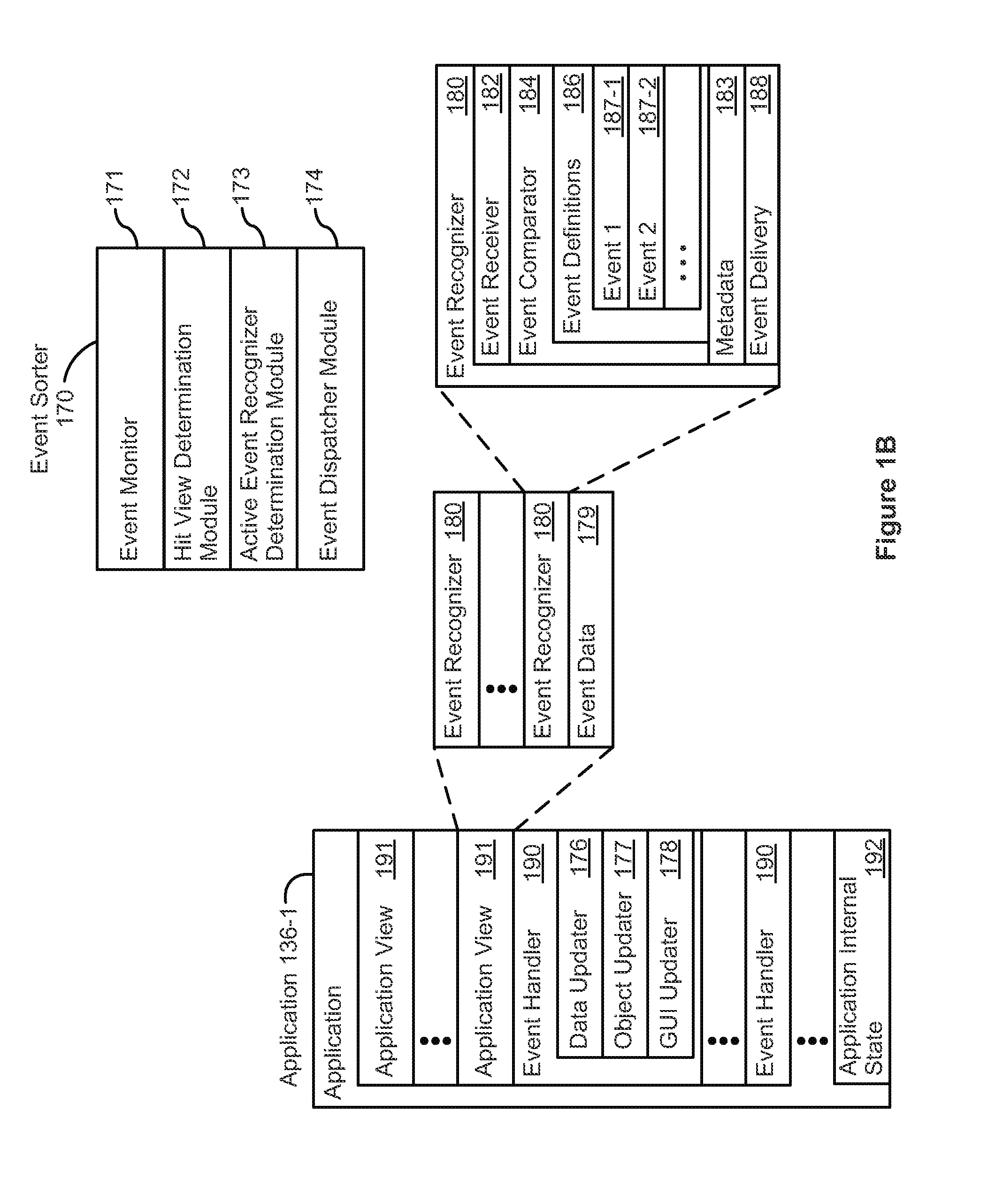
Patents
Literature
567results about How to "Efficient interface" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Speaker recognition
InactiveUS20170092278A1Increased efficiency , effectiveness , and user satisfactionFaster and efficient method and interfaceSpeech recognitionAcoustic propertyNatural language
A non-transitory computer-readable storage medium stores one or more programs including instructions, which when executed by an electronic device, cause the electronic device to receive natural-language speech input from one of a plurality of users, the natural-language speech input having a set of acoustic properties; and determine whether the natural-language speech input corresponds to both a user-customizable lexical trigger and a set of acoustic properties associated with the user; where in accordance with a determination that the natural language speech input corresponds to both a user-customizable lexical trigger and a set of acoustic properties associated with the user, invoke a virtual assistant; and in accordance with a determination that either the natural language speech input fails to correspond to a user-customizable lexical trigger or the natural-language speech input fails to have a set of acoustic properties associated with the user, forego invocation of a virtual assistant.
Owner:APPLE INC
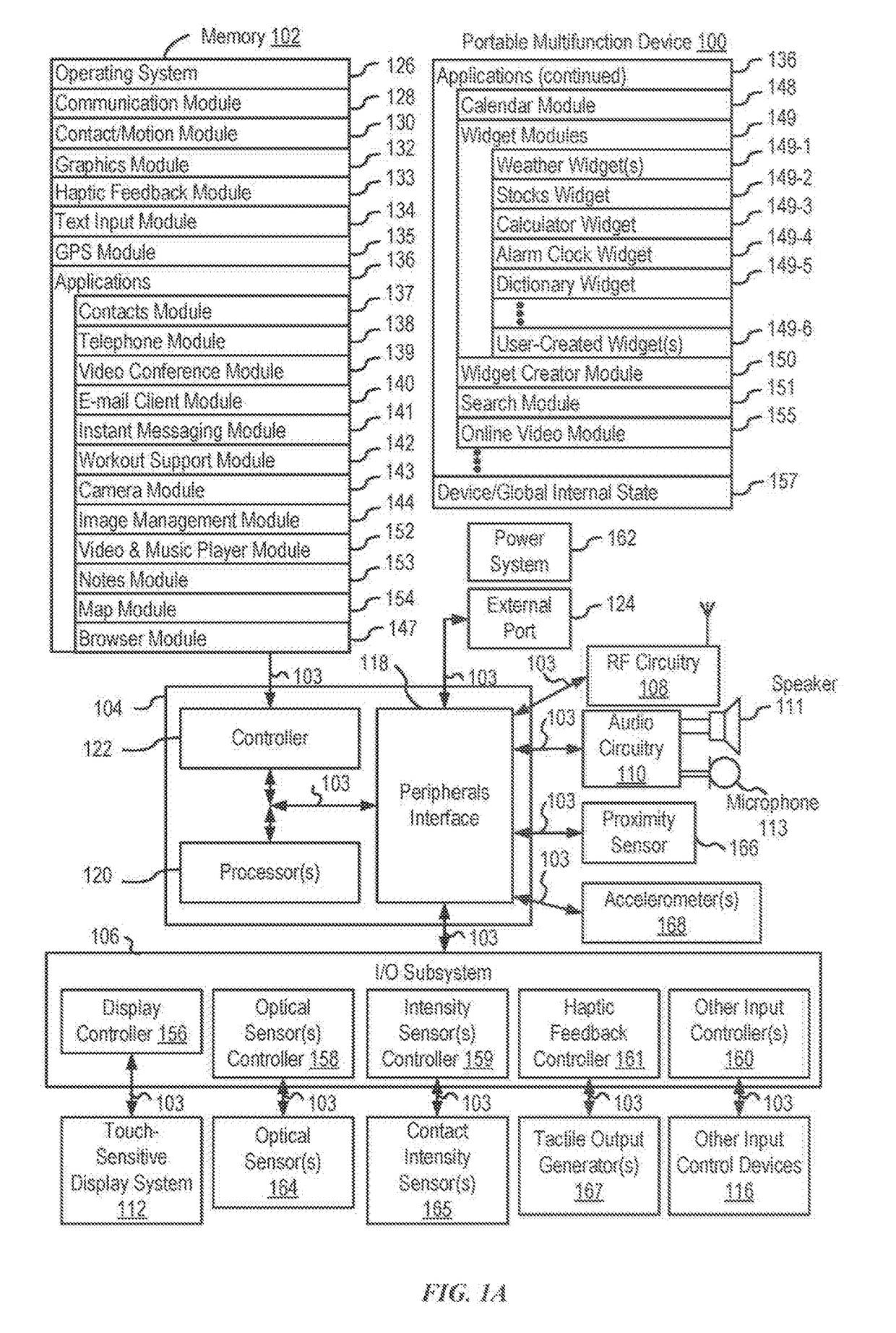
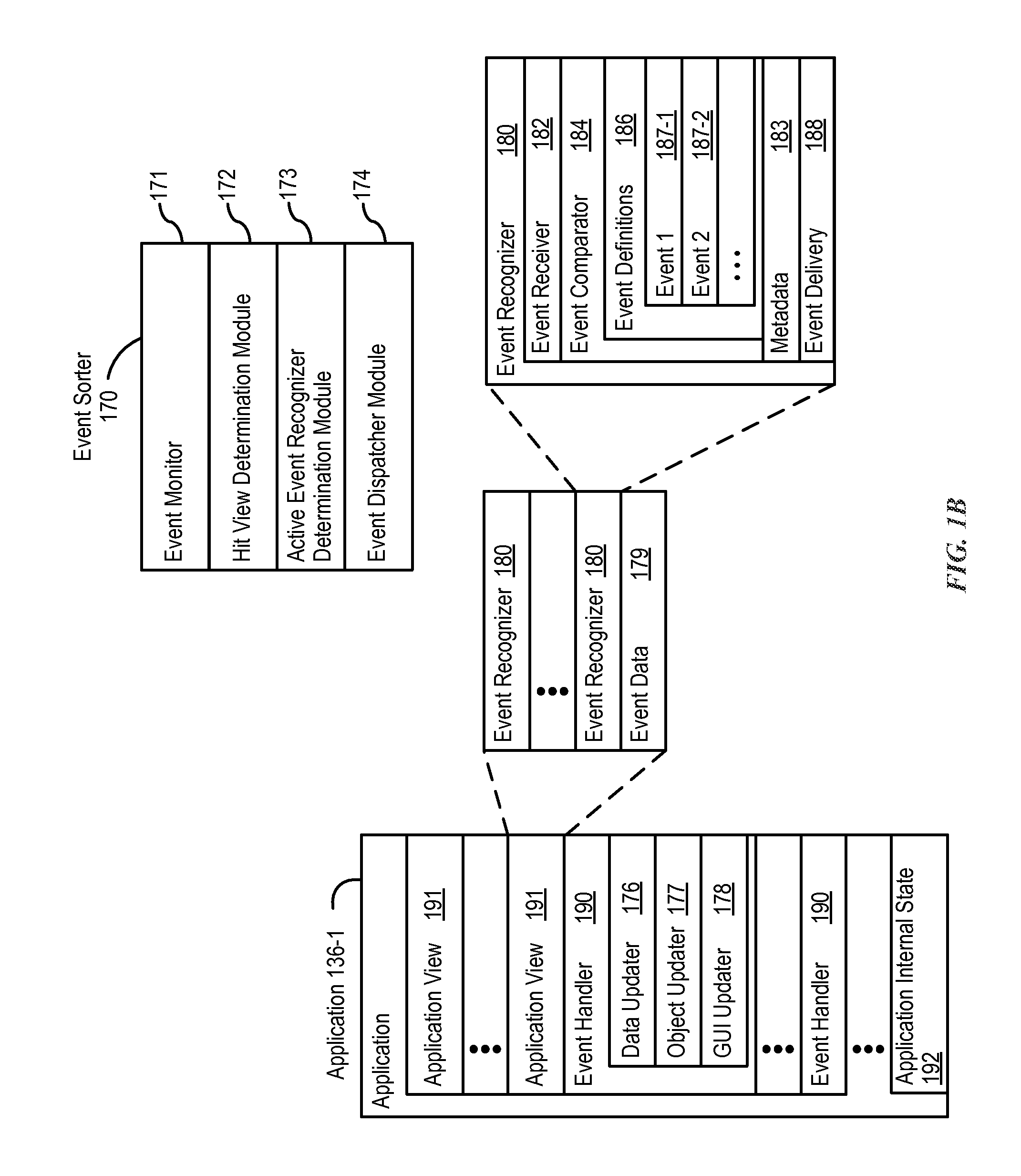
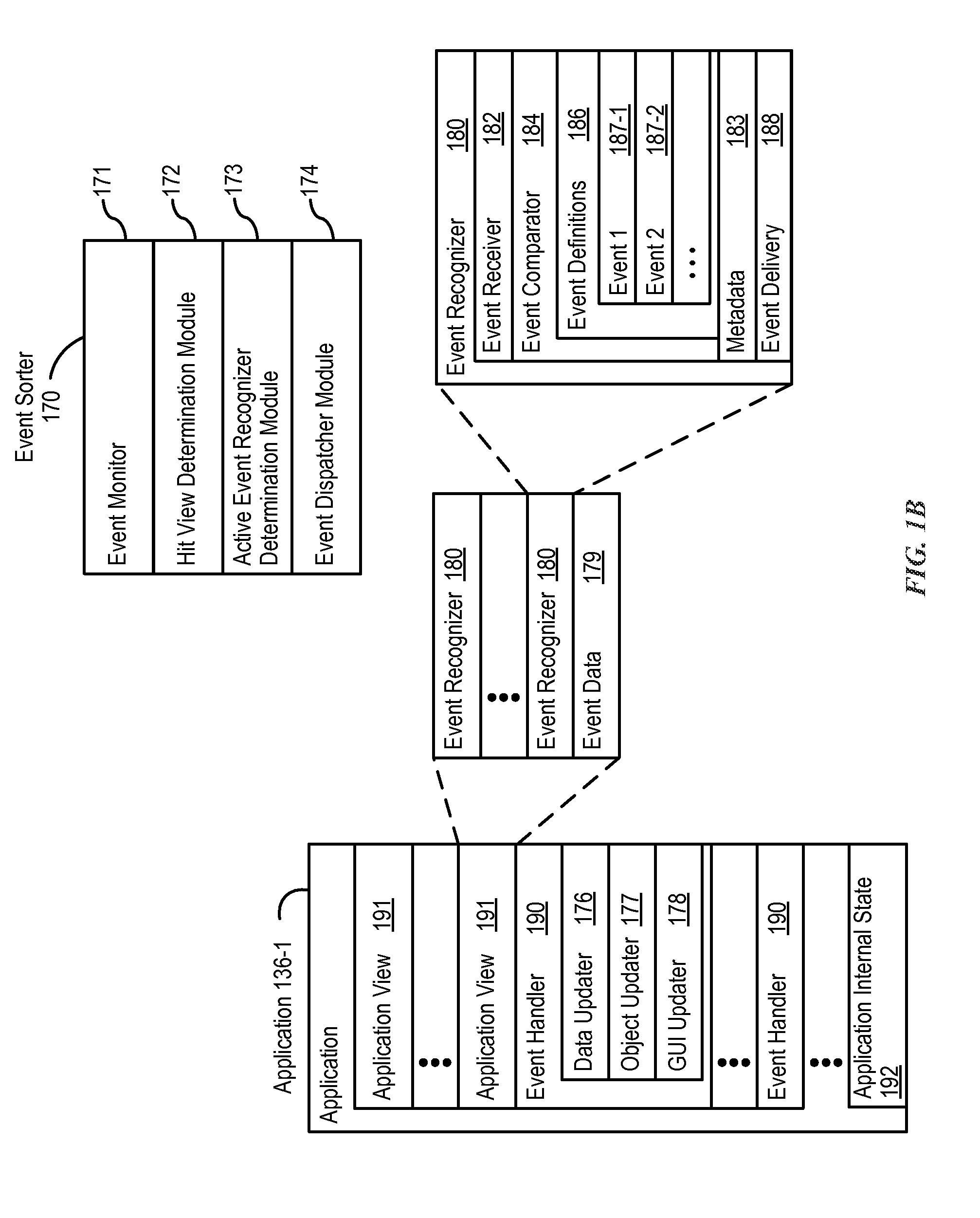
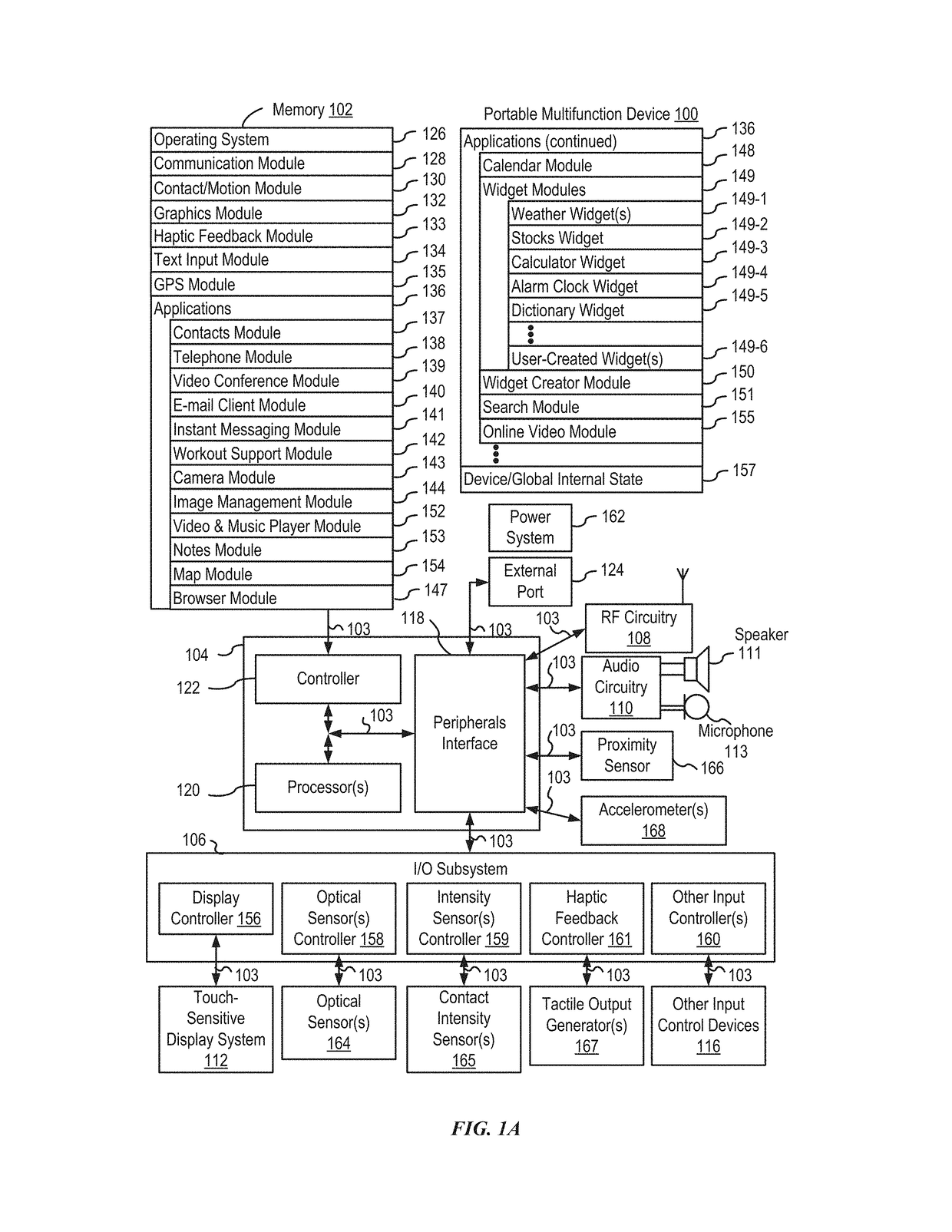
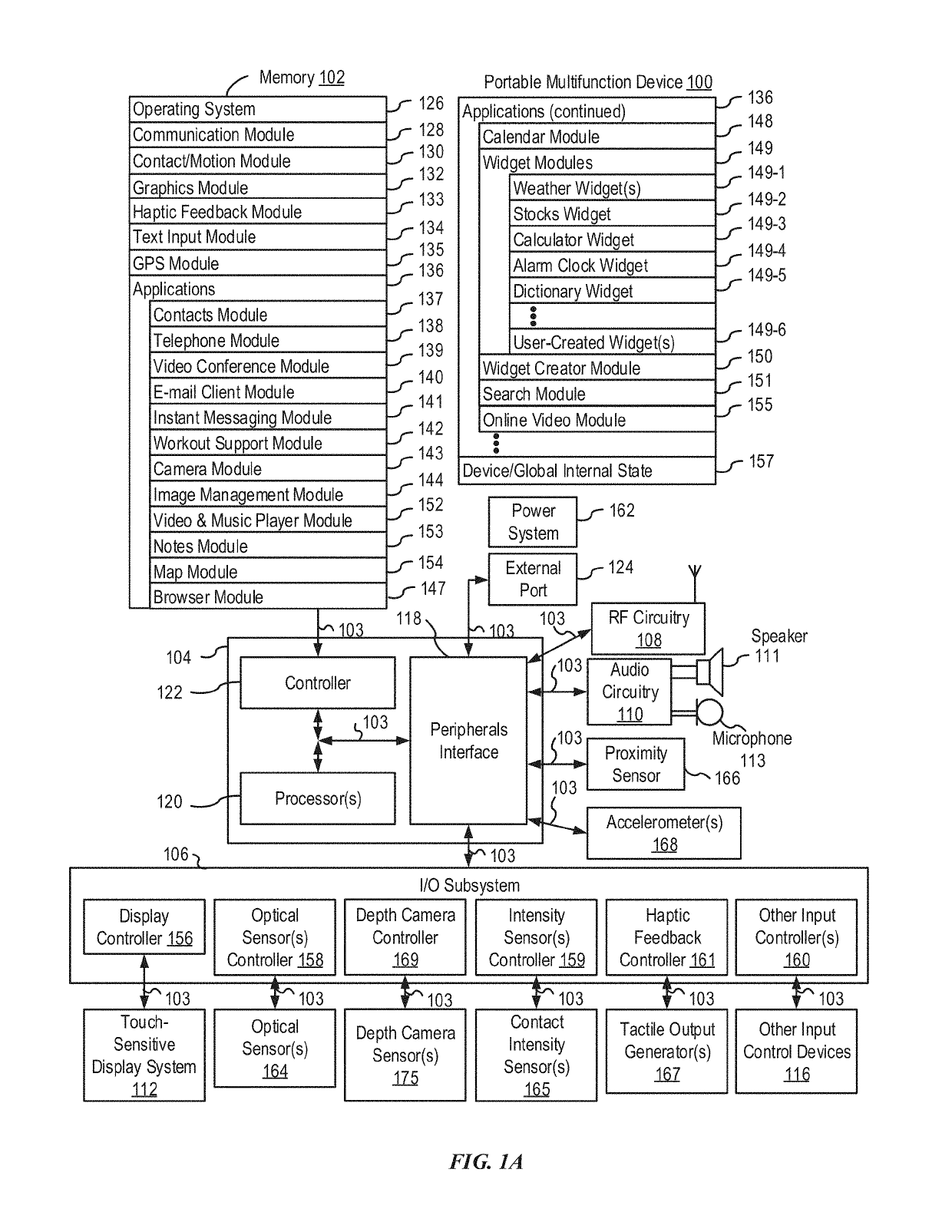
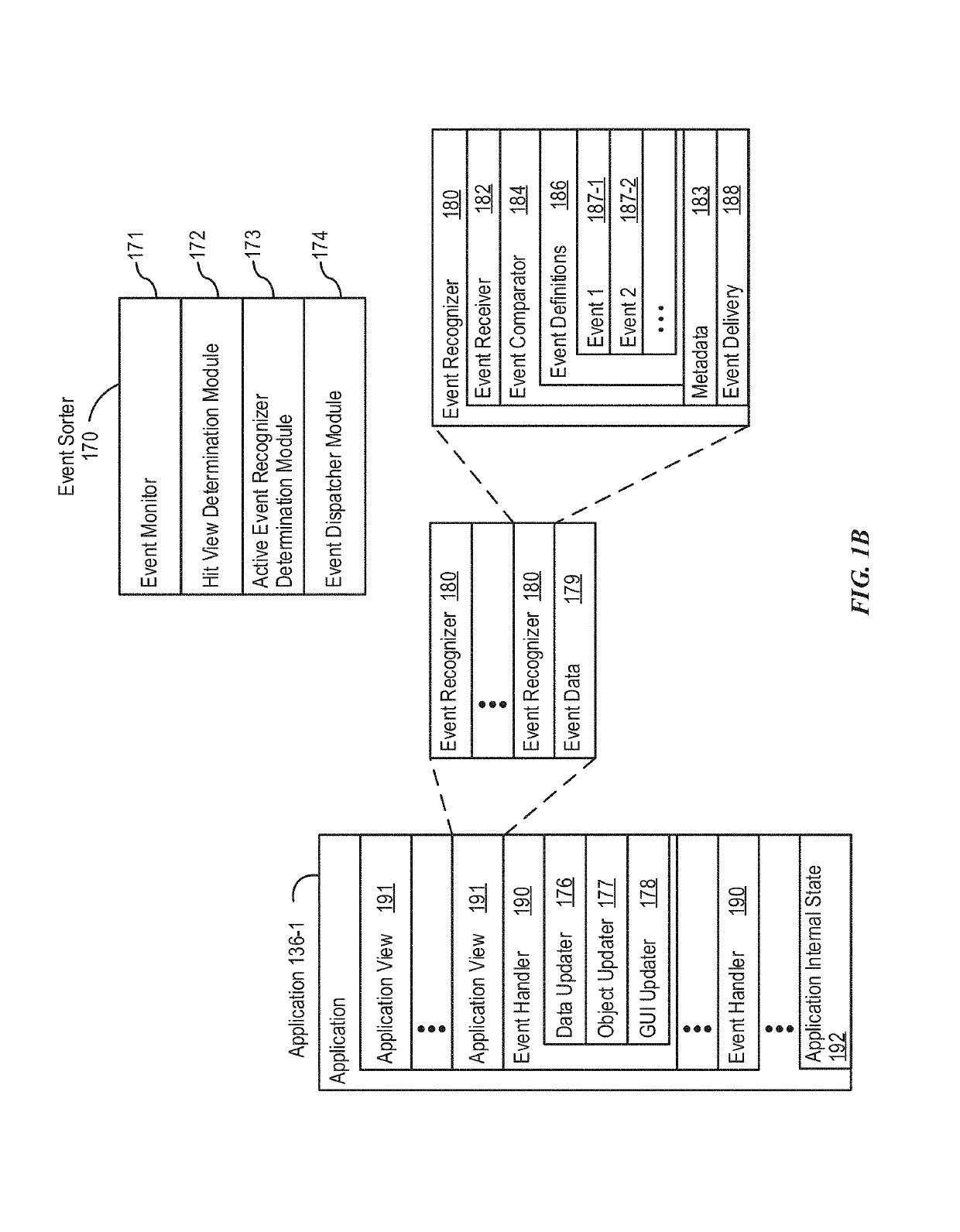
