Patents
Literature
849results about "Direction finders using ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic waves" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
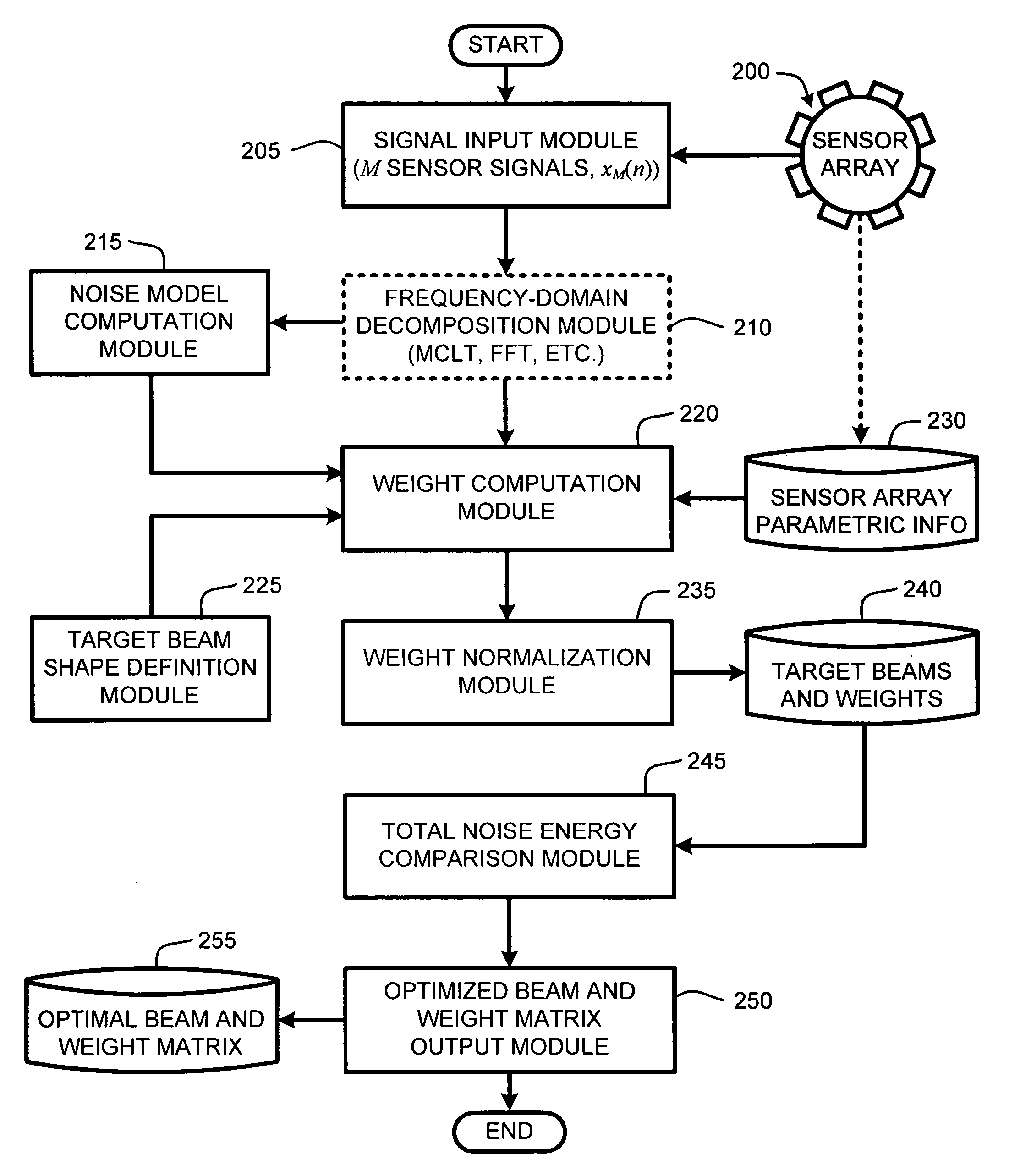
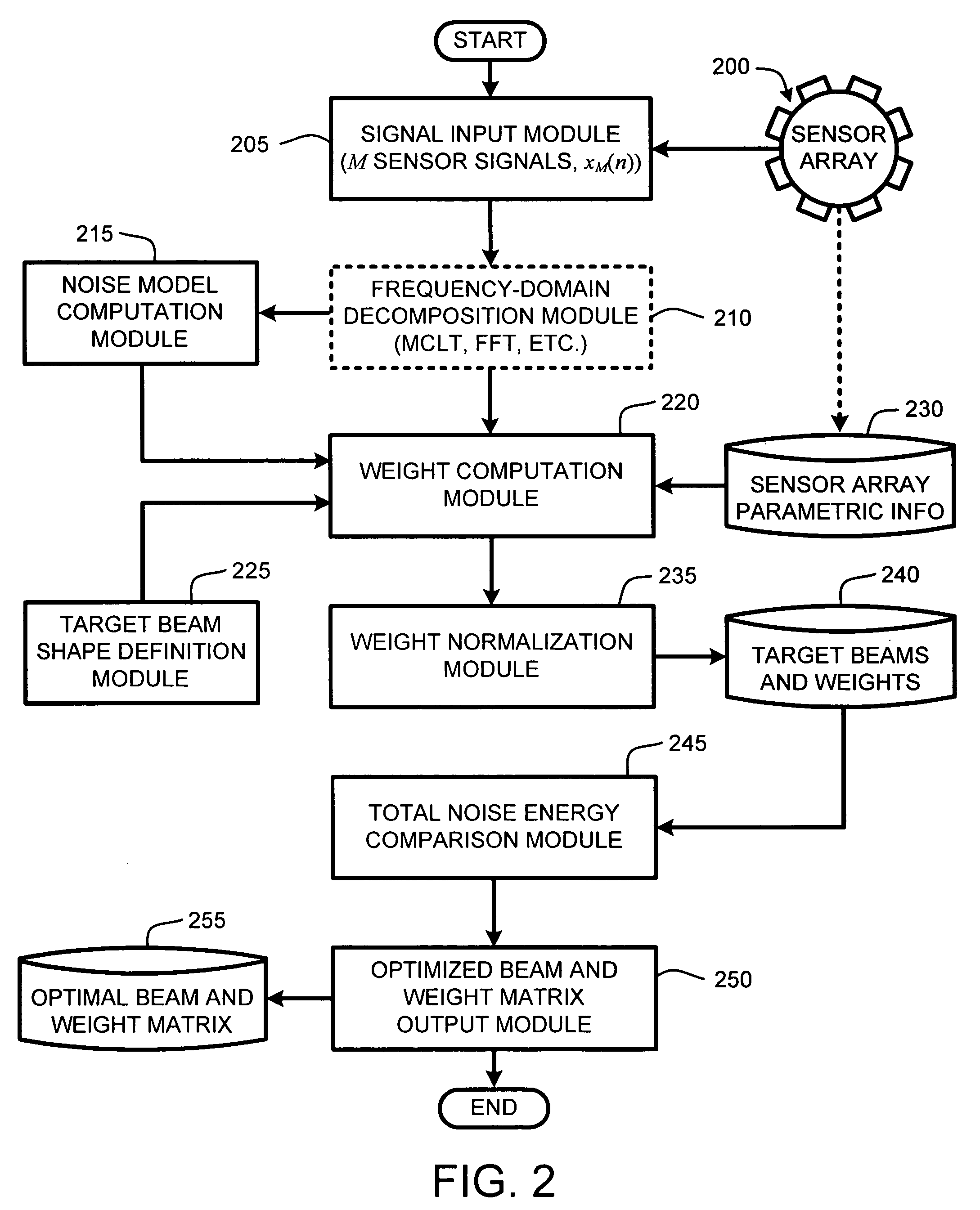
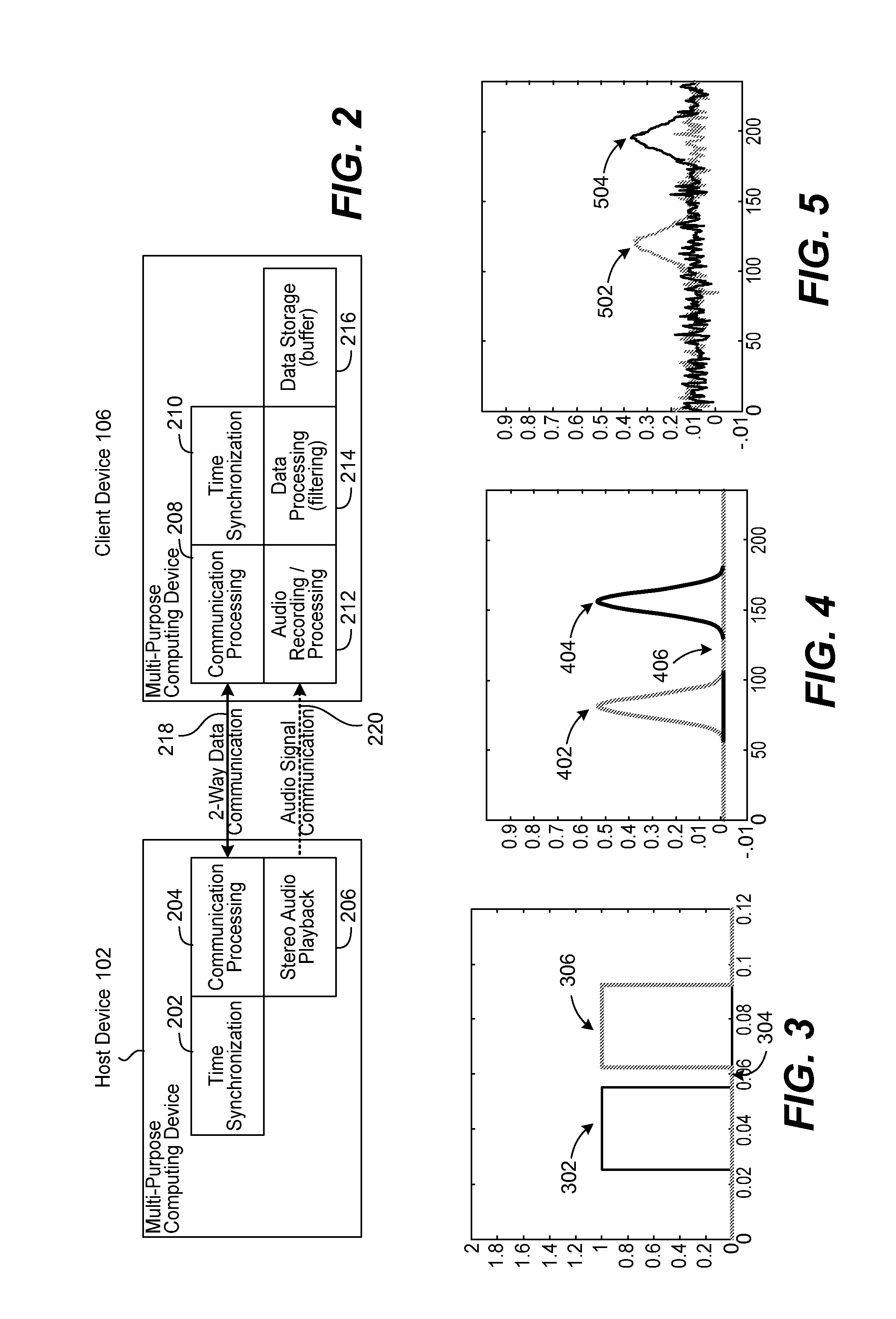
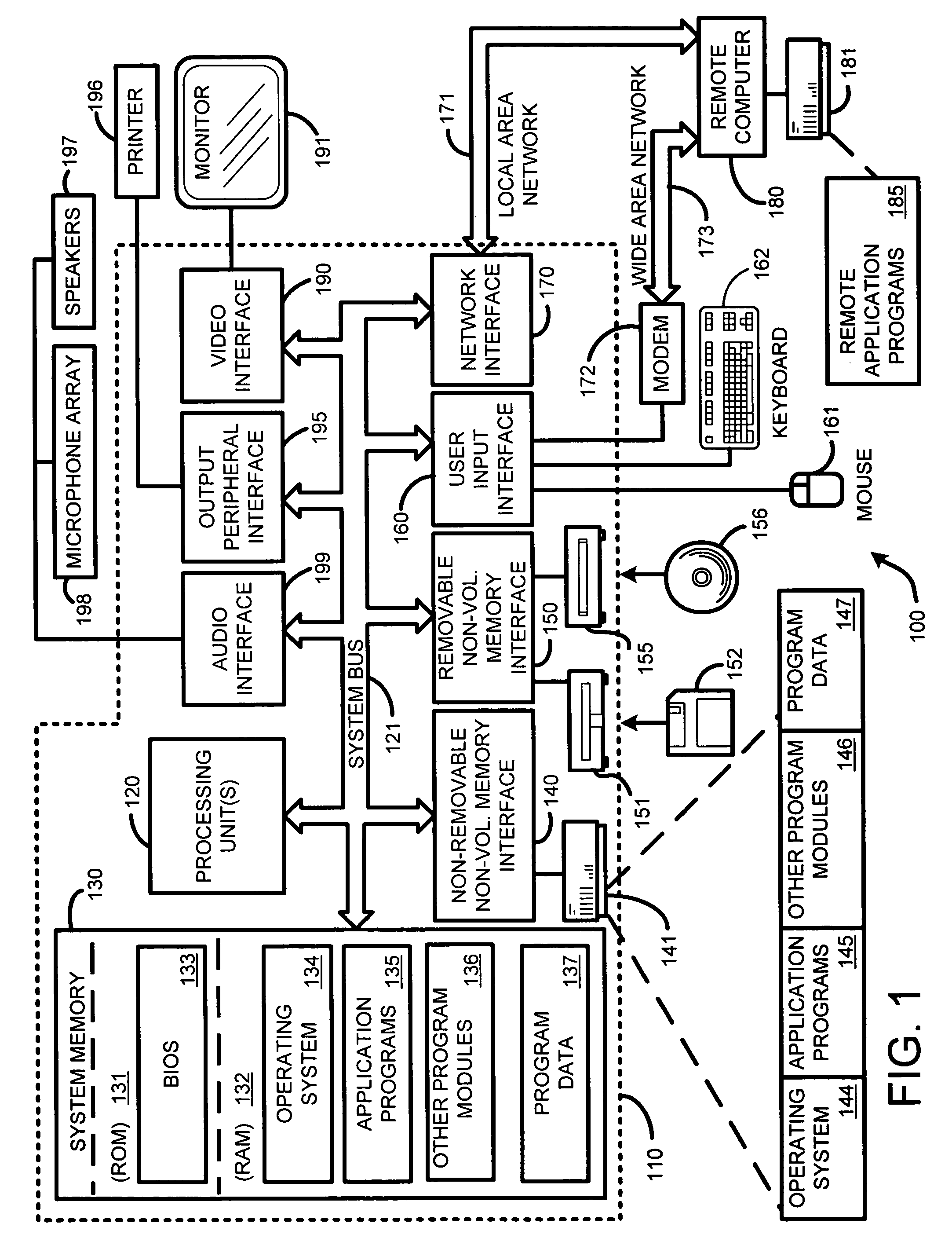
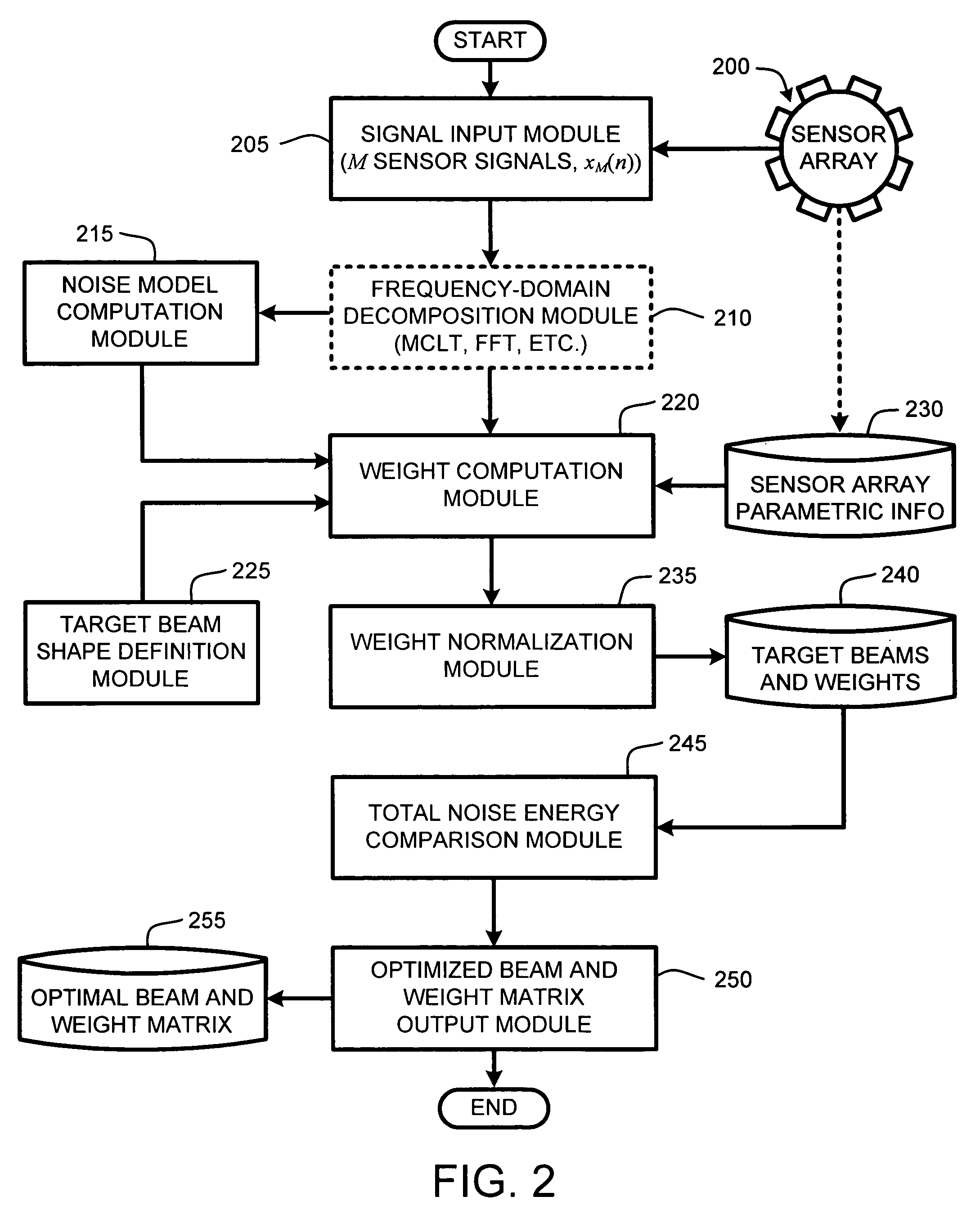
System and method for beamforming using a microphone array
InactiveUS20050195988A1Maximal noise suppressionIncrease widthPosition fixationMicrophones signal combinationEnvironmental noiseSound sources
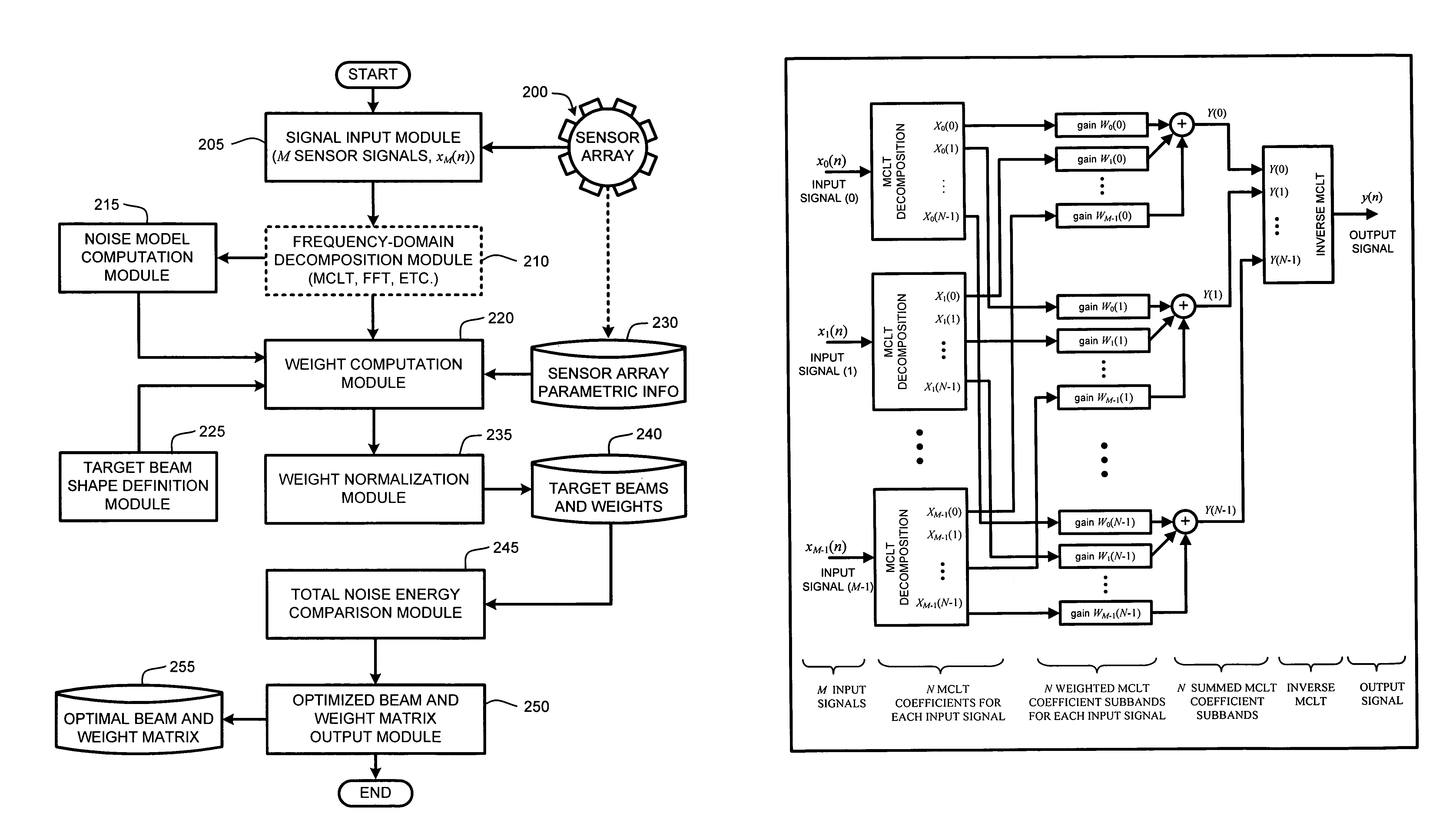
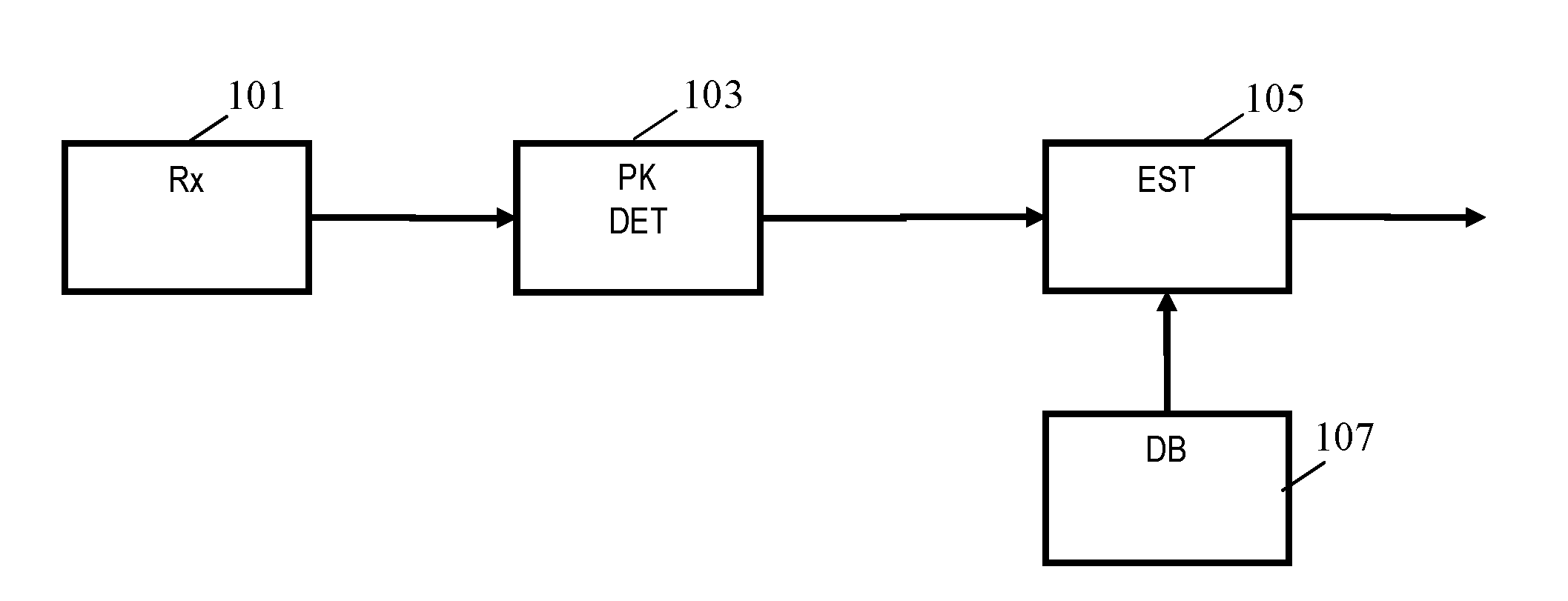
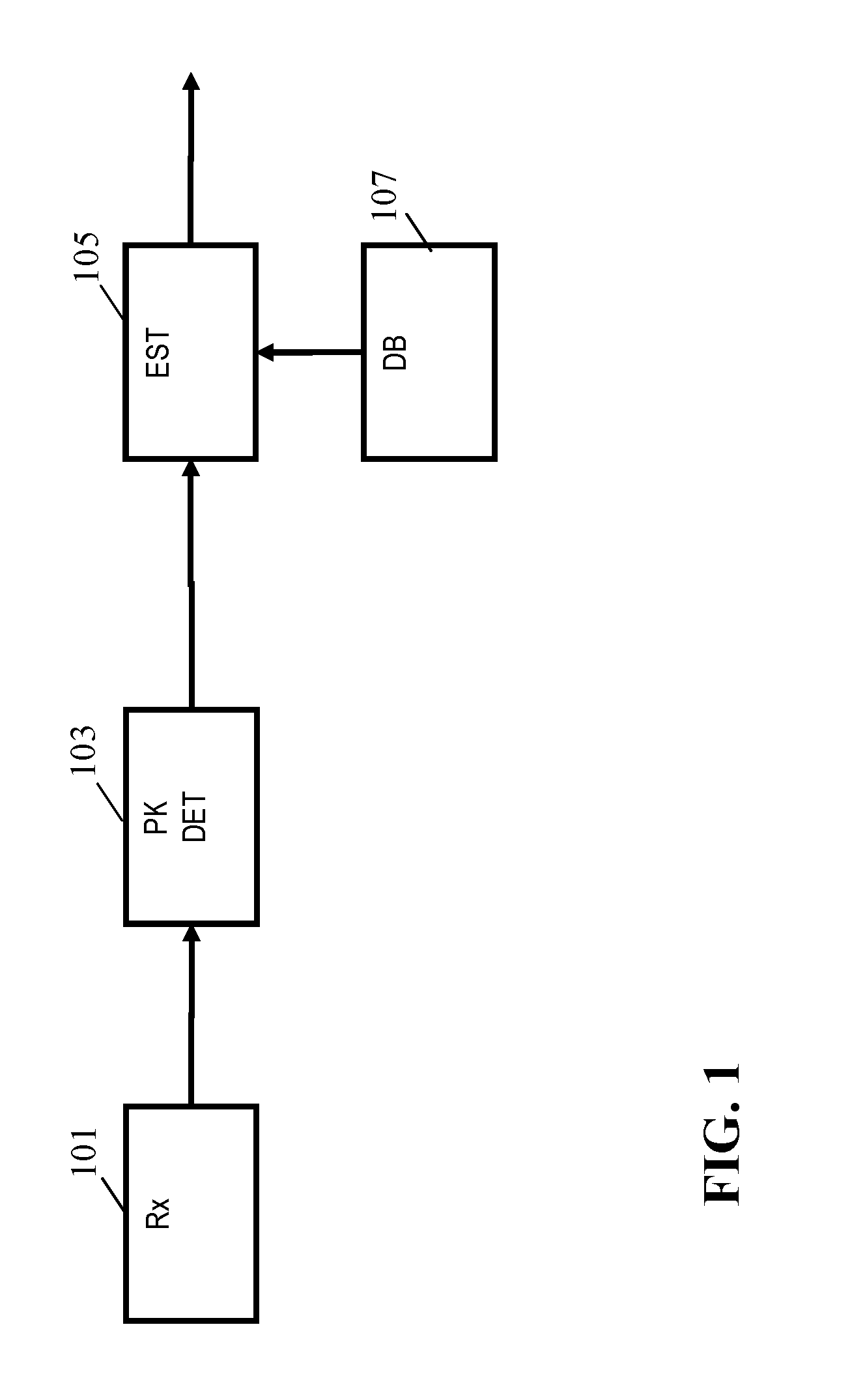
The ability to combine multiple audio signals captured from the microphones in a microphone array is frequently used in beamforming systems. Typically, beamforming involves processing the output audio signals of the microphone array in such a way as to make the microphone array act as a highly directional microphone. In other words, beamforming provides a “listening beam” which points to a particular sound source while often filtering out other sounds. A “generic beamformer,” as described herein automatically designs a set of beams (i.e., beamforming) that cover a desired angular space range within a prescribed search area. Beam design is a function of microphone geometry and operational characteristics, and also of noise models of the environment around the microphone array. One advantage of the generic beamformer is that it is applicable to any microphone array geometry and microphone type.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
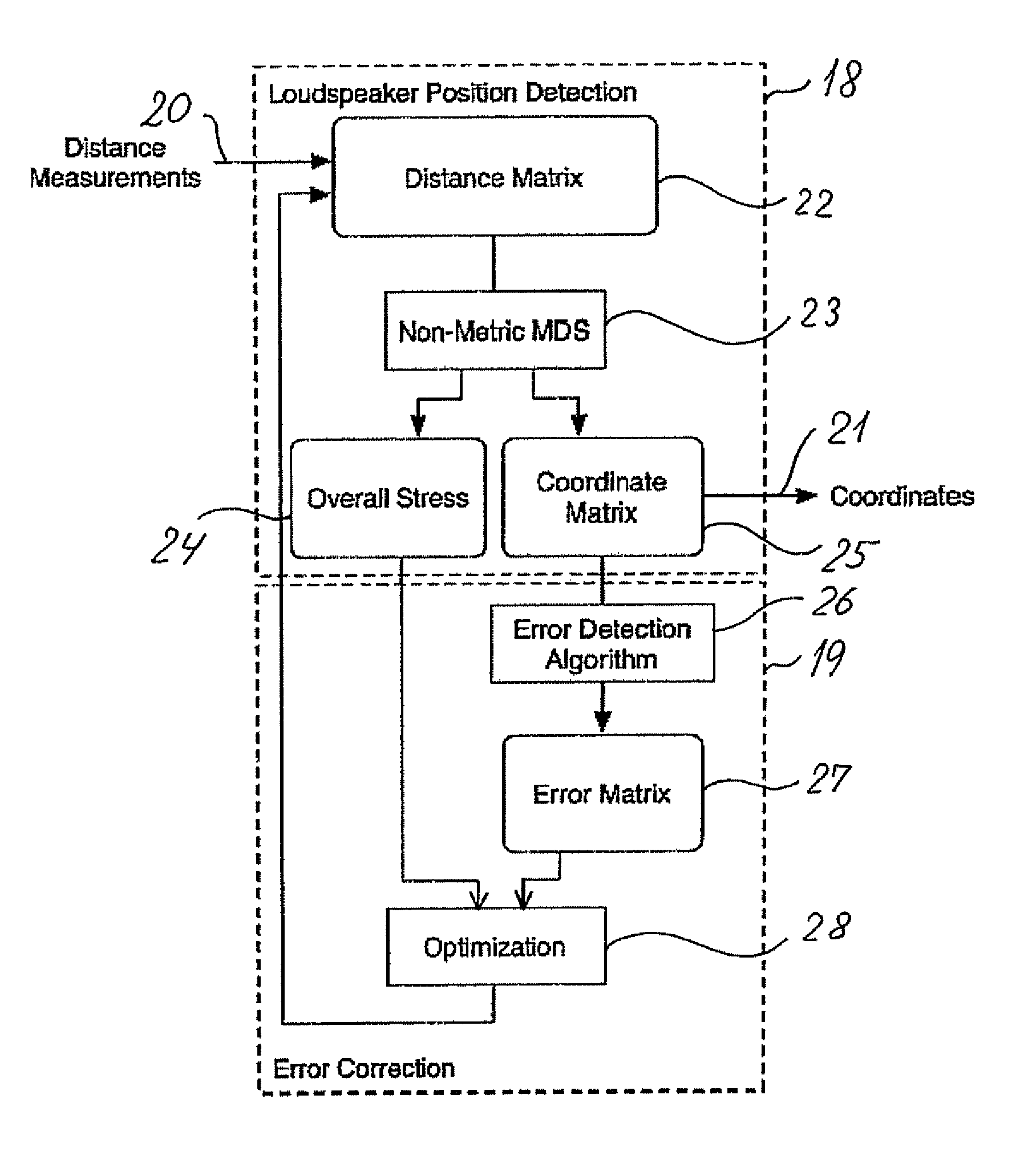
Loudspeaker position estimation
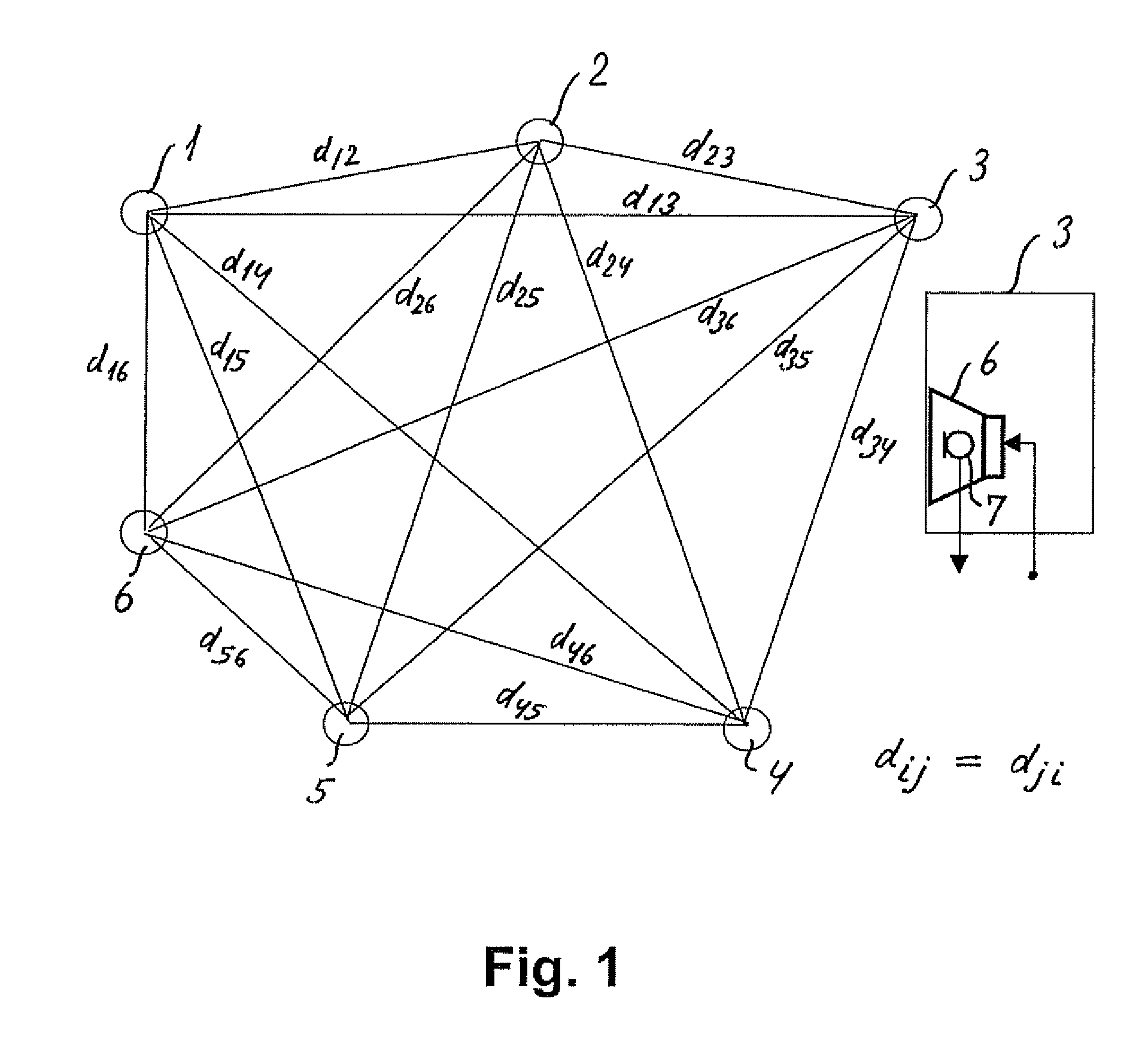
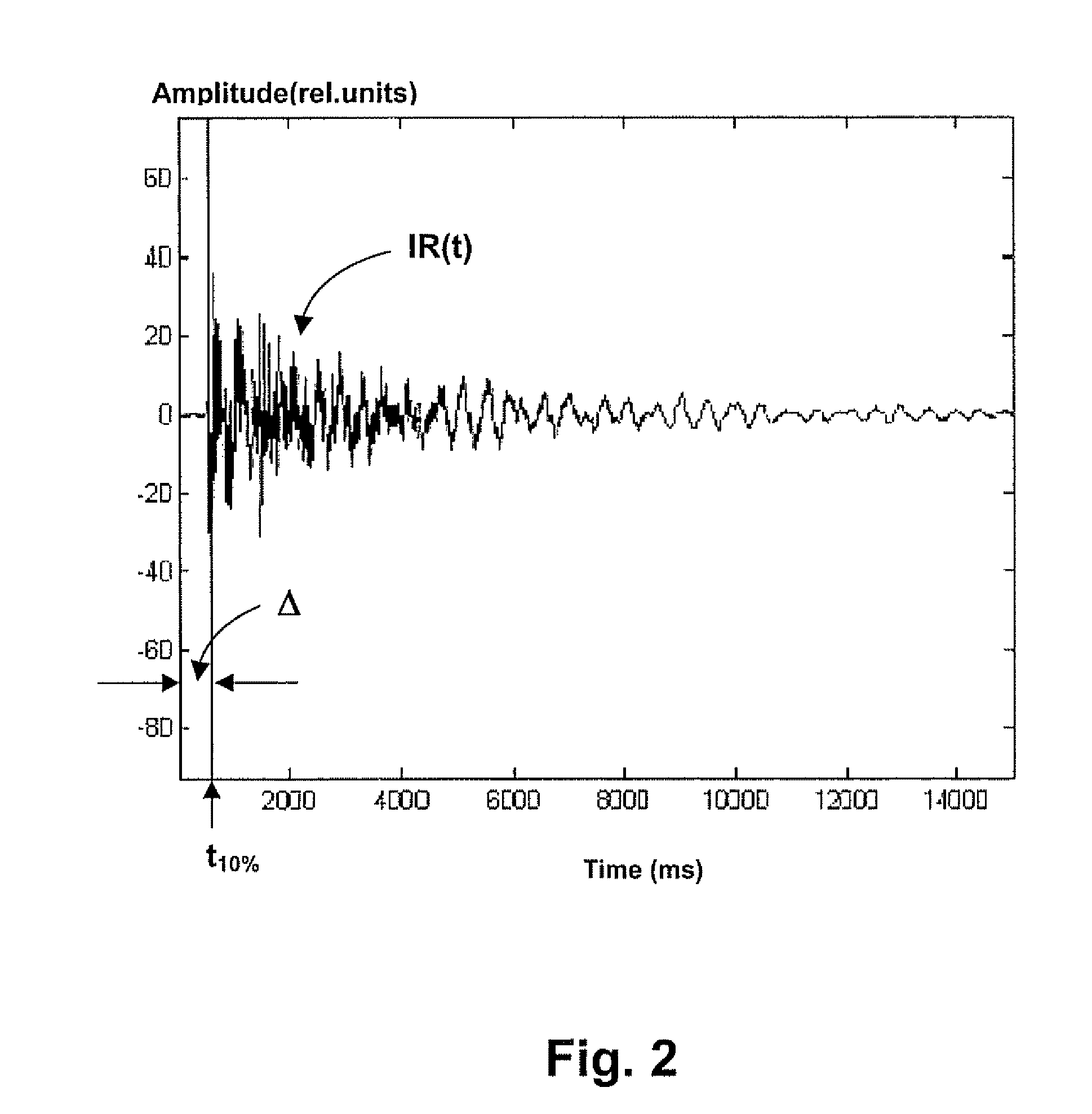
ActiveUS8279709B2Direction finders using ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic wavesLoudspeakersMultidimensional scalingDistance matrix
The invention relates to an automated estimation of the position (co-ordinates) of a set of loudspeakers in a ioom Based on measured impulse responses the distances between each pair of loudspeakers are estimated, thereby forming a distance matrix, and the resultant distance matrix is used by a multidimensional scaling (MDS) algorithm to estimate the co-ordinates of each individual loudspeaker An improved co-ordinate estimation can, if desired, be derived by utilizing the stress values provided by the MDS algorithm.
