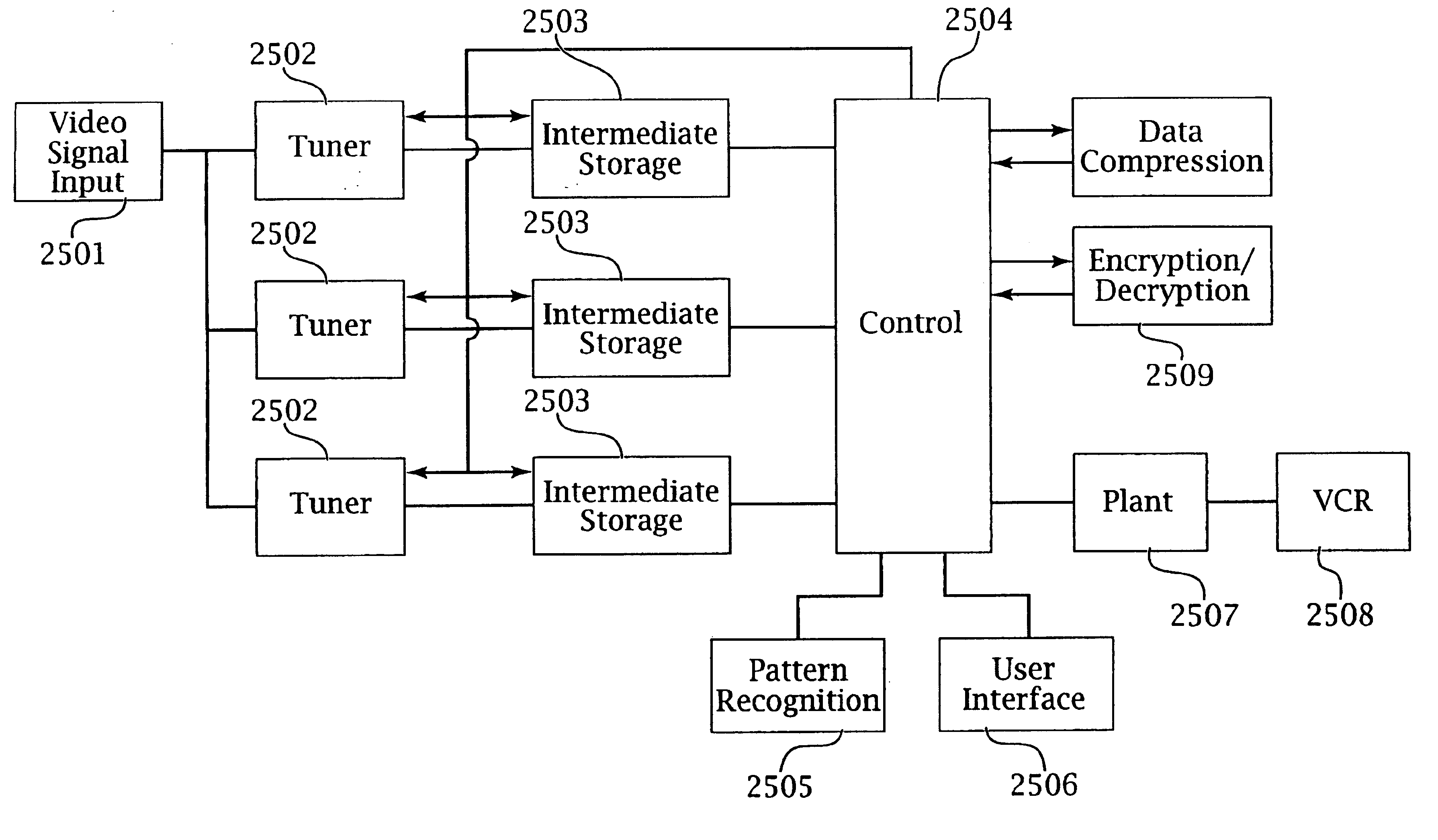
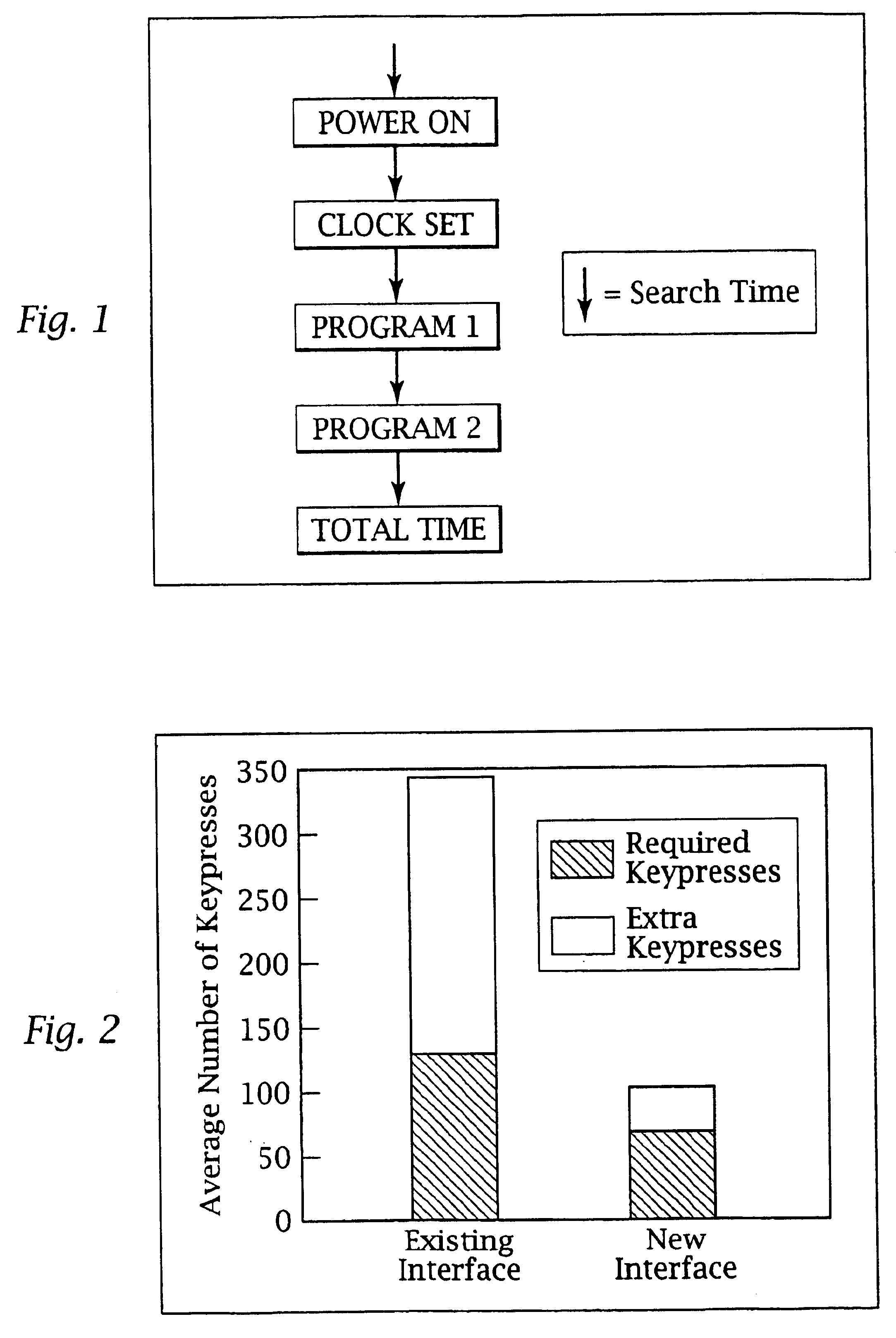
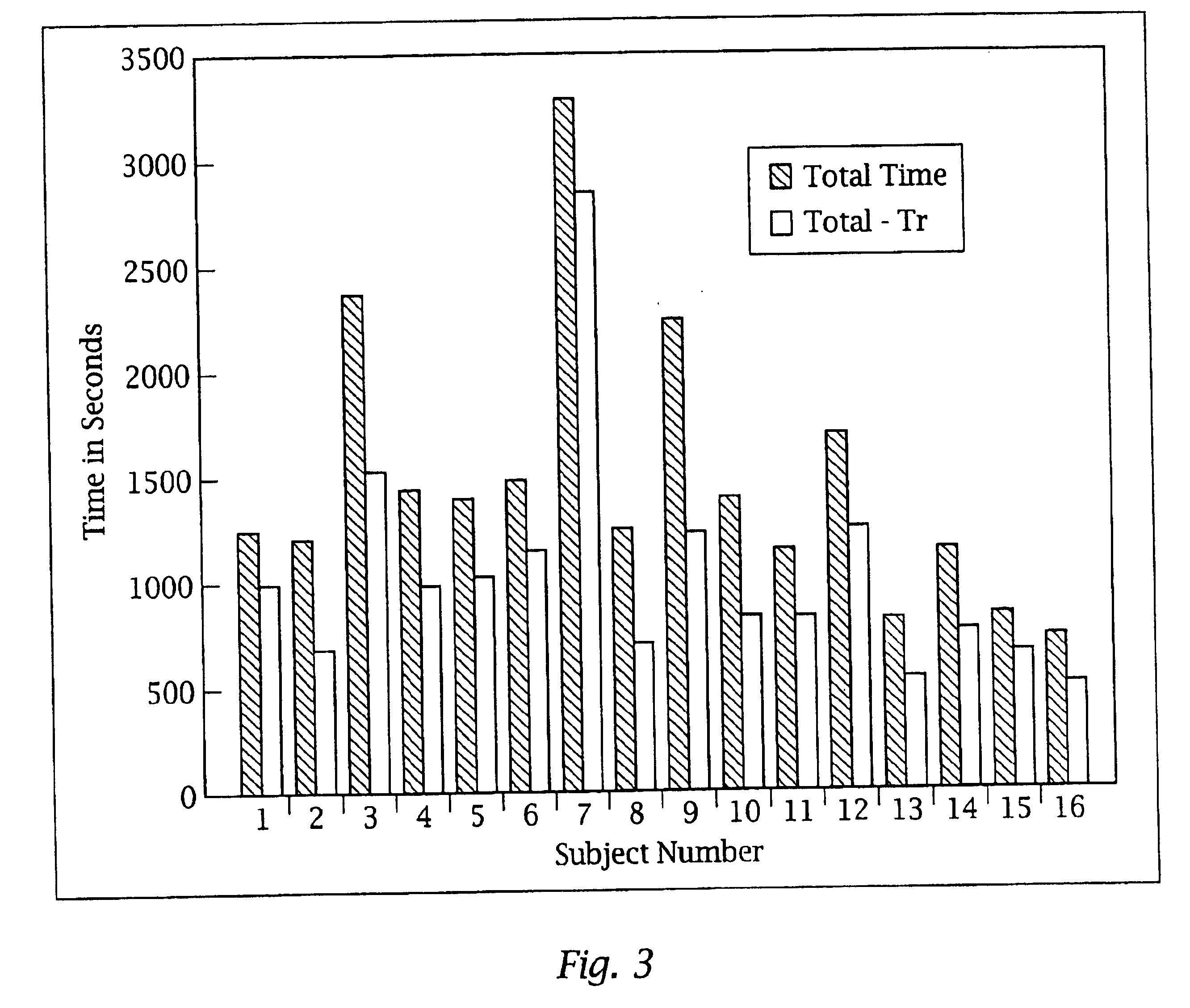
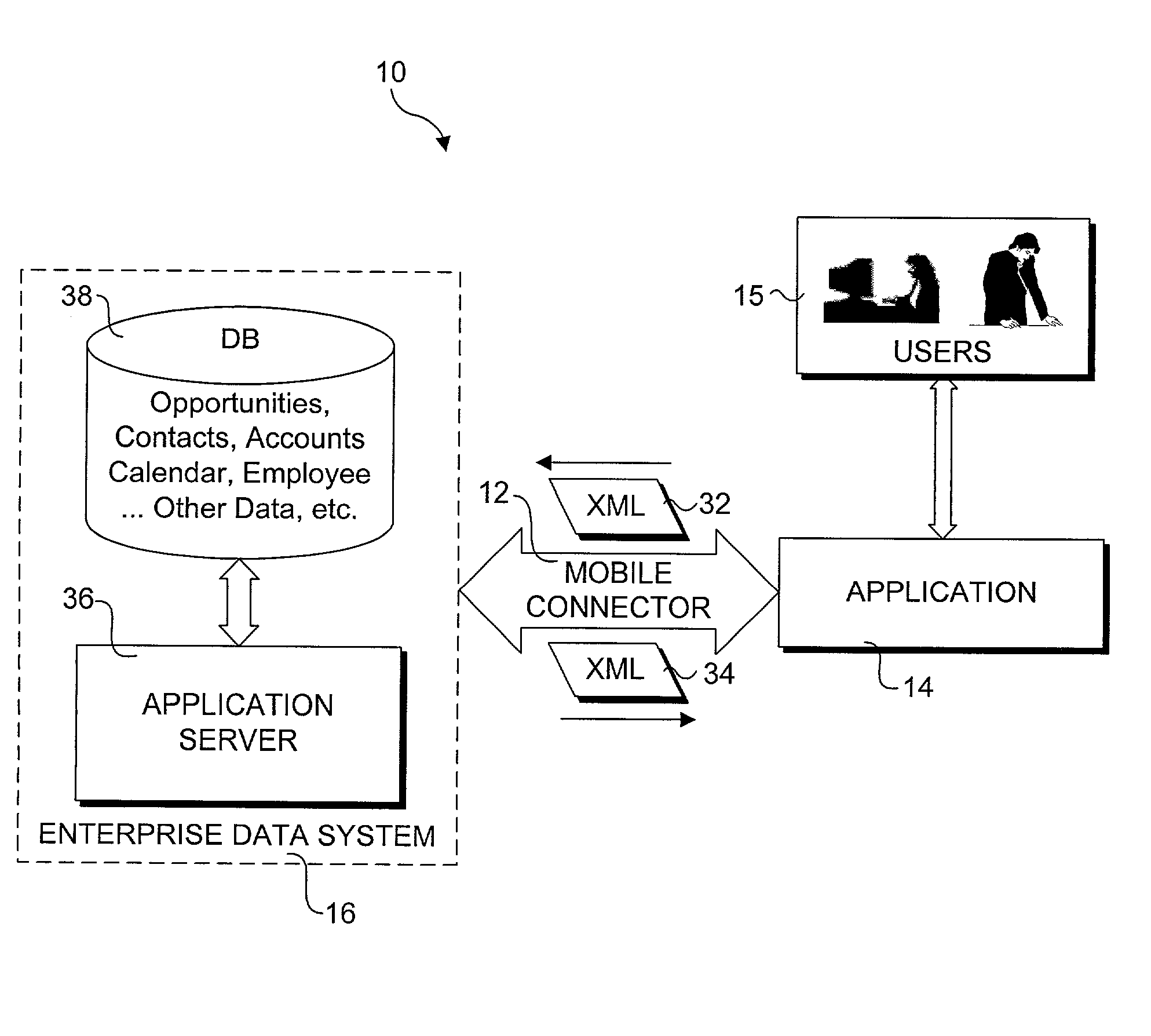
Patents
Literature
13251results about "Sound input/output" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
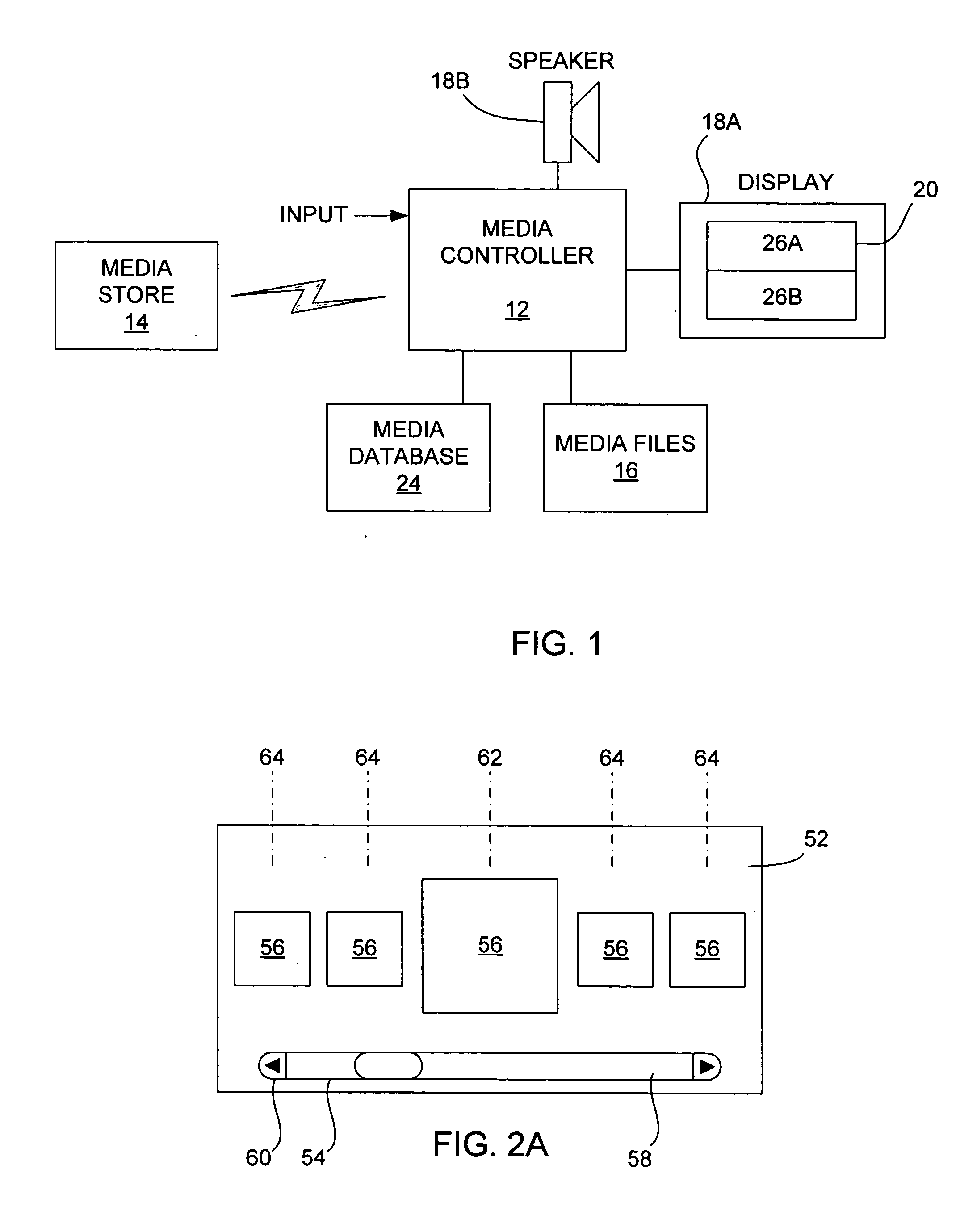
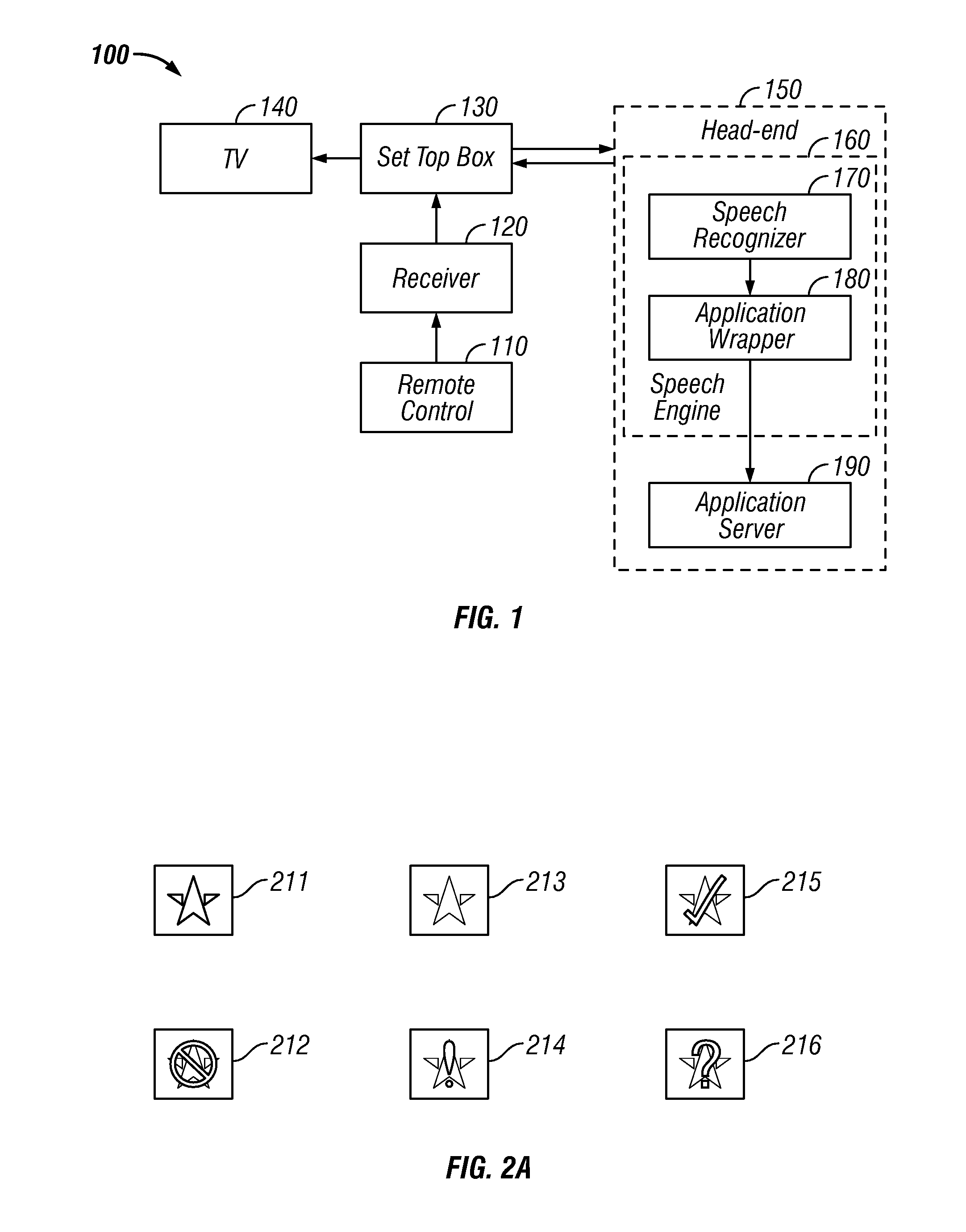
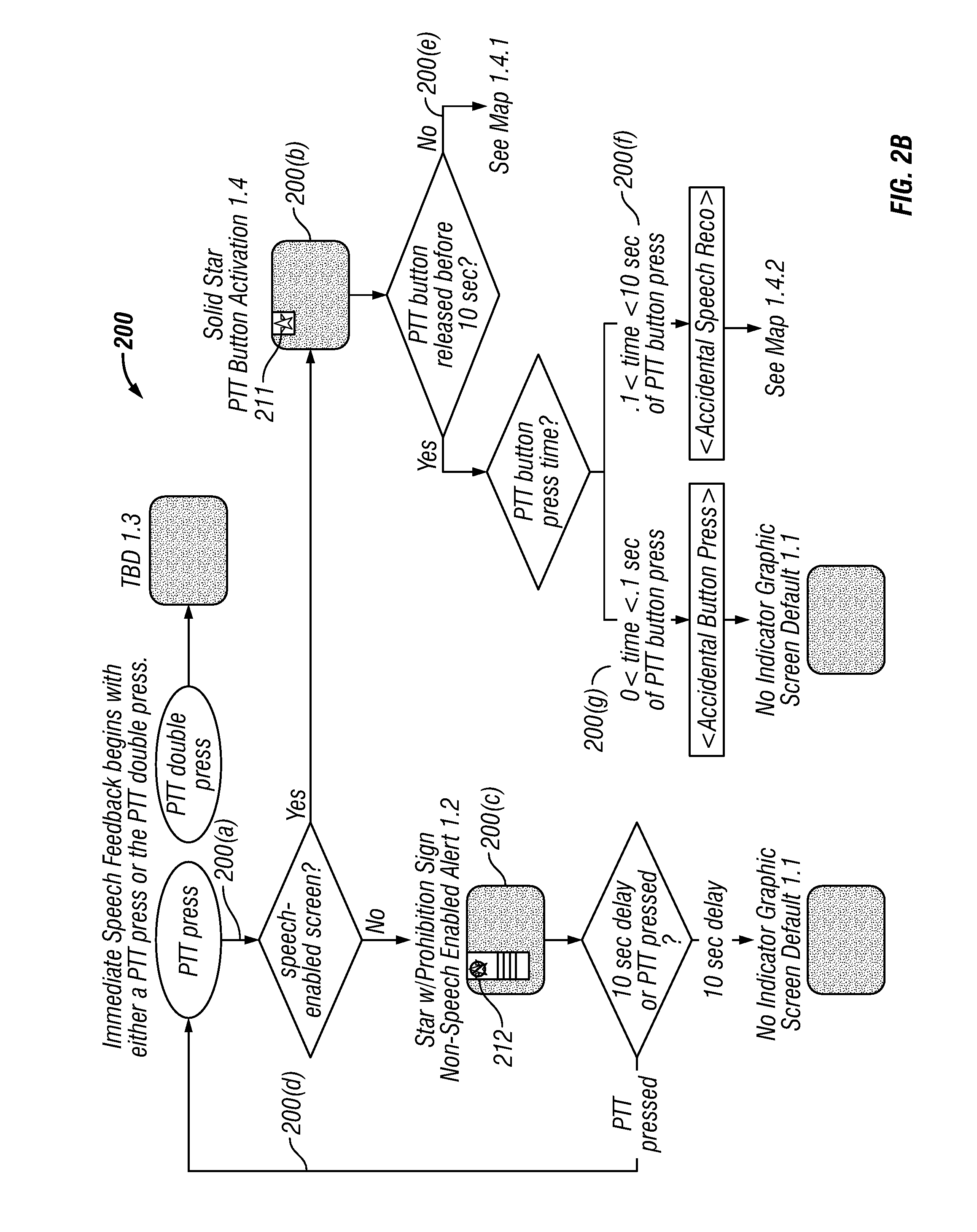
Intelligent electronic appliance system and method
InactiveUS6850252B1Minimize timeEasy to implementAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsCharacter and pattern recognitionAdaptive user interfaceDigital rights management
An intelligent electronic appliance preferably includes a user interface, data input and / or output port, and an intelligent processor. A preferred embodiment comprises a set top box for interacting with broadband media streams, with an adaptive user interface, content-based media processing and / or media metadata processing, and telecommunications integration. An adaptive user interface models the user, by observation, feedback, and / or explicit input, and presents a user interface and / or executes functions based on the user model. A content-based media processing system analyzes media content, for example audio and video, to understand the content, for example to generate content-descriptive metadata. A media metadata processing system operates on locally or remotely generated metadata to process the media in accordance with the metadata, which may be, for example, an electronic program guide, MPEG 7 data, and / or automatically generated format. A set top box preferably includes digital trick play effects, and incorporated digital rights management features.
