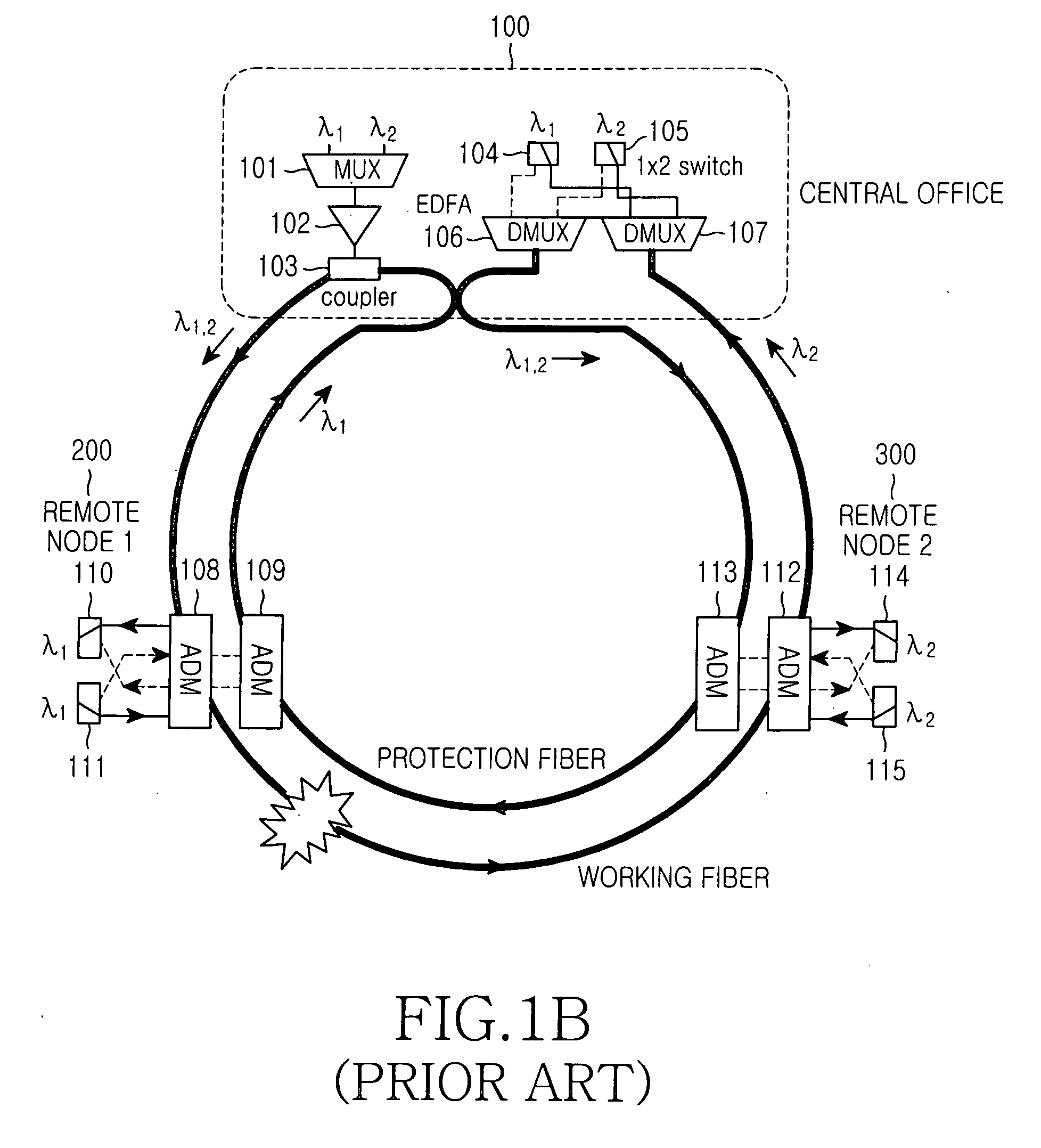
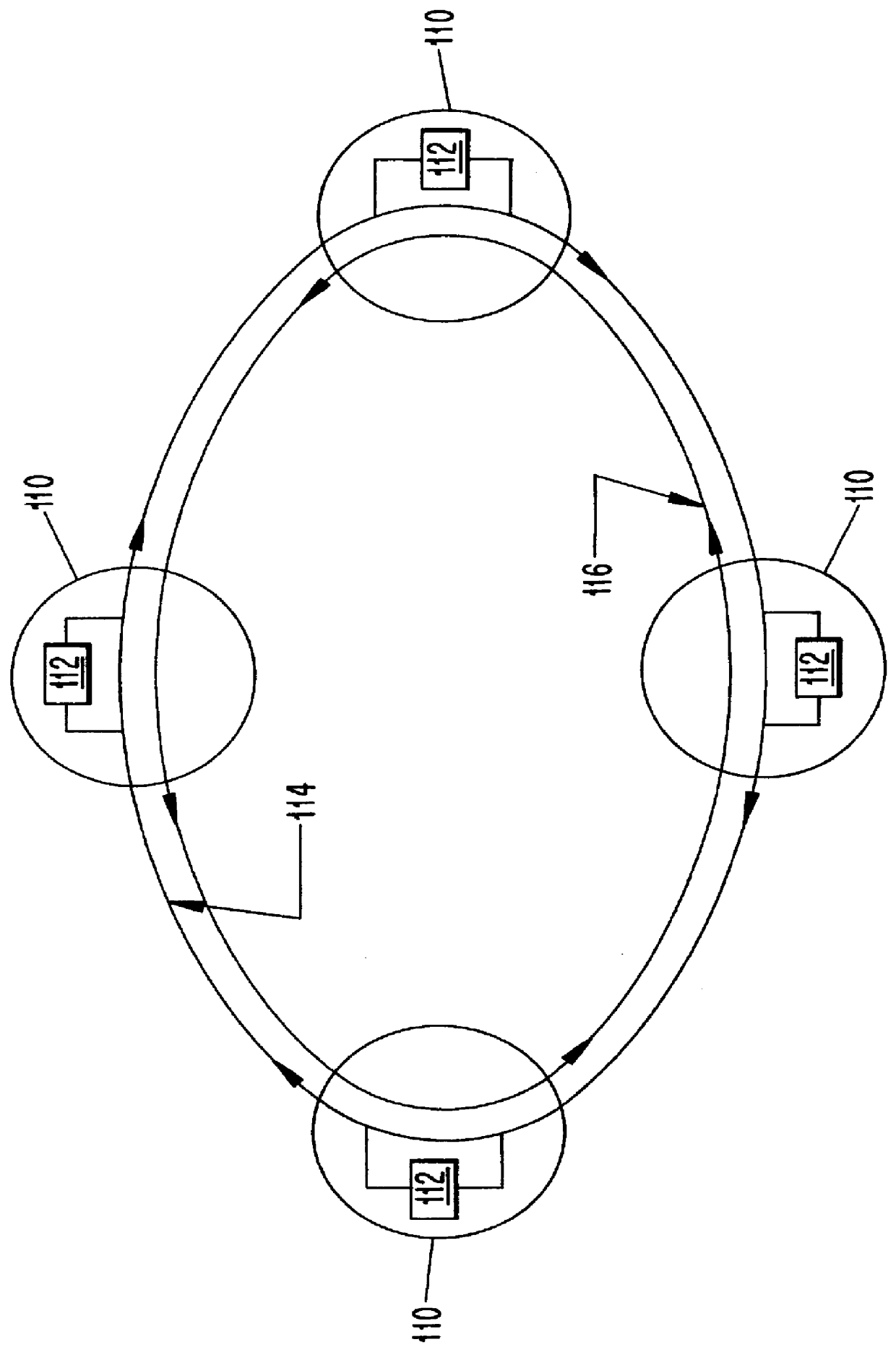
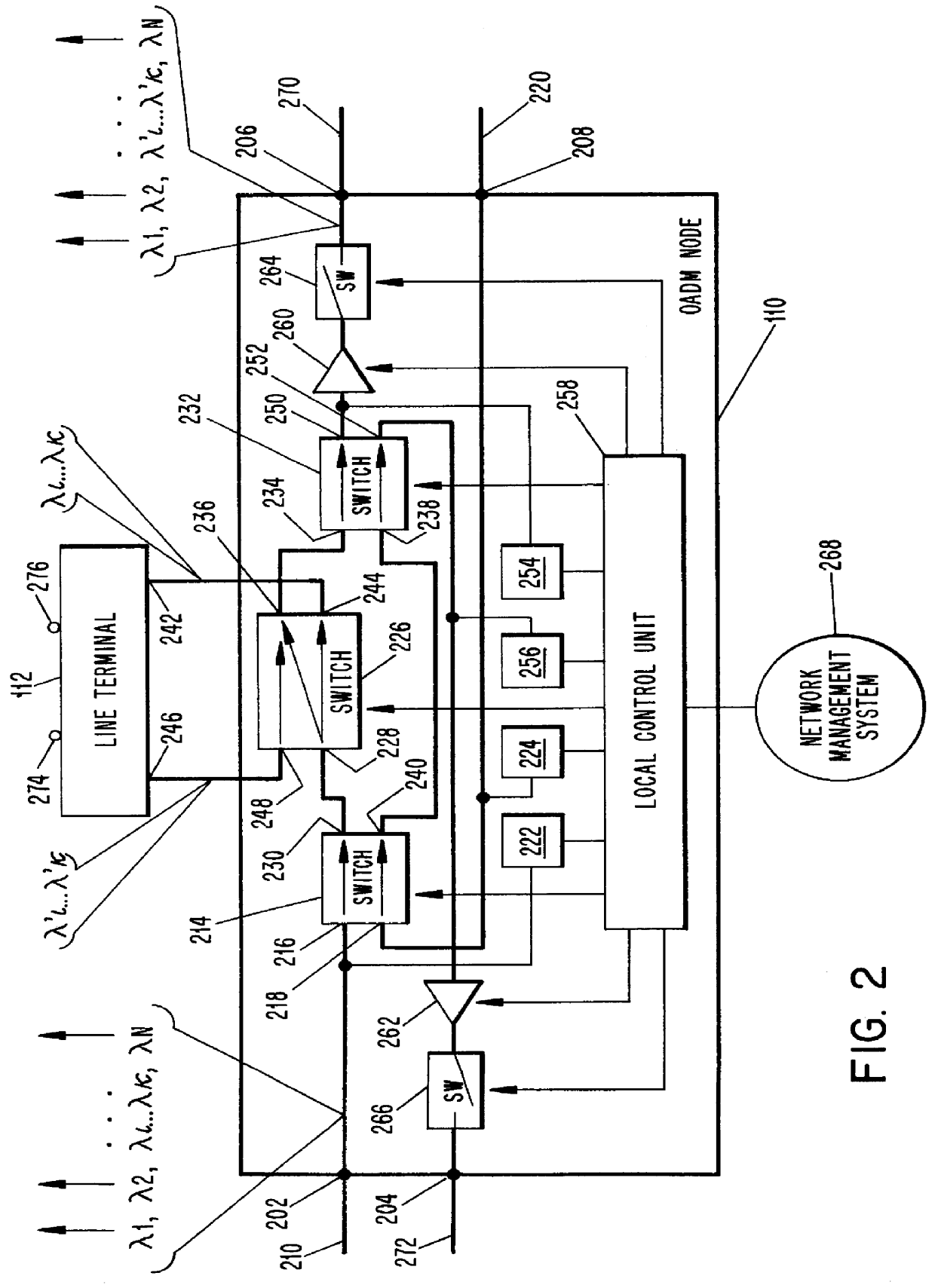
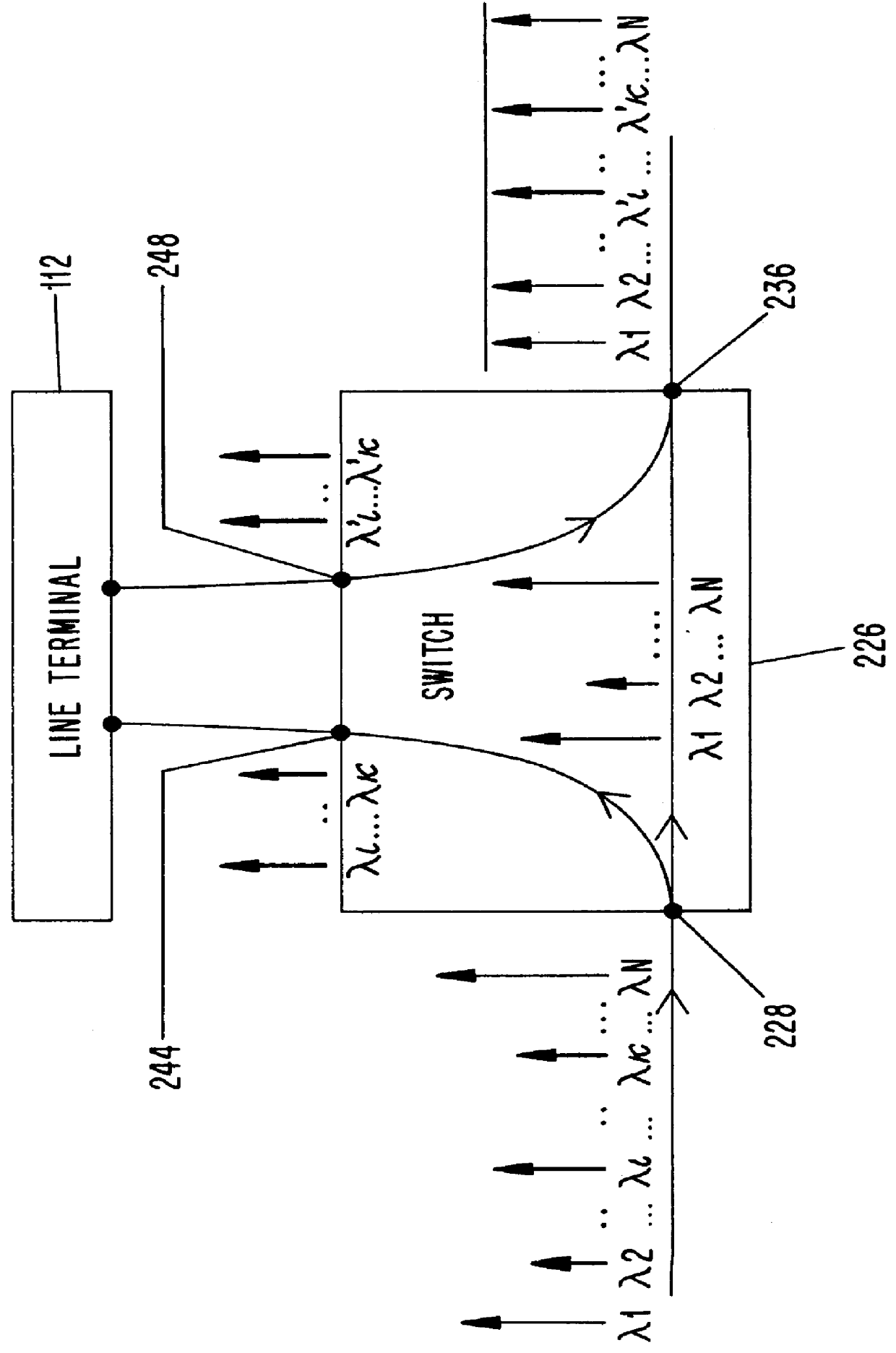
Patents
Literature
577results about "Ring-type electromagnetic networks" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
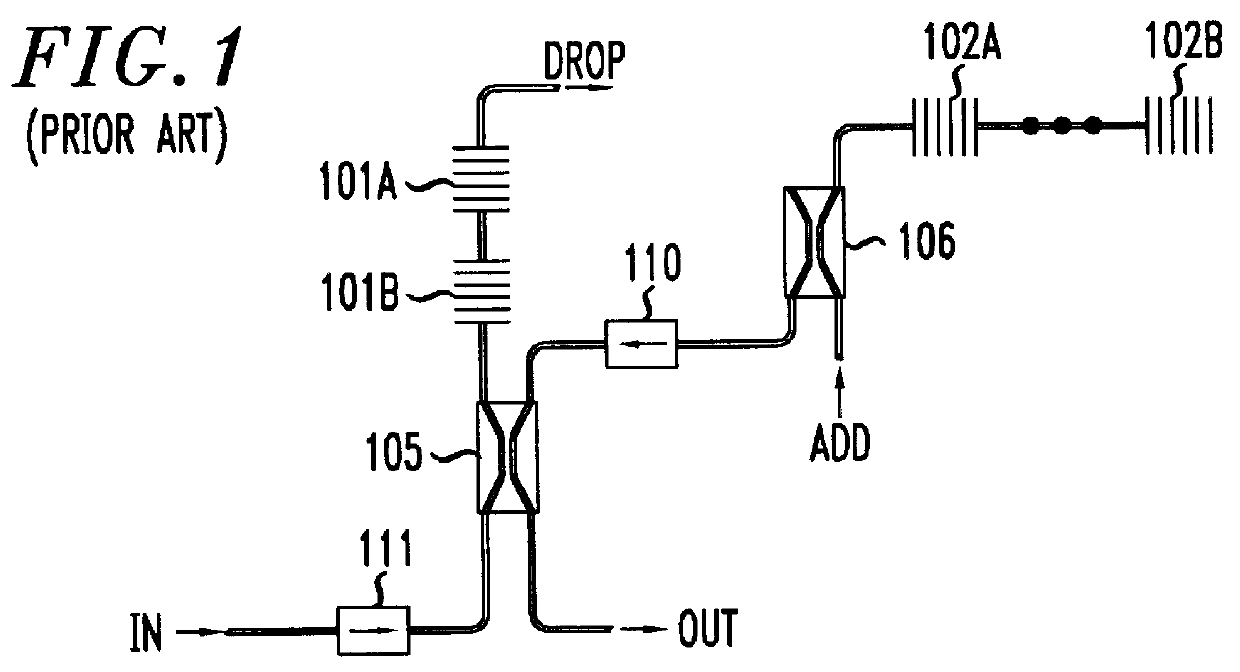
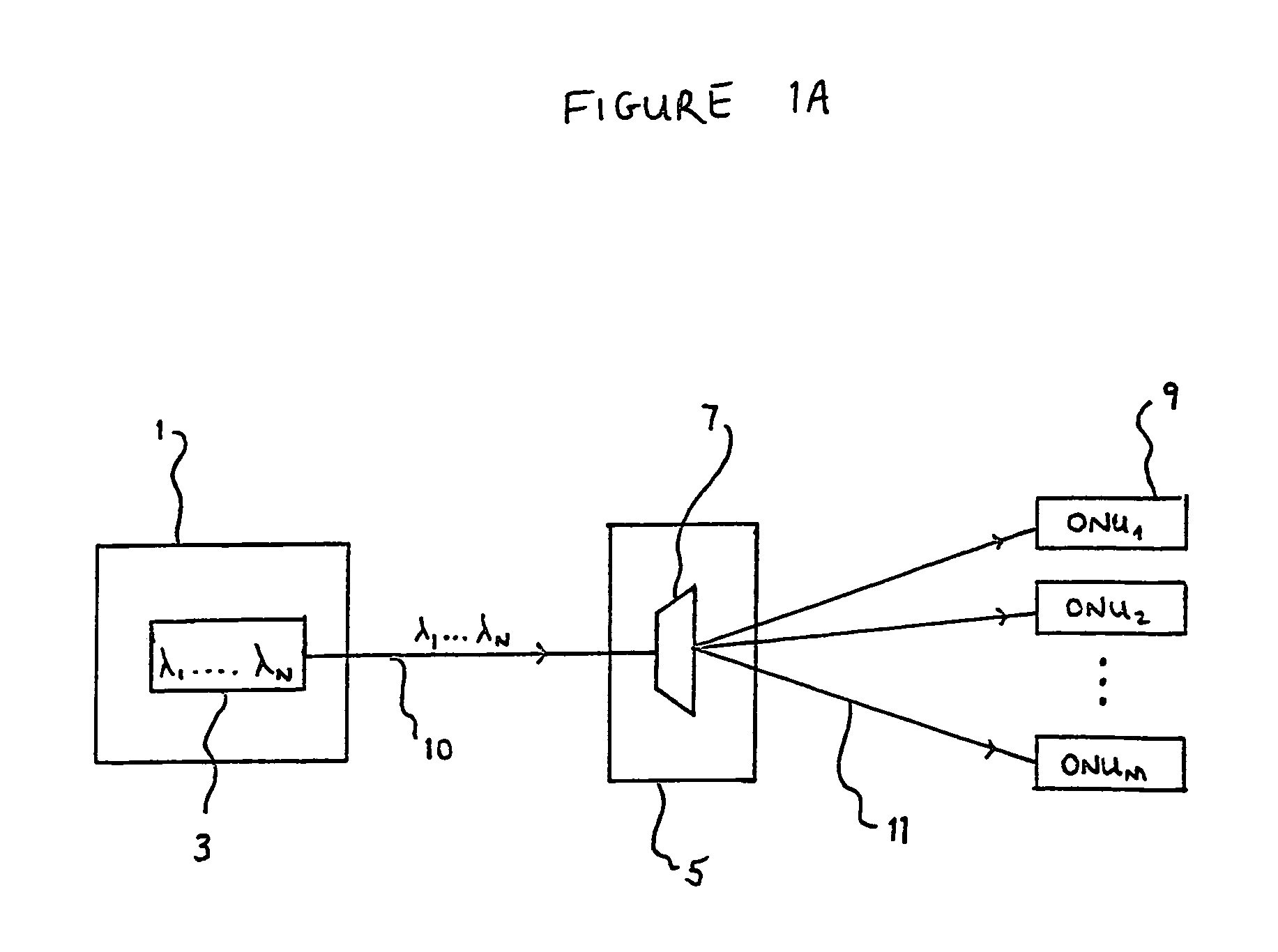
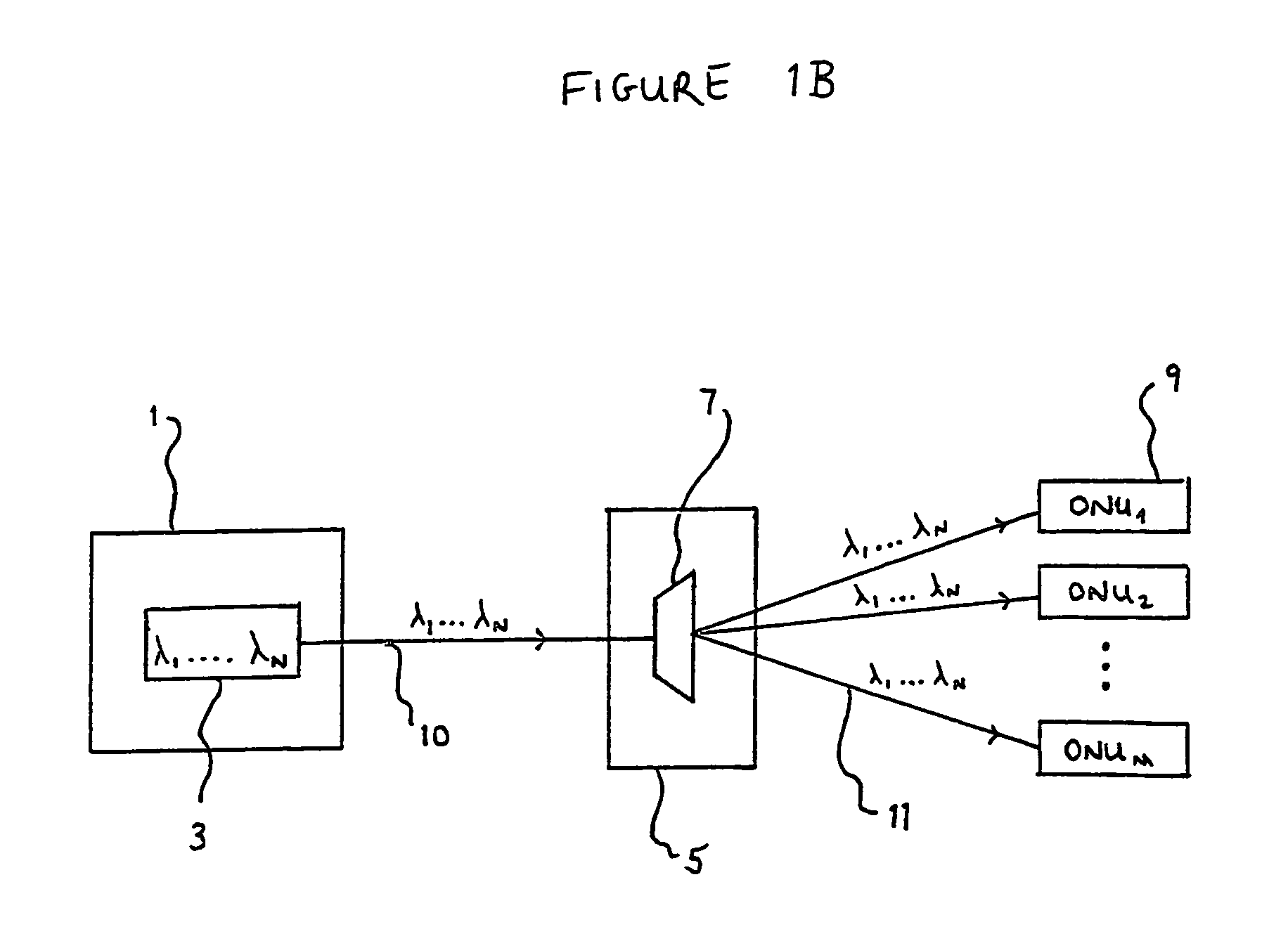
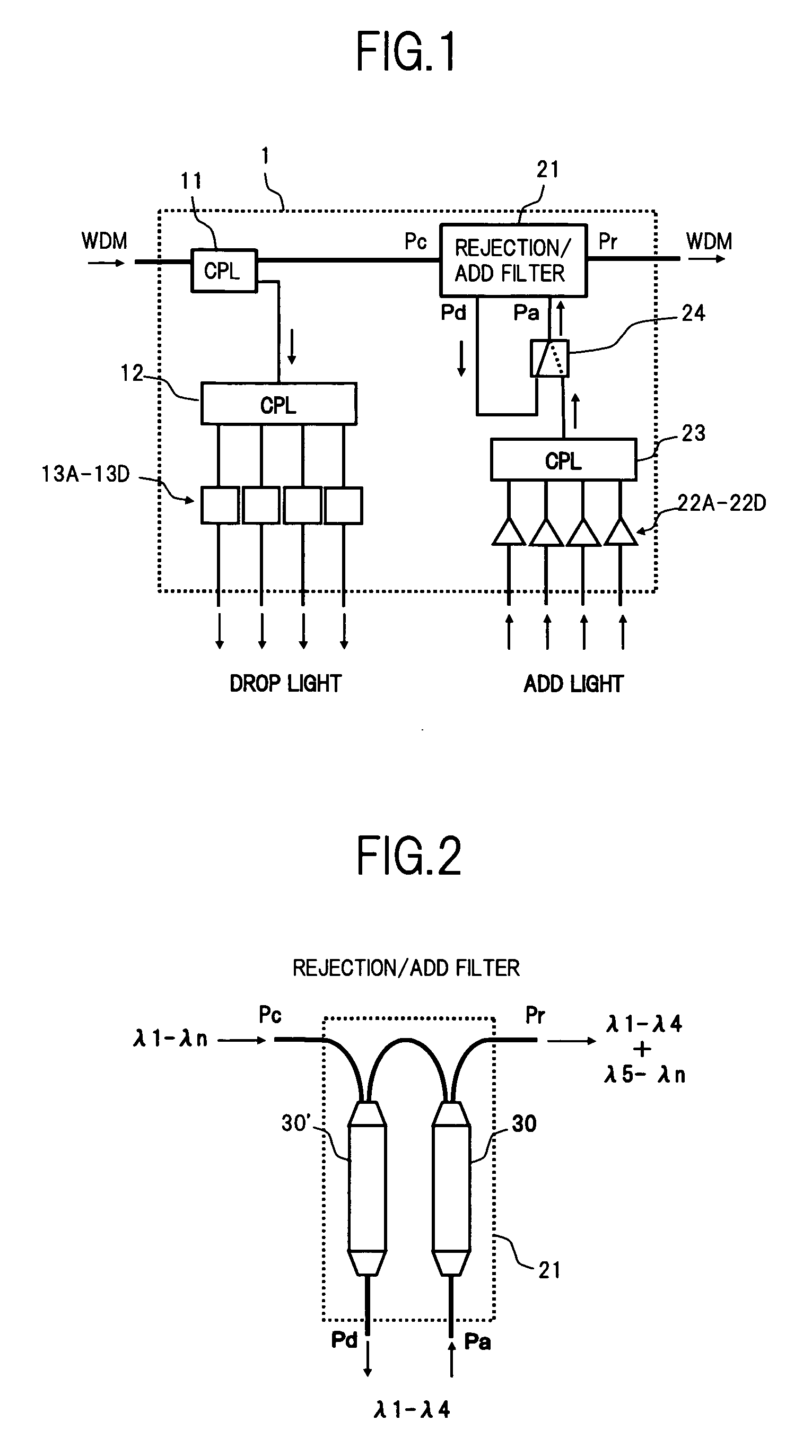
Wavelength-selective and loss-less optical add/drop multiplexer
InactiveUS6122095ALoss can be compensatedOvercomes shortcomingRing-type electromagnetic networksWavelength-division multiplex systemsFiberGrating
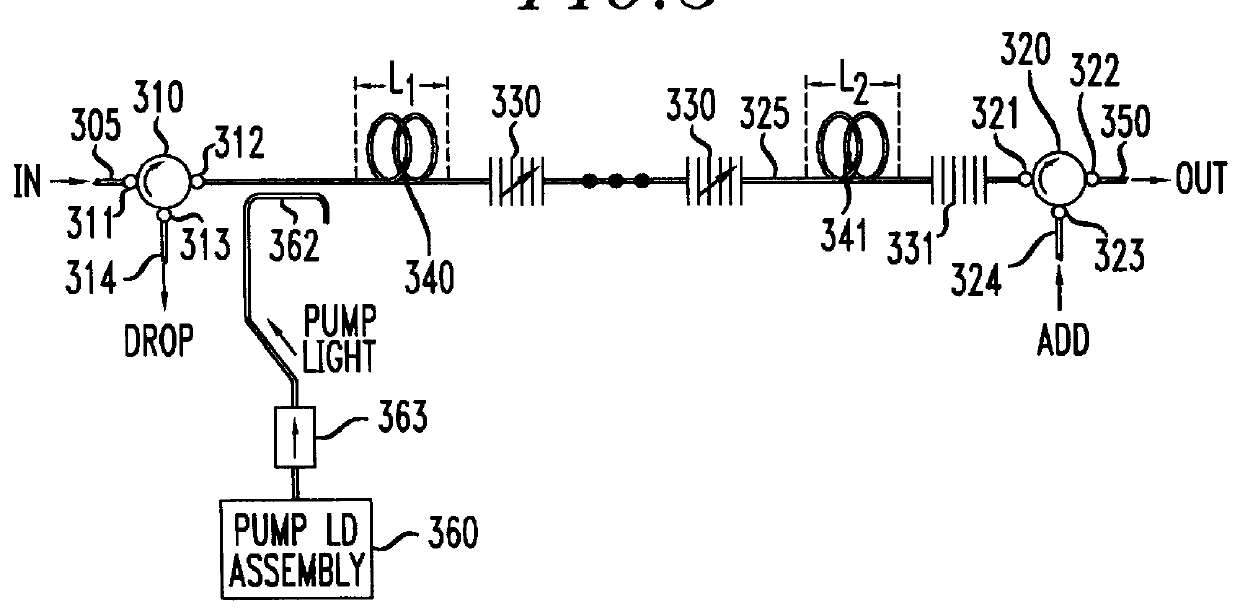
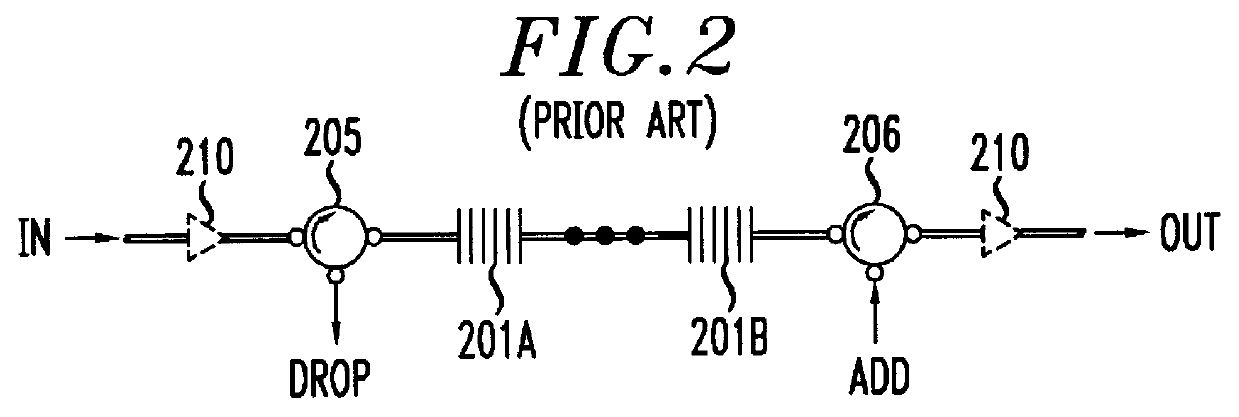
A loss-less, optical add / drop multiplexer according to the present invention includes a rare earth-doped fiber amplifier integrated with a wavelength-selective fiber path coupled between two directional optical transfer devices for selectively adding and dropping optical signals from a multi-wavelength signal, such as a wavelength division multiplexed optical signal. One or more fiber gratings are disposed along the length of the rare earth-doped fiber amplifier or between segments of the rare earth-doped fiber so that at least one grating is used for reflecting each optical signal that is expected to be added to or dropped from the multi-wavelength optical signal. By using this configuration, appropriate amplification is provided to compensate for losses in the add, drop, and through paths.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE +1
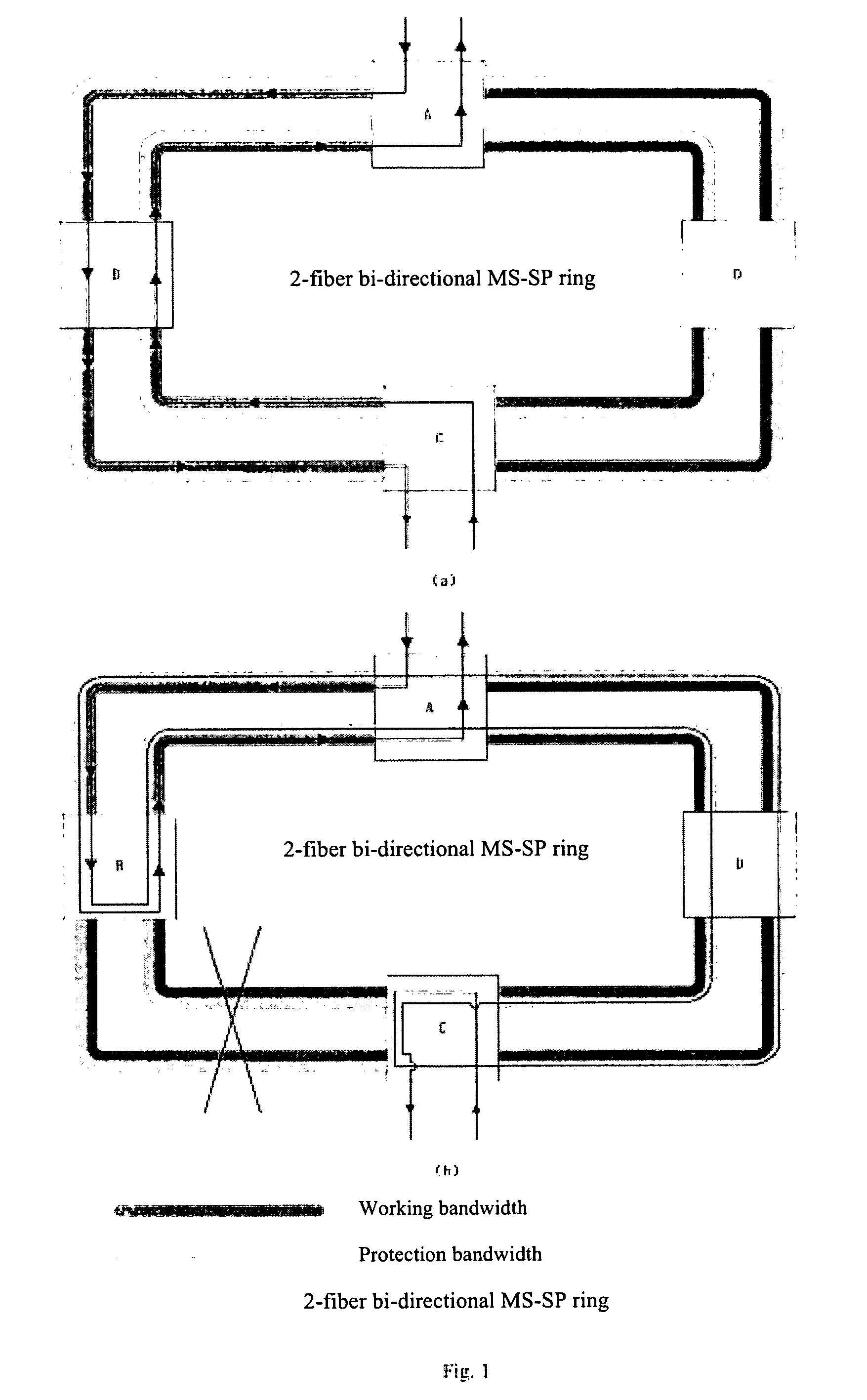
Self-healing network
InactiveUS6088141AShorten the timeRing-type electromagnetic networksLaser detailsSelf-healingProtection ring
PCT No. PCT / SE96 / 00794 Sec. 371 Date May 27, 1998 Sec. 102(e) Date May 27, 1998 PCT Filed Jun. 18, 1996 PCT Pub. No. WO97 / 01907 PCT Pub. Date Jan. 16, 1997A communication network system having at least three nodes, which are interconnected by transmission links carrying traffic to and from the nodes. The transmission links are divided into a working ring and a protection ring where the working ring and the protection ring can transmit traffic in opposite directions. A node is able to detect when an error occurs in the surrounding transmission links or the node itself. Each node can, by itself, divert traffic from the working ring to the protection ring and / or from the protection ring to the working ring. A recovery action is performed when the error is healed.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Optical path switch apparatus of optical LAN system
InactiveUS20060159388A1Suppressing networkSimple configurationMultiplex system selection arrangementsRing-type electromagnetic networksEngineeringPrism
In an optical LAN system, an optical connector is provided between the input and output optical fiber cables and each of the node devices. The optical connector includes a movable body (a switch body) having a prism. The movable body is switched selectively between a first position (a first state) at which the input and output optical fiber cables are optically connected to the node device and a second position (a second state) in which the input optical fiber cable and the output optical fiber cable are optically connected to each other in such a manner as to bypass the node device. This arrangement suppresses a network crash by means of a relatively simple configuration.