Owner:BANG & OLUFSEN
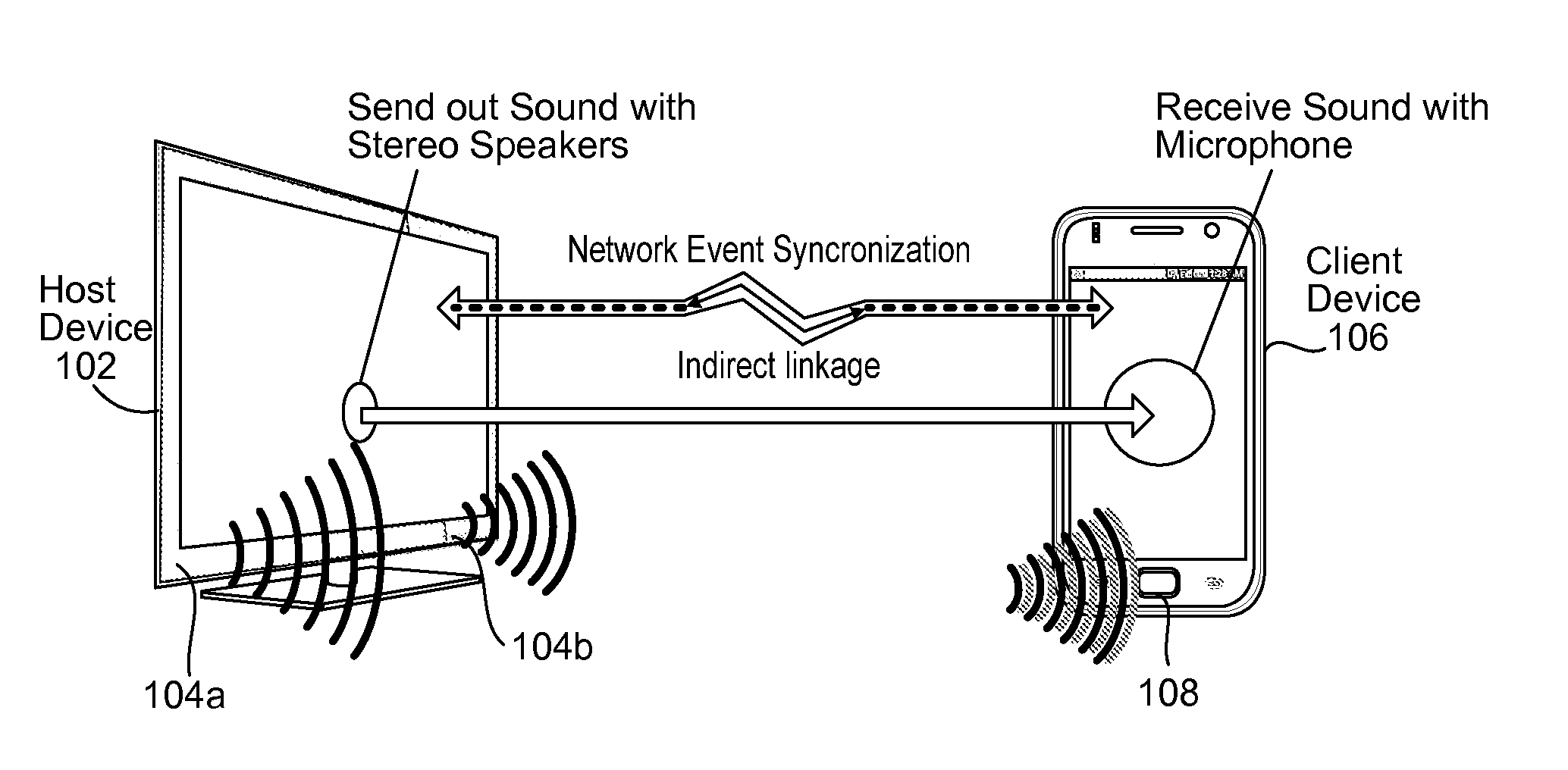
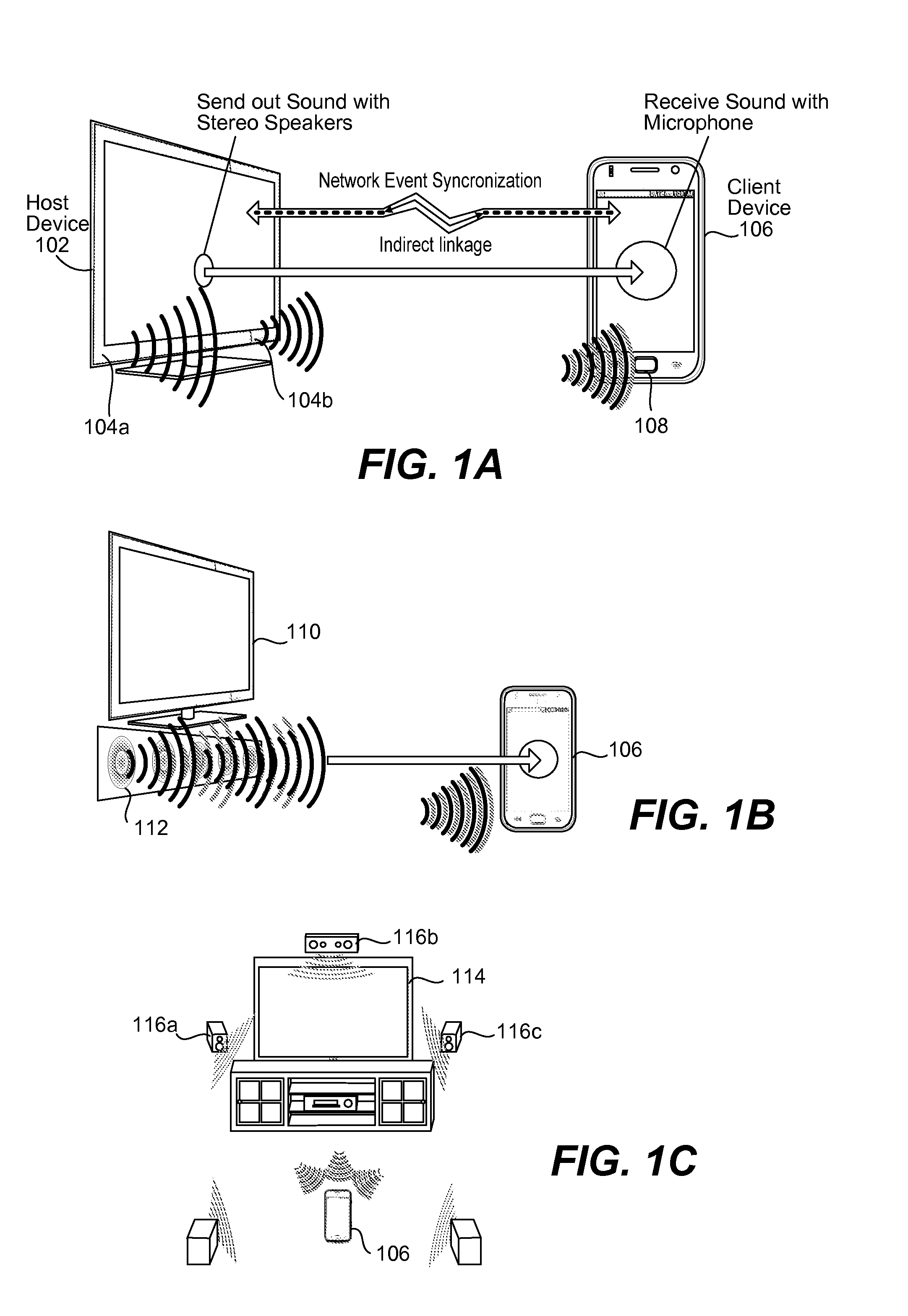
Position determination of devices using stereo audio
InactiveUS20120127831A1Direction finders using ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic wavesPosition fixationHand held devicesLoudspeaker
Methods and systems for determining and utilizing spatial correlative information relating to two or more devices to determine device positioning are described. Using audio signals emitted from stereo speakers, for example, associated with a first device and a microphone associated with the second device, the distance and angle between the two devices and as their relative positions can be determined. No other sensors or specialized accessories are needed on either device to calculate the distance and angles. The devices need only be loaded with the appropriate software which, when executed, is able to carry out steps of the present invention. The usefulness of one or both of the devices may be enhanced by knowing the distance and angle data between the devices. For example, one device may be a TV having stereo speakers and the other device may be a handheld device, such as a smartphone, having a microphone.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
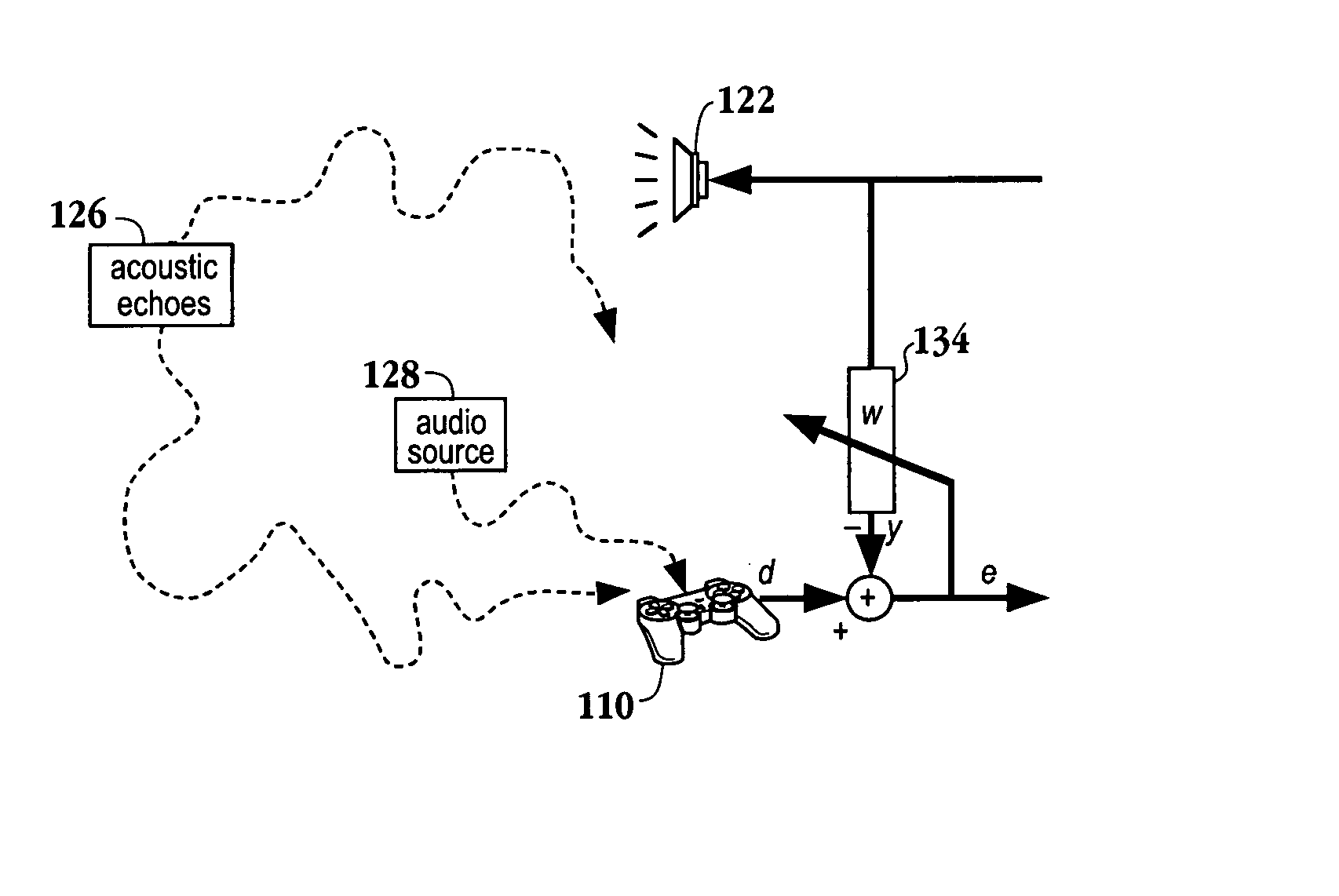
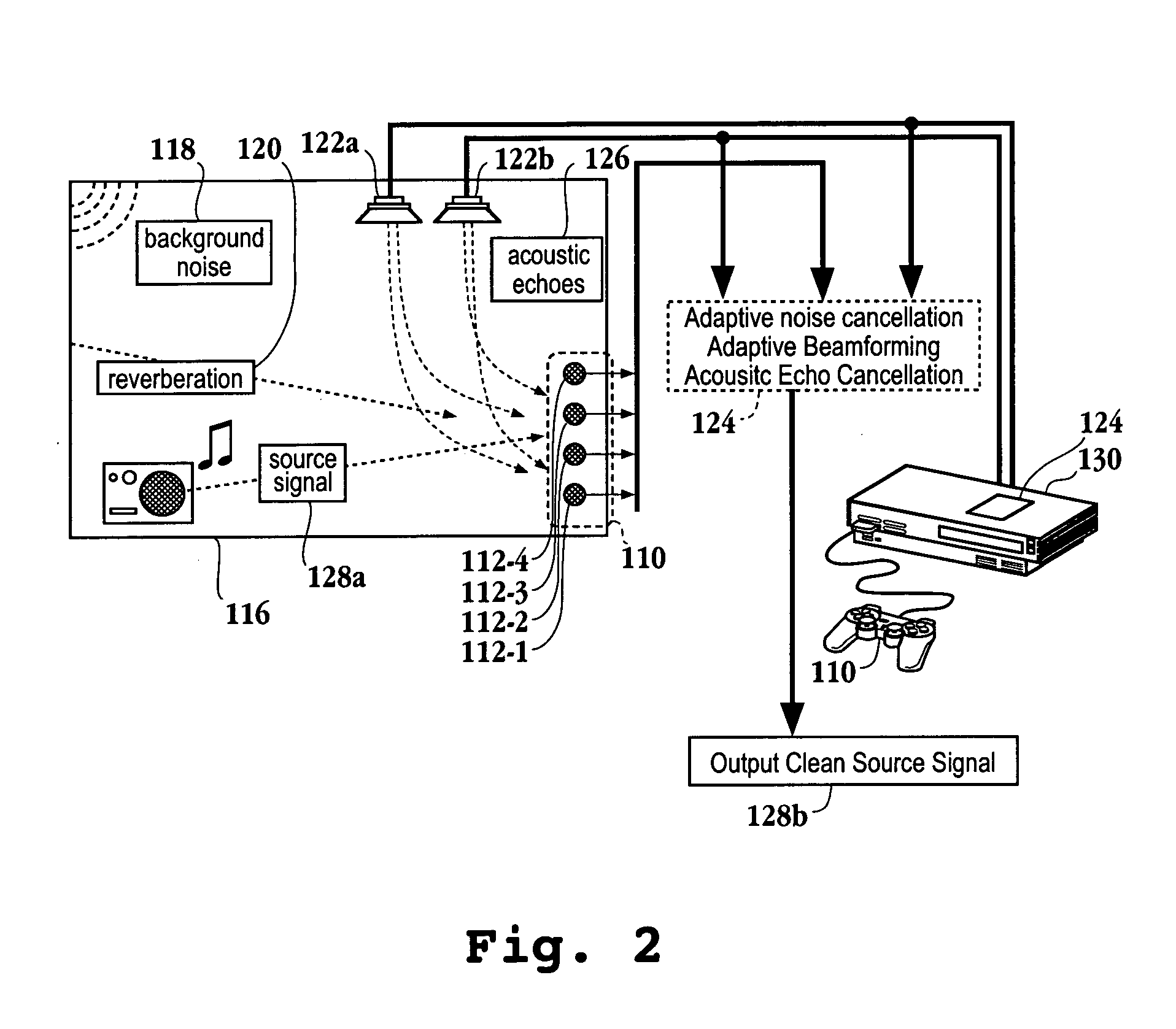
Audio input system
ActiveUS20050047611A1Reduce noiseAdditional componentDirection finders using ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic wavesMicrophones signal combinationSensor arrayTarget signal
A method for reducing noise associated with an audio signal received through a microphone sensor array is provided. The method initiates with enhancing a target signal component of the audio signal through a first filter. Simultaneously, the target signal component is blocked by a second filter. Then, the output of the first filter and the output of the second filter are combined in a manner to reduce noise without distorting the target signal. Next, an acoustic set-up associated with the audio signal is periodically monitored. Then, a value of the first filter and a value of the second filter are both calibrated based upon the acoustic set-up. A system capable of isolating a target audio signal from multiple noise sources, a video game controller, and an integrated circuit configured to isolate a target audio signal are included.
Owner:SONY COMPUTER ENTERTAINMENT INC
Wireless power transmission apparatus using ultrasound
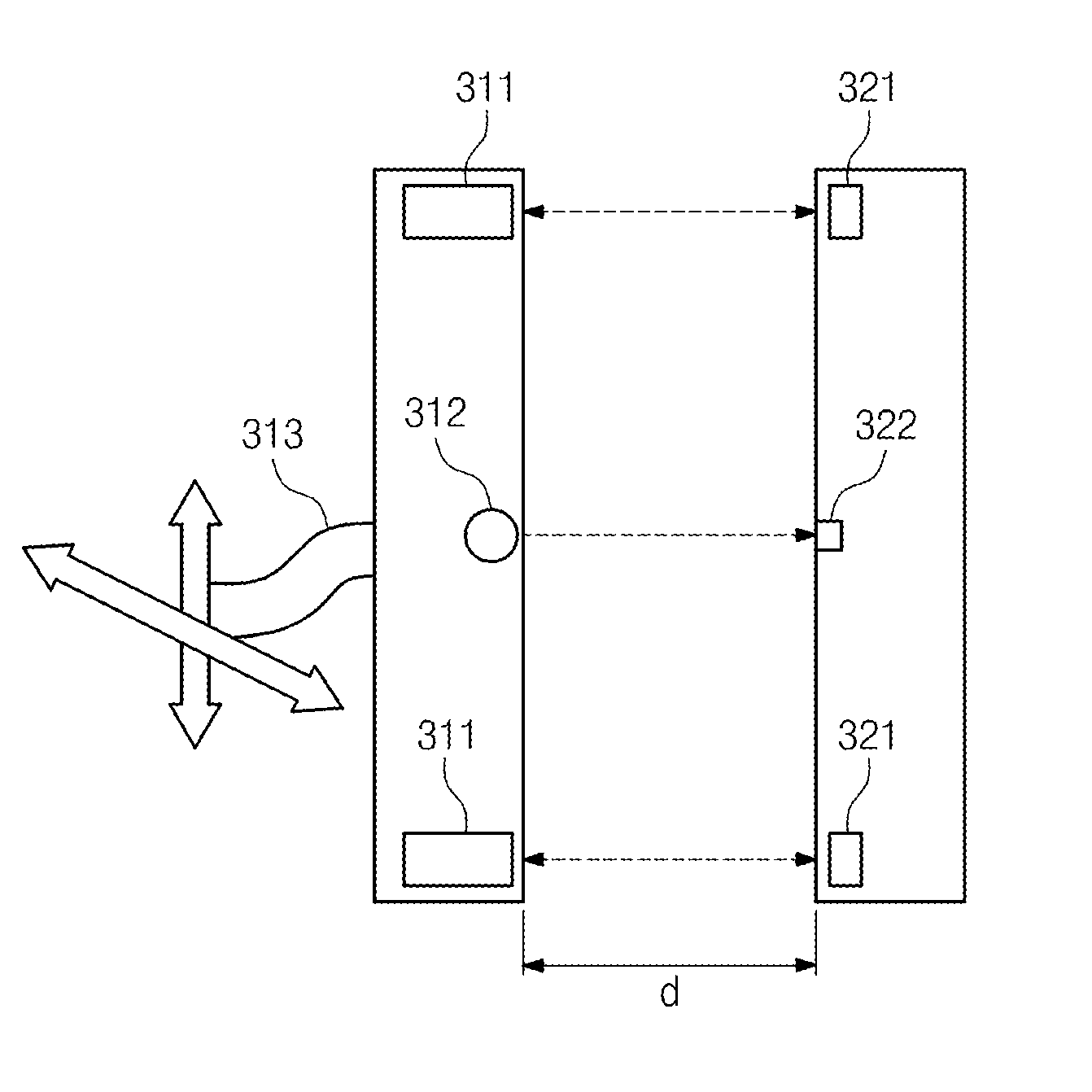
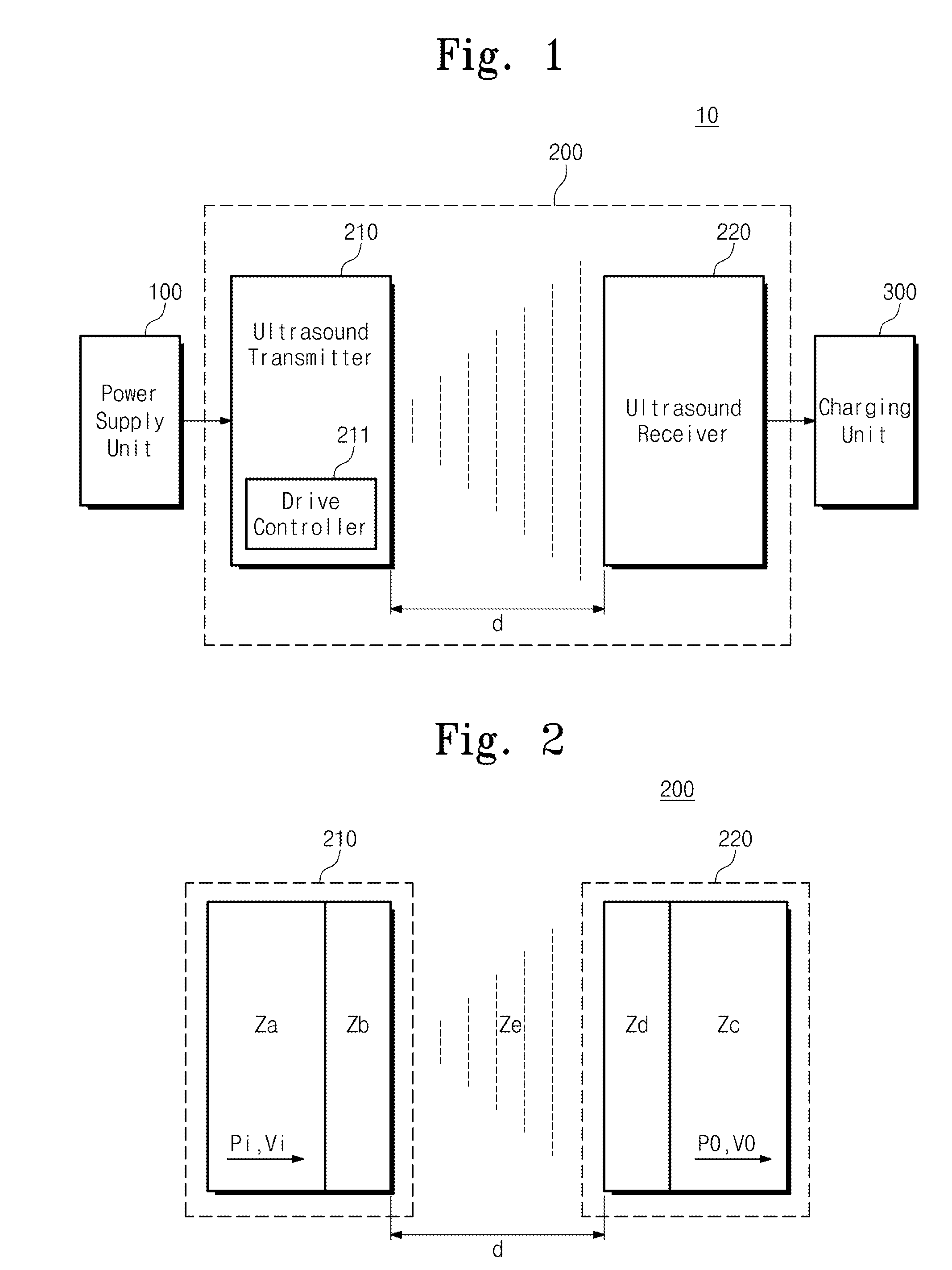
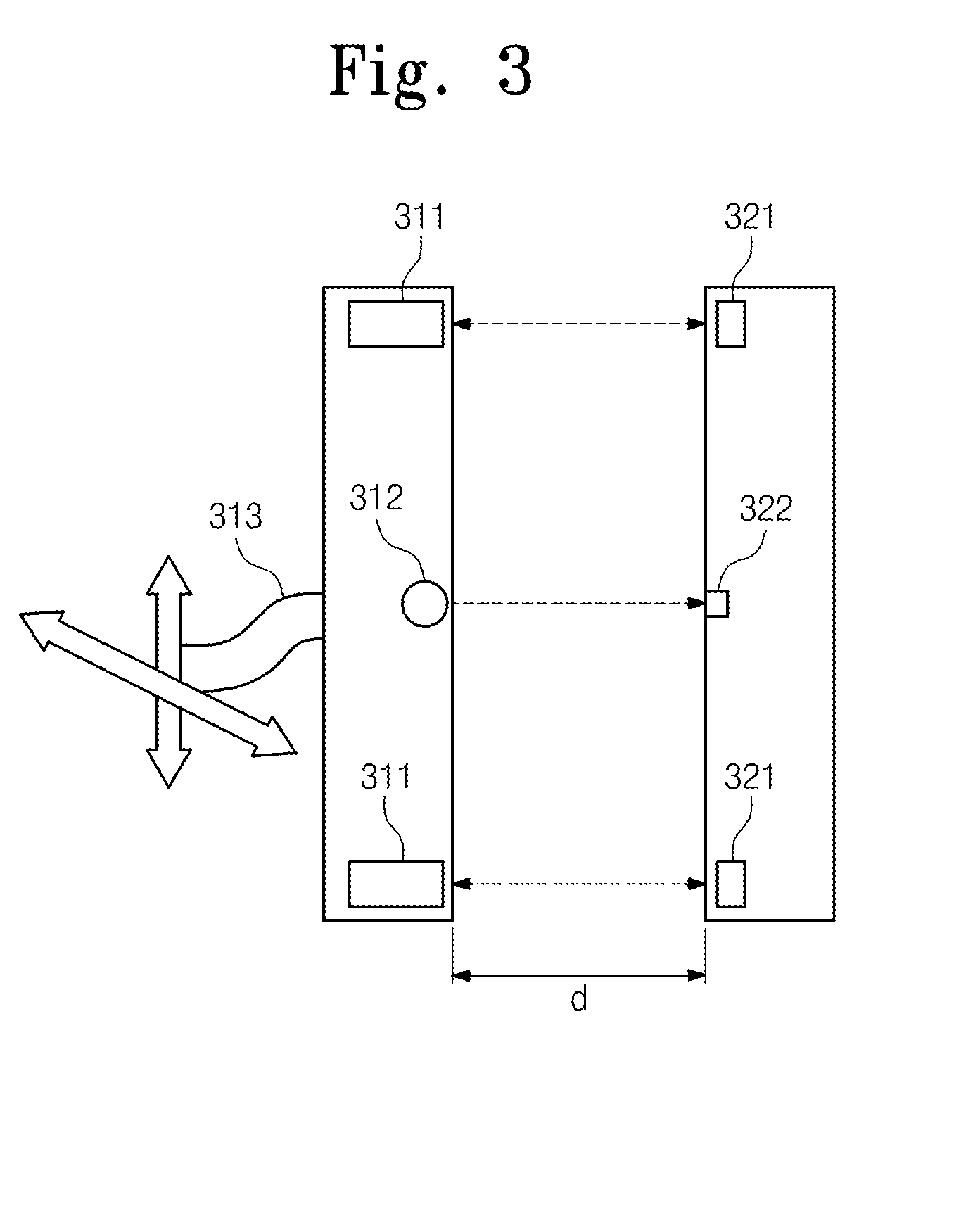
ActiveUS20150003207A1Improve efficiencyMultiple-port networksElectromagnetic wave systemElectric power transmissionSonification