Owner:BLANDING HOVENWEEP
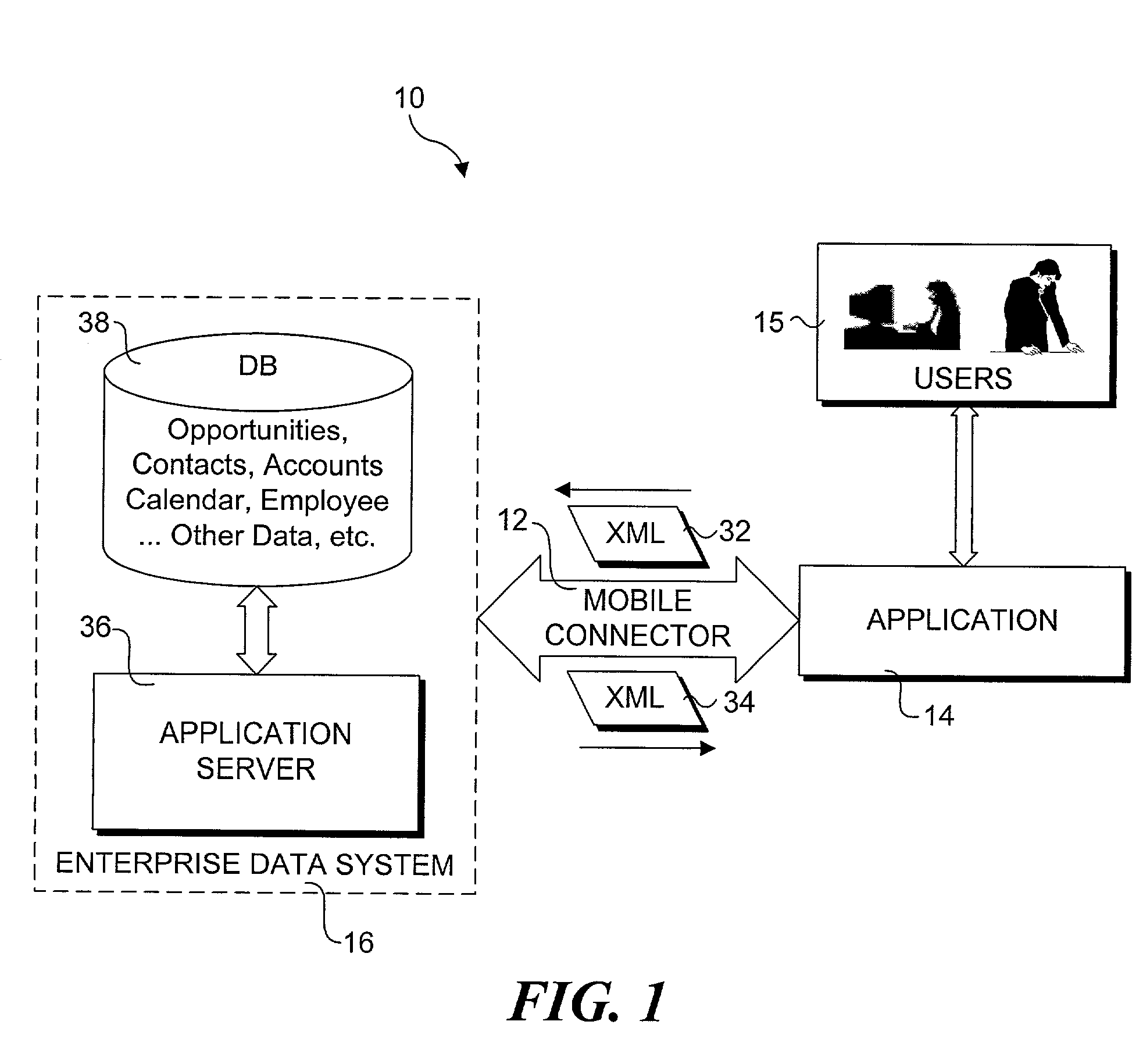
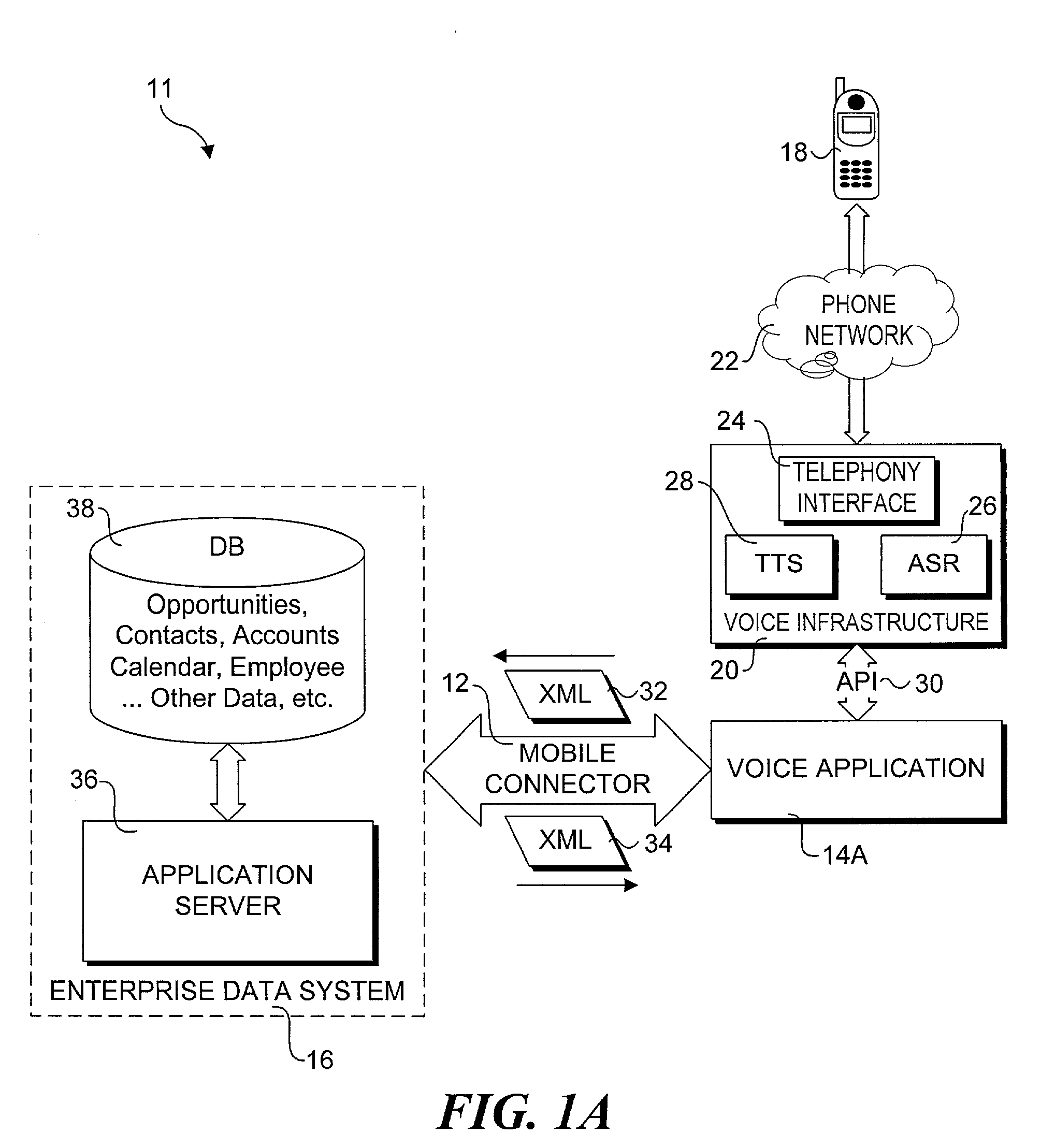
Method and system for enabling connectivity to a data system
A method and system that provides filtered data from a data system. In one embodiment the system includes an API (application programming interface) and associated software modules to enable third party applications to access an enterprise data system. Administrators are enabled to select specific user interface (UI) objects, such as screens, views, applets, columns and fields to voice or pass-through enable via a GUI that presents a tree depicting a hierarchy of the UI objects within a user interface of an application. An XSLT style sheet is then automatically generated to filter out data pertaining to UI objects that were not voice or pass-through enabled. In response to a request for data, unfiltered data are retrieved from the data system and a specified style sheet is applied to the unfiltered data to return filtered data pertaining to only those fields and columns that are voice or pass-through enabled.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
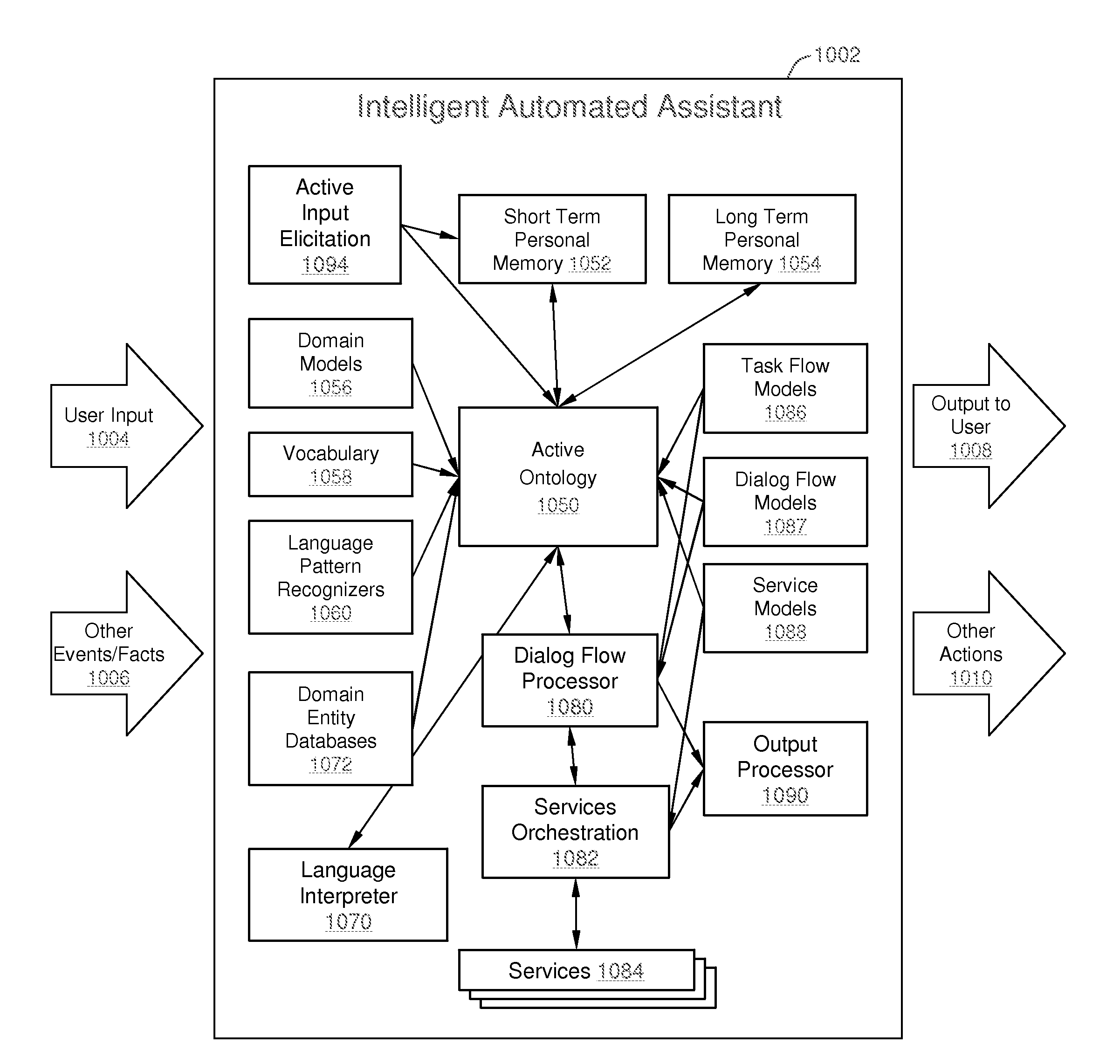
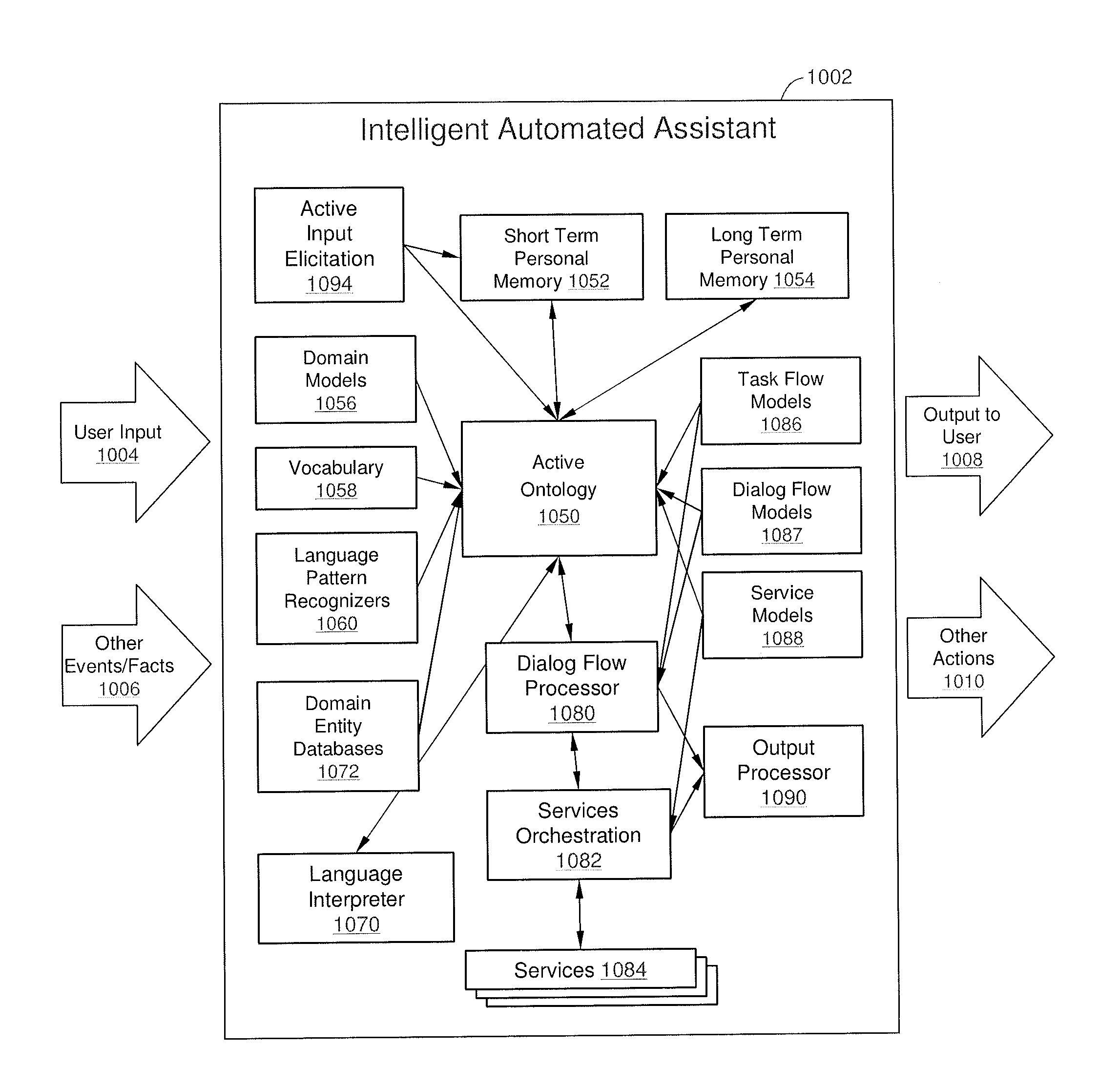
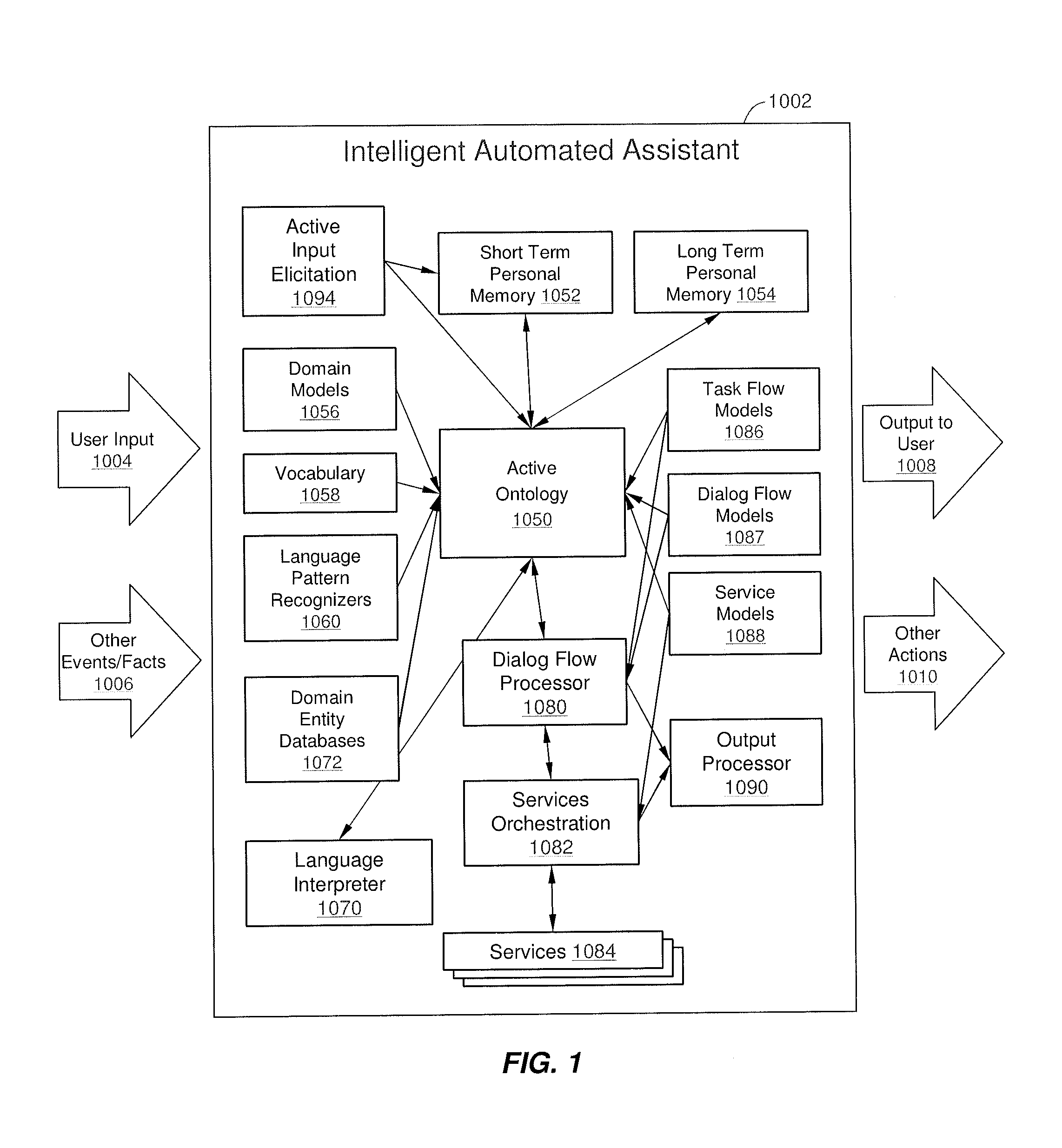
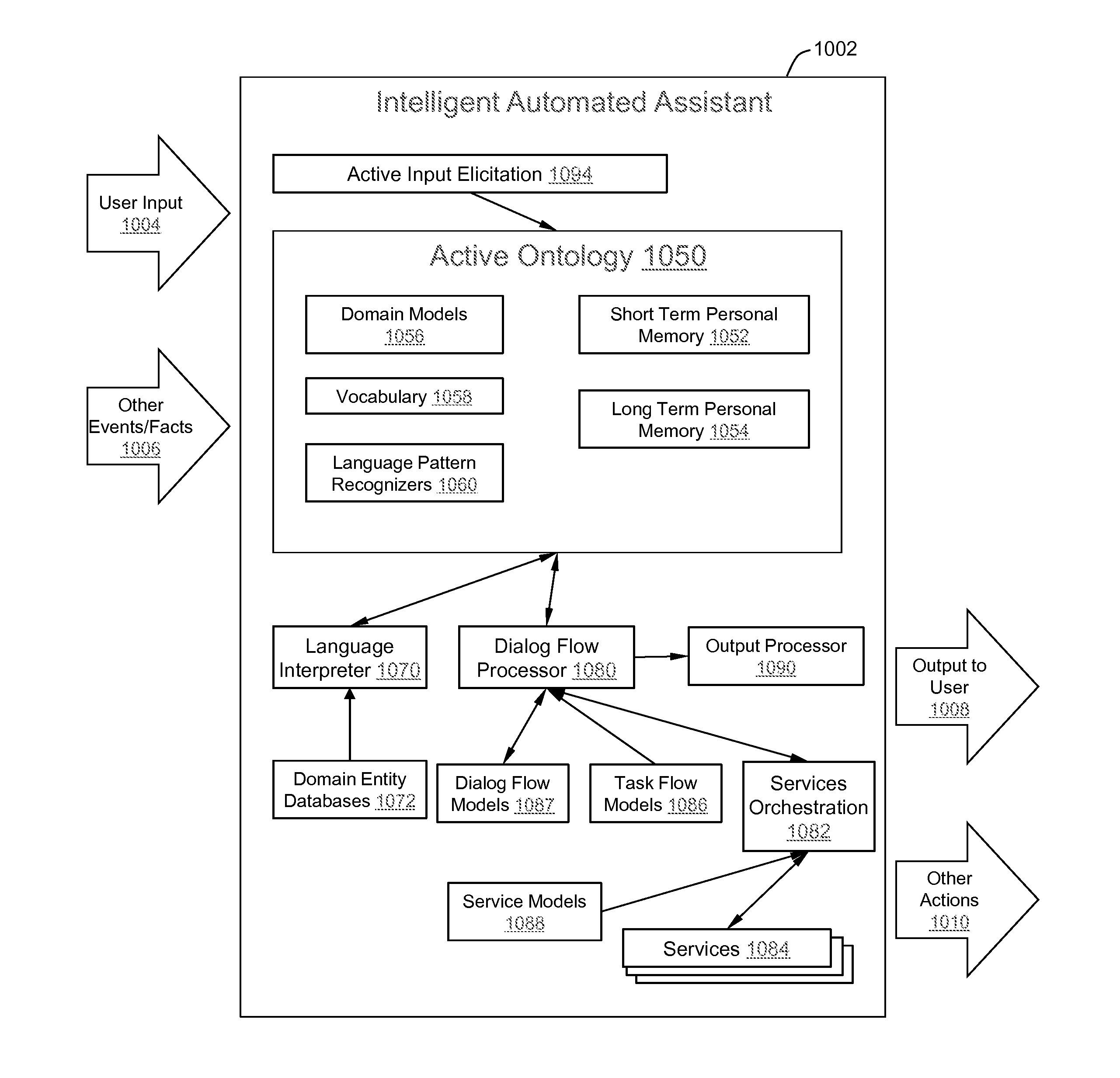
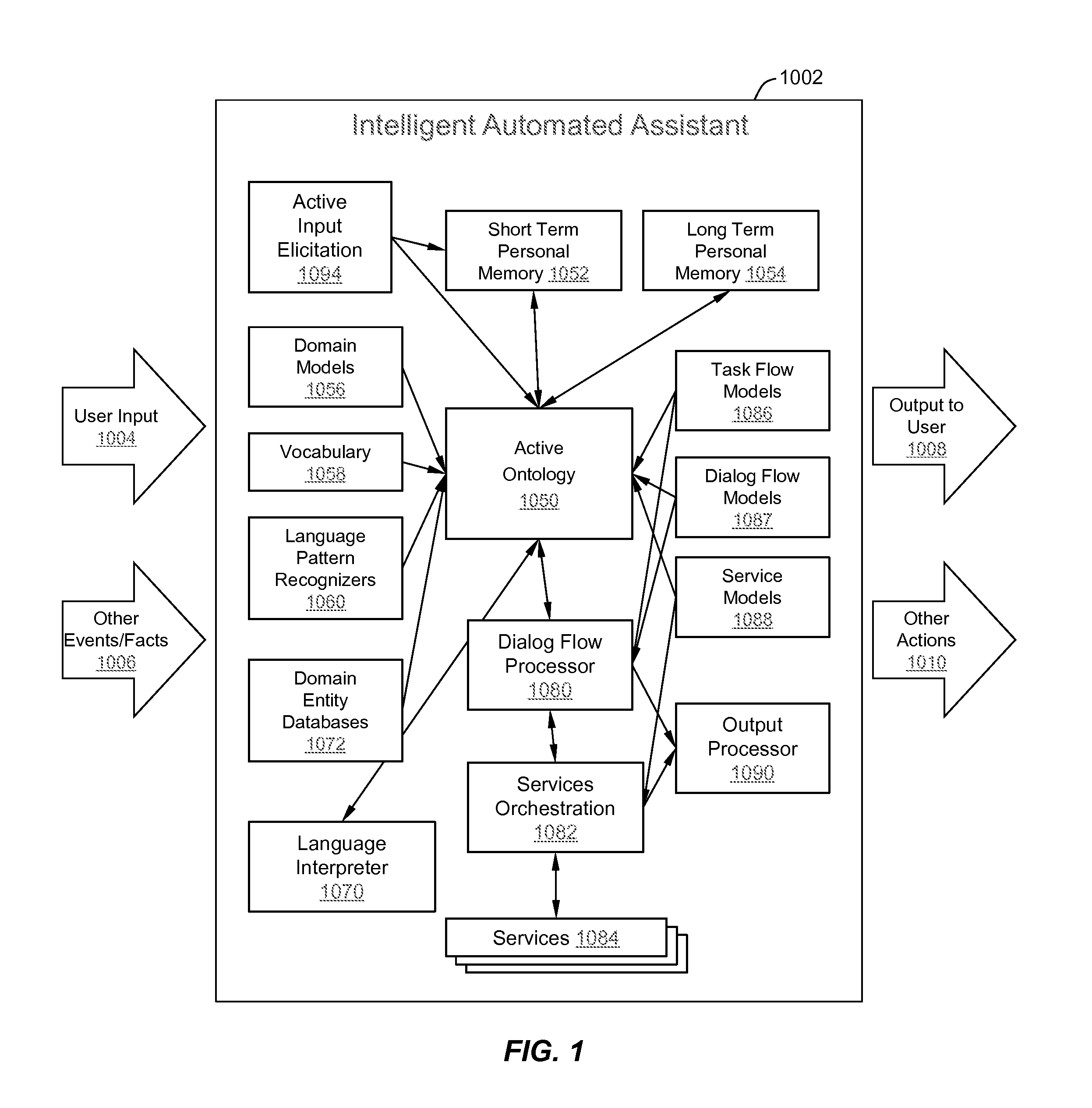
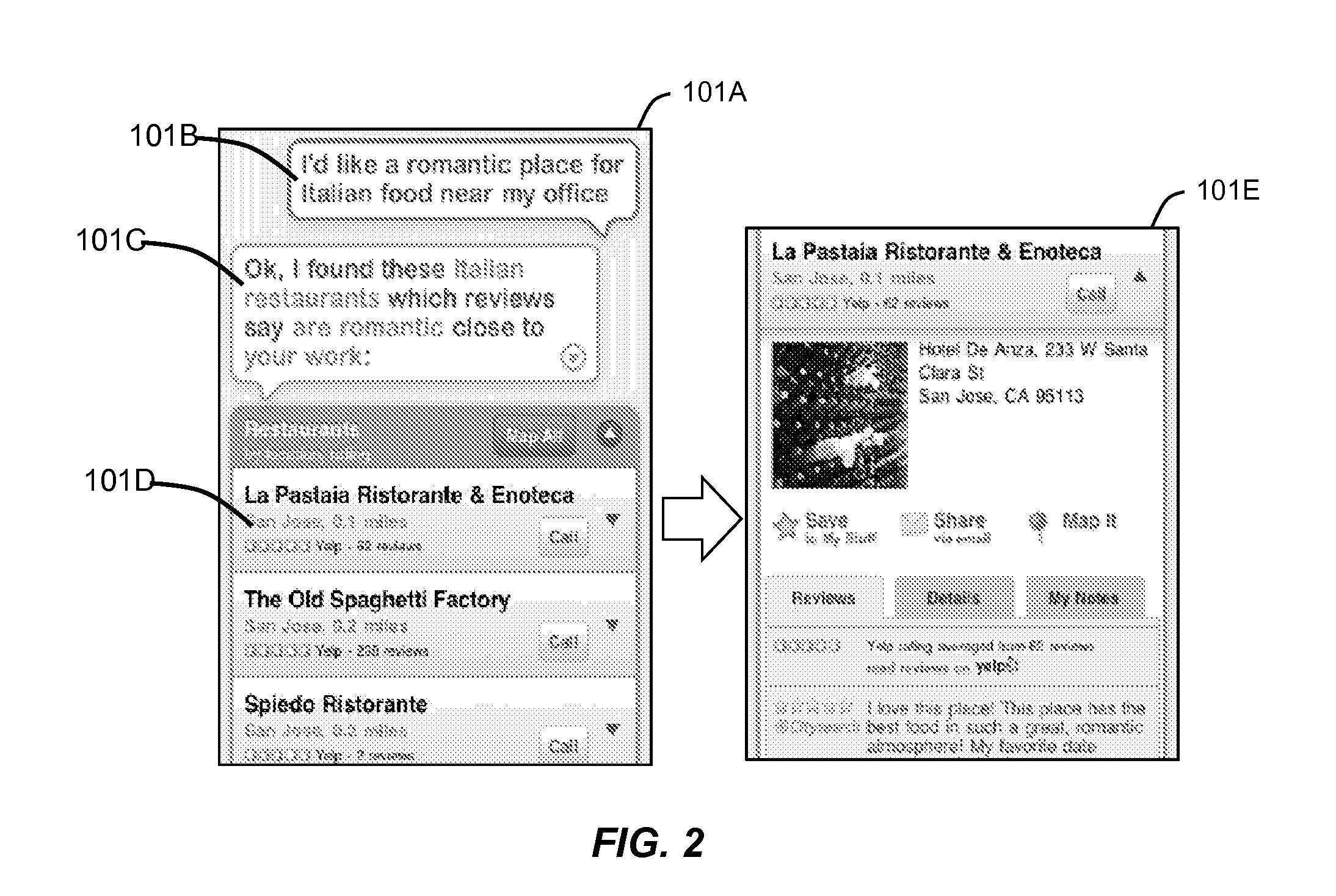
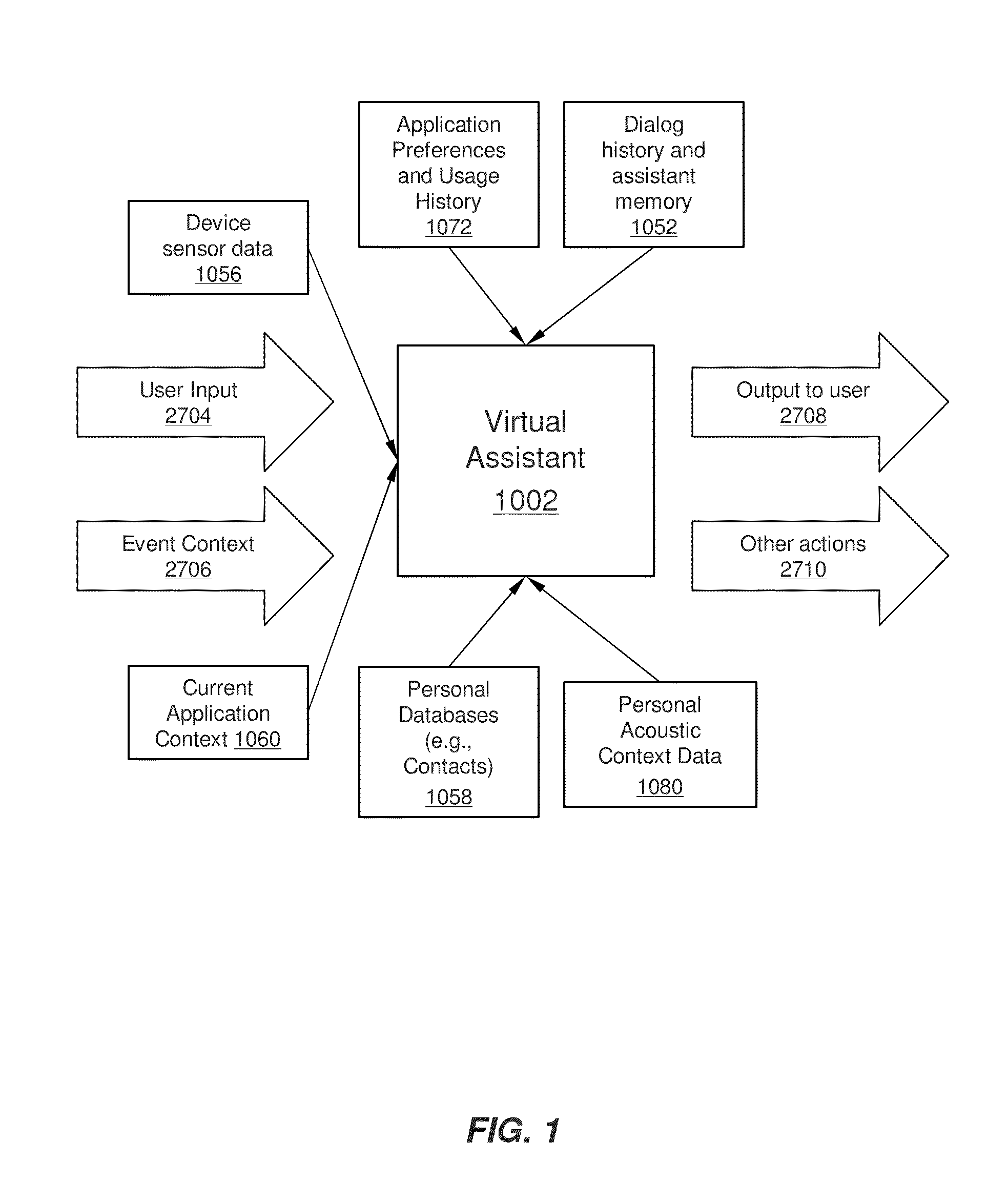
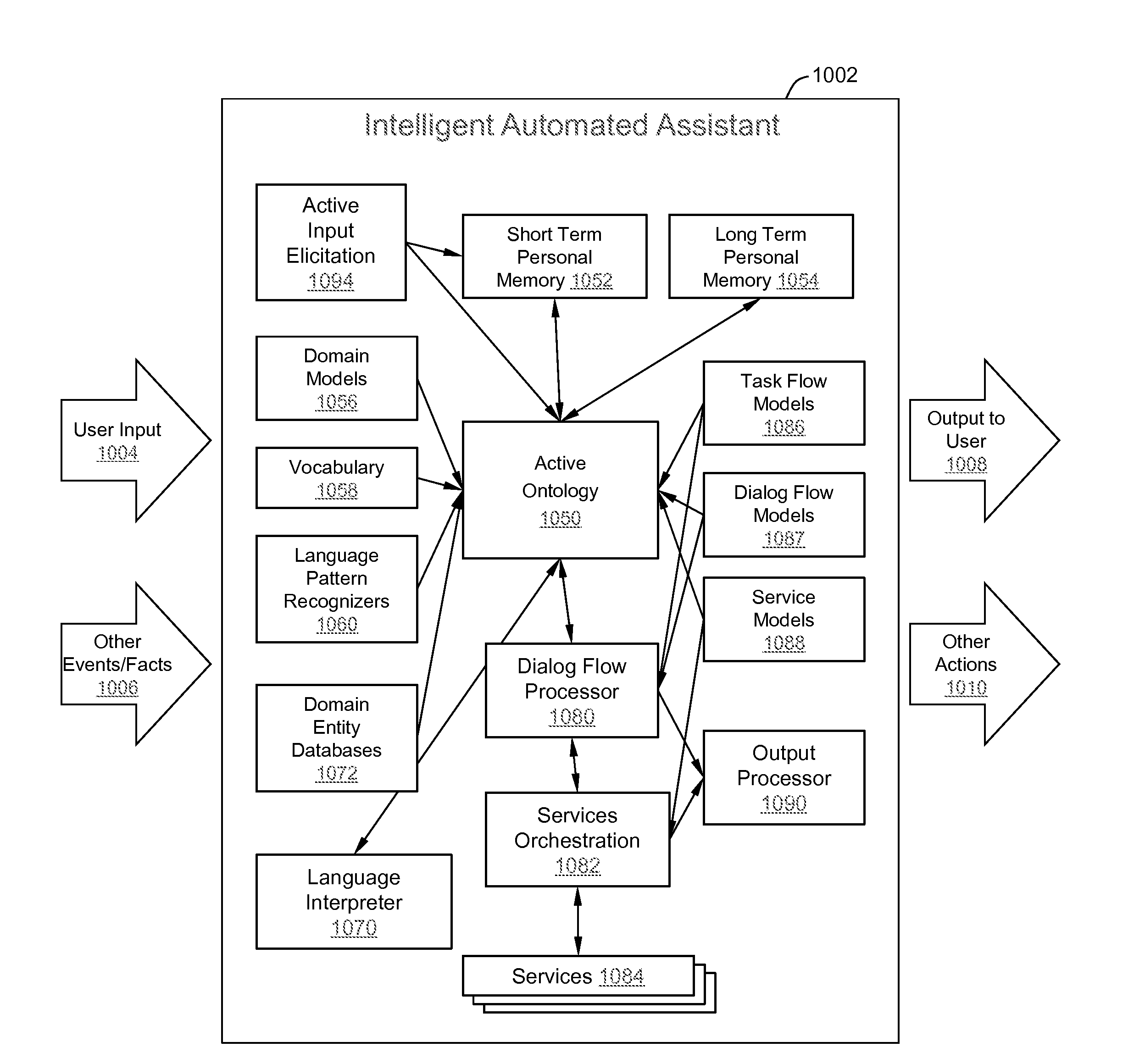
Intelligent Automated Assistant
ActiveUS20120016678A1Improve user interactionPromote effective engagementNatural language translationSemantic analysisService provisionSystem usage
