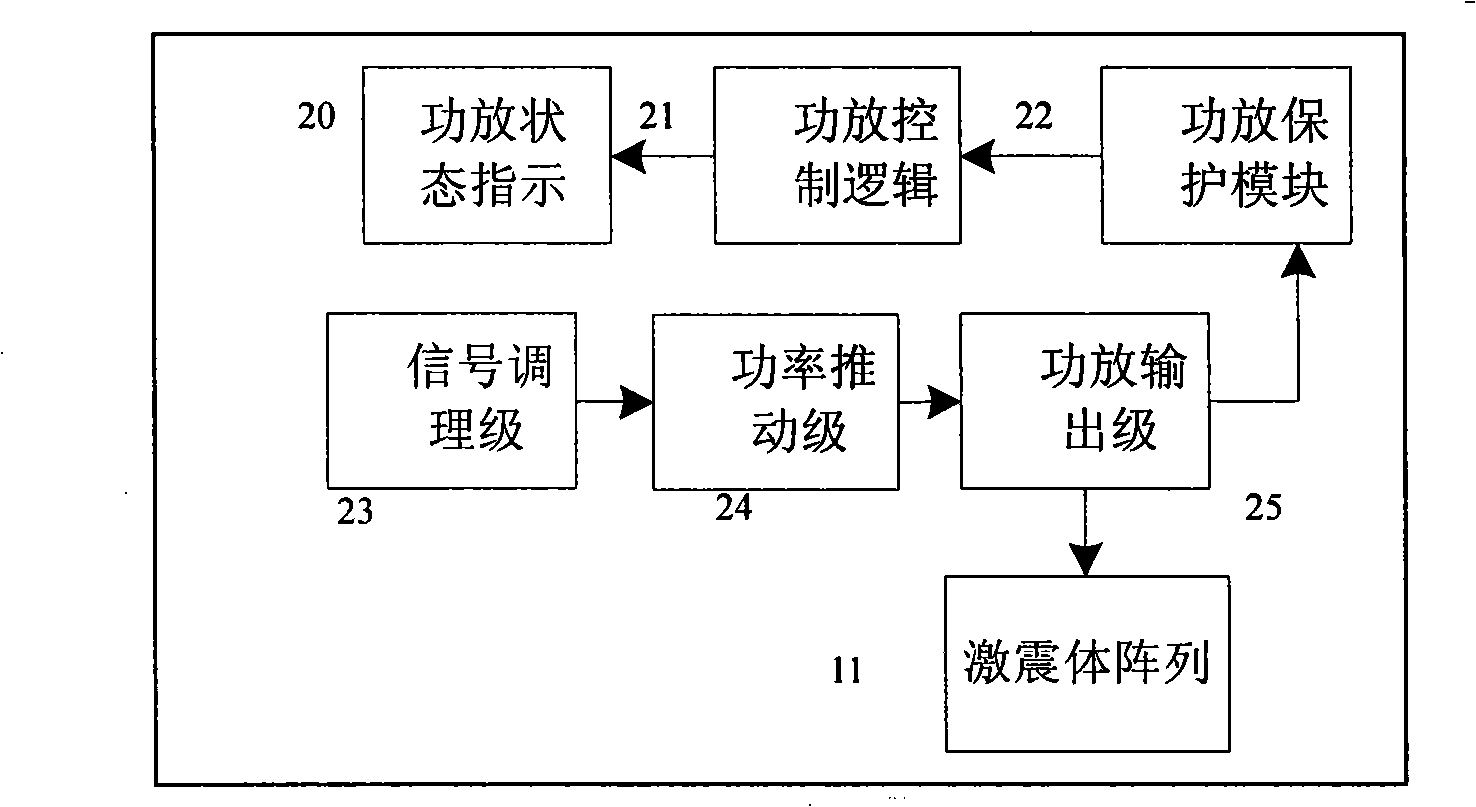
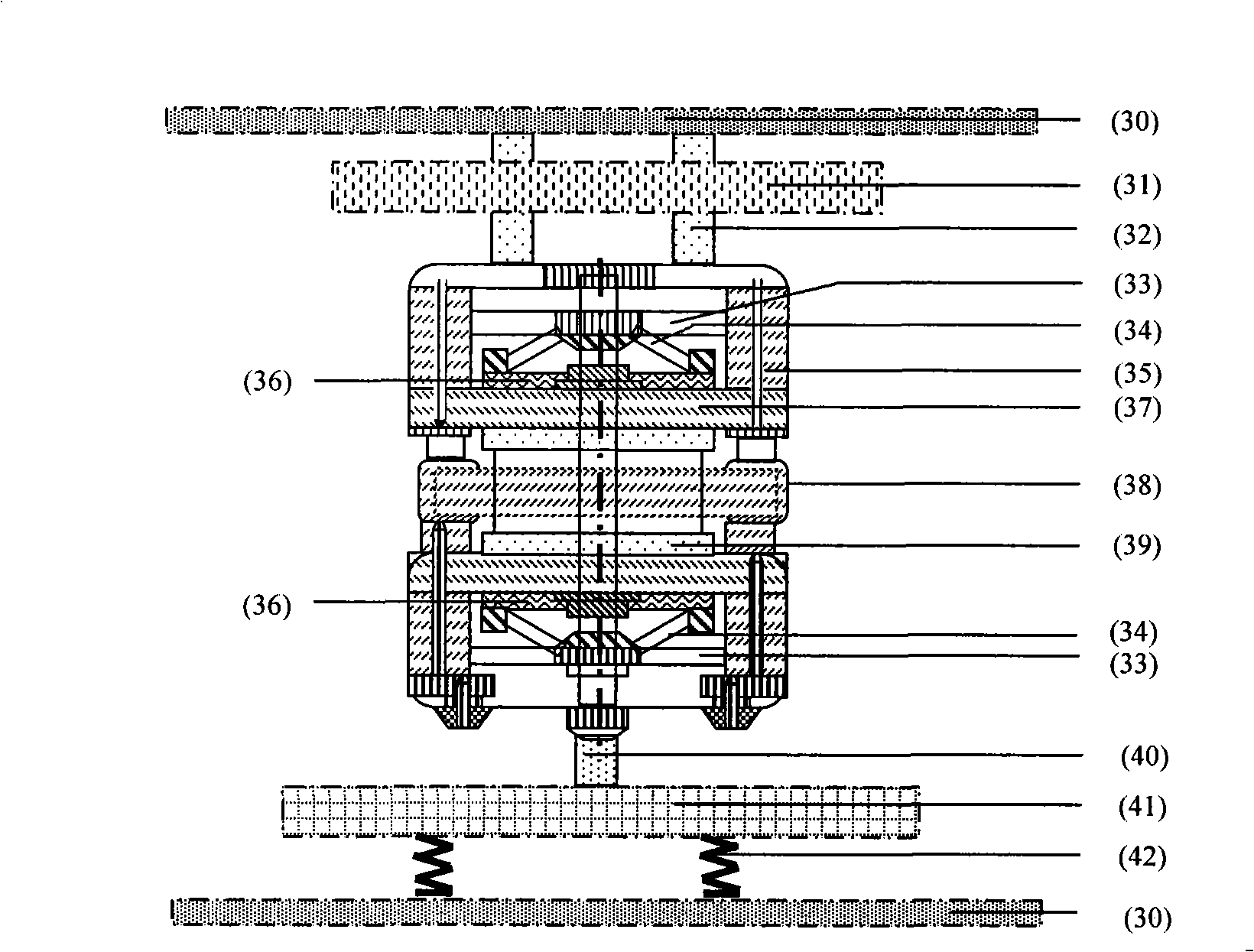
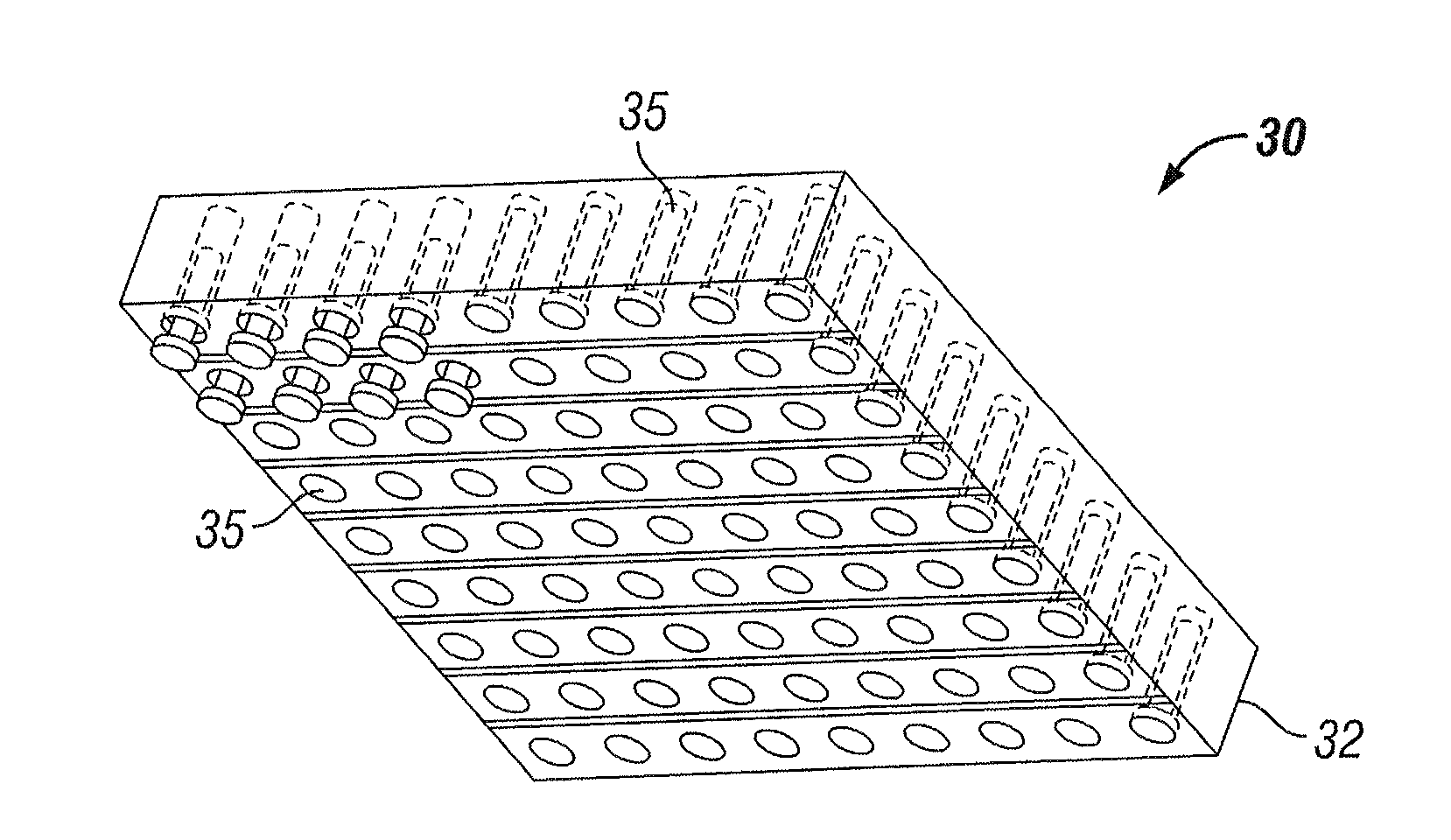
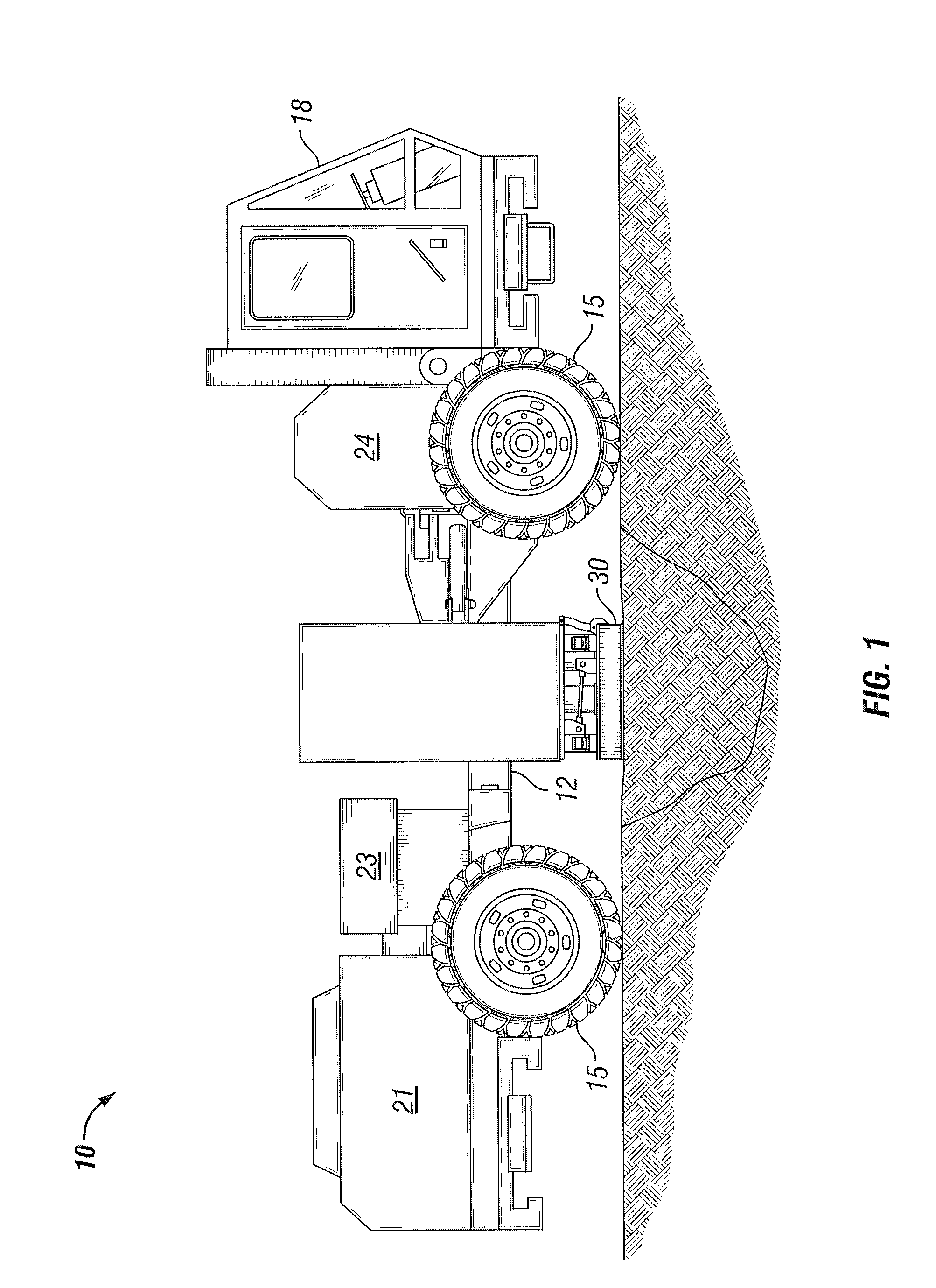
Patents
Literature
69 results about "Seismic vibrator" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
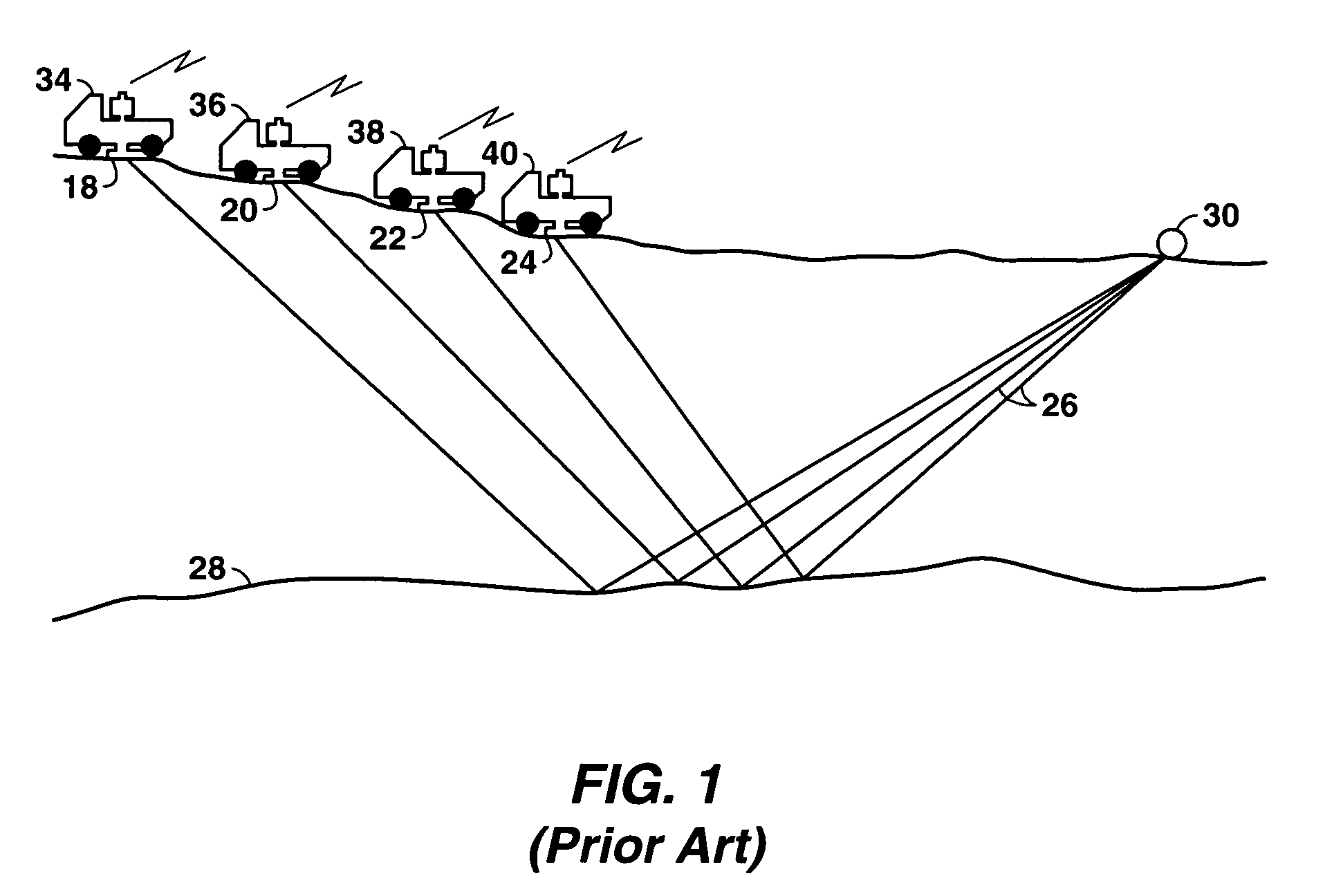
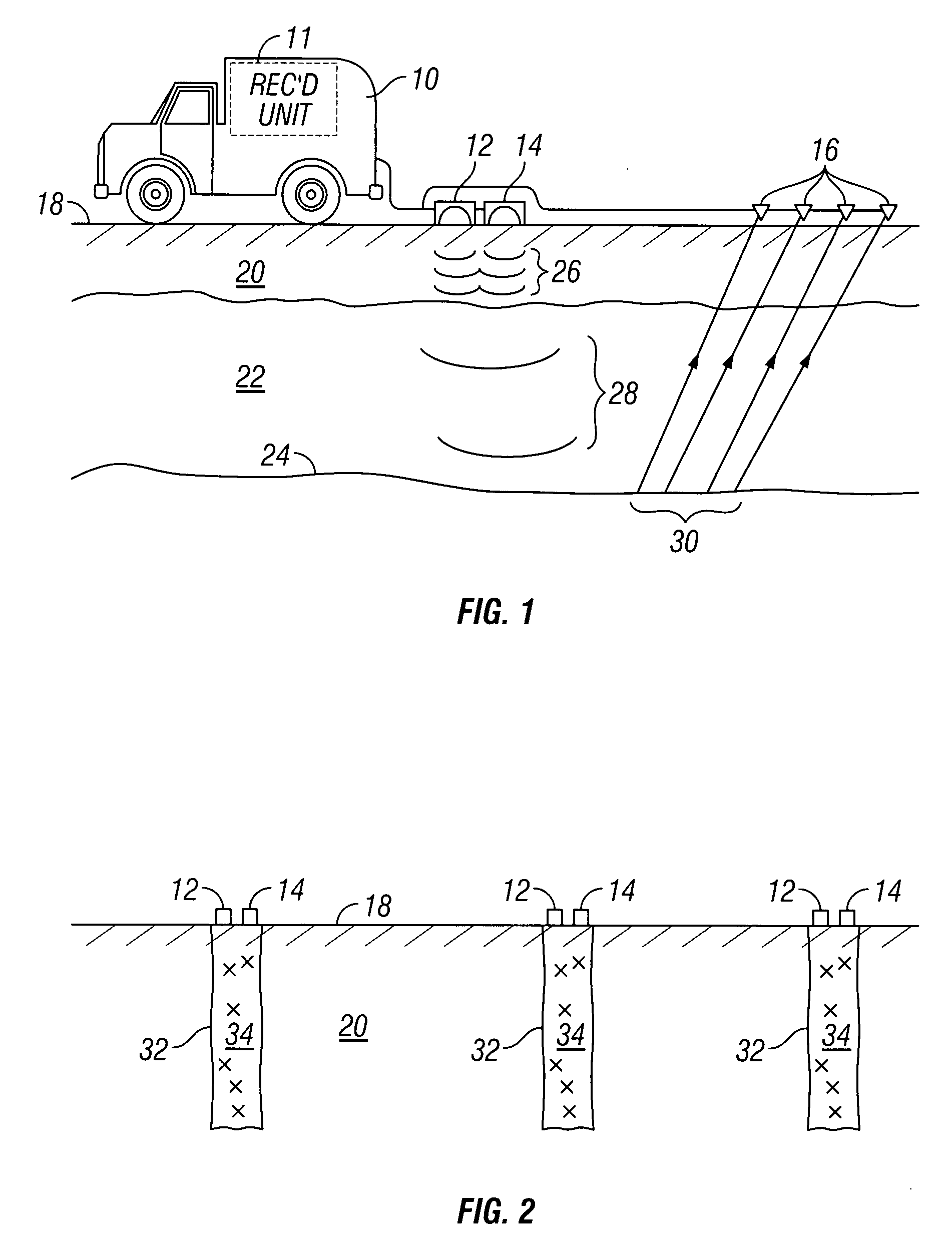
A seismic vibrator is a truck-mounted or buggy-mounted device that is capable of injecting low-frequency vibrations into the earth. It is one of a number of seismic sources used in reflection seismology. The ‘Vibroseis’ exploration technique (performed with vibrators) was developed by the Continental Oil Company (Conoco) during the 1950s and was a trademark until the company's patent lapsed.
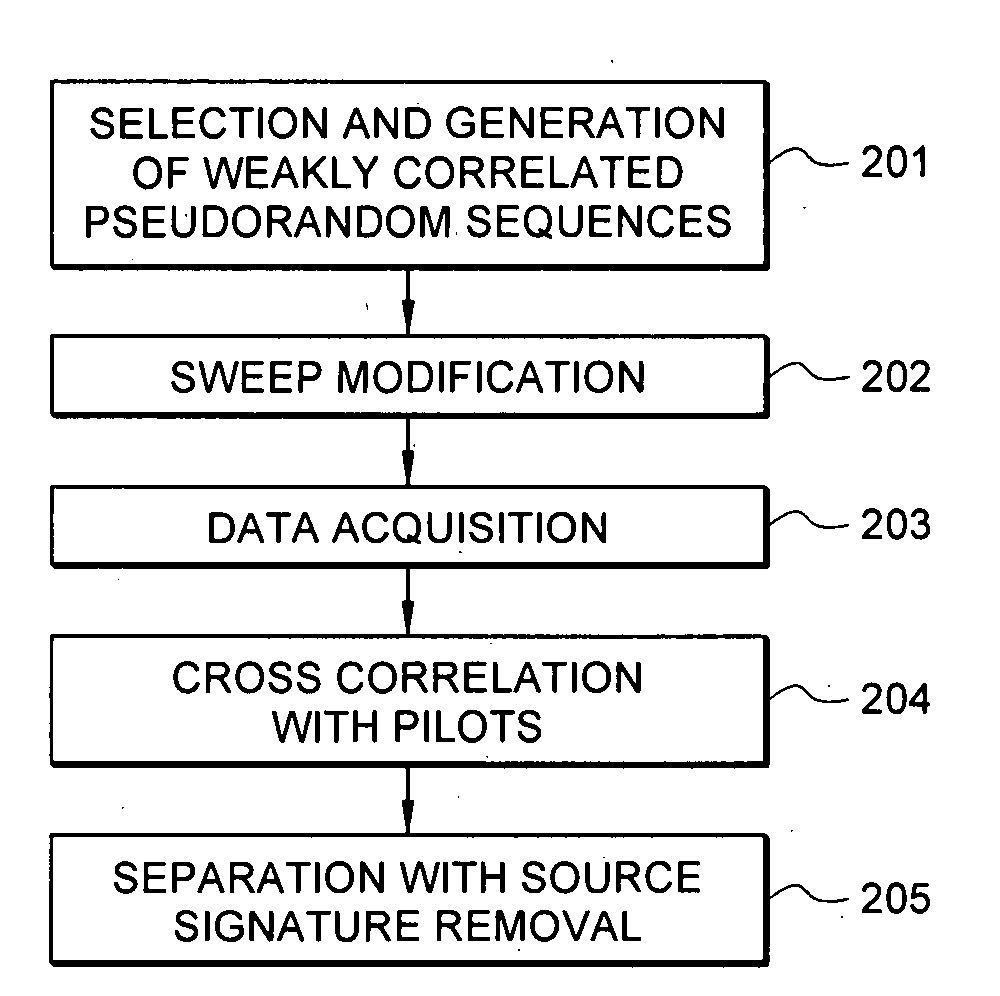
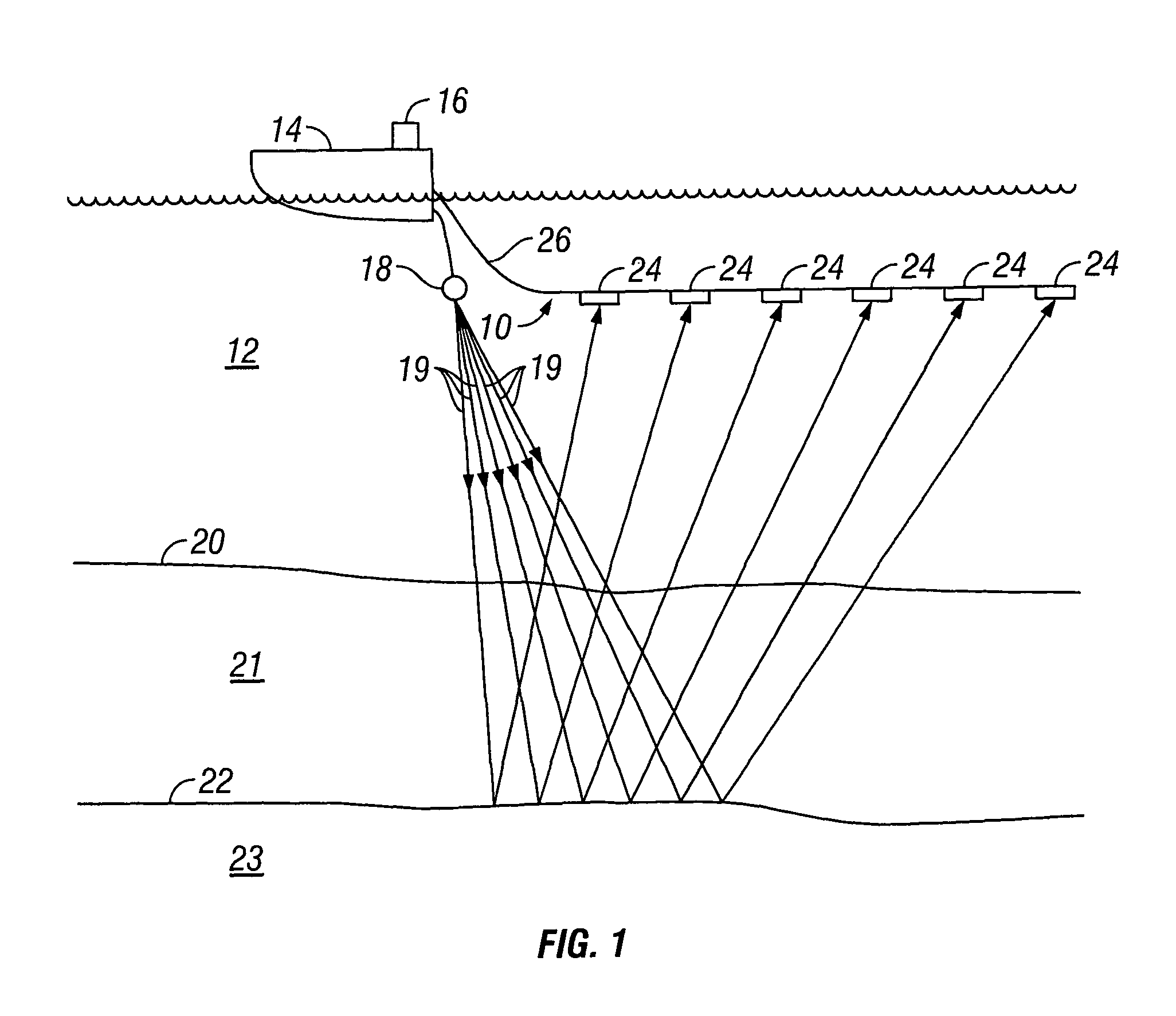
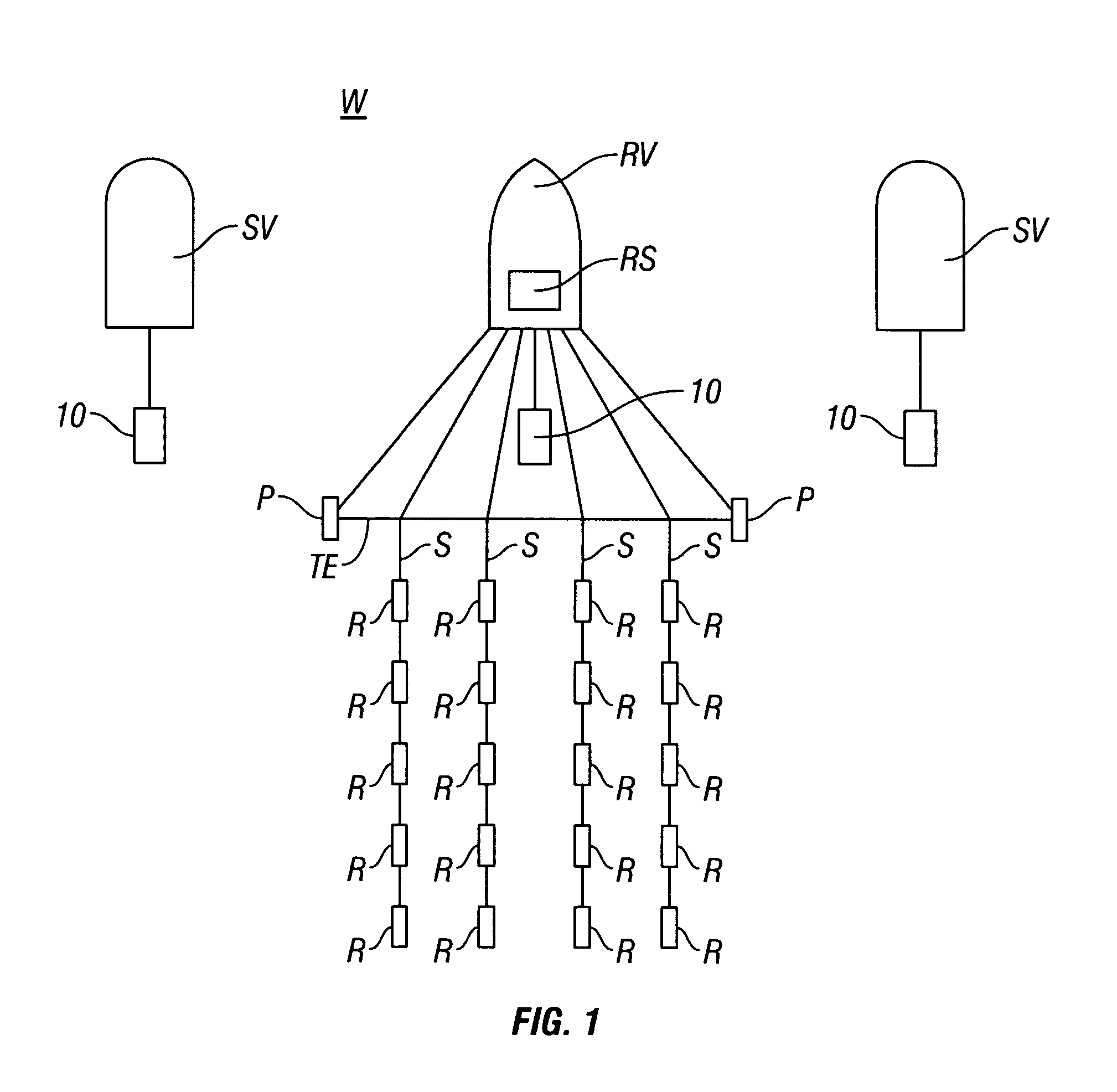
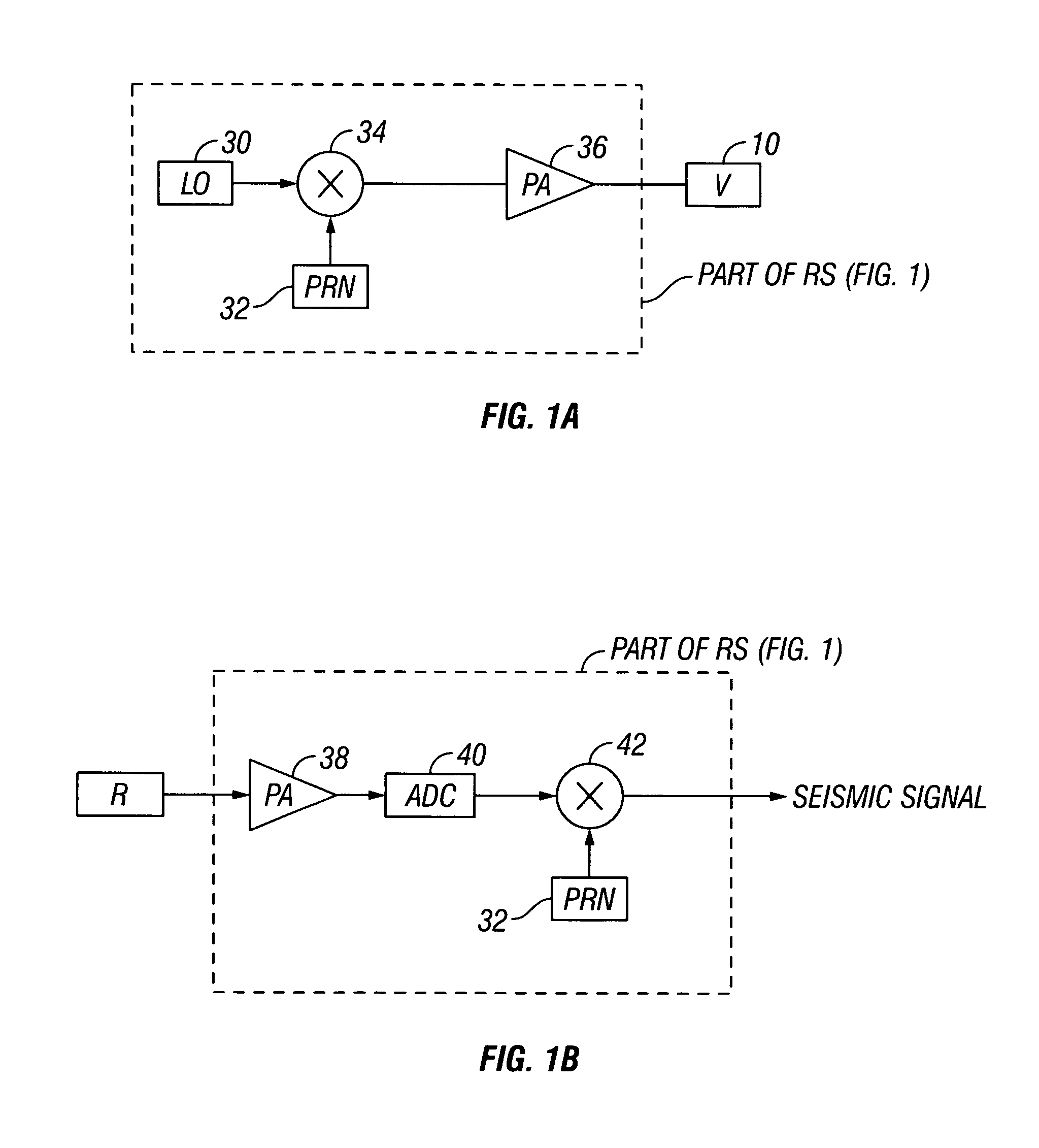
Efficient seismic data acquisition with source separation
ActiveUS20090010103A1Minimize crosstalkSeismic data acquisitionSeismic energy generationTime domainFrequency spectrum
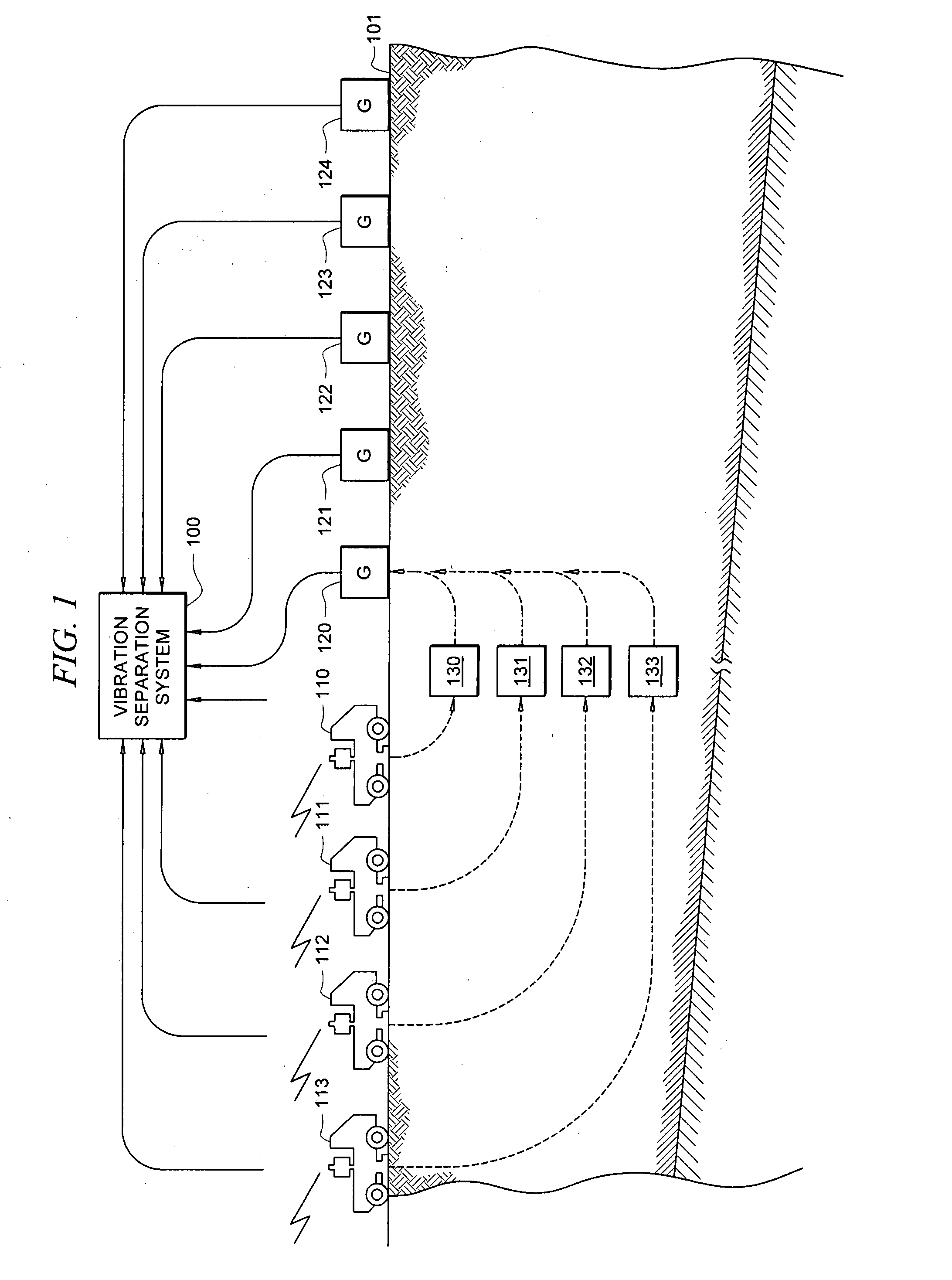
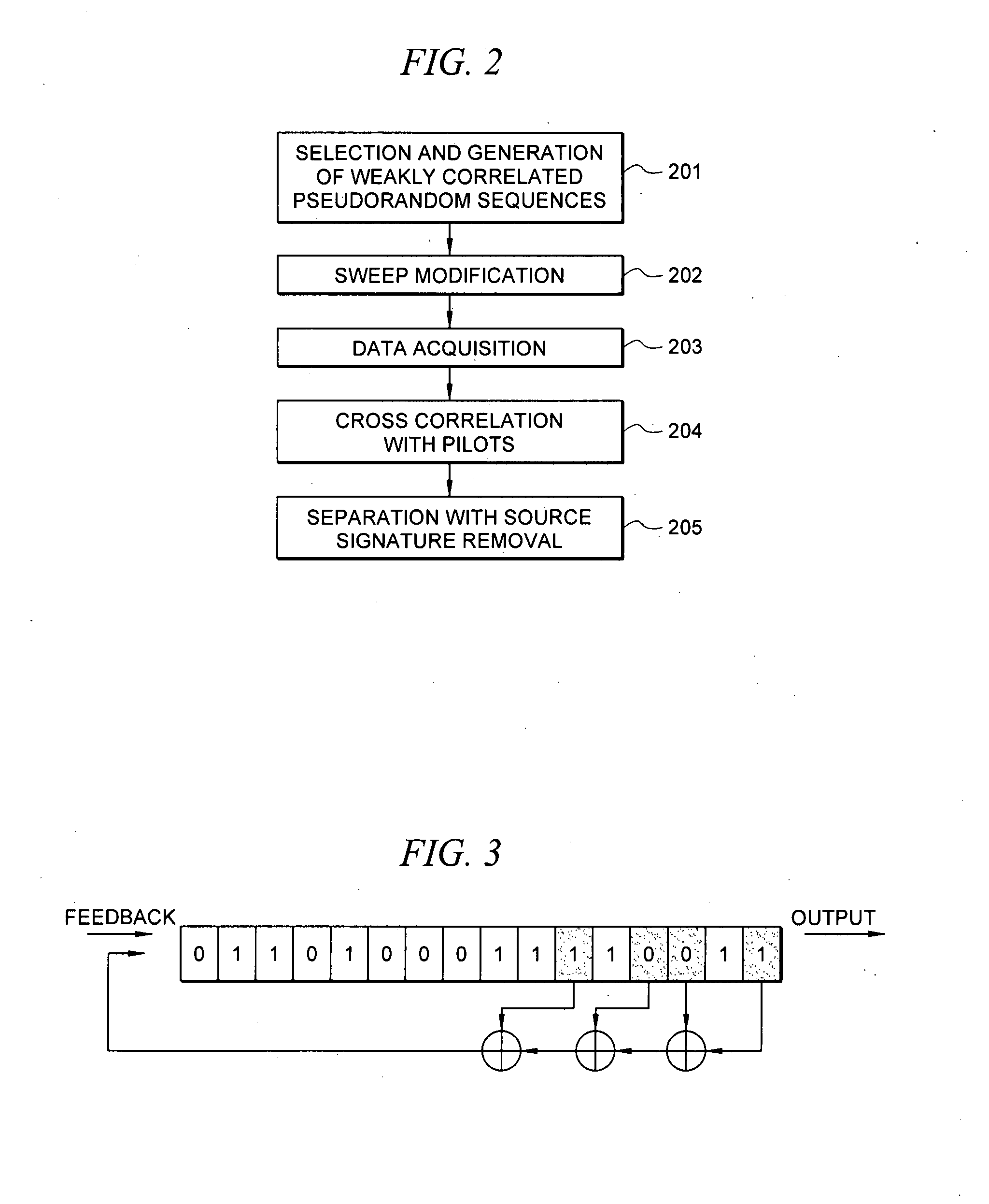
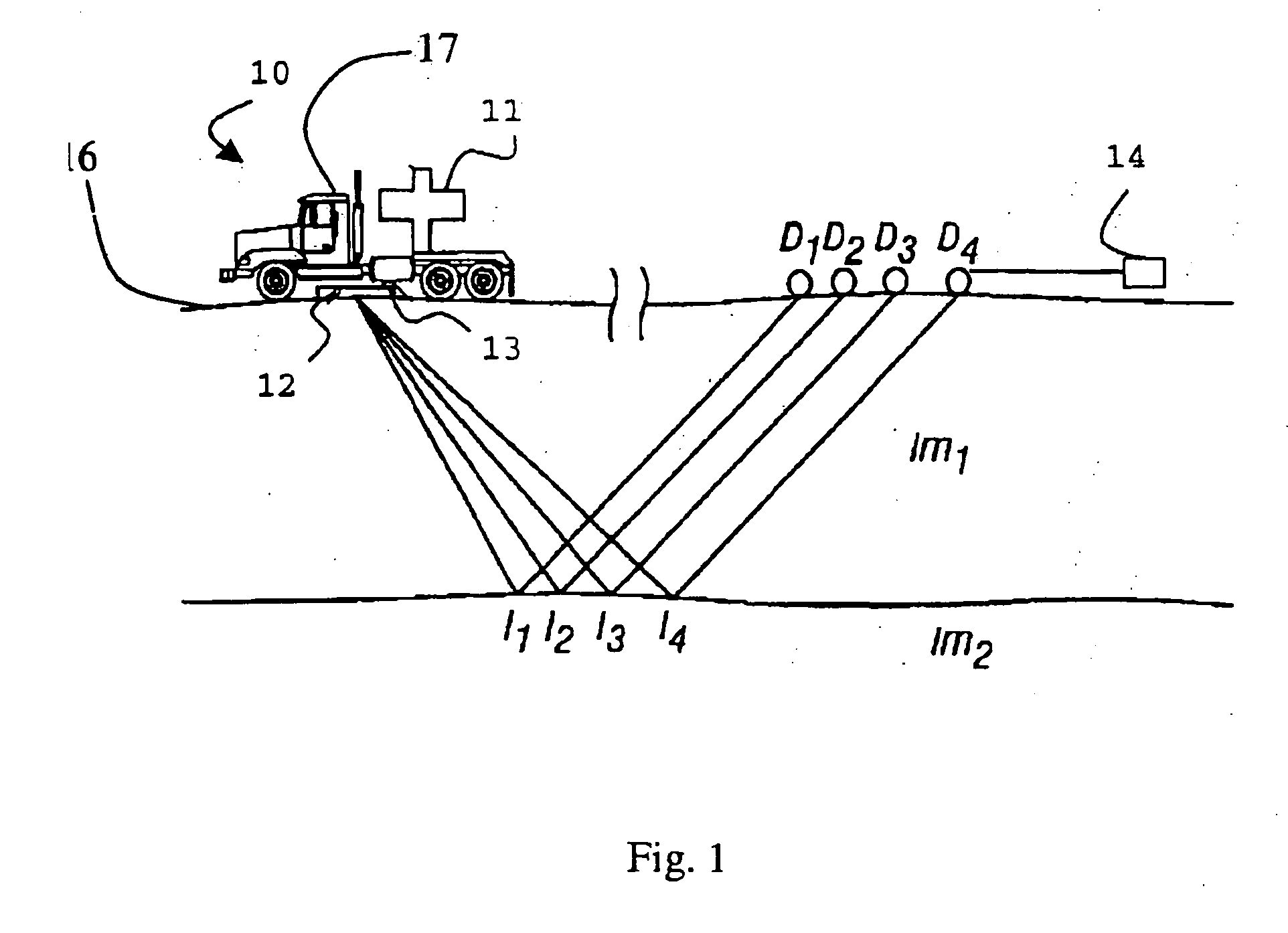
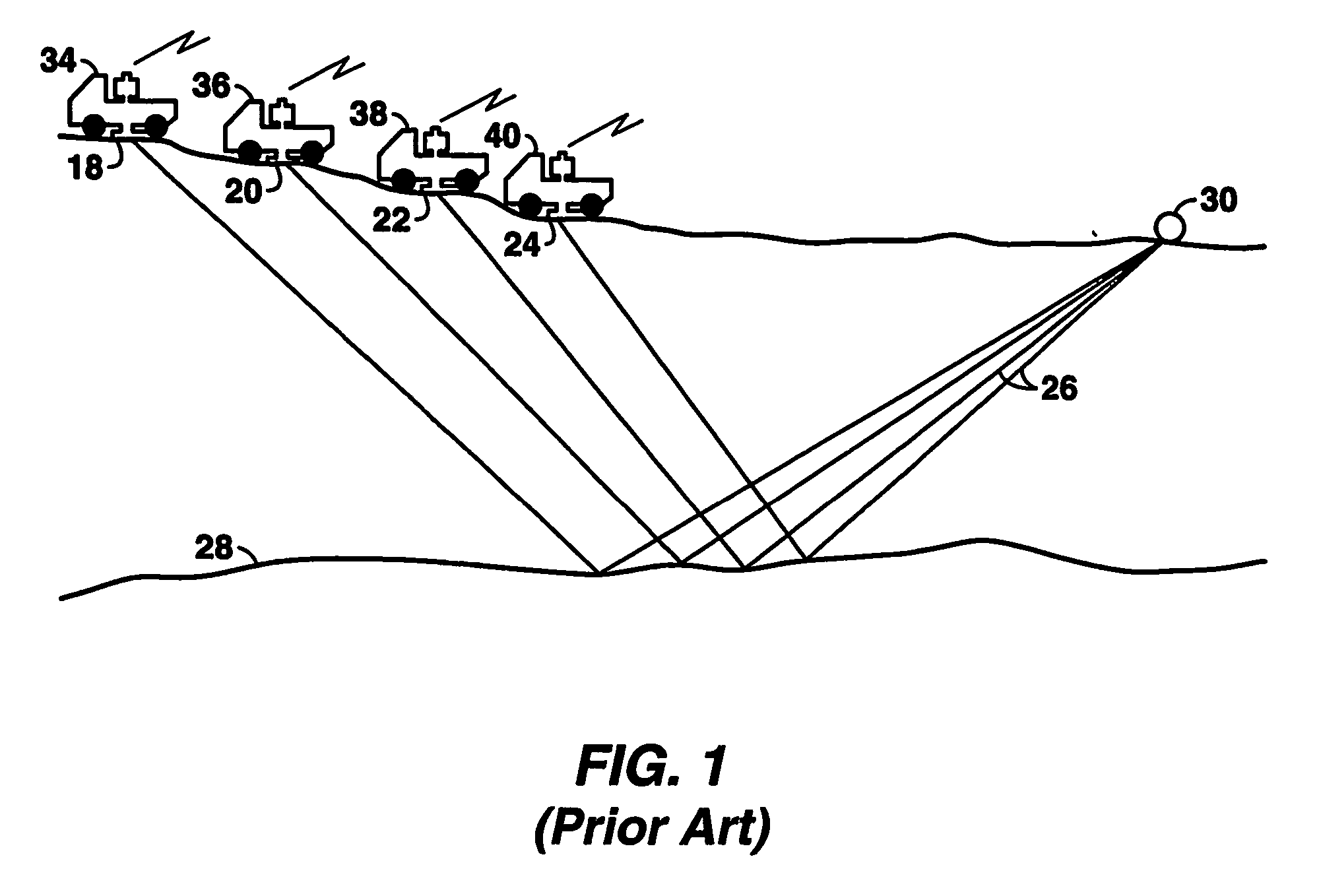
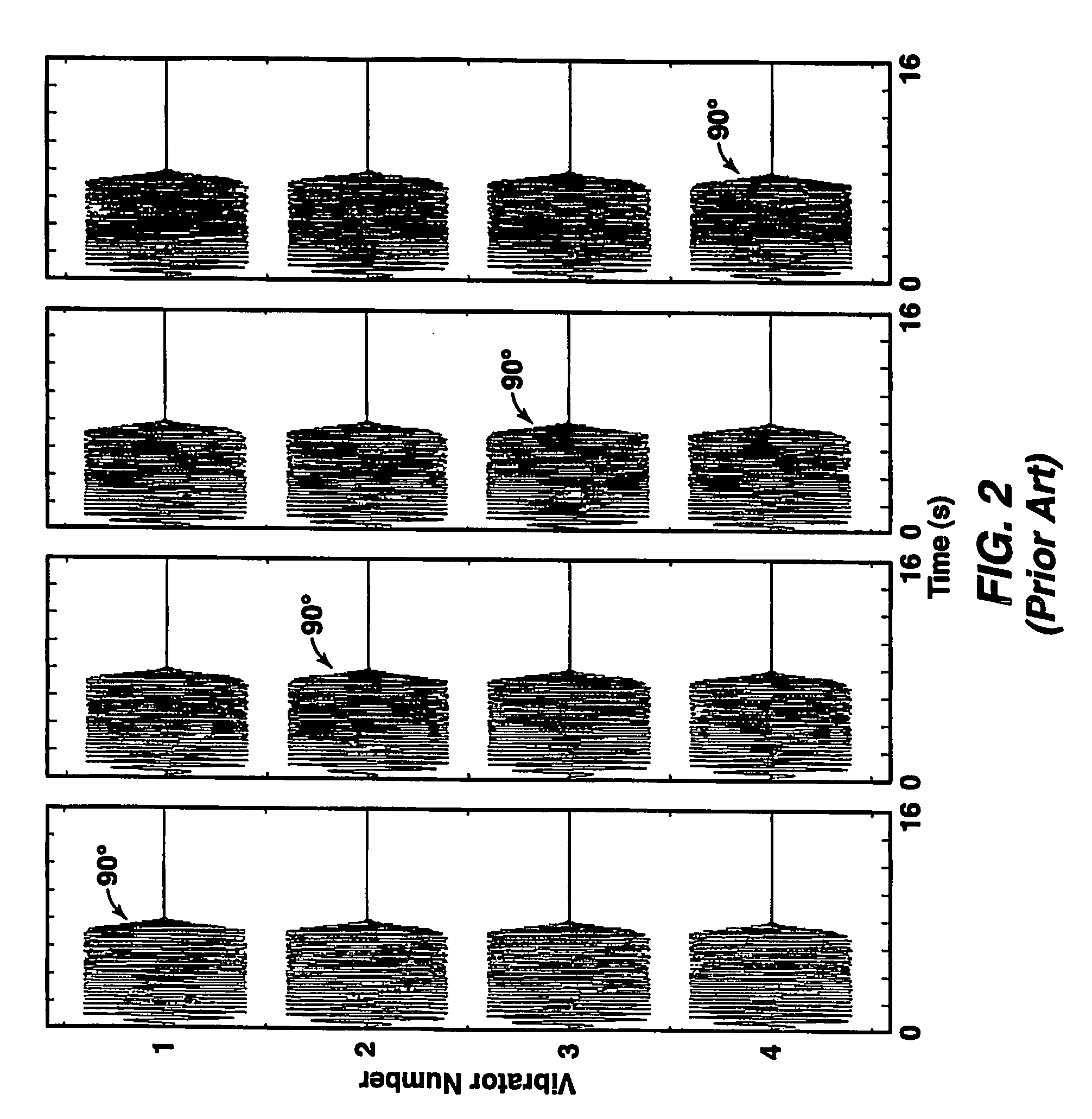
