Patents
Literature
4388 results about "Target signal" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
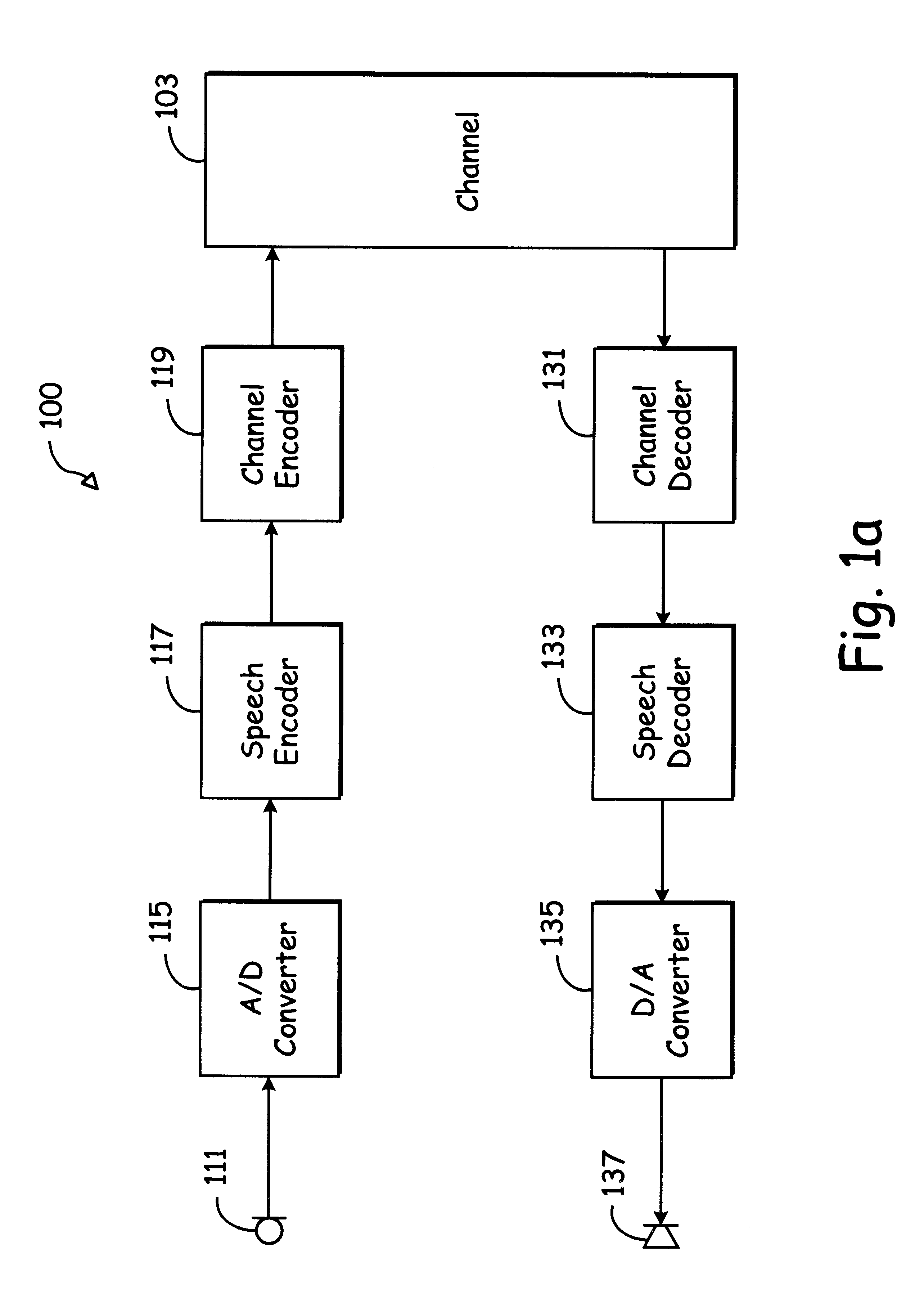
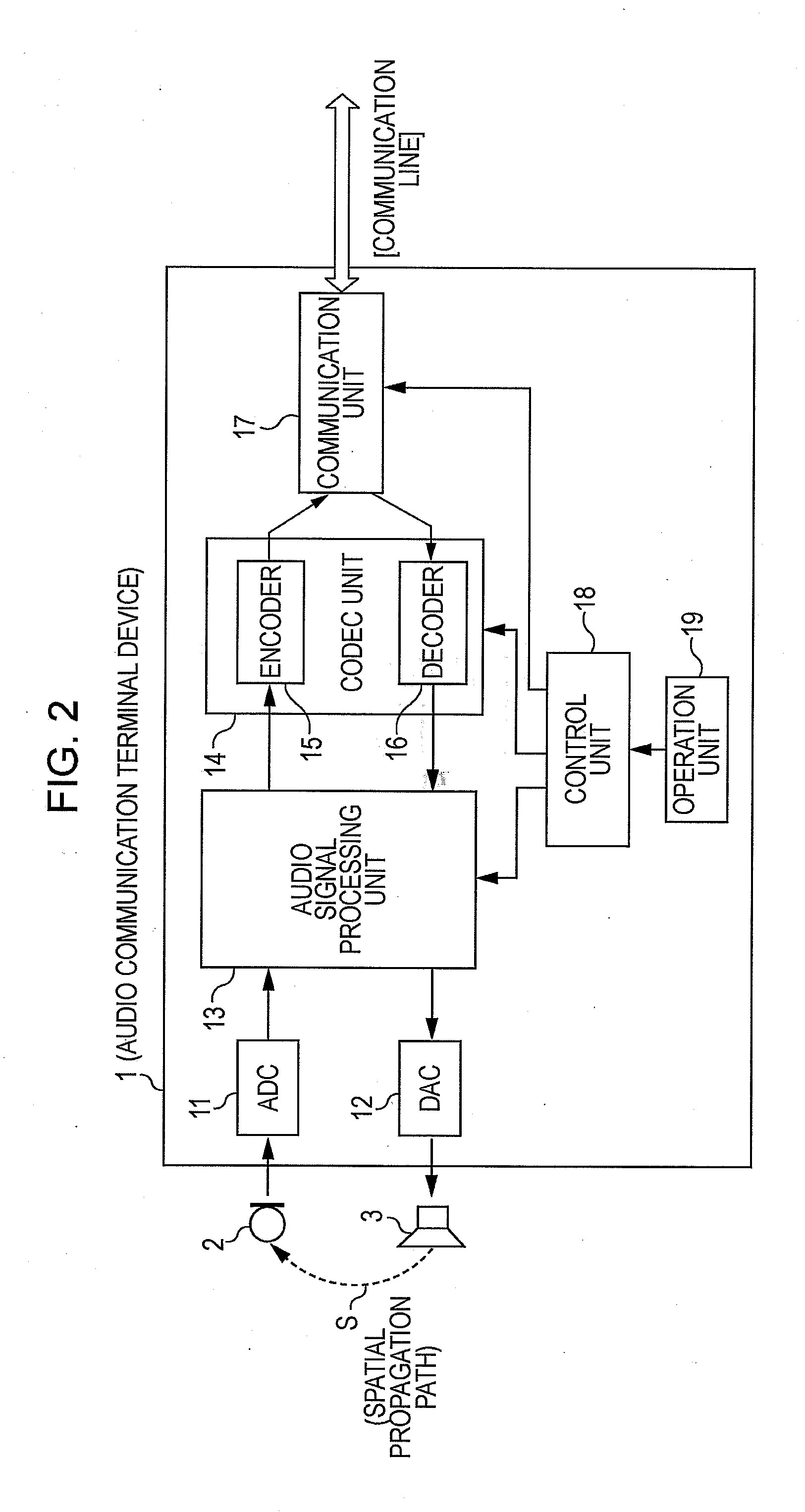
Audio input system
ActiveUS20050047611A1Reduce noiseAdditional componentDirection finders using ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic wavesMicrophones signal combinationSensor arrayTarget signal
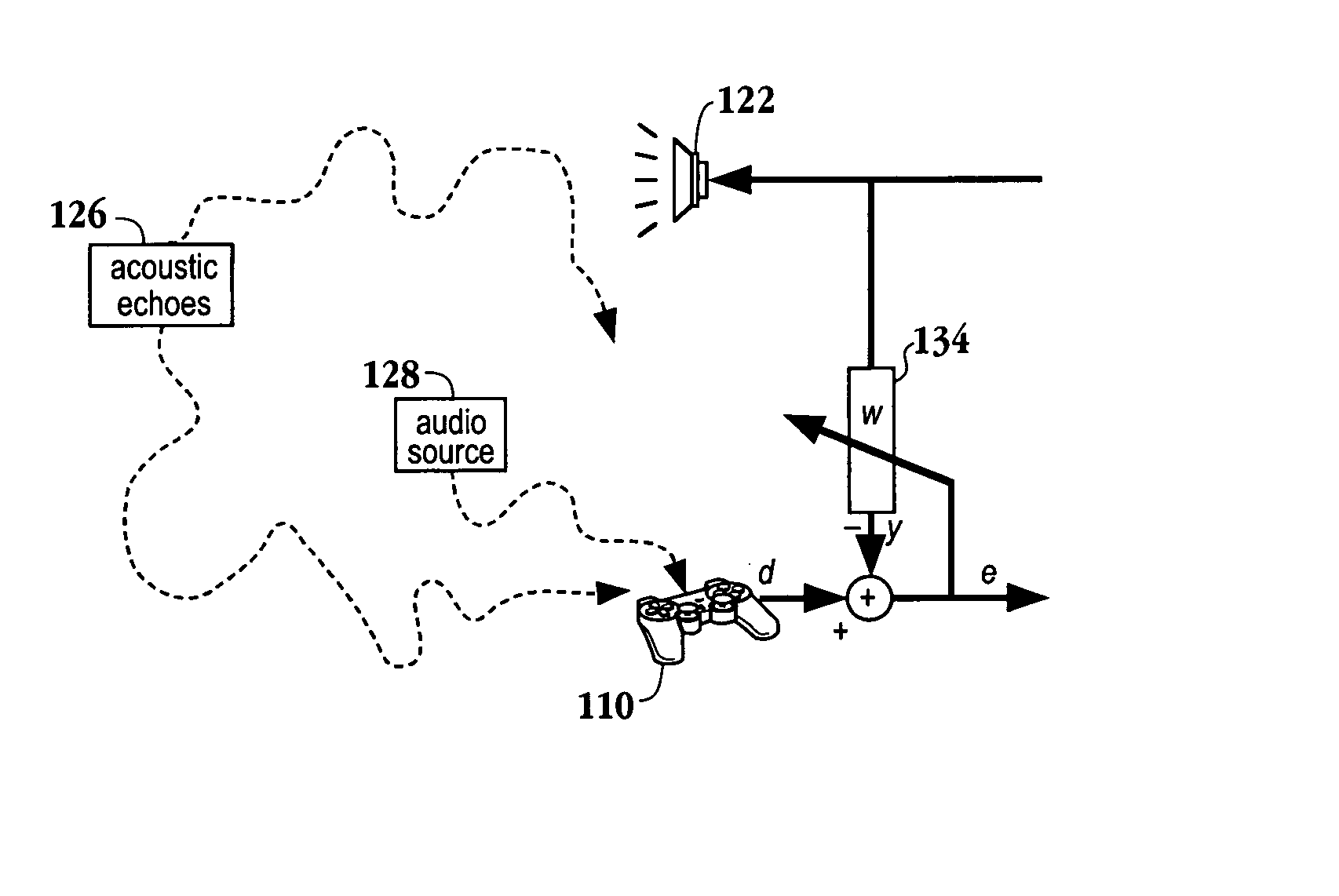
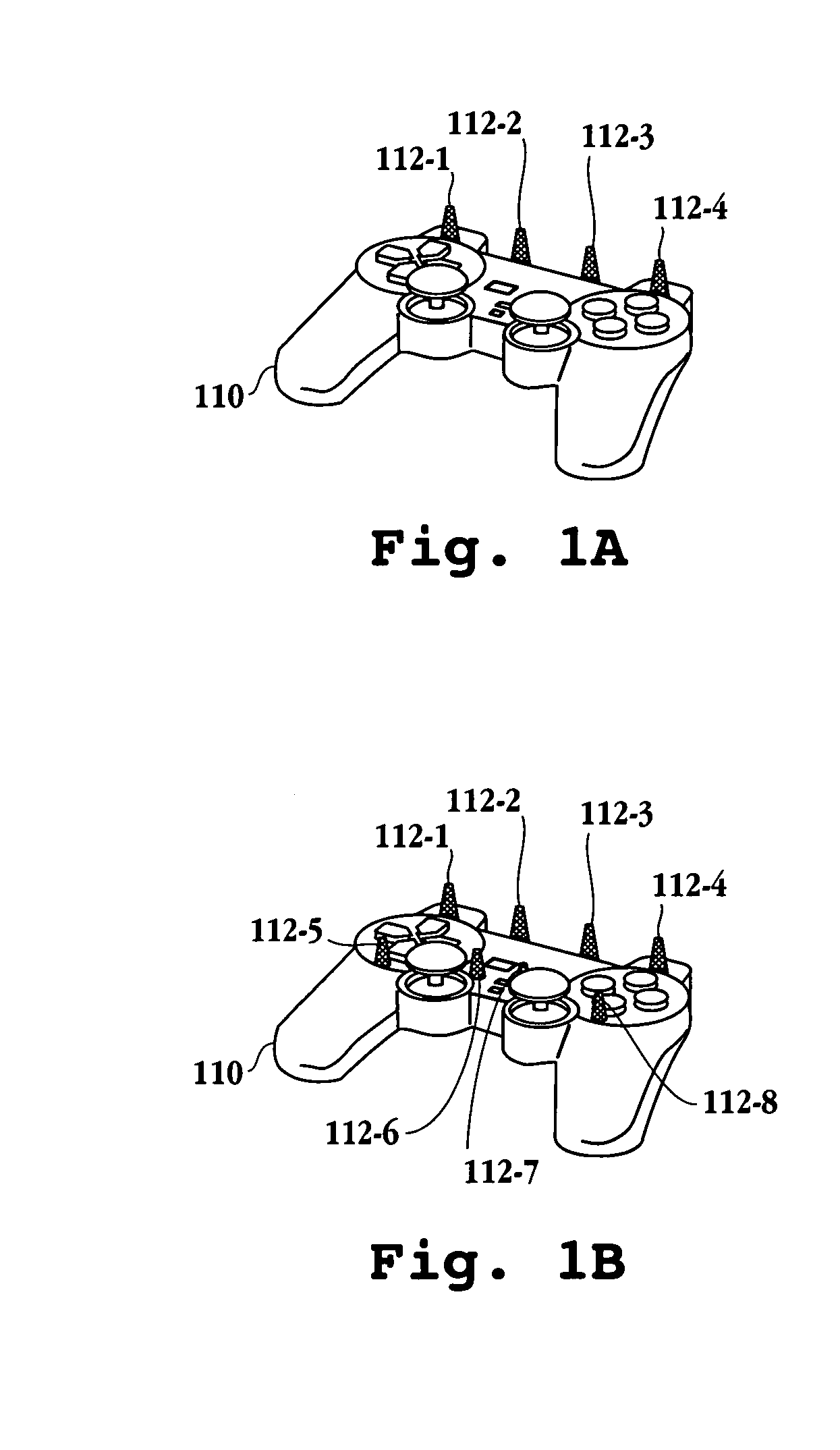
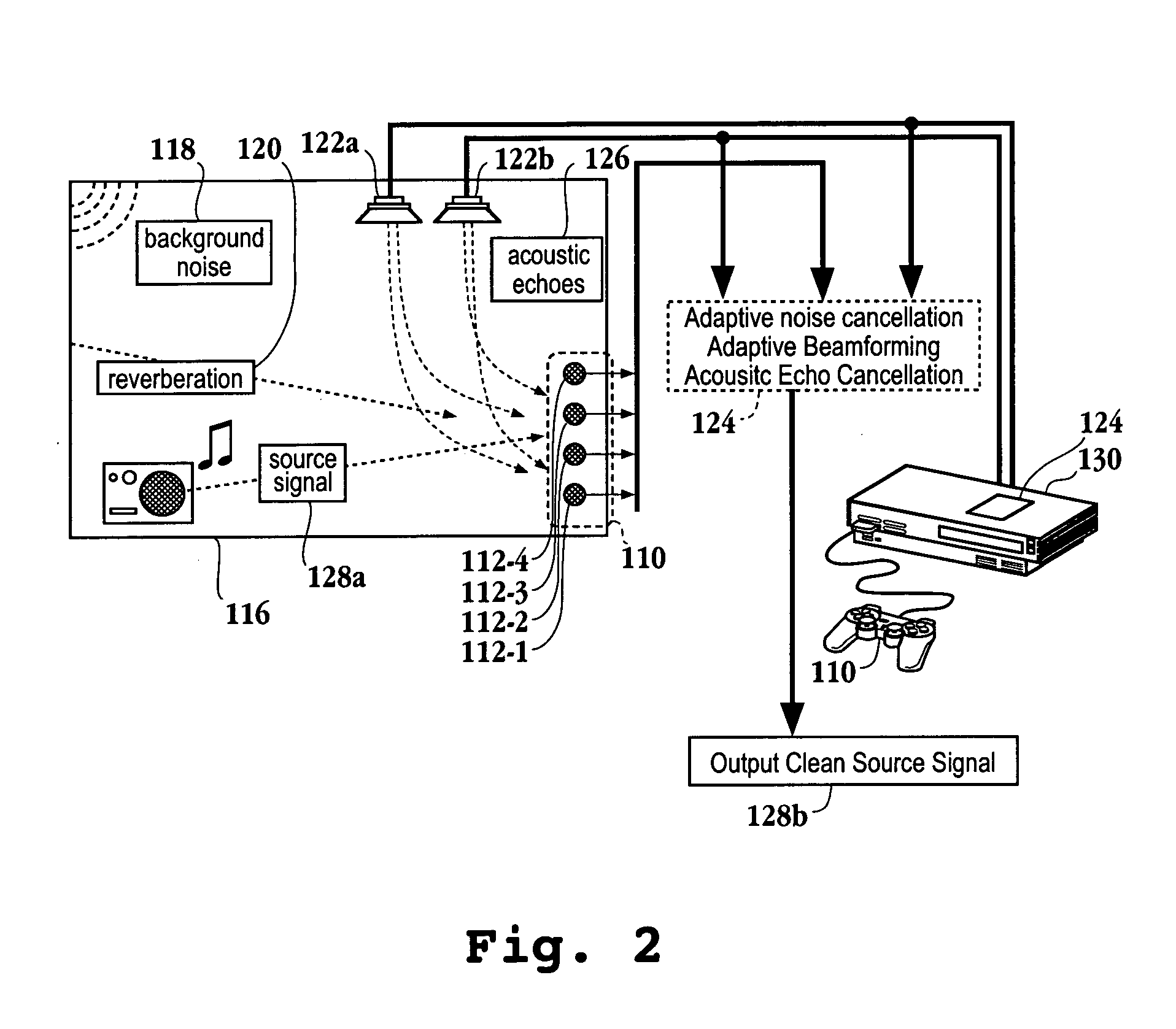
A method for reducing noise associated with an audio signal received through a microphone sensor array is provided. The method initiates with enhancing a target signal component of the audio signal through a first filter. Simultaneously, the target signal component is blocked by a second filter. Then, the output of the first filter and the output of the second filter are combined in a manner to reduce noise without distorting the target signal. Next, an acoustic set-up associated with the audio signal is periodically monitored. Then, a value of the first filter and a value of the second filter are both calibrated based upon the acoustic set-up. A system capable of isolating a target audio signal from multiple noise sources, a video game controller, and an integrated circuit configured to isolate a target audio signal are included.
Owner:SONY COMPUTER ENTERTAINMENT INC
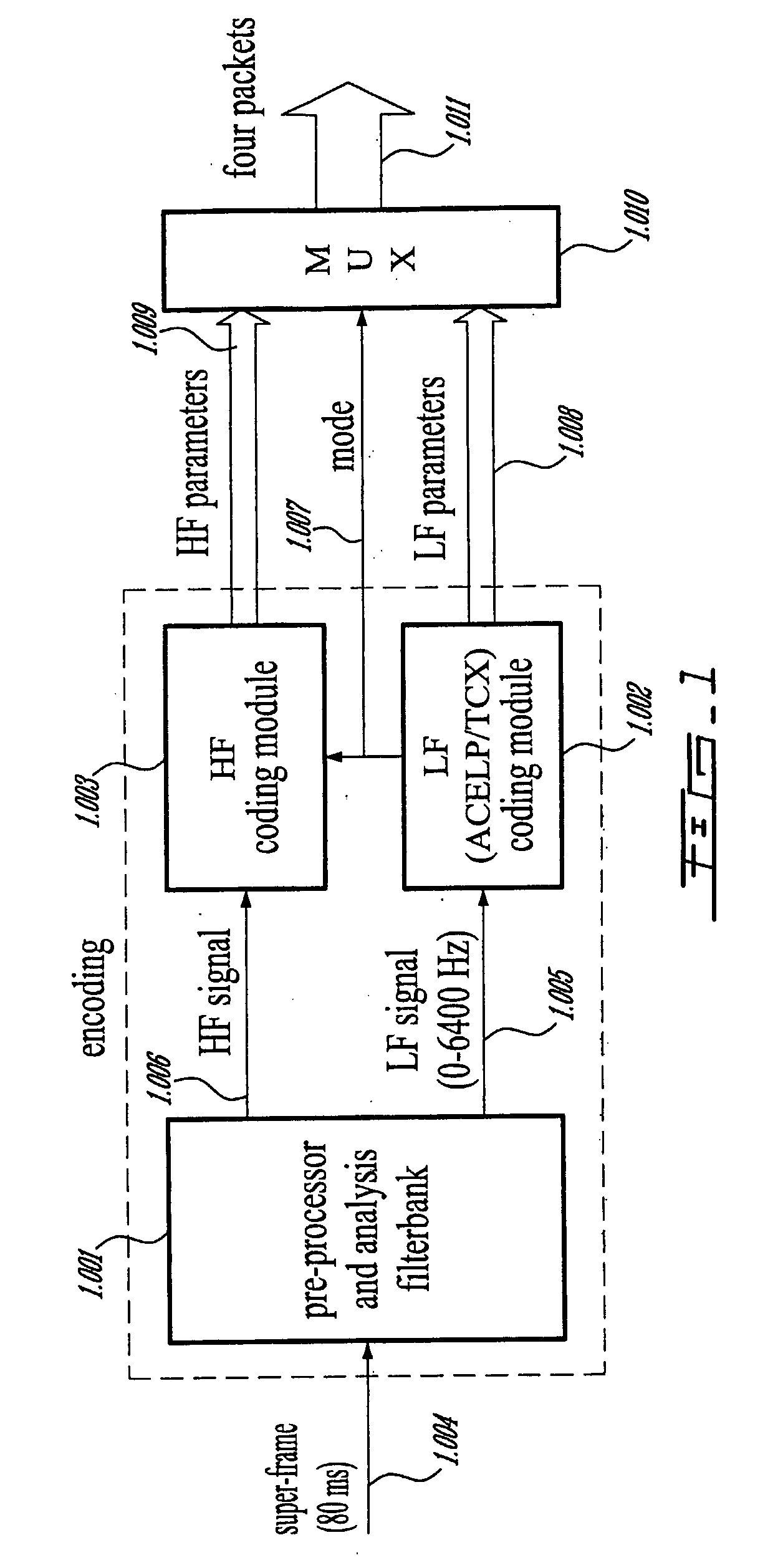
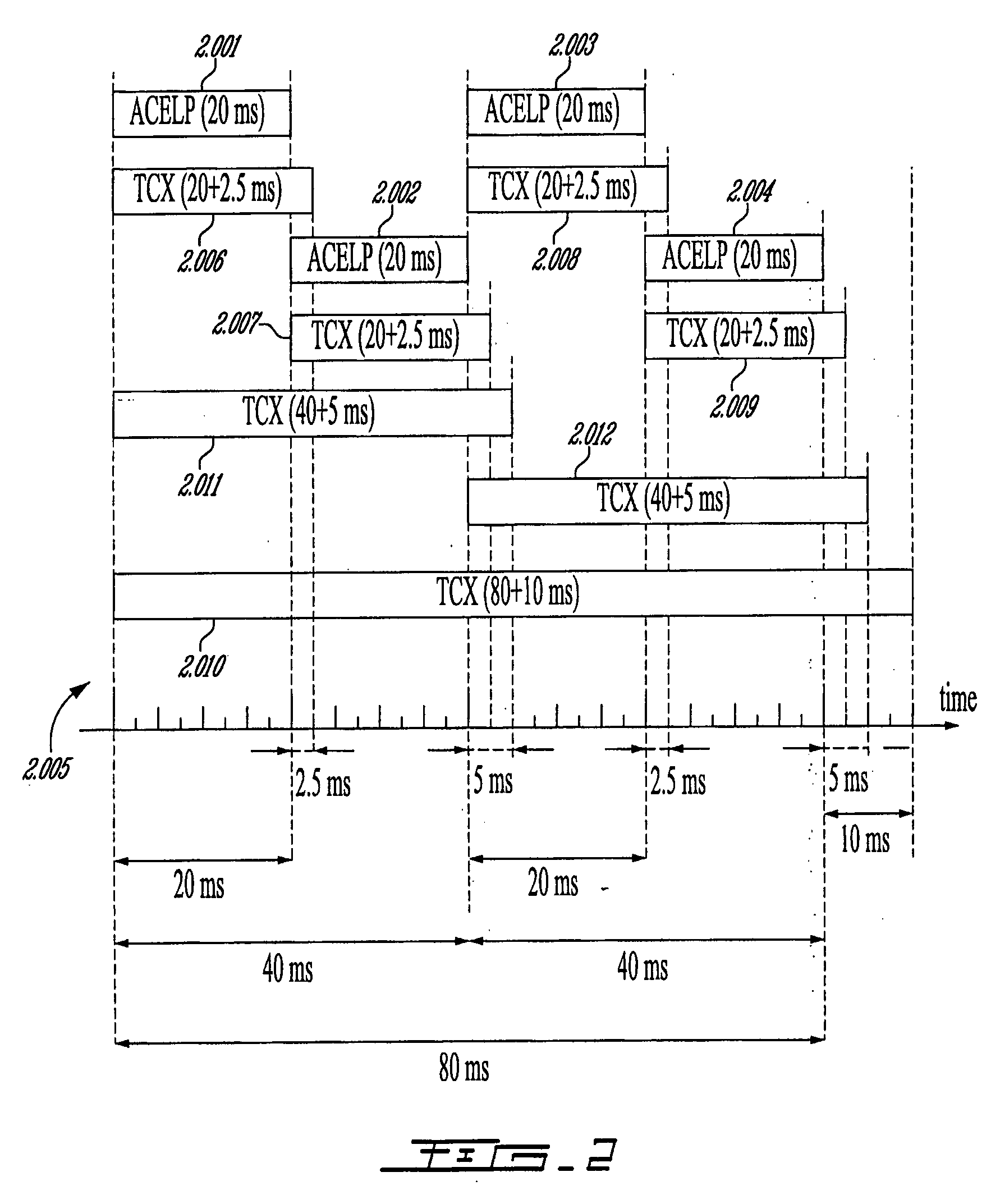
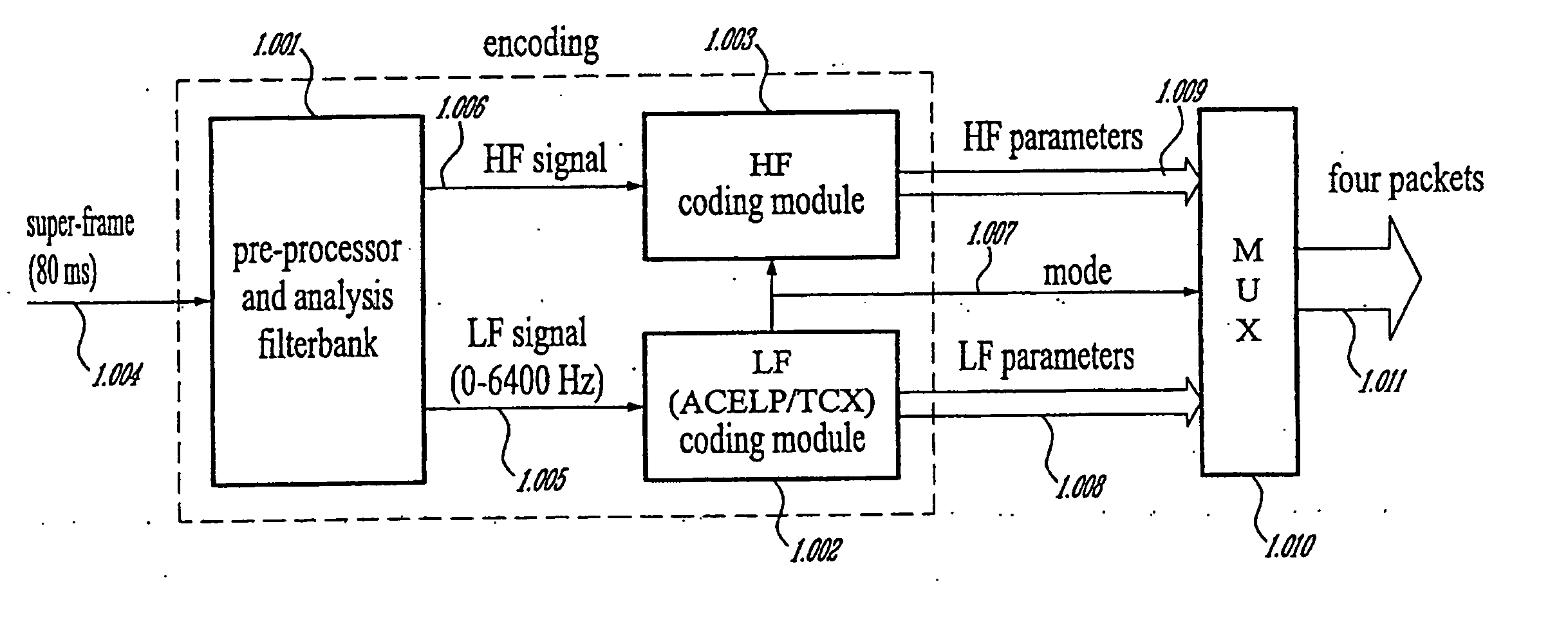
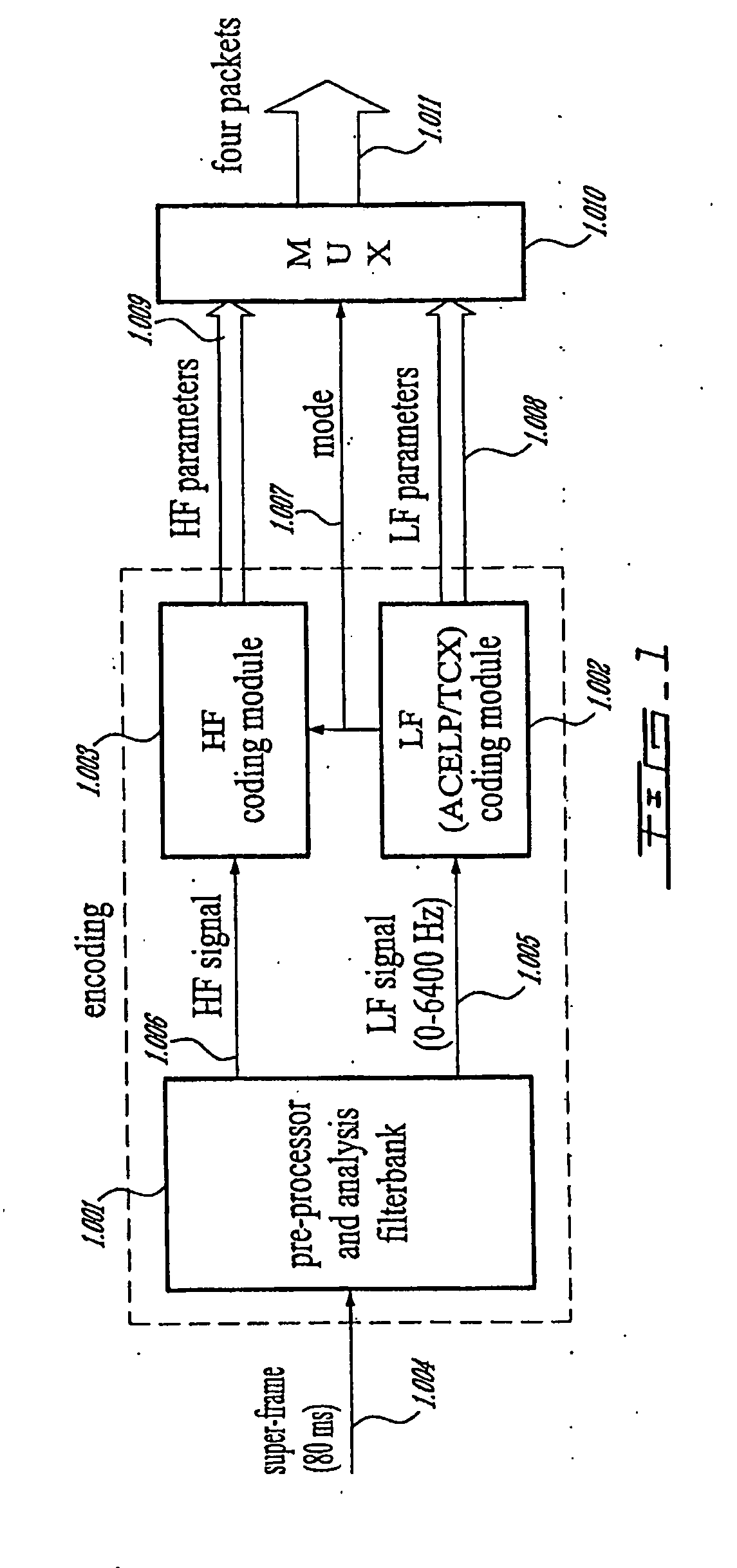
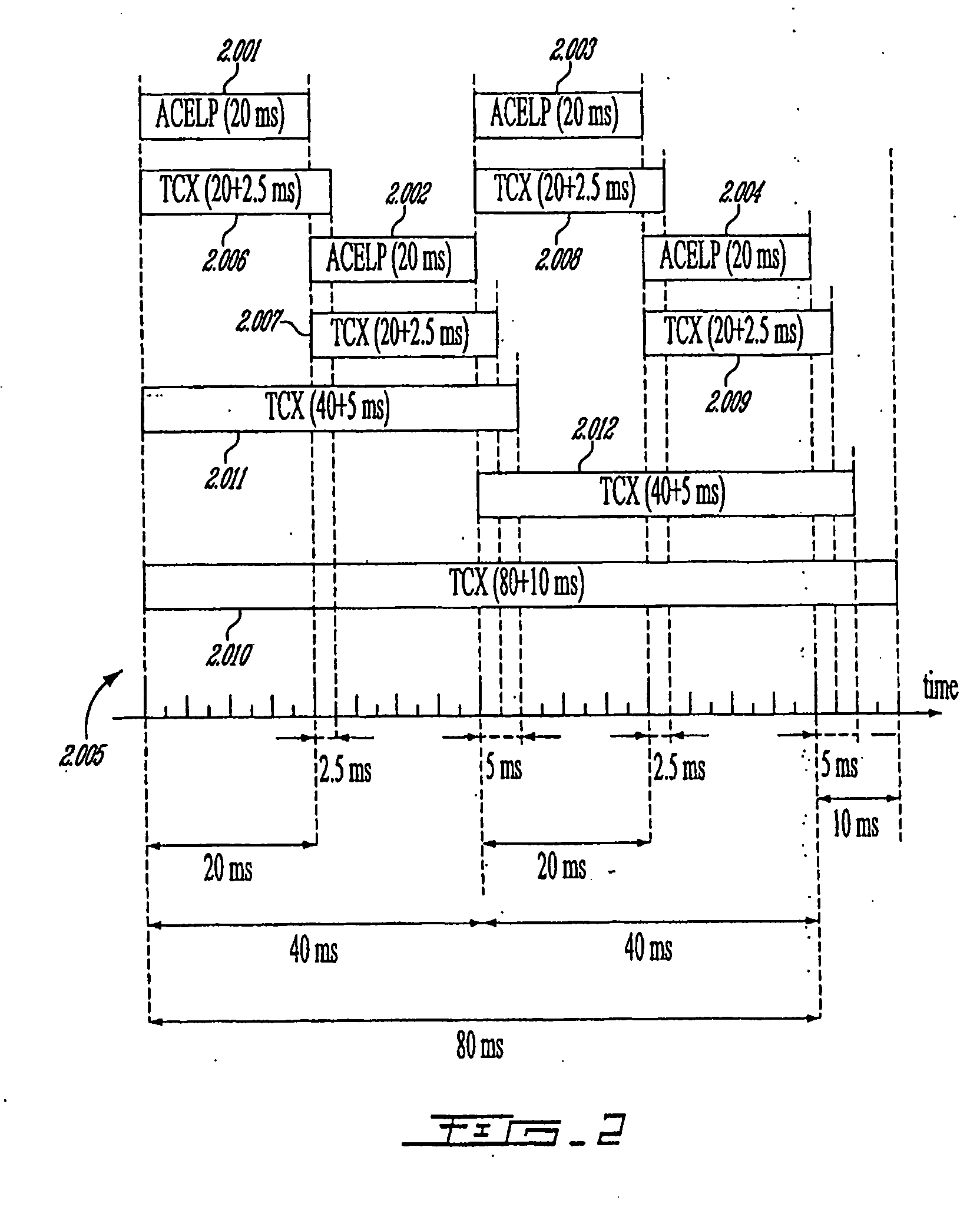
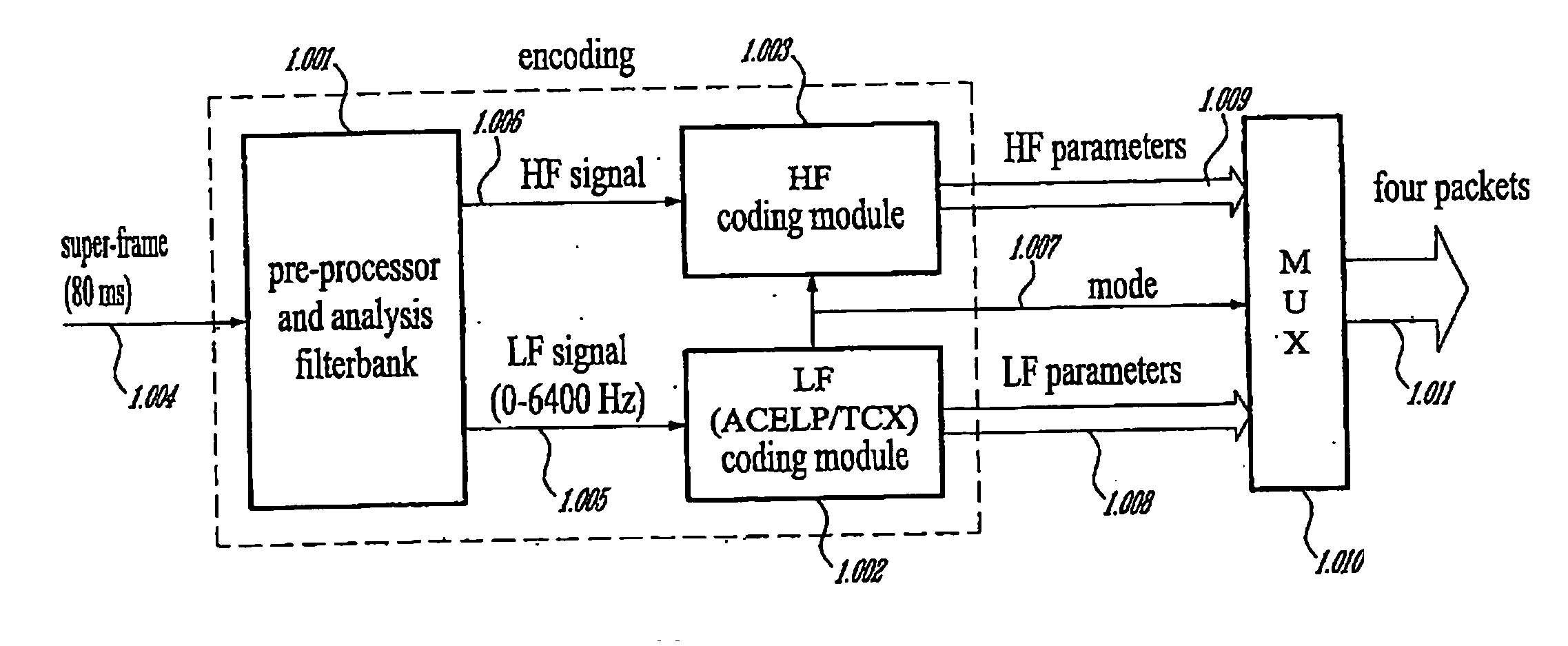
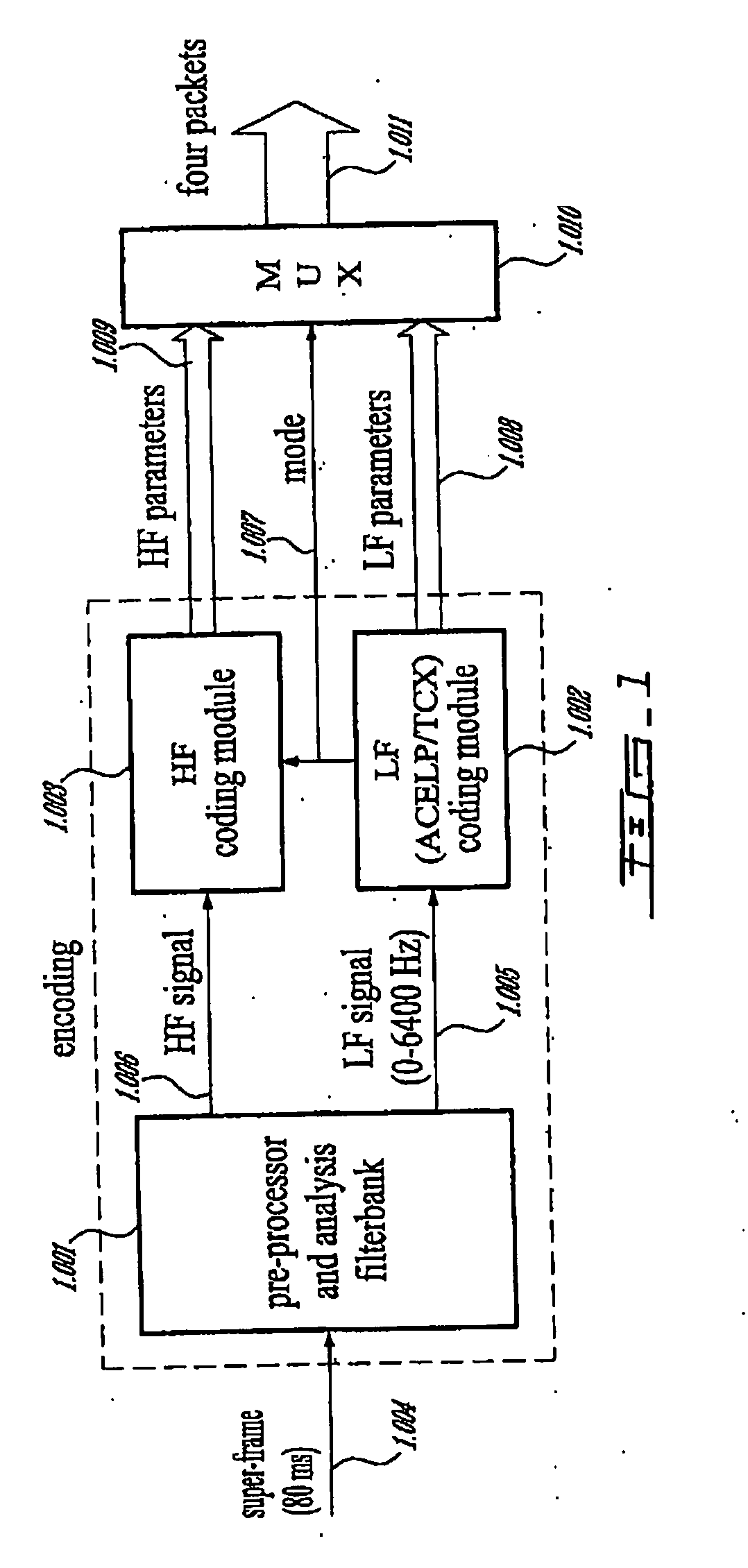
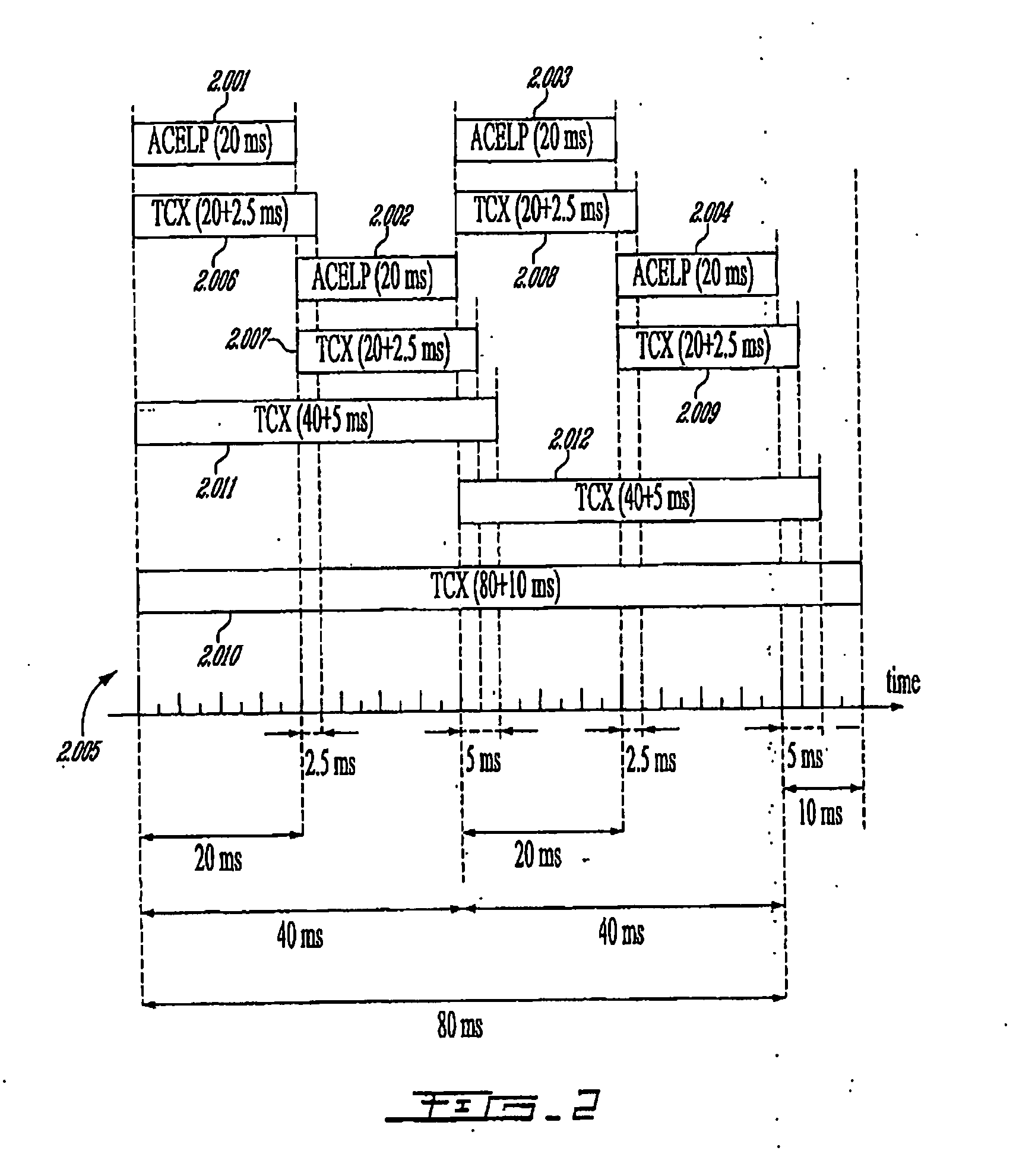
Methods and Devices for Low-Frequency Emphasis During Audio Compression Based on Acelp/Tcx
ActiveUS20070282603A1Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionBandwidth extensionFrequency spectrum
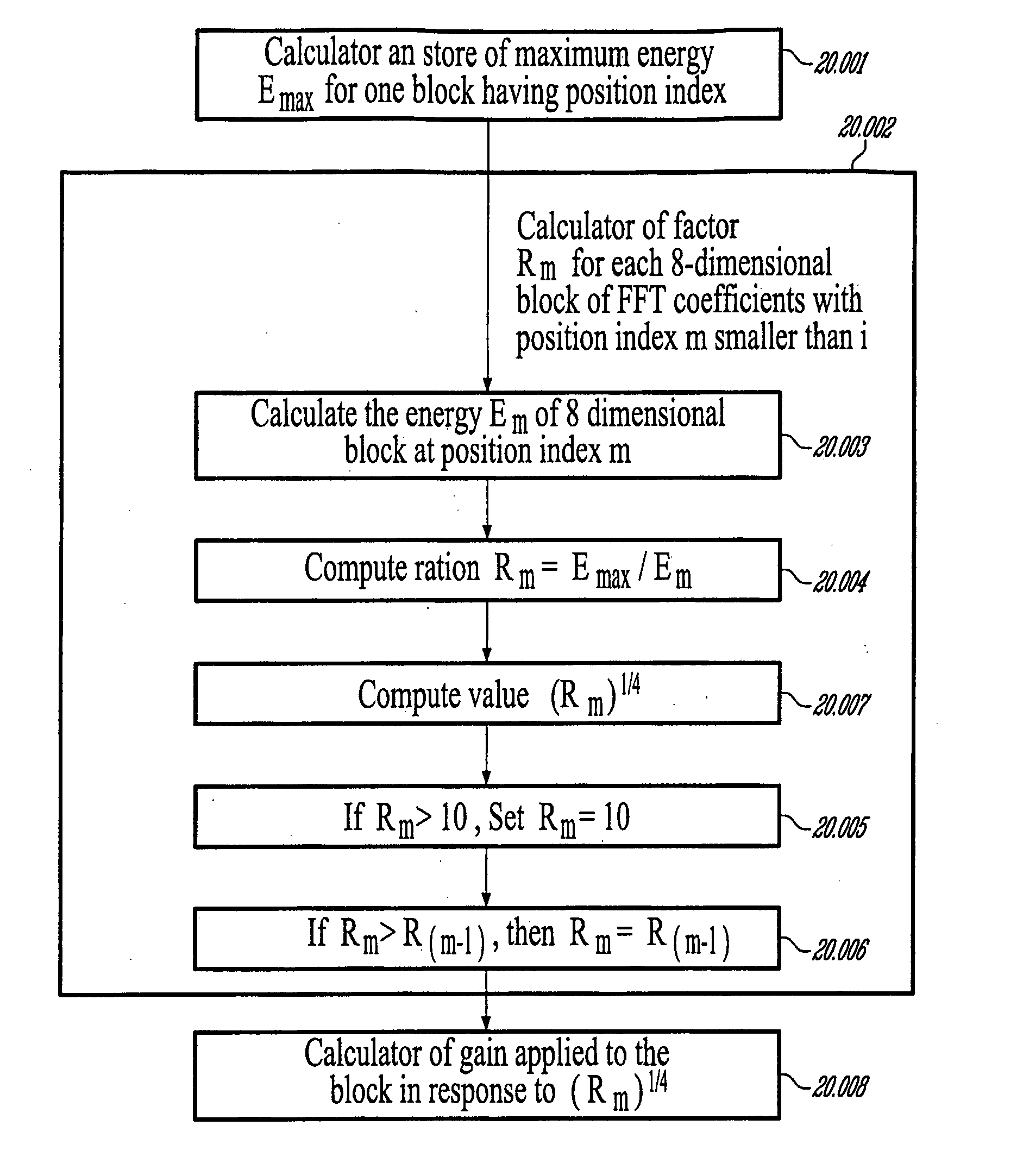
A first aspect of the present invention relates to a method for low-frequency emphasizing the spectrum of a sound signal transformed in a frequency domain and comprising transform coefficients grouped in a number of blocks, in which a maximum energy for one block is calculated and a position index of the block with maximum energy is determined, a factor is calculated for each block having a position index smaller than the position index of the block with maximum energy the calculated maximum energy and the energy of the block, and, for each block, a gain determining from the factor is applied to the transform coefficients of the block. Another aspect of the invention is concerned with an HF coding method for coding, through a bandwidth extension scheme, an HF signal obtained from separation of a full-bandwidth sound signal into the HF signal and a LF signal, in which an estimation of the an HF gain is calculated from LPC coefficients, the energy of the HF signal is calculated, the LF signal is processed to produce a synthesized version of the HF signal, the energy of the synthesized version of the HF signal is calculated, a ratio between the energy of the HF signal and the energy of the synthesized version of the HF signal is calculated and expressing as an HF gain, and a difference between the estimation of the HF gain and the HF gain is calculated to obtain a gain correction. A third aspect of the invention is concerned with a method for producing from a decoded target signal an overlap-add target signal in a current frame coded according to a first coding mode. According to this method, the decoded target signal of the current frame is windowed and a left portion of the window is skipped. A zero-input response of a weighting filter of the previous frame coded according to a second coding mode is calculated and windowed so that the zero-input response has an amplitude monotonically decreasing to zero after a predetermined time period. Finally, the calculated zero-input response is added to the decoded target signal to reconstruct the overlap-add target signal.
Owner:VOICEAGE CORP
Methods and devices for low-frequency emphasis during audio compression based on ACELP/TCX
ActiveUS20070225971A1Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionBandwidth extensionFrequency spectrum