An intelligent automated assistant system engages with the user in an integrated, conversational manner using natural language dialog, and invokes external services when appropriate to obtain information or perform various actions. The system can be implemented using any of a number of different platforms, such as the web, email, smartphone, and the like, or any combination thereof. In one embodiment, the system is based on sets of interrelated domains and tasks, and employs additional functionally powered by external services with which the system can interact.
Owner:APPLE INC
Head-mounted display apparatus for retaining a portable electronic device with display
Owner:APPLE INC
Methods and systems for indicating a clamping prediction
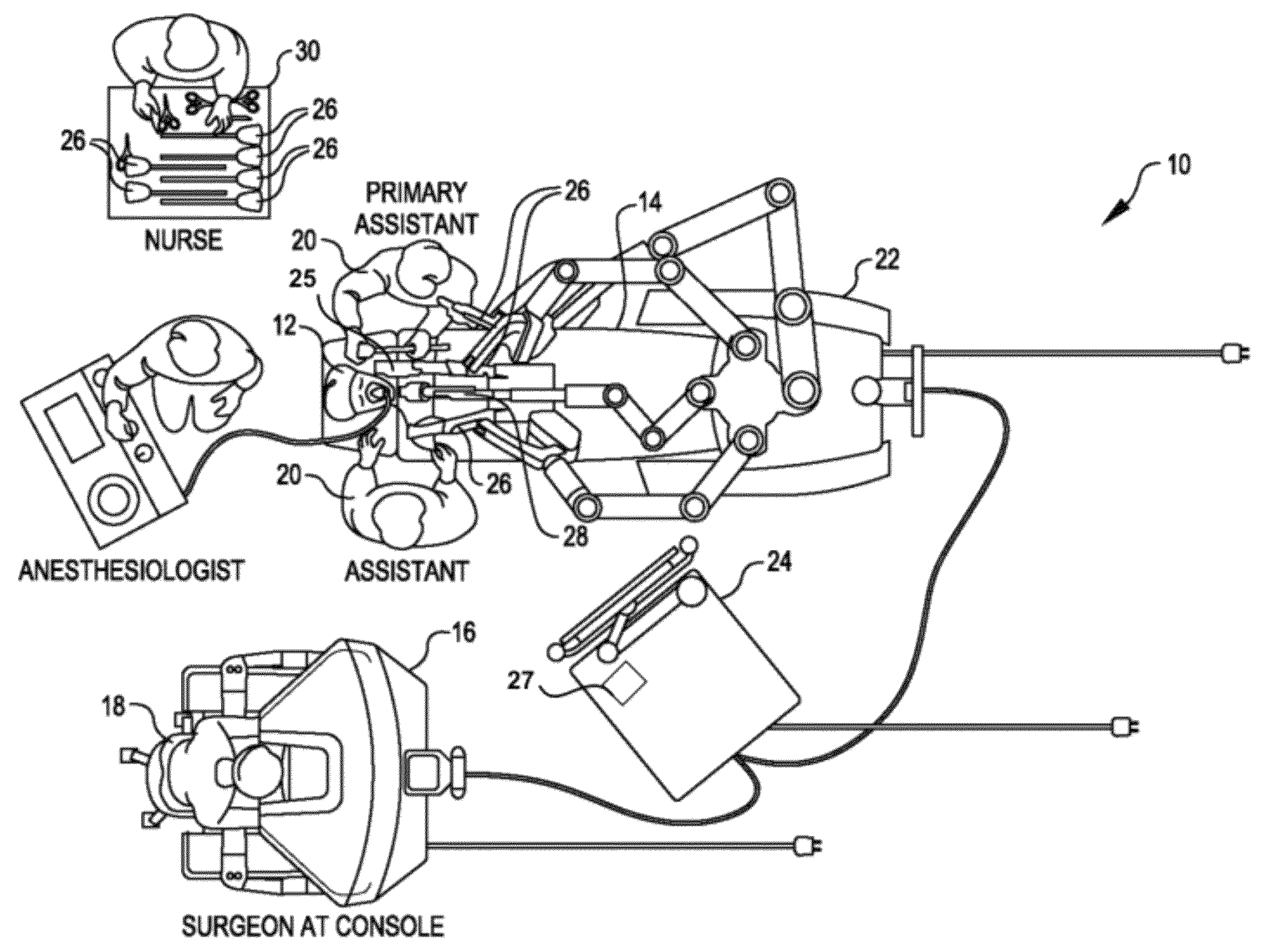
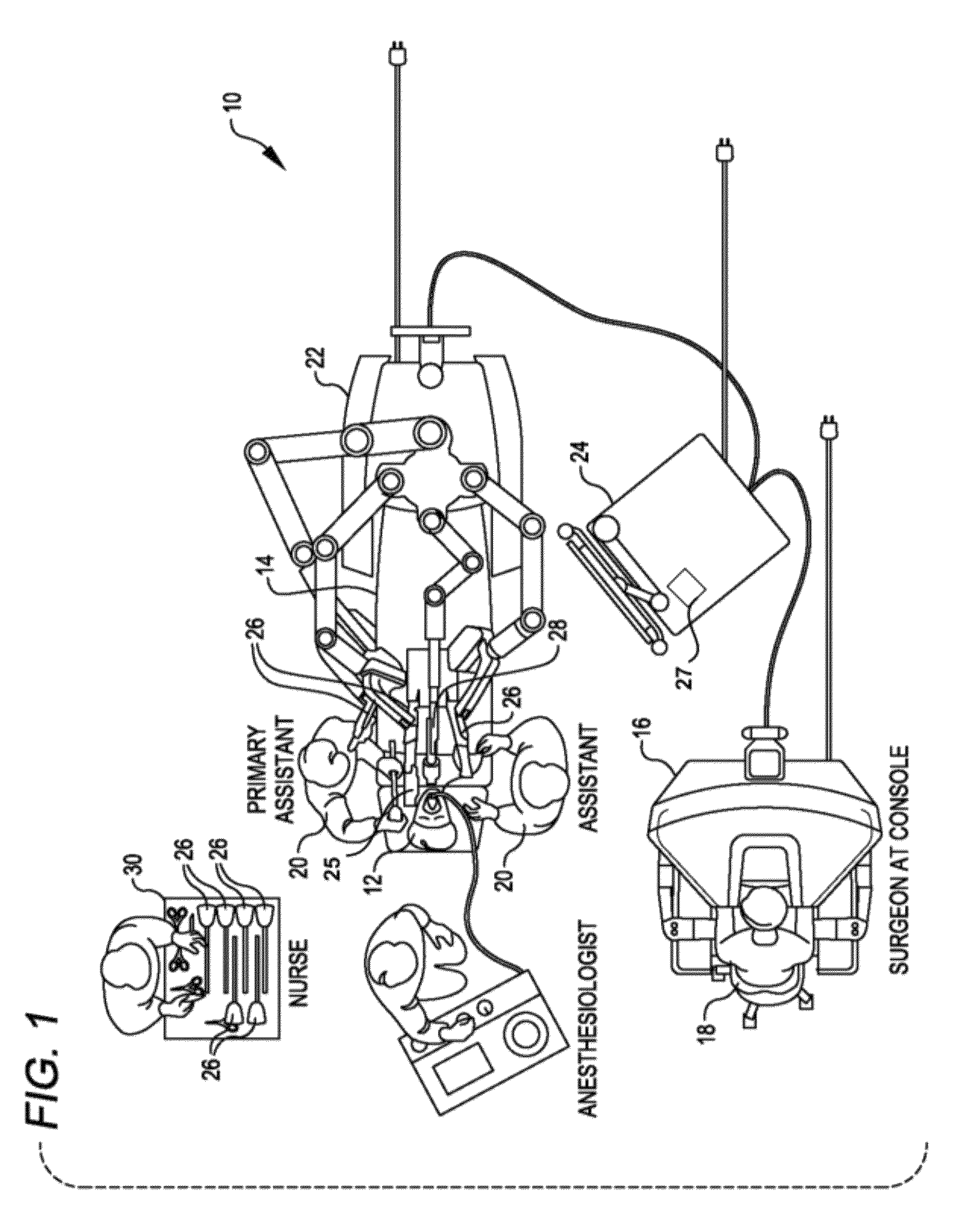
ActiveUS8989903B2Reduce the amount requiredReduce bleeding during staplingProgramme-controlled manipulatorDiagnosticsUser interfaceBody tissue
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
Mobile systems and methods of supporting natural language human-machine interactions
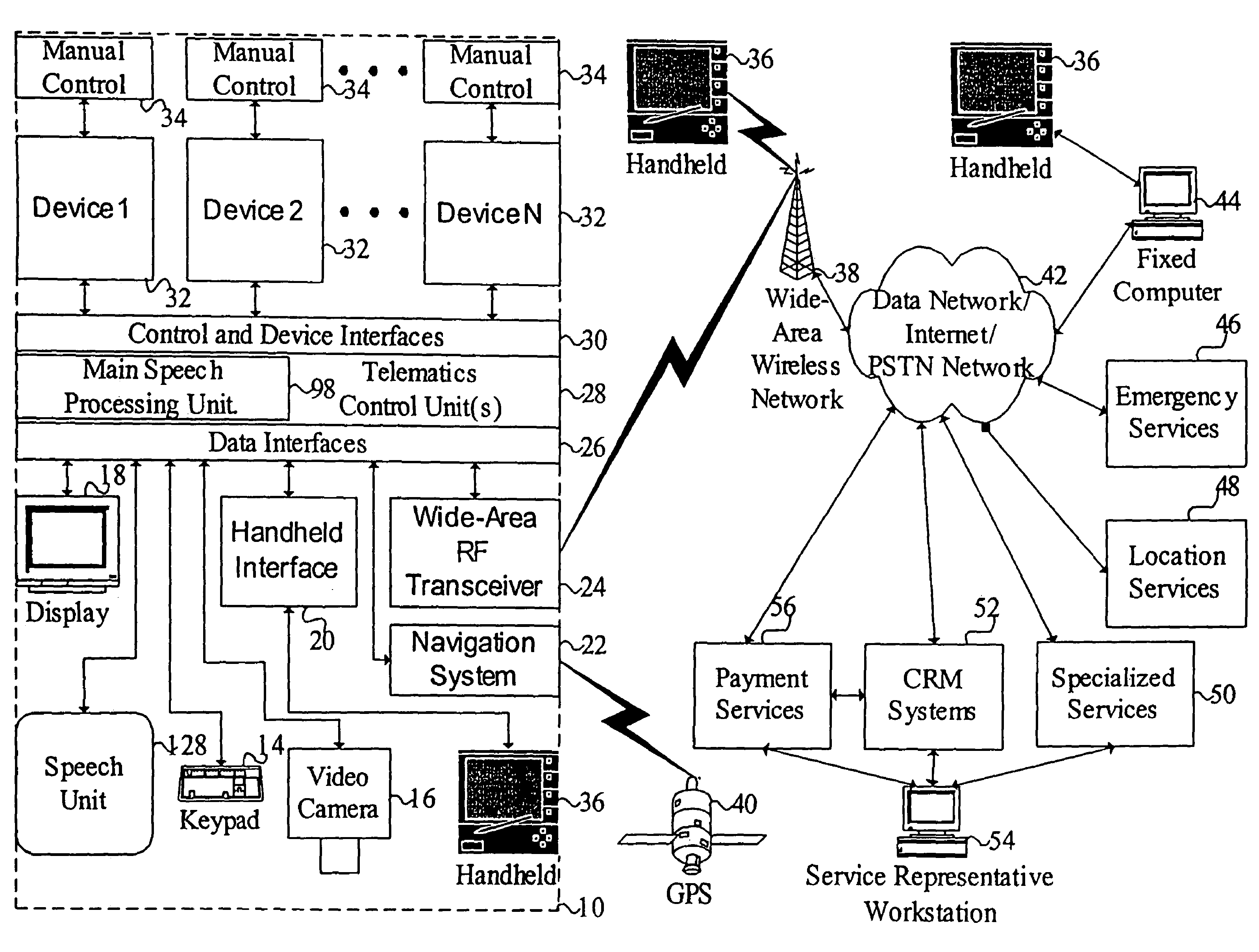
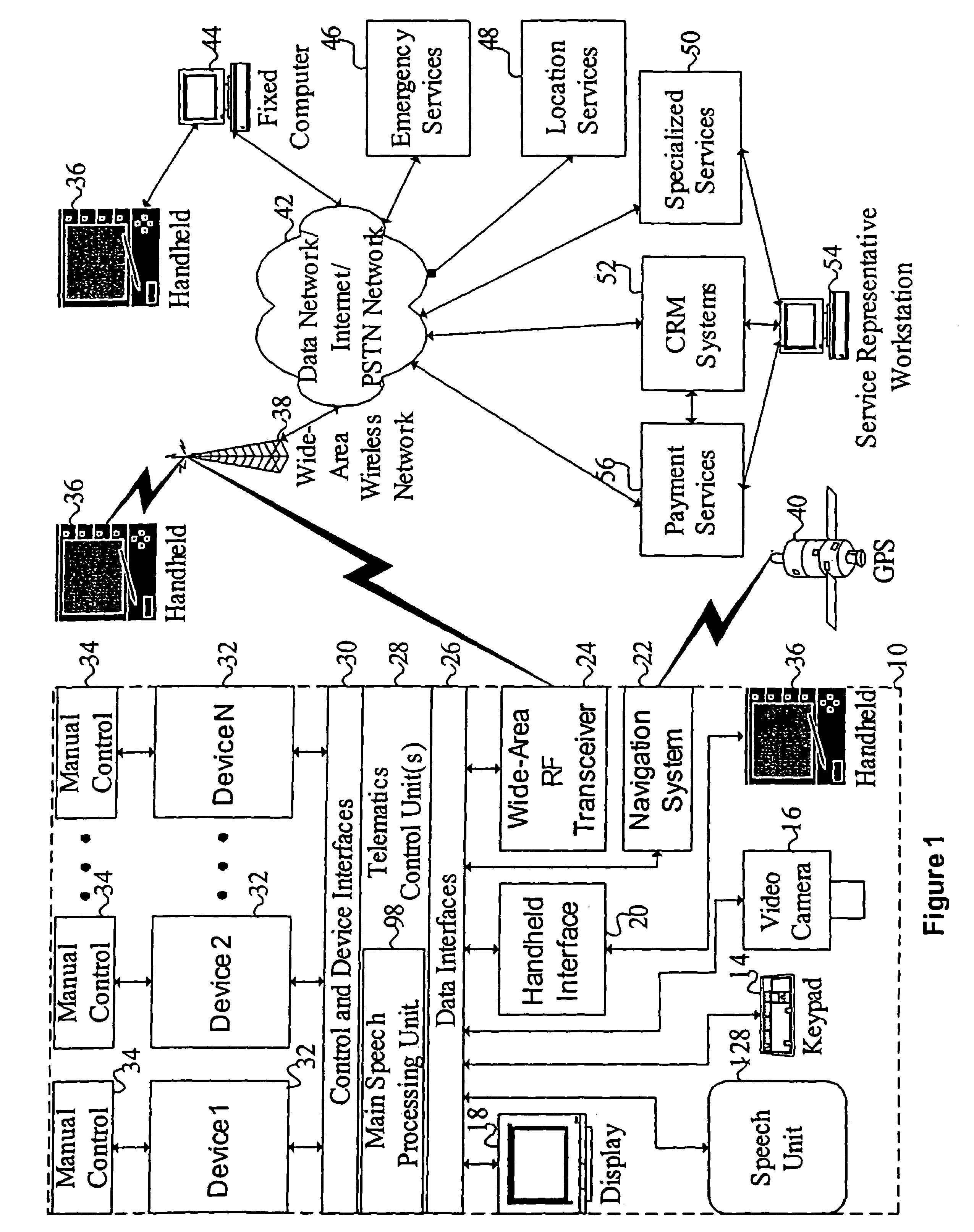
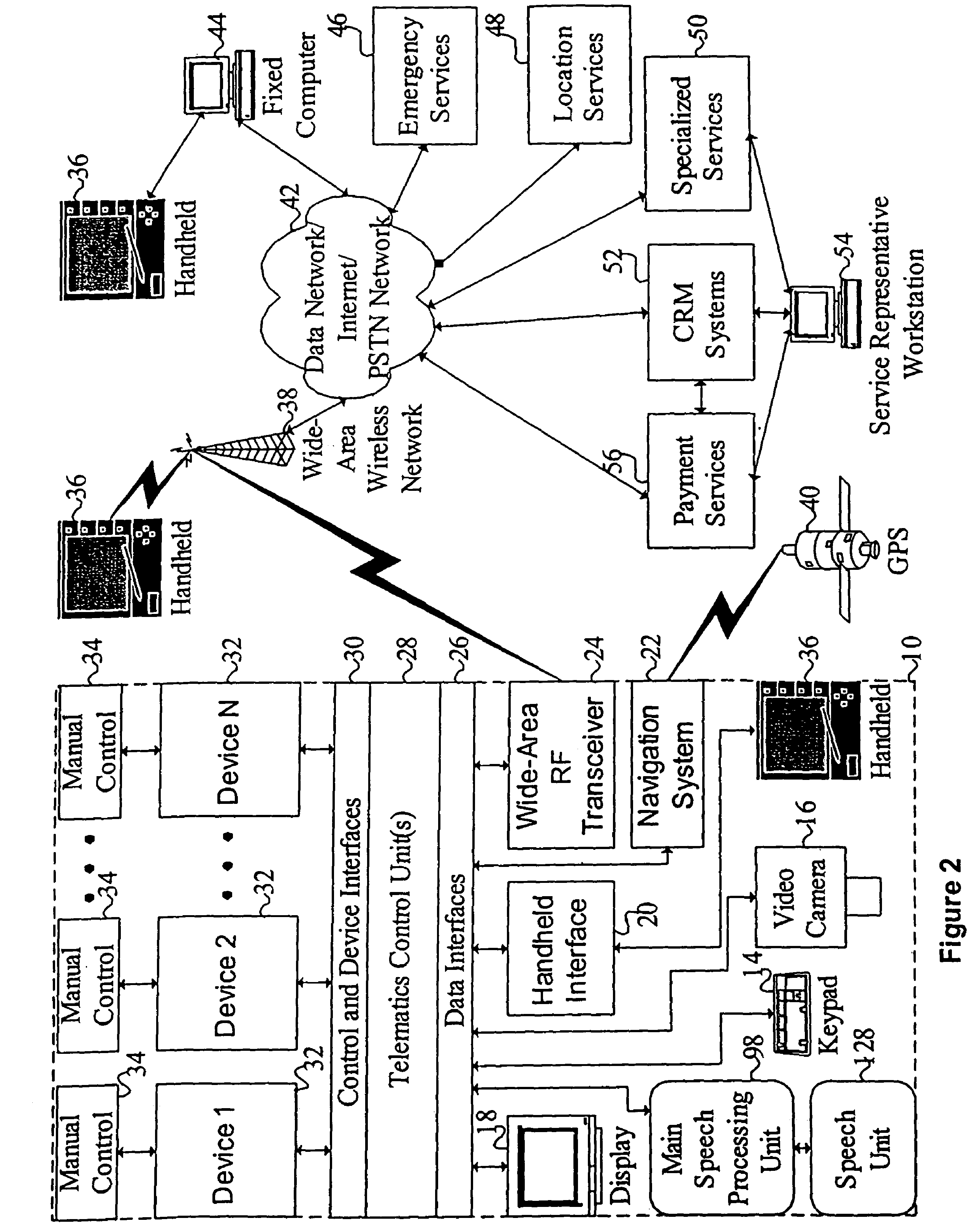
ActiveUS7949529B2Promotes feeling of naturalConvenient timeWeb data indexingDevices with voice recognitionTelematicsWide area network
A mobile system is provided that includes speech-based and non-speech-based interfaces for telematics applications. The mobile system identifies and uses context, prior information, domain knowledge, and user specific profile data to achieve a natural environment for users that submit requests and / or commands in multiple domains. The invention creates, stores and uses extensive personal profile information for each user, thereby improving the reliability of determining the context and presenting the expected results for a particular question or command. The invention may organize domain specific behavior and information into agents, that are distributable or updateable over a wide area network.