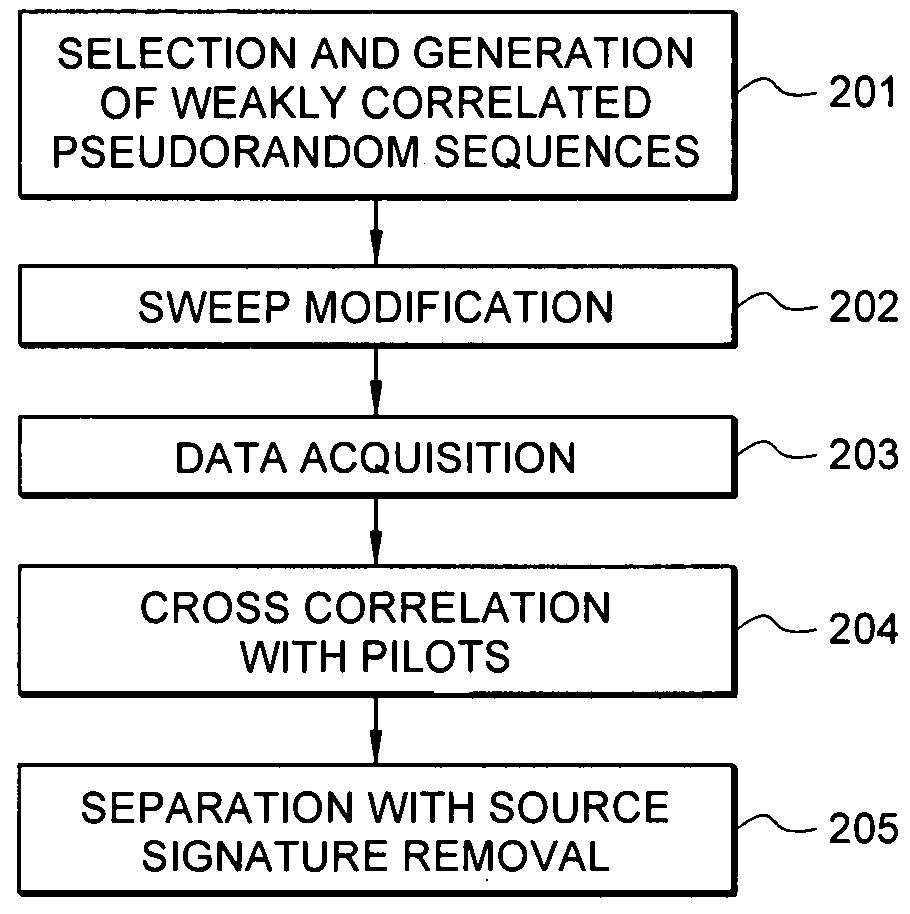
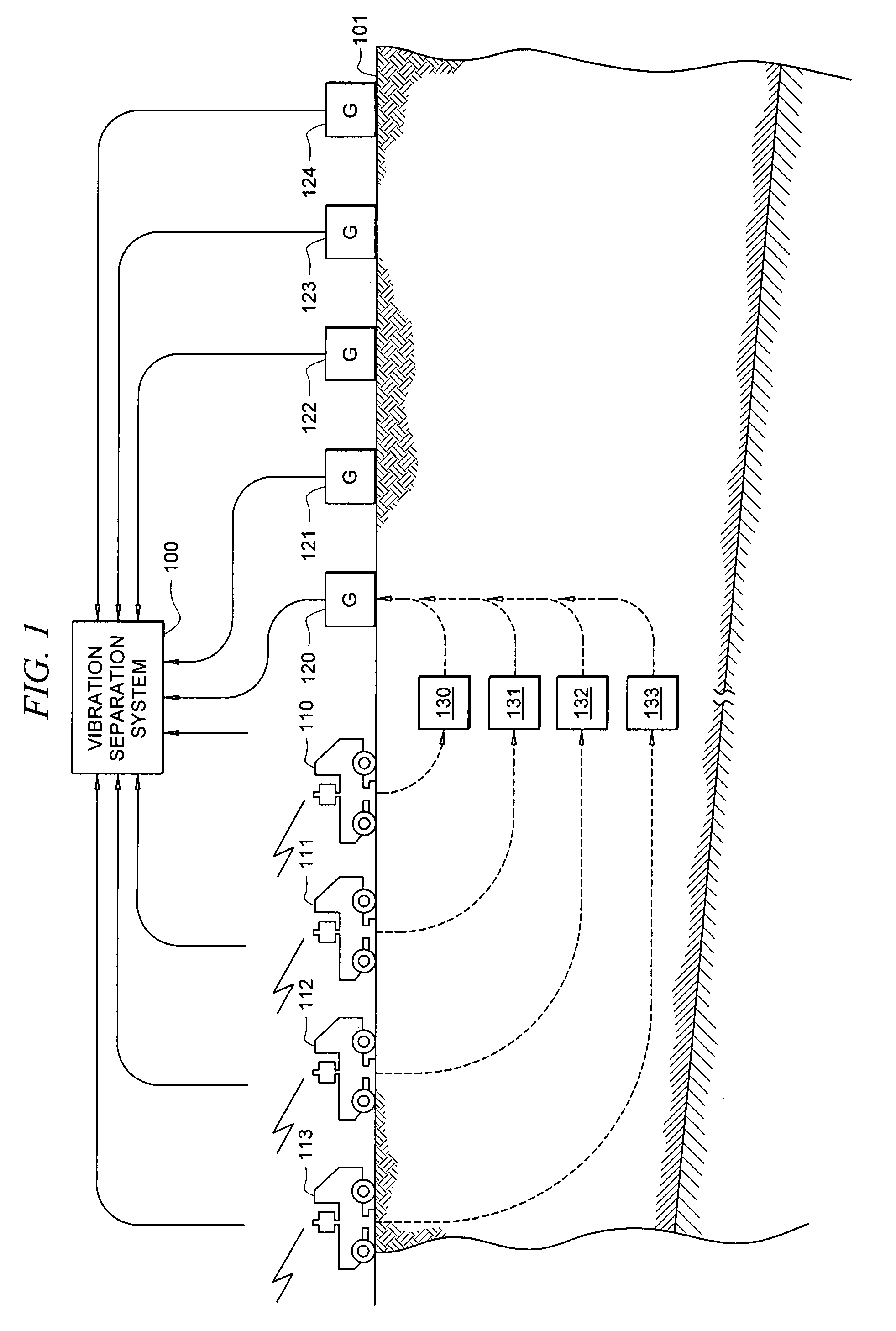
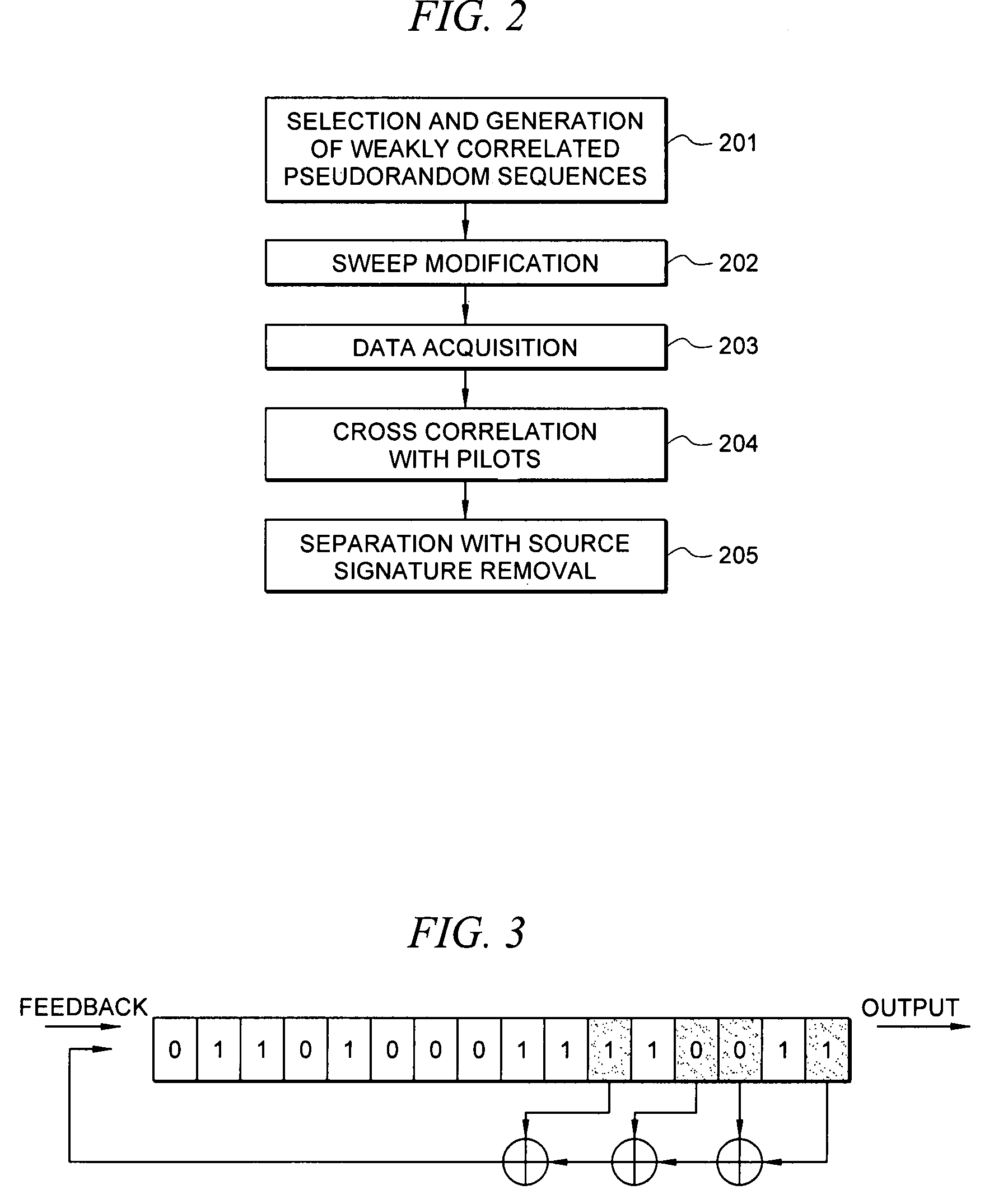
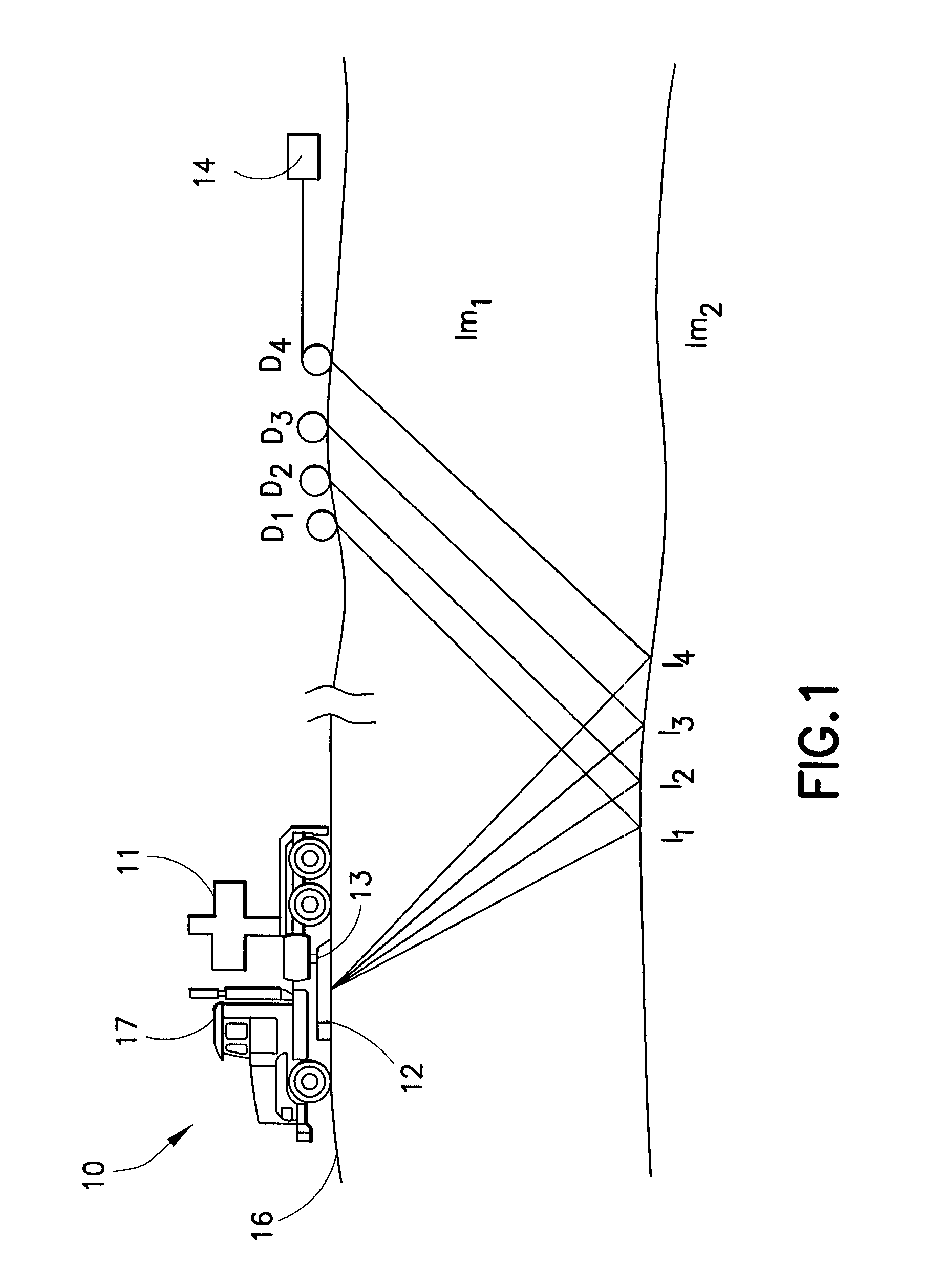
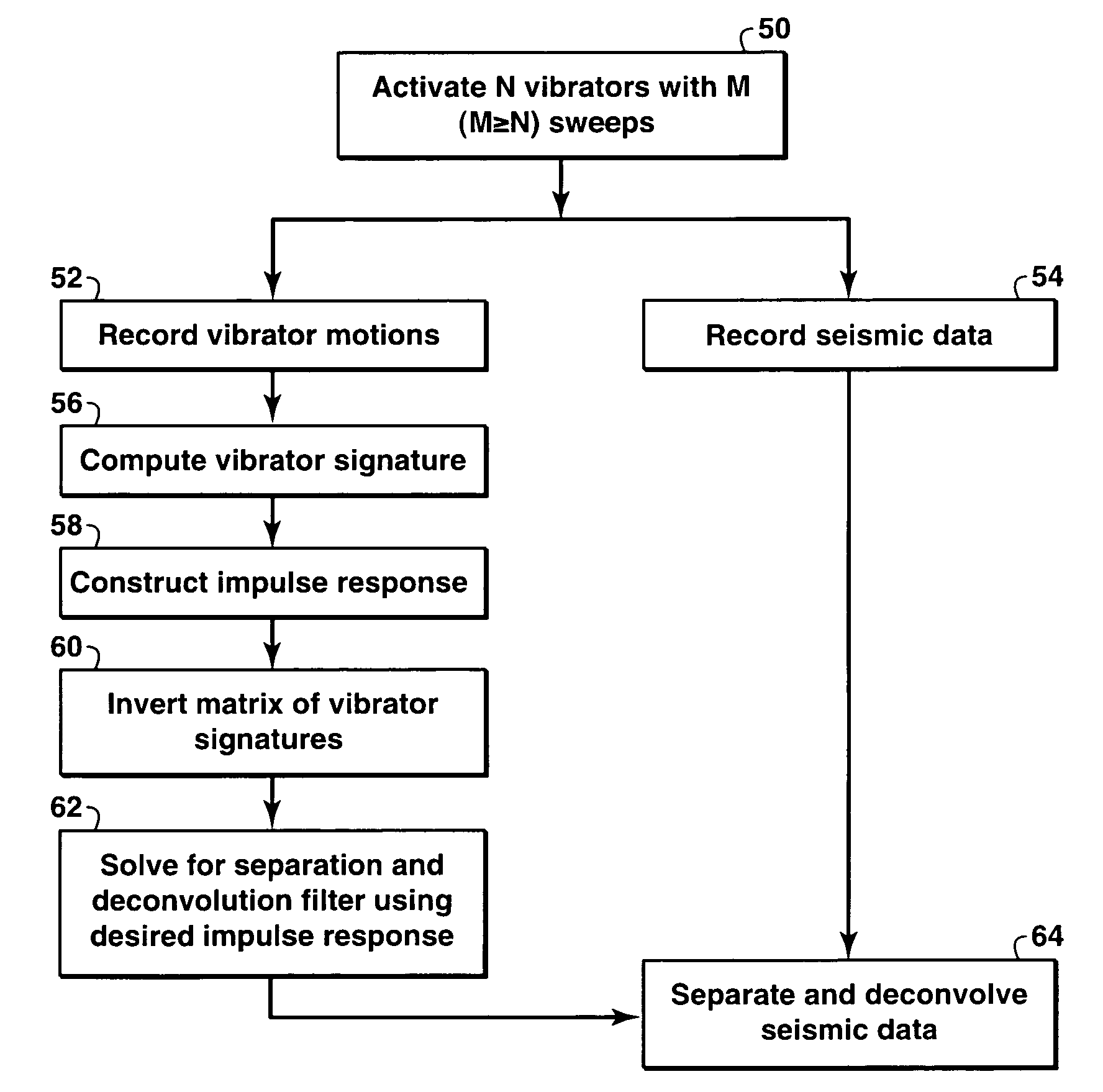
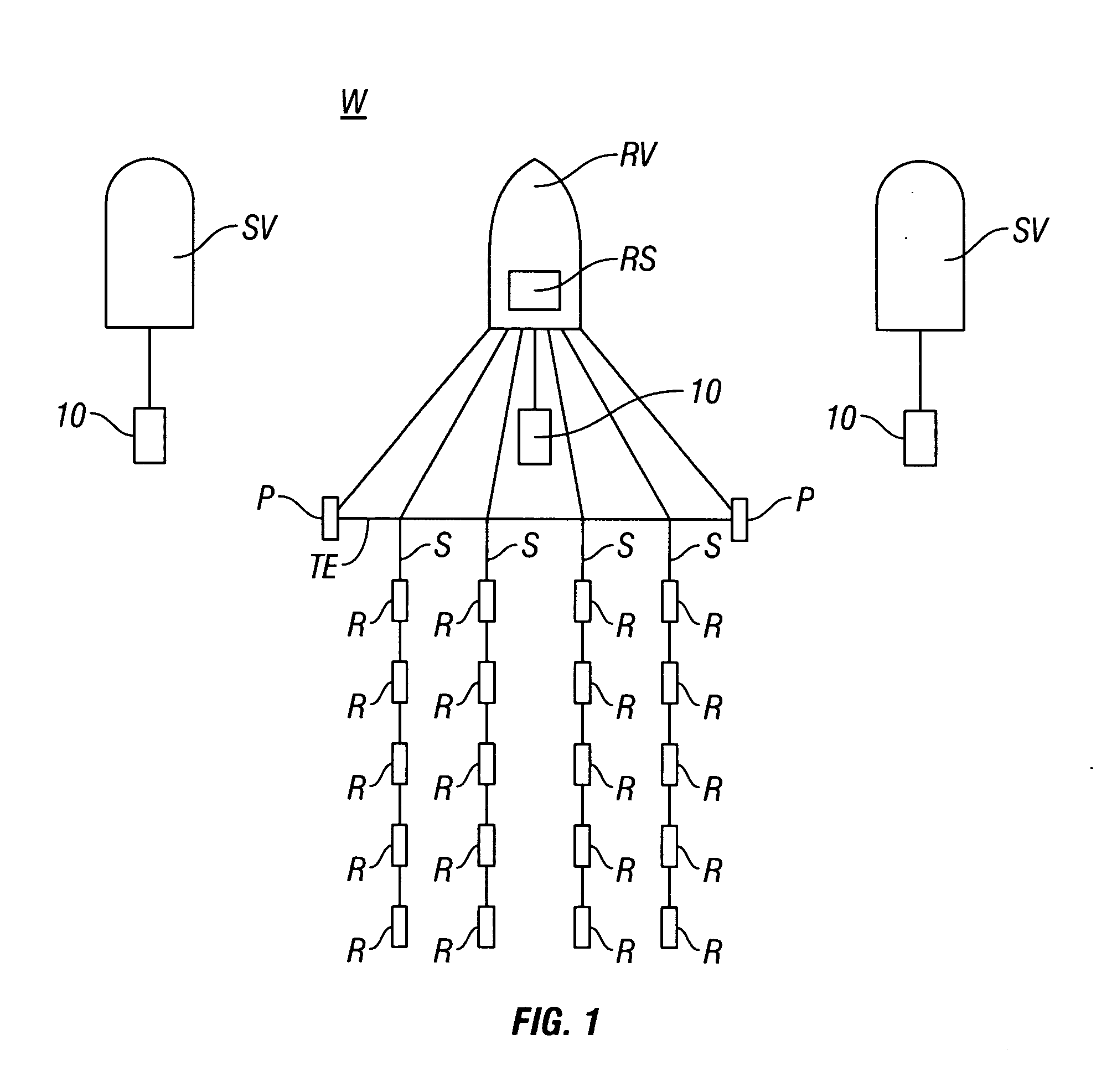
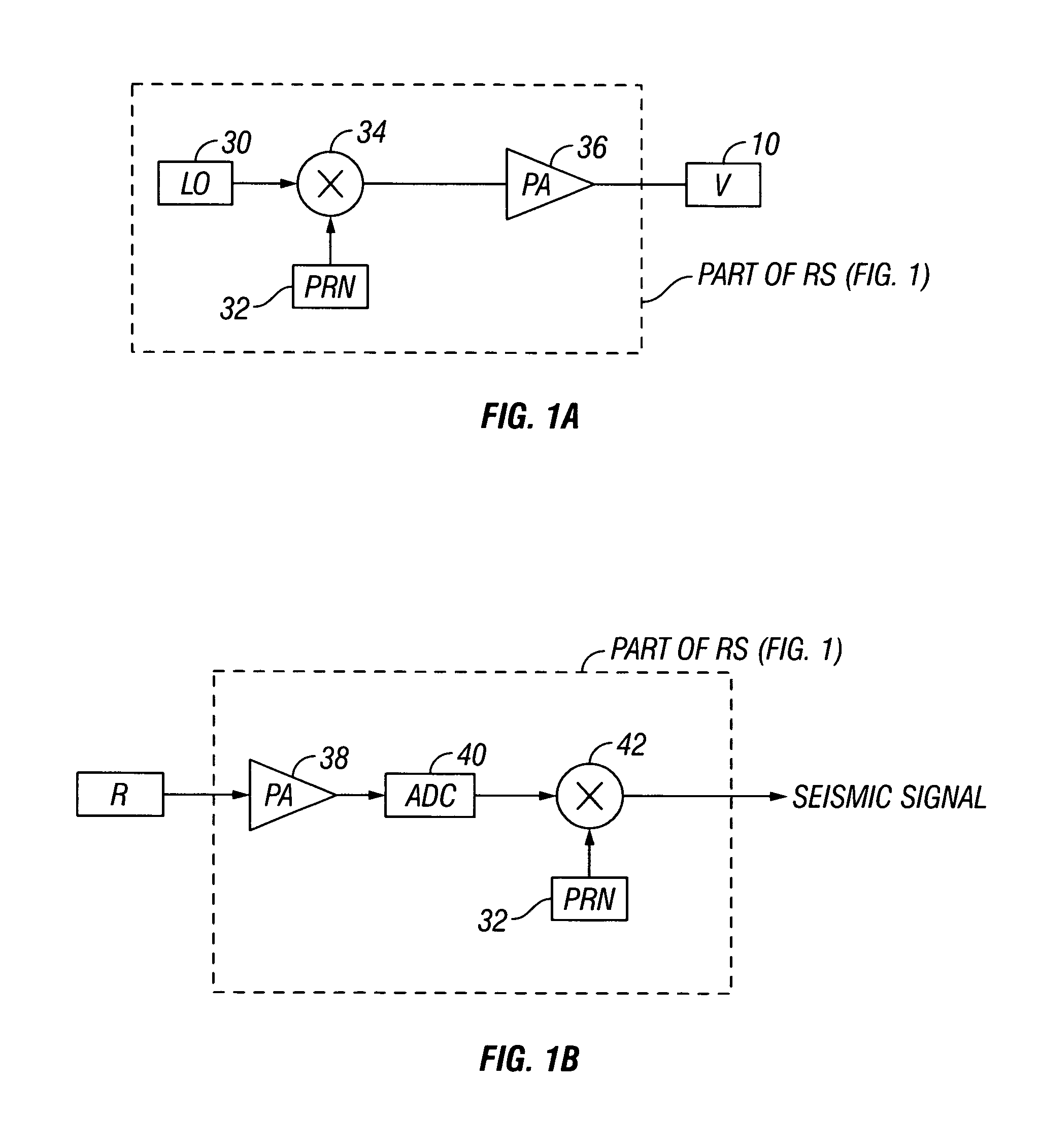
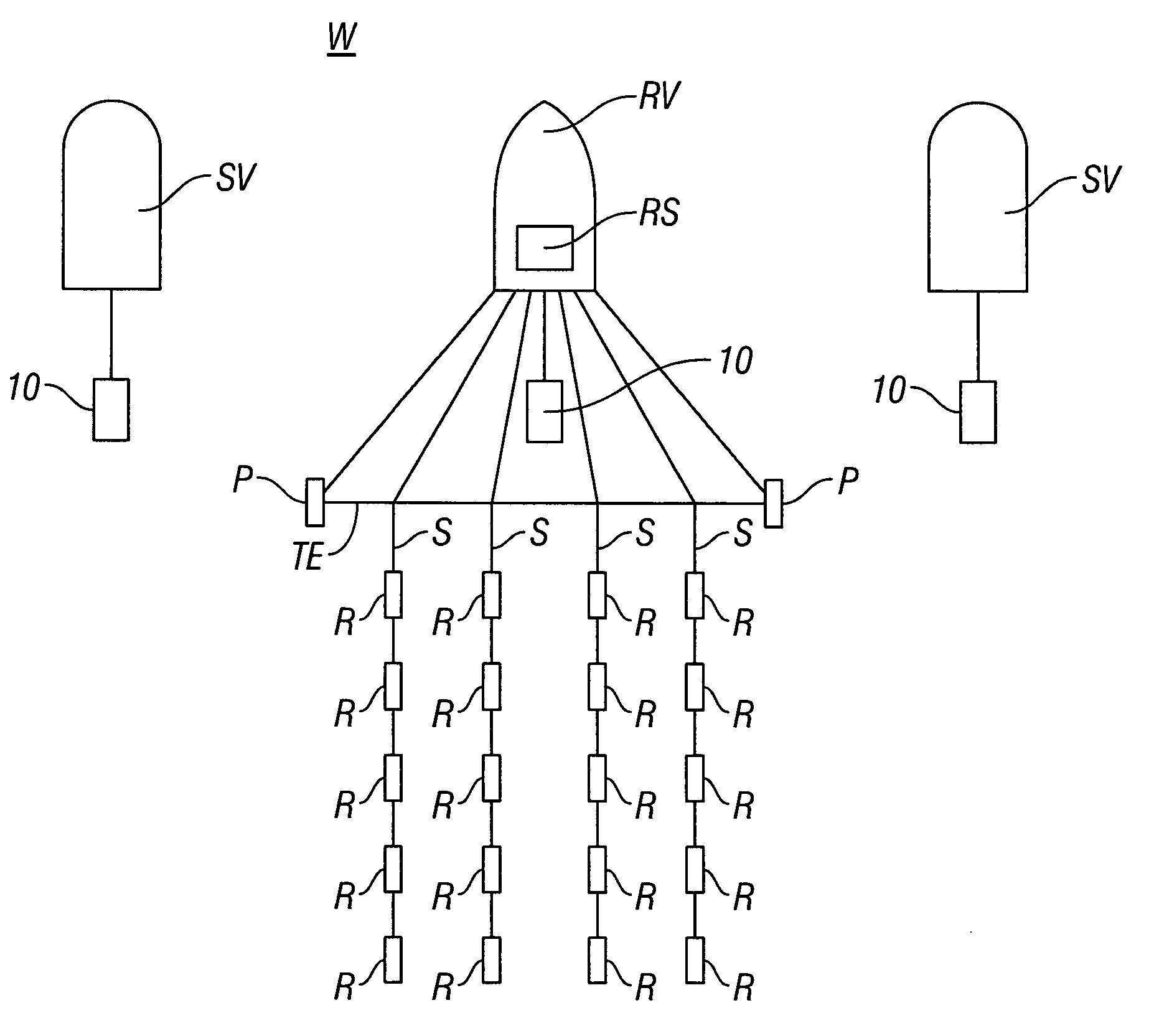
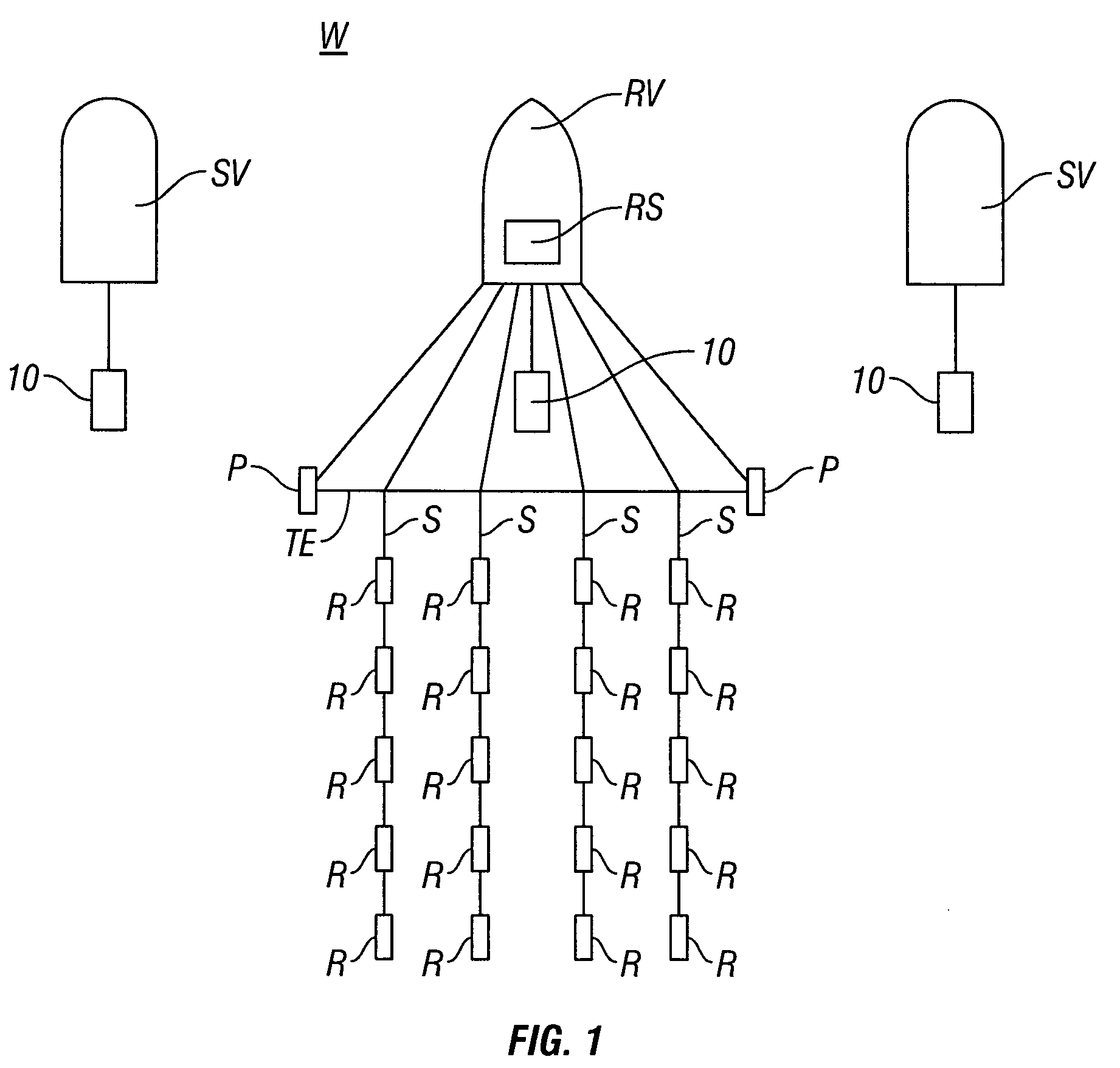
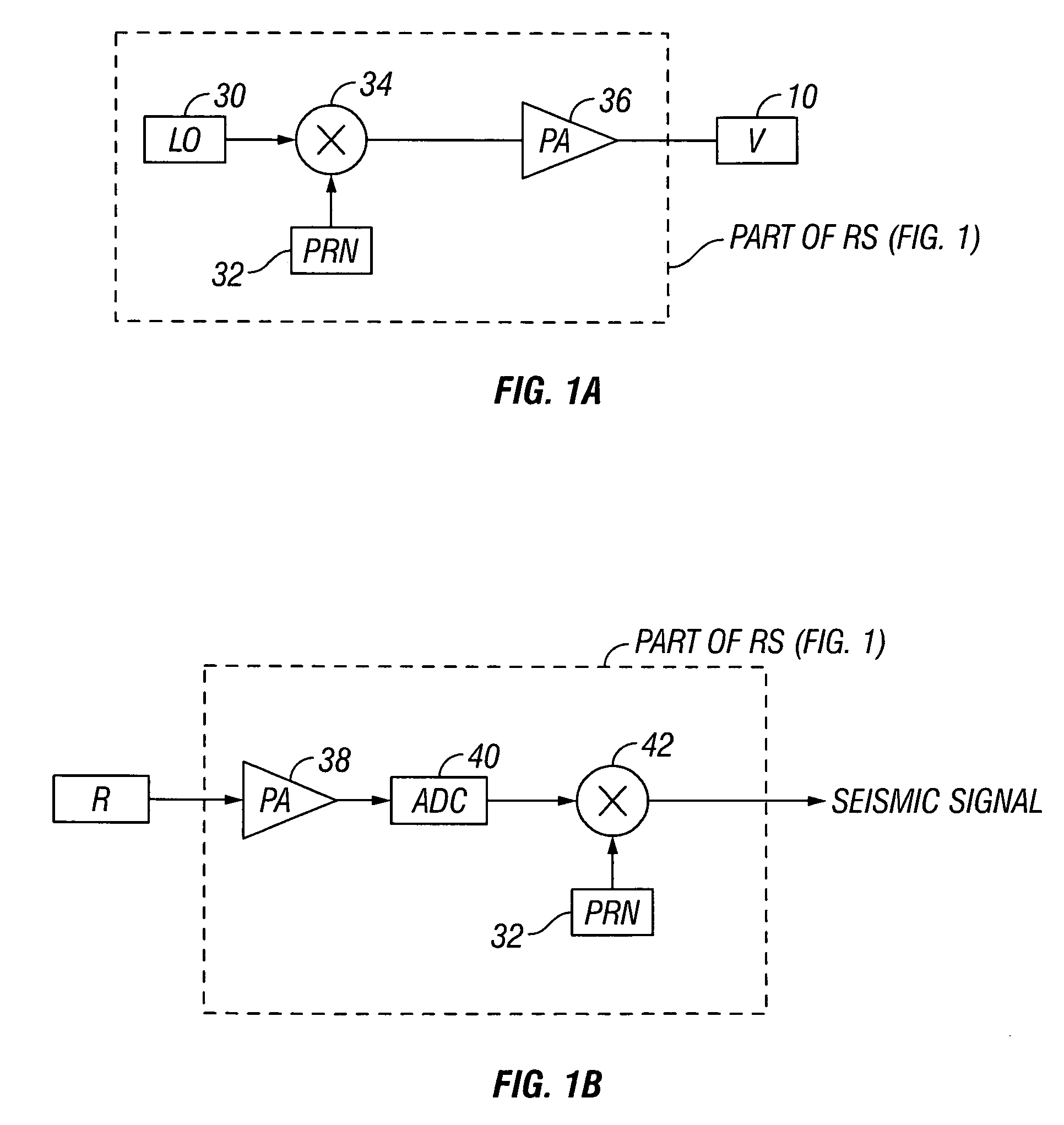
A method for the simultaneous operation of multiple seismic vibrators using unique modified pseudorandom sweeps and recovery of the transmission path response from each vibrator is disclosed. The vibrator sweeps are derived from pseudorandom binary sequences modified to be weakly correlated over a time window of interest, spectrally shaped and amplitude level compressed. Cross-correlation with each pilot signal is used to perform an initial separation of the composite received signal data set. Recordings of the motion of each vibrator are also cross-correlated with each pilot, windowed, and transformed to form a source cross-spectral density matrix in the frequency domain useful for source signature removal and for additional crosstalk-suppression between the separated records. After source signature removal in the frequency domain an inverse transform is applied to produce an estimate of each source-to-receiver earth response in the time domain. The method has application to both land and marine geophysical exploration.
