Patents
Literature
703results about "Seismic data acquisition" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
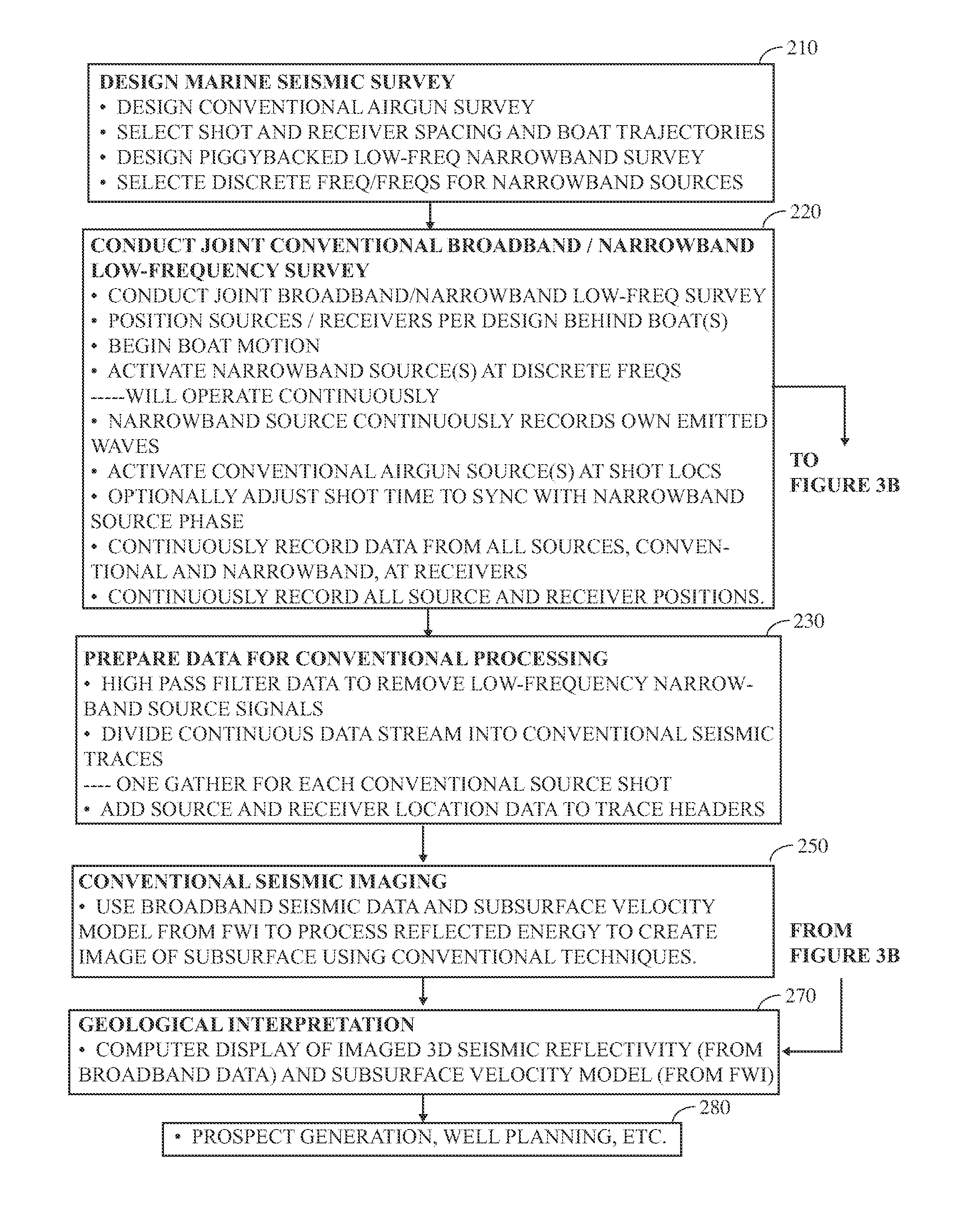
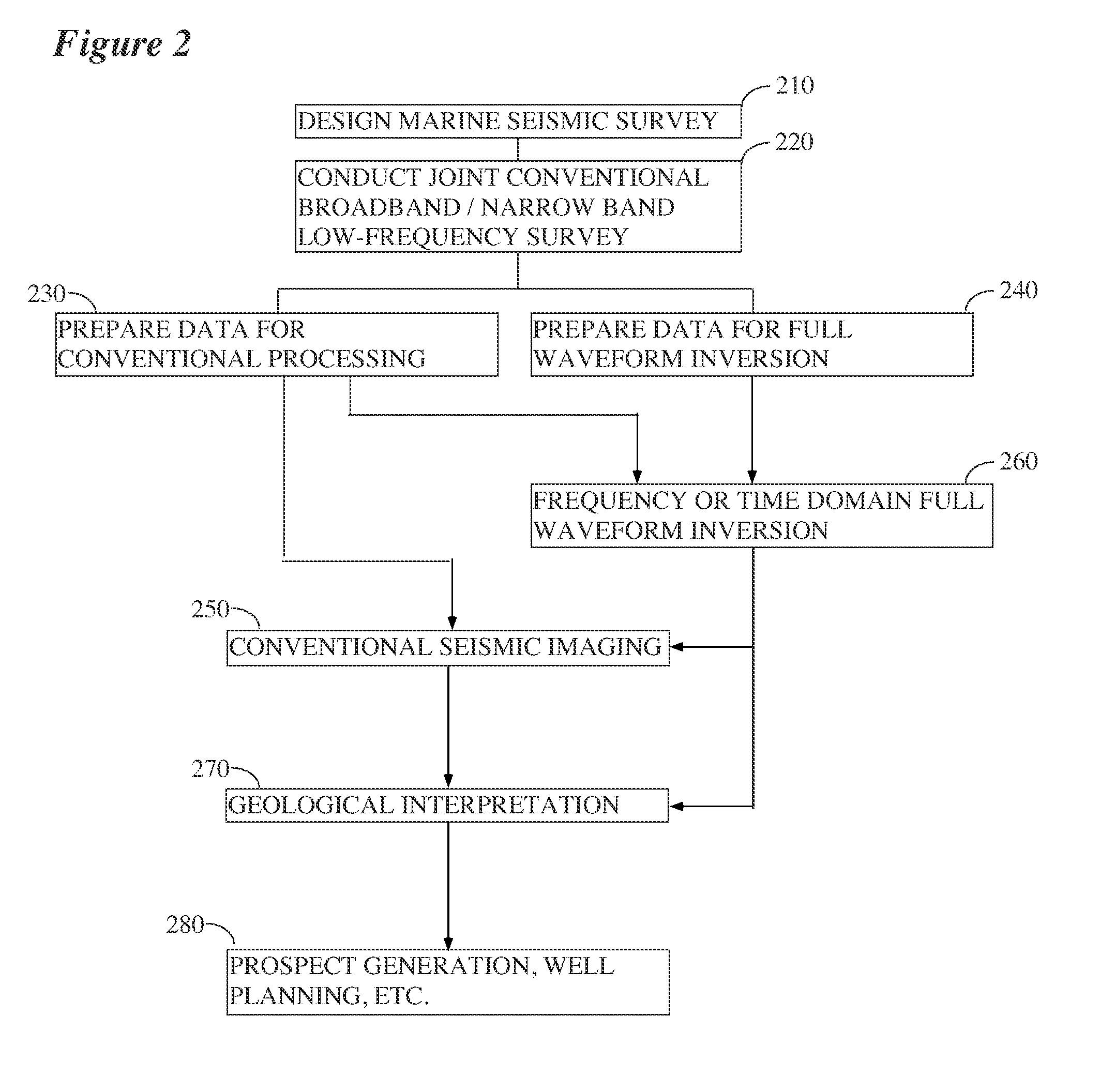
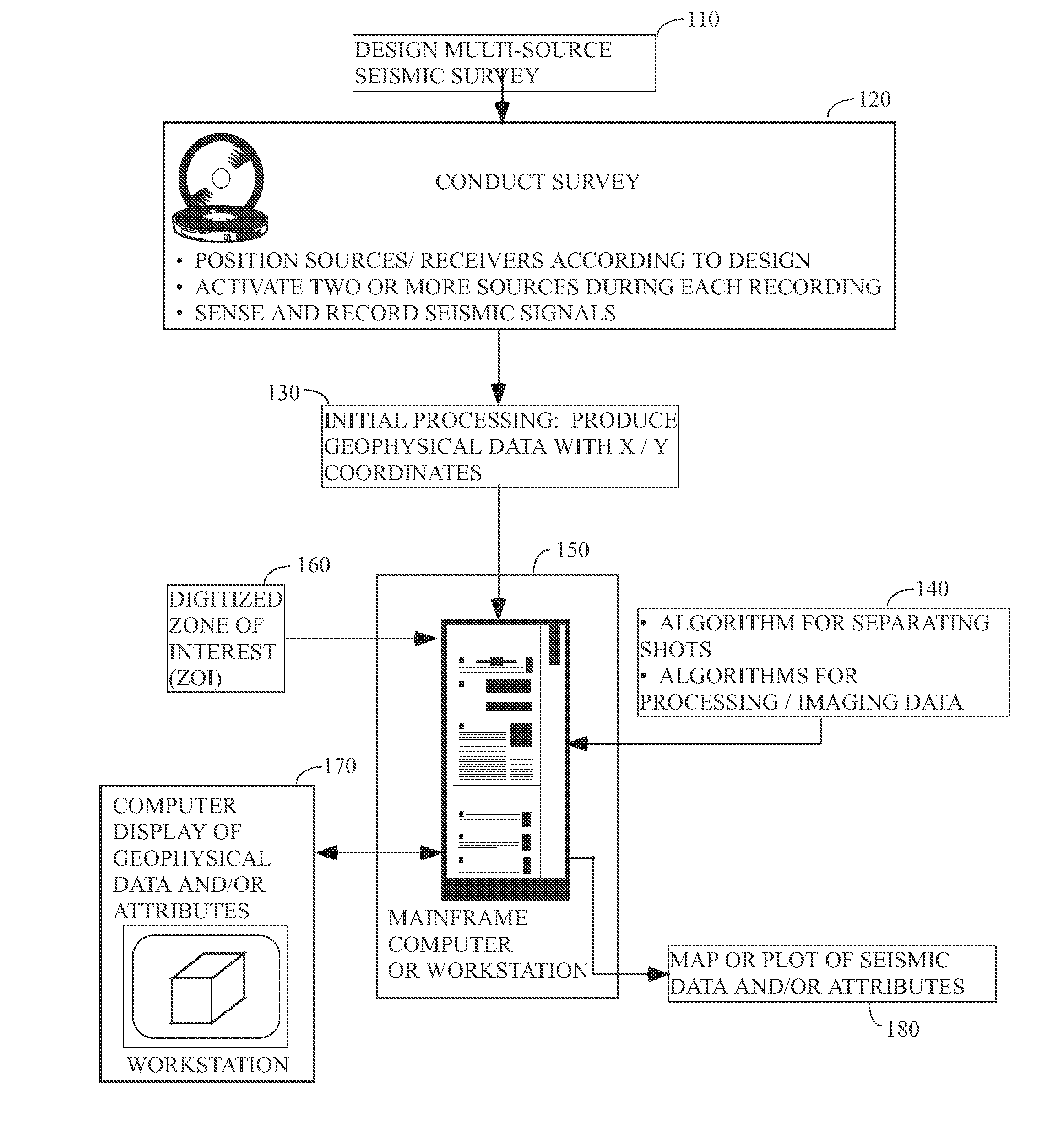
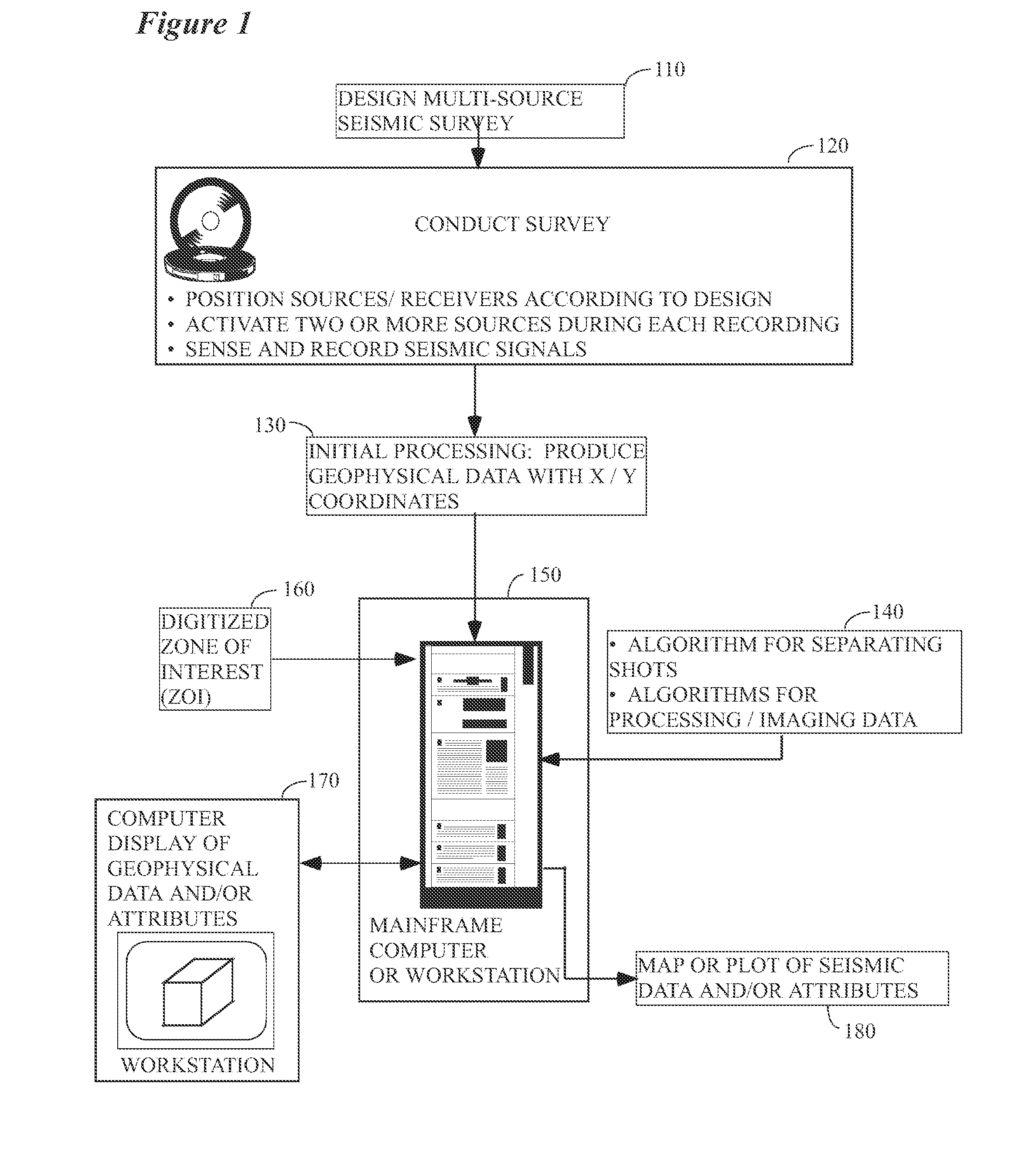
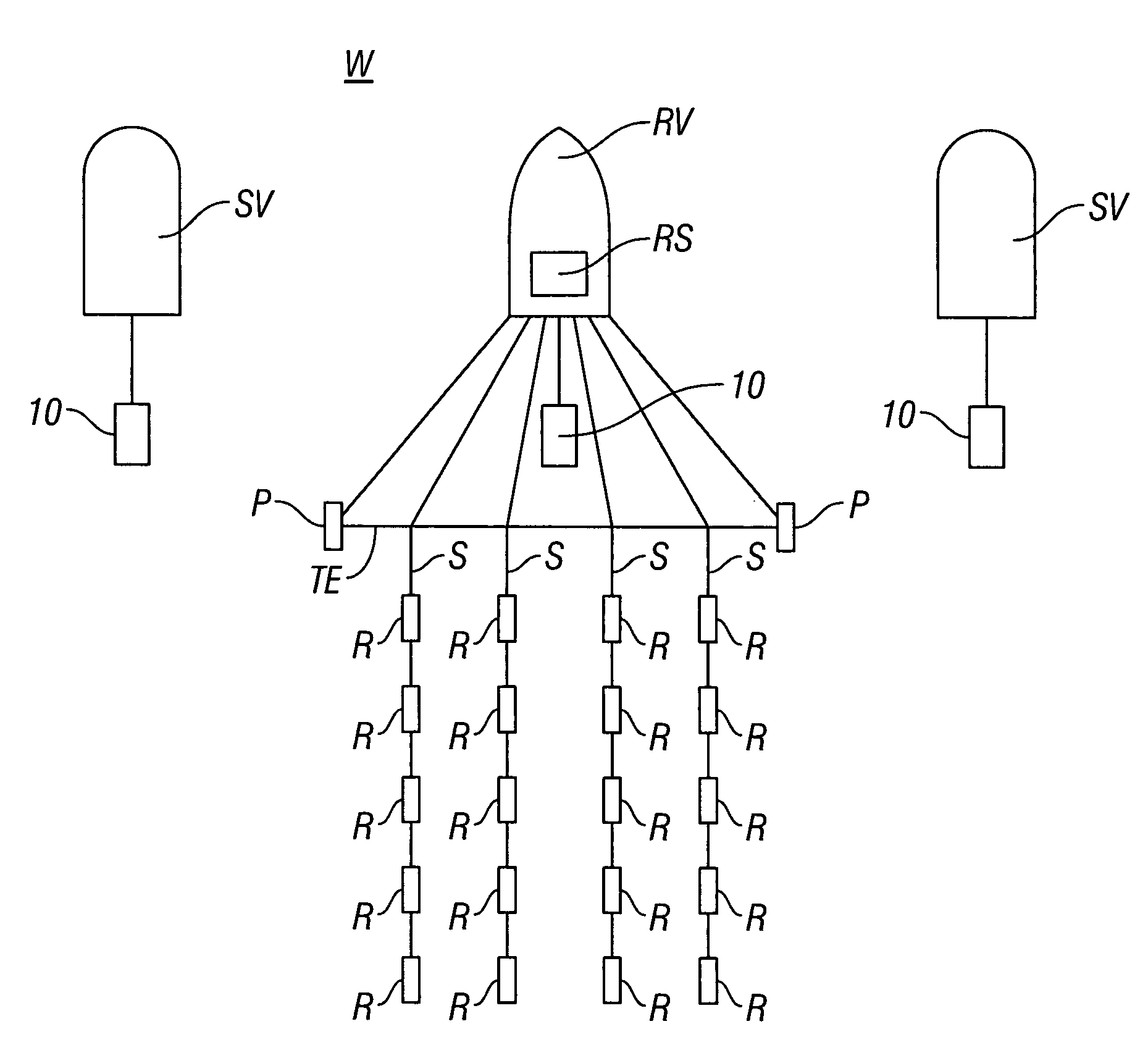
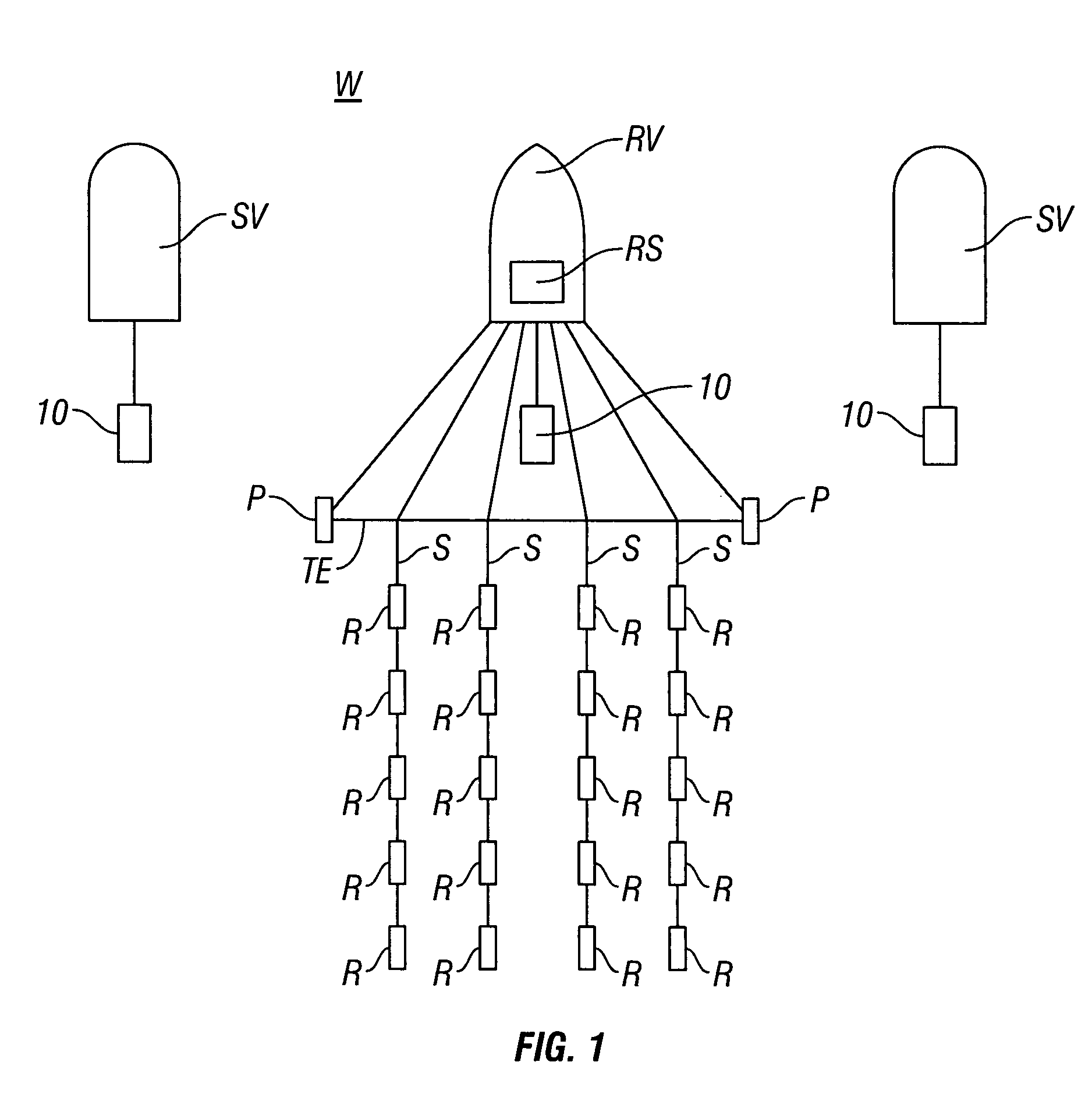
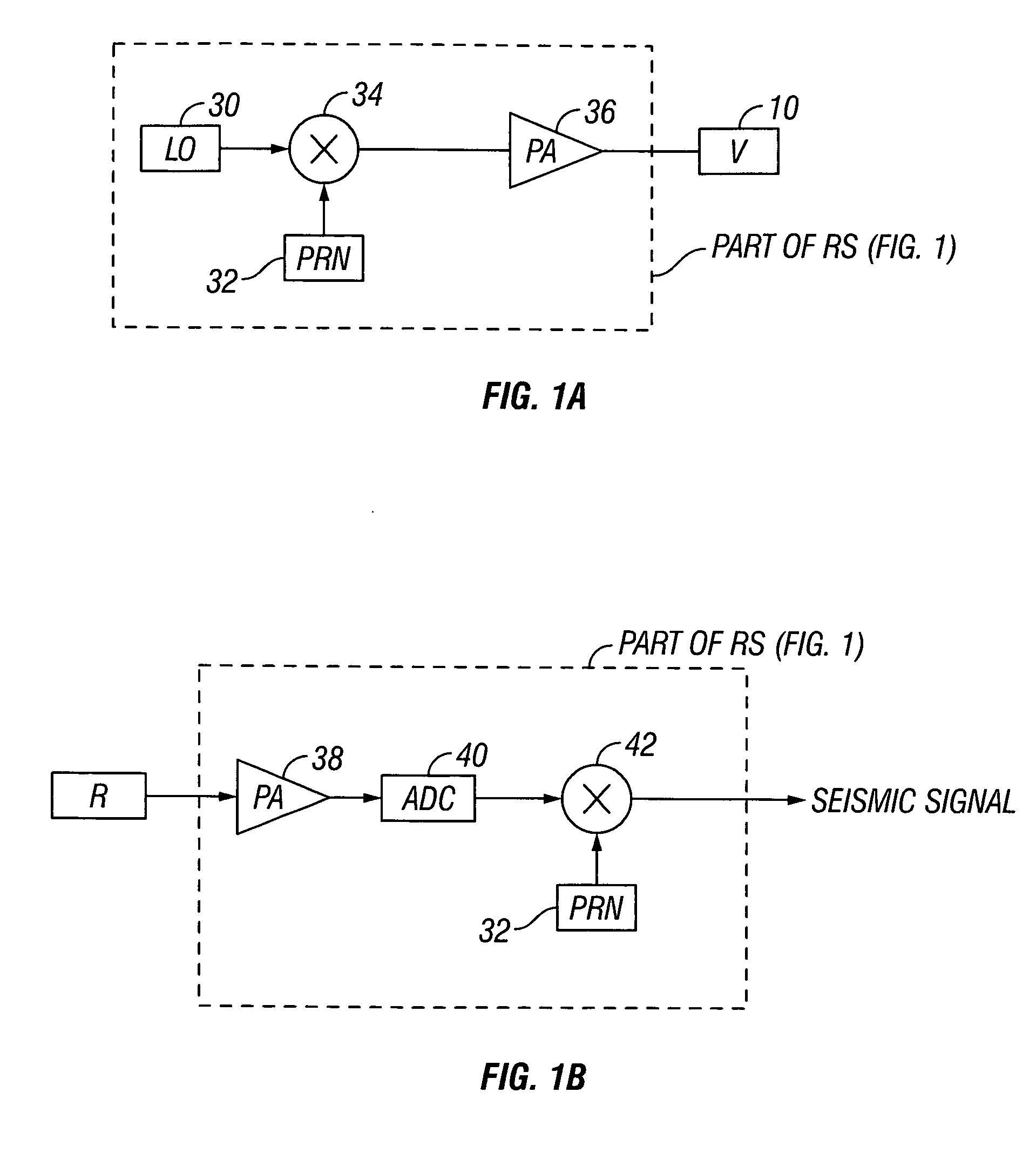
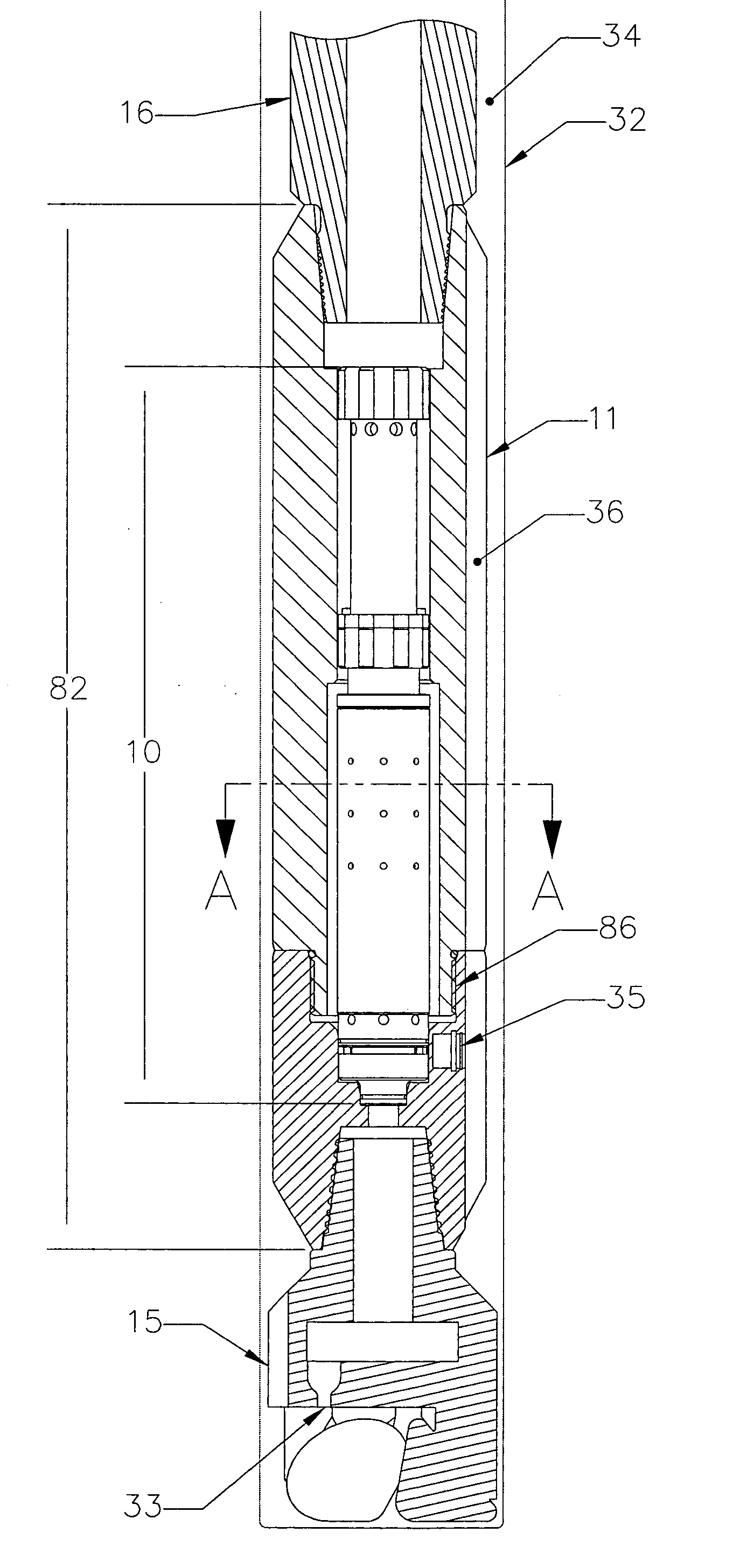
Seismic acquisition using narrowband seismic sources
ActiveUS20120155217A1Reduce crosstalkSpeed up the processSeismic data acquisitionSeismic signal processingMonochromatic colorFull waveform
There is provided herein a system and method of seismic data collection for land and marine data that utilizes narrowband to monochromatic low-frequency non-impulsive sources designed to optimize the ability of migration / inversion algorithms to image the subsurface of the Earth, in particular, full-waveform inversion.
