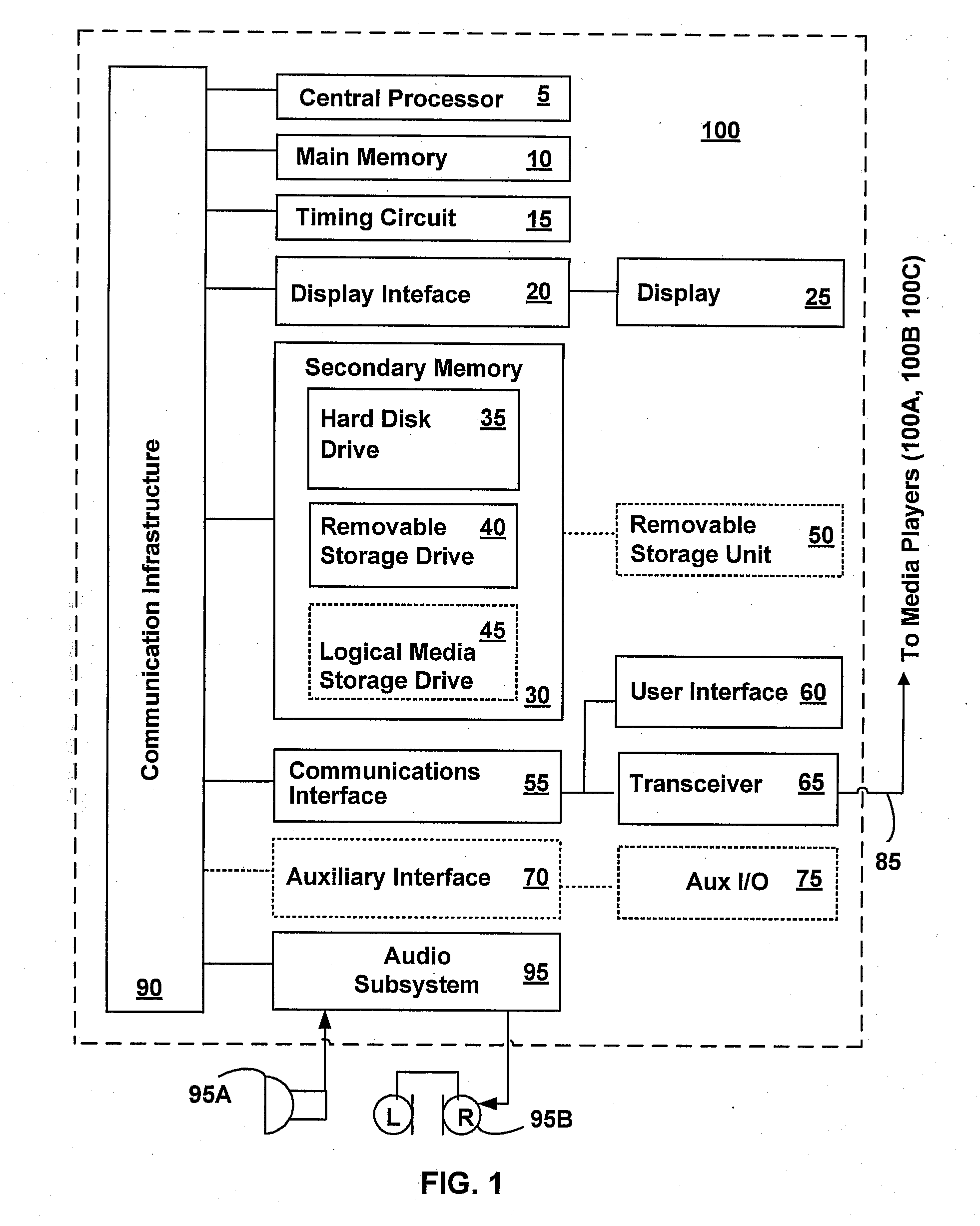
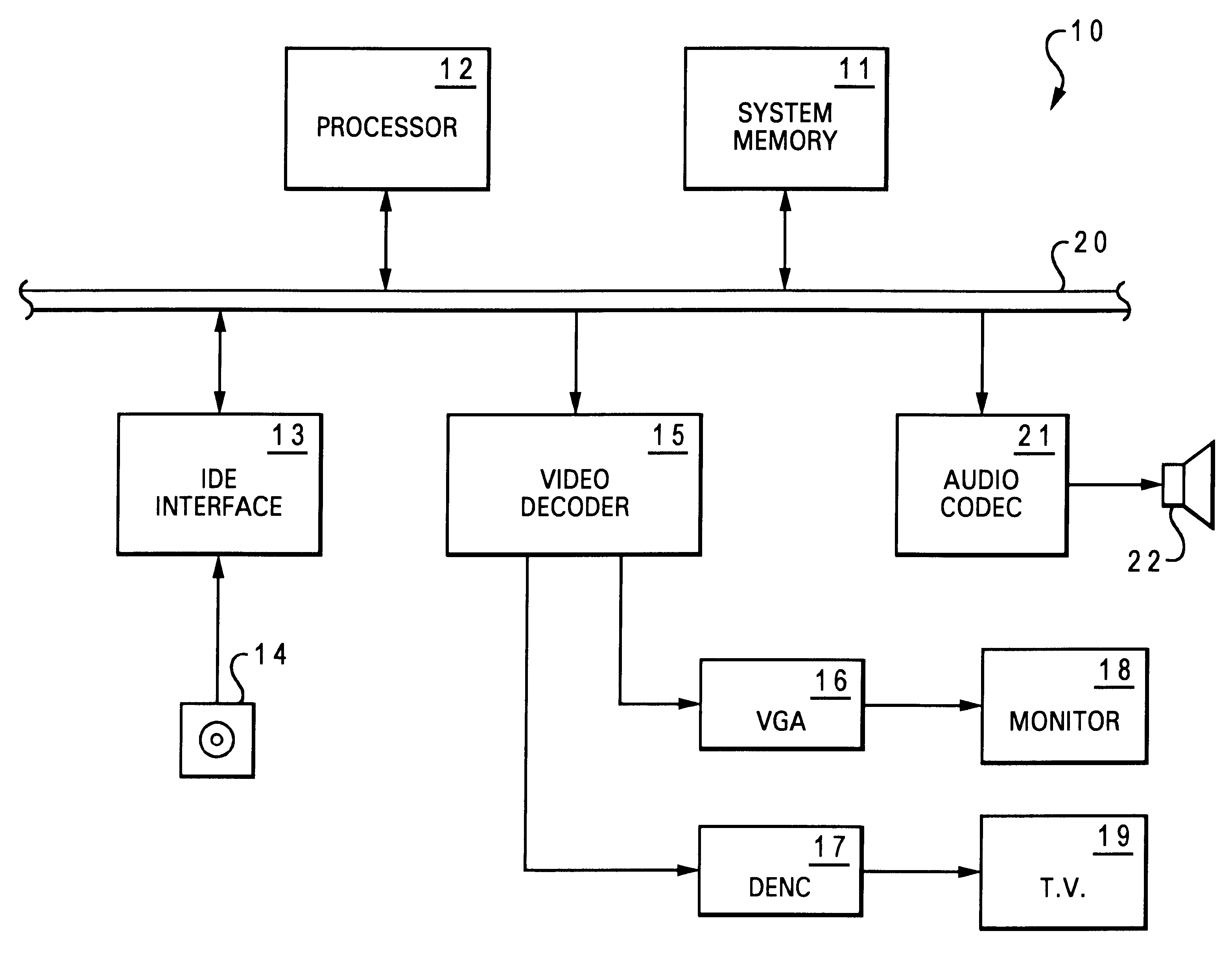
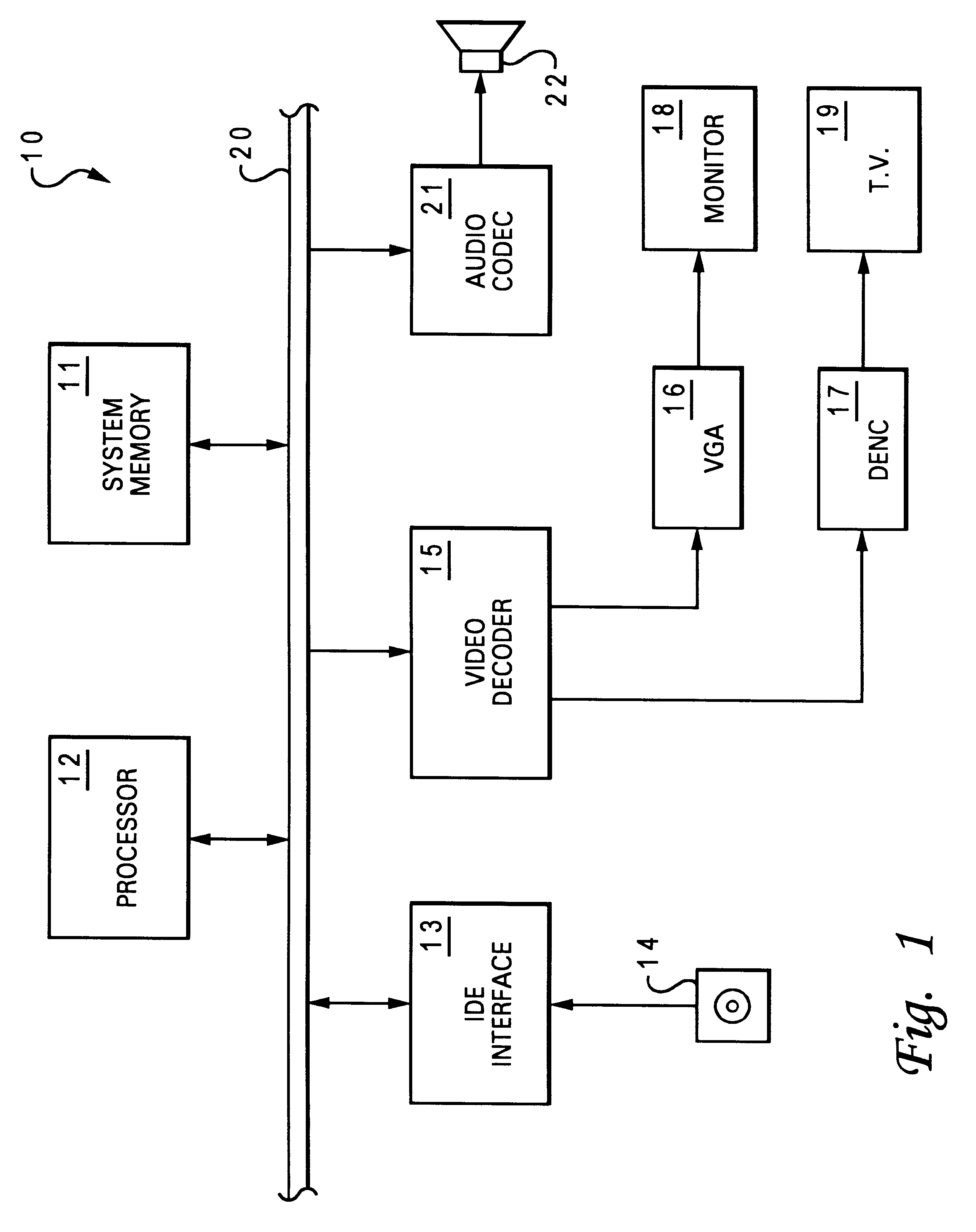
Patents
Literature
10849results about "Gain control" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
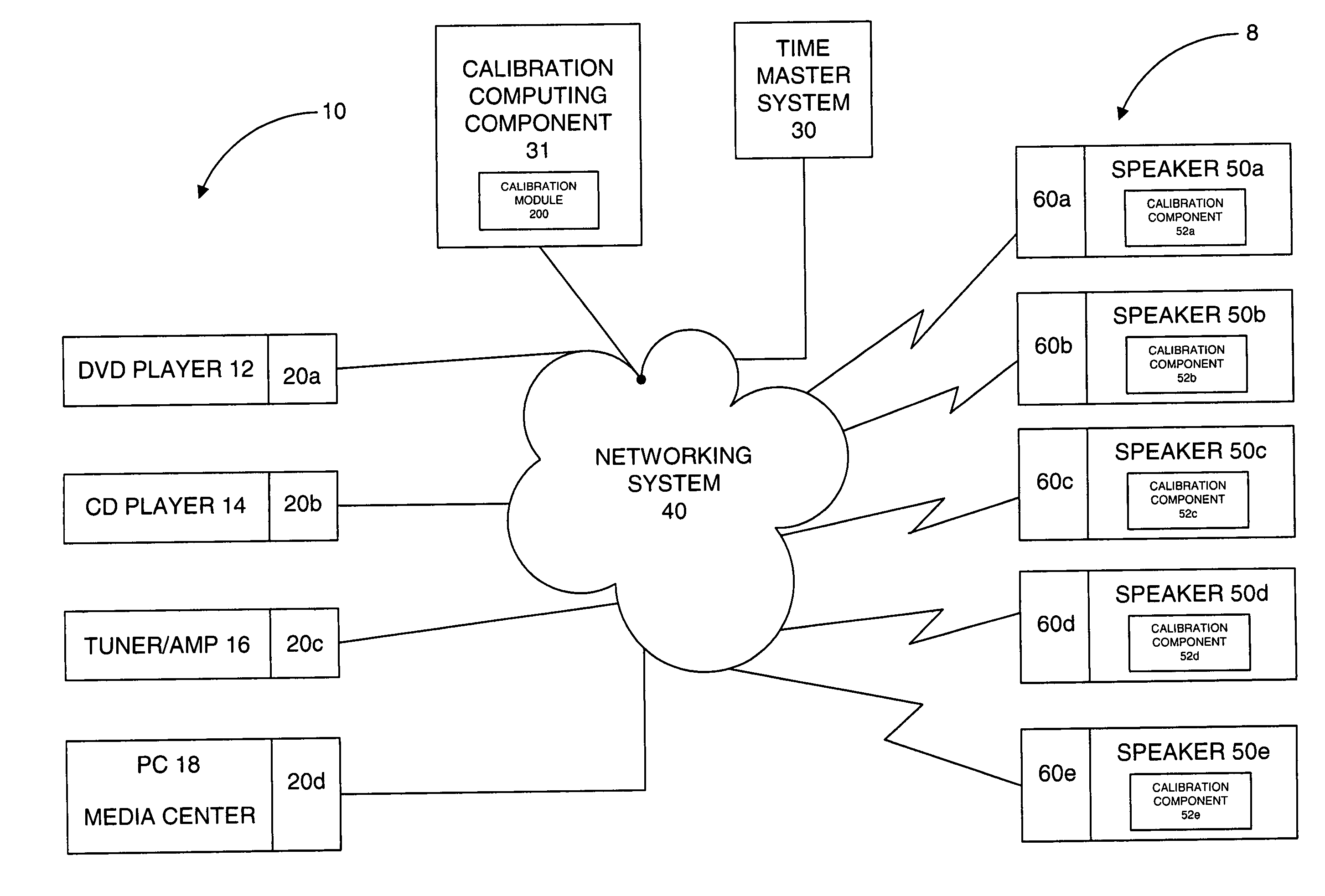
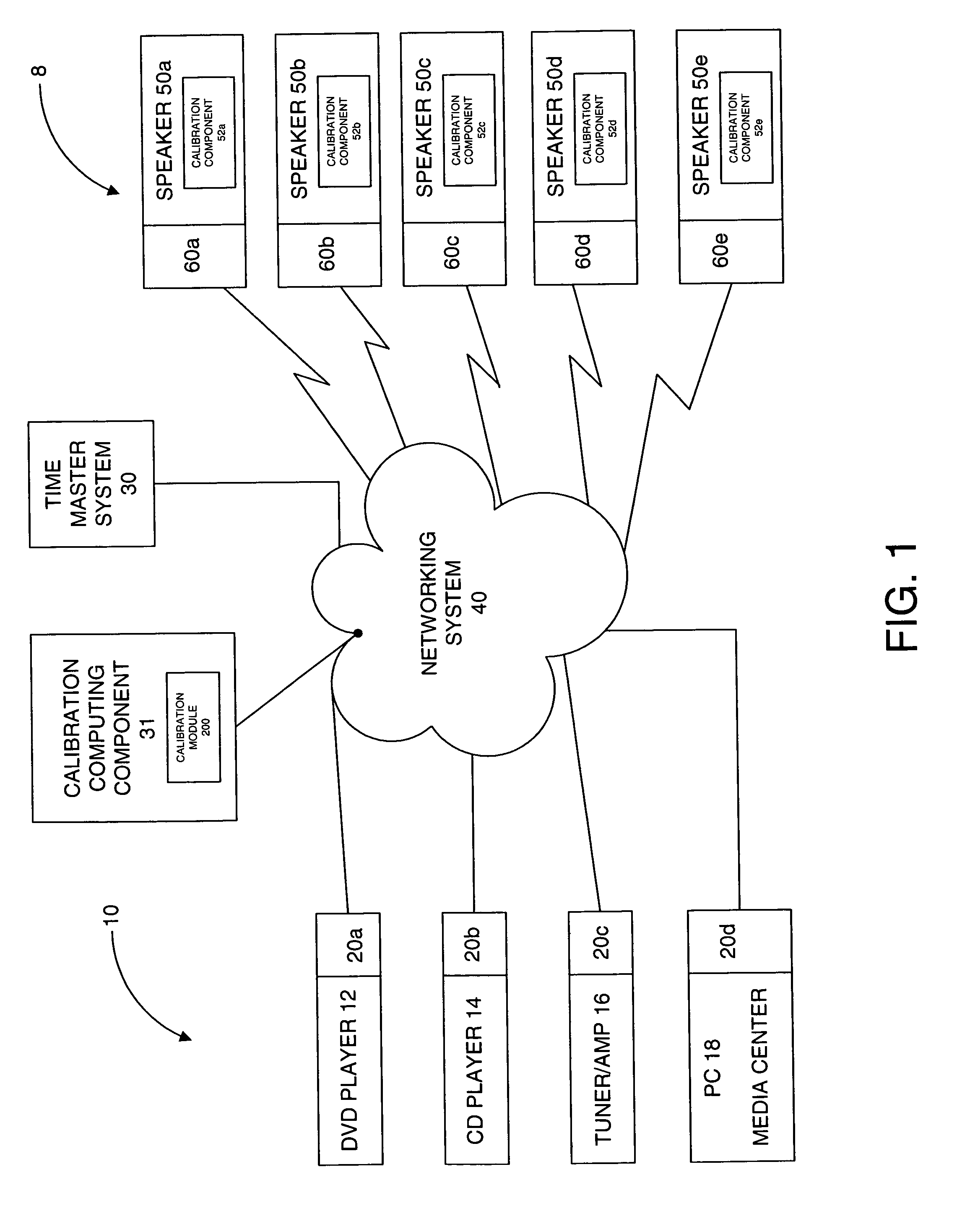
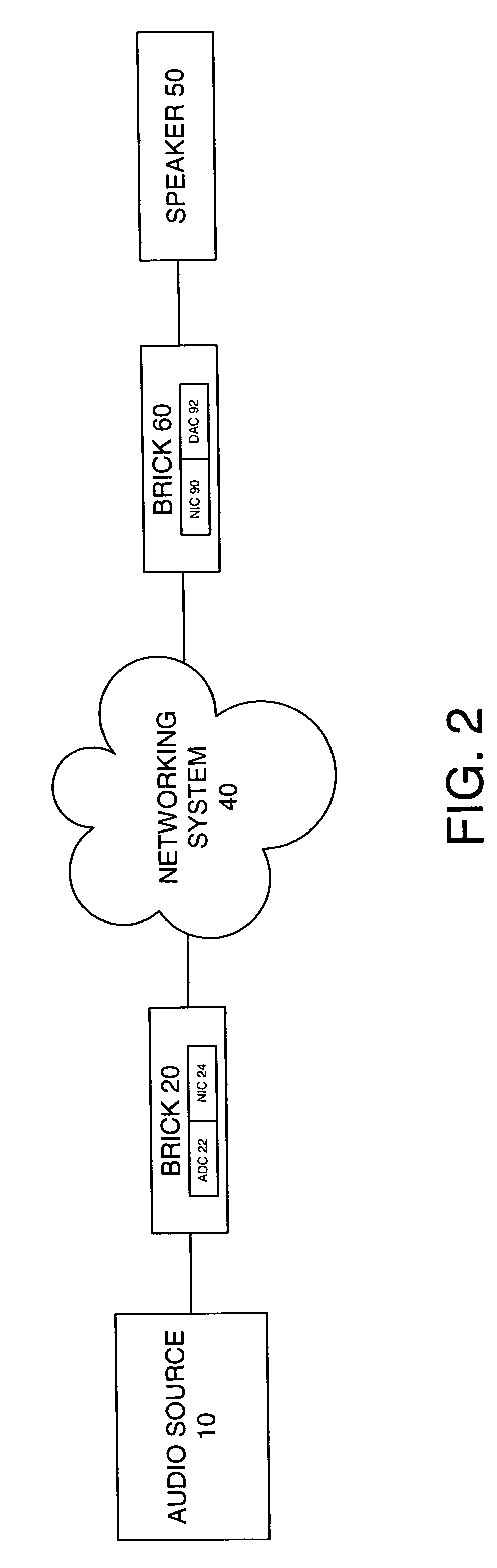
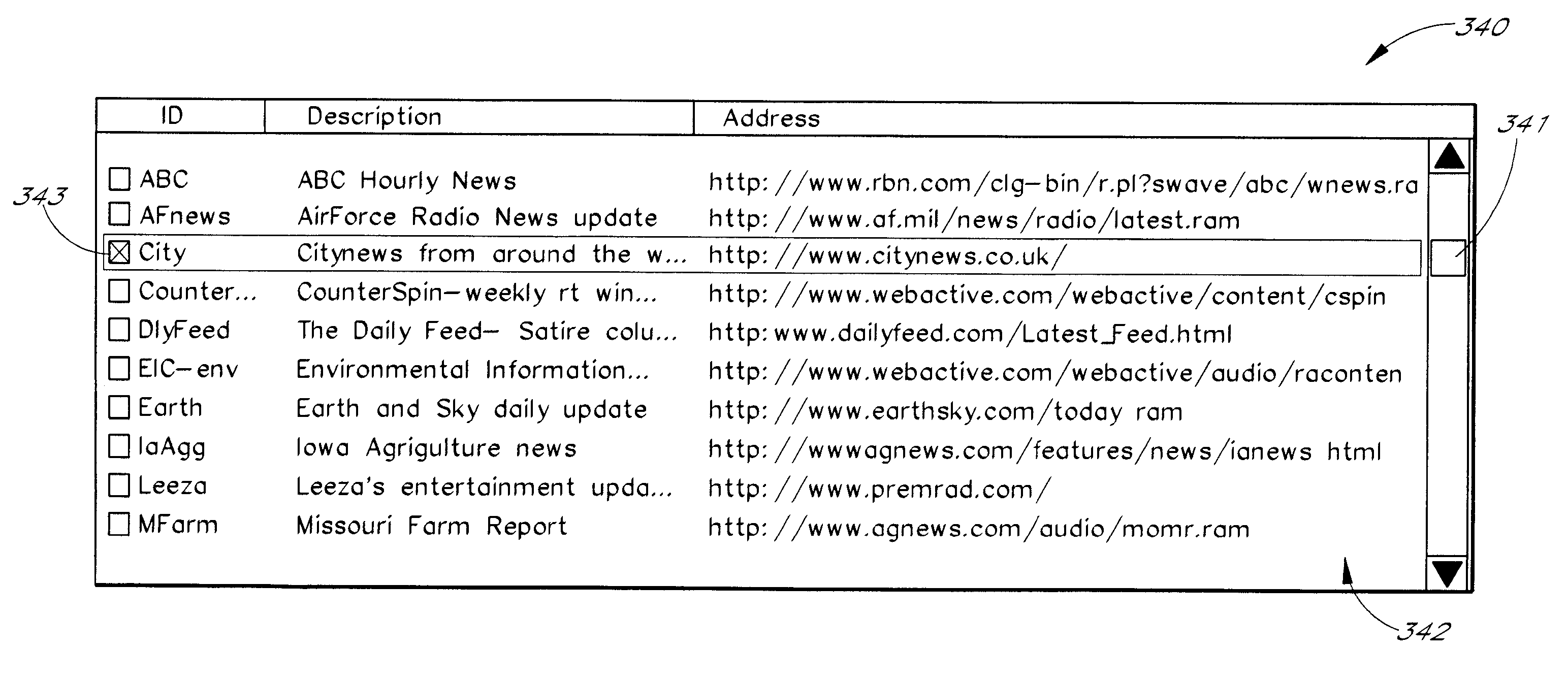
System and method for calibration of an acoustic system
The present invention is directed to a method and system for automatic calibration of an acoustic system. The acoustic system may include a source A / V device, calibration computing device, and multiple rendering devices. The calibration system may include a calibration component attached to each rendering device and a source calibration module. The calibration component on each rendering device includes a microphone. The source calibration module includes distance and optional angle calculation tools for automatically determining a distance between the rendering device and a specified reference point upon return of the test signal from the calibration component.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
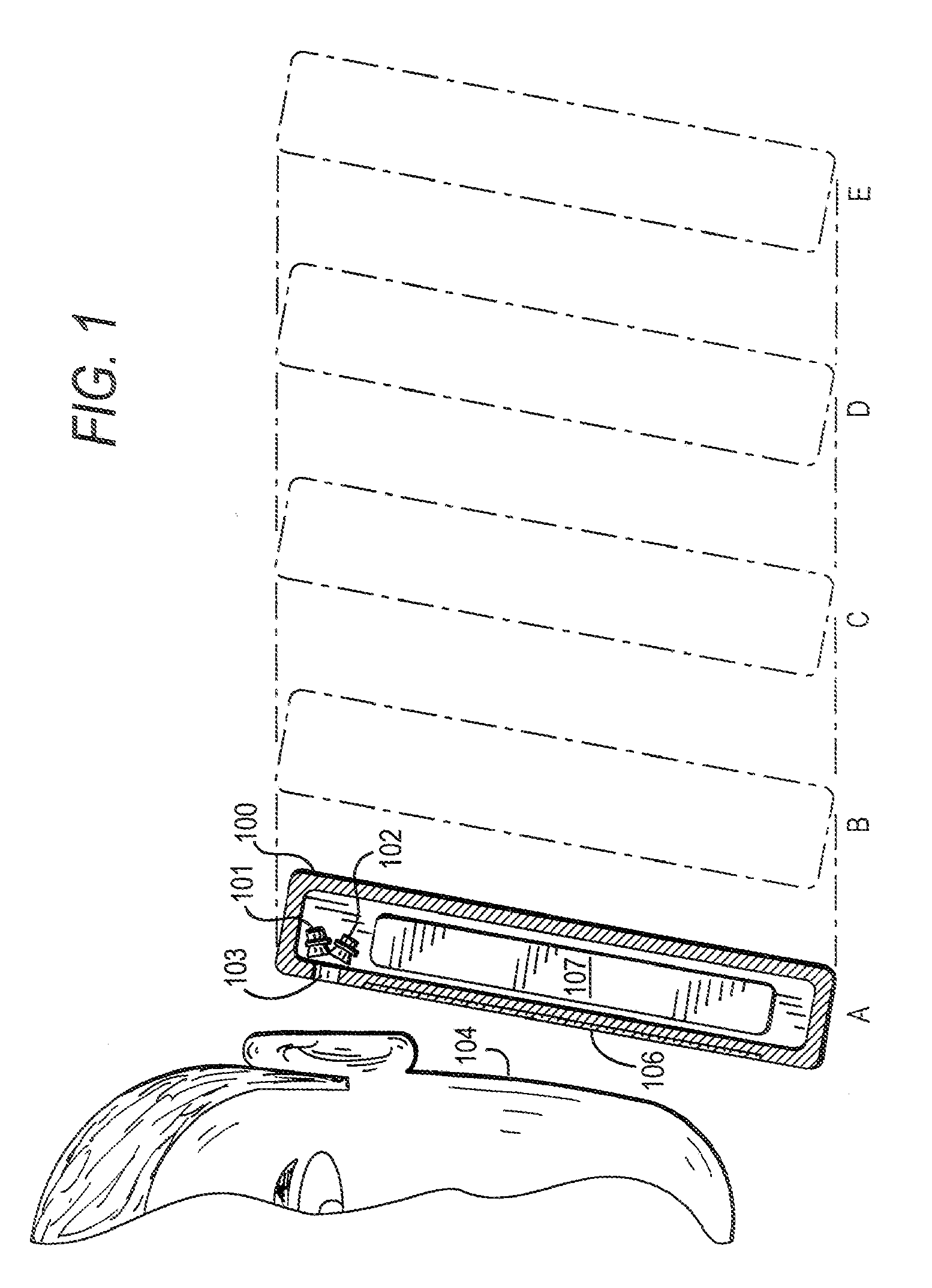
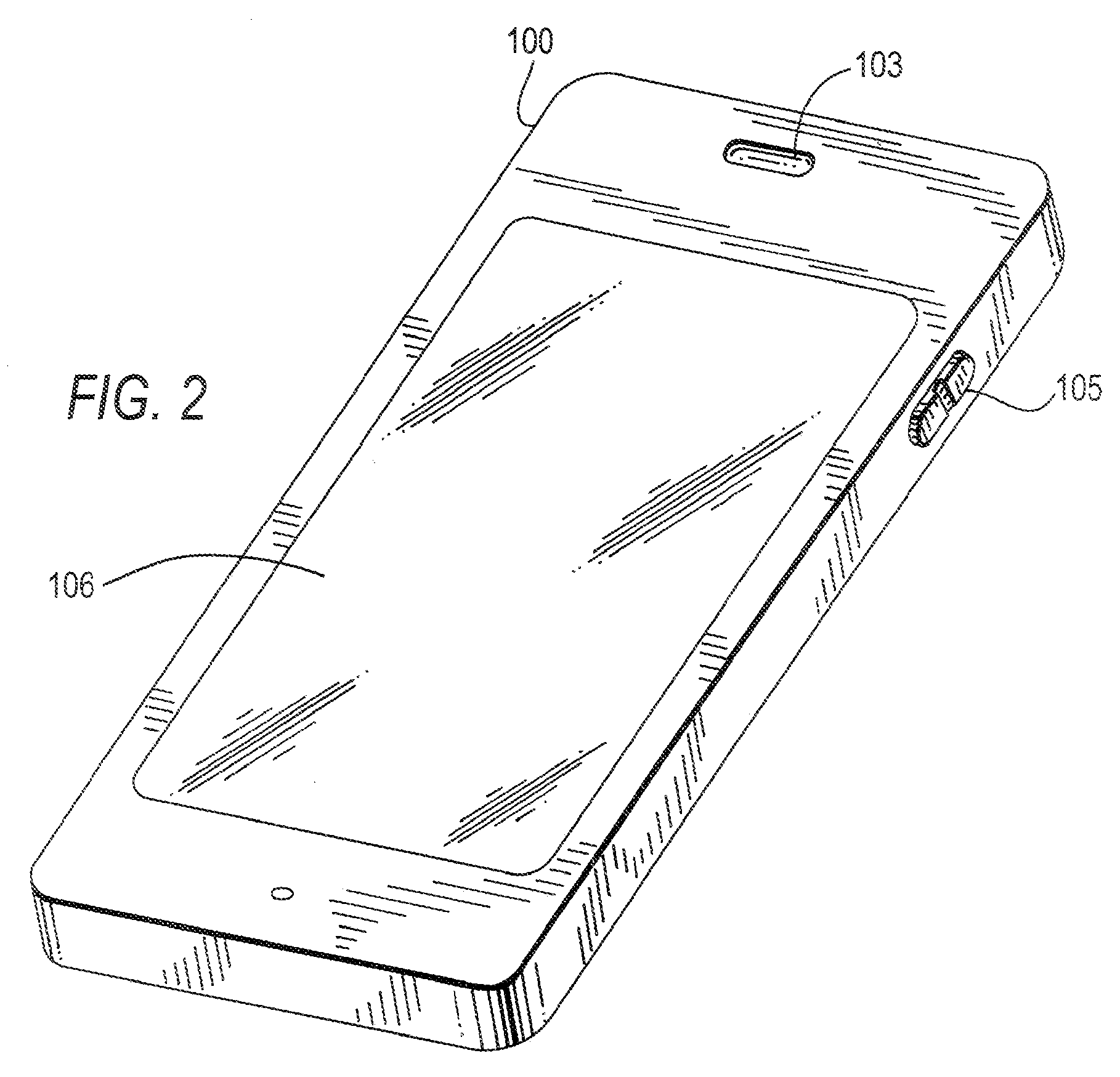
Automated response to and sensing of user activity in portable devices
ActiveUS7633076B2Input/output for user-computer interactionGain controlComputer scienceEquipment state
Owner:APPLE INC
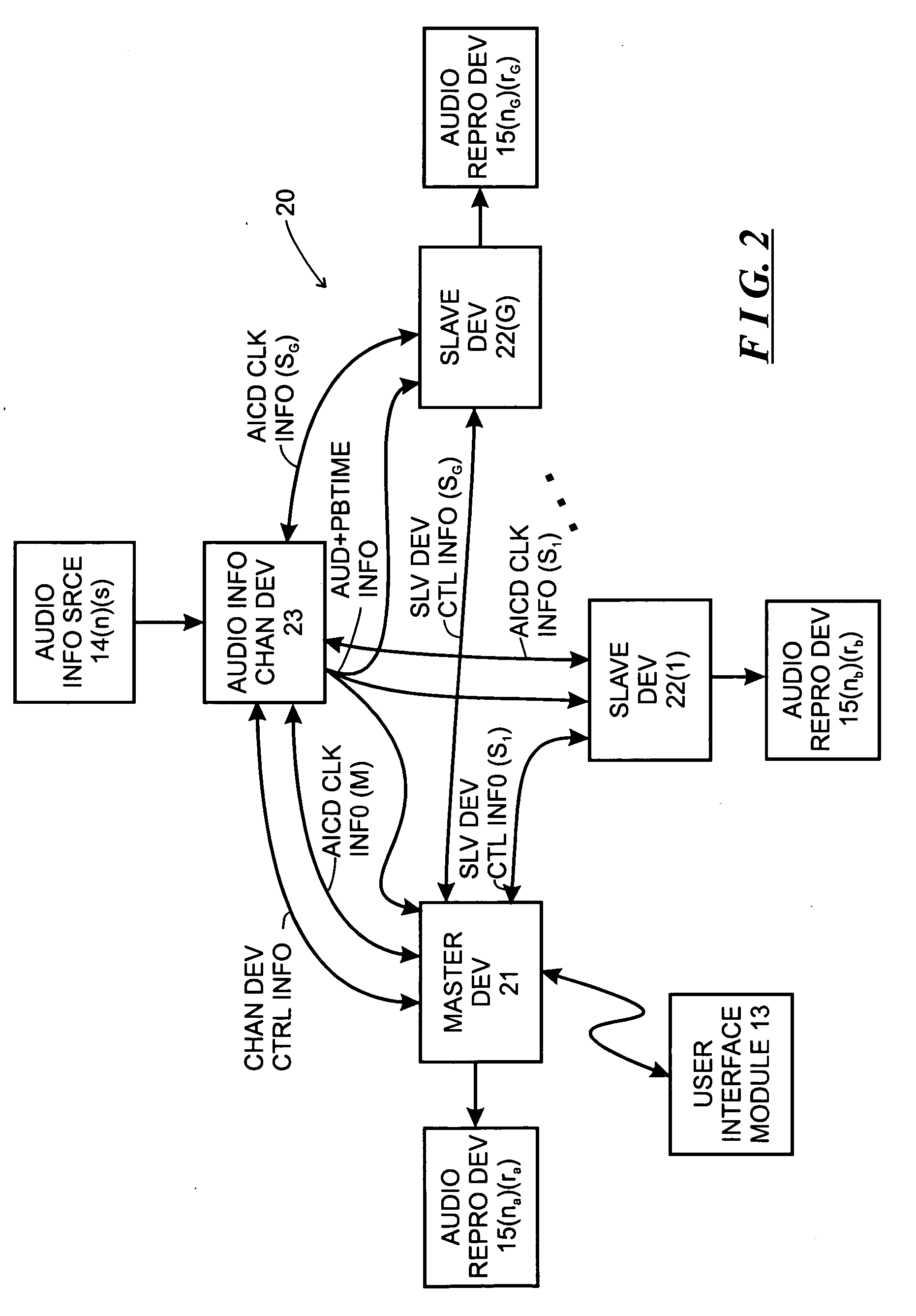
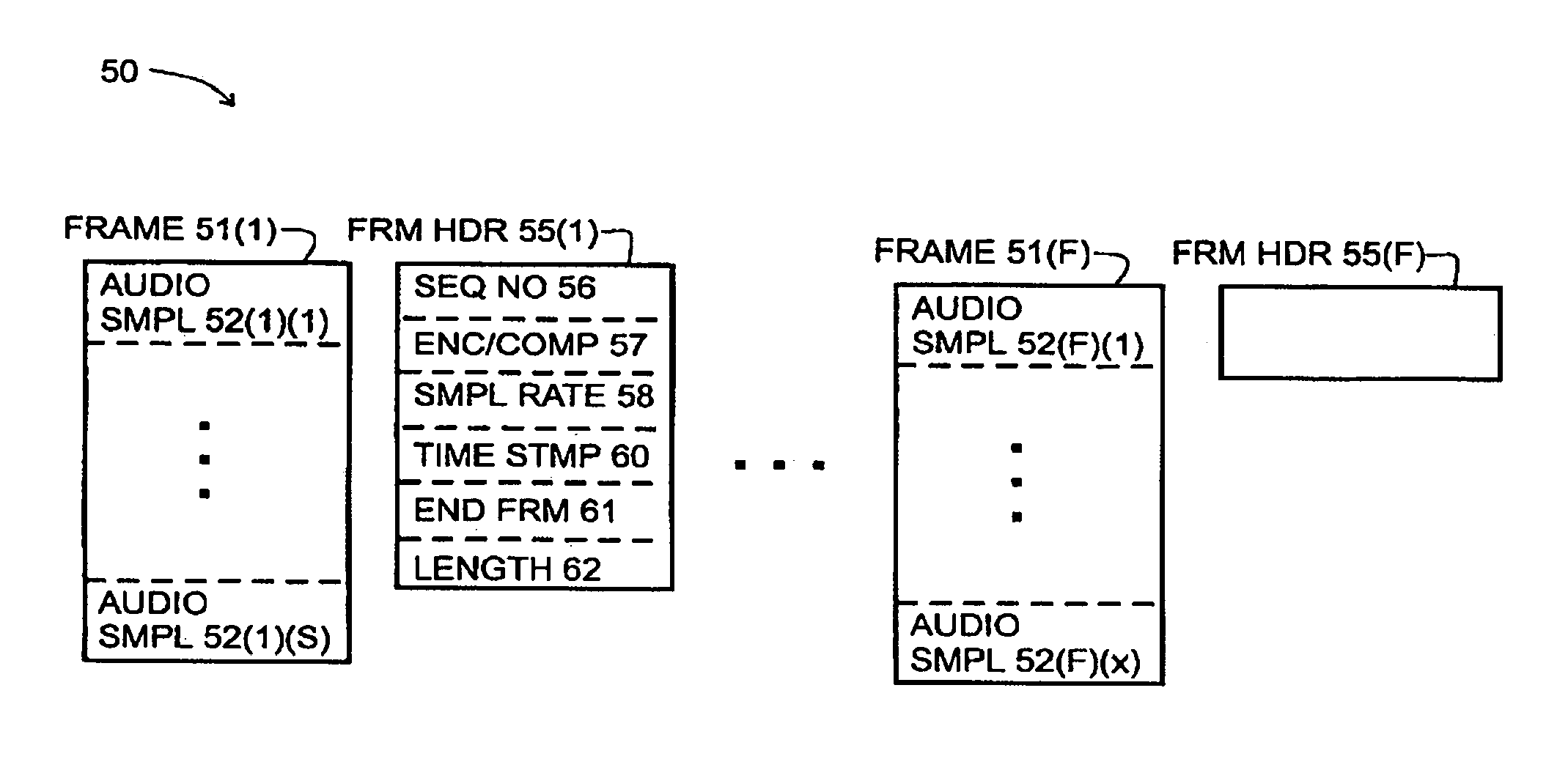
System and method for synchronizing operations among a plurality of independently clocked digital data processing devices
ActiveUS20070038999A1Maintenance operationTelevision system detailsGain controlElectronic data processingIndependent clock
A system is described for maintaining synchrony of operations among a plurality of devices that have independent clocking arrangements. The system includes a task distribution device that distributes tasks to a synchrony group comprising a plurality of devices that are to perform the tasks distributed by the task distribution device in synchrony. The task distribution device distributes each task to the members of the synchrony group over a network. Each task is associated with a time stamp that indicates a time, relative to a clock maintained by the task distribution device, at which the members of the synchrony group are to execute the task. Each member of the synchrony group periodically obtains from the task distribution device an indication of the current time indicated by its clock, determines a time differential between the task distribution device's clock and its respective clock and determines therefrom a time at which, according to its respective clock, the time stamp indicates that it is to execute the task.