Provided is a wireless power transmission apparatus. The apparatus includes an ultrasound transmitter generating an ultrasound signal in response to an external source voltage and transmitting the generated ultrasound signal to a medium layer and an ultrasound receiver receiving the ultrasound signal through the medium layer and converting the received ultrasound signal into a driving voltage. The ultrasound transmitter and receiver are manufactured to control impedance values thereof to be matched with each other and a distance between the ultrasound transmitter and receiver is controlled according to predetermined distance conditions.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Audio system and related method integrated with ultrasound communication functionality
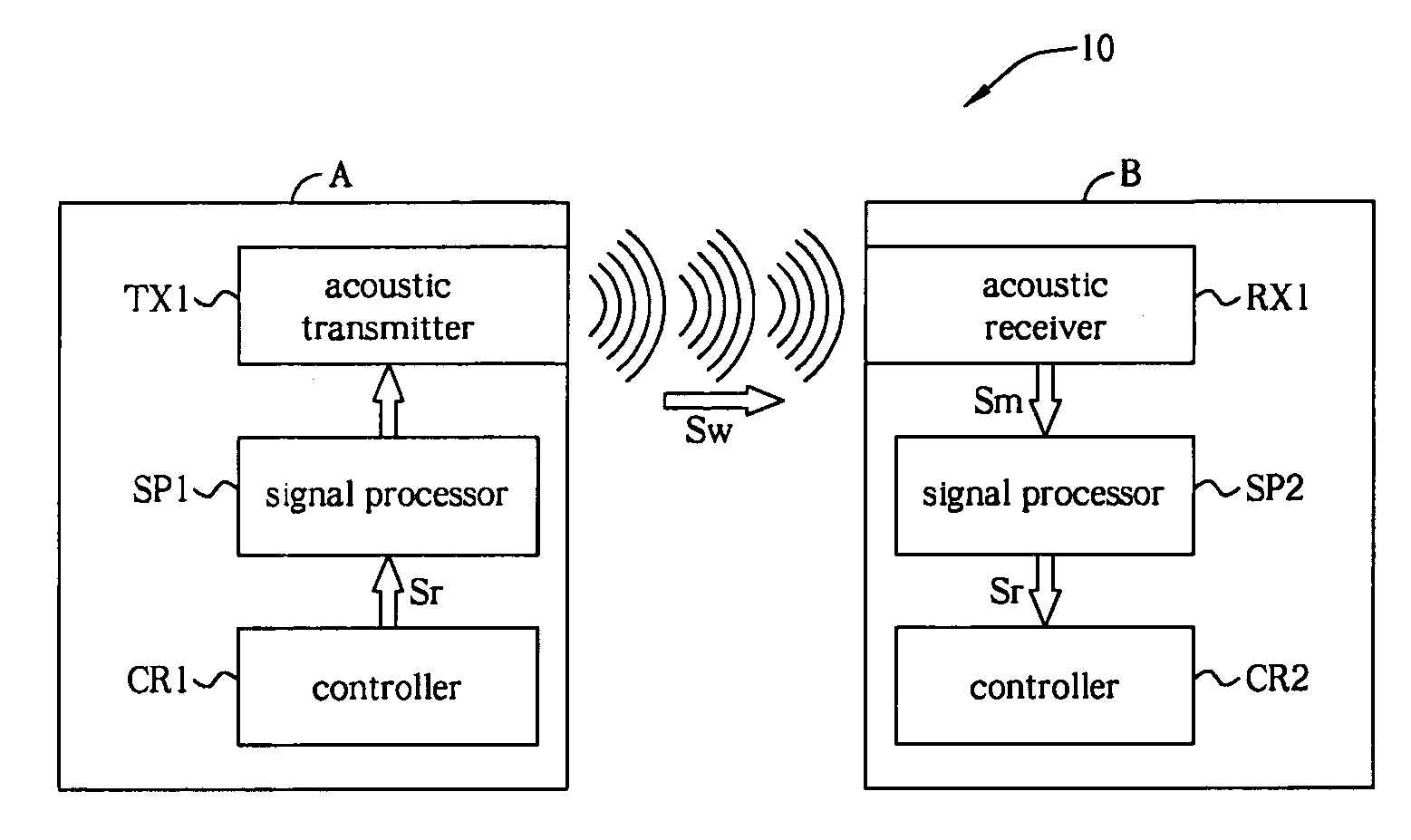
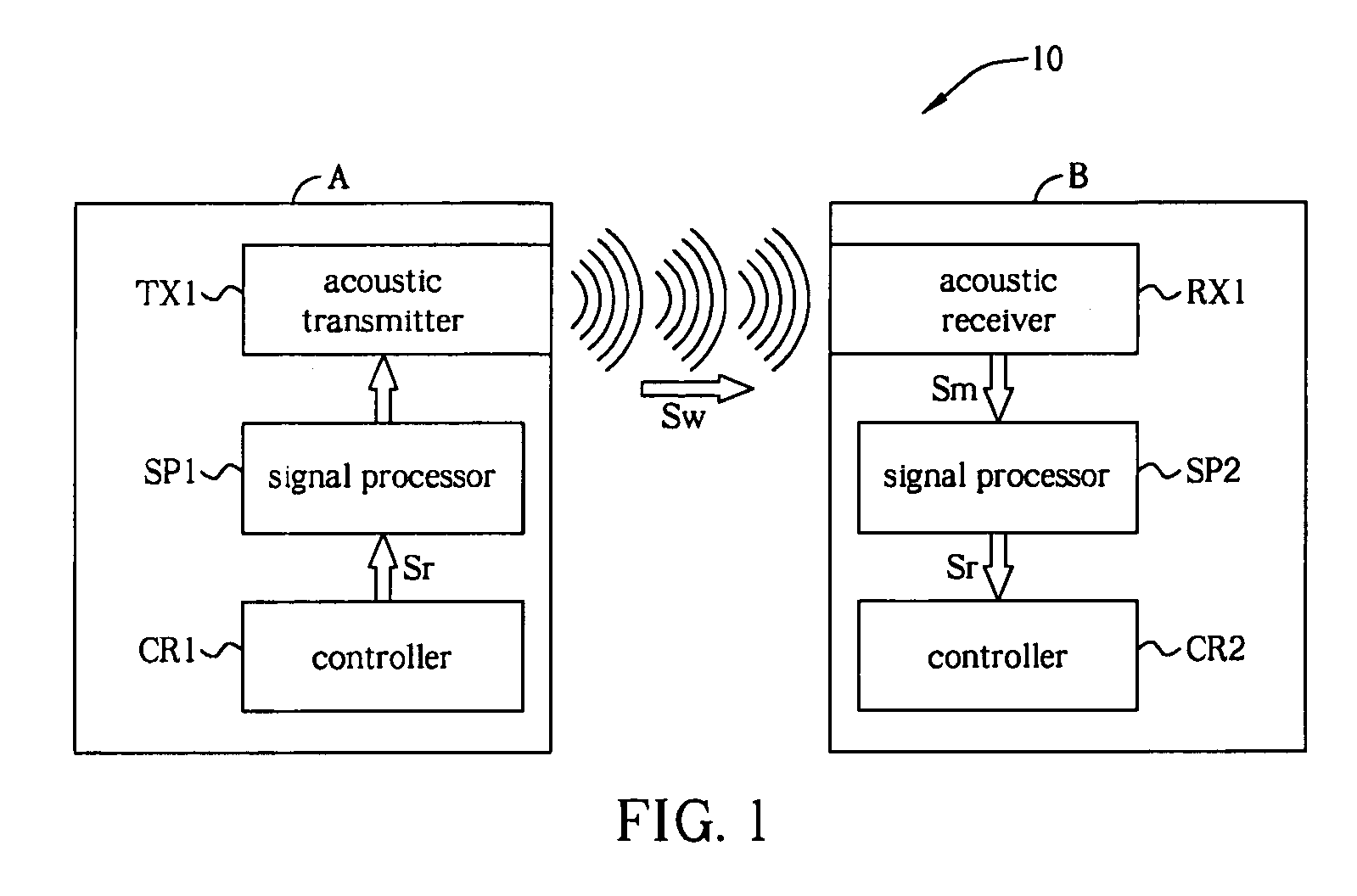
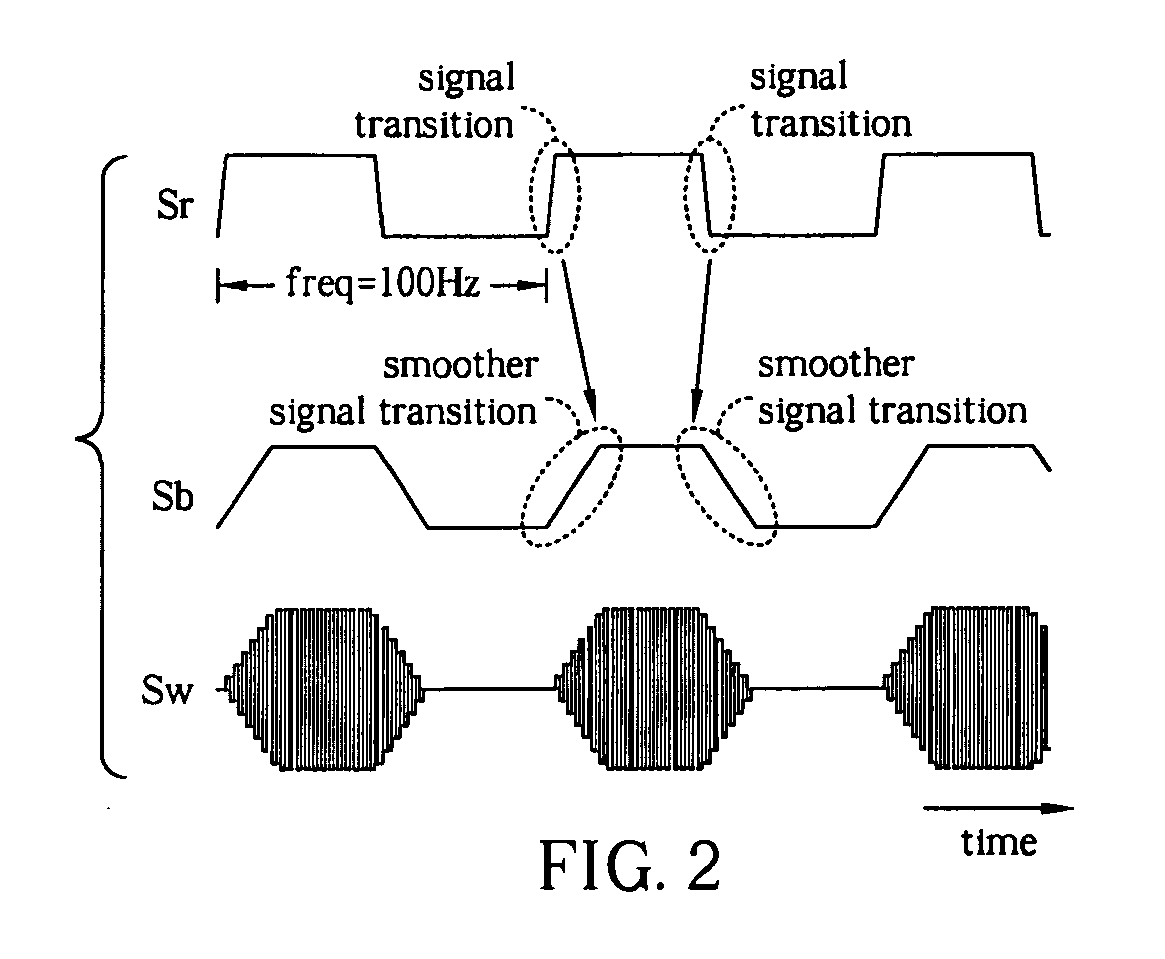
ActiveUS8160276B2Low costConveniences of remote communication can be widely prevailedDirection finders using ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic wavesSonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic transmissionSonificationLoudspeaker
Audio system and related method integrated with ultrasound communication functionality are provided. A communication transmitting device of proposed invention modulates a communication signal of communication functionality to a high-frequency sound and transmits the high-frequency sound by an ordinary audio transmitter. A communication receiving device of proposed invention receives the high-frequency sound with an ordinary audio receiver and demodulates it to retrieve the communication signal, and then the communication device can use the communication signal. The proposed audio sound transmitter / receiver can be implemented using low-cost audio speaker / microphone, such that a cost for implementing communication functionality can be reduced.
Owner:GENERALPLUS TECH INC
Acoustic Robust Synchronization Signaling for Acoustic Positioning System
InactiveUS20080084789A1Improve accuracyDirection finders using ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic wavesPosition fixationLocation detectionEngineering
A position detection system comprising positional element and positioning device, wherein the positional element transmits a continuously modulated acoustic waveform and a synchronization signal that is a sequence of at least two synchronization packets, each bearing timing data for the continuously modulated acoustic waveform. Additionally, the synchronization signal uses time hopping to support concurrent positioning of a plurality of positional elements.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
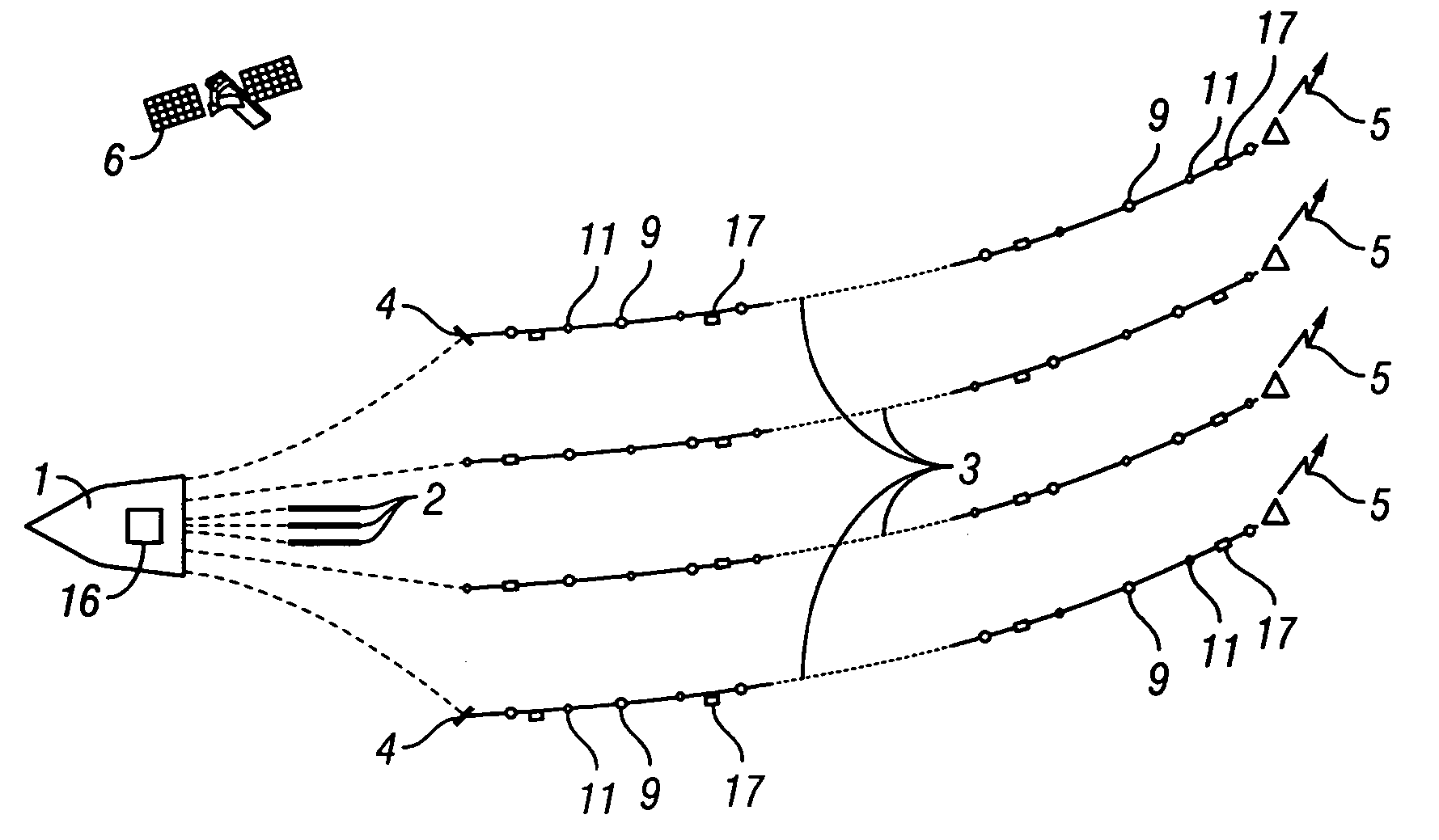
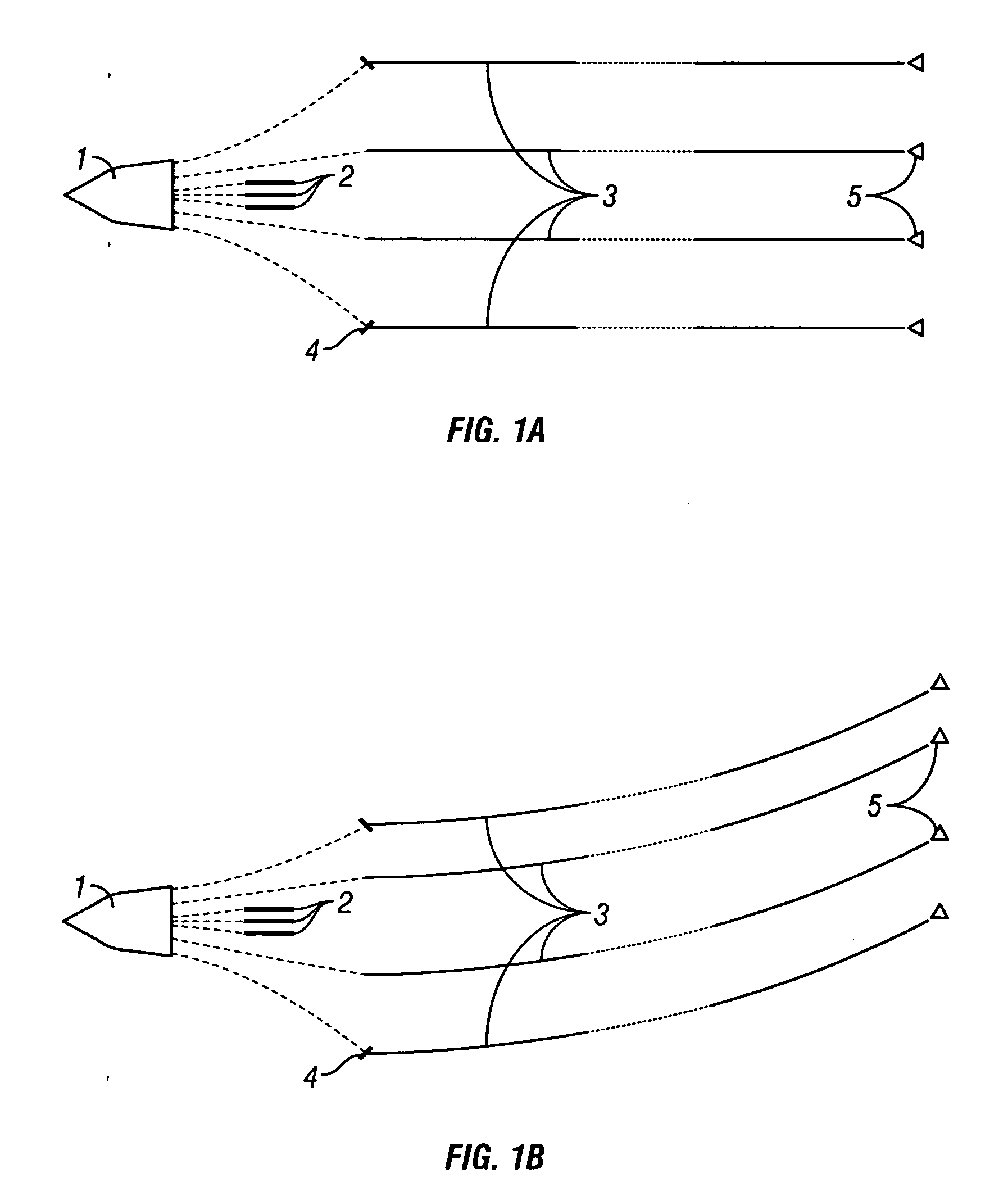
System and method for determining positions of towed marine seismic streamers
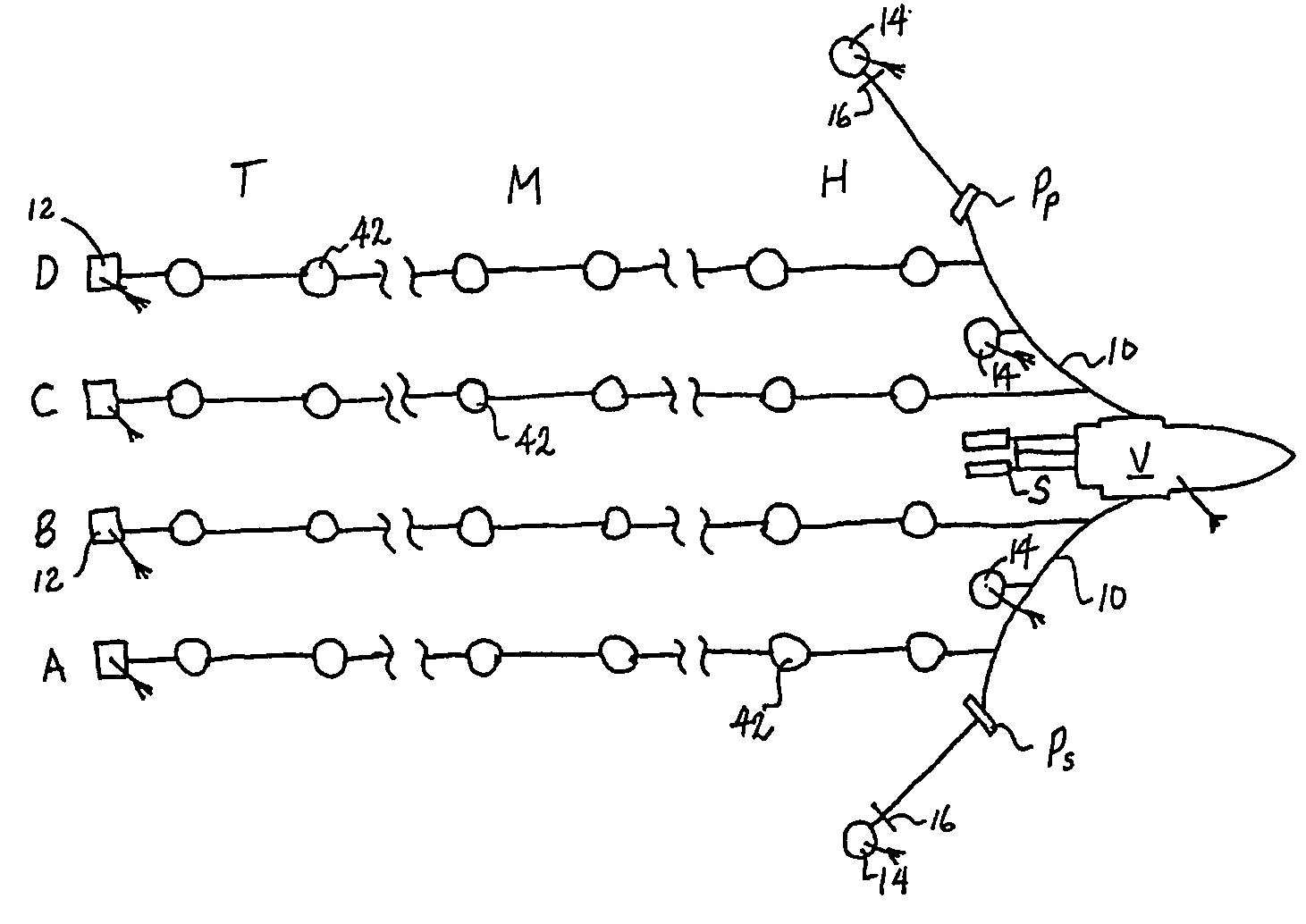
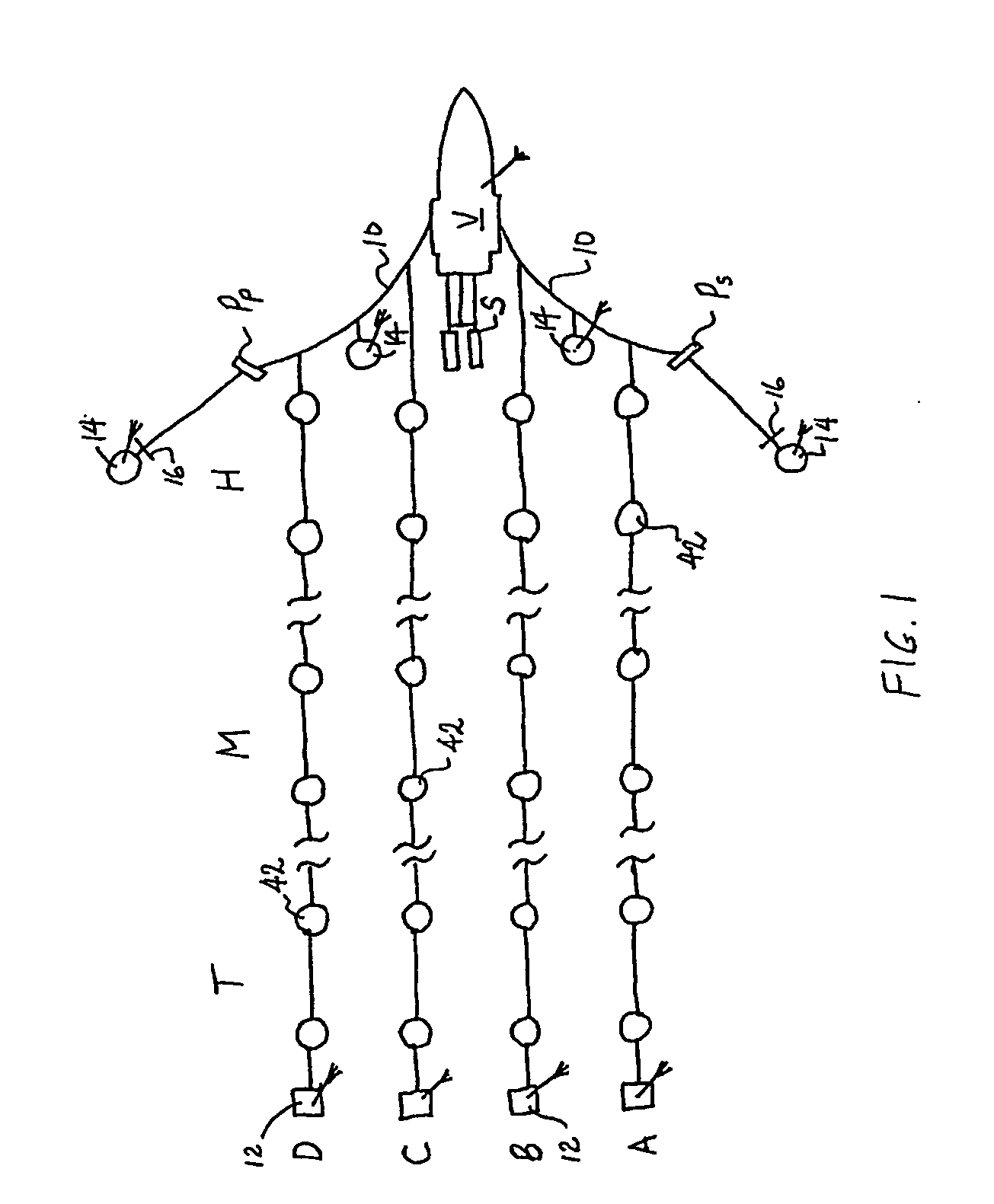
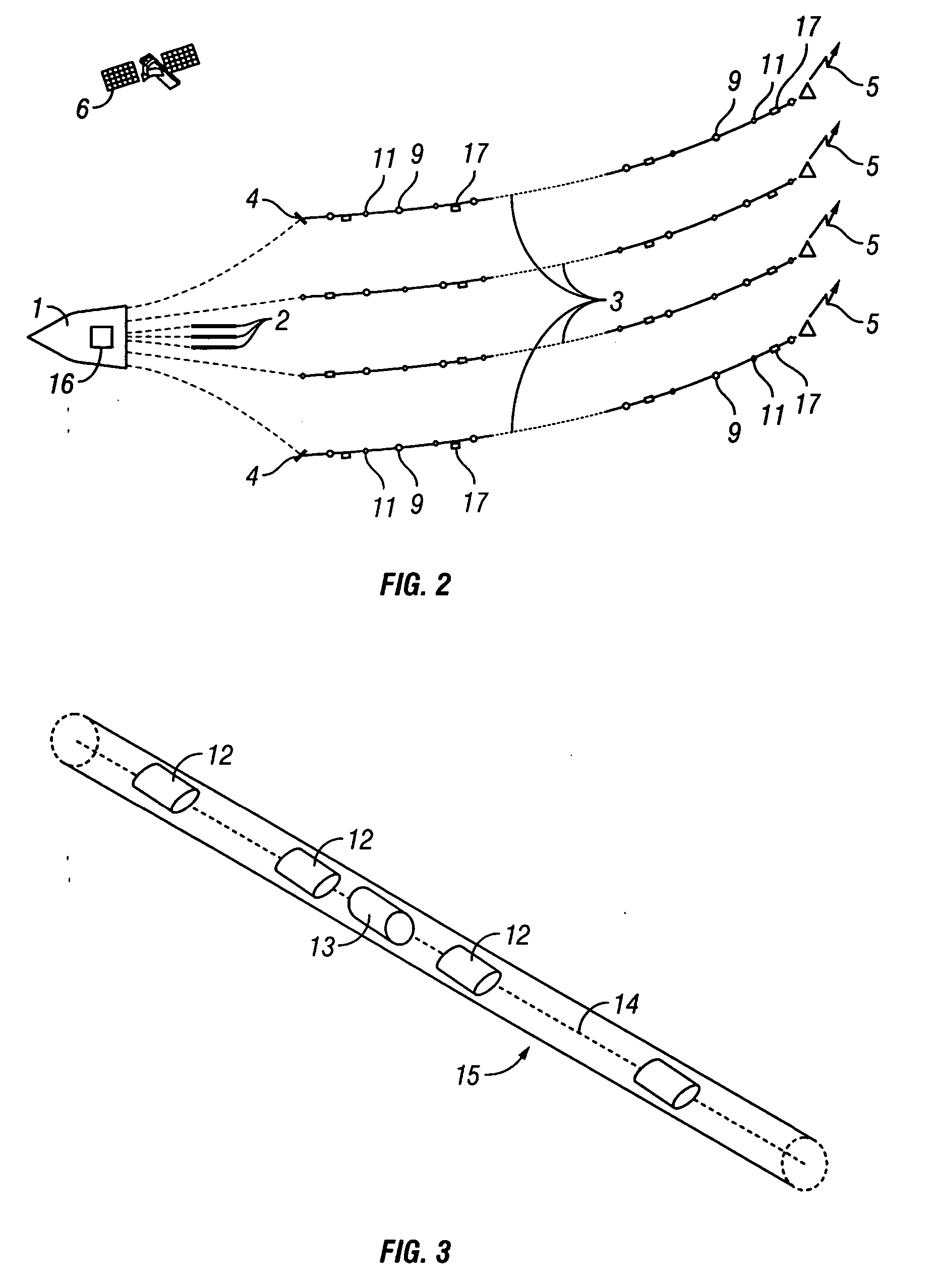
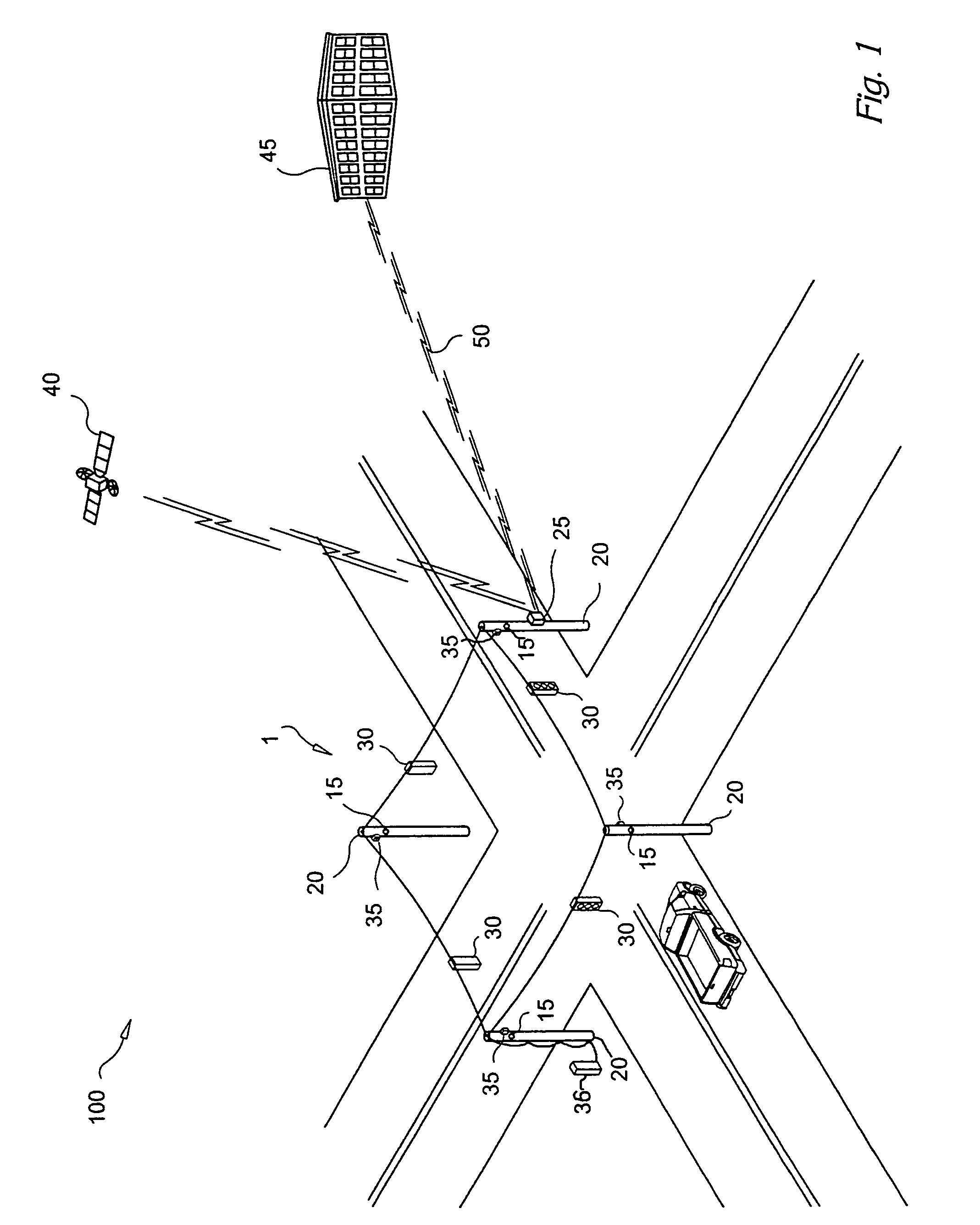
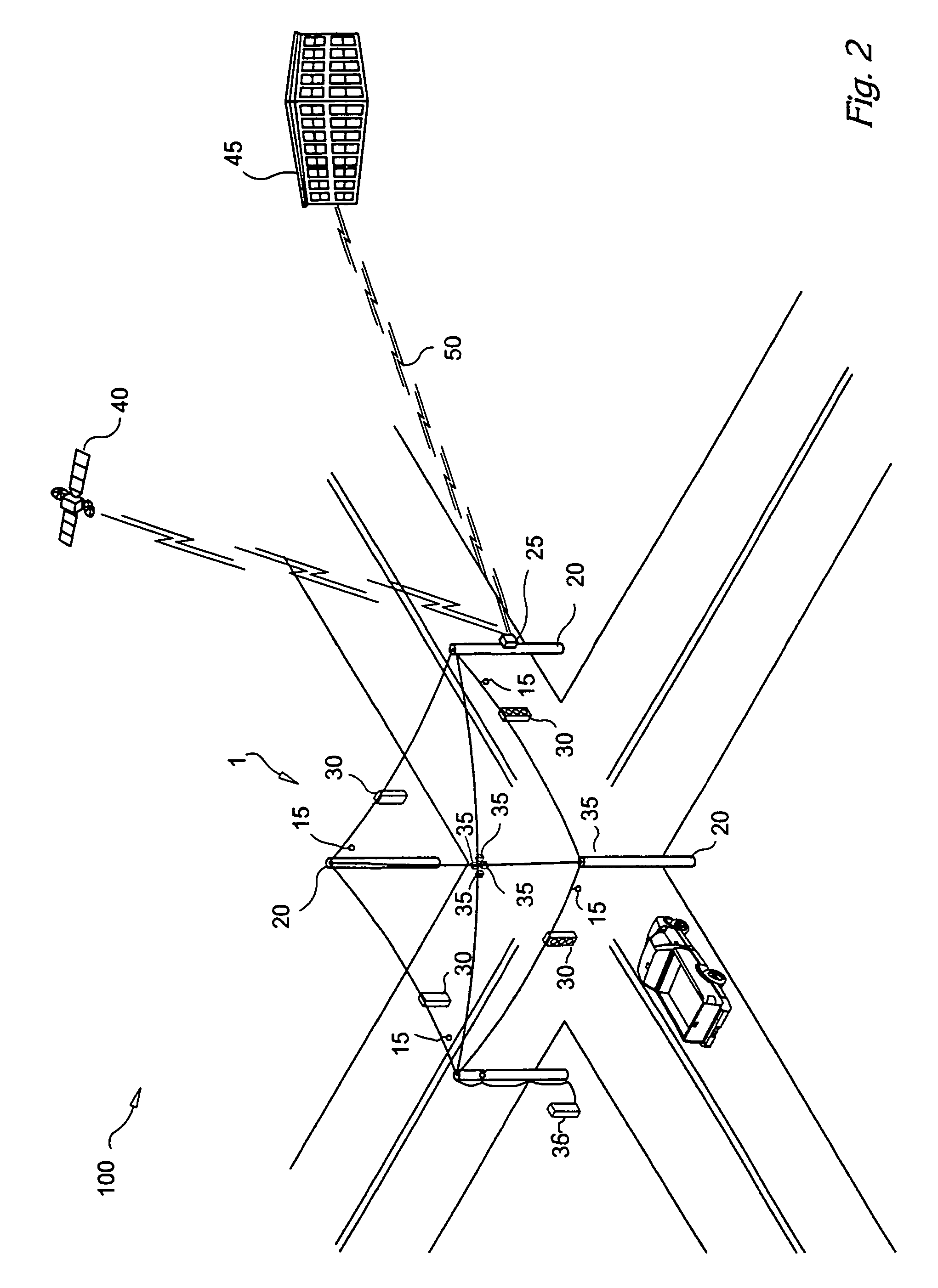
ActiveUS7376045B2Direction finders using ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic wavesMechanical vibrations separationBroadbandEngineering
Owner:PGS GEOPHYSICAL AS
Gps-based underwater cable positioning system
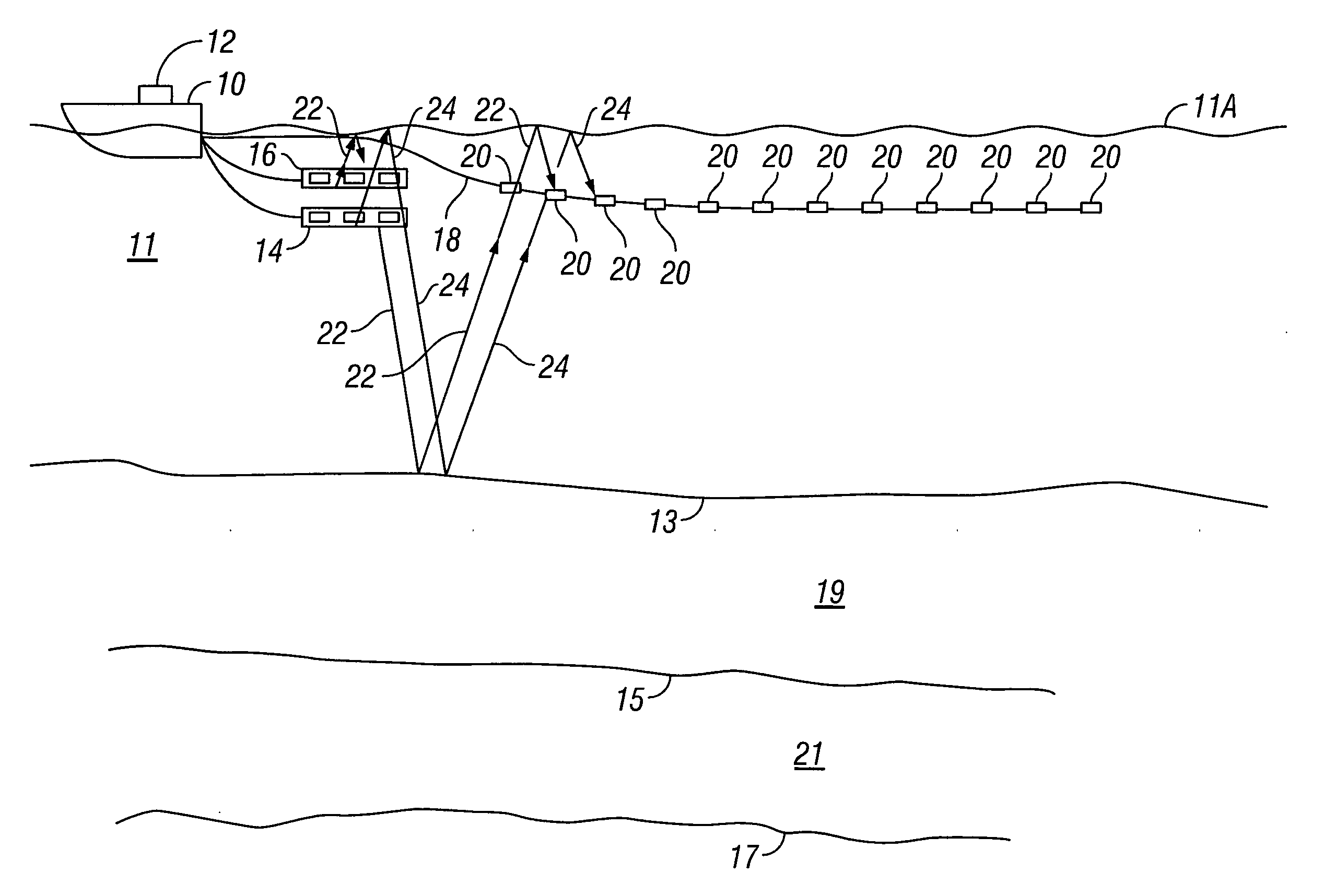
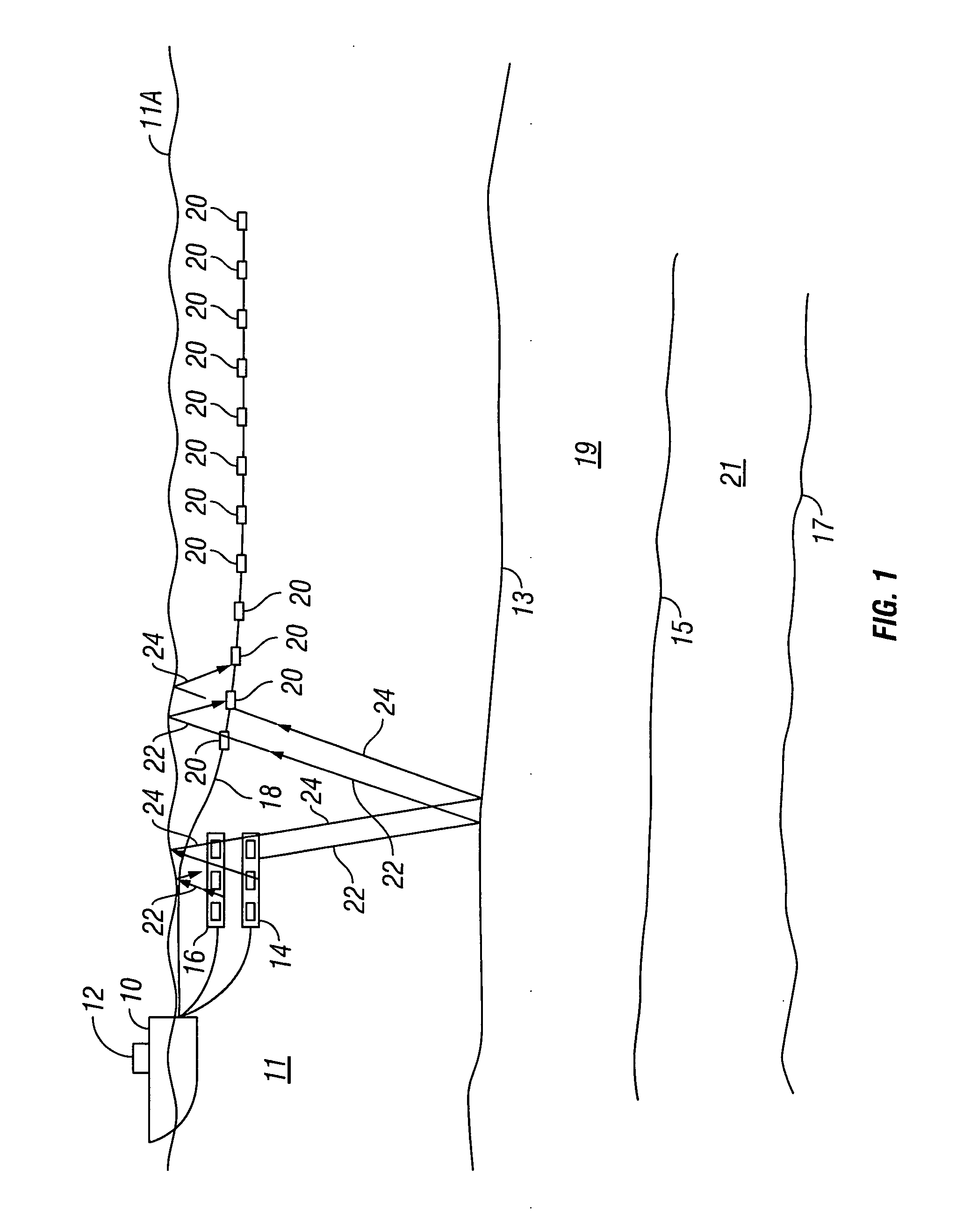
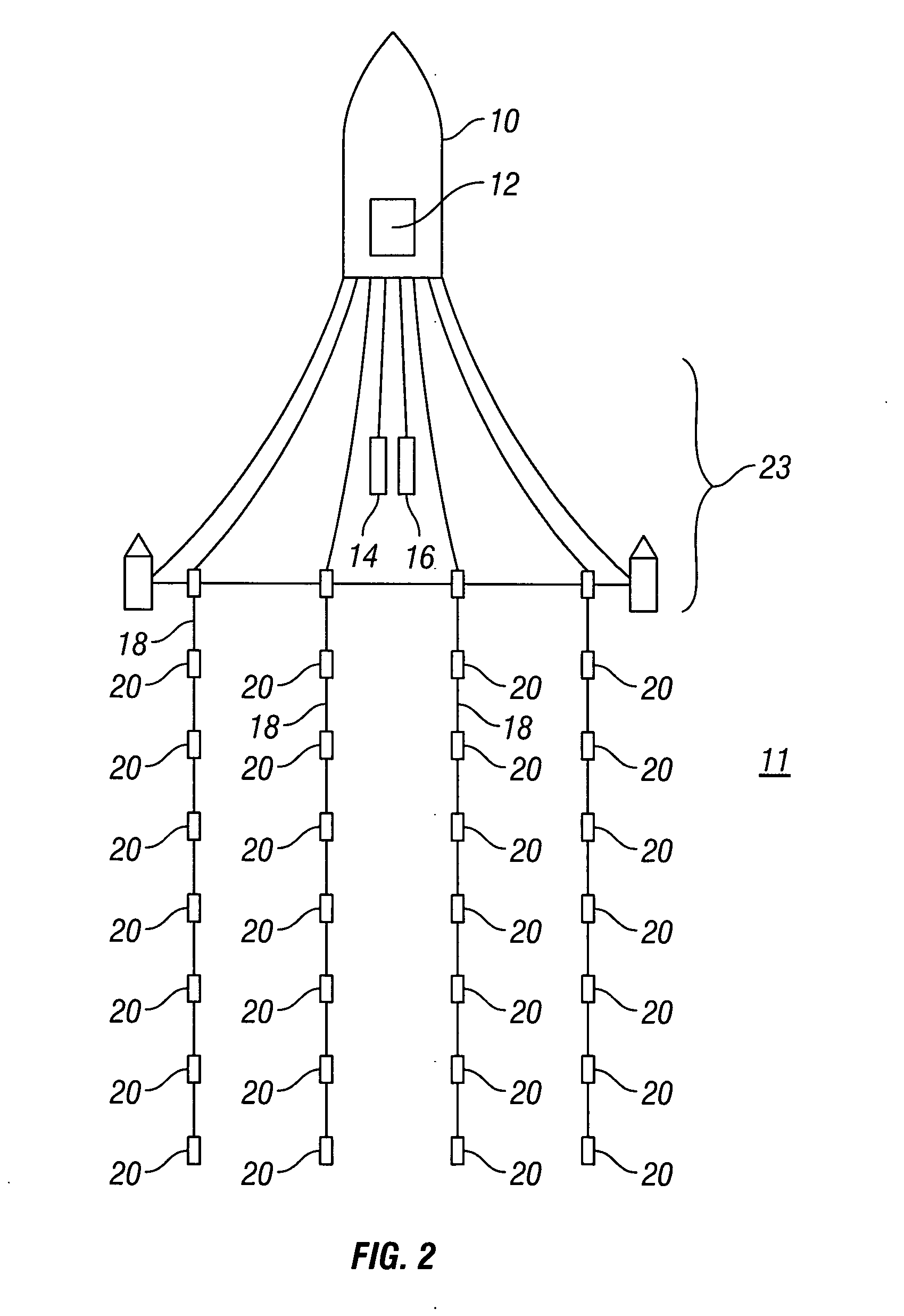
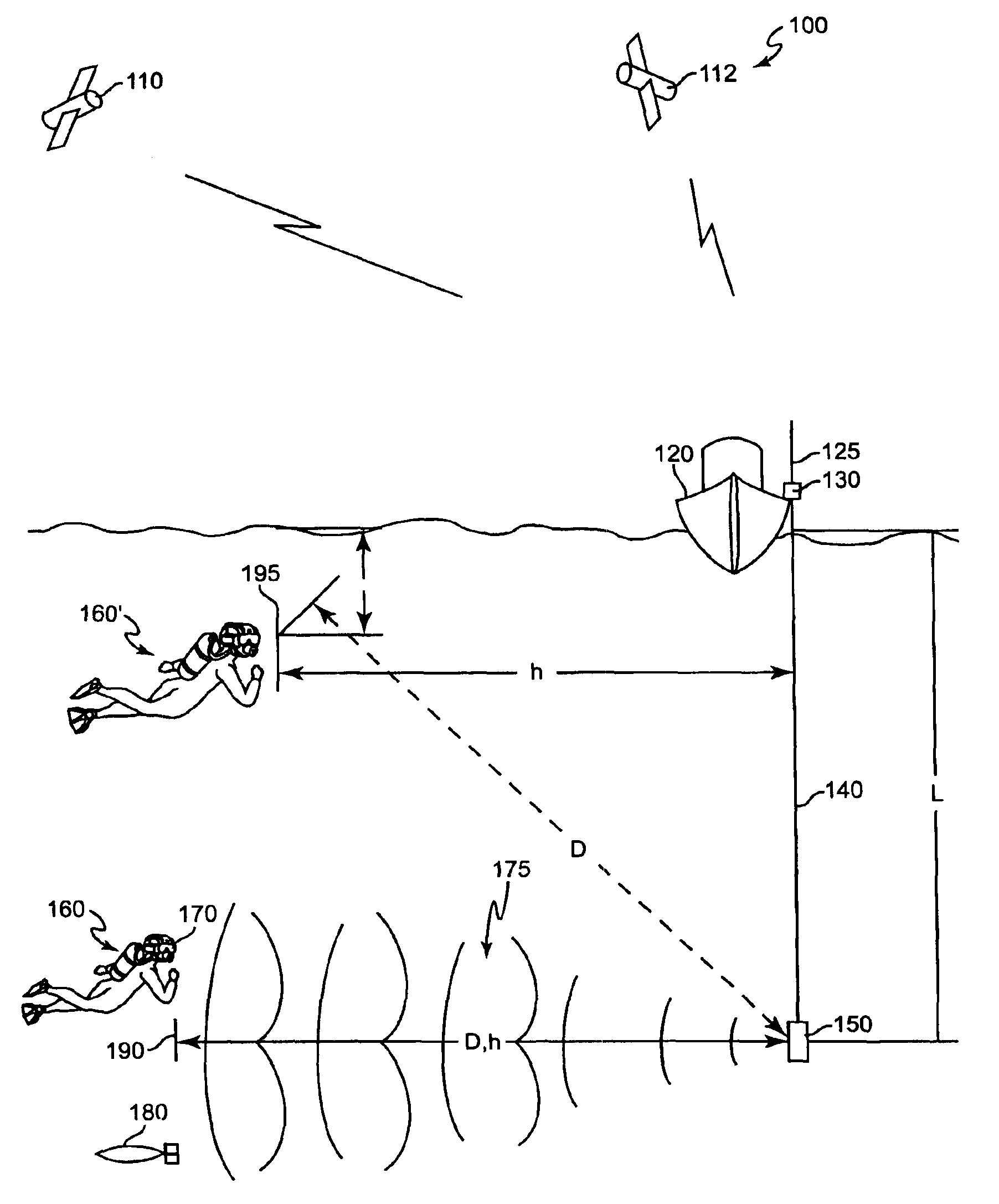
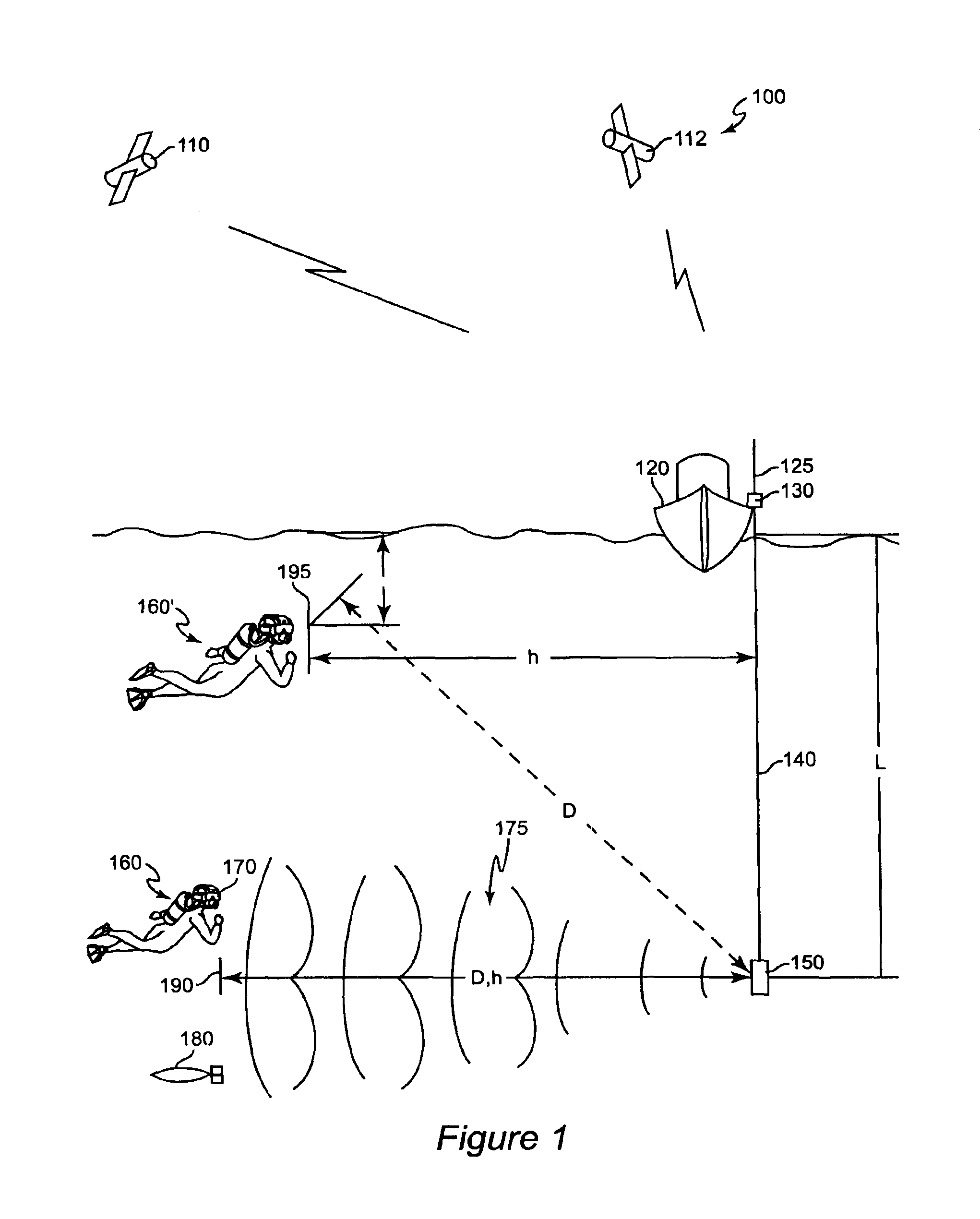