Owner:BP CORP NORTH AMERICA INC
Method and system for acquiring marine seismic data using multiple seismic sources
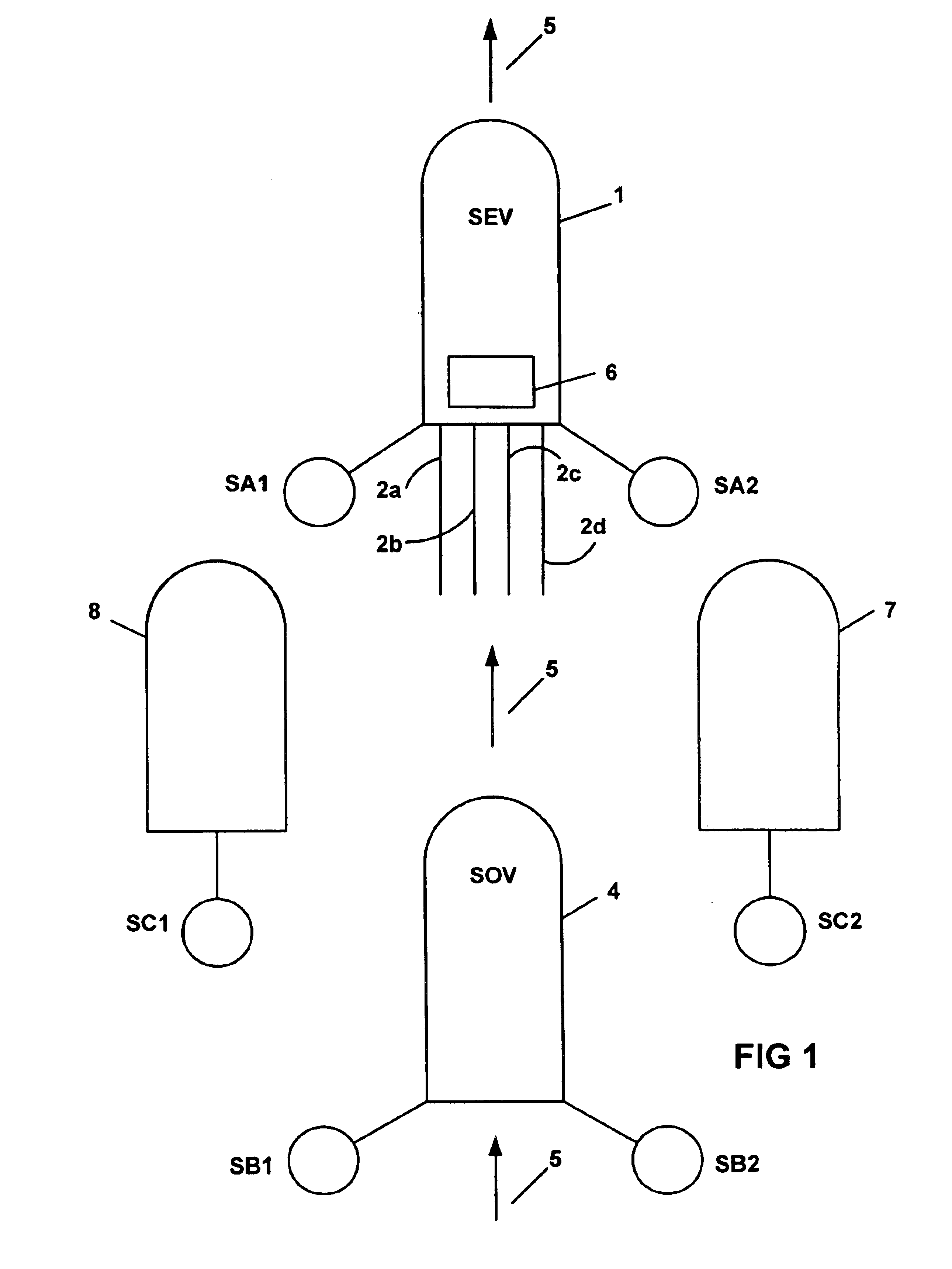
InactiveUS6906981B2Easy to foldIncrease the lengthSeismic data acquisitionSeismic energy generationSeismic surveySurveyor
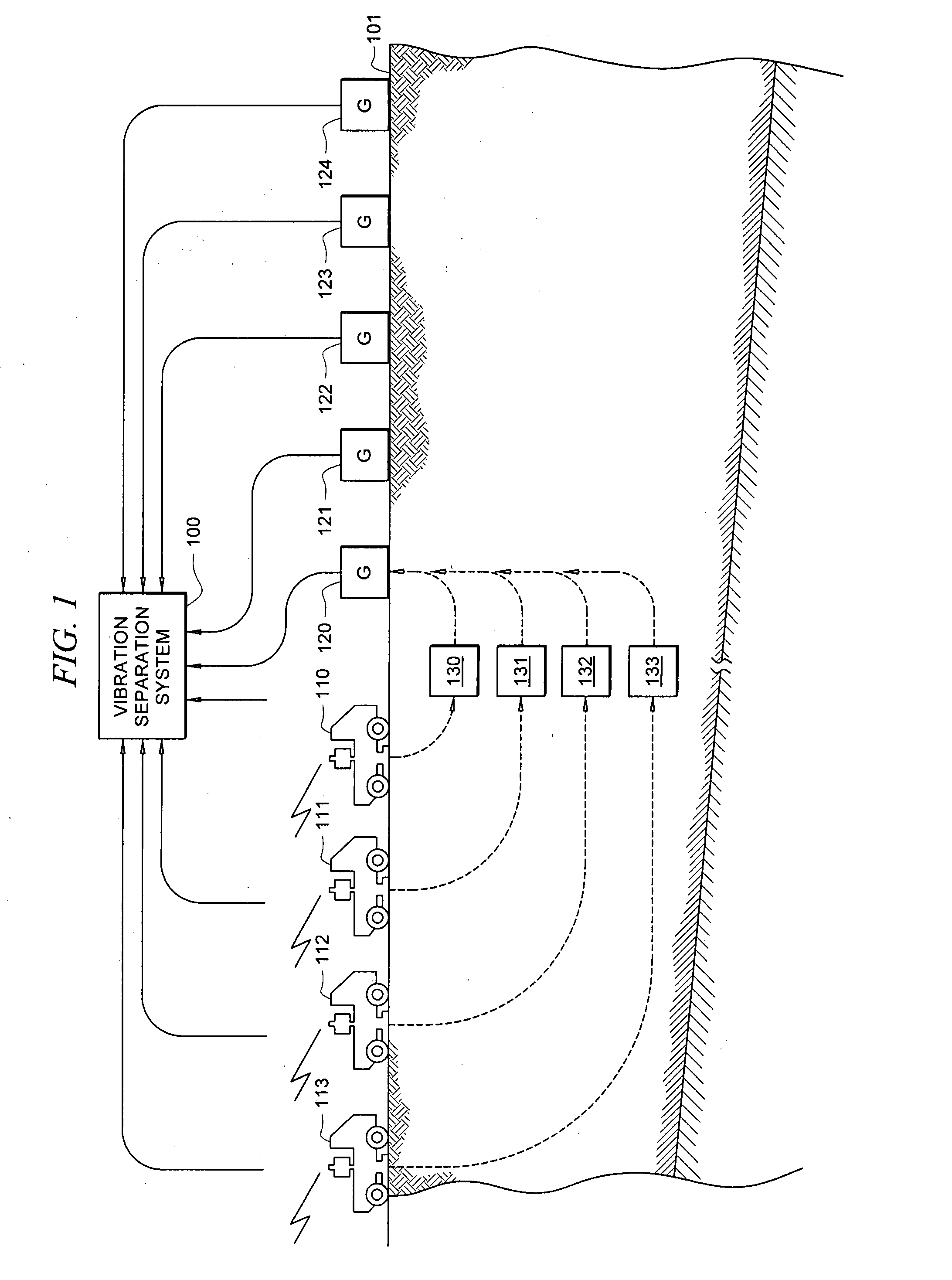
A method for seismic surveying is disclosed which includes towing a first seismic energy source and at least one seismic sensor system. A second seismic energy source is towed at a selected distance from the first source. The first seismic energy source and the second seismic energy source are actuated in a plurality of firing sequences. Each of the firing sequences includes firing of the first source, waiting a selected time firing the second source and recording signals generated by the seismic sensor system. The selected time between firing the first source and the second source is varied between successive ones of the firing sequences. The firing times of the first and second source are indexed so as to enable separate identification of seismic events originating from the first source and seismic events originating from the second source in detected seismic signals.
Owner:PGS GEOPHYSICAL AS
Method for separating independent simultaneous sources
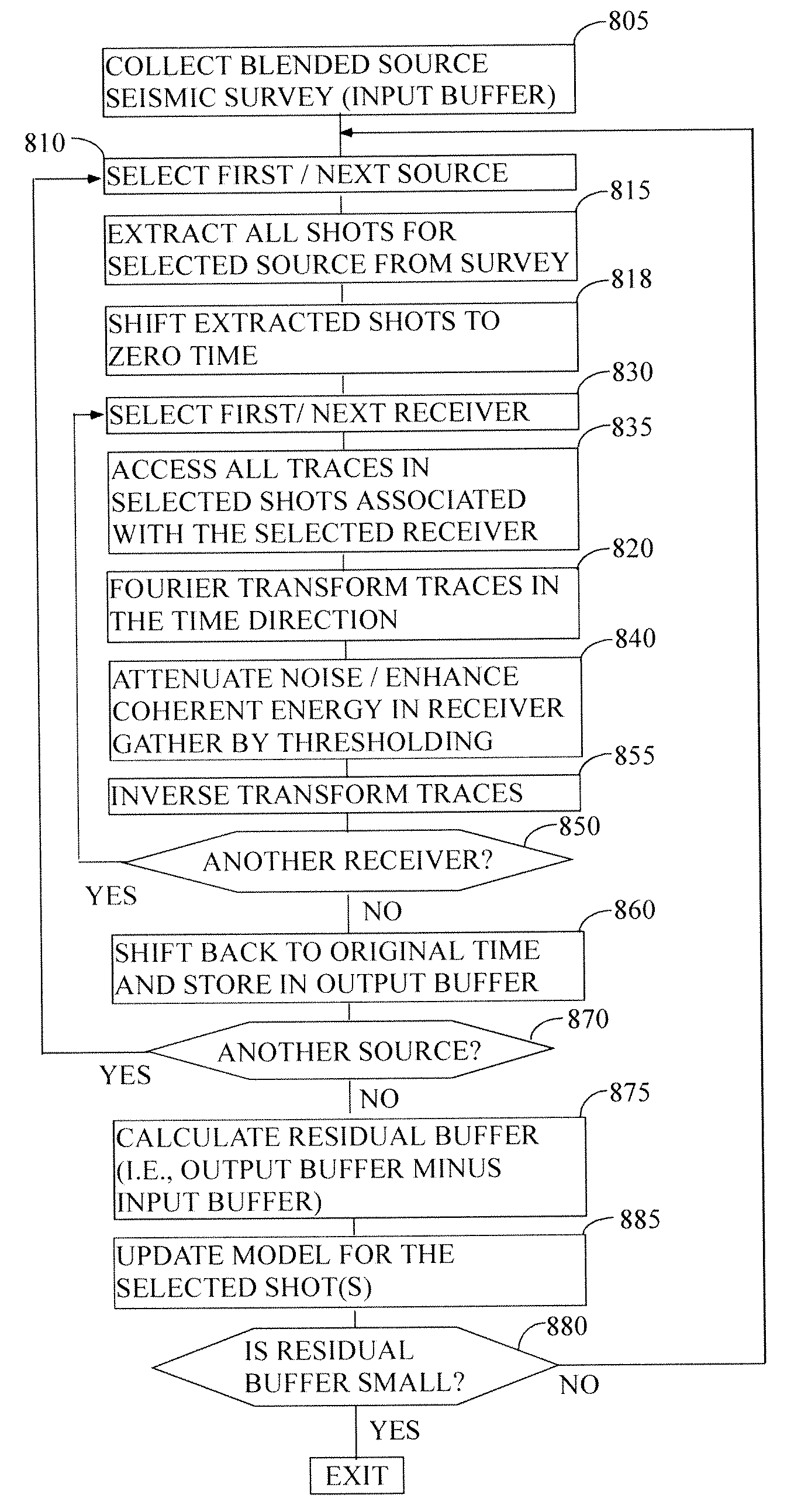
ActiveUS20100039894A1Easy accessEfficient collectionSeismic data acquisitionSeismic signal processingSeismic surveyStart time
Owner:BP CORP NORTH AMERICA INC
Hydraulic impulse generator and frequency sweep mechanism for borehole applications
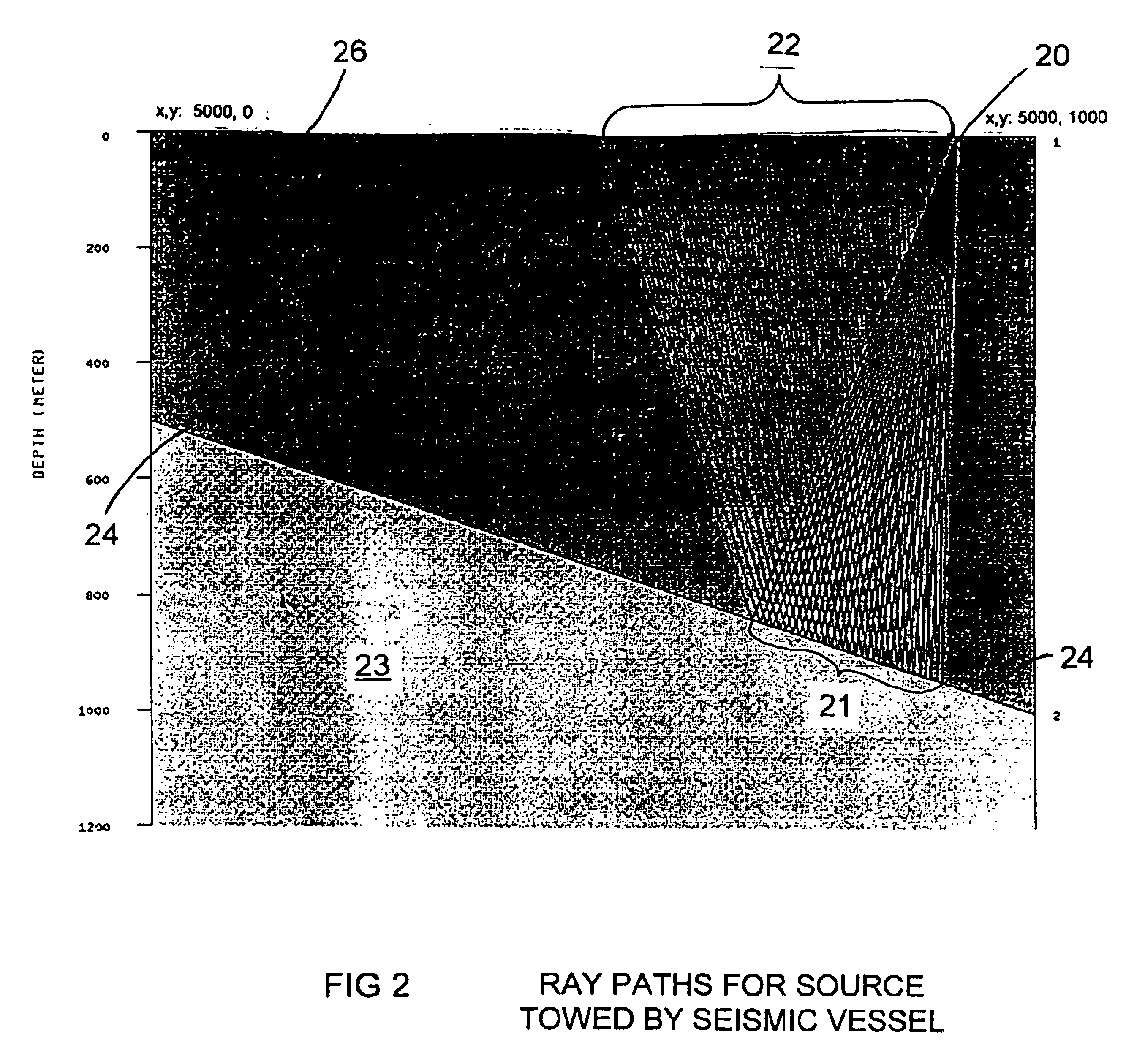
This invention discloses a valve that generates a hydraulic negative pressure pulse and a frequency modulator for the creation of a powerful, broadband swept impulse seismic signal at the drill bit during drilling operations. The signal can be received at monitoring points on the surface or underground locations using geophones. The time required for the seismic signal to travel from the source to the receiver directly and via reflections is used to calculate seismic velocity and other formation properties near the source and between the source and receiver. This information can be used for vertical seismic profiling of formations drilled, to check the location of the bit, or to detect the presence of abnormal pore pressure ahead of the bit. The hydraulic negative pressure pulse can also be used to enhance drilling and production of wells.
Owner:WELLS FARGO BANK NAT ASSOC +1
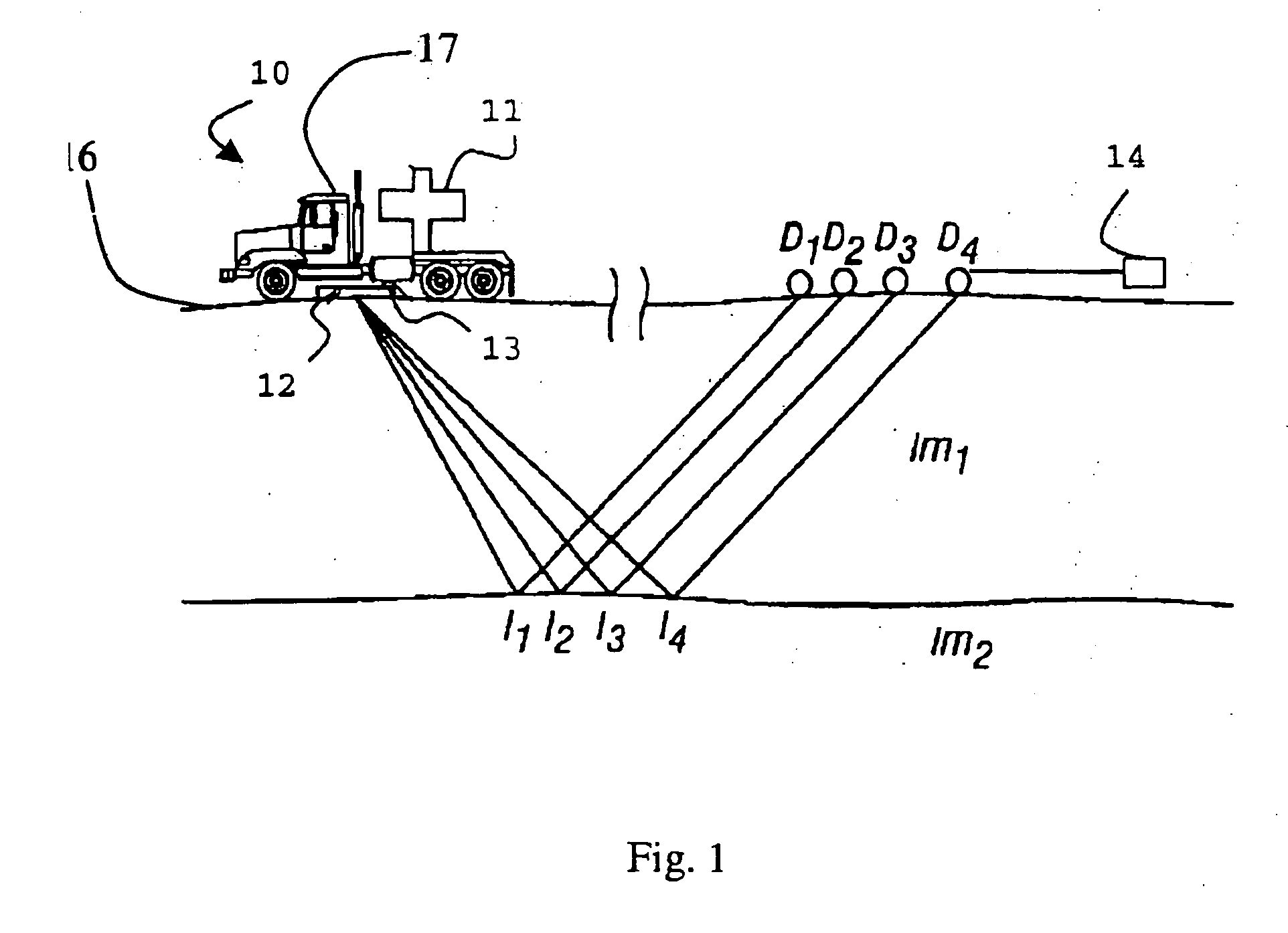
Method of seismic surveying
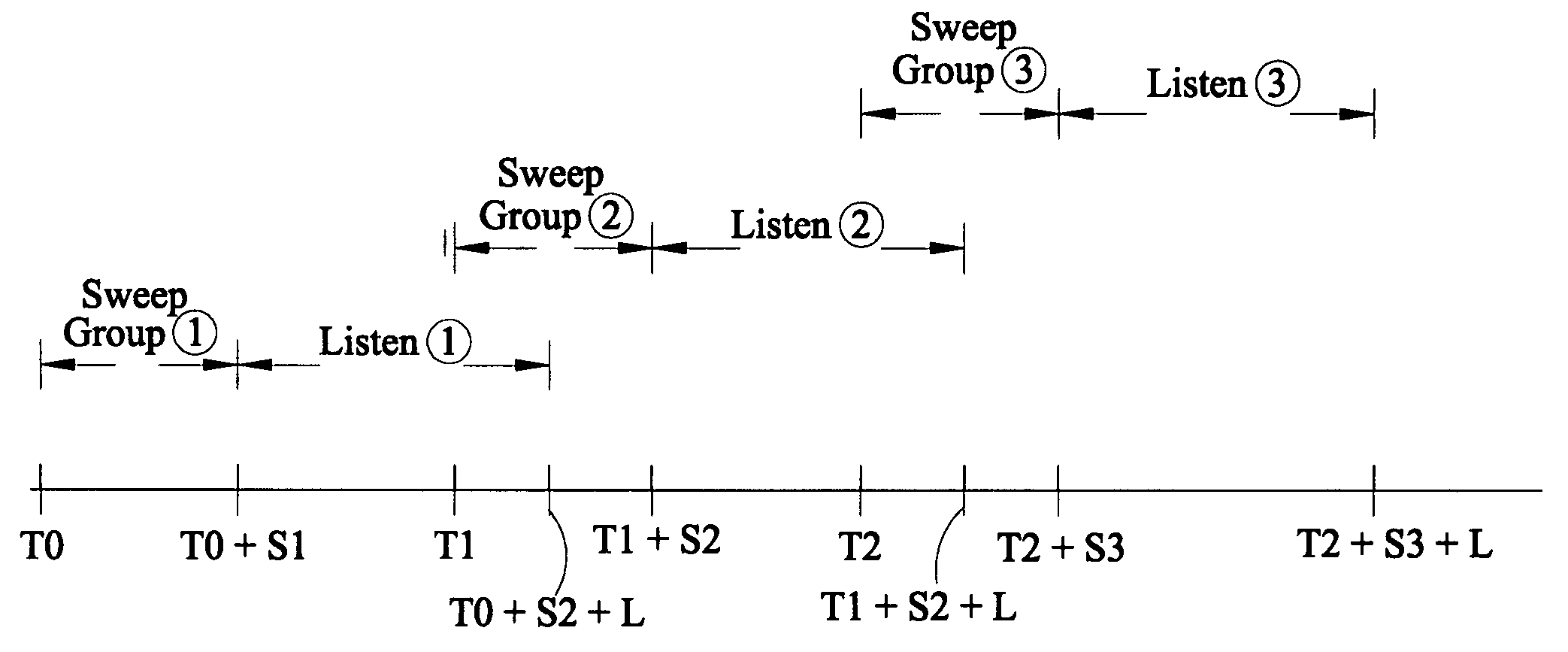
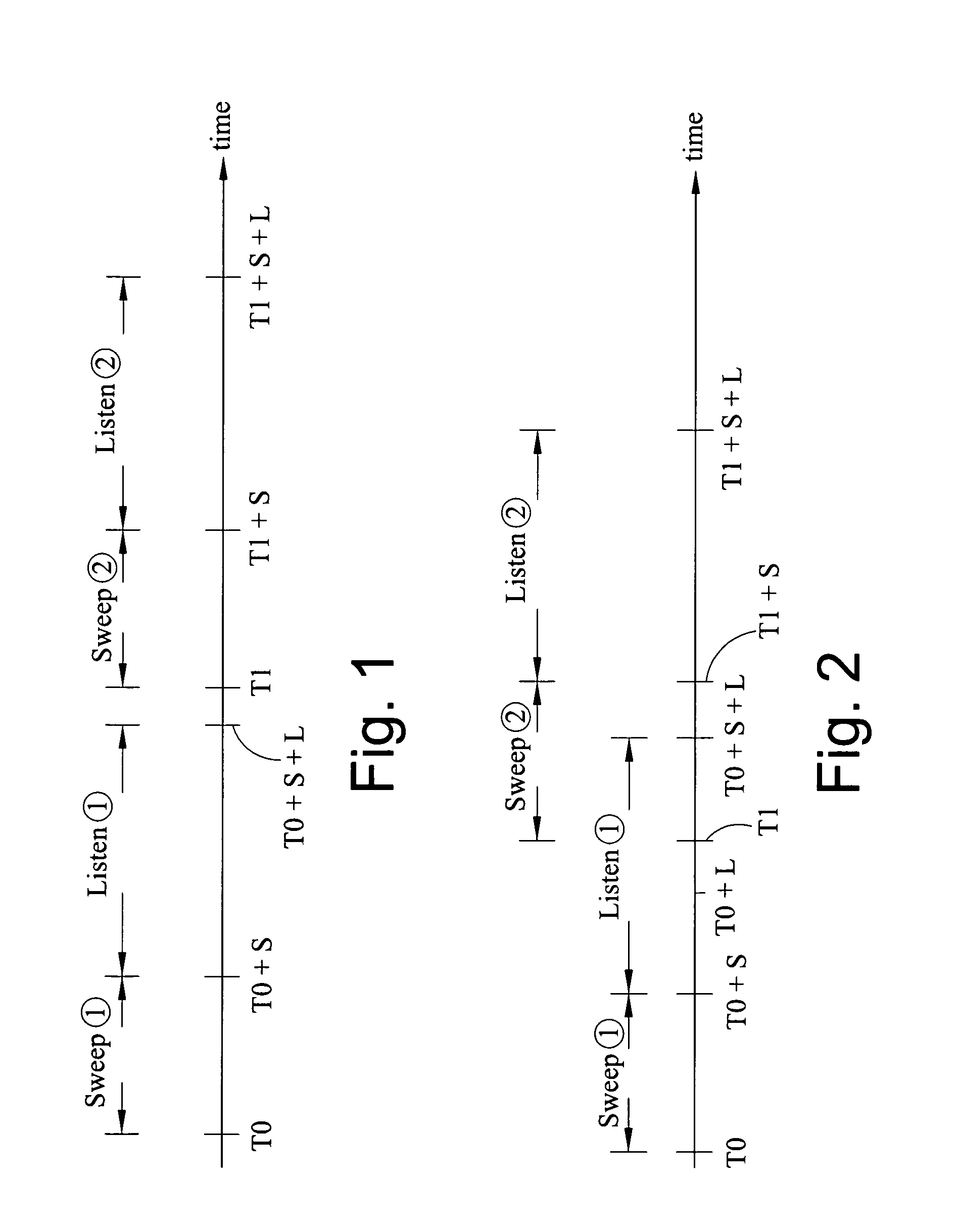
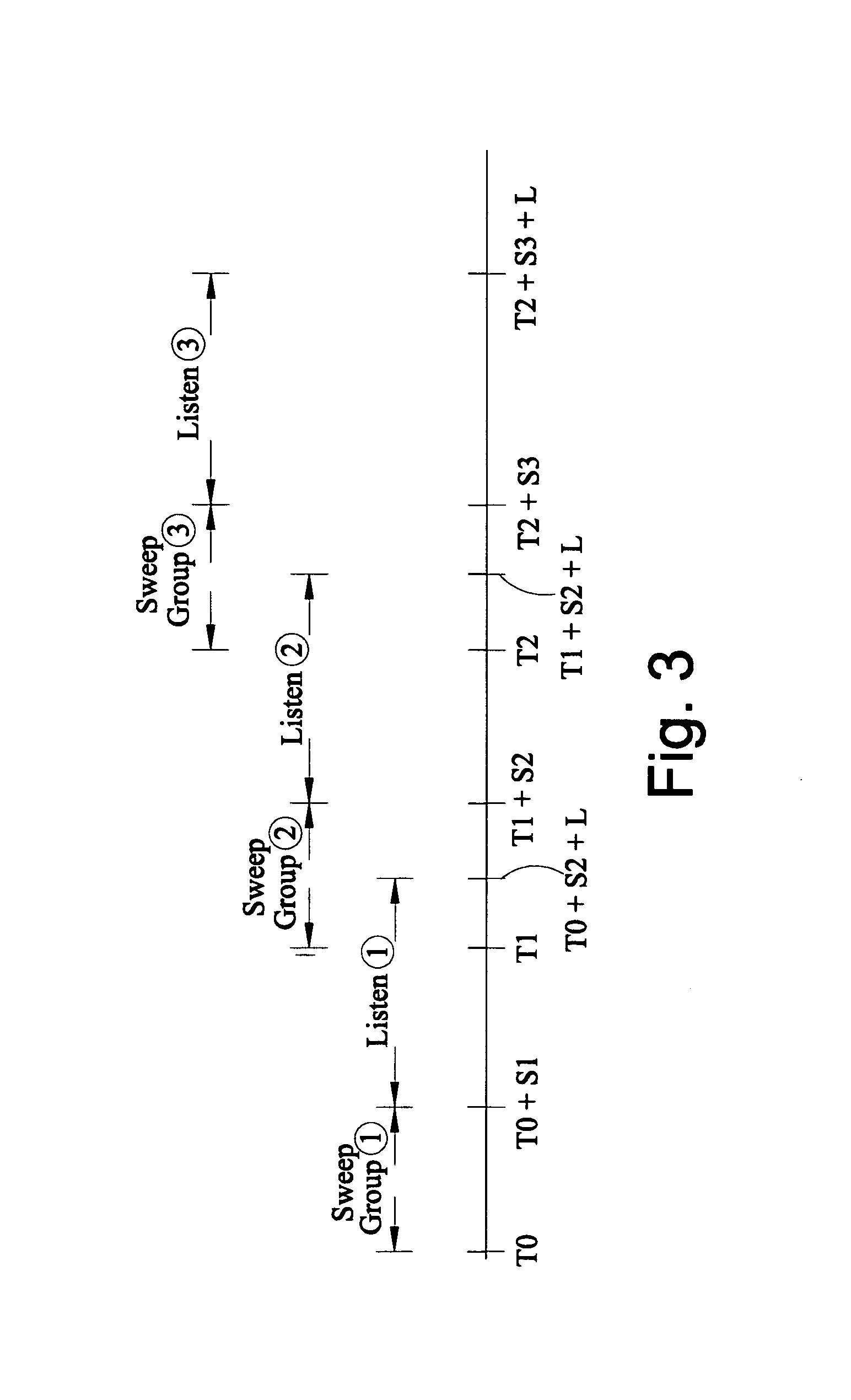
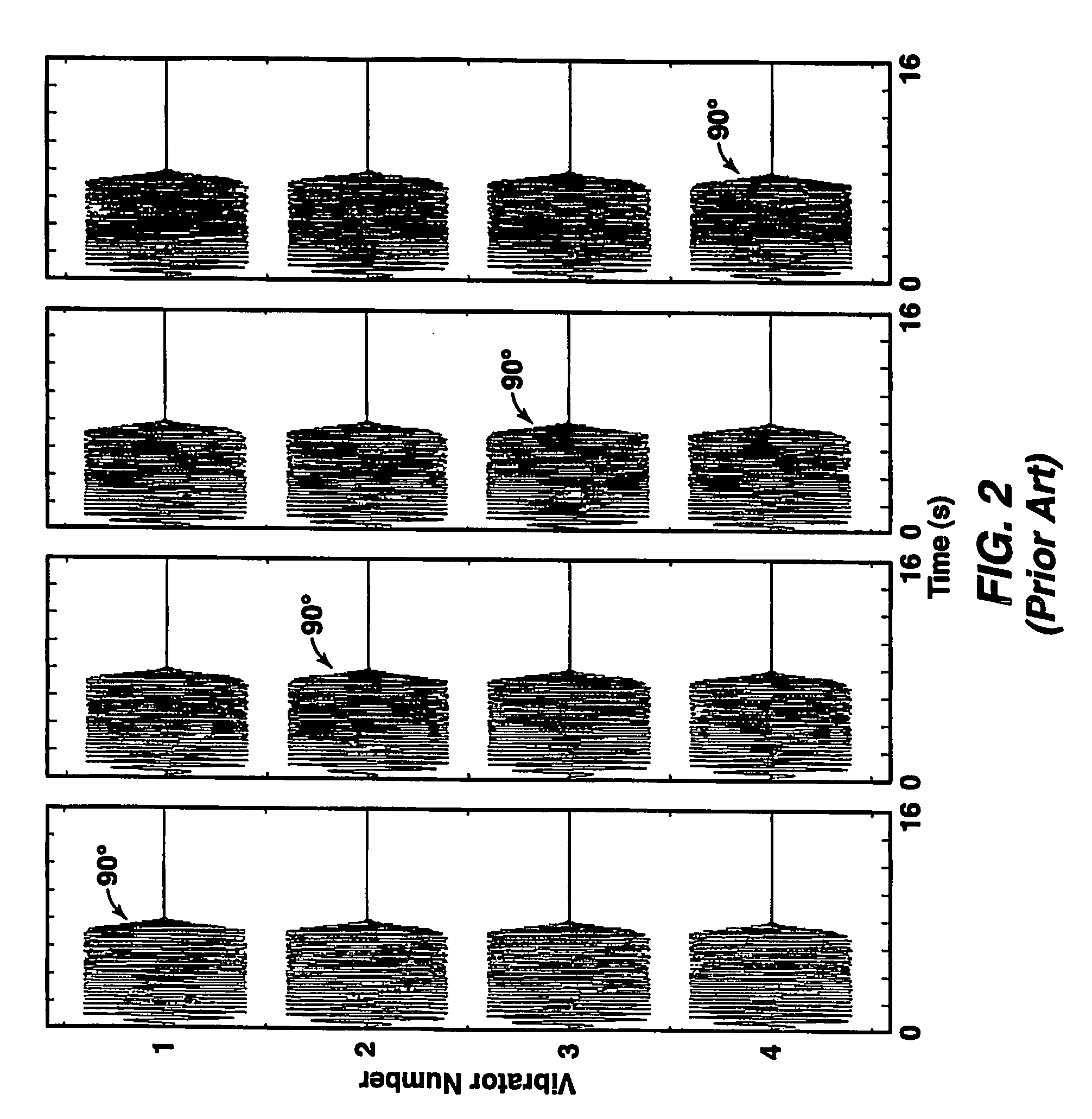
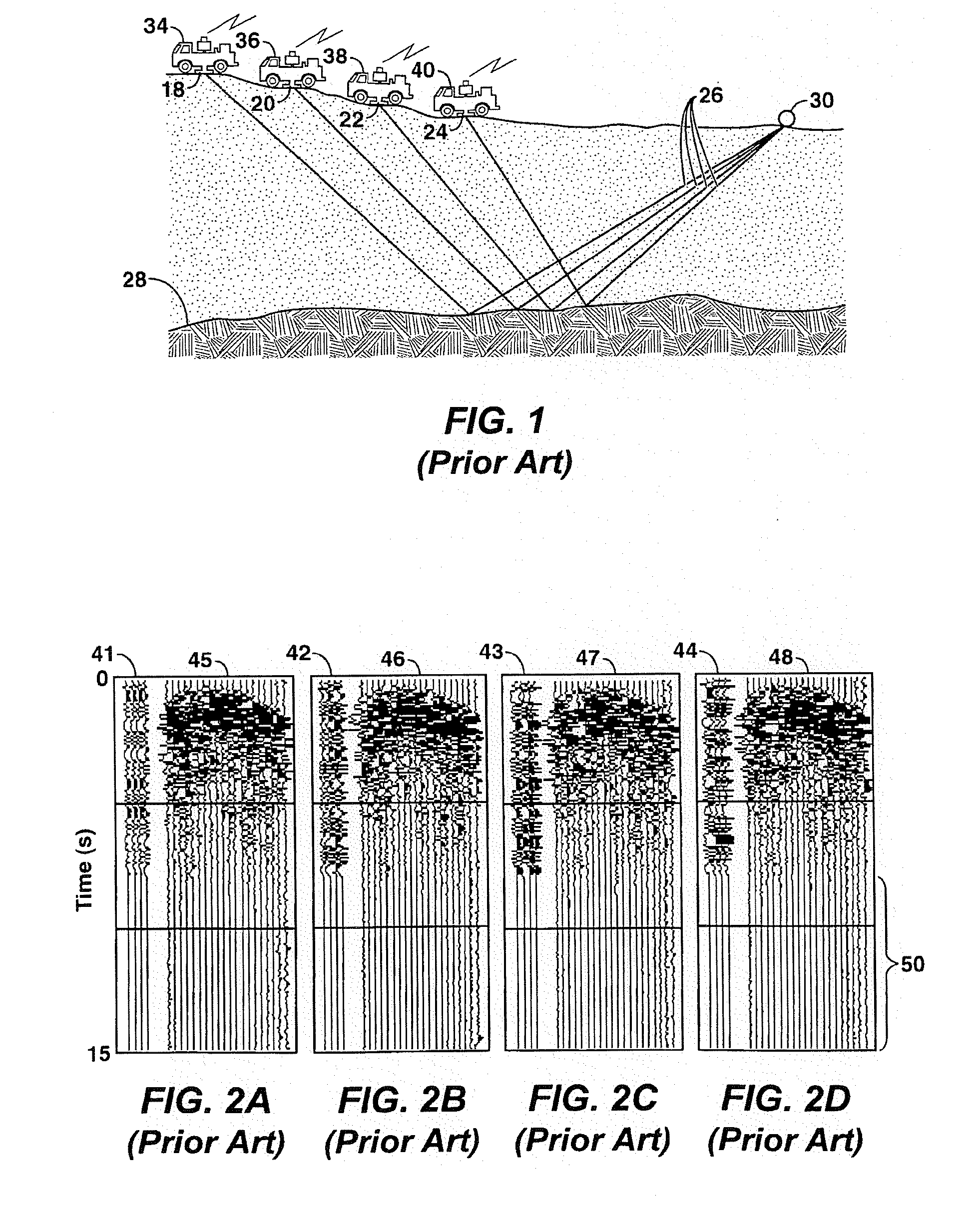
A method of seismic surveying comprising the steps of actuating the or each vibrator in a first vibrator group at time T0, and subsequently actuating the or each vibrator in a second vibrator group at time T1 that satisfies T0<T1<T0+S1+L where S1 is the sweep time of the first vibrator group and L is the listening time. At least one of the first vibrator group and the second vibrator group comprises at least two vibrators. The first group and the second group of vibrators may be the same group, or they may be different groups. This method enables the time required to complete a seismic survey to be reduced compared to the prior art “simultaneous shooting” and “slip-sweep shooting” techniques.In a case where the first group and the second group of vibrators are different, the method may further comprise actuating the or each vibrator in the first vibrator group at time T2, where T1<T2<T1+S2+L and S2 is the sweep time of the first vibrator group, and then actuating the or each vibrator in the second vibrator group at time T3 where T2<T3<T2+S1+L and where T3−T2≠T1−T0. The varying time delay between a shot of the first vibrator group and the corresponding shot of the second vibrator group means that harmonic noise will occur at different times in the shot records so that the noise may be eliminated by appropriately combining the shot records.
Owner:WESTERNGECO LLC
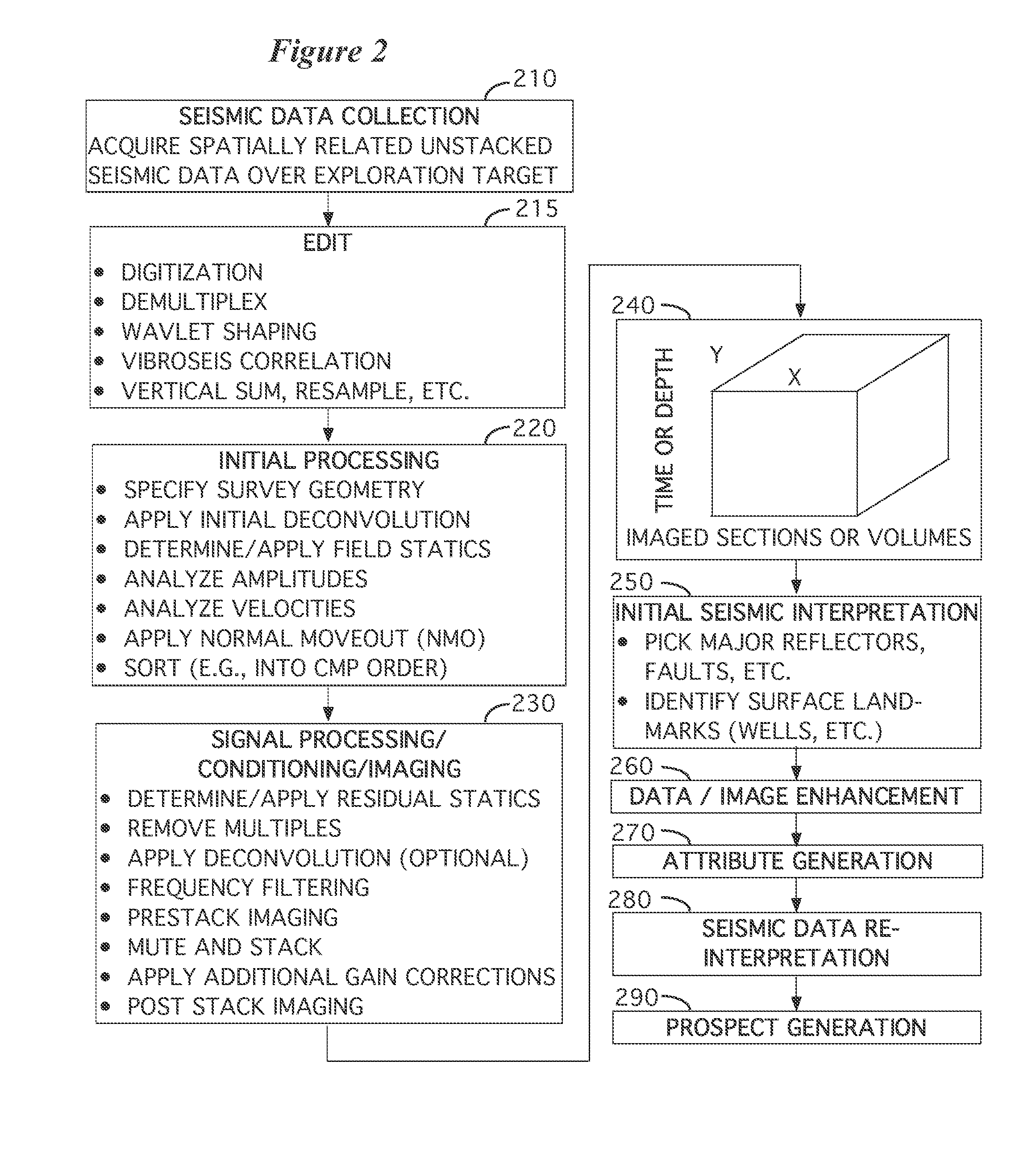
Coding and Decoding: Seismic Data Modeling, Acquisition and Processing
InactiveUS20070274155A1Seismic data acquisitionSeismic signal processingSource encodingData modeling