Owner:PACIFIC INDUSTRIAL CO LTD
Network managing apparatus, optical add/drop multiplexer, and network managing method
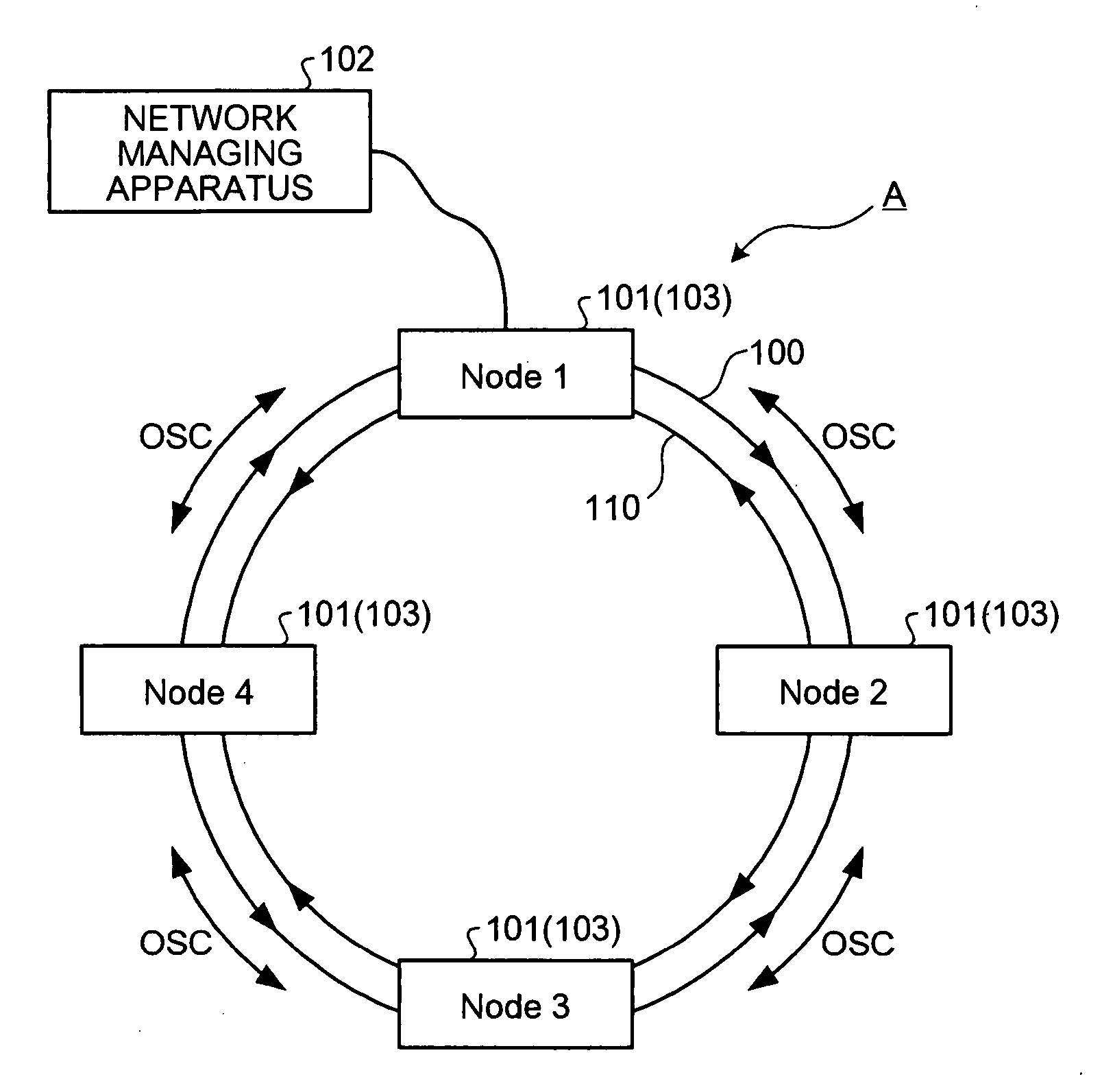
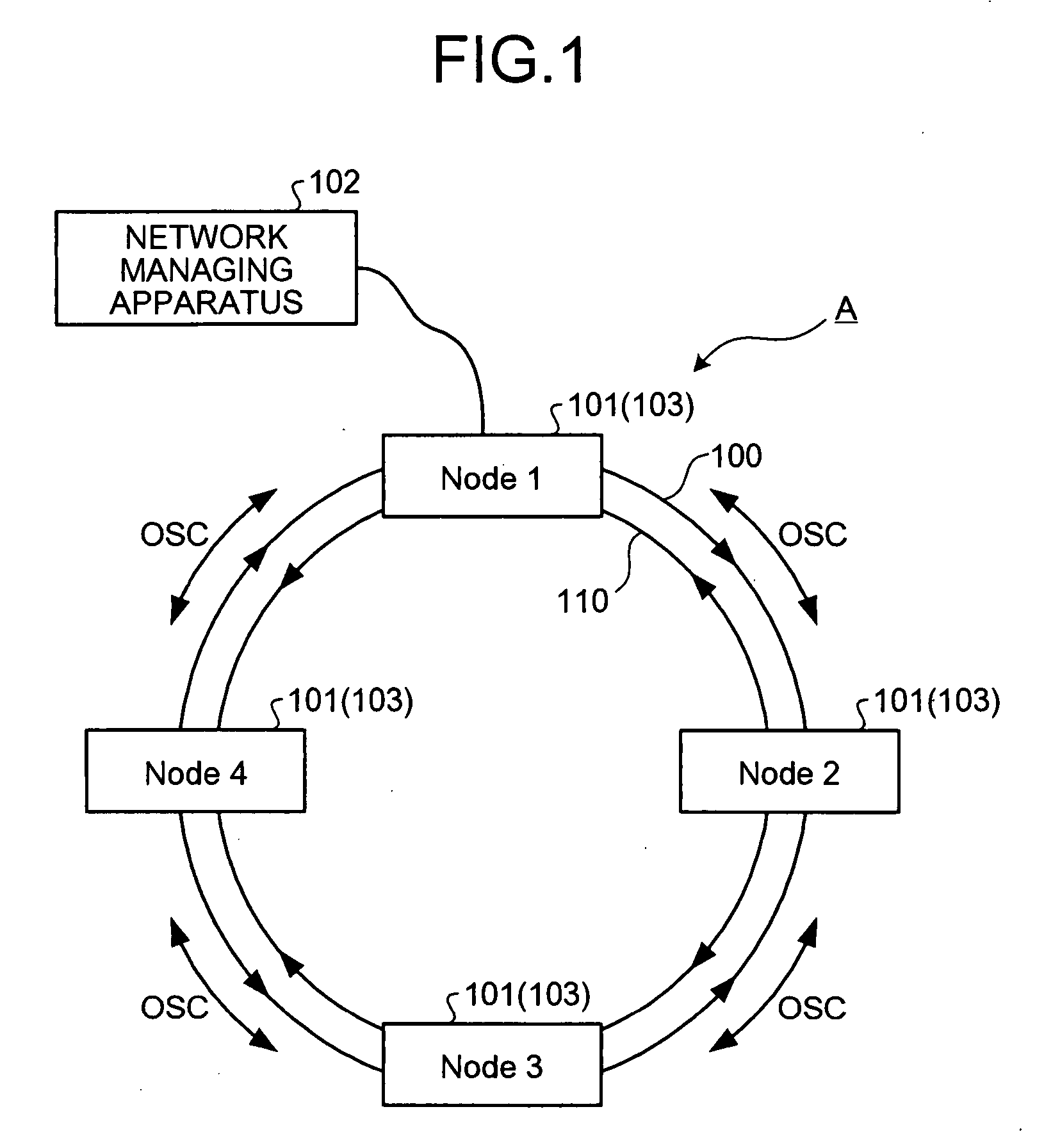
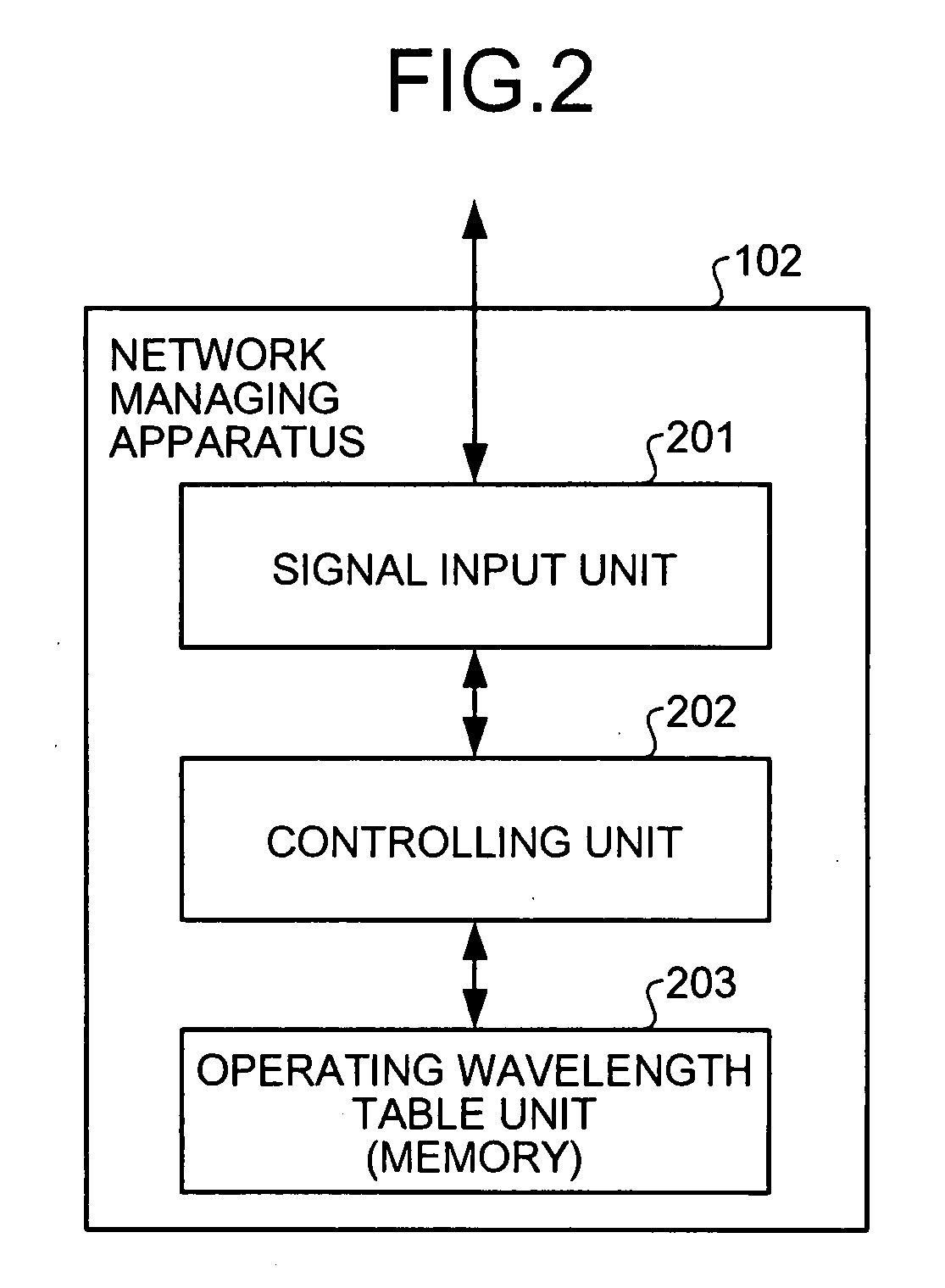
A network managing apparatus is connected to one of multiple OADM nodes that execute optical communication on an optical ring network configured by a two-line transmission path including of an active line and a backup line. The apparatus includes a storing unit that stores arrangement information of the OADM nodes and operating wavelength information of optical signals transmitted by the nodes. A controlling unit updates the operating wavelength information retained in the storing unit based on fault information from the OADM nodes and distributes the updated operating wavelength information to the OADM nodes.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
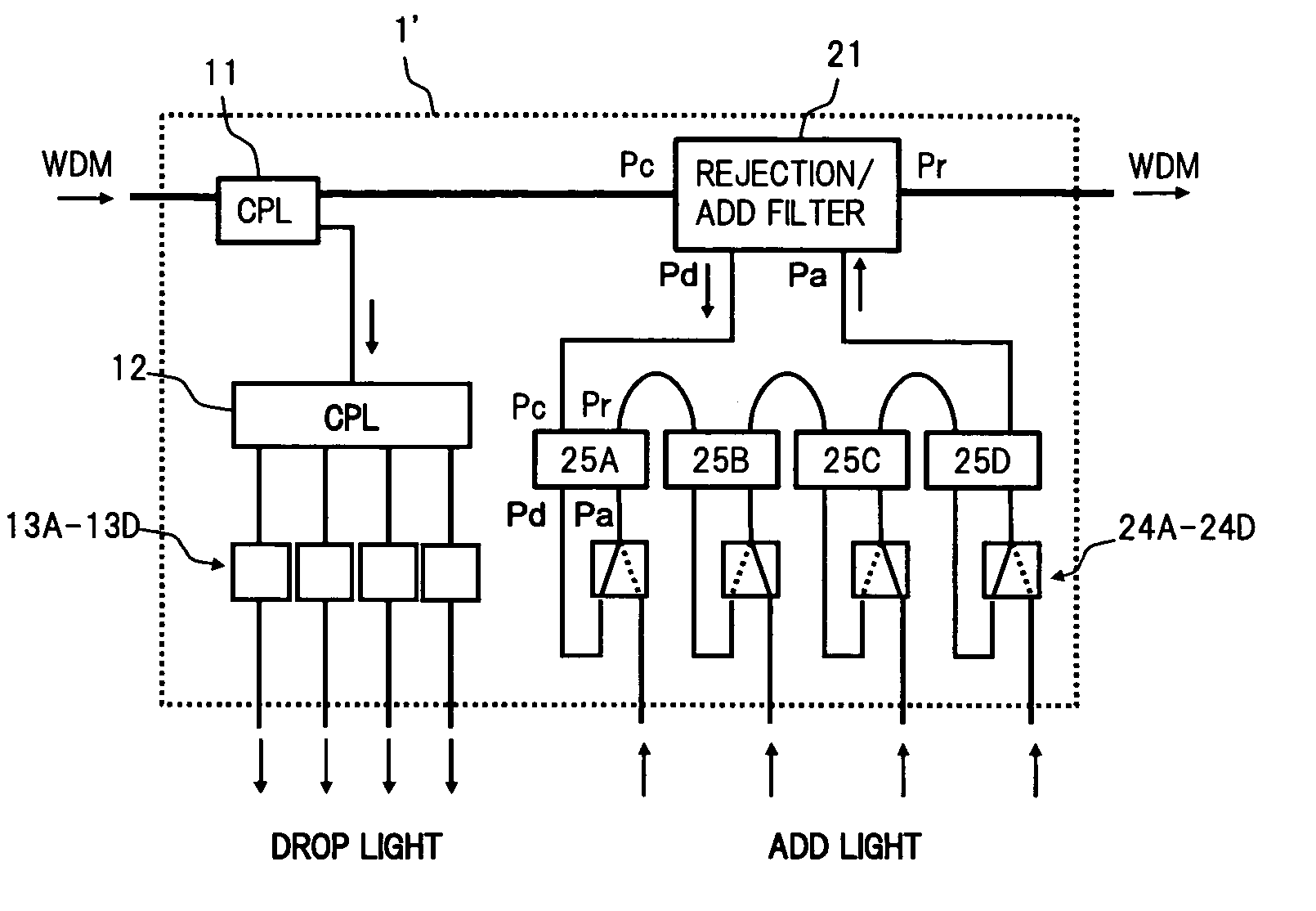
Optical add/drop multiplexer
ActiveUS20060034610A1Multiplex system selection arrangementsRing-type electromagnetic networksMultiplexerLength wave
A core unit arranged in a transmission path includes a through path for causing an input signal to an input port to pass through to an output port, a drop-side port 25a that drops the input signal having a predetermined wavelength, and an add-side port 25b that adds channel having a predetermined wavelength to the input light.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Optical communication network system
ActiveUS20060153496A1Quickly reconfiguredOptimizationMultiplex system selection arrangementsRing-type electromagnetic networksGratingLength wave
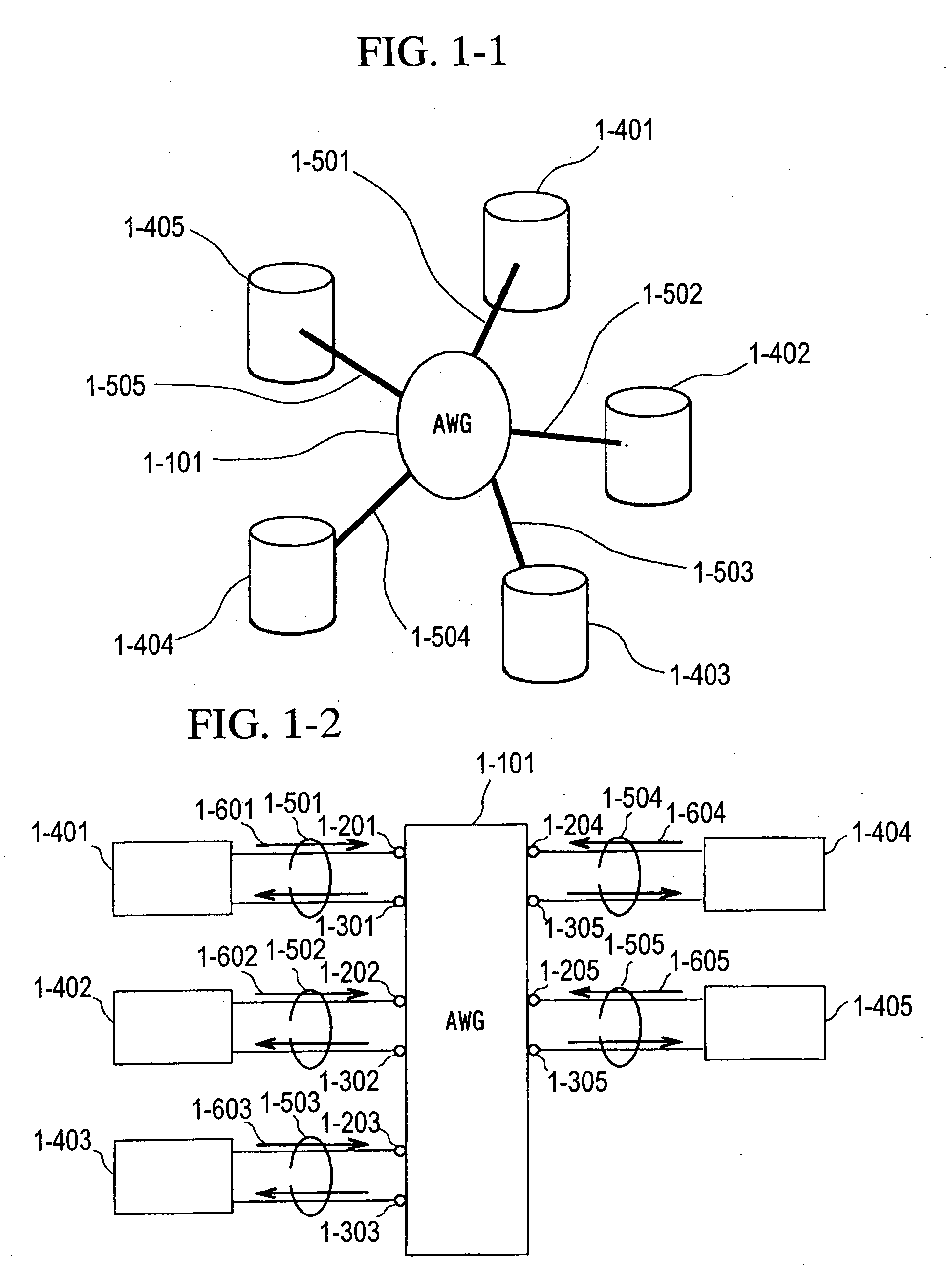
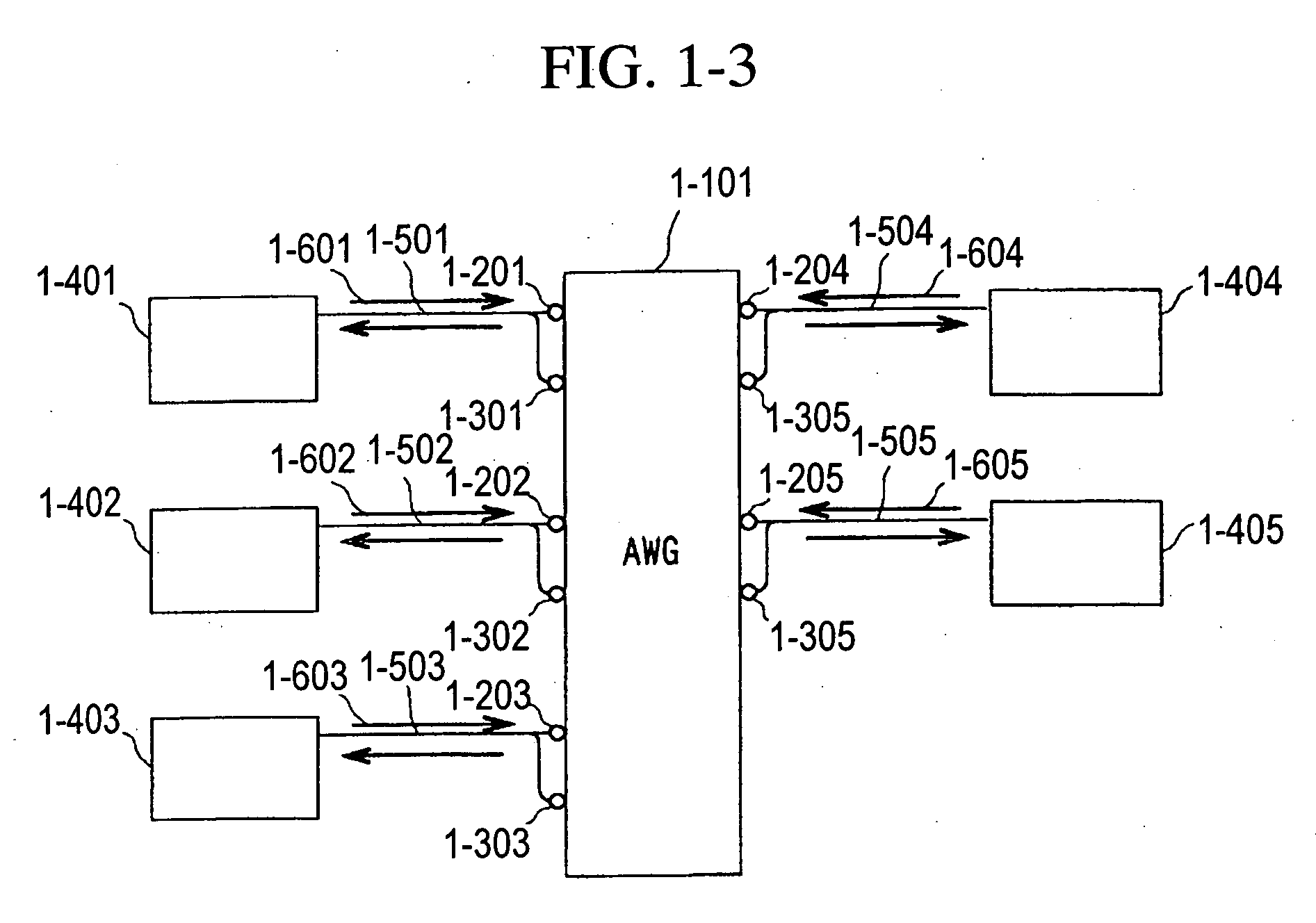
A fiber optic communication system includes a device of switching and setting wavelength of optical signals used in communication by network-node equipments, which sets the mapping of the wavelength of the optical signal used in communication by the network node equipments, and the input / output ports of an array waveguide grating (AWG), so as to construct a predetermined logical network topology by a plurality of network node equipments which are connected via optical fibers to the array waveguide grating that outputs optical signals inputted to optical input ports, to predetermined optical output ports in accordance with the wavelength thereof. As well as enabling a simple construction, it is easy to realize flexible network design, construction, and operation, and different network groups can also be easily connected to each other. Moreover, a fiber optic communication system having robust security and which can be stably operated even at the time of failure is realized at low cost.