A first aspect of the present invention relates to a method for low-frequency emphasizing the spectrum of a sound signal transformed in a frequency domain and comprising transform coefficients grouped in a number of blocks, in which a maximum energy for one block is calculated and a position index of the block with maximum energy is determined, a factor is calculated for each block having a position index smaller than the position index of the block with maximum energy the calculated maximum energy and the energy of the block, and, for each block, a gain determining from the factor is applied to the transform coefficients of the block. Another aspect of the invention is concerned with an HF coding method for coding, through a bandwidth extension scheme, an HF signal obtained from separation of a full-bandwidth sound signal into the HF signal and a LF signal, in which an estimation of the an HF gain is calculated from LPC coefficients, the energy of the HF signal is calculated, the LF signal is processed to produce a synthesized version of the HF signal, the energy of the synthesized version of the HF signal is calculated, a ratio between the energy of the HF signal and the energy of the synthesized version of the HF signal is calculated and expressing as an HF gain, and a difference between the estimation of the HF gain and the HF gain is calculated to obtain a gain correction. A third aspect of the invention is concerned with a method for producing from a decoded target signal an overlap-add target signal in a current frame coded according to a first coding mode. According to this method, the decoded target signal of the current frame is windowed and a left portion of the window is skipped. A zero-input response of a weighting filter of the previous frame coded according to a second coding mode is calculated and windowed so that the zero-input response has an amplitude monotonically decreasing to zero after a predetermined time period. Finally, the calculated zero-input response is added to the decoded target signal to reconstruct the overlap-add target signal.
Owner:VOICEAGE CORP
Methods and devices for low-frequency emphasis during audio compression based on ACELP/TCX
A first aspect of the present invention relates to a method for low-frequency emphasizing the spectrum of a sound signal transformed in a frequency domain and comprising transform coefficients grouped in a number of blocks, in which a maximum energy for one block is calculated and a position index of the block with maximum energy is determined, a factor is calculated for each block having a position index smaller than the position index of the block with maximum energy the calculated maximum energy and the energy of the block, and, for each block, a gain determining from the factor is applied to the transform coefficients of the block. Another aspect of the invention is concerned with an HF coding method for coding, through a bandwidth extension scheme, an HF signal obtained from separation of a full-bandwidth sound signal into the HF signal and a LF signal, in which an estimation of the an HF gain is calculated from LPC coefficients, the energy of the HF signal is calculated, the LF signal is processed to produce a synthesized version of the HF signal, the energy of the synthesized version of the HF signal is calculated, a ratio between the energy of the HF signal and the energy of the synthesized version of the HF signal is calculated and expressing as an HF gain, and a difference between the estimation of the HF gain and the HF gain is calculated to obtain a gain correction. A third aspect of the invention is concerned with a method for producing from a decoded target signal an overlap-add target signal in a current frame coded according to a first coding mode. According to this method, the decoded target signal of the current frame is windowed and a left portion of the window is skipped. A zero-input response of a weighting filter of the previous frame coded according to a second coding mode is calculated and windowed so that the zero-input response has an amplitude monotonically decreasing to zero after a predetermined time period. Finally, the calculated zero-input response is added to the decoded target signal to reconstruct the overlap-add target signal.
Owner:VOICEAGE CORP
Optical imaging of induced signals in vivo under ambient light conditions
InactiveUS6748259B1Rapid detection and imaging and localization and targetingHigh sensitivityInterferometric spectrometryNanoinformaticsImaging processingTarget signal
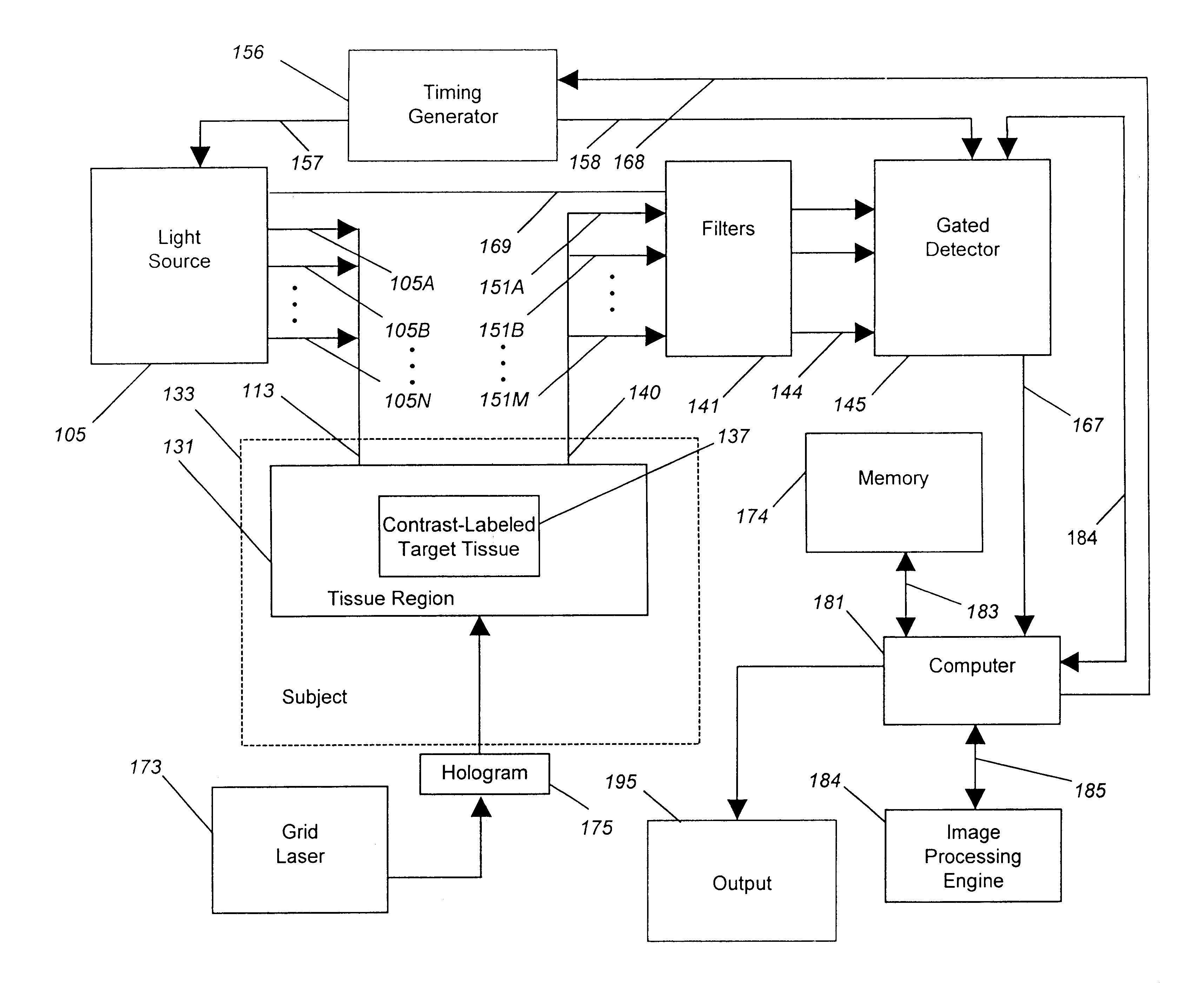
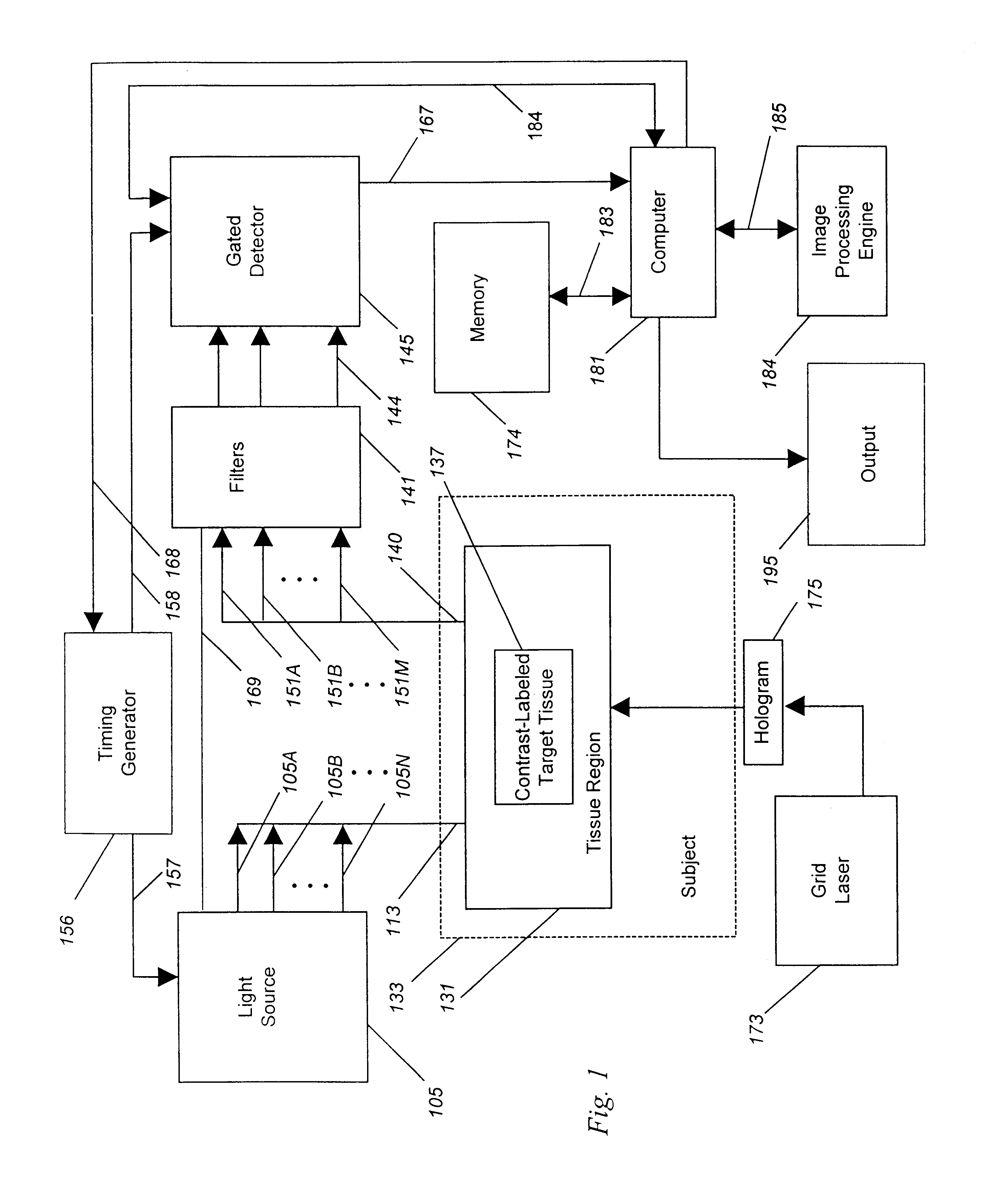
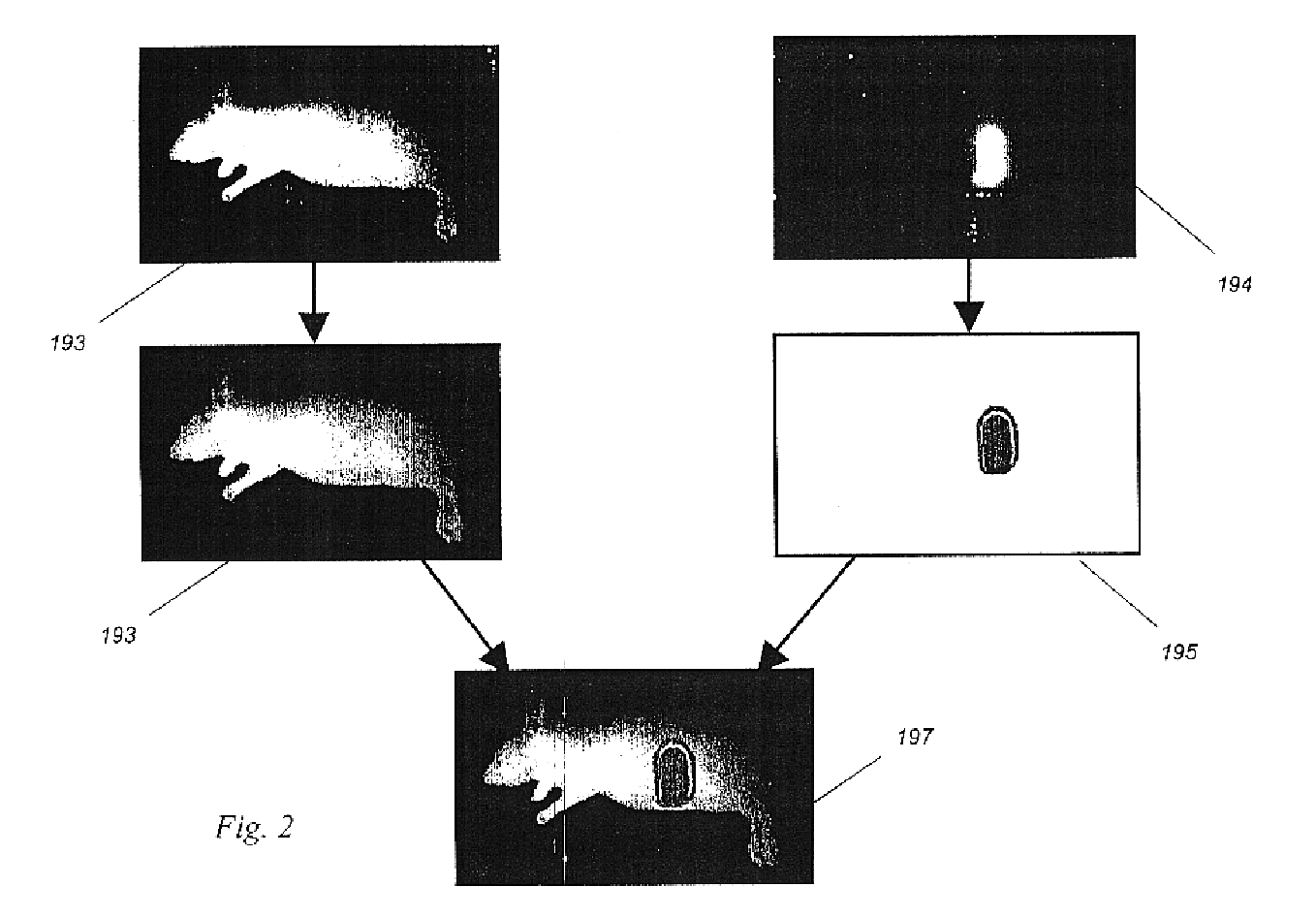
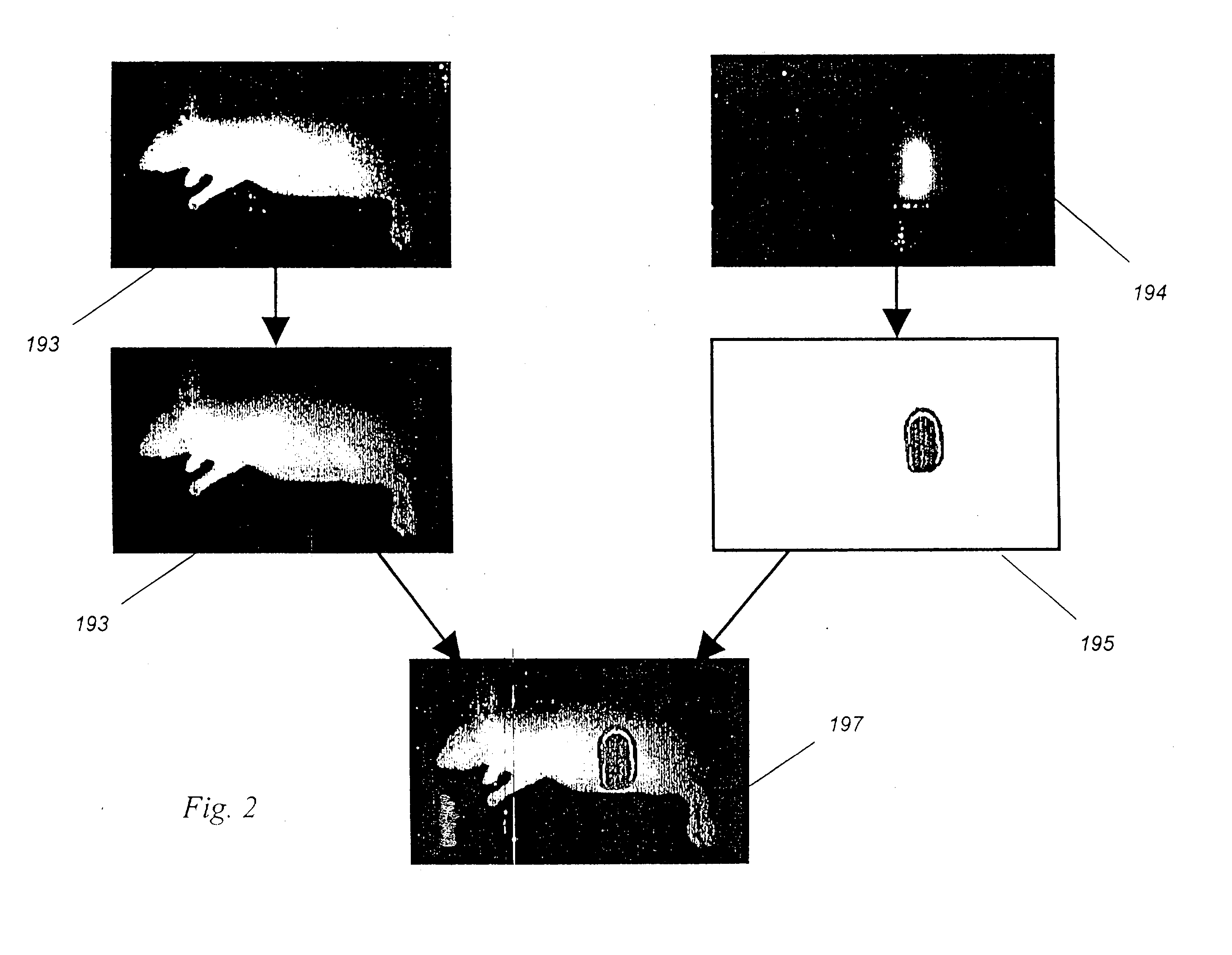
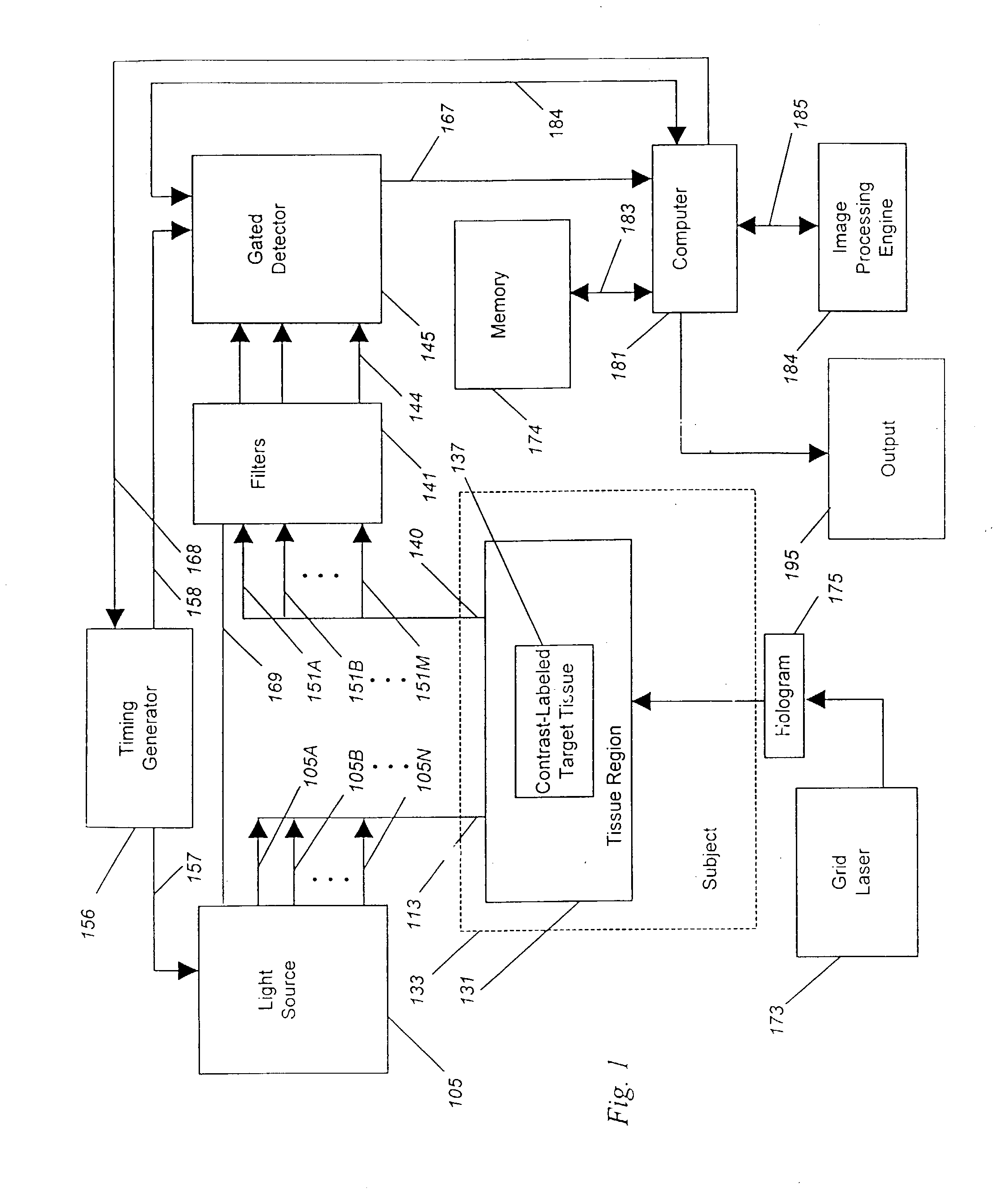
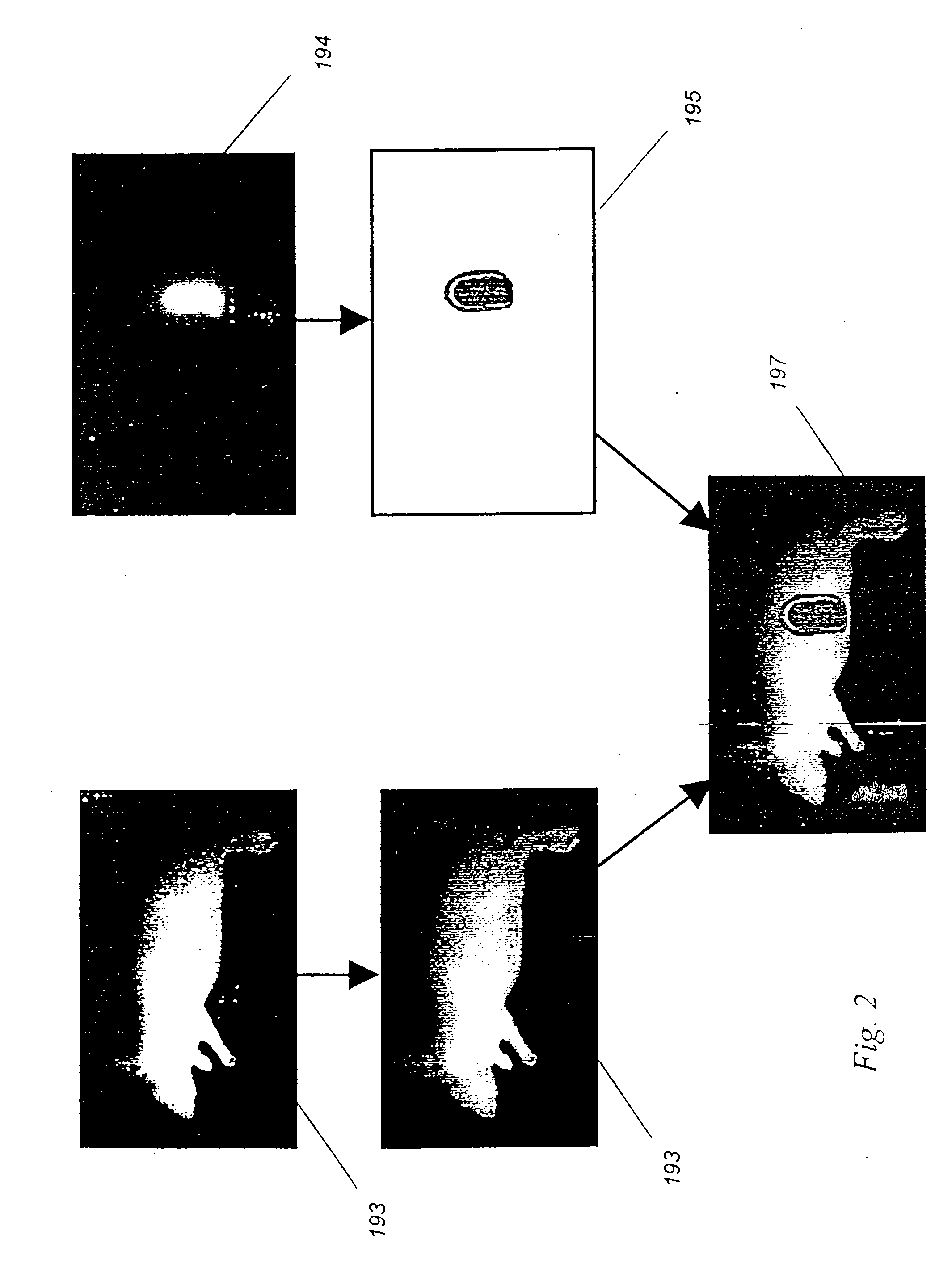
A method for detecting and localizing a target tissue within the body in the presence of ambient light in which an optical contrast agent is administered and allowed to become functionally localized within a contrast-labeled target tissue to be diagnosed. A light source is optically coupled to a tissue region potentially containing the contrast-labeled target tissue. A gated light detector is optically coupled to the tissue region and arranged to detect light substantially enriched in target signal as compared to ambient light, where the target signal is light that has passed into the contrast-labeled tissue region and been modified by the contrast agent. A computer receives signals from the detector, and passes these signals to memory for accumulation and storage, and to then to image processing engine for determination of the localization and distribution of the contrast agent. The computer also provides an output signal based upon the localization and distribution of the contrast agent, allowing trace amounts of the target tissue to be detected, located, or imaged. A system for carrying out the method is also described.
