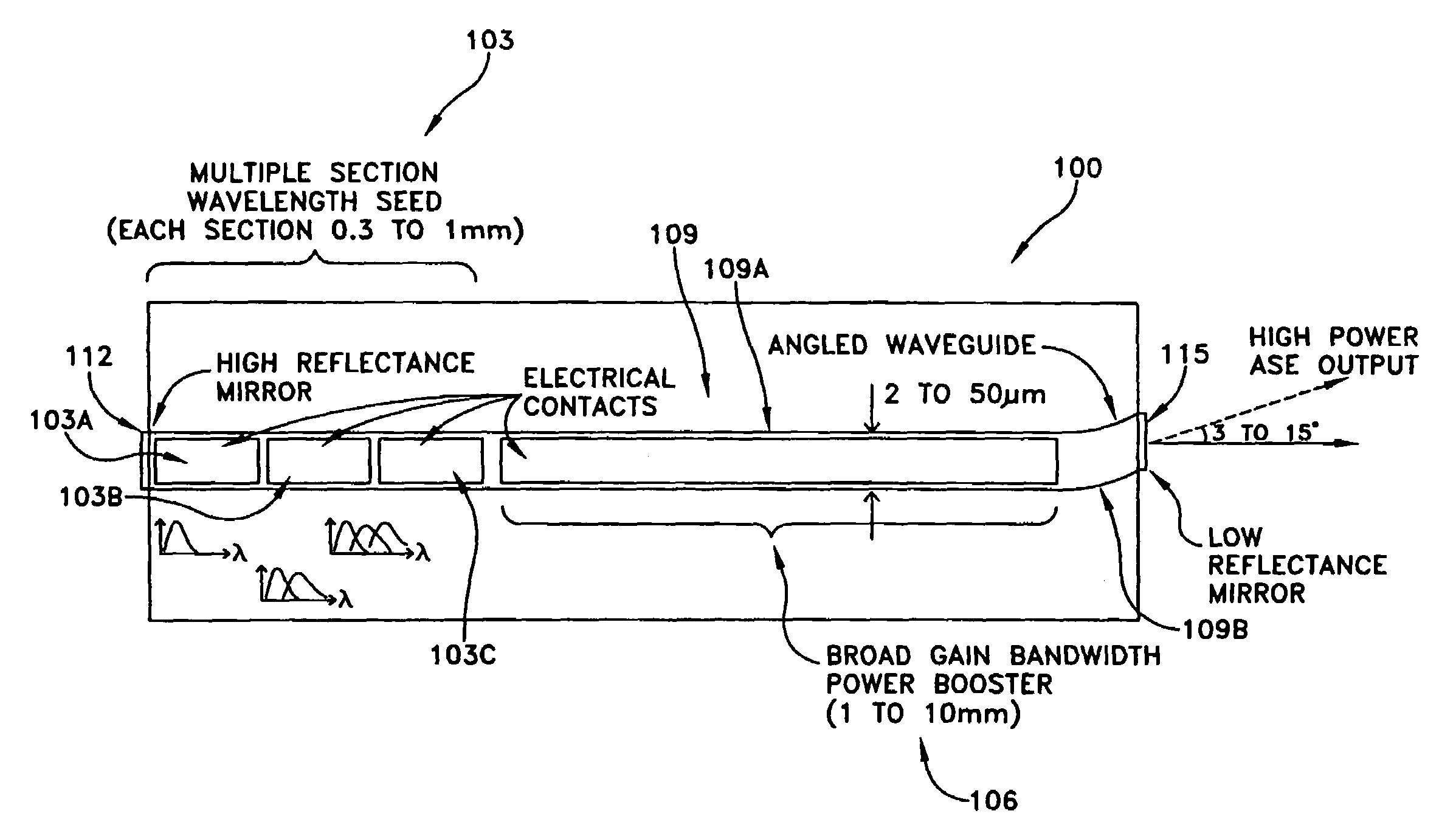
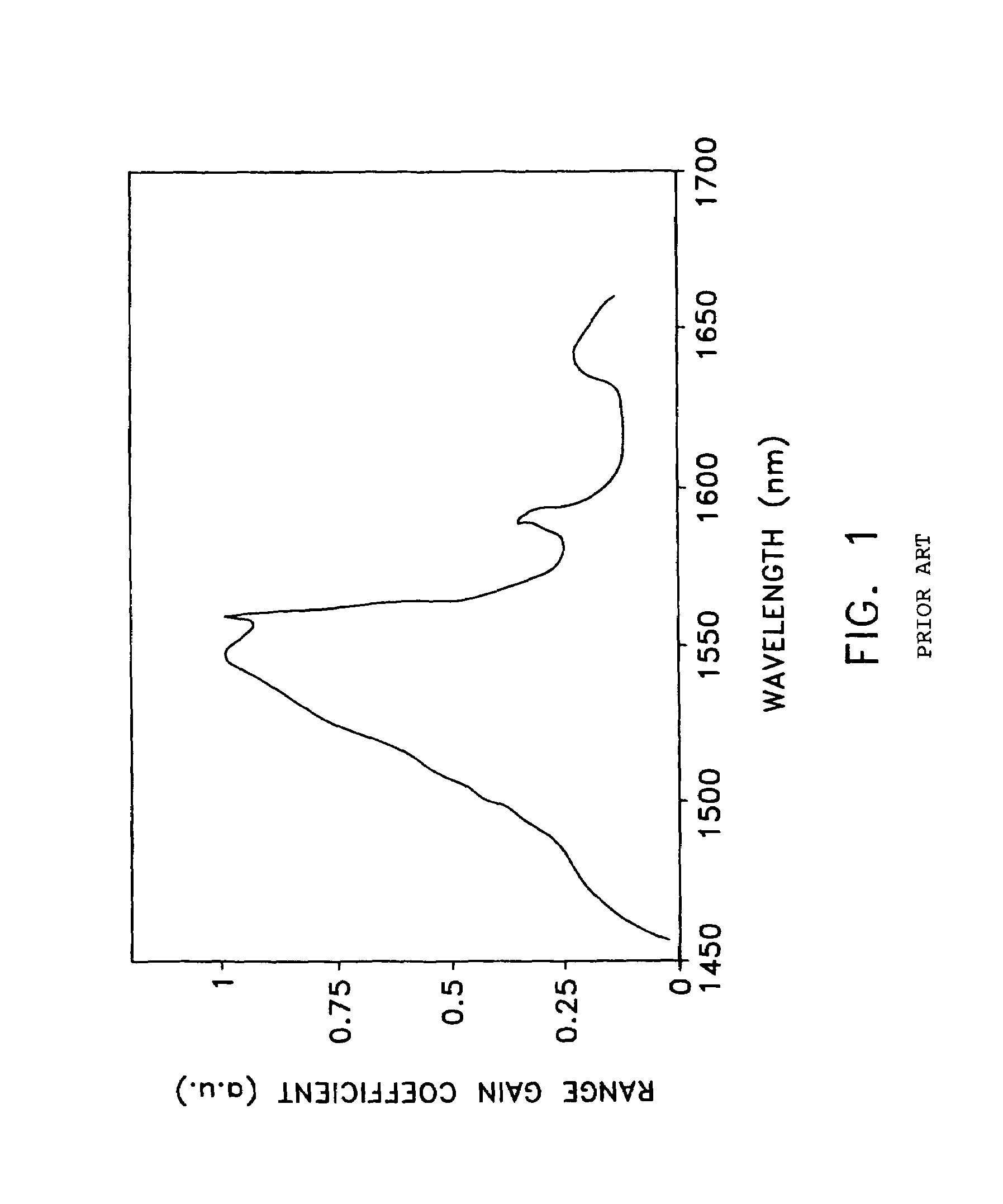
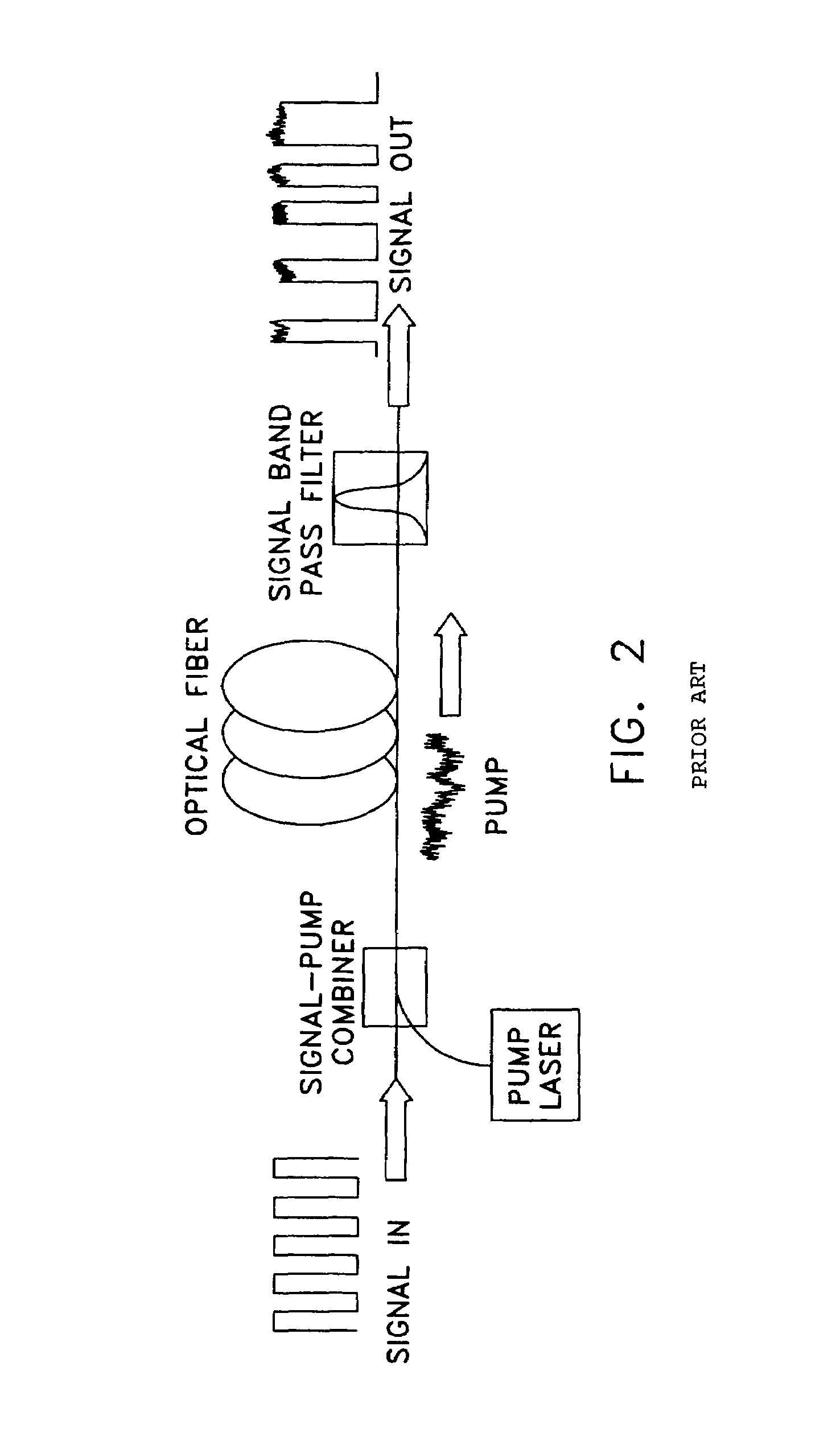
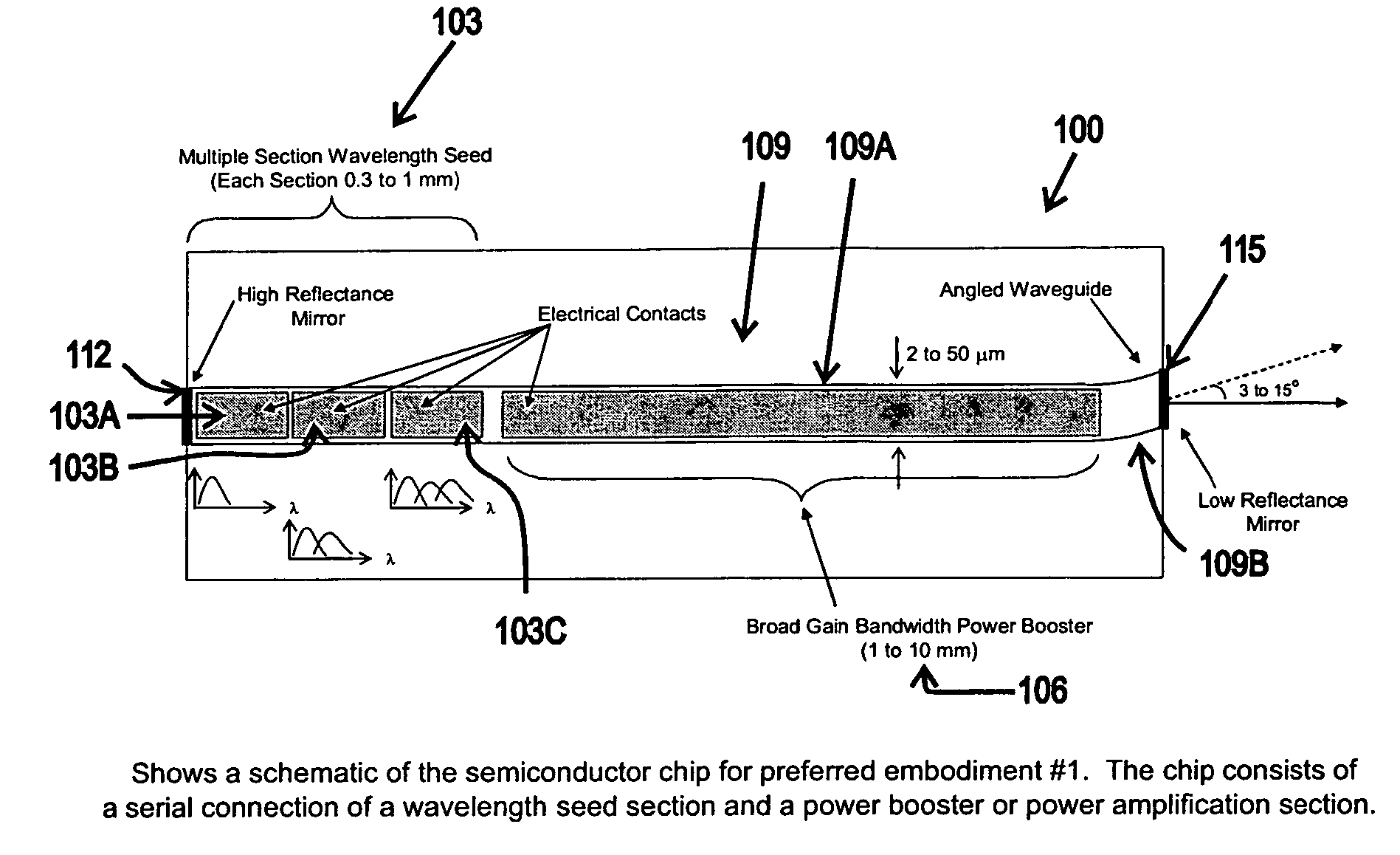
Patents
Literature
294 results about "Amplified spontaneous emission" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Amplified spontaneous emission (ASE) or superluminescence is light, produced by spontaneous emission, that has been optically amplified by the process of stimulated emission in a gain medium. It is inherent in the field of random lasers.
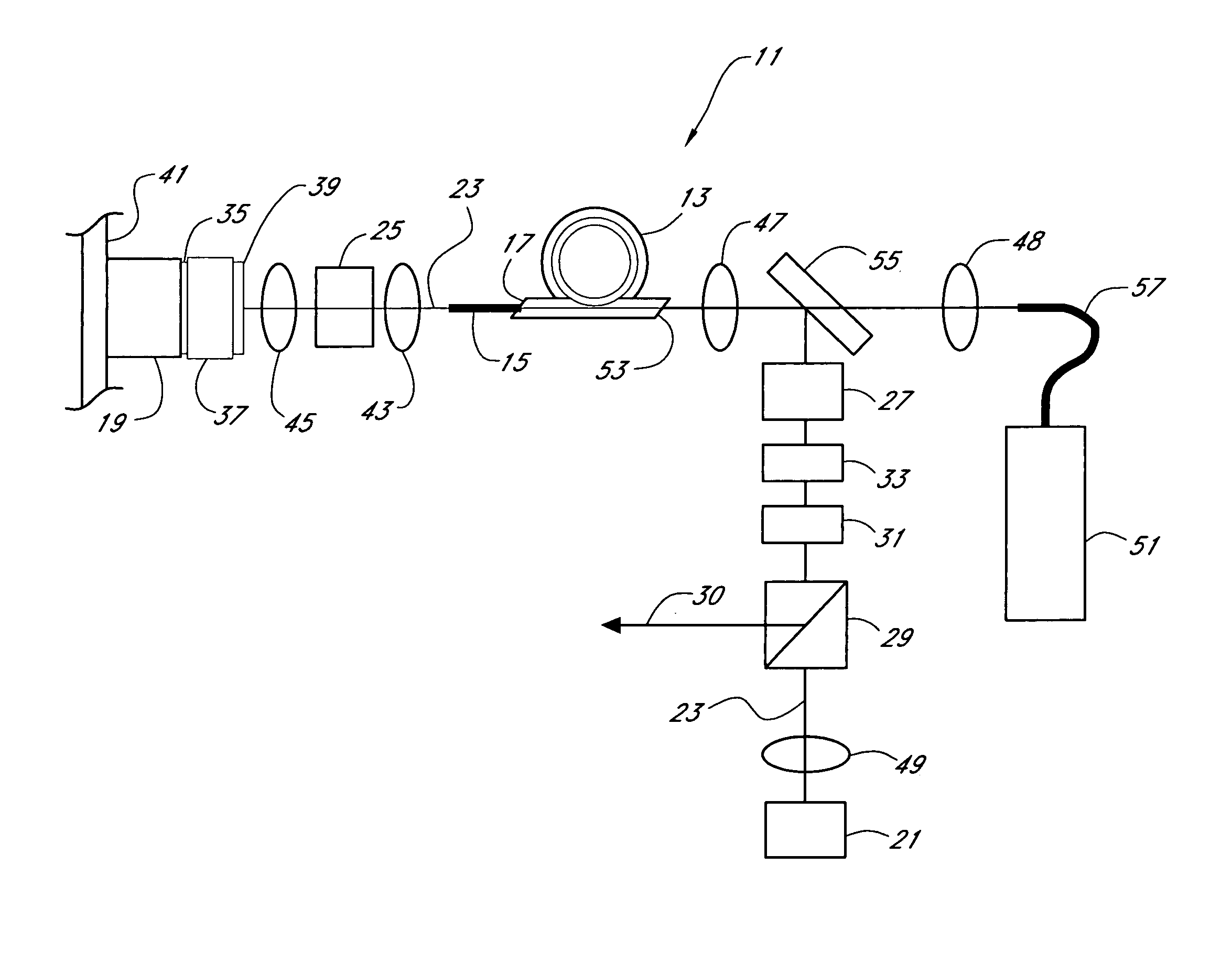
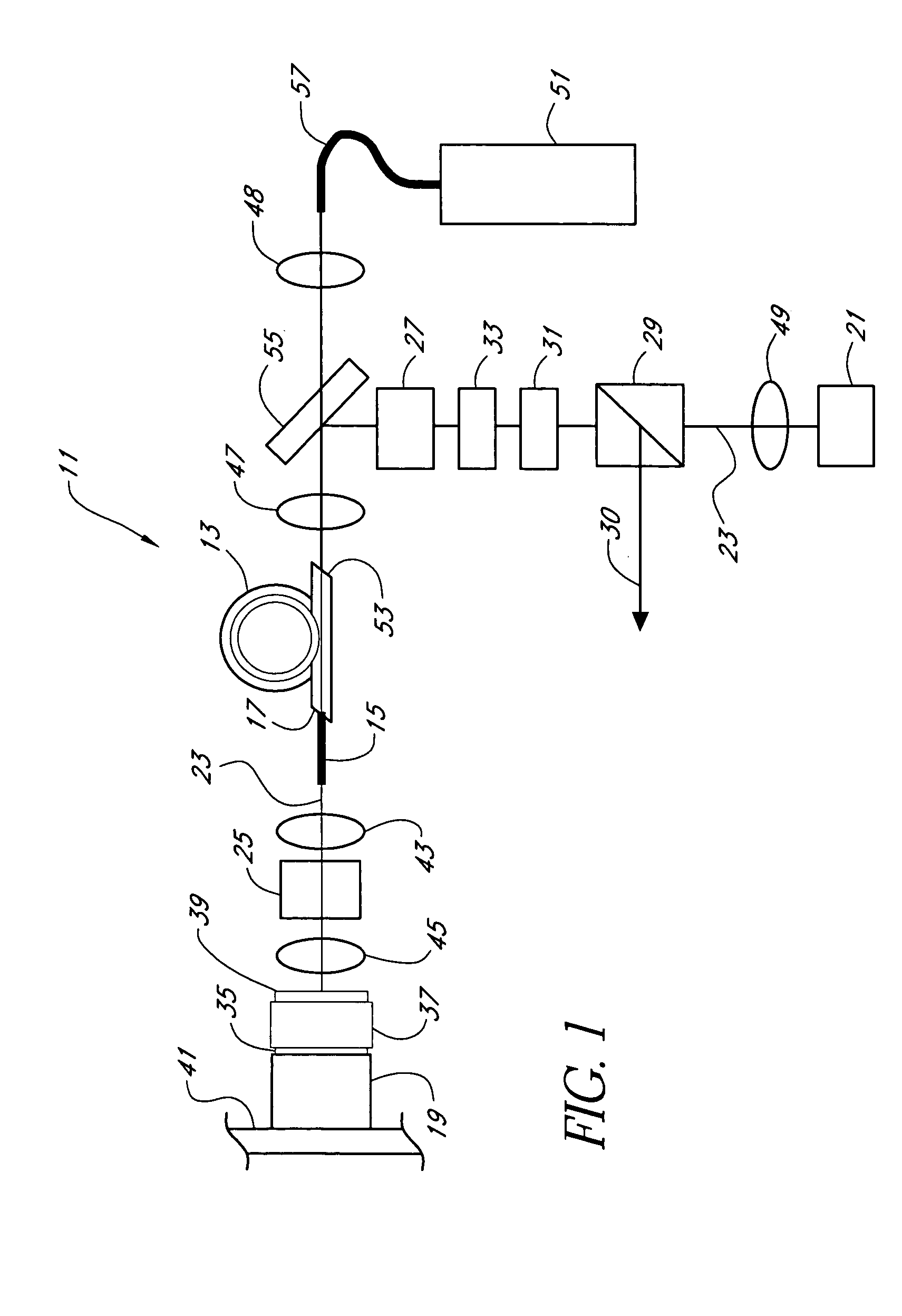
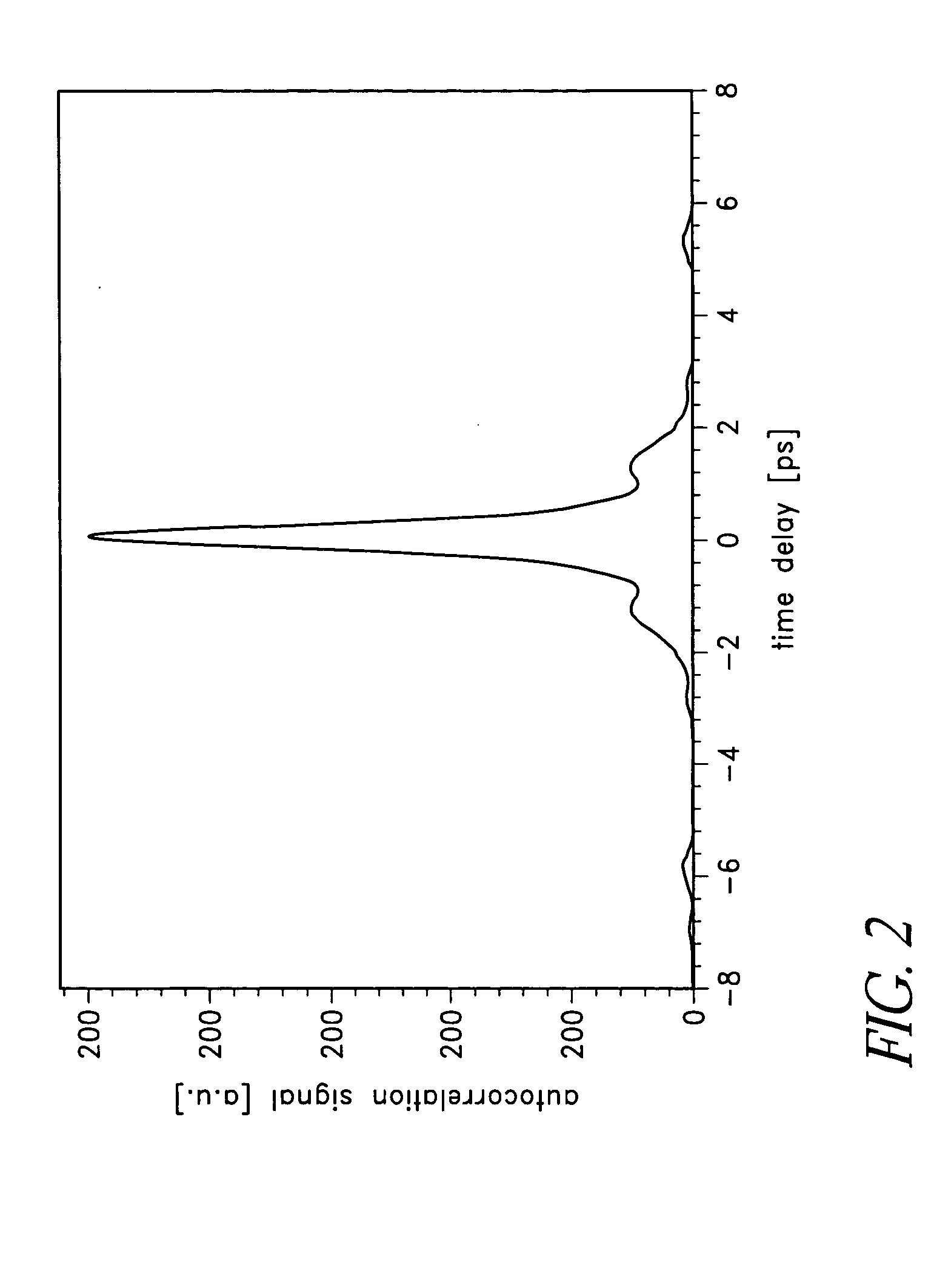
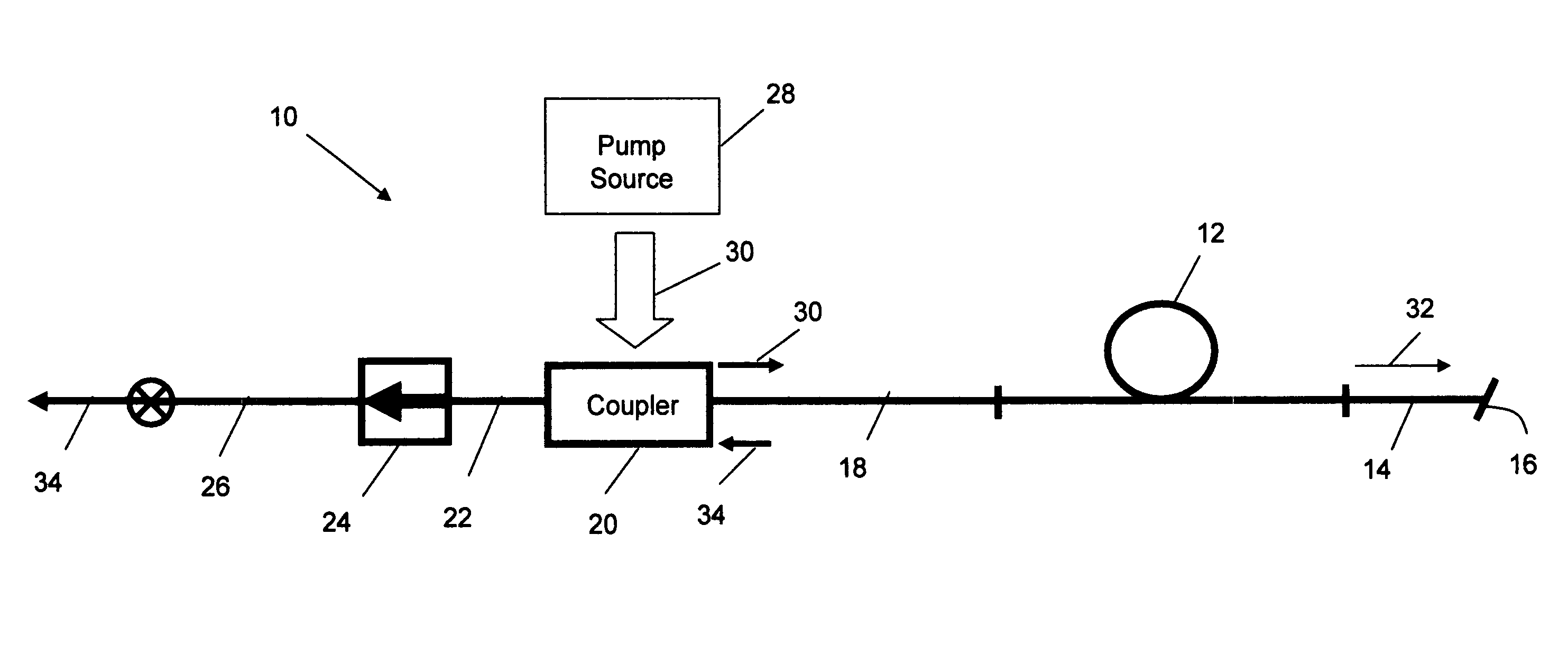
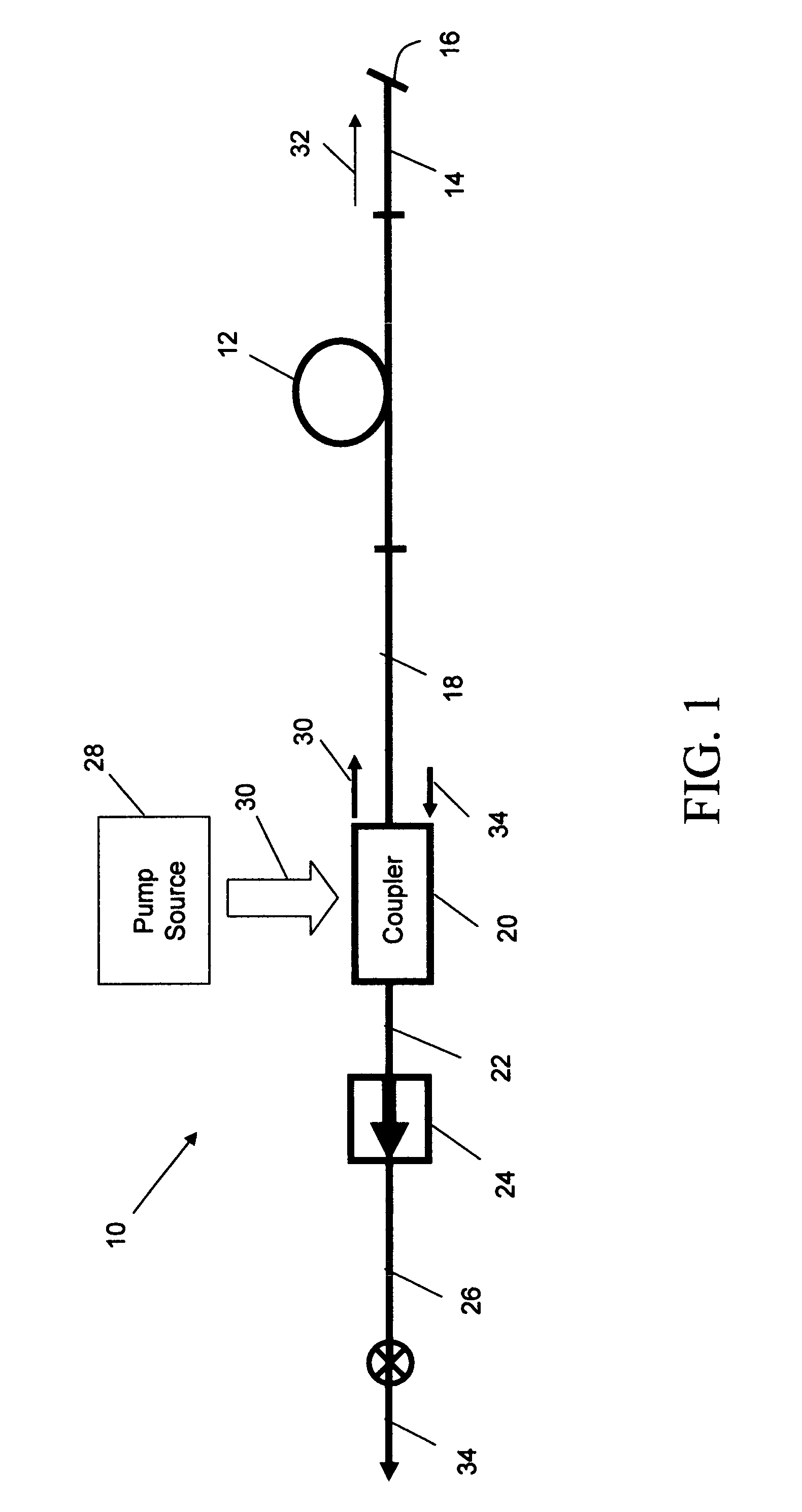
Mode-locked multi-mode fiber laser pulse source
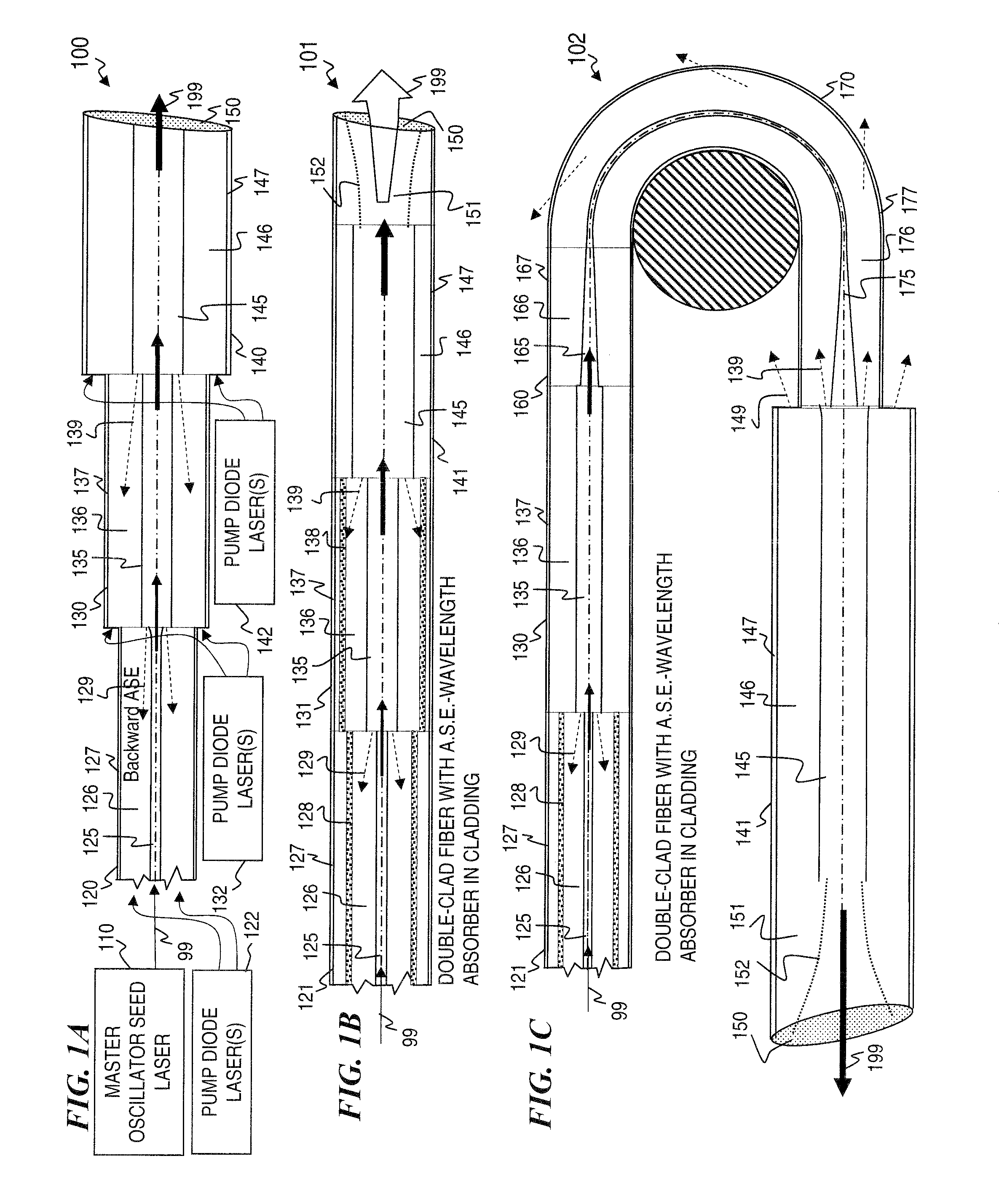
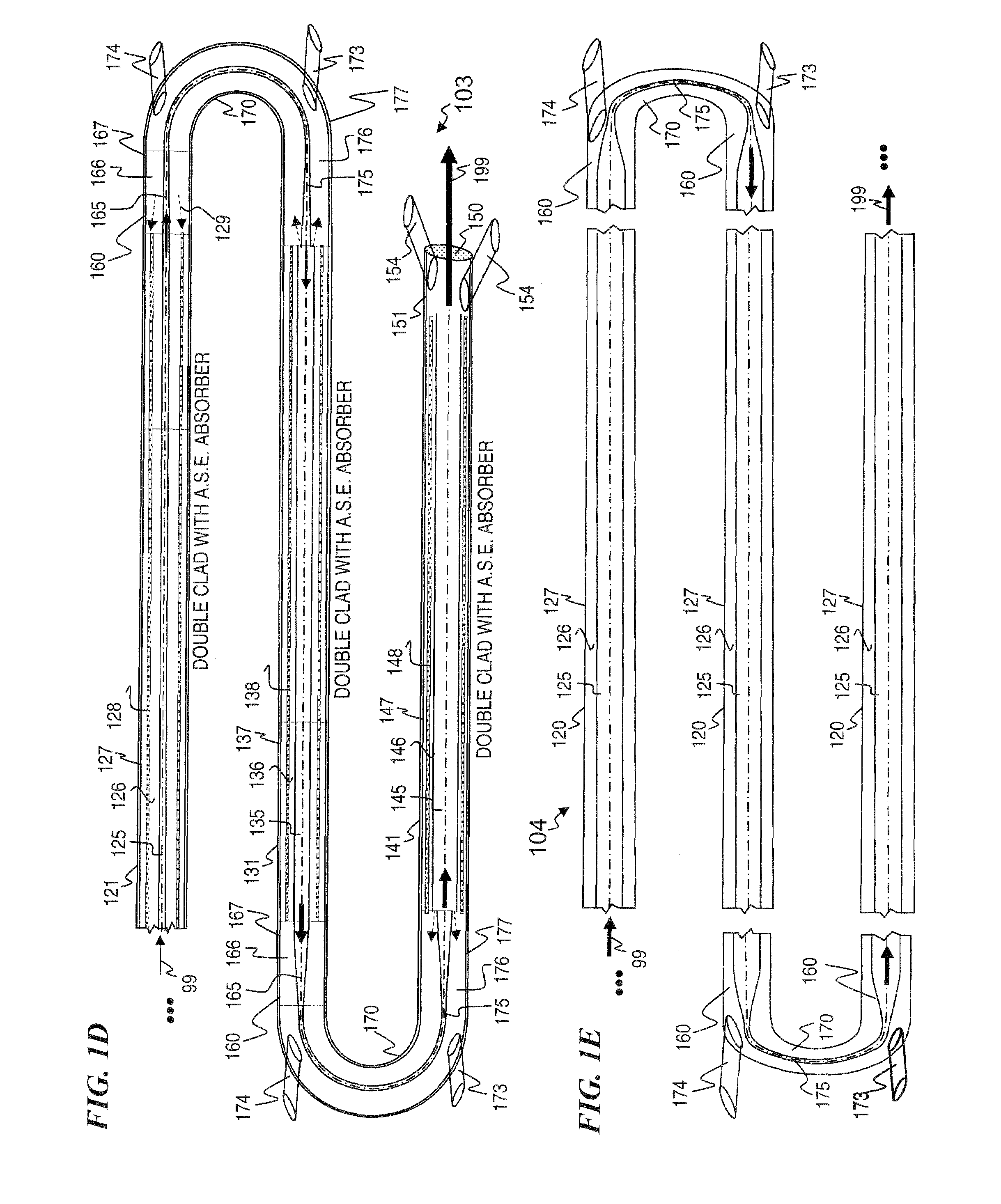
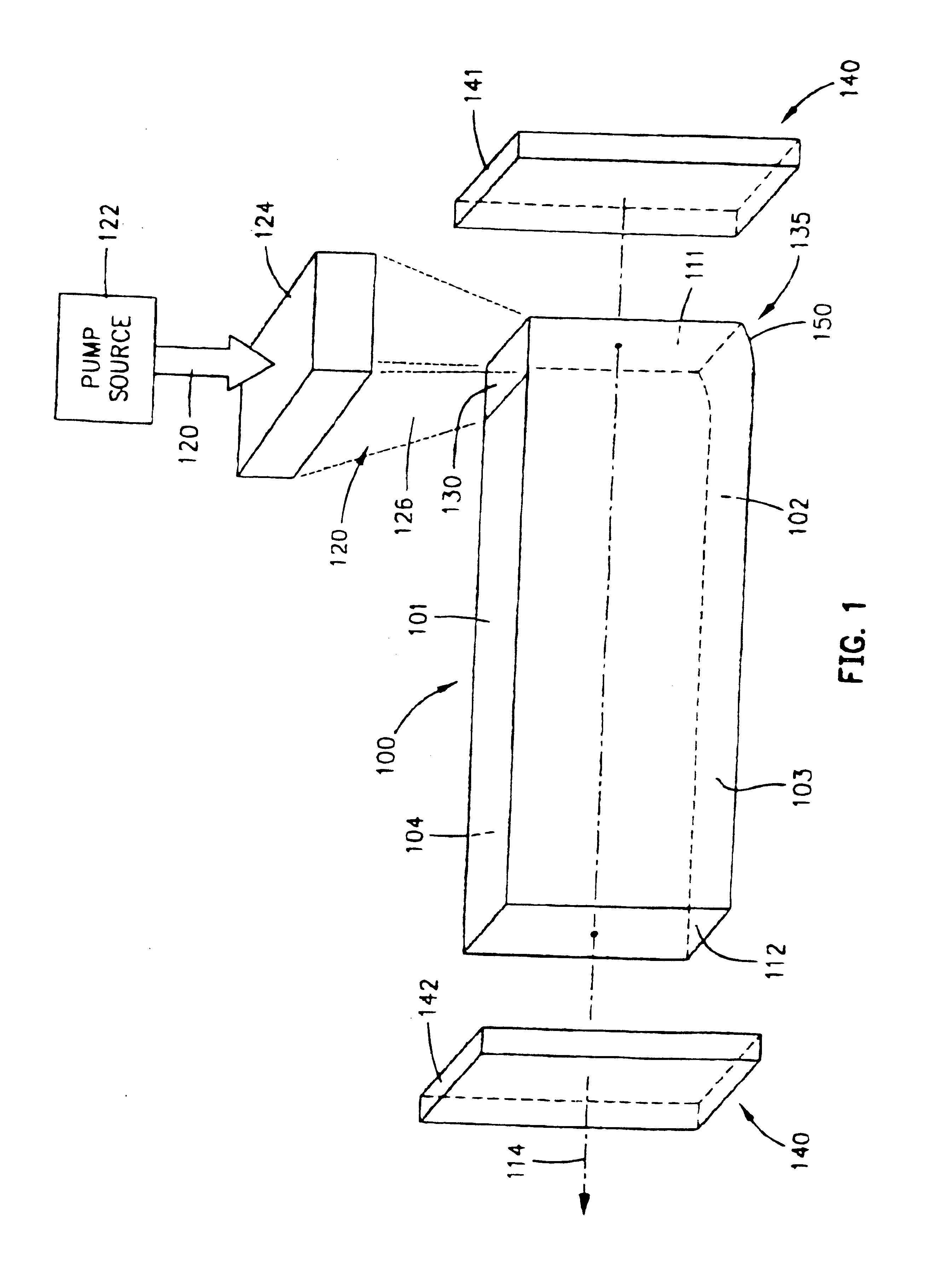
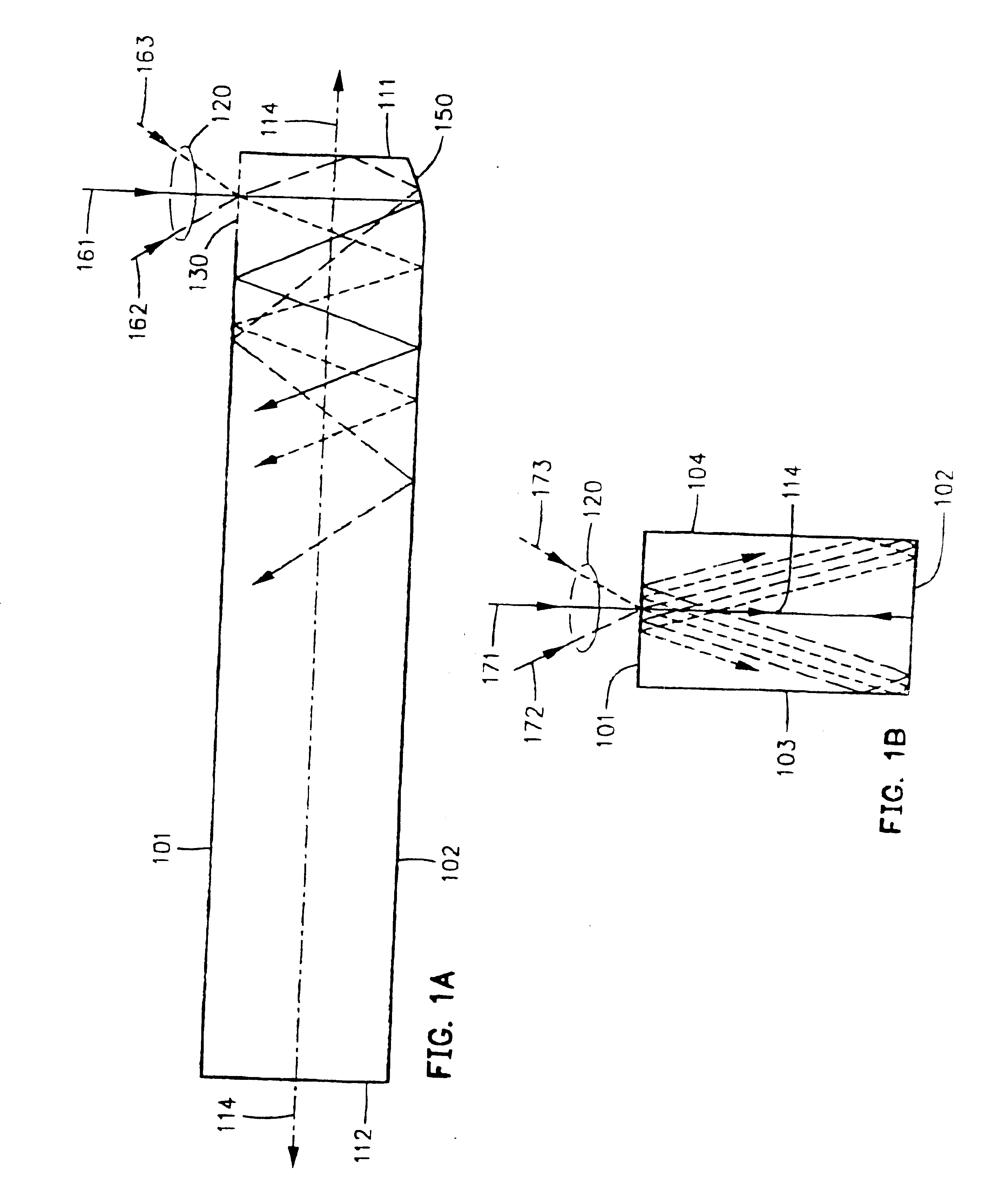
InactiveUS20050008044A1High energy storageIncrease the sectionCoupling light guidesActive medium shape and constructionHigh power lasersPeak value
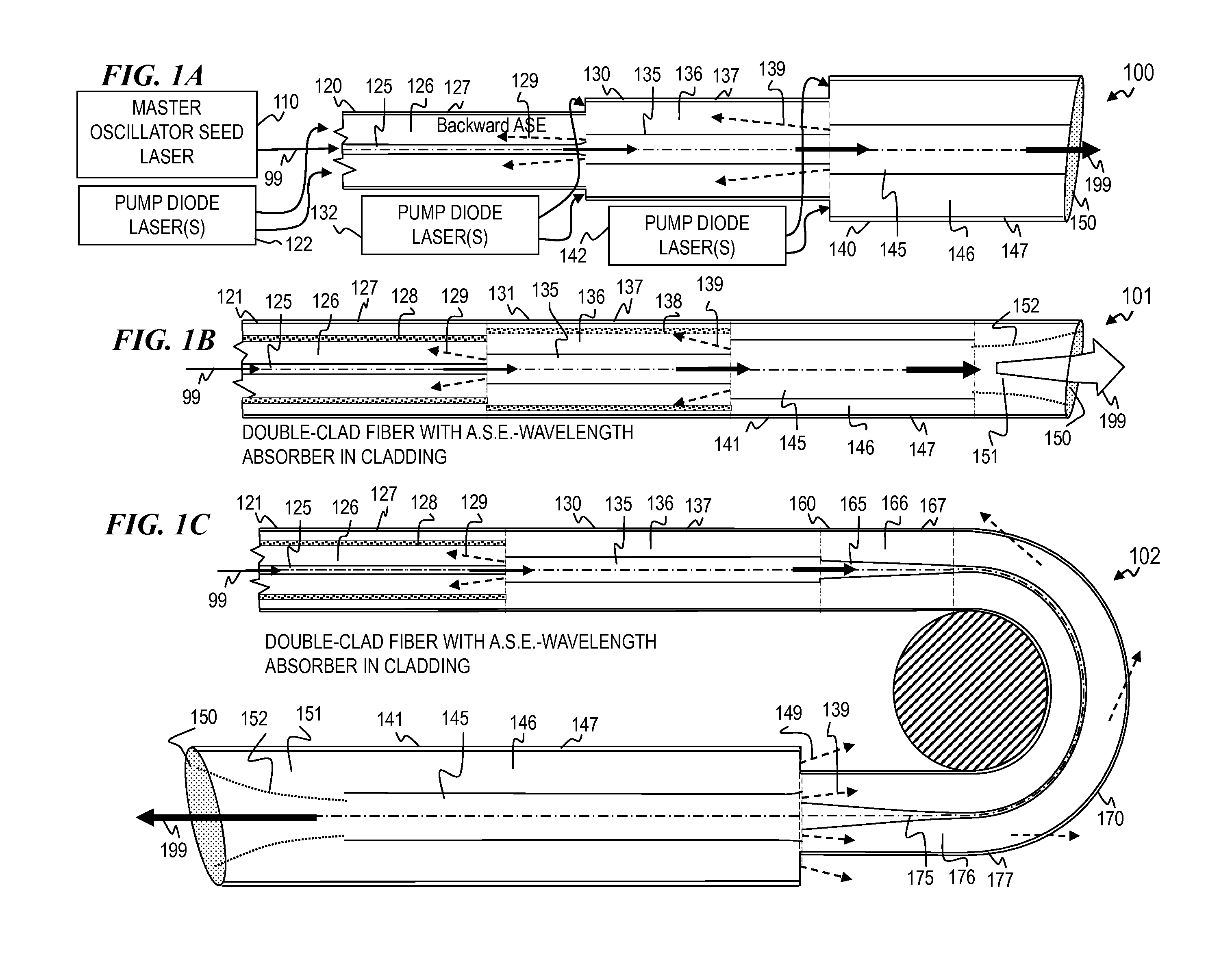
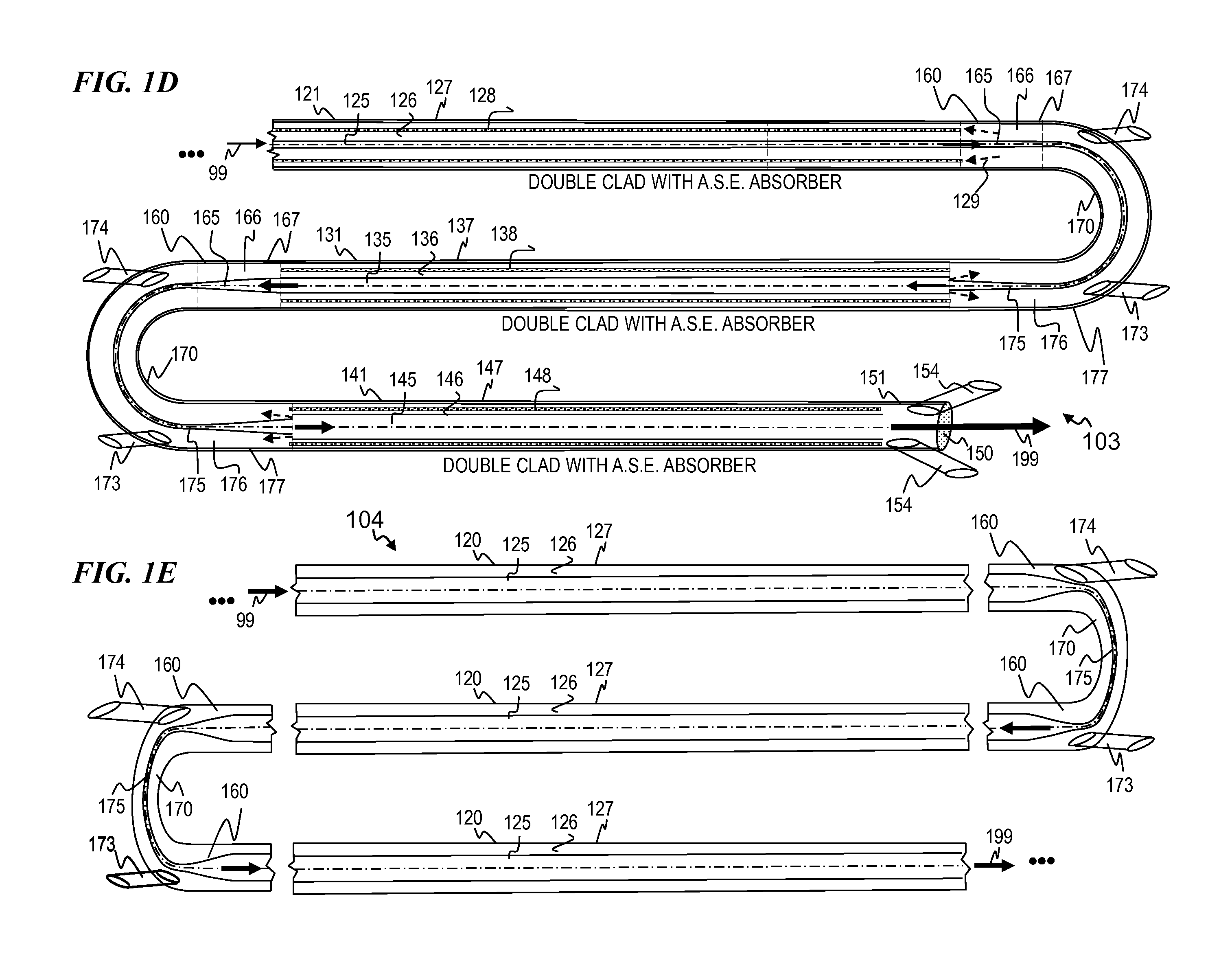
A laser utilizes a cavity design which allows the stable generation of high peak power pulses from mode-locked multi-mode fiber lasers, greatly extending the peak power limits of conventional mode-locked single-mode fiber lasers. Mode-locking may be induced by insertion of a saturable absorber into the cavity and by inserting one or more mode-filters to ensure the oscillation of the fundamental mode in the multi-mode fiber. The probability of damage of the absorber may be