A method for coding and decoding seismic data acquired, based on the concept of multishooting, is disclosed. In this concept, waves generated simultaneously from several locations at the surface of the earth, near the sea surface, at the sea floor, or inside a borehole propagate in the subsurface before being recorded at sensor locations as mixtures of various signals. The coding and decoding method for seismic data described here works with both instantaneous mixtures and convolutive mixtures. Furthermore, the mixtures can be underdetemined [i.e., the number of mixtures (K) is smaller than the number of seismic sources (I) associated with a multishot] or determined [i.e., the number of mixtures is equal to or greater than the number of sources). When mixtures are determined, we can reorganize our seismic data as zero-mean random variables and use the independent component analysis (ICA) or, alternatively, the principal component analysis (PCA) to decode. We can also alternatively take advantage of the sparsity of seismic data in our decoding process. When mixtures are underdetermined and the number of mixtures is at least two, we utilize higher-order statistics to overcome the underdeterminacy. Alternatively, we can use the constraint that seismic data are sparse to overcome the underdeterminacy. When mixtures are underdetermined and limited to single mixtures, we use a priori knowledge about seismic acquisition to computationally generate additional mixtures from the actual recorded mixtures. Then we organize our data as zero-mean random variables and use ICA or PCA to decode the data. The a priori knowledge includes source encoding, seismic acquisition geometries, and reference data collected for the purpose of aiding the decoding processing.The coding and decoding processes described can be used to acquire and process real seismic data in the field or in laboratories, and to model and process synthetic data.
Owner:IKELLE LUC T
Seismic prospecting method and device using simultaneous emission of seismic signals obtained by coding a signal by pseudo-random sequences
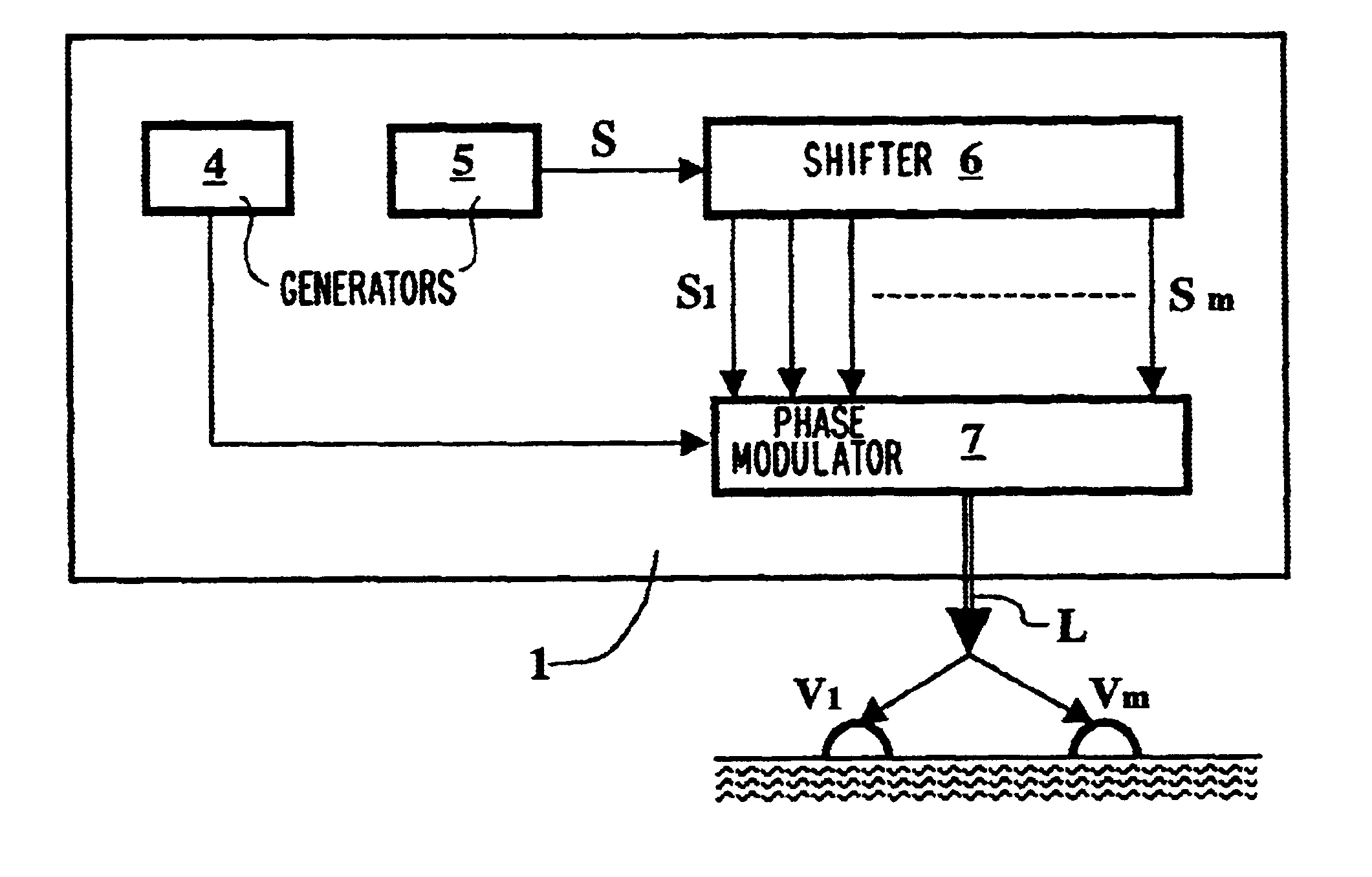
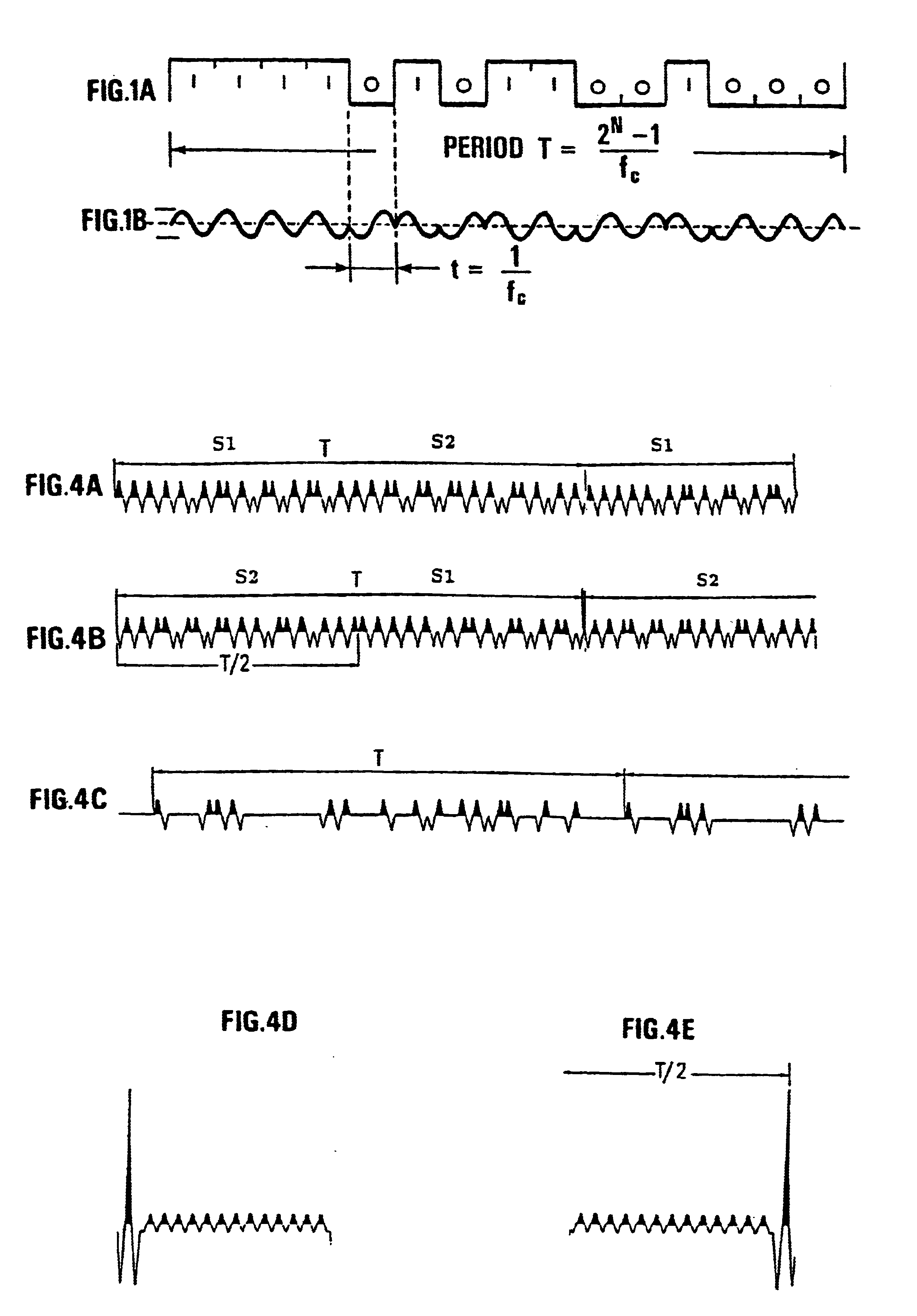
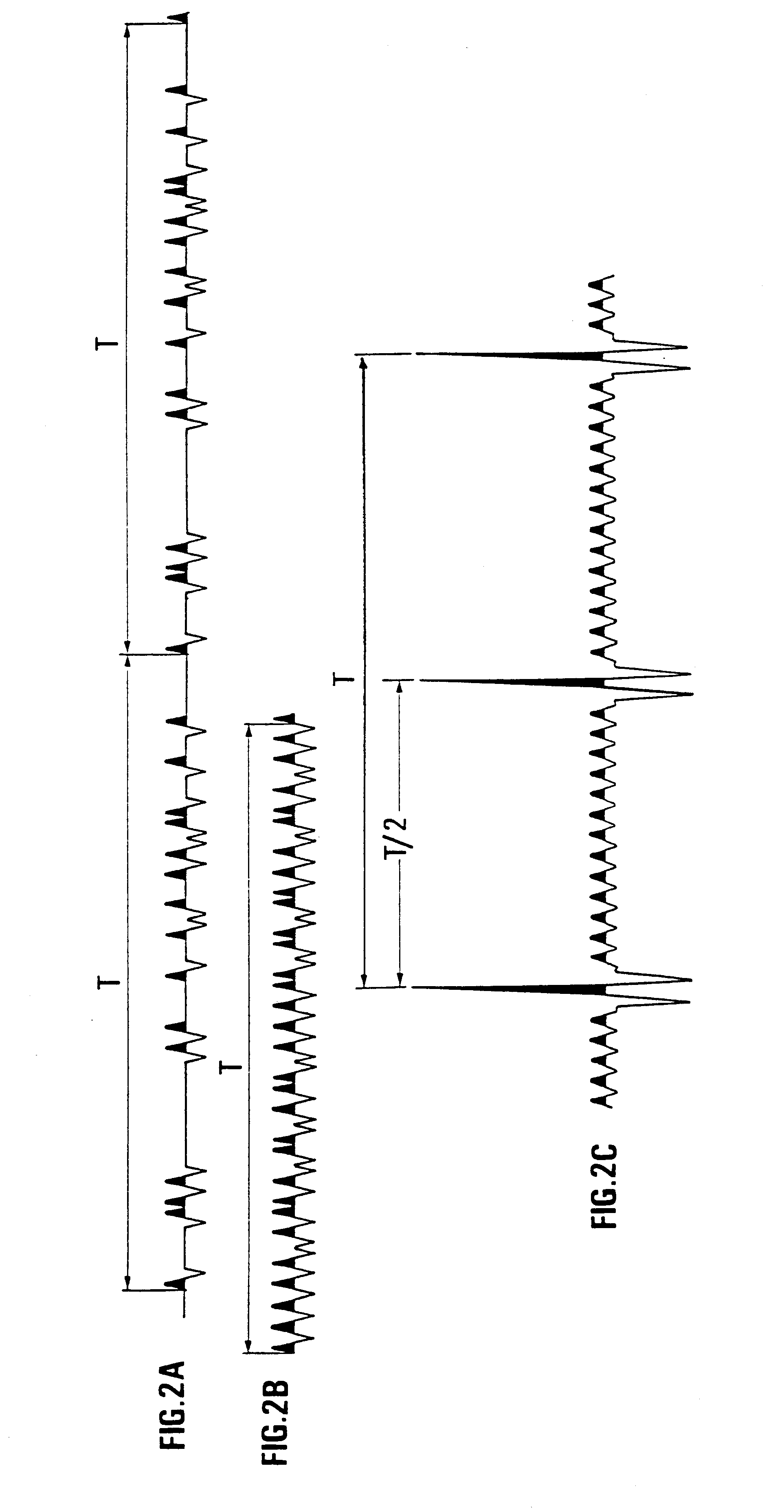
Seismic prospecting method and device using simultaneous emission of seismic signals obtained by coding a signal by pseudo-random sequences, and notably a periodic signal phase modulated by such sequences.Signals such as, for example, periodic signals phase modulated according to a pseudo-random code (binary for example), produced by a control unit, are for example emitted in the ground by means of vibrators, the seismic signals reflected by the subsoil discontinuities in response to the periodic signals emitted are picked up by receivers coupled with the formation and recorded in an acquisition and recording system. The periodic signals are emitted simultaneously by the vibrators. The control sequences of the coded periodic signals intended for all the vibrators are obtained either from the same random binary sequence with respective time lags evenly distributed over the length of the control sequence according to the number of vibrators used simultaneously (first mode), or from different sequences selected from among a group of sequences of minimum crosscorrelation (second mode), or by combining the two aforementioned modes. The respective contributions of the various vibrators are separated by correlating the signals received and recorded with signals constructed from the various control sequences obtained with time lags. The vibrators can be divided into several groups, the vibrators of each group being controlled by a binary sequence belonging to a minimum crosscorrelating group.Application: seismic prospecting or seismic monitoring of reservoirs for example.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
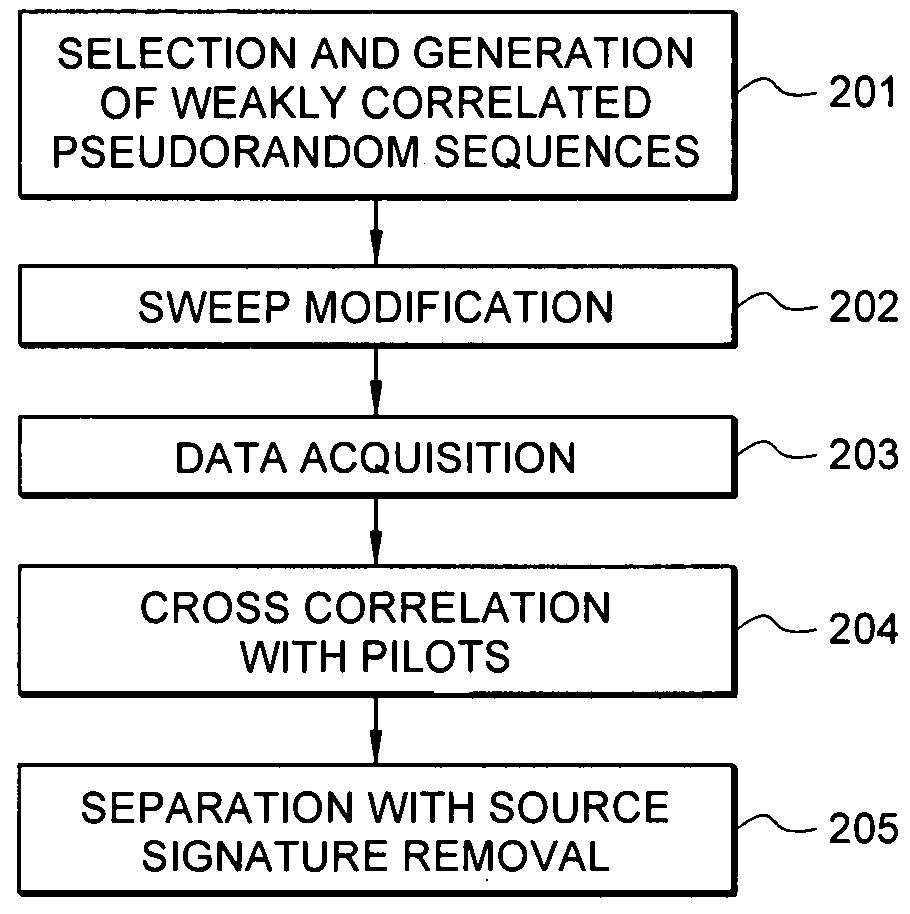
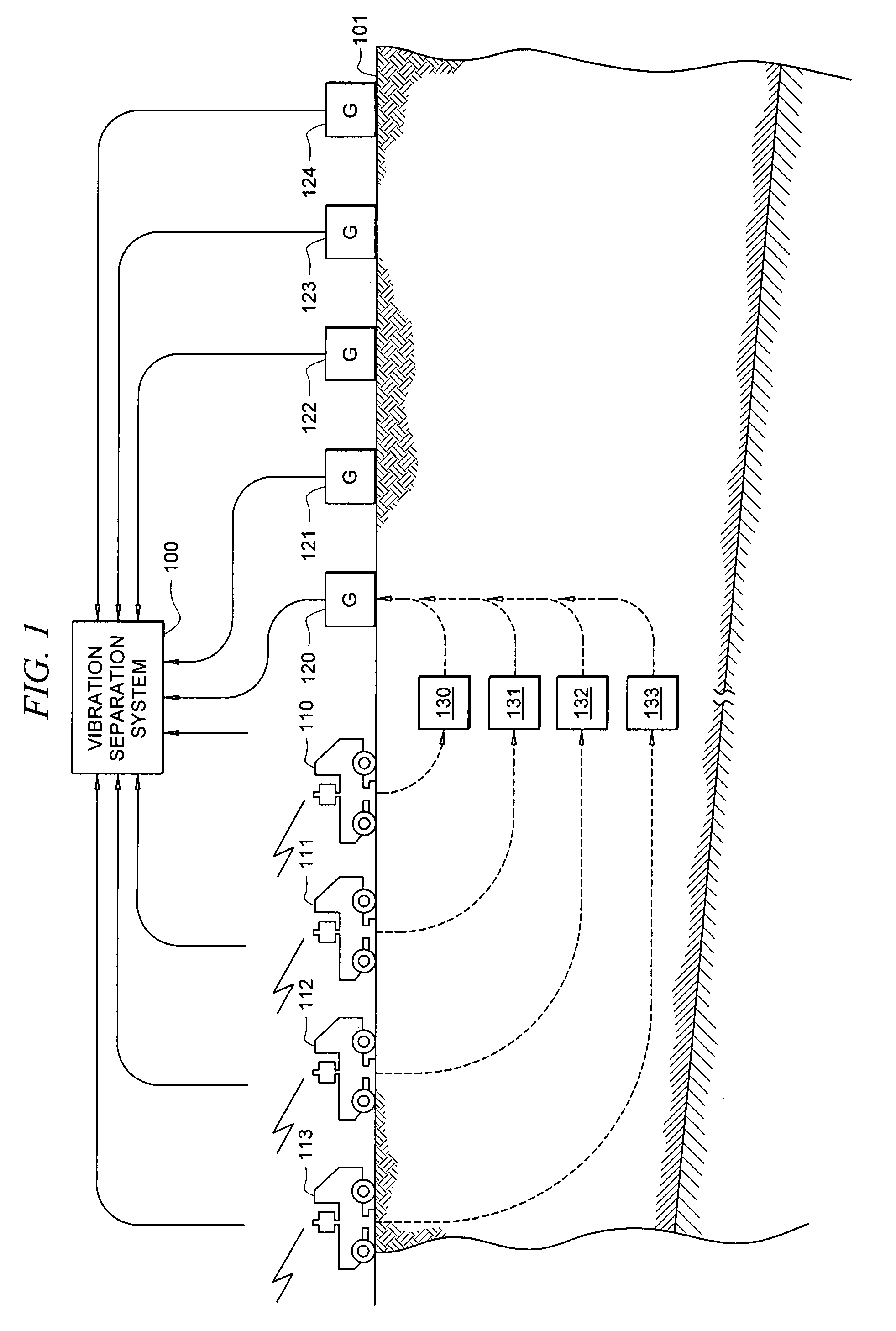
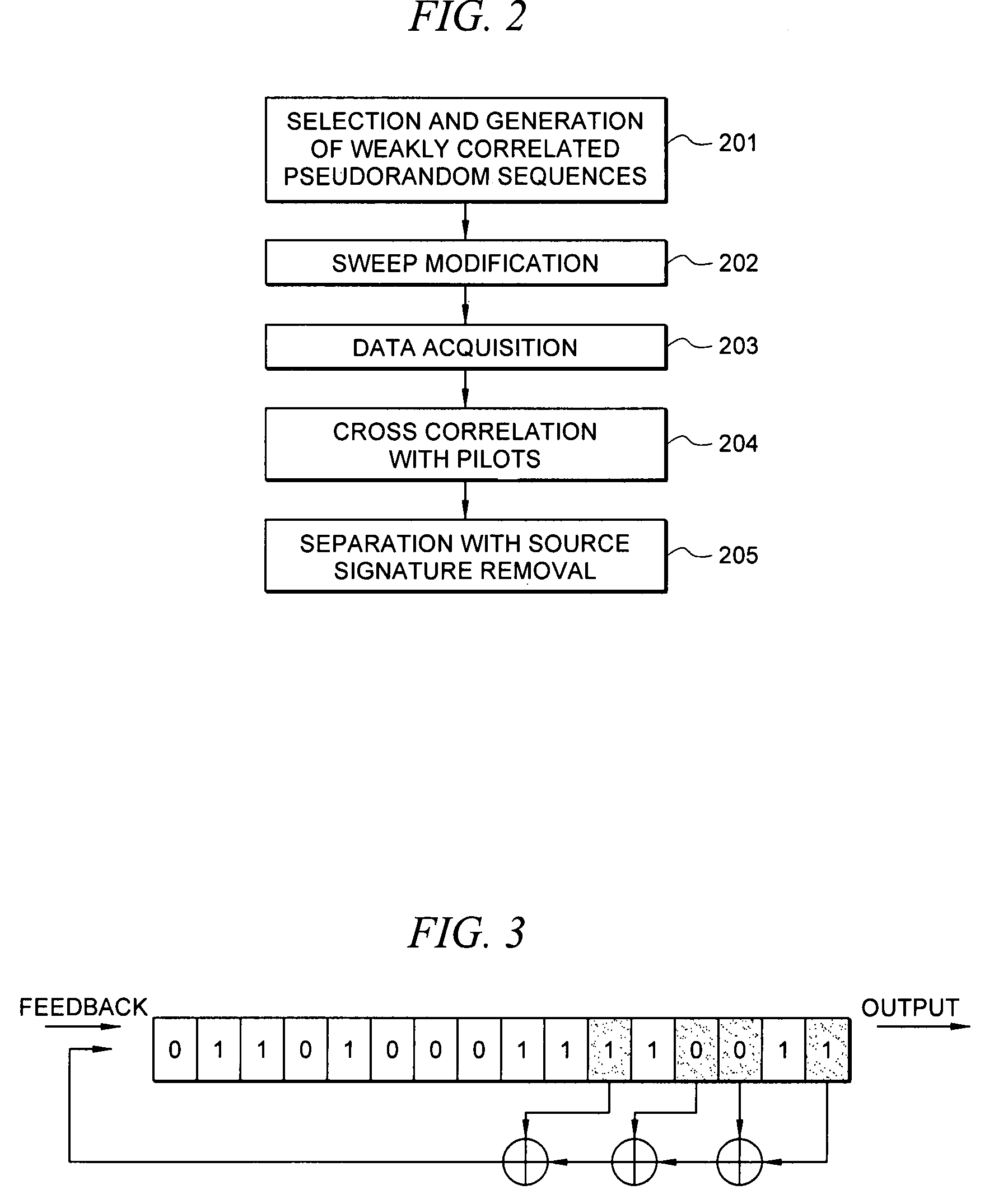
Efficient seismic data acquisition with source separation
ActiveUS20090010103A1Minimize crosstalkSeismic data acquisitionSeismic energy generationTime domainFrequency spectrum
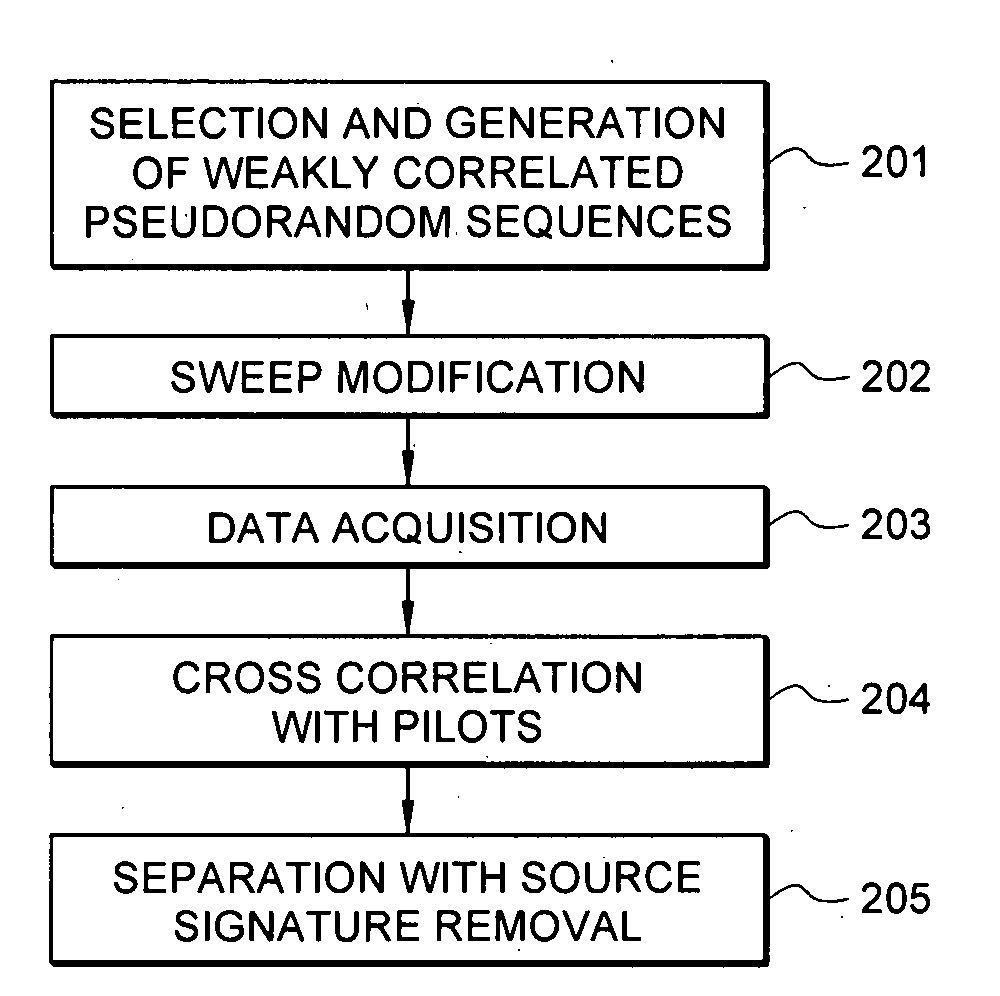
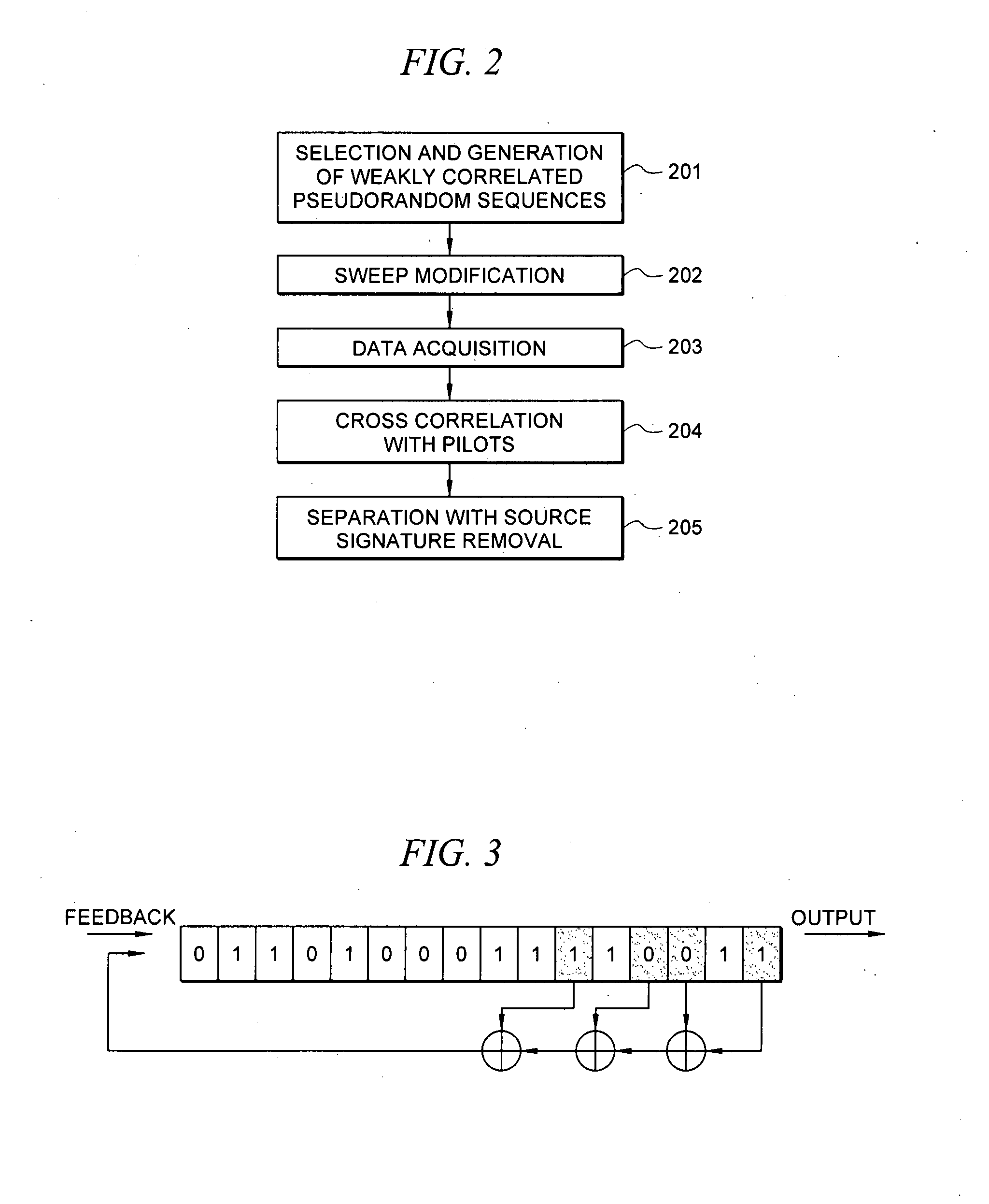
A method for the simultaneous operation of multiple seismic vibrators using unique modified pseudorandom sweeps and recovery of the transmission path response from each vibrator is disclosed. The vibrator sweeps are derived from pseudorandom binary sequences modified to be weakly correlated over a time window of interest, spectrally shaped and amplitude level compressed. Cross-correlation with each pilot signal is used to perform an initial separation of the composite received signal data set. Recordings of the motion of each vibrator are also cross-correlated with each pilot, windowed, and transformed to form a source cross-spectral density matrix in the frequency domain useful for source signature removal and for additional crosstalk-suppression between the separated records. After source signature removal in the frequency domain an inverse transform is applied to produce an estimate of each source-to-receiver earth response in the time domain. The method has application to both land and marine geophysical exploration.
