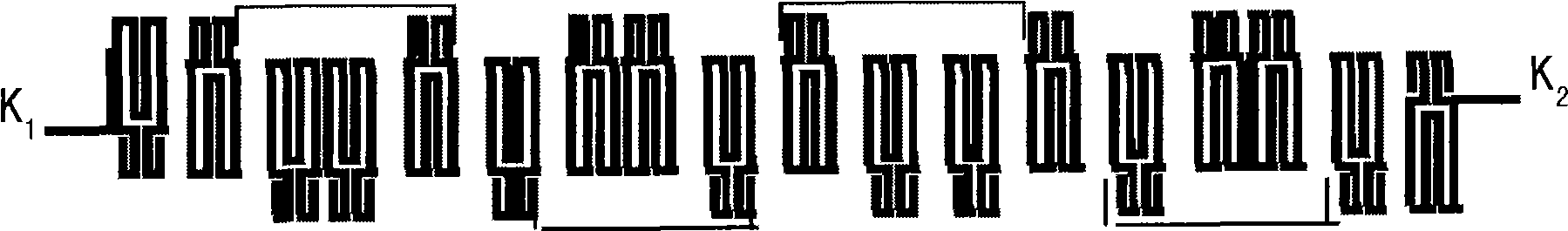Patents
Literature
478 results about "Band rejection" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
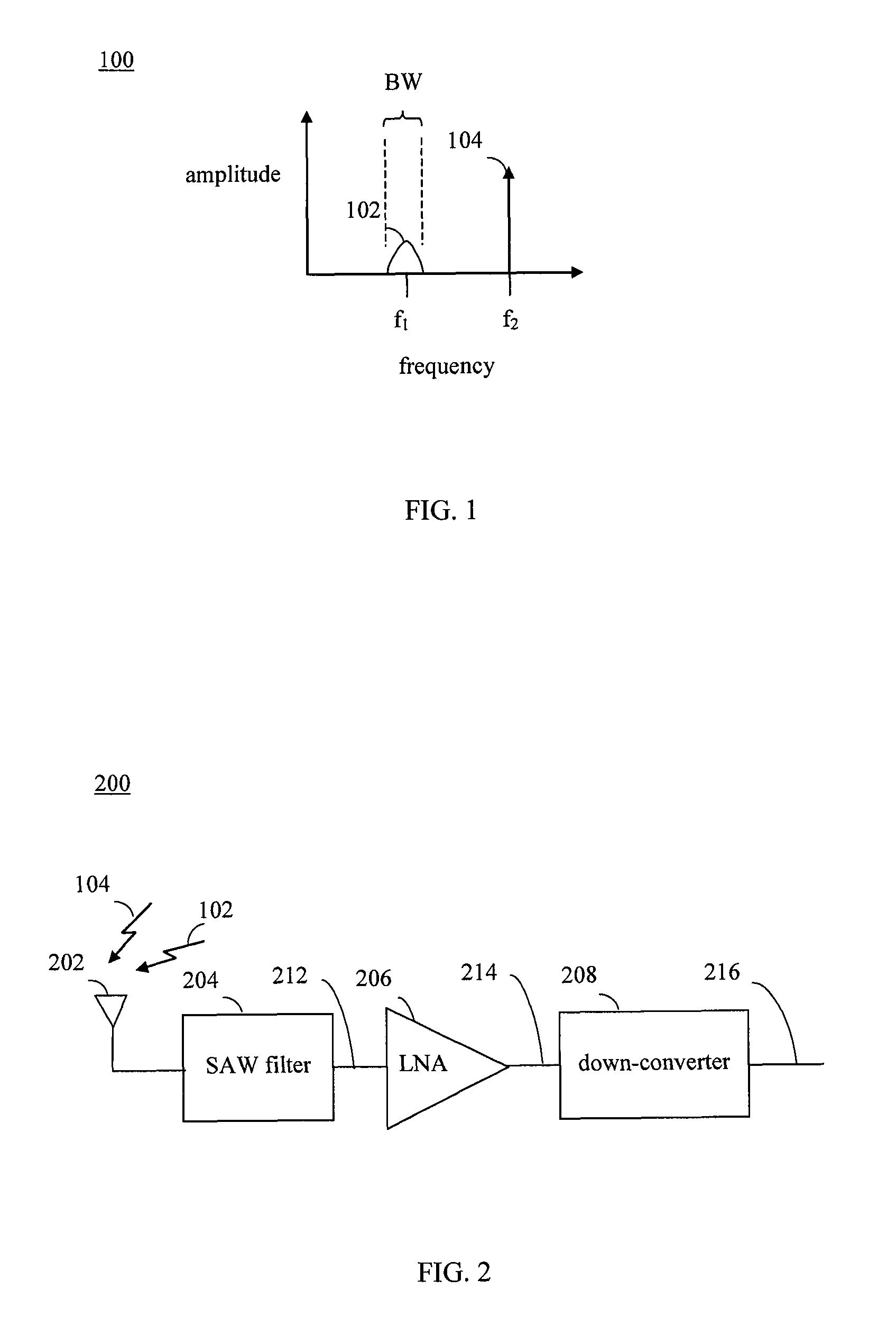
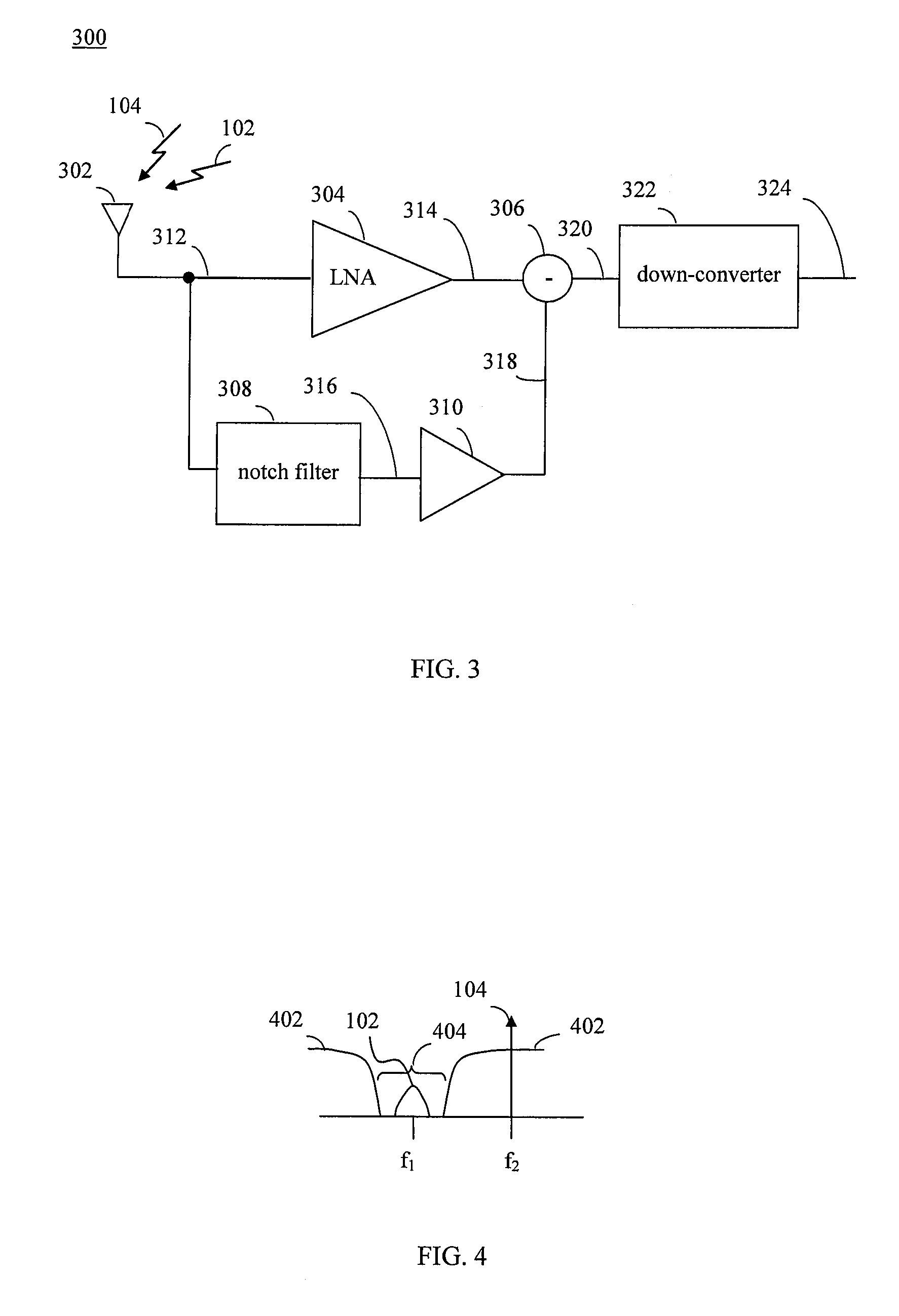
Band rejection is a phenomenon in waveform signals, where a certain frequency or range of frequencies are lost or removed from a source signal. The term band rejection, when used in electronic signal processing, refers to the deliberate removal of a known frequency range - for instance, to compensate for a known source of interference (such as noise from mains (household) electricity). A specific frequency is removed using a notch filter.
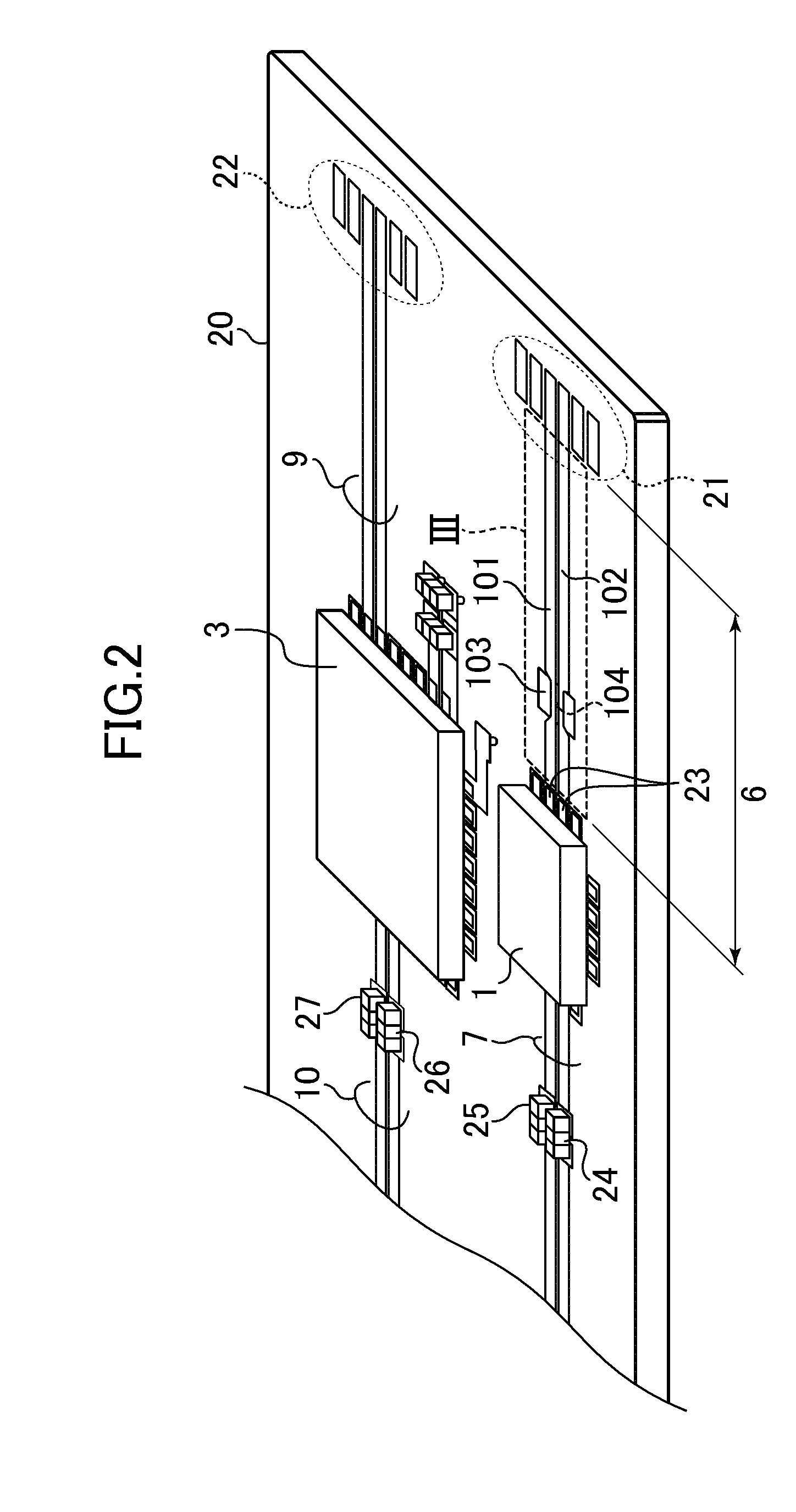
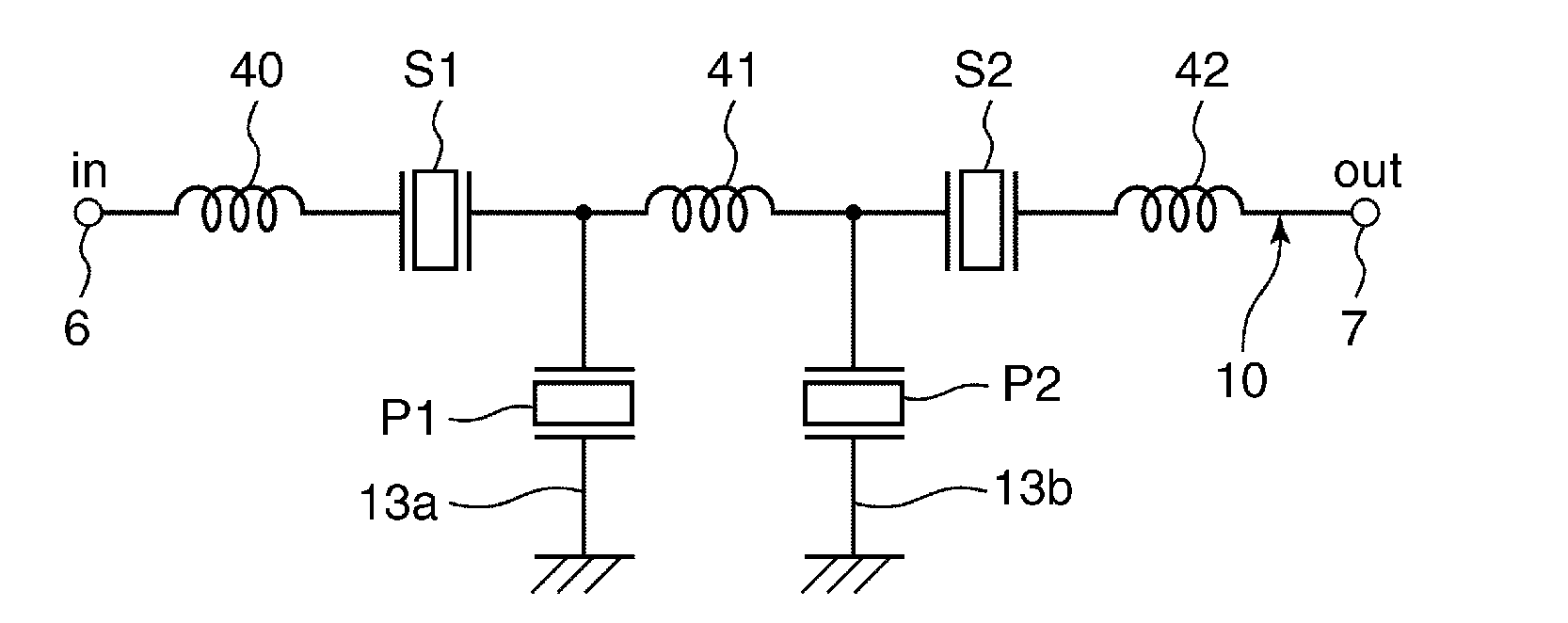
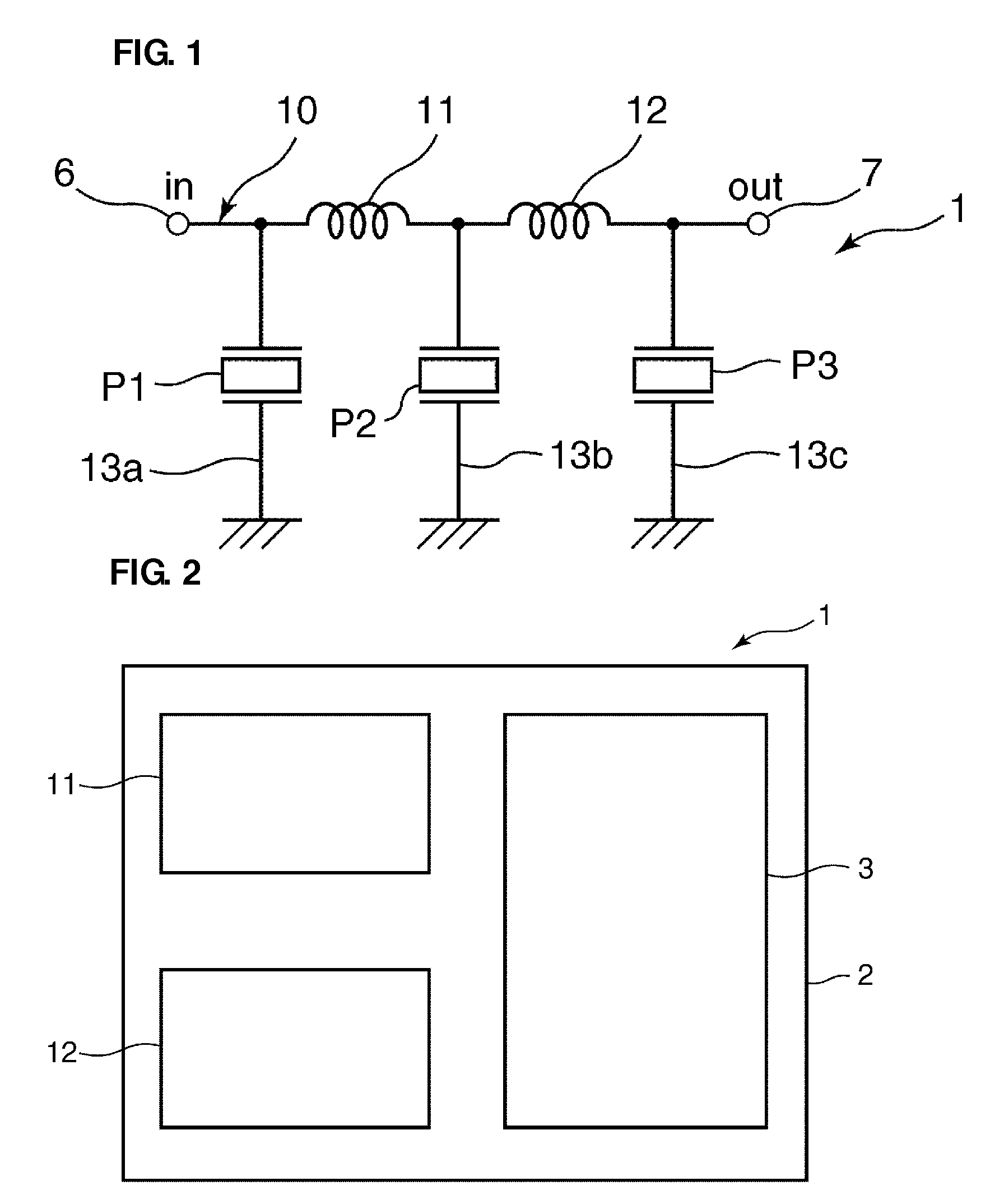
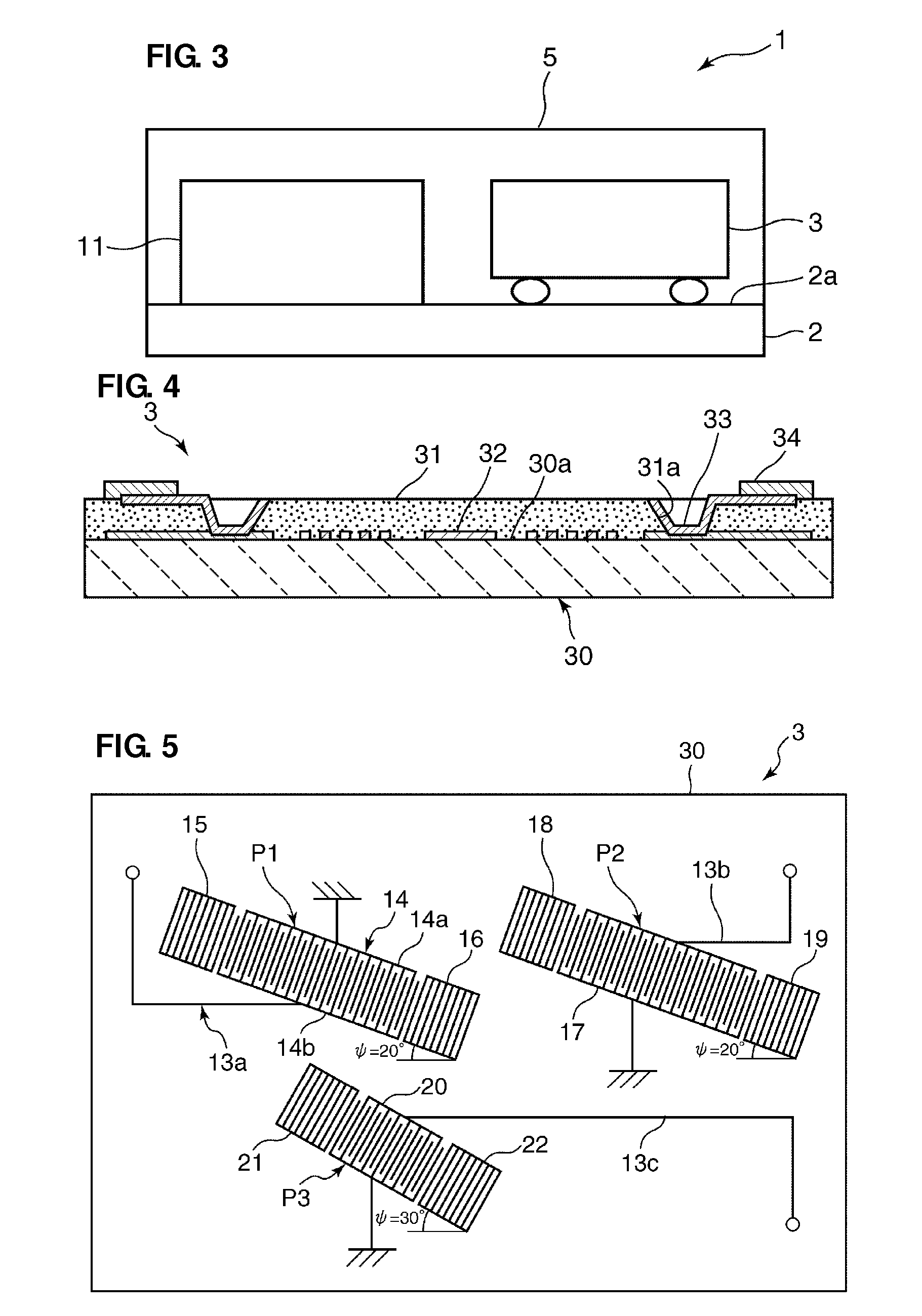
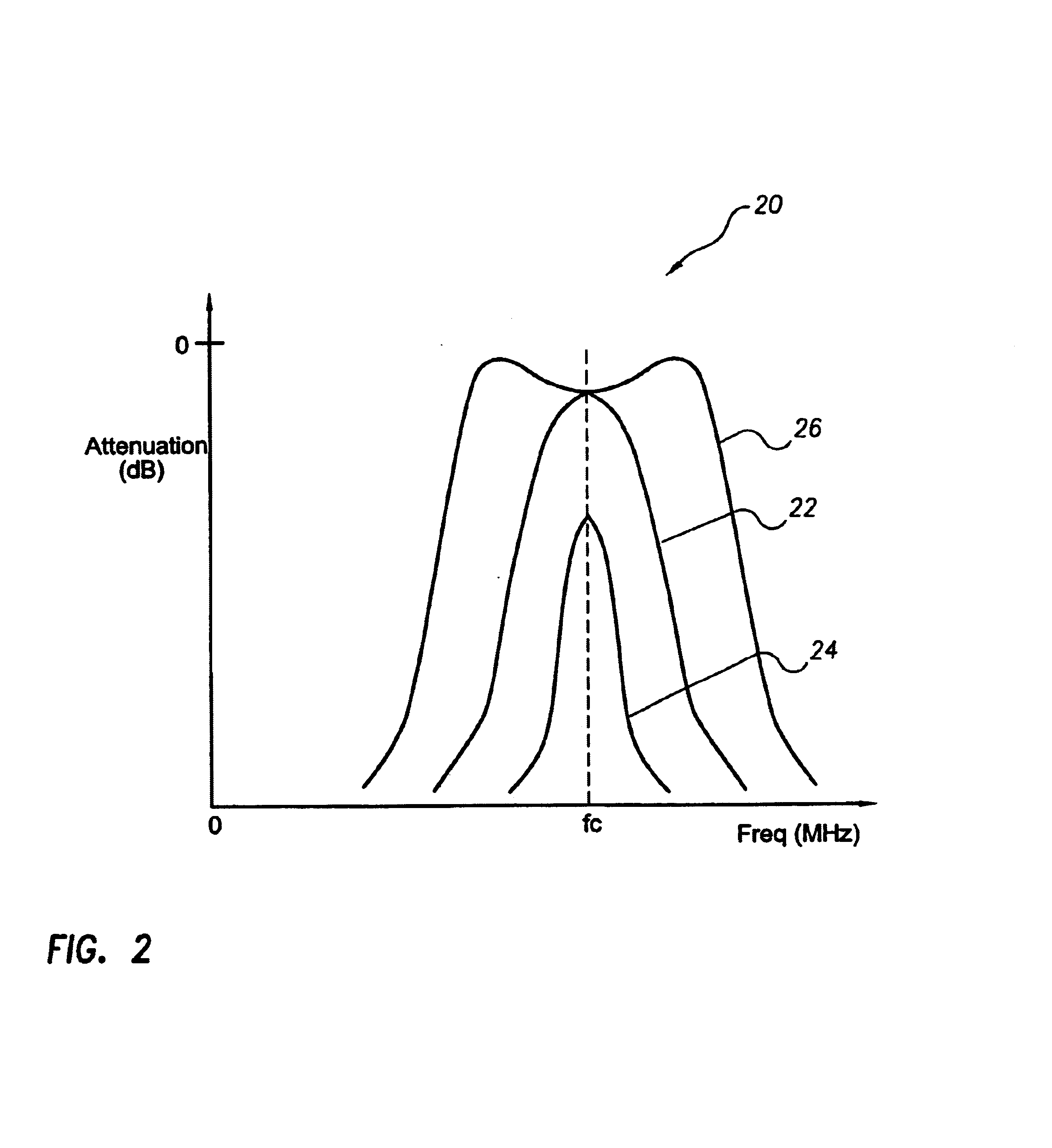
Reducing power consumption by taking advantage of superior in-circuit duplexer performance
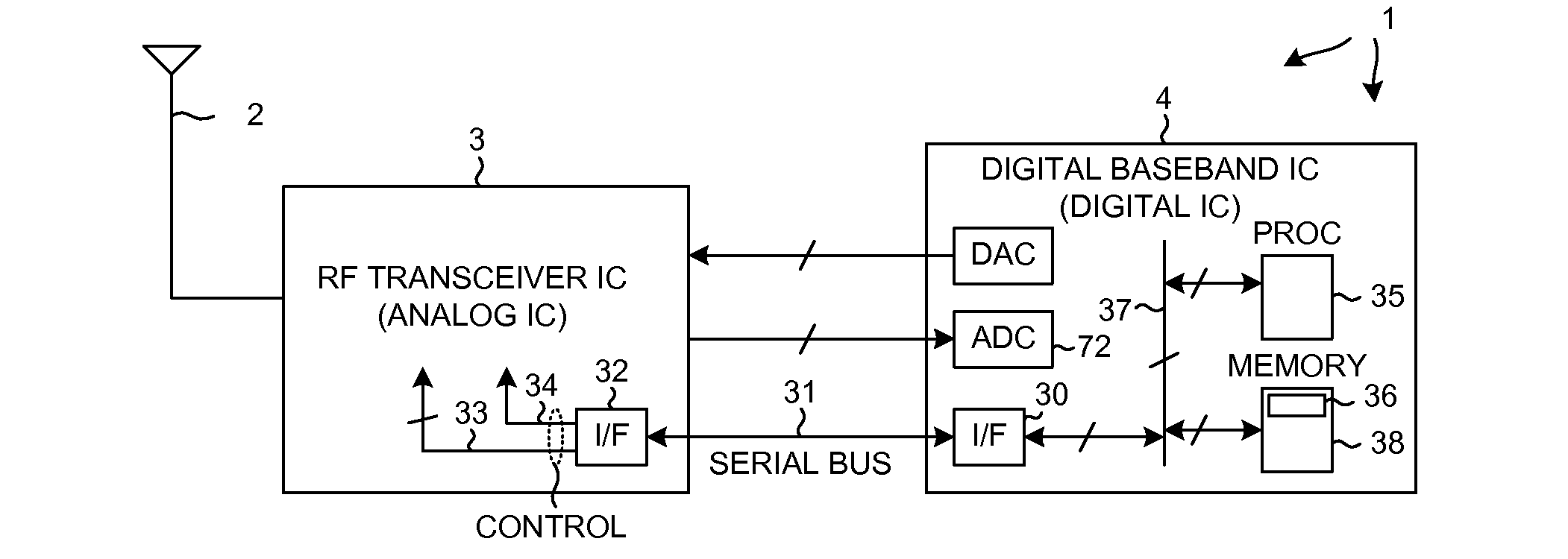
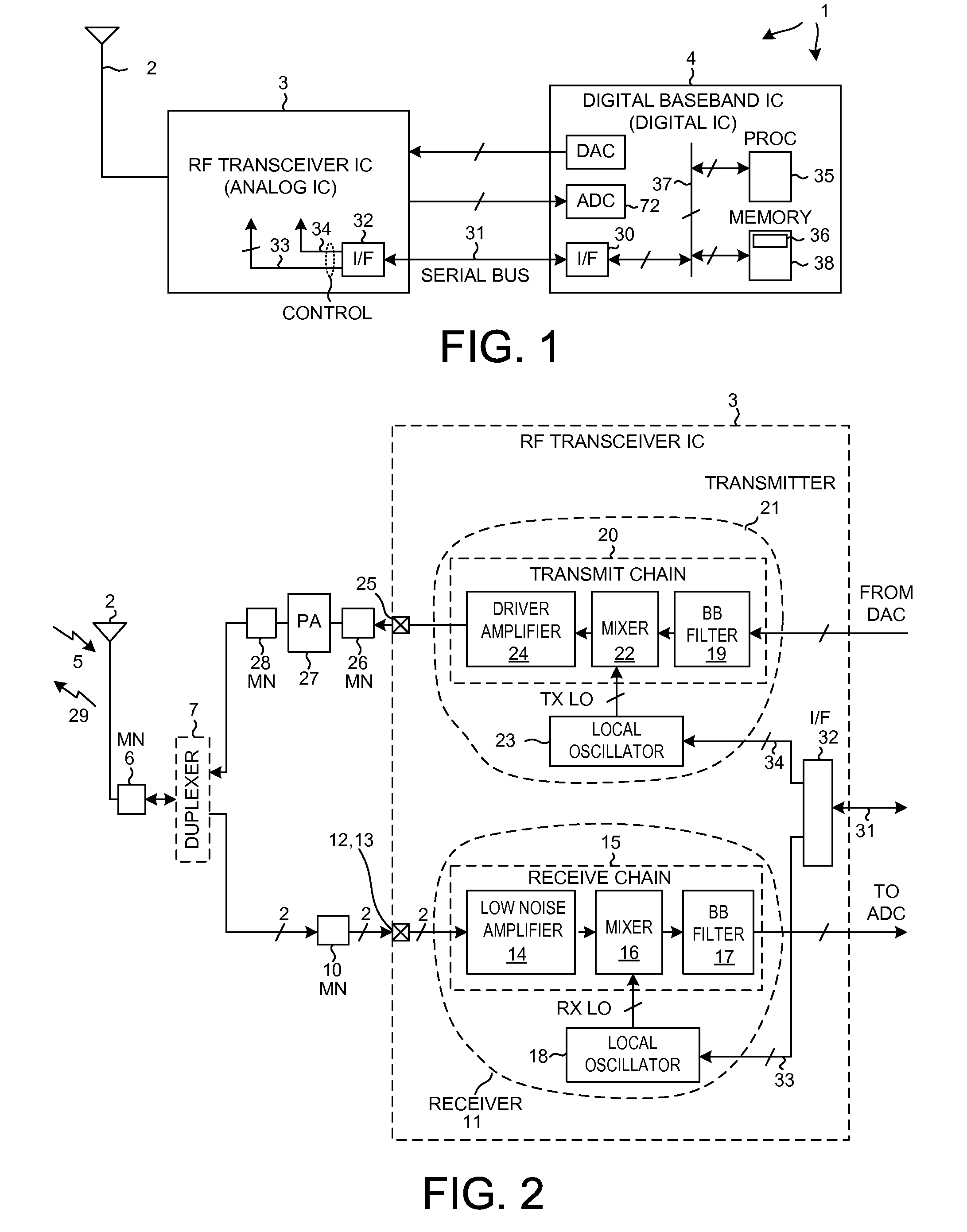
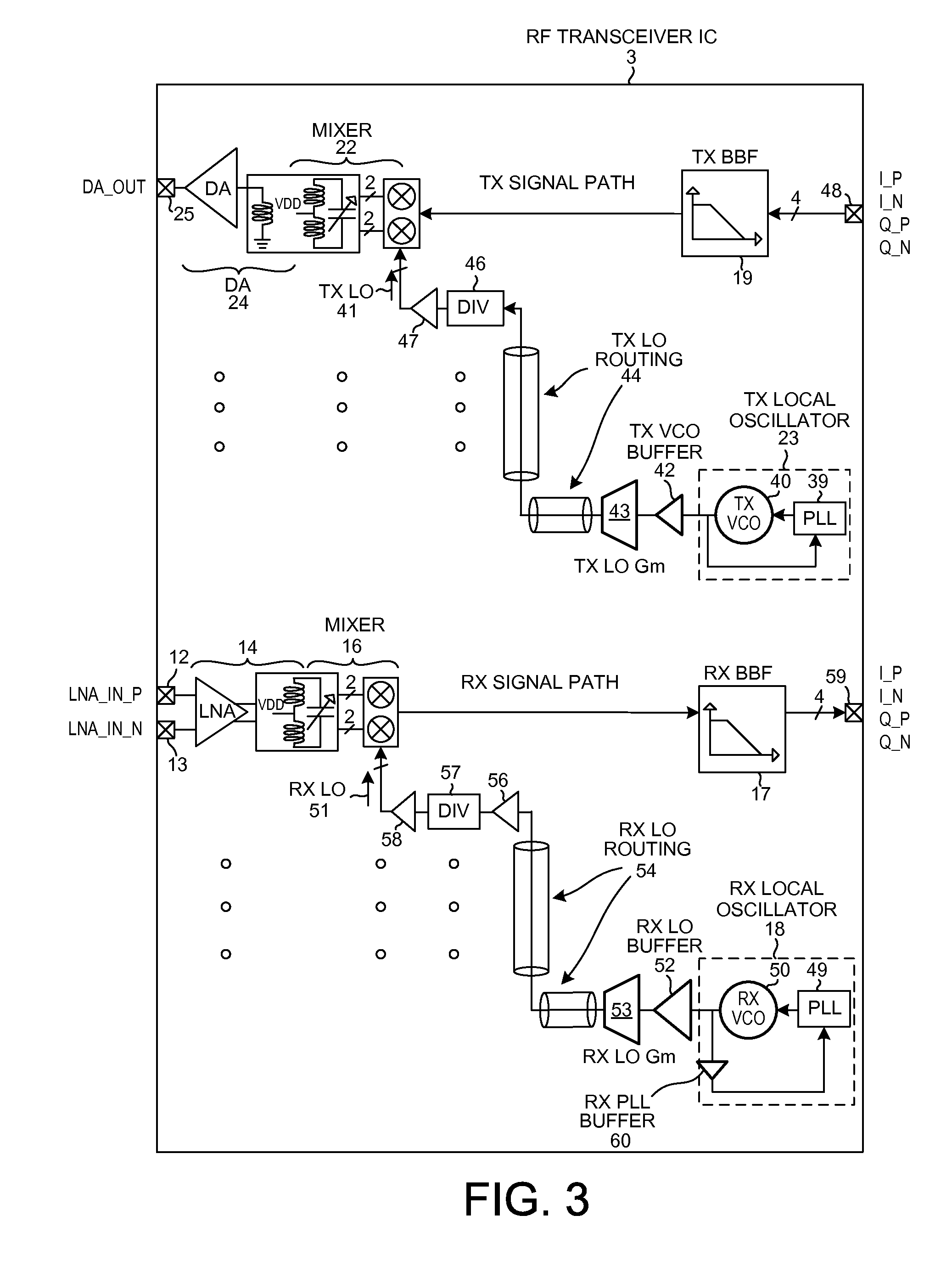
Although the duplexer in a full-duplex transceiver circuit may only be guaranteed by the duplexer manufacturer to have a transmit band rejection from its TX port to its RX port of a certain amount, and may only be guaranteed to have a receive band rejection of another amount, the actual transmit band rejection and the actual receive band rejection of a particular instance of the duplexer may be better than specified. Rather than consuming excess power in the receiver and / or transmitter in order to meet performance requirements assuming the duplexer only performs as well as specified, the duplexer's in-circuit performance is