ActiveUS20050180263A1Improve positioning geometryEnhanced signalBeacon systems using ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic wavesDirection finders using ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic wavesHydrophoneTransceiver
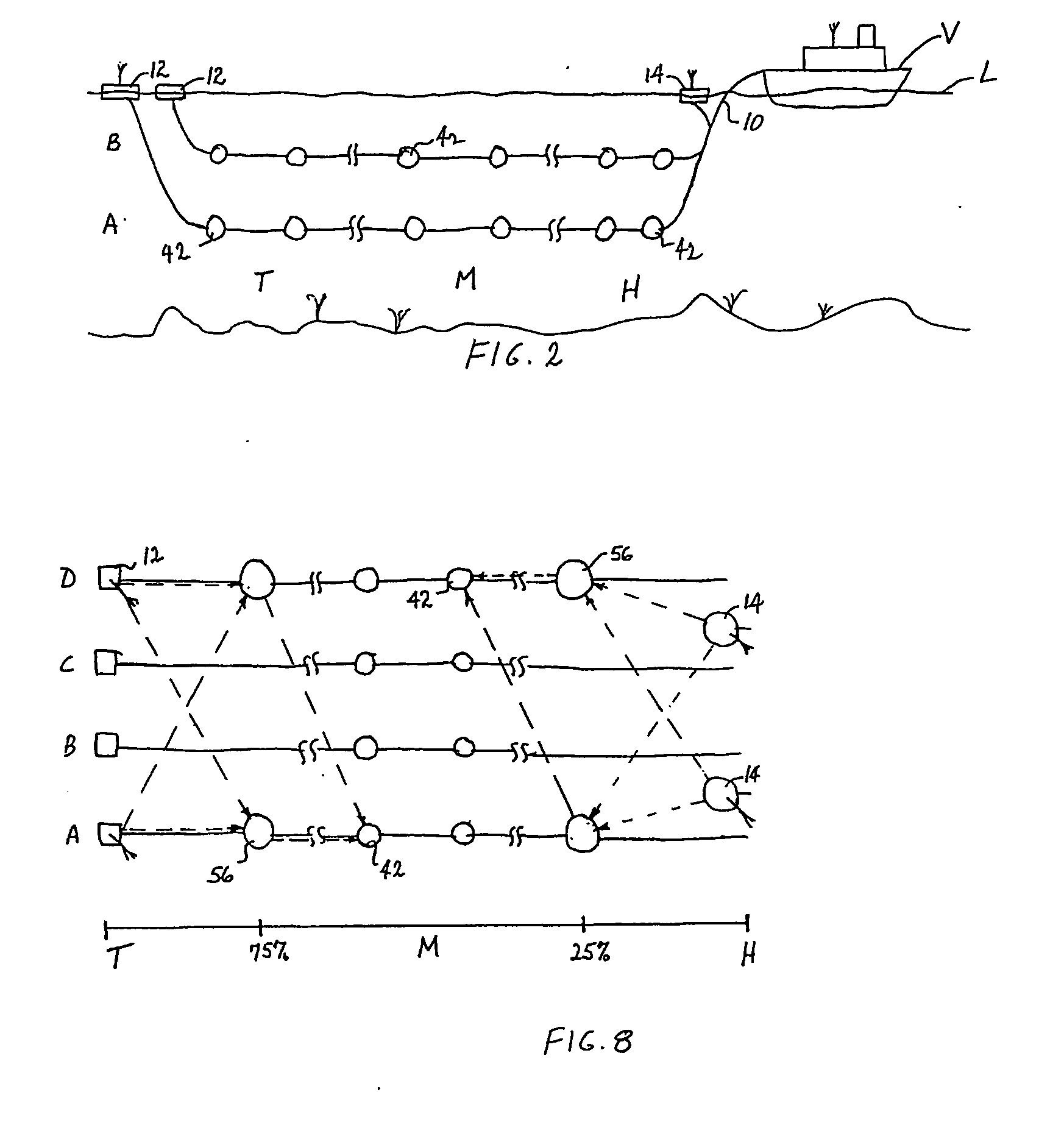
A GPS-based underwater cable positioning system for use in determining the shape and position of hydrophone streamers towed underwater behind survey vessels involved in marine seismic prospecting. The system includes a plurality of surface units towed behind the vessel. Each surface unit includes a GPS receiver to receive radio frequency GPS signals and to determine its positions. Each surface unit also has an acoustic transmitter to transmit an acoustic message signal representing its position and an optional time stamp into the water. Acoustic receiver units, attached spaced apart locations along one or more streamer cables, each include an acoustic receiver to receive the acoustic message signals from the surface units and to determine its position from the message signals. To augment the message signals from the surface units at locations distant from the surface units, acoustic transceiver units may be used. The acoustic transceiver units are attached to the streamer cables at ranges between the surface units and distant acoustic receiver units. The acoustic transceiver units each include an acoustic receiver that performs as the receivers in the acoustic receiver units and an acoustic transmitter to transmit acoustic message signals representing its position and an optional time stamp into the water to be received by the acoustic receiver units. In this way, the positions and shapes of towed streamer cables can be determined.
Owner:INPUT OUTPUT INC
Remote temperature sensing device
InactiveUS20100329301A1Reduce distanceThermometer detailsDirection finders using ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic wavesProximateTemperature difference
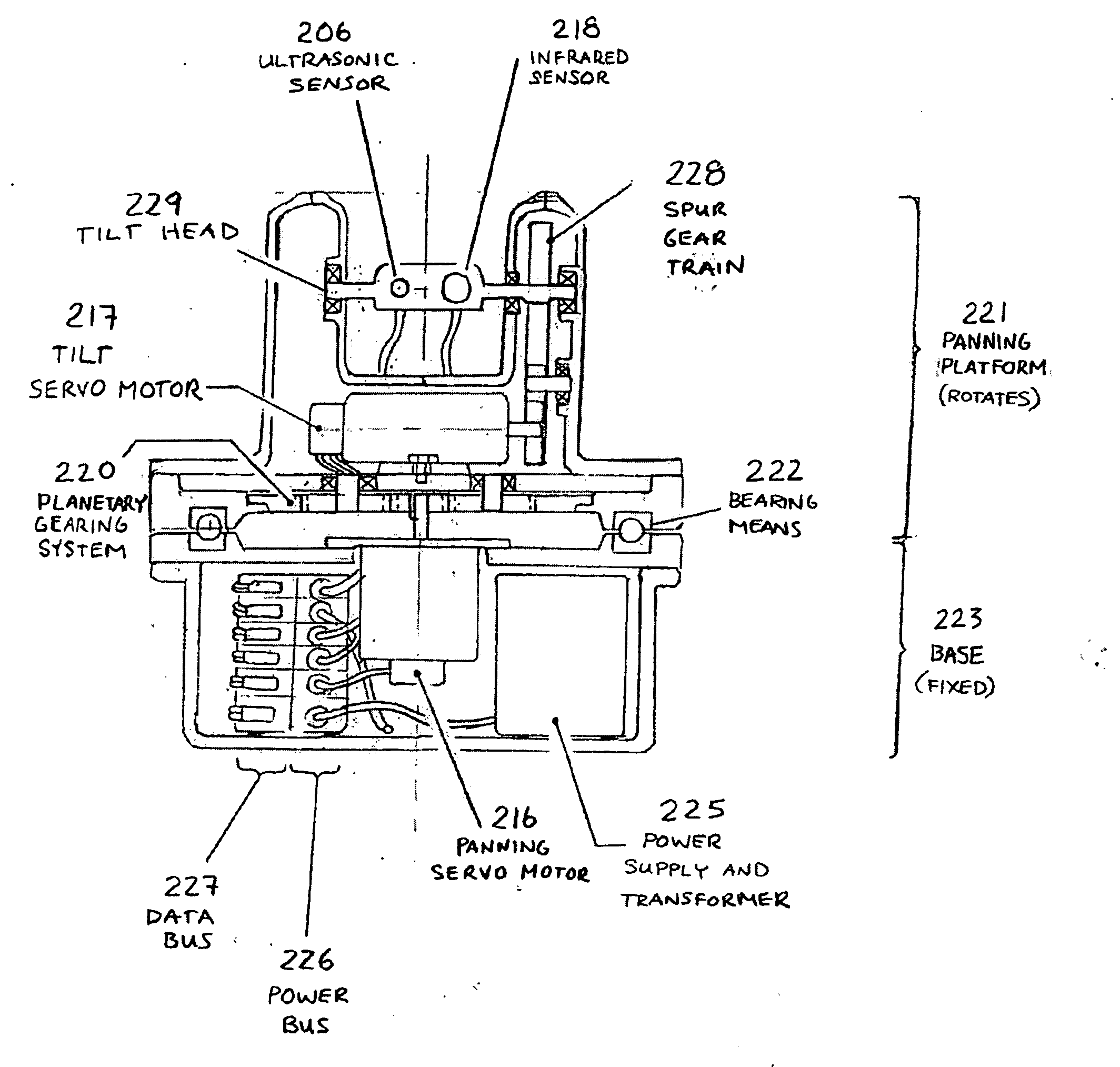
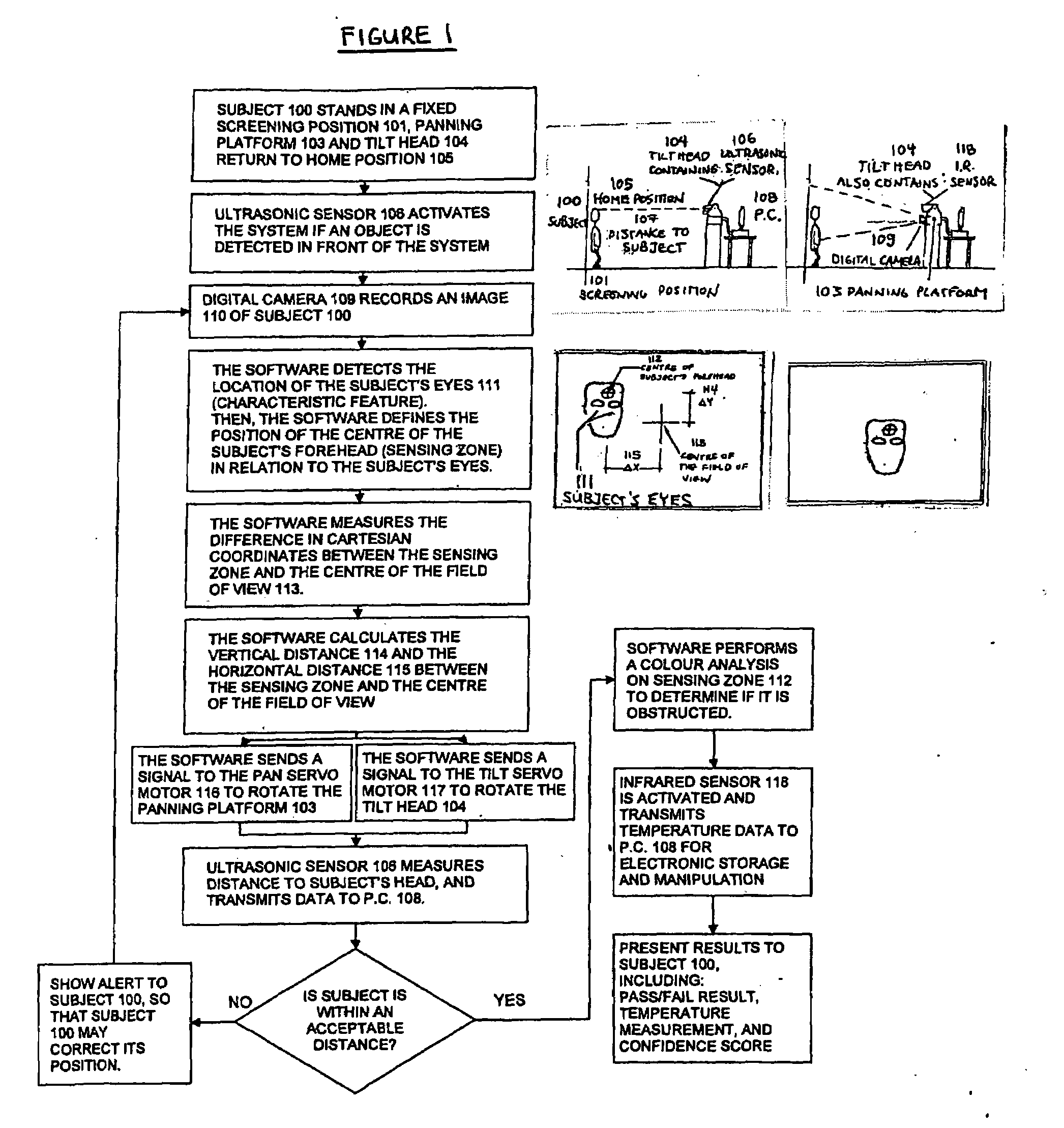
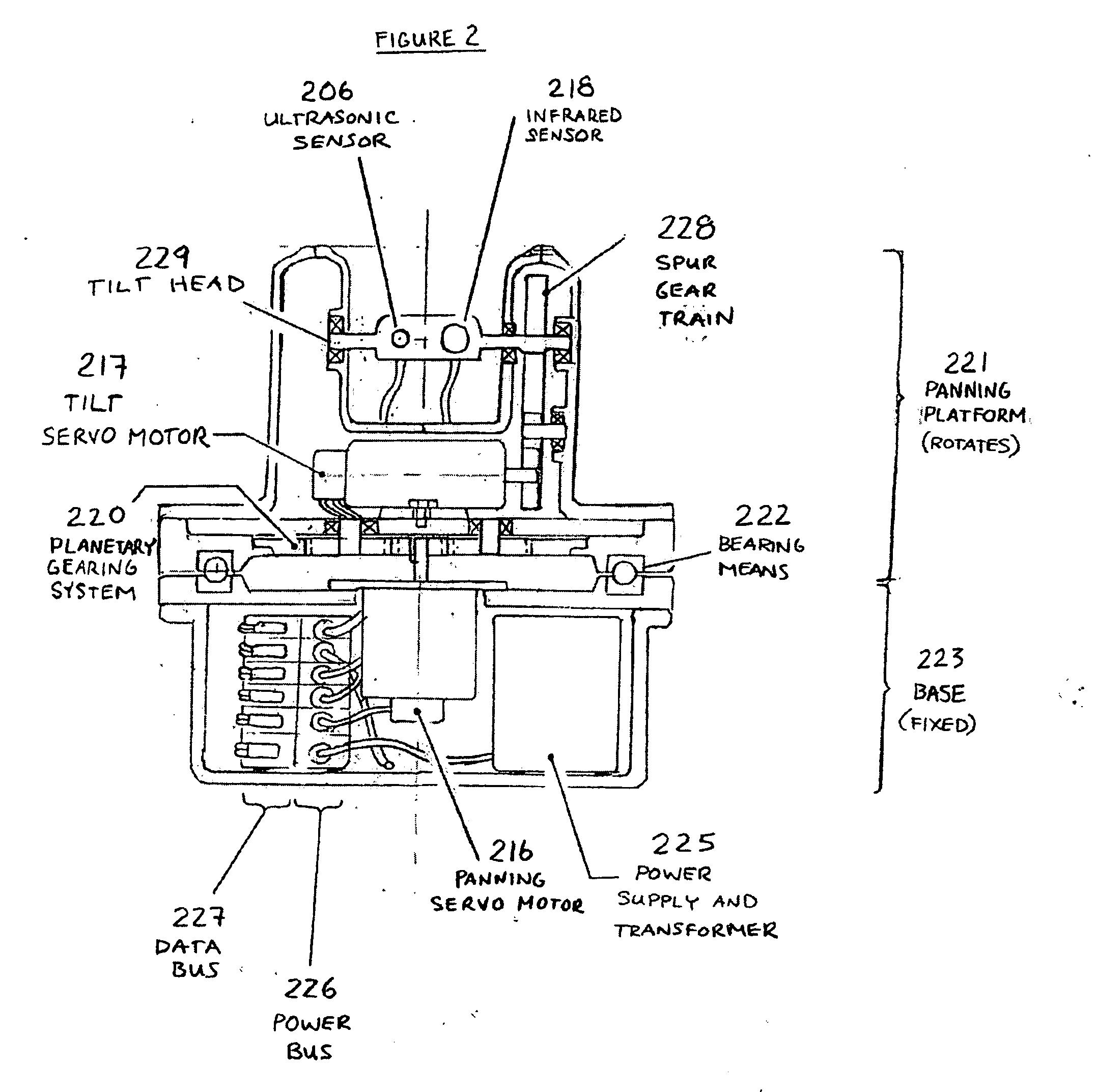
A temperature sensing device for remotely detecting the temperature of a subject having an identifying feature and a target zone in a fixed relationship to the identifying feature comprising: a distance sensor which measures the distance between the subject and the distance sensor; a temperature sensor for measuring a temperature difference in a sensing zone; a digital image capture device for capturing a digital image of the subject; a means of tilting at least the temperature sensor along at least one axis, and preferably tilting and panning along two axes; a controller that actuates the tilting means; and a support for supporting the distance sensor, the temperature sensor and the digital image capture device; wherein the controller tilts the distance sensor using the tilting means to reduce the distance between the target zone and the sensing zone; and a temperature sensor that measures a temperature difference proximate to the target zone, to detect elevated temperature illness in humans or animals.