Device, Method, and Graphical User Interface for Facilitating User Interaction with Controls in a User Interface
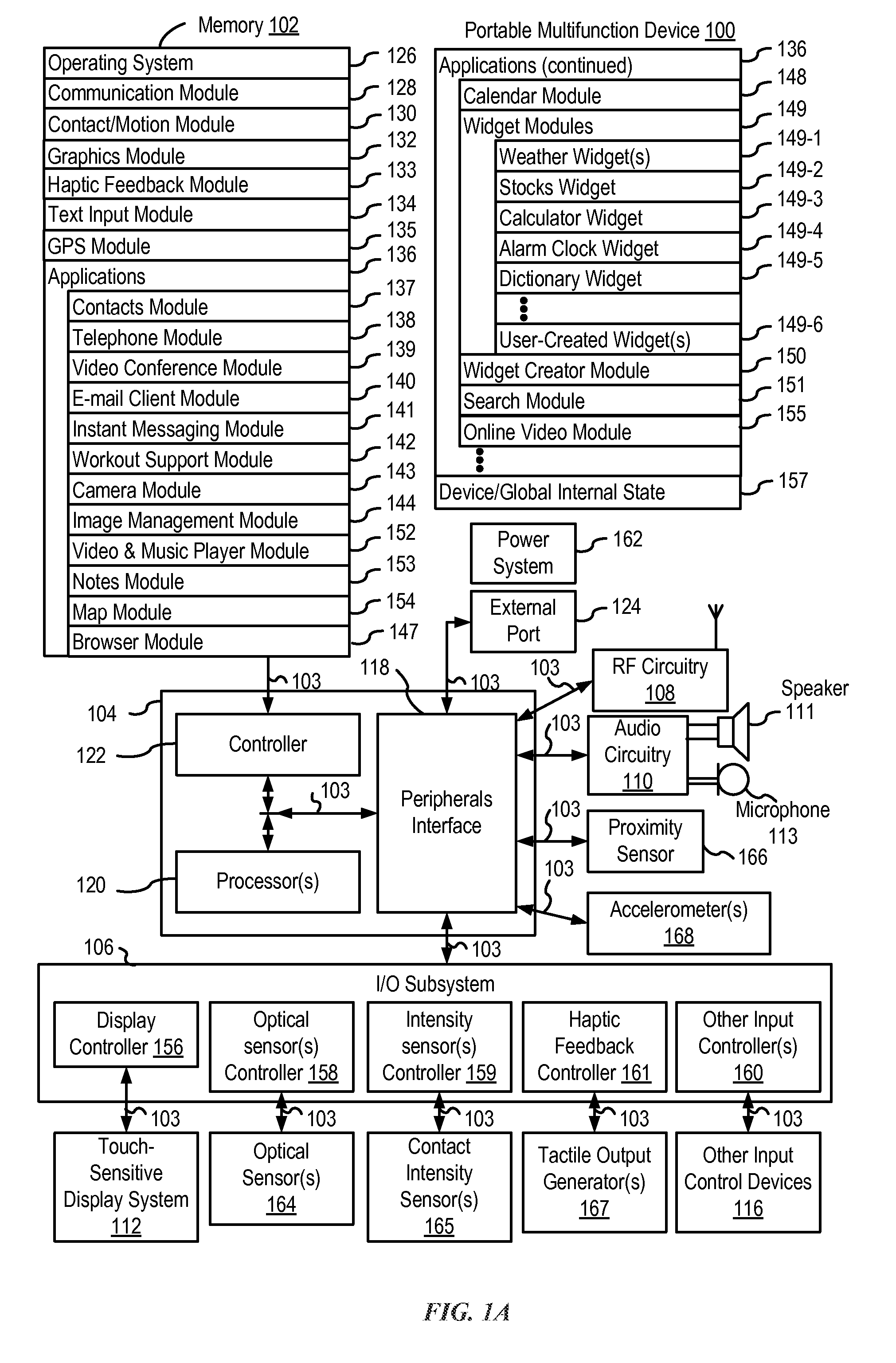
ActiveUS20150067513A1Faster and efficient methodFaster and efficient and interfaceInput/output processes for data processingPictoral communicationGraphicsGraphical user interface
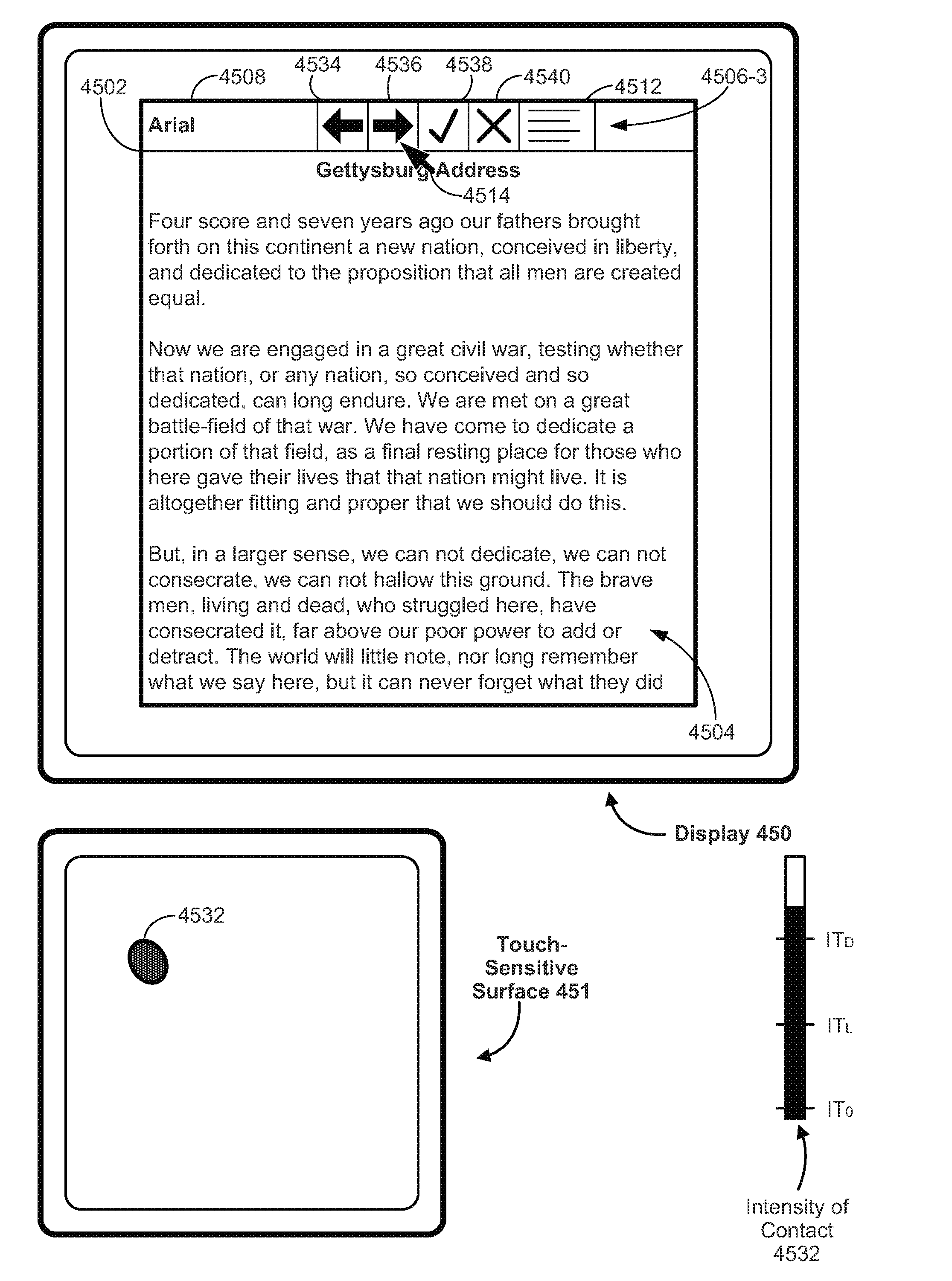
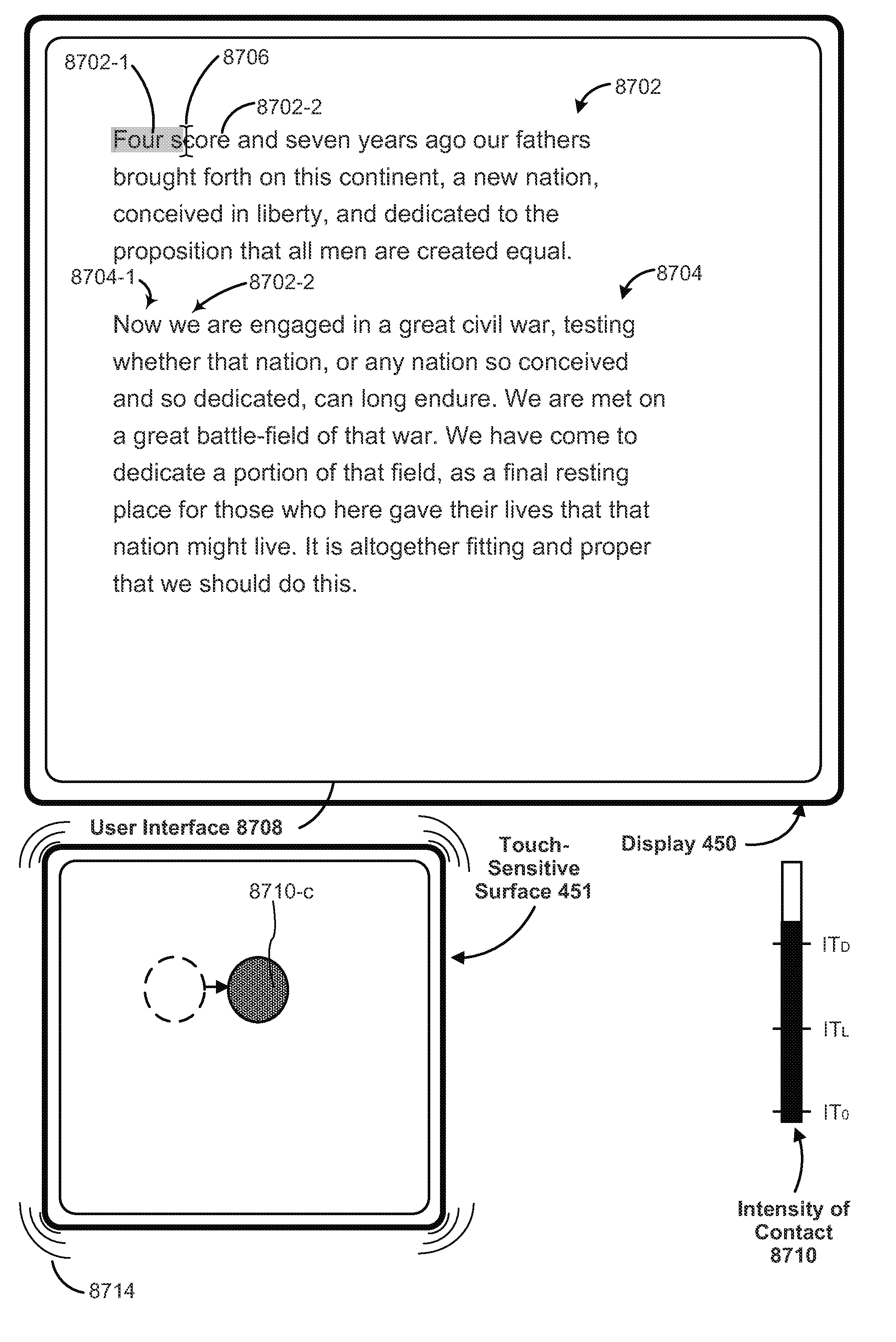
An electronic device, with a touch-sensitive surface and a display, includes one or more sensors to detect intensity of contacts with the touch-sensitive surface. The device displays, on the display, a first control for controlling a first operation. The device detects, on the touch-sensitive surface, a first input that corresponds to the first control; and in response to detecting the first input: in accordance with a determination that the first input meets first control-activation criteria but does not include a contact with a maximum intensity above a respective intensity threshold, the device performs the first operation; and in accordance with a determination that the first input includes a contact with an intensity above the respective intensity threshold, the device displays a second control for performing a second operation associated with the first operation.
Owner:APPLE INC
Device, Method, and Graphical User Interface for Forgoing Generation of Tactile Output for a Multi-Contact Gesture
ActiveUS20150149899A1Improve effectivenessImprove efficiencyInput/output for user-computer interactionPower supply for data processingGraphicsGraphical user interface
Owner:APPLE INC
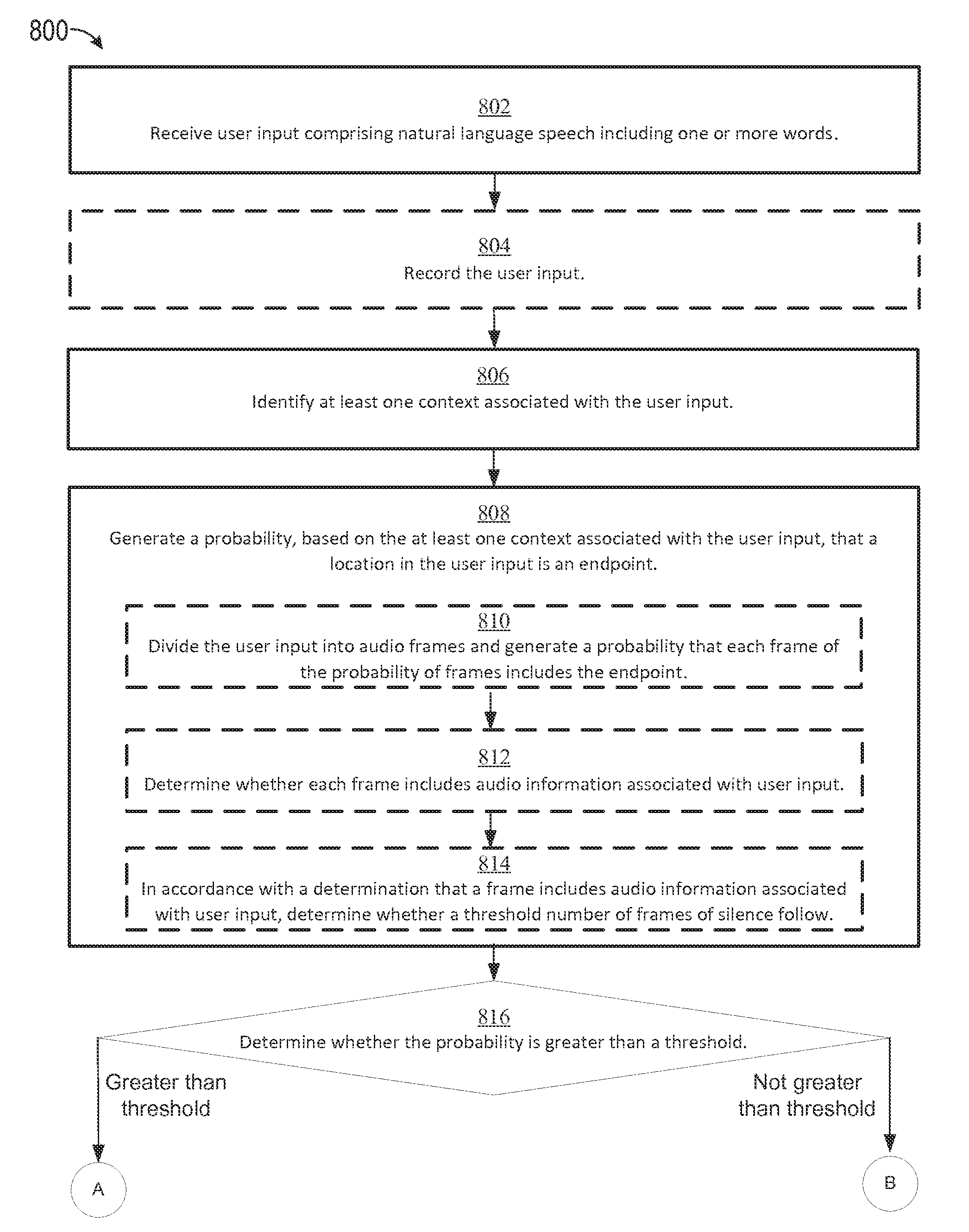
Context-based endpoint detection
ActiveUS20160358598A1Faster and efficient methodFaster and efficient and interfaceSpeech recognitionUser inputSpeech input
The present disclosure generally relates to context-based endpoint detection in user speech input. A method for identifying an endpoint of a spoken request by a user may include receiving user input of natural language speech including one or more words; identifying at least one context associated with the user input; generating a probability, based on the at least one context associated with the user input, that a location in the user input is an endpoint; determining whether the probability is greater than a threshold; and in accordance with a determination that the probability is greater than the threshold, identifying the location in the user input as the endpoint.
Owner:APPLE INC
Virtual assistant for media playback
InactiveUS20160378747A1Faster and efficient methodImprove effectivenessWeb data indexingSemantic analysisUser inputHuman–computer interaction
An exemplary method for identifying media may include receiving user input associated with a request for media, where that user input includes unstructured natural language speech including one or more words; identifying at least one context associated with the user input; causing a search for the media based on the at least one context and the user input; determining, based on the at least one context and the user input, at least one media item that satisfies the request; and in accordance with a determination that the at least one media item satisfies the request, obtaining the at least one media item.