measured as part of a transmitter-to-receiver isolation determination. Transmitter and / or receiver power settings are reduced where possible to take advantage of the measured better-than-specified in-circuit duplexer performance, while still meeting transceiver performance requirements. Power settings are not changed during normal transmit and receive mode operation.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Control apparatus
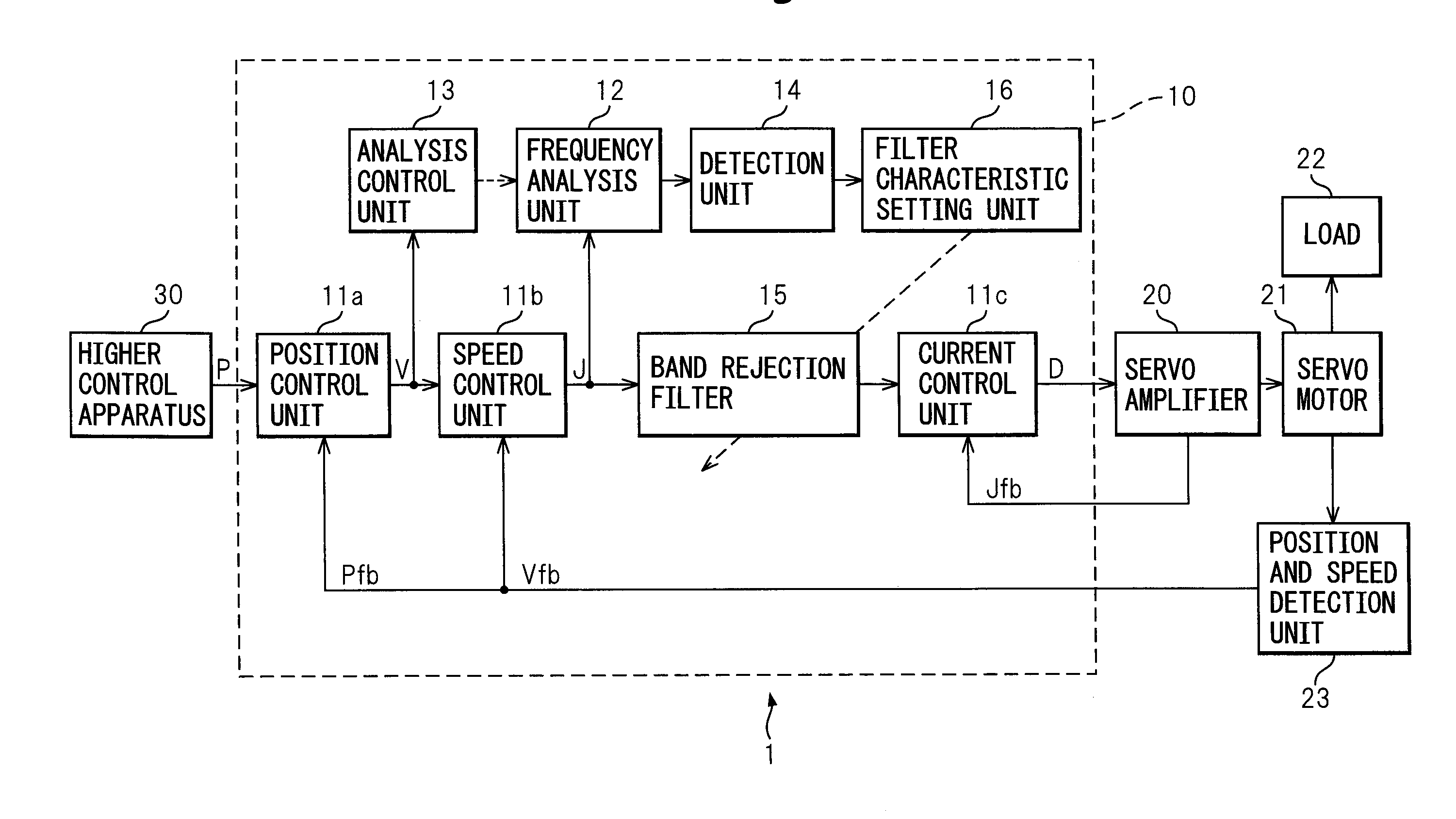
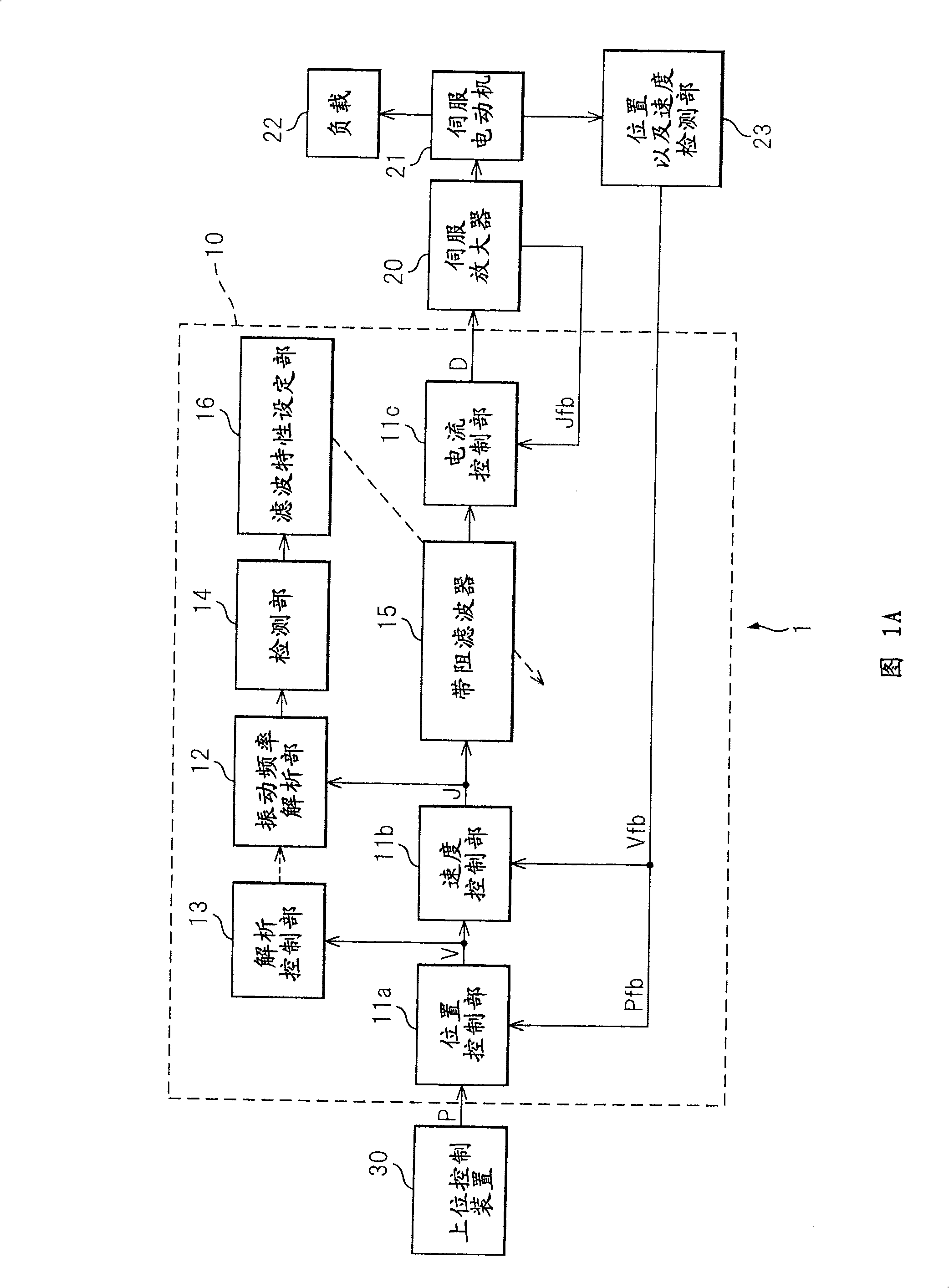
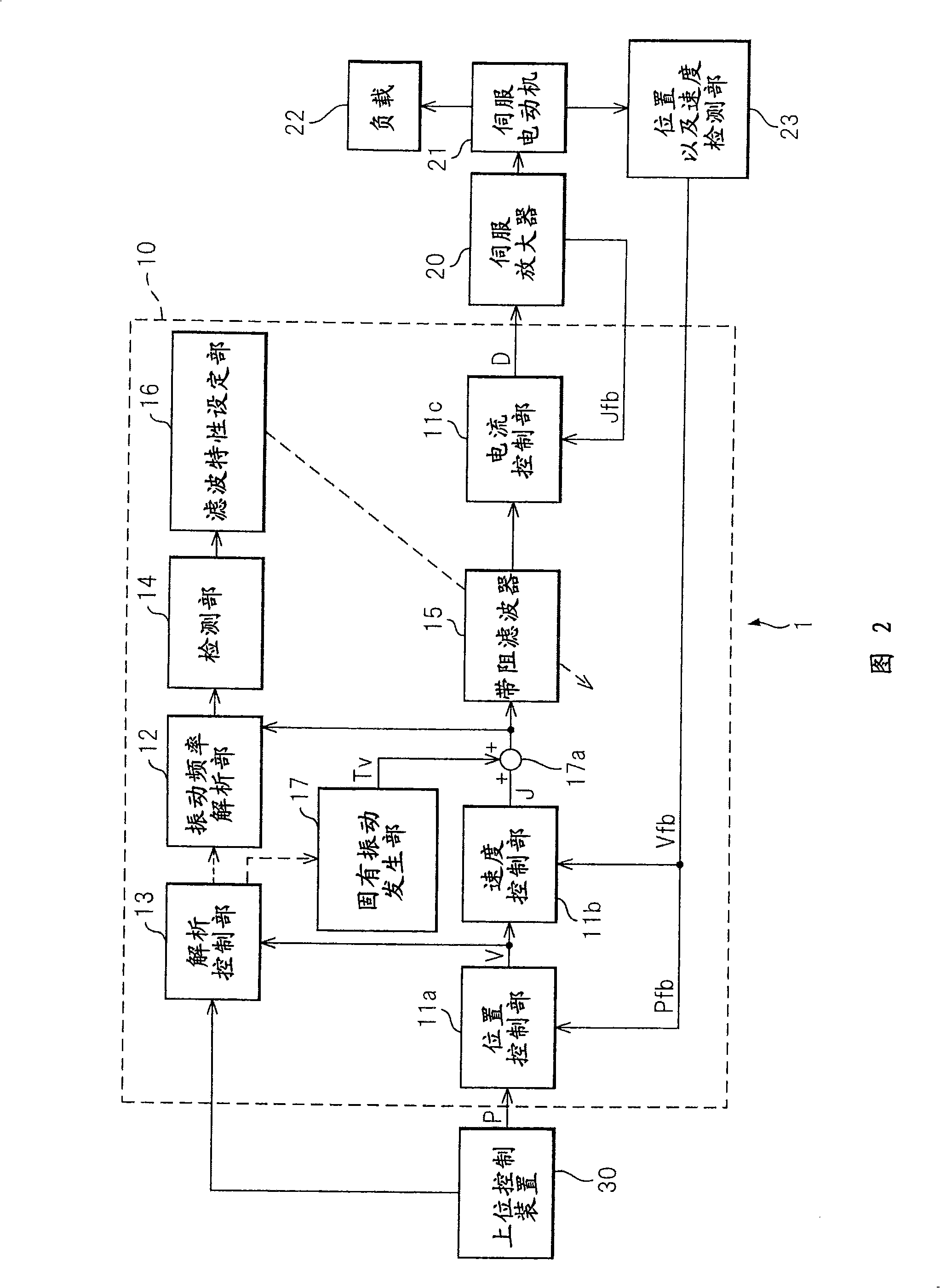
ActiveUS20090009128A1Accurate detectionReducing natural vibrationMechanical oscillations controlElectric motor controlControl signalBand-stop filter
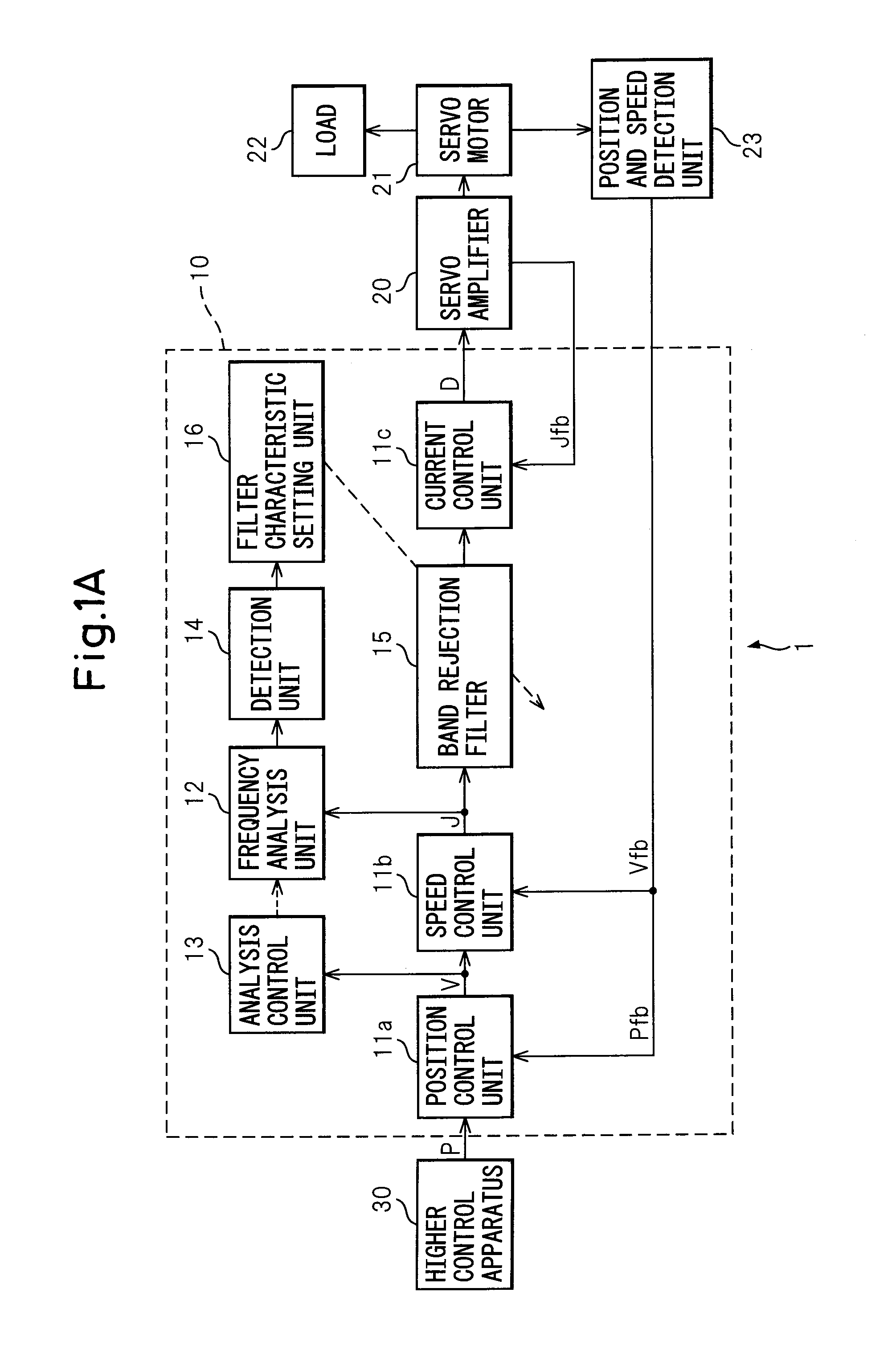
A control apparatus of the present invention comprising a control unit outputting a control signal controlling a servo motor and suppressing natural vibration of a controlled object including a motor and a machine driven by the motor while controlling the controlled object, comprising a frequency analysis unit analyzing a frequency component included in a torque command, an analysis control unit controlling the start or stopping of the frequency analysis unit, a detection unit detecting a natural frequency of the controlled object from an analysis result of the frequency analysis unit, a-band rejection filter receiving as input the torque command, stripping the command of the natural frequency component, and outputting the resultant command to the motor through a current control unit and servo amplifier, and a filter characteristic setting unit setting the frequency to be stripped at the filter based on the natural frequency detected by the detection unit.
