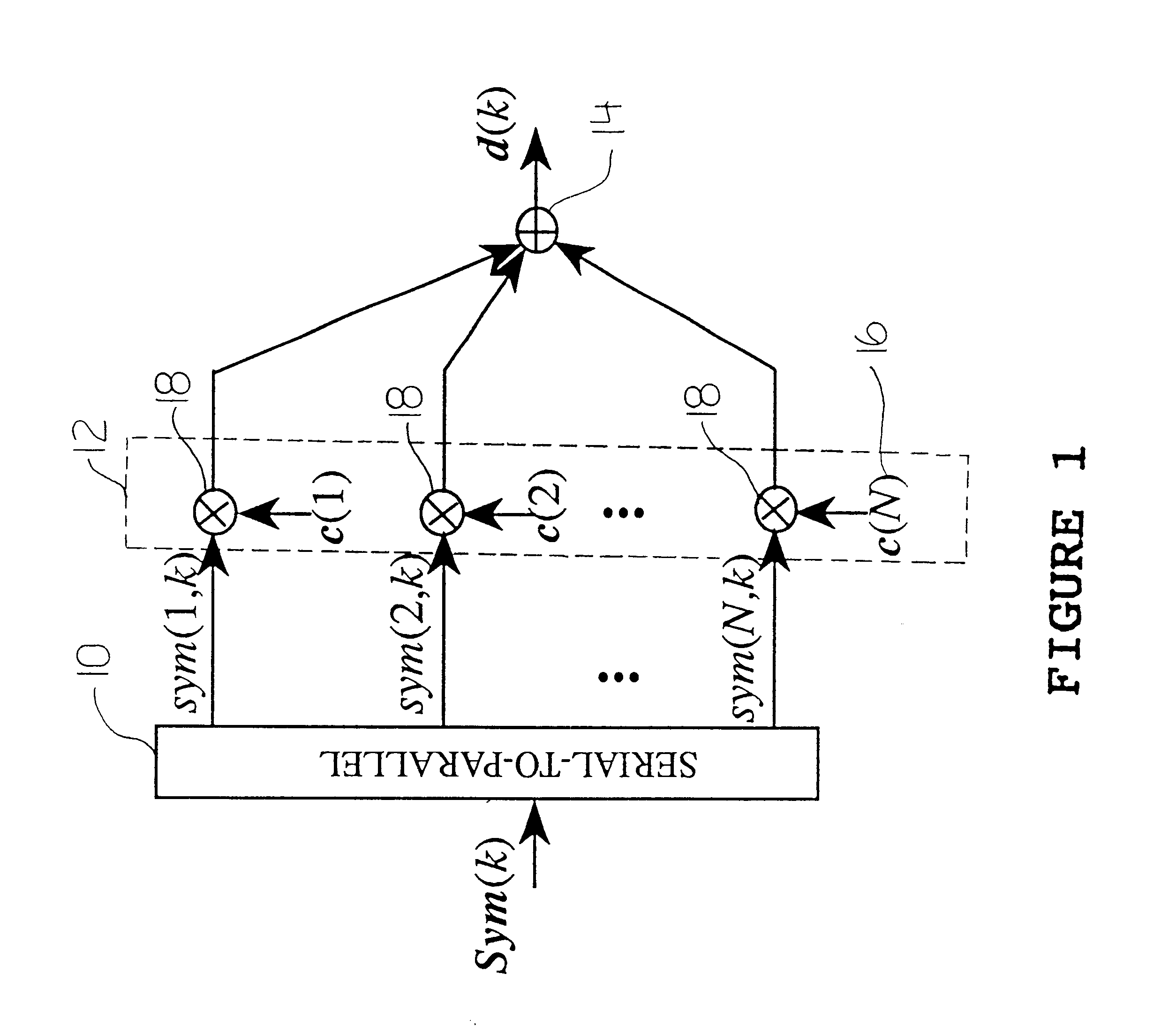
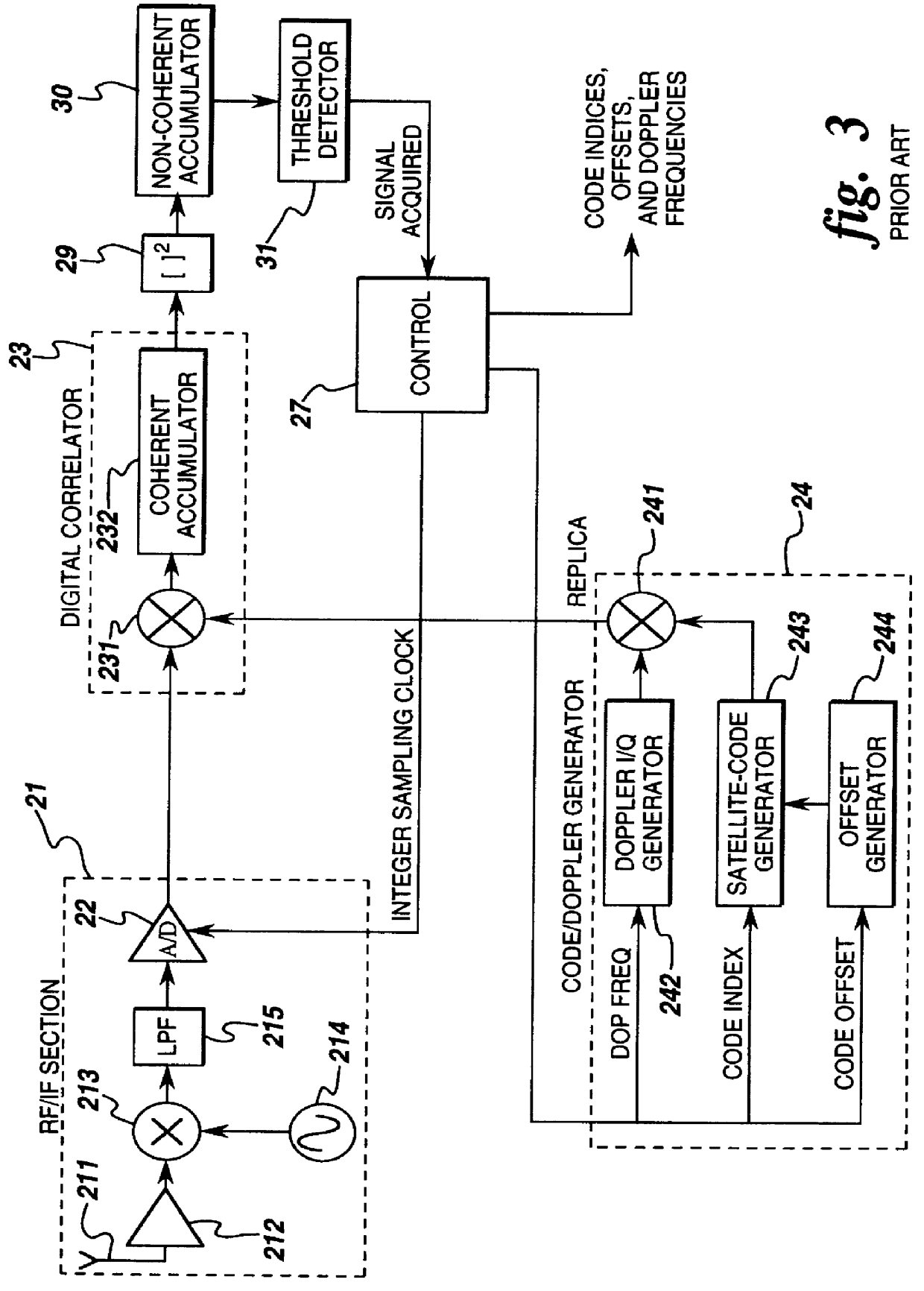
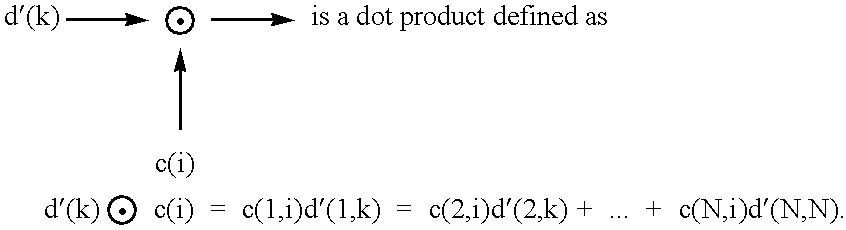Patents
Literature
511 results about "Direct-sequence spread spectrum" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
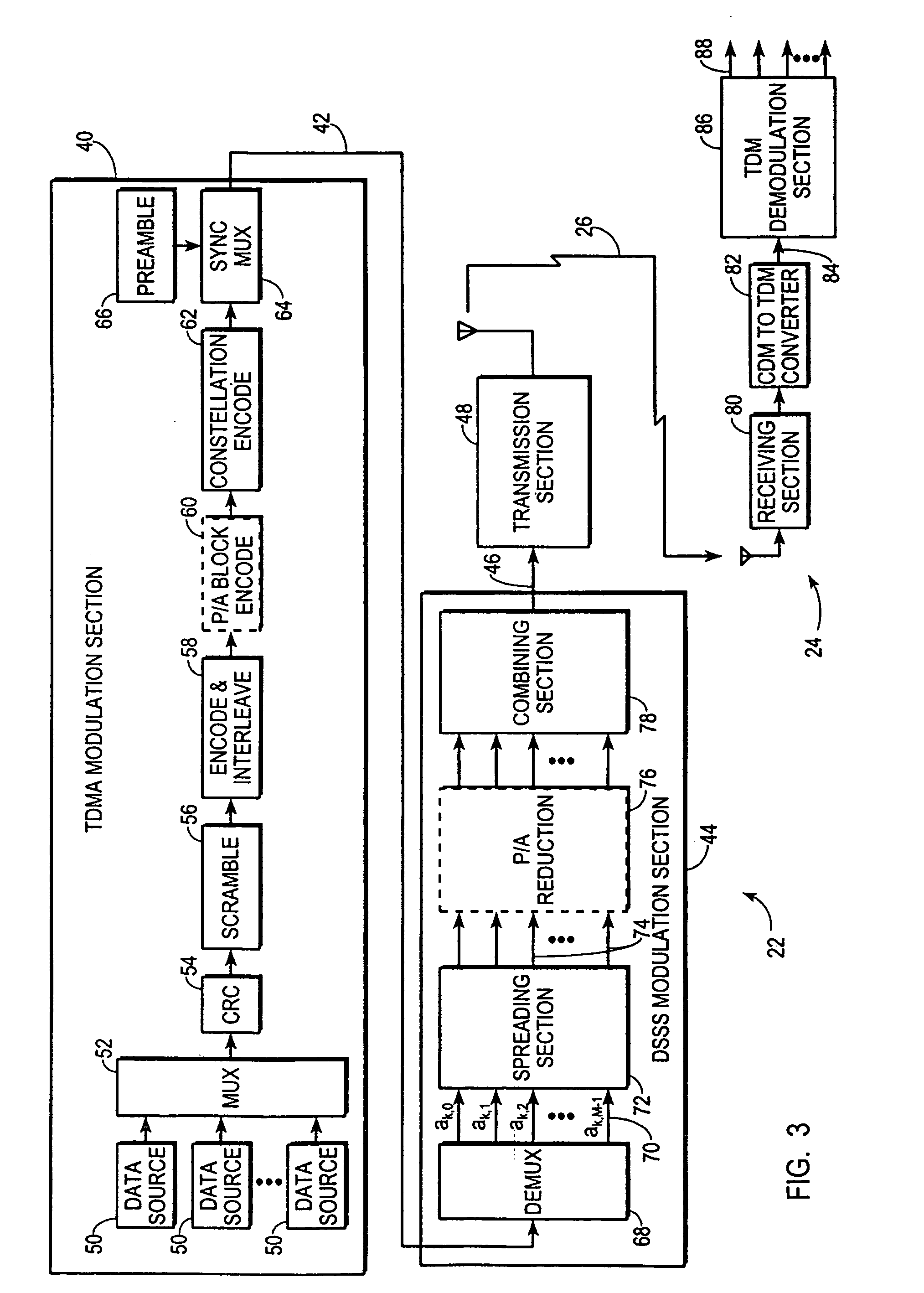
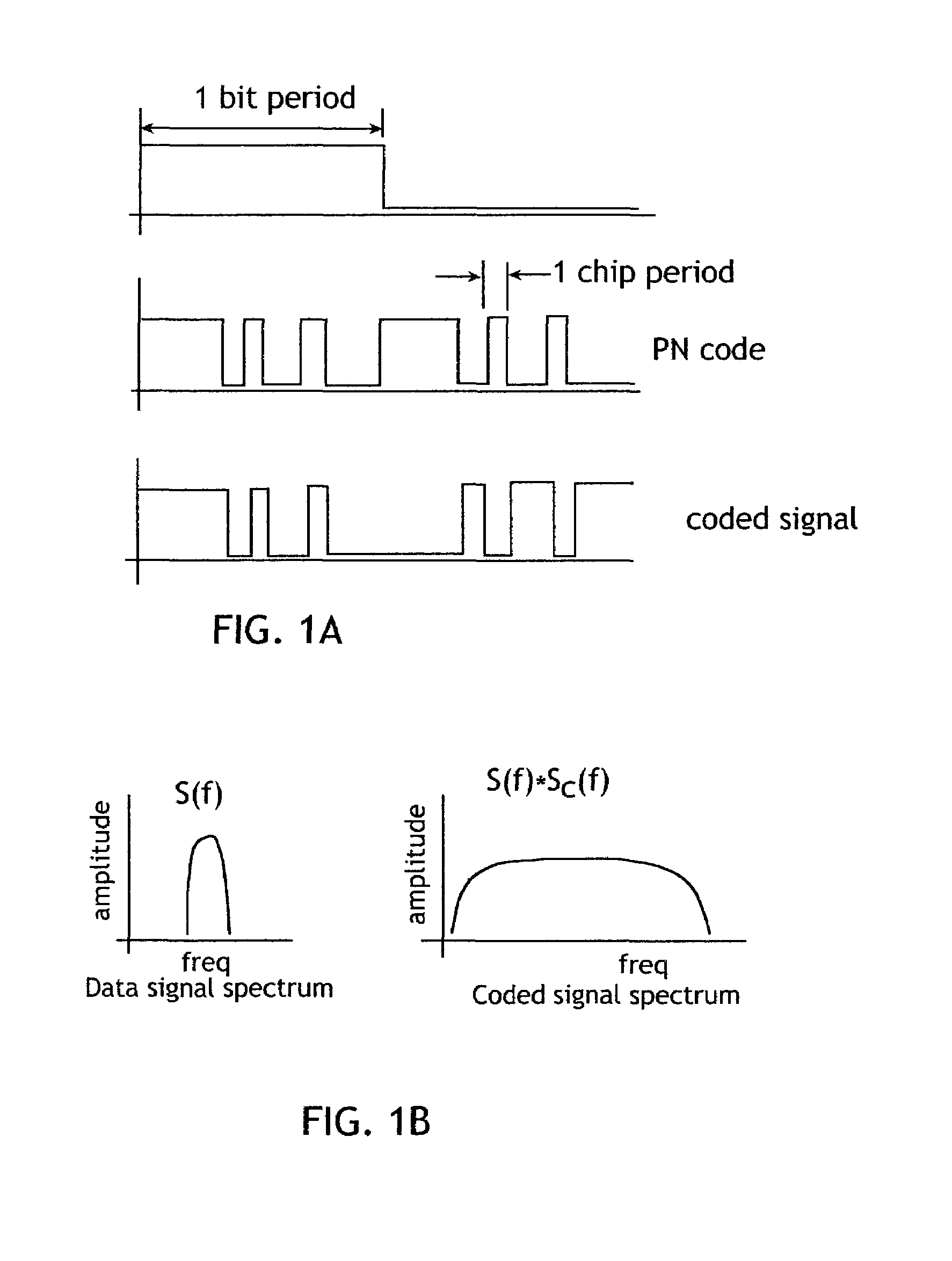
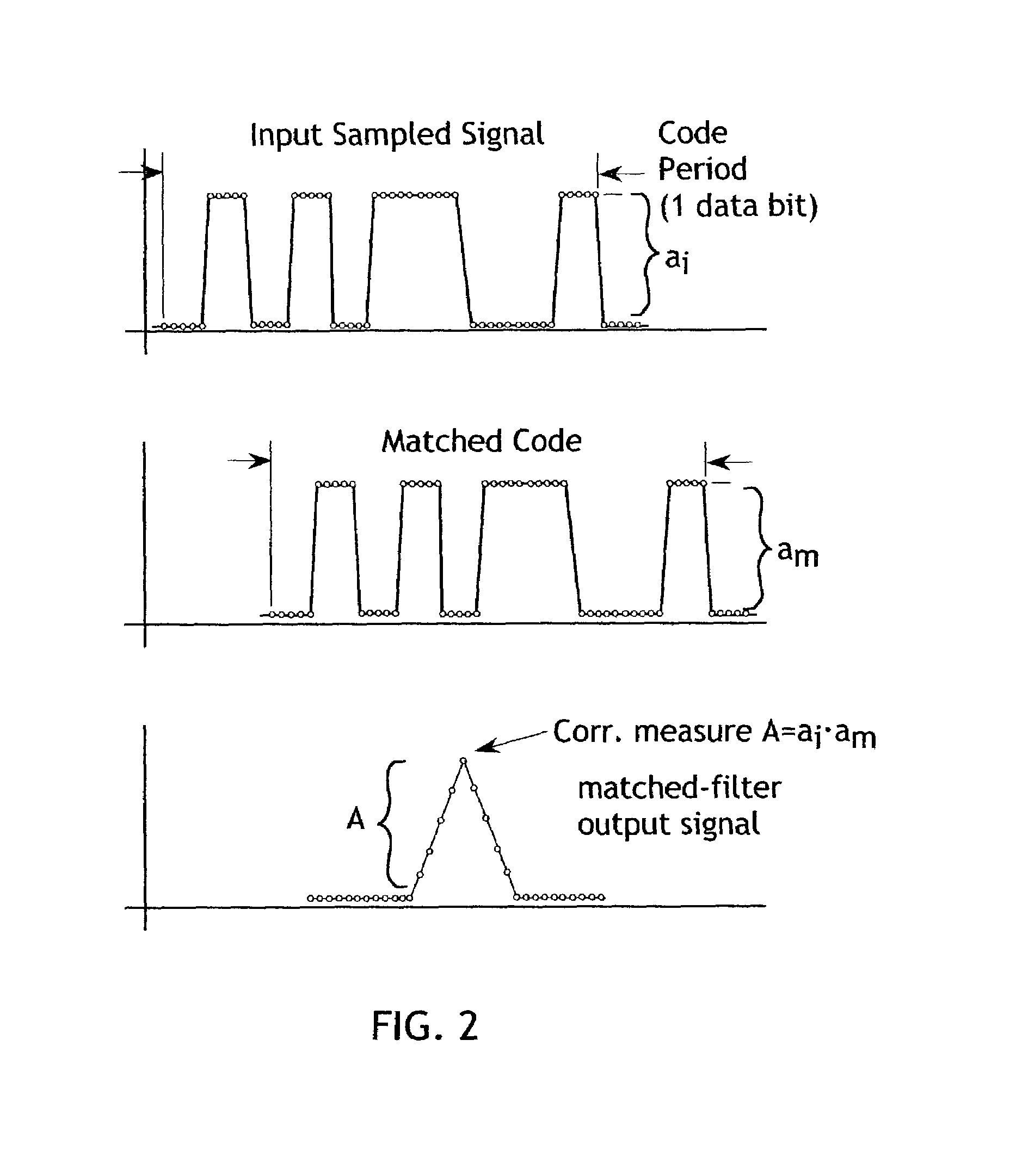
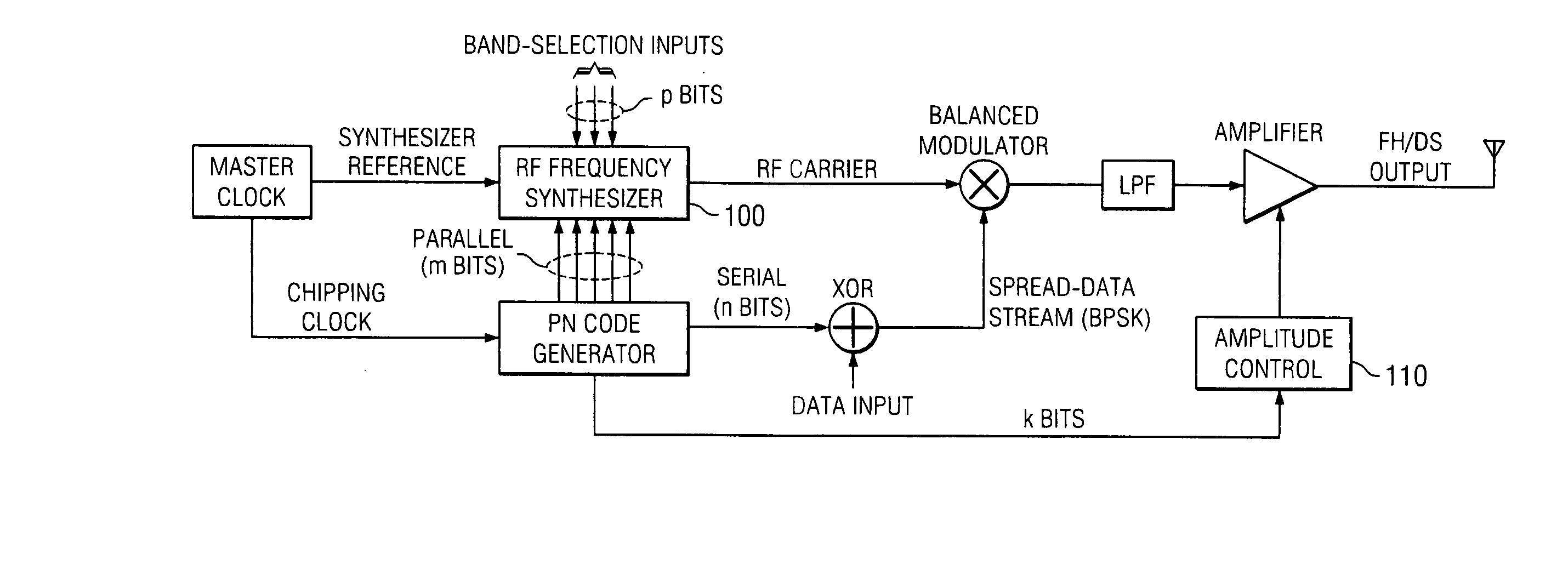
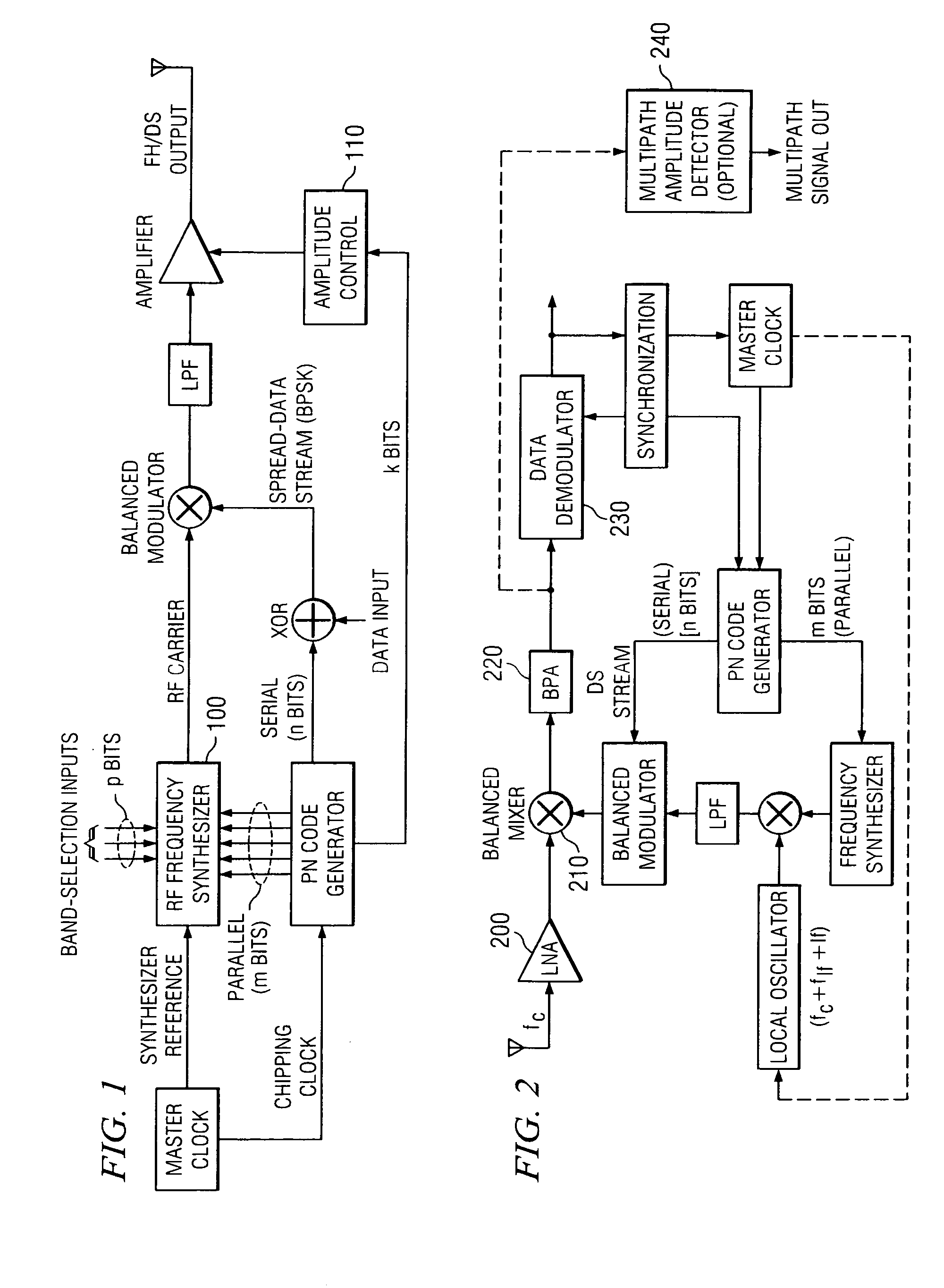
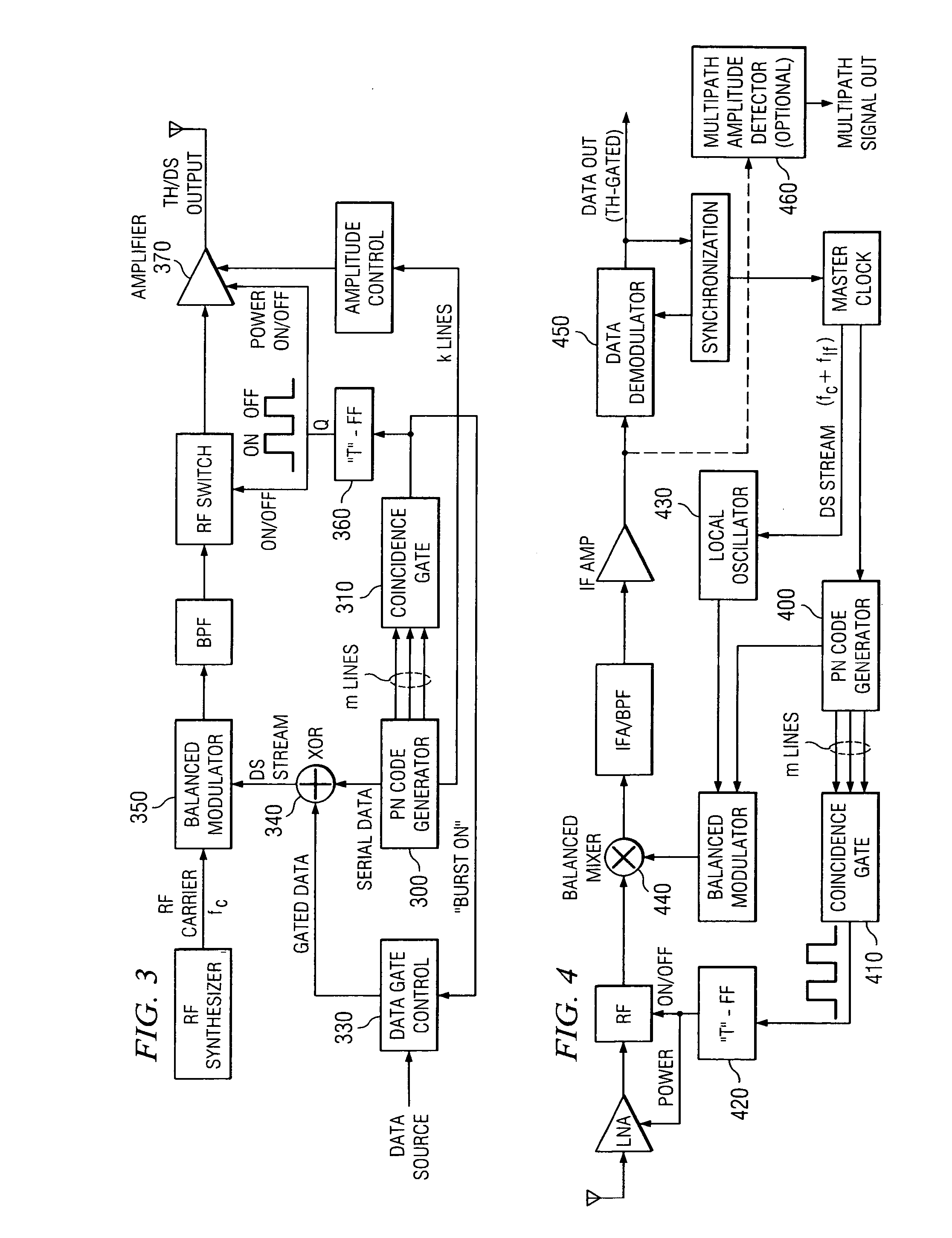
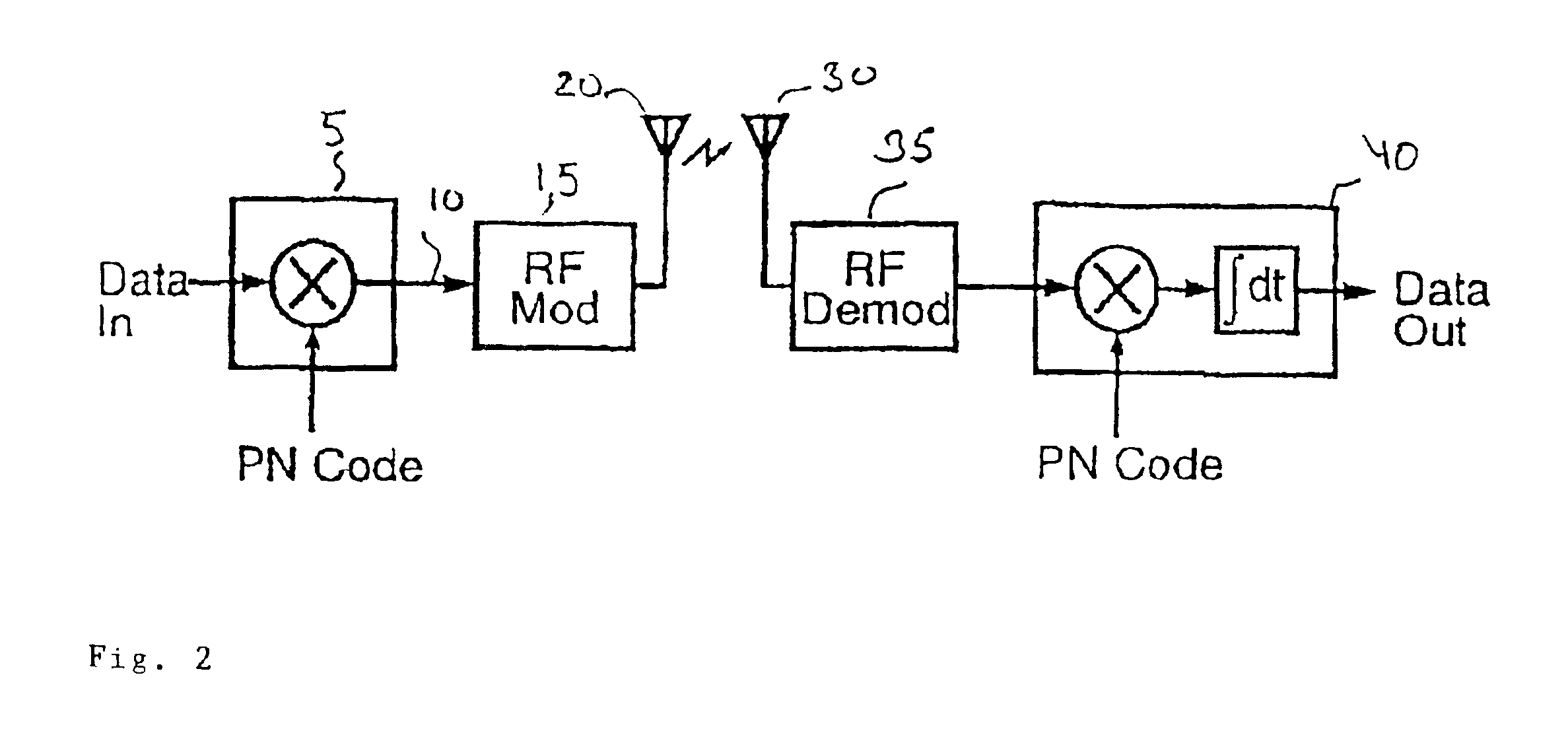
In telecommunications, direct-sequence spread spectrum (DSSS) is a spread spectrum modulation technique used to reduce overall signal interference. The spreading of this signal makes the resulting wideband channel more noisy, allowing for greater resistance to unintentional and intentional interference.
