Patents
Literature
42 results about "Generalized Multi-Protocol Label Switching" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
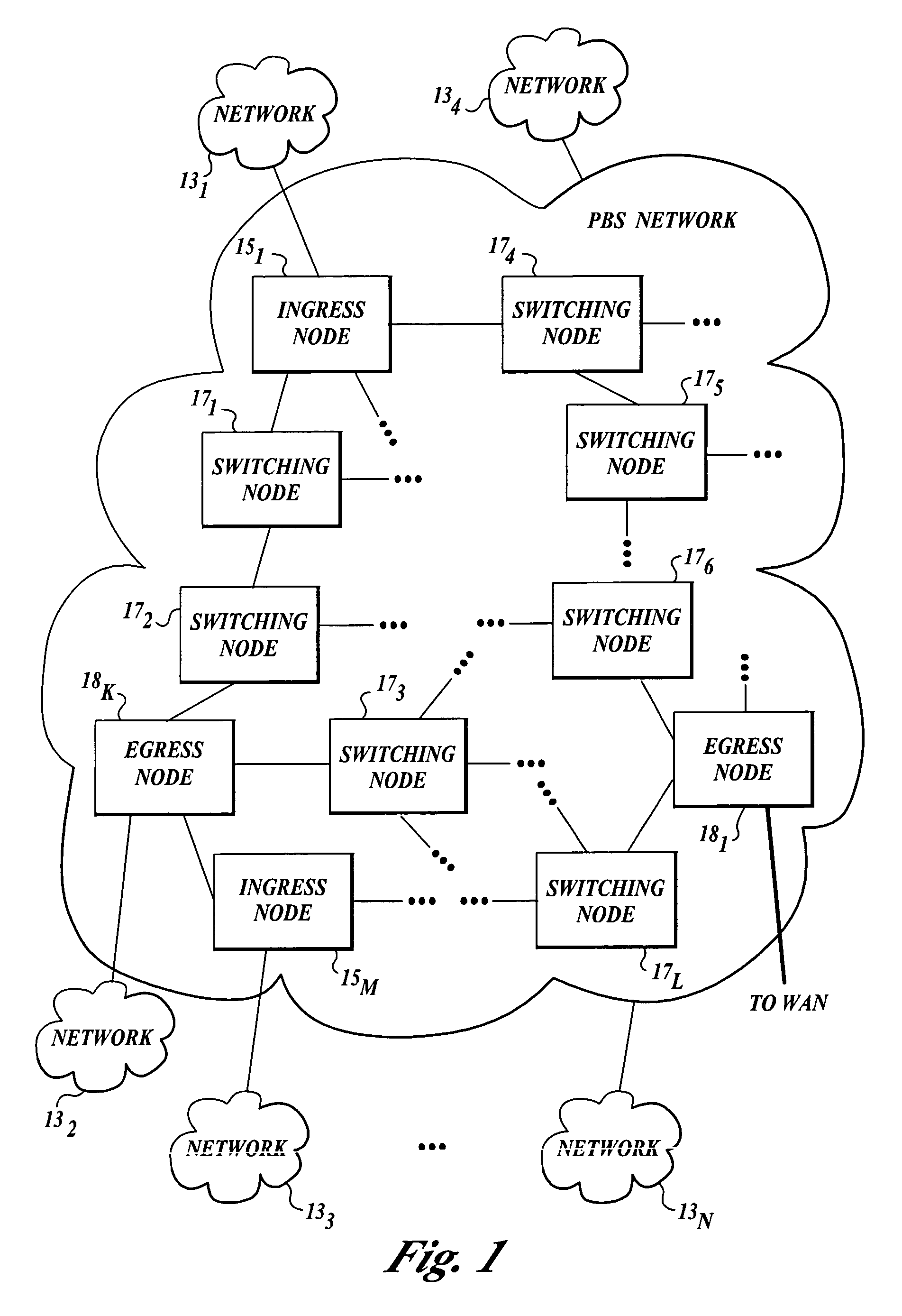
Generalized Multi-Protocol Label Switching (GMPLS) is a protocol suite extending MPLS to manage further classes of interfaces and switching technologies other than packet interfaces and switching, such as time division multiplexing, layer-2 switching, wavelength switching and fiber-switching.
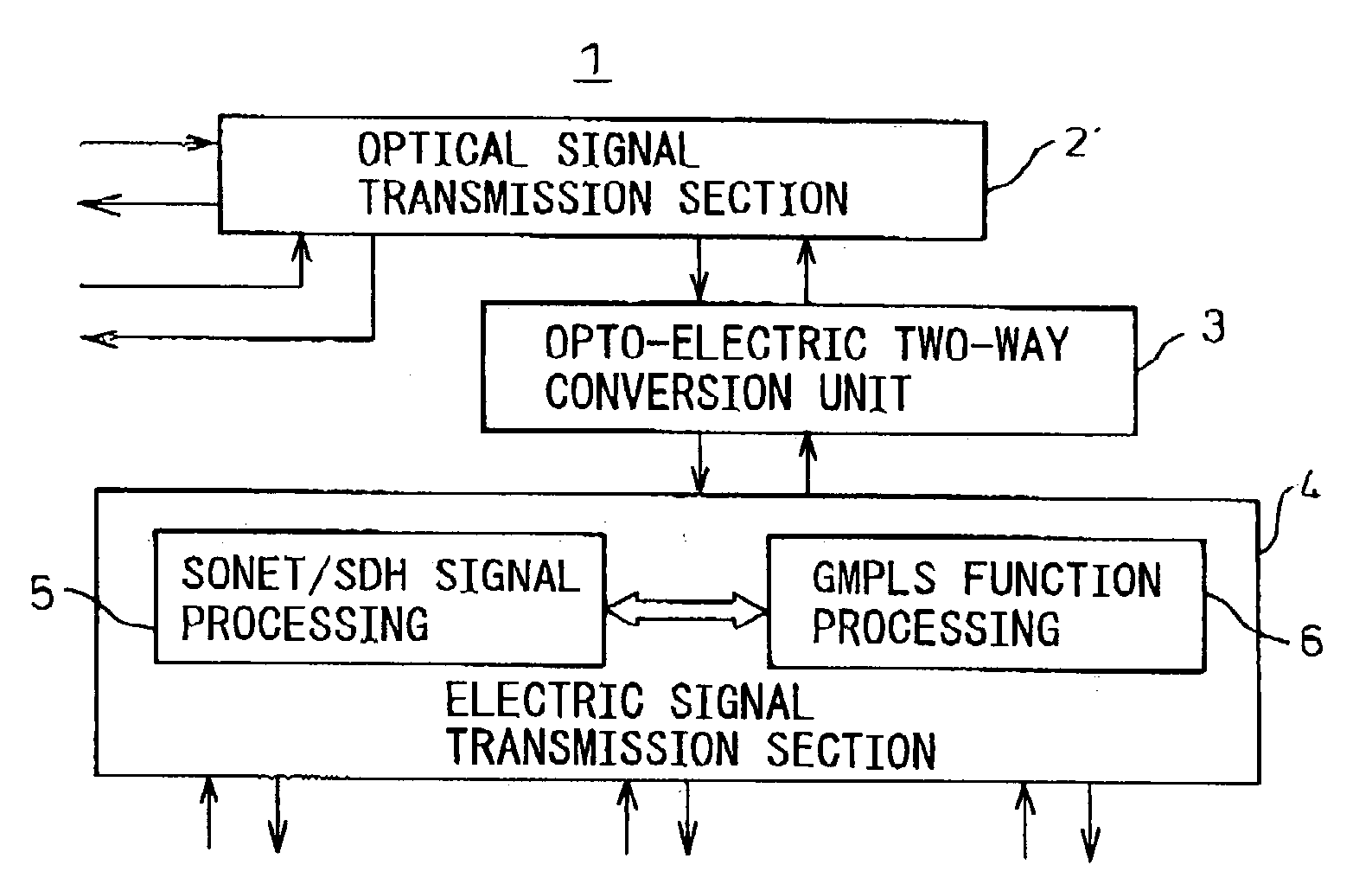
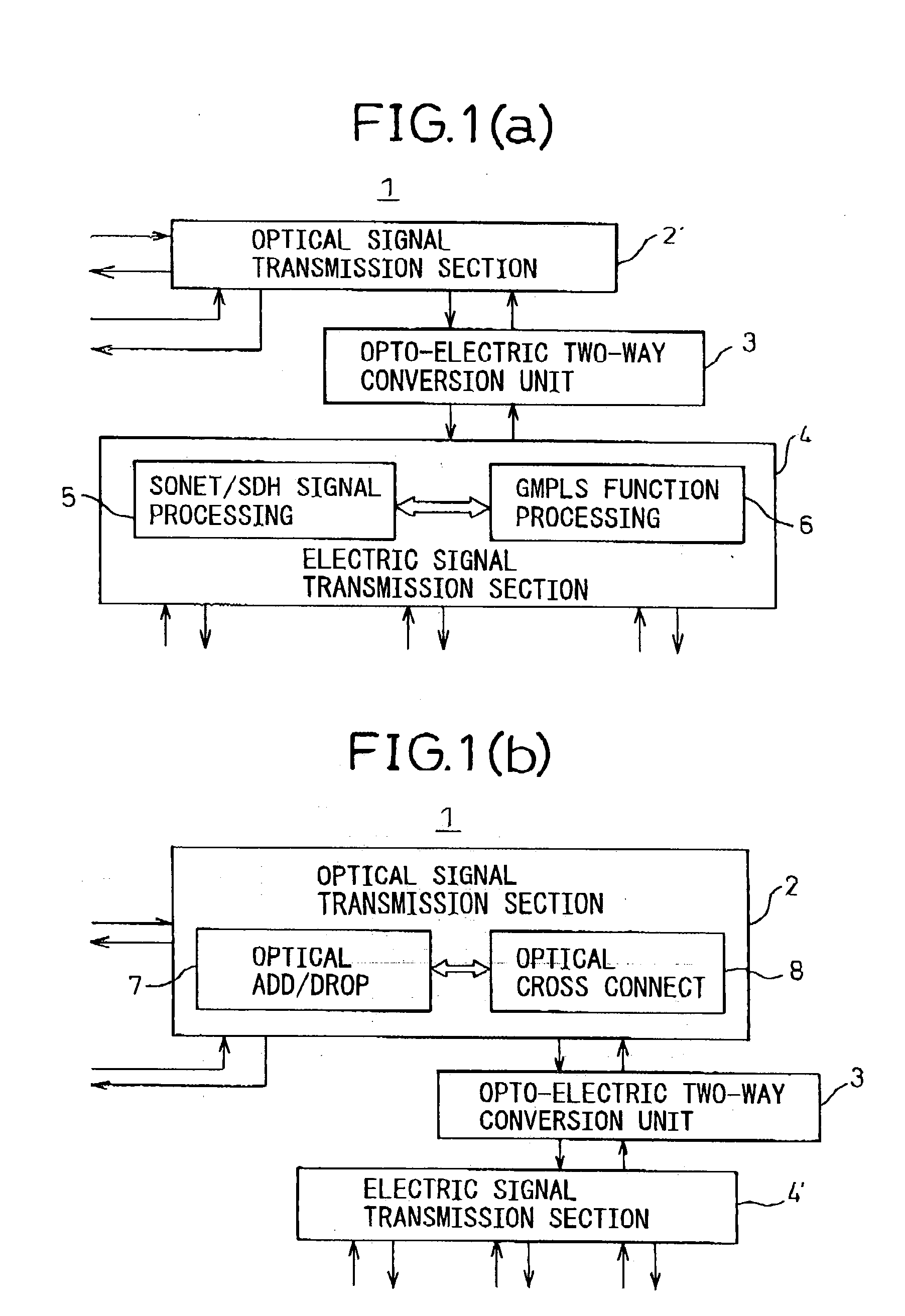
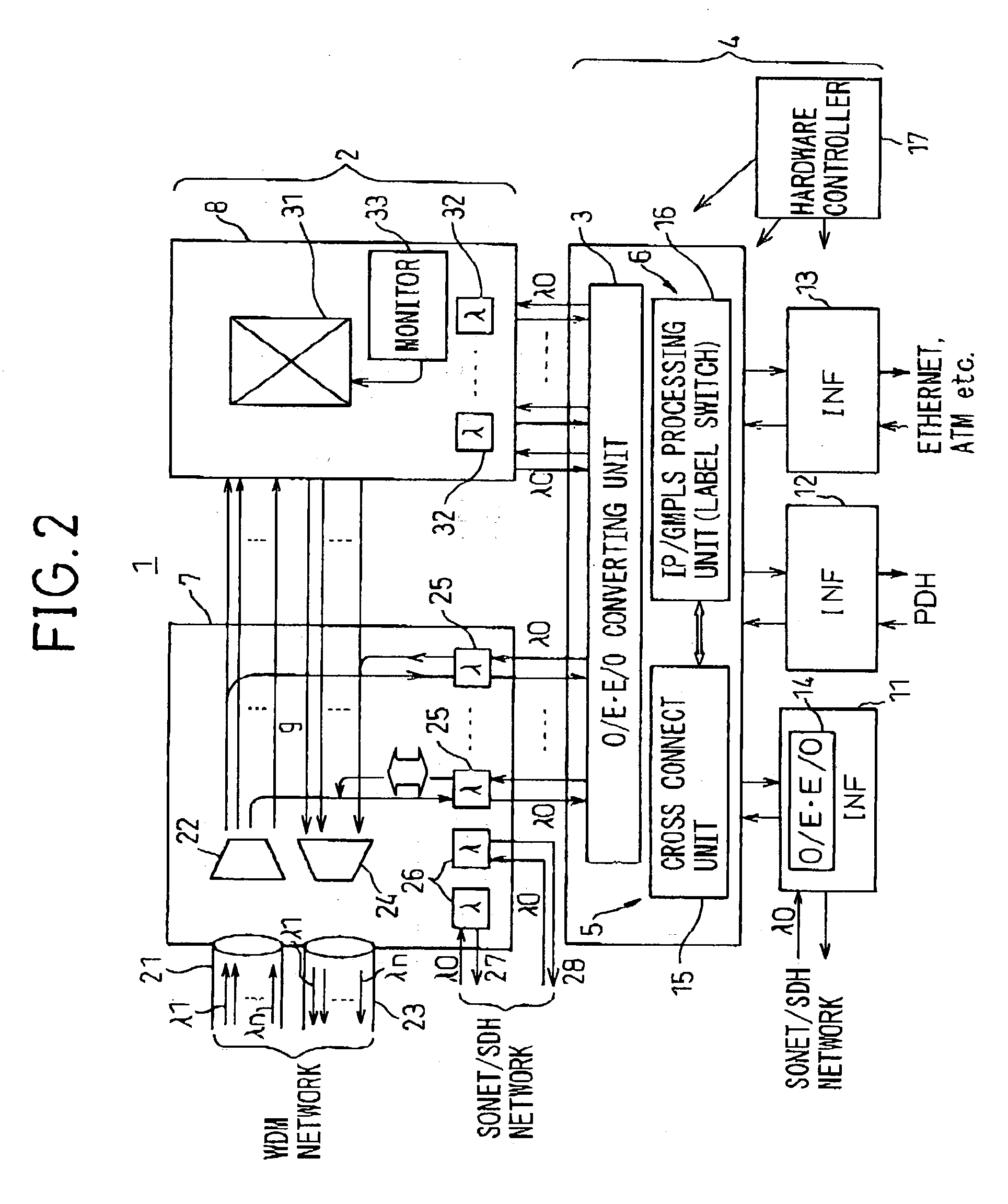
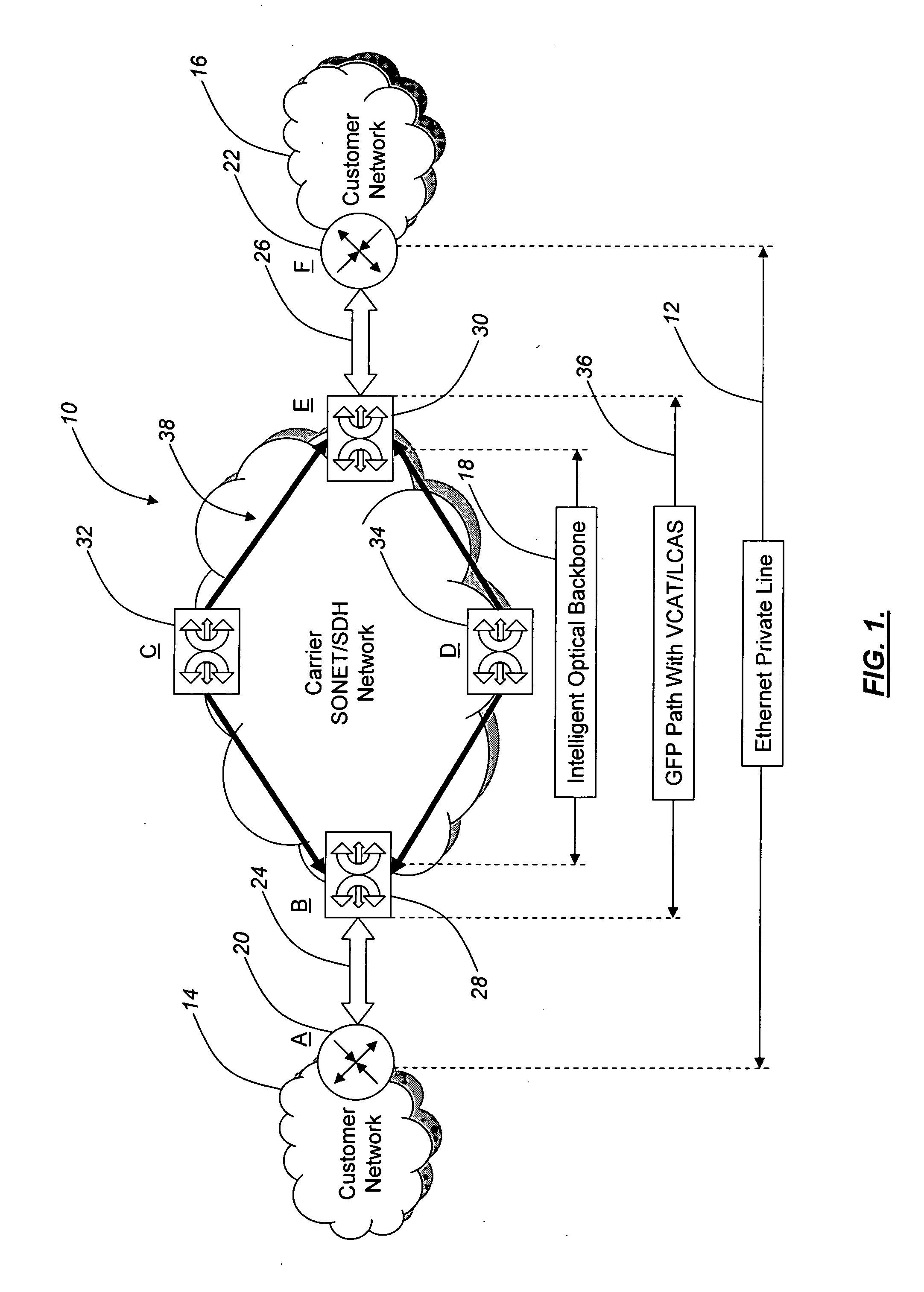
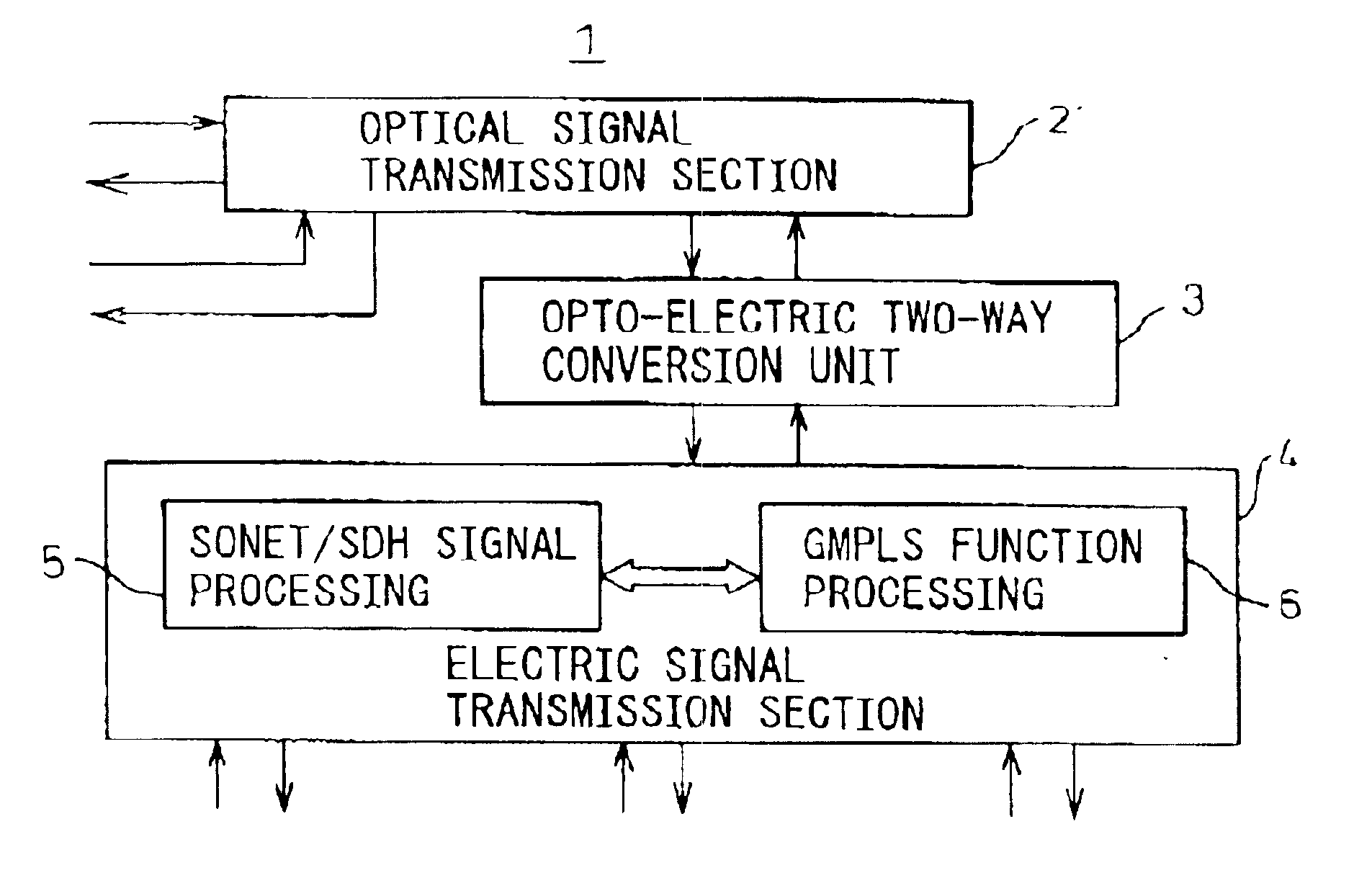
Transmission apparatus
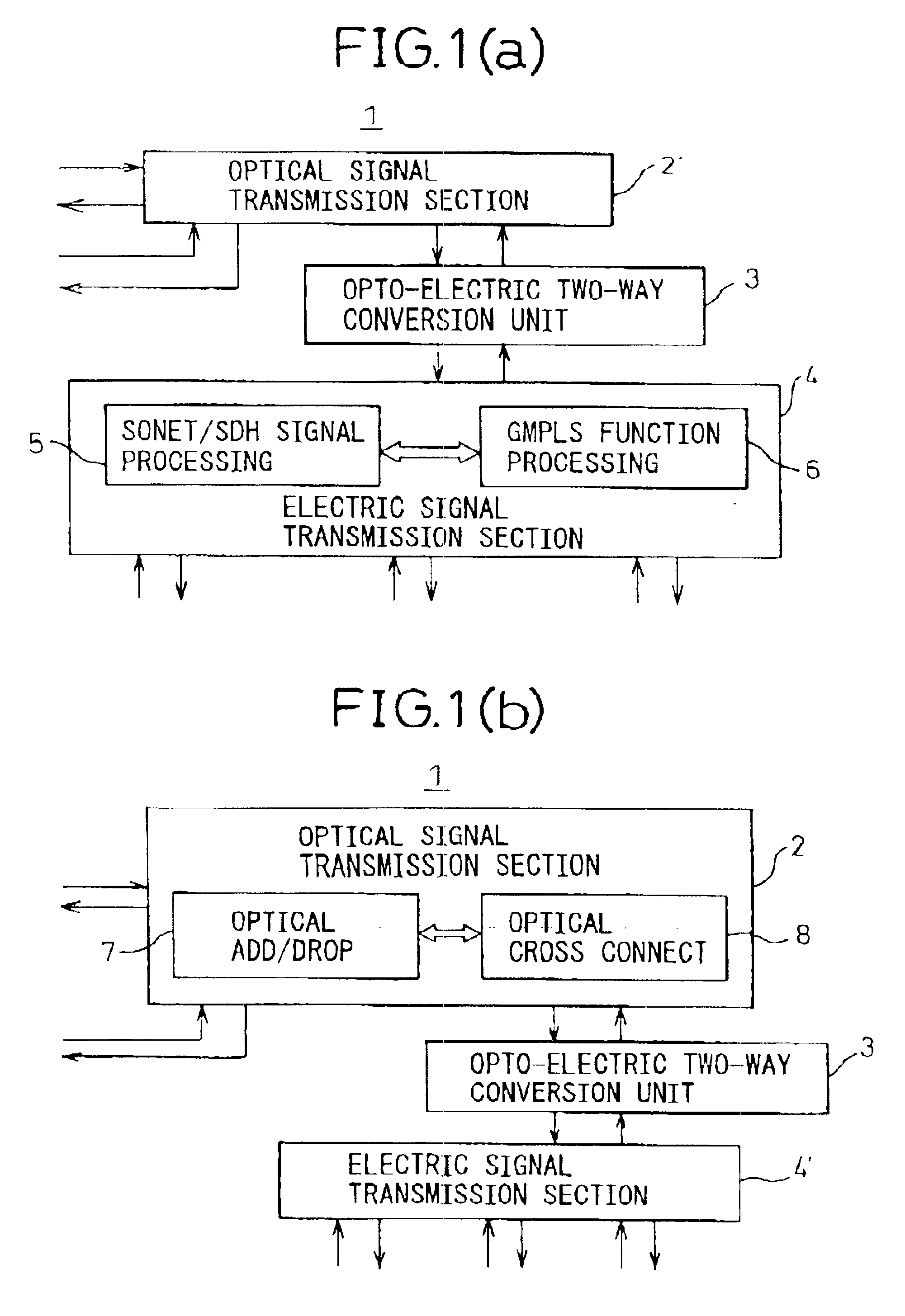
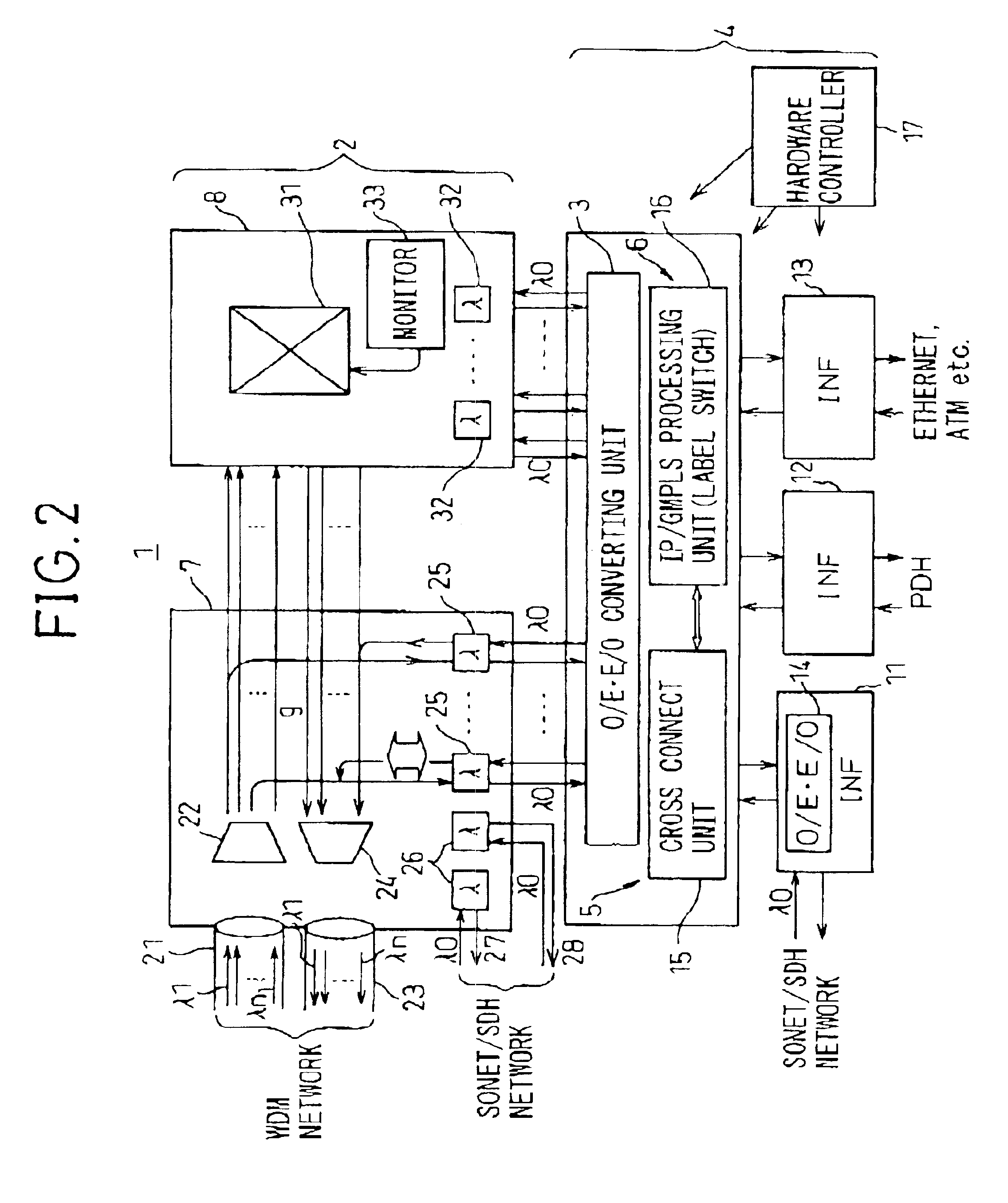
InactiveUS20030228093A1Multiplex system selection arrangementsRing-type electromagnetic networksCross connectionOpto electronic
A transmission apparatus for coupling an optical signal transmission section and an electrical signal transmission section through an opto-electric two-way conversion unit, where the electrical signal transmission section is comprised of a SONET / SDH signal processing function unit and a generalized multi protocol label switching (GMPLS) function processing function unit cooperating with that function unit and where the optical signal transmission section is comprised of an optical add / drop function unit for transferring an optical signal with the electrical signal transmission section through the conversion unit and an optical cross-connect function unit for switching paths in wavelength units of the optical signal with the electrical signal transmission section, whereby the capital cost and running costs of an optical network for transmitting an IP signal can be greatly reduced.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
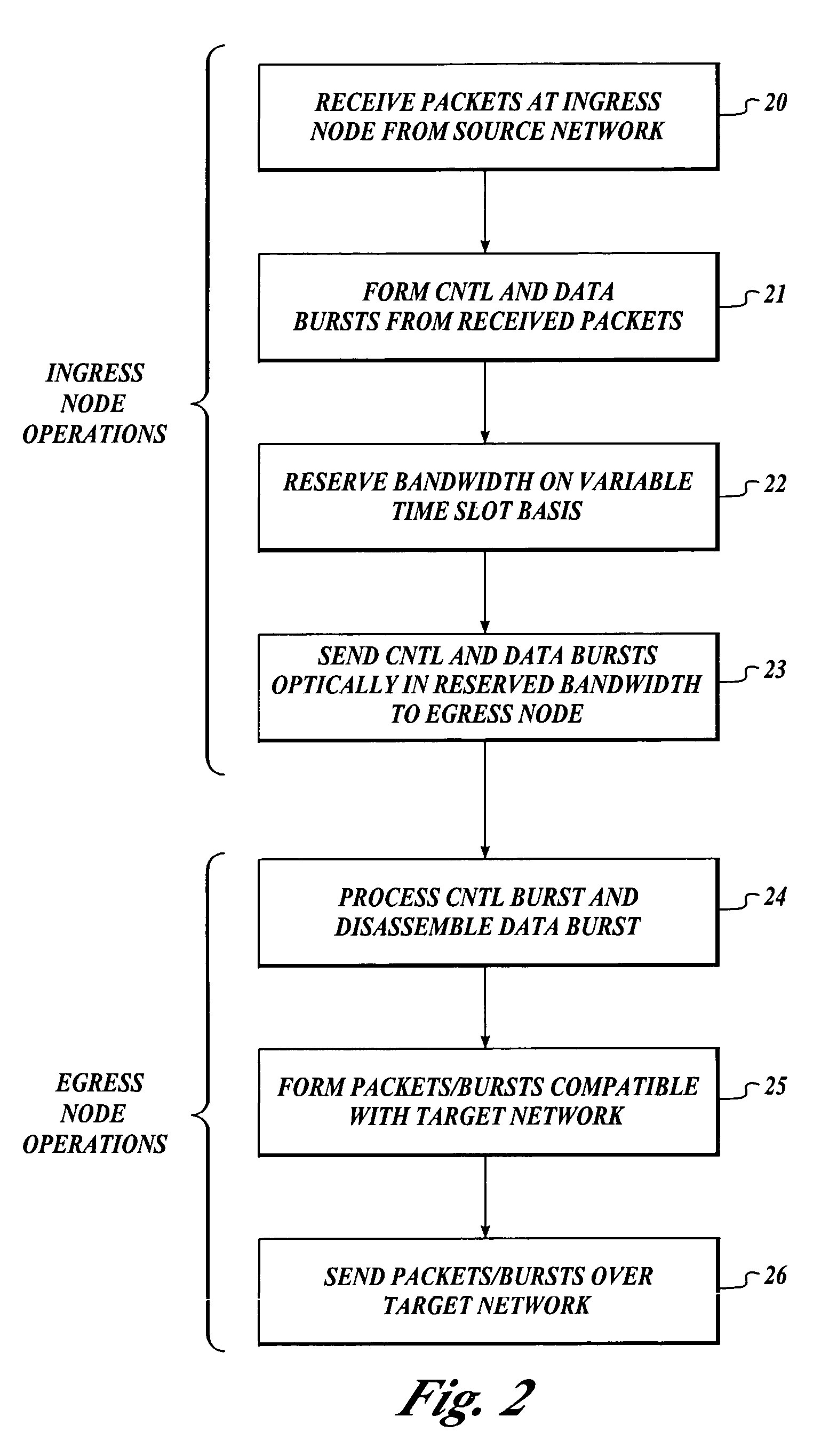
Method and apparatus for interfacing applications to LCAS for efficient SONET traffic flow control
InactiveUS20060018324A1Efficient interfaceError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsMultiprotocol Label SwitchingCross connection
