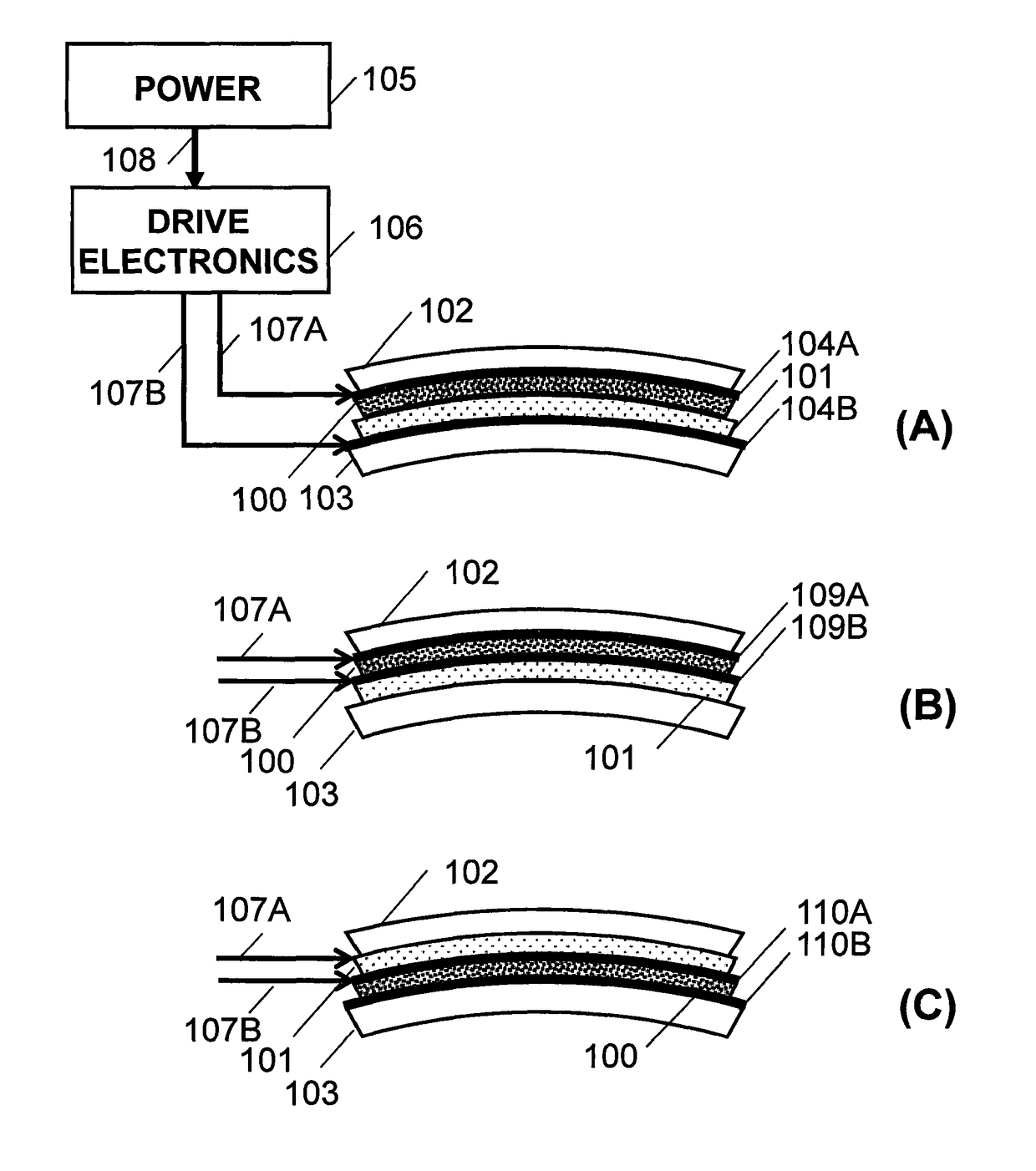
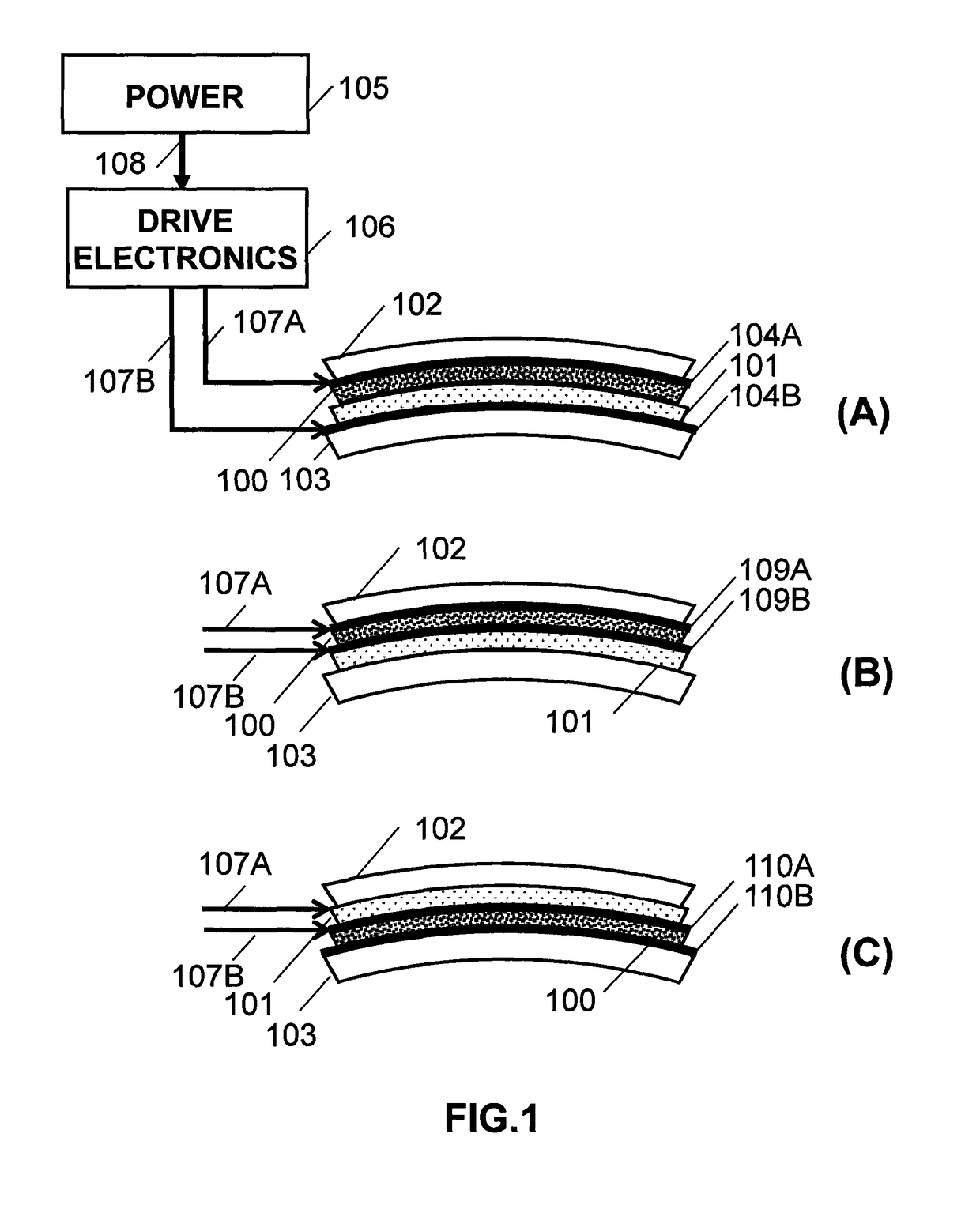
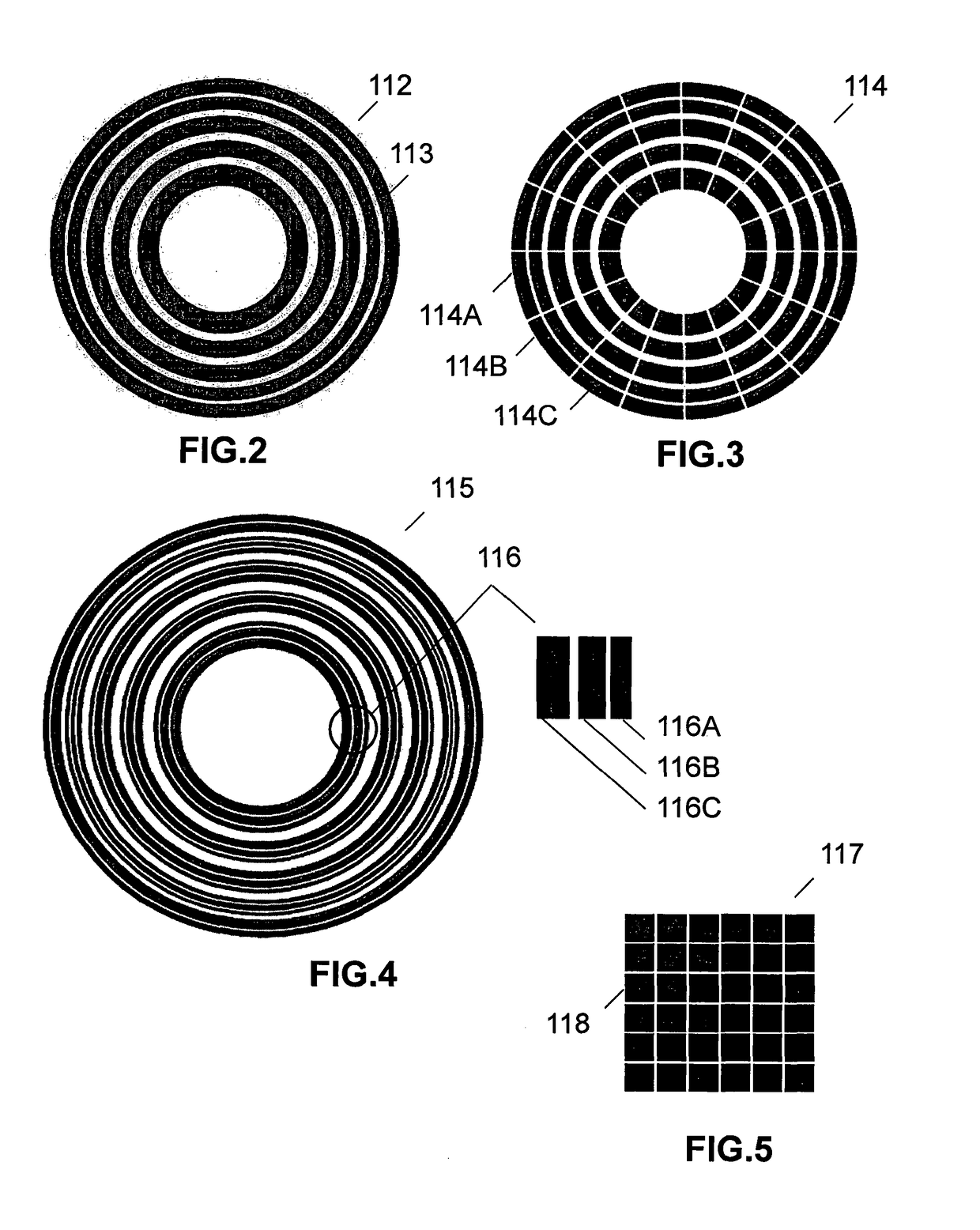
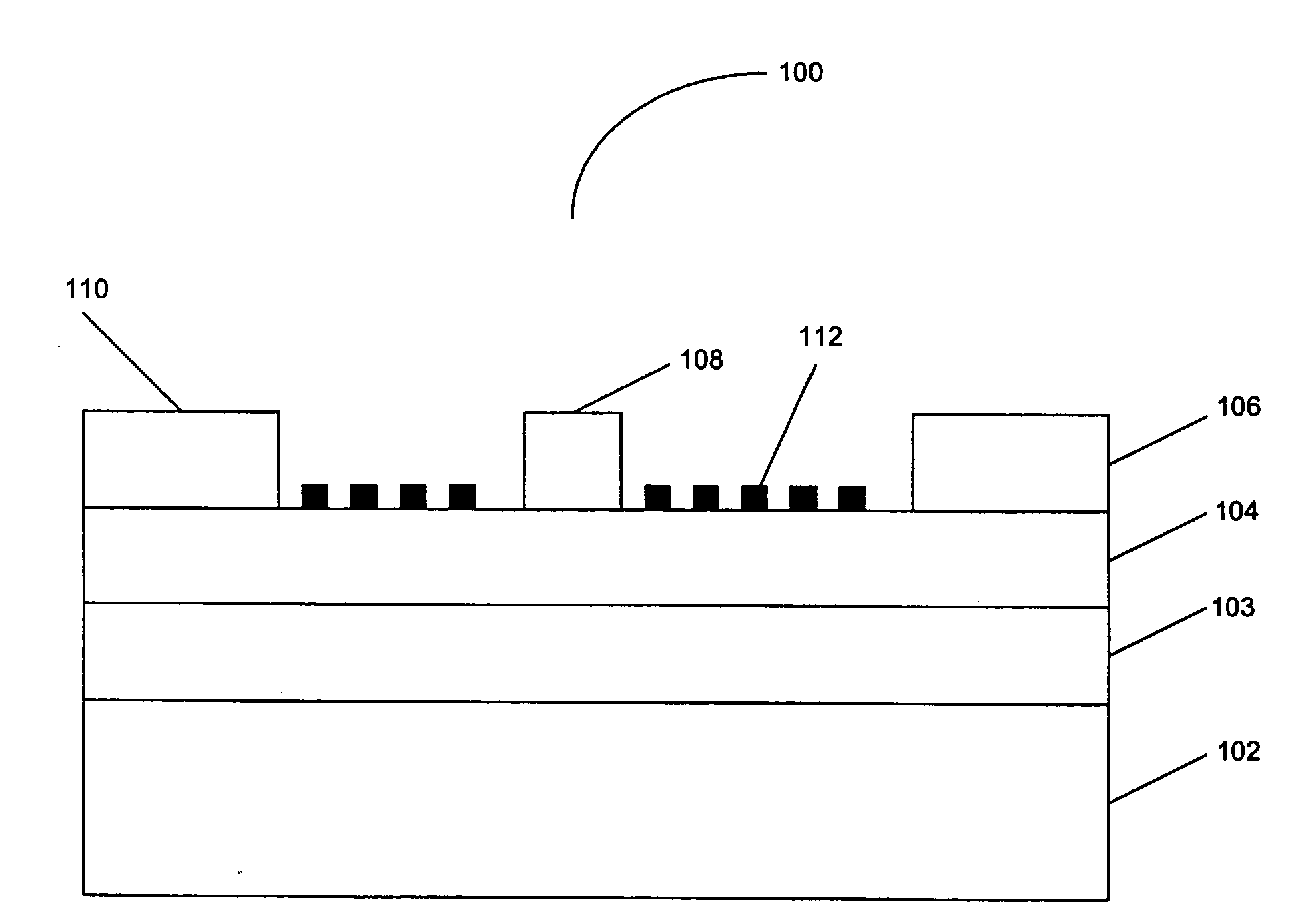
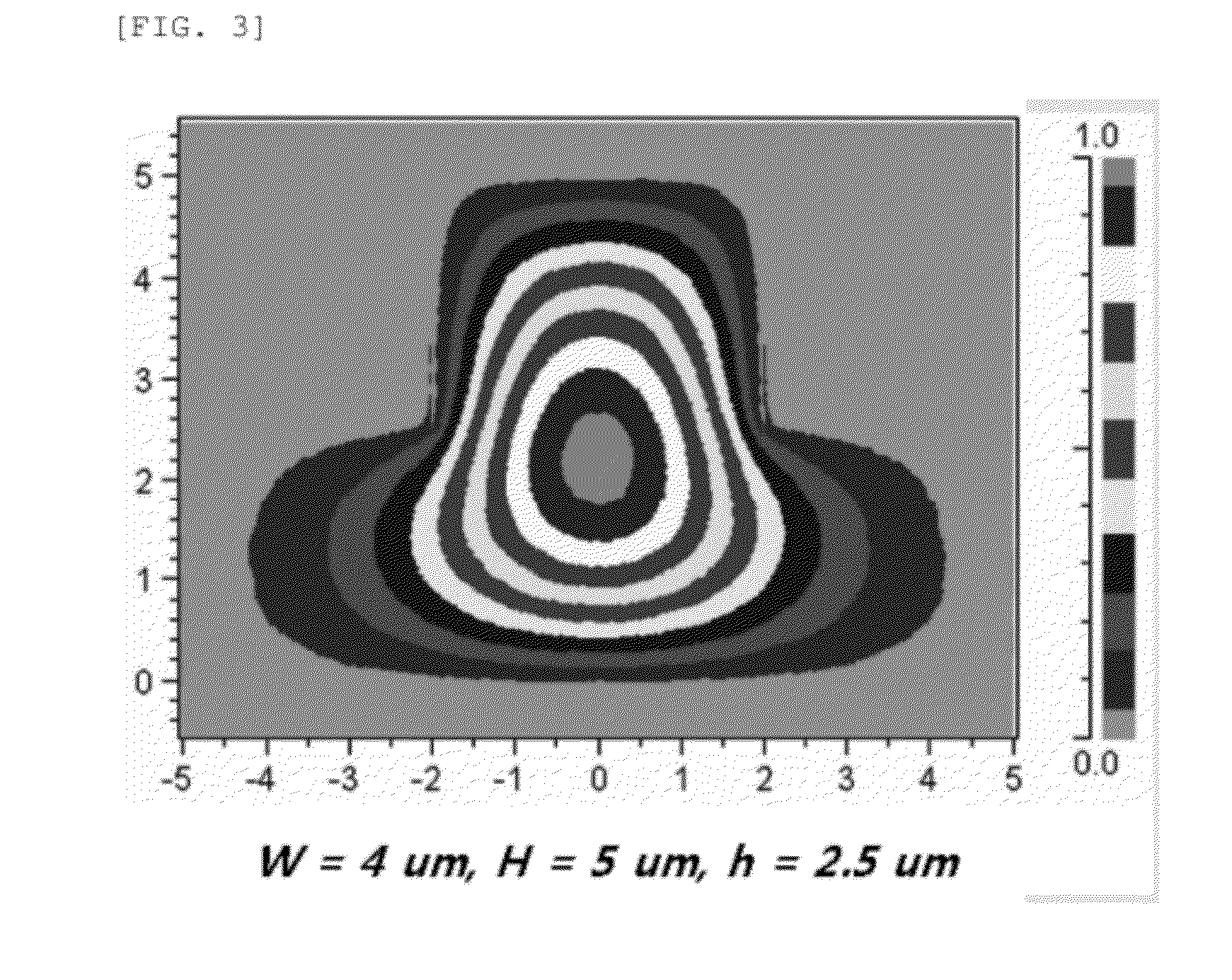
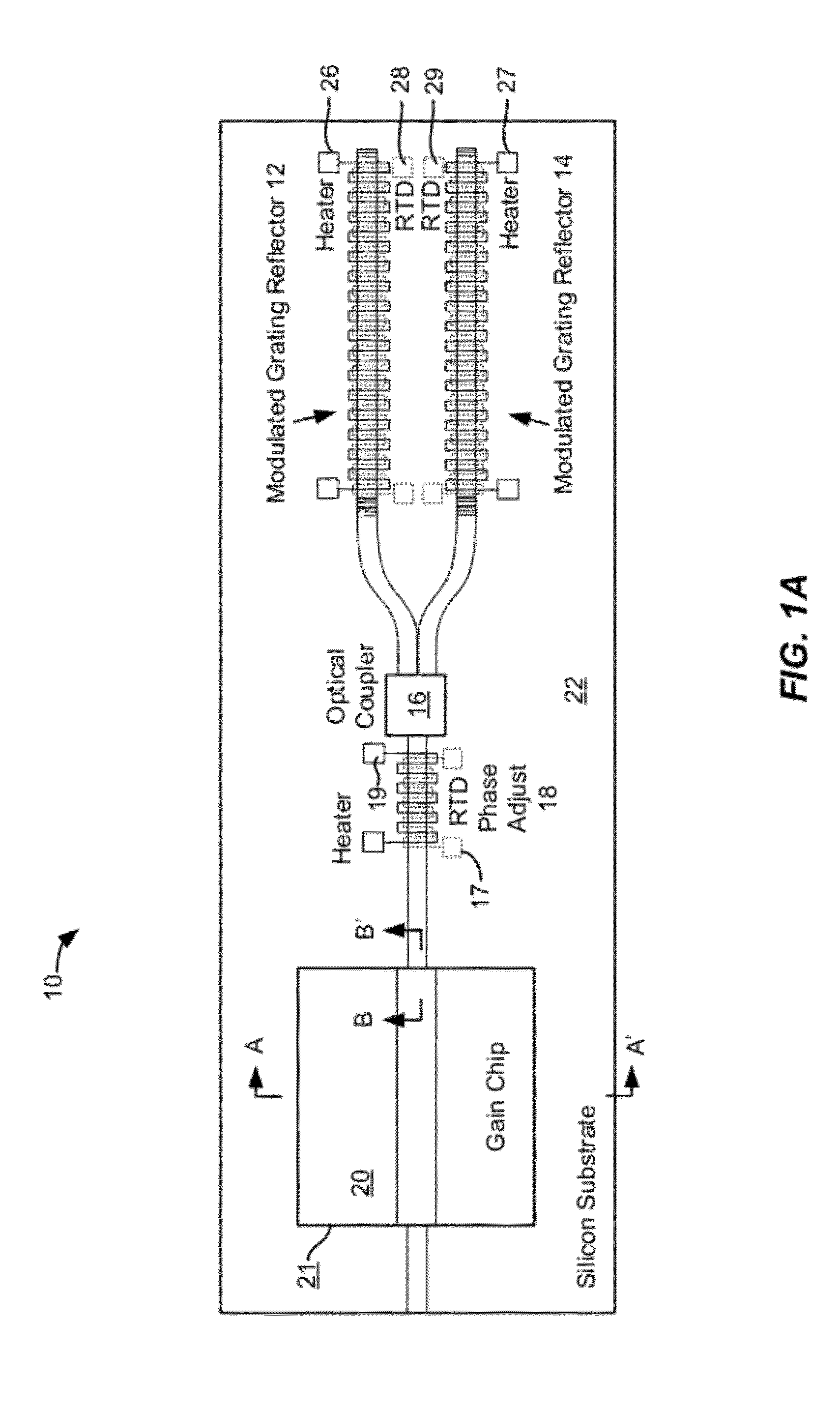
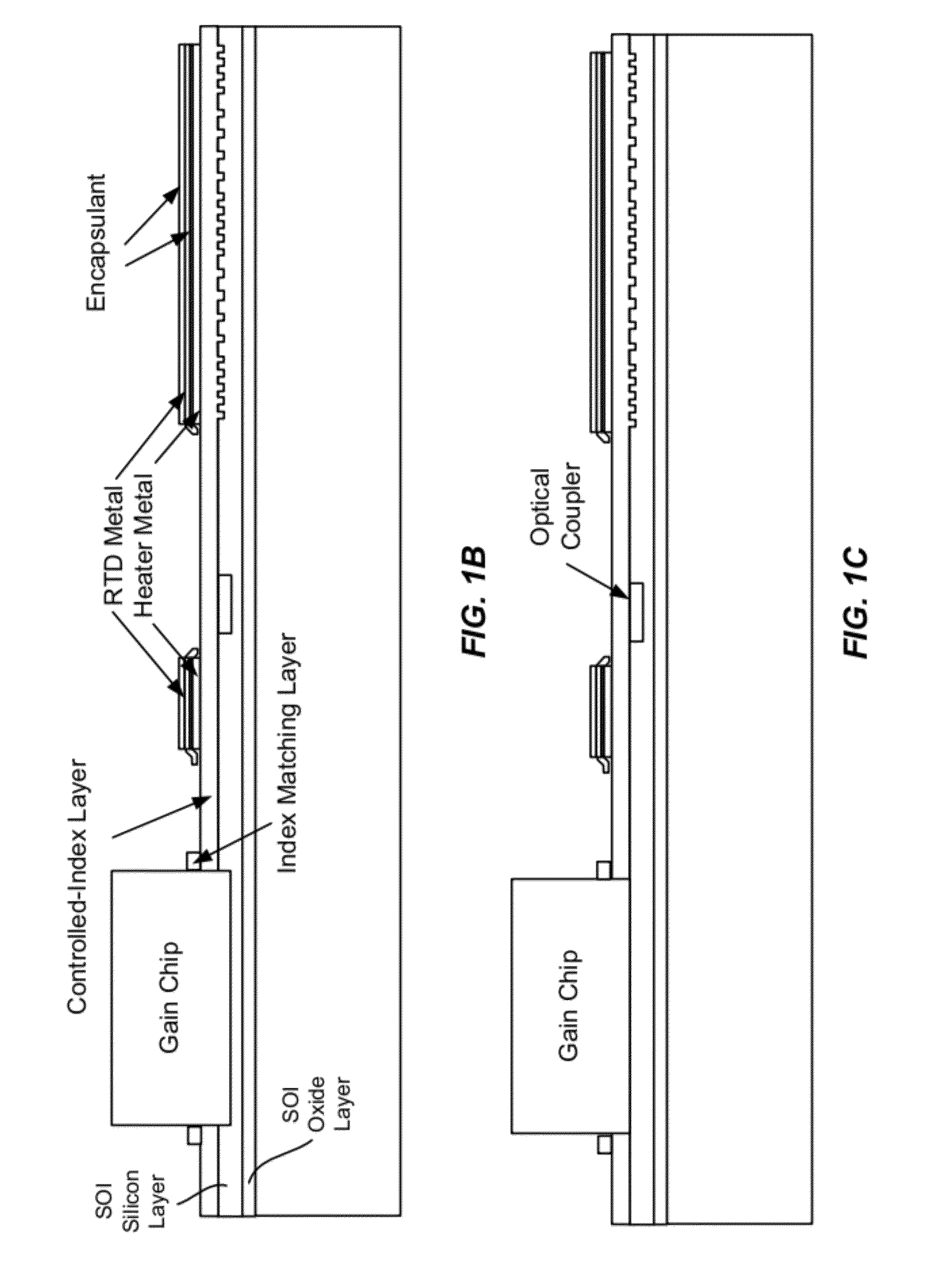
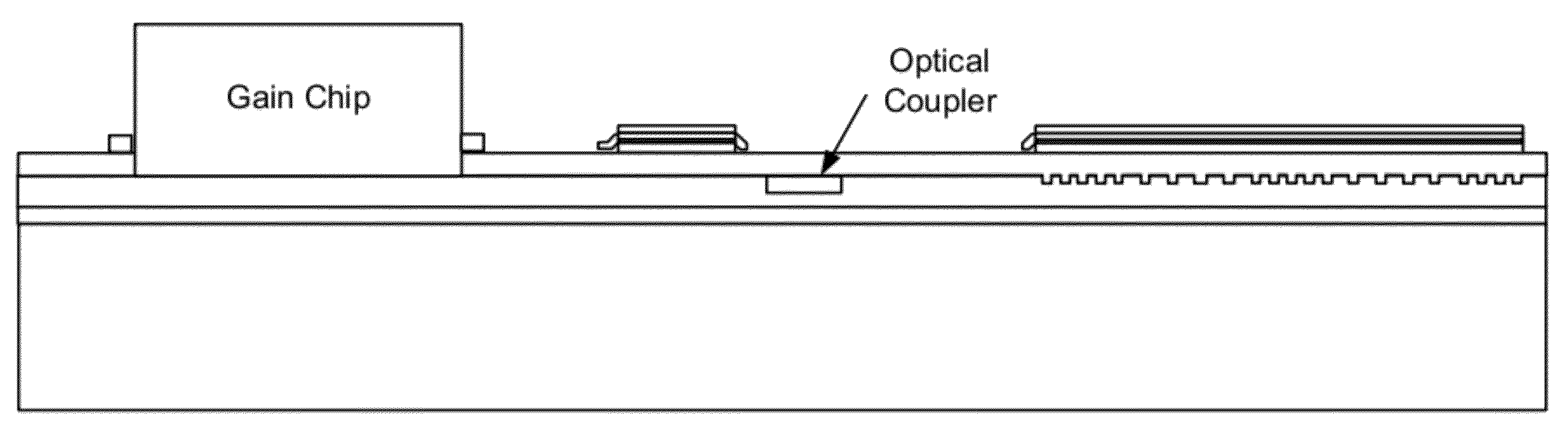
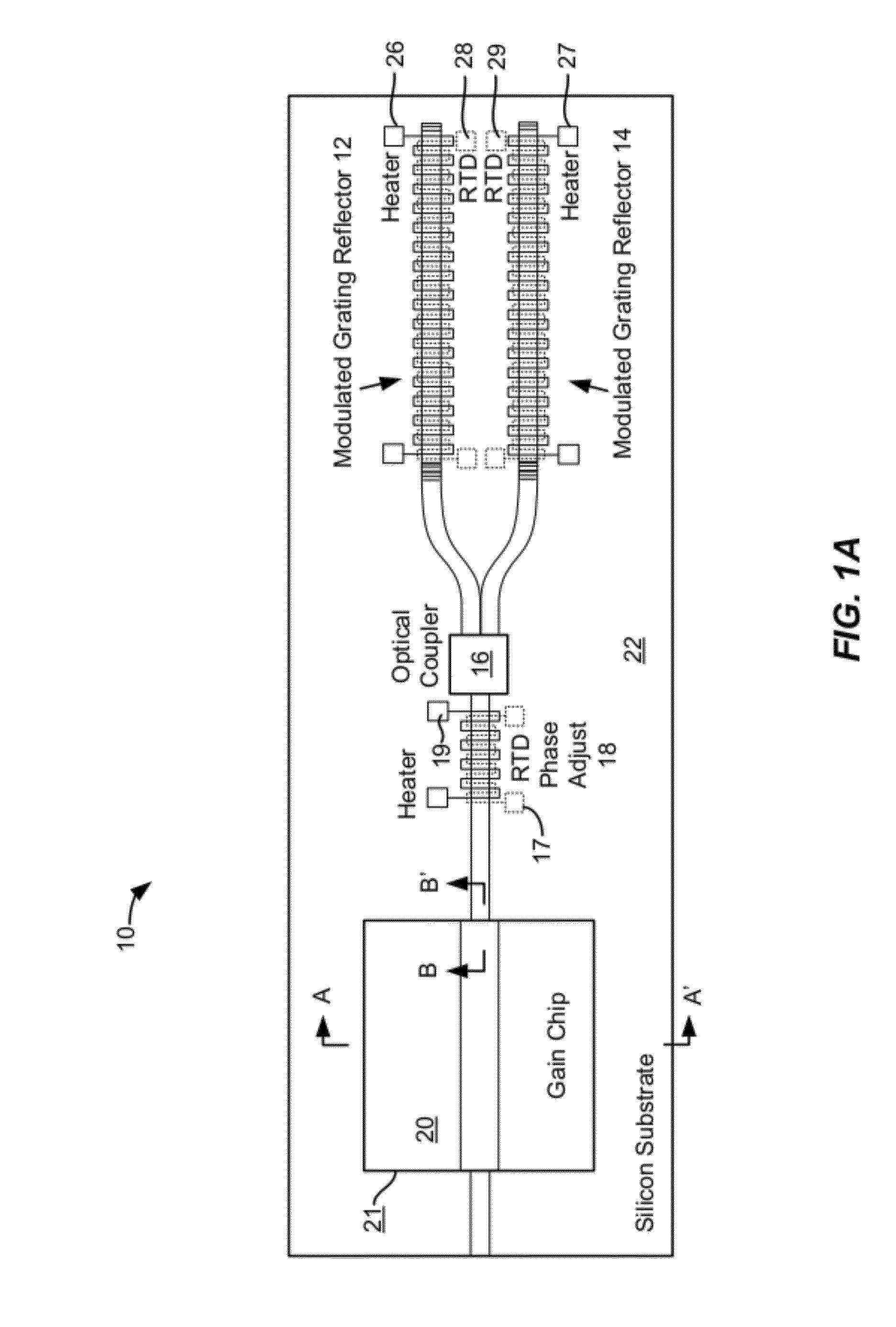
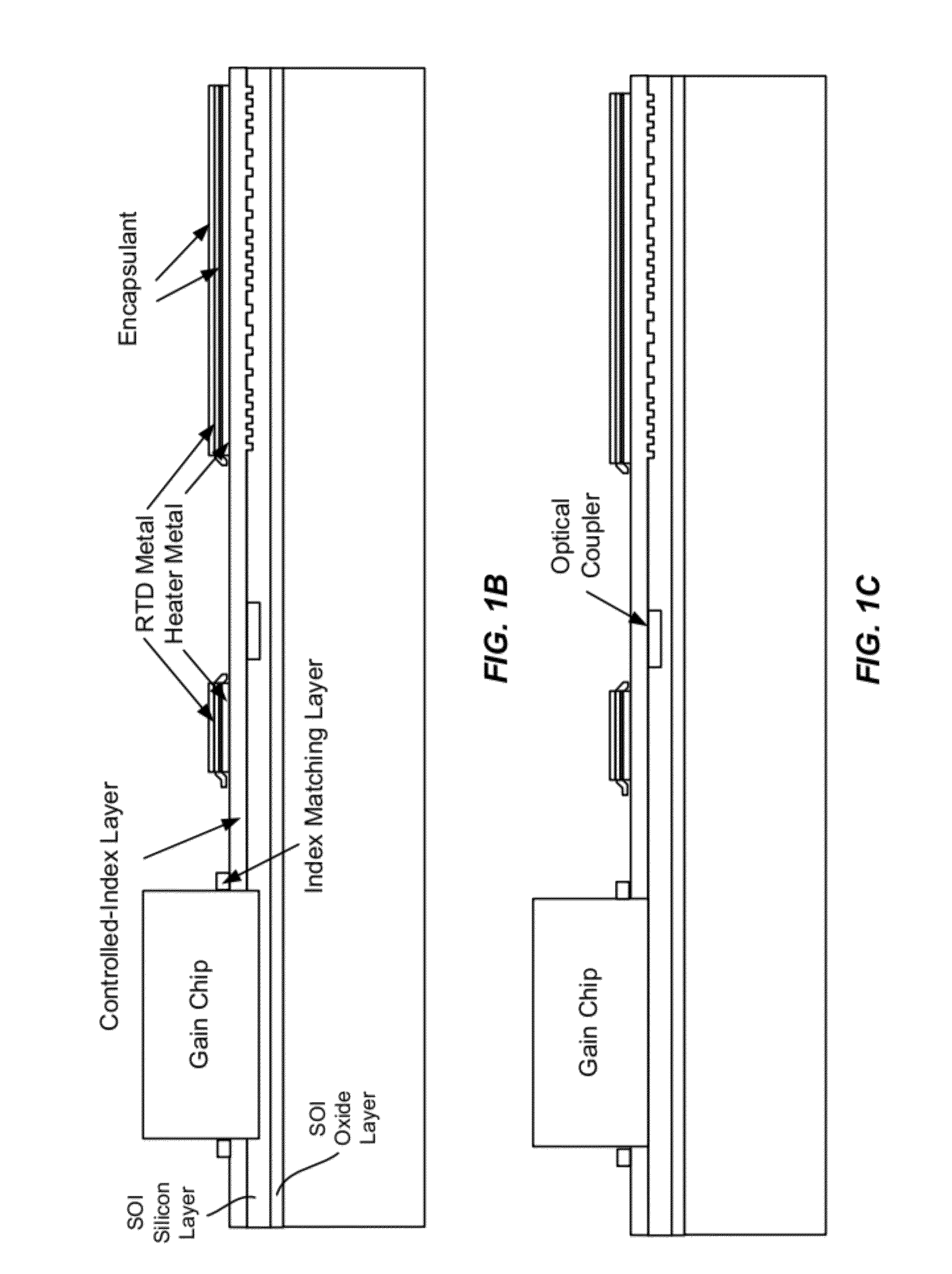
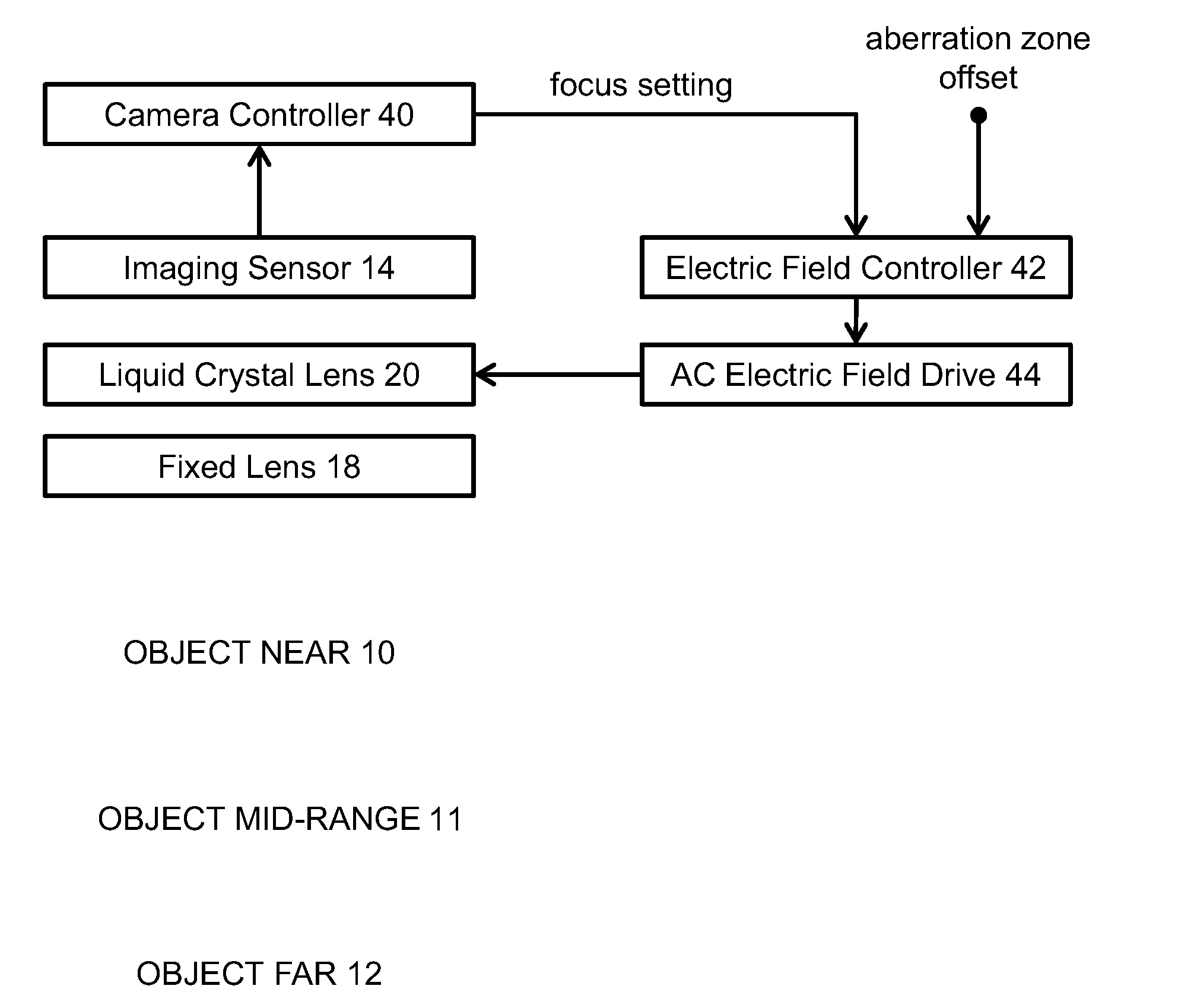
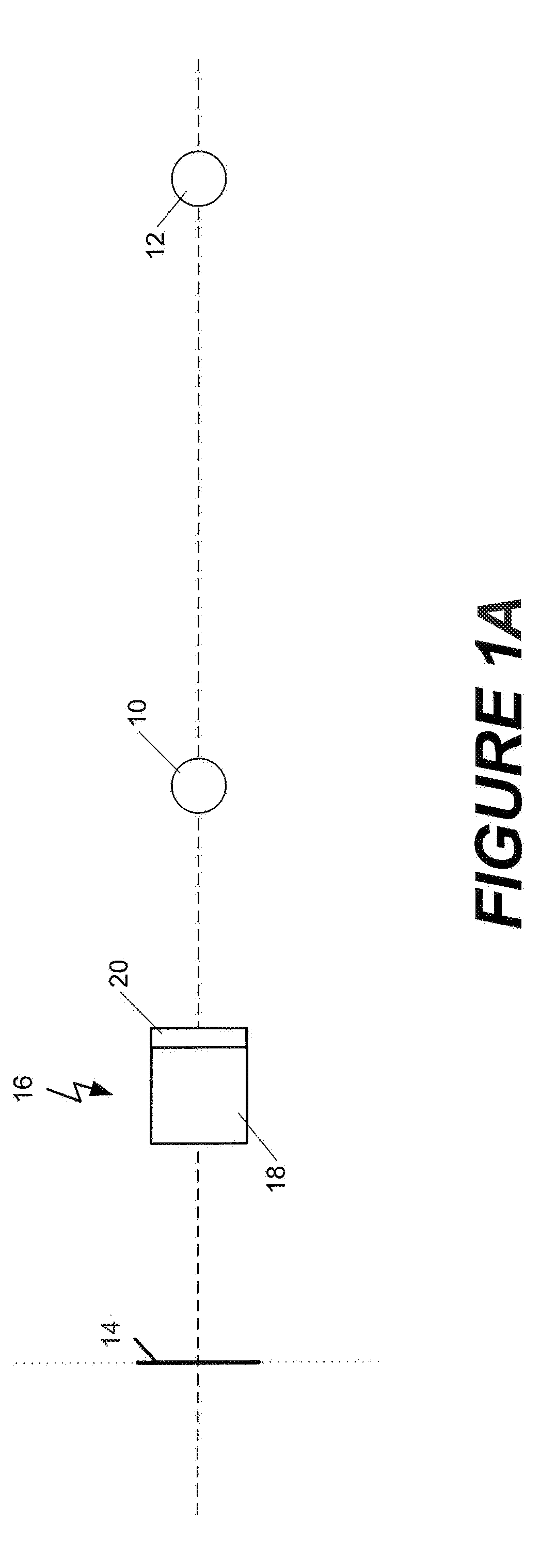
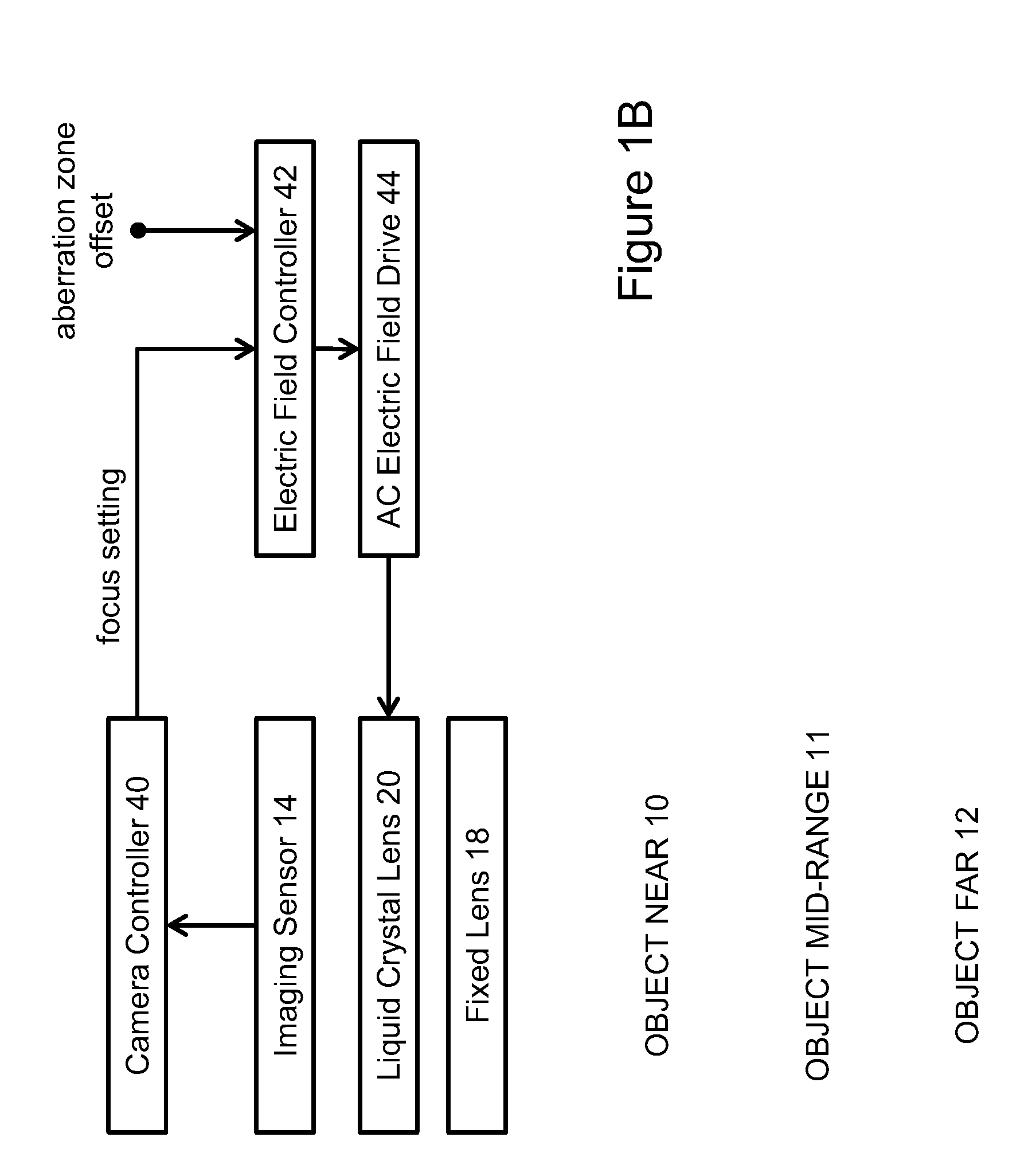
Patents
Literature
2225 results about "Tunable laser" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A tunable laser is a laser whose wavelength of operation can be altered in a controlled manner. While all laser gain media allow small shifts in output wavelength, only a few types of lasers allow continuous tuning over a significant wavelength range.
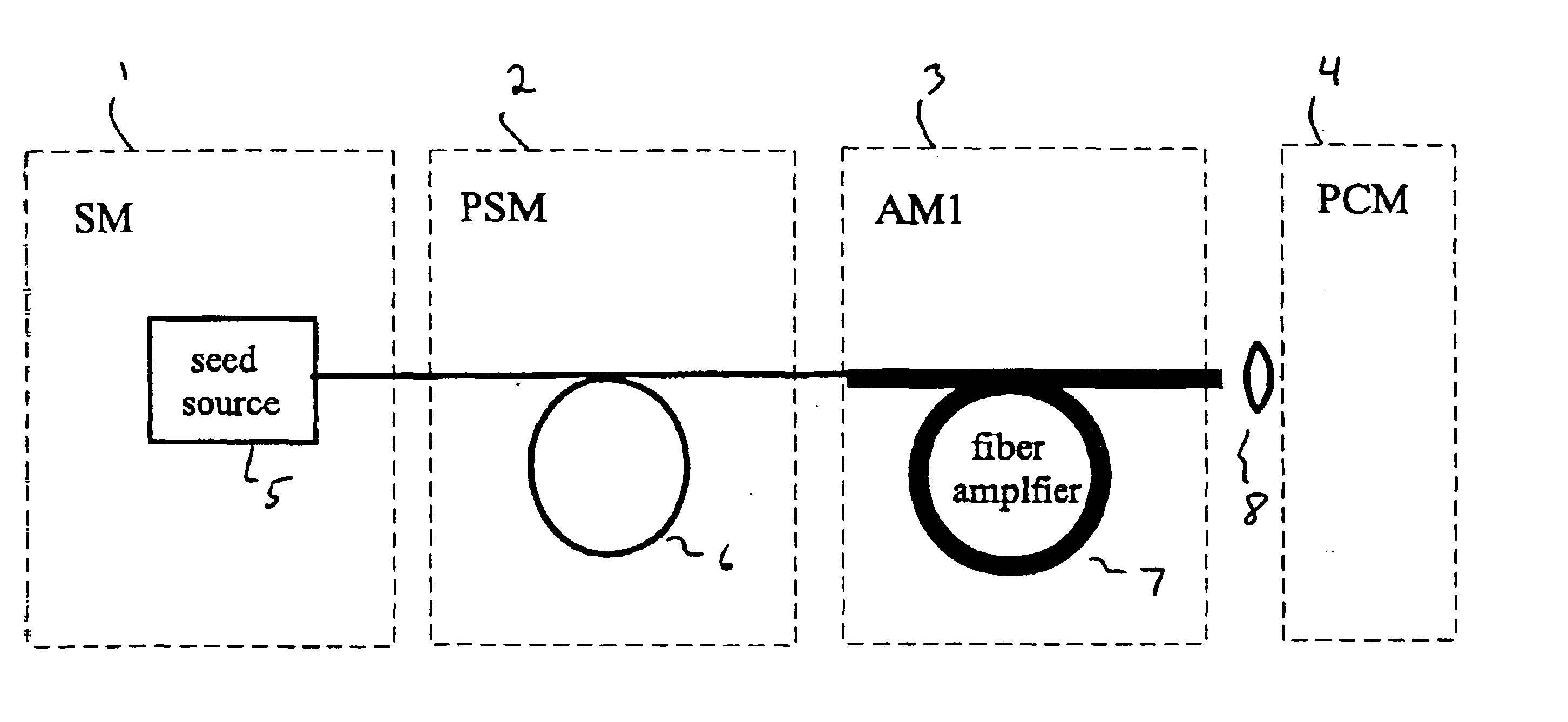
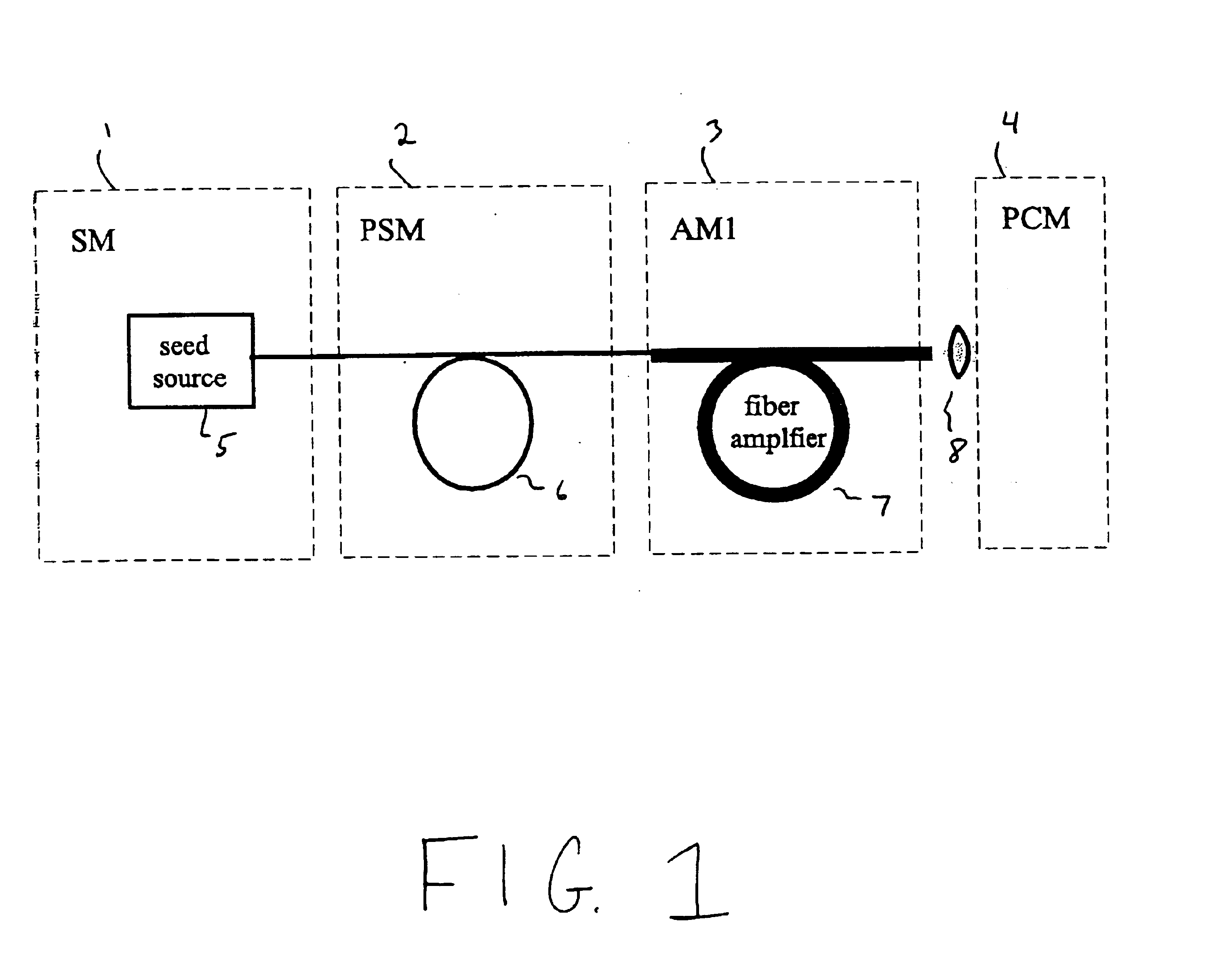
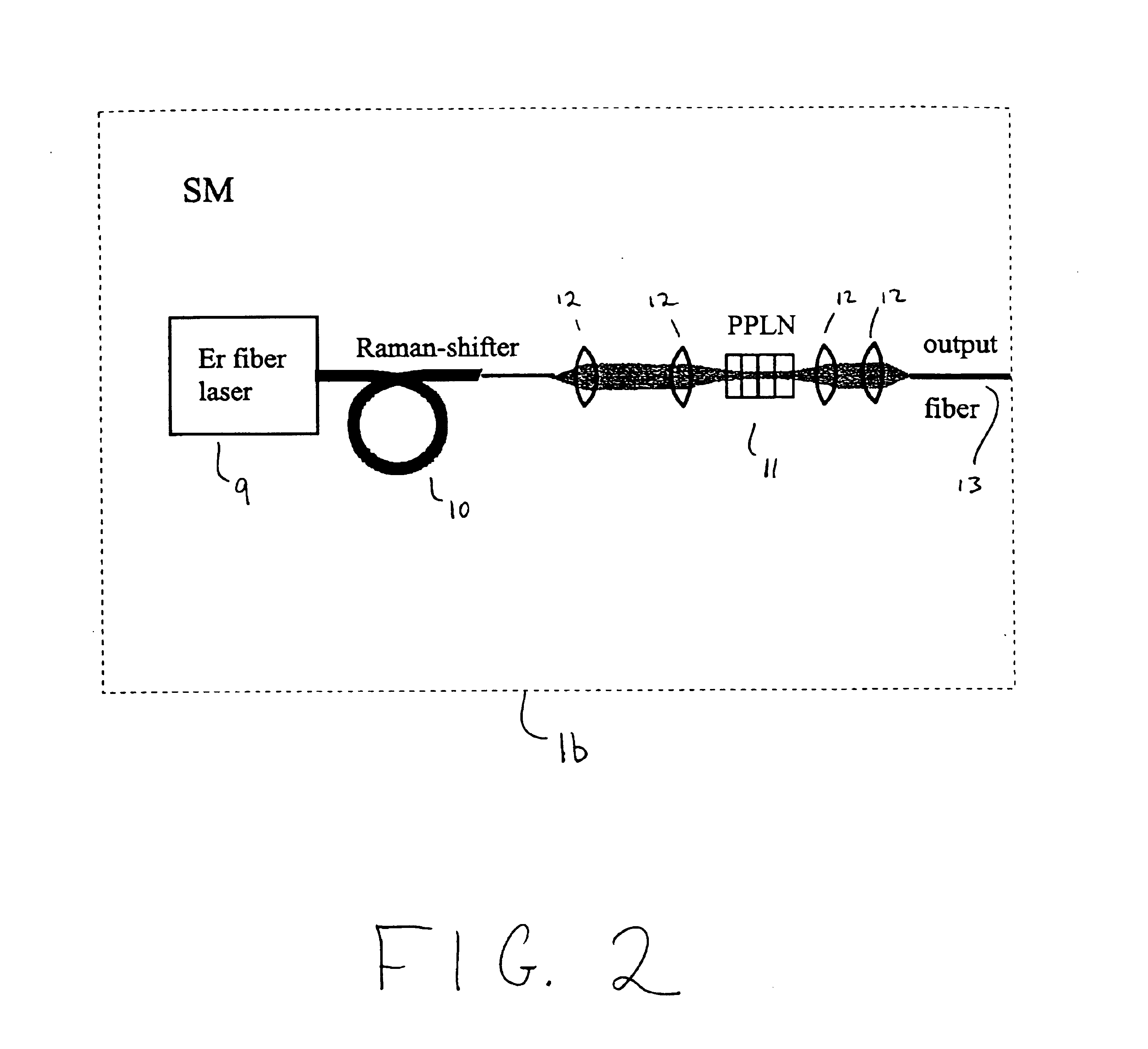
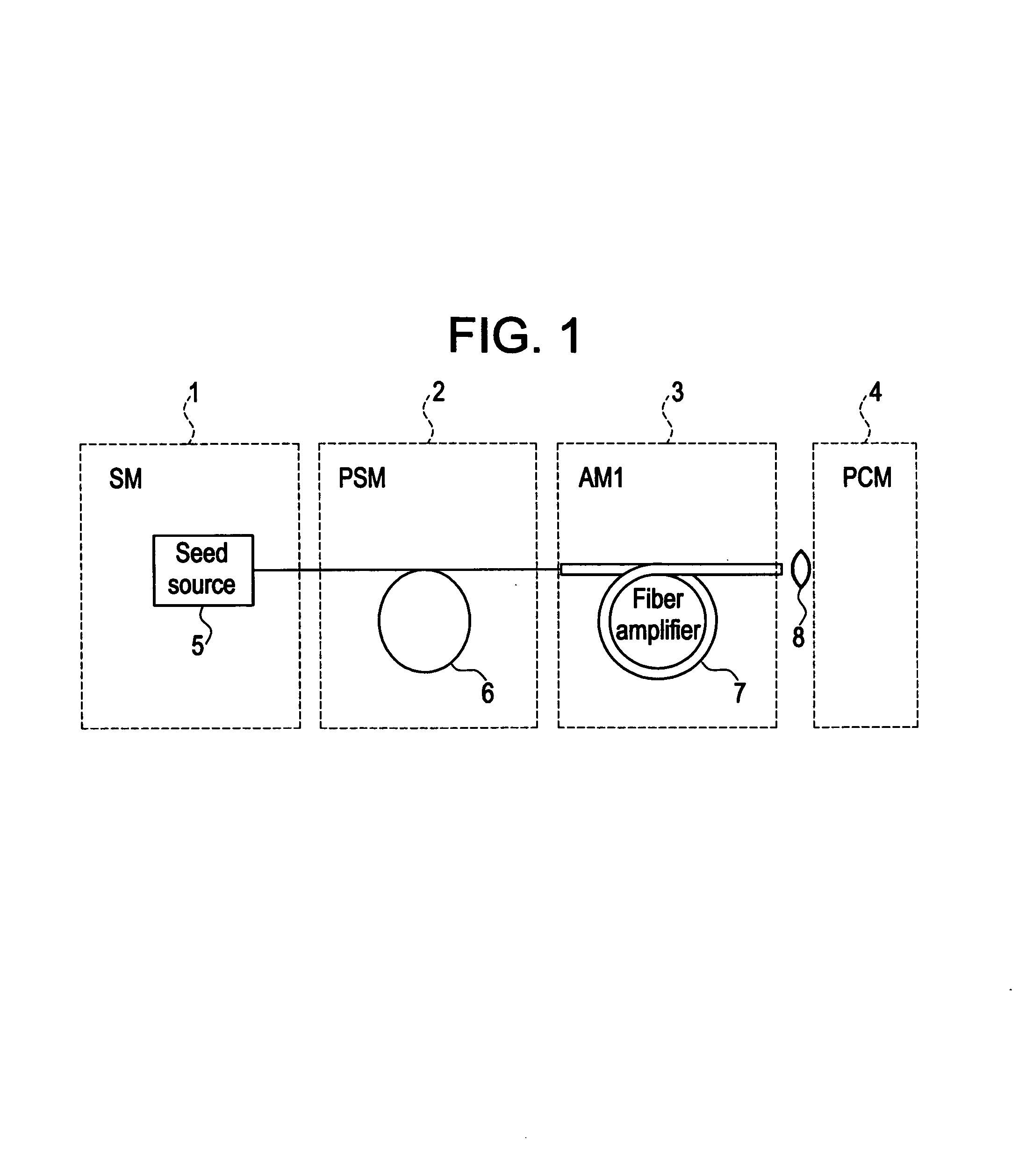
Modular, high energy, widely-tunable ultrafast fiber source
InactiveUS6885683B1High peak and high average powerReduce noiseCladded optical fibreLaser using scattering effectsNonlinear optical crystalHigh peak
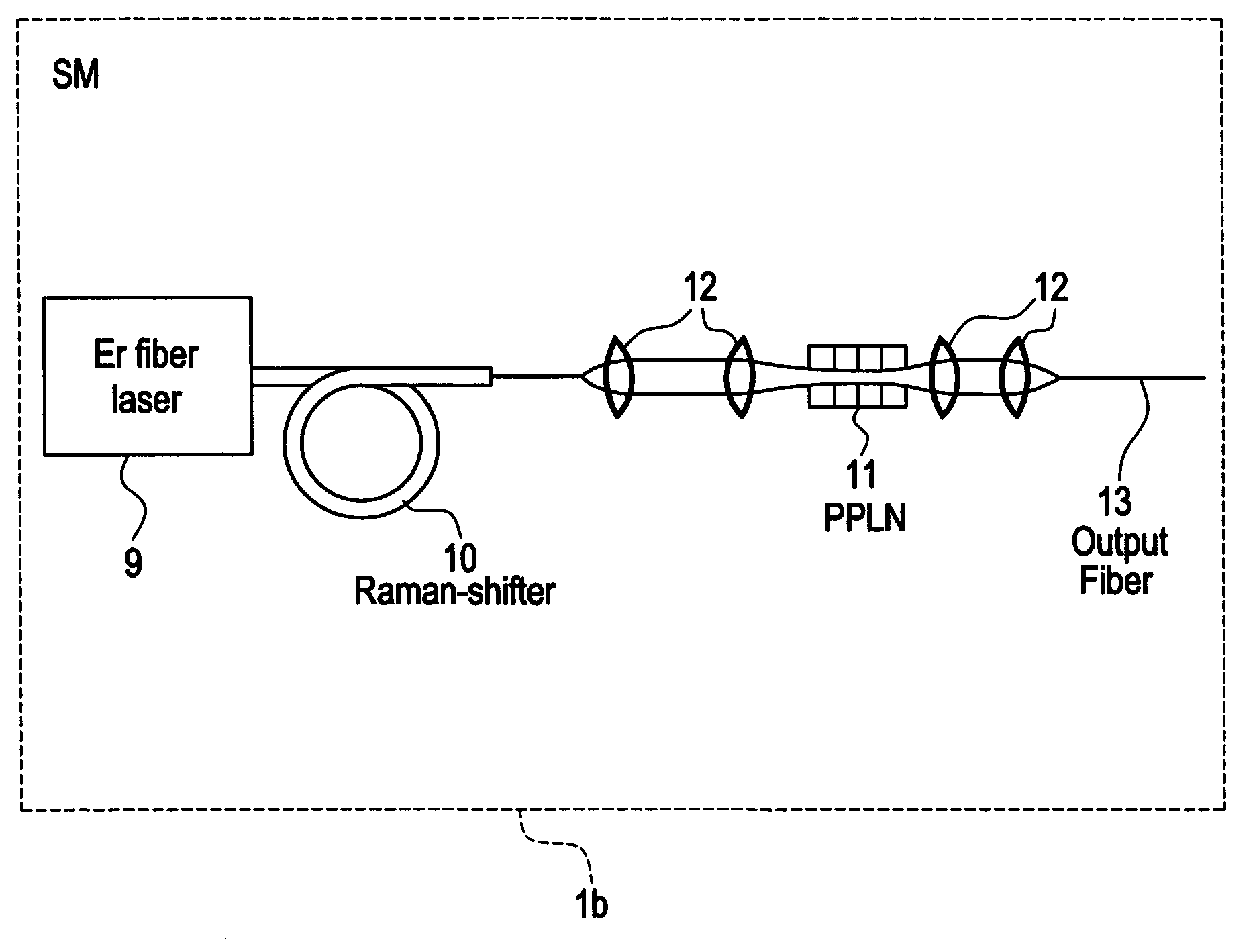
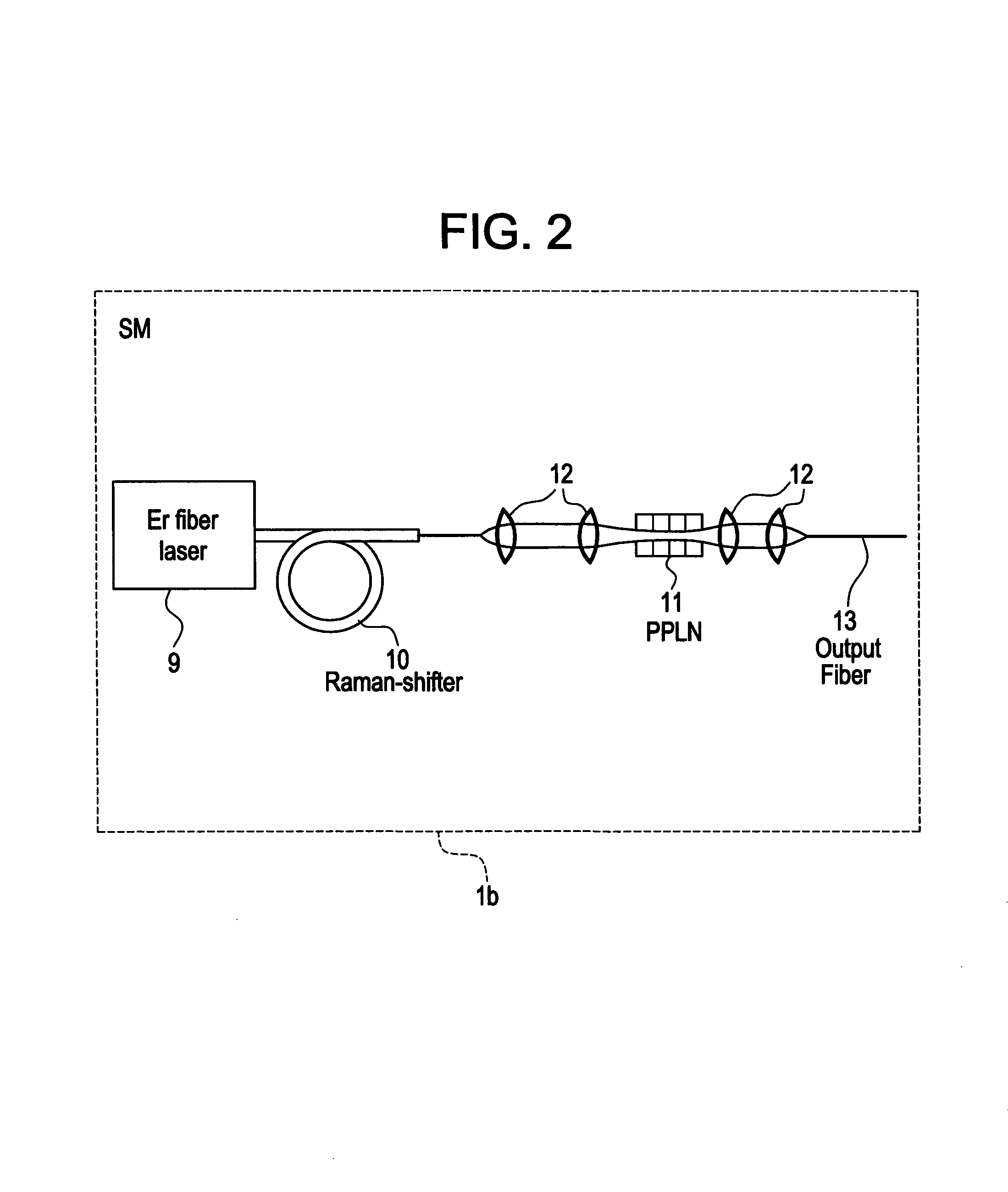
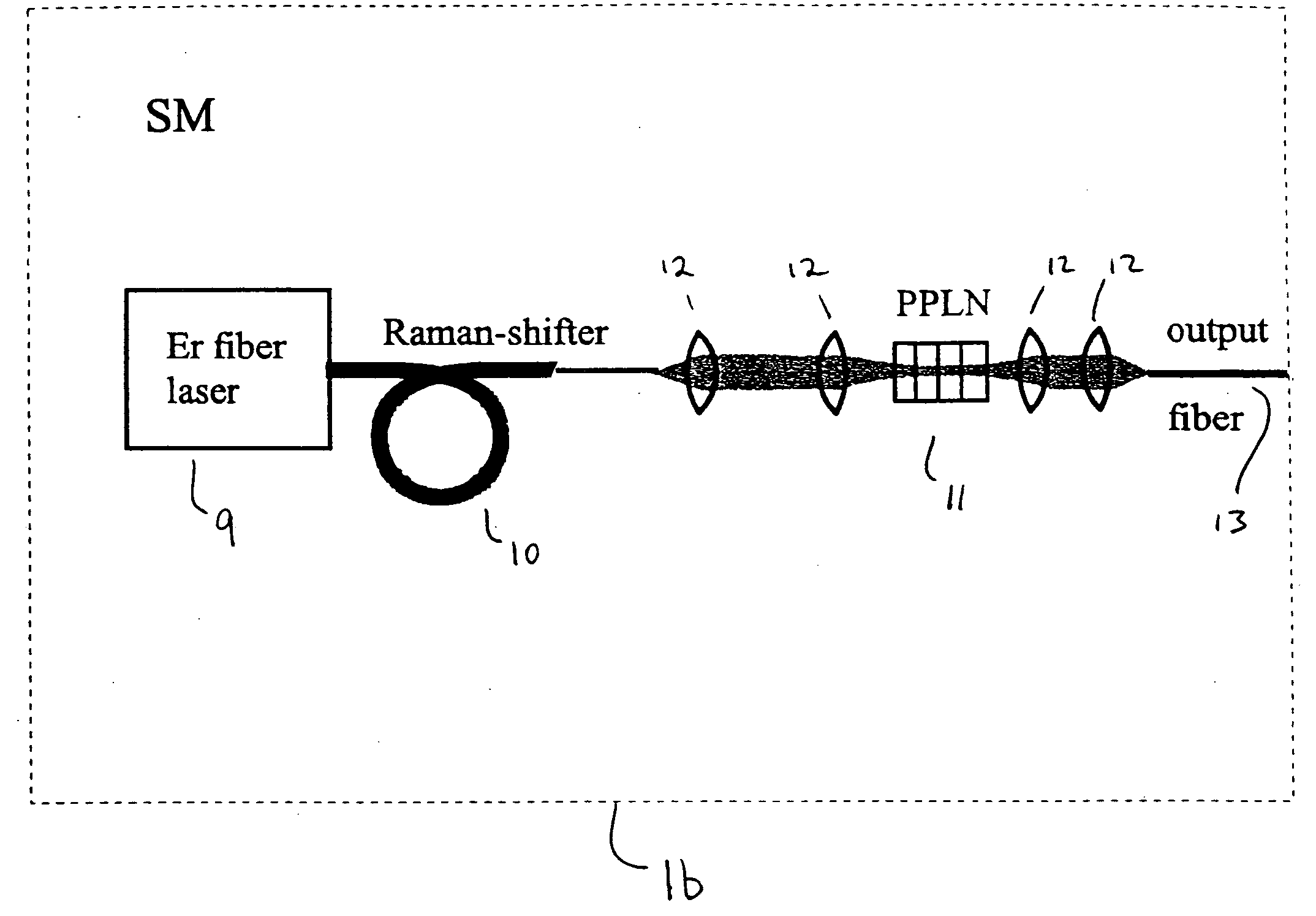
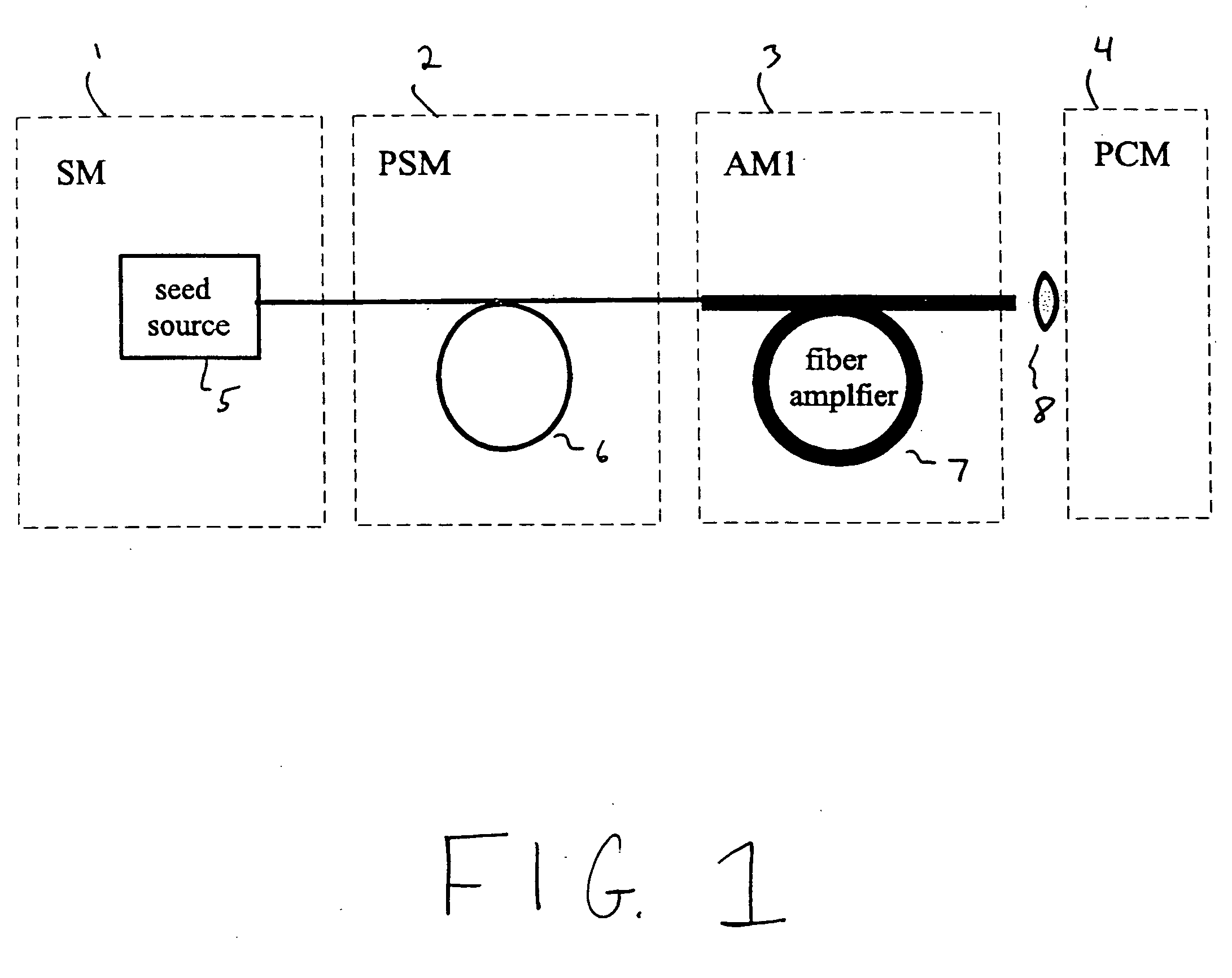
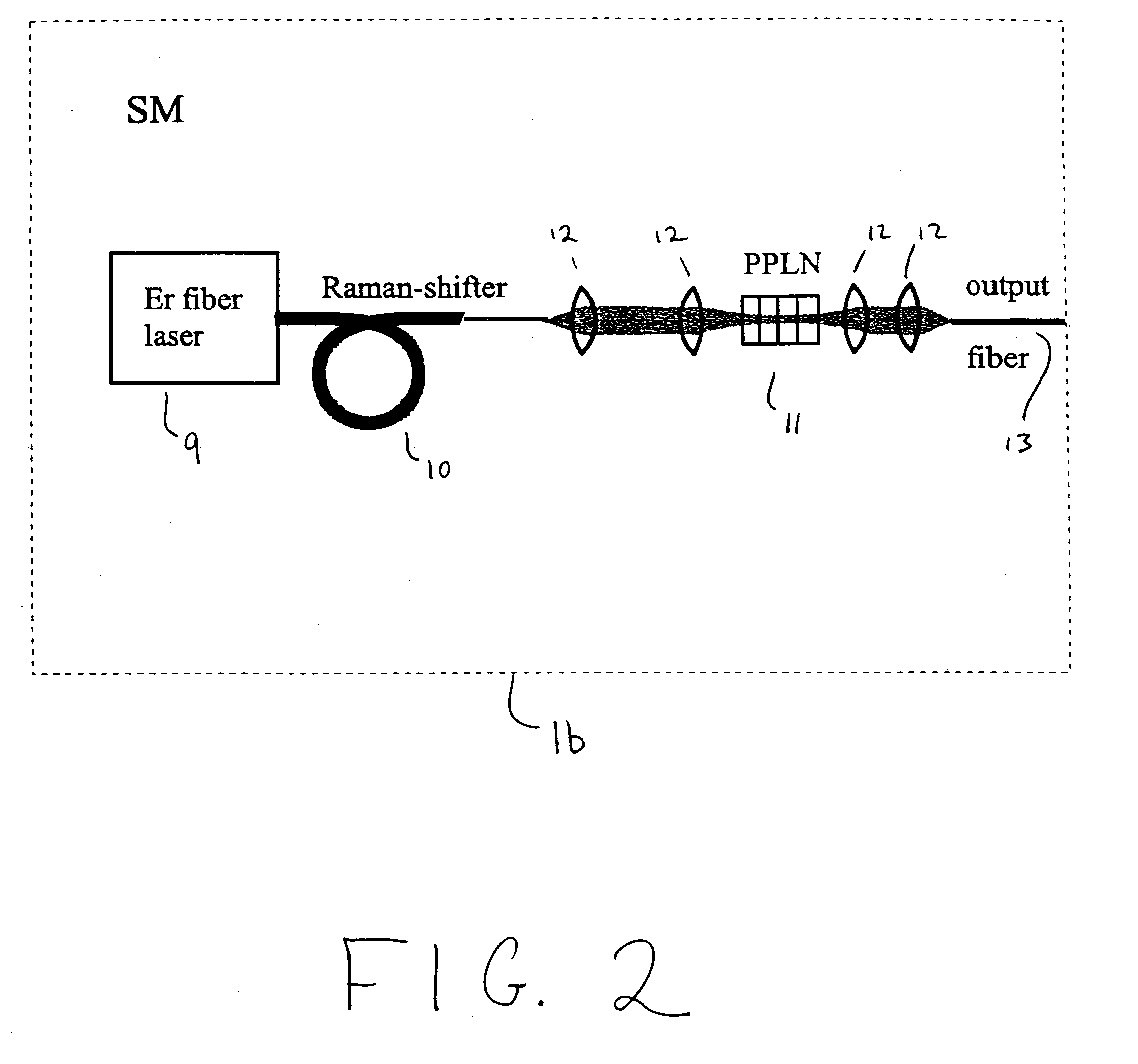