minimized by the insertion of an additional semiconductor optical power limiter into the cavity. To amplify and compress optical pulses in a multi-mode (MM) optical fiber, a single-mode is launched into the MM fiber by matching the modal profile of the fundamental mode of the MM fiber with a diffraction-limited optical mode at the launch end, The fundamental mode is preserved in the MM fiber by minimizing mode-coupling by using relatively short lengths of step-index MM fibers with a few hundred modes and by minimizing fiber perturbations. Doping is confined to the center of the fiber core to preferentially amplify the fundamental mode, to reduce amplified spontaneous emission and to allow gain-guiding of the fundamental mode. Gain-guiding allows for the design of systems with length-dependent and power-dependent diameters of the fundamental mode. To allow pumping with high-power laser diodes, a double-clad amplifier structure is employed. For applications in nonlinear pulse-compression, self phase modulation and dispersion in the optical fibers can be exploited. High-power optical pulses may be linearly compressed using bulk optics dispersive delay lines or by chirped fiber Bragg gratings written directly into the SM or MM optical fiber. High-power cw lasers operating in a single near-diffraction-limited mode may be constructed from MM fibers by incorporating effective mode-filters into the laser cavity. Regenerative fiber amplifiers may be constructed from MM fibers by careful control of the recirculating mode. Higher-power Q-switched fiber lasers may be constructed by exploiting the large energy stored in MM fiber amplifiers.