Owner:DIALECT LLC
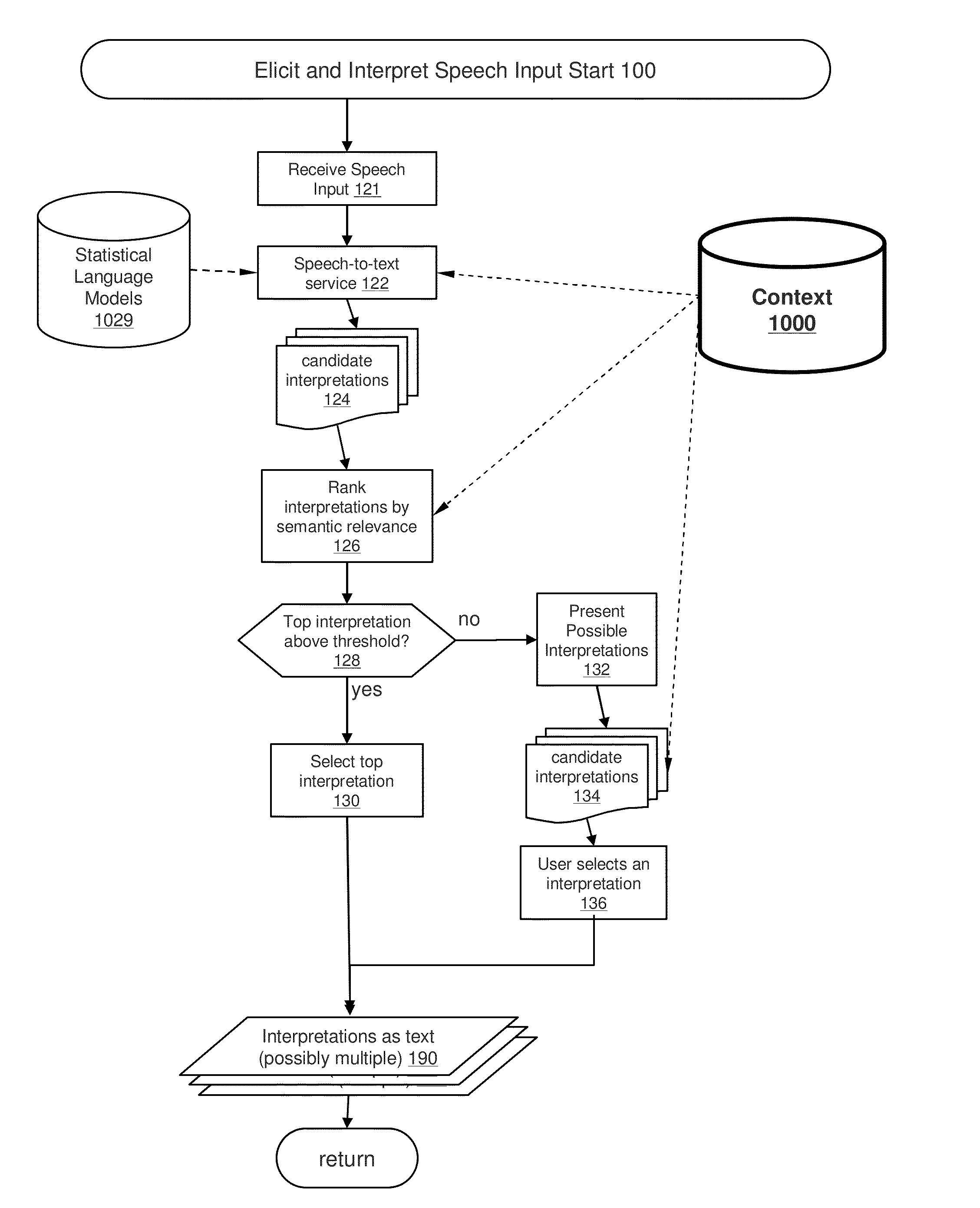
Consolidating Speech Recognition Results
InactiveUS20130073286A1Redundant elements are minimized or eliminatedChoose simpleSpeech recognitionSound input/outputRecognition algorithmSpeech identification
Candidate interpretations resulting from application of speech recognition algorithms to spoken input are presented in a consolidated manner that reduces redundancy. A list of candidate interpretations is generated, and each candidate interpretation is subdivided into time-based portions, forming a grid. Those time-based portions that duplicate portions from other candidate interpretations are removed from the grid. A user interface is provided that presents the user with an opportunity to select among the candidate interpretations; the user interface is configured to present these alternatives without duplicate elements.
Owner:APPLE INC
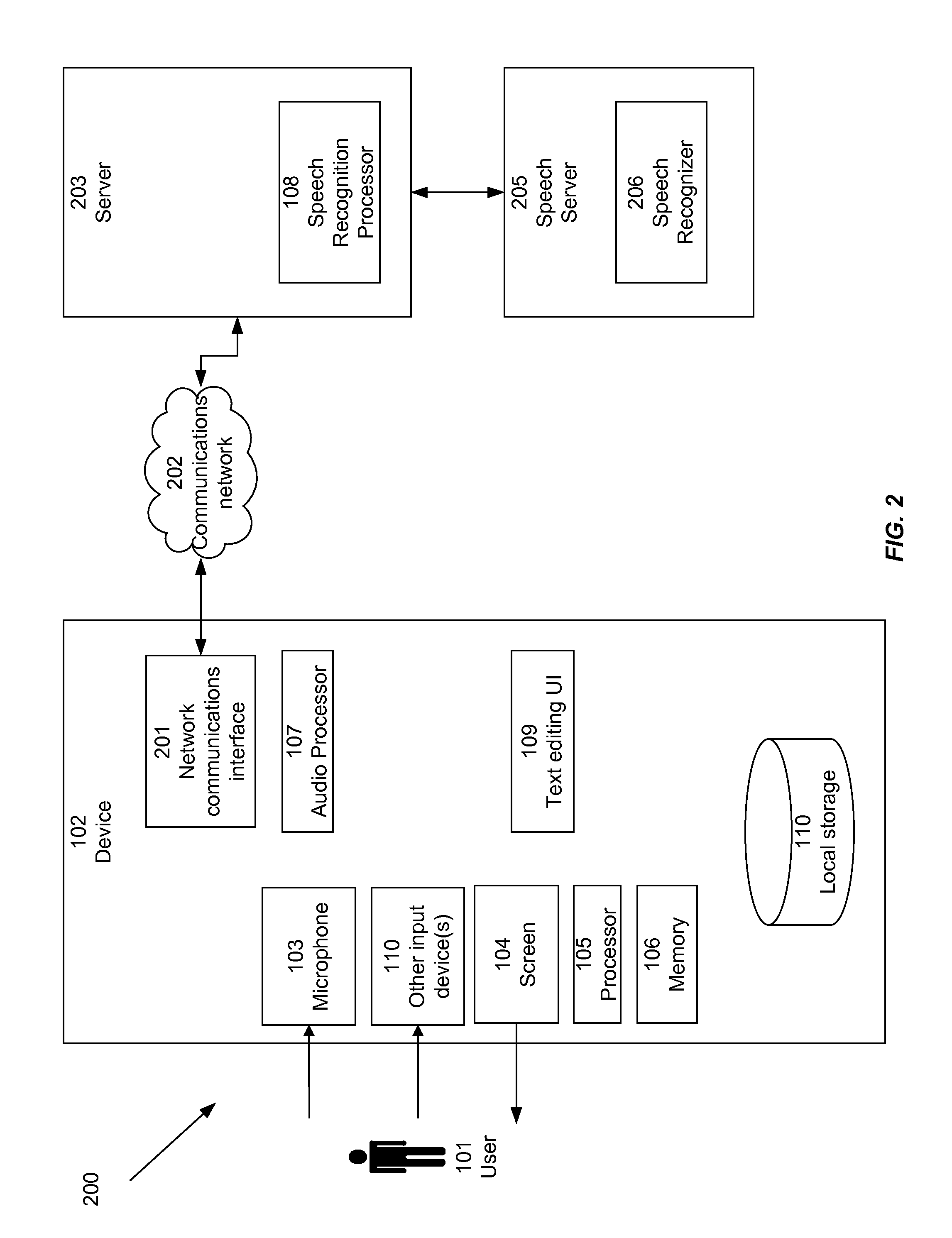
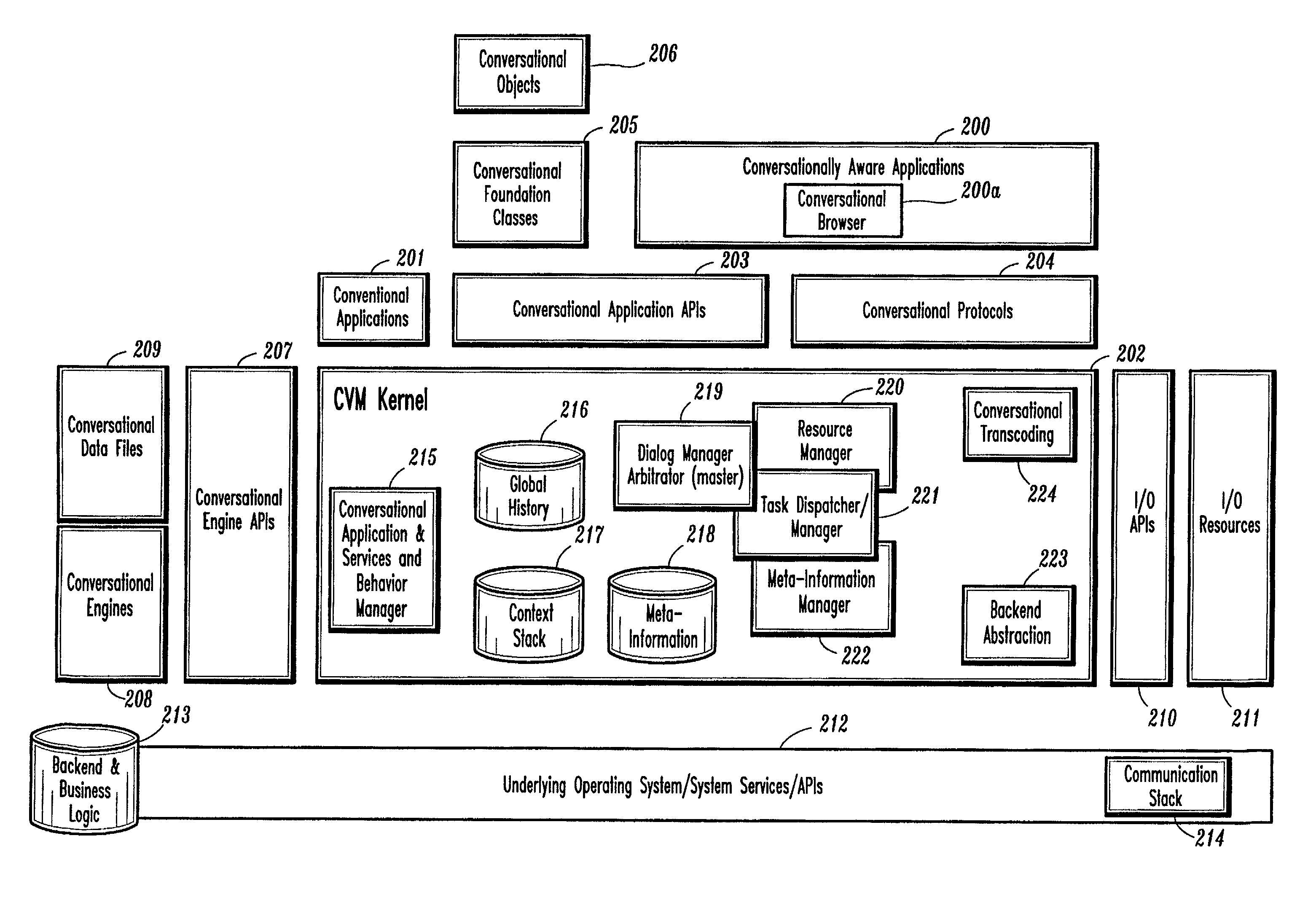
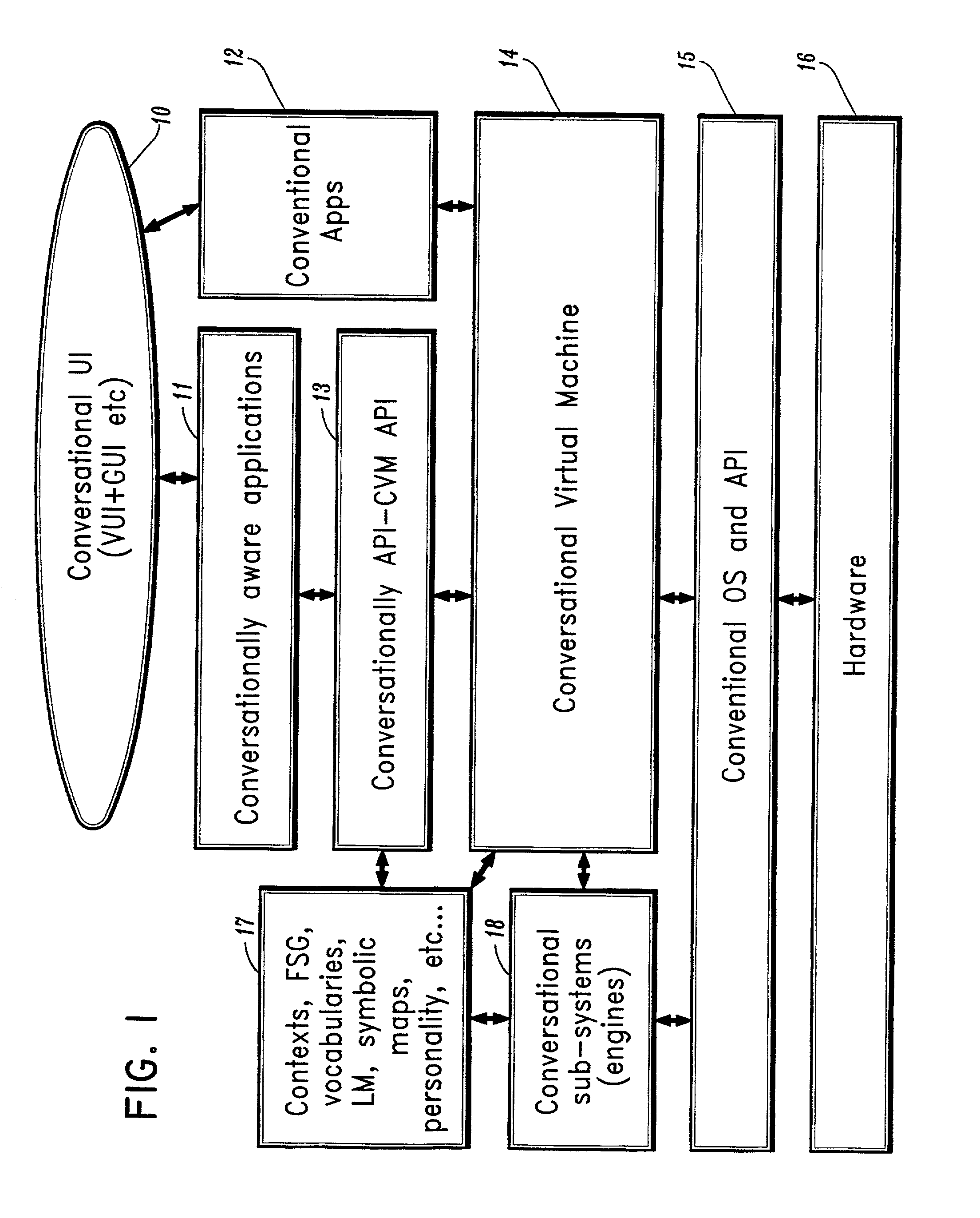
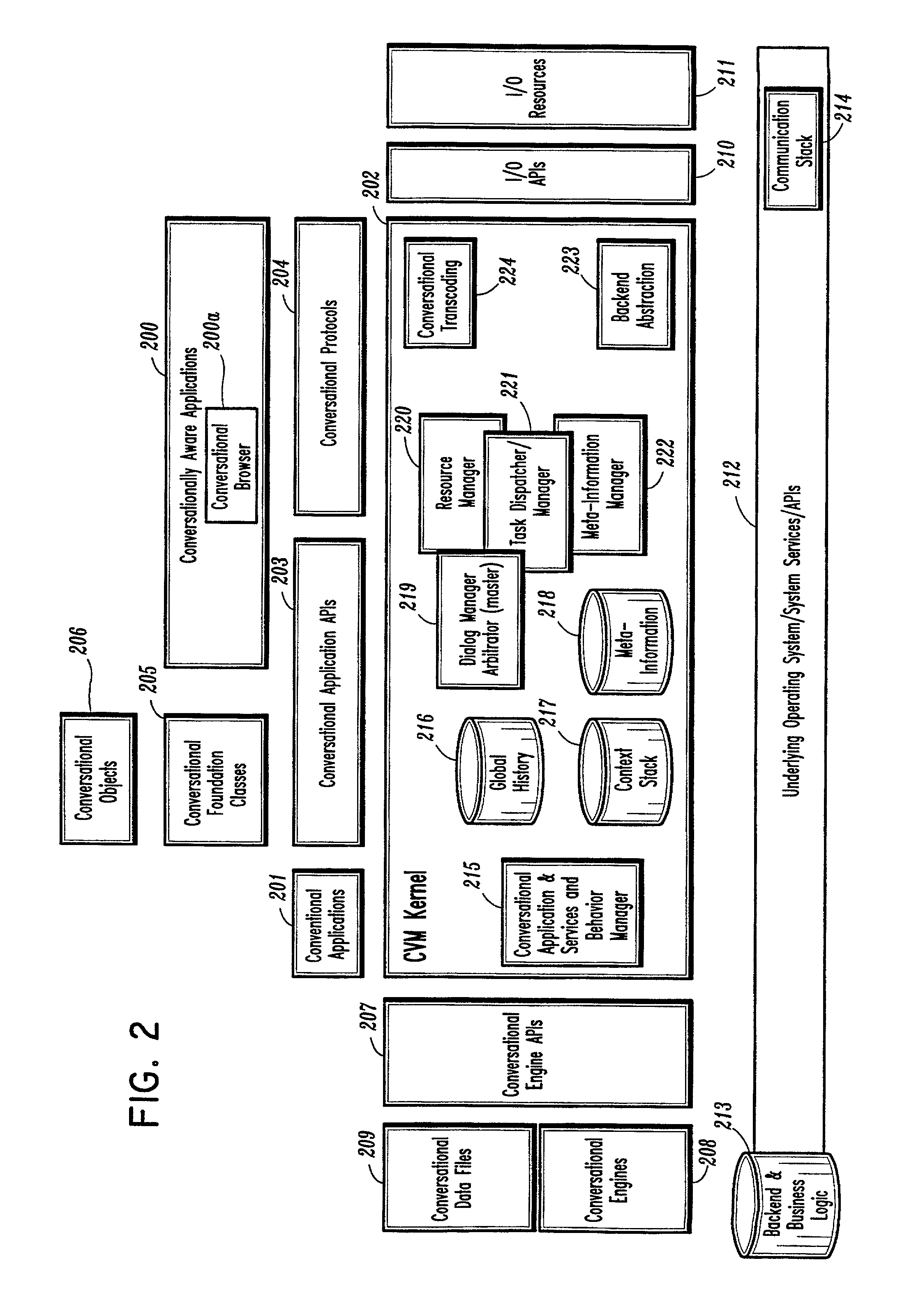
Conversational computing via conversational virtual machine
InactiveUS7137126B1Limitation for transferReduce degradationInterconnection arrangementsResource allocationConversational speechApplication software
A conversational computing system that provides a universal coordinated multi-modal conversational user interface (CUI) (10) across a plurality of conversationally aware applications (11) (i.e., applications that “speak” conversational protocols) and conventional applications (12). The conversationally aware maps, applications (11) communicate with a conversational kernel (14) via conversational application APIs (13). The conversational kernel (14) controls the dialog across applications and devices (local and networked) on the basis of their registered conversational capabilities and requirements and provides a unified conversational user interface and conversational services and behaviors. The conversational computing system may be built on top of a conventional operating system and APIs (15) and conventional device hardware (16). The conversational kernel (14) handles all I / O processing and controls conversational engines (18). The conversational kernel (14) converts voice requests into queries and converts outputs and results into spoken messages using conversational engines (18) and conversational arguments (17). The conversational application API (13) conveys all the information for the conversational kernel (14) to transform queries into application calls and conversely convert output into speech, appropriately sorted before being provided to the user.