A modular, compact and widely tunable laser system for the efficient generation of high peak and high average power ultrashort pulses. Modularity is ensured by the implementation of interchangeable amplifier components. System compactness is ensured by employing efficient fiber amplifiers, directly or indirectly pumped by diode lasers. Peak power handling capability of the fiber amplifiers is expanded by using optimized pulse shapes, as well as dispersively broadened pulses. After amplification, the dispersively stretched pulses can be re-compressed to nearly their bandwidth limit by the implementation of another set of dispersive delay lines. To ensure a wide tunability of the whole system, Raman-shifting of the compact sources of the ultrashort pulses in conjunction with frequency-conversion in nonlinear optical crystals can be implemented, or an Anti-Stokes fiber in conjunction with fiber amplifiers and Raman-shifters are used.
Owner:IMRA AMERICA
Azimuthally tunable multi-zone electrostatic chuck
ActiveUS20160345384A1Semiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementElectric heatingTunable laserEngineering
Implementations described herein provide a method for processing a substrate on a substrate support assembly which enables both lateral and azimuthal tuning of the heat transfer between an electrostatic chuck and a substrate. The method includes processing a first substrate using a first temperature profile on the ESC having primary heaters and spatially tunable heaters. A deviation profile is determined from a result of processing the first substrate from a target result profile. The first temperature profile is adjusted to a second temperature profile on the ESC based on the deviation profile. Adjusting to the second temperature profile includes incrementing the power to one or more spatially tunable heaters in one or more discrete locations corresponding to the deviations profile. A second substrate is then processed on the ESC using the second temperature profile.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Tunable laser light source
ActiveUS7099358B1Small distortionLittle noiseOptical resonator shape and constructionSemiconductor lasersLight beamPrism
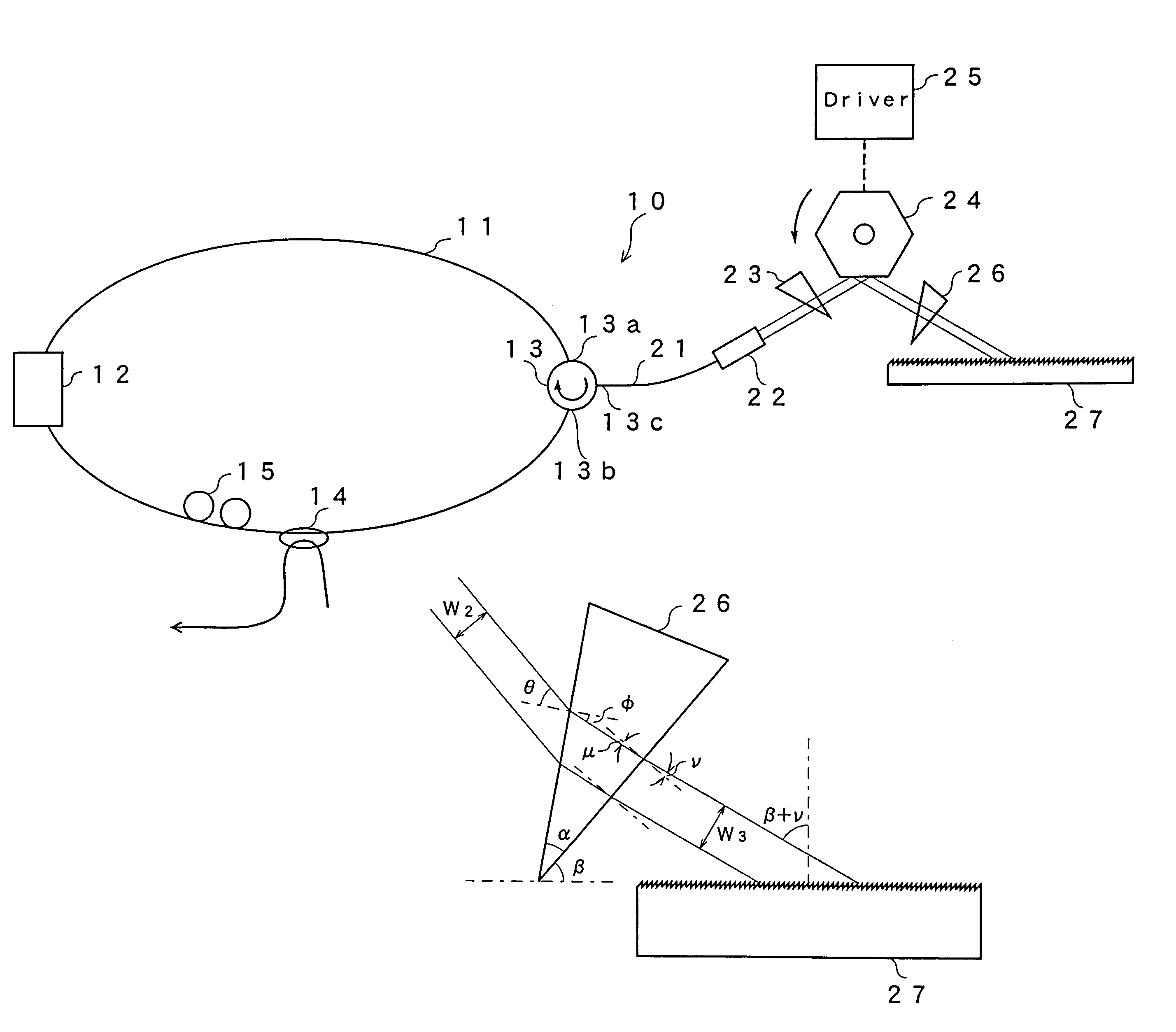
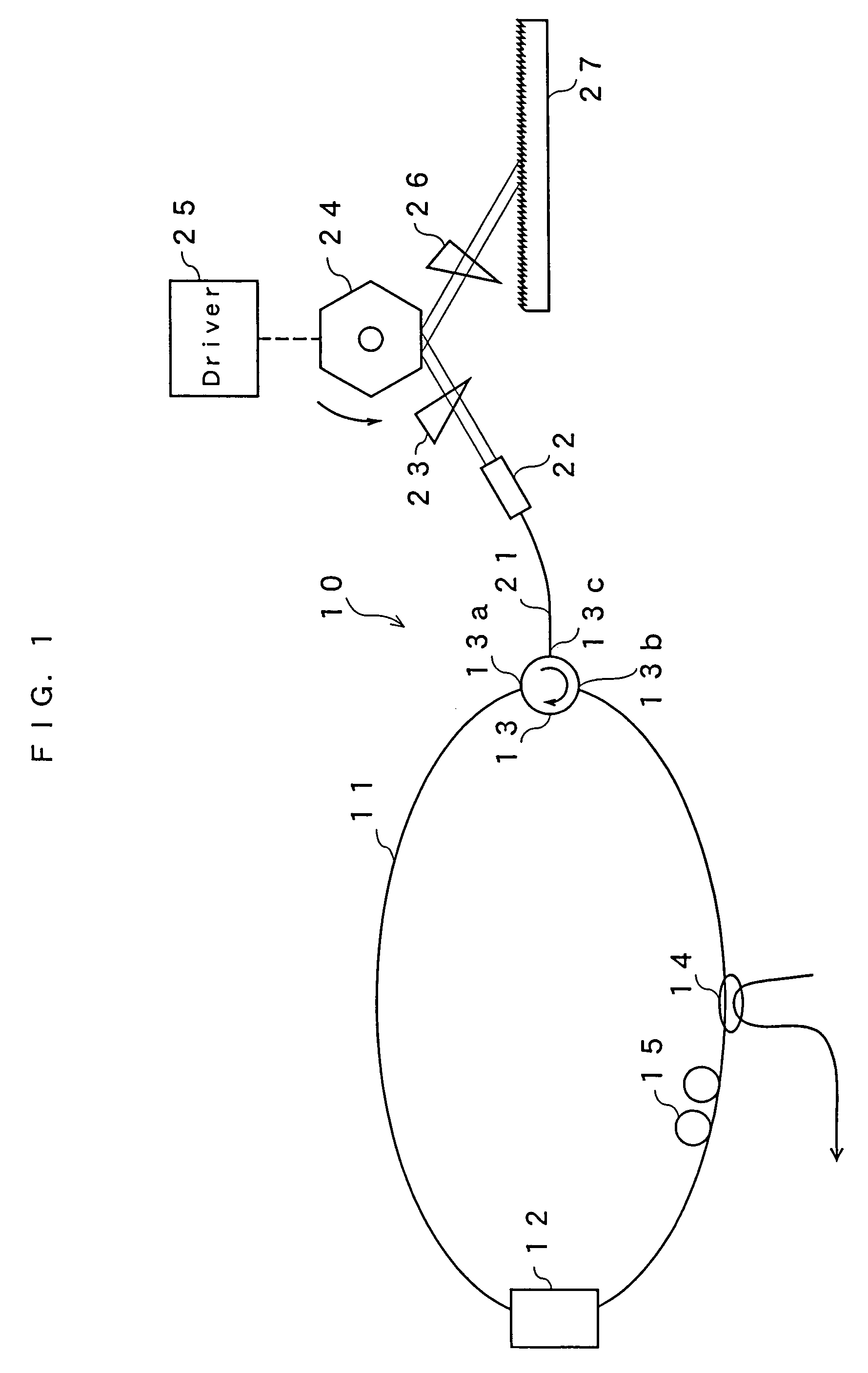
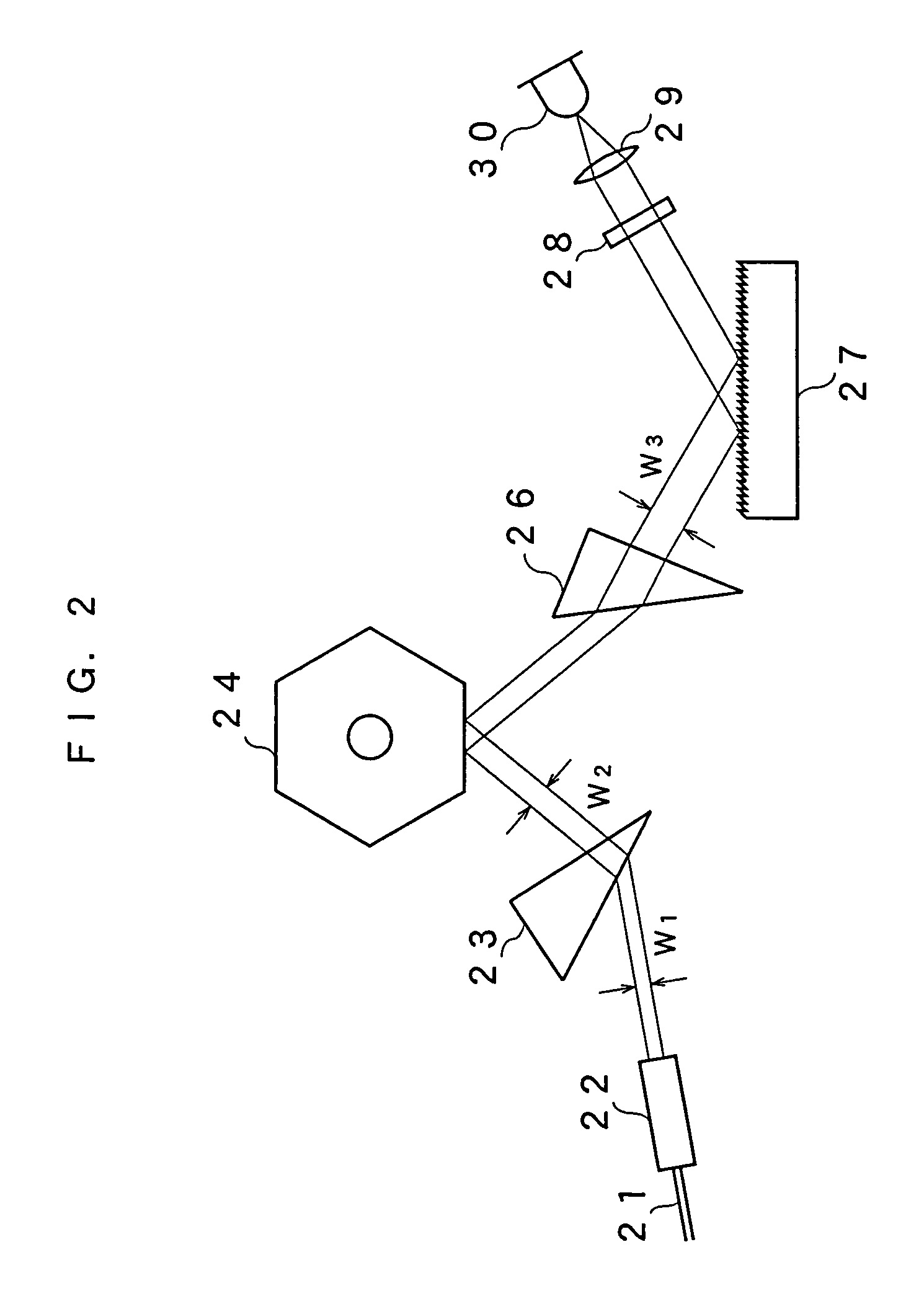
A gain medium 12 and a tunable filter are provided in an optical path of laser oscillation. The tunable filter has an optical beam deflector for periodically changing an optical beam at a constant angular speed, a prism 26 on which deflected light is made incident, and a diffraction grating 27. Appropriate selection of the apex angle α of the prism 26 and an angle β formed by the prism 26 and the diffraction grating 27 can provide a tunable laser light source for changing the oscillation frequency at high speed and a constant variation rate.
