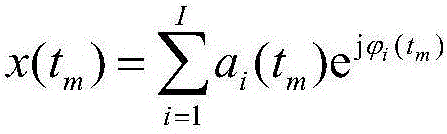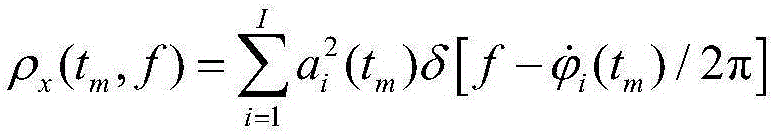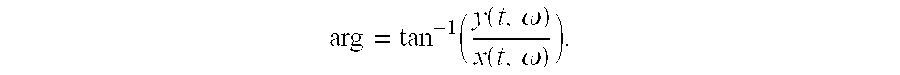Patents
Literature
127 results about "Time–frequency representation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
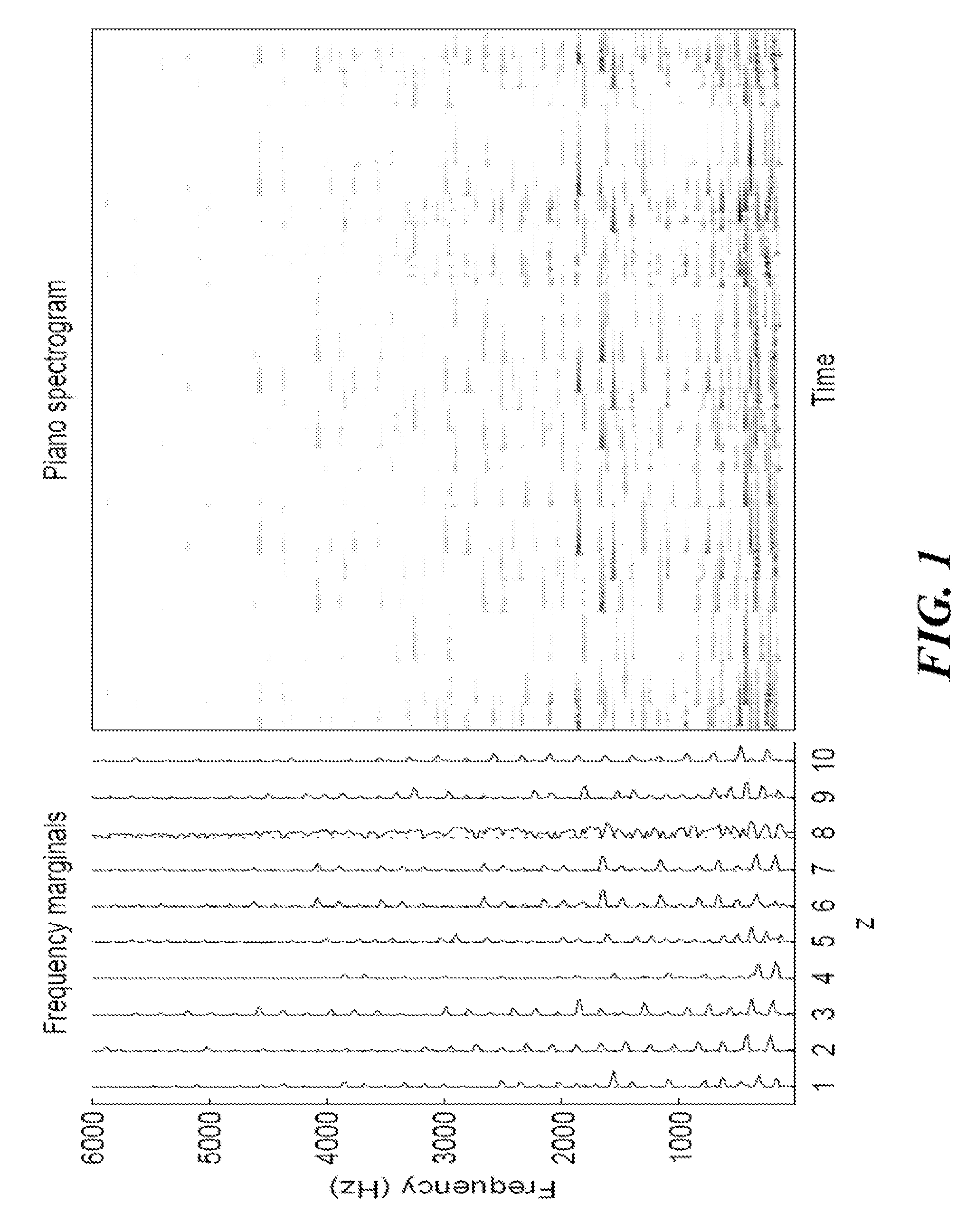
A time–frequency representation (TFR) is a view of a signal (taken to be a function of time) represented over both time and frequency. Time–frequency analysis means analysis into the time–frequency domain provided by a TFR. This is achieved by using a formulation often called "Time–Frequency Distribution", abbreviated as TFD.
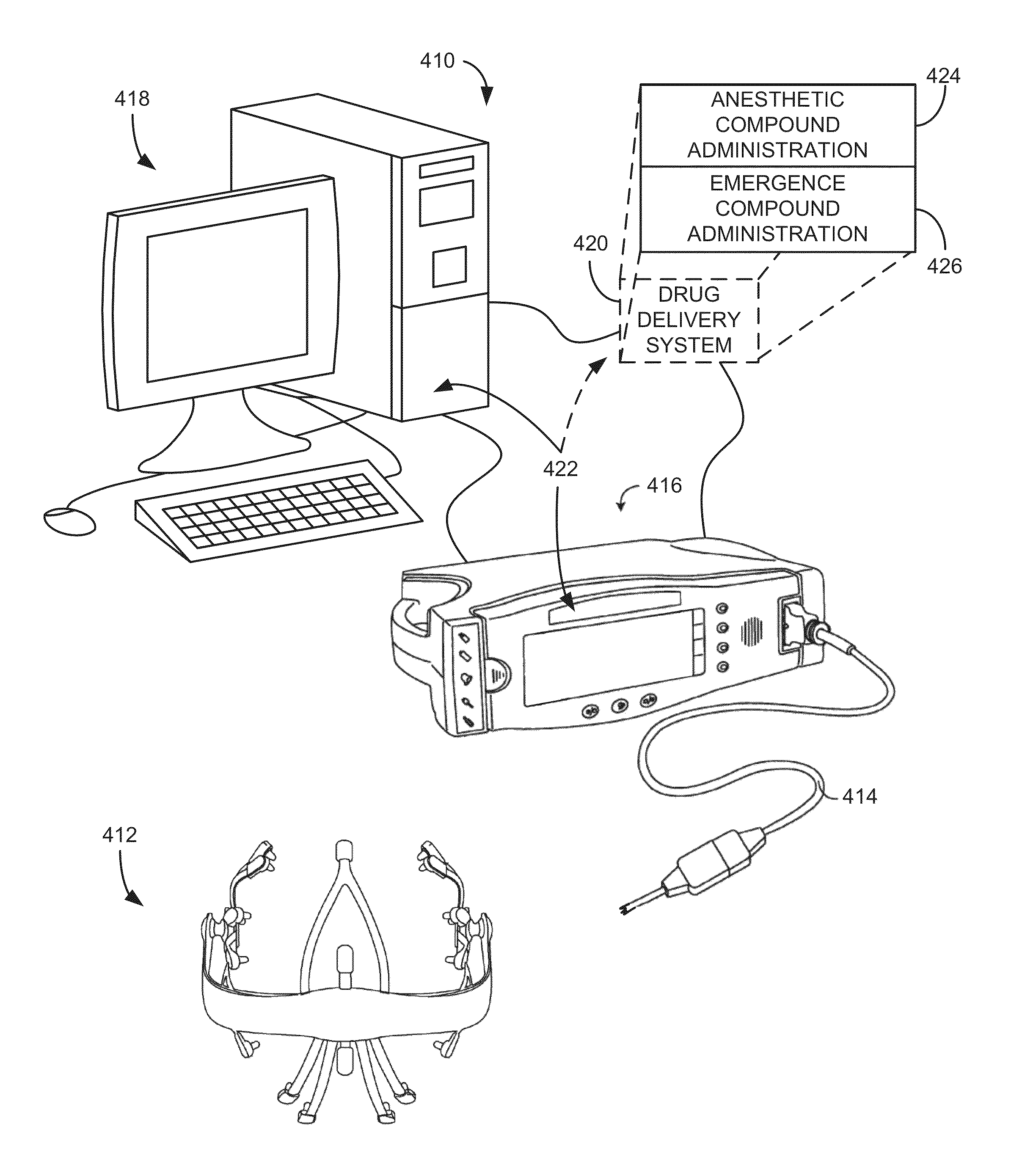
System and method for estimating high time-frequency resolution eeg spectrograms to monitor patient state
InactiveUS20140323897A1Accurate depictionImproved spectral analysisDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsFrequency spectrumDecomposition
A system and method for monitoring a patient includes a sensor configured to acquire physiological data from a patient and a processor configured to receive the physiological data from the at least one sensor. The processor is also configured to apply a spectral estimation framework that utilizes structured time-frequency representations defined by imposing, to the physiological data, a prior distributions on a time-frequency plane that enforces spectral estimates that are smooth in time and sparse in a frequency domain. The processor is further configured to perform an iteratively re-weighted least squares algorithm to perform yield a denoised time-varying spectral decomposition of the physiological data and generate a report indicating a physiological state of the patient.
Owner:BROWN EMERY N +3
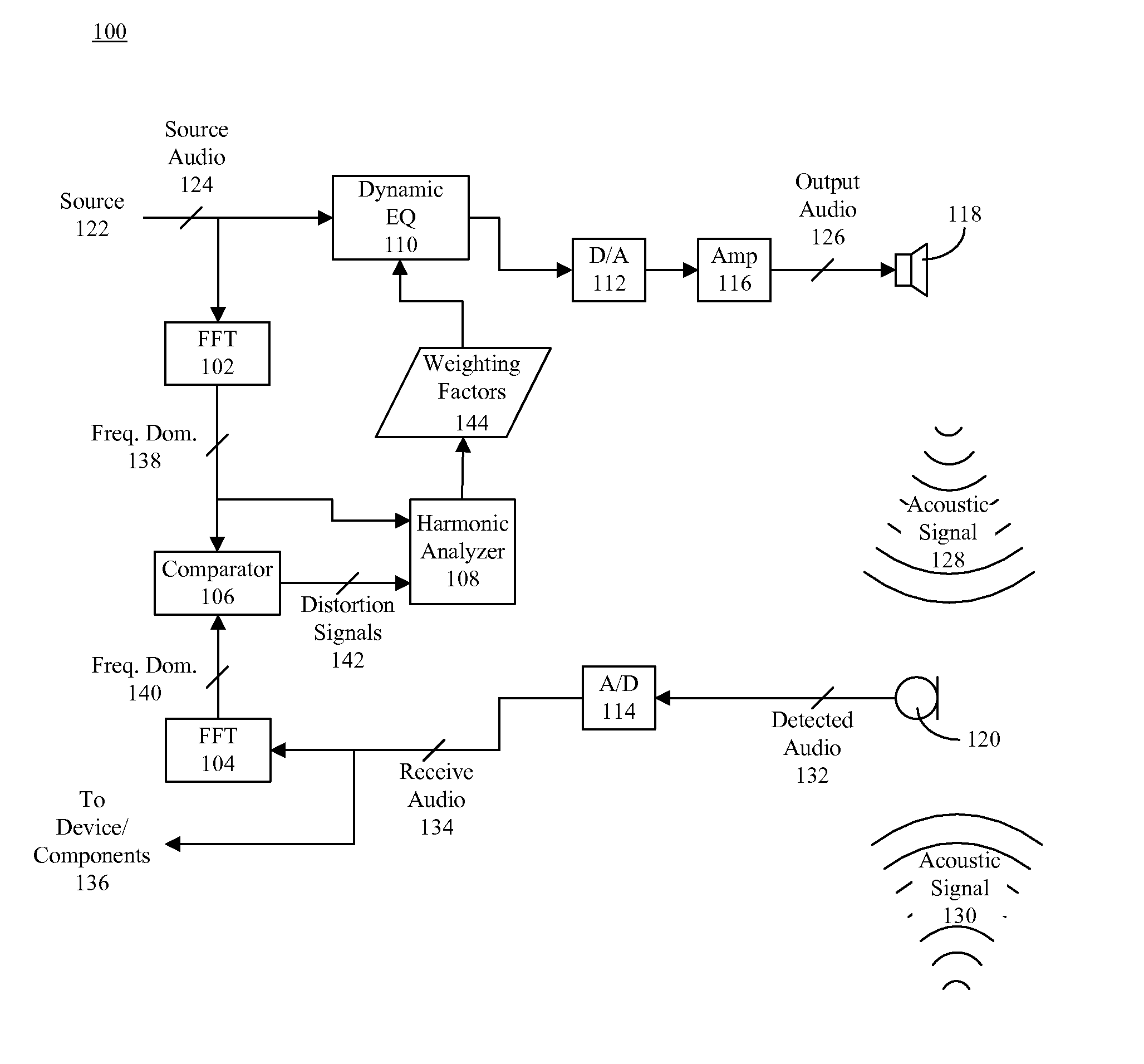
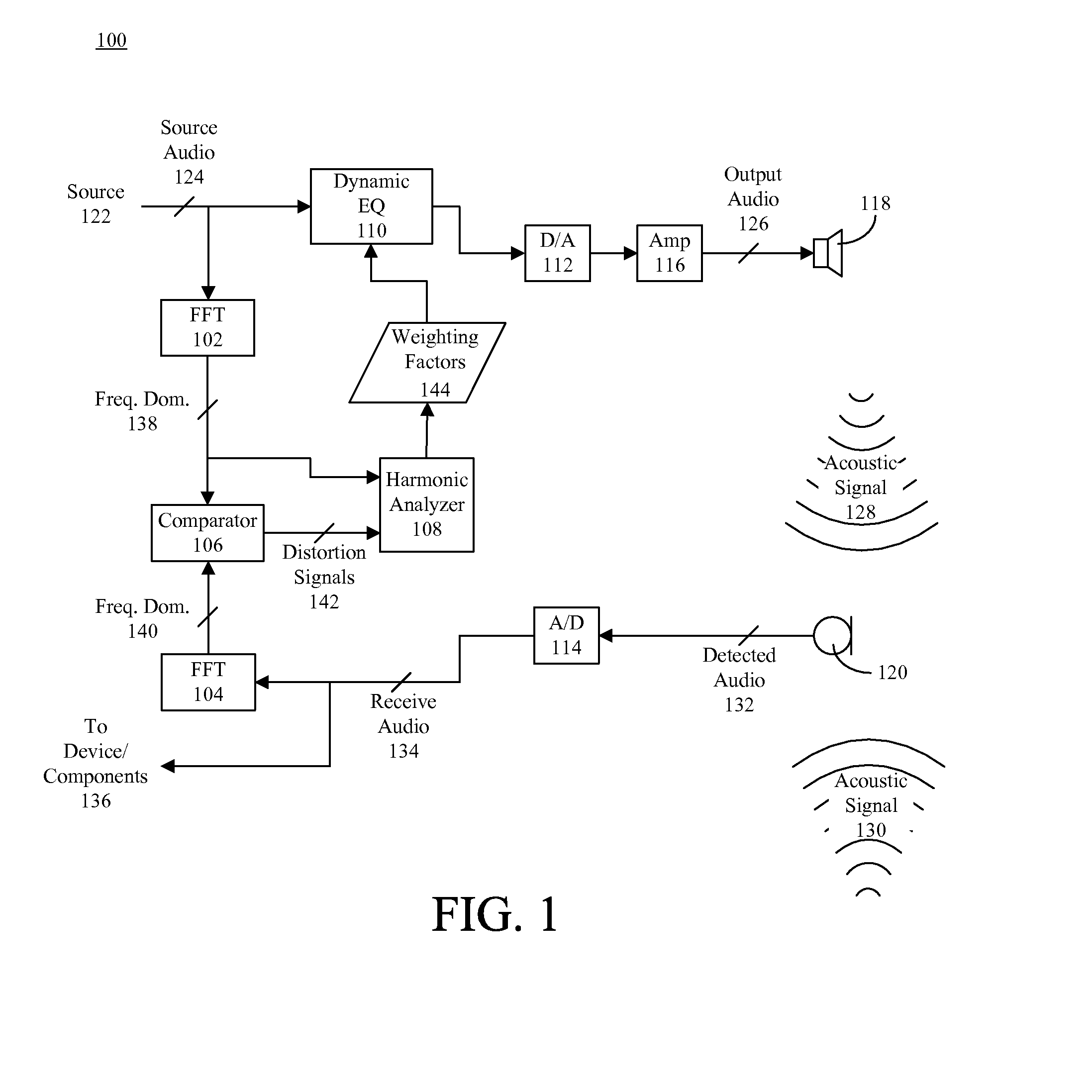
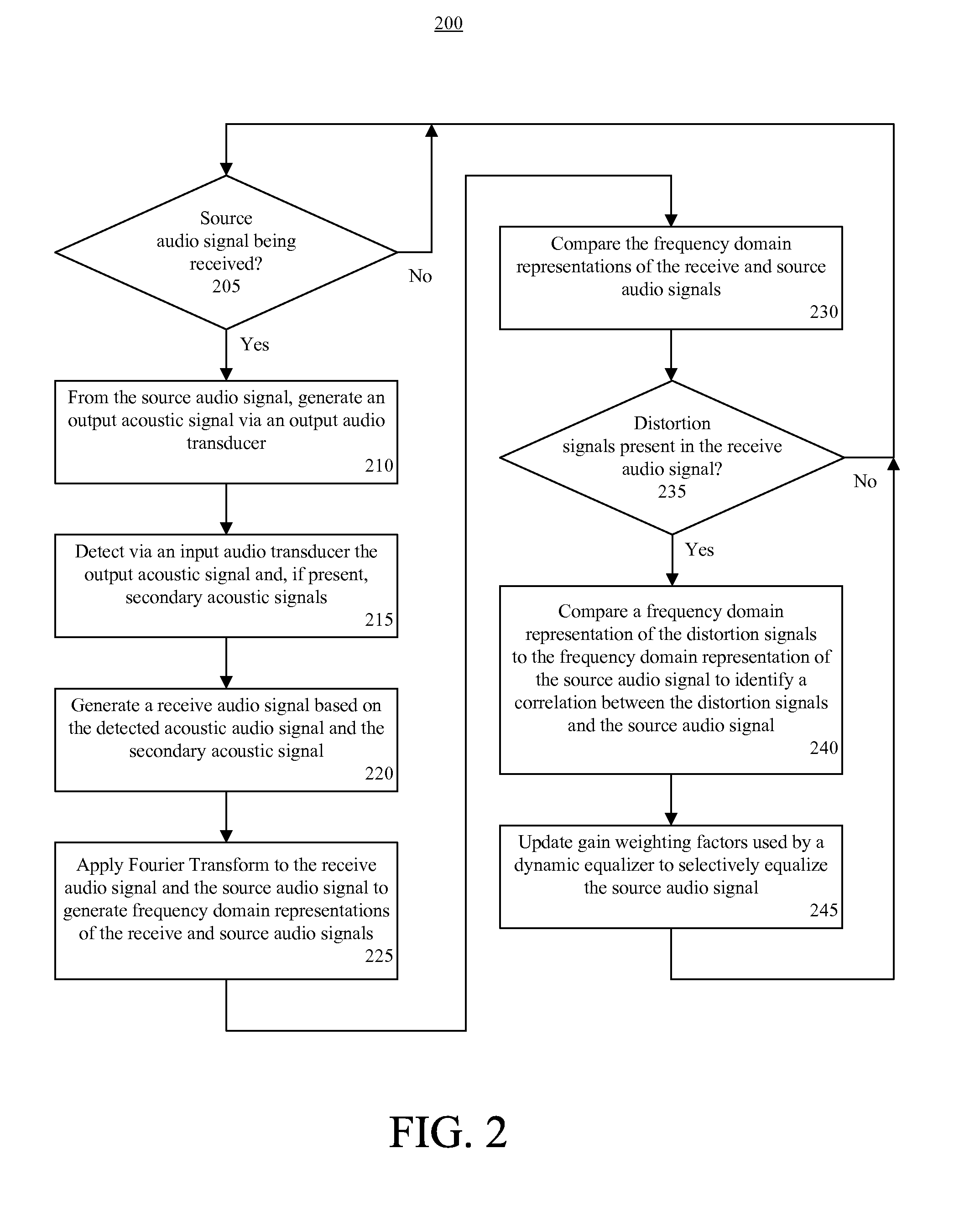
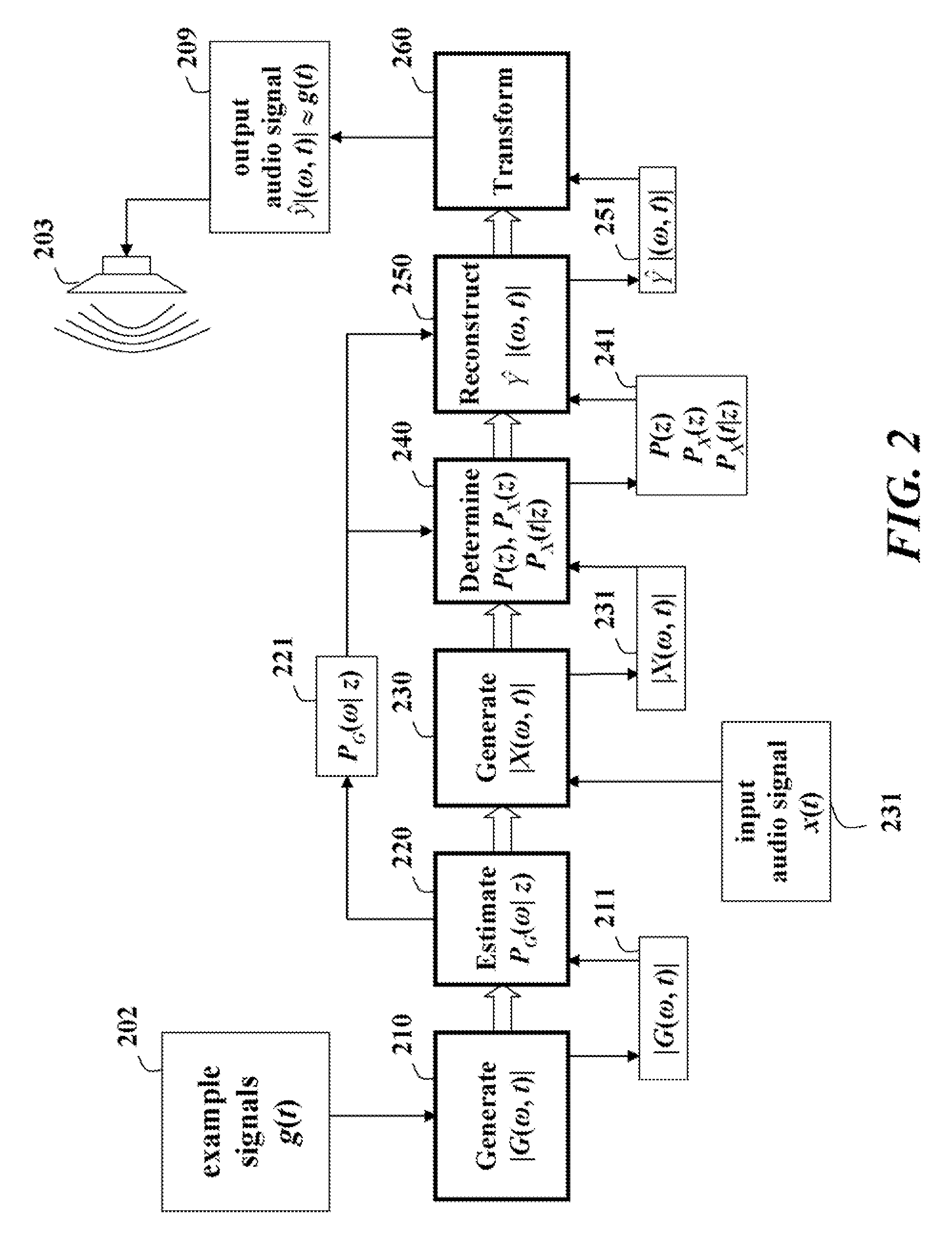
Dynamic distortion elimination for output audio
InactiveUS8045721B2Quality improvementInterconnection arrangementsGain controlTime–frequency representationComputer science
A method (200) for improving quality of output audio (126). The method can include detecting an output acoustic signal (128) and generating a receive audio signal (134) based, at least in part, on the detected output acoustic signal. A frequency domain representation (140) of the receive audio signal can be compared to a frequency domain representation (138) of a source audio signal (124) from which the output acoustic signal is generated. At least one distortion signal (142) in the receive audio signal can be identified, and the source audio signal can be selectively equalized to reduce an amplitude of the source audio signal at a frequency that correlates to the distortion signal.