Owner:SERCEL INC
Apparatus and method for imaging objects with wavefields
InactiveUS20070282200A1Vibration measurement in fluidMaterial analysis using microwave meansData setWave field
A transmission wave field imaging method, comprising the transmission of an incident wave field into an object, the incident wave field propagating into the object and, at least, partially scattering. Also includes the measuring of a wave field transmitted, at least in part, through an object to obtain a measured wave field, the measured wave field based, in part, on the incident wave field and the object. Additionally, the processing of the measured wave field utilizing a recursive reconstruction algorithm to generate an image data set representing at least one image of the object.
Owner:QT ULTRASOUND +1
Seismic acquisition method and system
ActiveUS20120147701A1Reduce impactReduce outputSeismic data acquisitionSeismic energy generationImaging qualityBiological activation
The maximum output of a seismic source array may be reduced by activating the individual seismic sources within these seismic source array in a pattern that is extended in time rather than by the presently employed conventional simultaneous activation of a large number of individual seismic sources. Methods are disclosed which take data shot with patterned sources and may use a sparse inversion method to create data with the about same image quality as that of conventional sources. In this manner the output of the maximum impulse of a seismic source array may be reduced by an amplitude factor of about 10 in the examples shown here, corresponding to a reduction of about 20 dB while maintaining virtually the same seismic image quality. The disclosed methods may be used in combination with any simultaneous sourcing technique. In addition, the disclosed methods may be used with a plurality of source arrays.
Owner:BP CORP NORTH AMERICA INC
Method for separating independent simultaneous sources
ActiveUS20100299070A1Easy accessEfficient collectionSeismic data acquisitionSeismic signal processingStart timeSeismic survey
Owner:BP CORP NORTH AMERICA INC
Construction and removal of scattered ground roll using interferometric methods
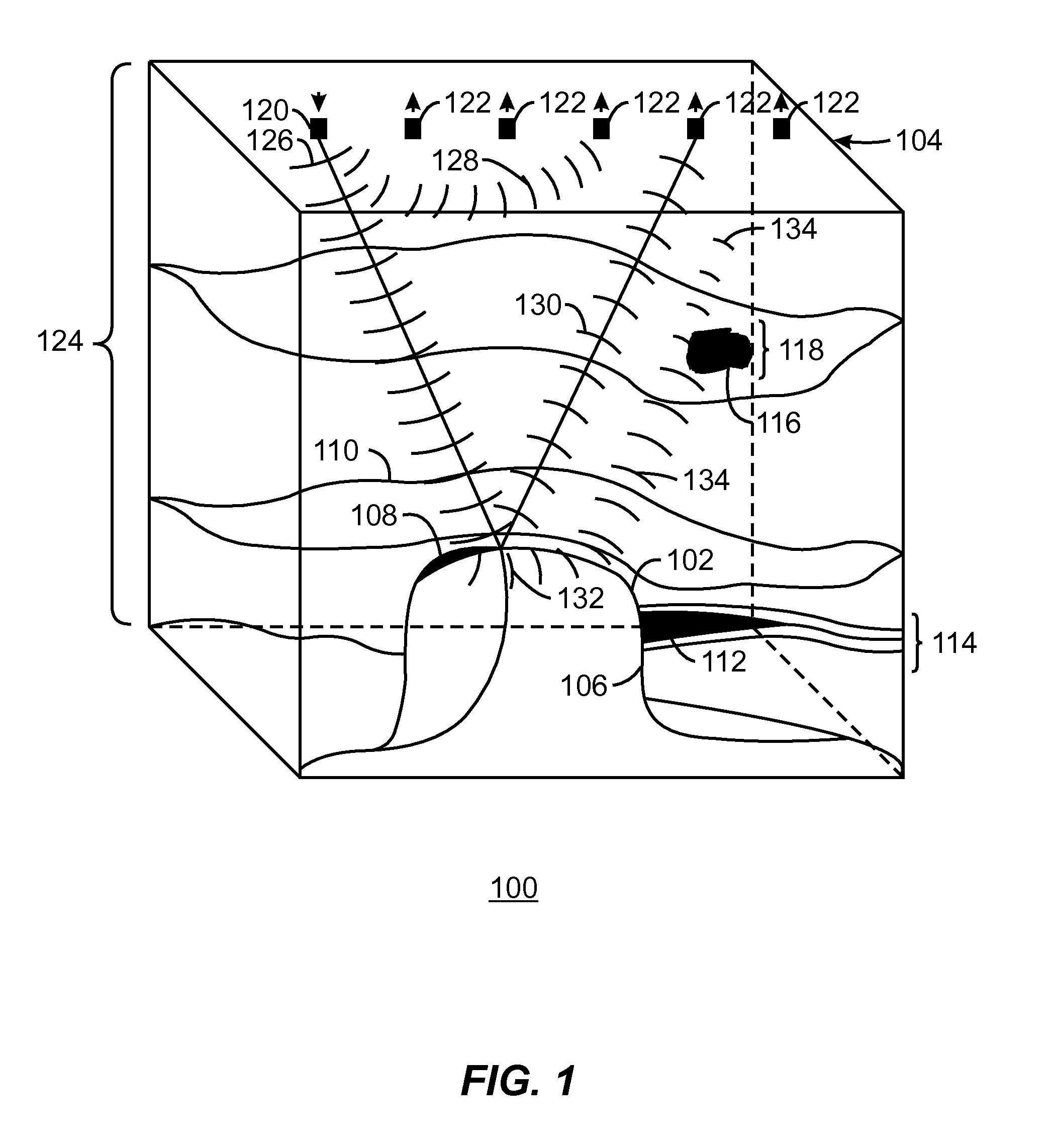
InactiveUS20070104028A1Interface is in effectSeismic data acquisitionSeismic signal processingData setWave field
A data set can be corrected for the effects of interface waves by interferometrically measuring an interface wavefield between each of a plurality of planned locations within a survey area; and correcting survey data acquired in the survey area for the interface waves. The interface wavefield may be interferometrically measured by receiving a wavefield including interface waves propagating within a survey area, the survey area including a plurality of planned survey locations therein; generating interface wave data representative of the received interface wavefield; and constructing a Green's function between each of the planned survey positions from the interface wave data. Other aspects include an apparatus by which the interface wavefield may be interferometrically measured and a computer apparatus programmed to correct the seismic data using the interferometrically measured interface wave data.
Owner:WESTERNGECO LLC
Distance- and frequency-separated swept-frequency seismic sources
InactiveUS20120147699A1Enhance simultaneous source separationEasy to separateSeismic data acquisitionSeismic signal recordingBandpass filteringFrequency separation
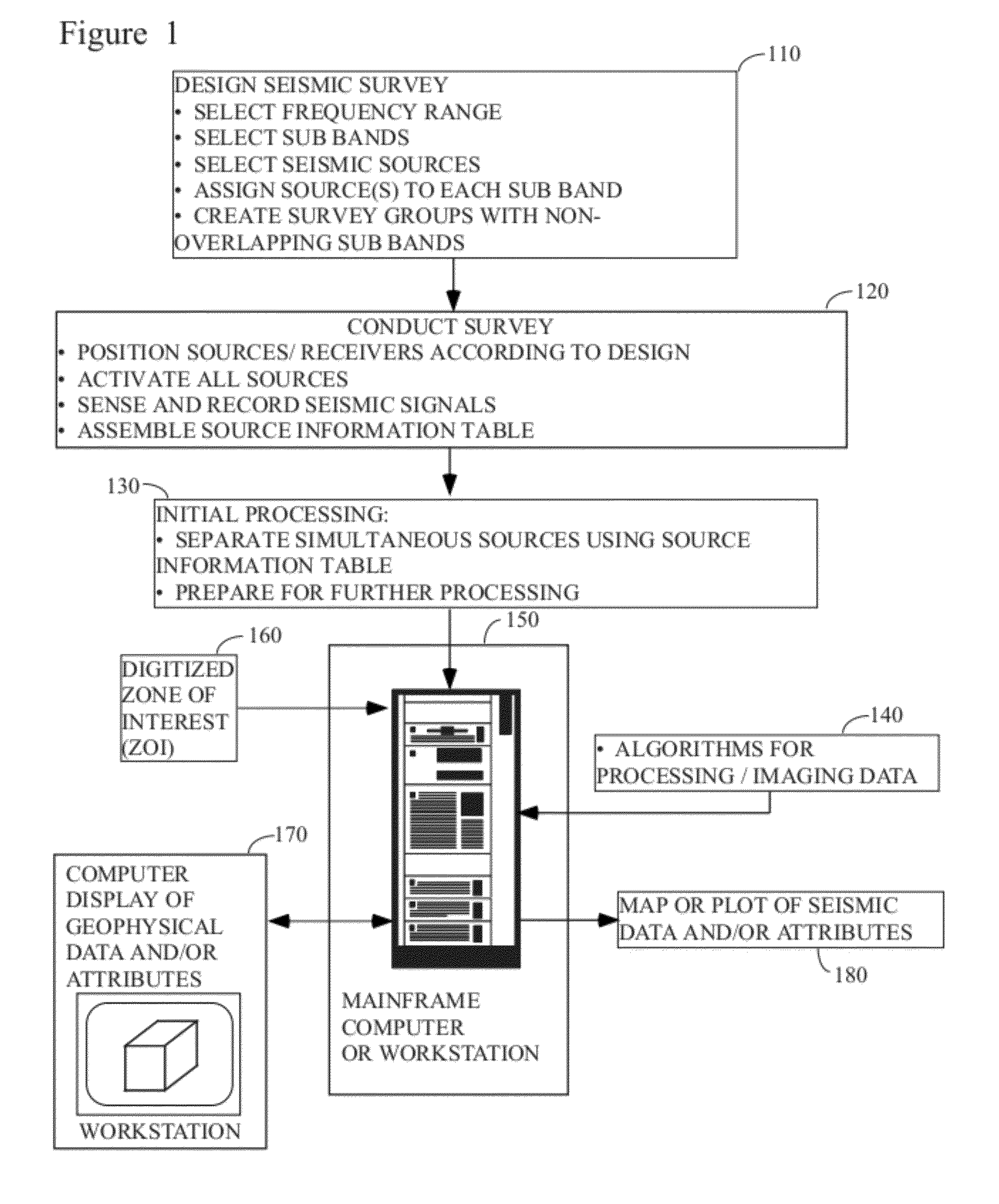
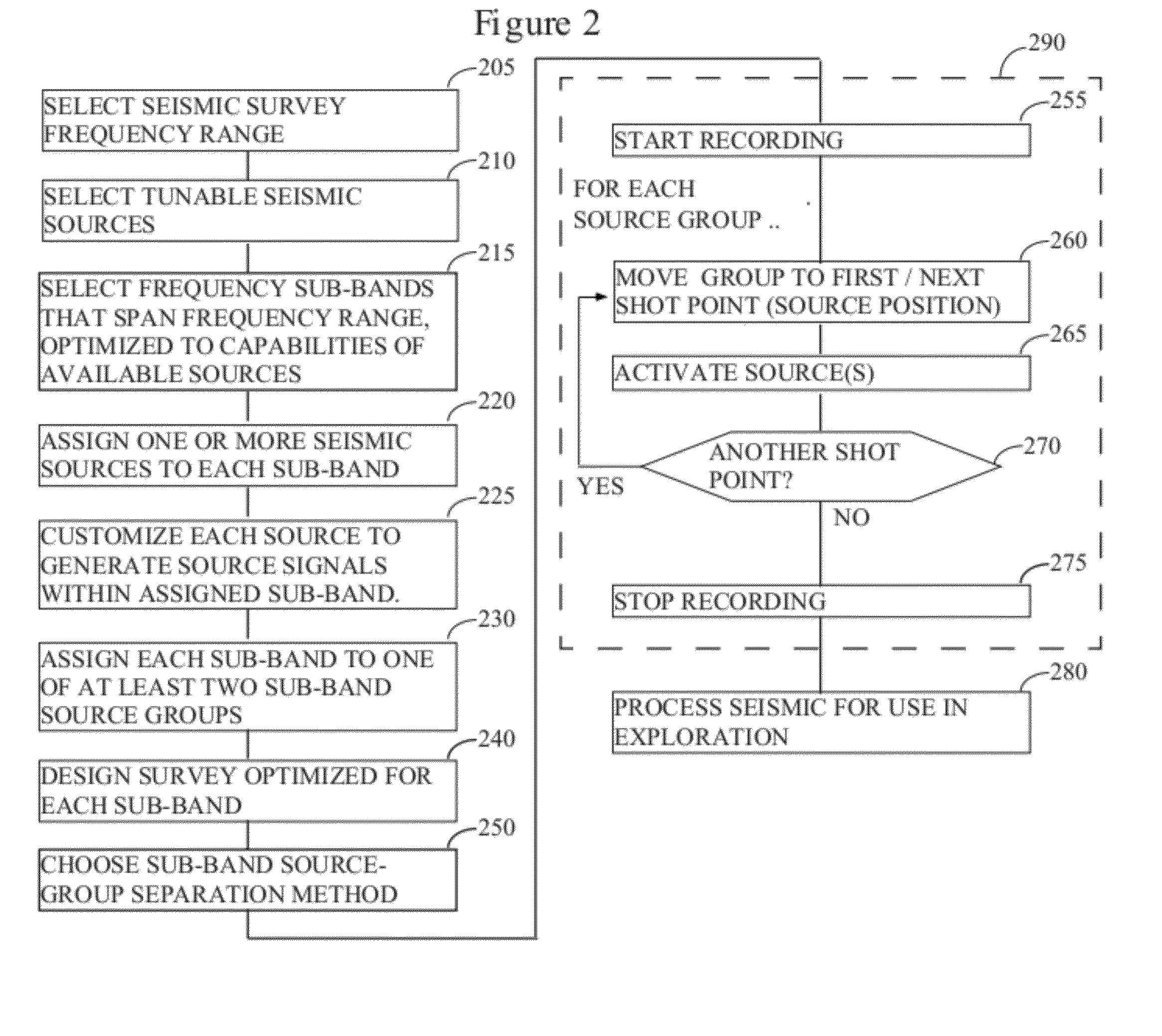
There is provided a method of seismic acquisition that utilizes a bank of restricted-bandwidth swept-frequency sub-band sources as a seismic source. Each seismic source will cover a restricted sub-band of frequencies, with all the sources taken together covering the full frequency range. Adjacent frequency bands may partially overlap, but non-adjacent frequency bands should not. The sources may be divided into two or more groups, with no sources covering adjacent frequency bands being placed in the same group. The sources within a group can then be separated by bandpass filtering or by conventional simultaneous source-separation techniques. The source groups may be operated simultaneously but separated in space, and the individual sources themselves may each operate independently, on a sweep schedule customized for that particular source.