Owner:SANTEC
Tunable laser transmitter with internal wavelength grid generators
InactiveUS6526071B1Laser optical resonator constructionSemiconductor laser arrangementsCapacitanceLaser transmitter
The present invention provides a continuously tunable external cavity laser (ECL) with a compact form factor and precise tuning to a selected center wavelength of a selected wavelength grid. The ECL may thus be utilized in telecom applications to generate the center wavelengths for any channel on the ITU or other optical grid. The ECL does not require a closed loop feedback. A novel tuning mechanism is disclosed which provides for electrical or mechanical tuning to a known position or electrical parameter, e.g., voltage, current or capacitance, with the required precision in the selected center wavelength arising as a result of a novel arrangement of a grid generator and a channel selector. The grid generator exhibits first pass bands which correspond to the spacing between individual channels of the selected wavelength grid and a finesse which suppresses side band modes of the laser. The channel selector exhibits second pass bands that are wider than the first pass bands. In an embodiment of the invention the second pass bands have a periodicity substantially corresponding with the separation between the shortest wavelength channel and the longest wavelength channel of the selected wavelength grid and a finesse which suppresses channels adjacent to the selected channel. The broad second pass bands of the channel selector reduce the sensitivity of the ECL to tuning variations about the selected channel, thus avoiding the requirement of a closed loop feedback system to control the channel selector.
Owner:NEWPORT CORP
Flexible 3-D Photonic Device
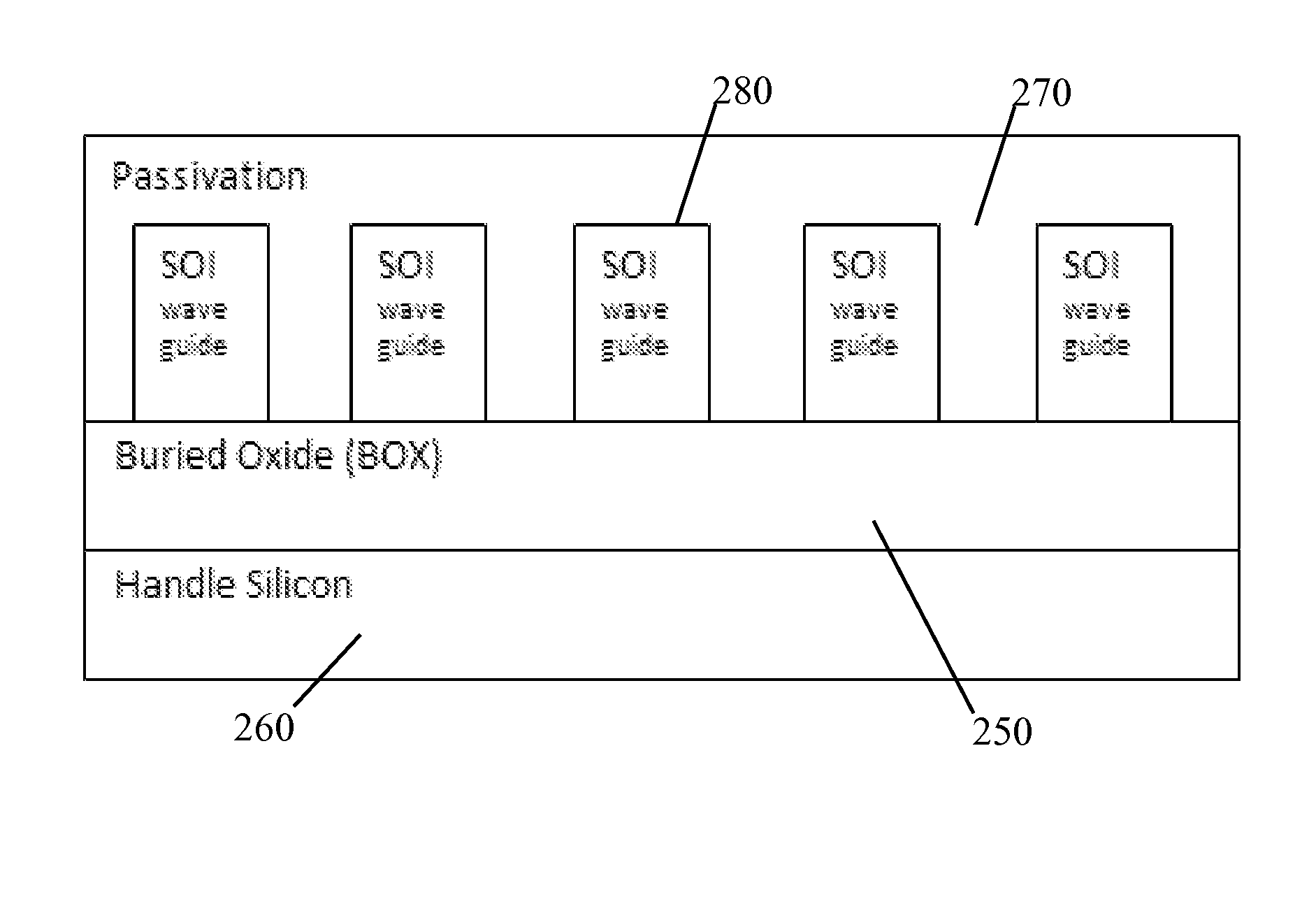
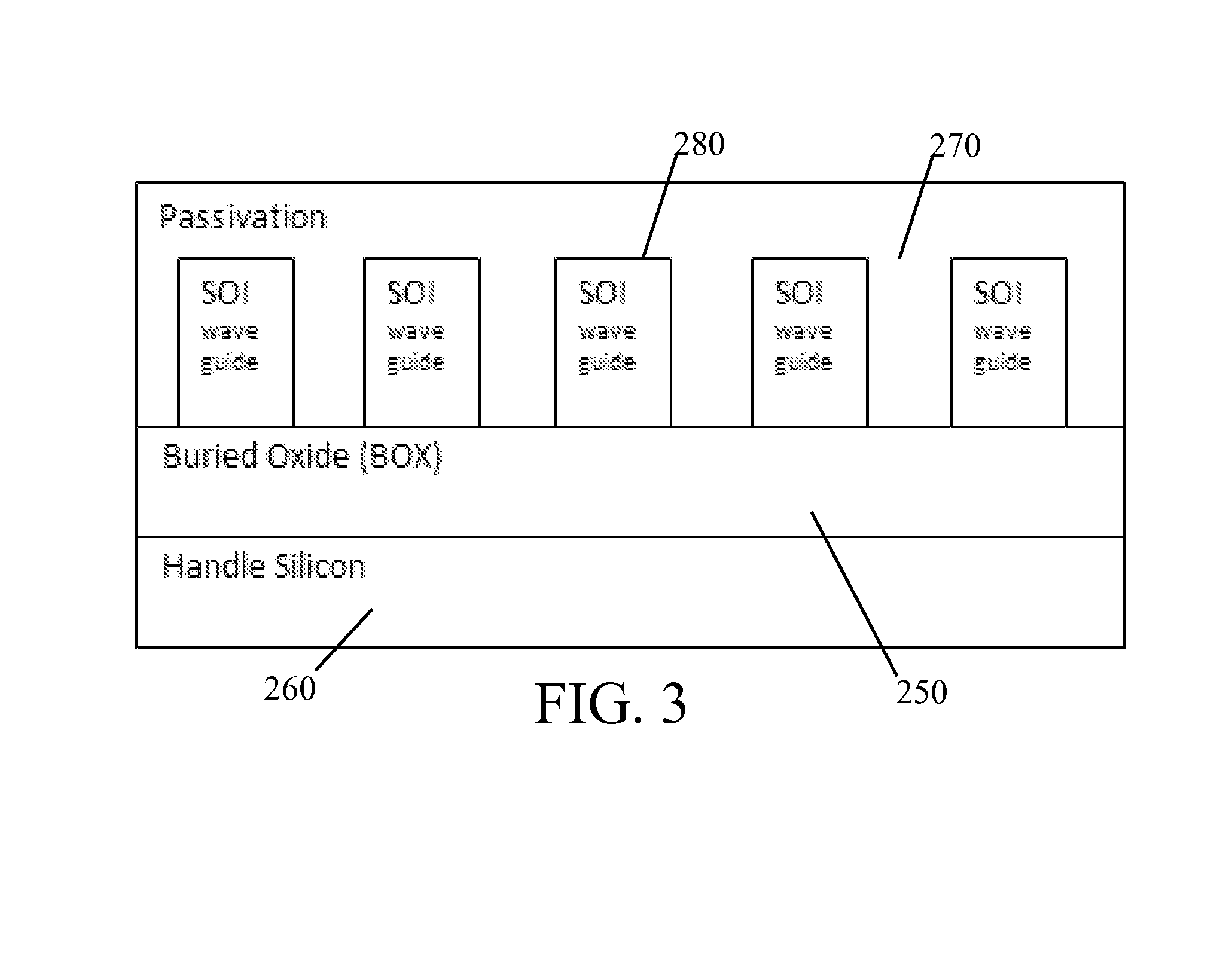
ActiveUS20140219604A1Function increaseSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOptical waveguide light guidePolymerPhoton
Three-dimensional flexible photonic integrated circuits on silicon are fabricated in semiconductor wafer form and then transferred to Silicon-on-Polymer (SOP) substrates. SOP provides flexibility for conformal mounting with devices capable of maintaining performance when dynamically deformed to allow routing of light in x, y and z directions. Bonding a wafer or individual die of III-V semiconductor, such as Gallium Arsenide or similar photonic material, to the flexible silicon creates an active region for lasers, amplifiers, modulators, and other photonic devices using standard processing. Mounting additional photonic devices to the opposite side of a flexible photonic waveguide produces a stack for three-dimensional devices. Multiple flexible photonic waveguides may be stacked to increase functionality by transferring light between stacked waveguides. The flexible photonic circuit allows for integration of photonic devices such as low threshold lasers, tunable lasers, and other photonic integrated circuits with flexible Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor (CMOS) integrated circuits.
Owner:AMERICAN SEMICON
Microwave tunable filter using microelectromechanical (MEMS) system
A microwave tunable filter having some advantages as follows: a) the integration of MEMS tunable filter and MMIC; b) the very low signal transmission loss and low dispersion; and c) the drastic variation and linear characteristic of frequency by means of MEMS capacitor and an external control signal. The microwave tunable MEMS filter includes a plurality of unit resonant cells, each unit resonant cell being formed by various serial and parallel combination of an inductor, a capacitor, a transmission line, and a variable MEMS capacitor, whereby capacitance variation of the variable MEMS capacitor in the unit resonant cell converts a resonant frequency of the unit resonant cell to thereby convert a center frequency of the filter.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Wavelength discretely tunable semiconductor laser
InactiveUS20020054614A1Increase output powerFast switching timeLaser optical resonator constructionOptical resonator shape and constructionWedge filter (device)Switching time
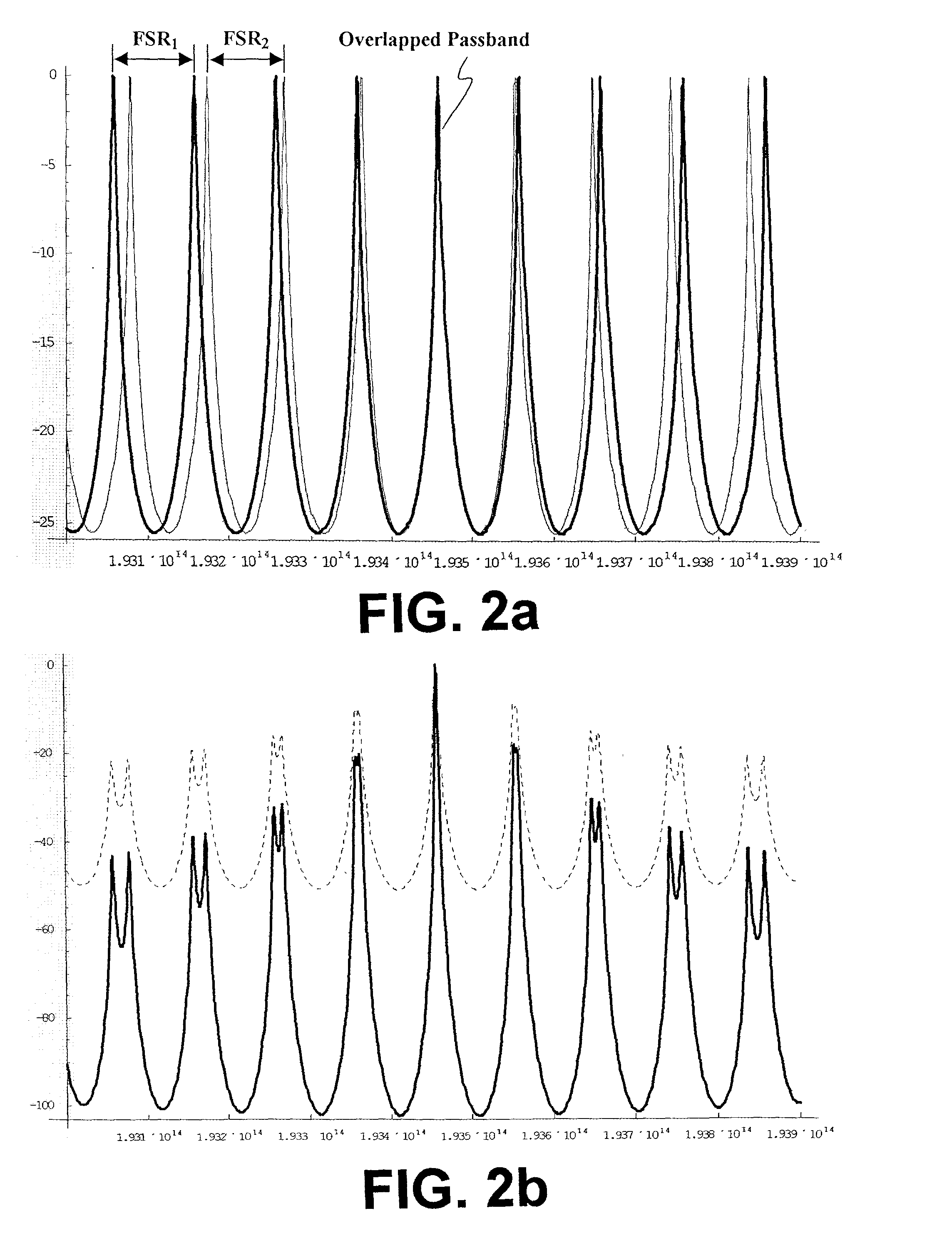
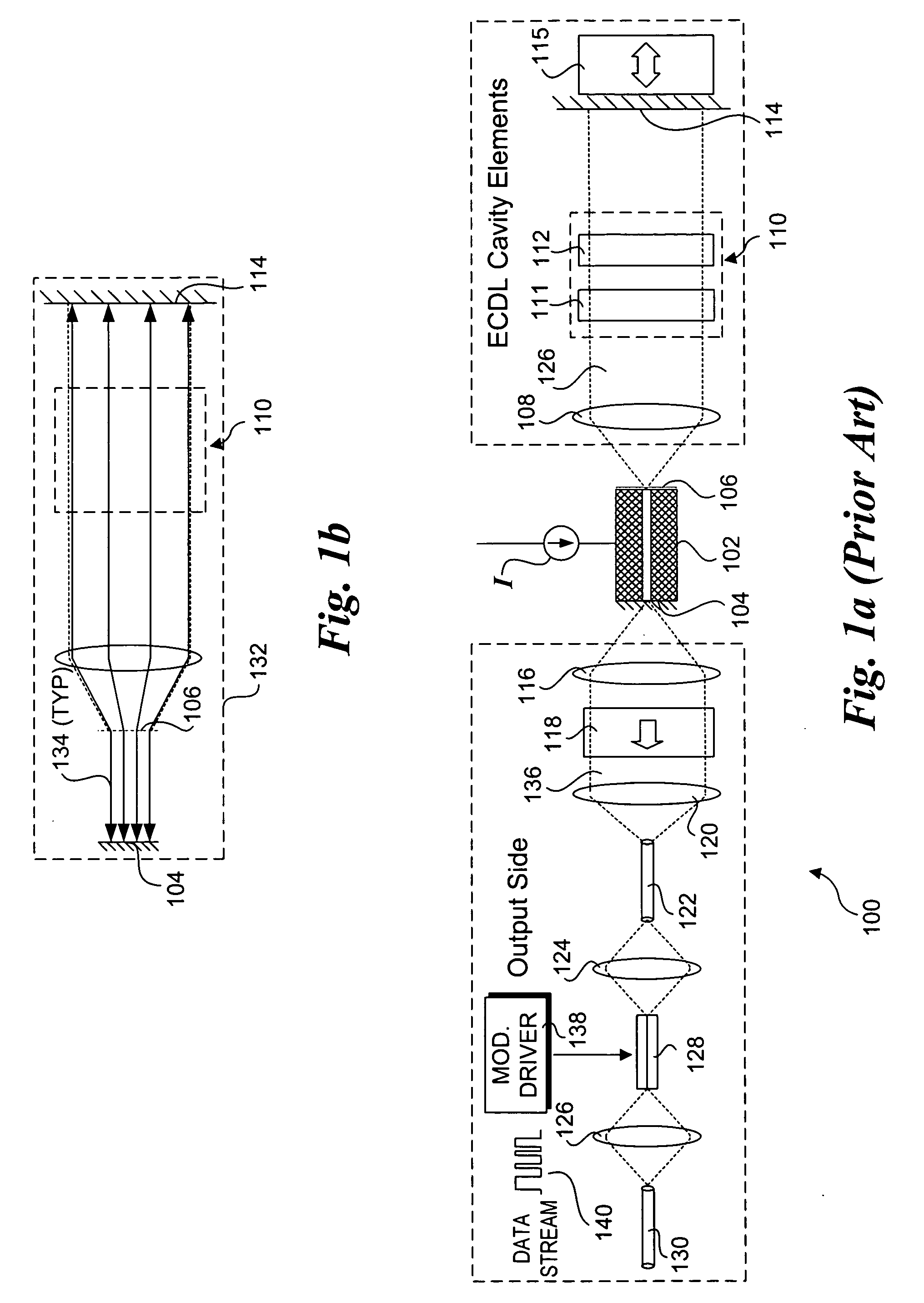
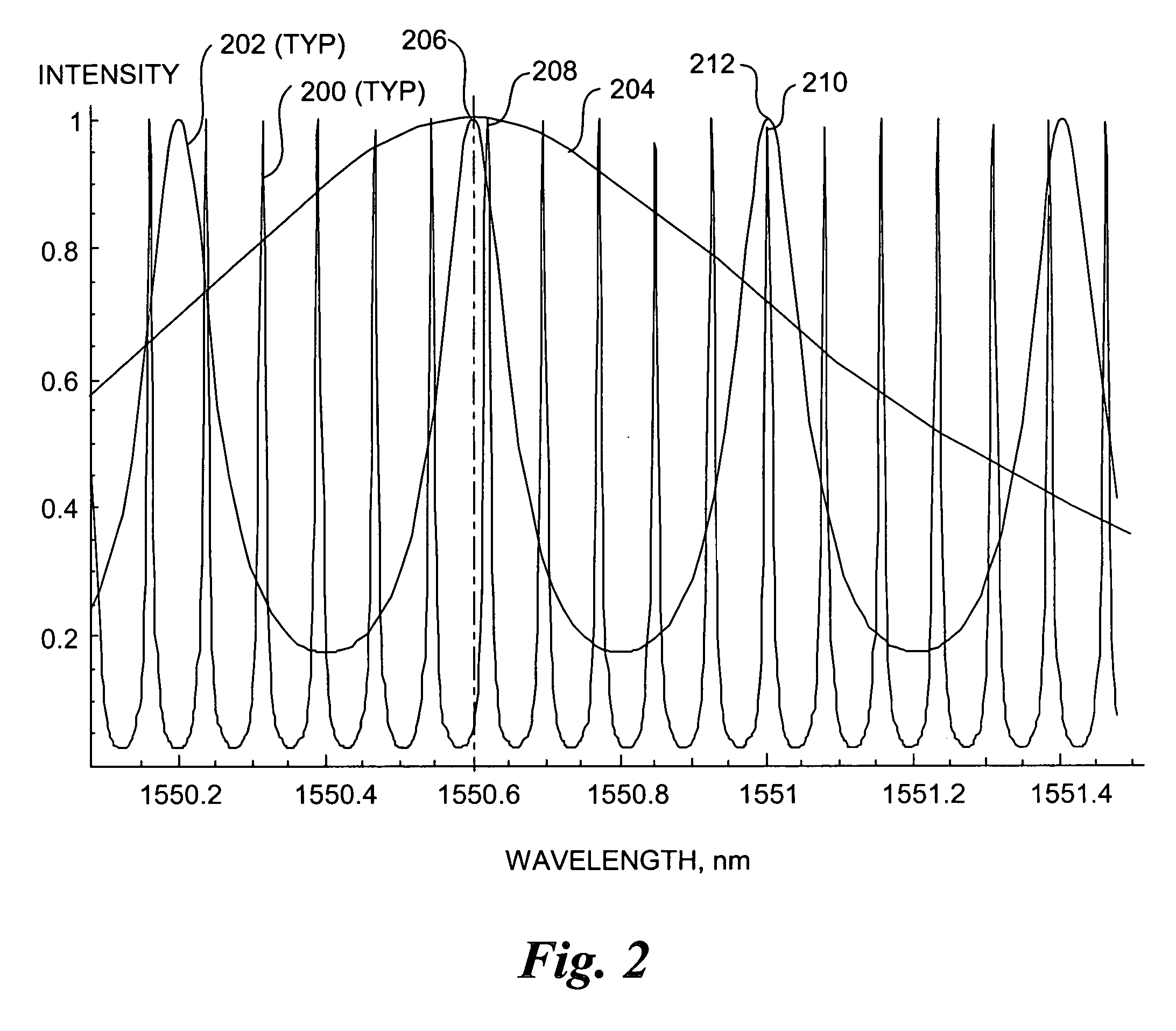
A wavelength discretely tunable semiconductor laser that addresses wide wavelength tuning range, is mode hopping free, has high output power, has fast wavelength switching time, is wavelength locking free and is relatively simple. Four exemplary embodiments disclosed herein utilize a wavelength discretely tunable semiconductor laser that comprises a discretely tunable filter and laser amplifier. In the first embodiment, the tuning element comprises a pair of cascade Fabry-Perot filters, each having a plurality of characteristic narrow transmission passbands that pass only the cavity mode under the passband. The spacing between the narrow transmission passbands are slightly different in one filter from the other filter so that only one passband from each filter can be overlapped in any given condition over the entire active element gain spectral range, thereby permitting lasing only at a single cavity mode passed by the cascade double filters. One of the two etalon filters can be made with a plurality of transmission passbands predetermined by industry, application and international standards, making this element an intra-cavity wavelength reference and eliminating further wavelength locking needs for the tunable laser. In a second embodiment, one of the two etalons is replaced by a wedge filter. The filter optical path change and thus the transmission passband shift are achieved by translating the wedge filter in a direction perpendicular to the optical axis. In a third embodiment, one of the two etalon filters is replaced by a polarization interference filter. The polarization interference filter consists of an electro-optically-tunable birefringent waveplate, a fixed birefringent waveplate, the laser cavity and T.E. polarization light emitted from the laser diode. In a fourth embodiment, the laser and wavelength tuning structure are integrated on a semiconductor substrate by epitaxy processes.
Owner:JIN HONG
Communication transceiver architecture
ActiveUS20070031150A1Reduce sensitivitySimplifies the transceiver architectureSatellite communication transmissionRadio transmissionLaser transmitterOptical axis
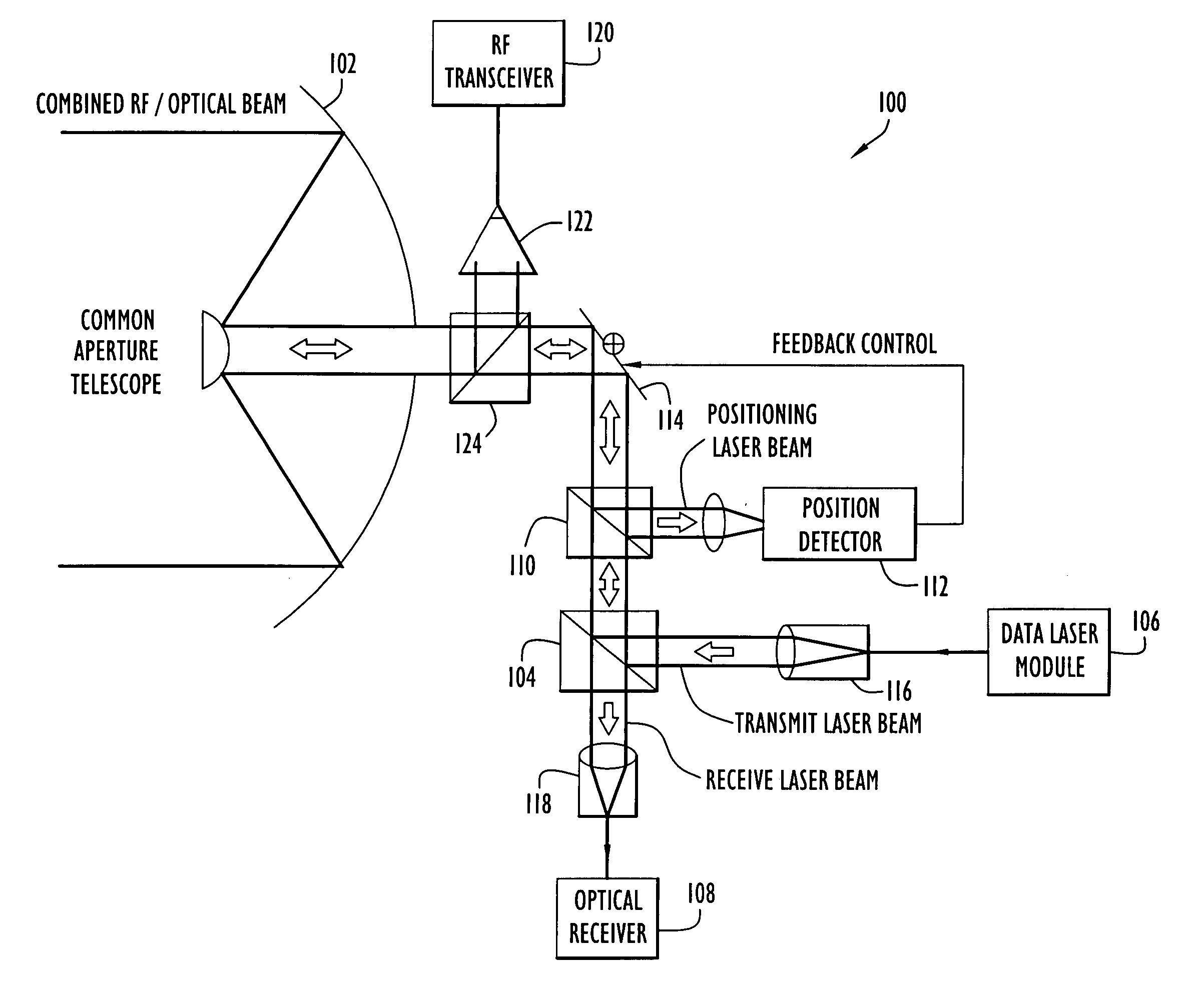
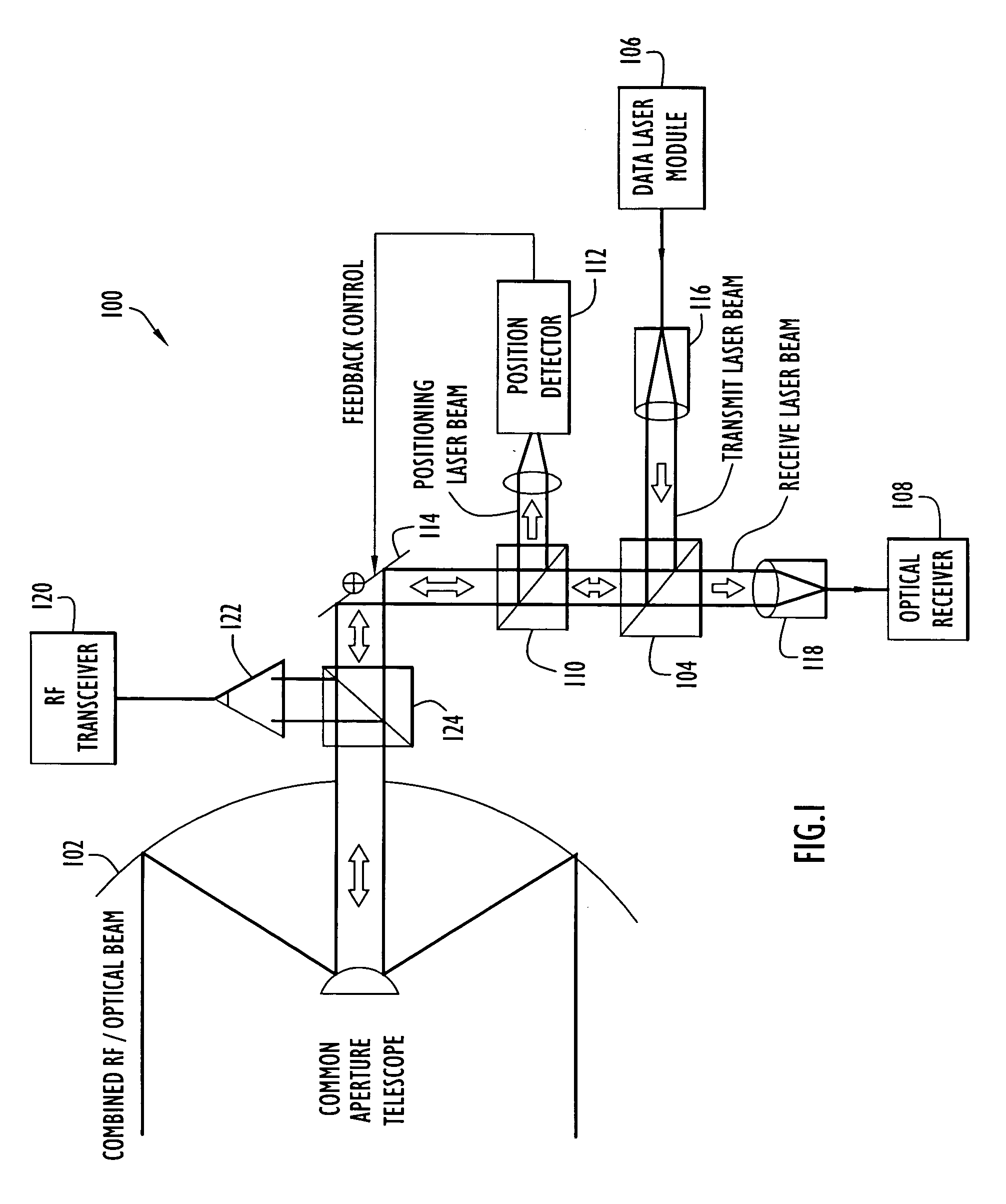
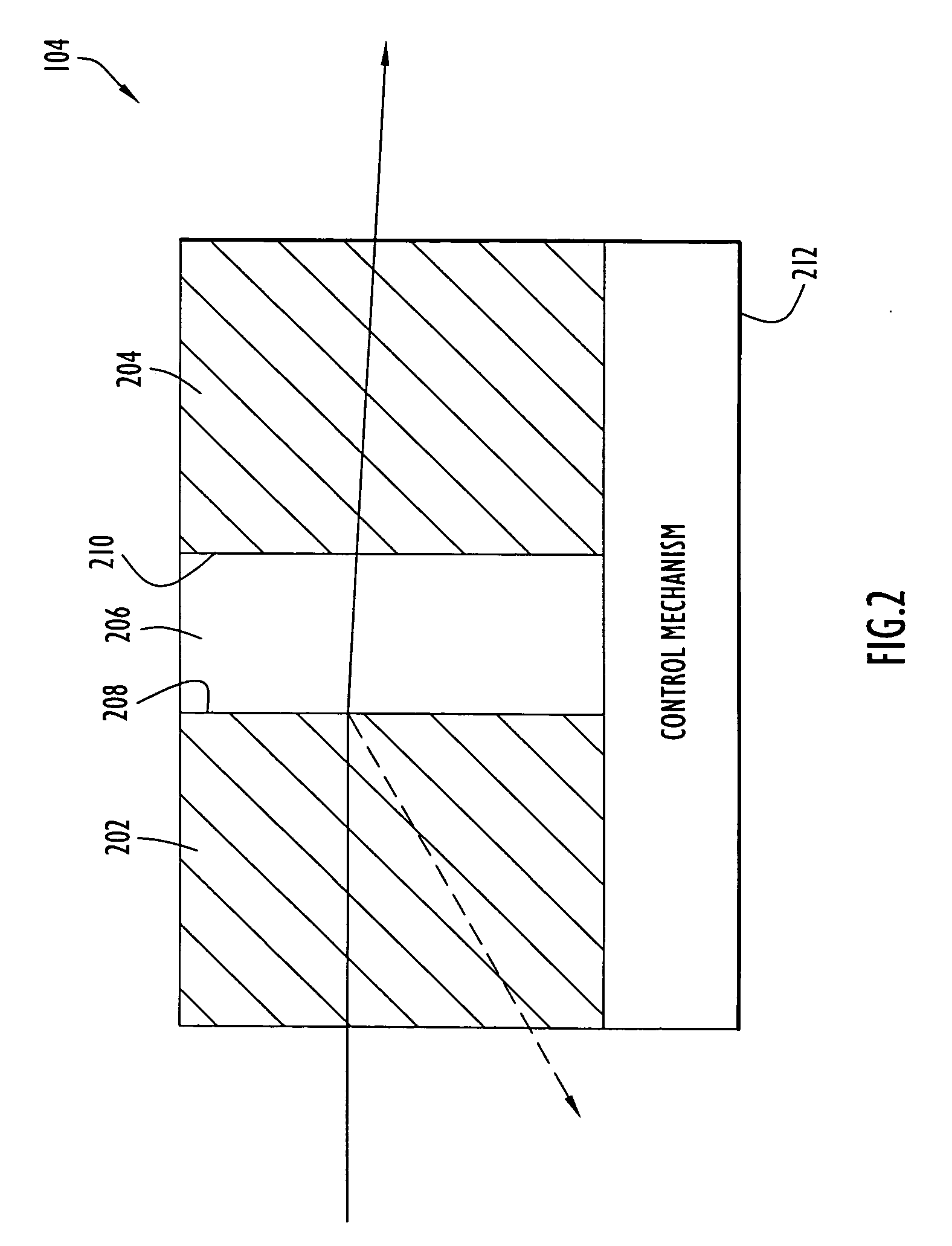
A free-space communication transceiver includes a telescope for transmitting and receiving laser beams, a tunable laser transmitter for generating a transmit laser beam modulated with data, a tunable optical receiver for processing a receive laser beam received from the telescope to recover data, and a tunable beamsplitter that directs the transmit laser beam to the telescope and directs the receive laser beam from the telescope to the optical receiver. Between the telescope and beamsplitter, the transmit and receive laser beams travel along a common optical axis as collinear collimated free-space beams. The transmit and receive laser beams operate at different wavelengths that can be interchanged, thereby support full-duplex operation. The beamsplitter employs a tunable etalon filter whose wavelength-dependent transmission characteristics are adjusted according to the transmit and receive wavelengths. Optionally, RF signals can additionally be couple to the common optical axis and transmitted and received by the telescope.