Owner:J FITNESS LLC
Optical imaging of induced signals in vivo under ambient light conditions
InactiveUS20040010192A1Rapid detection and imaging and localization and targetingUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsNanoinformaticsImaging processingTarget signal
A method for detecting and localizing a target tissue within the body in the presence of ambient light in which an optical contrast agent is administered and allowed to become functionally localized within a contrast-labeled target tissue to be diagnosed. A light source is optically coupled to a tissue region potentially containing the contrast-labeled target tissue. A gated light detector is optically coupled to the tissue region and arranged to detect light substantially enriched in target signal as compared to ambient light, where the target signal is light that has passed into the contrast-labeled tissue region and been modified by the contrast agent. A computer receives signals from the detector, and passes these signals to memory for accumulation and storage, and to then to image processing engine for determination of the localization and distribution of the contrast agent. The computer also provides an output signal based upon the localization and distribution of the contrast agent, allowing trace amounts of the target tissue to be detected, located, or imaged. A system for carrying out the method is also described.
Owner:J FITNESS LLC
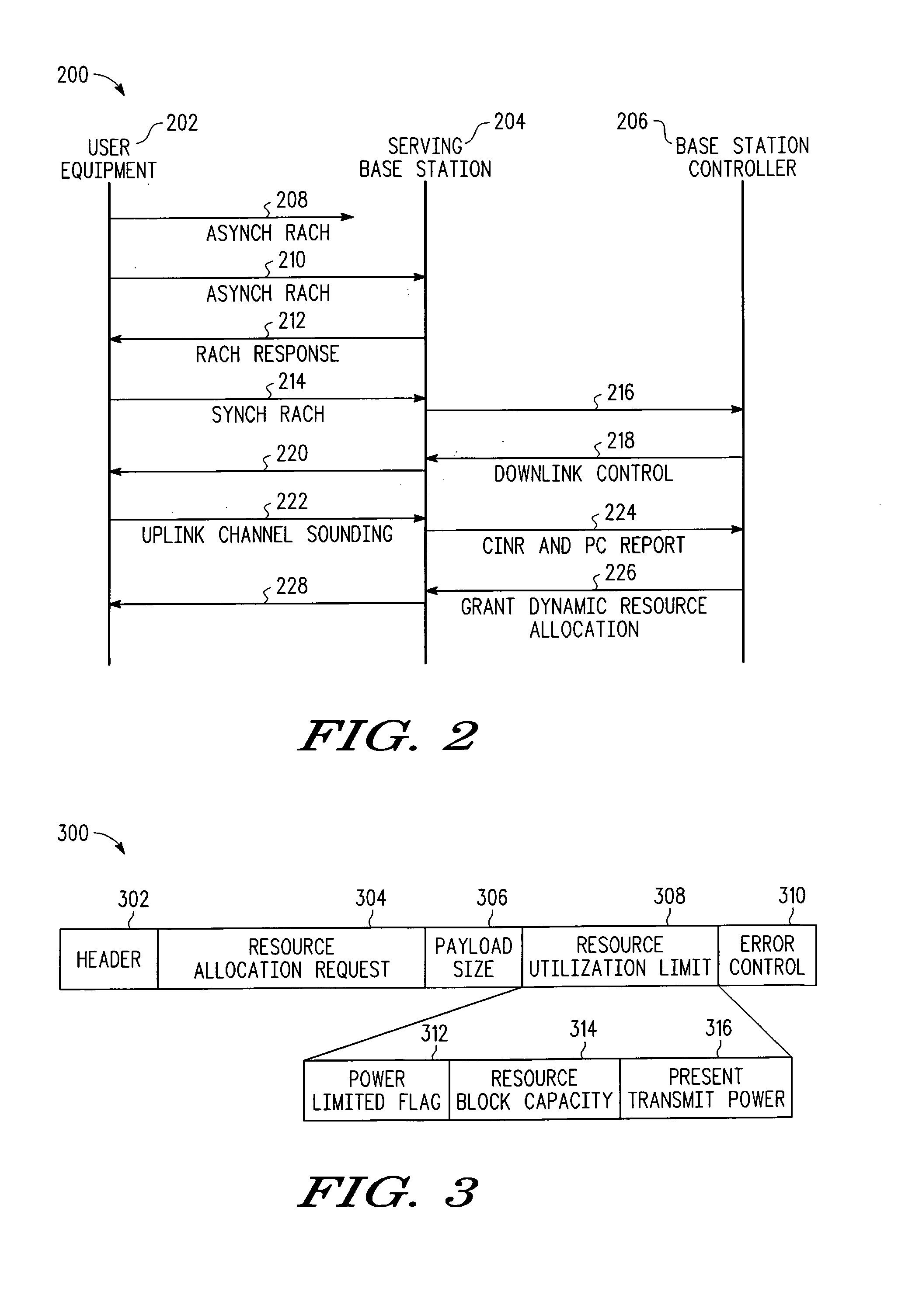
Resource allocation in a communication system
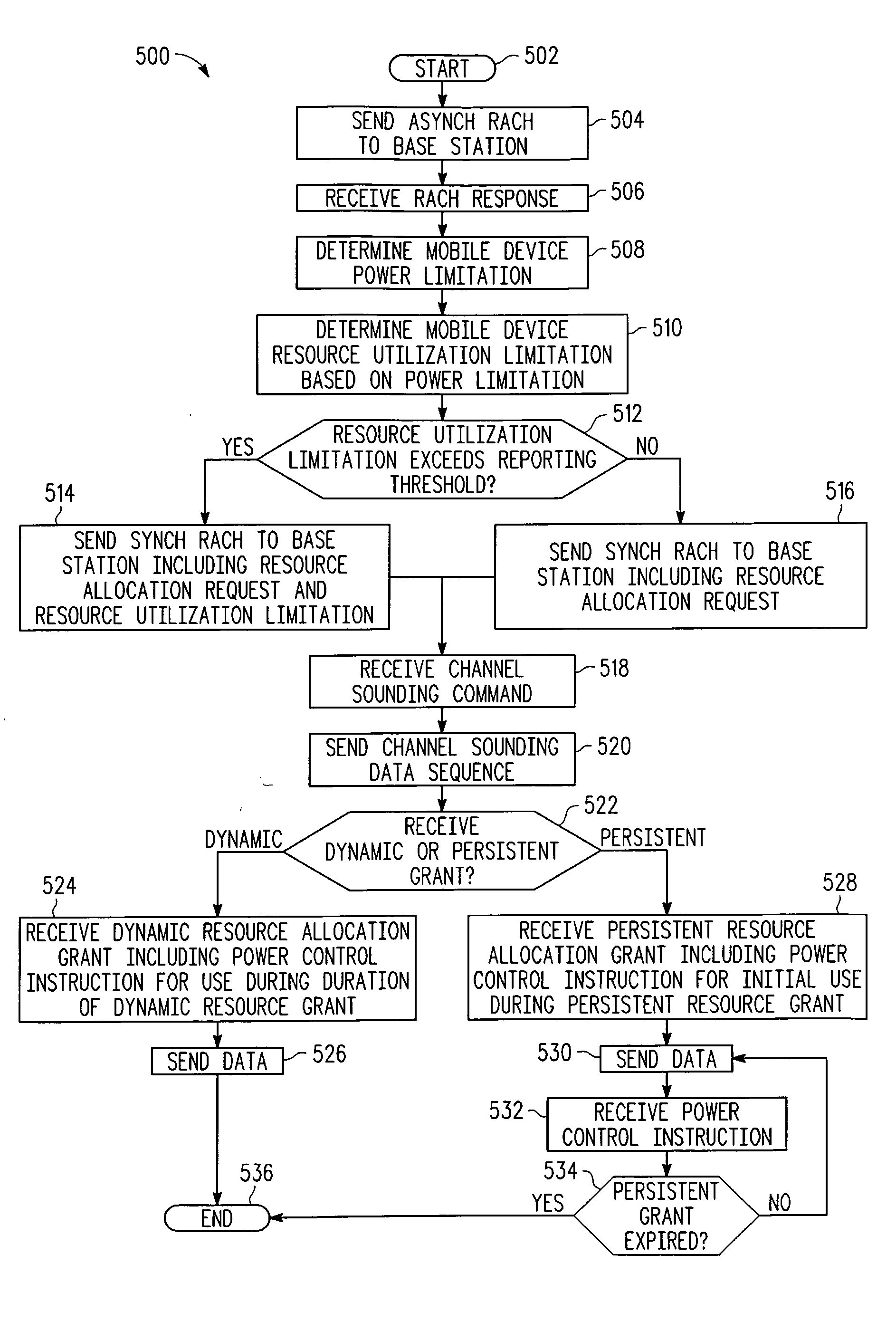
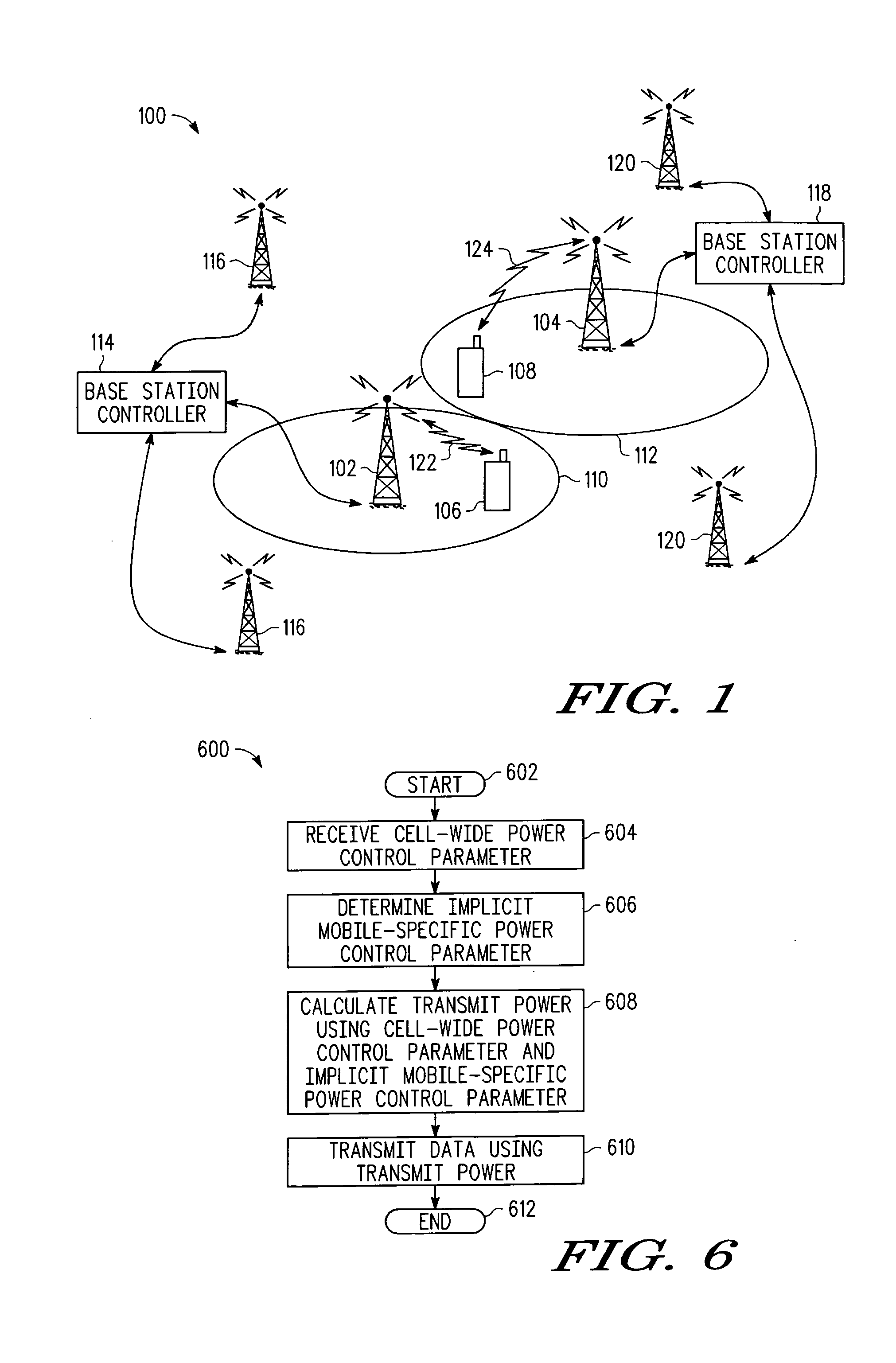
Methods and corresponding systems for determining a transmit power in a mobile device include receiving, in the mobile device, a cell-wide power control parameter related to a target receive power at a serving base station. Thereafter, a transmit power is calculated in response to the cell-wide power control parameter and an implicit mobile-specific power control parameter. The mobile device then transmits using the transmit power. The cell-wide power control parameter can be a cell target signal to interference-plus-noise ratio, or a fractional power control exponent. The implicit mobile-specific power control parameter can be a modulation and coding level previously used by the mobile device, or a downlink SINR level measured by the mobile device.
Owner:APPLE INC
Cellular system, mobile station, base station and transmission power control method as well as program to be executed for implementing the method
ActiveUS20050043051A1Quality is easy to controlQuality improvementPower managementTransmission control/equalisingInterference ratioTarget signal
In a cellular system, each mobile station concurrently linked to plural link base stations in soft handover state and receiving packet from the packet-transmitting base station controls a transmission power of an up-link dedicated physical channel based on a first transmission power control information included in down-link dedicated physical channels of the link base stations. In other state, the mobile station controls the transmission power based on a second transmission power control information included in a down-link dedicated physical channel of the packet-transmitting base station. This accelerates the power increase up to a target power level causing that the measured signal-to-interference-ratio at the packet-transmitting base station reaches a target signal-to-interference-ratio, thereby improving receiving quality of control signal from the mobile station at the packet-transmitting base station.
Owner:NEC CORP
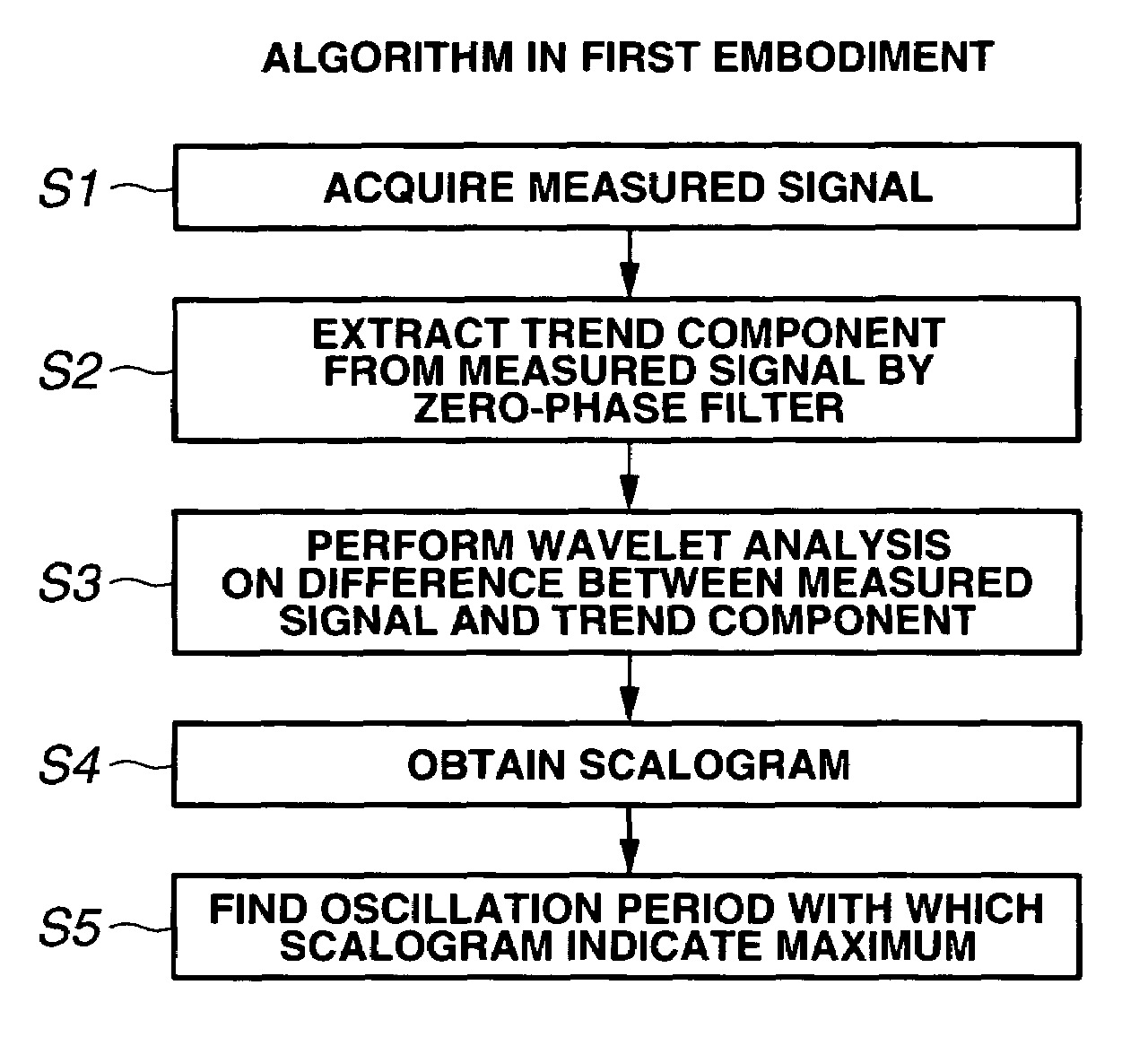
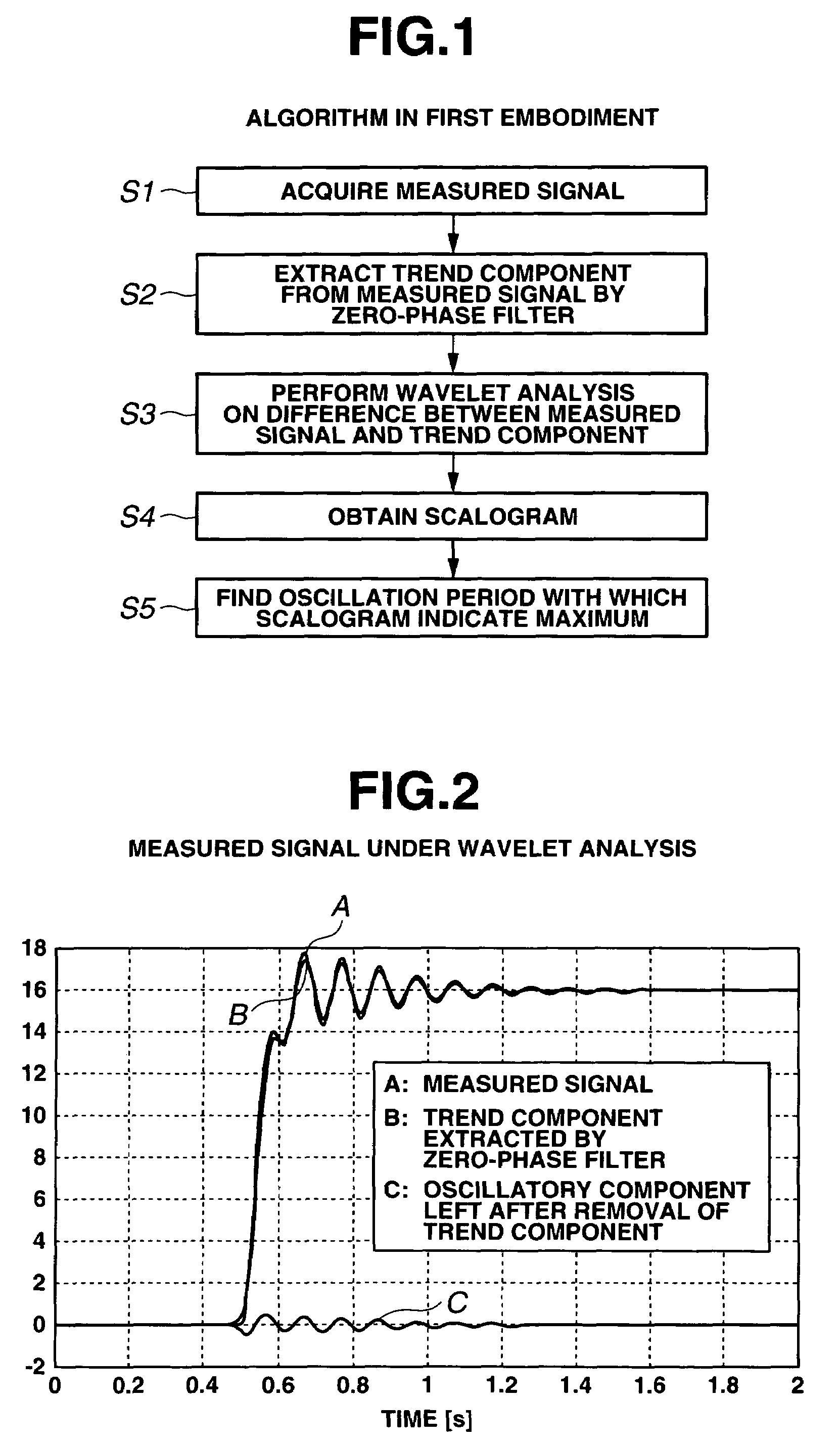
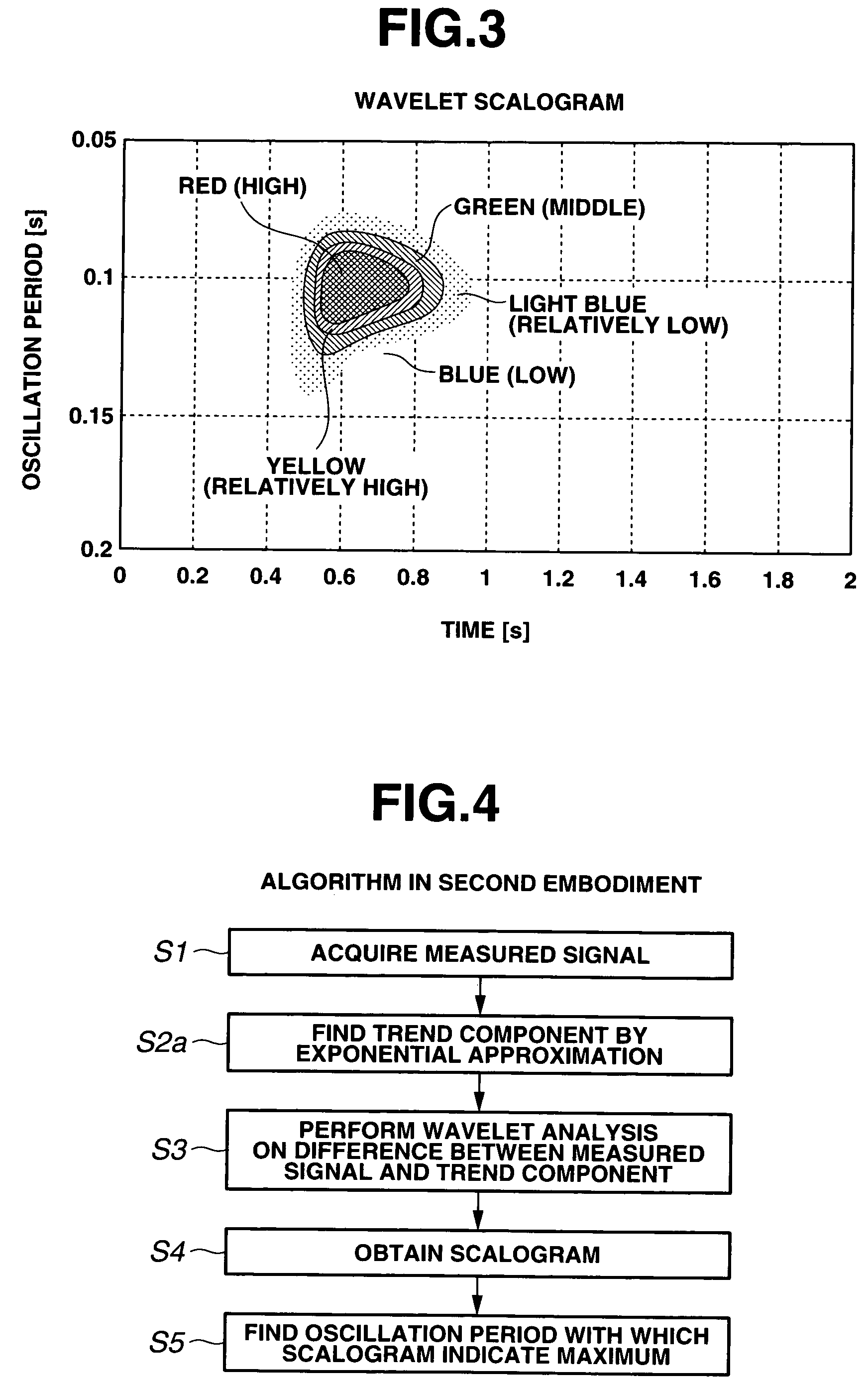
Method for analyzing signal waveform and analyzing vehicle dynamic characteristic
ActiveUS7523011B2Amplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceResistance/reactance/impedenceVehicle dynamicsWaveform analysis
A signal waveform analysis method includes: determining a trend component of an object signal by applying a zero-phase filter to the object signal; determining an oscillatory component of the object signal by removing the trend component from the object signal; determining a wavelet scalogram by performing a wavelet analysis on the oscillatory component; and determining an oscillation period of the object signal with which the wavelet scalogram indicates a maximum. The signal waveform analysis method is employed to evaluate vehicle dynamic characteristics.