Owner:SONOS
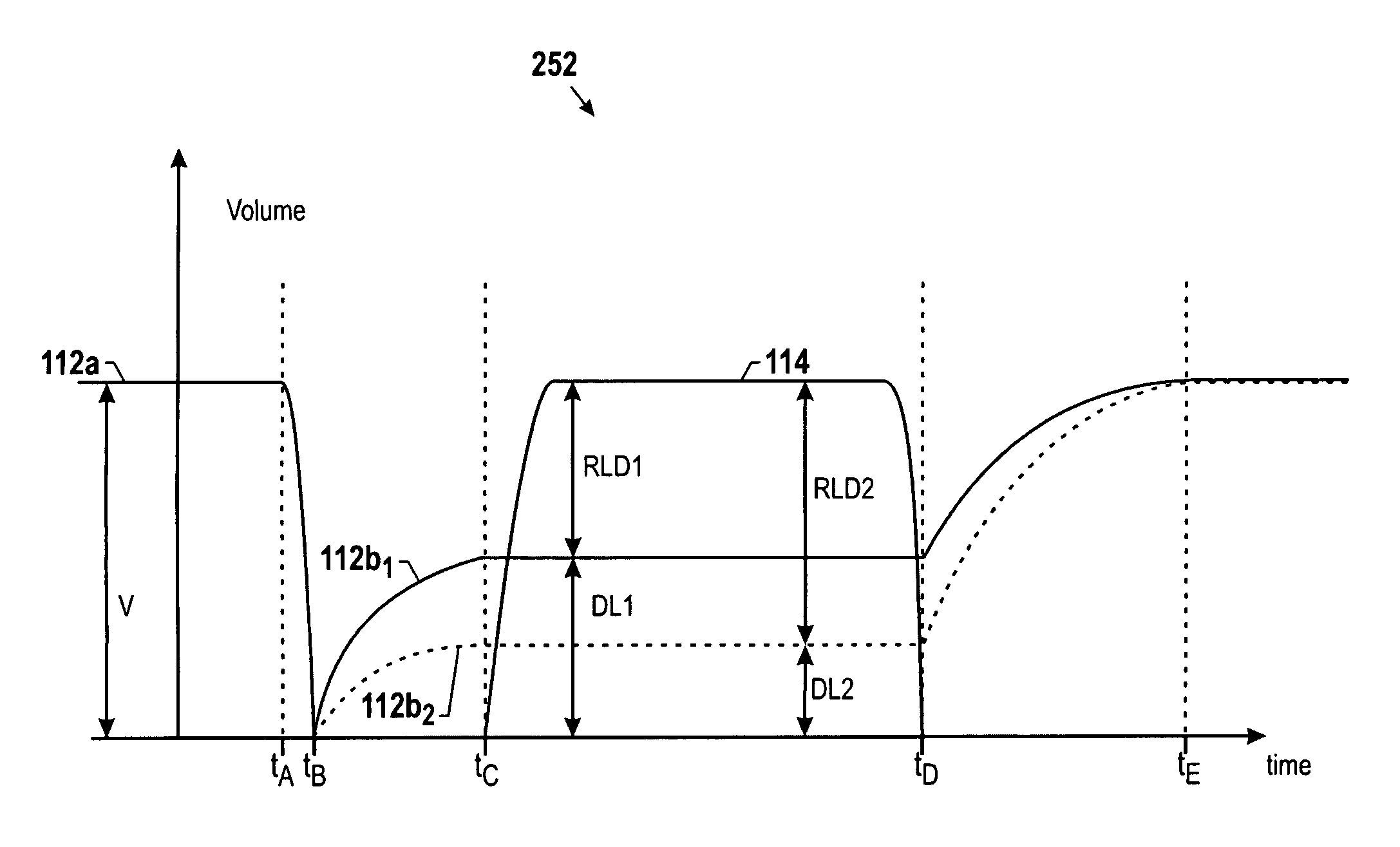
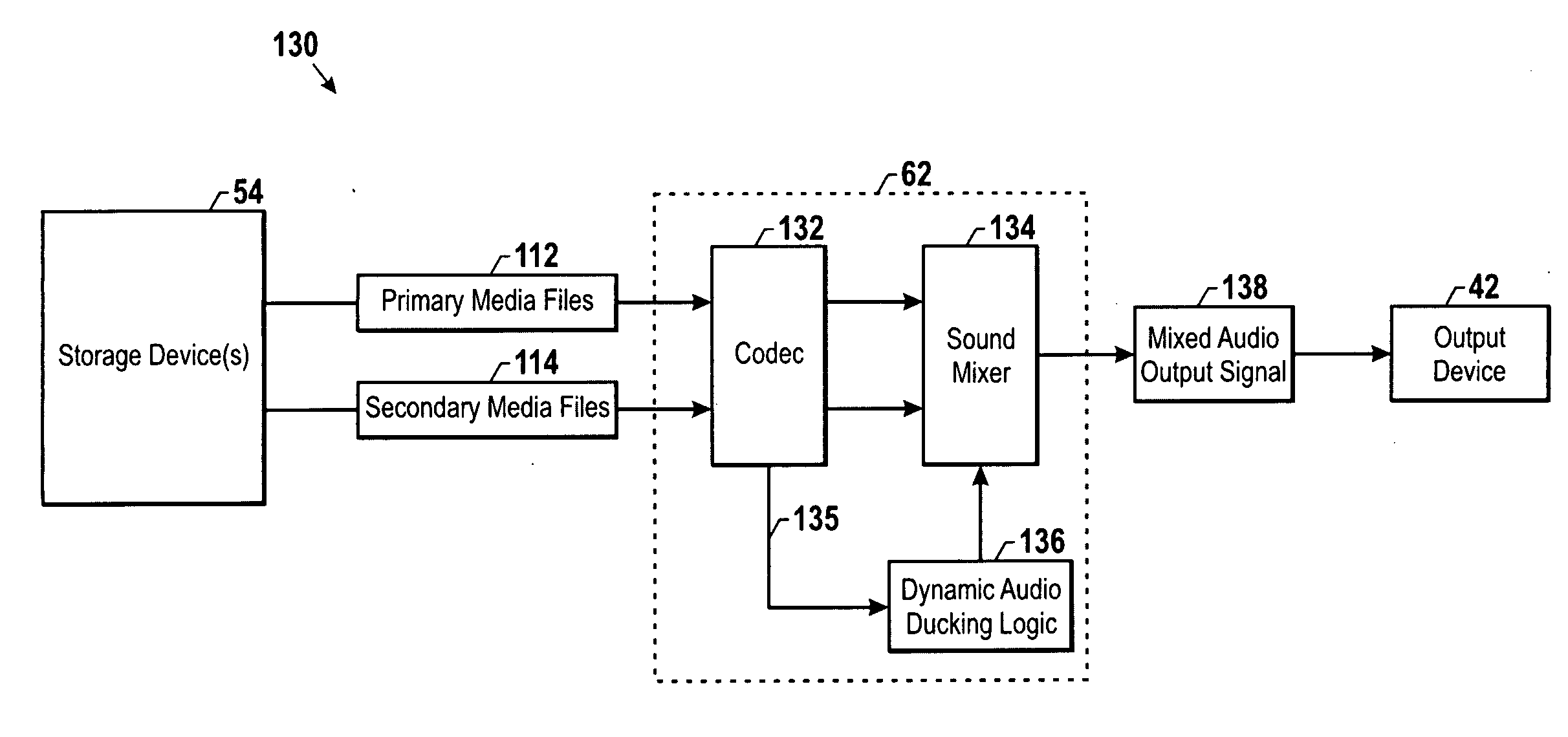
Dynamic audio ducking
Various dynamic audio ducking techniques are provided that may be applied where multiple audio streams, such as a primary audio stream and a secondary audio stream, are being played back simultaneously. For example, a secondary audio stream may include a voice announcement of one or more pieces of information pertaining to the primary audio stream, such as the name of the track or the name of the artist. In one embodiment, the primary audio data and the voice feedback data are initially analyzed to determine a loudness value. Based on their respective loudness values, the primary audio stream may be ducked during the period of simultaneous playback such that a relative loudness difference is generally maintained with respect to the loudness of the primary and secondary audio streams. Accordingly, the amount of ducking applied may be customized for each piece of audio data depending on its loudness characteristics.
Owner:APPLE INC
Dynamic audio ducking
Various dynamic audio ducking techniques are provided that may be applied where multiple audio streams, such as a primary audio stream and a secondary audio stream, are being played back simultaneously. For example, a secondary audio stream may include a voice announcement of one or more pieces of information pertaining to the primary audio stream, such as the name of the track or the name of the artist. In one embodiment, the primary audio data and the voice feedback data are initially analyzed to determine a loudness value. Based on their respective loudness values, the primary audio stream may be ducked during the period of simultaneous playback such that a relative loudness difference is generally maintained with respect to the loudness of the primary and secondary audio streams. Accordingly, the amount of ducking applied may be customized for each piece of audio data depending on its loudness characteristics.
Owner:APPLE INC
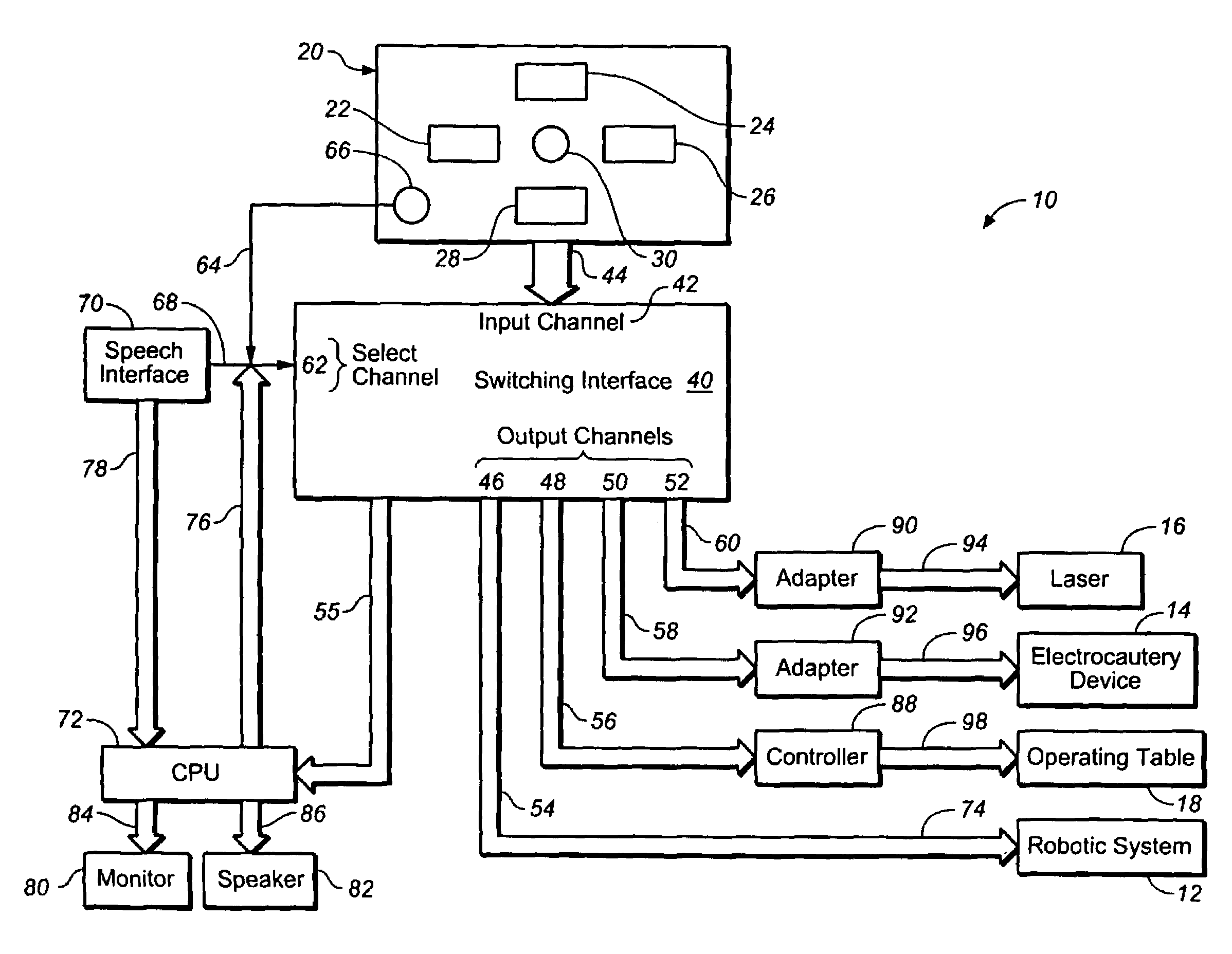
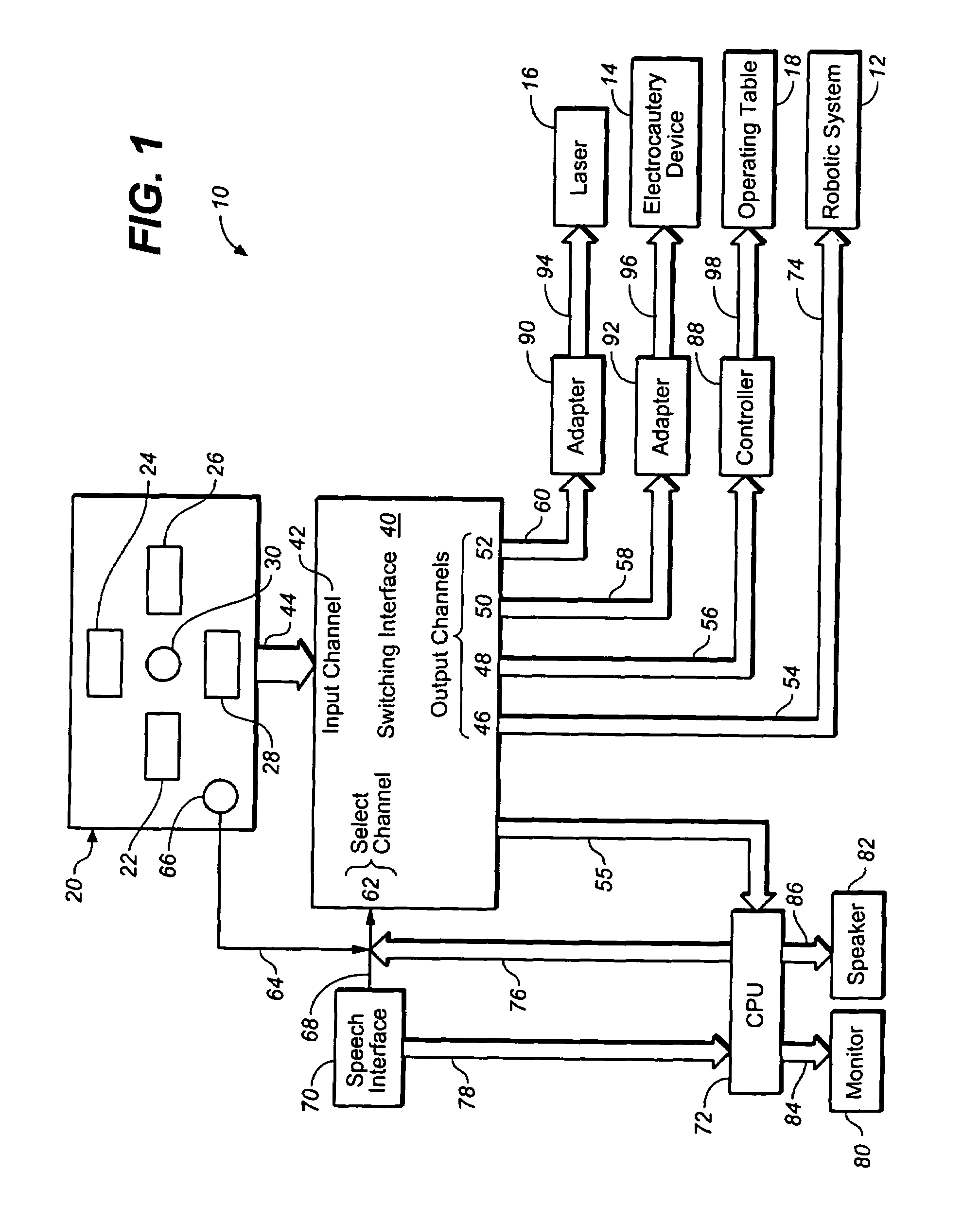
Multi-functional surgical control system and switching interface
An interface which allows a surgeon to operate multiple surgical devices from a single input device. The input device may be a foot pedal that provides output signals to actuate a number of different surgical devices. The surgical devices may include a robotic arm, a laser, an electrocautery device, or an operating table. The interface has an input channel that is coupled to the input device and a plurality of output channels that are coupled to the surgical devices. The interface also has a select input channel which can receive input commands to switch the input channel to one of the output channels. The select channel may be coupled to a speech interface that allows the surgeon to select one of the surgical devices with a voice command. The surgeon can operate any device by providing an input command which switches the input channel to the desired output channel.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
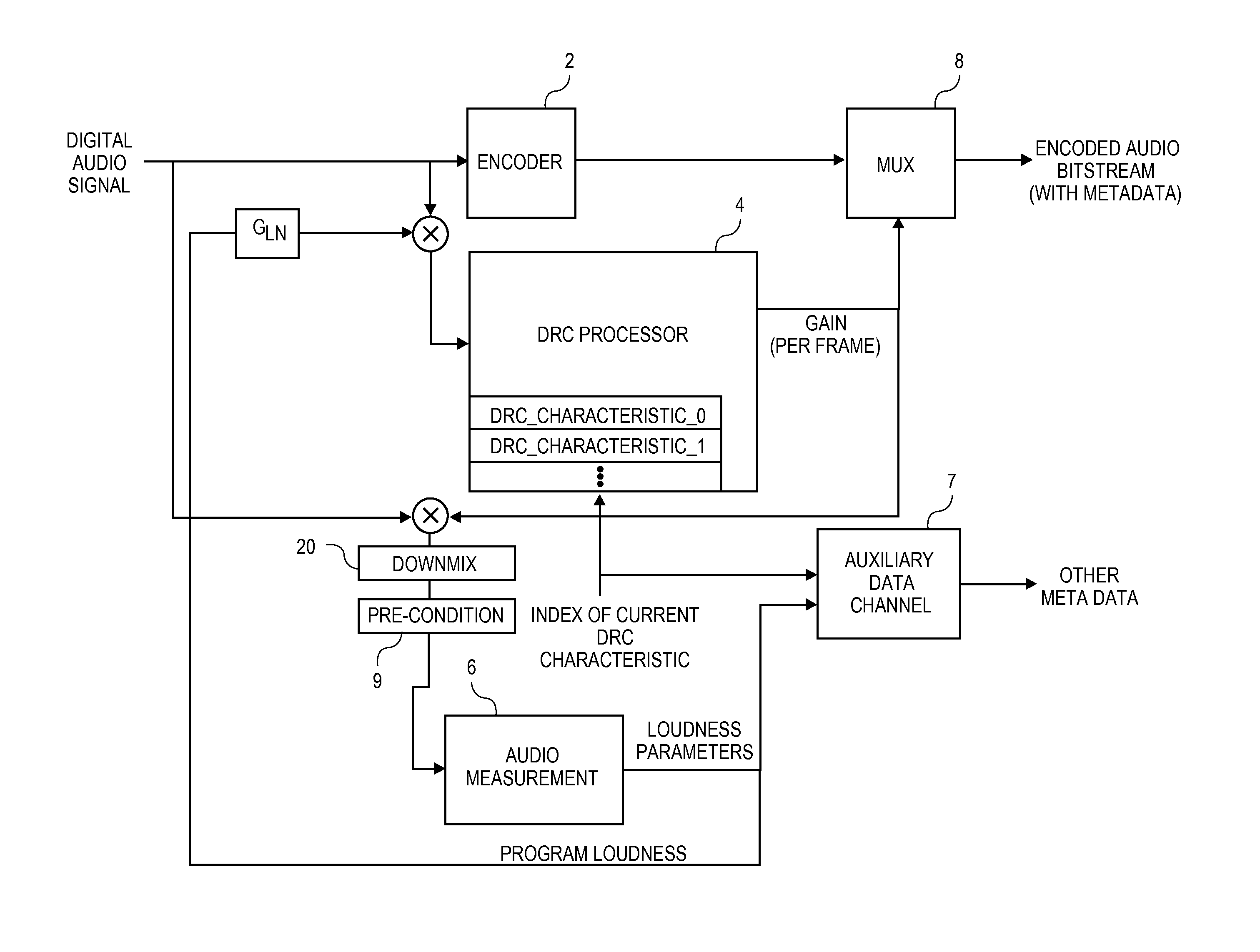
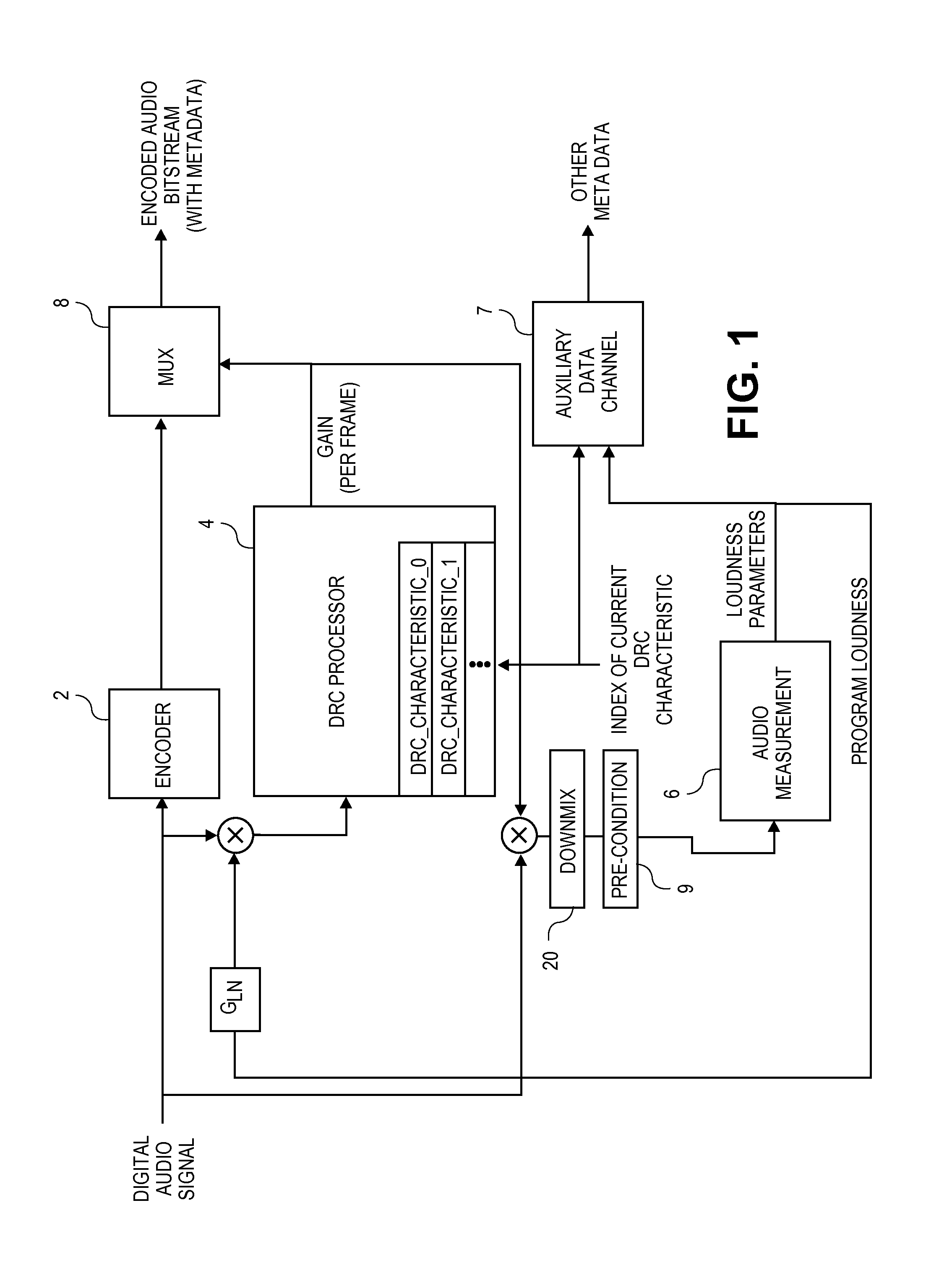
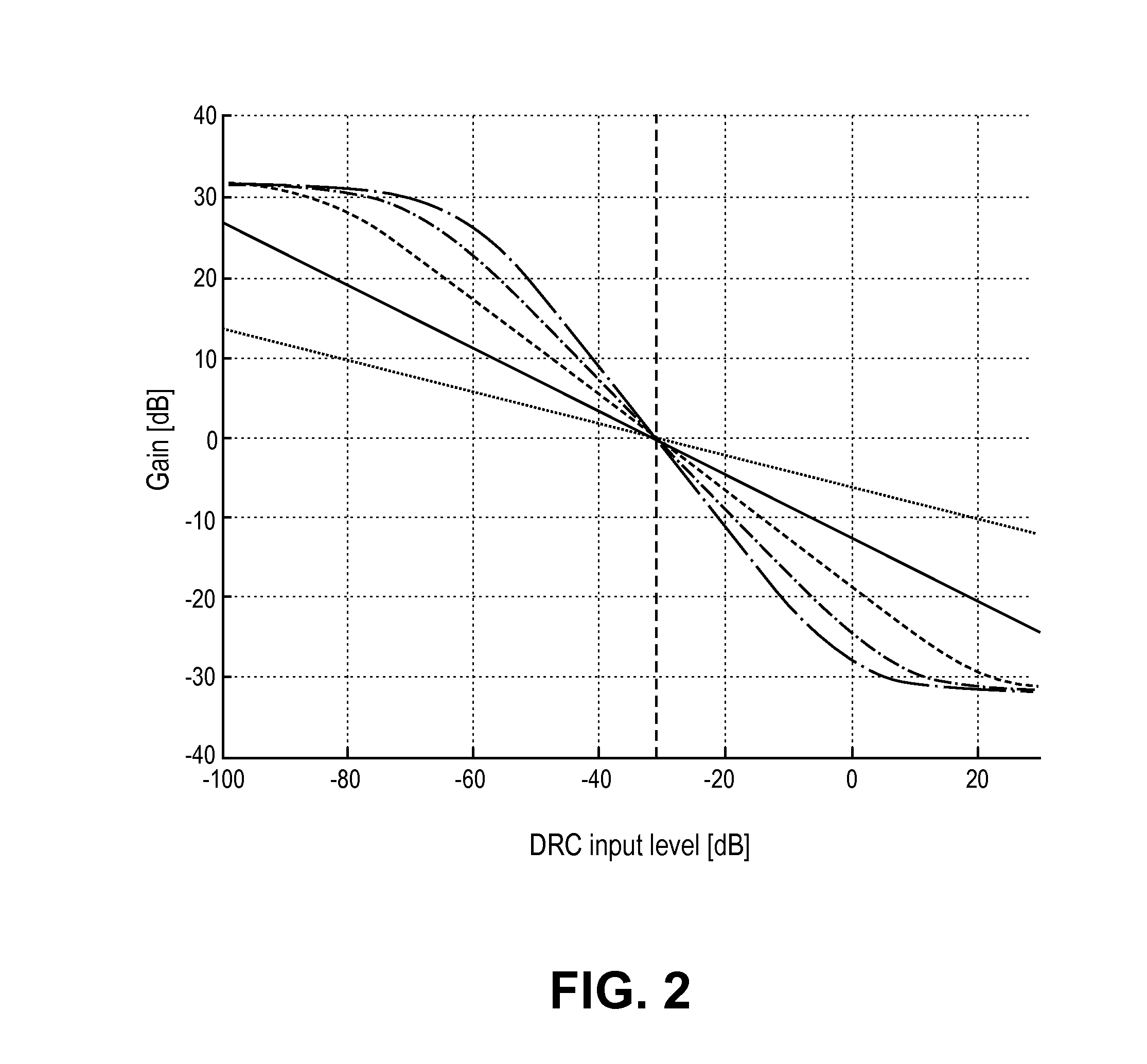
Metadata for loudness and dynamic range control
ActiveUS20140294200A1Improve the user's experience of playbackImprove experienceGain controlSpeech analysisAudio normalizationLoudness
An audio normalization gain value is applied to an audio signal to produce a normalized signal. The normalized signal is processed to compute dynamic range control (DRC) gain values in accordance with a selected one of several pre-defined DRC characteristics. The audio signal is encoded, and the DRC gain values are provided as metadata associated with the encoded audio signal. Several other embodiments are also described and claimed.
