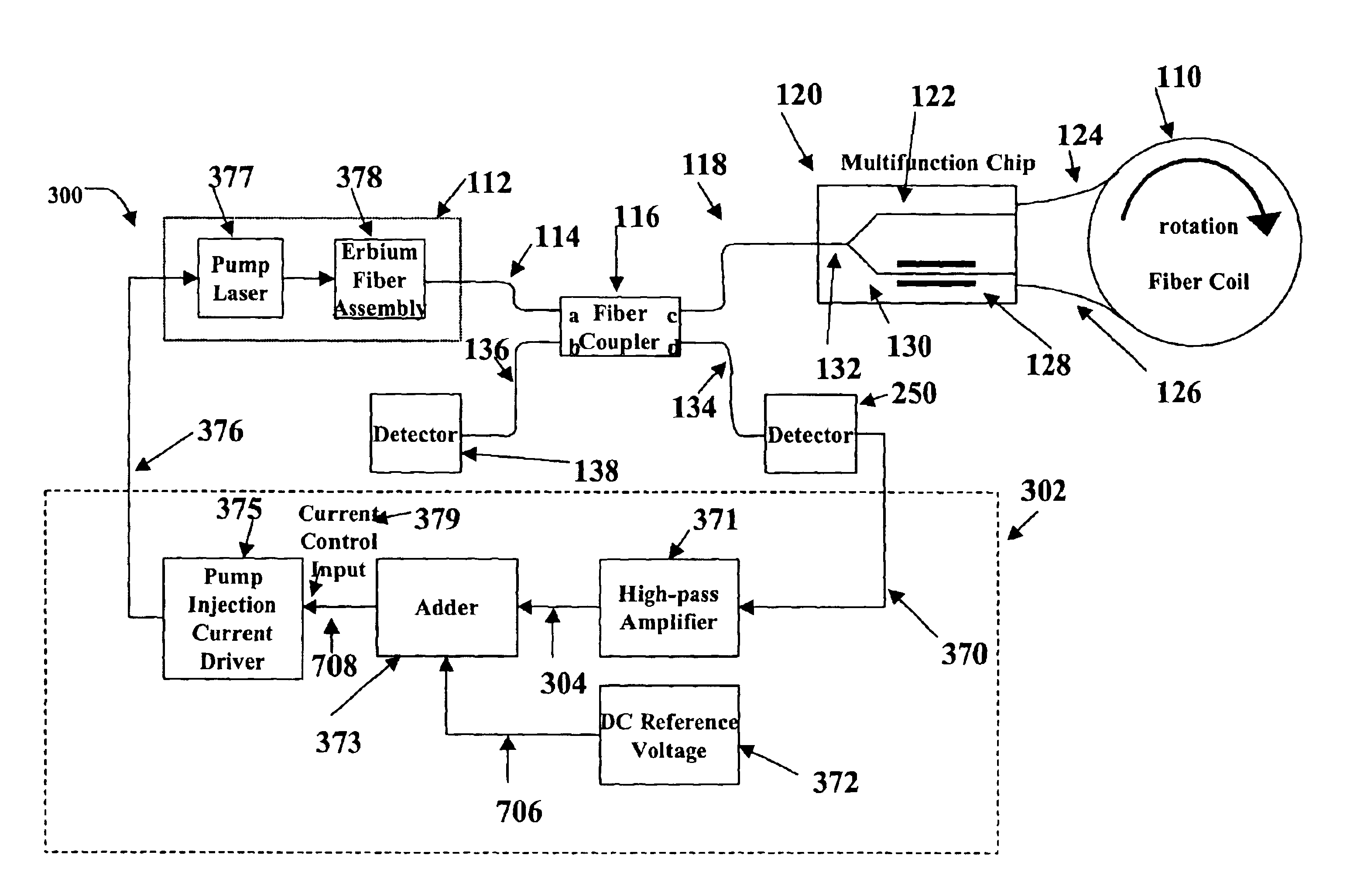
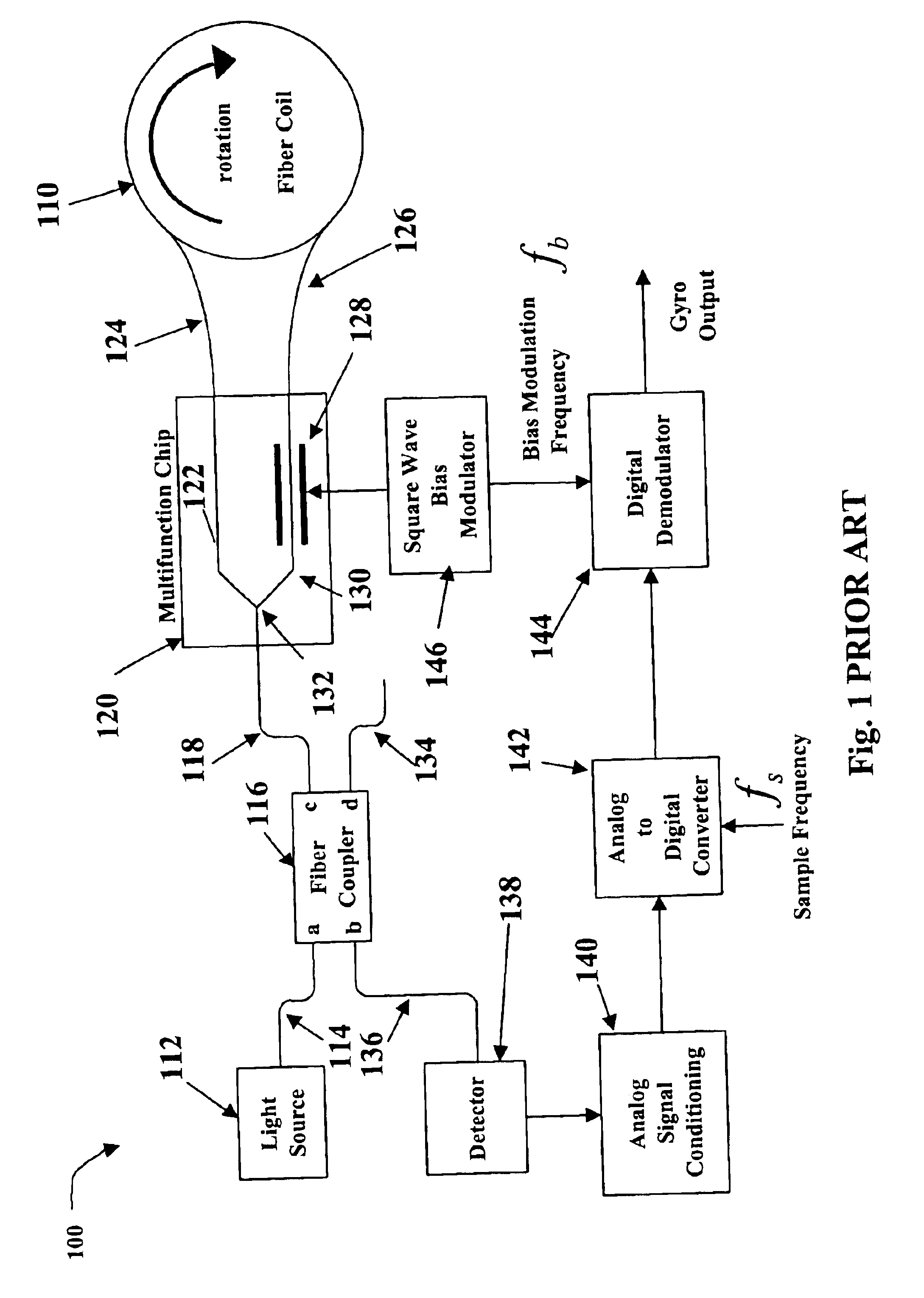
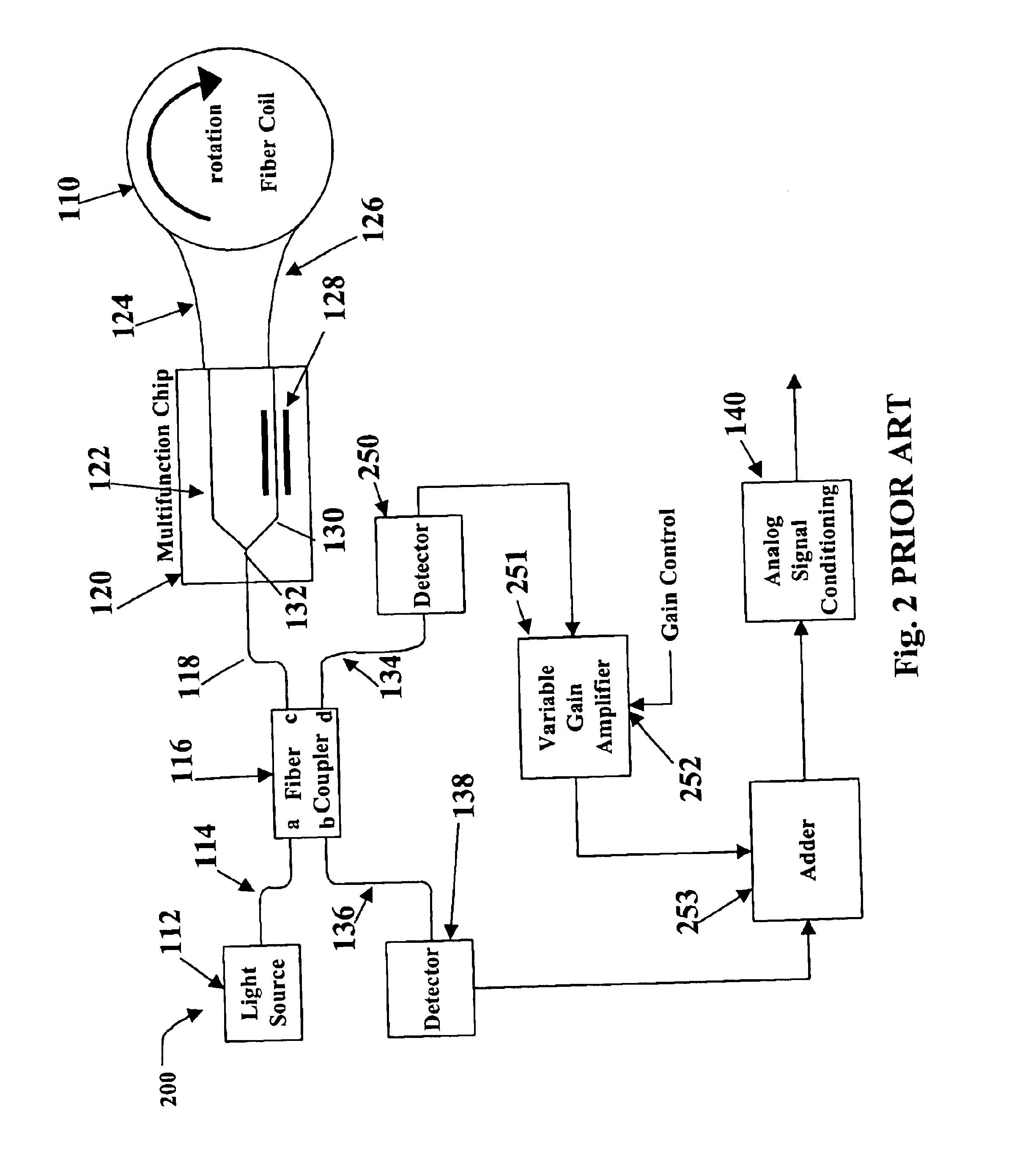
Relative intensity noise controller for fiber light sources
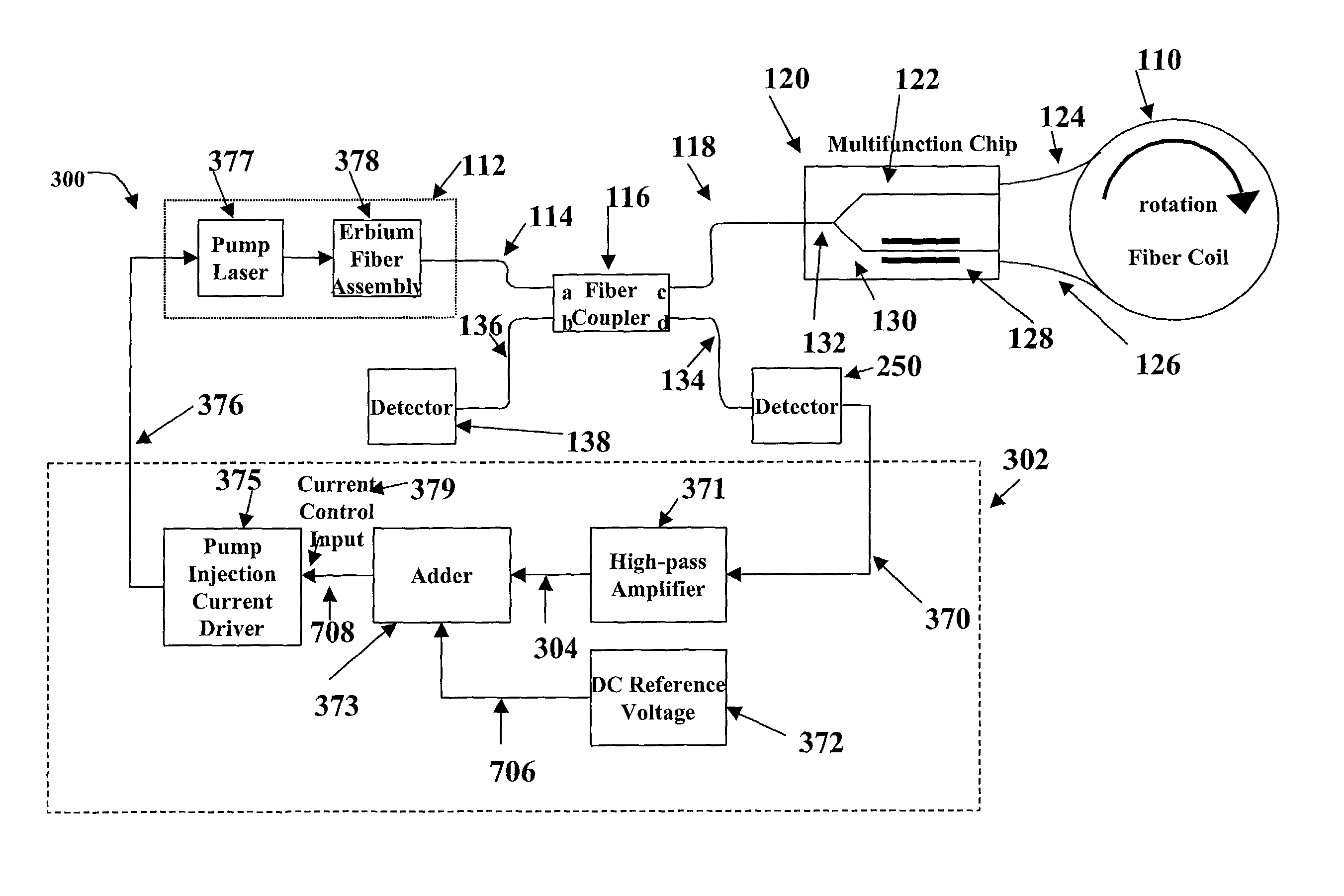
InactiveUS20030128365A1Sagnac effect gyrometersSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsFiberOctave
A system and method is provided which suppresses relative intensity noise in a fiber optic gyroscope by taking advantage of the frequency response of erbium fiber. In operation, the gain provided by the erbium fiber is added to the gain of the other components in the feedback loop to provide for stable loop performance up to about 250 kHz. The frequency response of the erbium fiber of about 3 kHz also provides a 6 db per octave roll-off, which, when used in a negative feedback control loop for controlling the current flowing to the gyroscope light source, allows for a relative intensity noise control loop with a bandwidth much greater than 3 kHz; this may be used in high performance gyroscope applications.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
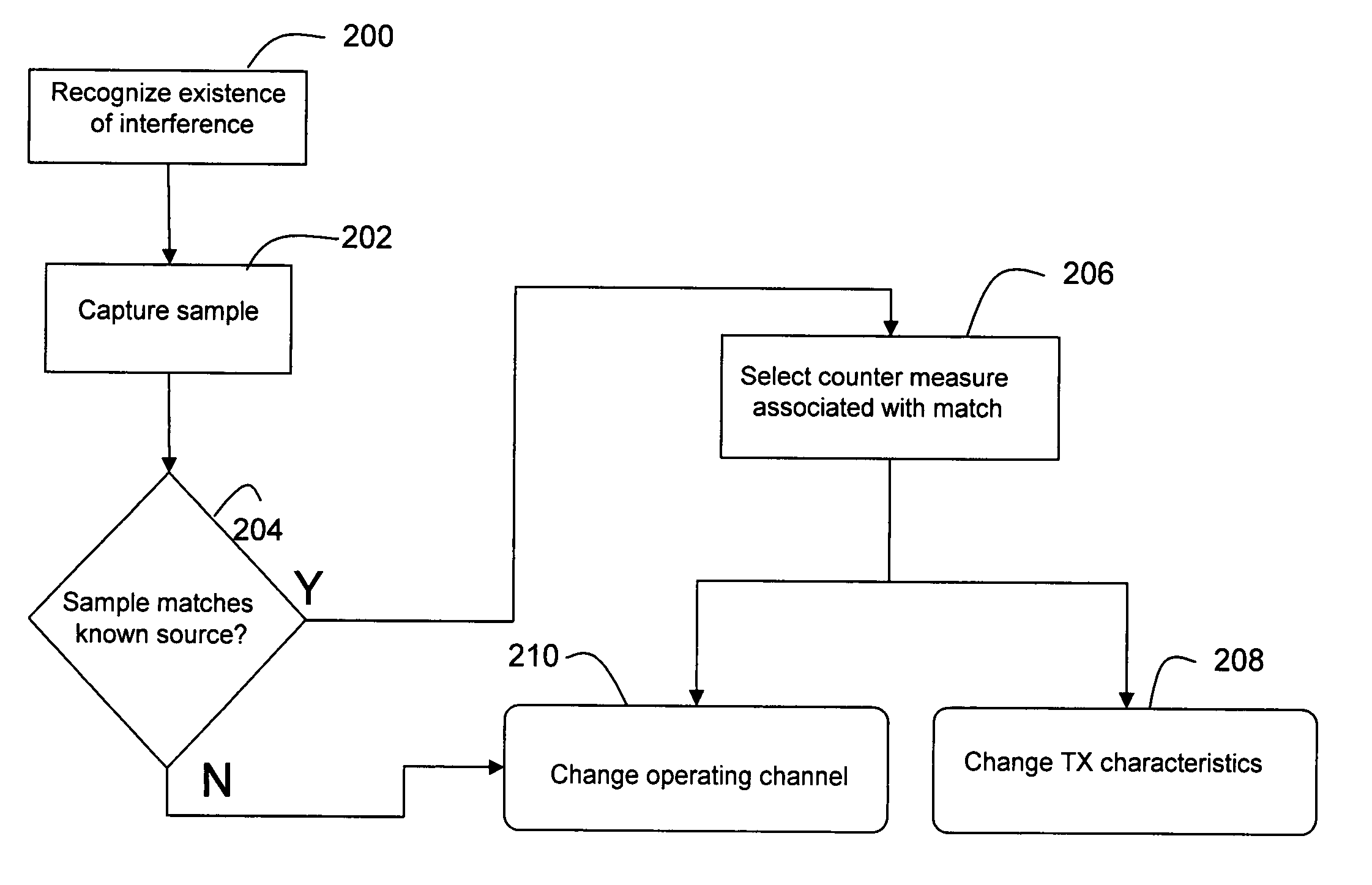
Remedial actions for interference in wireless LANs
InactiveUS20060171326A1Facilitate communicationIncrease powerPower managementFrequency-division multiplex detailsPulse periodTime duration