Owner:NIPPON TELEGRAPH & TELEPHONE CORP
Optical interconnection circuit among wavelength multiplexing chips, electro-optical device, and electronic apparatus
InactiveUS20040264867A1Easy to makeThe transmission is compactRing-type electromagnetic networksLaser detailsMultiplexingLength wave
To provide an optical interconnection circuit among wavelength multiplexing chips, capable of increasing signal transmission speed and of being easily made minute thereby being simply and easily fabricated, an electro-optical device, and an electronic apparatus, an optical interconnection circuit among wavelength multiplexing chips, which is disposed on a substrate, includes micro-tile shaped elements having a light emitting function or a light receiving function with wavelength selectivity.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
System and apparatus for radial optical distribution
ActiveUS20060165365A1Improving fiber organizationImproving routing managementRing-type electromagnetic networksOptical fibre/cable installationDistribution systemEngineering
Embodiments of the invention include an apparatus and system for managing and radially distributing optical fibers from a first location, such as a central office, to a plurality of destination locations, such as homes within a neighborhood. The apparatus includes a distribution panel having a central hub or ring, and both a plurality of optical input elements and a plurality of optical output elements disposed radially around the central hub. The optical input elements split the fibers coupled from the first location into a plurality of individual fibers that are routed to the central hub. The central hub radially distributes the plurality of fibers to appropriate optical output elements, which are coupled to destination fibers routed to the plurality of destination locations. The radial configuration of the apparatus provides a central breakout point for fiber distribution, thus improving fiber organization and routing management compared to conventional routing and distribution systems.
Owner:FURAKAWA ELECTRIC NORTH AMERICA INC
Apparatus and method for optical communication protection
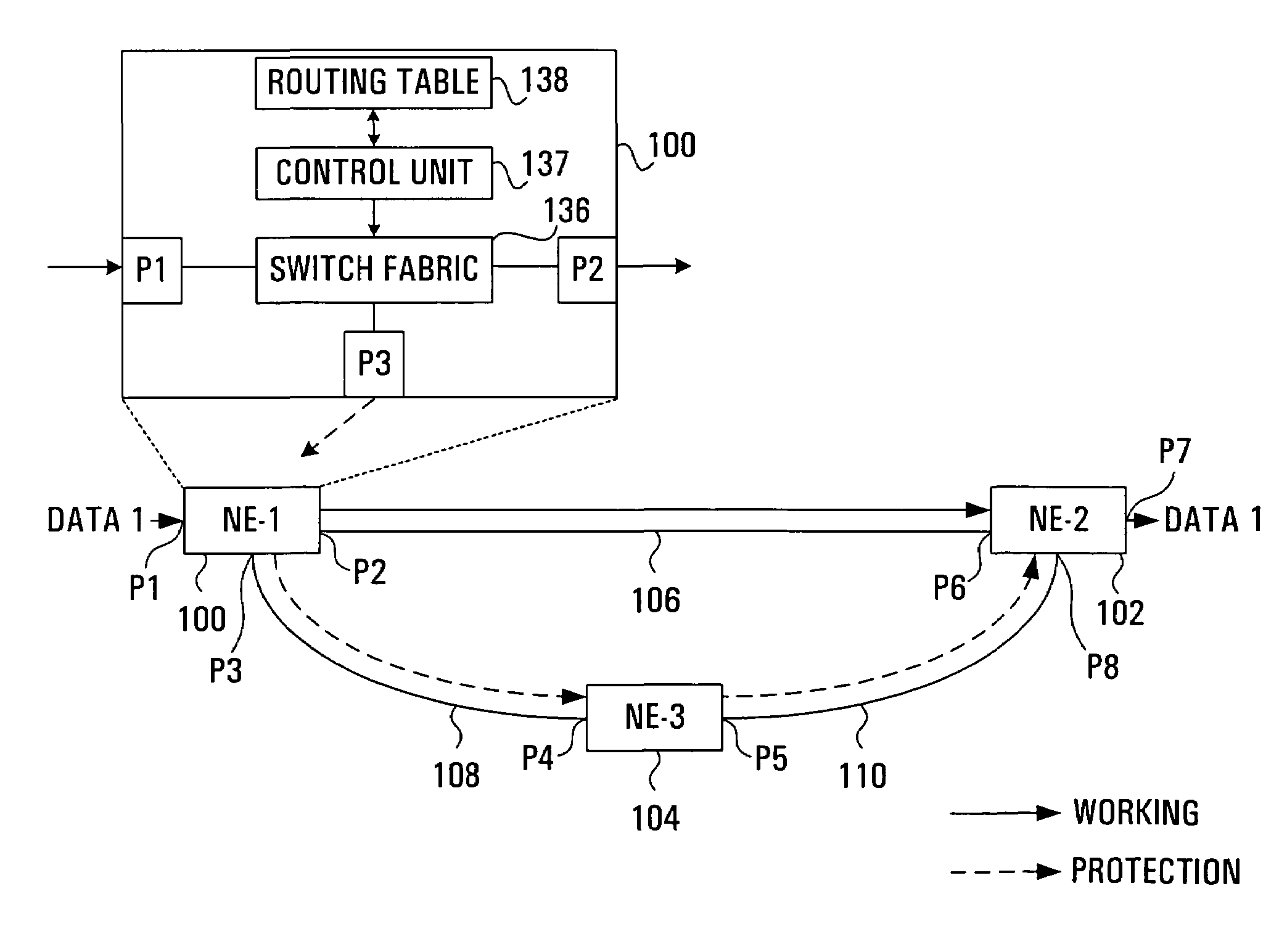
InactiveUS6934248B1Improve efficiencyRing-type electromagnetic networksError preventionTraffic capacityRouting table
Protection techniques within optical communication networks are extremely important. An alternative to a line protection scheme, as most current optical communication networks use, is to utilize a path protection technique in which working and protection paths that are desired are assigned during network setup. During normal operations, only the working path is configured within the network elements' switch fabric with protection paths being left unconfigured. If a failure indication is detected in the working path by a network element, a protection entry within a routing table of the network element is looked up to determine protection switching data that is required to switch the data traffic to the pre-assigned protection path. This protection switching data is inserted within the path overhead for the data traffic so that it can be communicated to all of the network elements that require their switch fabrics reconfigured to establish the protection path of communications. This protection technique allows for similar switching speed to that of line switching protection such as BLSR designs, but with an increase in efficiency in terms of protection bandwidth.
Owner:CIENA
Single-fiber protection in telecommunications networks
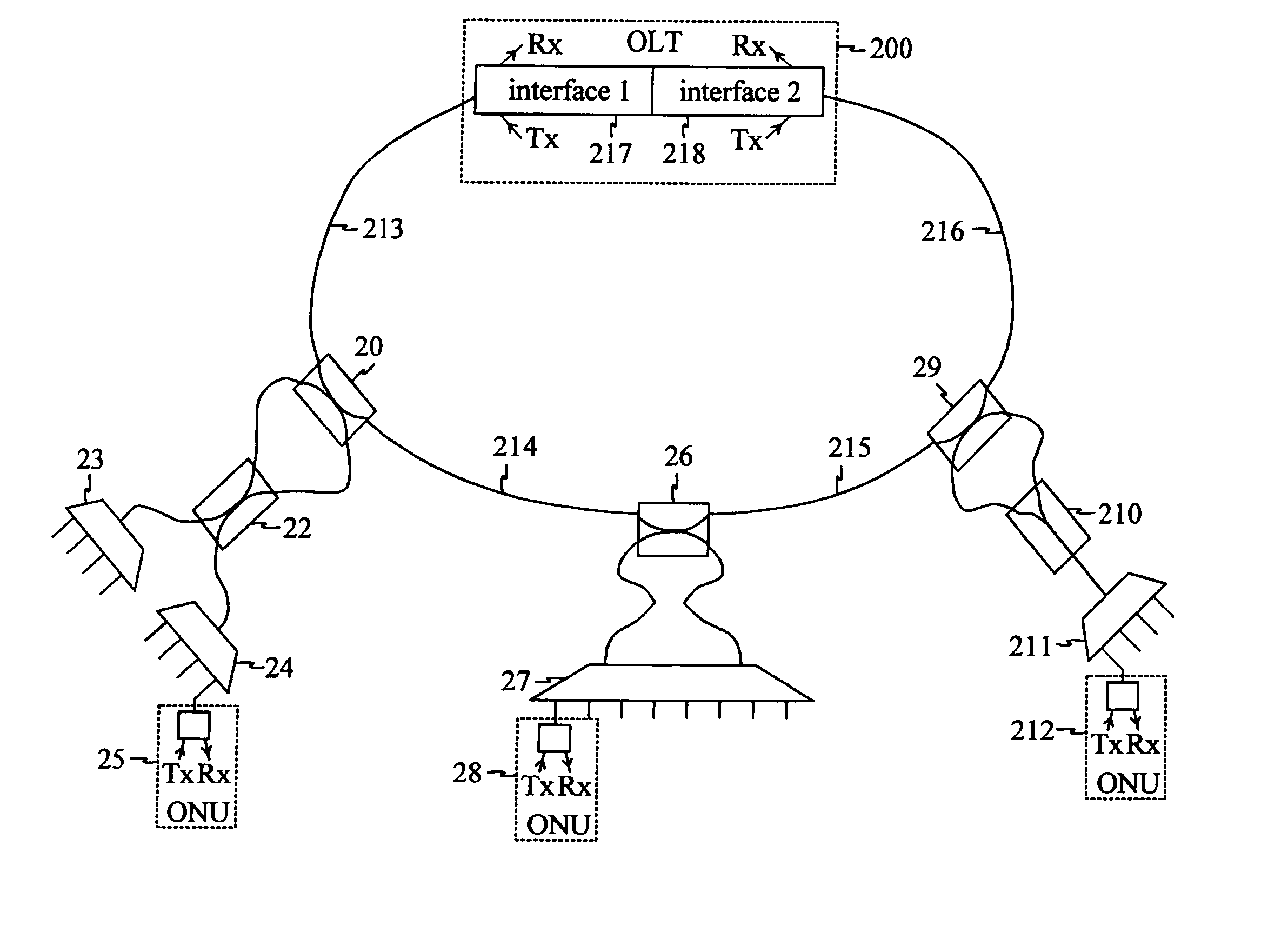
ActiveUS20050019031A1Efficient solutionCost-effectiveRing-type electromagnetic networksLaser detailsTelecommunications networkOptical power
A solution for detecting and recovering from a failure in a protected single-fiber passive optical network. A detector is used to detect the degradation in power level of optical signals. Furthermore, the invention discloses a variable symmetric split ratio approach to improve the number of splits (e.g. the number of ONUs). A single-fiber passive optical network is disclosed that uses a plurality of passive nodes connected in the optical fiber between the interfaces, wherein in the passive nodes 2-by-2 splitters / combiners are used to couple optical power from and into the optical fiber at a predetermined split ratio.
Owner:SCHOFIELD TECH
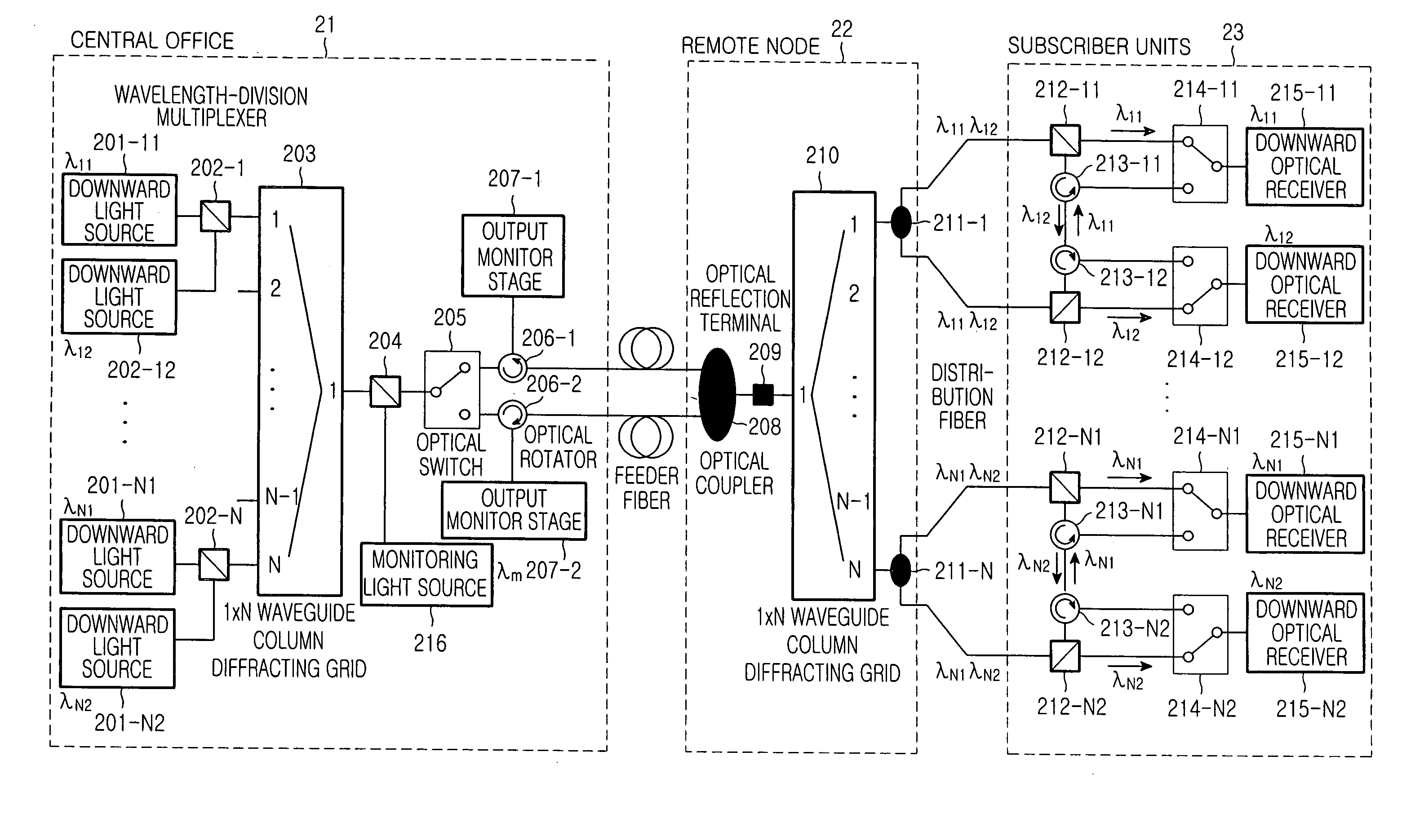
Wavelength-division multiplexed self-healing passive optical network
InactiveUS20050141892A1Detected accidentallyRing-type electromagnetic networksLaser detailsTelecommunicationsControl signal
A wavelength-division multiplexed self-healing passive optical network is capable of detecting cut-off and deterioration of feeder fiber and distribution fiber and restoring a network with a star structure. The network includes a central office, a remote node, and a plurality of subscriber units. Working and protection feeder fibers connect the central office to the remote node. A reflection unit at an end of the remote node connects to the central office for reflecting a monitoring optical signal transmitted from the central office. An output monitor stage at an end of the central office connects to the remote node for detecting the reflected monitoring optical signal and generating a control signal based on the presence of abnormality of the working and protection feeder fibers.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Add/drop multiplexer node
InactiveUS6134036AReduce noise levelReduce decreaseMultiplex system selection arrangementsRing-type electromagnetic networksMultiplexingMultiplexer
PCT No. PCT / SE96 / 00813 Sec. 371 Date Feb. 10, 1998 Sec. 102(e) Date Feb. 10, 1998 PCT Filed Jun. 20, 1996 PCT Pub. No. WO97 / 01897 PCT Pub. Date Jan. 16, 1997An add / drop multiplexer node in an optical network comprises an optical channel-selective switch. The switch is operable in bar and cross states and has a first input for the reception of optical multiplexed channels, a second input connected to an output on a line terminal associated with the node for adding channels, a first output, which is bar coupled to the first input and connected to a line terminal input for dropping channels and a second output, which is bar coupled to the second input. A predetermined number of channels to be dropped are selected and the channel-selective switch cross-couples non-selected channels from the first input to the second output.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
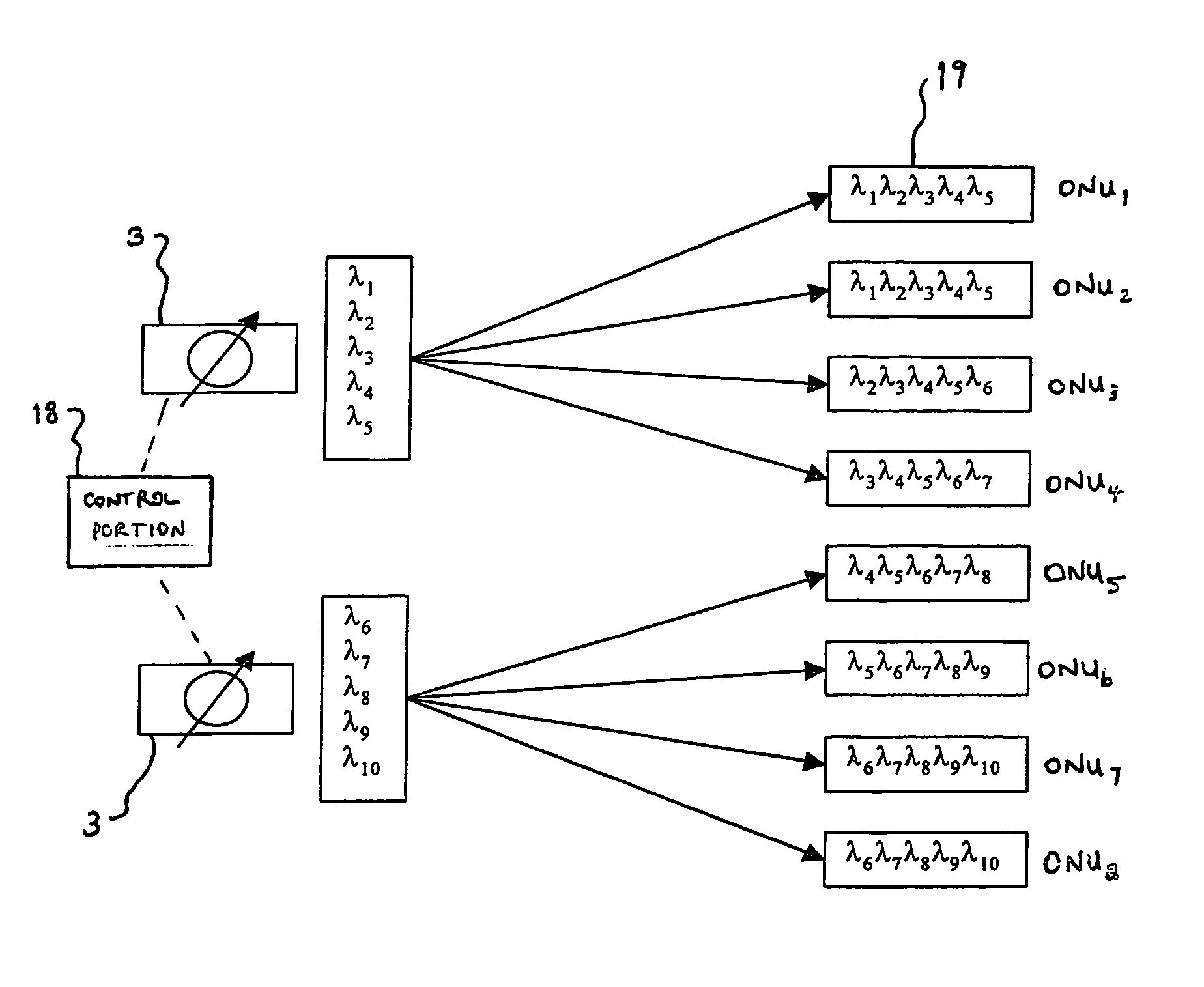
Optical network units preconfigured to accept predetermined subsets of wavelengths
InactiveUS7016608B1Multiplex system selection arrangementsRing-type electromagnetic networksLength waveOptical network unit
An optical network is provided which comprises a plurality of optical network units (19) and optical source means (3) connected and arranged to transmit light signals to each of the plurality of optical network units (19). The optical source means (3) are capable of transmitting light signals at one or more of a plurality of different wavelengths and at least one optical network unit (19) is operable to accept more than one of the said wavelengths. Further, each wavelength of the plurality is accepted by at least one of the optical network units (19) such that each such wavelength is accepted by a different subset of optical network units (19). The optical network further comprises control means (18) operable to cause the optical source means (3) to transmit light signals at one or more selected such wavelengths corresponding to respective desired subsets of the optical network units (19).