Owner:AUTOVISION TECH LTD
System and method for identifying and locating an acoustic event
InactiveUS6847587B2Improve “ view ”Eliminate riskDefence devicesDirection finders using ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic wavesEvent typeHost processor
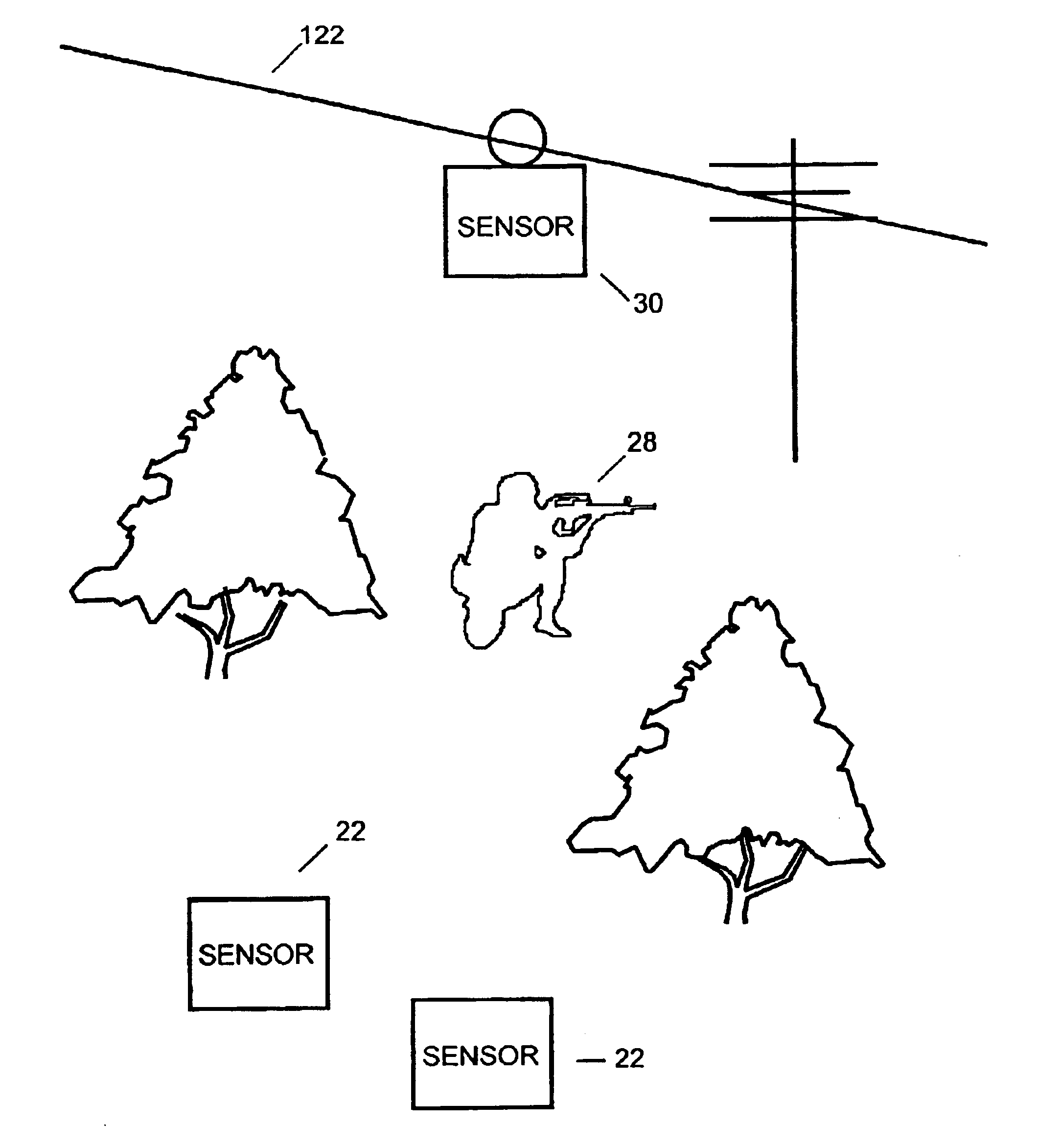
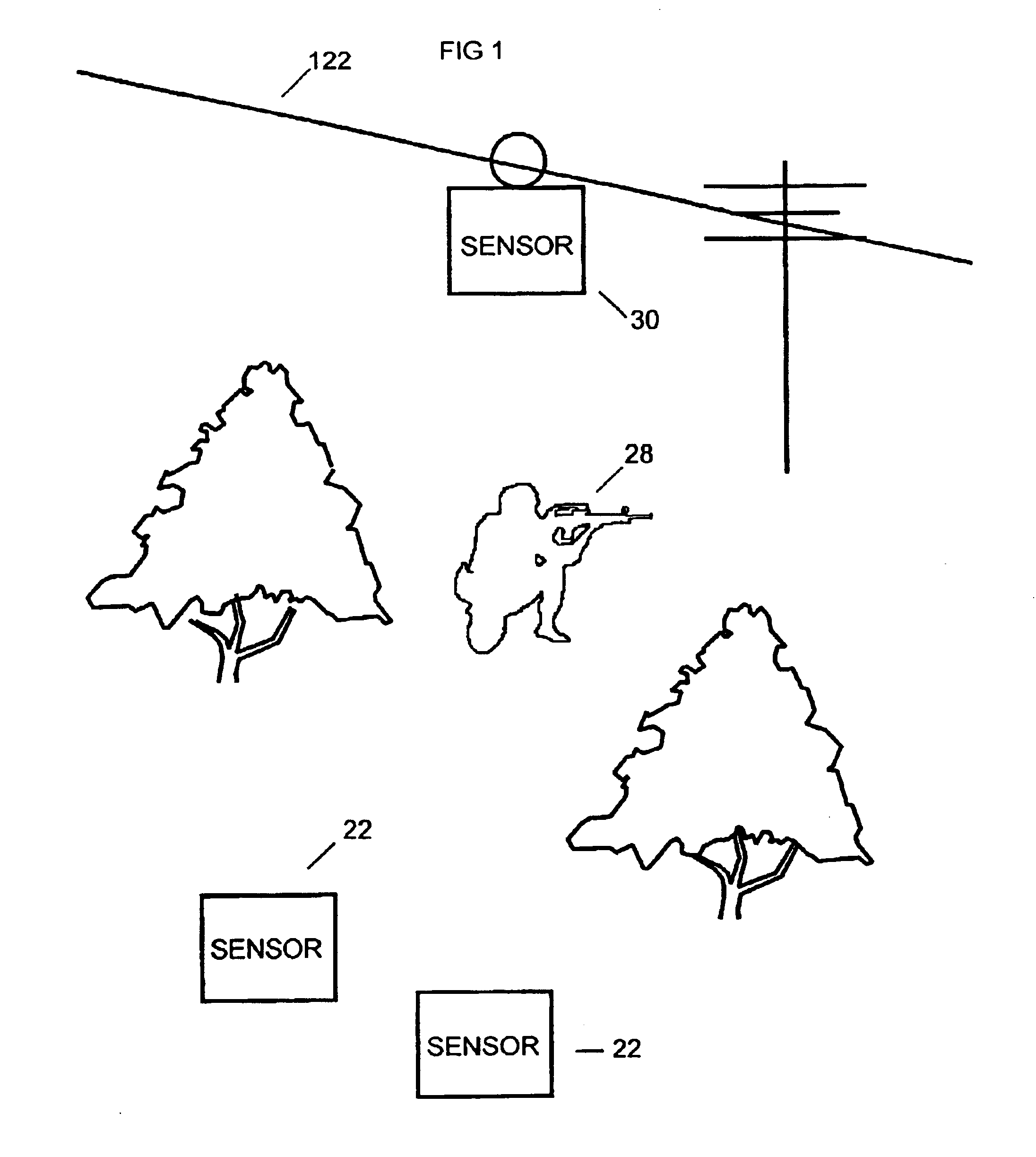
A system and method for detecting, identifying, and fixing the location of the source of an acoustic event. The inventive system includes: a plurality of sensors dispersed at somewhat regular intervals throughout a monitored area; a communication network adapted to deliver information from the sensors to a host processor; and a process within the host processor for determining, from the absolute times of arrival of an event at two or more sensors, a position of the source of the event. Acoustic events are detected and analyzed at each sensor so that the sensor transmits over the network: an identifier for the sensor; an identifier for the type of event; and a precise absolute time of arrival of the event at the sensor. In a preferred embodiment, the system also identifies the type of weapon firing a gunshot.
Owner:SHOTSPOTTER +2
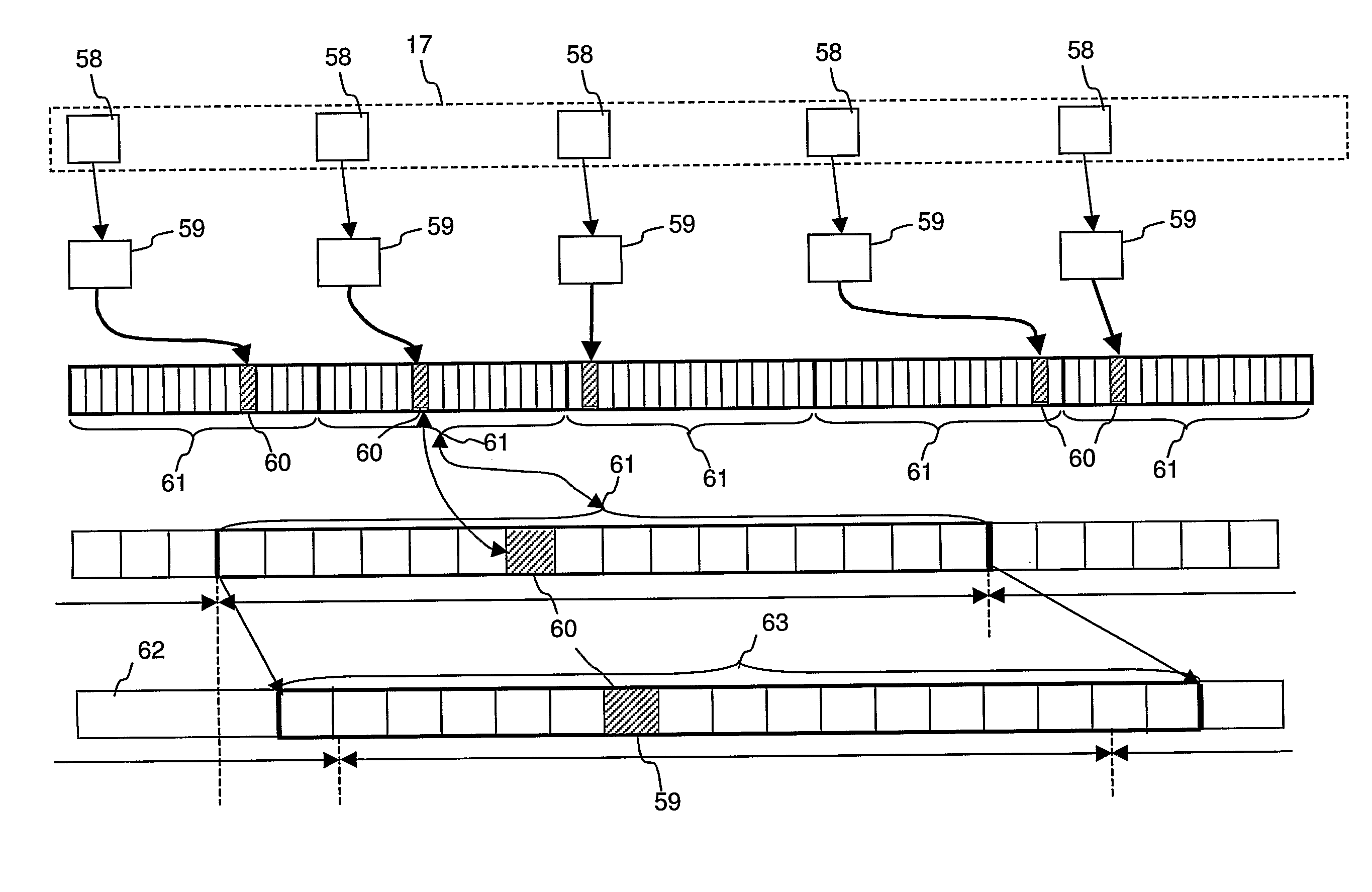
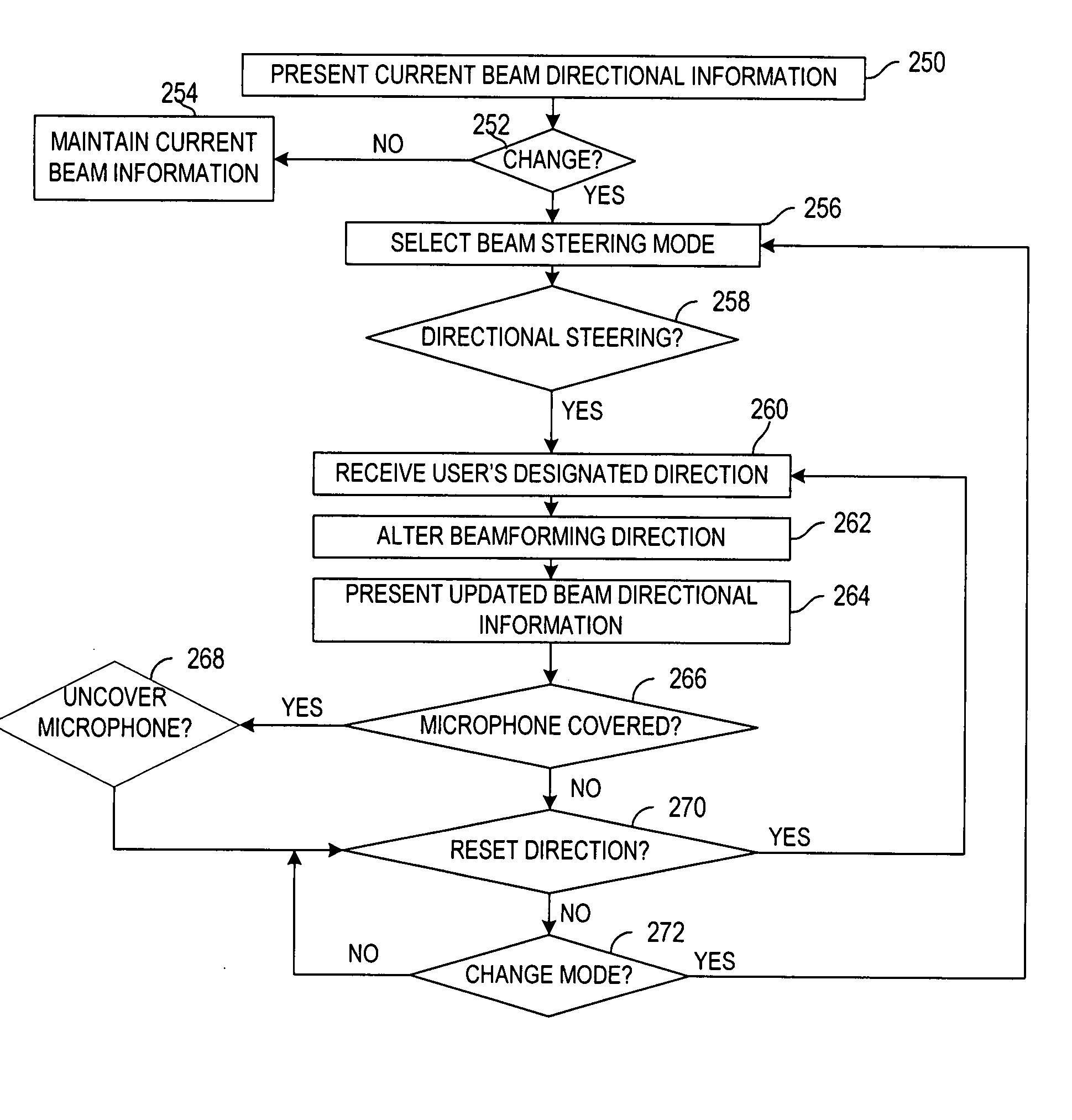
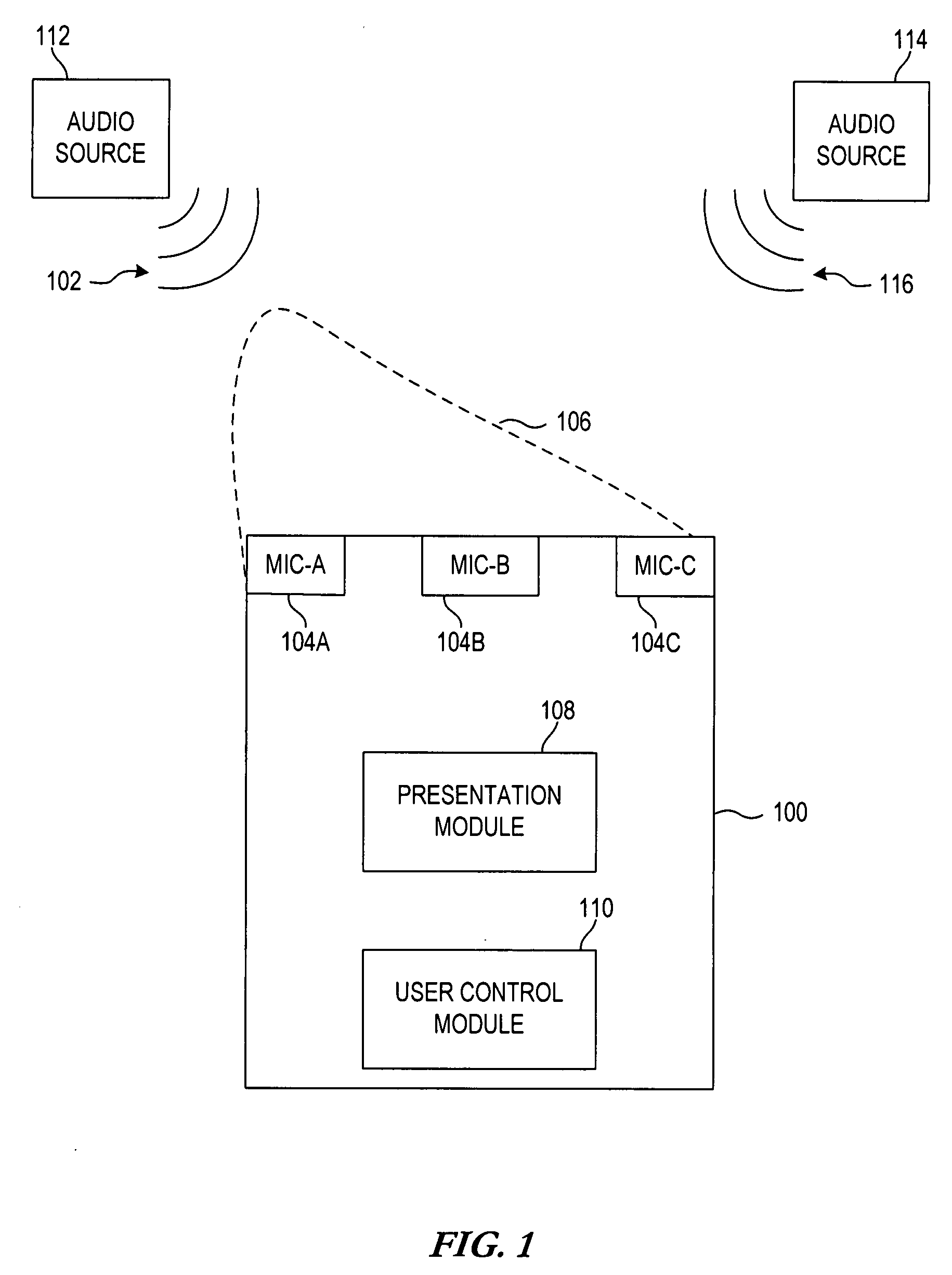
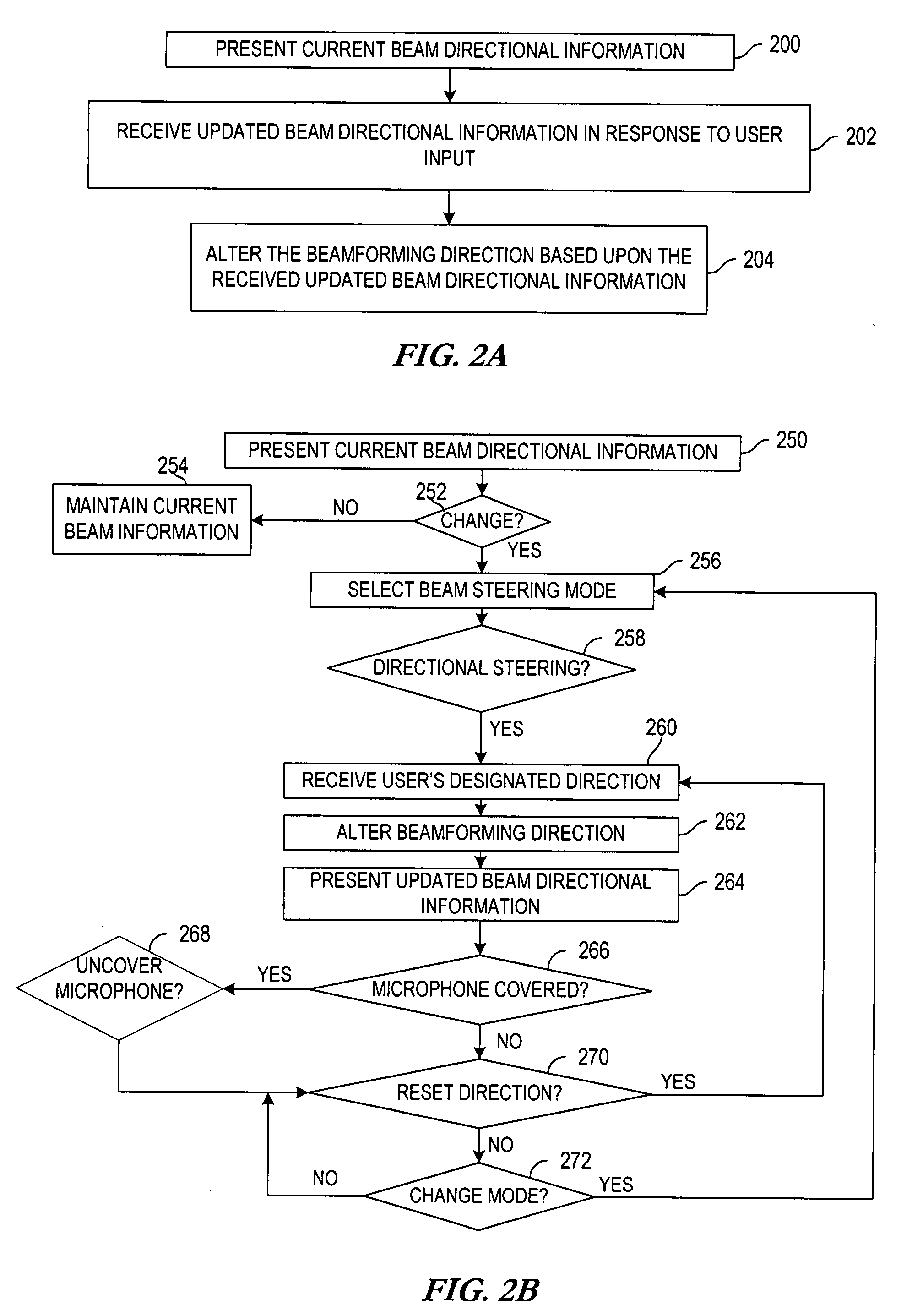
Methods and apparatuses for user controlled beamforming
InactiveUS20080259731A1Signal processingDirection finders using ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic wavesUser inputDirection information
A method for controlling beamforming in a device by a user of the device is provided. The method includes presenting current beam directional information via a user interface and receiving updated beam directional information in response to user input. The method also includes altering beamforming direction based upon the received updated beam directional information.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
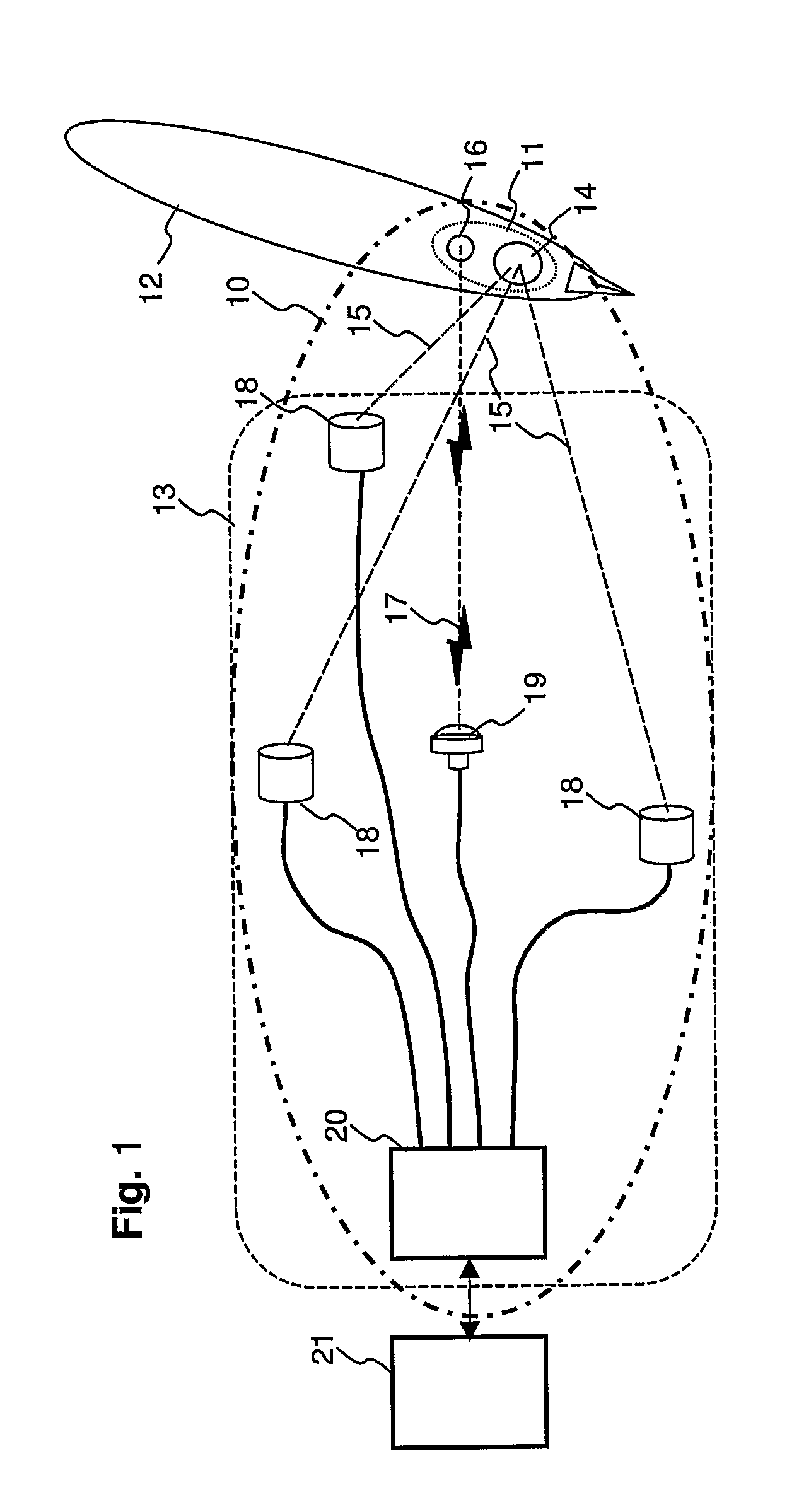
Ultrasonic tracking and locating system
ActiveUS20060013070A1Improve data transfer performanceDirection finders using ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic wavesPosition fixationUltrasonic sensorSonification
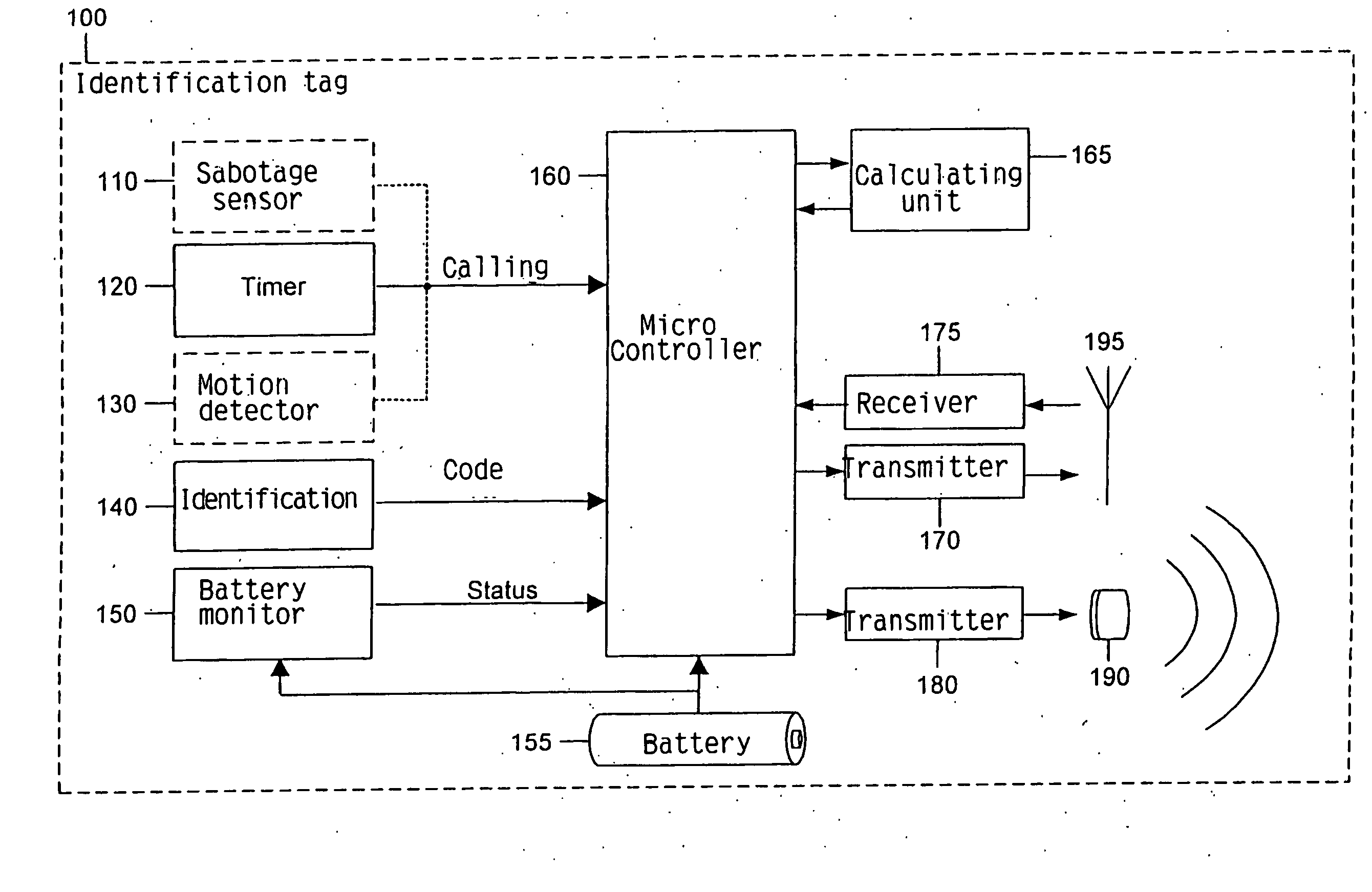
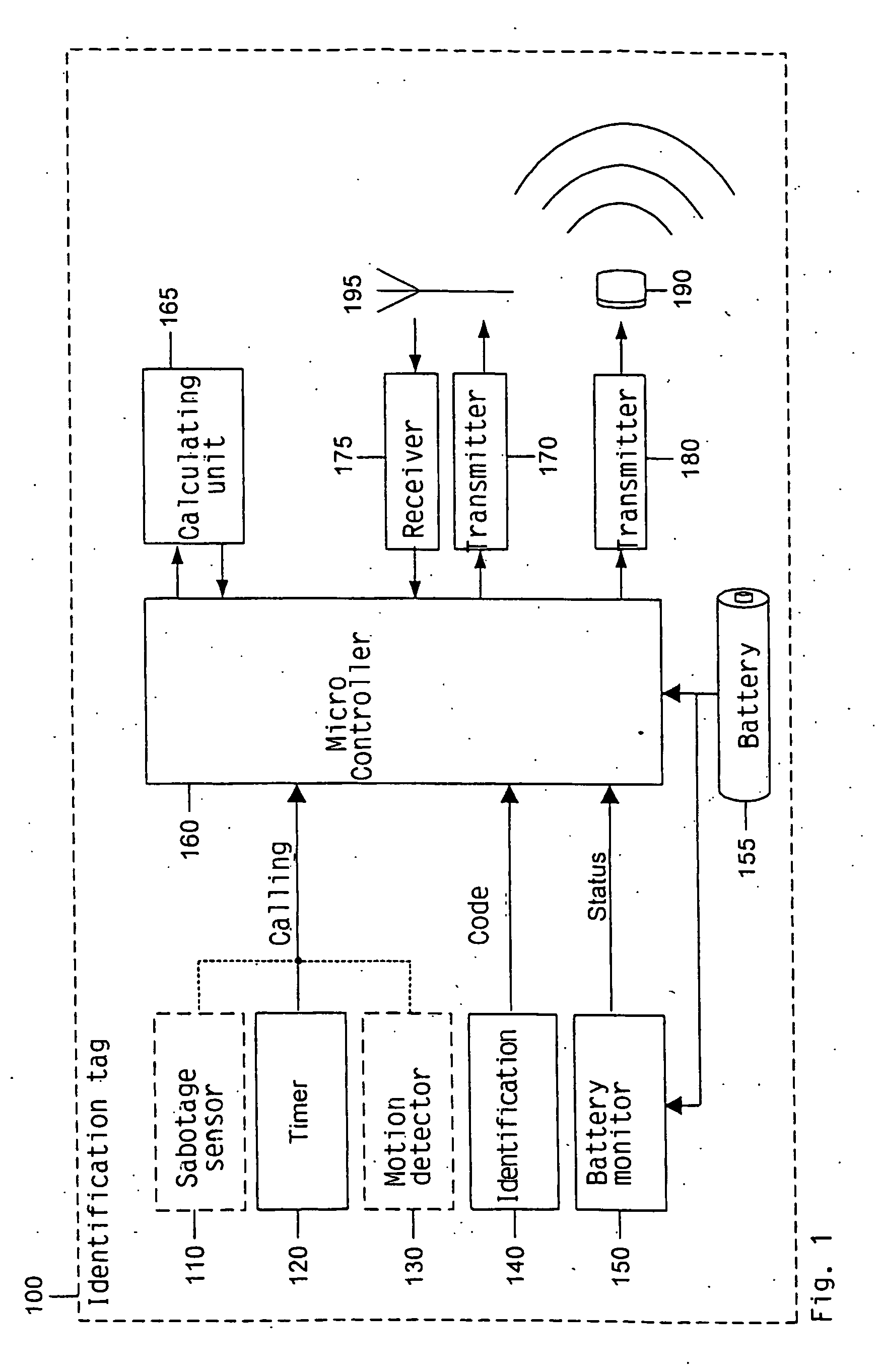
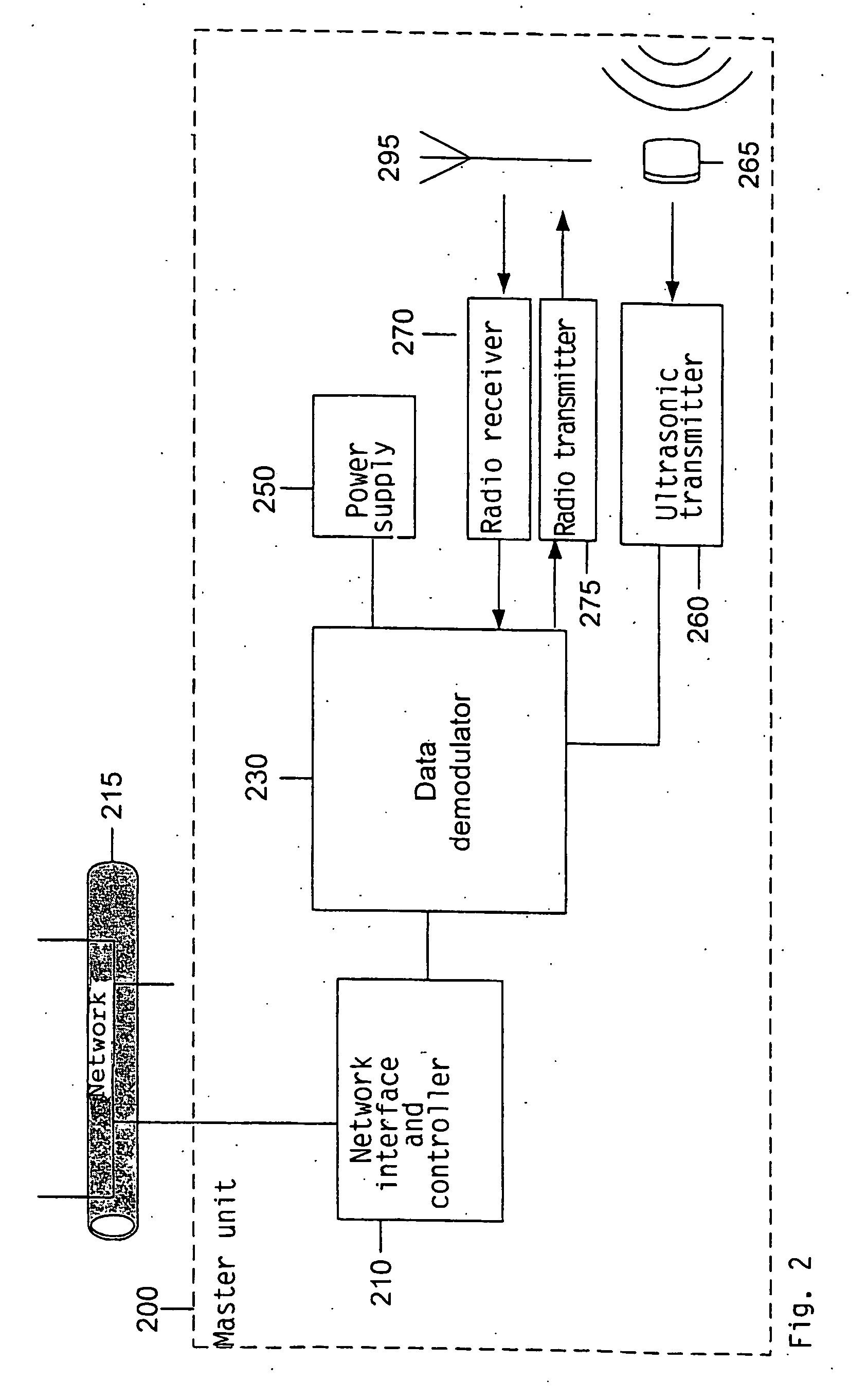
The invention relates to a method and a system for monitoring and position determination of objects and / or living beings within an area, such as, e.g. a room in a building. The system comprises a plurality of electronic units, called identification tags, which are attached to the objects that have to be monitored. Each identification tag has its own identification code (ID code) and is equipped with an ultrasonic transmitter, radio transmitter and radio receiver. The ultrasonic signals are recieved by one or more master and slave units which calculate transit time differences of ultrasonic pulses. This information together with the identification tags' ID code, identification of the room in which it is located, and any additional information are transmitted to a central processing unit which calculates the identification tag's position and presents it to a user of the system.
