Method for inhibiting amplified spontaneous emission of large-size sheet laser neodymium glass
A technology for amplifying spontaneous emission and flake lasers, applied in lasers, phonon exciters, laser parts, etc., it can solve the problems of high residual reflectivity, low yield, limited application, etc., and achieves low additional stress and easy operation. , Reduce the effect of laser damage and thermal damage
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0063] Embodiment 1, the method for suppressing and amplifying spontaneous emission of quadrilateral sheet laser neodymium glass,
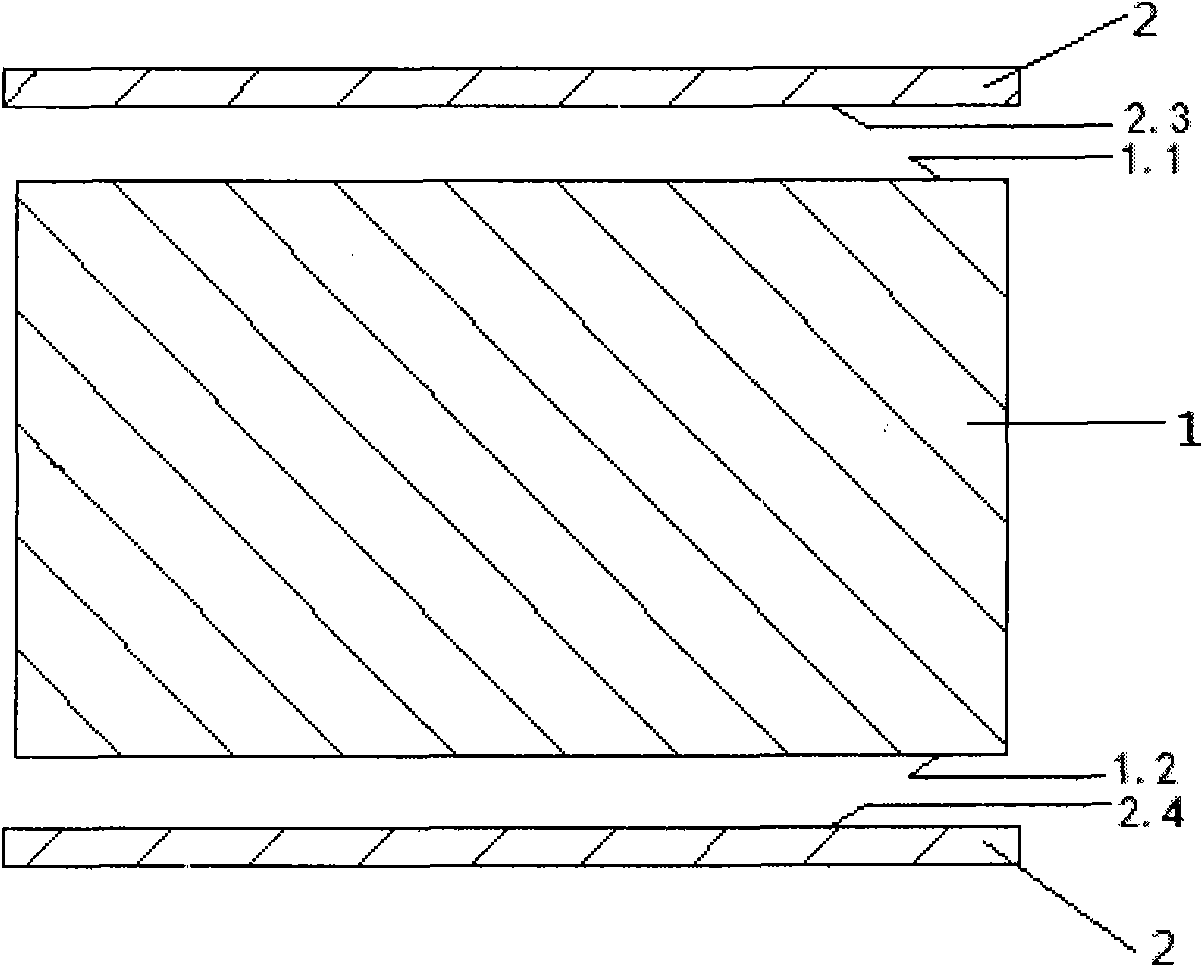
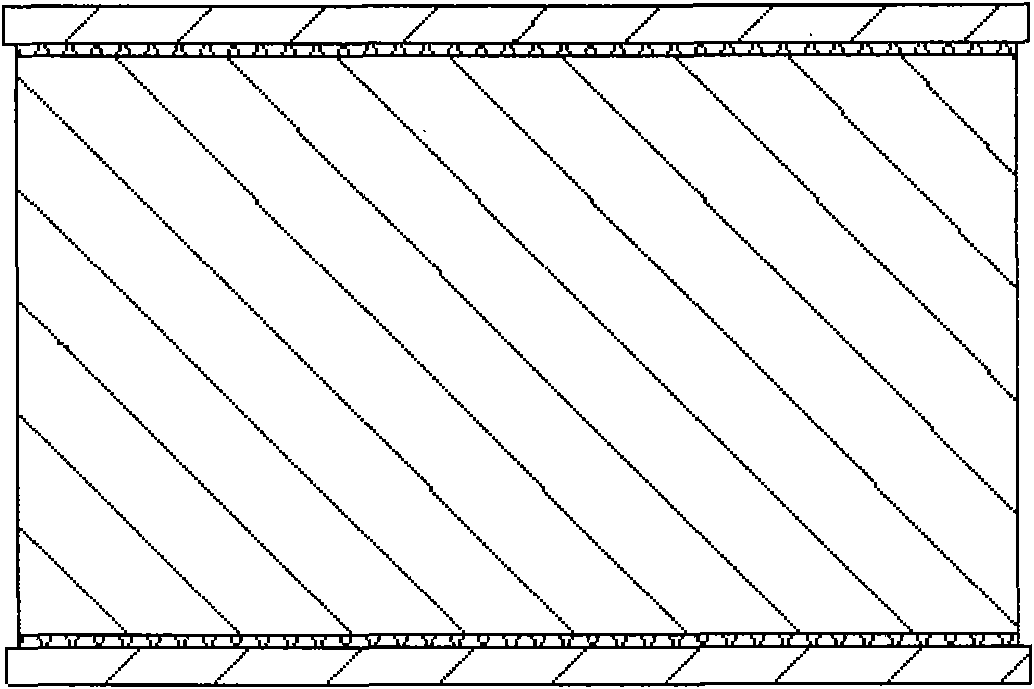
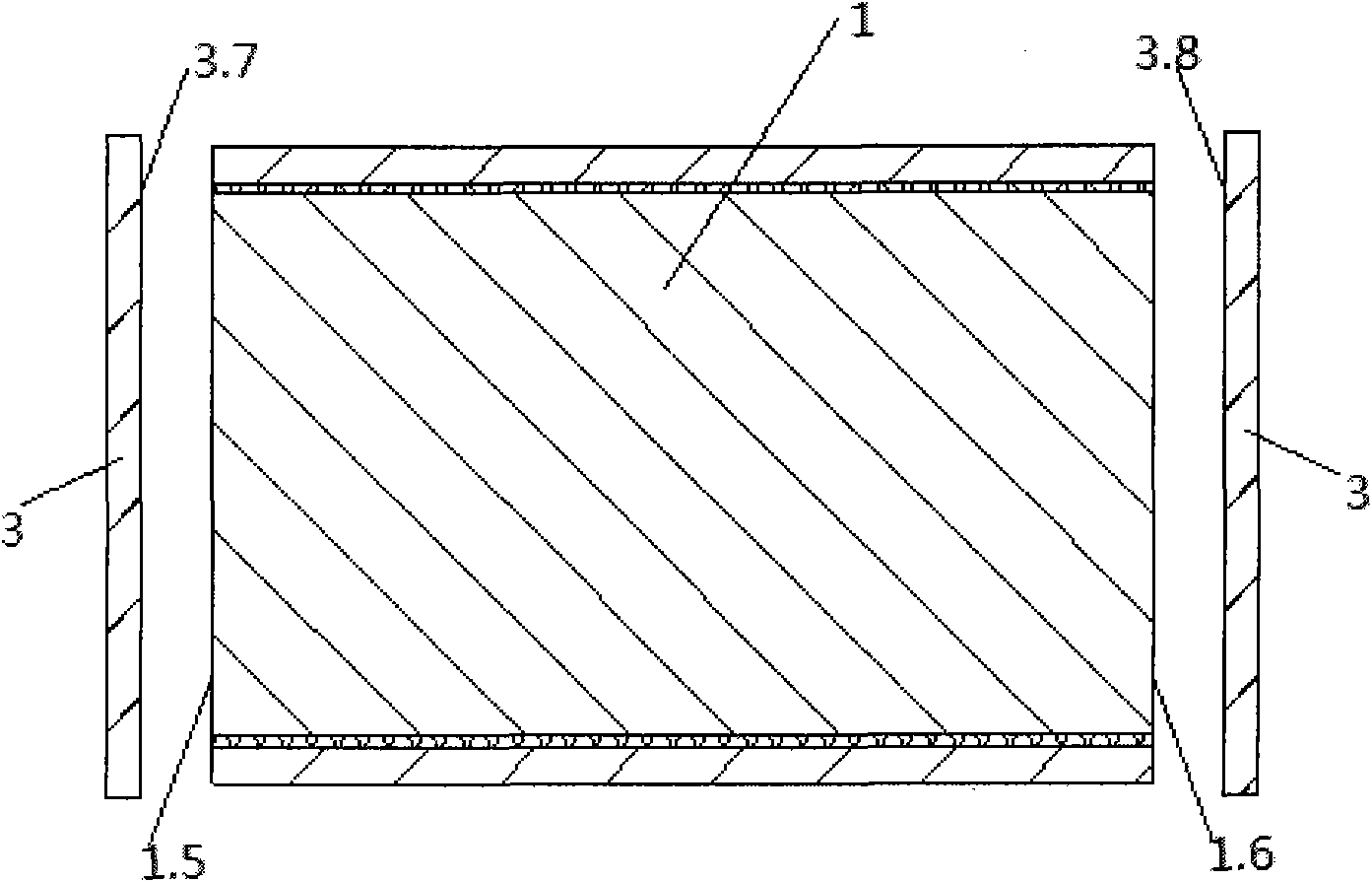
[0064] see Figure 1 to Figure 5 , figure 1 It is a schematic diagram of the arrangement of the long sides of the sheet-shaped laser neodymium glass and the absorbing glass strips in Example 1 of the present invention. figure 2 It is a schematic diagram of pasting the long side of the sheet-shaped laser neodymium glass and the absorbing glass slats in Example 1 of the present invention. image 3 It is a schematic diagram of the arrangement of the short sides of the sheet-shaped laser