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
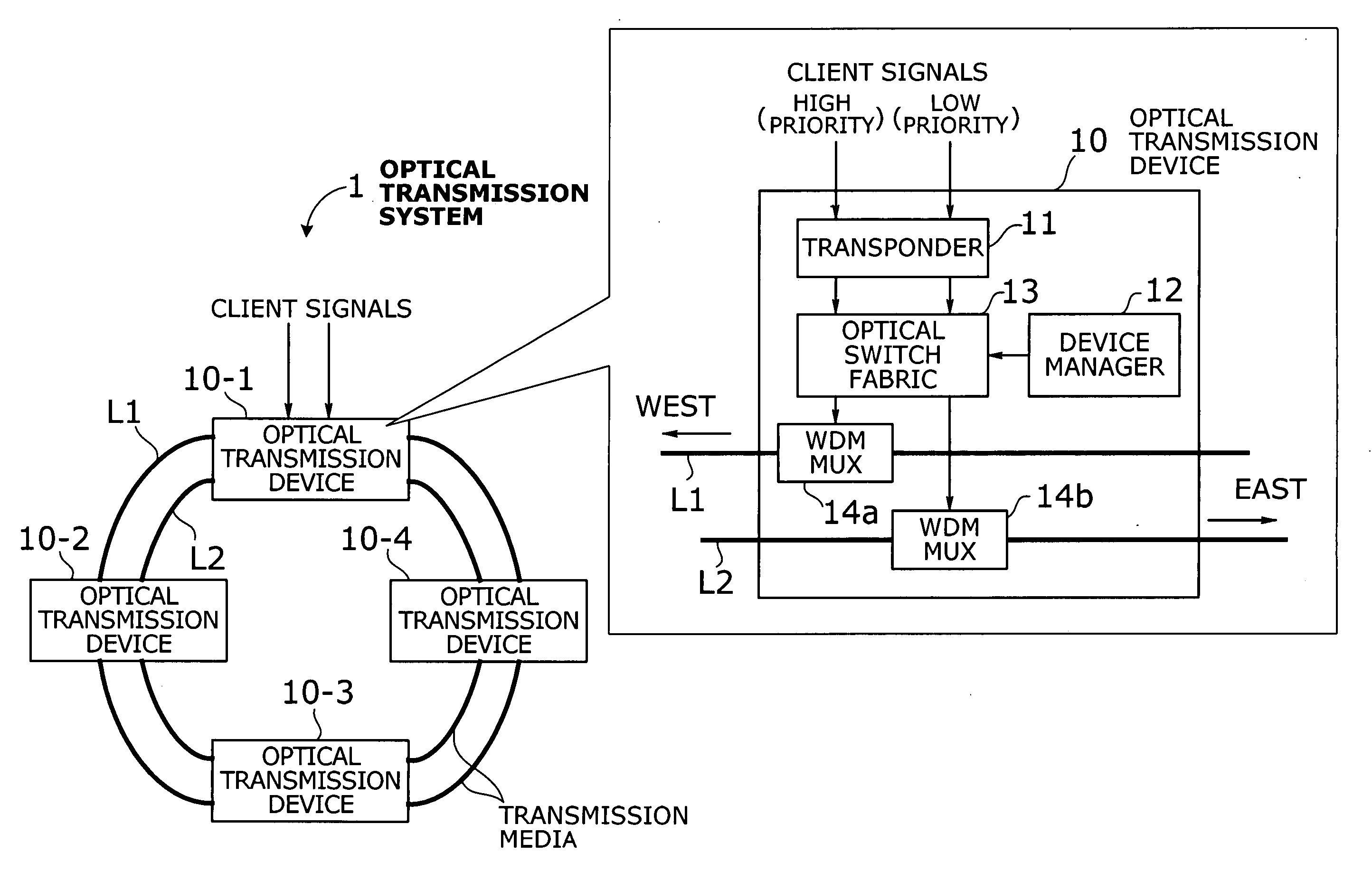
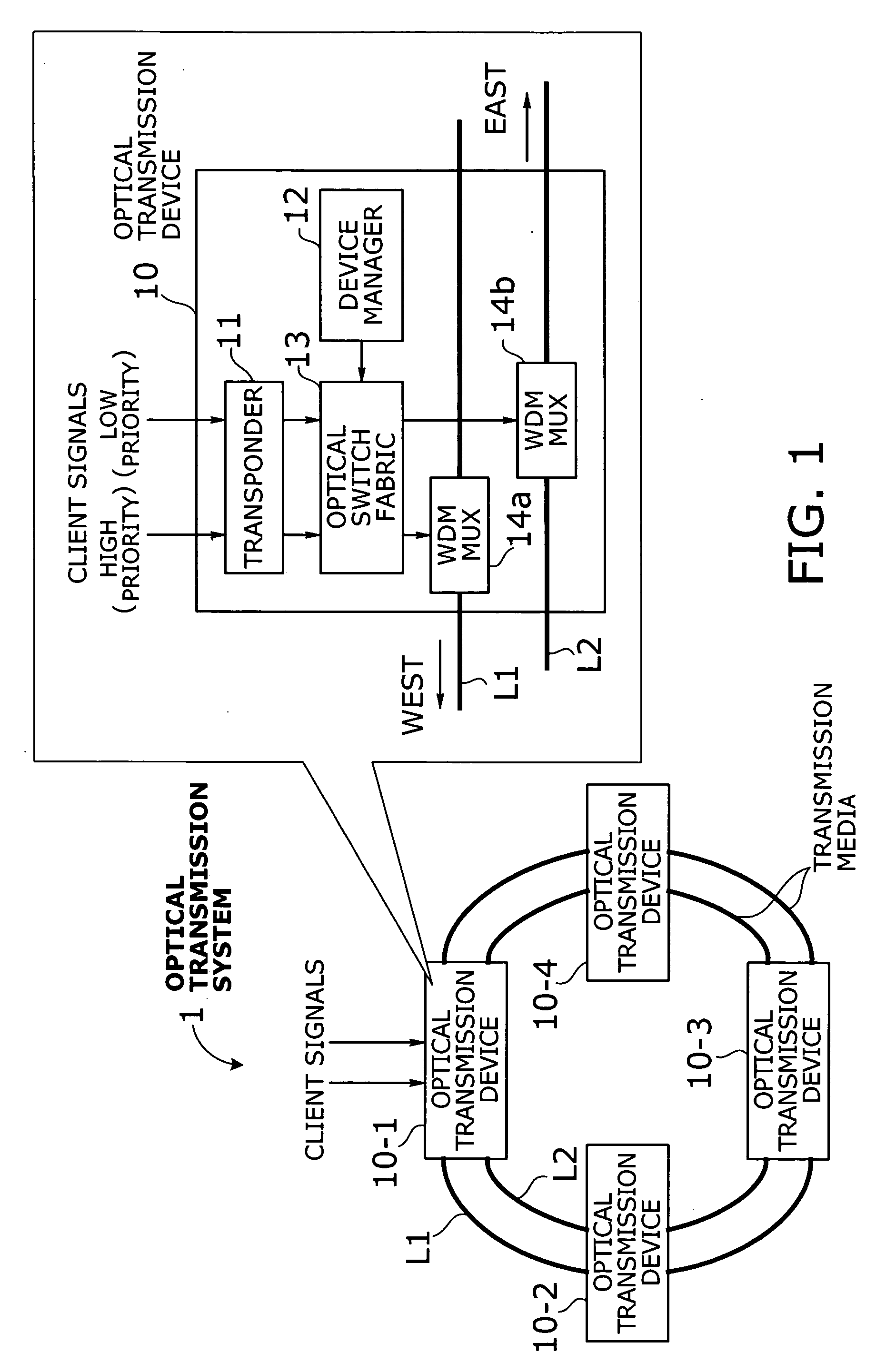
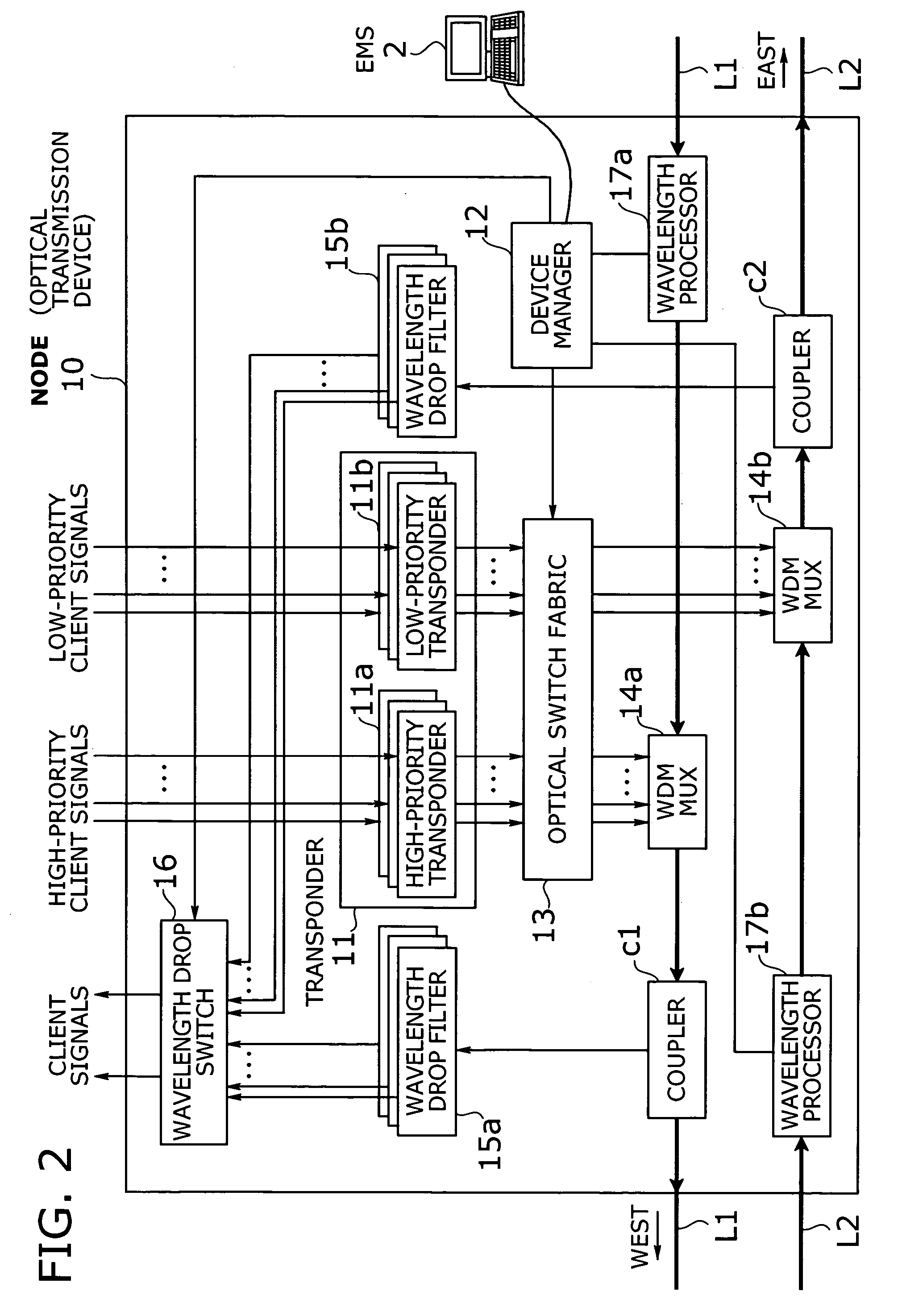
Optical transmission system with two-mode ring protection mechanism for prioritized client signals
InactiveUS20060013584A1Efficient use of bandwidthImprove fault toleranceRing-type electromagnetic networksWavelength-division multiplex systemsFault toleranceSurvivability
An optical transmission system that offers more efficient bandwidth usage in normal operation, as well as enhanced fault tolerance for higher service availability. A transponder converts high-priority and low-priority client signals into high-priority and low-priority wavelength signals to be added to network traffic. An optical switch fabric normally delivers high-priority and low-priority wavelength signals to high-priority and low-priority paths, respectively, where the two paths run in opposite directions. Such signals and paths are prioritized in terms of survivability against network failure. In case of a network failure, the optical switch fabric performs protection switching in either duplicate switching mode or path switchover mode depending on network failure information and drop wavelengths of each optical transmission device. In duplicate switching mode, high-priority wavelength signals are directed to both the high-priority and low-priority paths. In path switchover mode, they are routed to the low-priority path, instead of the high-priority path.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
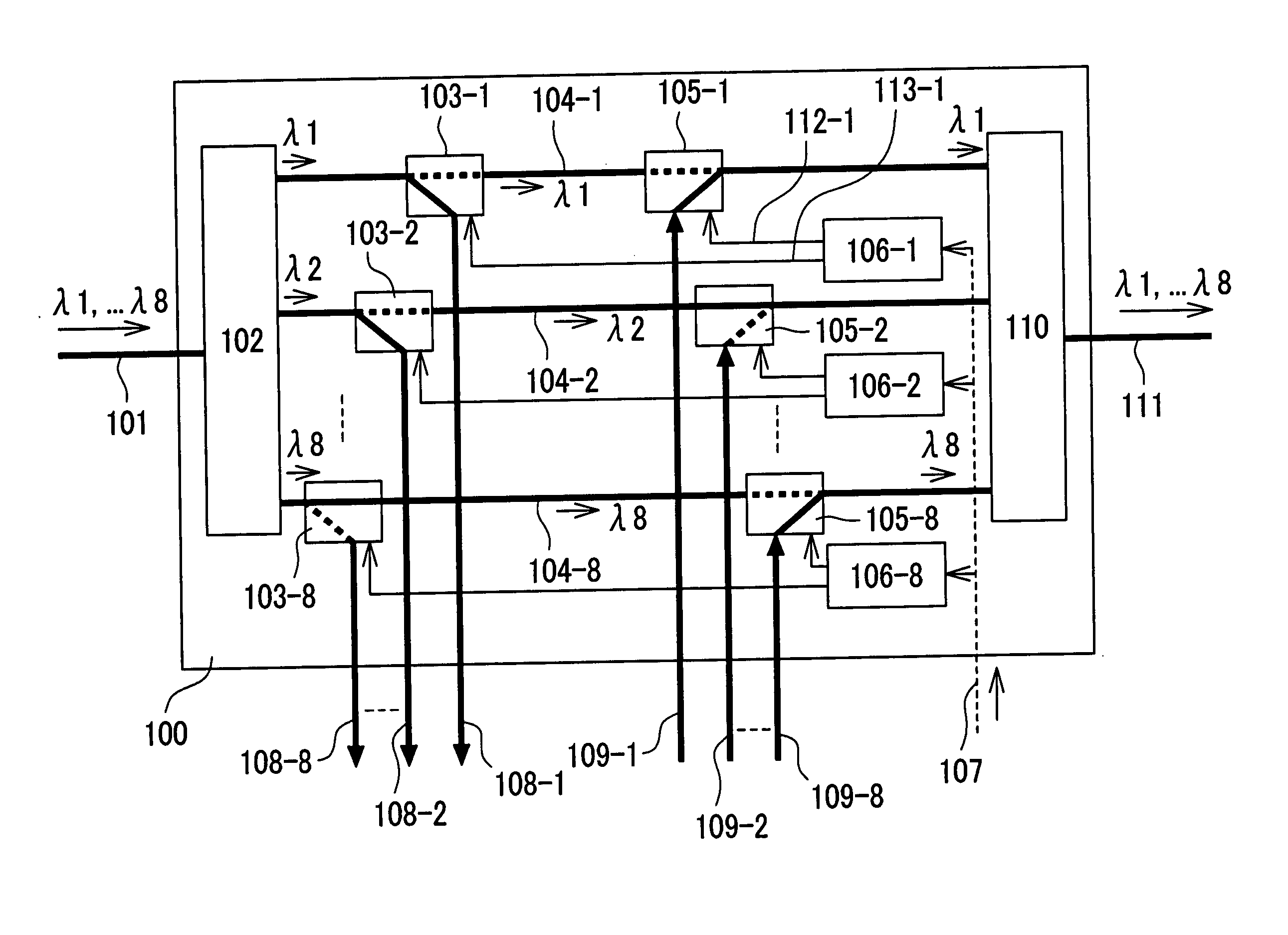
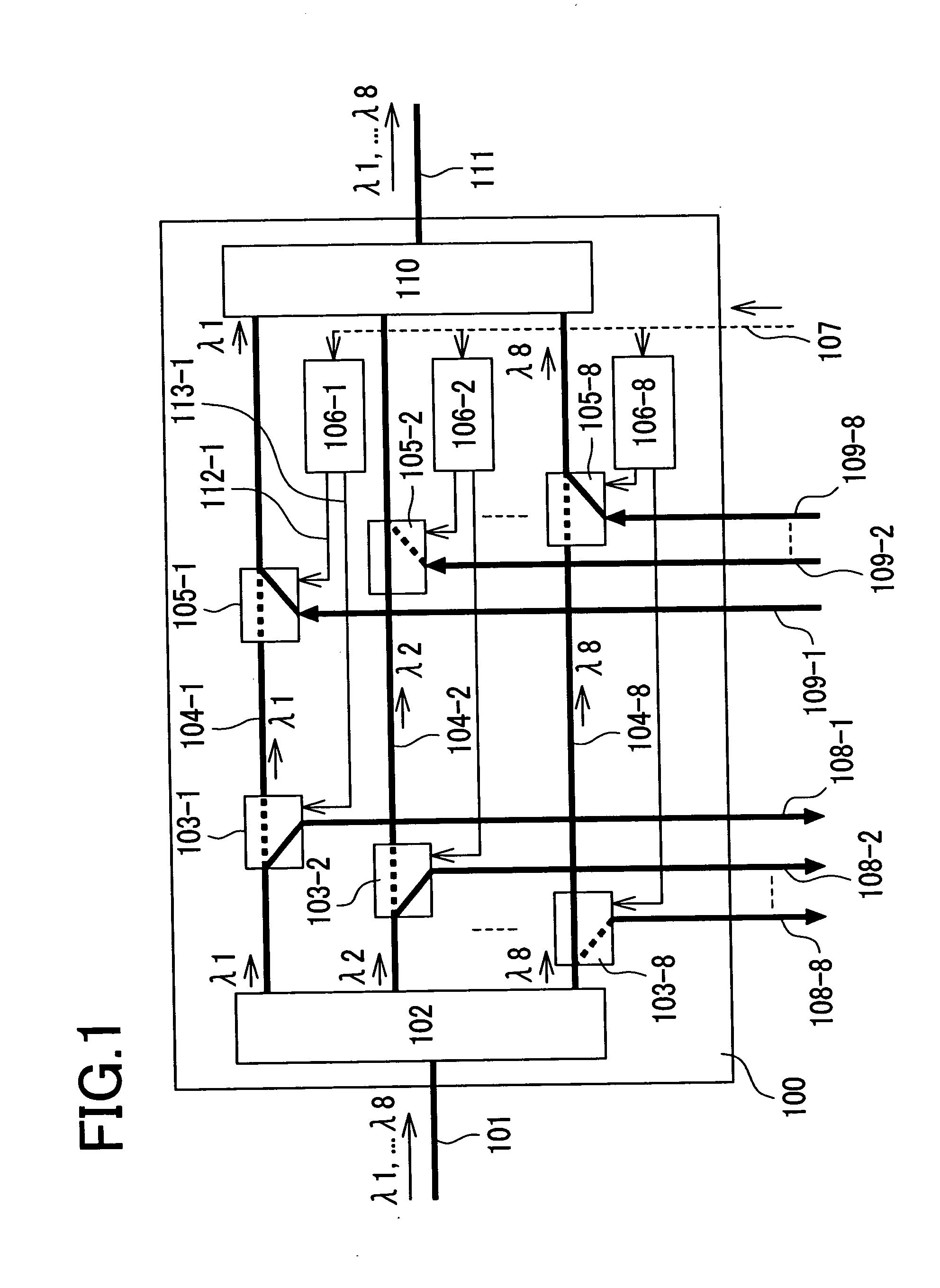
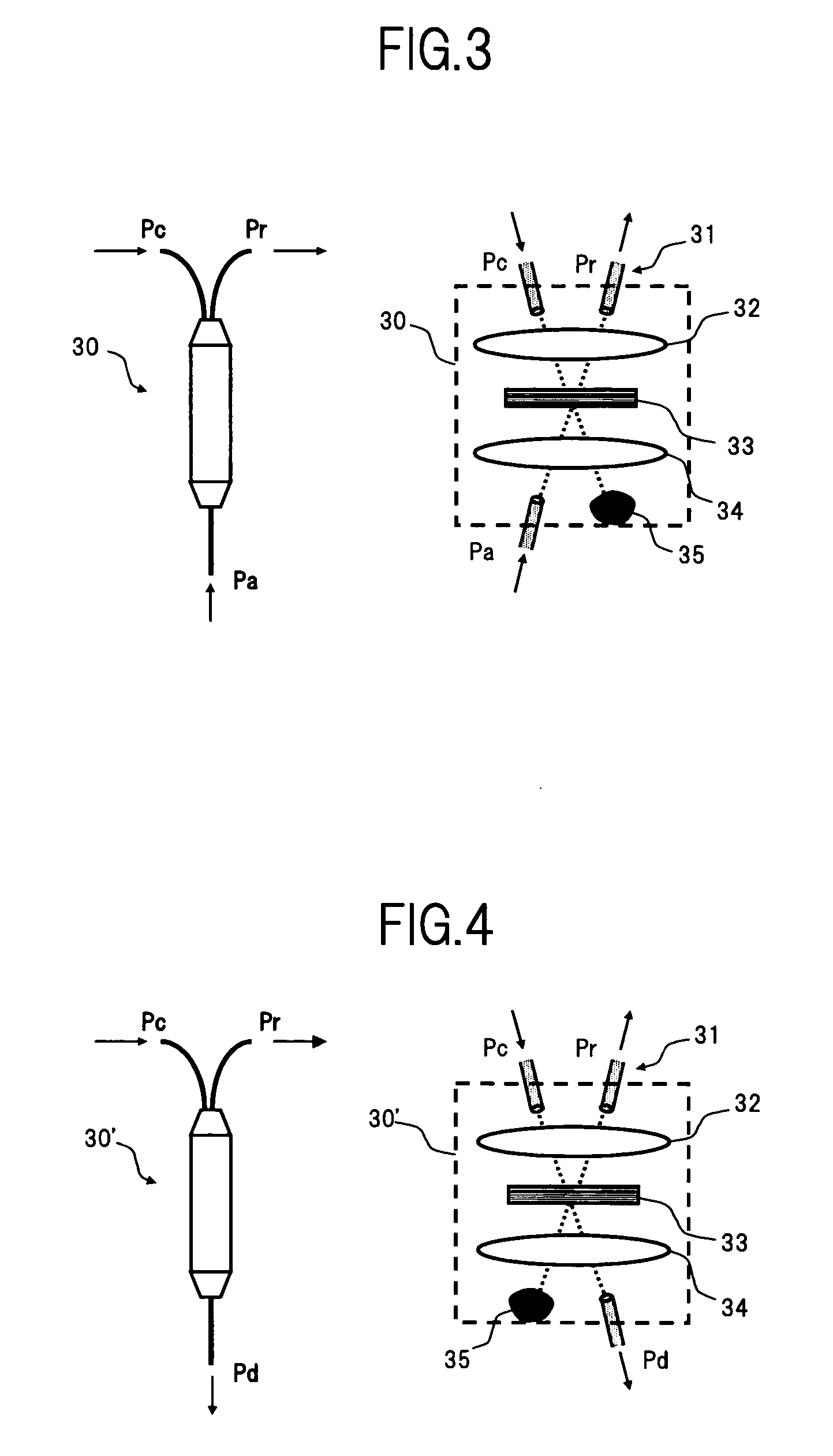
Optical add-drop multiplexer, and optical network equipment using the same
InactiveUS20060171717A1Achieve modularityRing-type electromagnetic networksWavelength-division multiplex systemsTransceiverOptical add-drop multiplexer
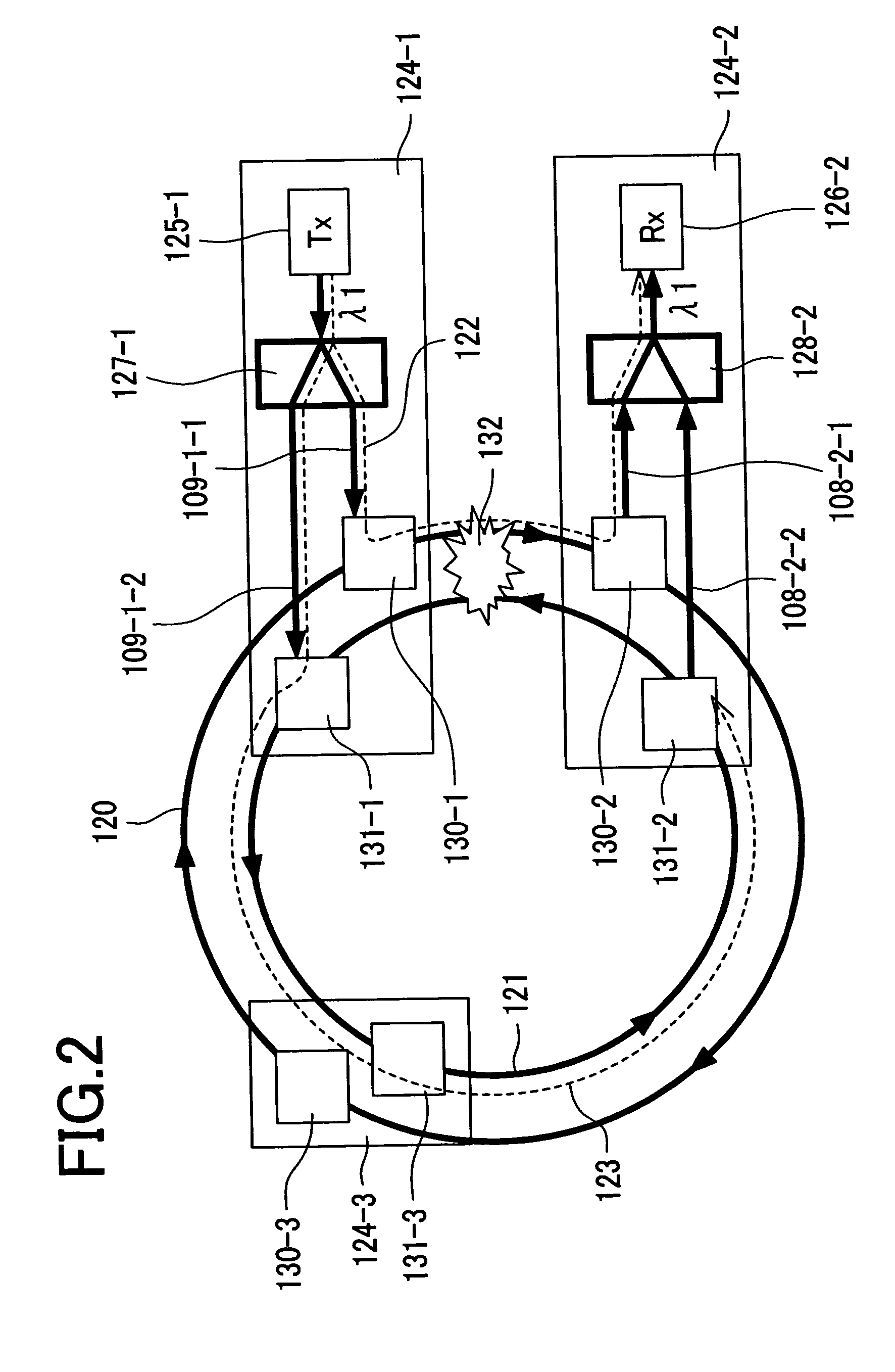
Heretofore, it was necessary to individually locate an optical switch, an optical switch control circuit, and the like, before and after an optical transceiver that performs optical protection. As a result, costs and the space for implementation increase, and a delay in services is also caused, which were the problems. For the purpose of solving the above problems, the present invention provides a simple optical protection method used in an optical add-drop multiplexer. Add switches 105-1 through 105-N and drop switches 103-1 through 103-N for optical signals corresponding to each wavelength in an optical add-drop multiplexer 100 are made controllable independently of one another. Add switches and drop switches of the active-side and backup-side optical add-drop multiplexers are switched by optical switch control circuits 106-1 through 106-N respectively to make a detour around a failure so that the optical protection is achieved.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Optical communication network system
ActiveUS7298974B2Quickly reconfiguredOptimizationMultiplex system selection arrangementsRing-type electromagnetic networksNetworked systemFiber-optic communication
A fiber optic communication system includes a device of switching and setting wavelength of optical signals used in communication by network-node equipments, which sets the mapping of the wavelength of the optical signal used in communication by the network node equipments, and the input / output ports of an array waveguide grating (AWG), so as to construct a predetermined logical network topology by a plurality of network node equipments which are connected via optical fibers to the array waveguide grating that outputs optical signals inputted to optical input ports, to predetermined optical output ports in accordance with the wavelength thereof. As well as enabling a simple construction, it is easy to realize flexible network design, construction, and operation, and different network groups can also be easily connected to each other. Moreover, a fiber optic communication system having robust security and which can be stably operated even at the time of failure is realized at low cost.
Owner:NIPPON TELEGRAPH & TELEPHONE CORP
Radio base station with multiple radio frequency heads
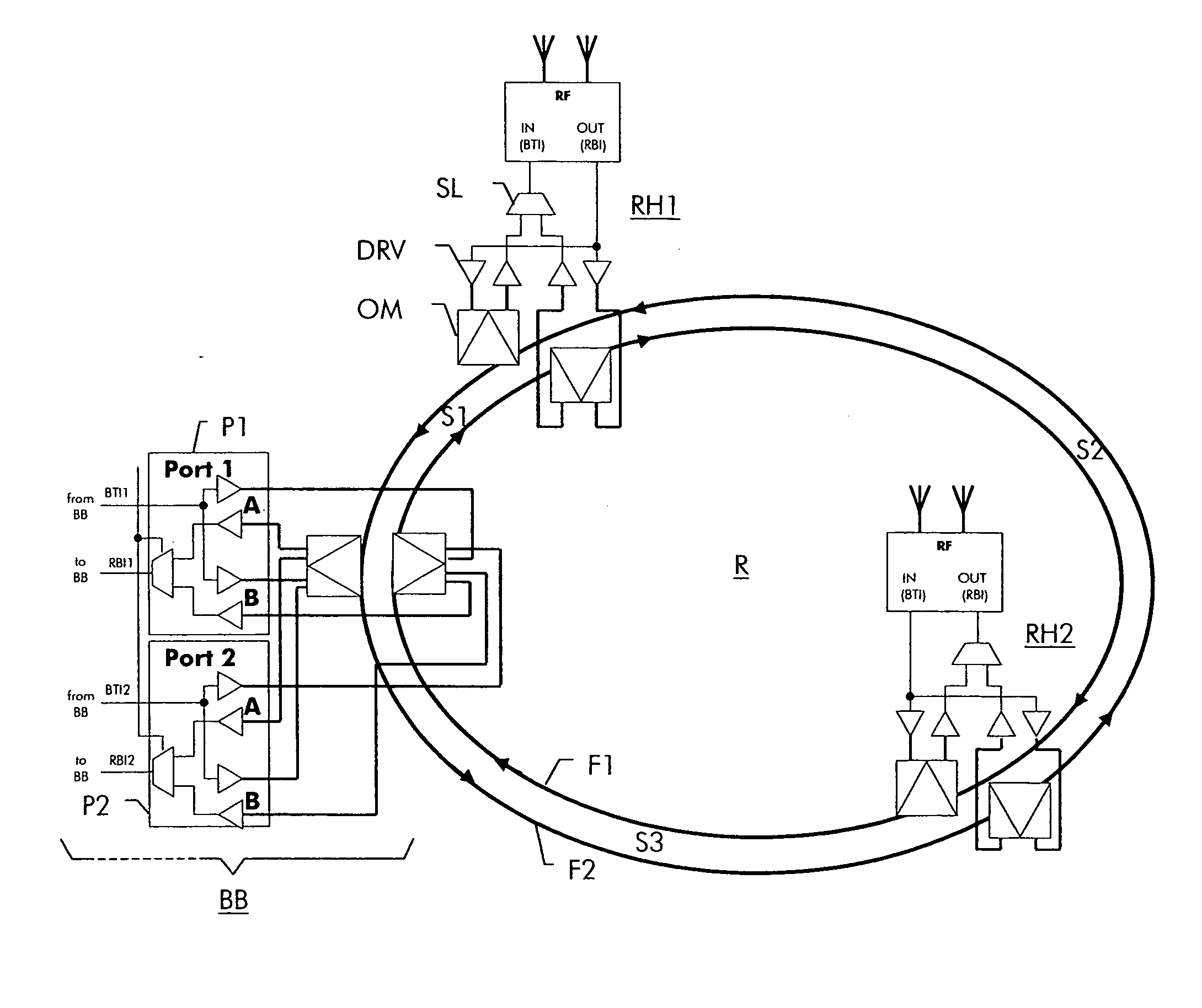
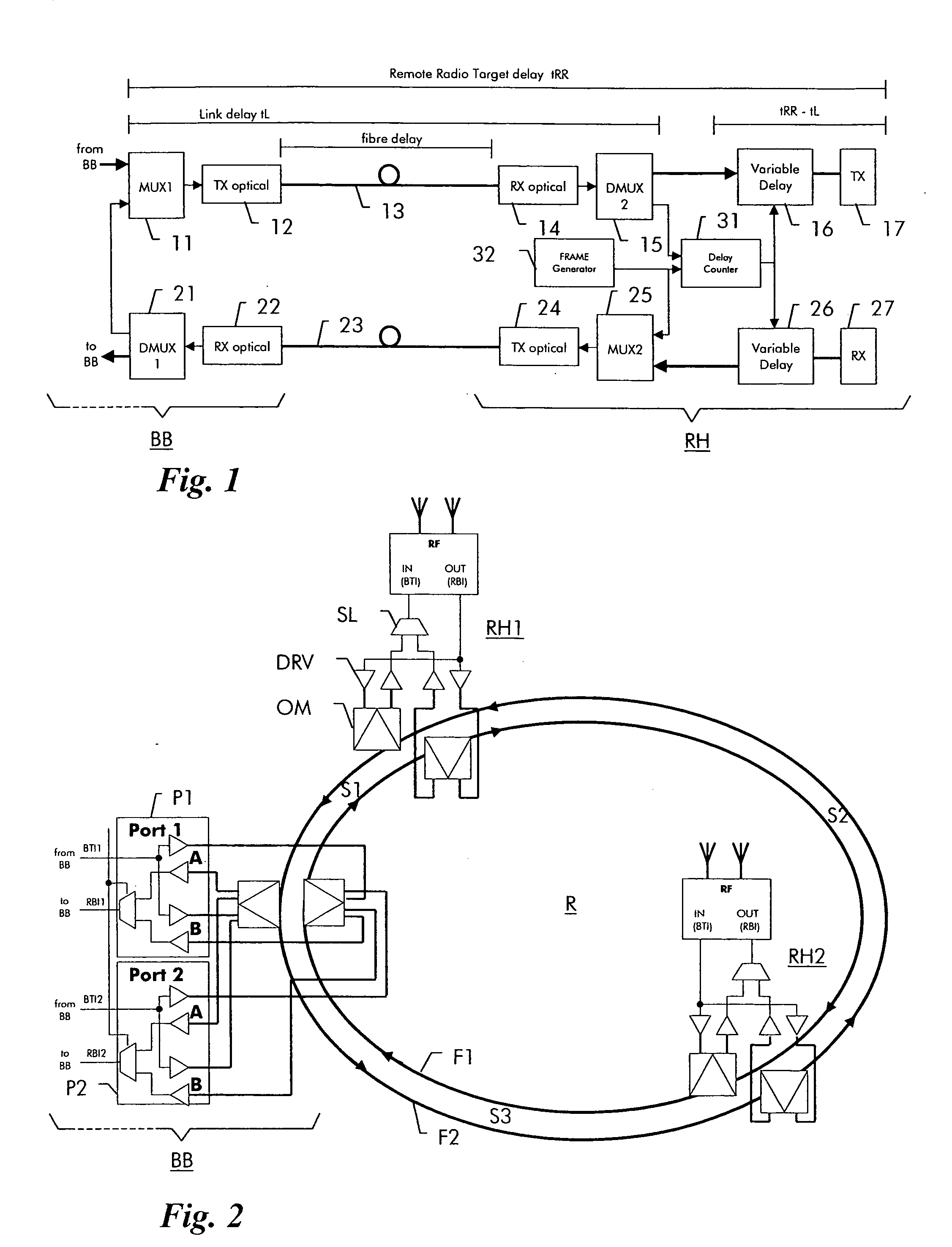
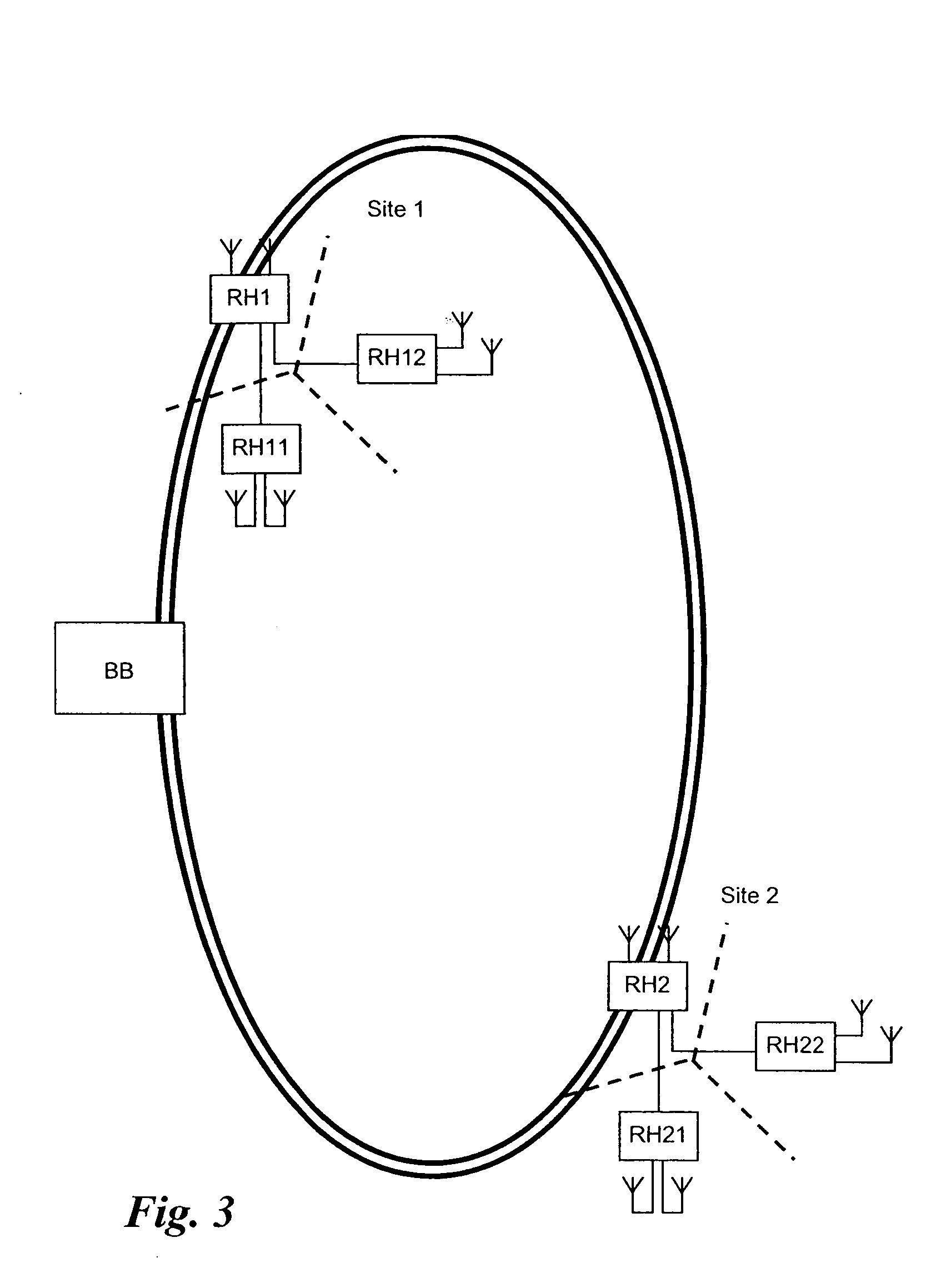
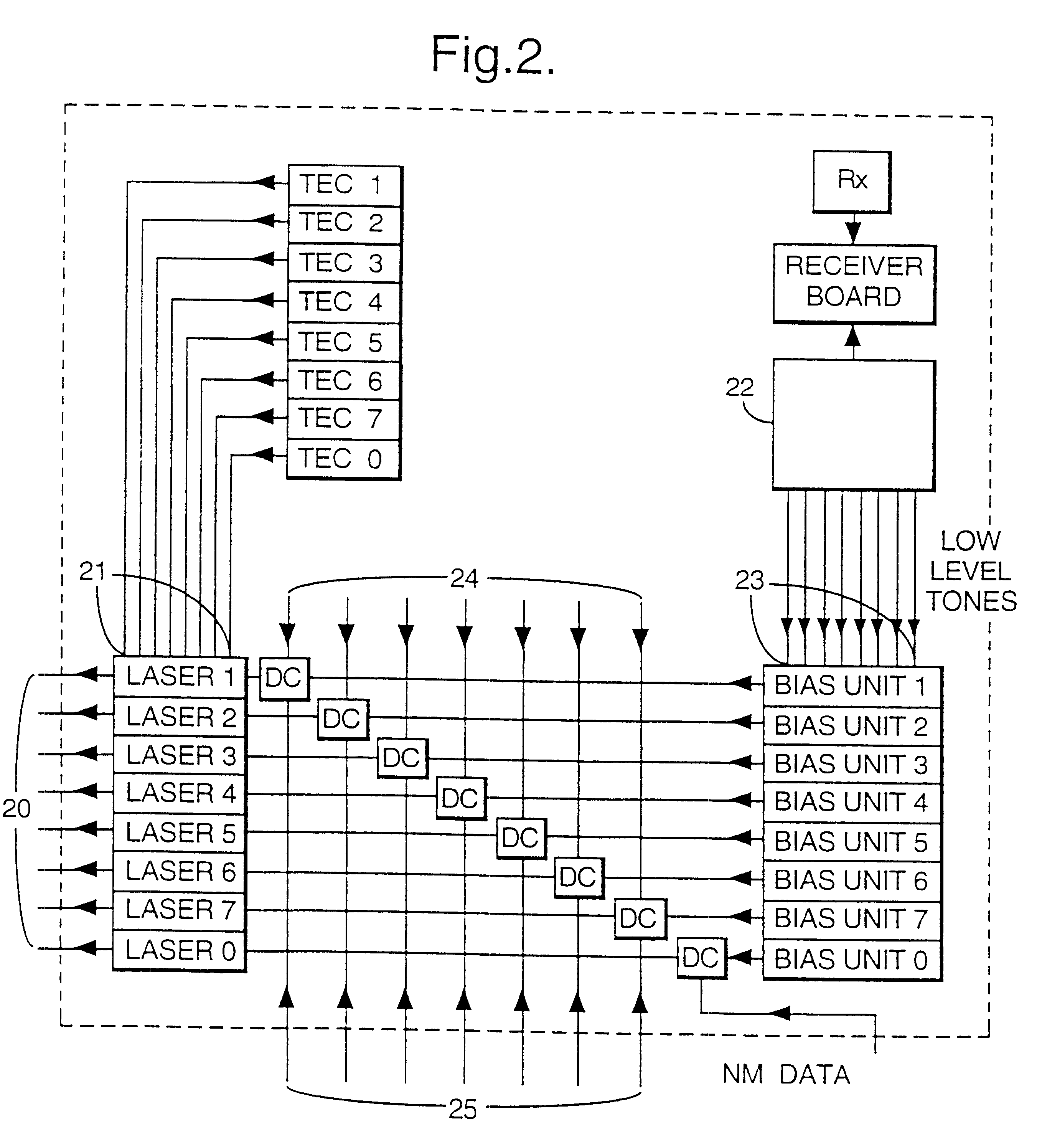
InactiveUS20050152695A1Simpler and clean installationImprove securityRing-type electromagnetic networksLaser detailsFiberPropagation delay
A radio base station has a baseband unit (BB) and multiple RF heads (RH1, RH2), which are interconnected by means of a bi-directional two-fiber optical ring (R). Each RF head (RH1, RH2) has a delay counter (31) for determining a propagation delay (tL) on the ring (R) and a variable delay circuit (16, 26) for compensating a difference between the propagation delay on the ring and a predefined target delay (tRR). The delay counter counts (31) the delay between a test signal sent on the first fiber (F1) of the ring to the baseband unit and a received test signal looped back by the baseband unit on the second fiber (F2) of the ring.