Owner:APPLE INC
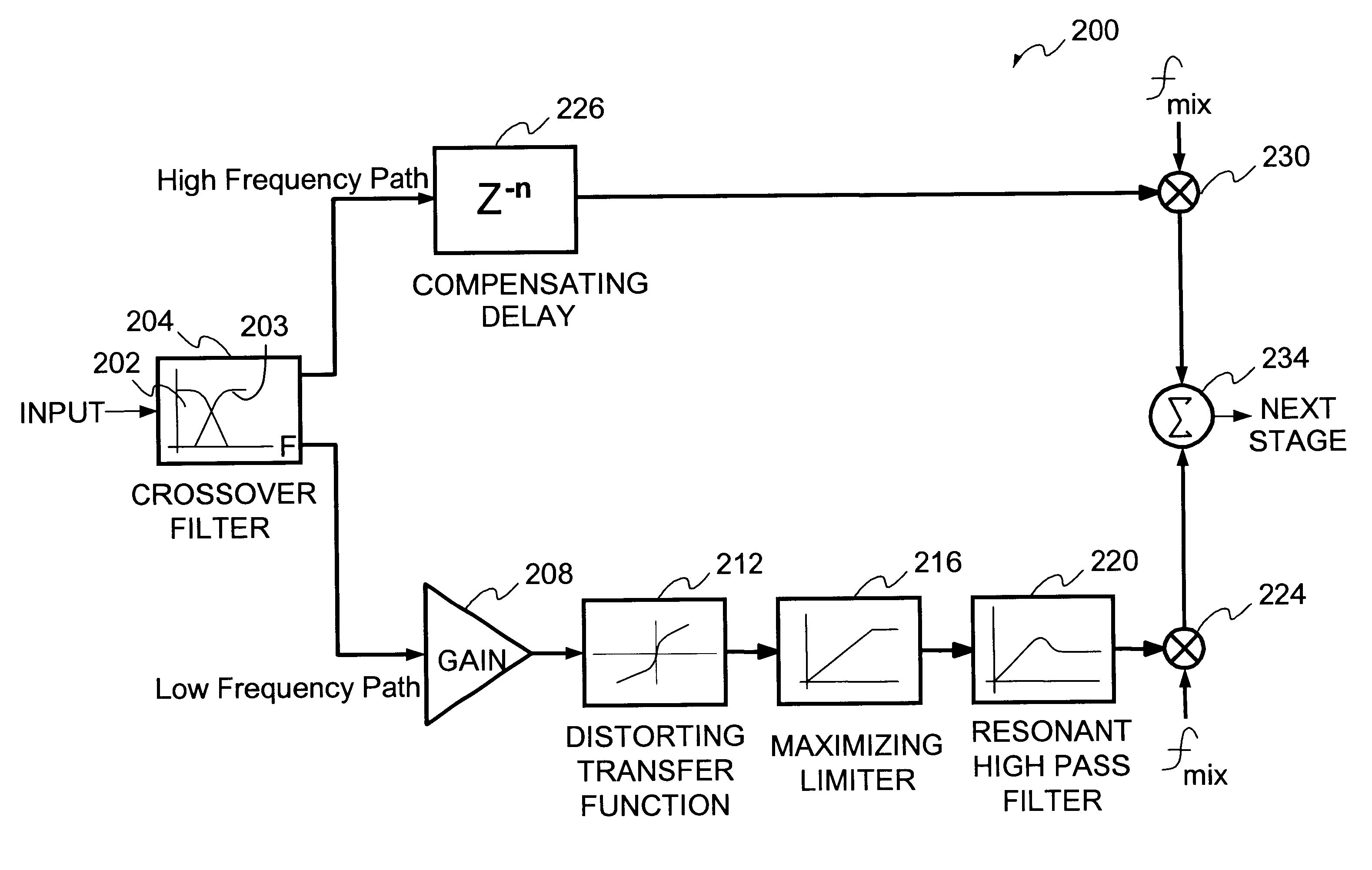
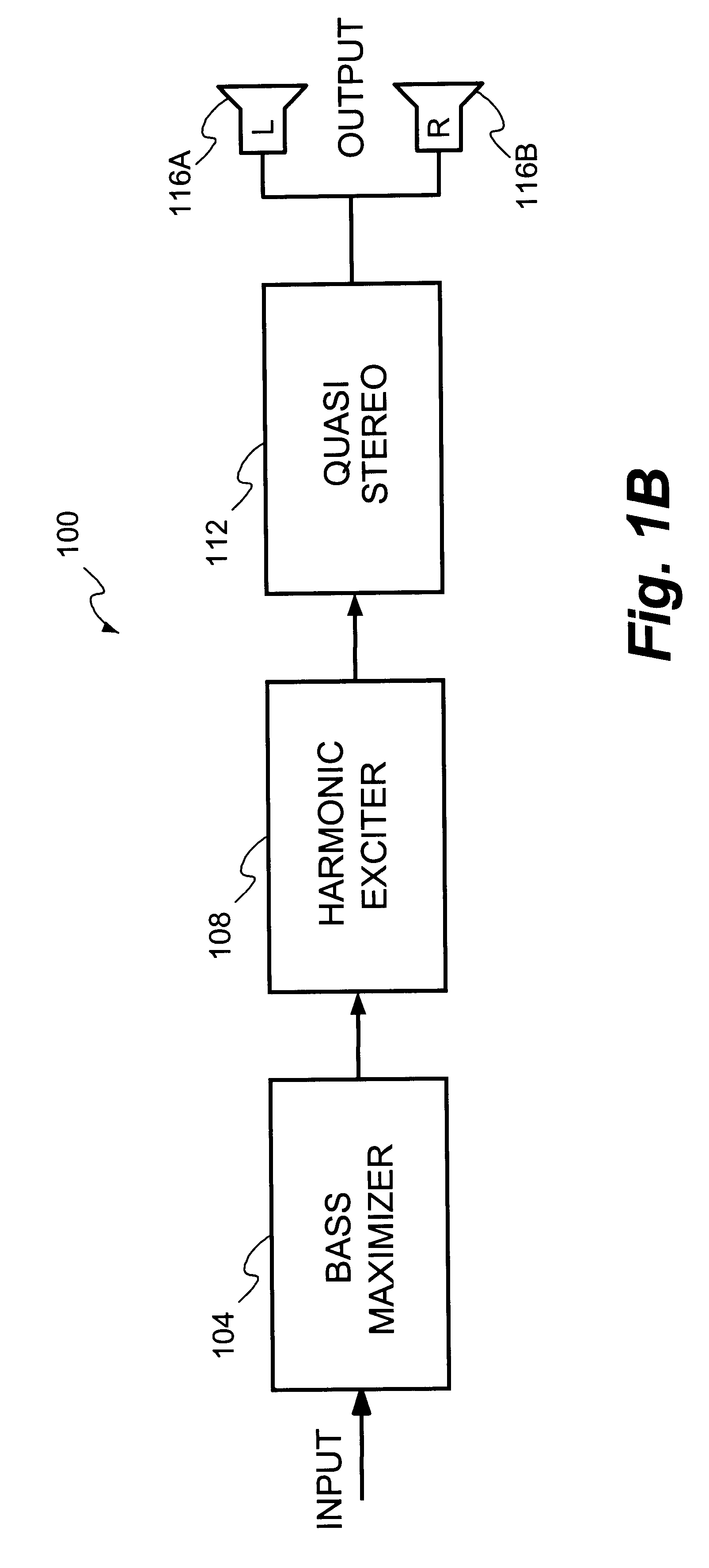
Method and system for enhancing audio signals
InactiveUS6606388B1Facilitates separate modificationFacilitates enhancementElectrophonic musical instrumentsGain controlHarmonicComputer module
A technique for enhancing audio signals generated from compressed digital audio files is described. The technique uses a Bass Maximizer module, a Harmonic Exciter module and a Quasi Stereo module. The Bass Exciter module enhances the intensity, depth and punch of the bass audio content by creating harmonic sequences from low frequency components contained in the original input signal. The Harmonic Exciter module adds to the treble audio content of the original input signal by generating harmonic series from the high frequency components contained in the input signal. The Quasi Stereo Module creates a stereo image of the enhanced input signal by adding and subtracting delayed and filtered versions of the enhanced input signal with itself to create left and right channeled stereo-like outputs. The technique provides a useful tool to regenerate from an audio signal more pleasant and joyful sounds.
Owner:ARBORETUM SYST
Adjustment of acoustic properties based on proximity detection
One or more acoustic transducers of a device may be adjusted based on automatic detection of device proximity to the user. In a mobile telephone, when the user is using the receiver and holding the telephone against his / her ear, if the telephone detects that the user has moved the telephone further from his / her ear, the telephone will raise the receiver volume. Similarly, if the user is using the speaker, the telephone will adjust the speaker volume as user distance from the telephone changes. In another embodiment the telephone may fade between the receiver and the speaker. Volume is not the only acoustic property that could be adjusted according to user proximity. Frequency response is another property that could be adjusted, such as using appropriate electronic filtering, or by turning on another transducer that is not otherwise being used.
Owner:APPLE INC
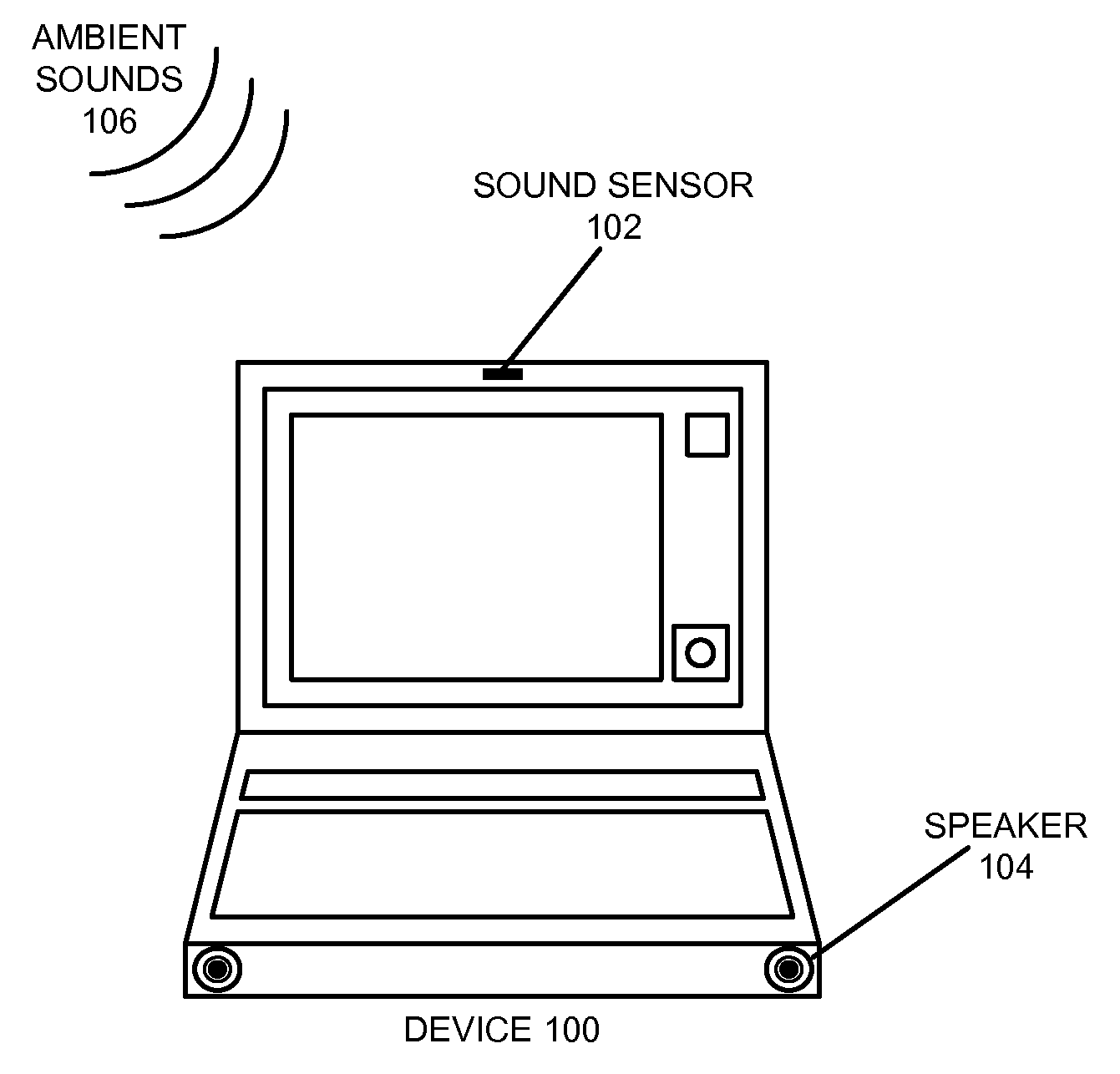
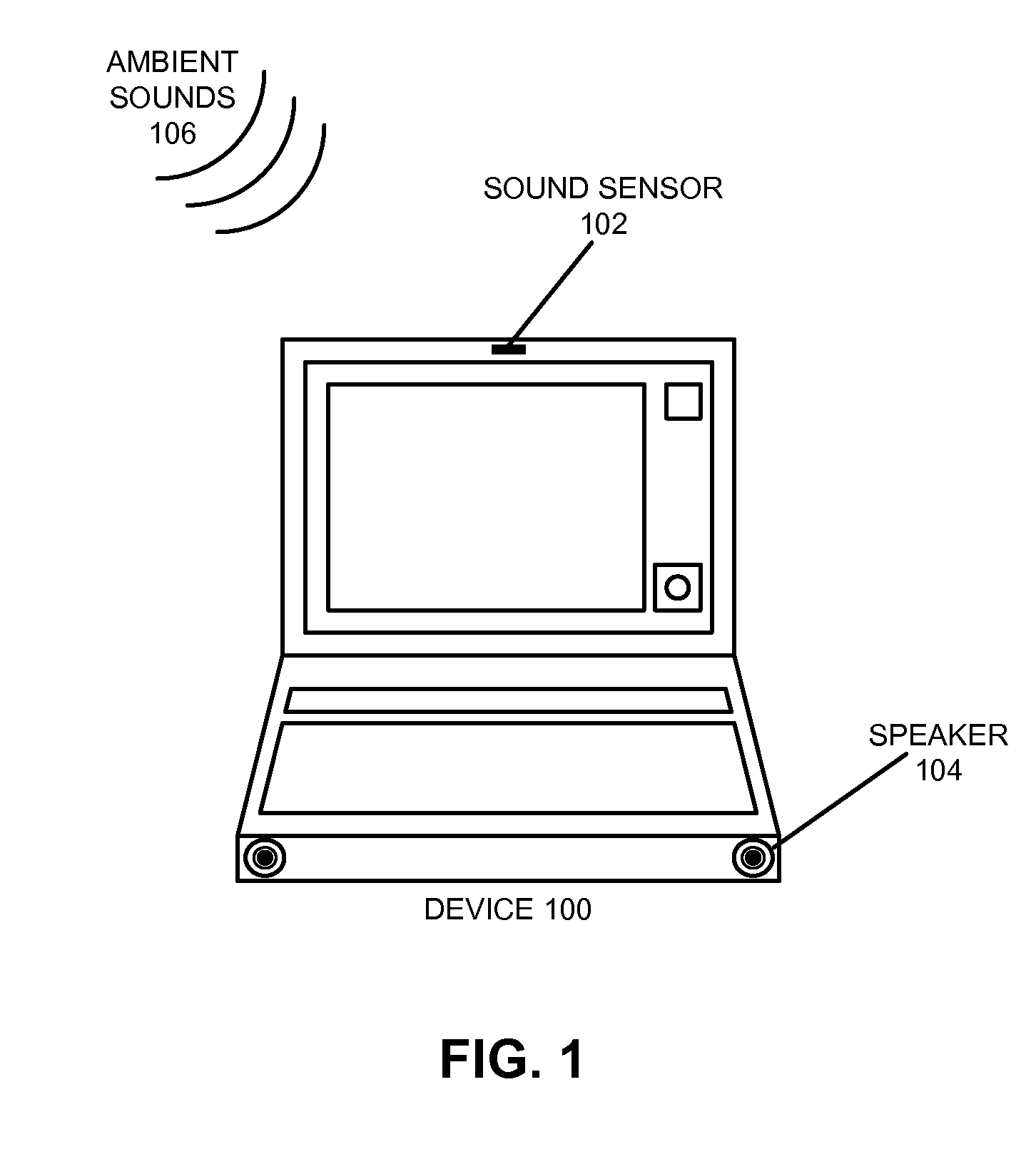
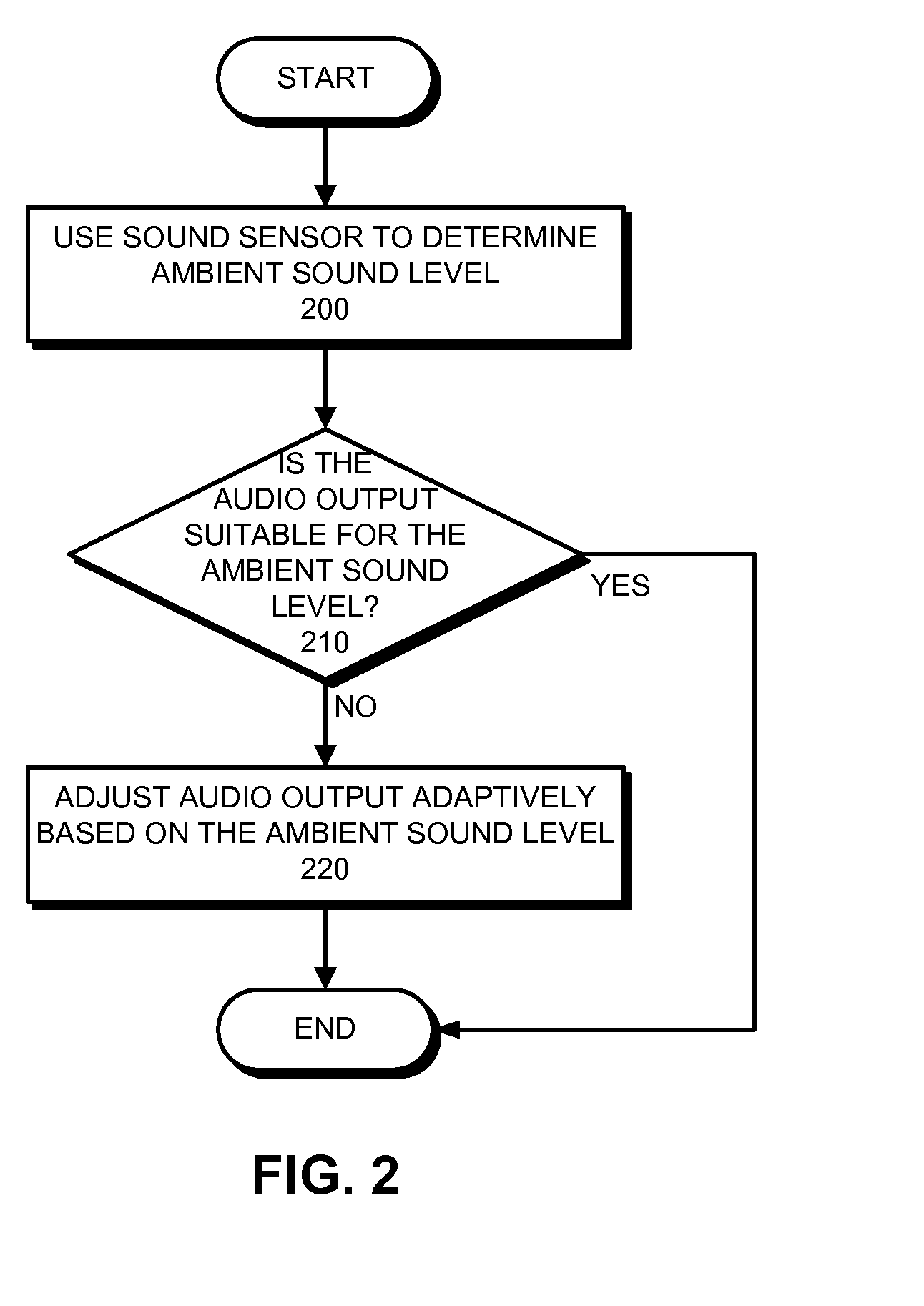
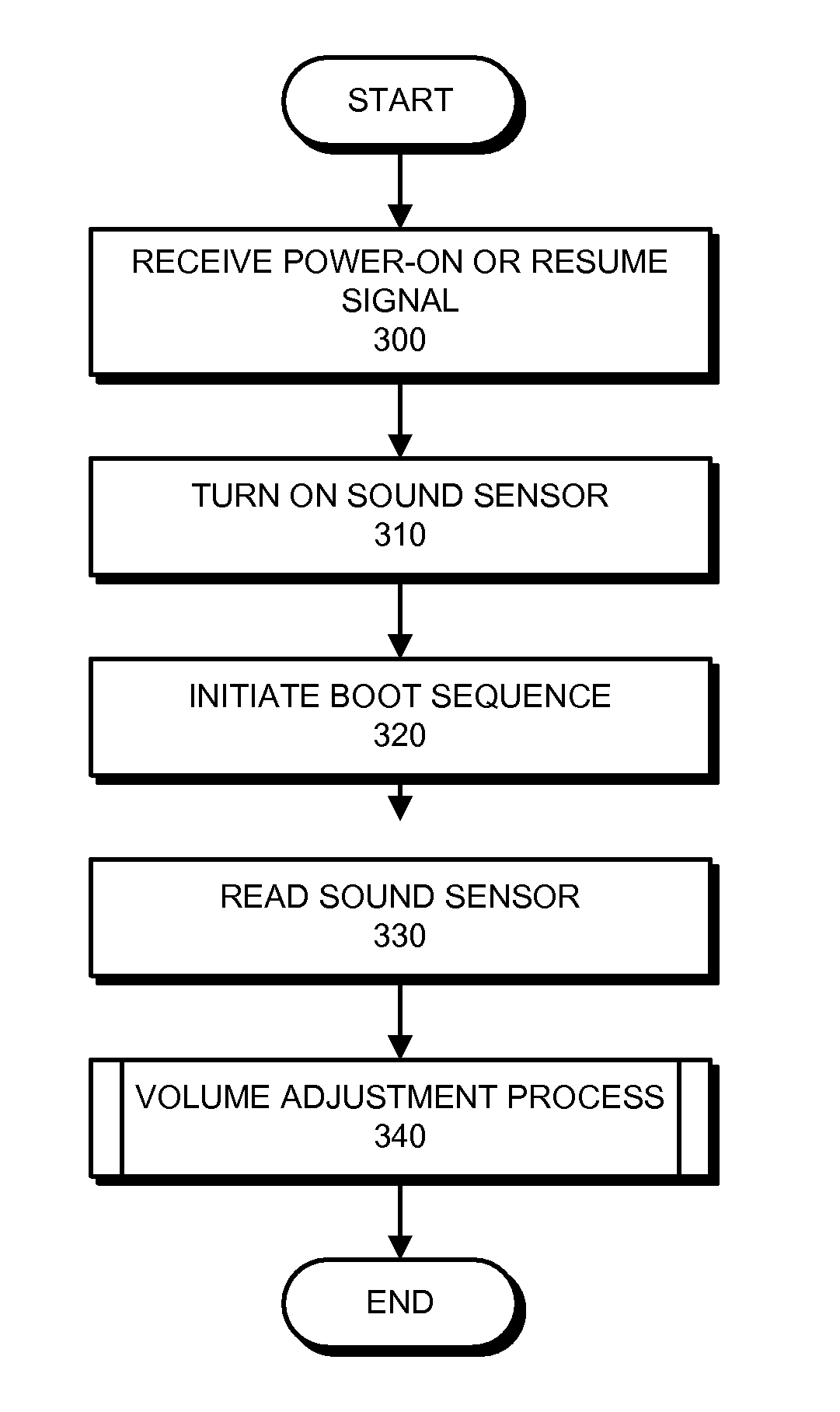
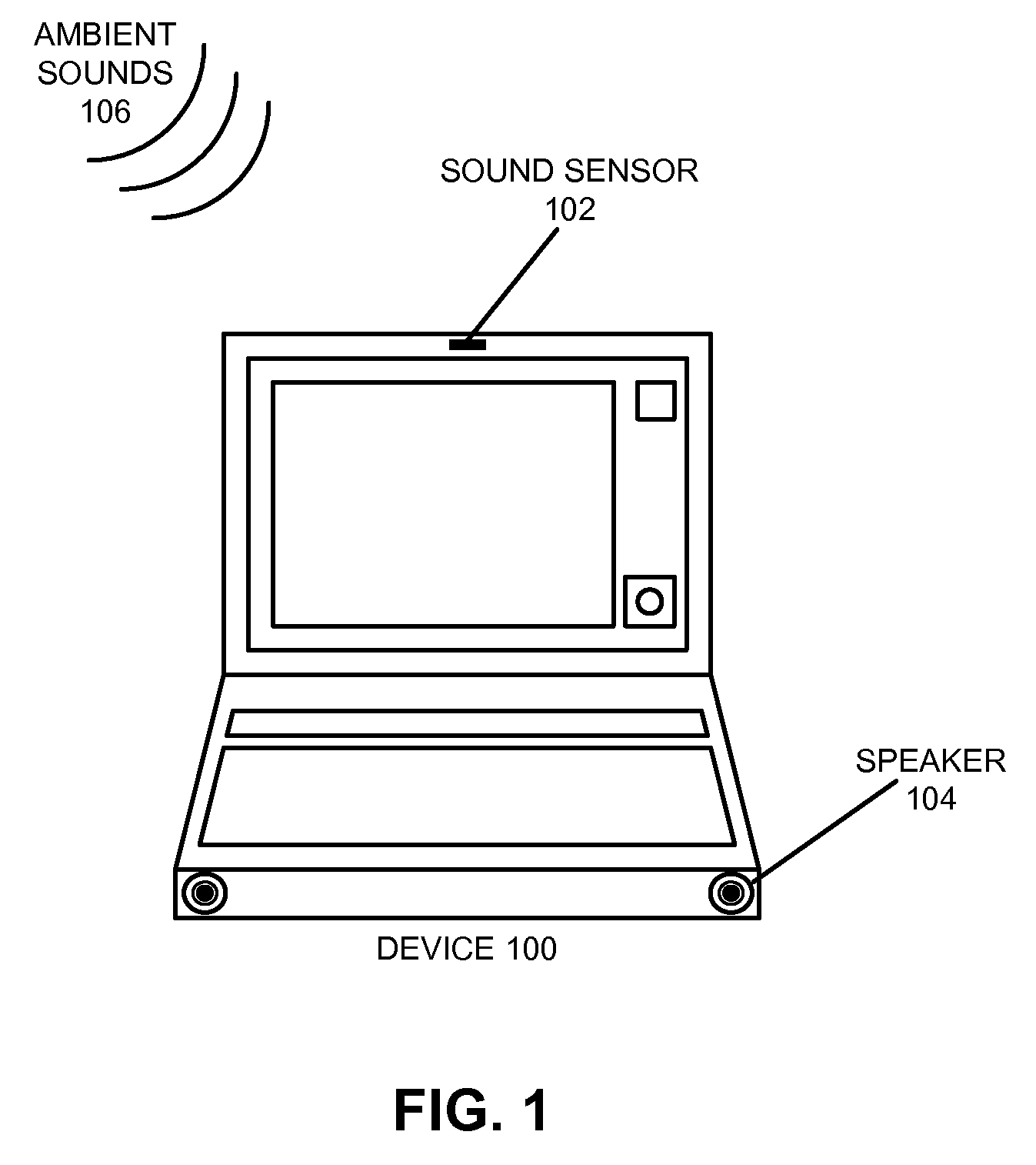
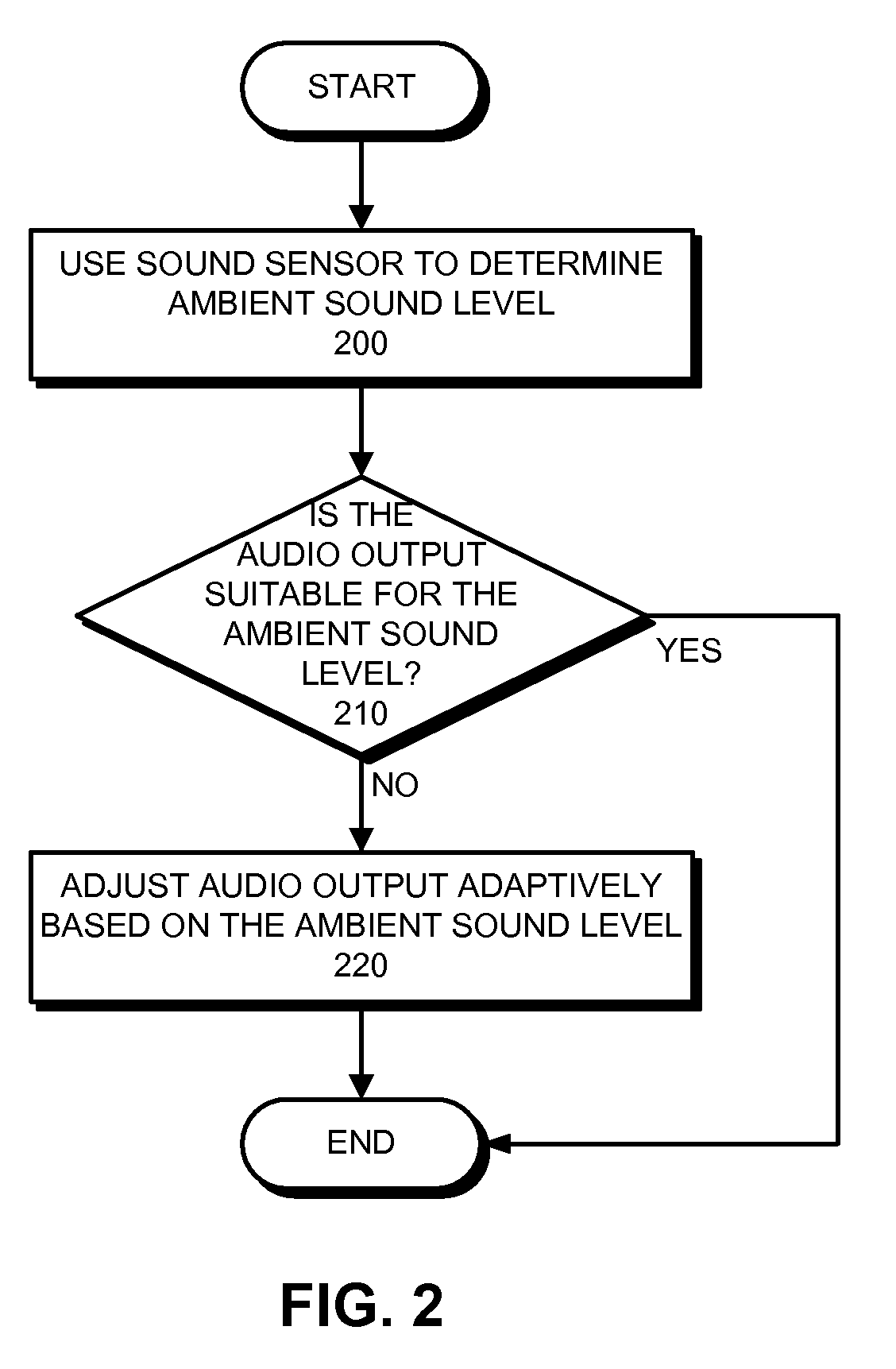
Method and apparatus for using a sound sensor to adjust the audio output for a device
ActiveUS20090022329A1Ameliorates potentially-disruptive audio outputsGain controlTransducer casings/cabinets/supportsSelf adaptiveComputer science
One embodiment of the present invention provides a system that uses a sound sensor to adjust the audio output of a device. During operation, the system uses the sound sensor to determine an ambient sound level for the environment in the proximity of the device. The system then adjusts a volume setting for the device adaptively based on the determined ambient sound level. Adaptively adjusting the volume setting allows the device to adapt to its audio environment and ameliorates potentially-disruptive audio outputs.