Owner:FANUC LTD
Differential transmission circuit and information processing system
ActiveUS20120269522A1Increase costSuppress electromagnetic radiationCross-talk/noise/interference reductionPrinted circuit aspectsInformation processingElectrical conductor
A differential transmission circuit includes a grounded conductive layer, a pair of transmission line conductors, a conductive film and a via hole which connects the grounded conductive layer to the conductive film. The differential transmission circuit further includes a straight-line region which is present in the differential transmission circuit through which a differential transmission signal output by a driving circuit is transmitted and in which the pair of transmission line conductors extends parallel so as to have a first width, and a band rejection filter region in which the pair of transmission line conductors planarly overlaps the conductive film and extends parallel so as to have a second width narrower than the first width and a common mode of the differential transmission signal is attenuated at one of the frequencies which are natural number multiples of a frequency corresponding to the predetermined bit rate.
Owner:LUMENTUM JAPAN INC
Band rejection filter
ActiveUS20110090026A1Improve clarityLarge attenuation amountMultiple-port networksUltrasound attenuationElectromechanical coupling coefficient
An inexpensive compact band rejection filter realizes a high sharpness of a filter characteristic at ends of passbands and has a large attenuation. In the band rejection filter, at least one of a plurality of elastic wave resonators, which contributes to formation of a transition band, has a propagation angle larger than those of the other elastic wave resonators. Accordingly, the at least one of the plurality of elastic wave resonators which contributes to the formation of the transition band has an electromechanical coupling coefficient that is smaller than electromechanical coupling coefficients of the other elastic wave resonators.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
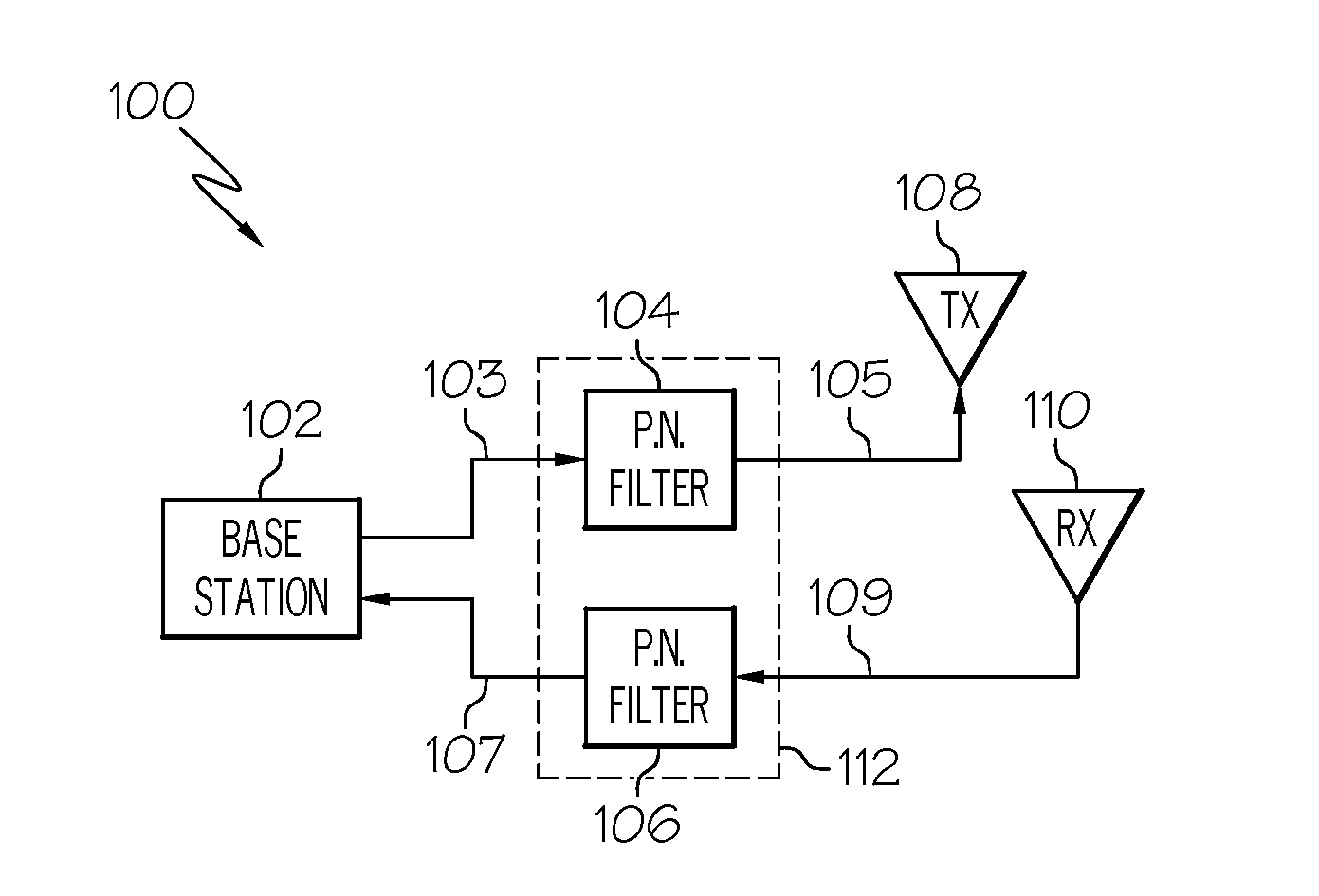
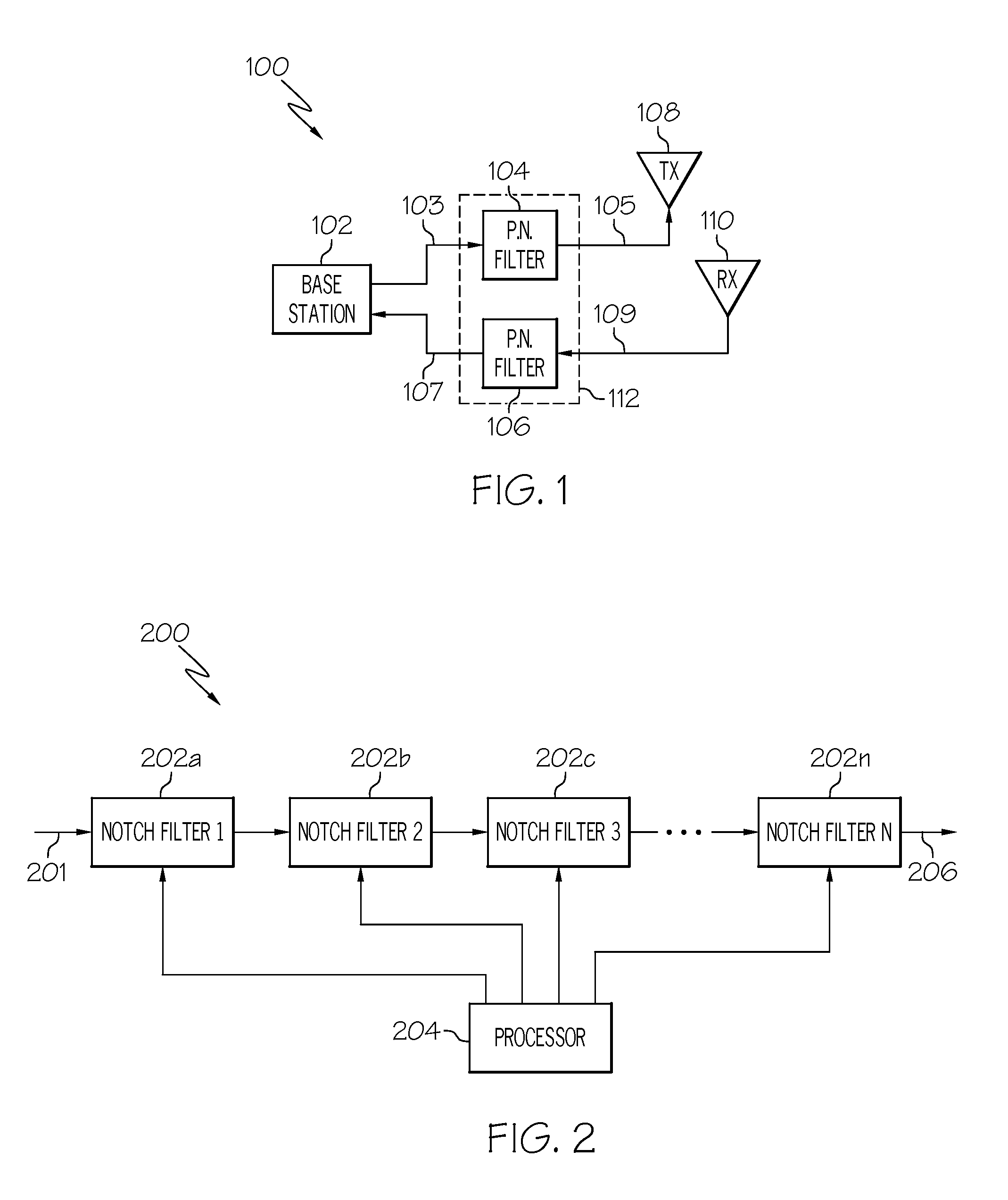
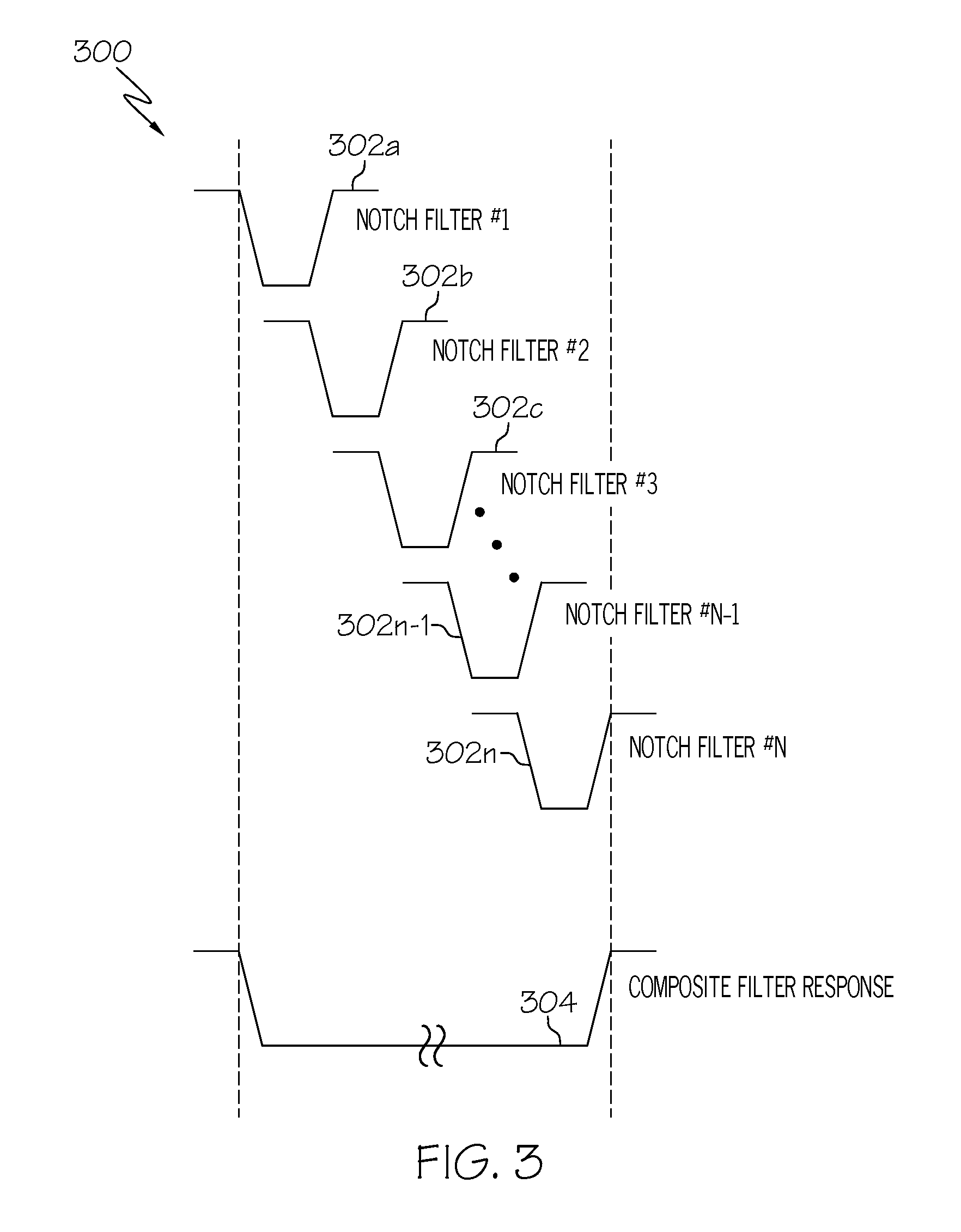
System and method for selectively rejecting frequency bands in wireless communication systems
InactiveUS20090075644A1Rapid reconfigurationRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsWireless commuication servicesBandpass filteringCommunications system
A system and method for selectively rejecting frequency bands in wireless communication systems are disclosed. For example, the system provides a software-selective band rejection technique using multiple cascaded band rejection filters that can remove undesired sub-bands within the RF pass band of the wireless communication system, subsystem or network involved. Thus, the system enables the remaining or desired sub-bands in that RF pass band to be passed. Consequently, the software-oriented band rejection approach enables a designer, operator or user to rapidly configure or reconfigure its designated bands or sub-bands (e.g., on an application-by-application basis) without having to procure and install new bandpass filter hardware or other filter hardware.
Owner:COMMSCOPE TECH LLC +1
Filtering antenna with low profile, wide band and high gain
ActiveCN105591197ASimple structureEasy to processRadiating elements structural formsAntenna earthingsElectromagnetic metasurfaceBroadband
The invention discloses a filtering antenna with low profile, wide band and high gain. The antenna comprises an electromagnetic super-surface radiator and a feed part. The electromagnetic super-surface is constituted by non-uniformly small electrical units and is used as a high-efficiency radiator so that the bandwidth and gain of antenna are increased. At the same time, radiation zero points can be produced, and frequency selectivity can be increased through adjusting roll-off degree of an upper edge of a pass-band. According to the antenna, discrete micro-strip coupling slits are creatively used for feeding; metal via holes are introduced in between the micro-strip and floor; good filtering effect of low frequency stop band is guaranteed; roll-off degree of pass-band lower edges is increased. According to the invention, electromagnetic super-surface with filtering effect is creatively designed and is applied in filtering antenna; the antenna structure is simple and no complicated filtering circuit is used; The height is only 0.06[lambda]0; 10dB impedance bandwidth is 28.4%; antenna loss is low and efficiency reaches up to 95%; in-band average gain is 8.2dBi; out-band rejection is over 20dB; the stop-band is wide.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Multichannel low-stray-light spectrograph based on area array detector
InactiveCN102175324AEffective correctionAccurate measurementRadiation pyrometrySpectrometry/spectrophotometry/monochromatorsFull waveSpectrograph
The invention relates to a multichannel low-stray-light spectrograph based on an area array detector, belonging to the field of spectral analysis instruments. The spectrograph comprises an optical platform and a light signal acquisition device, and is characterized in that the area array detector serves as the optical platform; a plurality of band-rejection filters are processed and formed along the spectrum distribution direction on the window of one channel by using an imaging film-coating method; the condition of the change of the stray light received by each area of the detector is measured in real time; and by using the channel as a reference channel, the stray light of the whole spectral analysis instrument is efficiently corrected in real time. By using the spectrograph provided by the invention, the measured stray light in a full-wave band scope of a spectral analysis system is efficiently corrected. The multichannel low-stray-light spectrograph can be applied to measuring various photo-chromic parameters, such as spectrum characteristics, absorbance value, and the like of a to-be-measured sample.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Test system for radio frequency index
InactiveCN102571239ASolve block index testEliminate the effects ofTransmitters monitoringIndex testTest efficiency
The invention provides a test system for a radio frequency index. The test system comprises a multiplexer, a RRU (Radio Remote Unit), a tester and a signal source, wherein a common port of the multiplexer is connected with an antenna port of the RRU; one or more band-pass filter ports in the multiplexer are connected with the tester through a first attenuator and is used for testing a radio frequency index of a downlink signal; a first output port of the signal source is directly connected with a first band-rejection filter port in the multiplexer and is used for outputting an uplink interference signal; and a second output port of the signal source is connected with a second band-rejection filter port in the multiplexer through a second attenuator and is used for outputting an uplink useful signal and testing the radio frequency index of the uplink signal. By adopting the test system for the radio frequency index, the simultaneous test for uplink and downlink indexes is realized, the block index test is performed under TX rated power, the influence of test environment on the RRU performance is eliminated, and the test efficiency is increased.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Microstripline waveguide converter
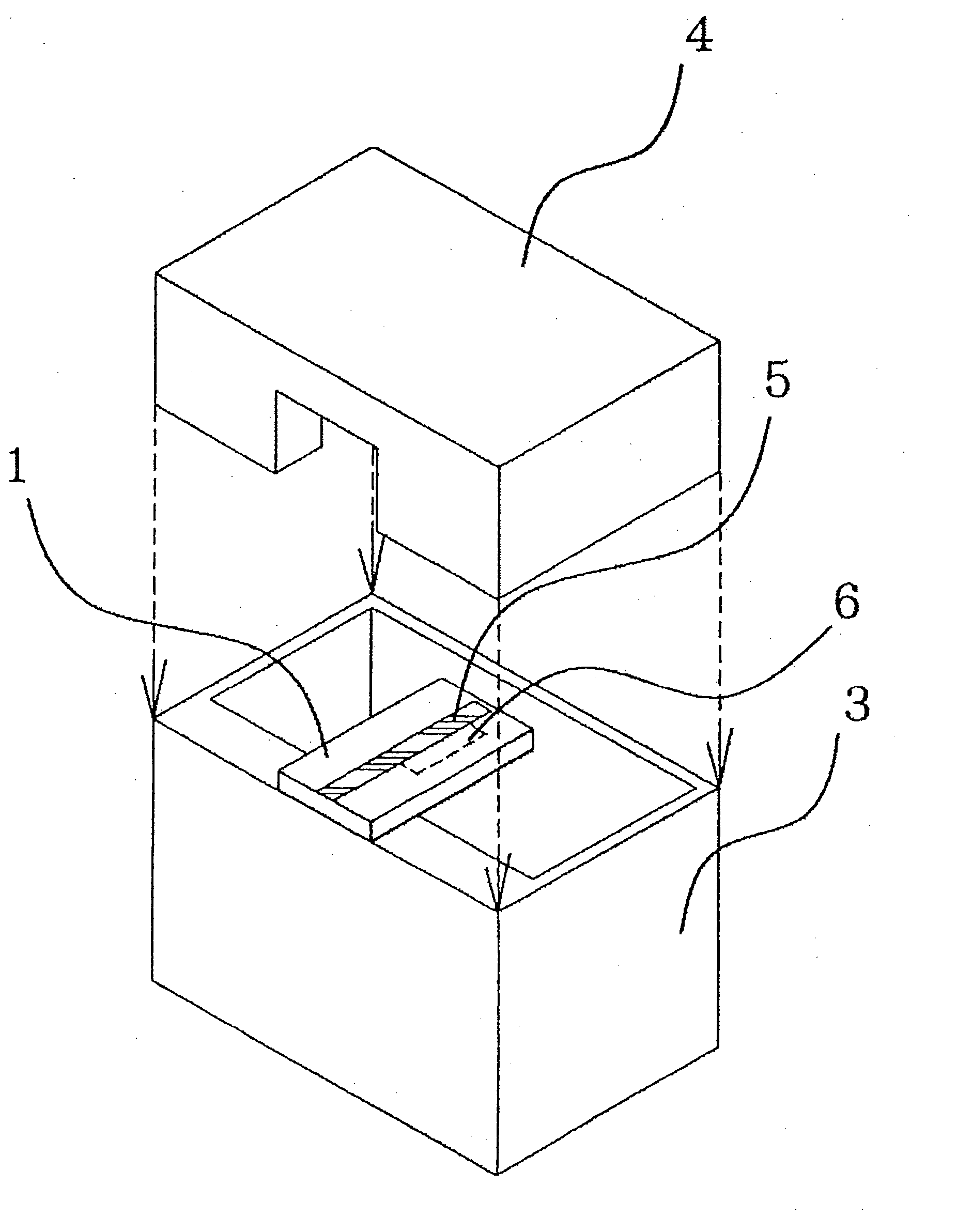
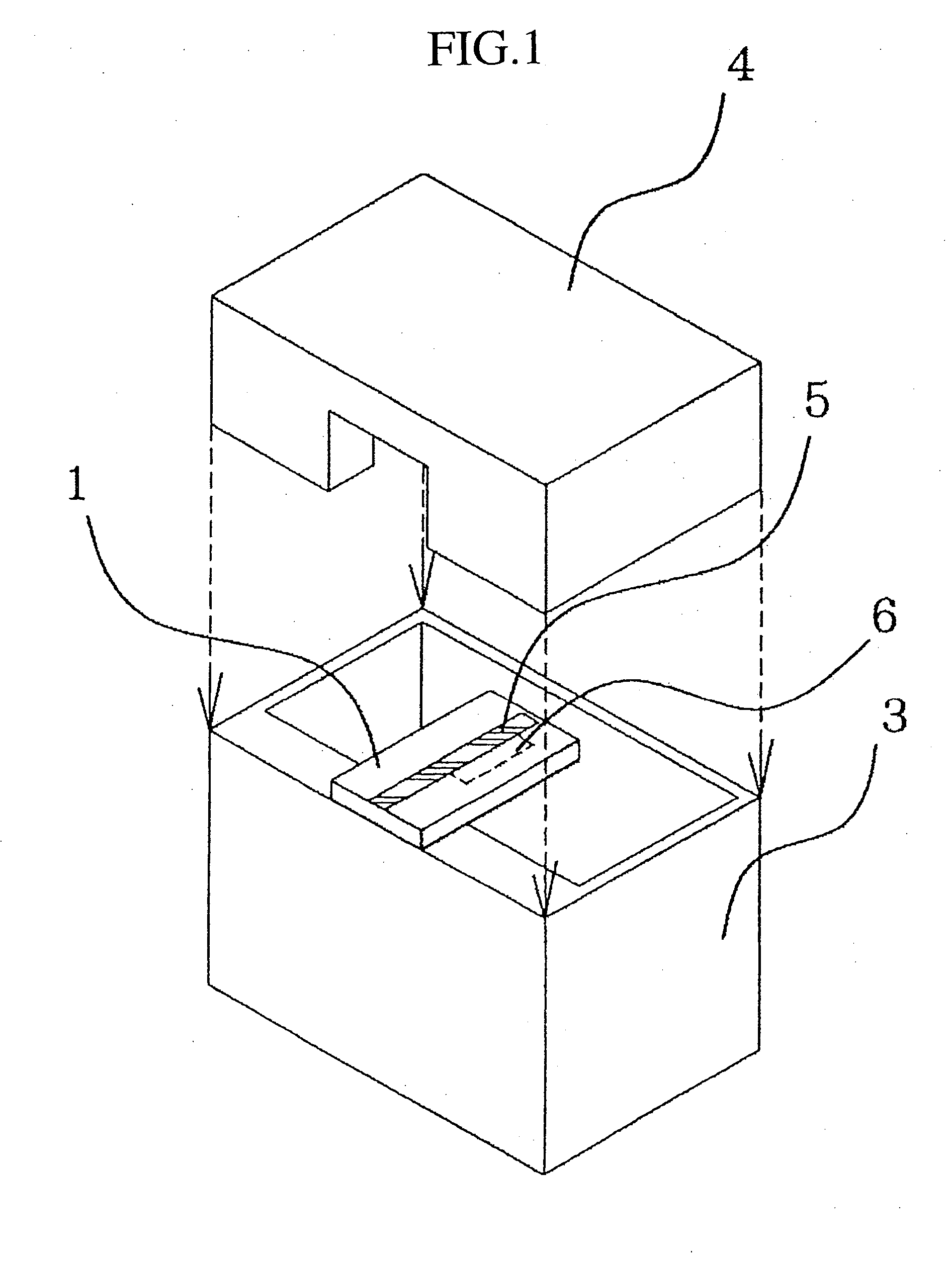
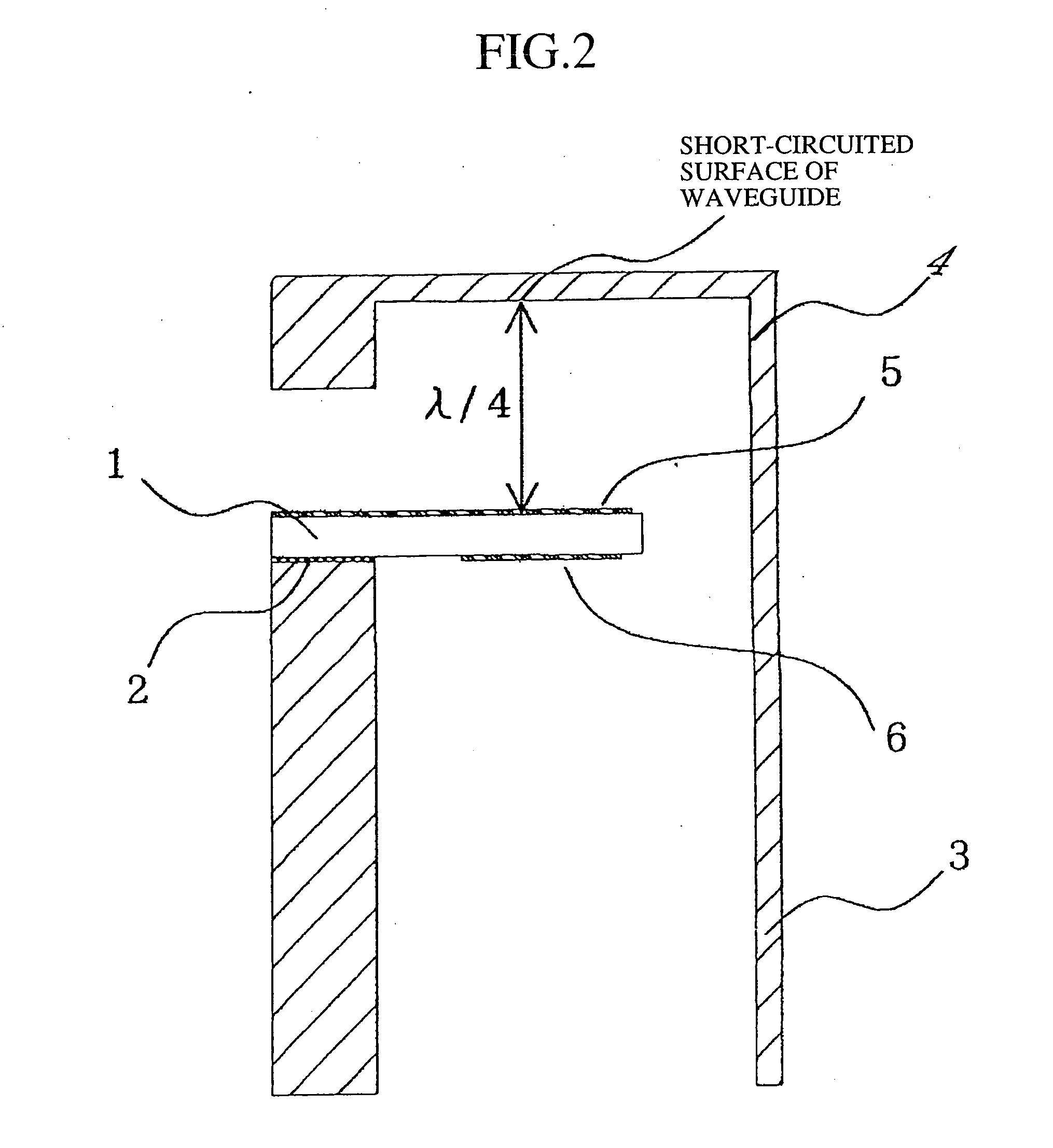
InactiveUS20050200424A1Small sizeElimination of the working process of connecting the filterOne-port networksCoupling devicesElectrical conductorBand shape
In the inside of the converting portion of a microstripline waveguide converter, on the backside surface of a dielectric substrate, which constitutes, for example, a “stripline antenna,” a strip conductor pattern, which serves as a half-wavelength strip resonator, is disposed, to thereby add a band rejection function to the converter. The size of the converter is thereby reduced.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Complementary opening resonance ring and defect ground structure half module substrate integrated waveguide dual-band filter