Owner:APPLE INC
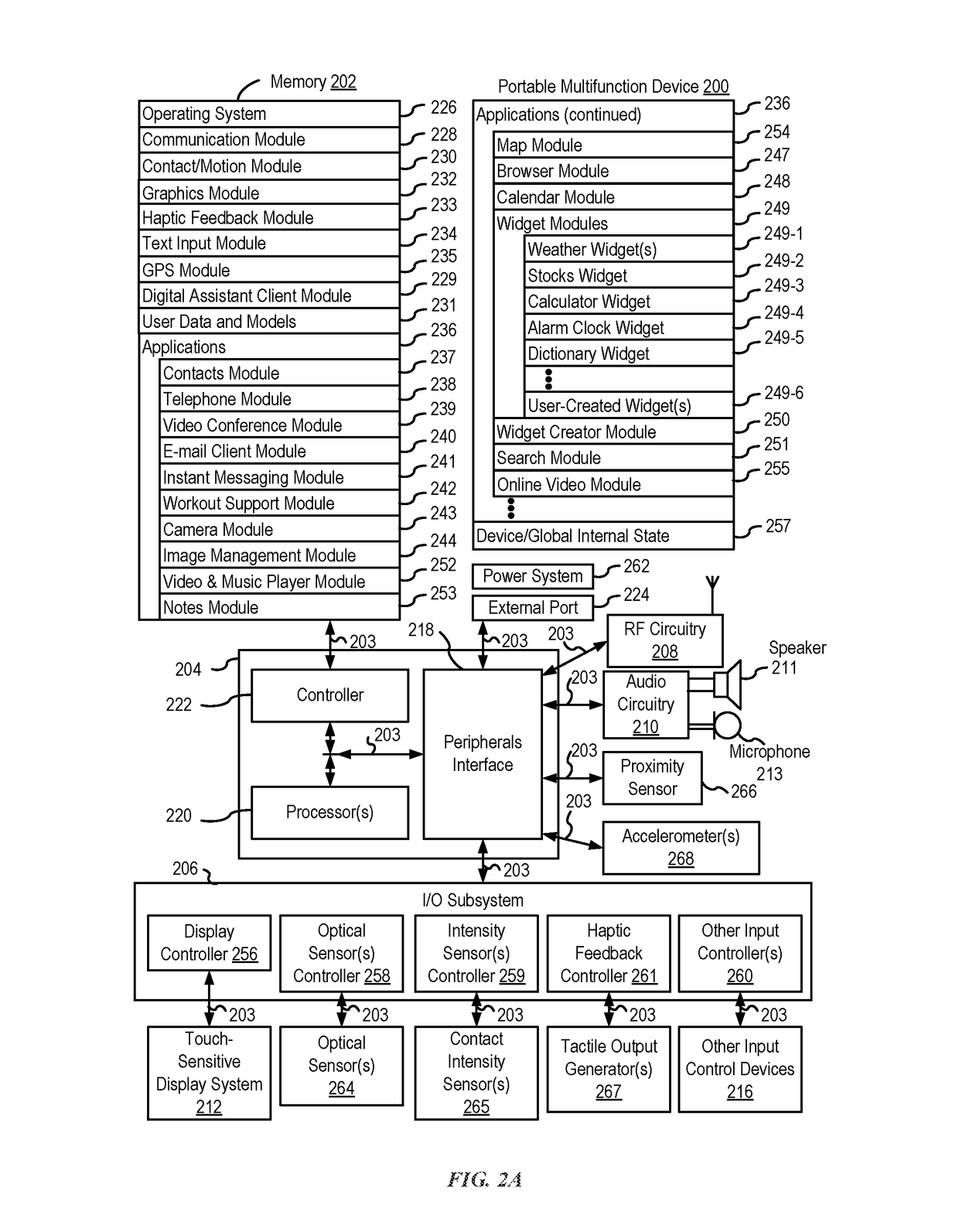
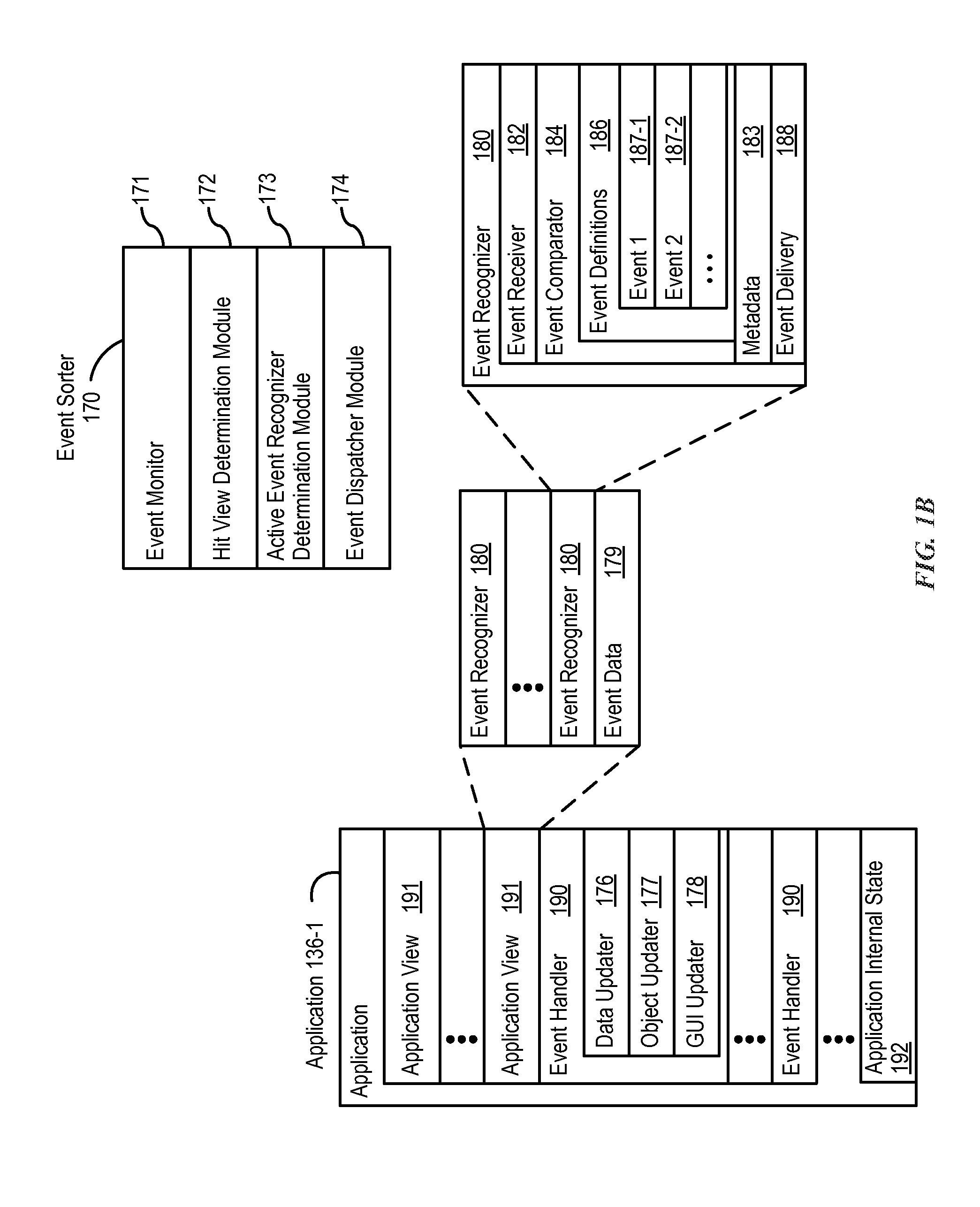
Devices, Methods, and Graphical User Interfaces for Manipulating User Interface Objects with Visual and/or Haptic Feedback
ActiveUS20170046024A1Faster and efficient methodReduce the numberInput/output for user-computer interactionNatural language data processingGraphicsGraphical user interface
A device concurrently displays a background user interface and a first version of a notification associated with a first application. The device detects a first contact at a location that corresponds to the first version of the notification. In response to the detection, and upon a determination that the contact meets application-launching criteria, the device initiates a process to launch the first application. In response to the detecting, and upon a determination that the contact meets notification-expansion criteria, where the notification-expansion criteria require that the characteristic intensity of the contact meet a preview intensity threshold, the device displays a second version of the notification, where the second version of the notification has a size larger than the first version, includes expanded notification content that is not displayed in the first version, and is overlaid on the background user interface.
Owner:APPLE INC
Methods and interfaces for home media control
ActiveUS20180335903A1Faster and efficient methodFaster and efficient and interfaceSubstation equipmentSound input/outputMedia controlsComputer hardware
The present disclosure generally relates to interfaces and techniques for media playback on one or more devices. In accordance with some embodiments, an electronic device includes a display, one or more processors, and memory. The electronic device receives user input and, in response to receiving the user input, displays, on the display, a multi-device interface that includes: one or more indicators associated with a plurality of available playback devices that are connected to the device and available to initiate playback of media from the device, and a media playback status of the plurality of available playback devices.
Owner:APPLE INC
Device, Method, and Graphical User Interface for Managing Concurrently Open Software Applications
ActiveUS20110252381A1Faster and efficient method and interfaceReduce cognitive loadExecution for user interfacesInput/output processes for data processingGraphicsGraphical user interface
Owner:APPLE INC
Unconventional virtual assistant interactions
ActiveUS20170132199A1Faster and efficient methodFaster and efficient and interfaceDigital data information retrievalNatural language data processingHuman–computer interactionProgram plan
Owner:APPLE INC
Dictation that allows editing
InactiveUS20170263248A1Faster and efficient methodFaster and efficient and interfaceNatural language data processingSpeech recognitionUser inputWorld Wide Web
An electronic device implements dictation-based editing of textual data. The device receives a natural-language user input and determines whether the natural-language user input includes a predefined editing command. If the natural-language user input includes the predefined editing command, the device modifies the textual data in accordance with the predefined editing command. If the natural-language user input does not include the predefined editing command, the device transcribes the natural-language user input and adds the transcribed text to the textual data.
Owner:APPLE INC
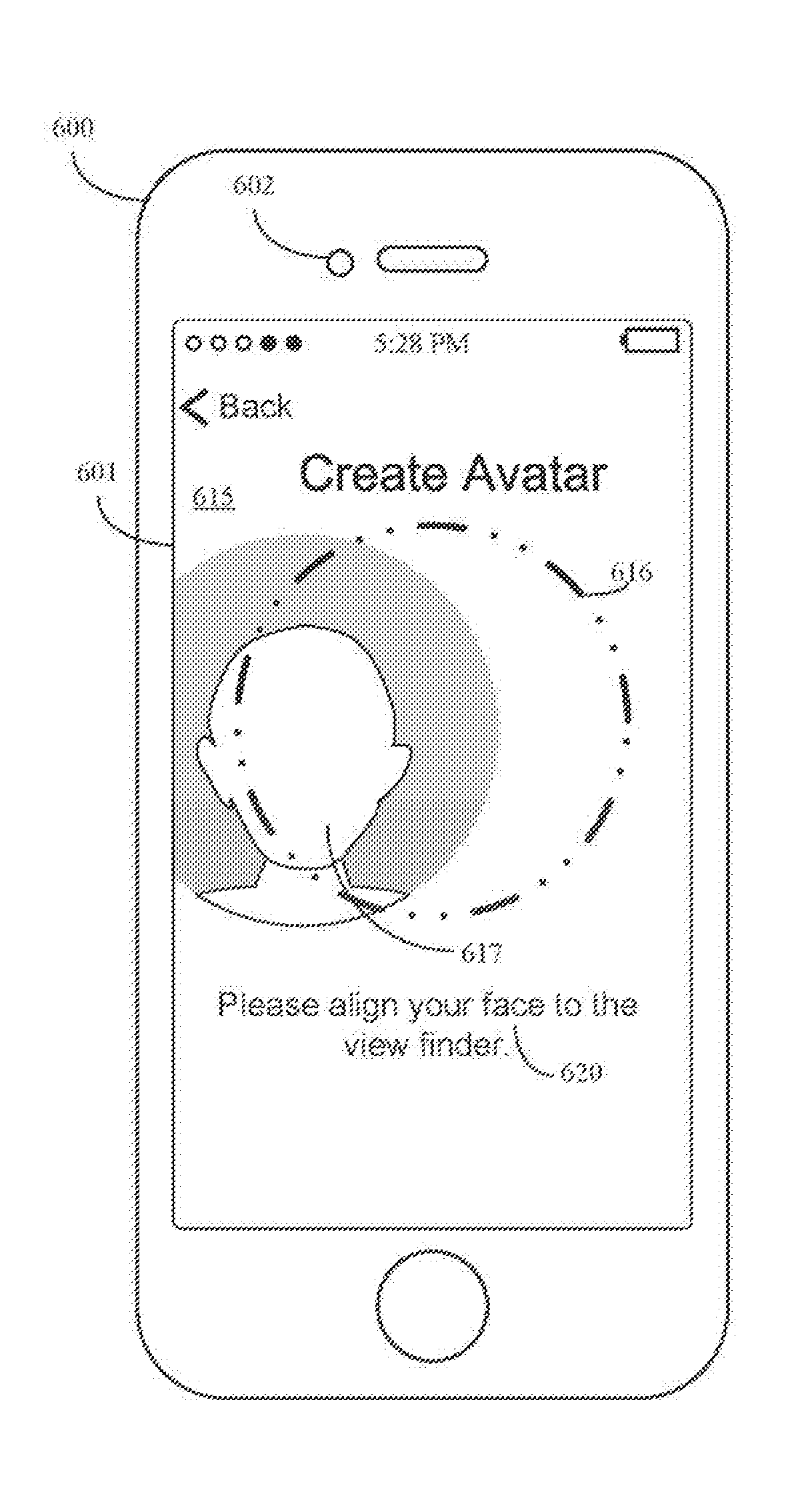
Avatar creation and editing
ActiveUS20180091732A1Faster and efficient method and interfaceReduce cognitive loadImage enhancementTelevision system detailsHuman–computer interactionImaging data
The present disclosure generally relates to creating and editing user avatars. In some examples, guidance is provided to a user while capturing image data for use in generating a user-specific avatar. In some examples, a user interface allows a user to intuitively customize a user avatar. In some examples, avatars are generated for a messaging session based on an avatar model for a user of the messaging application. In some examples, an avatar editing interface updates a user avatar in response to gestures and based on the type of gesture and the avatar feature that is selected for editing.