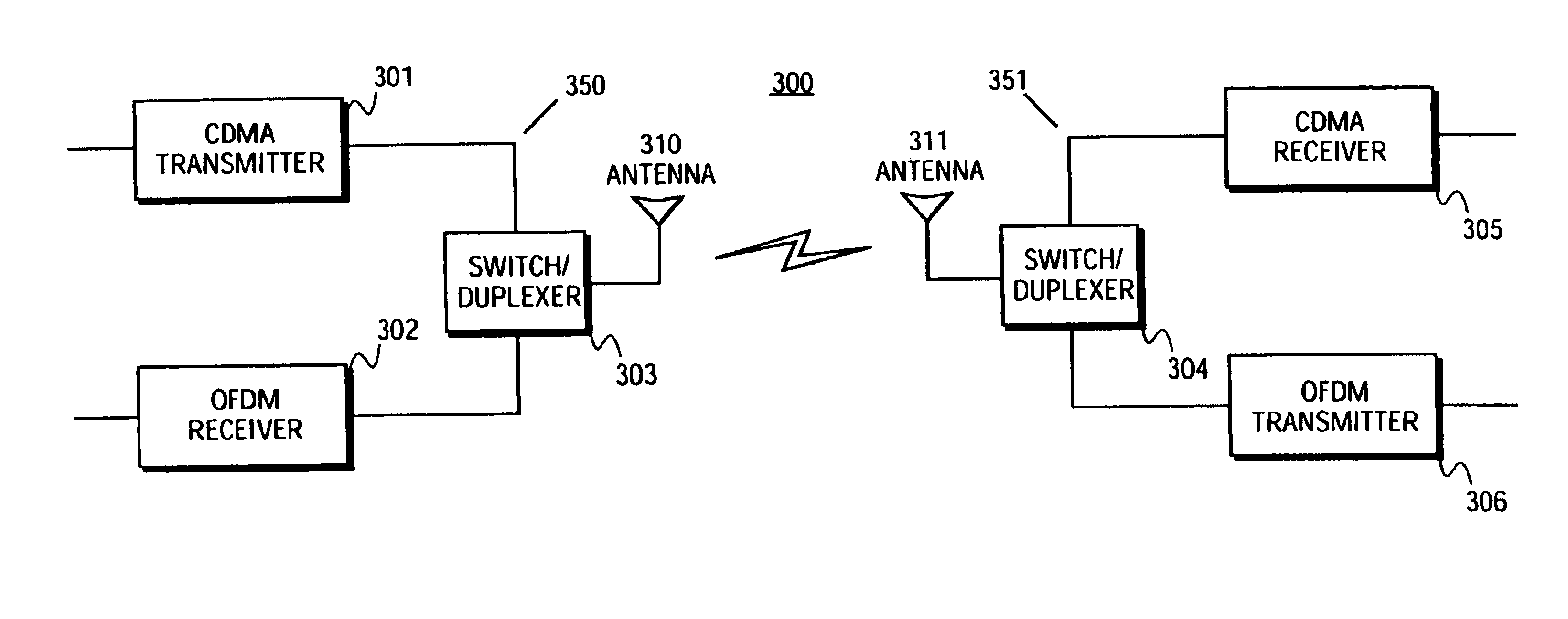
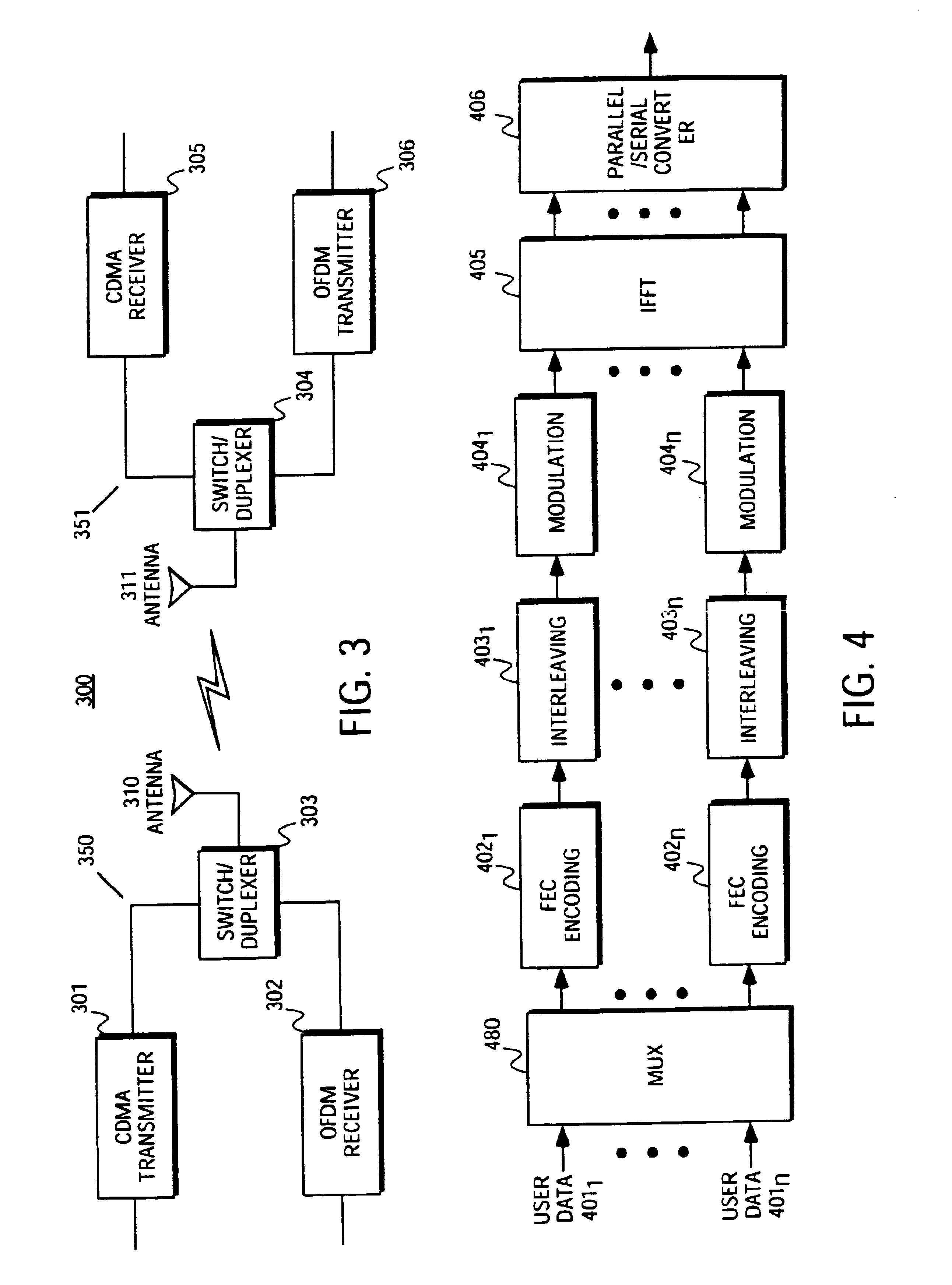
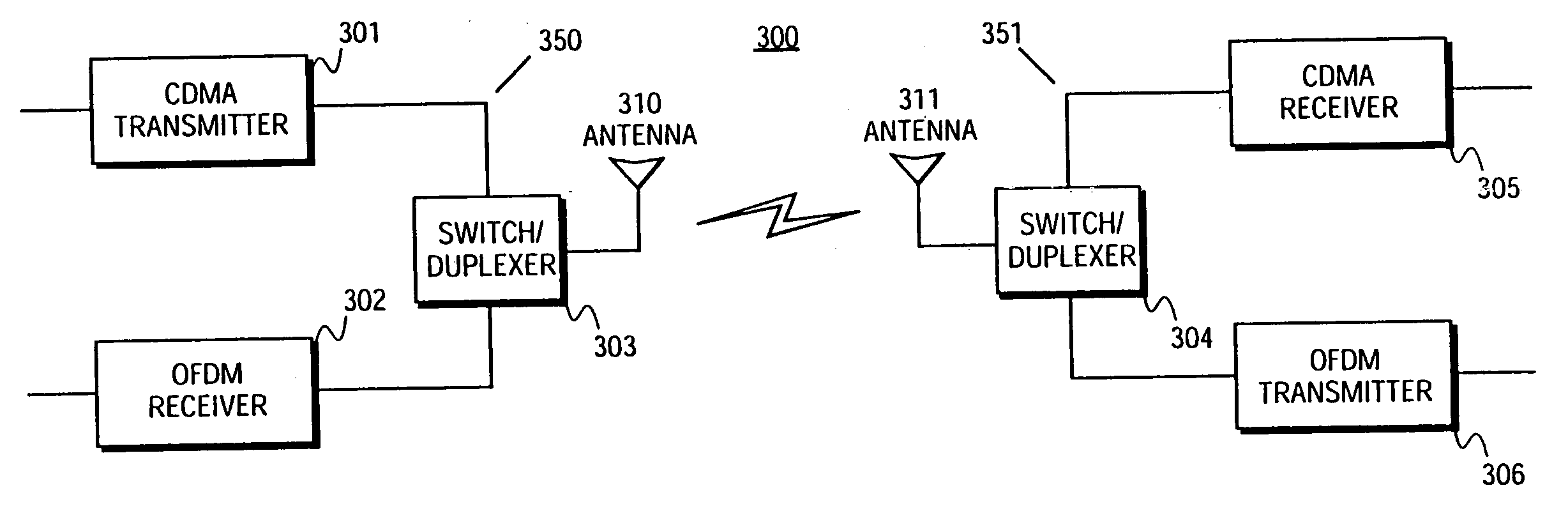
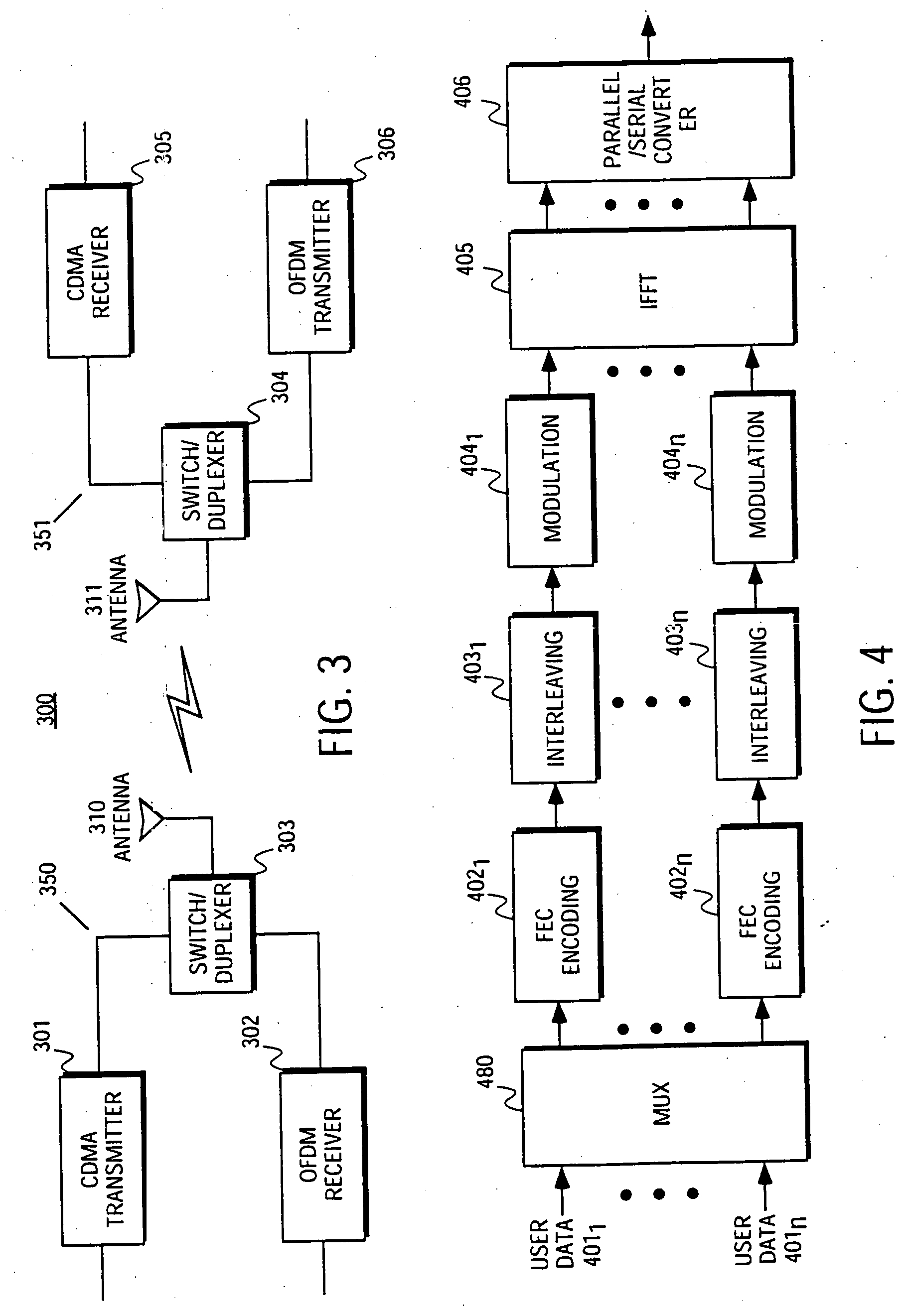
Communication system using OFDM for one direction and DSSS for another direction
InactiveUS6940827B2Power managementTransmission path divisionCommunications systemTelecommunications
A method and apparatus for wireless communication are described. In one embodiment, a method for communicating with a subscriber comprises transmitting orthogonal frequency domain multiplexing (OFDM) signals to the subscriber, and receiving direct-sequence spread spectrum (DSSS) signals from the subscriber.
Owner:ADAPTIX +1
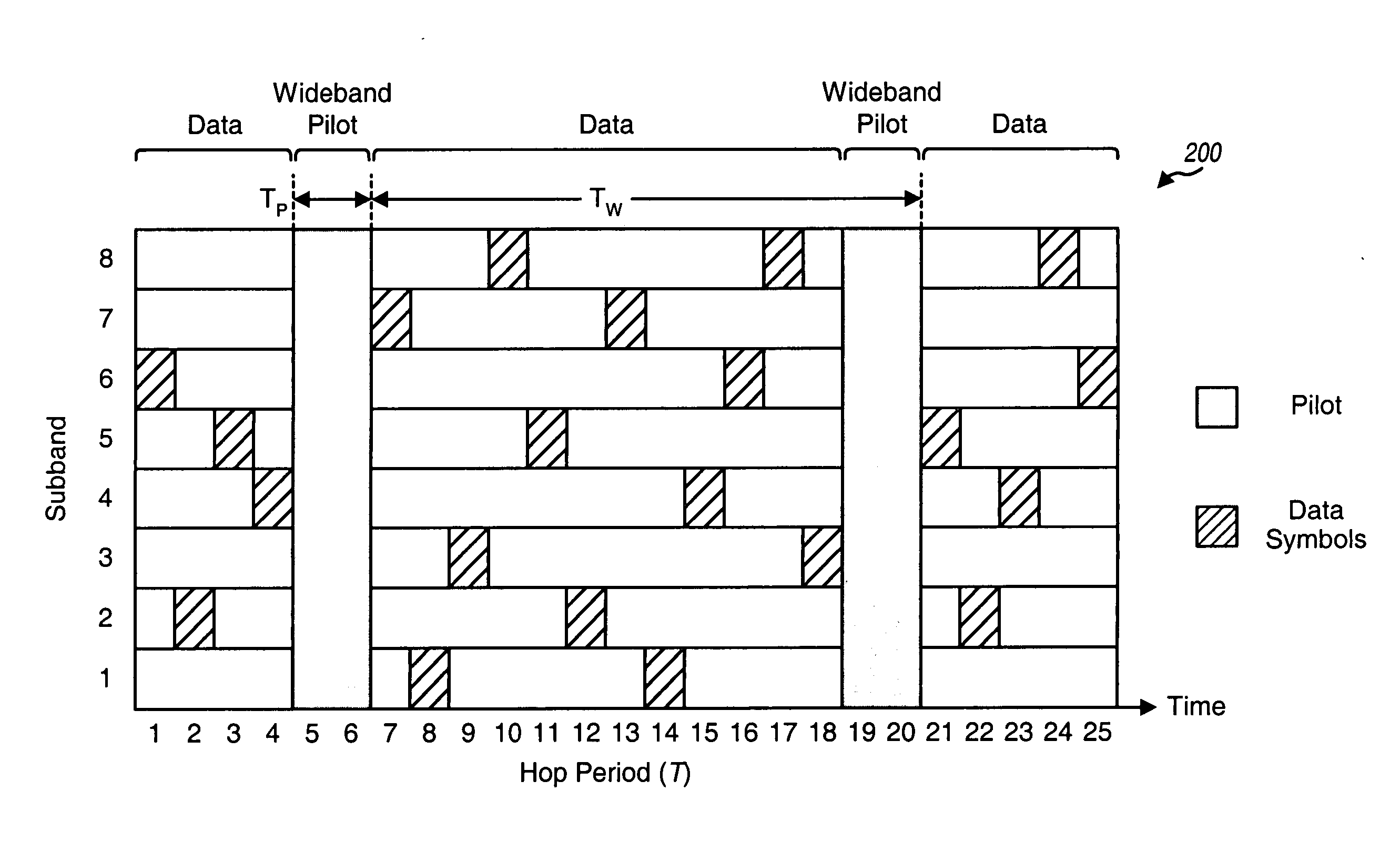
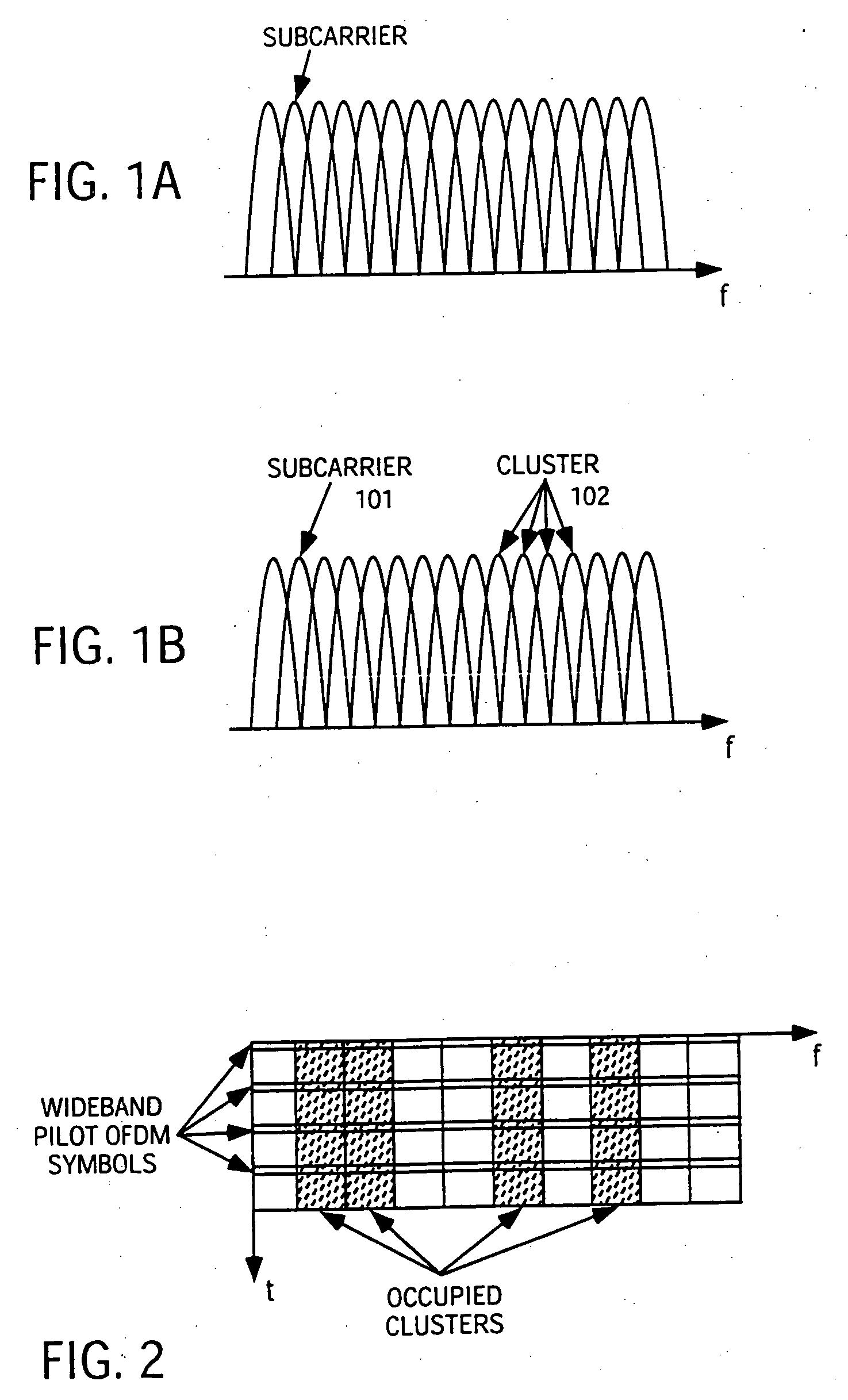
Fast frequency hopping with a code division multiplexed pilot in an OFDMA system
ActiveUS20040228267A1Fast frequency hoppingImprove interferenceTransmission path divisionTime-division multiplexCommunications systemTransmitted power
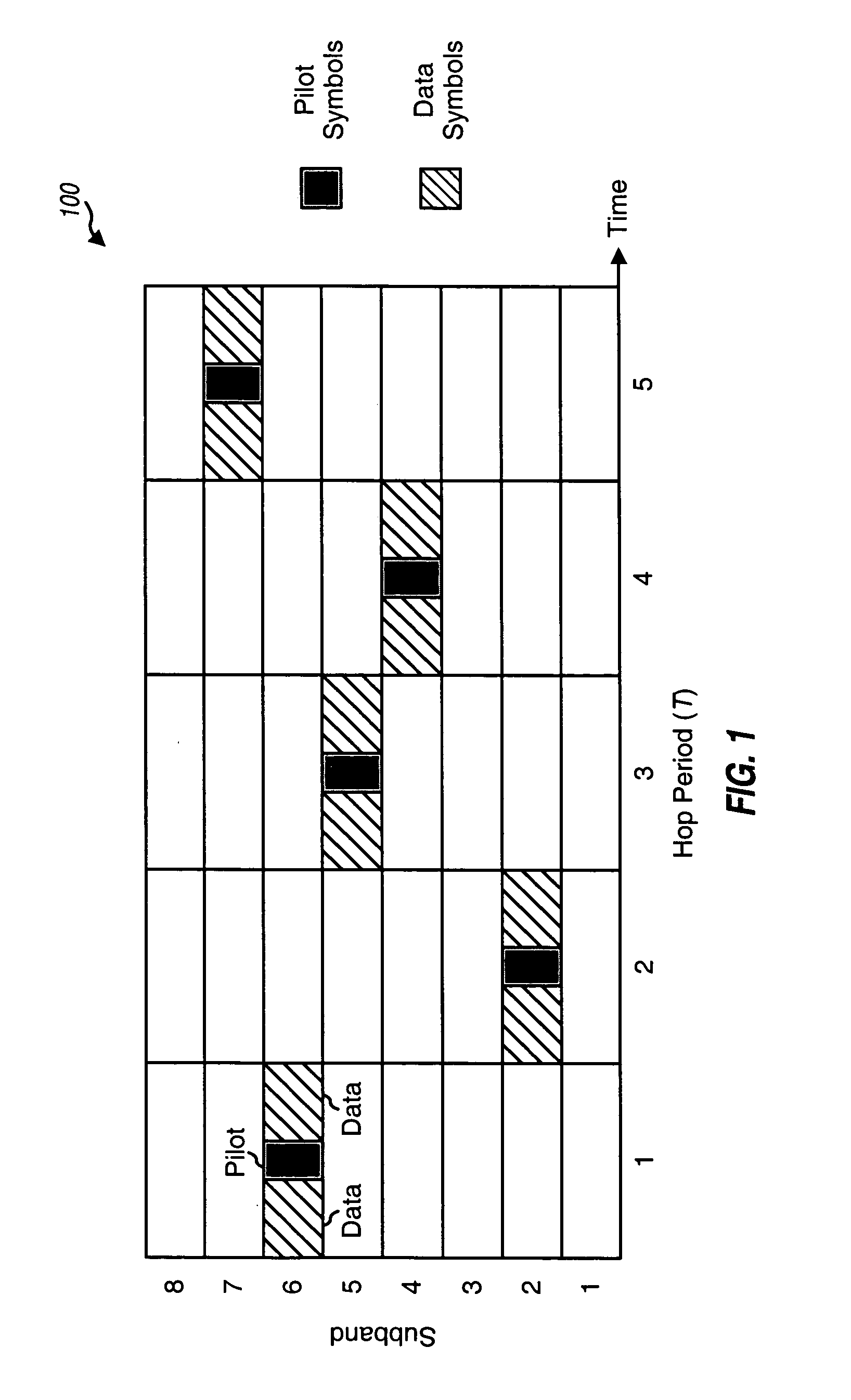
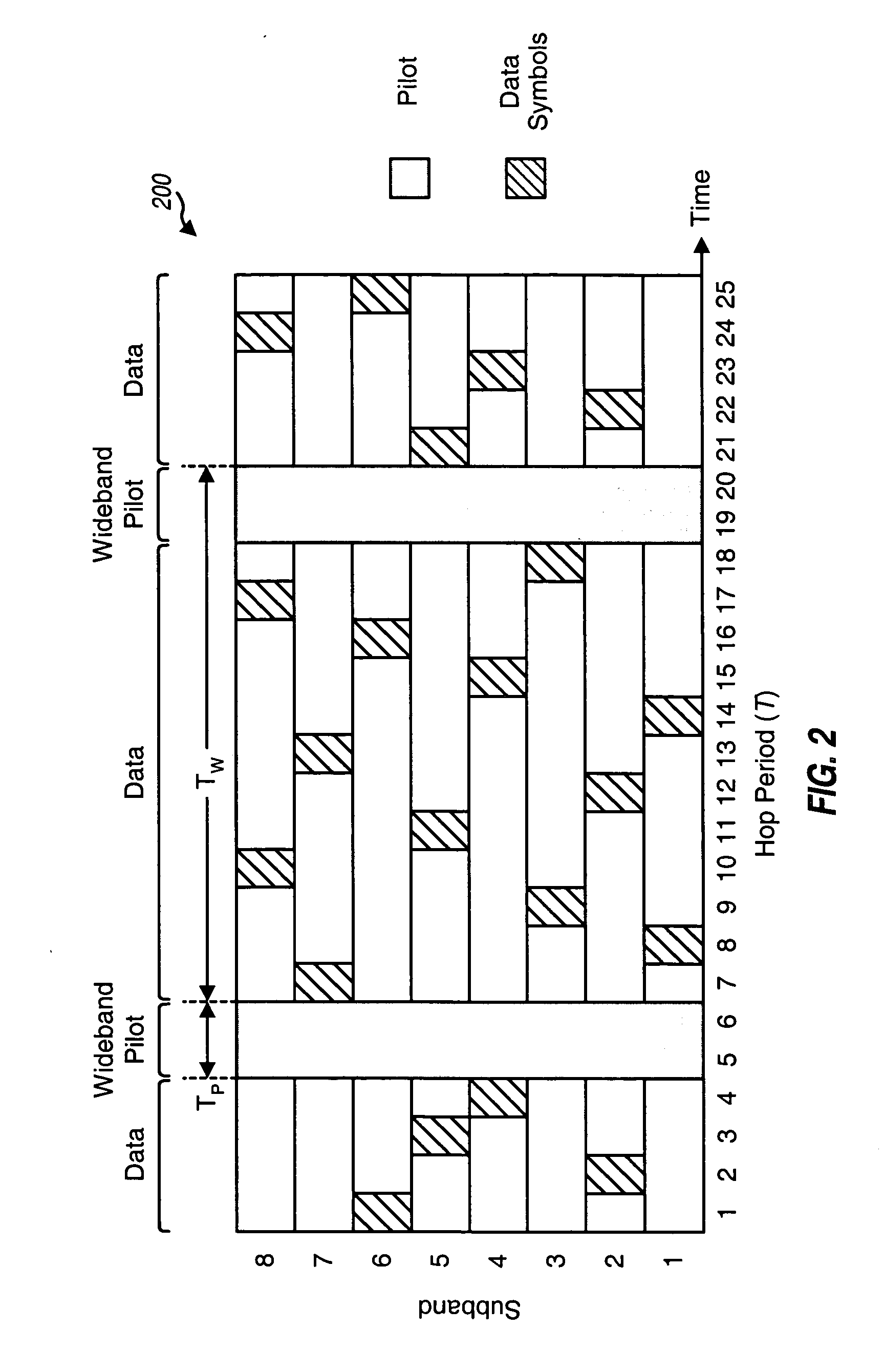
Techniques are provided to support fast frequency hopping with a code division multiplexed (CDM) pilot in a multi-carrier communication system (e.g., an OFDMA system). Each transmitter (e.g., each terminal) in the system transmits a wideband pilot on all subbands to allow a receiver (e.g., a base station) to estimate the entire channel response at the same time. The wideband pilot for each transmitter may be generated using direct sequence spread spectrum processing and based on a pseudo-random number (PN) code assigned to that transmitter. This allows the receiver to individually identify and recover multiple wideband pilots transmitted concurrently by multiple transmitters. For a time division multiplexed (TDM) / CDM pilot transmission scheme, each transmitter transmits the wideband pilot in bursts. For a continuous CDM pilot transmission scheme, each transmitter continuously transmits the wideband pilot, albeit at a low transmit power level. Any frequency hopping rate may be supported without impacting pilot overhead.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Short range spread-spectrum radiolocation system and method
InactiveUS6556942B1Sufficient gross rangingLow costDirection finders using radio wavesBeacon systems using radio wavesData setTriangulation
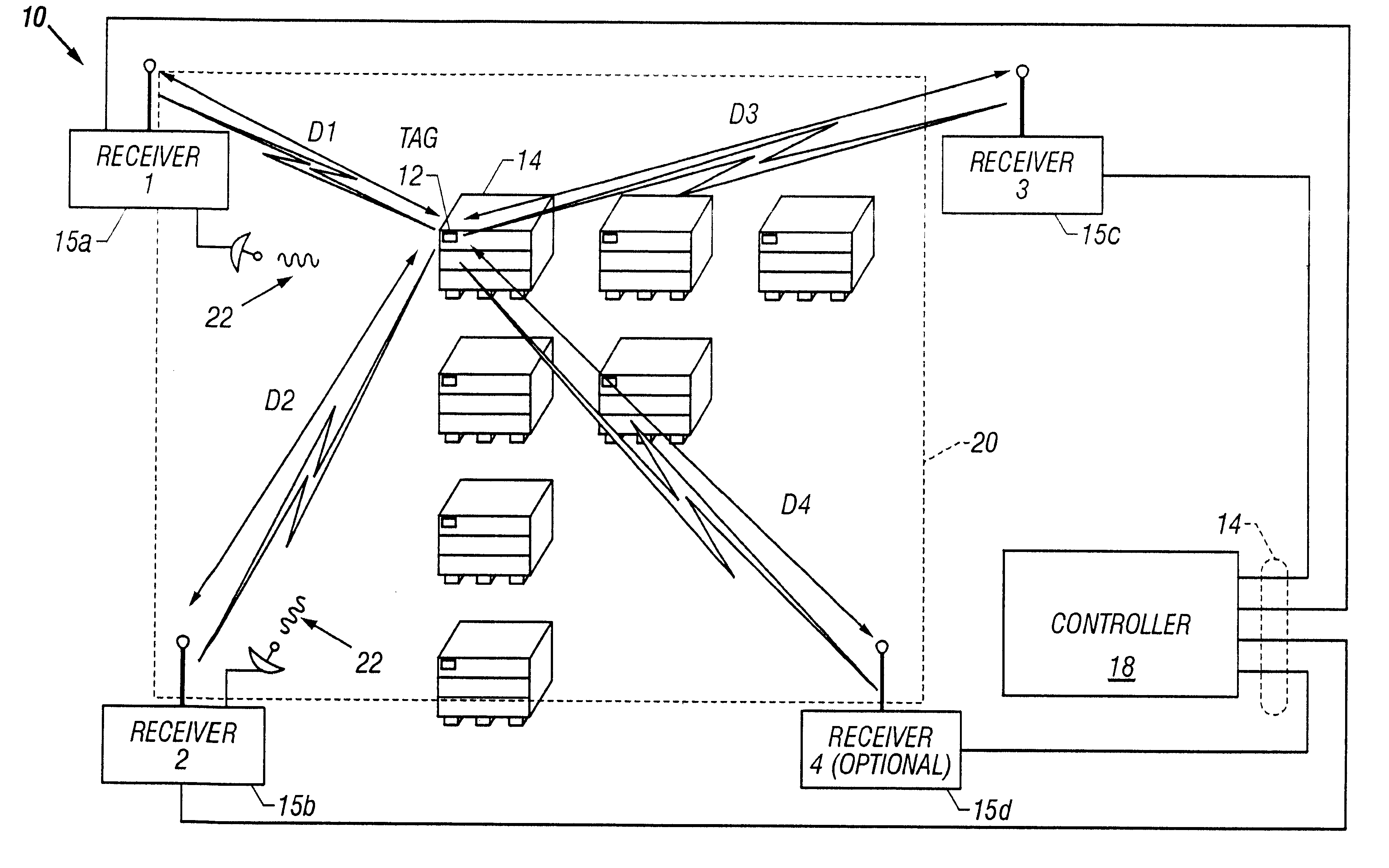
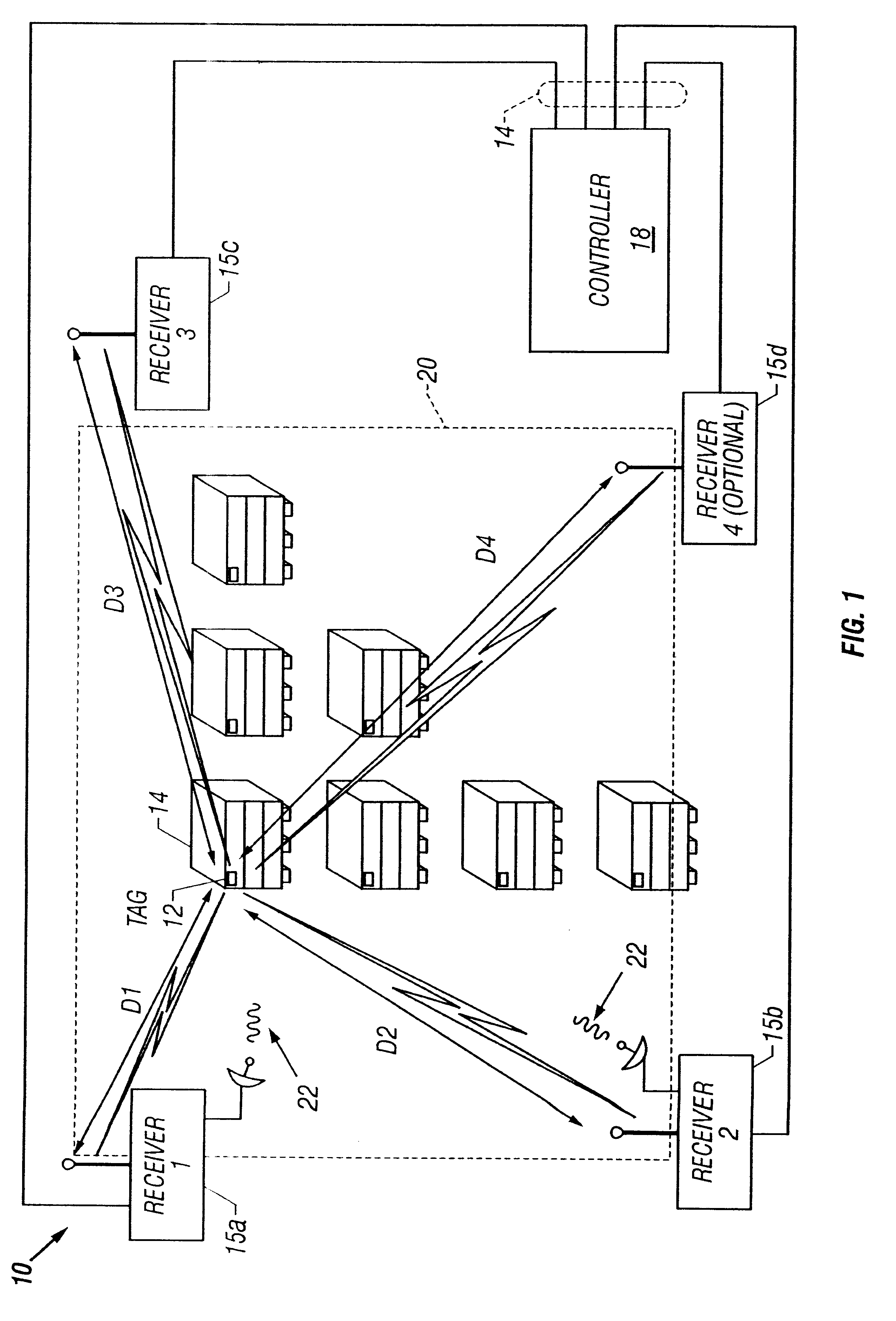
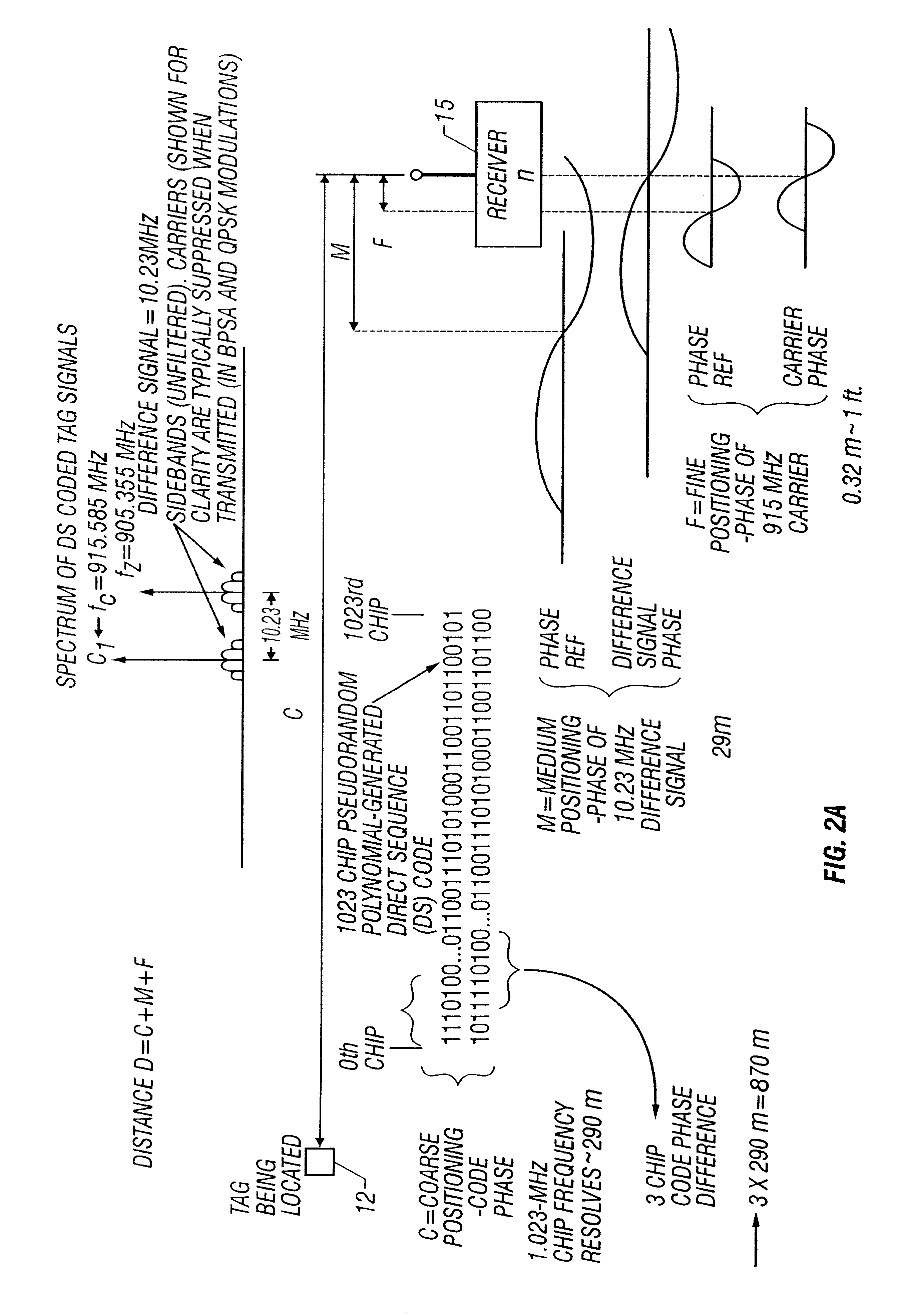
A short range radiolocation system and associated methods that allow the location of an item, such as equipment, containers, pallets, vehicles, or personnel, within a defined area. A small, battery powered, self-contained tag is provided to an item to be located. The tag includes a spread-spectrum transmitter that transmits a spread-spectrum code and identification information. A plurality of receivers positioned about the area receive signals from a transmitting tag. The position of the tag, and hence the item, is located by triangulation. The system employs three different ranging techniques for providing coarse, intermediate, and fine spatial position resolution. Coarse positioning information is provided by use of direct-sequence code phase transmitted as a spread-spectrum signal. Intermediate positioning information is provided by the use of a difference signal transmitted with the direct-sequence spread-spectrum code. Fine positioning information is provided by use of carrier phase measurements. An algorithm is employed to combine the three data sets to provide accurate location measurements.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
Array Antenna System and Spread Spectrum Beamformer Method
InactiveUS20090103593A1Simple designEasy to processMultiplex code generationRadio transmissionMultiplexingTransceiver
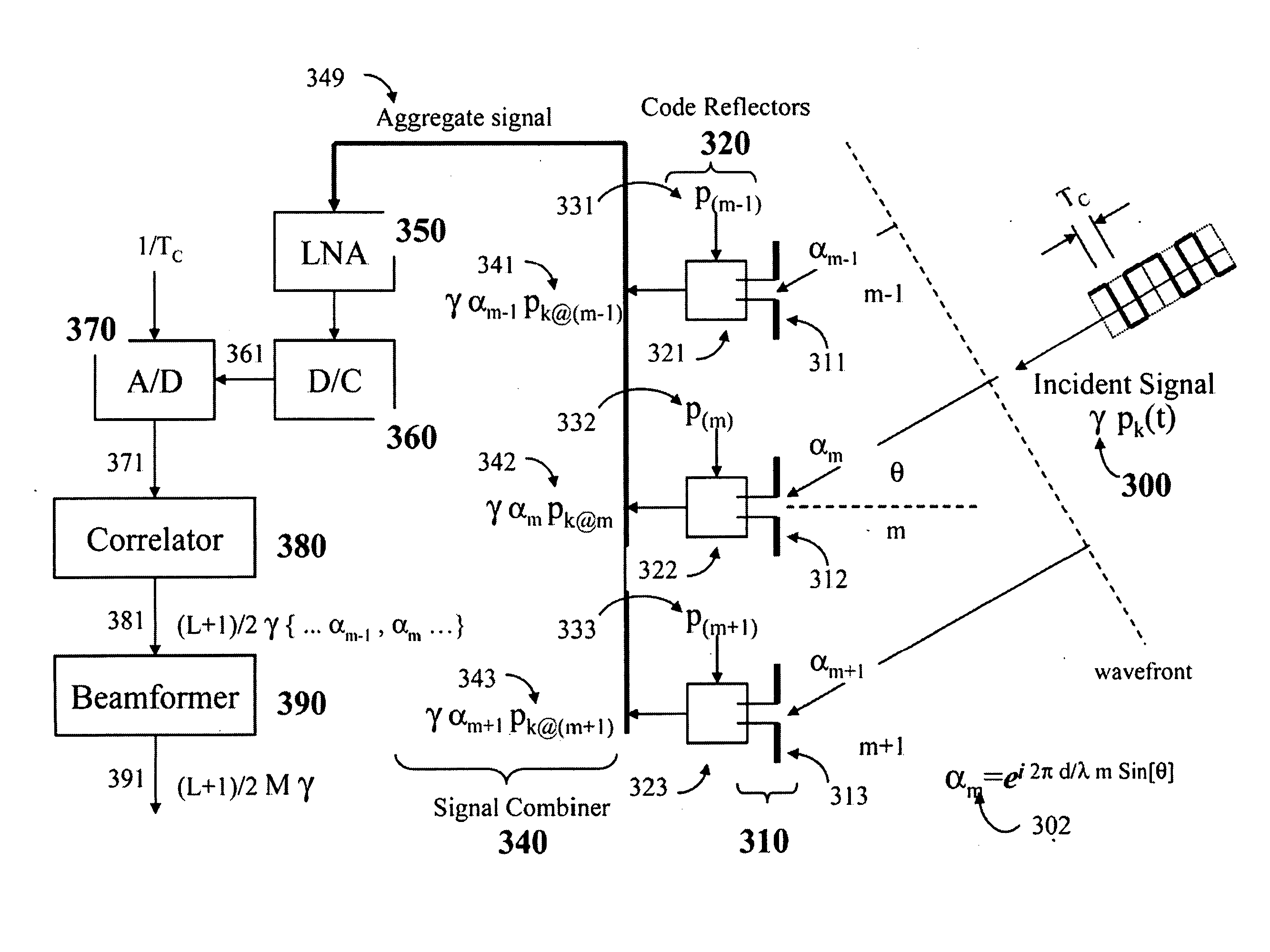