Owner:GOOGLE TECHNOLOGY HOLDINGS LLC
Method for Visualizing the Directional Sound Activity of a Multichannel Audio Signal
ActiveUS20180084367A1Simple and clear visualizationIntuitive visualizationStereophonic circuit arrangementsSpeech analysisGraphicsSound sources
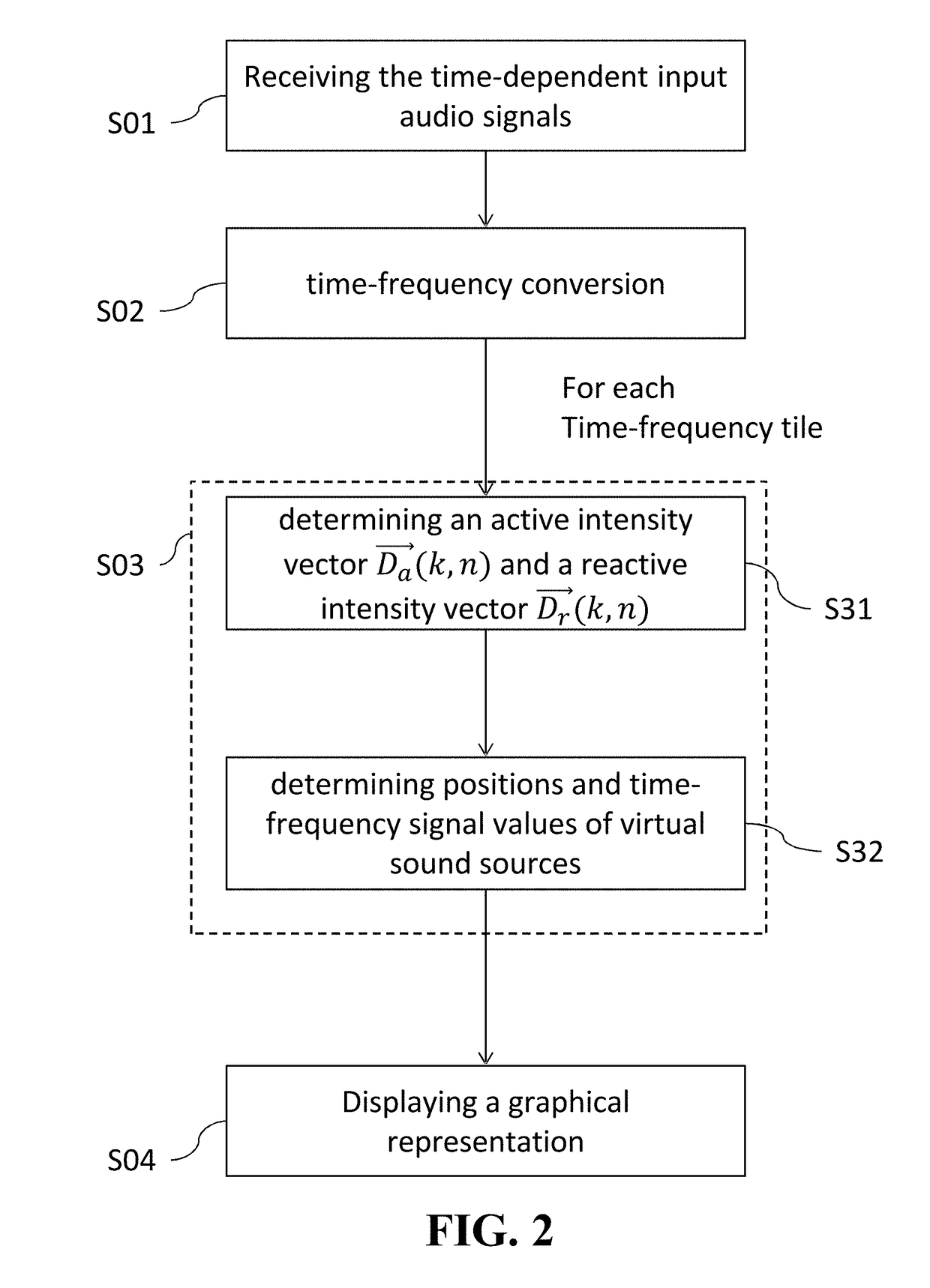
A method for visualizing a directional sound activity of a multichannel audio signal, wherein the multichannel audio signal comprises time-dependent input audio signals, comprising determining a directional sound activity vector from virtual sound sources determined from an active directional vector and a reactive directional vector determined from time-frequency representations of different input audio signals for each one of a plurality of time-frequency tiles; determining a contribution of each one of said directional sound activity vectors within sub-divisions of space on the basis of directivity information related to each sub-divisions of space and directional sound activity level within said sub-division of space by summing said contributions; displaying a visualization of the directional sound activity of the multichannel audio signal by a graphical representation of directional sound activity level within said sub-division of space.
Owner:A VOLUTE
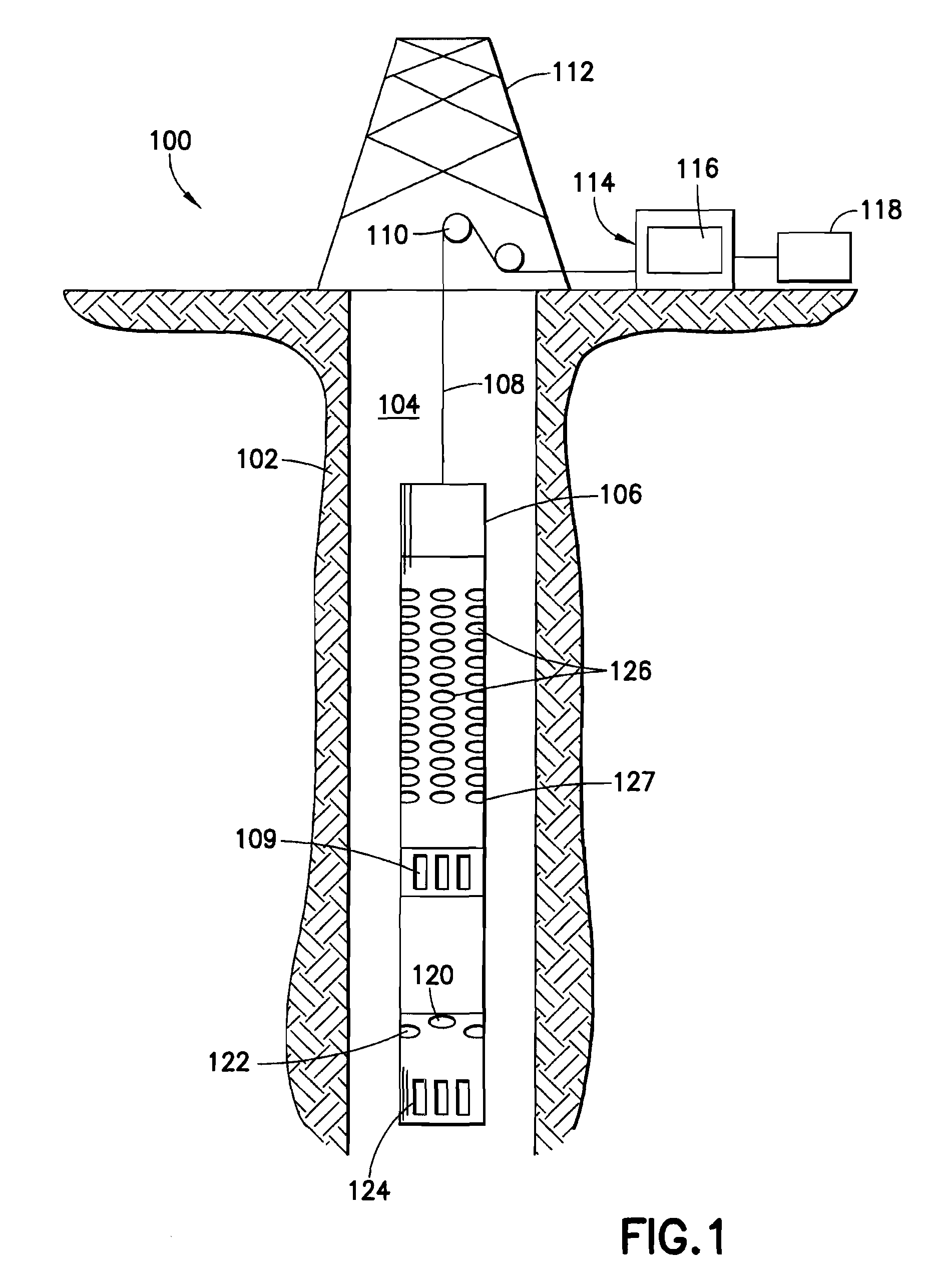
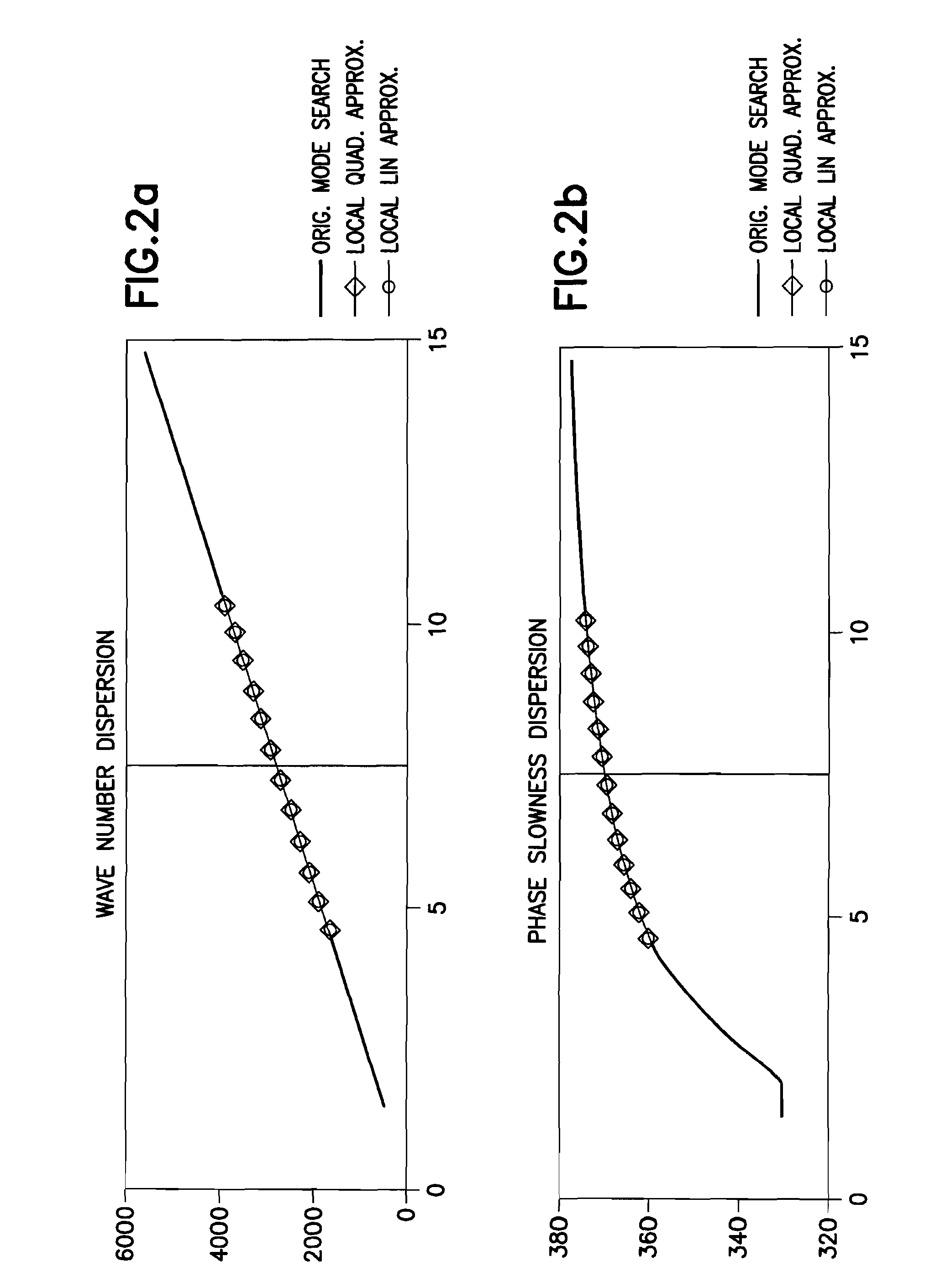
Dispersion extraction for acoustic data using time frequency analysis
ActiveUS20090067286A1Efficient identificationSeismic signal processingSeismology for water-loggingSensor arrayDispersion curve
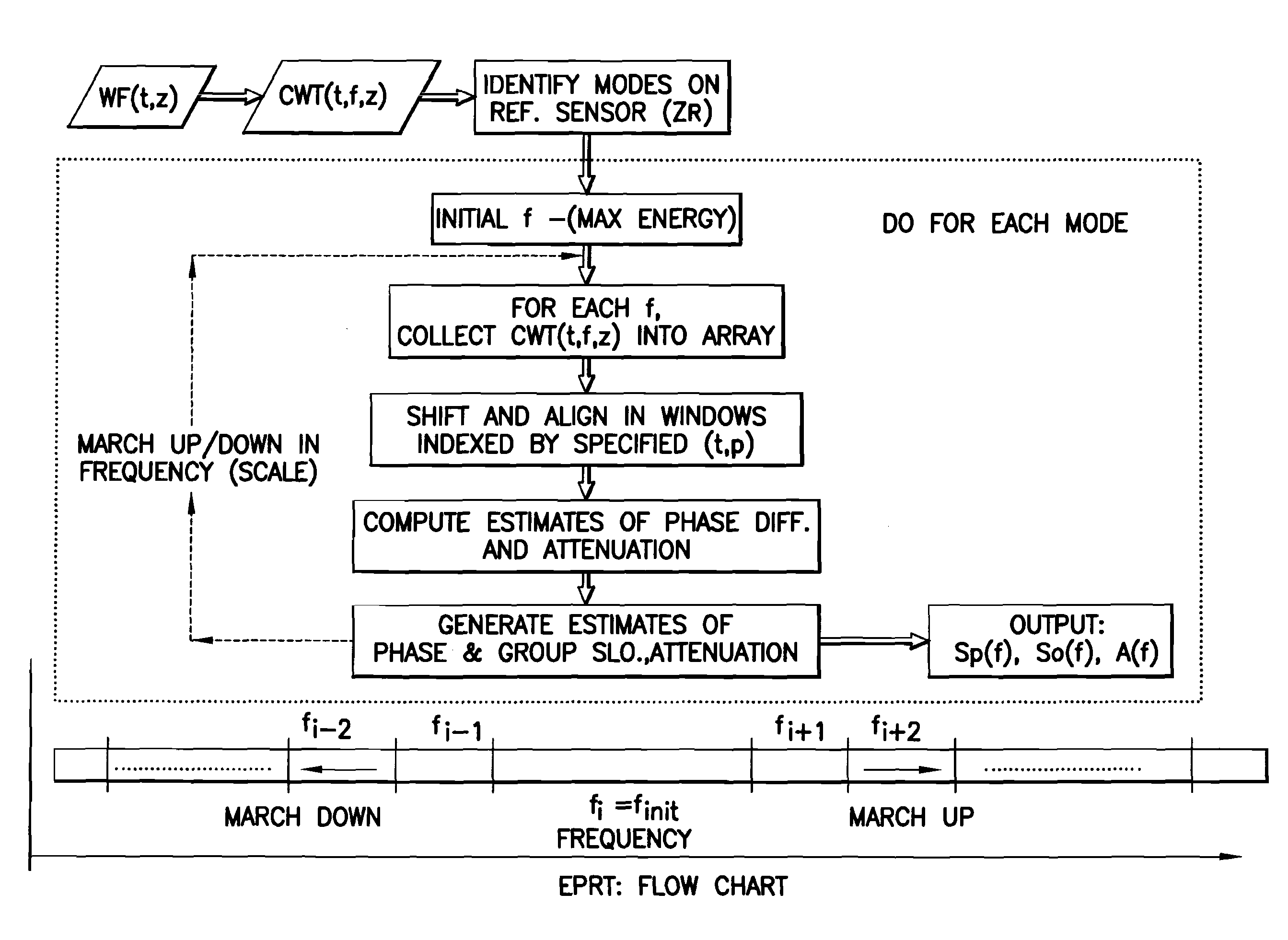
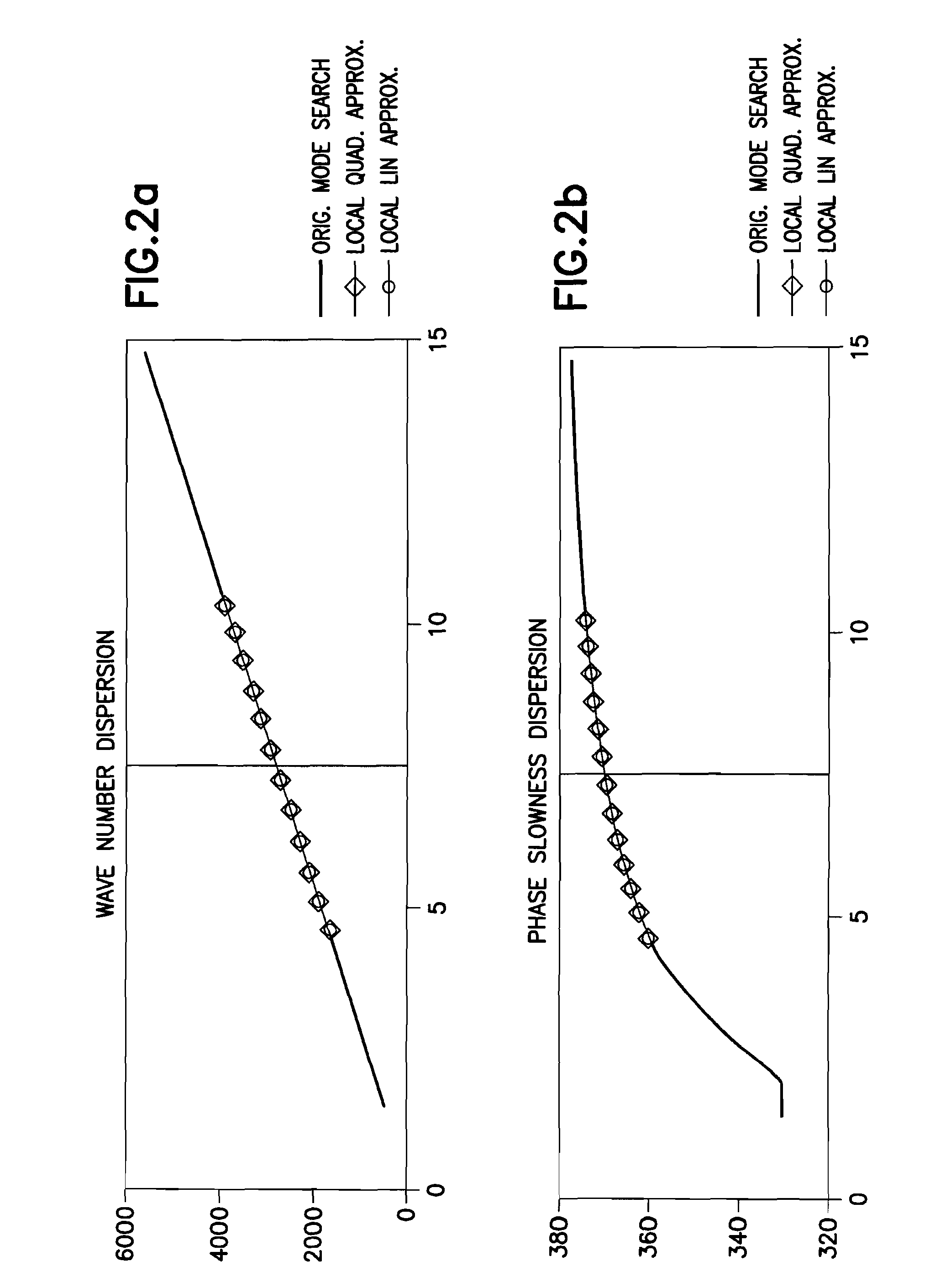
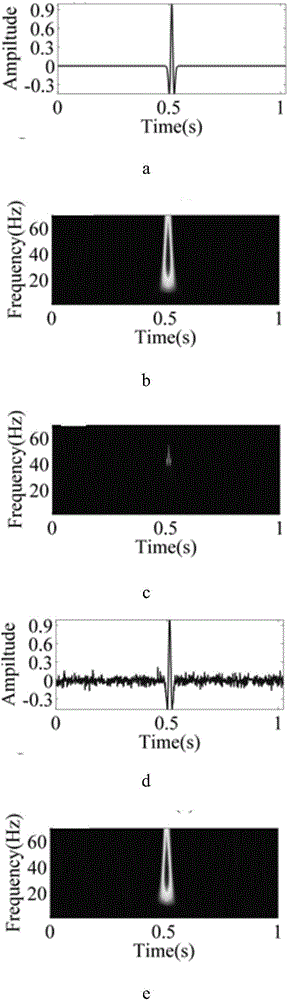
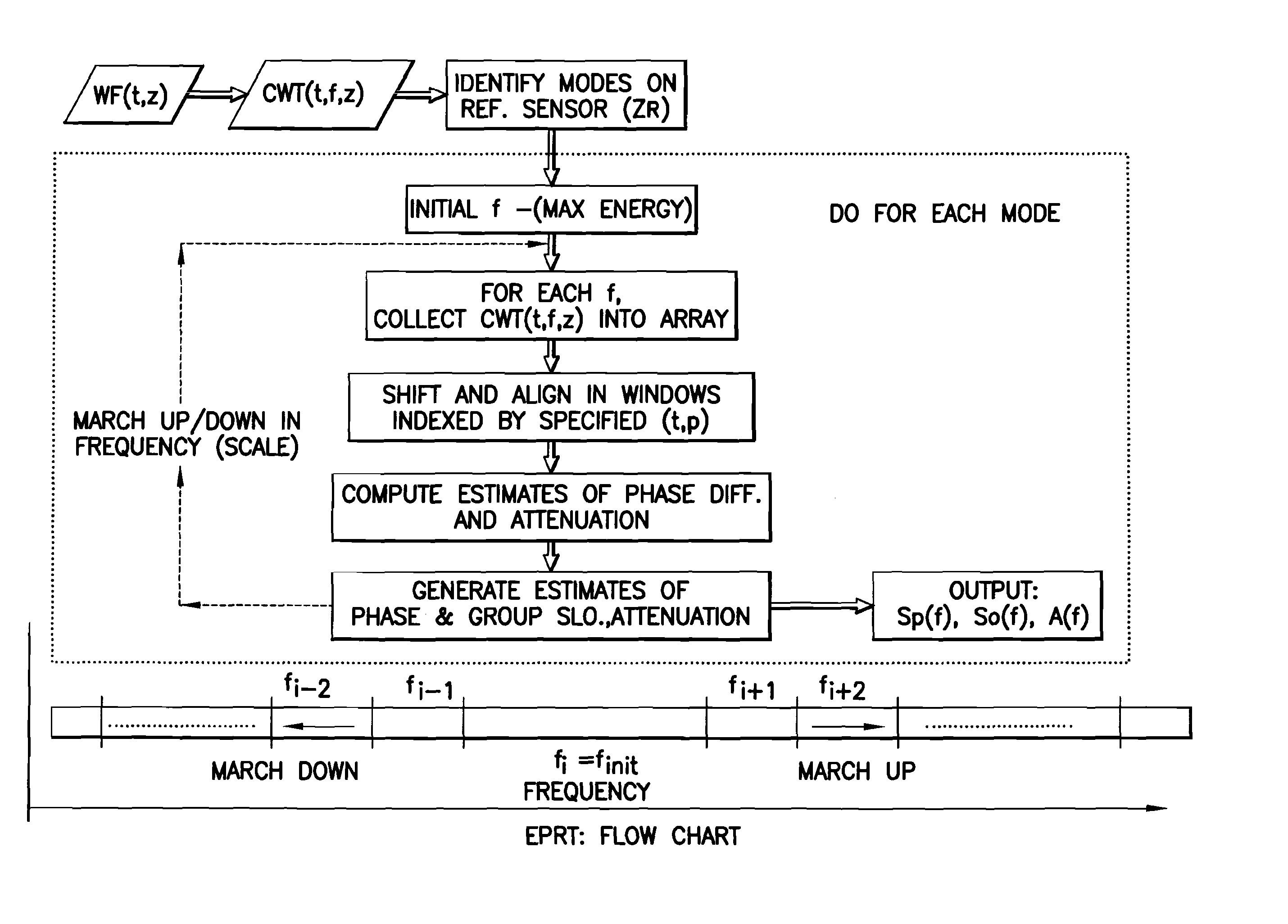
This invention pertains to the extraction of the slowness dispersion characteristics of acoustic waves received by an array of two or more sensors by the application of a continuous wavelet transform on the received array waveforms (data). This produces a time-frequency map of the data for each sensor that facilitates the separation of the propagating components thereon. Two different methods are described to achieve the dispersion extraction by exploiting the time frequency localization of the propagating mode and the continuity of the dispersion curve as a function of frequency. The first method uses some features on the modulus map such as the peak to determine the time locus of the energy of each mode as a function of frequency. The second method uses a new modified Radon transform applied to the coefficients of the time frequency representation of the waveform traces received by the aforementioned sensors. Both methods are appropriate for automated extraction of the dispersion estimates from the data without the need for expert user input or supervision
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Speech recognition system and method for generating phonotic estimates
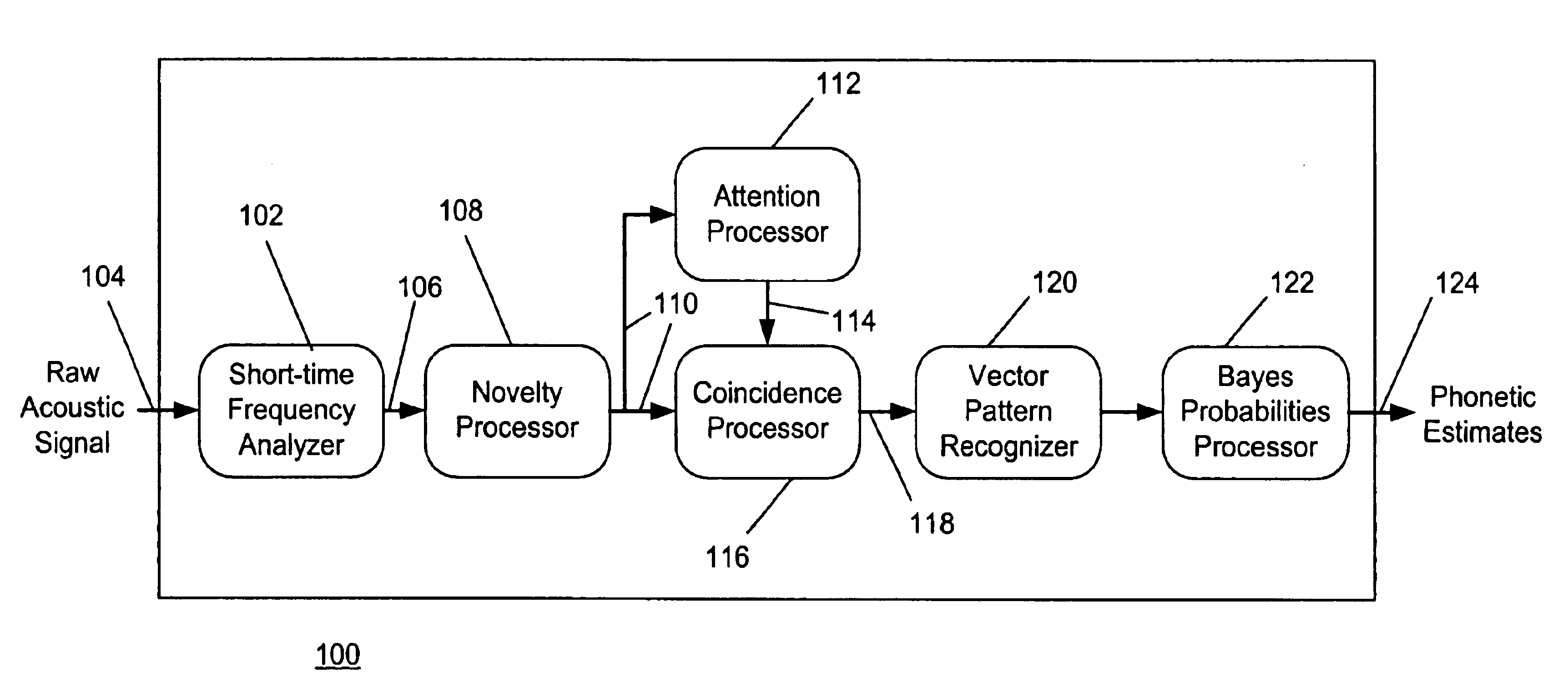
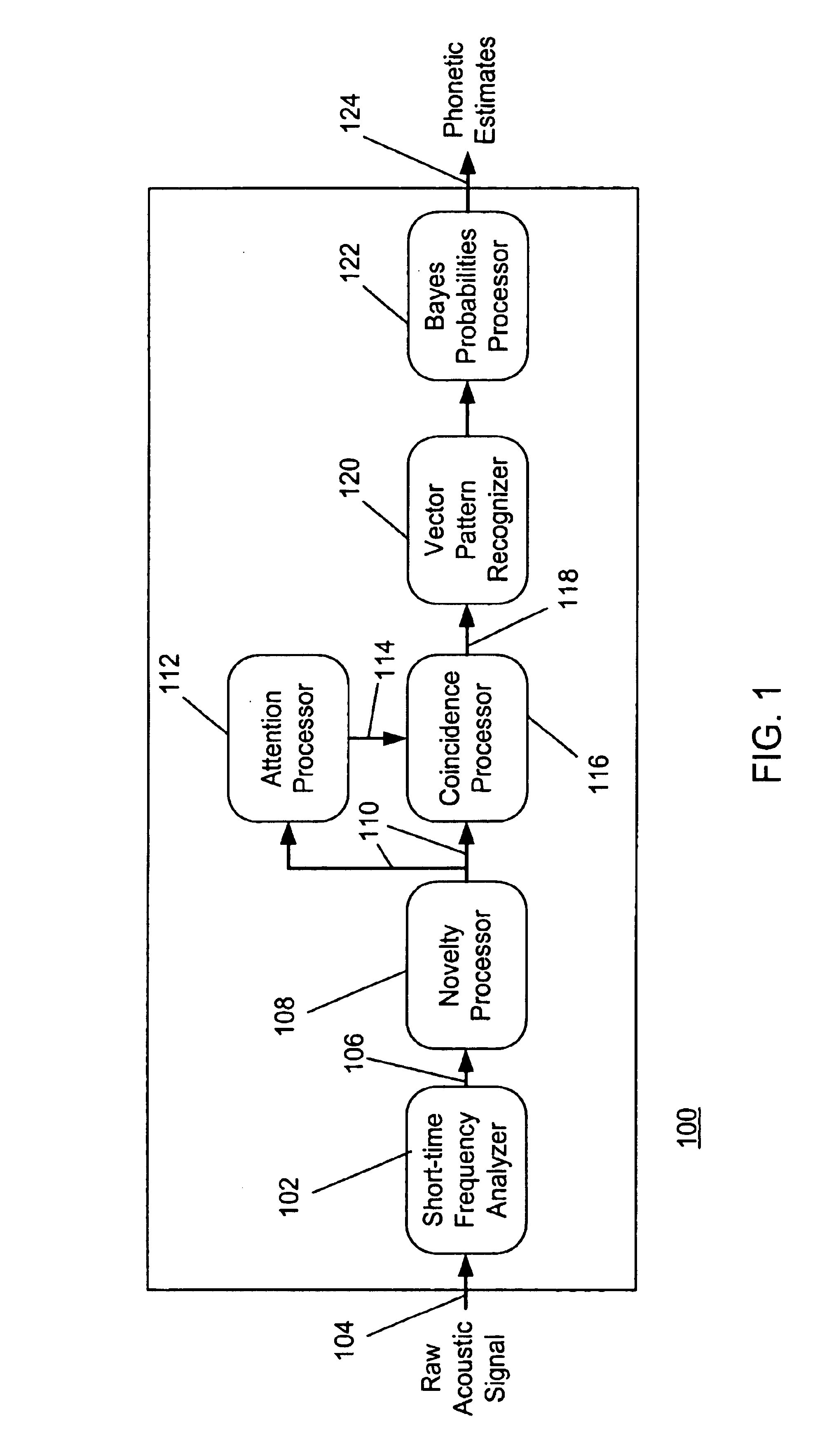
InactiveUS6868380B2Simplify subsequent processing stepsAvoid difficultySpeech recognitionMarketingCo-occurrenceSpeech identification
A speech recognition system for transforming an acoustic signal into a stream of phonetic estimates includes a frequency analyzer for generating a short-time frequency representation of the acoustic signal. A novelty processor separates background components of the representation from region of interest components of the representation. The output of the novelty processor includes the region of interest components of the representation according to the novelty parameters. An attention processor produces a gating signal as a function of the novelty output according to attention parameters. A coincidence processor produces information regarding co-occurrences between samples of the novelty output over time and frequency. The coincidence processor selectively gates the coincidence output as a function of the gating signal according to one or more coincidence parameters. A vector pattern recognizer and a probability processor receives the gated coincidence output and produces a phonetic estimate stream representative of acoustic signal.