The invention discloses a complementary opening resonance ring and defect ground structure half module substrate integrated waveguide dual-band filter. The dual frequency-band filter is realized by using two resonators. The dual frequency-band filter is a complementary opening resonance ring defect ground structure which is characterized in that a top layer metal is arranged on a medium substrate, a top layer metal ground is arranged on a grounding metal surface, a complementary opening resonance ring structure is etched in the top layer metal and a grounding metal paster is etched. A line of metal through holes, microstrip lines, impedance matching units, an input feed wire and an output feed wire are arranged at one edge of the top layer metal. The complementary opening resonance ring structure can generate one passband and can generate a transmission zero point at the same time; the complementary opening resonance ring defect ground structure and the microstrip lines can generate one passband by coupling, can generate one transmission zero point at the same time and are cascaded to form the dual-band filter. According to the filter, two transmission zero points are introduced, so the out-of-band rejection is improved, the passband selectivity is improved, and the external quality factor is improved by adopting a conical gradual feeding mode.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY
Novel cross coupling substrate integrated waveguide band-pass filter
InactiveCN103326093AMeet the high performance requirements of the designSimplify structural complexityWaveguide type devicesCapacitanceResonant cavity
The invention discloses a novel cross coupling substrate integrated waveguide band-pass filter. The filter comprises basic resonant units, wherein rectangular resonant cavities serve as the basic resonant units. Magnetic coupling is achieved among the resonant cavities in a windowing mode. S-shaped grooves are formed to achieve electrical coupling, and input and output are achieved by the adoption of a micro-strip-line and coplanar-waveguide structure. The rectangular SIW resonant cavities are formed by loading of periodic metal through holes in medium substrates. The electrical coupling is achieved through the structure that the S-shaped grooves with symmetrical central axes are formed in the upper metal face and the lower metal face of the two cavities, debugging is convenient, processing is easy, and the structure is suitable for the miniaturization design of the filter. The micro-strip-line and coplanar-waveguide structure is adopted for the input and the output, and the structure is that coplanar waveguides are directly connected with an input 50-Ohm micro strip line and an output 50-Ohm micro strip line, so that an extra transitional design is not needed for matching of ports, and complexity is simplified. The filter is compact in structure, improves out-of-band rejection, has better properties of restraining strays and separating signals, and meets requirements for the miniaturization and high properties of modernization radio communication.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Lamination sheet type wave filter and method for producing the same
InactiveCN101404485ARaise the sensory valueLarge inductance inductorMultiple-port networksCapacitanceElectrical conductor
The invention belongs to the technical field of electronic components and relates to a multi-layer chip filter and a preparation method thereof. The filter leads in ceramics and ferrite in the same chip and simultaneously realizes large inductance and large capacitance; wherein, the inductance consists of a hollow inductance (a 'magnetic core' is a ceramic material) and a magnetic core induction (the magnetic chip is ferrite material). The hollow inductance is characterized by small inductance value, large quality factor, high self-resonance frequency, and the like, thus being capable of better broadening the working frequency section of the filter; the magnetic core inductance has the characteristics of large inductance value, low self-resonance frequency, and the like, thus better reducing the in-band insertion loss of a filter with a low cut-off frequency and improving the effect of the transmission signal of the filter. The preparation method of the multi-layer chip filter includes the steps such as material preparing, casting, punching, pore filling, conductor printing, chip overlapping, isostatic pressing, gumming, sintering, etc. The filter has the advantages of small size, large rectangle degree, large out-band rejection as well as broad working frequency. The preparation method has high controllability and can be compatible with the technique of the existing chip components.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
YIG (Yttrium Iron Garnet) band rejection filter based on planar resonant coupling structure and fabrication method of YIG band rejection filter
ActiveCN106252802ACompact designImproved tuning sensitivityWaveguide type devicesSputteringGadolinium gallium garnet
The invention discloses a YIG (Yttrium Iron Garnet) band rejection filter based on a planar resonant coupling structure and a fabrication method of the YIG band rejection filter. The filter comprises a YIG band rejection filter and a driver, wherein the YIG band rejection filter comprises a resonant cavity, a planar resonant coupling structure, a permanent-magnet biasing magnetic path and an excitation coil, the planar resonant coupling structure is arranged in the resonant cavity, and the permanent-magnet biasing magnetic path provides a stable magnetic field for the resonant cavity. With the adoption of a mode of arranging a YIG thin film on a front surface of GGG (Gadolinium gallium garnet) glass and photoetching a coplanar waveguide circuit on the YIG thin film by sputtering, the planar resonant coupling structure is formed, a traditional spherical three-dimensional coupling structured YIG band rejection resonant coupling structure is substituted, and the technical defect existing in the traditional structure is also overcome. In the processing technology, The YIG thin film is first photoetched to a required shape according to a product shape needed to fabricate, and then the GGG glass is cut along appearance; and the defect of edge breakage or damage of the YIG thin film easily caused by directly cutting the YIG thin film based on a GGG substrate is overcome.
Owner:SOUTHWEST INST OF APPLIED MAGNETICS
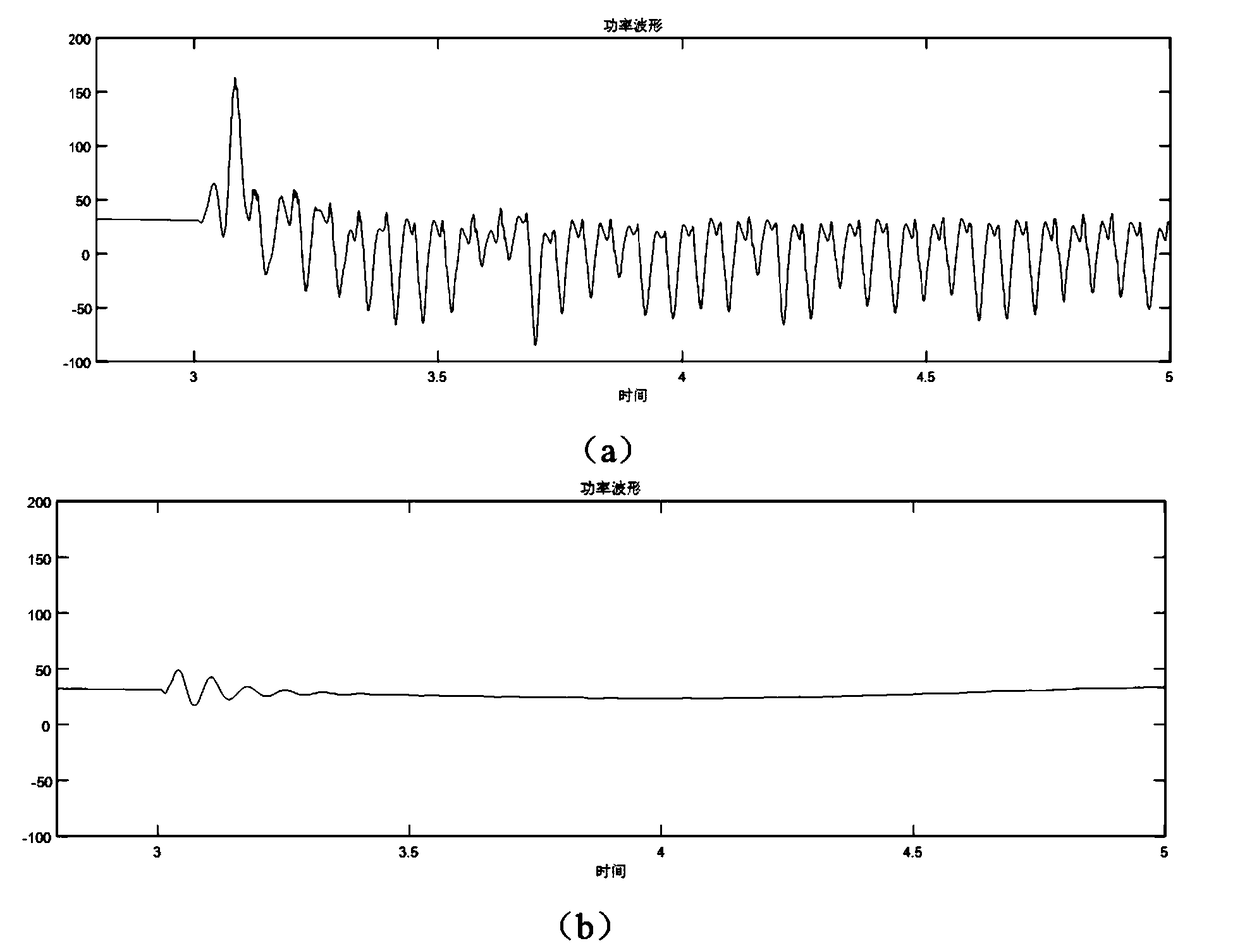
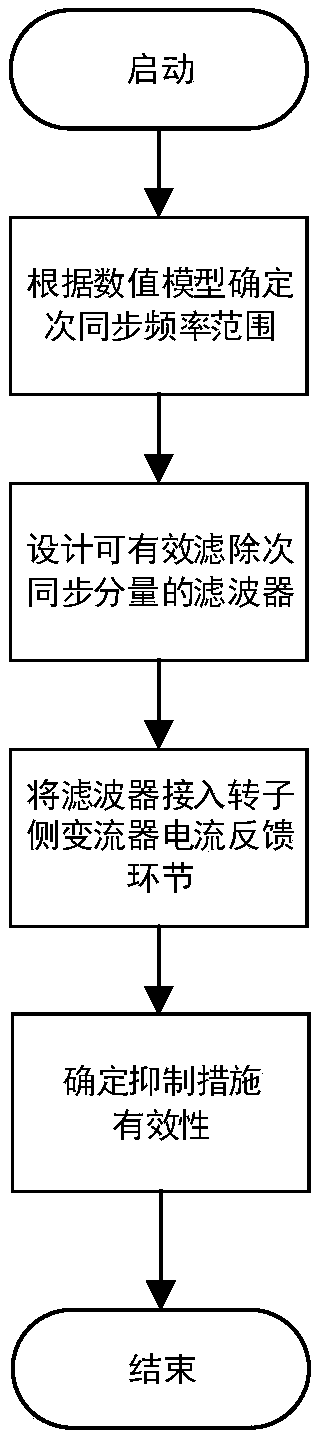
Method used for inhibiting double-fed wind power plant grid connection subsynchronous oscillation
ActiveCN108631338AGuaranteed uptimeImprove stabilitySingle network parallel feeding arrangementsPower oscillations reduction/preventionElectricityElectric power system
The invention discloses a method used for inhibiting double-fed wind power plant grid connection subsynchronous oscillation. First, according to a numerical model of a grid-connected double-fed wind power plant, the frequency range of subsynchronous oscillation that may occur is determined. Then a phase compensation technology is employed for designing a corresponding band rejection filter. Finally, the designed band rejection filter is connected to a current feedback link of converter current inner loop of a rotor side of a double-fed fan. According to the invention, subsynchronous control mutual action of the double-fed wind power plant can be inhibited effectively, so that a distinct inhibition effect on double-fed wind power plant grid connection subsynchronous oscillation is realized.The method has significant realistic meaning in ensuring safe and stable operation of a power system.
Owner:ELECTRIC POWER RESEARCH INSTITUTE OF STATE GRID NINGXIA ELECTRIC POWER COMPANY +1
Narrow band-pass tuned resonator filter topologies having high selectivity, low insertion loss and improved out-of-band rejection over extended frequency ranges
InactiveUS7078987B1Increase valueLow insertion lossMultiple-port networksWaveguide type devicesCapacitanceOut of band rejection
A tuned resonator circuit topology is disclosed that permits implementation of narrow band-pass filters having high loaded Q and optimal coupling (for low insertion loss) using a parallel tuned resonator topology at frequencies in the 1 to 2 GHz range and beyond. The topology consists of a mirror image of the parallel tuned circuit about the signal line of a conventional parallel tuned circuit to effect a cancellation of virtually all of the induced currents between the inductive elements of the resonators. This reduction in induced currents reduces the magnetic coupling between the resonators, thereby offsetting the increase in overall coupling between the resonators as frequency increases, and thereby serves to maintain optimal coupling between the resonators as the frequency of operation increases. Moreover, the mirror image topology increases the parallelism between the inductive elements in the resonators, thereby decreasing the inductance values and permitting an increase in capacitance values. Increasing the capacitance values of the resonators effectively offsets the decrease in the loaded Q as frequency is increased. The topology works for any number of parallel resonators. As the resolution of the manufacturing process decreases (e.g. from printed circuit board to integrated circuit processes), the range of operating frequencies scales with the increase in resolution.