The present invention provides methods and apparatuses for interfacing high-layer applications to Link Capacity Adjustment Scheme (LCAS) on Synchronous Optical Network / Synchronous Digital Hierarchy (SONET / SDH) edge nodes. These applications include high-level control protocols, such as Generalized Multiprotocol Label Switching (GMPLS) and Optical Switching and Routing Protocol (OSRP), and user-initiated cross-connect creation and termination. The present invention provides a mechanism that is capable of mapping SONET / SDH connections to Virtual Concatenated Groups (VCGs), thus enabling an efficient interface for operators to control and manage the connections via LCAS. As part of the mechanism, the existing LCAS protocol state machine is enhanced such that the operators can shut down bi-directional SONET / SDH flows from a single edge node, as opposed to from both source and sink nodes, as provided for by existing specifications.
Owner:CIENA
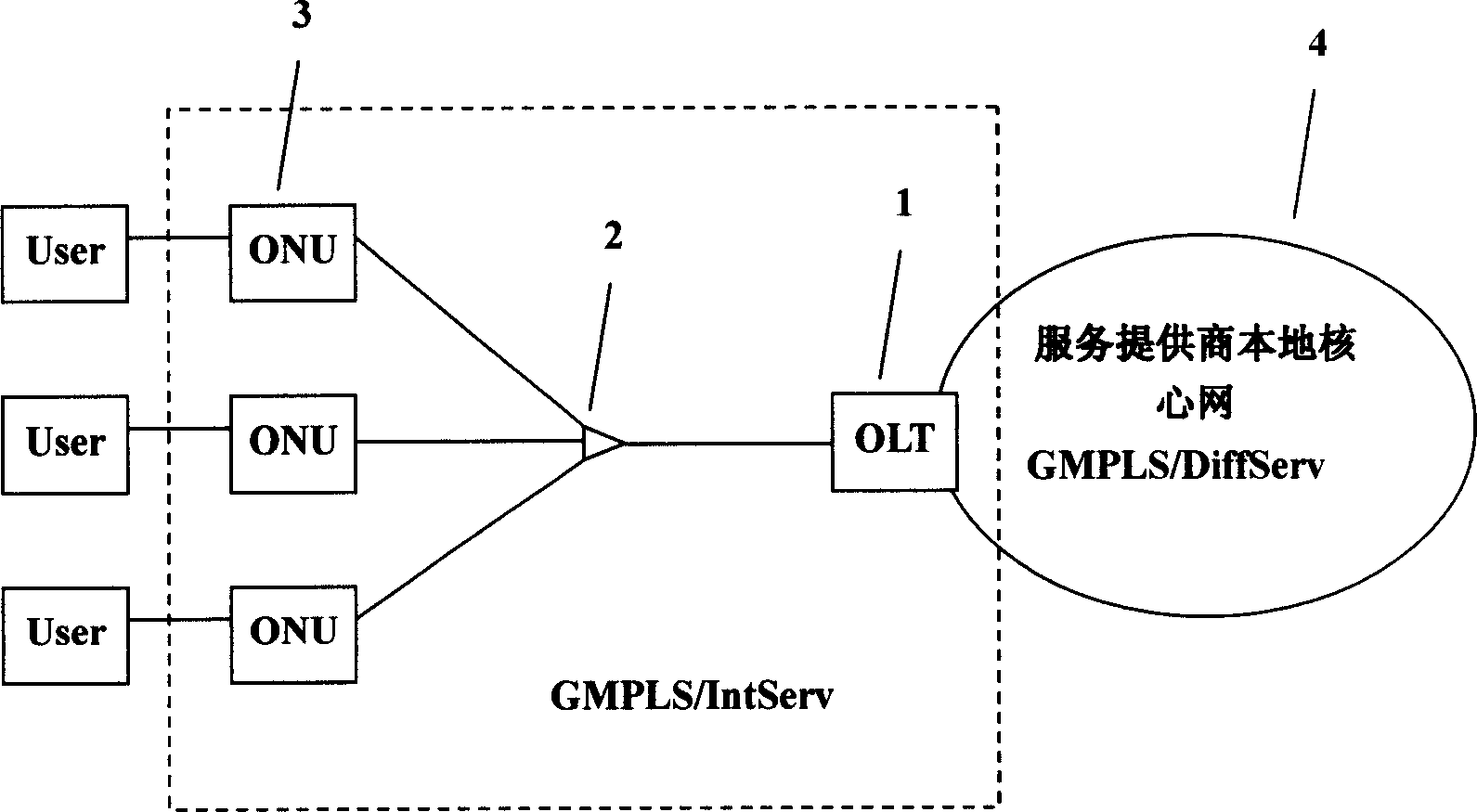
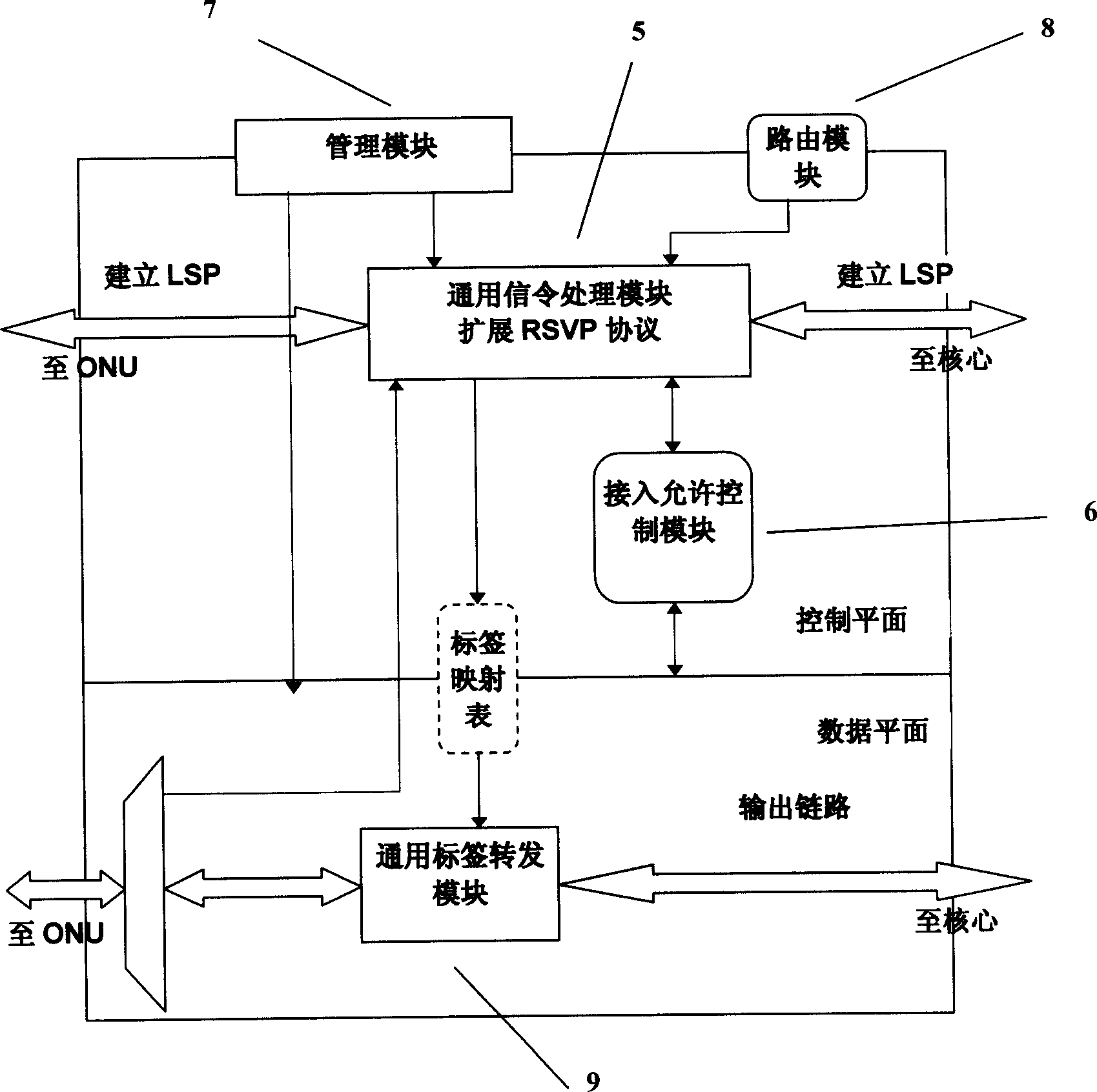
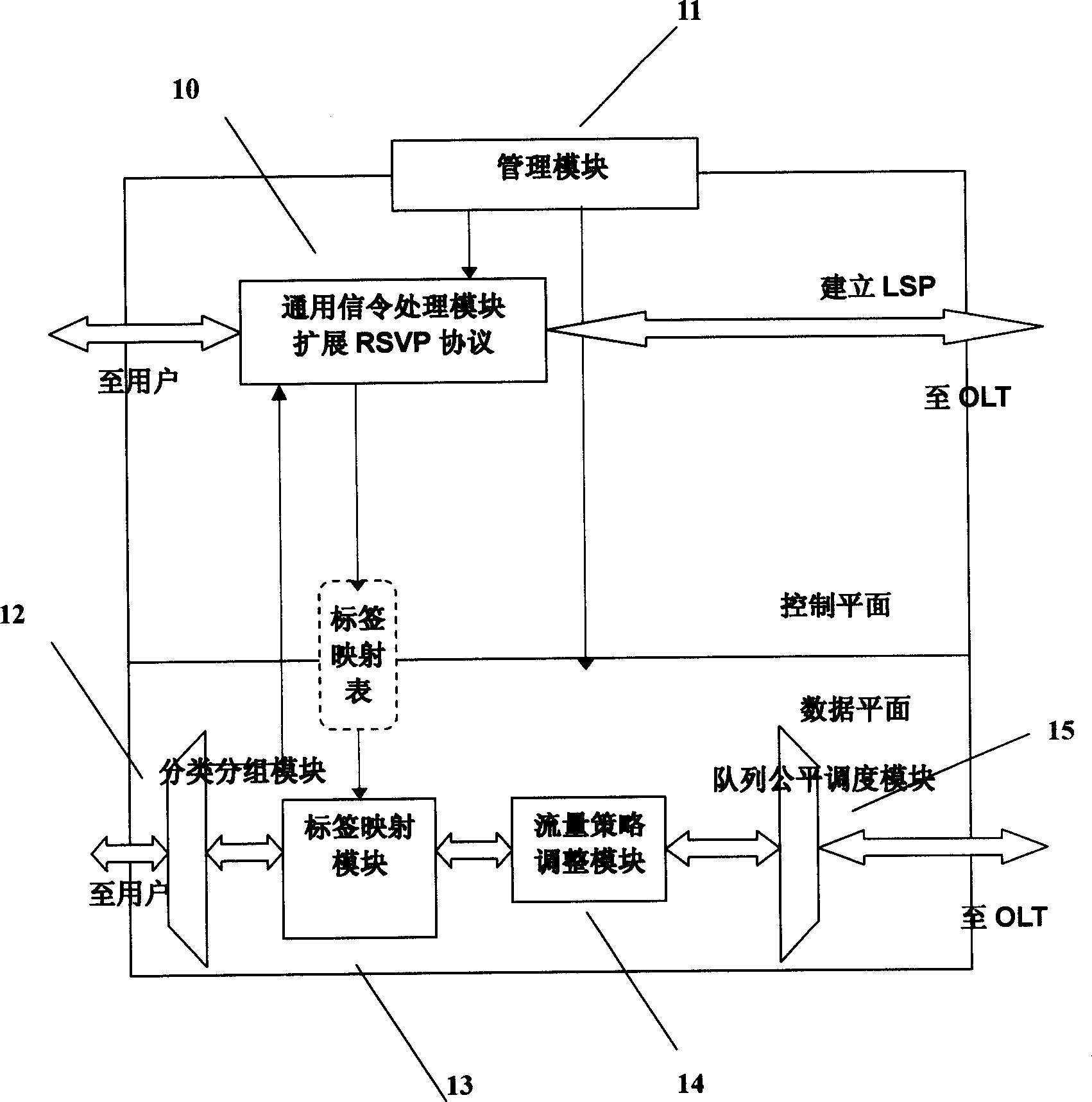
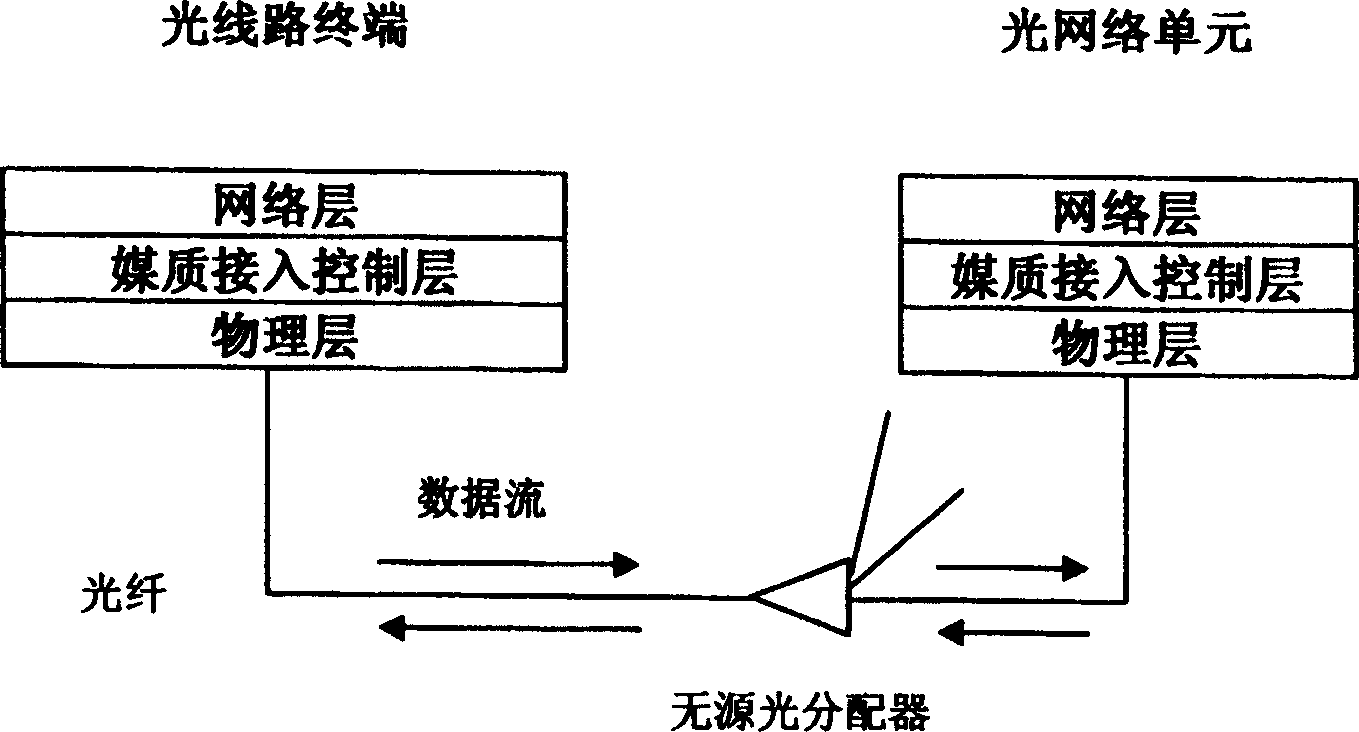
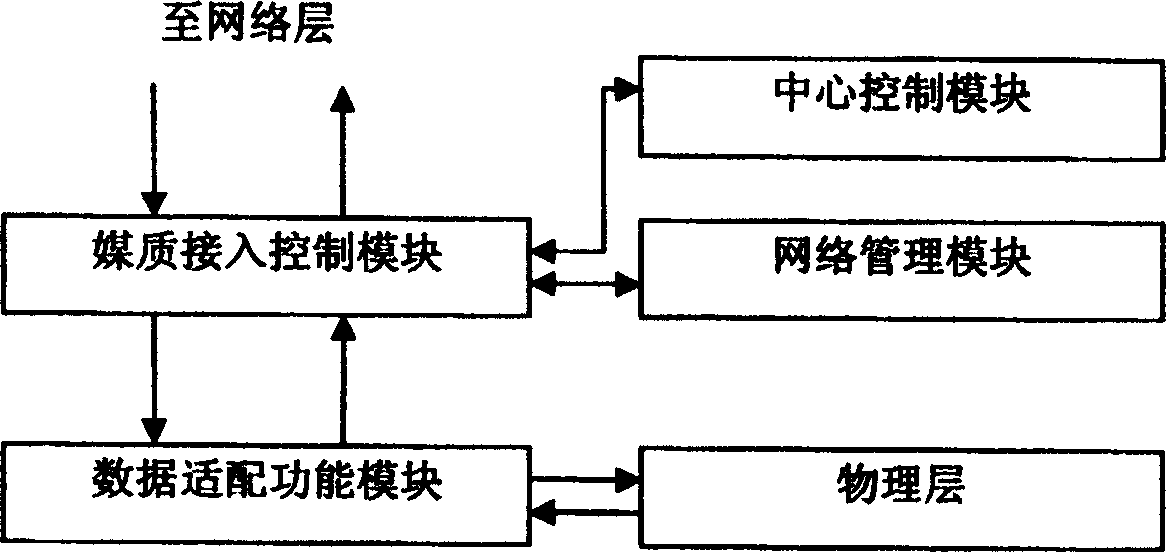
Passive optical network system based on generalized multiprotocol label switching (GMPLS) protocol
InactiveCN1725756ARealize intelligenceRealize intelligent controlTransmissionTelecommunications linkMultiprotocol Label Switching
A passive optical network system based on label exchanging protocol of universal multi-protocol is prepared as connecting optical line terminal OLT to multiple optical network unit ONU by wideband passive optical distribution network , using OLT and ONU as edge router and GMPLS domain of said exchanging protocol for being connected to the other GMPLS router in said multi-protocol by communication link , using OLT as intermediate router of integrated service in system individually for controlling all communication activities , using ONU as inlet router of integrated service in system for executing command of OLT .