Owner:PERATON INC
Modular, high energy, widely-tunable ultrafast fiber source
InactiveUS7167300B2High peak and high average powerReduce noiseLaser using scattering effectsCladded optical fibreHigh peakHigh energy
Owner:IMRA AMERICA
Tunable laser having liquid crystal waveguide
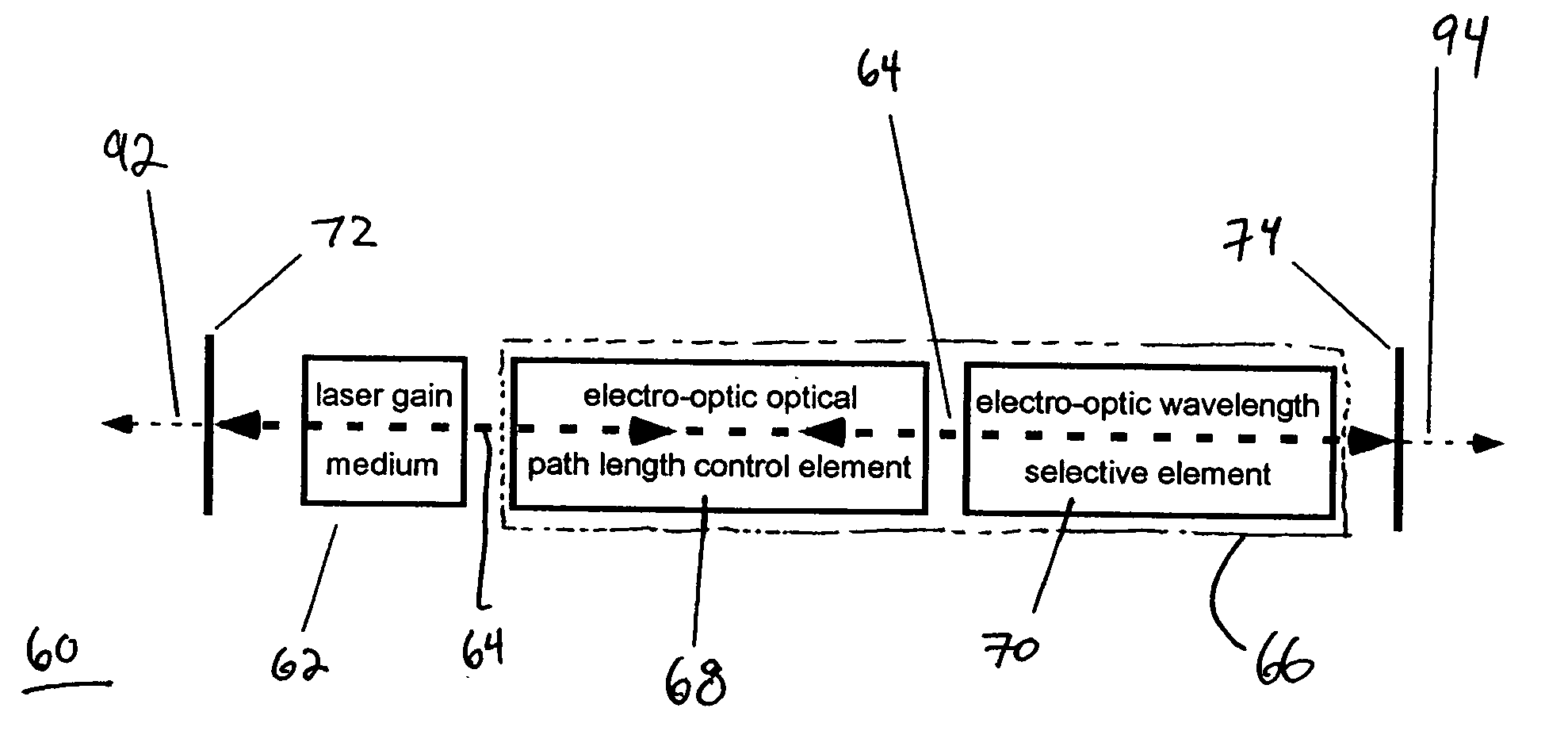
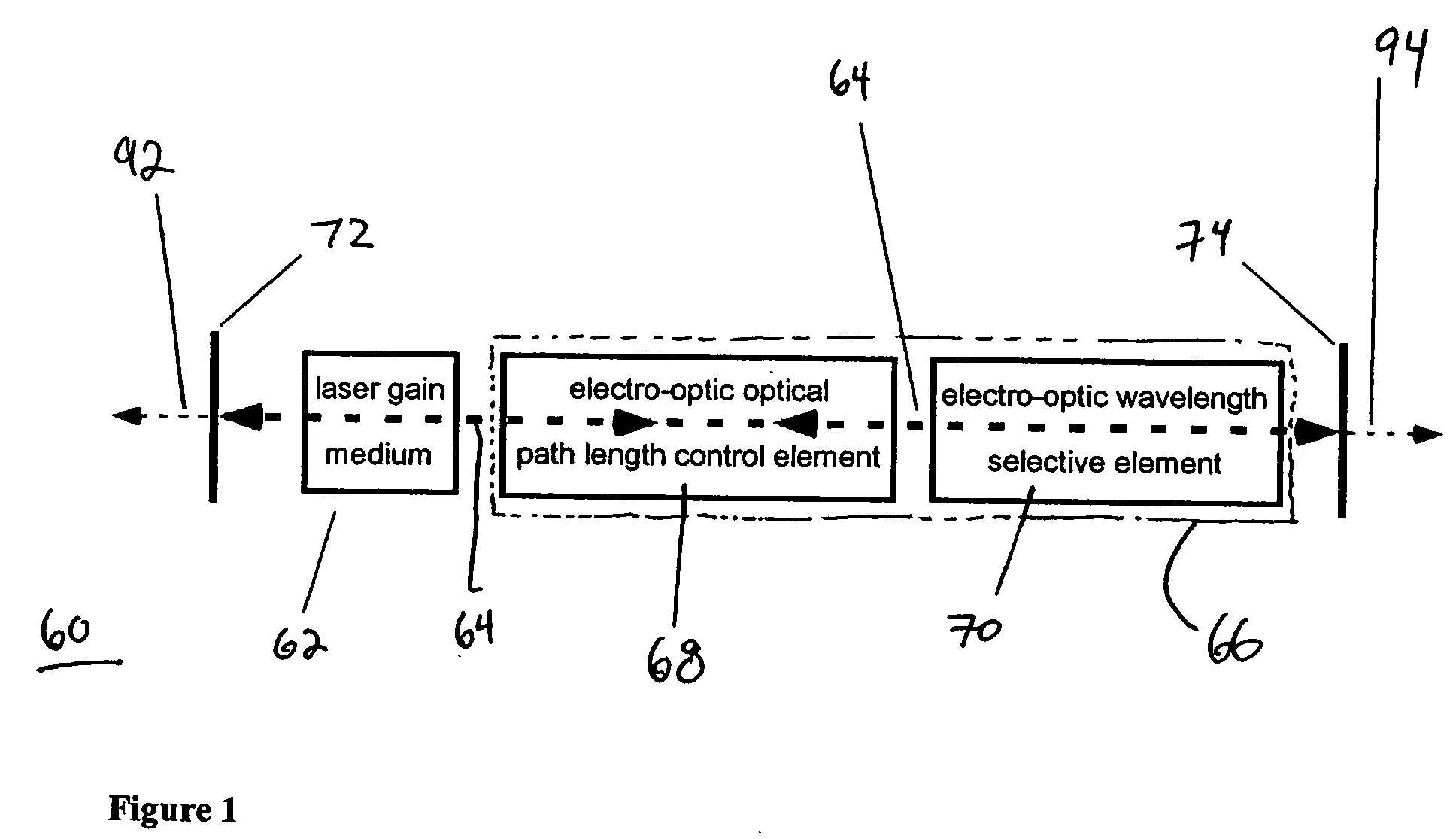
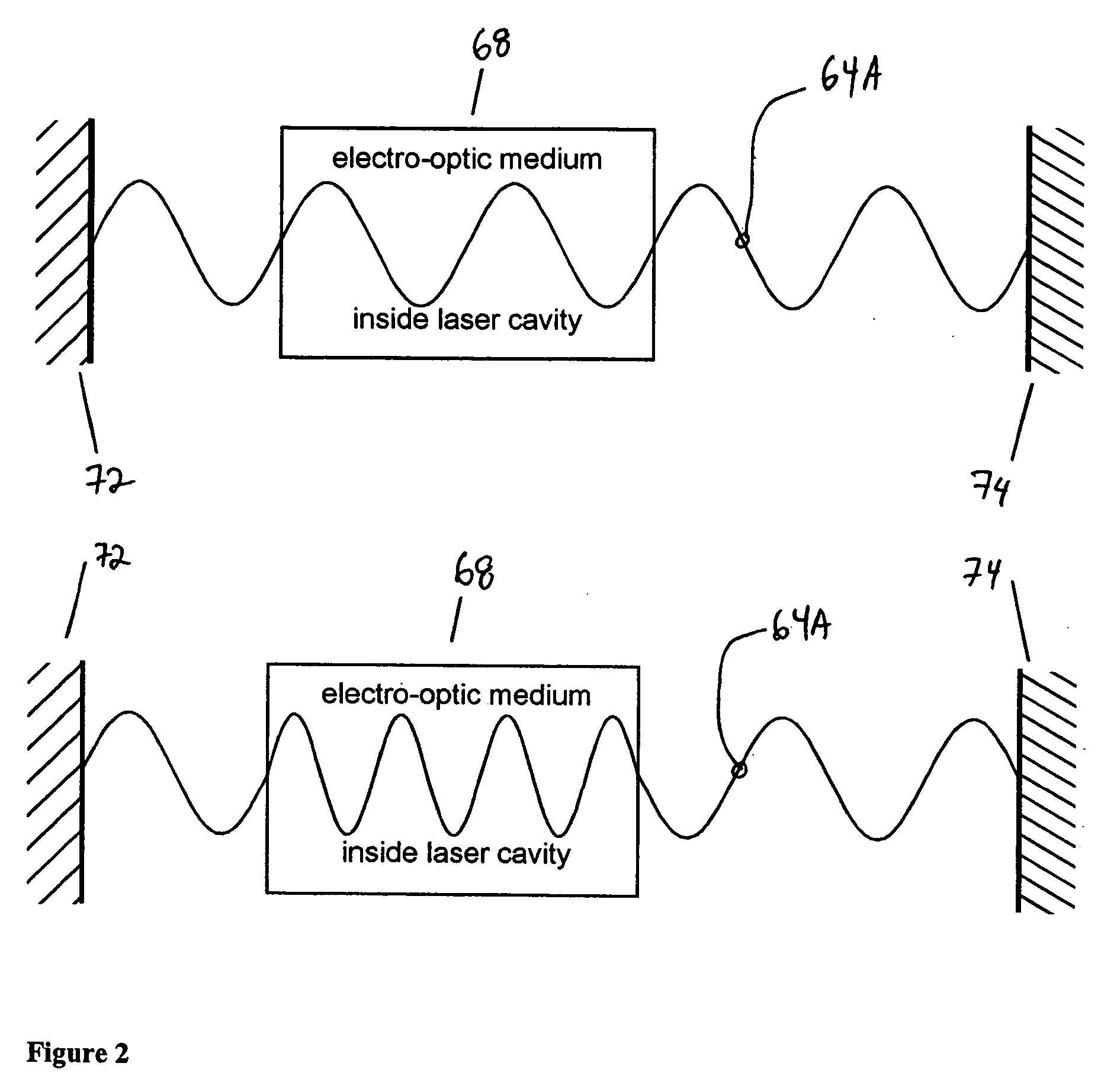
A tunable laser for providing a laser beam with a selectable wavelength. In one example, the tunable laser includes a gain medium for generating the laser beam; a waveguide for processing the laser beam, the waveguide having liquid crystal material or other electro-optic material disposed therein; an optical path length control element disposed within said waveguide for controlling an effective optical path length of the laser cavity; and a wavelength selective element for controlling the wavelength of the laser beam. The tunable laser may be designed without any moving mechanical parts if desired.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
Modular, high energy, widely-tunable ultrafast fiber source
InactiveUS20050163426A1High peak and high average powerReduce noiseLaser using scattering effectsCladded optical fibreHigh peakHigh energy
A modular, compact and widely tunable laser system for the efficient generation of high peak and high average power ultrashort pulses. Modularity is ensured by the implementation of interchangeable amplifier components. System compactness is ensured by employing efficient fiber amplifiers, directly or indirectly pumped by diode lasers. Peak power handling capability of the fiber amplifiers is expanded by using optimized pulse shapes, as well as dispersively broadened pulses. Dispersive broadening is introduced by dispersive pulse stretching in the presence of self-phase modulation and gain, resulting in the formation of high-power parabolic pulses. In addition, dispersive broadening is also introduced by simple fiber delay lines or chirped fiber gratings, resulting in a further increase of the energy handling ability of the fiber amplifiers. The phase of the pulses in the dispersive delay line is controlled to quartic order by the use of fibers with varying amounts of waveguide dispersion or by controlling the chirp of the fiber gratings. After amplification, the dispersively stretched pulses can be re-compressed to nearly their bandwidth limit by the implementation of another set of dispersive delay lines. To ensure a wide tunability of the whole system, Raman-shifting of the compact sources of ultrashort pulses in conjunction with frequency-conversion in nonlinear optical crystals can be implemented, or an Anti-Stokes fiber in conjunction with fiber amplifiers and Raman-shifters are used. A particularly compact implementation of the whole system uses fiber oscillators in conjunction with fiber amplifiers. Additionally, long, distributed, positive dispersion optical amplifiers are used to improve transmission characteristics of an optical communication system. Finally, an optical communication system utilizes a Raman amplifier fiber pumped by a train of Raman-shifted, wavelength-tunable pump pulses, to thereby amplify an optical signal which counterpropogates within the Raman amplifier fiber with respect to the pump pulses.
Owner:IMRA AMERICA
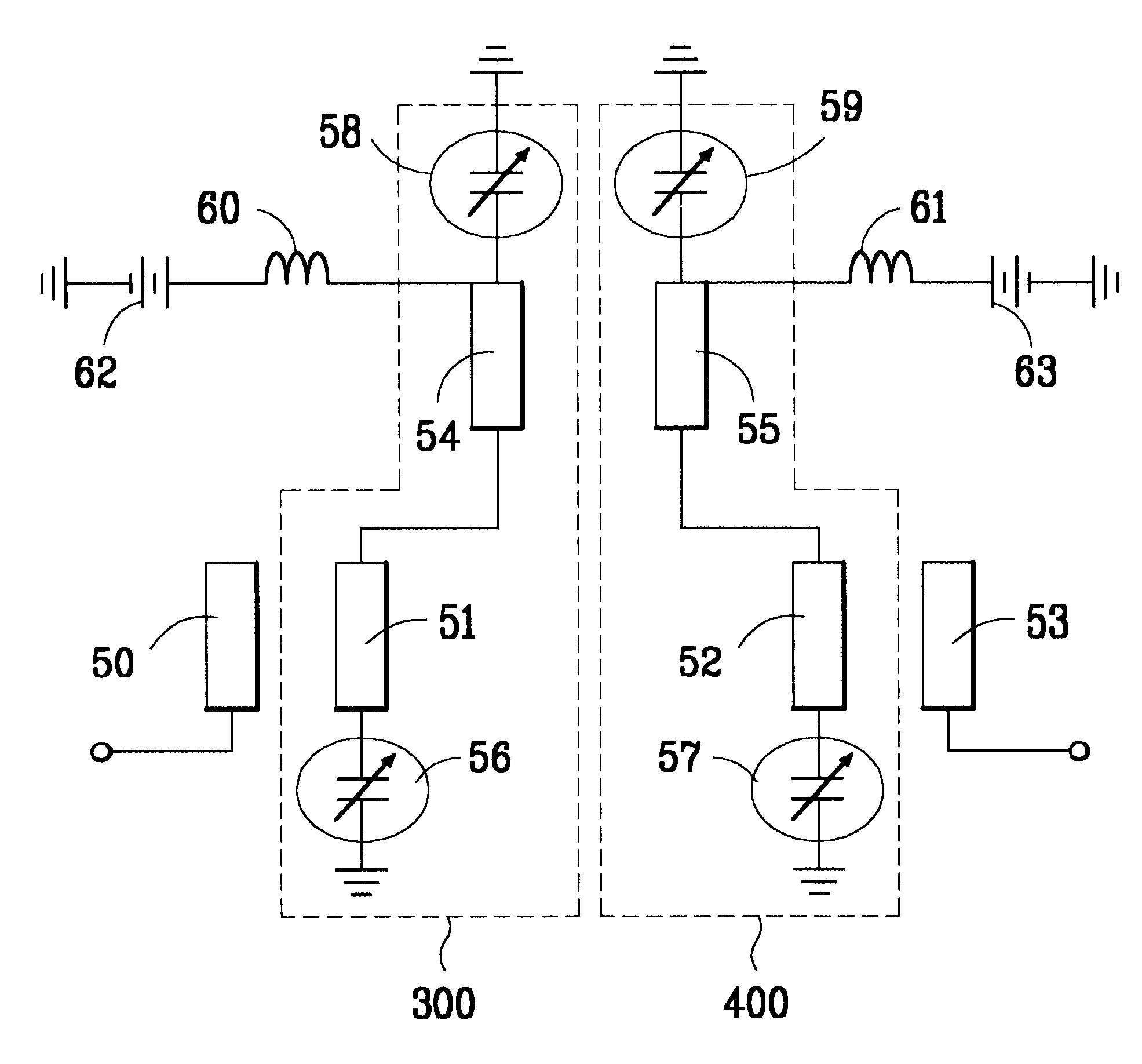
Semi-integrated designs for external cavity tunable lasers
ActiveUS20050213618A1Laser detailsLaser optical resonator constructionExternal cavity diode laserPhase control
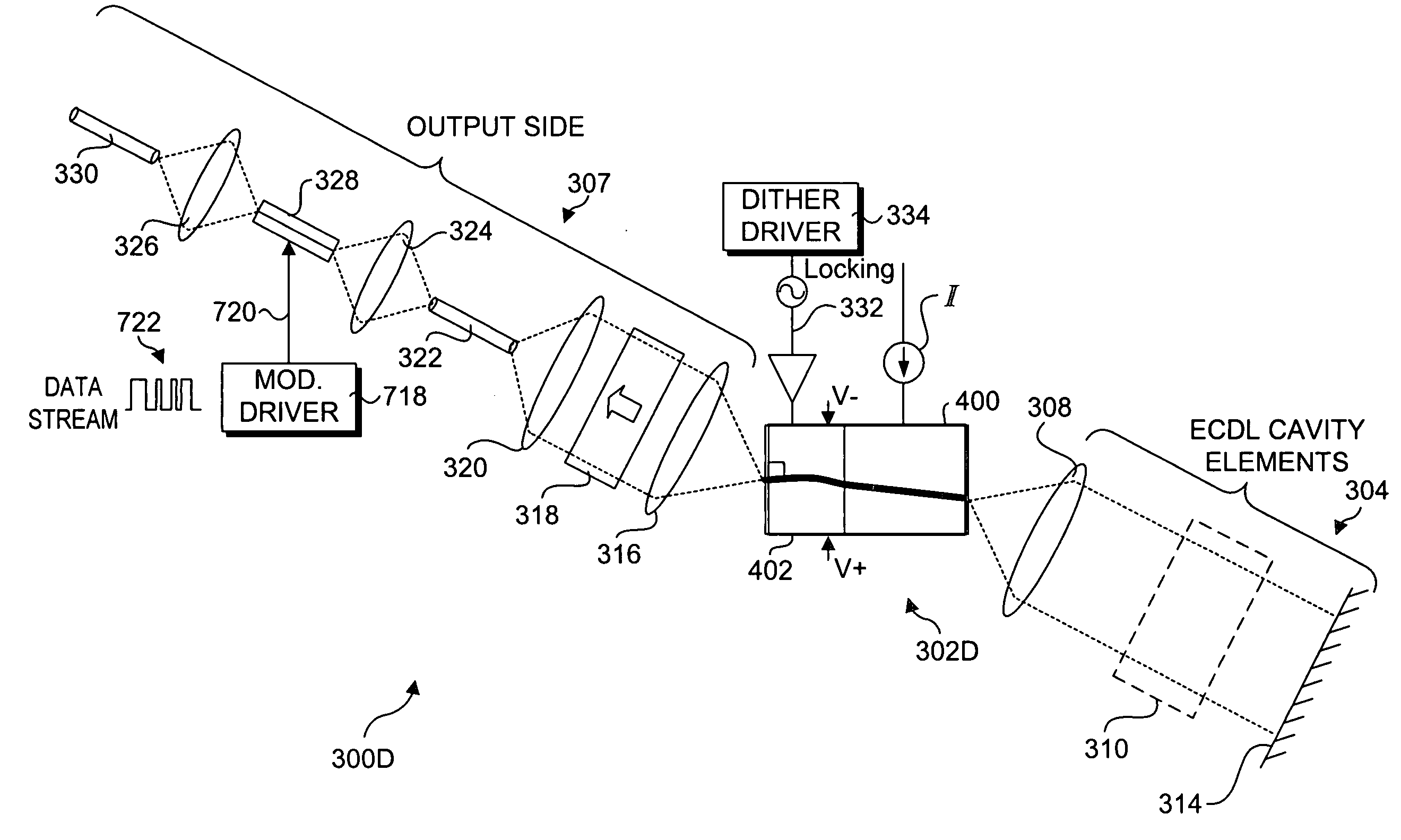
Semi-integrated external cavity diode laser (ECDL) designs including integrated structures comprising a gain section, phase control section, and optional modulator section. Each integrated structure includes a waveguide that passes through each of the sections. A mirror is defined in the structure to define one end of a laser cavity. A reflective element is disposed generally opposite a rear facet of the gain section, forming an external cavity therebetween. A tunable filter is disposed in the external cavity to effectuate tuning of the laser. During operation, a modulated drive signal is provided to the phase control section. This modulates an optical path length of the laser cavity, which produces an intensity (amplitude) modulation in the laser output. A detector is employed to produce a feedback signal indicative of the intensity modulation that is used for tuning the laser in accordance with a wavelength locking servo loop. Upon passing through the modulator section, an optical signal is modulated with data.