Owner:FERMANN MARTIN E +1
Method and apparatus for optical gain fiber having segments of differing core sizes
ActiveUS7768700B1Enhanced energy extractionReduce the amount requiredLaser using scattering effectsFibre transmissionFiberBandpass filtering
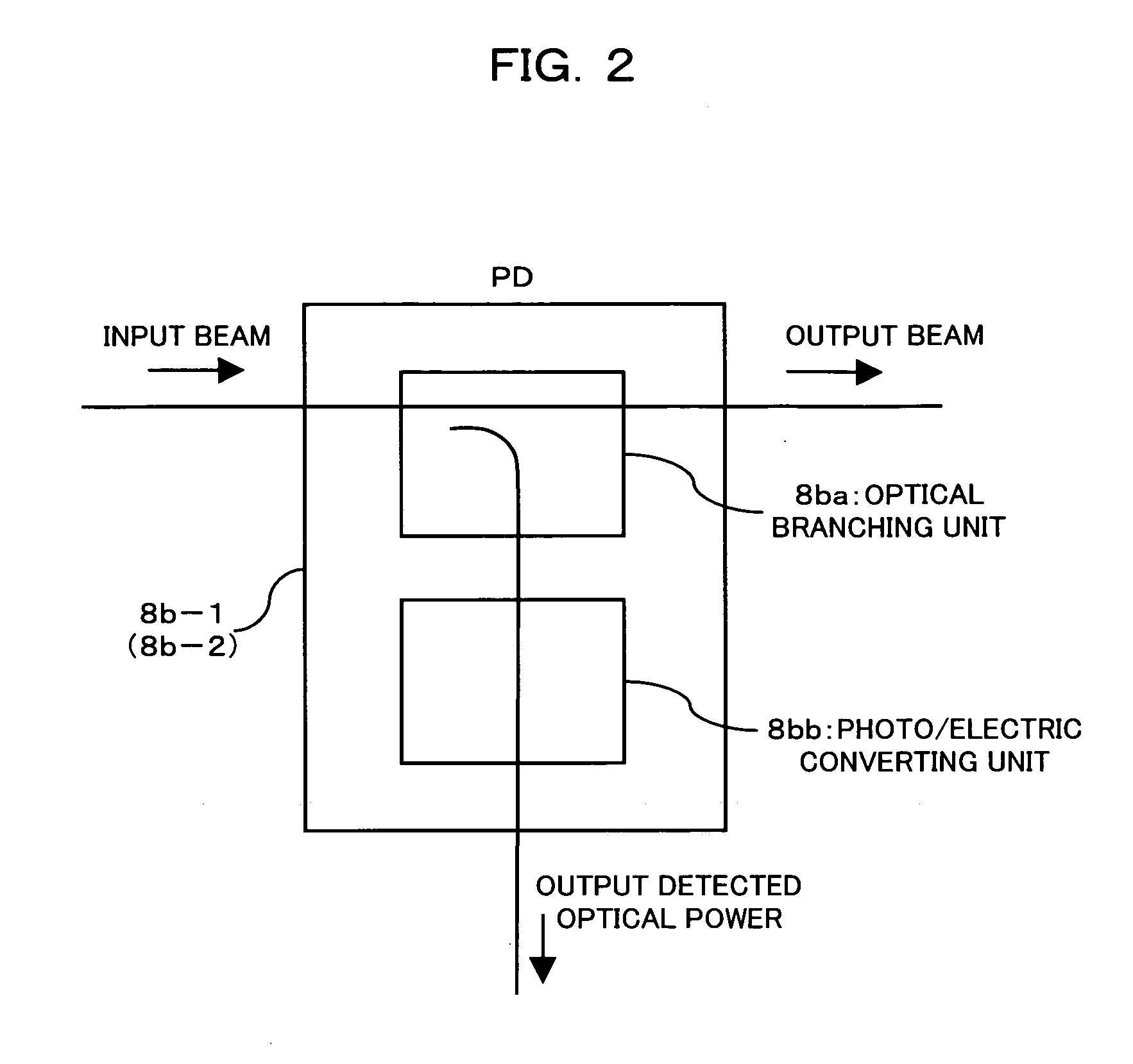
Apparatus and method for amplifying laser signals using segments of fibers of differing core diameters and / or differing cladding diameters to suppress amplified spontaneous emission and non-linear effects such as four-wave mixing (FWM), self-phase modulation, and stimulated Brillouin and / or Raman scattering (SBS / SRS). In some embodiments, different core sizes have different sideband spacings (spacing between the desired signal and wavelength-shifted lobes). Changing core sizes and providing phase mismatches prevent buildup of non-linear effects. Some embodiments further include a bandpass filter to remove signal other than the desired signal wavelength and / or a time gate to remove signal at times other than during the desired signal pulse. Some embodiments include photonic-crystal structures to define the core for the signal and / or the inner cladding for the pump. Some embodiments include an inner glass cladding to confine the signal in the core and an outer glass cladding to confine pump light in the inner cladding.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
High-gain diode-pumped laser amplifier
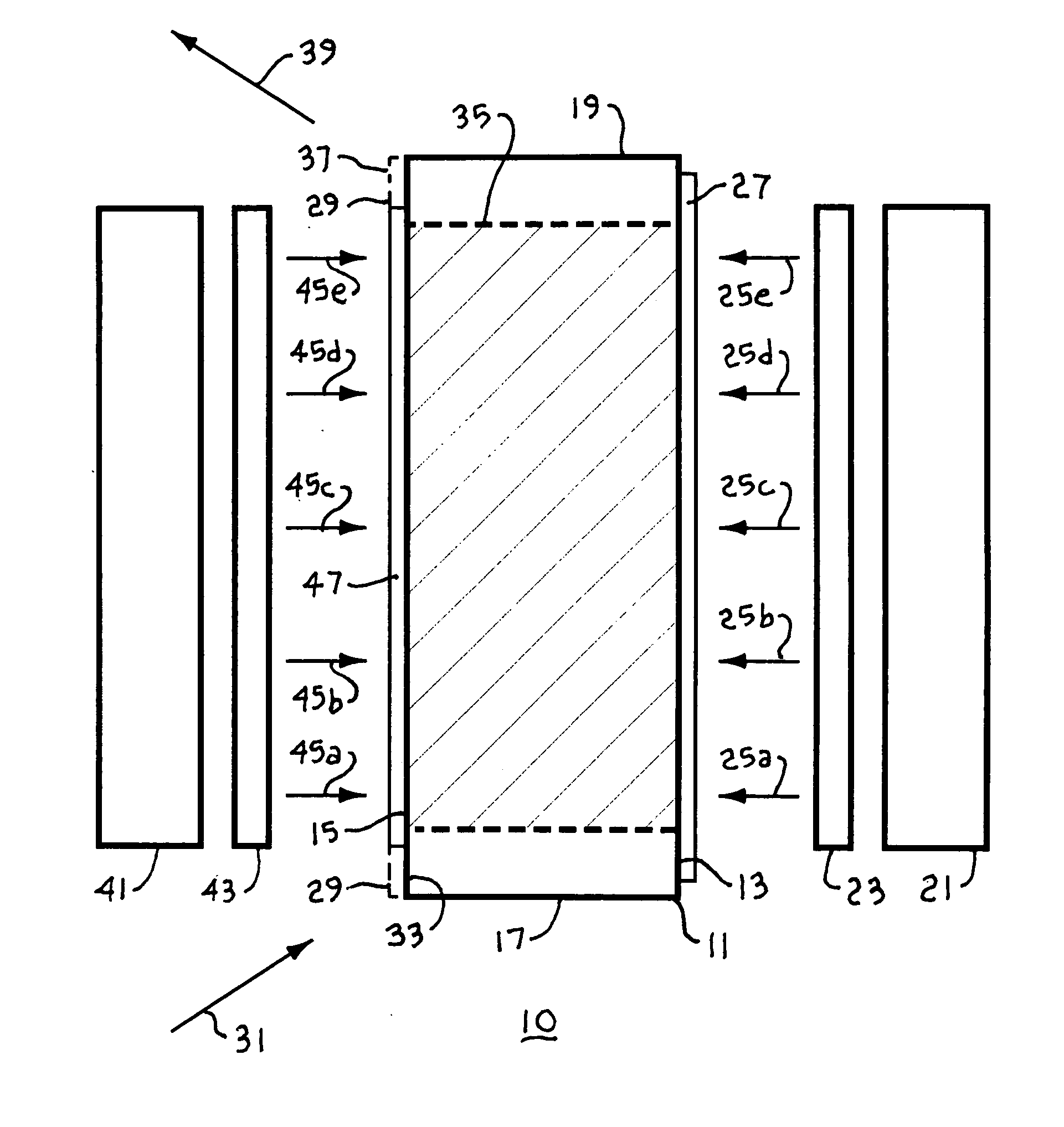
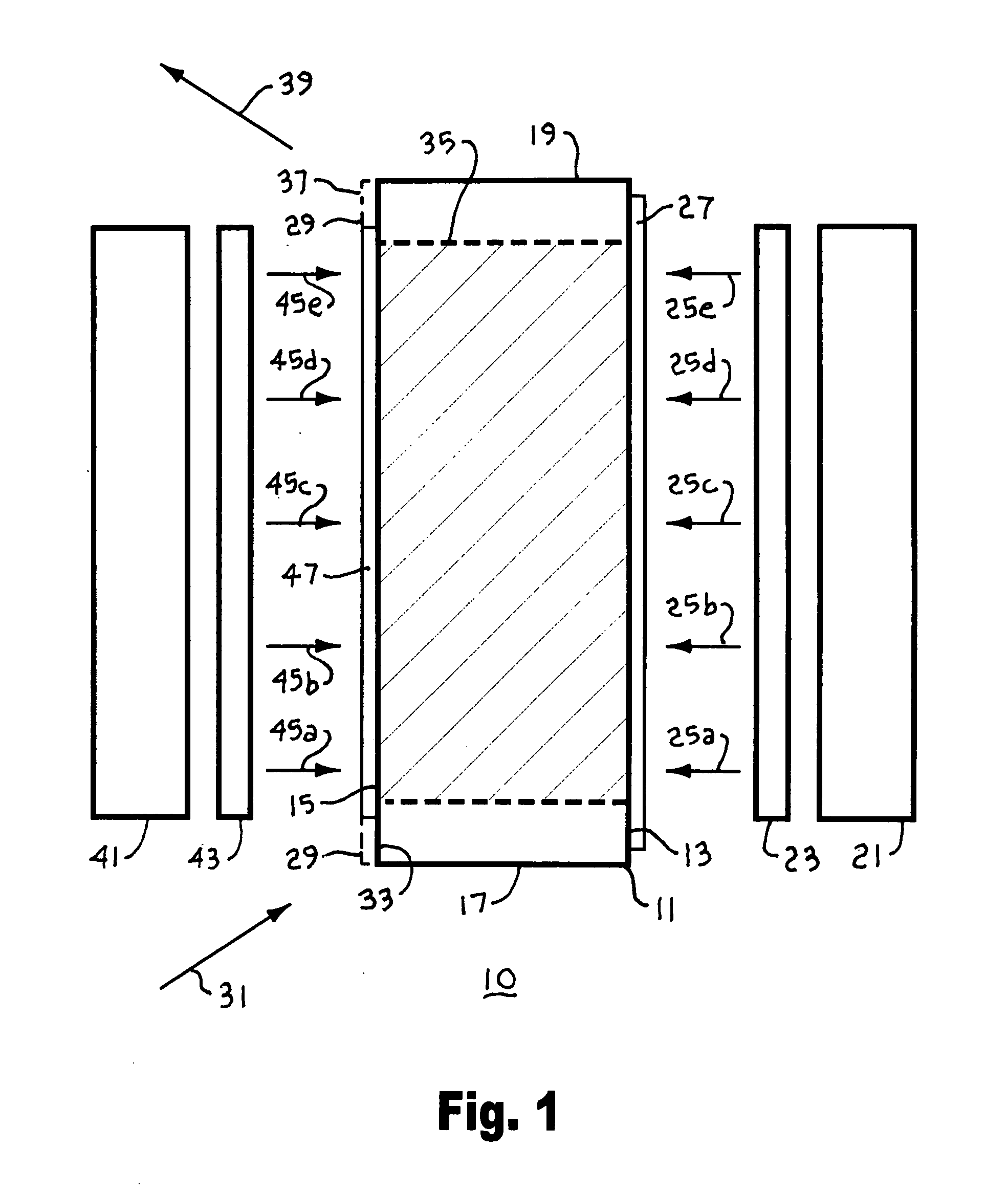
InactiveUS20060114961A1Minimize parasitic amplified spontaneous emissionActive medium shape and constructionOptical devices for laserAudio power amplifierOptical coating
A laser amplifier includes a laser active slab with a source of pump power to amplify an input laser beam, the laser active slab including a block of laser active material having opposed lateral faces defining a wedge lateral dihedral angle, opposed longitudinal faces, and opposed parallel transverse faces, the wedge lateral dihedral angle specified to minimize parasitic amplified spontaneous emission. The source of pump power may be one or more laser diode bars and microlenses producing a gain sheet in the laser active slab. The lateral faces may include optical coatings highly transmitting at a wavelength of the pump power and highly reflecting at a lasing wavelength to provide a folded path for the input laser beam though the gain sheet. The laser amplifier may optionally include one or more external mirrors highly reflecting at the lasing wavelength positioned and oriented to provide one or more additional zig-zag passes through the gain sheet for the input laser beam and to provide a multi-pass-amplified laser beam.
Owner:MANNI JEFFREY G
Apparatus and method for a high-gain double-clad amplifier
ActiveUS7526167B1Suppress instabilityEffectiveLaser detailsOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingFiberLength wave
An optical apparatus design and method for suppressing cladding-mode gain in fiber- and other waveguide-amplification devices. In some embodiments, a signal-wavelength-absorbing core or region is included within the pump cladding or the pump waveguide, in order to absorb signal-wavelength radiation that occurs in the regions where only pump-wavelength radiation is wanted. This absorbing region prevents cladding-mode gain, thus preserving more pump-wavelength excitation for amplifying the desired signal radiation. In other embodiments, the refractive-index profile of the fiber or other waveguide is adjusted to reduce the numeric aperture and thus reduce the angle of light that will remain in the cladding. Since amplified spontaneous emission (ASE) occurs at all angles, a lower-NA fiber will leak a higher proportion of ASE (since a relatively lower portion of the ASE radiation is within the smaller angle that is retained within a low-NA fiber), while pump light, which was introduced into the fiber within the lower-NA angle will remain in the cladding.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
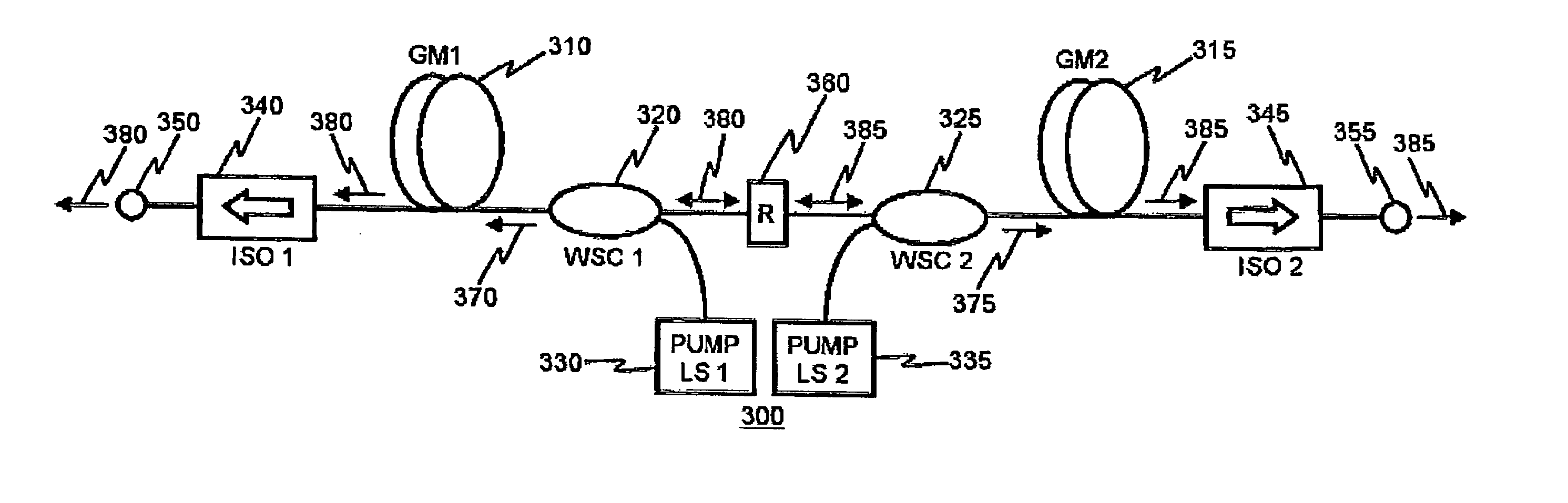
Method for locking Raman gains of target and Raman OFA (optical fiber amplifier)
ActiveCN102307068ADark current has little effectLarge range of valuesLaser detailsElectromagnetic transmissionAutomatic controlAudio power amplifier
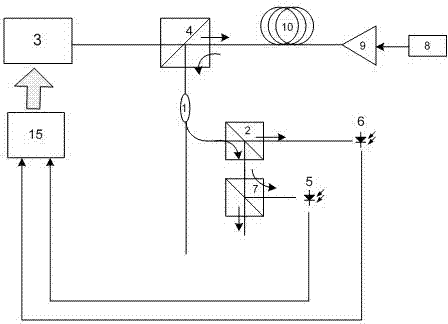
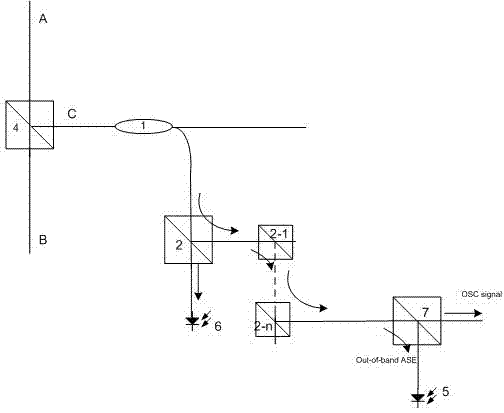
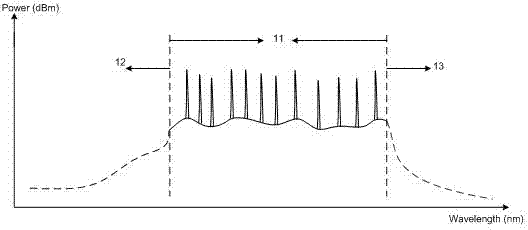
The invention discloses a method for locking Raman gains of a target and a Raman OFA (optical fiber amplifier). The OFA comprises a coupler and a control unit, wherein the control unit comprises a gain locking module; and a detection circuit formed by a filter and an optical power detector is connected between the output end of the coupler and the input end of the control unit. In the method, the control unit is utilized to adjust the power of a pump laser, thus the power of detected OOB (out of band) ASE (amplified spontaneous emission) optical signals is consistent with that of the targeted OOB ASE optical signals, and the amplification gains of the target is locked. The optical path structure of the OFA is simple, the Raman gains can be configured flexibly in accordance with the circuit conditions, and the gains of the Raman OFA can be automatically controlled and locked.
Owner:GUANGXUN SCI & TECH WUHAN
Dual-port broadband light source with independently controllable output powers
InactiveUS20050069252A1Increase output powerSatisfactory output efficiencyLaser output parameters controlActive medium materialBroadband light sourceAmplified spontaneous emission
A dual-port broadband light source with independently controllable output powers includes a broadband light source having a first gain medium pumped by an input pump light in order to output a first amplified spontaneous emission through both ends thereof. A second gain medium pumped by another input pump light in order to output a second amplified spontaneous emission through both ends thereof. A reflector disposed between the opposite ends of the first and second gain mediums to reflect the input first and second amplified spontaneous emissions. The first and second amplified spontaneous emissions output from the first and second gain mediums are then output to the outside through first and second output terminals.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
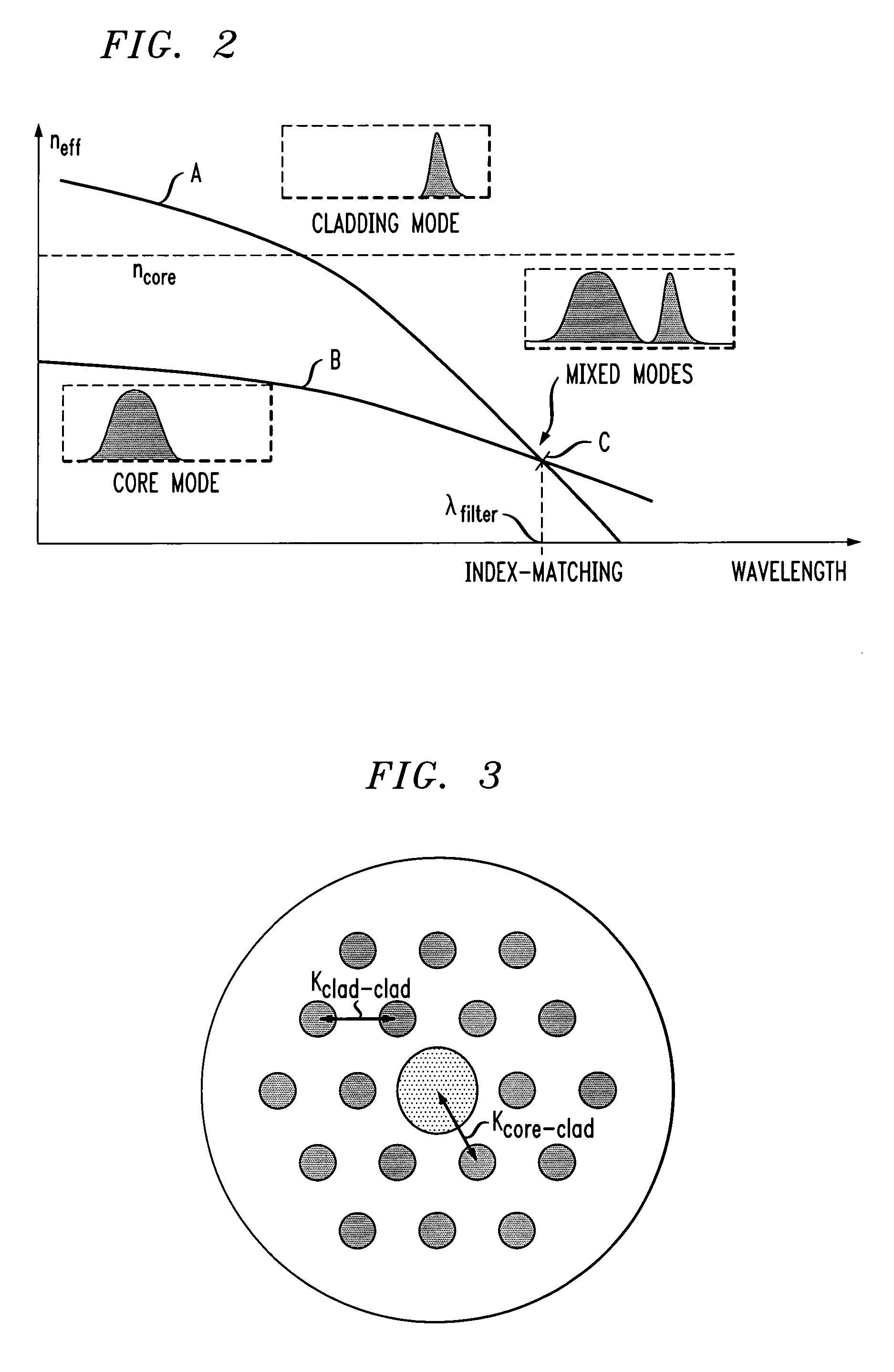
Optical fiber filter for suppression of amplified spontaneous emission
ActiveUS7272287B2Enhanced spontaneous emissionCoupling light guidesMulticore optical fibreTotal internal reflectionRefractive index
An in-line, distributed optical fiber filter comprises a core region with a raised refractive index (with respect to the surrounding cladding material) so as to allow for total internal reflection (TIR) of the desired transmission wavelength(s). One or more raised index features are formed within the cladding region and are configured so as to result in mode mixing between the cladding mode and core mode at determined wavelength(s) to be removed by filtering. The parameters associated with determining the proper core specifications and cladding specifications can be separately determined to provide for enhanced performance in terms of both filtering unwanted signals and propagation of desired communication signals.
Owner:FURAKAWA ELECTRIC NORTH AMERICA INC
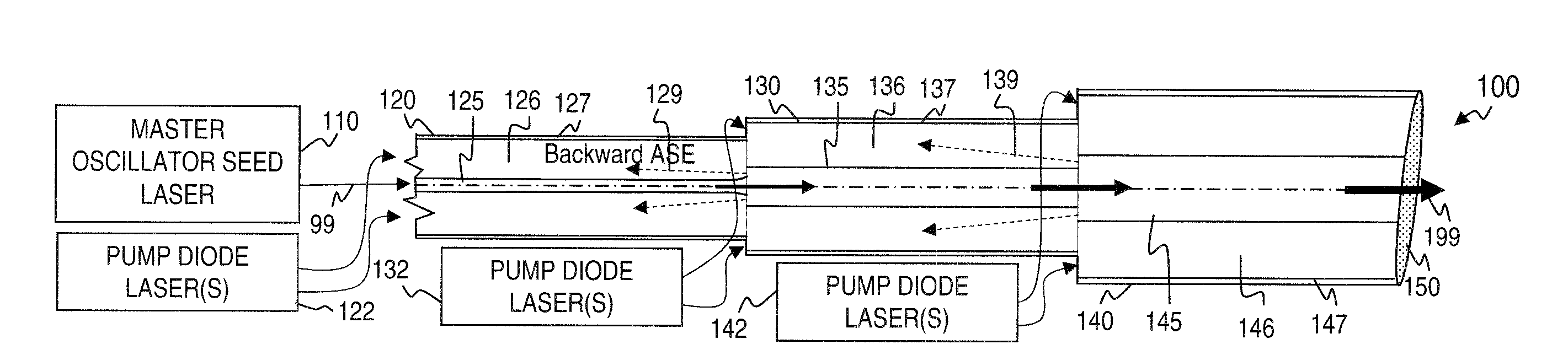
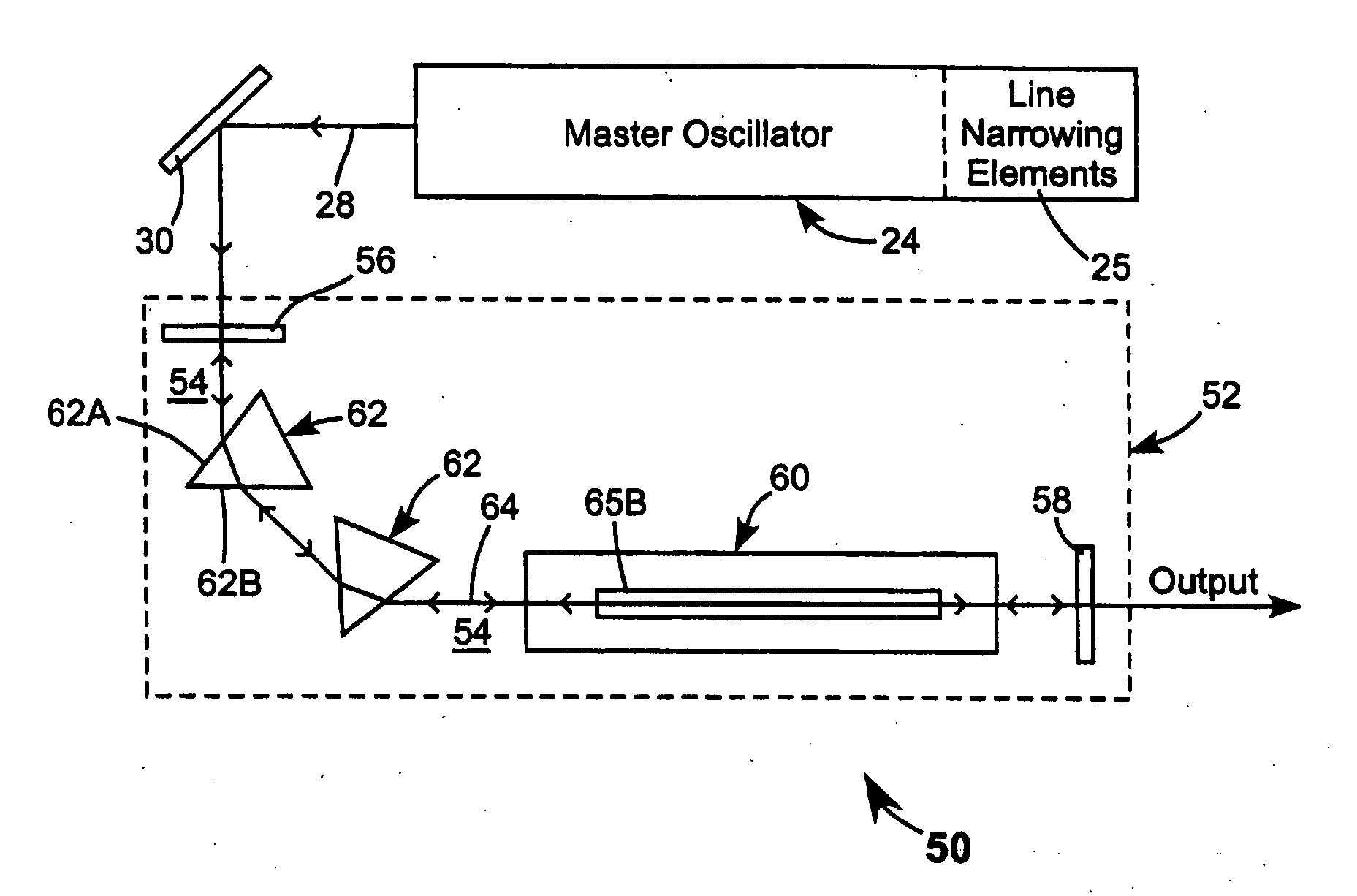
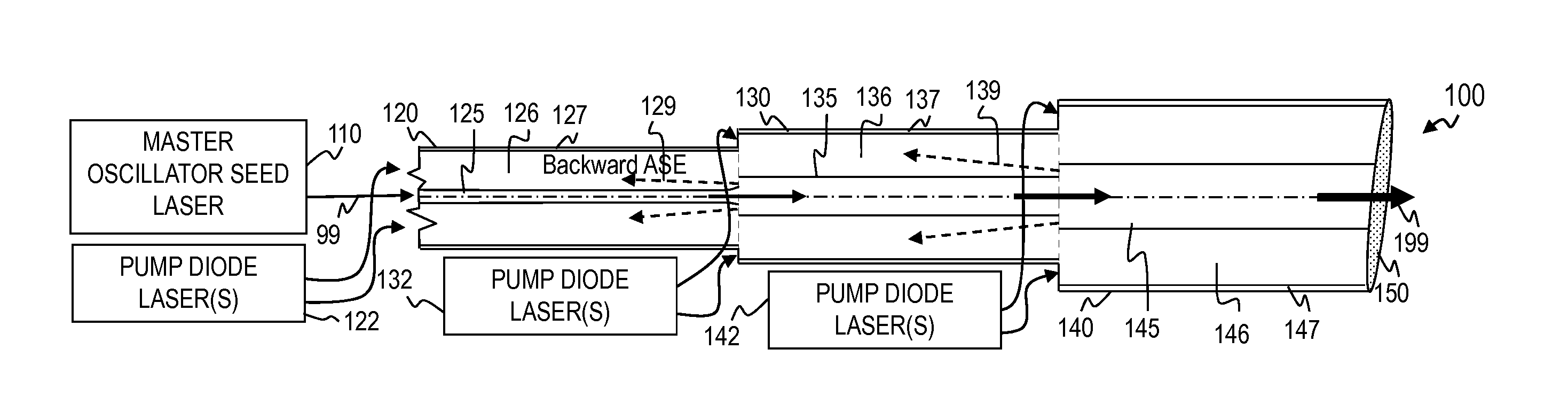
Bandwidth-limited and long pulse master oscillator power oscillator laser systems
InactiveUS20060007978A1Limited bandwidthAvoid short lengthOptical resonator shape and constructionActive medium materialMaster oscillatorLong pulse
Laser systems have a line-narrowed master oscillator and a power oscillator for amplifying the output of the master oscillator. The power oscillator includes optical arrangements for limiting the bandwidth of radiation that can be amplified. The limited amplification bandwidth of the power oscillator is relatively broad compared to that of the output of the master oscillator, but narrower than would be the case without the bandwidth limiting arrangements. The bandwidth narrowing arrangements of the power oscillator function primarily to restrict the bandwidth of amplified spontaneous emission generated by the power oscillator.