Owner:APPLE INC
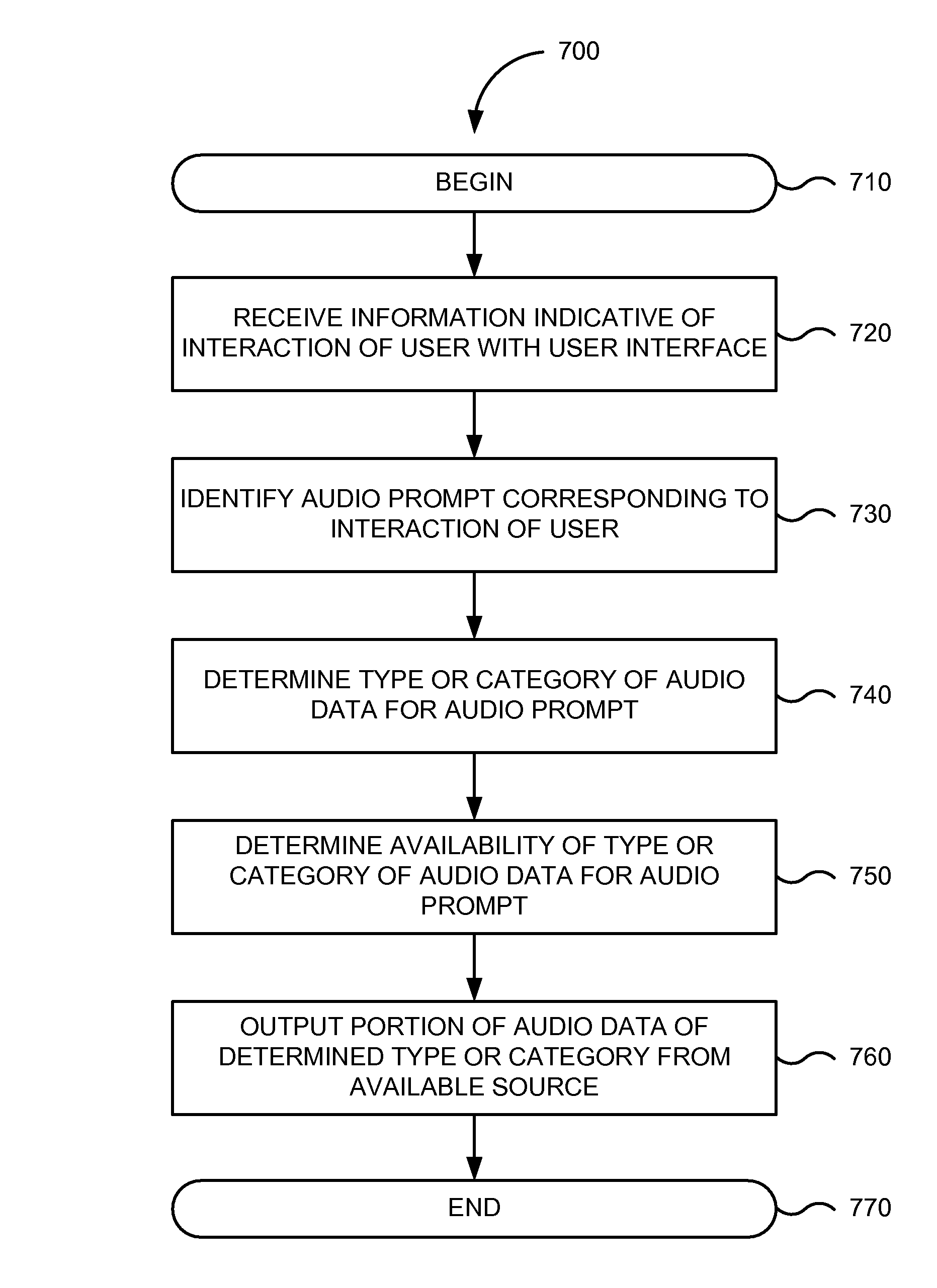
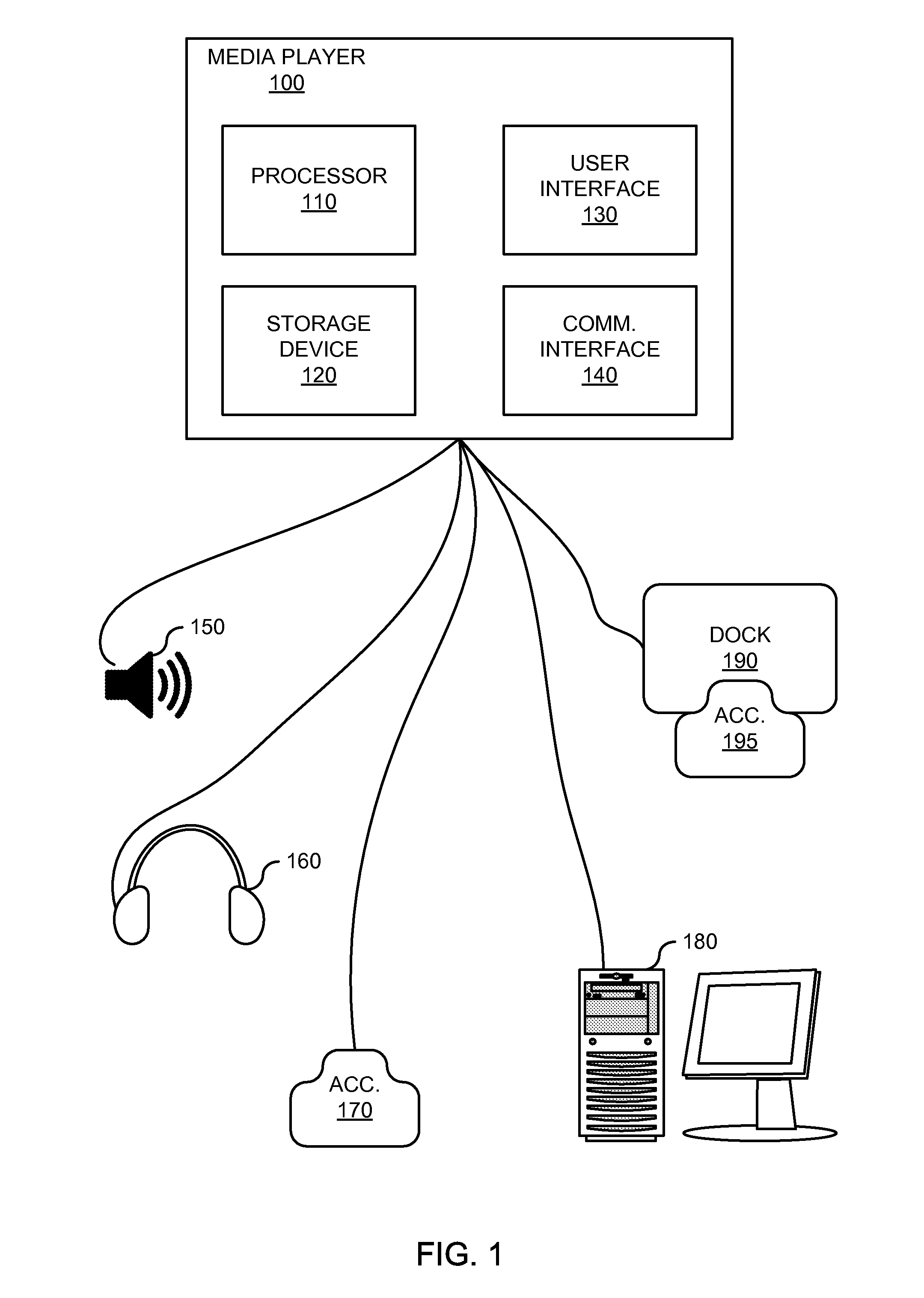
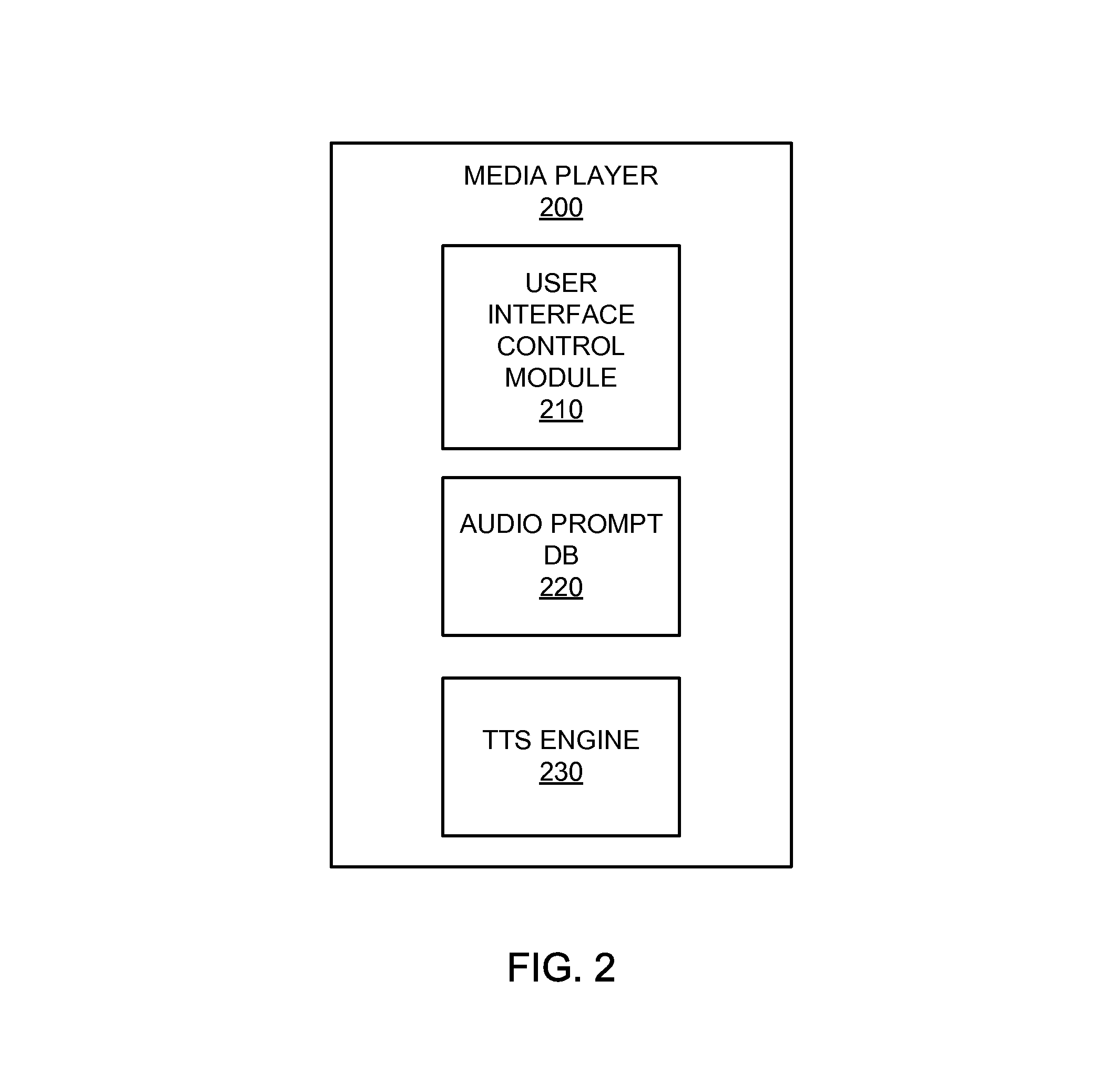
Audio user interface
InactiveUS8898568B2User may experienceImprove experienceInstruments for road network navigationGain controlNatural user interfaceHuman–computer interaction
An audio user interface that provides audio prompts that help a user interact with a user interface of an electronic device is disclosed. The audio prompts can provide audio indicators that allow a user to focus his or her visual attention upon other tasks such as driving an automobile, exercising, or crossing a street, yet still enable the user to interact with the user interface. An intelligent path can provide access to different types of audio prompts from a variety of different sources. The different types of audio prompts may be presented based on availability of a particular type of audio prompt. As examples, the audio prompts may include pre-recorded voice audio, such as celebrity voices or cartoon characters, obtained from a dedicate voice server. Absent availability of pre-recorded or synthesized audio data, non-voice audio prompts may be provided.
Owner:APPLE INC
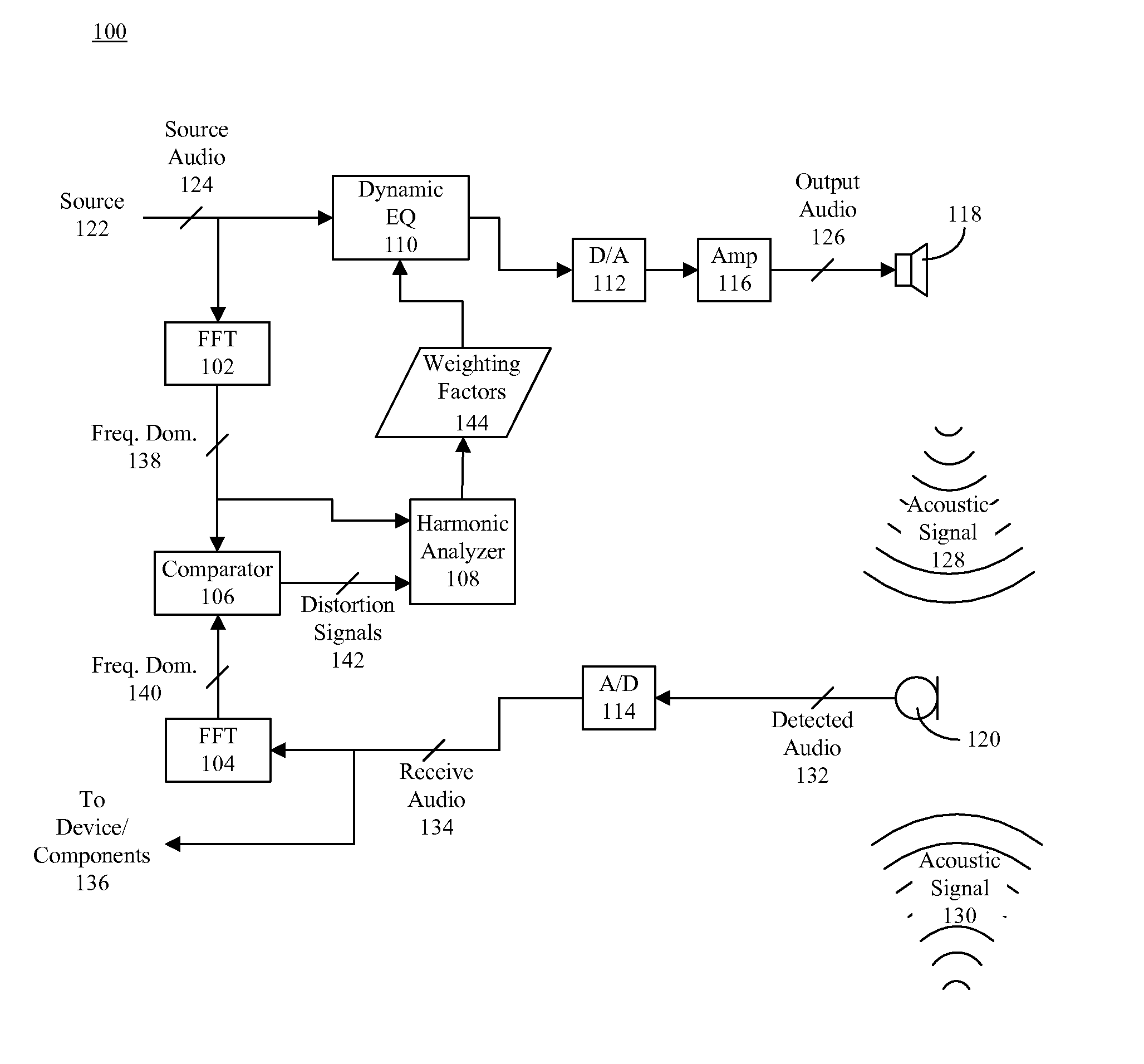
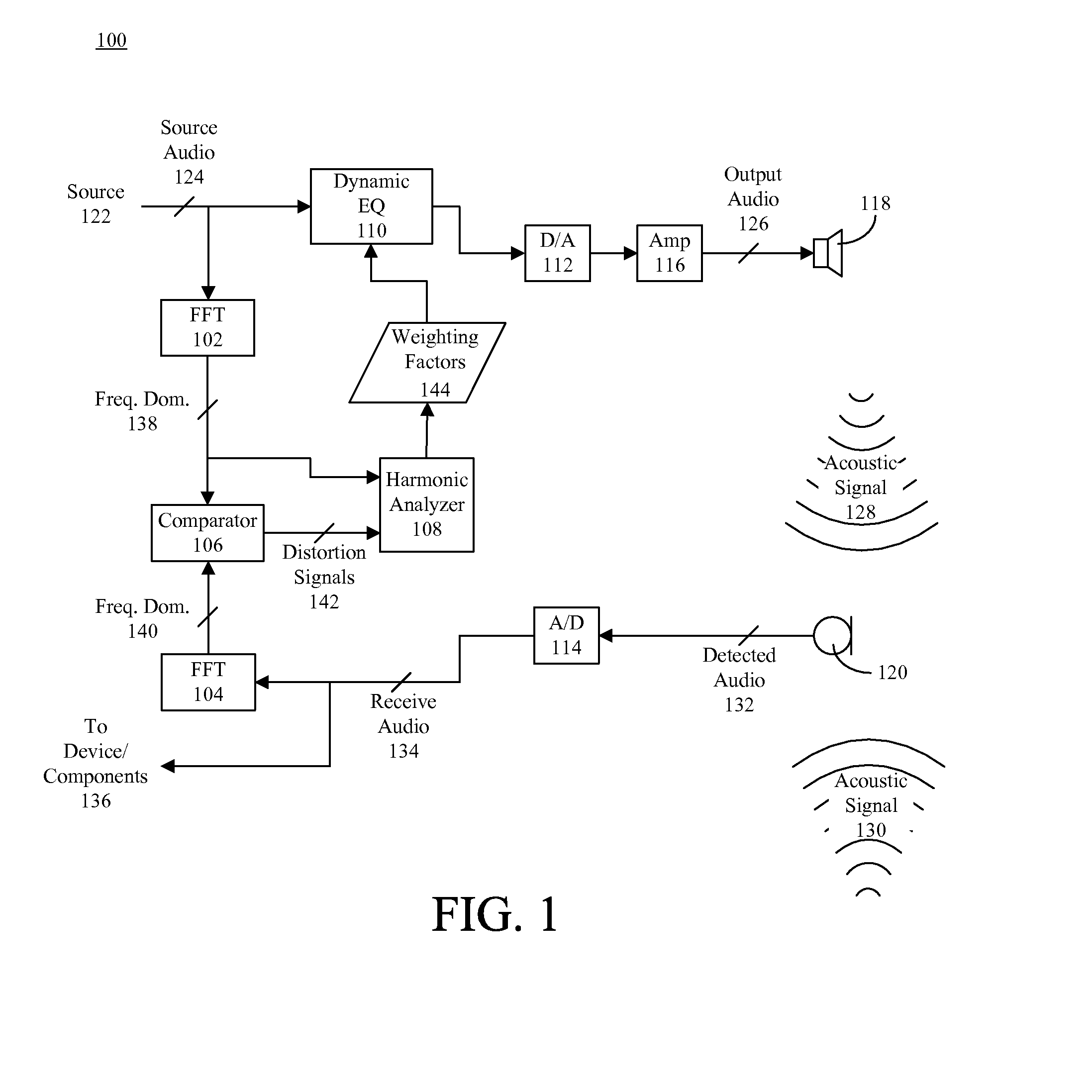
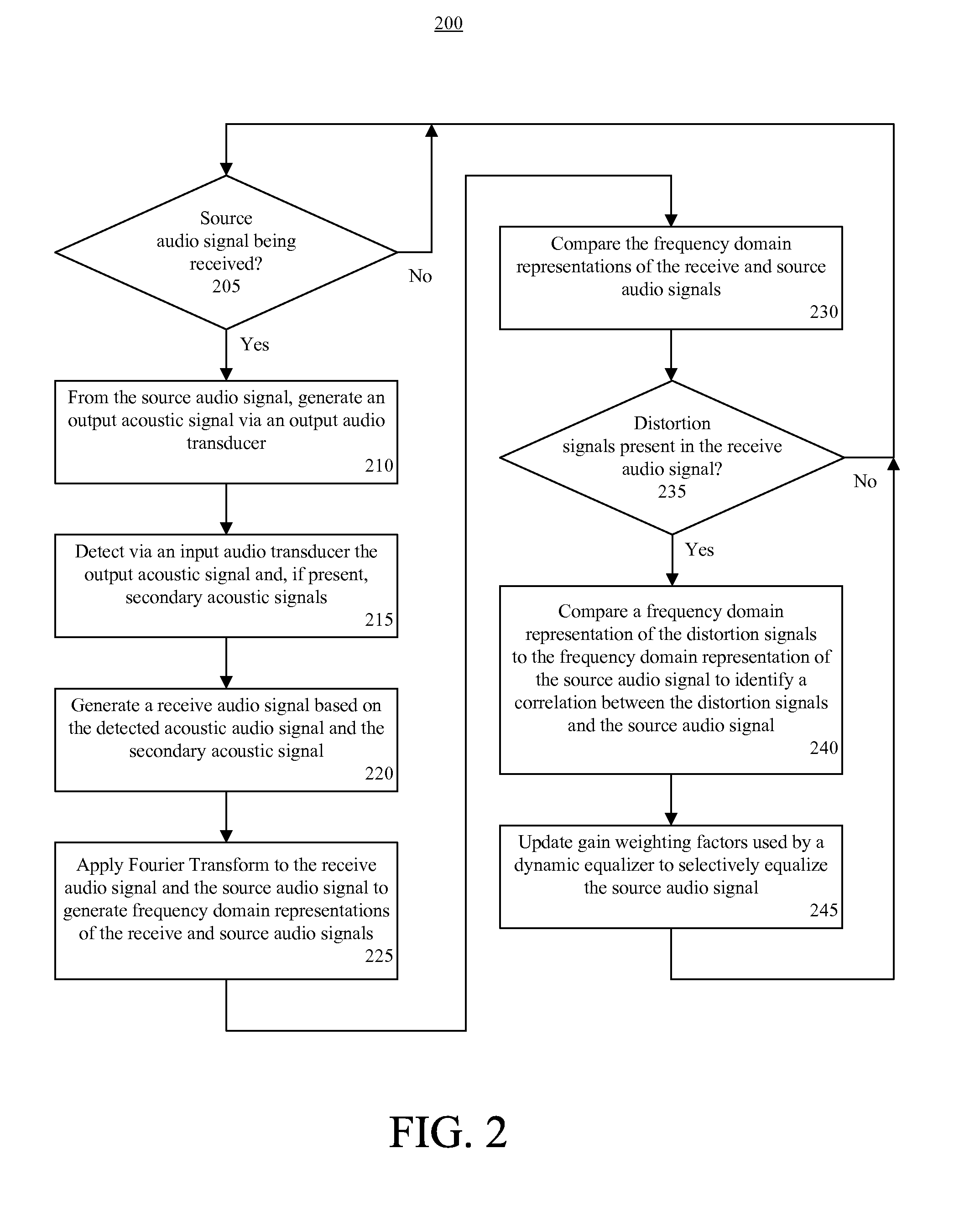
Dynamic distortion elimination for output audio
InactiveUS8045721B2Quality improvementInterconnection arrangementsGain controlTime–frequency representationComputer science
A method (200) for improving quality of output audio (126). The method can include detecting an output acoustic signal (128) and generating a receive audio signal (134) based, at least in part, on the detected output acoustic signal. A frequency domain representation (140) of the receive audio signal can be compared to a frequency domain representation (138) of a source audio signal (124) from which the output acoustic signal is generated. At least one distortion signal (142) in the receive audio signal can be identified, and the source audio signal can be selectively equalized to reduce an amplitude of the source audio signal at a frequency that correlates to the distortion signal.