Owner:NEOPHOTONICS CORP
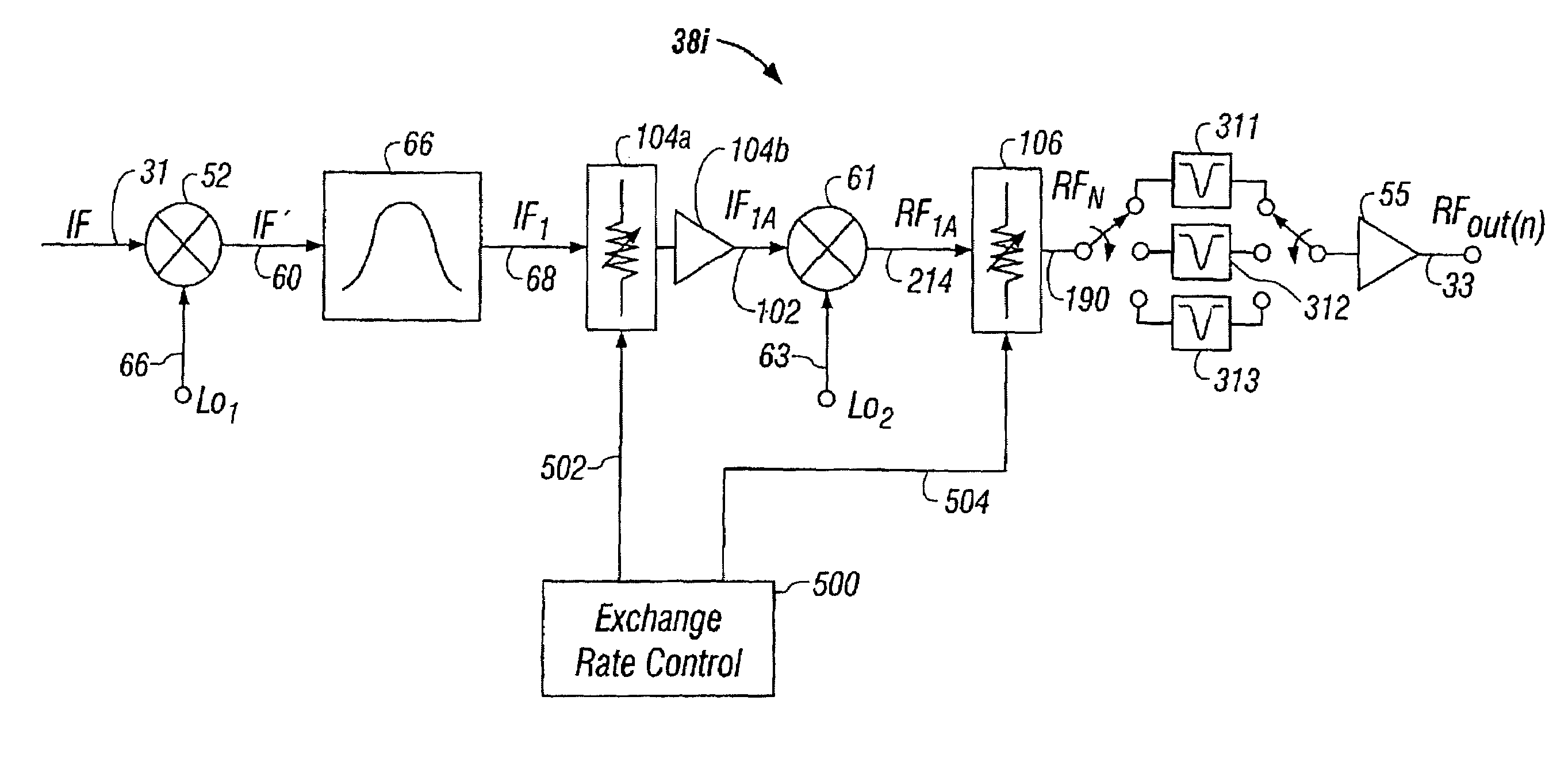
Agile frequency converter for multichannel systems using IF-RF level exhange and tunable filters
InactiveUS7003275B1Increasing unloaded QReduced insertion lossResonant long antennasFrequency-division multiplex detailsMicrocontrollerFrequency changer
Agile frequency converter and method, IF-RF level exchange process, and notch filtering techniques. System noise and spurious levels generated by channel frequency conversion is reduced in applications requiring broadband combining of frequency converters to form multichannel composite signal. Converter employs two-stage frequency conversion process, with gain exchange system using variable pre-mixer gain and variable post-mixer attenuation to maintain constant RF output signal power level. For those few conversion frequencies where distortion component(s) cannot be filtered without degrading desired signal, IF-RF level exchange is optimized for meeting the carrier-to-distortion (C / D) ratio specifications at slight expense of noise level for that channel only, while still meeting aggregate combined carrier-to-noise (C / N) specification requirements. Optimal apportionment of level exchange for each channel depends on specific frequency rejection capability of spurious components and is matched to filtering capability and stored within non-volatile memory of a microcontroller used in the frequency converter.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
Distributed disturbance sensing device and the related demodulation method based on polarization sensitive optical frequency domain reflectometry
ActiveUS20140176937A1Long test distanceImprove spatial resolutionReflectometers dealing with polarizationSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementInformation analysisS-matrix
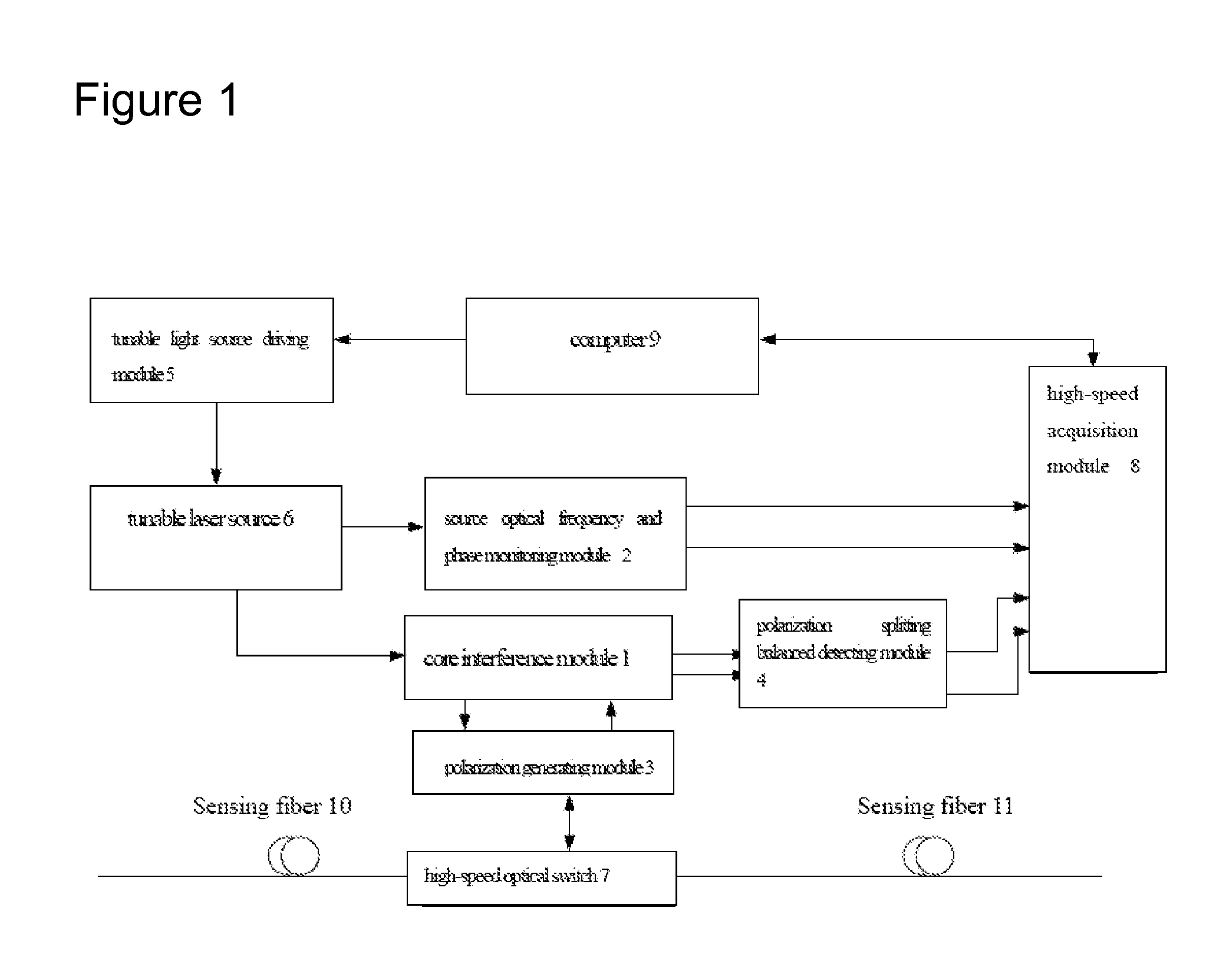
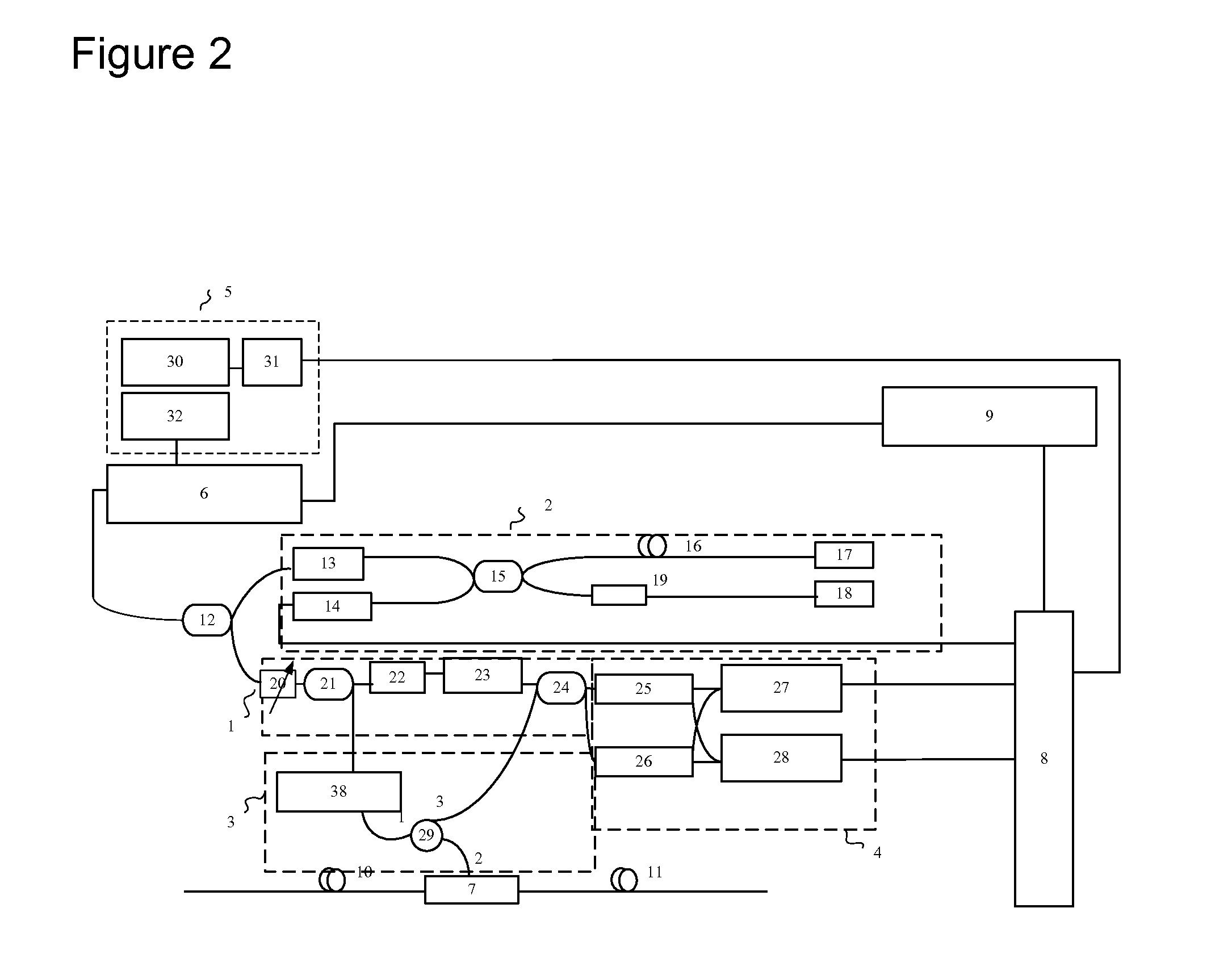
This invention relates to a distributed disturbance sensing device based on polarization sensitive optical frequency domain reflectometry (OFDR) and the related demodulation thereof. The device, adopting OFDR, polarization controlling and analysis techniques, consists of a ultra-narrow linewidth tunable laser source module, polarization generating and polarization splitting balanced detecting module, laser source optical frequency and phase monitoring module, high-speed optical switch and so on to establish a large-scale and long-distance optical sensing network. The demodulation method consists of analysis the polarization information from sensing optical fiber, the method of suppressing and compensating of the non-linear optical frequency and the laser phase noise, super-resolution analyzing, advanced denoising method and the polarization information analysis method based on Jones and Mueller's matrices using distributed wave plate model of optical fiber.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
System and methods for optical stimulation of neural tissues
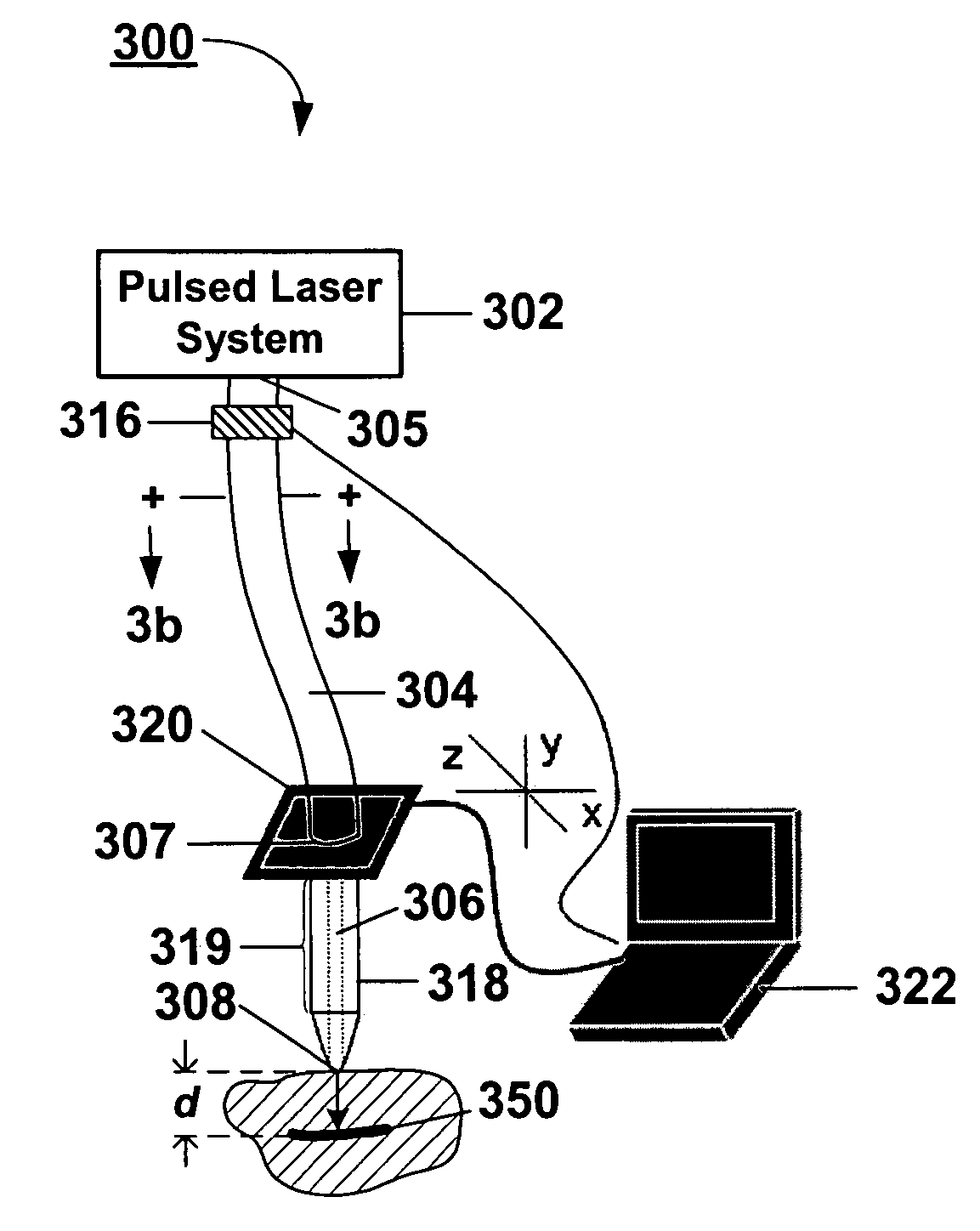
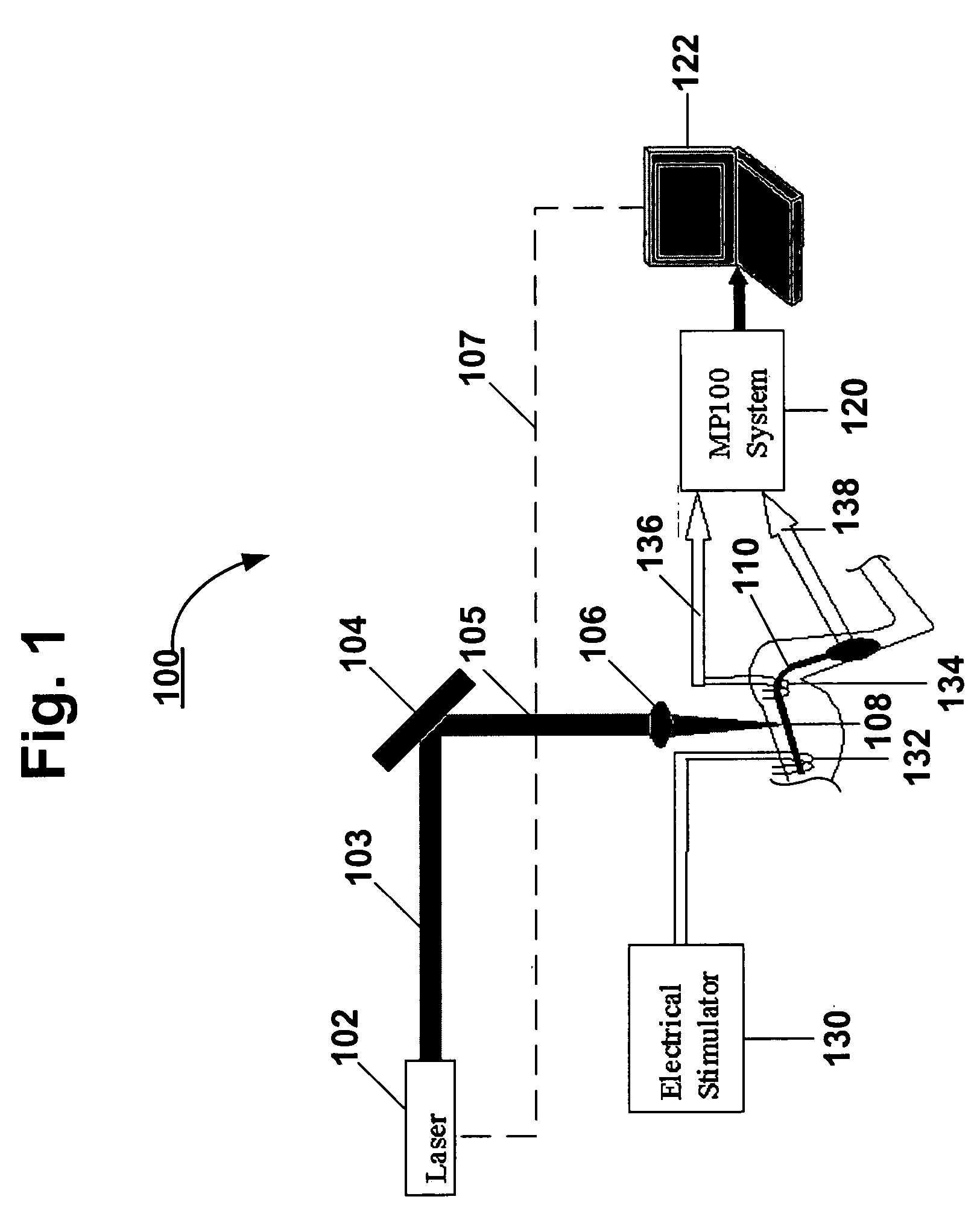
The present invention, in one aspect, relates to a system for stimulating neural tissue of a living subject. The system comprises an energy source capable of generating optical energy, a connector having a first end and a second end capable of transmitting optical energy, and a probe operably coupled to the second end of the connector and having an end portion for delivering optical energy to a target neural tissue. In one embodiment, the energy source comprises a tunable laser.
Owner:VANDERBILT UNIV
Tunable temperature controlled substrate support assembly
ActiveUS20160027678A1Heater elementsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingTemperature controlEngineering
Implementations described herein provide a substrate support assembly which enables both lateral and azimuthal tuning of the heat transfer between an electrostatic chuck and a heating assembly. The substrate support assembly comprises a body having a substrate support surface and a lower surface, one or more main resistive heaters disposed in the body, a plurality of spatially tunable heaters disposed in the body, and a spatially tunable heater controller coupled to the plurality of spatially tunable heaters, the spatially tunable heater controller configured to independently control an output one of the plurality of spatially tunable heaters relative to another of the plurality of spatially tunable heaters.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Electrically focus-tunable lens
An electrically focus-tunable lens having a passive lens and a liquid crystal diffractive lens both sandwiched between a first transparent substrate with a first electrode applied to one surface and a second transparent substrate with a second electrode applied to one surface. The electrodes are operative to apply at least one voltage across the liquid crystal diffractive lens
Owner:DIGILENS
III-V photonic integration on silicon
ActiveUS20070170417A1Minimize limitationFinal product manufactureRadiation controlled devicesCMOSCoupling
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
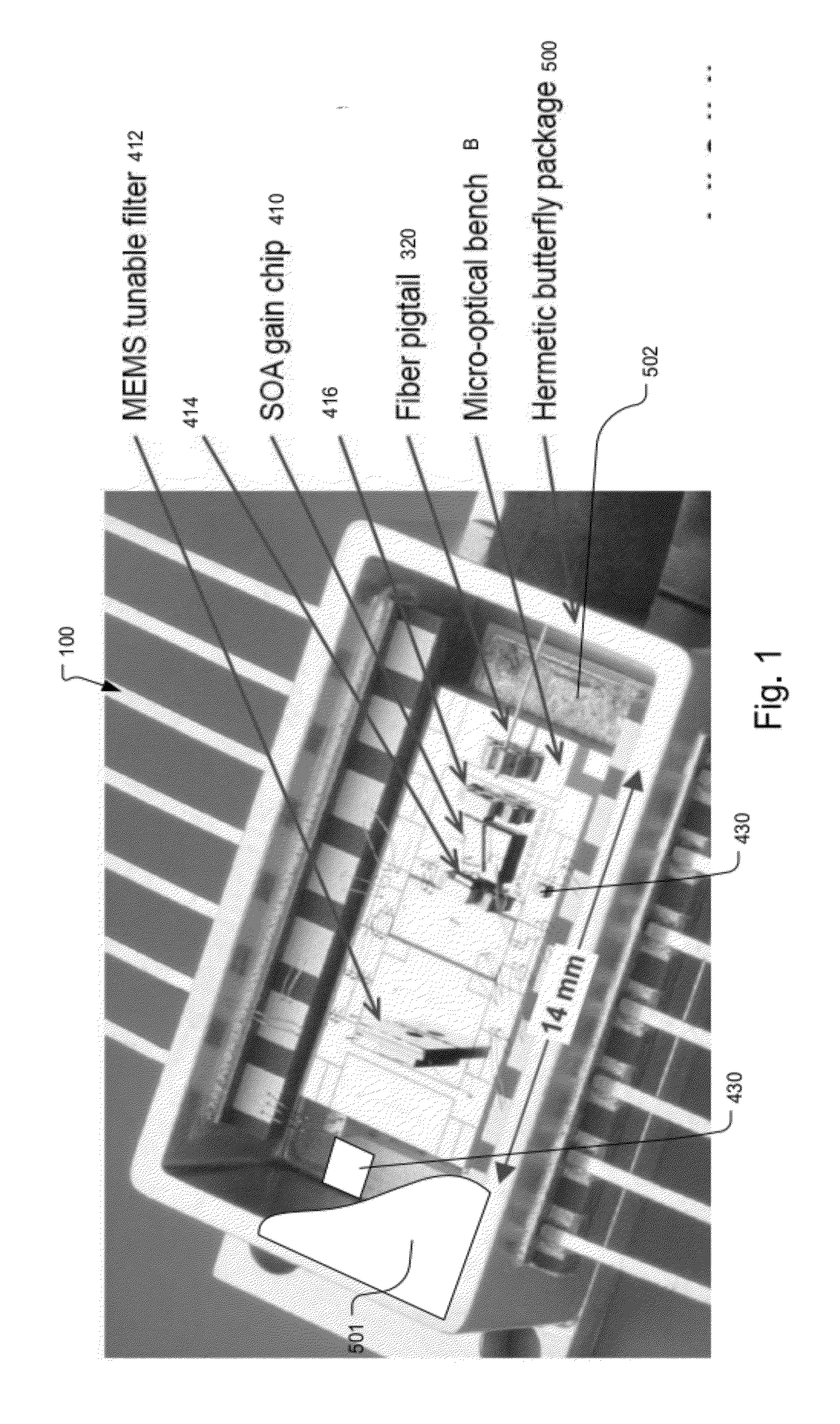
Method and System for Avoiding Package Induced Failure in Swept Semiconductor Source
ActiveUS20120257210A1Eliminate trace organicEliminate trace organicsLaser detailsUsing optical meansTunable laserPhysics
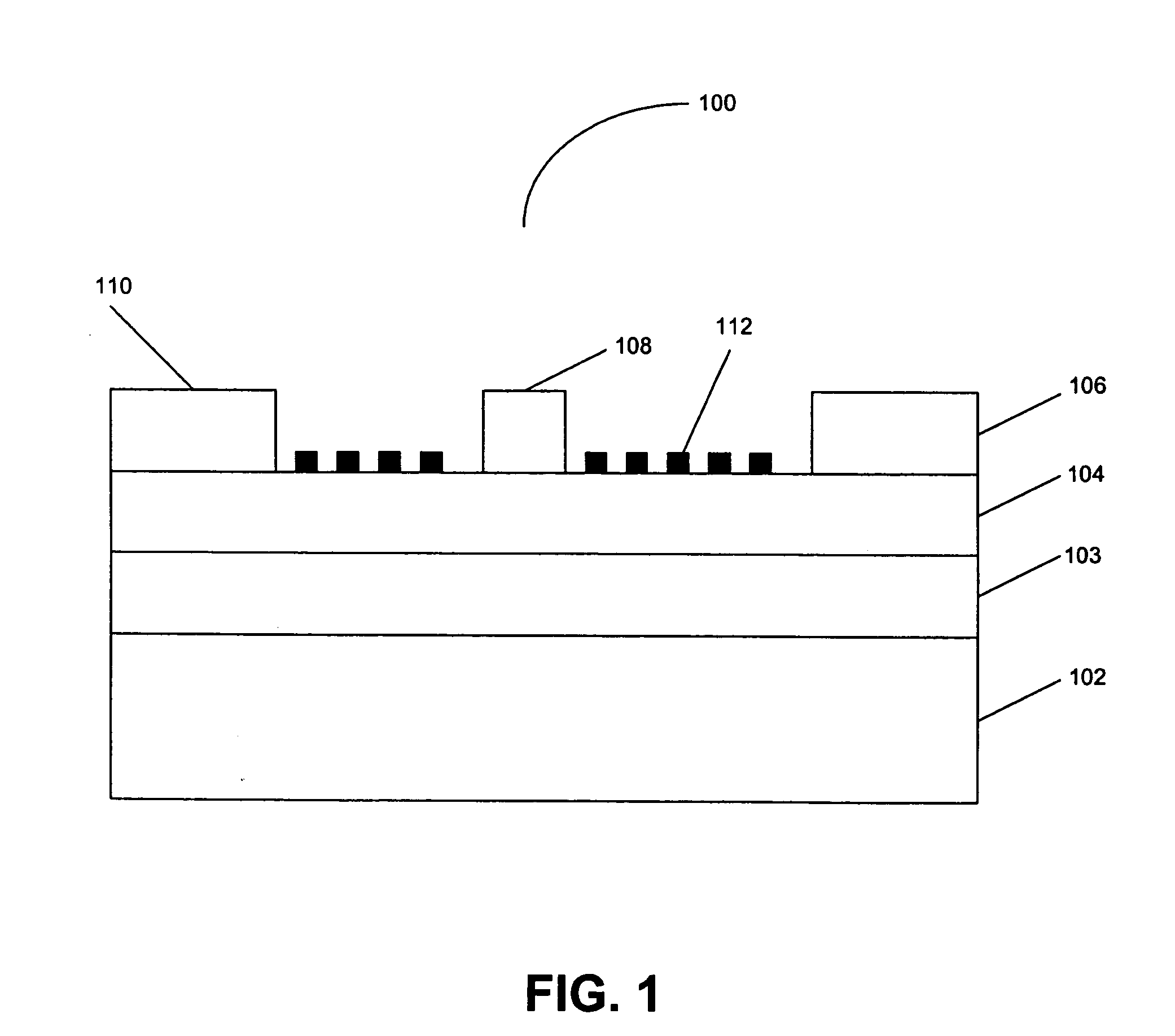
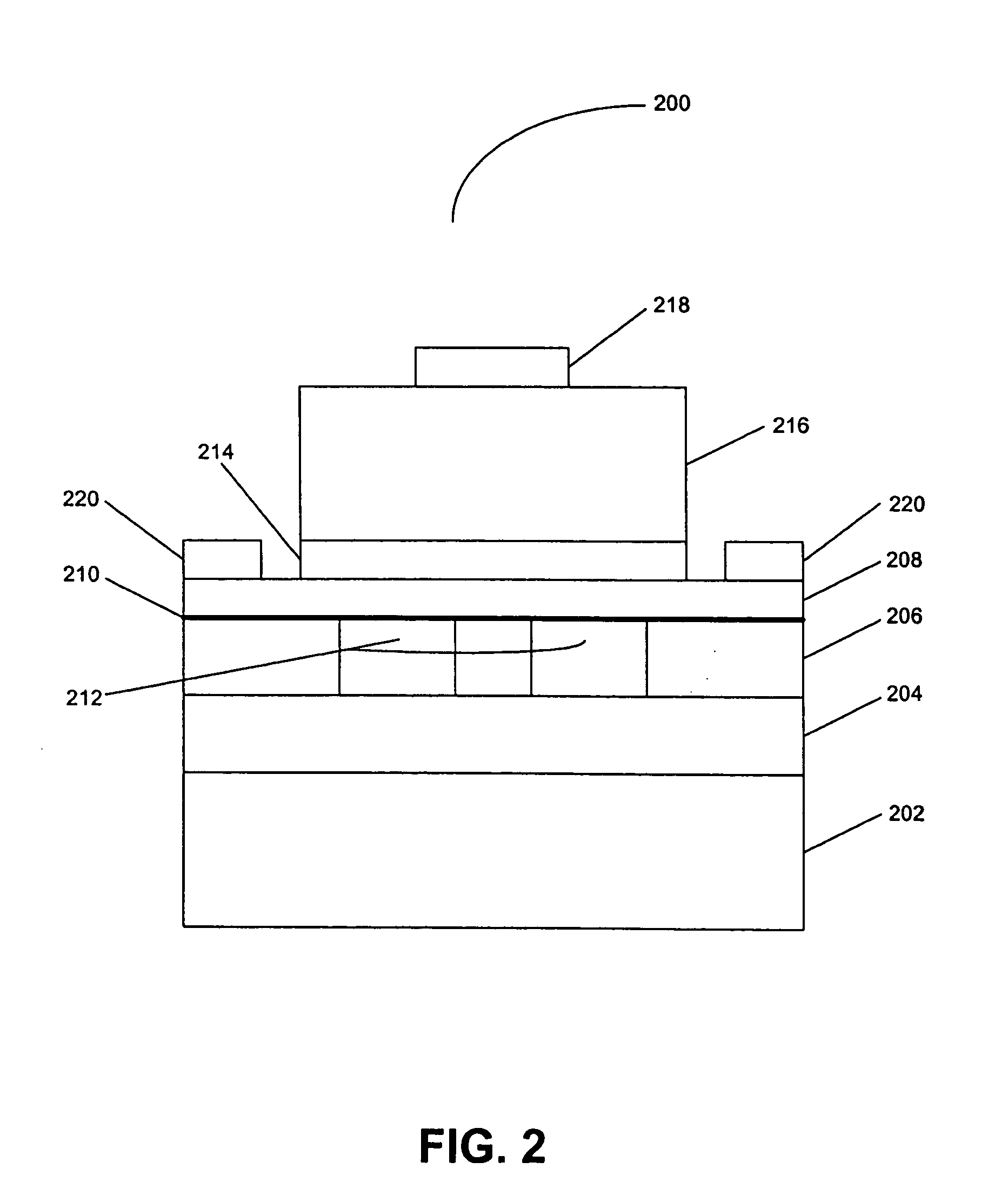
Dry oxygen, dry air, or other gases such as ozone are hermetically sealed within the package of the external cavity laser or ASE swept source to avoid packaging-induced failure or PIF. PIF due to hydrocarbon breakdown at optical interfaces with high power densities is believed to occur at the SLED and / or SOA facets as well as the tunable Fabry-Perot reflector / filter elements and / or output fiber. Because the laser is an external cavity tunable laser and the configuration of the ASE swept sources, the power output can be low while the internal power at surfaces can be high leading to PIF at output powers much lower than the 50 mW.