Owner:SERCEL INC
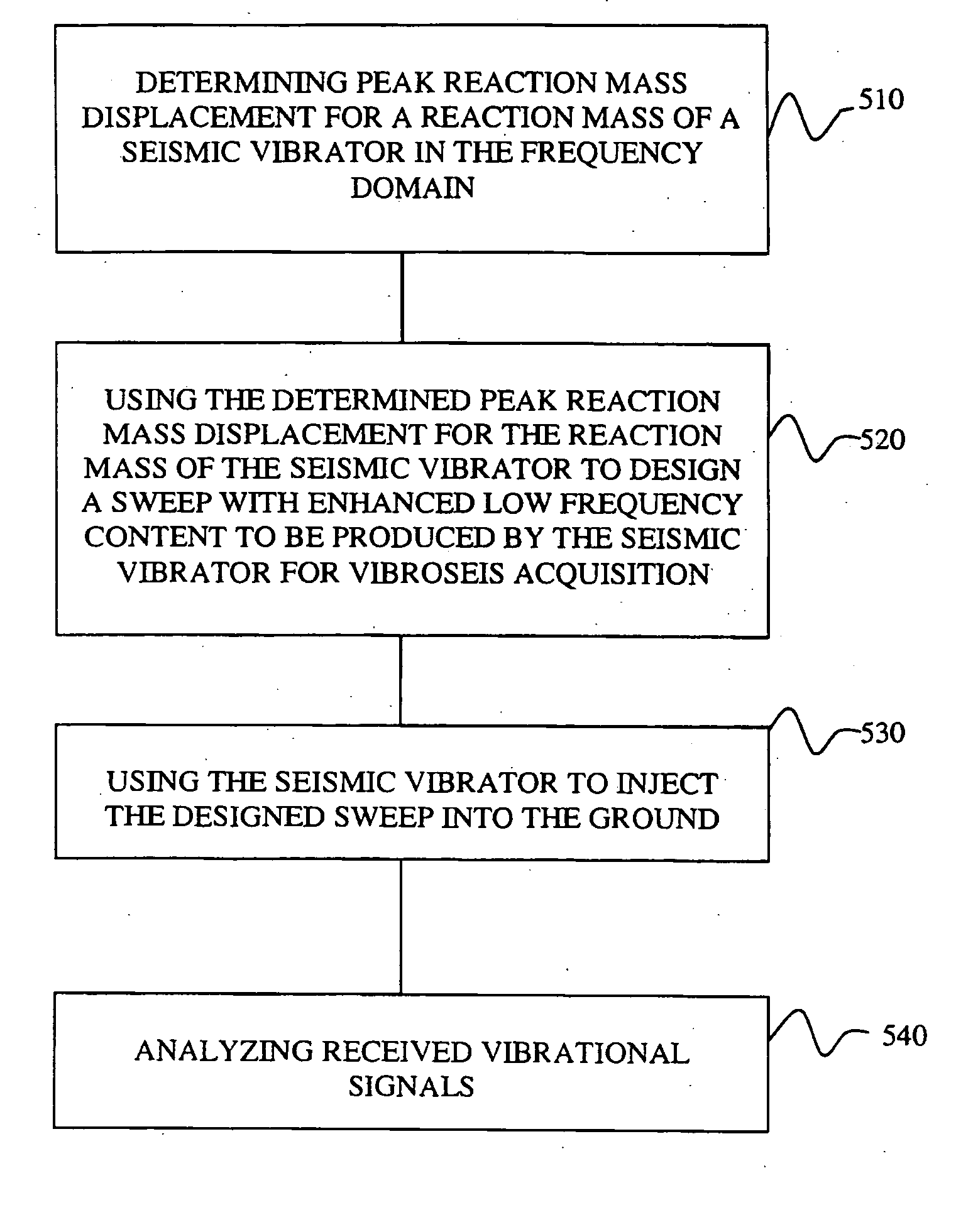
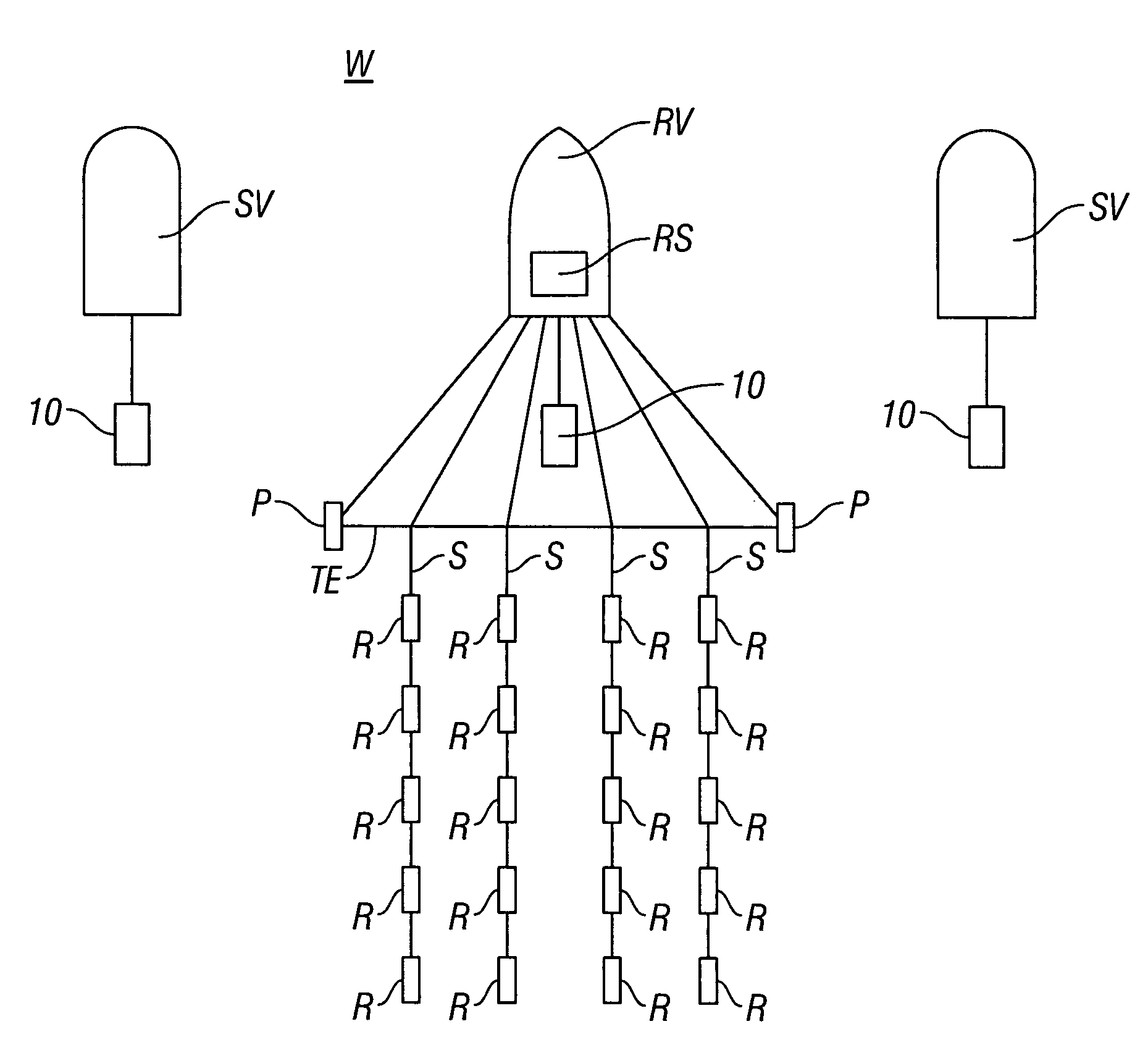
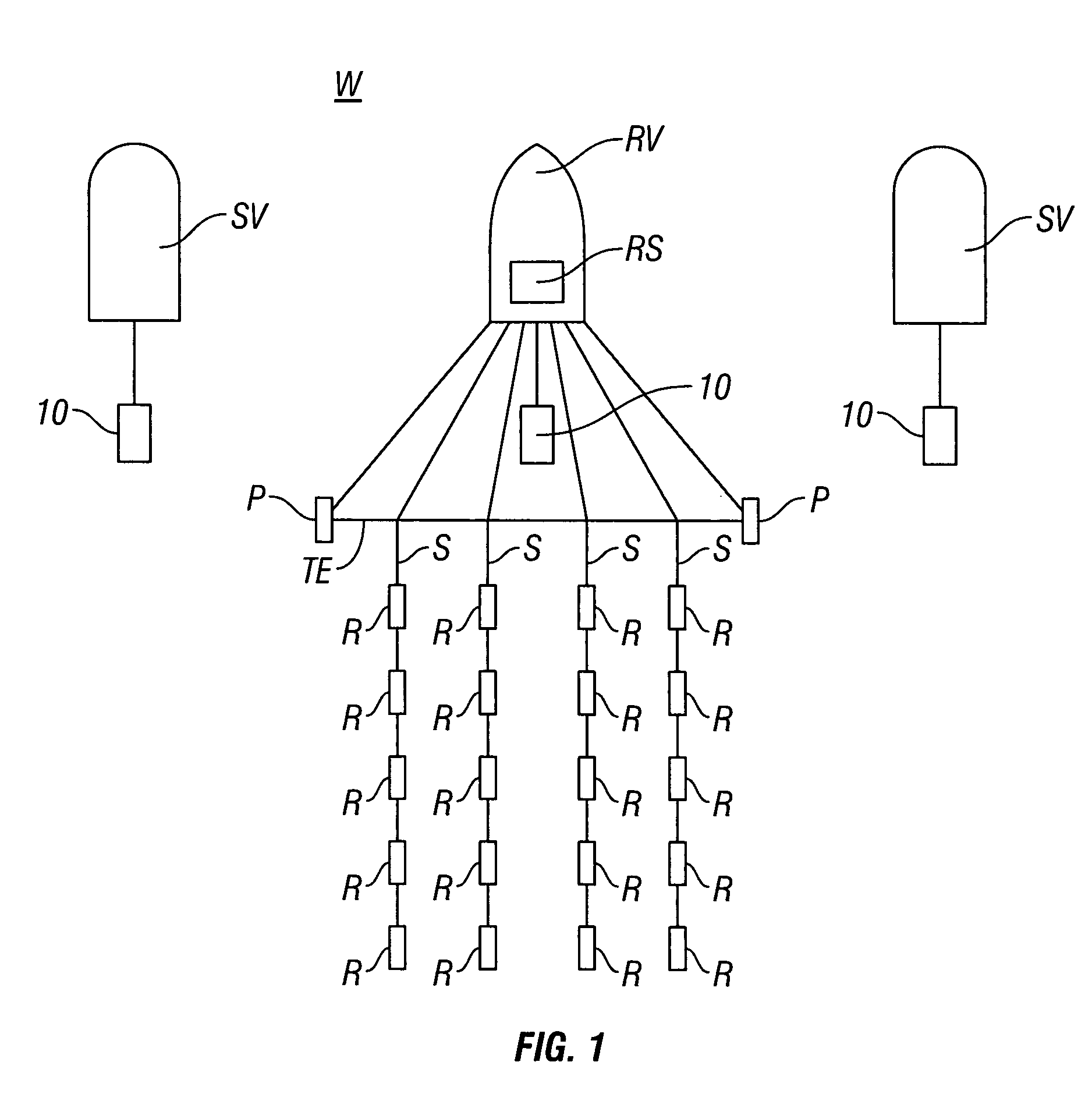
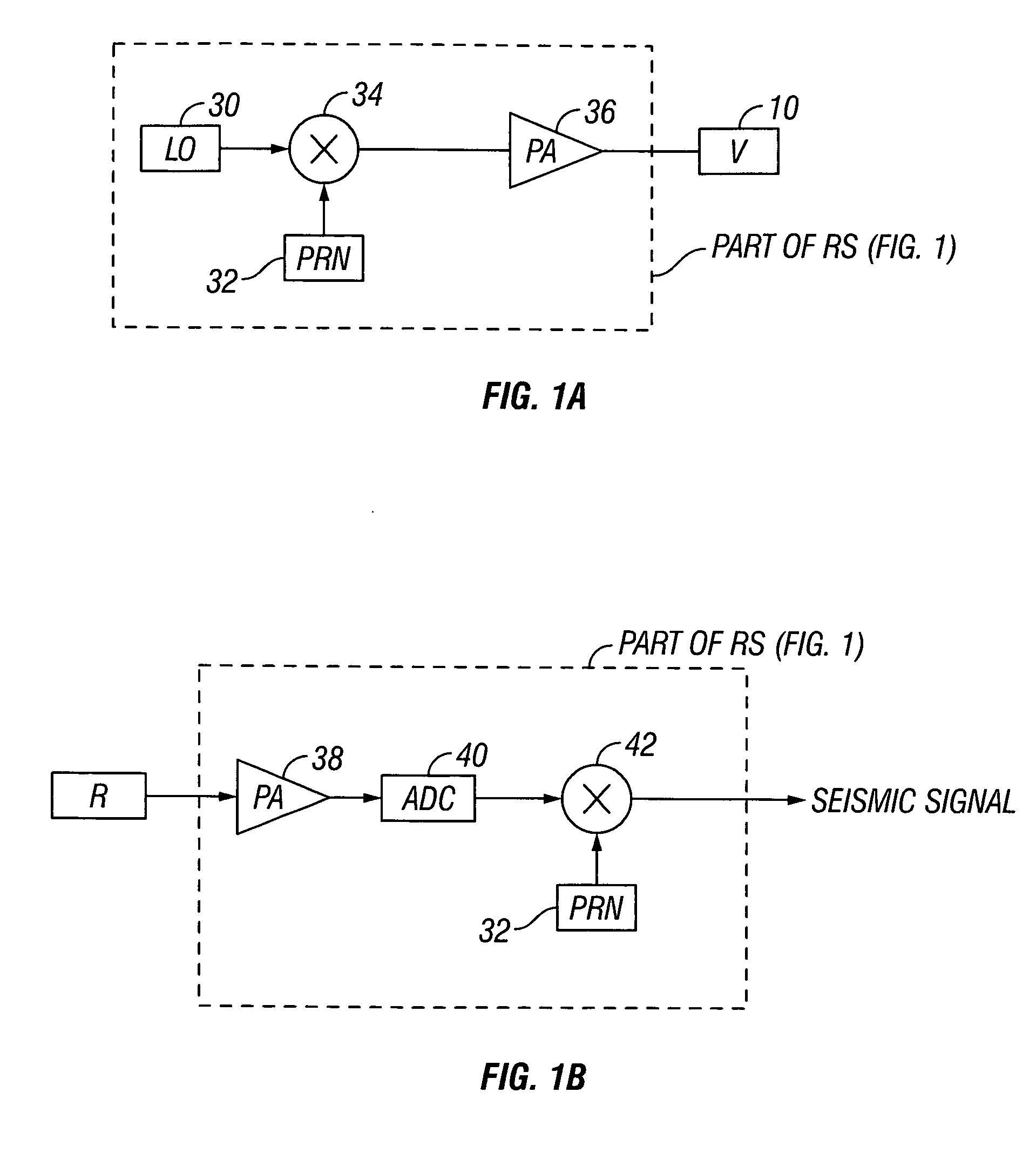
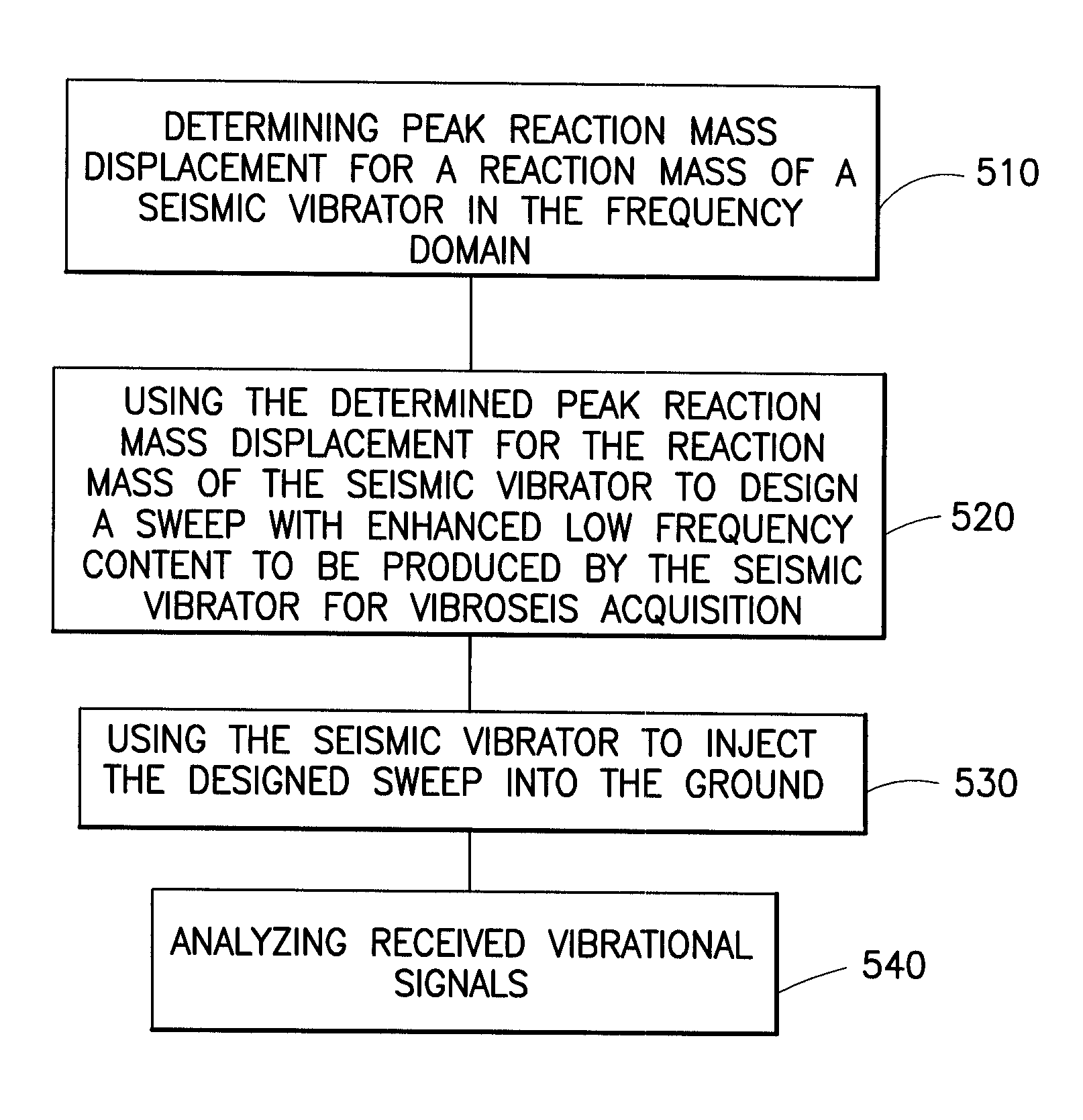
Systems and methods for enhancing low-frequency content in vibroseis acquisition
ActiveUS20070133354A1Enhanced/optimized amplitudeImprove errorSeismic data acquisitionSeismic signal processingEngineeringUltimate tensile strength
This invention relates in general to vibroseis and, more specifically, but not by way of limitation, to the enhancement and / or signal strength optimization of low frequency content of seismic signals for use in surveying boreholes and / or subsurface earth formations. In embodiments of the present invention, physical properties of a seismic vibrator may be analyzed and used to provide for determination of a driving force necessary to drive a reaction mass to produce a sweep signal with enhanced low frequency content for injection into the ground for vibroseis. In certain aspects, the physical properties may be considered independent of any geophysical properties related to operation of the seismic vibrator.