Owner:MEIDENSHA ELECTRIC MFG CO LTD +1
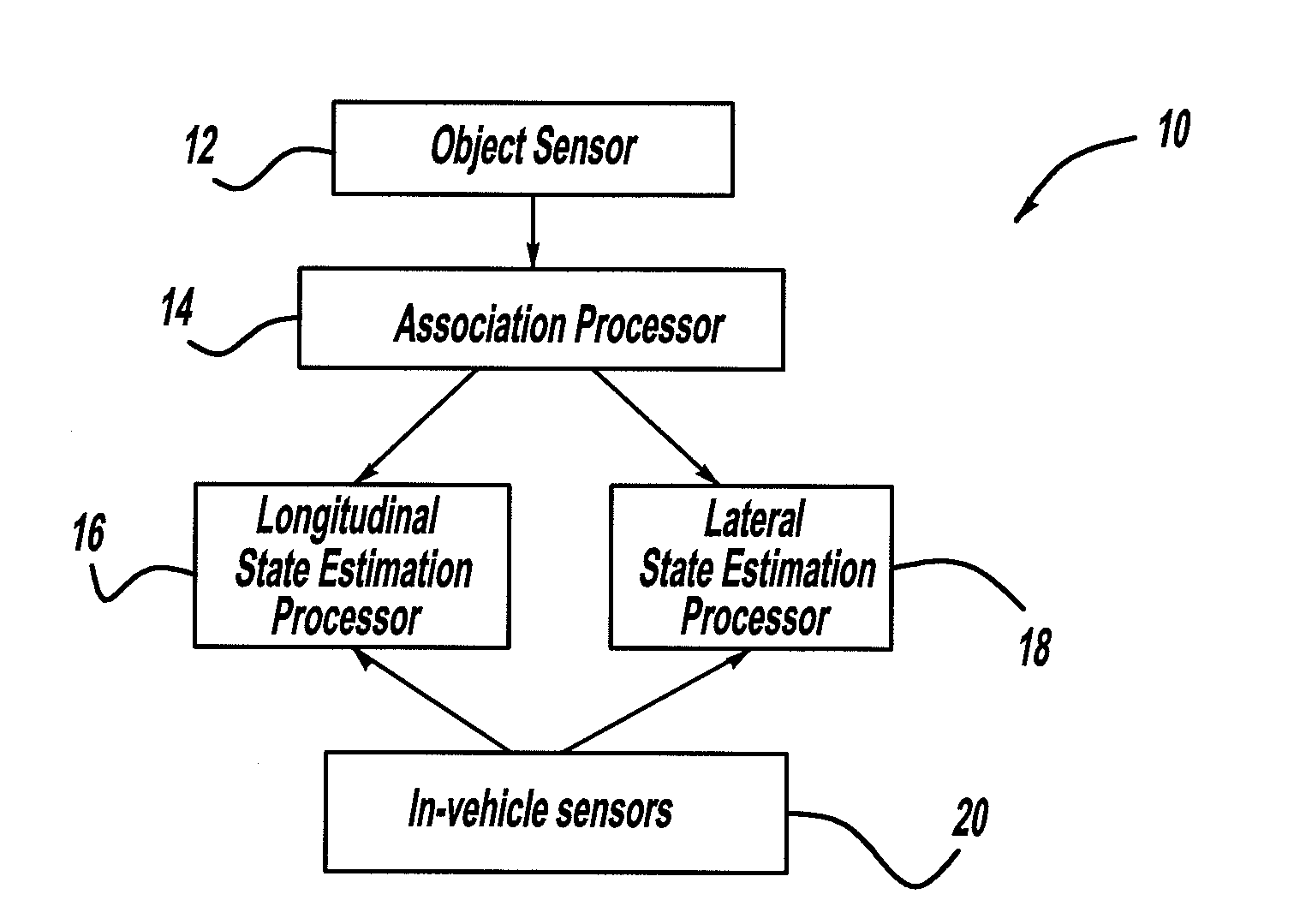
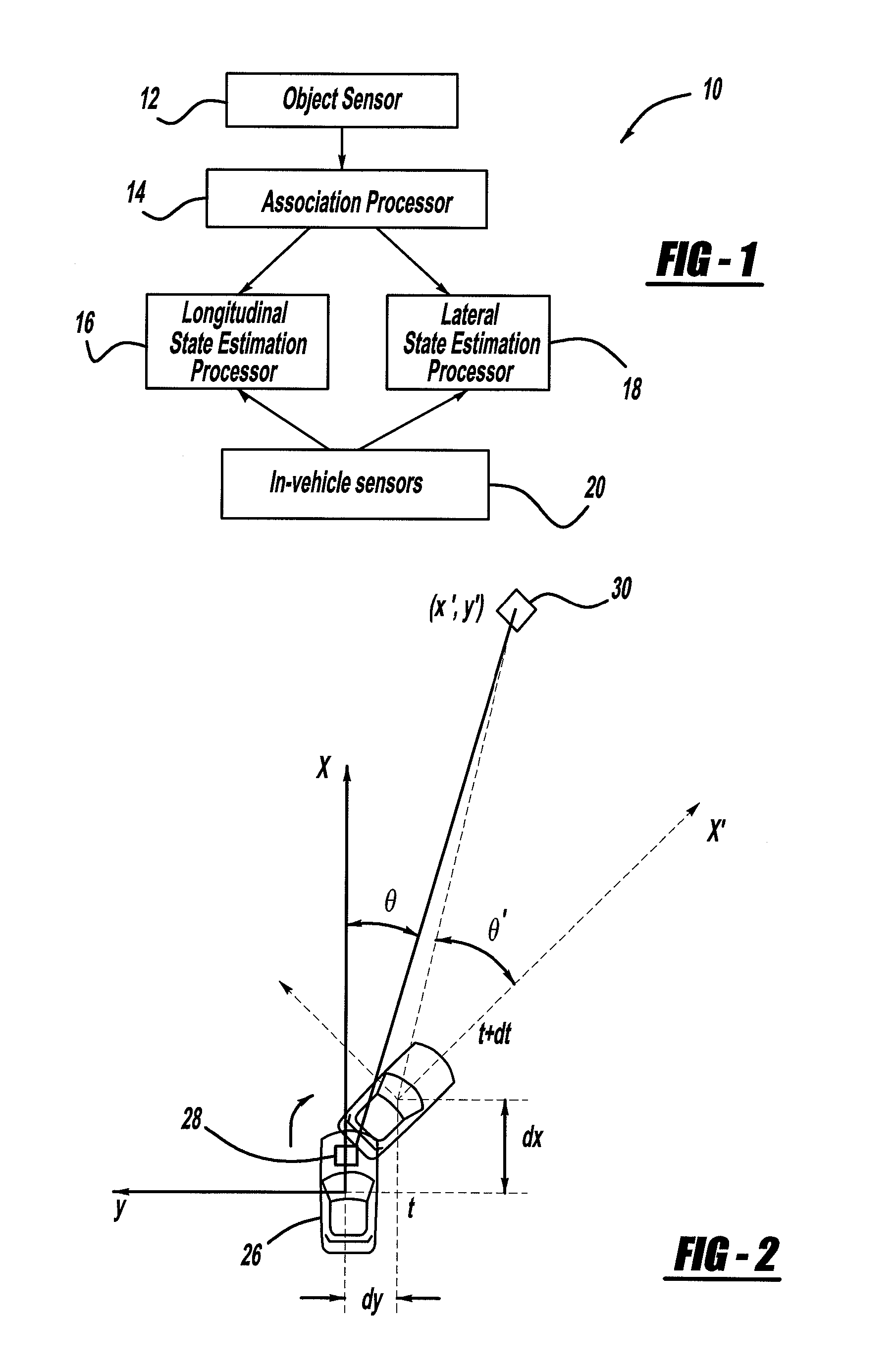
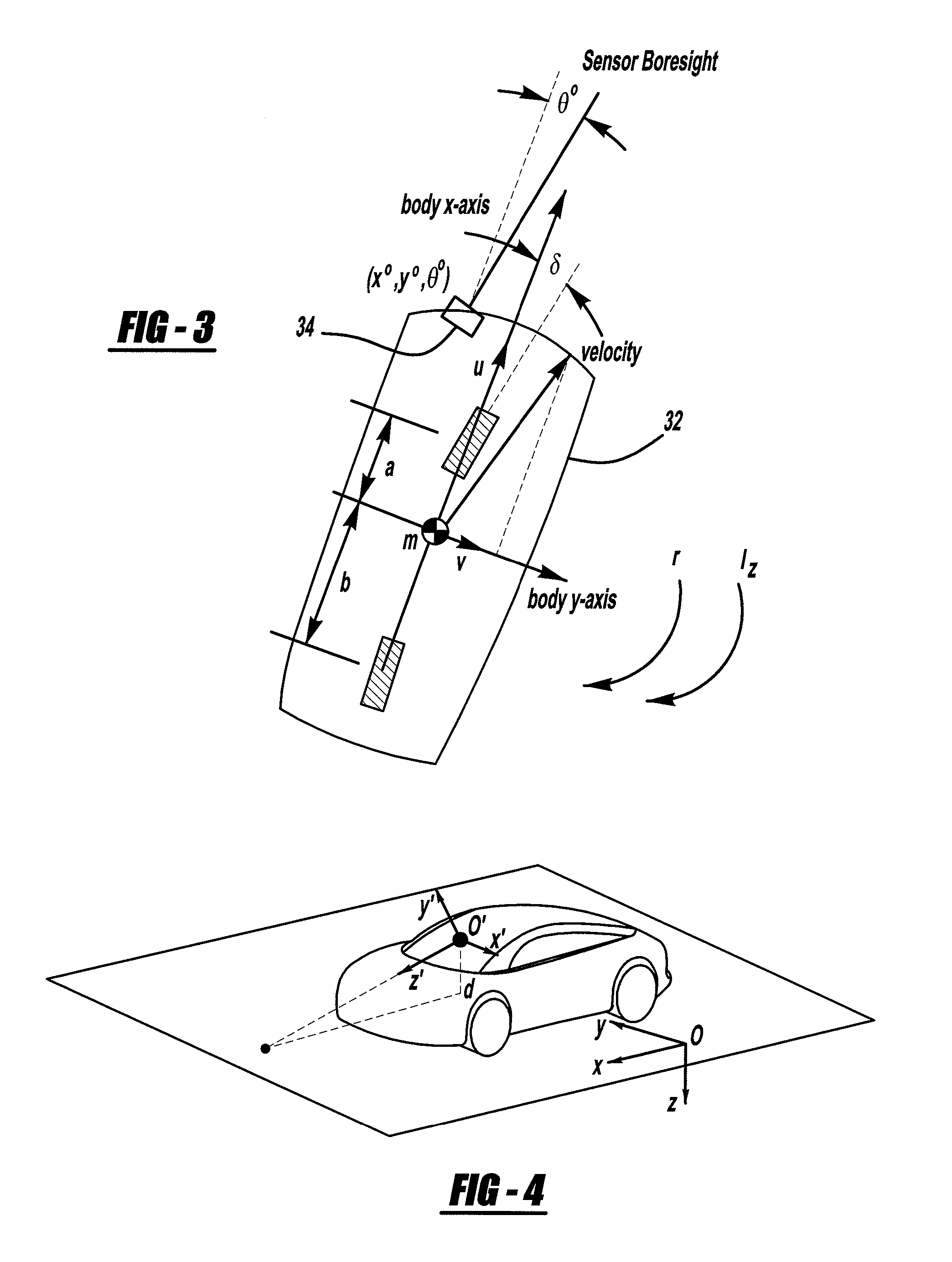
Radar, Lidar and camera enhanced methods for vehicle dynamics estimation
ActiveUS20100017128A1Anti-collision systemsComplex mathematical operationsVehicle dynamicsMultiple frame
A system for estimation vehicle dynamics, including vehicle position and velocity, using a stationary object. The system includes an object sensor that provides object signals of the stationary object. The system also includes in-vehicle sensors that provide signals representative of vehicle motion. The system also includes an association processor that receives the object signals, and provides object tracking through multiple frames of data. The system also includes a longitudinal state estimation processor that receives the object signals and the sensor signals, and provides a correction of the vehicle speed in a forward direction. The system also includes a lateral state estimation processor that receives the object signals and the sensor signals, and provides a correction of the vehicle speed in the lateral direction.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
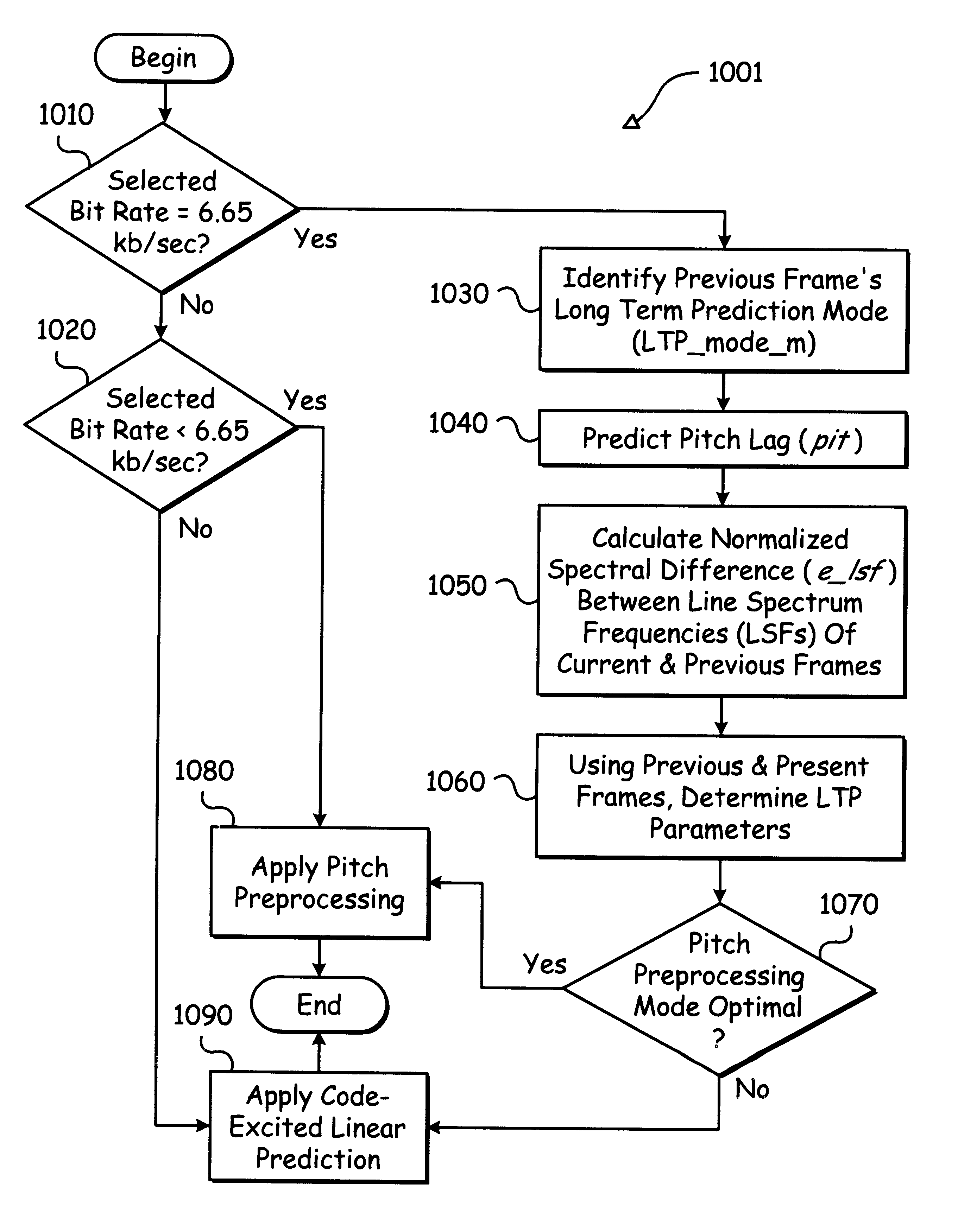
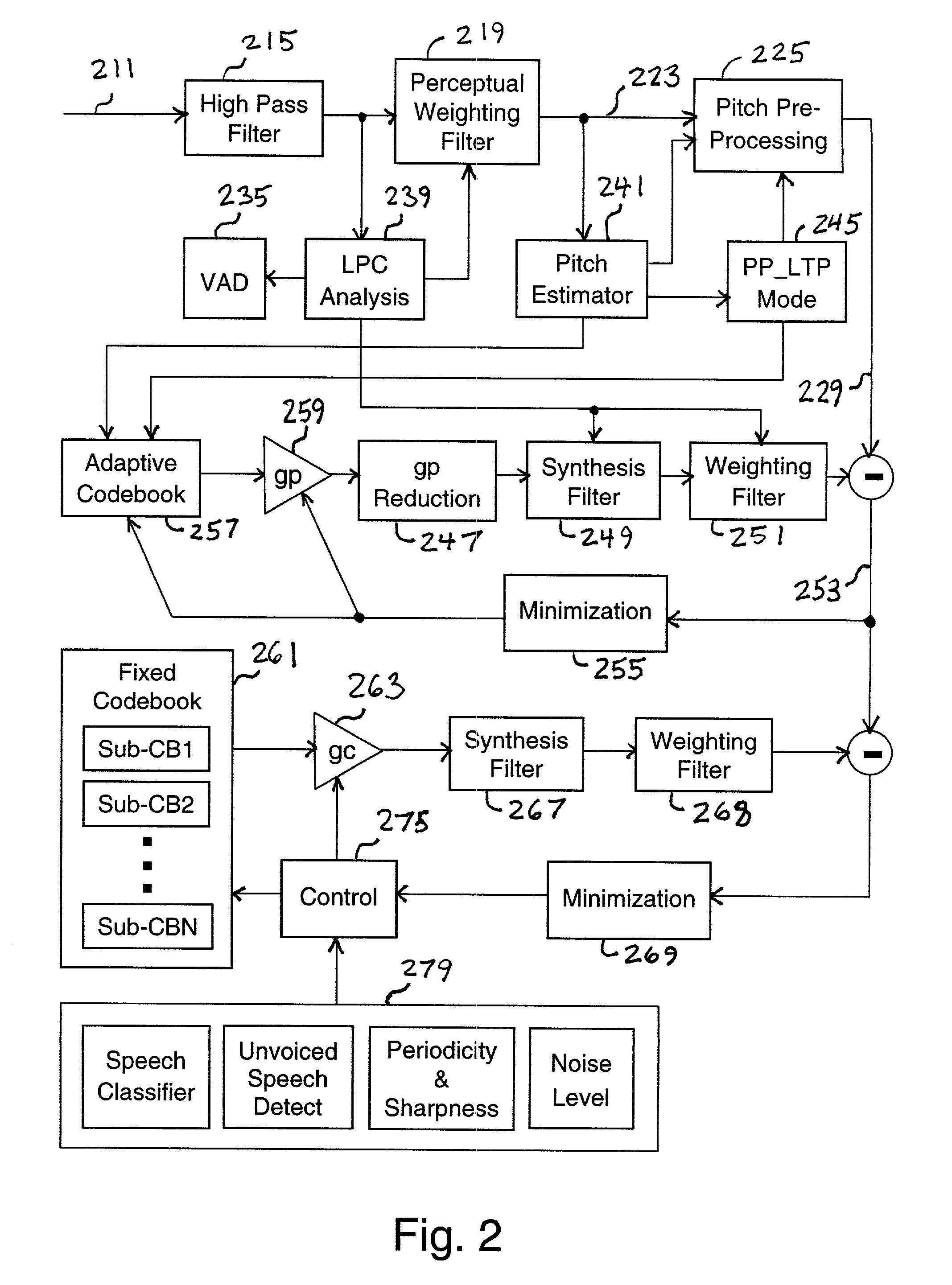
Speech encoder adaptively applying pitch preprocessing with warping of target signal
A multi-rate speech codec supports a plurality of encoding bit rate modes by adaptively selecting encoding bit rate modes to match communication channel restrictions. In higher bit rate encoding modes, an accurate representation of speech through CELP (code excited linear prediction) and other associated modeling parameters are generated for higher quality decoding and reproduction. A speech encoder employing various encoding schemes based upon parameters including an available transmission bit rate. In addition, the speech encoder is operable to identify and apply an optimal encoding scheme for a given speech signal. The speech encoder may be applied code-excited linear prediction when the available bit rate is above a predetermined upper threshold. Pitch preprocessing, including continuous warping, may be applied when it is below a predetermined lower threshold. The encoder considers varying characteristics of the speech signal including the long term prediction mode of a previous frame, and a spectral difference between the line spectral frequencies of a current and a previous frame, a predicted pitch lag, an open loop pitch lag, a closed loop pitch lag, a pitch gain, and a pitch correlation.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
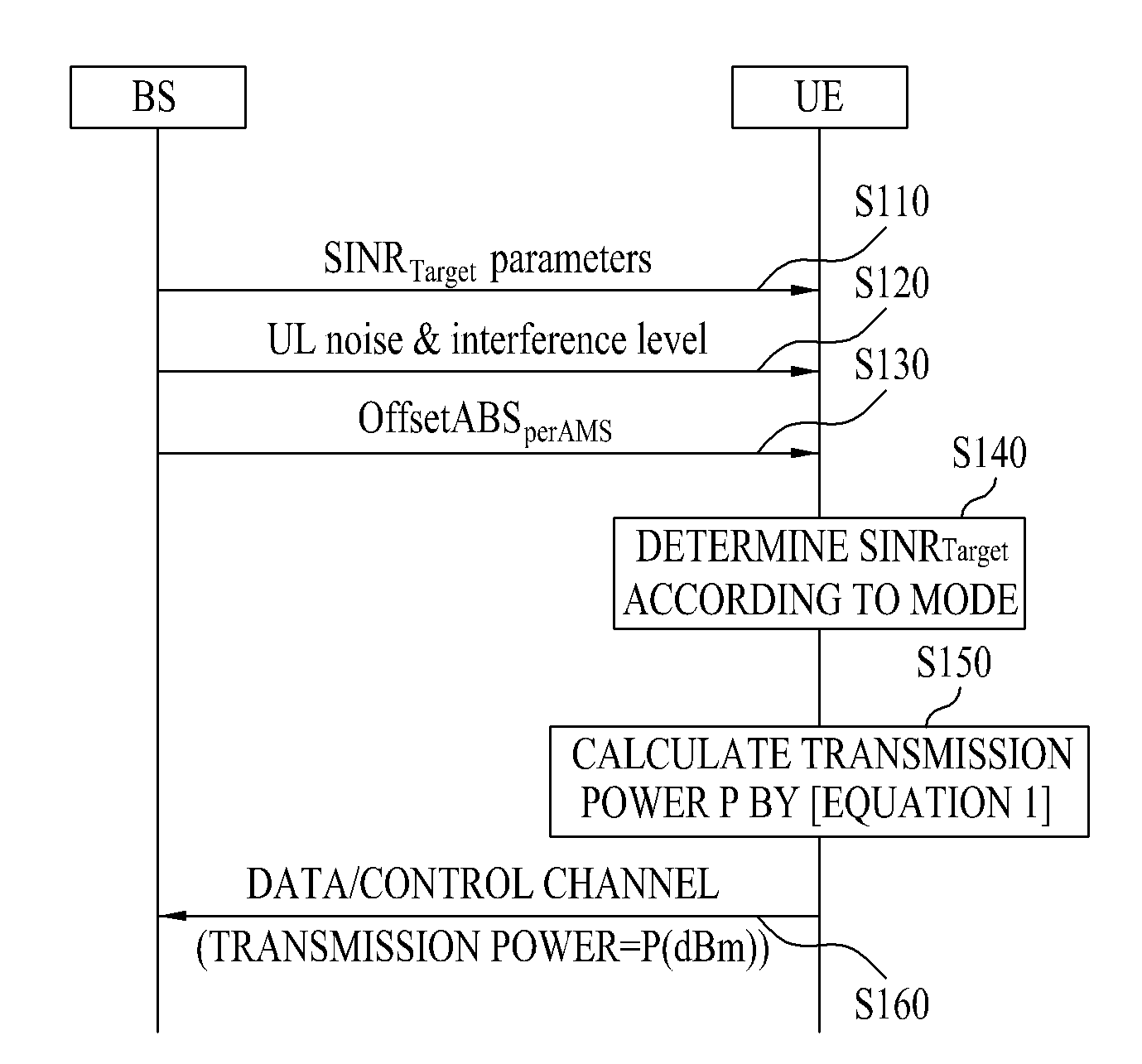
Method and apparatus for controlling uplink power in a wireless communication system
InactiveUS20110098076A1Improve service qualityMaintain stabilityPower managementError preventionCommunications systemTarget signal
A method and apparatus for controlling uplink power in a wireless communication system are disclosed. The uplink power controlling method includes receiving target Signal-to-Interference plus Noise Ratio (SINR) parameters and an uplink noise and interference level from a base station, determining an uplink power based on a target SINR and an estimated average power level of noise and interference of a user equipment, the target SINR being determined using the target SINR parameters and the estimated average power level of noise and interference of the user equipment being calculated using the uplink noise and interference level, and receiving at least one of selectively transmitted first and second offsets from the base station and adjusting the uplink power based on the received at least one of the first and second offsets.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
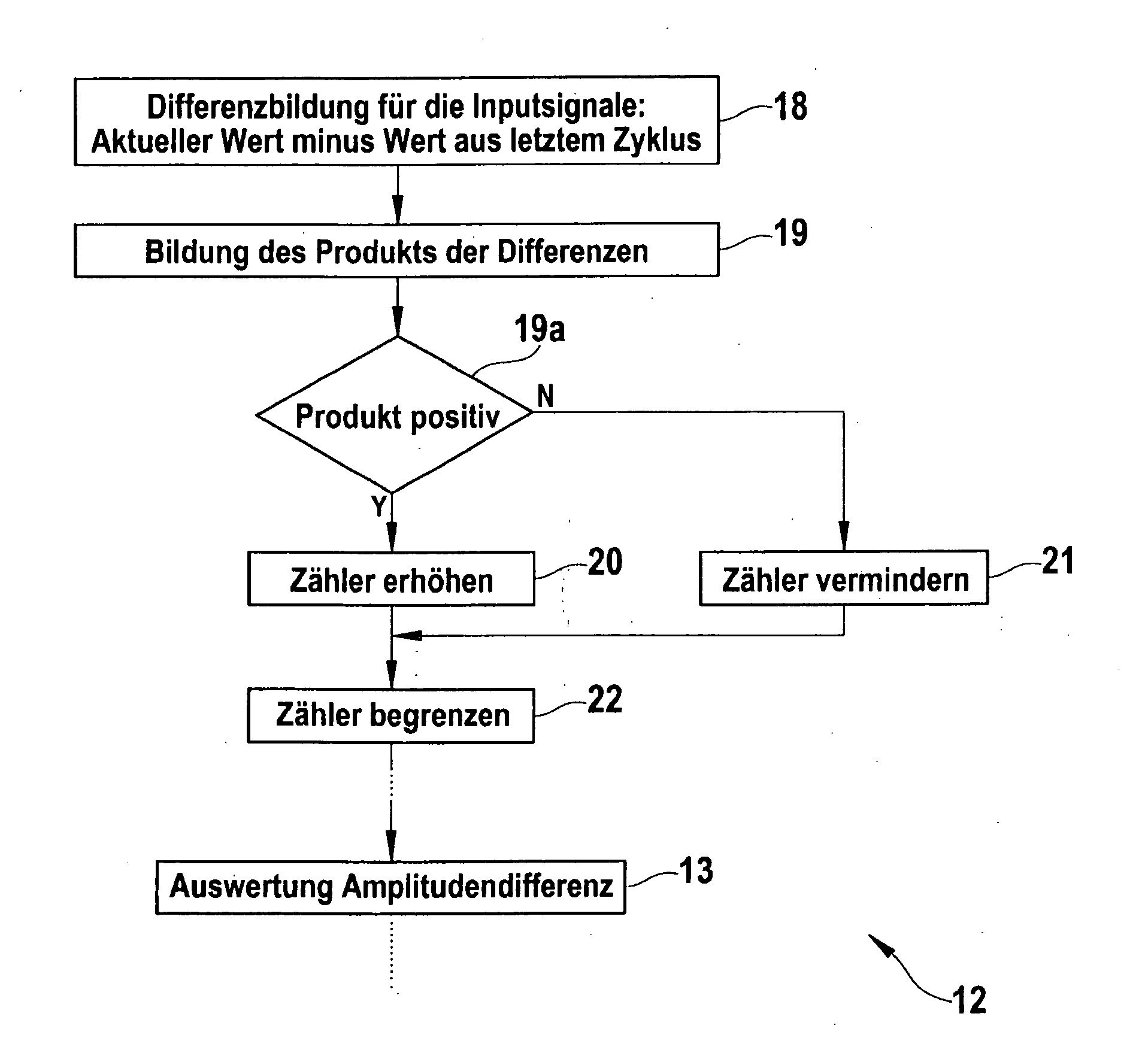
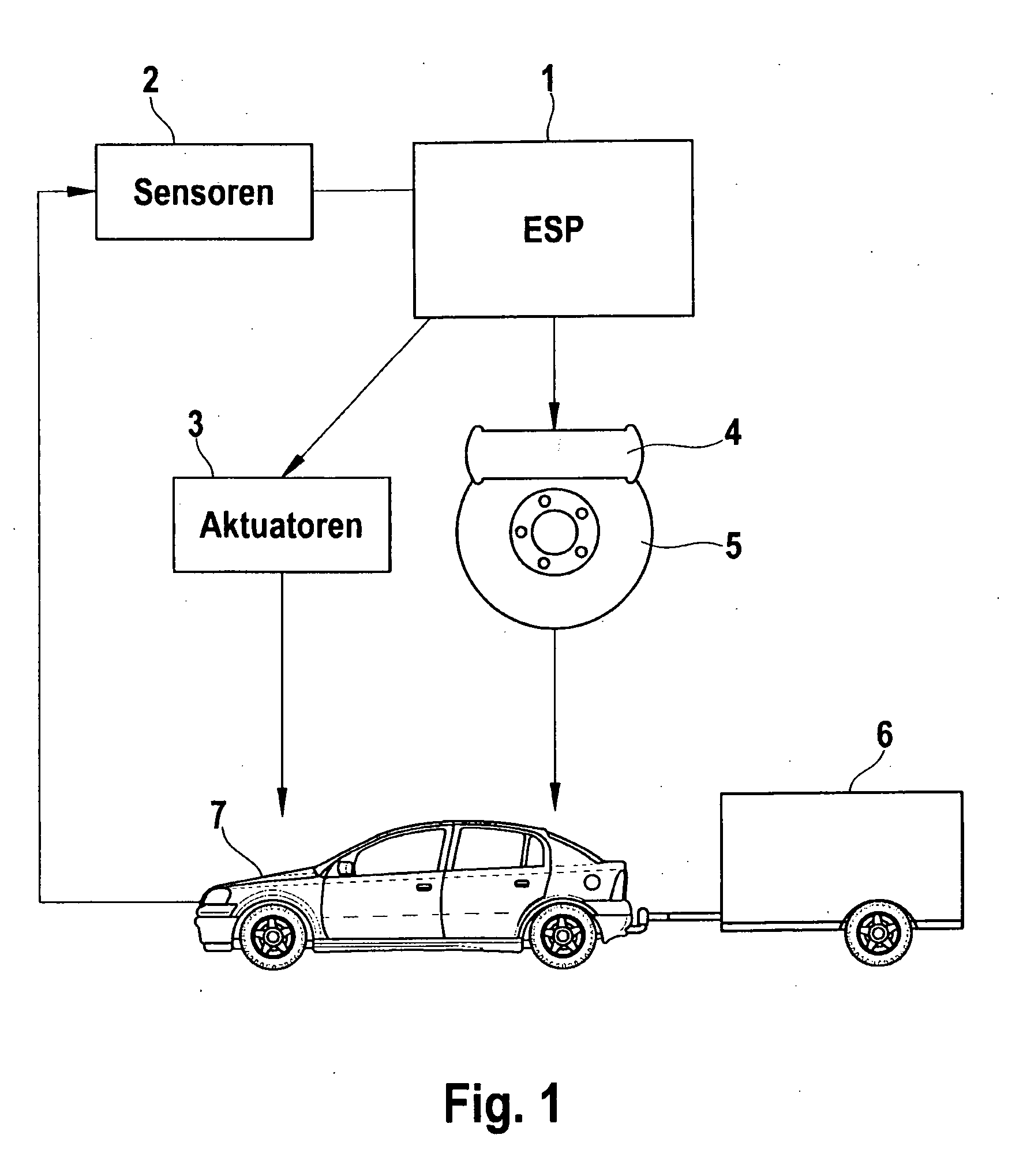
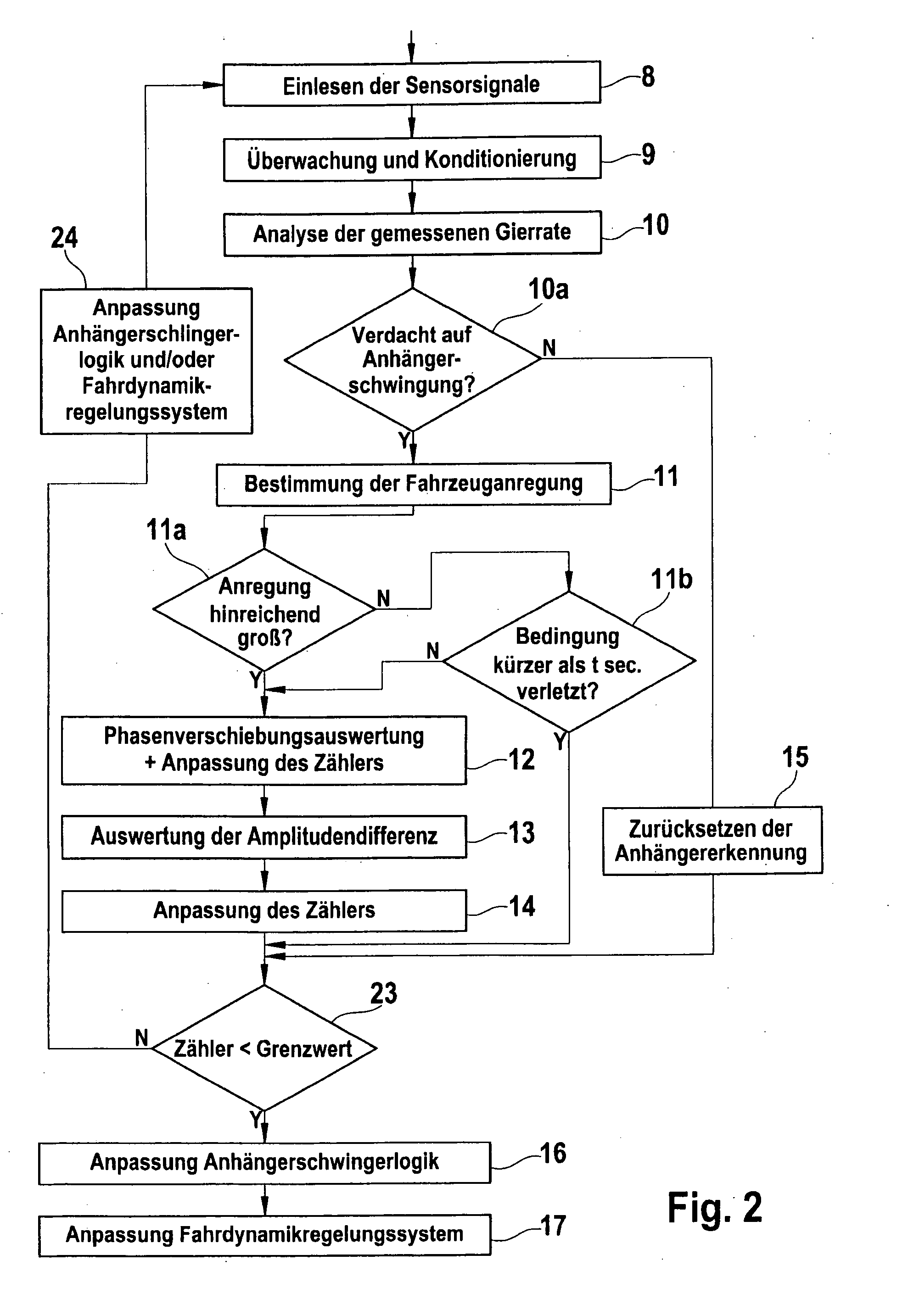
Method and Control Device for Identifying a Trailer Operation of a Towing Vehicle
InactiveUS20090306861A1Reliable identificationImprove reliabilityDigital data processing detailsAutomatic initiationsVehicle dynamicsControl system
In a method for identifying a trailering mode in the context of a towing vehicle, in particular as part of a vehicle dynamics control system having a trailer roll logic function for stabilizing the combination of towing vehicle and trailer, that identification of the trailering mode is accomplished by a comparison of an actual signal characterizing the vehicle state with a corresponding target signal.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
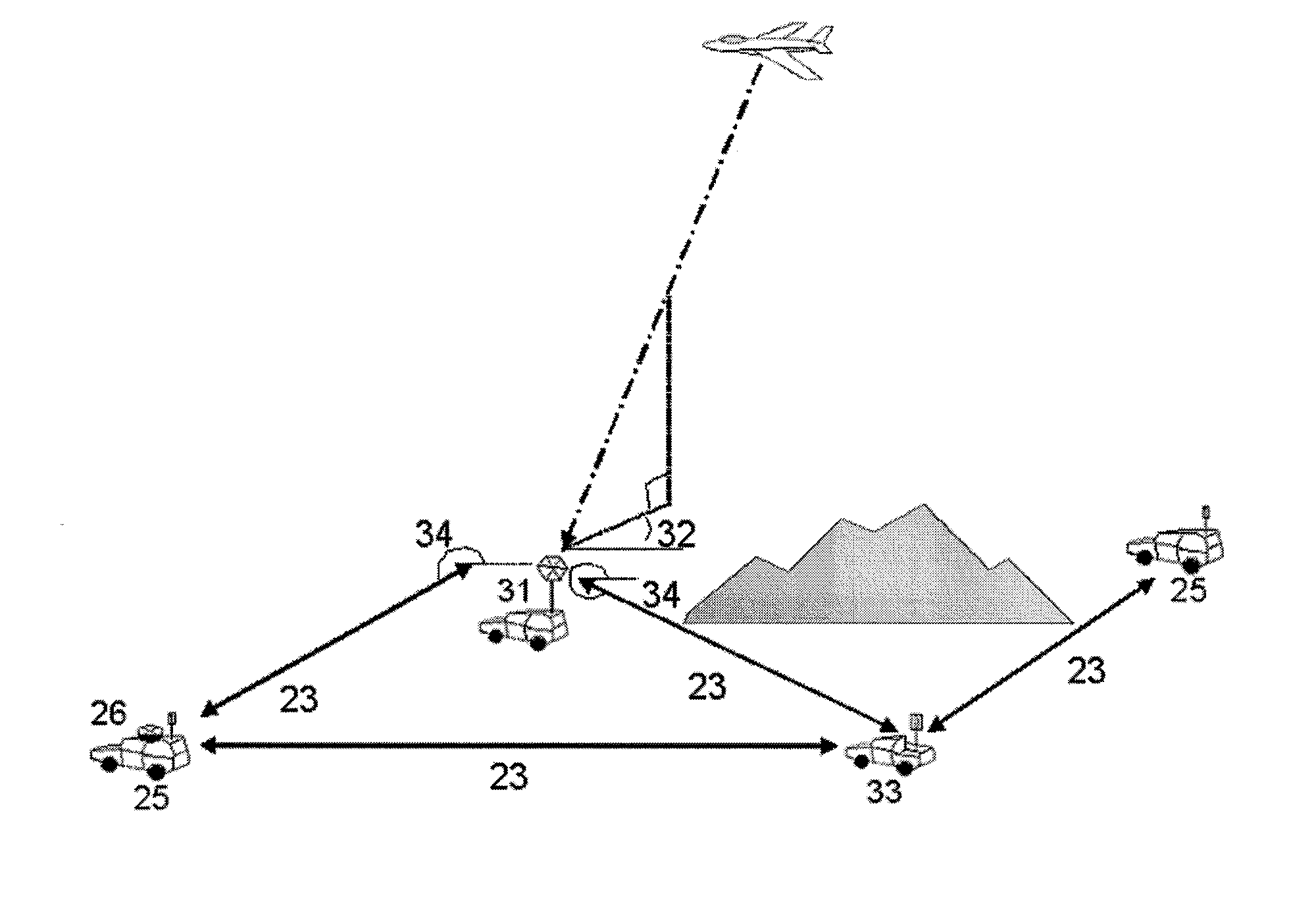
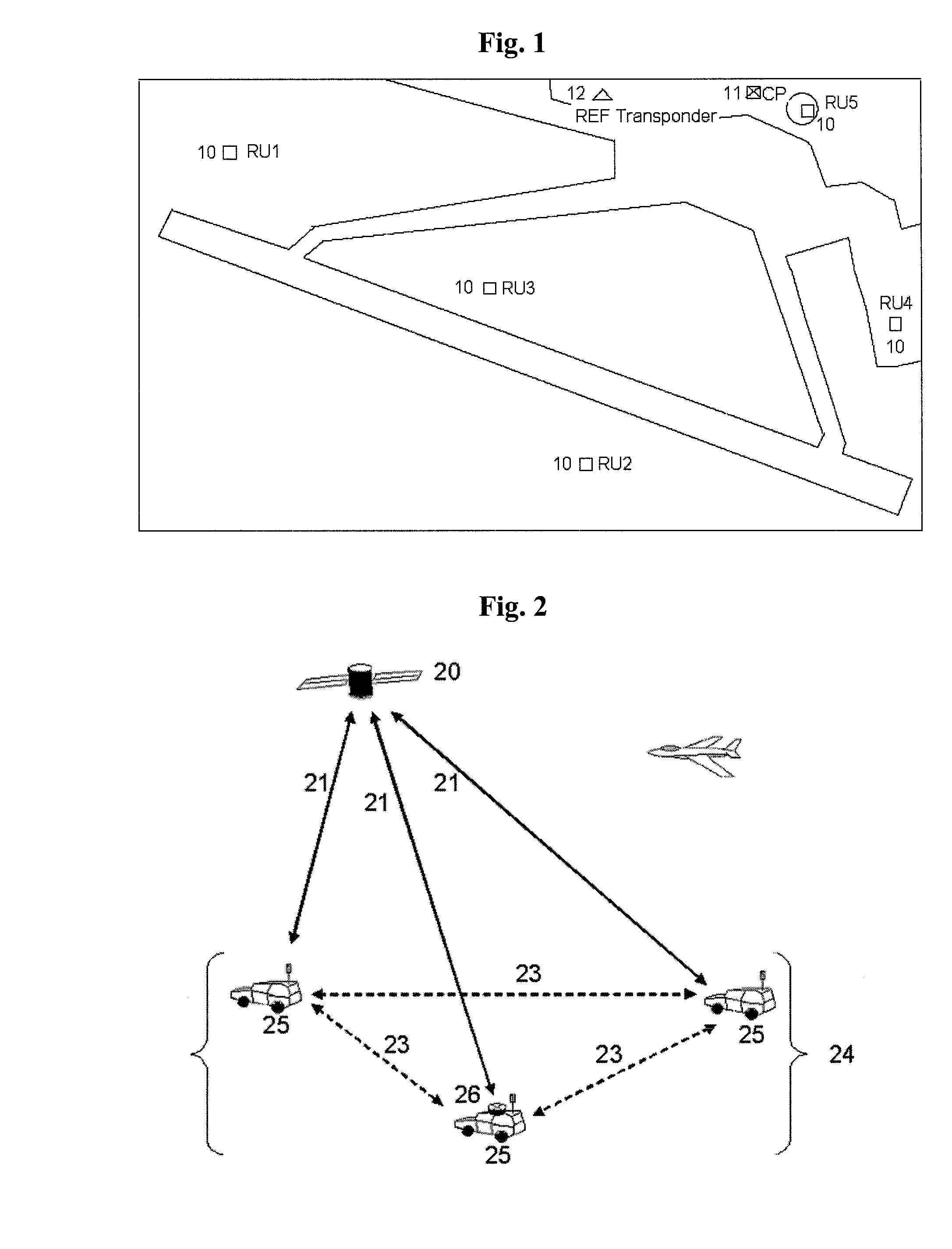
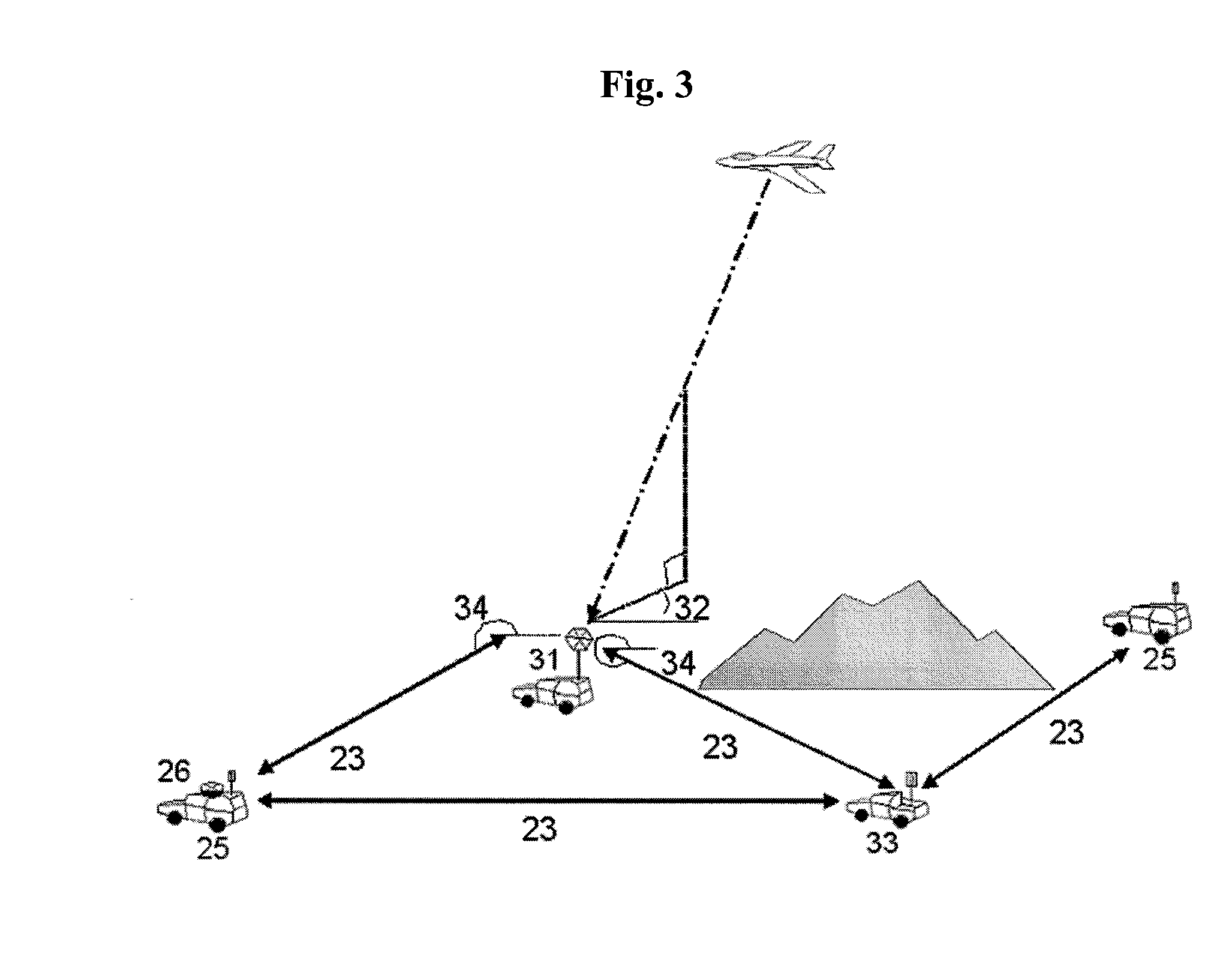
System and method for multilaterating a position of a target using mobile remote receiving units
ActiveUS20070247368A1Direction finders using radio wavesPosition fixationTarget signalMultilateration