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Mesh restoration in optical transport networks
The present disclosure provides mesh restoration systems and methods with Optical Transport Network (OTN) links using a signaling and routing protocol, such as Optical Signaling and Routing Protocol (OSRP), Automatically Switched Optical Network (ASON), Generalized Multi Protocol Label Switching (GMPLS), and the like. The present invention includes an optical node, network, and method using the signaling and routing protocol for OTN lines of differing bandwidth granularities. The present invention utilizes OTN overhead for in-band signaling and may include capability for supporting SONET / SDH lines as well as OTN lines in the same system using the signaling and routing protocol.
Owner:CIENA
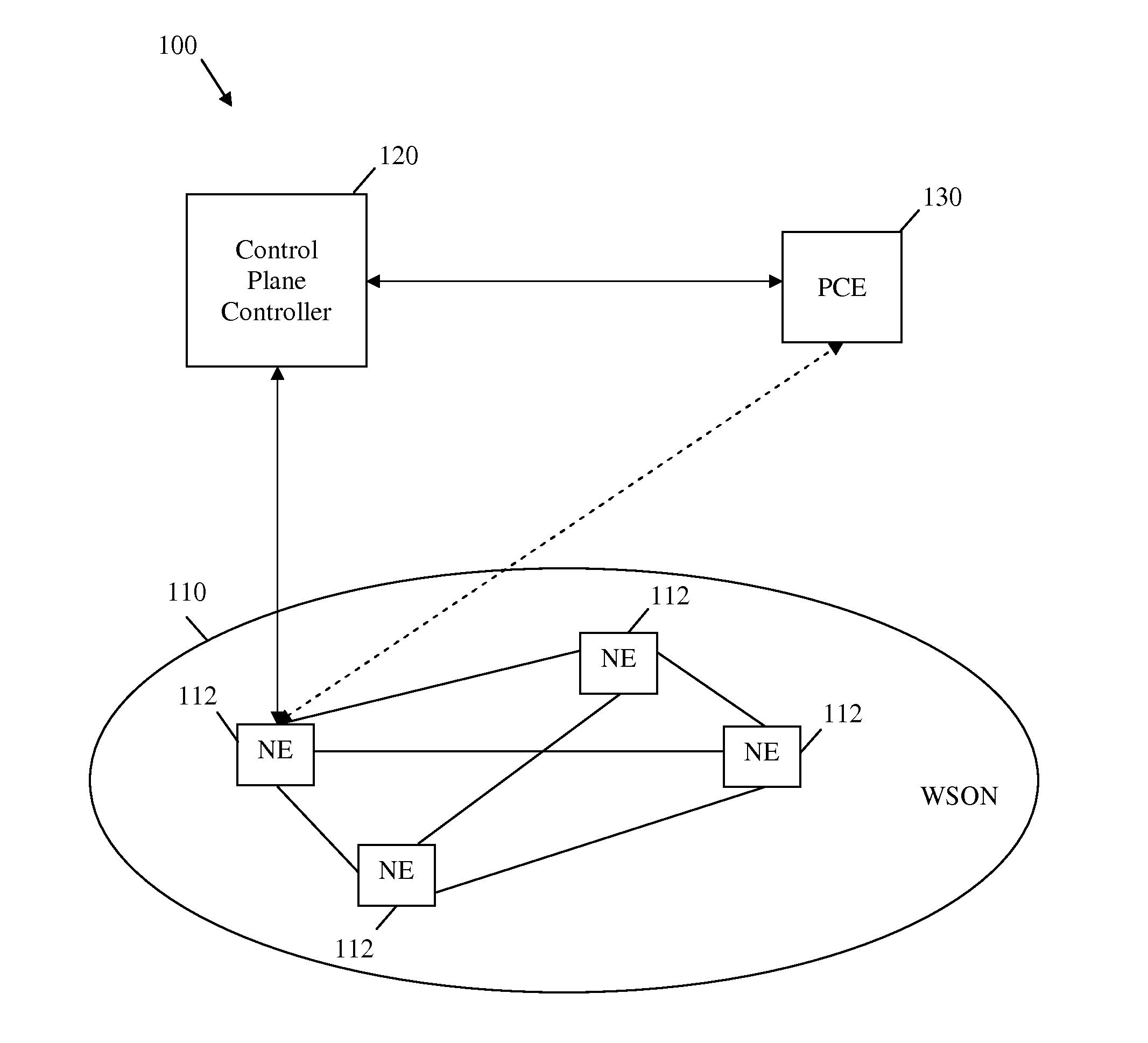
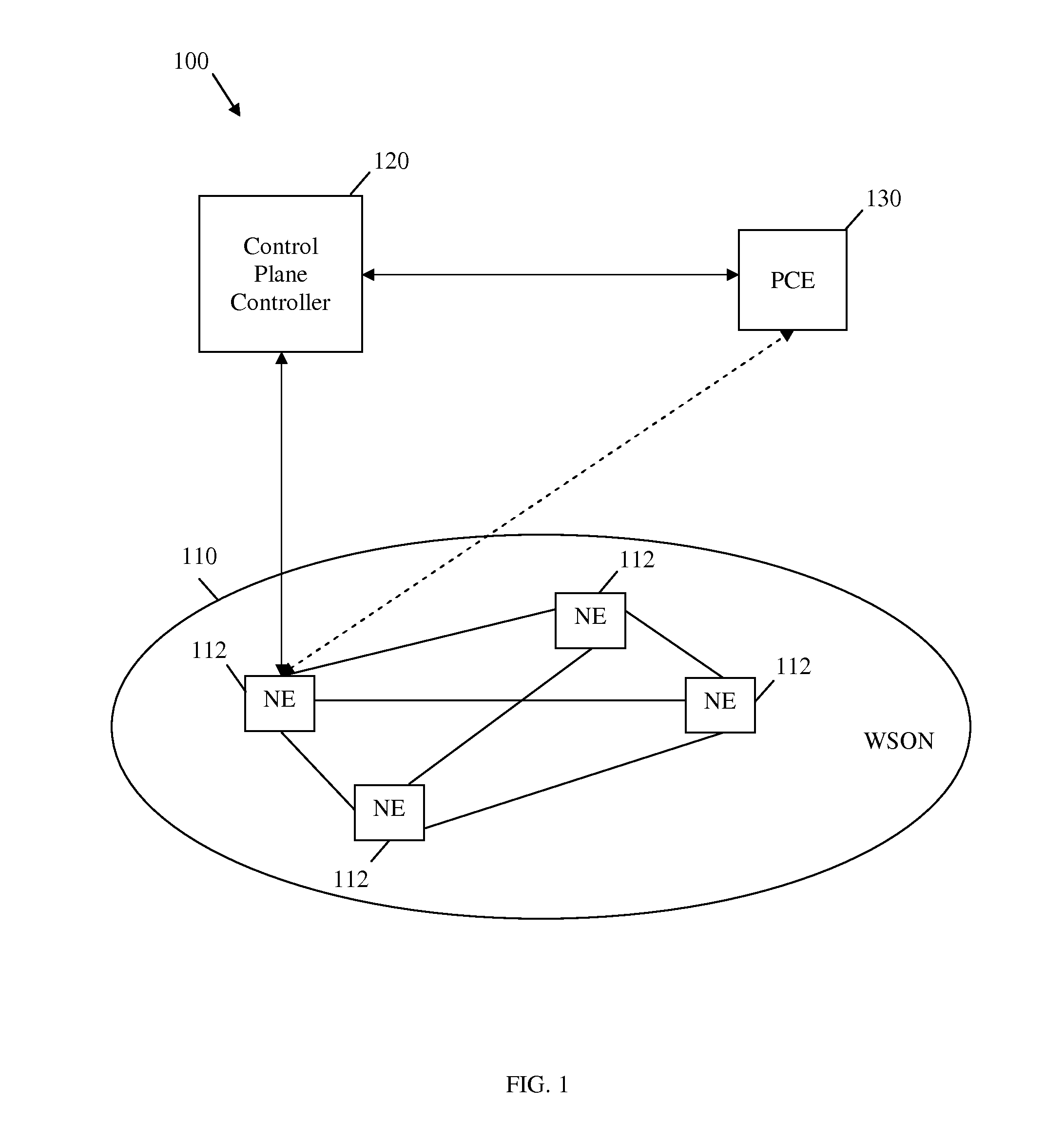
Method for Characterizing Wavelength Switched Optical Network Signal Characteristics and Network Element compatibility Constraints for Generalized Multi-Protocol Label Switching
ActiveUS20110081147A1Multiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsMultiplexingWavelength switched optical network
An apparatus comprising a path computation element (PCE) configured to perform a path computation using signal compatibility constraints information for a network element (NE) in a wavelength switched optical network (WSON), wherein the signal constraints information are communicated at a Generalized Multi-Protocol Label Switching (GMPLS) control plane layer and comprise a plurality of signal attributes and a plurality of NE compatibility constraints. A network component comprising a transmitter unit configured to transmit signal compatibility constraints via GMPLS signaling, wherein the signal compatibility constraints define the signal compatibility constraints for a NE in a WSON. A method comprising receiving signal compatibility constraints for a NE in a WSON, performing a path calculation based on the signal compatibility constraints for the NE, and sending signal compatibility constraints associated with a computed path.
Owner:FUTUREWEI TECH INC
Transmission apparatus
InactiveUS6850660B2Low costMultiplex system selection arrangementsRing-type electromagnetic networksCross connectionEngineering
A transmission apparatus for coupling an optical signal transmission section and an electrical signal transmission section through an opto-electric two-way conversion unit, where the electrical signal transmission section is comprised of a SONET / SDH signal processing function unit and a generalized multi protocol label switching (GMPLS) function processing function unit cooperating with that function unit and where the optical signal transmission section is comprised of an optical add / drop function unit for transferring an optical signal with the electrical signal transmission section through the conversion unit and an optical cross-connect function unit for switching paths in wavelength units of the optical signal with the electrical signal transmission section, whereby the capital cost and running costs of an optical network for transmitting an IP signal can be greatly reduced.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Method for realizing passive light network running and managing
InactiveCN1592302AReduce occupancyImprove transmission efficiencyTransmissionTraffic capacityNetwork management
A method for realizing passive light network operation and management is that general labels of the general multiprotocol label exchange protocol are applied to realize data forward multiple addressing base, the labels are taken as the basis of data service sorting forward. The label exchange path is applied to realize the forward of direct user end to user end, the strengthened route protocol is used to realize uniform flow engineering of passive light network and back bone network, the strengthened signaling protocol is used to realize the uniform label distribution of the passive light network and back bone network and the network management structure is applied to realize a uniform network management platform of the passive light network and backbone network.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Generic multi-protocol label switching (GMPLS)-based label space architecture for optical switched networks
ActiveUS7272310B2Multiplex system selection arrangementsData switching by path configurationExchange networkPhotonics
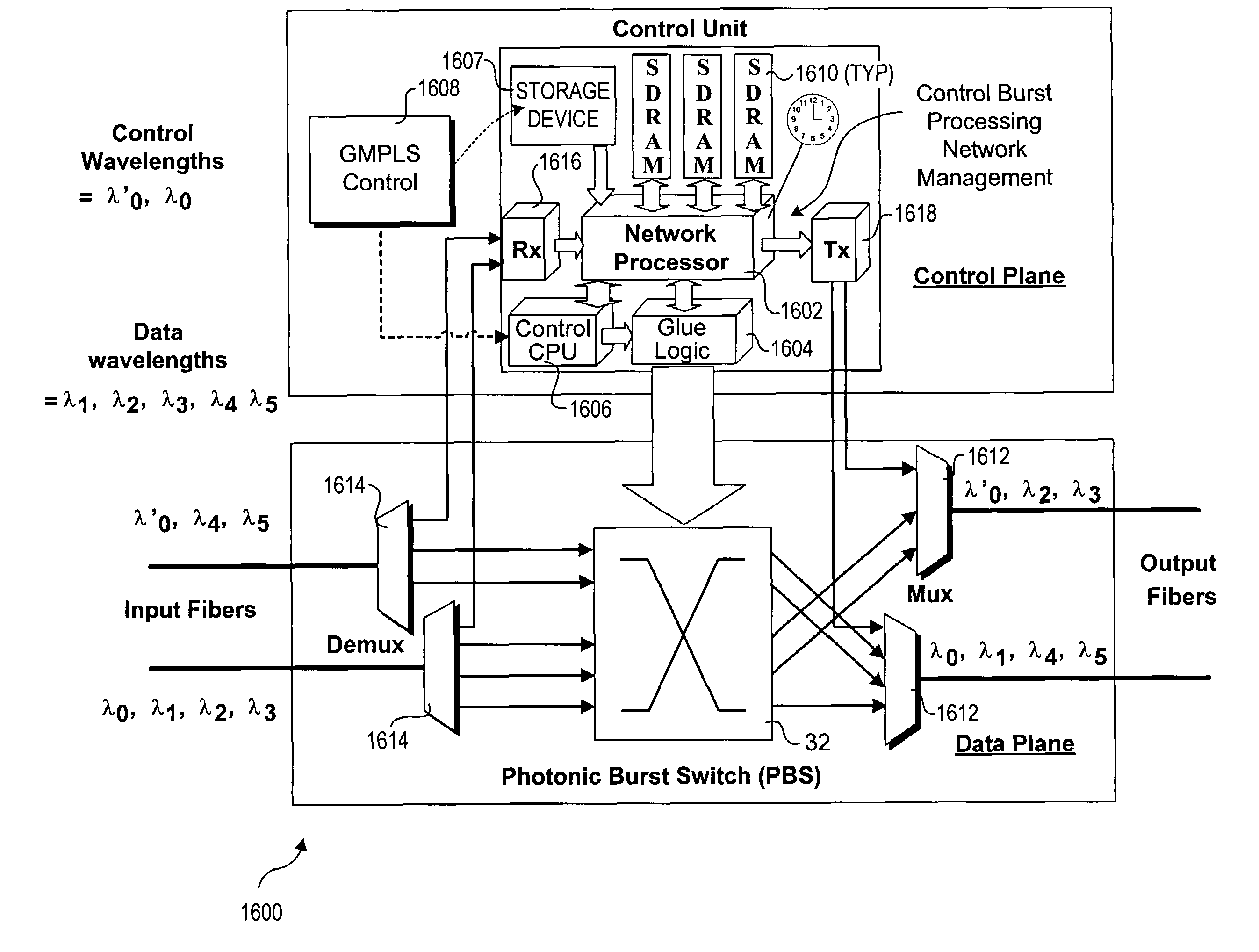
An architecture and method for performing coarse-grain reservation of lightpaths within wavelength-division-multiplexed (WDM) based photonic burst switched (PBS) networks with variable time slot provisioning. The method employs a generalized multi-protocol label switched (GMPLS)-based PBS label that includes information identifying each lightpath segment in a selected lightpath route. A resource reservation request is passed between nodes during a forward traversal of the route, wherein each node is queried to determine whether it has transmission resources (i.e., a route lightpath segment) available during a future timeframe. Soft reservations are made for each lightpath segment that is available using information contained in a corresponding label. If all lightpath segments for a selected route are available, the soft reservations turn into hard reservations. The stored reservations enable quick routing of control burst that are employed for routing data during scheduled use of the lightpaths.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Gmpls control of ethernet
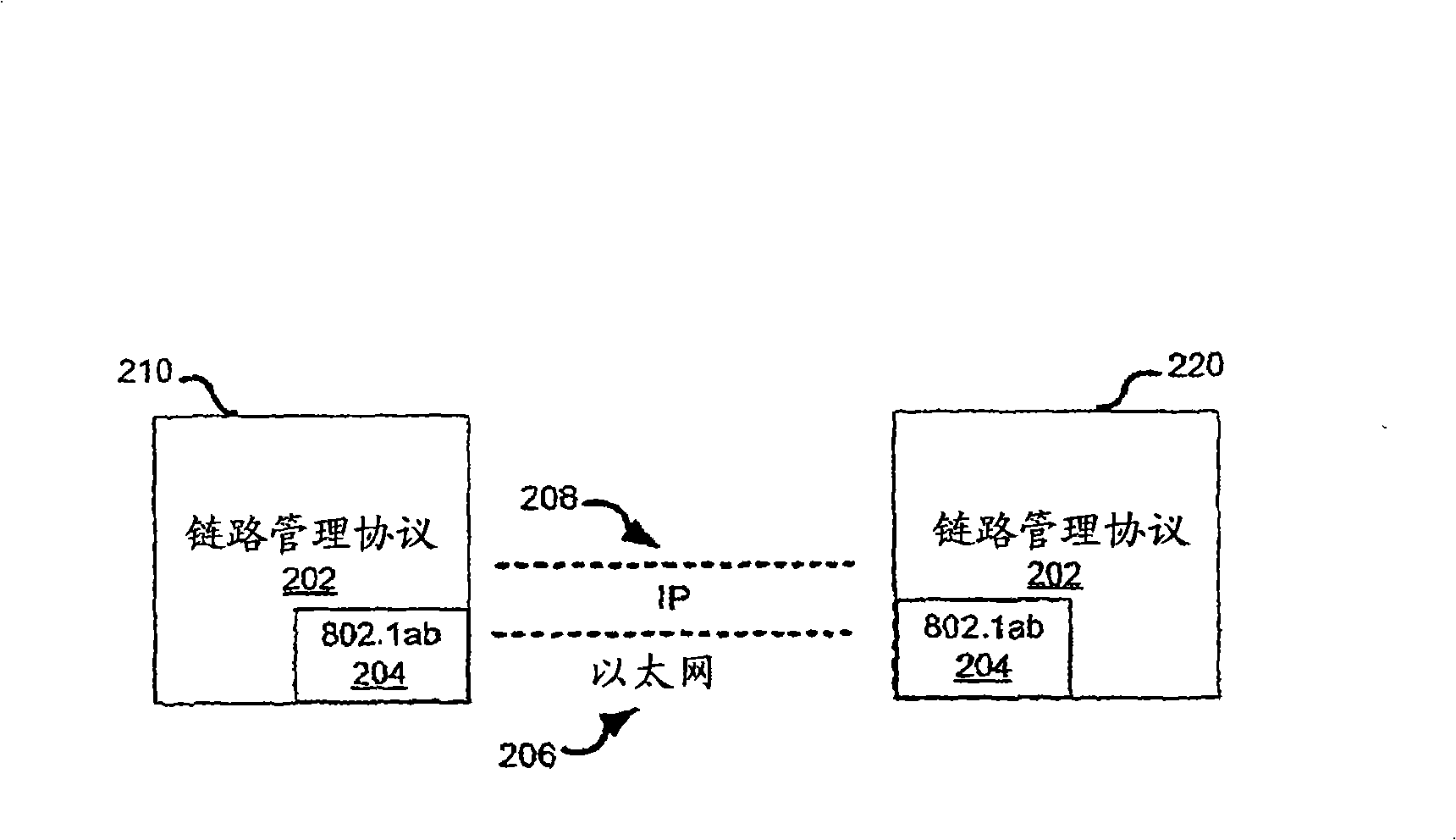
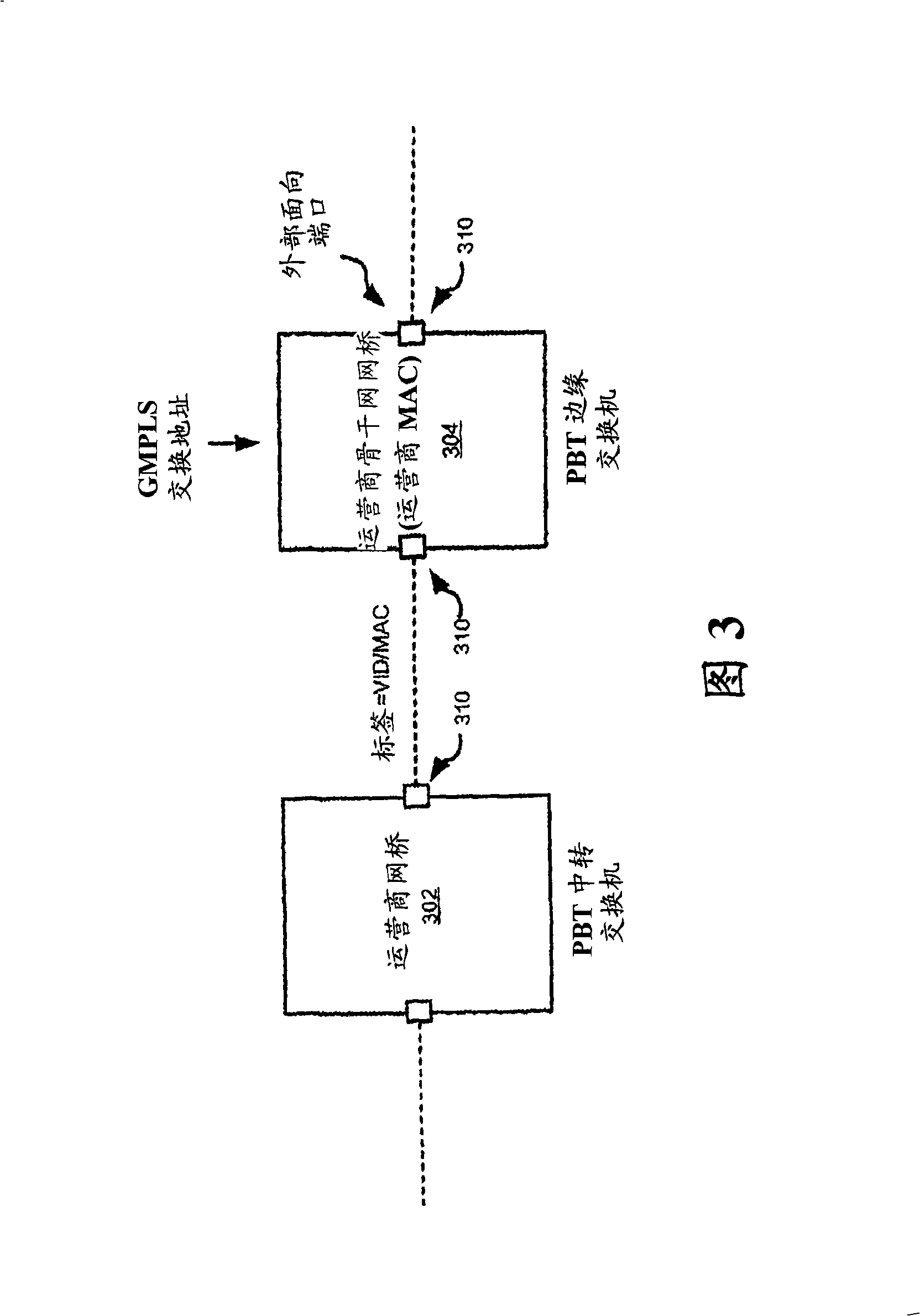
Ethernet provider backbone transport (PBT) paths are controlled utilizing Generalized Multi-protocol Label Switching (GMPLS) signaling protocol. A path between edge nodes is identified by a combination of a VID and destination MAC address in a VID / MAC tuple populated in the forwarding tables of intermediary nodes. To establish the PBT path, a path calculation is performed from the originator node to the terminator node through the network. The originating node then sends a GMPLS label object with a suggested VID / MAC to identify the path to the terminator. The intermediary nodes or bridges forward the object to the terminating node. The terminating node then offers a VID / MAC tuple in a GMPLS label object in response. When the intermediary nodes forward the response from the terminating node to the originator, the appropriate forwarding labels are then installed in the forwarding tables of each node utilizing the associated VID / MAC tuples.