Owner:ARRIS ENTERPRISES LLC
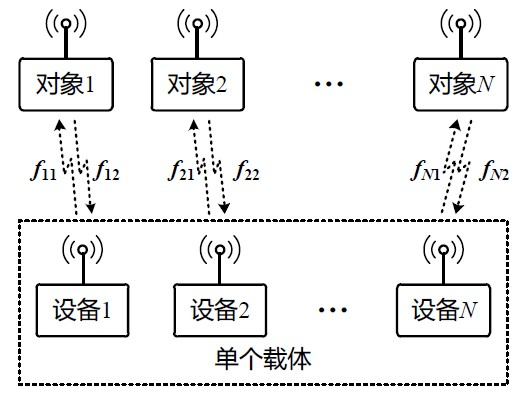
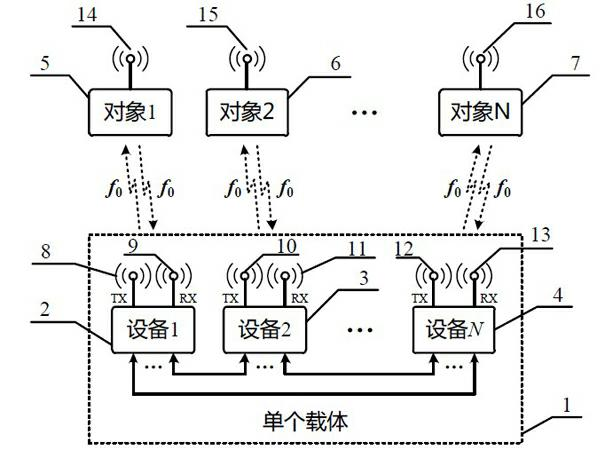
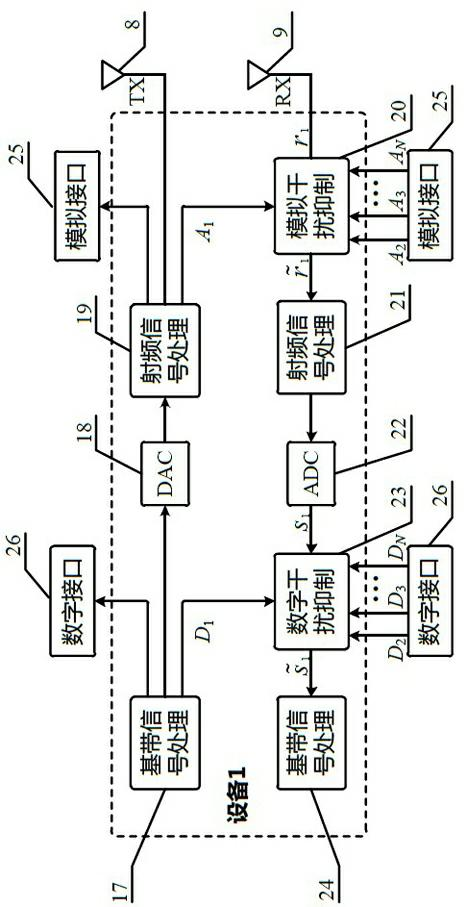
Method for simultaneous common-frequency work of a plurality of pieces of electromagnetic equipment in single carrier
ActiveCN102594463AImprove spectrum utilizationThe spectrum planning problem is simpleTransmission noise suppressionTelecommunicationsFrequency spectrum
The invention discloses a method for the simultaneous common-frequency work of a plurality of pieces of electromagnetic equipment in a single carrier. By the method, a plurality of pieces of equipment in the single carrier with a finite area or volume can simultaneously transmit and receive electromagnetic waves to normally communicate with the outside under the conditions of same working frequency range and partial overlapping or adjacency. Digital interfaces and analogue interfaces are required by each piece of equipment, and are connected with one another for the transmission of transmitted signals of each piece of equipment. The influence of the transmitted signals on received signals can be eliminated by analogue interference suppression and digital interference suppression in a receiving flow of each piece of equipment. By the method, a frequency spectrum utilization rate can be greatly increased, requirements for a clutter and harmonic outer-of-band rejection technology can be lowered, and difficulty in system upgrading and expansion can be lowered.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Broadband dual-polarization base station filter antenna element and array without external filter circuit
PendingCN109004340AGood radiation characteristicsStable radiation characteristicsAntenna supports/mountingsRadiating elements structural formsOut of band rejectionBroadband
The invention discloses a broadband dual-polarization base station filter antenna unit without an external filter circuit and an array thereof. The antenna unit is arranged in the middle of the reflector. The antenna comprises an oscillator arm, a balun and two parasitic metal rings. The vibrator arm is provided with a microstrip line branch, is connected through the balun, and is fed through thebalun, and the balun is provided with a feeder line. The upper part and the lower part of the vibrator arm are respectively provided with parasitic metal rings. The antenna unit has the characteristics of compact and simple structure. The invention realizes good out-of-band rejection effect and has good frequency selectivity without cascading filter, thus avoiding filter insertion loss. The invention realizes high polarization isolation, and realizes stable pattern in wide frequency band at the same time.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Dielectric filter, antenna duplexer, and communications appliance
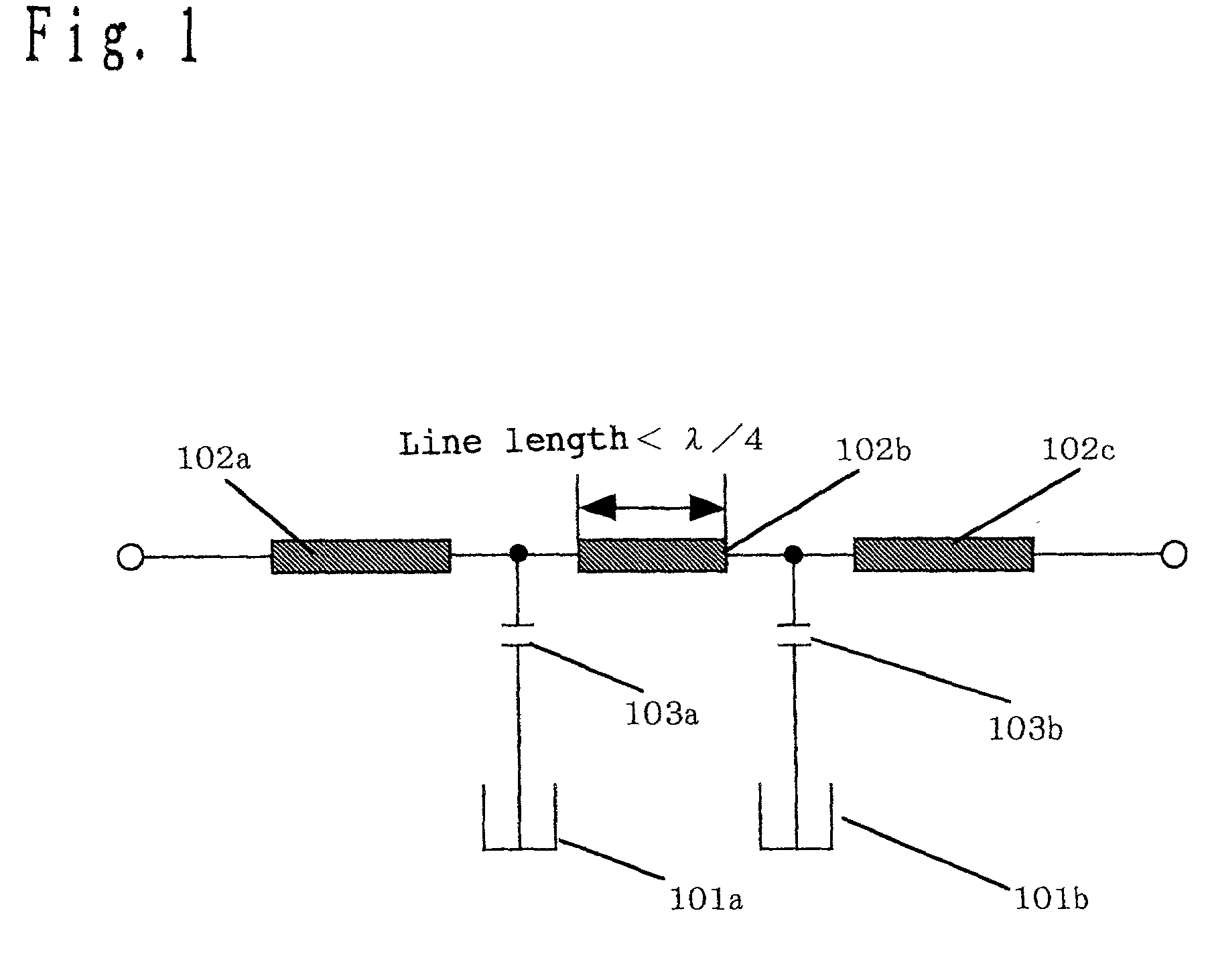
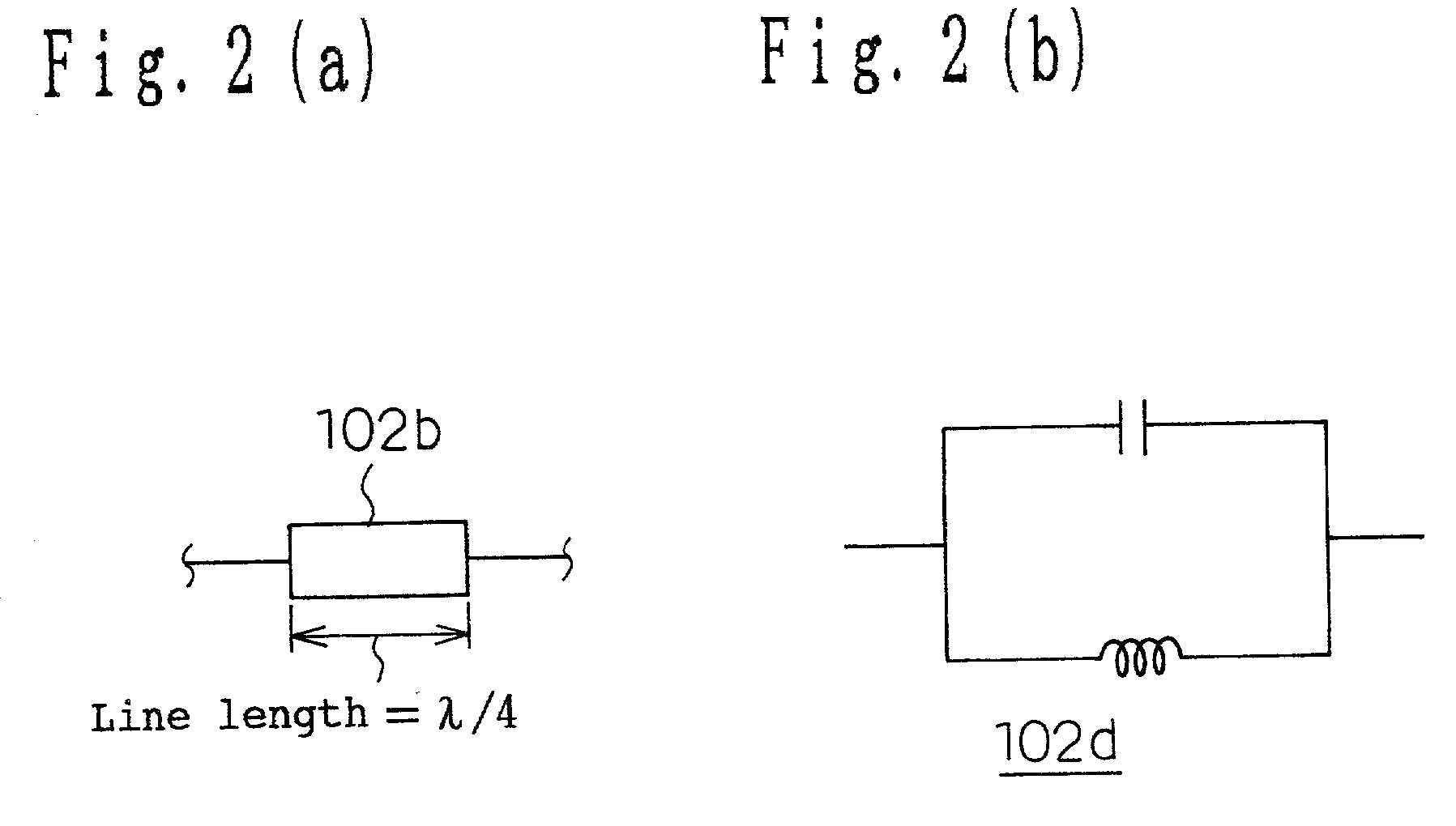
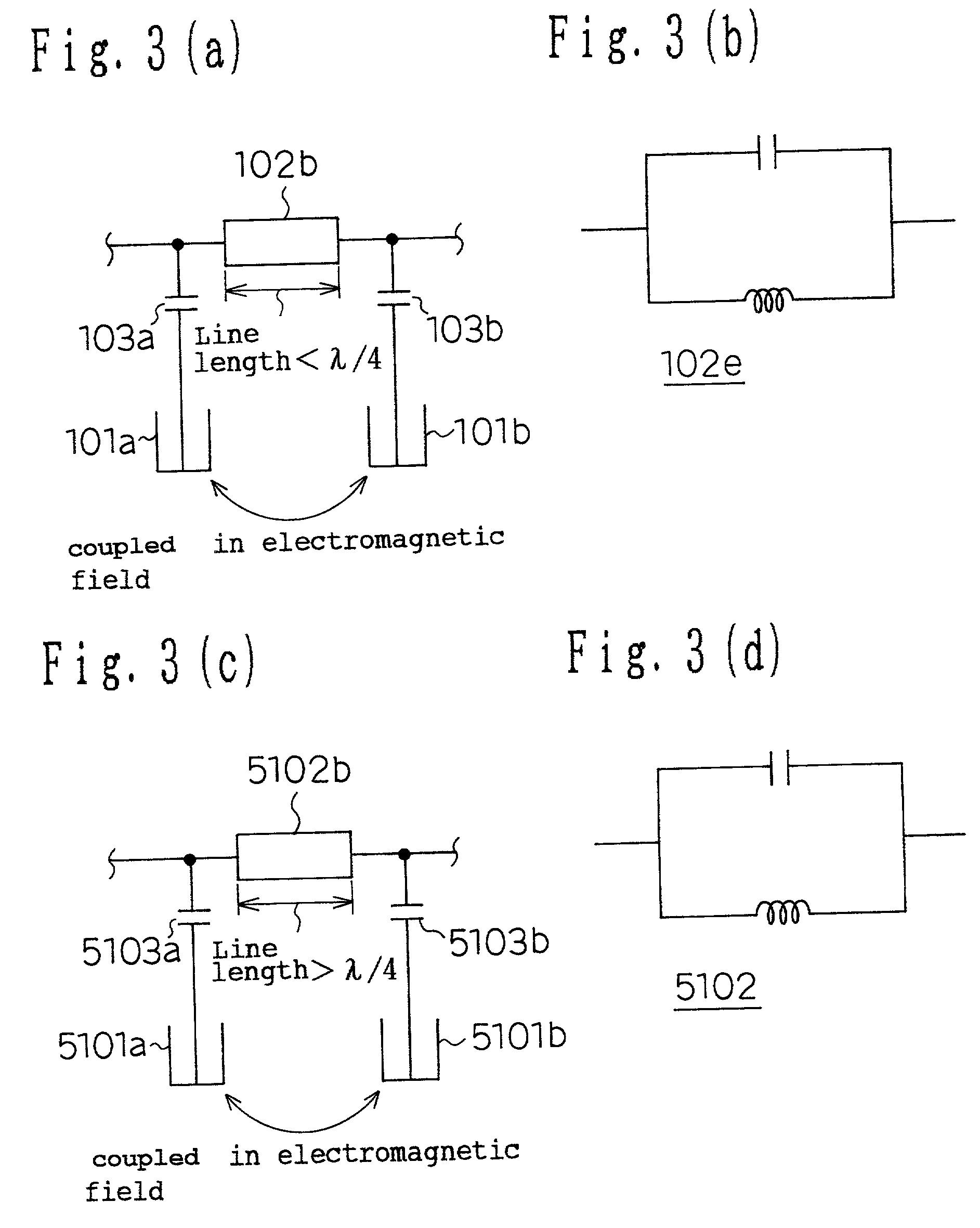
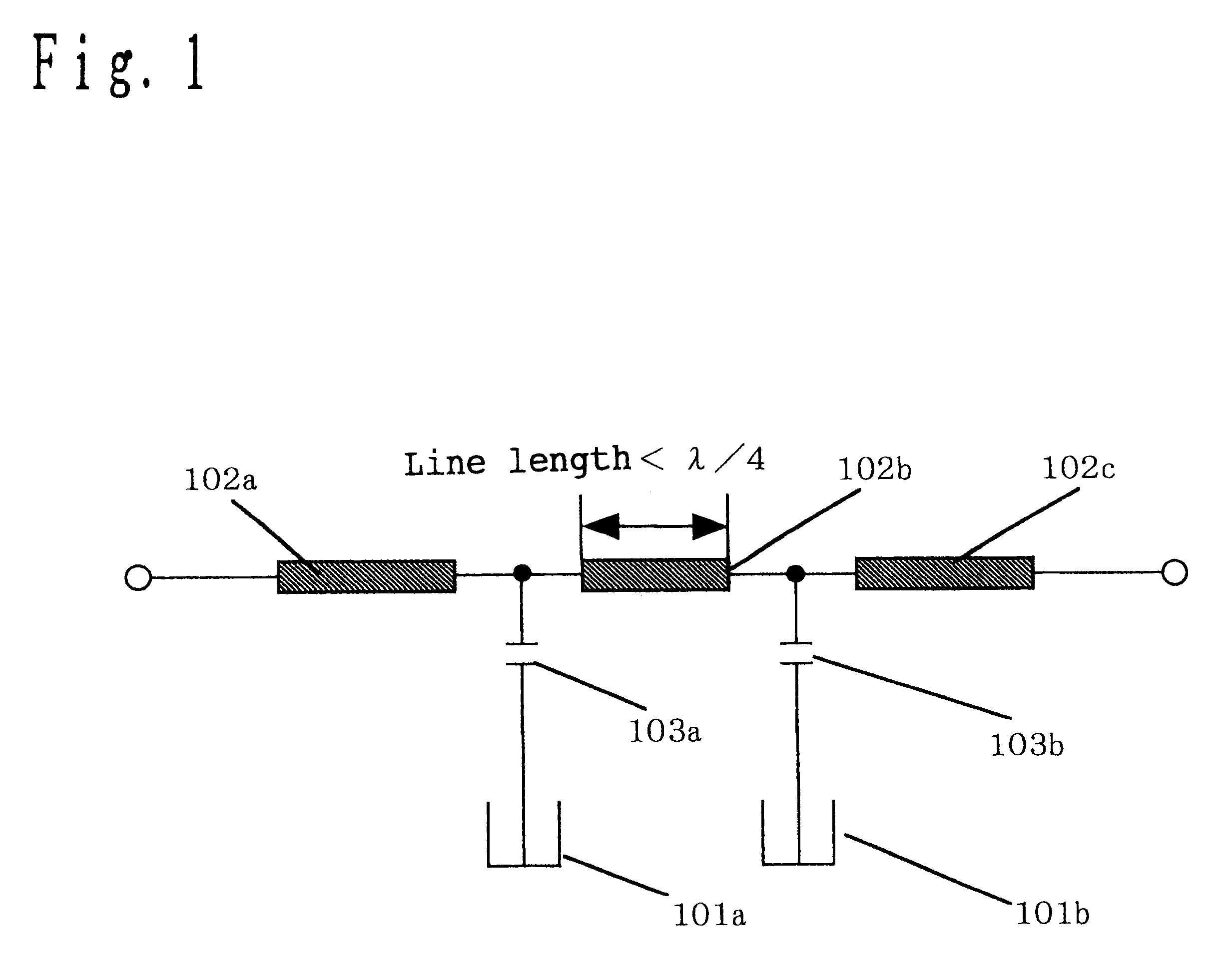
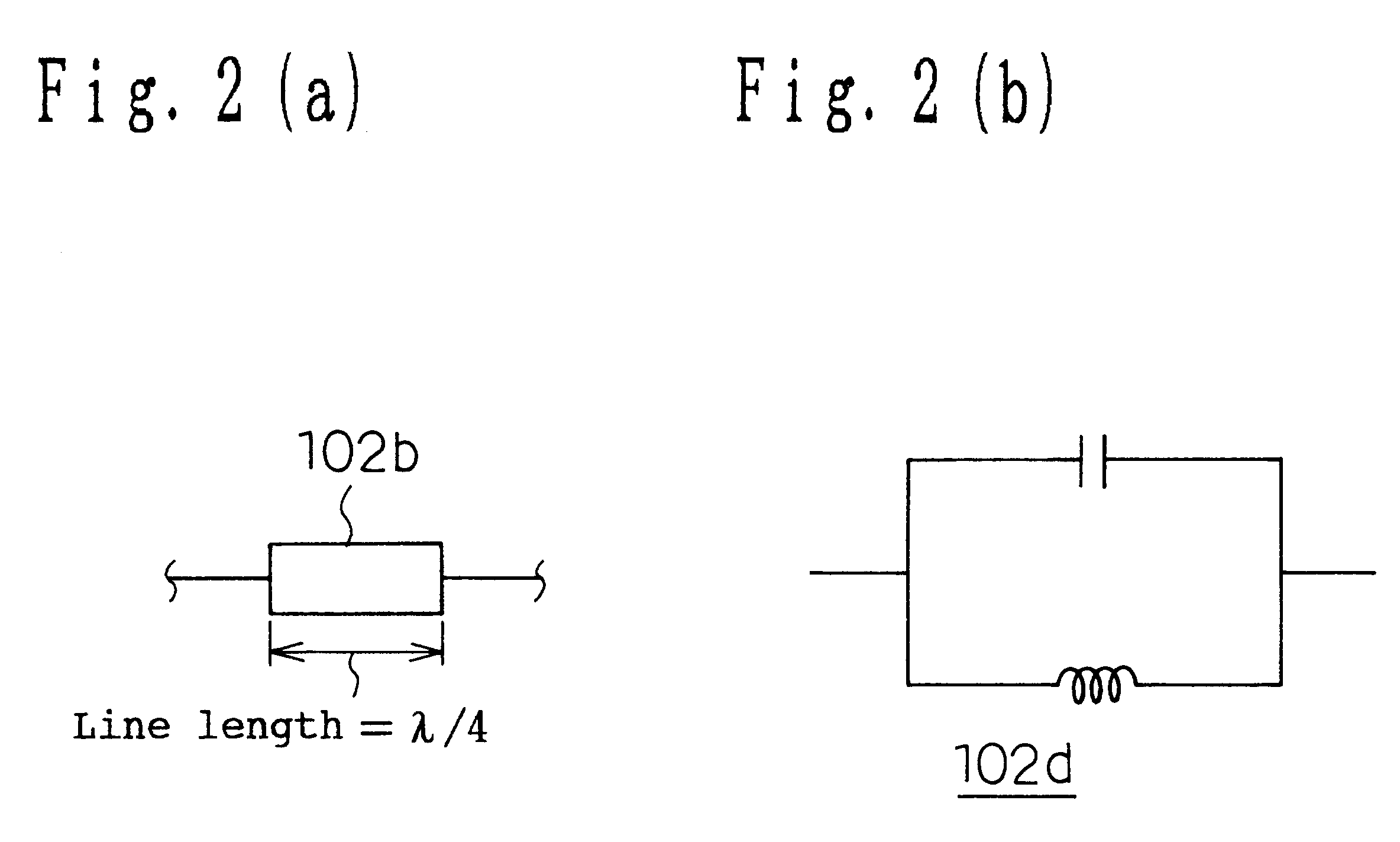
A dielectric filter, has a plurality of resonators; and at least one transmission line provided among said plurality of resonators, wherein a band rejection characteristic is formed around a resonance frequency of said resonator, and a line length of said transmission line is shorter than ¼ of a wavelength corresponding to the resonance frequency of said resonator.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Control apparatus
ActiveCN101339438ADetect natural vibration frequencyReduce natural vibrationElectric motor controlMechanical oscillations controlAudio power amplifierControl signal
Owner:FANUC LTD
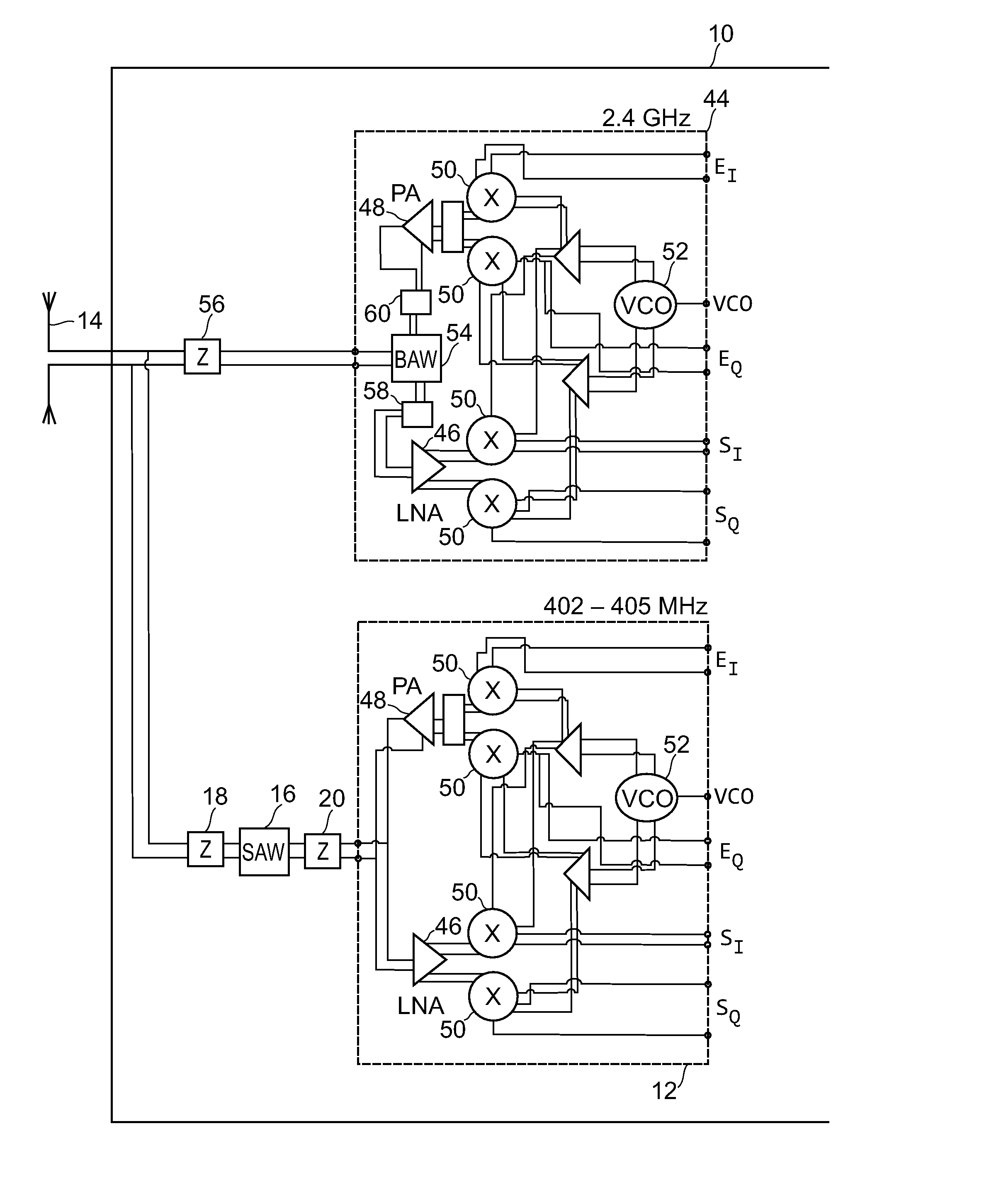
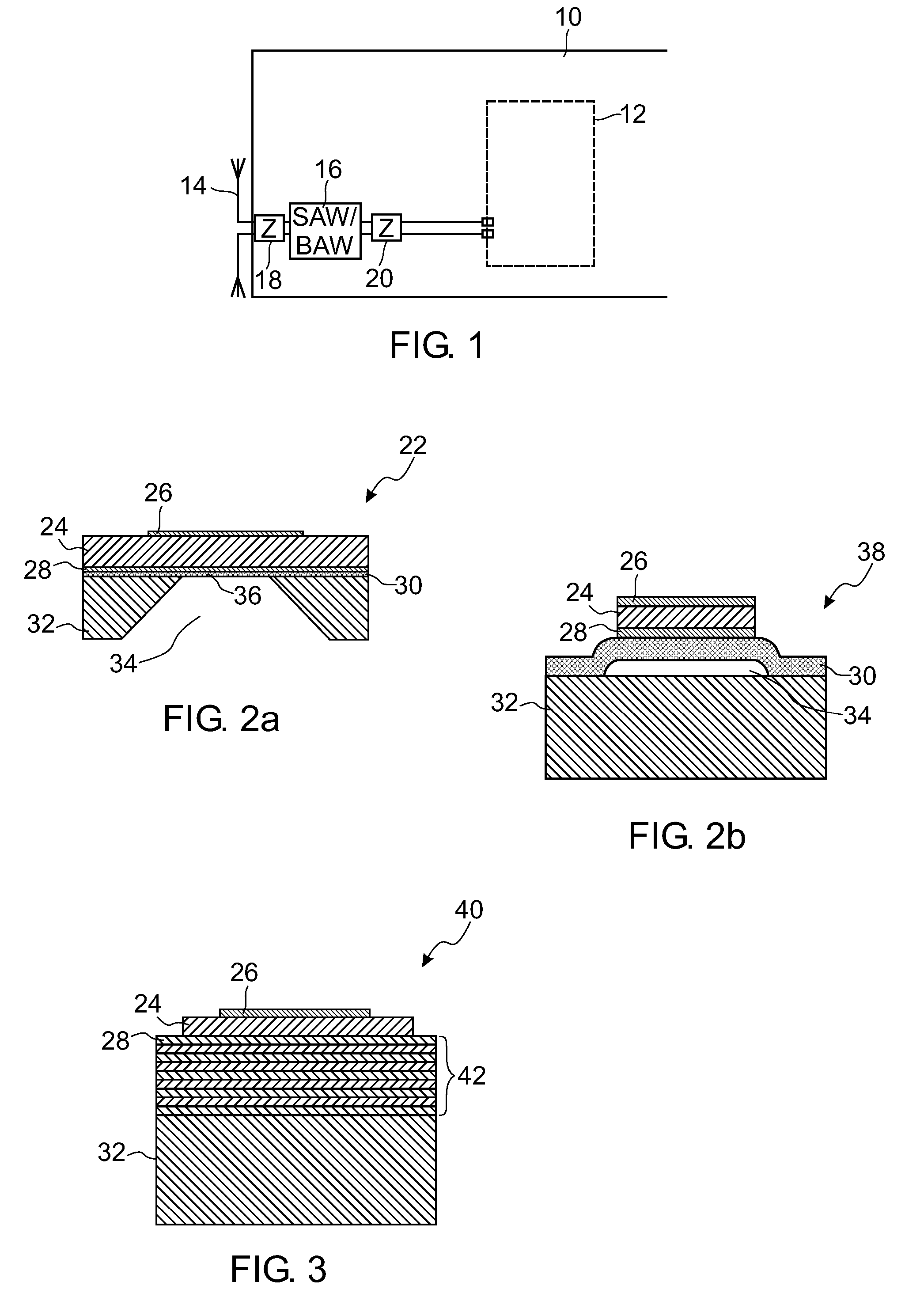
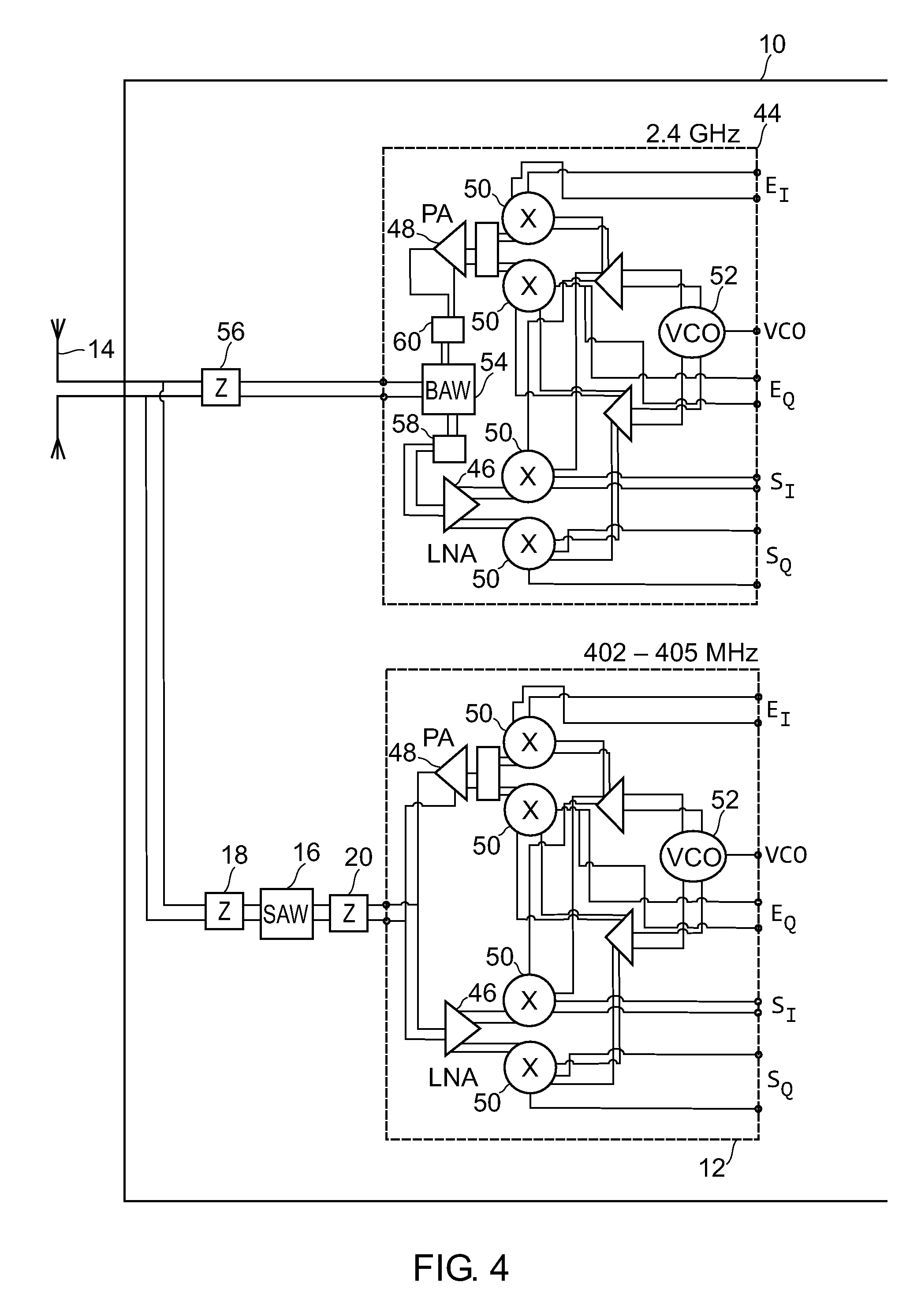
RF telemetry for an active medical device such as an implant or programmer for an implant
ActiveUS20070279149A1MiniaturizationLow costElectrotherapyImpedence networksAcoustic waveMulti-band device
RF telemetry for an active medical device such as active implant or programmer for such implant. The device includes at least one RF antenna (14), and at least one RF telemetry transmitter / receiver (44) with, for coupling to the antenna, an associated band rejection filter (54). The band rejection filter (54) comprises at least one volume acoustic wave BAW resonator (40) of the SMR type with insulation by Bragg acoustic reflector (42). The device can be a multi-band device comprising a plurality of RF transmitters / receivers (12, 44) operating in respective distinct bands of frequencies such as the 402˜405-MHz, 863˜870-MHz, 902˜928-MHz and 2.4-GHz bands or by UWB transmission.