A method for transmitting digital beamformed signals in a transmit array antenna apparatus utilizing a single transceiver with one power amplifier, one up-frequency converter and one digital-to-analog converter for said array transmit antenna apparatus comprising the steps of: generating a first set of direct-sequence spread spectrum codes; generating a plurality of weights, each weight being a beamforming amplitude and phase or delay for each element; generating a direct-sequence spread spectrum multiplexed signal containing such weights while using one of such first-set codes per element; converting such an multiplexed signal to a convenient radio frequency; amplifying and transmitting such a multiplexed radio frequency signal to the elements; generating a second set of direct-sequence spread spectrum codes; extracting a radio frequency signal with direction-bearing weight information at each element while using a subset of codes from the second set; generating a third set of direct-sequence spread spectrum codes at each element; transmitting a signal with array gain beamformed towards a specific direction while using a transmit array apparatus composed of spaced elements, such a transmit beamformed signal being a radio frequency signal, a direct-sequence spread spectrum radio frequency signal containing a subset of codes from the third set, or a sequence of radio frequency pulses that have short duration and high power.
Owner:APPLIED RADAR
Power efficient receiver
InactiveUS6028887AReduce power consumptionShorten the timePosition fixationBeacon systemsPower efficientDirect-sequence spread spectrum
A direct sequence spread spectrum receiver samples an incoming signal and stores the sample in memory. Power is then inhibited to the tuner of the receiver to minimize power consumption. The signal sample may be read from memory when necessary to process the signal without further signal acquisition. Power to other receiver sections may be selectively controlled to minimize power consumption. Such a receiver is useful in global positioning satellite (GPS) signal processing where the receiver has a limited power supply.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Digital spread spectrum methods and apparatus for testing aircraft wiring
InactiveUS7069163B2Efficient implementationElectronic circuit testingTesting electric installations on transportOriginal dataData signal
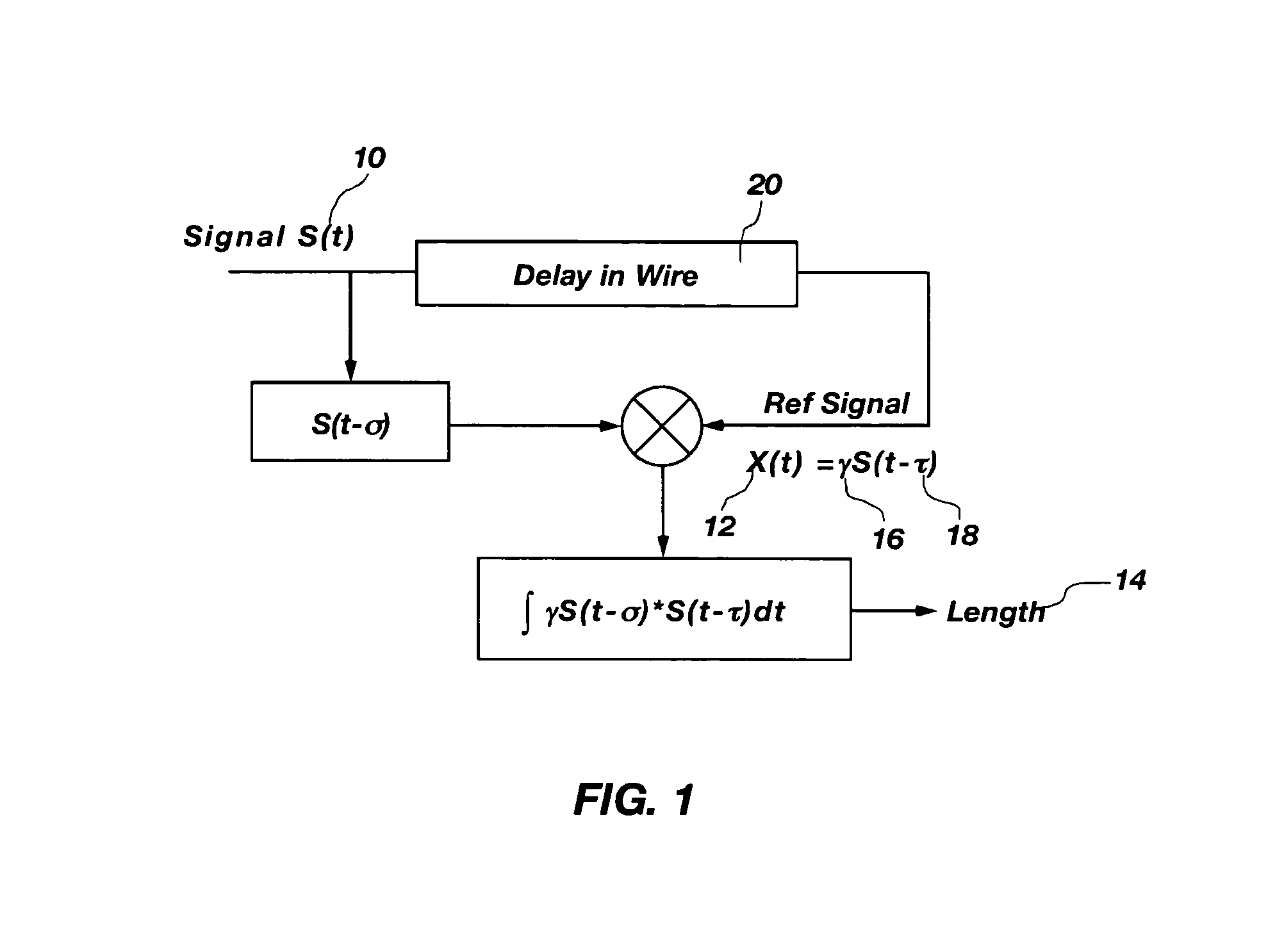
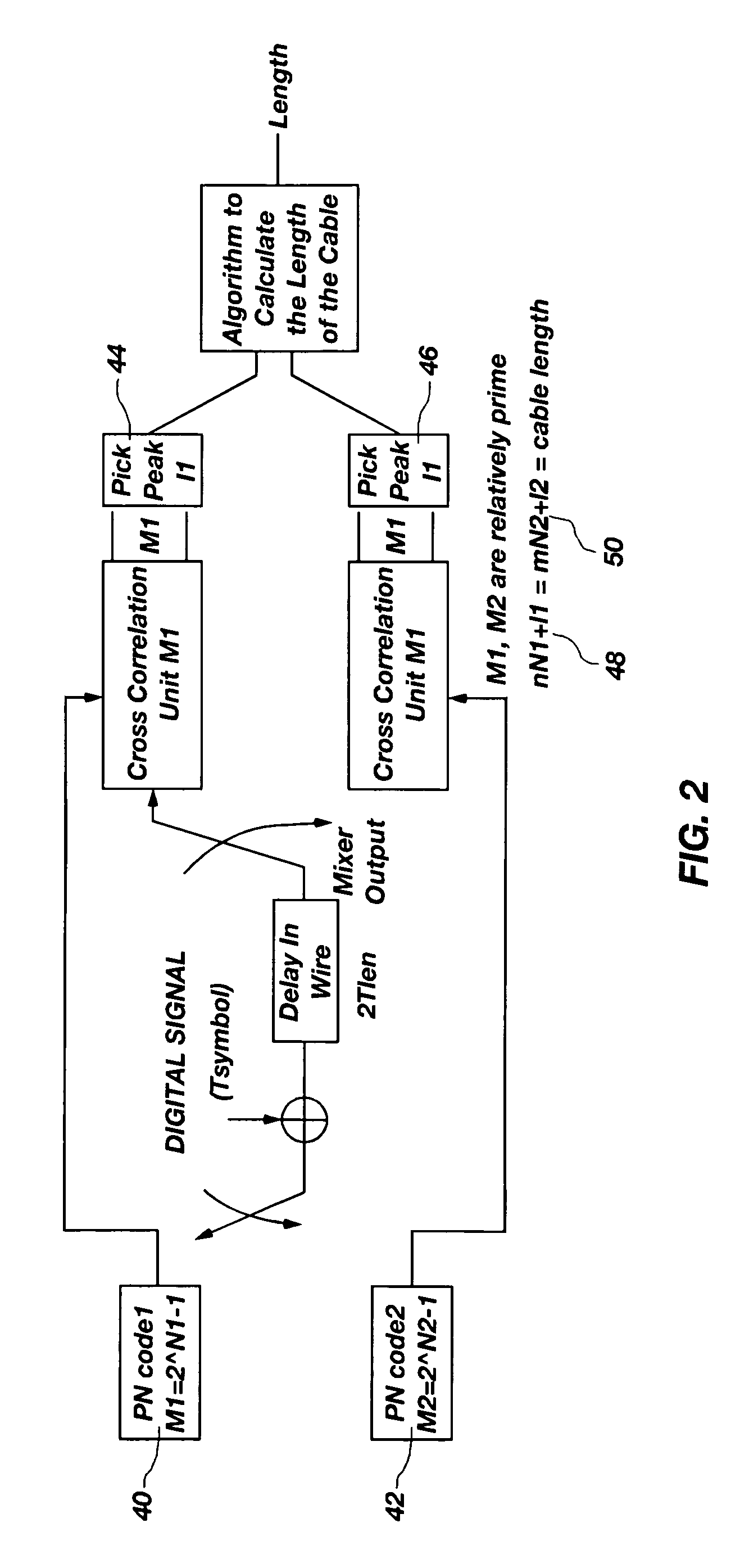
A system and method that utilizes direct sequence spread spectrum signal (DSSS) encoding to enable testing of a live wire, wherein an original data signal is modified and then transmitted along the wire, and a reflected signal is collected and analyzed using correlation techniques to determine characteristics of the live wire, including the location of a fault.
Owner:UTAH STATE UNIVERSITY
Multicode direct sequence spread spectrum
InactiveUSRE37802E1Improve throughputReduce ICISecret communicationMulti-frequency code systemsFrequency spectrumDirect-sequence spread spectrum
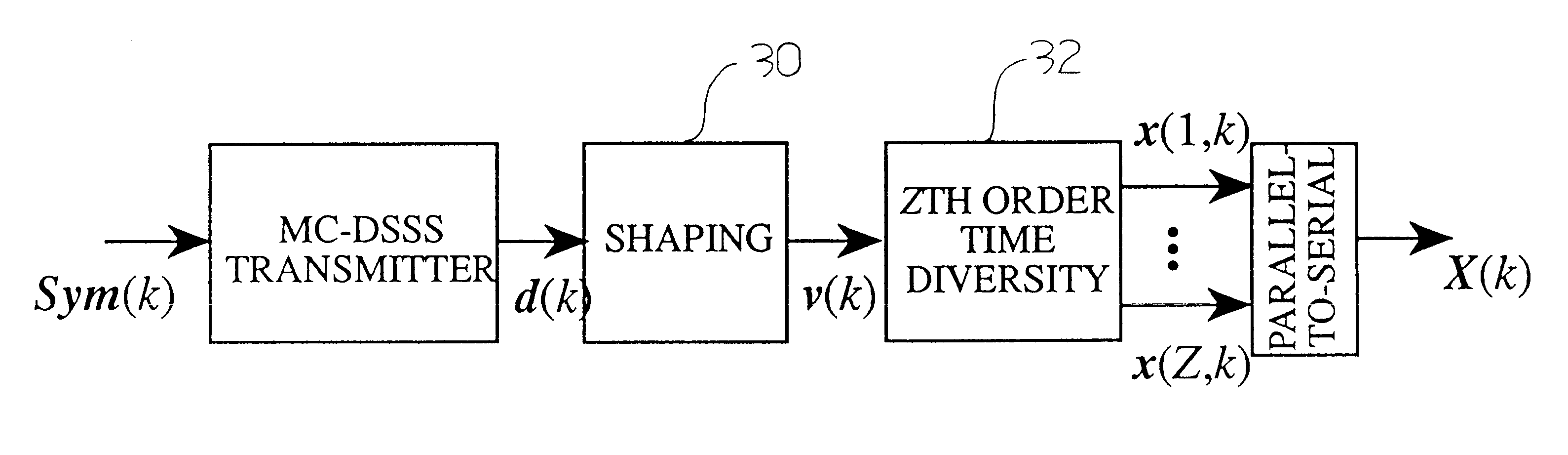
In this patent, we present MultiCode Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum (MC-DSSS) which is a modulation scheme that assigns up to N DSSS codes to an individual user where N is the number of chips per DSSS code. When viewed as DSSS, MC-DSSS requires up to N correlators (or equivalently up to N Matched Filters) at the receiver with a complexity of the order of N2 operations. In addition, a non ideal communication channel can cause InterCode Interference (ICI), i.e., interference between the N DSSS codes. In this patent, we introduce new DSSS codes, which we refer to as the "MC" codes. Such codes allow the information in a MC-DSSS signal to be decoded in a sequence of low complexity parallel operations which reduce the ICI. In addition to low complexity decoding and reduced ICI. MC-DSSS using the MC codes has the following advantages: (1) it does not require the stringent synchronization DSSS requires, (2) it does not require the stringent carrier recovery DSSS requires and (3) it is spectrally efficient.