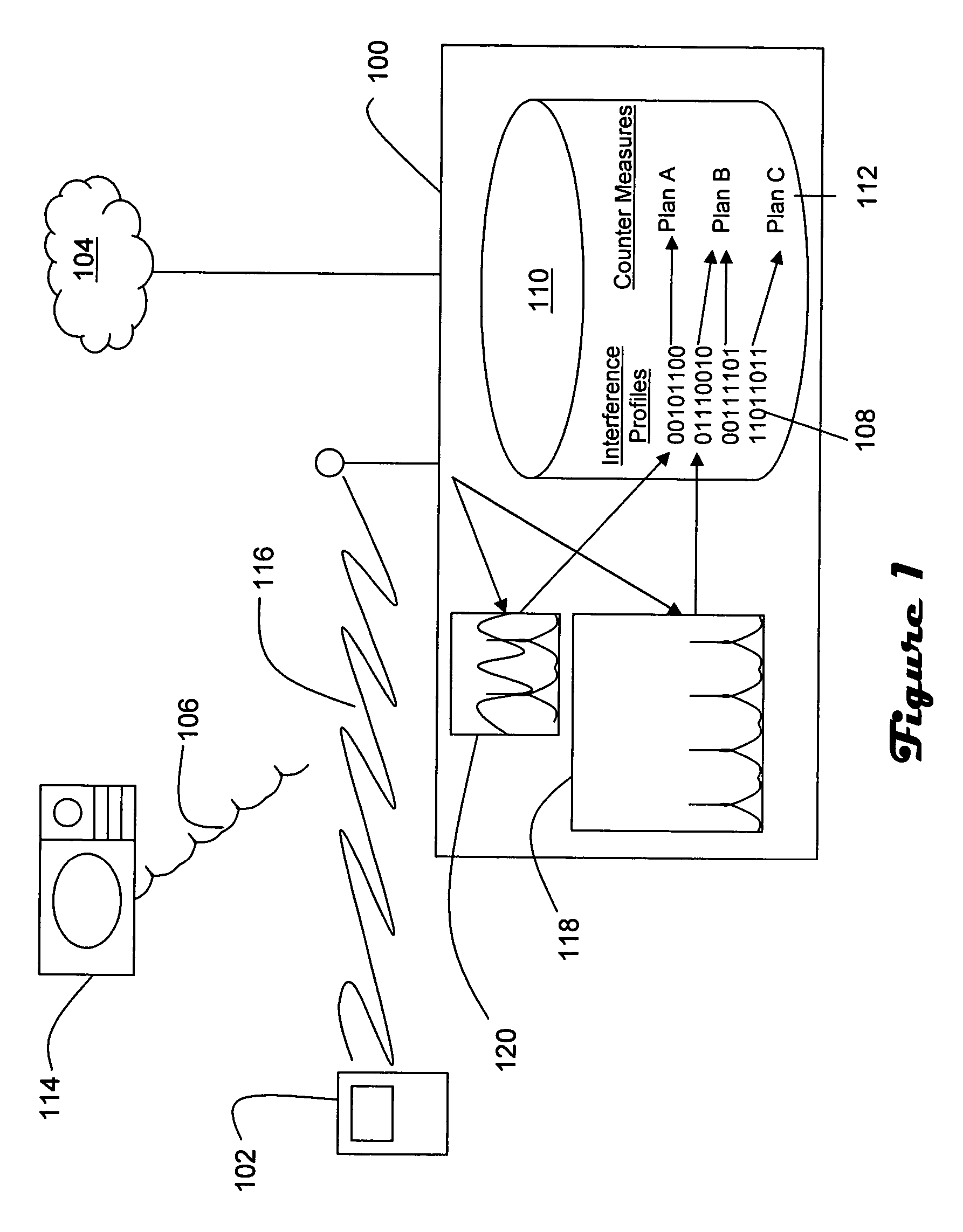
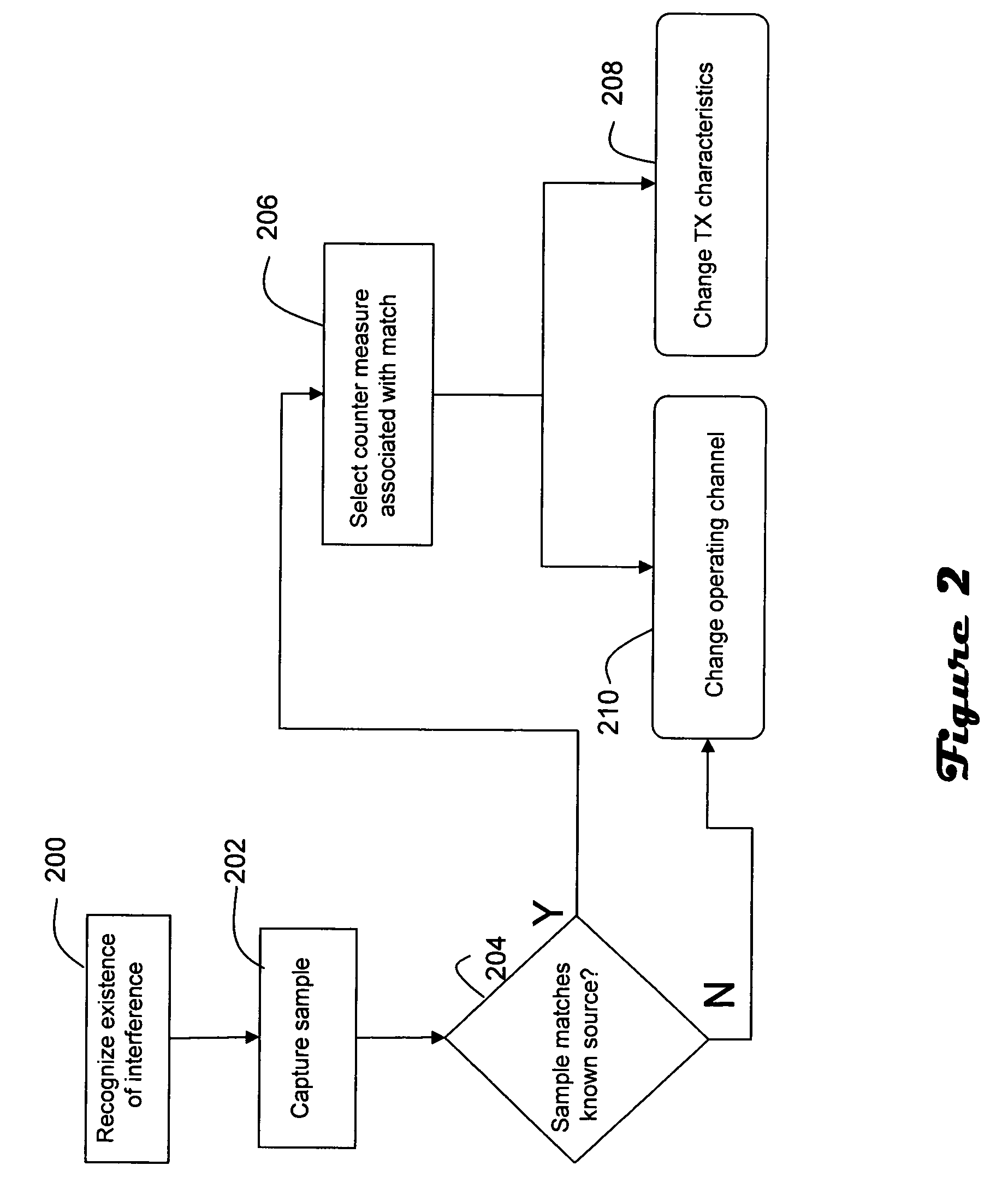
In a wireless network having an access point and at least one wireless end device, the access point is operable to differentiate between normal communications and interference from another device in order to capture a sample of the interference, determine whether the interference originates from a known type of device, and prompt remedial actions such as moving communications to a distant channel, increasing transmission power, changing data rate, and packet fragmentation based on whether the interference originates from a known type of device. Interference pulse duration may be used to at least initially narrow the possible sources of interference. Pulse period may be employed to differentiate between interference sources which exhibit similar pulse duration. If pulse duration and period are not sufficient to identify the interference source then other characteristics may be examined, such as pulse waveform, roll off and period in relation to local power frequency. In the case of microwave interference it is generally best to move to a distant channel. Increased transmission power and packet fragmentation can be used to maintain communications while scanning for a new channel.