Owner:BP CORP NORTH AMERICA INC
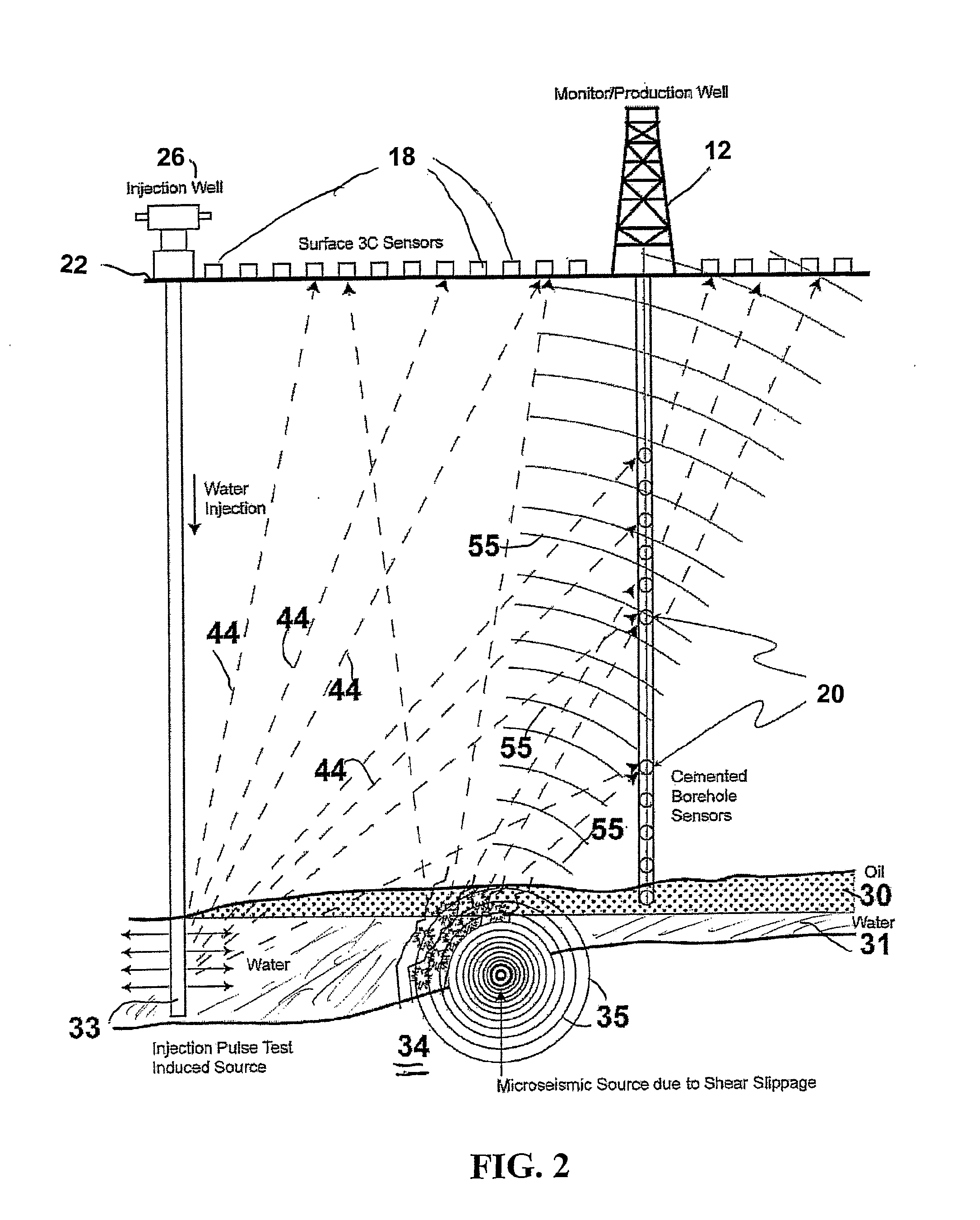
Continuous Reservoir Monitoring for Fluid Pathways Using Microseismic Data
InactiveUS20090299637A1Easy to manageOptimization StrategyElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSurveySeismic energyReservoir monitoring
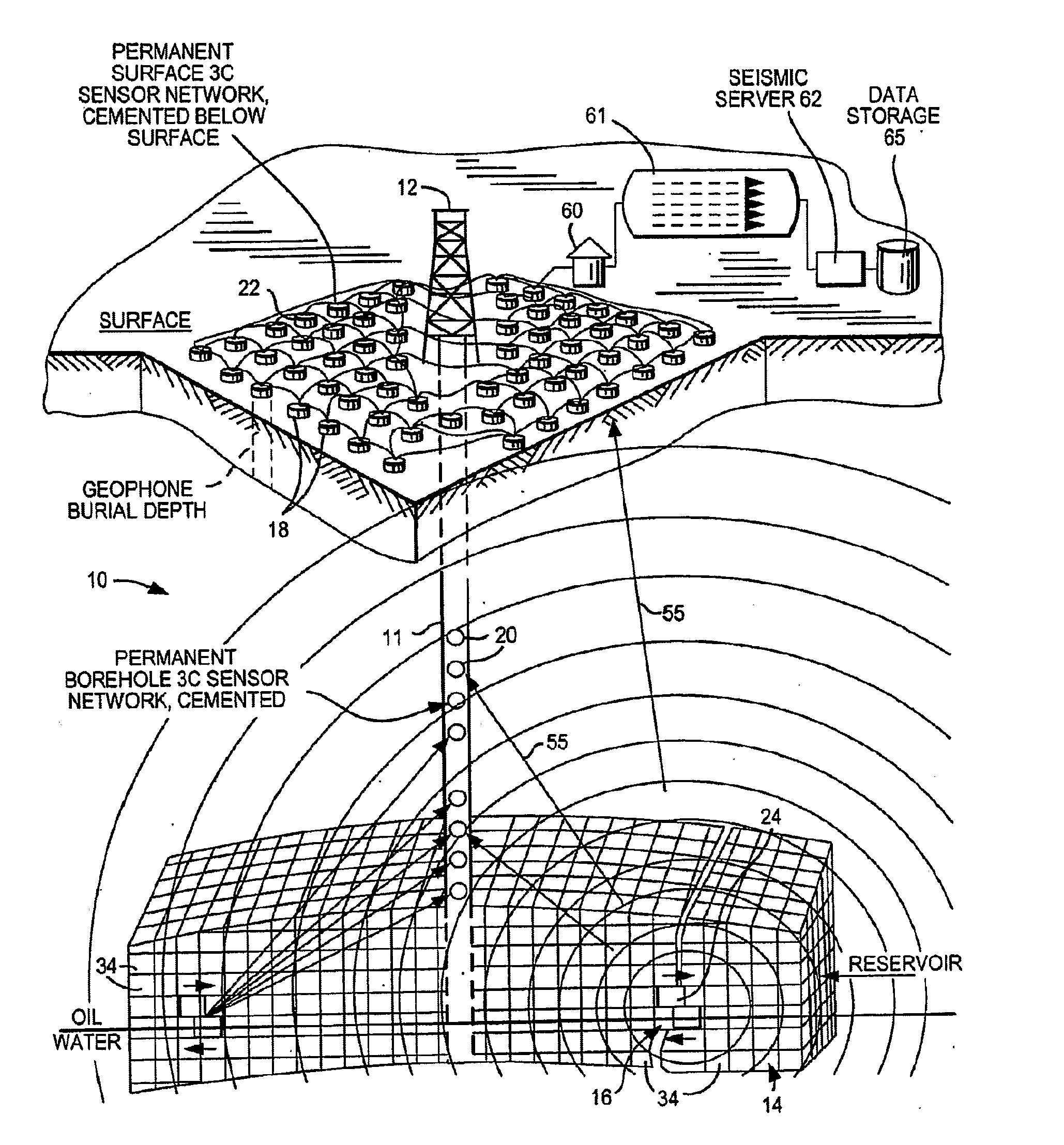
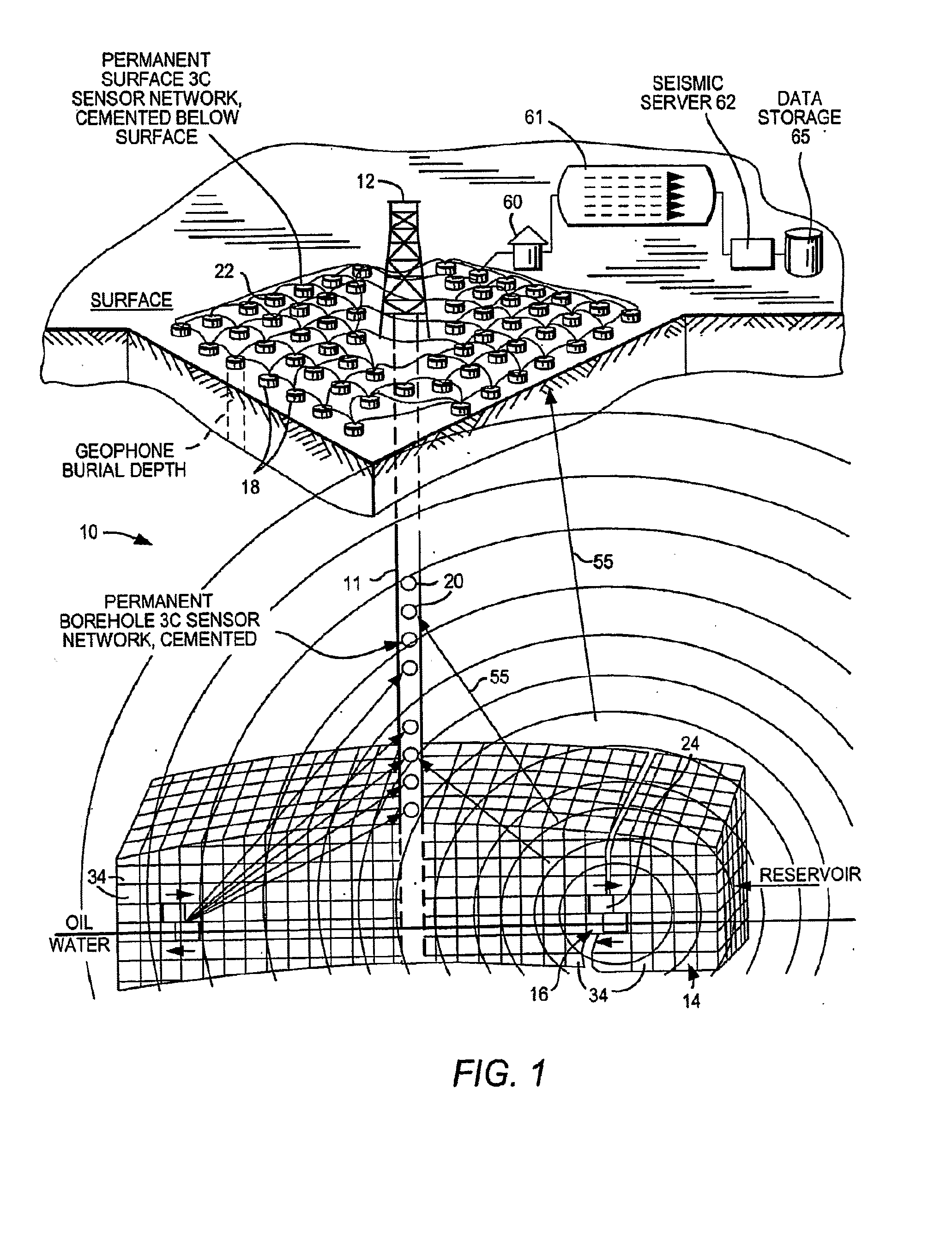
A system and method monitor a hydrocarbon reservoir for drainage in volumetric three dimensions. Monitoring between wells is imperative for optimum reservoir management and is achieved by mapping the hydrocarbon fluid pathways in a producing reservoir. Unlike conventional 4D or time-lapse reflection seismic imaging systems that use a controlled active seismic source and records reflected seismic energy at receivers, the system and method exploit the minute vibrations, or micro-earthquakes generated in the reservoir layers that are induced by fluid movement. These microseisms are detected as the fluids move in the reservoir.
Owner:SAUDI ARABIAN OIL CO
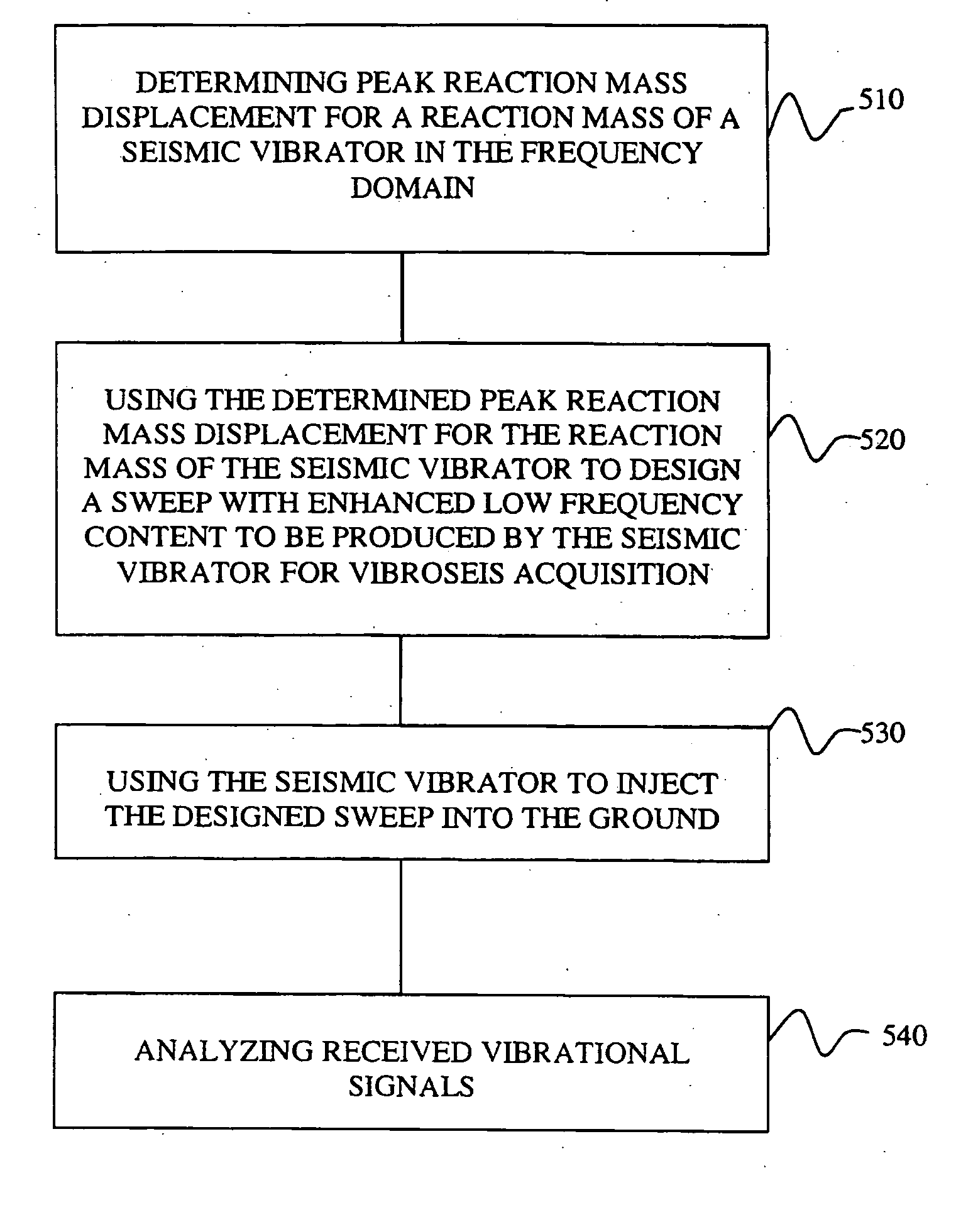
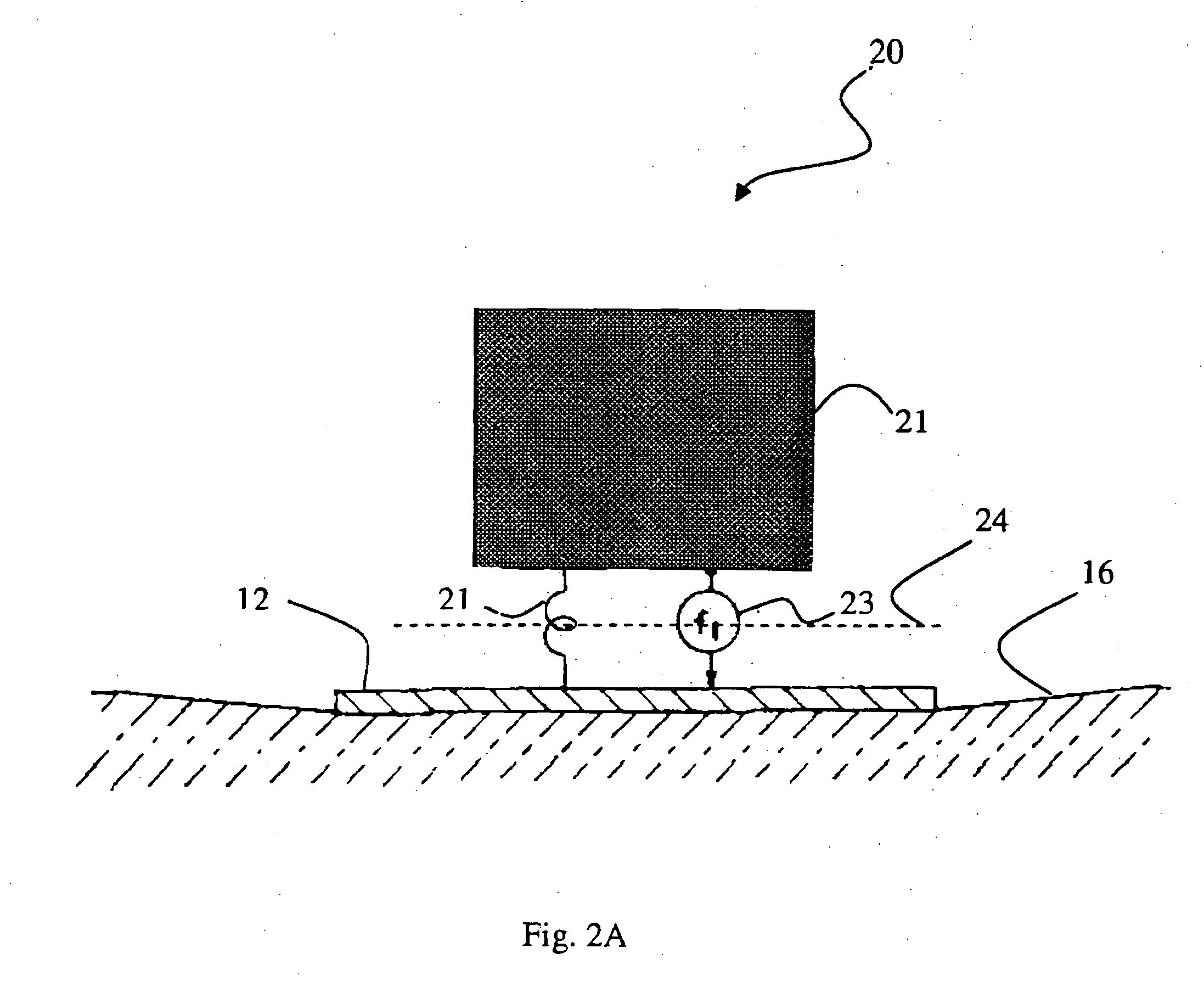
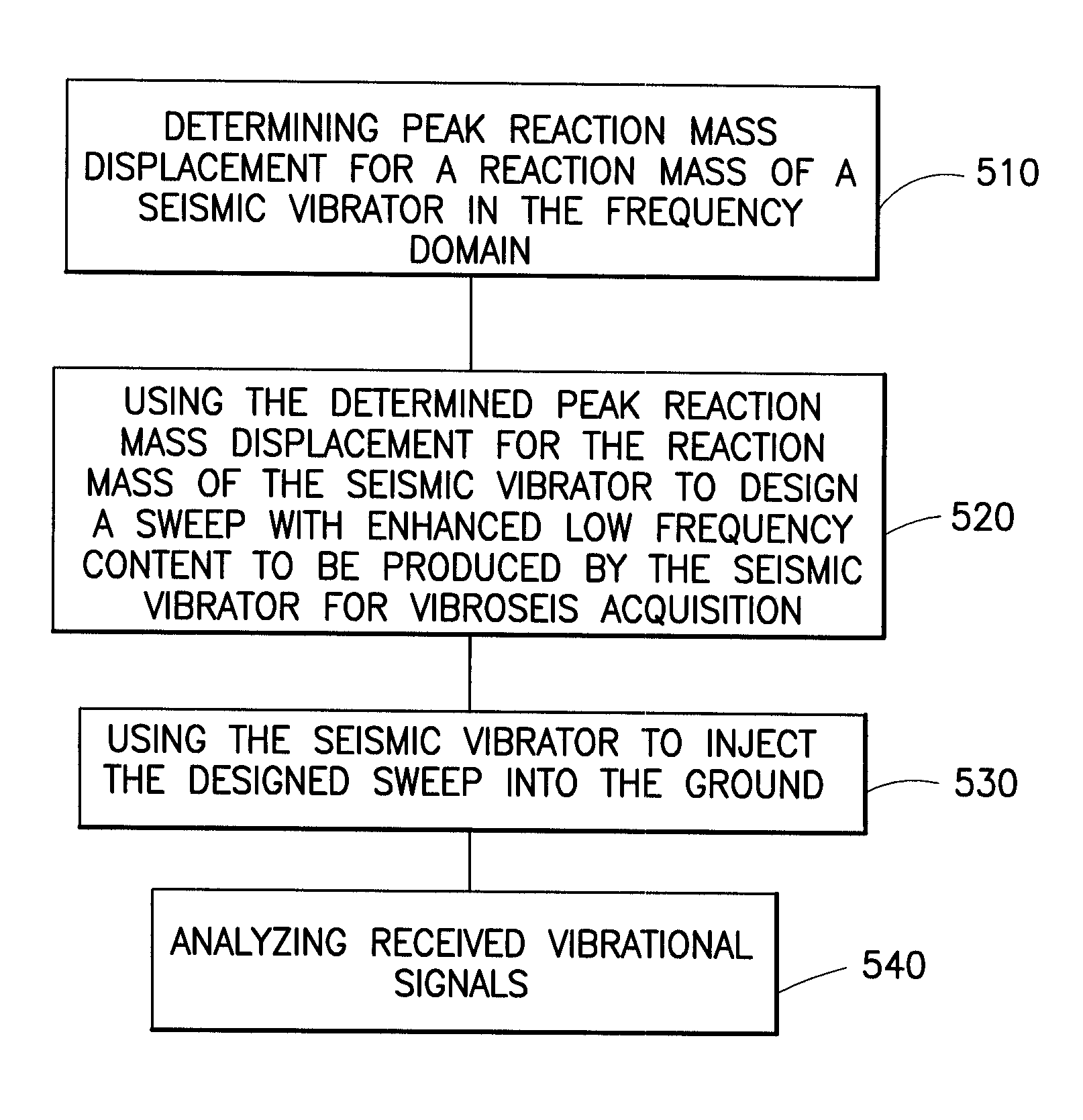
Systems and methods for enhancing low-frequency content in vibroseis acquisition
ActiveUS20070133354A1Enhanced/optimized amplitudeImprove errorSeismic data acquisitionSeismic signal processingEngineeringUltimate tensile strength
This invention relates in general to vibroseis and, more specifically, but not by way of limitation, to the enhancement and / or signal strength optimization of low frequency content of seismic signals for use in surveying boreholes and / or subsurface earth formations. In embodiments of the present invention, physical properties of a seismic vibrator may be analyzed and used to provide for determination of a driving force necessary to drive a reaction mass to produce a sweep signal with enhanced low frequency content for injection into the ground for vibroseis. In certain aspects, the physical properties may be considered independent of any geophysical properties related to operation of the seismic vibrator.
Owner:WESTERNGECO LLC
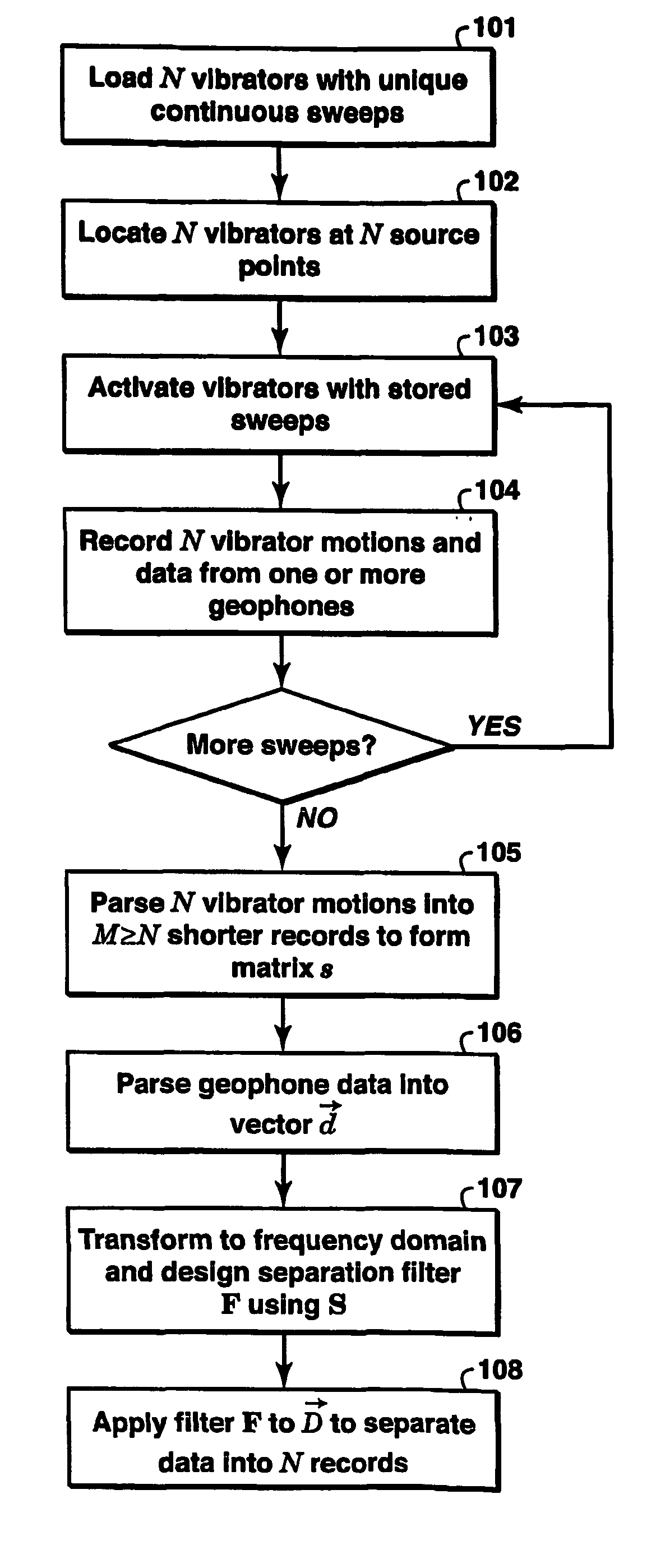
Method for continuous sweepting and separtion of multiple seismic vibrators
InactiveUS20060164916A1Reduce harmonic noiseReduce noiseSeismic data acquisitionSeismic signal processingContinuous scanningFourier transform on finite groups
A method for simultaneously operating multiple seismic vibrators using continuous sweeps (little or no “listening” time between sweeps) for each vibrator, and recovering the separated seismic responses for each vibrator with the earth signature removed. Each vibrator is given a unique, continuous pilot signal. The earth response to the motion of each vibrator is measured or estimated. The vibrator motion records for each vibrator and the combined seismic data record for all the vibrators are parsed into separate shorter records. The shorter records are then used to form a system of simultaneous linear equations in the Fourier transform domain, following the HFVS method of Sallas and Allen. The equations are then solved for the separated earth responses.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL UPSTREAM RES CO
Efficient seismic data acquisition with source separation
A method for the simultaneous operation of multiple seismic vibrators using unique modified pseudorandom sweeps and recovery of the transmission path response from each vibrator is disclosed. The vibrator sweeps are derived from pseudorandom binary sequences modified to be weakly correlated over a time window of interest, spectrally shaped and amplitude level compressed. Cross-correlation with each pilot signal is used to perform an initial separation of the composite received signal data set. Recordings of the motion of each vibrator are also cross-correlated with each pilot, windowed, and transformed to form a source cross-spectral density matrix in the frequency domain useful for source signature removal and for additional crosstalk-suppression between the separated records. After source signature removal in the frequency domain an inverse transform is applied to produce an estimate of each source-to-receiver earth response in the time domain. The method has application to both land and marine geophysical exploration.