Owner:GOOGLE TECHNOLOGY HOLDINGS LLC
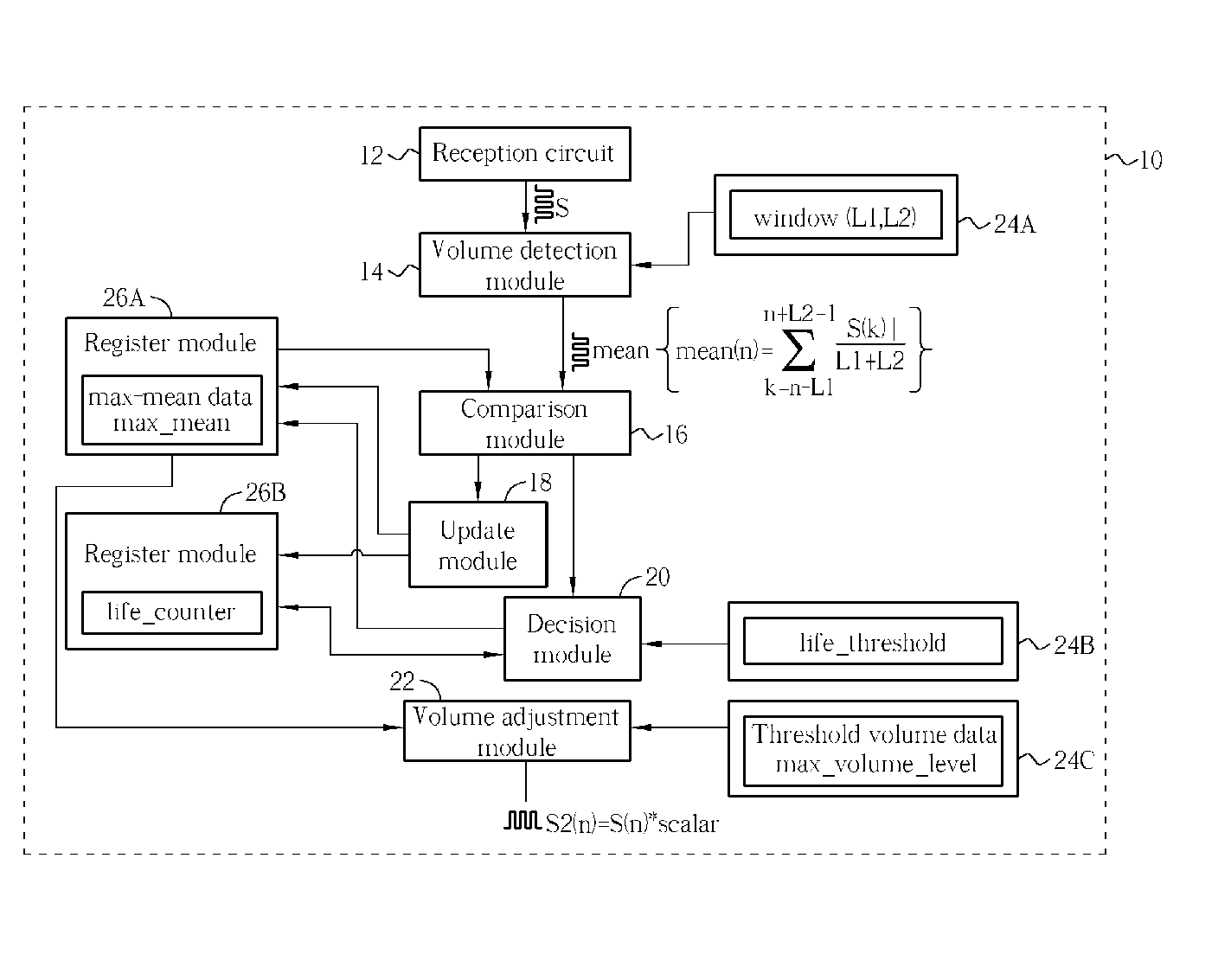
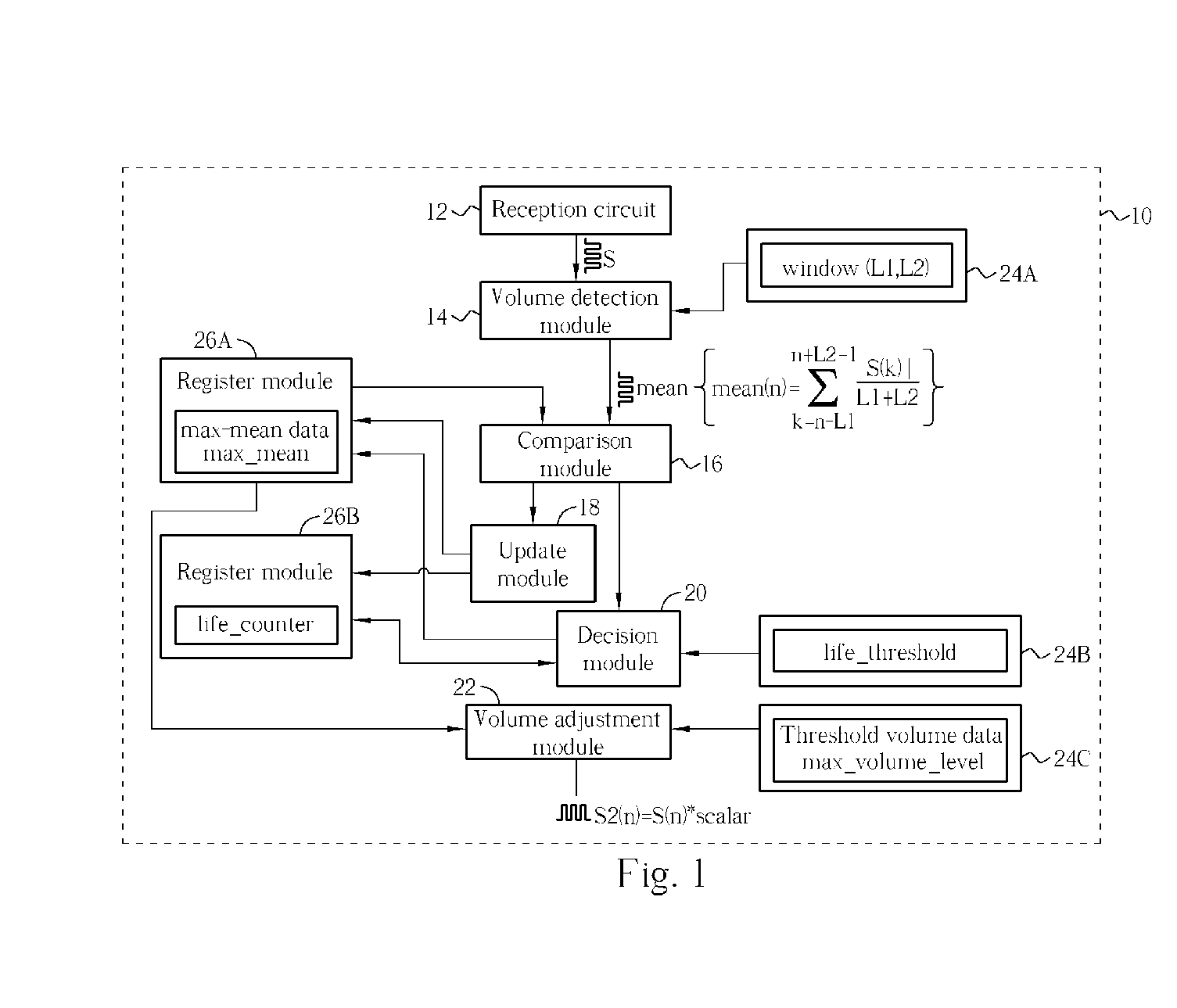
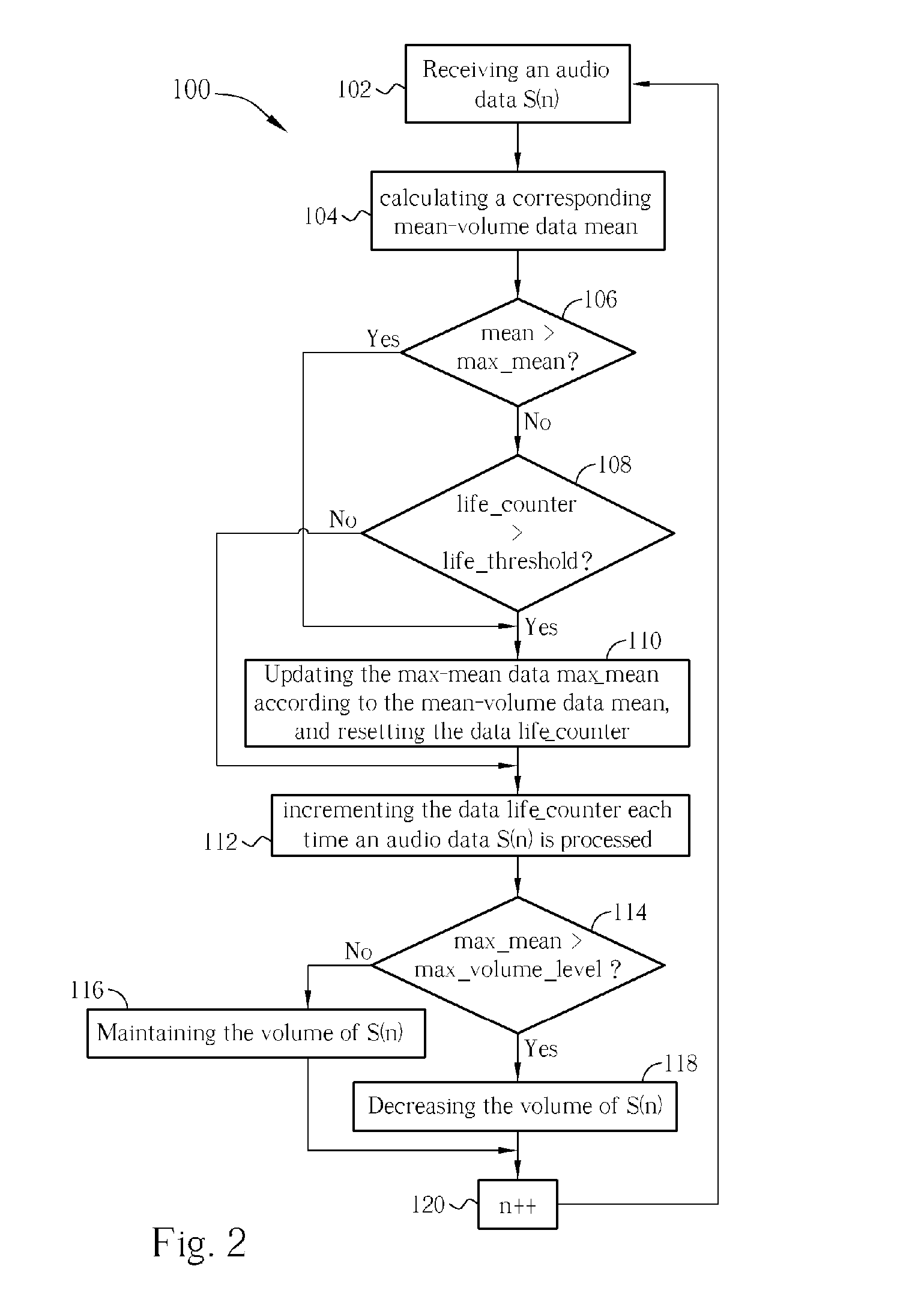
Methods and related circuit for automatic audio volume level control
Methods and related circuit for automatic volume-tracking and controlling of an audio signal. The audio signal has a plurality of sampled audio data, and the method includes: for each of the audio data, calculating a mean-volume data according to neighboring audio data; if the mean-volume data is larger than a recorded max-mean data, then updating the max-mean data, otherwise keeping the max-mean data not updated; and recording whether the max-mean data is updated. After performing aforementioned steps for a predetermined number of audio data, if the max-mean data is still not updated, then updating the max-mean data according to current mean-volume data. Thus the max-mean data can reflects local maximum volume of the audio signal, and the invention can control the volume of the audio signal accordingly.
Owner:ALICORP
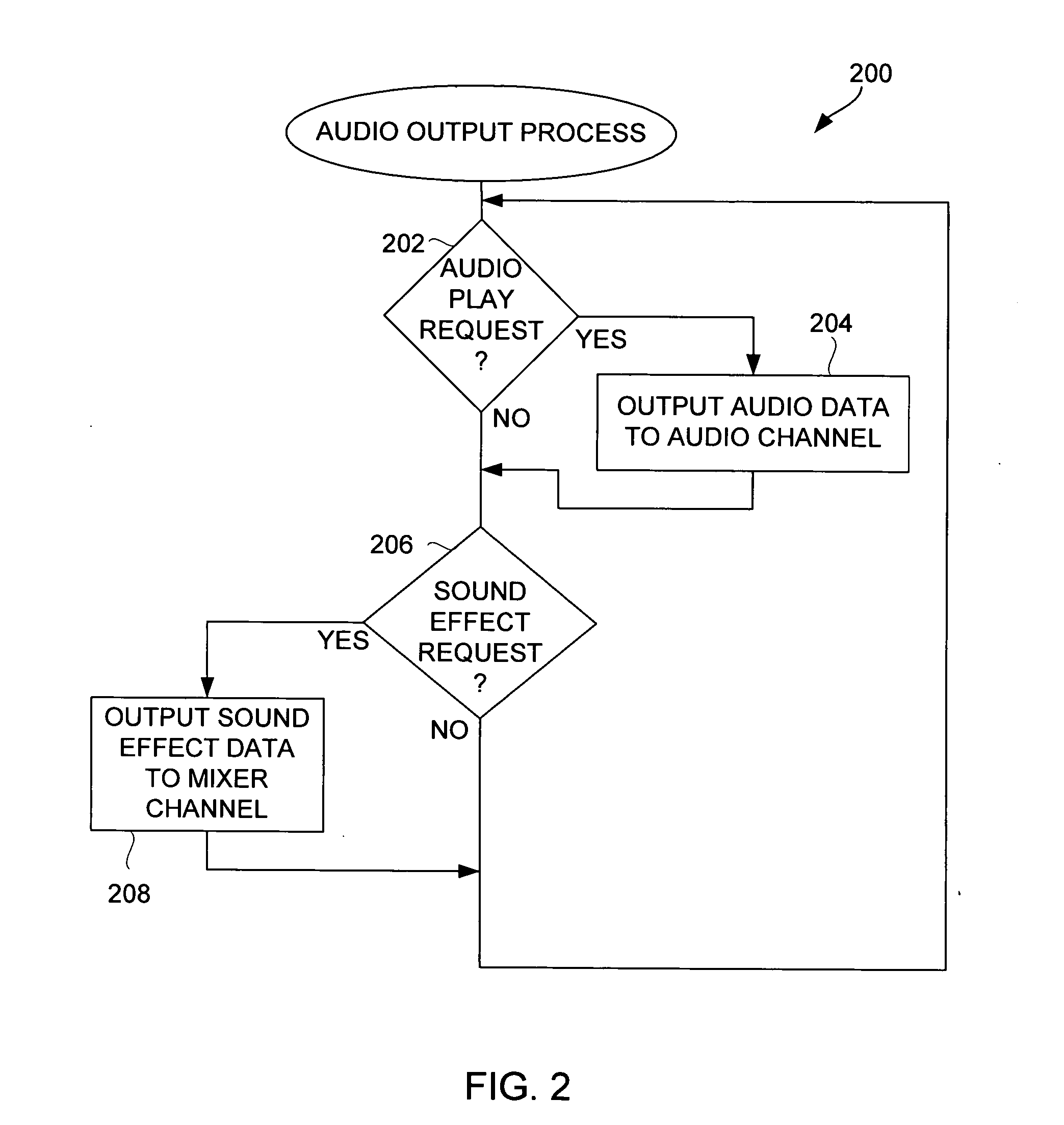
Techniques for presenting sound effects on a portable media player
ActiveUS20060274905A1Good choiceProvide feedbackElectrophonic musical instrumentsGain controlAuditory feedbackLoudspeaker
Improved techniques for presenting sound effects at a portable media device are disclosed. The sound effects can be output as audio sounds to an internal speaker, an external speaker, or both. In addition, the audio sounds for the sound effects can be output together with other audio sounds pertaining to media assets (e.g., audio tracks being played). In one embodiment, the sound effects can serve to provide auditory feedback to a user of the portable media device. A user interface can facilitate a user's selection of sound effect usages, types or characteristics.
Owner:APPLE INC
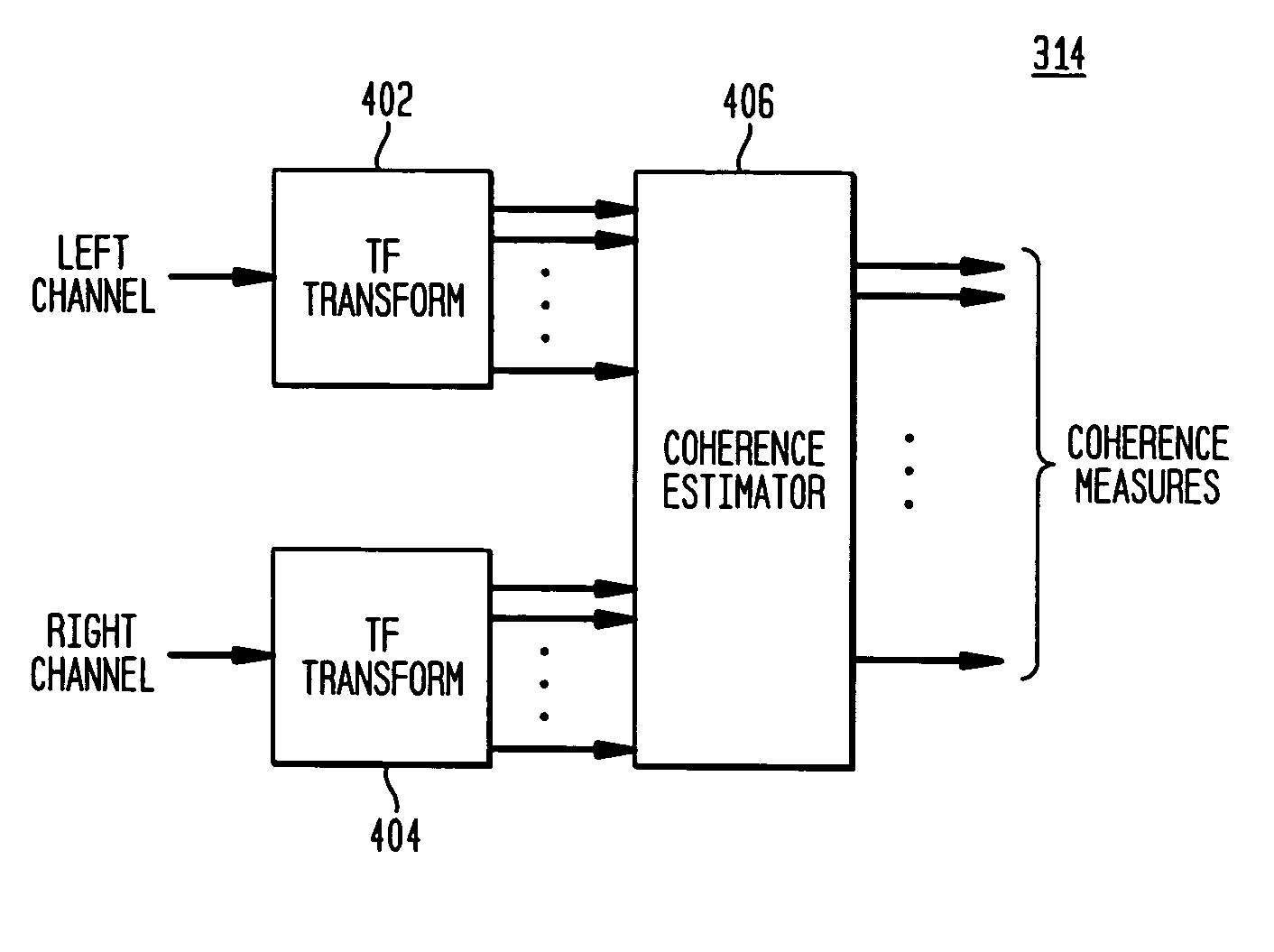
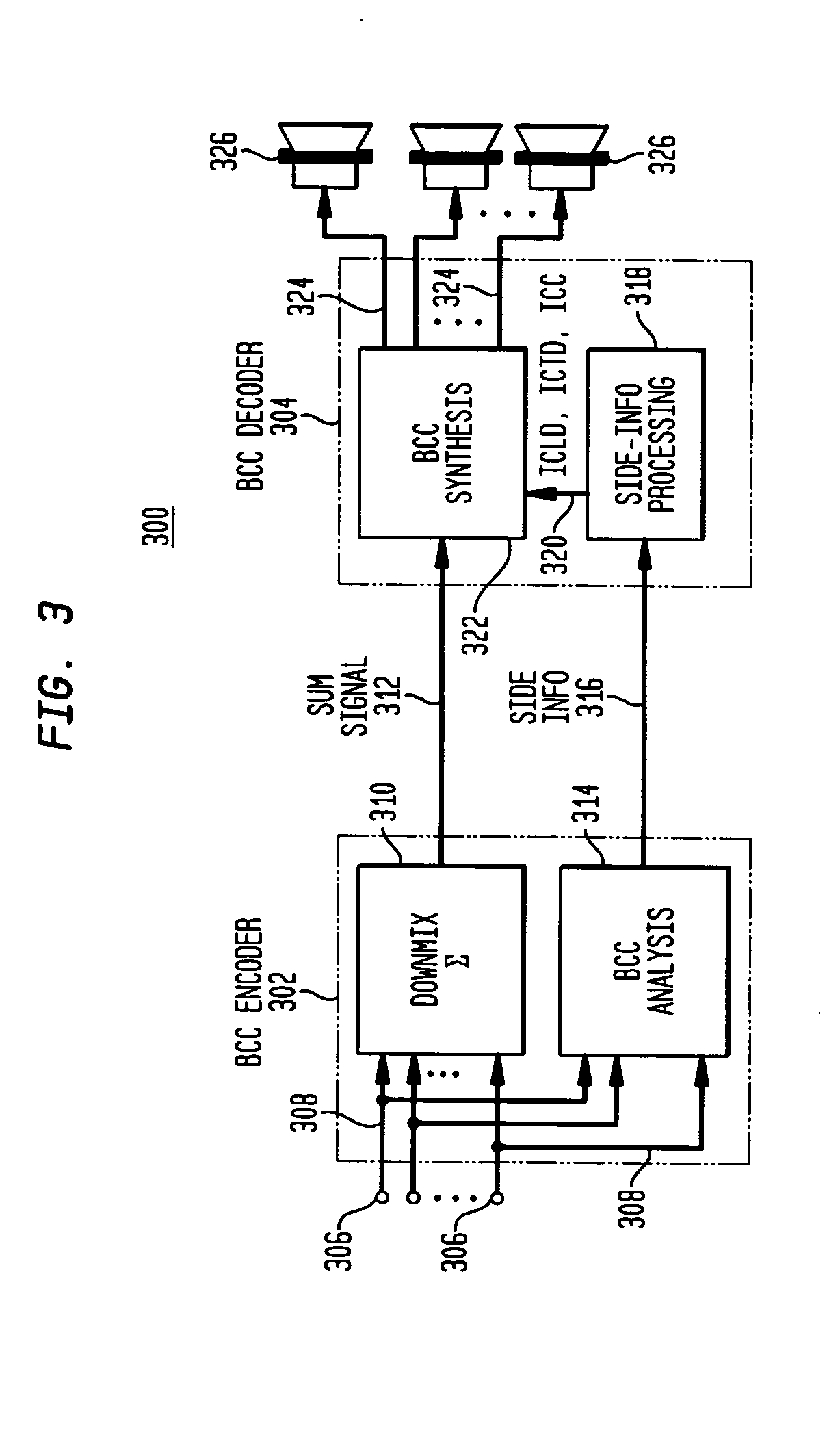
Late reverberation-based synthesis of auditory scenes
ActiveUS20050180579A1Reduce transmission bandwidth requirementsReduce bandwidth requirementsGain controlSpeech analysisComputation complexityChannel correlation
A scheme for stereo and multi-channel synthesis of inter-channel correlation (ICC) (normalized cross-correlation) cues for parametric stereo and multi-channel coding. The scheme synthesizes ICC cues such that they approximate those of the original. For that purpose, diffuse audio channels are generated and mixed with the transmitted combined (e.g., sum) signal(s). The diffuse audio channels are preferably generated using relatively long filters with exponentially decaying Gaussian impulse responses. Such impulse responses generate diffuse sound similar to late reverberation. An alternative implementation for reduced computational complexity is proposed, where inter-channel level difference (ICLD), inter-channel time difference (ICTD), and ICC synthesis are all carried out in the domain of a single short-time Fourier transform (STFT), including the filtering for diffuse sound generation.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Method and apparatus for using a sound sensor to adjust the audio output for a device
ActiveUS8306235B2Ameliorates potentially-disruptive audio outputsGain controlTransducer casings/cabinets/supportsEngineeringAudio frequency
One embodiment of the present invention provides a system that uses a sound sensor to adjust the audio output of a device. During operation, the system uses the sound sensor to determine an ambient sound level for the environment in the proximity of the device. The system then adjusts a volume setting for the device adaptively based on the determined ambient sound level. Adaptively adjusting the volume setting allows the device to adapt to its audio environment and ameliorates potentially-disruptive audio outputs.
Owner:APPLE INC
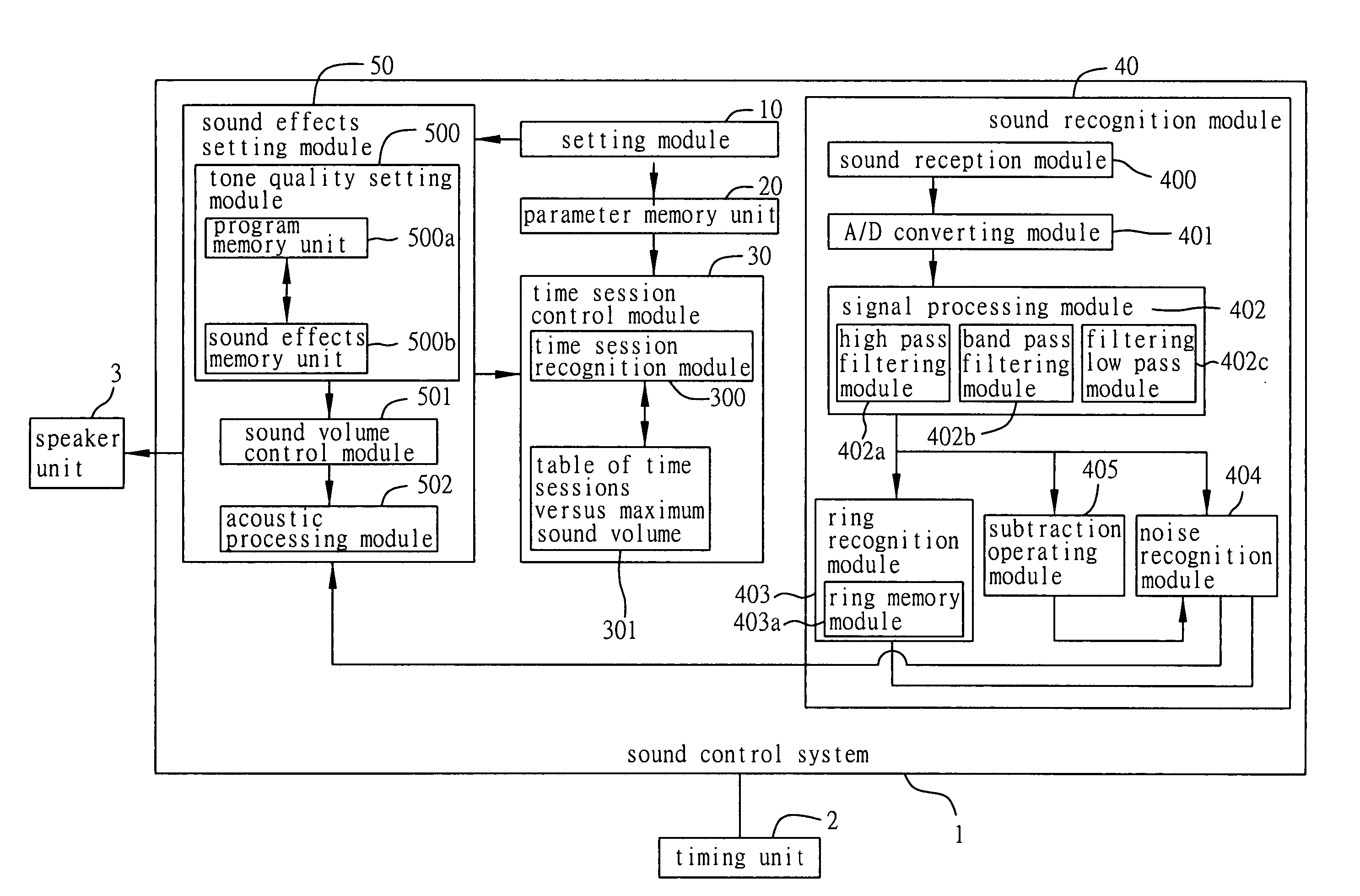
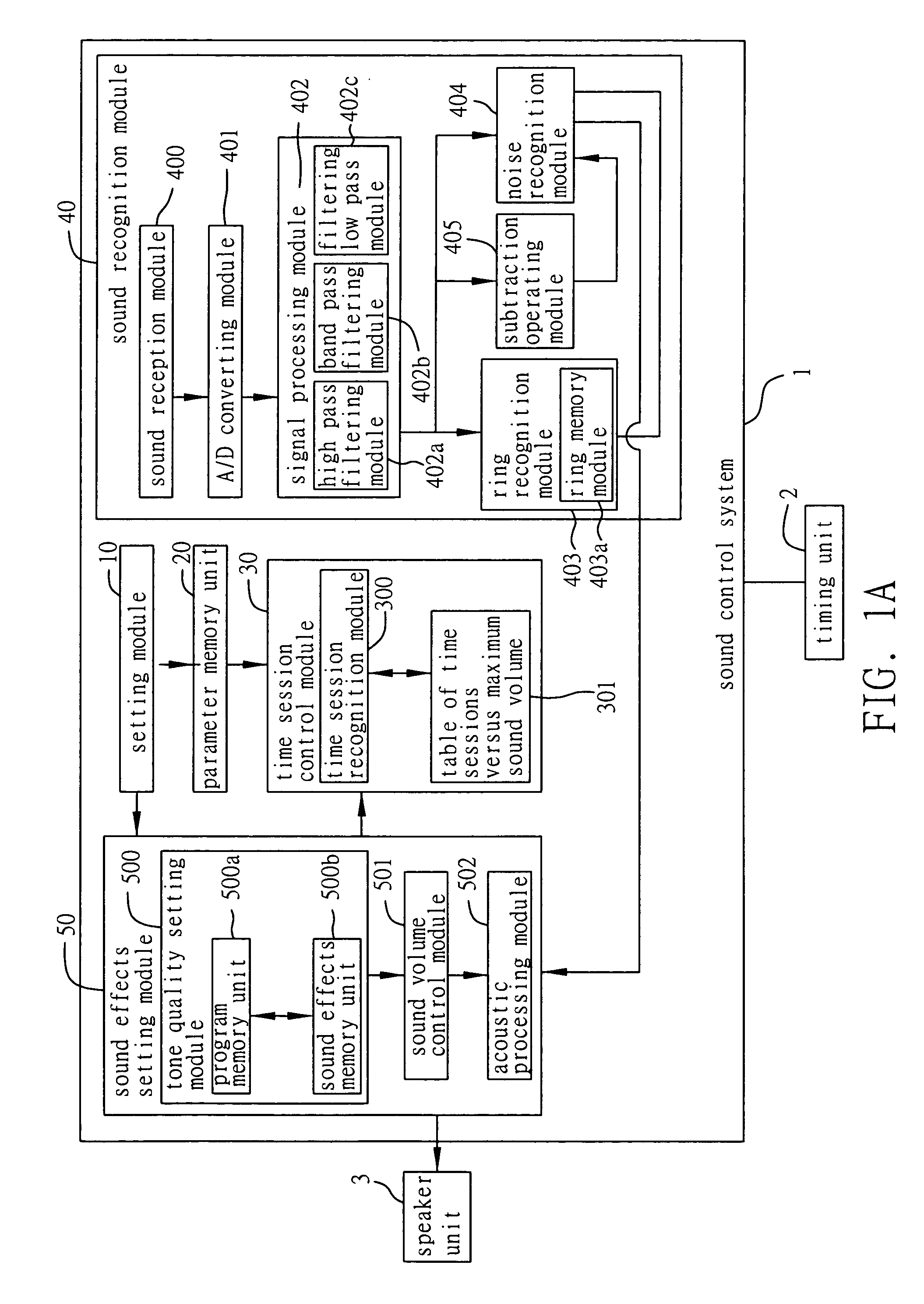
Sound control system and method
InactiveUS20060018492A1Realize automatic adjustmentImprove soundGain controlTwo-channel systemsControl systemSession control
A sound control system and method applicable to an electronic device having a timing unit. A setting module is provided to set predetermined conditions and corresponding sound volume parameters. A time session control module retrieves the sound volume parameter corresponding to a present condition obtained by the timing unit. Then, a corresponding sound output signal to be outputted by a speaker unit connected to the sound control system is set via a sound effects module according to the sound volume parameter and a sound signal around the electronic device that is received and recognized by a sound recognition module. By such arrangement, the sound control system and method allow the electronic device to provide the user with optimal sound effects depending on the environment and the user's preferences.