Owner:PICCATA FUND LIABILITY
Band-pass high-order analog filter backed hybrid receiver equalization
InactiveUS20080069191A1Multiple-port networksDelay line applicationsTransceiverDifferential signaling
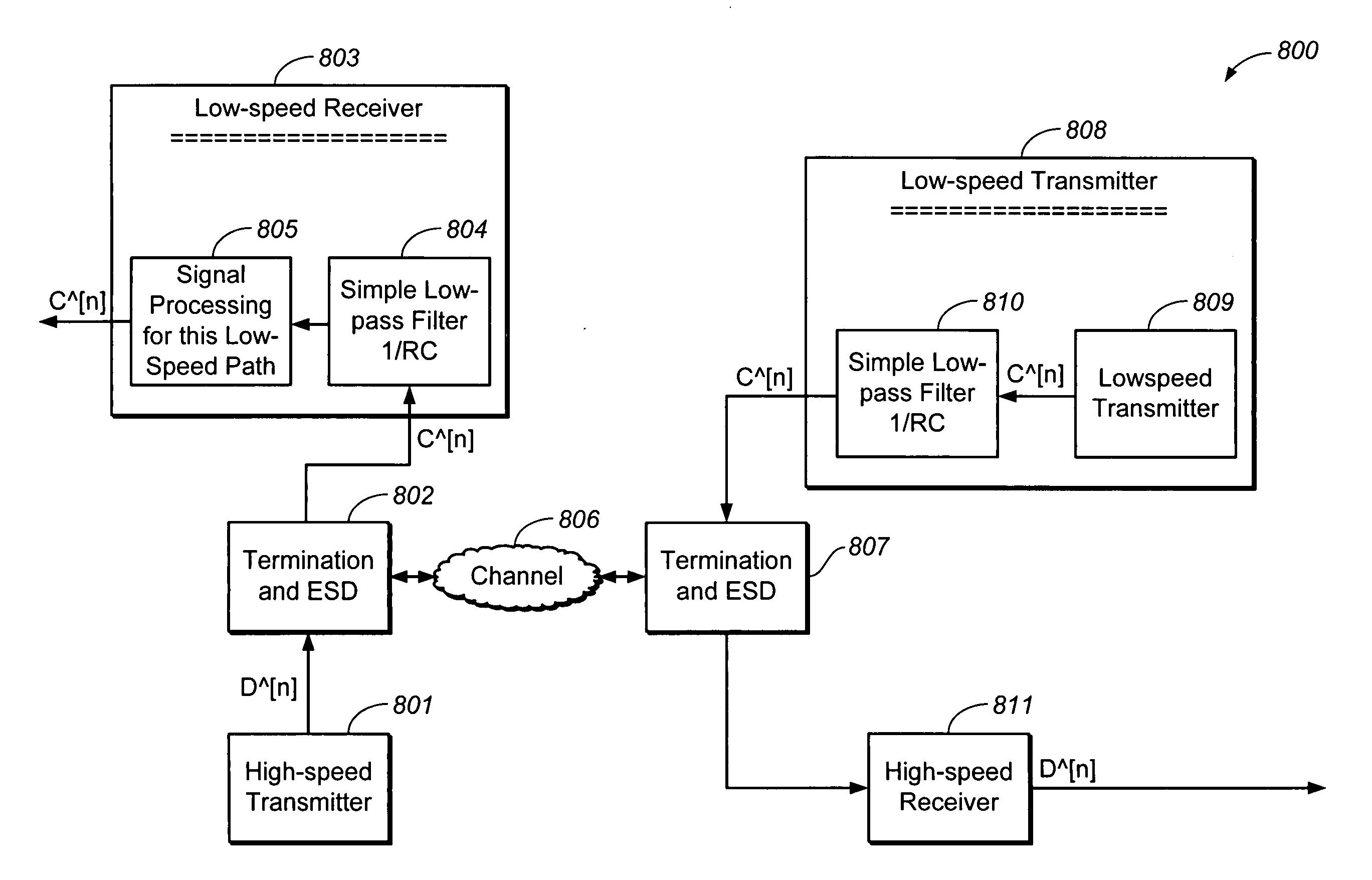
A system and a method for channel equalization are provided. A linear equalizer using a continuous-time linear equalization and a decision feedback equalizer using a discrete-time decision feedback equalization are integrated together from a hybrid receiver equalizer. The continuous-time linear equalization scheme and the discrete-time decision feedback equalization scheme are blended using a joint adaptation algorithm to form an equalization scheme for inter-symbol interference cancellation in the hybrid receiver equalizer. The hybrid receiver equalizer controls crosstalk while maintaining signal bandwidth and linearity of a signal by the high-order high frequency roll-off of the linear equalizer used. Using this configuration, the hybrid receiver equalizer eliminates the need for adaptive bandwidth controller used in conventional low-pass receiver equalization schemes. The hybrid receiver equalizer can be used in receivers for dual-speed simultaneous transmission on the same physical link. The hybrid receiver equalizer can also be used in receivers for simultaneous forward and back-channel transmission using differential-signaling in multi-Gbps transceivers.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
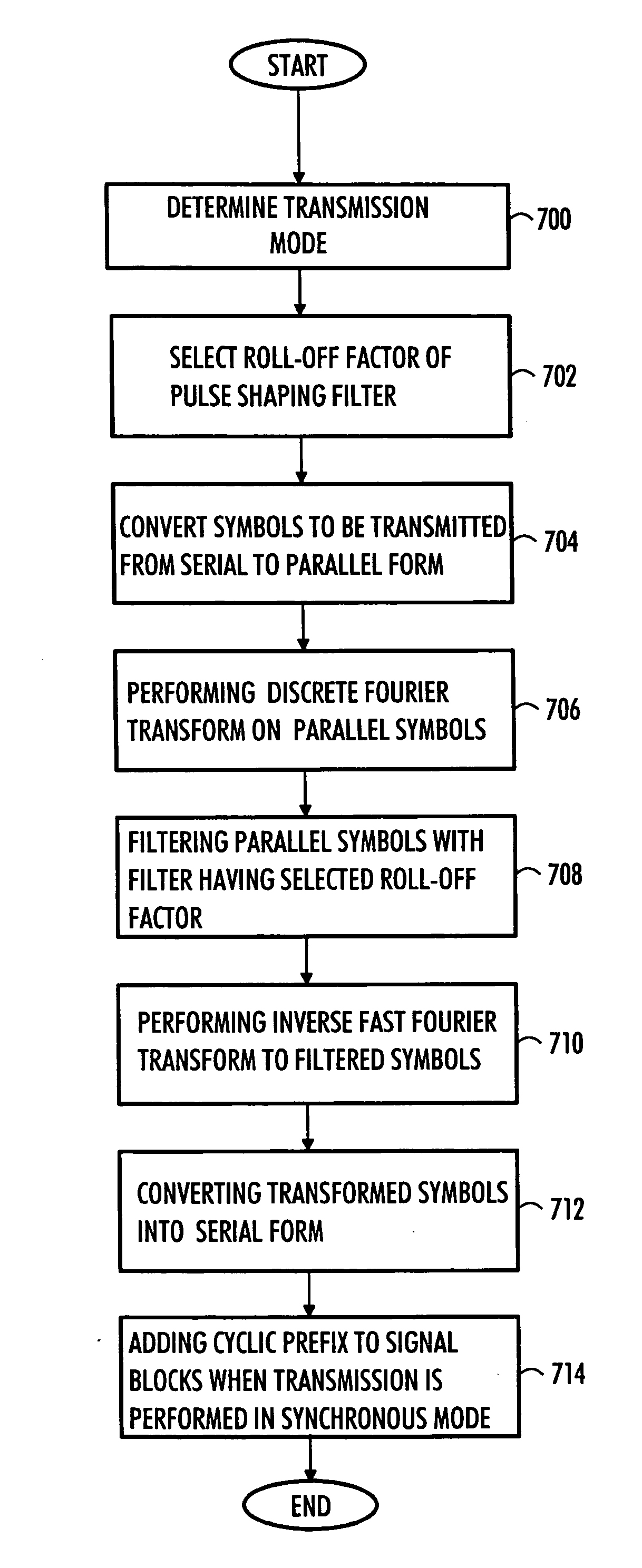
Controlling filter in connection with cyclic transmission format
A method for controlling a filter, a transmitter, a receiver and an apparatus are provided. The apparatus comprises a filter configured to filter signal blocks to be transmitted in a cyclic transmission form and a controller configured to select a roll-off factor of the filter for a signal block depending on whether transmission is performed in a synchronous or an asynchronous mode.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
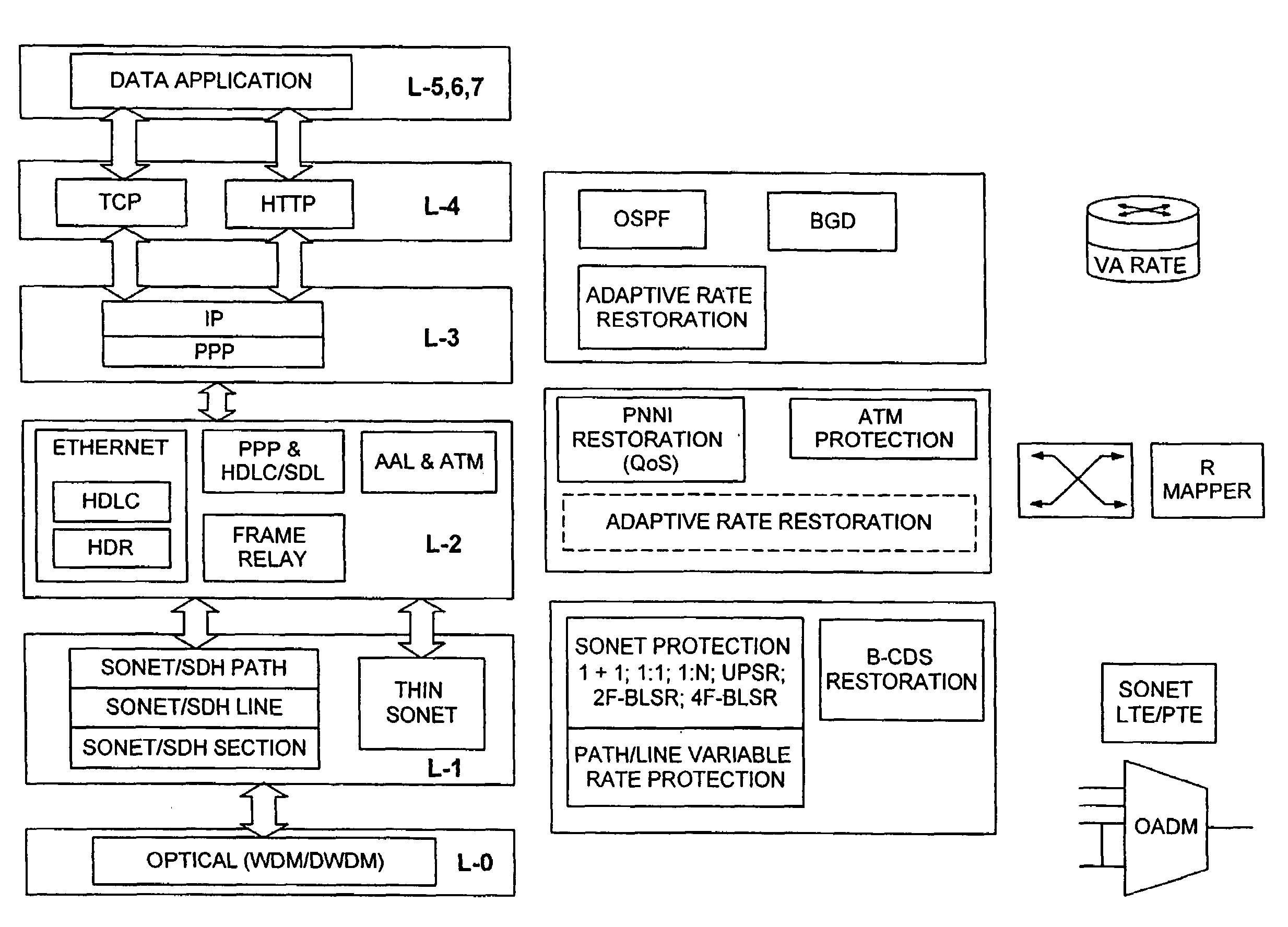
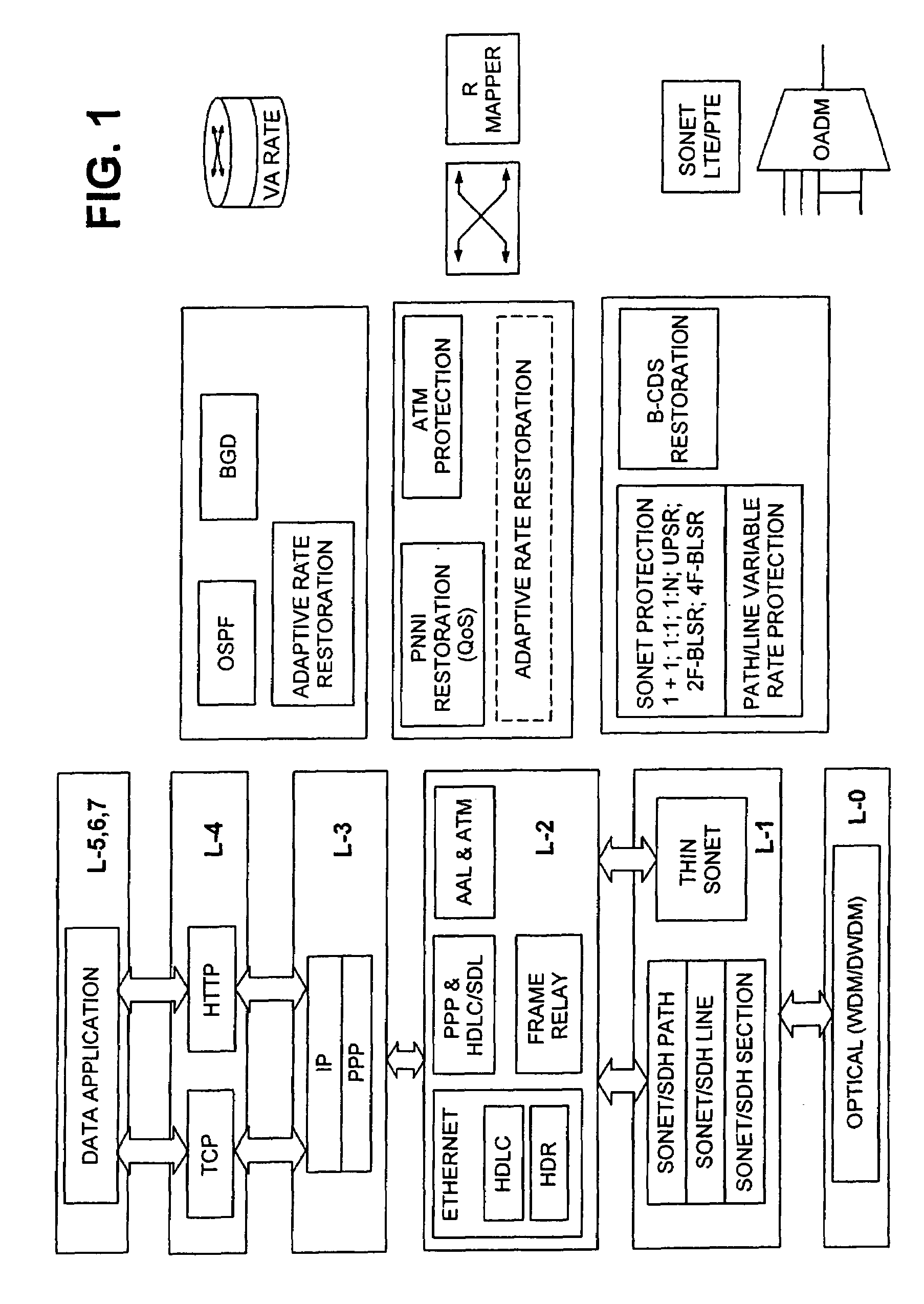
Adaptive rate traffic recovery mechanism for communication networks
A traffic recovery mechanism for communication networks uses a layer-1 adaptive rate protection scheme that compliments layer-3 restoration mechanisms. The protection scheme allocates less bandwidth to the traffic during a protection switch than during the normal operating conditions. This scheme allows the network to roll off more gracefully from the perspective of the applications routed through it. Rate adaptation is effected by a new interface between the data equipment and the transport network, which switches information transfer rate between two or more predetermined levels.