Owner:ELIZA
Method for intelligently diagnosing rotating machine fault feature based on deep CNN model
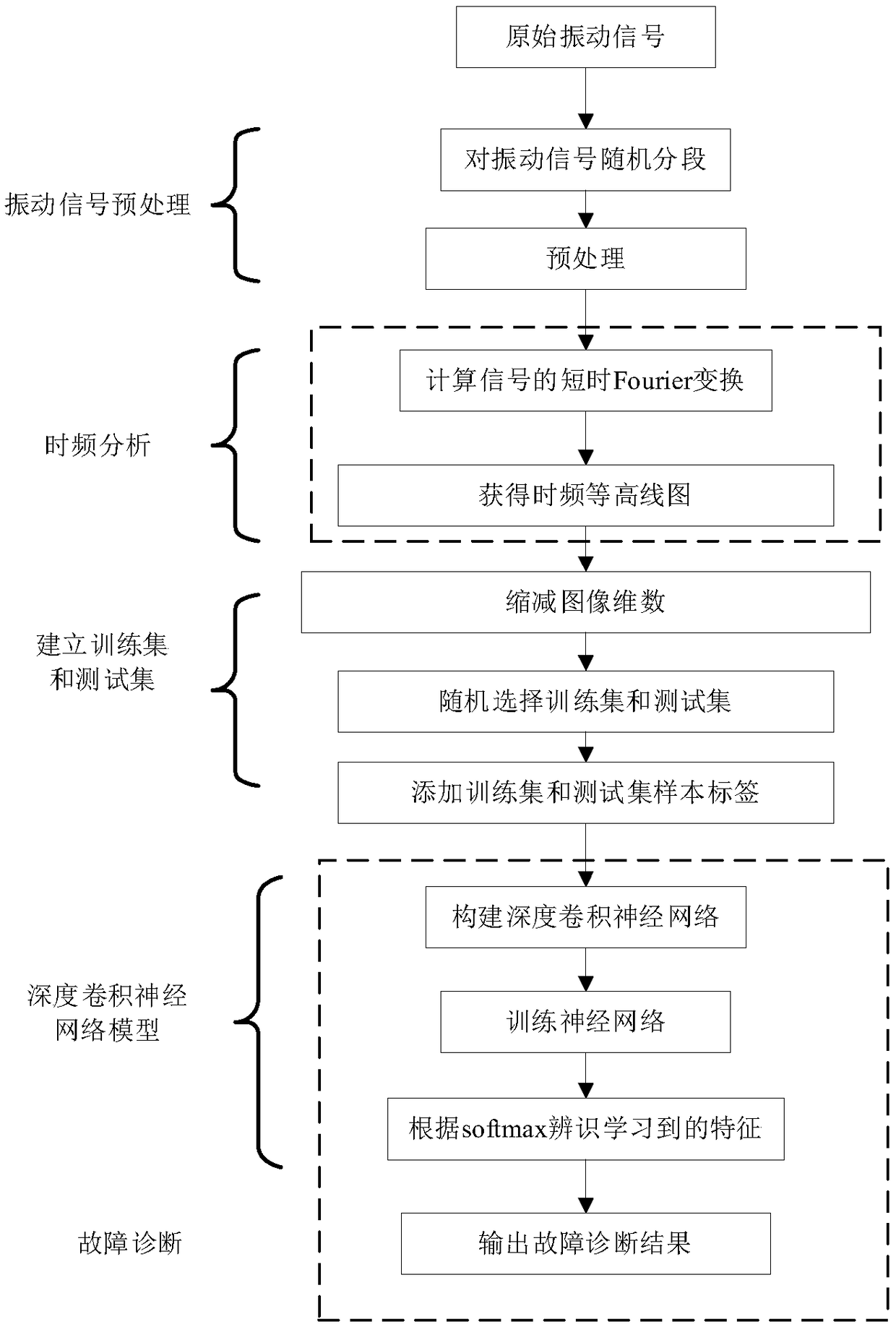
ActiveCN108830127AAccurately reflect the characteristicsAvoid featuresCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesAlgorithmNetwork model
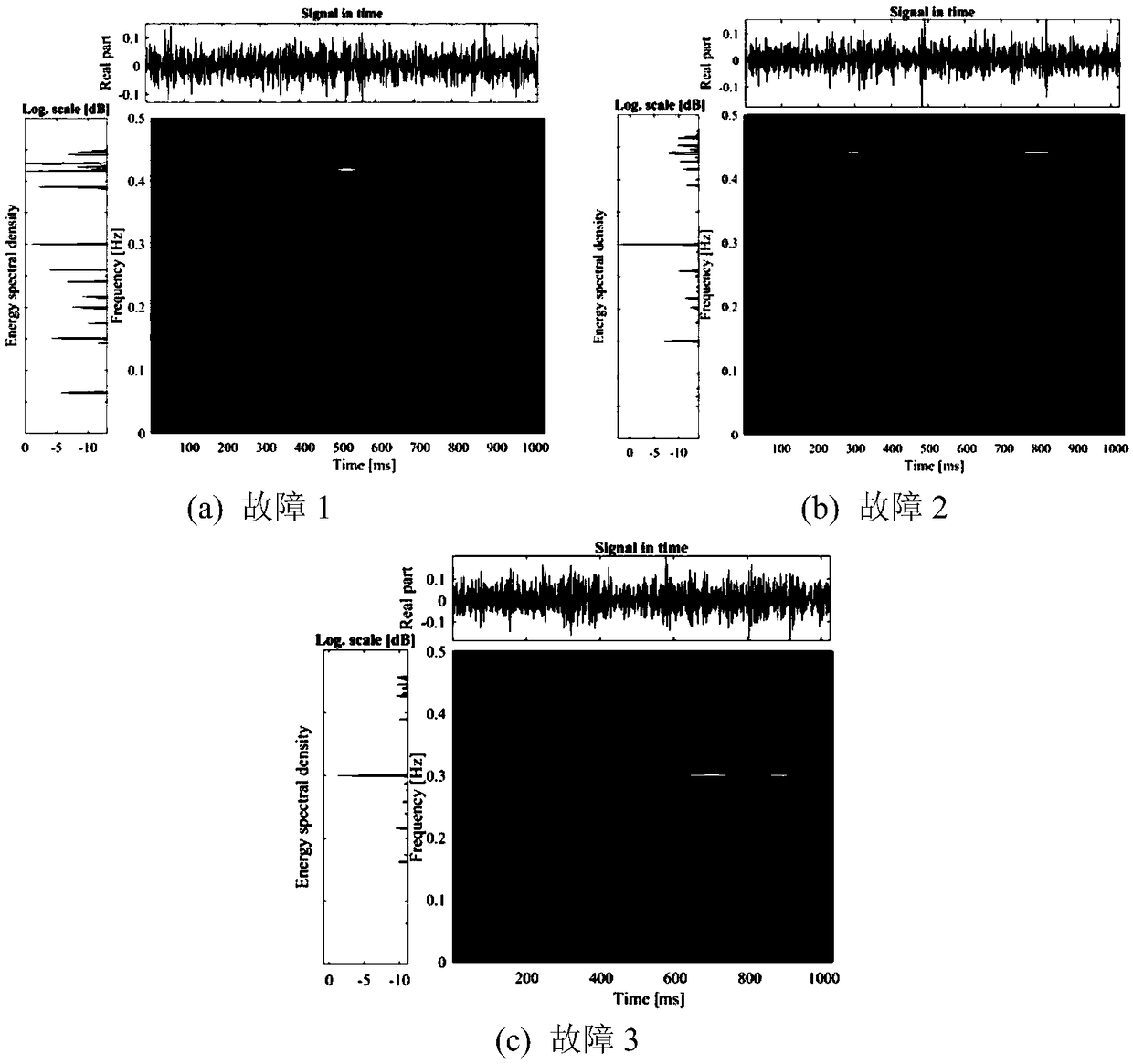
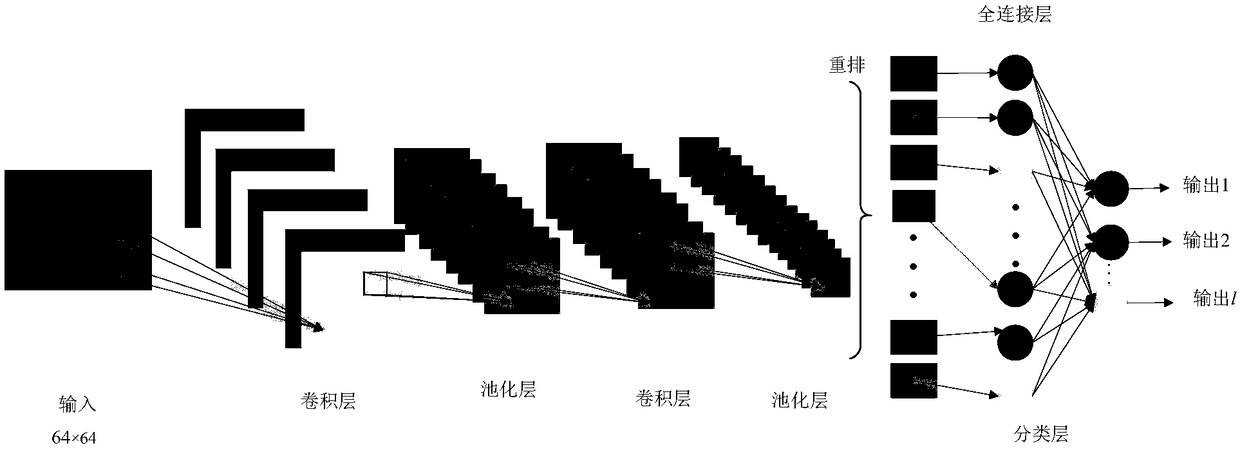
The invention discloses a method for intelligently diagnosing a rotating machine fault feature based on a deep CNN model. The method comprises: (1) acquiring rotating machine fault vibration signal data, segmenting the data and performing de-trend item preprocessing; (2) performing short-time Fourier time-frequency transform analysis on the signal data to obtain the time-frequency representation of each vibration signal, and displaying the time-frequency representation with a pseudo-color map; (3) reducing the image resolution by an interpolation method and superimposing respective images to form a training sample and a test sample as inputs of the CNN; (4) constructing the deep CNN model including an input layer, two convolution layers, two pooling layers, a fully connected layer, and a softmax classification layer and an output layer; and (5) introducing the training sample into the model for training, obtaining a convolution feature, a pooling feature and a neural network structuralparameter, and diagnosing unknown fault signals according to the constructed deep CNN. The method has better accuracy and stability than an existing time-domain or frequency-domain method.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
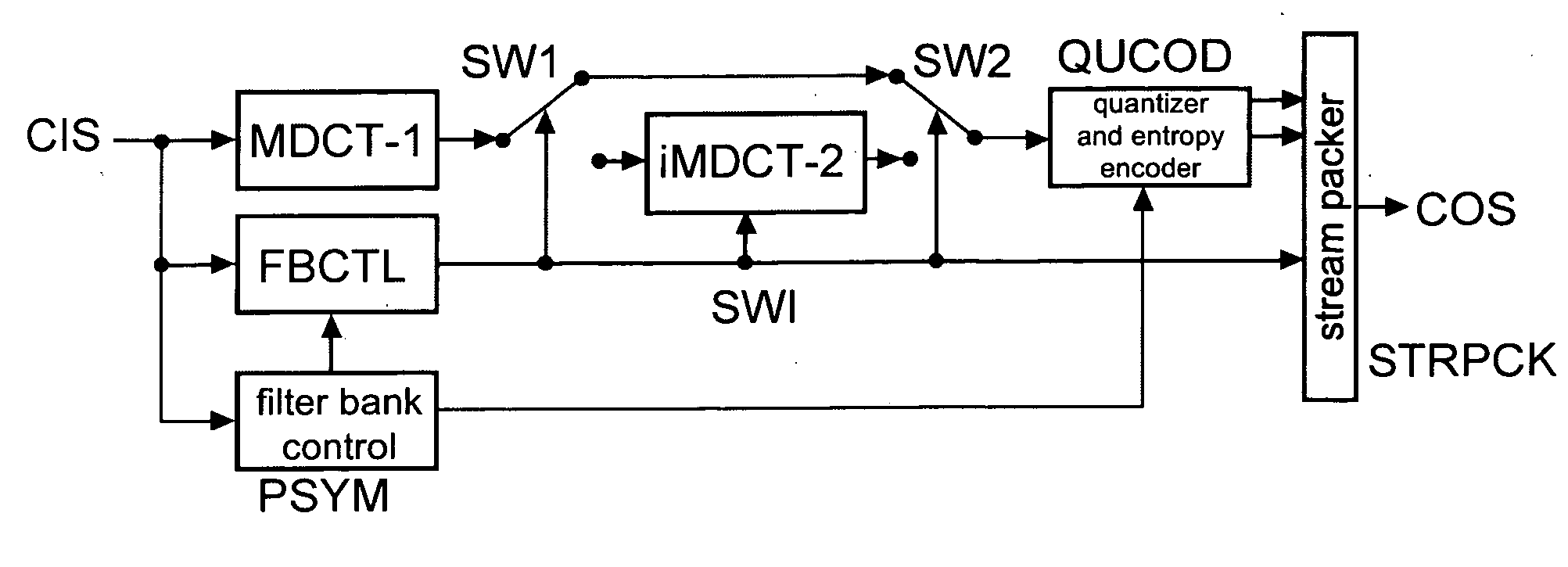
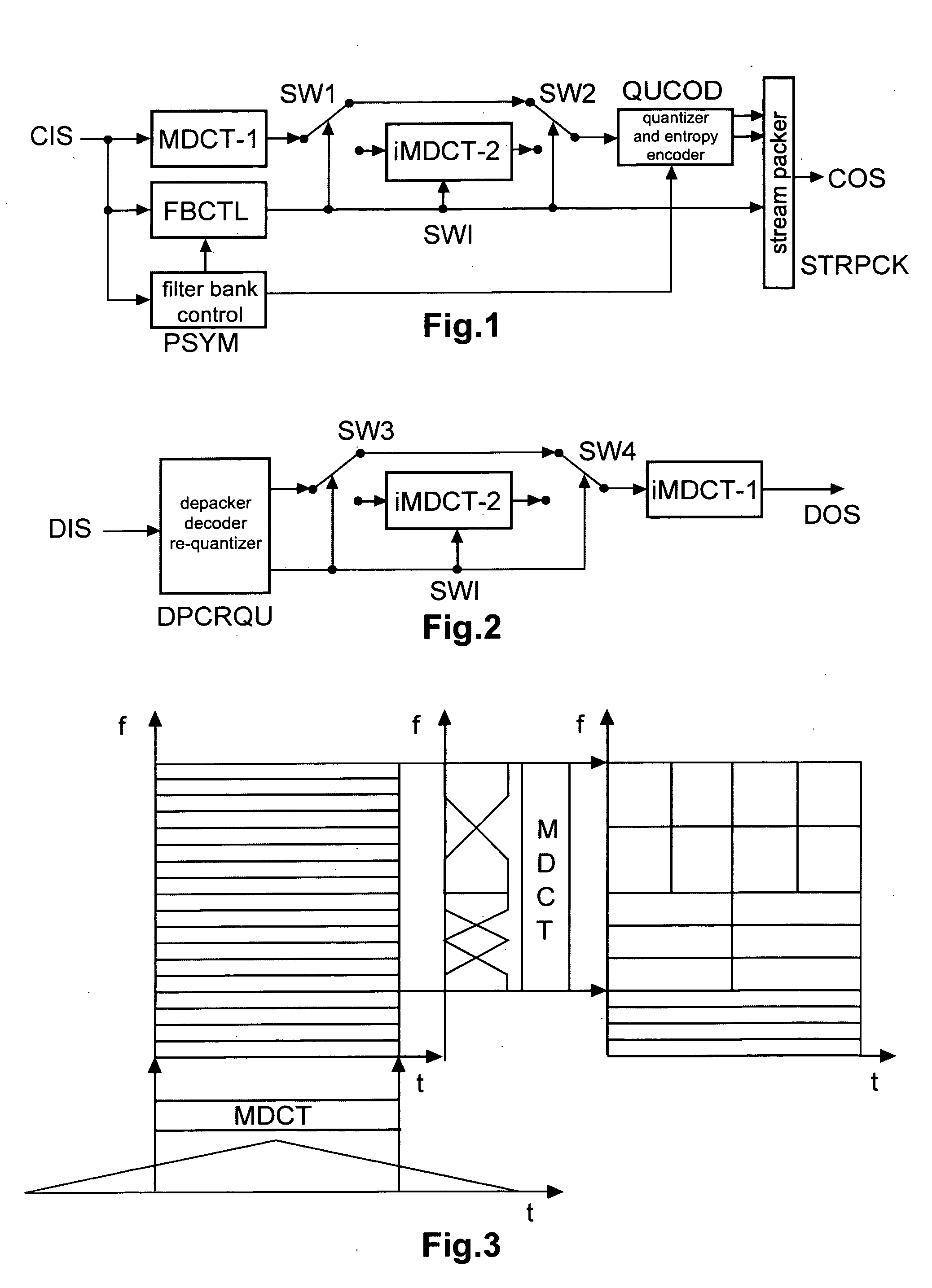
Method and apparatus for encoding and decoding an audio signal using adaptively switched temporal resolution in the spectral domain
ActiveUS20090012797A1Quality improvementReduce encoding delaySpeech synthesisTemporal resolutionFrequency spectrum
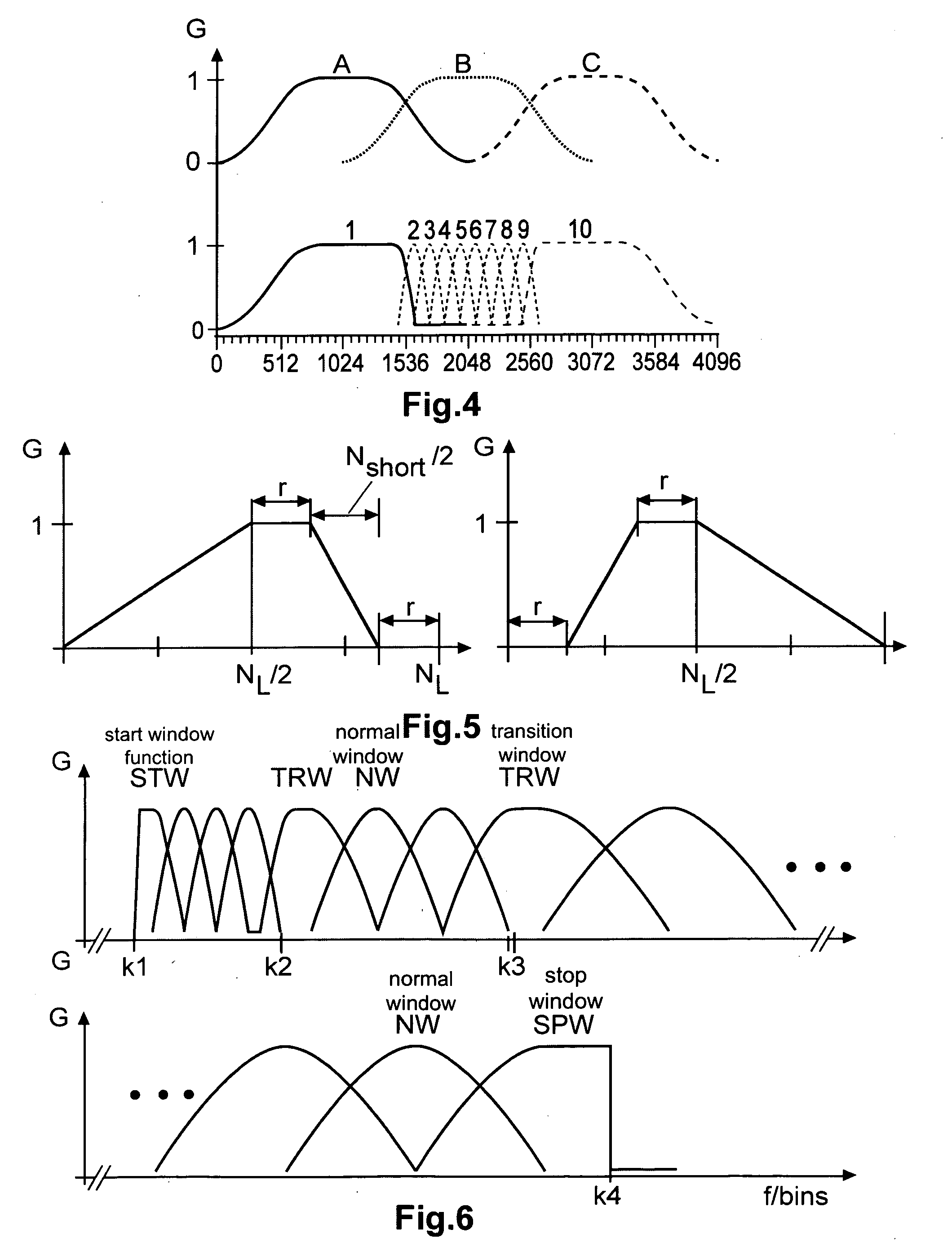
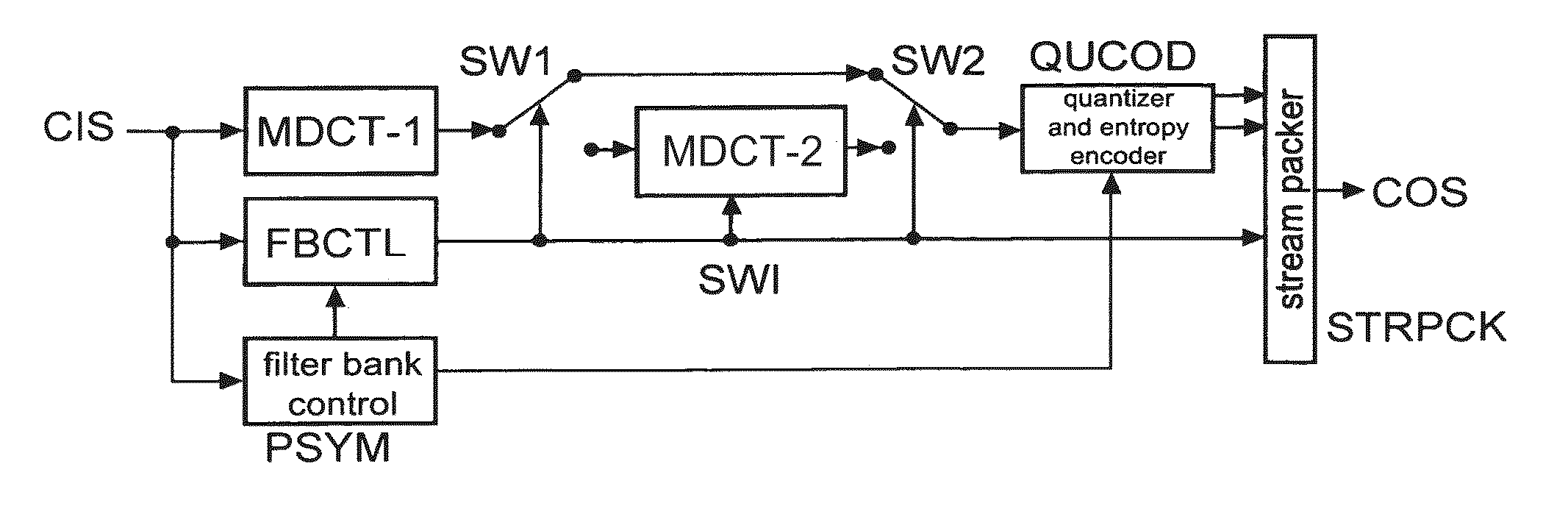
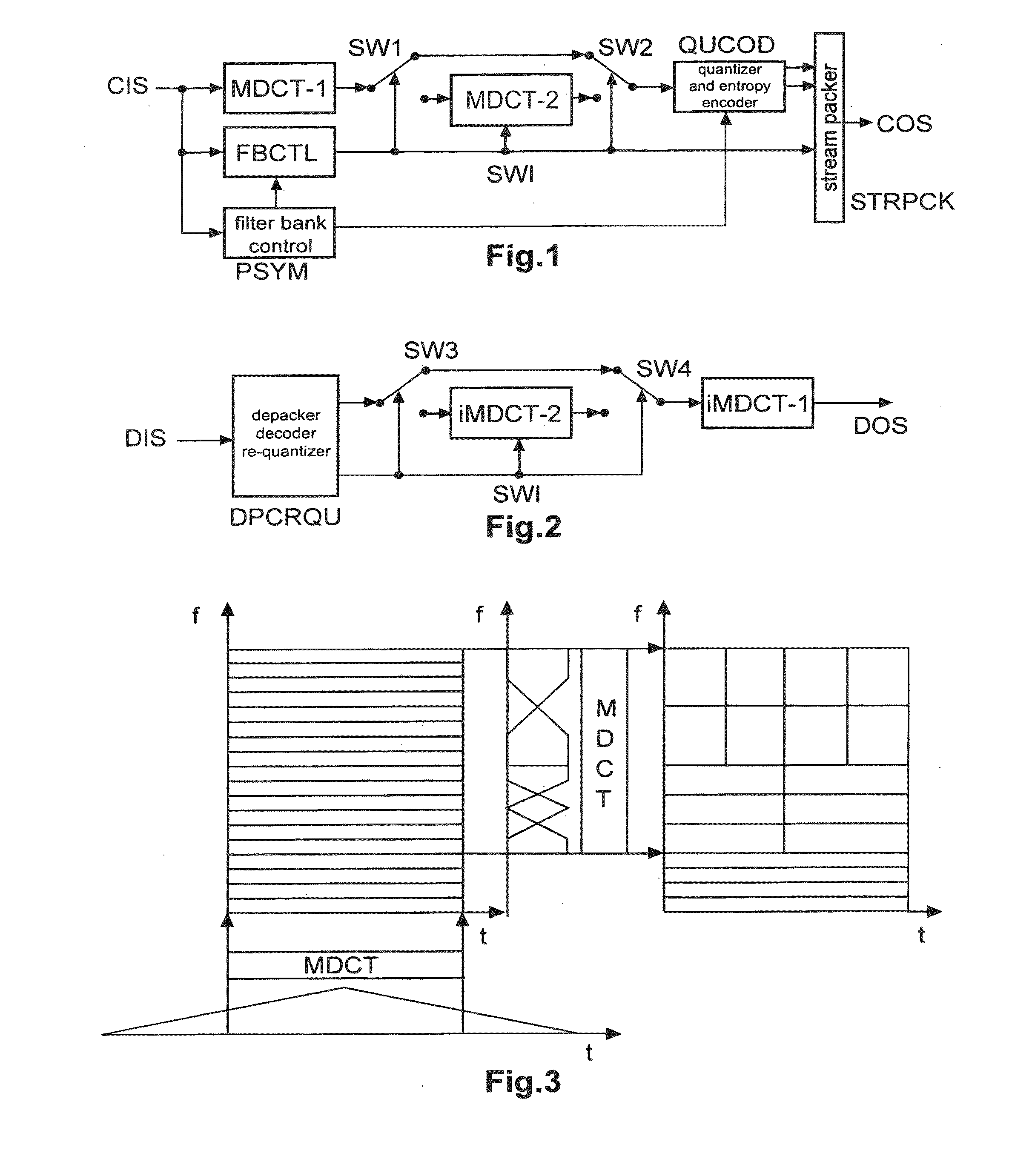
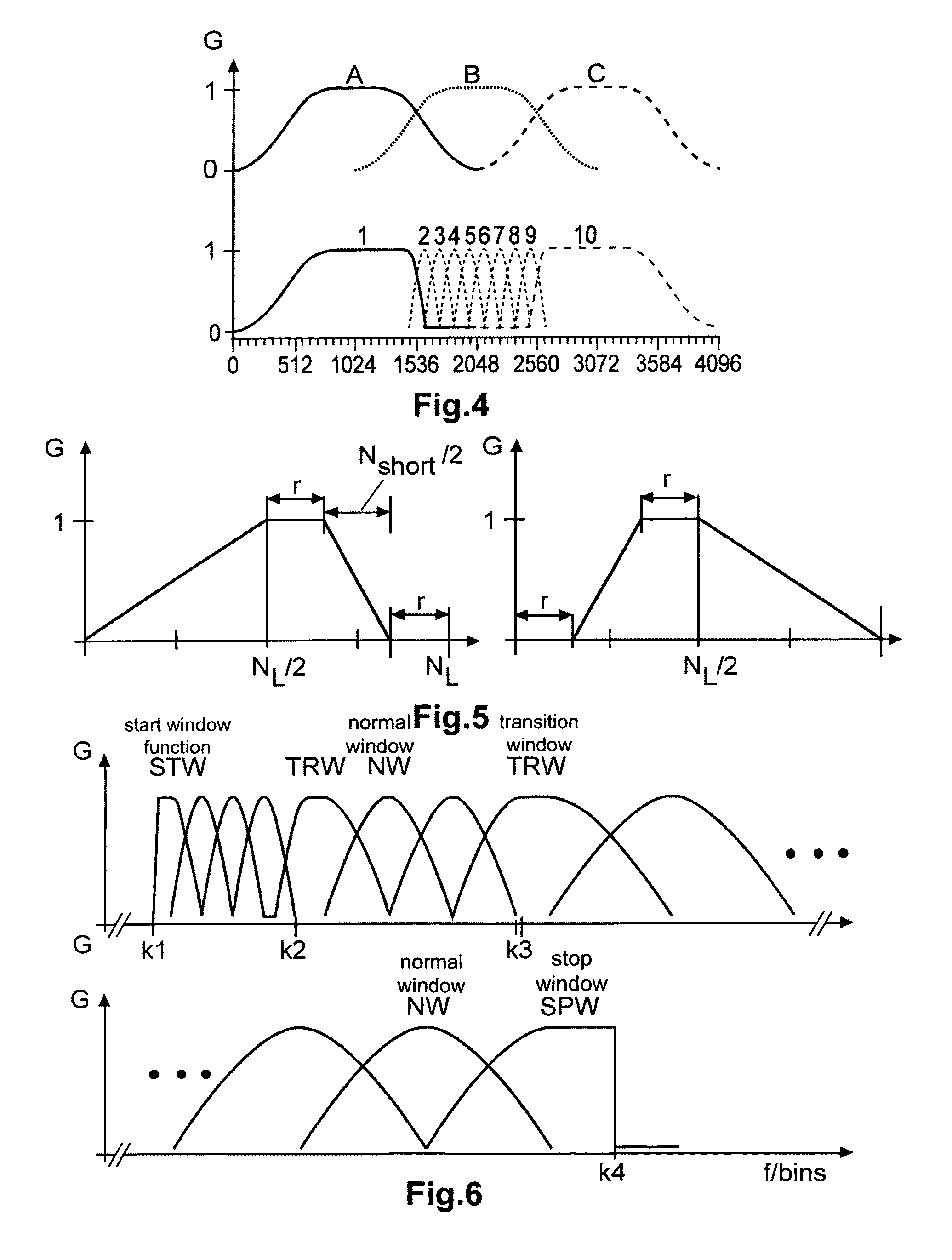
Perceptual audio codecs make use of filter banks and MDCT in order to achieve a compact representation of the audio signal, by removing redundancy and irrelevancy from the original audio signal. During quasi-stationary parts of the audio signal a high frequency resolution of the filter bank is advantageous in order to achieve a high coding gain, but this high frequency resolution is coupled to a coarse temporal resolution that becomes a problem during transient signal parts by producing audible pre-echo effects. The invention achieves improved coding / decoding quality by applying on top of the output of a first filter bank a second non-uniform filter bank, i.e. a cascaded MDCT. The inventive codec uses switching to an additional extension filter bank (or multi-resolution filter bank) in order to re-group the time-frequency representation during transient or fast changing audio signal sections. By applying a corresponding switching control, pre-echo effects are avoided and a high coding gain and a low coding delay are achieved.