A method of multilaterating the position of a target, including the steps of deploying a plurality of time synchronized receiving units in a network that allows the receiving units to communicate with a central processor; receiving a target signal from the target at each receiving unit; determining a time of arrival for the target signal at each receiving unit; determining position data for each receiving unit at the time when the target signal is received at each respective receiving unit; and using the time of arrival and position data for each receiving unit to determine the position of the target by multilateration. A system for carrying out the method is also disclosed.
Owner:SAAB INC
Speech encoder adaptively applying pitch preprocessing with warping of target signal
InactiveUS20010023395A1Efficient and effective of signalReduce bitrateSpeech analysisTarget signalClosed loop
A multi-rate speech codec supports a plurality of encoding bit rate modes by adaptively selecting encoding bit rate modes to match communication channel restrictions. In higher bit rate encoding modes, an accurate representation of speech through CELP (code excited linear prediction) and other associated modeling parameters are generated for higher quality decoding and reproduction. A speech encoder employing various encoding schemes based upon parameters including an available transmission bit rate. In addition, the speech encoder is operable to identify and apply an optimal encoding scheme for a given speech signal. The speech encoder may be applied code-excited linear prediction when the available bit rate is above a predetermined upper threshold. Pitch preprocessing, including continuous warping, may be applied when it is below a predetermined lower threshold. The encoder considers varying characteristics of the speech signal including the long term prediction mode of a previous frame, and a spectral difference between the line spectral frequencies of a current and a previous frame, a predicted pitch lag, an open loop pitch lag, a closed loop pitch lag, a pitch gain, and a pitch correlation.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
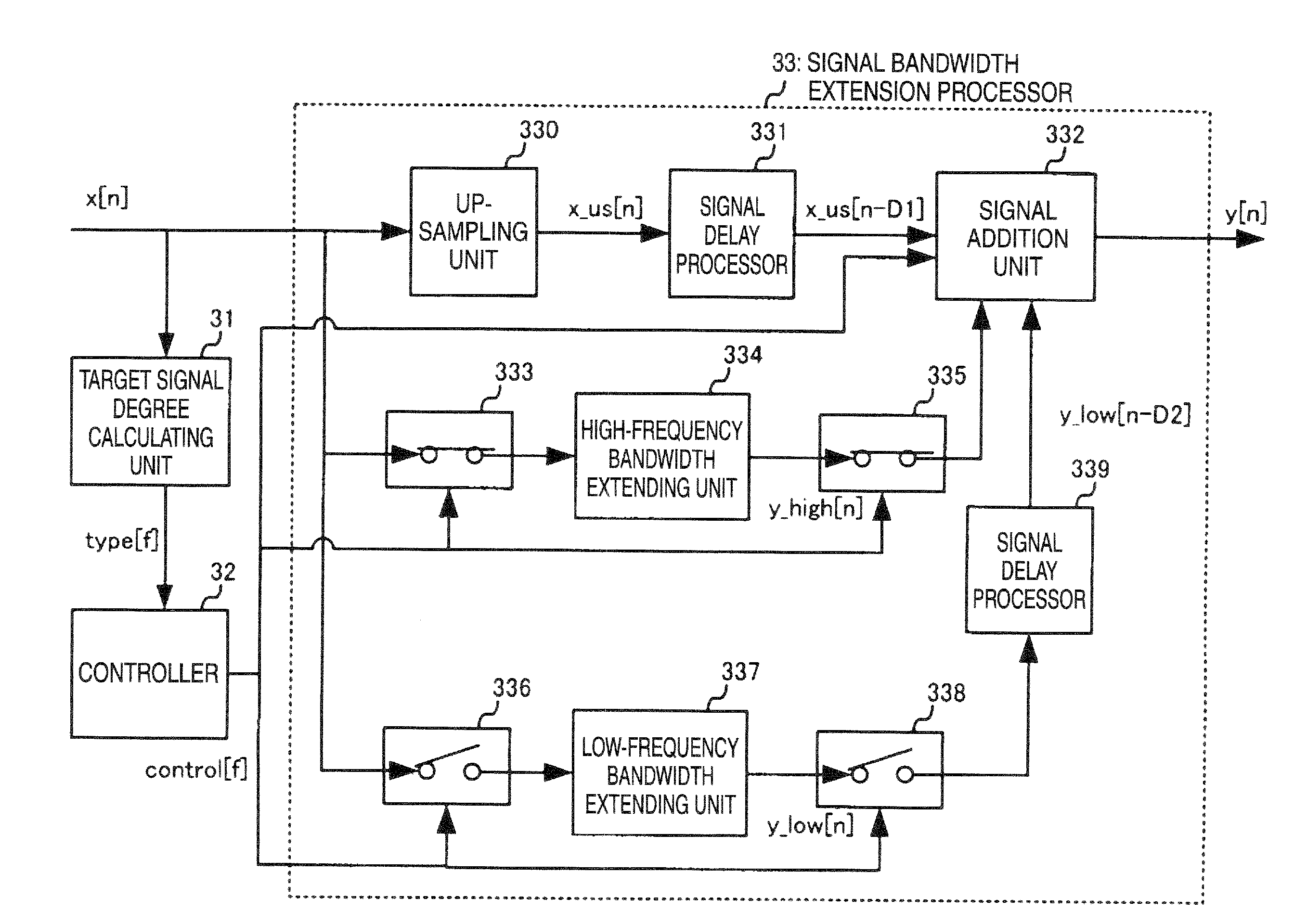
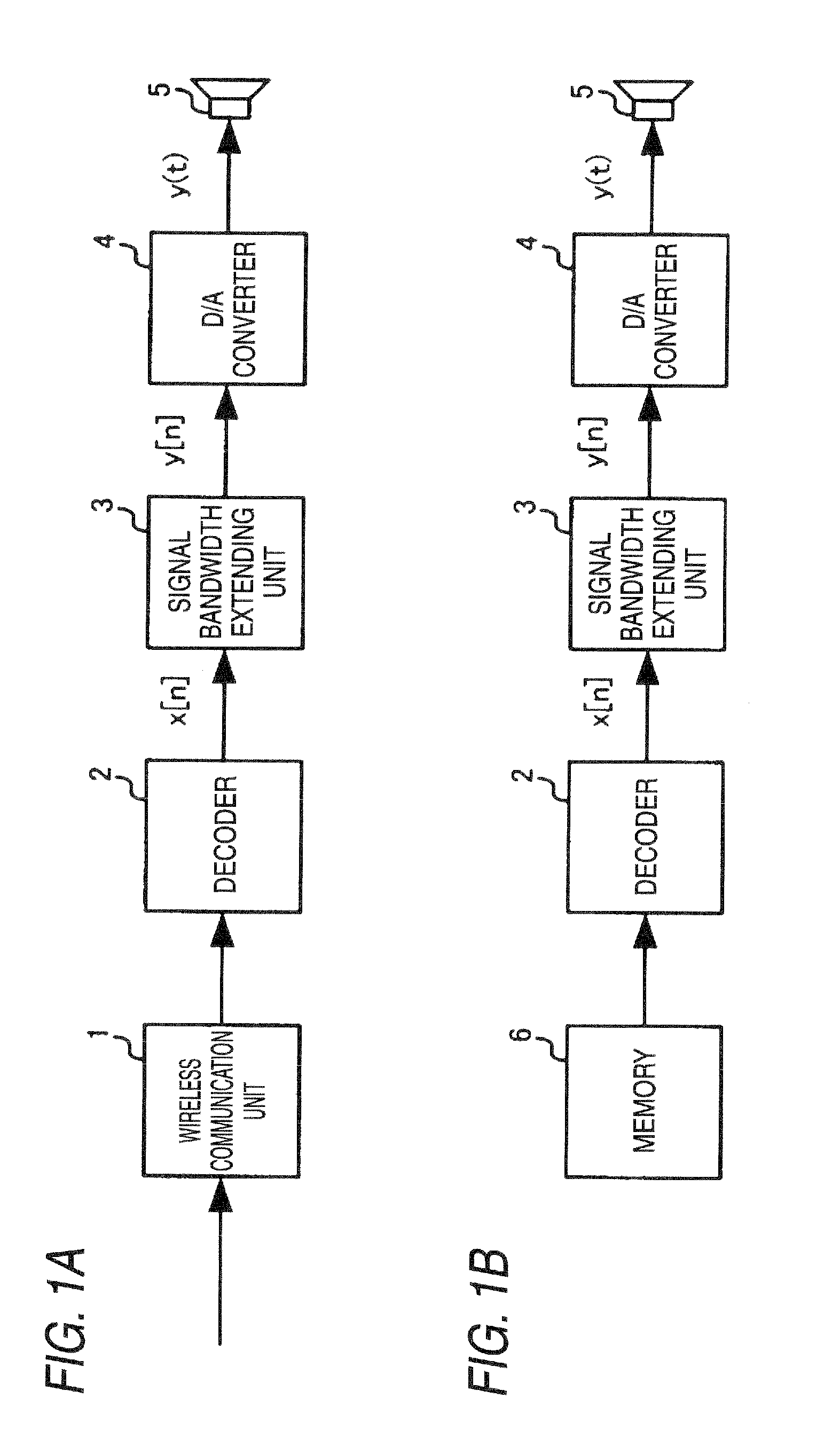
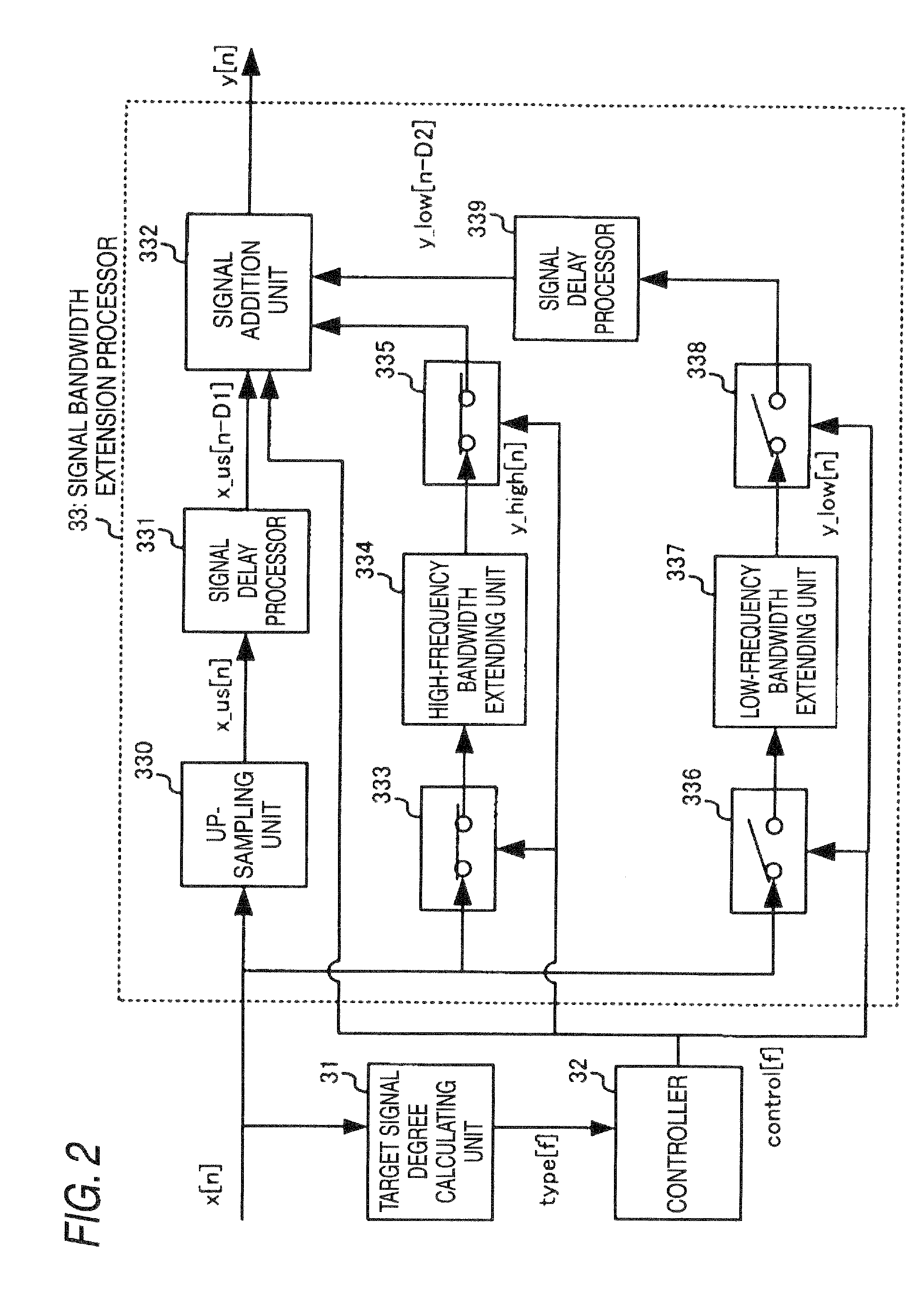
Signal bandwidth extending apparatus
A signal bandwidth extending apparatus including: a bandwidth extending section configured to extend a frequency bandwidth of a target signal, the target signal included in an input signal; a calculating section configured to calculate a degree of the target signal included in the input signal; and a controller configured to change a method of extending the frequency bandwidth by the bandwidth extending section according to a result of the calculating section.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Method of evaluating a readout signal, and optical disc apparatus
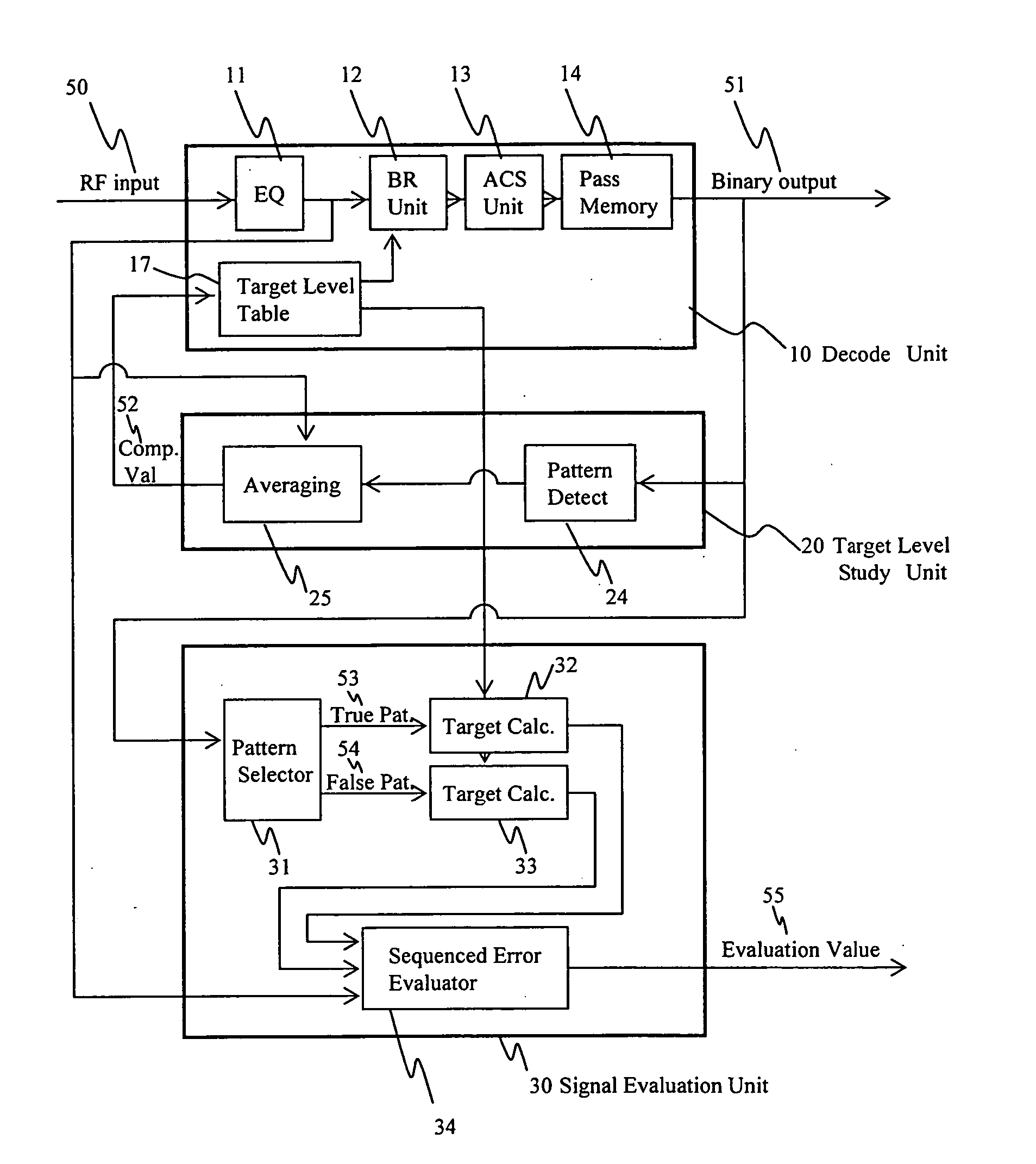
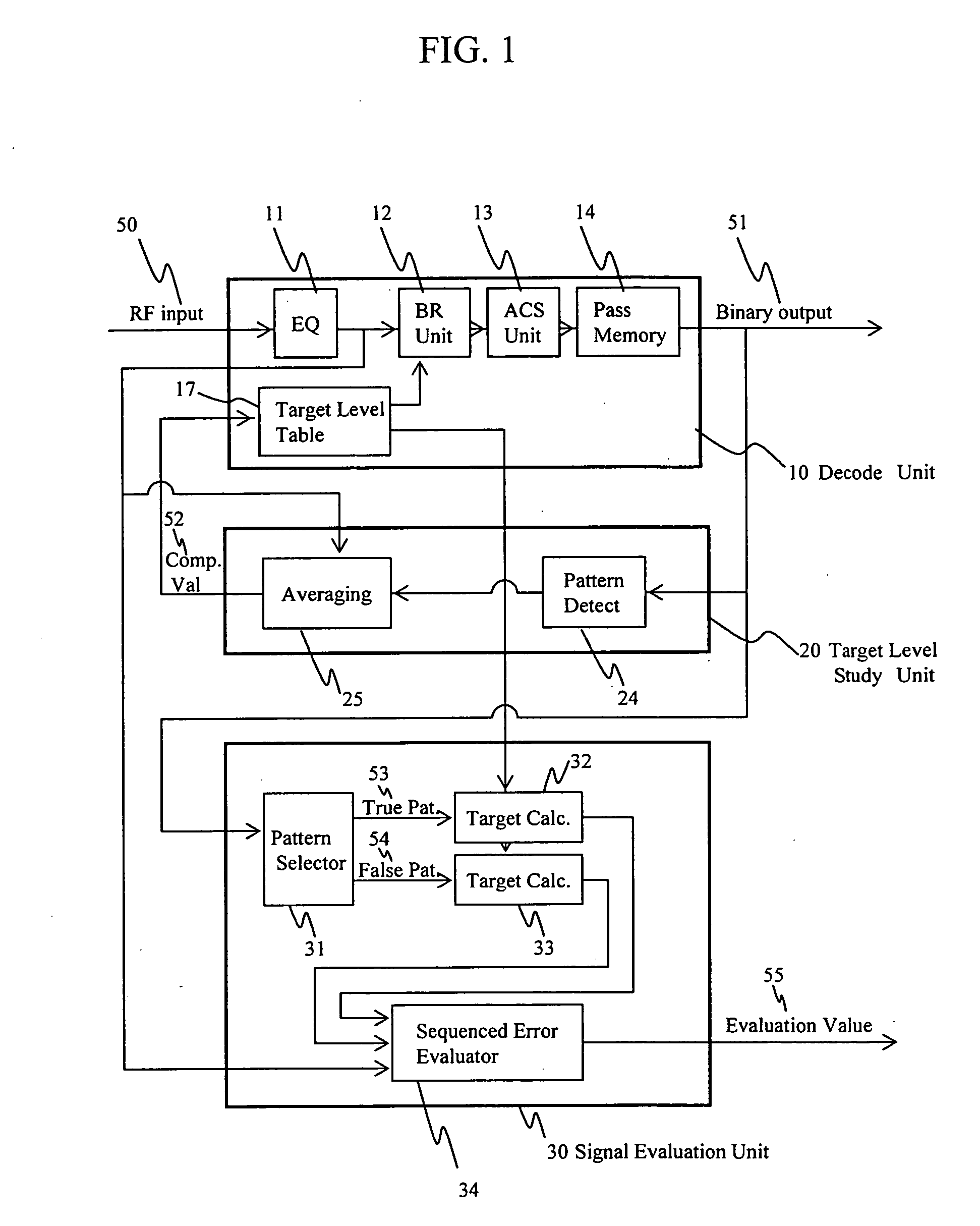
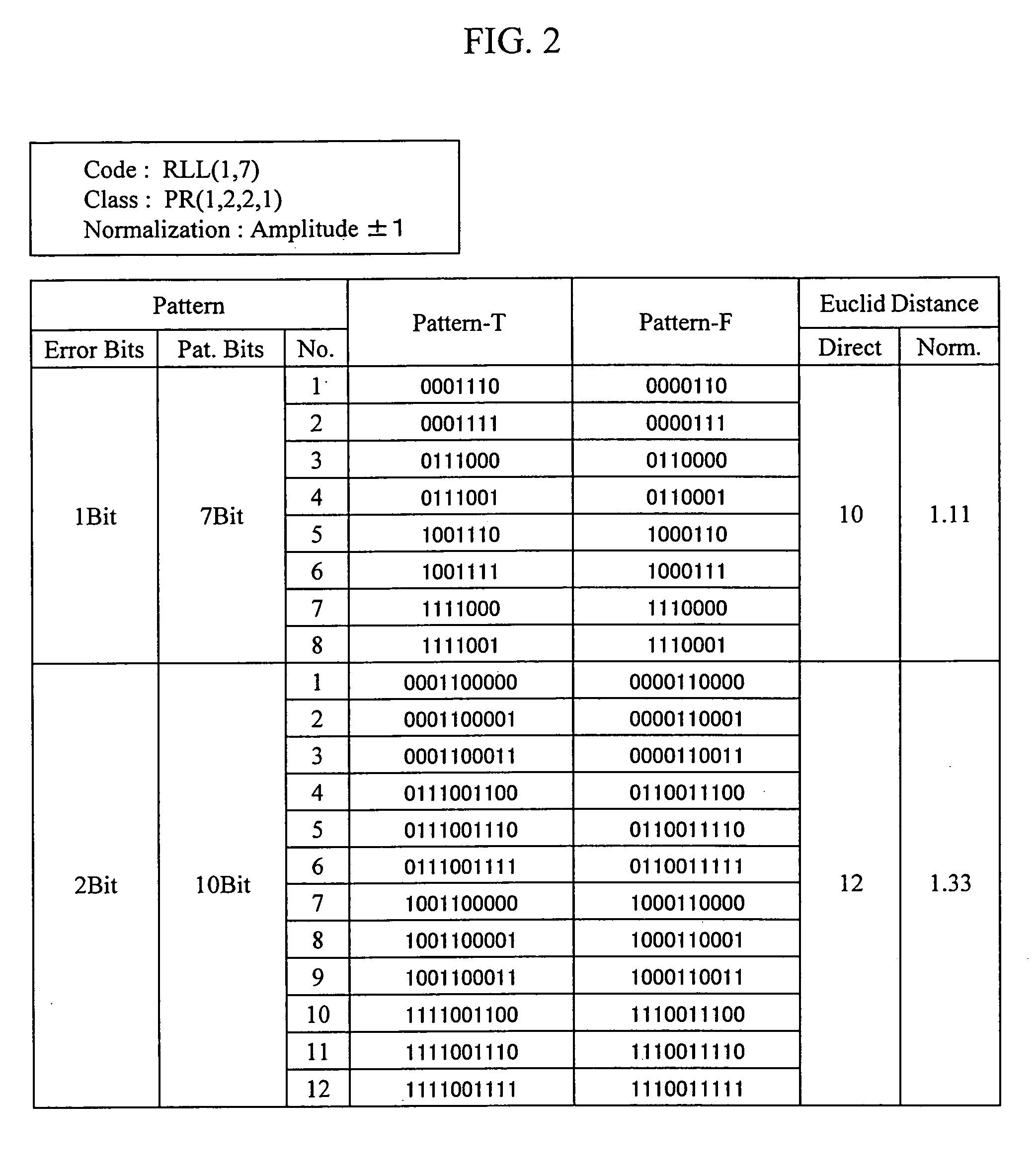
InactiveUS20050249318A1Precise positioningAccurate assessmentModification of read/write signalsOptical beam sourcesViterbi decoderSignal quality
A method of evaluating the quality of a read signal from the viewpoint of the detection margin of a Viterbi decoder in the PRML method in which a target signal level varies depending on the read signal, and an optical disc apparatus implementing the method. A method of evaluating the quality of a signal pattern comprising a combination of minimum run lengths from the viewpoint of edge shift, and an optical disc apparatus implementing the method. From the target signal level that varies depending on the read signal, a target signal is generated based on a decoding result, and an error target signal is generated in which the decoding result is edge-shifted. The signal quality is evaluated by calculating a Euclidean distance between these signals and the read signal. A virtual state that is not included in the Viterbi decoder and that is less than the minimum run length is defined, and a target signal level for the virtual state is generated using a target signal level table inside the Viterbi decoder, based on the concept of convolution. In this way, the signal quality can be evaluated by the same method as mentioned above even in cases where the pattern of a combination of the minimum run lengths has edge-shifted.
Owner:HITACHI-LG DATA STORAGE +1
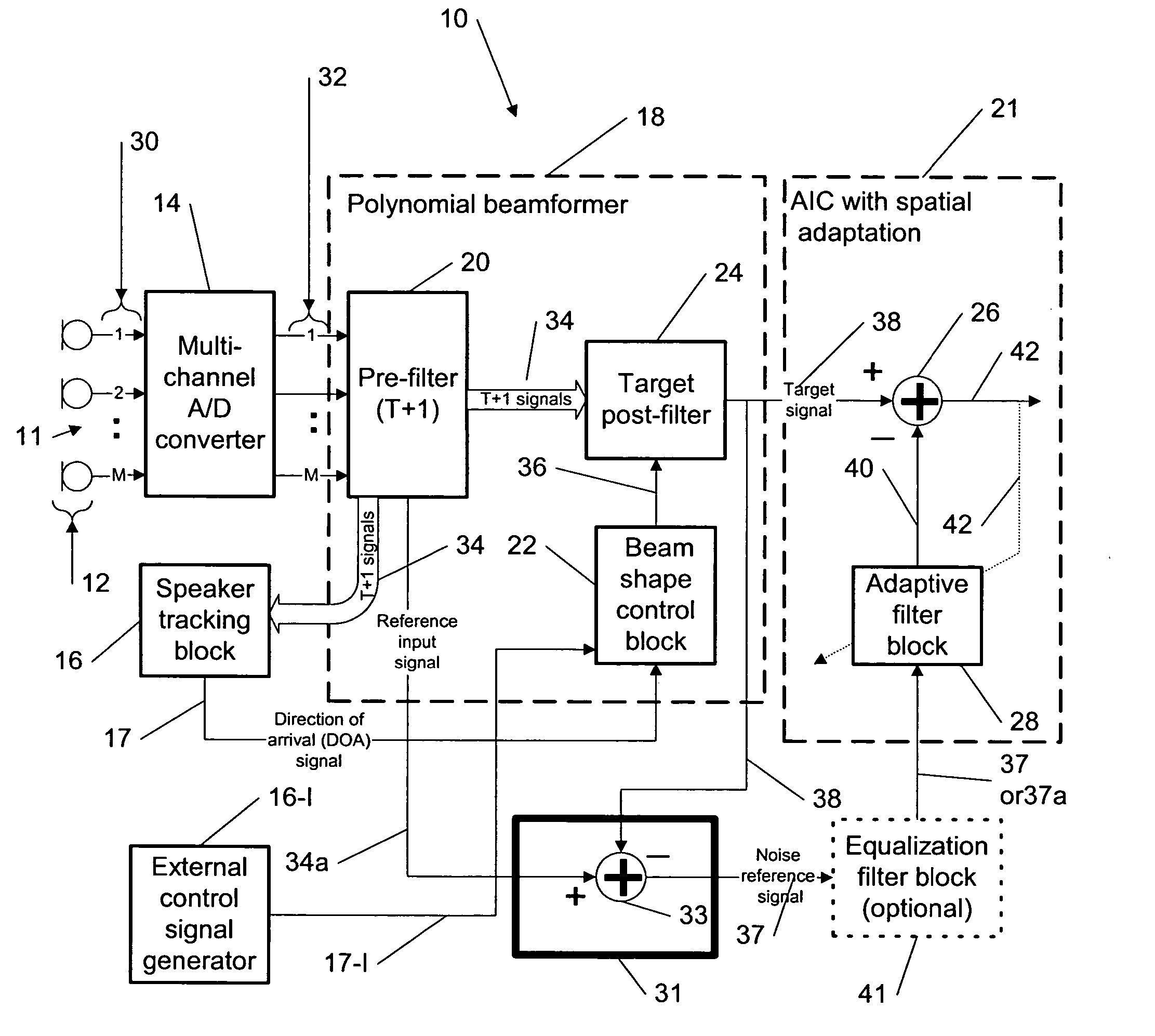
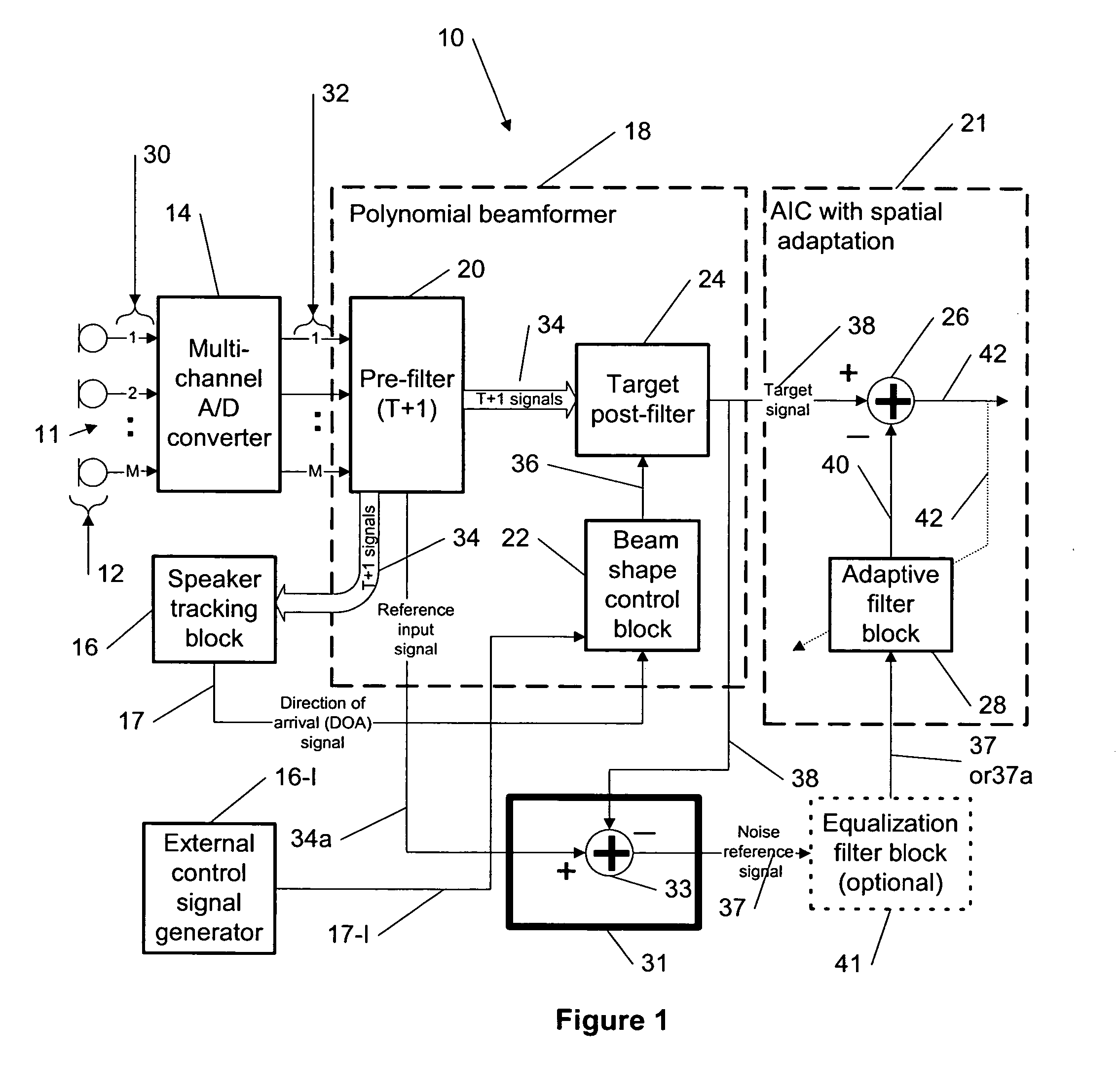
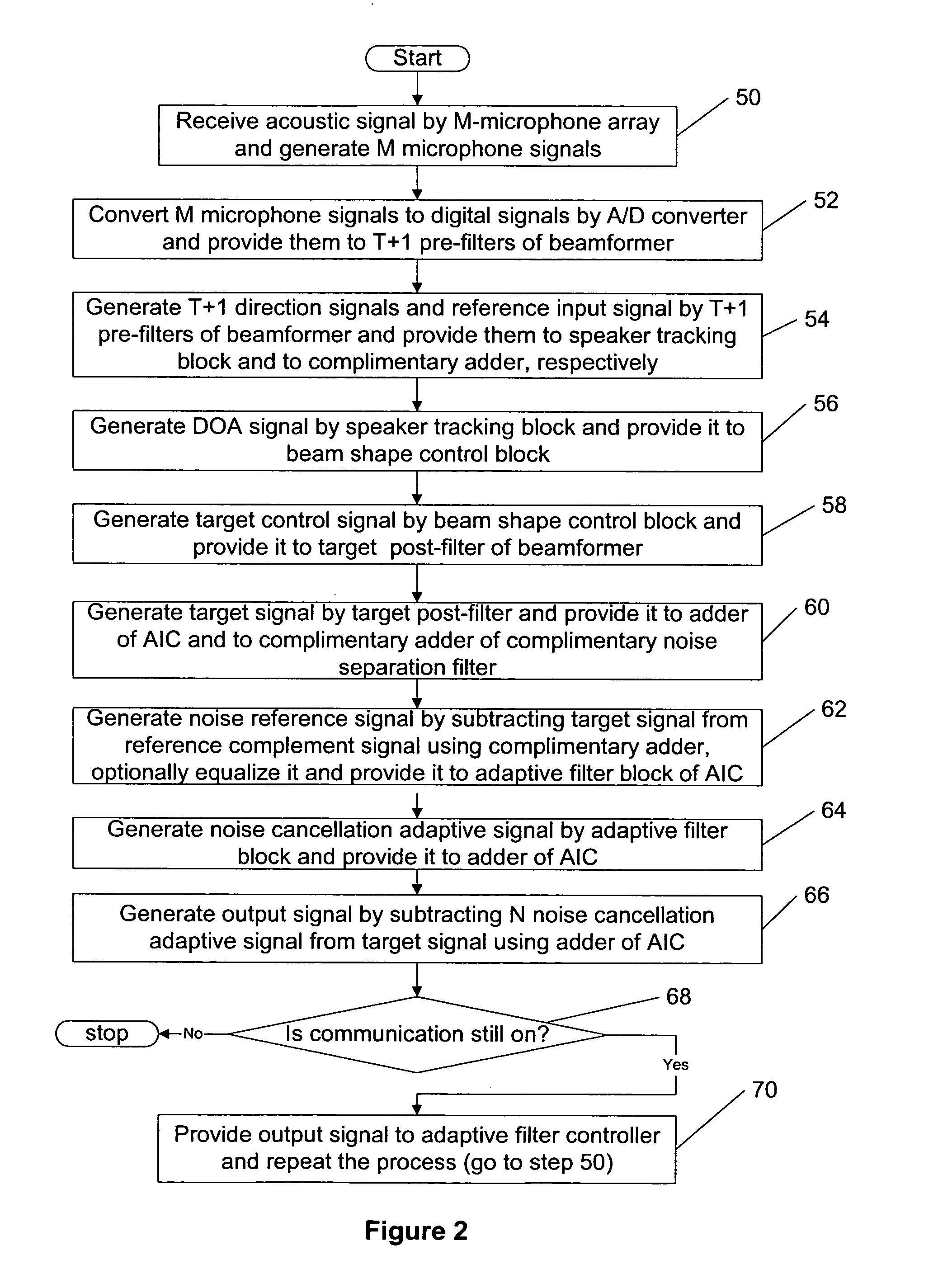
Method for efficient beamforming using a complementary noise separation filter
ActiveUS20050141731A1High computational complexityEfficient implementationSignal processingEar treatmentAdaptive filterInterference canceller
This invention describes a method for efficient beamforming for generalized sidelobe canceling using complementary noise separation filtering for generating a noise reference for adaptation performance of an adaptive interference canceller (AIC). The adaptive filter provides noise estimates to be subtracted from the desired signal path providing further noise reduction in the system output. More specifically, the present invention relates to a multi-microphone beamforming system similar to a generalized sidelobe canceller (GSC) structure, but the difference with the conventional GSC method is that the complementary filter used for desired signal blocking can be realized with a simple subtraction without compromising the beam steering flexibility of the polynomial beamforming filter front end using the desired target signal and the complementary background noise estimate signal, respectively, with the complexity of one complementary filter and one sum beamformer.