Owner:CIENA
Relative intensity noise controller with maximum gain at frequencies at or above the bias modulation frequency or with second order feedback for fiber light sources
InactiveUS6765678B2Speed measurement using gyroscopic effectsSagnac effect gyrometersFiberNegative feedback
A system and method is provided which suppresses relative intensity noise in a fiber optic gyroscope by taking advantage of the frequency response of erbium fiber. In operation, the gain provided by the erbium fiber is added to the gain of the other components in the feedback loop to provide for stable loop performance up to about 250 kHz. The frequency response of the erbium fiber of about 3 kHz also provides a 6 db per octave roll-off, which, when used in a negative feedback control loop for controlling the current flowing to the gyroscope light source, allows for a relative intensity noise control loop with a bandwidth much greater than 3 kHz; this may be used in high performance gyroscope applications.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
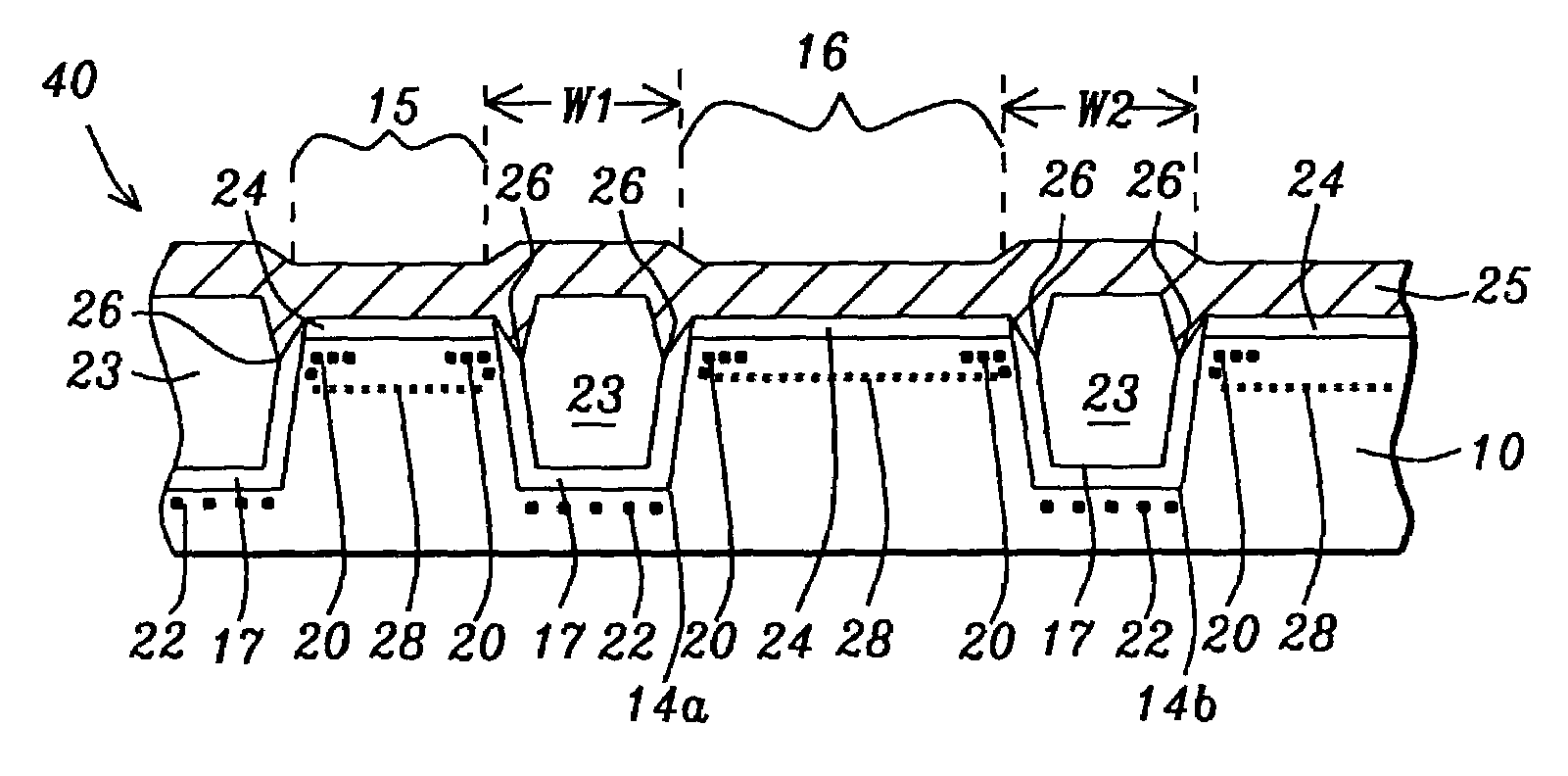
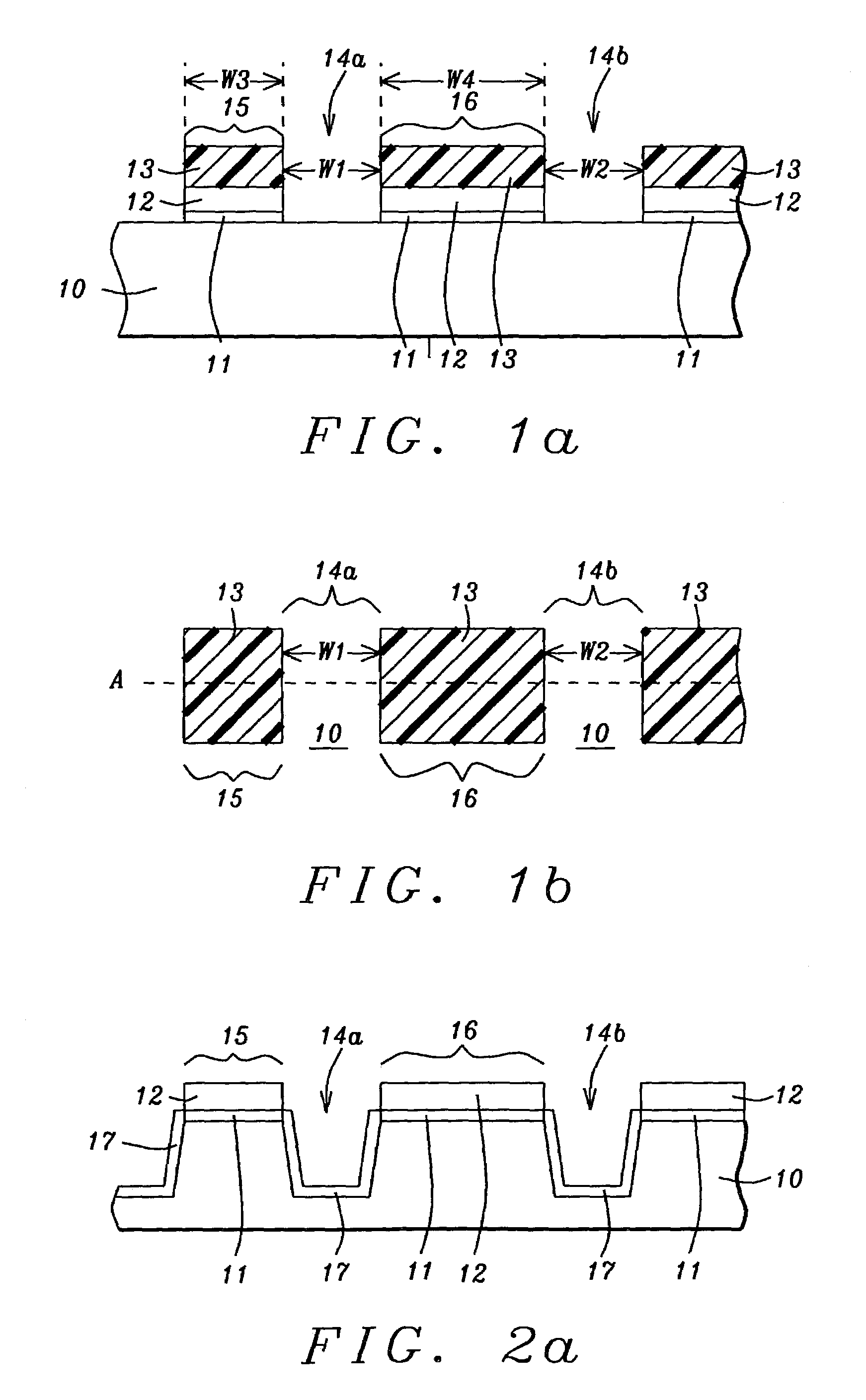
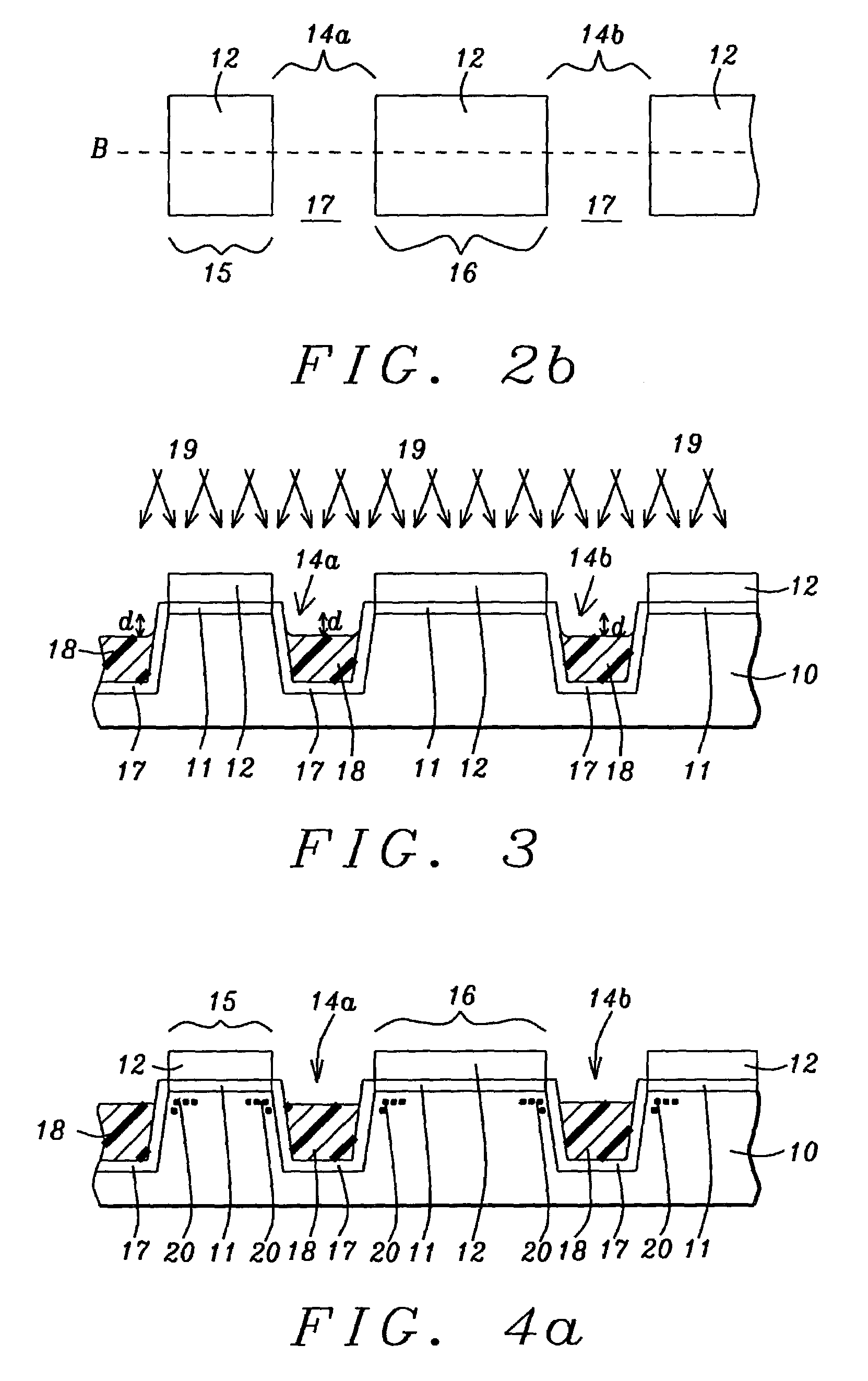
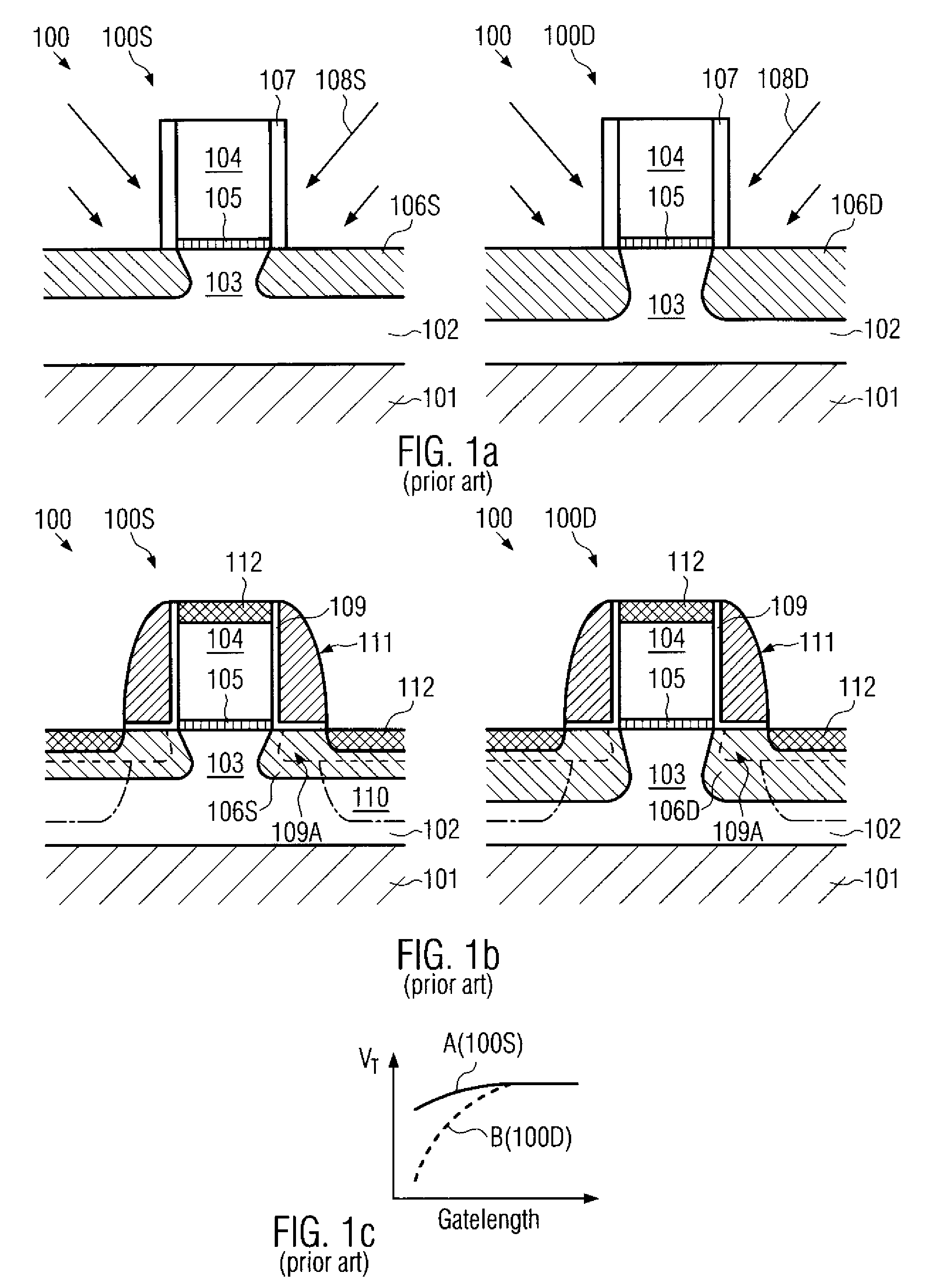
Narrow width effect improvement with photoresist plug process and STI corner ion implantation
InactiveUS7071515B2Improving the reverse narrow width effectIncrease widthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesGate dielectricIndium
A method to reduce the inverse narrow width effect in NMOS transistors is described. An oxide liner is deposited in a shallow trench that is formed to isolate active areas in a substrate. A photoresist plug is formed in the shallow trench and is recessed below the top of the substrate to expose the top portion of the oxide liner. An angled indium implant through the oxide liner into the substrate is then performed. The plug is removed and an insulator is deposited to fill the trenches. After planarization and wet etch steps, formation of a gate dielectric layer and a patterned gate layer, the NMOS transistor exhibits an improved Vt roll-off of 40 to 45 mVolts for both long and short channels. The improvement is achieved with no degradation in junction or isolation performance. The indium implant dose and angle may be varied to provide flexibility to the process.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Transmission circuit
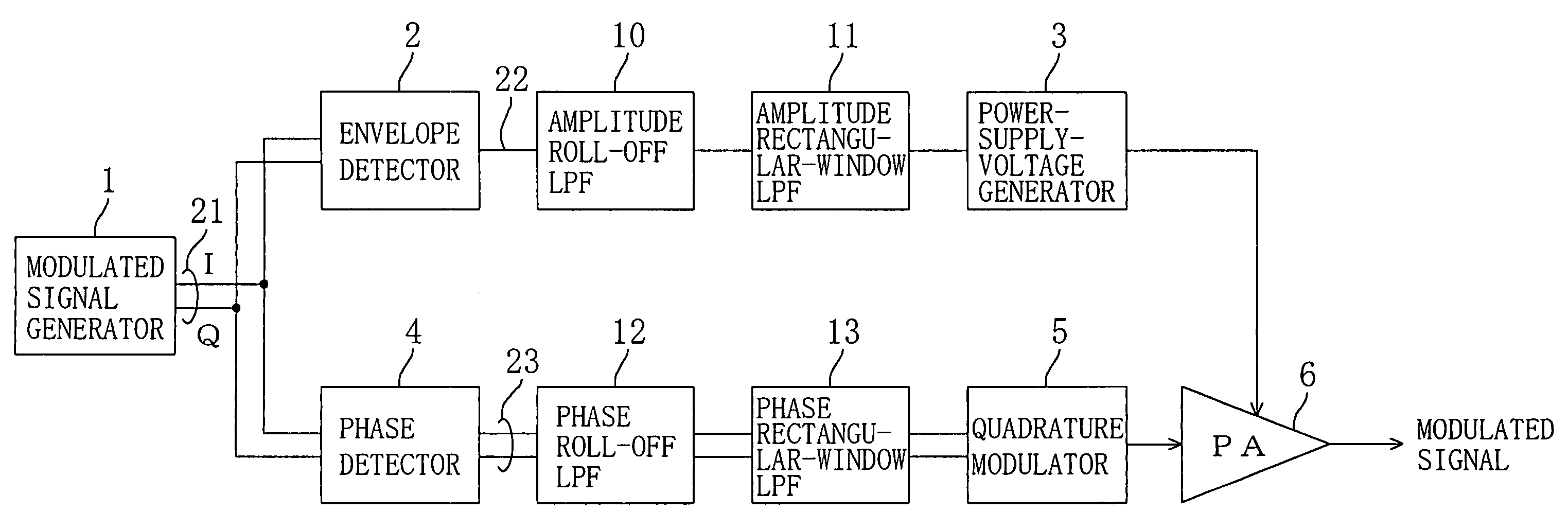
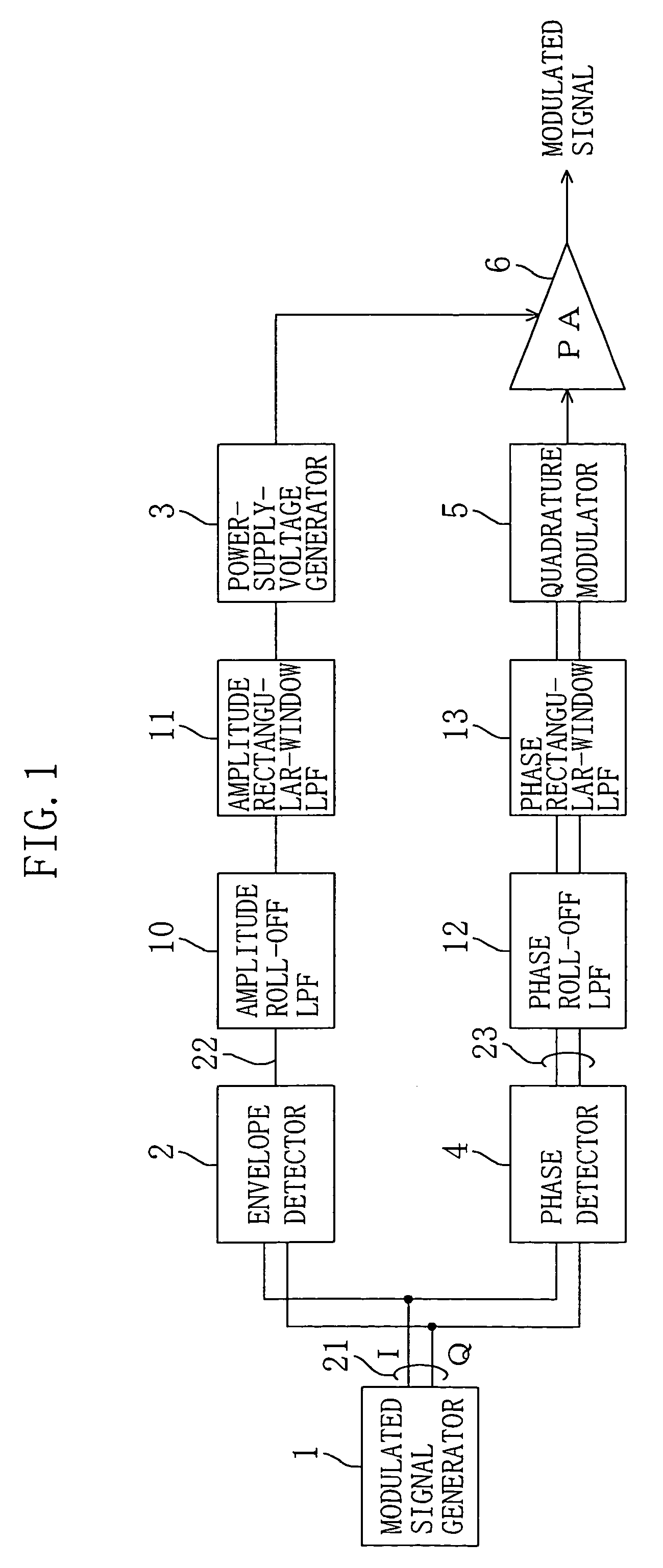
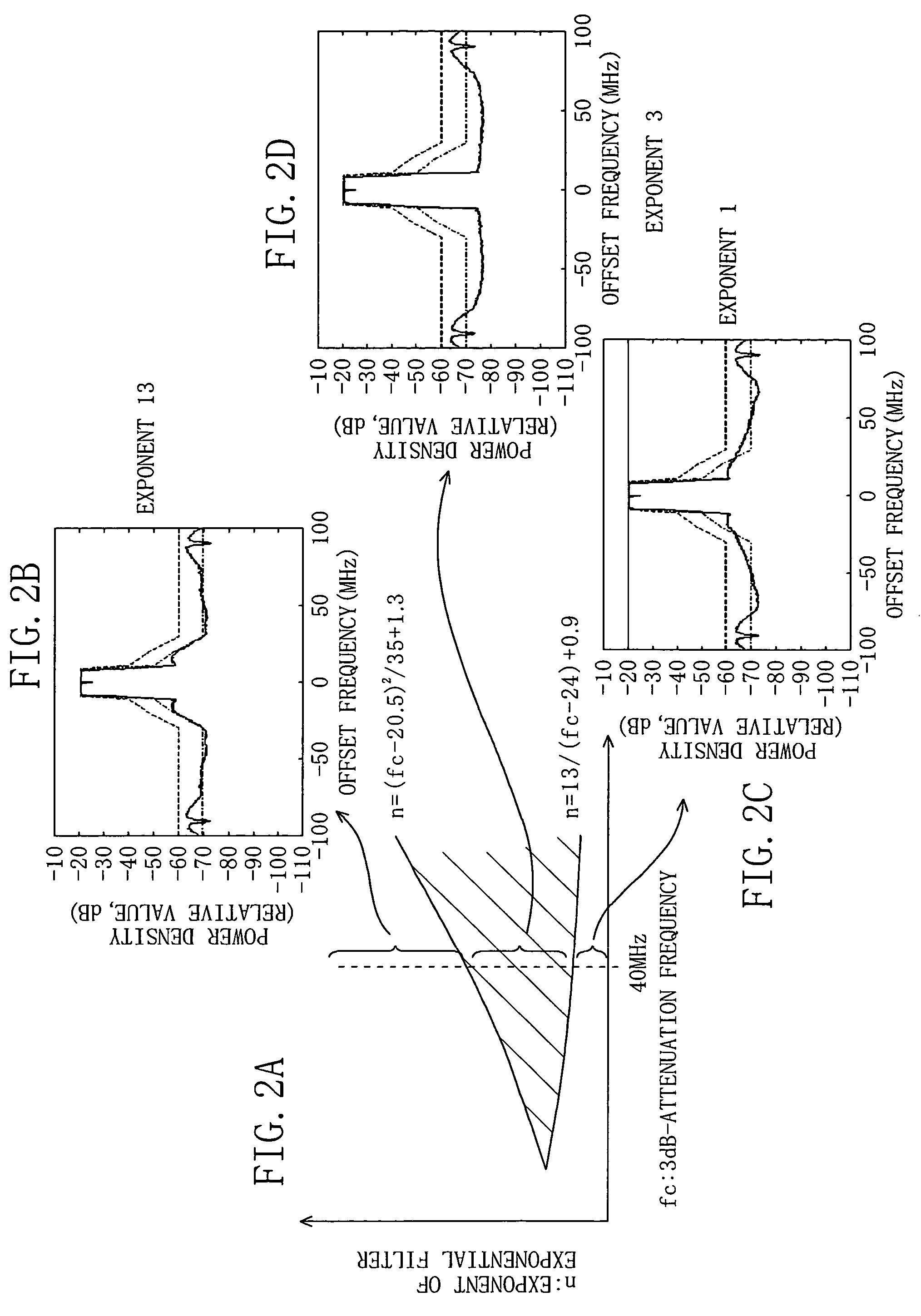
ActiveUS7092683B2Suppress deterioration of spectrumEasy to operateResonant long antennasModulation with suppressed carrierPhase detectorSignal generator