Owner:UNILOC 2017 LLC
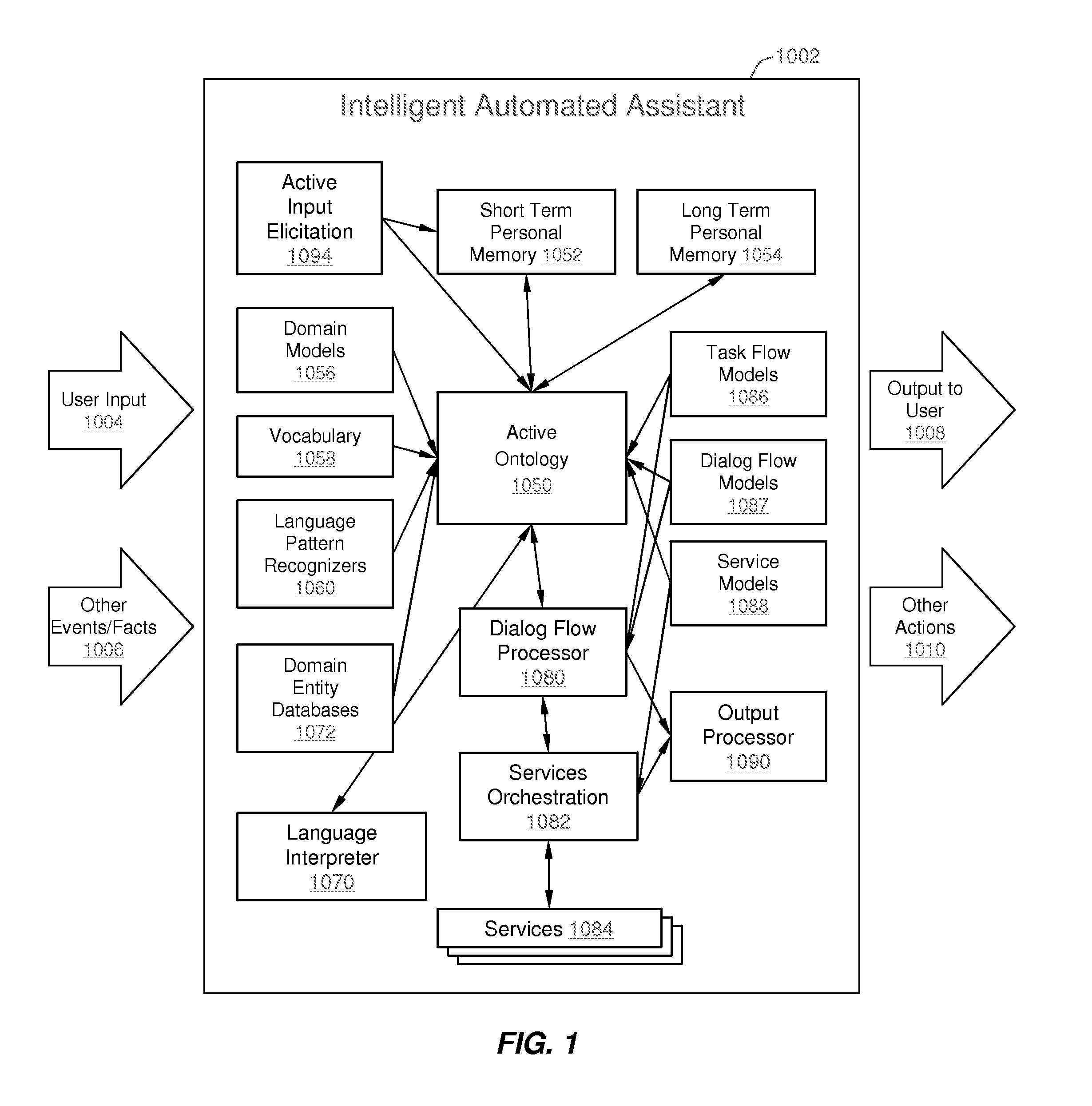
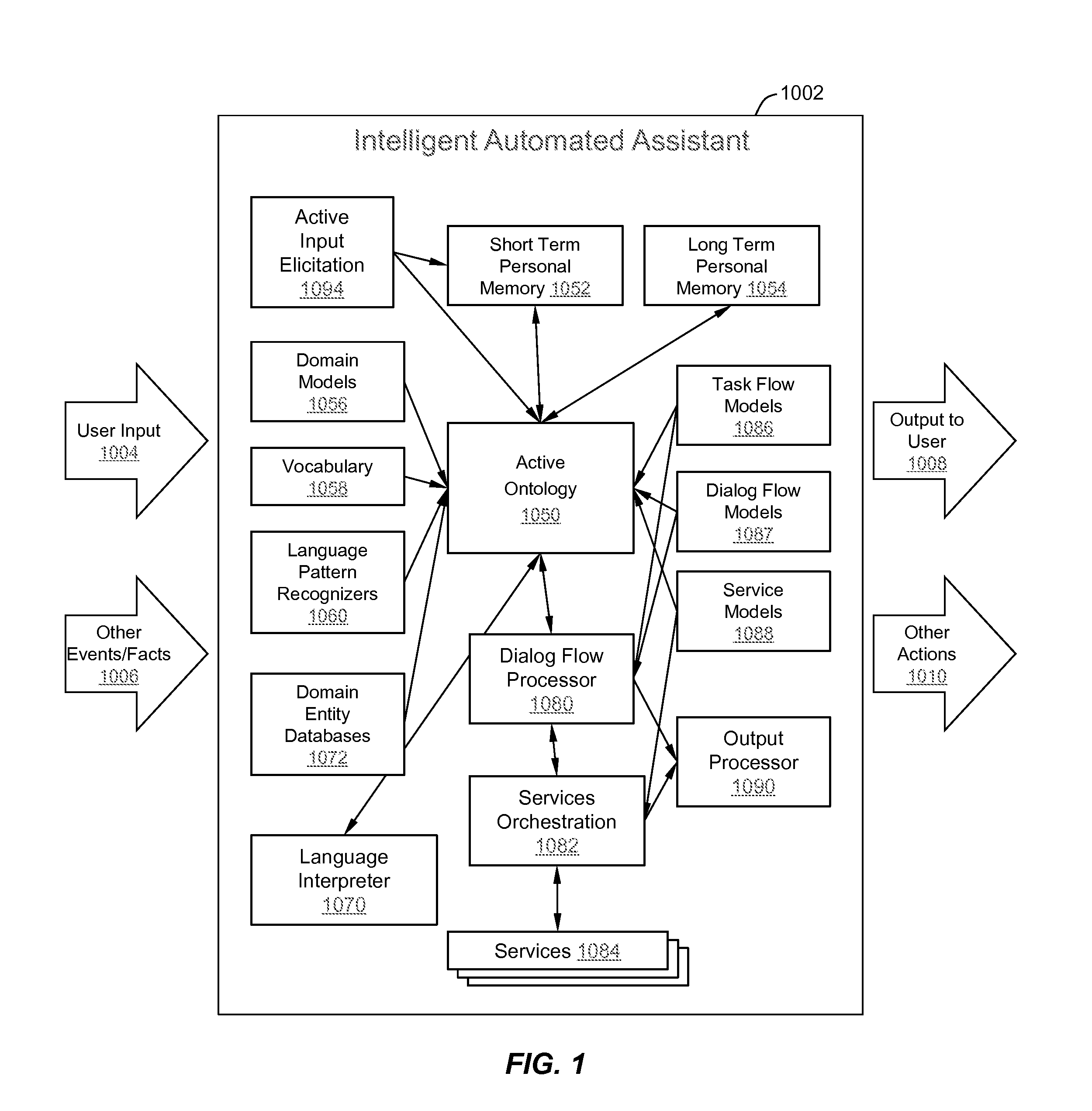
Intelligent Automated Assistant
ActiveUS20120245944A1Improve user interactionEffectively engageNatural language translationSemantic analysisService provisionComputer science
The intelligent automated assistant system engages with the user in an integrated, conversational manner using natural language dialog, and invokes external services when appropriate to obtain information or perform various actions. The system can be implemented using any of a number of different platforms, such as the web, email, smartphone, and the like, or any combination thereof. In one embodiment, the system is based on sets of interrelated domains and tasks, and employs additional functionally powered by external services with which the system can interact.
Owner:APPLE INC
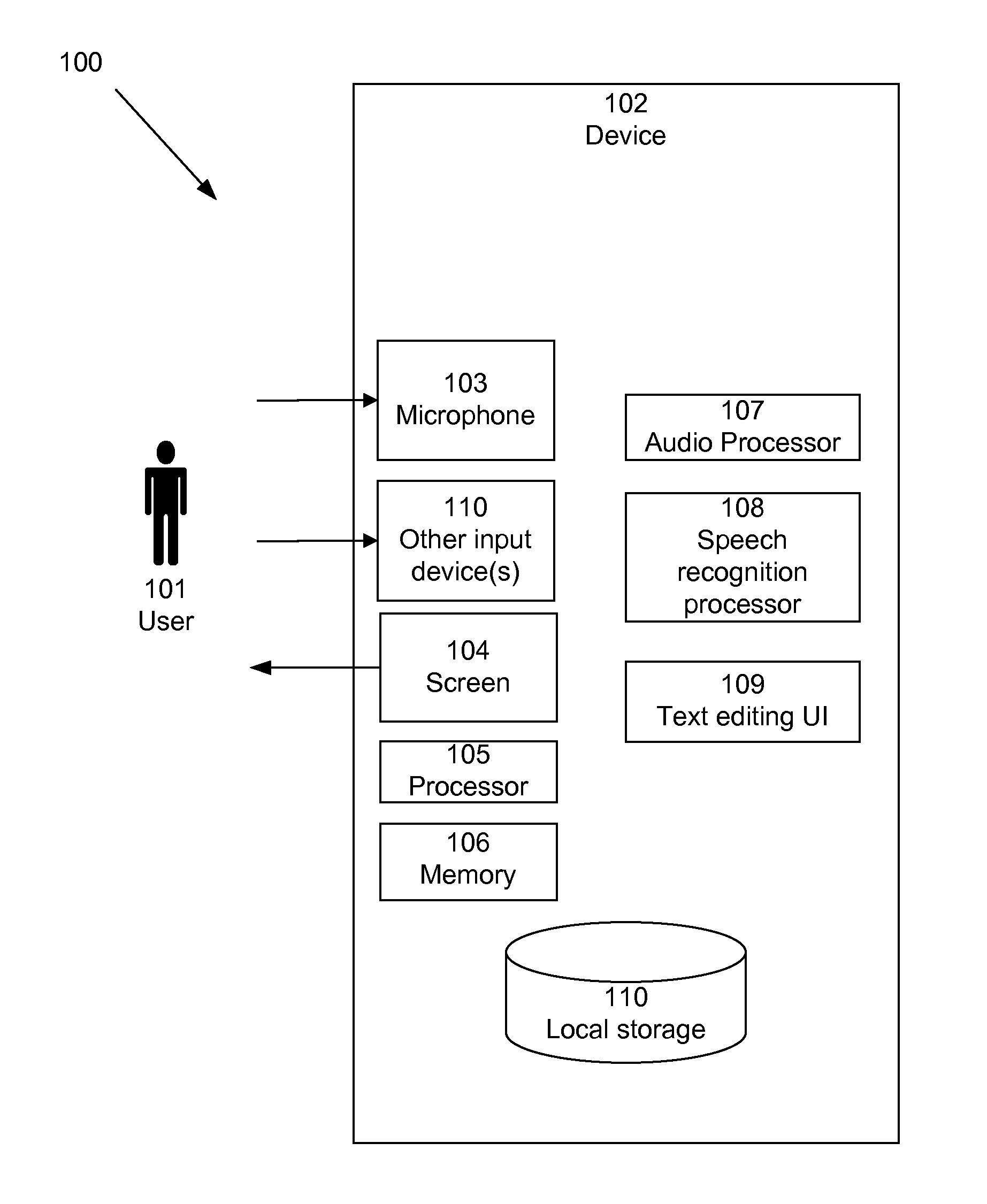
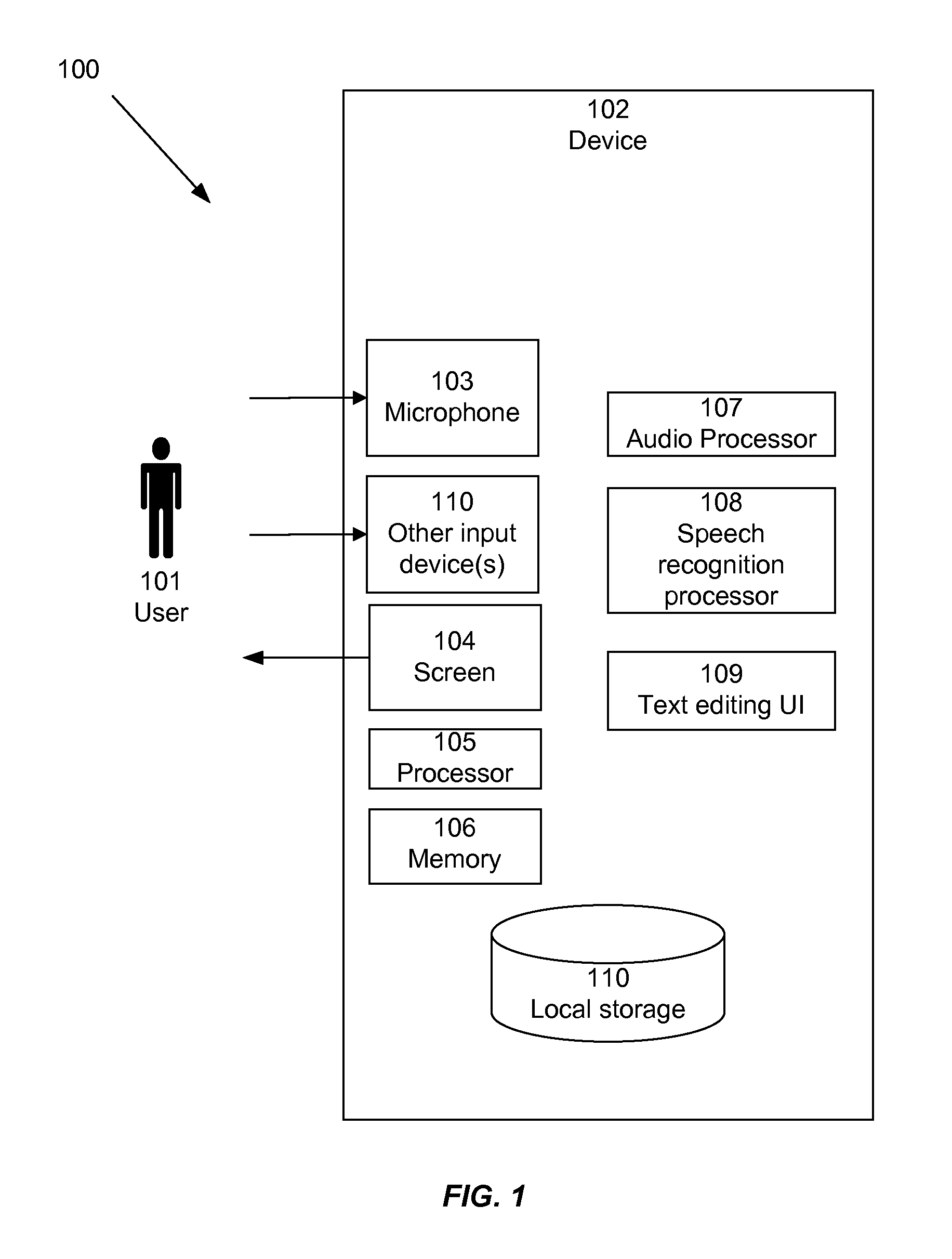
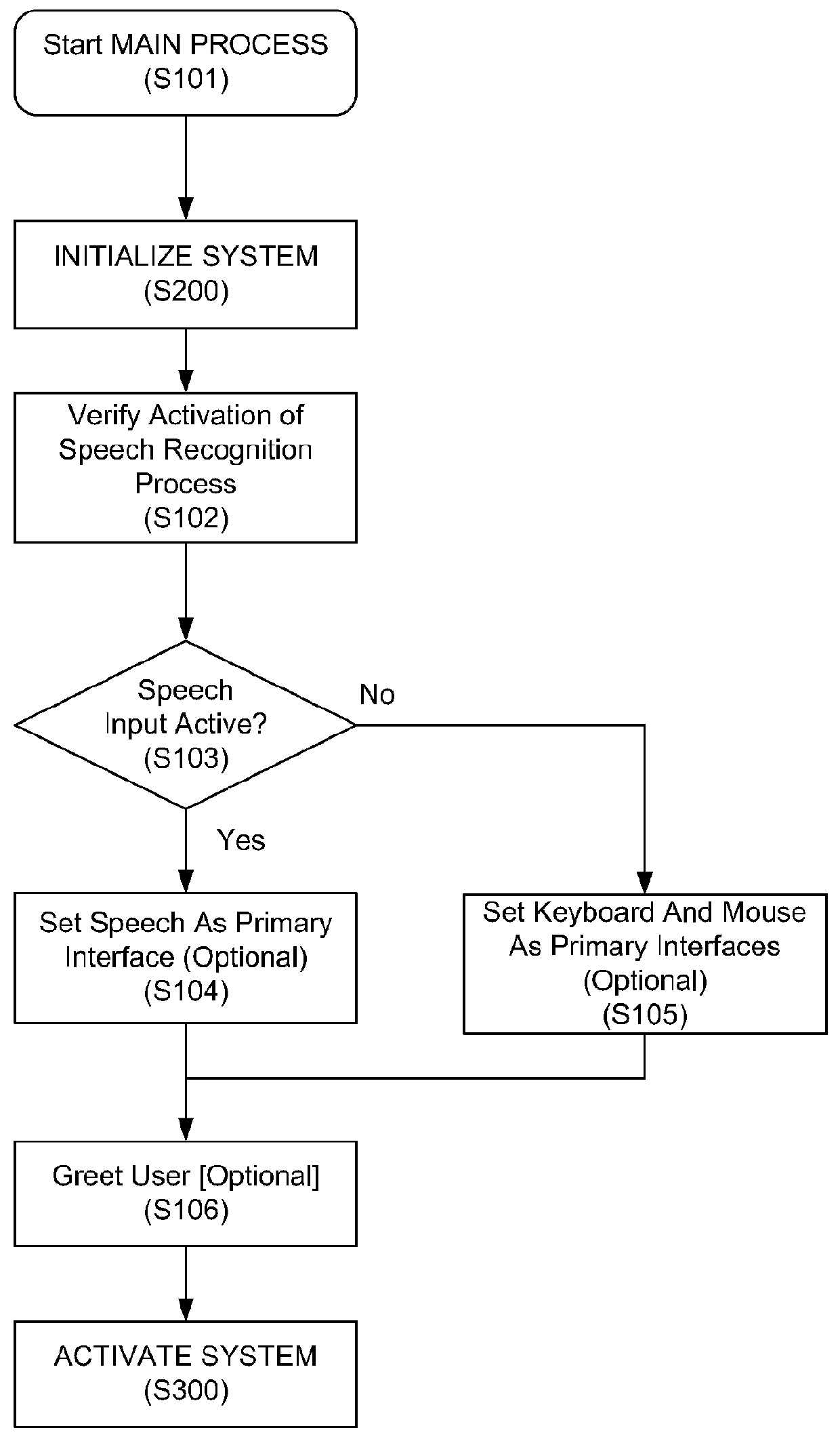
Speech interface system and method for control and interaction with applications on a computing system
ActiveUS8165886B1Reduce ambiguityImprove integritySound input/outputSpeech recognitionSpeech inputApplication software
A speech processing system which exploits statistical modeling and formal logic to receive and process speech input, which may represent data to be received, such as dictation, or commands to be processed by an operating system, application or process. A command dictionary and dynamic grammars are used in processing speech input to identify, disambiguate and extract commands. The logical processing scheme ensures that putative commands are complete and unambiguous before processing. Context sensitivity may be employed to differentiate data and commands. A multi faceted graphic user interface may be provided for interaction with a user to speech enable interaction with applications and processes that do not necessarily have native support for speech input.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
System and method for an integrated, multi-modal, multi-device natural language voice services environment
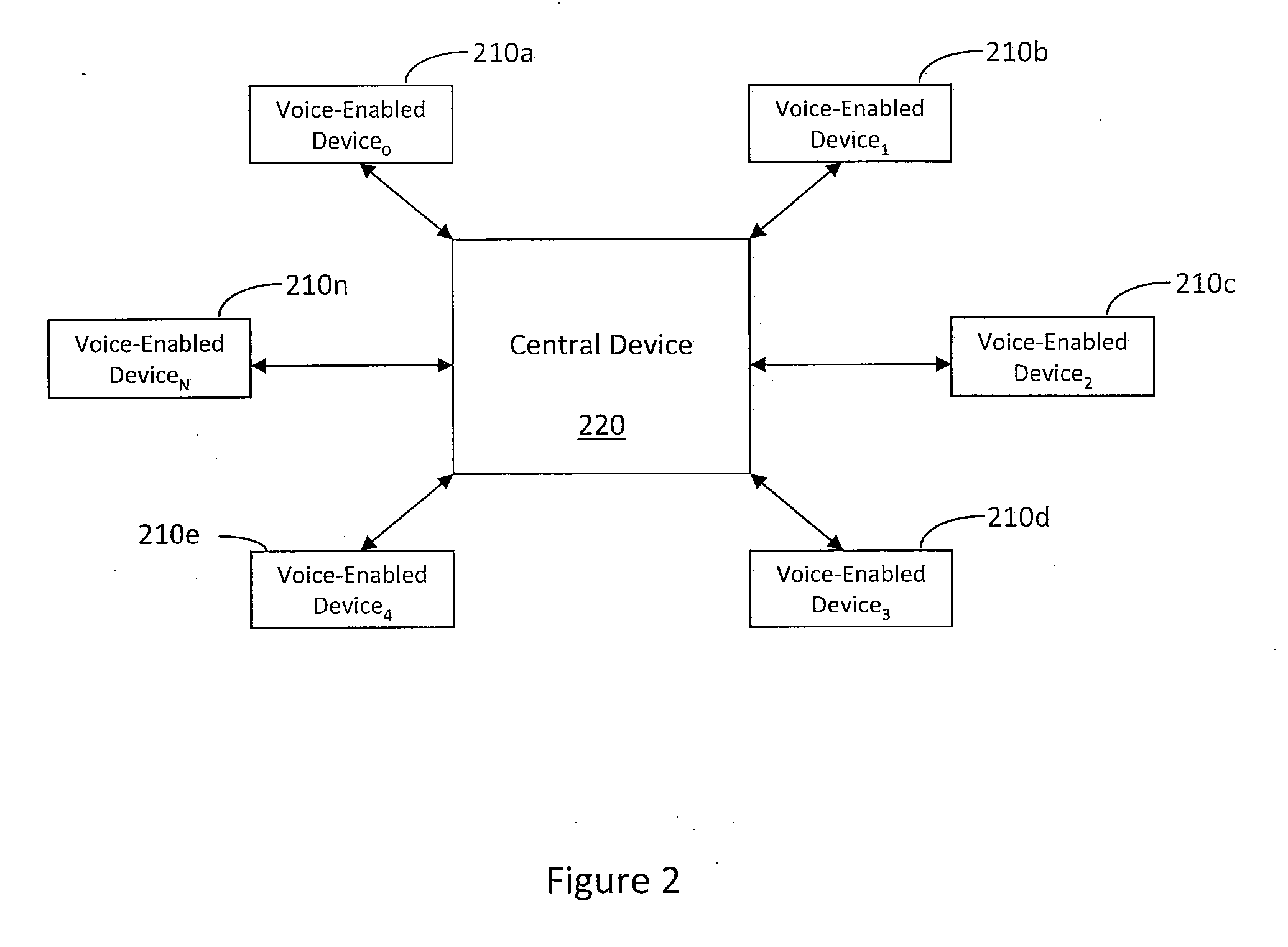
A system and method for an integrated, multi-modal, multi-device natural language voice services environment may be provided. In particular, the environment may include a plurality of voice-enabled devices each having intent determination capabilities for processing multi-modal natural language inputs in addition to knowledge of the intent determination capabilities of other devices in the environment. Further, the environment may be arranged in a centralized manner, a distributed peer-to-peer manner, or various combinations thereof. As such, the various devices may cooperate to determine intent of multi-modal natural language inputs, and commands, queries, or other requests may be routed to one or more of the devices best suited to take action in response thereto.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Multi-access mode electronic personal assistant
InactiveUS6895558B1Digital data information retrievalMultiplex communicationVocal responseData access
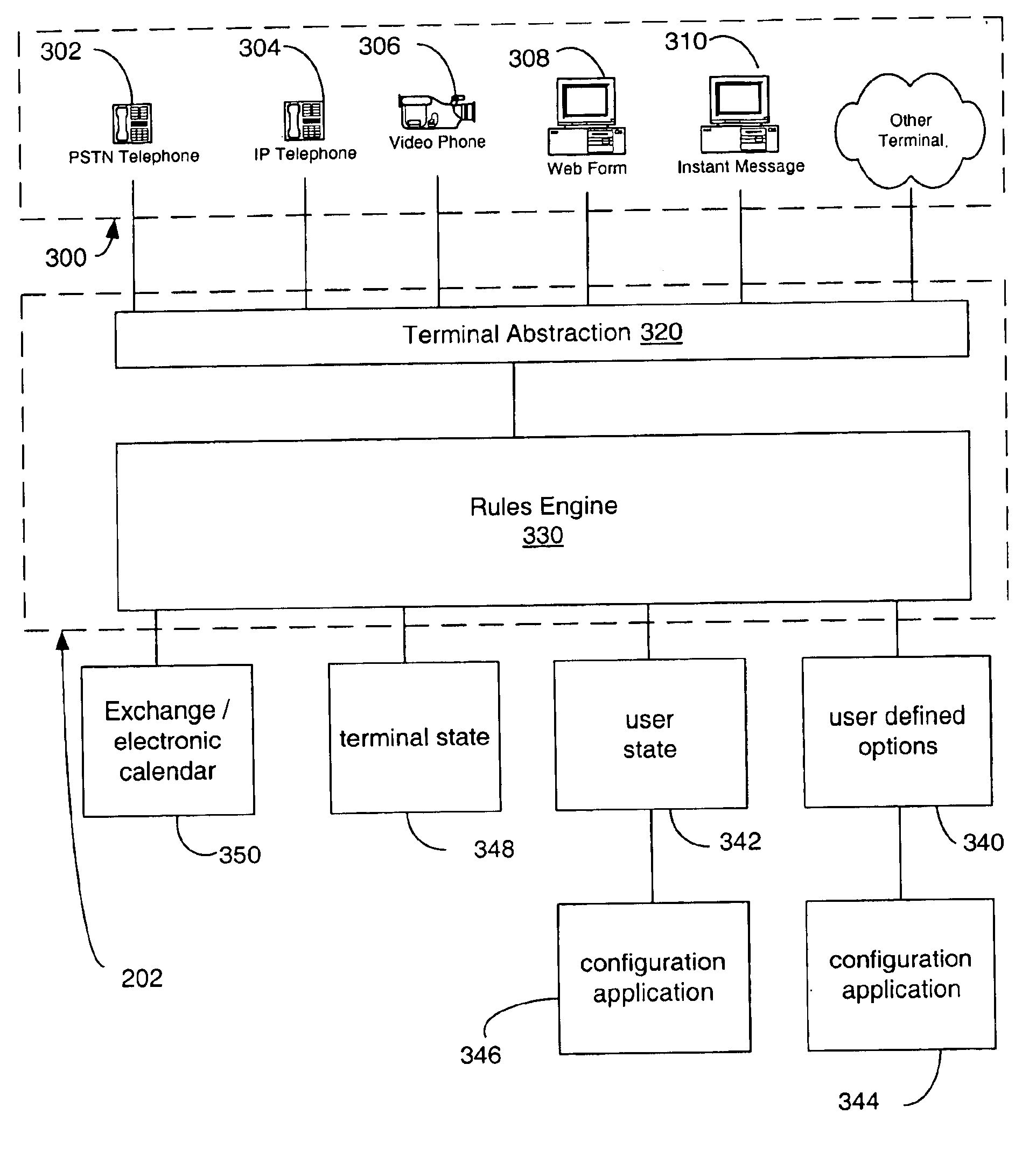
A system enables communication between server resources and a wide spectrum of end-terminals to enable access to the resources of both converged and non-converged networks via voice and / or electronically generated commands. An electronic personal assistant (ePA) incorporates generalizing / abstracting communications channels, data and resources provided through a converged computer / telephony system interface such that the data and resources are readily accessed by a variety of interface formats including a voice interface or data interface. A set of applications provides dual interfaces for rendering services and data based upon the manner in which a user accesses the data. An electronic personal assistant in accordance with an embodiment of the invention provides voice / data access to web pages, email, file shares, etc. A voice-based resource server authenticates a user by receiving vocal responses to one or more requests variably selected and issued by a speaker recognition-based authentication facility. Thereafter an application proxy is created.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Automatically Adapting User Interfaces for Hands-Free Interaction
ActiveUS20130275875A1Adjusting operationAdapt to the environmentSound input/outputSpeech recognitionUser inputHands free
The method includes automatically, without user input and without regard to whether a digital assistant application has been separately invoked by a user, determining that the electronic device is in a vehicle. In some implementations, determining that the electronic device is in a vehicle comprises detecting that the electronic device is in communication with the vehicle (e.g., via a wired or wireless communication techniques and / or protocols). The method also includes, responsive to the determining, invoking a listening mode of a virtual assistant implemented by the electronic device. In some implementations, the method also includes limiting the ability of a user to view visual output presented by the electronic device, provide typed input to the electronic device, and the like.