Owner:GUANGDONG OPPO MOBILE TELECOMM CORP LTD
Method and apparatus for encoding and decoding an audio signal using adaptively switched temporal resolution in the spectral domain
ActiveUS8095359B2Quality improvementReduce encoding delaySpeech synthesisTemporal resolutionFrequency spectrum
Owner:GUANGDONG OPPO MOBILE TELECOMM CORP LTD
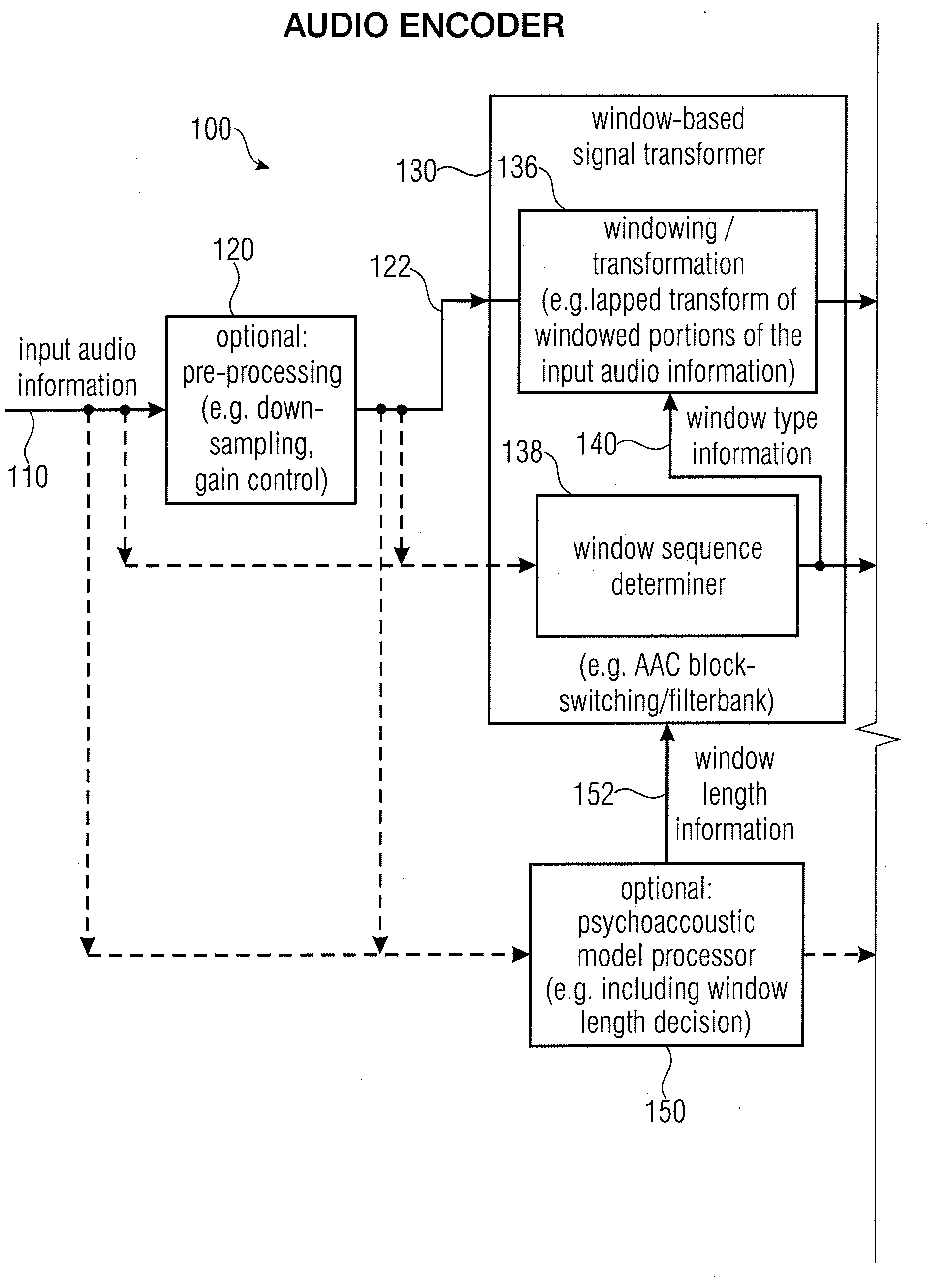
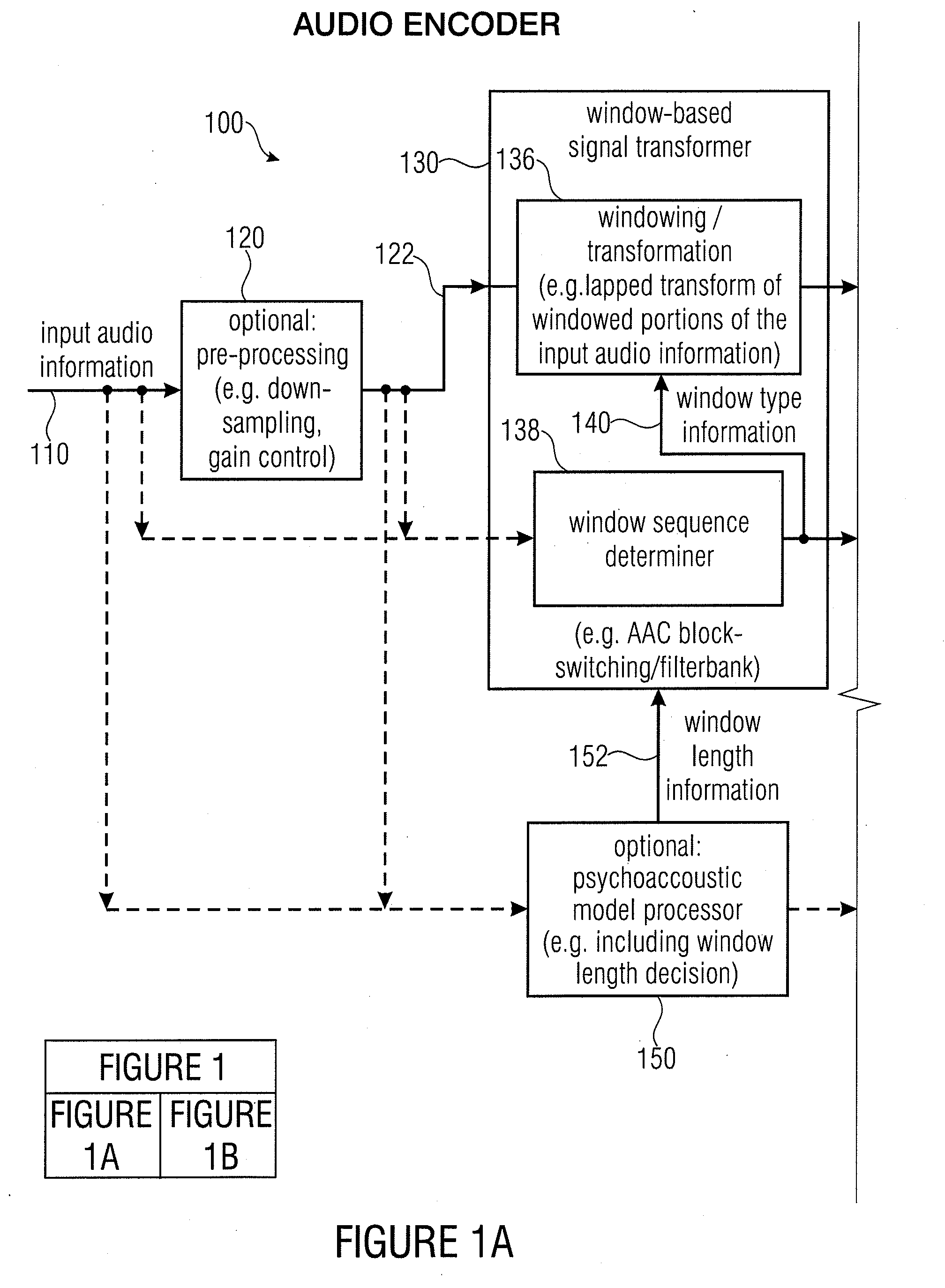
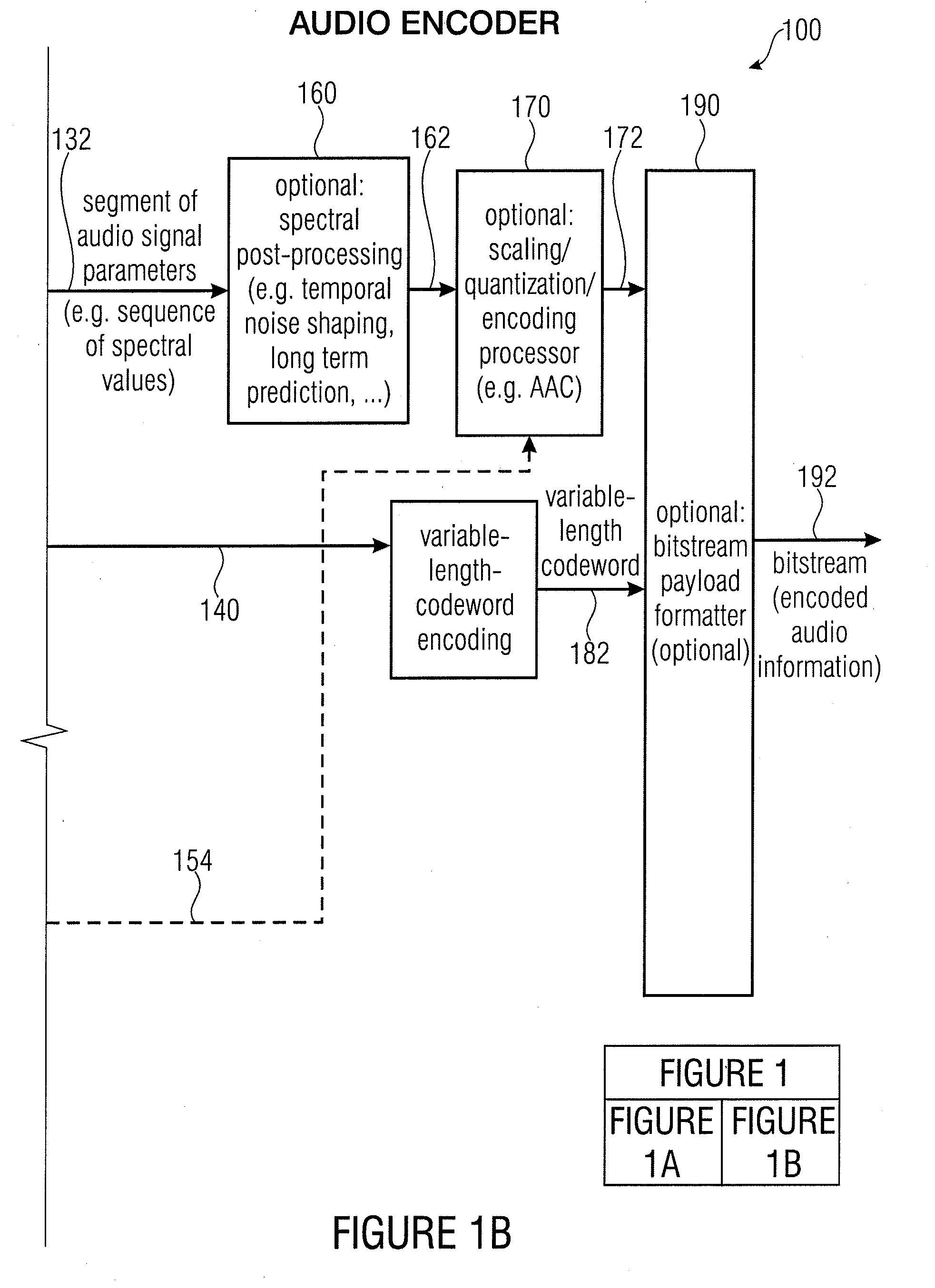
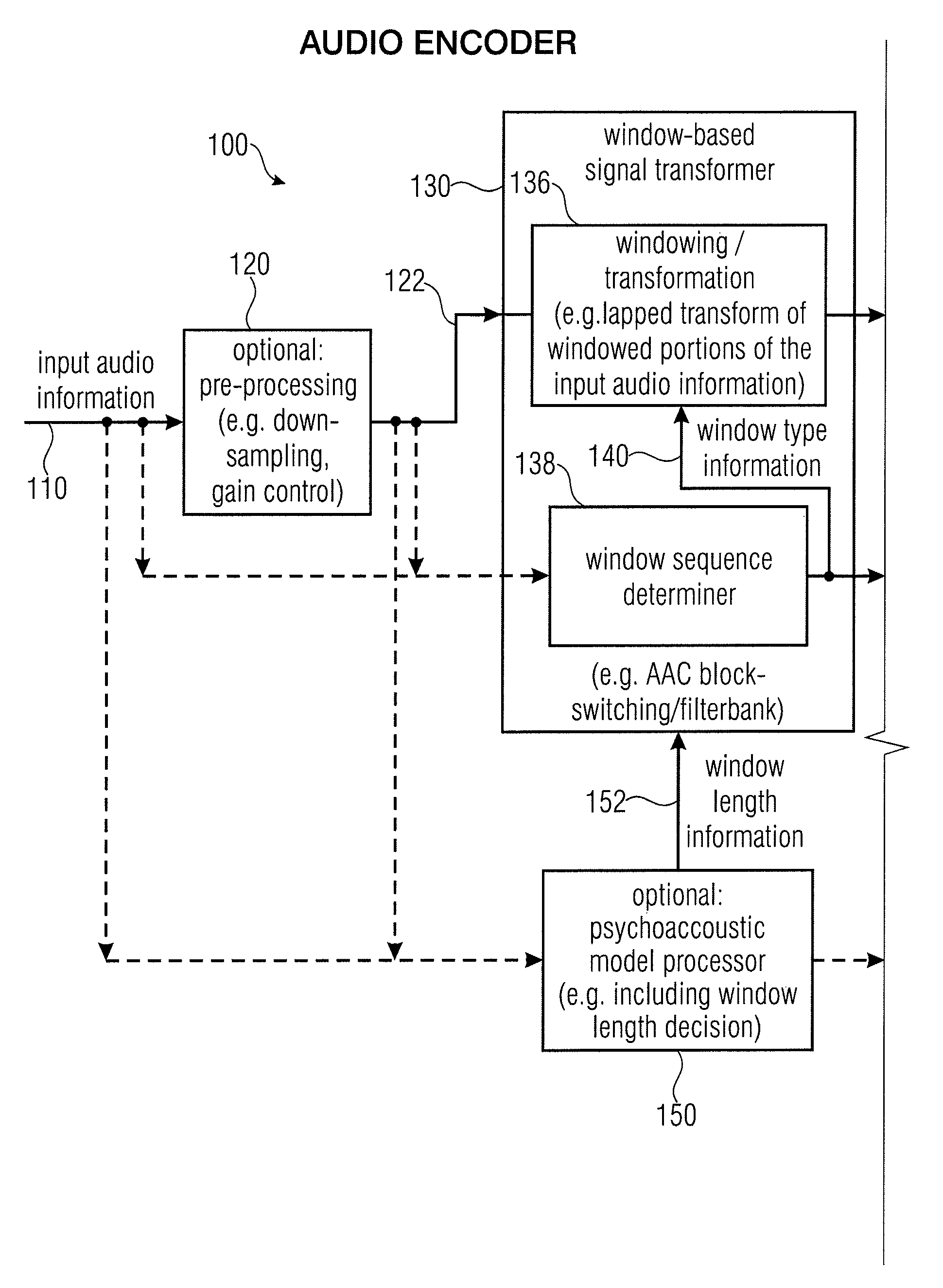
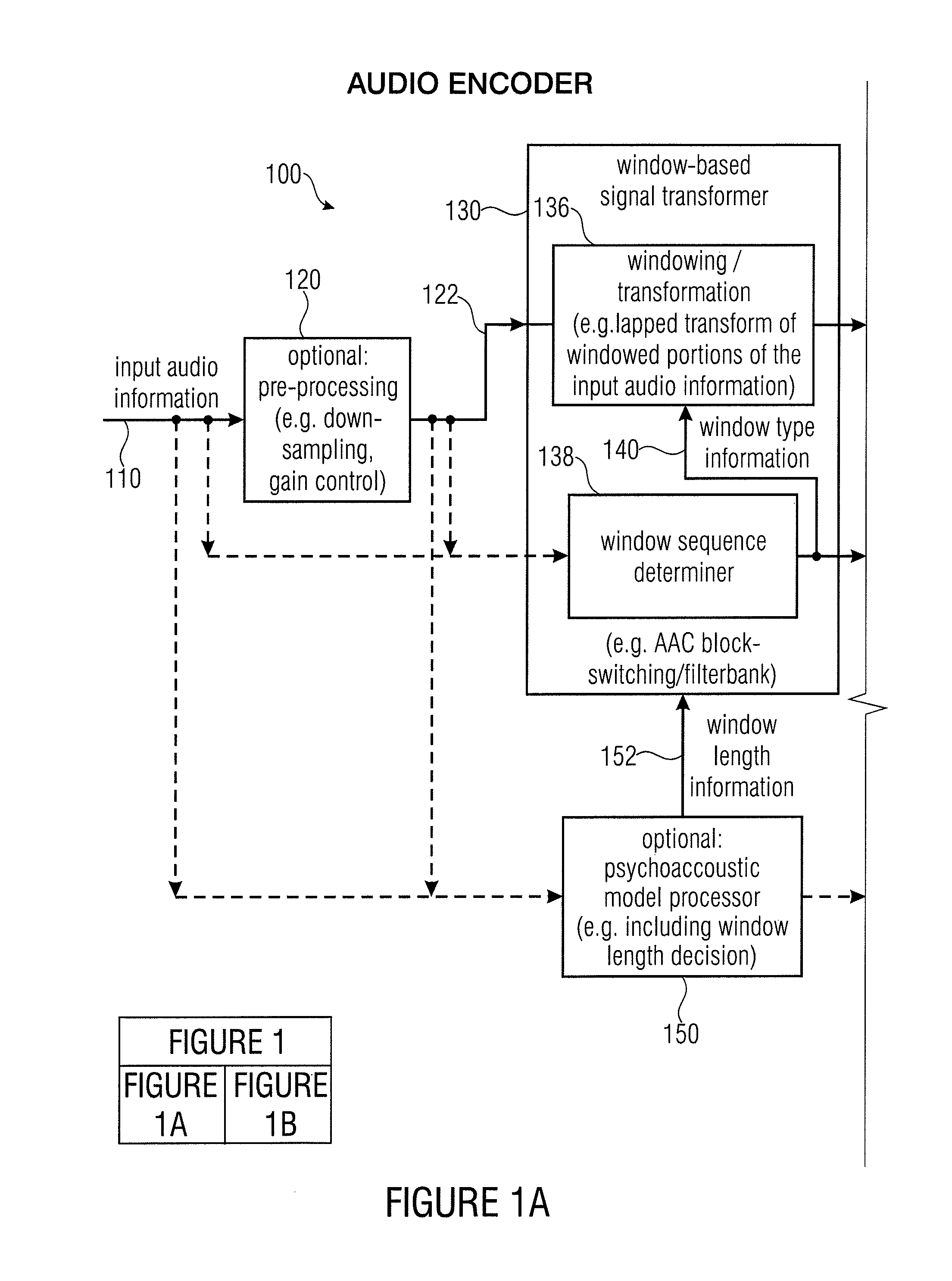
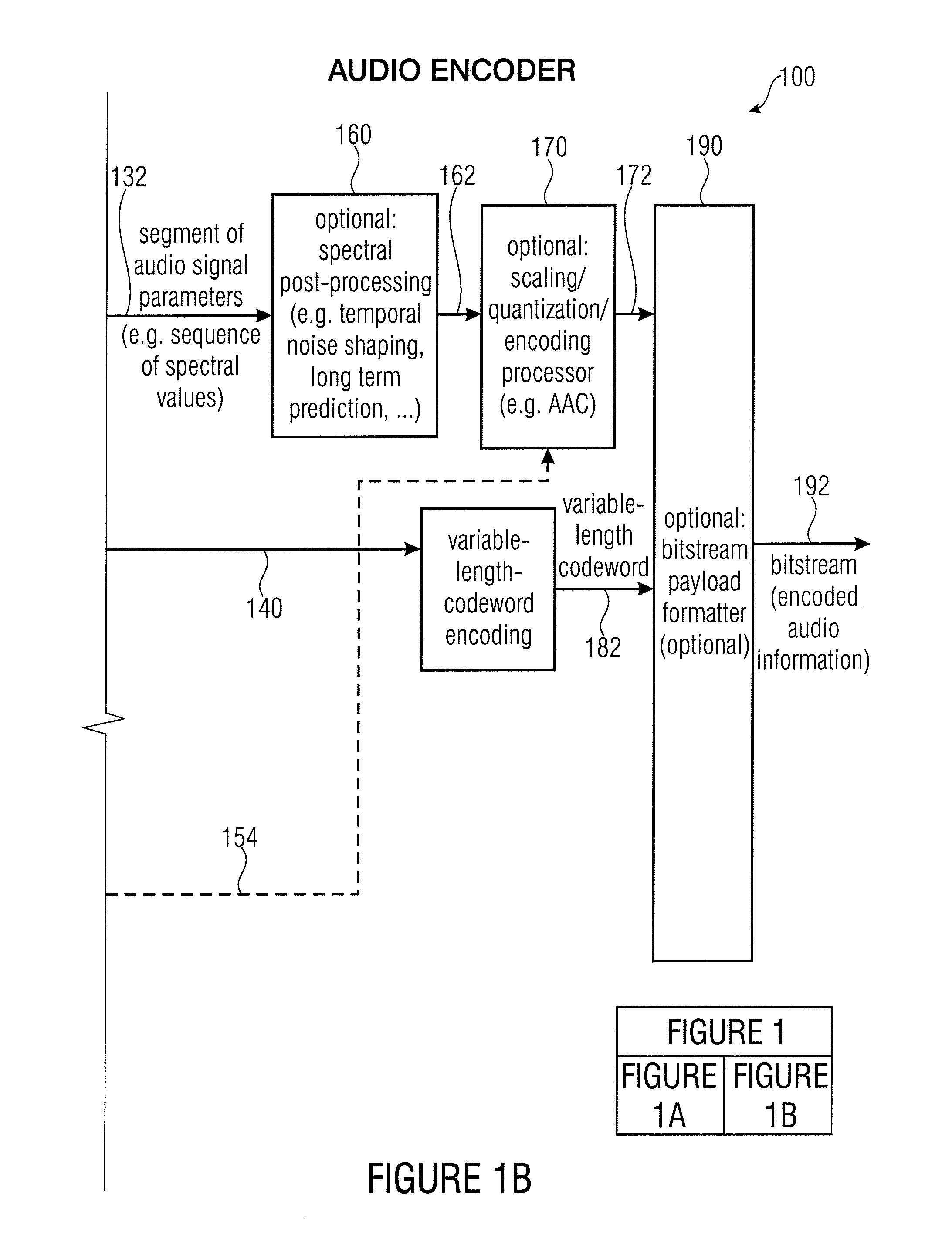
Audio encoder, audio decoder, encoded audio information, methods for encoding and decoding an audio signal and computer program
An audio decoder for providing a decoded audio information on the basis of an encoded audio information includes a window-based signal transformer configured to map a time-frequency representation, which is described by the encoded audio information, to a time-domain representation. The window-based signal transformer is configured to select a window, out of a plurality of windows including windows of different transition slopes and windows of different transform length, on the basis of a window information. The audio decoder includes a window selector configured to evaluate a variable-codeword-length window information in order to select a window for a processing of a given portion of the time-frequency representation associated with a given frame of the audio information.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
Method for Expanding Audio Signal Bandwidth
InactiveUS20090048846A1High frequencyAvoid problemsSpeech analysisTime domainTime–frequency representation
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
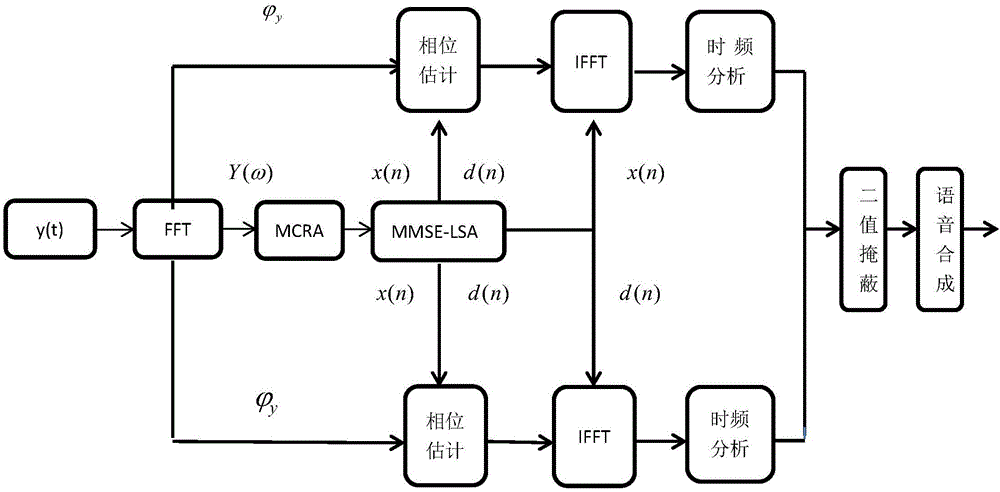
Voice enhancement method for fusing phase estimation and human ear hearing characteristics in digital hearing aid
ActiveCN105741849AQuality improvementEnhanced auditory characteristicsSpeech analysisNoise power spectrumGammatone filter
The invention discloses a voice enhancement method for fusing phase estimation and human ear hearing characteristics in a digital hearing aid, comprising steps of obtaining a frequency domain expression mode containing noise through Fourier transformation, adopting a minimum value control recursive average method to obtain a noise power spectrum, obtaining initial enhancement voice and a noise amplitude spectrum, obtaining the initial enhancement voice and noise through correcting the phase of the voice and the noise through improving the phase estimation of the voice distortion under the low signal-to-noise ratio environment, performing filtering processing on the initial enhancement voice and the noise through a gammatone filter assembly which simulates the working mechanism of the artificial cochlea, performing analysis on the time frequency of the gammatone filter assembly to obtain the time frequency expression form consisting of time frequency units, using the hearing characteristics of the human ear to calculate binary mast containing noise in the time frequency domain, and using the mask value to obtain the enhanced voice after synthesis.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