Owner:WESTERNGECO LLC
Method for continuous sweepting and separtion of multiple seismic vibrators
InactiveUS20060164916A1Reduce harmonic noiseReduce noiseSeismic data acquisitionSeismic signal processingContinuous scanningFourier transform on finite groups
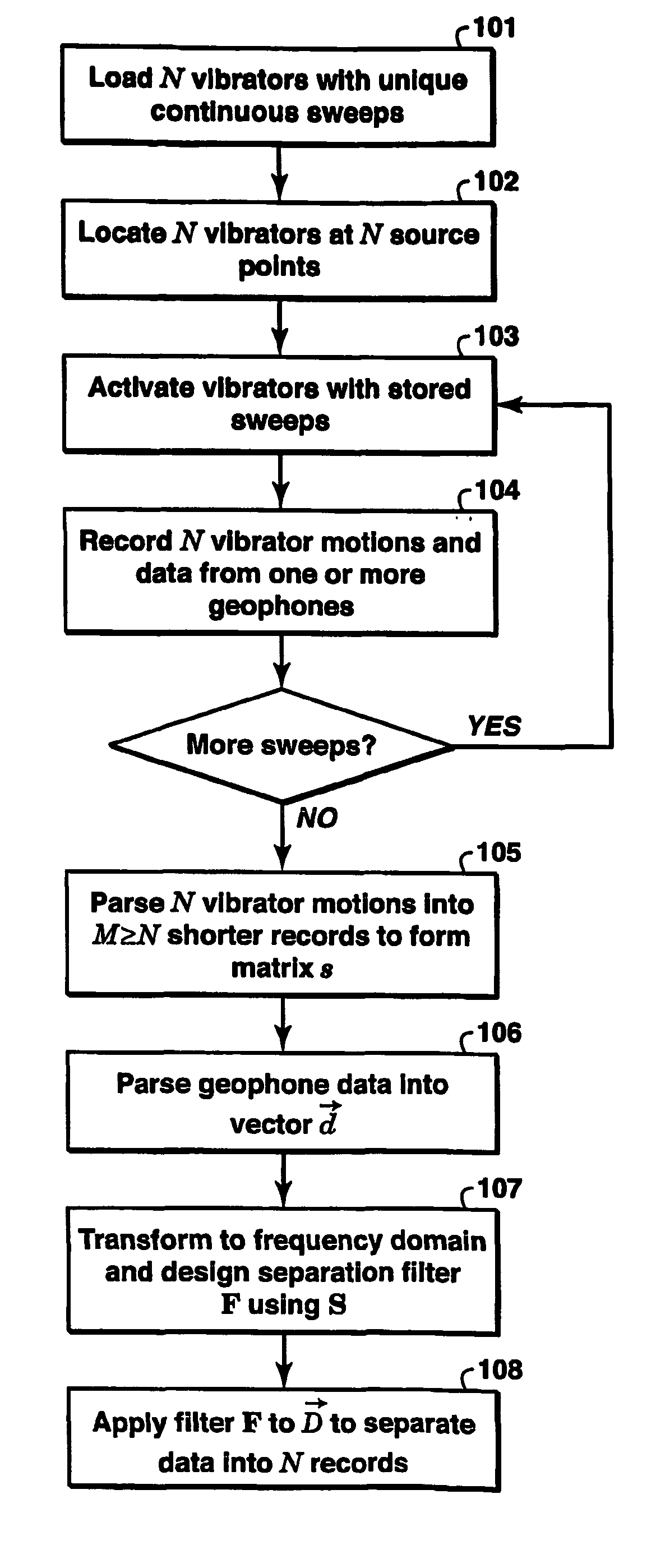
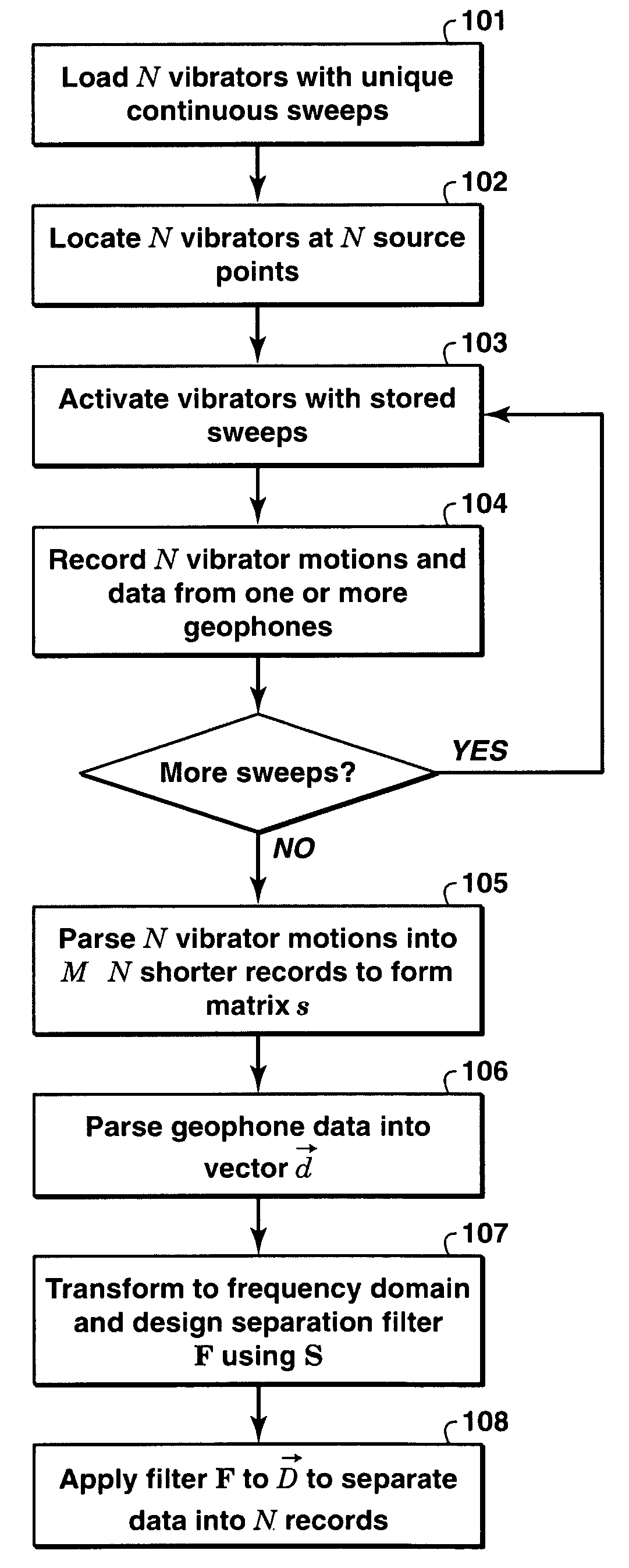
A method for simultaneously operating multiple seismic vibrators using continuous sweeps (little or no “listening” time between sweeps) for each vibrator, and recovering the separated seismic responses for each vibrator with the earth signature removed. Each vibrator is given a unique, continuous pilot signal. The earth response to the motion of each vibrator is measured or estimated. The vibrator motion records for each vibrator and the combined seismic data record for all the vibrators are parsed into separate shorter records. The shorter records are then used to form a system of simultaneous linear equations in the Fourier transform domain, following the HFVS method of Sallas and Allen. The equations are then solved for the separated earth responses.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL UPSTREAM RES CO
Efficient seismic data acquisition with source separation
A method for the simultaneous operation of multiple seismic vibrators using unique modified pseudorandom sweeps and recovery of the transmission path response from each vibrator is disclosed. The vibrator sweeps are derived from pseudorandom binary sequences modified to be weakly correlated over a time window of interest, spectrally shaped and amplitude level compressed. Cross-correlation with each pilot signal is used to perform an initial separation of the composite received signal data set. Recordings of the motion of each vibrator are also cross-correlated with each pilot, windowed, and transformed to form a source cross-spectral density matrix in the frequency domain useful for source signature removal and for additional crosstalk-suppression between the separated records. After source signature removal in the frequency domain an inverse transform is applied to produce an estimate of each source-to-receiver earth response in the time domain. The method has application to both land and marine geophysical exploration.
Owner:SERCEL INC
Method for optimizing energy output of from a seismic vibrator array
InactiveUS20100118647A1Seismic data acquisitionSeismology for water-covered areasSeismic energySeismic vibrator
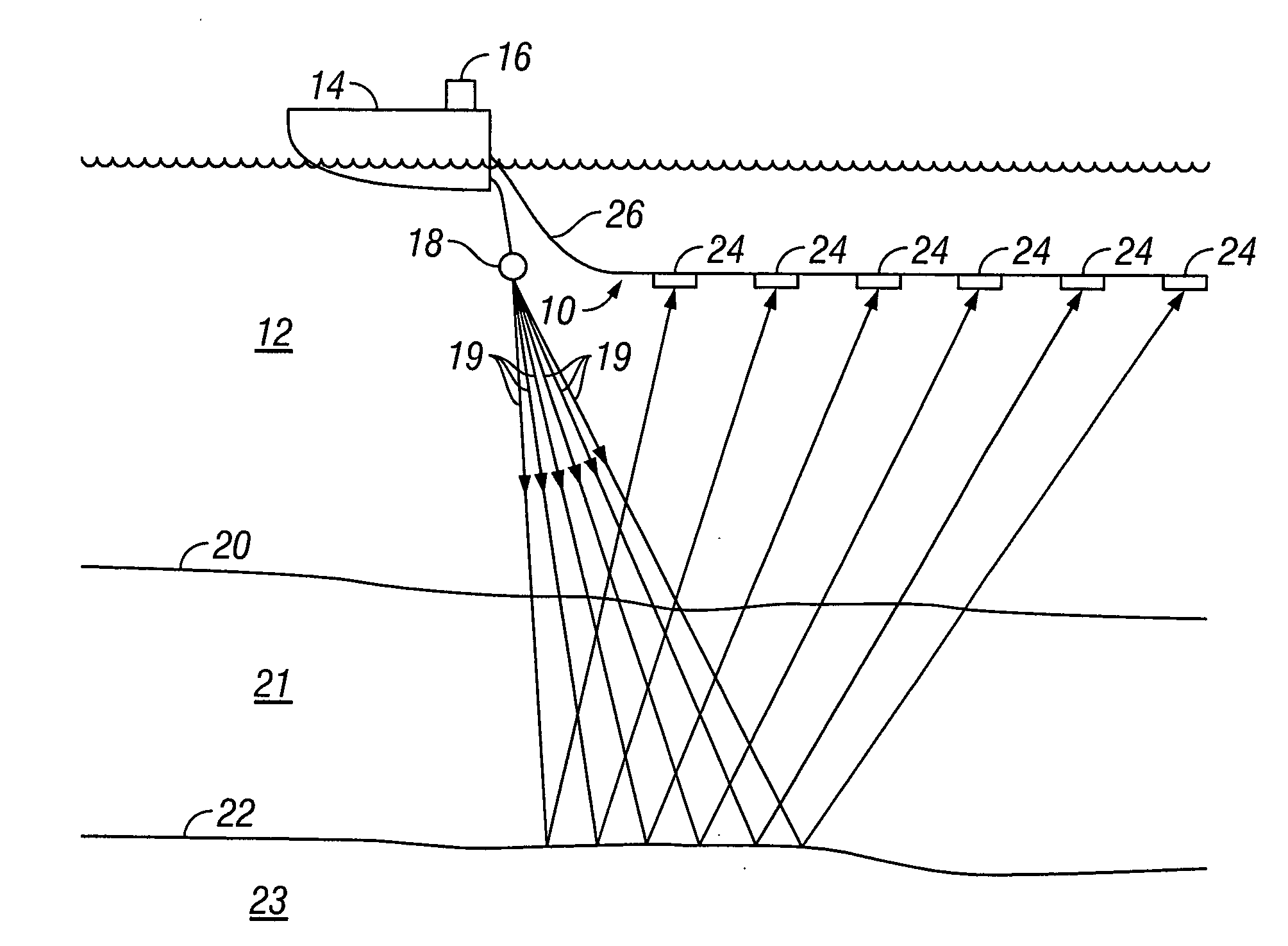
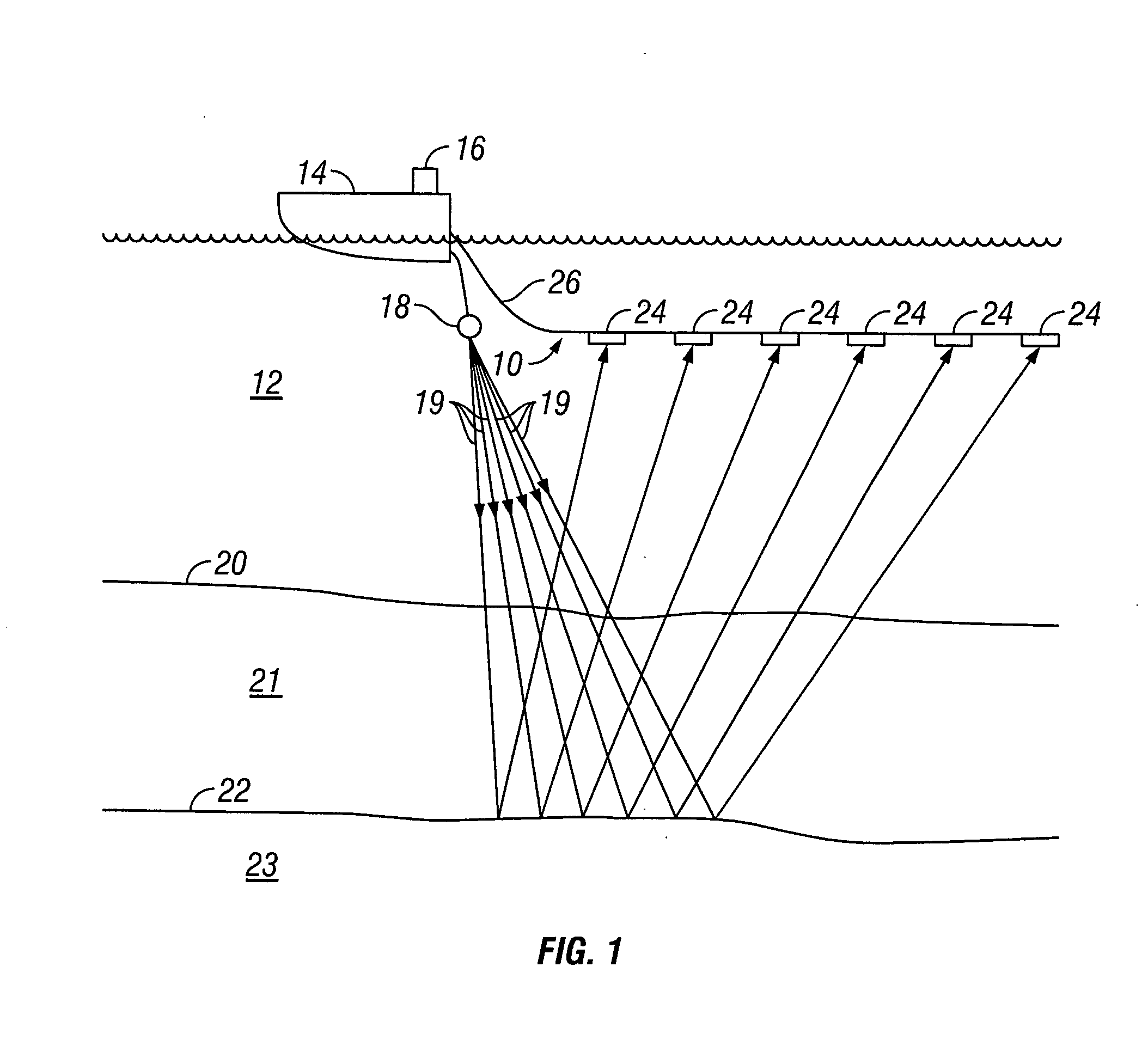
A method for generating seismic energy for subsurface surveying includes operating a first seismic vibrator and operating at least a second seismic vibrator in a body of water substantially contemporaneously with the operating the first seismic vibrator. Each vibrator has a different selected frequency response, and the vibrators each are operated at a depth in the water such that a surface ghost amplifies a downward output of each vibrator within a selected frequency range. A signal used to drive each vibrator has a frequency range corresponding to the frequency range of each vibrator.
Owner:PGS GEOPHYSICAL AS
Systems and methods for enhancing low-frequency content in vibroseis acquisition
ActiveUS7327633B2Enhanced/optimized amplitudeImprove errorSeismic data acquisitionSeismic signal processingEngineeringUltimate tensile strength
This invention relates in general to vibroseis and, more specifically, but not by way of limitation, to the enhancement and / or signal strength optimization of low frequency content of seismic signals for use in surveying boreholes and / or subsurface earth formations. In embodiments of the present invention, physical properties of a seismic vibrator may be analyzed and used to provide for determination of a driving force necessary to drive a reaction mass to produce a sweep signal with enhanced low frequency content for injection into the ground for vibroseis. In certain aspects, the physical properties may be considered independent of any geophysical properties related to operation of the seismic vibrator.
Owner:WESTERNGECO LLC
Shaped high frequency vibratory source