Owner:NORTEL NETWORKS LTD
Method and related apparatus for establishing link-diverse traffic paths in a telecommunications network
ActiveUS20150172171A1Multiplex system selection arrangementsOptical multiplexService modelTelecommunications link
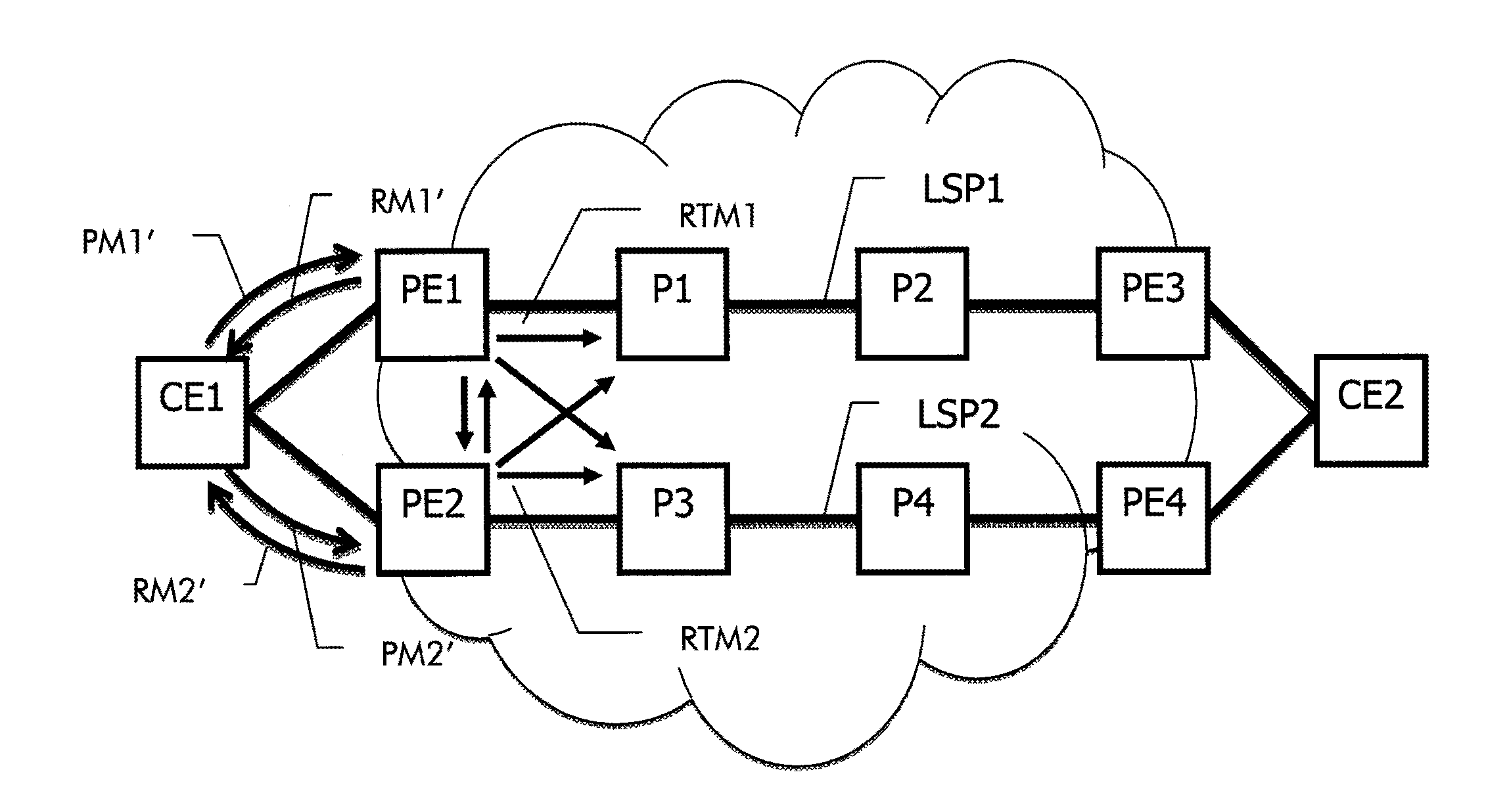
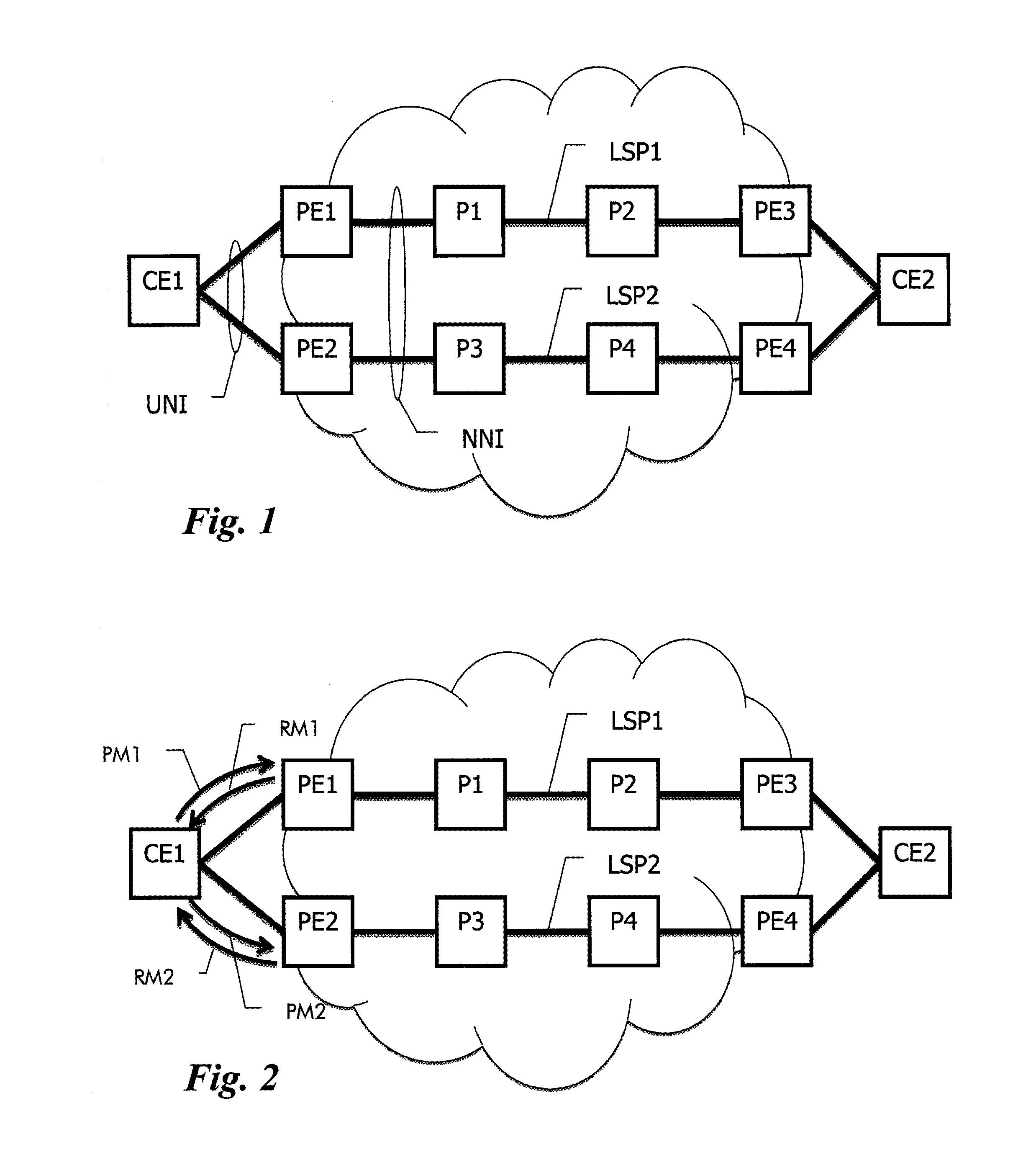
In order to achieve path diversity for dual-homed User-Network Interface clients connected to a Generalized Multiprotocol Label Switching control plane enabled transport network that is operated in an overlay mode, the overlay extension service model is enhanced by adding shared constraint information for path diversity in the optical transport network. In particular, within the provider network, shared constraint information of a first traffic path is determined and a data element indicative of the shared constraint information is returned by a first provider edge node to a customer edge device via a User-Network Interface. When the customer edge device requests a second traffic path through the provider network to be established from a second provider edge node and to be disjoint from said first traffic path, the customer edge device forwards the data element to the second provider edge node to enable path calculation of the second traffic path using the shared constraint information as exclusion list.
Owner:RPX CORP
Mesh restoration in optical transport networks
The present disclosure provides mesh restoration systems and methods with Optical Transport Network (OTN) links using a signaling and routing protocol, such as Optical Signaling and Routing Protocol (OSRP), Automatically Switched Optical Network (ASON), Generalized Multi Protocol Label Switching (GMPLS), and the like. The present invention includes an optical node, network, and method using the signaling and routing protocol for OTN lines of differing bandwidth granularities. The present invention utilizes OTN overhead for in-band signaling and may include capability for supporting SONET / SDH lines as well as OTN lines in the same system using the signaling and routing protocol.
Owner:CIENA
Wide area multi-service communications network based on dynamic channel switching
InactiveUS7149210B2Efficient transportEfficient use ofMultiplex system selection arrangementsHybrid switching systemsWide areaDynamic channel
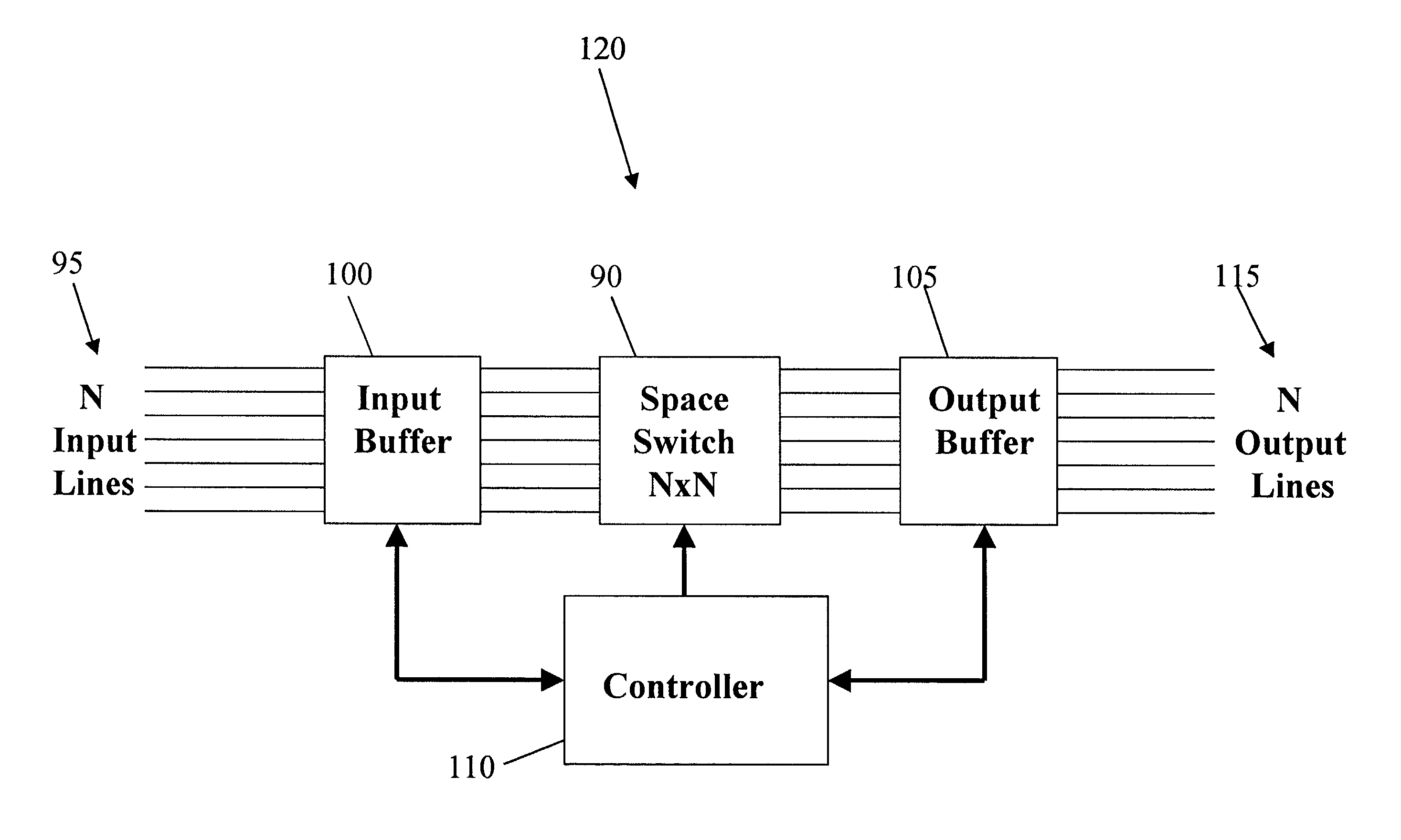
A networking approach is disclosed that combines the advantages of circuit switching and packet switching in an integrated communications network. With this approach, control signals are separated from the data and transmitted separately in a common control channel. Control and signaling operation can be viewed as a logical extension of generalized multi-protocol label switching (GMPLS). A variable number of data channels are dynamically assigned to each connection through the network. Channels are quickly switched in to accommodate the data flow through a connection and switched out when they are no longer needed. With this dynamic channel switching approach, a continuous data stream is not altered as it transverses the network and data channels are efficiently utilized even if the data source is bursty. The proposed approach is compatible with legacy networks and can provide a mechanism for convergence of circuit switching and packet switching. Most of the benefit of the proposed approach can be achieved with modifying only network and server equipment, but not necessarily client equipment, to support dynamic channel switching.
Owner:DEMARTINO KEVIN A
Method and device for gmpls based multilayer link management in a multilayer network
InactiveUS20130265880A1Function increaseImprove protectionError preventionTransmission systemsMultiprotocol Label SwitchingLink management
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Method, device and system for fusing IP and light
ActiveCN101860769ADoes not affect forwarding performanceMultiplex system selection arrangementsData switching networksVirtual LANThe Internet
The invention provides a method, a device and a system for fusing IP and light. The method comprises the following steps of: sending a request for establishing a user network interface to light network equipment; receiving a universal multi-protocol label switching label returned by the light network equipment; and converting the universal multi-protocol label switching label into a virtual local area network identifier of an Ethernet sub interface, and performing communication by using the Ethernet sub interface. The universal multi-protocol label switching label is converted into the virtual local area network ID of the established Ethernet sub interface so that the common Internet / multi-protocol label switch can be applied to a universal multi-protocol label switching user network interface and the fusion of the IP and the light is realized.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
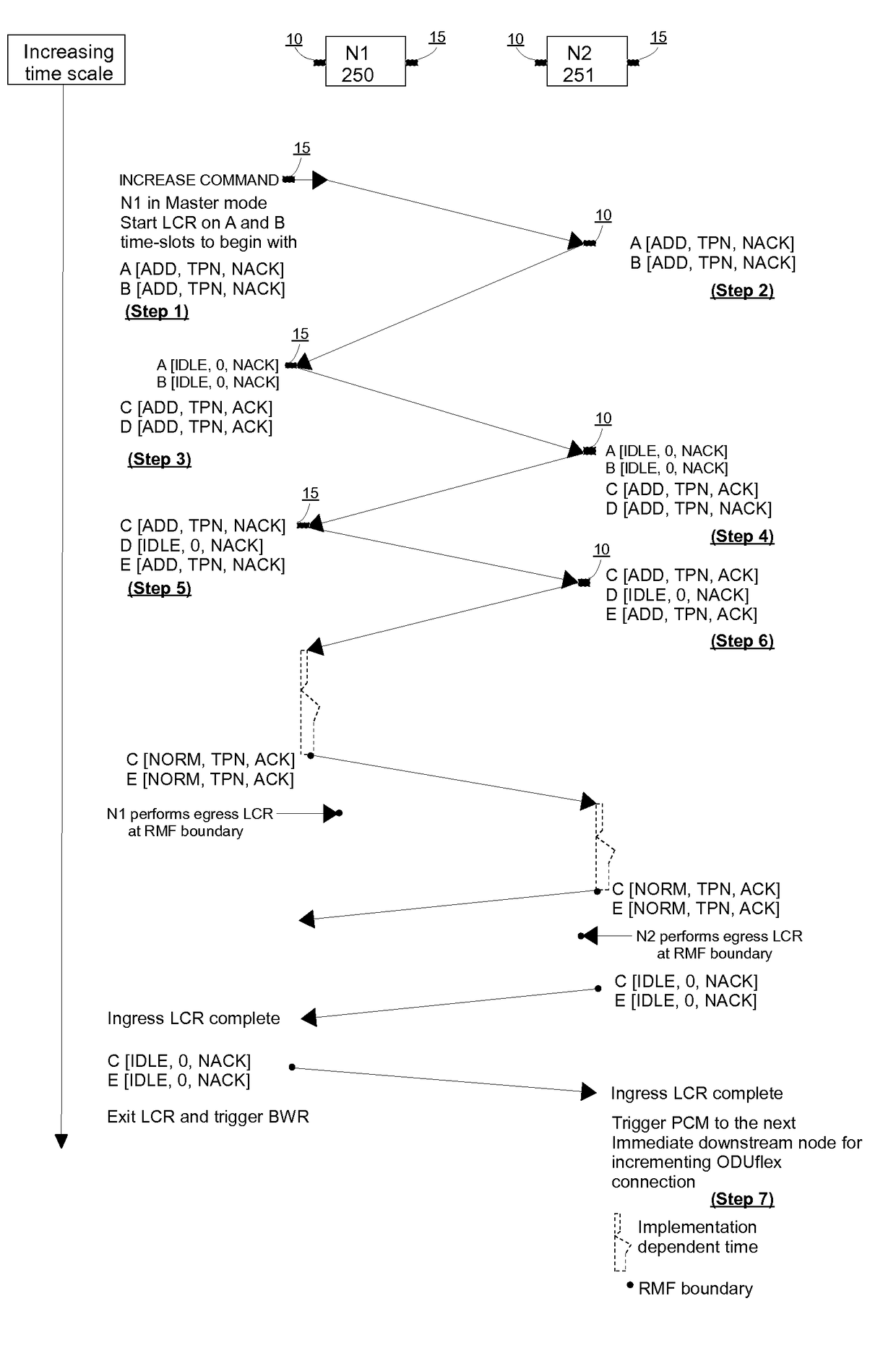
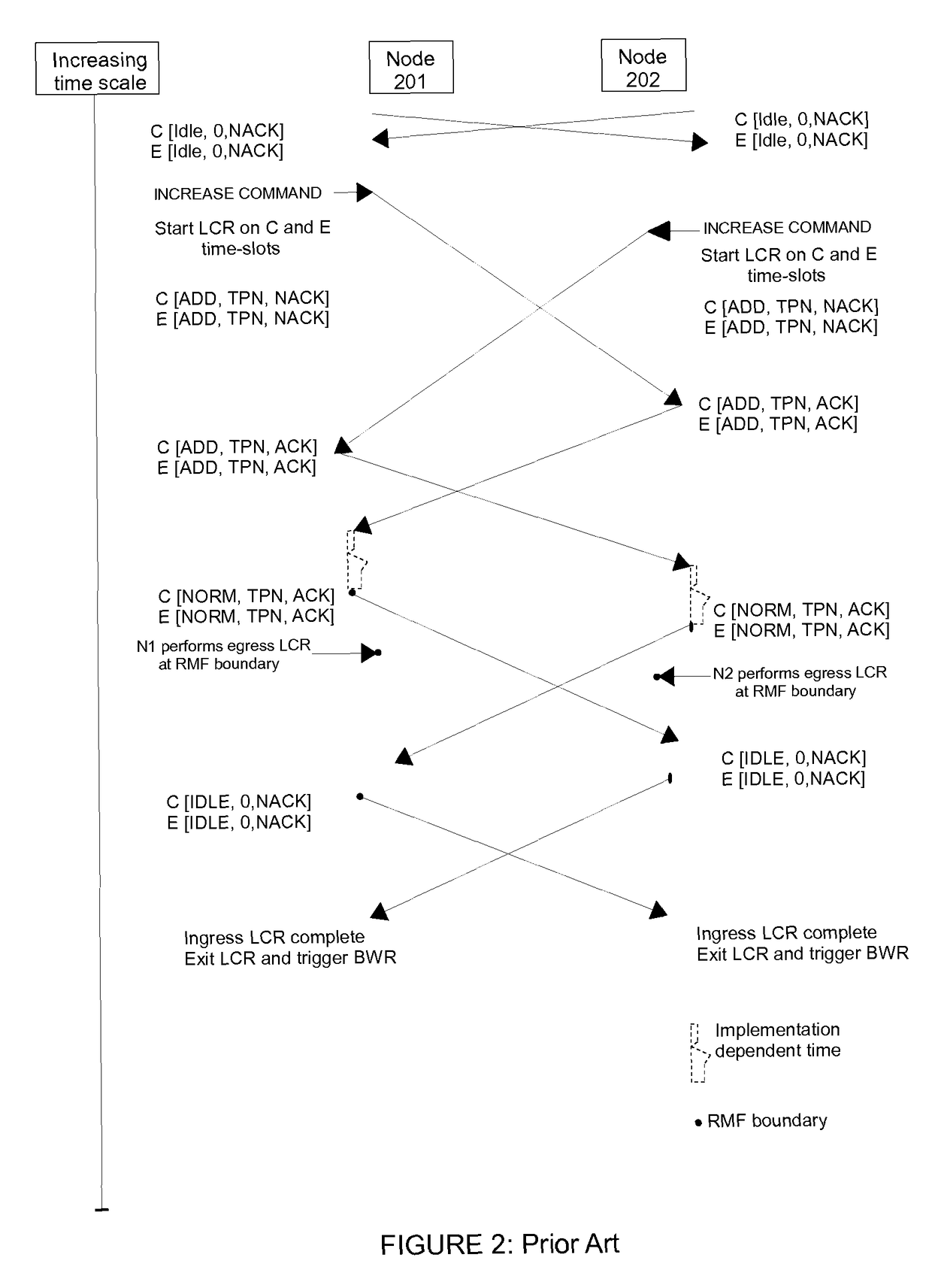
Dynamic hitless ODUflex resizing in optical transport networks
ActiveUS20140079402A1Well formedTime-division optical multiplex systemsTime-division multiplexNetwork managementMulti protocol
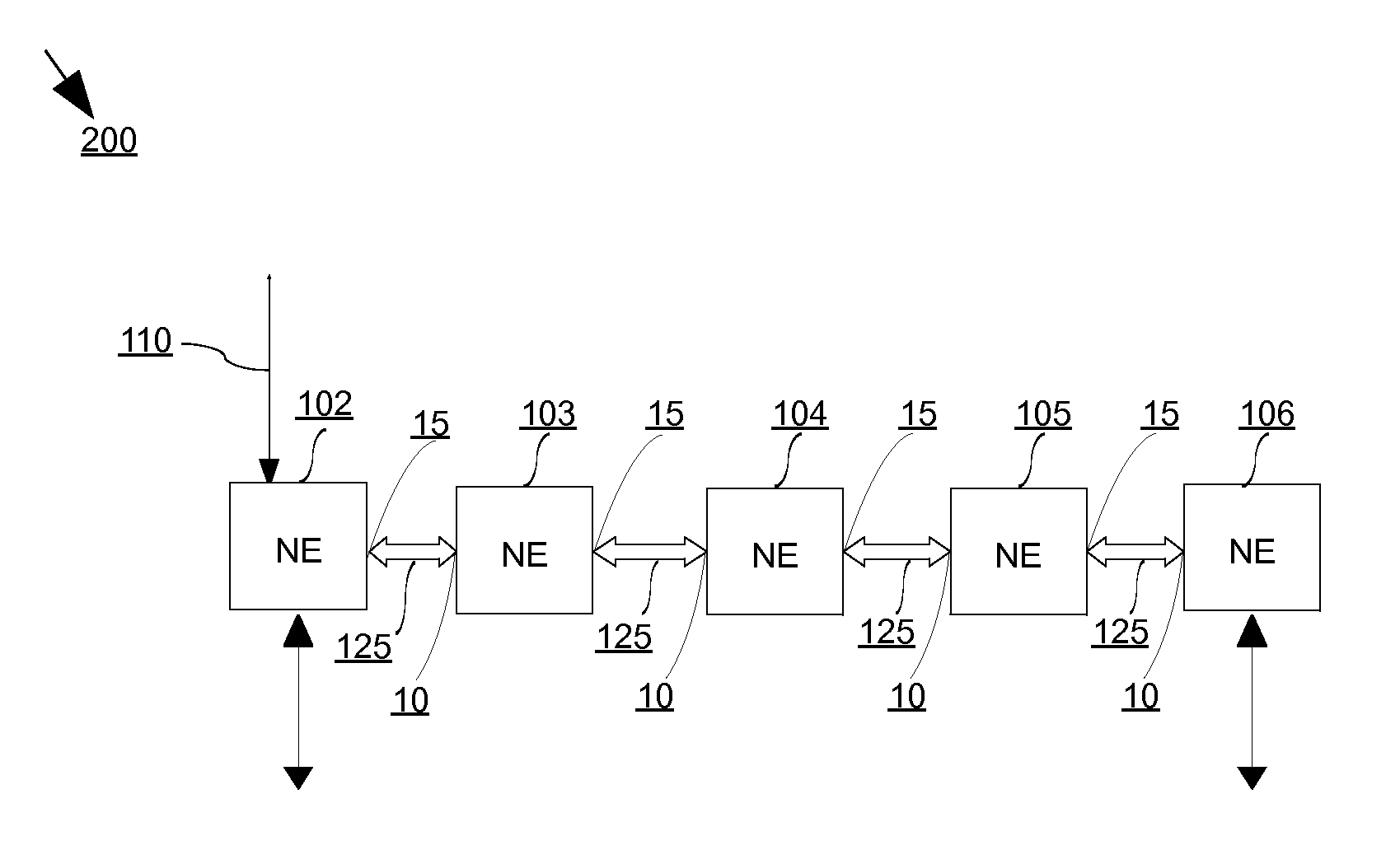
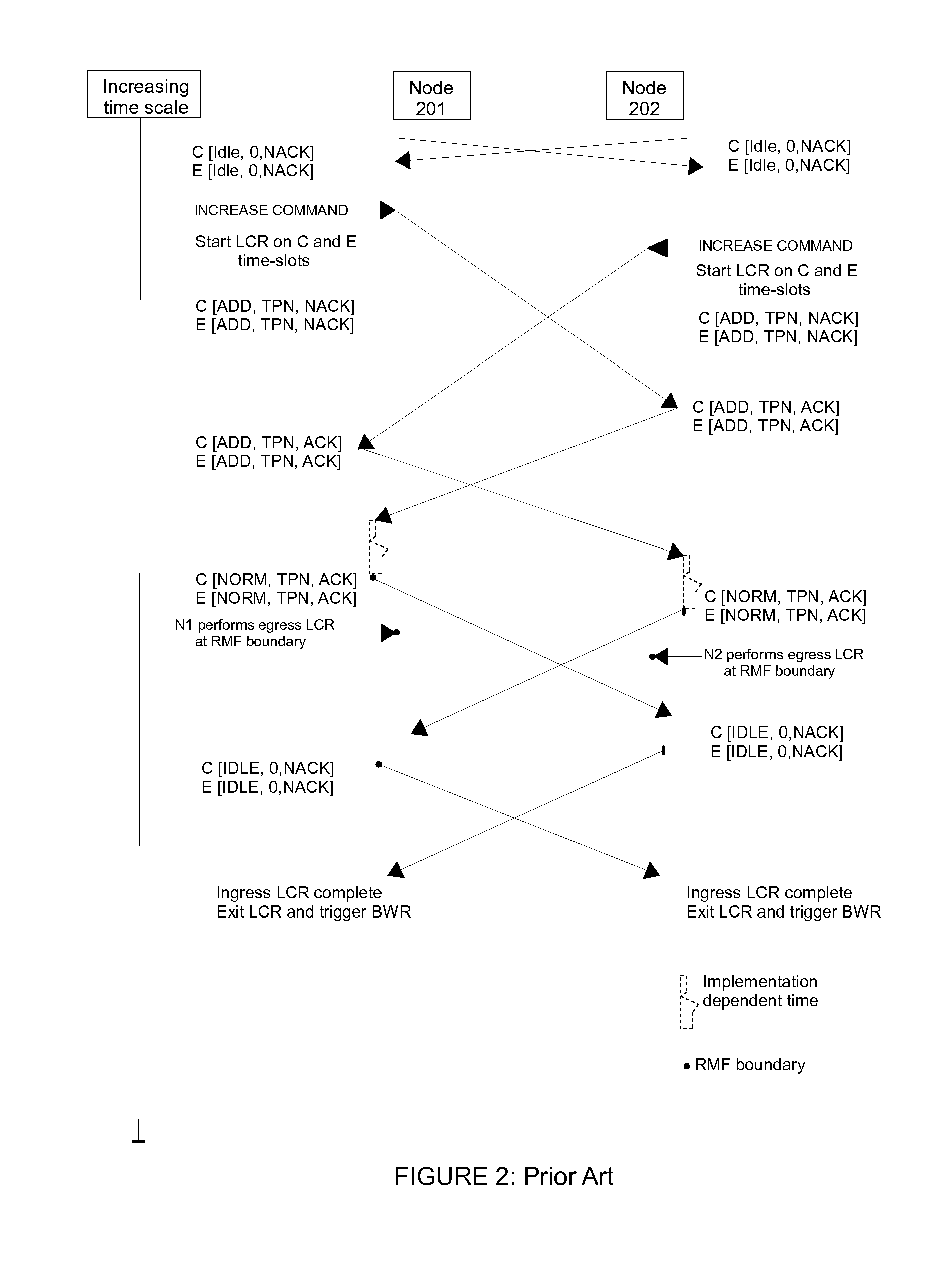
The present invention and its embodiments are made to provide for dynamic hitless resizing in optical transport network without any identification of matching time slots by the Network Management System (NMS) or any control plane signaling including Generalised Multi Protocol Label Switching (GMPLS). An aspect of the invention provides for a method of hitless ODUflex connection resizing in an optical transport network by incrementing or decrementing the ODUflex connection between the nodes, based on an indication command given to a source node for bandwidth increase or decrease, by identifying and matching at least one time slot through Link Connection Resizing (LCR) protocol message exchanges. Another aspect of the invention provides for a method of hitless ODUflex connection resizing in an optical transport network by decrementing the matching time slot used for the incrementing operation, in case of unsuccessful incrementing operation between nodes.