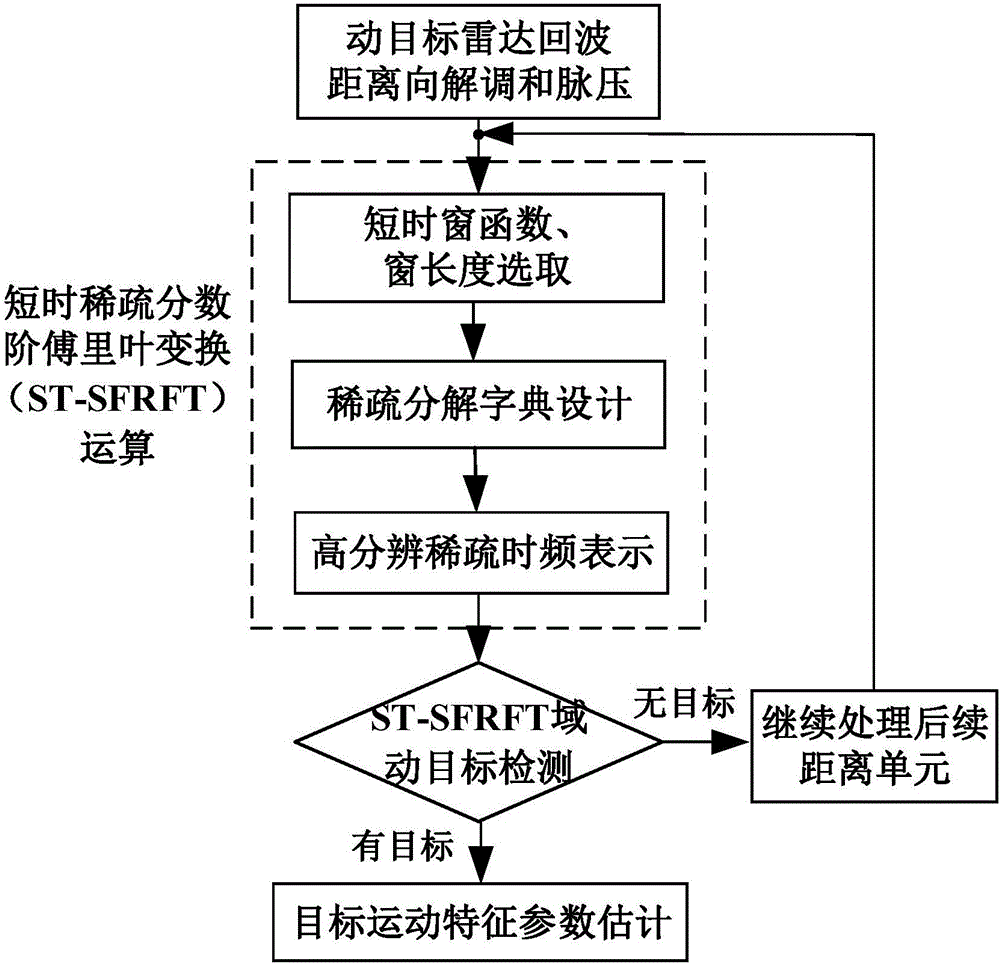
Radar moving target detection method based on short-time sparse fractional Fourier transform (ST-SFRFT)
ActiveCN106526568AImplement time-frequency representationGuaranteed energy concentrationRadio wave reradiation/reflectionDecompositionTarget signal
The invention relates to a radar moving target detection method based on short-time sparse fractional Fourier transform (ST-SFRFT), and belongs to the technical field of radar signal processing and detection. The method comprises the steps of: performing radar echo demodulation and pulse compression to realize high range resolution, and selecting a range unit to be detected; performing spare time-frequency analysis parameter initialization, comprising selection of a short-time window function and a window length and design of a sparse decomposition dictionary; performing ST-SFRFT operation for spare optimization solution, thus completing high-resolution spare time-frequency representation of moving target echo; traversing all range search units, performing moving target signal spare domain detection and estimating a target moving parameter. By adopting a high-resolution spare representation method, high-resolution and low-complexity time-frequency representation of time-varying signals is realized at the time frequency-spare domain; and the method is suitable for analyzing the time varying non-stability of signals, suppresses background clutter while improving energy concentration of moving target signals, and significantly improves the radar moving target detection and parameter estimation capability.
Owner:NAVAL AVIATION UNIV
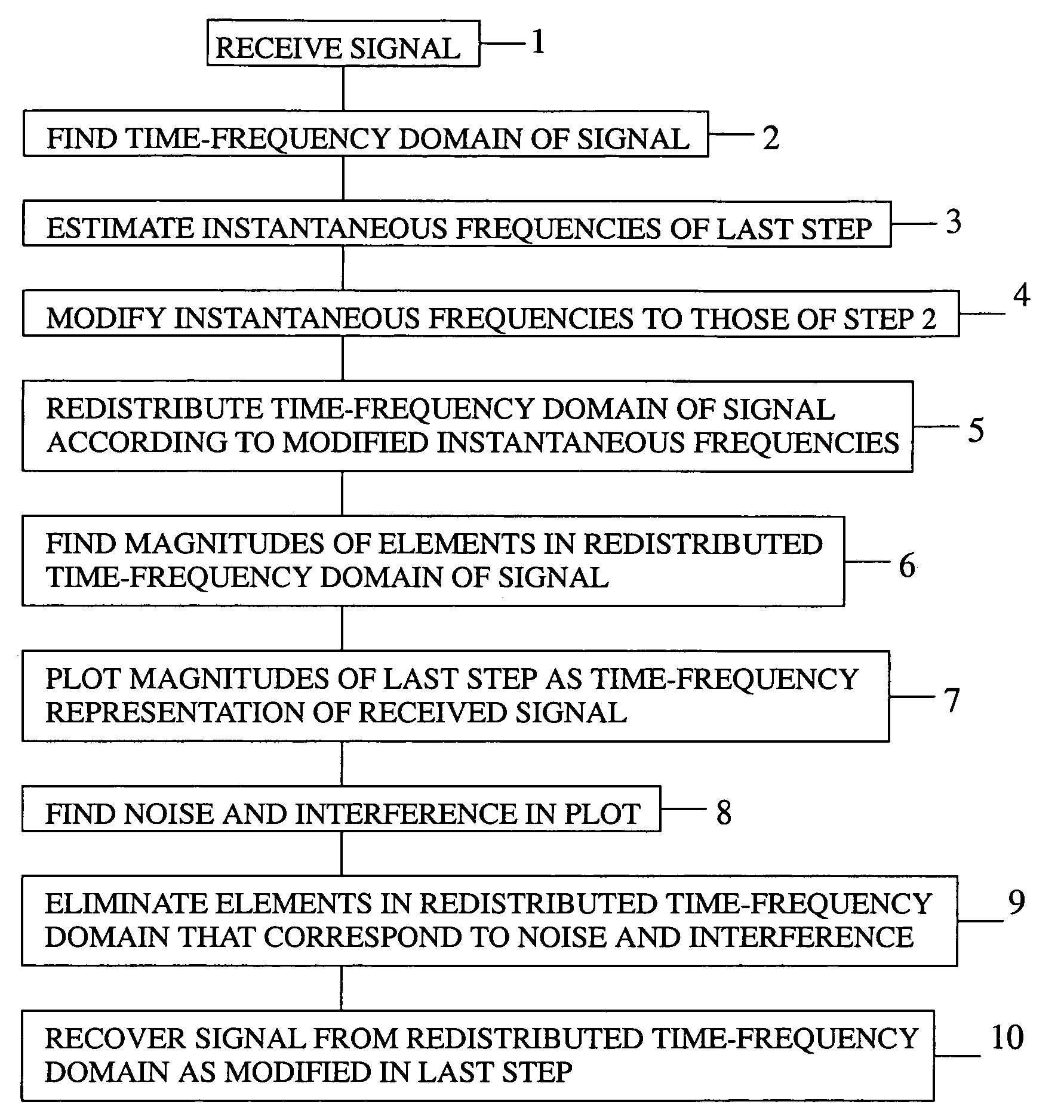
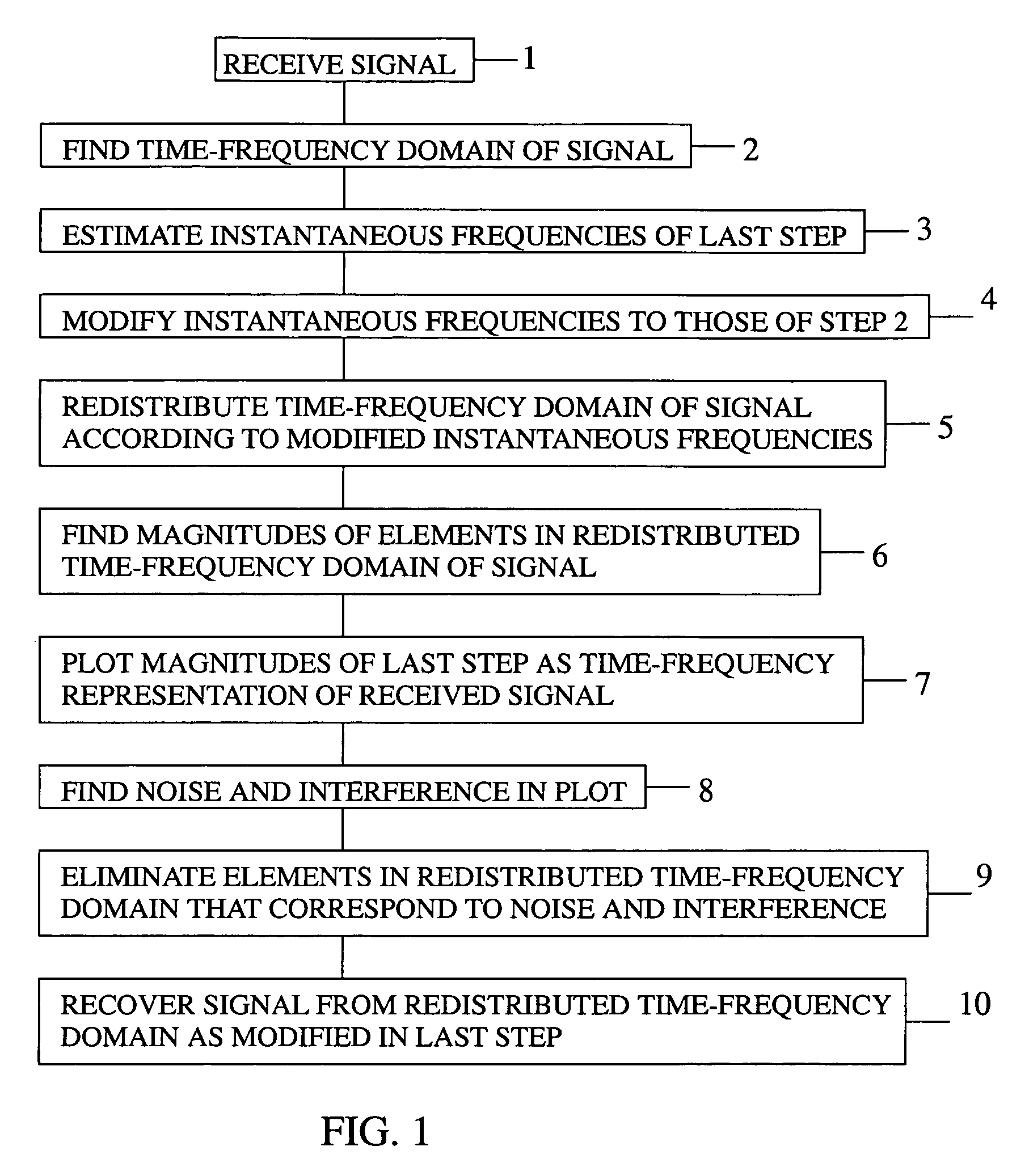
Method of removing noise and interference from signal
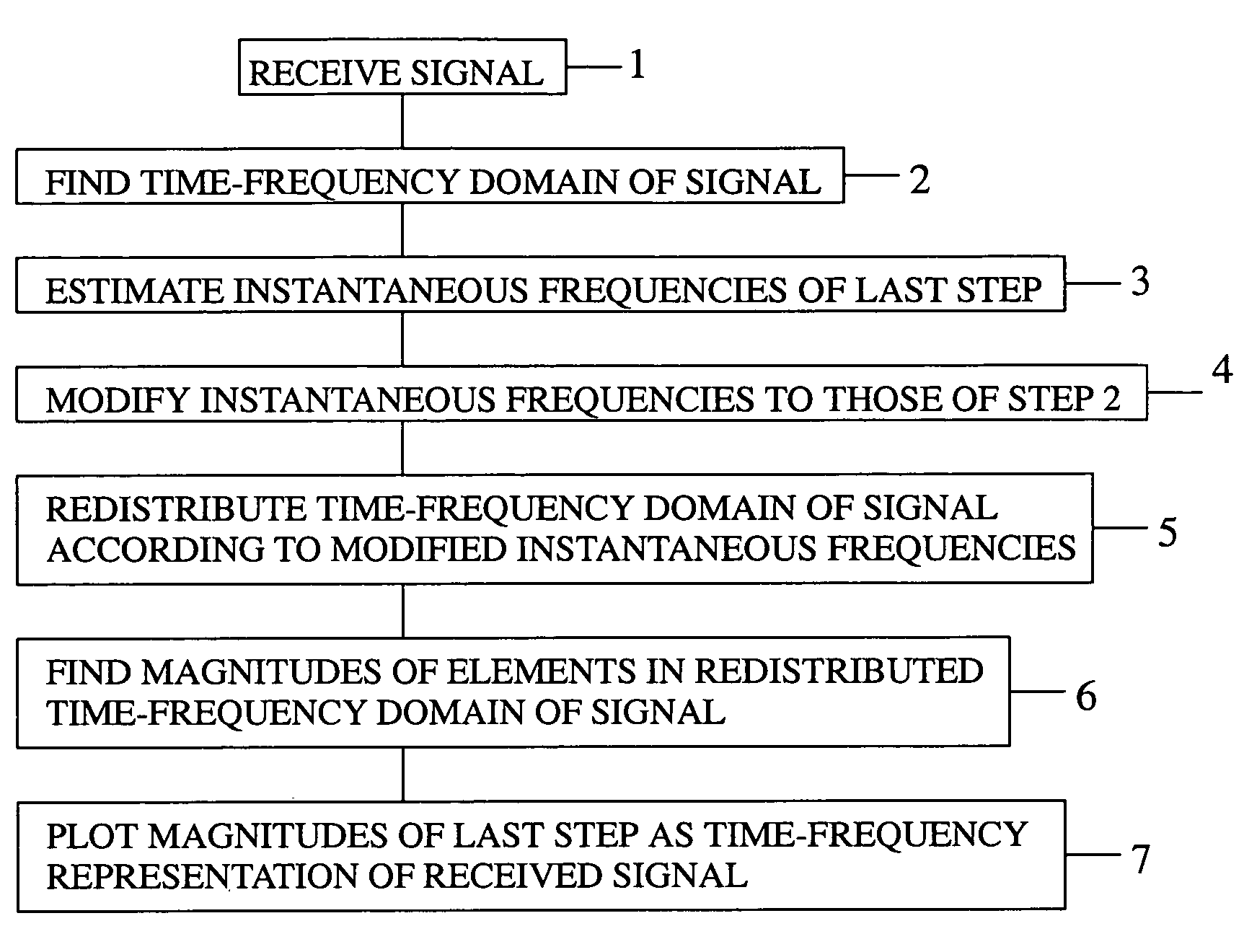
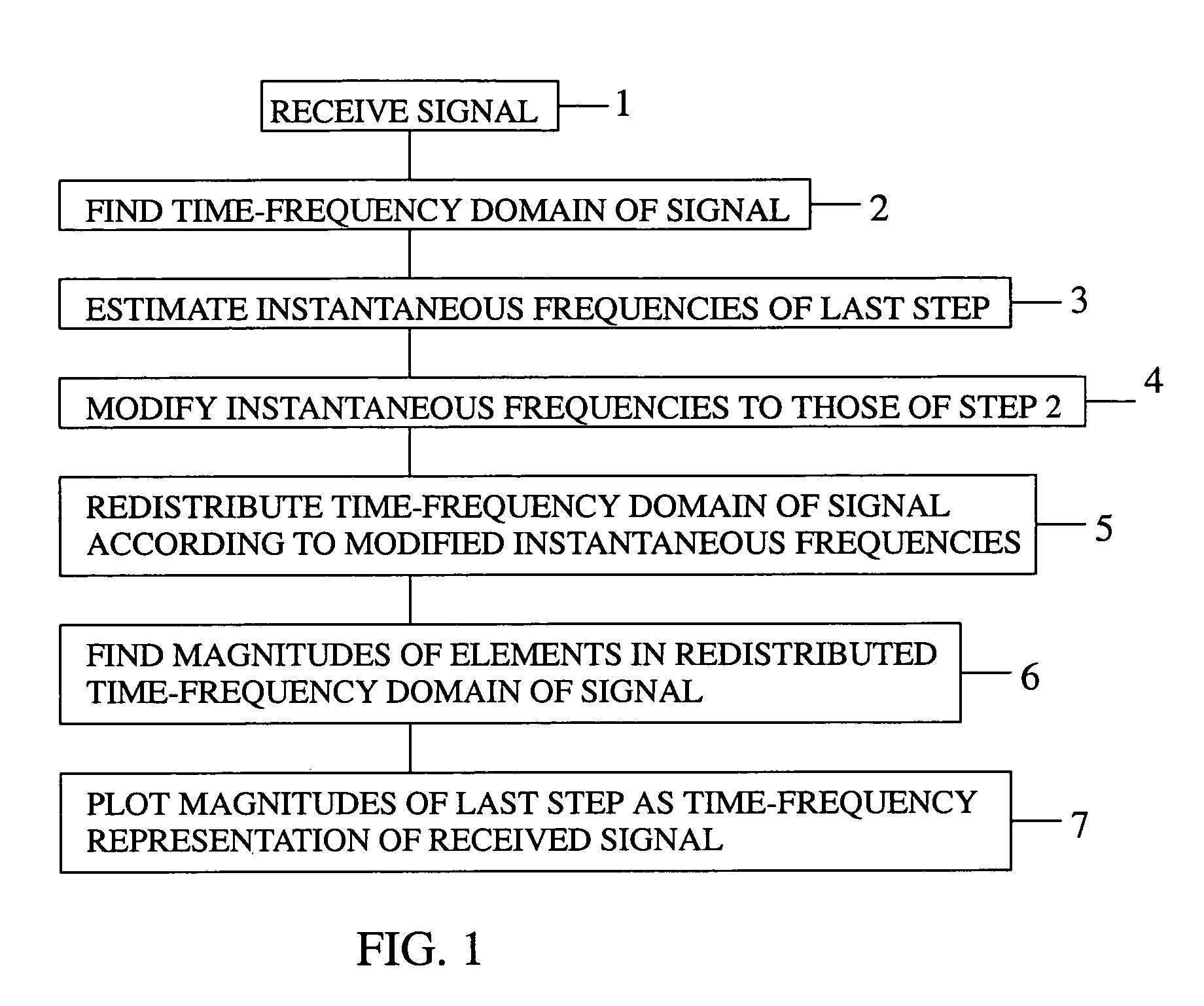
ActiveUS7676046B1Remove noiseEliminate interferenceError preventionBroadcast information characterisationTime–frequency representationElectrical and Electronics engineering
A method of removing noise and interference from a signal by receiving the signal, calculating a joint time-frequency domain of the signal, estimating instantaneous frequencies of the joint time-frequency domain, modifying each estimated instantaneous frequency, if necessary, to correspond to a frequency of the joint time-frequency domain to which it most closely compares, redistributing the elements within the joint time-frequency domain according to the estimated instantaneous frequencies as modified, computing a magnitude for each element in the joint time-frequency domain as redistributed, plotting the results as the time-frequency representation of the signal, identifying in the plot any noise and interference components in the received signal, eliminating from the redistributed joint time-frequency domain elements that correspond to noise and interference, and recovering a signal devoid of noise and interference from the modified redistributed joint time-frequency domain.