Owner:APPLE INC
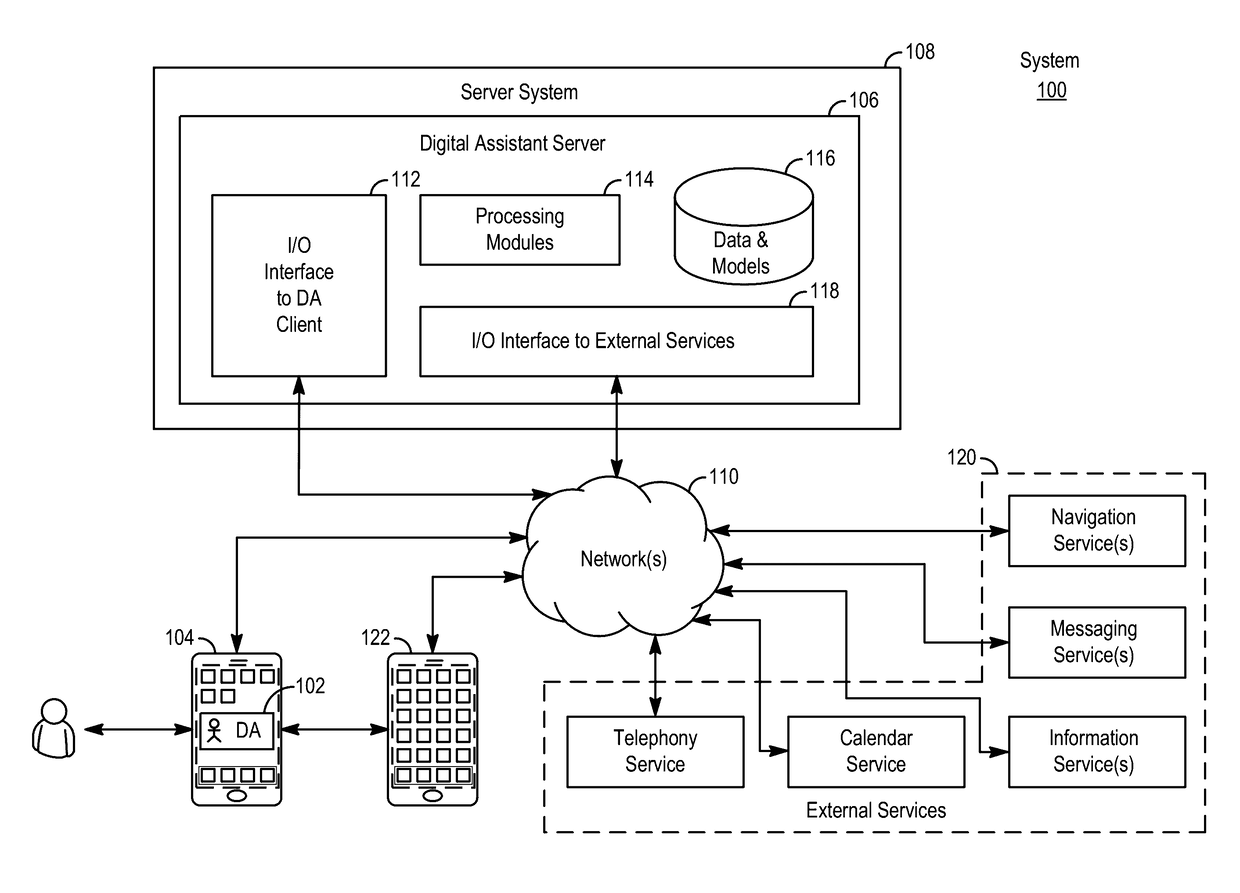
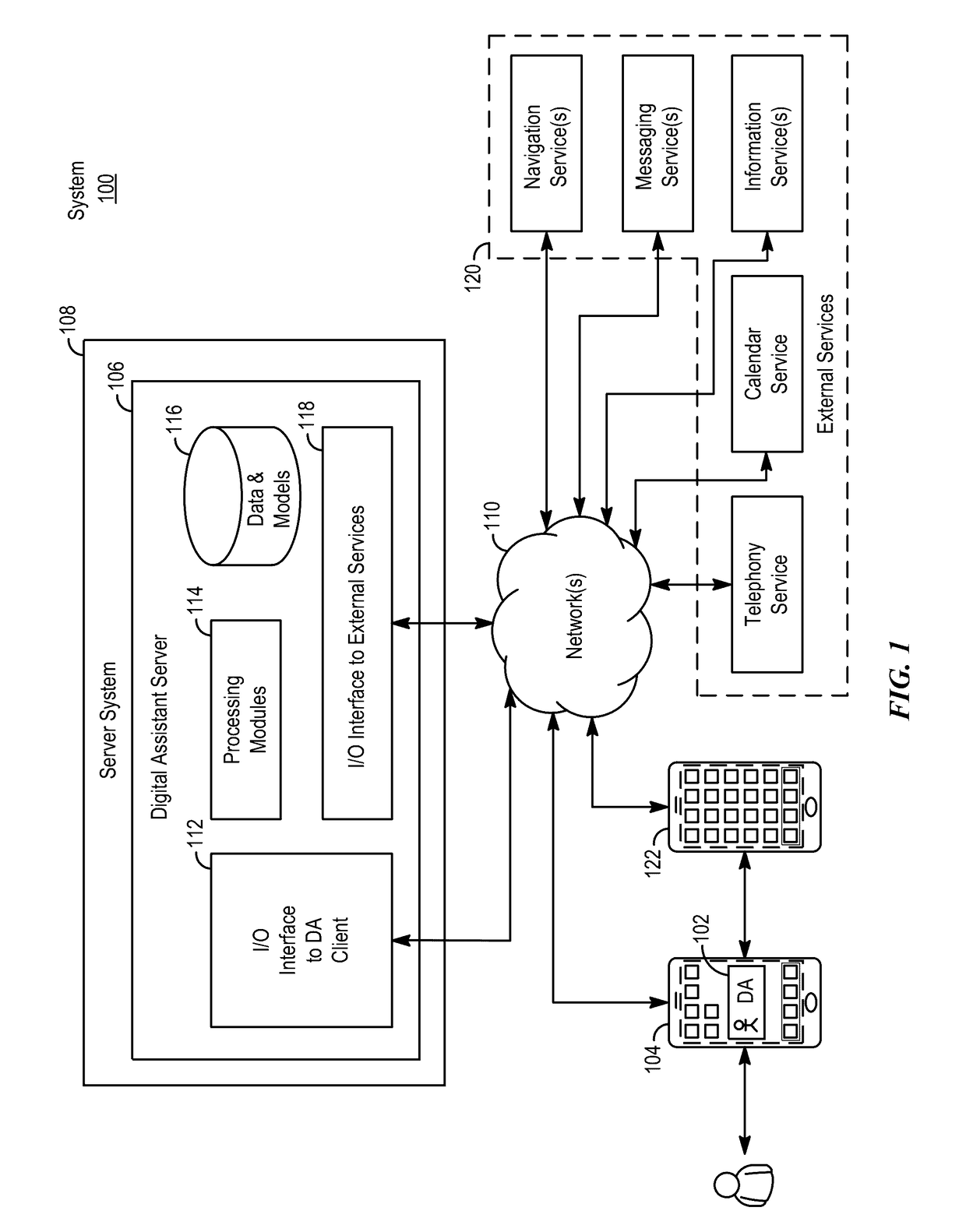
Zero latency digital assistant
ActiveUS20170068513A1Faster and efficient methodFaster and efficient and interfaceInput/output to record carriersDevices with voice recognitionUser inputHuman–computer interaction
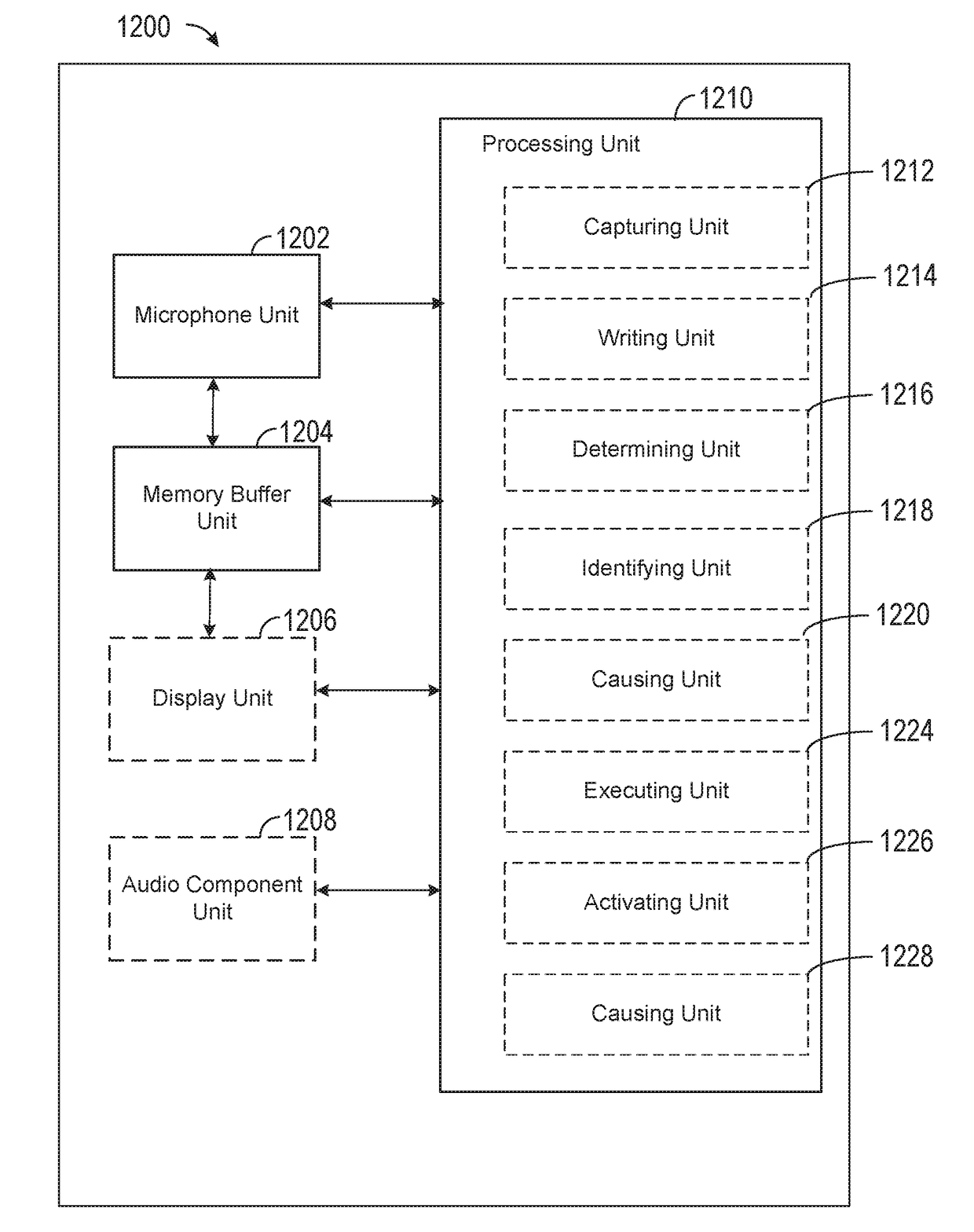
An electronic device can implement a zero-latency digital assistant by capturing audio input from a microphone and using a first processor to write audio data representing the captured audio input to a memory buffer. In response to detecting a user input while capturing the audio input, the device can determine whether the user input meets a predetermined criteria. If the user input meets the criteria, the device can use a second processor to identify and execute a task based on at least a portion of the contents of the memory buffer.
Owner:APPLE INC
Distributed personal assistant
ActiveUS20170068550A1Faster and efficient methodReduce cognitive loadProgram initiation/switchingArtificial lifeReal-time computing
An exemplary method for using a virtual assistant may include, at an electronic device configured to transmit and receive data, receiving a user request for a service from a virtual assistant; determining at least one task to perform in response to the user request; estimating at least one performance characteristic for completion of the at least one task with the electronic device, based on at least one heuristic; based on the estimating, determining whether to execute the at least one task at the electronic device; in accordance with a determination to execute the at least one task at the electronic device, causing the execution of the at least one task at the electronic device; in accordance with a determination to execute the at least one task outside the electronic device: generating executable code for carrying out the least one task; and transmitting the executable code from the electronic device.
Owner:APPLE INC
Virtual assistant for media playback
ActiveUS20190220246A1Faster and efficient methodReduce cognitive loadSemantic analysisMetadata multimedia retrievalUser inputHuman–computer interaction
An exemplary method for identifying media may include receiving user input associated with a request for media, where that user input includes unstructured natural language speech including one or more words; identifying at least one context associated with the user input; causing a search for the media based on the at least one context and the user input; determining, based on the at least one context and the user input, at least one media item that satisfies the request; and in accordance with a determination that the at least one media item satisfies the request, obtaining the at least one media item.
Owner:APPLE INC
Method and apparatus for allocating processor resources in a logically partitioned computer system
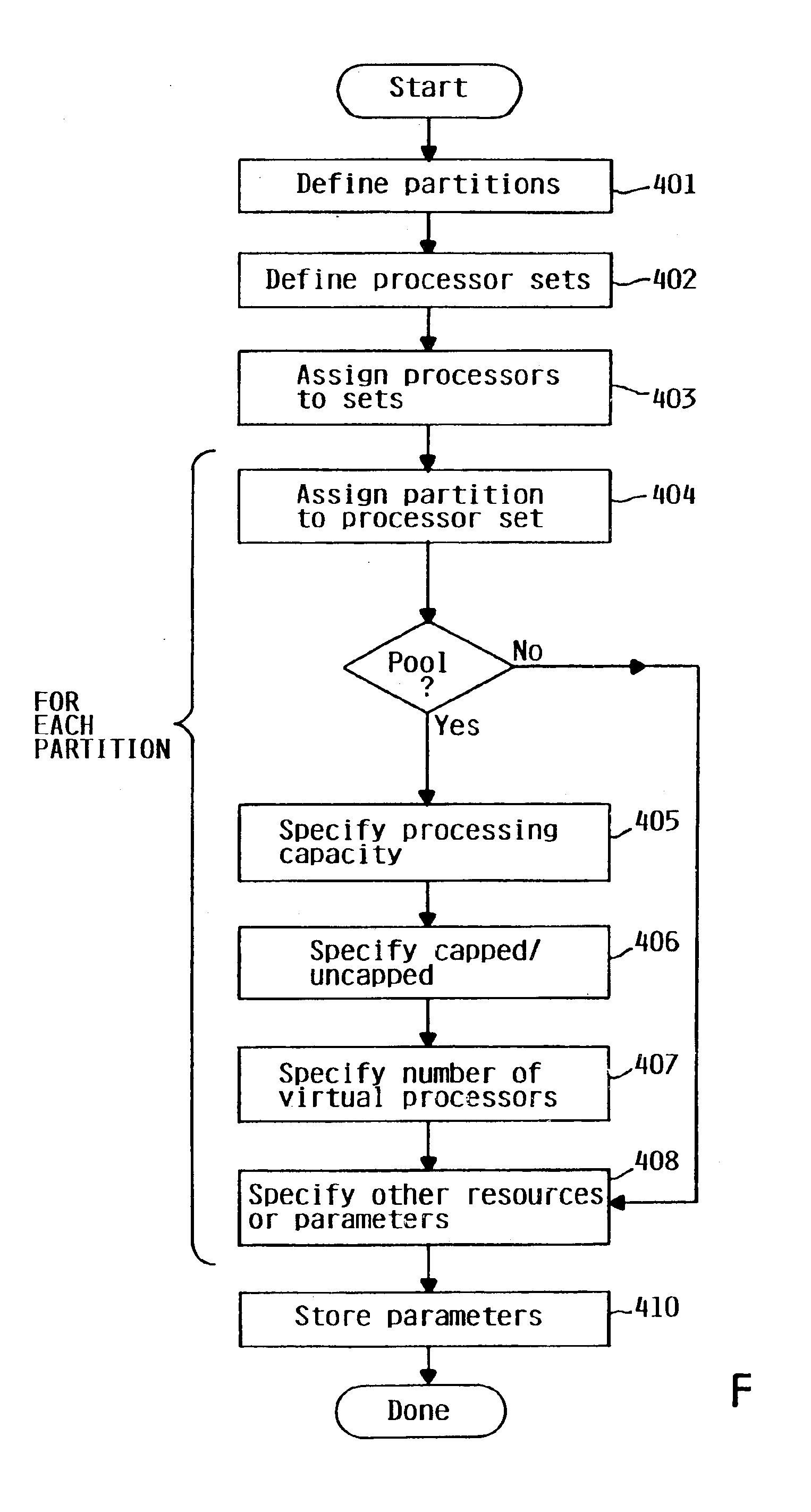
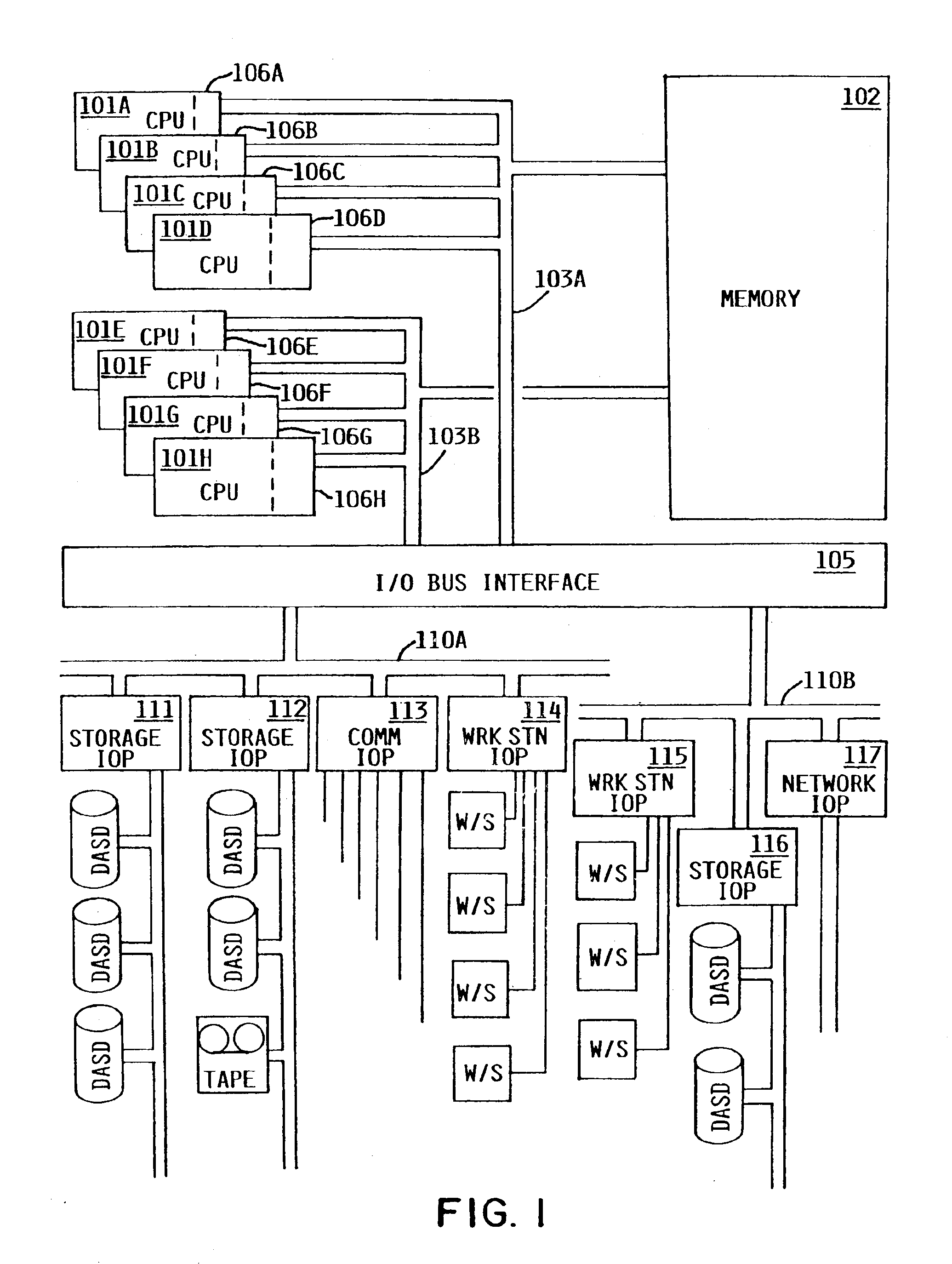
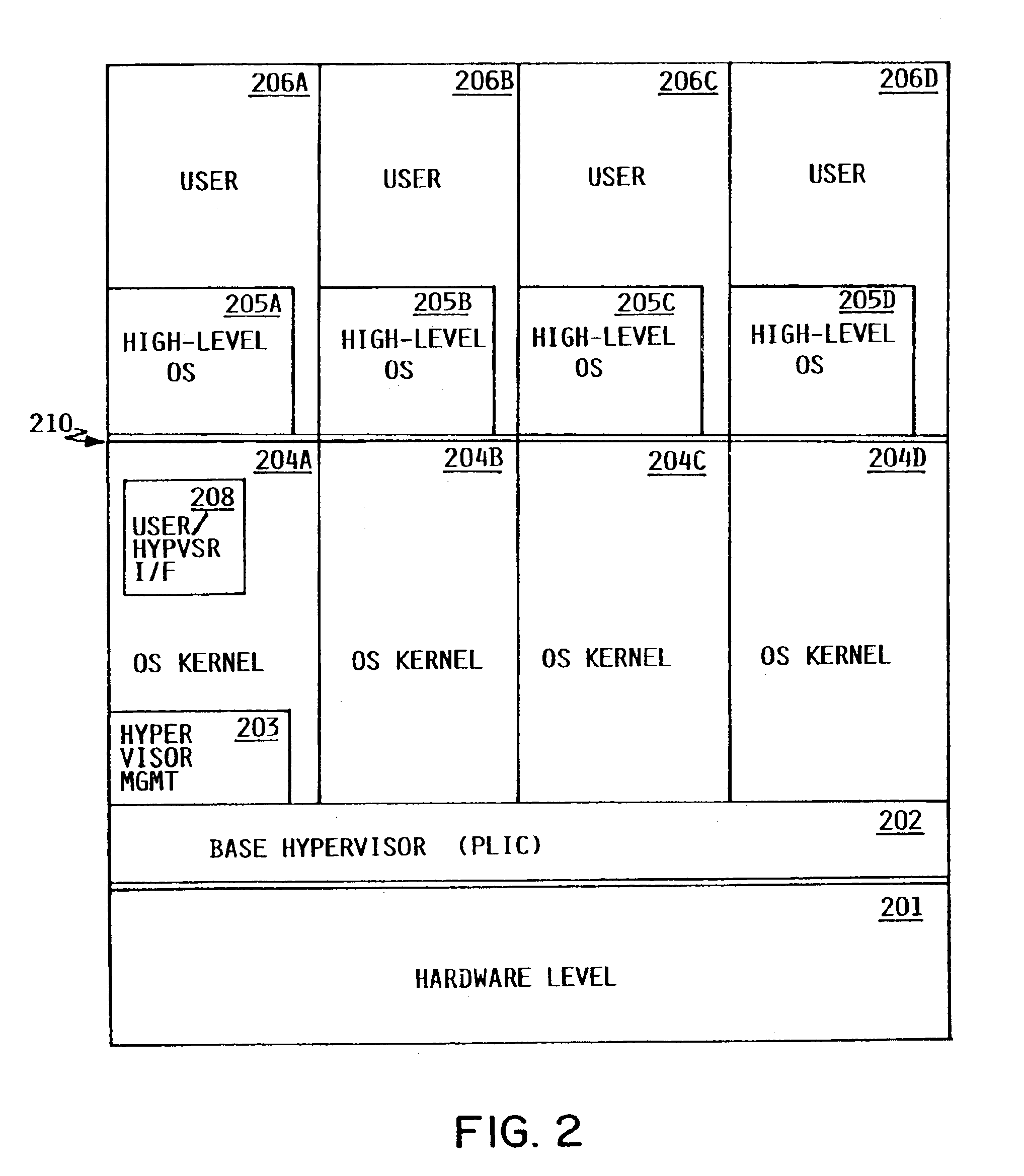
InactiveUS6957435B2Efficient interfaceResource allocationGeneral purpose stored program computerComputer architectureComputerized system
A processor allocation mechanism for a logically partitionable computer system allows an administrator to specify processing capability allocable to each partition as an equivalent number of processors, where the processing capability may be specified as a non-integer value. This processing capability value is unaffected by changes to the processing capability values of other partitions. The administrator may designate multiple sets of processors, assigning each physical processor of the system to a respective processor set. Each logical partition is constrained to execute in an assigned processor set, which may be shared by more than one partition. Preferably, the administrator may designate a logical partition as either capped, meaning that a partition can not use excess idle capacity of the processors, or uncapped, meaning that it can.
Owner:IBM CORP
User interface for camera effects
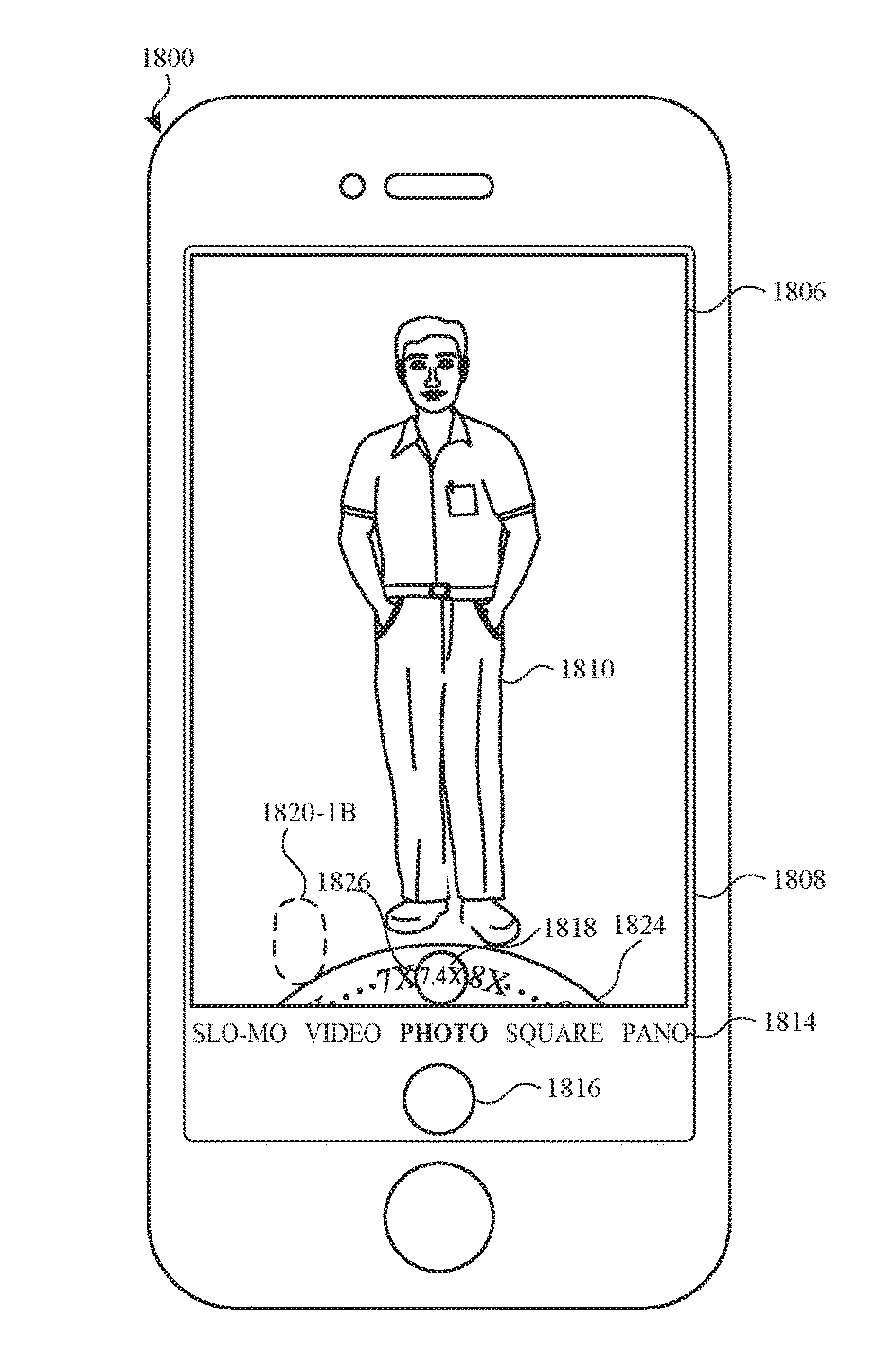
ActiveUS9716825B1Faster and efficient methodFaster and efficient and interfaceTelevision system detailsImage enhancementDigital zoomMagnification