Owner:EXCELITAS TECH
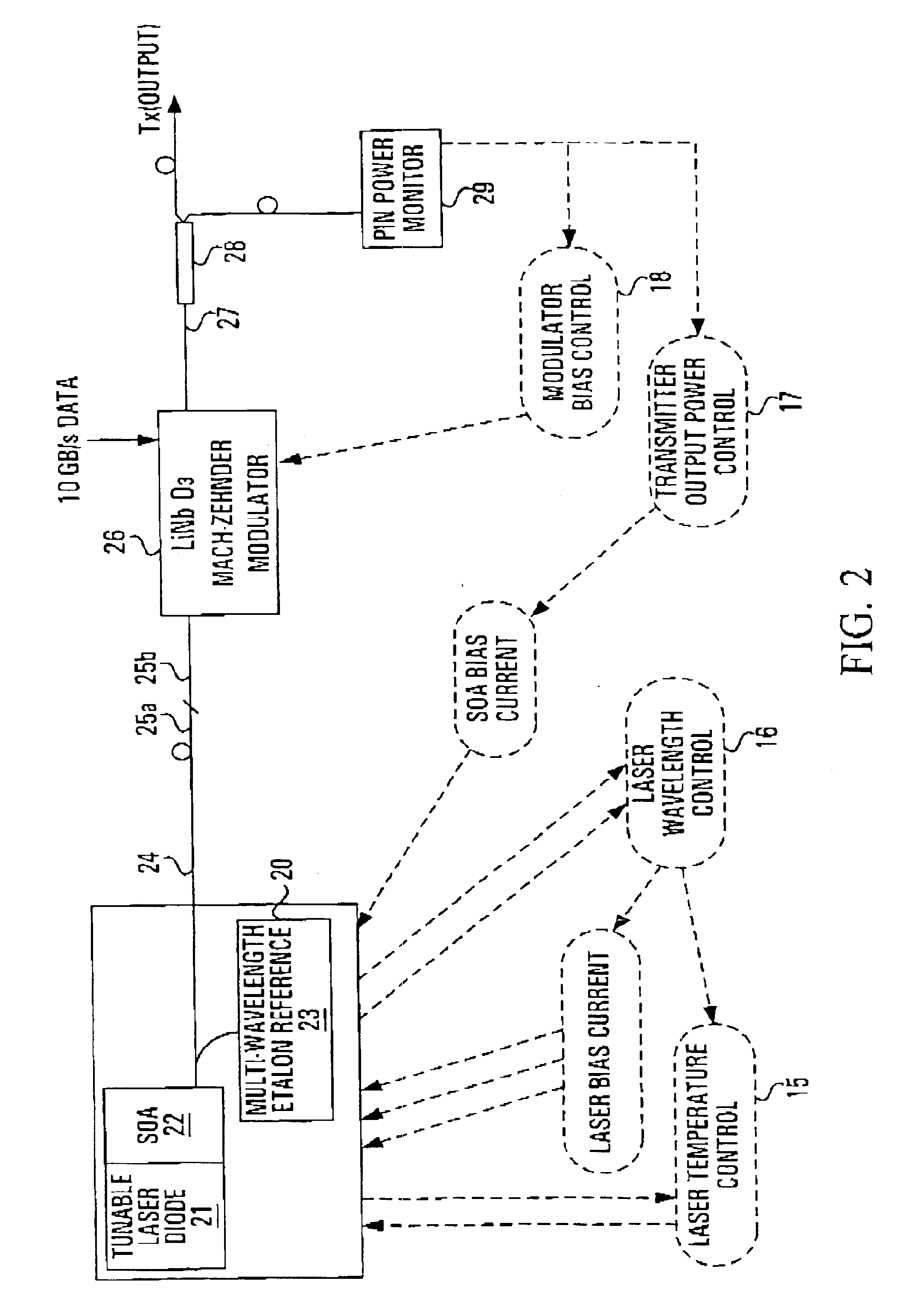
Tunable laser source with monolithically integrated interferometric optical modulator
A monolithically-integrated semiconductor optical transmitter that can index tune to any transmission wavelength in a given range, wherein the range is larger than that achievable by the maximum refractive index tuning allowed by the semiconductor material itself (i.e. Δλ / λ>Δn / n). In practice, this tuning range is >15 nm. The transmitter includes a Mach-Zehnder (MZ) modulator monolithically integrated with a widely tunable laser and a semiconductor optical amplifier (SOA). By using an interferometric modulation, the transmitter can dynamically control the chirp in the resulting modulated signal over the wide tuning range of the laser.
Owner:LUMENTUM OPERATIONS LLC
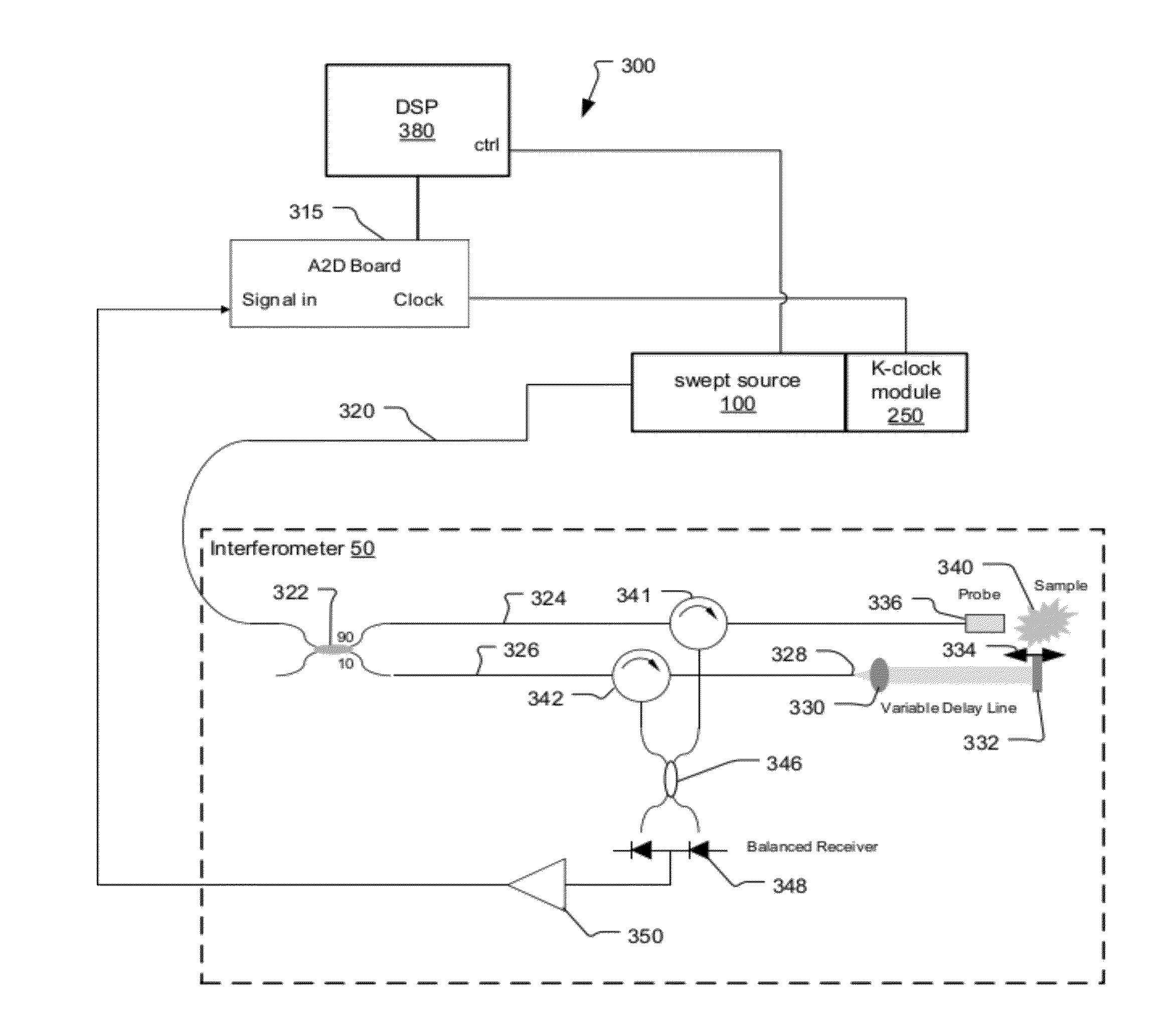
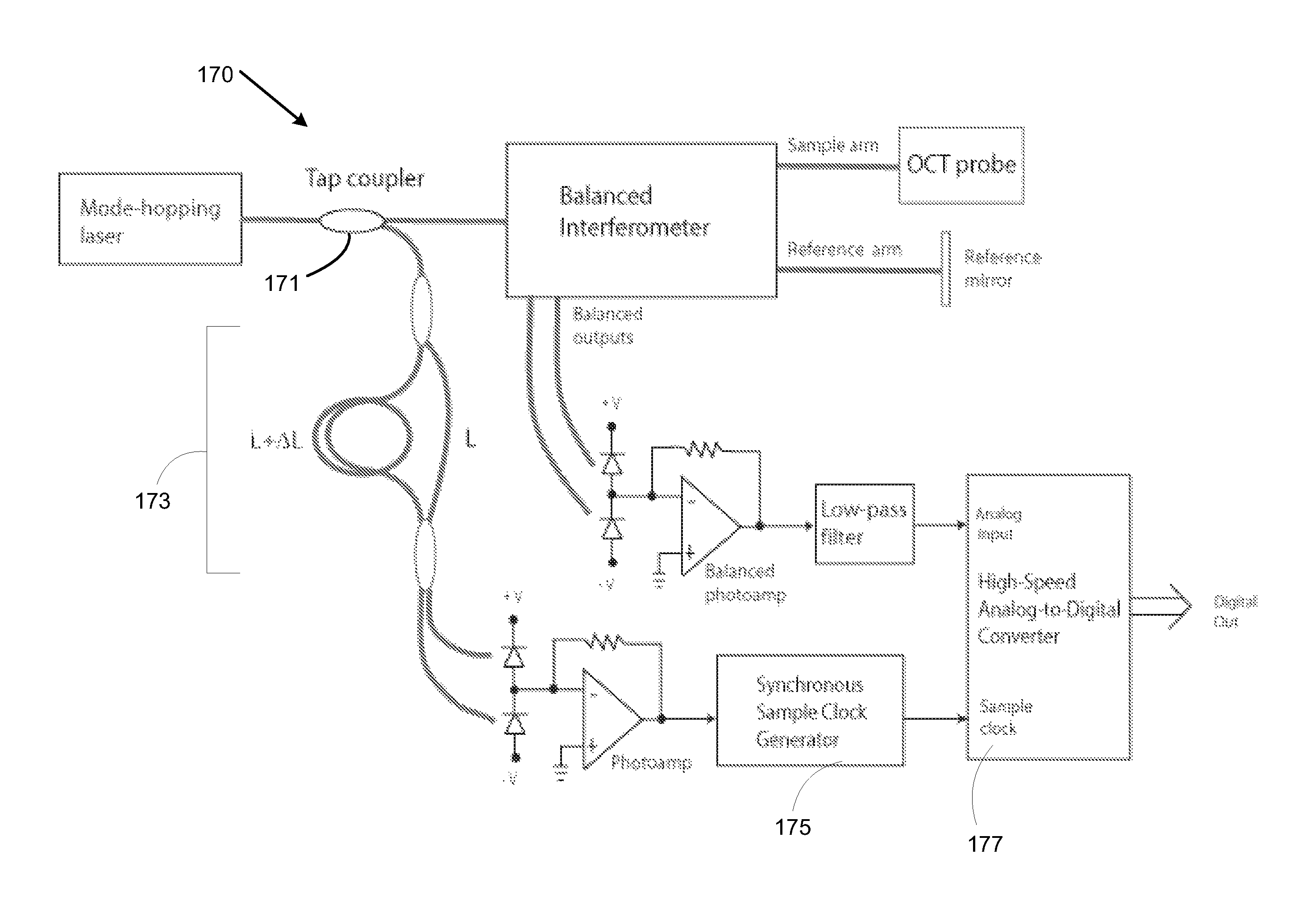
Swept mode-hopping laser system, methods, and devices for frequency-domain optical coherence tomography
ActiveUS8582109B1Intensity fluctuationShort transition timeLaser detailsUsing optical meansLaser lightOptical communication
In part, the invention relates to frequency-domain optical coherence tomography system. The system includes a tunable laser comprising a laser output for transmitting laser light and a laser cavity having a length L, a gain element disposed within the laser cavity; a tunable wavelength selective element disposed within the laser cavity; a reference reflector disposed outside of the laser cavity; an interferometer in optical communication with the laser output and the reference reflector, wherein the interferometer is configured to transmit a portion of the laser light to a sample and combine light scattered from the sample with light scattered from the reference reflector; and a detector in optical communication with the interferometer that receives the combination of light scattered from the sample and the light scattered from the reference reflector and transforms the combination of light into an electronic signal comprising measurement data with respect to the sample.
Owner:LIGHTLAB IMAGING
III-V photonic integration on silicon
ActiveUS8110823B2Minimize limitationFinal product manufactureRadiation controlled devicesCMOSCoupling
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
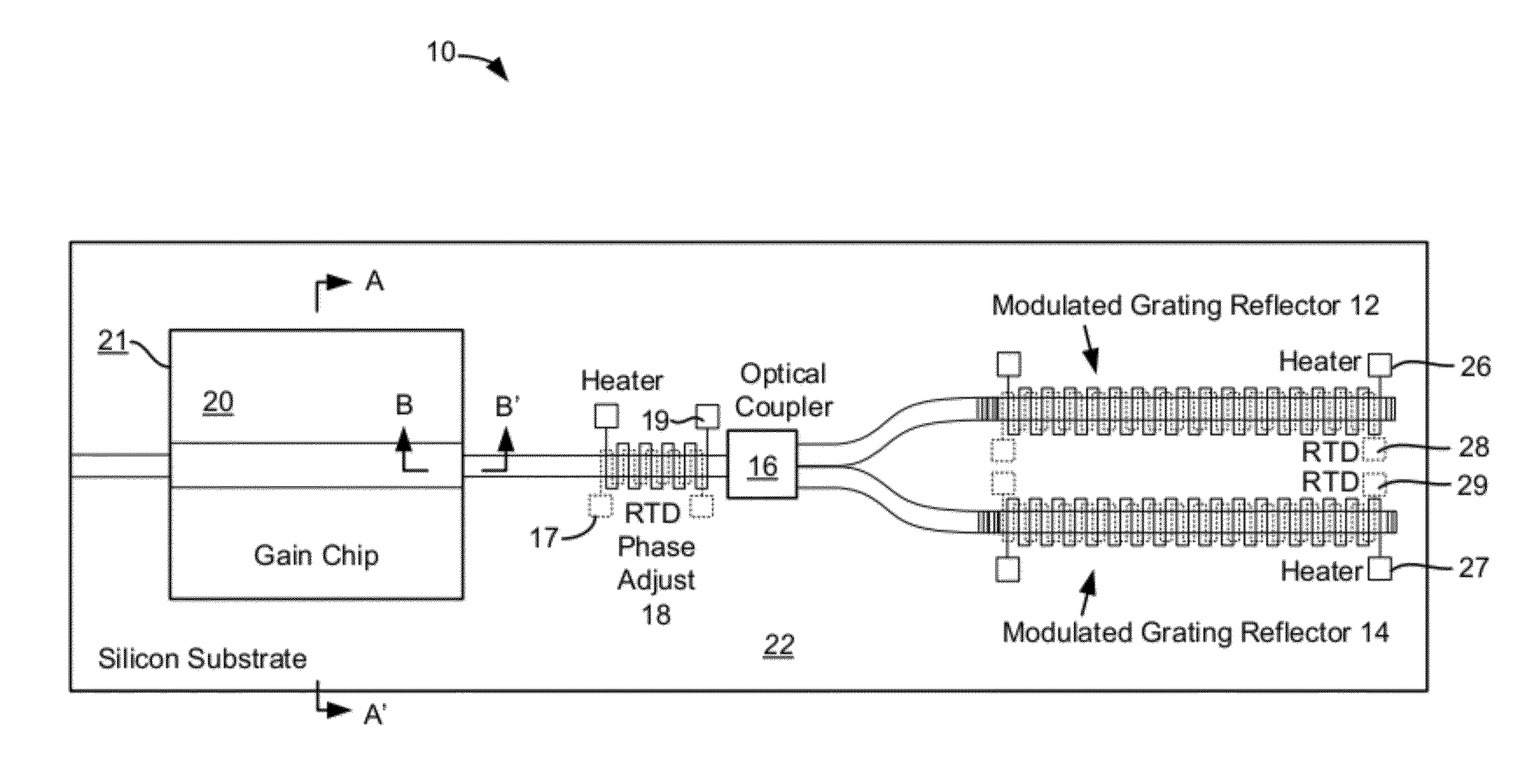
External cavity tunable laser module
InactiveUS20120099611A1Reliably tunedImprove production yieldLaser detailsSemiconductor lasersGratingLength wave
Provided is a wavelength tunable external cavity semiconductor laser module by a thermo-optic effect of a semiconductor optical waveguide. The wavelength tunable external cavity semiconductor laser module includes: a light source generating wideband light; a semiconductor optical waveguide having one end optically coupled to the light source; a Bragg grating formed on the optical waveguide; a thin film heater provided at an upper portion of the Bragg grating and controlling a reflection band of the Bragg grating by a thermo-electric effect; a first temperature sensor provided at an upper portion of the optical waveguide; a thermoelectric cooler (TEC) provided at a lower portion of the optical waveguide; a heat insulating layer provided between the optical waveguide and the TEC; and an optical fiber optically coupled to the other end of the optical waveguide.
Owner:MEL TELECOM
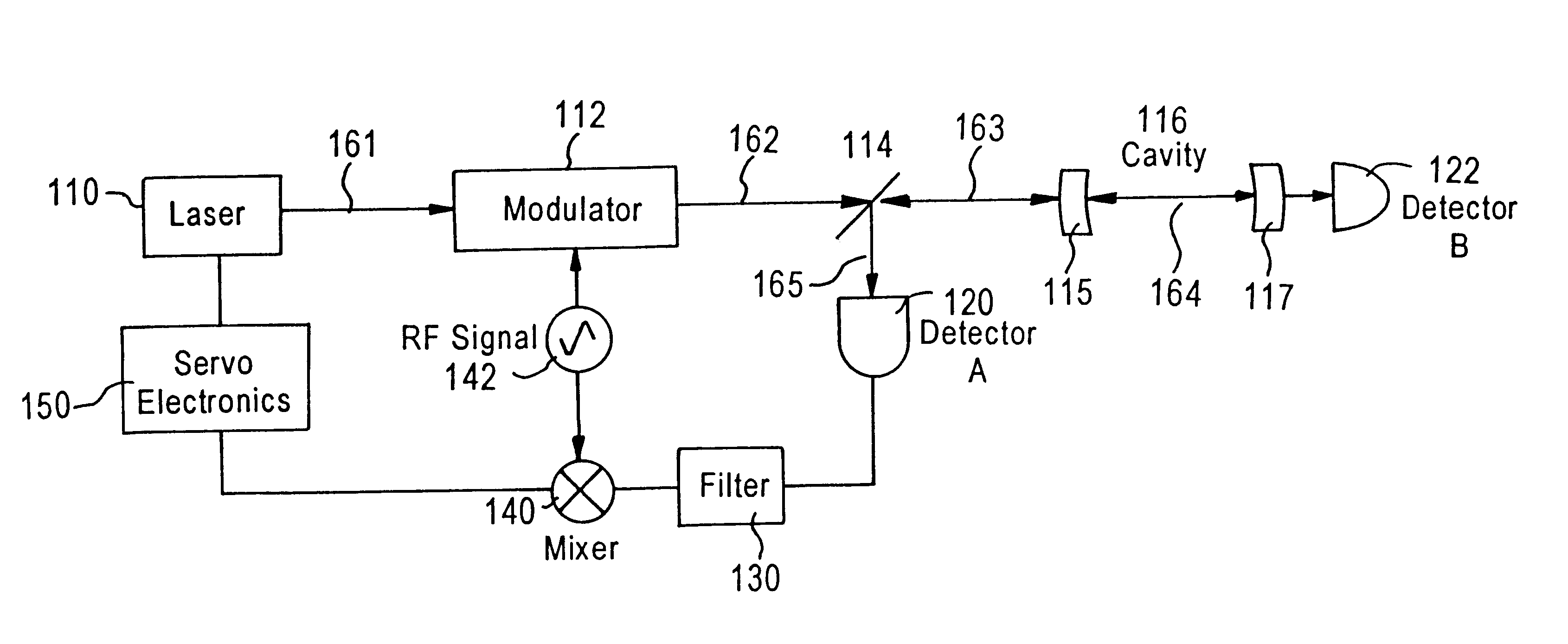
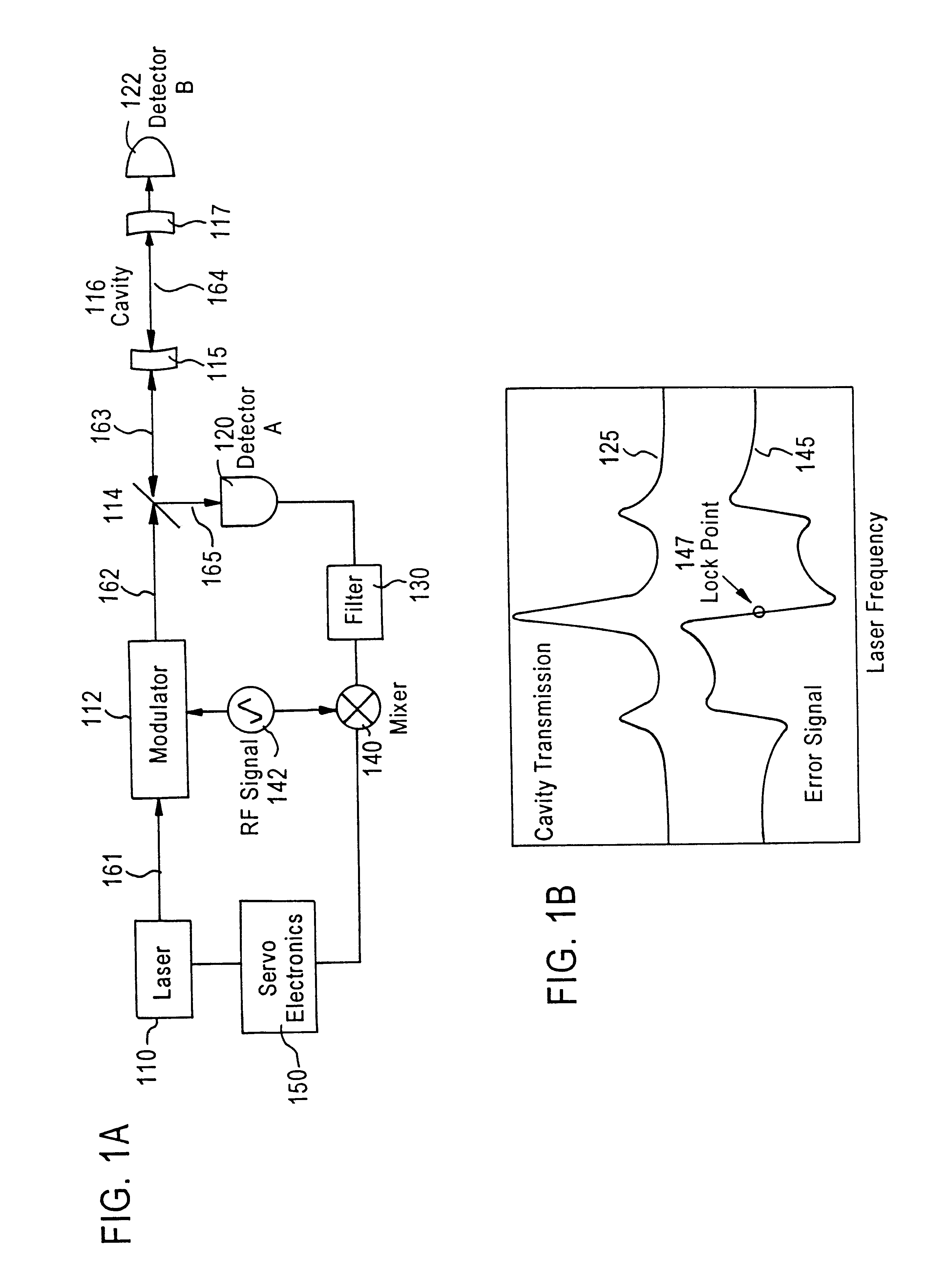
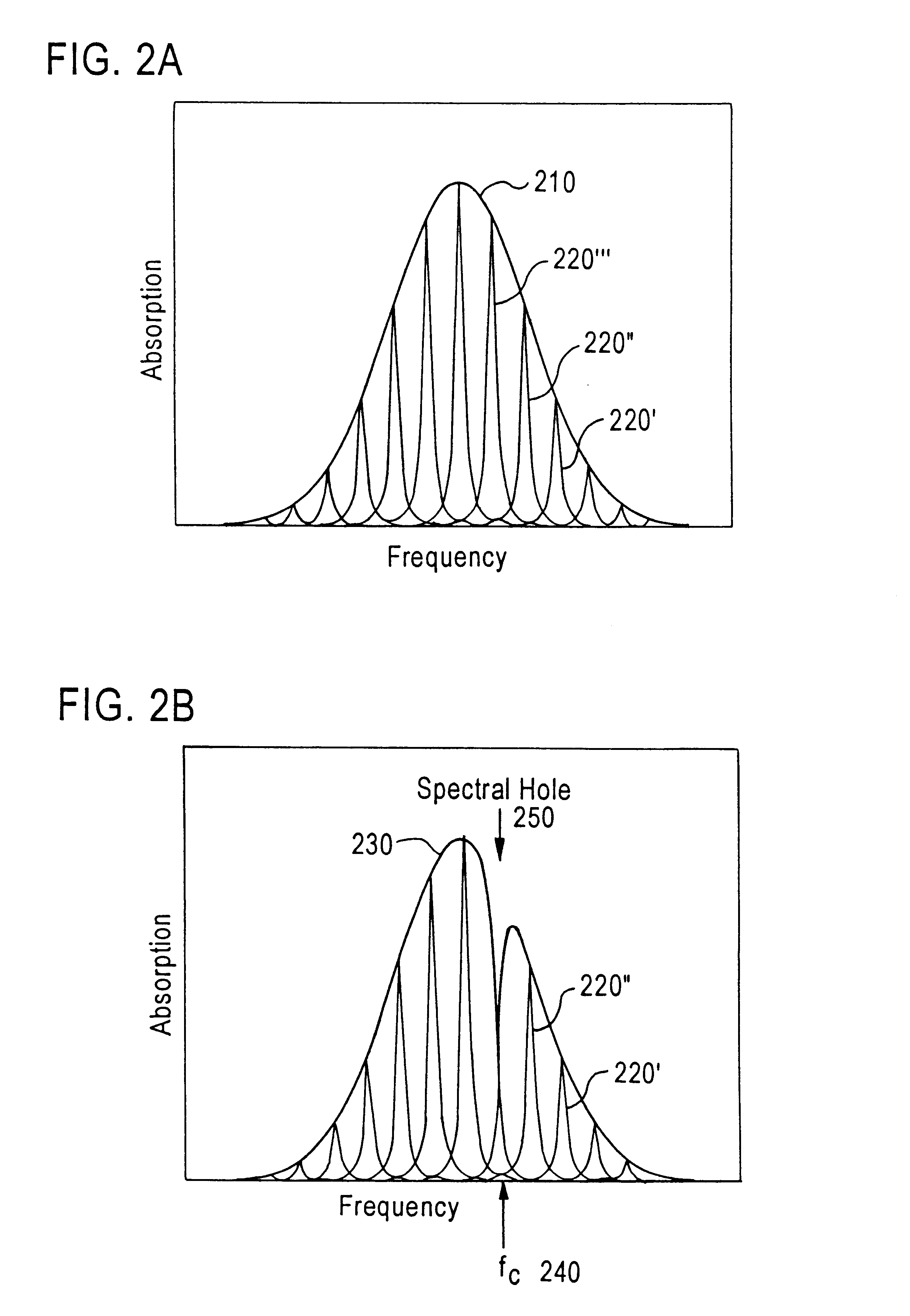
Laser frequency stabilizer using transient spectral hole burning
InactiveUS6654394B1Laser frequency stabilizationLaser detailsSemiconductor lasersFrequency stabilizationSpectral hole burning
Techniques for stabilizing a laser at a selectable frequency include splitting an output beam from an electrically adjustable laser into a first beam and a second beam. The second beam is transmitted through a modulator. Then the second beam is transmitted through a transient spectral hole burning material onto a detector. The laser is electronically adjusted in response to a detector output from the detector which senses the changes in the modulated second beam after it passes through the transient spectral hole burning material. Additions here to encompass the mode-locked case?