Owner:WI LAN INC
Pre-acquisition frequency offset removal in a GPS receiver
InactiveUS6151353AReduce power consumptionShorten the timePower managementPosition fixationGps receiverLocal oscillator
A direct sequence spread spectrum receiver samples an incoming signal and stores the sample in memory. Prior to sampling and storage, the incoming signal is translated to an IF signal. Also prior to storage, the IF signal is corrected for a frequency offset signal. The frequency offset may be caused by many sources, Doppler shift or local oscillator error, for example. Once the signal is corrected for the frequency offset, the signal sample is stored in memory. The signal sample is read from memory as necessary to process the signal. Such a receiver is useful in global positioning satellite (GPS) signal processing where the incoming signal contains several satellite transmissions encoded with CDMA encoding.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
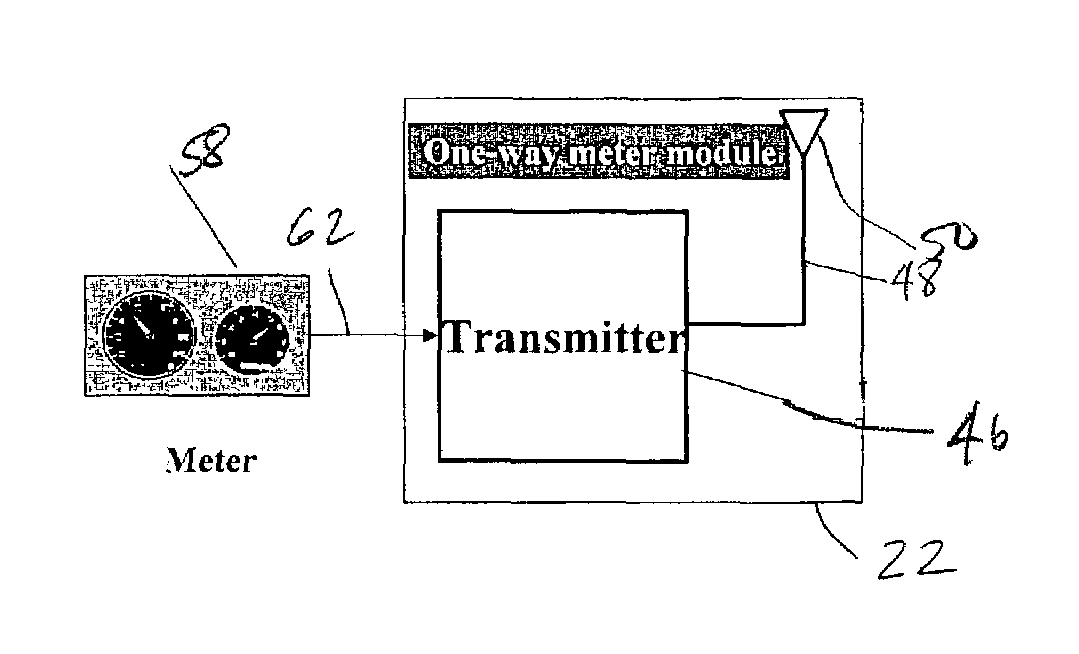
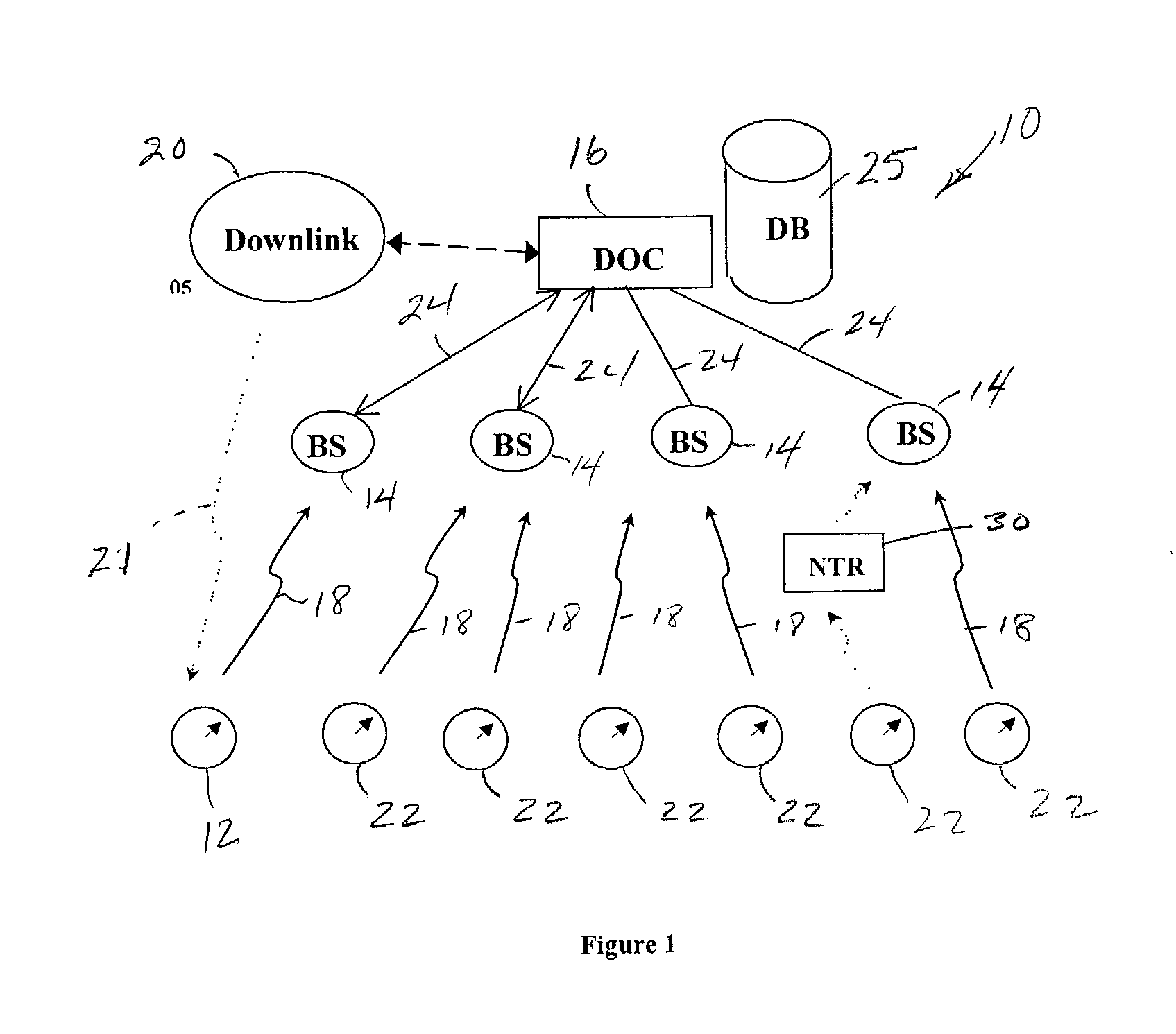
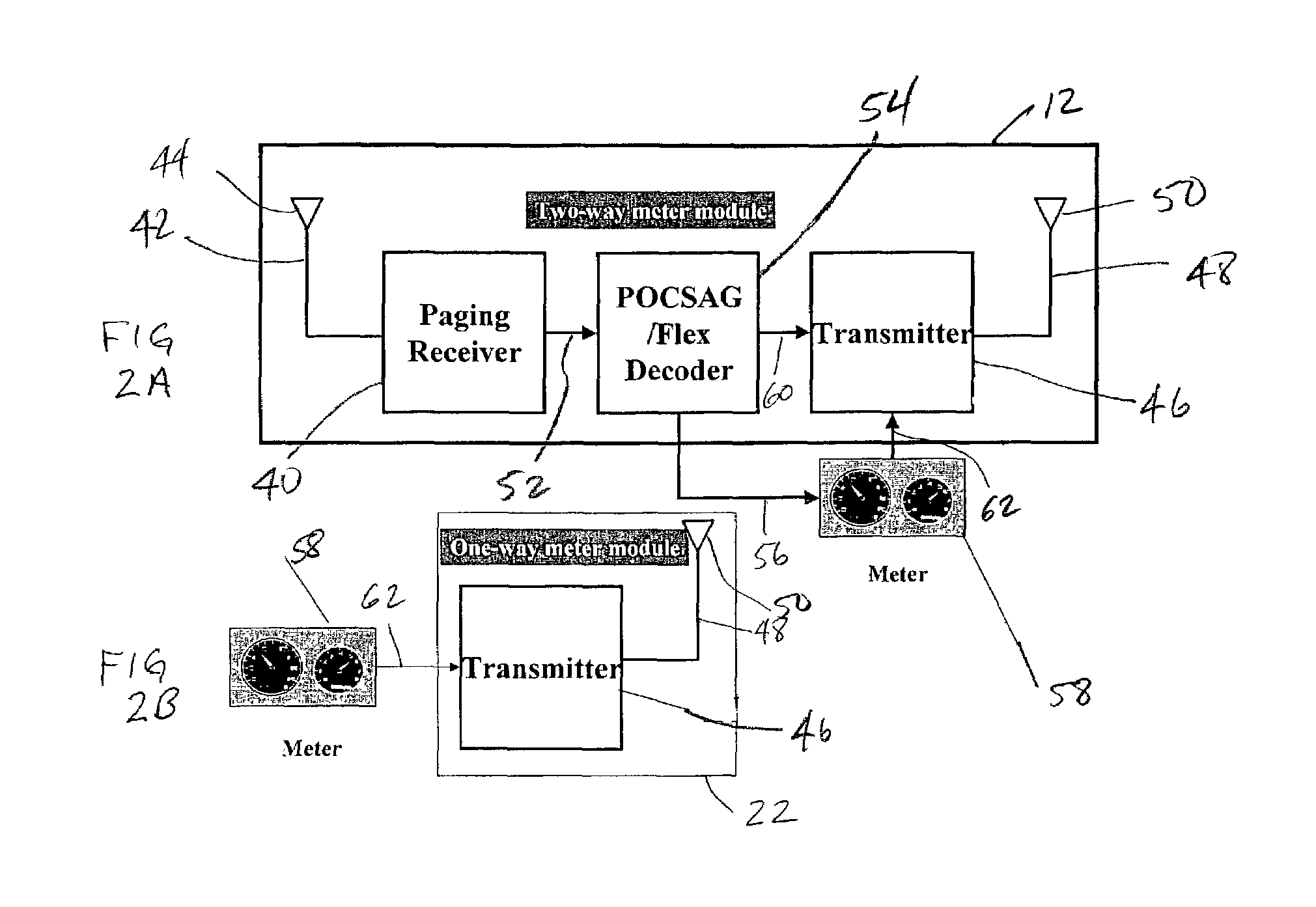
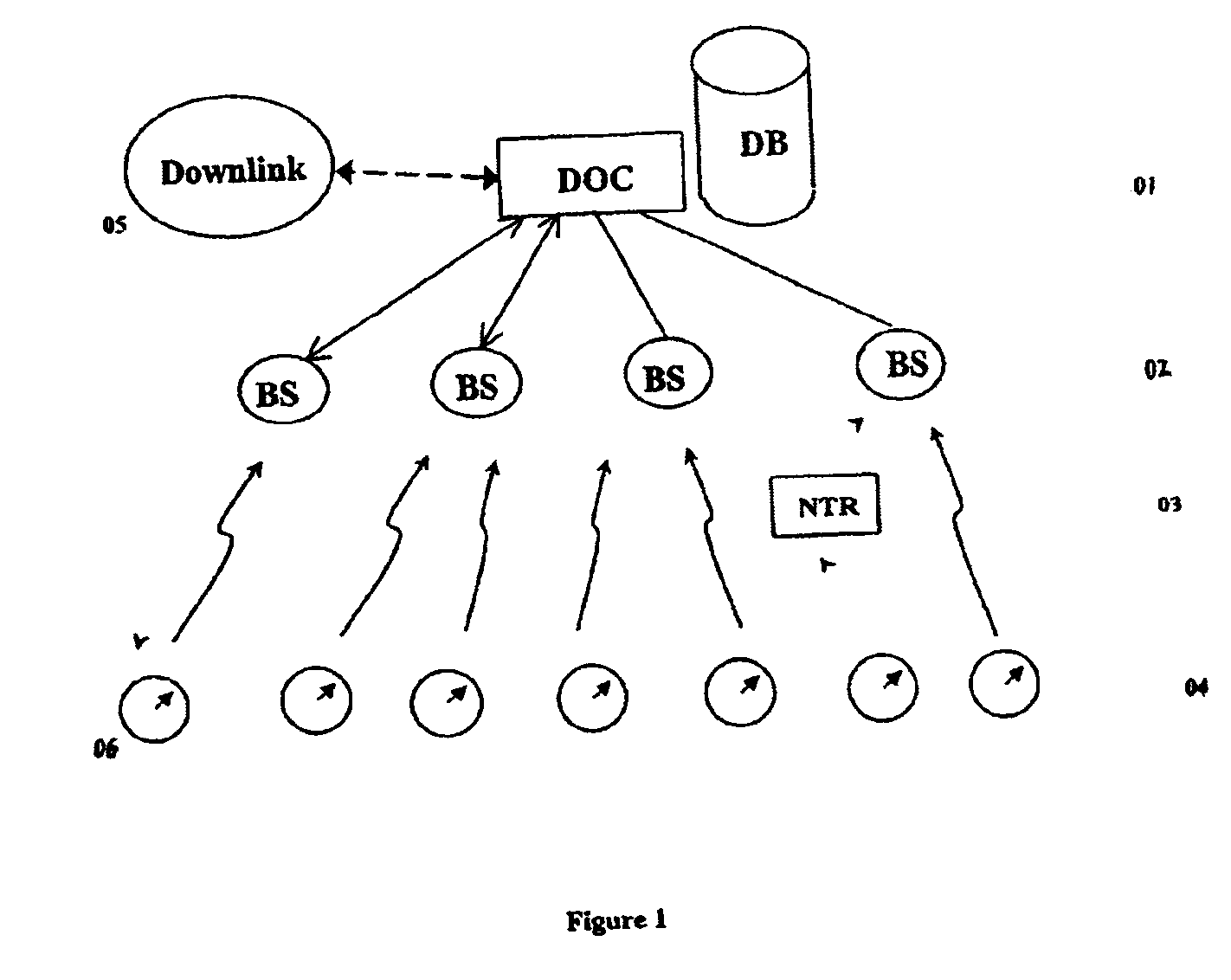
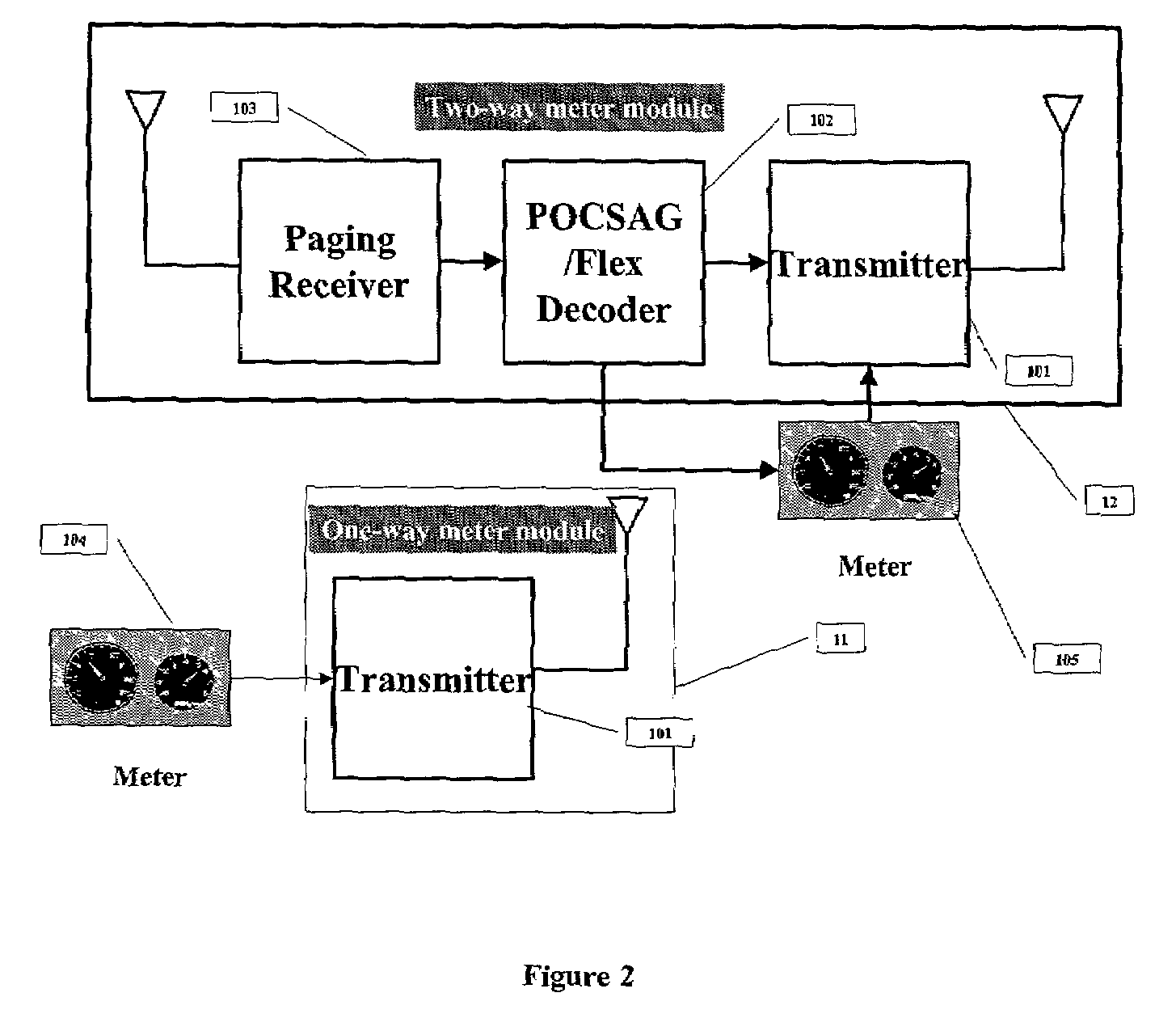
Modular wireless fixed network for wide-area metering data collection and meter module apparatus
InactiveUS7012546B1Increase flexibilityIncrease capacityElectric signal transmission systemsTariff metering apparatusTransceiverData acquisition
A one way direct sequence spread spectrum (DSSS) communications wide-area network is the data collection channel (uplink) of an automatic meter reading (AMR) system, and a paging network, or other suitable communication channel is the optional forward (downlink) channel. The communications network may include one-way meter modules (transmitters) each communicatively coupled to a corresponding electric, gas or water utility meter, and may include two-way meter modules (transceivers) each coupled to such a corresponding utility meter. The meter modules monitor, store, encode and periodically transmit metering data via radio signals (air messages) in an appropriate RF channel. Metering data air messages are collected by a network of receiver Base Stations (BS) and forwarded to a Data Operations Center (DOC), which acts as a metering data gateway. The reception range of each base station is typically over 5 miles in urban areas, allowing sparse infrastructure deployment for a wide variety of metering data collection applications.
Owner:SENSUS USA
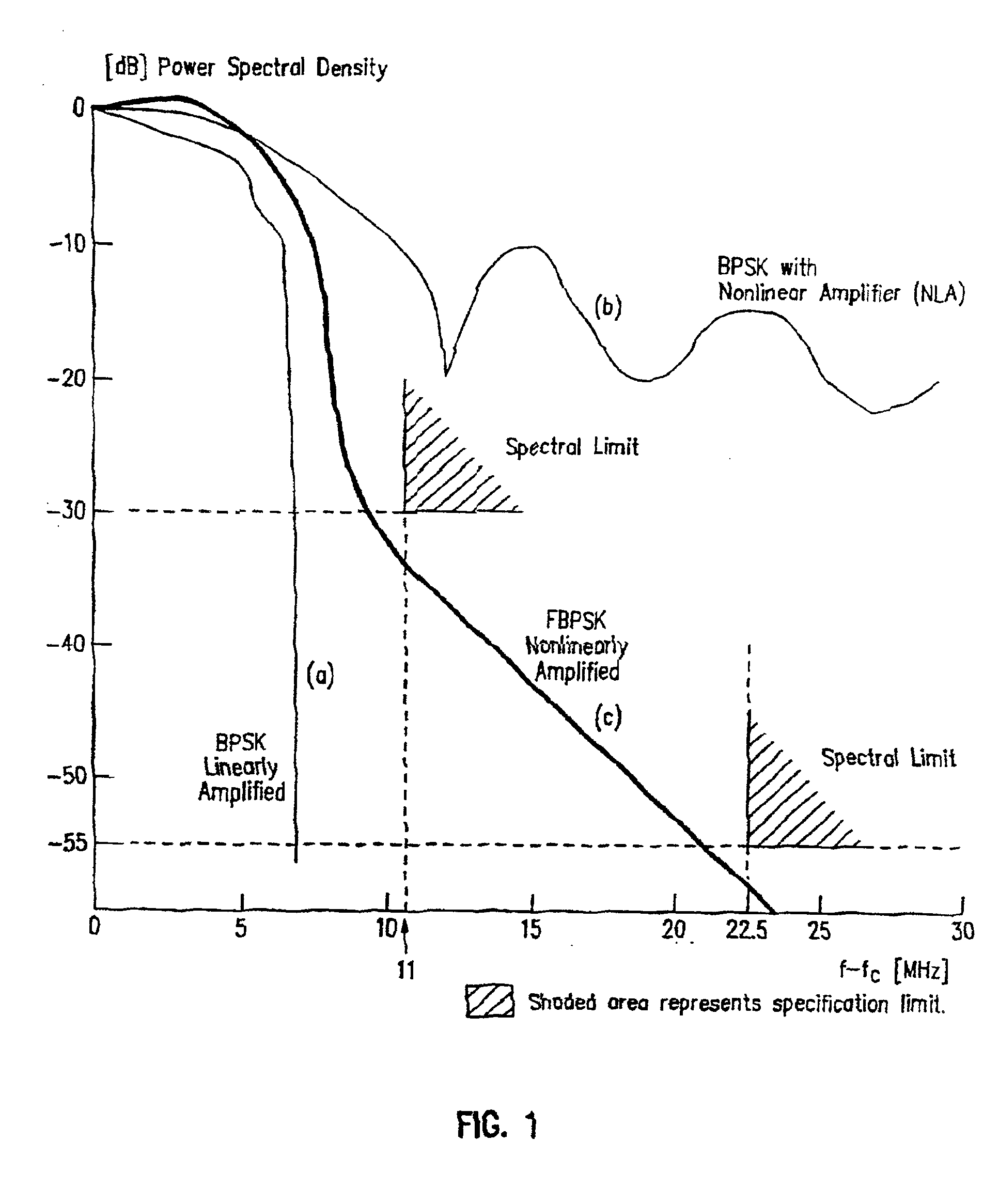
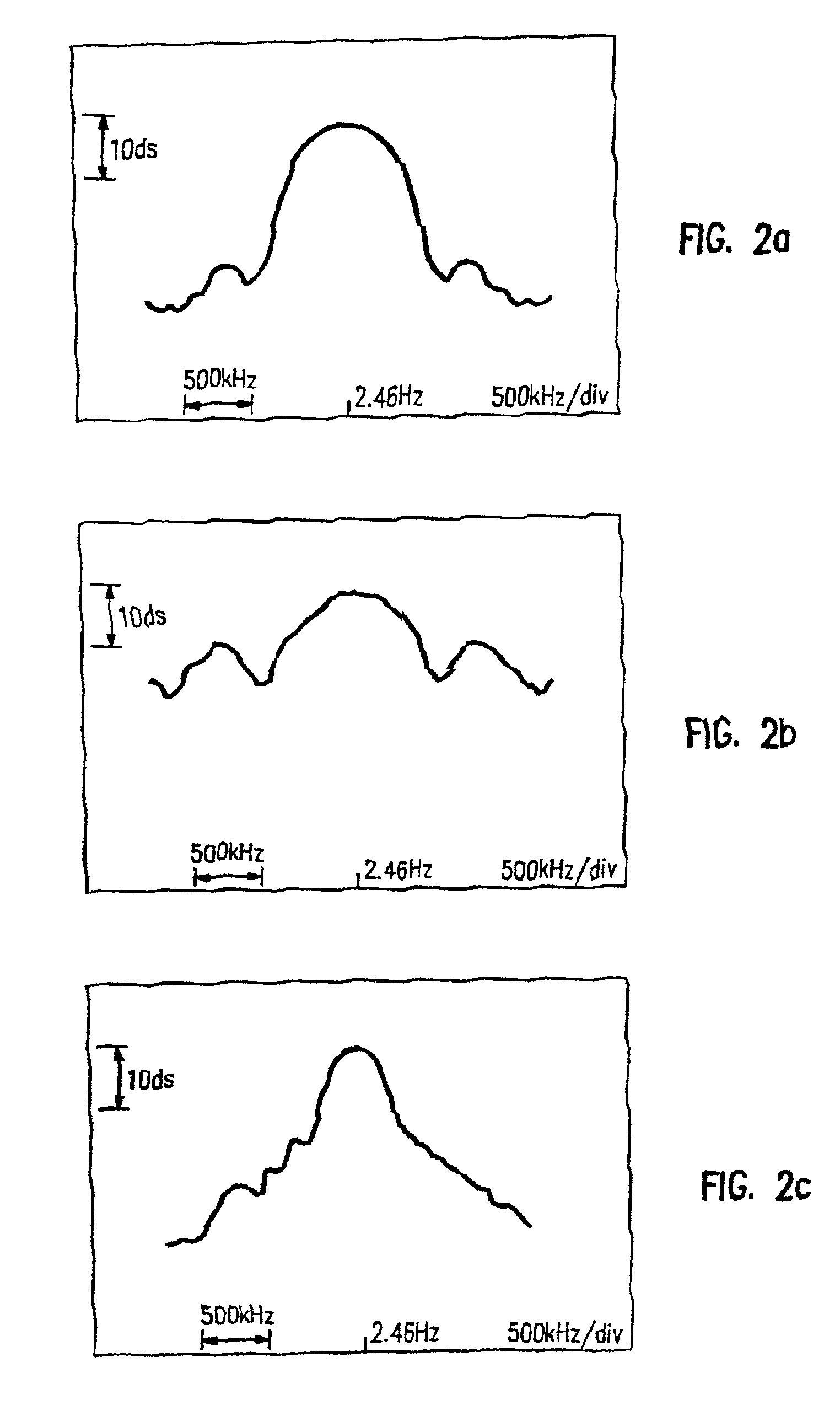
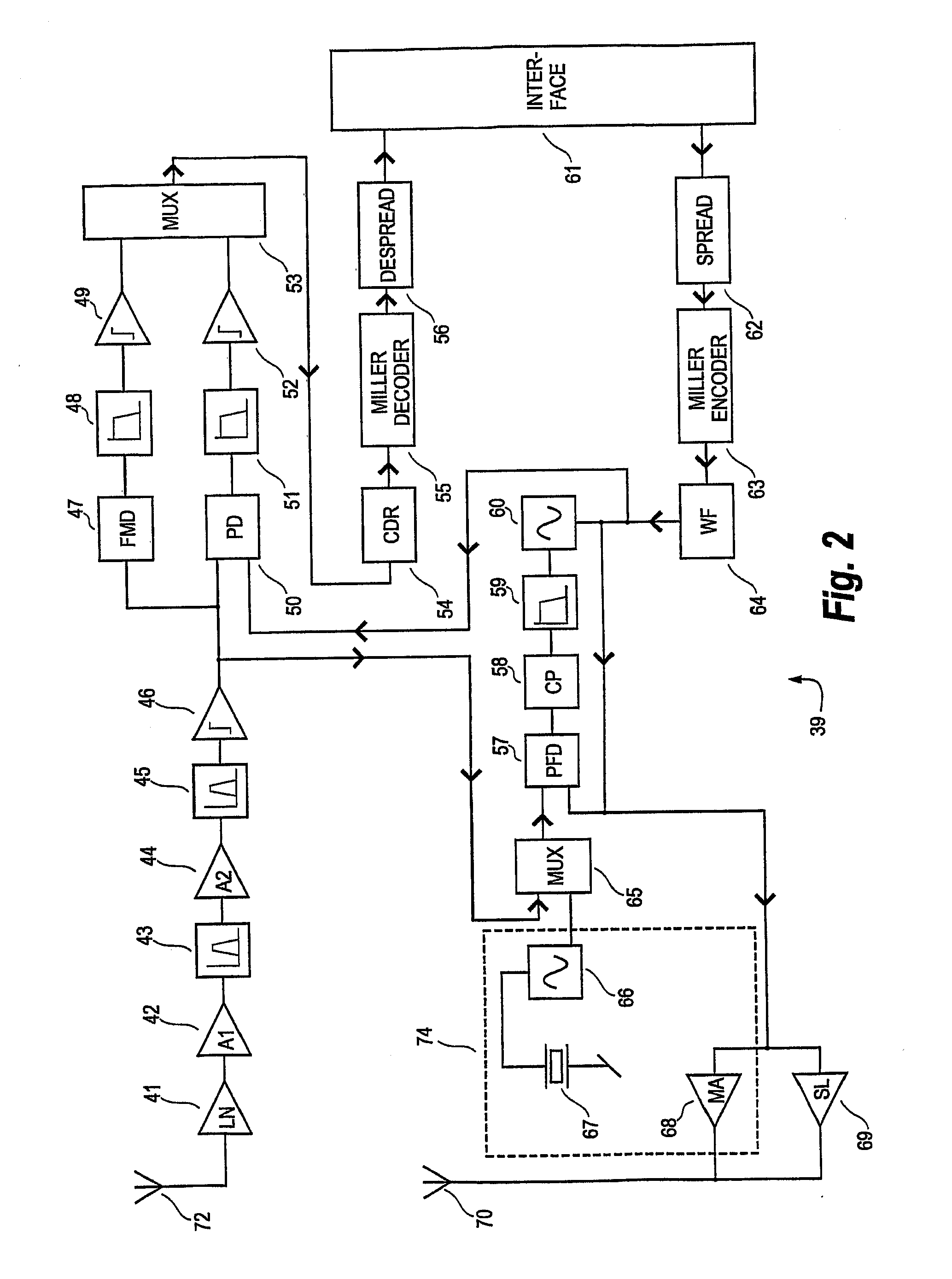
FMOD transceivers including continuous and burst operated TDMA, FDMA, spread spectrum CDMA, WCDMA and CSMA
InactiveUS6928101B2Improve performanceLow costAsymmetric modulation circuitsPhase-modulated carrier systemsModem deviceFrequency spectrum
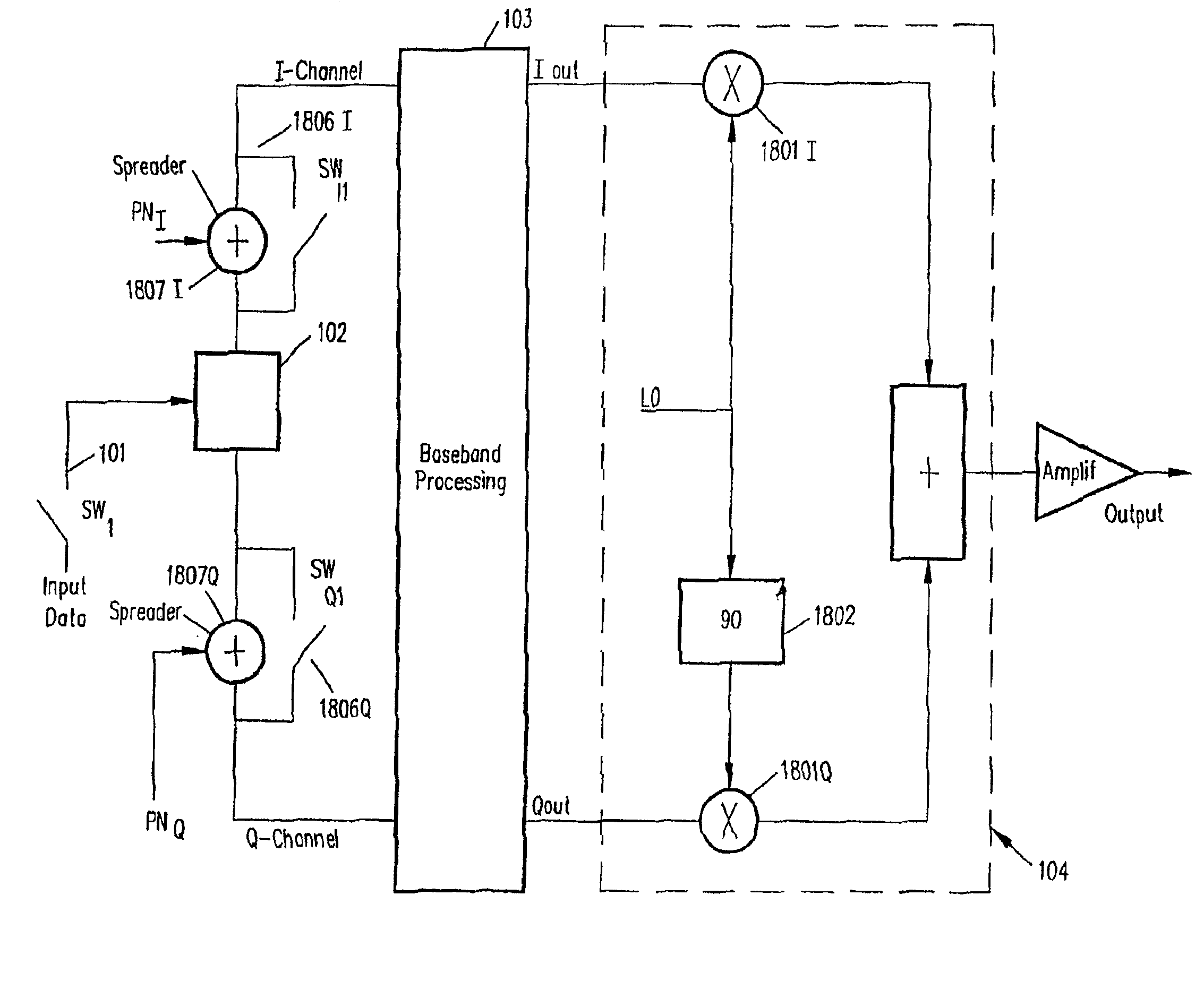
Binary and Quadrature Feher's Modulation (F-Modulation, or FMOD) Transmitter-Receiver systems and circuits exhibit reduced envelope fluctuation and peak radiation, and increased efficiency. A subclass of these systems has a constant envelope. They advantageously provide lower power operation with improved performance including robust BER performance, and compatibility with both linearly and nonlinearly amplified narrow spectrum, and without disadvantages of conventional BPSK, DBPSK QPSK and pi / 4-QPSK. Feher's BPSK (FBPSK) is an improved efficiency transmitter which is compatible with conventional BPSK receivers. FBPSK modems are based on using quadrature structure where Q-channel data is inserted in quadrature with I-channel data for certain applications. The Q-channel data may be “offset” from the I-channel data by an amount selectable between zero and a specified time. Further improvement in the spectrum is attained using correlation between I and Q channels. FBPSK modem is shown to meet the IEEE 802.11 specified spectral direct sequence spread spectrum mask (−30 dB point) for wireless LAN, and leads to an output power gain of 6.5 dB over conventional BPSK modems. The cross-coupled quadrature FMOD structure is also suitable for continuous mode and for burst operated TDMA, FDMA, CDMA, WCDMA and CSMA Frequency Modulation Quadrature AM (QAM), QPSK and offset QPSK, as well as pi / 4-shifted QPSK modems / processors. Reduced modulation index Gaussian FSK (GFSK), multilevel FM and cross-coupled Quadrature Amplitude Modulated (QAM) transmitters and combinations of these modulations and corresponding coherent demodulators are disclosed. Controlled rise and fall time descriptions of burst operated systems are included.