Owner:TEJAS NETWORKS
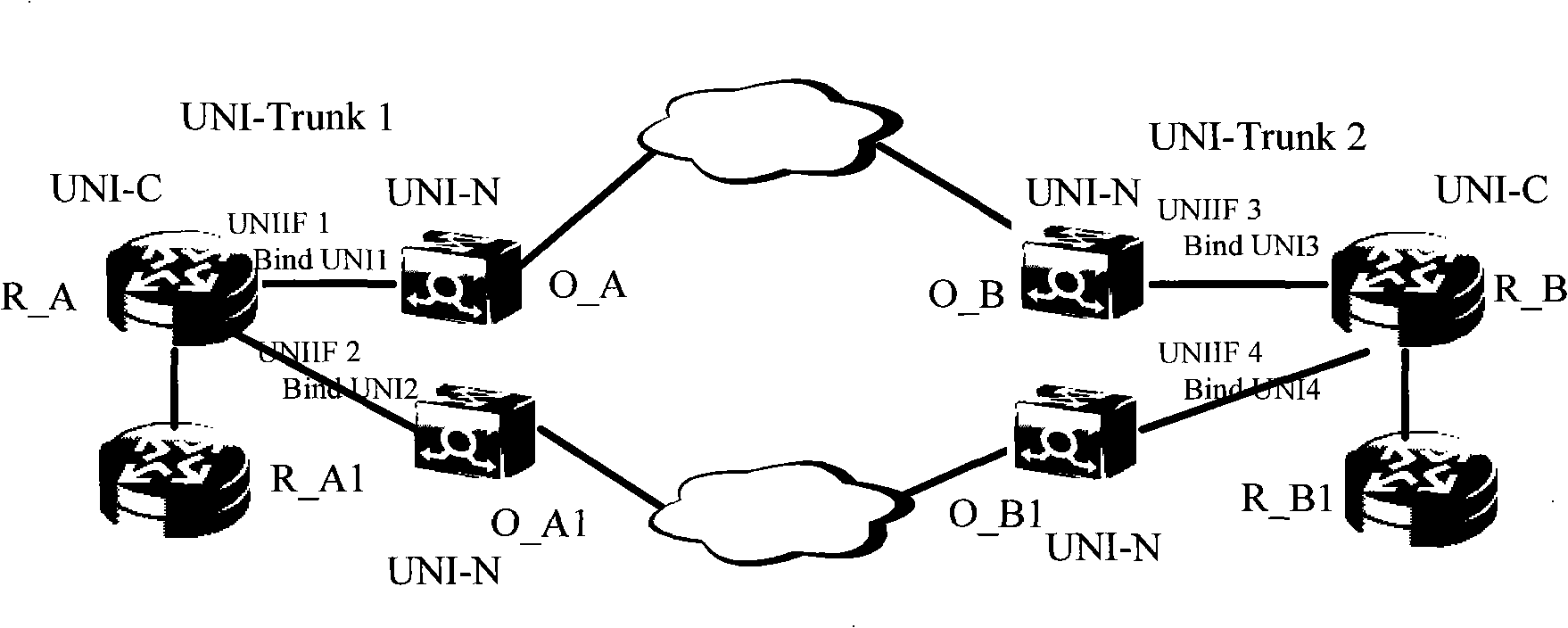
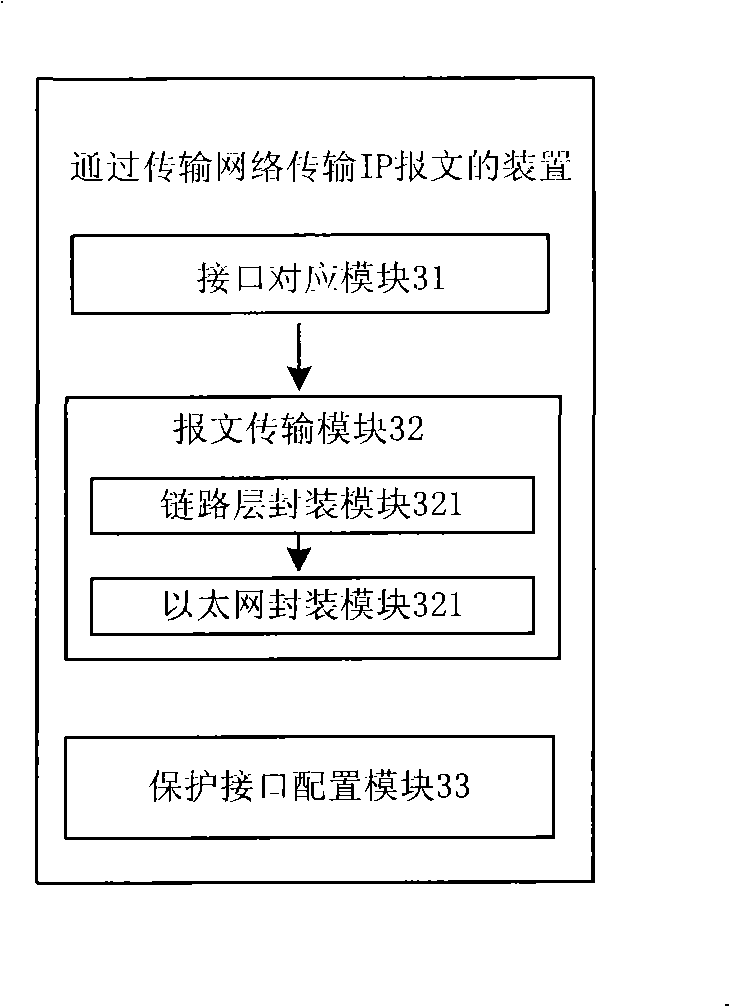
Method and device for transmitting IP message through transmission network
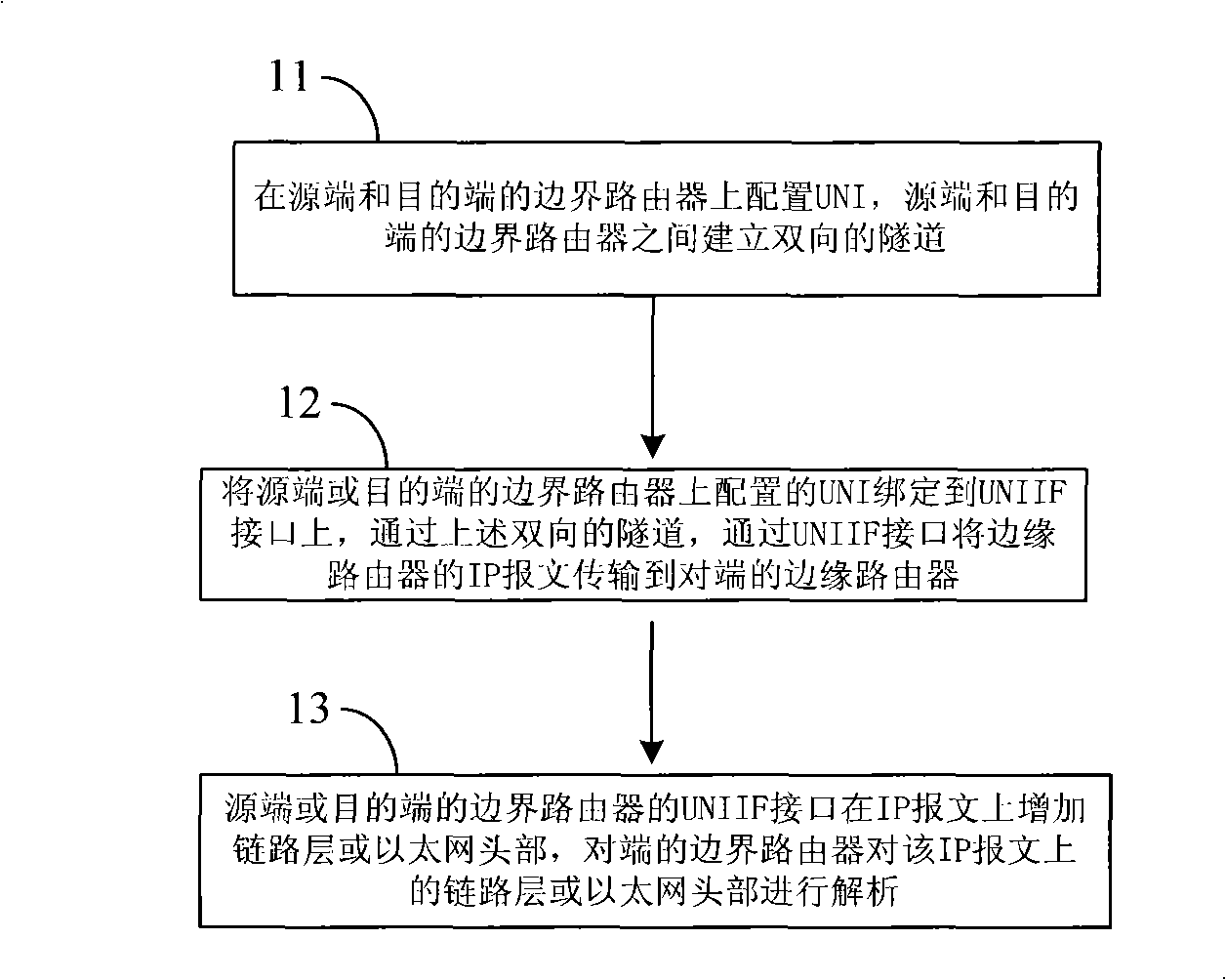
The embodiment of the invention provides a method and a device for transmitting IP message through transmission network. An UNIIF (access from UNI to a transmission network) interface is created on edge routers of a source terminal and a objective terminal in a general multiprotocol label switching network, and the UNIIF interface corresponds to a bidirectional tunnel between the source terminal router and the objective terminal router. The IP message of the edge router of the source terminal or the objective terminal enters the tunnel through the UNIIF interface, and IP message is transmitted to a edge router of a opposite terminal through the tunnel. The present invention realizes transmission of the IP business message through the transmission network and guarantees isolation of the establishment of the UNI business on a border router and establishment of IP business.
Owner:深圳市智通天下科技服务有限公司
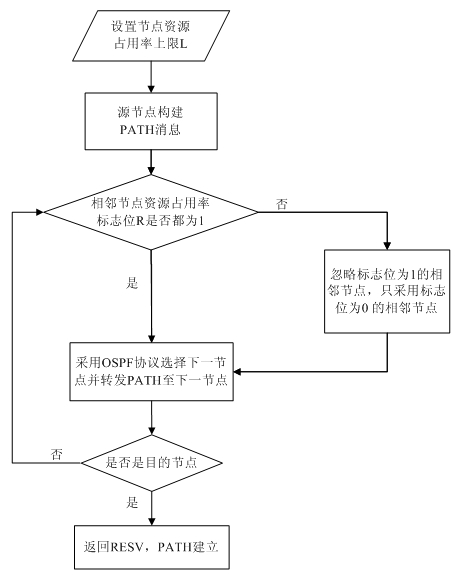
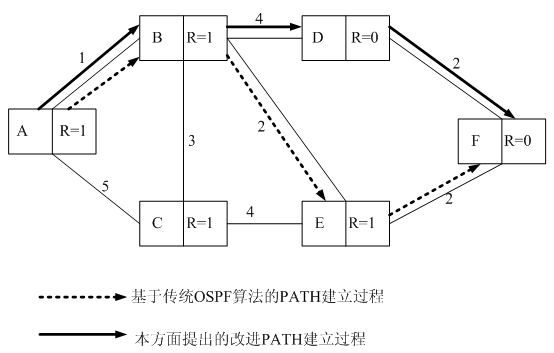
Method for implementing traffic engineering in GMPLS/OBS (generalized multi-protocol label switching/optical burst switching) network
InactiveCN102685004AEase congestion rateReduce the probability of packet lossData switching networksInternet traffic engineeringPacket loss
The invention discloses a method for implementing traffic engineering in a GMPLS / OBS (generalized multi-protocol label switching / optical burst switching) network. In the method, a label switching path is built by the aid of the shortest path algorithm taking the resource occupancy rate of current nodes as a constraint condition. The method particularly includes the steps: acquiring nodes in the GMPLS / OBS network and storing resource occupancy rate information of all adjacent nodes; firstly judging whether the resource occupancy rate of the adjacent nodes in the current nodes is smaller than a preset resource occupancy rate threshold or not when building a TE (traffic engineering) tunnel between a source node and a host node, and selecting the shortest path as a next node from the adjacent nodes with the resource occupancy rate smaller than the preset resource occupancy rate threshold by a routing algorithm if the resource occupancy rate of the adjacent nodes in the current nodes is smaller than the preset resource occupancy rate threshold; selecting the shortest path as a next node from all the adjacent nodes in the current nodes by the routing algorithm if not; and deducing the rest by analogy until the selected next node is the host node. By the method, the blocking rate of a link circuit can be decreased, business packet loss is decreased, a traffic engineering mechanism of the network is efficiently implemented, and the transmission property of the GMPLS / OBS network is improved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Test method of difference time delay of optical network
InactiveCN101877800AImprove stabilityImprove reliabilityMultiplex system selection arrangementsTime delaysNetwork packet
The invention relates to a test method of the difference time delay of an optical network, belonging to the technical field of communication. The test method comprises the following steps of: initializing, sending test data packets testing link communication to a terminal end or a source end through a loopback link by a service triggering module; carrying out state update on the terminal end and the source end, and then sending a request for establishing a label switching path to a GMPLS (Generalized Multi-Protocol Label Switching) control plane by the service triggering module; recording path establishment successful time T1 and starting the switching processing of the test data packets by the service triggering module to obtain switching time T2; and subtracting the path establishment successful time T1 with the switching time T2 so as to obtain solved label switching path (including one-way and two-way paths) establishment difference time delay. The method and the technical scheme capable of simply, conveniently, fast and accurately measuring the path establishment difference time delay of the control plane and a data plane have convenient implementation and low cost and can help users to better learn about the dynamic characteristics of the GMPLS optical network.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