Owner:APPLE INC
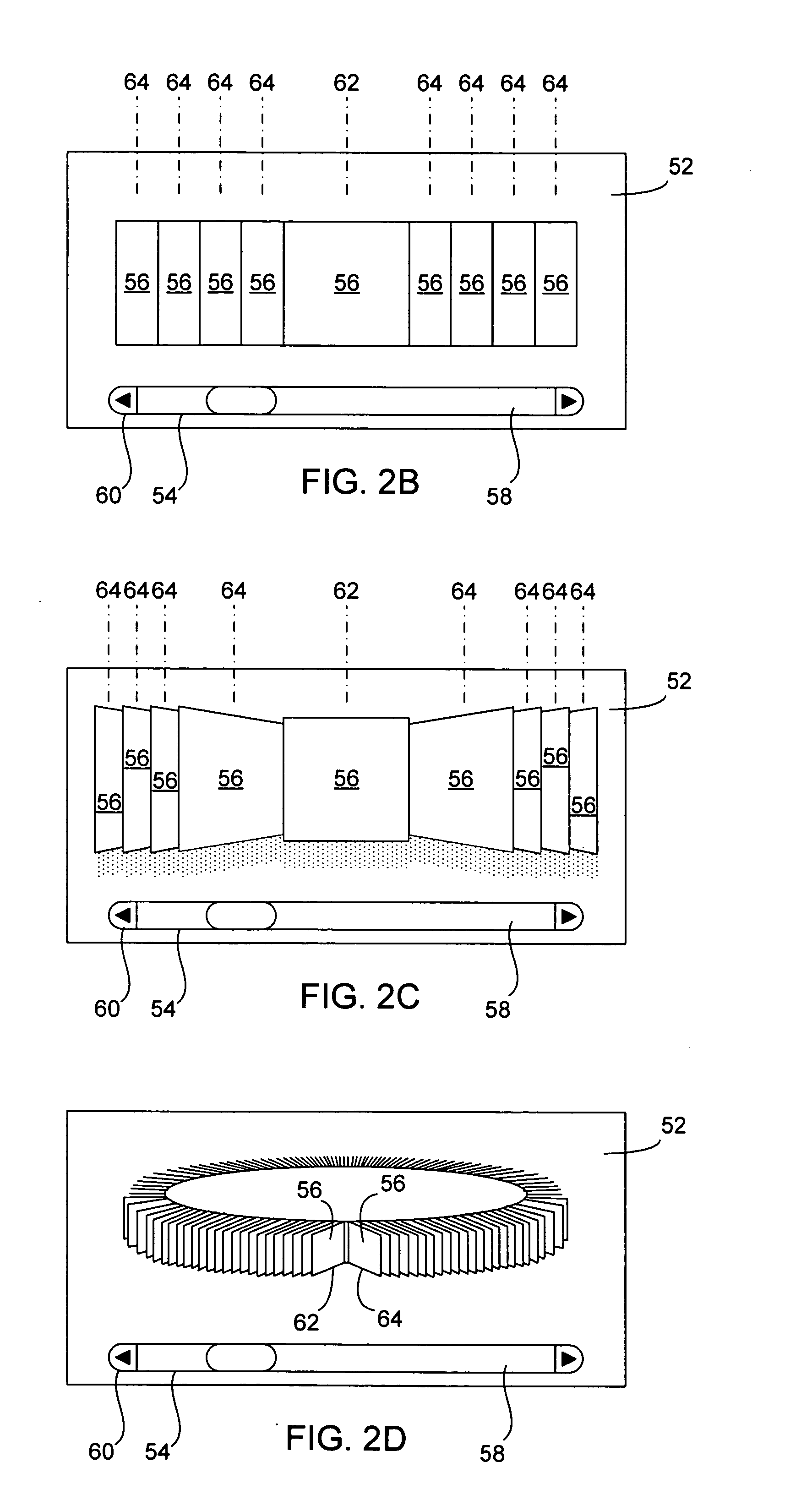
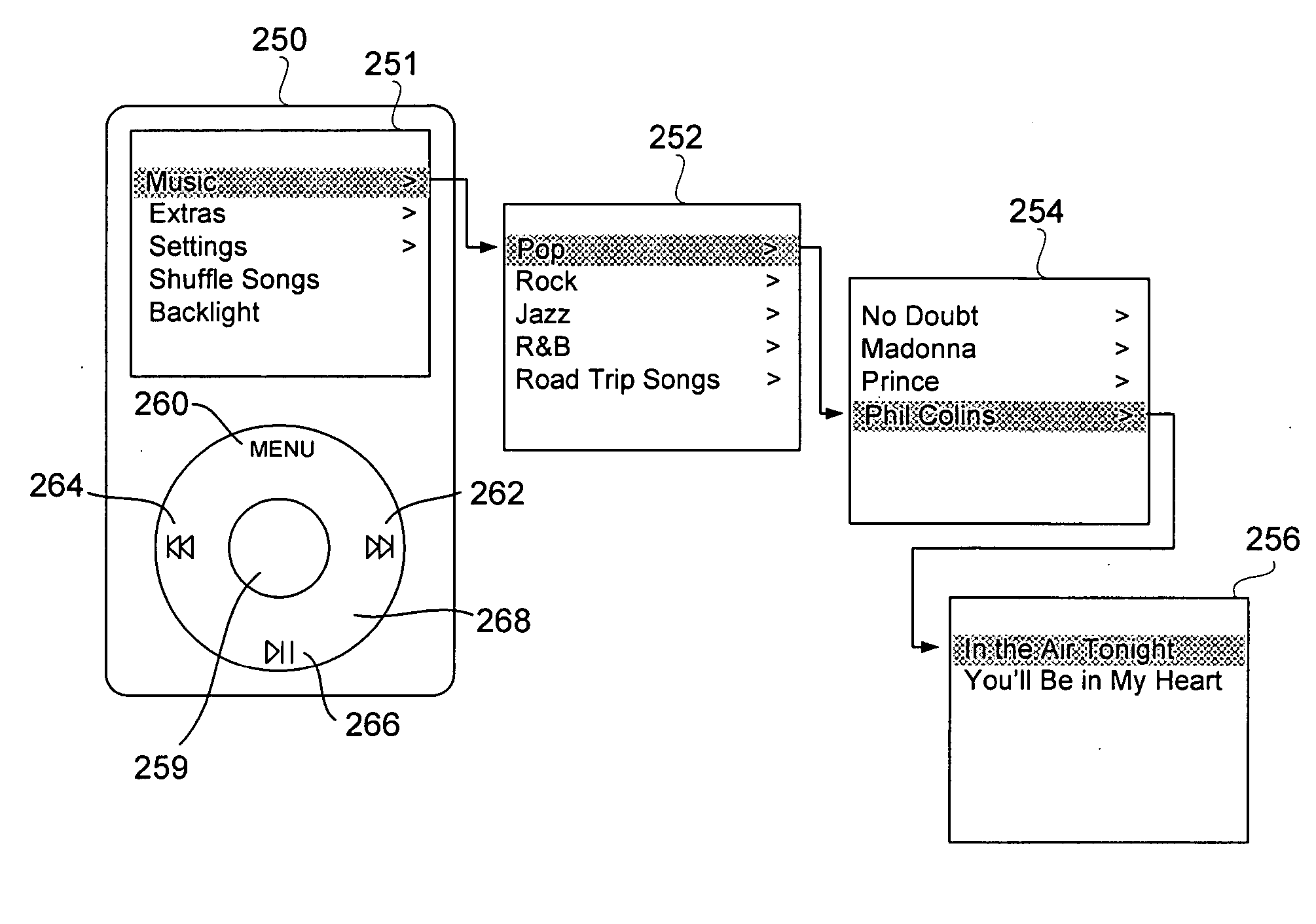
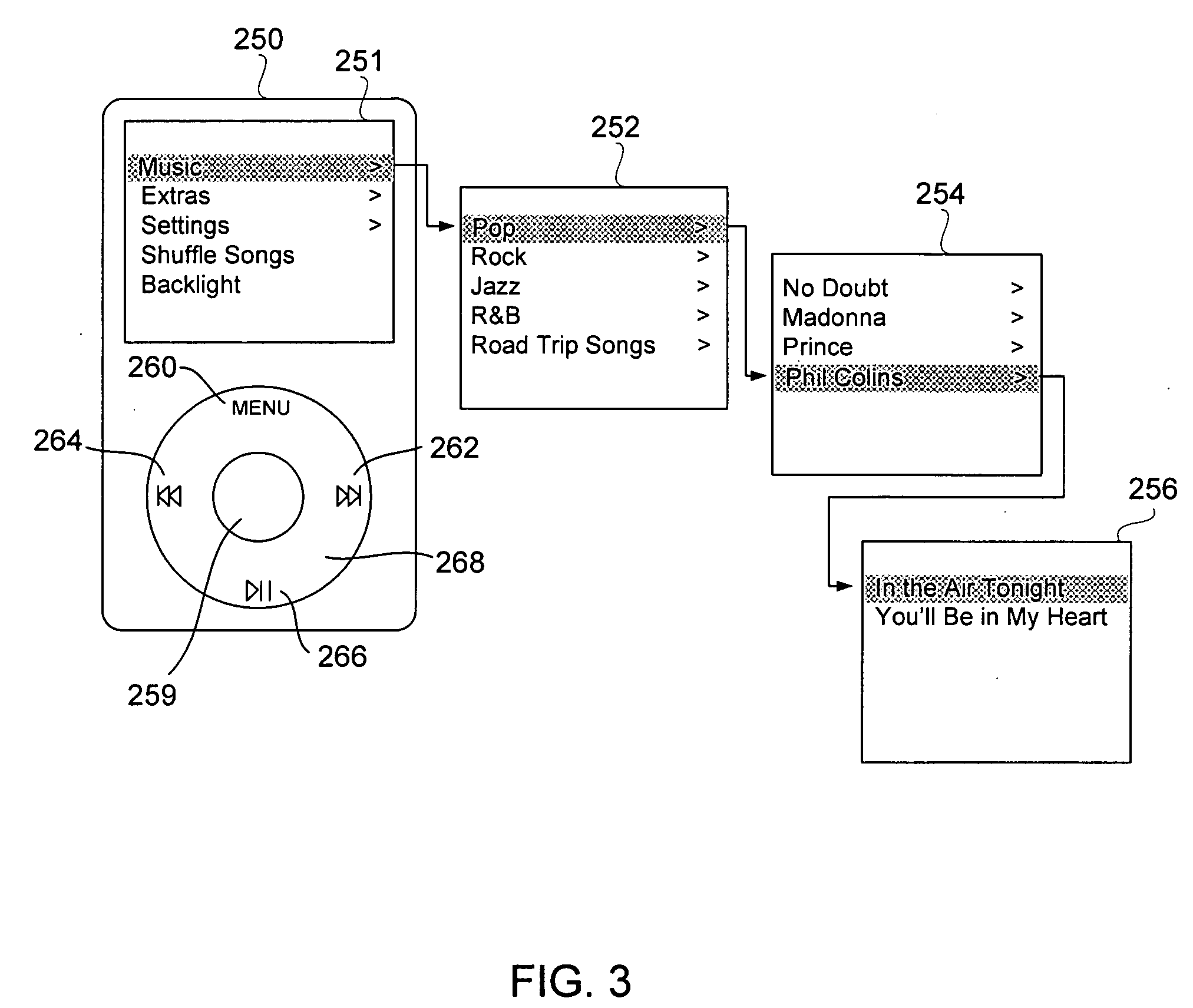
Media manager with integrated browsers
ActiveUS20080066016A1Metadata audio data retrievalSound input/outputGraphicsGraphical user interface
Methods and systems that improve the way media is played, sorted, modified, stored and cataloged are disclosed. One aspect relates to a browse window that allows a user to navigate through and select images that are related to media items. Another aspect relates to a graphical user interface of a media management program that utilizes multiple browse windows. Another aspect relates to simultaneously displayed media browse windows whose operations are integrated together so that the content shown therein is automatically synched when selections are made. Another aspect relates to resetting browsed content to the currently playing media.
Owner:APPLE INC
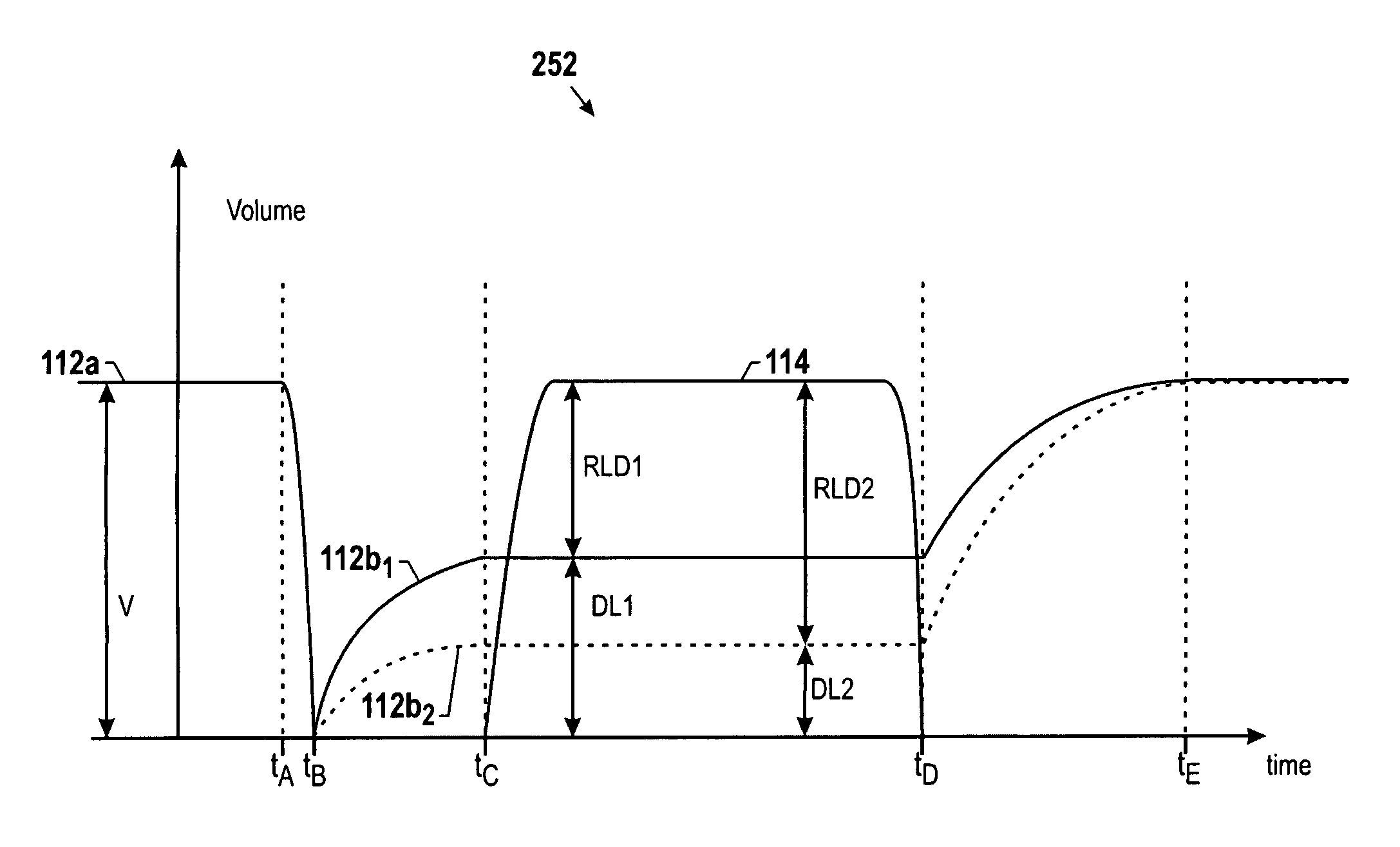
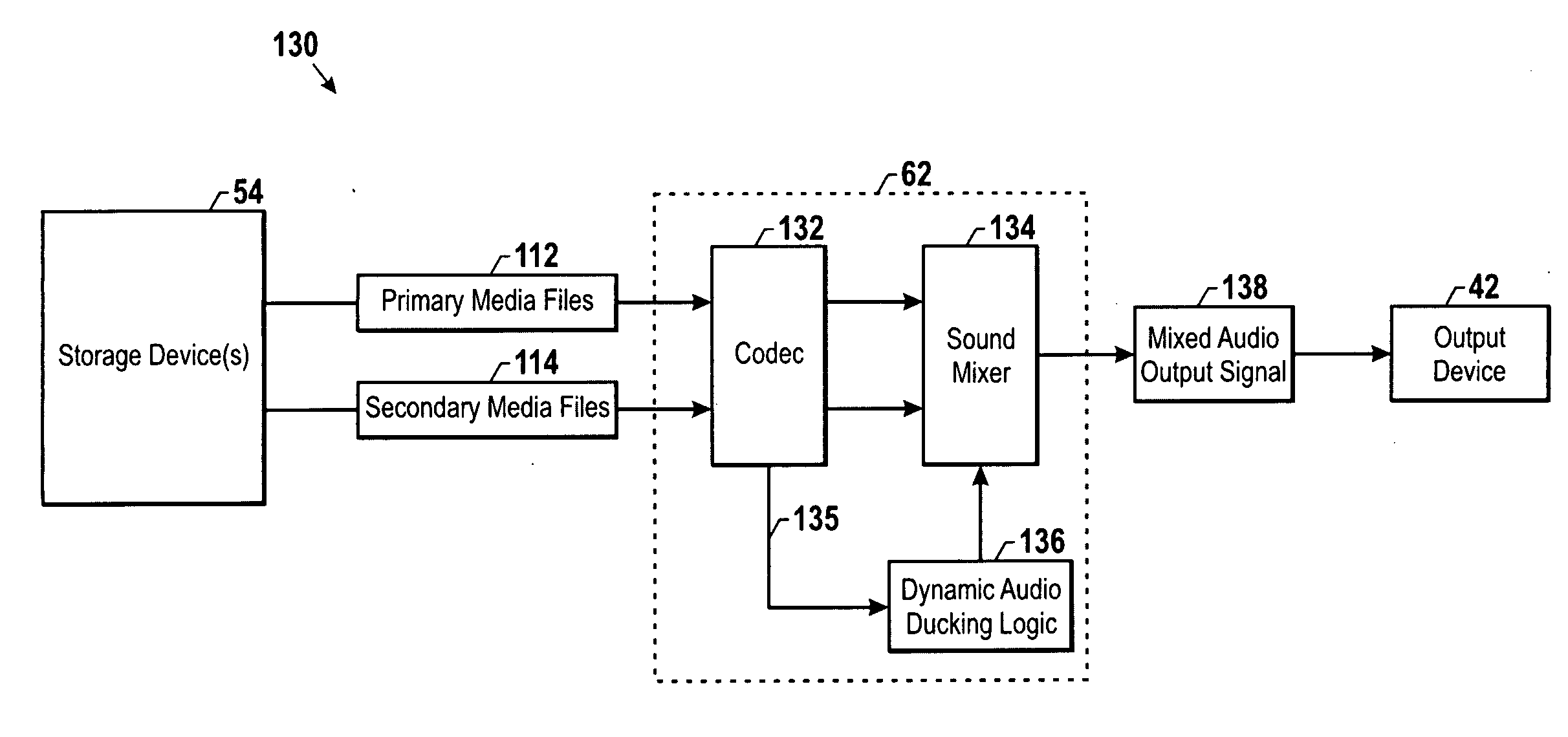
Dynamic audio ducking
Various dynamic audio ducking techniques are provided that may be applied where multiple audio streams, such as a primary audio stream and a secondary audio stream, are being played back simultaneously. For example, a secondary audio stream may include a voice announcement of one or more pieces of information pertaining to the primary audio stream, such as the name of the track or the name of the artist. In one embodiment, the primary audio data and the voice feedback data are initially analyzed to determine a loudness value. Based on their respective loudness values, the primary audio stream may be ducked during the period of simultaneous playback such that a relative loudness difference is generally maintained with respect to the loudness of the primary and secondary audio streams. Accordingly, the amount of ducking applied may be customized for each piece of audio data depending on its loudness characteristics.
Owner:APPLE INC
Dynamic audio ducking
Various dynamic audio ducking techniques are provided that may be applied where multiple audio streams, such as a primary audio stream and a secondary audio stream, are being played back simultaneously. For example, a secondary audio stream may include a voice announcement of one or more pieces of information pertaining to the primary audio stream, such as the name of the track or the name of the artist. In one embodiment, the primary audio data and the voice feedback data are initially analyzed to determine a loudness value. Based on their respective loudness values, the primary audio stream may be ducked during the period of simultaneous playback such that a relative loudness difference is generally maintained with respect to the loudness of the primary and secondary audio streams. Accordingly, the amount of ducking applied may be customized for each piece of audio data depending on its loudness characteristics.