A transmission circuit includes: a modulated signal generator for outputting a modulated signal; an envelope detector for outputting an amplitude modulated voltage; an amplitude roll-off LPF for attenuating the amplitude modulated voltage by using a damping property represented by an exponential function in which an argument is exponentially proportional to a frequency; a power-supply-voltage generator for generating a power supply voltage in accordance with an amplitude value of the amplitude modulated voltage; a phase detector for outputting a phase modulated signal; a phase roll-off LPF for attenuating the phase modulated signal by using a damping property represented by an exponential function in which an argument is exponentially proportional to an offset frequency with respect to a center frequency; and an RF power amplifier.
Owner:GK BRIDGE 1
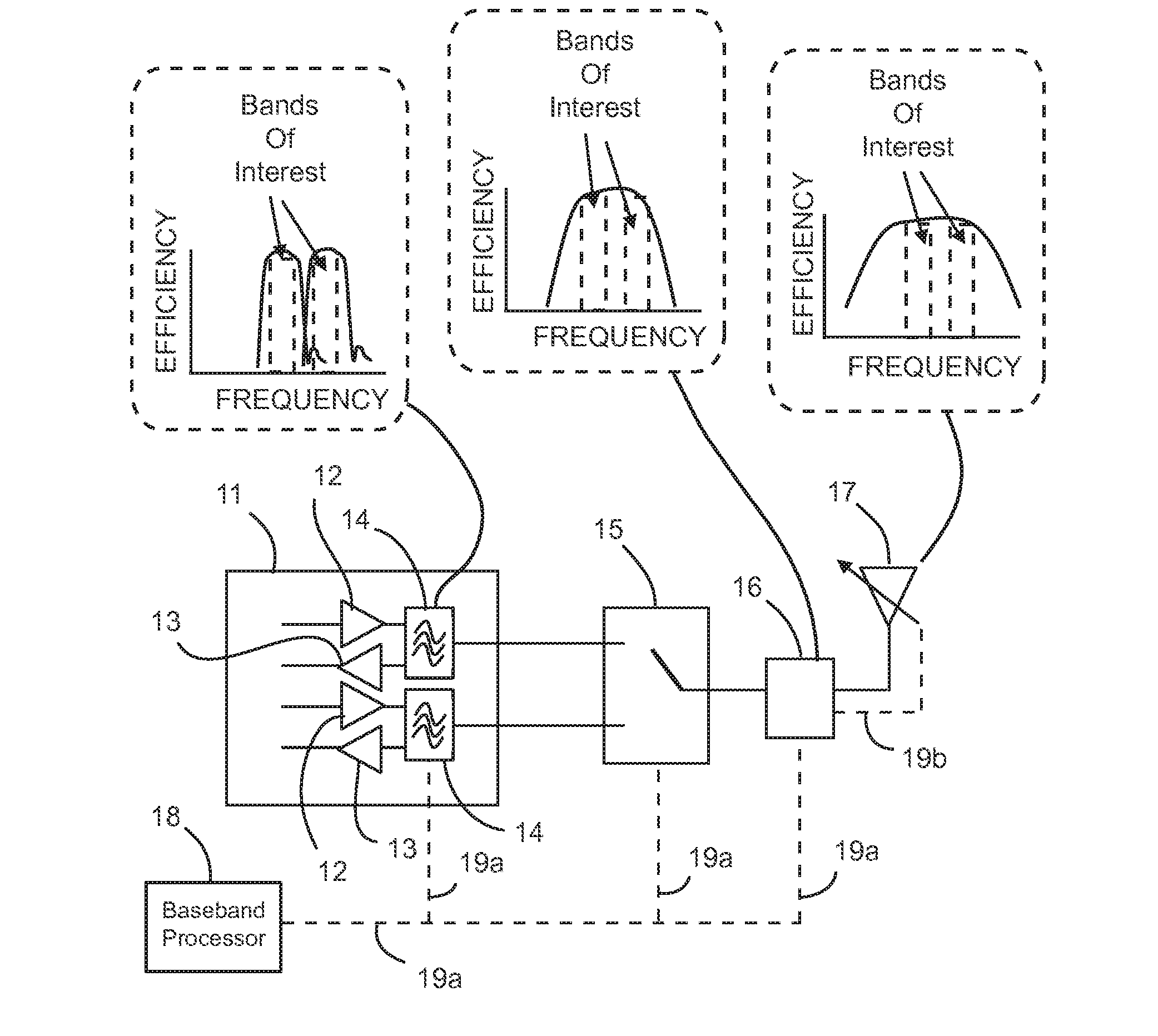
Apparatus and method for selecting modulation and filter roll-off to meet power and bandwidth requirements
ActiveUS20070218942A1Maximize power efficiencyMaintaining required bandwidth efficiencyEnergy efficient ICTFrequency-division multiplex detailsFrequency spectrumRoll-off
A base station for use in a wireless network that communicates according to a multi-carrier protocol. The base station receives an uplink signal transmitted by a first subscriber station. The first subscriber station transmits using a configurable spectral shaping filter and a selectable modulation order. The base station determines a required bandwidth efficiency associated with the first subscriber station and, in response to the determination, selects a first modulation order and a first filter parameter to be used by the first subscriber station. Advantageously, the base station selects the first modulation order and the first filter parameter in order to maximize a power efficiency of the first subscriber station while maintaining the required bandwidth efficiency.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Directed dipole antenna
InactiveUS7358922B2Optimized horizontal plane radiation patternImproved roll-offAntenna supports/mountingsIndividually energised antenna arraysDipole antennaRoll-off
A dual polarized variable beam tilt antenna having a superior Sector Power Ratio (SPR). The antenna may have slant 45 degree dipole radiating elements including directors, and may be disposed on a plurality of tilted element trays to orient an antenna boresight downtilt. The directors may be disposed above or about the respective dipole radiating elements. The antenna has a beam front-to-side ratio exceeding 20 dB, a horizontal beam front-to-back ratio exceeding 40 dB, a high-roll off, and is operable over an expanded frequency range.