Owner:COHERENT GMBH
Parallel optical fiber amplifier with high power conversion
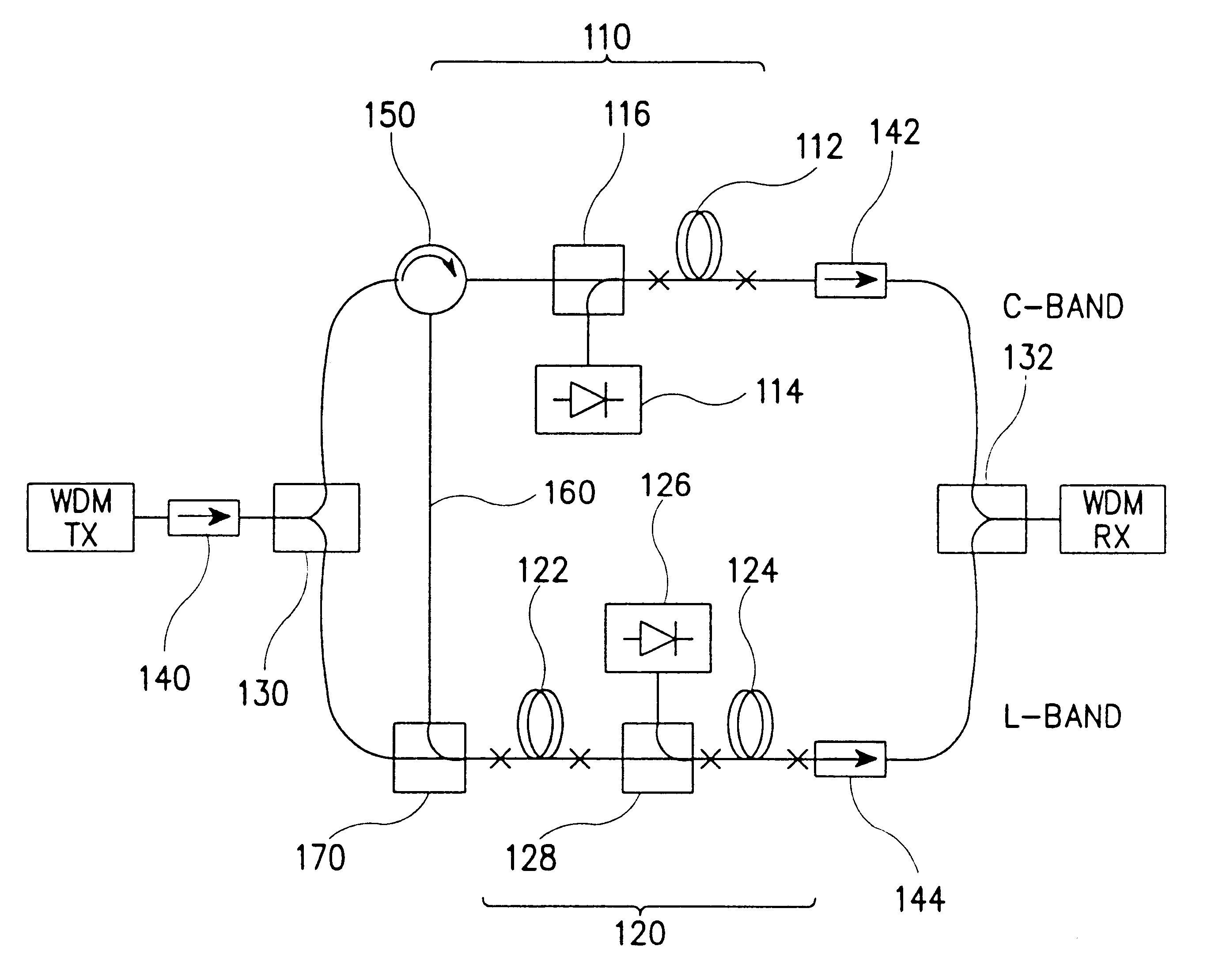
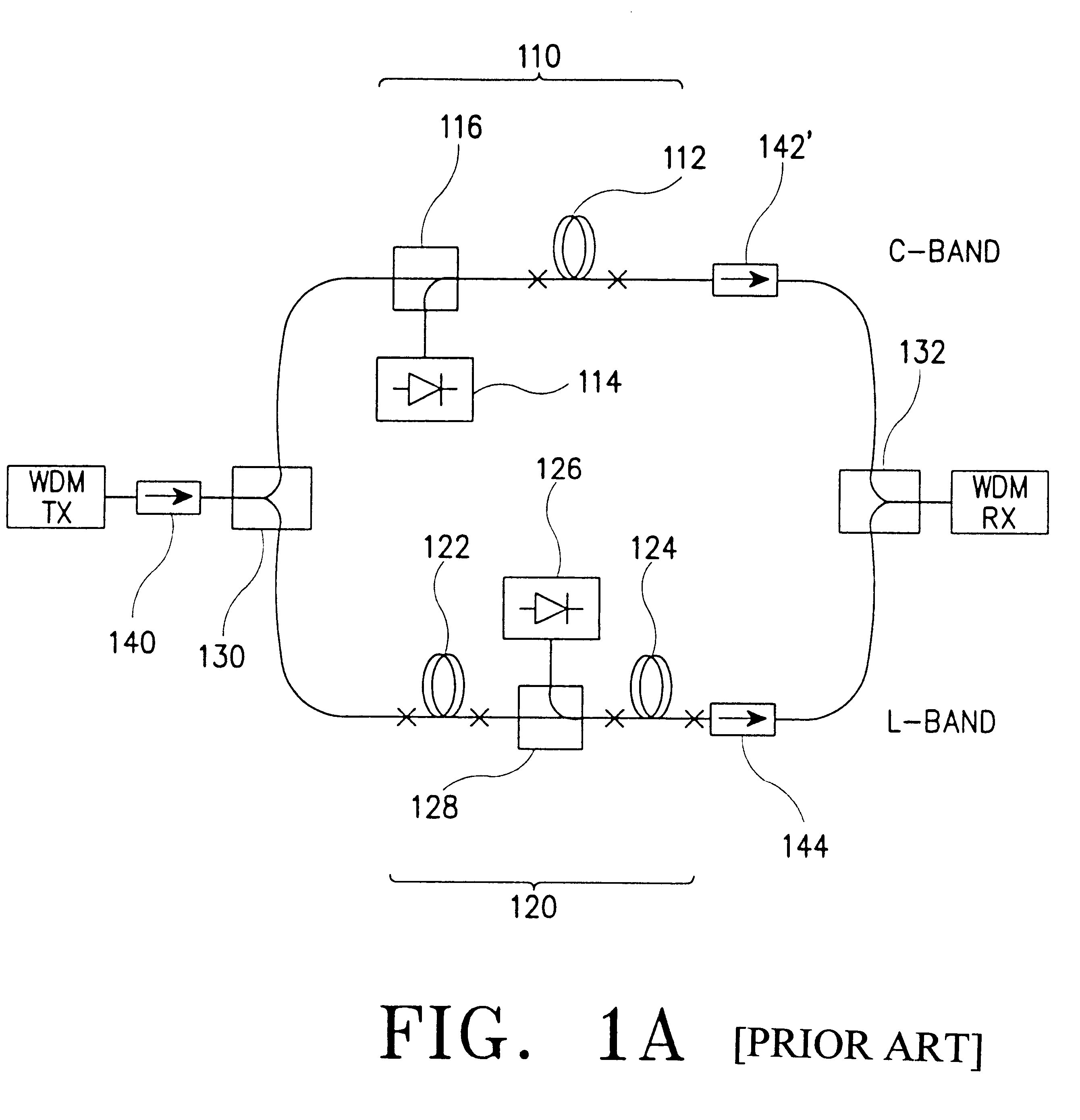
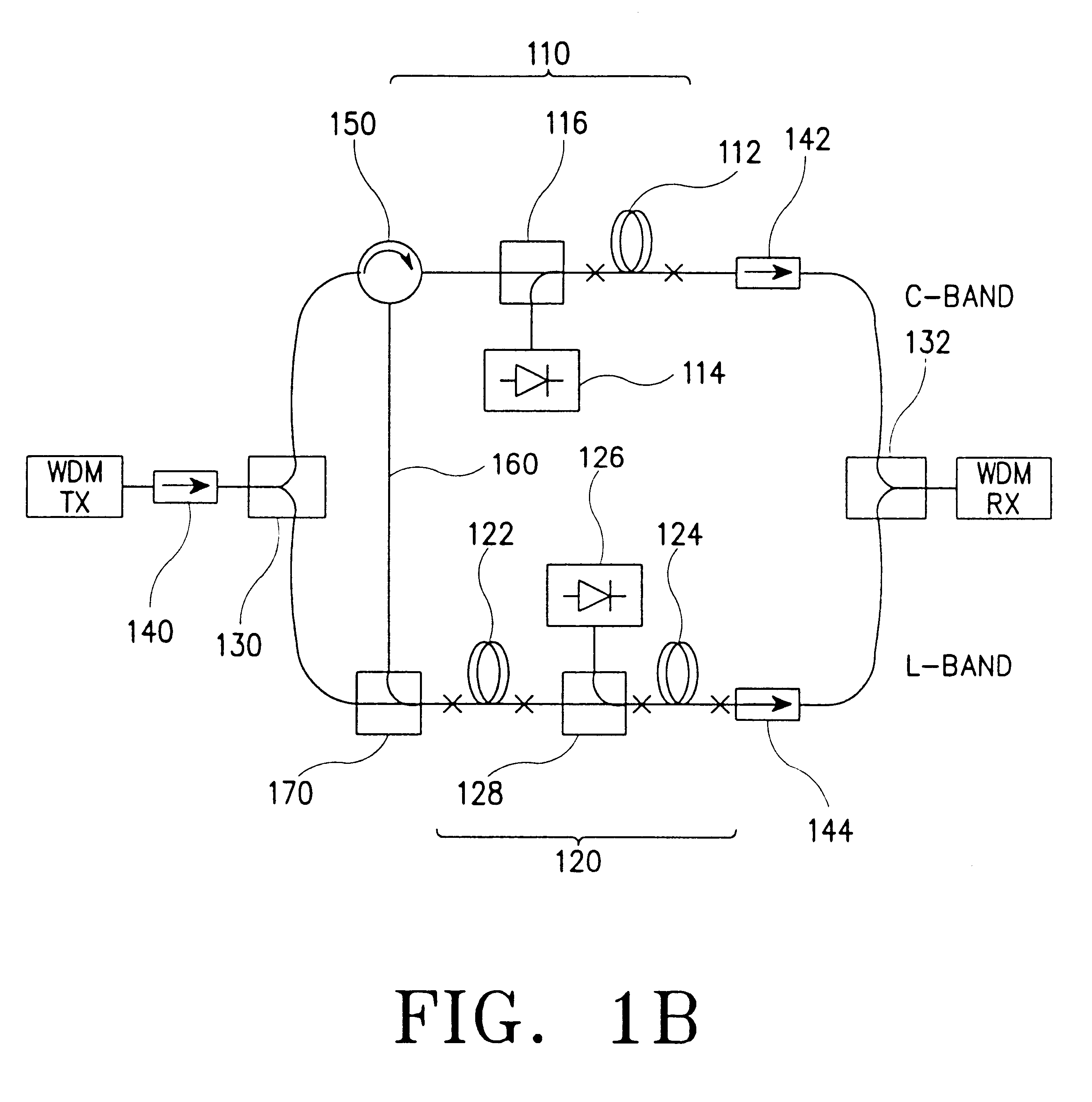
InactiveUS6317254B1Improve power conversion efficiencyCladded optical fibreExcitation process/apparatusOptical fiber amplifiersL band edfa
A parallel optical fiber amplifier having a configuration in which a C-band silica-based erbium-doped fiber amplifier (EDFA) stage and an L-band EDFA stage are coupled together in parallel in such a fashion that a reverse amplified spontaneous emission (ASE) light emitted from the C-band and / or L-band EDFA stage is reused as a secondary pumping source for an amplification in the L-band EDFA stage. In the optical fiber amplifier of the present invention, the reverse ASE light emitted from the C-band EDFA stage and the reverse ASE light emitted from the L-band EDFA stages supplied to the L-band EDFA stage so that they can be reused for improving the power conversion efficiency of the entire system and for reducing the noise factor thereof.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Unbalanced interferometer based fiber bragg grating (FBG) demodulation system and method
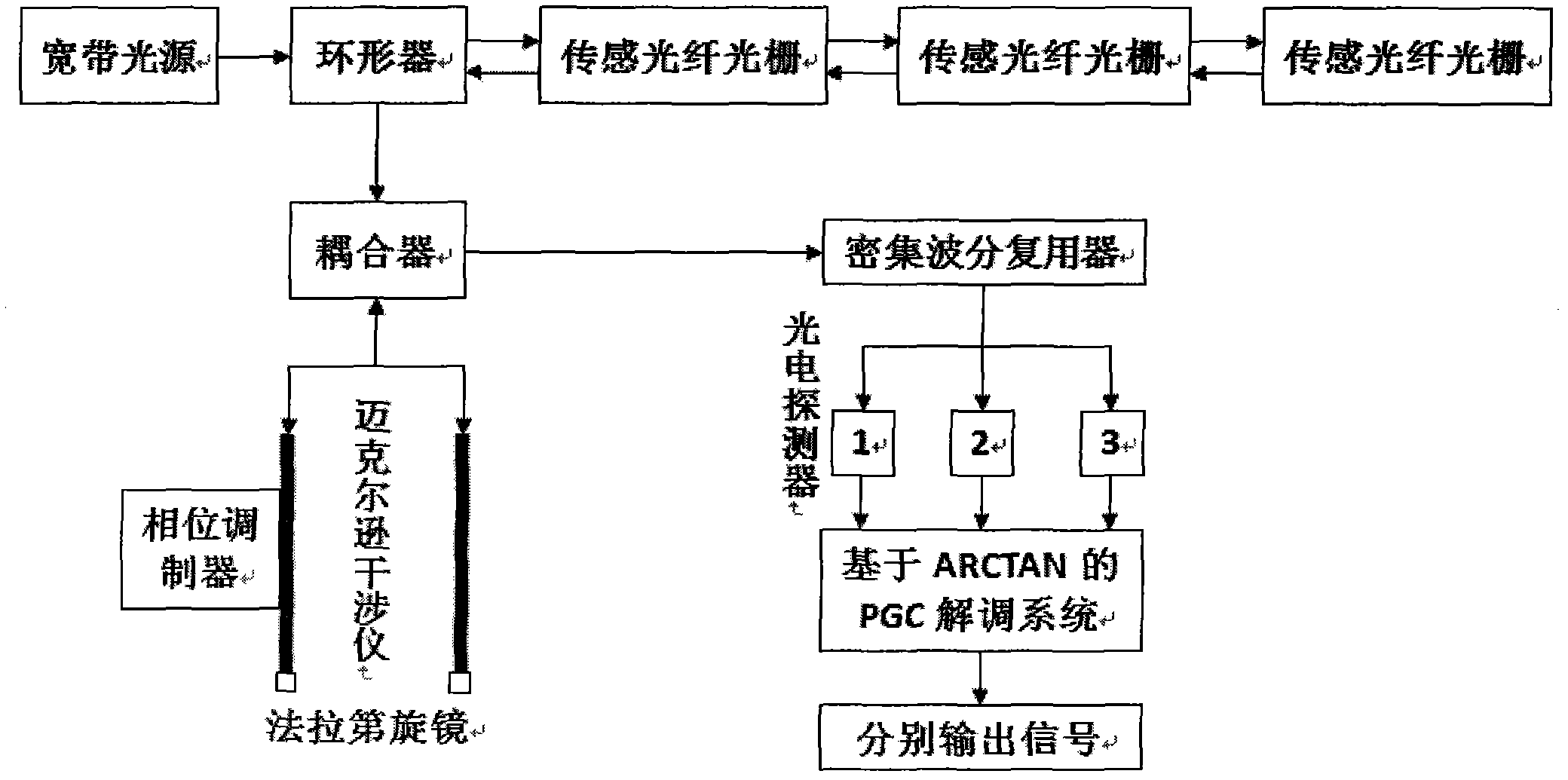
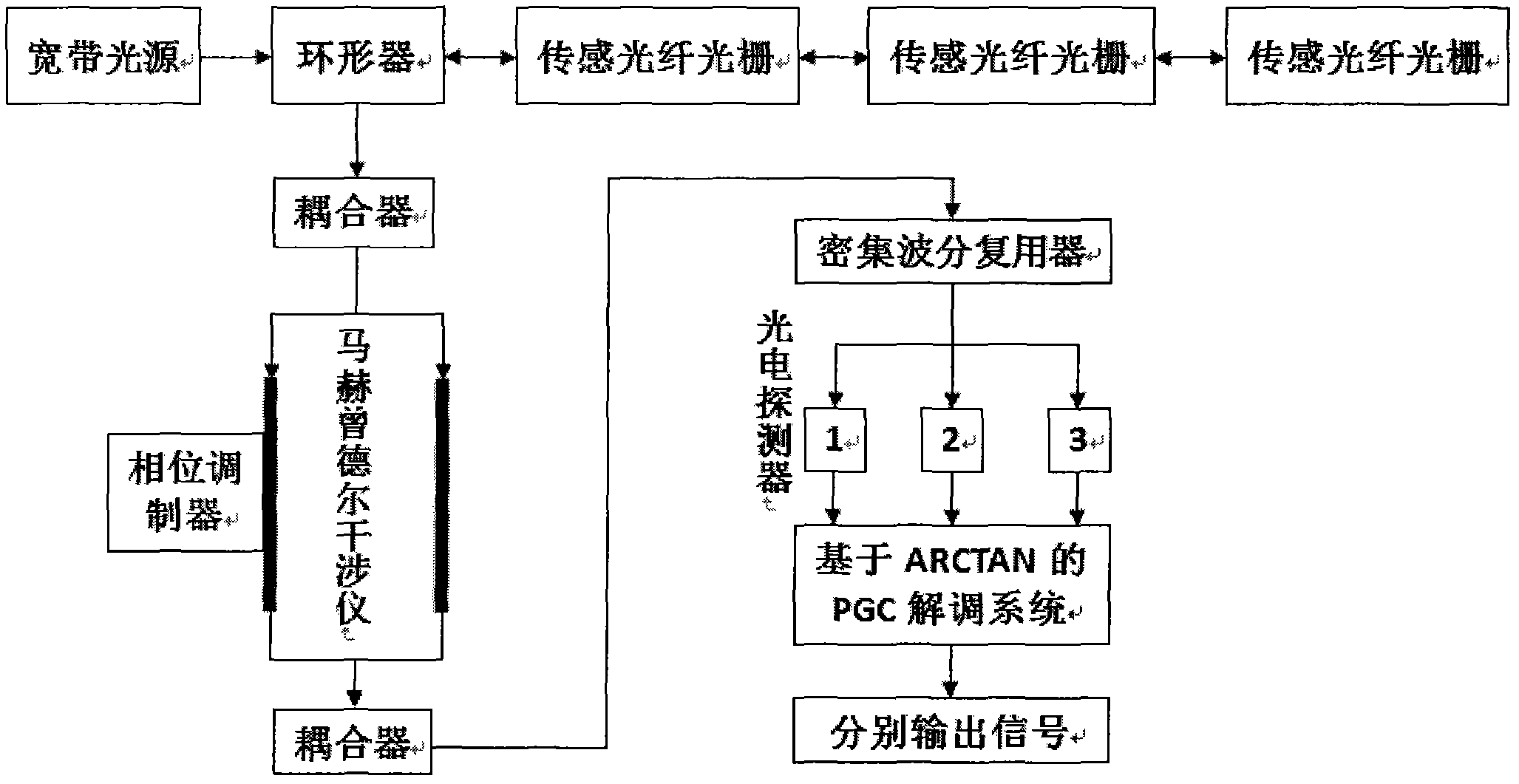
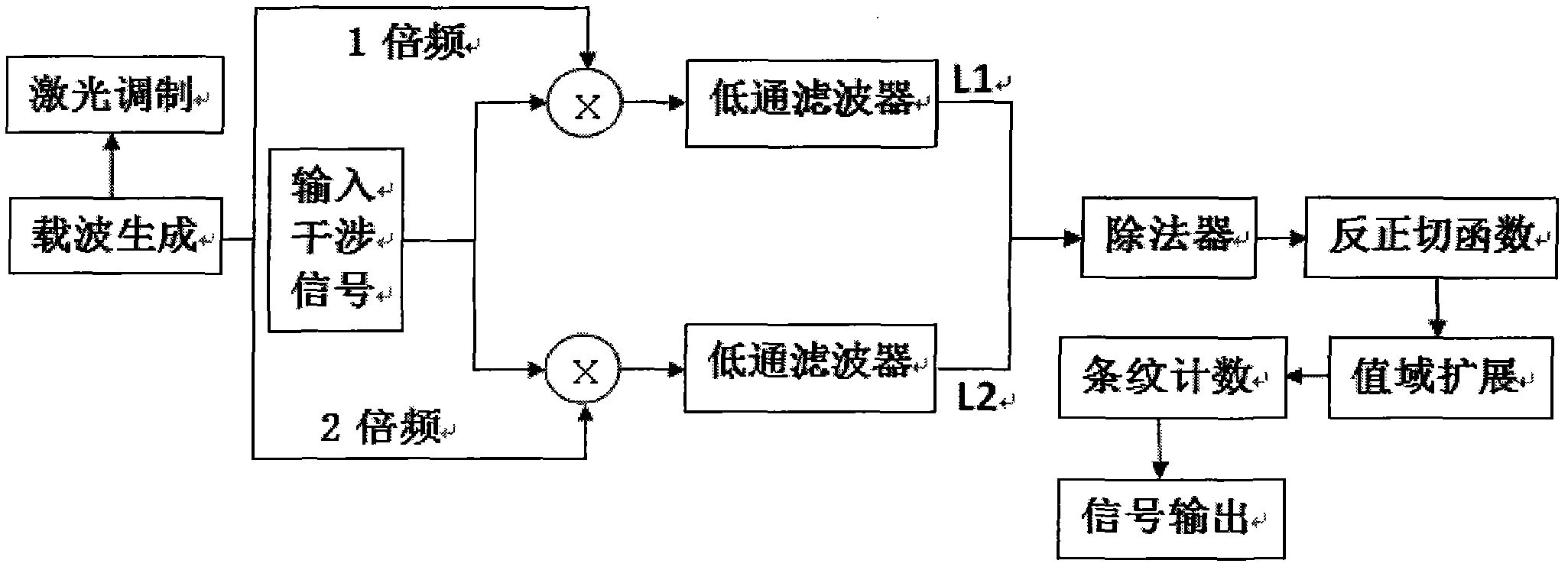
InactiveCN102147552AResponsiveHigh sensitivityLight demodulationConverting sensor output opticallyGratingAcousto-optics
The invention relates to an unbalanced interferometer based fiber bragg grating (FBG) demodulation system and method, belonging to the technical field of fiber optic sensing. The system sequentially passes through a superluminescent diode (SLD) or an amplified spontaneous emission (ASE) broadband light source, an optic isolator, a circulator or a coupler, and a fiber bragg grating and returns back to the circulator or the coupler, and then passes through the coupler, an unbalanced Michelson interferometer with two channels and a Faraday rotator mirror and returns back to an interferometer and the coupler or passes through a Mach-Zehnder interferometer with two channels and the coupler, wherein one channel of the interferometer is wound around a piezoelectric ceramic or an electrooptical modulator, and an acousto-optic modulator, finally passes through a dense wave division multiplexer and a photoelectric detector and is connected with an ARCTAN based PGC (Phase Generation Carrier) signal response demodulation module. The invention has the advantages; by adopting the combination of the an FBG sensor and ARCTAN-based PGC phase modulation, the system has high sensitivity, large dynamic range and good linearity, good response to an abrupt signal and easiness of multiplexing, low cost and easiness of implementing.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
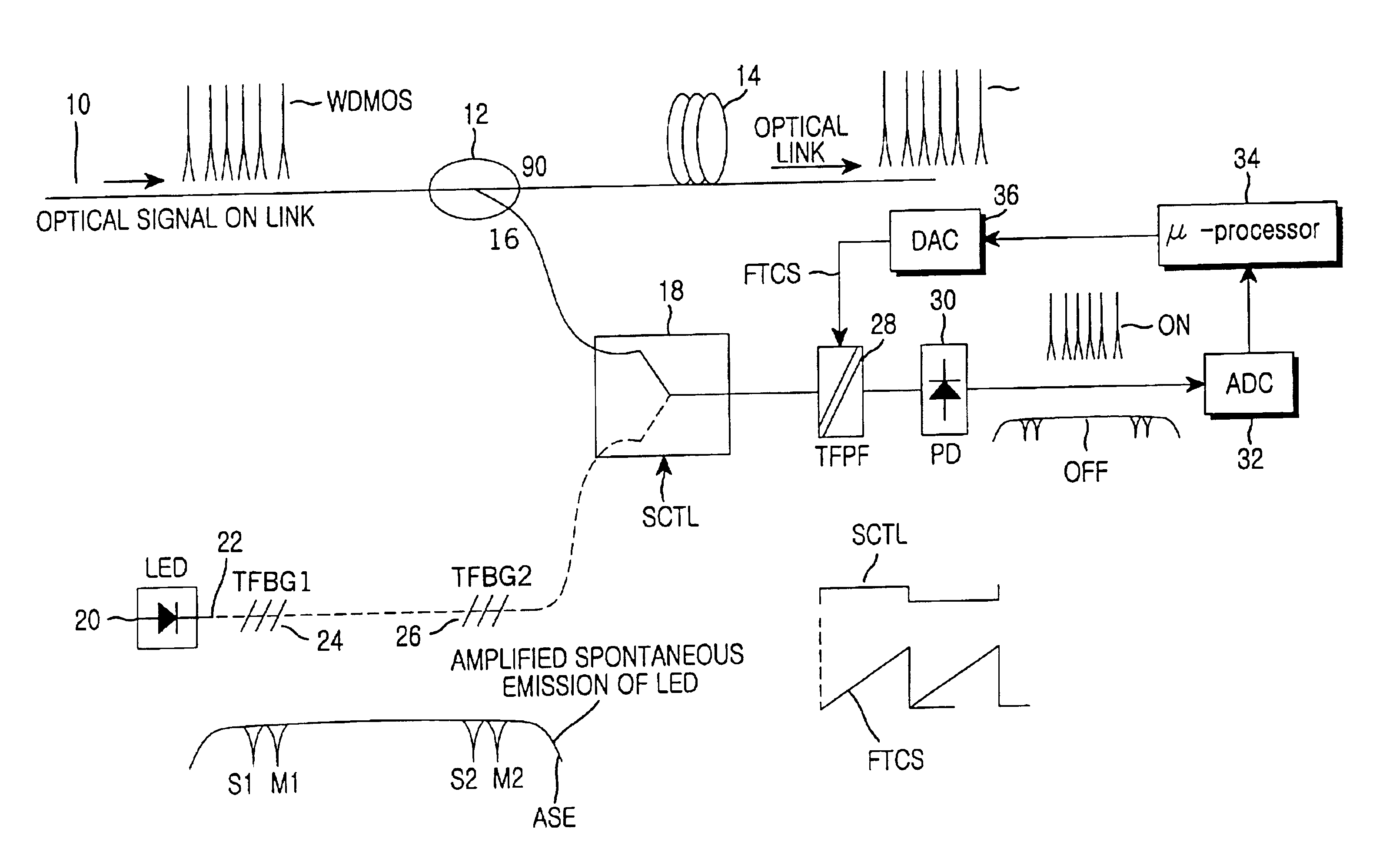
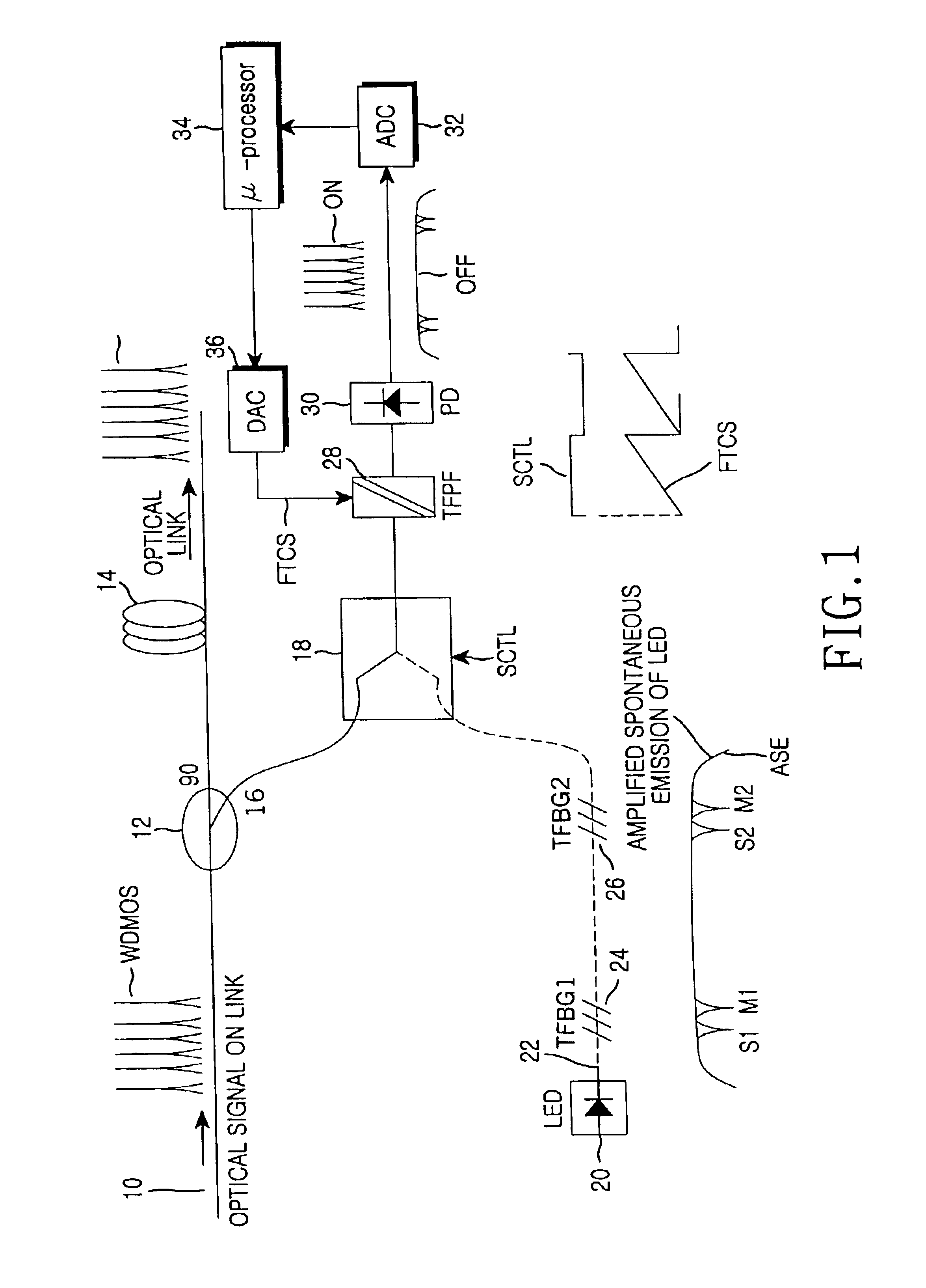
Method and apparatus for monitoring optical signal performance in wavelength division multiplexing system
InactiveUS6839131B2High resolutionMonitor performanceRadiation pyrometryMaterial analysis by optical meansFiberControl signal