Owner:SONITOR TECH
System and method for beamforming using a microphone array
InactiveUS7415117B2Maximal noise suppressionIncrease widthPosition fixationMicrophones signal combinationSound sourcesEngineering
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
System and method for determining positions of towed marine seismic streamers
ActiveUS20070091719A1Reduce cross-correlationDirection finders using ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic wavesMechanical vibrations separationEngineeringBroadband
A system comprises a plurality of acoustic transmitters, mounted inside the streamers, adapted to transmit broadband signals having low cross-correlation between the signals of different transmitters; a plurality of acoustic receivers, mounted inside the streamers, adapted to receive the signals from the transmitters; at least one processor adapted to cross-correlate the signals received at the receivers with copies of transmitter signals to determine identities of the transmitters of the received signals and to determine travel times of the received signals; and a main processor adapted to convert the travel times to distances between the identified transmitters and the receivers and to determine relative positions of the streamers from the distances.
Owner:PGS GEOPHYSICAL AS
Method for aquiring and processing marine seismic data to extract and constructively use the up-going and down-going wave-fields emitted by the source(s)
InactiveUS20100008184A1Direction finders using ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic wavesSeismic signal processingSurface oceanPhase shifted
A method for acquisition and processing of marine seismic signals to extract up-going and down- going wave-fields from a seismic energy source includes deploying at least two marine seismic energy sources at different depths in a body of water. These seismic energy sources are actuated with known time delays that are varied from shot record to shot record. Seismic signals from sources deployed at different depths are recorded simultaneously. Seismic energy corresponding to each of the sources is extracted from the recorded seismic signals. Up-going and down-going wave-fields are extracted from the sources deployed at different depths using the extracted seismic energy therefrom. A method includes the separated up-going and down-going wave-fields are propagated to a water surface or a common reference, the up-going or the down-going wave-field is 180 degree phase shifted, and the signals from these modified up-going and down-going wave-fields are summed.
Owner:PGS GEOPHYSICAL AS
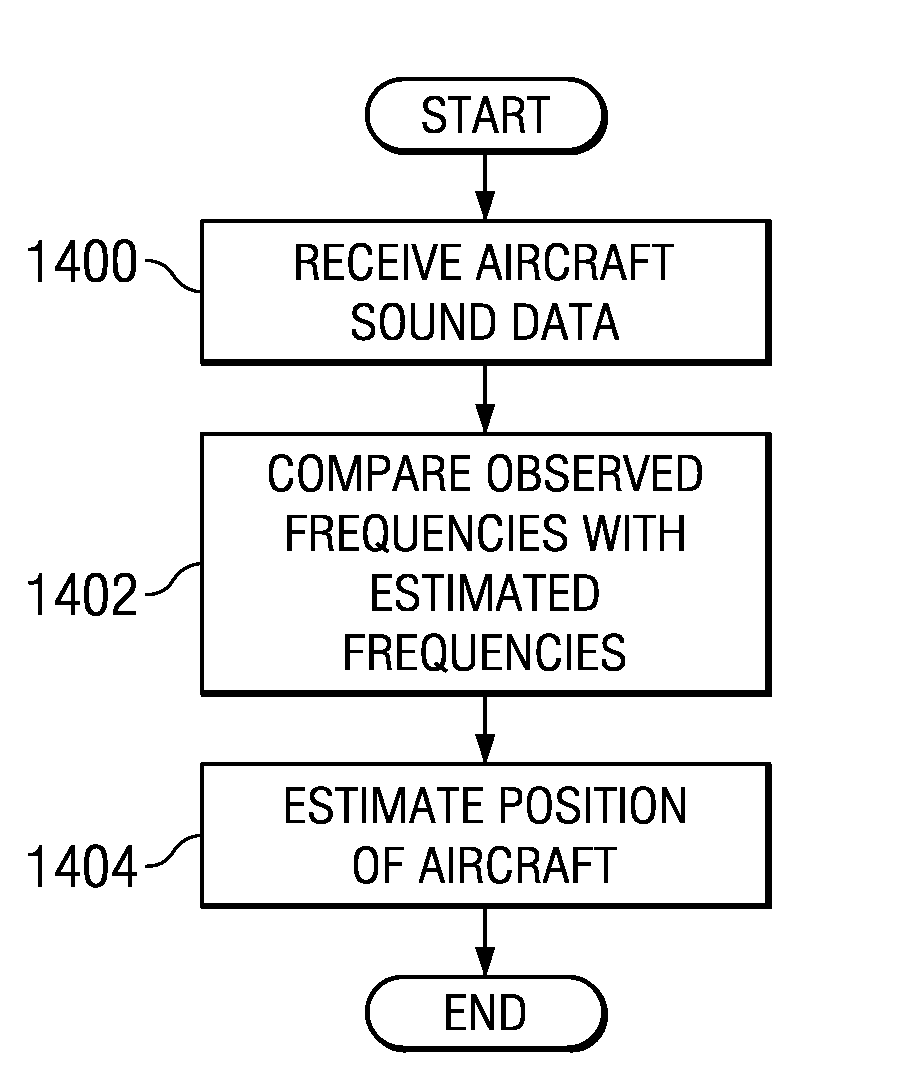
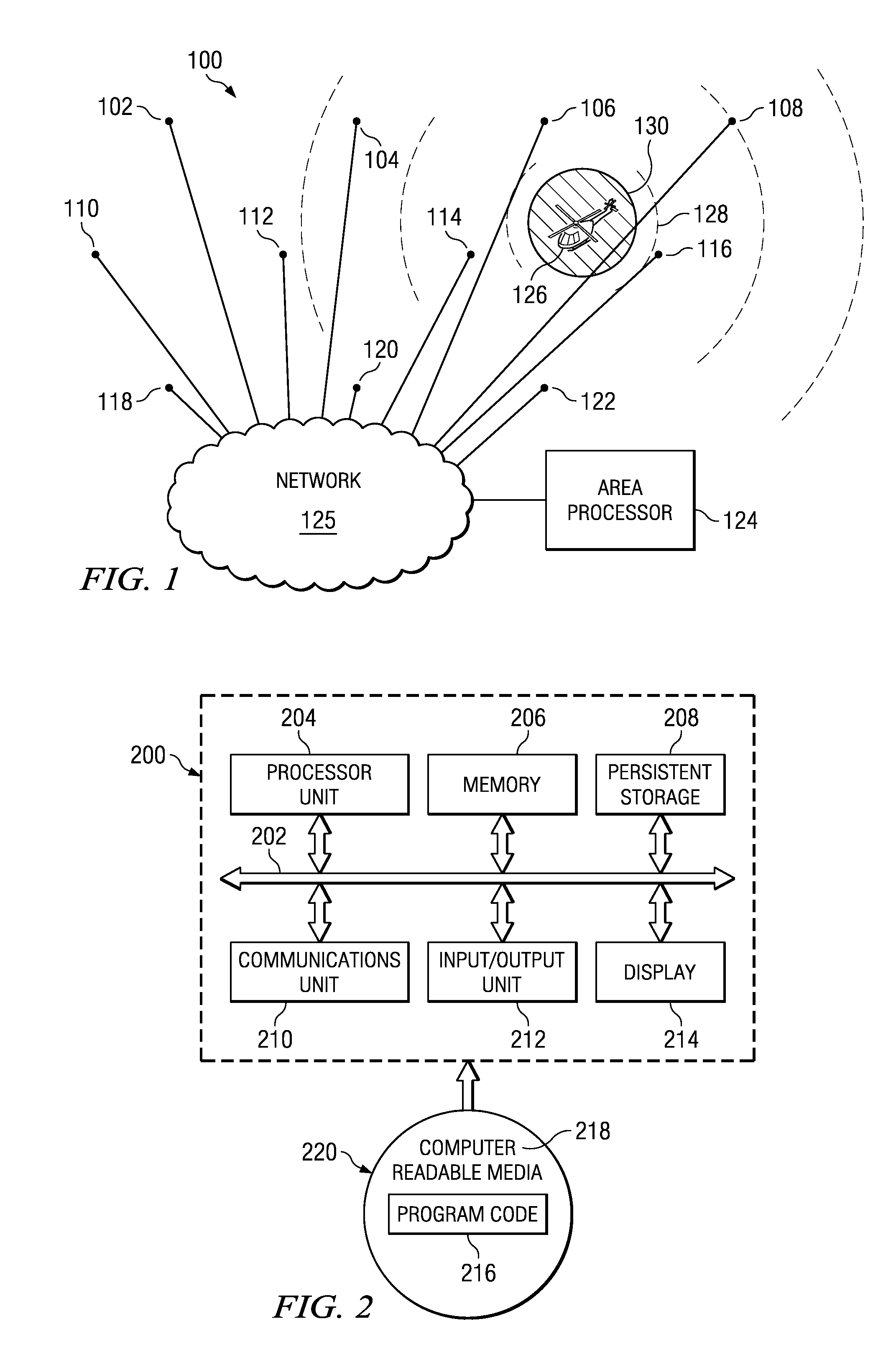
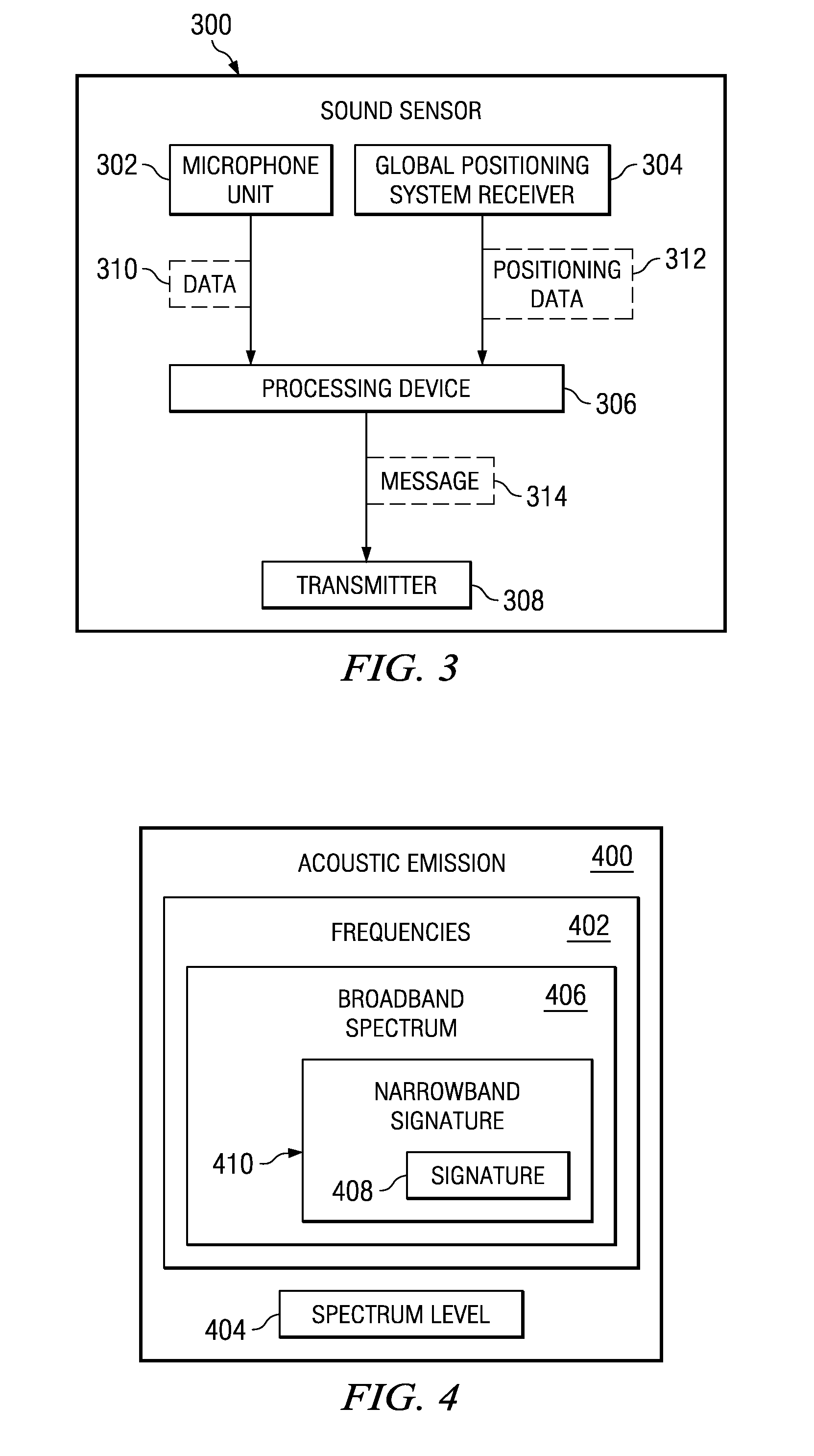
Acoustic wide area air surveillance system
ActiveUS20090257314A1Direction finders using ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic wavesPosition fixationLocation detectionWide area
A method and apparatus for detecting an aircraft. The method is provided for wide area tracking of aircraft. An acoustic emission of the aircraft is detected from a plurality of locations. A position of the aircraft at a set of times is estimated by comparing a set of harmonically related Doppler shifted frequencies for the acoustic emission to an expected zero Doppler shifted frequency of the aircraft to form an estimated position. The position of the aircraft and a heading of the aircraft are tracked using the estimated position. The aircraft type is classified based on the corresponding set of zero Doppler frequencies at each acoustic sensor.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Robot mechanism for inspection of live-line suspension insulator string
ActiveUS20100100239A1Inspection is accurateProgramme controlVibration measurement in solidsControl theoryElectric wire
Disclosed herein is a robot mechanism for inspection of a live-line suspension insulator string. A robot body of the robot mechanism reciprocates along the live-line suspension insulator string and includes upper and lower robot frames configured to encircle the insulator string, a battery module provided to either end of the robot body, an actuation module for moving the robot body along the insulator string, an inspection module for electrically inspecting an insulator, a connection module for coupling the robot body to an installation / dismantlement mechanism, a wing opening / closing module for manually separating the robot body from the insulator string, a measurement module for measuring electrical properties of the insulator, a controller for controlling operation of the robot body, and a crack detection unit for detecting cracks formed in the insulator.
Owner:KOREA ELECTRIC POWER CORP
Sensor fusion system and vehicle control system therewith
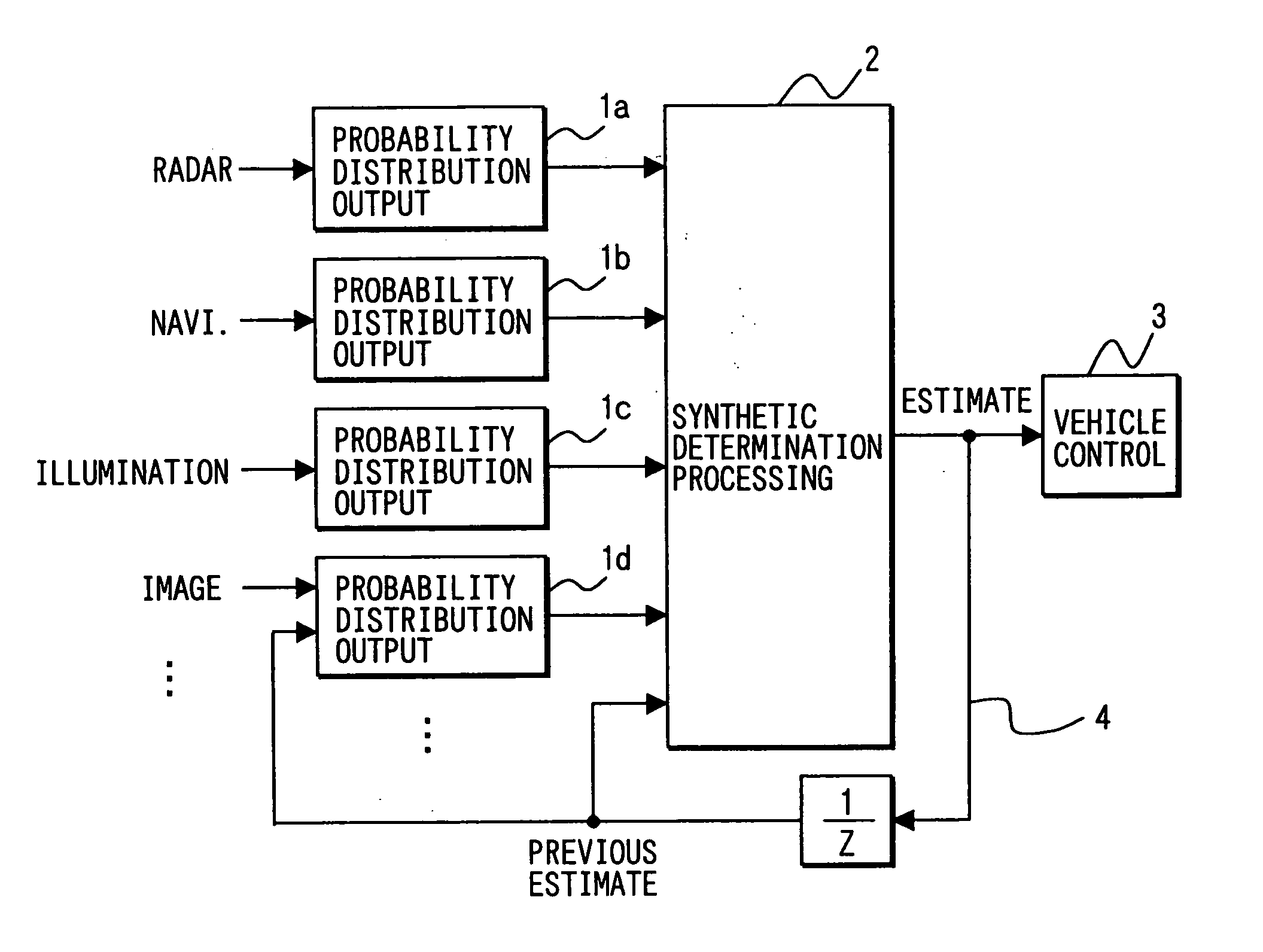
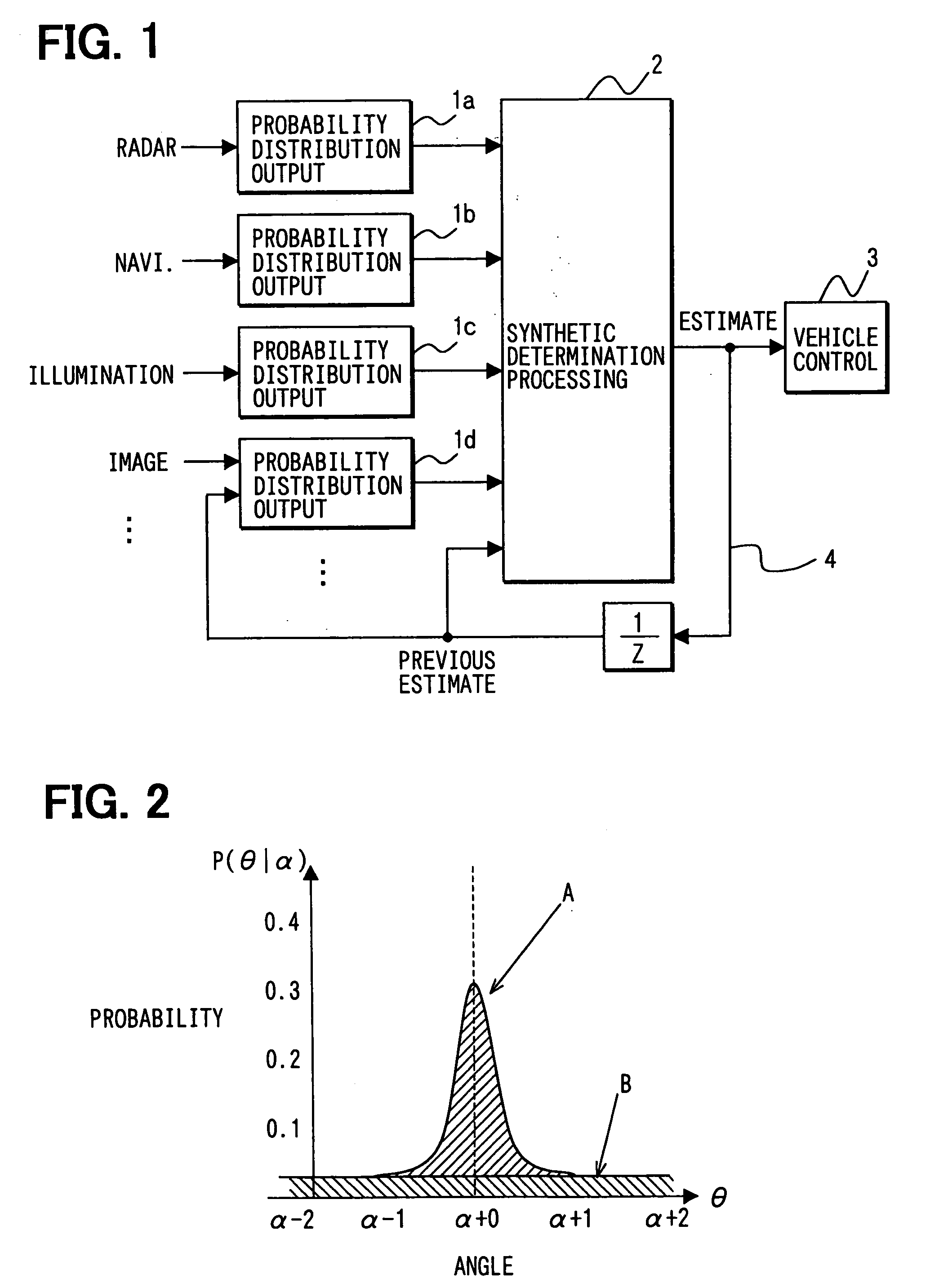
InactiveUS20050125154A1Improve reusabilityImprove versatilityImage analysisVehicle fittingsAlgorithmControl system
Each of multiple probability distribution outputting units computes a probability distribution of a data value detected by the corresponding sensor or algorithm in an image recognition processing or the like. The respective probability distributions of the multiple probability distribution outputting units are given as outputs to a synthetic determination processing unit. Data formats of the outputs to the synthetic determination processing unit can be thereby standardized. Hence, the synthetic determination processing unit is exempted from considering which type of sensor or algorithm each of the outputs is based upon. Even when a sensor or algorithm is added or changed, the same data-fusing algorithm in the synthetic determination processing unit can be uniformly used.