Owner:COMMSCOPE TECH LLC
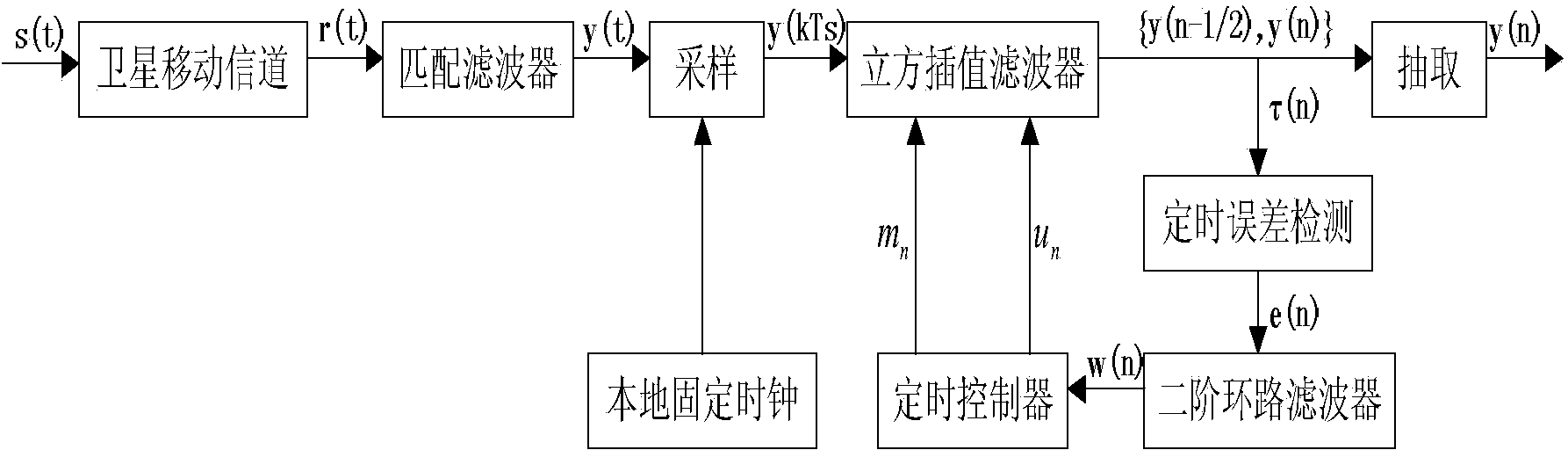
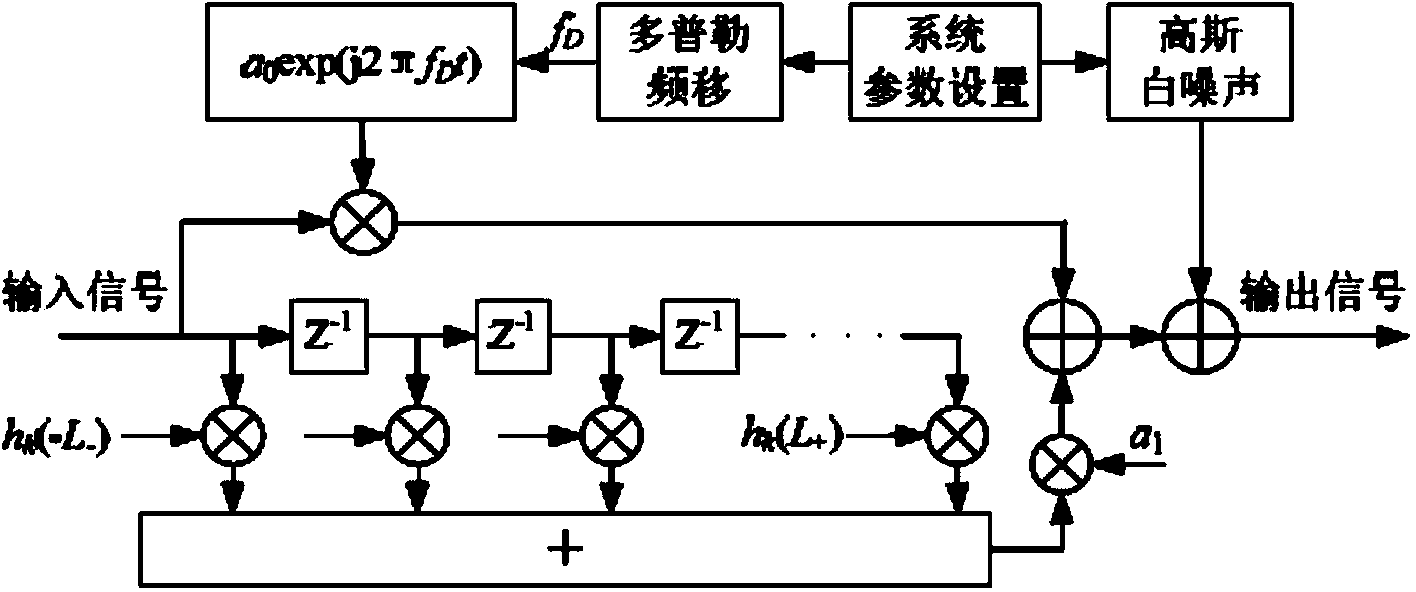
Satellite communication timing synchronization error detection method based on full-digital receiving
ActiveCN103457680AEliminate timing error skewEasy to lockReceivers monitoringSynchronising arrangementTime informationCoded element
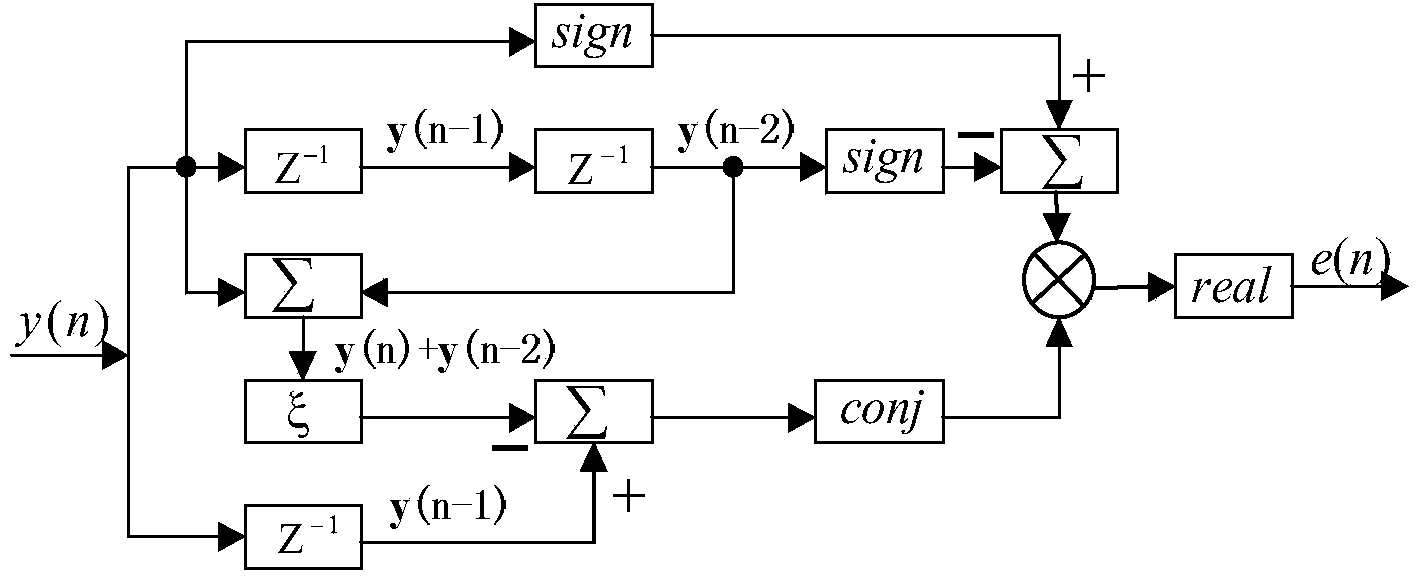
Disclosed is a satellite communication timing synchronization error detection method based on full-digital receiving. In view of wide application of a Gardner algorithm in a timing synchronization loop and the limitation of the Gardner algorithm to band-limited signals, when polarity jump happens to two adjacent symbols, after two adjacent code elements are utilized for cosine roll-off forming filtering, the relation between samples of two best sampling points and the sample of a middle point of the two best sampling points is utilized, the effect of different adjacent symbols to the middle value is firstly taken into consideration and the effect value is calculated according to the minimum mean-square error criterion, and is then eliminated; when polarity jump does not happen to the adjacent symbols, how to reduce self noise generated by the situation that timing information can not be acquired is taken into consideration. A sign function sign (.) in an E-Gardner algorithm is utilized to solve the problem. Under the satellite channel environment, the enhancing algorithm is simple in structure, under the condition of a small roll-off coefficient, the performance of QPSK modulating signal clock capturing and error detection is improved, and the satellite communication timing synchronization error detection method based on full-digital receiving can effectively eliminate self-noise and reduce system resource consumption.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
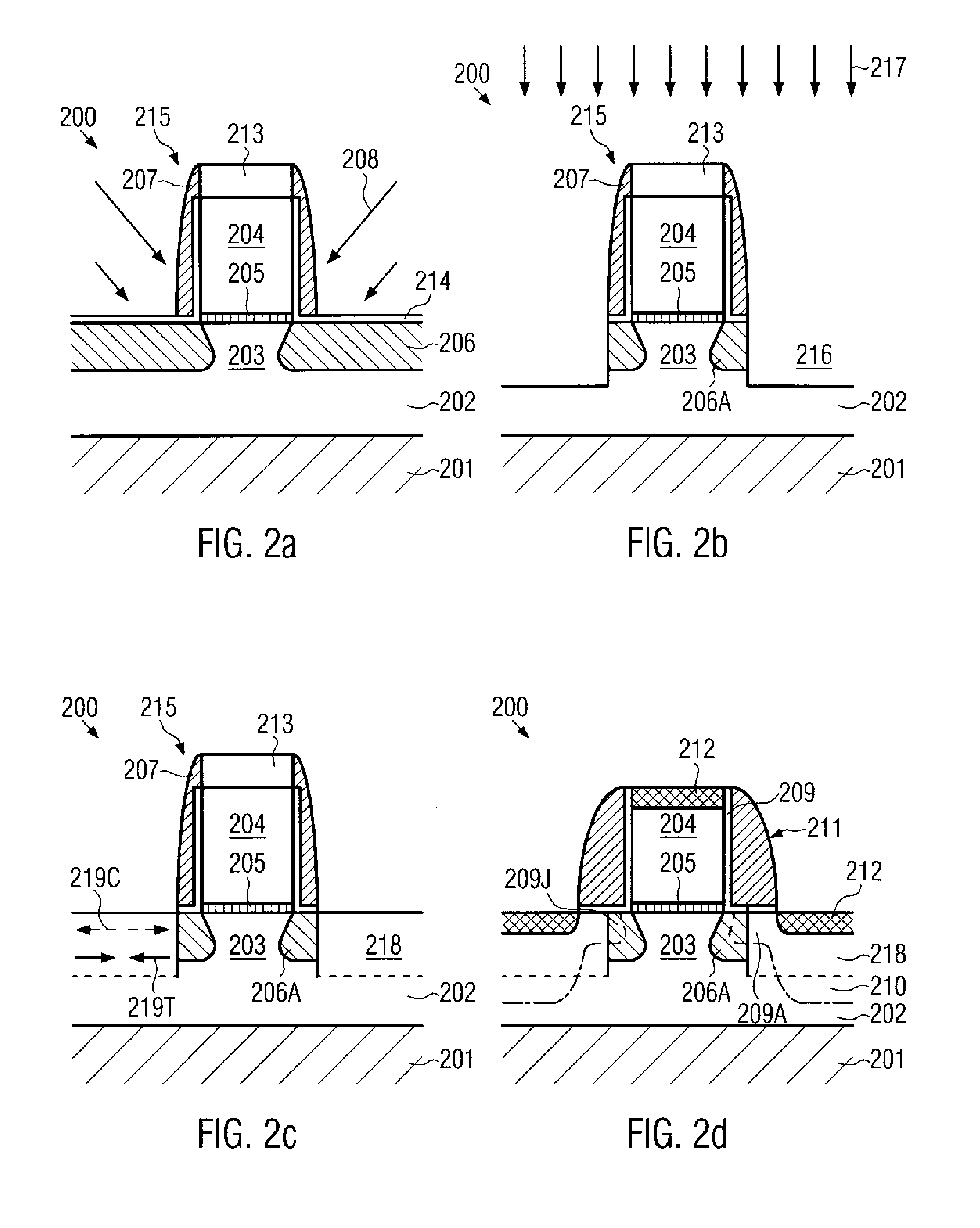
Transistor device having an increased threshold stability without drive current degradation
ActiveUS20070202641A1Improve behaviorReduced threshold varianceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesDriving currentSemiconductor materials
By removing a portion of a halo region or by avoiding the formation of the halo region within the extension region, which may be subsequently formed on the basis of a re-grown semiconductor material, the threshold roll off behavior may be significantly improved, wherein an enhanced current drive capability may simultaneously be achieved.
Owner:OCEAN SEMICON LLC
Filtering antenna with low profile, wide band and high gain
ActiveCN105591197ASimple structureEasy to processRadiating elements structural formsAntenna earthingsElectromagnetic metasurfaceBroadband
The invention discloses a filtering antenna with low profile, wide band and high gain. The antenna comprises an electromagnetic super-surface radiator and a feed part. The electromagnetic super-surface is constituted by non-uniformly small electrical units and is used as a high-efficiency radiator so that the bandwidth and gain of antenna are increased. At the same time, radiation zero points can be produced, and frequency selectivity can be increased through adjusting roll-off degree of an upper edge of a pass-band. According to the antenna, discrete micro-strip coupling slits are creatively used for feeding; metal via holes are introduced in between the micro-strip and floor; good filtering effect of low frequency stop band is guaranteed; roll-off degree of pass-band lower edges is increased. According to the invention, electromagnetic super-surface with filtering effect is creatively designed and is applied in filtering antenna; the antenna structure is simple and no complicated filtering circuit is used; The height is only 0.06[lambda]0; 10dB impedance bandwidth is 28.4%; antenna loss is low and efficiency reaches up to 95%; in-band average gain is 8.2dBi; out-band rejection is over 20dB; the stop-band is wide.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Interference resistant modulation method for digital television terrestrial broadcast transmitter
InactiveCN101420408AFrequency synchronizationTime synchronizationTelevision system detailsError preventionTime domainInterference resistance
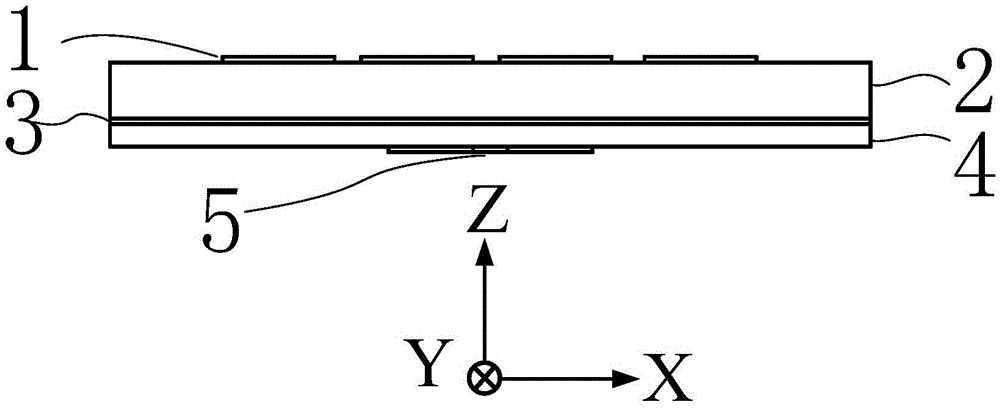
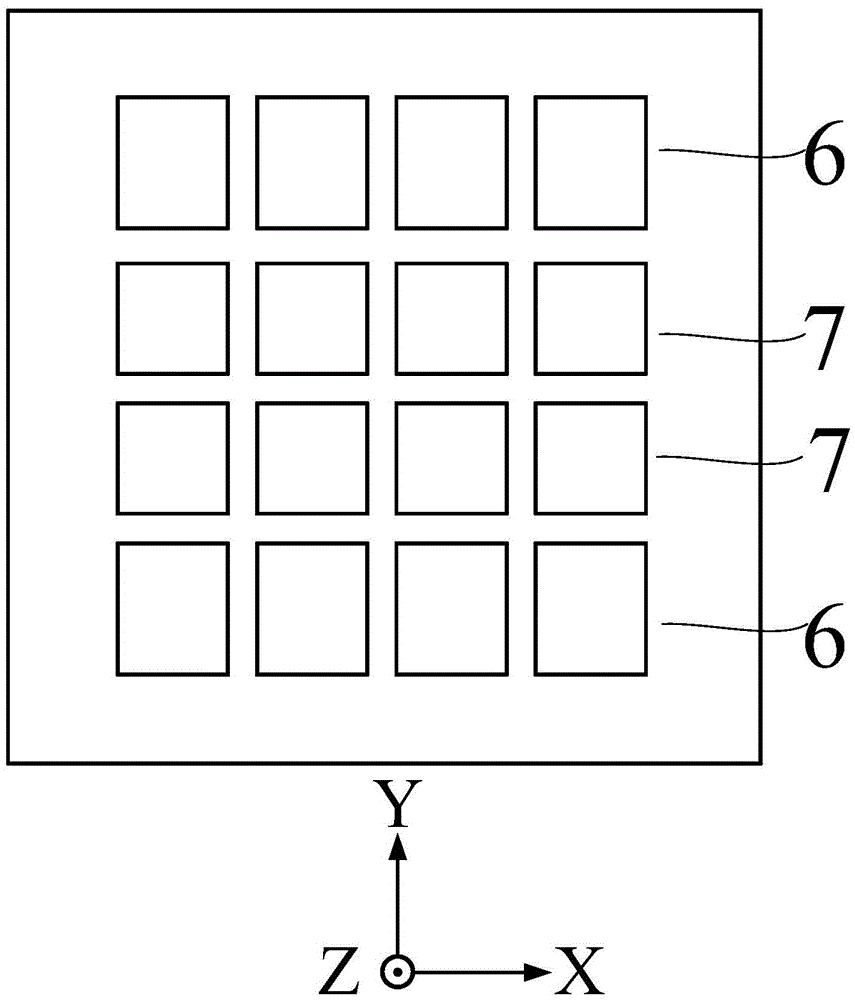
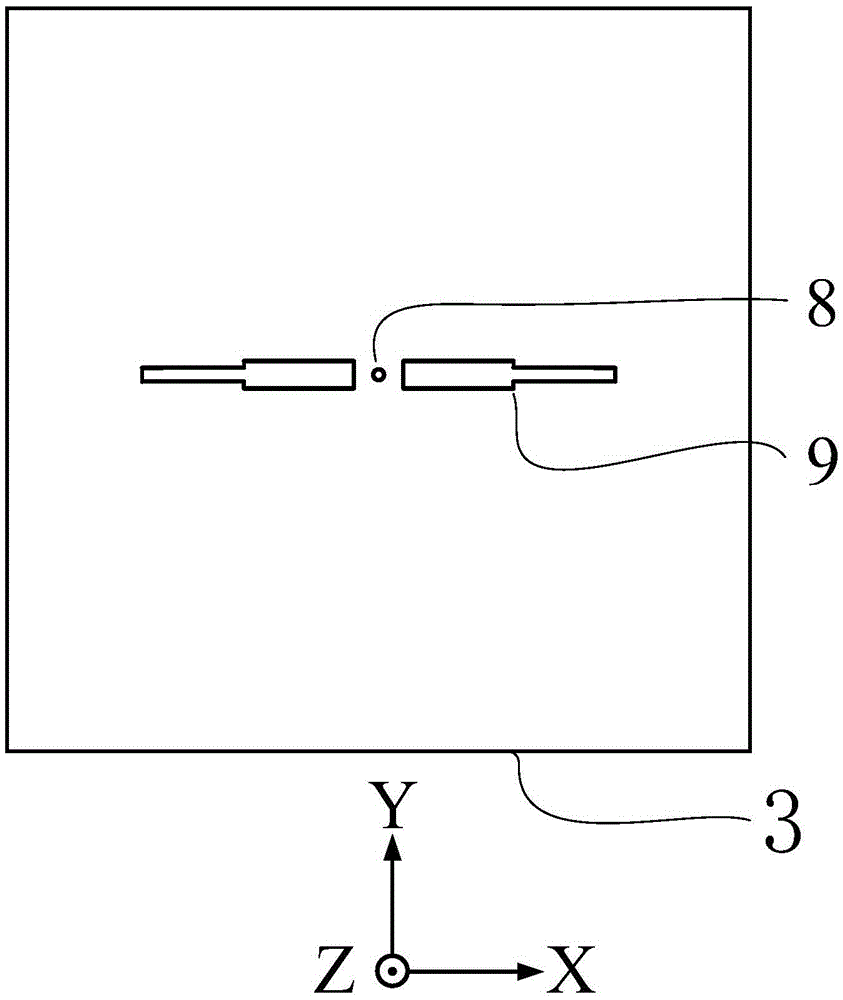
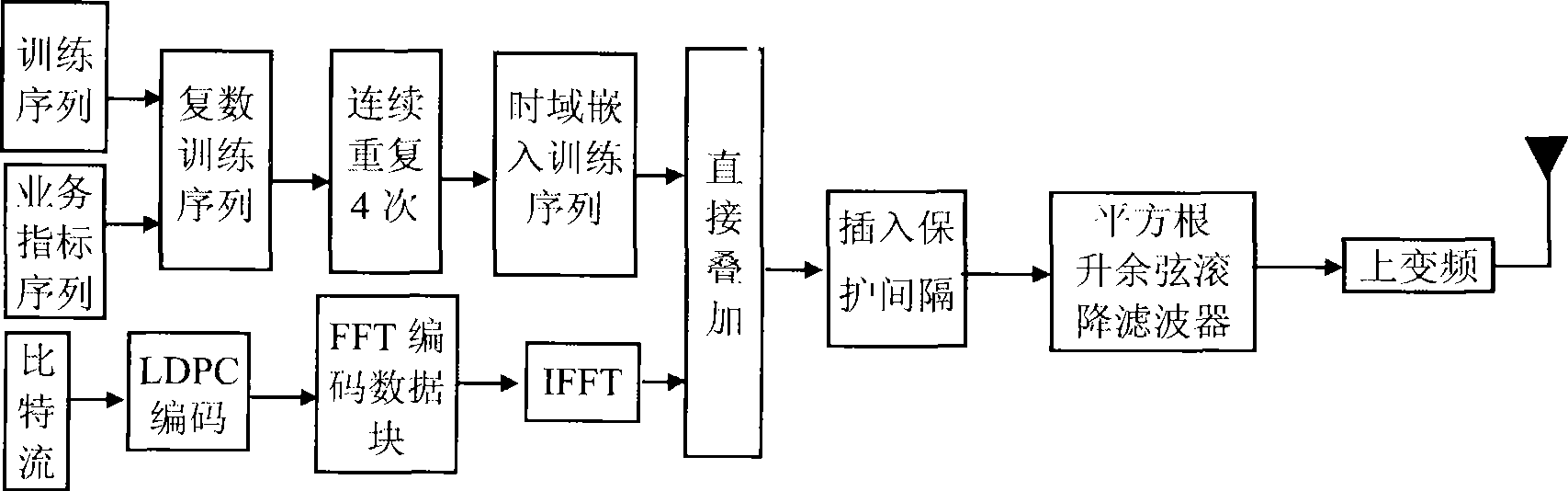
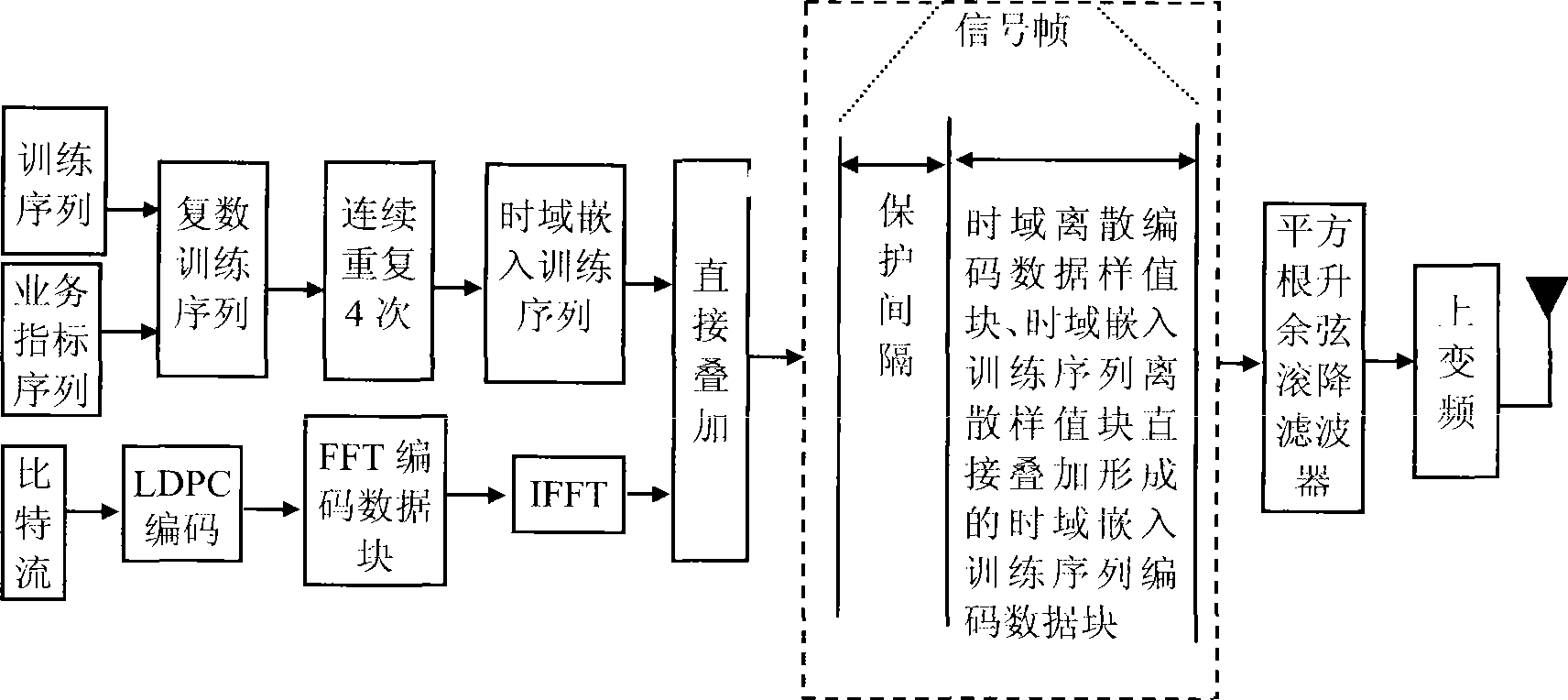