Owner:MONTANA STATE UNIVERSITY
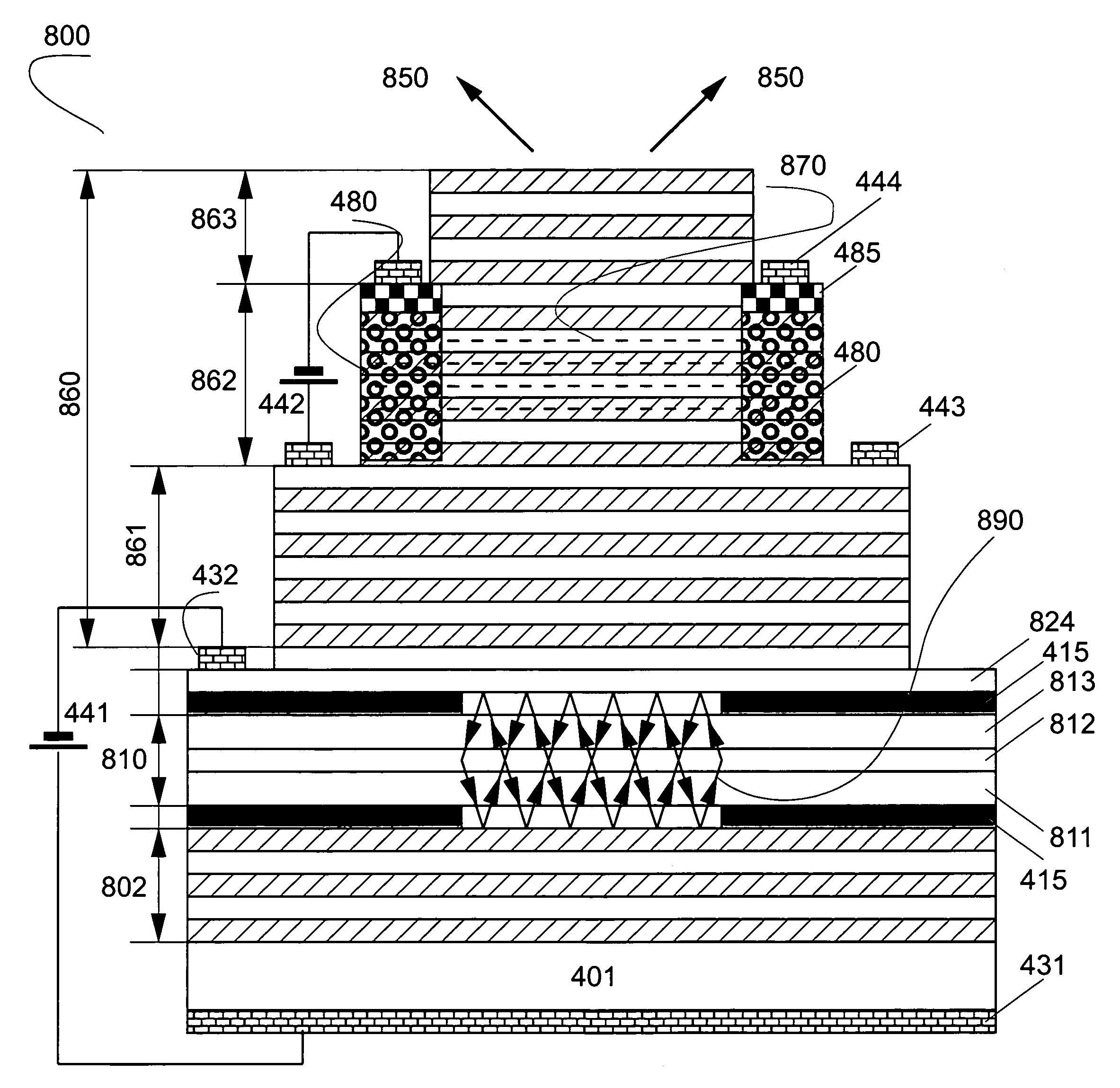
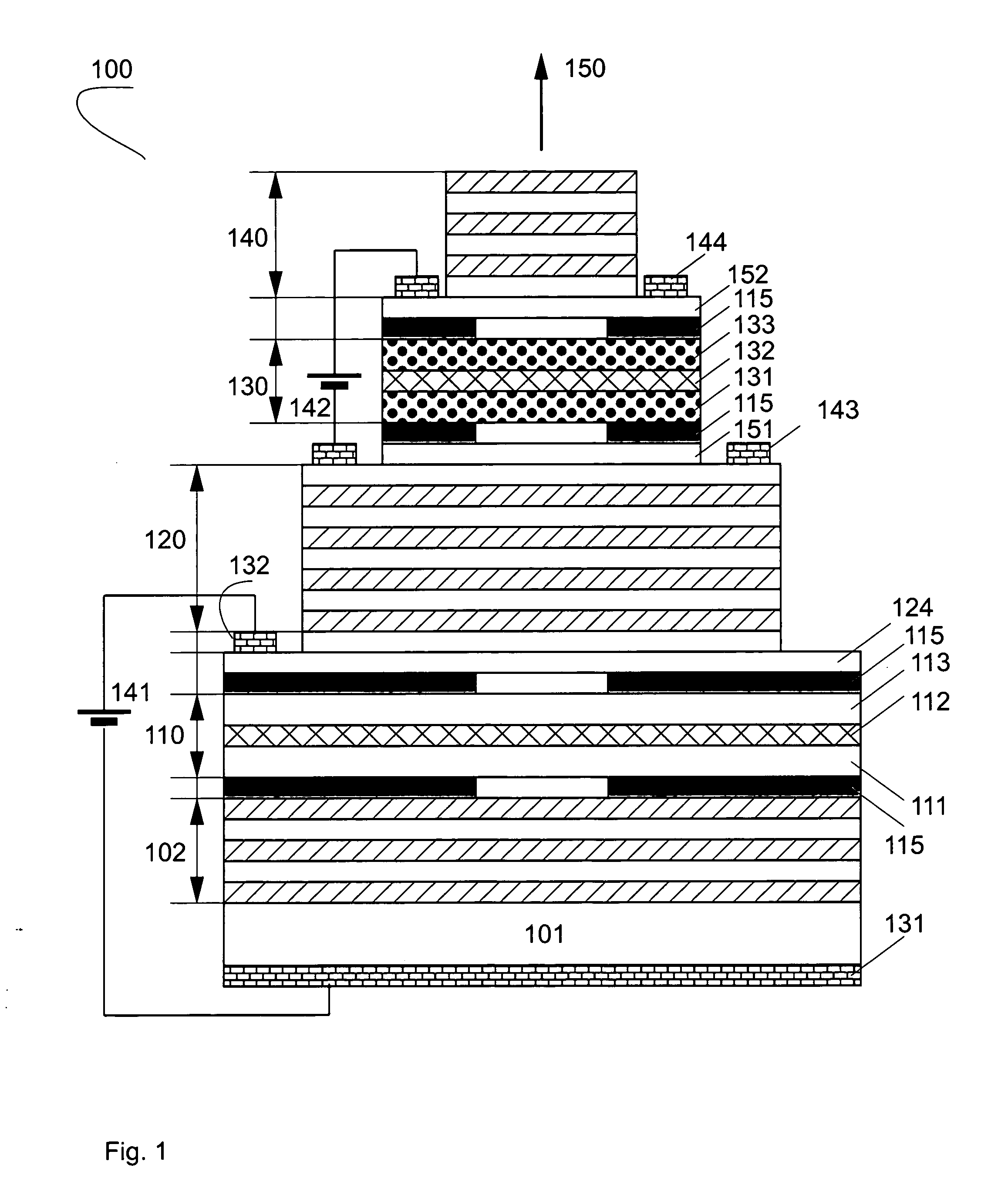
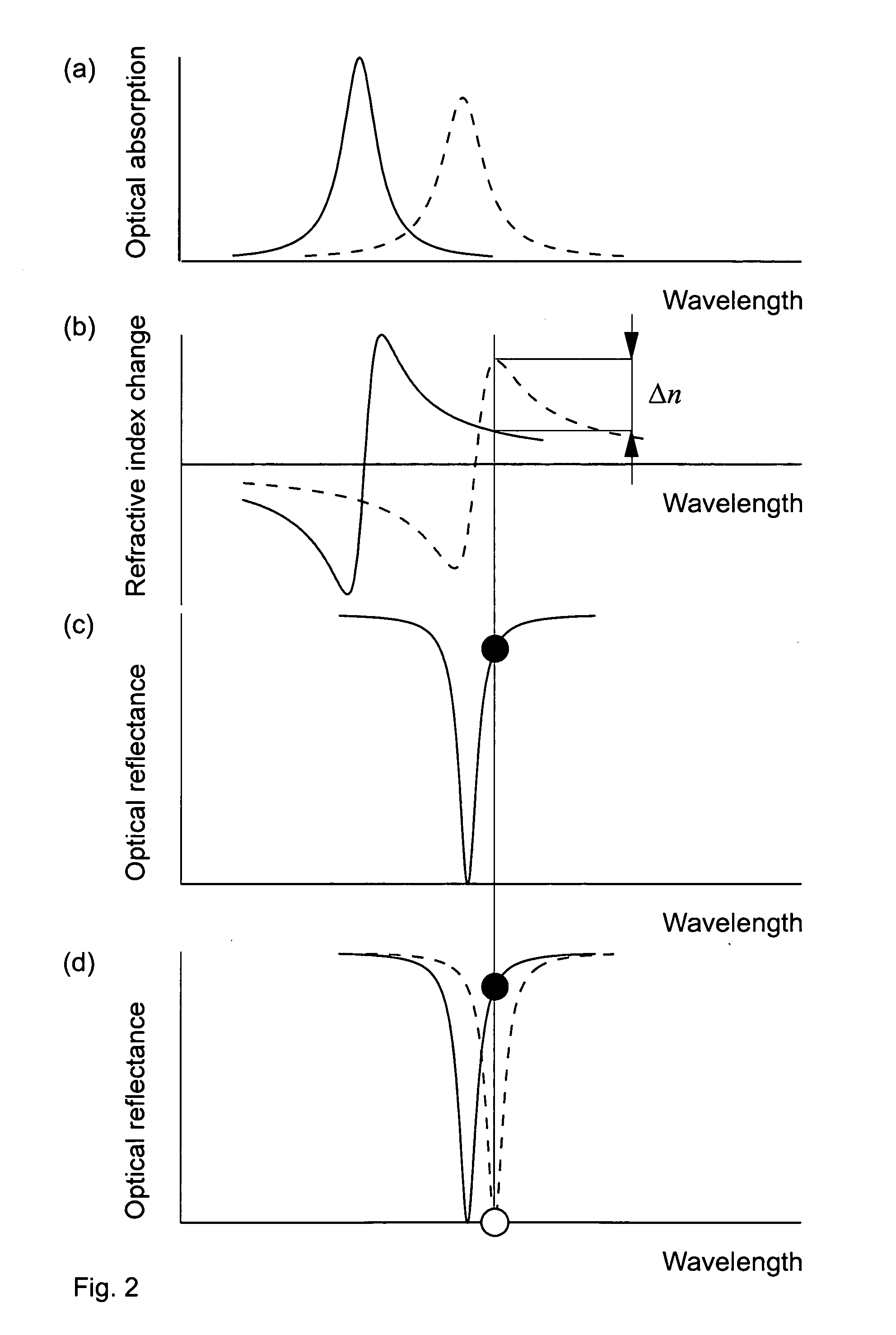
Electrooptically Bragg-reflector stopband-tunable optoelectronic device for high-speed data transfer
ActiveUS20070291808A1Modulated transmittance of the multilayer interference reflectorLaser detailsSolid-state devicesPhotodetectorIntensity modulation
A device contains at least one wavelength-tunable multilayer interference reflector controlled by an applied voltage and at least one cavity. The stopband edge wavelength of the wavelength-tunable multilayer interference reflector is preferably electrooptically tuned using the quantum confined Stark effect in the vicinity of the cavity mode (or a composite cavity mode), resulting in a modulated transmittance of the multilayer interference reflector. A light-emitting medium is preferably introduced in the cavity or in one of the cavities permitting the optoelectronic device to work as an intensity-modulated light-emitting diode or diode laser by applying an injection current. The device preferably contains at least three electric contacts to apply forward or reverse bias and may operate as a vertical cavity surface emitting light-emitter or modulator or as an edge-emitting light emitter or modulator. Using a multilayer interference reflector containing tunable section allows also obtaining a wavelength-tunable laser or a wavelength-tunable resonant cavity photodetector in the case where the optical field profile in the active cavity or cavities is affected by the stopband wavelength shift. Adding additional modulator sections enables applications in semiconductor optical amplifiers, frequency converters or lock-in optical amplifiers.
Owner:CONNECTOR OPTICS
Method and system for hybrid integration of a tunable laser for a cable TV transmitter
InactiveUS20120057079A1Reduce power consumptionSmall sizeTelevision system detailsLaser detailsReflectance spectroscopyEngineering
A cable television transmitter includes a substrate including a silicon material, control electronics disposed in the substrate, and a gain medium coupled to the substrate. The gain medium includes a compound semiconductor material. The cable television transmitter also includes an optical modulator optically coupled to the gain medium and electrically coupled to the control electronics, a waveguide disposed in the substrate and optically coupled to the gain medium, a first wavelength selective element characterized by a first reflectance spectrum and disposed in the substrate, and a second wavelength selective element characterized by a second reflectance spectrum and disposed in the substrate. The cable television transmitter further includes an optical coupler disposed in the substrate and joining the first wavelength selective element, the second wavelength selective element, and the waveguide and an output mirror.
Owner:SKORPIOS TECH
Method and system for hybrid integration of a tunable laser and a phase modulator
InactiveUS20120057610A1Reduce power consumptionSmall sizeLaser detailsSemiconductor lasersReflectance spectroscopyLength wave
A tunable laser includes a substrate comprising a silicon material and a gain medium coupled to the substrate. The gain medium includes a compound semiconductor material. The tunable laser also includes an optical modulator optically coupled to the gain medium, a phase modulator optically coupled to the optical modulator, and a waveguide disposed in the substrate and optically coupled to the gain medium. The tunable laser further includes a first wavelength selective element characterized by a first reflectance spectrum and disposed in the substrate, a second wavelength selective element characterized by a second reflectance spectrum and disposed in the substrate, an optical coupler disposed in the substrate and joining the first wavelength selective element, the second wavelength selective element, and the waveguide, and an output mirror.
Owner:SKORPIOS TECH
Tunable liquid lens with reduced aberration
InactiveUS20090213321A1Reduce impactTelevision system detailsProjector focusing arrangementPhotovoltaic detectorsPhotodetector
A tunable optical imaging system uses a fixed lens and a tunable liquid crystal lens that is operated only outside of an operational range of high aberration. A voltage range applied to change the optical power of the liquid crystal lens is limited to a continuous tunable range of low aberration. The relative positioning between the lens and a corresponding photodetector, and the relative lens powers of a fixed lens and the tunable lens, may be selected to compensate for any optical power offsets resulting from the limitation of the voltage range of the tunable lens. The lens may be operated in either positive tunability or negative tunability mode.
Owner:POINT FINANCIAL
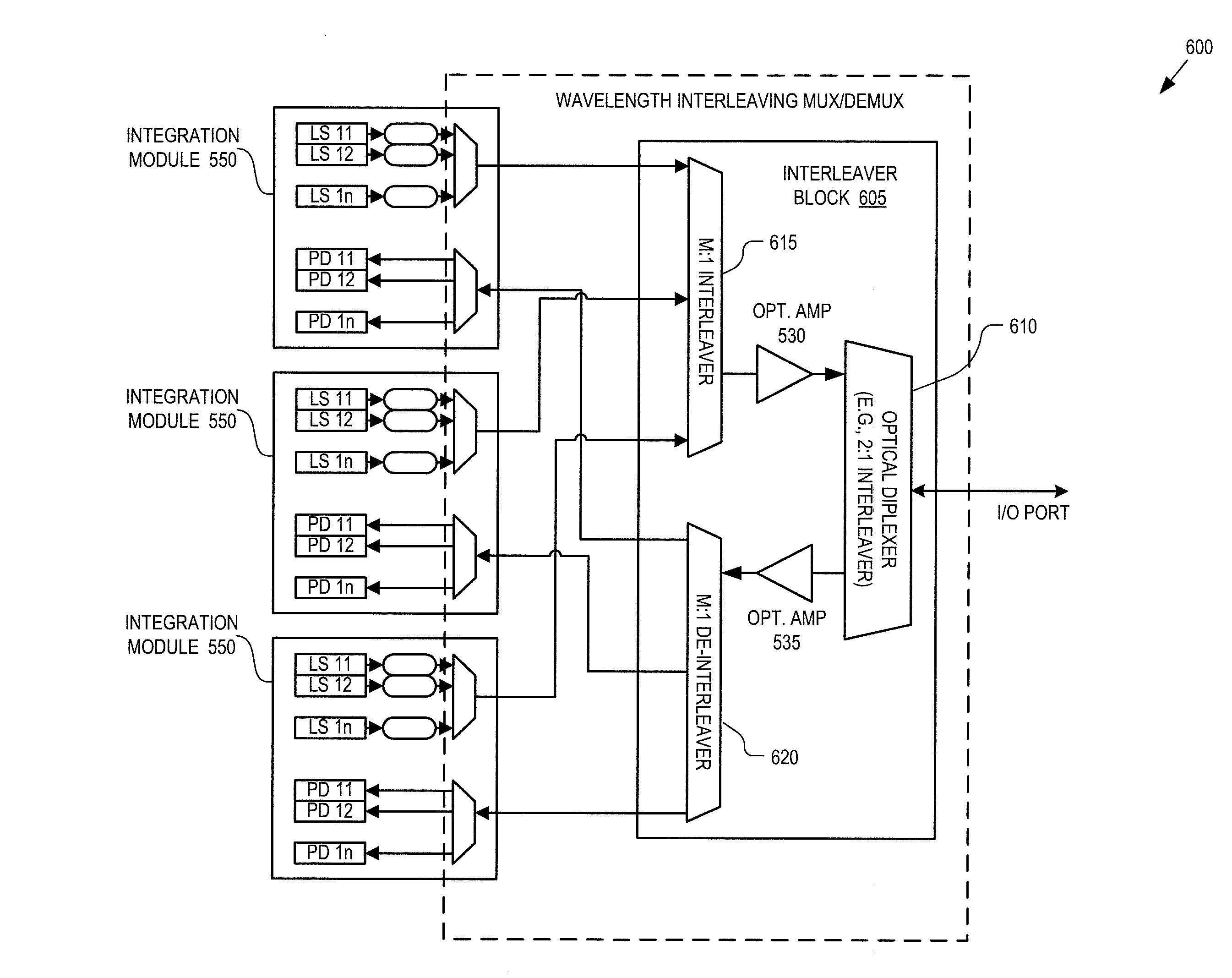
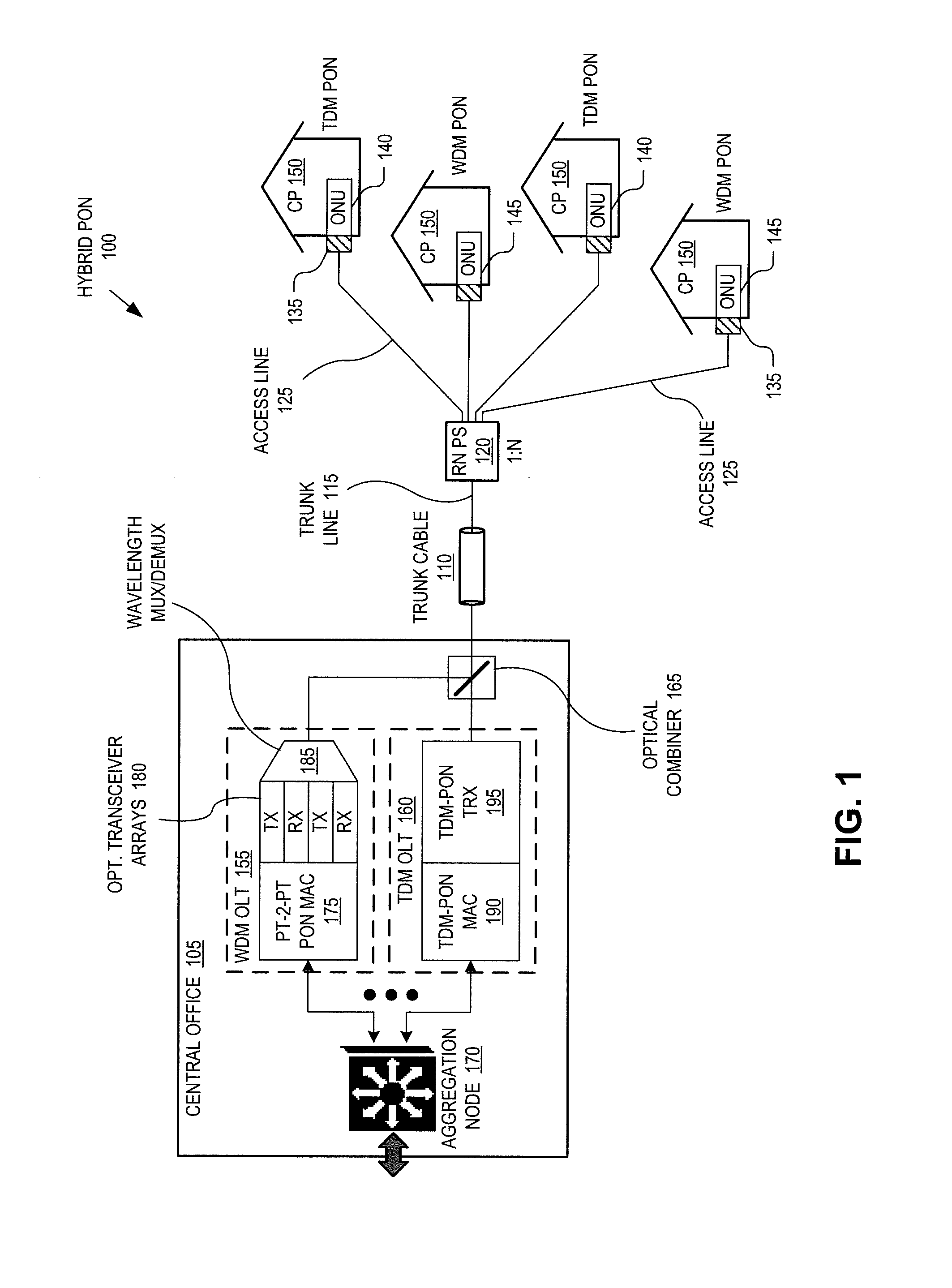
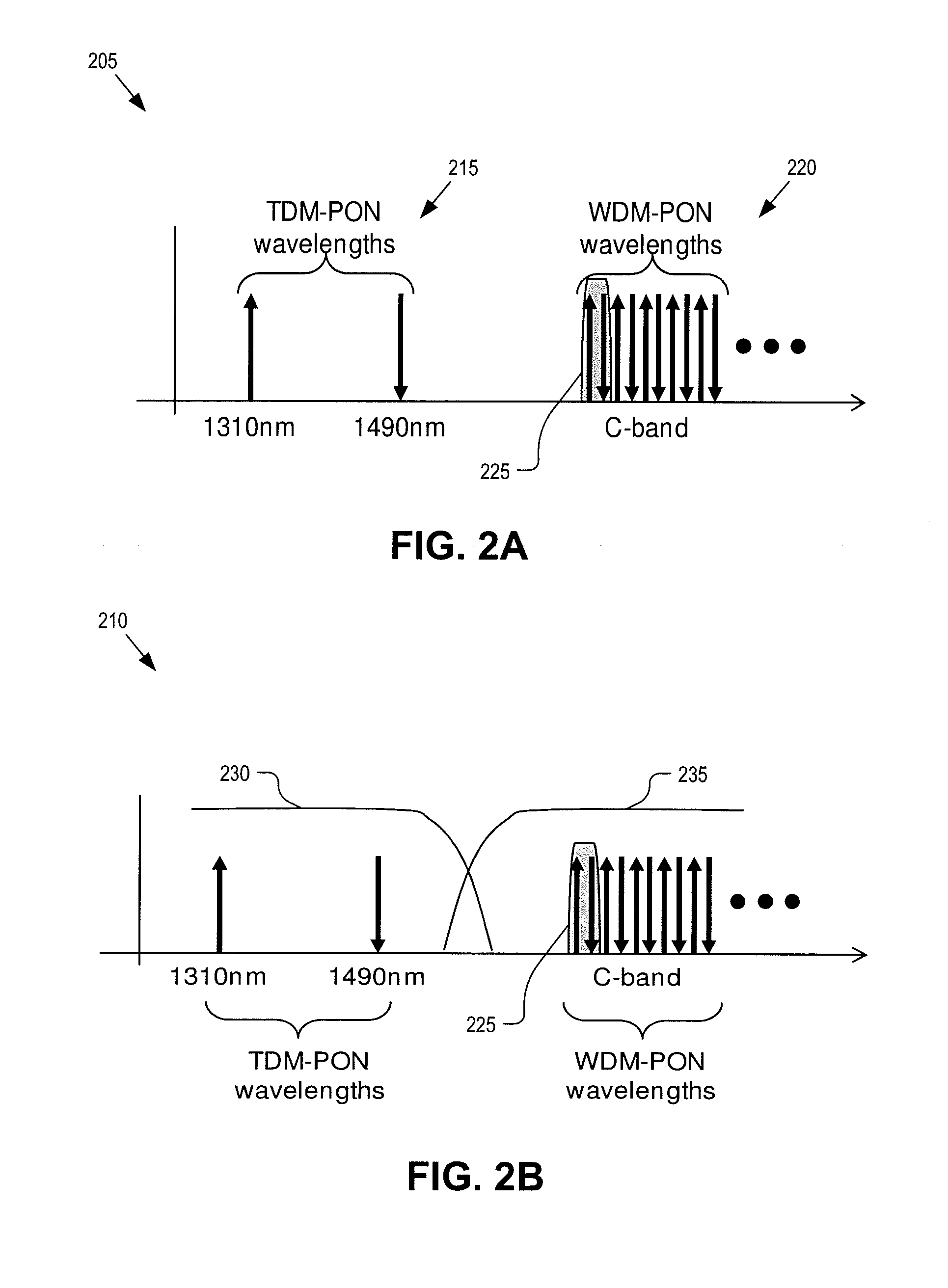
Passive optical network with asymmetric modulation scheme
A passive optical network couples a WDM optical line terminal (“OLT”) to WDM optical network units (“ONUs”). The WDM OLT includes an optical transmitter array with coherent transmitters to generate downstream WDM signals encoded using phase modulation, an optical receiver array with direct detection photo-detectors to receive upstream WDM signals encoded with amplitude modulation, and an optical diplexer optically coupled to the optical transmitter array and the optical receiver array. The WDM ONU includes a tunable optical transmitter having a first tunable laser source coupled to generate a selectable upstream carrier wavelength and direct amplitude modulation circuitry coupled to amplitude modulate the first tunable laser source and a tunable optical receiver having coherent detection circuitry to demodulate phase information from the downstream WDM signals and a second tunable laser source operated as a local oscillator and coupled to tune to a selectable downstream carrier wavelength.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
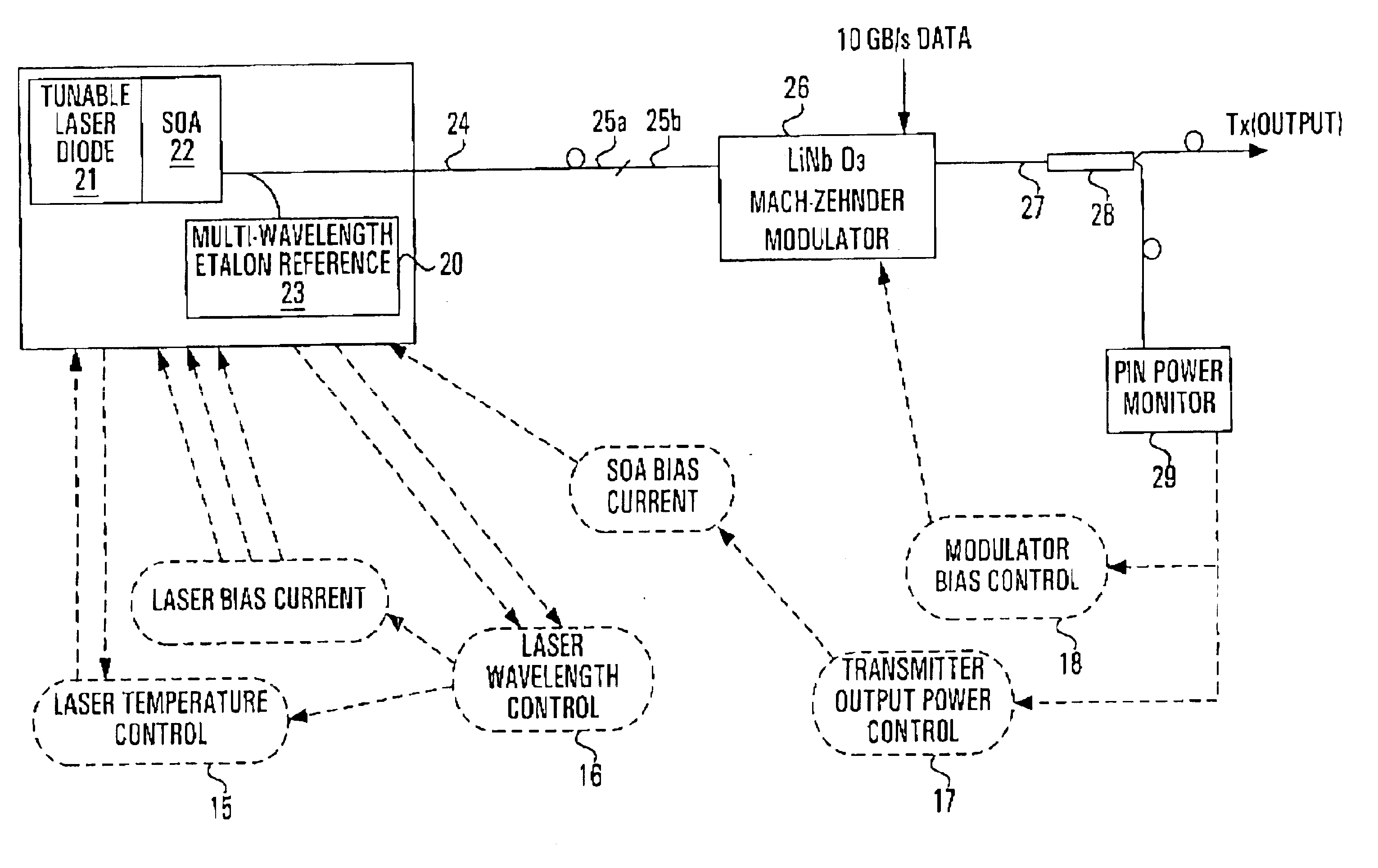
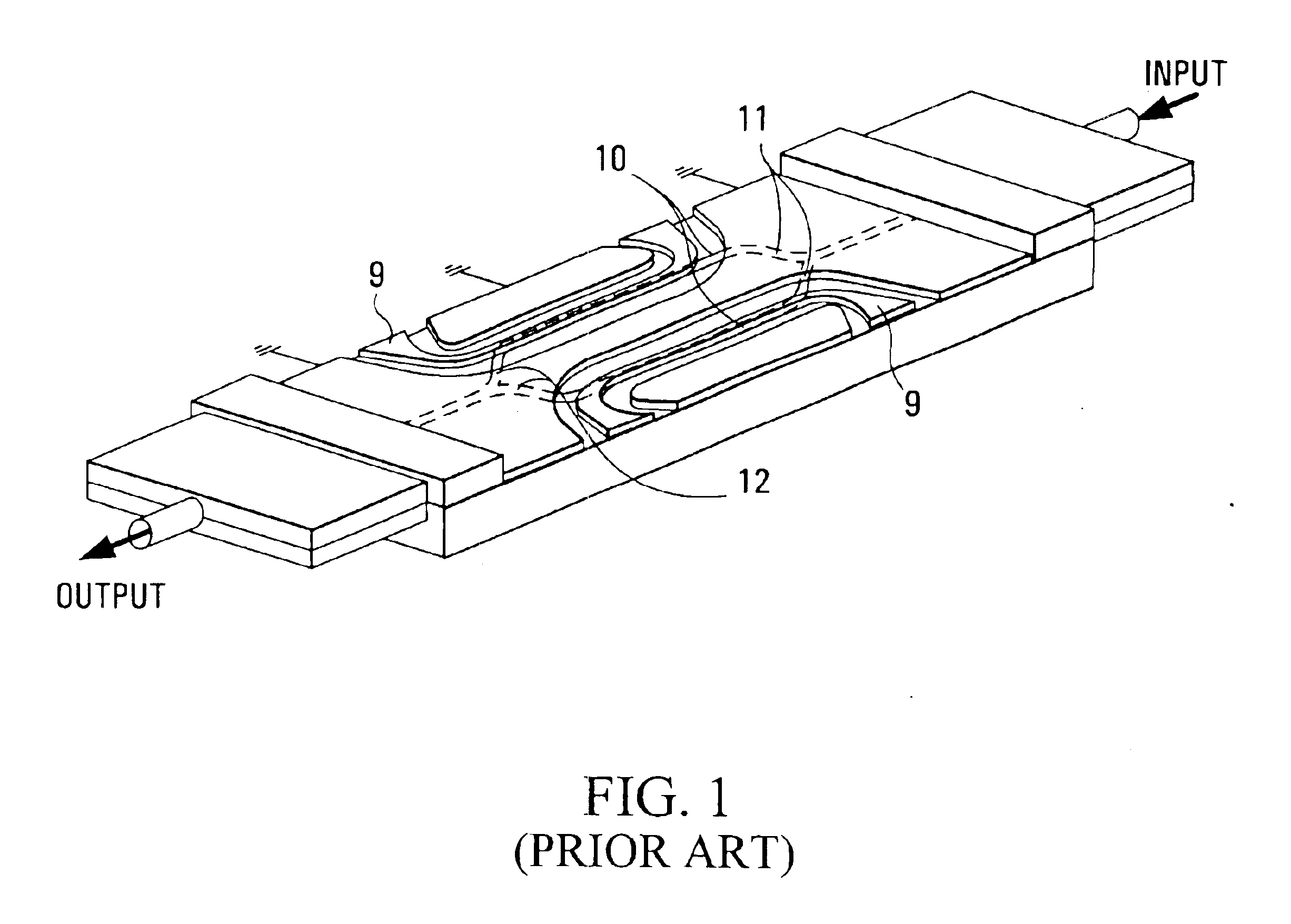
Use of amplified spontaneous emission from a semiconductor optical amplifier to minimize channel interference during initialization of an externally modulated DWDM transmitter
InactiveUS6842587B1Reduce output powerStabilize output powerElectromagnetic transmittersOptical pathPhysics
A semiconductor optical amplifier (SOA) is placed in the optical path between the tunable laser and the external modulator on a DWDM optical transmitter. The modulator transfer function is measured using low-level amplified spontaneous emission light output from the SOA in order to find the modulator bias corresponding to minimum transmission. The external modulator is biased to the point of minimum transmission to reduce the transmitter output power during laser turn-on. The SOA bias is also turned off to provide further attenuation as the laser is turned on. Similarly, to avoid emitting off-wavelength light during wavelength changes, the transmitter output is attenuated with a combination of low SOA bias current and biasing the modulator to its minimum transmission point. In both cases, the laser wavelength is allowed to stabilize without interfering with adjacent DWDM channels.
Owner:CIENA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com