Owner:SERCEL INC
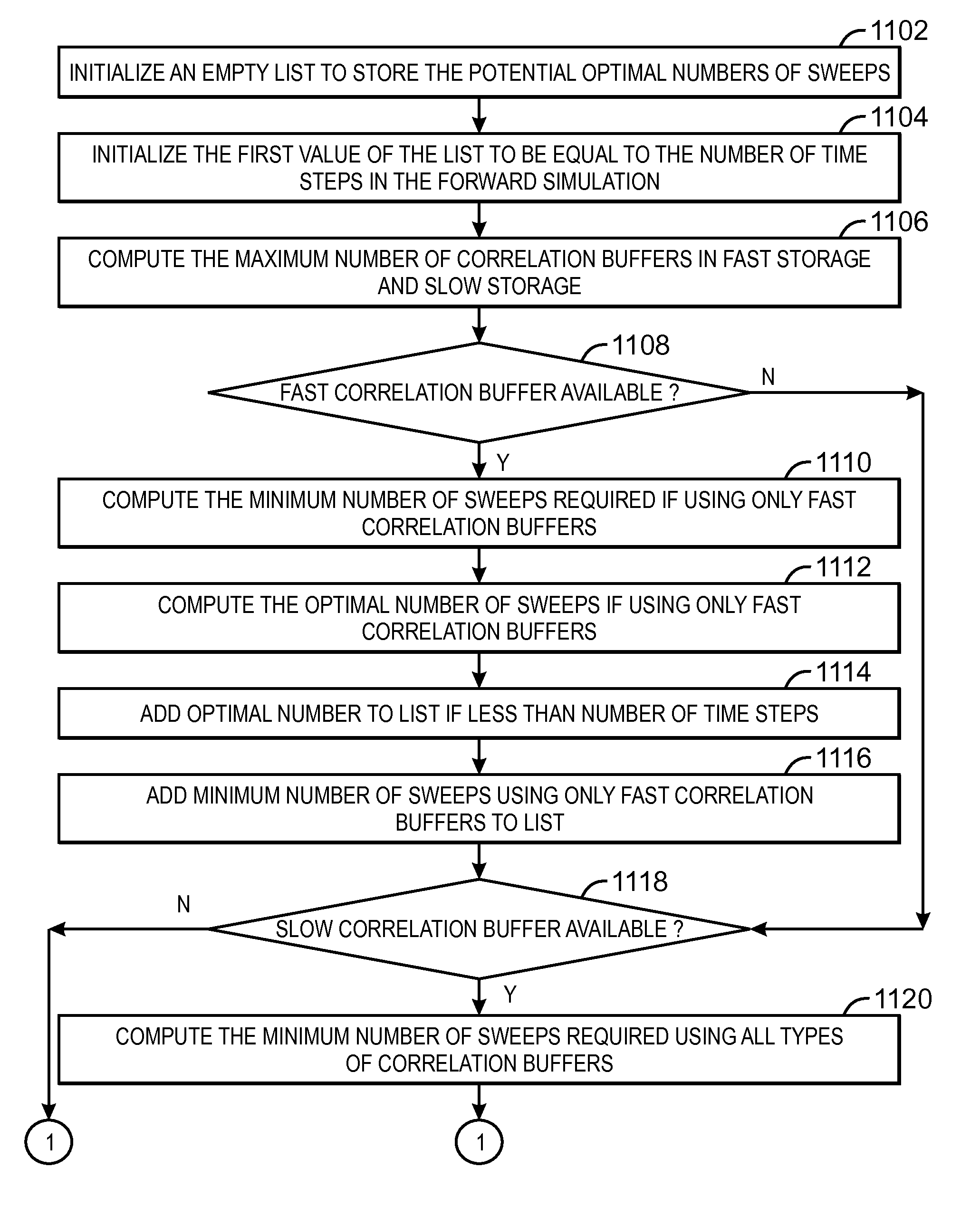
Method and system for checkpointing during simulations
ActiveUS20110288831A1Reduce computing costMinimal costAcoustic presence detectionSeismic data acquisitionParallel computingComputer memory
Method and system for more efficient checkpointing strategy in cross correlating (316) a forward (328) and backward (308) propagated wave such as in migrating (326) or inverting seismic data. The checkpointing strategy includes storing in memory forward simulation data at a checkpointed time step, wherein the stored data are sufficient to do a cross correlation at that time step but not to restart the forward simulation. At other checkpoints, a greater amount of data sufficient to restart the simulation may be stored in memory (314). Methods are disclosed for finding an optimal combination, i.e. one that minimizes computation time (1132), of the two types of checkpoints for a given amount of computer memory (1004), and for locating a checkpoint at an optimal time step (306, 1214, 1310). The optimal checkpointing strategy (1002) also may optimize (1408) on use of fast (1402) vs. slow (1404) storage.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL UPSTREAM RES CO
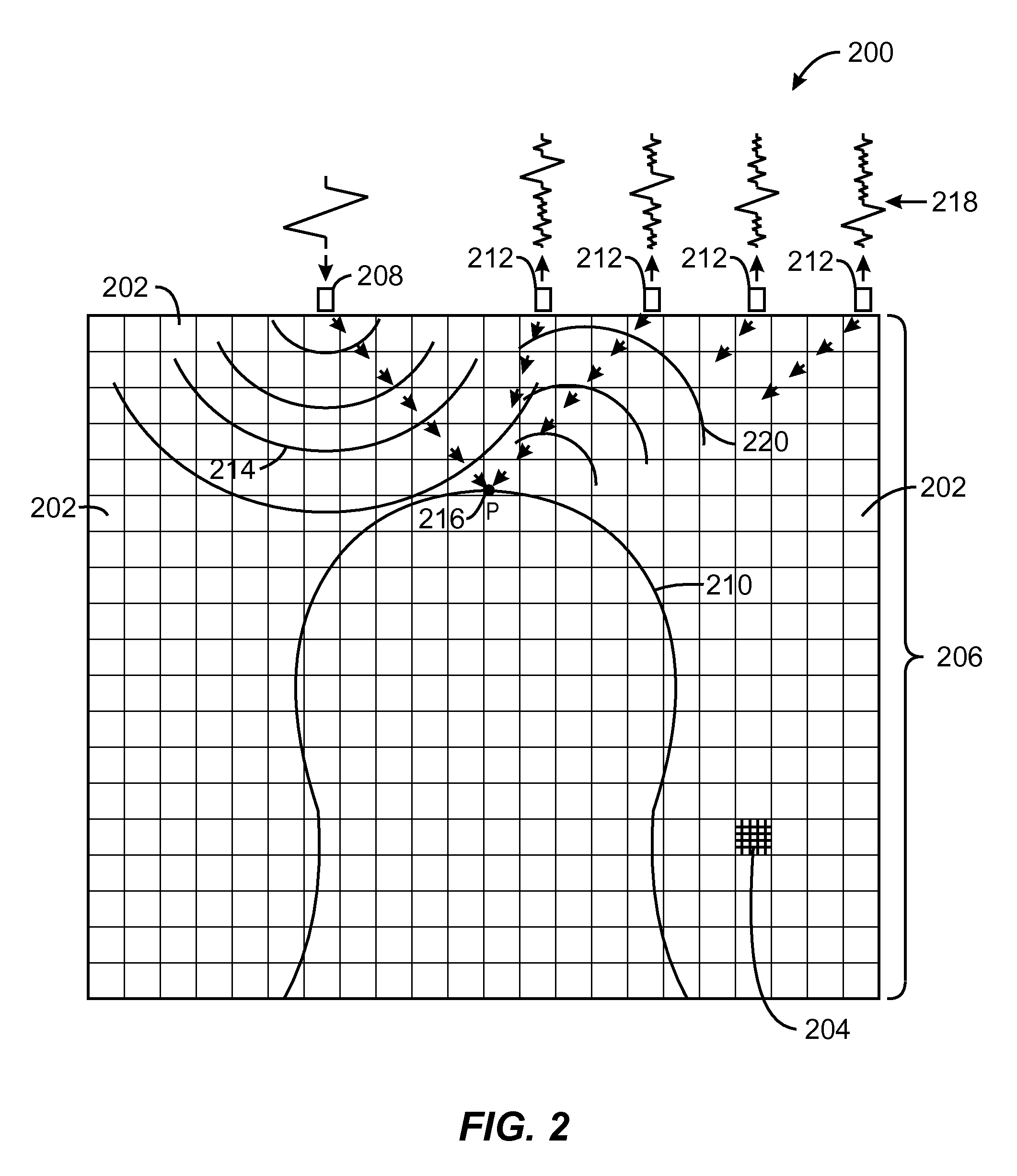
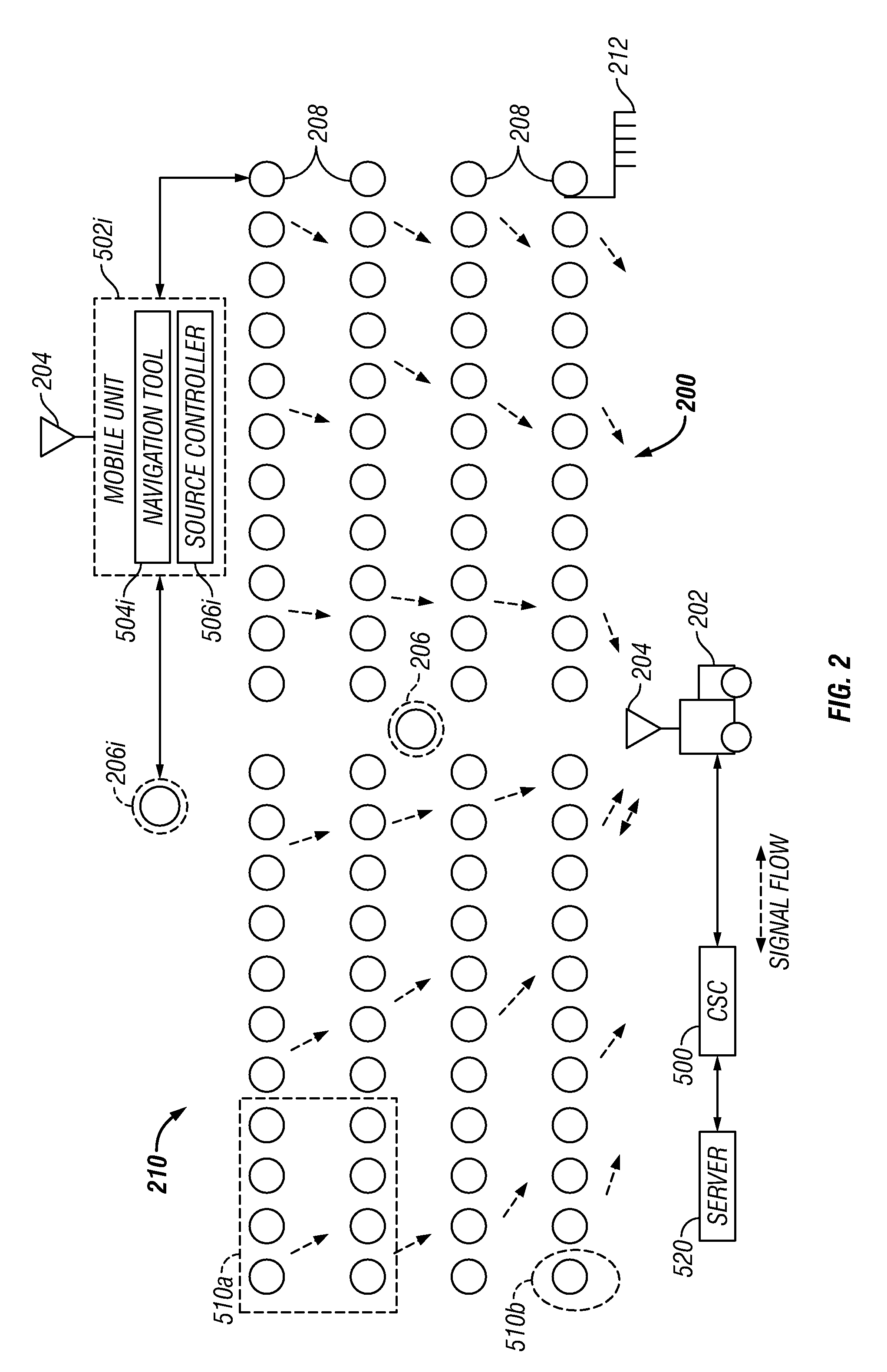
One Touch Data Acquisition
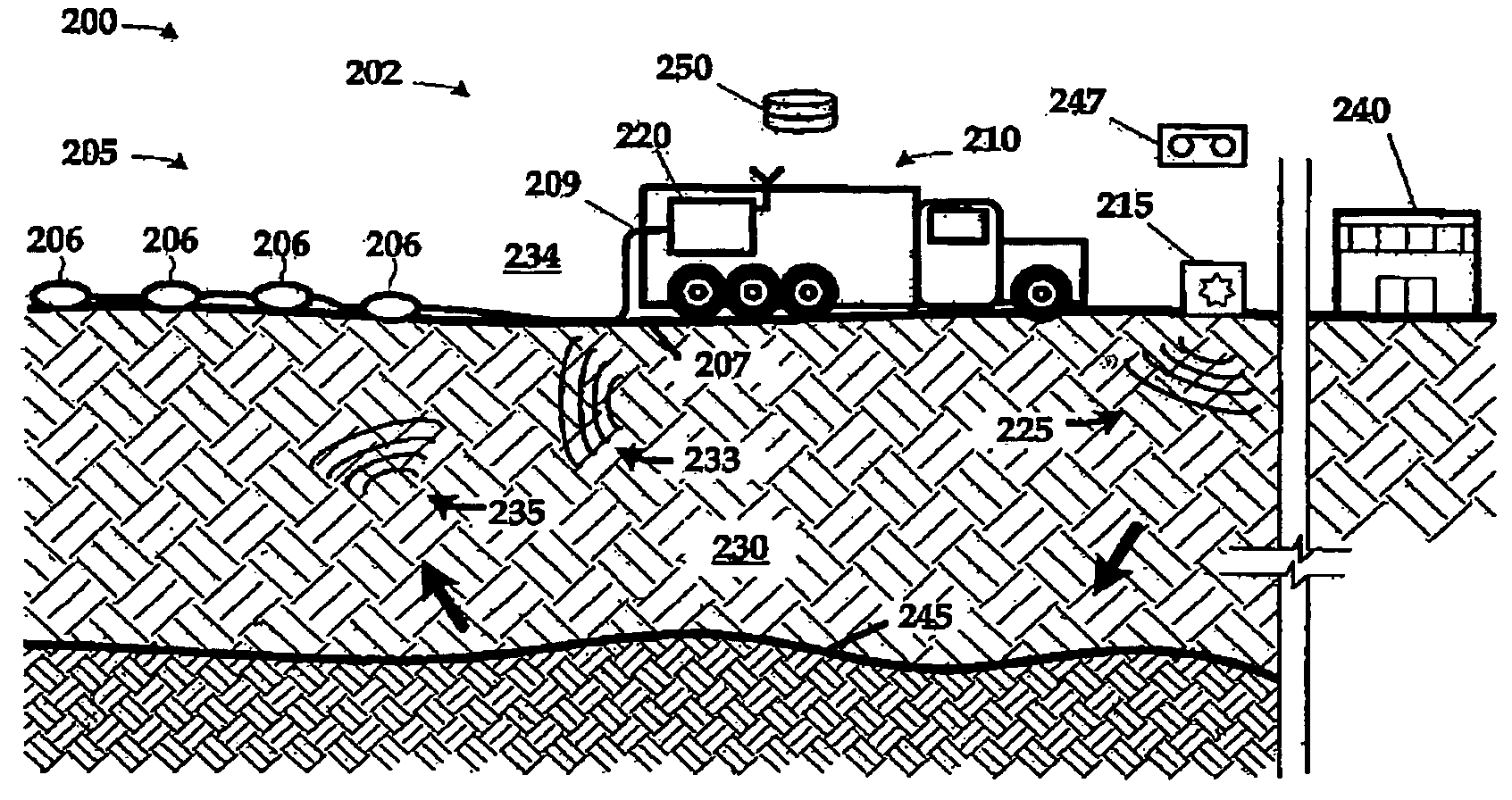
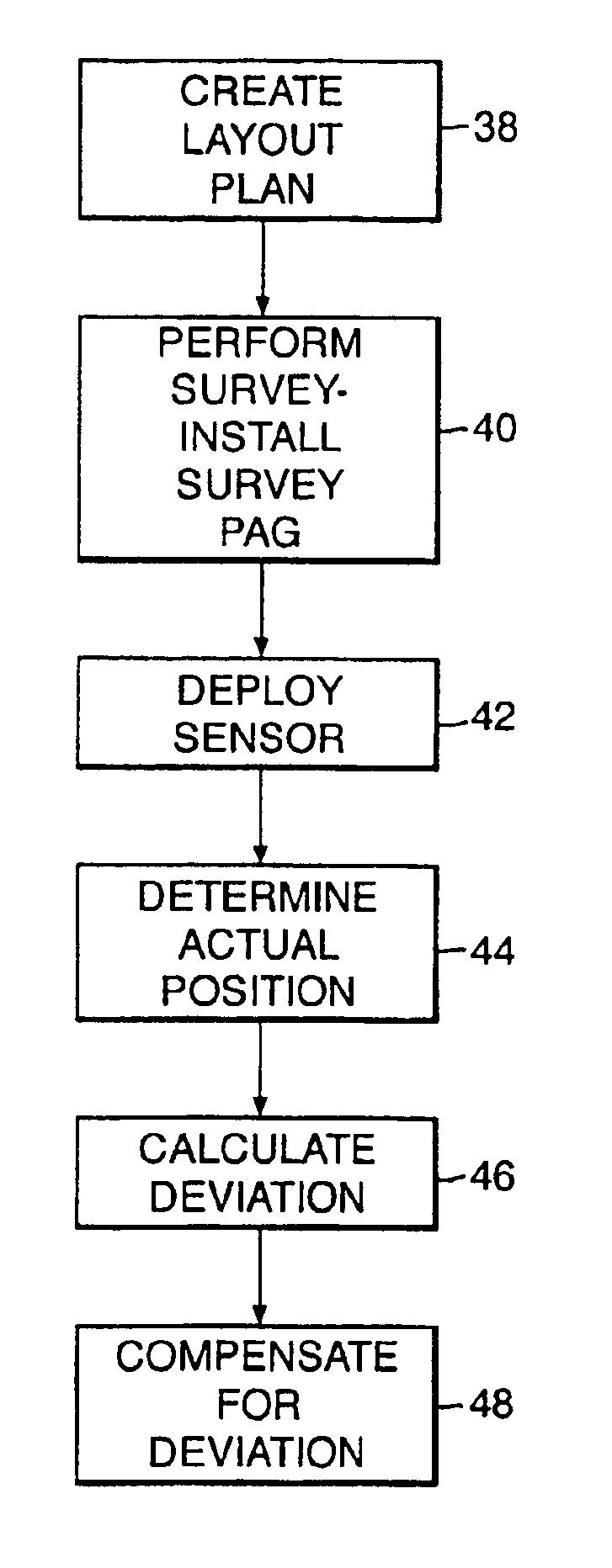
A seismic spread has a plurality of seismic stations positioned over a terrain of interest and a controller programmed to automate the data acquisition activity. In one aspect, the present disclosure provides a method for forming a seismic spread by developing a preliminary map of suggested locations for seismic devices and later forming a final map having in-field determined location data for the seismic devices. Each suggested location is represented by a virtual flag used to navigate to each suggested location. A seismic device is placed at each suggested location and the precise location of the each placed seismic devices is determined by a navigation device. The determined locations are used to form a second map based on the determined location of the one or more of the placed seismic devices. Using the virtual flag eliminates having to survey the terrain and place physical markers and later remove those physical markers. It is emphasized that this abstract is provided to comply with the rules requiring an abstract which will allow a searcher or other reader to quickly ascertain the subject matter of the technical disclosure. It is submitted with the understanding that it will not be used to interpret or limit the scope or meaning of the claims. (37 CFR 1.72(b)
Owner:INOVA
Method for optimizing energy output of from a seismic vibrator array
InactiveUS20100118647A1Seismic data acquisitionSeismology for water-covered areasSeismic energySeismic vibrator
A method for generating seismic energy for subsurface surveying includes operating a first seismic vibrator and operating at least a second seismic vibrator in a body of water substantially contemporaneously with the operating the first seismic vibrator. Each vibrator has a different selected frequency response, and the vibrators each are operated at a depth in the water such that a surface ghost amplifies a downward output of each vibrator within a selected frequency range. A signal used to drive each vibrator has a frequency range corresponding to the frequency range of each vibrator.
Owner:PGS GEOPHYSICAL AS
Hydraulic impulse generator and frequency sweep mechanism for borehole applications
ActiveUS20050178558A1Travel can be limitedEliminate water hammer effectSurveyOperating means/releasing devices for valvesGeophoneSeismic velocity
This invention discloses a valve that generates a hydraulic negative pressure pulse and a frequency modulator for the creation of a powerful, broadband swept impulse seismic signal at the drill bit during drilling operations. The signal can be received at monitoring points on the surface or underground locations using geophones. The time required for the seismic signal to travel from the source to the receiver directly and via reflections is used to calculate seismic velocity and other formation properties near the source and between the source and receiver. This information can be used for vertical seismic profiling of formations drilled, to check the location of the bit, or to detect the presence of abnormal pore pressure ahead of the bit. The hydraulic negative pressure pulse can also be used to enhance drilling and production of wells.
Owner:WELLS FARGO BANK NAT ASSOC +1
Data offload and charging systems and methods
InactiveUS20050246137A1Batteries circuit arrangementsError detection/correctionTelecommunications linkData acquisition
Apparatus and methods are provided for simultaneously retrieving data from multiple data acquisition units and for recharging such data acquisition units. The data offload and charging unit comprises a frame that defines stations for holding the data acquisition units and a host computer. A combined power and communications port at each such station is adapted to interface with one of the data acquisition units such that power may flow from the data offload and charger unit to that data acquisition unit and data may flow from that data acquisition unit to the host computer substantially simultaneously. Communications links are provided between the host computer and each combined power and communications port.
Owner:ASCEND GEO
Method and system for transmission of seismic data
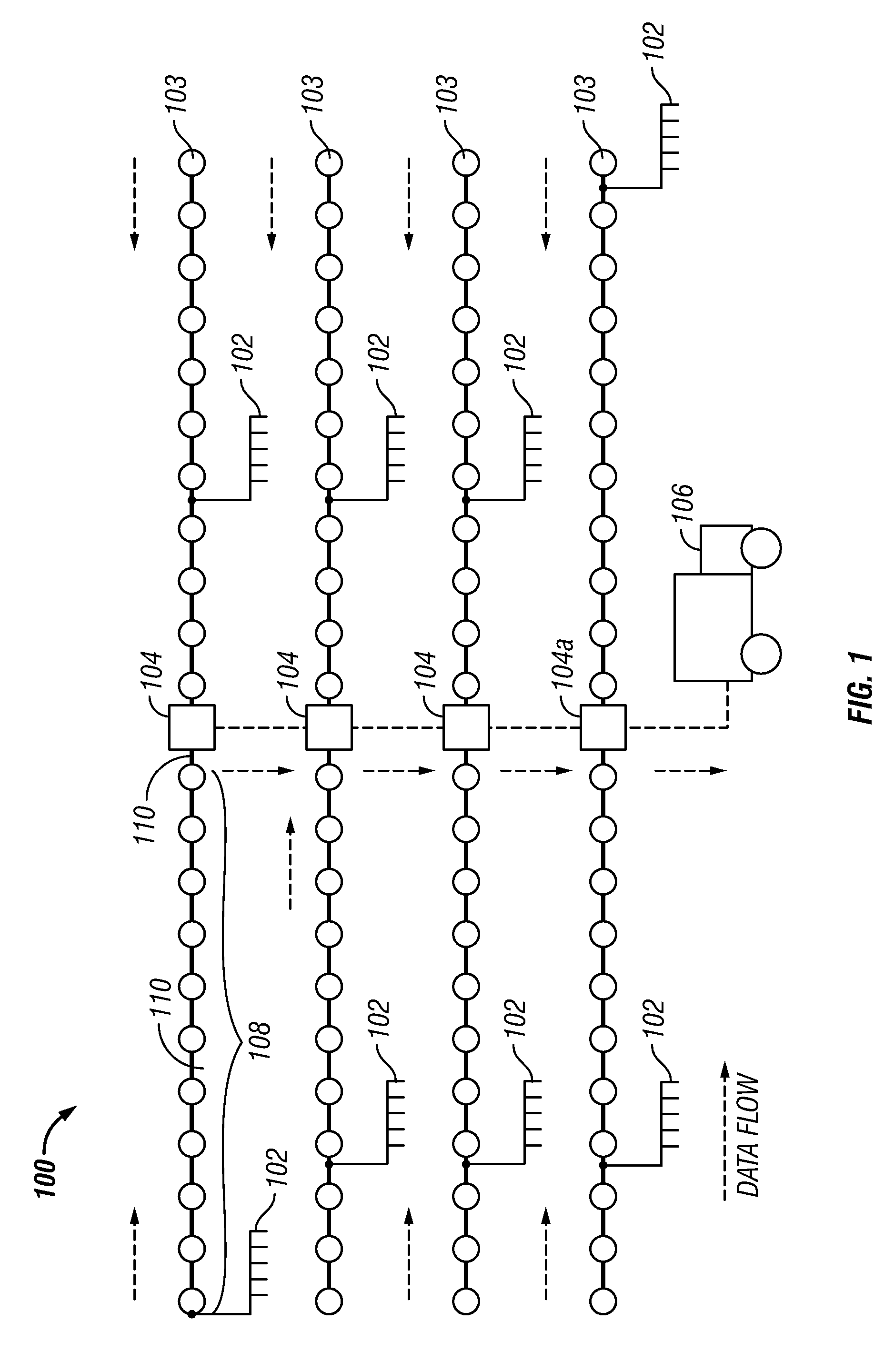
ActiveUS20050114033A1Reduce in quantityLess powerSeismic data acquisitionSeismic signal transmissionRadio receiverTransmitter
The transmission method utilizes multiple seismic acquisition units within an array as intermediate short range radio receivers / transmitters to pass collected seismic data in relay fashion back to a control station. Any one seismic unit in the array is capable of transmitting radio signals to several other seismic units positioned within radio range of the transmitting unit, thus allowing the system to select an optimal transmission path. Utilizing an array of seismic units permits transmission routes back to a control station to be varied as needed. In transmissions from the most remote seismic unit to the control station, each unit within a string receives seismic data from other units and transmits the received seismic data along with the receiving unit's locally stored seismic data. Preferably, as a transmission is passed along a chain, it is bounced between seismic units so as to be relayed by each unit in the array.