Owner:RPX CORP
System and method for configuring optical circuits
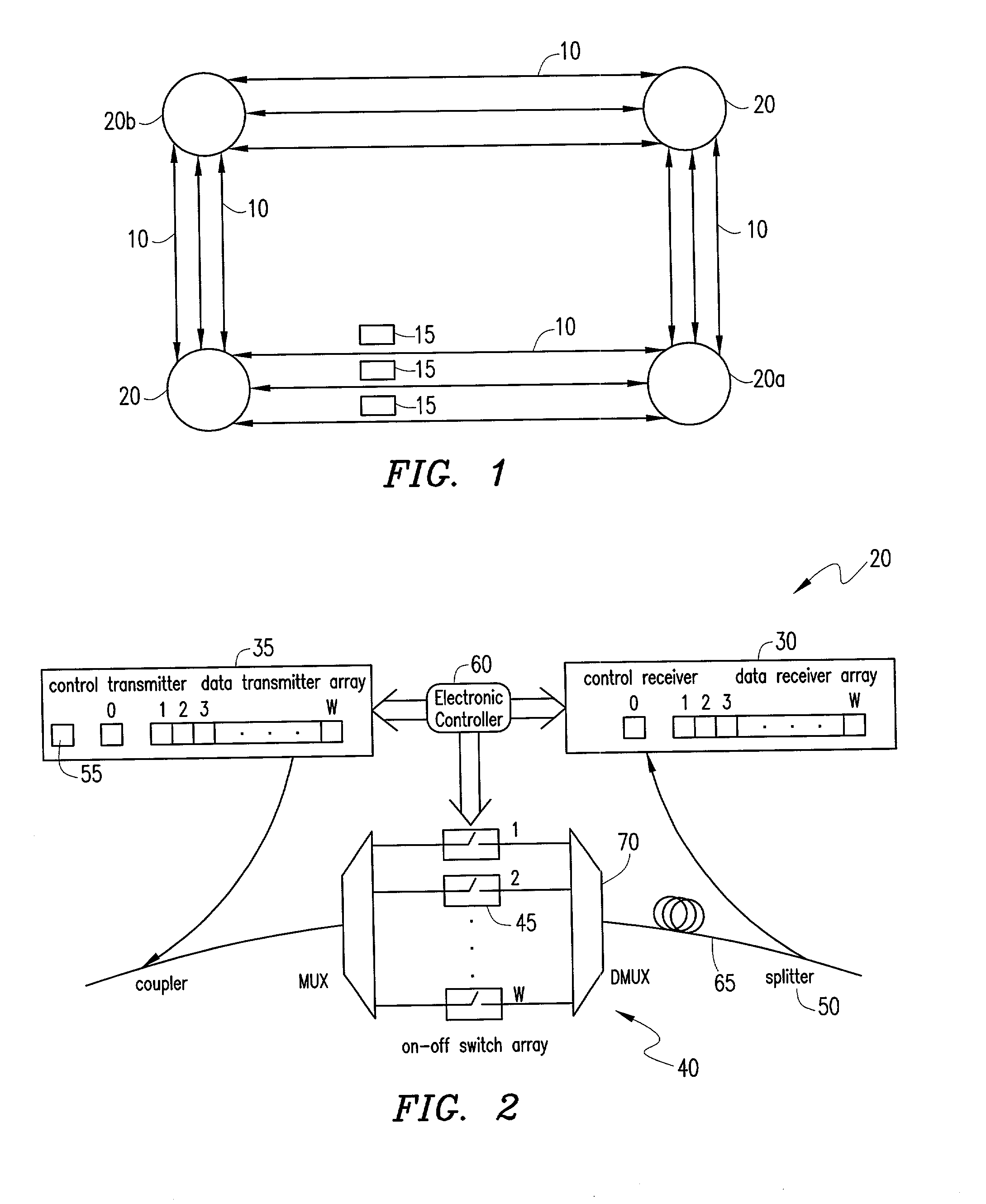
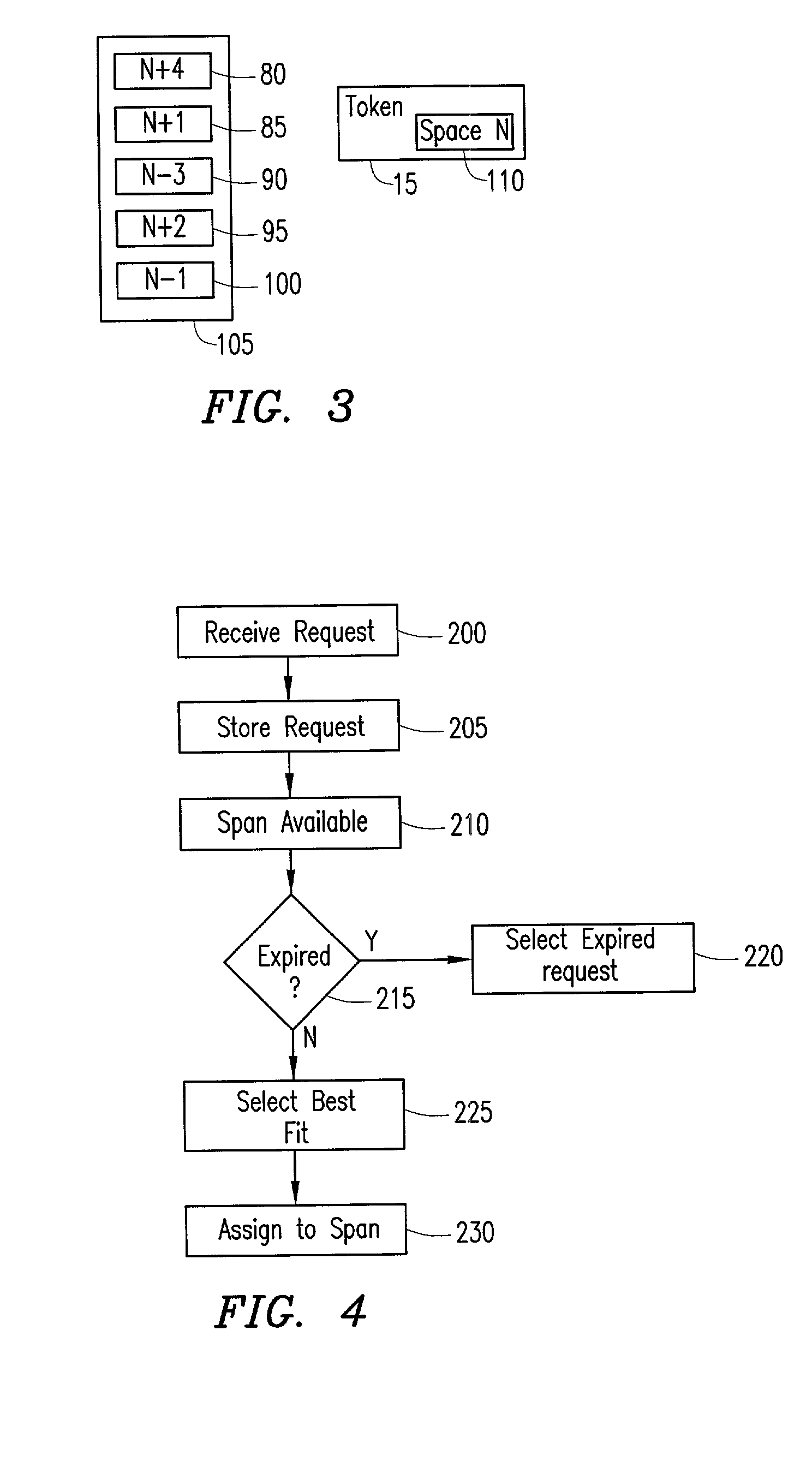
A system and method for configuring lightpaths within an optical circuit wherein the source node stores requests for a lightpath between the source node and the destination node. Upon receipt of a token at the source node indicating an available space within a wavelength, the source node selects a request stored within the queue based upon a best fit window protocol. A lightpath is then established between the source node and the destination node responsive to a selected request.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
PON system
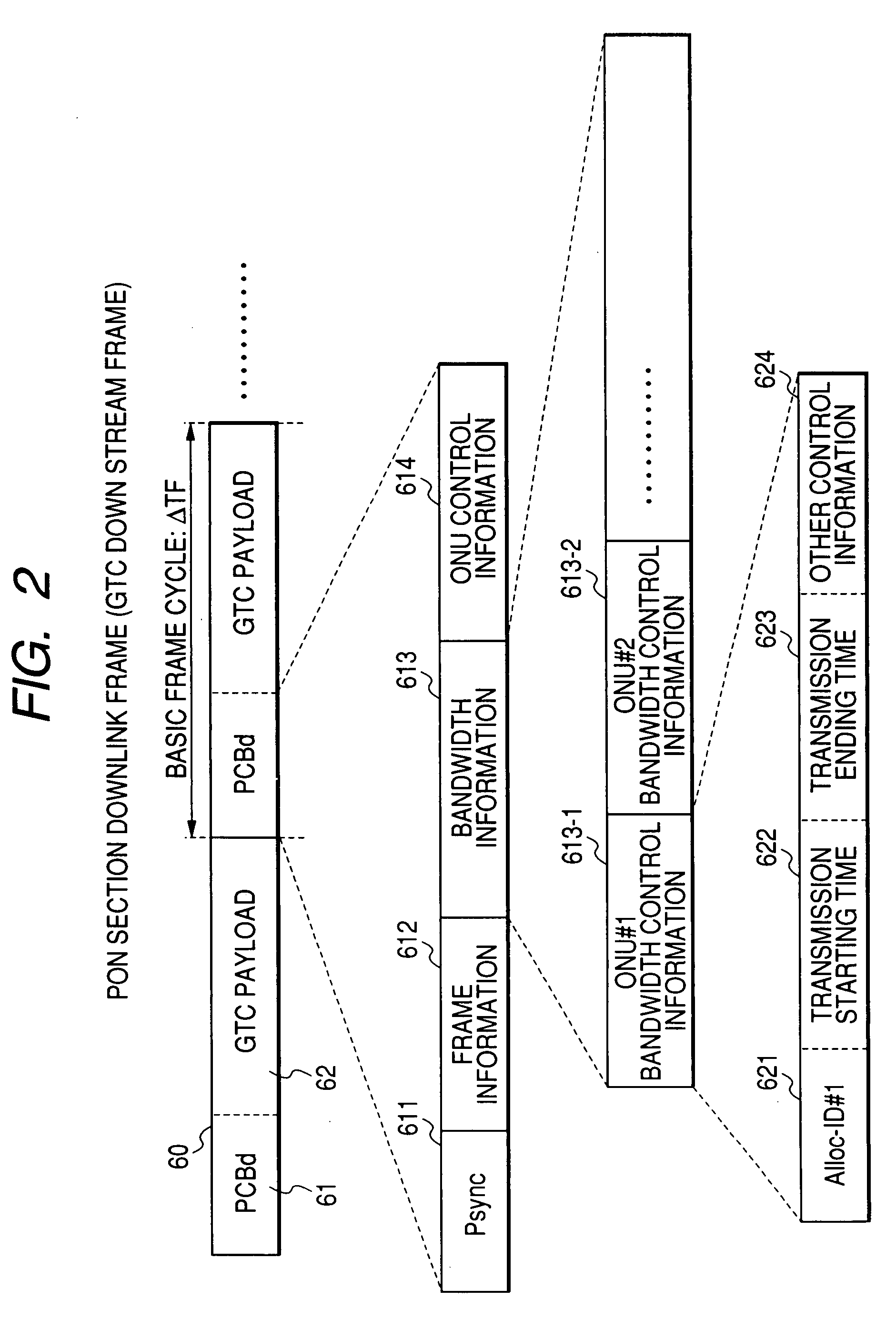
InactiveUS20070237177A1Surplus bandwidthReduce data volumeMultiplex system selection arrangementsRing-type electromagnetic networksNormal modeDistributed computing
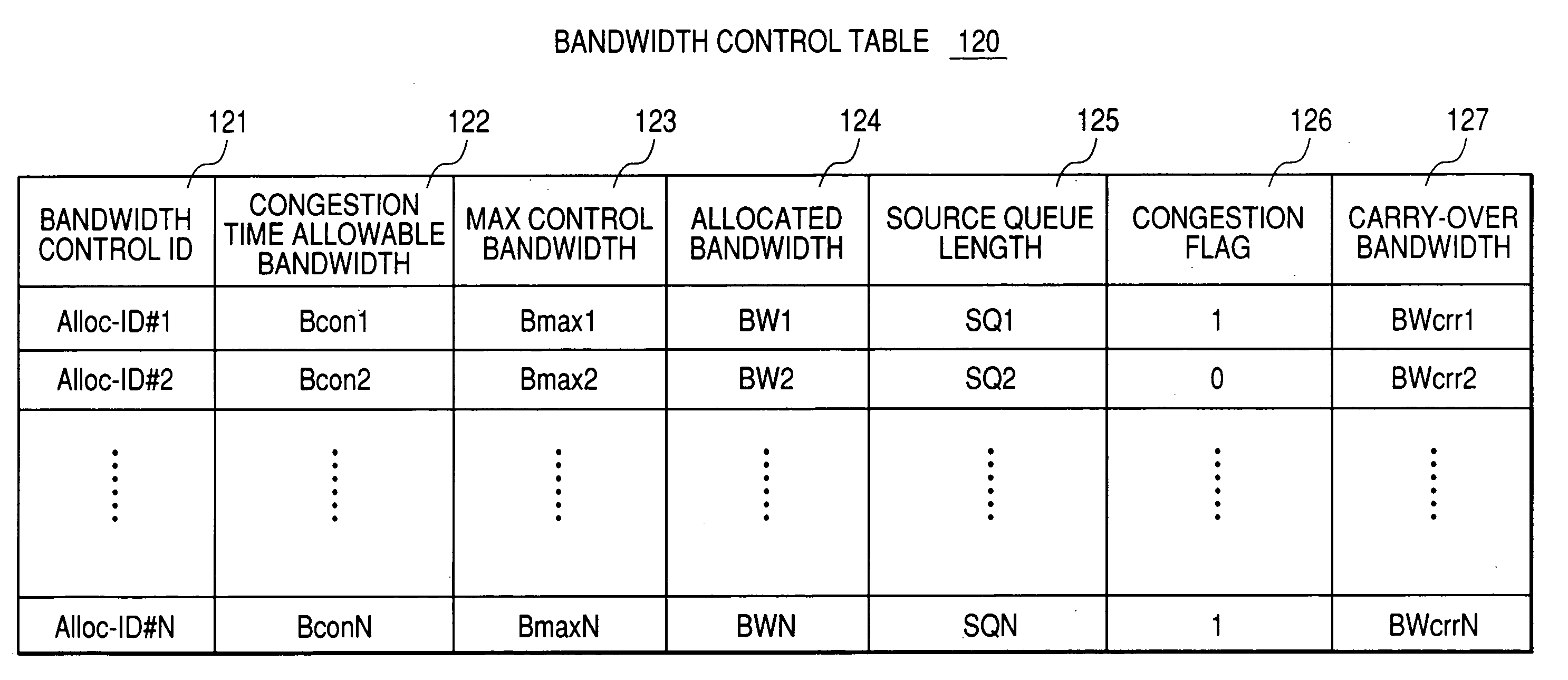
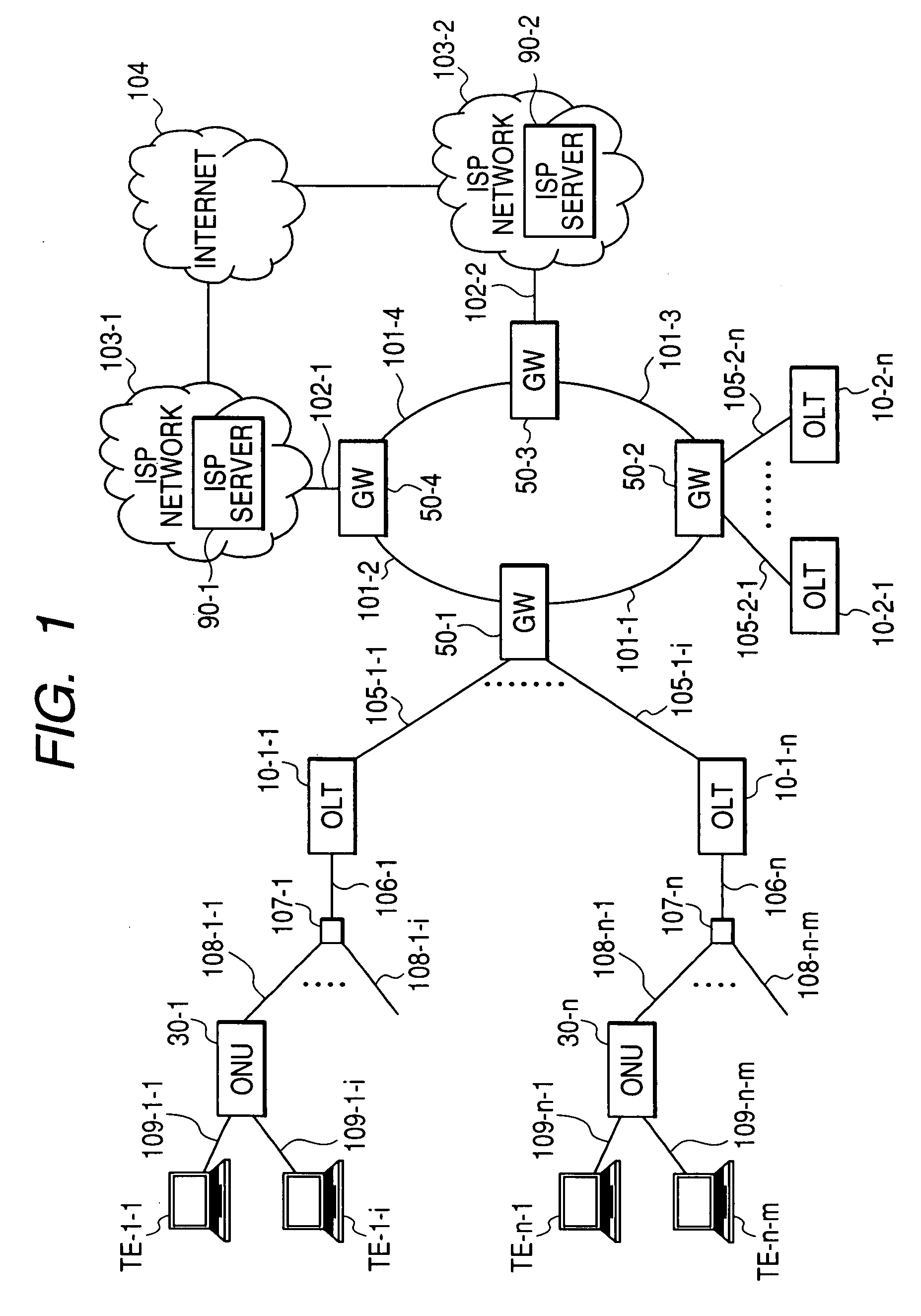
Disclosed herewith is a PON system and a bandwidth controlling method capable of controlling congestion with use of an upstream bandwidth in a PON section efficiently when congestion occurs in a gateway (GW) connected to an OLT. An OLT connected to a plurality of ONUs through a passive optical network (PON) and to a gateway (GW) through a communication line, when receiving a congestion occurrence notice indicating a congestion occurred output number from a GW, identifies the identifier of the ONU that is using a GW output line having the congestion output port number and shifts the bandwidth controlling of the PON section in a normal mode for allocating a bandwidth to each ONU normally to that in a bandwidth suppression mode for allocating a congestion time allowable bandwidth that is less than the current bandwidth to the ONU having the identified ONU identifier and a bandwidth to each of other ONUs according to its transmission queue length.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
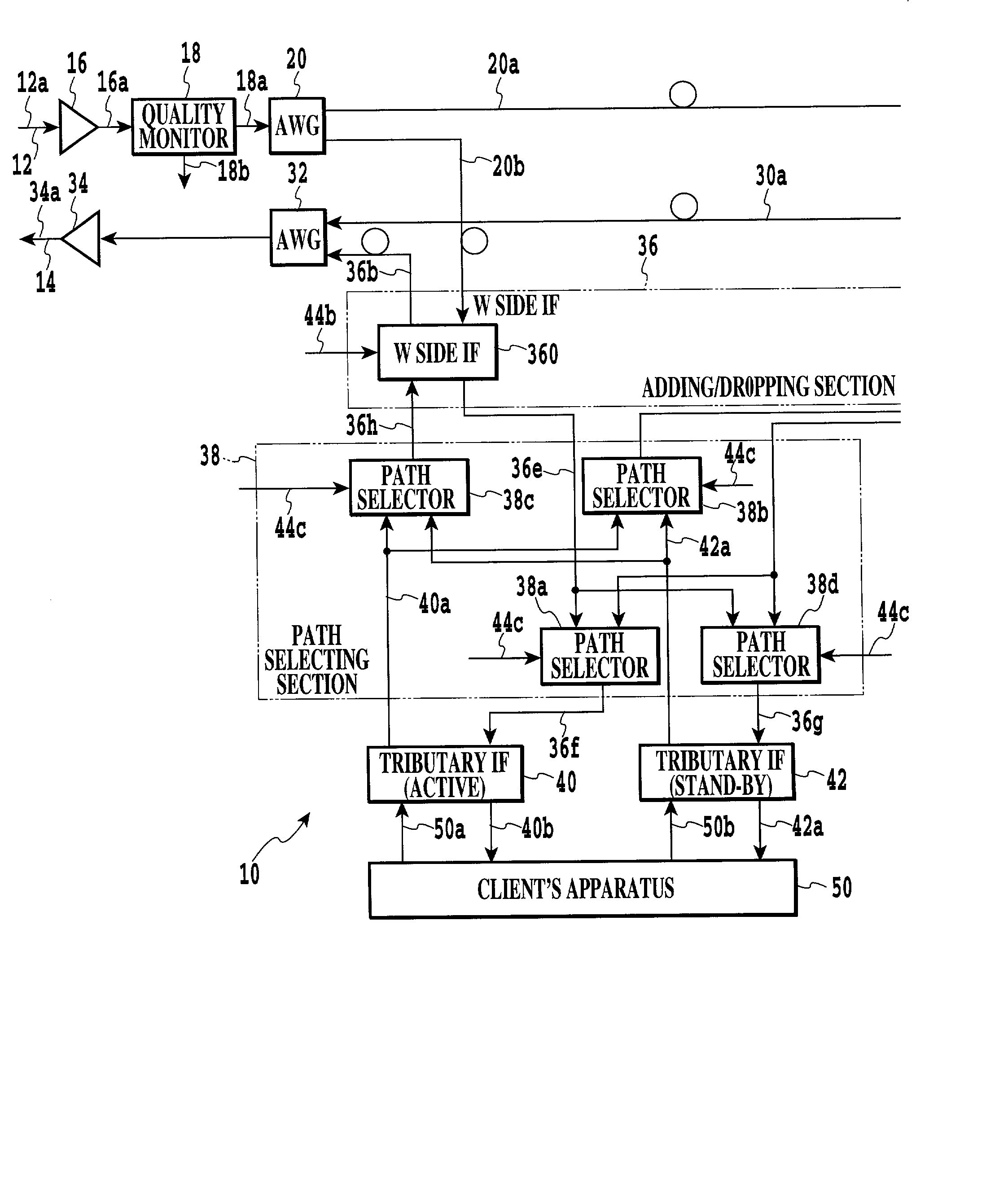
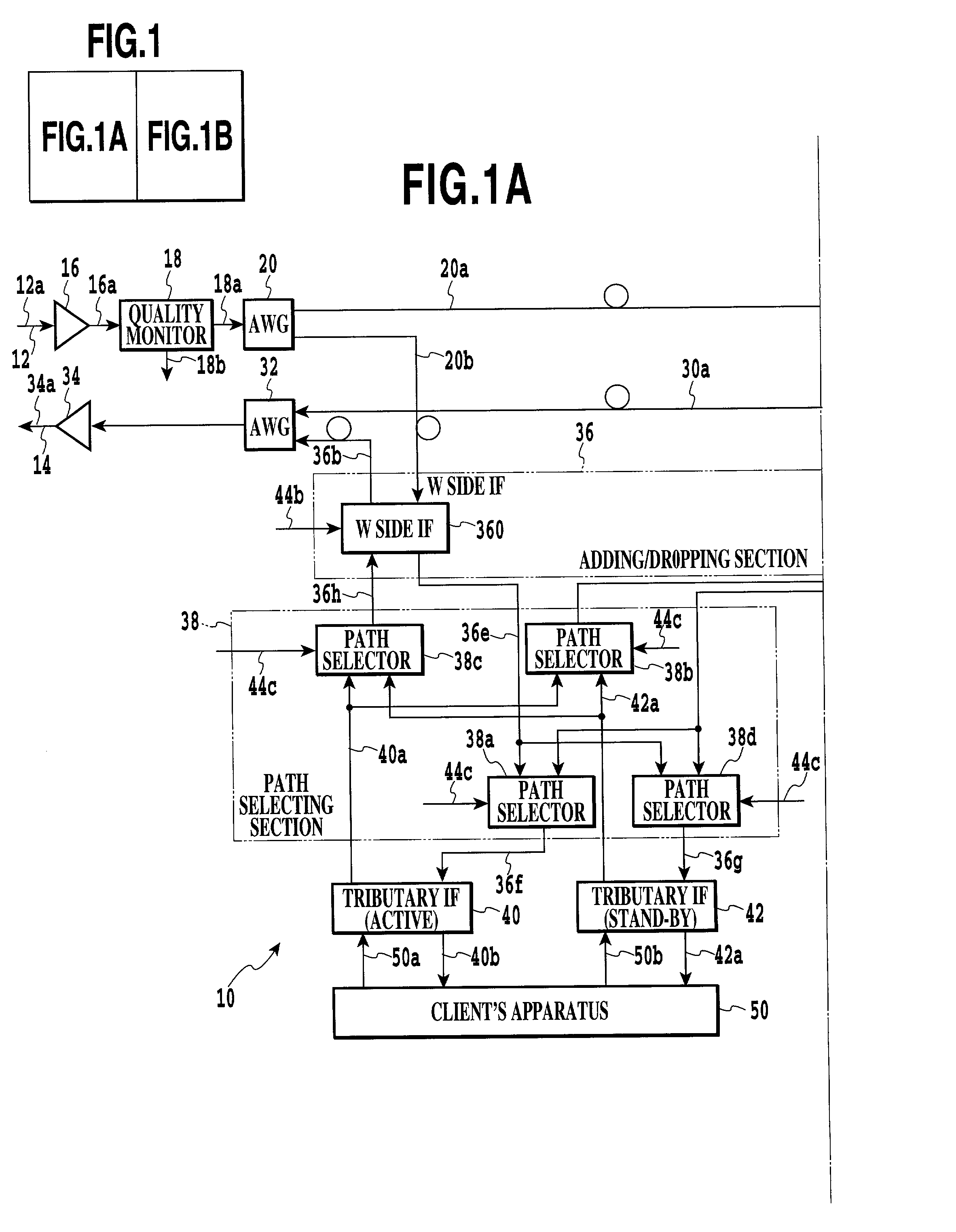
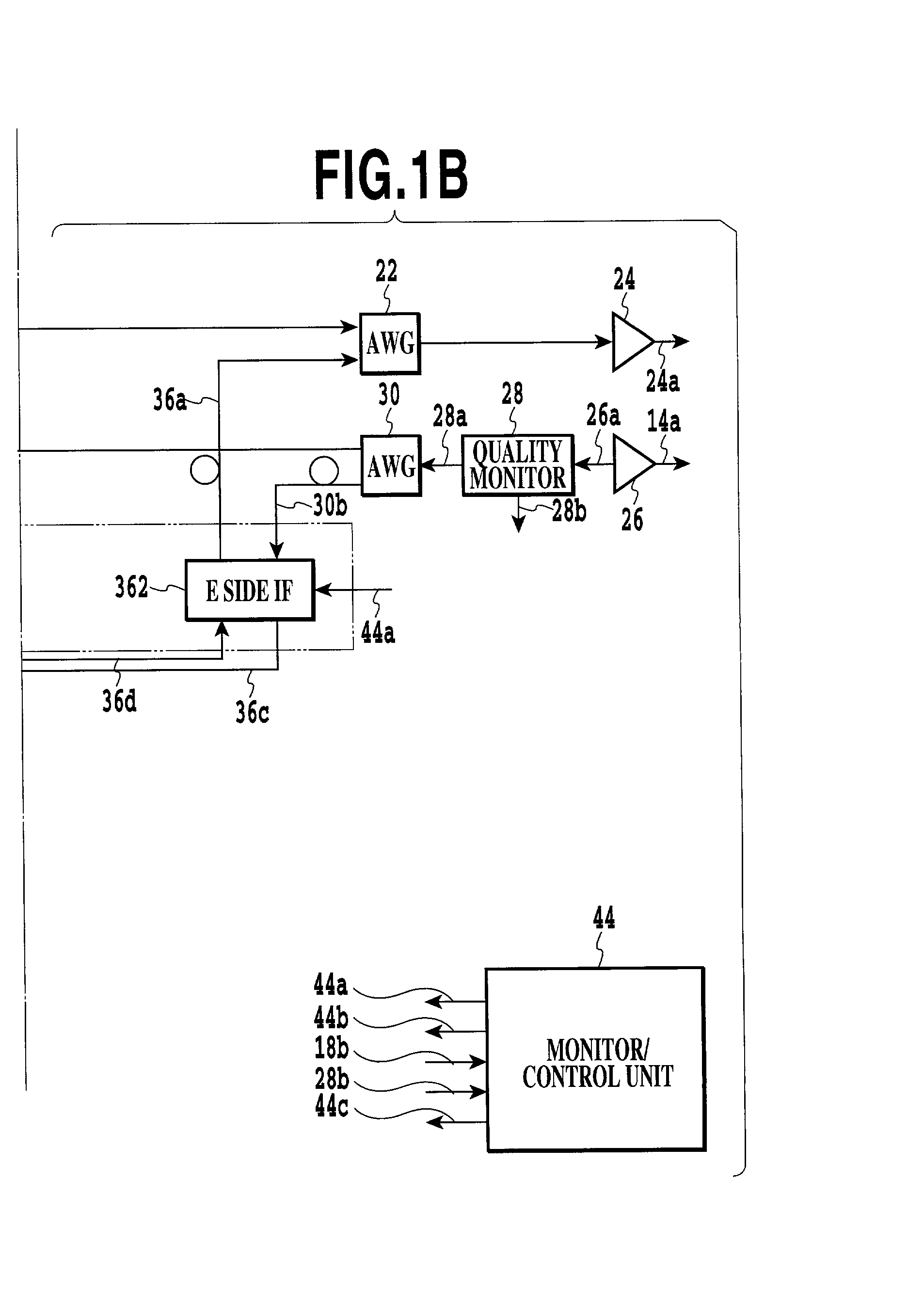
Optical transmission apparatus with an optimal routing and data transmitting capability and a method of determining an optimal route on optical transmission
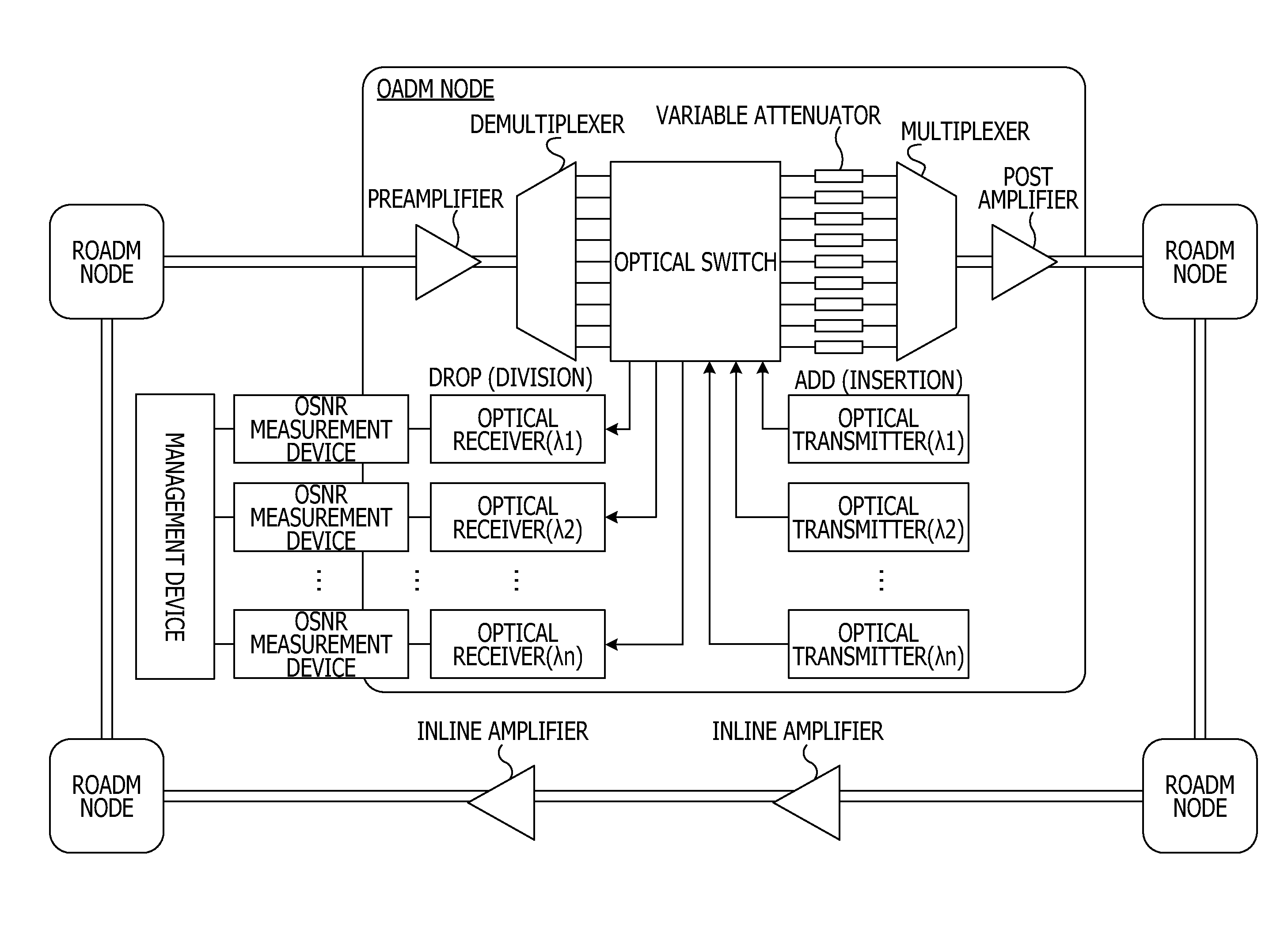
An optical transmission apparatus implemented as an OADM (Optical Add / Drop Multiplexer) includes quality monitors each for monitoring the quality of a signal arriving on a particular optical transmission path. A monitor / control unit converts quality signals output from the quality monitors to path-by-path bit error rates, or estimation values, and compares them to select a route. The monitor / control unit then generates a metric value "1" for the route selected and adds it to one of identical metric values, which are assigned to routes to the same destination, that corresponds to the route selected. The monitor / control unit can therefore select a route closer to actual transmission path conditions. A method of determining an optimal route for optical transfer is also disclosed.
Owner:OKI ELECTRIC IND CO LTD