ActiveUS7436734B2Improved noise suppressionSeismic data acquisitionSeismic signal processingConvolution filterBiological activation
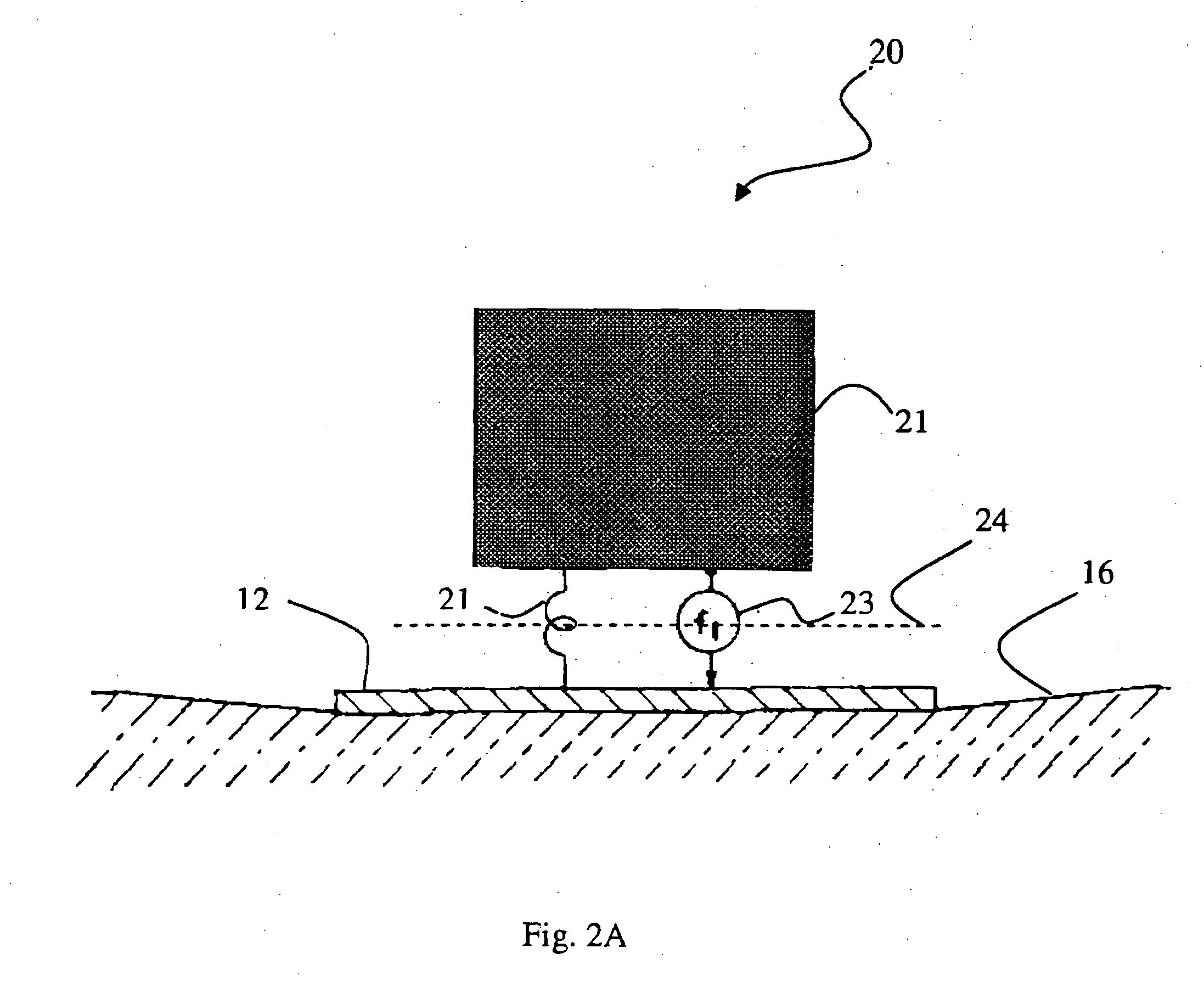
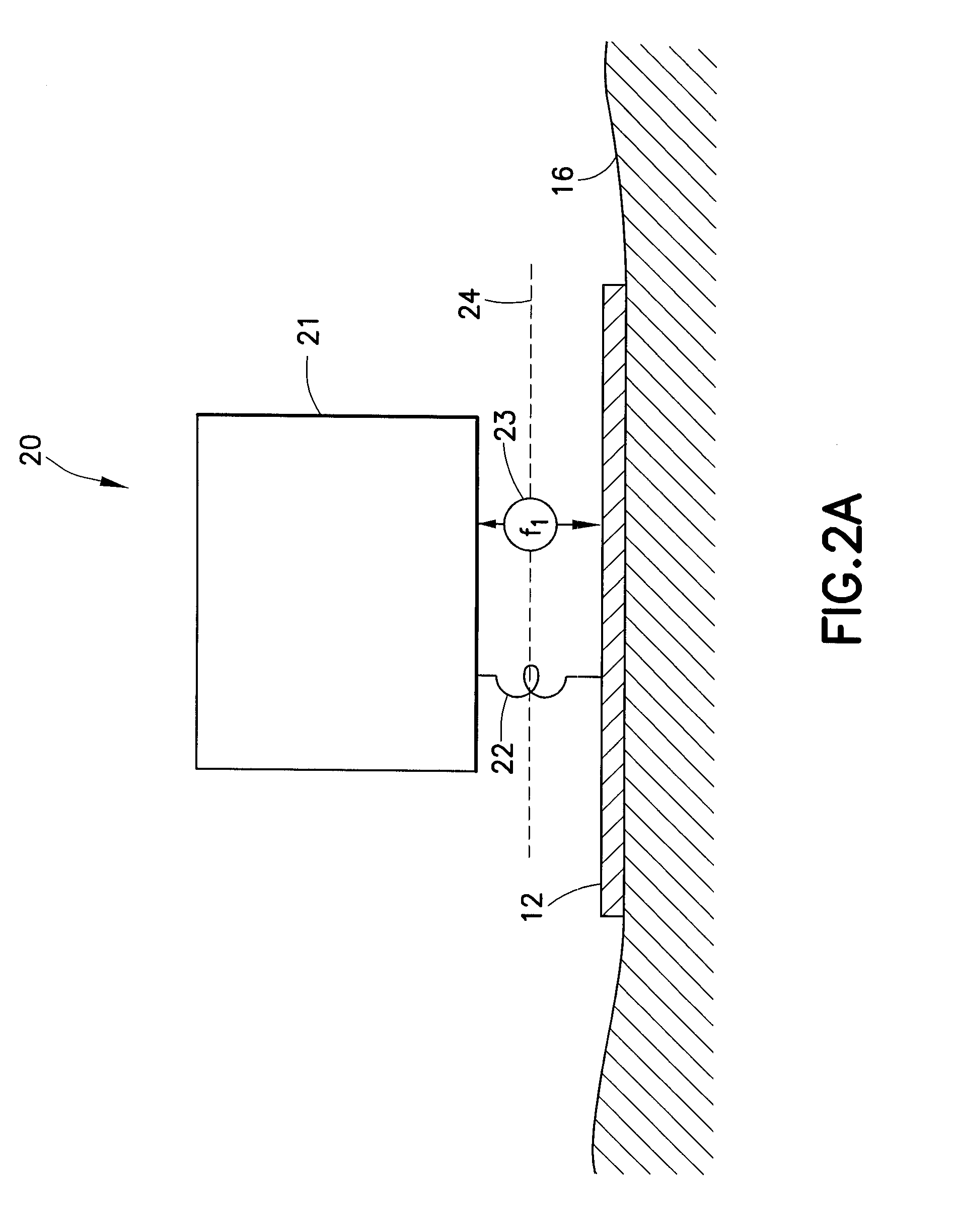
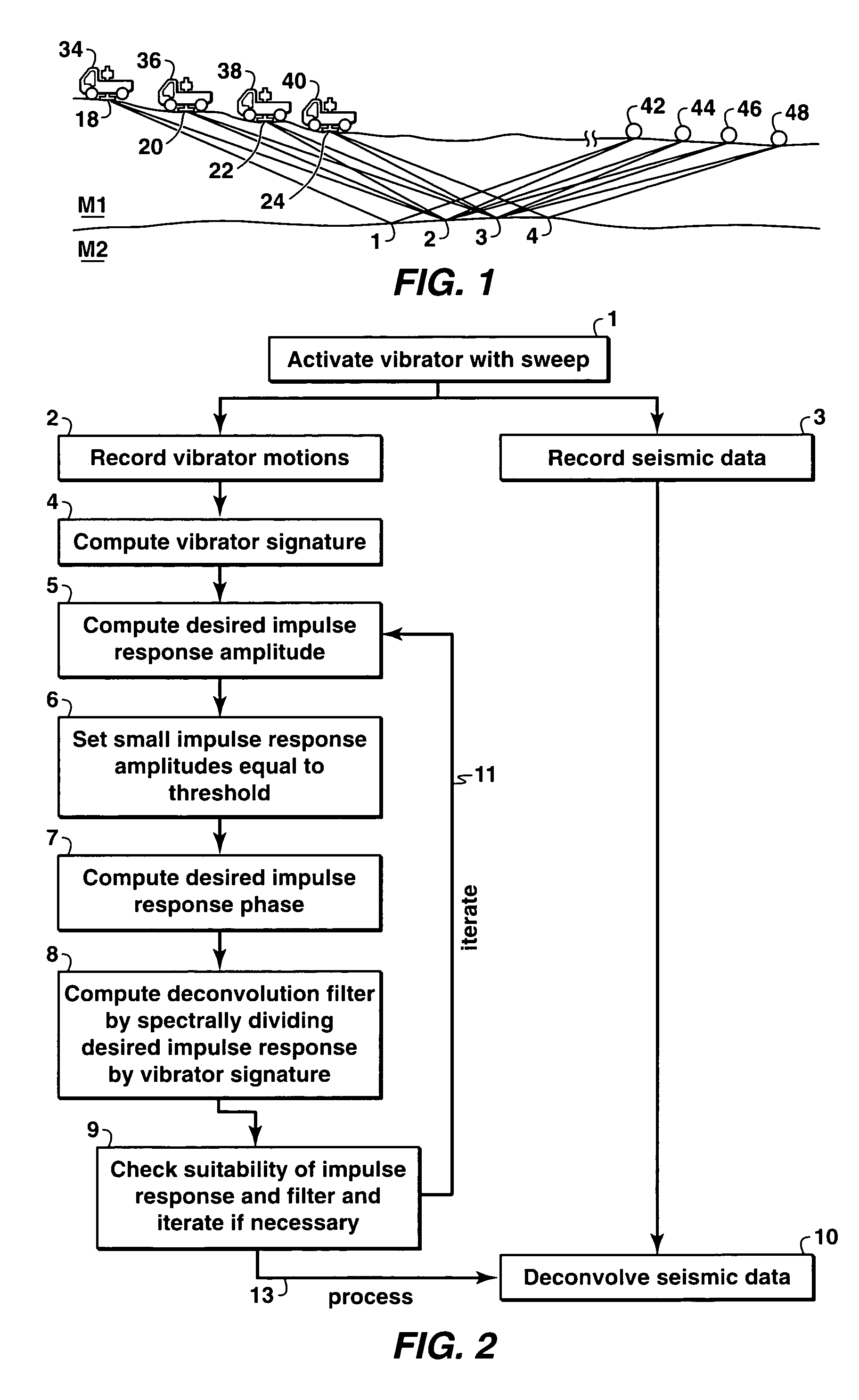
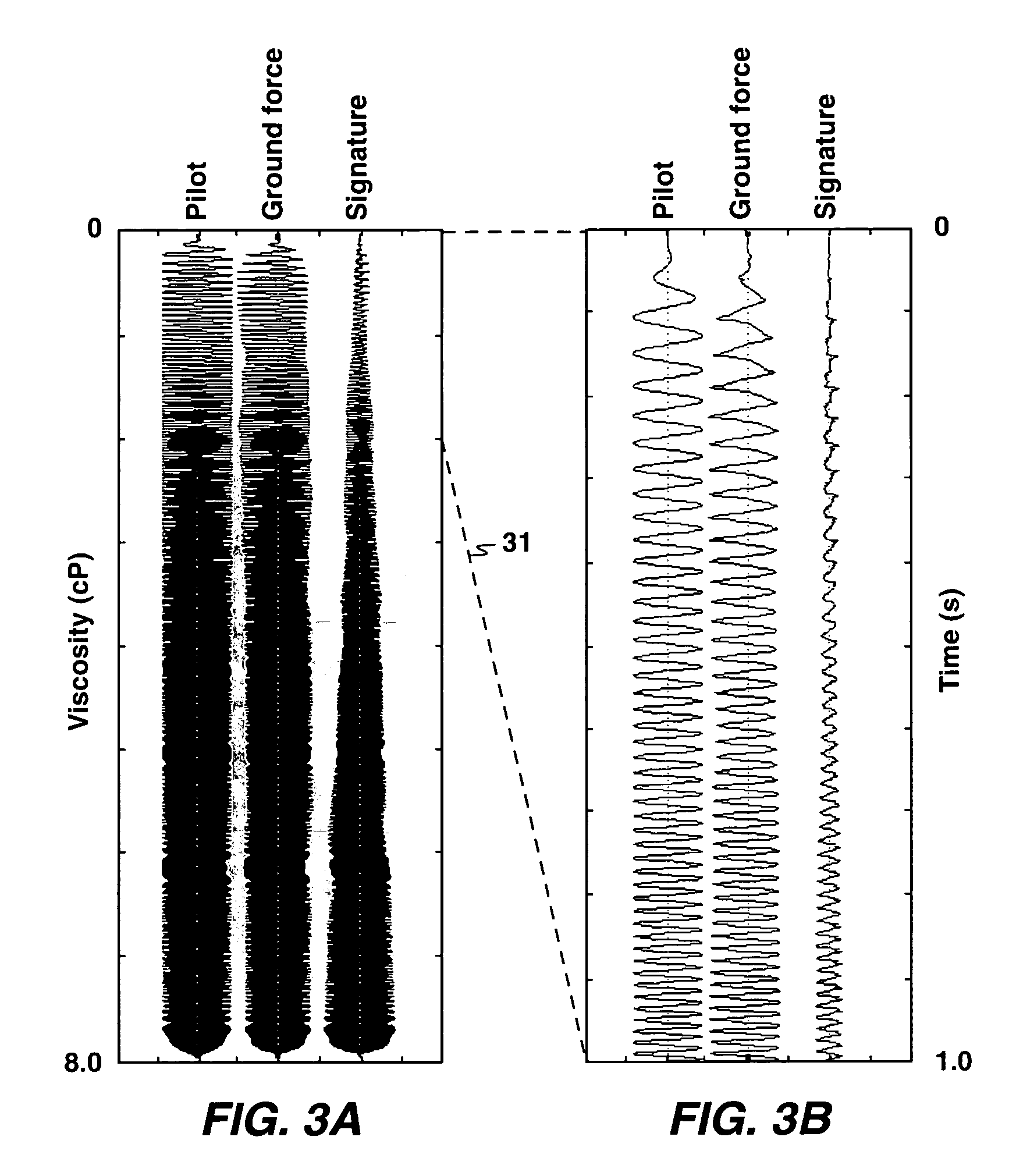
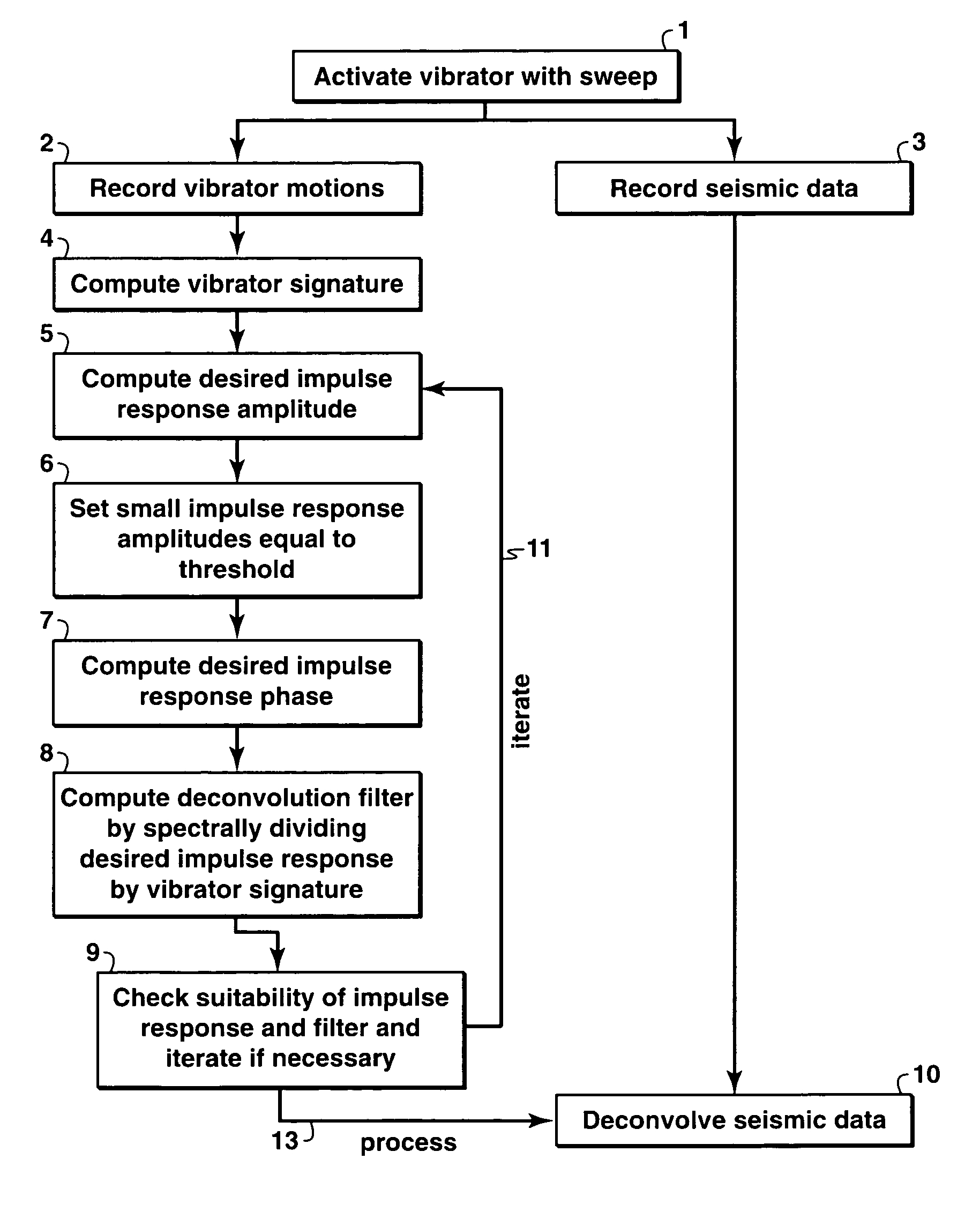
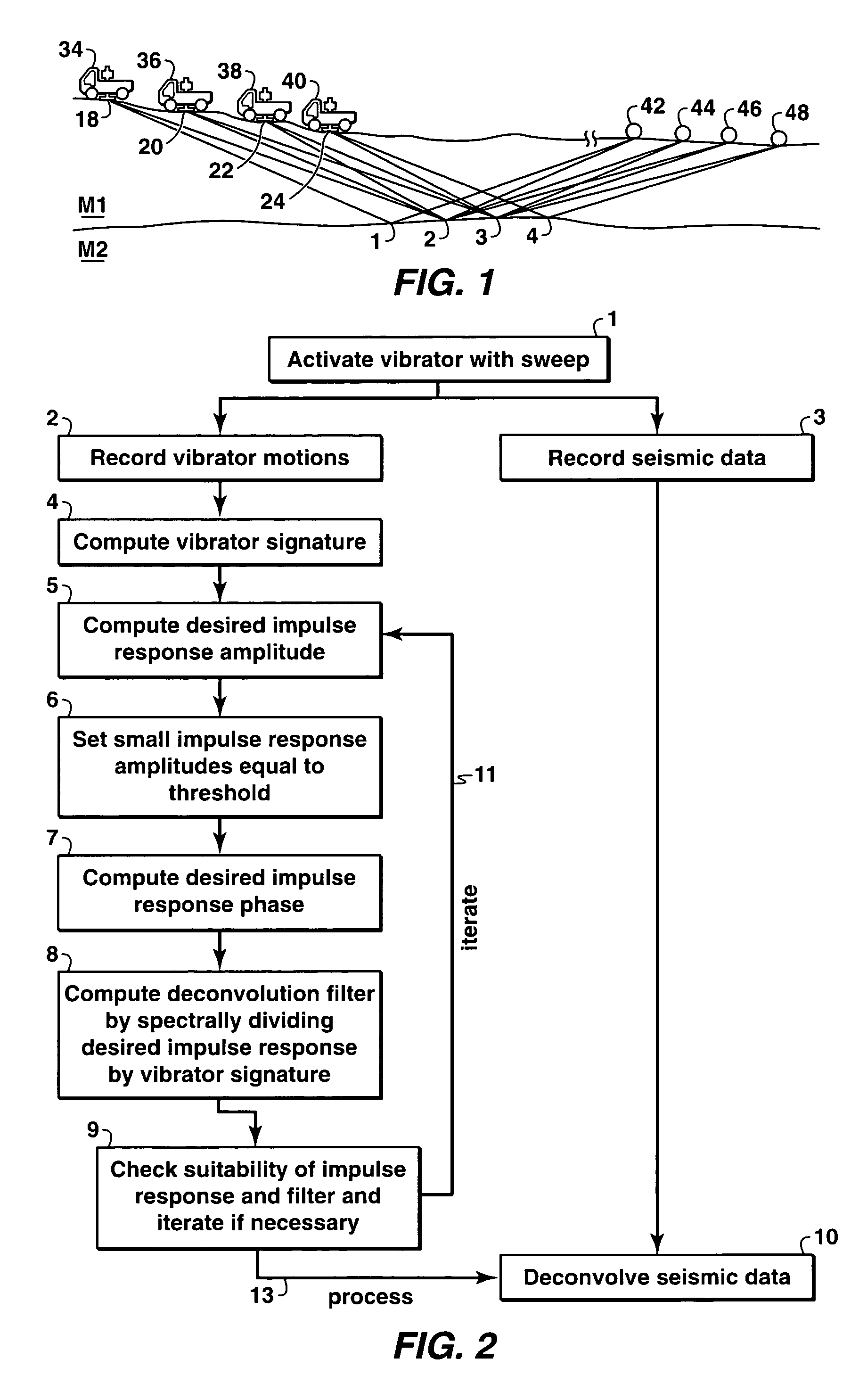
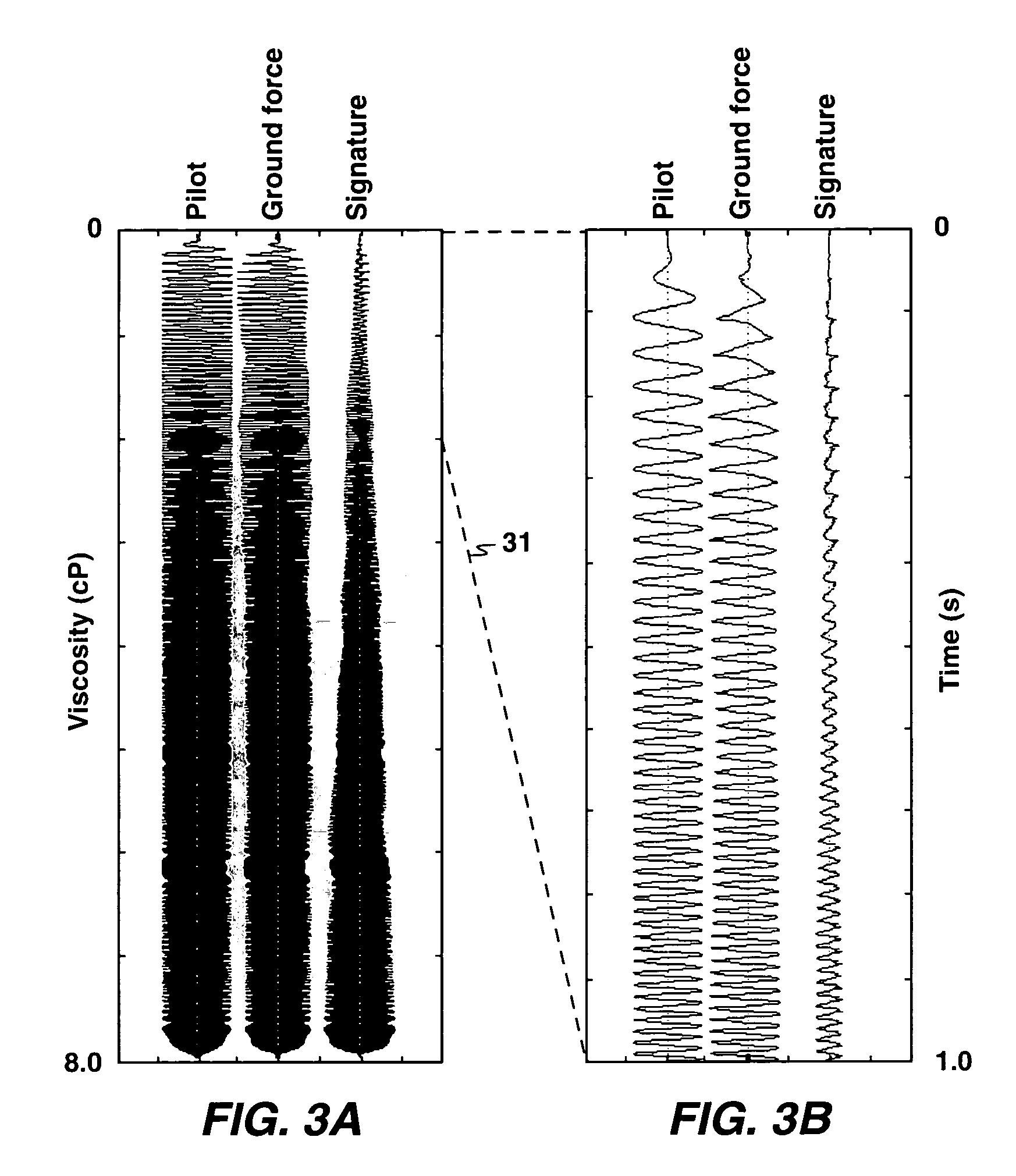
The present invention is a method of processing seismic data in which one or more seismic vibrators are activated with one or more pilot signals and vibrator motions are recorded along with seismic data. Vibrator signatures are computed from measured vibrator motions, such as the ground force signal. A desired impulse response is specified from either a measured vibrator motion or from test data or field data from a location near the location from which the seismic data was acquired. A deconvolution filter is computed from the impulse response and the vibrator signature. Alternatively, a single separation and deconvolution filter is derived from the impulse response and from vibrator signatures from multiple vibrators and sweeps. The deconvolution or deconvolution and separation filter is used to process the seismic data. The vibrators are then moved to a new location, and the activation is repeated.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL UPSTREAM RES CO
Shaped high frequency vibratory source
ActiveUS20060250891A1Improved noise suppressionSeismic data acquisitionSeismic signal processingConvolution filterBiological activation
The present invention is a method of processing seismic data in which one or more seismic vibrators are activated with one or more pilot signals and vibrator motions are recorded along with seismic data. Vibrator signatures are computed from measured vibrator motions, such as the ground force signal. A desired impulse response is specified from either a measured vibrator motion or from test data or field data from a location near the location from which the seismic data was acquired. A deconvolution filter is computed from the impulse response and the vibrator signature. Alternatively, a single separation and deconvolution filter is derived from the impulse response and from vibrator signatures from multiple vibrators and sweeps. The deconvolution or deconvolution and separation filter is used to process the seismic data. The vibrators are then moved to a new location, and the activation is repeated.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL UPSTREAM RES CO
Control system for marine vibrators and seismic acquisition system using such control system
Owner:PGS GEOPHYSICAL AS
Method for generating spread spectrum driver signals for a seismic vibrator array using multiple biphase modulation operations in each driver signal chip
ActiveUS20110038225A1Seismic data acquisitionSound producing devicesDirect-sequence spread spectrumVircator
A method for generating seismic energy for subsurface surveying include operating a first seismic vibrator above an area of the subsurface to be surveyed and operating at least a second seismic vibrator above the area substantially contemporaneously with the operating the first seismic vibrator. The first and the second vibrators each have a different selected frequency response. The first and second vibrators each is operated by a same direct sequence spread spectrum signal, wherein a different number of modulation operations for each logical value in the direct sequence spread spectrum signal is selected for each vibrator.
Owner:PGS GEOPHYSICAL AS
Control system for marine vibrators and seismic acquisition system using such control system
A method for controlling output of a marine seismic vibrator includes operating the vibrator using a predetermined driver signal. A vibrator output signal is measured at at least two different places on the vibrator. The at least two measured vibrator output signals are used to determine a corrected driver signal, wherein the corrected driver signal results in fewer harmonics of fundamental frequencies in the vibrator output. The vibrator is operated using the corrected driver signal.