An apparatus for monitoring a wavelength division multiplexed optical signal transmitted onto a main optical path includes: an amplified spontaneous light emitter for generating an amplified spontaneous emission signal and transmitting the same to onto a reference optical path; at least one fiber bragg grating for sending out an amplified spontaneous emission signal having a reference wavelength by reflecting or absorbing only that part of the amplified spontaneous emission signal which consists of a reflection wavelength or an absorbance wavelength; an optical switch for outputting at least one of the wavelength division multiplexed optical signals branched from the main optical path or one of the amplified spontaneous emissions including the reference wavelengths in response to a switching control signal input; a tunable optical filter for filtering the optical signal outputted from the optical switch using varied filter characteristics, and for outputting the filtered optical signal; and a control unit for measuring an optical wavelength, an optical power and an optical signal to noise ratio of the wavelength division multiplexed optical signal based on the analyzed reference wavelength.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Monolithic semiconductor light source with spectral controllability
InactiveUS20050201675A1Induce Raman amplification of optical signalIncrease powerCoupling light guidesActive medium shape and constructionBroadbandAmplified spontaneous emission
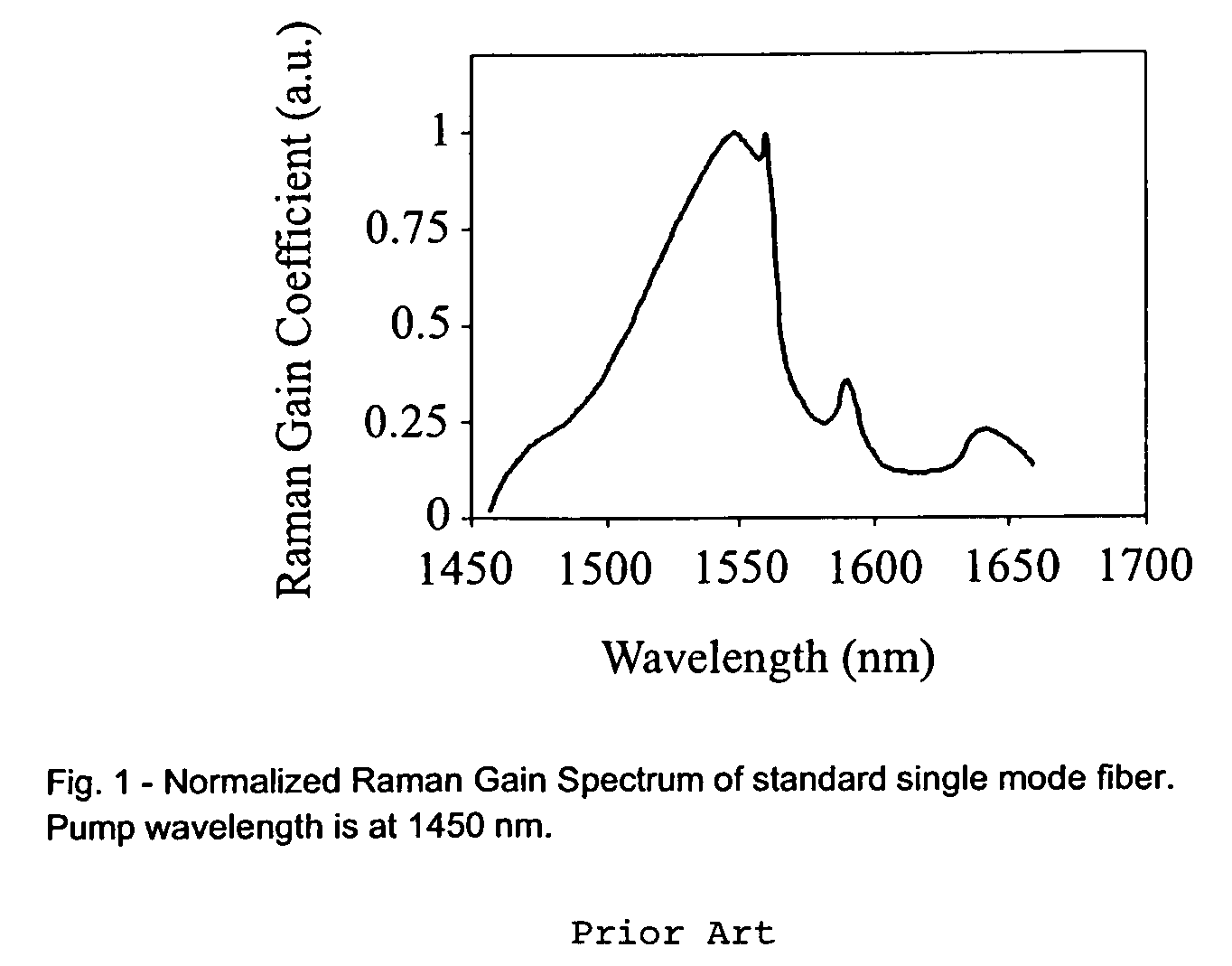
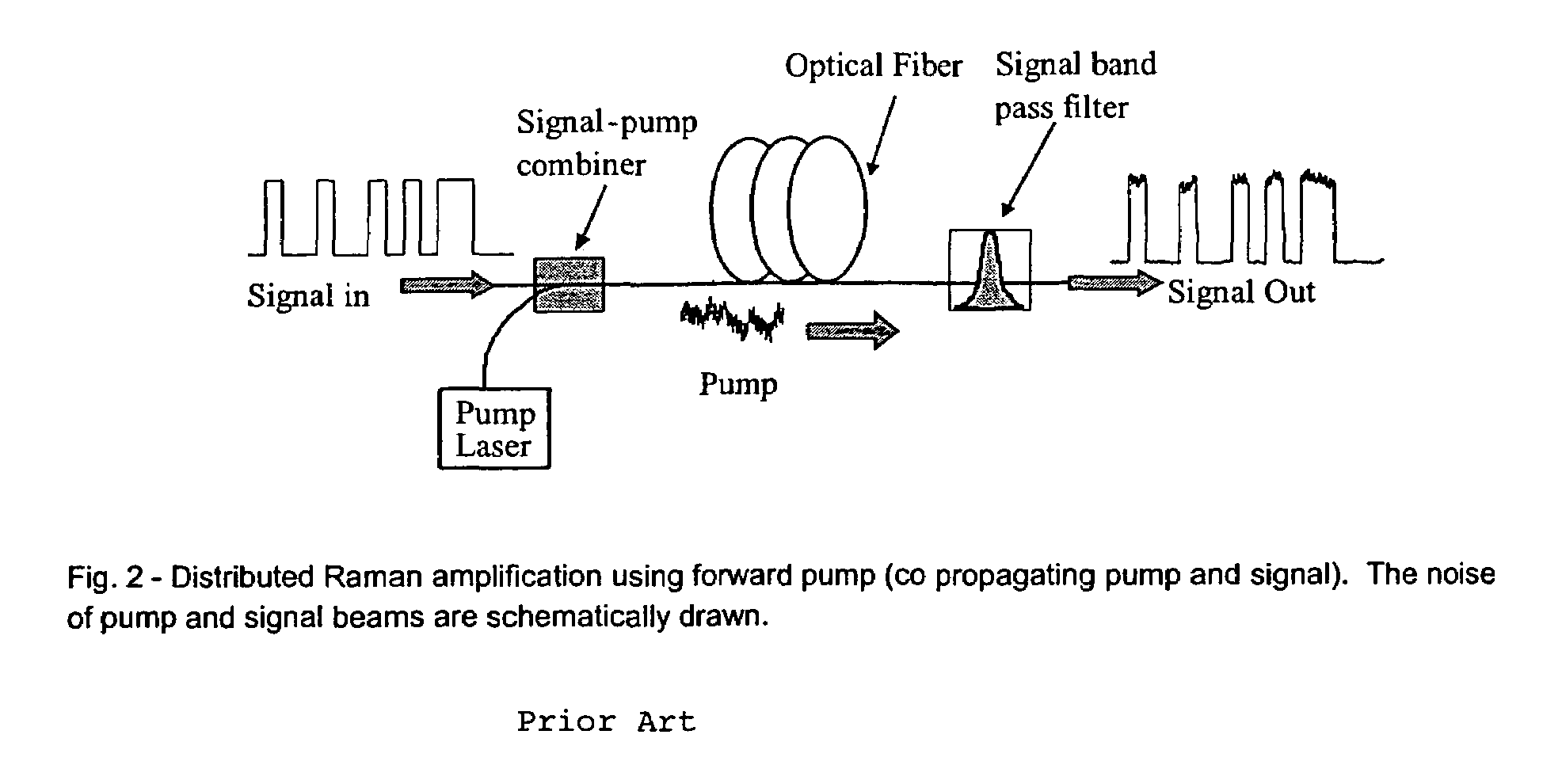
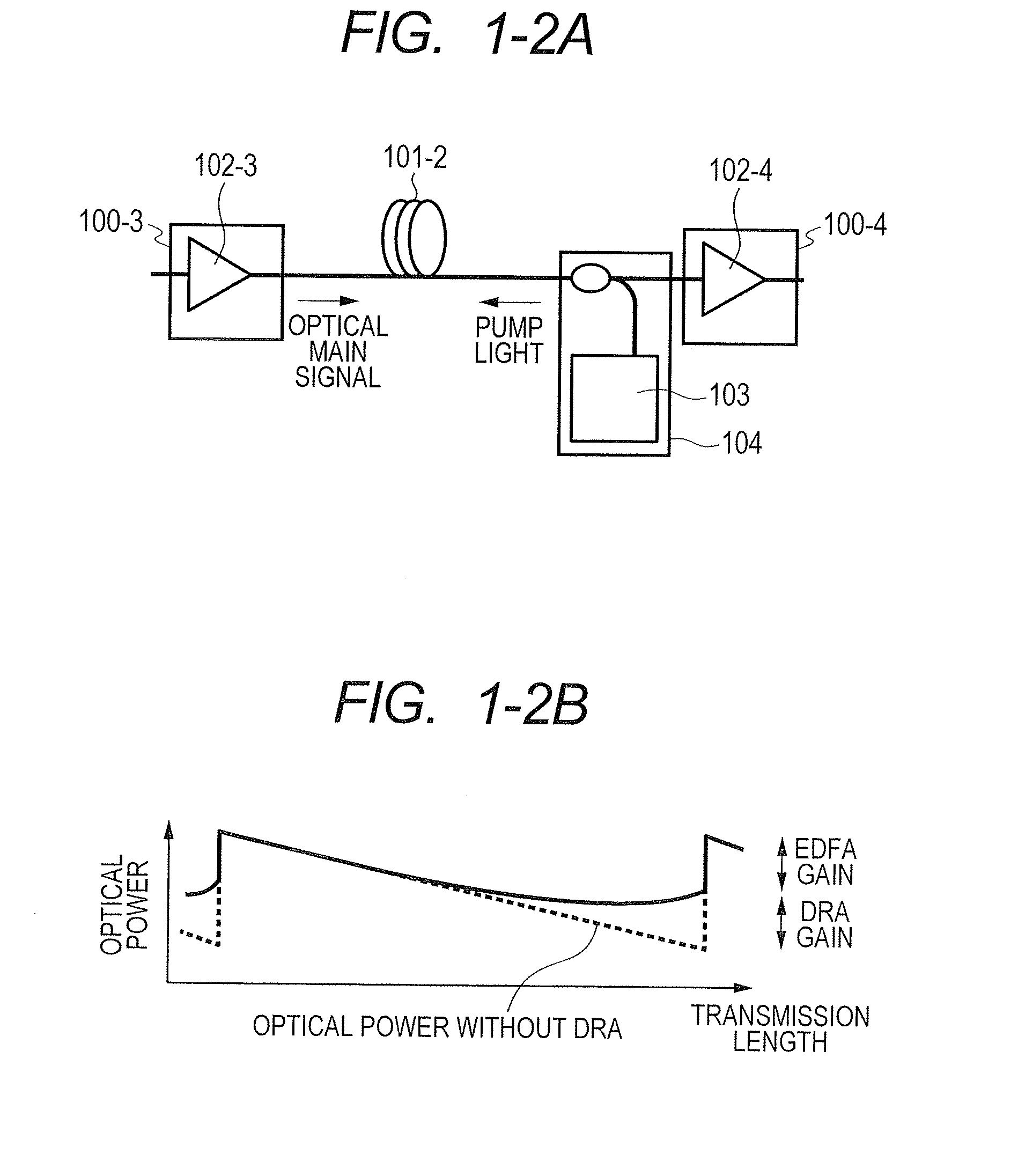
The invention is in the field of distributed Raman amplification for digital and analog transmission applications and other applications, e.g., instrumentation and imaging applications, including HFC-CATV applications. In particular, the invention uses a high power broadband source of amplified spontaneous emission (ASE) as the Raman pump source for improved system performance. The invention also includes methods for constructing such a high-power broadband Raman pump.
Owner:AHURA CORP
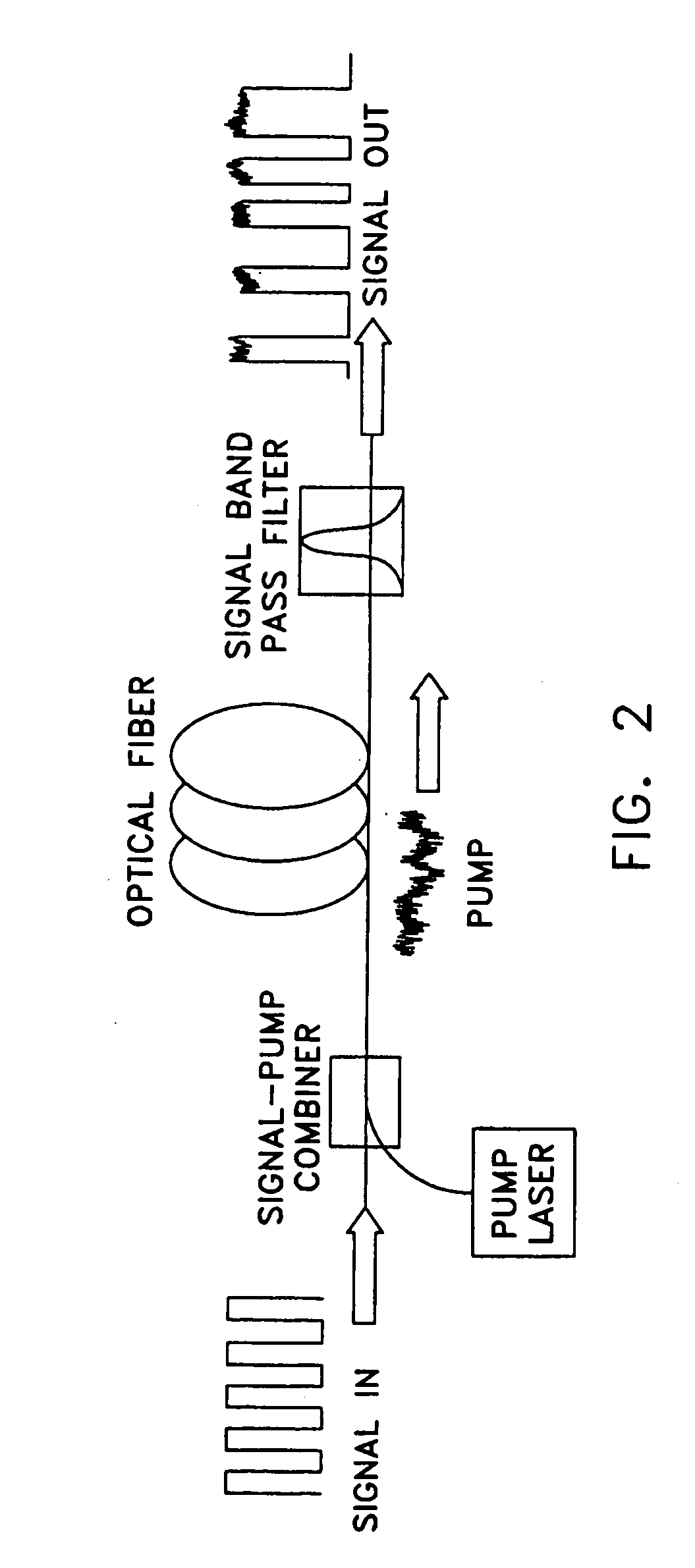
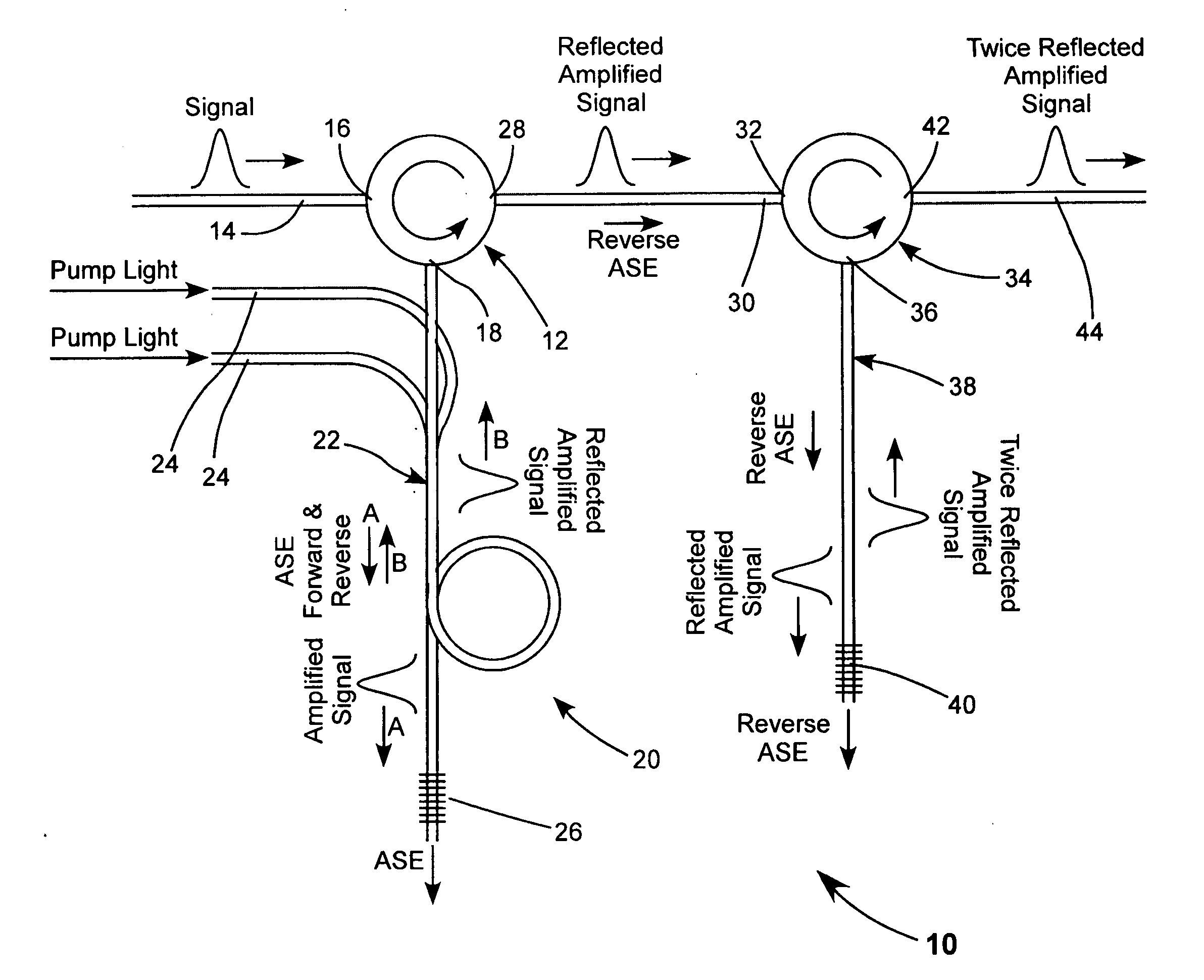
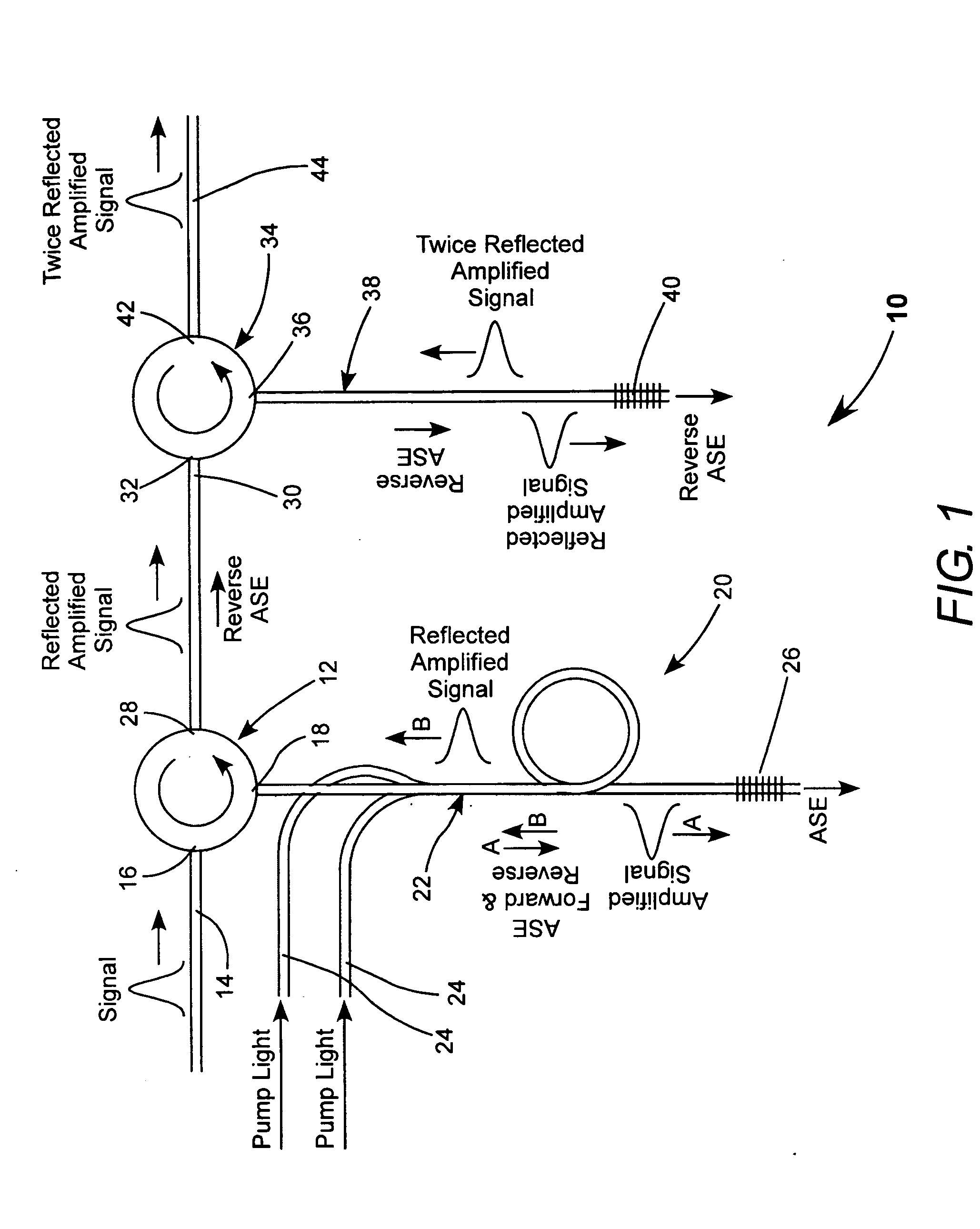
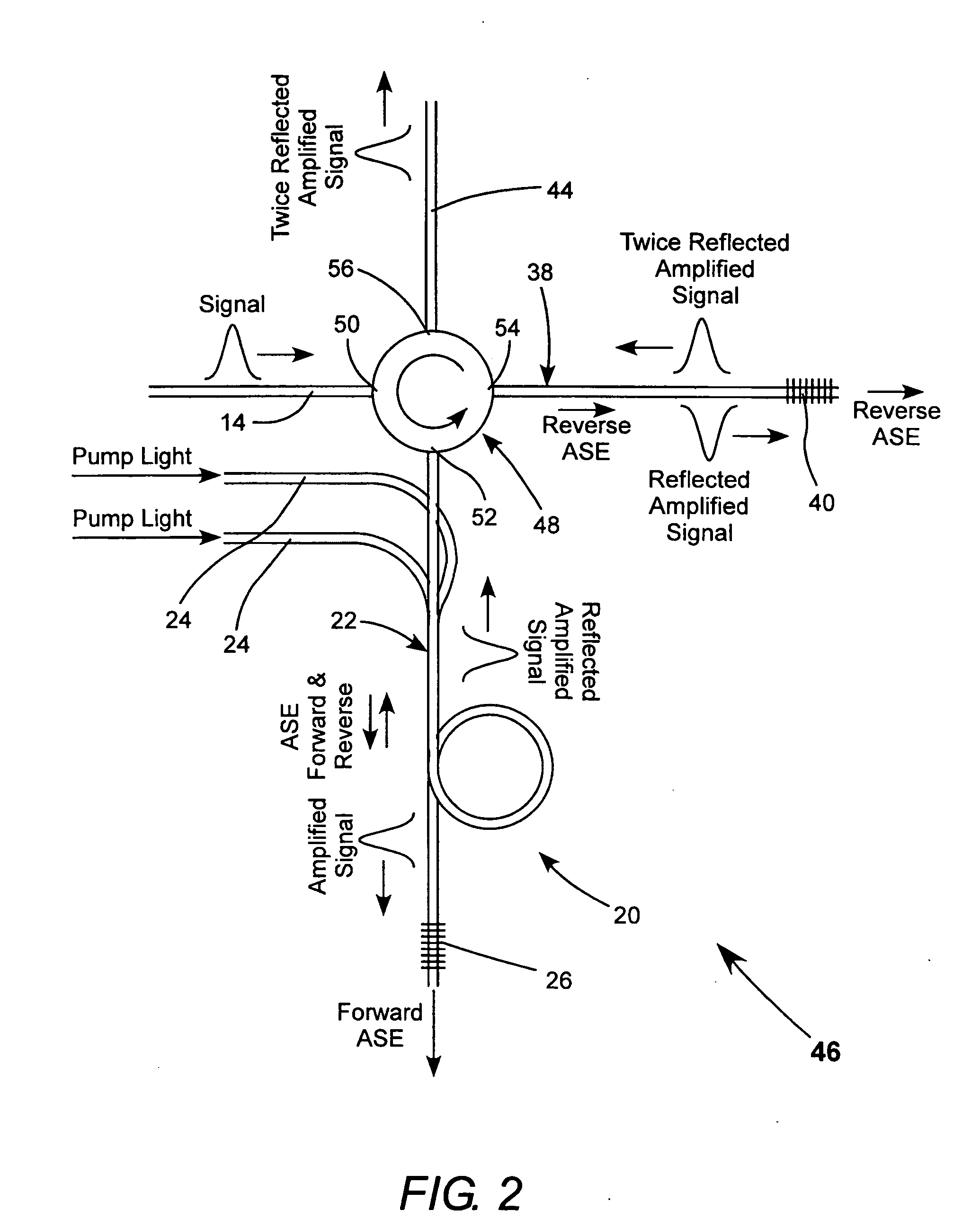
Fiber amplifier with suppression of amplified spontaneous emission
A fiber amplifier module for amplifying a signal pulse includes an optically pumped double-pass fiber amplifier in which a fiber Bragg grating reflects an amplified pulse in between the first and second amplification passes, and transmits most forward-propagating amplified spontaneous emission (ASE) generated by the optical pumping. The reflected amplified pulse from the double-pass amplifier, and reverse-propagating ASE generated by the optical pumping are reflected from another fiber Bragg grating that again reflects the amplified pulse and transmits most of the ASE. The twice-reflected amplified pulse can be delivered from the amplifier as an output pulse or passed to another amplifier module for further amplification. The amplifier fiber is operated in a saturated or near saturated mode. This reduces amplification of any portion of the forward-propagating ASE that is reflected into reverse propagation by the fiber Bragg grating of the double-pass amplifier.