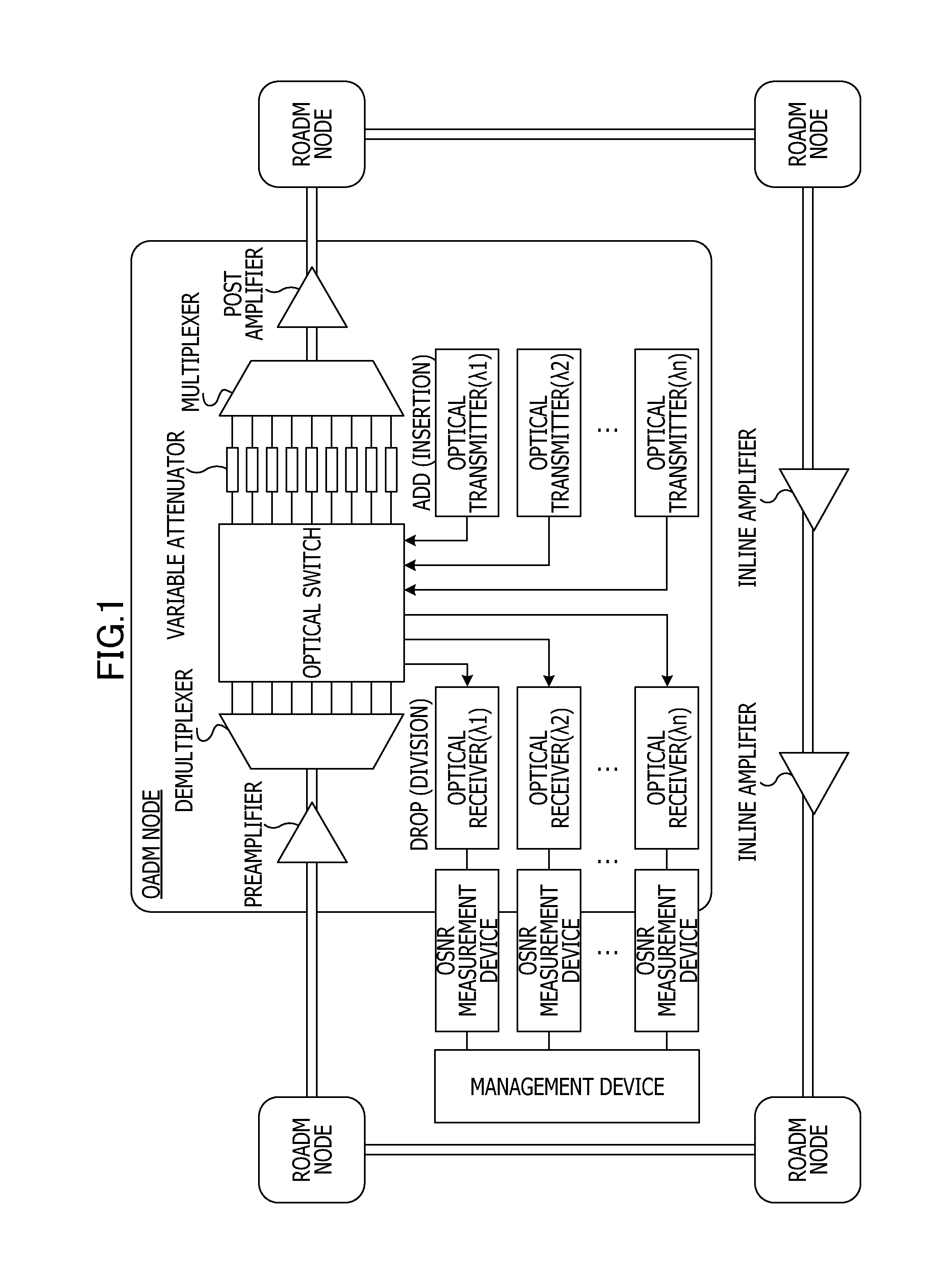
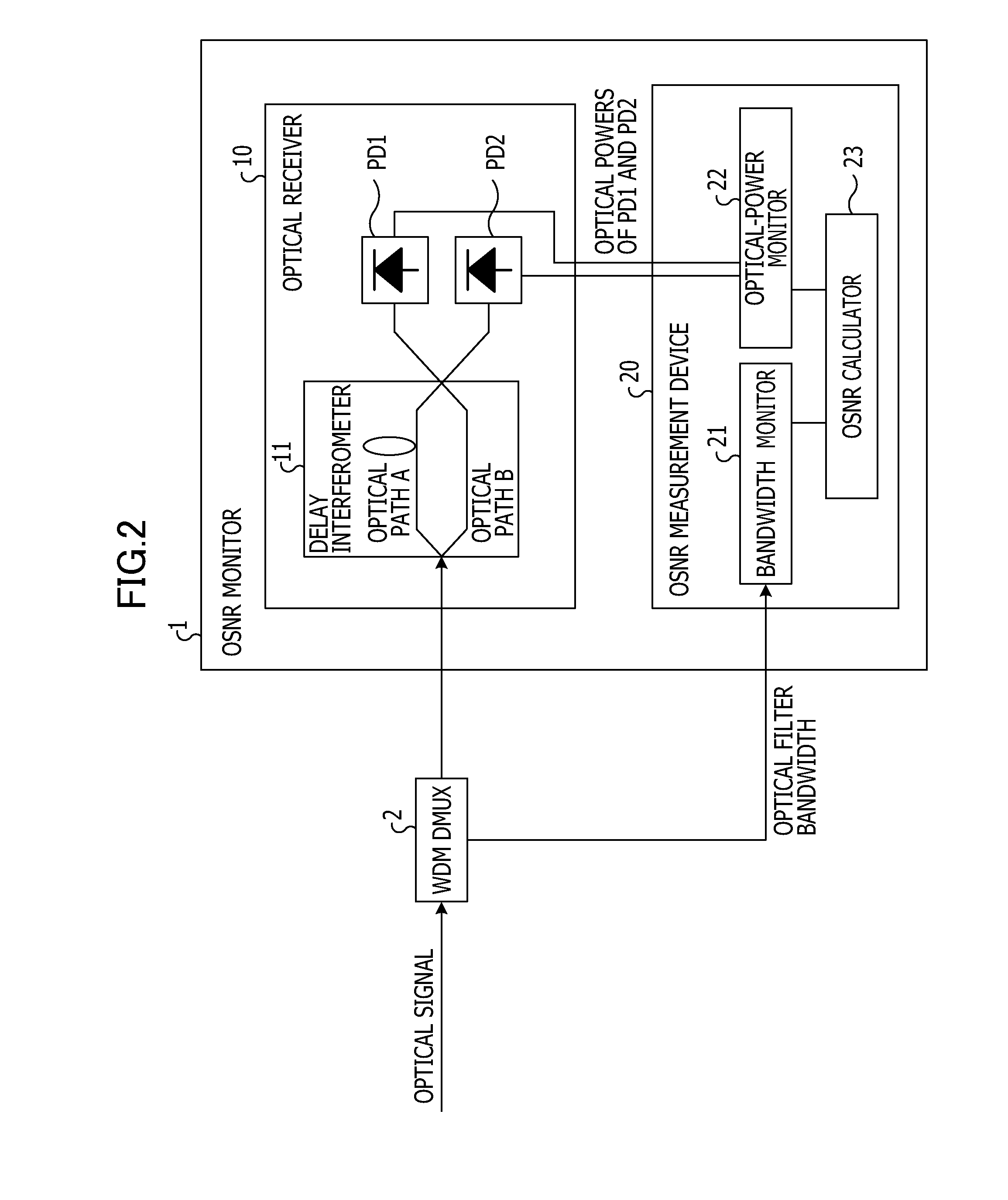
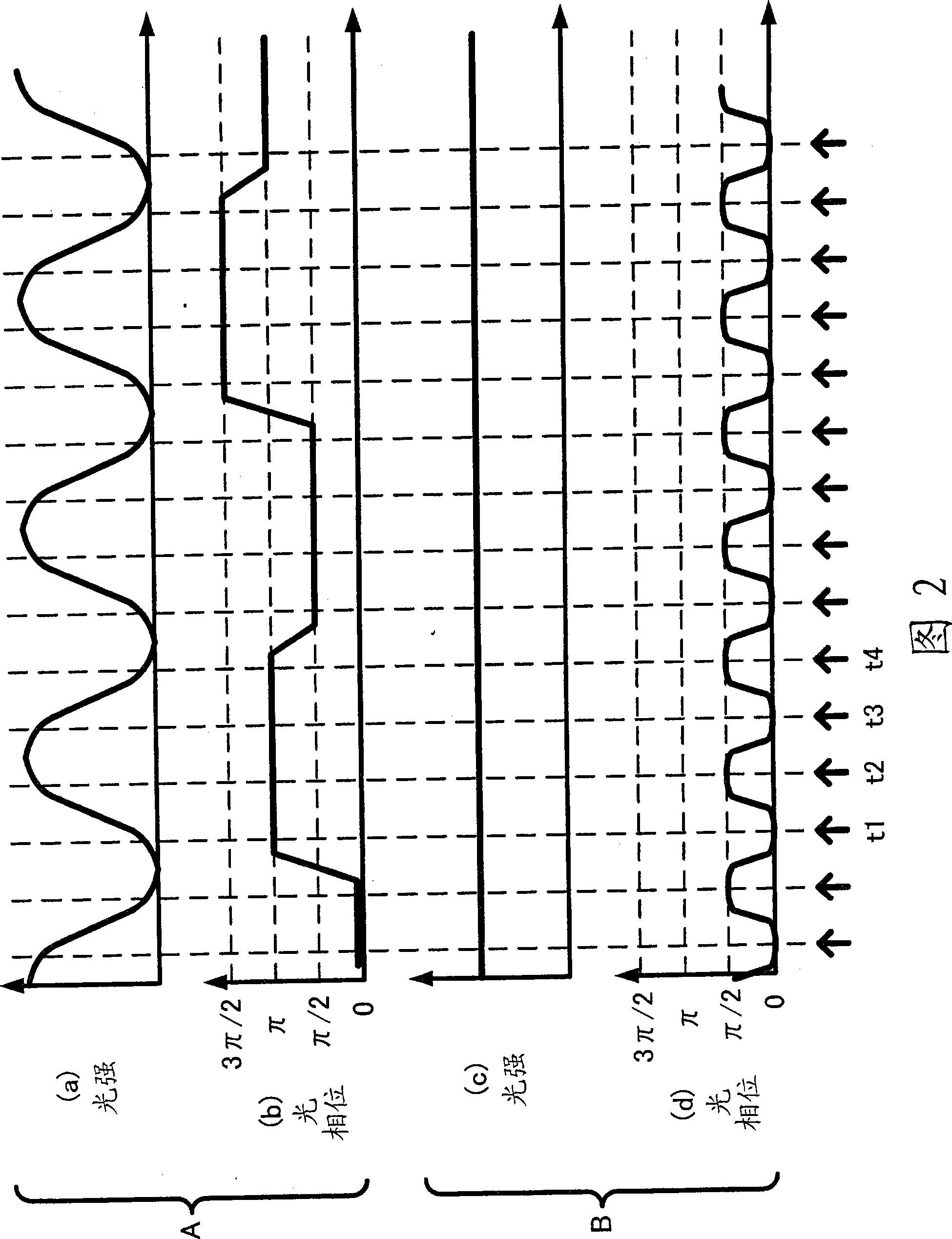
Osnr monitor device and osnr measurement device
InactiveUS20100322622A1Ring-type electromagnetic networksWavelength-division multiplex systemsMeasurement deviceOptical power
An OSNR monitor device includes an optical receiver including a delay interferometer which inputs an optical signal in accordance with a given bandwidth and outputs two optical signals and causes the optical signals to interfere with each other and optical detectors which outputs currents in accordance with optical powers of the optical signals output from the interferometer, an optical power monitor configured to obtain the optical powers of the optical signals received by the optical detectors included in the optical receiver, and an OSNR calculator configured to calculate an optical signal-to-noise ratio in accordance with the optical powers obtained from the optical power monitor and the reception bandwidth.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Coherent light receiving system
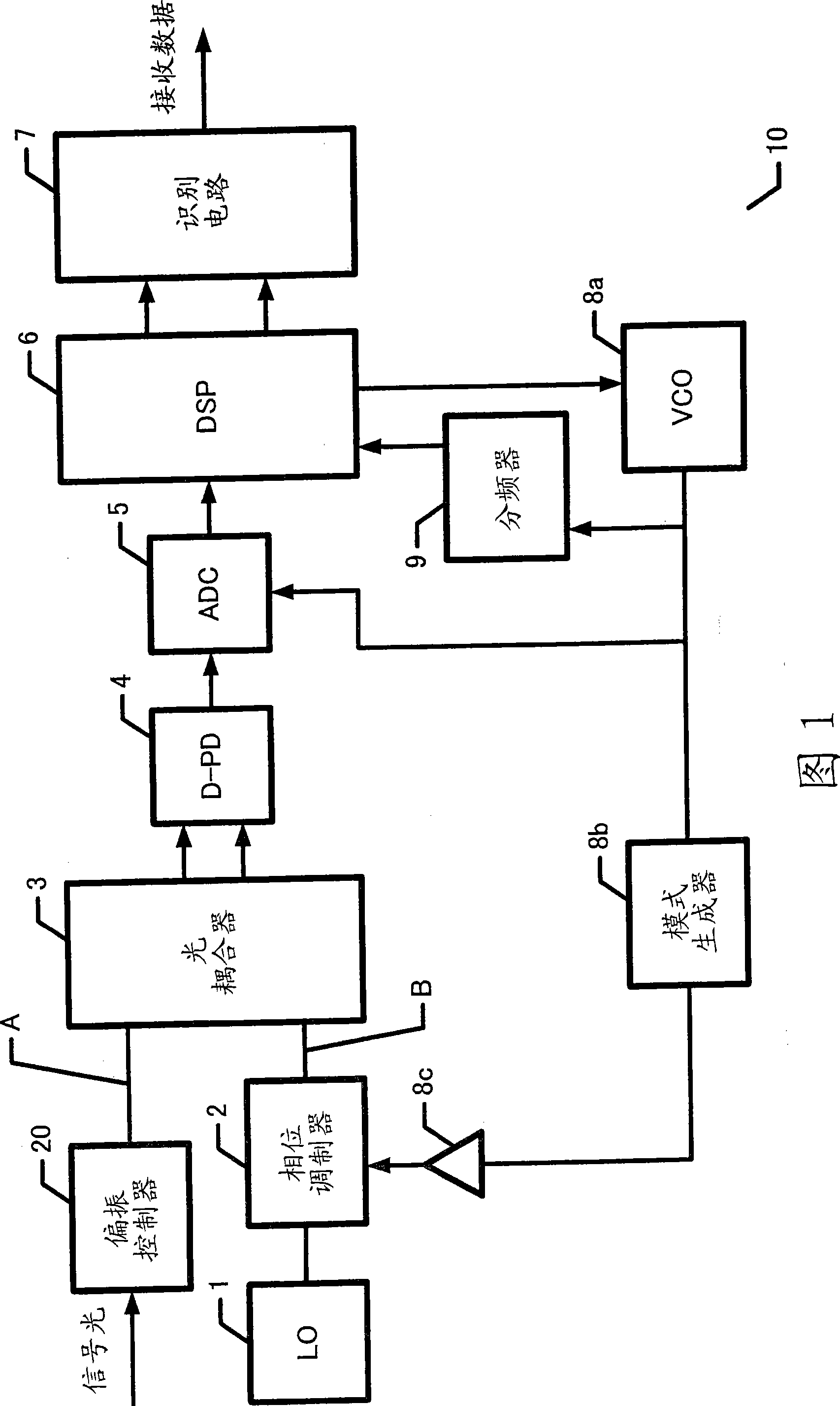
InactiveCN101369851ARing-type electromagnetic networksWavelength-division multiplex systemsDigital signal processingLocal oscillator
The invention provides a coherent light receiving system. In order to reduce the size and simplify the structure of a coherent light receiver, the coherent light receiver includes an optical mixer for coupling local oscillator light and reception signal light, a photoelectric converter for photoelectrically converting light coupled in the optical mixer, a reception data processing unit for extracting reception data included in the reception signal light through digital signal processing for processing the coupled signal converted into an electrical signal by the photoelectric converter, based on a first clock, and a modulator for modulating the local oscillator light or the reception signal light inputted to the optical mixer respectively, by using a clock phase-synchronized with the first clock used for the digital signal processing in the reception data processing unit.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
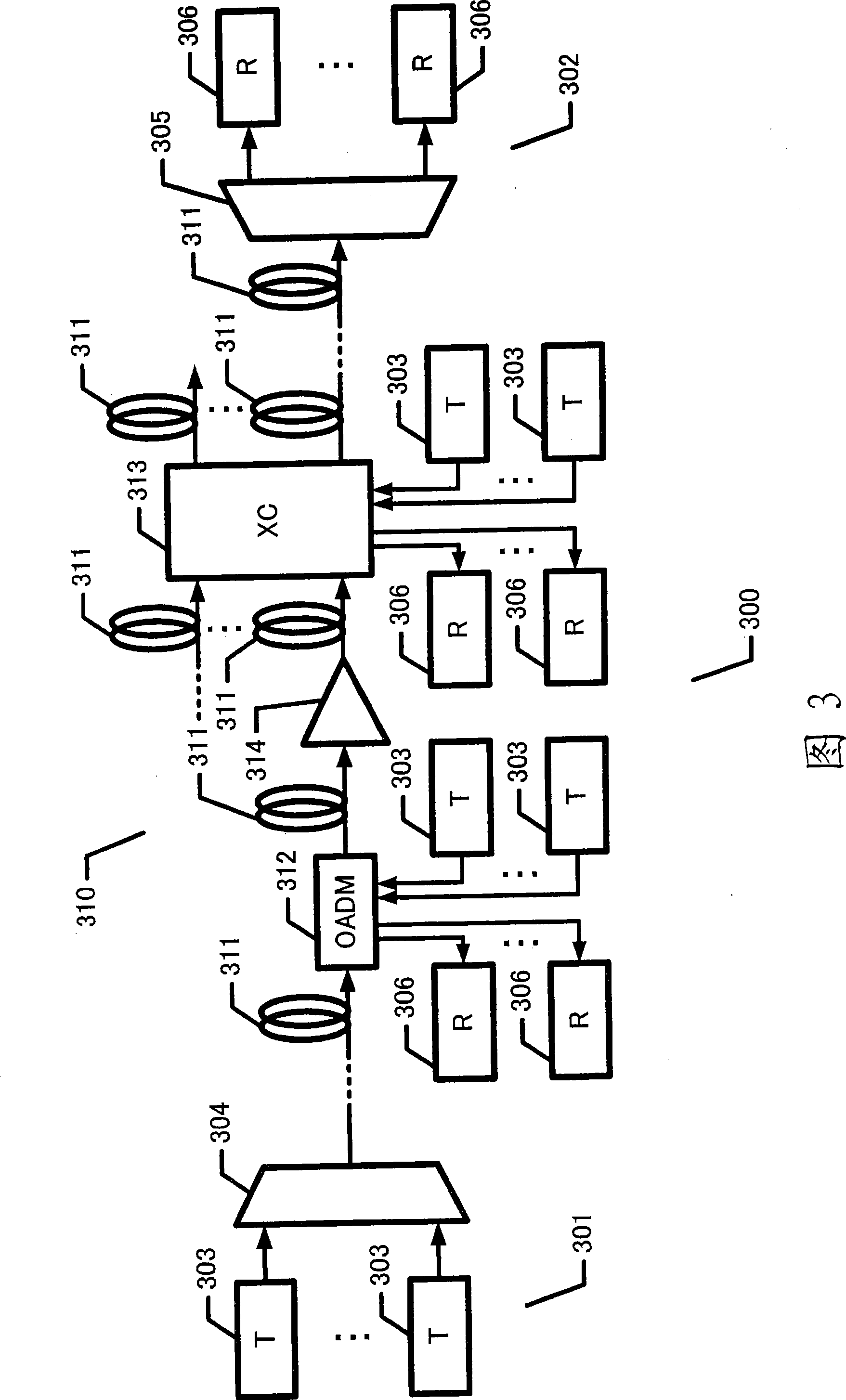
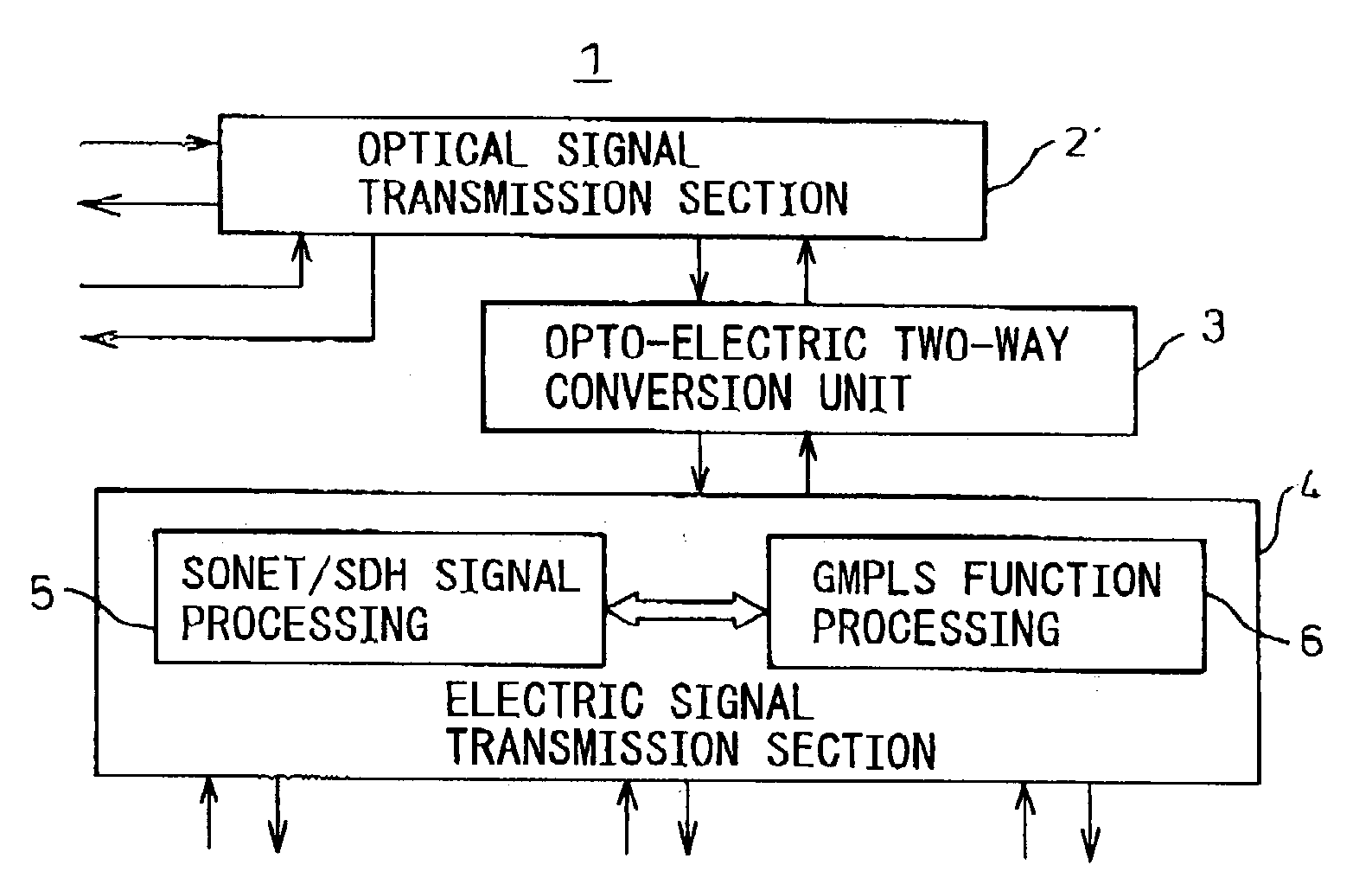
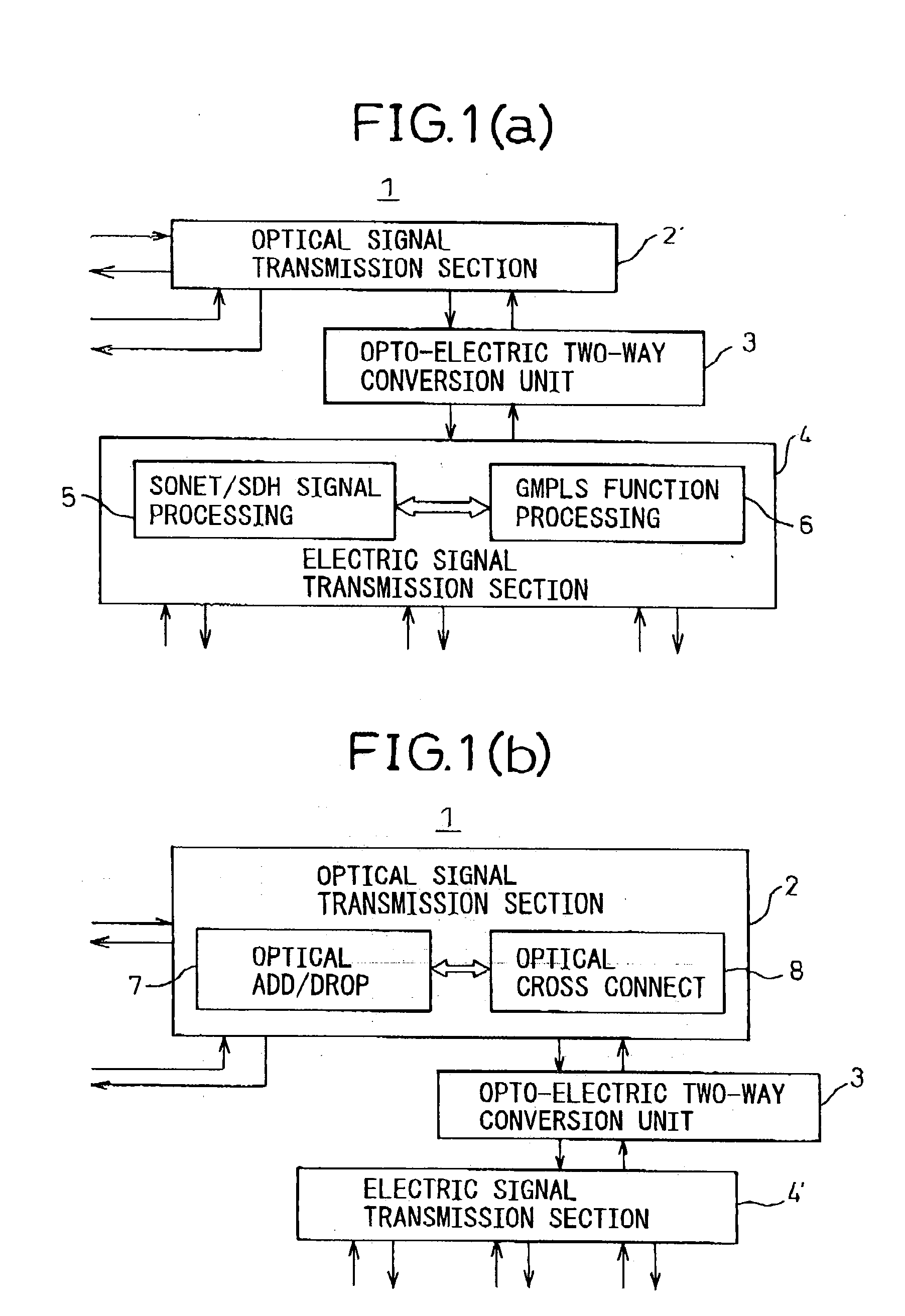
Transmission apparatus
InactiveUS20030228093A1Multiplex system selection arrangementsRing-type electromagnetic networksCross connectionOpto electronic
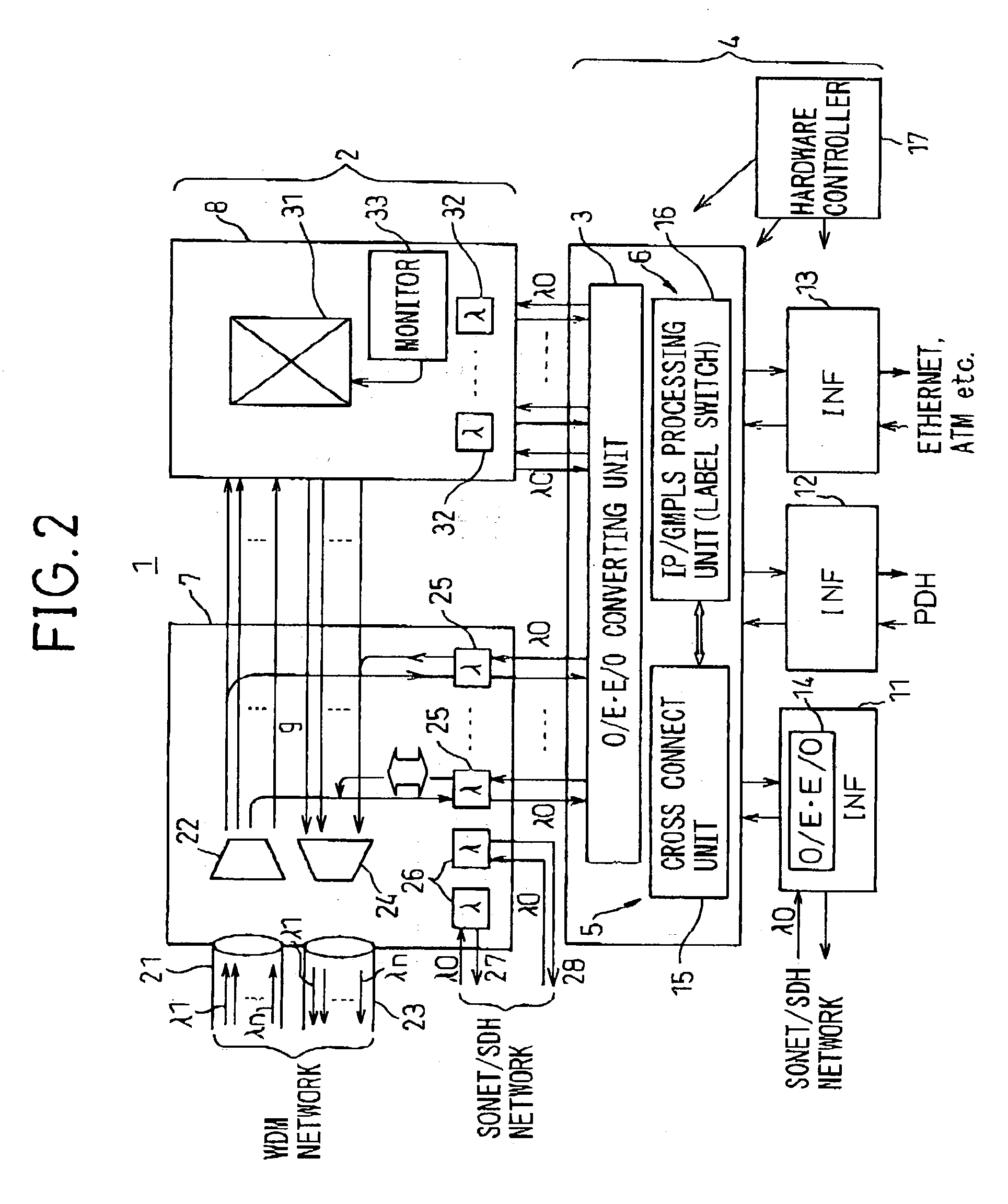
A transmission apparatus for coupling an optical signal transmission section and an electrical signal transmission section through an opto-electric two-way conversion unit, where the electrical signal transmission section is comprised of a SONET / SDH signal processing function unit and a generalized multi protocol label switching (GMPLS) function processing function unit cooperating with that function unit and where the optical signal transmission section is comprised of an optical add / drop function unit for transferring an optical signal with the electrical signal transmission section through the conversion unit and an optical cross-connect function unit for switching paths in wavelength units of the optical signal with the electrical signal transmission section, whereby the capital cost and running costs of an optical network for transmitting an IP signal can be greatly reduced.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