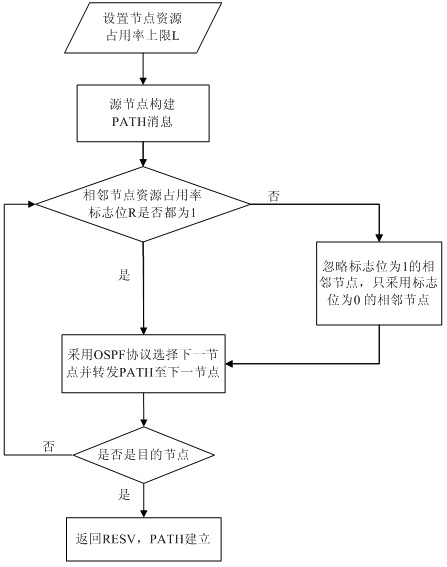
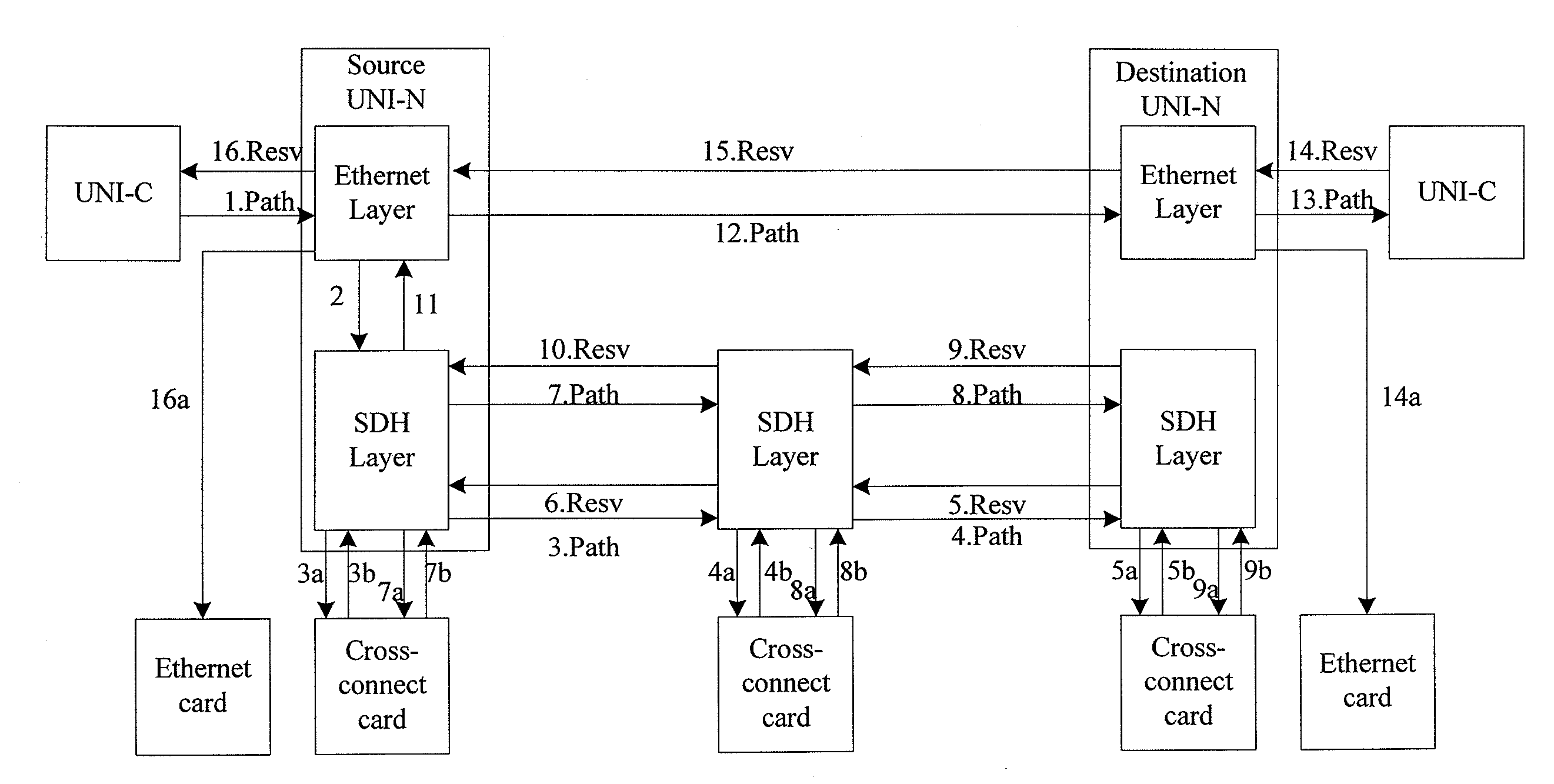
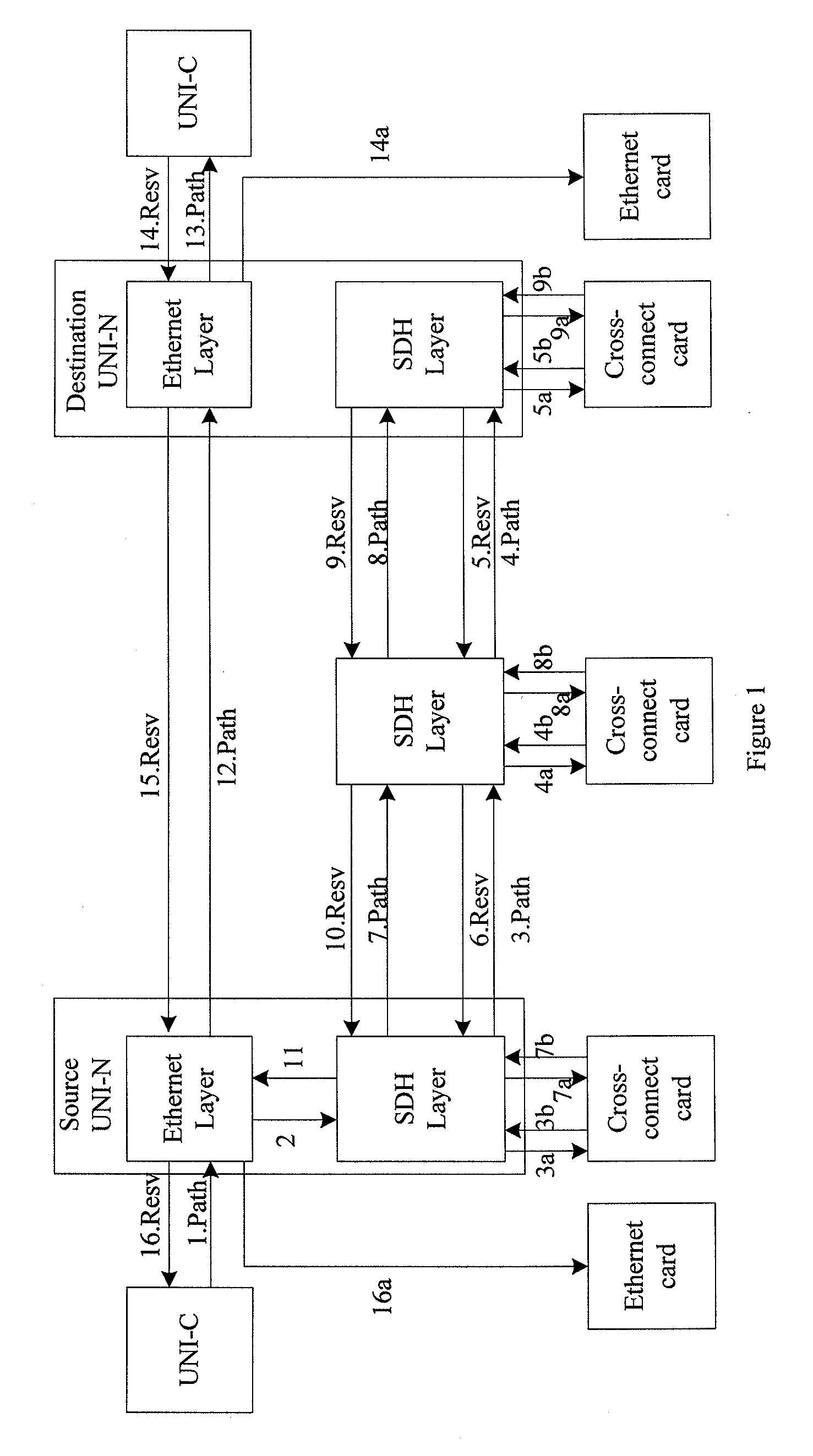
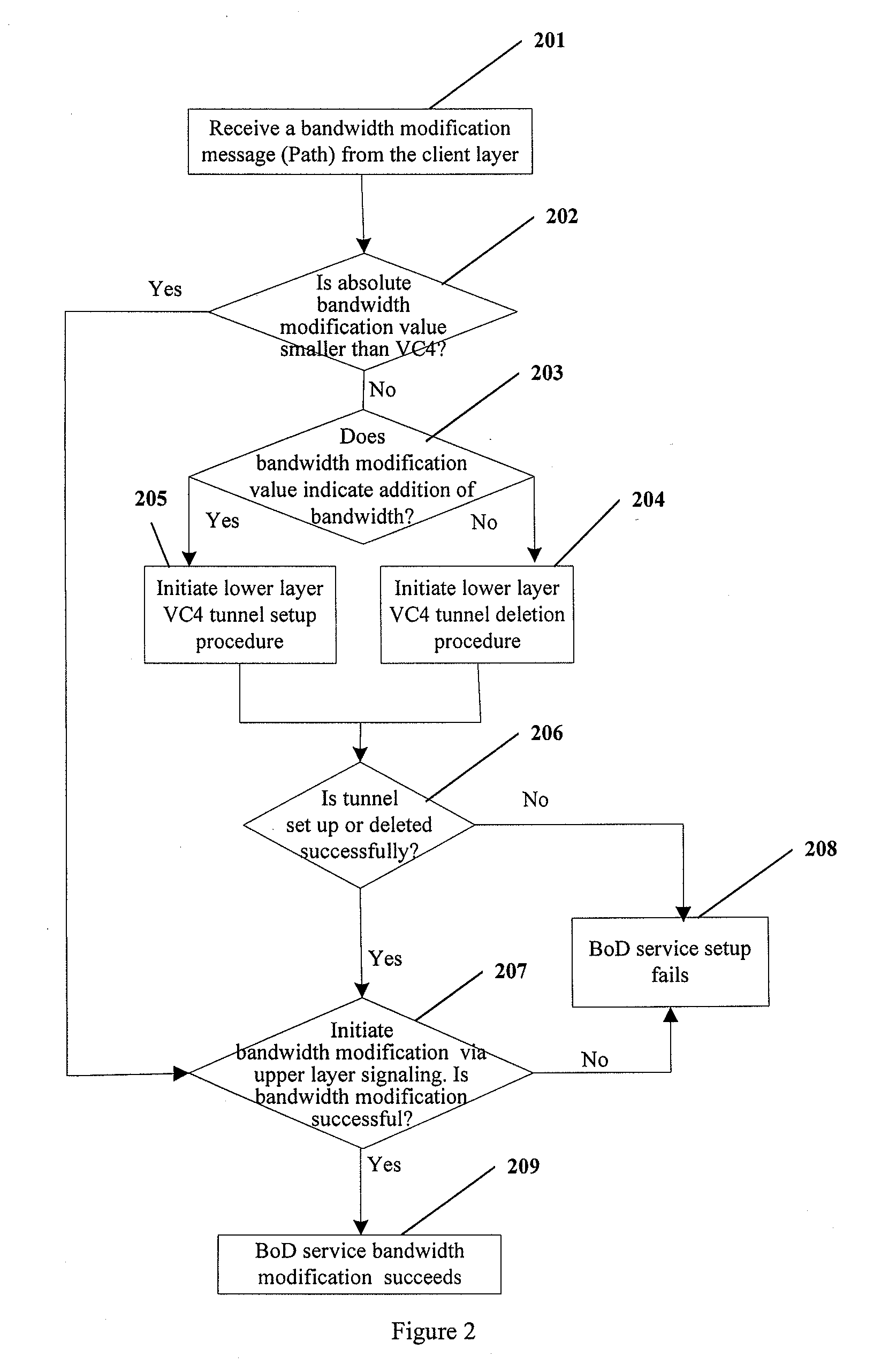
Method and apparatus for modifying bandwidth in bandwidth on demand services
InactiveUS20090122811A1Easy to set upTime-division multiplexStore-and-forward switching systemsTraffic capacityLink Capacity Adjustment Scheme
A method for modifying bandwidth in a Bandwidth on Demand (BoD) service includes: a User Network Interface (UNI) client (UNI-C) sends the BoD service based bandwidth modification message to a UNI network (UNI-N) via control plane signaling, the bandwidth modification message carrying a bandwidth modification value; the UNI-N modifies bandwidth according to the bandwidth modification amount and a lower layer tunnel granularity. An apparatus for modifying bandwidth in a BoD service is also disclosed. According to the present invention, by adopting Generalized Multi-Protocol Label Switching (GMPLS) on the control plane and Link Capacity Adjustment Scheme (LCAS), Virtual Concatenation (VC) and Generic Framing Procedure (GFP) on the transport plane, the BoD service can be automatically set up and a client is able to modify service bandwidth according to changes of service traffic dynamically in real time.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
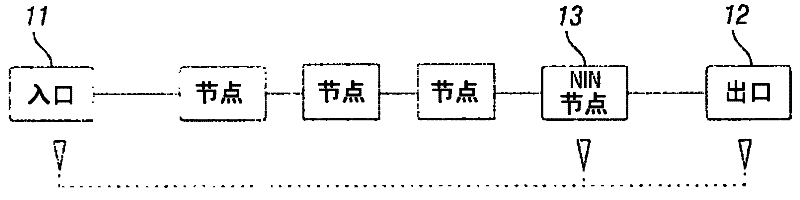
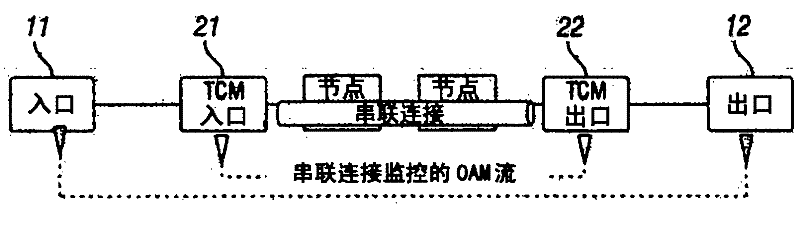
Network connection segment monitoring
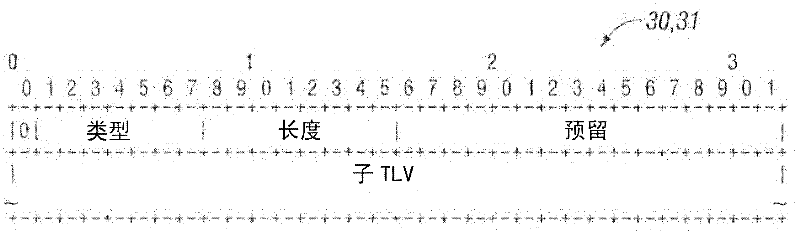
A method and ingress node for configuring intermediate OAM monitoring entities to monitor the quality of segments of a communication connection between an ingress node and an egress node. The ingress node constructs an object that includes technology-independent OAM parameters, identities of the OAM monitoring entities to be configured, and technology- specific attributes, wherein the technology-independent OAM parameters define an OAM type and desired monitoring actions by each of the identified OAM monitoring entities, and the technology-specific attributes define descriptors for configuring the 0AM monitoring entities in accordance with a communication protocol utilized for the connection. The ingress node utilizes Generalized Multi-Protocol Label Switching, GMPLS, signaling to send the object to the OAM monitoring entities. The object may be a Hop Attributes sub-object or a Label Switching Protocol, LSP, Attributes object including a Segment OAM Configuration Type-Length-Value, TLV, field that includes the technology-independent OAM parameters and technology-specific attributes.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
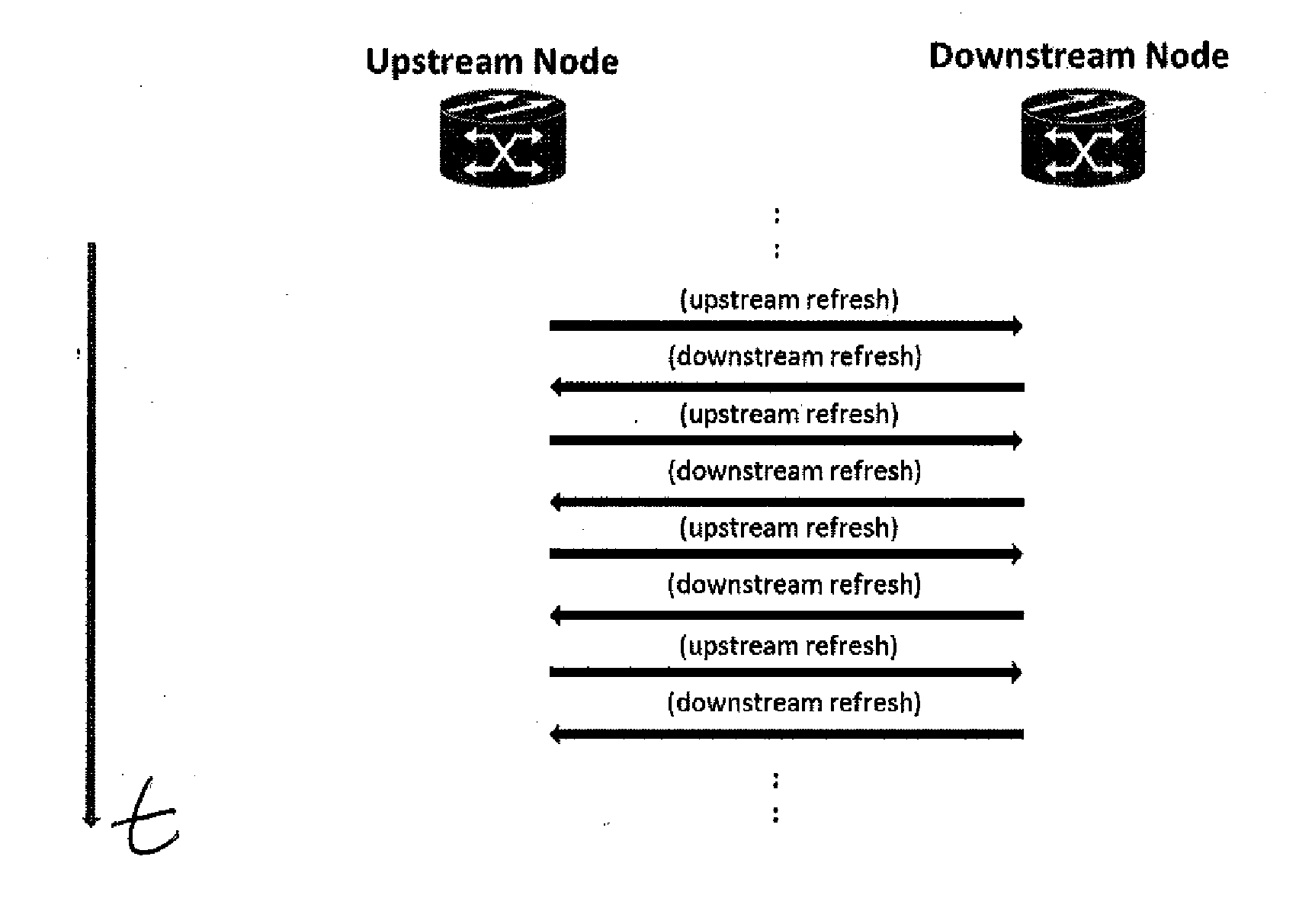
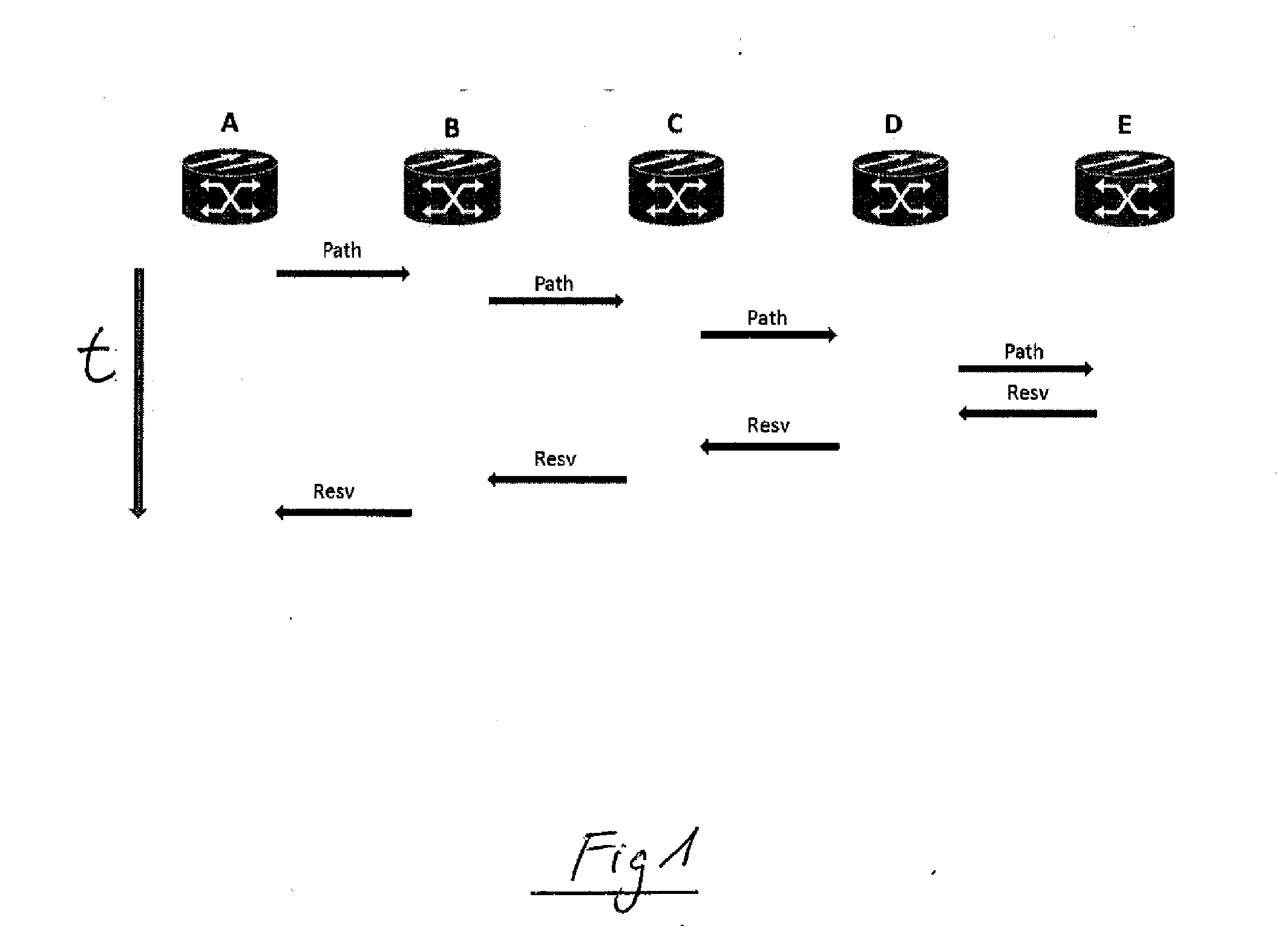
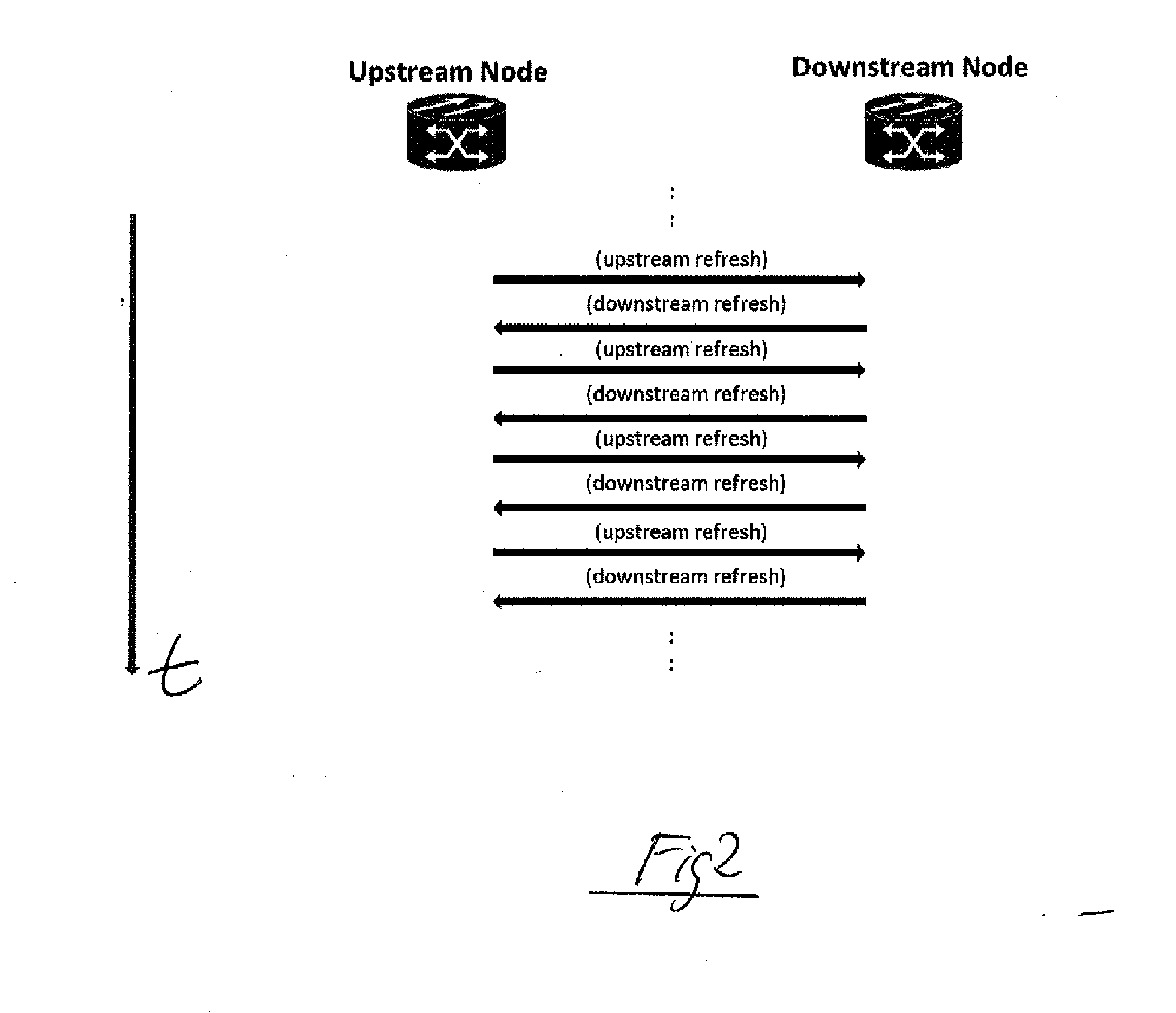
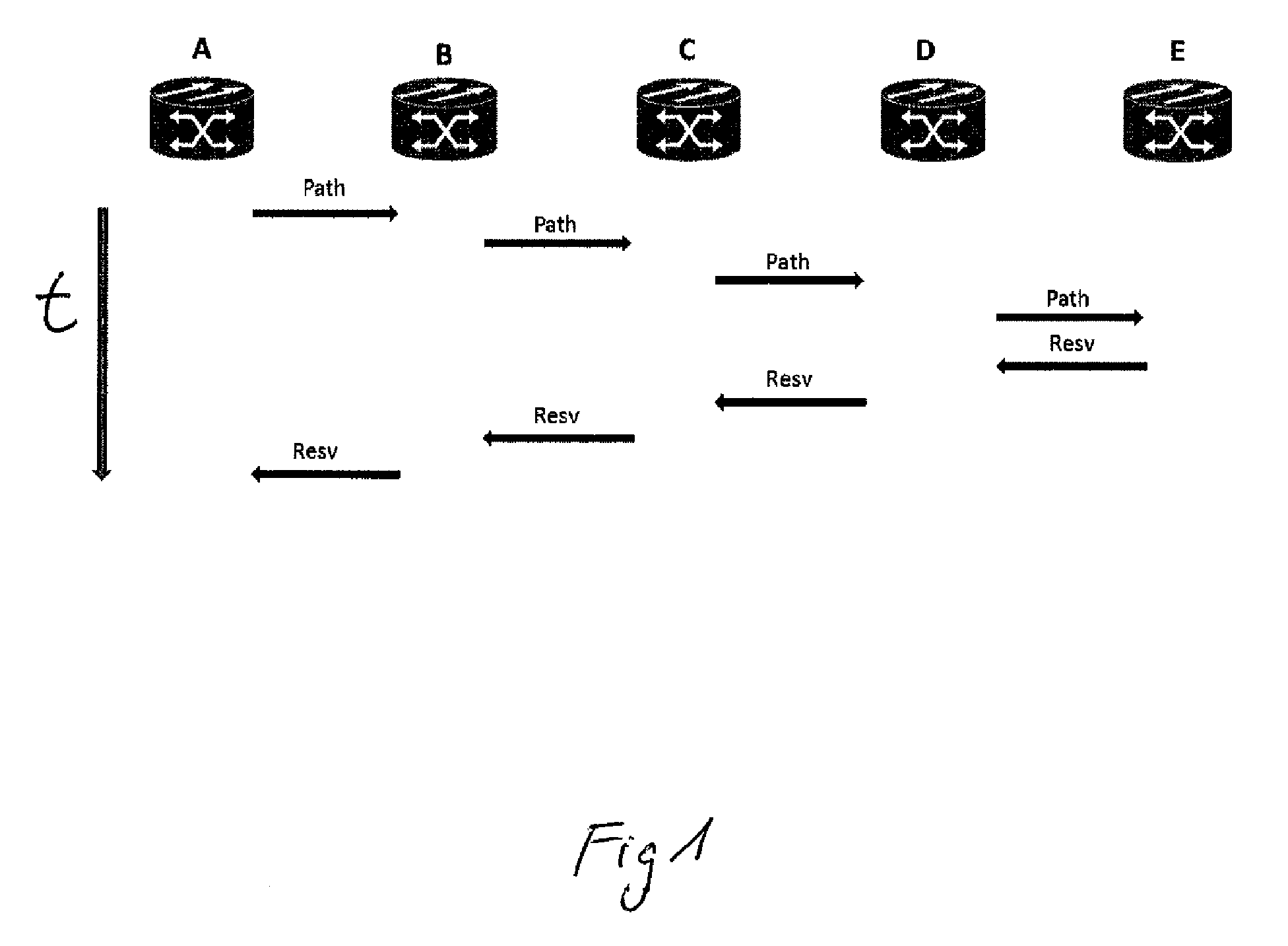
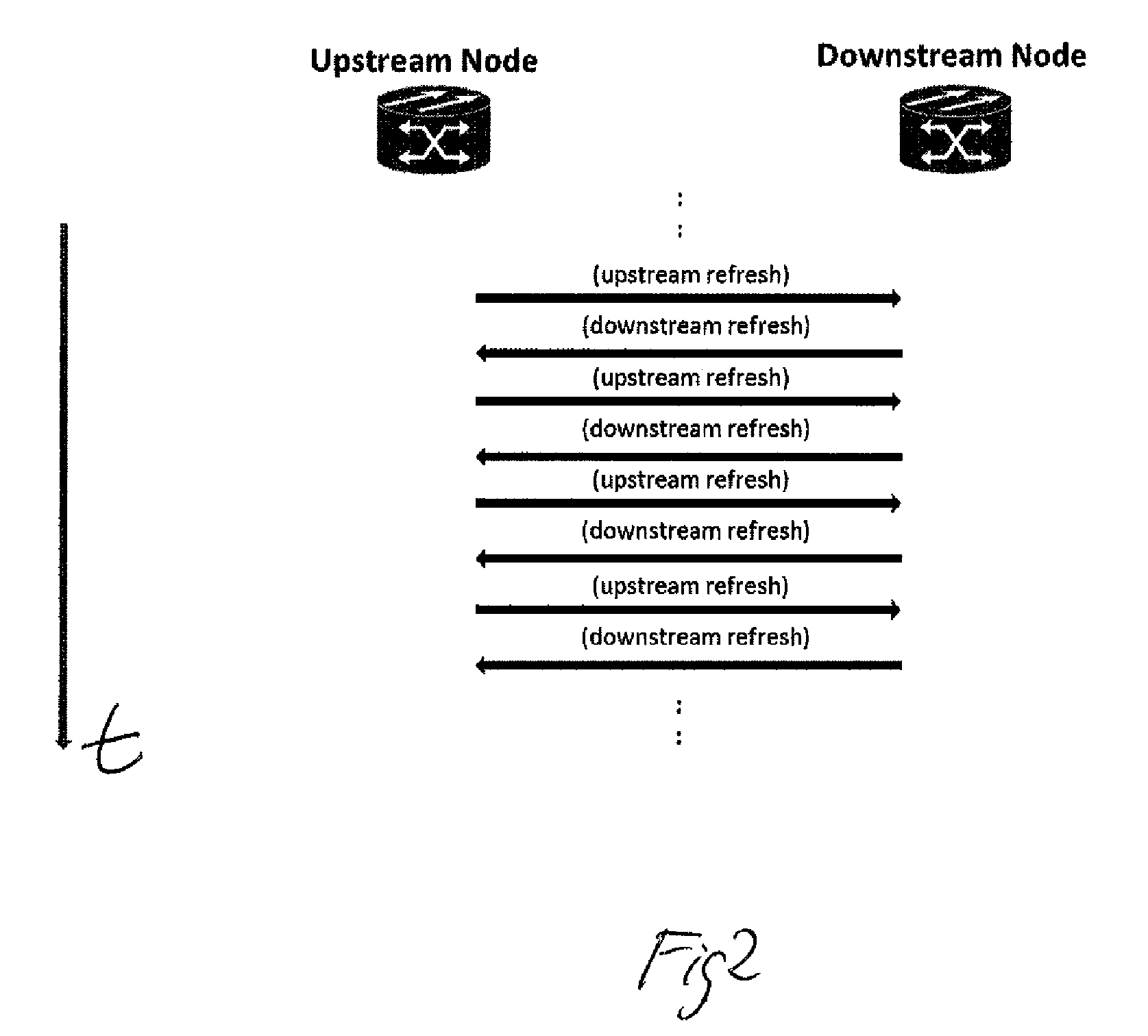
Method for managing services in a generalized-multi-protocol label switching, gmpls, controlled network
A Generalized-Multi-Protocol Label Switching controlled network is described, as is a method for managing services in the network under conditions of disrupted control plane connectivity. Nodes of the network use a Resource Reservation Protocol with Traffic Engineering extension, RSVP-TE, to allocate and provision resources of the network. Each of the nodes is adapted to evaluate local RSVP Path or Resv state data after having sent at least one signaling message to a receiving neighboring node without receipt of an acknowledgement message from said receiving node within a configurable time to determine an IP address of a node being located after the non-responsive receiving node along a service path of a service in a downstream or upstream direction. Each node is adapted to send the signaling message to the determined IP address of the next node located behind the non-responsive receiving node along the service path.