Owner:SORIN CRM
Multi-frequency single negative-permittivity metamaterial and preparation method thereof
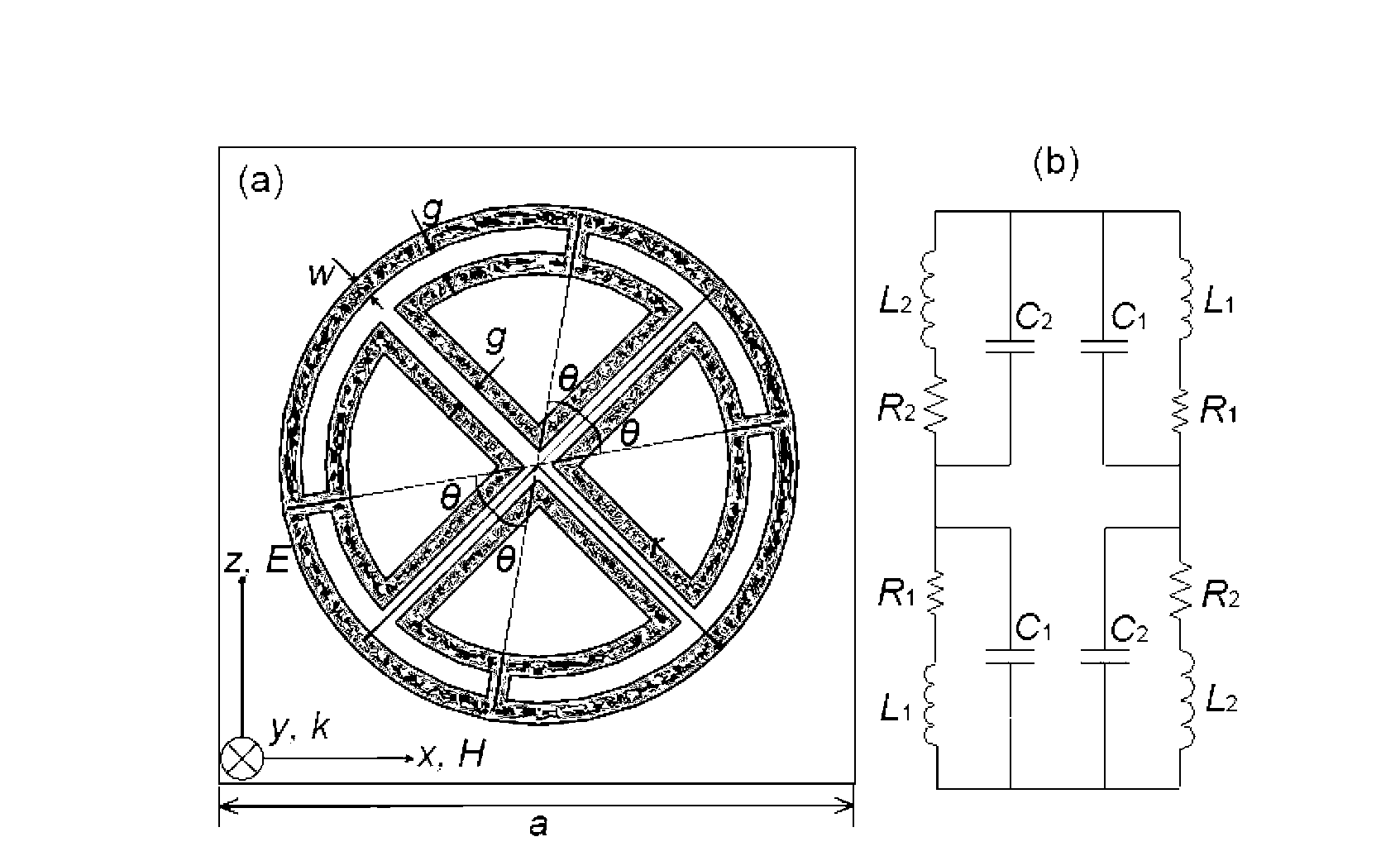
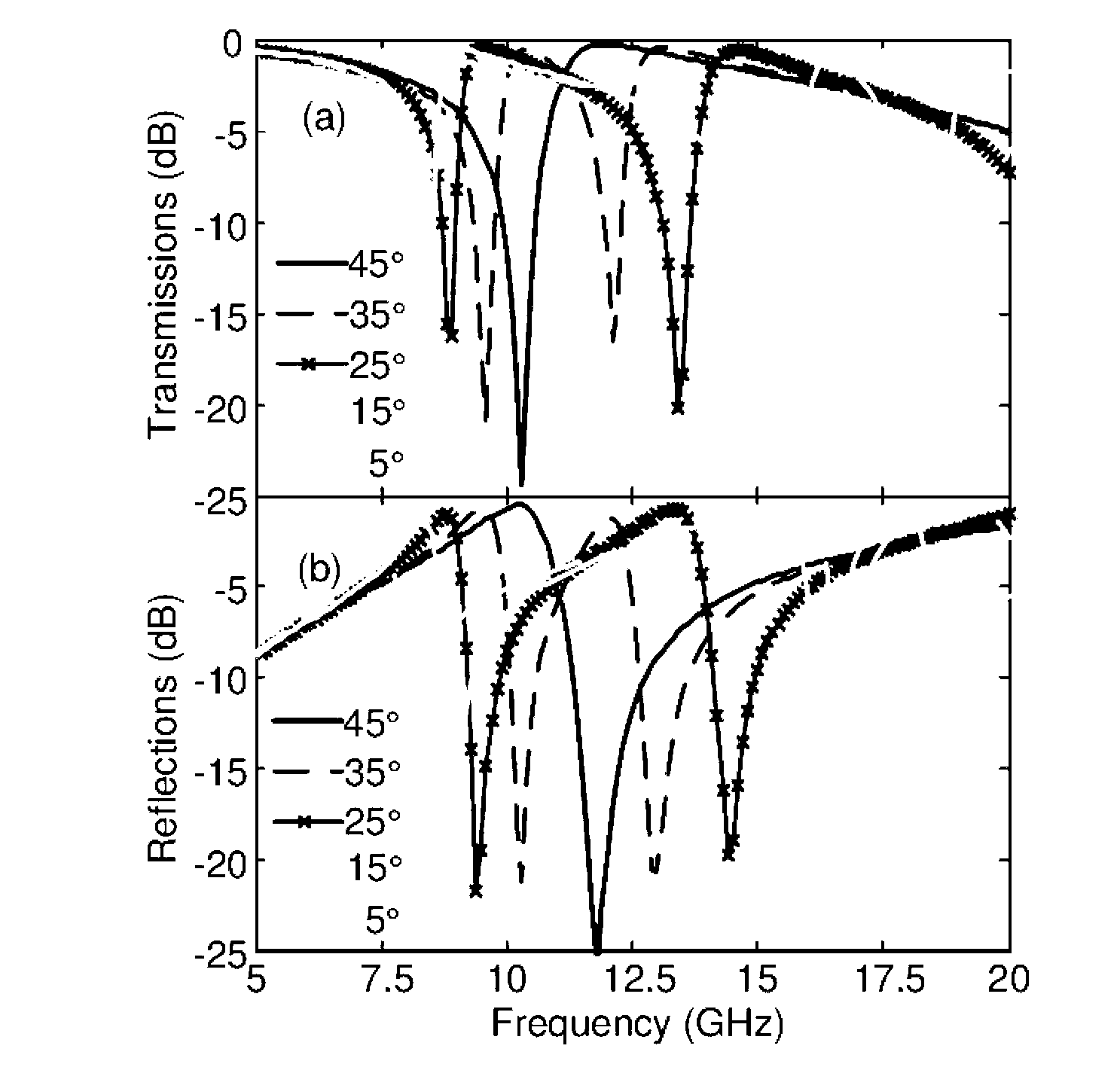
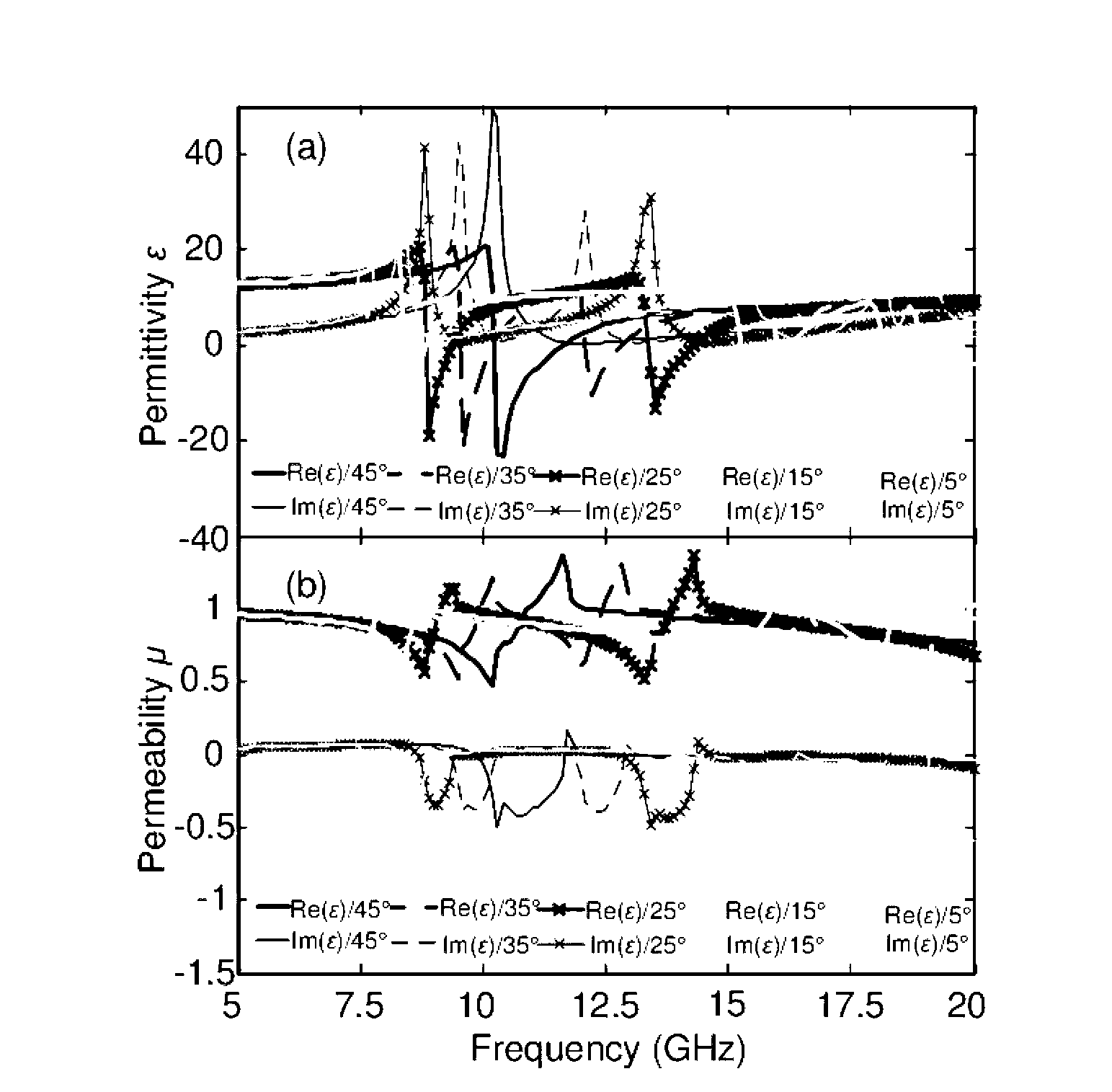
InactiveCN103178352AAdjustable negative dielectric constantSimple manufacturing methodAntennasEpoxyMicrowave
The invention provides a multi-frequency single negative-permittivity metamaterial and a preparation method thereof and belongs to the technical field of microwave electromagnetic materials. A substrate of the multi-frequency single negative-permittivity metamaterial is an epoxy resin PCB (printed circuit board) substrate, and a basic structure unit is a metal double-ring crisscrossed resonance structure based on stub connection. The preparation method includes: calculating an included angle between a straight line where a stub of the metal double-ring crisscrossed resonance structure is located and a channel through a negative-permittivity resonance frequency range to be regulated; and etching the metal double-ring crisscrossed resonance structure on one side of the epoxy resin PCB substrate by circuit etching technology. The preparation method of the multi-frequency single negative-permittivity metamaterial is simple and easy, frequency range of the multi-frequency single negative-permittivity metamaterial prepared by the preparation method is simple to adjust and stable in performance, and the multi-frequency single negative-permittivity metamaterial can be used for designing and researching multi-frequency negative refractive index metamaterial, multi-frequency band-pass / band-rejection filter, multi-frequency electromagnetic invisible materials, absorbing materials and the like.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONIC SCI & TECH OF CHINA +1
Dielectric filter, antenna duplexer, and communications appliance
A dielectric filter including a plurality of resonators, and at least one transmission line provided among said plurality of resonators. A band rejection characteristic is formed around a resonance frequency of the resonator, and a line length of the transmission line is shorter than ¼ of a wavelength corresponding to the resonance frequency of the resonator.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
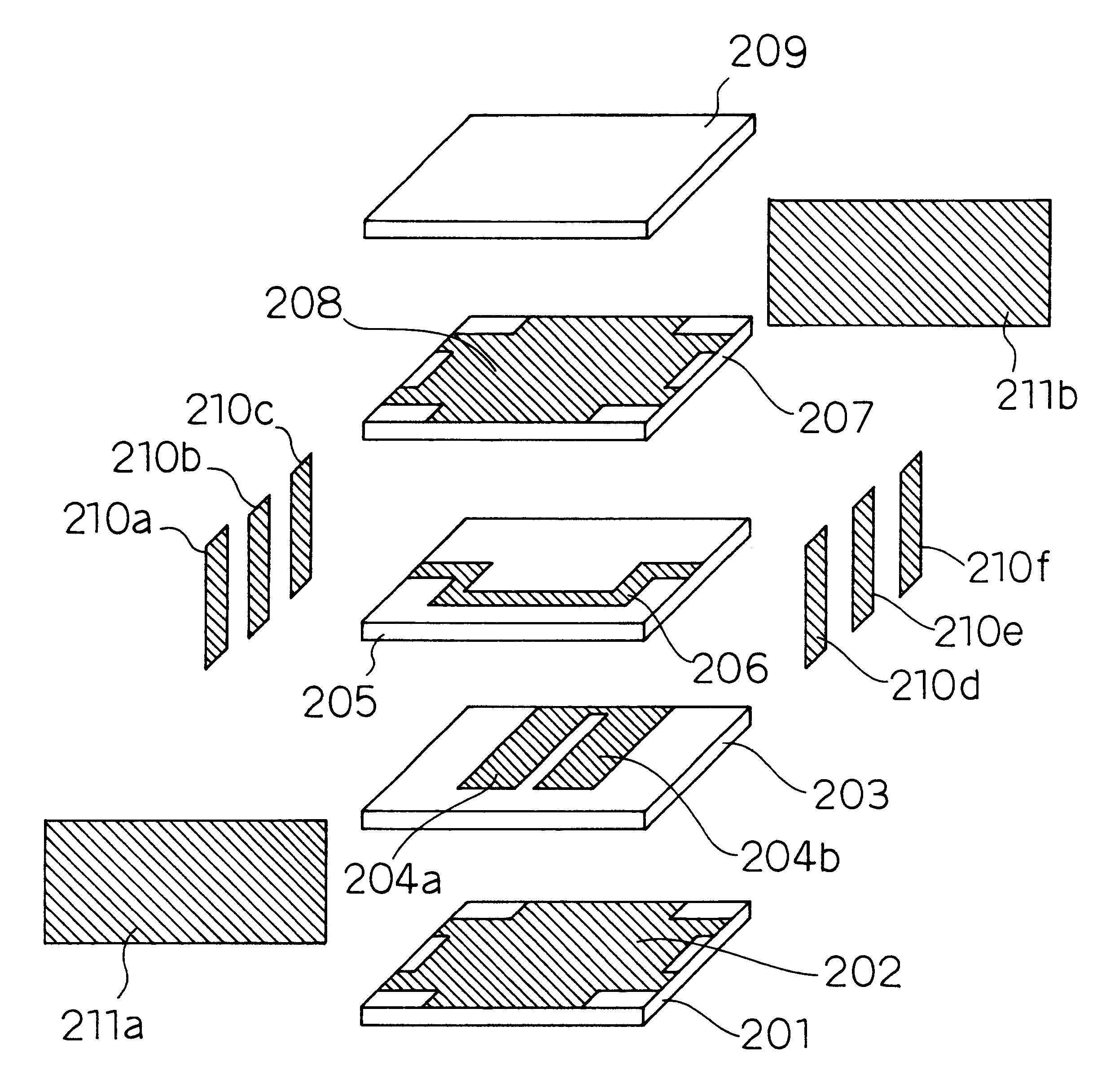
Coupling method of microstrip filter and microstrip resonator thereof
ActiveCN101546854AEfficient use ofSmall parasitic couplingResonatorsCoupling devicesCapacitanceMicrostrip resonators
The invention relates to a coupling method of a microstrip filter and a microstrip resonator thereof. The resonator comprises a group of finger-inserting capacitors comprising microstrips, a group of double-helix curved inductors and a group of blocky capacitors formed with ground, wherein the microstrip comprises an upper-layer superconducting film, a lower-layer superconducting film and an artificial monocrystal medium positioned between the upper-layer and the lower-layer superconducting films; the finger-inserting capacitors are connected in parallel with the double-helix curved inductors, and the finger-inserting capacitors and the double-helix curved inductors connected in parallel are serially connected with the blocky capacitors; a line in the finger-inserting capacitors of the first resonator, which has the same charge polarity with an outermost line of the finger-inserting capacitor of the second resonator is shortened or cut off completely; and the outermost line of the finger-inserting capacitors of the second resonator is elongated and bent, extends into a line shortened or cut off completely in the finger-inserting capacitors of the first resonator and is coupled with two adjacent lines in the finger-inserting capacitors of the first resonator. The filter has less insertion loss, large out-band rejection, high band-edge gradient and good group delay performance.