Owner:PGS GEOPHYSICAL AS
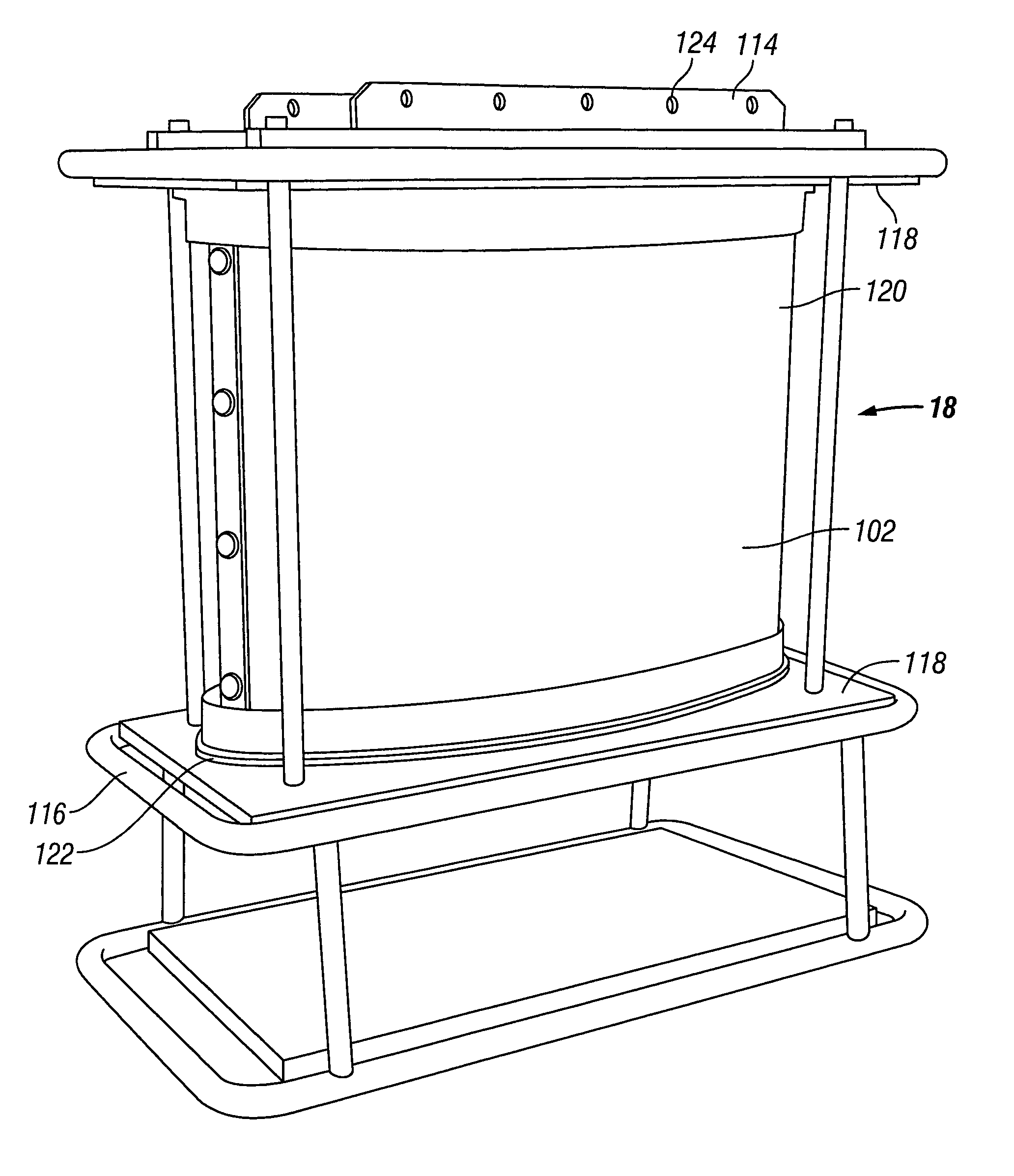
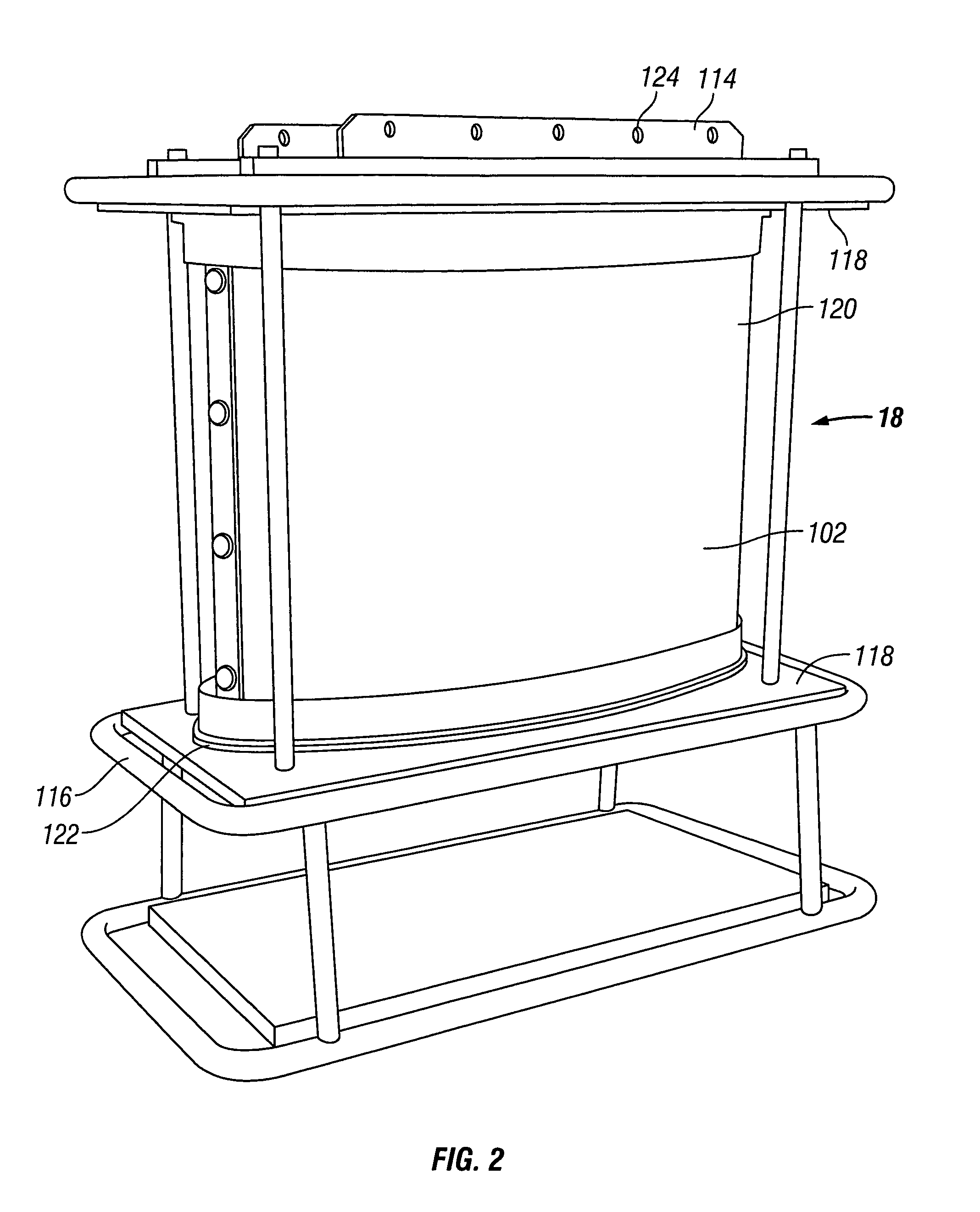
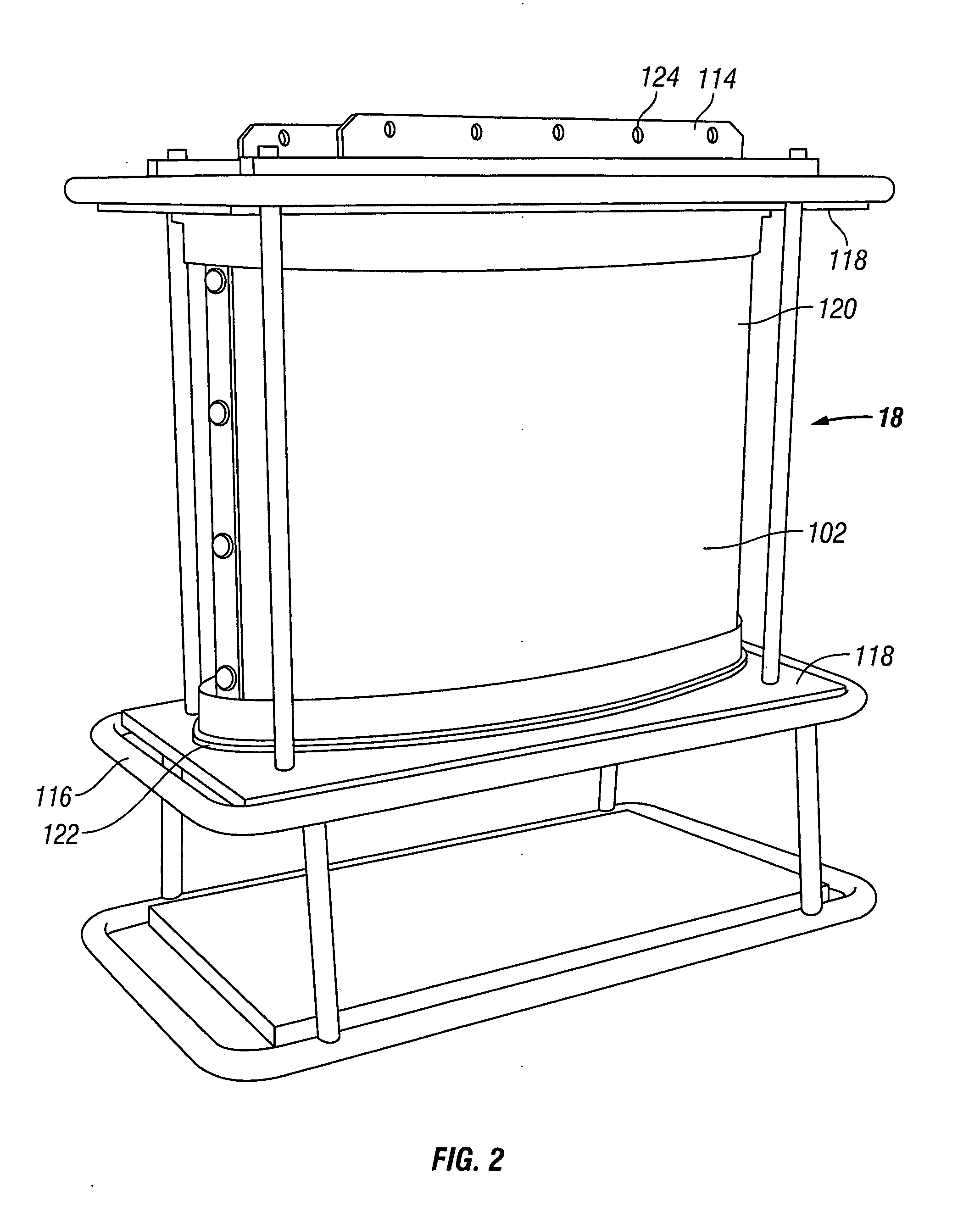
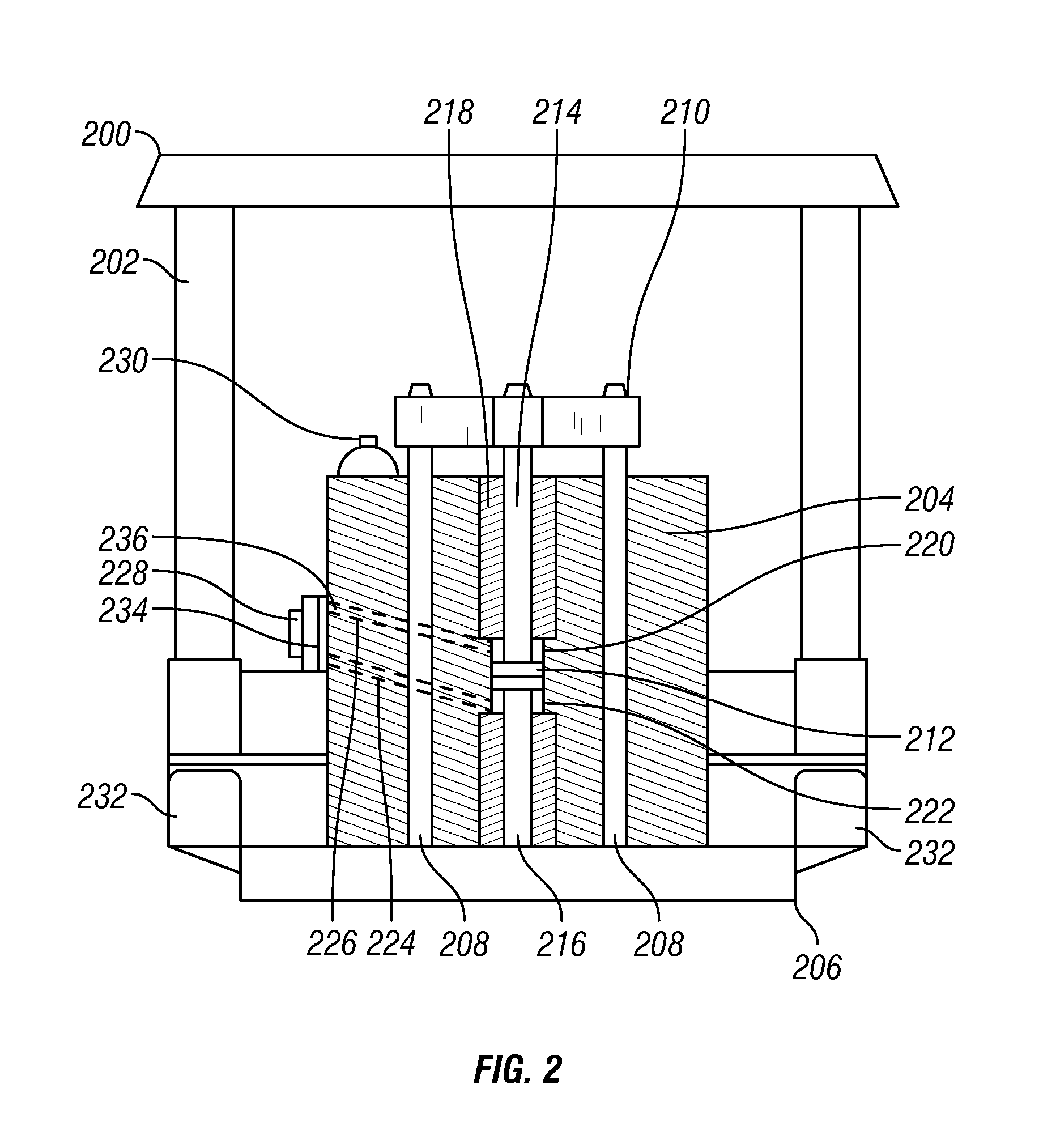
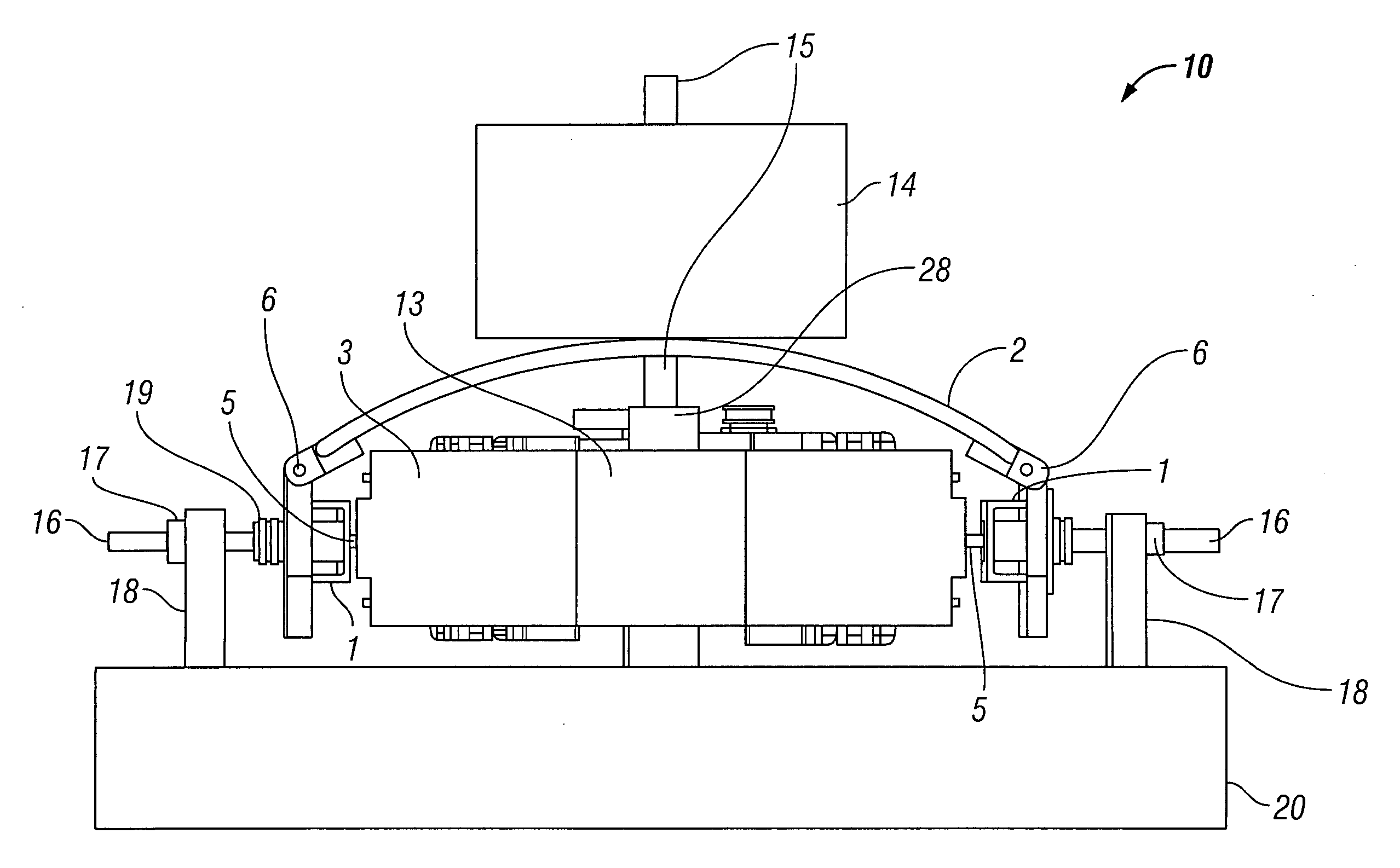
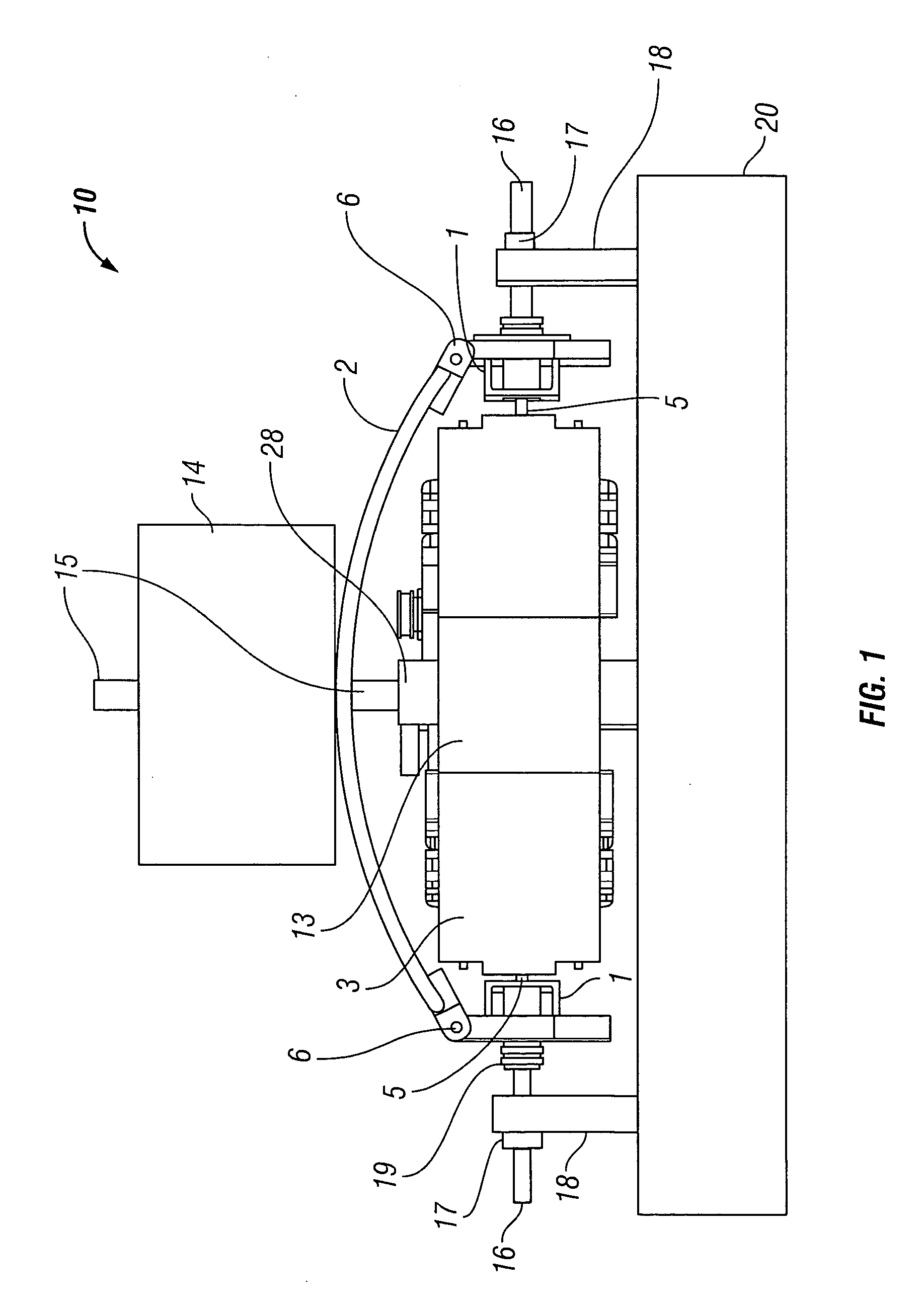
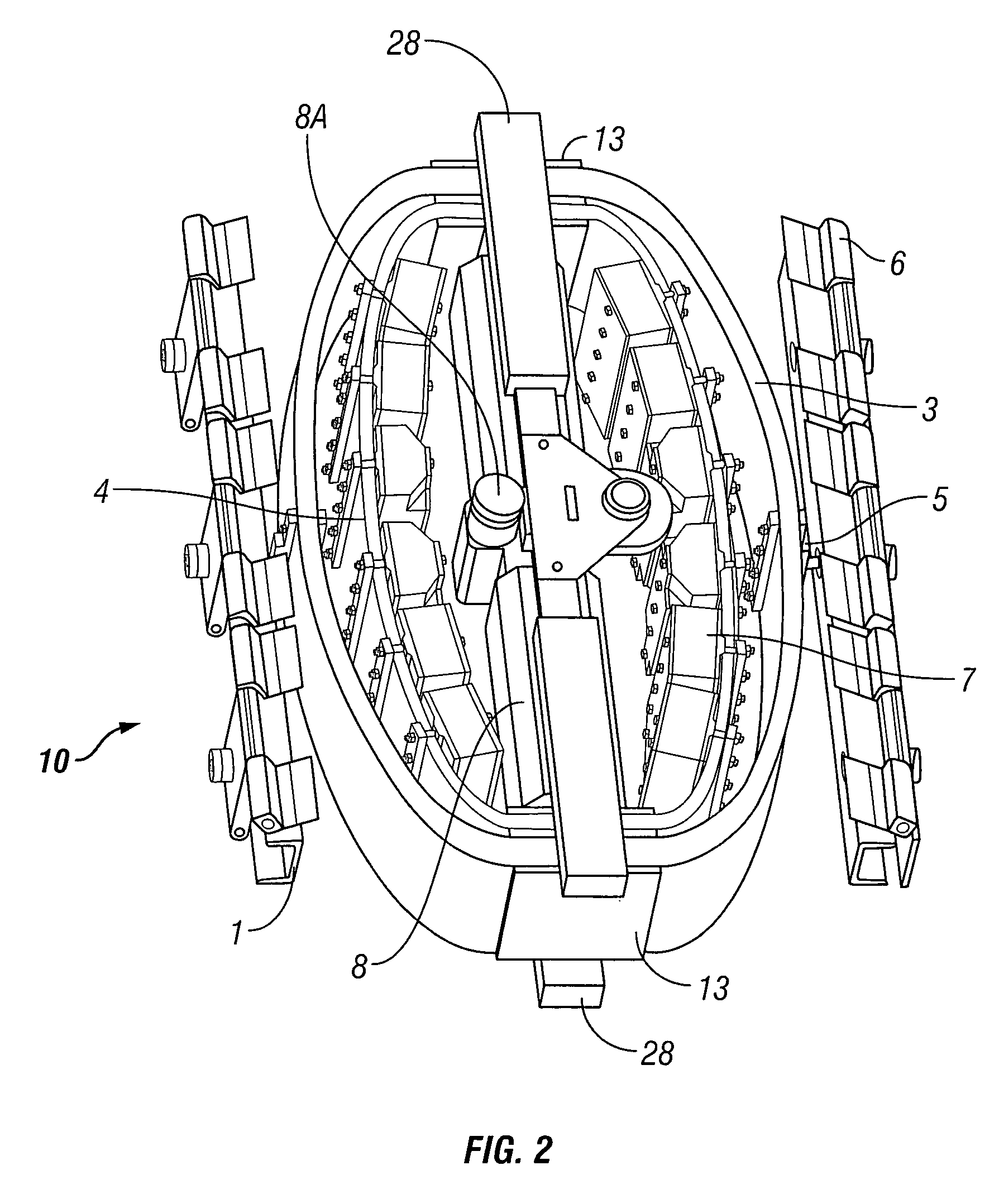
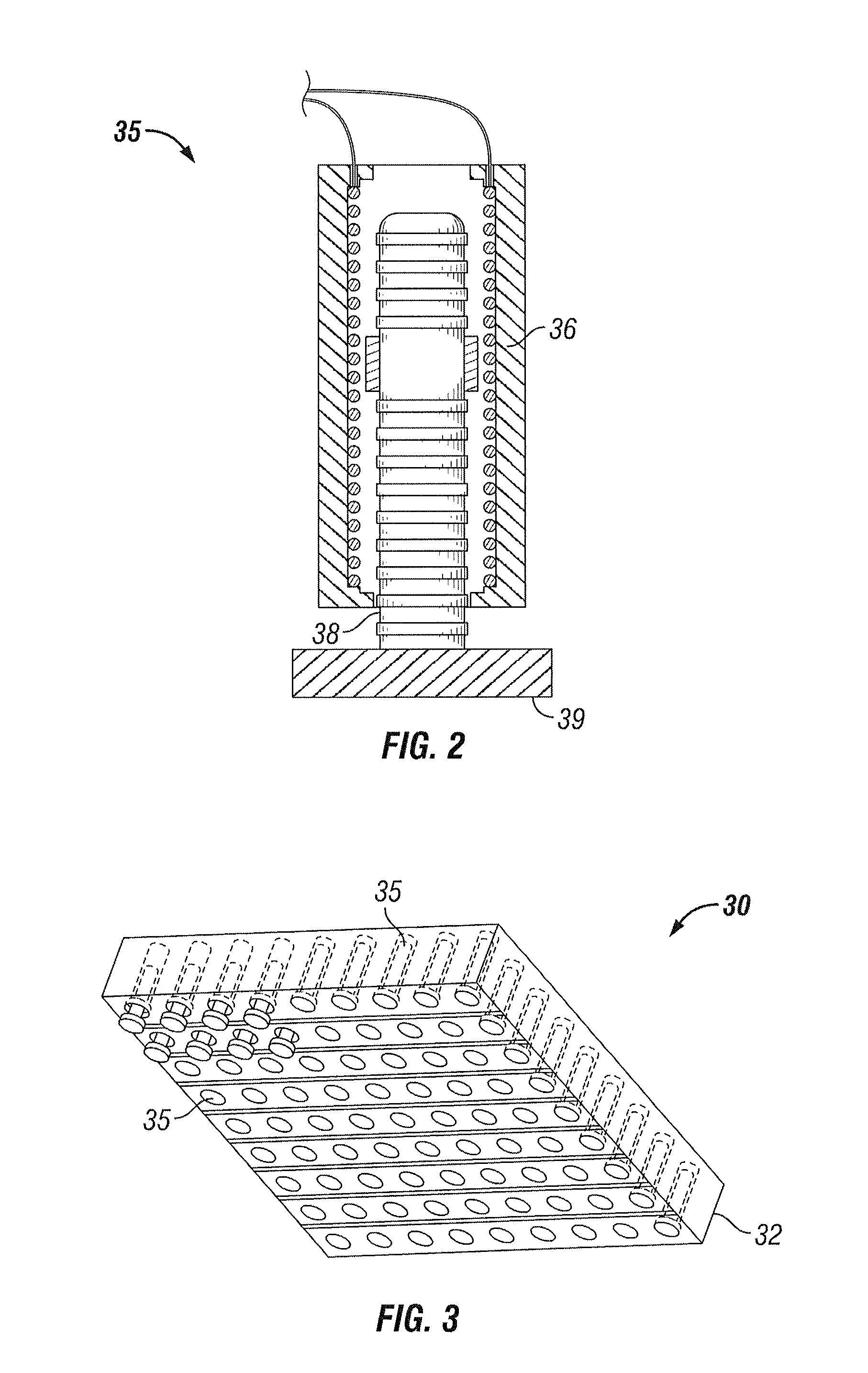
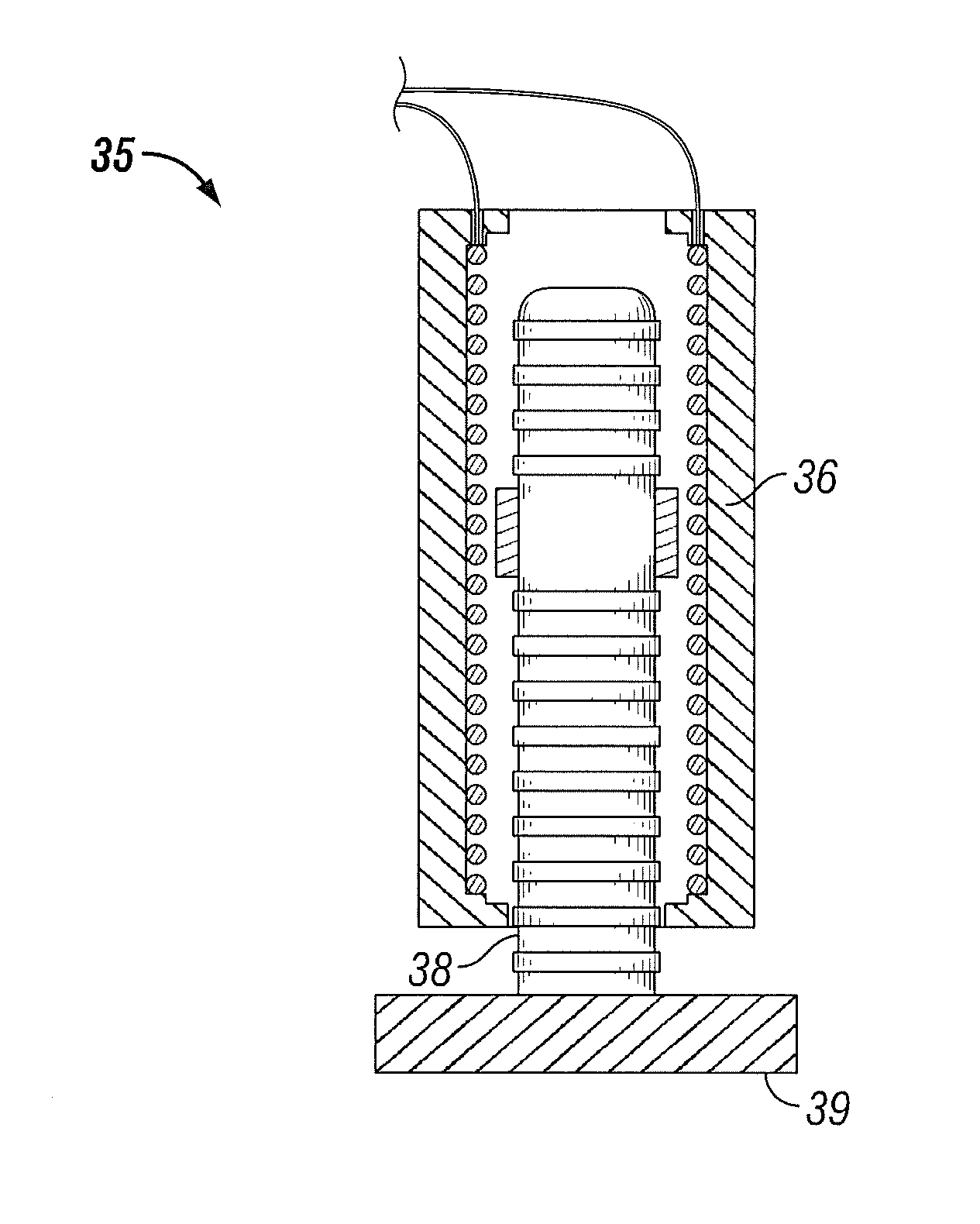
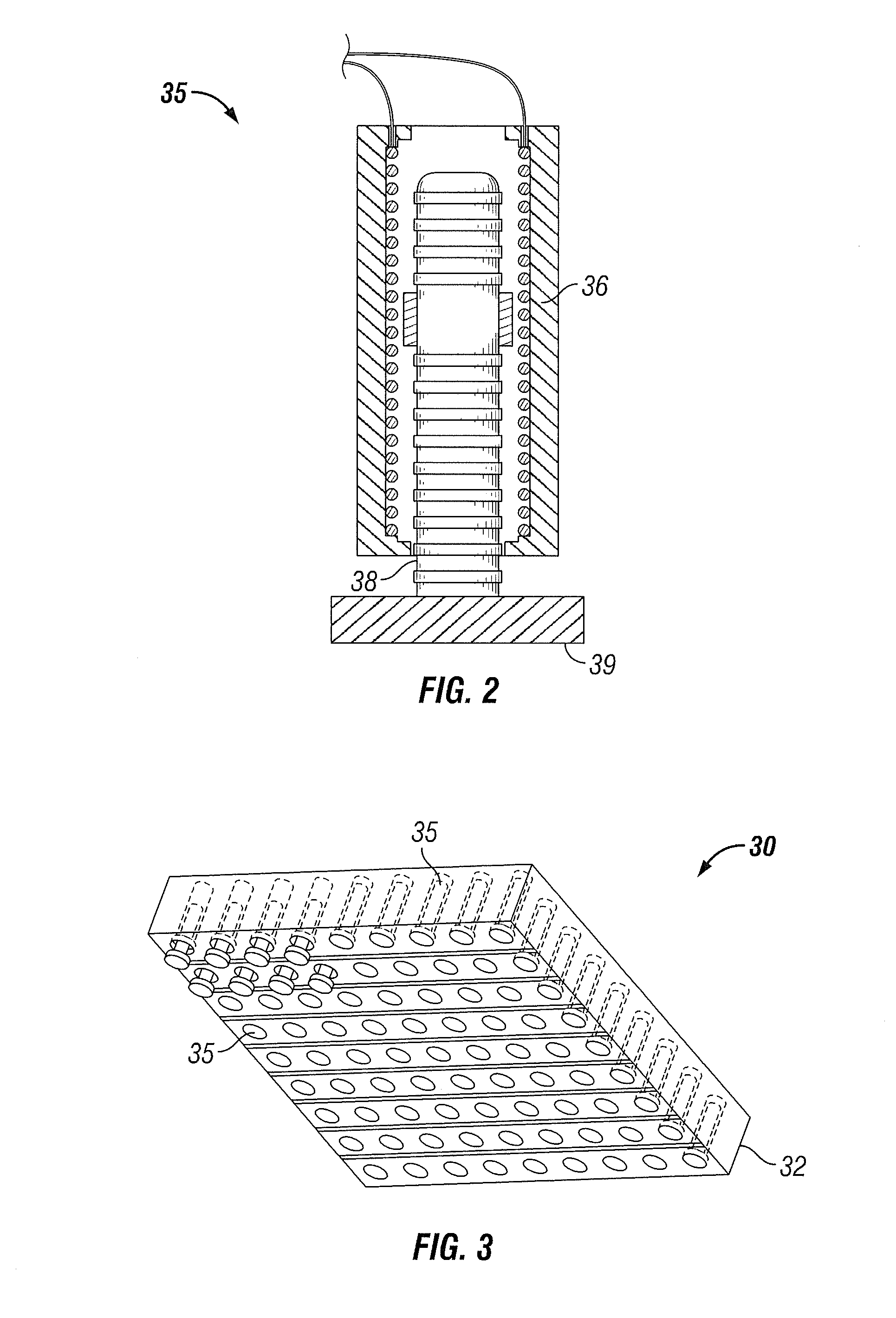
Seismic vibrator having multiple resonant frequencies in the seismic frequency band using multiple spring and mass arrangements to reduce required reactive mass
InactiveUS7881158B2Seismic energy generationMagnetostrictive transducersTransducerClassical mechanics
A seismic vibrator includes a transducer, a reactive mass, a base plate to couple motion of the reactive mass to subsurface formations and a linkage system configured to couple motion of the transducer to the reactive mass and the base plate. The linkage system cooperates with the reactive mass and the transducer to define a first resonant frequency and a second resonant frequency within a range of 1 to 300 Hz.
Owner:PGS GEOPHYSICAL AS
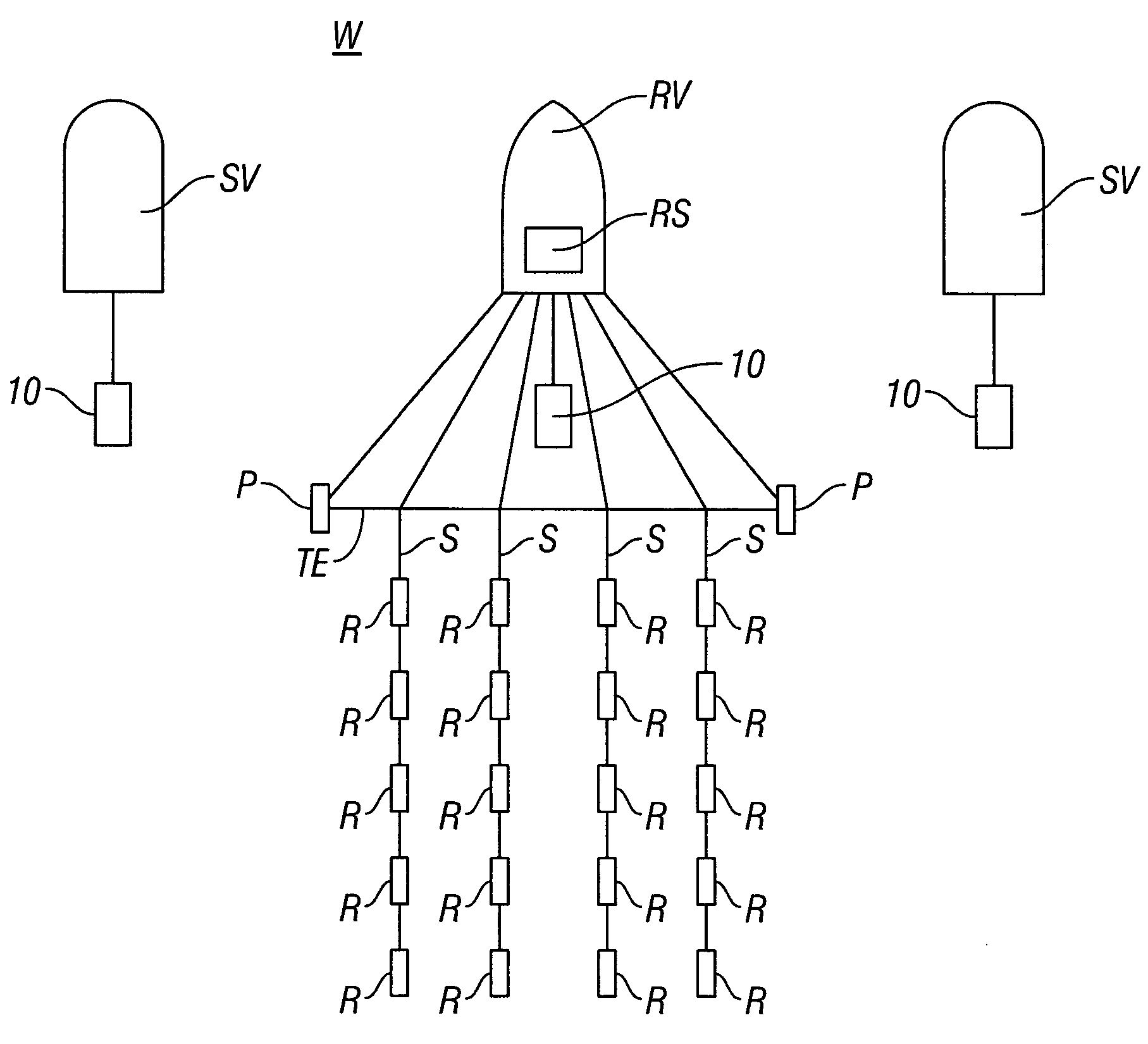
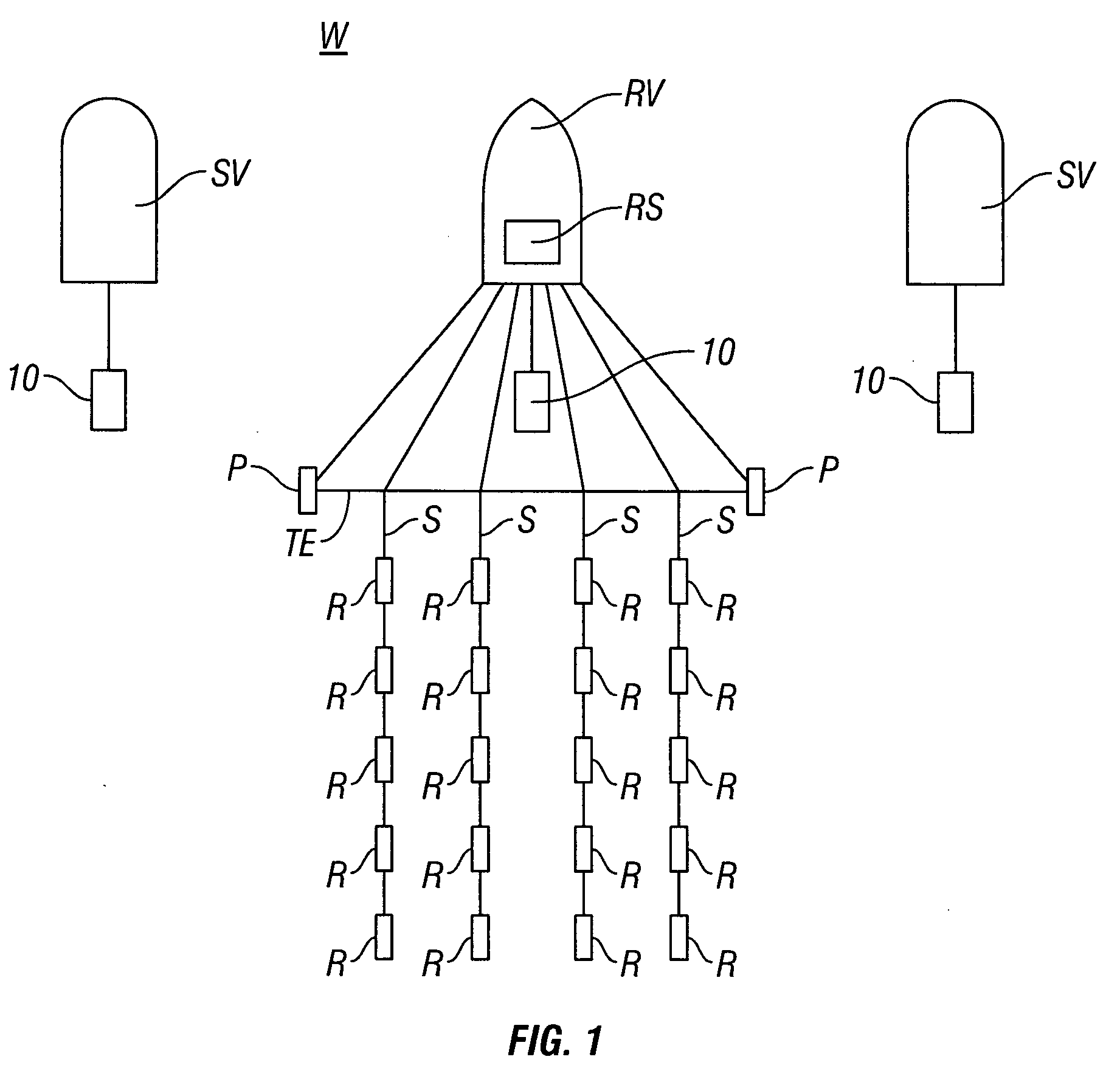
Seismic vibrator array and method for using
ActiveUS8094514B2Seismic data acquisitionSeismology for water-covered areasSeismic energySeismic vibrator
A method for generating seismic energy for subsurface surveying includes operating a first seismic vibrator and operating at least a second seismic vibrator substantially contemporaneously with the operating the first seismic vibrator. A driver signal to each of the first and the at least a second seismic vibrators that are substantially uncorrelated with each other.
Owner:PGS GEOPHYSICAL AS
Method for continuous sweeping and separation of multiple seismic vibrators
ActiveUS20080205193A1Reduce noiseSeismic data acquisitionSeismic signal processingContinuous scanningFourier transform on finite groups
A method for simultaneously operating multiple seismic vibrators using continuous sweeps (little or no “listening” time between sweeps) for each vibrator, and recovering the separated seismic responses for each vibrator with the earth signature removed. Each vibrator is given a unique, continuous pilot signal. The earth response to the motion of each vibrator is measured or estimated. The vibrator motion records for each vibrator and the combined seismic data record for all the vibrators are parsed into separate shorter records. The shorter records are then used to form a system of simultaneous linear equations in the Fourier transform domain, following the HFVS method of Sallas and Allen. The equations are then solved for the separated earth responses.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL UPSTREAM RES CO
Seismic vibrator array and method for using
ActiveUS20100118646A1Seismic data acquisitionSeismic signal processingSeismic energySeismic vibrator
A method for generating seismic energy for subsurface surveying includes operating a first seismic vibrator and operating at least a second seismic vibrator substantially contemporaneously with the operating the first seismic vibrator. A driver signal to each of the first and the at least a second seismic vibrators that are substantially uncorrelated with each other.
Owner:PGS GEOPHYSICAL AS
Method for operating marine seismic vibrator array to enhance low frequency output
A method for operating marine seismic vibrators includes towing at least a first and a second marine seismic vibrator in a body of water beneath the hull of a vessel. At least a third marine seismic vibrator is towed at a selected depth in the water other than beneath the hull of the vessel. The at least first, second and third vibrators are operated to sweep through respective frequency ranges. The first and second frequency ranges have lowermost frequencies and uppermost frequencies respectively differing by a selected sub-harmonic frequency range. The third frequency range has a lowermost frequency at least equal to the uppermost frequency of one of the first and second frequency ranges and traverses a seismic frequency range of interest.