Owner:INVENTEC CORP
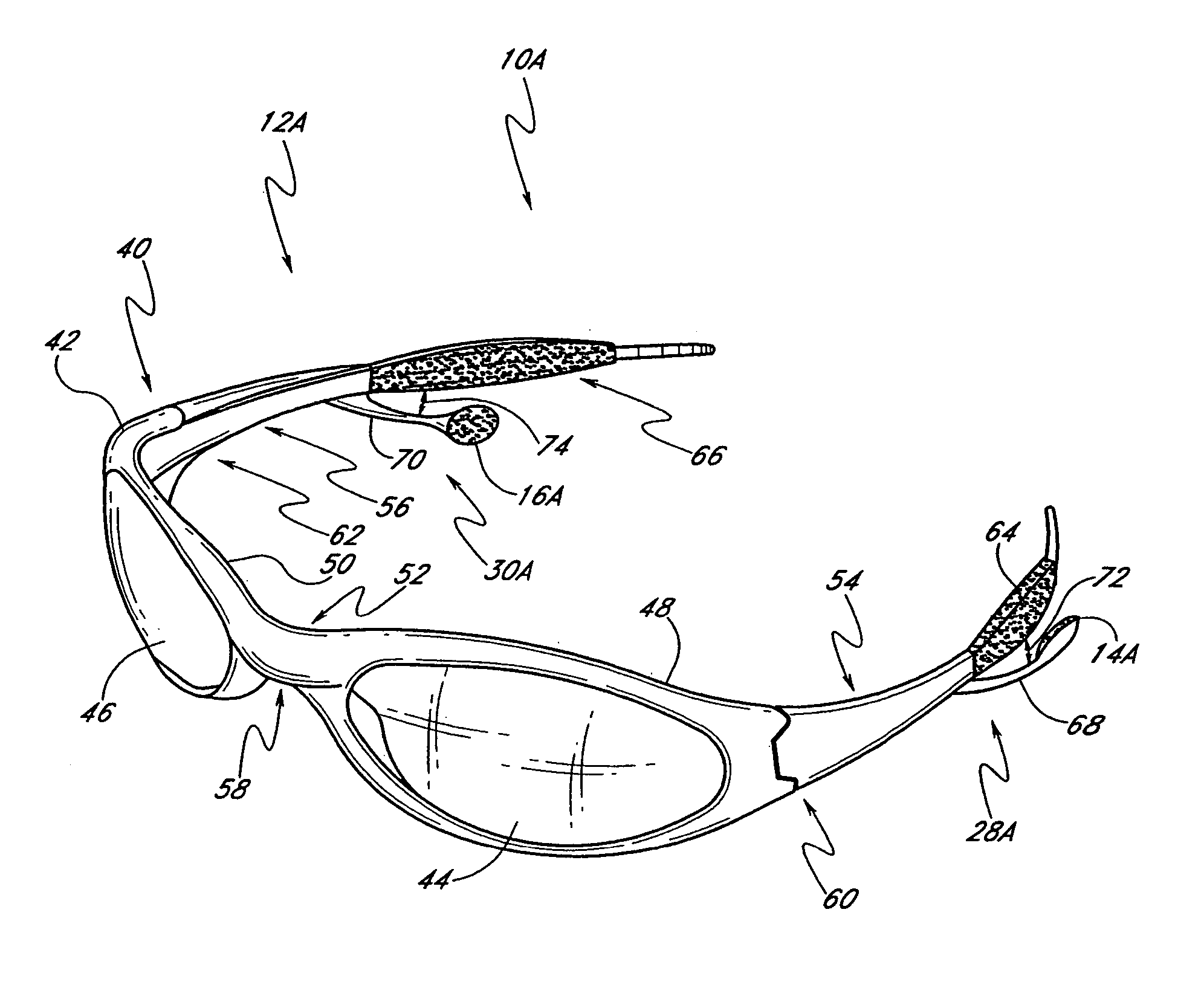
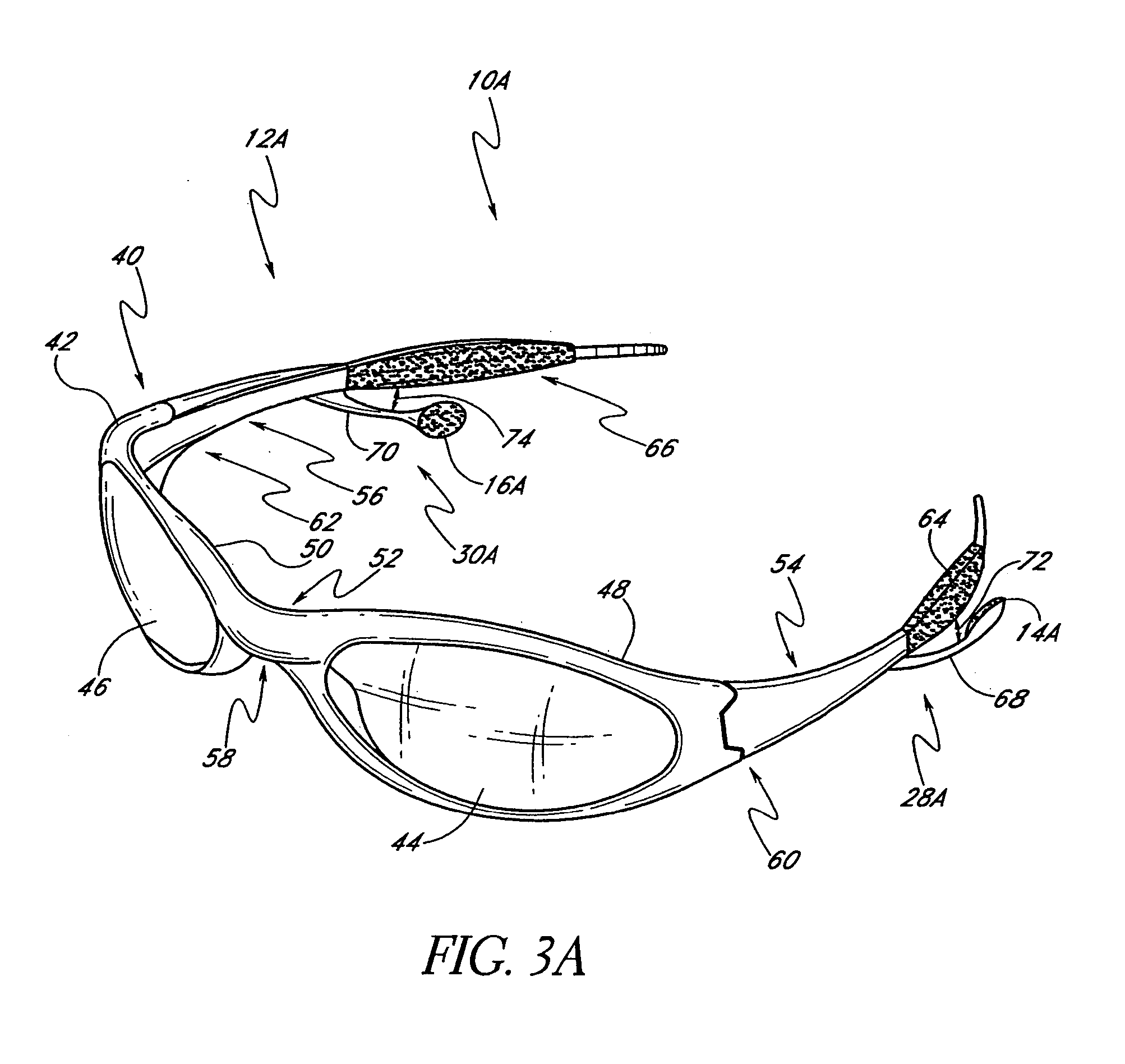
Wireless interactive headset
A wearable wireless audio device includes a support, an electronics circuit, and a speaker. The support includes a first ear stem and an orbital, and is configured to support at least one lens in a wearer's field of view. The electronics circuit is supported by the support and is configured to receive at least one digital audio file and generate an audio signal indicative of the at least one digital audio file. The speaker is supported by the support, and is directed toward at least one of the wearer's ears. The speaker is configured to convert the audio signal into sound. The speaker has a speaker face, and the speaker is configured to rotate from a first position in which the speaker face is substantially parallel to a yz-plane to a second position in which the speaker is inclined at an angle with respect to the yz-plane. The speaker is coupled to the support with a speaker pivot, and is configured to rotate about the speaker pivot while maintaining the speaker face substantially parallel to a yz-plane. The speaker is configured to move along an axis substantially parallel to a z-axis with respect to the support.
Owner:OAKLEY INC
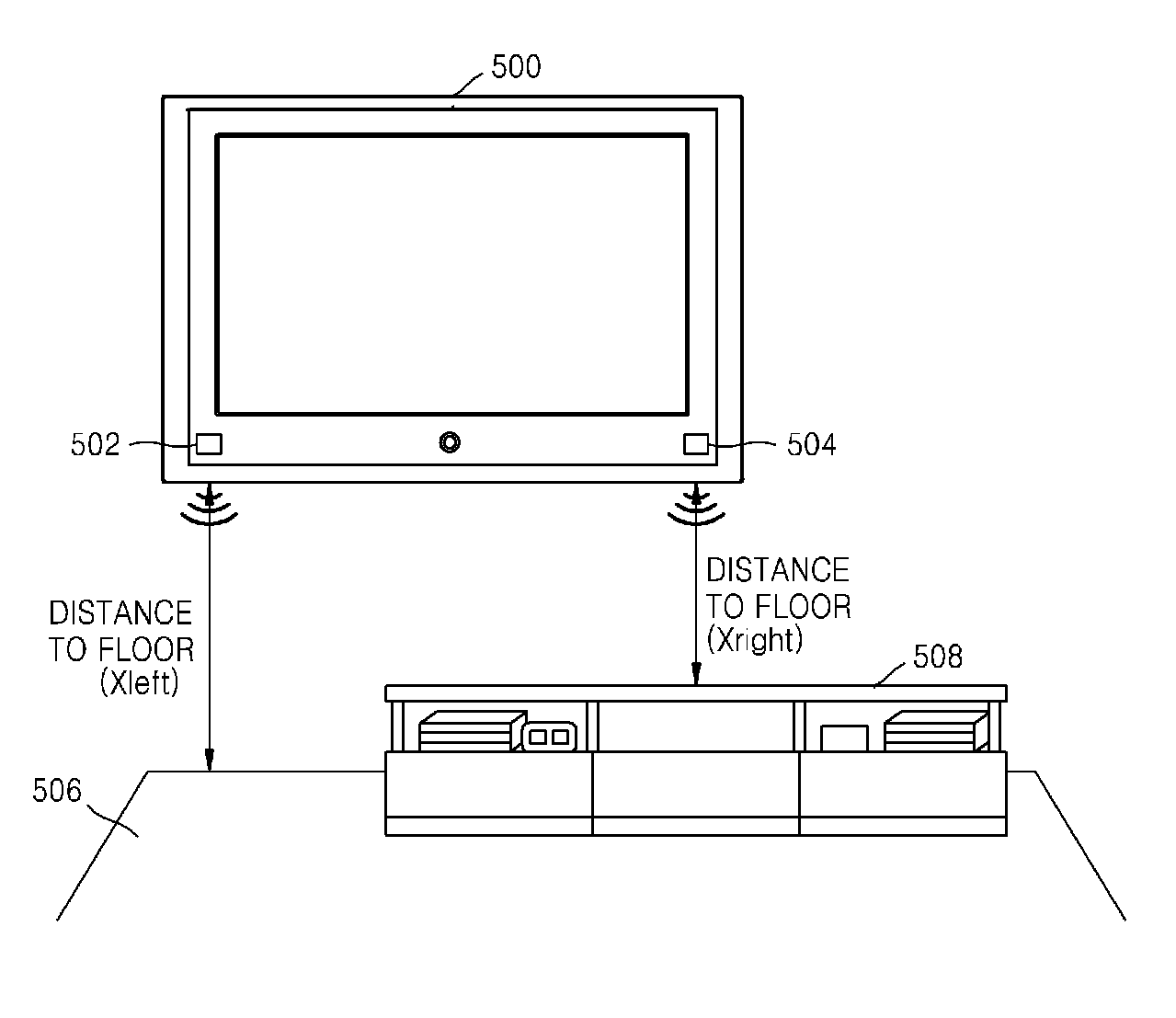
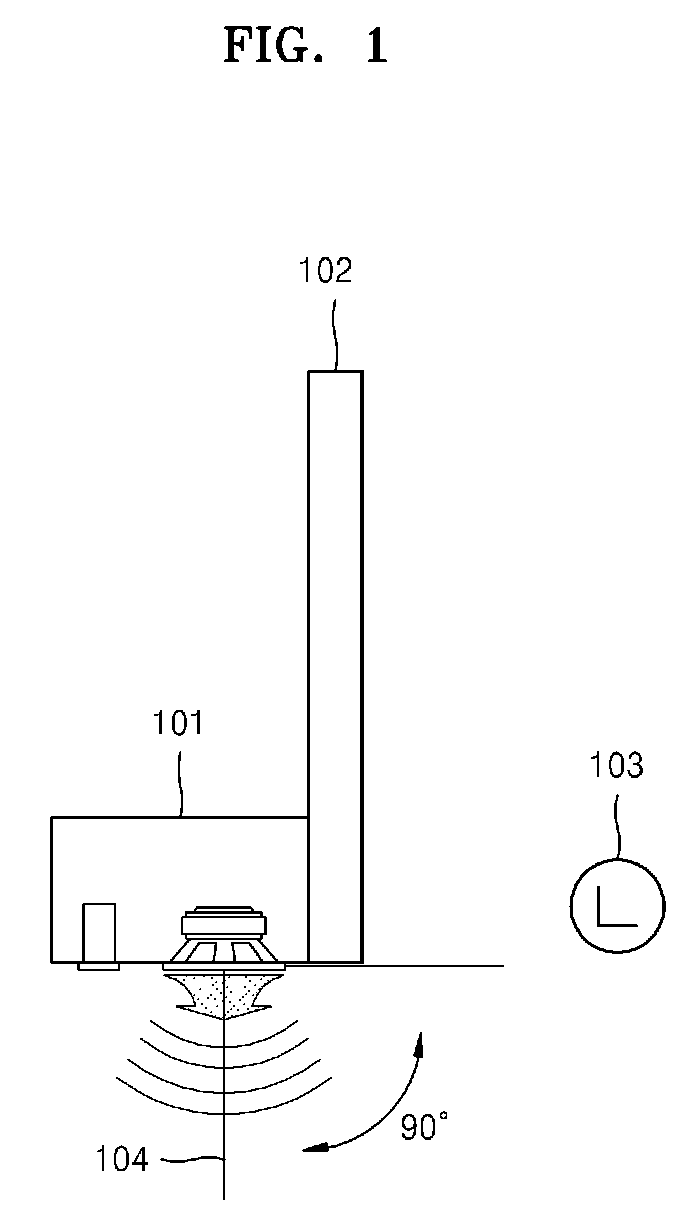
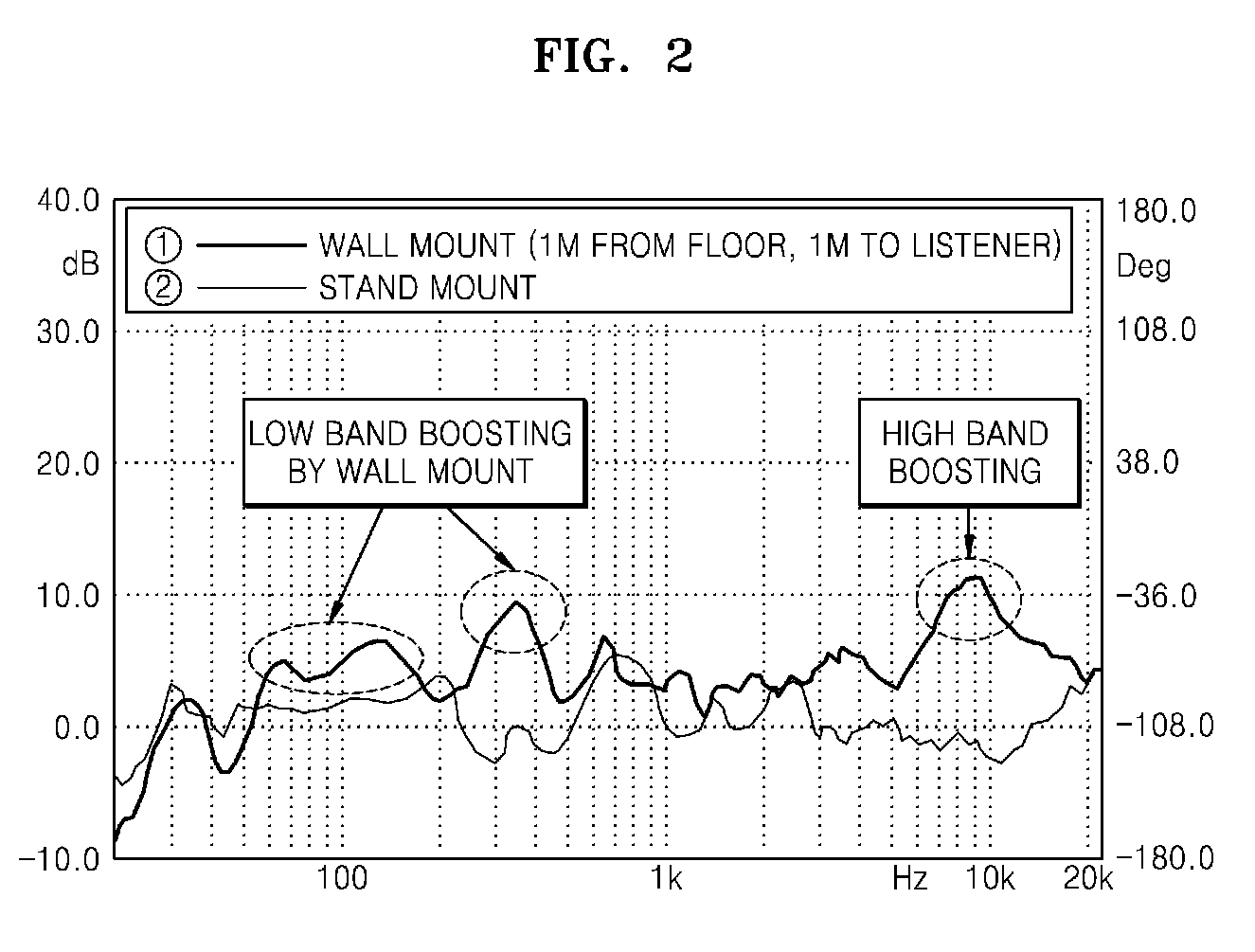
Method of compensating for audio frequency characteristics and audio/video apparatus using the method
A method of compensating for spatial audio frequency characteristics that varies in accordance with a mounting condition of a down firing speaker of an audio / video (AV) apparatus includes calculating a listening distance between the AV apparatus and a listener, calculating a distance between a speaker mounted on the AV apparatus and a neighboring reflective surface, setting a spatial frequency compensation filter value and a speaker frequency characteristic compensation filter value based on the calculated distances, and compensating for frequency characteristics of an audio signal by combining the spatial frequency compensation filter value and the speaker frequency characteristic compensation filter value.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Network-enabled audio device
InactiveUS20070089132A1Optimize allocationReception of a broadcast from the World Wide Web is no more complicatedTelevision system detailsGain controlThe InternetDisplay device
A network-enabled audio device that provides a display device that allows the user to select playlists of music much like a jukebox is disclosed. The user can compose playlists from disk files, CD's, Internet streaming audio broadcasts, online music sites, and other audio sources. The user can also select a desired Web broadcast from a list of available Web broadcasts. In addition, the user can play standard audio CD's and MP3 encoded CD's and have access to local AM / FM stations. Further, the software, the user controls, and the display in the network-enabled audio device are operably configured and connected such that the user can listen to playlists that include CD's and other audio sources just as the user would choose a playlist in a jukebox. The user accesses a server site via a PC and the Internet. From the server