Owner:III HLDG 3
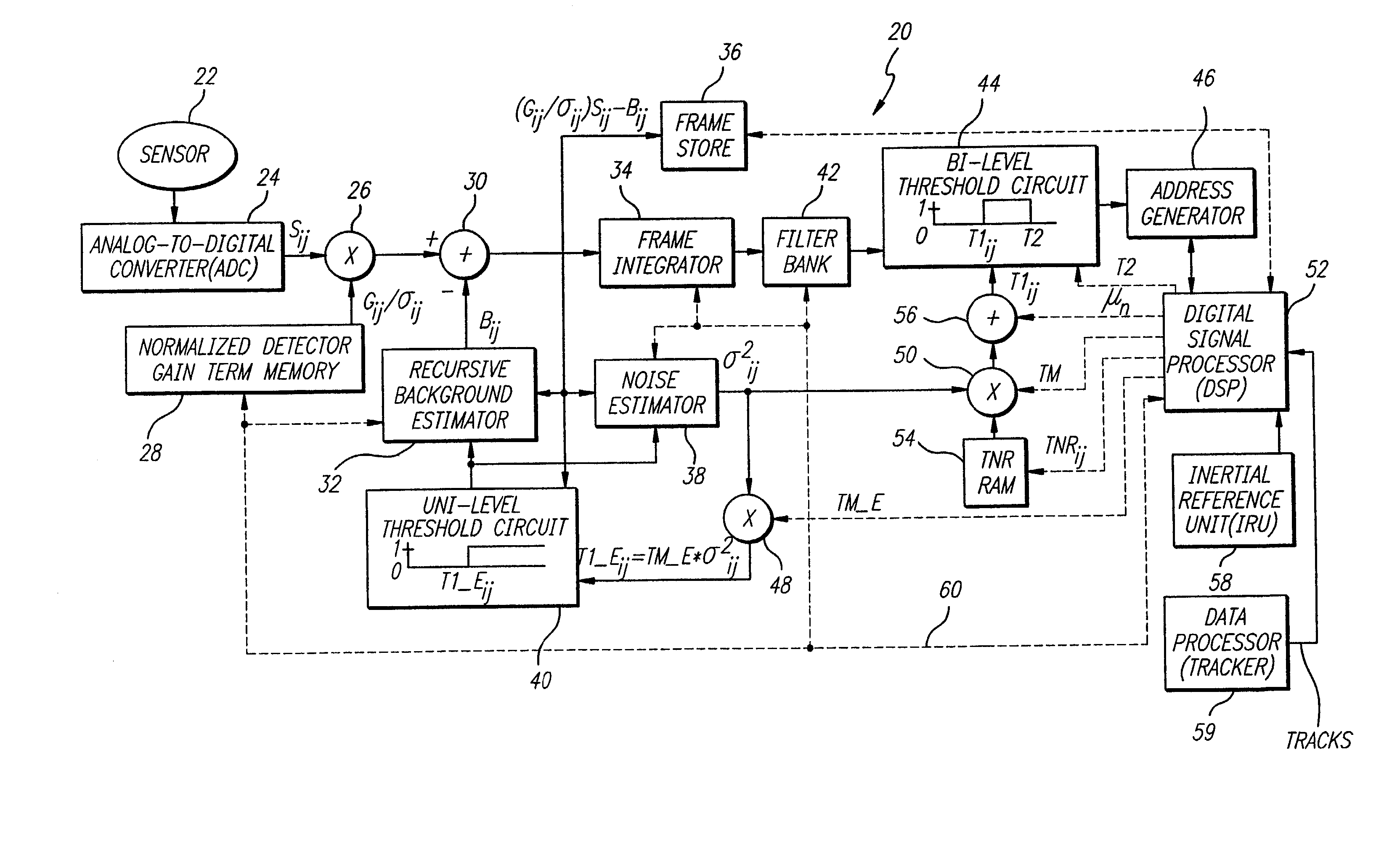
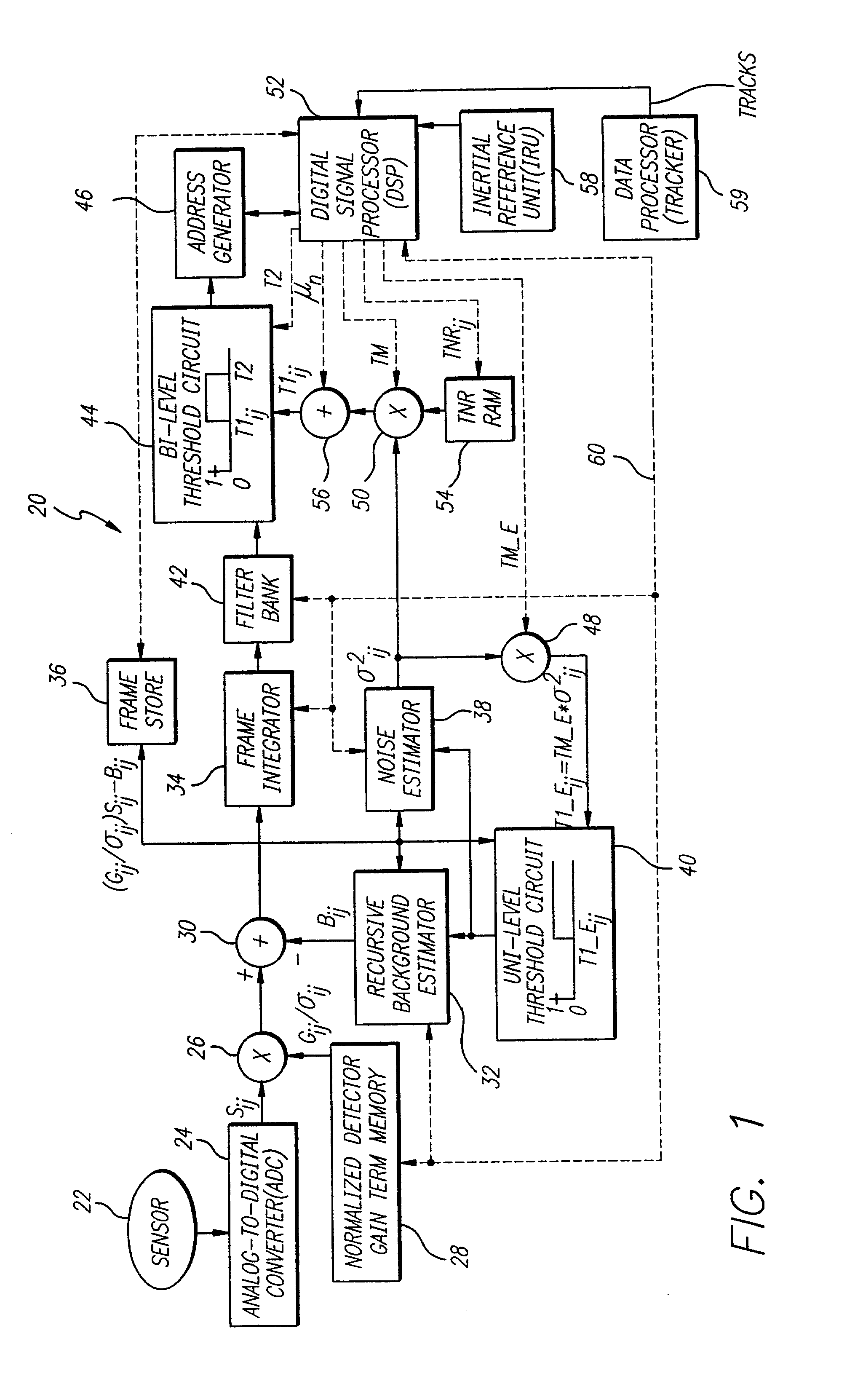
Accurate target detection system
InactiveUS20020084414A1Television system detailsMaterial analysis by optical meansElectricityIntegrator
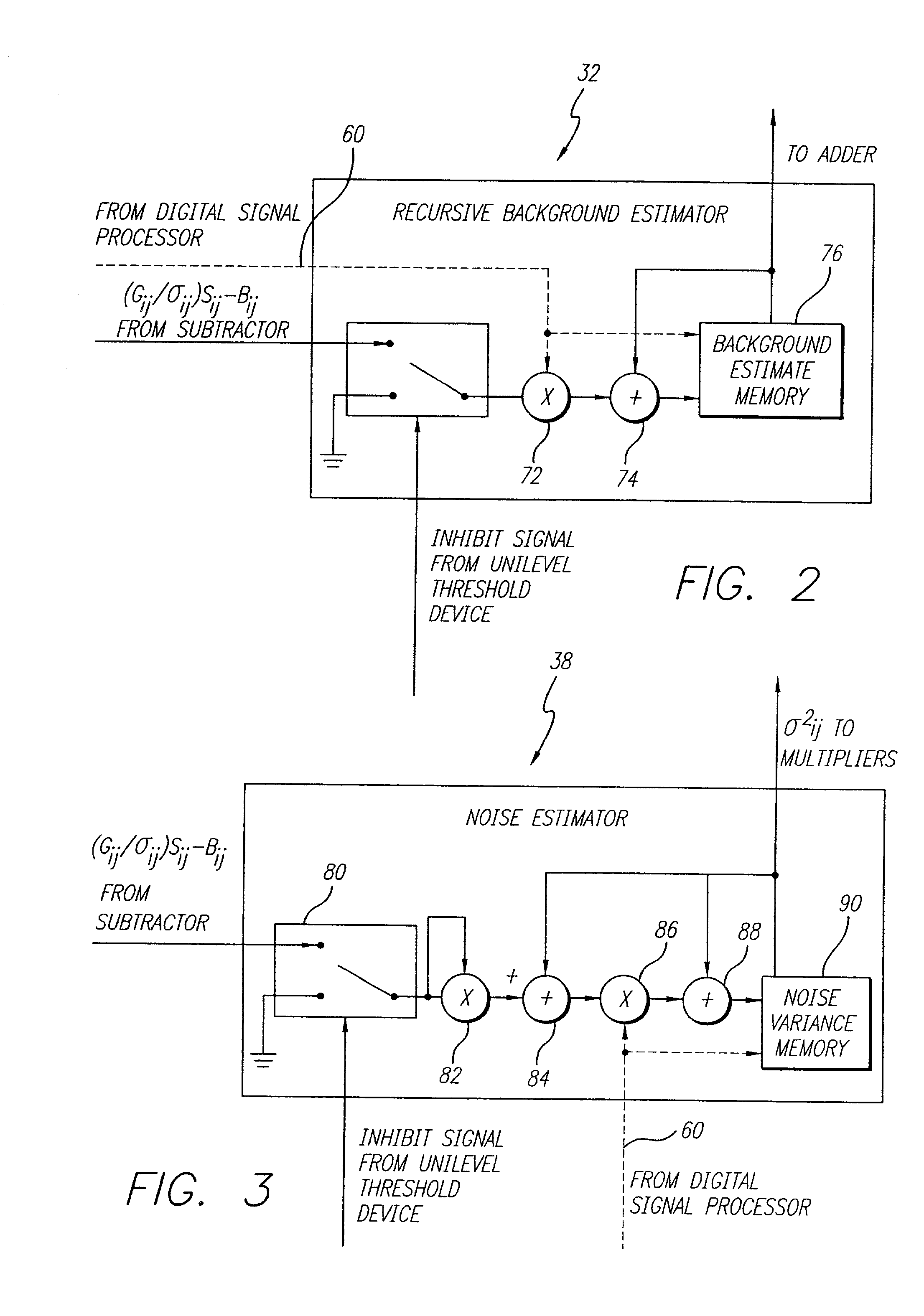
An accurate target detection system. The system includes a sensor (22) that receives electromagnetic signals and provides electrical signals in response thereto. A non-uniformity correction circuit (28, 38, 52) corrects non-uniformities in the sensor (22) based on the electrical signals and provides calibrated electrical signals in response thereto. A third circuit (30, 32, 34, 38, 42, 44, 52) determines if a target signal is present within the calibrated electrical signals and provides a target detection signal in response thereto. A fourth circuit (38, 40, 48) selectively activates or deactivates the non-uniformity correction circuit (28, 38, 52) based on the target detection signal. In a specific embodiment, the sensor (22) is an array of electromagnetic energy detectors (22), each detector providing an electrical detector output signal The non-uniformity correction circuit (28, 38, and 52) includes circuit for compensating for gain, background, and noise non-uniformities (28, 38, and 52) in the electromagnetic energy detectors. The non-uniformity correction circuit (28, 38, and 52) includes a detector gain term memory (28) for storing detector gain compensation values. The detector gain compensation values are normalized by noise estimates unique to each of the detectors. The third circuit (30, 32, 34, 38, 42, 44, and 52) includes a signal enhancement circuit for reducing noise (34, 42) in the calibrated electrical signals. The third circuit (30, 32, 34, 38, 42, 44, and 52) includes a noise estimation circuit (32, 38) that estimates noise in each of the detector output signals and provides noise estimates in response thereto. The noise estimation circuit (32, 38) further includes a noise estimator circuit (38) and a recursive background estimator (32). The third circuit (30, 32, 34, 38, 42, 44, 52) further includes a subtractor (30) for subtracting background from the calibrated electrical signals and providing background subtracted signals in response thereto. The signal enhancement circuit (34, 42) includes a frame integrator circuit for adding frames of image data (34), each frame containing data corresponding to the background subtracted signals and providing summed frames in response thereto. The third circuit (30, 32, 34, 38, 42, 44, 52) includes a first threshold circuit (44) for comparing the filtered signal to a first threshold and a second threshold and providing a threshold exceedance signal if the filtered signal is between the first threshold and the second threshold.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Method and apparatus for generating a flip angle schedule for a spin echo train pulse sequence
ActiveUS20080319301A1Reduced refocusing flip angleMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringTarget signalPulse sequence
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
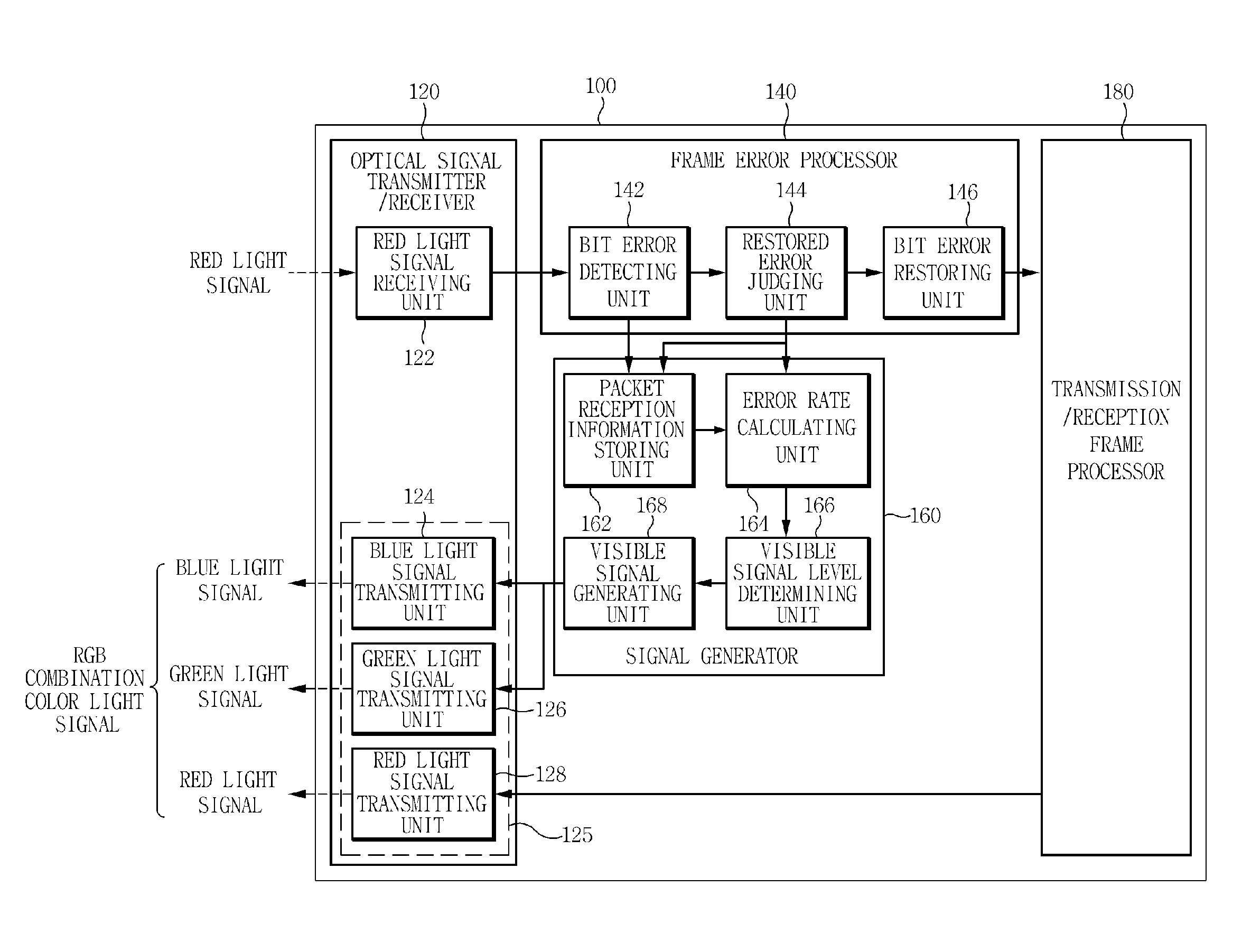
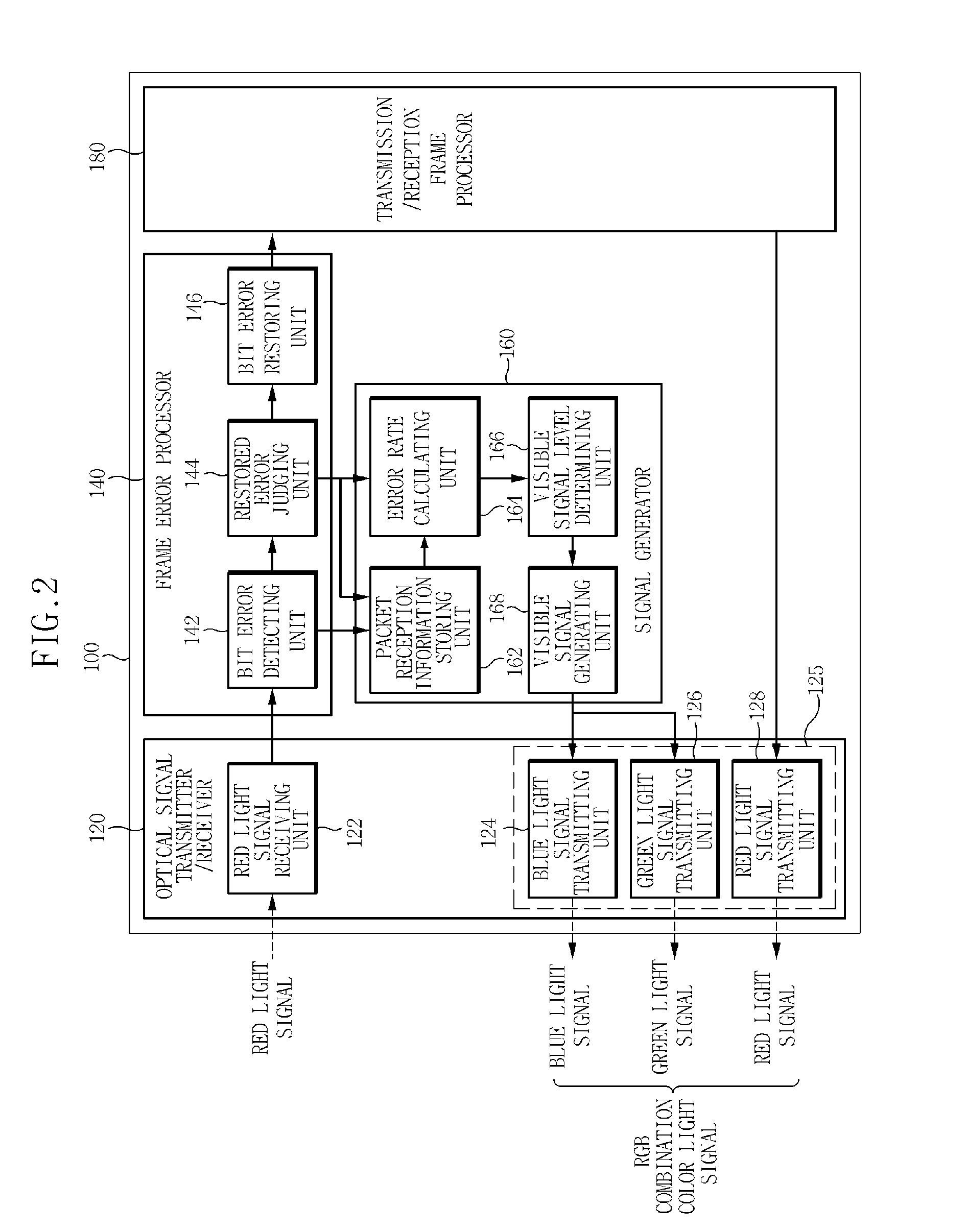
Apparatus for visible light communication indicating communication quality using RGB color mixing and method thereof
InactiveUS20110026918A1Reception quality of dataRapidly and stably transmit dataClose-range type systemsTransmission monitoringCommunication qualityTarget signal
A visible light communication apparatus of the present invention includes: a target signal receiver filtering only a signal having a target wavelength from a visible light received signal received from a transmitting terminal; a signal generator judging a reception quality of the visible light received signal by using characteristics of the signal having the target wavelength and generating a visible signal by using at least one light source having a wavelength different from the target wavelength in accordance with the reception quality; and an optical signal transmitter transmitting the signal having the target wavelength for transmitting data together with the visible signal and changing a light emitting color of a visible light transmitted signal.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
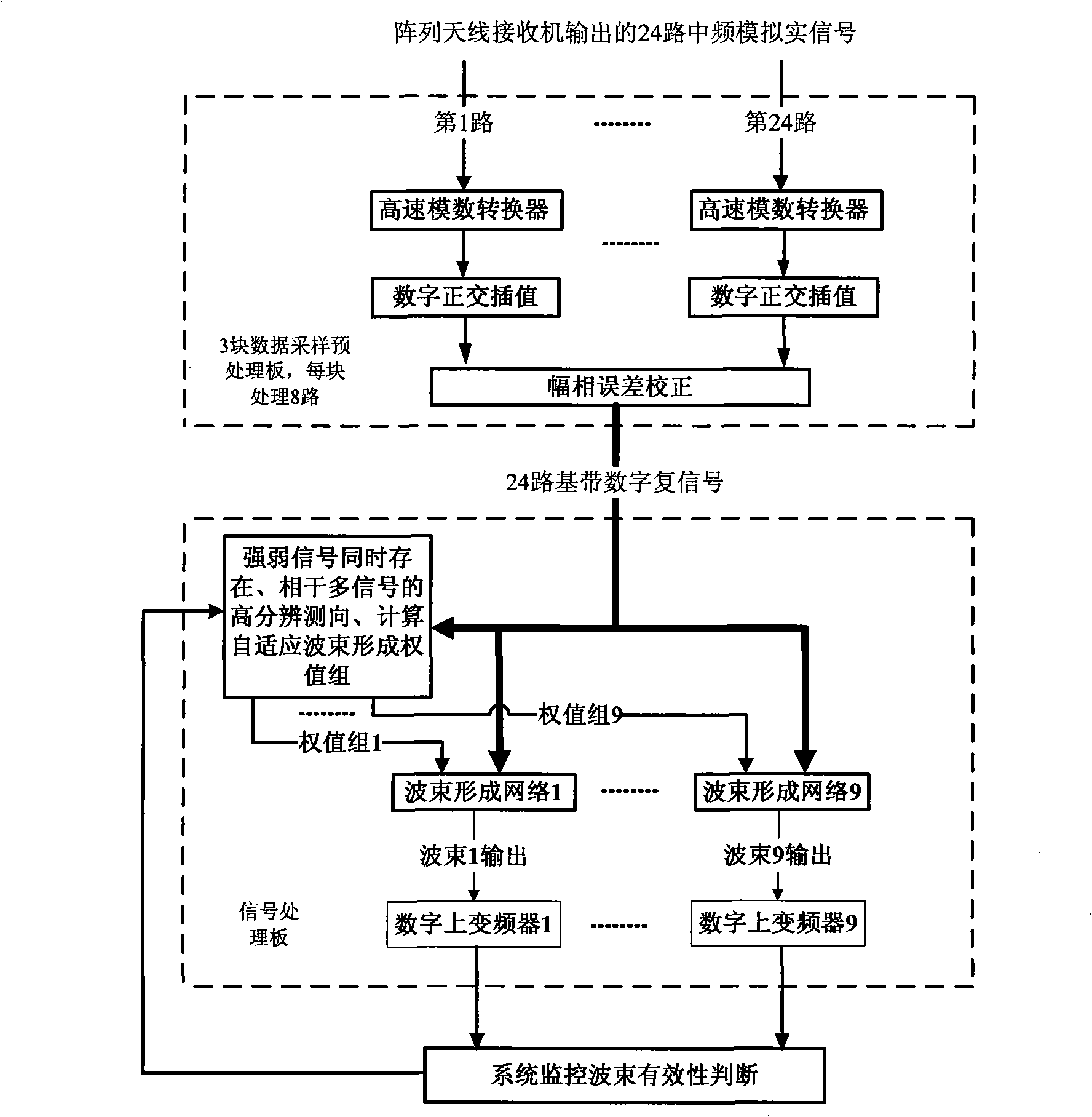
Phased array digital multi-beam forming machine for electron reconnaissance
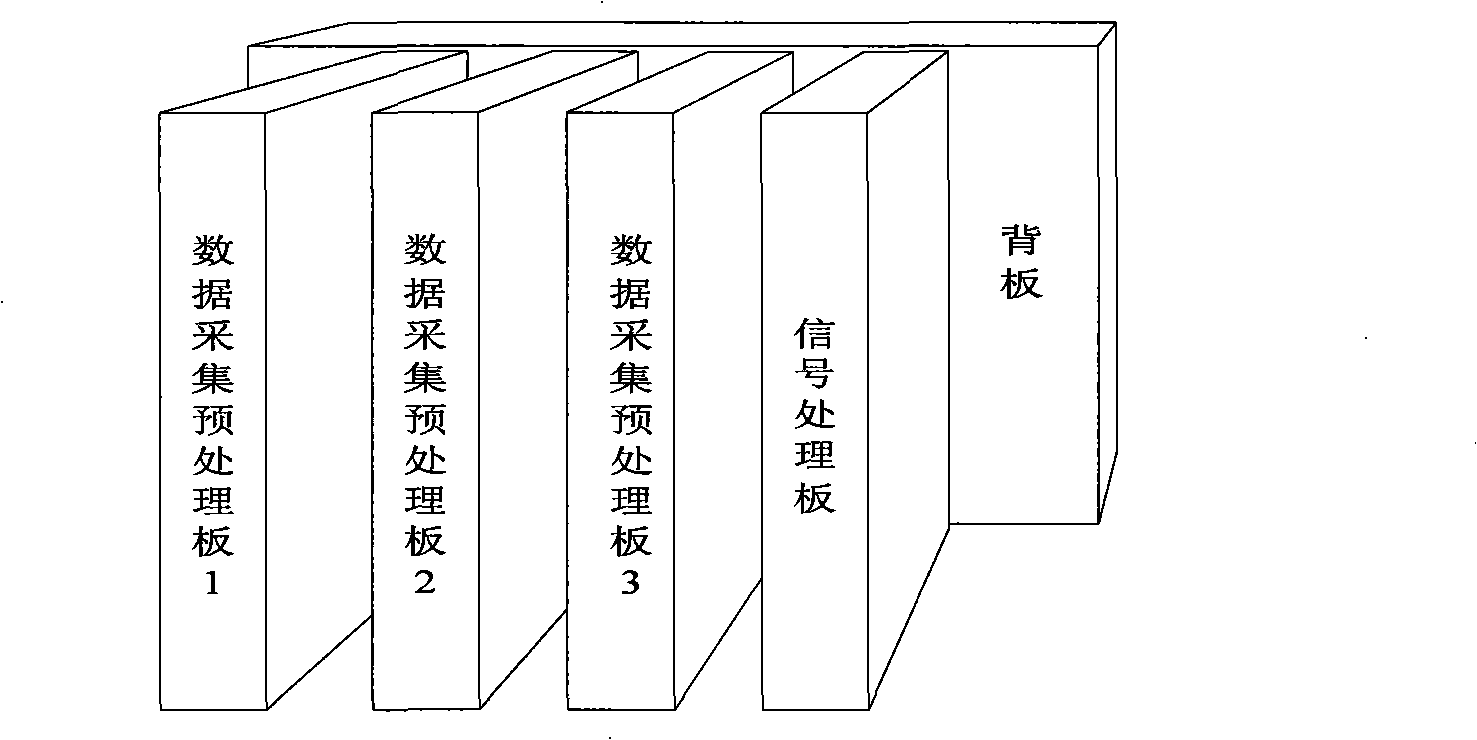
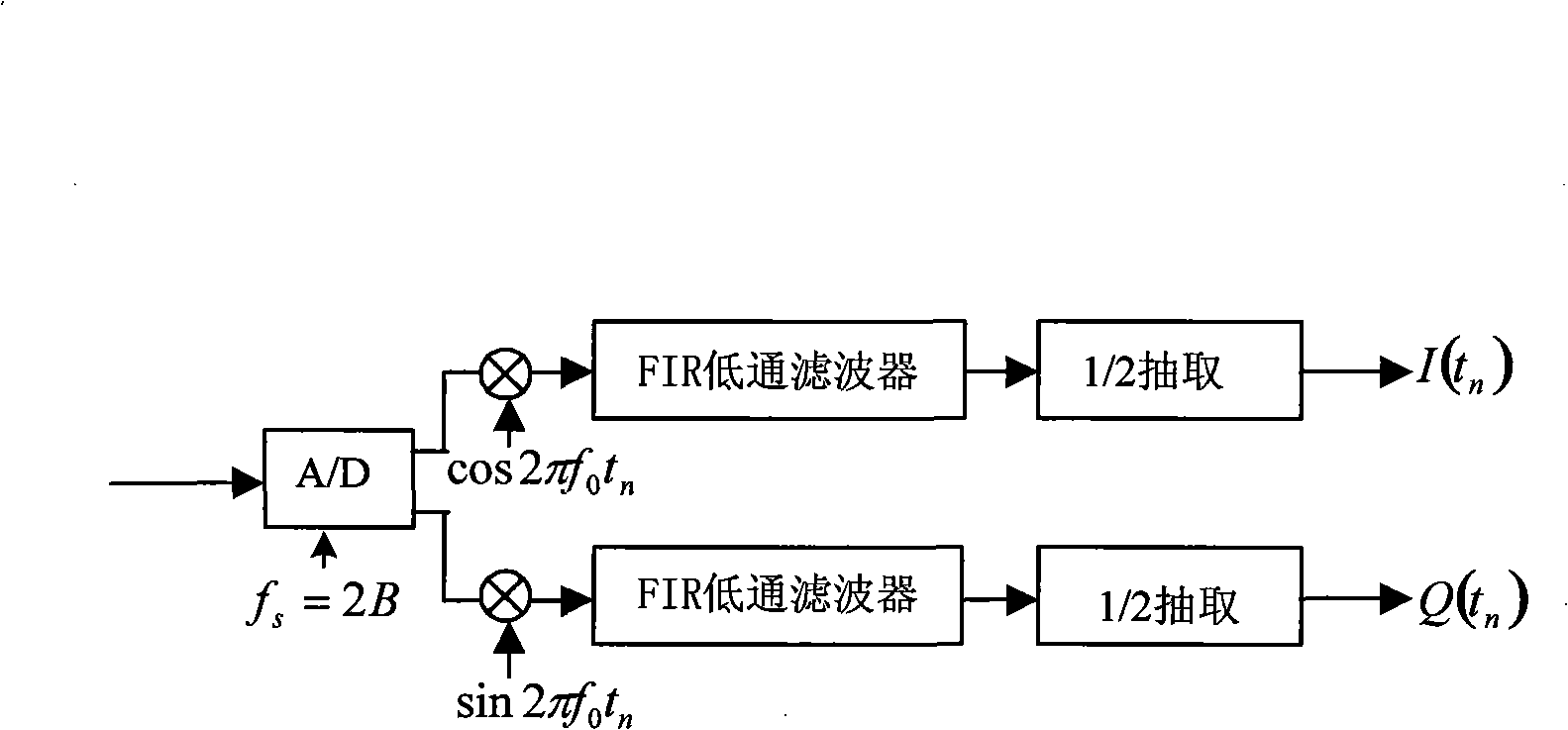
InactiveCN101349741AGuaranteed median alignmentGuaranteed bit alignmentRadio wave finder detailsRadio wave direction/deviation determination systemsIntermediate frequencyData acquisition