Owner:INTEL CORP
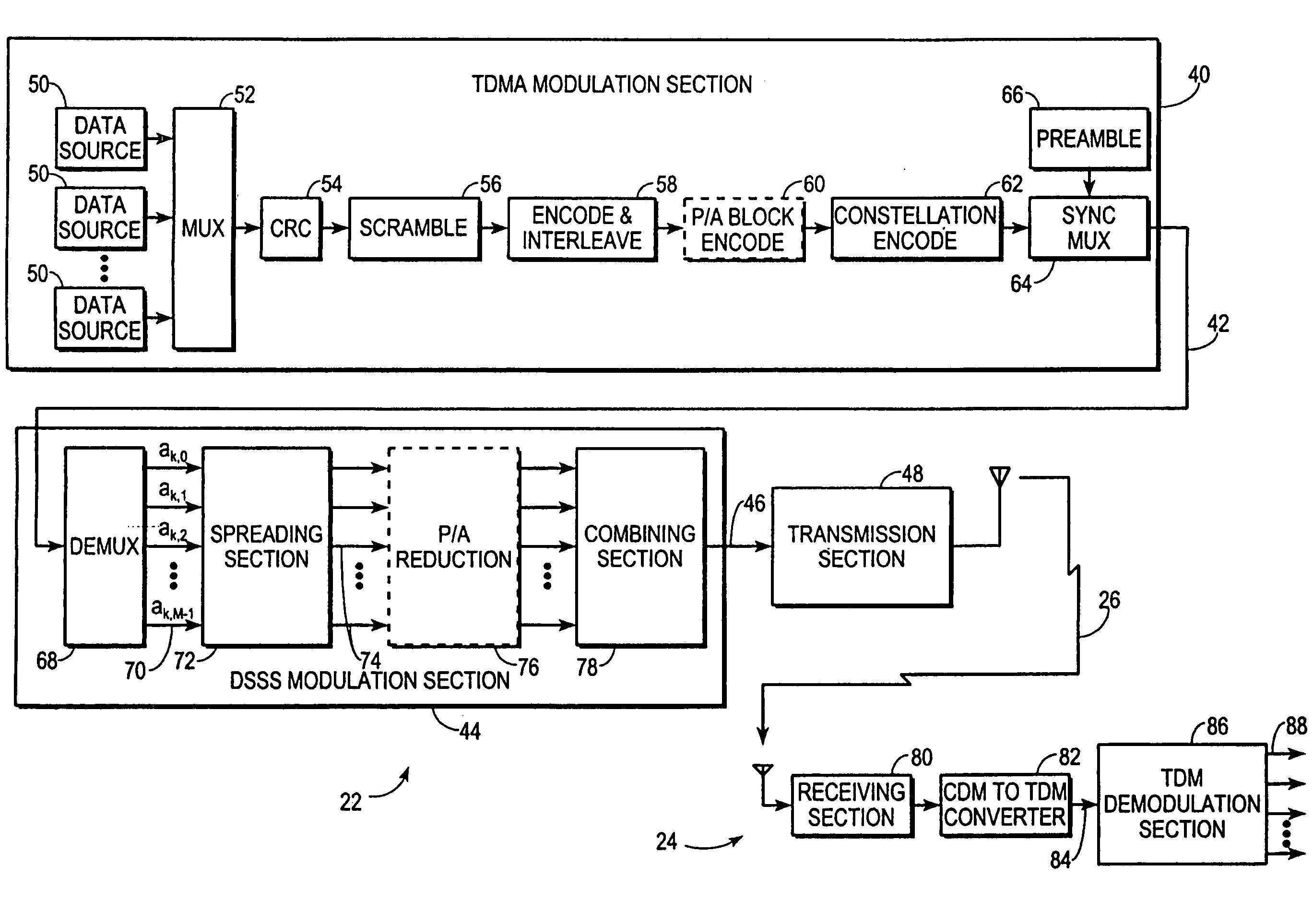
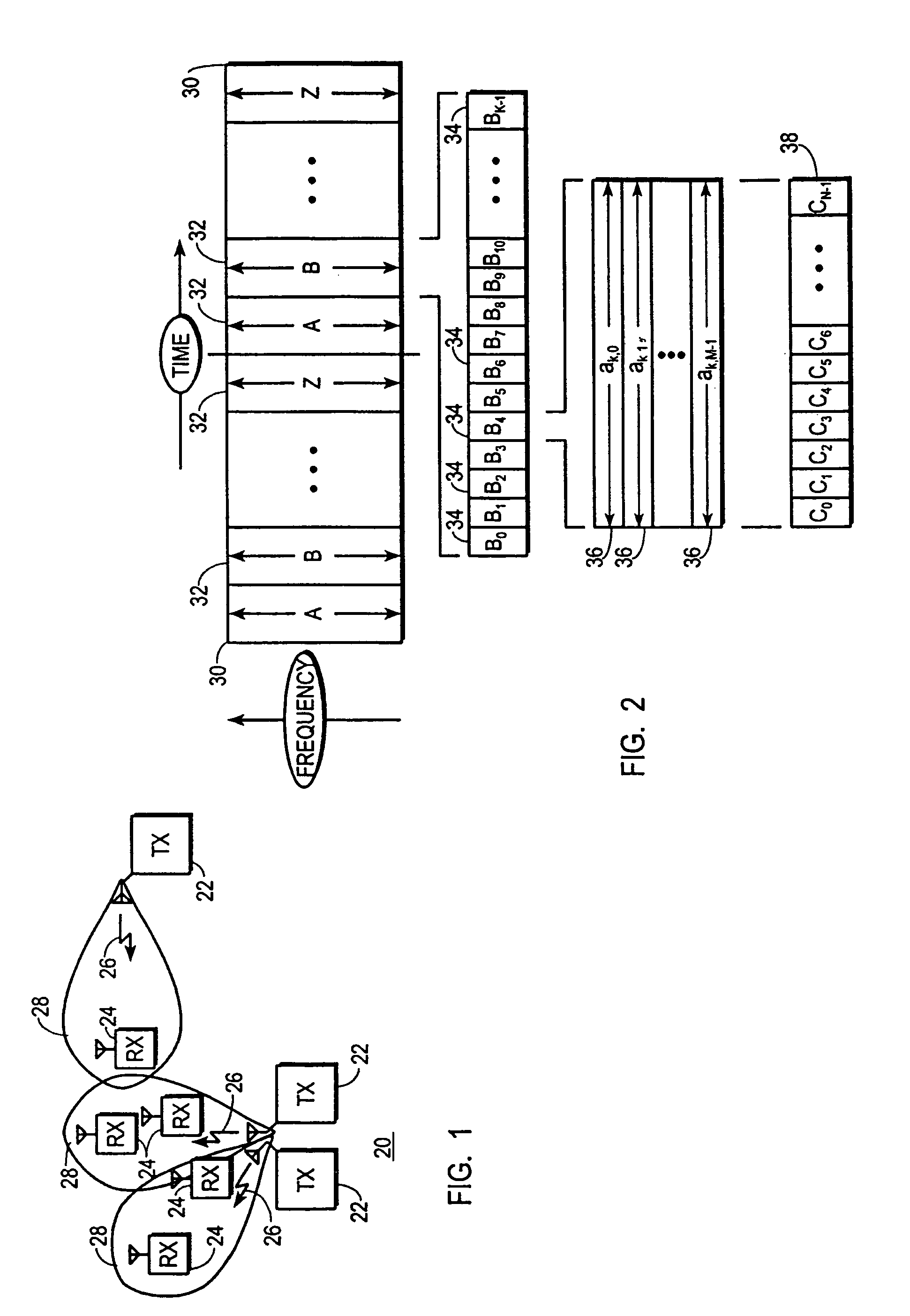
CDMA/TDMA communication method and apparatus for wireless communication using cyclic spreading codes
A communication system (20) uses TDMA techniques to distinguish intended recipients of a communication signal (26) from one another, and direct sequence spread spectrum (DSSS) techniques to encode and distinguish diverse parallel substreams (70, 74) of each user's data stream. Parallel unspread substreams (70) are spread using cyclic variations of a common spreading code (38). In one embodiment, the common spreading code (38) is chosen for low aperiodic autocorrelation sidelobes and a substantially flat spectral analysis. In another embodiment the common spreading code (38) is chosen for low periodic autocorrelation sidelobes and a substantially flat spectral analysis. In one embodiment, the use of cyclic variations of the spreading code (38) along with a cyclic prefix (114) enables the mathematical communicative matrix multiplication property, thereby permitting equalization for multipath to occur following or in conjunction with despreading.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL VENTURES HOLDING 81 LLC
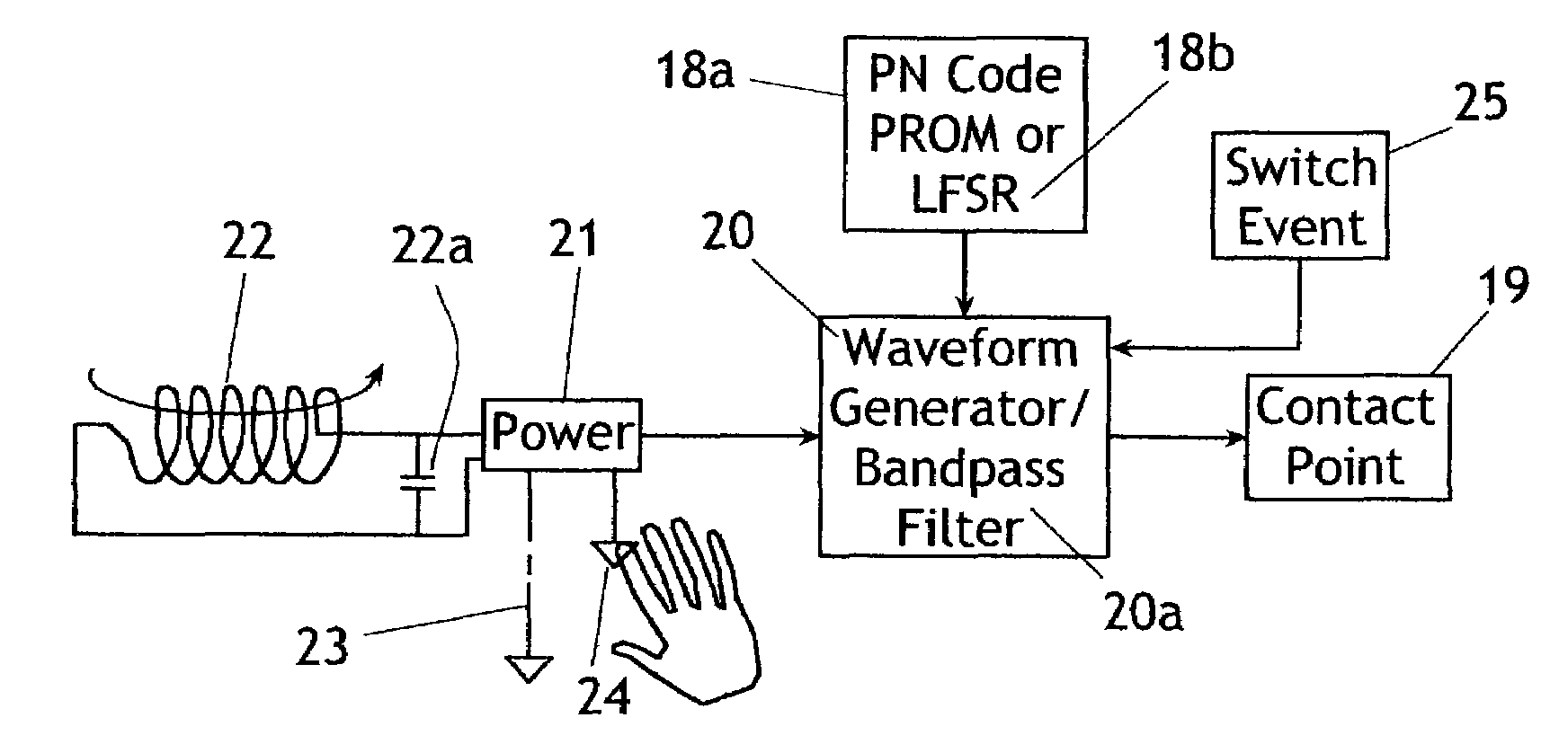
Method and apparatus for a touch sensitive system employing direct sequence spread spectrum (DSSS) technology
InactiveUS7084860B1Easy to identifyAccurate location trackingTransmission systemsCathode-ray tube indicatorsSemi activeTouch Senses
A touch sensing apparatus for receiving input from one or more touch stimulating devices employs a direct sequence spread spectrum (DSSS) signaling arrangement to transmit signals from the touch stimulating devices for identification and location determination. Active devices are powered by an EM field and generate a touch stimulating signal that is spread spectrum encoded for identification, and signal pickups in a propagation layer receive the touch stimulation signals which are identified by the DSSS encoding and located using received signal strength (RSS) techniques. Semi-active devices are powered by an EM field and receive code instructions to generate specific spread spectrum signals and generate a touch-stimulating signal. Touch stimulating devices are either tethered or tether-free, and powered by batteries or EM fields.
Owner:INTERTACTILE TECH CORP
GPS receiver with efficient signal acquisition
InactiveUS6118808AReduce power consumptionShorten the timePosition fixationSynchronisation signal speed/phase controlMemory bankGps receiver
A direct sequence spread spectrum receiver samples an incoming signal and translates the signal to an IF signal. The IF signal is sampled and stored in memory. In one embodiment, the memory consists of two memory banks which alternately receive sample segments. During a write period to one of the memory banks, the other memory bank supplies its output to a processor. This continues in a ping-pong manner. In another embodiment, a single memory bank is filled and read as necessary, the receiver ignoring incoming signal until the processor has completed processing the sample available at the output of the memory. Such a receiver is useful in global positioning satellite (GPS) signal processing where the incoming signal contains several satellite transmissions encoded with CDMA encoding.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
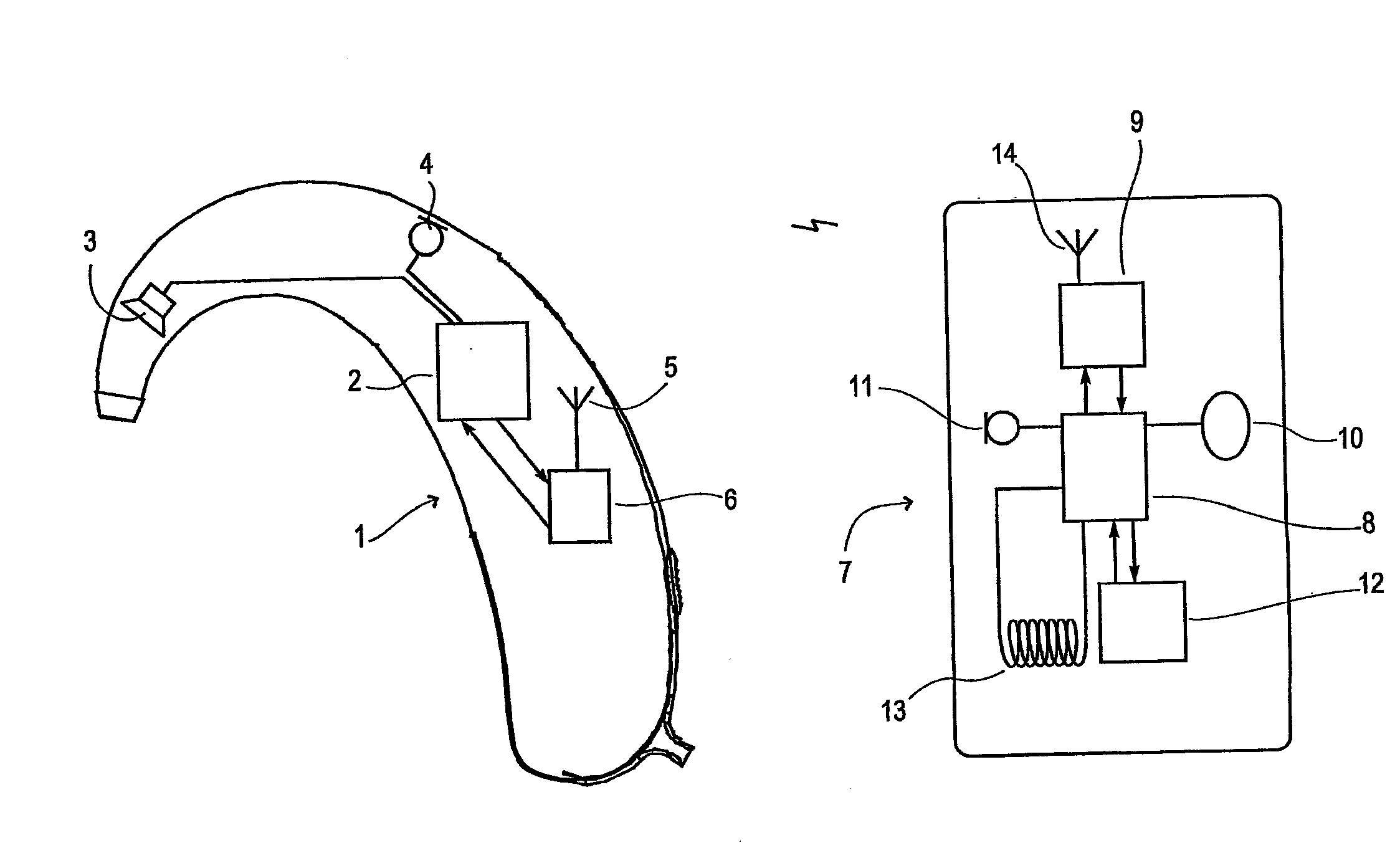
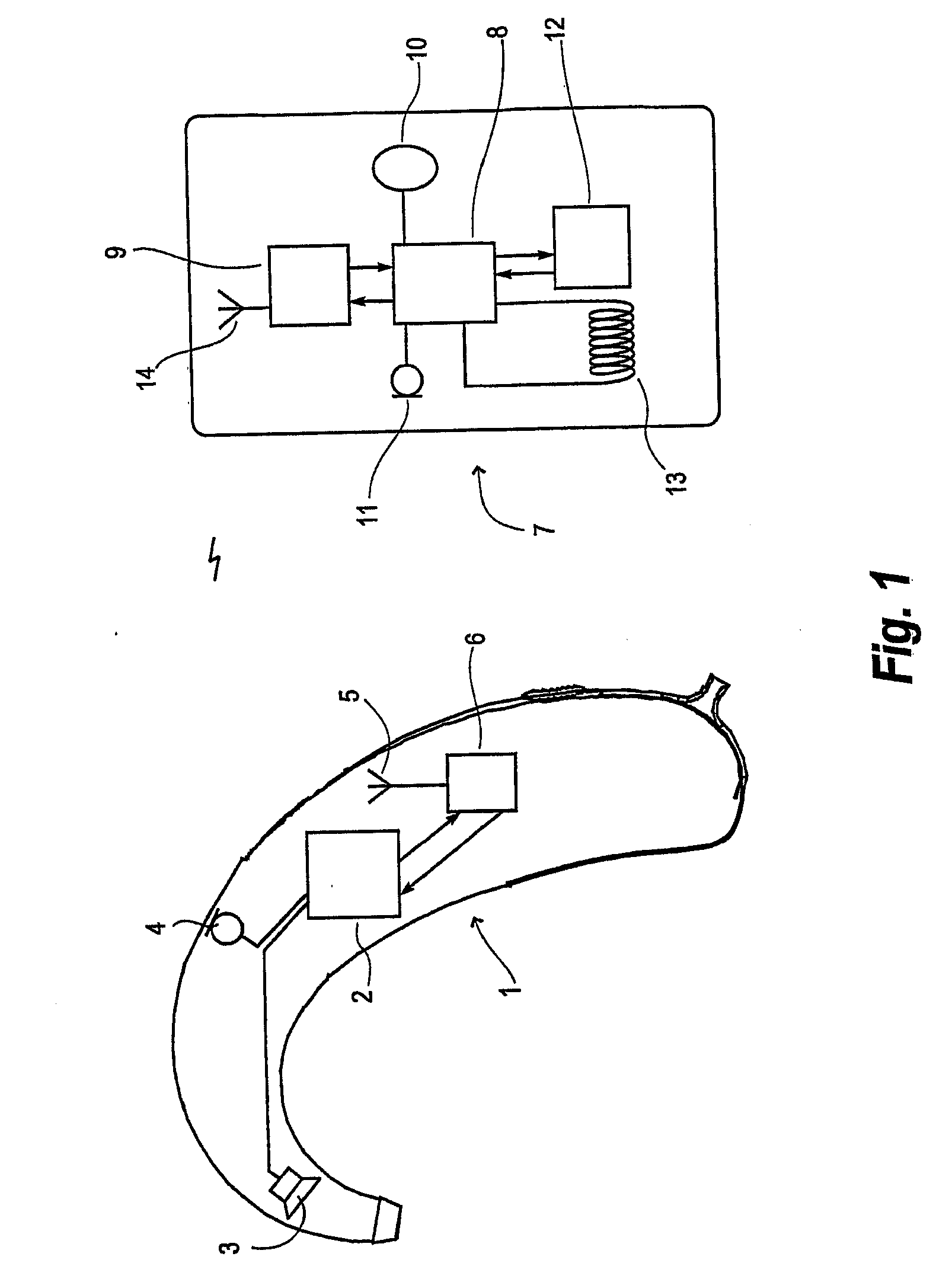
Apparatus and method for operating a hearing aid
InactiveUS20070269065A1Reduce power consumptionEliminate needDeaf aid adaptationHearing aidDirect-sequence spread spectrum
A programmable hearing aid including means for receiving and transmitting data wirelessly from and to a portable module being in proximity to said hearing aid. Said portable module has means for transmitting audio signals, fitting data or special instructions to the hearing aid processor and including means for receiving data transmitted from said hearing aid, including data representing a monitoring of real-time signal processing parameters in the hearing aid. A preferred embodiment of the hearing aid / portable module combination utilizes Miller-coded direct sequence spread-spectrum radio signal transmitters and receivers for transmitting and receiving data between the heading aid and the portable module. This enables remote controlling or monitoring of, transmitting audio to, or programming of a hearing aid without the need for external connectors.