site, the user obtains a list of the devices in his or her Internet Personal Audio Network (IPAN) and what songs are on those devices. The IPAN includes an IPAN server, an IPAN client, and IPAN software stored on the network-enabled audio device. Thus, the network-enabled audio device provides people who are or are not comfortable with computers a way of taking music from various sources and putting it into one place for listening pleasure. In one embodiment, the Personal Computer (PC) is used to compose the playlists, but the user is able to listen to playlists and other audio sources without using the PC.
Owner:GOLDEN IP LLC
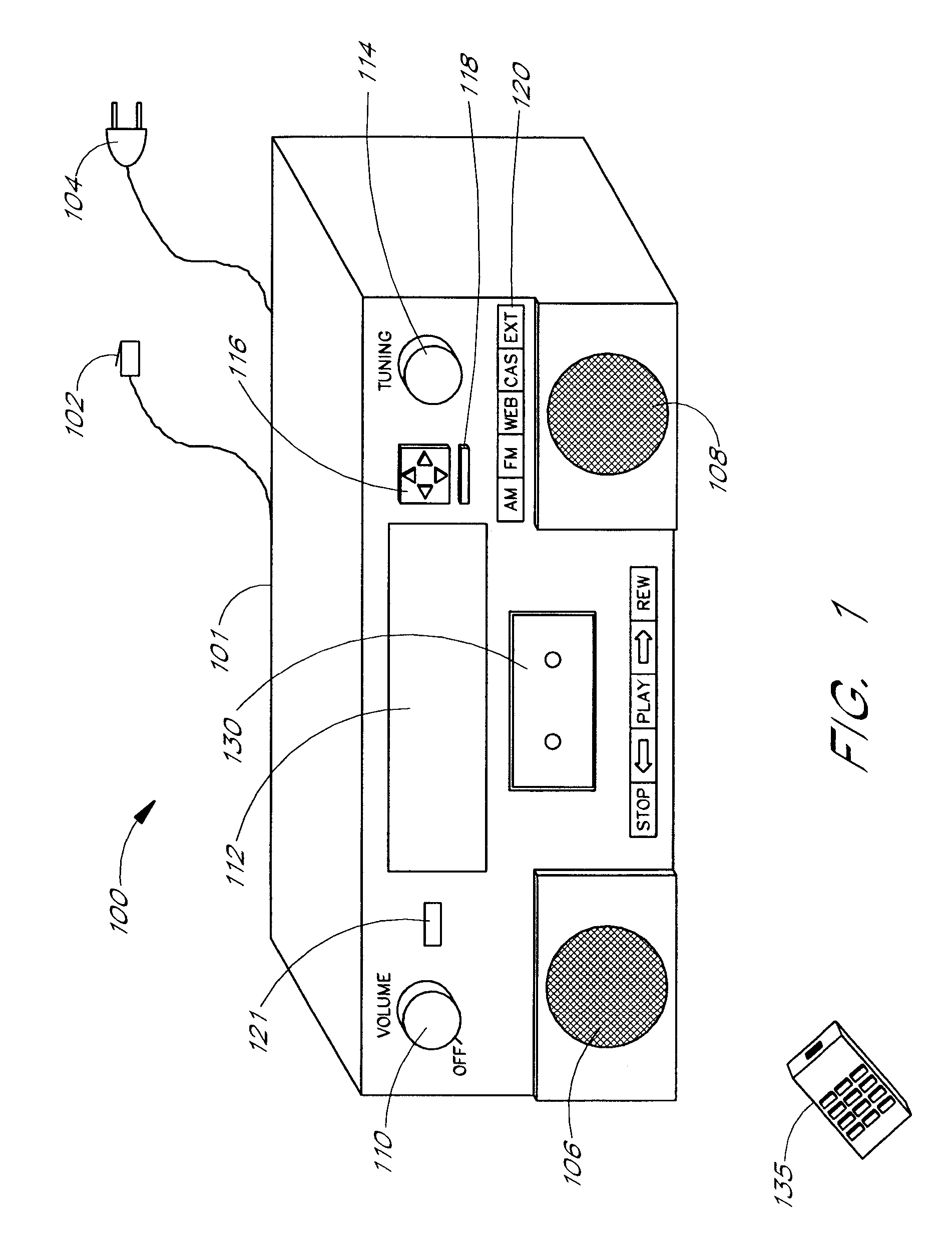
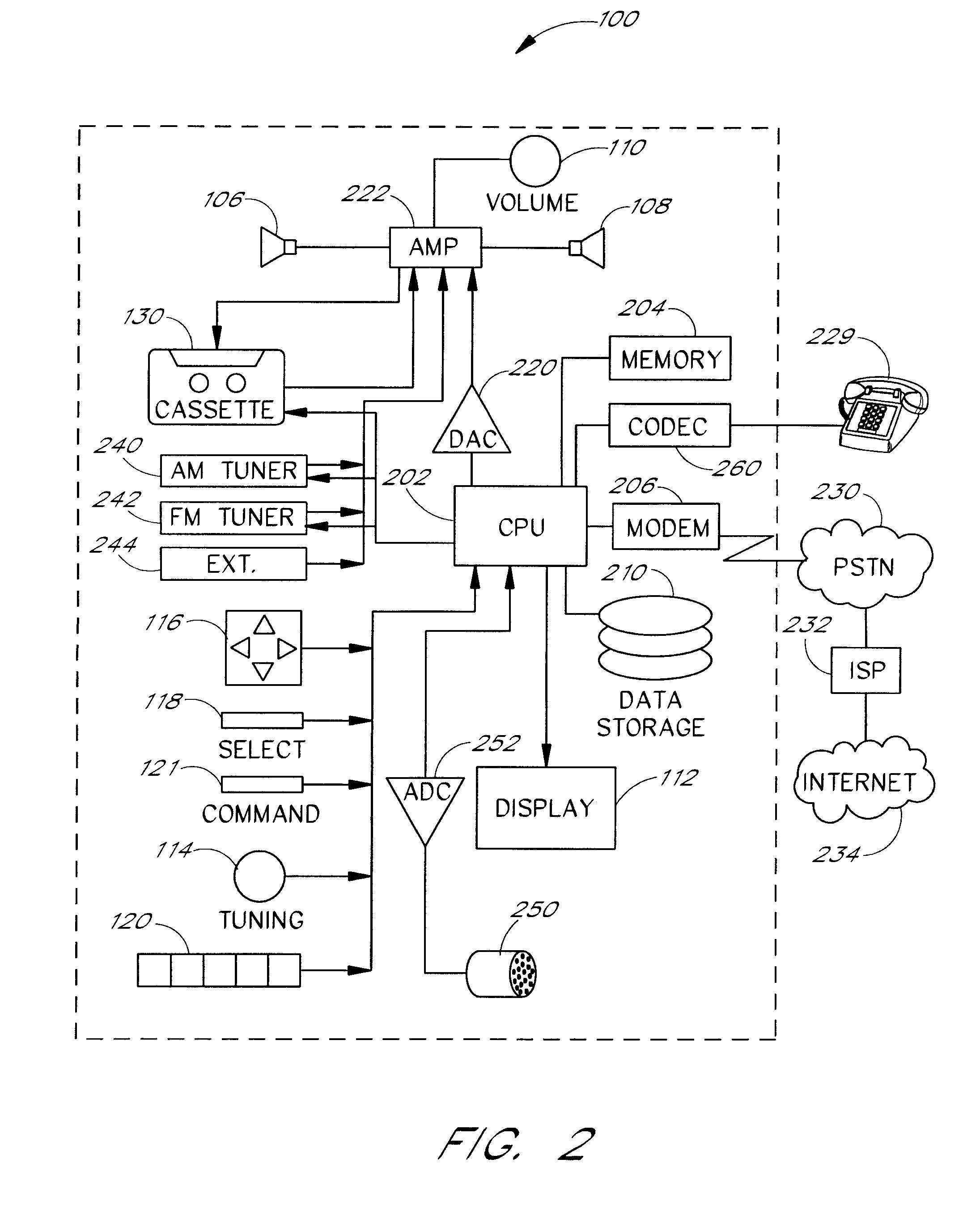
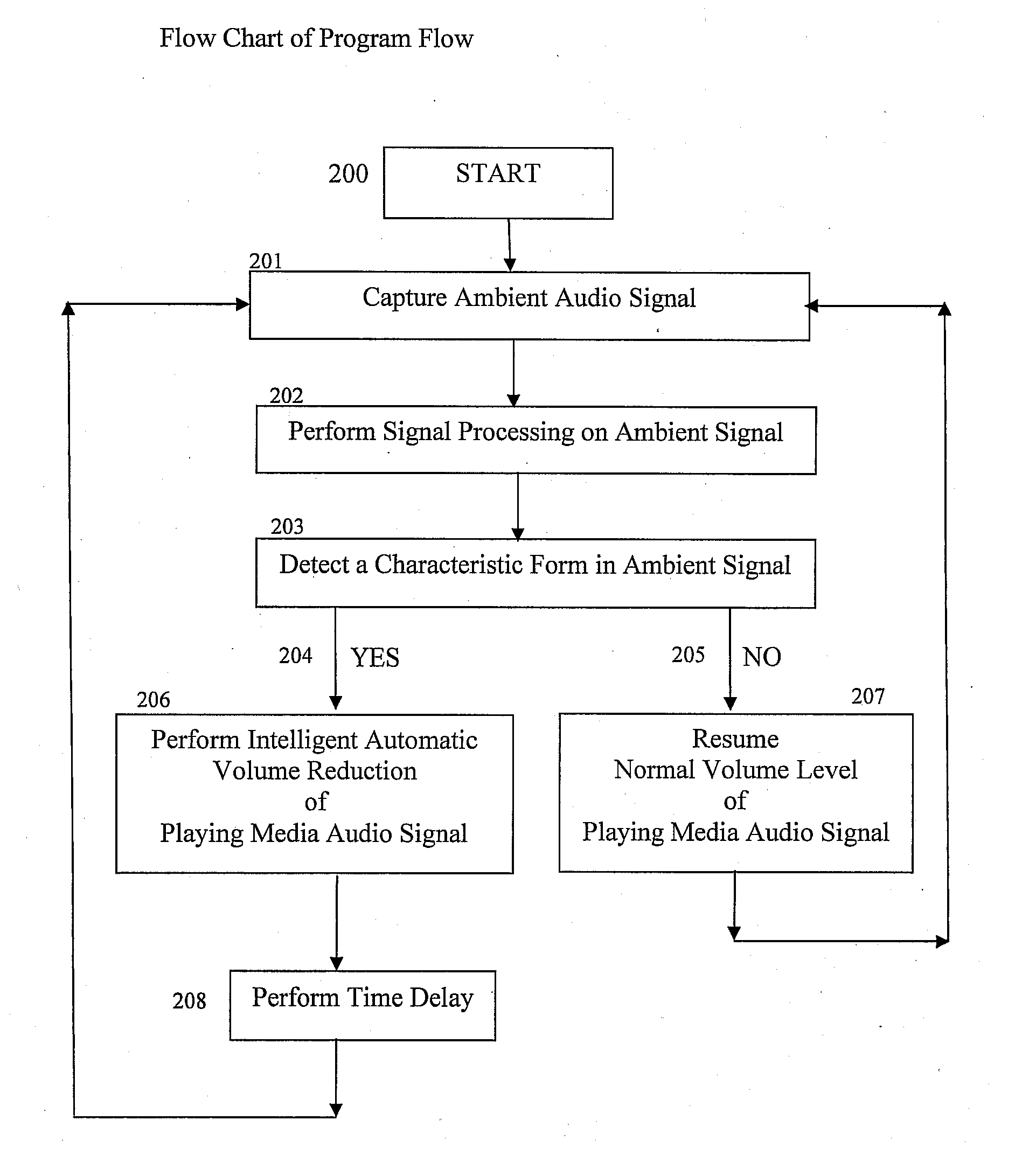
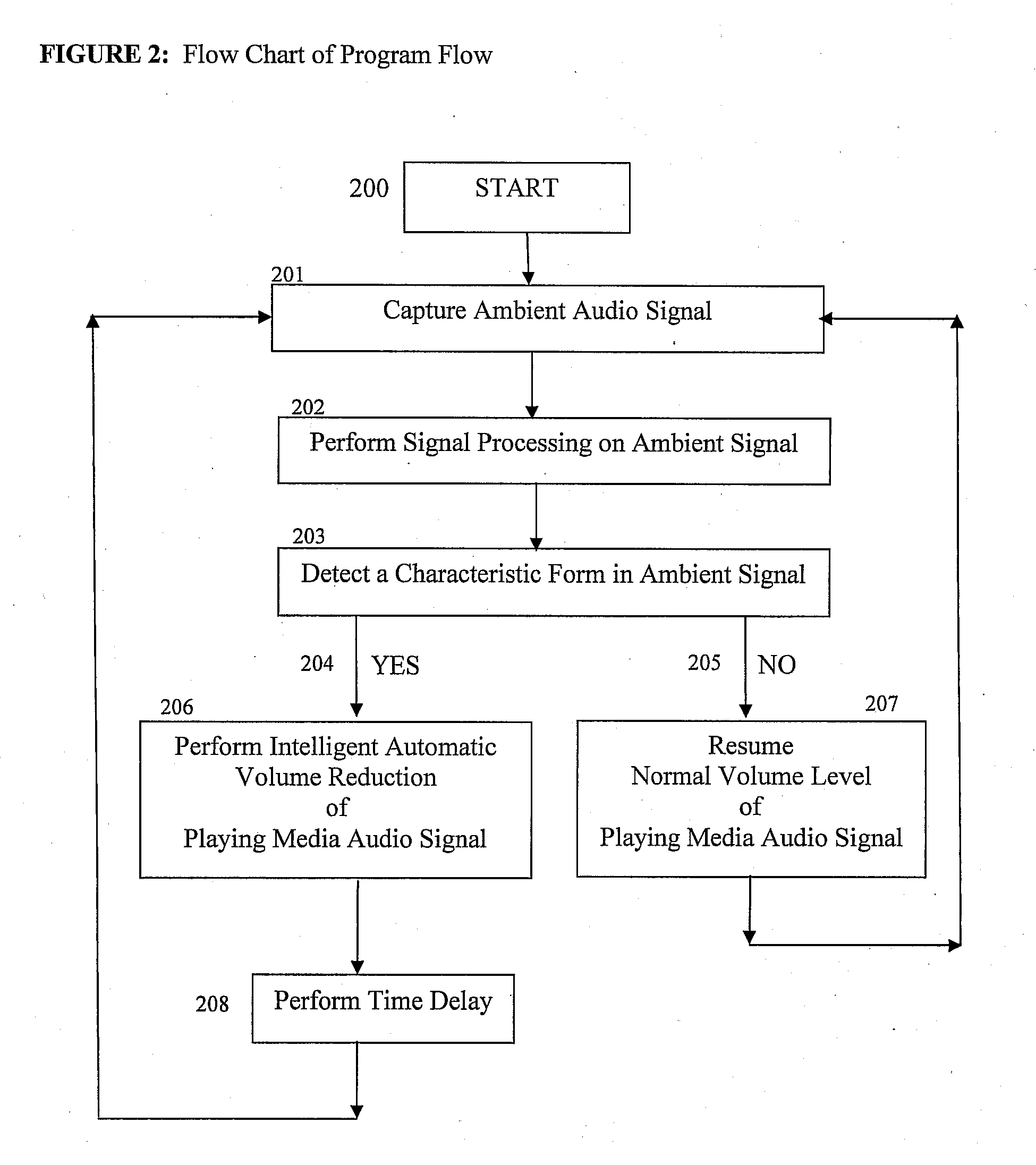
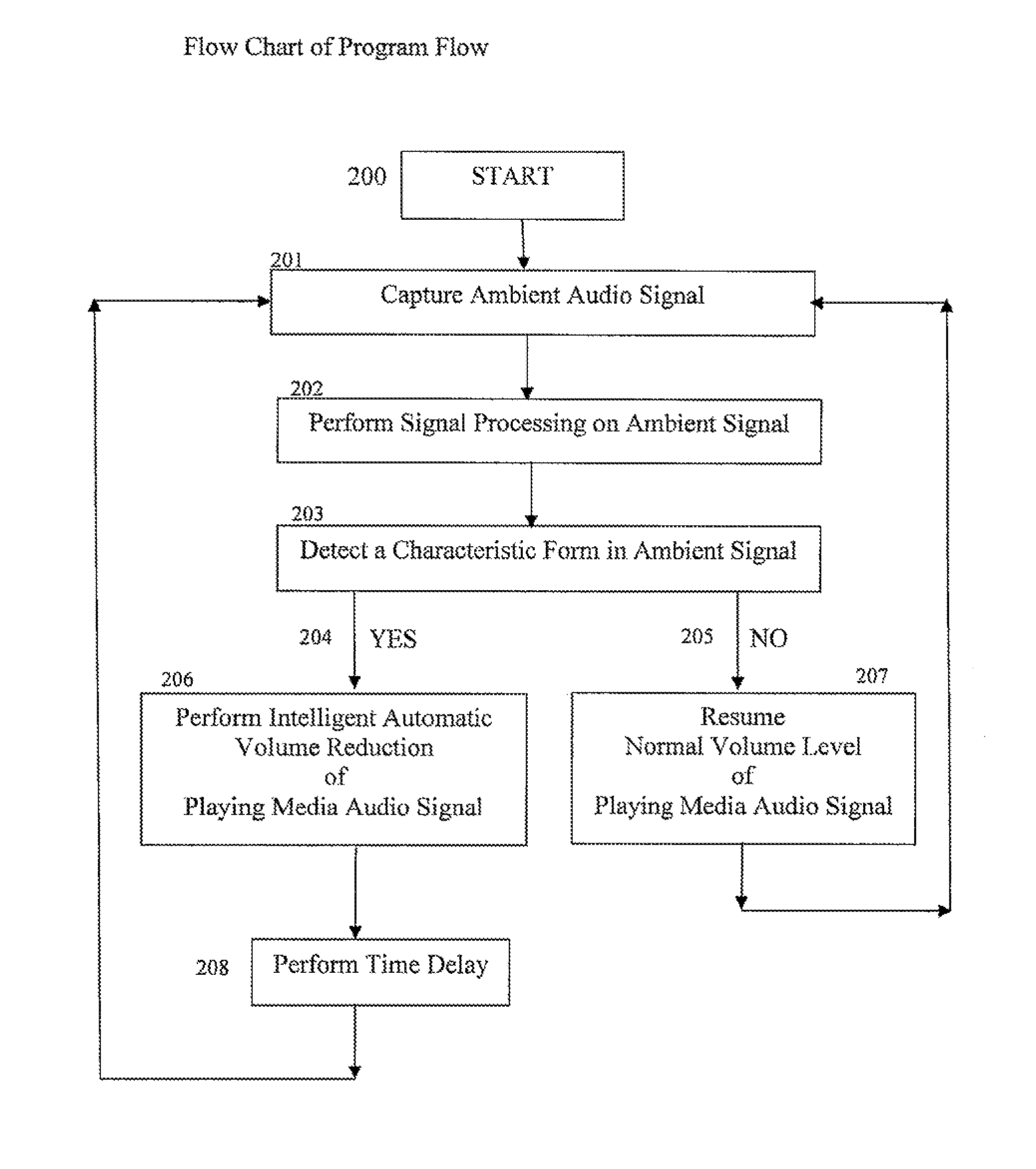
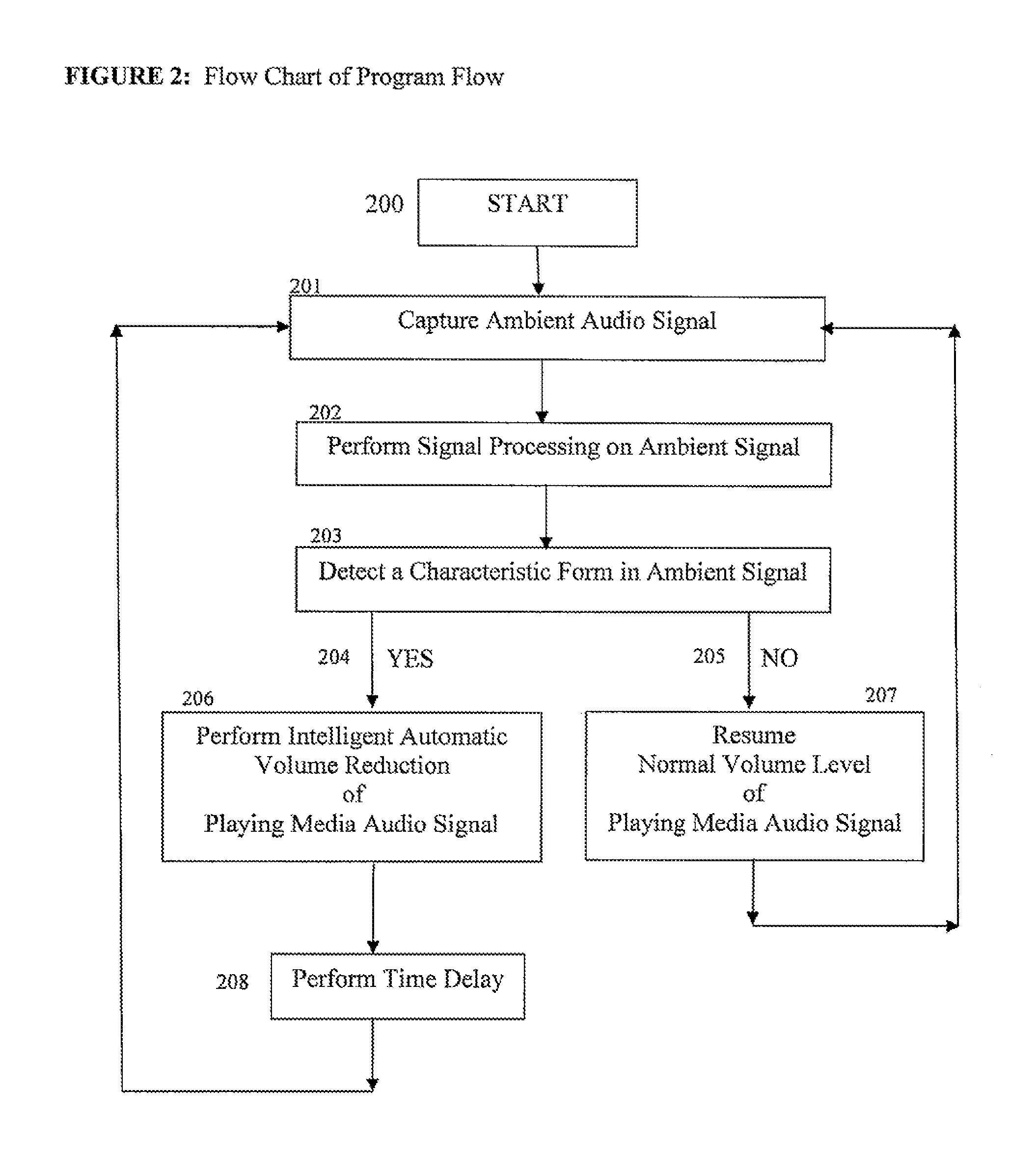
Ambient sound responsive media player
InactiveUS20070189544A1Reduce outputRecording carrier detailsGain controlComputer scienceAudio frequency
Some embodiments of the present invention provide a method of adjusting an output of a media player comprising capturing an ambient audio signal; processing the ambient audio signal to determine whether one or more characteristic forms are present within the ambient audio signal; and reducing an output of a media player from a first volume to a second volume if the one or more characteristic forms are present within the ambient audio signal. The characteristic forms may be, for example, a name or personal identifier of a user of the media player, the voice of a user of the media player, or an alarm or siren.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
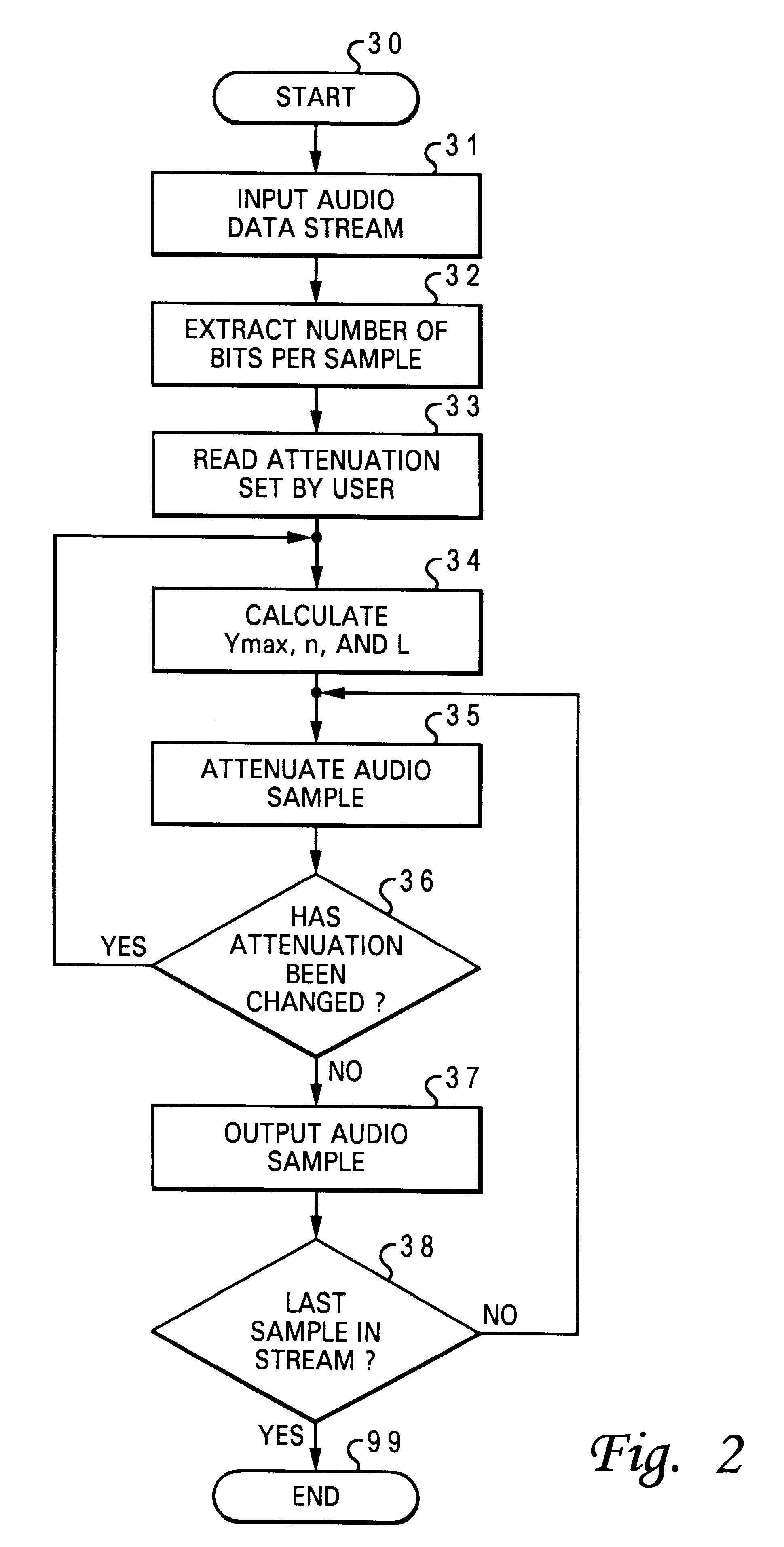
Method and system for selectively and variably attenuating audio data
InactiveUS6498855B1Gain controlVolume compression/expansion in digital/coded amplifiersData streamComputer science
A method and system for selectively and variably attenuating audio data are disclosed. A high-volume control value as selected by a user is first received, and this high-volume control value defines a volume output level for high amplitude audio samples. An attenuation factor is then determined by utilizing the high-volume control value. Each sample from an incoming audio data stream is conditionally attenuated with the attenuation factor such that high amplitude audio data get compressed while low amplitude audio data remain unaffected. Finally, the attenuated samples are sent to an output.
Owner:IBM CORP
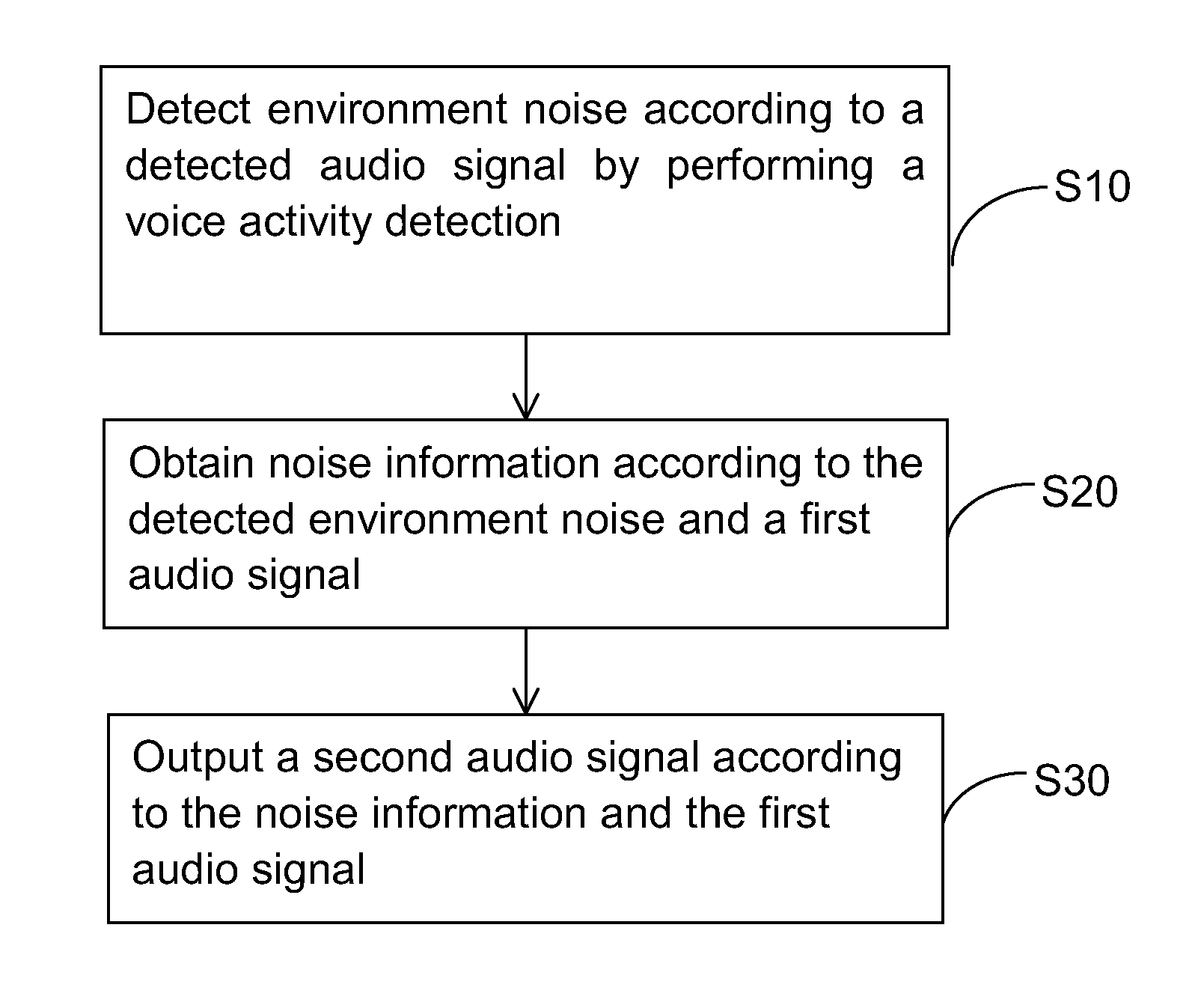
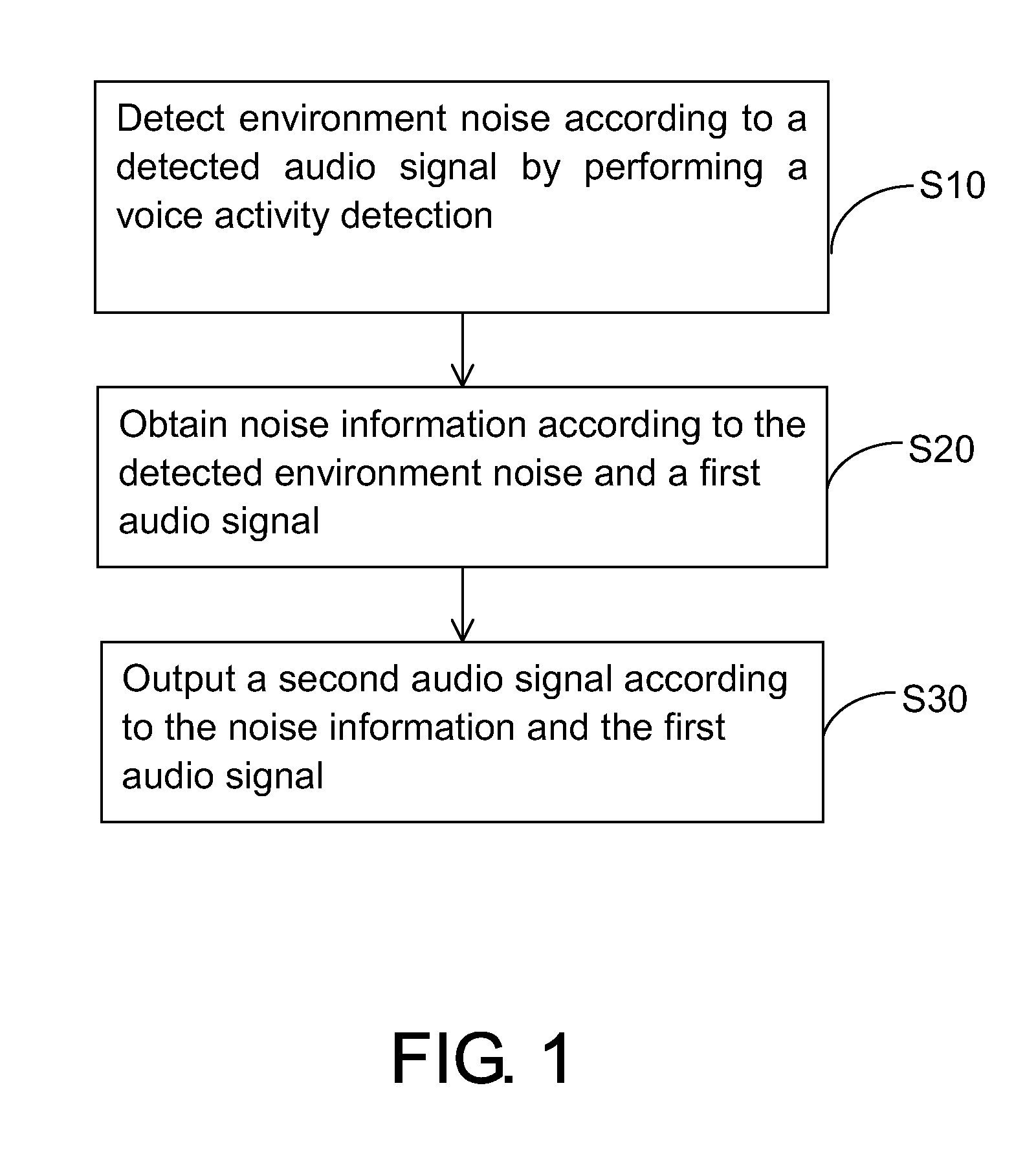
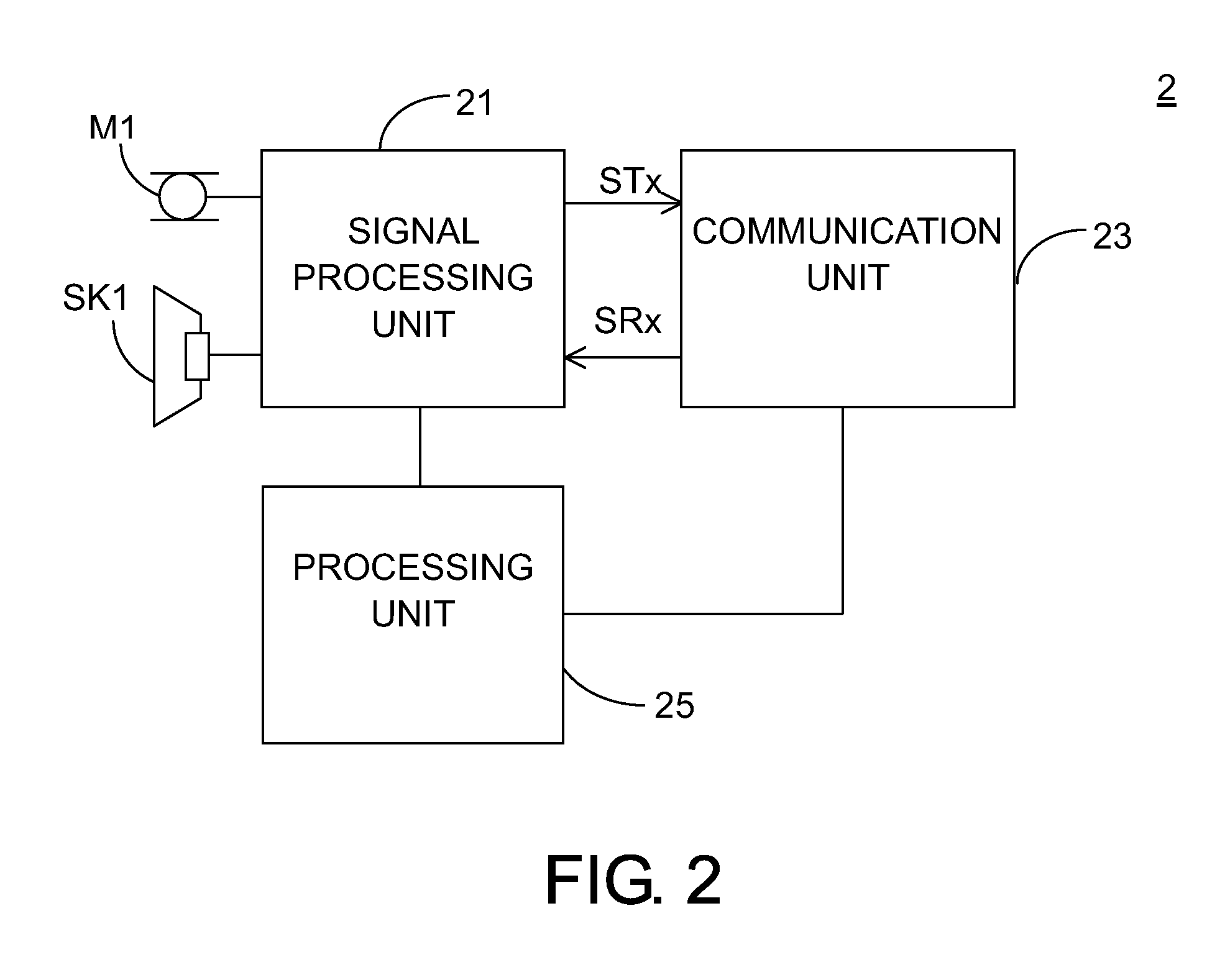
Method and apparatus for audio intelligibility enhancement and computing apparatus
Method and apparatus for audio intelligibility enhancement and computing apparatus are provided. The method includes the following steps. Environment noise is detected by performing voice activity detection according to a detected audio signal from at least a microphone of a computing device. Noise information is obtained according to the detected environment noise and a first audio signal. A second audio signal is outputted by boosting the first audio signal under an adjustable headroom by the computing device according to the noise information and the first audio signal.