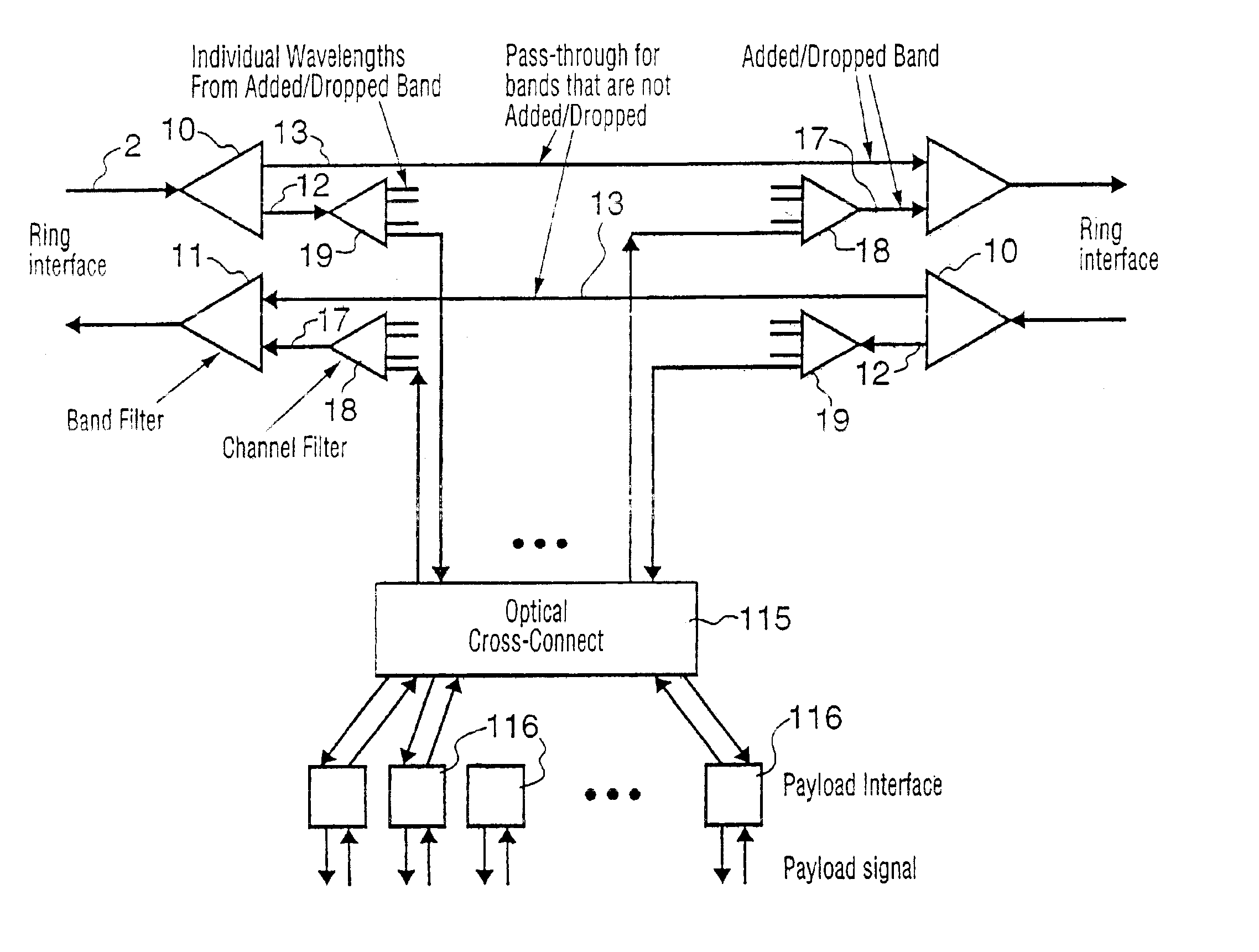
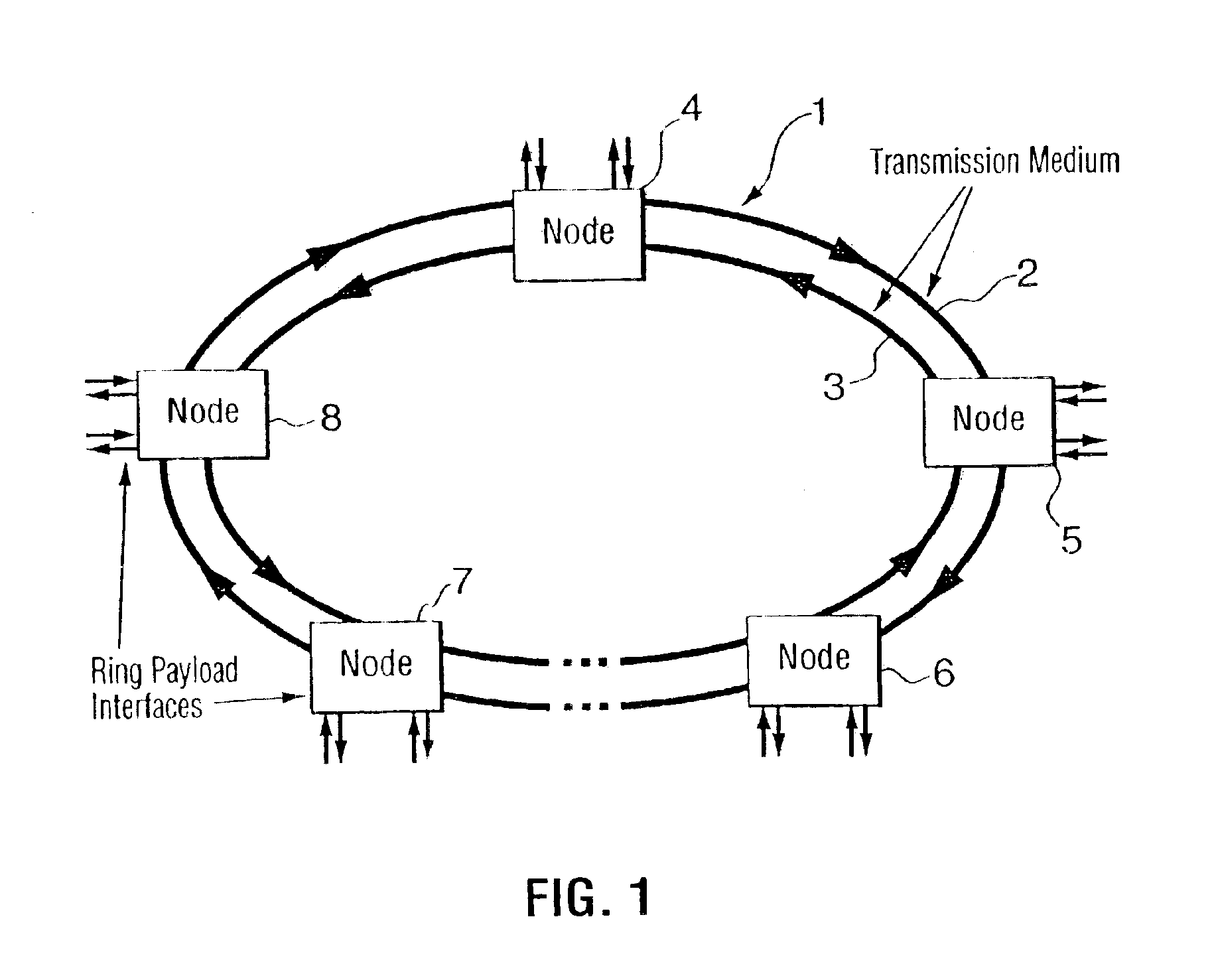
WDM optical network with passive pass-through at each node
InactiveUS6892032B2Minimal lossReduce lossMultiplex system selection arrangementsRing-type electromagnetic networksPath lengthWdm optical networks
A communications network has a plurality of nodes interconnected by an optical transmission medium. The transmission medium is capable of a carrying a plurality of wavelengths organized into bands. A filter at each node for drops a band associated therewith and passively forwards other bands through the transmission medium. A device is provided at each node for adding a band to the transmission medium. Communication can be established directly between a pair of nodes in the network sharing a common band without the active intervention of any intervening node. This allows the network to be protocol independent. Also, the low losses incurred by the passive filters permit relatively long path lengths without optical amplification.
Owner:CIENA
Wavelength and path assignment in wavelength division multiplexed ring networks
ActiveUS7088920B2Ring-type electromagnetic networksWavelength-division multiplex systemsRing networkWdm optical networks
A method is provided for establishing a service connection between first and second network nodes in a WDM optical network for a plurality of network users. The method begins by receiving, from each network user, user-preferences prioritizing a plurality of decision criteria defining preferable characteristics of the service connection. Next, a prescribed algorithm is used to select a path and a channel wavelength at which information is to be conveyed over the path between the first and second nodes. The selection is based on the plurality of decision criteria as prioritized in accordance with the user-preferences. Finally, the first and second network nodes are interconnected over the selected path with the selected channel wavelength.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Meshed optical network
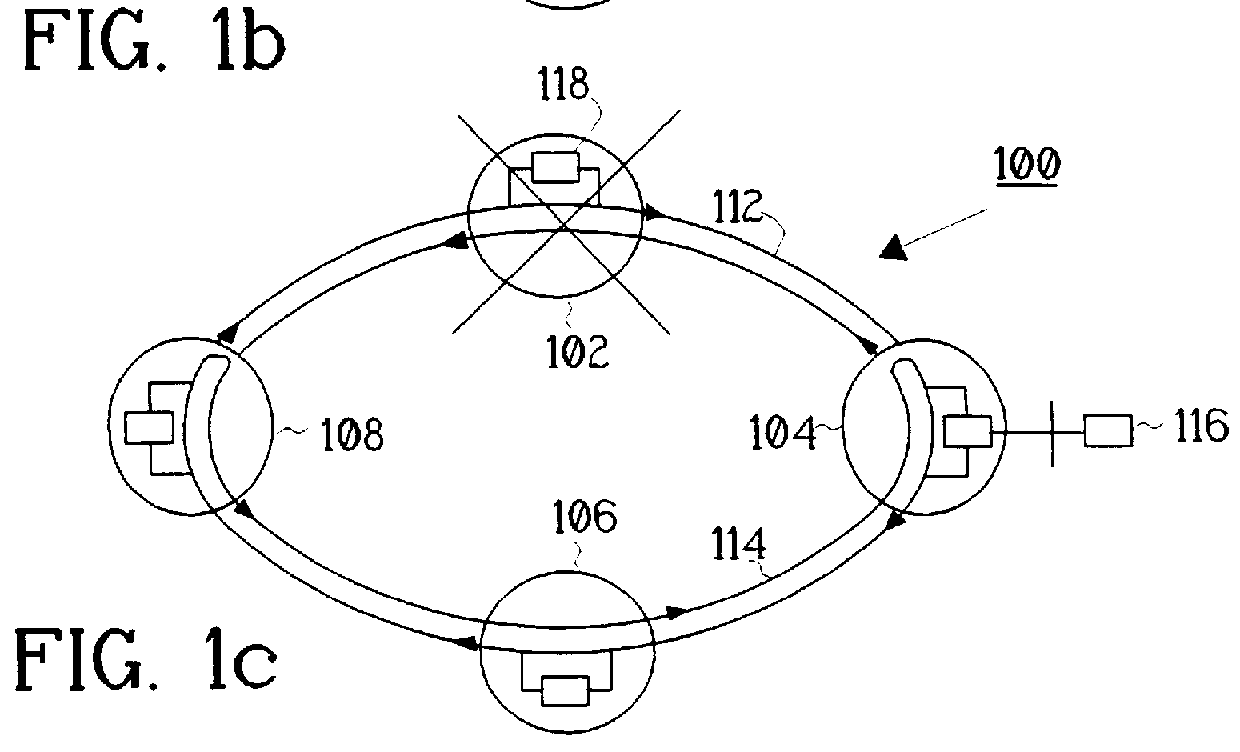
InactiveUS6414767B1Improve robustnessMinimal control overheadWavelength-division multiplex systemsData switching by path configurationWavelength channelsWaveguide
An optical network includes interconnected via an NxN WDM router. The nodes are connected to an optical waveguide ring having a duplex structure. A first set of optical waveguides connects the transmitters in the nodes and a second set of optical waveguides connects the receivers in the nodes. The NxN wavelength router is connected across the ring between the first set of optical waveguides and the second set of optical waveguides. Each of the nodes is able to communicate with any other of the nodes on a respective wavelength channel via the router.