Owner:INST OF PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
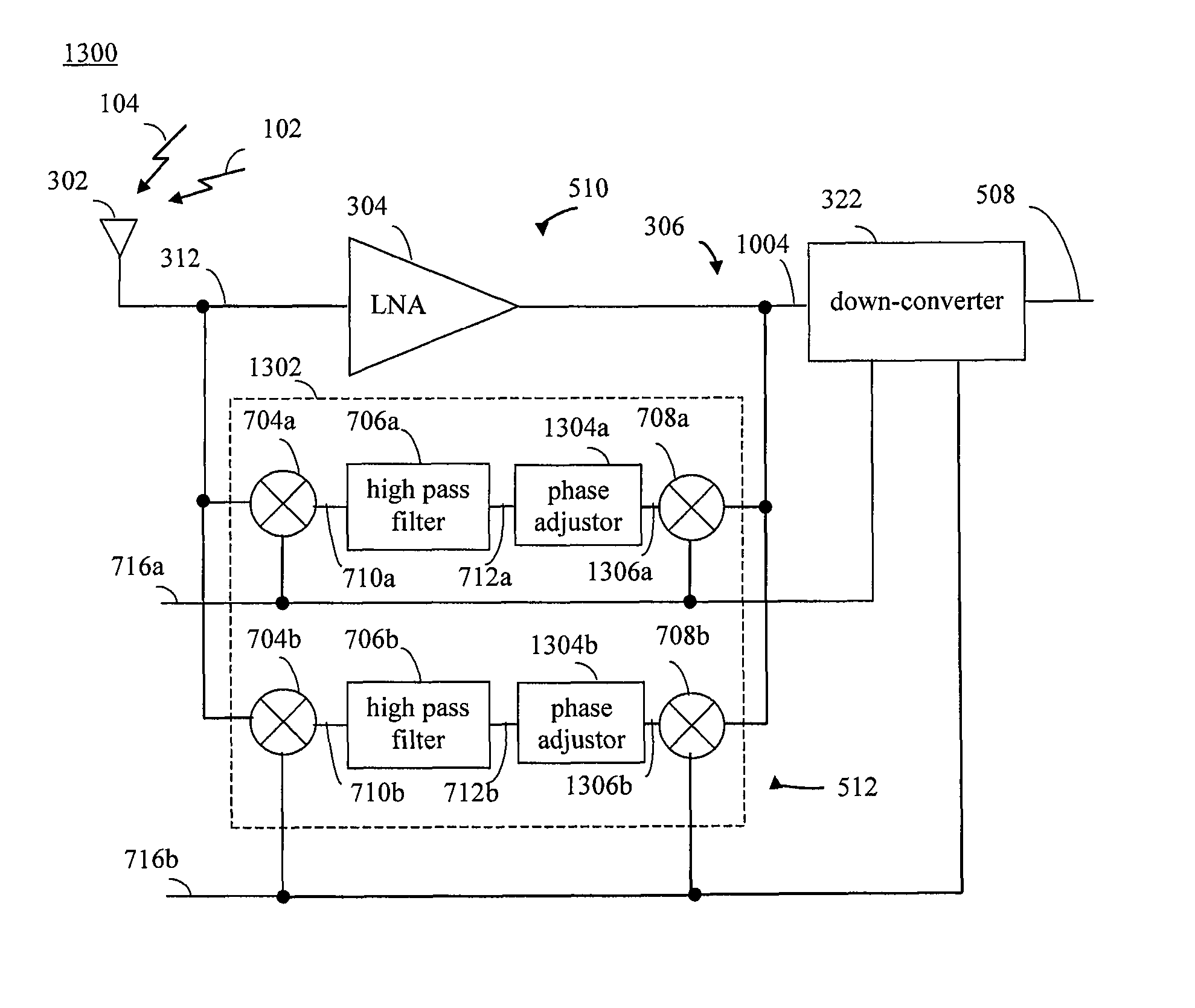
Radio frequency filtering technique with auto calibrated stop-band rejection
Methods, systems, and apparatuses for filtering received radio frequency signals are provided. A first RF communication signal is received that includes a desired information signal portion and an undesired blocker signal portion that is offset in frequency from the desired portion. The first RF communication signal is amplified in a first signal path and is filtered in a second signal path. The filtering of the first RF communication signal in the second signal path includes: down-converting the first RF communication signal to a down-converted signal, high pass filtering the down-converted signal, and up-converting the high pass filtered down-converted signal to a second RF communication signal. The filtering of the first RF communication signal filters out the desired information signal portion from the second signal path. A signal phase is adjusted in the second signal path to match phase shifts between the first and second signal paths. The second RF communication signal is subtracted from the amplified first RF communication signal to generate a third RF communication signal. Third RF communication signal includes the desired information signal portion but does not include the blocker signal, which is canceled during the subtraction.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Characterization method and device of tunable laser
ActiveCN105826811AIncrease flexibilityImprove accuracyLaser detailsLaser optical resonator constructionBeam splitterControl signal
The invention relates to a characterization method and device of a tunable laser, which are used for realizing rapid and accurate characterization of the tunable laser, have universality, and are suitable for a tunable laser having an arbitrary number of control signals. The method includes the following steps: output light of the tunable laser is coupled into an optical fiber, and is then split into two paths through a beam splitter, one path passes through an optical band-pass optical filter, the other path passes through an optical band rejection filter, and central wavelengths of the optical band-pass filter and the optical band rejection filter are set at a target wavelength [lambda]0, and are then connected to a detector; control signals of the tunable laser are changed and optical power detected by the detector is collected through a computer or a microprocessor; and an initial control signal combination is generated randomly, a ratio R of the optical power P1 that passes through the optical band-pass filter and the optical power P2 that passes through the optical band rejection filter is used as a criterion for optimization, and a control signal combination required by stable output of the target wavelength [lambda]0 is searched through an optimization algorithm.
Owner:宁波元芯光电子科技有限公司
High relative bandwidth dual frequency combiner
ActiveCN101478071ARealize splitting and combiningMultiple ways of splitting and combiningWaveguide type devicesPower capabilityBand-pass filter
The invention discloses a double-frequency combiner with high relative bandwidth, which comprises a band rejection filter arranged on a chamber and used for enabling ultra wide band signals to pass and a band filter used for enabling relative narrow band signals to pass. The band rejection filter comprises a conduction band. The band filter comprises a plurality of harmonic oscillation columns. After the band rejection filter is combined with the band filter, the signals are output through a common port. A combination part is arranged on the harmonic oscillation column of the band filter close to the common port. The combination part is coupled with the conduction band by means of slot coupling to couple signals between the two filters. The double-frequency combiner with high relative bandwidth widens the range of use of the combiner, and overcomes the limitation that the conventional combined can only be used in the mobile communication system; in addition, as sufficient gaps are reserved between the internal parts, the power capability is improved. Furthermore, the invention has the advantages of high electric indices, low cost, simple process and the like.
Owner:COMBA TELECOM TECH (GUANGZHOU) CO LTD
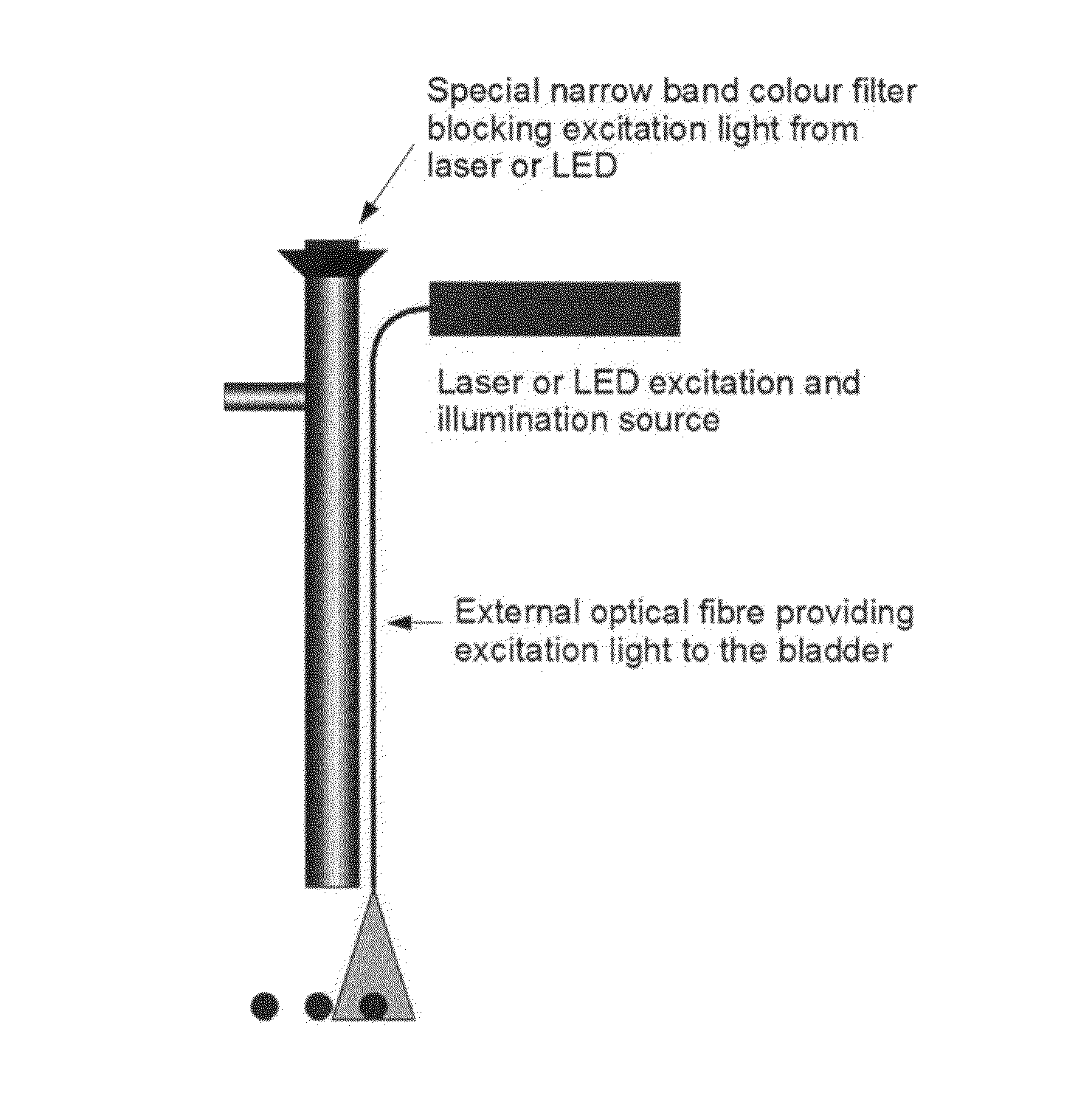
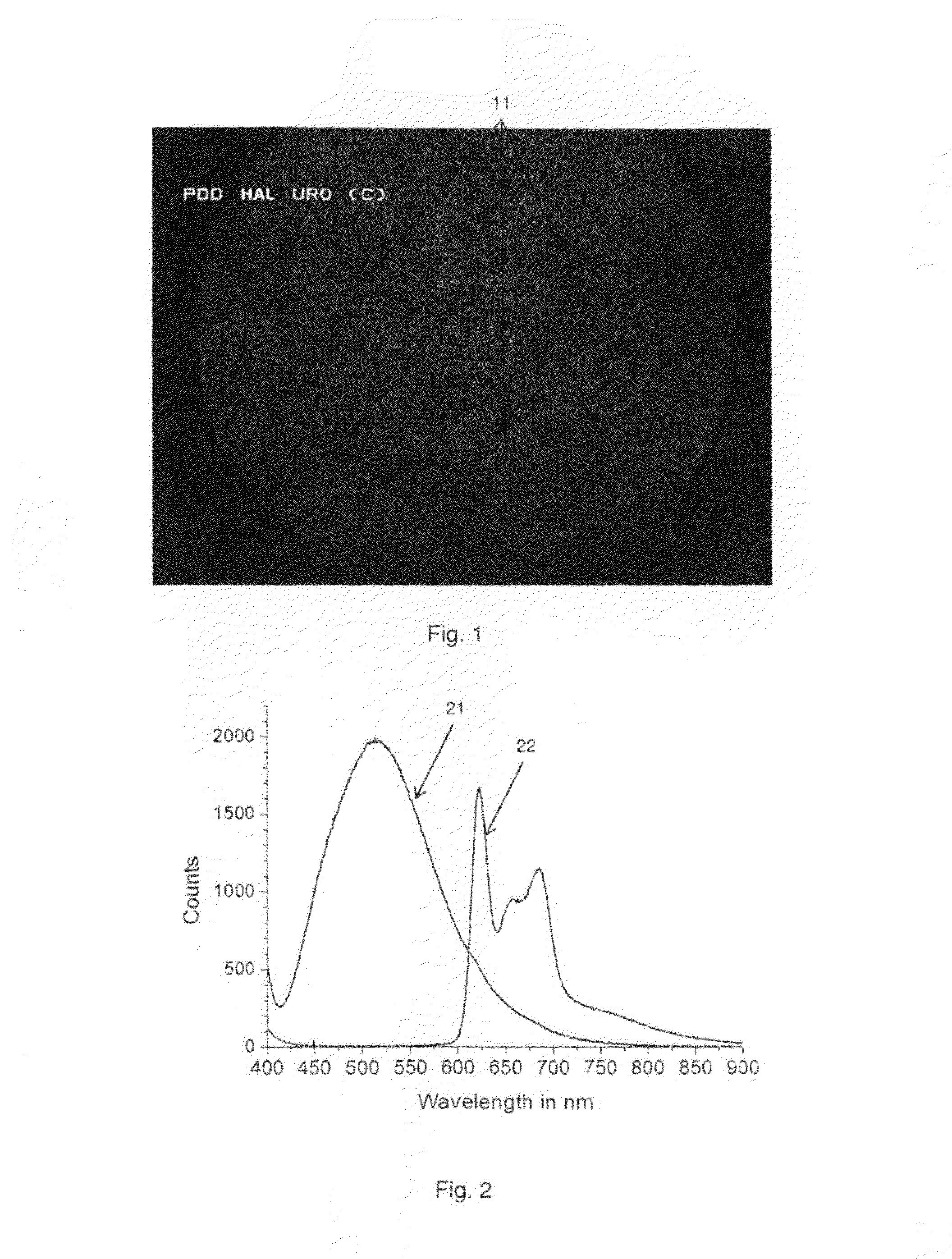
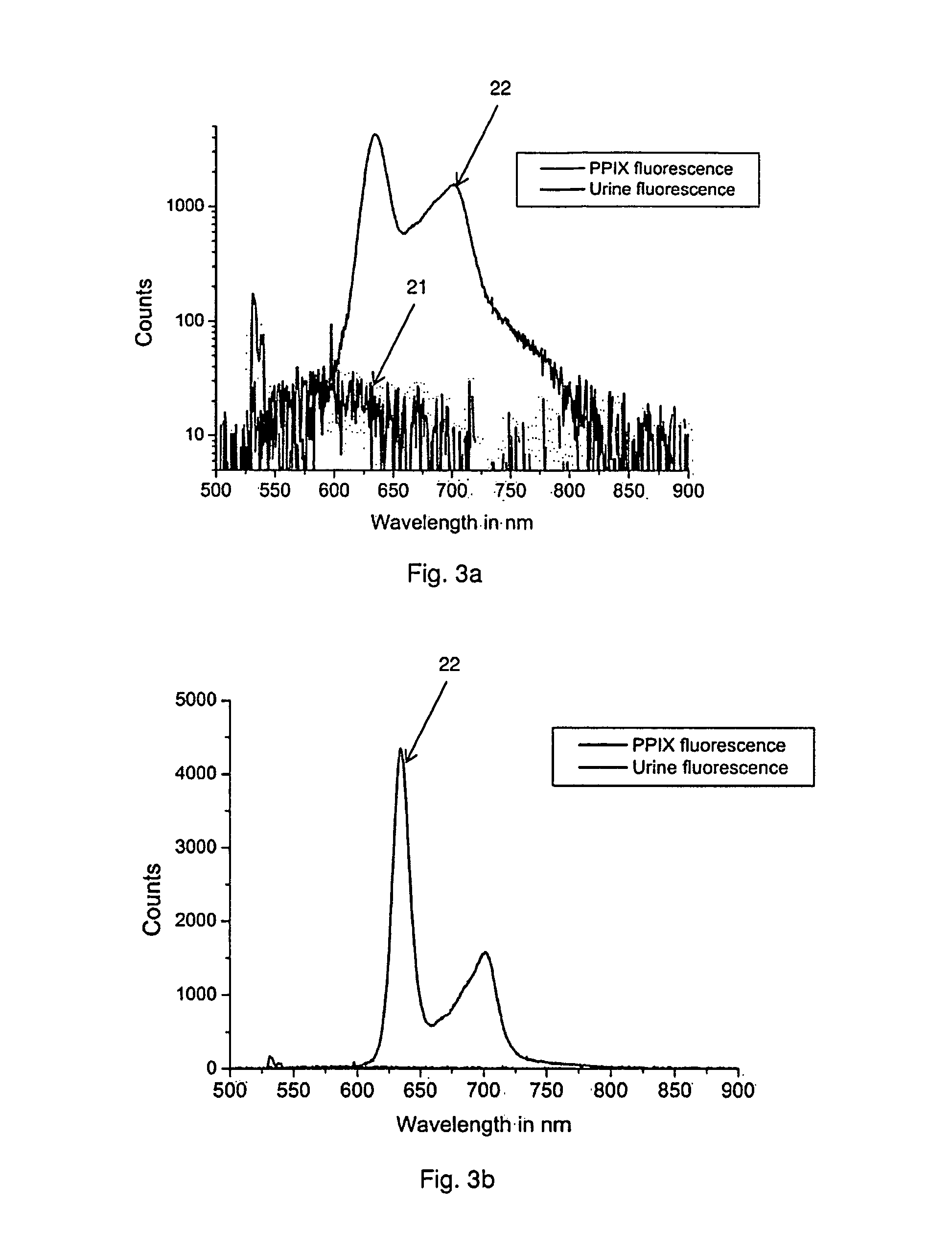
Illumination System for Endoscopic Applications
InactiveUS20150088001A1Easy diagnosisImprove treatmentCosmonautic condition simulationsMechanical apparatusBand-stop filterLighting system