Owner:PGS GEOPHYSICAL AS
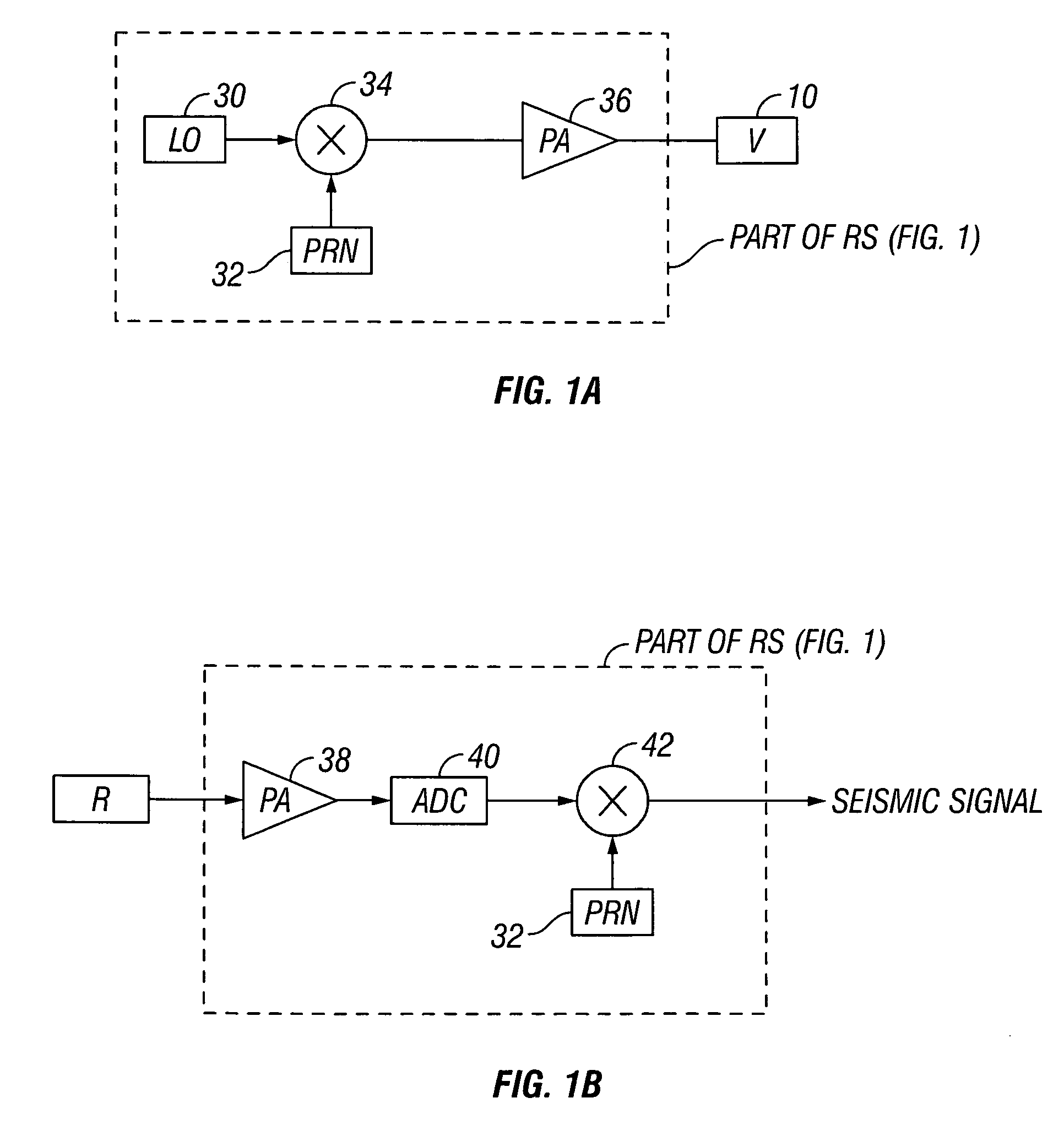
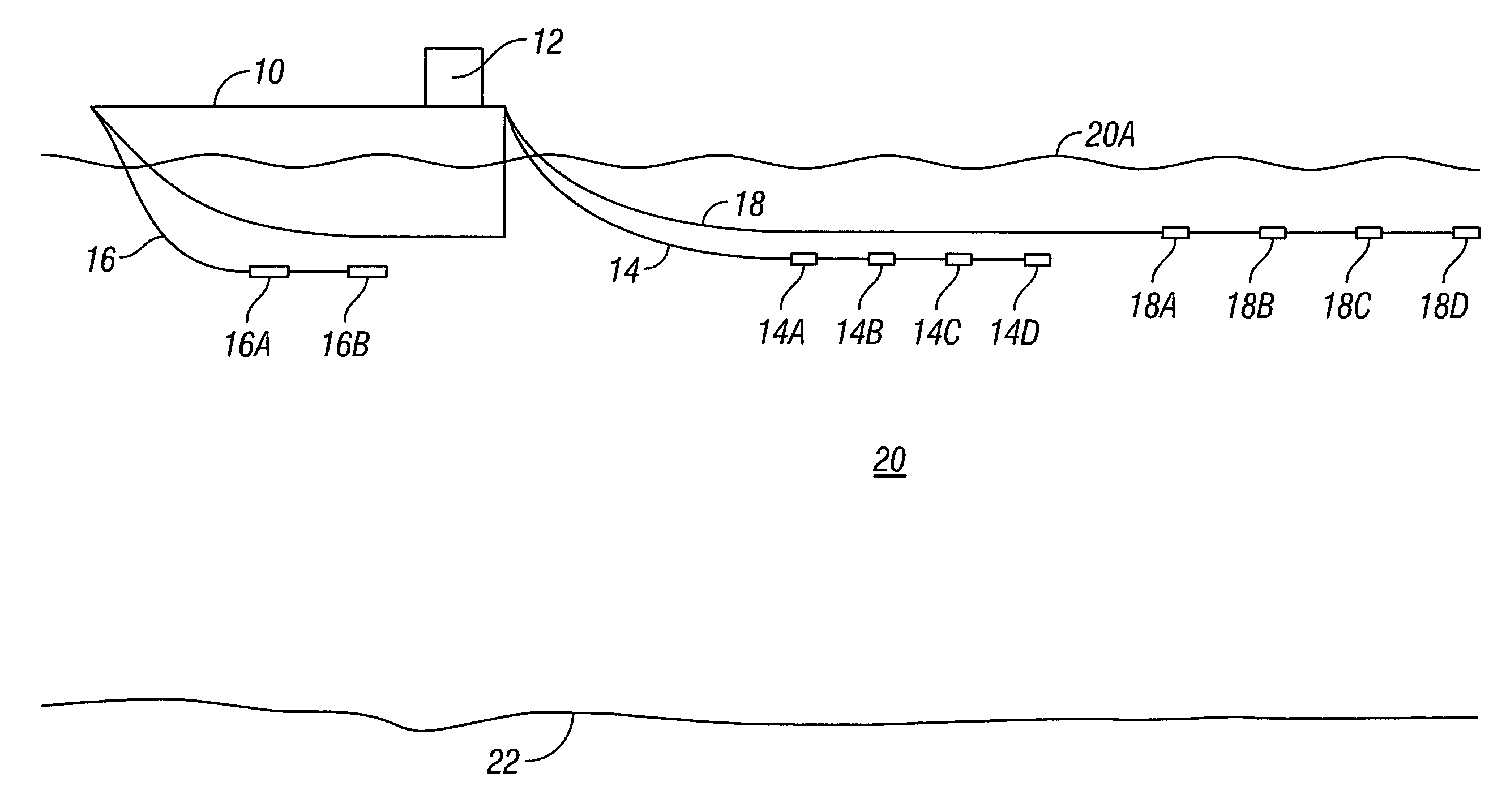
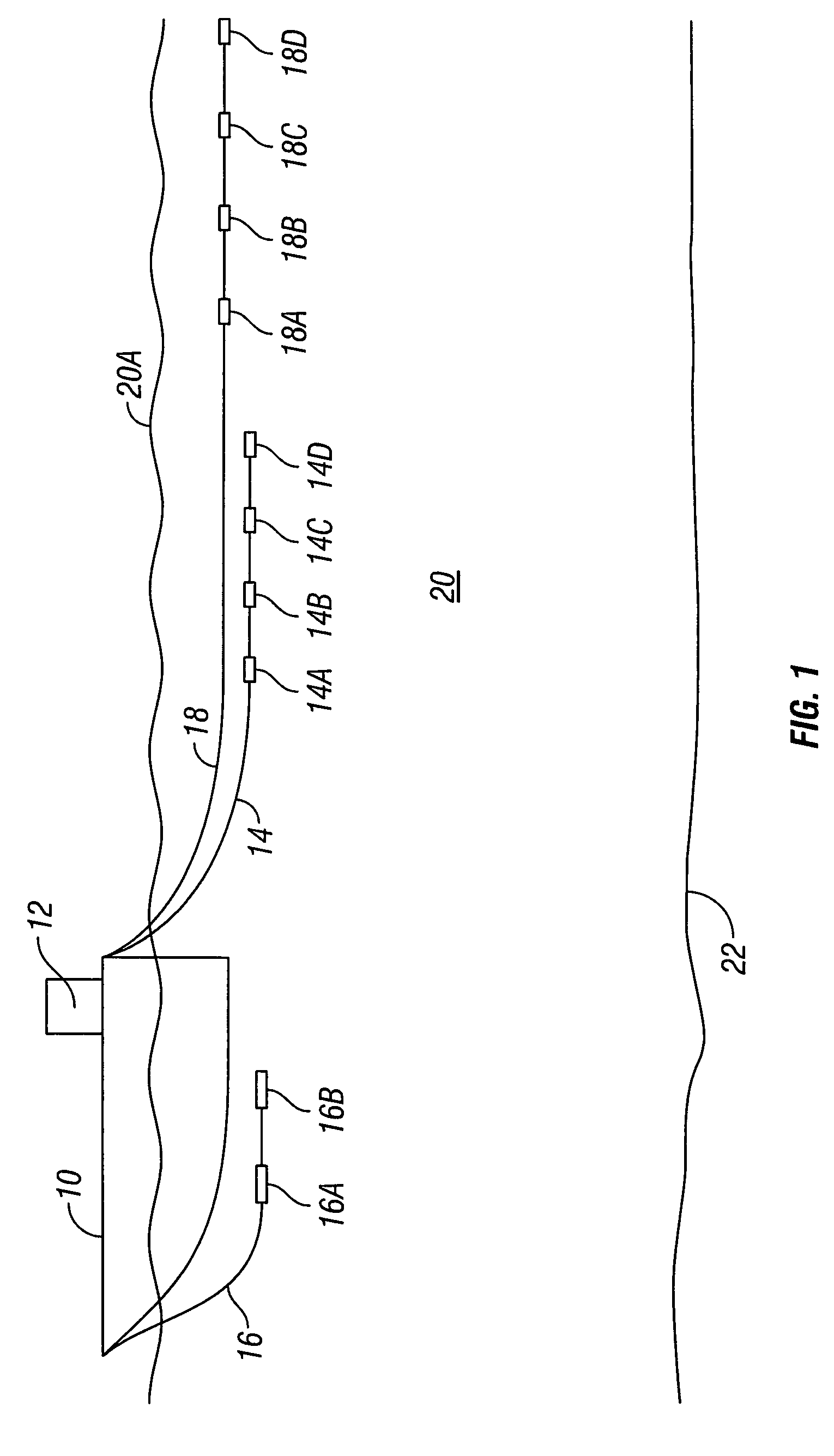
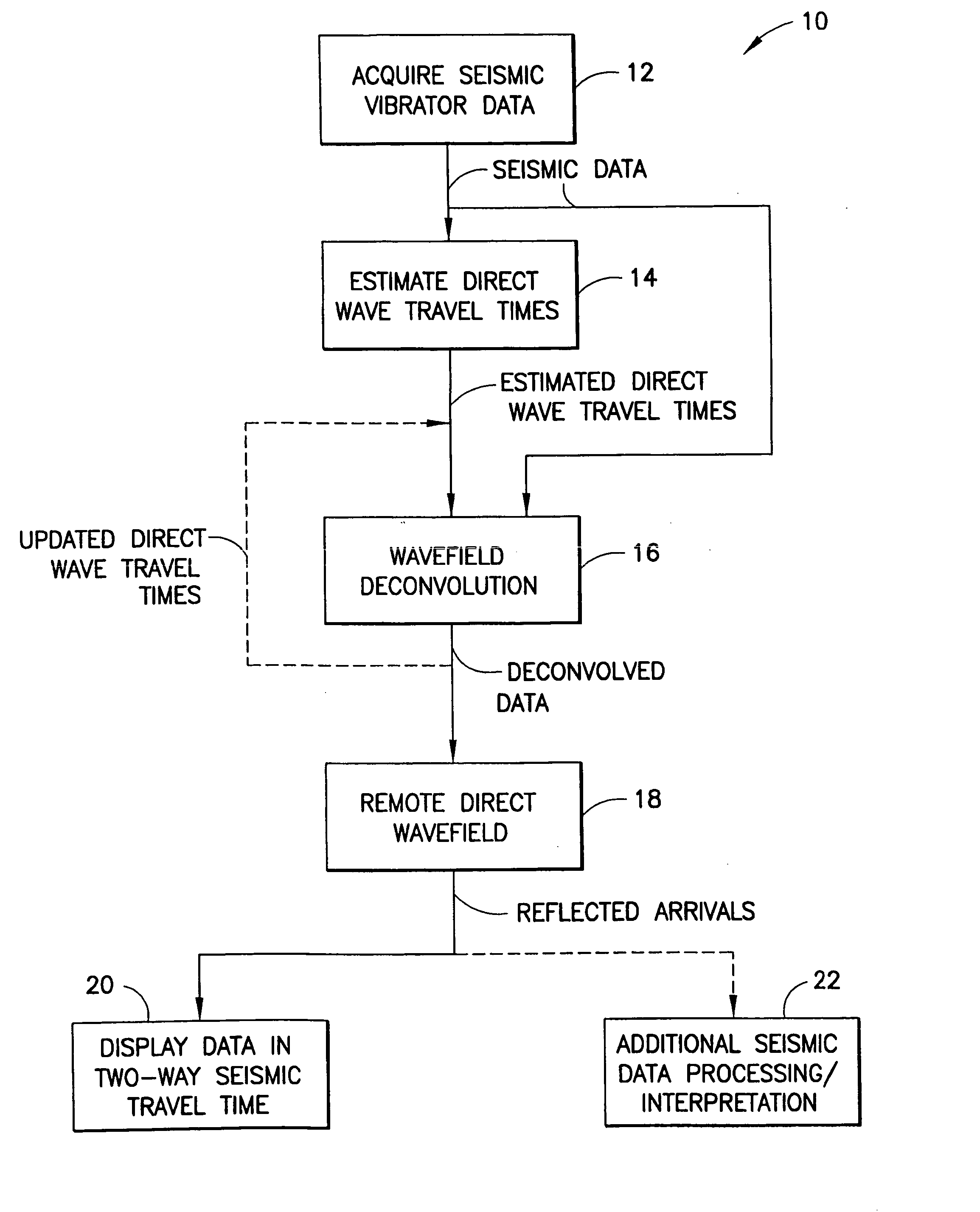
High-frequency processing of seismic vibrator data
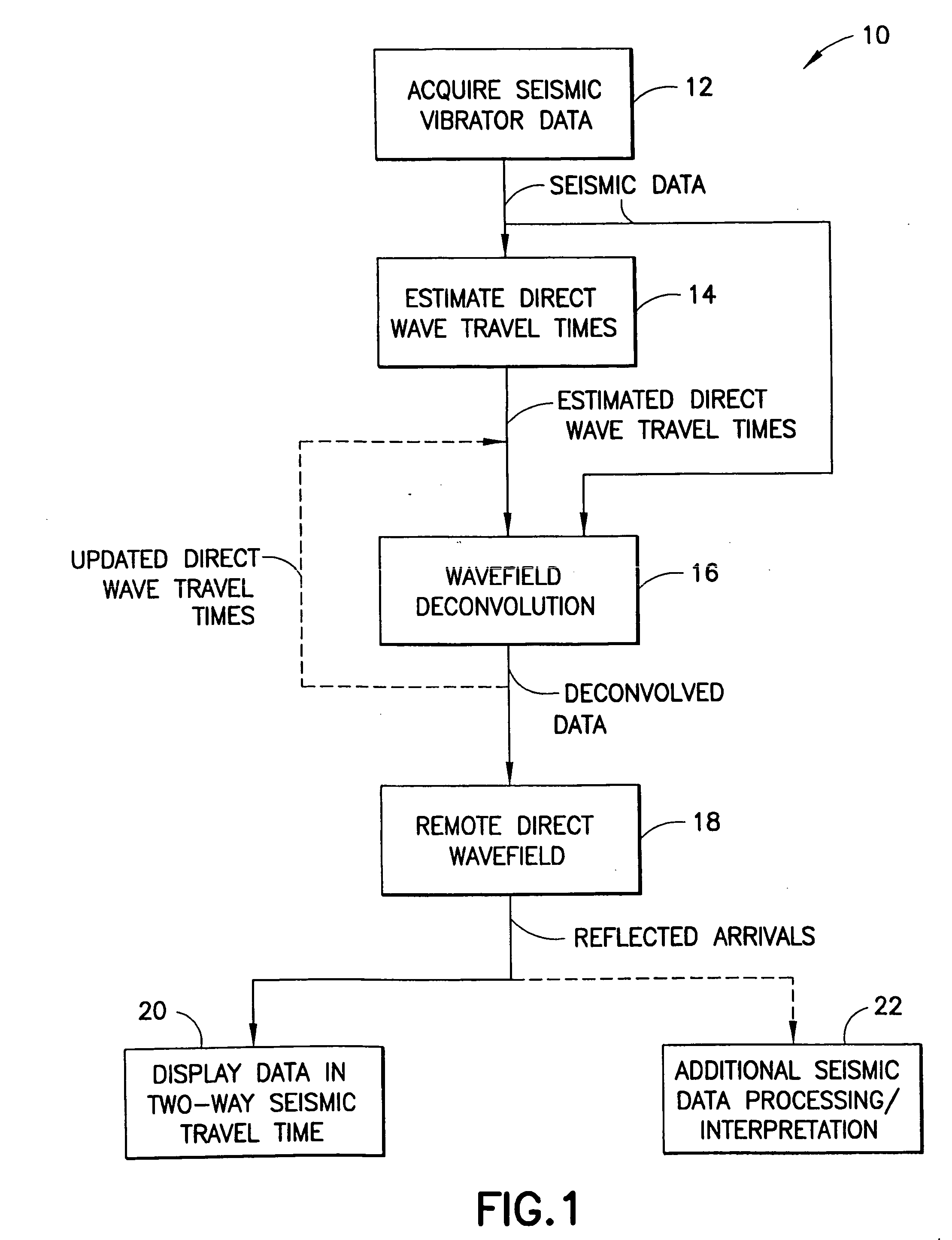
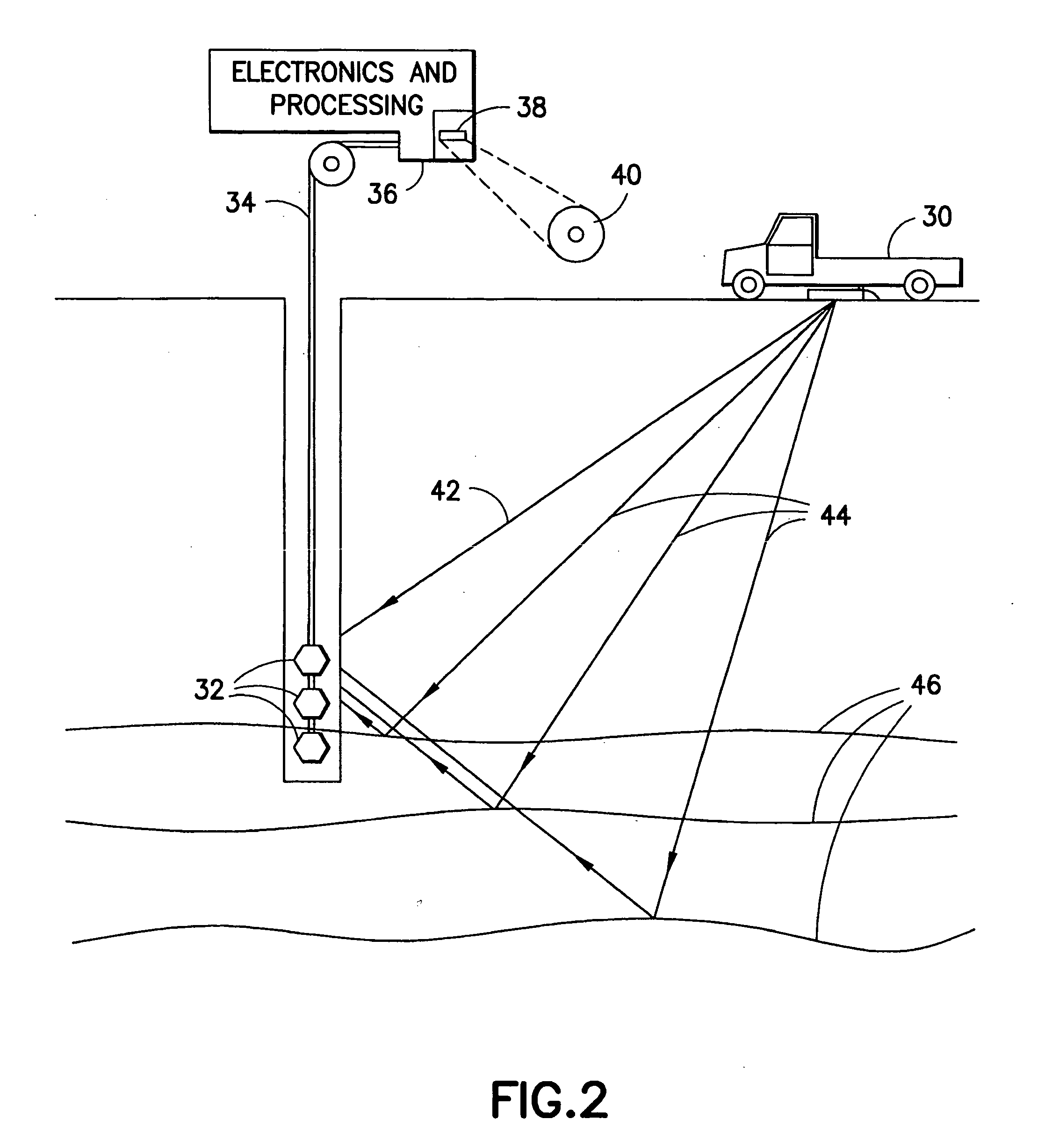
A method of processing seismic data obtained using a seismic vibrator that includes estimating travel times of direct wave arrivals between the seismic vibrator and an array of seismic receiver locations and wavefield deconvolving the seismic data using the direct wave arrival travel times. Also a related method of producing a high-frequency geological subsurface image that includes acquiring seismic data having significant harmonic energy using a seismic vibrator, estimating direct wave arrival travel times between the seismic vibrator and an array of seismic receiver locations, wavefield deconvolving the seismic data using the estimated direct wave arrival travel times, and using the wavefield deconvolved seismic data to produce a high-frequency geological subsurface image. A further related computer useable medium having computer readable program code means embodied therein practicing the inventive method.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Apparatus and Method for Generating A Seismic Source Signal
A seismic source signal generator includes a mass, a primary accumulator and a secondary accumulator, the secondary accumulator having an internal volume smaller than an internal volume of the primary accumulator. A method for generating a signal using a seismic vibrator includes operating the seismic vibrator using hydraulic fluid, damping hydraulic pressure deviations in the hydraulic fluid using a first accumulator in hydraulic communication with the hydraulic fluid, and damping pressure deviations in the hydraulic fluid using a second accumulator in hydraulic communication with the hydraulic fluid, the second accumulator having an internal volume smaller than an internal volume of the first accumulator.
Owner:INOVA
Method for generating spread spectrum driver signals for a seismic vibrator array using multiple biphase modulation operations in each driver signal chip
ActiveUS8335127B2Seismic data acquisitionSound producing devicesDirect-sequence spread spectrumVircator
A method for generating seismic energy for subsurface surveying include operating a first seismic vibrator above an area of the subsurface to be surveyed and operating at least a second seismic vibrator above the area substantially contemporaneously with the operating the first seismic vibrator. The first and the second vibrators each have a different selected frequency response. The first and second vibrators each is operated by a same direct sequence spread spectrum signal, wherein a different number of modulation operations for each logical value in the direct sequence spread spectrum signal is selected for each vibrator.
Owner:PGS GEOPHYSICAL AS
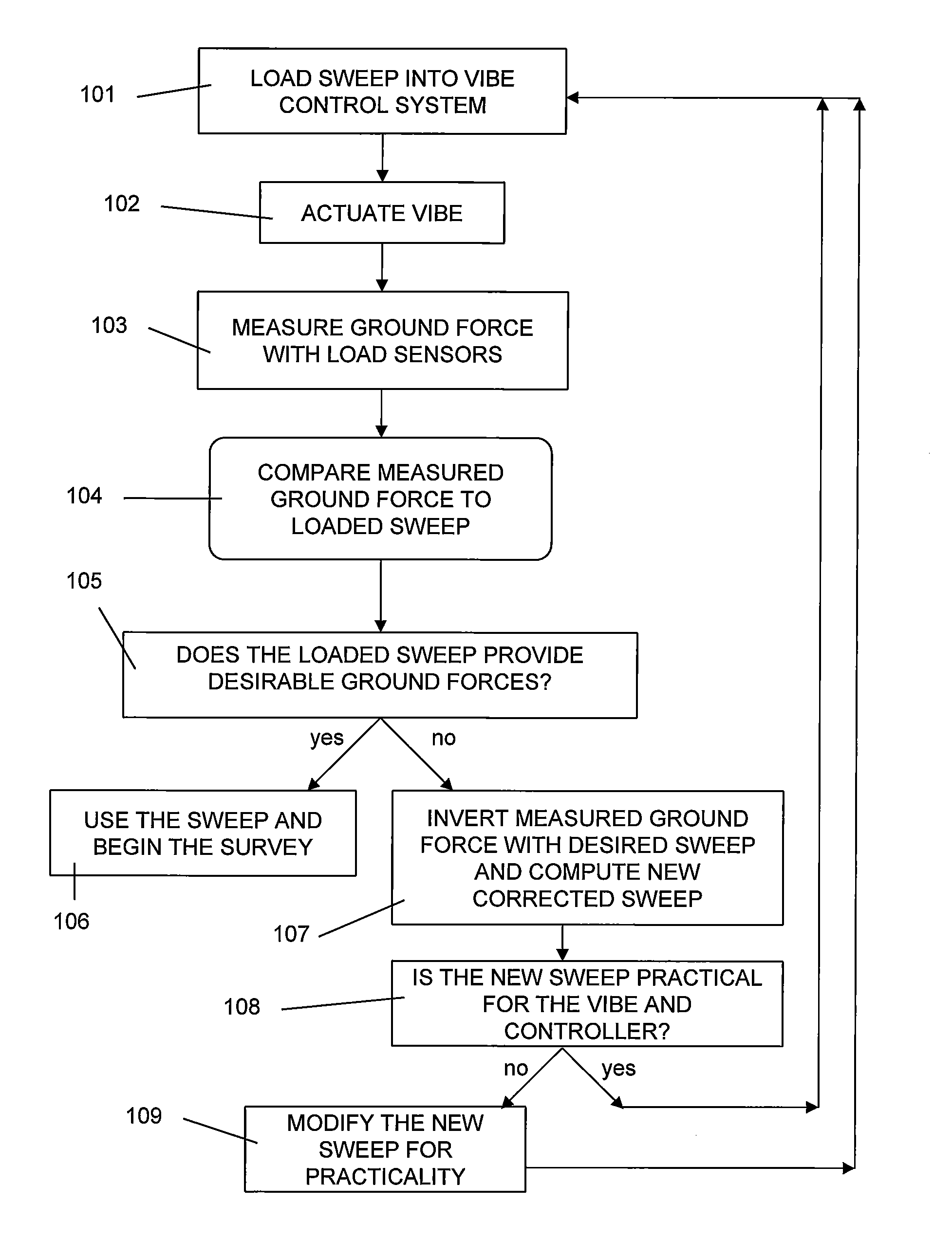
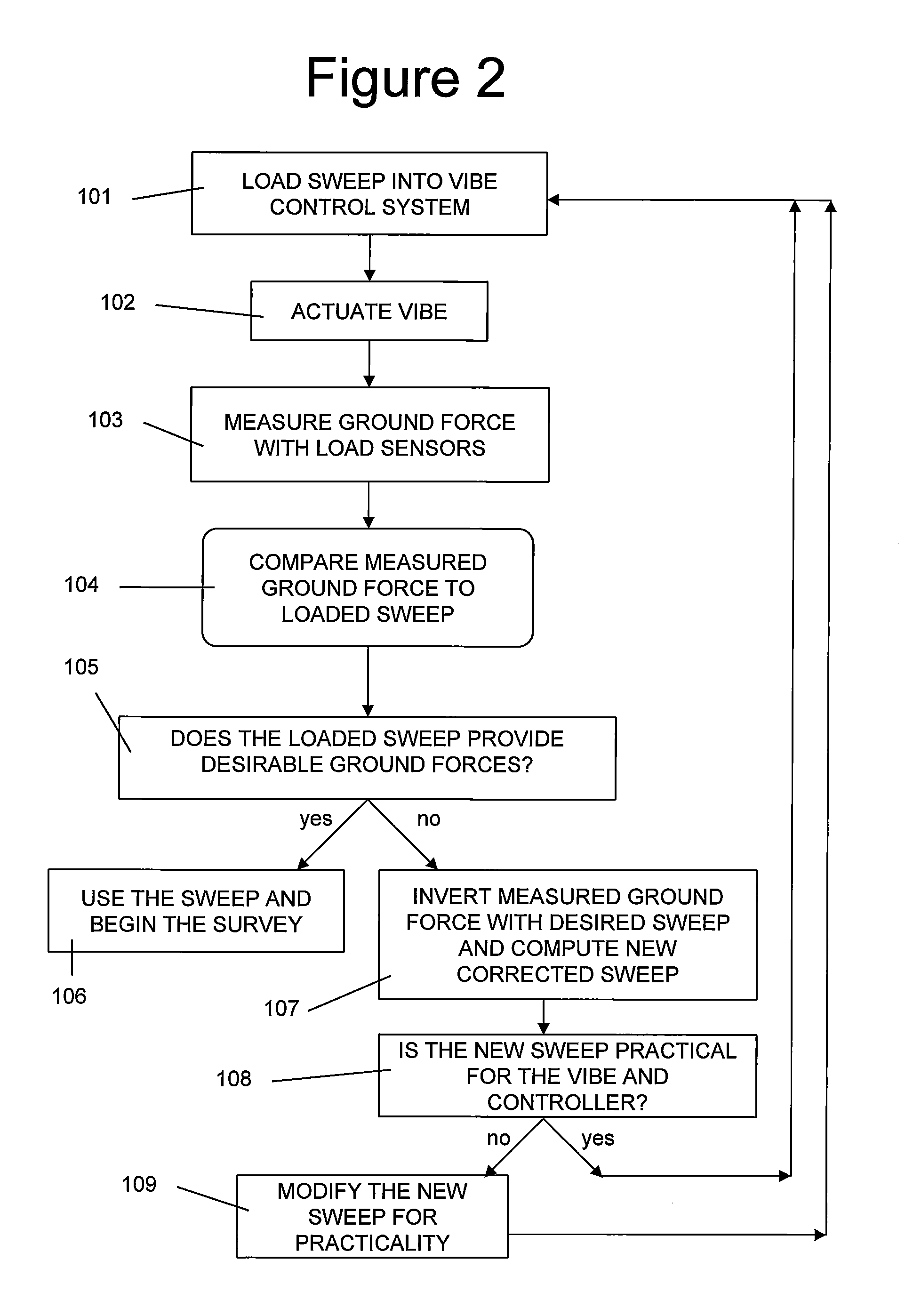
Method for creating an improved sweep for a seismic source
InactiveUS20120037445A1Wide bandwidthSeismic data acquisitionSeismic energy generationEngineeringLoad cell
An adapted seismic vibrator for obtaining a true ground force comprising: a baseplate pad; a baseplate drive system, wherein the drive system is connected to the baseplate pad and moves the baseplate pad up and down; a vibrator controller electronics, wherein the electronics are connected to the drive system and causes the drive system to move the baseplate pad up and down; and a plurality of load cell sensors disposed between the baseplate pad and ground, wherein the sensors measure the vibrator output force during a sweep. A method of obtaining a true ground force sweep comprising the steps of: using the load cell sensors to measure an actual output force of a seismic vibrator and electronics to obtain an actual ground force data; using inversion to invert the actual ground force data and desired original pilot sweep to obtain a revised pilot sweep that produces a true ground force sweep; and entering the true ground force sweep into the electronics.
Owner:CONOCOPHILLIPS CO
Superheterodyne seismic vibrator and method
InactiveUS20090086574A1Seismic data acquisitionSeismology for water-loggingAcoustic energyLinear medium
A seismic energy source includes at least a first and a second acoustic radiator operatively coupled to a non-linear medium proximate an upper limit of formations in the Earth's subsurface. The first and second acoustic radiators are configured to convert electrical energy directly into acoustic energy. The source includes means for operating the first and the second acoustic radiator at respective first and second frequencies. The first and second frequencies are selected such that substantially no acoustic energy propagates through the non-linear medium. The first and the second frequencies are selected such that a difference therebetween is swept through a range of frequencies of seismic energy capable of propagating through the Earth's subsurface to at least one acoustic impedance boundary within the Earth's subsurface.
Owner:PGS ONSHORE INC
Method for operating marine seismic vibrator array to enhance low frequency output
A method for operating marine seismic vibrators includes towing at least a first and a second marine seismic vibrator in a body of water beneath the hull of a vessel. At least a third marine seismic vibrator is towed at a selected depth in the water other than beneath the hull of the vessel. The at least first, second and third vibrators are operated to sweep through respective frequency ranges. The first and second frequency ranges have lowermost frequencies and uppermost frequencies respectively differing by a selected sub-harmonic frequency range. The third frequency range has a lowermost frequency at least equal to the uppermost frequency of one of the first and second frequency ranges and traverses a seismic frequency range of interest.
Owner:PGS GEOPHYSICAL AS
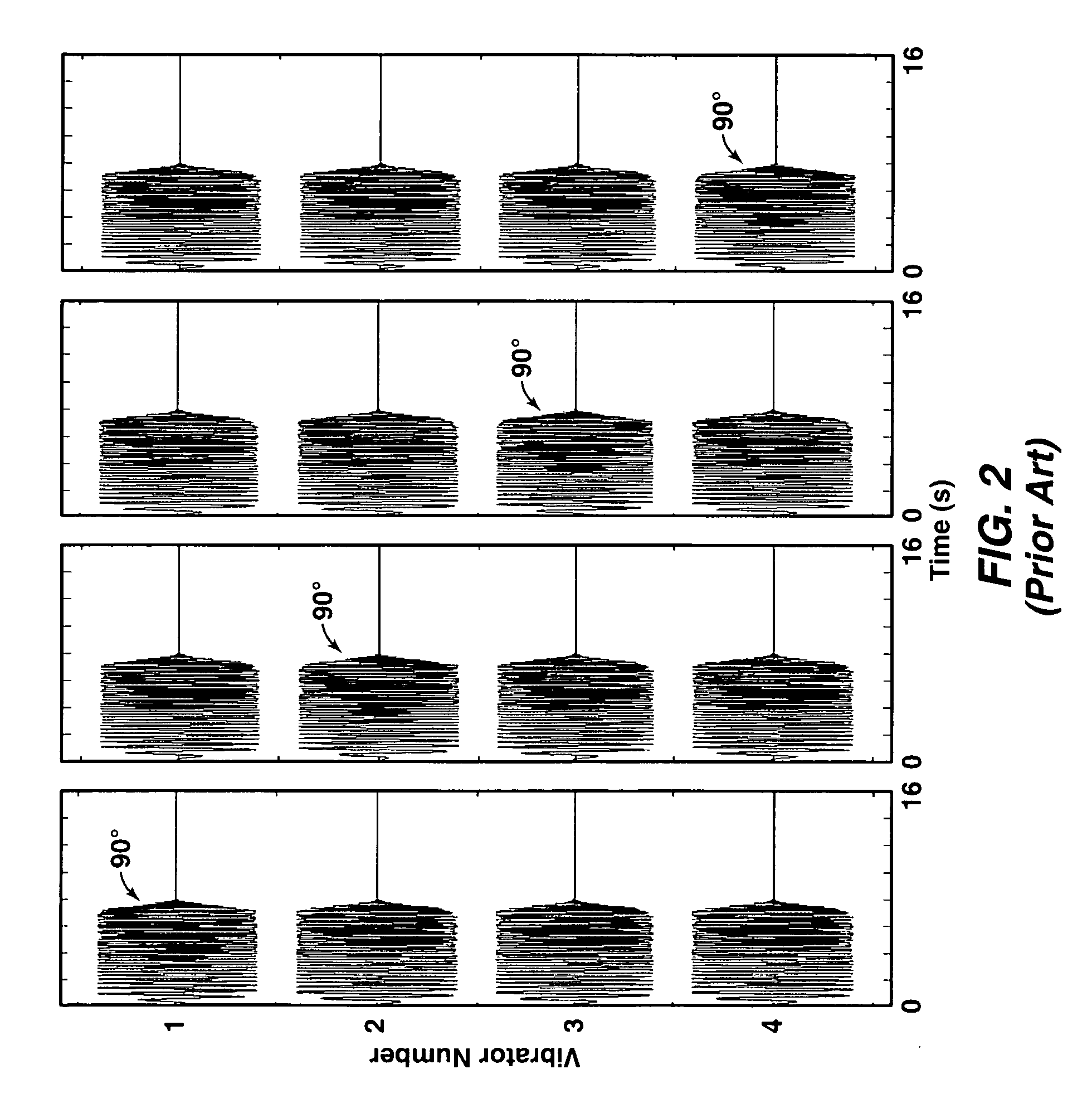
Adjacent shot interference suppressing method and device for independent simultaneous sweeping seismic data of seismic vibrators
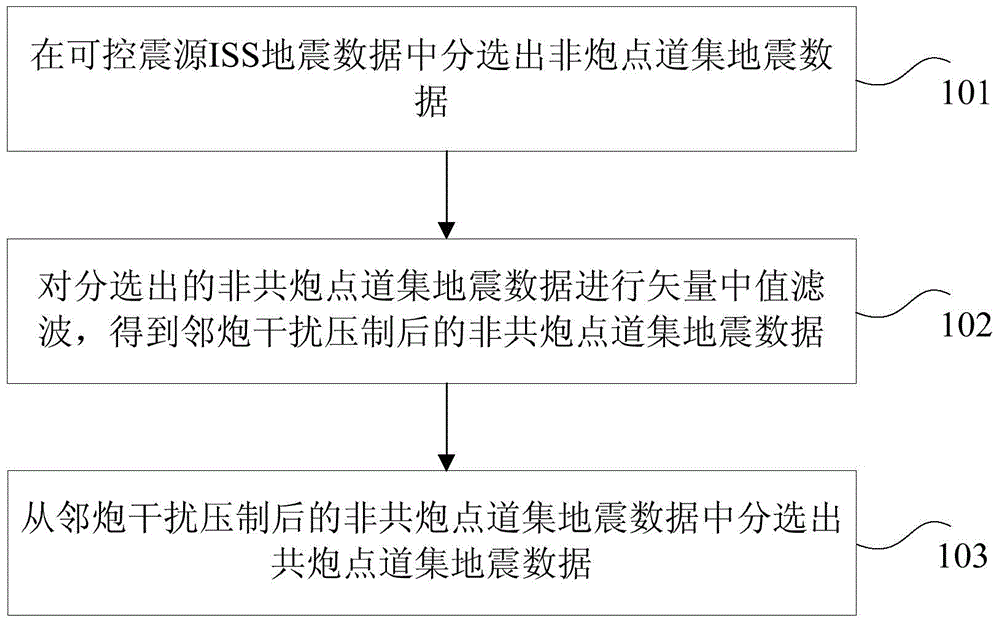
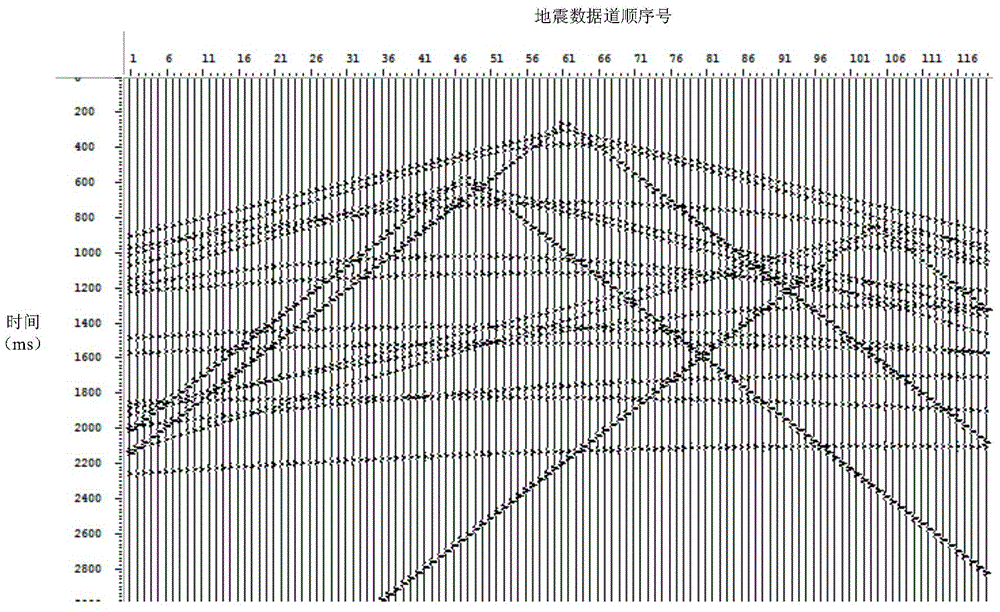
ActiveCN104597499ATroubleshoot technical issues with low accuracyImprove accuracySeismic signal processingSeismic vibratorShot point
The invention discloses an adjacent shot interference suppressing method and device for independent simultaneous sweeping seismic data of seismic vibrators. The adjacent shot interference suppressing method includes that separating non-common shot point gather seismic data from ISS seismic data of the seismic vibrators; carrying out vector median filtering on the separated non-common shot point gather seismic data to obtain non-common shot point gather seismic data performed with adjacent shot interference suppressing; separating common shot point gather seismic data from the non-common shot point gather seismic data performed with the adjacent shot interference suppressing. The adjacent shot interference suppressing method and device for the independent simultaneous sweeping seismic data of the seismic vibrators solve the technical problem of low seismic data precision of the prior art, realize to effectively eliminate the adjacent shot interference in the ISS seismic data and enable the seismic data precision to be improved.