Owner:APPLE INC
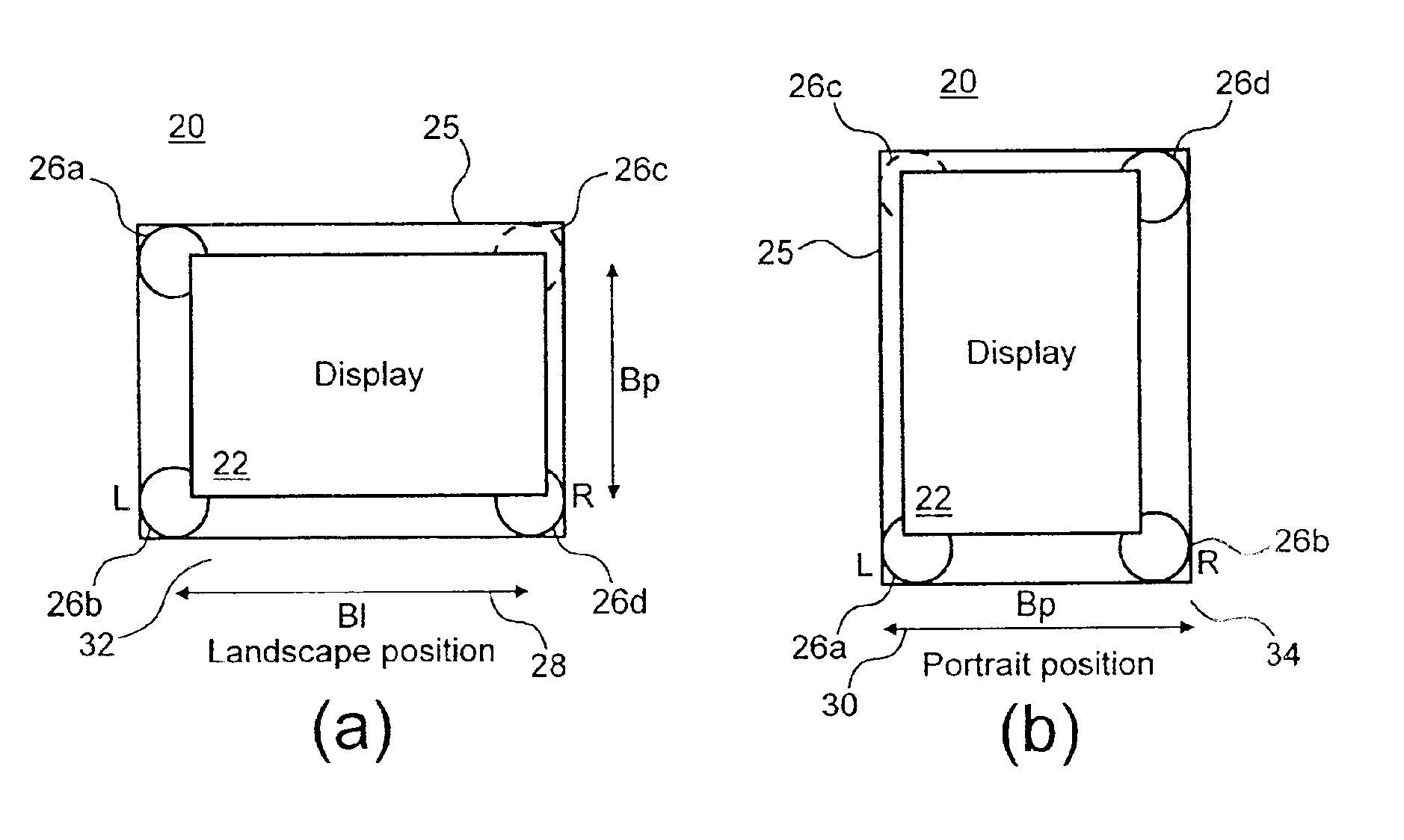
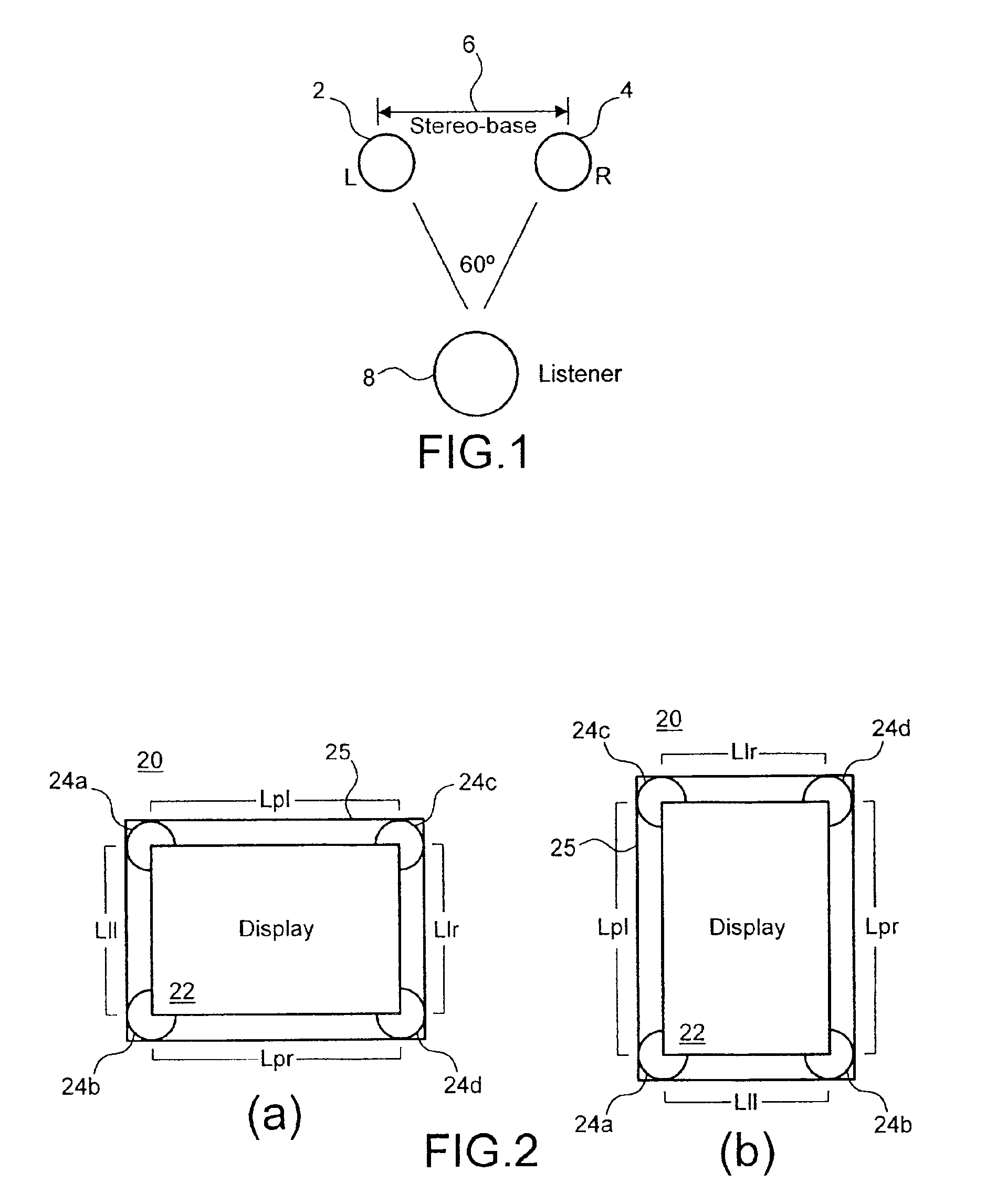
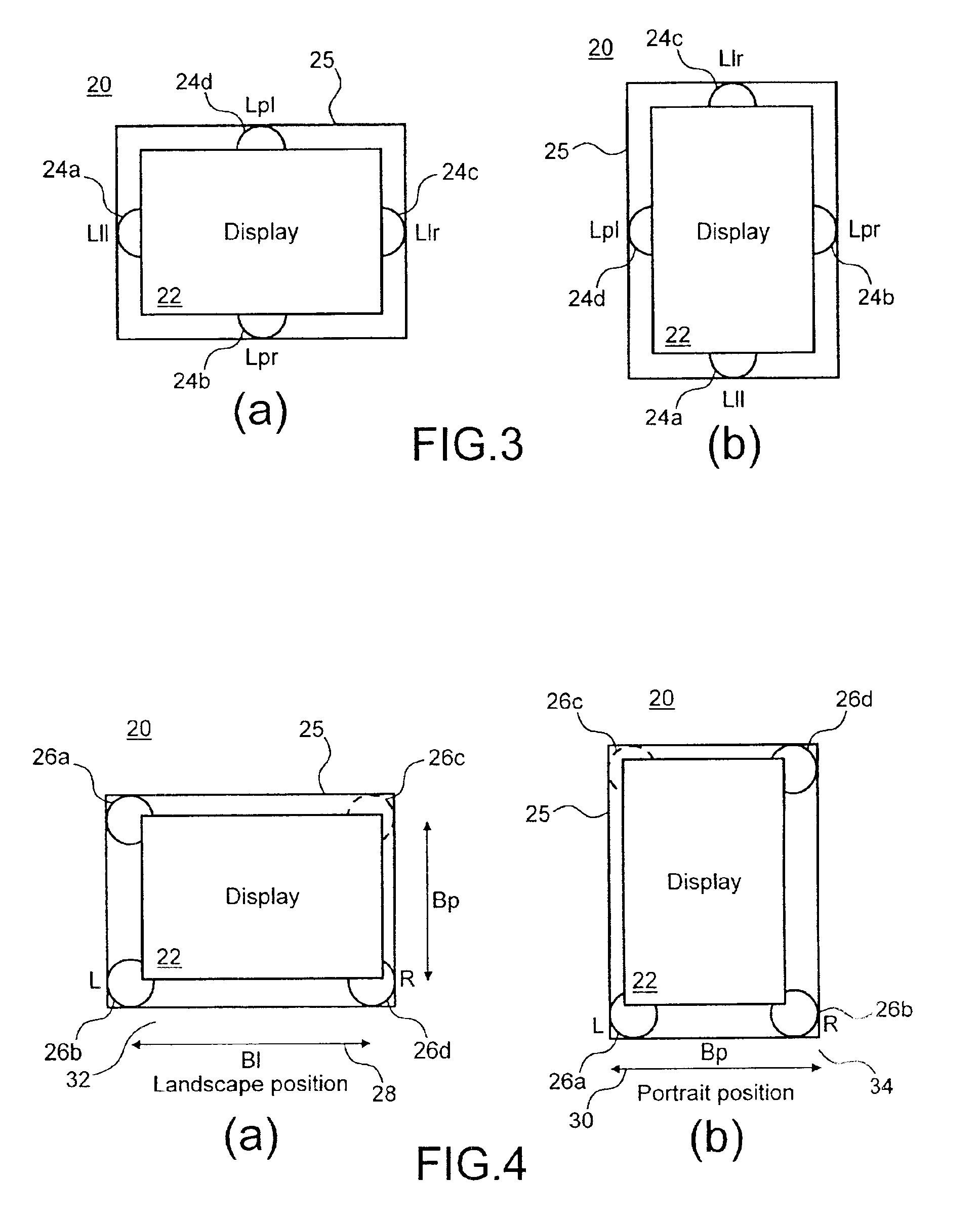
Stereophonic reproduction maintaining means and methods for operation in horizontal and vertical A/V appliance positions
InactiveUS6882335B2Improved audio listeningEnhance the imageTelevision system detailsDevices with sensorDisplay deviceEngineering
Display apparatus including a display and an orientation sensitive interface mechanism is disclosed. In an exemplary embodiment, the orientation sensitive interface includes first and second loudspeaker pairs. The first loudspeaker pair includes first and second loudspeakers and the second loudspeaker pair includes the second and third loudspeaker. The first and second loudspeaker pairs are disposed along transverse directions to each other. The display apparatus comprises a switch which switches between the first loudspeaker pair and the second loudspeaker pair. By providing the respective loudspeaker pairs, and switching between them, it is possible to orient the display apparatus in transverse directions corresponding to respective loudspeaker pairs, yet maintain a substantially stereophonic reproduction for each orientation.
Owner:HTC CORP
System and method for supporting interactive user interface operations and storage medium
InactiveUS7426467B2Easy to operateMeet demandInput/output for user-computer interactionTelevision system detailsAnimationCommand system
There is provided a system for supporting interactive operations for inputting user commands to a household electric apparatus such as a television set / monitor and information apparatuses. According to the system for supporting interactive operations applying an animated character called a personified assistant interacting with a user based on speech synthesis and animation, realizing a user-friendly user interface and simultaneously making it possible to meet a demand for complex commands or providing an entry for services. Further, since the system is provided with a command system producing an effect close to human natural language, the user can easily operate the apparatus with a feeling close to ordinary human conversation.
Owner:SONY CORP
Competing devices responding to voice triggers
At a first electronic device with a display and a microphone: sampling audio input using the first microphone; in accordance with the sampling of audio input using the first microphone, sending stop instructions to a second electronic device with a second microphone, the second electronic device external to the first electronic device, wherein the second electronic device is configured to respond to audio input received using the second microphone, and wherein the stop instructions instruct the second electronic device to forgo responding to audio input received using the second microphone, wherein responding to audio input received using the second microphone comprises providing perceptible output.
Owner:APPLE INC
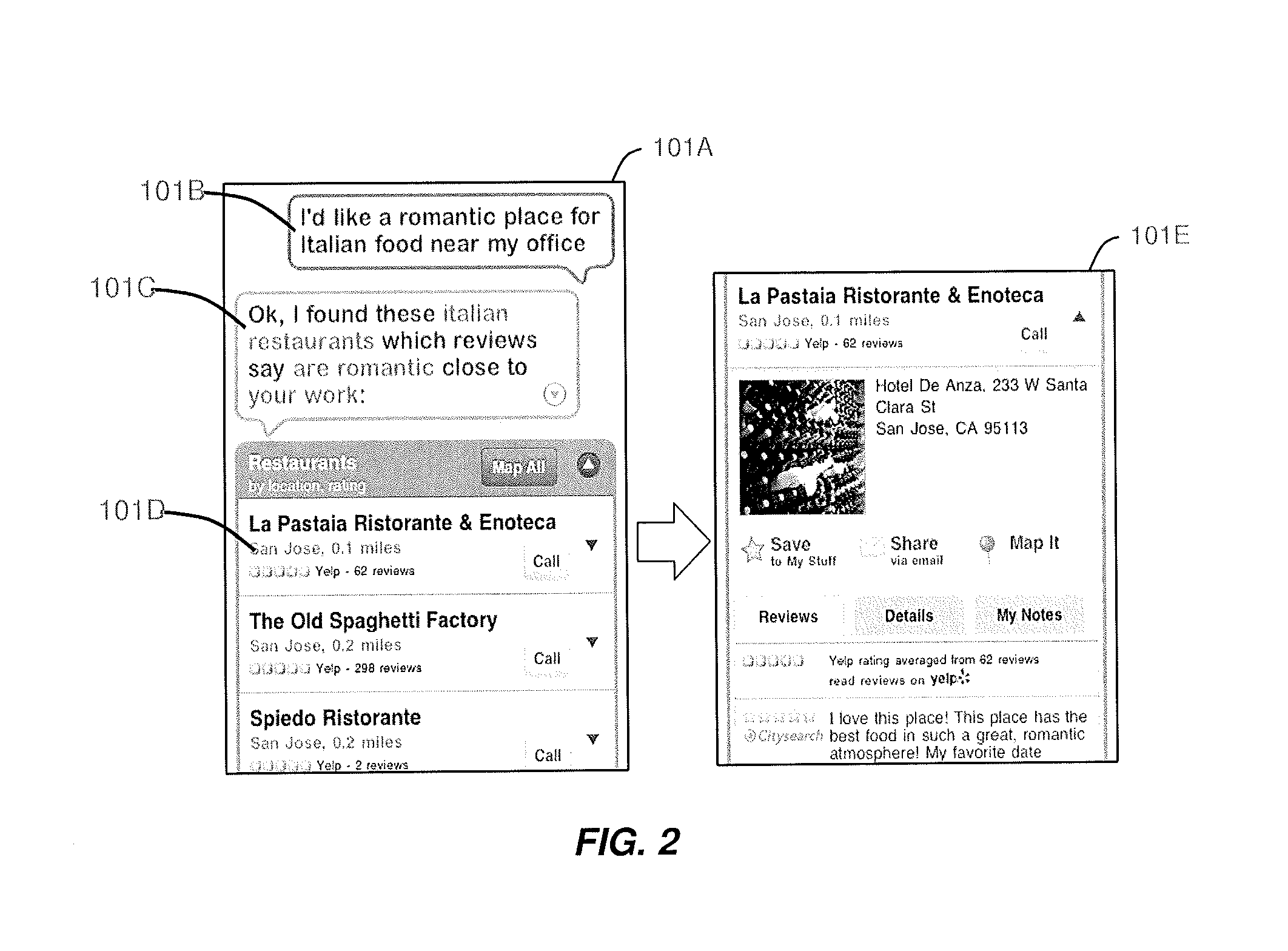
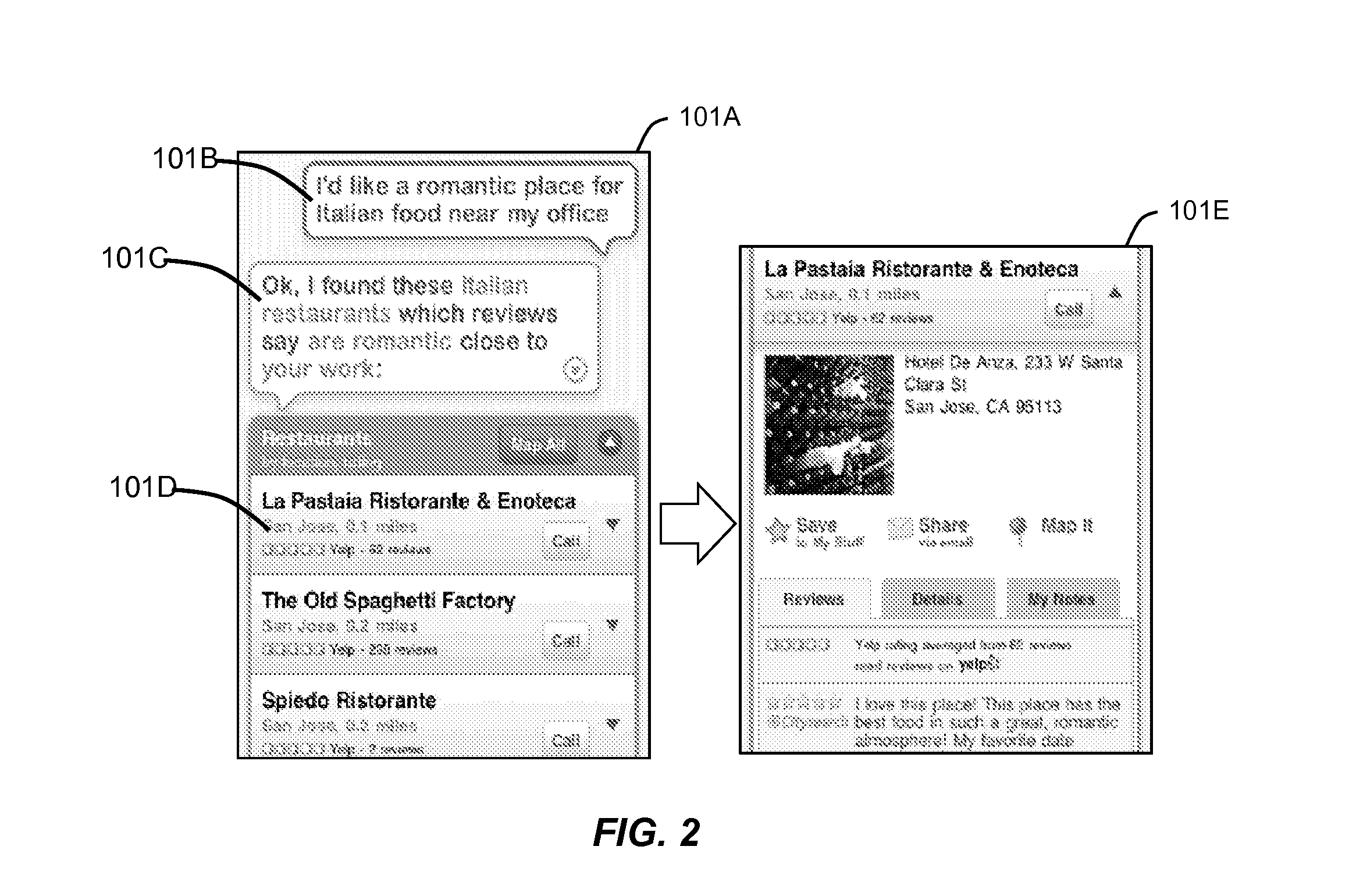
Prioritizing Selection Criteria by Automated Assistant
ActiveUS20130111348A1Improve user interactionEffectively engageNatural language translationSemantic analysisSelection criterionSpeech input
Methods, systems, and computer readable storage medium related to operating an intelligent digital assistant are disclosed. A user request is received, the user request including at least a speech input received from a user. The user request including the speech input is processed to obtain a representation of user intent for identifying items of a selection domain based on at least one selection criterion. A prompt is provided to the user, the prompt presenting two or more properties relevant to items of the selection domain and requesting the user to specify relative importance between the two or more properties. A listing of search results is provided to the user, where the listing of search results has been obtained based on the at least one selection criterion and the relative importance provided by the user.
Owner:APPLE INC
Audio user interface for computing devices
ActiveUS20060095848A1Easy to carryEfficient leveragingRecord information storageCarrier indicating arrangementsHand heldHand held devices
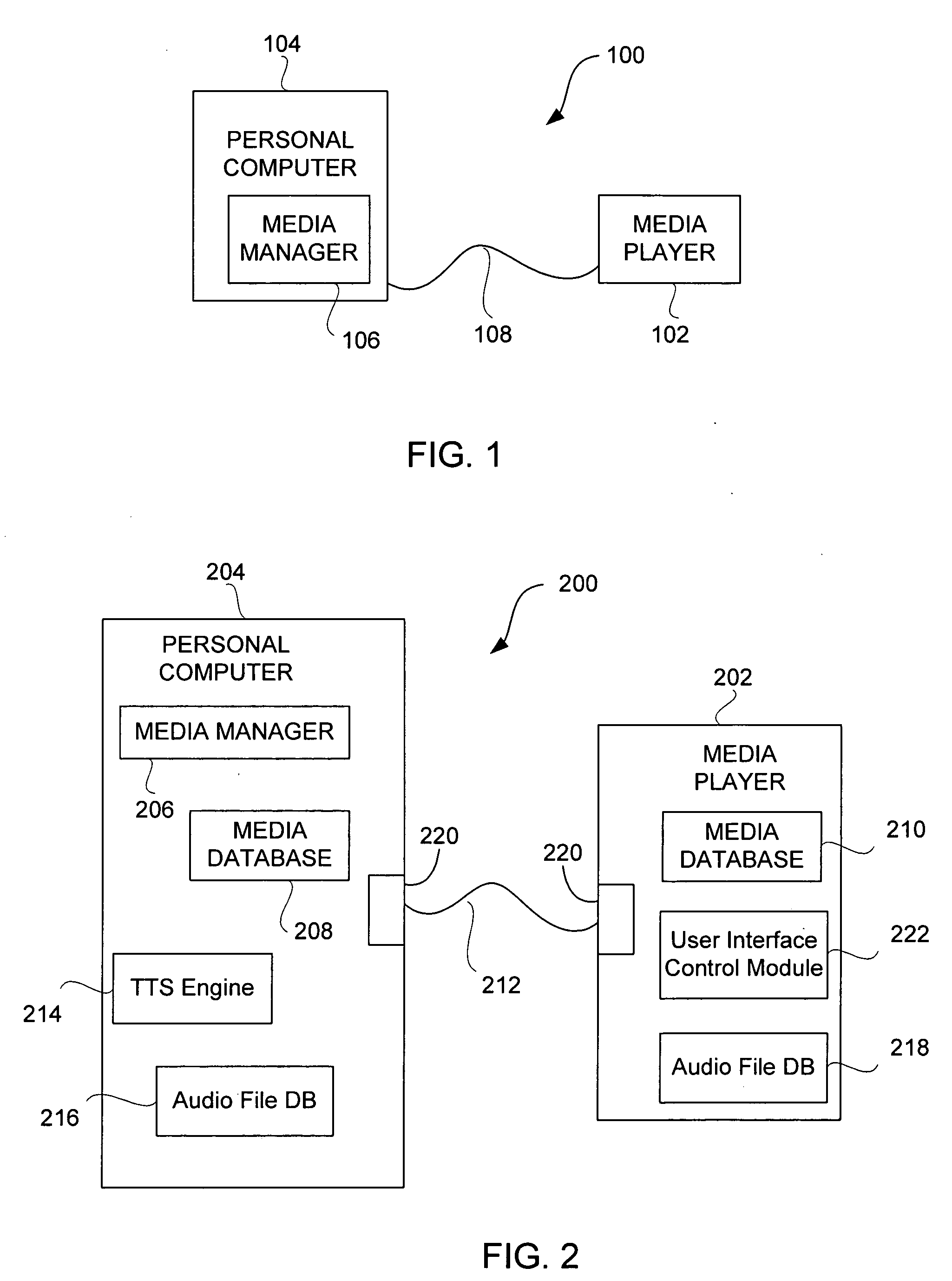
An audio user interface that generates audio prompts that help a user interact with a user interface of a device is disclosed. One aspect of the present invention pertains to techniques for providing the audio user interface by efficiently leveraging the computing resources of a host computer system. The relatively powerful computing resources of the host computer can convert text strings into audio files that are then transferred to the computing device. The host system performs the process intensive text-to-speech conversion so that a computing device, such as a hand-held device, only needs to perform the less intensive task of playing the audio file. The computing device can be, for example, a media player such as an MP3 player, a mobile phone, or a personal digital assistant.
Owner:APPLE INC
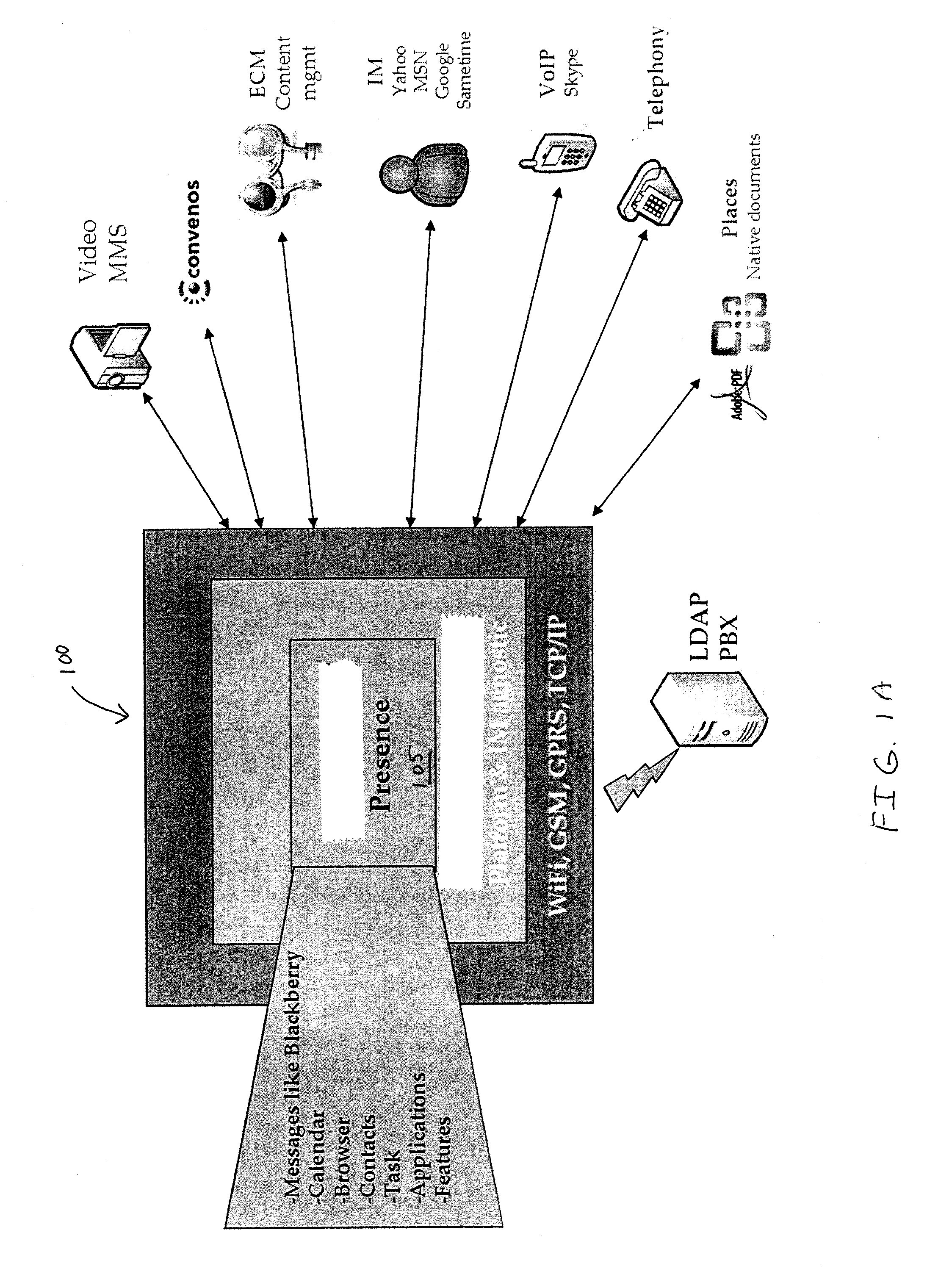
Apparatus, system, method, and computer program product for collaboration via one or more networks
InactiveUS20090019367A1Work well togetherFacilitate conferencing and collaborationDigital data protectionMultiple digital computer combinationsVirtual conferenceSpeech sound
A collaboration architecture supports virtual meetings, including web conferencing and collaboration. Presence information is aggregated from different types of communication services to provide a generic representation of presence. In one implementation, collaboration lifecycle management is provided to manage meetings over the lifecycle of a project. Audio options include voice over internet protocol (VoIP) and conventional PTSN phone networks, which are supported in one implementation by an audio conferencing server.