Owner:WIDEX AS
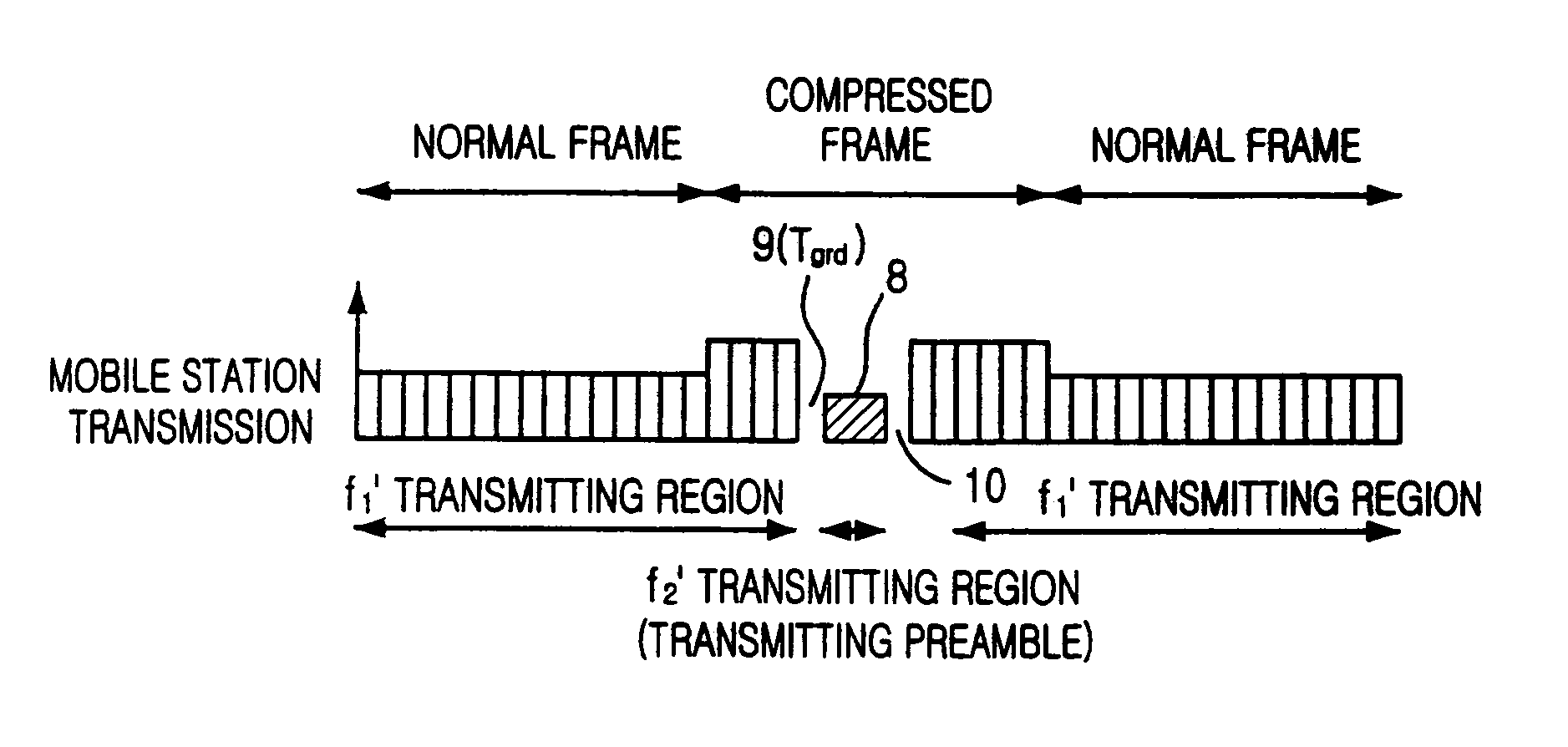
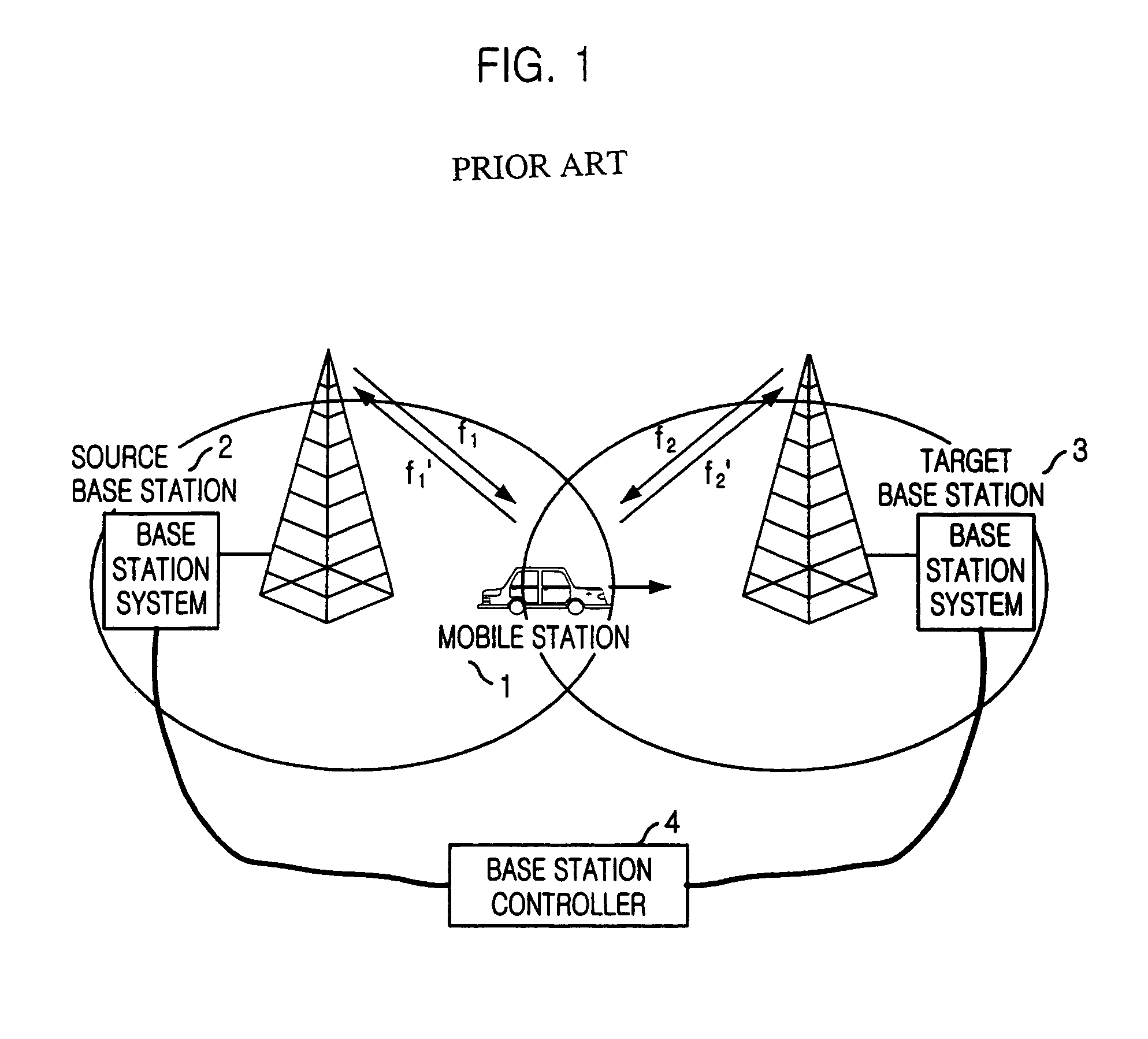
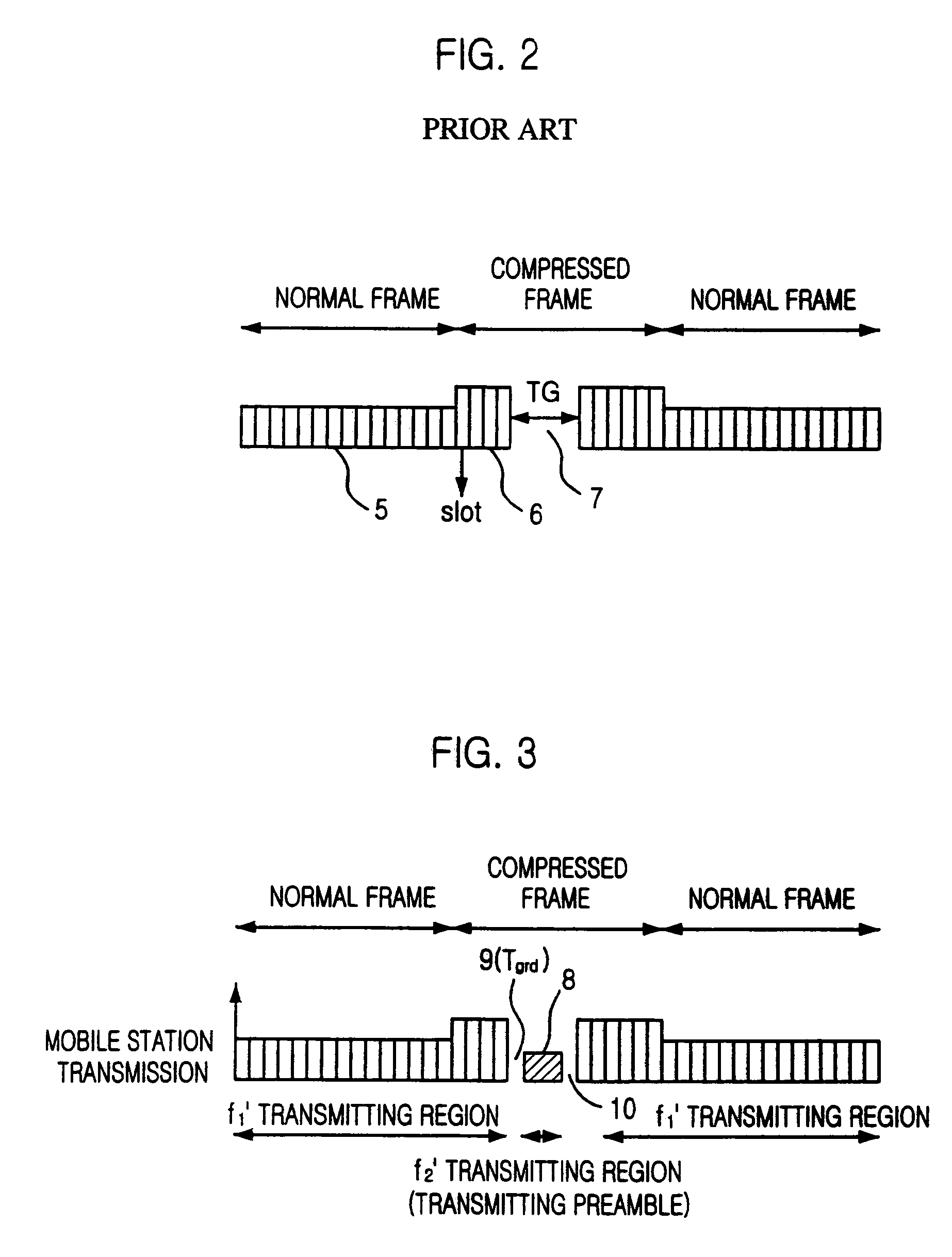
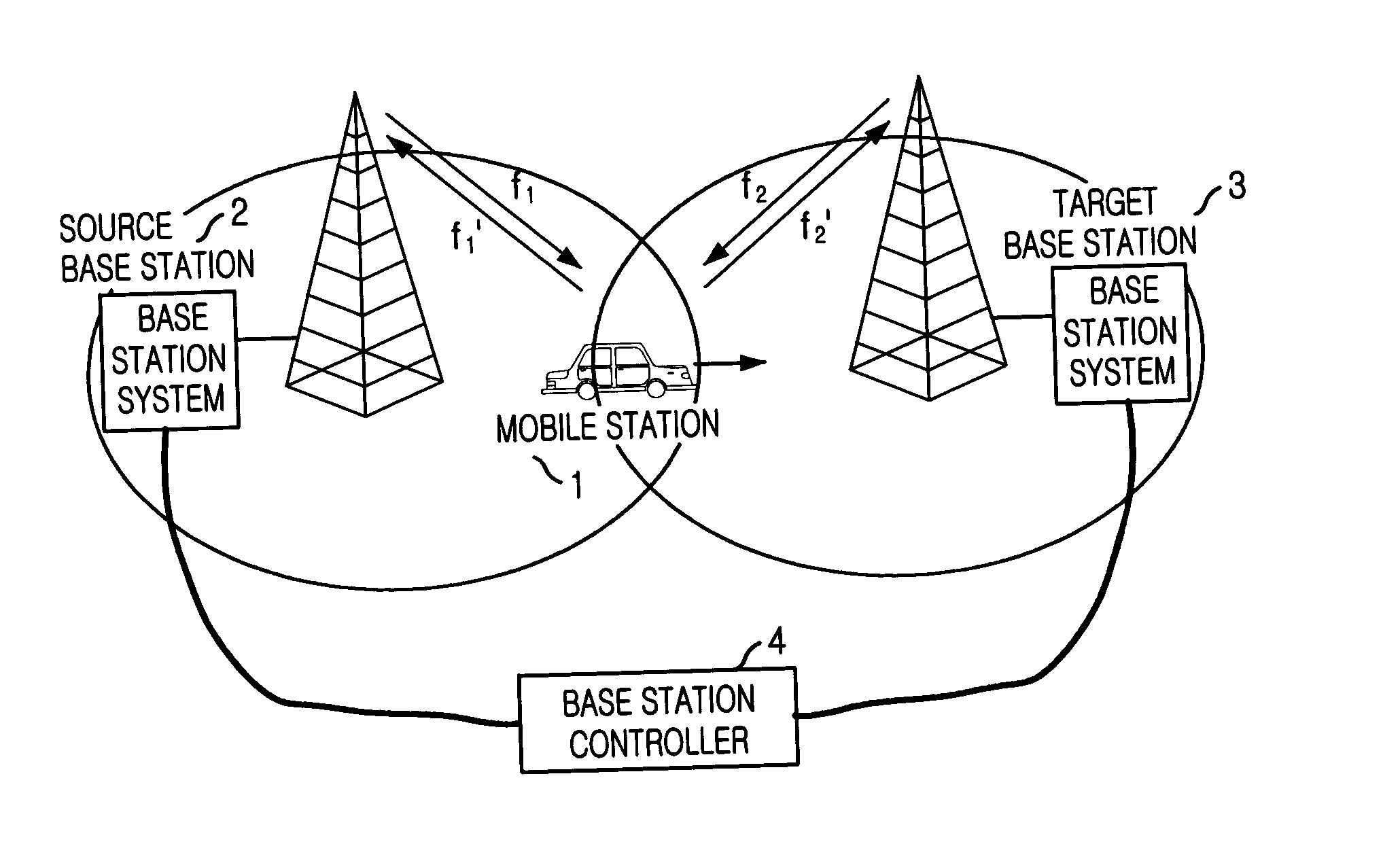
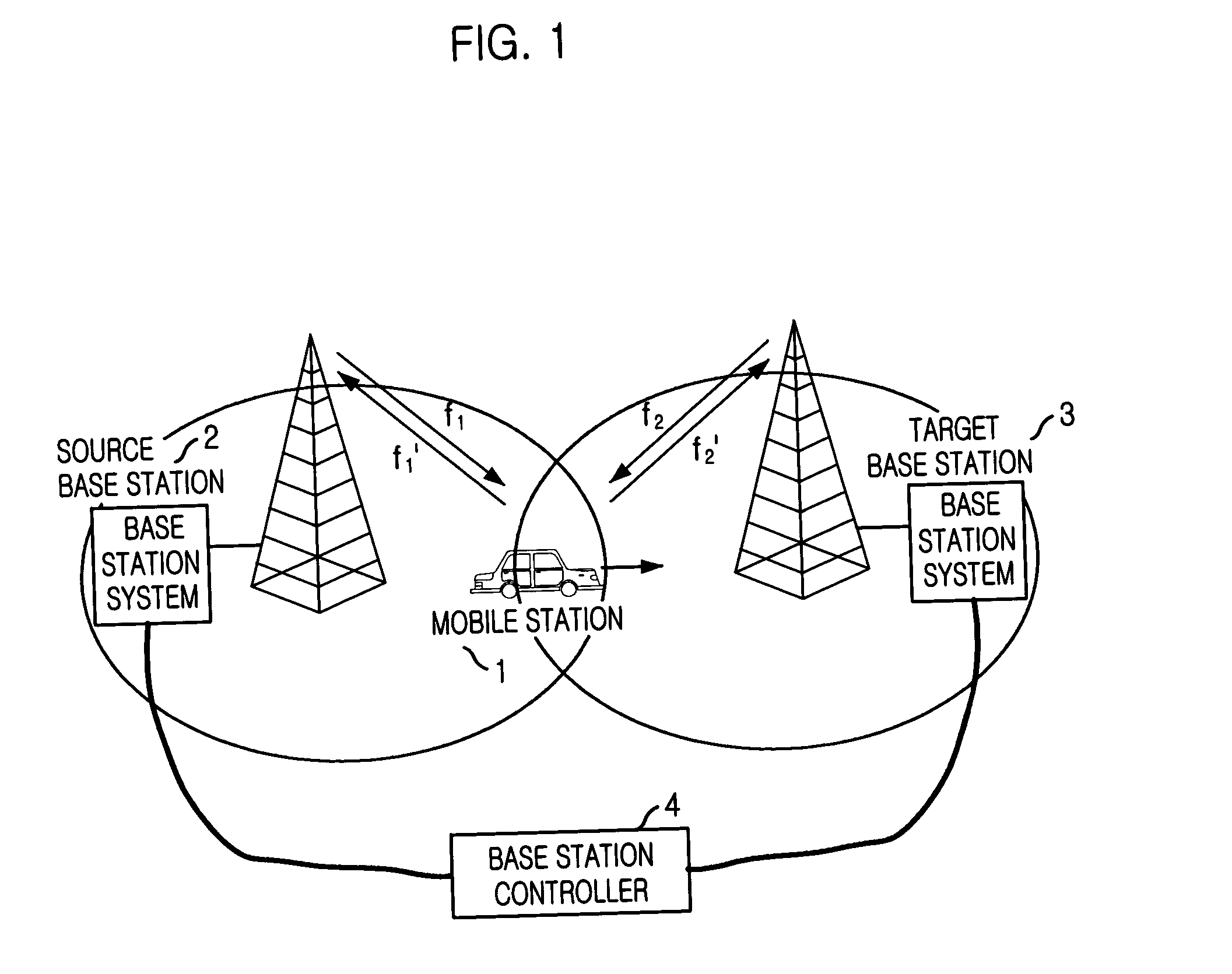
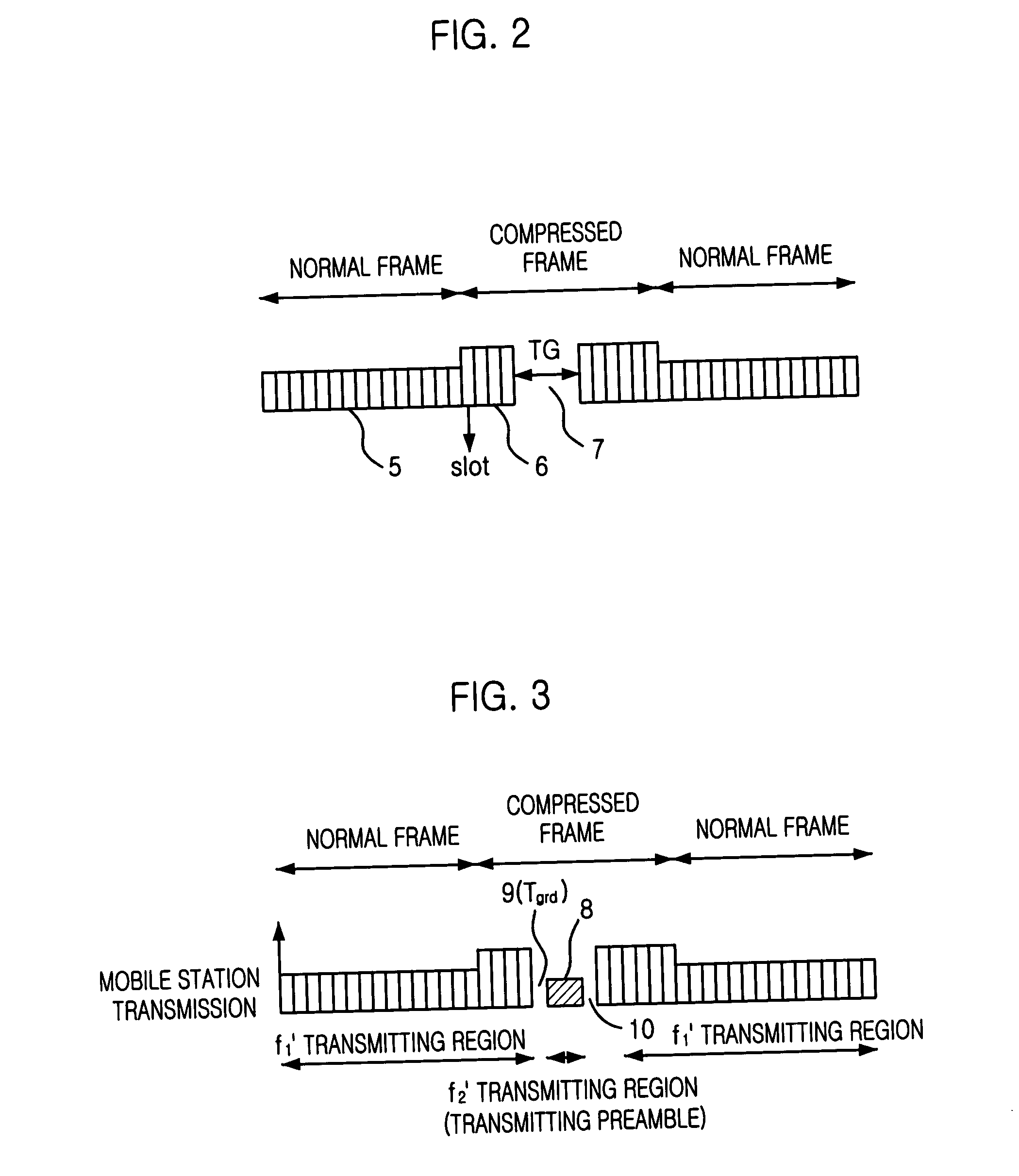
Method for seamless inter-frequency hard handover in radio communication system
InactiveUS7376424B2Synchronisation arrangementRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsCommunications systemTransceiver
A method for seamless inter-frequency hard handover in a radio communication system is disclosed. The method for seamless inter-frequency hard handover includes the steps of: a) at a mobile station, blocking a first uplink carrier frequency used for communication, transmitting a direct sequence spread preamable signal through a second uplink carrier frequency for a short time, and continuously performing the communication through the first uplink carrier frequency: and h) at a target base transciever station, acquiring an uplink synchronization of a mobile station based on the preamble before performing handover.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Method for seamless inter-frequency hard handover in radio communication system
InactiveUS20040053614A1Synchronisation arrangementRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsCommunications systemCarrier signal
A method for seamless inter-frequency hard handover in a radio communication system is disclosed. The method for seamless inter-frequency hard handover includes the steps of: a) at a mobile station, blocking a first uplink carrier frequency used for communication, transmitting a direct sequence spread preamable signal through a second uplink carrier frequency for a short time, and continuously performing the communication through the first uplink carrier frequency: and h) at a target base transciever station, acquiring an uplink synchronization of a mobile station based on the preamble before performing handover.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Hybrid spread spectrum radio system
InactiveUS20080019422A1Improve securityGood signalTransmissionTelecommunicationsDirect-sequence spread spectrum
Systems and methods are described for hybrid spread spectrum radio systems. A method, includes receiving a hybrid spread spectrum signal including: fast frequency hopping demodulating and direct sequence demodulating a direct sequence spread spectrum signal, wherein multiple frequency hops occur within a single data-bit time and each bit is represented by chip transmissions at multiple frequencies
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
Method and apparatus for addition data transmission and reception in digital broadcast system
InactiveUS20130142219A1Maintain backward compatibilityPlural information simultaneous broadcastSimultaneous/sequential multiple television signal transmissionIntermediate frequencyDigital radio
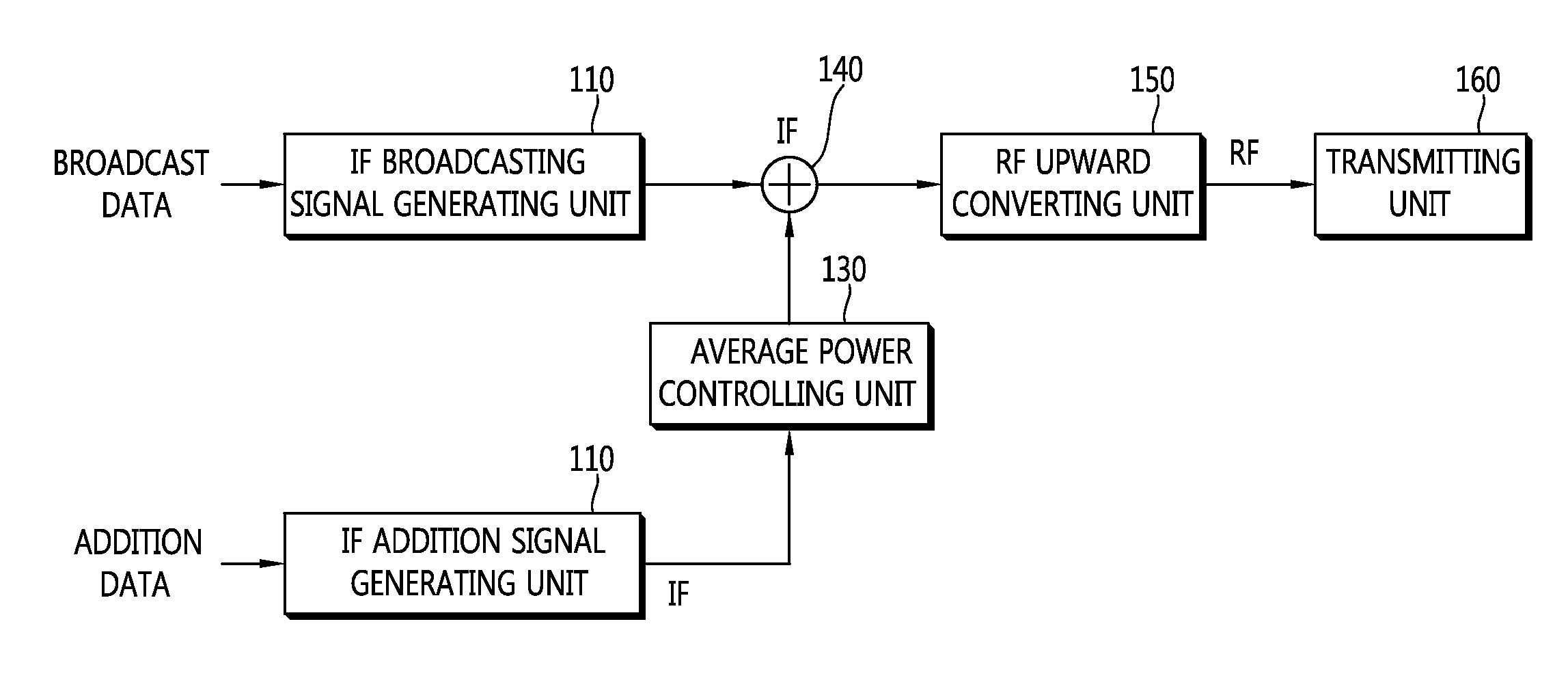
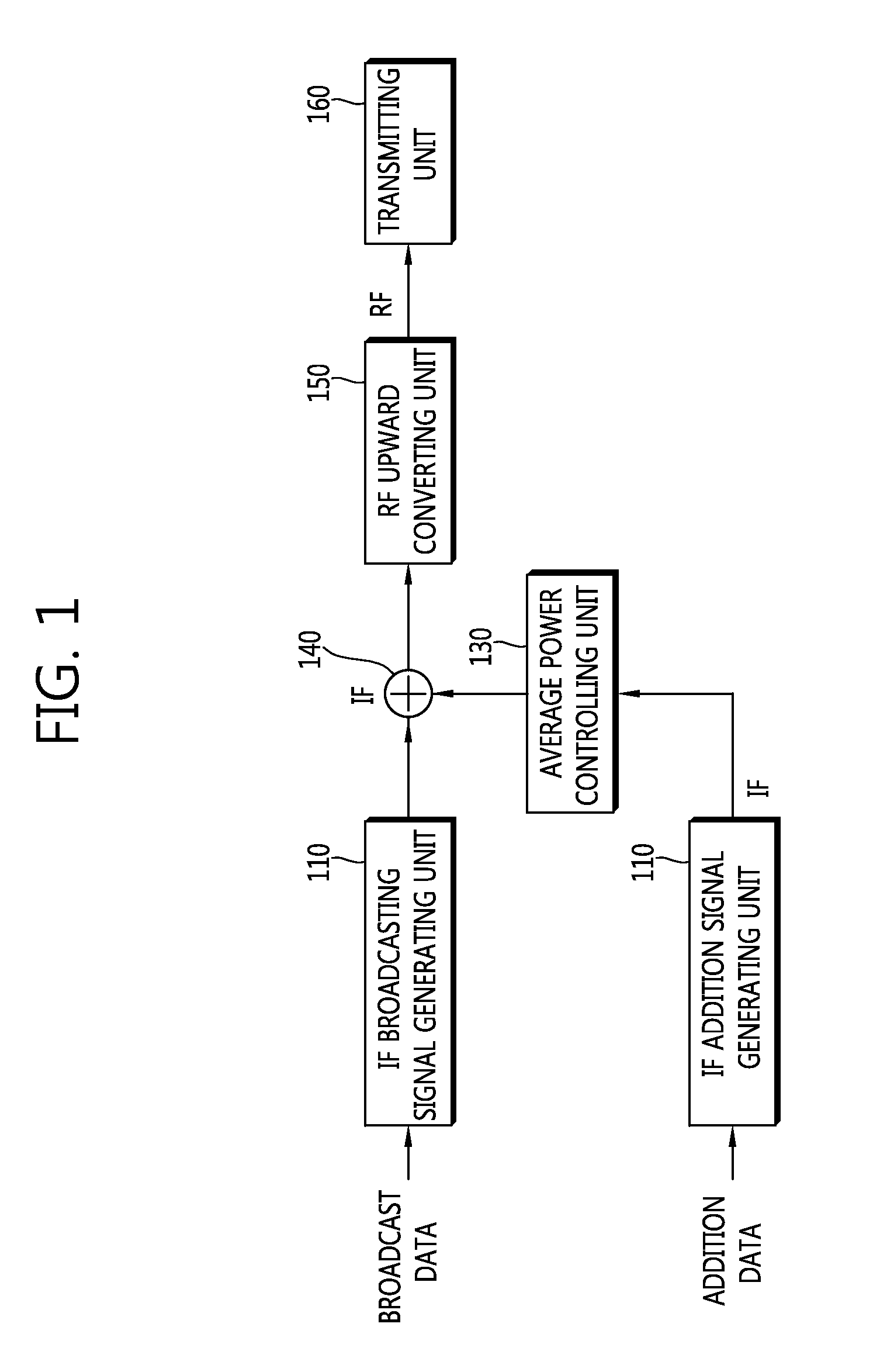
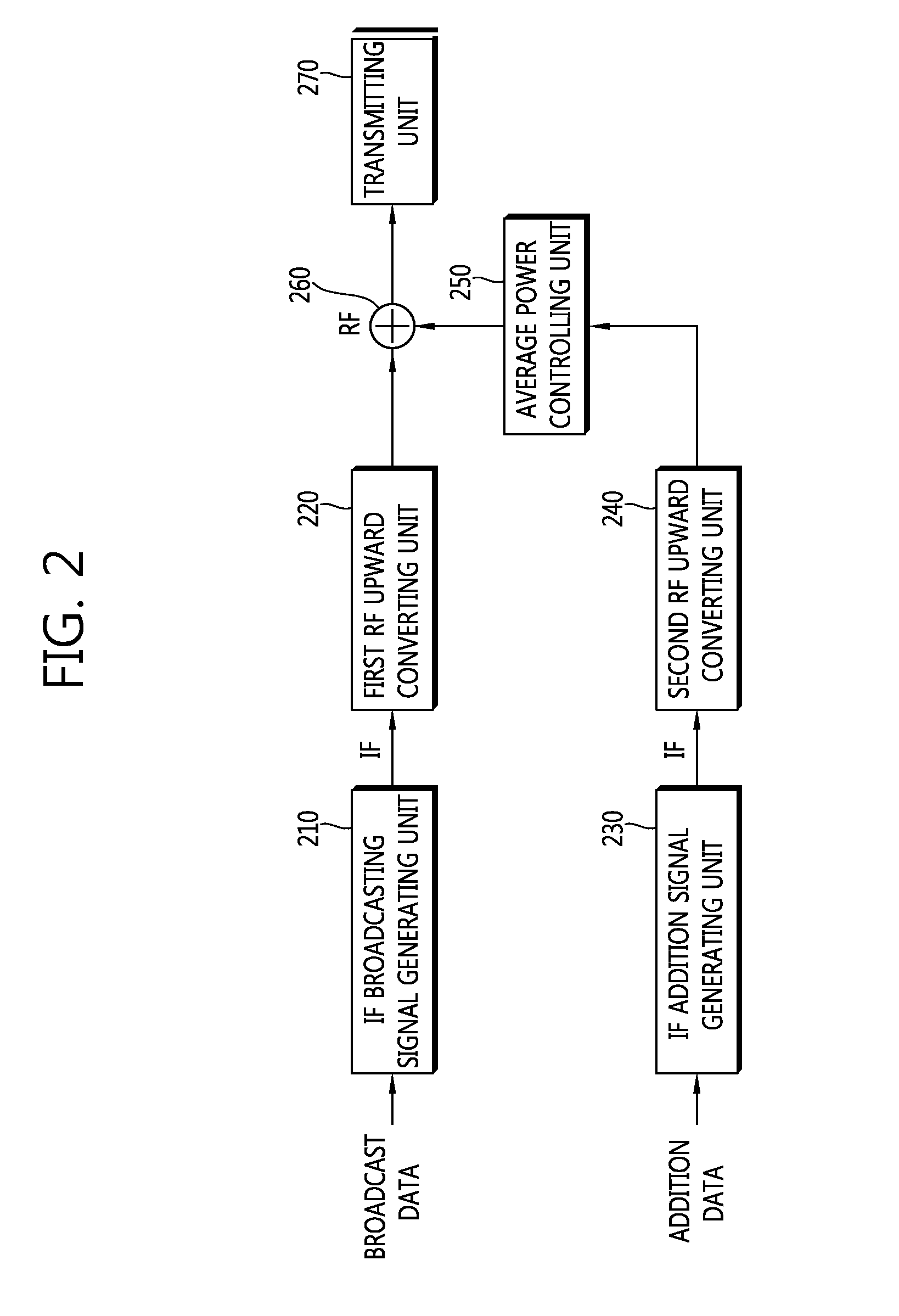
Provided are an apparatus for addition data transmission includes: an IF broadcasting signal generating unit receiving the broadcast data, and FEC and modulation of the received broadcast data to generate a broadcasting signal in an intermediate frequency (IF) band; an IF addition signal generating unit receiving the addition data to generate an addition signal in the IF band by using direct sequence spread spectrum (DSSS); an average power controlling unit controlling average power of the addition signal in the IF band; a signal combining unit combining the broadcasting signal in the IF band and the addition signal in the IF band to generate a combination signal; an RF upward converting unit upwardly converting the combination signal in a signal in a radio frequency (RF) band to a combination signal in the RF band; and a transmitting unit transmitting the combination signal in the RF band.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST +2
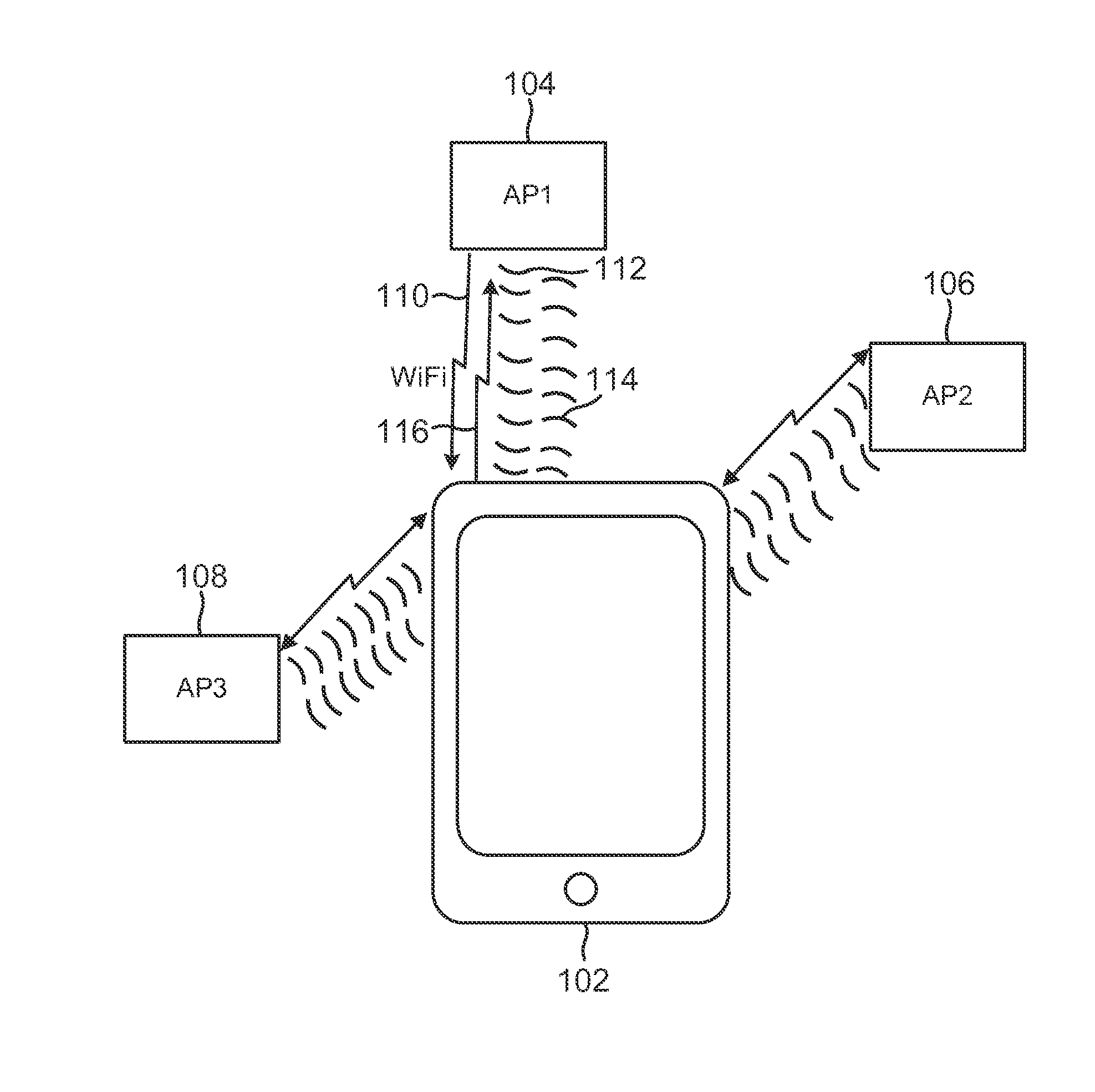
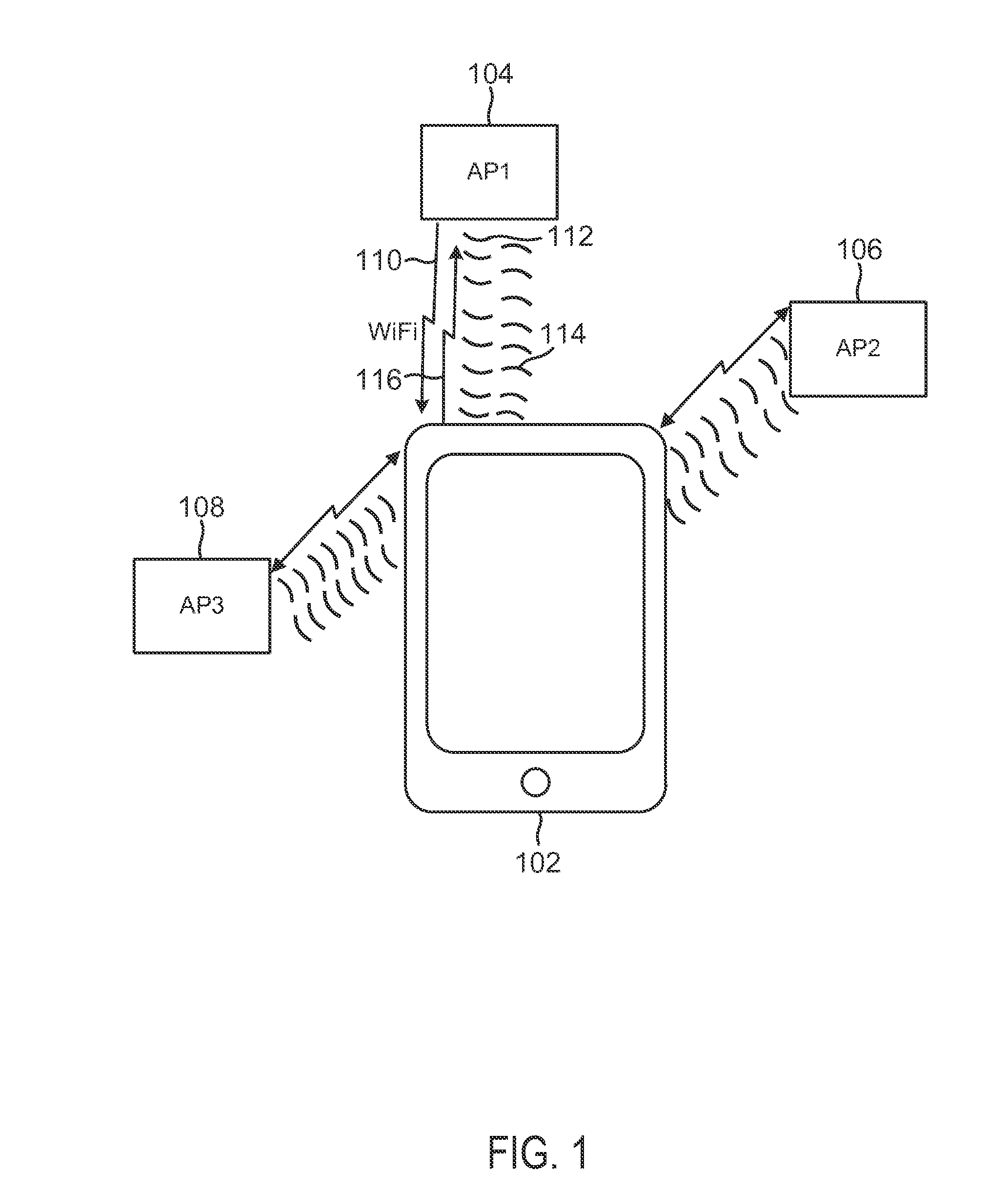
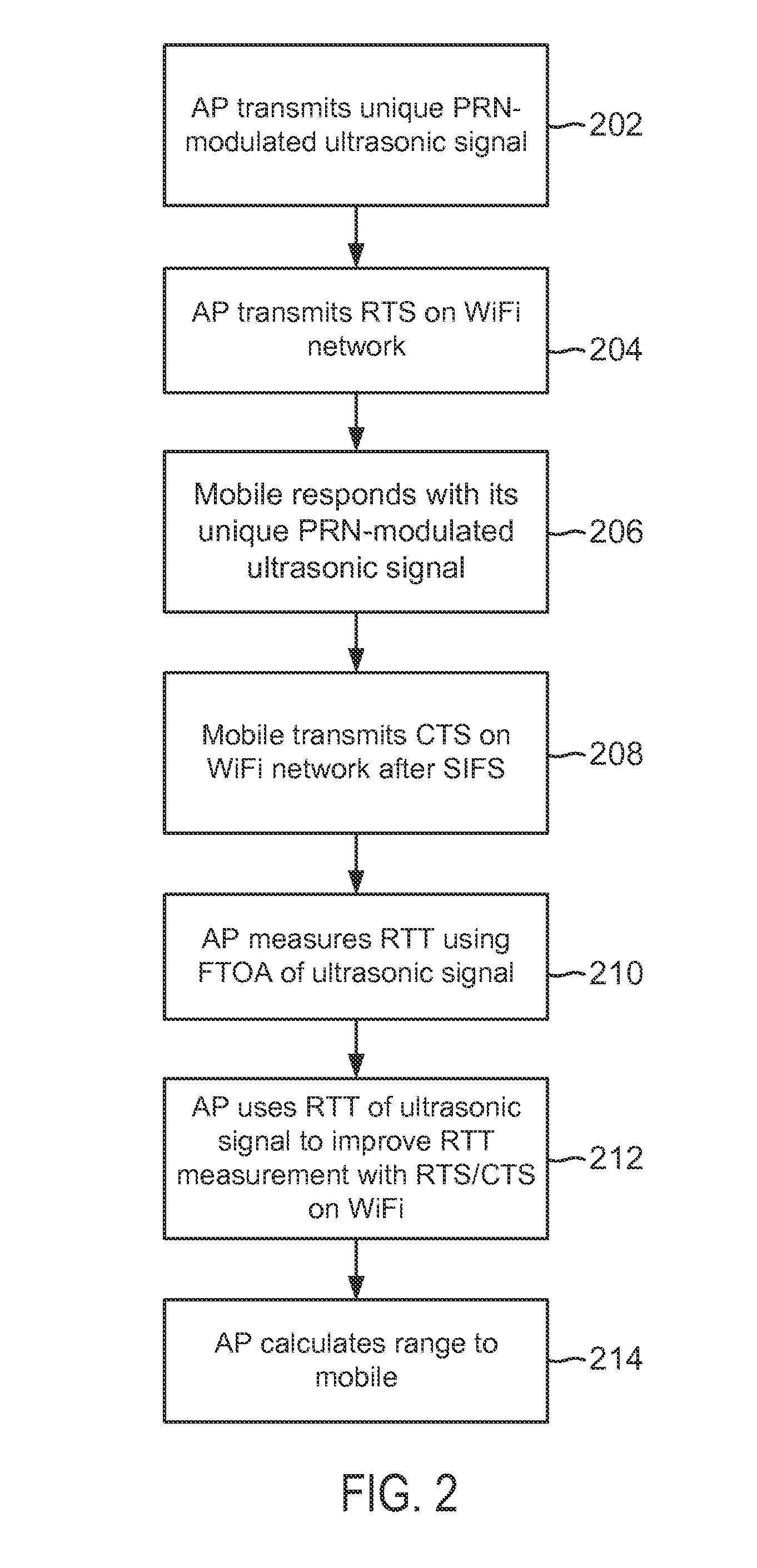
Ranging using wi-fi and ultrasound measurements communication
InactiveUS20140253389A1Improve range determinationImprove accuracyDirection finders using radio wavesPosition fixationWi-FiCommunications system
System and methods are disclosed to use ultrasonic (US) and WiFi signals to improve range determination between devices in WiFi-based position or range estimation systems. Such systems may leverage existing WiFi infrastructure and US-capable sensors such as speakers and microphones as US transducers. US ranging between devices may be performed using round-trip time (RTT) or one-way measurements. To enable US ranging between a device and multiple US transmitters simultaneously, the US signal from each US transmitters or from the device may be modulated with a unique pseudo-random number (PRN) using direct sequence spread spectrum (DSSS). The transmission of US signals may be synchronized with the transmission of WiFi beacons which may contain data fields that contain the PRN sequence used to modulate the synchronous US signal. In RTT ranging, a receiving device receiving an US signal transmission may respond with its own PRN-modulated US signal synchronized to its WiFi beacon.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