Owner:COHERENT INC
Semiconductor-type processing for solid-state lasers
InactiveUS20050195726A1Improve performanceImproved profileLaser detailsRadiation applicationsAudio power amplifierEngineering
The present invention includes a method of fabricating an optically-pumped disk-array solid-state laser amplifier having one or more disks, wherein one or more of the one or more disks having two opposed surfaces, including the steps of patterning a photoresist mask on one or more of the two opposed surfaces of the one or more disks and processing the one or more disks through the patterned photoresist mask, whereby the temperature profile improved radially across the disk's surface, amplified spontaneous emission are reduced, or combinations thereof.
Owner:COHERENT INC
Active Optical Fibers With Wavelength-Selective Filtering Mechanism, Method of Production and Their Use
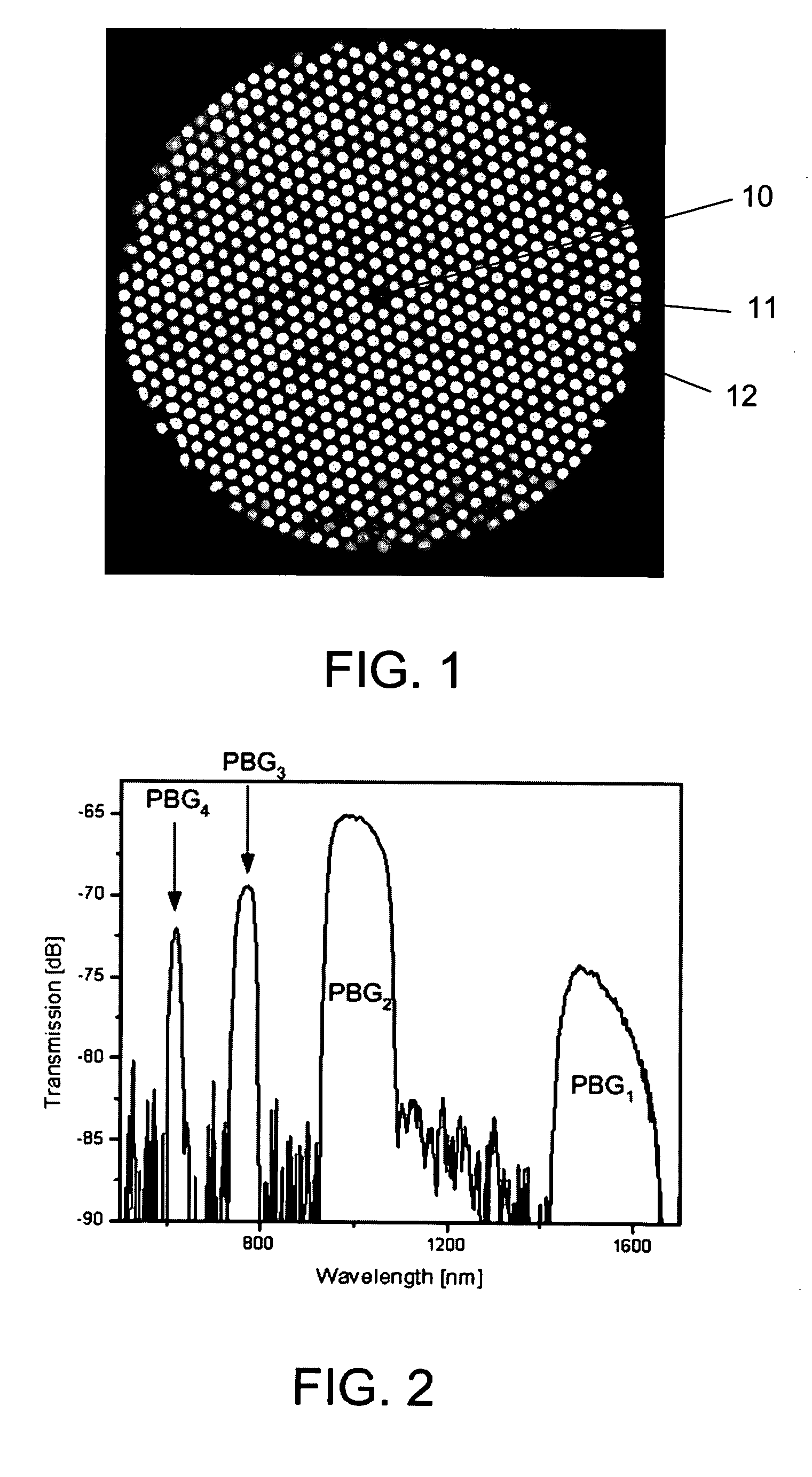
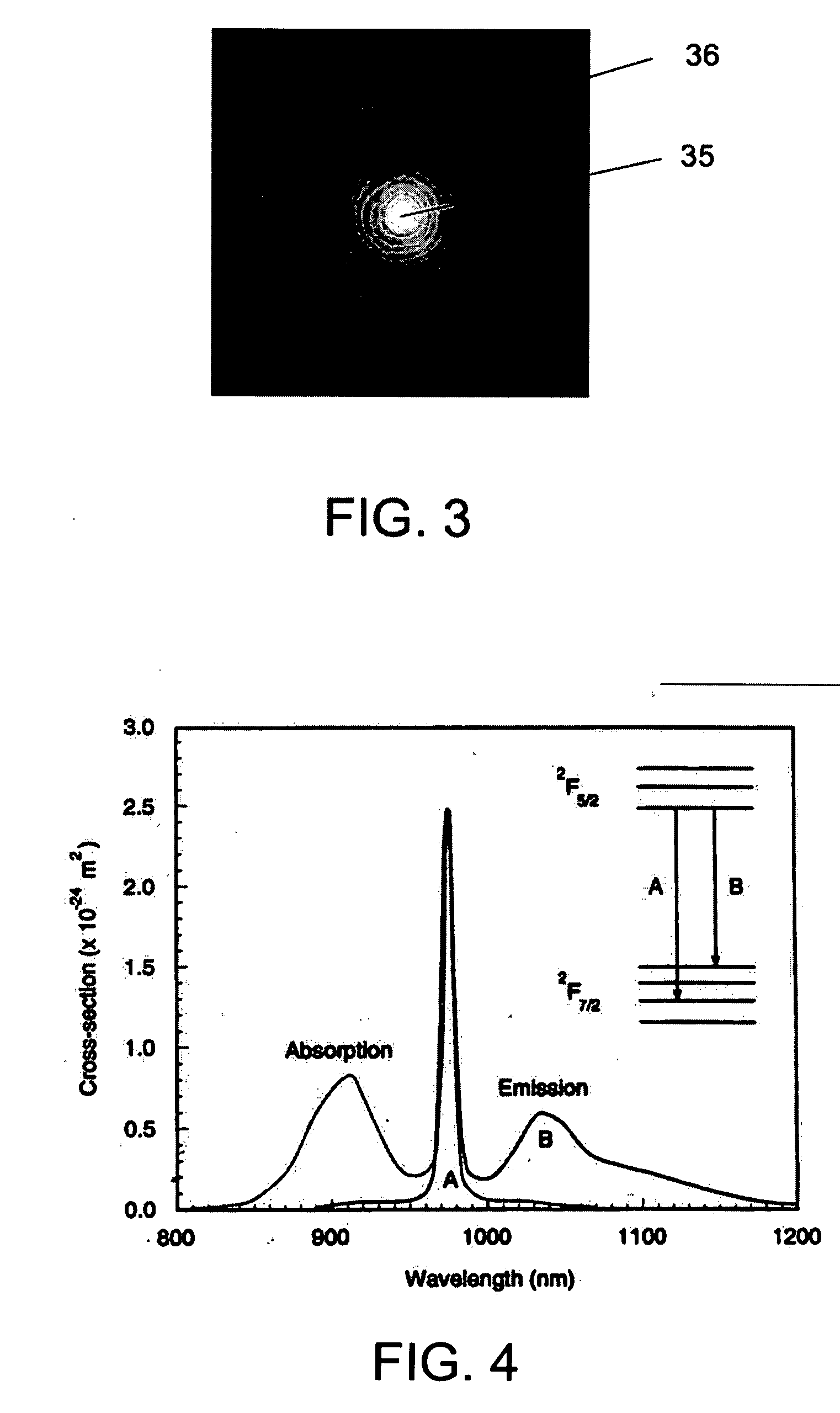
ActiveUS20090168149A1Efficient amplificationEnhanced spontaneous emissionOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingFibre transmissionPhotonic bandgapPhotonics
The invention relates to optical fibers for use in optical amplification of light, such as in optical fiber amplifiers and lasers and for use in delivery of high power light, in particular to a scheme for reducing amplified spontaneous emission at undesired wavelengths. The invention further relates to articles, methods and use. An object of the invention is achieved by a micro-structured optical fiber, which is adapted to guide light by the photonic bandgap effect and to have one or more pass bands and at least one stop-band over a wavelength range from λstop1 to λstop2. In an aspect of the invention, the at least one stop-band provides filter functions that suppress nonlinear effects. In another aspect, the core region is actively doped, and the active material has an emission spectrum with a higher value of the emission cross section σE at a wavelength λASE between λstop1 and λstop2 than outside said wavelength range such that amplified spontaneous emission and lasing within the wavelength range from λstop1 to λstop2 is reduced. In still another aspect, the optical fiber exhibits photonic bandgaps at different wavelength ranges in different radial directions of a cross section of the optical fiber.
Owner:NKT PHOTONICS
Monolithic semiconductor light source with spectral controllability
InactiveUS7190861B2Coupling light guidesElectromagnetic transmissionBroadbandAmplified spontaneous emission
The invention is in the field of distributed Raman amplification for digital and analog transmission applications and other applications, e.g., instrumentation and imaging applications, including HFC-CATV applications. In particular, the invention uses a high power broadband source of amplified spontaneous emission (ASE) as the Raman pump source for improved system performance. The invention also includes methods for constructing such a high-power broadband Raman pump.
Owner:AHURA CORP
System for amplifying optical signals
InactiveUS7215836B2Laser using scattering effectsLaser optical resonator constructionBroadbandAmplified spontaneous emission
The invention is in the field of distributed Raman amplification for digital and analog transmission applications and other applications, e.g., instrumentation and imaging applications, including HFC-CATV applications. In particular, the invention uses a high power broadband source of amplified spontaneous emission (ASE) as the Raman pump source for improved system performance. The invention also includes methods for constructing such a high-power broadband Raman pump.
Owner:AHURA CORP
Gain media edge treatment to suppress amplified spontaneous emission in a high power laser
InactiveUS20050254536A1Minimizing thermally induced stressSuppress parasitic oscillationActive medium materialActive medium shape and constructionElastomerHigh power lasers
A novel method and apparatus for suppressing ASE and parasitic oscillation modes in a high average power laser is introduced. By roughening one or more peripheral edges of a solid-state crystal or ceramic laser gain media and by bonding such edges using a substantially high index bonding elastomer or epoxy to a predetermined electromagnetic absorbing arranged adjacent to the entire outer surface of the peripheral edges of the roughened laser gain media, ASE and parasitic oscillation modes can be effectively suppressed.
Owner:LAWRENCE LIVERMORE NAT SECURITY LLC
Noise figure measurement of optical amplifiers by power substitution
InactiveUS6226117B1Limited resolution bandwidthOpen spaceMaterial analysis by optical meansOptical resonator shape and constructionEngineeringAmplified spontaneous emission
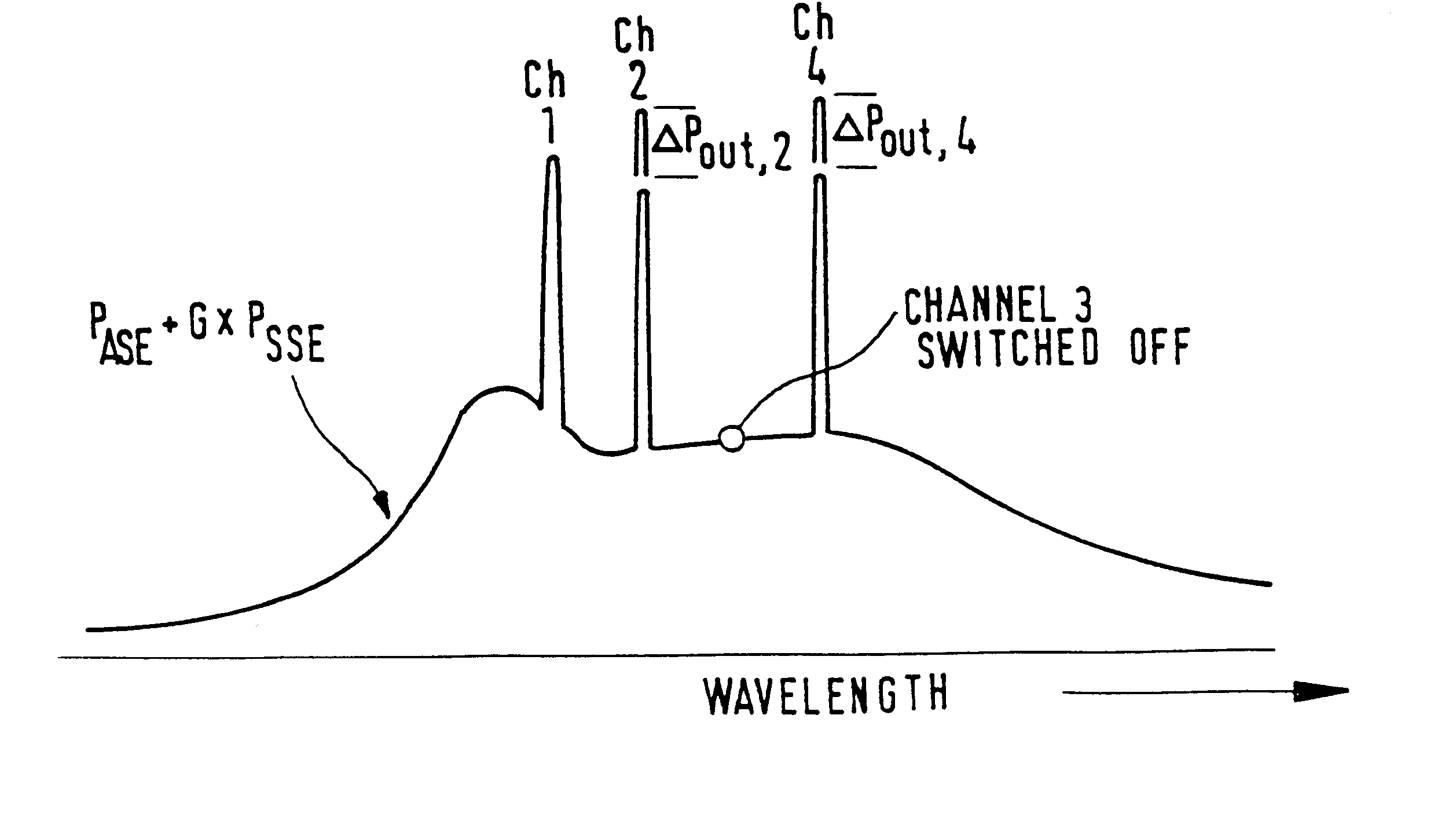
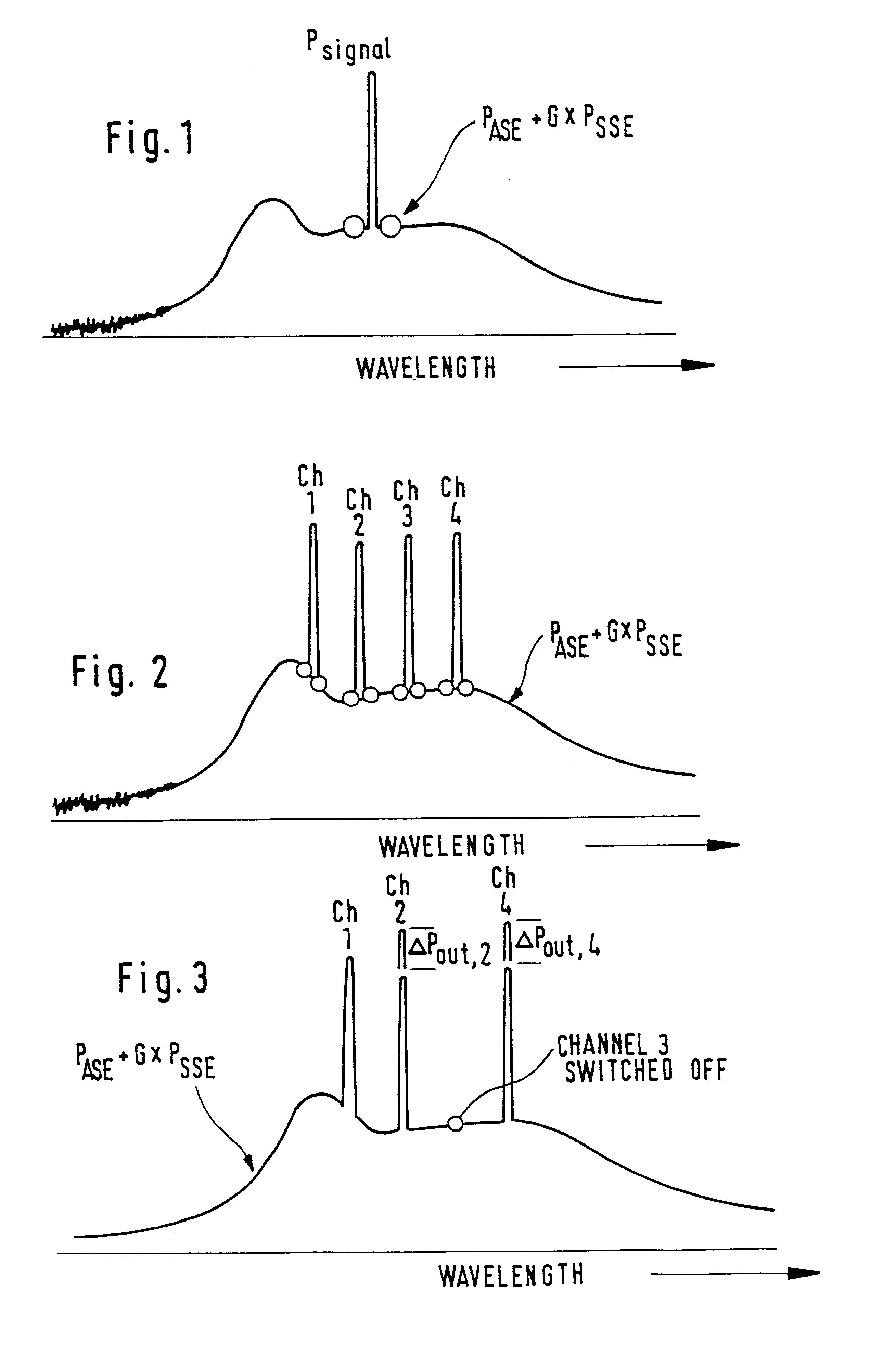
Described is a noise figure measurement for optical amplifiers by disabling a signal of a channel before the measurement of the amplified spontaneous emission for that channel and by distributing a power equivalent which is substantially equal to the power of the signal of the disabled channel, at at least one other wavelength. The noise figure measurement can be used as well in multi-channel applications such as WDM, as in a single channel operation.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
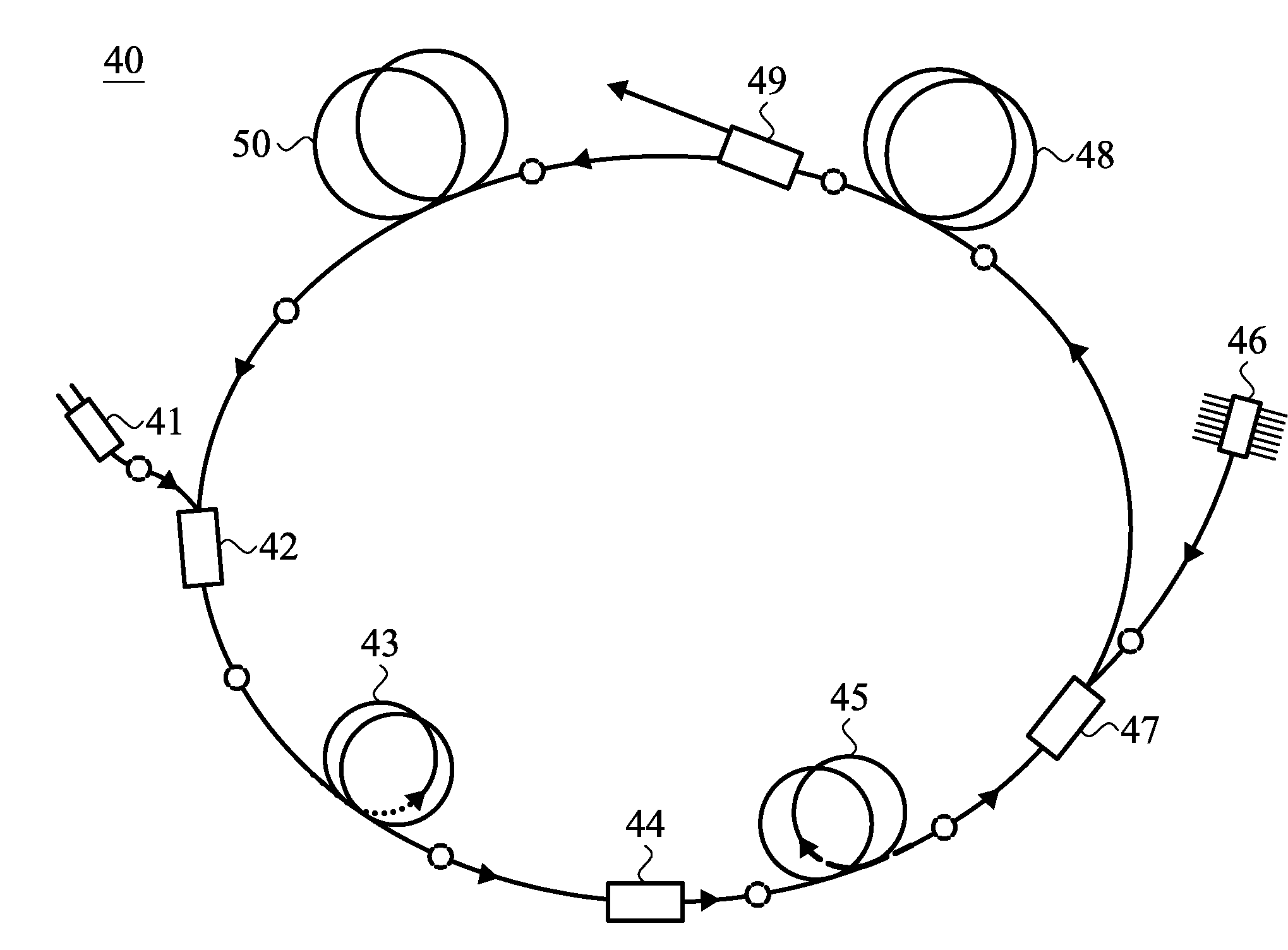
Ring or linear cavity of all-fiber-based ultra short pulse laser system and method of operating the same
InactiveUS20110158265A1Shorten the maintenance periodLaser using scattering effectsExcitation process/apparatusFiberMode-locking
A ring-cavity or linear-cavity all-fiber-based ultra short pulse laser system and method of operating the same are provided. The all-fiber-based ultra short pulse laser system includes a pulse pump light source, a gain fiber, a first fiber signal pump combining unit, a broadband optical isolator, a fiber saturable absorber, an assistant light source, a second fiber signal pump combining unit, and a light coupling output. The first fiber signal pump combining unit is respectively connected to the pulse pump light source and the gain fiber to emit broadband amplified spontaneous emission, then the broadband amplified spontaneous emission passes through the broadband optical isolator. The second fiber signal pump combining unit is respectively connected to the assistant light source and the fiber saturable absorber. An ASE signal actively provides passive mode locking of the cavity, and the light coupling output partially outputs the laser. A dispersion fiber controls the temporal width.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Apparatus and method for optical gain fiber having segments of differing core sizes
ActiveUS8089689B1Easy extractionReduce the amount requiredLaser using scattering effectsFibre transmissionFiberBandpass filtering
Apparatus and method for amplifying laser signals using segments of fibers of differing core diameters and / or differing cladding diameters to suppress amplified spontaneous emission and non-linear effects such as four-wave mixing (FWM), self-phase modulation, and stimulated Brillouin and / or Raman scattering (SBS / SRS). In some embodiments, different core sizes have different sideband spacings (spacing between the desired signal and wavelength-shifted lobes). Changing core sizes and providing phase mismatches prevent buildup of non-linear effects. Some embodiments further include a bandpass filter to remove signal other than the desired signal wavelength and / or a time gate to remove signal at times other than during the desired signal pulse. Some embodiments include photonic-crystal structures to define the core for the signal and / or the inner cladding for the pump. Some embodiments include an inner glass cladding to confine the signal in the core and an outer glass cladding to confine pump light in the inner cladding.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN ACULIGHT CORP
Standoff detection using coherent backscattered spectroscopy
InactiveUS20080258071A1Emission spectroscopyMaterial analysis by optical meansGas phaseDecomposition
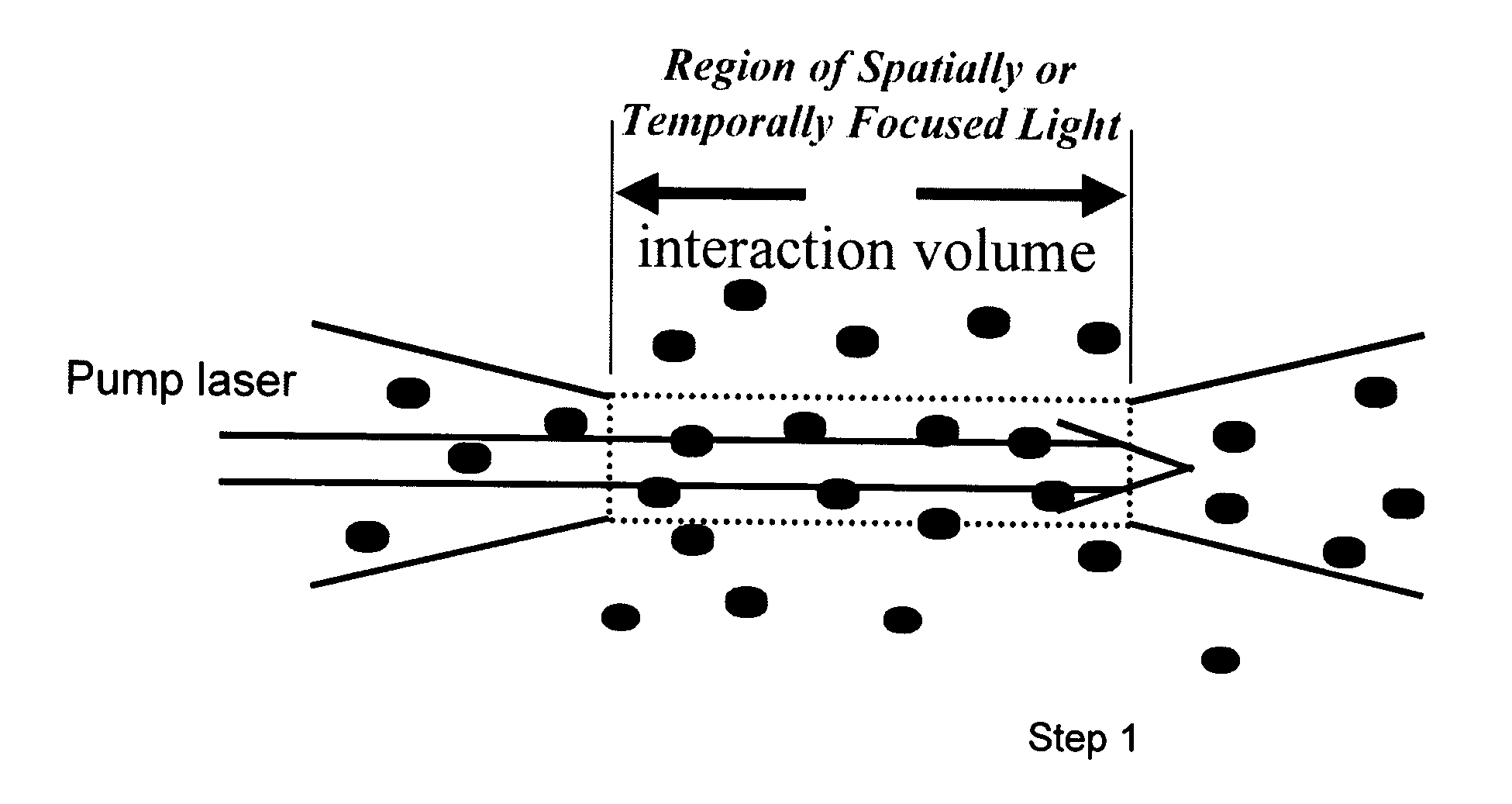
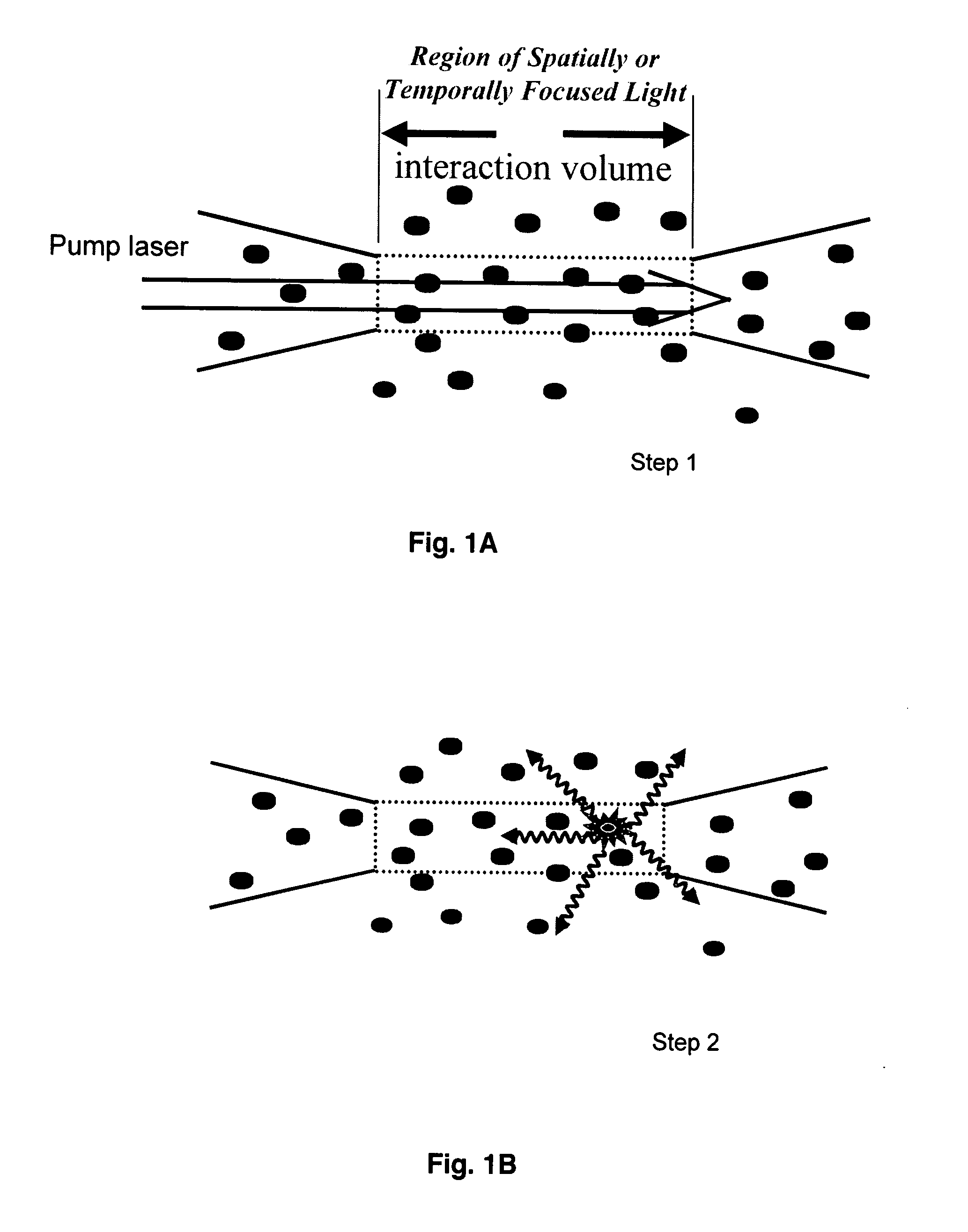
Provided herein are methods for detecting vapor-phase materials and / or photofragments thereof including energetic materials and decomposition products thereof, molecules or analytes at a stand-off distance. The methods provide for the stimulation of the ground state vapor phase to an excited state using a high fluence temporally and spatially focused ultraviolet laser pulse. The detection of back-scattered amplified spontaneous emission from the excited state vapor-phase material indicates the presence of the vapor phase materials.