The present disclosure generally relates to user interfaces. In some examples, the electronic device transitions between user interfaces for capturing photos based on data received from a first camera and a second camera. In some examples, the electronic device provides enhanced zooming capabilities that result in visual pleasing results for a displayed digital viewfinder and for captured videos. In some examples, the electronic device provides user interfaces for transitioning a digital viewfinder between a first camera with an applied digital zoom to a second camera with no digital zoom. In some examples, the electronic device prepares to capture media at various magnification levels. In some examples, the electronic device enhanced capabilities for navigating through a plurality of values.
Owner:APPLE INC
User interface for manipulating user interface objects with magnetic properties
ActiveUS20150370529A1Improve effectivenessImprove efficiencyInput/output for user-computer interactionCathode-ray tube indicatorsDisplay deviceHuman–computer interaction
The present disclosure relates to user interfaces for manipulating user interface objects. A device, including a display and a rotatable input mechanism, is described in relation to manipulating user interface objects. In some examples, the manipulation of the object is a scroll, zoom, or rotate of the object. In other examples, objects are selected in accordance with simulated magnetic properties.
Owner:APPLE INC
Proactive assistant with memory assistance
InactiveUS20170091612A1Faster and efficient methodFaster and efficient and interfaceNatural language translationArtificial lifeArray data structureDatabase
A non-transitory computer-readable storage medium stores one or more programs including instructions, which when executed by an electronic device of a user, cause the electronic device to generate at least one experiential data structure accessible to a virtual assistant; modify at least one experiential data structure with one or more annotations associated with the experiential data structure, utilizing the virtual assistant; store at least one experiential data structure; receive a natural-language user request for service from the virtual assistant, and output information responsive to the user request using at least one experiential data structure. The experiential data structure is a data structure that includes an organized set of data associated with at least one of the user and the electronic device at a particular point in time.
Owner:APPLE INC
User interface for manipulating user interface objects with magnetic properties
ActiveUS10001817B2Reduce cognitive loadExtension of timeDetails for portable computersSound input/outputDisplay deviceHuman–computer interaction
The present disclosure relates to user interfaces for manipulating user interface objects. A device, including a display and a rotatable input mechanism, is described in relation to manipulating user interface objects. In some examples, the manipulation of the object is a scroll, zoom, or rotate of the object. In other examples, objects are selected in accordance with simulated magnetic properties.
Owner:APPLE INC
Activity and workout updates
ActiveUS20170354845A1Faster and efficient methodFaster and efficient and interfacePhysical therapies and activitiesHealth-index calculationMulti segmentHuman–computer interaction
The present disclosure generally relates to navigating, viewing, and sharing activity and workout data and interacting with workout and / or activity applications. In some examples, scrolling of activity data is based on the content being displayed. In some examples, friends' activity data may be viewed. In some examples, a notification and workout data for a friend's completed workout is received and displayed. In some example, the activity data received from friends is viewed and managed. In some examples, workout data for a multi-segment workout is displayed in a three-dimensional stack on a map. In some examples, a workout application operates in a limited mode until a touch input is received with a characteristic intensity that is greater than a threshold intensity.
Owner:APPLE INC
User interface for loyalty accounts and private label accounts for a wearable device
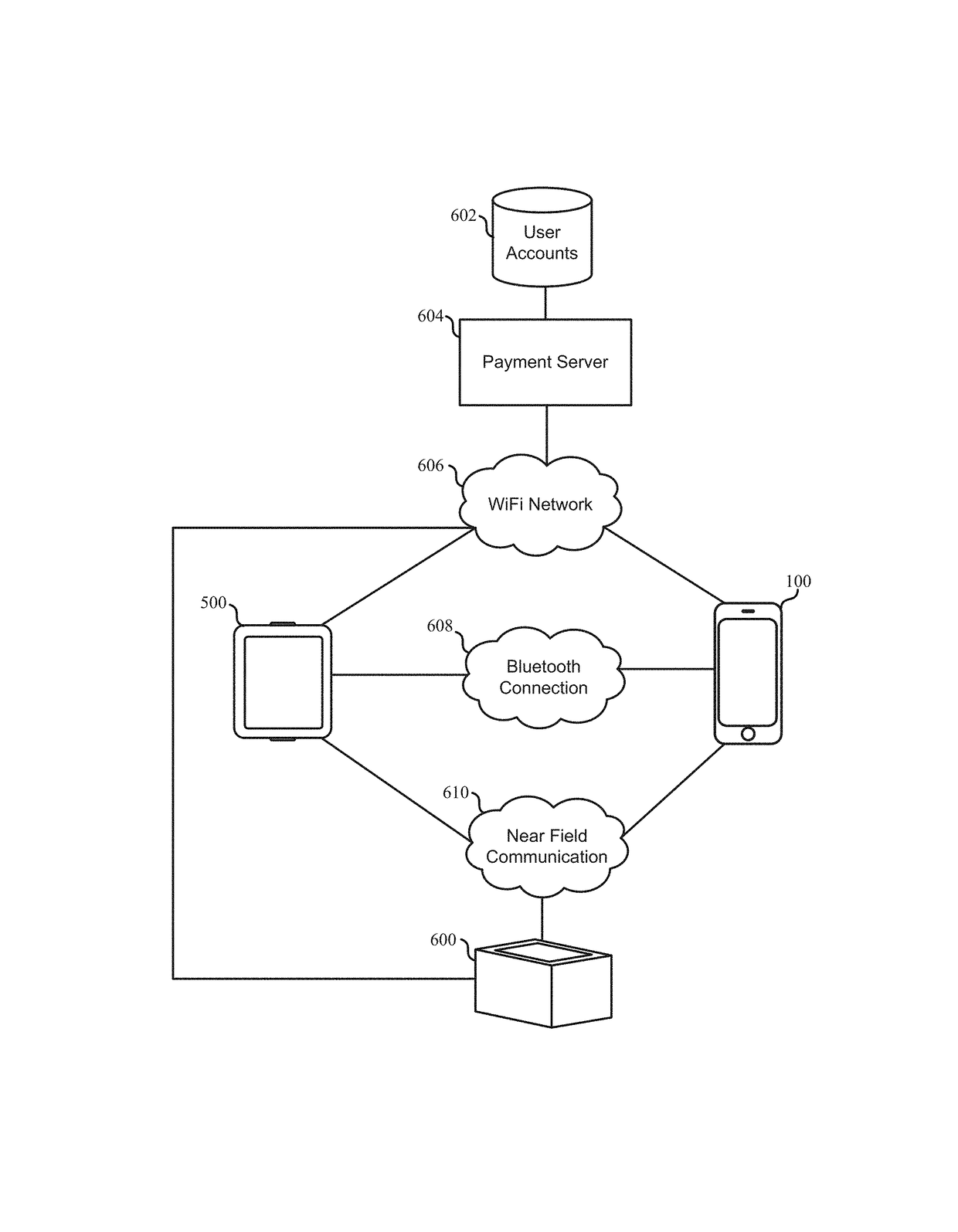
ActiveUS20160358180A1Improve effectivenessImprove efficiencyApparatus for meter-controlled dispensingPoint-of-sale network systemsHuman–computer interactionWearable Electronic Device
The present disclosure generally relates to the use of loyalty accounts, private label payment accounts, and general payment accounts using a wearable electronic device with an electronic wallet. Various accounts are linked to the electronic device. In some examples, the electronic device is NFC-enabled. The electronic device may be used to provide loyalty account information and payment account information to a payment terminal, such as an NFC-enabled payment terminal.