The present invention discloses a method for modulating digital television ground broadcasting transmitter based on insertion training sequence and LDPC code, wherein the method comprises the following steps: 1) forming an FFT coded data block with the input bit flow through LDPC coding; 2) switching the FFT coded data block to a time domain discrete coded data sample block through IFFT; 3) forming a complex training sequence discrete sample block with a mode that a training sequence is used as a real part sequence and an operational indicator sequence is used as an imaginary part sequence; 4) continuously repeating the complex training sequence for four times to form a time domain insertion training sequence discrete sample block; 5) directly overlapping the time domain discrete coded data sample block with the time domain insertion training sequence discrete sample block for forming a time domain insertion training sequence coded data block; 6) inserting a circulating prefix into the time domain insertion training sequence coded data block for forming a signal frame; 7) forming a signal frame pulse with a square-root raised cosine roll-off filter; and 8) upconverting the baseband signal to the carrier.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
Synthesis method for an active polyphase filter
InactiveUS7098731B1Improve the level ofOscillations generatorsTransmissionElectrical conductorSynthesis methods
A fully-integrated continuous-time active complex bandpass IF filter that may contain transmission zeros yielding much sharper roll-off than that of an all-pole filter is implemented using transconductors and capacitors only. Each of the filter second-Order sections realizes a pair of complex poles and a may realize a double imaginary axis zero. Since the transconductors are electronically tunable the positions of filter zeros and poles are adjustable using an automatic tuning system. In each filter section the value of different transconductors are modified to separately change the pole frequency, its Q-factor and the zero frequency. Each pole and zero are separately tuned, which achieves a higher level of tuning accuracy than in case where all poles and zeros were adjusted simultaneously.
Owner:WYSZYNSKI ADAM S
Frequency stabilization of chopper-stabilized amplifiers
InactiveUS7209000B2Negative-feedback-circuit arrangementsAmplifier modifications to raise efficiencyFrequency stabilizationAudio power amplifier
Frequency stabilization of chopper-stabilized amplifiers using multipath hybrid double-nested Miller compensation. The compensation may provide a desired 6 dB / oct roll off for both instrumentation amplifiers and operational amplifiers. Various embodiments are disclosed.
Owner:MAXIM INTEGRATED PROD INC
Method and system for spectral stitching of tunable semiconductor sources
ActiveUS7324569B2Effectively wider scan bandLaser detailsSpectrometry/spectrophotometry/monochromatorsDriving currentSpectral bands
A multi semiconductor source tunable spectroscopy system has two or more semiconductor sources for generating tunable optical signals that are tunable over different spectral bands. The system enables the combination of these tunable signals to form an output signal that is tunable over a combined band including these individual spectral bands of the separate semiconductor sources. The system further compensates for spectral roll-off associated with the semiconductor sources. Specifically, near the limits of the semiconductor sources' spectral bands, the power in the tunable signal tends to degrade or decrease. The system compensates for this roll-off using drive current control, attenuators, or electronic compensation.
Owner:EXCELITAS TECH
Surface-acoustic-wave filters with poles of attenuation created by impedance circuits
InactiveUSRE37639E1Improve frequency characteristicsIncreasing stopband attenuationMultiple-port networksPiezoelectric/electrostrictive/magnetostrictive devicesUltrasound attenuationAcoustic wave
A surface-acoustic-wave filter couples a two-port surface-acoustic-wave resonator filter circuit coupled in parallel or in series with a two-port impedance circuit. The two-port impedance circuit has an impedance that creates a pole of attenuation, by making the open-circuit impedance of the surface-acoustic-wave filter equal to the short-circuit impedance. High attenuation over a wide range of stopband frequencies is obtained in this way, combined with steep roll-off between the passband and stopband.