Owner:DENSO CORP
High Speed Metrology with Numerically Controlled Machines
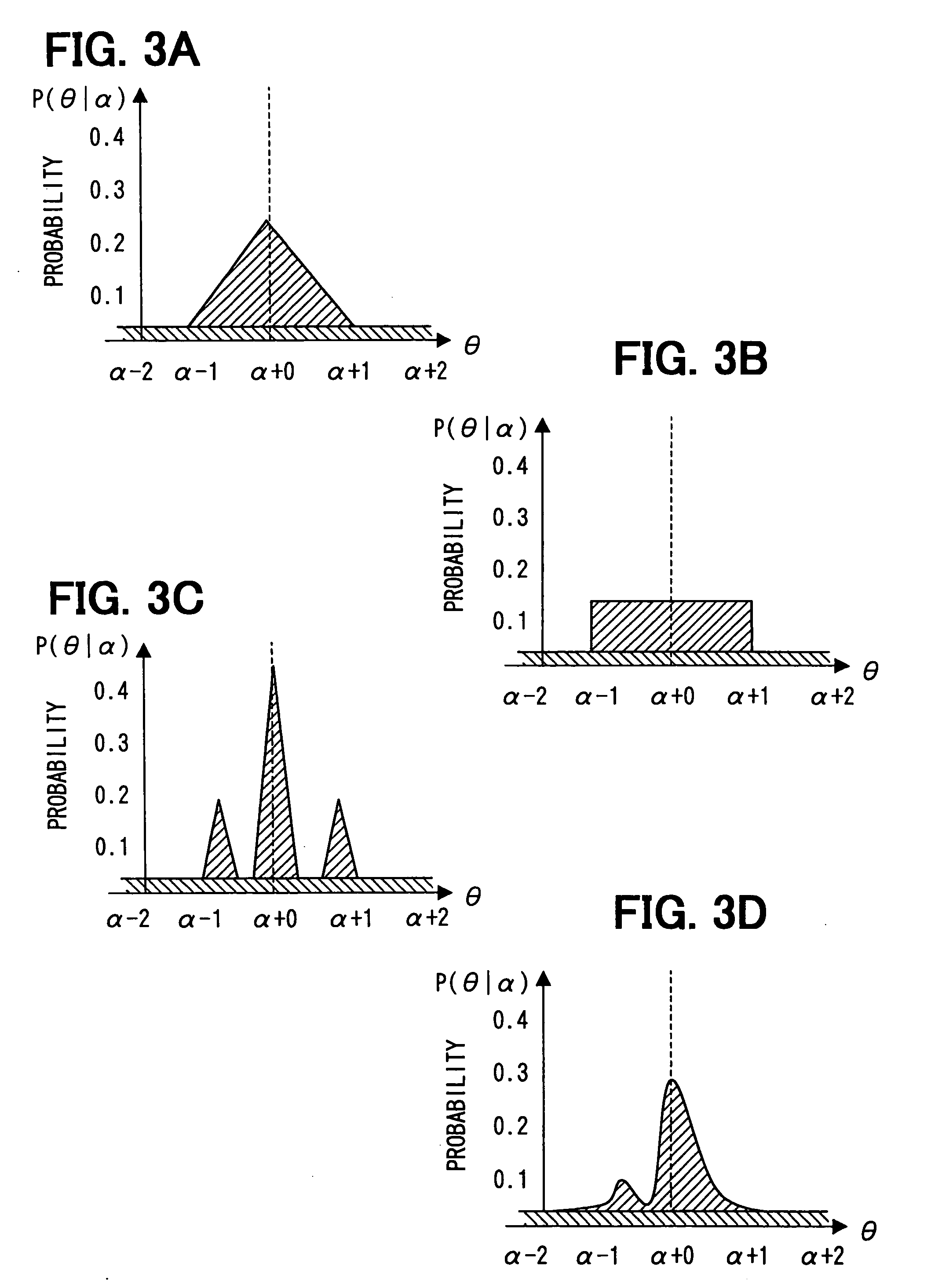
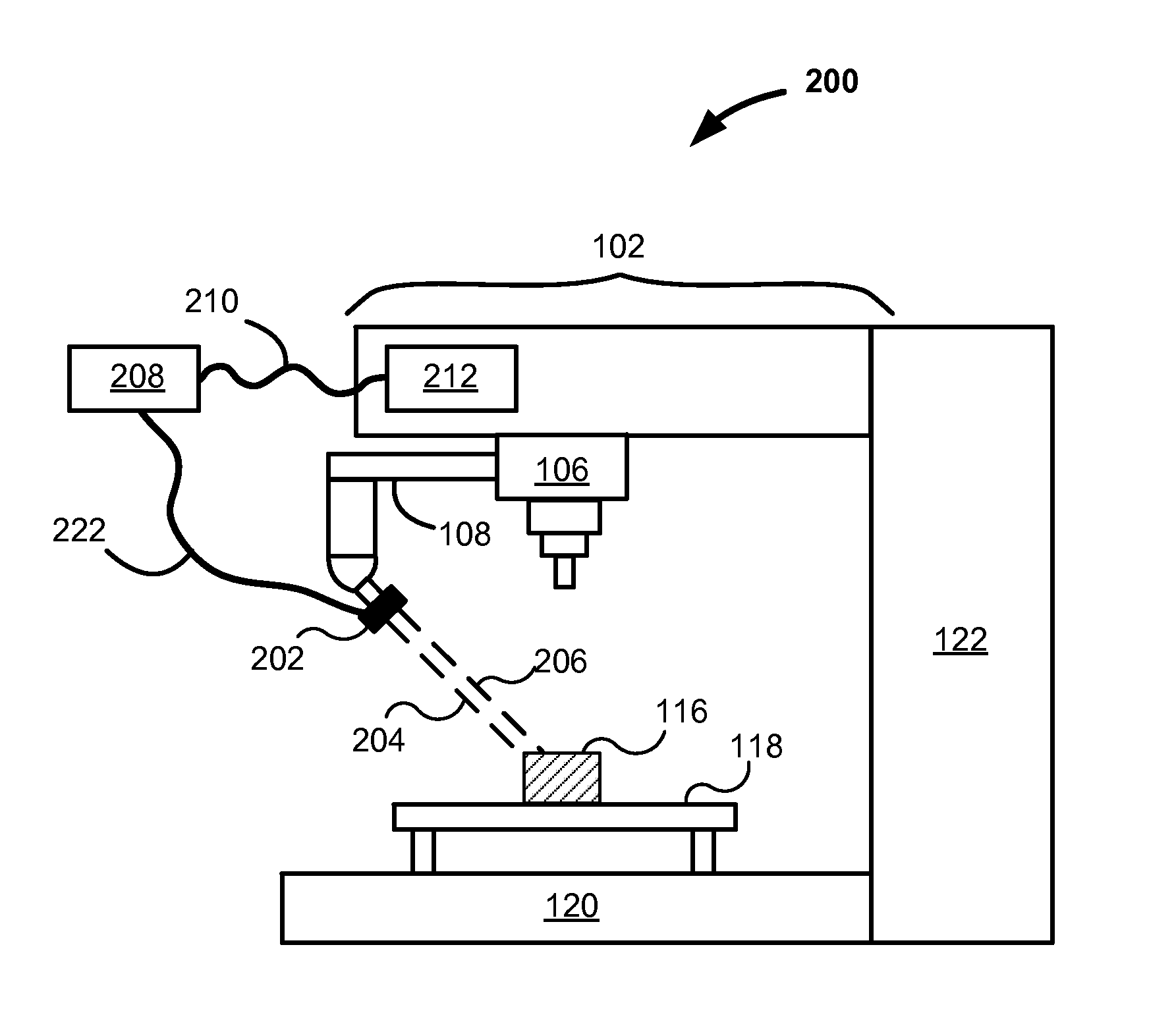
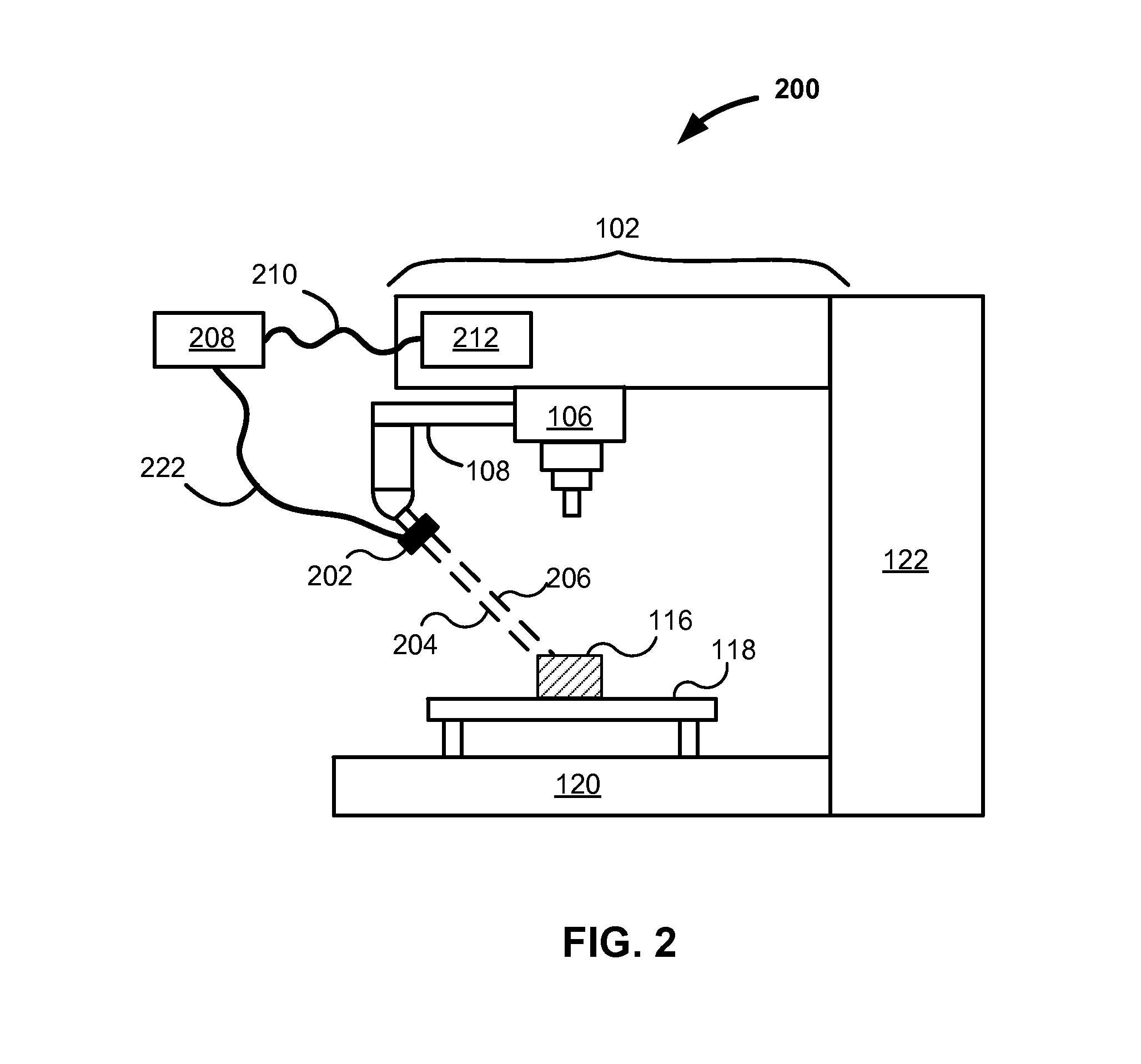
ActiveUS20140157610A1Accurate verificationTight stack-up toleranceVibration measurement in solidsAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesNumerical controlMetrology
Systems, apparatuses and methods are described for integrating an electronic metrology sensor with precision production equipment such as computer numerically controlled (CNC) machines. For example, a laser distance measuring sensor is used. Measurements are taken at a relatively high sample rate and converted into a format compatible with other data generated or accepted by the CNC machine. Measurements from the sensor are synchronized with the position of the arm of the machine such as through the use of offsets. Processing yields a detailed and highly accurate three-dimensional map of a workpiece in the machine. Applicable metrology instruments include other near continuously reading non-destructive characterization instruments such as contact and non-contact dimensional, eddy current, ultra-sound, and X-Ray Fluorescence (XRF) sensors. Various uses of measurements include: multiple component matching, correction of machine drift, closed loop control of machines, and verification of product tolerances via substantially complete serialized dimensional quality control.
Owner:GRALE TECH
Method for determining, recording and sending GPS location data in an underwater environment
InactiveUS6941226B2Accurately and effectively employingDigital data processing detailsPosition fixationSonarGps receiver
Underwater position determination is provided by combining sonar-derived ranging data between a sonar receiver and a sonar transmitter with GPS position data to provide geographically-referenced position data accurately representing the position of a sonar receiver carried or worn by a diver or submersible vehicle. Function and accuracy enhancements are provided to compensate for diver and sonar transmitter and depth difference and differences of sonar signal propagation speed as well as several techniques of compensation for change of position of the GPS receiver and for logging diver and / or vehicle path.
Owner:VIAVI SOLUTIONS INC
Modular intelligent transportation system
InactiveUS7983835B2High bandwidthLow costControlling traffic signalsAnalogue computers for vehiclesTelecommunications linkTelecommunications
Owner:THE WILFRED J AND LOUISETTE G LAGASSEY IRREVOCABLE TRUST ROGER J MORGAN TRUSTEE
Autonomous ultrasonic indoor tracking system
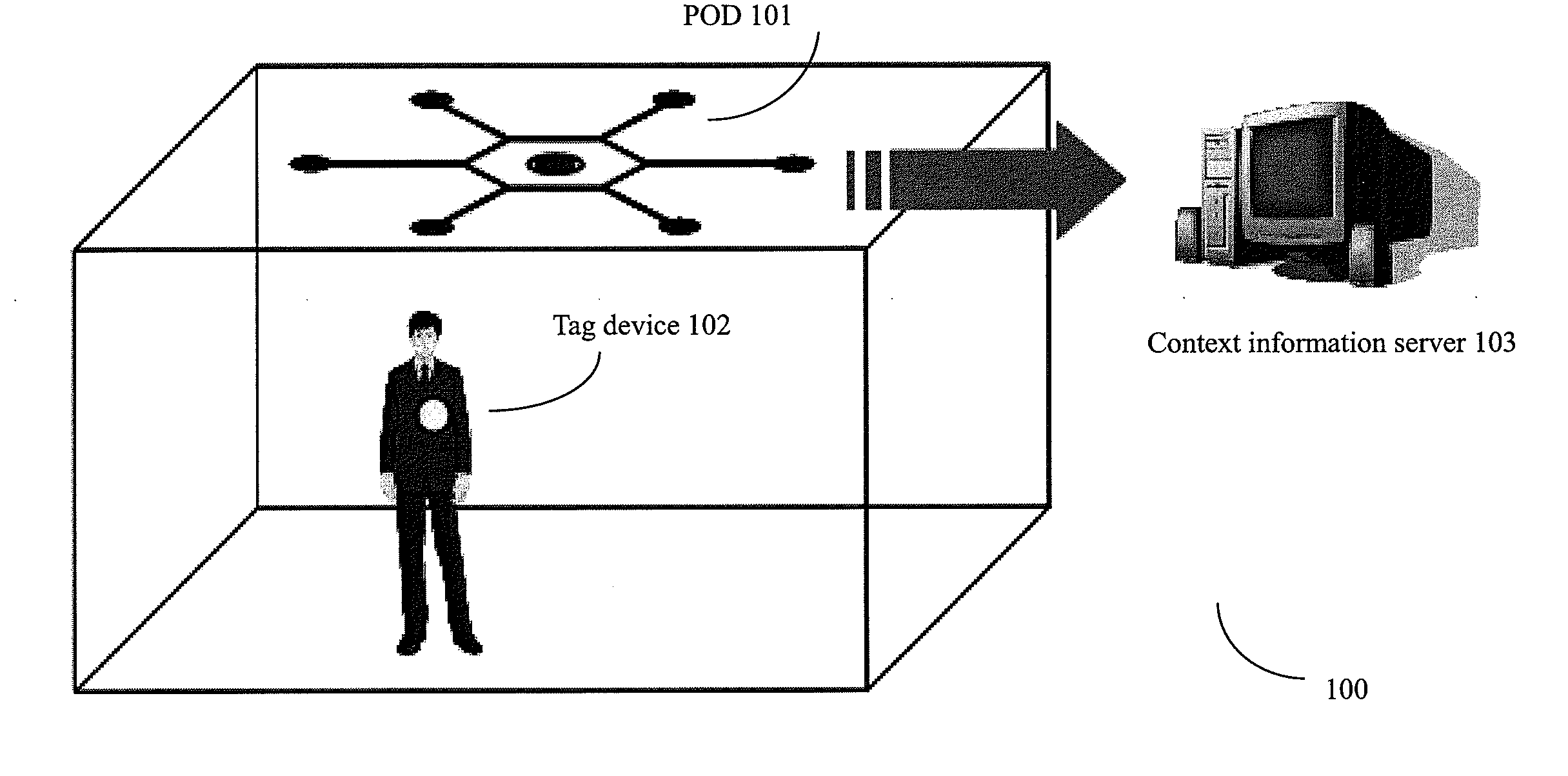
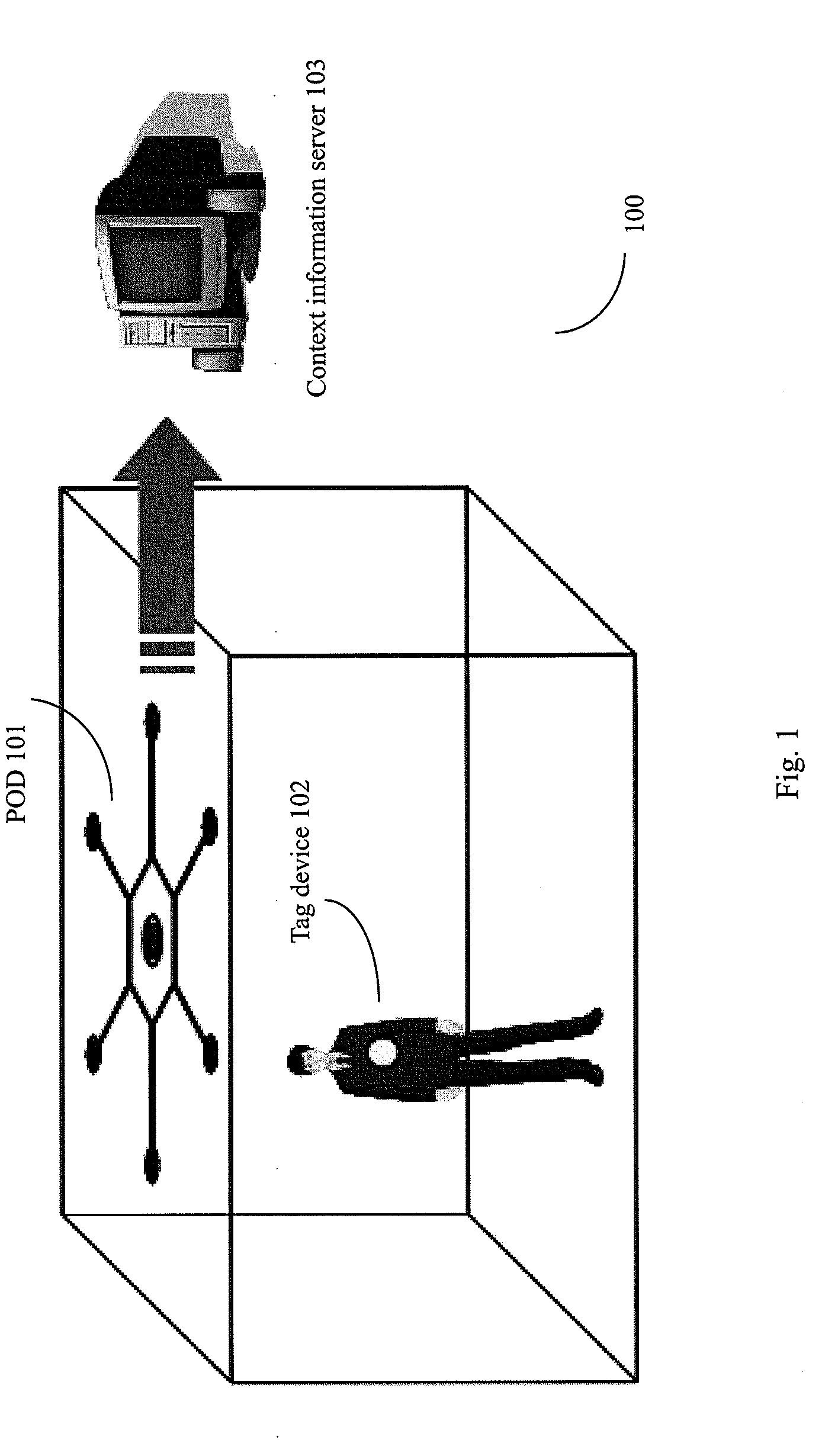
InactiveUS20090190441A1Easy to deployImprove accuracyDirection finders using ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic wavesPosition fixationSonificationEngineering
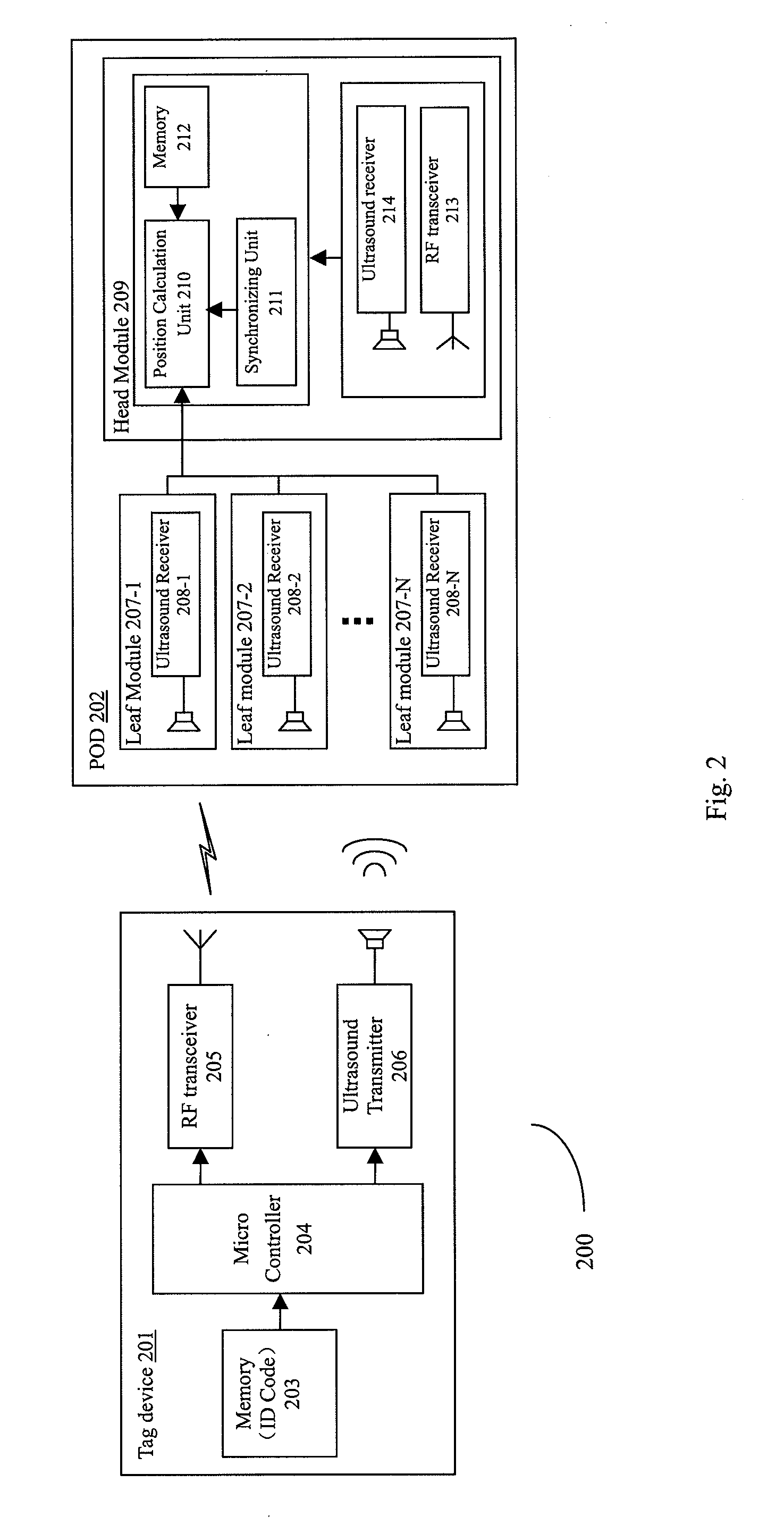
The present invention provides a Positioning on One Device (POD) for locating and tracking objects and an autonomous ultrasound indoor track system (AUITS) and method for locating objects by using the POD. The AUITS can comprise: a tag device installed on a mobile object, which includes radio frequency (RF) and ultrasound transmitters for transmitting RF and ultrasound signals; and a POD for receiving the RF and ultrasound signals transmitted from the tag device to locate the mobile object. The POD can comprise: a plurality of leaf modules, each of the leaf modules including a positioning signal receiver for receiving the positioning signals (e.g. ultrasound signal) transmitted from the tag device, wherein there is a known structural topology relationship between the plurality of leaf modules. Then, the positioning signal detection times from respective positioning signal receivers and the structural topology relationship of the POD can be used for calculation of the position of the object. Compared with the prior arts, the POD and the AUITS system of the present invention presents several advantages, such as high accuracy, easy deployment, calibration free, low cost, in-device coordination, and flexibility.
Owner:NEC (CHINA) CO LTD
Displaying dynamic caller identity during point-to-point and multipoint audio/videoconference
InactiveUS20100085415A1Improve accuracyImprove recognition accuracyDirection finders using ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic wavesTelevision conference systemsMultiple inputKnowledge transfer
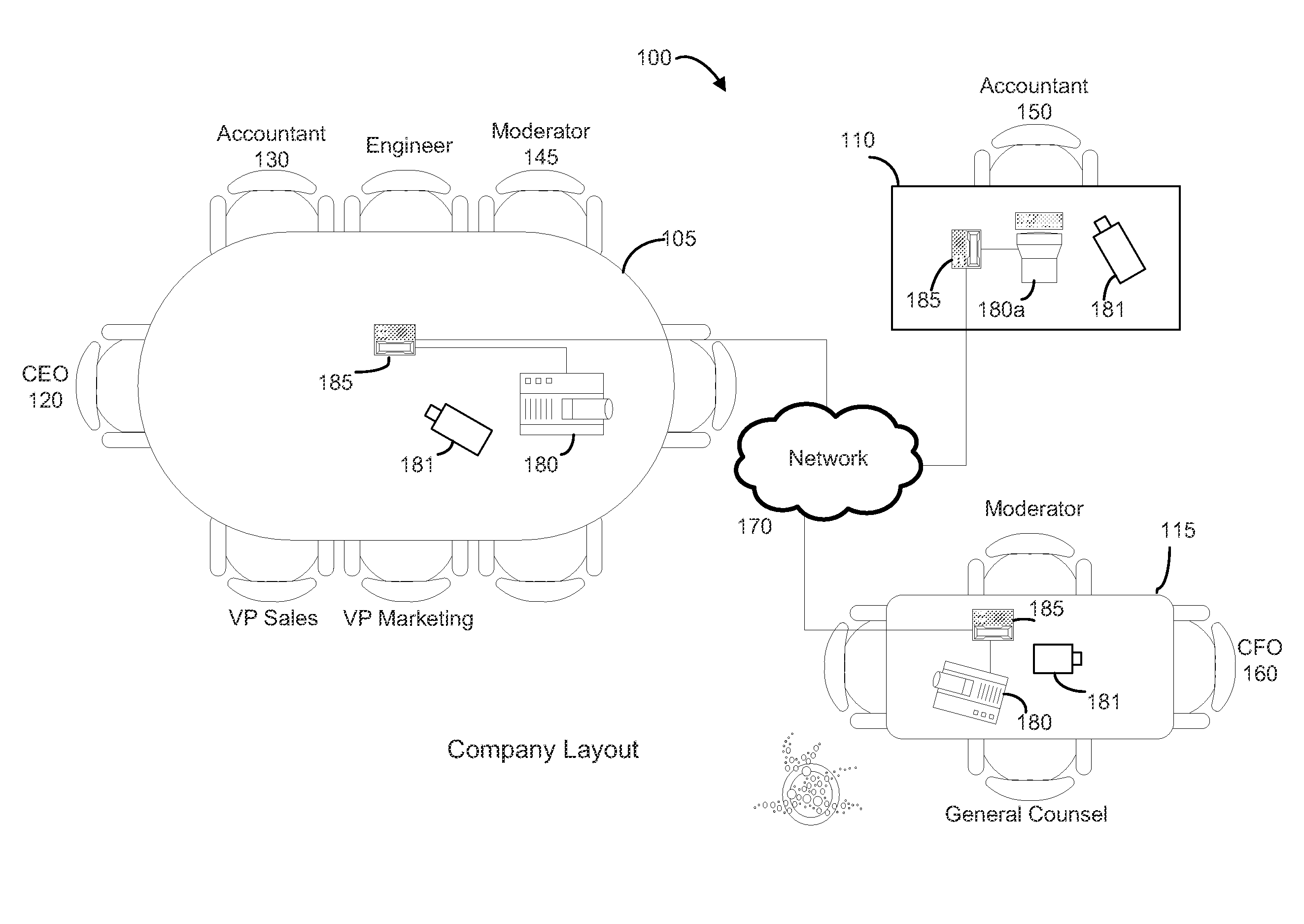
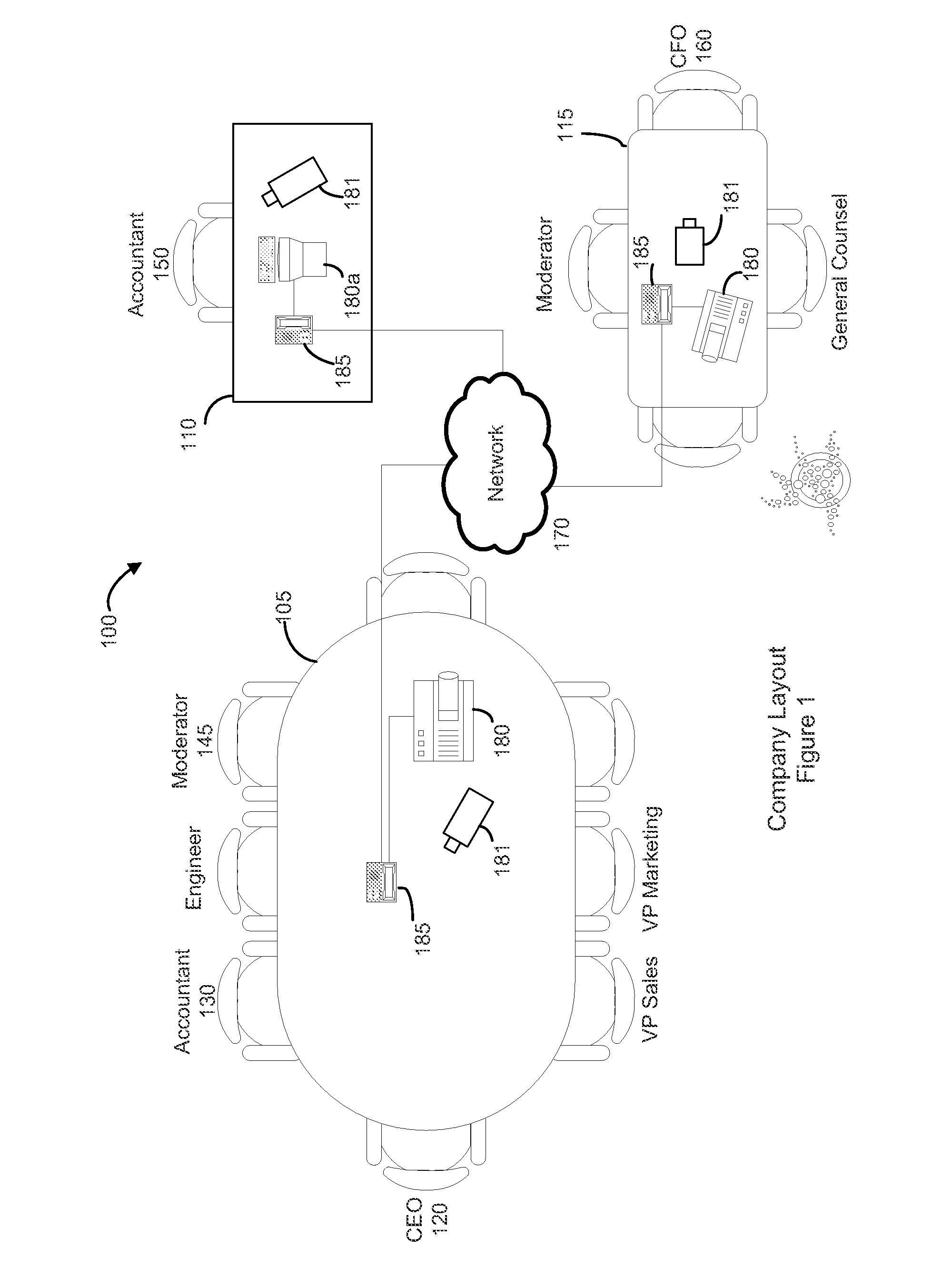
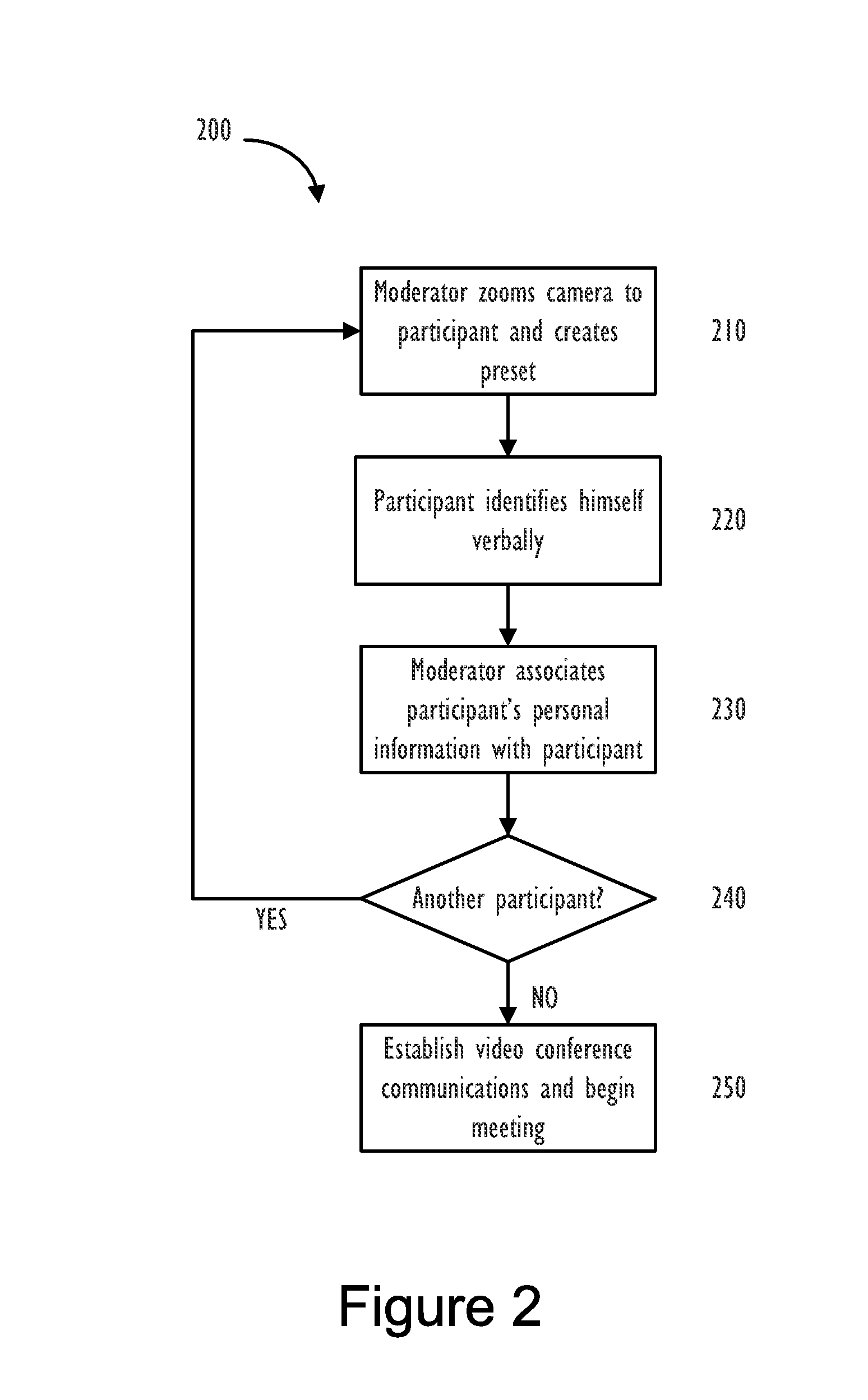
A method for efficiently determining and displaying pertinent information determined from multiple input and calculated parameters associated with a videoconference call. The method for efficiently determining and displaying this personal information is performed using input from the user at an endpoint and calculated information throughout the videoconference to present personal information, about the currently speaking person, to all participants. Videoconferencing systems are typically used by multiple people at multiple locations. The method of this disclosure allows for more user interaction and knowledge transfer amongst the participants. By sharing information between the different locations participants are more aware of who is speaking at any given time and the importance to be applied to what that particular person is saying.