Owner:NATIONAL SECURITY AGENCY
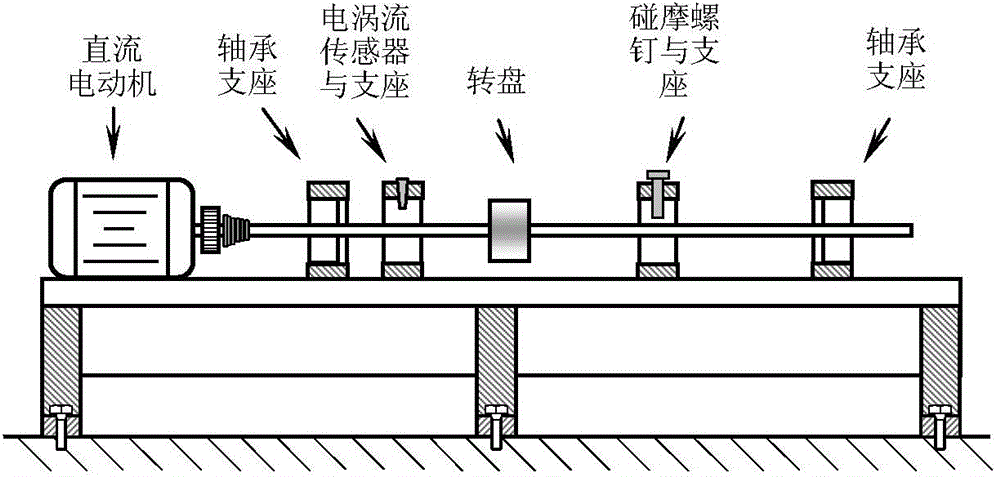
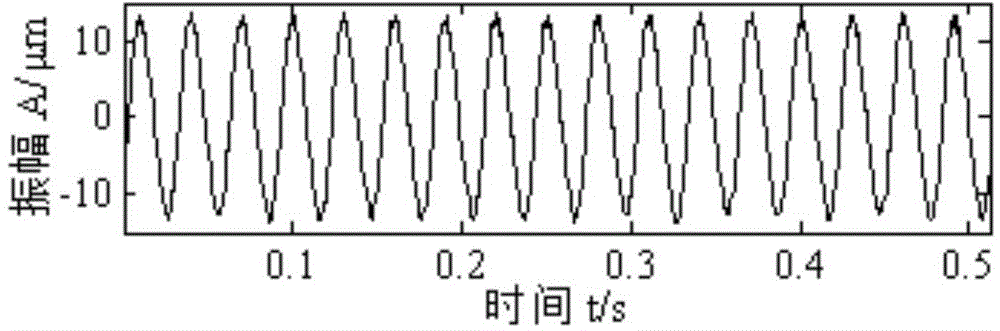
Rotor rub impact fault detection method based on nonlinear compression conversion and rotor rub impact fault detection system based on nonlinear compression conversion
ActiveCN104634526AApplicable to online health monitoringReliable resultsVibration measurement in solidsVibration testingFrequency spectrumEngineering
The invention discloses a rotor rub impact fault detection method based on nonlinear compression conversion and a rotor rub impact fault detection system based on nonlinear compression conversion, and the method and the system are used for detecting the rub impact fault of a rotor system in a rotating machine. The method comprises the following steps of performing nonlinear compression conversion on a vibration signal of the rotor system so as to obtain time-frequency representation of the vibration signal; calculating the instantaneous frequency of the vibration signal in combination with the time-frequency representation; further calculating the frequency spectrum of a vibration part of the instantaneous frequency; if fr is the rotating frequency of the rotor system, the maximal spectrum peak of the frequency spectrum is within a range of [0.99fr,1.01fr] and the amplitude value is greater than 2% of the rotating frequency, judging that the rotor system has a rub impact fault; otherwise, judging that the rotor system does not has a rub impact fault. The system is implemented on the basis of the method and is capable of facilitating application of the method. By virtue of the method and the system, whether the rub impact fault exists or not can be accurately judged, and the result is rapid and reliable; the method and the system are simple and easy and are applicable to online health monitoring of a rotor.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
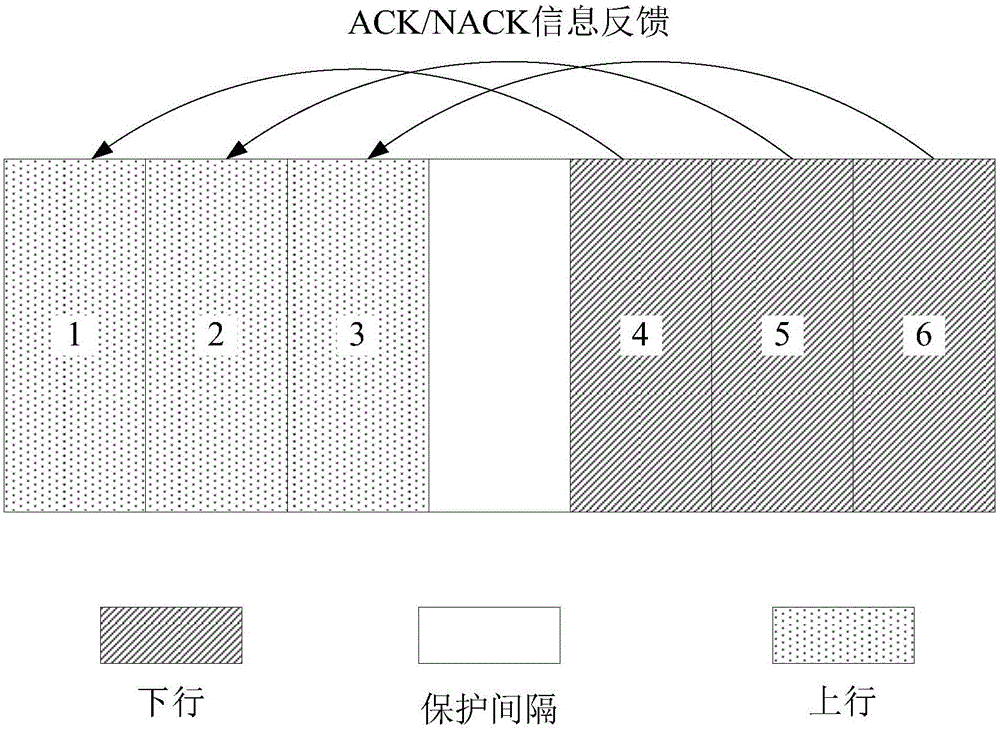
Information feedback method of uplink data and correlation equipment
InactiveCN106301700ASmall feedback delayLower latencyError prevention/detection by using return channelTransmission path multiple useTime delaysNetwork packet
An embodiment of the invention provides an information feedback method of uplink data. The method comprises the following steps of generating response feedback indication information corresponding to an uplink data packet, wherein the response feedback indication information is used for indicating a time frequency position aiming at ACK / NACK information feedback of the uplink data packet; according to the response feedback indication information, determining the time frequency position aiming at the ACK / NACK information feedback of the uplink data packet; and on the determined time frequency position, feeding back the ACK / NACK information aiming at the uplink data packet. Besides, the embodiment of the invention also provides a base station and the terminal. By using the information feedback method of the uplink data, time delay of the ACK / NACK information feedback of the uplink data can be effectively reduced.
Owner:YULONG COMPUTER TELECOMM SCI (SHENZHEN) CO LTD
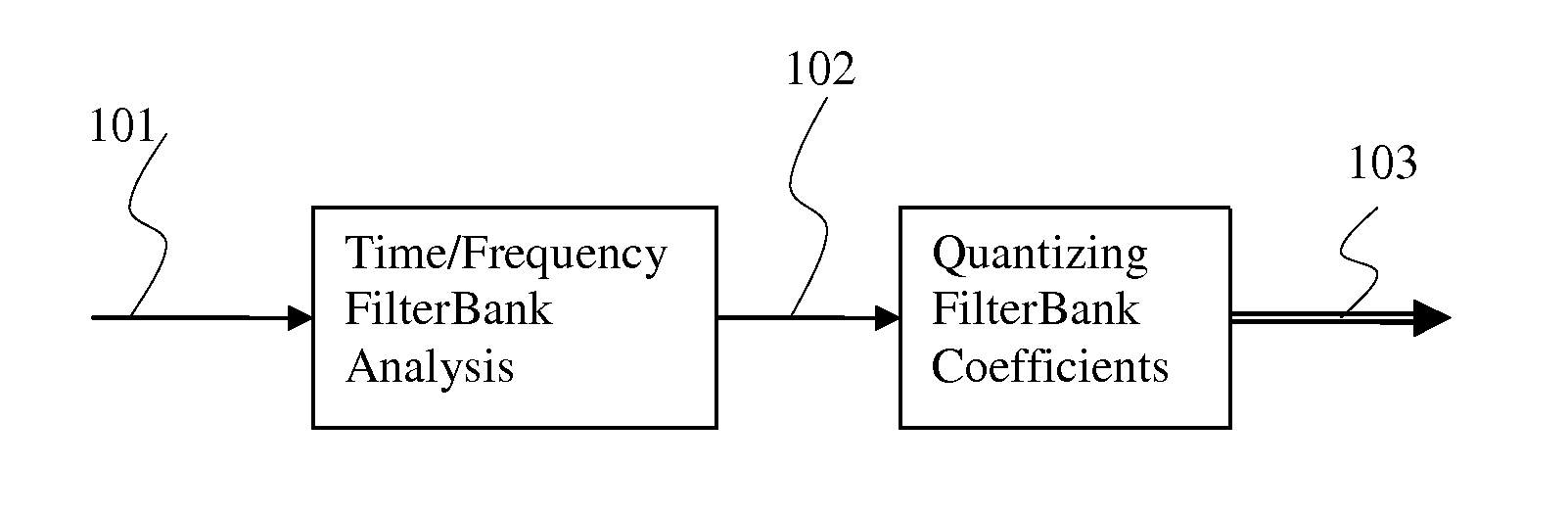
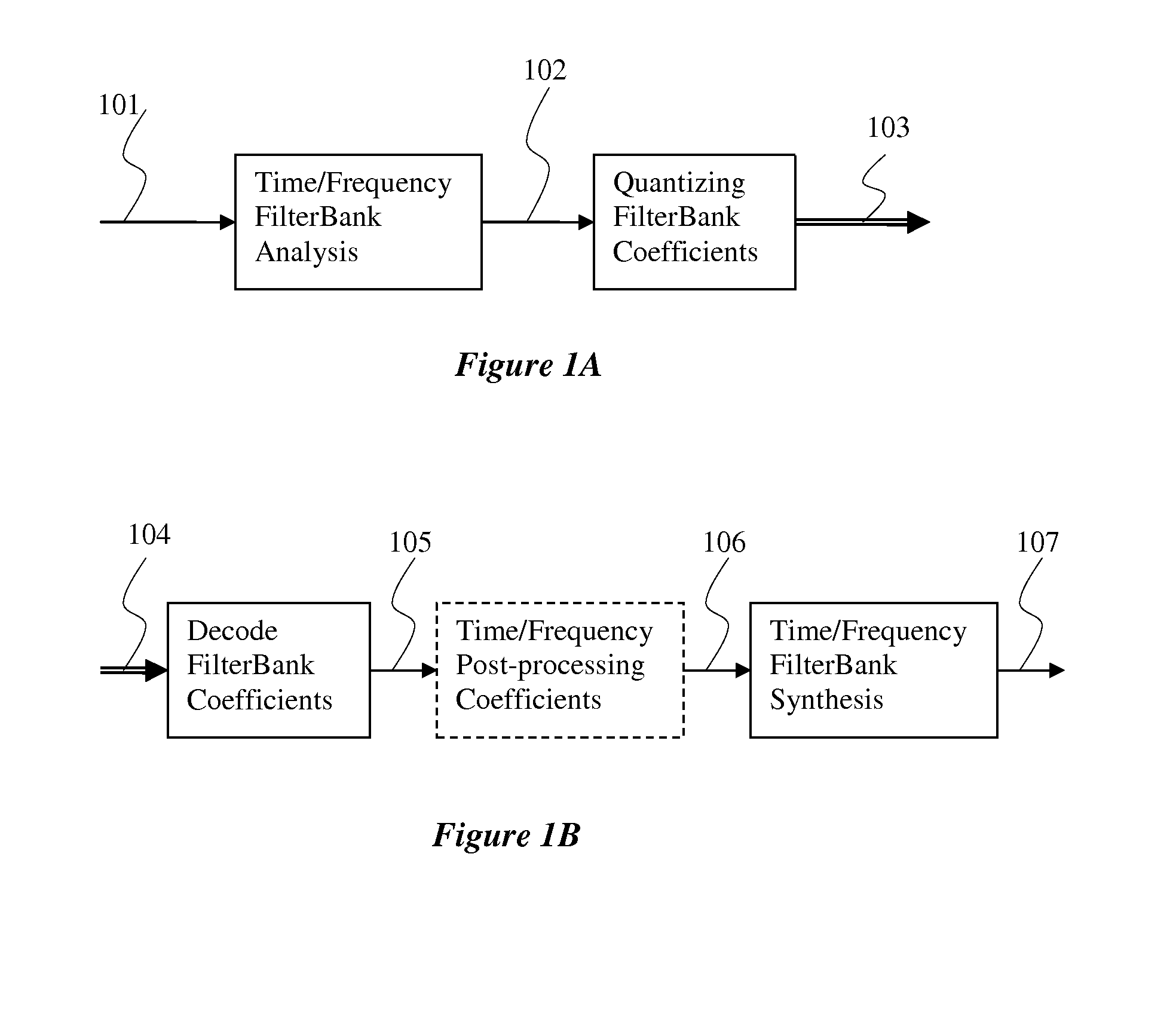
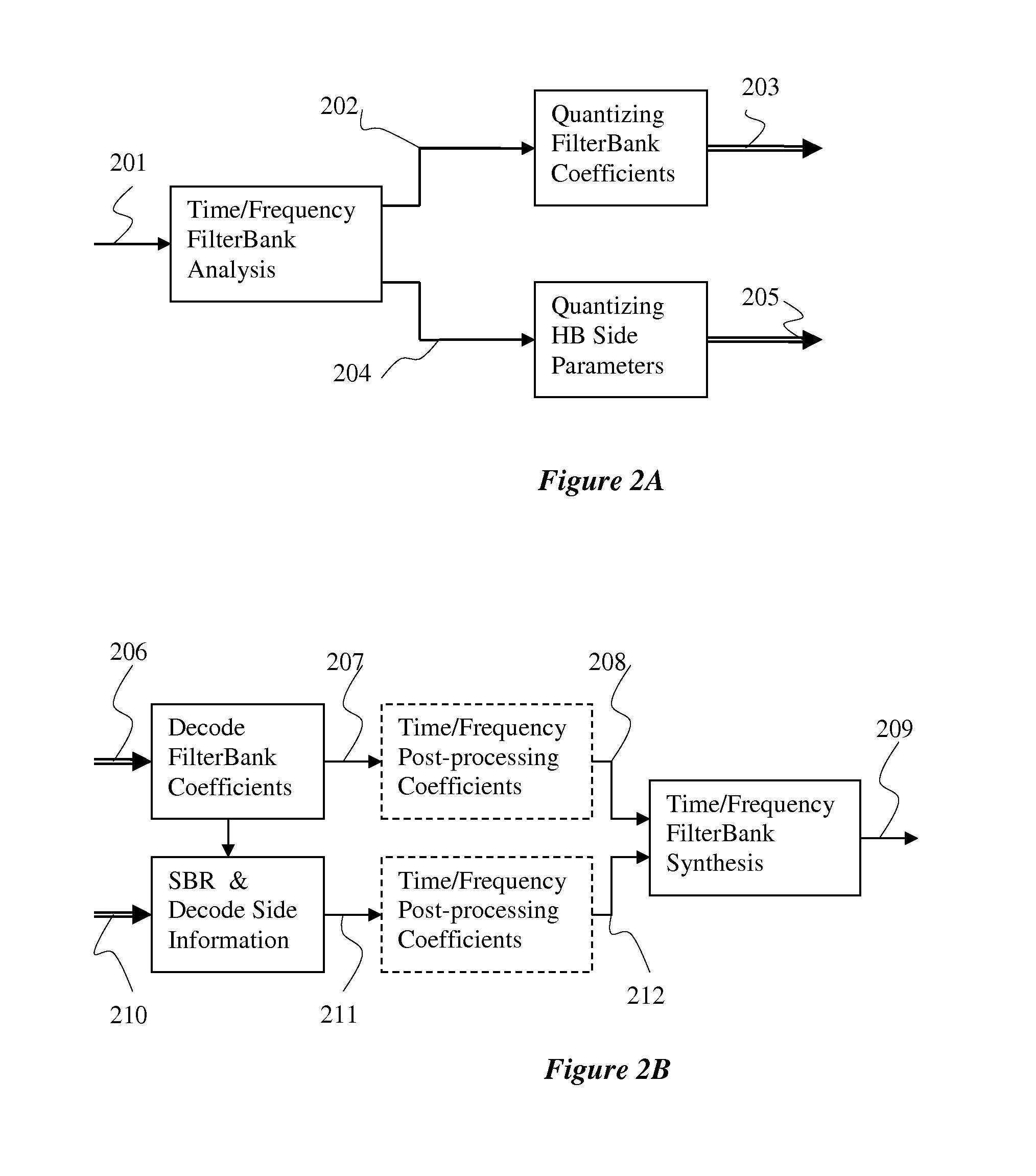
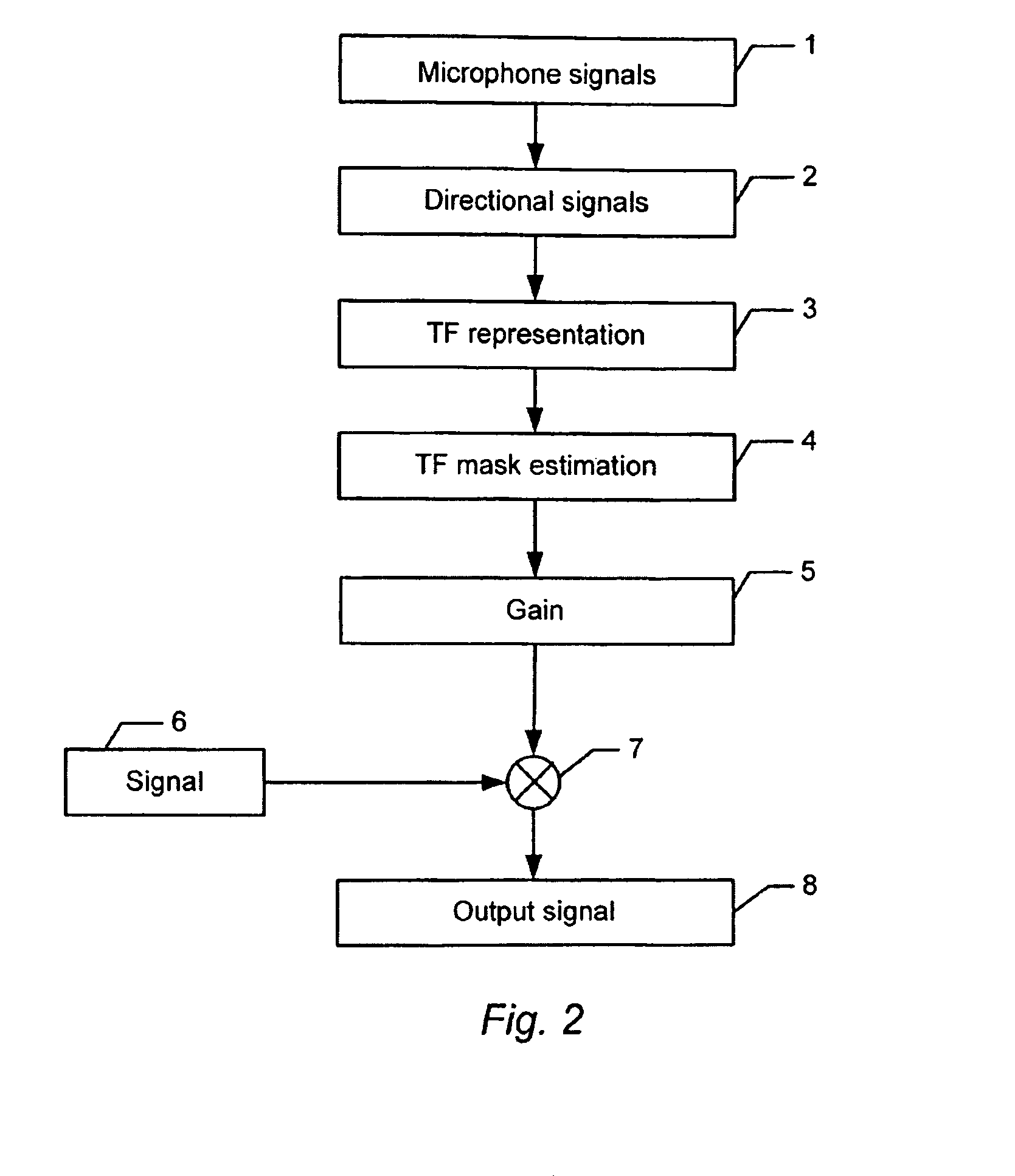
Time/Frequency Two Dimension Post-processing
In accordance with an embodiment, a time-frequency post-processing method of improving perceptual quality of a decoded audio signal, the method includes determining a time-frequency representation (such as filter bank analysis and synthesis) of an audio signal, estimating a time-frequency energy distribution of an audio signal from a time-frequency filter bank, computing a modification gain for each time-frequency representation point to have a modified time-frequency representation, and outputting audio signal from a modified time-frequency representation.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Time/frequency two dimension post-processing
In accordance with an embodiment, a time-frequency post-processing method of improving perceptual quality of a decoded audio signal, the method includes determining a time-frequency representation (such as filter bank analysis and synthesis) of an audio signal, estimating a time-frequency energy distribution of an audio signal from a time-frequency filter bank, computing a modification gain for each time-frequency representation point to have a modified time-frequency representation, and outputting audio signal from a modified time-frequency representation.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
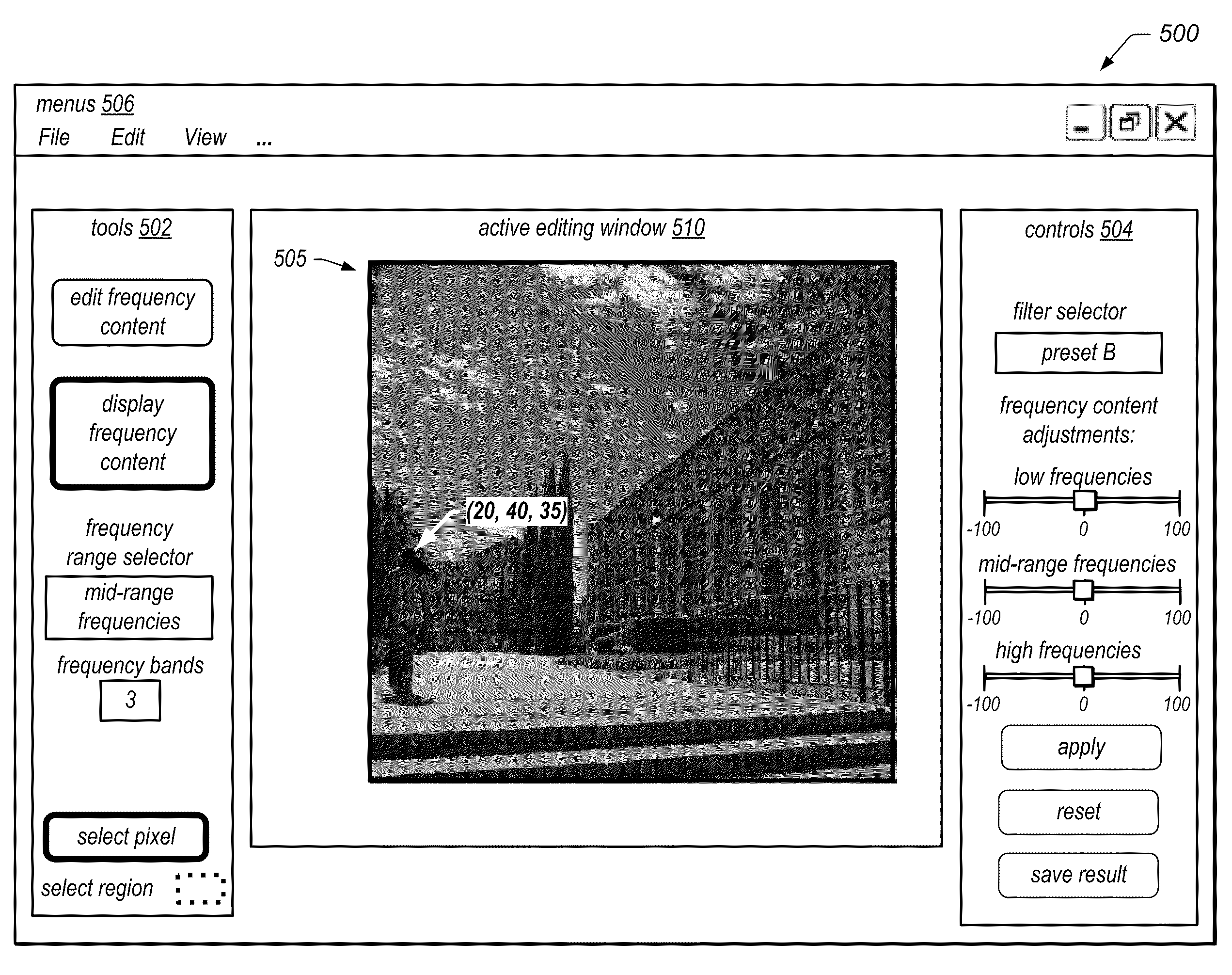
System and Method for Editing Frequency Content of Images
ActiveUS20130121614A1Improve accuracyLimit its operationImage enhancementCharacter and pattern recognitionTime–frequency representationMultiple frequency
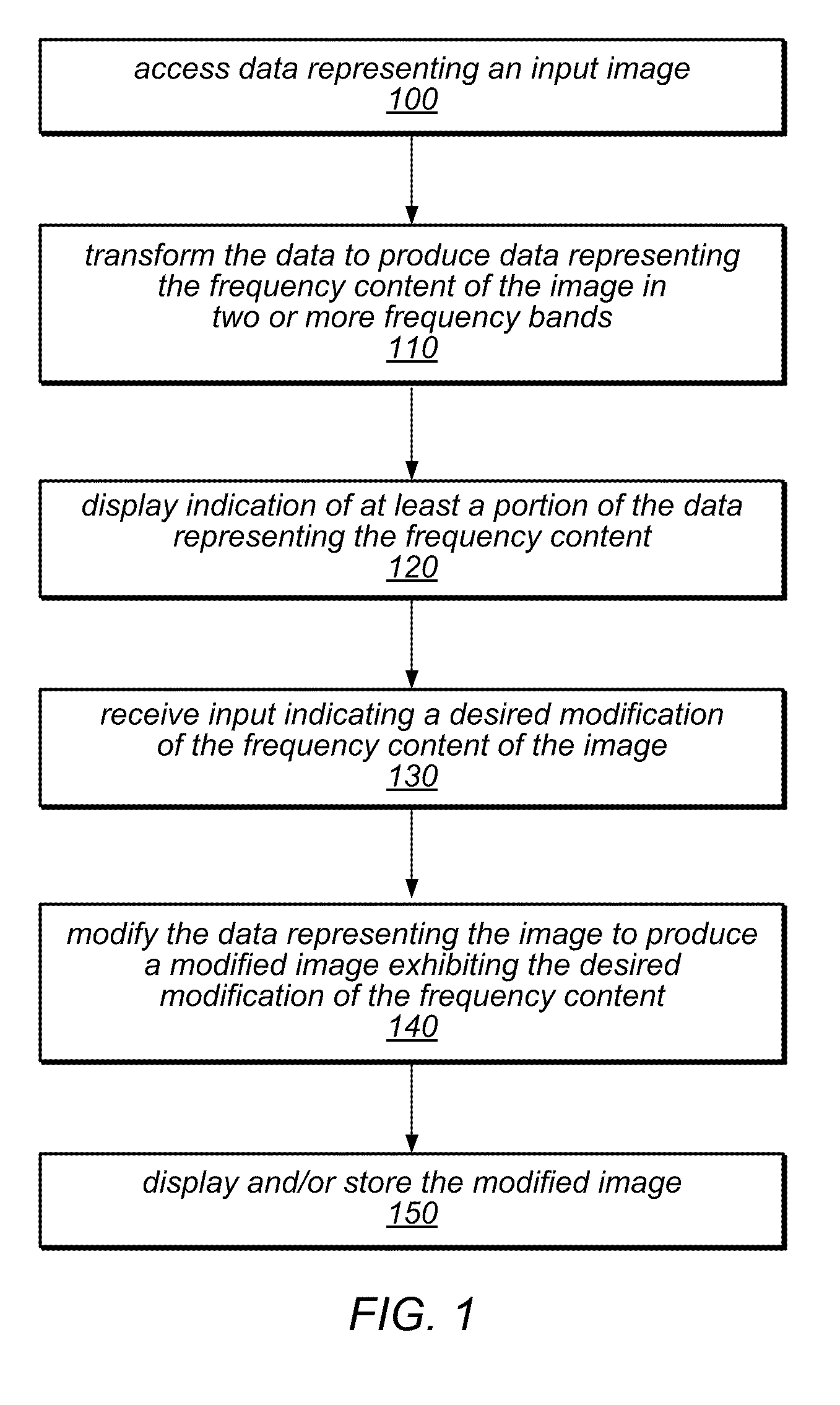
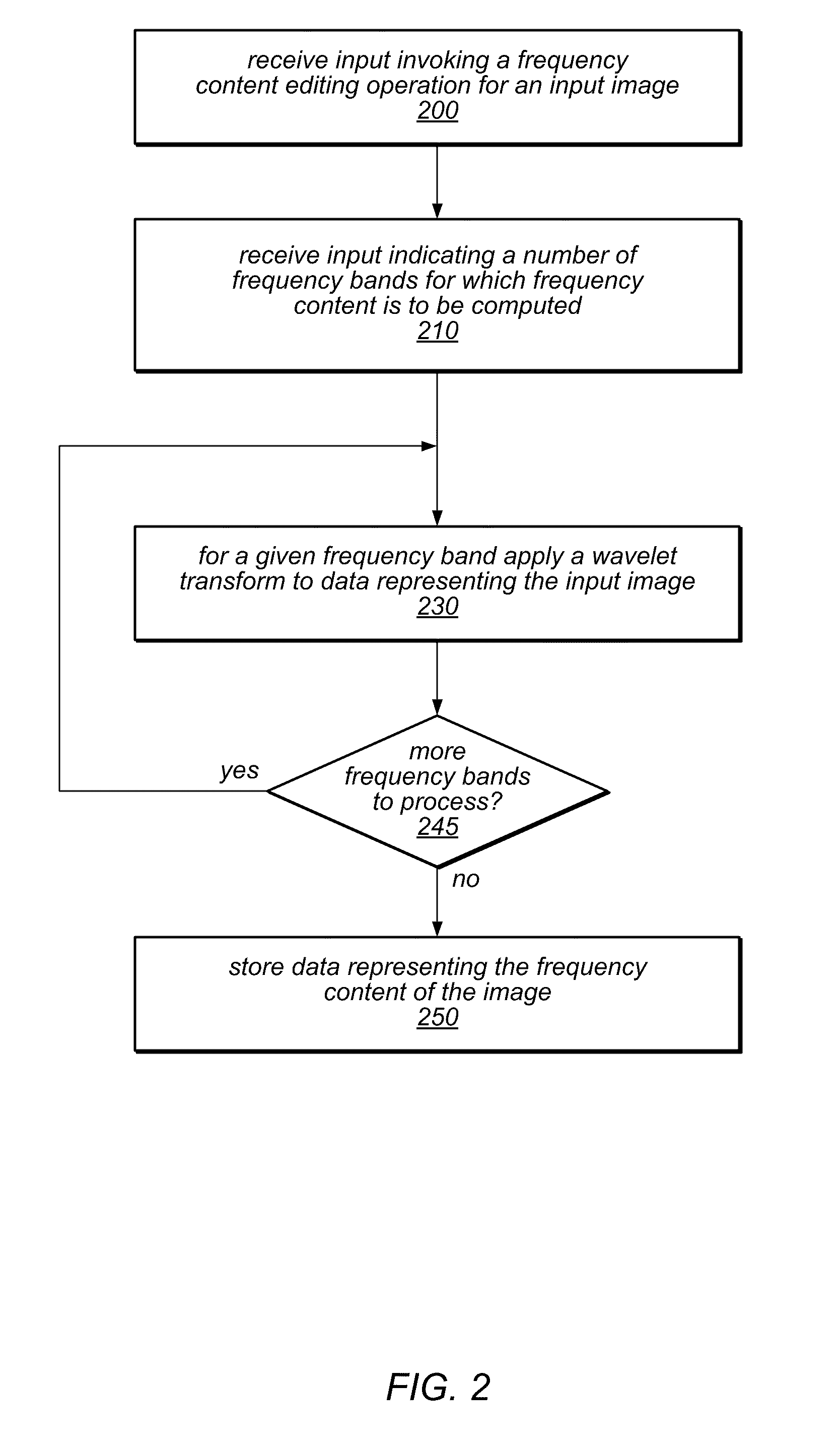
Systems, methods, and computer-readable storage media for editing the frequency content of an image may provide an intuitive interface for examining and / or modifying the frequency content. The methods may include accessing image data, performing a wavelet transform of the image data (or another MRA technique) to produce a time-frequency representation (TFR) of the image representing frequency content in multiple frequency bands, and displaying an indication of the frequency content of the image by displaying a sub-image of the TFR or numerical data representing the frequency content at selected pixels. In response to receiving input specifying a desired frequency content modification, the methods may include performing a Fourier transform of the image data to produce frequency content data, modifying the frequency content data, and performing an inverse transformation of the modified data to produce modified image data. The modification may be applied globally or to a selected portion of the image.
Owner:ADOBE INC
Method of generating time-frequency signal representation preserving phase information