Owner:CONVENOUS
Interface for a Virtual Digital Assistant
The digital assistant displays a digital assistant object in an object region of a display screen. The digital assistant then obtains at least one information item based on a speech input from a user. Upon determining that the at least one information item can be displayed in its entirety in the display region of the display screen, the digital assistant displays the at least one information item in the display region, where the display region and the object region are not visually distinguishable from one another. Upon determining that the at least one information item cannot be displayed in its entirety in the display region of the video display screen, the digital assistant displays a portion of the at least one information item in the display region, where the display region and the object region are visually distinguishable from one another.
Owner:APPLE INC
Hand-ear user interface for hand-held device
InactiveUS6978127B1Small sizeInput/output for user-computer interactionInterconnection arrangementsInformation processingPersonalization
A hand-held information processing device, such as a mobile phone, has a thumb wheel that lets the user scan a circular array of options. Each respective one of the options is represented by a respective audio output that gets played out when the wheel is turned a notch up or down. This enables the user to select an option with one hand and without having to look at the device. It also allows for a form factor smaller than that of a conventional mobile phones since a keypad is not needed for entering digits to make a call from a personalized directory.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Disambiguation Based on Active Input Elicitation by Intelligent Automated Assistant
ActiveUS20130110515A1Improve user interactionEffectively engageNatural language translationSemantic analysisUser inputSpeech input
Owner:APPLE INC
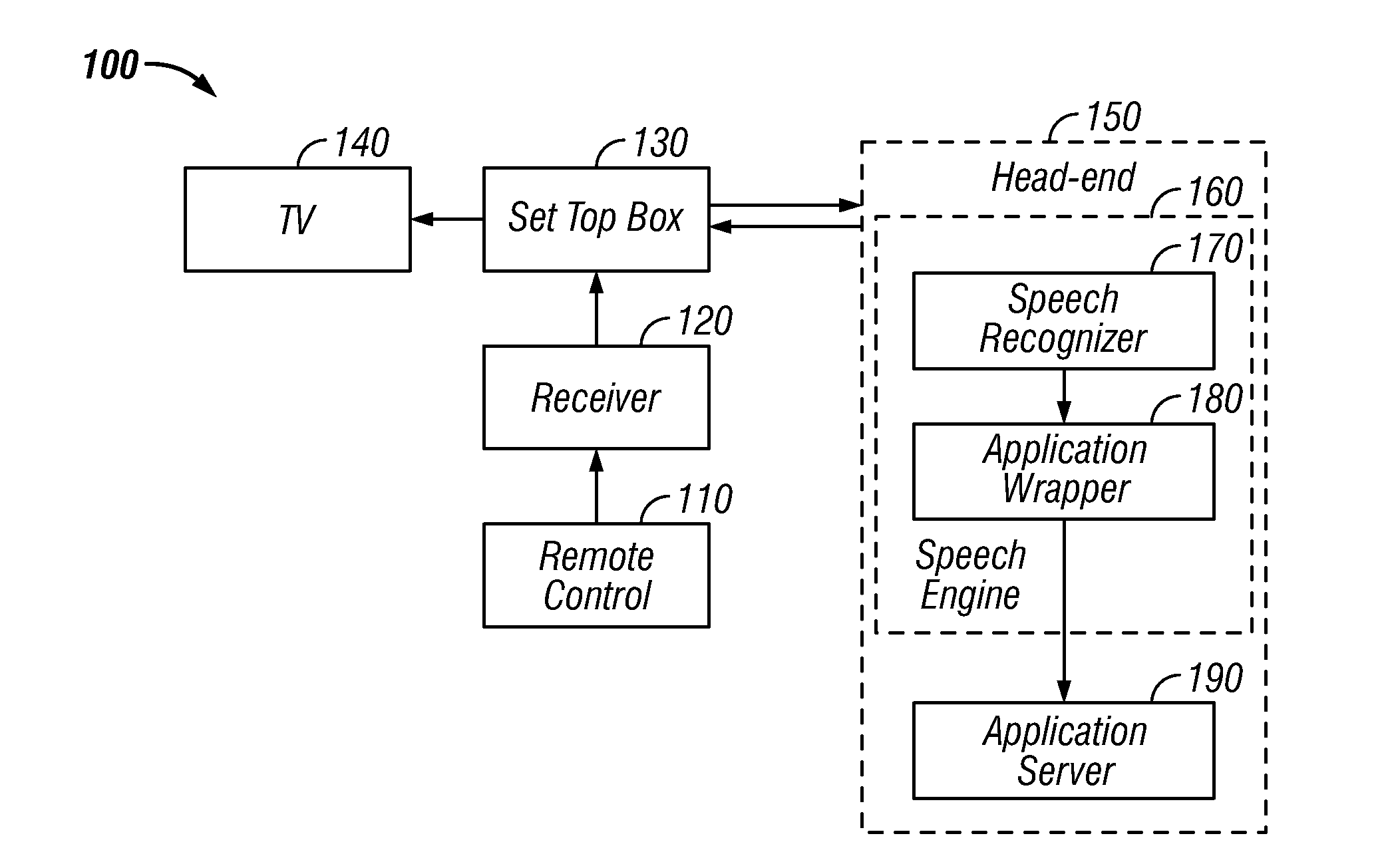
Global speech user interface
ActiveUS20080120112A1Good informationInput/output for user-computer interactionTelevision system detailsTelevision screenApplication software
A global speech user interface (GSUI) comprises an input system to receive a user's spoken command, a feedback system along with a set of feedback overlays to give the user information on the progress of his spoken requests, a set of visual cues on the television screen to help the user understand what he can say, a help system, and a model for navigation among applications. The interface is extensible to make it easy to add new applications.
Owner:PROMPTU SYST CORP
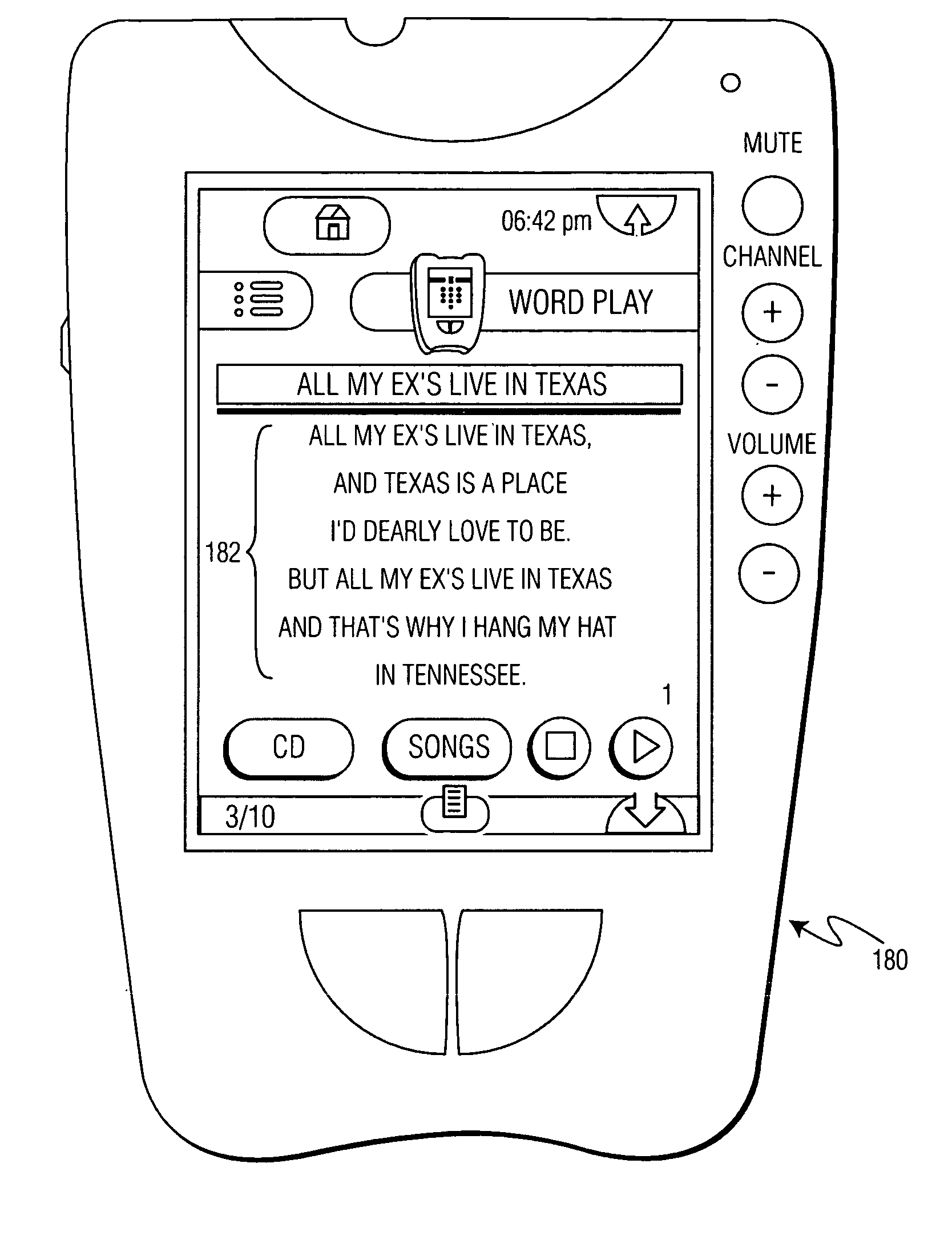
Synchronizing text/visual information with audio playback
InactiveUS7058889B2Particular applicabilityElectrophonic musical instrumentsAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsTimestampDisplay device
A method of synchronizing visual information with audio playback includes the steps of selecting a desired audio file from a list stored in memory associated with a display device, sending a signal from the display device to a separate playback device to cause the separate playback device to start playing the desired audio file; and displaying visual information associated with the desired audio file on the display device in accordance with timestamp data such that the visual information is displayed synchronously with the playing of the desired audio file, wherein the commencement of playing the desired audio file and the commencement of the displaying step are a function of the signal from the display device.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Systems and methods to select media content
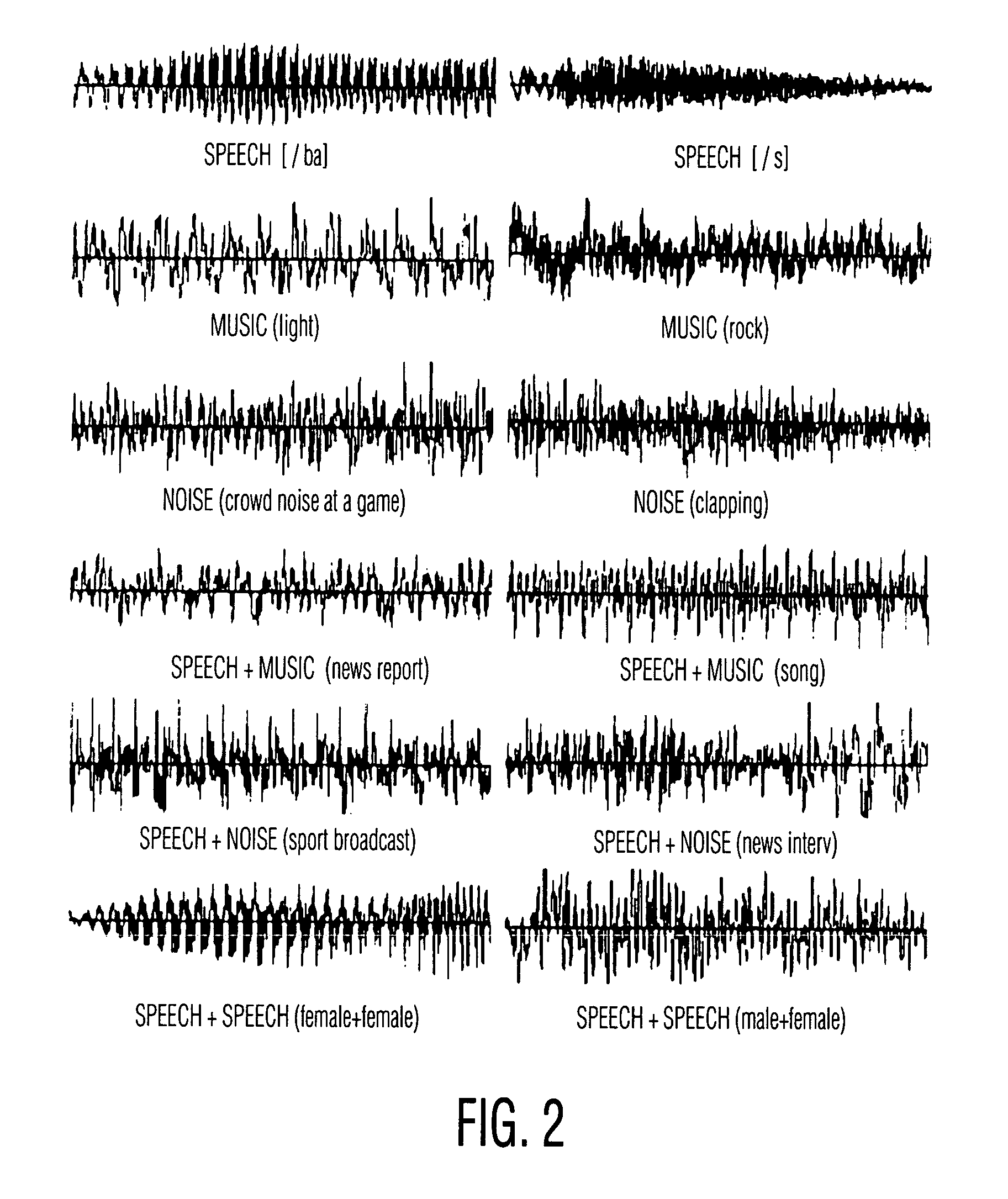
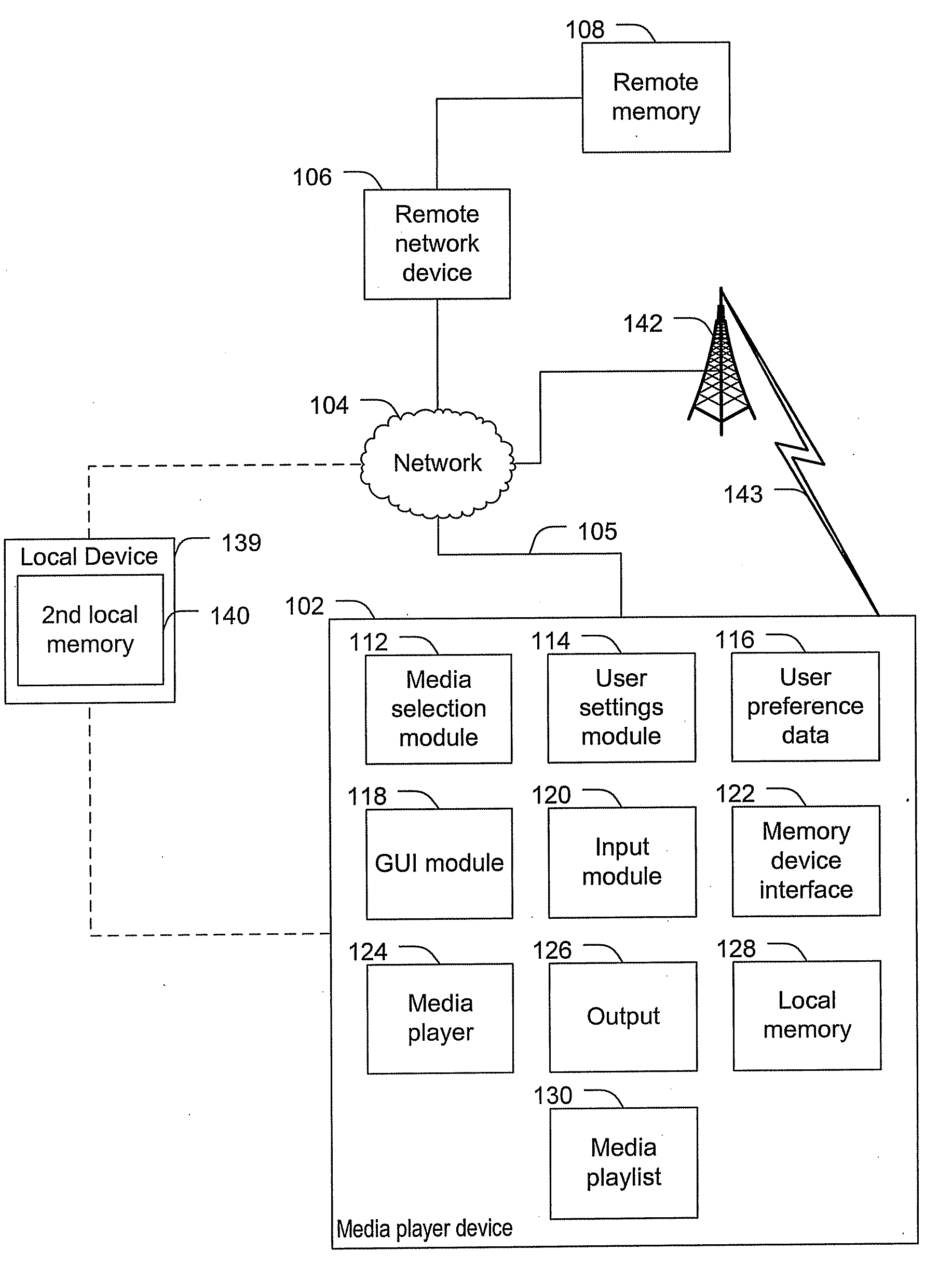
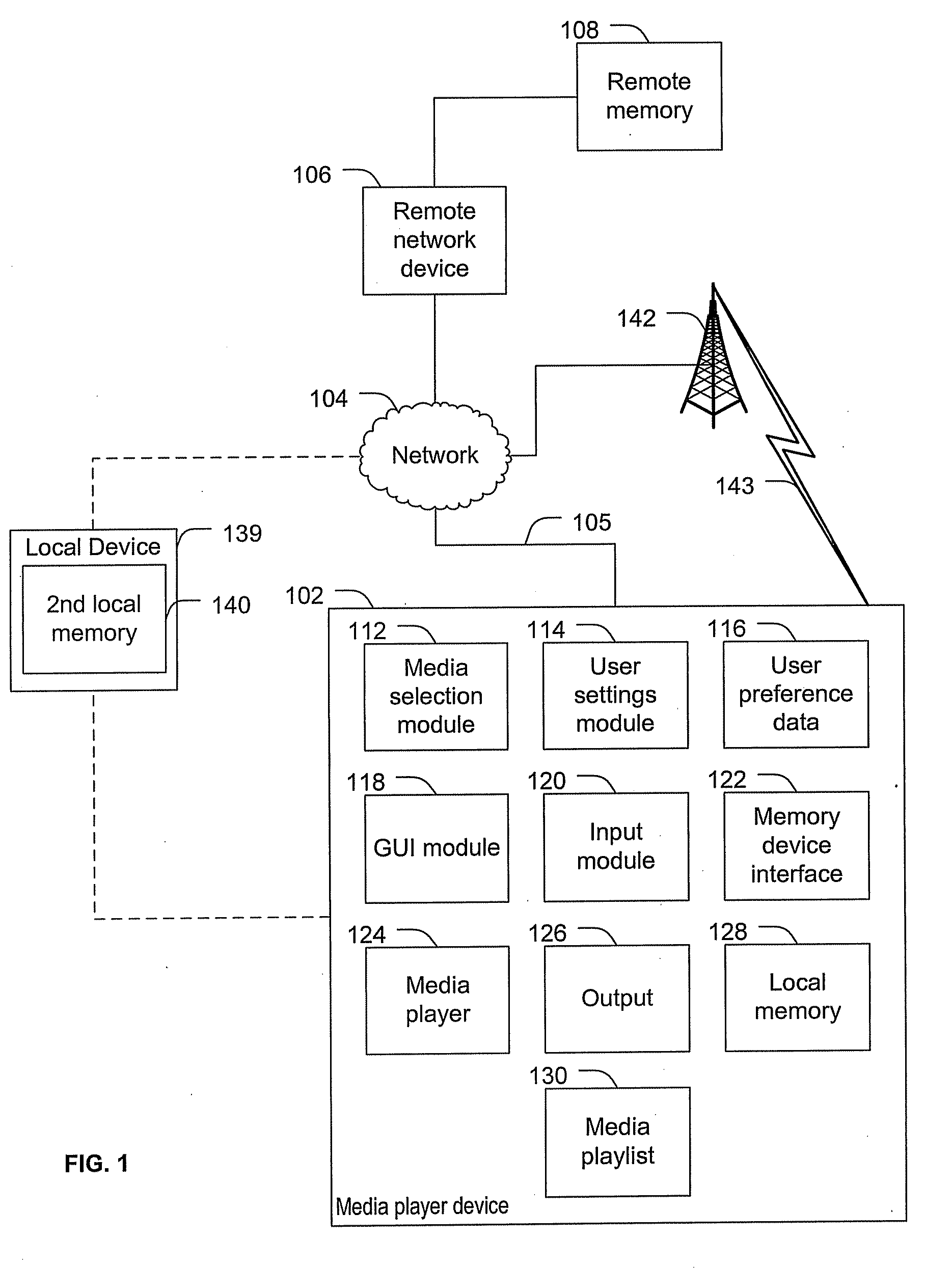
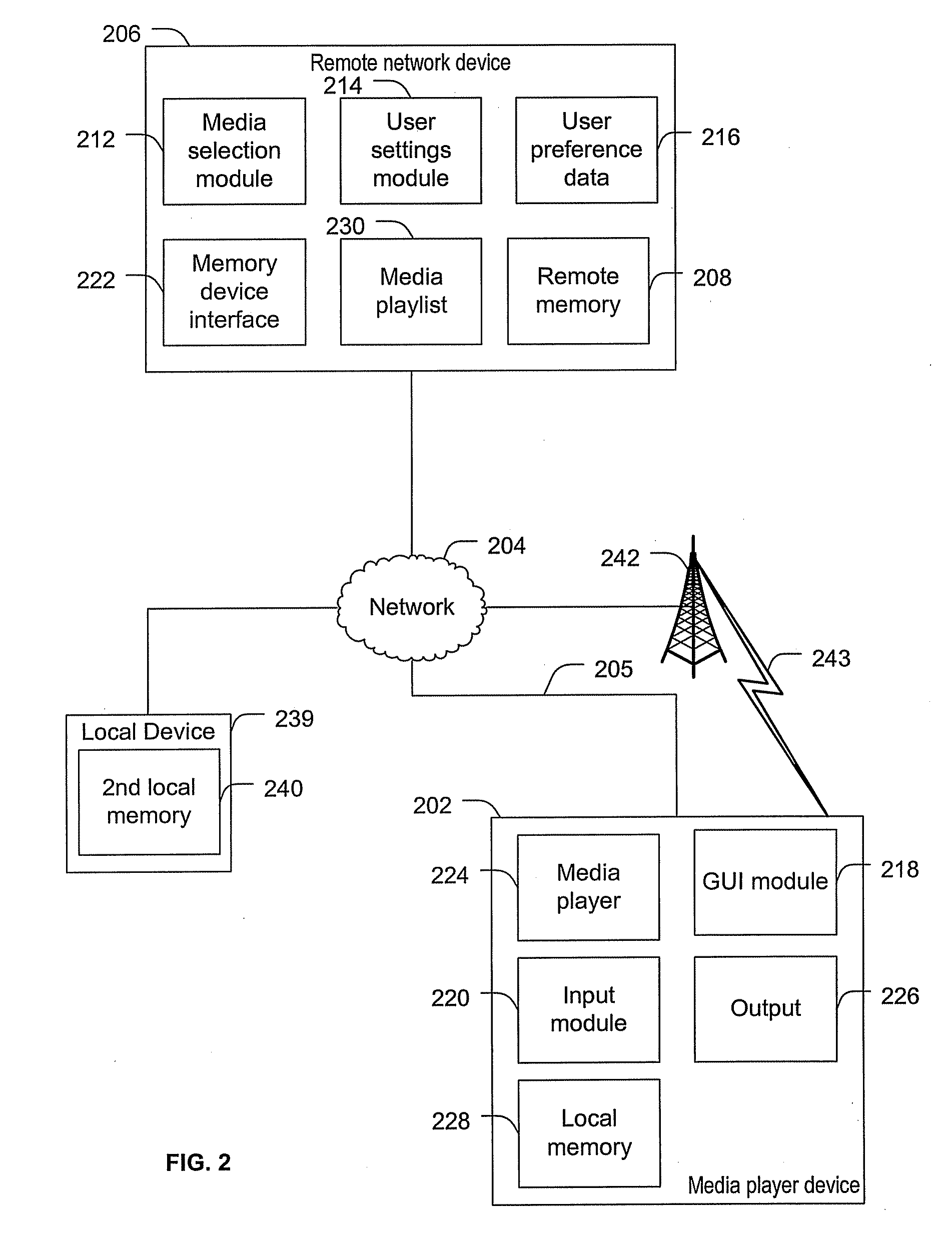
ActiveUS20100131895A1Multiple digital computer combinationsSound input/outputUser definedDynamic choice
Systems and methods to select media content are provided. A method includes dynamically selecting content items for presentation via a media player based on user media selection settings. The user media selection settings specify a proportion of a first category of media content to be presented and a proportion of at least one second category of media content to be presented. The at least one second category includes a user defined category. First media content is associated with the first category based on an intrinsic property of the first media content and second media content is associated with the user defined category based on a property that is not intrinsic to the second media content. The method also includes generating an output stream presenting the dynamically selected content items.
Owner:AT&T INTPROP I L P
Methods and systems for generating a zoomable graphical user interface
ActiveUS20050005241A1Easy and rapid selectionSmooth navigationTelevision system detailsMultimedia data browsing/visualisationGraphicsGraphical user interface
Owner:DRNC HLDG INC
Facilitating the sending of multimedia as a message
ActiveUS20150312184A1Function increaseEasy to editTexturing/coloringTelevision systemsElectronic communicationMedia content
One or more embodiments described herein include methods and systems of sending multimedia content items as electronic communications. More specifically, systems and methods described herein provide user the ability to easily and effectively select multimedia content items stored on a computing device for inclusion in a communication session without navigating away from the communication session. Additionally, systems and methods described herein provide a user the ability to edit multimedia content items for inclusion in the communication session.
Owner:META PLATFORMS INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com