Owner:BRITISH TELECOMM PLC
Optical network and arrangement and method in such network
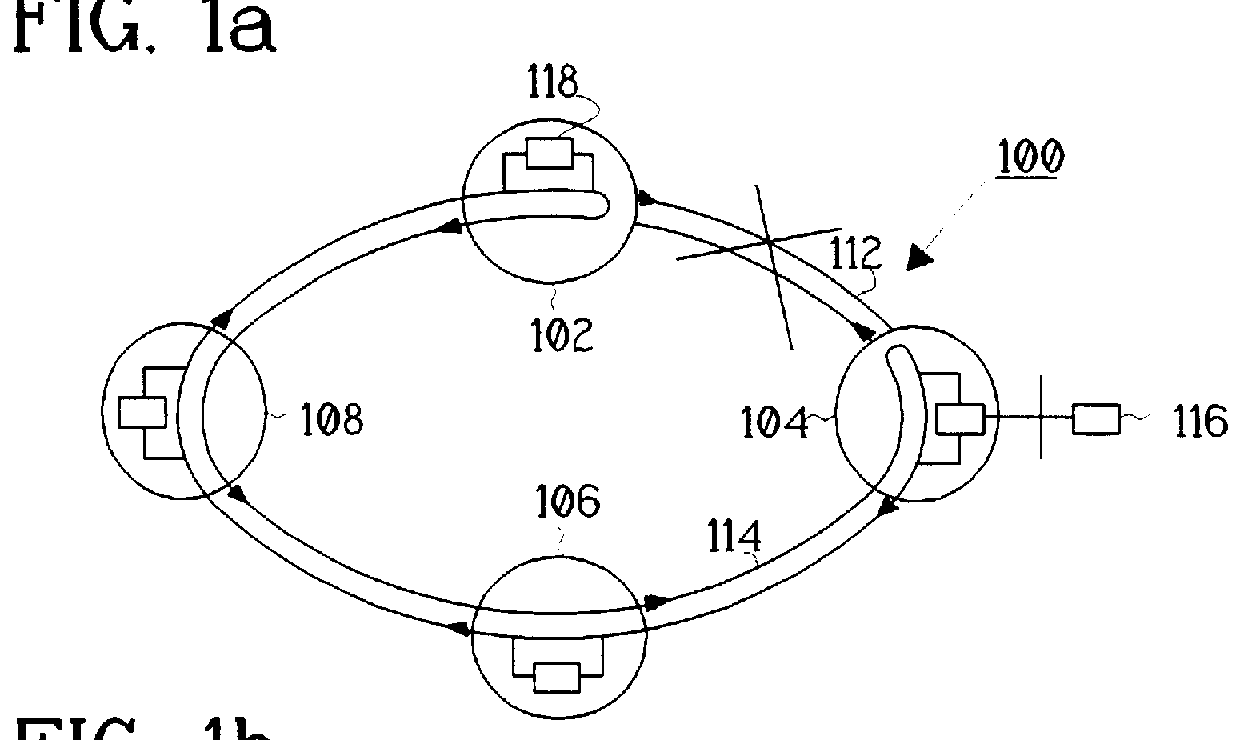
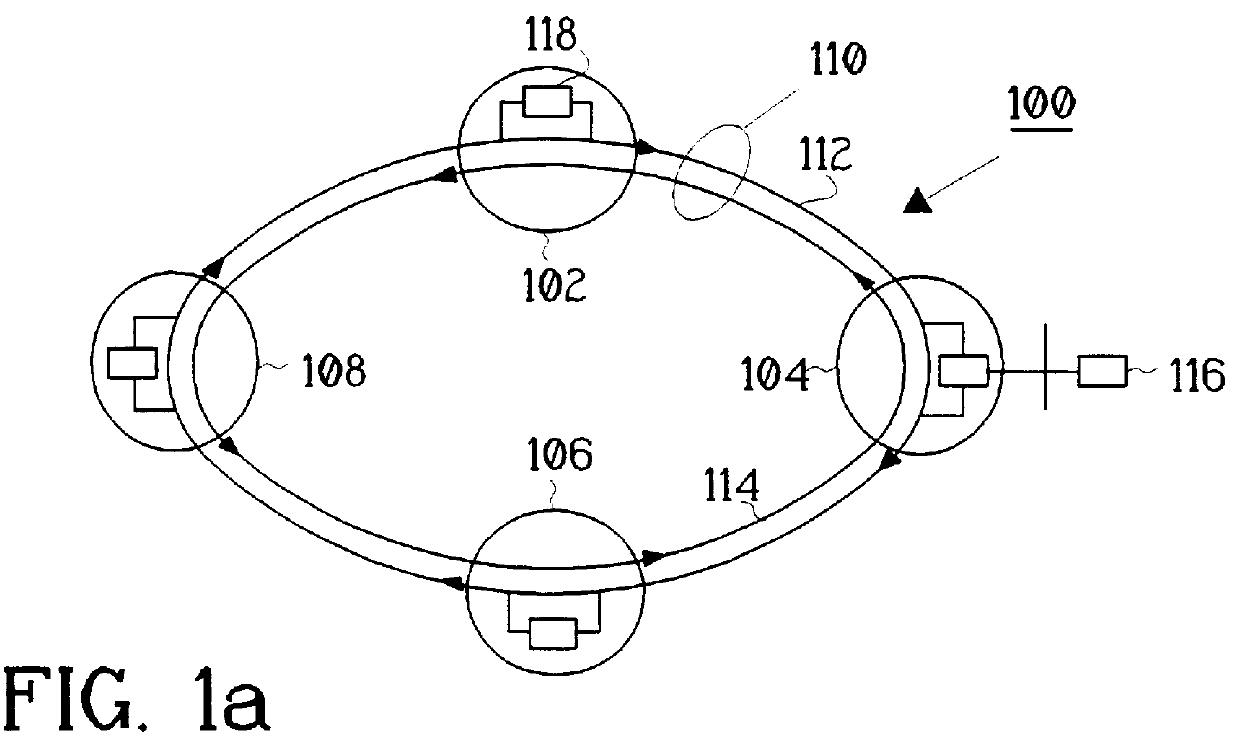
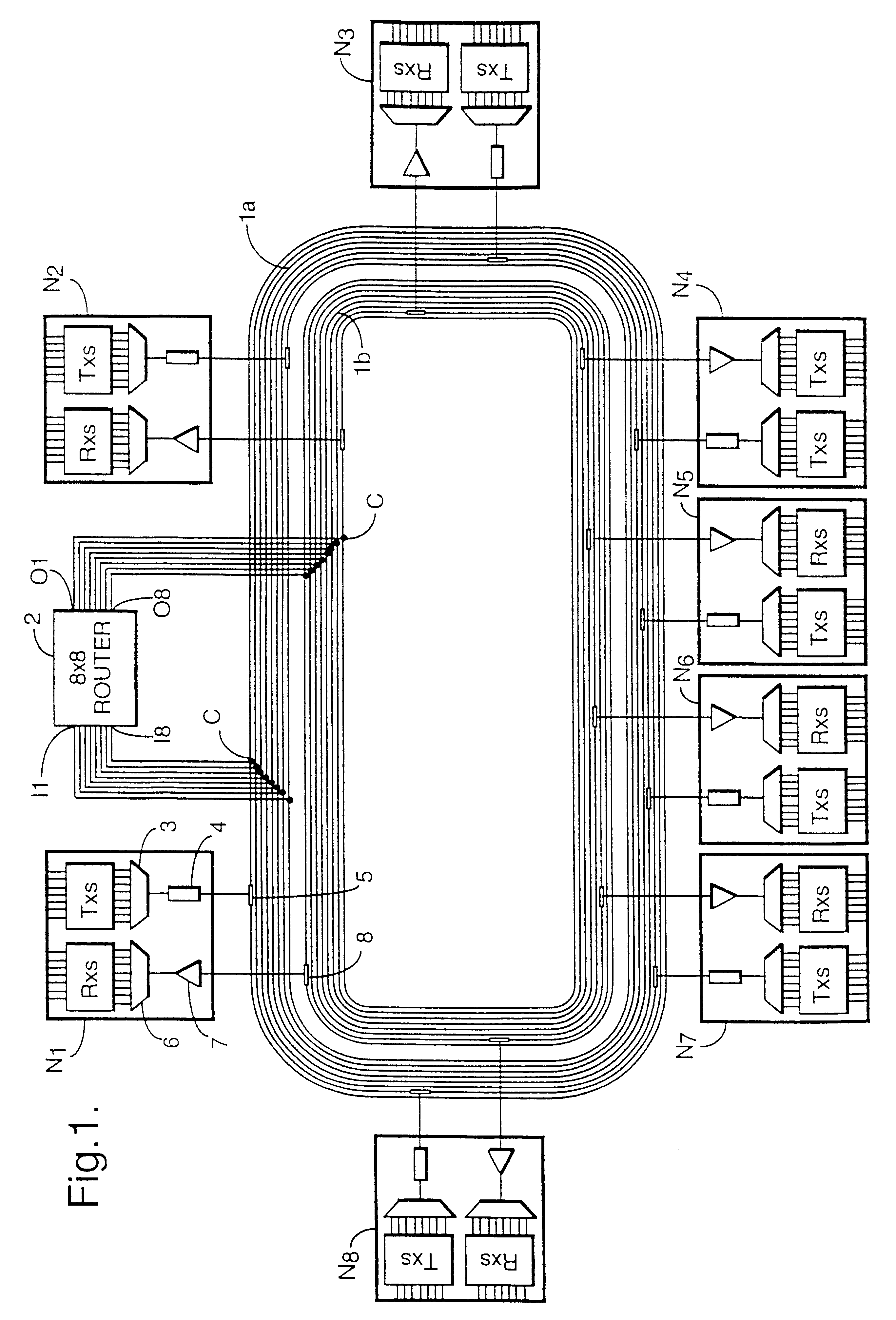
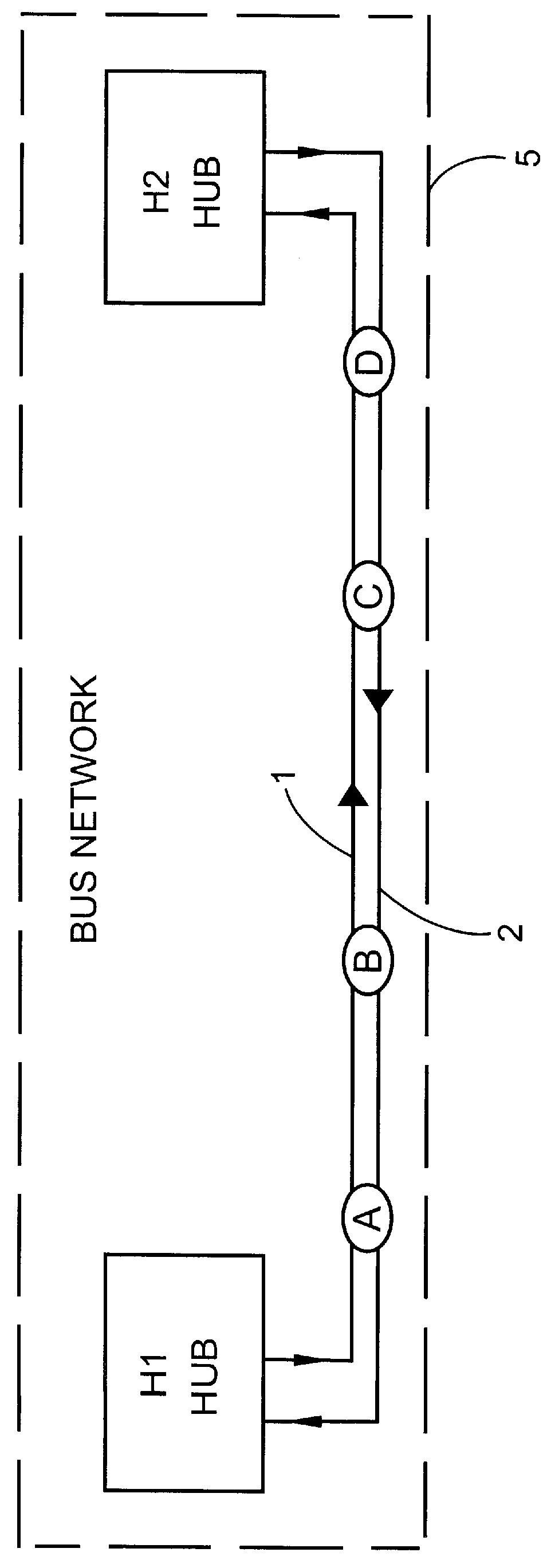
PCT No. PCT / SE96 / 00374 Sec. 371 Date Dec. 29, 1997 Sec. 102(e) Date Dec. 29, 1997 PCT Filed Mar. 26, 1996 PCT Pub. No. WO96 / 31964 PCT Pub. Date Oct. 10, 1996An optical network which is arranged to ensure communication between nodes in a lower-order loop and a higher-order loop when there is an interruption in the lower-order loop or in the event of hub failure. Each lower-order loop consists of a bus network with hubs and one or a plurality of nodes. Two optical fibers connect the nodes in each bus network and are used for communication in opposite directions between the nodes. Each bus network comprises precisely two hubs of which the first closes the bus network end at the first end thereof and the second closes the bus network at the other end. The hubs connect the bus networks in a lower-order loop and join this loop to a higher-order loop. Each node in the bus network is arranged to communicate with each hub. Channel allocation can be carried out so that channels received in one node are re-used for transmission on the same fiber from the same node.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
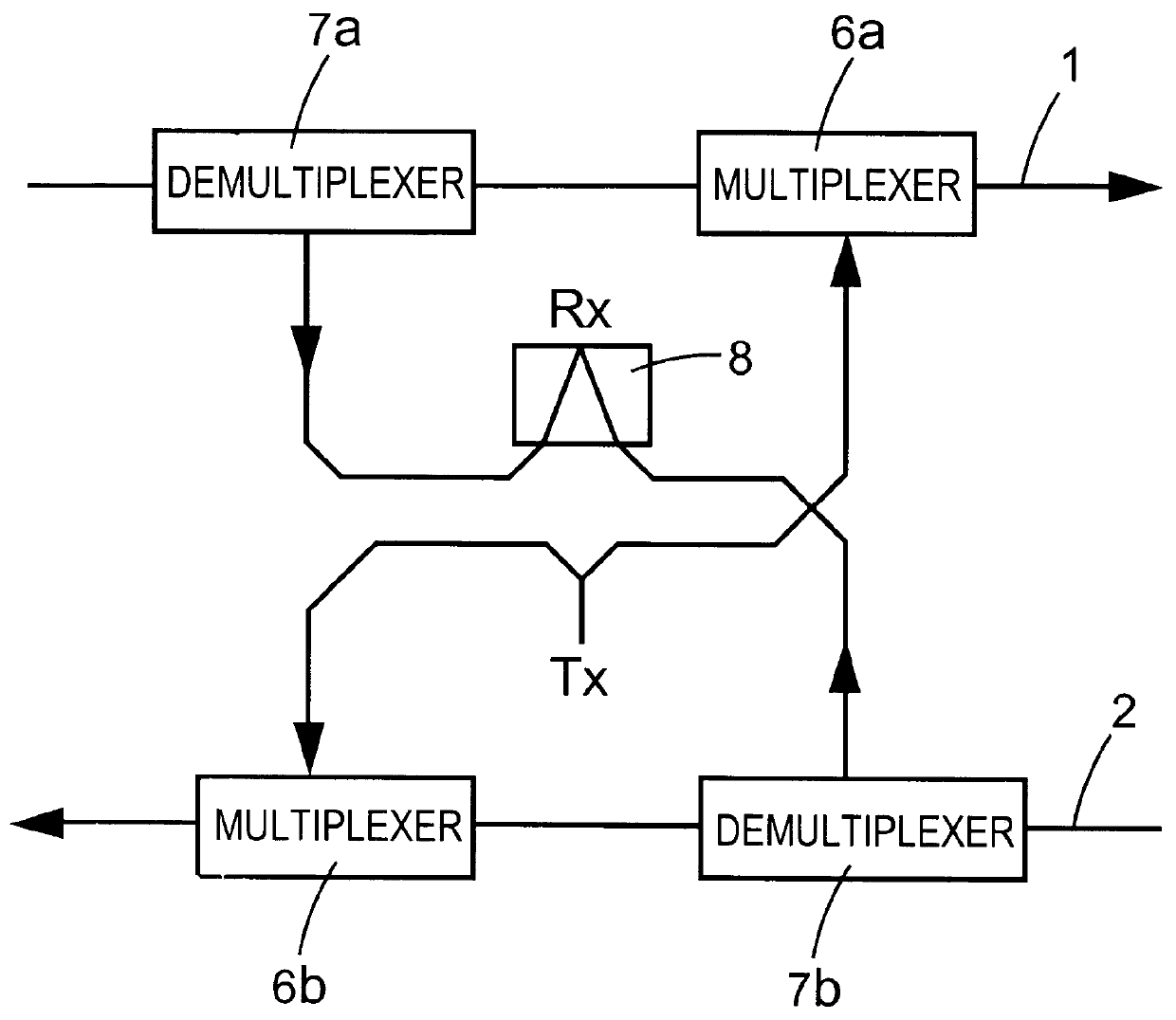
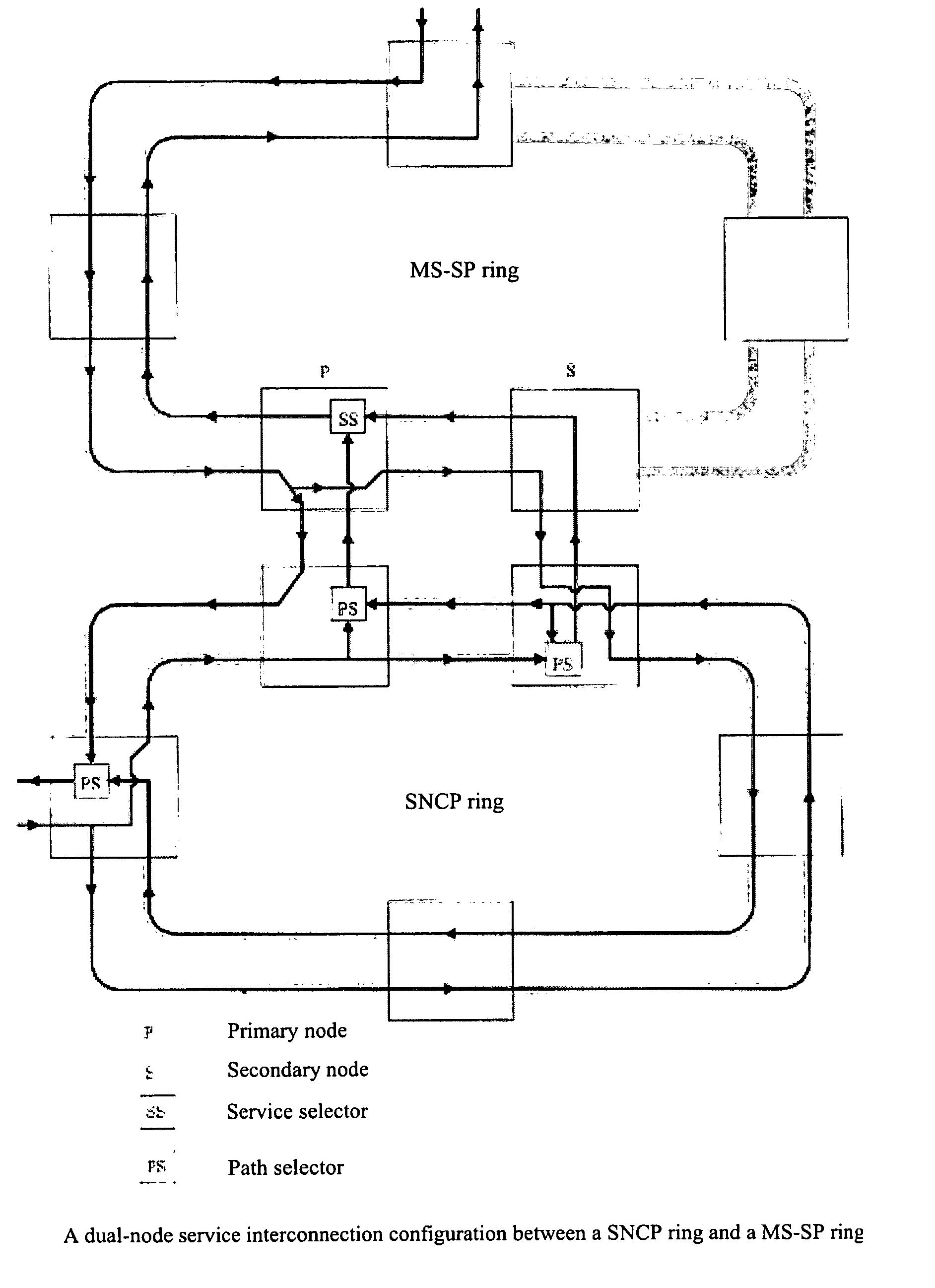
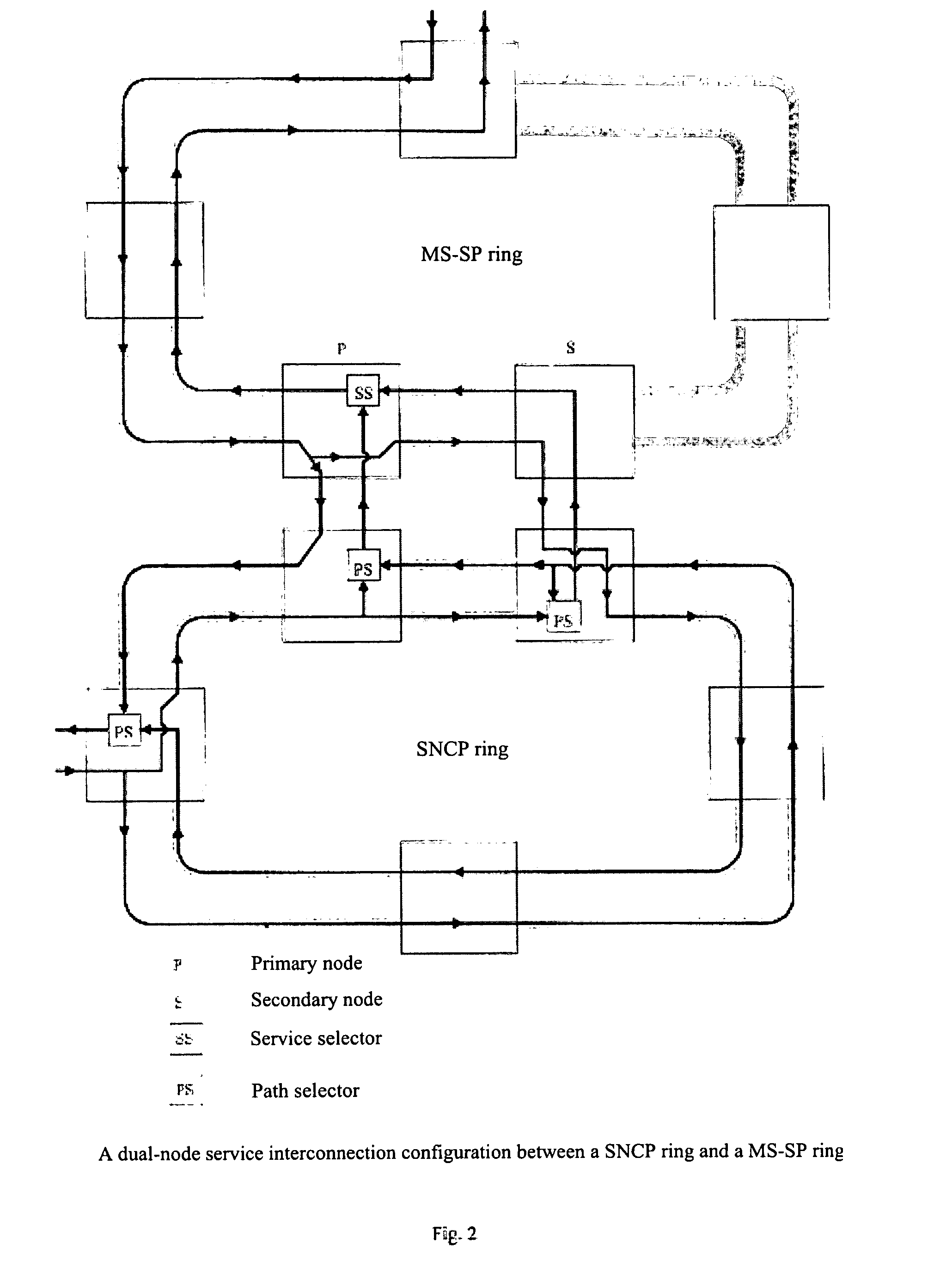
Exchange structure and a method of connection configuration between the optical networks
InactiveUS20070014573A1Improve reliabilityEasy networkingRing-type electromagnetic networksOptical multiplexRing networkInterconnection
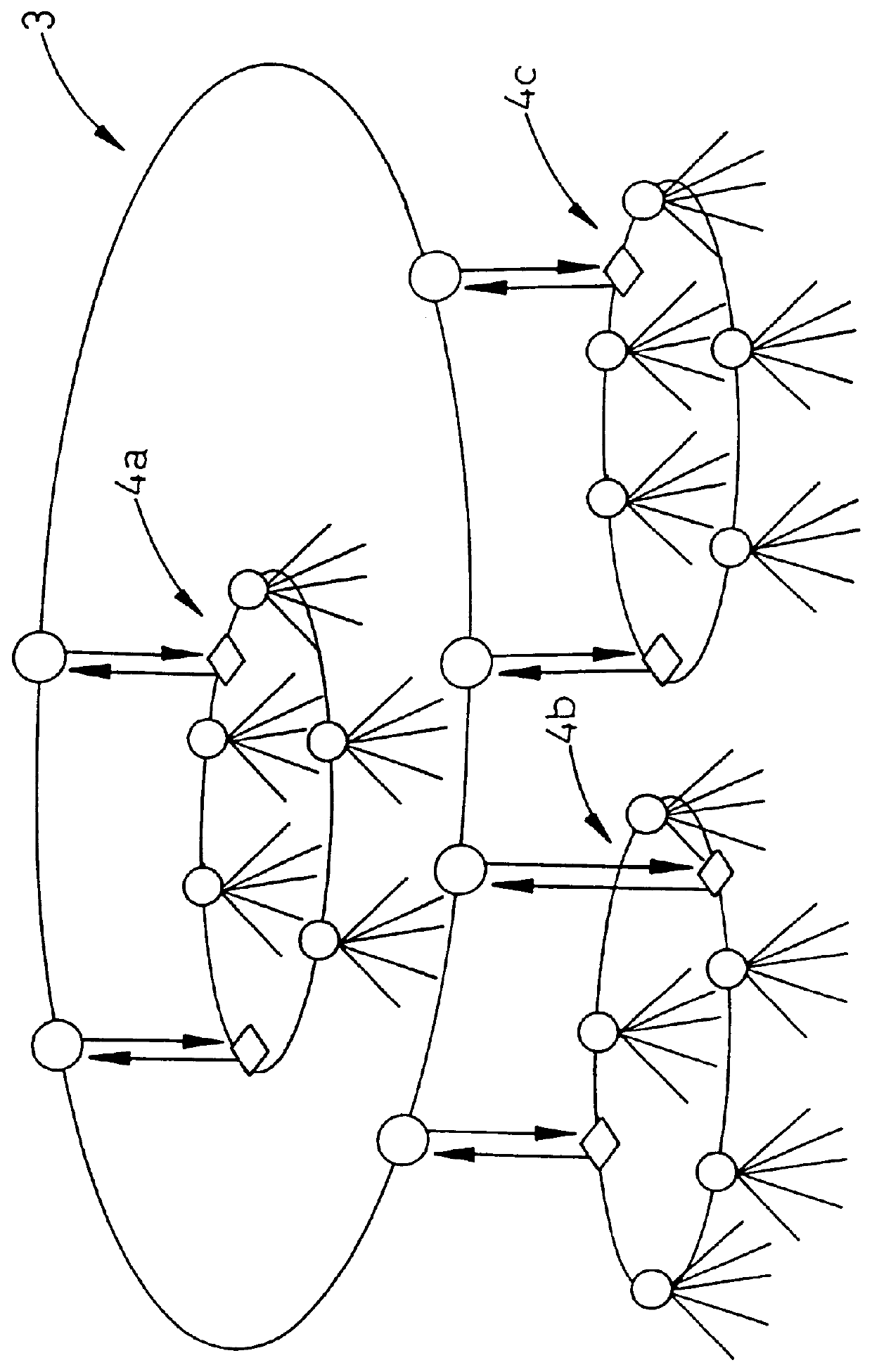
The invention discloses an interconnection structure and a method for configuring path between the optical networks. The optical network includes a first network and a second network, the first network and the second network each has a number of nodes, a first node of the first network connects with a third node of the second network, a second node of the first network connects with a fourth node of the second network. The method comprises the steps of: setting-up a first path between one of the first node and the second node and another node of the first network; and at least by one link of the link between the first node and the third node and that between the second node and the fourth node, and by the first path, said another node of the first network communicates for path with another node of the second network. By the dual-node interconnection structure and the path configuration shceme of this invention between a ring network and a mesh network, and between mesh networks, the respective advantages of the ring network and the mesh metwork in regard to protection and restoration can be combined effectively, and the existing internetworking schemes between the rings are also compatible.
Owner:WEI XUEQIN +2
Ring type optical transmission system and optical apparatus connected to same
InactiveUS20060115210A1Simplify device configurationEasy to useRing-type electromagnetic networksWavelength-division multiplex systemsCommunications systemTransfer system
In the ring type optical communication system of the present invention, in each OADM arranged on a ring network, an optical signal which has the same wavelength as the add wavelength assigned to a local node, of the optical signals of each wavelength contained in WDM light input from on the ring, is extracted from a drop port Pd without being terminated by a rejection / add filter, and input to an optical switch. In the optical switch, either one of the optical signal extracted from the rejection / add filter, or the add light added onto the ring from the local node, is selected, and the selected light is applied to the add port Pa of the rejection / add filter. As a result, communication between a central station and optional OADM nodes, and multicast communication over a plurality of ring networks can be realized by means of a simple node configuration.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
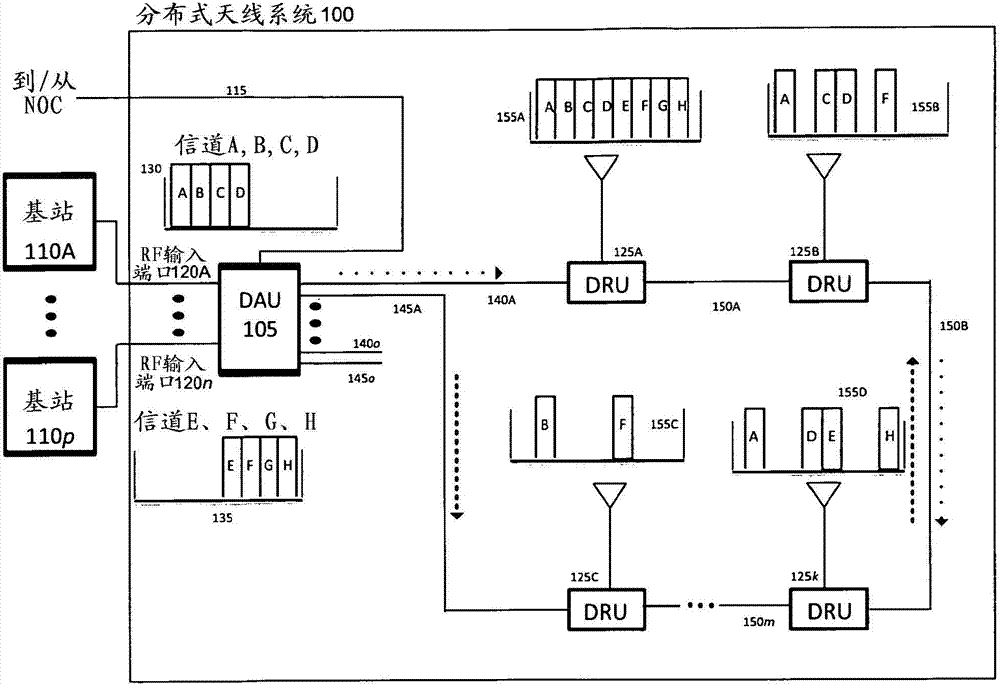
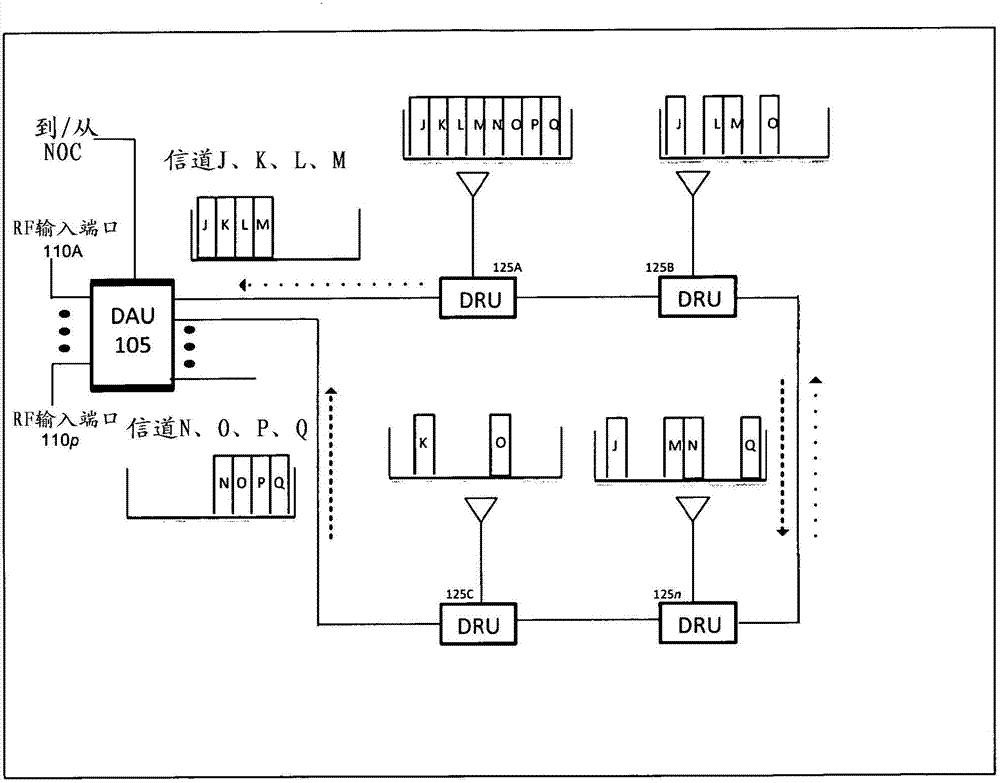
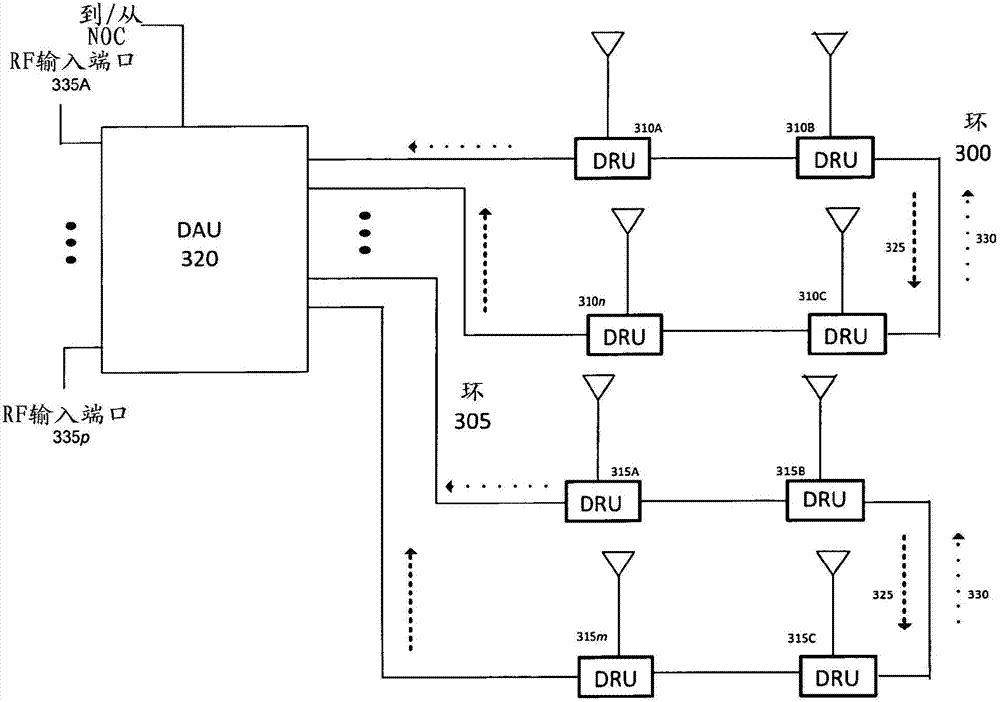
Daisy-chained ring of remote units for a distributed antenna system
ActiveCN103201958AImprove efficiencyIncrease flow capacityRing-type electromagnetic networksHybrid transportDistributed antenna systemMulti carrier
The present disclosure is a novel utility of a software defined radio (SDR) based Distributed Antenna System (DAS) that is field reconfigurable and support multi-modulation schemes (modulation-independent), multi-carriers, multi-frequency bands and multi-channels. More specifically, the present invention relates to a DAS utilizing one or more Daisy-Chained Rings of Remote Units. The present invention enables a high degree of flexibility to manage, control, enhance, facilitate the usage and performance of a distributed wireless network such as Flexible Simulcast, automatic traffic load-balancing, network and radio resource optimization, network calibration, autonomous / assisted commissioning, carrier pooling, automatic frequency selection, frequency carrier placement, traffic monitoring, traffic tagging, pilot beacon, etc. As a result, a DAS in accordance with the present invention can increase the efficiency and traffic capacity of the operators' wireless network.
Owner:DALI SYST LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com