Owner:ADVA OPTICAL NETWORKING SE
Method, system, and device for implementing service forwarding
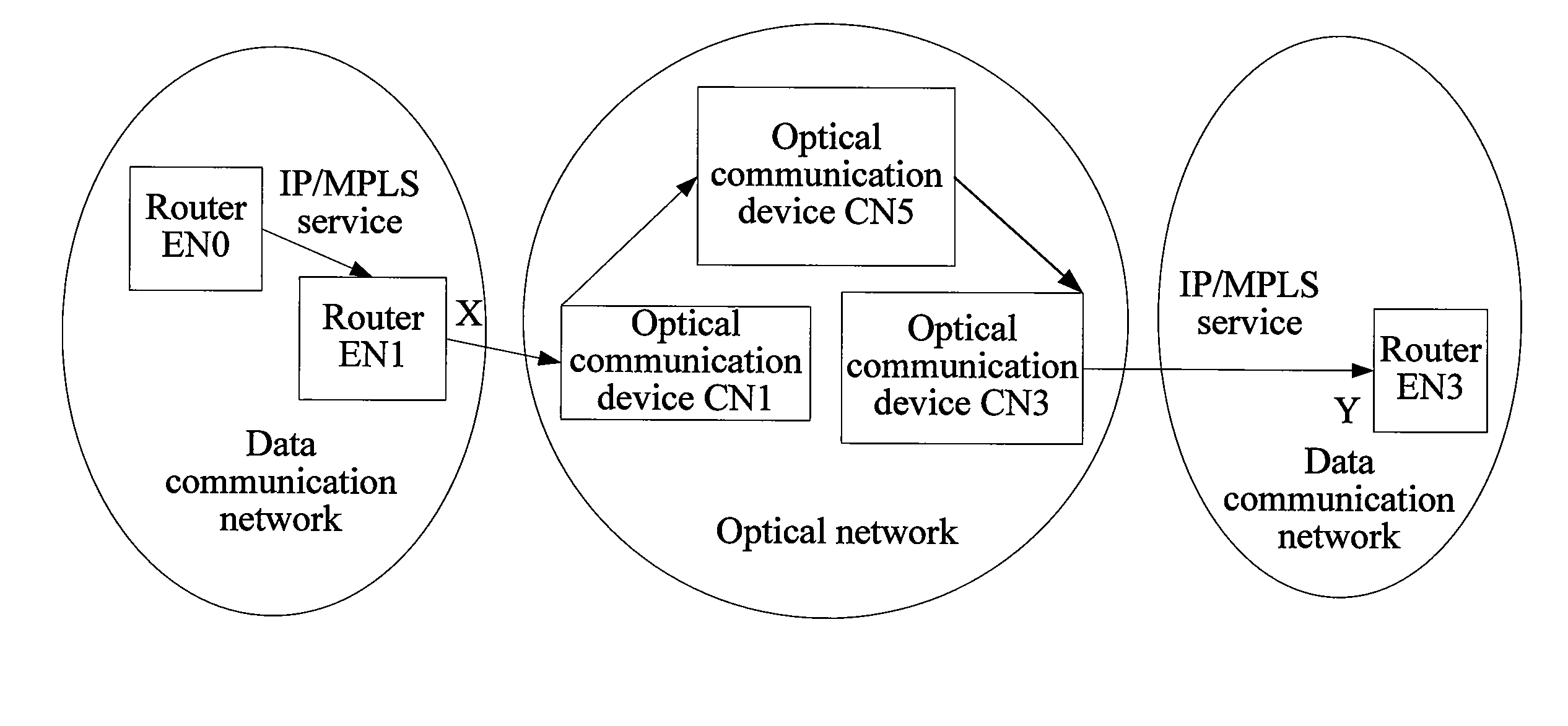
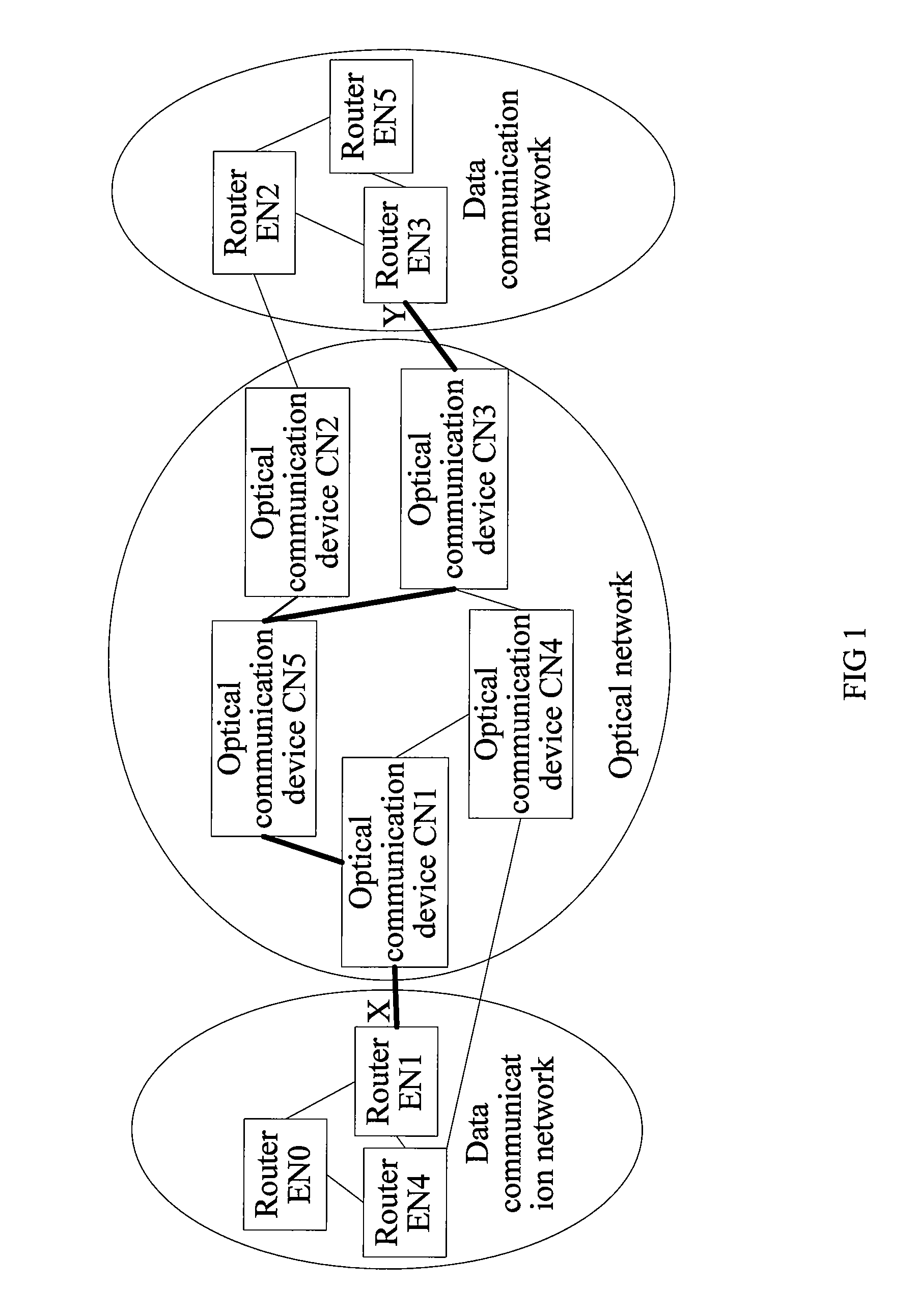
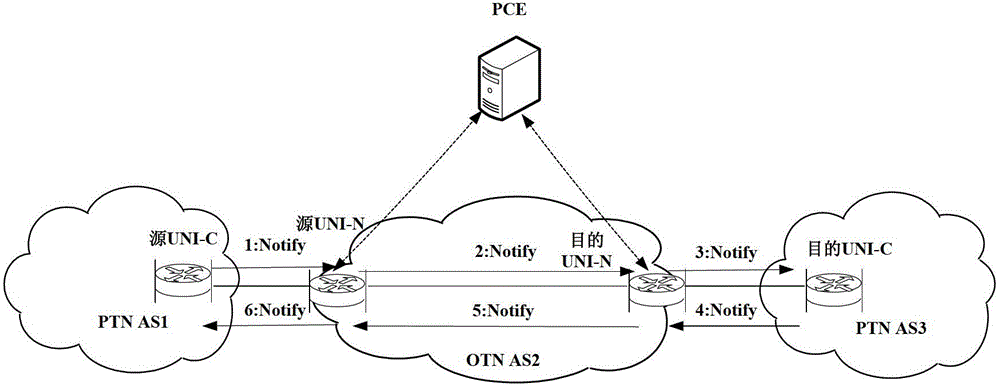
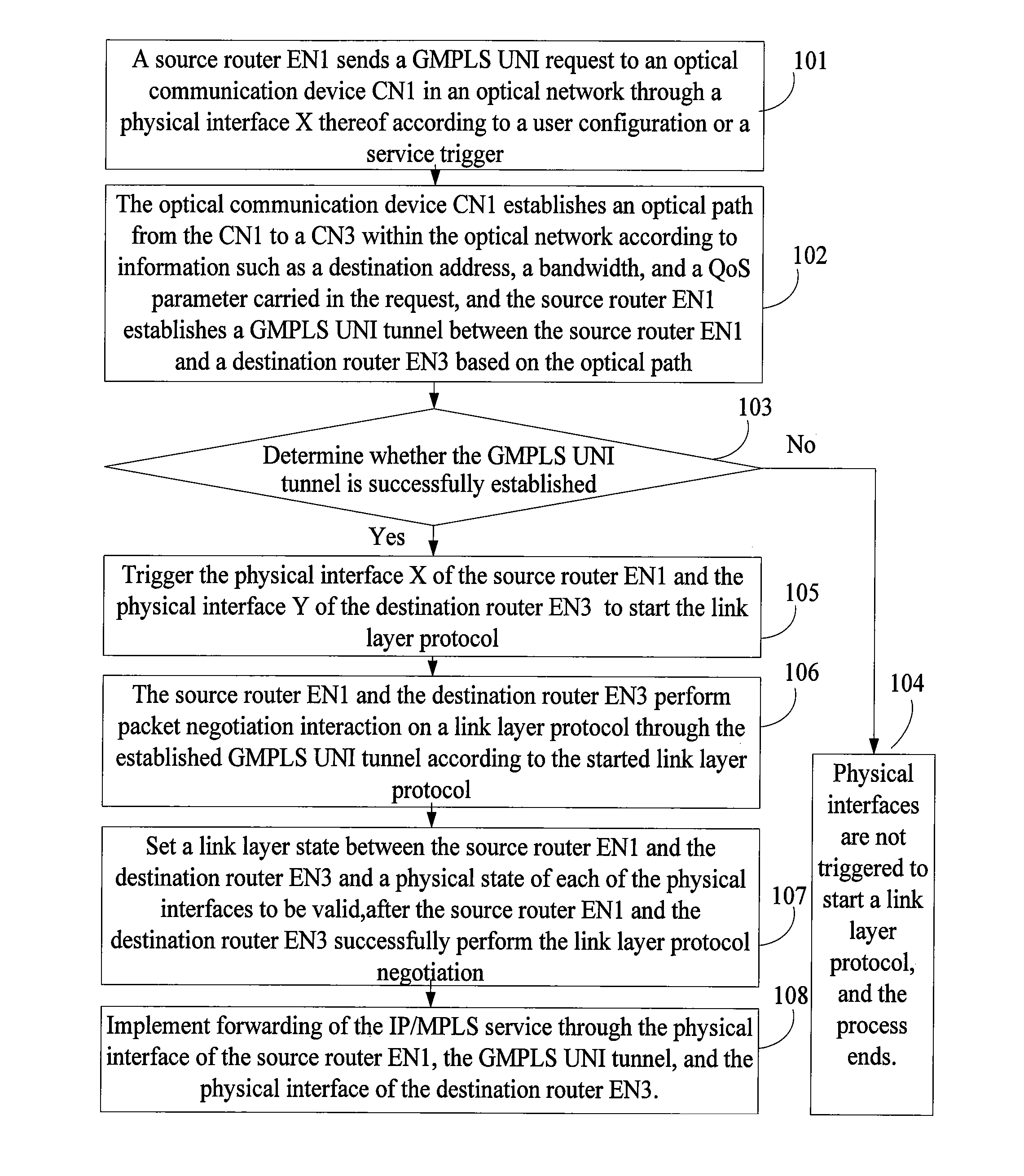
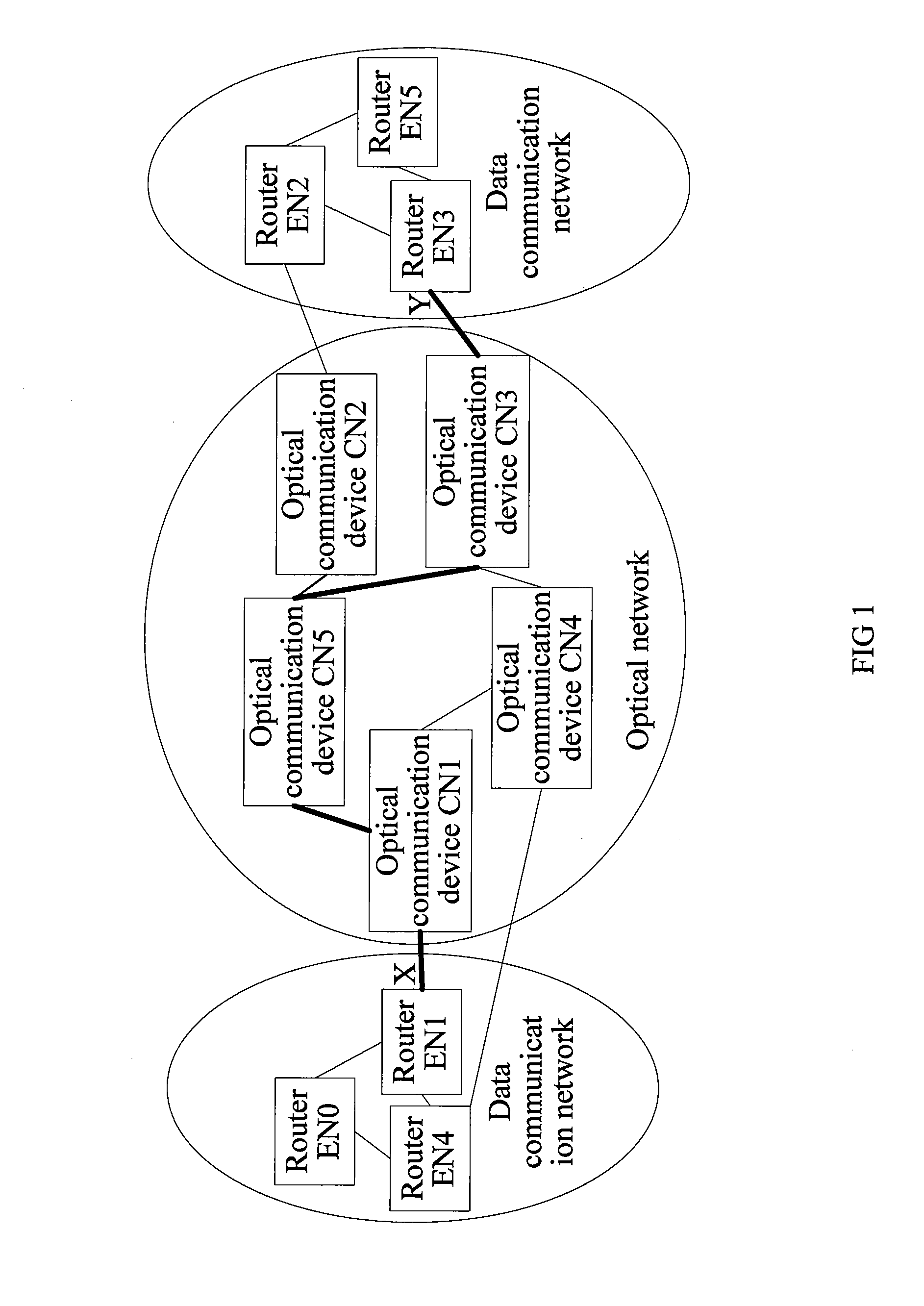
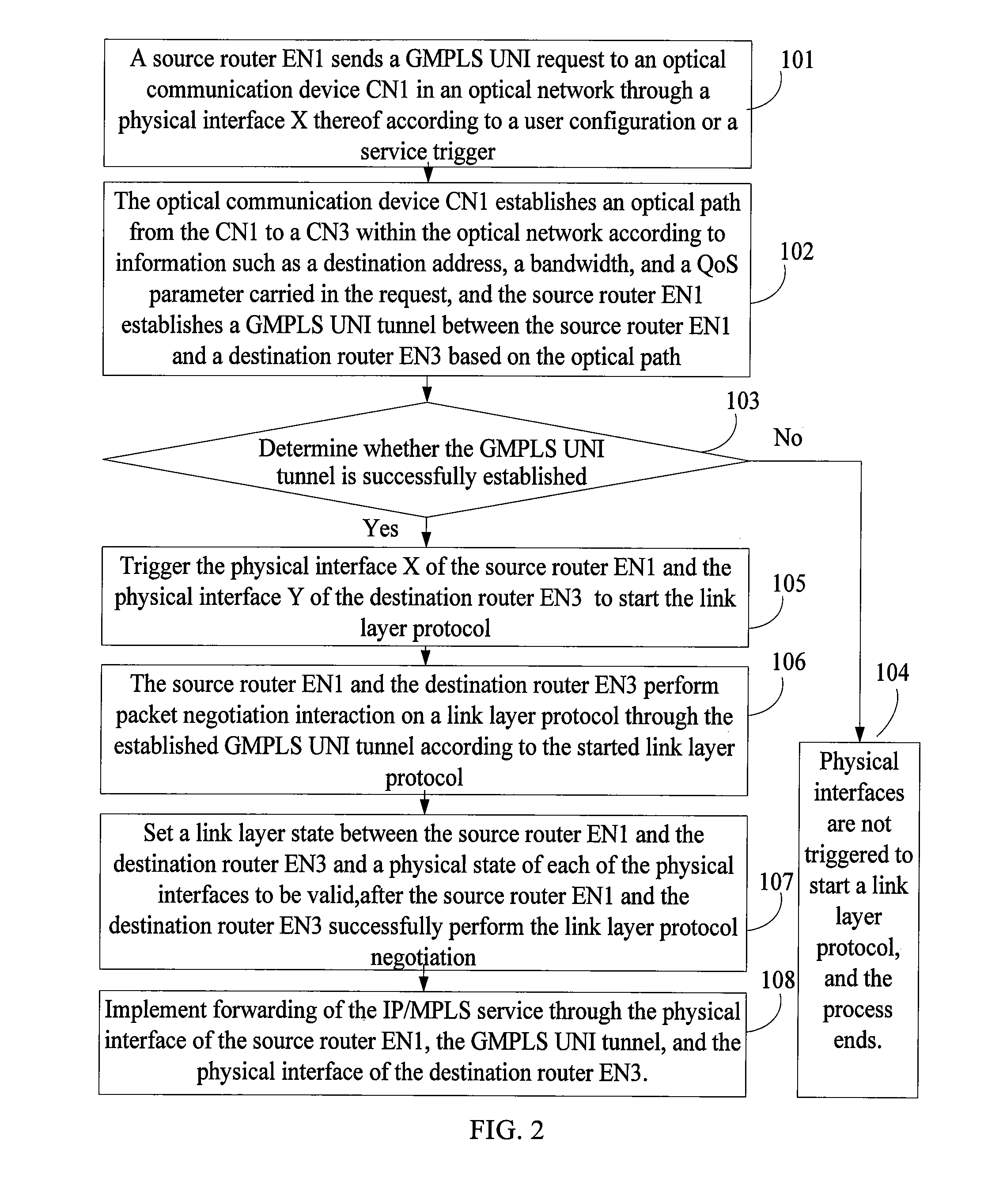
InactiveUS8902909B2Implementation complexity can be reducedDegrade reconstructionMultiplex system selection arrangementsData switching by path configurationMulti protocolForwarding plane
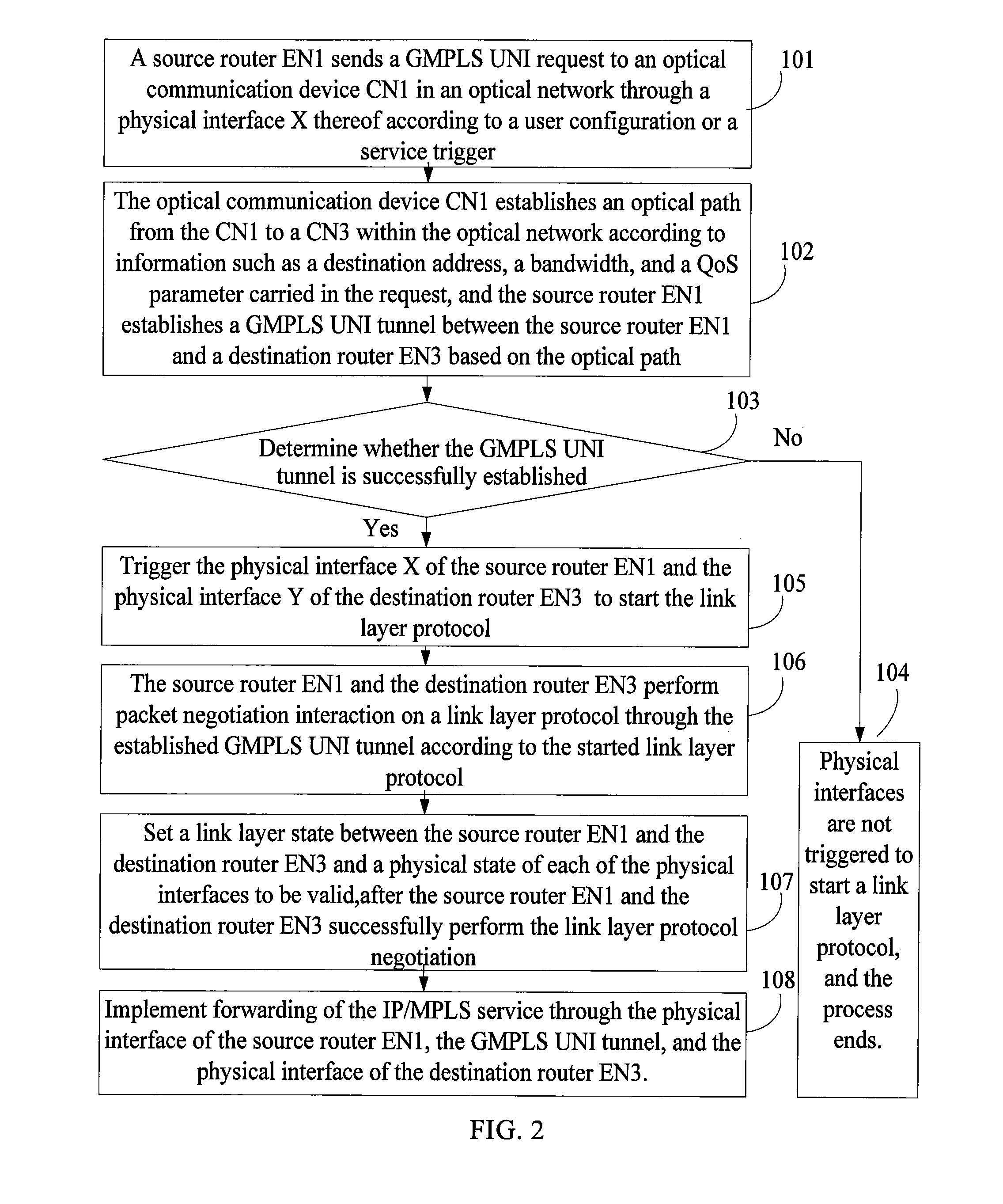
In the field of communications, a method, a system, and a device for implementing service forwarding are disclosed. The method includes: establishing an optical network tunnel between data communication devices; triggering physical interfaces of the data communication devices directly connected to an optical network to start a link layer protocol after the optical network tunnel is successfully established; performing, by the data communication devices, link layer negotiation through the optical network tunnel according to the link layer protocol; setting a link layer state between the data communication devices and a physical state of the physical interfaces to be valid after the link layer negotiation is performed successfully; and implementing, service forwarding, by the data communication devices through the optical network tunnel after the link layer state and the physical state of the physical interfaces are set to be valid. In this way, Internet Protocol (IP) / Multi-Protocol Label Switching (MPLS) service forwarding of the data communication devices is implemented, implementation complexity of bearing the IP / MPLS service over a Generalized Multi-Protocol Label Switching User-Network Interface (GMPLS UNI) tunnel is reduced, reconstruction on an IP / MPLS control plane and a forwarding plane is decreased, and forwarding performance is improved.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Method and related apparatus for establishing link-diverse traffic paths in a telecommunications network
ActiveUS9559944B2Multiplex system selection arrangementsData switching by path configurationService modelTelecommunications link
In order to achieve path diversity for dual-homed User-Network Interface clients connected to a Generalized Multiprotocol Label Switching control plane enabled transport network that is operated in an overlay mode, the overlay extension service model is enhanced by adding shared constraint information for path diversity in the optical transport network. In particular, within the provider network, shared constraint information of a first traffic path is determined and a data element indicative of the shared constraint information is returned by a first provider edge node to a customer edge device via a User-Network Interface. When the customer edge device requests a second traffic path through the provider network to be established from a second provider edge node and to be disjoint from said first traffic path, the customer edge device forwards the data element to the second provider edge node to enable path calculation of the second traffic path using the shared constraint information as exclusion list.