The invention discloses a phased array digital multi-beam generator for electronic reconnaissance, for the high resolution direction measurement having strong and weak signals or coherent multi signals, and forming the multi-target signal into anti-interference digital multi-beam to form a multi-beam process: first, in a data acquisition pretreatment board, an AD samples intermediate frequency analogue real signals output by each array antenna receiver, a DPS and a FPGA chip are cooperated to complete quadrate sampling and amplitude phase error correction; the intermediate frequency analogue actual signals are converted into a baseband digital complex signal and the amplitude phase error between the multi channels is corrected; a LVDS channel transmits the baseband digital complex signal to a signal processing board, the DPS completes the high resolution direction measurement having strong and weak signals or coherent multi signals and calculates the weight value group formed by the adaptive beam; the weight value group is added into the wave beam in the signal processing board FPGA to form a network; completing forming anti-interference digital multi-beam of the multi-target signal; an up frequency converter converts the output of the anti-interference digital multi-beam into needed intermediate frequency analogue signal.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Methods and compositions for delivering polynucleotides
Methods and compositions for delivering polynucleotides are provided. One embodiment provides a non-viral vector comprising a recombinant polynucleotide-binding protein comprising a protein transduction domain operably linked to a targeting signal. Methods for modifying the genome of non-nuclear organelles are also provided.
Owner:GENCIA
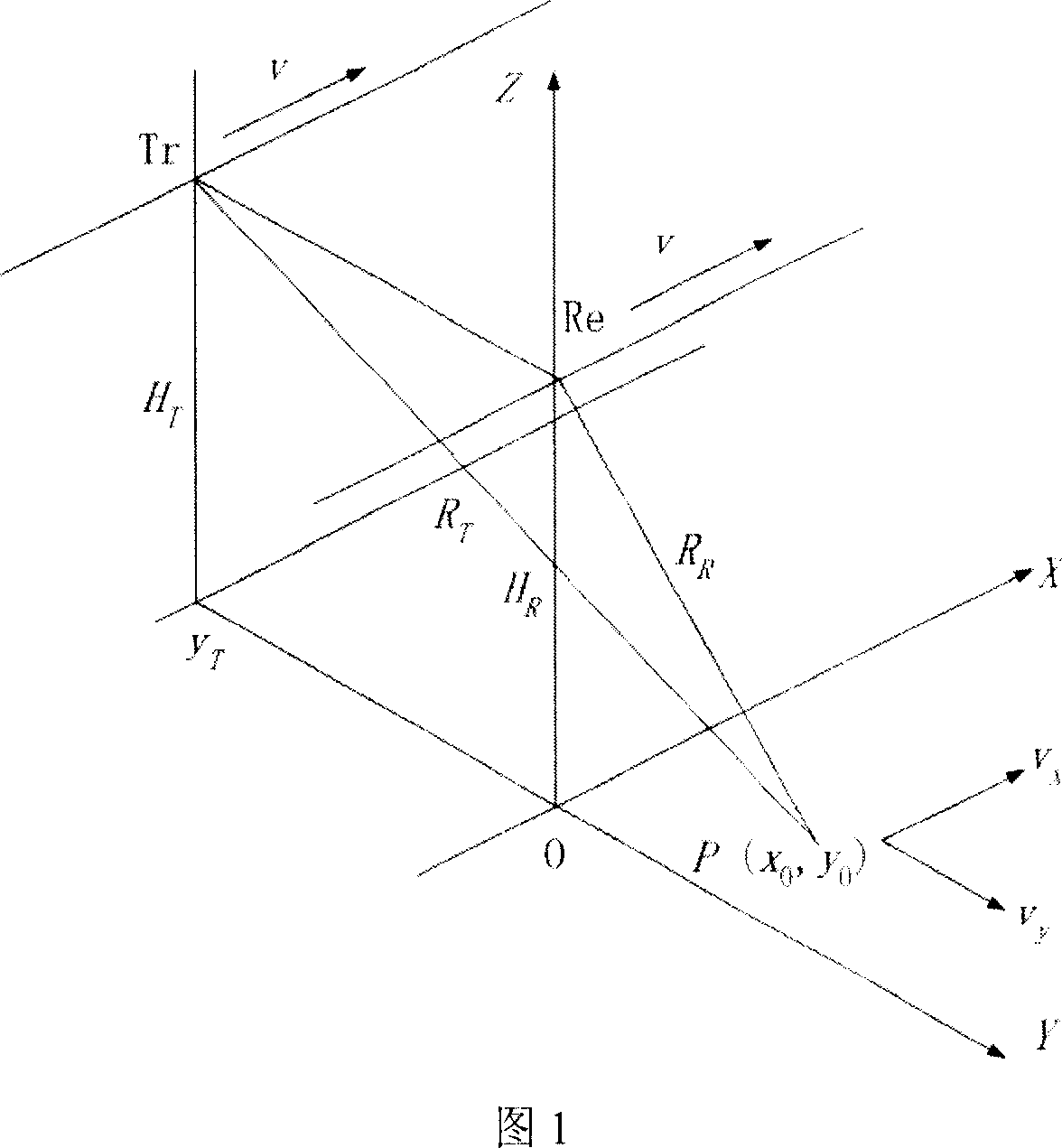
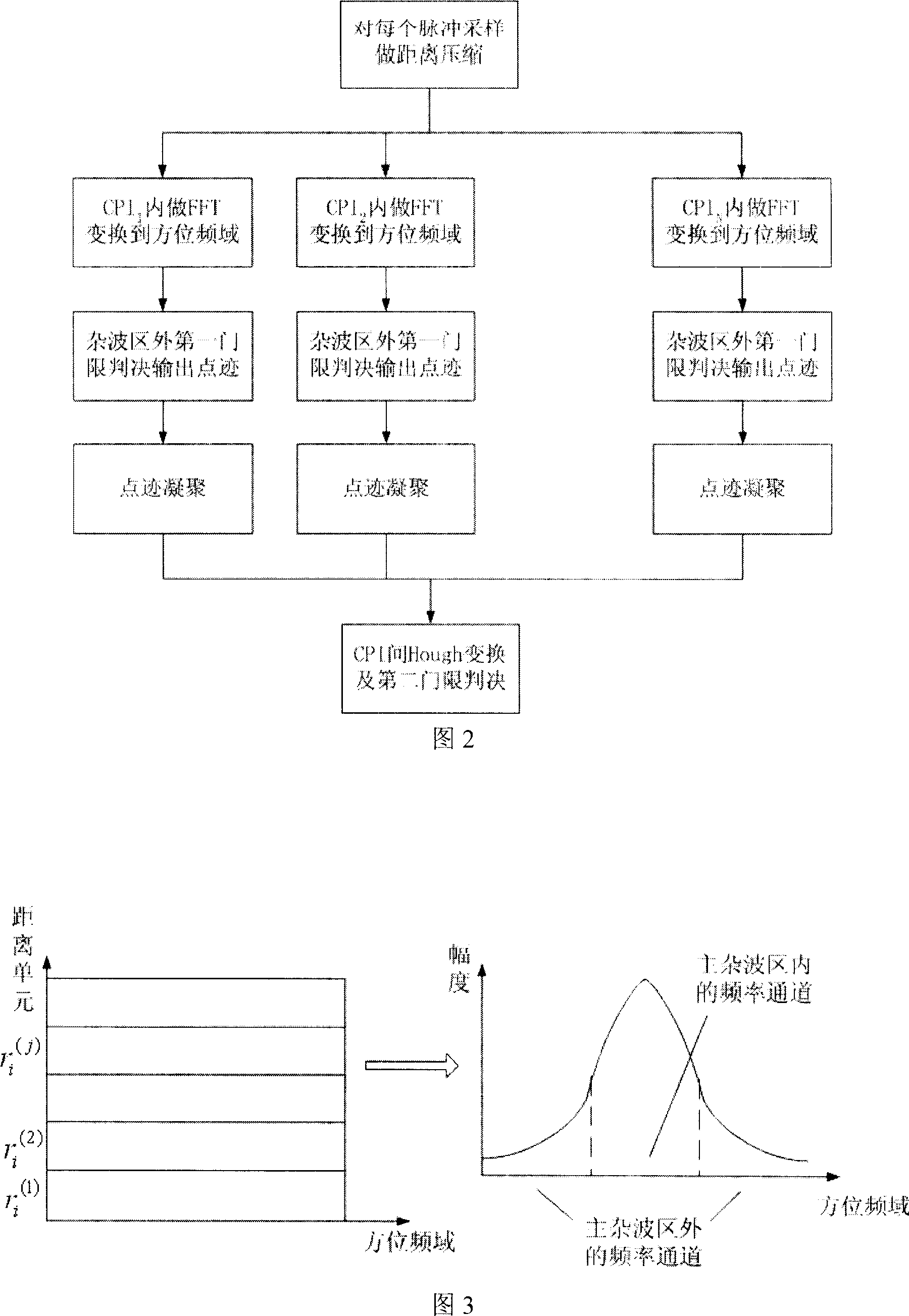
Double-threshold constant false alurm motion target detecting method of double base synthetic aperture radar
A detection method of double-threshold constant false alarm movement object on double-base synthetic aperture radar includes finalizing distance compression of various pulse-sampling, dividing orientation time to be multiple CPI, carrying out FFT in each CPI to enter orientation frequency domain, comparing data amplitude of frequency channel at external of clutter region with the first threshold and outputting point trace, making coagulation on point trace, making Hough transform in point trace domain and making decision of the second threshold.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Multi-fractal detection method of targets in FRFT (Fractional Fourier Transformation) domain sea clutter
ActiveCN102967854AReduce the demand for signal-to-clutter ratio in target detectionThe need to reduce the signal-to-clutter ratioWave based measurement systemsTime domainTarget signal
The invention discloses a multi-fractal detection method of targets in FRFT (Fractional Fourier Transformation) domain sea clutter and belongs to the radar signal processing field. According to the conventional multi-fractal detection methods of targets in sea clutter, echo sequences in the radar time domain are processed directly, and therefore detection performance of weak moving targets in strong sea clutter background is poor. The multi-fractal detection method of targets in FRFT domain sea clutter is characterized in that fractional Fourier transformation is organically combined with the multi-fractal processing method, and the generalized Hurst index number of the sea-clutter fractional Fourier transformation spectrum is extracted to form detection statistics by comprehensively utilizing the advantage that the fractional Fourier transformation is capable of effectively improving the signal to clutter ratio of the moving target on the sea surface and the feature that the multi-fractal characteristic is capable of breaking the tether of the signal to clutter ratio to a certain extent. The detection method comprehensively utilizes the advantages of phase-coherent accumulation and multi-fractal theory and has excellent separating capability on the weak moving targets in sea clutter; and simultaneously, the method is also suitable for tracking target signals in nonuniform fractal clutter and has popularization and application values.
Owner:NAVAL AERONAUTICAL & ASTRONAUTICAL UNIV PLA
Sound signal processor and delay time setting method
InactiveUS20100183163A1Increase flexibilityInterconnection arrangementsSubstation speech amplifiersAdaptive filterTarget signal
An echo canceller formed of an adaptive filter is designed such that even under a condition where a system transmission delay is undefined, an appropriate delay time can be set in a delay circuit that absorbs a system delay, and that an effective echo cancellation effect can always be achieved. A time difference of a transmission path until a reproduction audio signal input to the delay circuit is input as a processing target signal of an adaptive filter system through a space between a speaker and a microphone is determined, and the delay time corresponding to this time difference is set in the delay circuit. At this time, the speaker and the microphone are placed so that the distance therebetween is small, and the delay time of the delay circuit is set to 0. Thus, the determined time difference indicates a system transmission delay in the above transmission path. That is, an accurate delay time corresponding to the system transmission delay can be set in the delay circuit.