Owner:MAGSEIS FF LLC
Seismic data acquisition method and apparatus
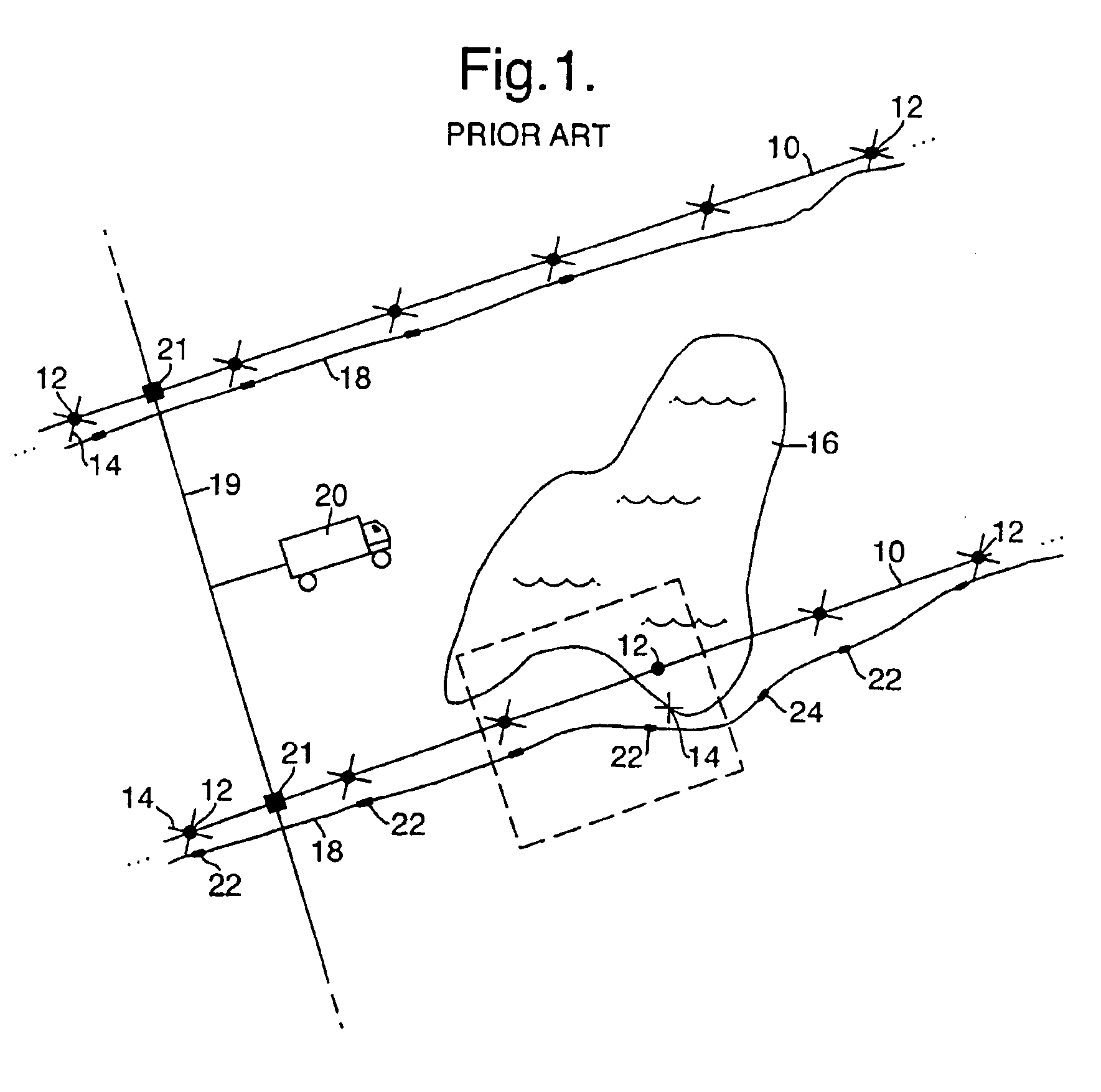
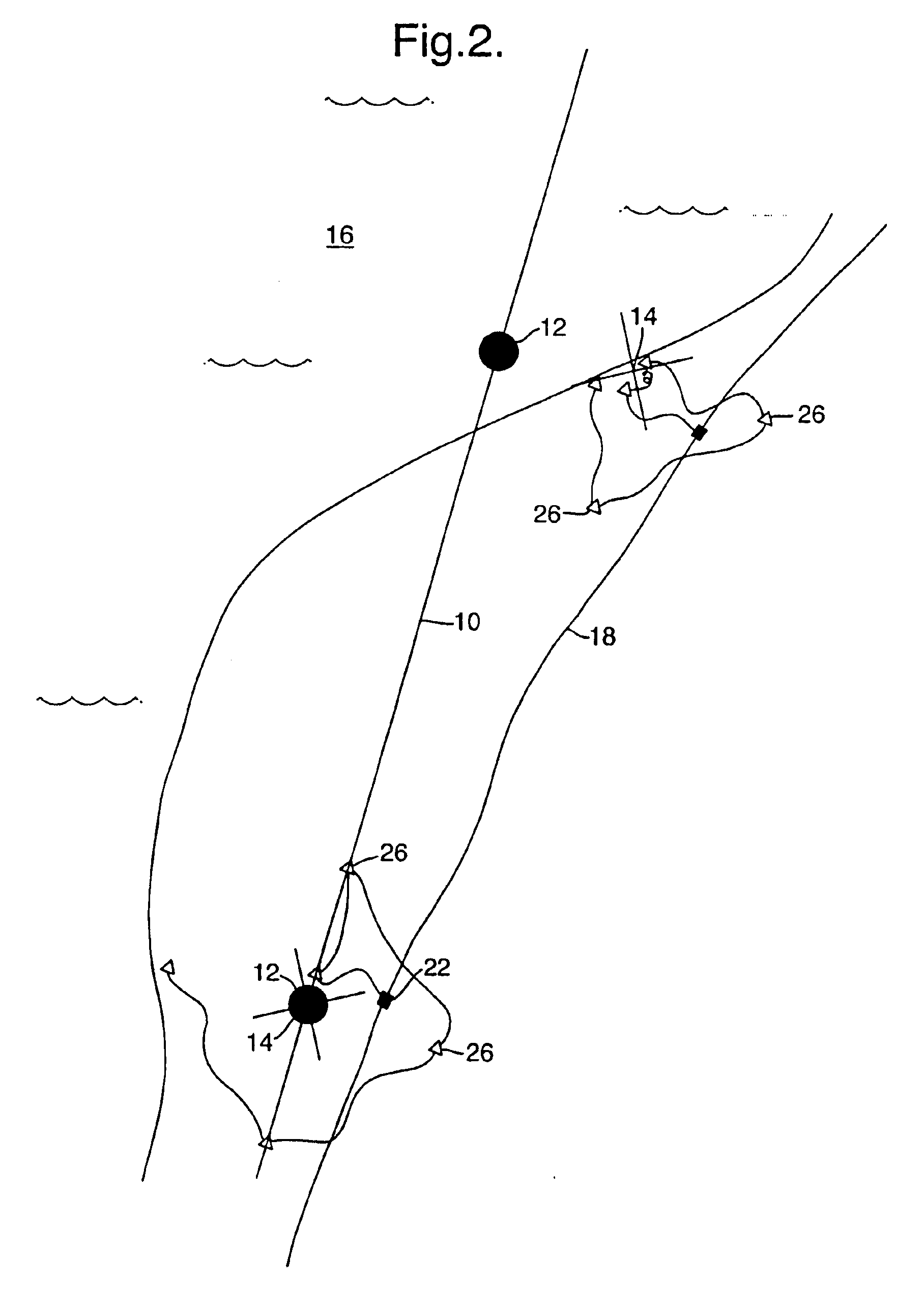
InactiveUS6847896B1Avoid smallEasy and faster lay-outDirection finders using ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic wavesSeismic data acquisitionData acquisitionGeophysics
A method of acquiring seismic data adapted for a land or transition zone environment including placing a location identifier in a particular location, placing a seismic sensor near the location identifier, reading the location identifer using a seismic data cable, recording seismic data acquired by the seismic sensor using the seismic data cable, and assigning sensor position coordinates to the seismic data based on measured position coordinates of the location identifier. The invention also includes an apparatus adapted for seismic data acquisition in a land or transition zone environment including a location identifier, a seismic senor capable of being placed near the location identifier, a seismic data cable, means for reading the location identifier using the seismic data cable, means for recording seismic data acquired by the seismic sensor using the seismic data cable, and means for assigning sensor position coordinates to the seismic data based on measured position coordinates of the location identifier.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
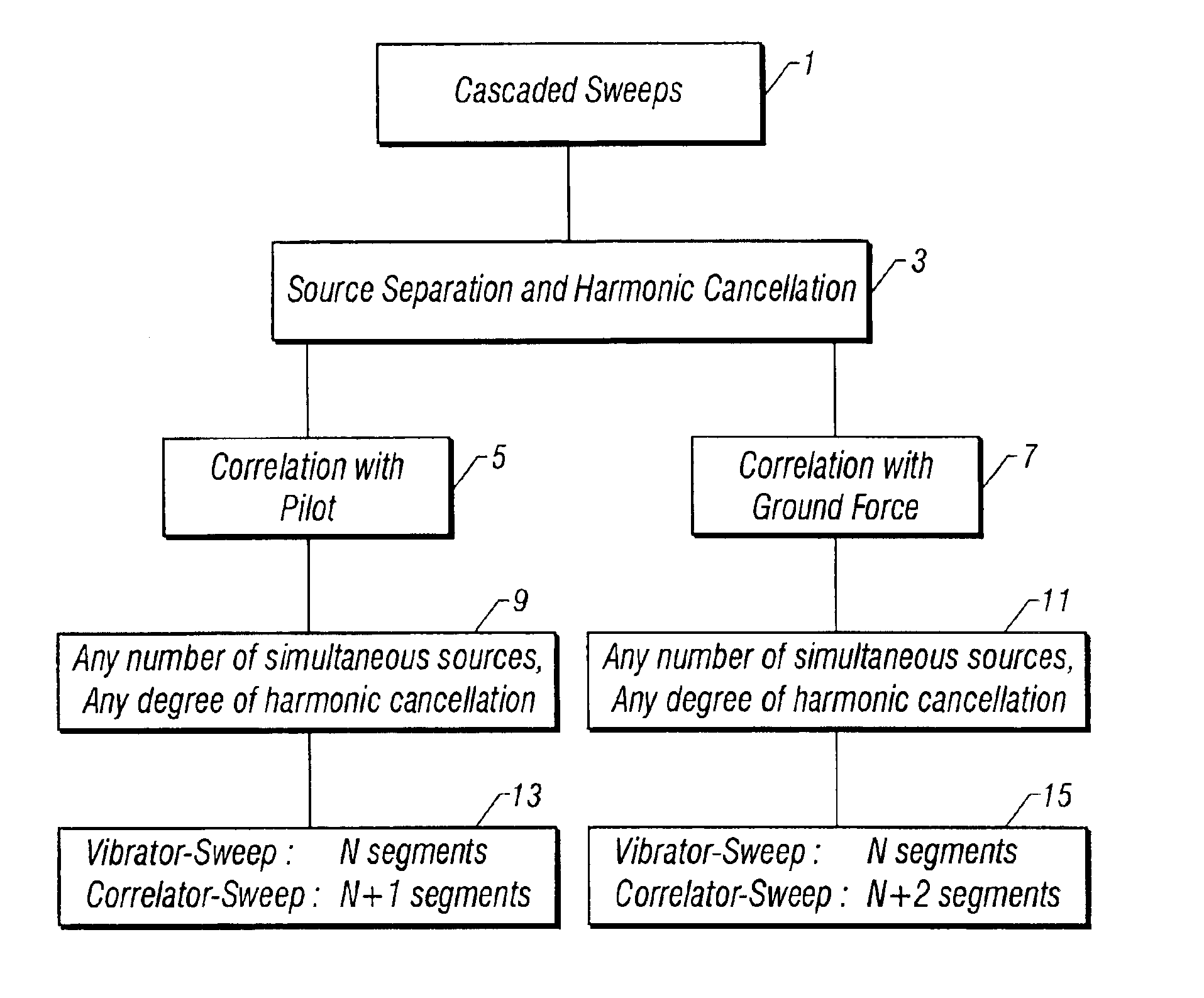
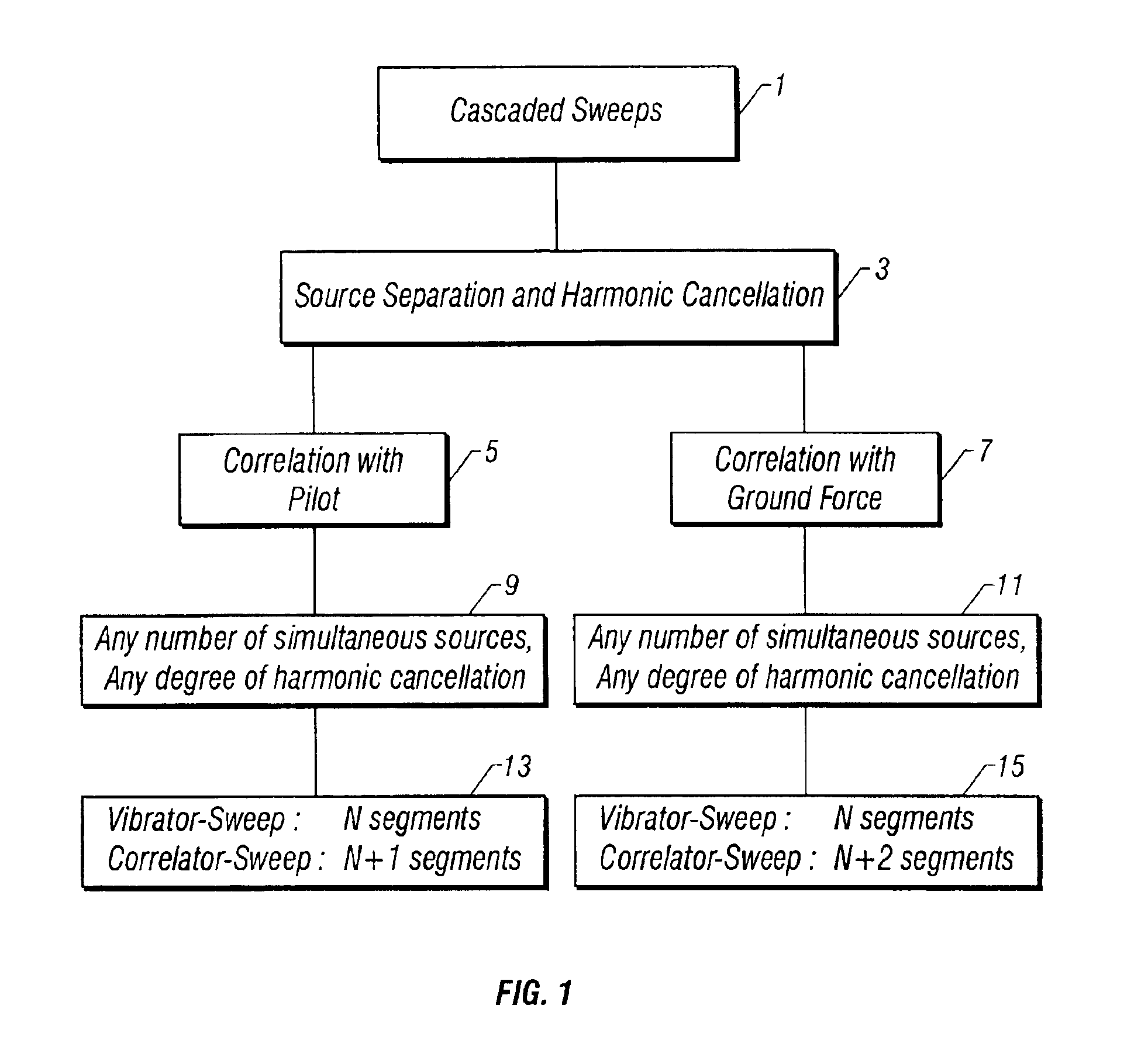
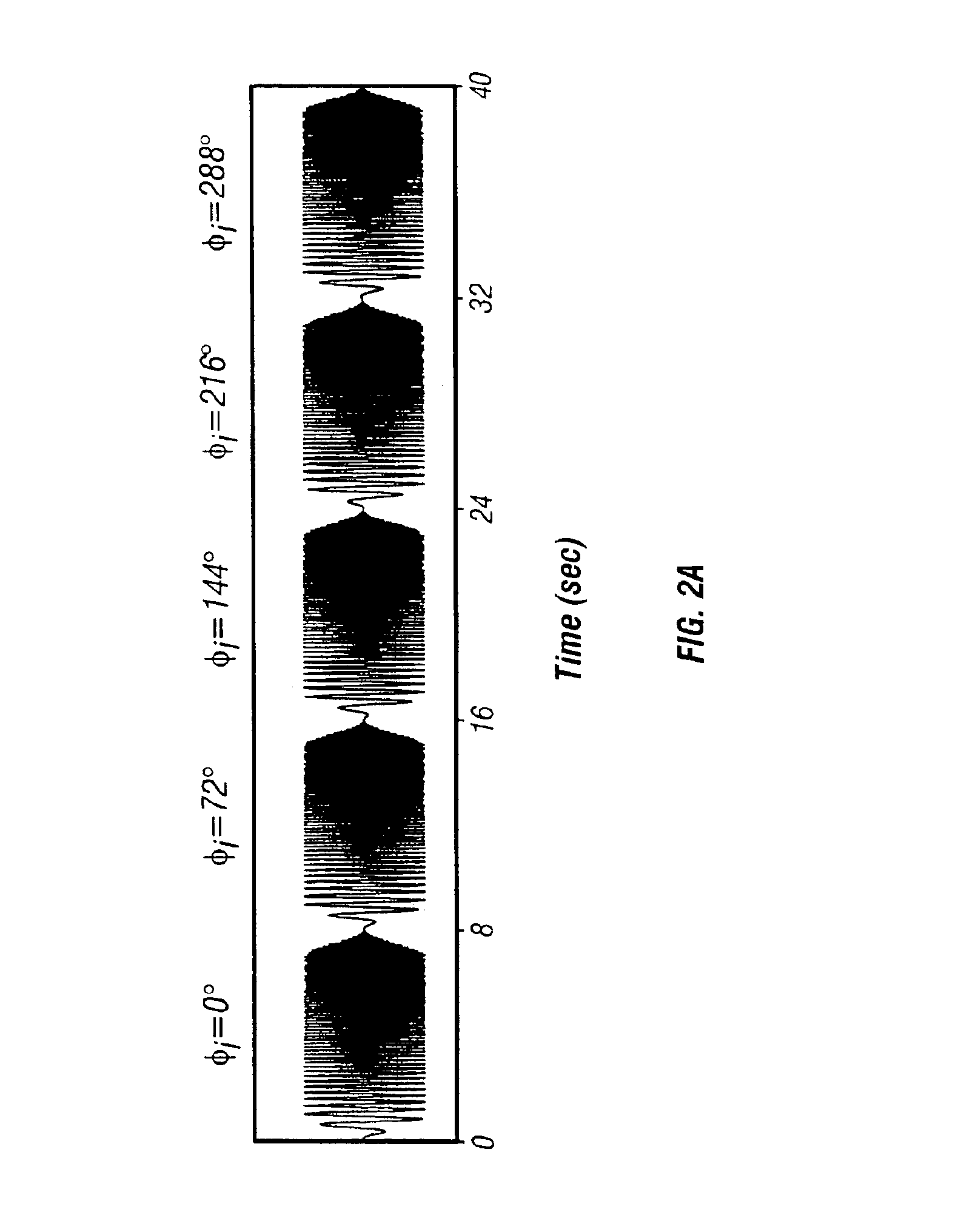
Method of using cascaded sweeps for source coding and harmonic cancellation
A method of seismic surveying using one or more vibrational seismic energy sources activated by sweep signals. The highest order harmonic that has sufficient strength to cause significant harmonic distortion of a sweep segment is determined. A number of sweep segments in excess of the number of sources is selected. Initial phase angles are selected for each sweep segment of each seismic energy source so that substantially all harmonics up to and including the highest order harmonic are suppressed. Using cascaded sweeps, seismic data are acquired and processed to substantially attenuate harmonics upto the selected order.
Owner:WESTERNGECO LLC
Systems and methods for enhancing low-frequency content in vibroseis acquisition
ActiveUS7327633B2Enhanced/optimized amplitudeImprove errorSeismic data acquisitionSeismic signal processingEngineeringUltimate tensile strength
This invention relates in general to vibroseis and, more specifically, but not by way of limitation, to the enhancement and / or signal strength optimization of low frequency content of seismic signals for use in surveying boreholes and / or subsurface earth formations. In embodiments of the present invention, physical properties of a seismic vibrator may be analyzed and used to provide for determination of a driving force necessary to drive a reaction mass to produce a sweep signal with enhanced low frequency content for injection into the ground for vibroseis. In certain aspects, the physical properties may be considered independent of any geophysical properties related to operation of the seismic vibrator.
Owner:WESTERNGECO LLC
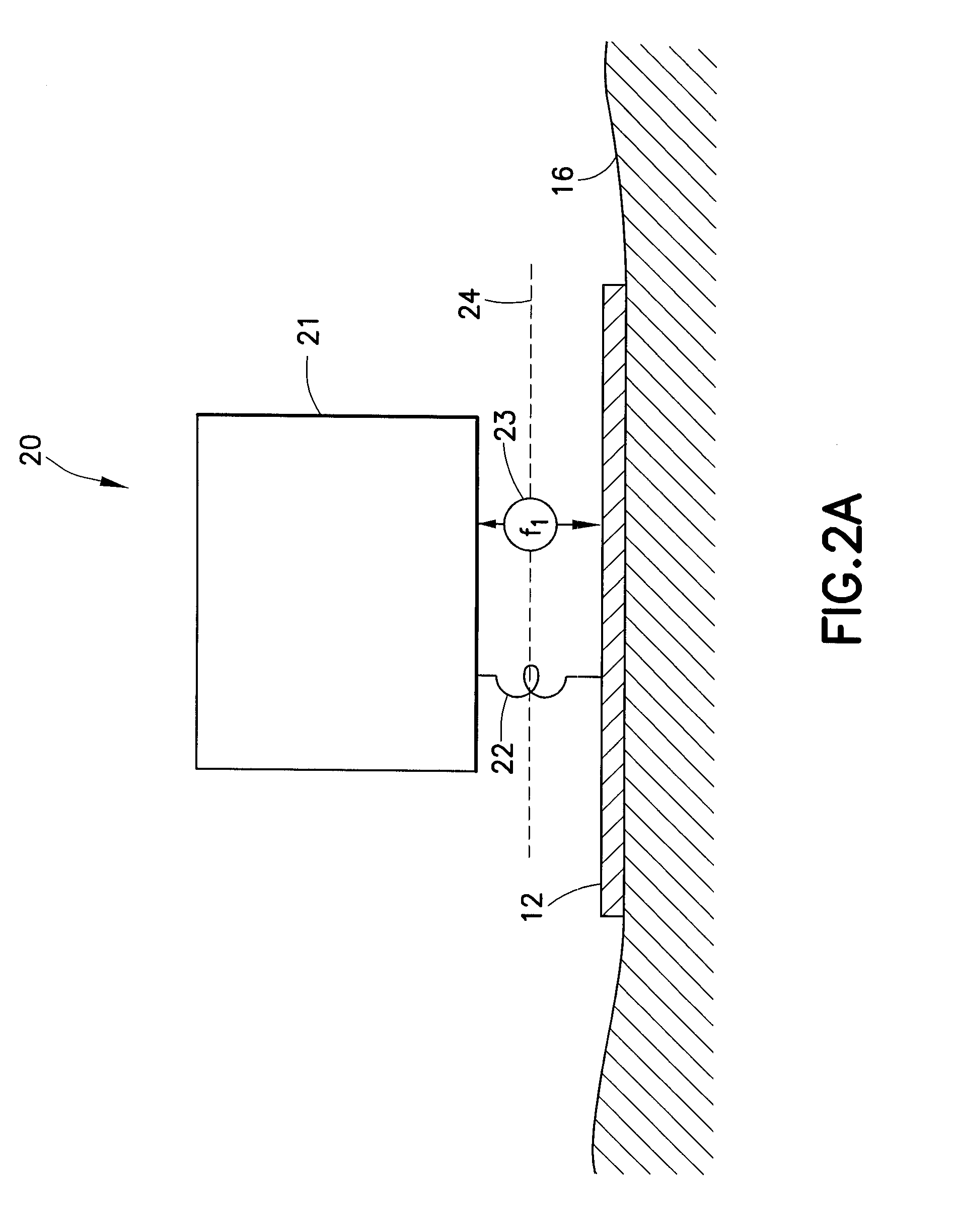
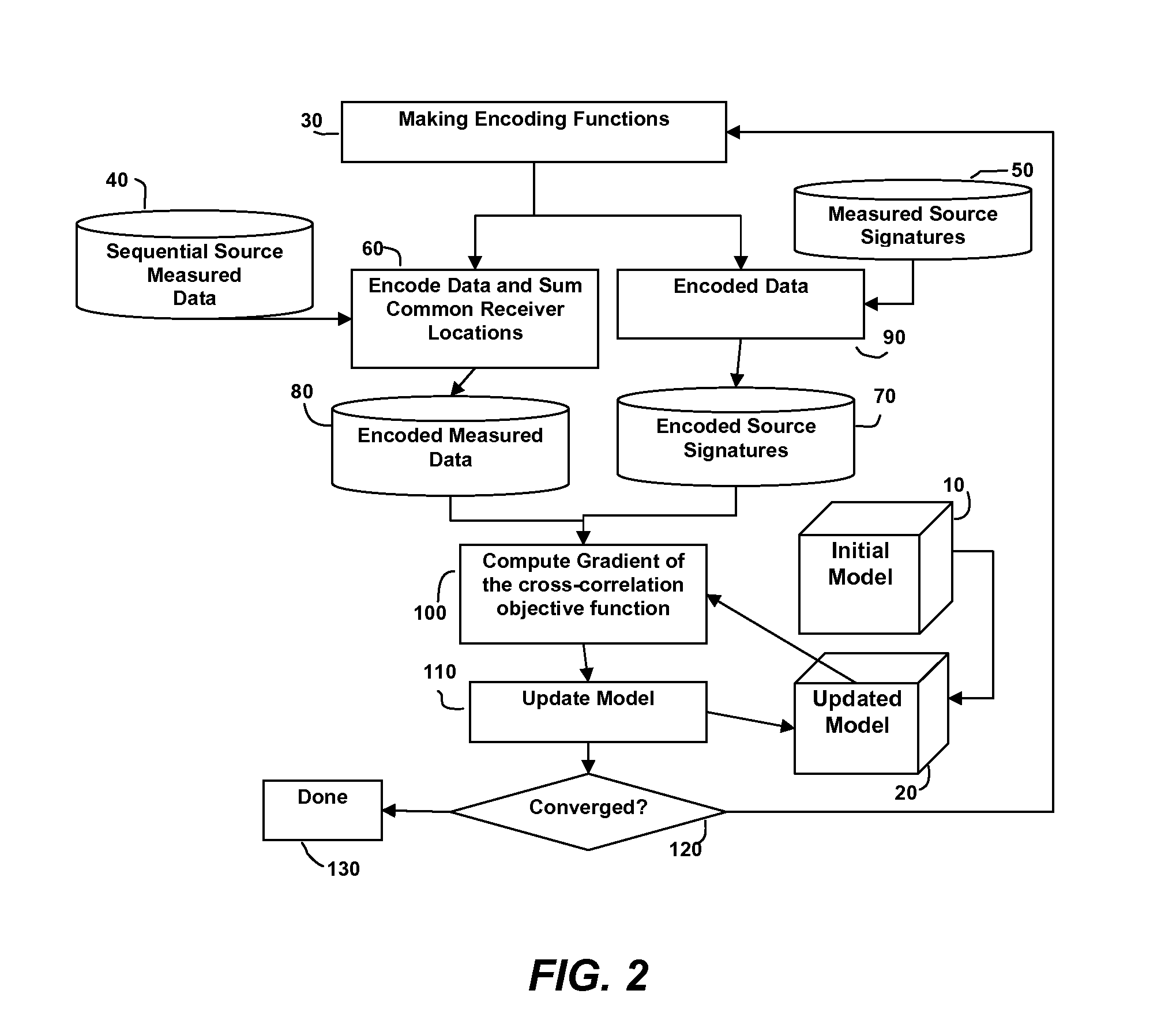
Simultaneous Source Inversion for Marine Streamer Data With Cross-Correlation Objective Function
ActiveUS20120143506A1Seismic data acquisitionSeismology for water-covered areasData acquisitionPhysical property
Method for simultaneous full-wavefield inversion of gathers of source (or receiver) encoded (30) geophysical data (80) to determine a physical properties model (20) for a subsurface region, especially suitable for surveys where fixed-receiver geometry conditions were not satisfied in the data acquisition (40). The inversion involves optimization of a cross-correlation objective function (100).