Owner:HTC CORP
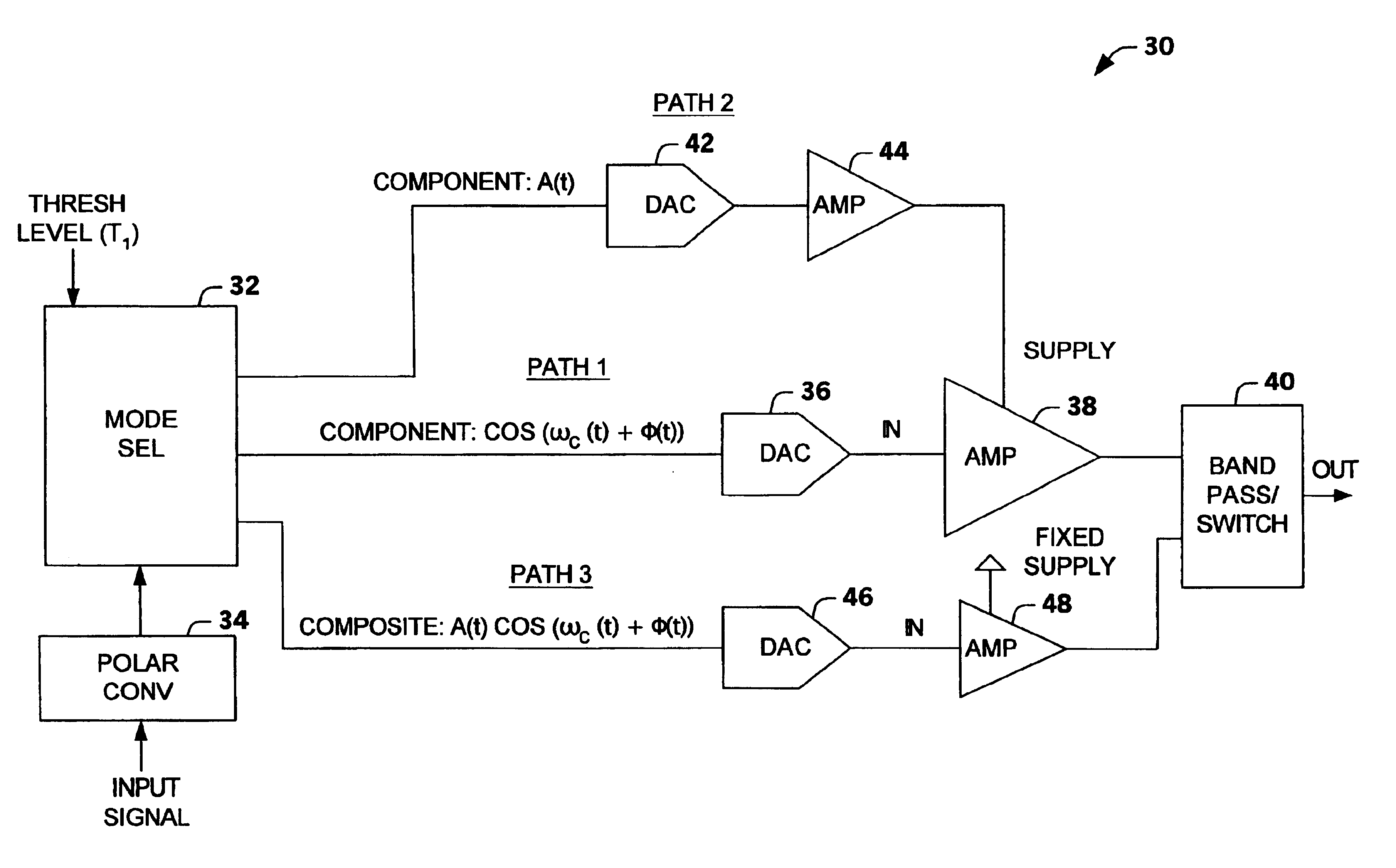
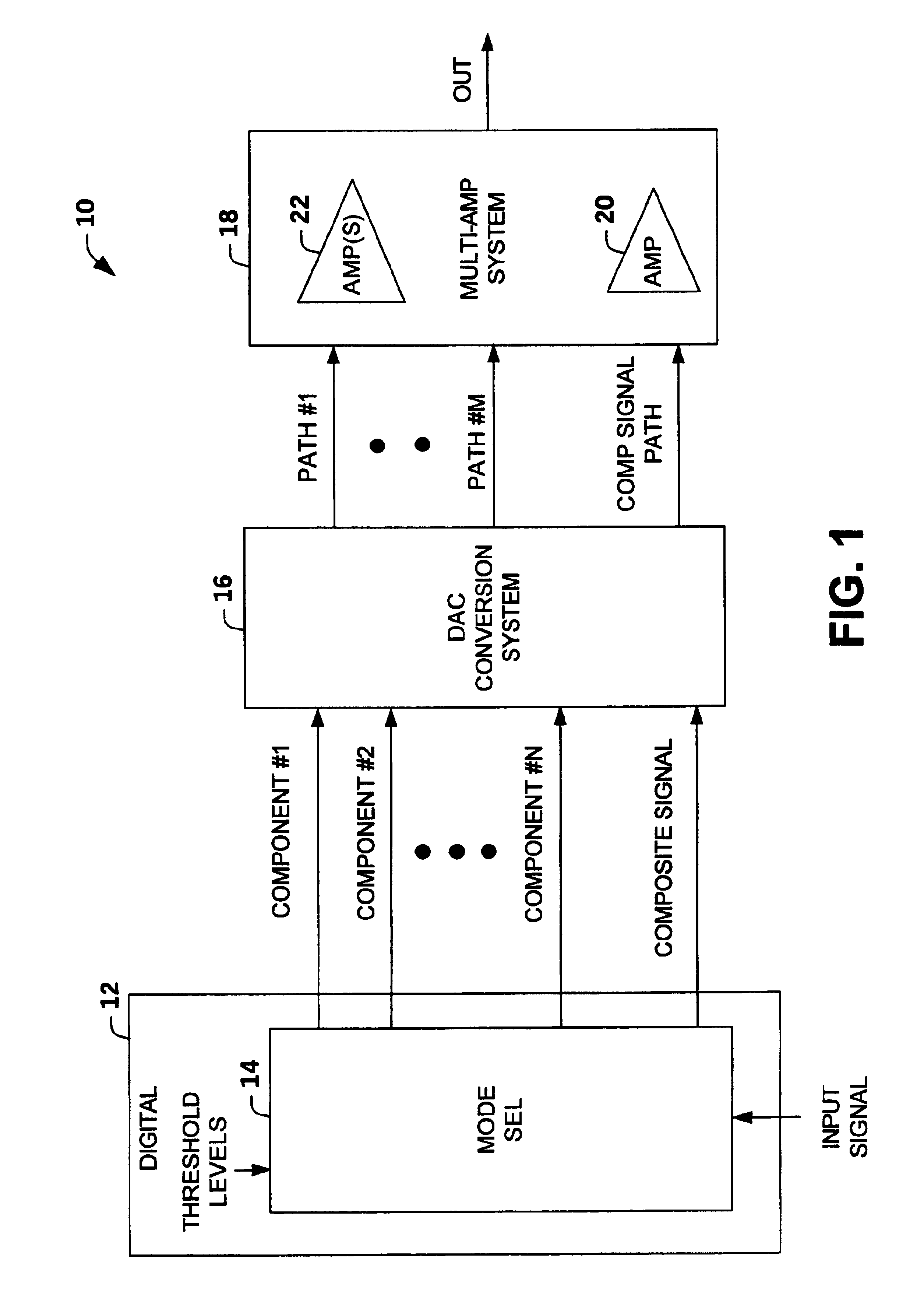
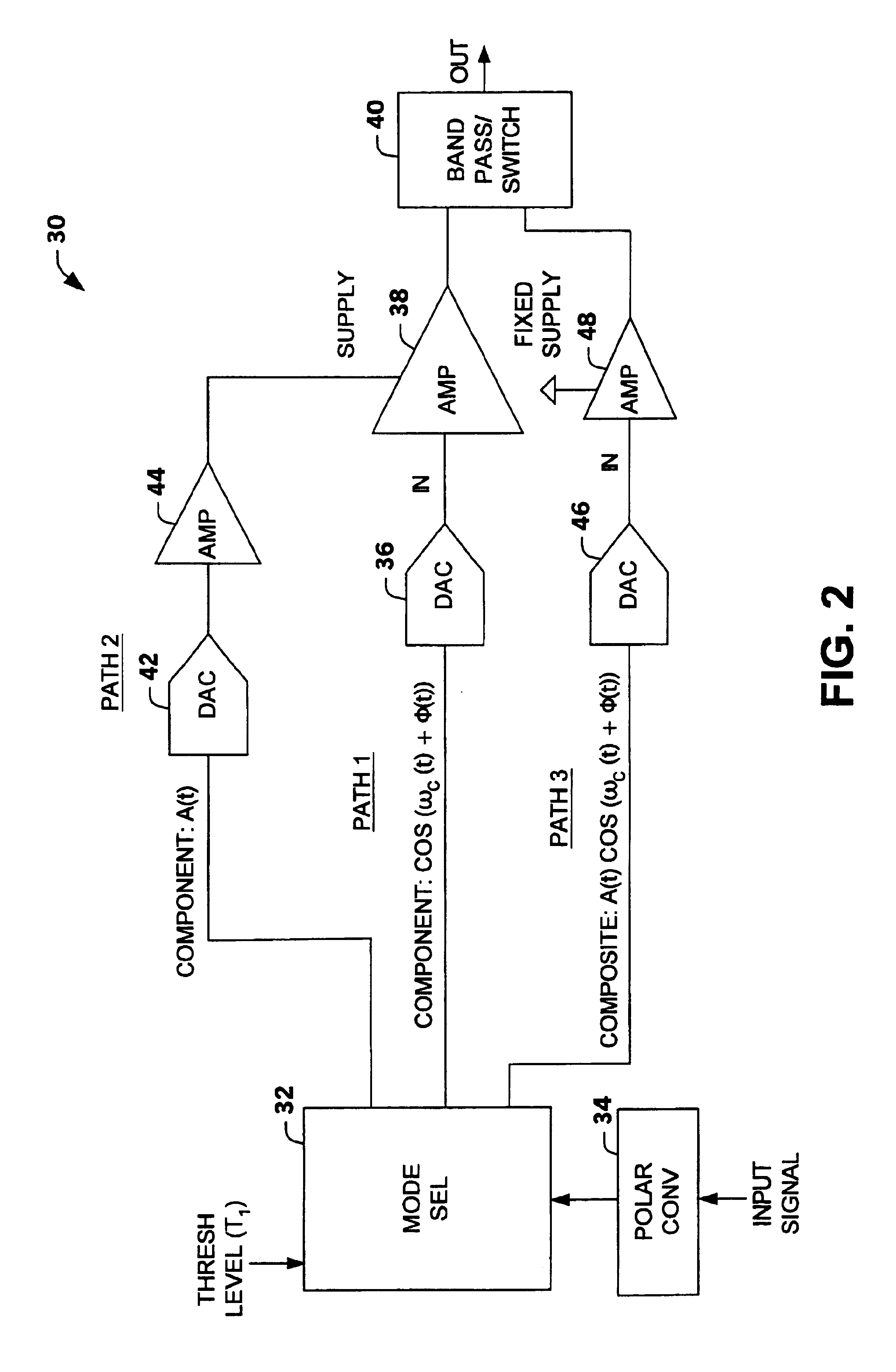
Multi-mode multi-amplifier architecture
InactiveUS6853244B2Amplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionGain controlAudio power amplifierEngineering
An amplification architecture or system is provided having a multiple amplifier system that switches modes of operation between operation in a component mode and a composite mode based on a characteristic of an input signal relative to a threshold level. In the component mode, the components of the input signal are employed to different terminals of the multiple amplifier system that provide a reconstructed amplified representation of the input signal. In the composite mode, the input signal is amplified to provide an amplified representation of the input signal.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
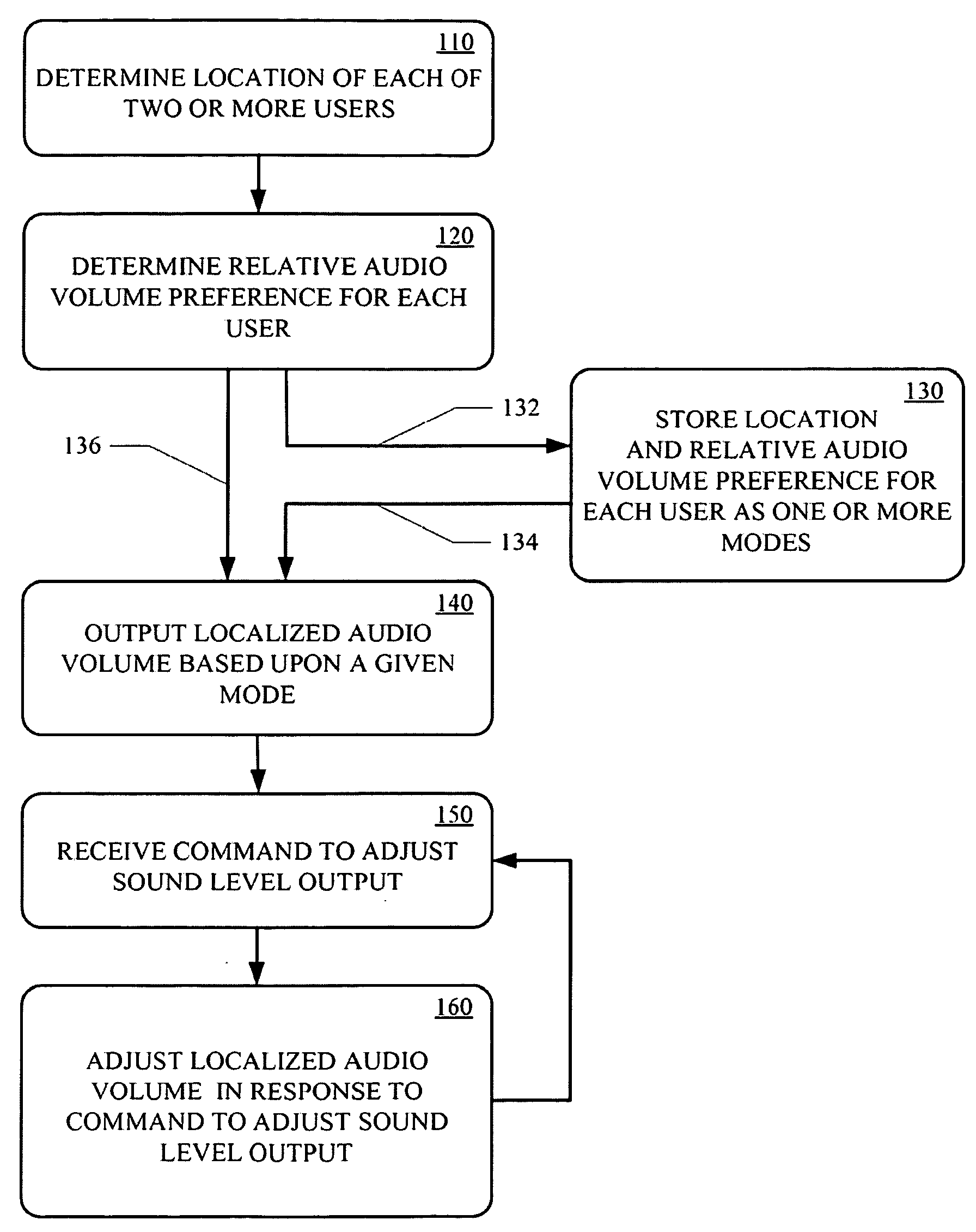
Techniques for personalizing audio levels
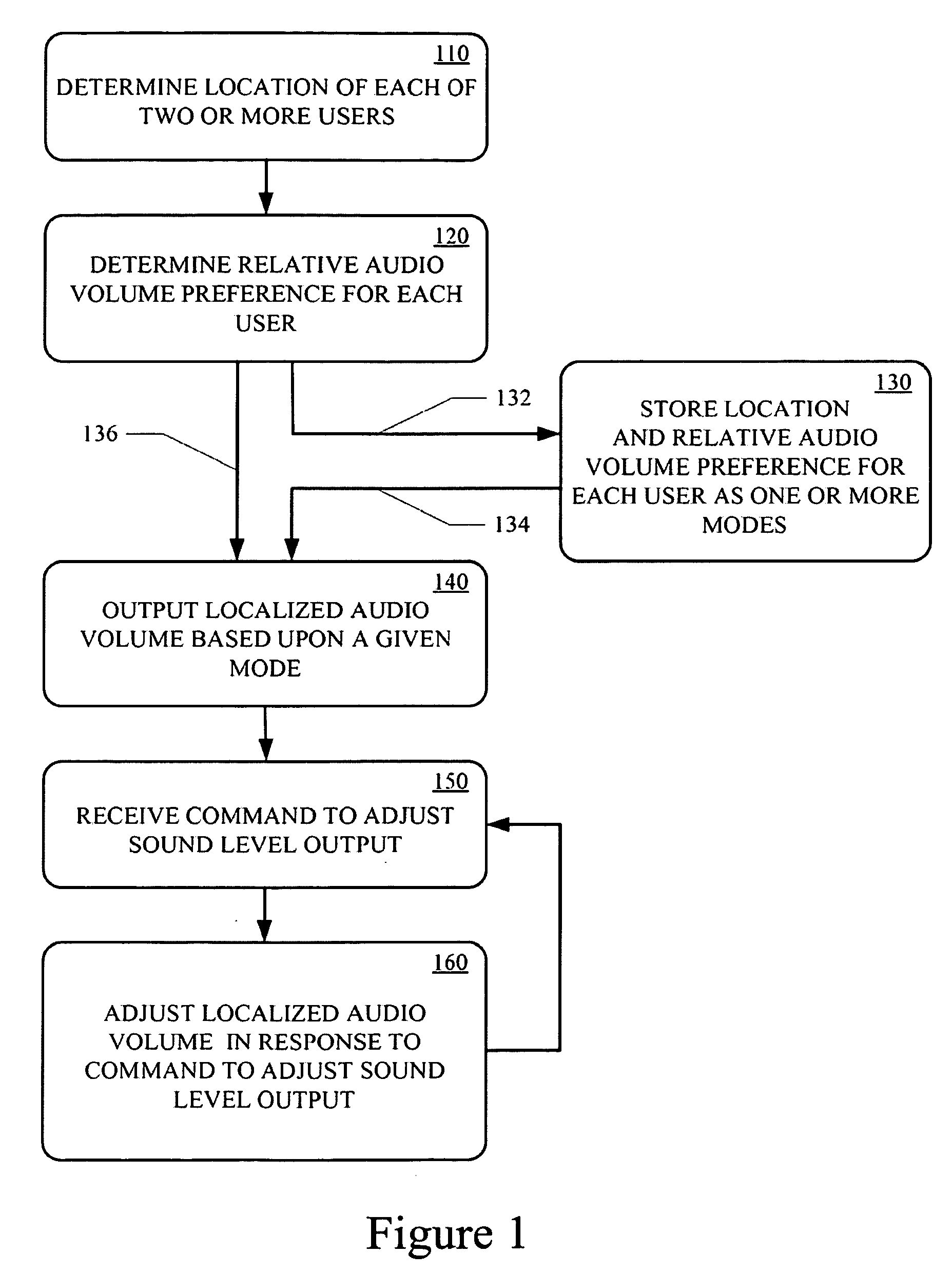
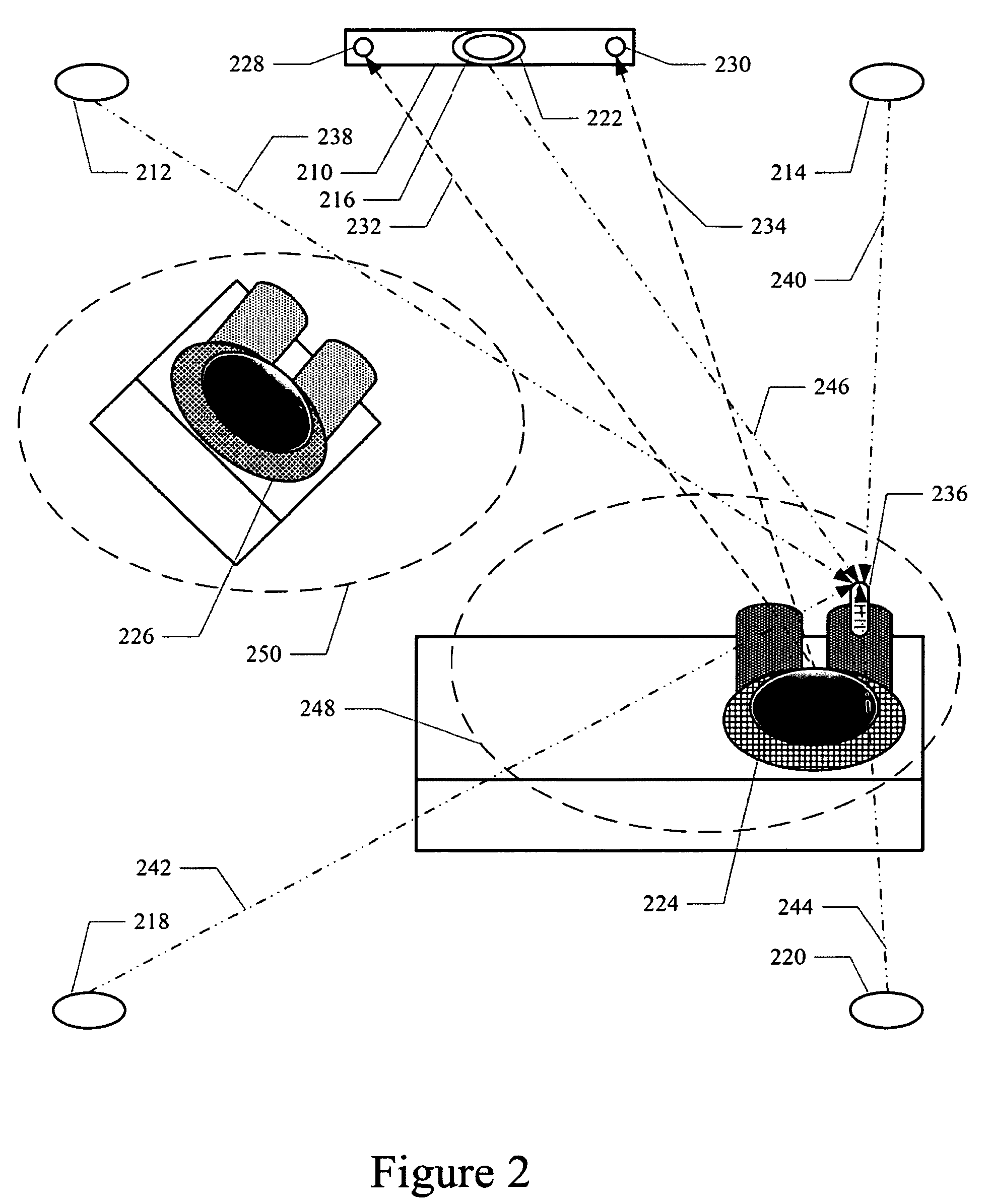
Techniques for personalizing audio levels, in accordance with embodiments of the present technology, provide different audio volumes to different locations in a room allowing for two or more users to enjoy the same audio content at different volumes. Differential level and delay compensation filtering based on a position of each of a plurality of speakers, the location of each user and the preferred relative audio volume of each user are utilized to produce different effective audio levels in localized regions of a room.
Owner:SONY CORP +1
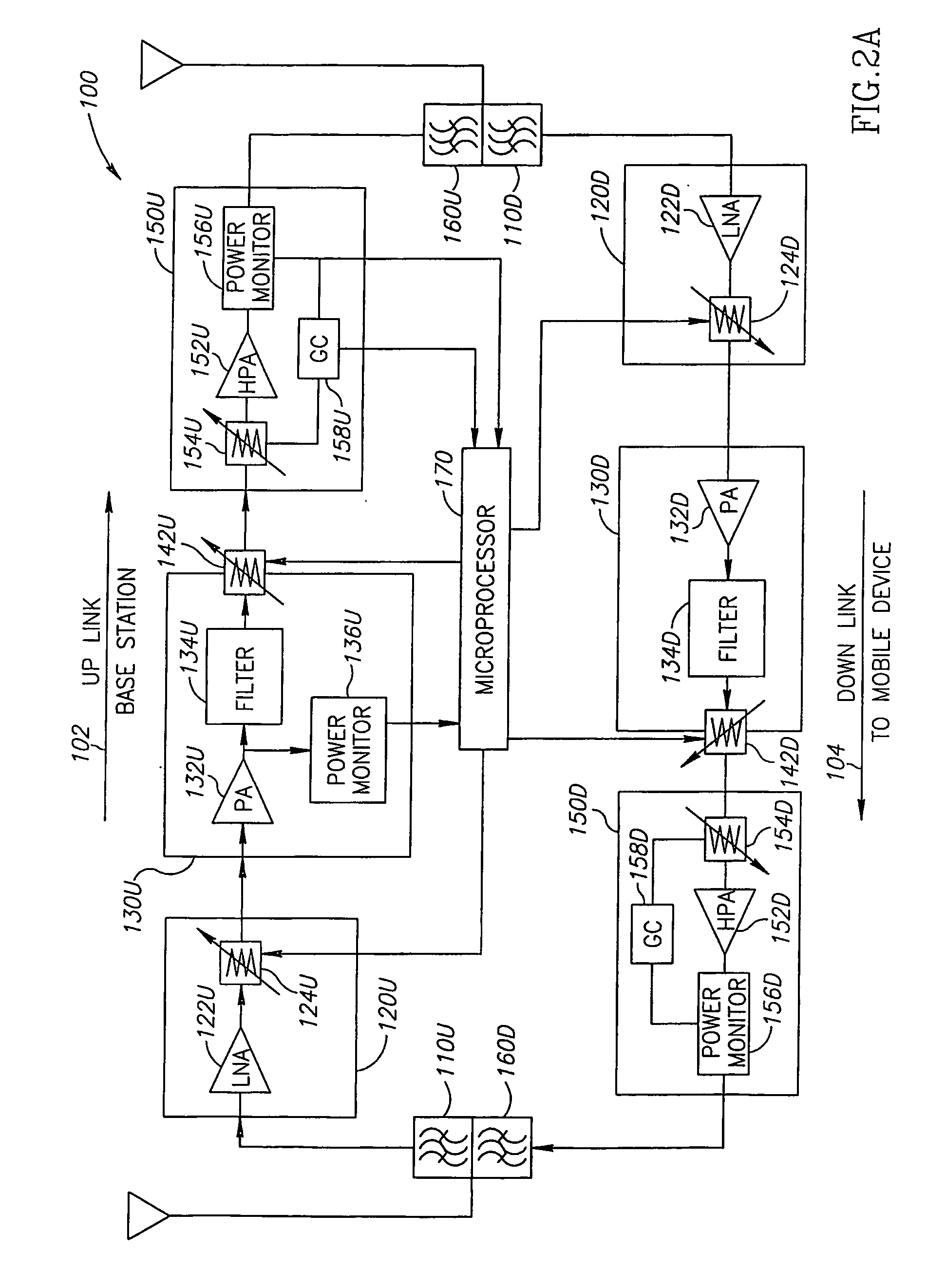
Method for automatic control of rf level of a repeater
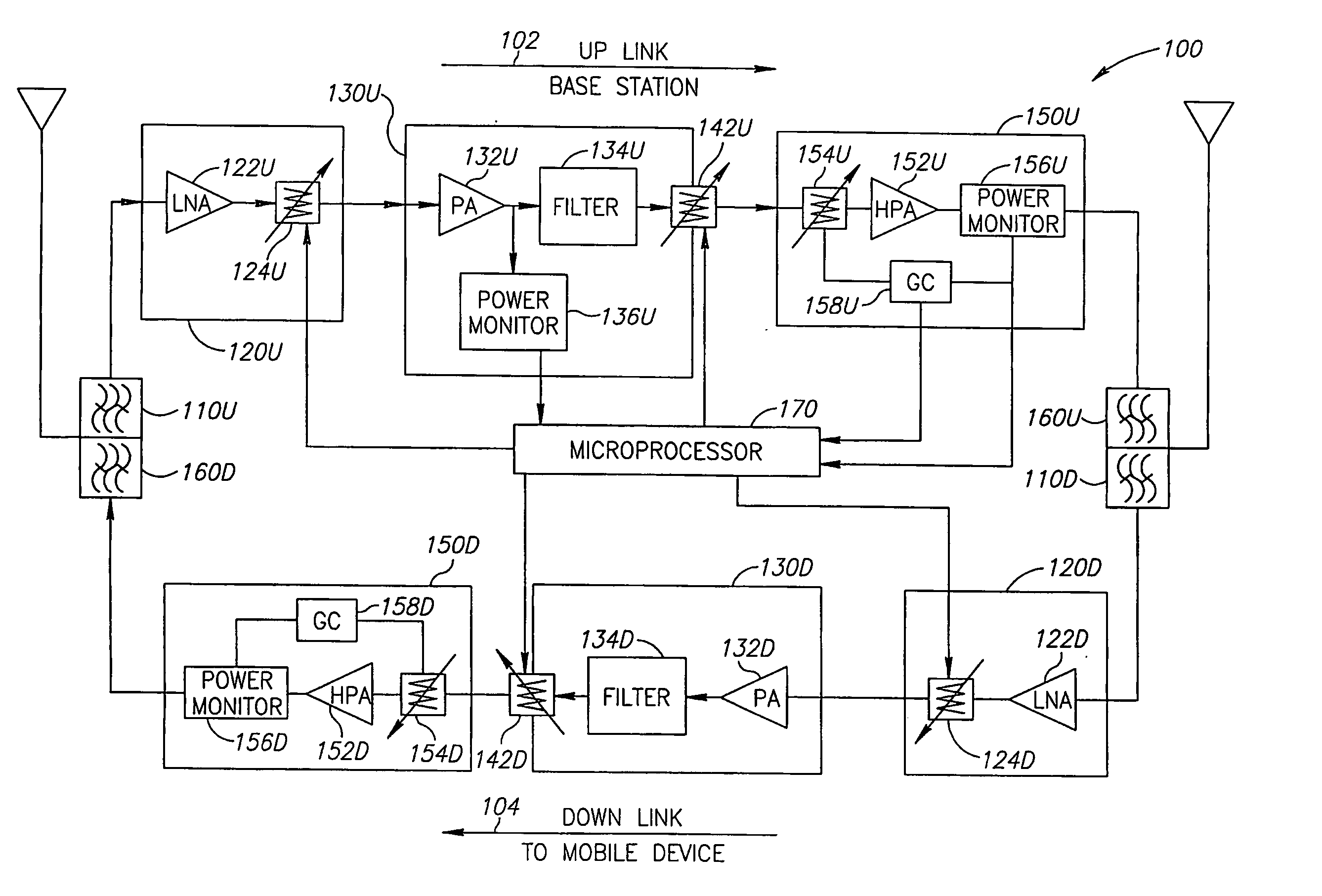
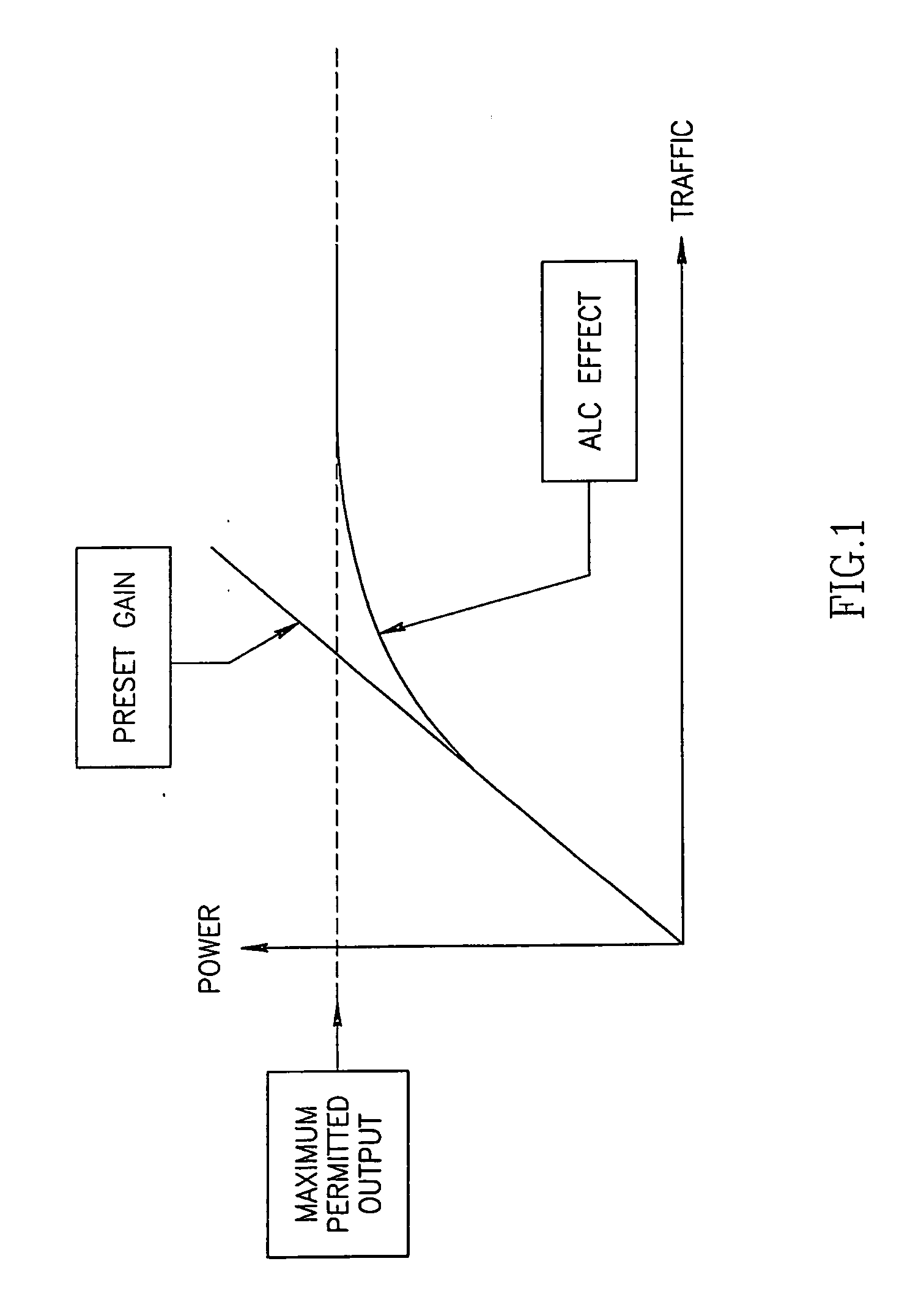
A method and apparatus for controlling an output power level of a radio frequency (RF) repeater (100 or 200). A system includes a receiver to receive a signal, a filtering unit configured to pass frequency components at or around a frequency band of a predetermined communication channel, an attenuator (124 or 142) to produce an attenuated signal by attenuating a parameter of the signal, a power amplifier (150) to adjust the output power level of repeater to a desired level by adjusting the gain of one or more components of the system, and a microprocessor (170) to receive an input responsive to the output power level of the repeater and, in response to the input, to transfer control signals to the receiver and the attenuator. The method includes sampling traffic load characteristics during operation of a network and adjusting a gain of one or more components of the repeater based on the traffic load characteristics.
Owner:AXELL WIRELESS
Network-enabled audio device
InactiveUS20070089135A1Reception of a broadcast from the World Wide Web is no more complicatedOptimize allocationTelevision system detailsGain controlThe InternetDisplay device
A network-enabled audio device that provides a display device that allows the user to select playlists of music much like a jukebox is disclosed. The user can compose playlists from disk files, CD's, Internet streaming audio broadcasts, online music sites, and other audio sources. The user can also select a desired Web broadcast from a list of available Web broadcasts. In addition, the user can play standard audio CD's and MP3 encoded CD's and have access to local AM / FM stations. Further, the software, the user controls, and the display in the network-enabled audio device are operably configured and connected such that the user can listen to playlists that include CD's and other audio sources just as the user would choose a playlist in a jukebox. The user accesses a server site via a PC and the Internet. From the server site, the user obtains a list of the devices in his or her Internet Personal Audio Network (IPAN) and what songs are on those devices. The IPAN includes an IPAN server, an IPAN client, and IPAN software stored on the network-enabled audio device. Thus, the network-enabled audio device provides people who are or are not comfortable with computers a way of taking music from various sources and putting it into one place for listening pleasure. In one embodiment, the Personal Computer (PC) is used to compose the playlists, but the user is able to listen to playlists and other audio sources without using the PC.
Owner:GOLDEN IP LLC
Systems and methods for synchronizing operations among a plurality of independently clocked digital data processing devices without a voltage controlled crystal oscillator
ActiveUS20120029671A1Television system detailsDigital data processing detailsDigital dataEngineering
Owner:SONOS
Ambient sound responsive media player
Some embodiments of the present invention provide a method of adjusting an output of a media player comprising capturing an ambient audio signal; processing the ambient audio signal to determine whether one or more characteristic forms are present within the ambient audio signal; and reducing an output of a media player from a first volume to a second volume if the one or more characteristic forms are present within the ambient audio signal. The characteristic forms may be, for example, a name or personal identifier of a user of the media player, the voice of a user of the media player, or an alarm or siren.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
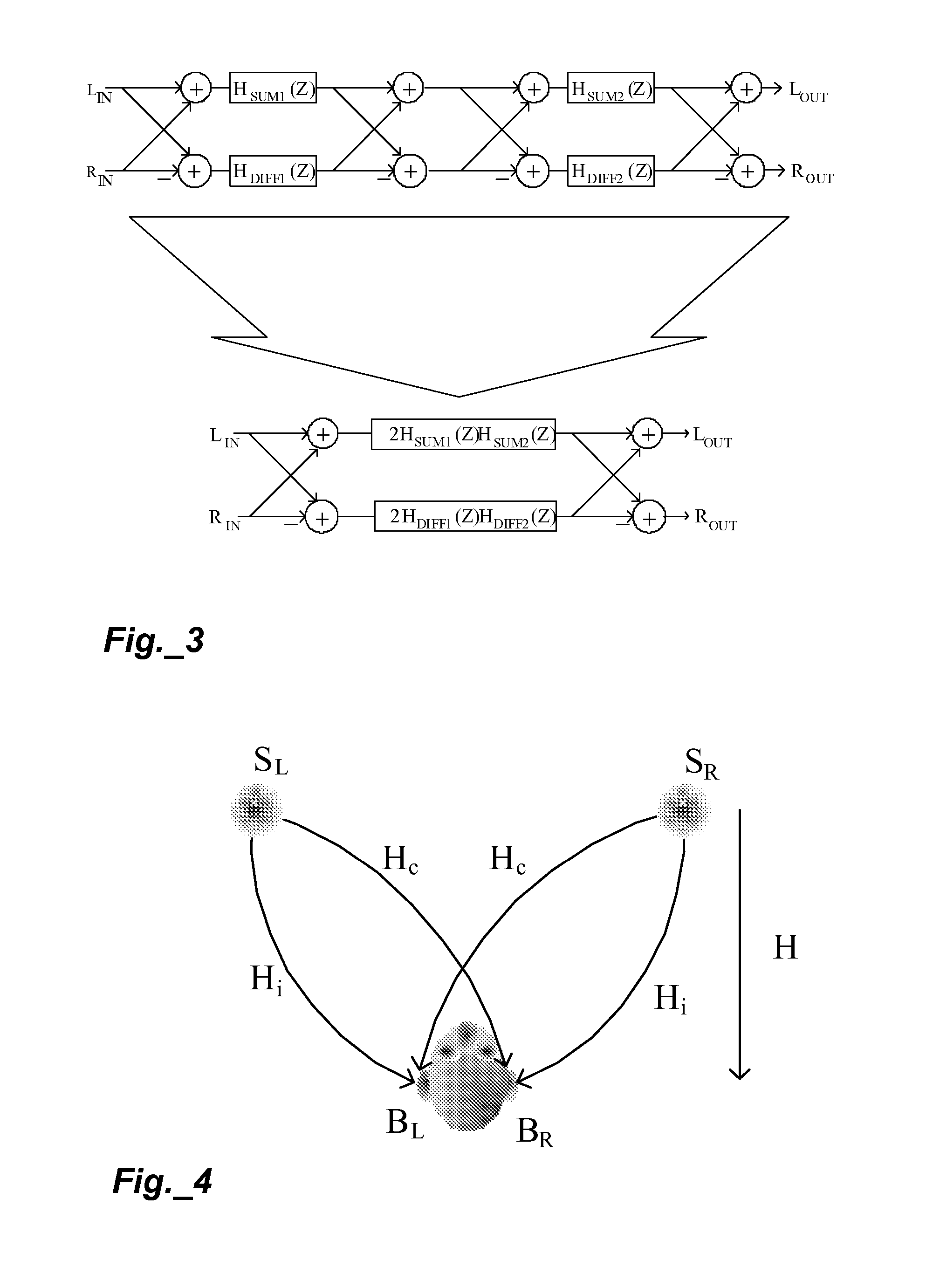
Spatial audio enhancement processing method and apparatus
The present invention describes techniques that can be used to provide novel methods of spatial audio rendering using adapted M-S matrix shuffler topologies. Such techniques include headphone and loudspeaker-based binaural signal simulation and rendering, stereo expansion, multichannel upmix and pseudo multichannel surround rendering.
Owner:CREATIVE TECH CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com