Owner:POLYCOM INC
Determination of a room dimension estimate
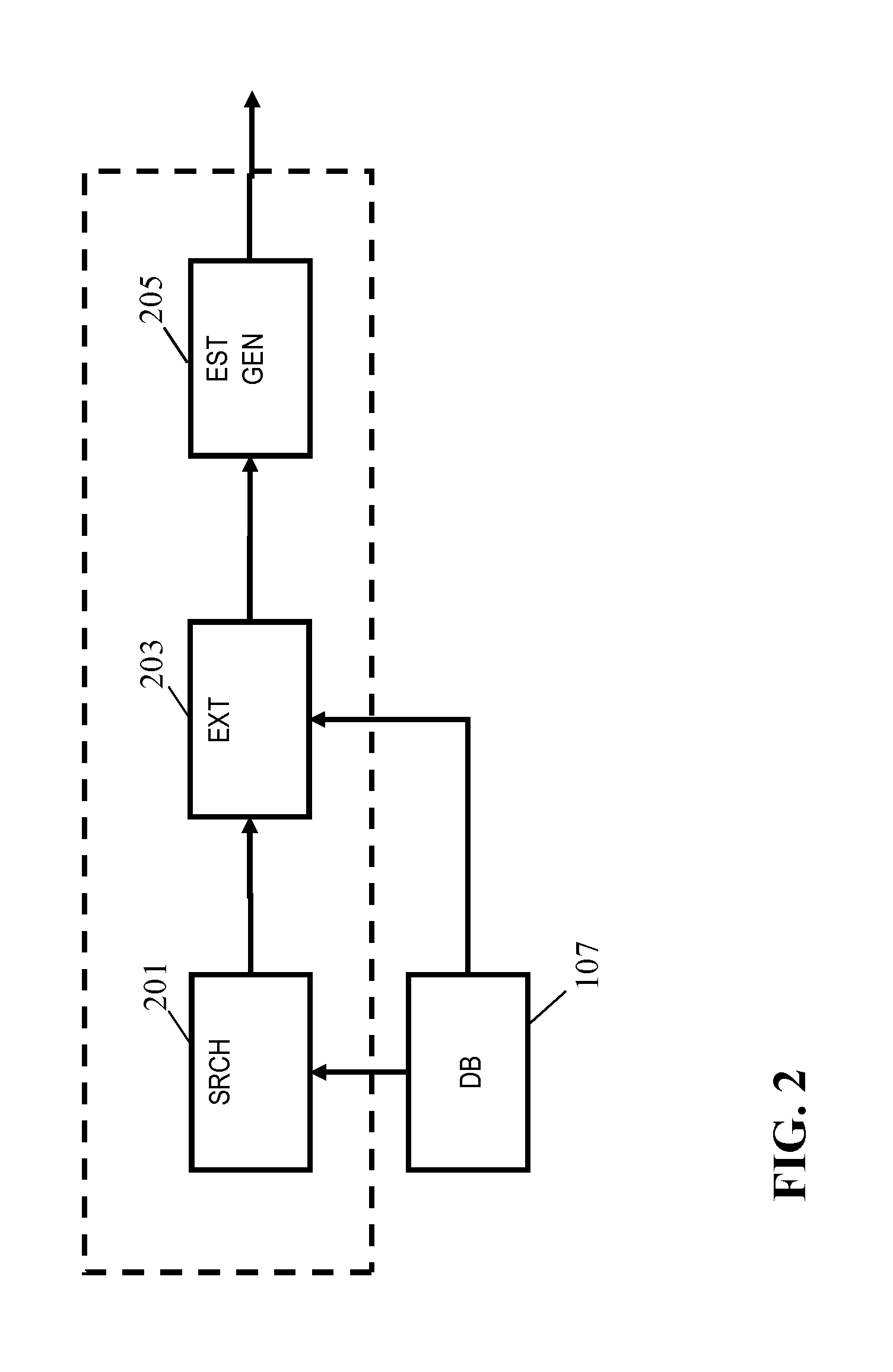
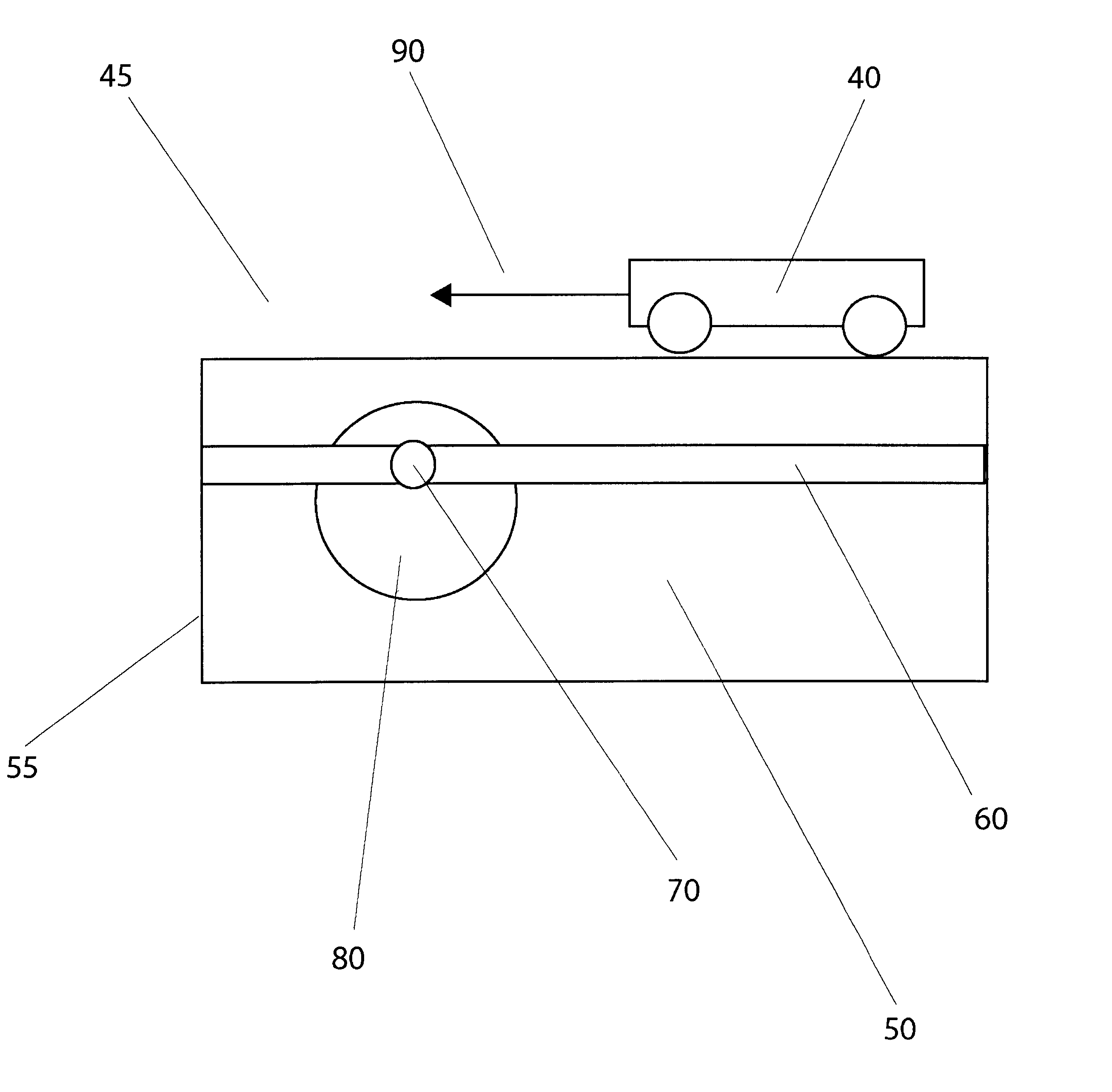
ActiveUS20160061597A1Improved and facilitated determinationWell representedDirection finders using ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic wavesUsing subsonic/sonic/ultrasonic vibration meansPeak valuePeak oil
An apparatus for determining a room dimension estimate comprises a receiver (101) providing an acoustic room response e.g. generated from acoustic measurements. A peak detector (103) detects a set of peaks in the acoustic room response in a frequency interval having an upper frequency of no more than 400 Hz. A store (107) comprises a set of peak profiles with associated room dimension data, and an estimator (105) determines the room dimension estimate from the associated room dimension data and a comparison of the set of peaks to the peak profiles. The estimator may perform the steps of first finding a matching peak profile for the set of peaks from the set of peak profiles; extracting first room dimension data associated with the matching peak profile(s) from the store; and determining the room dimension estimate in response to the first room dimension data. The peak profiles may represent calculated Eigenfrequencies.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Method and apparatus for detecting leaks in buried pipes by using a selected combination of geophysical instruments
InactiveUS6667709B1Material analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesVibration measurement in fluidEngineeringWave speed
A method and apparatus for detecting and locating leaks in buried pipes is disclosed in which ground penetrating radar, induction, acoustic, and vacuum excavation systems are selected based on soil conditions and then employed in selected combinations. The conductivity and wave speed of the soil are used in the selection process and in the process of detecting and locating a leak based on the measurements obtained from the selected combination of detection systems.
Owner:UNDERGROUND IMAGING TECH +1
Vigilante acoustic detection, location and response system
InactiveUS20100226210A1Direction finders using ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic wavesPosition fixationEngineeringOmni directional
A system and method for detecting the exact location of an acoustic event, the system comprising a plurality of variably spaced sensors, wherein each sensor comprises an omnidirectional microphone for detecting the acoustic event; a global positioning system (GPS); and a transmitter receiver for transmitting (i) the time that the acoustic event arrived at a particular sensor and (ii) the location of the particular sensor at the time the acoustic event arrived at the particular sensor; and a central processor radio-linked to the plurality of variably spaced sensors comprising a software program comprising at least one algorithm for determining the location of the acoustic event.
Owner:KORDIS THOMAS F +1
Seismic data acquisition method and apparatus
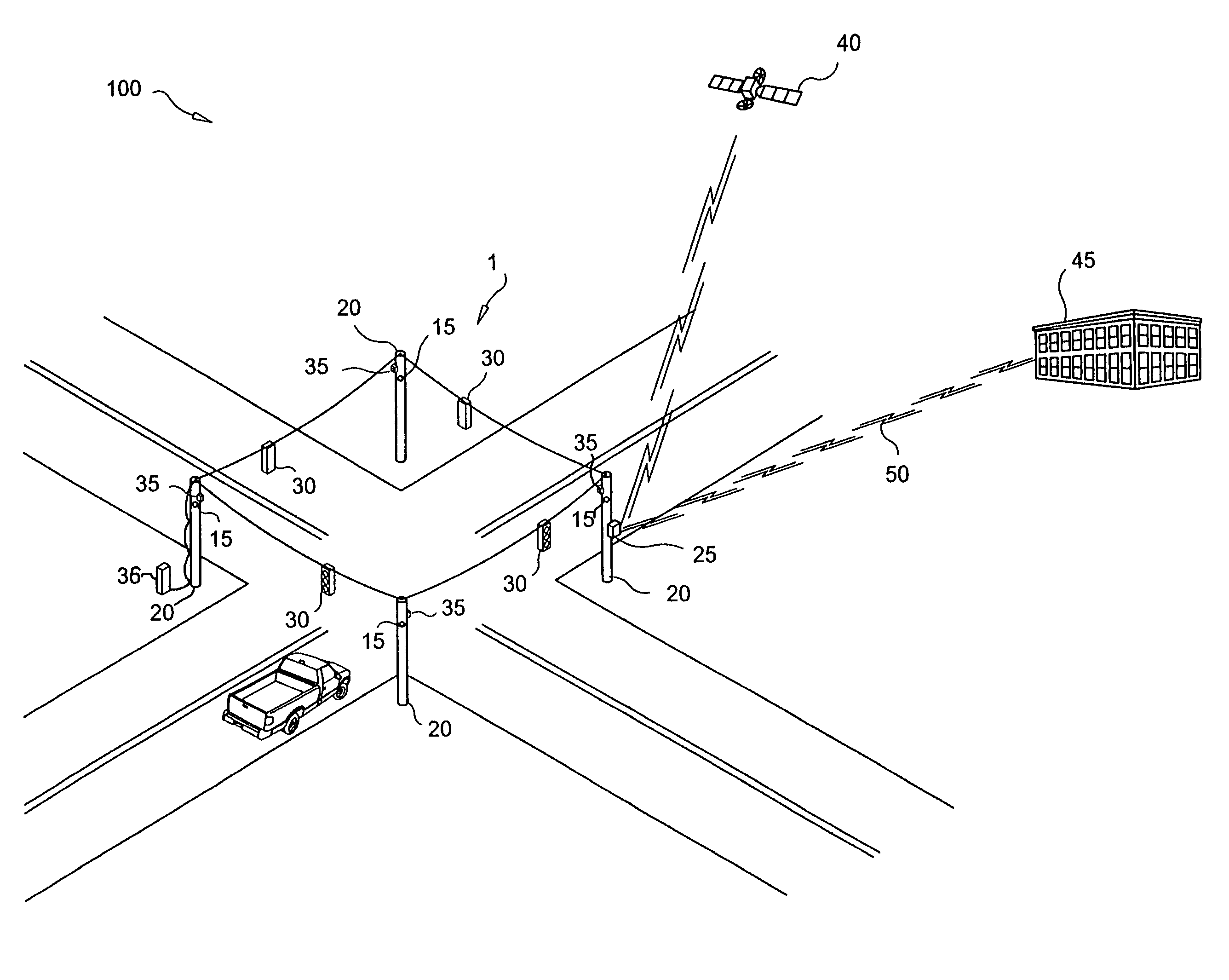
InactiveUS6847896B1Avoid smallEasy and faster lay-outDirection finders using ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic wavesSeismic data acquisitionData acquisitionGeophysics
A method of acquiring seismic data adapted for a land or transition zone environment including placing a location identifier in a particular location, placing a seismic sensor near the location identifier, reading the location identifer using a seismic data cable, recording seismic data acquired by the seismic sensor using the seismic data cable, and assigning sensor position coordinates to the seismic data based on measured position coordinates of the location identifier. The invention also includes an apparatus adapted for seismic data acquisition in a land or transition zone environment including a location identifier, a seismic senor capable of being placed near the location identifier, a seismic data cable, means for reading the location identifier using the seismic data cable, means for recording seismic data acquired by the seismic sensor using the seismic data cable, and means for assigning sensor position coordinates to the seismic data based on measured position coordinates of the location identifier.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Symmetrical Multi-Path Method For Determining the Distance Between Two Transmitter-Receivers
ActiveUS20080231498A1Improve accuracyImprove distance accuracyOptical rangefindersDirection finders using ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic wavesMulti pathTransmitter
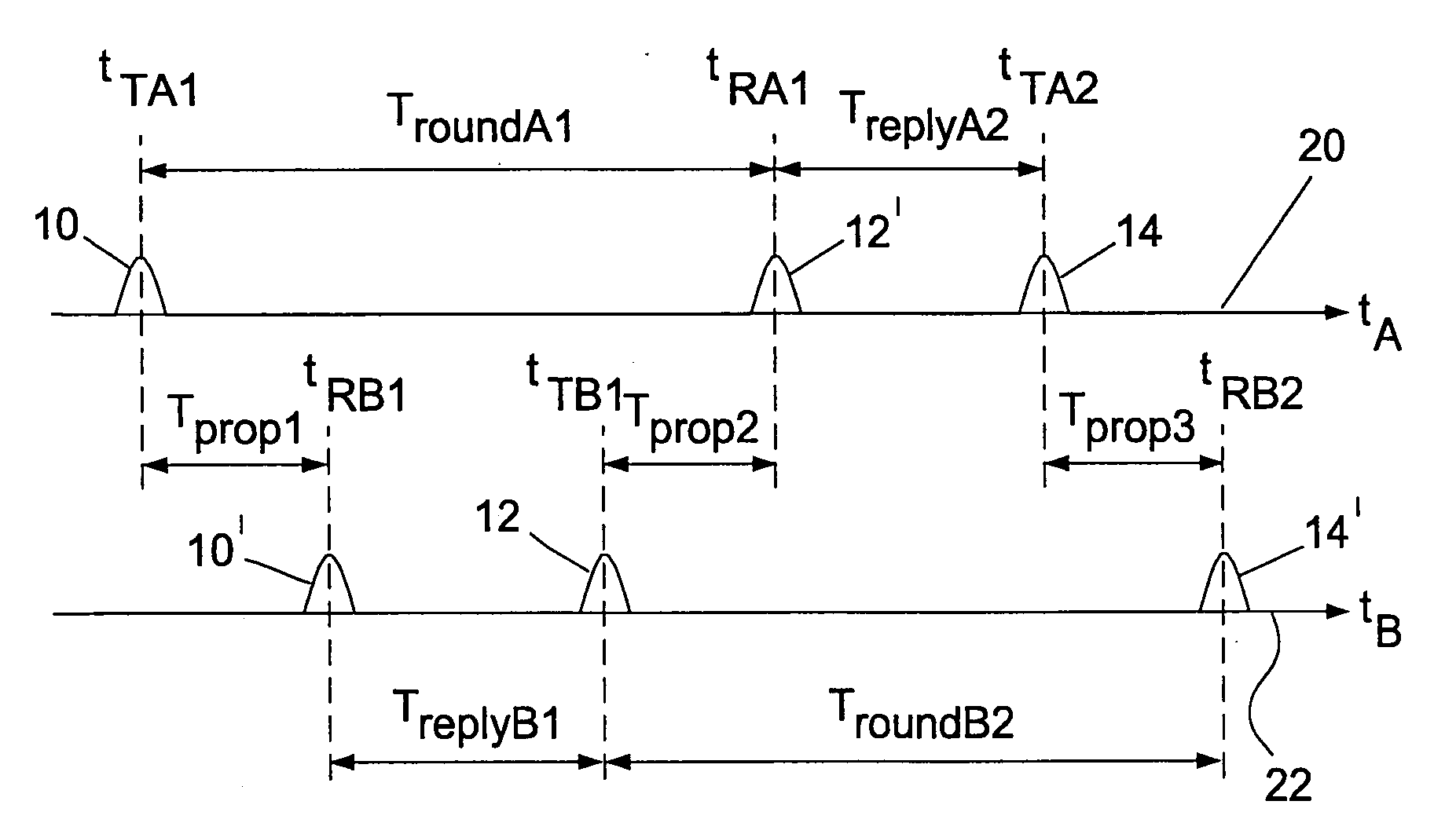
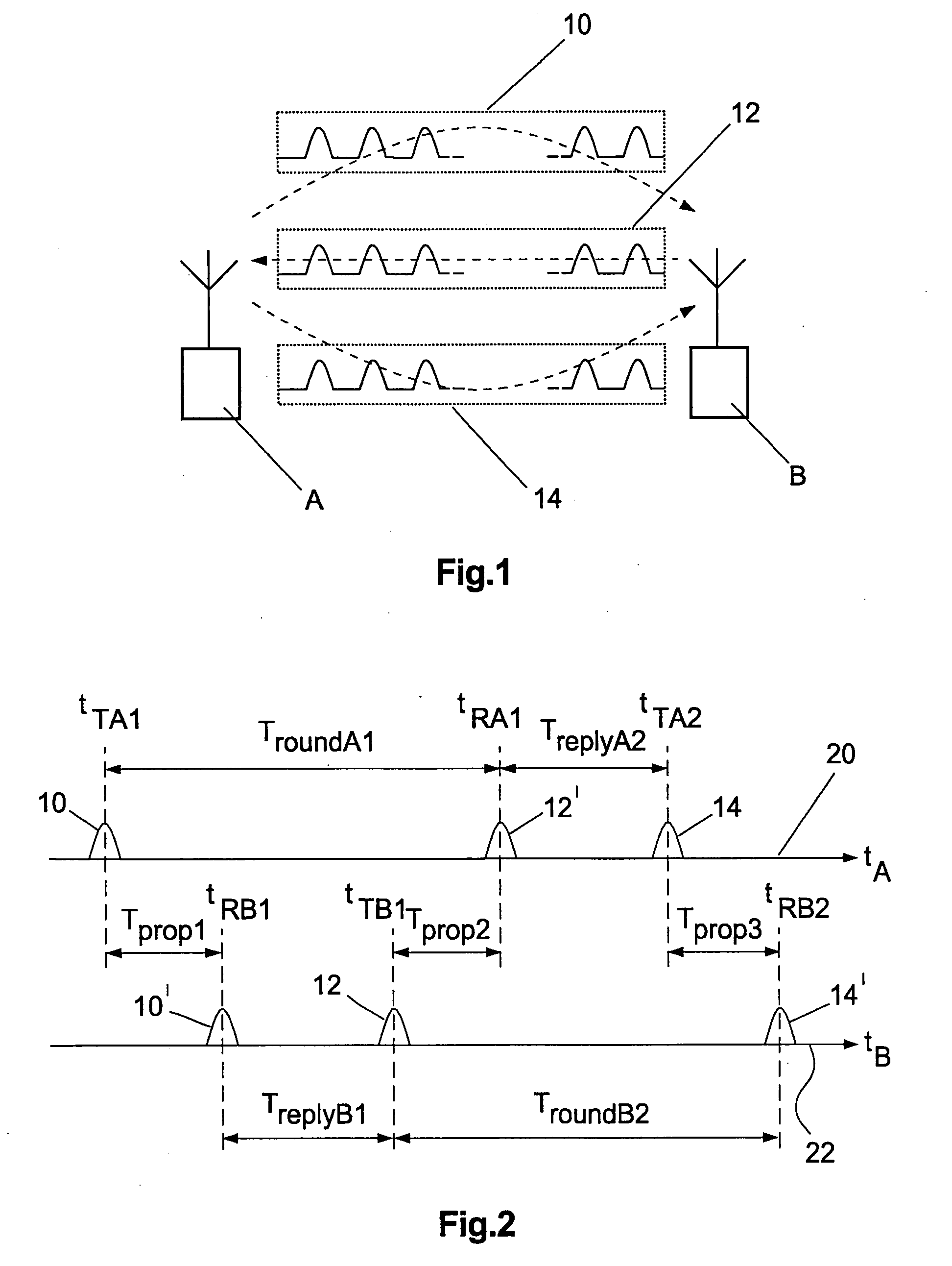
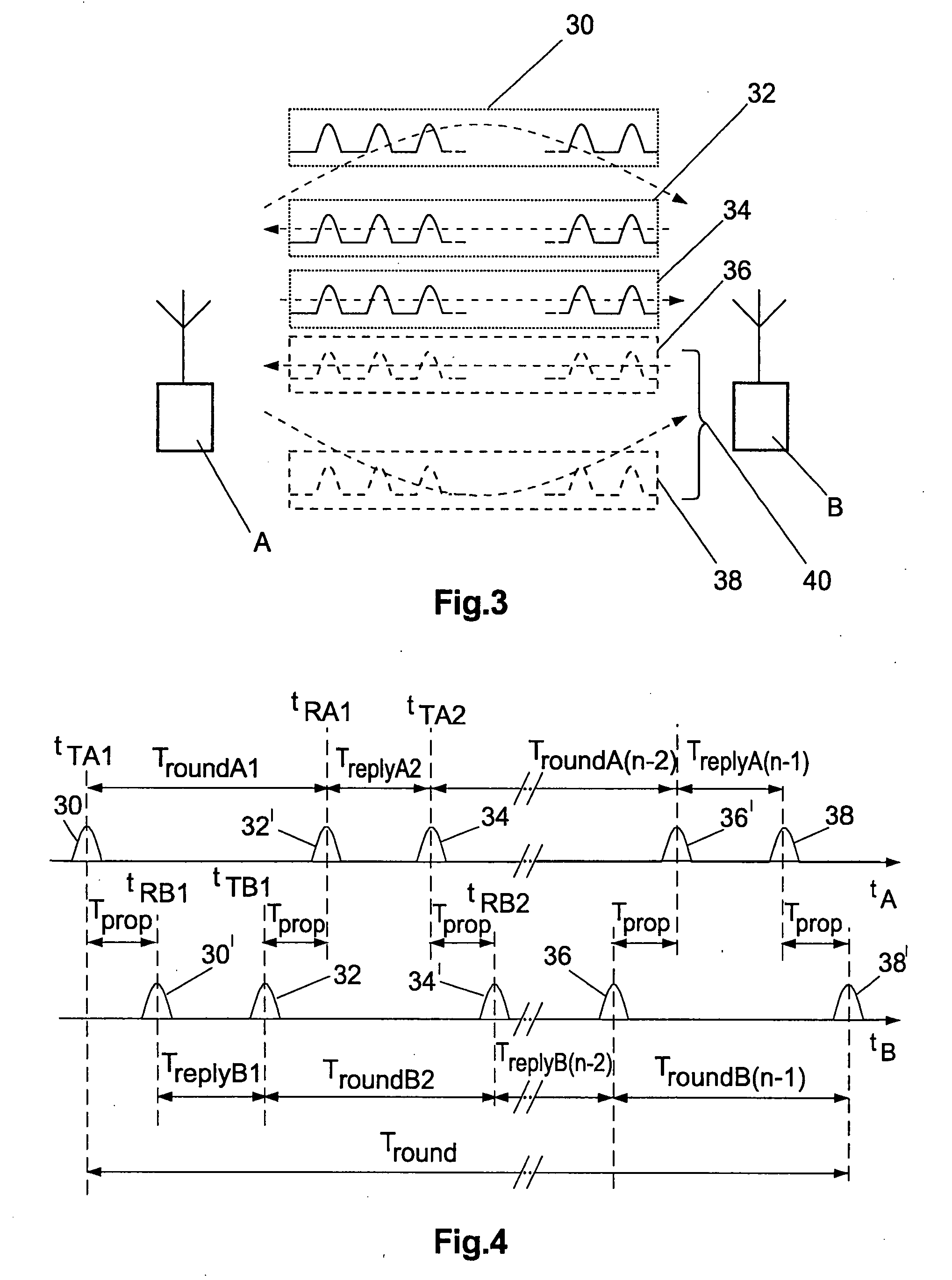
The invention relates to a symmetrical multi-path method for determining the spatial distance between two transmitter-receivers. Both transmitter-receivers set off at least one signal round in each case. A signal round comprises the steps:a) transmitting at least one request data frame of a first transmitter-receiver to a second transmitter-receiver at a request transmitting time (TTA1, TTB2),b) receiving the request data frame at the second transmitter-receiver at a request receiving time (TRB1, TRA2),c) transmitting a reply data frame from the second transmitter-receiver to the first transmitter-receiver at a reply transmitting time (TTB1, TTA2), which has a respective reply time interval (TreplyB1, TreplyA2) from the request receiving time (TRB1, TRA2) and detecting the reply time interval,d) receiving the reply data frame at the first transmitter-receiver setting off the signal round and detecting an allocated reply receiving time (TRA1, TRB2).The signal rounds are performed in such a way that the reply time intervals (TreplyA2, TreplyB1) are either identical or have a difference, in the case of performing more than one signal round set off by each transmitter-receiver an average difference, the amount of which is a maximum of 200 microseconds.
Owner:NANOTRON GES FUR MIKROTECHN
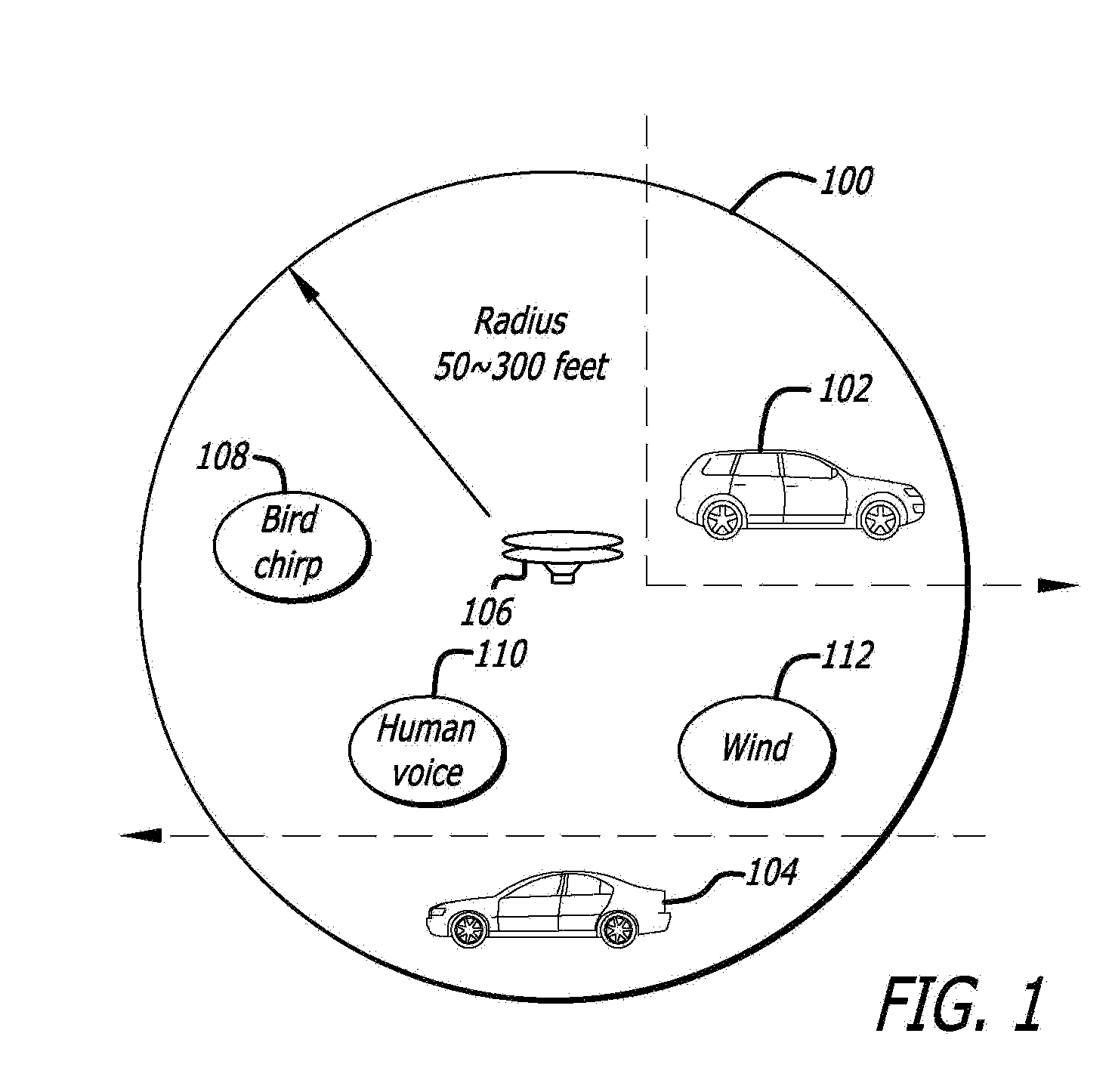
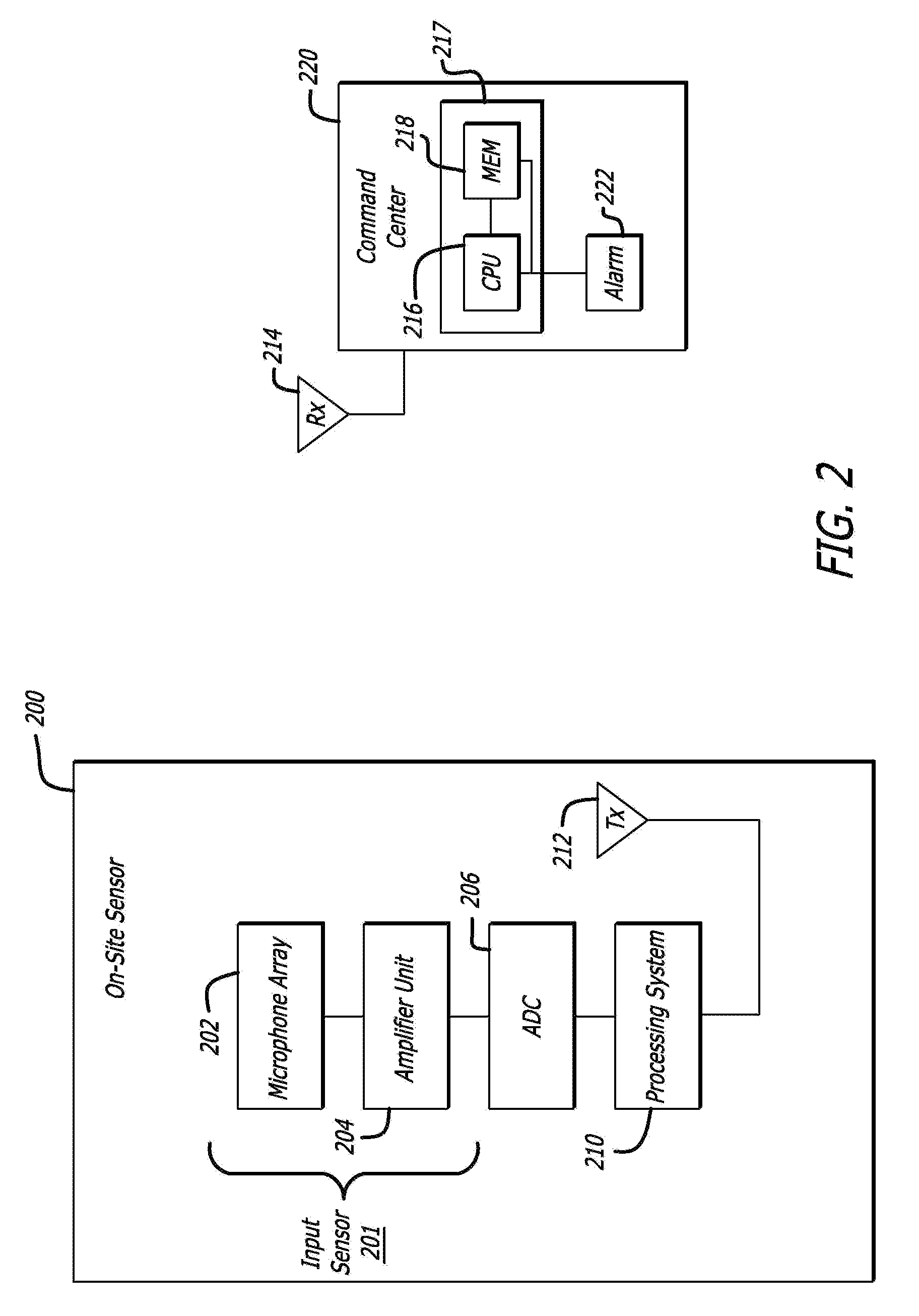
Detection and classification of running vehicles based on acoustic signatures
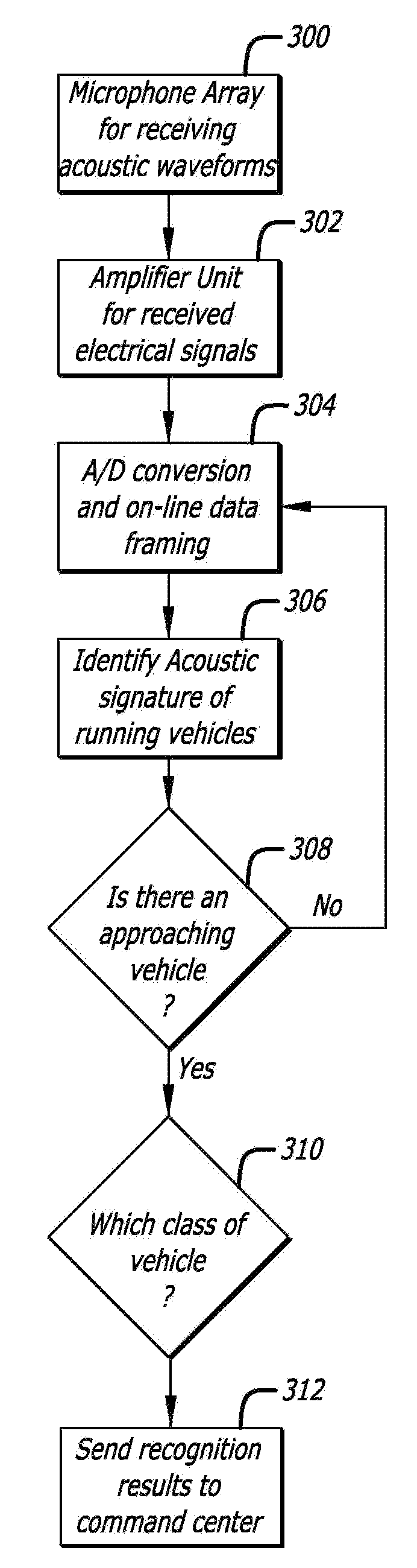
ActiveUS20090115635A1Analogue computers for vehiclesVibration measurement in fluidFeature vectorSynaptic weight
A method and apparatus for identifying running vehicles in an area to be monitored using acoustic signature recognition. The apparatus includes an input sensor for capturing an acoustic waveform produced by a vehicle source, and a processing system. The waveform is digitized and divided into frames. Each frame is filtered into a plurality of gammatone filtered signals. At least one spectral feature vector is computed for each frame. The vectors are integrated across a plurality of frames to create a spectro-temporal representation of the vehicle waveform. In a training mode, values from the spectro-temporal representation are used as inputs to a Nonlinear Hebbian learning function to extract acoustic signatures and synaptic weights. In an active mode, the synaptic weights and acoustic signatures are used as patterns in a supervised associative network to identify whether a vehicle is present in the area to be monitored. In response to a vehicle being present, the class of vehicle is identified. Results may be provided to a central computer.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com