Owner:RPX CORP
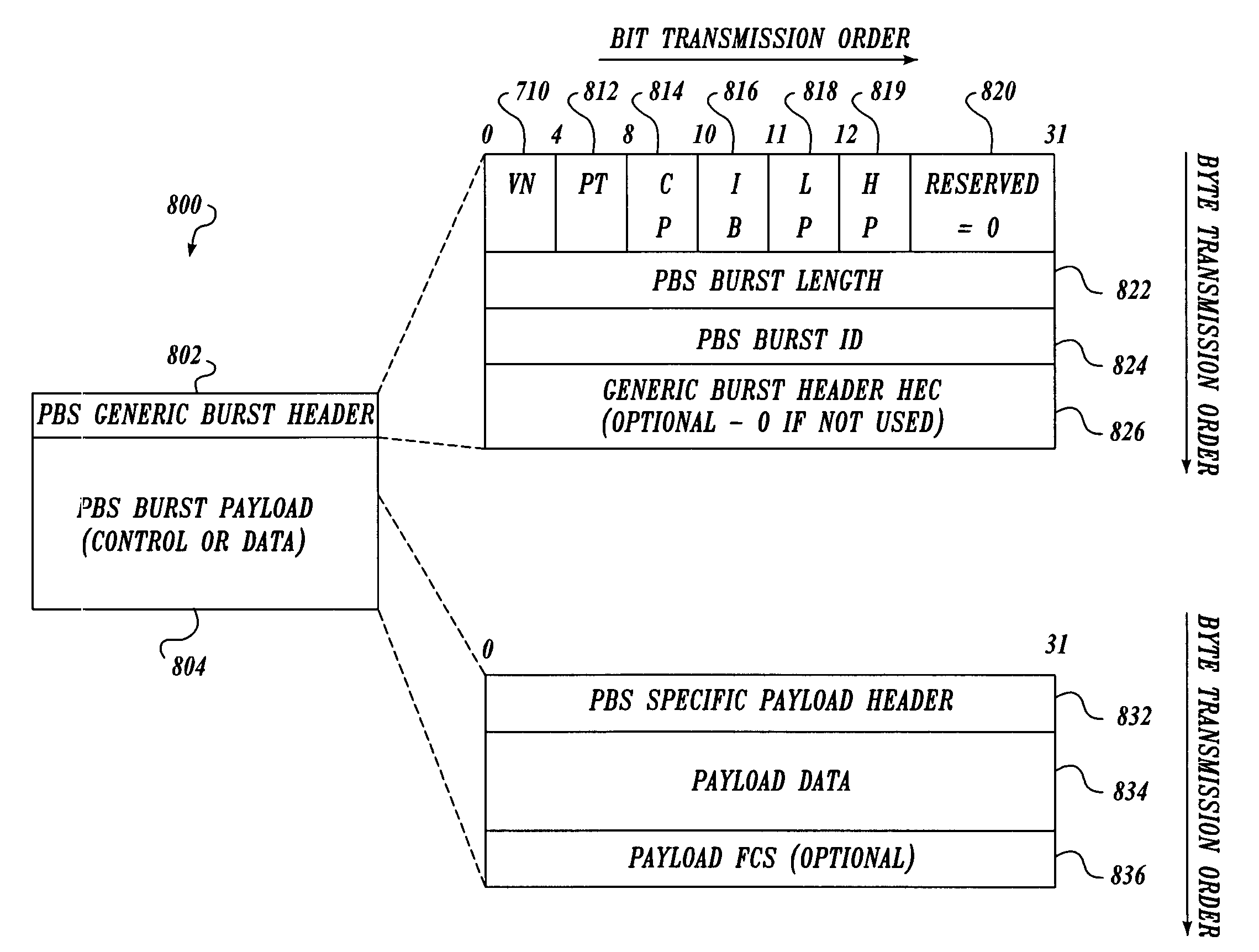
Method and system to frame and format optical control and data bursts in WDM-based photonic burst switched networks
InactiveUS7848649B2Multiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsExchange networkPhotonics
A wavelength-division-multiplexed based photonic burst switched (PBS) network, which includes edge and switching nodes, optically communicate information formatted into PBS control and data burst frames. Each PBS data burst frame is associated with a PBS control burst frame. A PBS burst frame includes a PBS burst header and burst payload having fields to indicate whether: (a) the PBS burst frame is a PBS control burst; (b) the control burst is transmitted on a wavelength different from that of the associated PBS data burst; and (c) the PBS burst frame has a label for use in a generalized multi-protocol label swapping (GMPLS)-based control system. The PBS burst payload frame includes fields to indicate (a) specific PBS payload information; (b) PBS data payload; and (c) an optional PBS payload frame check sequence (FCS) for error detection.
Owner:INTEL CORP
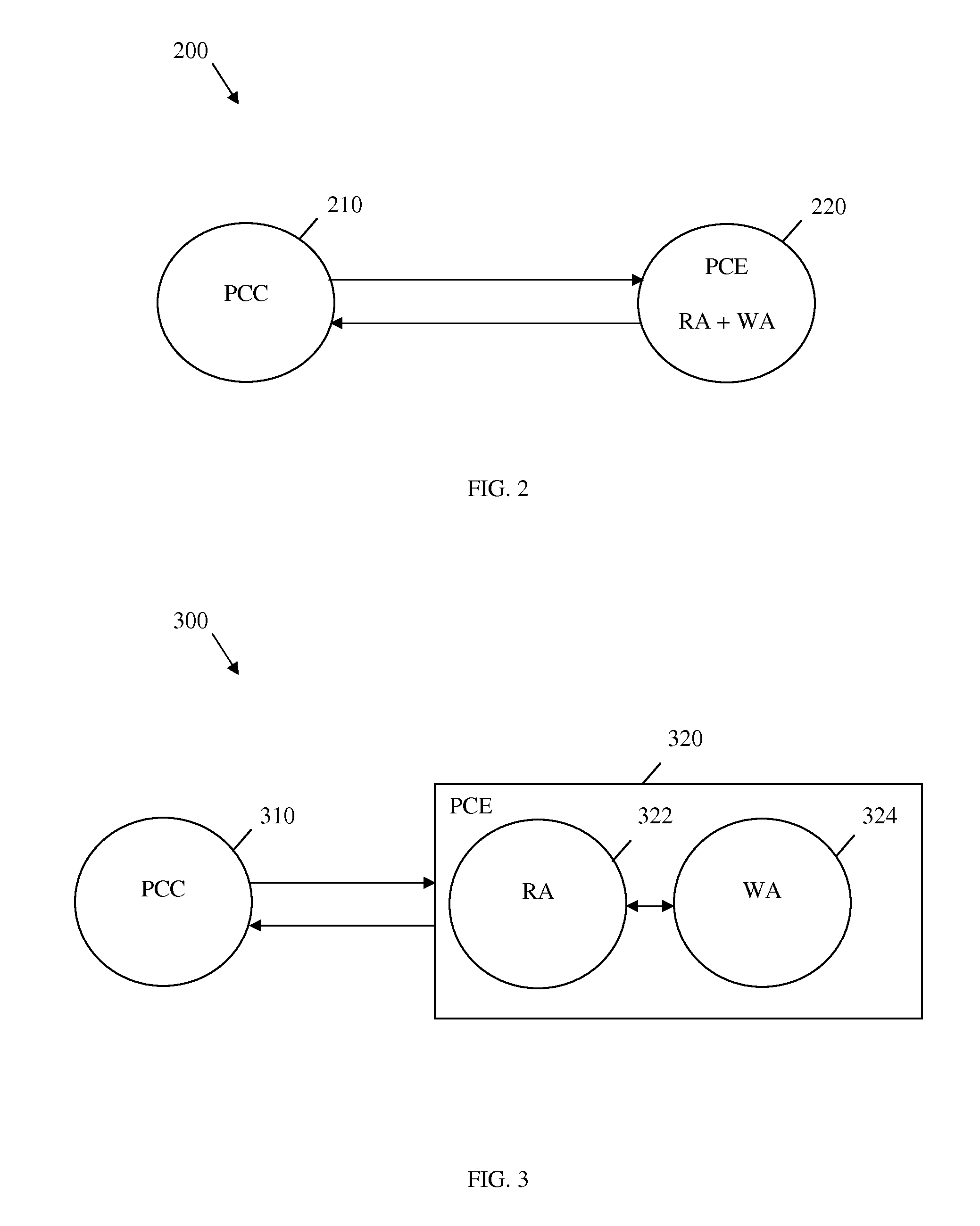
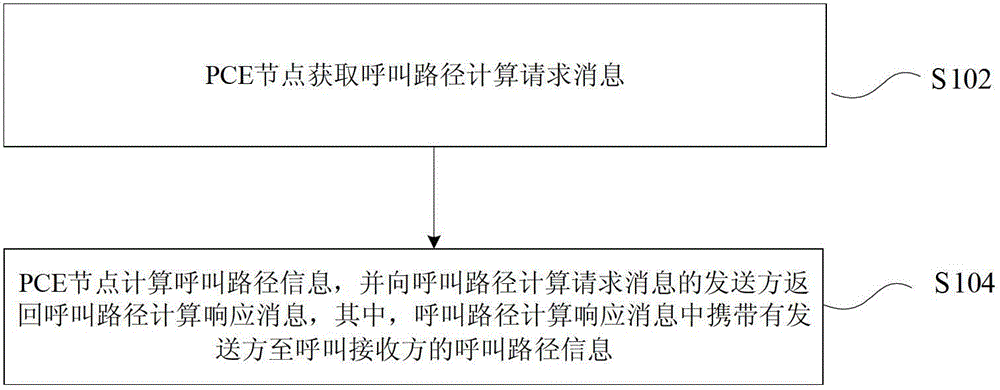
Method and system for acquiring call path information
ActiveCN102724111ARealize dynamic path calculationSolve the problem that the path information from the source node to the destination node cannot be obtained during the callData switching networksPath computation elementGeneralized Multi-Protocol Label Switching
The invention discloses a method and a system for acquiring call path information. The method comprises the steps as follows: acquiring a call path calculation request message by a PCE (Path Computation Element) node, wherein the call path calculation request message is used for acquiring call path information from a sending party of the call path calculation request message to a call receiving party from the PCE node, the sending party comprises a call path source node, and the call receiving party comprises a call path destination node; and calculating the call path information by the PCE node, and returning a call path calculation response message to the sending party, wherein the call path calculation response message carries the call path information. According to the technical scheme provided by the invention, dynamic path calculation of GMPLS (Generalized Multi-Protocol Label Switching) call is realized in a cross-domain network.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Method, system, and device for implementing service forwarding
InactiveUS20110222847A1Service degradationImprove forwarding performanceMultiplex system selection arrangementsTransmission monitoringMulti protocolComputer science
In the field of communications, a method, a system, and a device for implementing service forwarding are disclosed. The method includes: establishing an optical network tunnel between data communication devices; triggering physical interfaces of the data communication devices directly connected to an optical network to start a link layer protocol after the optical network tunnel is successfully established; performing, by the data communication devices, link layer negotiation through the optical network tunnel according to the link layer protocol; setting a link layer state between the data communication devices and a physical state of the physical interfaces to be valid after the link layer negotiation is performed successfully; and implementing, service forwarding, by the data communication devices through the optical network tunnel after the link layer state and the physical state of the physical interfaces are set to be valid. In this way, Internet Protocol (IP) / Multi-Protocol Label Switching (MPLS) service forwarding of the data communication devices is implemented, implementation complexity of bearing the IP / MPLS service over a Generalized Multi-Protocol Label Switching User-Network Interface (GMPLS UNI) tunnel is reduced, reconstruction on an IP / MPLS control plane and a forwarding plane is decreased, and forwarding performance is improved.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Method and apparatus for interfacing applications to LCAS for efficient SONET traffic flow control
InactiveUS7680128B2Efficient interfaceError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsLink Capacity Adjustment SchemeCross connection
The present invention provides methods and apparatuses for interfacing high-layer applications to Link Capacity Adjustment Scheme (LCAS) on Synchronous Optical Network / Synchronous Digital Hierarchy (SONET / SDH) edge nodes. These applications include high-level control protocols, such as Generalized Multiprotocol Label Switching (GMPLS) and Optical Switching and Routing Protocol (OSRP), and user-initiated cross-connect creation and termination. The present invention provides a mechanism that is capable of mapping SONET / SDH connections to Virtual Concatenated Groups (VCGs), thus enabling an efficient interface for operators to control and manage the connections via LCAS. As part of the mechanism, the existing LCAS protocol state machine is enhanced such that the operators can shut down bi-directional SONET / SDH flows from a single edge node, as opposed to from both source and sink nodes, as provided for by existing specifications.
Owner:CIENA
Method for managing services in a generalized-multi-protocol label switching, GMPLS, controlled network
A Generalized-Multi-Protocol Label Switching controlled network is described, as is a method for managing services in the network under conditions of disrupted control plane connectivity. Nodes of the network use a Resource Reservation Protocol with Traffic Engineering extension, RSVP-TE, to allocate and provision resources of the network. Each of the nodes is adapted to evaluate local RSVP Path or Resv state data after having sent at least one signaling message to a receiving neighboring node without receipt of an acknowledgement message from said receiving node within a configurable time to determine an IP address of a node being located after the non-responsive receiving node along a service path of a service in a downstream or upstream direction. Each node is adapted to send the signaling message to the determined IP address of the next node located behind the non-responsive receiving node along the service path.
Owner:ADTRAN NETWORKS SE
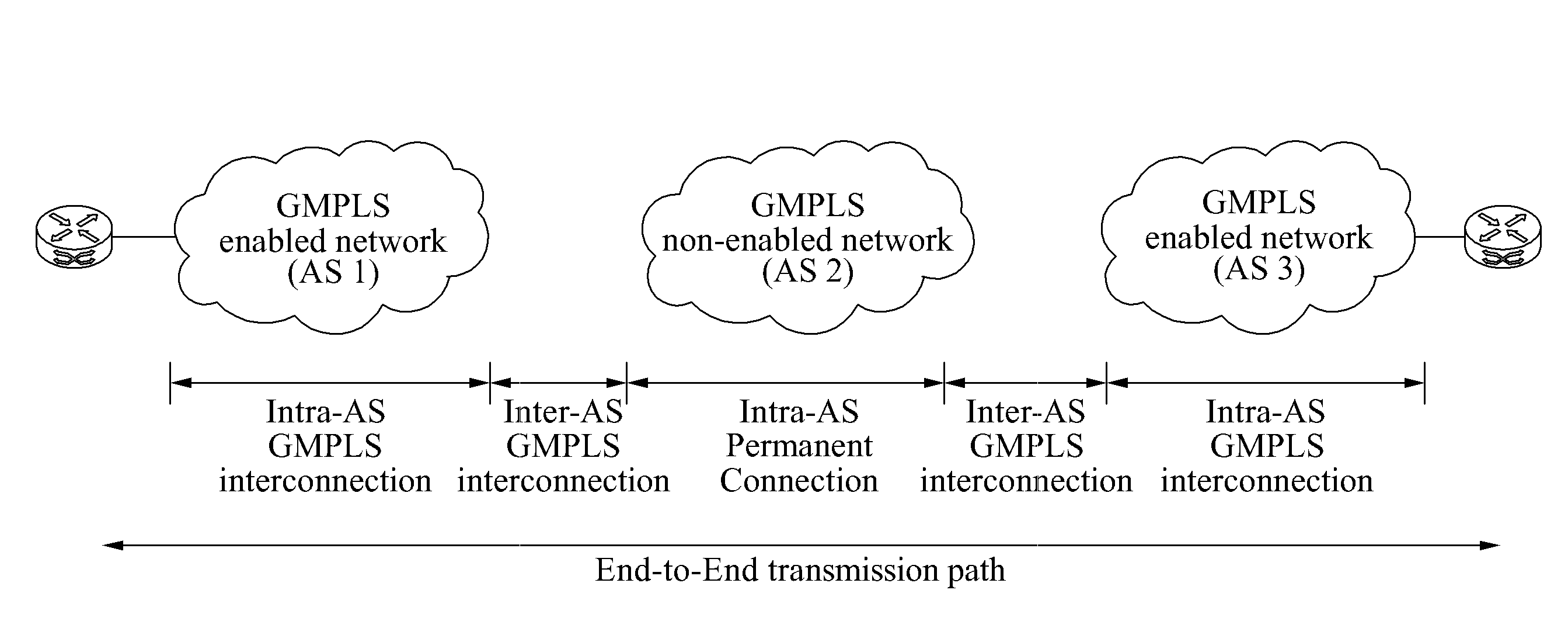
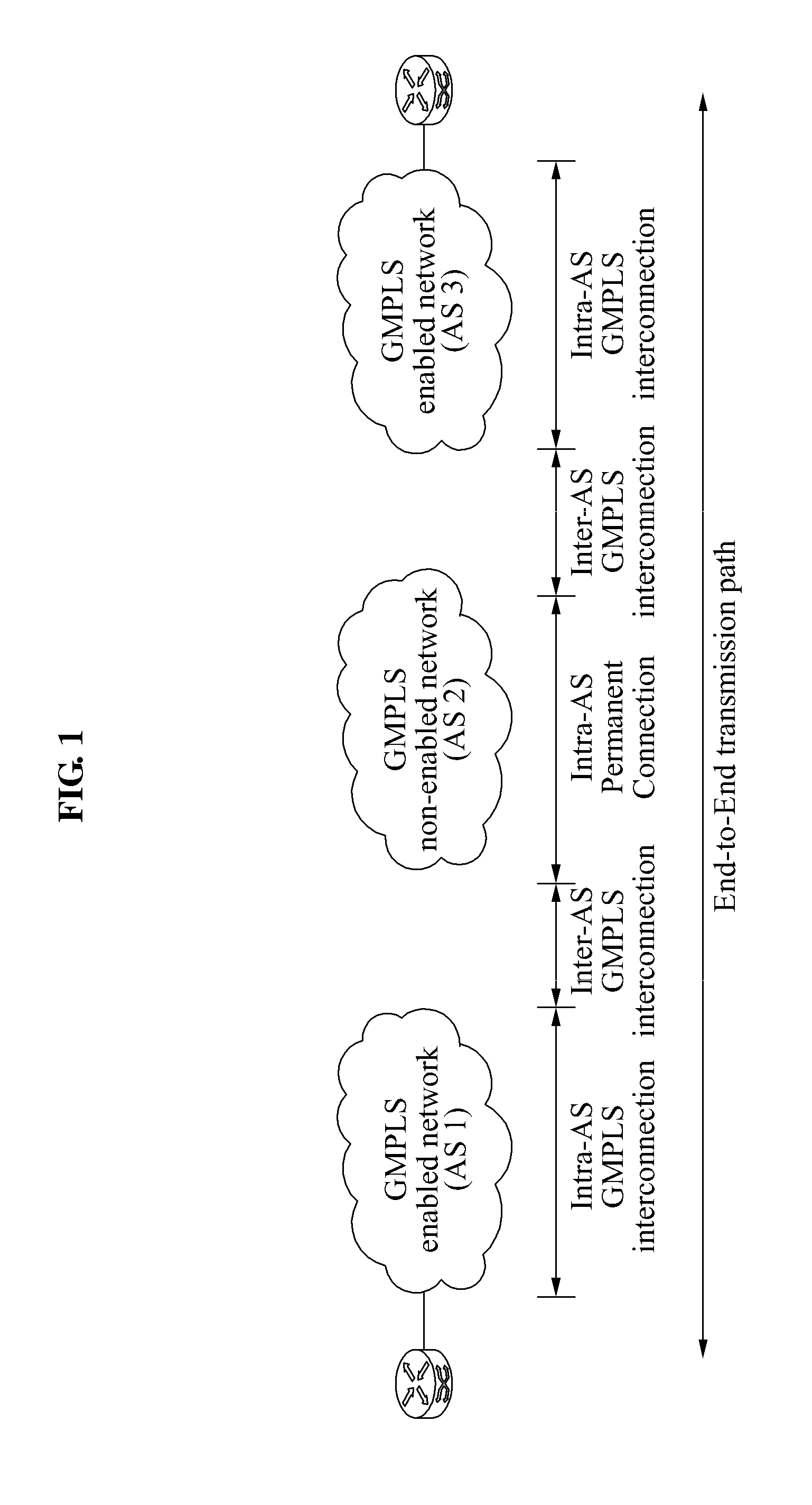
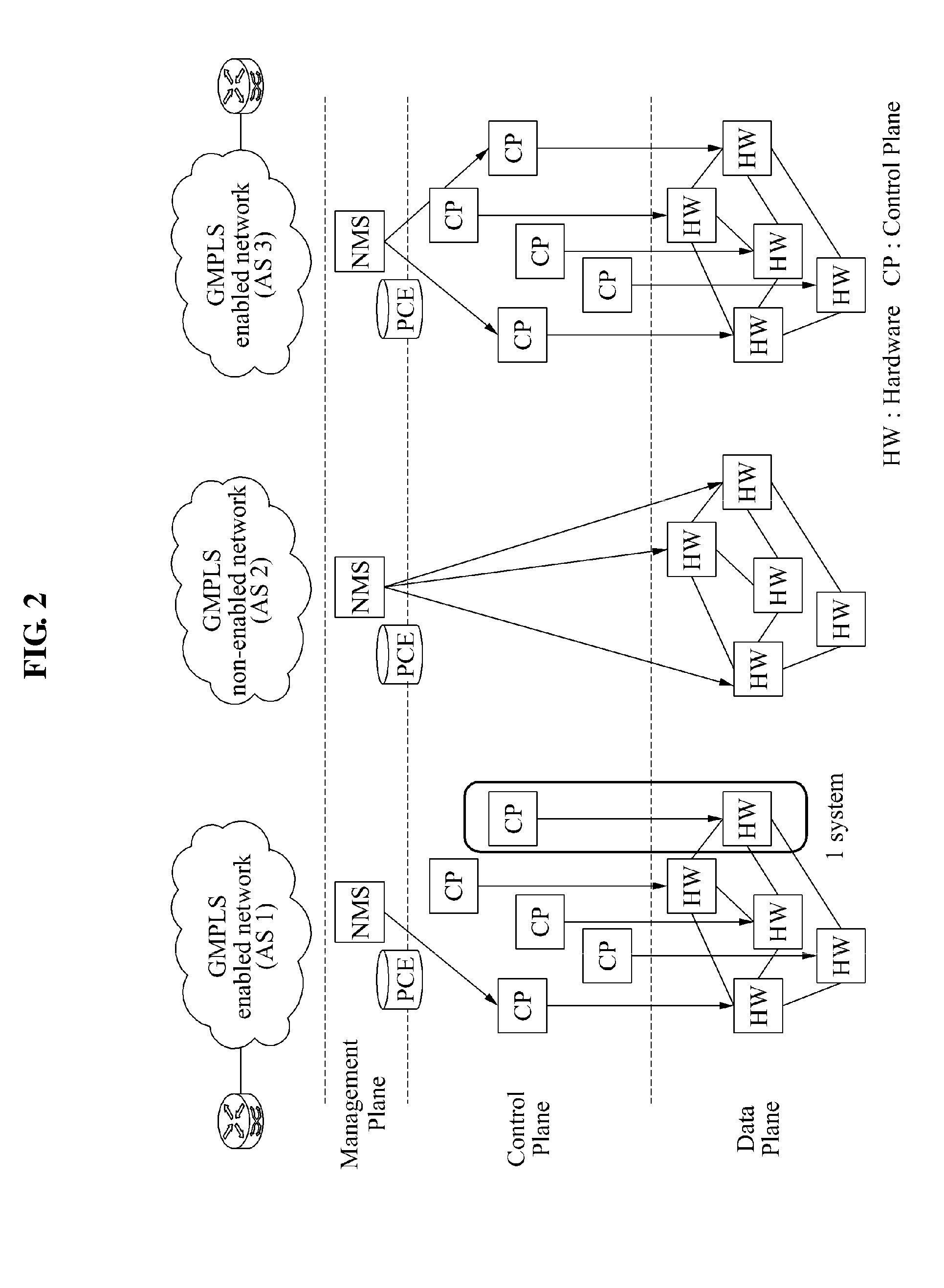
Gmpls non-enabled network gateway and operating method for routing between gmpls enabled network and gmpls non-enabled network
InactiveUS20120128003A1Reduce burden of expenseReduce administrative burdenData switching by path configurationBorder Gateway ProtocolMultiprotocol Label Switching
A generalized multiprotocol label switching (GMPLS) non-enabled network gateway for routing between a GMPLS enabled network and a GMPLS non-enabled network for connection between the GMPLS enabled network and the GMPLS non-enabled network, and an operating method for the GMPLS non-enabled network gateway are provided. The GMPLS non-enabled network gateway may include a border gateway protocol (BGP) routing unit to exchange routing information between a first GMPLS enabled network and a third GMPLS enabled network using a BGP, and a resource reservation protocol signaling unit to search for a path to another network using the routing information and to perform inter-autonomous system (AS) signaling by including a control plane of the first GMPLS enabled network or the third GMPLS enabled network and a signaling interface applying an out-of-band method.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Dynamic hitless ODUflex resizing in optical transport networks
ActiveUS9722723B2Time-division optical multiplex systemsTime-division multiplexNetwork managementMulti protocol
The present invention and its embodiments are made to provide for dynamic hitless resizing in optical transport network without any identification of matching time slots by the Network Management System (NMS) or any control plane signaling including Generalised Multi Protocol Label Switching (GMPLS). An aspect of the invention provides for a method of hitless ODUflex connection resizing in an optical transport network by incrementing or decrementing the ODUflex connection between the nodes, based on an indication command given to a source node for bandwidth increase or decrease, by identifying and matching at least one time slot through Link Connection Resizing (LCR) protocol message exchanges. Another aspect of the invention provides for a method of hitless ODUflex connection resizing in an optical transport network by decrementing the matching time slot used for the incrementing operation, in case of unsuccessful incrementing operation between nodes.
Owner:TEJAS NETWORKS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com