A method of generating a time-frequency representation of a signal that preserves phase information by receiving the signal, calculating a joint time-frequency domain of the signal, estimating instantaneous frequencies of the joint time-frequency domain, modifying each estimated instantaneous frequency, if necessary, to correspond to a frequency of the joint time-frequency domain to which it most closely compares, redistributing the elements within the joint time-frequency domain according to the estimated instantaneous frequencies as modified, computing a magnitude for each element in the joint time-frequency domain as redistributed, and plotting the results as the time-frequency representation of the signal.
Owner:NATIONAL SECURITY AGENCY
Audio encoder, audio decoder, encoded audio information, methods for encoding and decoding an audio signal and computer program
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
Synchronous extrusion and transformation-based earthquake weighting average instantaneous frequency extracting method
InactiveCN106291700AClearly portrayedClear featuresSeismic signal processingTime–frequency representationNoise suppression
The invention discloses a synchronous extrusion and transformation-based earthquake weighting average instantaneous frequency extracting method. On the basis of three-parameter wavelet transformation, energy rearrangement is conducted by evaluating a rearrangement rule (instantaneous frequency) to obtain more accurate and sparser time frequency representation, so that an effective signal energy distribution space is determined accurately; on this basis, threshold de-noising is introduced to perform noise suppression; finally a method for evaluating noise-containing signal weighing instantaneous frequency is provided. The calculation result of the method has high noise-resistant performance and precision by calculating the instantaneous frequency of noise-free and noise-containing synthetic seismic record and comparing the noise-resistant performance of different methods; when the method is applied to actual data, the characteristic of a reservoir stratum can be clearly described.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Dispersion extraction for acoustic data using time frequency analysis
This invention pertains to the extraction of the slowness dispersion characteristics of acoustic waves received by an array of two or more sensors by the application of a continuous wavelet transform on the received array waveforms (data). This produces a time-frequency map of the data for each sensor that facilitates the separation of the propagating components thereon. Two different methods are described to achieve the dispersion extraction by exploiting the time frequency localization of the propagating mode and the continuity of the dispersion curve as a function of frequency. The first method uses some features on the modulus map such as the peak to determine the time locus of the energy of each mode as a function of frequency. The second method uses a new modified Radon transform applied to the coefficients of the time frequency representation of the waveform traces received by the aforementioned sensors. Both methods are appropriate for automated extraction of the dispersion estimates from the data without the need for expert user input or supervision.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Multi-microphone method for estimation of target and noise spectral variances
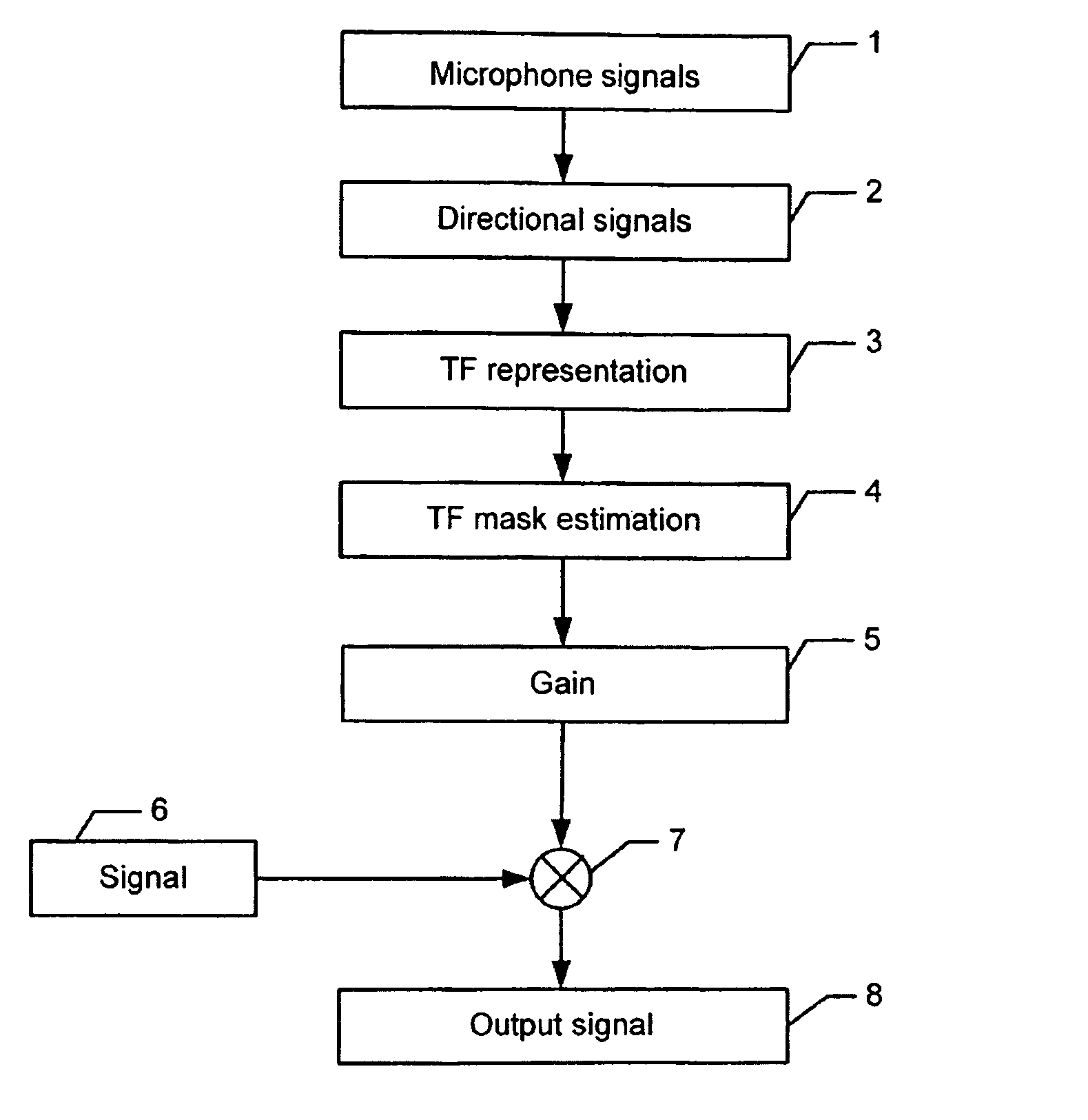
InactiveCN104902418AImprove intelligibilitySpeech analysisMicrophones signal combinationTarget signalTime–frequency representation
The application relates to an audio processing system and a method of processing a noisy (e.g. reverberant) signal comprising first (v) and optionally second (w) noise signal components and a target signal component (x), the method comprising a) Providing or receiving a time-frequency representation Y i (k,m) of a noisy audio signal y i at an i th input unit, i=1, 2, ..., M, where M‰¥2; b) Providing (e.g. predefined spatial) characteristics of said target signal component and said noise signal component(s); and c) Estimating spectral variances or scaled versions thereof » v, »x of said first noise signal component v (representing reverberation) and said target signal component x, respectively, said estimates of »v and »x being jointly optimal in maximum likelihood sense, based on the statistical assumptions that a) the time-frequency representations Y i (k,m), X i (k,m), and V i (k,m) (and W i (k,m) ) of respective signals y i (n), and signal components x i , and v i (and w i ) are zero-mean, complex-valued Gaussian distributed, b) that each of them are statistically independent across time m and frequency k, and c) that X i (k,m) and V i (k,m) (and W i (k,m)) are uncorrelated. An advantage of the invention is that it provides the basis for an improved intelligibility of an input speech signal. The invention may e.g. be used for hearing assistance devices, e.g. hearing aids.
Owner:OTICON
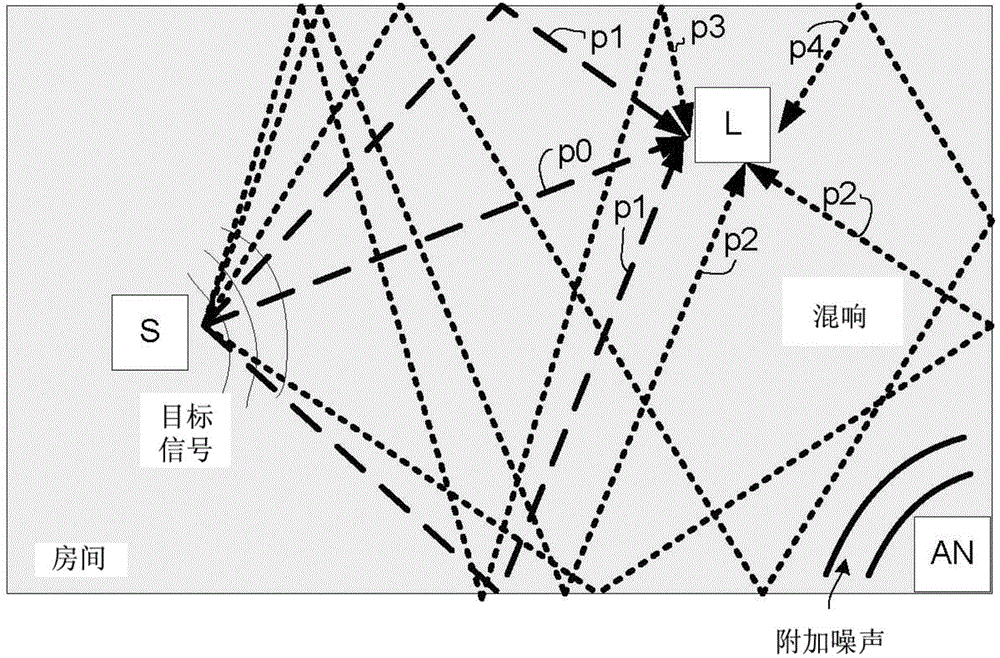
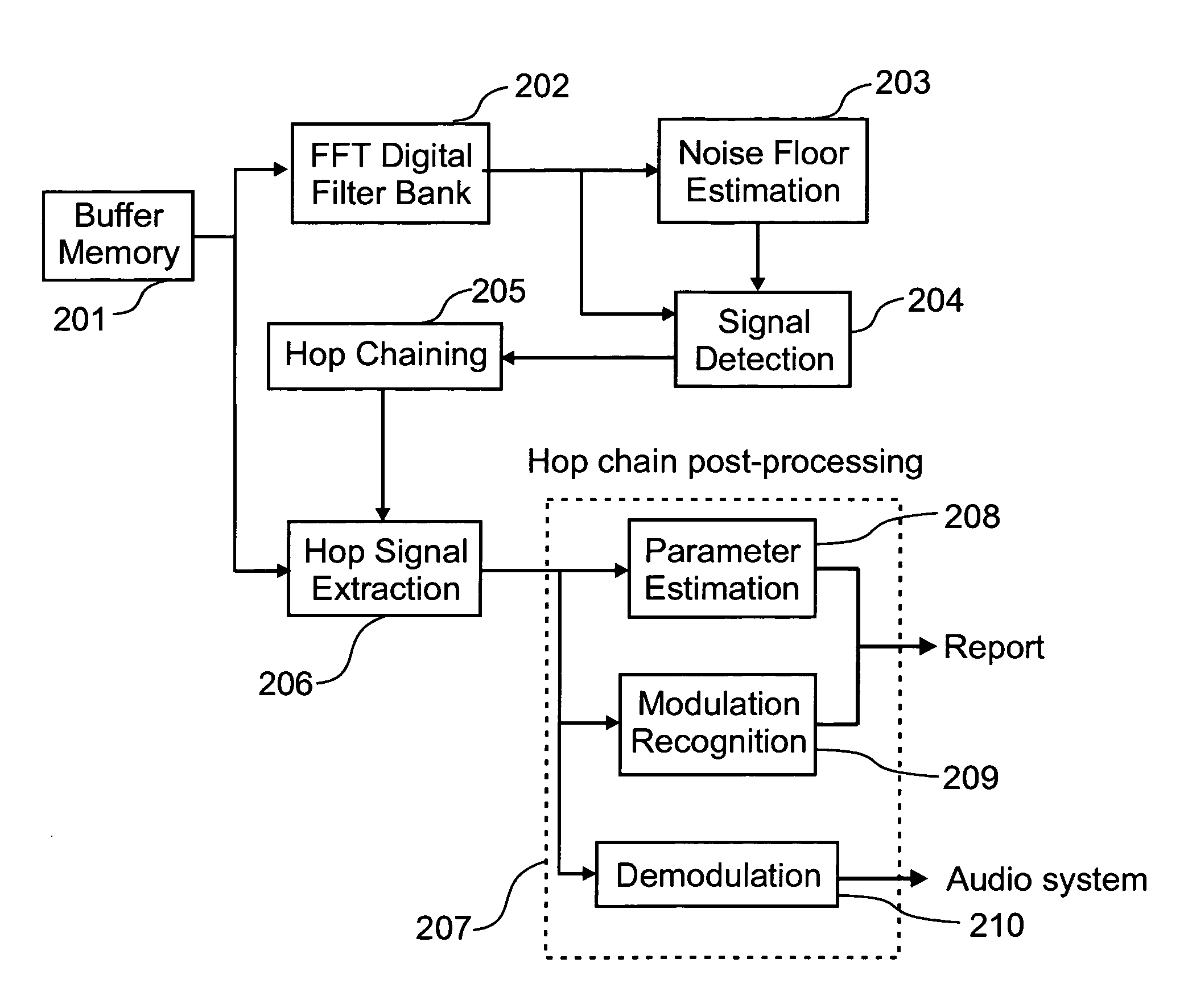
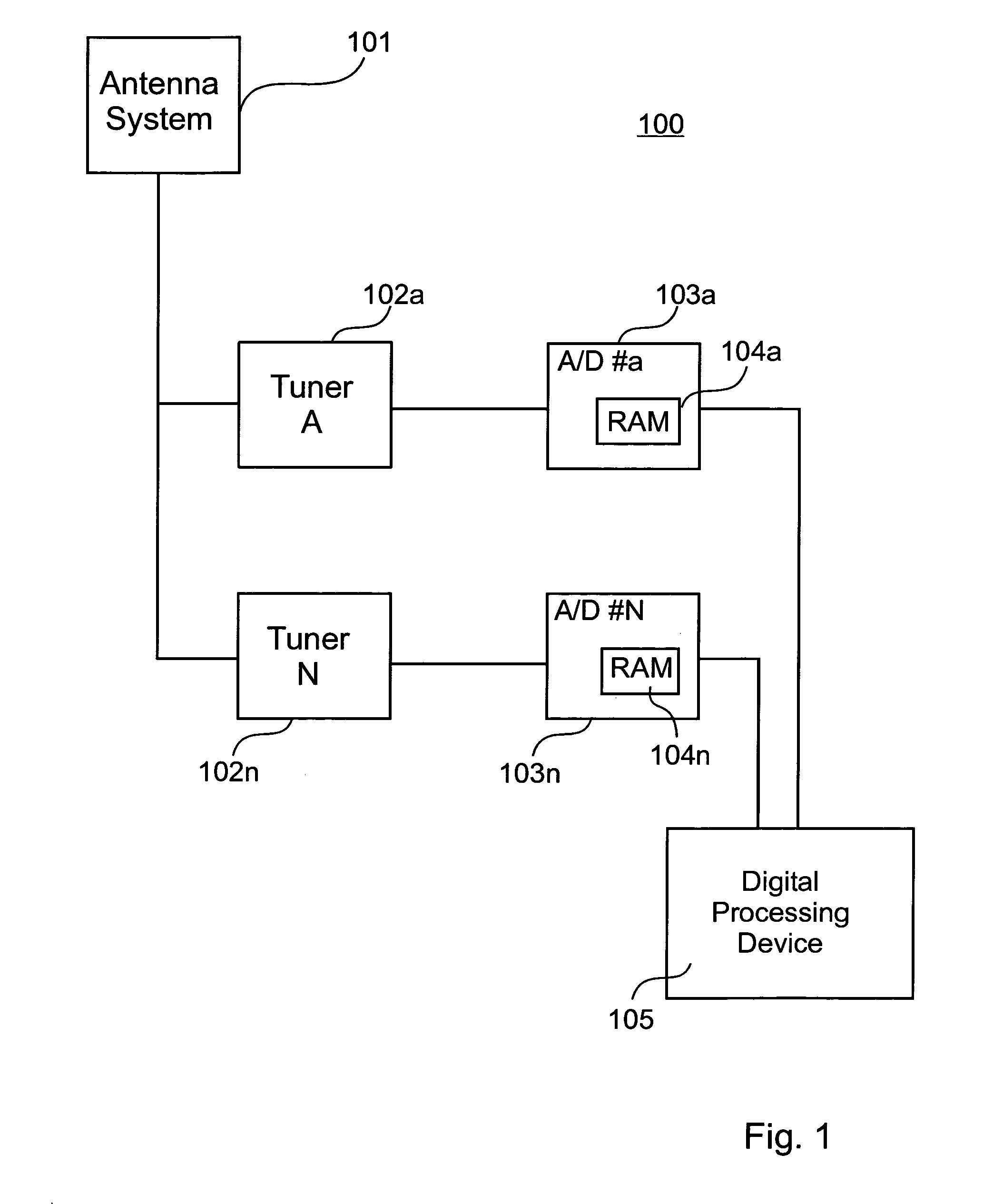
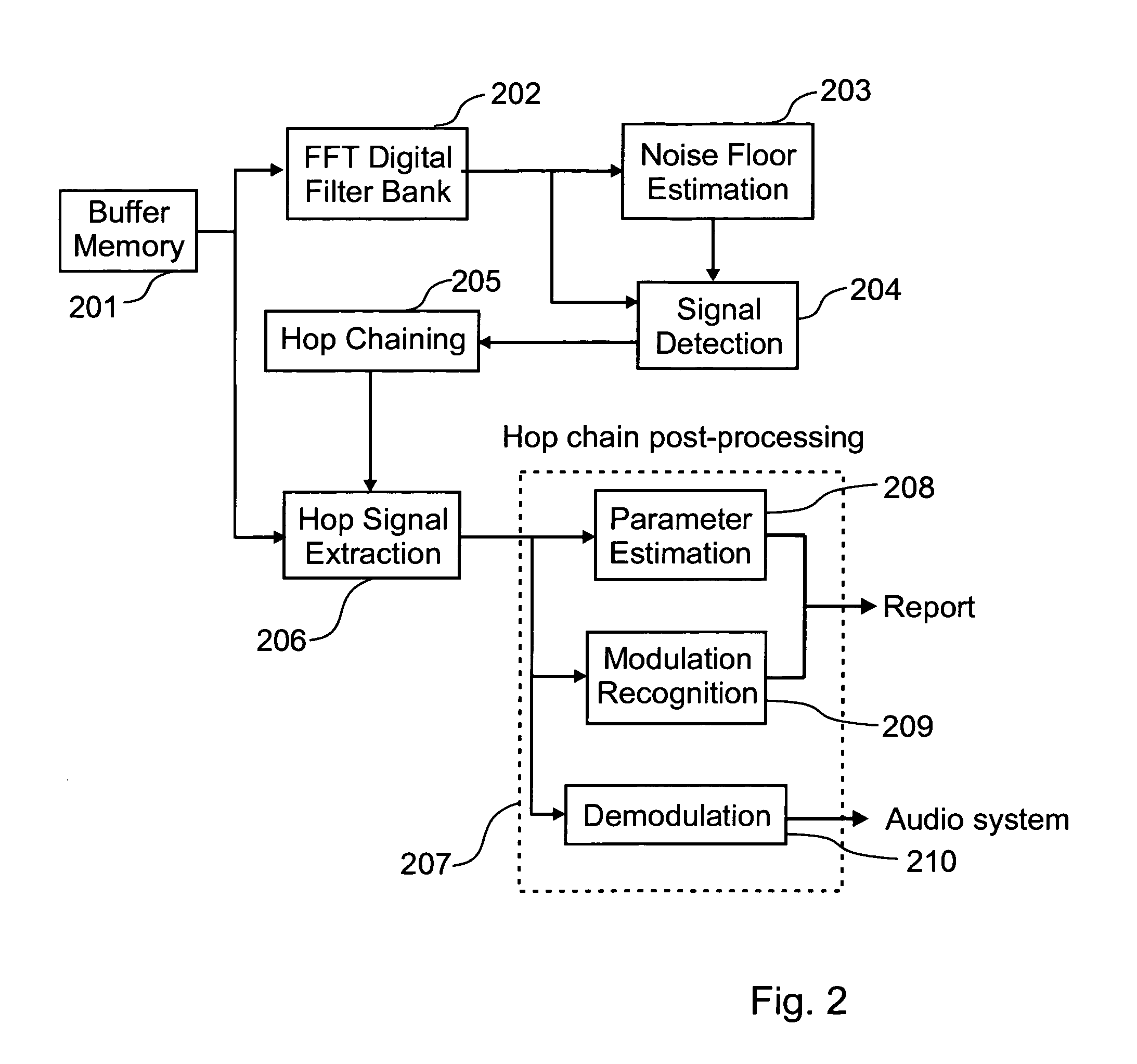
Automatic signal extraction and analysis from time-frequency representation
The problem of operationally analyzing spread spectrum frequency-hopping transmissions has been known since the invention of frequency-hopping radios. A frequency-hopping radio transmits a communication using small signal segments of data making up the transmission in accordance to a set of predetermined parameters. In this type of transmission each small segment of data is transmitted at a different frequency, one after another, until the transmission is completed. In some cases, it may be desirable to analyze these radio transmissions and to be able to determine radio spectrum usage and provide a mean to report on interference in frequency bands where multiple types of transmissions are possible. A novel method of isolating multiple transmission signals that are transmitted using frequency-hopping and apparatus is thus proposed which receives at least a transmission and performs operations within frequency bands of the received transmission in order to monitor and characterize signal energy therein.