Owner:HANGER SOLUTIONS LLC
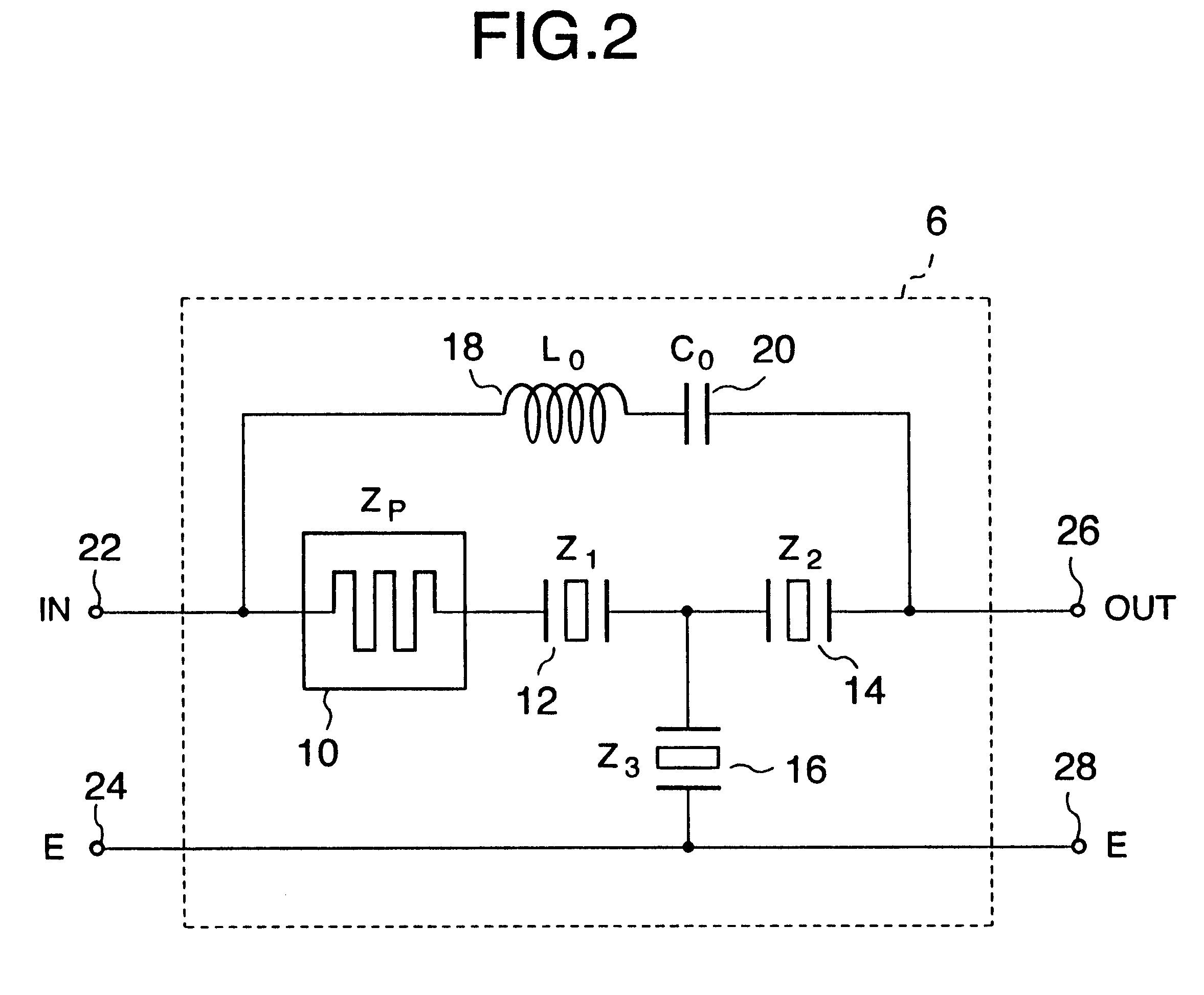
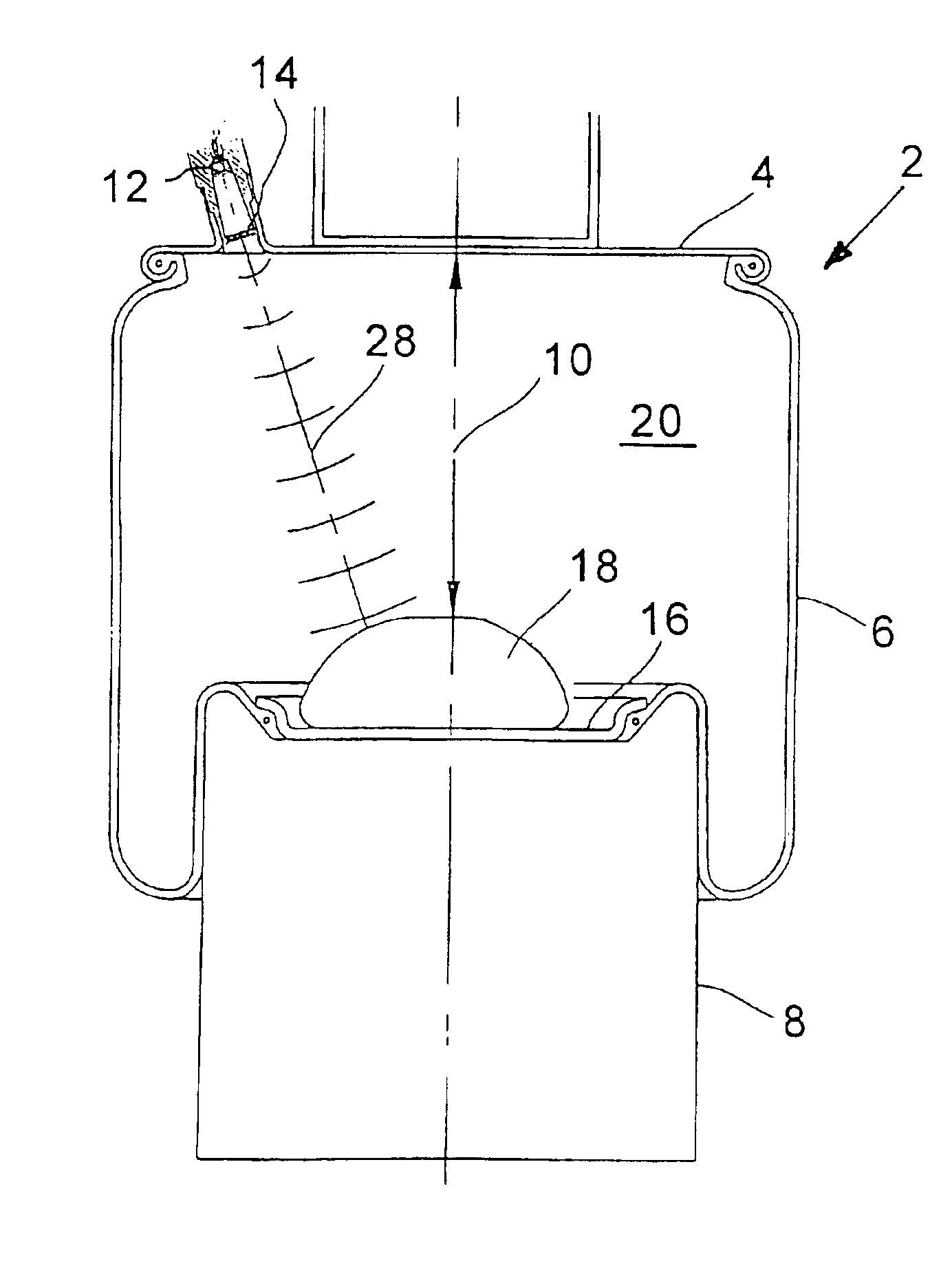
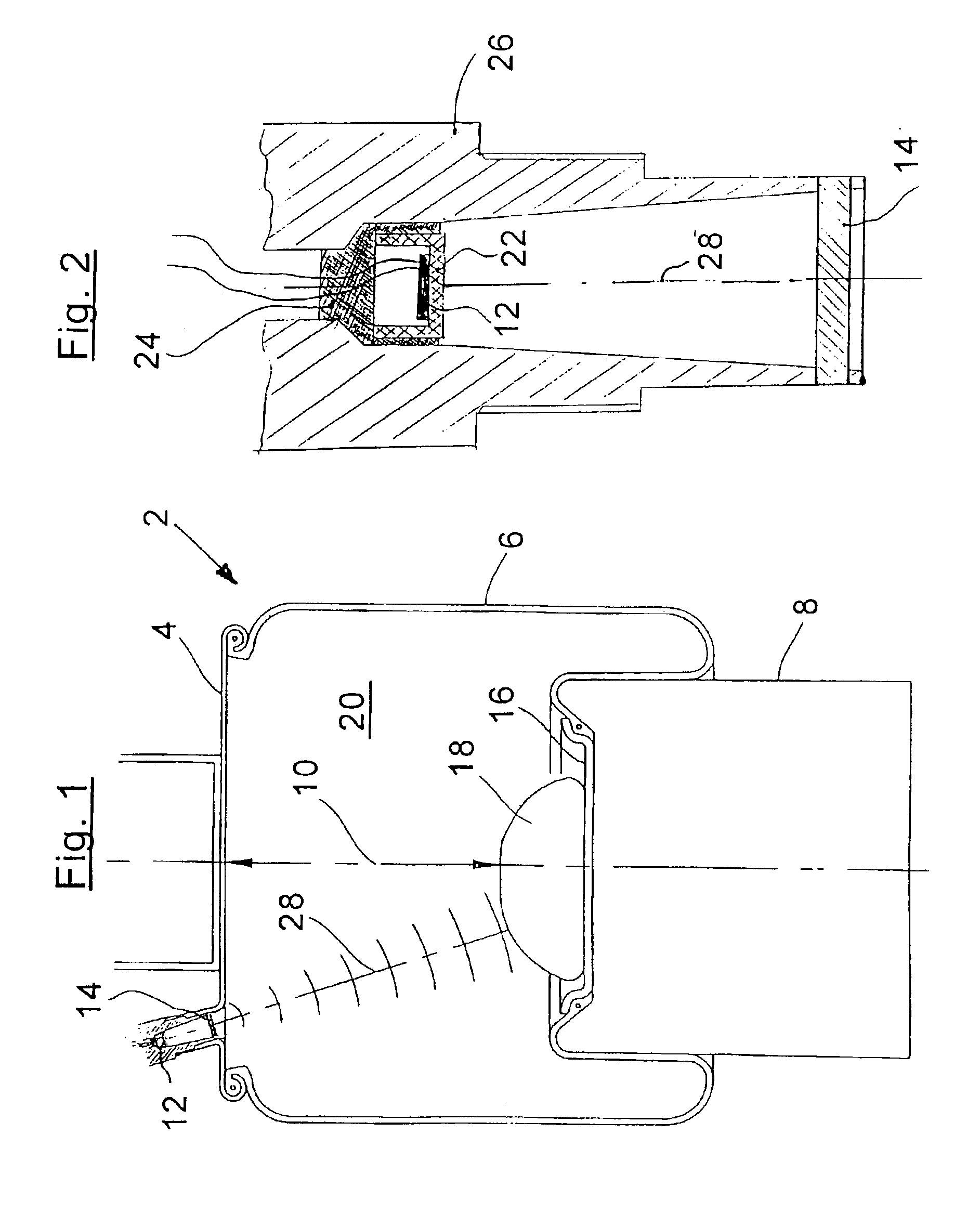
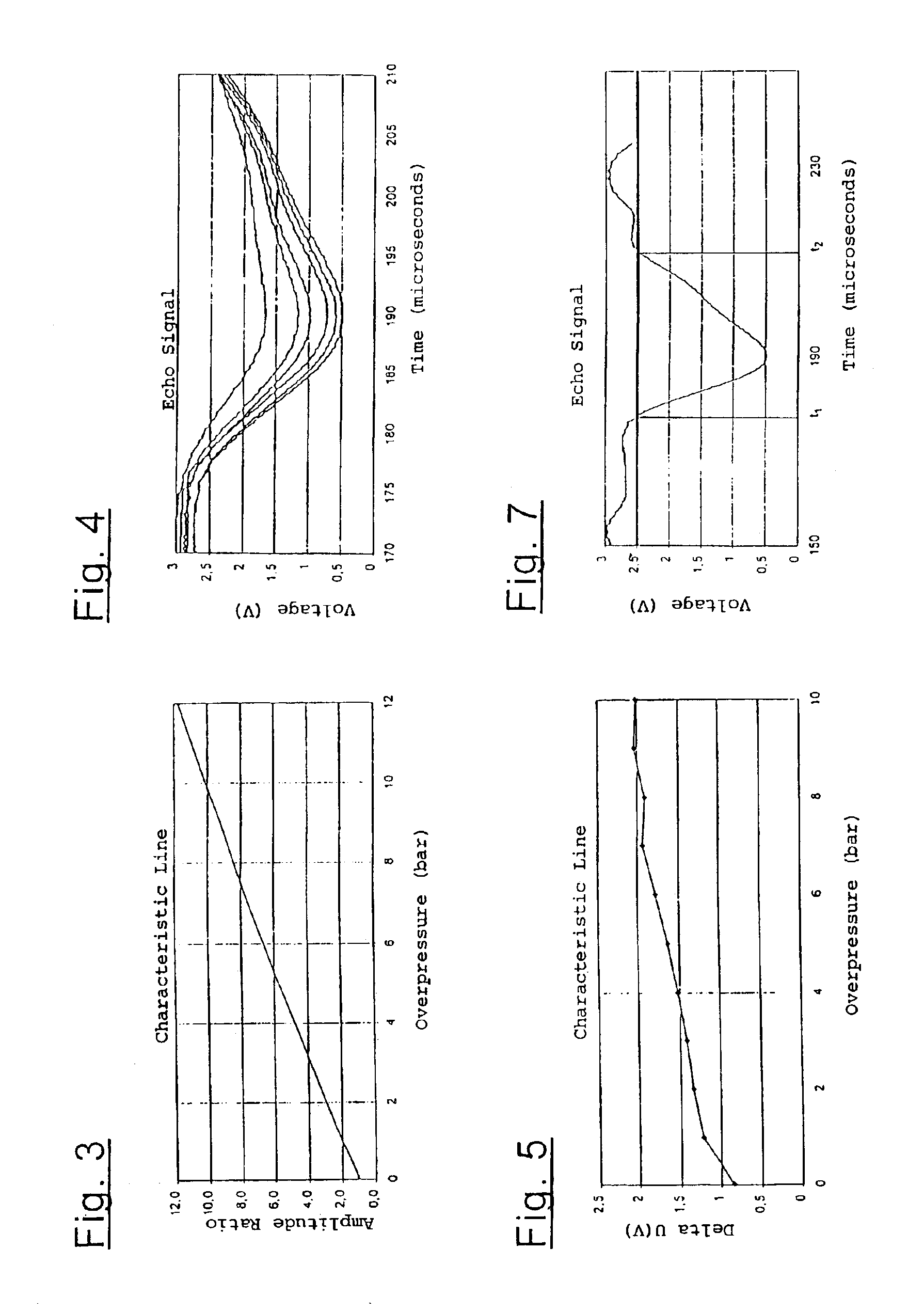
Method for determining the pressure present in the interior space of an air spring for a motor vehicle and apparatus for carrying out the method
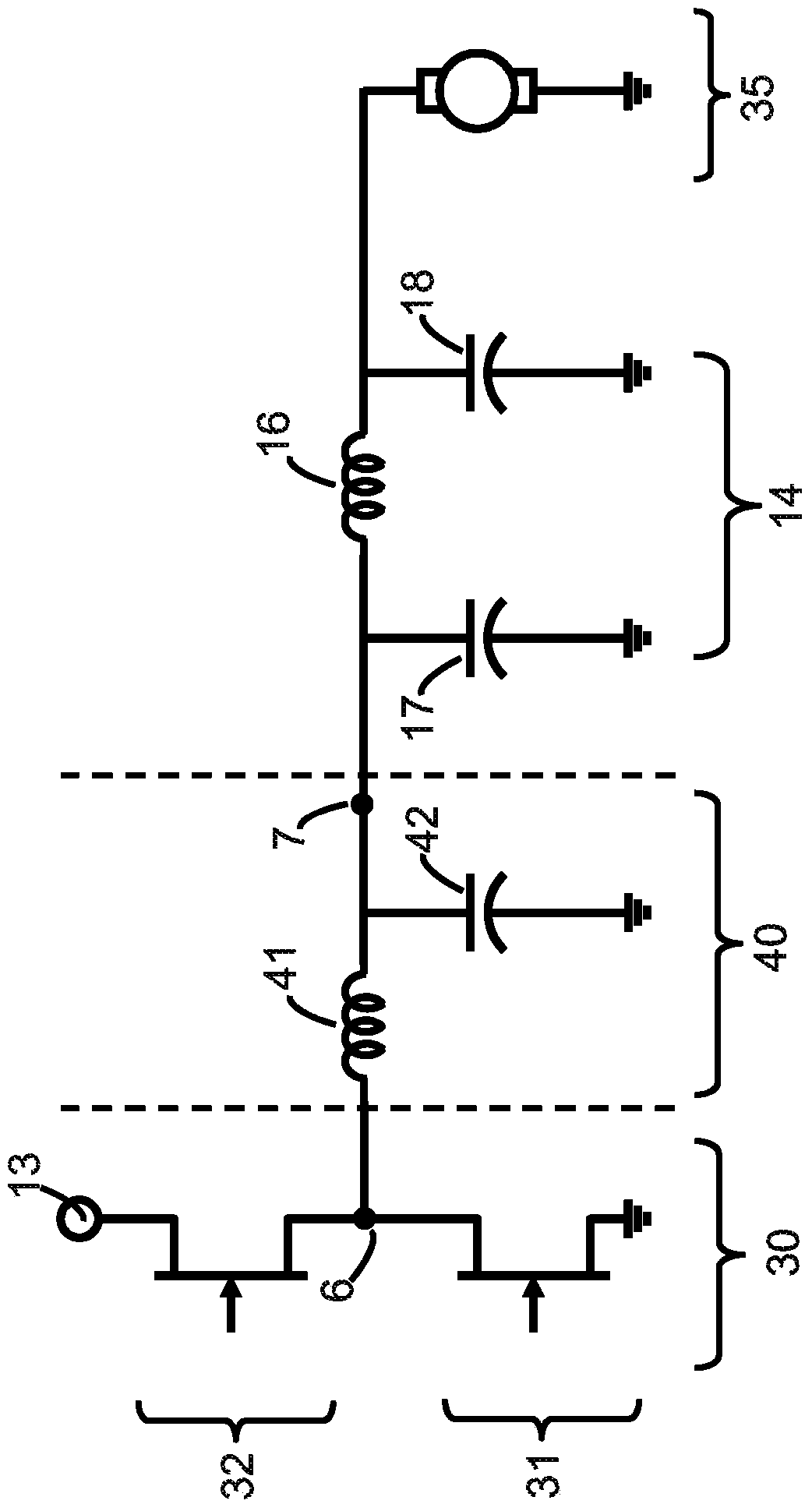
InactiveUS6931930B2Cost-effective and precisely functioningReduce complexityVibration measurement in fluidMagnetic property measurementsUltrasonic sensorAmbient pressure
An ultrasonic pulse / echo measurement arrangement includes an ultrasonic transducer (12), which is mounted spatially fixed on an air spring cover plate (4). The arrangement further includes a fixedly mounted reference reflector (14), a target reflector (16) mounted on a roll-off piston (8) or on the bumper (18) as well as a transmitter / receiver evaluation electronic circuit (30). The running time as well as the amplitude of the reference signal is evaluated to precisely determine the pressure present in the interior space of the air spring. The ultrasonic transducer (12) has a λ / 4-adaptation layer (22), whose impedance does not correspond to the geometric mean of the impedances of the ultrasonic transducer (12) and the ambient air of the interior space (20) of the air spring, but rather, is a mismatch. The evaluation electronic circuit (30) can be calibrated at ambient pressure for the determination of the inner pressure of the air spring. Preferably, the pressure measuring method according to the invention is also used to determine the running-time dependent spring height in an air spring (2) of a motor vehicle.
Owner:VAHRENWALDER STRASSE 9
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com