Owner:EXXONMOBIL UPSTREAM RES CO
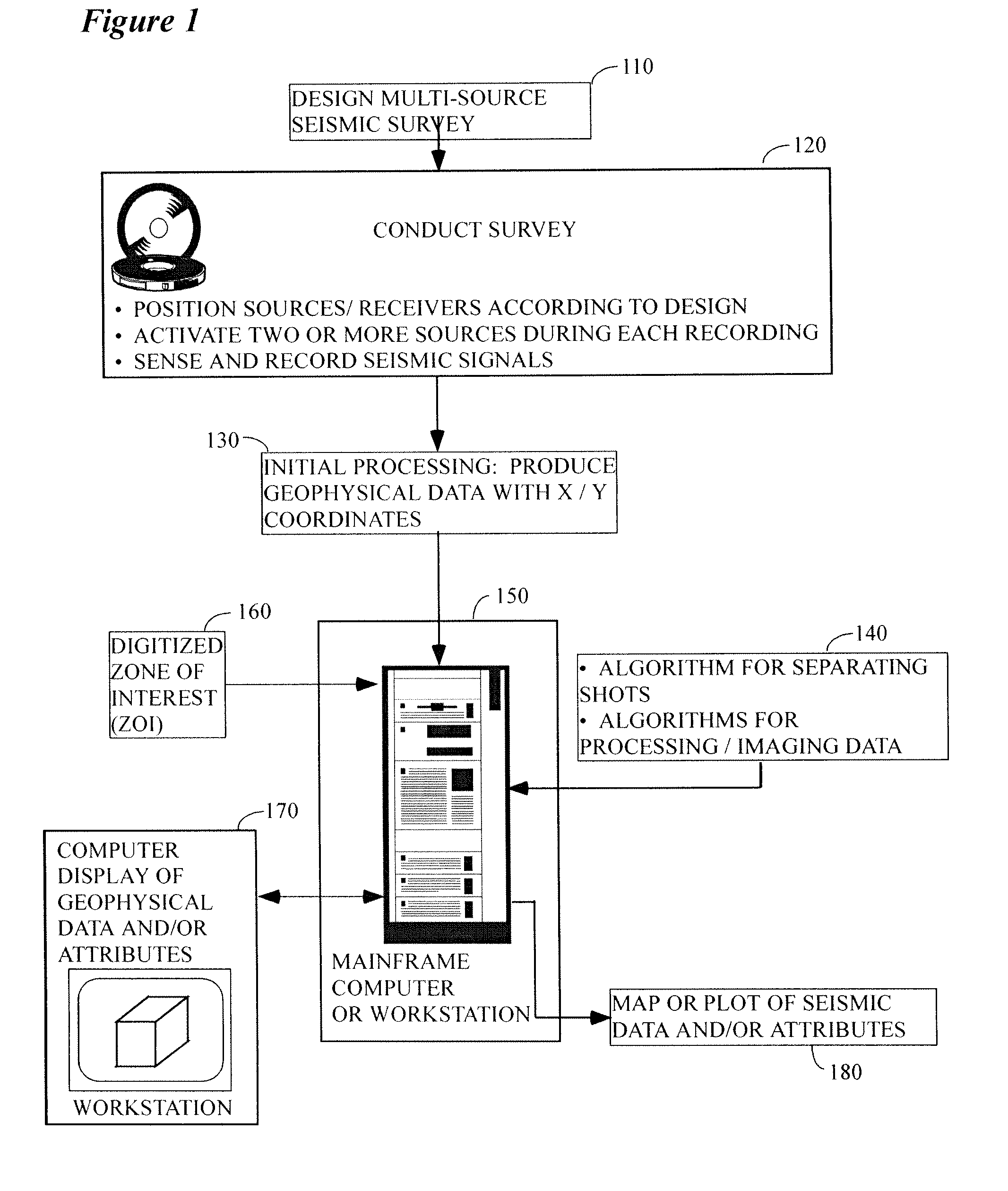
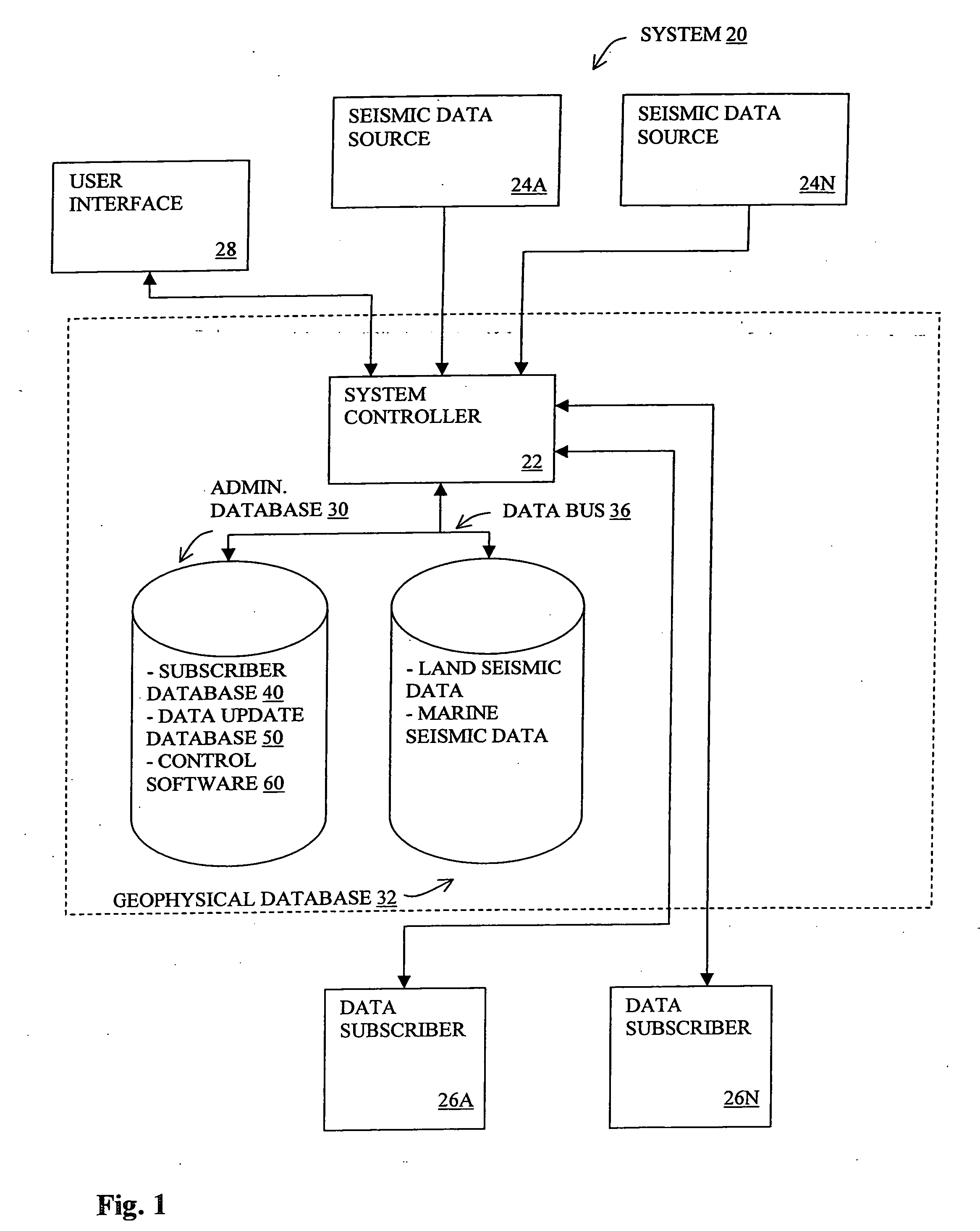
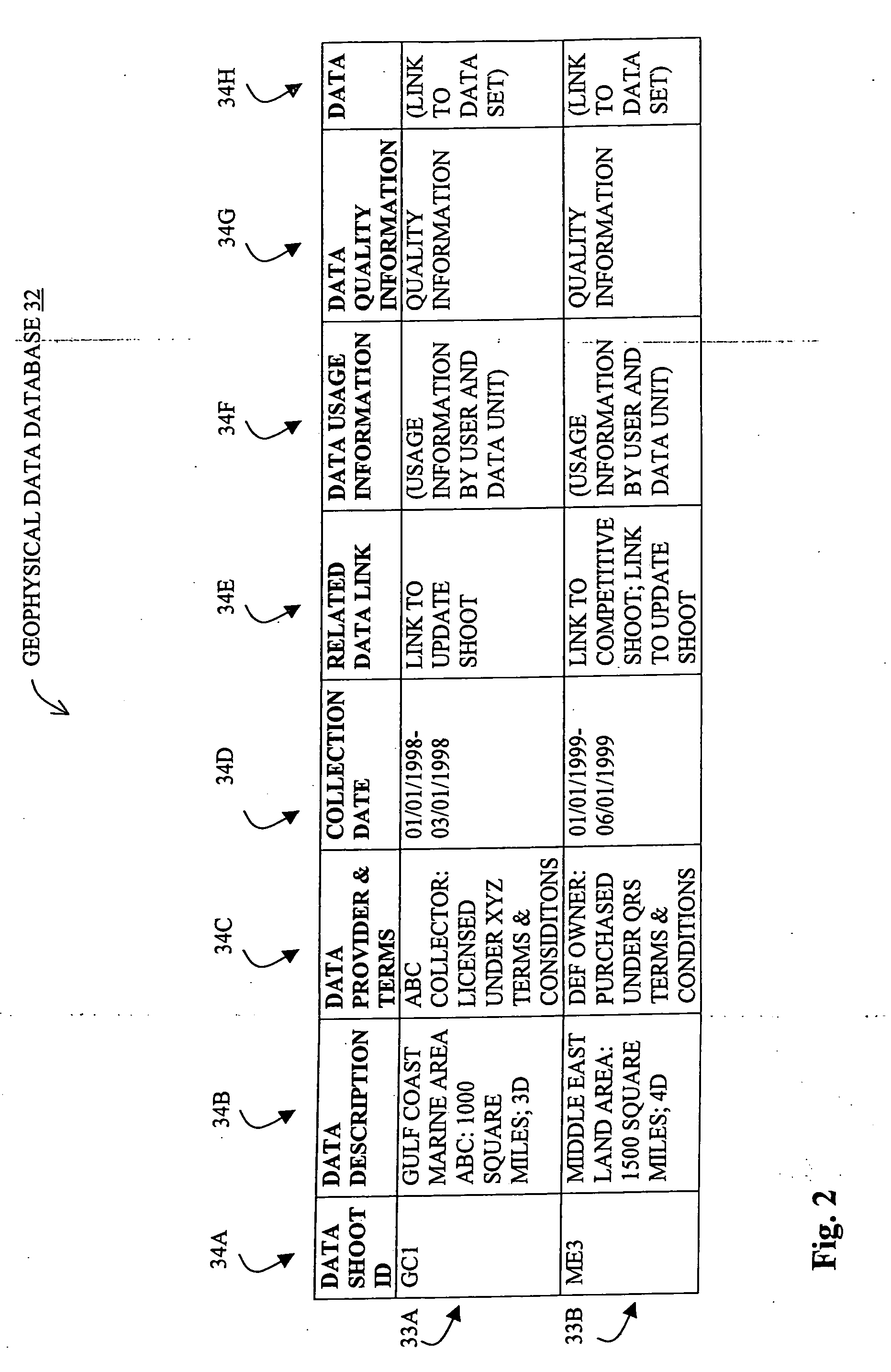
Methods and systems for selecting and acquiring data to update a geophysical database
InactiveUS20050228725A1Seismic data acquisitionBuying/selling/leasing transactionsData providerFull data
Methods and systems for collecting, managing, distributing and updating geophysical data primarily for E&P companies include in one embodiment the sale of subscriptions entitling paid subscribers access to all subscribed data including both preview and full data. Initial and subsequent data providers are preferably compensated from subscriber fees and may be compensated based on relative subscriber use of data. Data subscriptions can include for subscribers the right to vote or otherwise provide input relating to desired data updates. Data updates are preferably purchased based on competitive bids. The inventive systems and methods diminish much of the risk and uncertainty associated with the collection, management, distribution and updating of geophysical data under current methodologies, making the process more efficient and cost-effective for participating parties.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
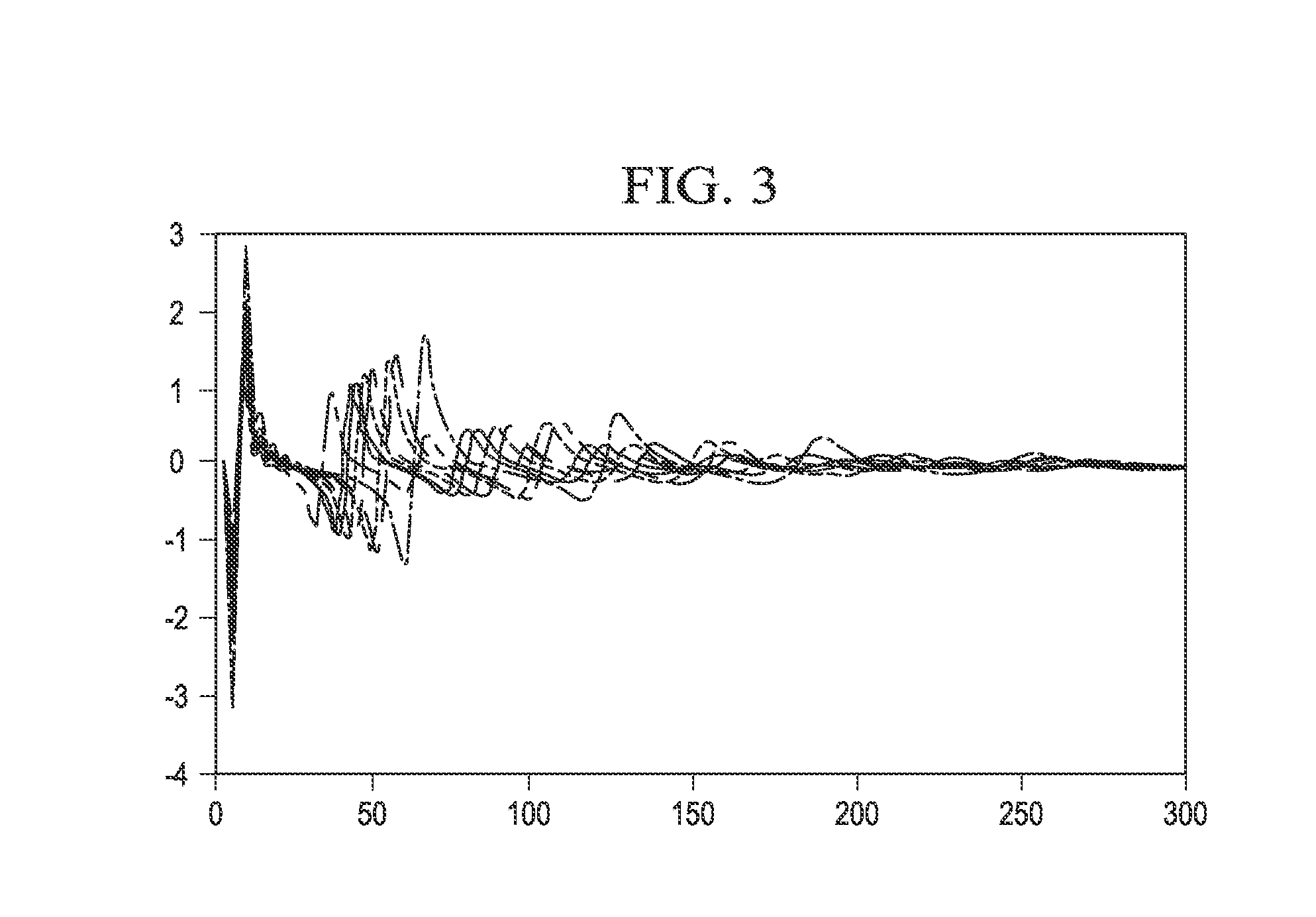
Separation and Noise Removal for Multiple Vibratory Source Seismic Data
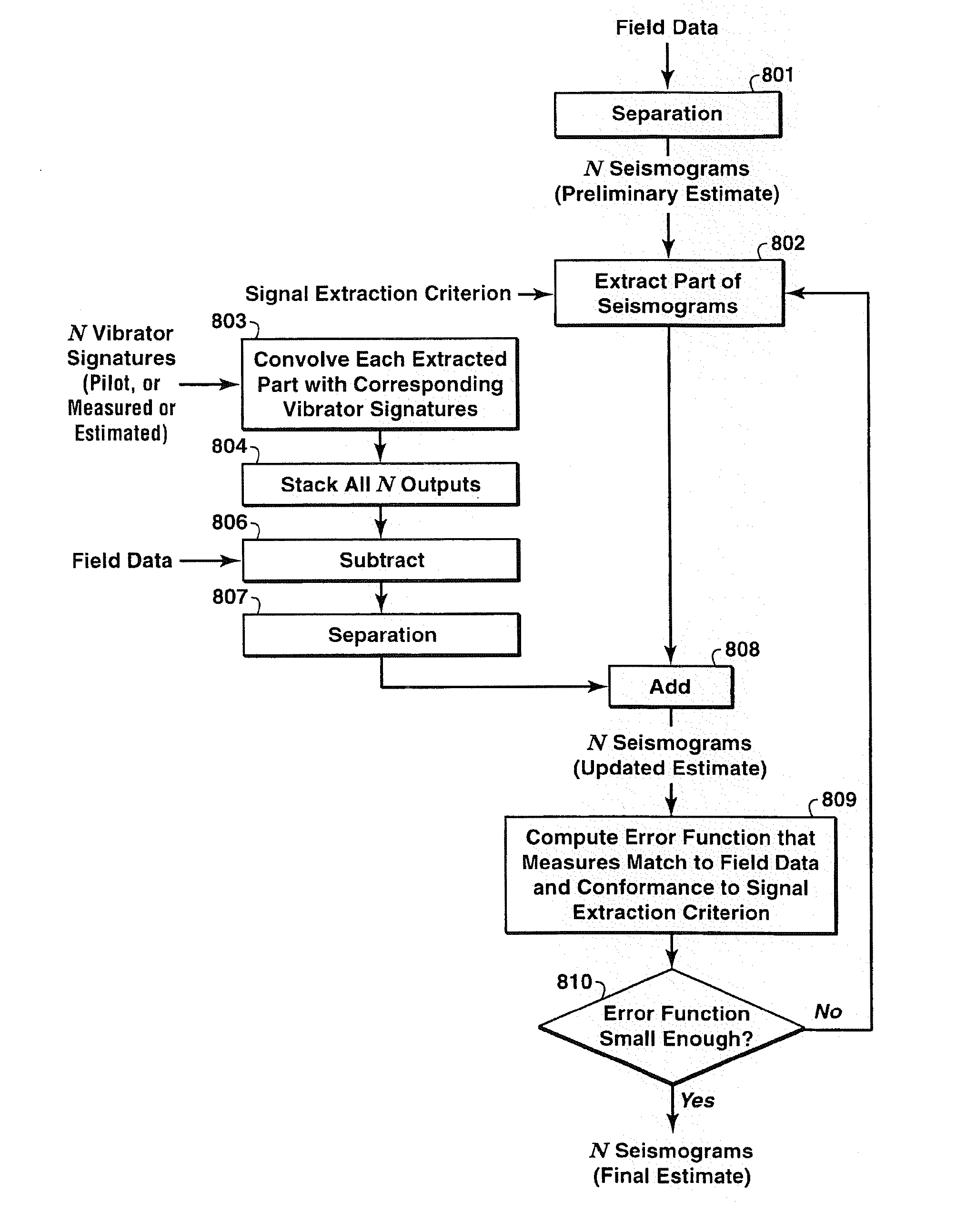
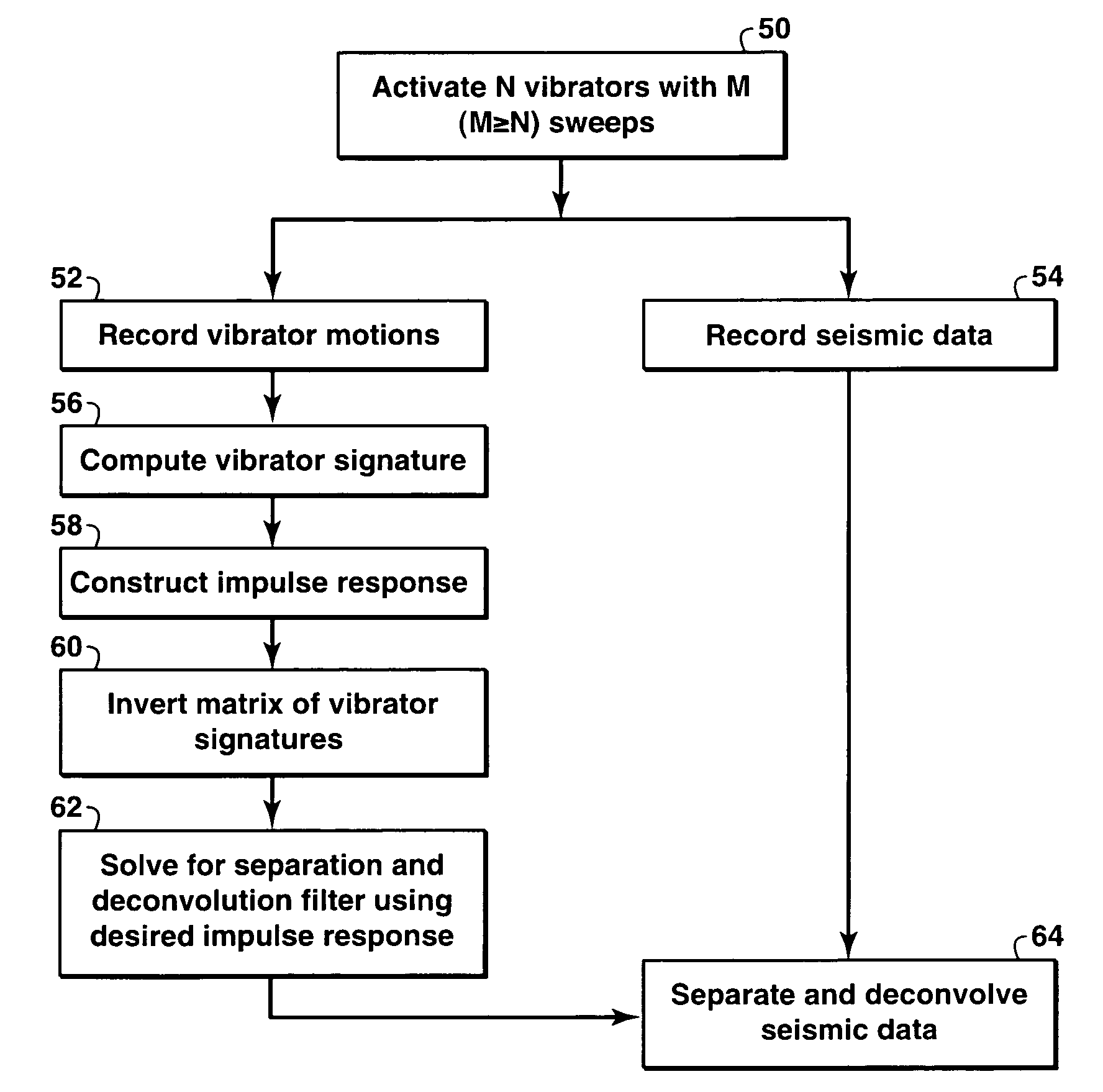
The invention discloses a way to recover separated seismograms with reduced interference noise by processing vibroseis data recorded (or computer simulated) with multiple vibrators shaking simultaneously or nearly simultaneously (200). A preliminary estimate of the separated seismograms is used to obtain improved seismograms (201). The preliminary estimate is convolved with the vibrator signature and then used to update the seismogram. Primary criteria for performing the update include fitting the field data and satisfying typical criteria of noise-free seismograms (202). Alternative ways to update are disclosed, including signal extraction, modeled noise extraction, constrained optimization based separation, and penalized least-squares based separation. The method is particularly suited for removing noise caused by separating the combined record into separate records for each vibrator, and is advantageous where the number of sweeps is fewer than the number of vibrators (200).
Owner:EXXONMOBIL UPSTREAM RES CO
Shaped high frequency vibratory source
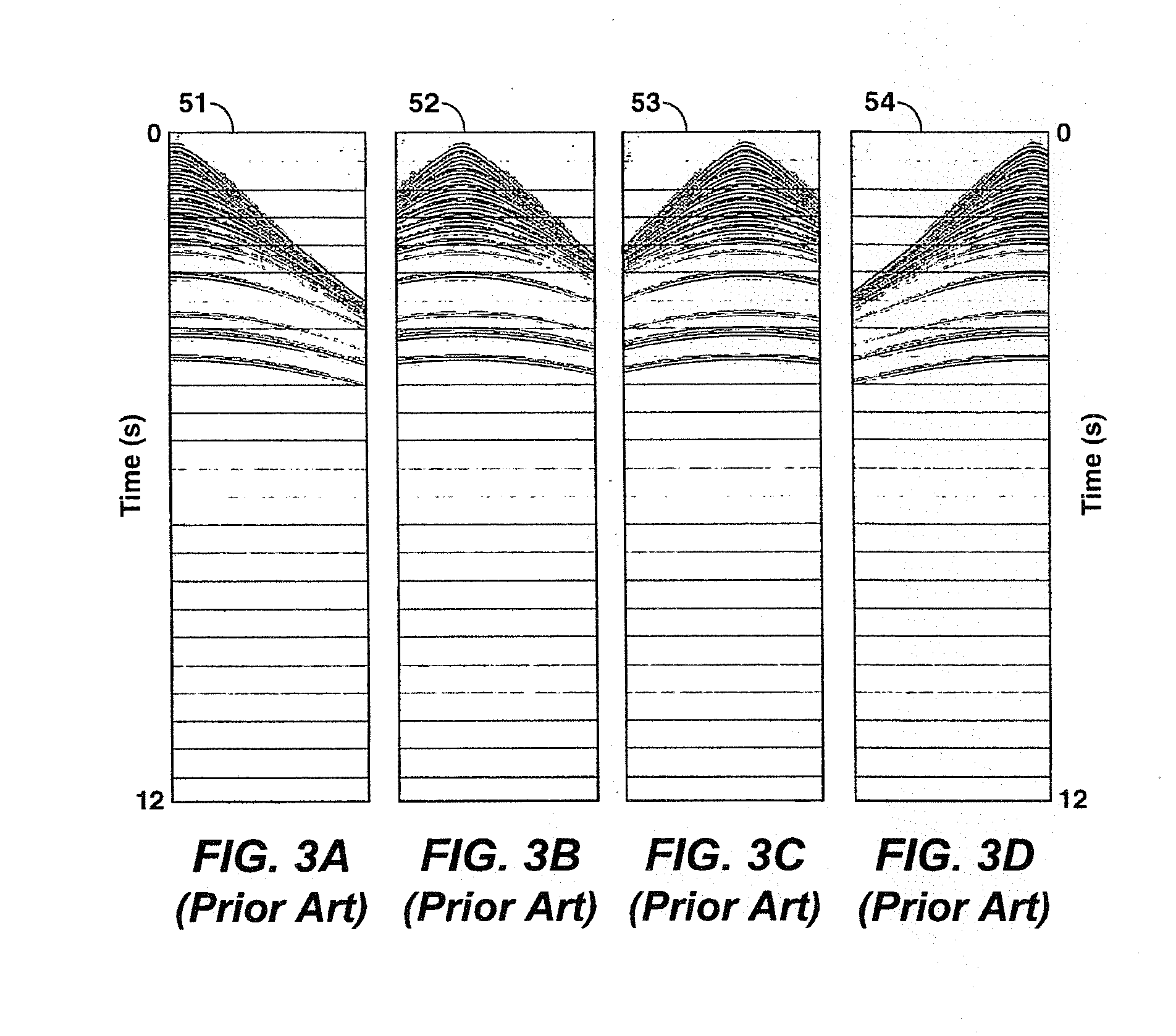
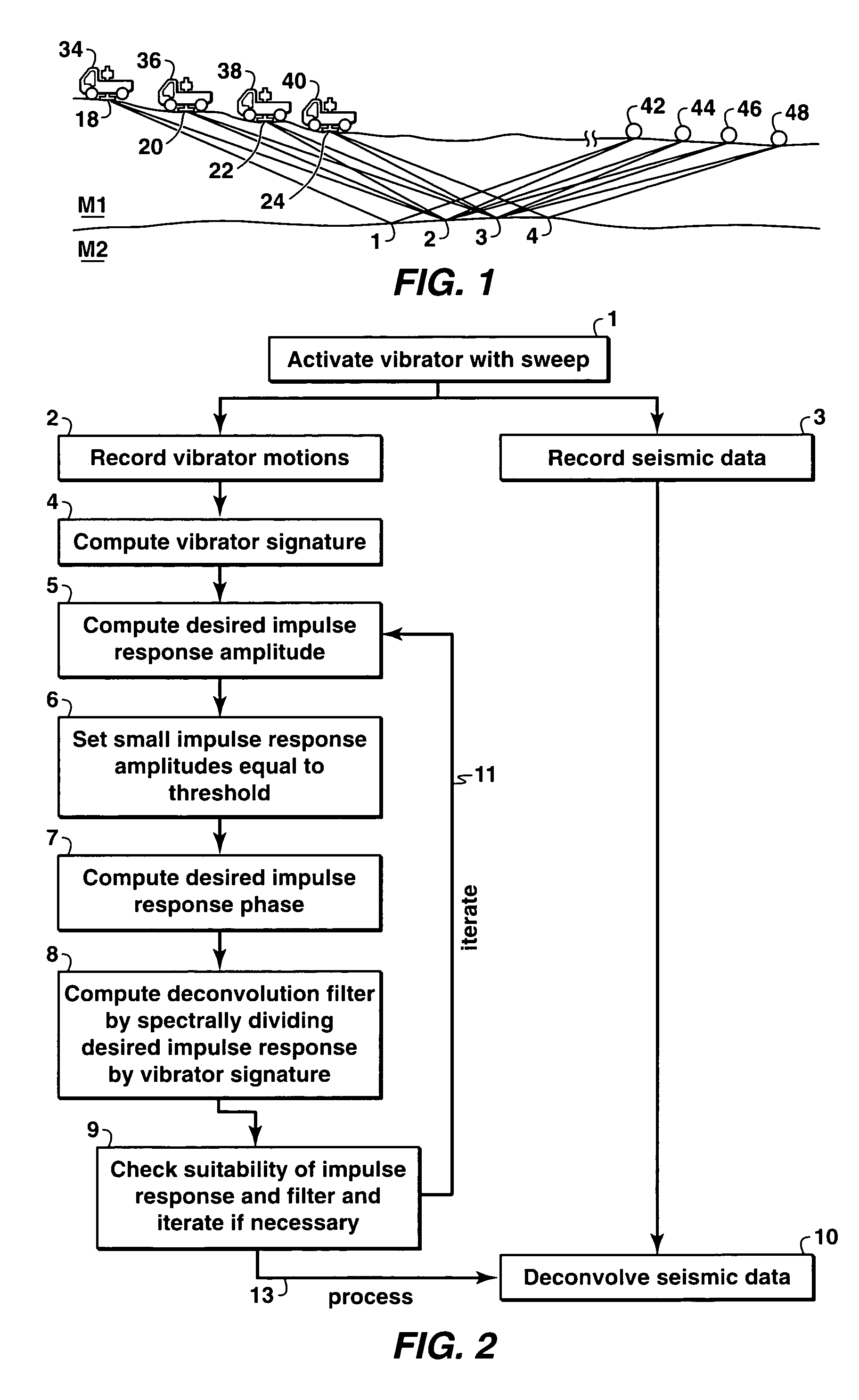
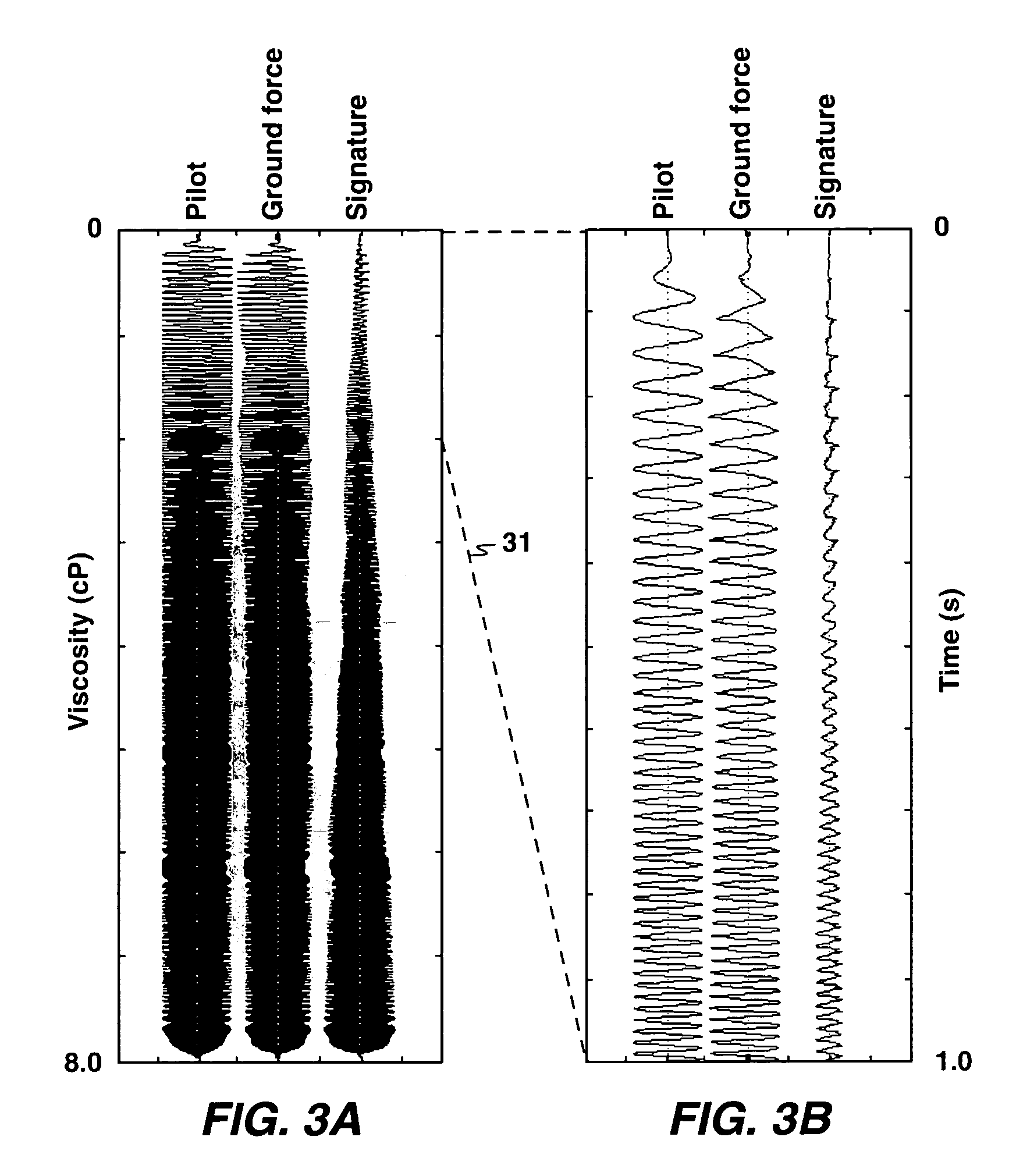
ActiveUS7436734B2Improved noise suppressionSeismic data acquisitionSeismic signal processingConvolution filterBiological activation
The present invention is a method of processing seismic data in which one or more seismic vibrators are activated with one or more pilot signals and vibrator motions are recorded along with seismic data. Vibrator signatures are computed from measured vibrator motions, such as the ground force signal. A desired impulse response is specified from either a measured vibrator motion or from test data or field data from a location near the location from which the seismic data was acquired. A deconvolution filter is computed from the impulse response and the vibrator signature. Alternatively, a single separation and deconvolution filter is derived from the impulse response and from vibrator signatures from multiple vibrators and sweeps. The deconvolution or deconvolution and separation filter is used to process the seismic data. The vibrators are then moved to a new location, and the activation is repeated.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL UPSTREAM RES CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com