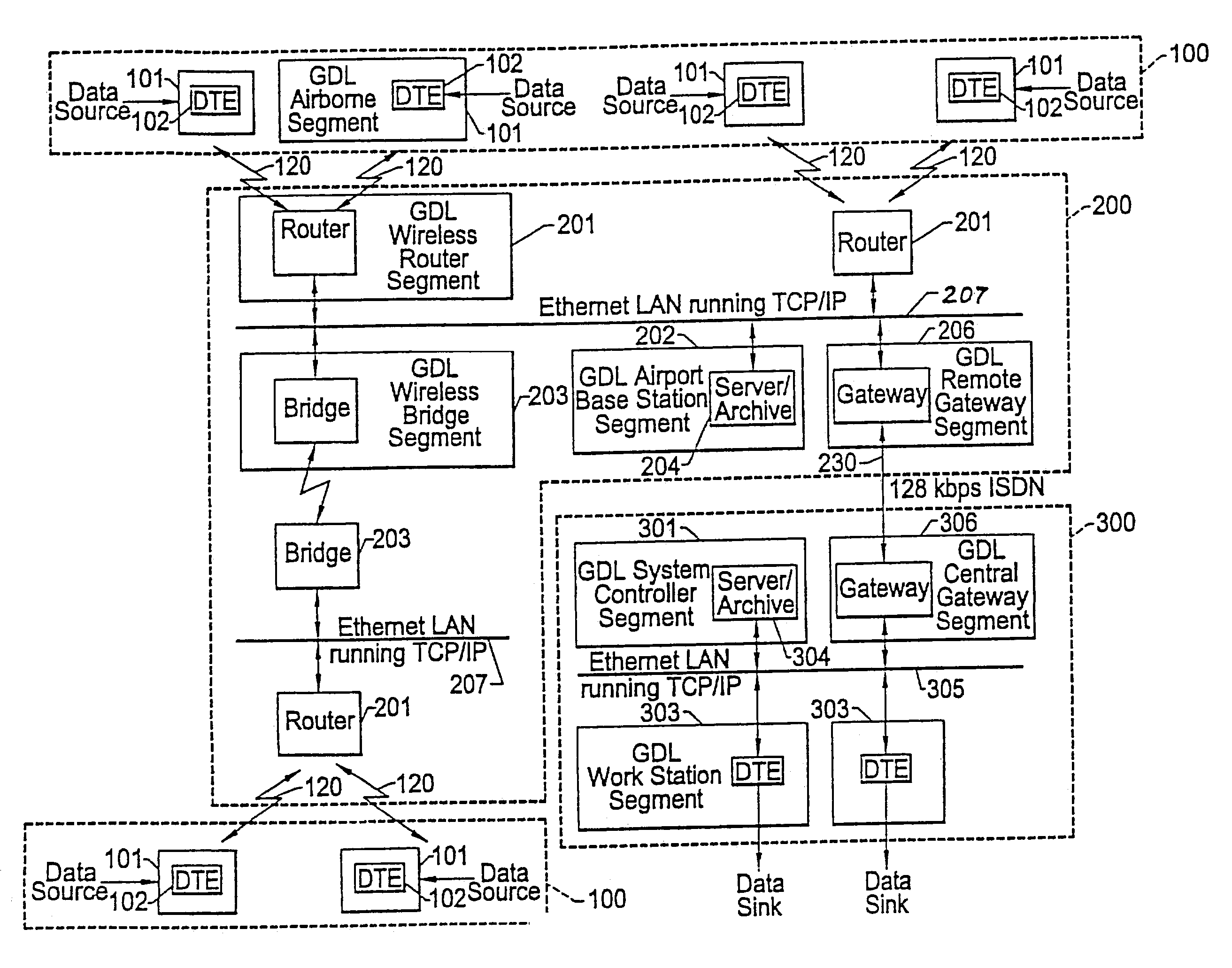
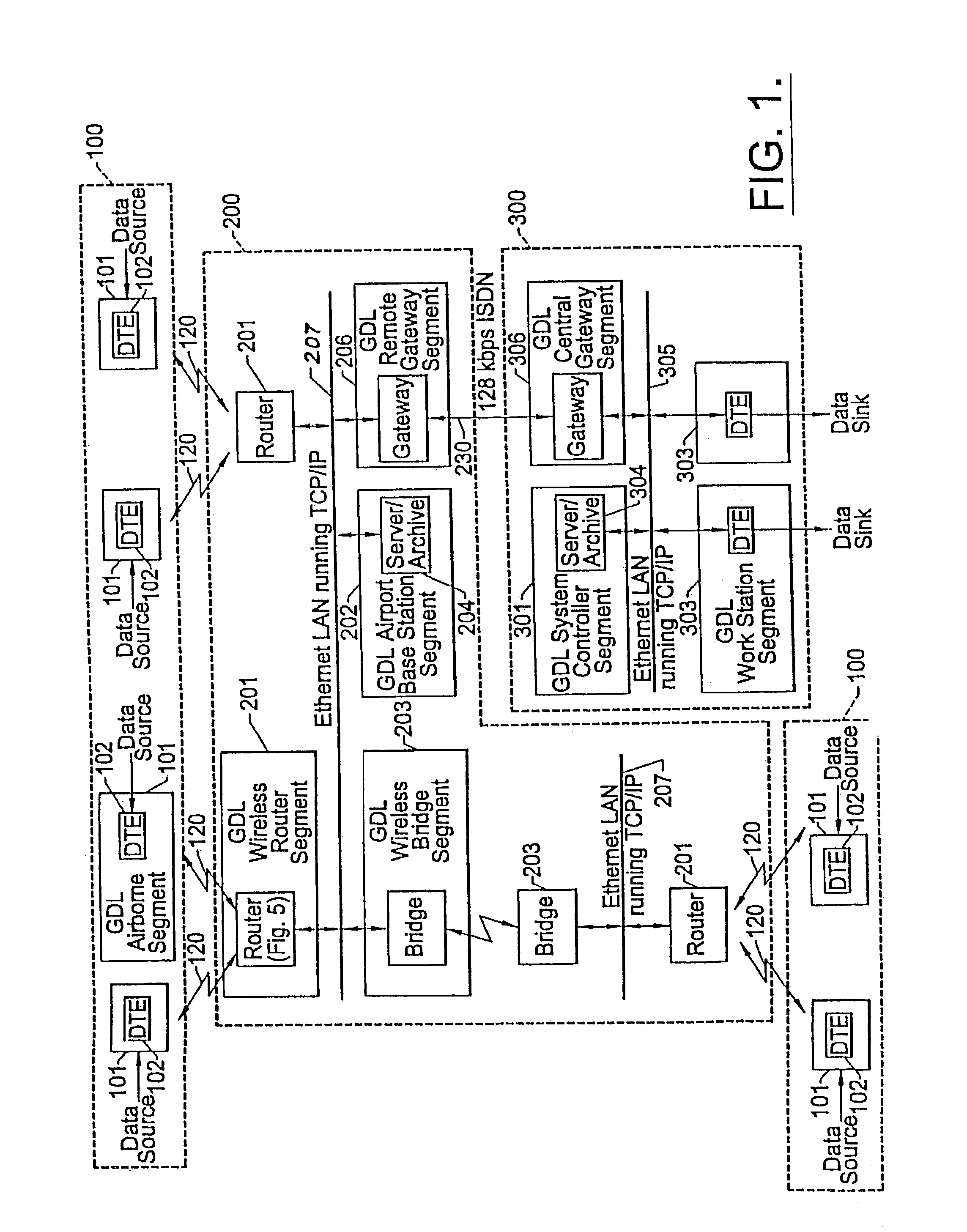
Wireless, ground link-based aircraft data communication method
InactiveUS6990319B2Increasing transmit power levelReliable receptionControl safety arrangementsRadio transmissionCommunications systemFlight vehicle
A flight information communication system has a plurality of RF direct sequence spread spectrum ground data links that link respective aircraft-resident subsystems, in each of which a copy of its flight performance data is stored, with airport-located subsystems. The airport-located subsystems are coupled by way communication paths, such as land line telephone links, to a remote flight operations control center. At the flight operations control center, flight performance data downlinked from plural aircraft parked at different airports is analyzed. In addition, the flight control center may be employed to direct the uploading of in-flight data files, such as audio, video and navigation files from the airport-located subsystems to the aircraft.
Owner:HARRIS CORP
Relay wireless sensor network routing method based on energy balance and distance cooperation
InactiveCN101489275AData transmission is stableShorten the timeEnergy efficient ICTNetwork topologiesEnergy balancedInformation data
A wireless sensor network routing method based on energy equalization and distance cooperation relates to data fusion and routing technique of wireless sensor network, and is typically used for clustering routing technique. According to a given regulation, the sensor nodes in the wireless sensor network are divided to cluster head node, relay node and cluster member node. The energy consumption of whole wireless sensor network is fully equalized and the effective usage factor of energy is increased. An energy threshold LT is introduced for realizing the smooth transition of roles between nodes, saving the cluster generation time and reducing the energy consumption. Single-hop communication is adopted in the cluster. Direct sequence spread spectrum is applied. Each cluster uses a unique cluster spreading code. All nodes in the cluster use the unique cluster spreading code for transmitting data to the cluster head and the inter-cluster interference is effectively reduced. The method of the invention can obtain purpose of prolonging the survival time of network under the precondition that the information data is reliably, effectively and accurately transmitted to the base station.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Method to minimize compatibility error in hierarchical modulation using variable phase
InactiveUS20050113040A1Increase volumeIncrease the amount of dataSpatial transmit diversityPhase-modulated carrier systemsDirect-sequence spread spectrumComputer science
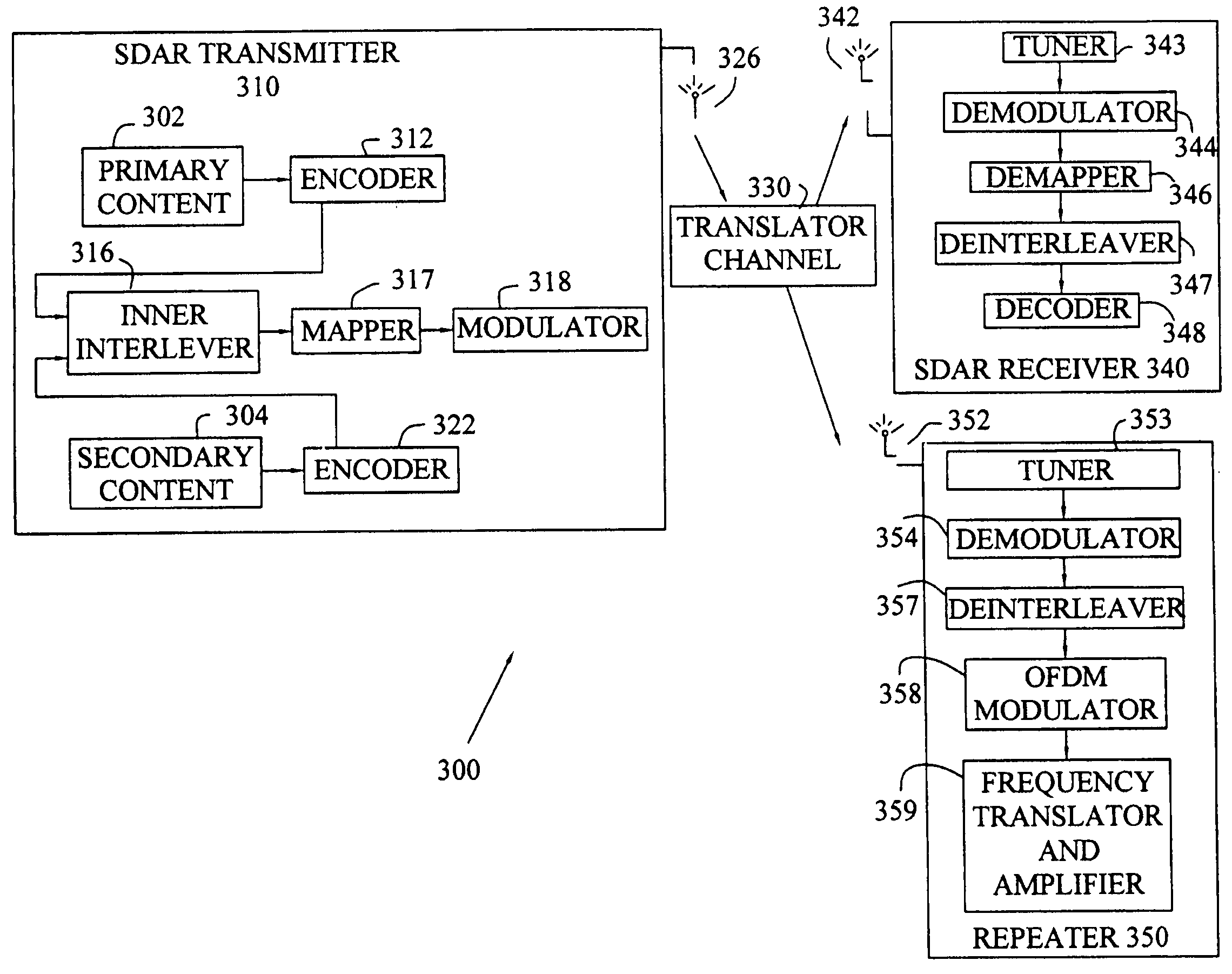
The present invention provides a method, receiver and transmitter for use in a SDAR system. The method involves generating a first modulated signal based on first input data. Additional modulation is superimposed on the first modulated signal based on additional input data, being spread across a plurality of symbols in the first modulated signal in a predetermined pattern to generate a modified signal which is then transmitted. The modified signal is decoded by performing a first demodulation of the first modulated signal then additional demodulation is performed to obtain additional input data. The superimposing step uses a plurality of offset sequence values to add the additional modulation to the first modulated signal. The offset sequence may appear as a pseudo-random distribution of offset sequence values, and may include at least one zero offset value. Alternatively, the additional modulated signal may be a fromed as a direct sequence spread spectrum modulation and the offset sequence appearing as a pseudo-noise distribution. A Hadamard matrix sequence may be used as the direct sequence code.
Owner:DELPHI TECH INC
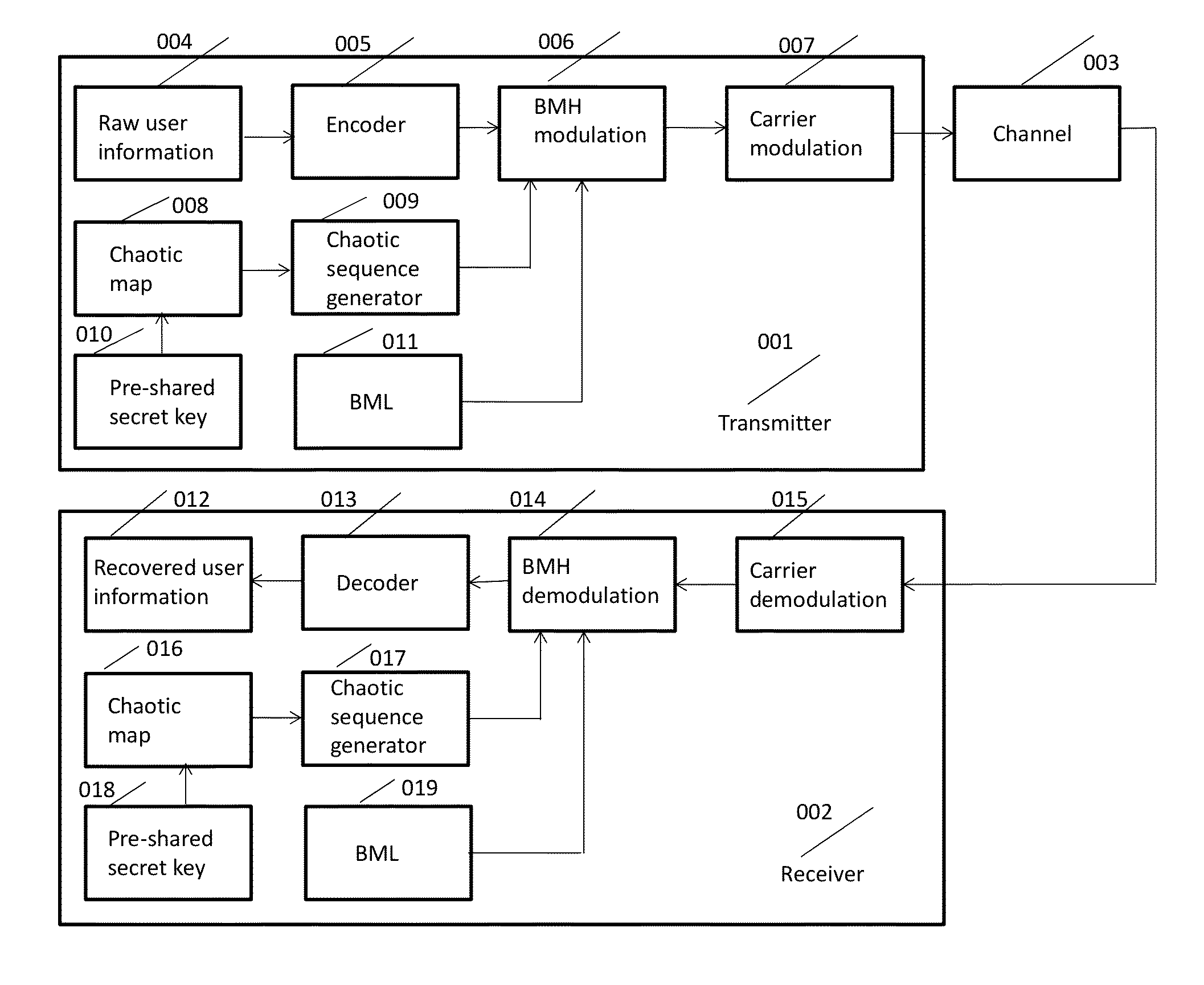
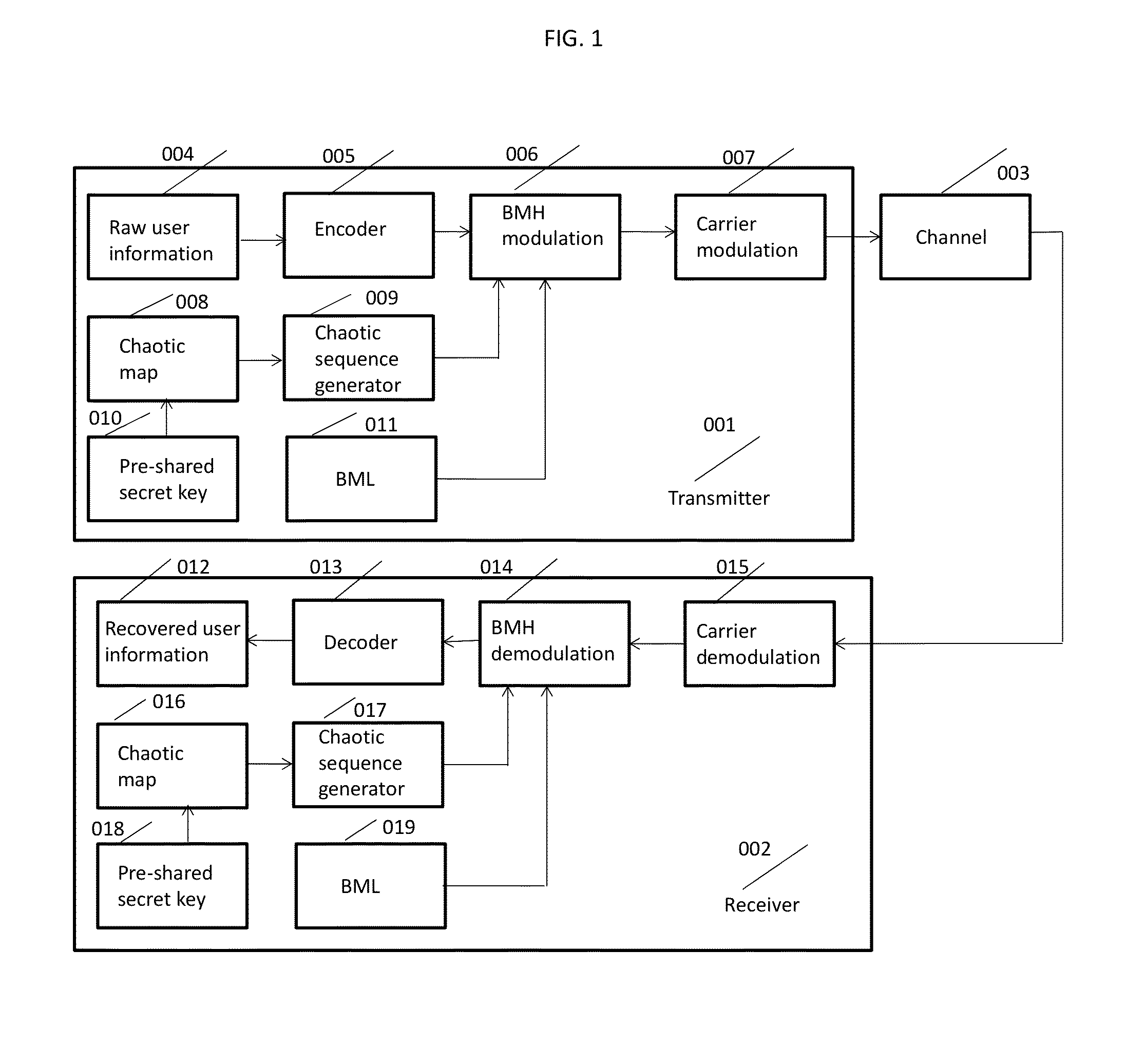
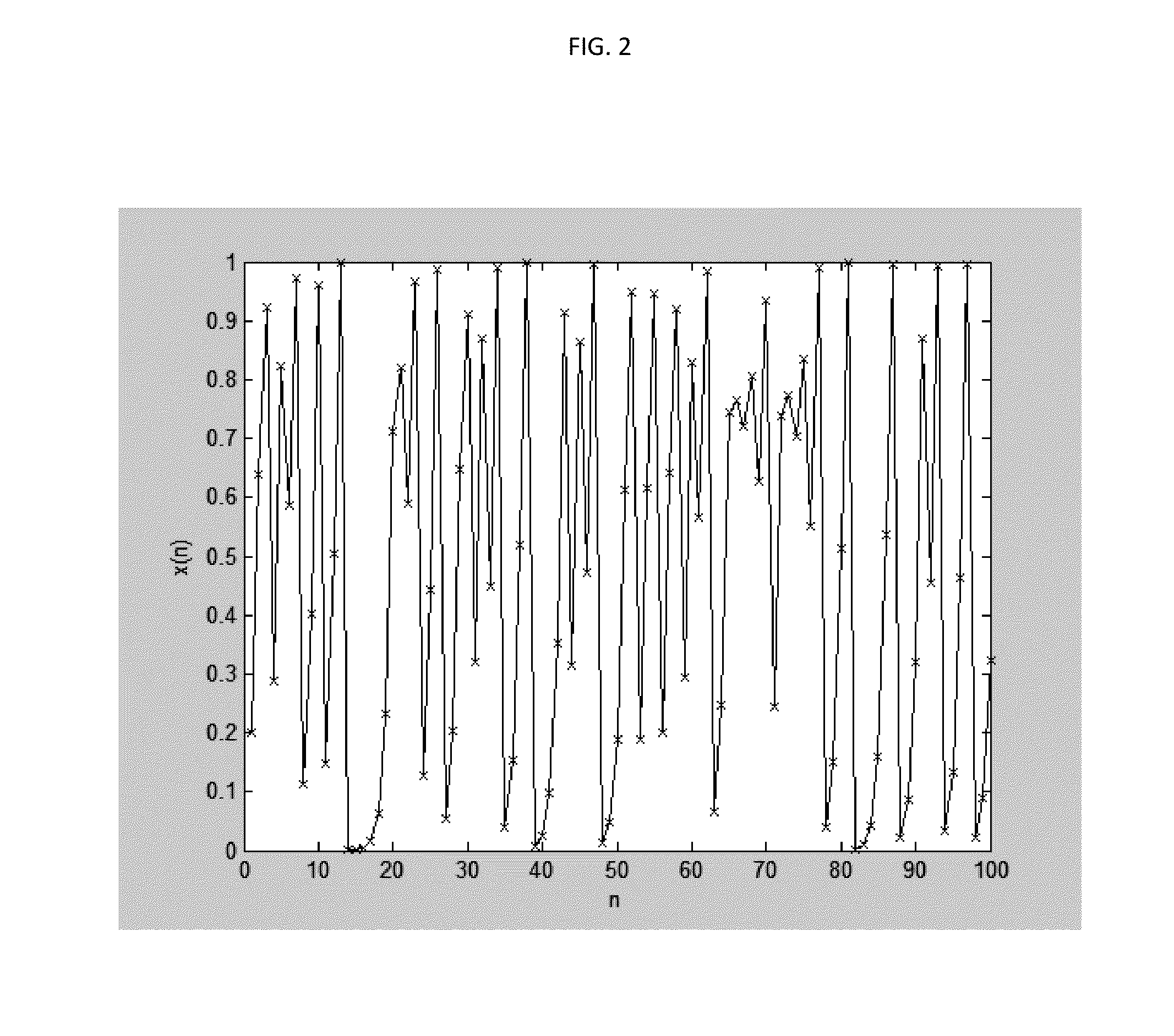
Chaotic Baseband Modulation Hopping Based Post-Quantum Physical-Layer Encryption
A post-quantum physical-layer encryption / decryption system based on chaotic Baseband Modulation Hopping (BMH). The baseband constellation, mapping, power level, and phase will vary symbol-by-symbol according to assigned random sequences. Pre-shared secret keys are used as the chaotic system parameters, initialization, and quantization parameters to generate the BMH codes. The BMH physical-layer encryption / decryption system can be combined with digital-domain based encryption algorithms such as AES, code-based post-quantum cryptography, and other physical-layer secure communication techniques such as Frequency Hopping (FH) and Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum (DSSS). It can also be combined with Quantum Key Distribution (QKD) to provide mutual authenticated key distribution. This invention can be applied to all kinds of communication systems including wireless (radio frequency, optical, quantum channel, sonar) and wire (optical fiber, power-line, telephone line, wire quantum channel, etc.), single carrier and multi-carrier, OFDM, MIMO channels.