Owner:BC P INC CHINA NAT PETROLEUM CORP +1
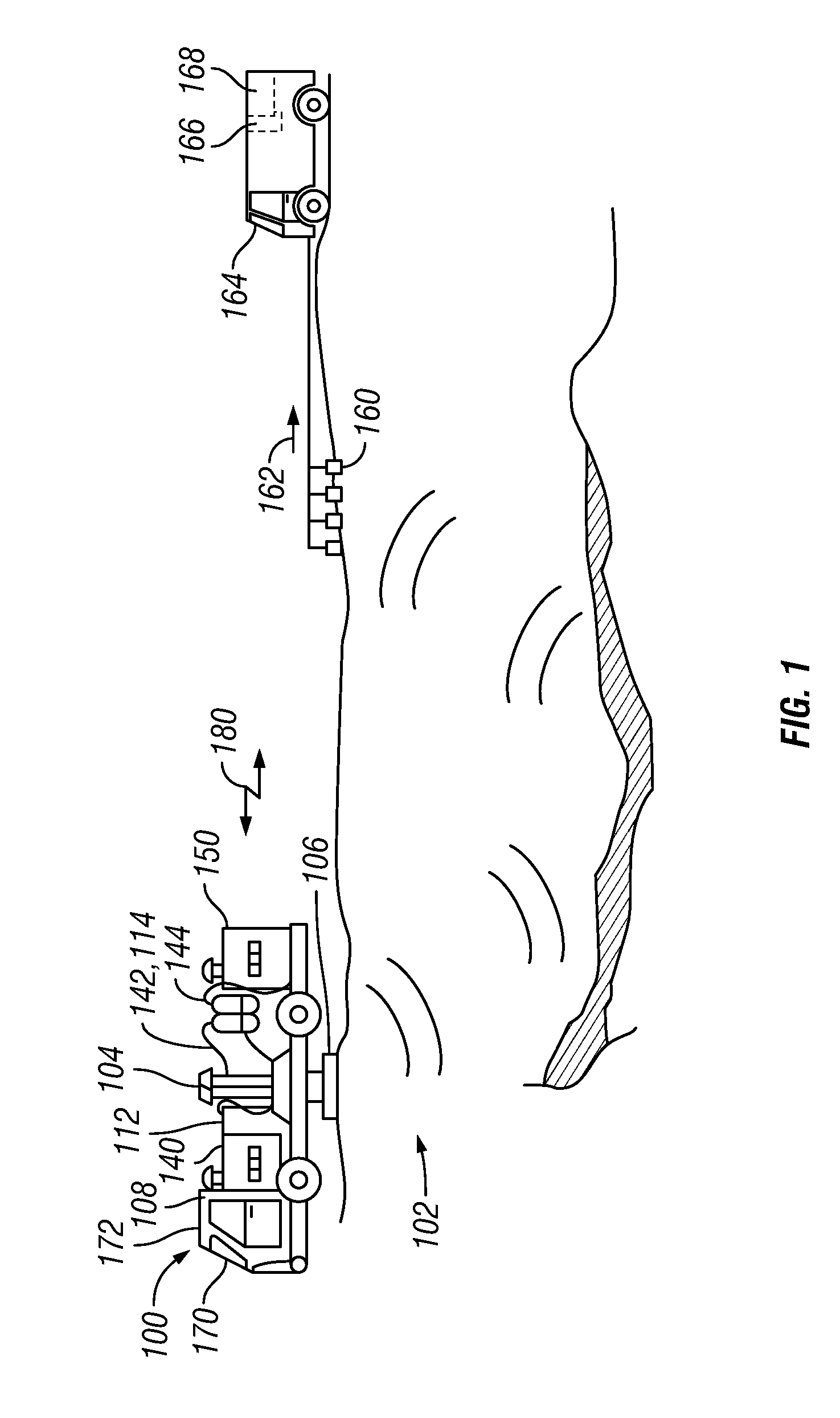
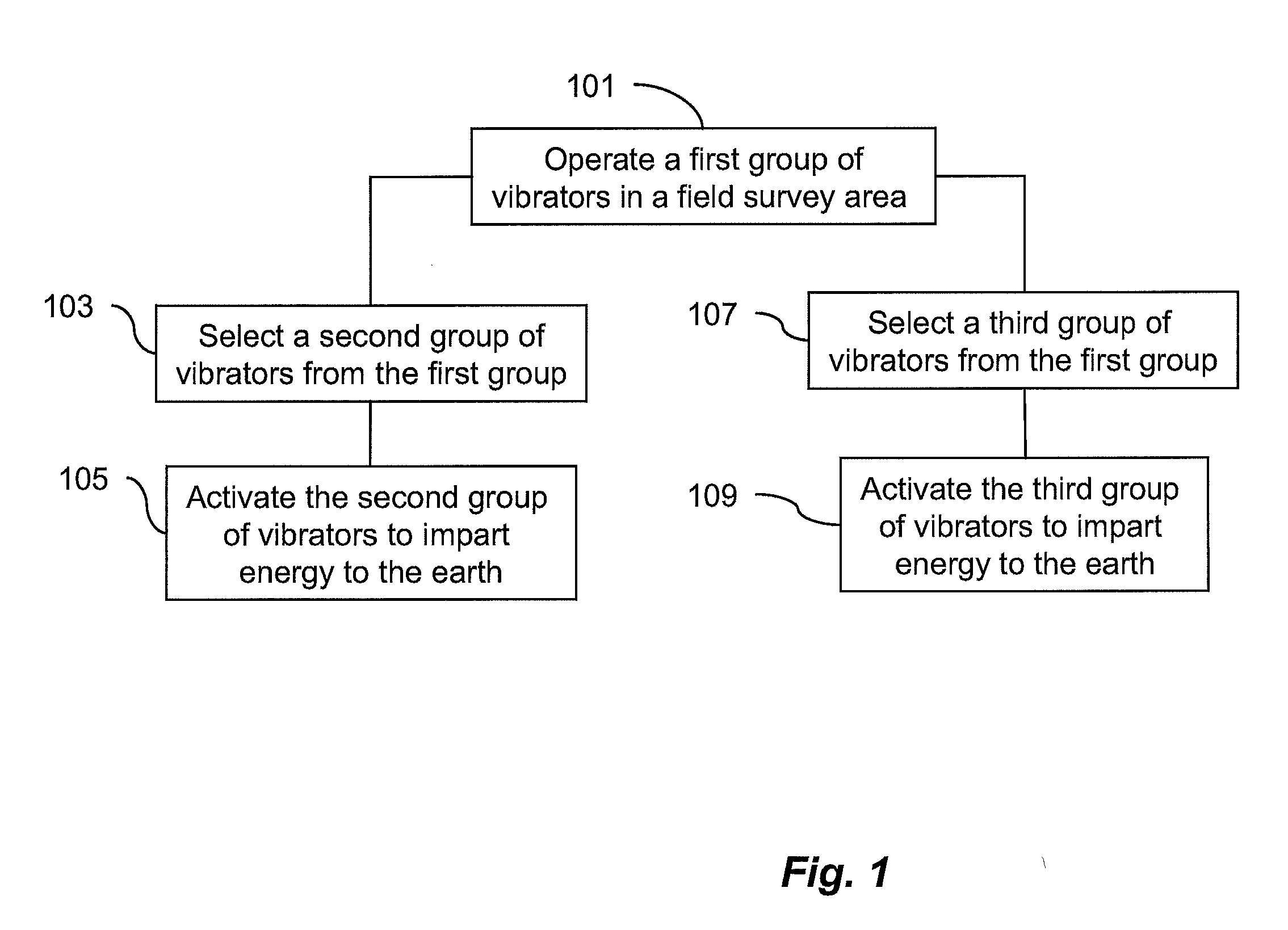
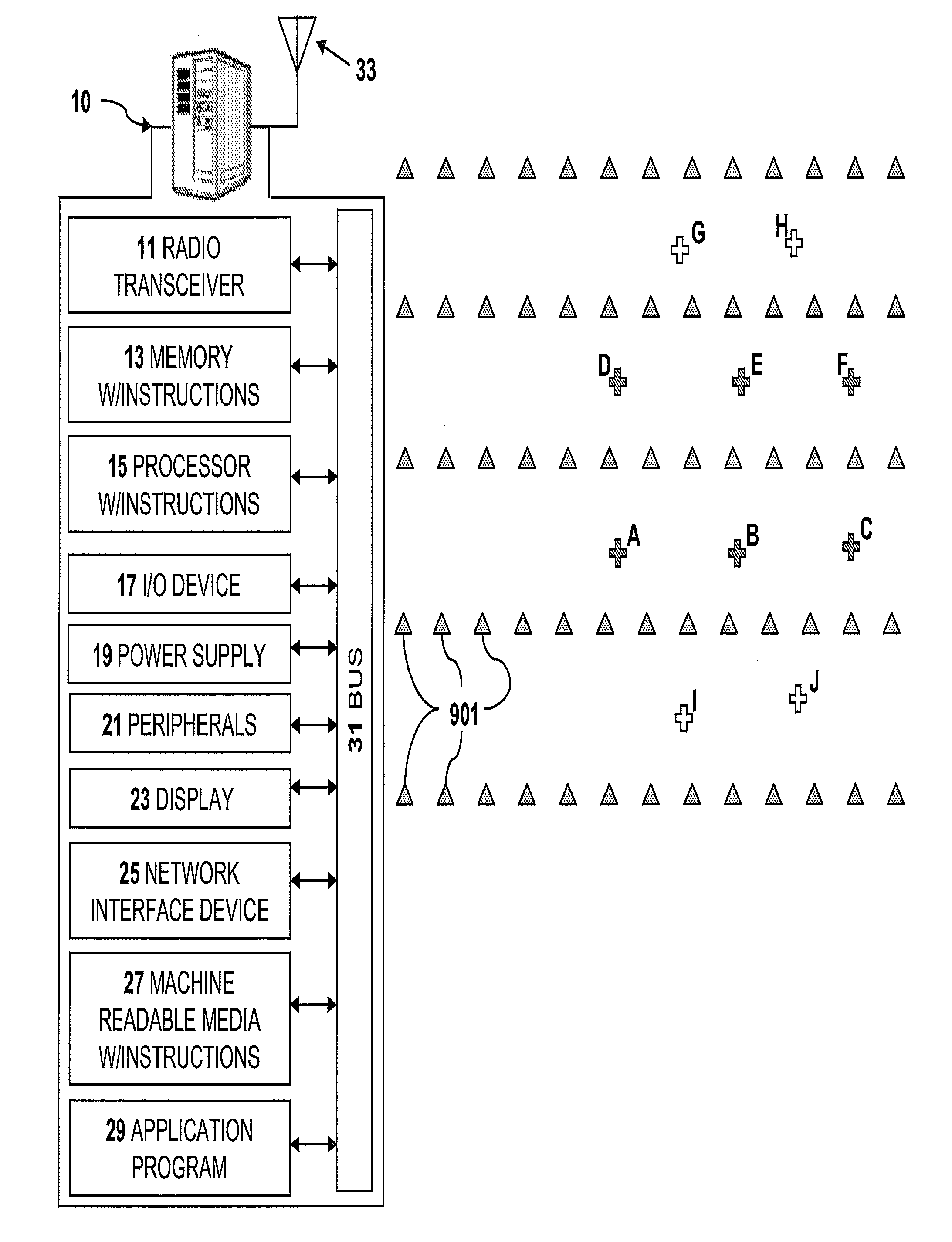
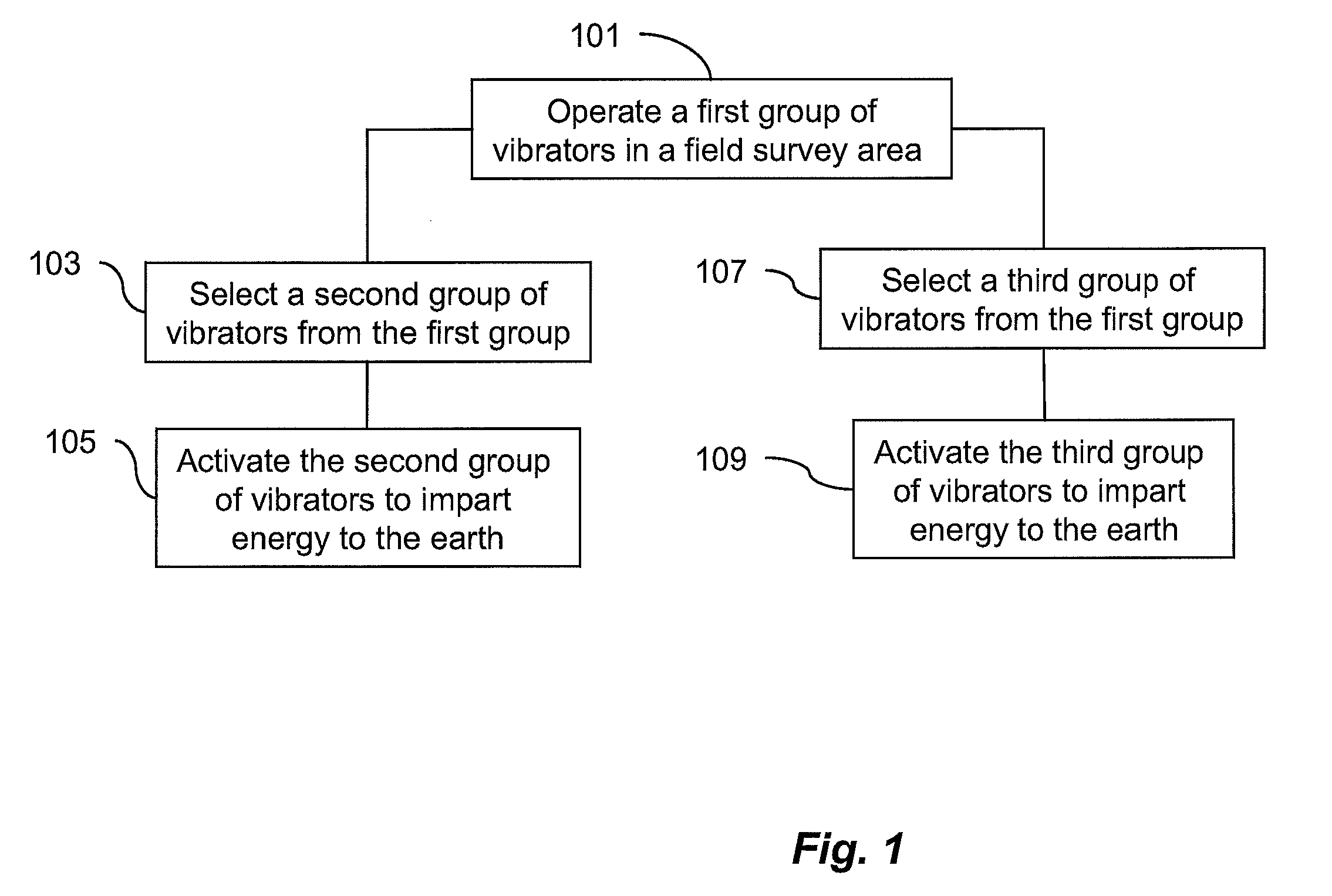
Dynamic source parameter selection for seismic vibrator data acquisition
A method and system of operating single vibrator source points for seismic data acquisition includes acquiring real-time field survey locations for a first plurality of seismic vibrators, determining at least one geometrical relationship between each of the first plurality of seismic vibrators as a function of the field survey locations, selecting a second plurality of seismic vibrators from the first plurality of vibrators as a function of the at least one geometrical relationship, selecting source parameter data for the second plurality of seismic vibrators as a function of the field survey locations and driving the second plurality of seismic vibrators to propagate seismic energy into the earth. A third plurality of vibrators is selected based on geometrical relationships and associated source parameters are determined based on vibrator locations. Multiple vibrator groups may acquire data continuously without interruption.
Owner:CONOCOPHILLIPS CO
Seismic vibrator
InactiveUS20090321175A1Seismic energy generationMagnetostrictive transducersTransducerClassical mechanics
A seismic vibrator includes a transducer, a reactive mass, a base plate to couple motion of the reactive mass to subsurface formations and a linkage system configured to couple motion of the transducer to the reactive mass and the base plate. The linkage system cooperates with the reactive mass and the transducer to define a first resonant frequency and a second resonant frequency within a range of 1 to 300 Hz.
Owner:PGS GEOPHYSICAL AS
Dynamic source parameter selection for seismic vibrator data acquisition
A method and system of operating single vibrator source points for seismic data acquisition includes acquiring real-time field survey locations for a first plurality of seismic vibrators, determining at least one geometrical relationship between each of the first plurality of seismic vibrators as a function of the field survey locations, selecting a second plurality of seismic vibrators from the first plurality of vibrators as a function of the at least one geometrical relationship, selecting source parameter data for the second plurality of seismic vibrators as a function of the field survey locations and driving the second plurality of seismic vibrators to propagate seismic energy into the earth. A third plurality of vibrators is selected based on geometrical relationships and associated source parameters are determined based on vibrator locations. Multiple vibrator groups may acquire data continuously without interruption.
Owner:CONOCOPHILLIPS CO
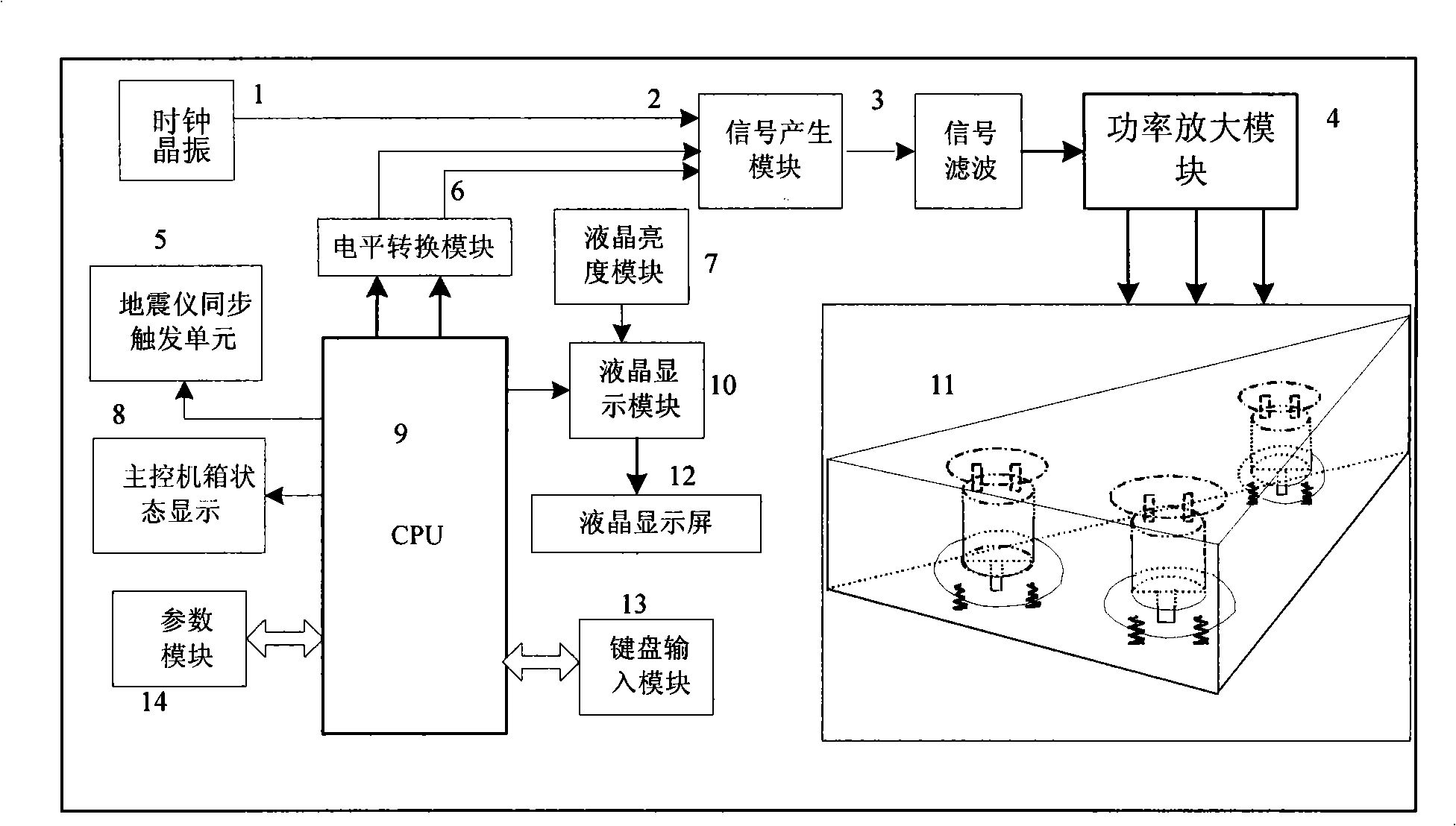
Sea electromagnetical type shallow layer earthquake controllable earthquake focus system
InactiveCN101285891AEnergy output optimizationMeet the requirements of high-resolution seismic explorationSeismic energy generationSurface oceanAlloy
The invention relates to a vibroseis device for marine geophysical exploration, in particular to a marine electromagnetic type shallow seismic vibrator system. The system is formed by a main controller and a vibration generator array. The main controller consists of a CPU, a seismograph synchronizer trigging unit, a parameter module, an electric level switching module, a signal generating module and a power amplifying module. The vibration generator array is fixed onto a steel shelf by a fixing substrate. A fixing bracket, magnetic steel, a magnetic polar plate and an iron core are rigidly connected with a housing. Moving coils are fixed on a middle axle of the vibration generator. The middle axle of a vibration generator is connected with a moving substrate. The moving coils are connected with a load bearing spring by aluminum alloy. The load bearing spring is fixed onto the housing through rivets. A supporting spring which is connected with the moving substrate by bolts is fixed onto the steel shelf through the bolts. The system is comparatively high in scanning frequency section of signal up to 1 to 1500Hz, good in repeatability of the signal, and optimal in the energy output of the vibration generator. The system meets the requirements of high resolution earthquake exploration at marine shallow layers and solves the influence of marine earthquake exploration carriers on seismic focus.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
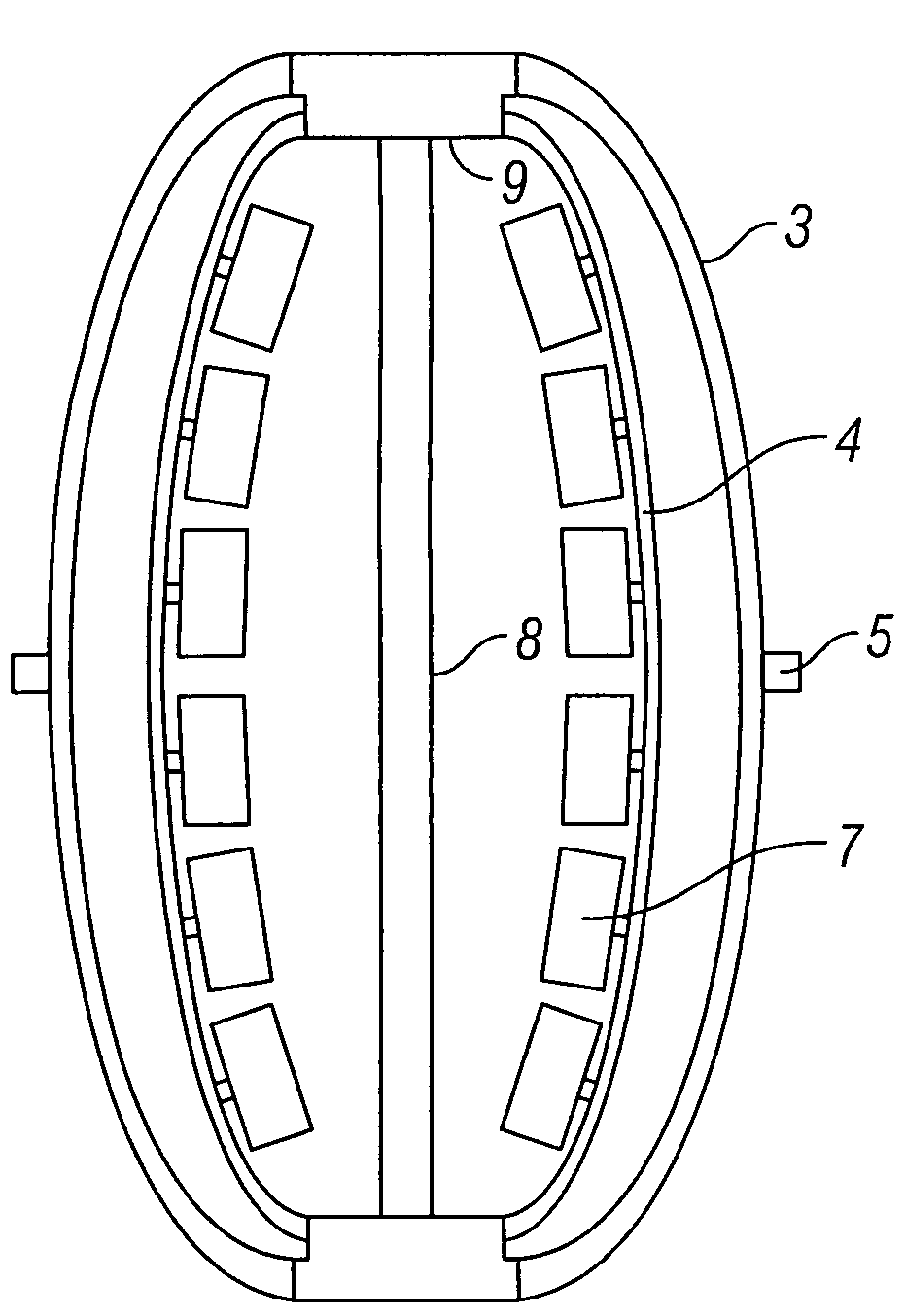
Constant energy displacements
ActiveUS20130308422A1Effectively to impartSeismic data acquisitionSeismic signal receiversAcoustic energyElectric power
An electric sweep type seismic vibrator source of the type used in seismic prospecting for hydrocarbons is provided. In one example, the source uses an engine and generator combination to create electric power for all systems on the source such as driving a frame of linear electric motors that direct a rod or piston to contact the ground in a recurring fashion along with driving the source from location to location through a survey area. A foot is arranged on the bottom end of the rod or piston for contact with the ground and by engaging the grid of motors to push down against the ground in a rapid progression, acoustic energy is created and delivered into the ground for geophones to sense and record.
Owner:CONOCOPHILLIPS CO
Vibrator source system for improved seismic imaging
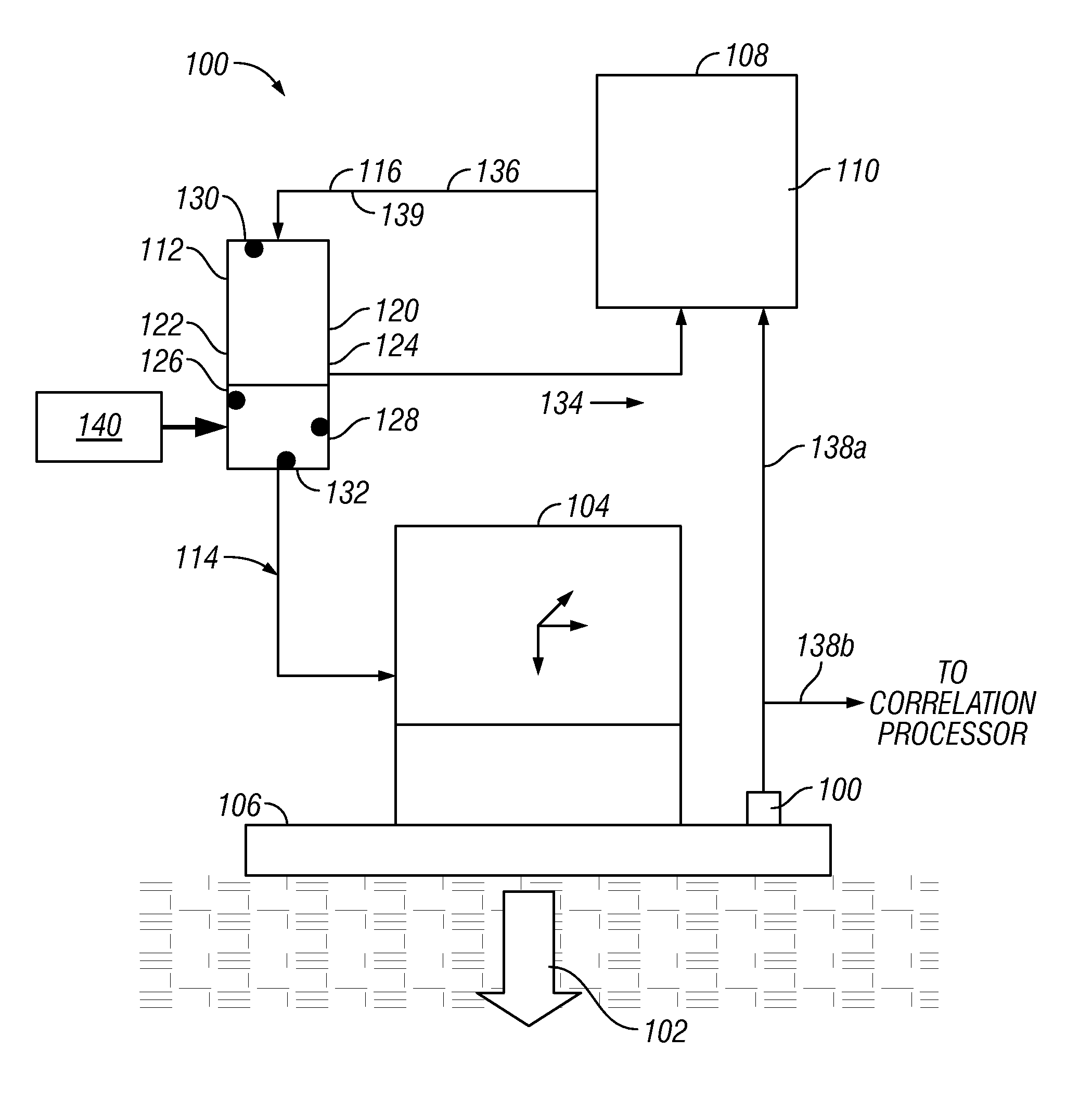
InactiveUS20130201793A1Improve performanceImprove of seismic dataSeismic signal processingAccelerometerSignal on
A system for modeling the output signal emanating from a seismic vibrator based on a superposed collection of damped harmonic oscillators, whose critical parameters are determined from signals from accelerometers on the baseplate and reaction mass portions of the vibrator together with the input force (pilot sweep). This modeled output signal is a more accurate representation of the seismic signal that propagates into the earth and may be used in the cross-correlation process to significantly enhance the accuracy of the recorded seismic data. Additionally, by modeling the output signal on a shot by shot basis, any changes in the ground's surface can be monitored and / or documented, and, if required, the sweep parameters can be varied shot by shot for optimum performance.
Owner:ROWSE SPENCER LEWIS +1
Distinctive land seismic sweep
ActiveUS20130286780A1Effectively to impartBiocideSeismic data acquisitionAcoustic energyHydrocotyle bowlesioides
The invention is an electric sweep type seismic vibrator source of the type used in seismic prospecting for hydrocarbons. The source uses an engine and generator combination to create electric power for all systems on the source such as driving a frame of linear electric motors that direct a rod or piston to contact the ground in a recurring fashion along with driving the source from location to location through a survey area. Preferably a foot is arranged on the bottom end of the rod or piston for contact with the ground and by engaging the grid of motors to push down against the ground in a rapid progression, acoustic energy is created and delivered into the ground for geophones to sense and record. However, the rapid progression of pulses or sweep of seismic energy is delivered in a distinctive fashion as compared to a conventional upsweep or downsweep and the distinctiveness is also achieved by creating a designed cadence or timing such that each pulse in a series of pulses is not delivered in a regular timing. Several similar seismic sources may be employed where each is provided with its own distinctive series of pulses such that each may be identified within the data record and source separation from a number of seismic sources may be accomplished.
Owner:CONOCOPHILLIPS CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com