Owner:SONY CORP
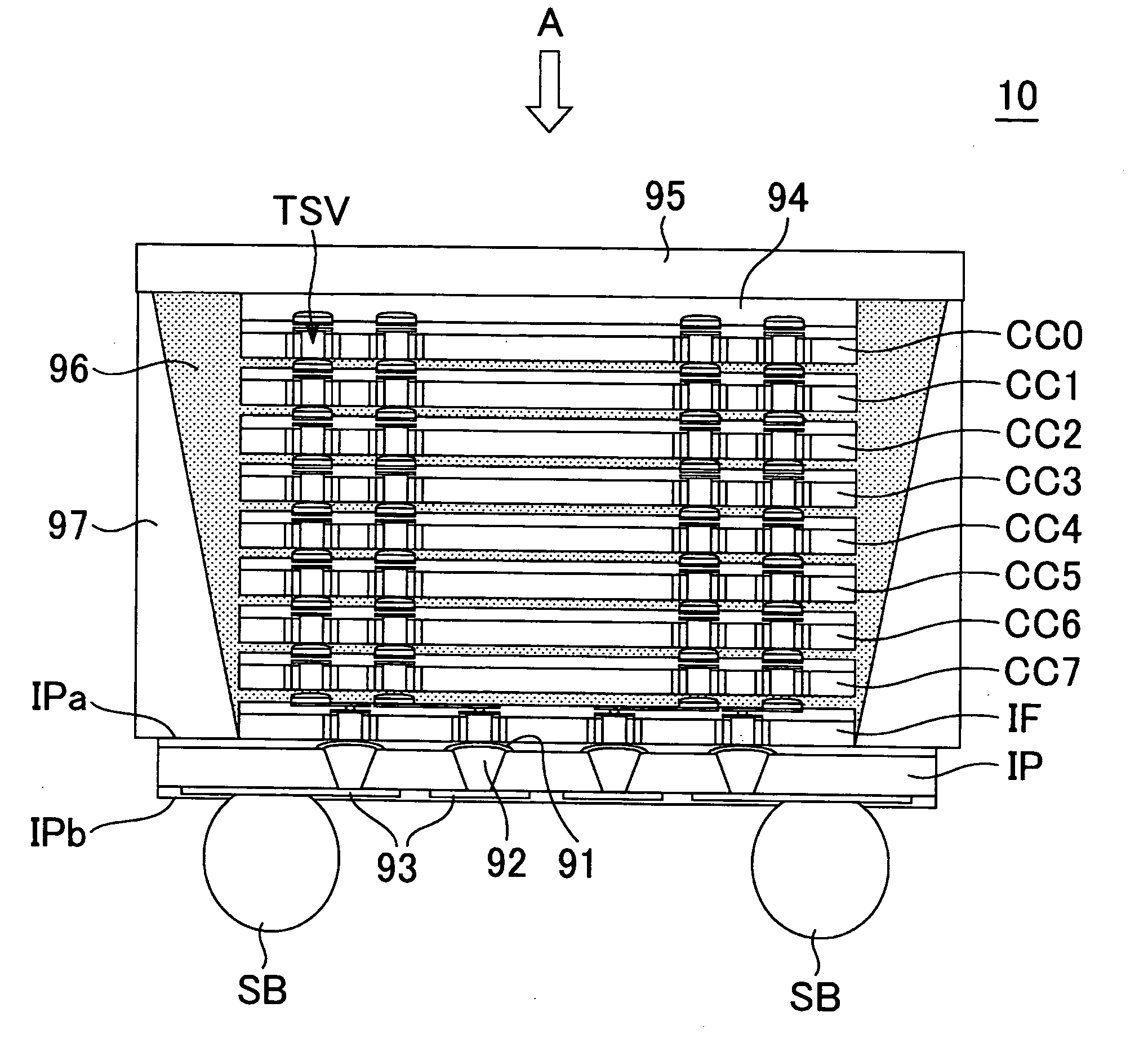
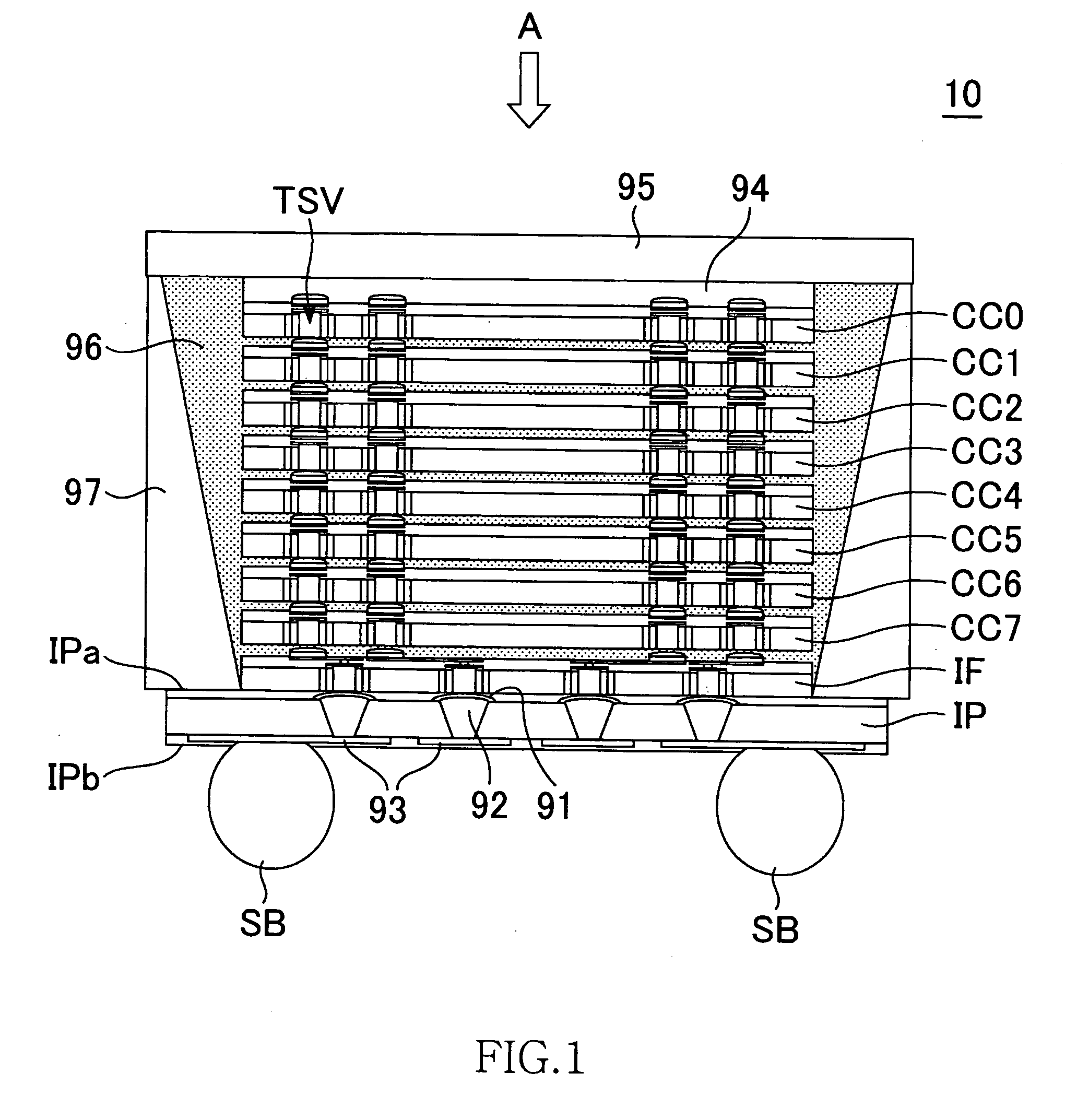
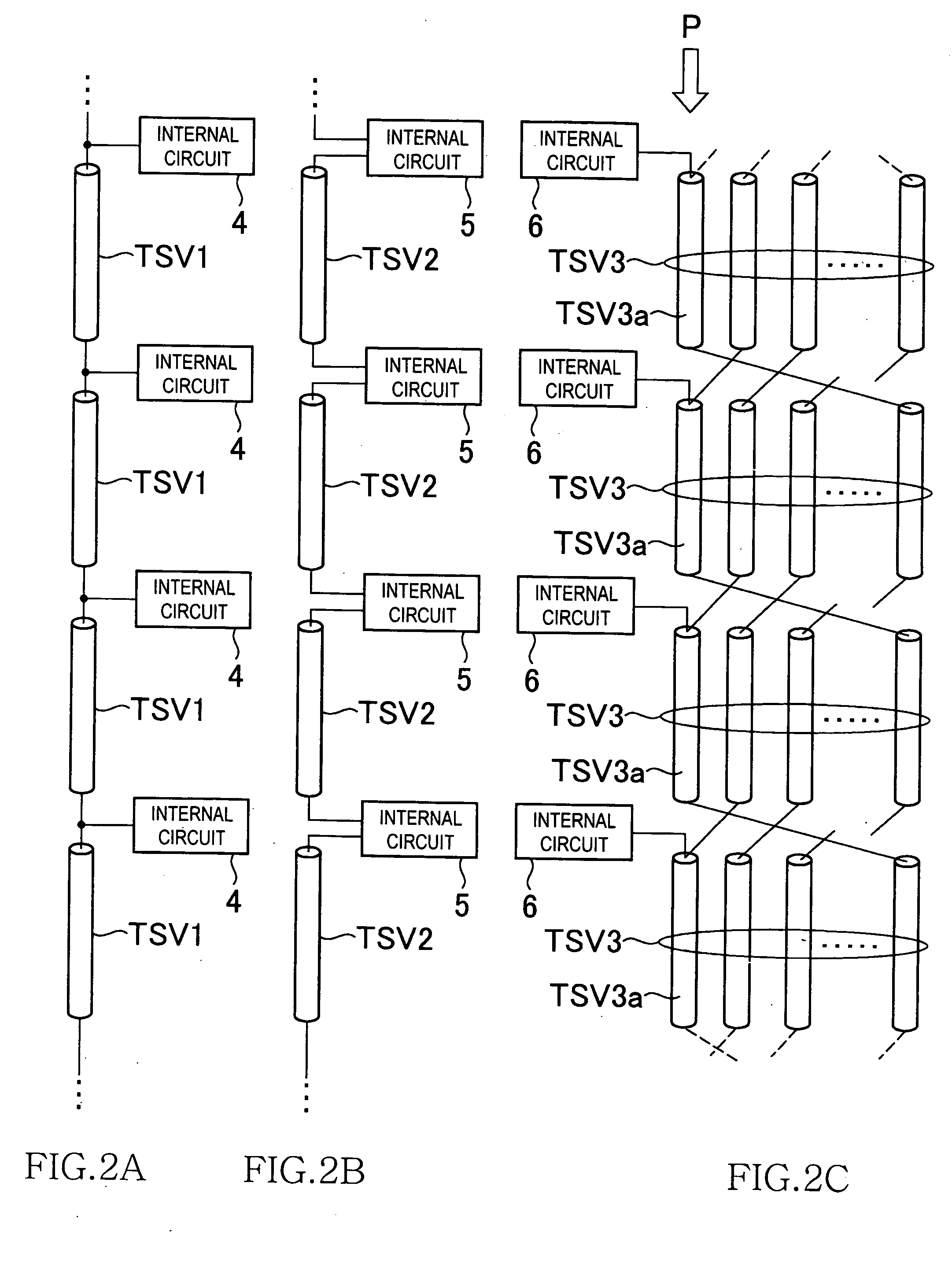
Semiconductor device semiconductor device testing method, and data processing system
InactiveUS20110175639A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesElectricityData processing system
To provide a semiconductor device including an interface chip and a core chip and a measurement-target signal line and a reference signal line each including a through silicon via provided in the core chip and electrically connecting the interface chip and the core chip. The interface chip outputs a test clock generated by a first signal generation circuit to the core chip. The core chip includes a second signal generation circuit that generates a predetermined measurement signal from the test clock, and outputs the predetermined measurement signal to the measurement-target signal line and the reference signal line in a simultaneous manner. Further, the interface chip detects a phase difference of a plurality of predetermined measurement signals input via the measurement-target signal line and the reference signal line by an operational amplifier, and outputs a test result to a determination circuit.
Owner:LONGITUDE SEMICON S A R L
General signal generator for radar target simulation
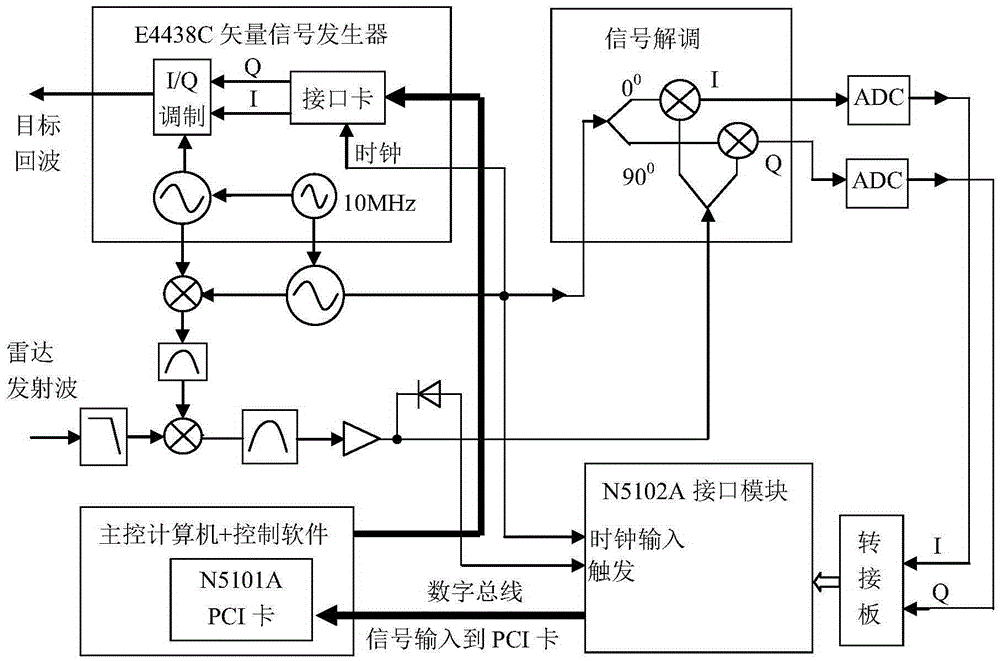
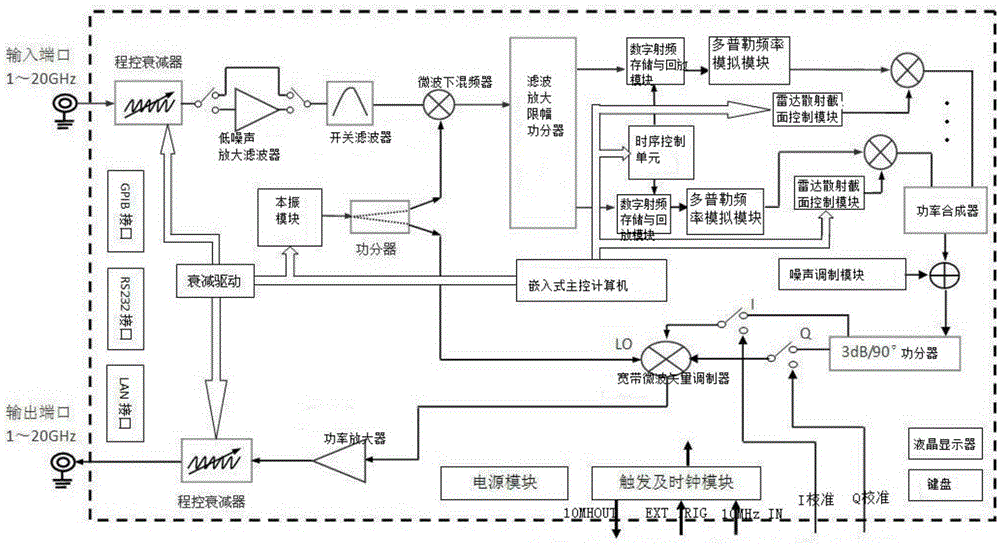
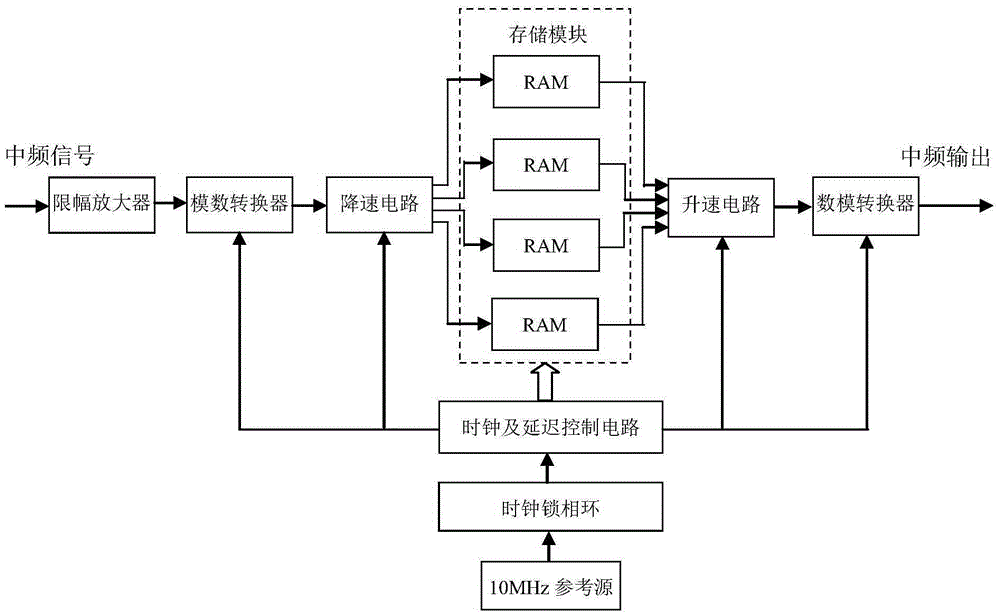
InactiveCN105403870AControllable distanceEasy to control speedWave based measurement systemsSequence controlRadar systems
The invention, which relates to the technical field of the radar target simulation, discloses a general signal generator for radar target simulation. With the signal generator, a defect that the existing radar target signal generator is based on a special-purpose signal generator and only serve a radar system with a specific type in terms of frequency band coverage and function setting and thus the application range is limited can be solved. The signal generator comprises an embedded main control computer, a timing sequence control unit, an attenuation drive, a local oscillation module, a filtering, amplifying and limiting amplitude power divider, a plurality of digital radio frequency storage and playback modules, a plurality of Doppler frequency simulation modules, a radar cross section control module, a noise modulation module, a microwave down mixer, and IQ up mixing unit and the like. The output terminal of the microwave down mixer is connected with the filtering, amplifying and limiting amplitude power divider; the multiple digital radio frequency storage and playback modules are connected to the filtering, amplifying and limiting amplitude power divider; and the output terminal of each digital radio frequency storage and playback module is connected with one Doppler frequency simulation module.
Owner:THE 41ST INST OF CHINA ELECTRONICS TECH GRP
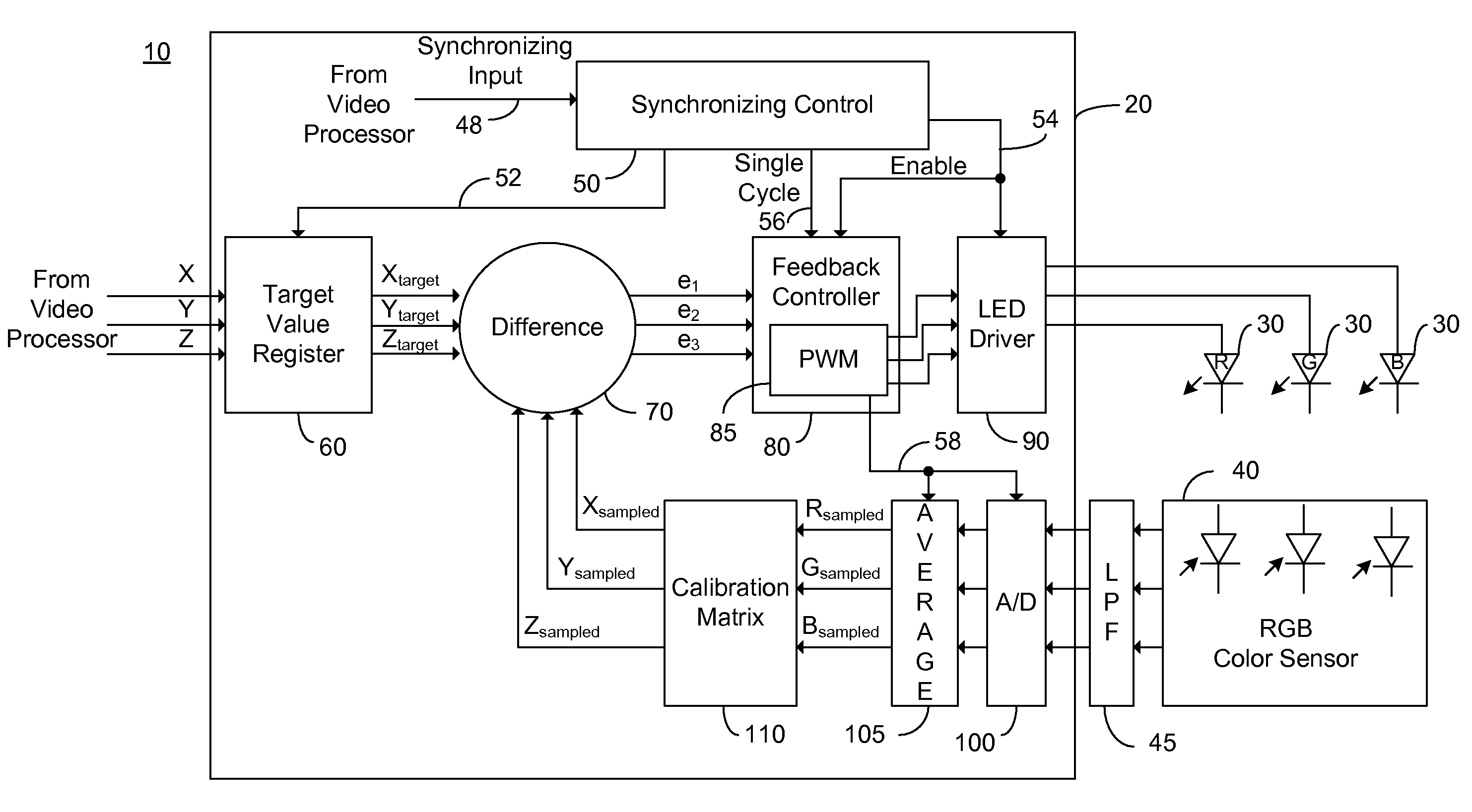
Color Control for Dynamic Scanning Backlight
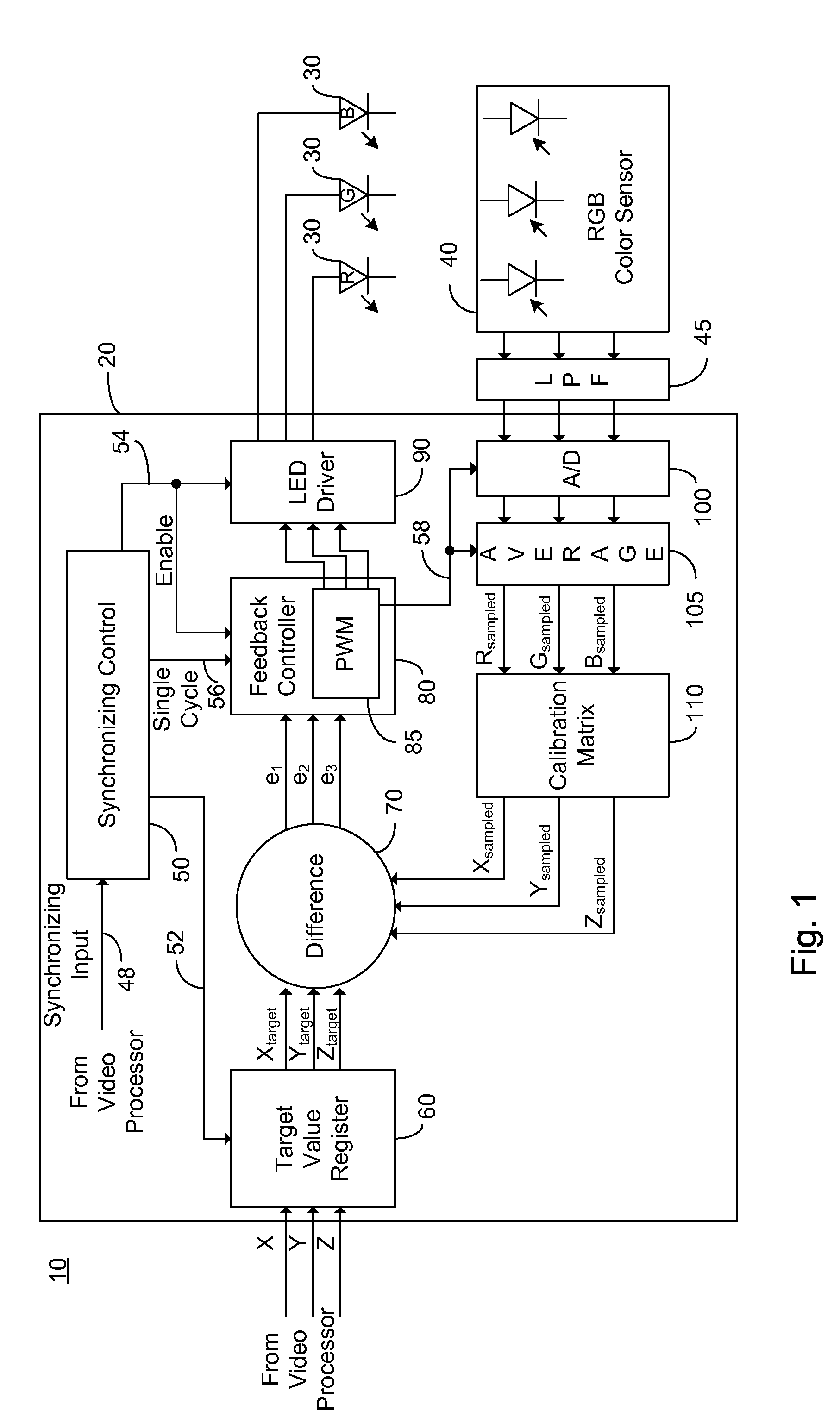
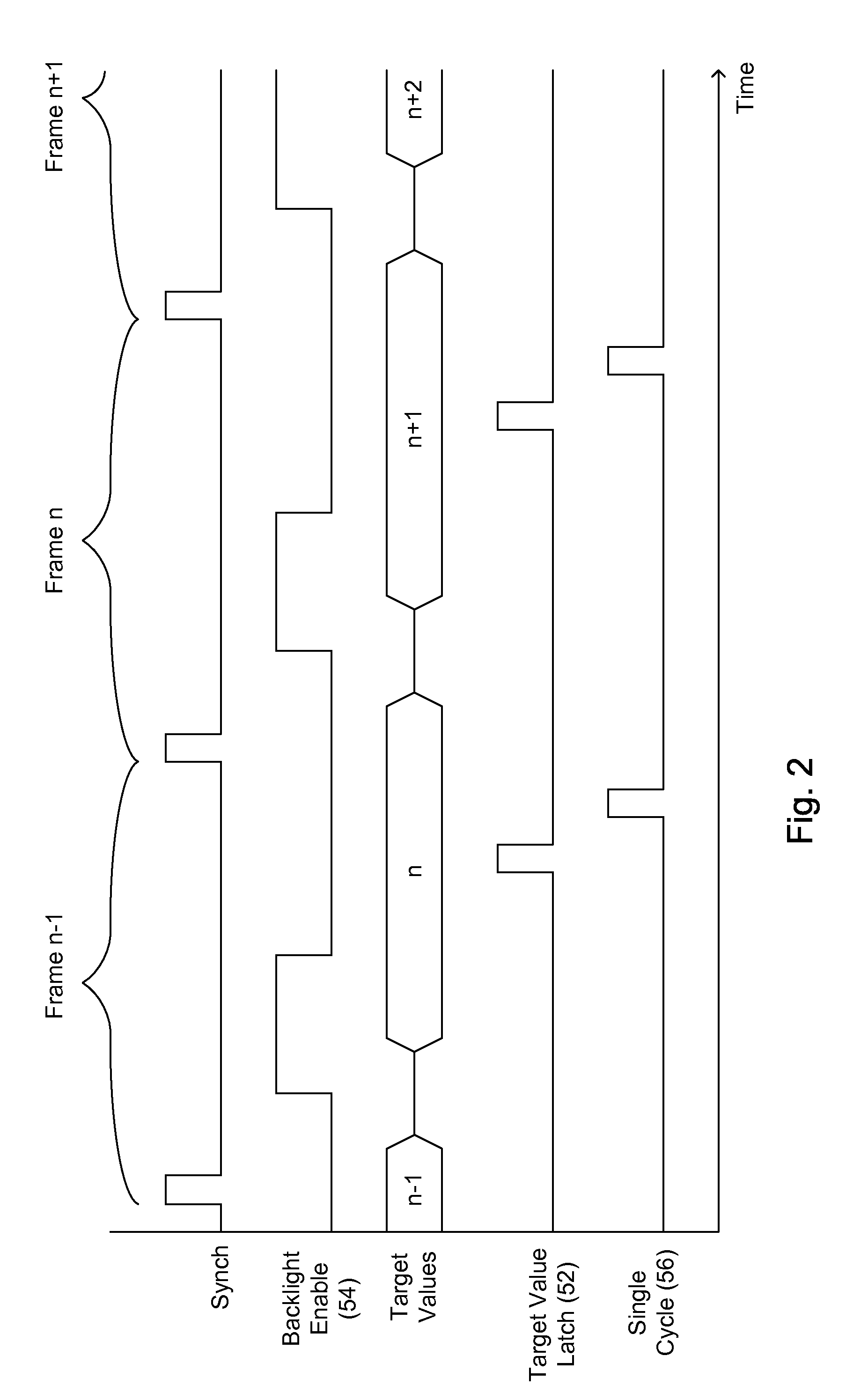
A method of controlling the output of a luminaire by receiving a first target signal associated with a first frame; generating a first light output control signal for an on time portion of the first frame, the light output control signal responsive to the received first target signal; sampling a light output during the on time portion of the first frame, the light output being responsive to the first light output control signal; receiving a second target signal associated with a second frame, the second frame following the first frame; comparing the received second target signal with the sampled light output of the on time portion of the first frame; and generating an error signal responsive to the comparing.
Owner:POLARIS POWERLED TECH LLC
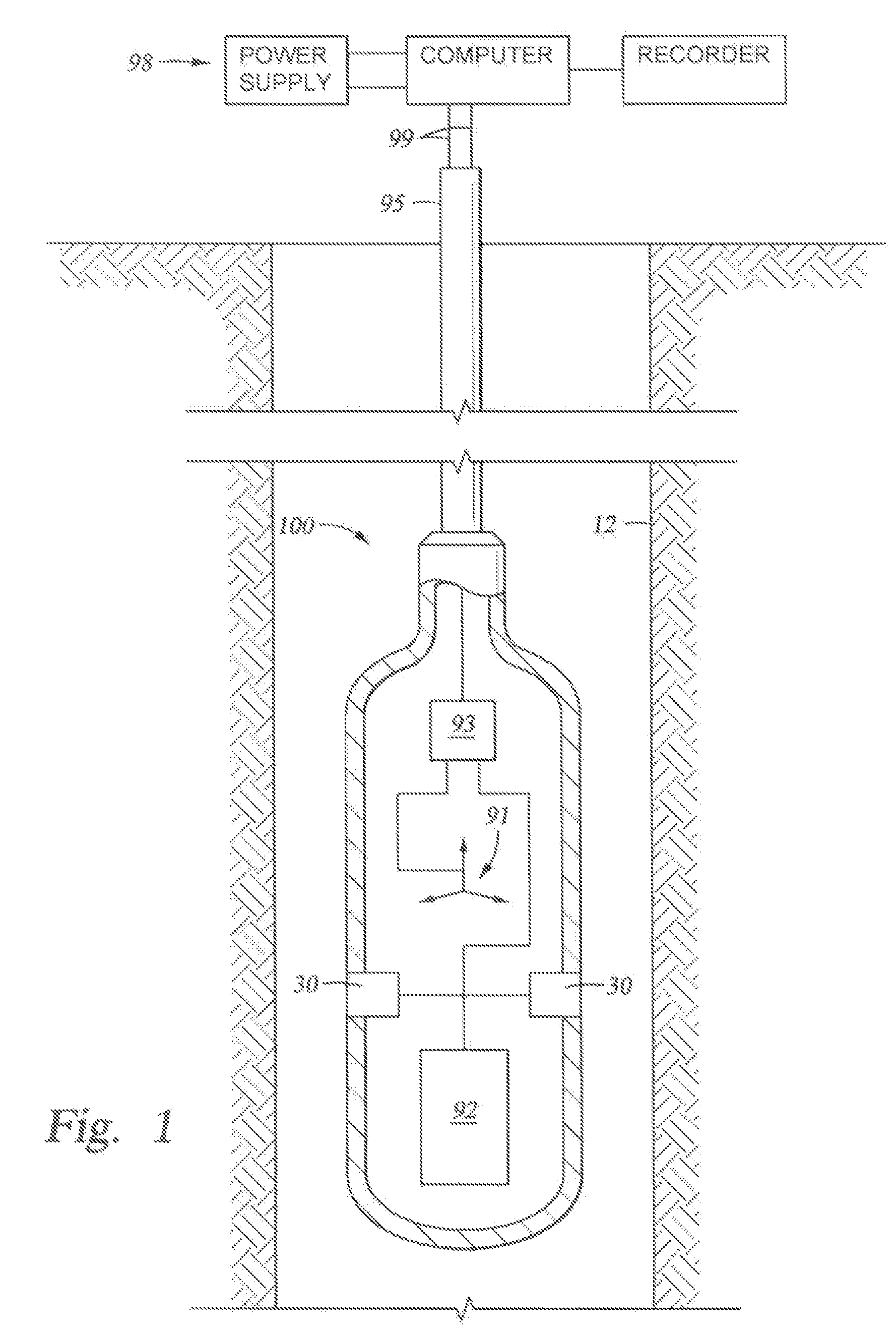
Enclosures for Containing Transducers and Electronics on a Downhole Tool
An enclosure for housing a transducer and electronics for disposal on a downhole tool. A transducer is disposed at an angle with respect to a longitudinal axis of the enclosure, wherein the enclosure contains a fluid surrounding the transducer. Enclosures also include transducers linked to motor means for selective rotation of the transducers within the enclosure. Enclosures with transducer arrays for phased or targeted signal transmission / detection.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com