Owner:HER MAJESTY THE QUEEN & RIGHT OF CANADA REPRESENTED BY THE MIN OF IND
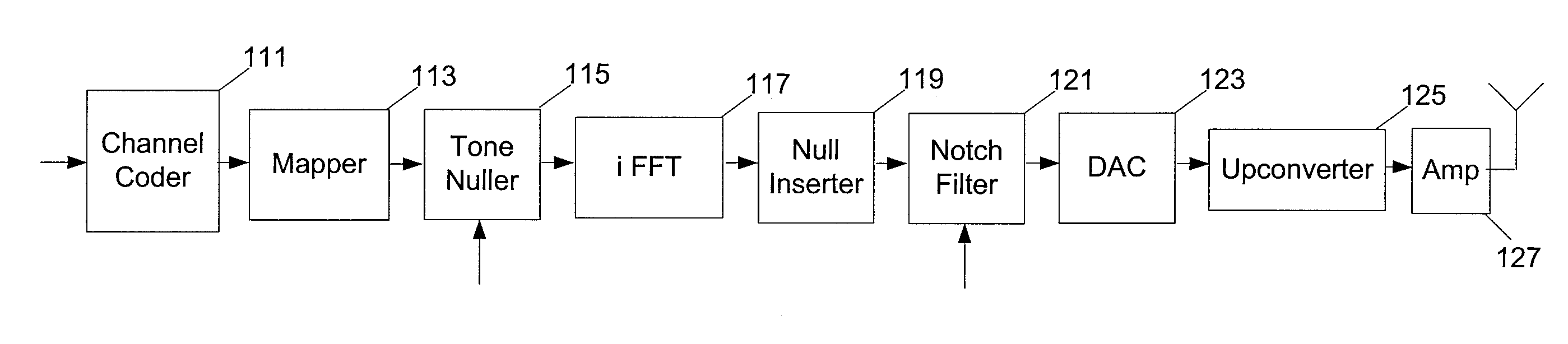
Notch filtering for OFDM system with null postfix
ActiveUS20080056395A1Reduce communicationTransmission path divisionCriteria allocationTime domainFrequency spectrum
Transmission systems and methods for reducing interference by wideband communication systems with narrowband communications systems are disclosed. In some embodiments an ultrawideband system employing orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) with a null post-fix nulls symbols for sub-carriers at potentially interfering frequencies prior to transformation to the time domain and filters a time domain representation using a notch filter to further reduce spectral components at the potentially interfering frequencies. In further embodiments pre-emphasis is applied to a frequency domain representation of symbols to reduce ripples introduced by the notch filter.
Owner:REALTEK SEMICON CORP +1
Seismic data attenuation compensation method in synchronous extrusion transform domain
ActiveCN107390267ACompensation for degradationCompensation stabilizationSeismic signal processingUltrasound attenuationImage resolution
The invention discloses a seismic data attenuation compensation method in a synchronous extrusion transform domain. In the synchronous extrusion transform domain, the attenuation compensation process is represented as an inverse problem with L1 norm regularization, solving is carried out through an iterative re-weighting algorithm, and thus, stabilized attenuation compensation is realized. Synchronous extrusion transform can suppress diffusion of time frequency energy, a more sparse and highly-localized time frequency representation is obtained, and thus, attenuation compensation on nonstationary seismic signals is facilitated. The method uses the sparse properties of signals in the synchronous extrusion transform domain, the L1 norm regularization method is introduced to stabilize the attenuation compensation process, and a noise amplification problem is thus avoided. The disclosed method is used to realize compensation on seismic attenuation effects, the seismic data resolution can be enhanced, and convenience is brought to subsequent seismic inversion and reservoir description.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Listening device providing enhanced localization cues, its use and a method
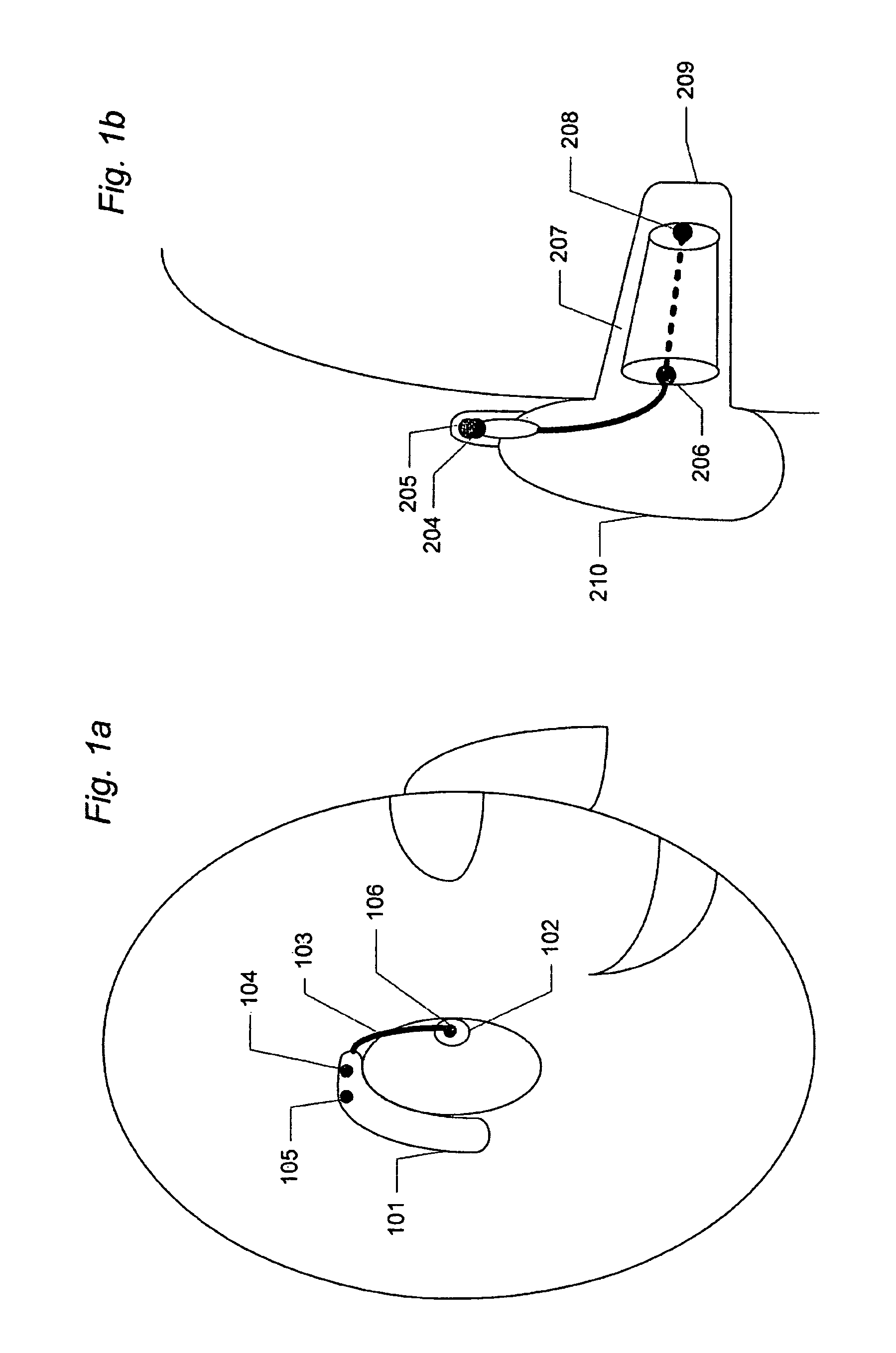
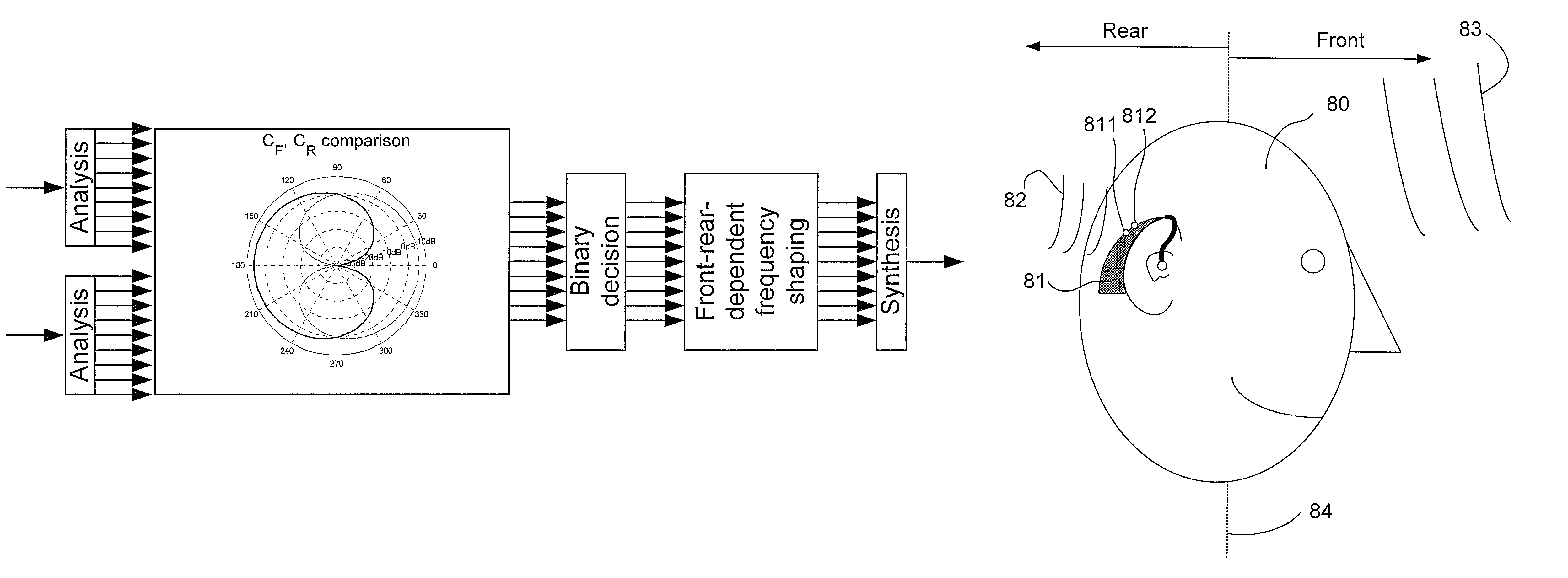
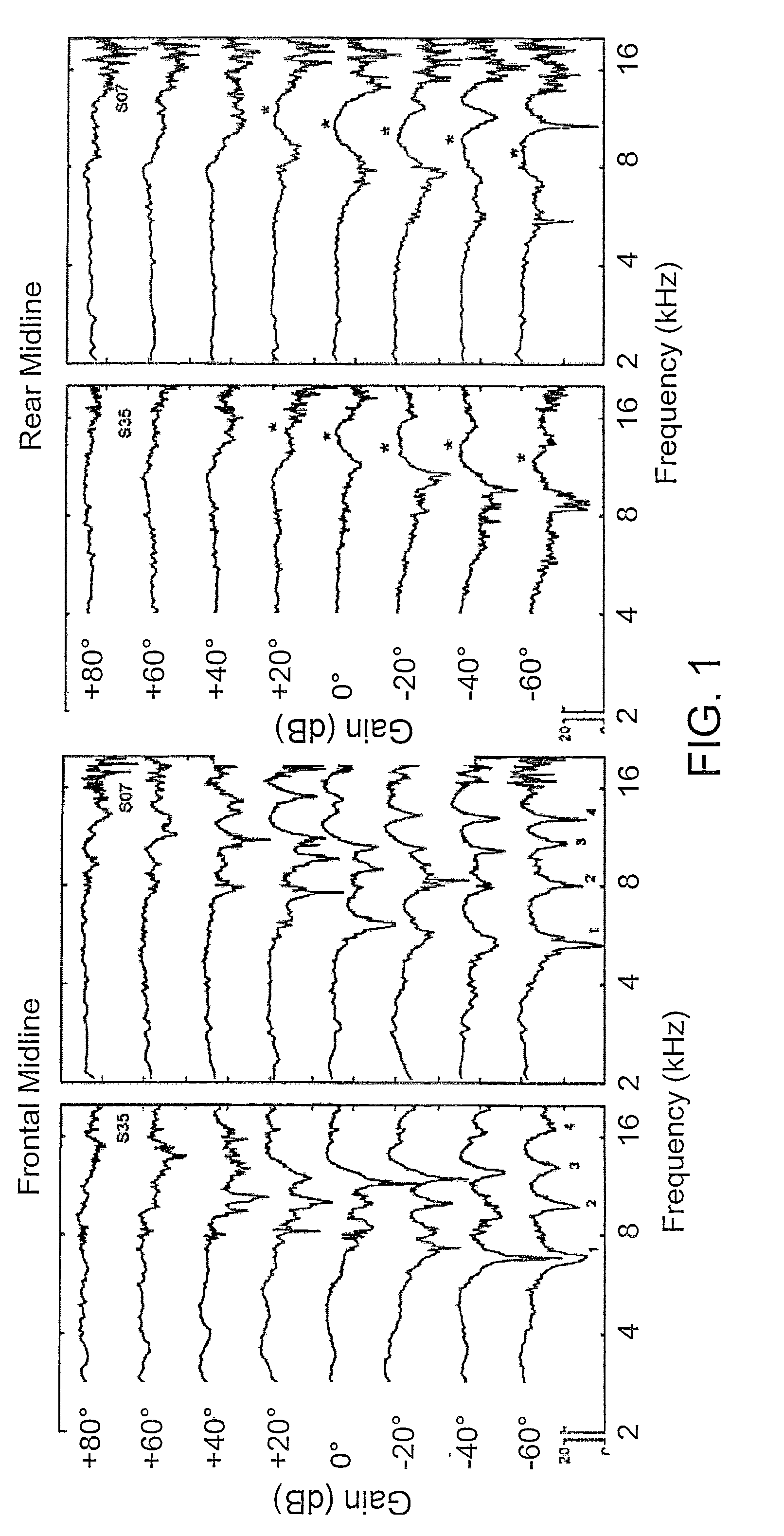
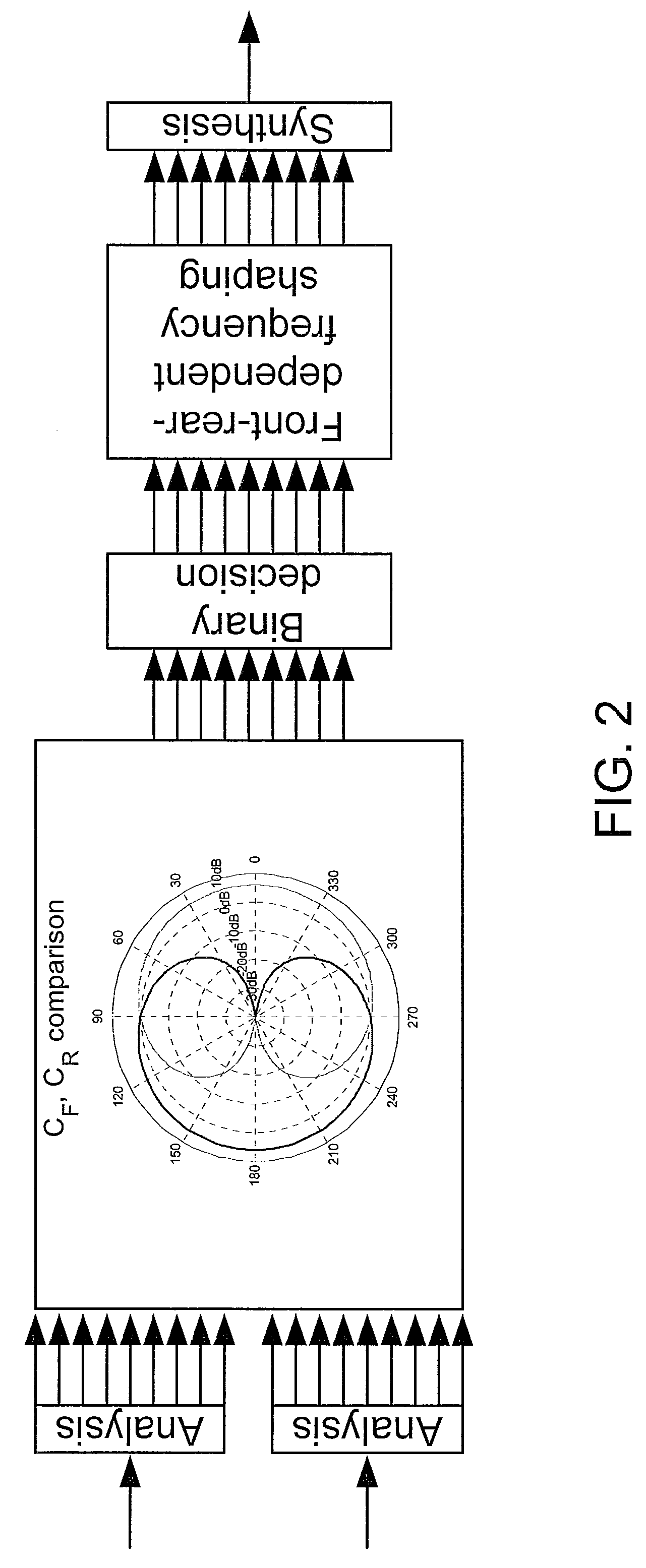
ActiveUS8526647B2Good estimateImprove localizationEar supported setsSets with pocket amplifiersFrequency UnitHearing apparatus
A listening device includes an ear-part for being worn in or at an ear of a user, a microphone system including at least two microphones each converting an input sound to an electrical microphone signal, and a TF-conversion unit for providing a time-frequency representation of the at least two microphone signals. Each signal representation includes complex or real values of the signal in a particular time-frequency unit. The listening device also includes a DIR-unit with a directionality system providing a weighted sum of the at least two electrical microphone signals thereby providing at least two directional microphone signals having maximum sensitivity in spatially different directions and a combined microphone signal. Each time-frequency unit of the combined signal is attributable to a particular direction. A frequency shaping-unit modifies one or more selected time-frequency units to indicate directional cues of input sounds providing an improved directional output signal.
Owner:OTICON
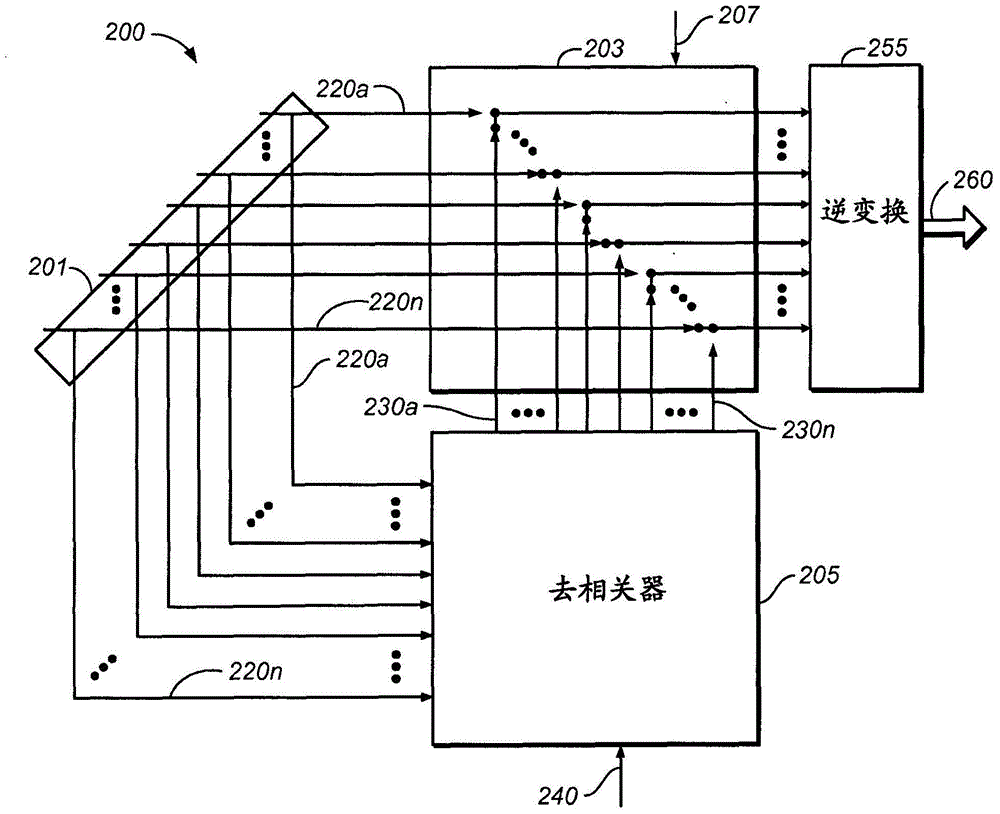
Signal decorrelation in an audio processing system
Audio processing methods may involve receiving audio data corresponding to a plurality of audio channels. The audio data may include a frequency domain representation corresponding to filterbank coefficients of an audio encoding or processing system. A decorrelation process may be performed with the same filterbank coefficients used by the audio encoding or processing system. The decorrelation process may be performed without converting coefficients of the frequency domain representation to another frequency domain or time domain representation. The decorrelation process may involve selective or signal-adaptive decorrelation of specific channels and / or specific frequency bands. The decorrelation process may involve applying a decorrelation filter to a portion of the received audio data to produce filtered audio data. The decorrelation process may involve using a non-hierarchal mixer to combine a direct portion of the received audio data with the filtered audio data according to spatial parameters.
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
Method for detecting period transient state characteristic in signal
InactiveCN101344427AImplement automatic detectionRealize cycle judgmentVibration measurement in solidsMachine gearing/transmission testingTransient stateTime–frequency representation
The invention discloses a test method of periodic transient characteristics in signals, uses a sensing device for inputting and implementing analog-to-digital conversion, obtains a signal x(t), and detects whether the transient characteristics with a period T1, T2 or Tm exist in the signal x(t), where m is a positive integer. The test method is characterized in that the test method comprises the following steps: the time frequency decomposition of the signal x(t) is implemented, and the time frequency representation TFRX(t, f) of the signal characteristics is obtained; m polar coordinate mappings are respectively built according to the periods T1, T2 or Tm; each mapping is represented on a polar coordinate figure; when enhanced characteristic representation appears in the polar coordinate figure that is corresponding to the period Tn (n lies in a closed interval between 1 and m), whether the transient characteristics with the period Tn exist in the detected signal is decided. The test method of the periodic transient characteristics in signals conveniently realizes period deciding, improves the efficiency and the accuracy of period deciding, can realize automatic detection of the periodic transient characteristics, and is particularly applicable to automatic failure identification of mechanical equipment.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com