Owner:APPLE INC
Condition-based activation of a user interface
InactiveUS20160357354A1Improve effectivenessImprove efficiencyAcoustic time signalsDigital data processing detailsDisplay deviceOperation mode
Owner:APPLE INC
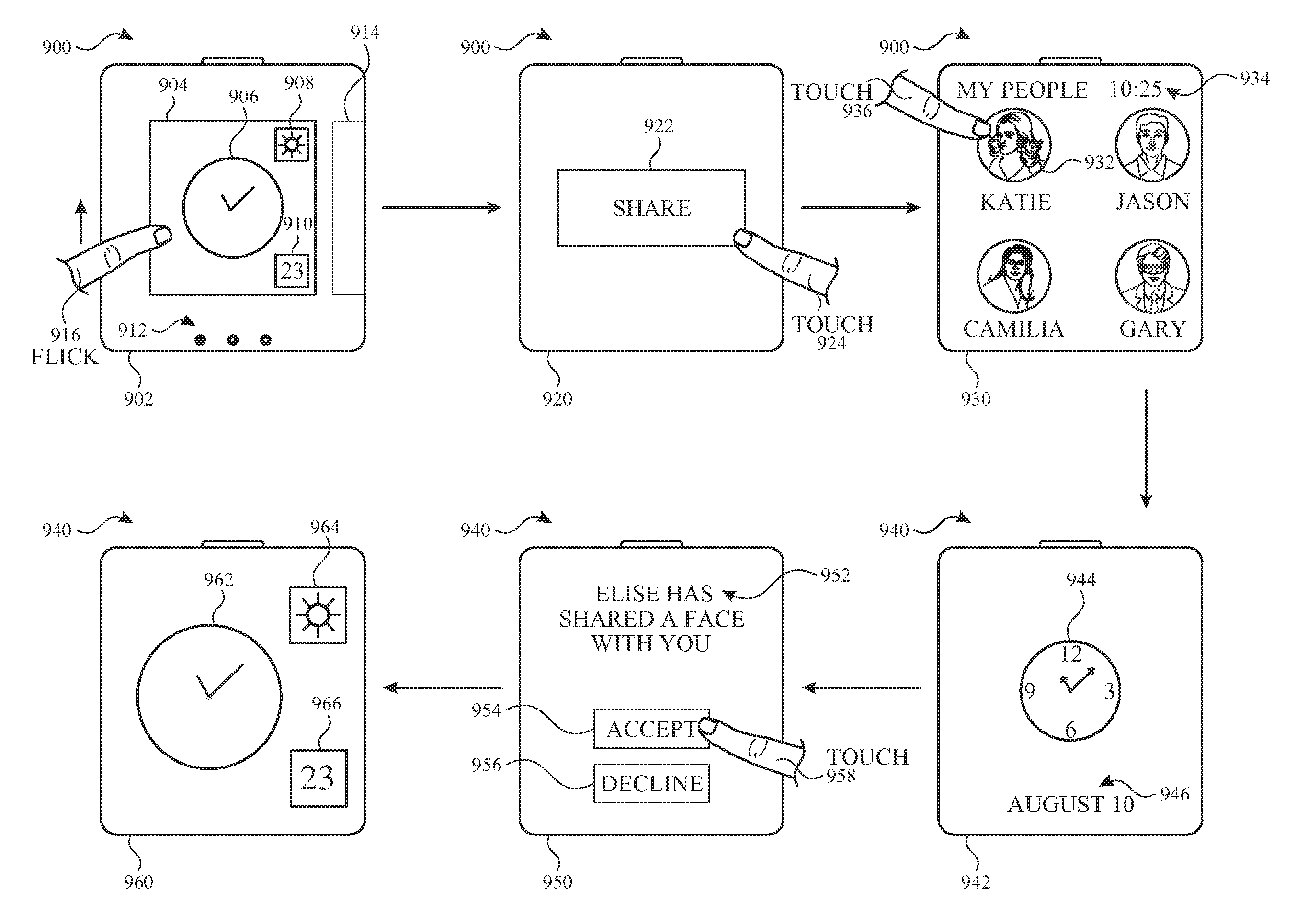
Sharing user-configurable graphical constructs
InactiveUS20160261675A1Faster and efficient methodReduce cognitive loadService provisioningInformation formatGraphicsContext specific
Methods for sharing user-configurable graphical constructs, e.g., for use with a portable multifunction device, are disclosed. The methods described herein allow for sharing user-configurable graphical constructs, such as context-specific user interfaces and emoji graphical objects that contain independently configurable graphical elements. Further disclosed are non-transitory computer-readable storage media, systems, and devices configured to perform the methods described herein.
Owner:APPLE INC
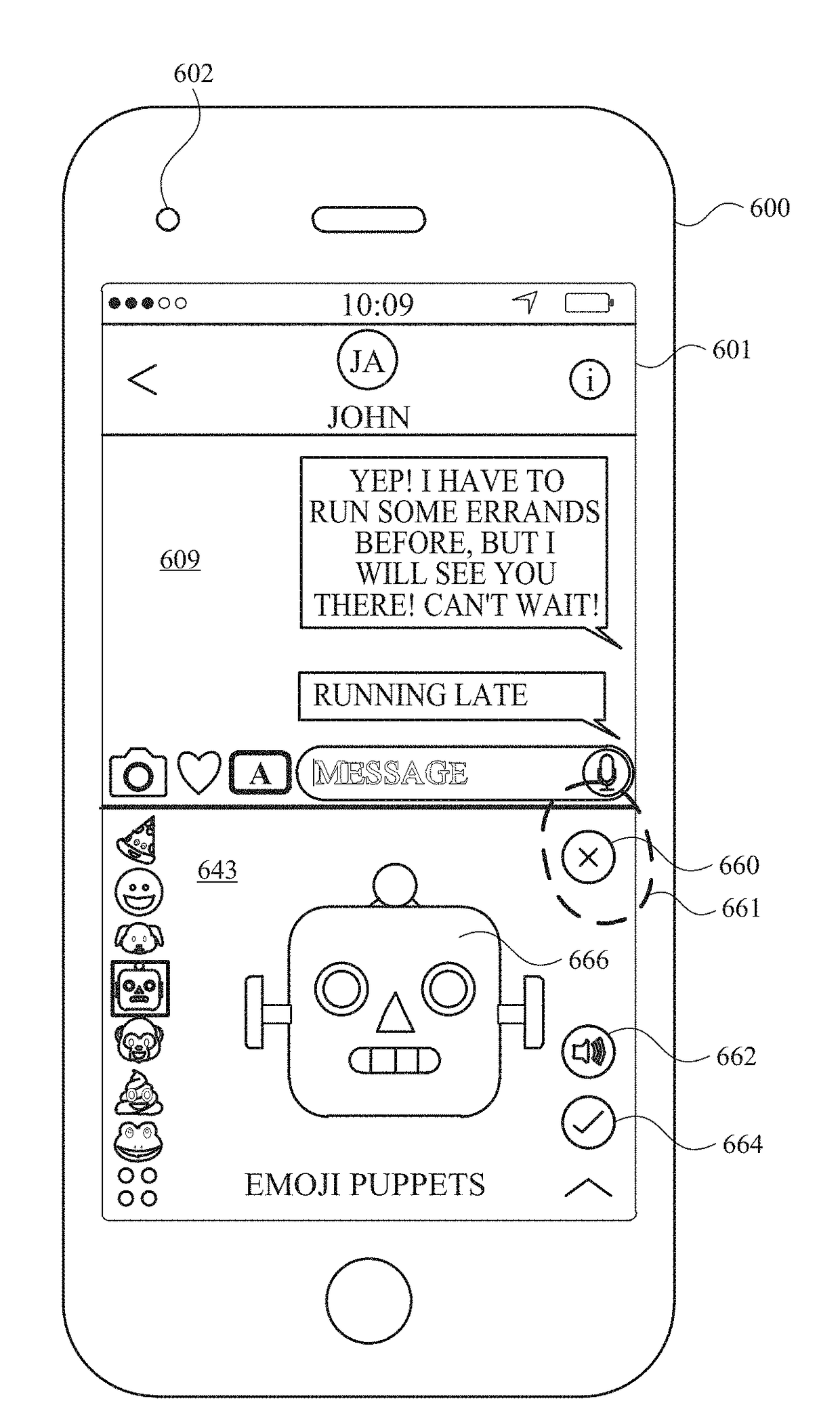
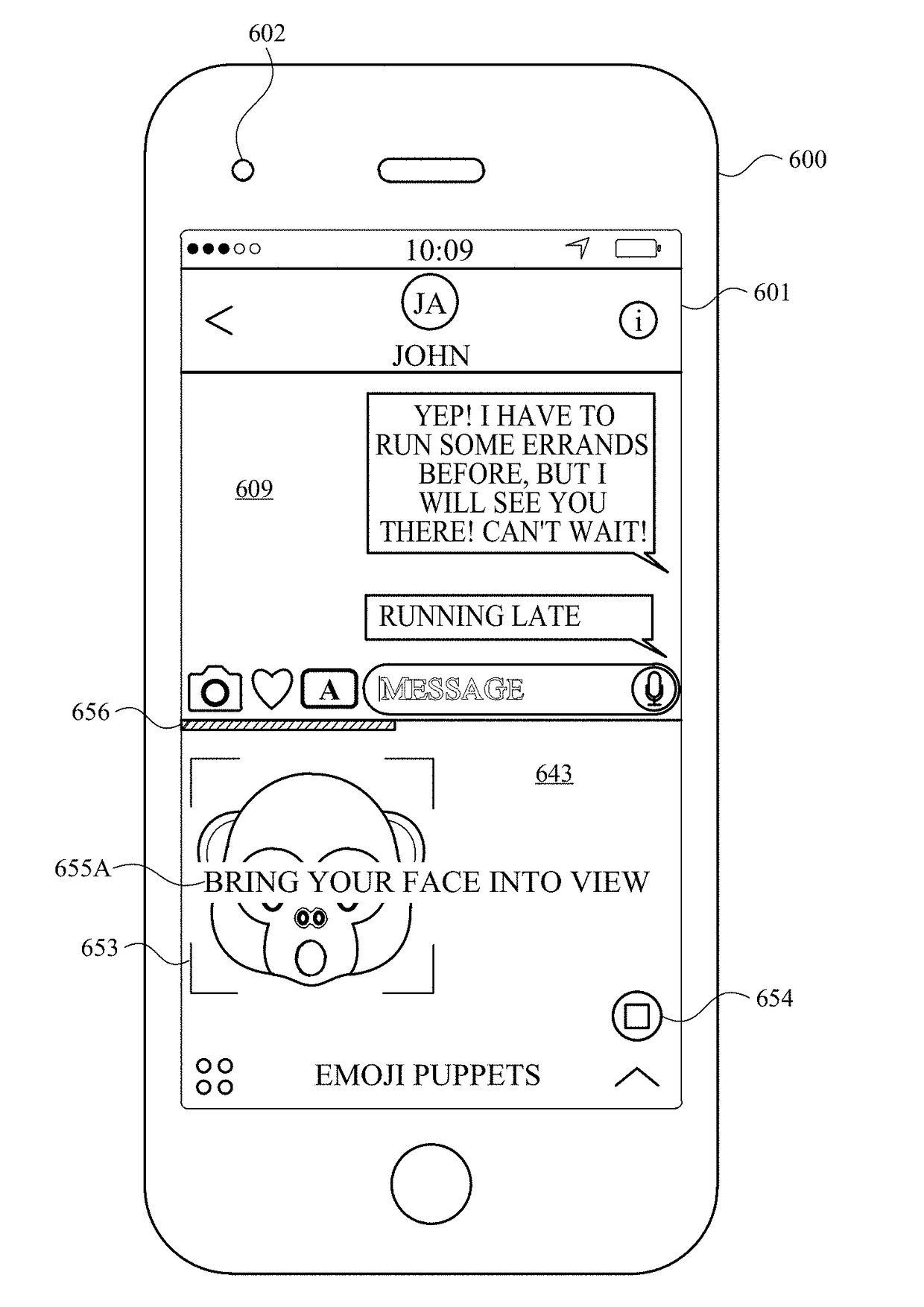
Emoji recording and sending
ActiveUS20180336715A1Faster and efficient methodFaster and efficient and interfaceTelevision system detailsSubstation equipmentComputer graphics (images)Ophthalmology
The present disclosure generally relates to generating and modifying virtual avatars. An electronic device having a camera and a display apparatus displays a virtual avatar that changes appearance in response to changes in a face in a field of view of the camera. In response to detecting changes in one or more physical features of the face in the field of view of the camera, the electronic device modifies one or more features of the virtual avatar.