neodymium glass and the absorbing glass slabs in Embodiment 1 of the present invention. Figure 4 It is a schematic diagram of pasting the long side of the sheet-shaped laser neodymium glass and the absorbing glass slats in Example 1 of the present invention. Figure 5 It is a schematic diagram of the structure of the sheet-shaped laser neodymium glass according t...
Embodiment 2
[0080] The shape and implementation steps of this embodiment are the same as embodiment 1, the difference is:
[0081] The absorption glass is phosphate glass doped with copper oxide, and the weight percentage of the absorption glass doped with copper oxide is 0.5%.
[0082] The external dimensions of the absorbing glass slabs are 2 mm or more longer than the sides of the laser neodymium glass in the longitudinal direction, and 1 mm or more wider than the thickness of the laser neodymium glass in the width direction of the absorbing glass. The optical plane is treated with an acid solution, moved to a clean room for coupling treatment, cleaned and dried, and ready for operation. The organic adhesive is treated by suction filtration under reduced pressure to remove fine solid matter in the organic adhesive. The said absorbing glass is tightly bonded to the side of said laser neodymium glass by using said organic adhesive. Controlling the thickness of the organic adhesive laye...
Embodiment 3
[0085] Example 3: Method for Suppressing Amplified Spontaneous Emission by Octagonal Sheet Laser Neodymium Glass
[0086] see Figure 6 to Figure 9 , Image 6 It is a schematic diagram of arrangement of octagonal sheet-shaped laser neodymium glass with four hypotenuses and absorbing glass slats in Embodiment 3. Figure 7 It is a structural schematic diagram of the four hypotenuses of the octagonal sheet-shaped laser neodymium glass and the absorbing glass slats of the third embodiment. Figure 8 It is a schematic diagram of the arrangement of octagonal sheet-shaped laser neodymium glass with four straight sides and absorbing glass slats in Embodiment 3. Figure 9 It is a structural schematic diagram of octagonal sheet laser neodymium glass in Example 3 after shape shaping and precise polishing of the light-transmitting surface.
[0087] Select the absorbing glass and organic adhesive that match the laser neodymium glass, the same as in Example 1. The weight percent of the ab...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com