Owner:ARNOLD BRADLEY R +3
Optical communication module and optical fiber communication system
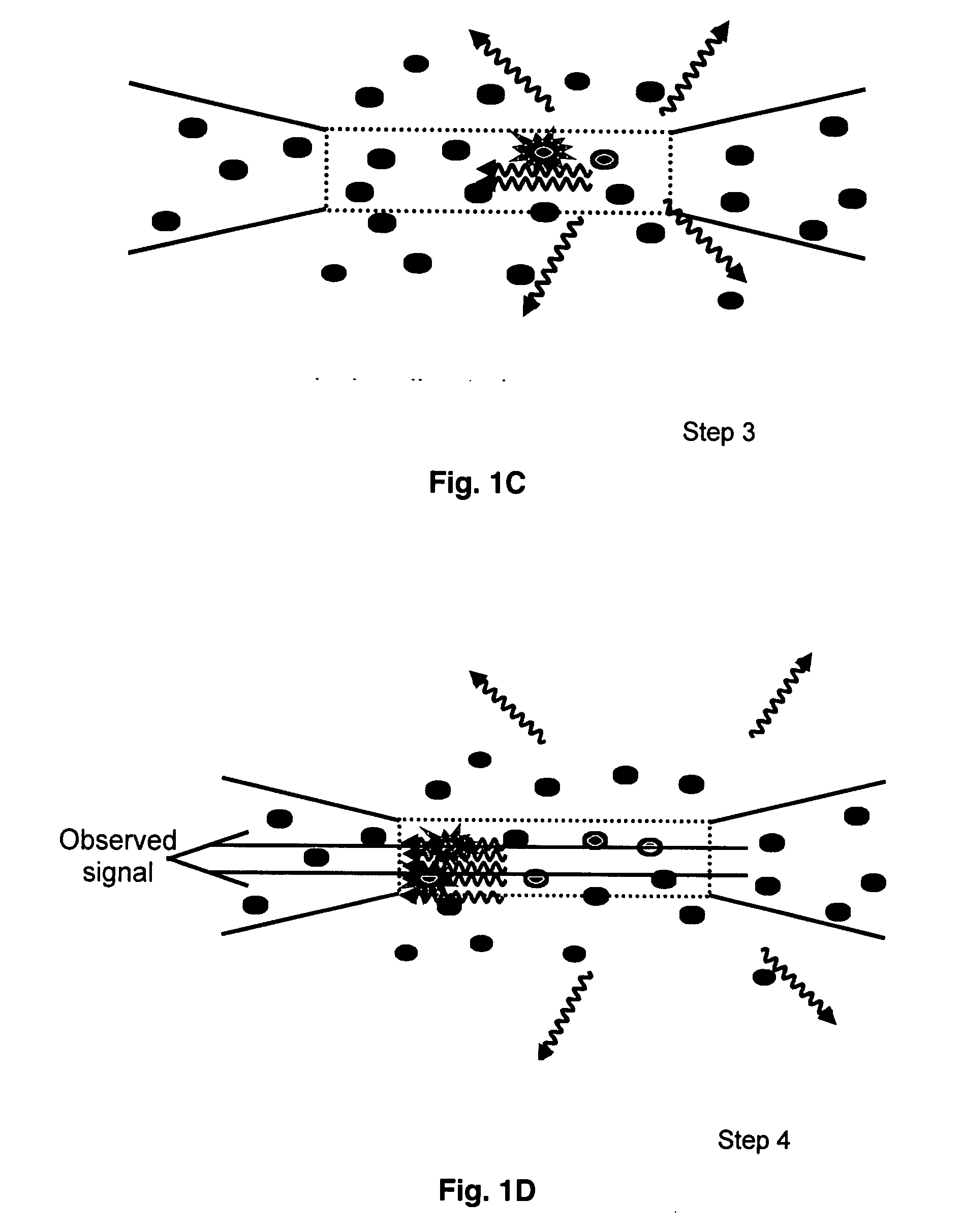
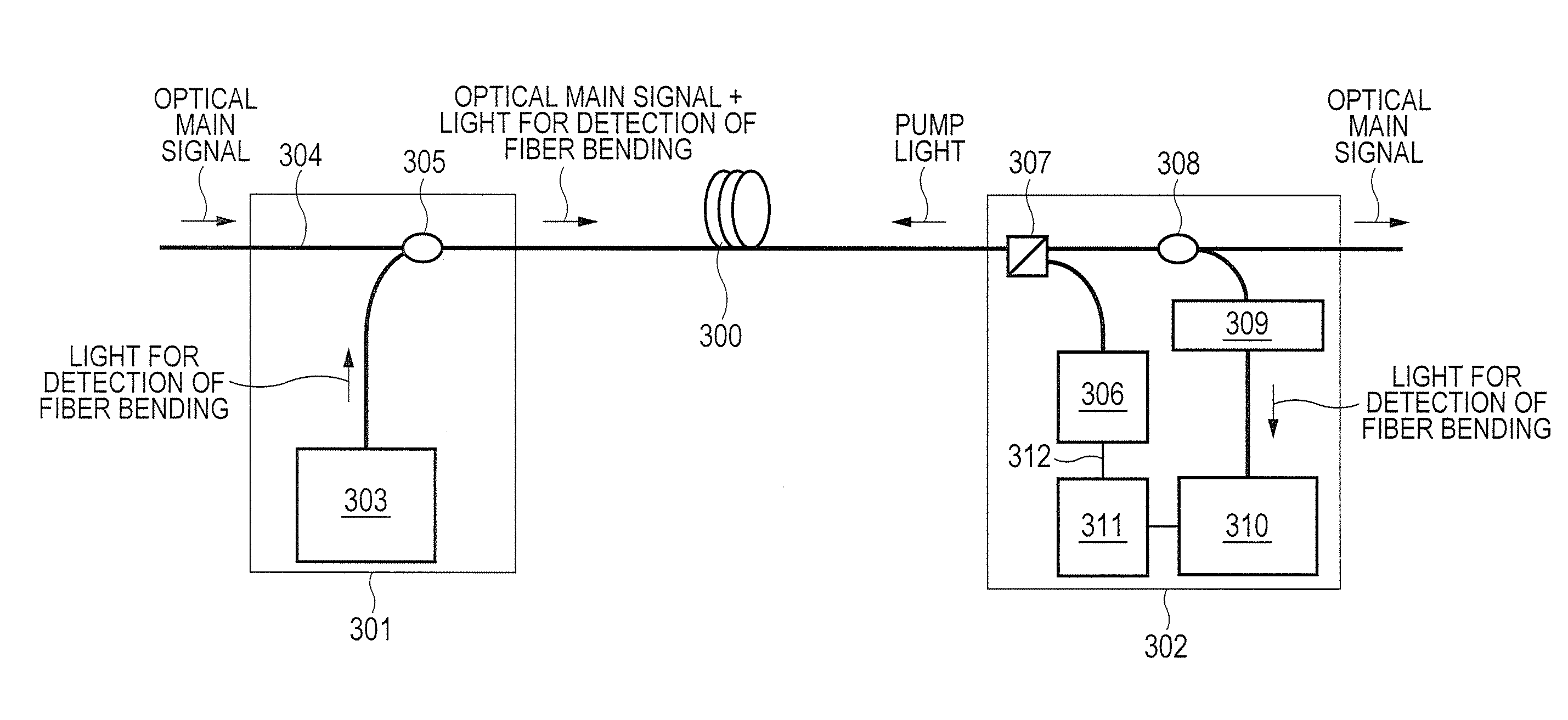
InactiveUS20120224168A1Improve accuracyHigh-precision detectionRadiation pyrometryMaterial analysis by optical meansFiberStimulate raman scattering
Bending of an optical fiber where a heat may be generated by a high output power can be detected without using a dedicated light source. An optical communication module that outputs a continuous wave light generated by at least one light source to an optical fiber transmission line, includes: (1) a loss measurement unit that measures a loss of an amplified spontaneous emission generated by allowing the continuous wave light output from the light source to create stimulated Raman scattering in the optical fiber transmission line; (2) a fiber abnormality analyzer that detects the abnormal state of the optical fiber transmission line on the basis of loss information on the ASE measured by the loss measurement unit; and (3) a light source controller that controls a supply state of the continuous wave light from the light source on the basis of the detection of the fiber abnormality analyzer.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
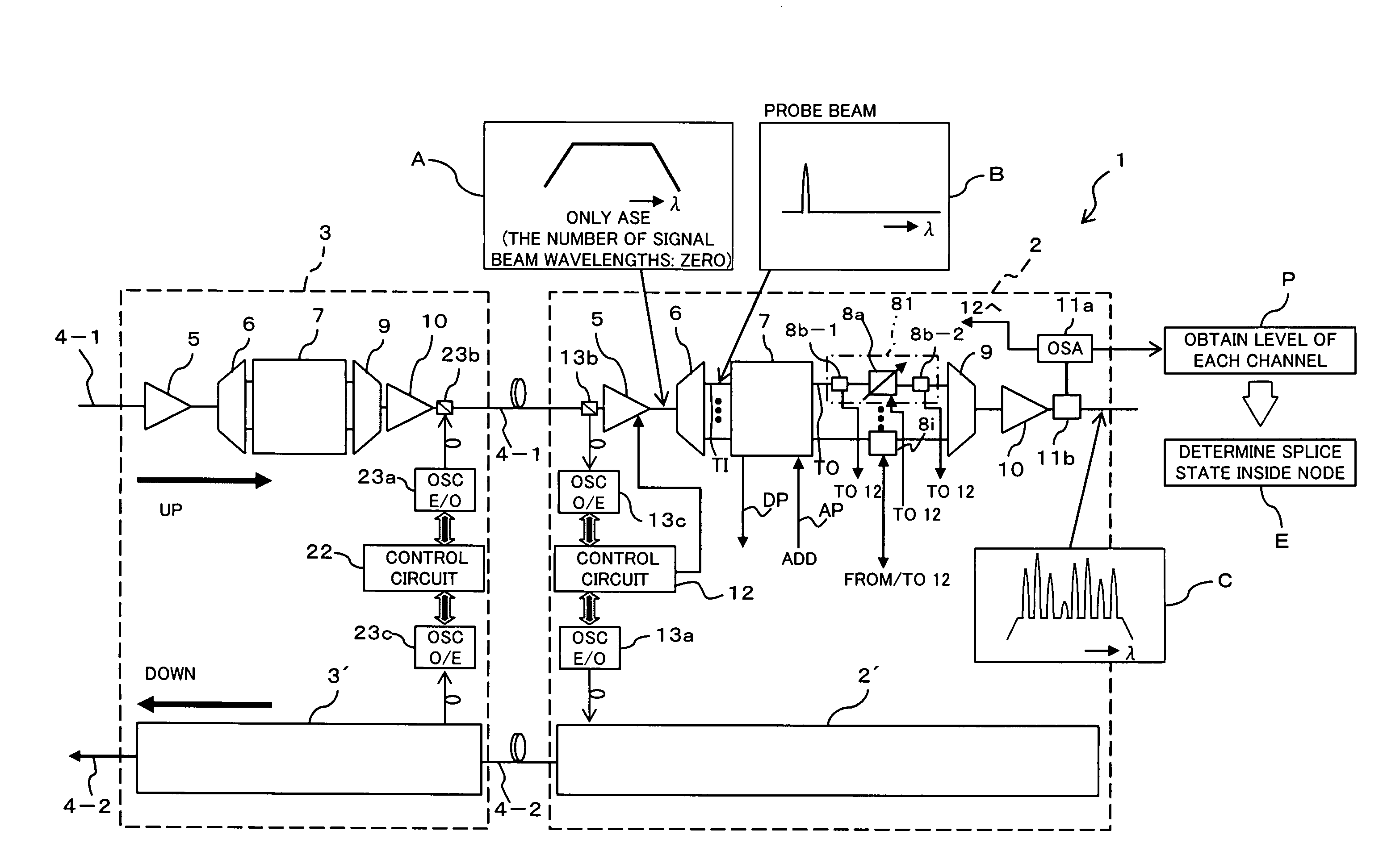
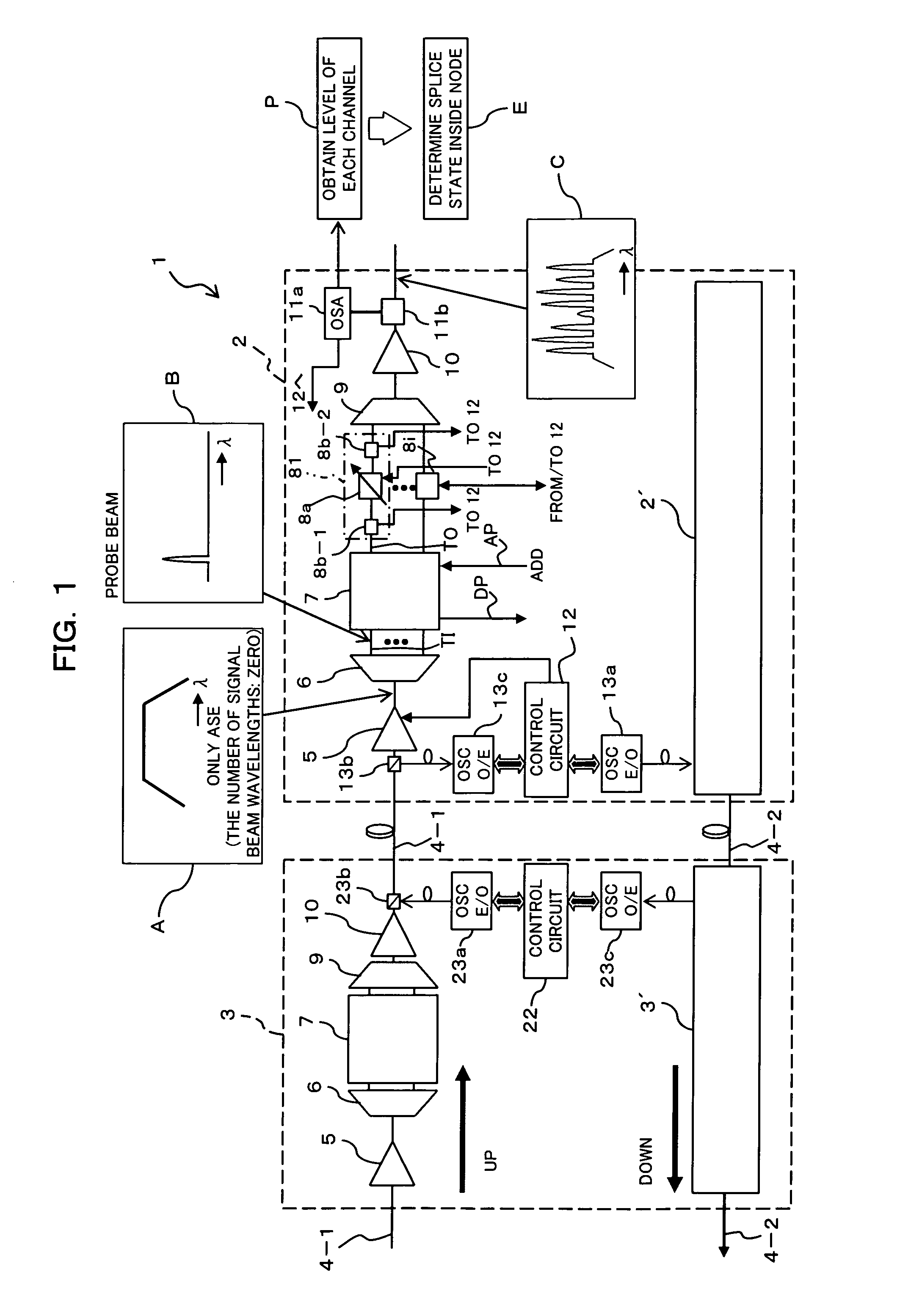
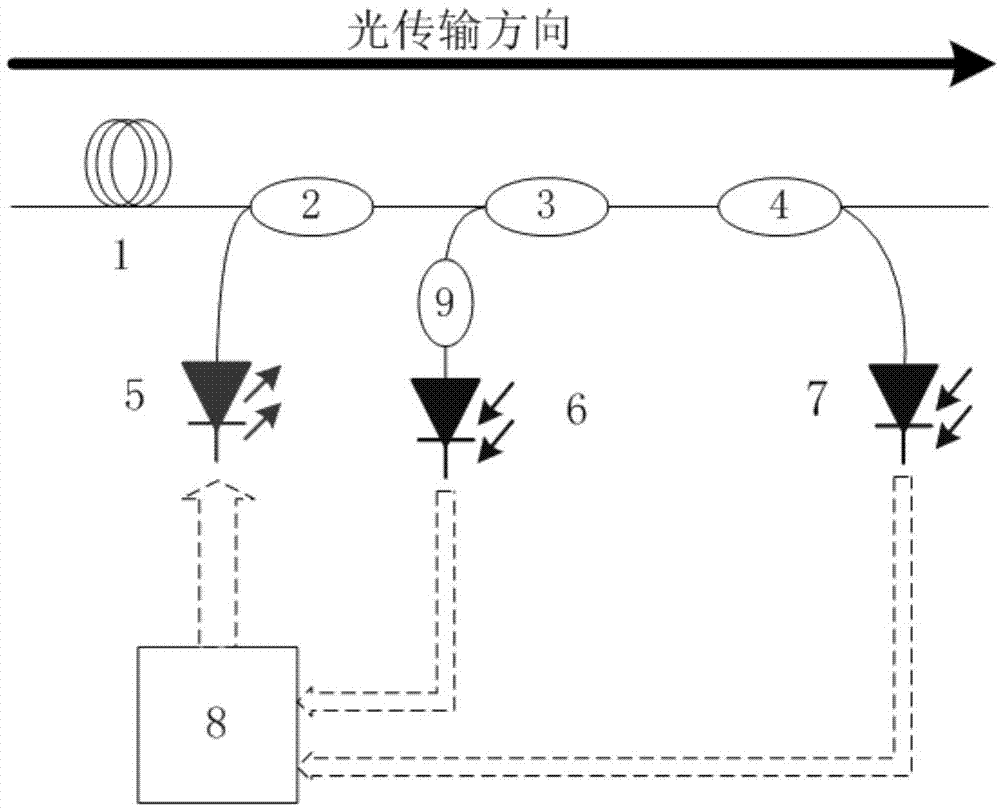
Optical transmission apparatus, continuity testing method therein, and optical transmission system
InactiveUS20060269284A1Short timeLow costRing-type electromagnetic networksWavelength-division multiplex systemsOptical propagationContinuity test
An optical transmission apparatus comprises a preamplifier controlling unit for controlling a preamplifier so that amplified spontaneous emission including all wavelength bands of a wavelength-multiplexed signal beam is outputted toward a wavelength demultiplexing unit, with the wavelength-multiplexed signal beam not inputted, power monitors for monitoring optical powers of the amplified spontaneous emission fed from the preamplifier and wavelength-demultiplexed by the wavelength demultiplexing unit, and a determining unit for determining the continuity state of an optical propagation path of each wavelength component on the basis of a result of monitoring by the power monitors. The optical transmission apparatus allows the continuity test on optical propagation paths of channels including a channel not used at the time of a start of the operation to be made easier than the known techniques.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
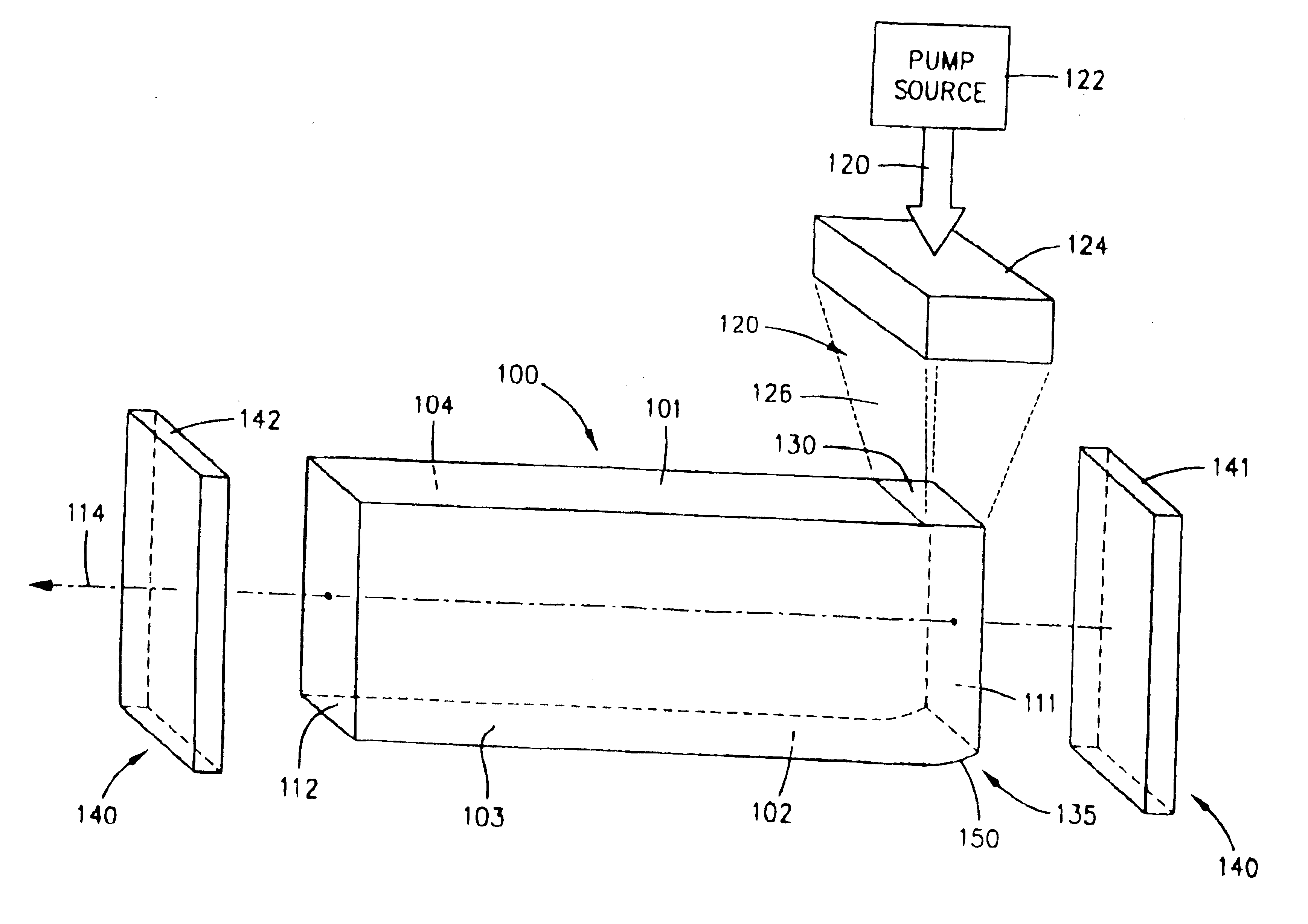
Laser with gain medium configured to provide an integrated optical pump cavity
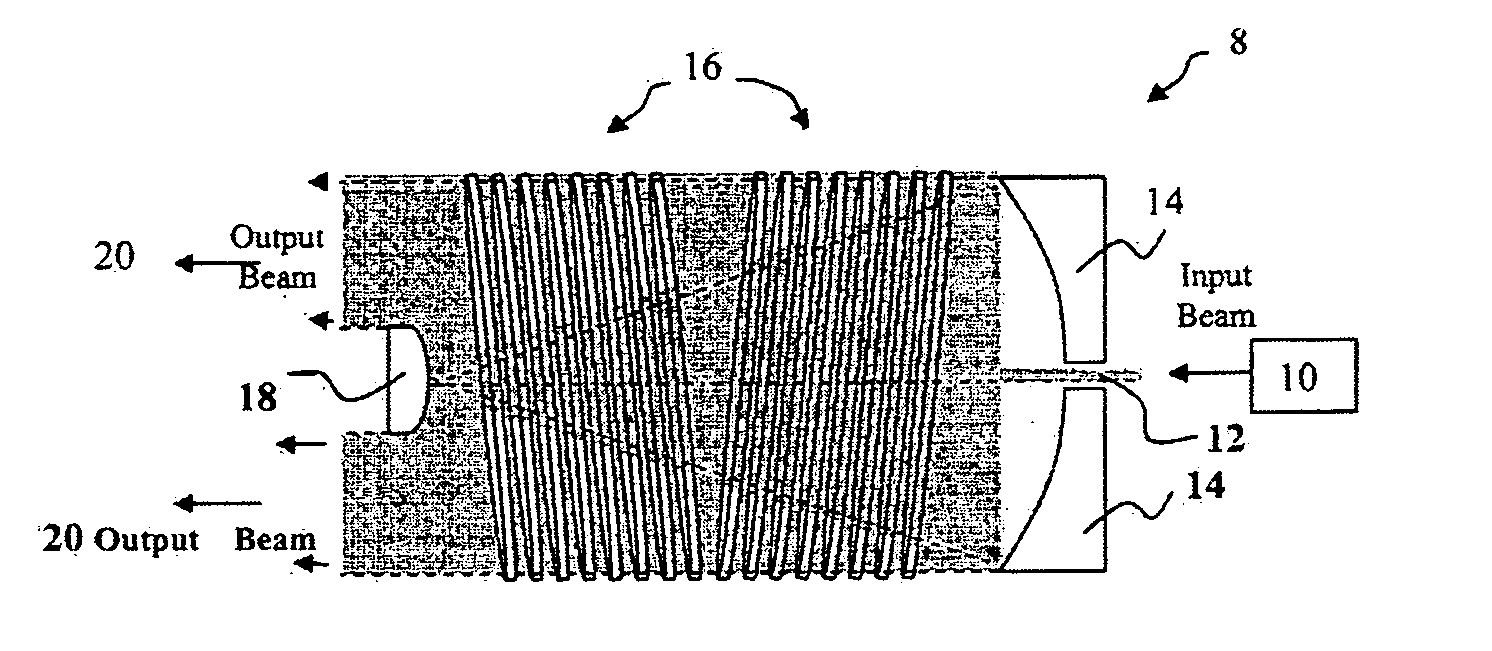
InactiveUS20020057725A1Reduce lossEfficient extractionOptical resonator shape and constructionActive medium shape and constructionDopantOptical pumping
An optically-pumped laser having a gain medium configured to provide a low loss, three-dimensional integrated optical pump cavity that substantially confines optical pump radiation within the lasing volume, which is particularly useful for efficiently pumping solid state gain media that has low pump dopant concentration. The integrated pump cavity includes a plurality of boundaries contiguous with the gain medium. An optical pump source such as a laser diode array supplies optical pump radiation that is input into the gain medium through one or more pump cavity windows with a propagation direction transverse to a laser axis defined through the gain medium. In some embodiments, an optical surface is situated opposite the window to approximately recollimate the input pump radiation. The optical pump cavity may be designed to concentrate the optical pump radiation and approximately uniformly pump the entire volume of the lasing medium. In one such embodiment, the pump cavity includes opposing converging surfaces that concentrate the optical pump radiation as it projects along the laser axis. Embodiments are disclosed in which a solid state gain medium has coatings that operate to suppress amplified spontaneous emission ("ASE"). Some embodiments also include heat sinks that directly contact the transverse boundaries and control the temperature distribution within the gain medium in a predetermined manner.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Fiber grating temperature sensing system for detecting temperatures of inflammables and explosives
ActiveCN102680139AHigh precisionHigh sensitivityThermometers using physical/chemical changesDigital signal processingFiber gratings
The invention provides a fiber grating temperature sensing system for detecting temperatures of inflammables and explosives. The system comprises an amplified spontaneous emission (ASE) broadband source, a circulator, an optical switch, an optical switch drive device, a fiber Bragg grating (FBG) temperature sensor, a holographic volume phase grating, a collimating lens, a condenser lens, a photoelectric detector, a control circuit, a digital signal processing (DSP) circuit, a storage and an upper computer, wherein the FBG temperature sensor is stuck onto the surfaces of the inflammables and explosives, and wavelength drifting information is demodulated by utilizing a holographic volume phase grating demodulation method, so that temperature variation of the FBG temperature sensor is obtained, namely, the temperature variation of the inflammables and explosives, and the temperature of the inflammable and explosive is finally obtained. Fiber grating temperature sensing system for detecting temperatures of inflammables and explosives has the advantages that the sensitivity and the stability are high, optical fiber sensors have strong anti-electromagnetic interference, anti-shaking, moisture resistant, corrosion resistant and the like competences, therefore the system can also be used normally for a long time in severe environments. The optical fiber sensors have the advantages of being light in weight, small in size and the like.