Owner:APPLE INC
Method and apparatus for managing and accessing depth data in a computer graphics system
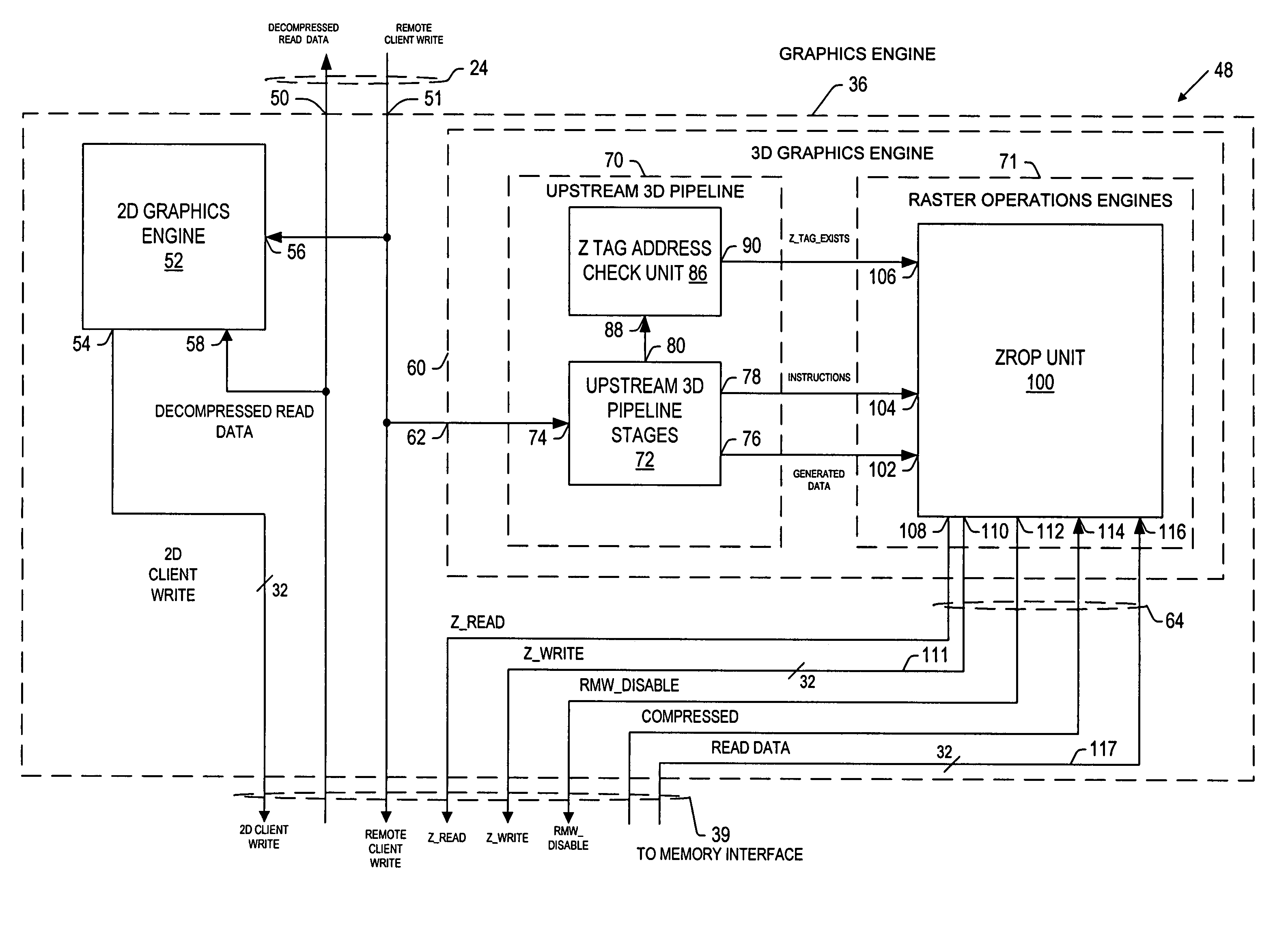
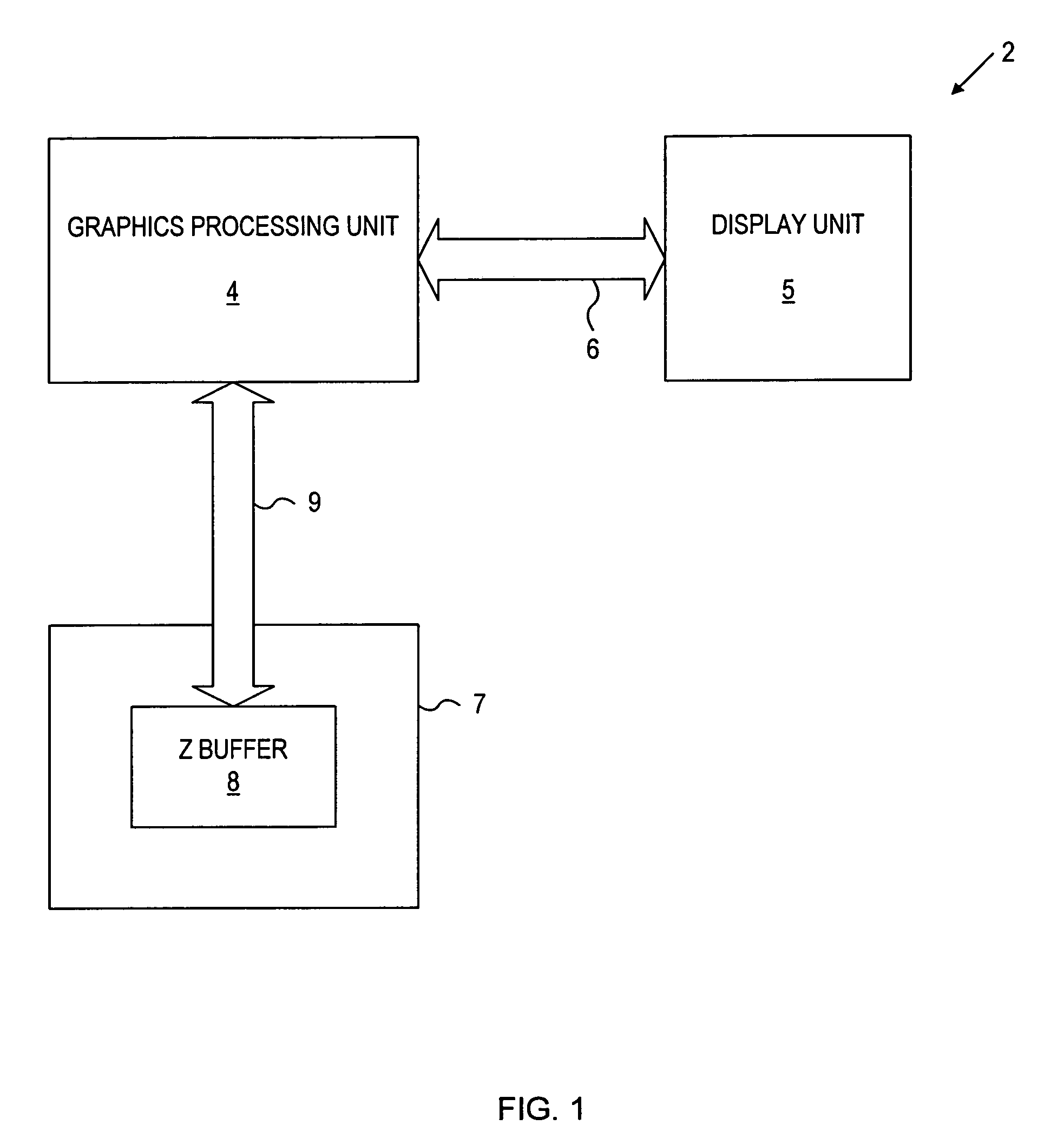
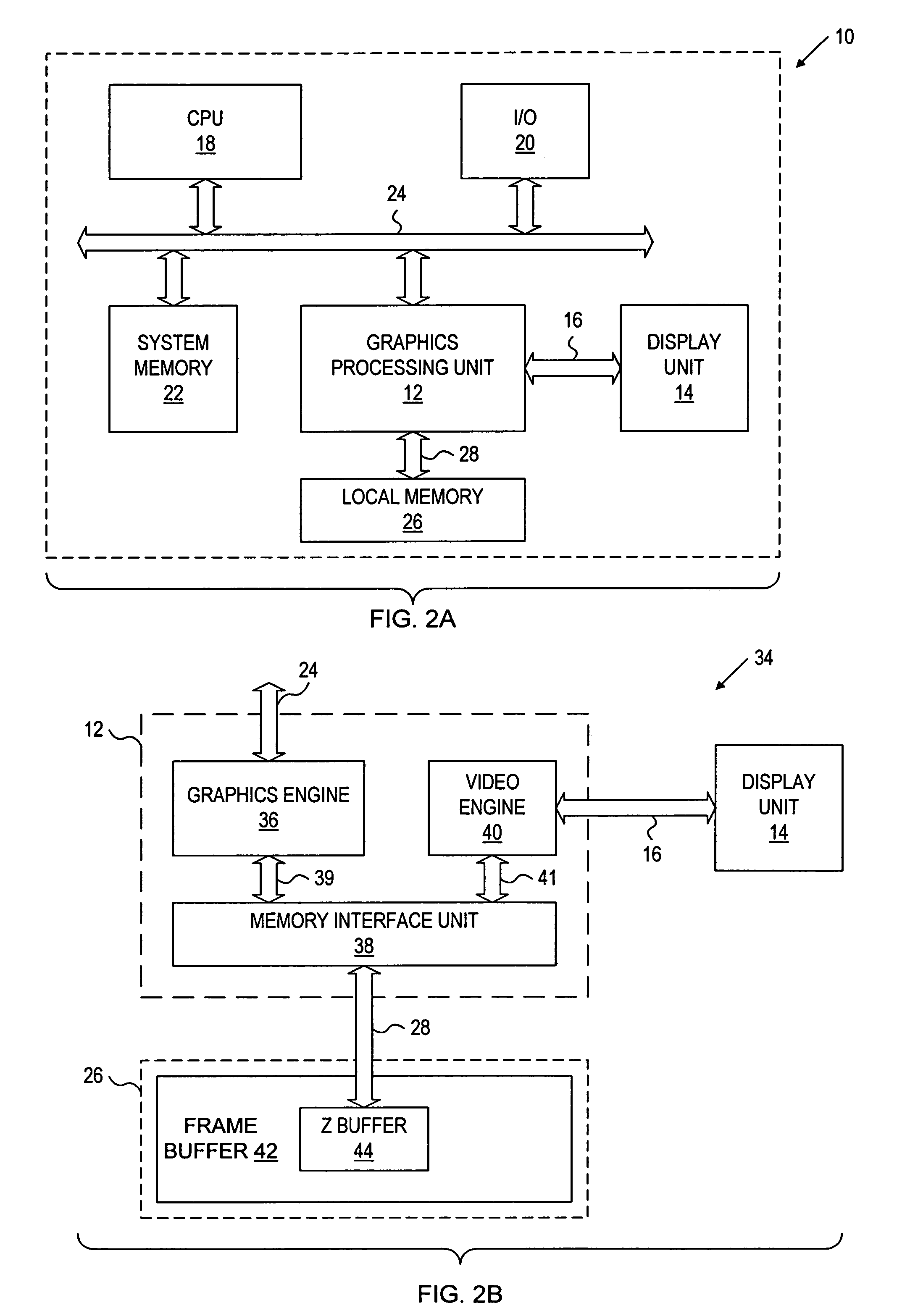
A computer graphics system provides for processing image data including Z data for use in displaying three-dimensional images on a display unit. The system includes: a depth buffer providing for temporary storage of Z data; and a graphics processing unit having a graphics engine for generating image data including Z data, and a memory interface unit communicatively coupled to the graphics engine and communicatively coupled to the depth buffer via a depth buffer interface. The graphics processing unit is operative to compress at least a portion of the generated Z data, to write the compressed portion of Z data to the depth buffer via the depth buffer interface in a compressed format, to read portions of compressed Z data from the depth buffer via the depth buffer interface, and to decompress the compressed Z data read from the buffer. An advantage of the present invention is that effective Z data bandwidth through the depth buffer interface is maximized in order to facilitate fast depth buffer access operations.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
User interface for manipulating user interface objects with magnetic properties
InactiveUS20160170624A1Improve effectivenessImprove efficiencyTime-pieces with integrated devicesDetails for portable computersDisplay deviceHuman–computer interaction
The present disclosure relates to user interfaces for manipulating user interface objects. A device, including a display and a rotatable input mechanism, is described in relation to manipulating user interface objects. In some examples, the manipulation of the object is a scroll, zoom, or rotate of the object. In other examples, objects are selected in accordance with simulated magnetic properties.
Owner:APPLE INC
Emoji recording and sending
ActiveUS20180335930A1Faster and efficient method and interfaceIncreased efficiency and effectiveness and user satisfactionTelevision system detailsColor television detailsElectronic equipmentField of view
The present disclosure generally relates to generating and modifying virtual avatars. An electronic device having a camera and a display apparatus displays a virtual avatar that changes appearance in response to changes in a face in a field of view of the camera. In response to detecting changes in one or more physical features of the face in the field of view of the camera, the electronic device modifies one or more features of the virtual avatar.
Owner:APPLE INC
User interfaces for stored-value accounts
ActiveUS9842330B1Faster and efficient methodFaster and efficient and interfaceFinanceCoin/paper handlersPaymentUser input
In some examples, an account is provisioned onto an electronic device. In some examples, the device receives a value to fund the account provisioned on the electronic device. In some examples, the electronic device transacts with a contactless transaction terminal using the provisioned account and displays an indication of the transaction. In some examples, the electronic device transmits information corresponding to the provisioned account without checking for authentication. In some examples, the device receives user input initiating a process for moving the account from a first device to a second device. In some examples, the device receives account payment credentials from a second device when a set of payment criteria are met.
Owner:APPLE INC
Creative camera
ActiveUS10270983B1Faster and efficient methodFaster and efficient and interfaceImage enhancementTelevision system detailsComputer visionVisual perception
Owner:APPLE INC
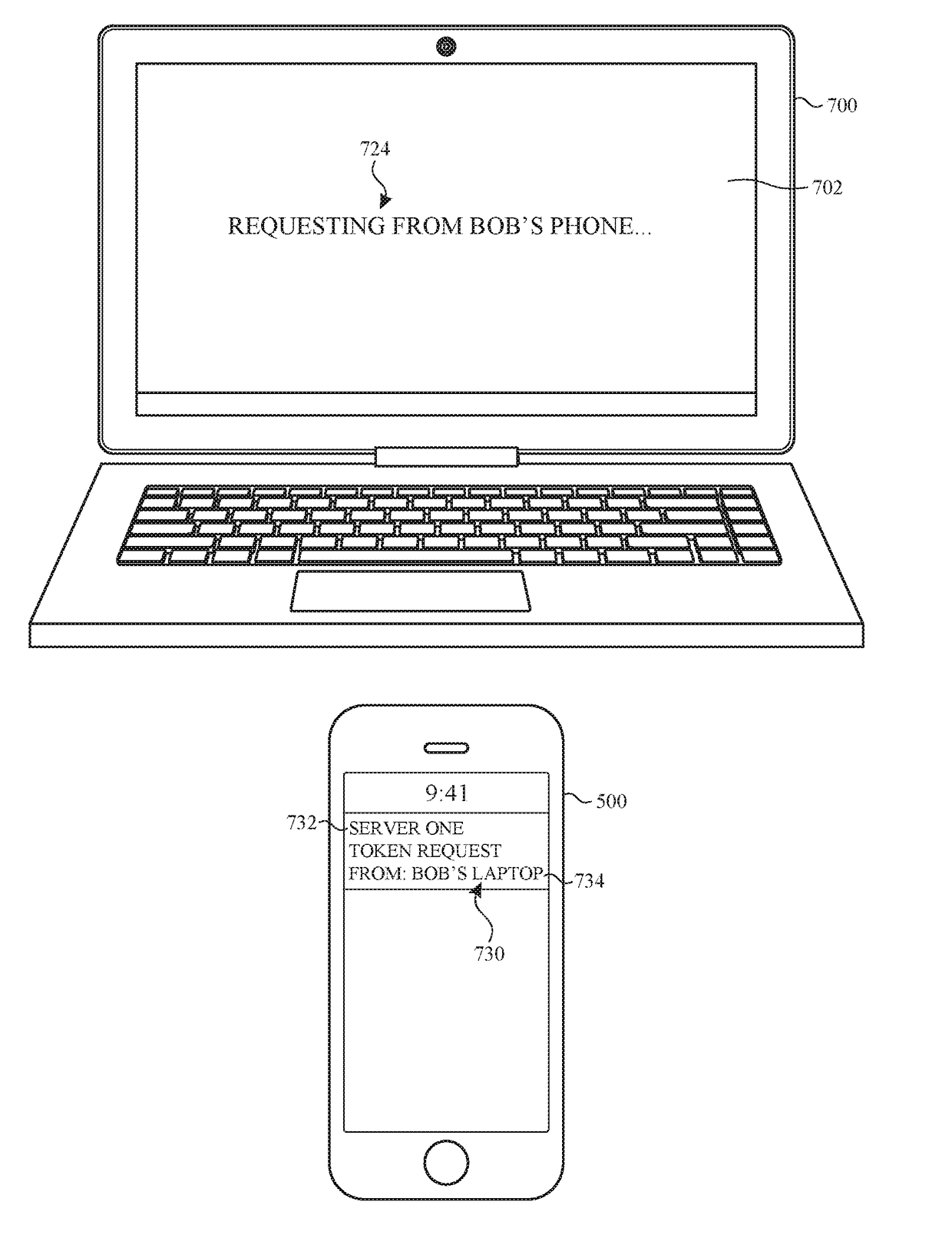
User interface for a device requesting remote authorization
ActiveUS20170339151A1Faster and efficient methodImprove effectivenessUser identity/authority verificationPayment architectureComputer hardwareNetwork connection
The present disclosure generally relates to techniques for managing a remote authorization to proceed with an action, such as creating a secure network connection. In some examples, a requesting device receives selection of one or more options. The requesting device transmits a request to proceed with an action to an authenticating device. The authenticating device concurrently displays an indication of the request to proceed with the action, information about the selected one or more options, and an indication of the requesting device. The authenticating device receives authorization to proceed with the action and transmits a response to the requesting device regarding the request to proceed with the action.
Owner:APPLE INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com