The present disclosure relates to an illumination system for endoscopic applications comprising at least one substantially monochromatic light source having a predefined central wavelength between 400 and 500 nm or between 500 and 550 nm, an optical transmission path adapted to guide light emanating from the light source to an endoscopic region of examination, and an optical band-rejection filter, wherein the illumination system is adapted to illuminate at least a part of the region of examination by generating autofluorescence in surrounding tissue, and the band-rejection filter is adapted to attenuate at least said light source wavelength to a viewer and wherein said light source is the single light source in the illumination system. A further embodiment relates to an endoscope for examining a body cavity comprising tissue, the endoscope comprising a source of light consisting of a substantially monochromatic light source having a predefined central wavelength between 400 and 550 nm, means for guiding light from the substantially monochromatic light source towards at least a part of the tissue, and at least one band-rejection filter adapted to attenuate at least said central wavelength, wherein the substantially monochromatic light source is configured to generate autofluorescence in the irradiated tissue such that the irradiated tissue is observable, and wherein the endoscope is configured to display at least a part of the irradiated tissue through said band-rejection filter. A system for photodynamic diagnosis and / or therapy of bladder cancer is further disclosed herein.
Owner:DANMARKS TEKNISKE UNIV +1
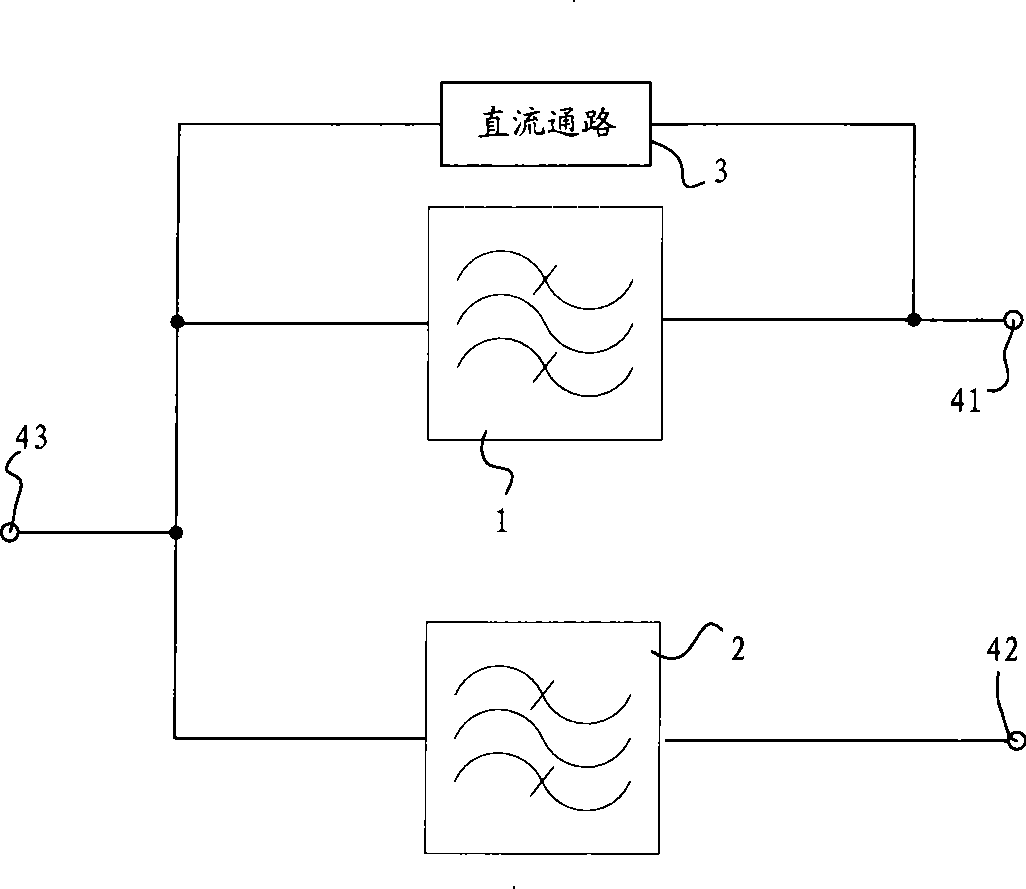
Antenna system with high isolation characteristics
ActiveUS20140139391A1Antenna couplingsIndependent non-interacting antenna combinationsMain branchCoupling
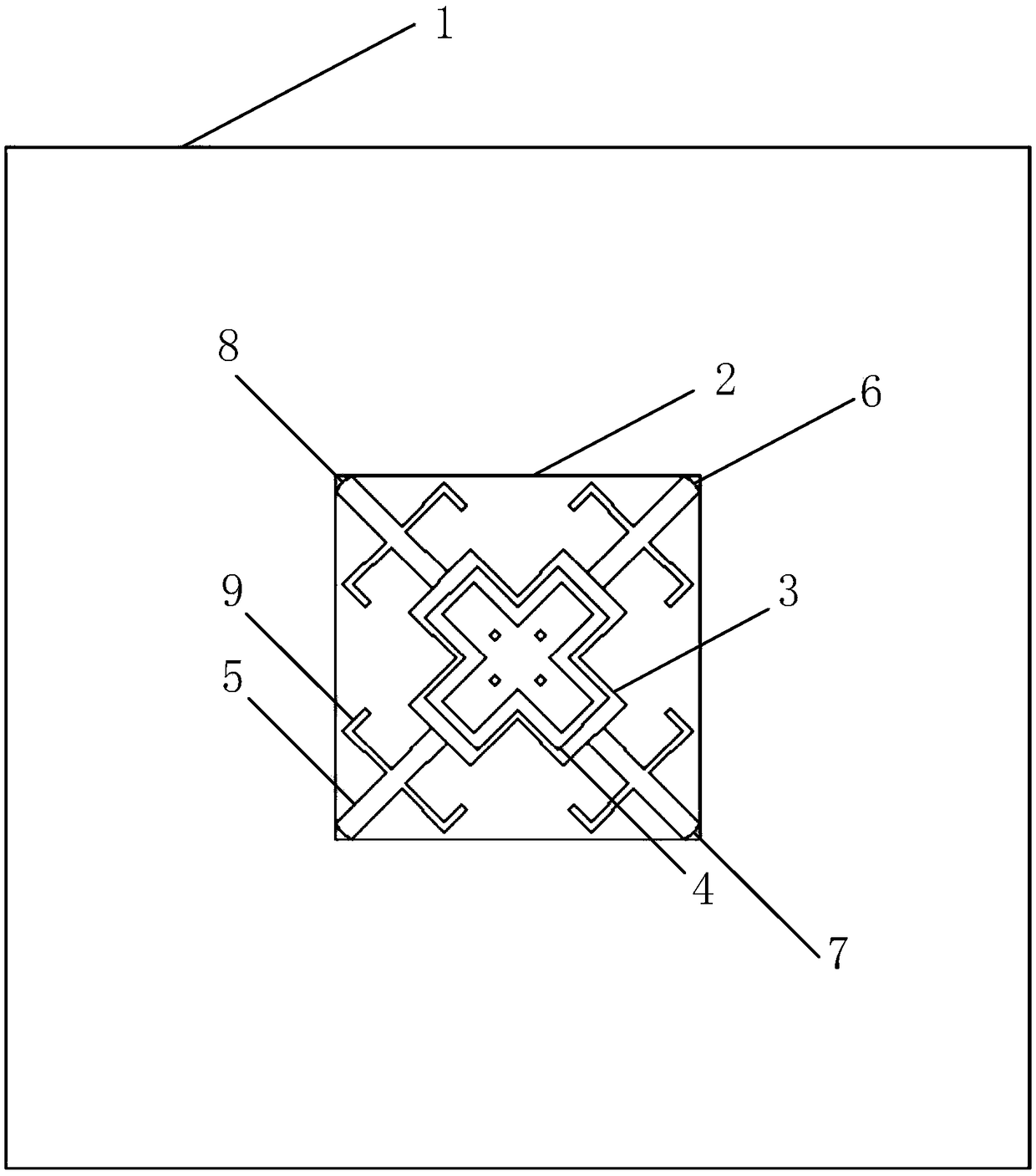
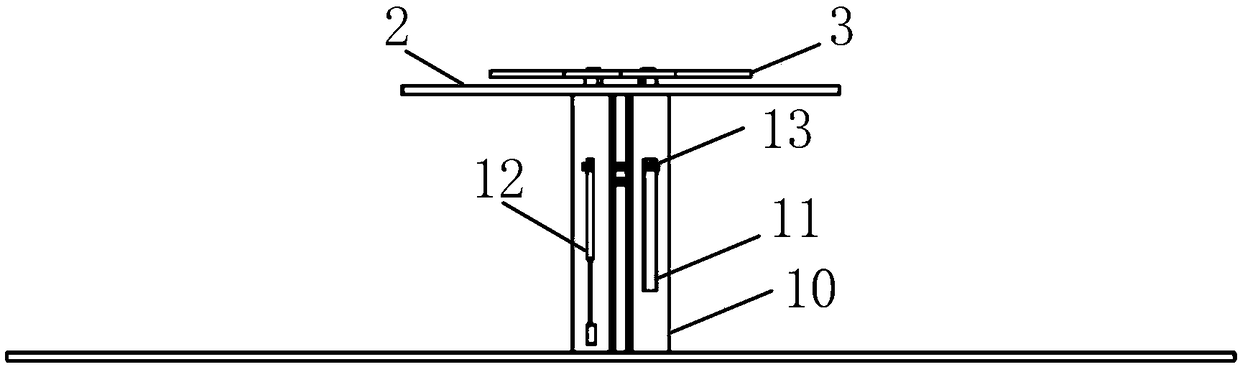
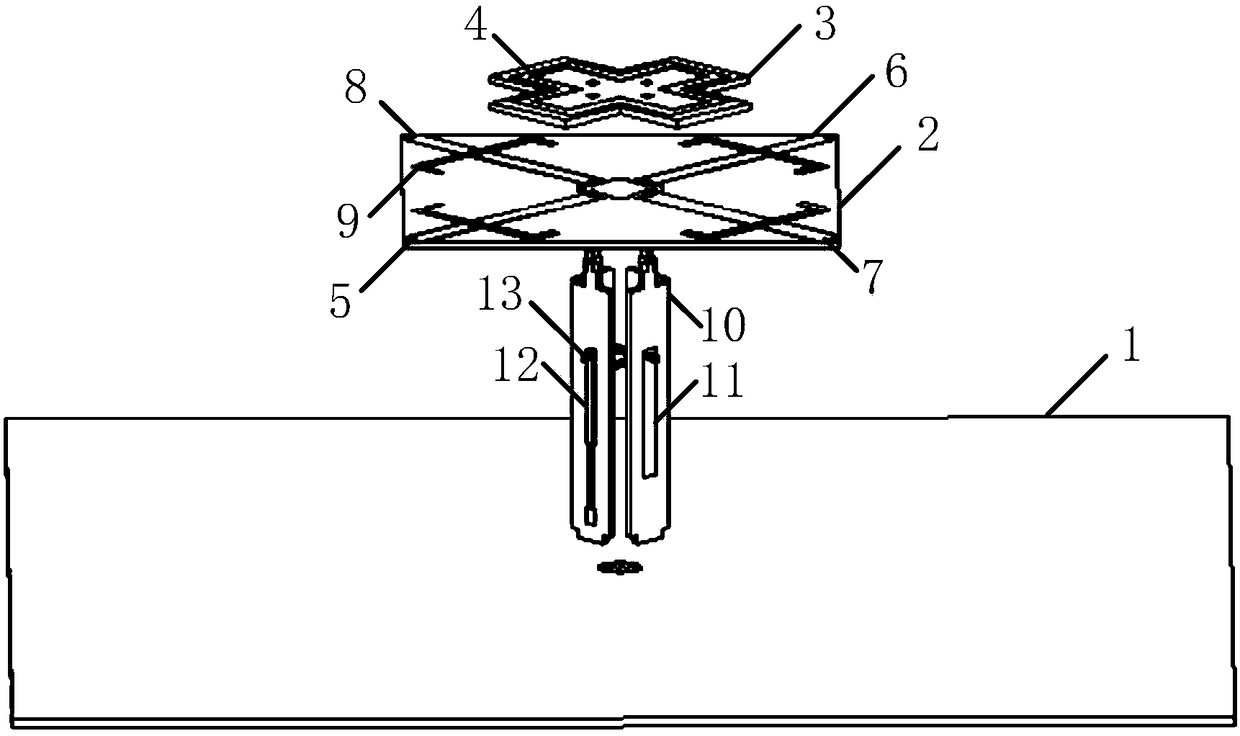
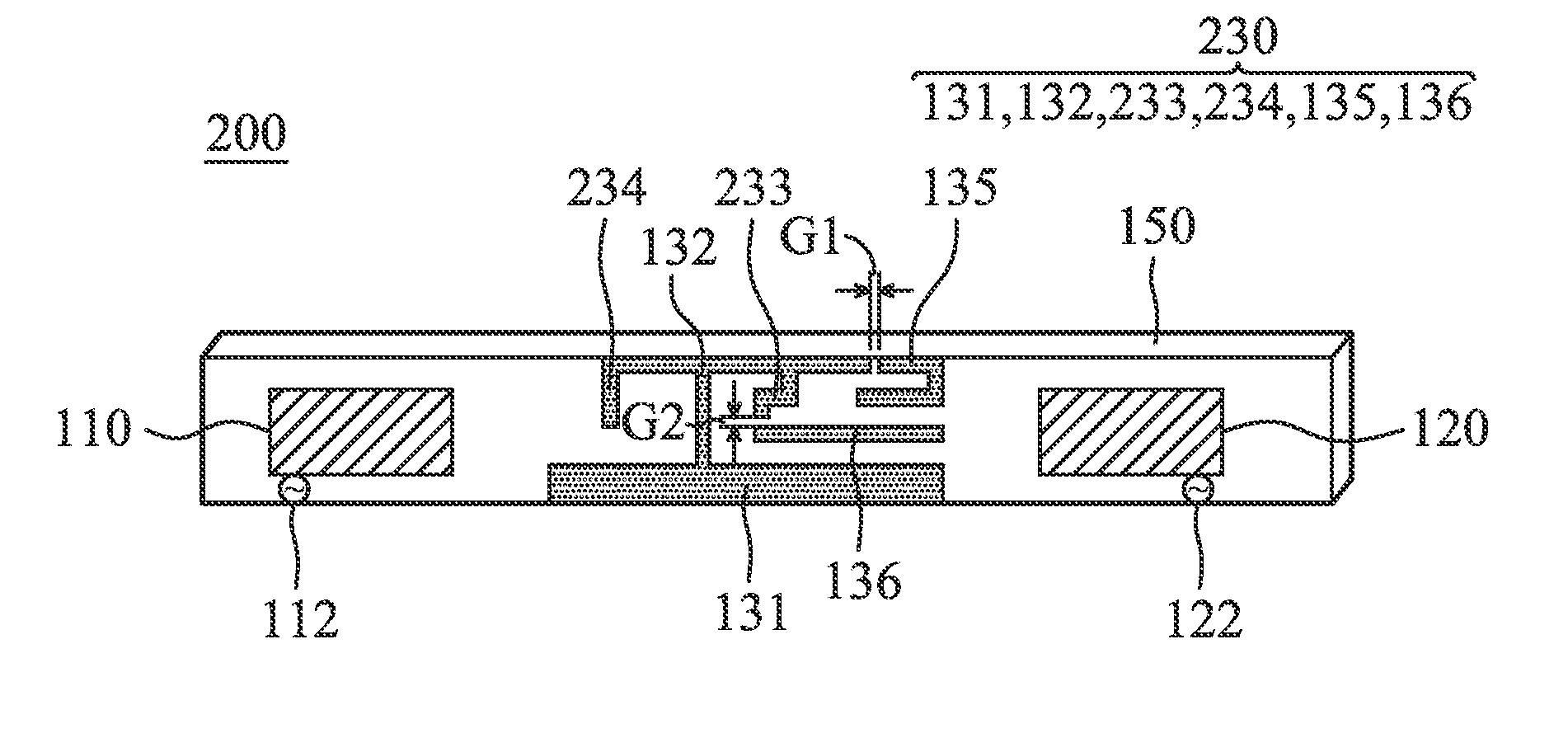
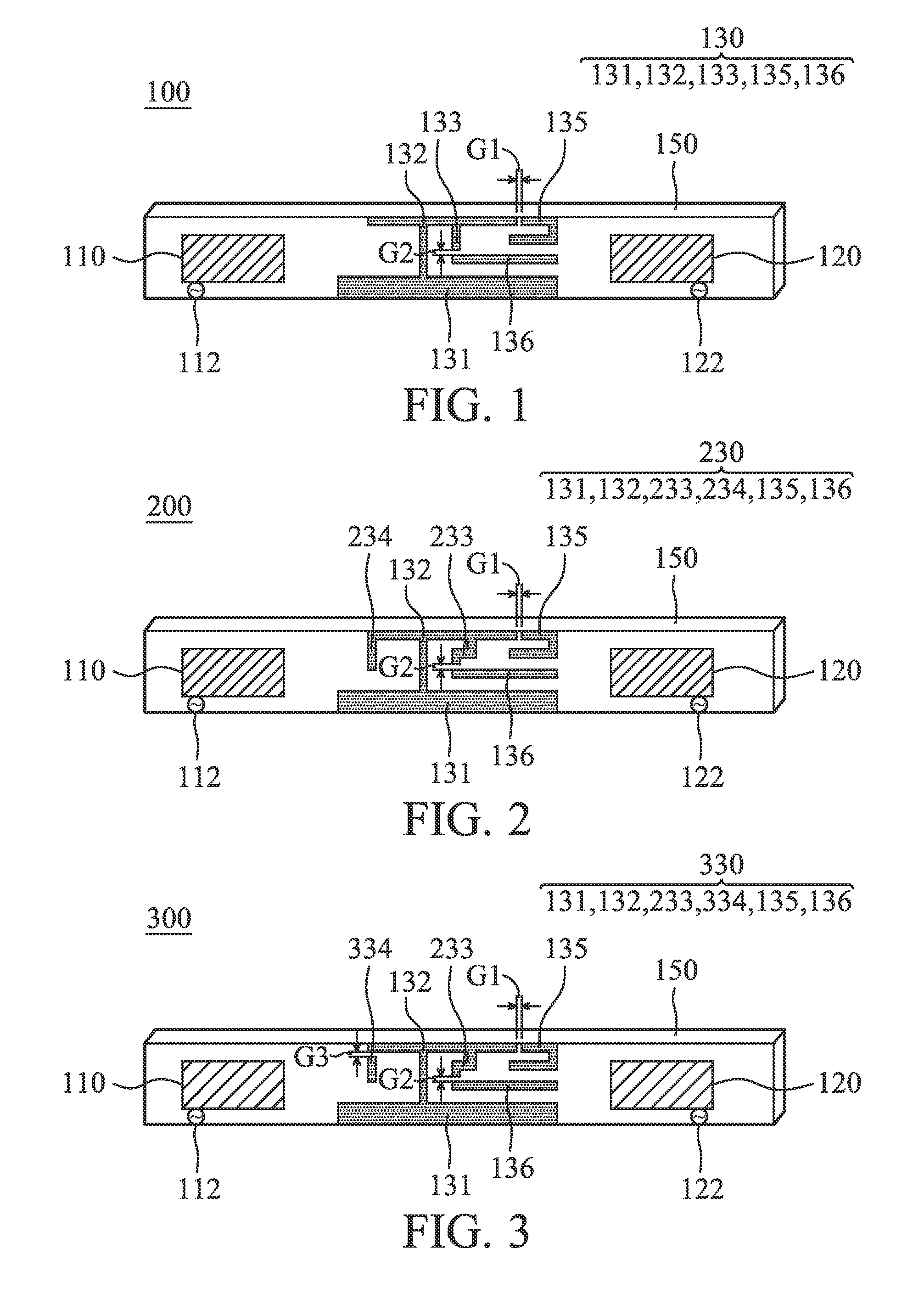
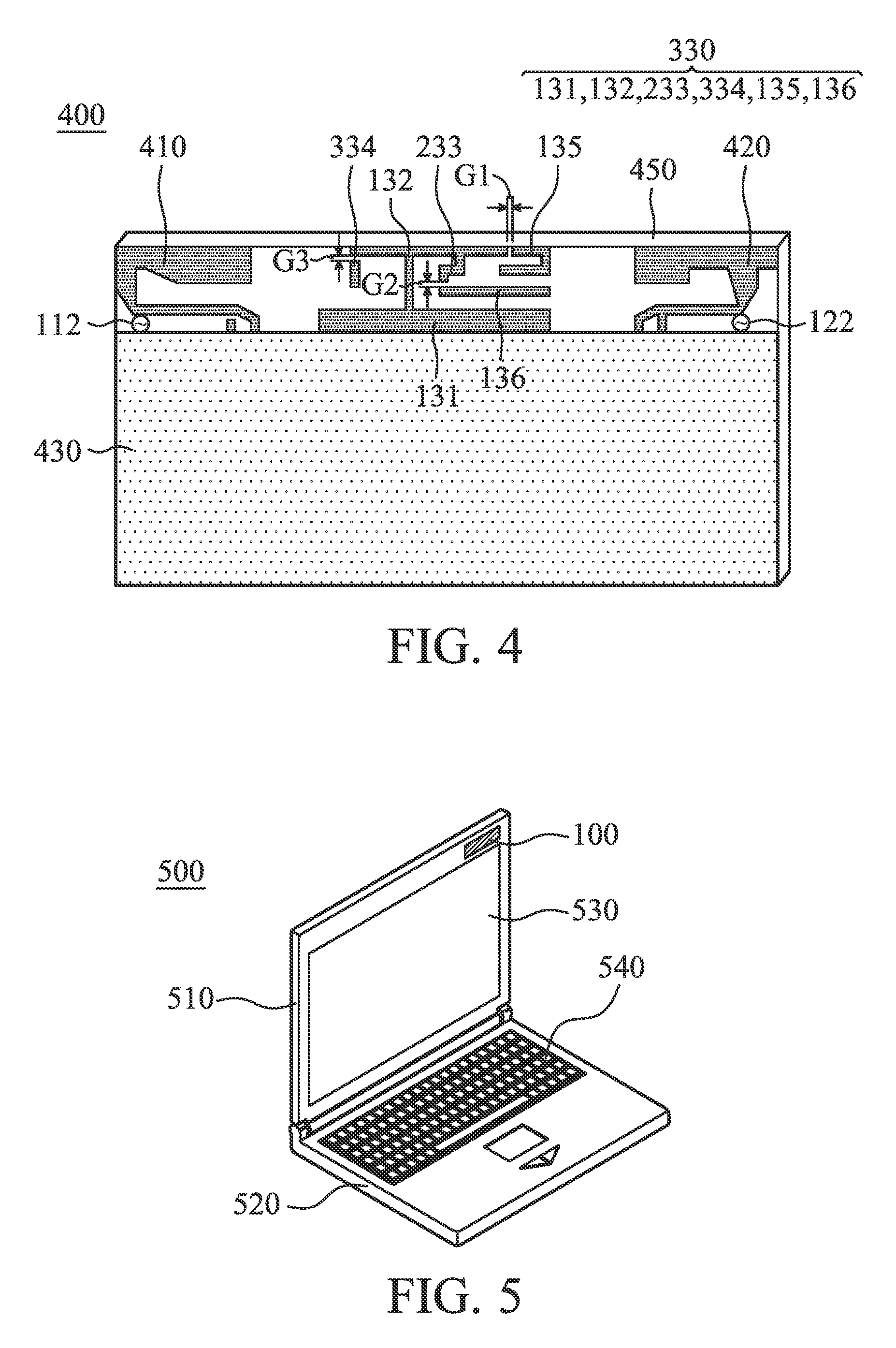
An antenna system includes a first antenna, a second antenna, a band rejection filter, and a dielectric substrate. The band rejection filter is substantially disposed between the first antenna and the second antenna. The band rejection filter includes a protruded ground element, a main branch, a first extension branch, a first additional branch, and a second additional branch. The main branch substantially has a T-shape. The first extension branch is coupled to the main branch. The first additional branch is separated from the main branch, and a first coupling gap is formed between the first additional branch and the main branch. The second additional branch is separated from the main branch, and a second coupling gap is formed between the second additional branch and the first extension branch. The band rejection filter is configured to improve the isolation between the first antenna and the second antenna.
Owner:QUANTA COMPUTER INC
High-stop-band rejection low radar cross section transmission array antenna
ActiveCN110048240ACo-absorptionAchieve high stop-band rejection characteristicsWaveguide hornsAntenna couplingsOut of band interferenceHorn antenna
The invention discloses a high-stop-band rejection low radar cross section transmission array antenna, belongs to the technical field of wireless communication technologies and radars, and particularly relates to the technologies that the transmission array antenna enhances the capability of suppressing out-of-band interference signals, reduces the radar cross section (RCS) and the like. The high-stop-band rejection low RCS transmission array antenna adopts a horn antenna for feeding, a high-stop-band transmission unit, a high-frequency band-stop frequency selection surface and a dual-polarization band-pass resistance frequency selection surface are integrated, and independent control over transmission characteristics and RCS reduction characteristics is achieved by adjusting correspondingparameters of the units. The high-stop-band rejection low RCS transmission array antenna has the beneficial effects that 1, the high-stop-band rejection degree and low-RCS transmission array antennaunit structure is provided; 2, the suppression capability of the antenna on out-of-band interference signals is obviously improved; and 3, the low-frequency structure and the high-frequency structureare used as the design of the dual-polarization band-pass resistance frequency selection surface floor, so that the reduction of the RCS in an ultra wide band is realized.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
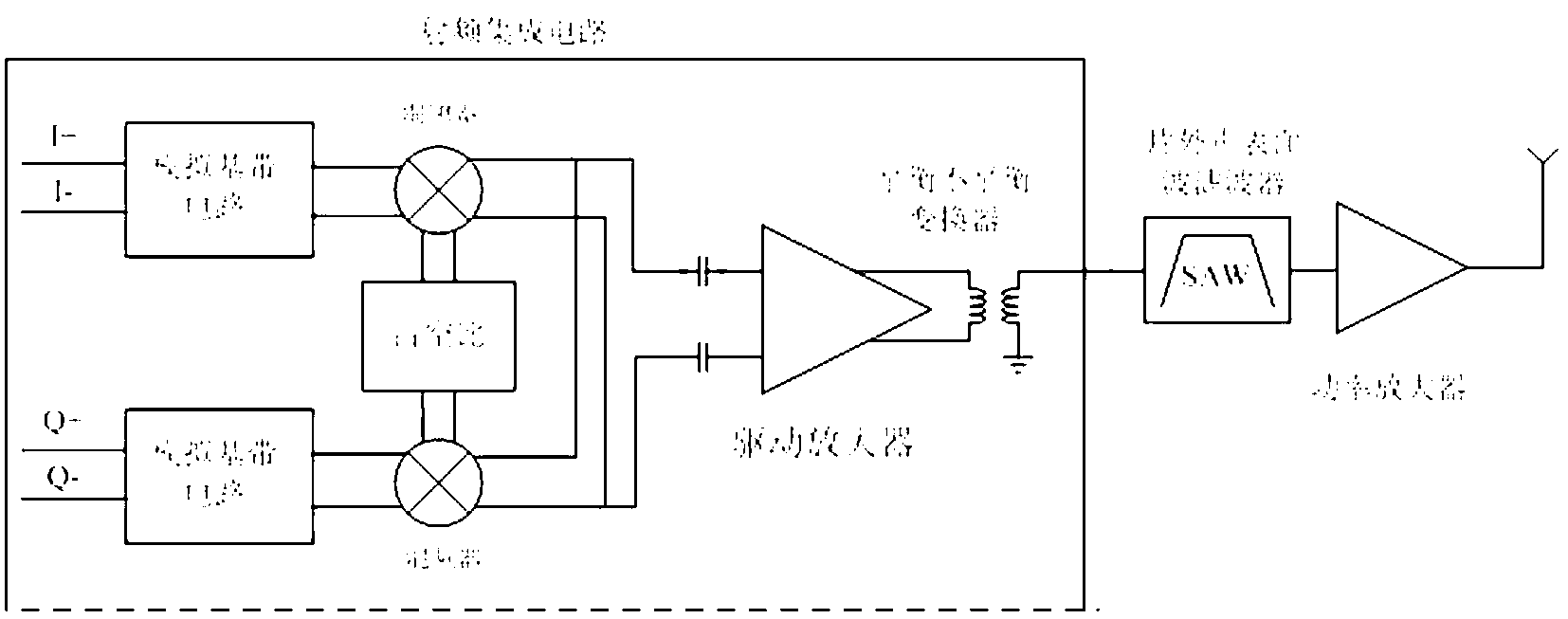
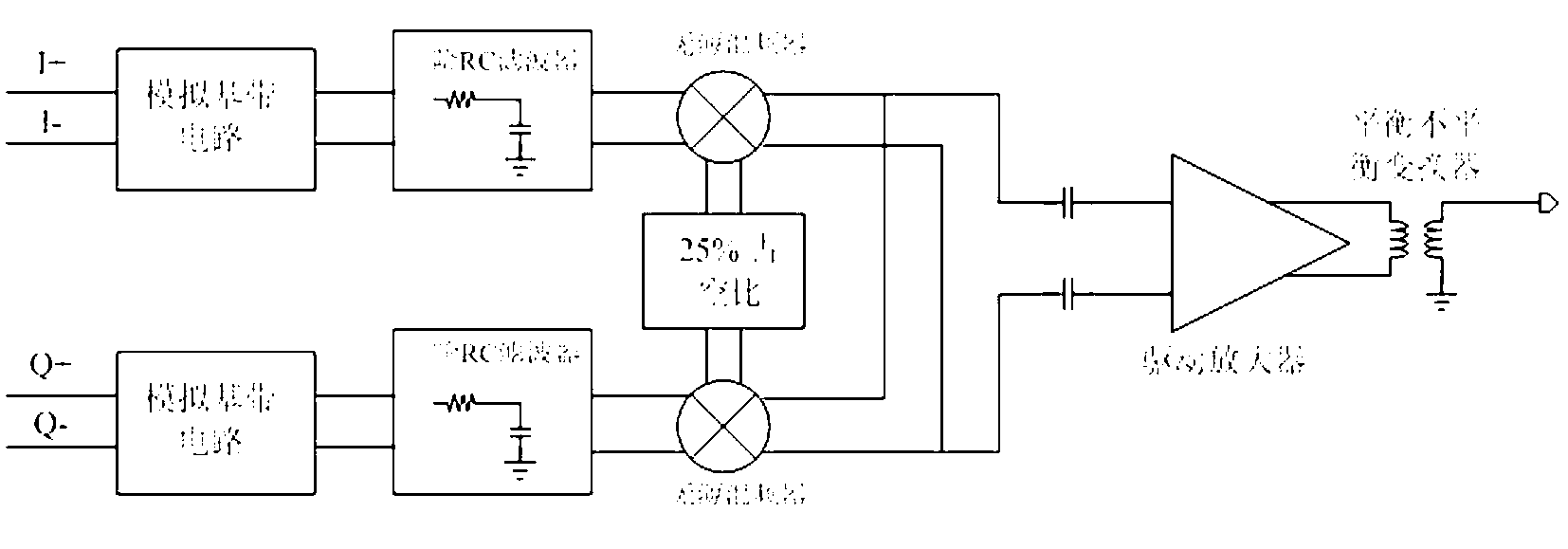
Wireless transmitter and band rejection filter
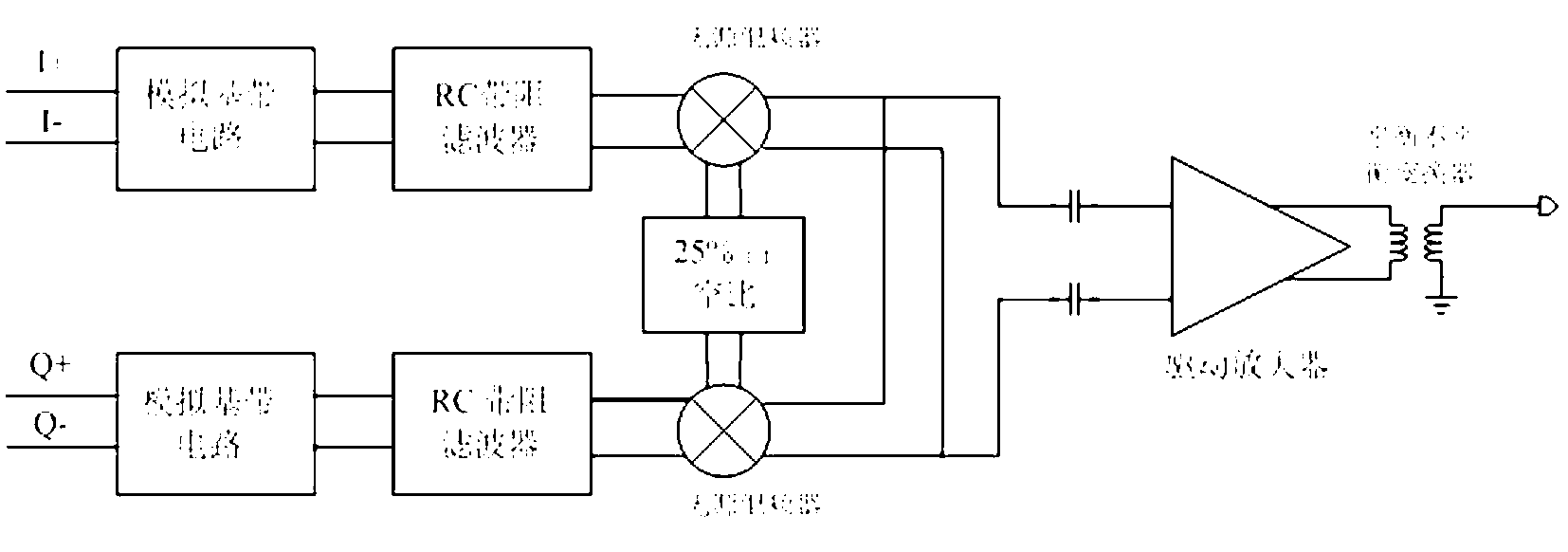
ActiveCN103187982ALow far-end noise characteristicsLess noise at the far endMultiple-port networksTransmissionAudio power amplifierBand-stop filter
The invention discloses a wireless transmitter and a band rejection filter. The wireless transmitter comprises an analog base band circuit, a passive RC band rejection filter, a passive mixer, a driving amplifier and a balanced-unbalanced converter. A band rejection frequency point of the passive RC band rejection filter is a far-end noise frequency point, and the filter is utilized for filtering out far-end noise of the analog base band circuit. The far-end noise contributed by the analog base band circuit is greatly reduced, in addition, a passive achieving manner is utilized by the band rejection filter so as to ensure that noise induced by the band rejection filter is very low and the characteristic of extremely low far-end noise of a whole wireless transmitter system is achieved.
Owner:NATIONZ TECH INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com