Owner:山东双测安全信息技术产业研究院有限公司
Method for inhibiting amplified spontaneous emission of large-size sheet laser neodymium glass
ActiveCN101976796ASimple processEasy to operateOptical resonator shape and constructionHigh power lasersAdhesive
The invention relates to a method for inhibiting the amplified spontaneous emission of large-size sheet laser neodymium glass, which comprises the following steps of: (1) selecting absorbing glass matched with the sheet laser neodymium glass and an organic adhesive; (2) processing and adhering the sheet laser neodymium glass and an absorbing glass strip; (3) precisely polishing a light pass surface of the sheet laser neodymium glass, and the like. The method can effectively inhibit the amplified spontaneous emission and parasitic oscillation of the large-size sheet laser neodymium glass; gain performance approximates the theoretical calculation level; and the glass has high stability and meets the using requirement of a high-power laser device.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
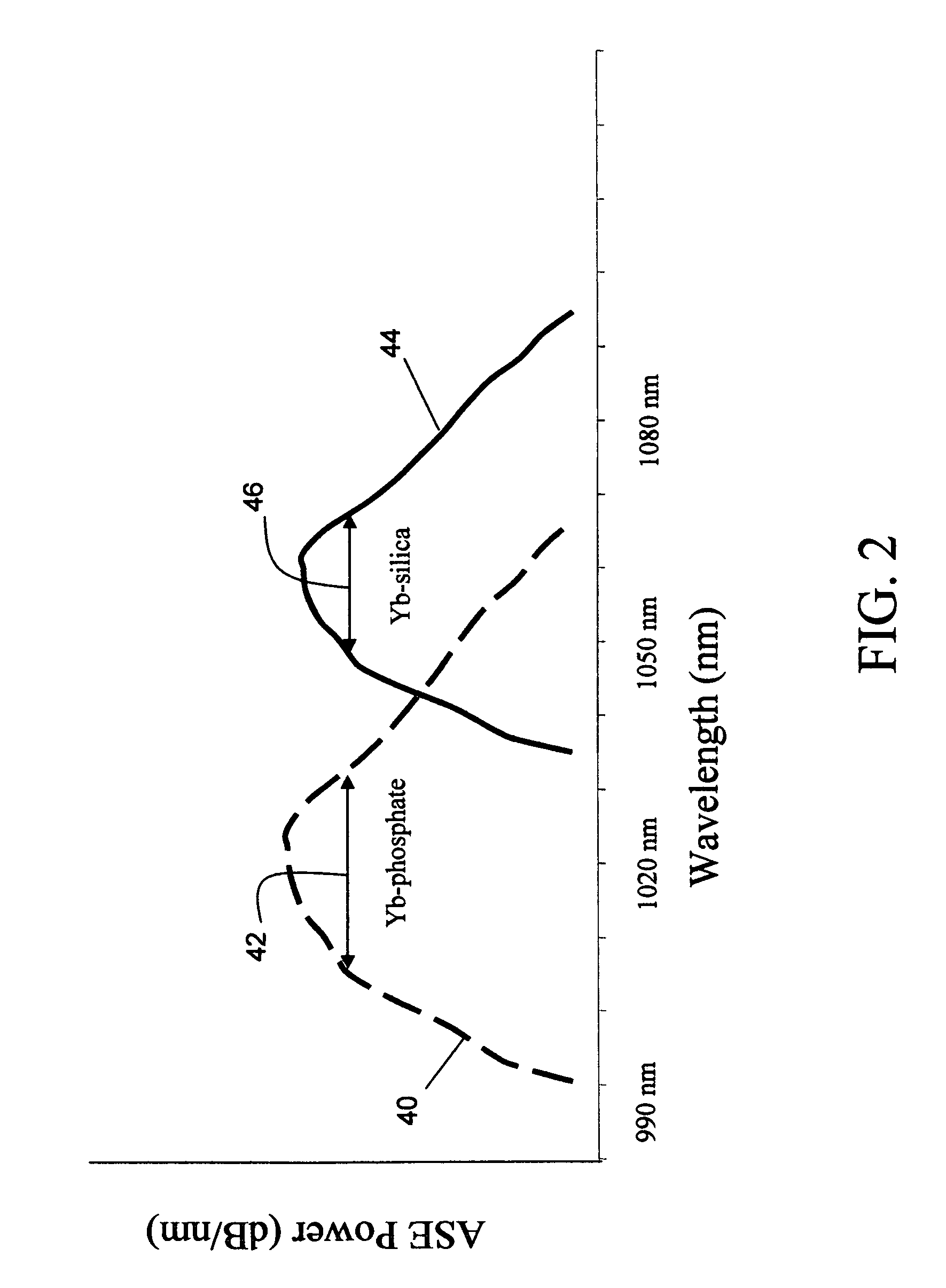
1-mum phosphate-glass fiber amplified spontaneous emission (ASE) source
ActiveUS7423803B1High levelImprove stabilityLaser using scattering effectsFibre transmissionHigh concentrationPhosphate glass
A phosphate glass 1-μm fiber ASE source provides high power and broadband emission that covers wavelengths on the short side of Yb-doped silica. A single-mode fiber formed from phosphate glass is doped with highly elevated concentrations of Yb dopants 0.5-30 wt. % and typically 2-10 wt. %, far higher than either silica or germano-silicate. The high concentration of Yb dopant absorbs the pump in a short length, typically 10-150 cm instead of tens of meters, to provide high saturated output power and a shifted emission spectrum. The excess power allows the fiber ASE source to be configured to provide the output powers, emission bandwidth and stability desired by many applications. Furthermore, the ASE can be configured to emit a nearly Gaussian spectral profile without sacrificing power or bandwidth. The backward emission spectrum of Yb-doped phosphate glass is centered near 1020 nm instead of 1060, which allows the ASE source to cover wavelength on the short side of Yb-doped silica, which may be important in certain applications such as ophthalmic OCT where water absorption has a transparency window.
Owner:NP PHOTONICS A CORP OF DELAWARE
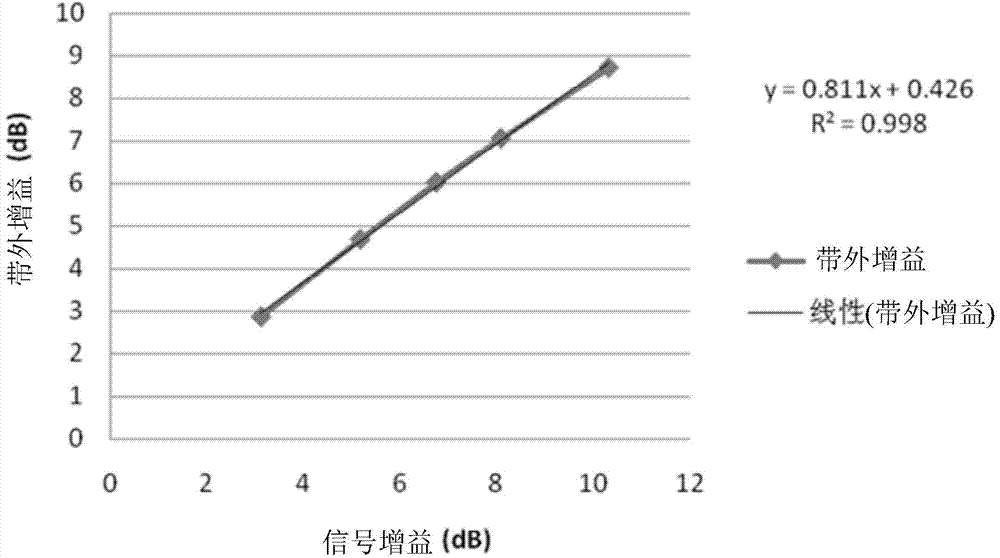
Raman fiber amplifier and automatic gain control method thereof
The invention an automatic gain control method of a Raman fiber amplifier. The automatic gain control method includes extracting in-band or out-of-band ASE (amplified spontaneous emission) power; adjusting power of a pumping laser to enable output power of the Raman fiber amplifier (RFA) and ASE power generated by the RFA to tend to meeting a formula (3): PaseT=10*log(KG*10(Pout / 10)+CG), wherein PaseT, Pout refer to theoretical value of the ASE power generated by the RFA and the Raman output power respectively, and unit is dBm; G refers to Raman gain, and unit is dB; KG and CG refer to slope and intercept value under the gain. The automatic gain control method is wide in application range, can be used for gain control of Raman amplifiers small in input light power change and can be applied to gain control of Raman amplifiers quite wide in input light power change range.
Owner:WUXI TACLINK OPTOELECTRONICS TECH CO LTD
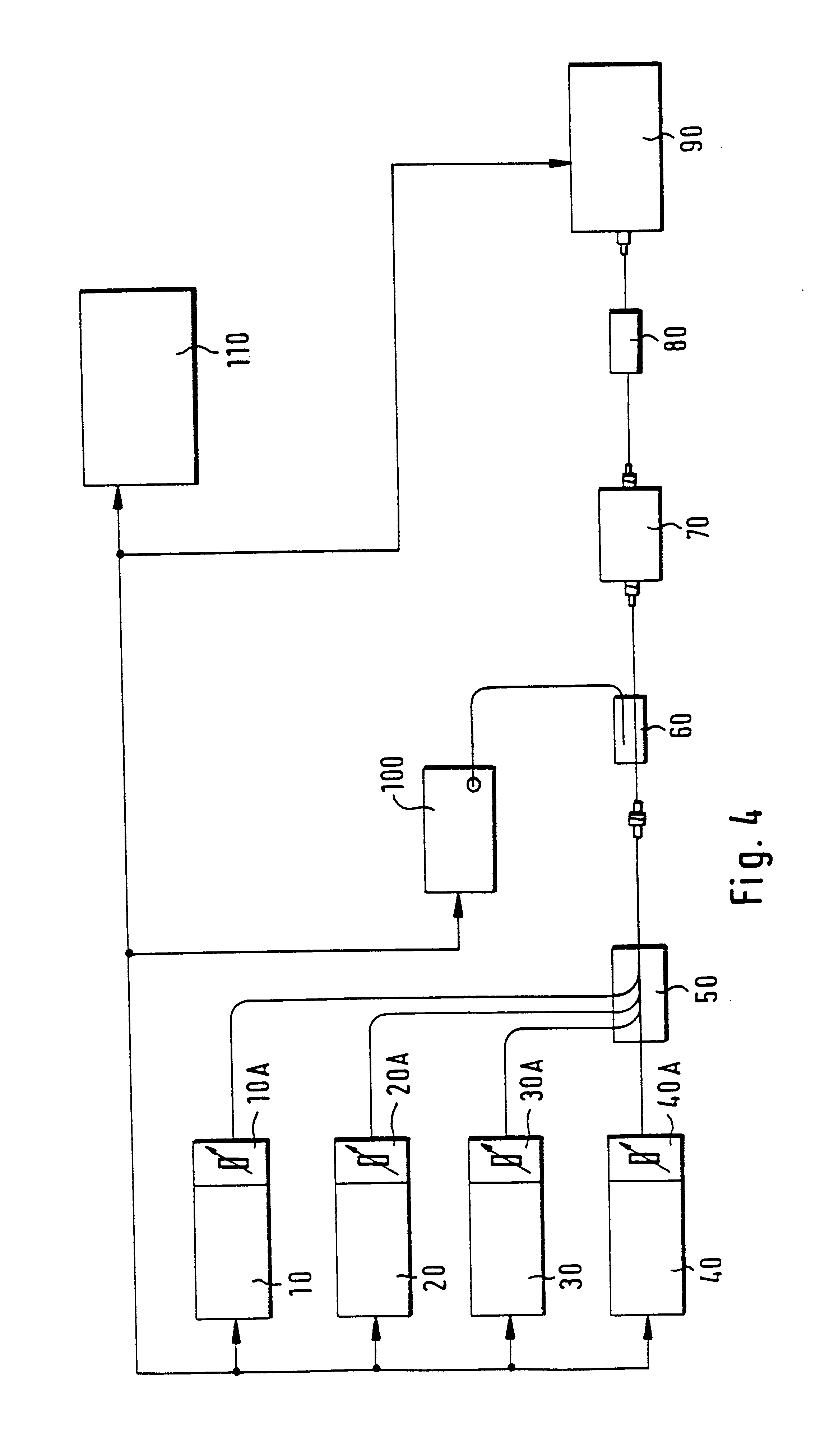
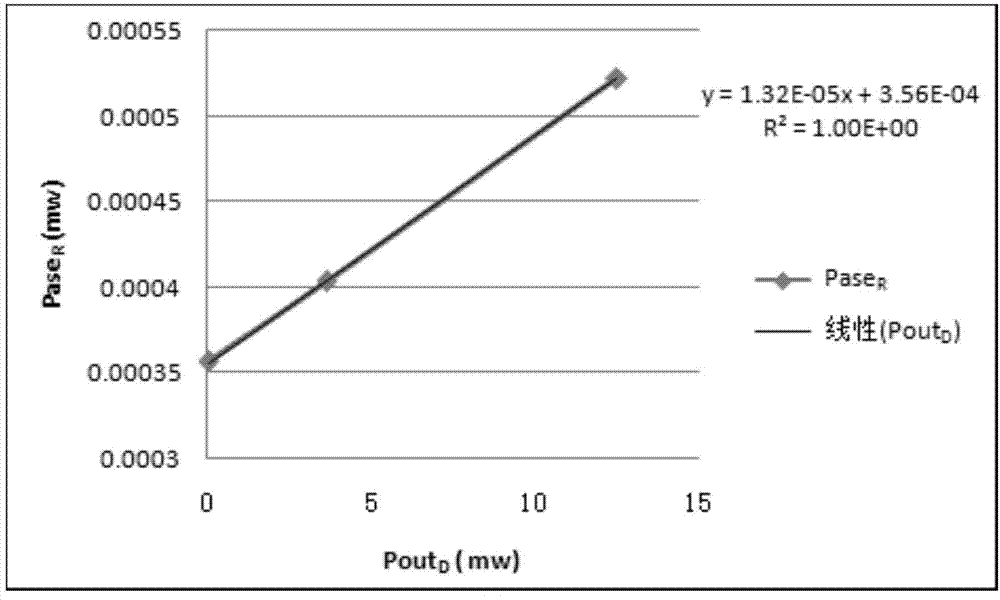
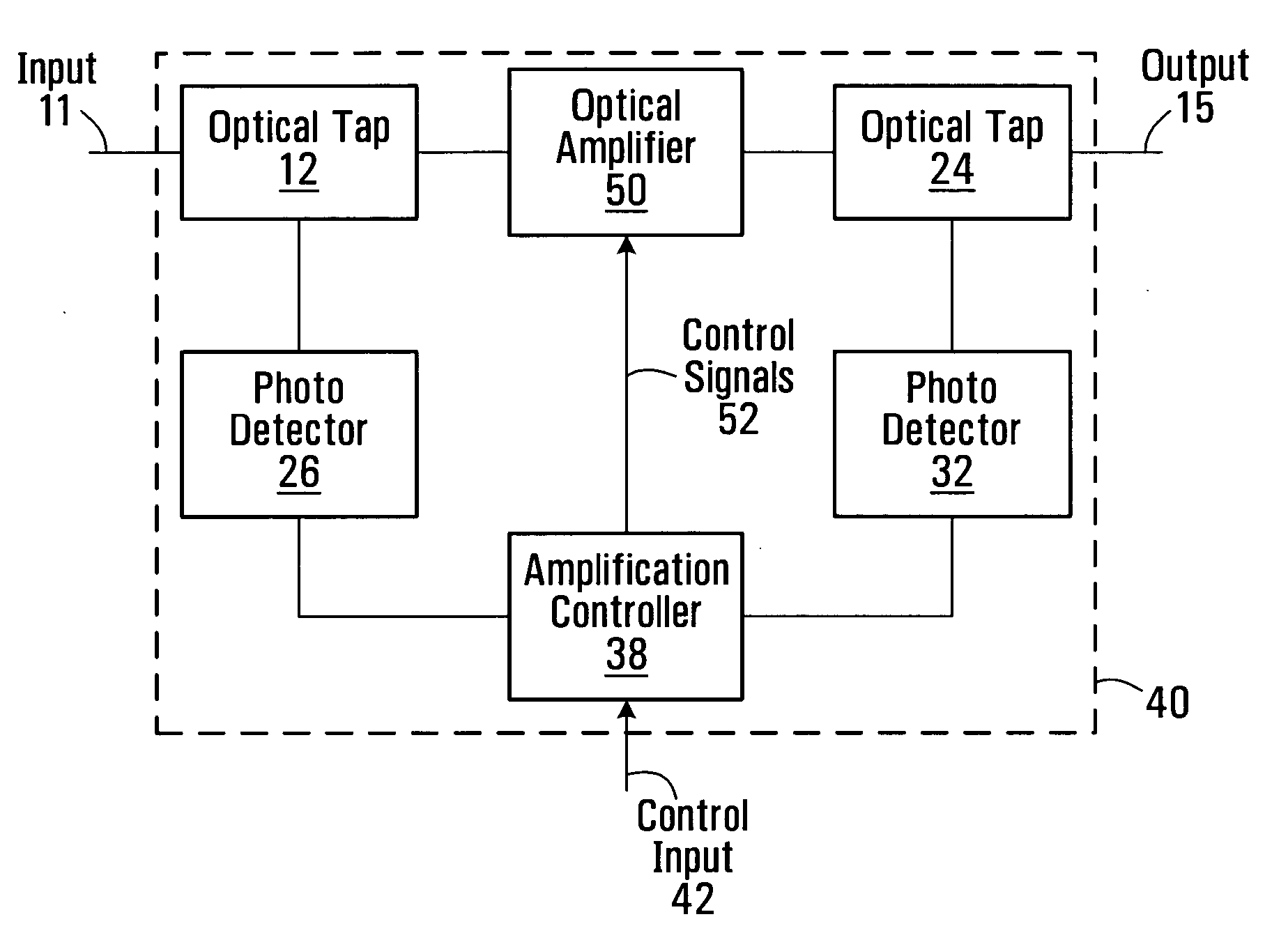
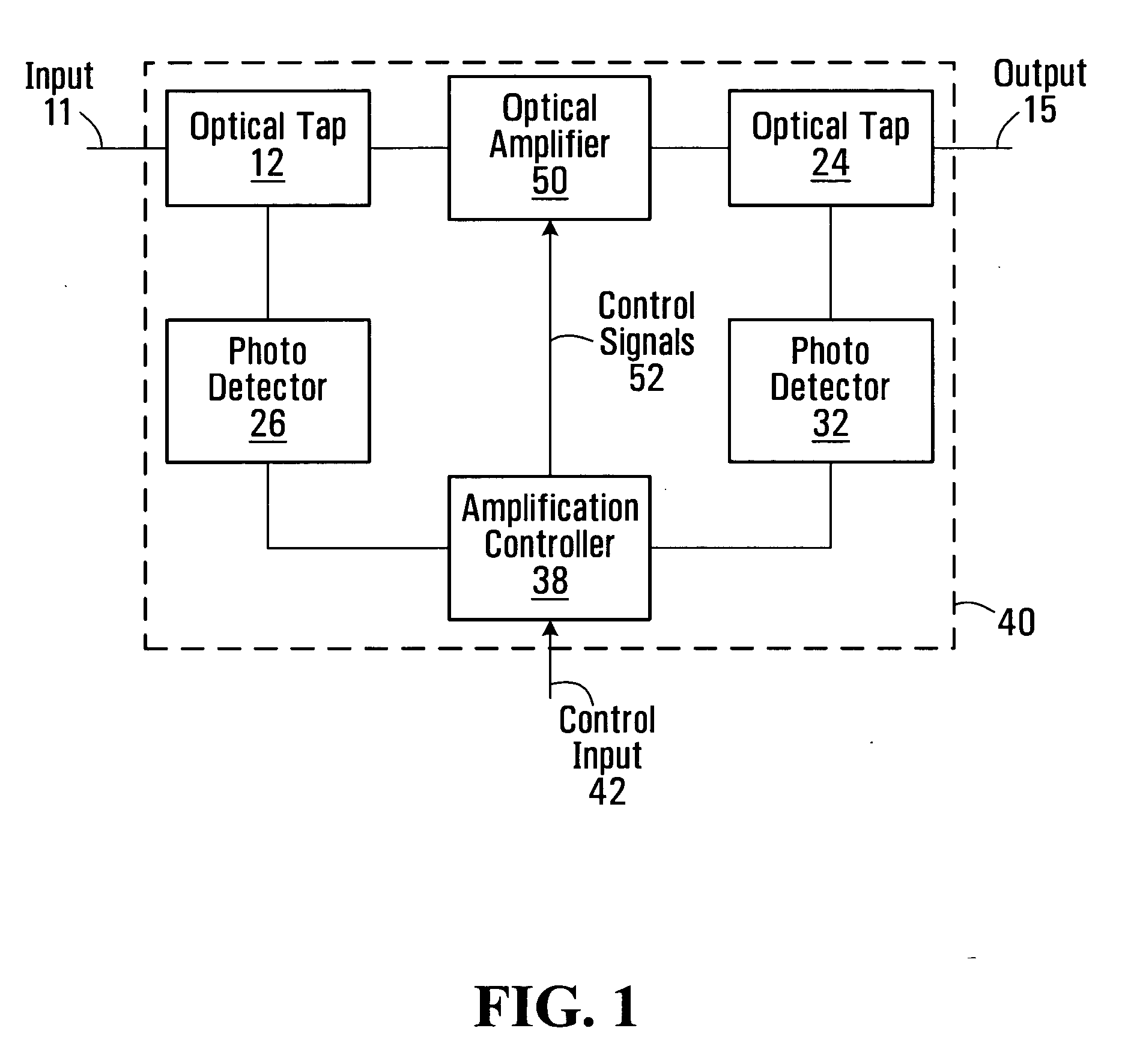
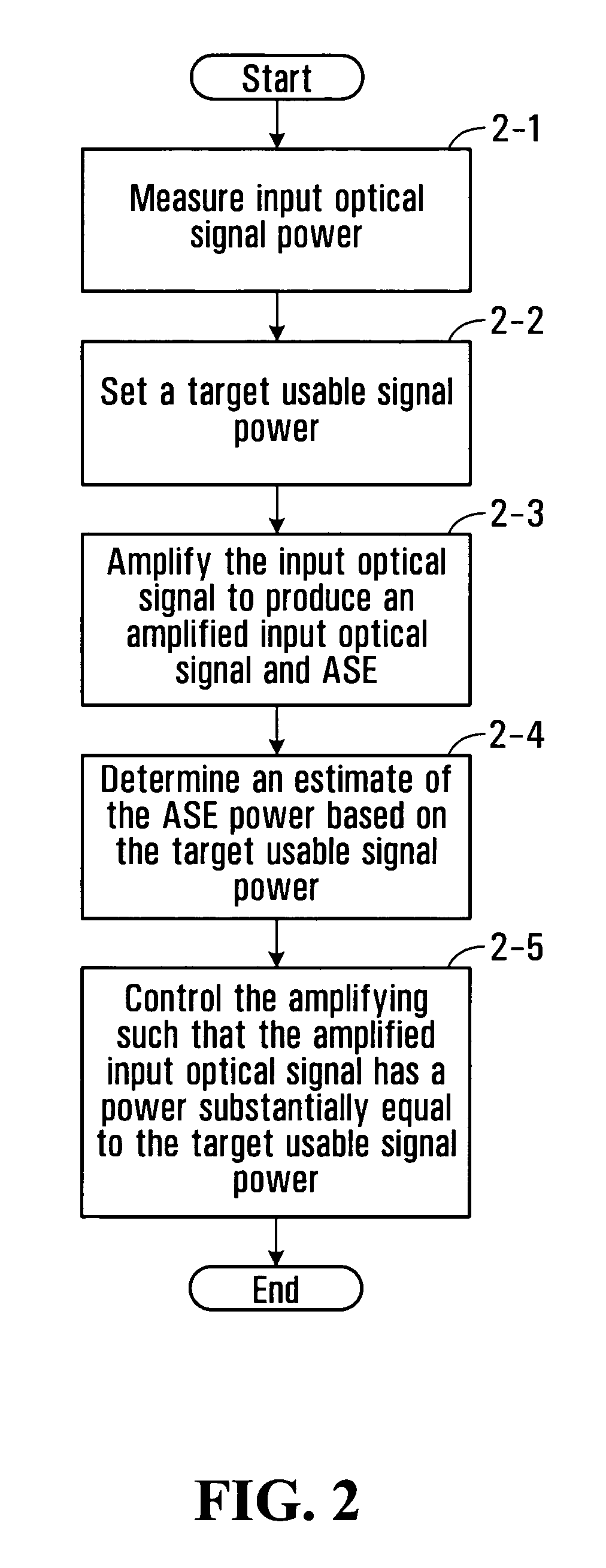
Method and apparatus for amplified spontaneous emission corrected automatic signal power control of an optical amplifier
An optical amplifier system and controller and a method for automatically controlling the usable signal power of an optical amplifier are provided. The method differentiates between the total optical power that includes the amplified spontaneous emission (ASE), and the useful amplified optical signal power at the output of the amplifier. The optical amplifier system comprises an optical amplifier, a first and a second photodetector operable to measure the power of the input and output signals of the optical amplifier and an amplification controller with a control input. The amplification controller is operable to compensate for the ASE power when operating in automatic signal power control mode.
Owner:JUMIPER NETWORKS INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com