Owner:LI WENHUA +1
Communication system using OFDM for one direction and DSSS for another direction
InactiveUS20060067278A1Power managementTransmission path divisionCommunications systemDirect-sequence spread spectrum
A method and apparatus for wireless communication are described. In one embodiment, a method for communicating with a subscriber comprises transmitting orthogonal frequency domain multiplexing (OFDM) signals to the subscriber, and receiving direct-sequence spread spectrum (DSSS) signals from the subscriber.
Owner:SDR HLDG L L C +2
Synchronized binaural hearing system
InactiveUS6839447B2Accurately determineReduce power consumptionHeadphones for stereophonic communicationFrequency-modulated carrier systemsProsthesisEngineering
A wireless binaural hearing aid system that utilises direct sequence spread spectrum technology to synchronize operation between individual hearing prostheses is provided.
Owner:GN HEARING AS
An easy-to-realize method and device for full digital frequency conversion
InactiveCN101262240AImprove versatilityIncrease working frequencyModulation transferenceTransmissionControl signalIntermediate frequency
The invention discloses an all digital frequency converting method and a device thereof, being easily realized for hardware. The method and the device are essentially used for sample rate convertion of rational number-times of baseband signals and the convertion of the baseband signals and the intermediate frequency signals in digital communication. Under the coordination of control signals and enabling signals, the convertion of signal sample rate can be finished and the convertion of the baseband signals and the intermediate signals can be finished through the reasonable matching of variable integral number-times wave filtering and fraction-times interpolation. The system of the invention essentially comprises a frequency mixer, a cascade connection integral comb filter, a fraction-time interpolating device, a half-band filter, a signal shaping filter, a power detection module and a control interface. The configurable hardware implemented structure of the invention is applicable to a plurality of modulation methods, has the advantages of low resource consumption and good portability, and is used for various wireless communication systems such as multilevel phase shift keying (MPSK), orthogonal frequency division multiplex (OFDM), direct sequence spread spectrum (DSSS) and continuous phase modulation (CPM), etc.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Precise tracking and measuring method of high dynamic signal of air fleet link
InactiveCN101776752ASolve the defect of poor precisionRadio wave reradiation/reflectionDigital signal processingAviation
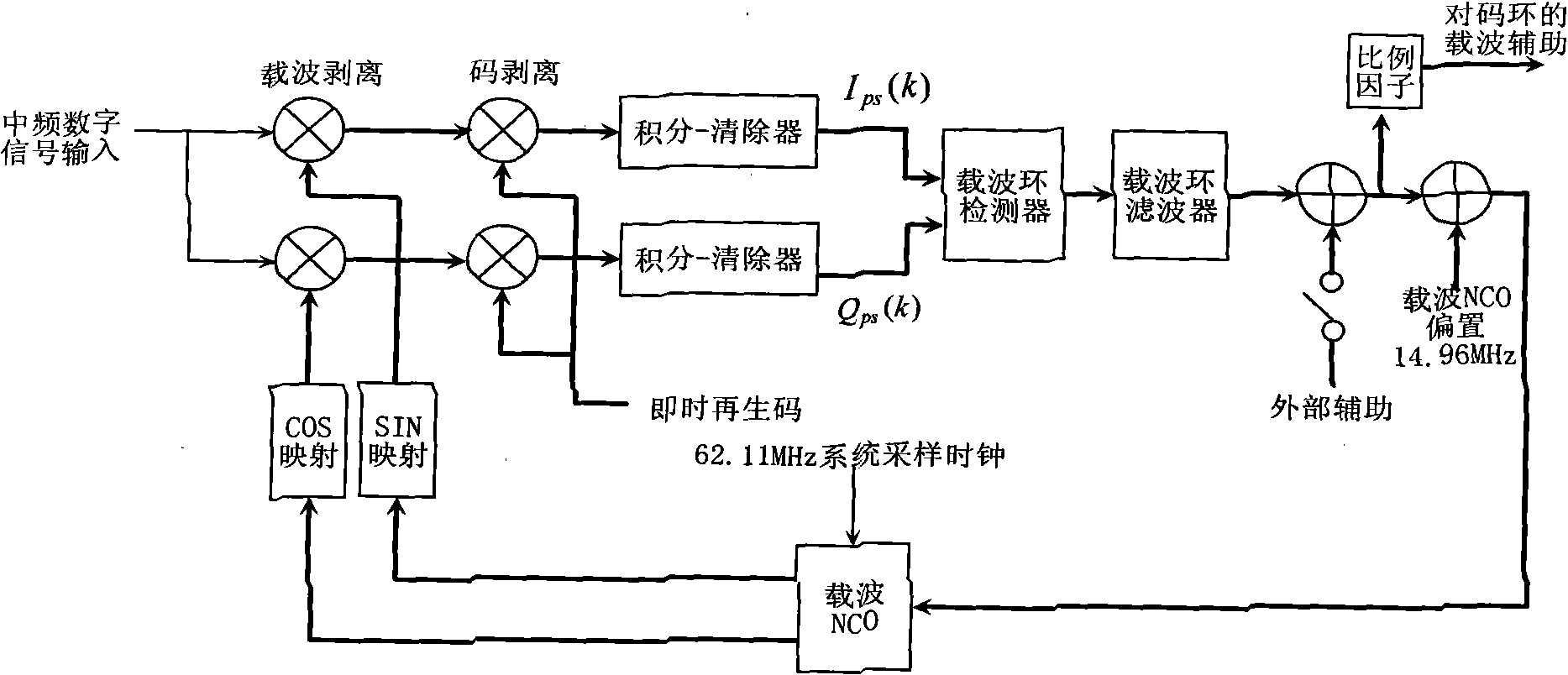
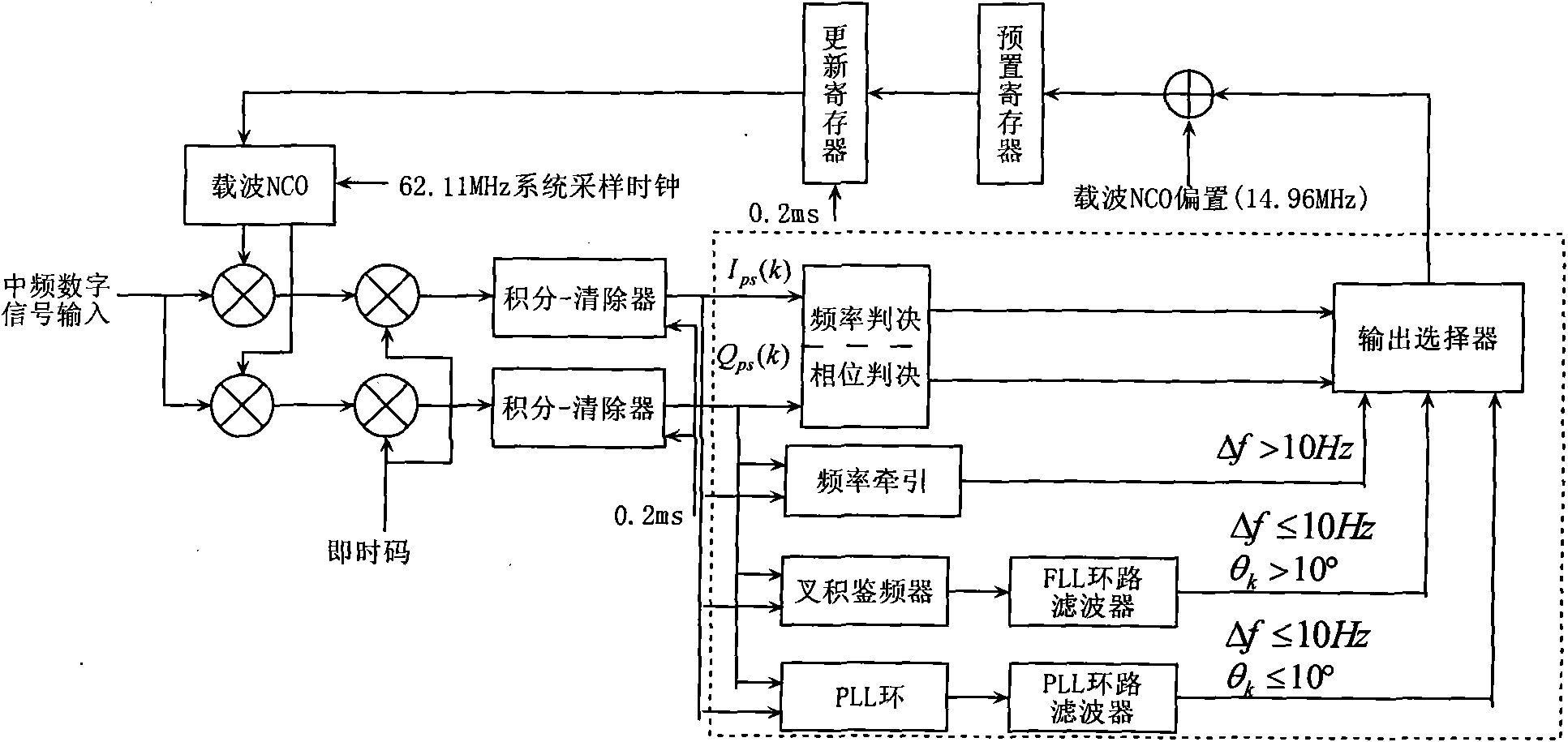
The invention relates to a precise tracking and measuring method of a high dynamic signal of an air fleet link, belonging to the technical field of aeronautical data links and radio navigation, and aiming at providing a precise tracking and measuring method of the high dynamic signal the an air fleet link and an implementation structure to solve the problems in the prior art. The invention provides a system framework of the precise tracking and measuring method of the high dynamic signal of the air fleet link, which can be implemented on a digital signal processor (DSP) and a FPGA (field programmable gate array) of a circuit board, and overcomes the defects of the unfavorable precision of a traditional high dynamic receiver by utilizing a double-loop structure of a frequency tracking loop of carrier tracking and a phase locking loop as well as a code phase locking loop to realize the high precise tracking under a high dynamic condition. The method can be widely applied to satellite navigation receivers, range measurement systems and communication systems based on a quiescent carrier modulation direct sequence spread spectrum system.
Owner:NAT SPACE SCI CENT CAS
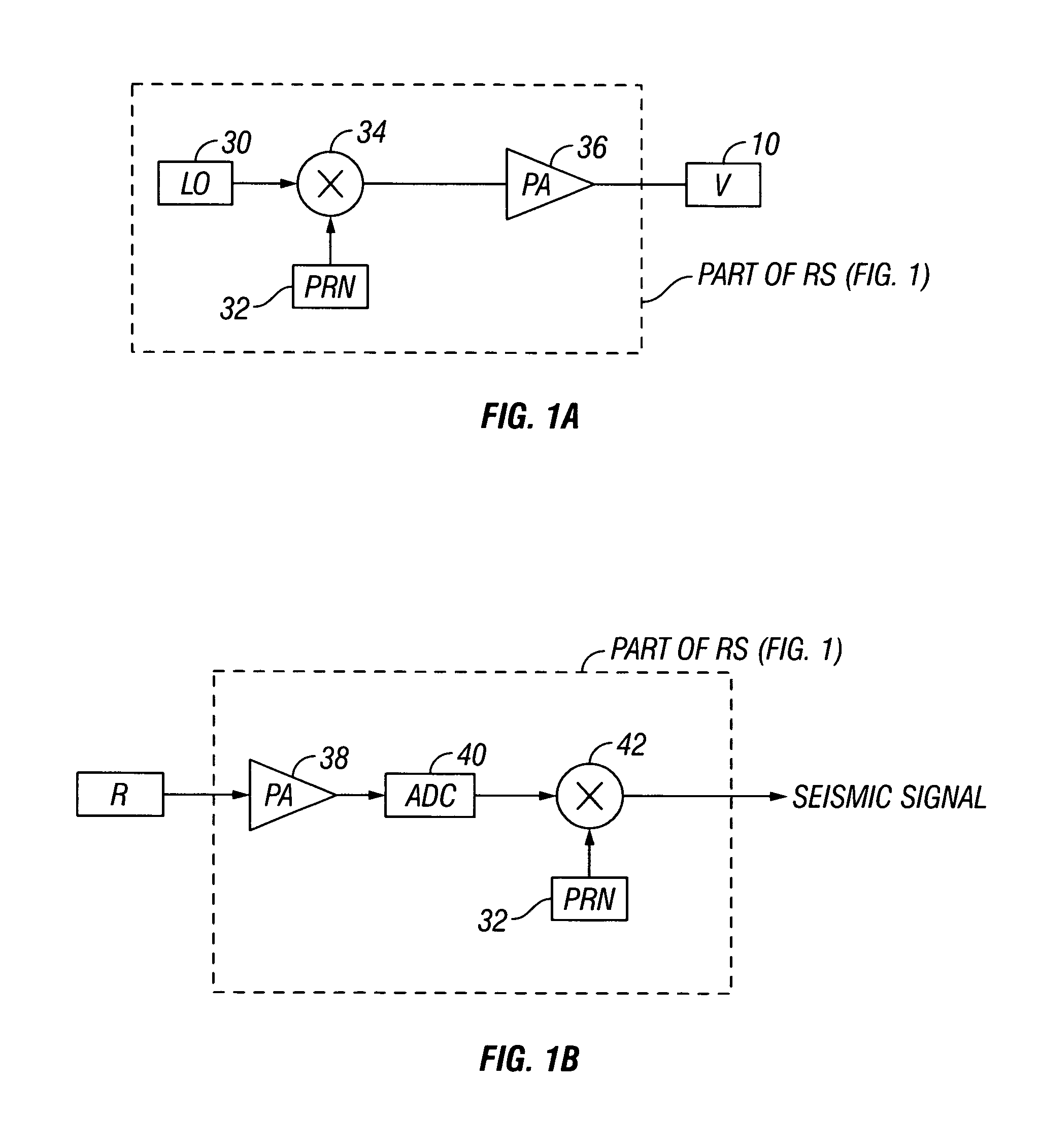
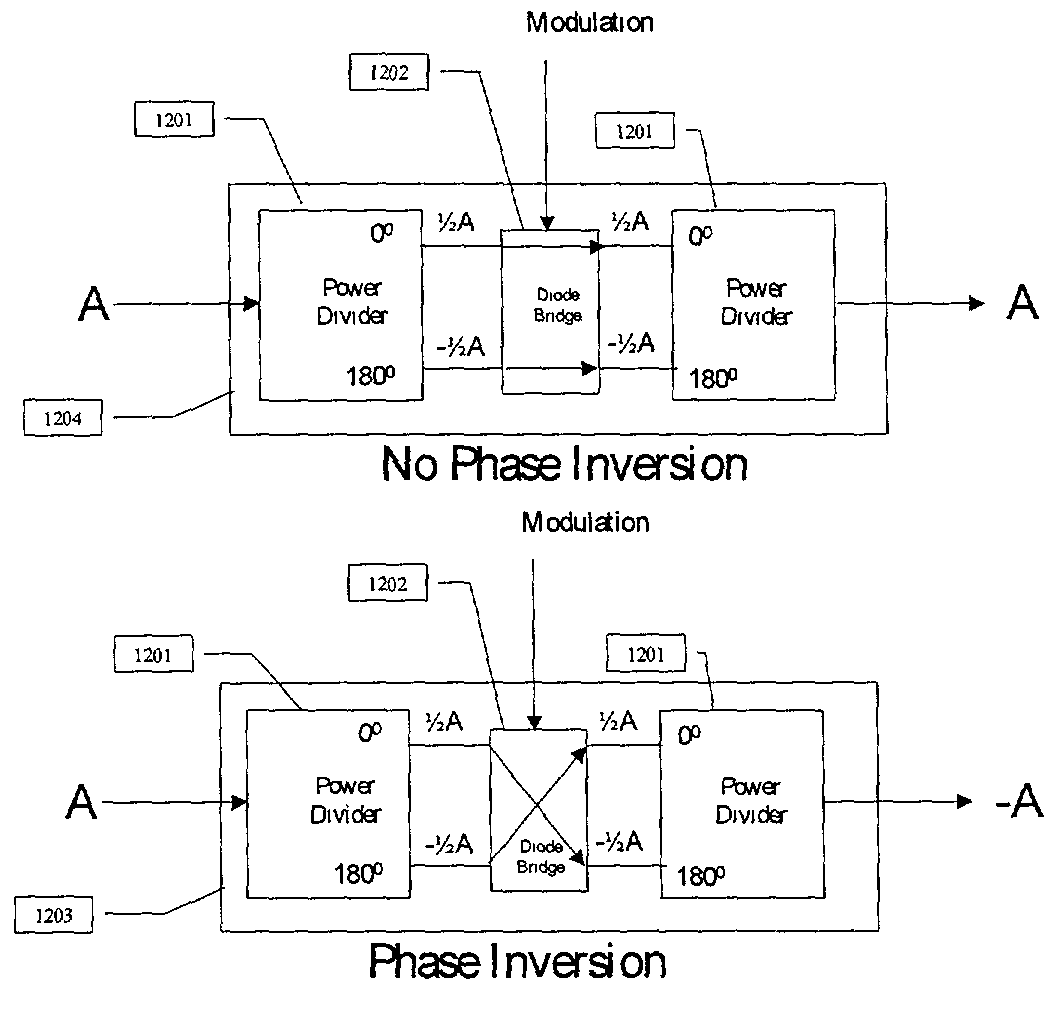
Method for generating spread spectrum driver signals for a seismic vibrator array using multiple biphase modulation operations in each driver signal chip
ActiveUS20110038225A1Seismic data acquisitionSound producing devicesDirect-sequence spread spectrumVircator
A method for generating seismic energy for subsurface surveying include operating a first seismic vibrator above an area of the subsurface to be surveyed and operating at least a second seismic vibrator above the area substantially contemporaneously with the operating the first seismic vibrator. The first and the second vibrators each have a different selected frequency response. The first and second vibrators each is operated by a same direct sequence spread spectrum signal, wherein a different number of modulation operations for each logical value in the direct sequence spread spectrum signal is selected for each vibrator.
Owner:PGS GEOPHYSICAL AS
Modular wireless fixed network for wide-area metering data collection and meter module apparatus
InactiveUS7009530B2Electric signal transmission systemsFrequency-division multiplex detailsWide areaModularity
A one-way direct sequence spread spectrum (DSSS) communications wide-area network is used as the data collection channel (uplink) of an automatic meter reading (AMR) application and a paging network, or other suitable downlink network, is used as an optional forward (downlink) channel in a cost-effective manner. The network is simple to deploy, highly scalable and modular. It offers a wide range of service options, from basic daily meter readings to advanced applications based on interval consumption data, to full two-way applications, while keeping the system's deployment and ongoing costs proportional to the service options and capacity requirements selected for various segments of the meter population. A high-output-power meter module is introduced, which provides significant benefits when operating on the network.
Owner:NEXUSDATA 1993 LTD
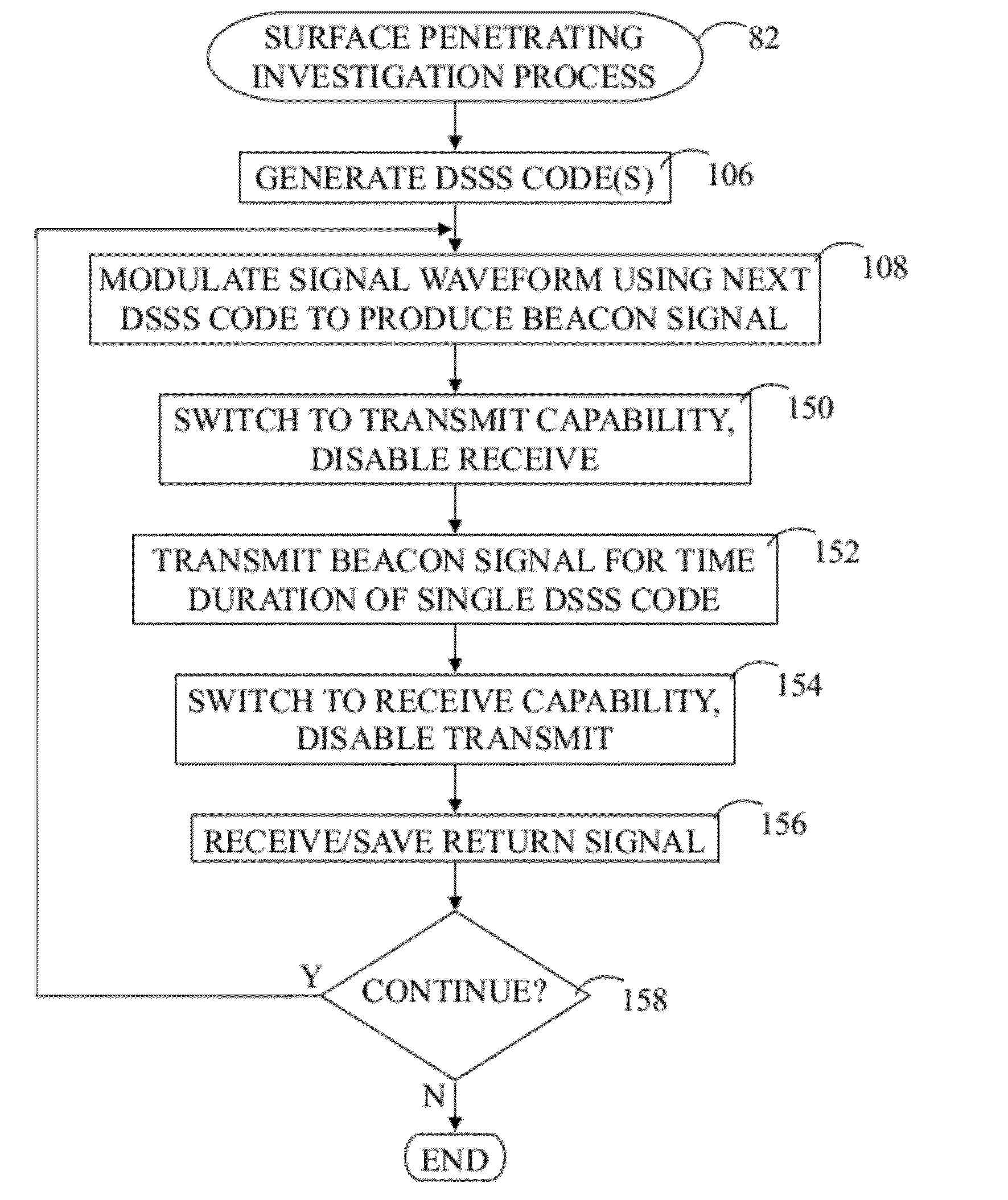
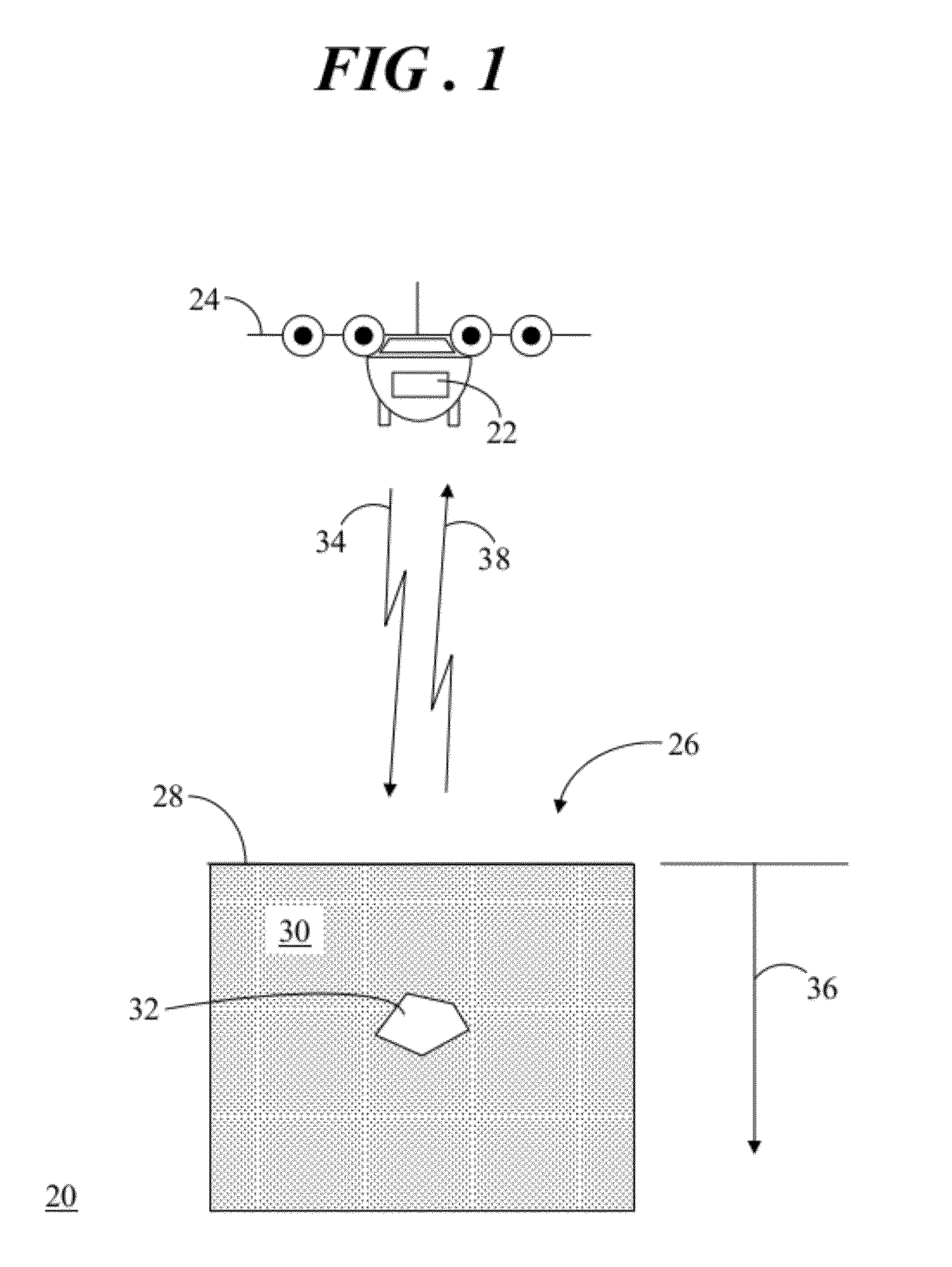
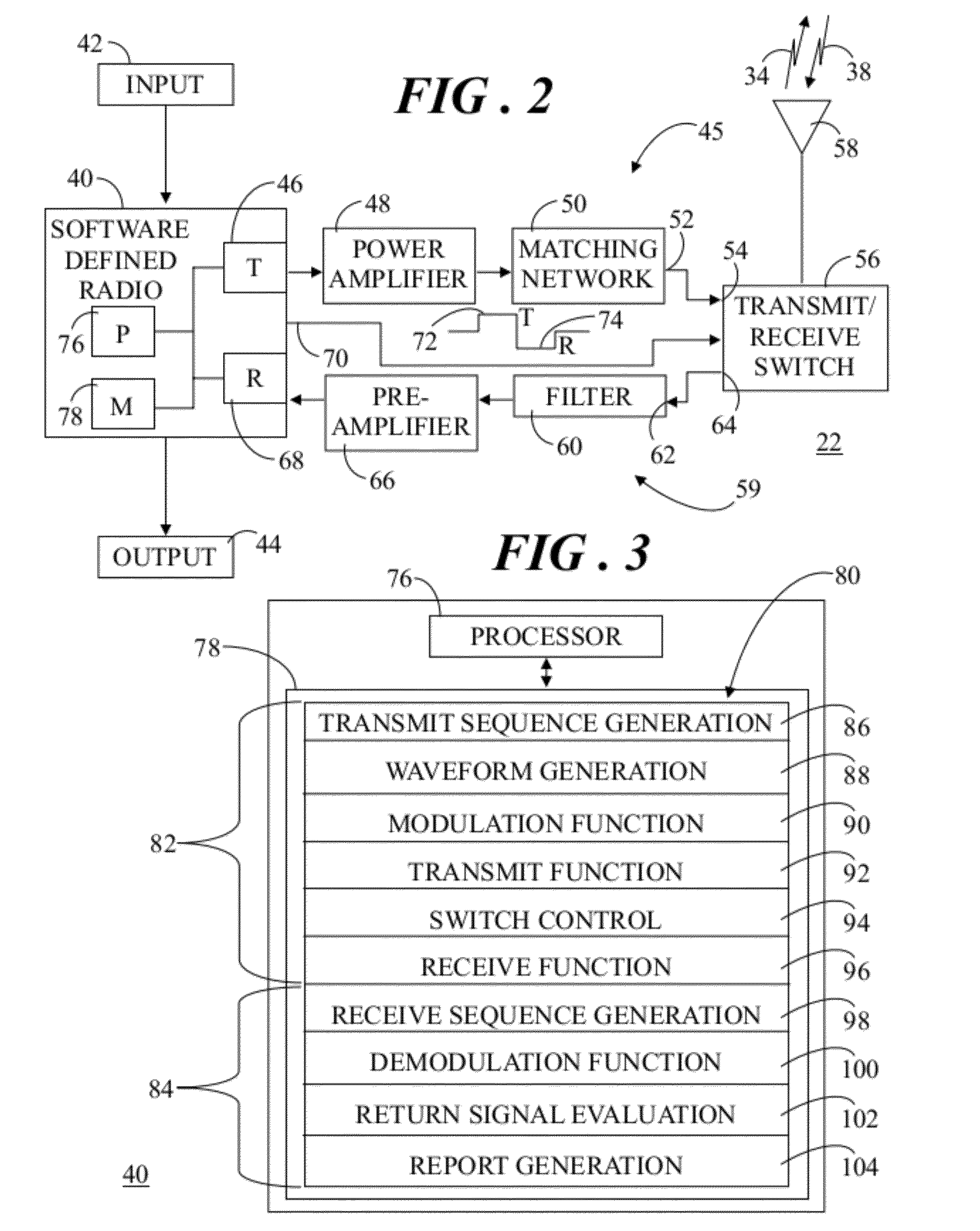
Surface penetrating radar system and target zone investigation methodology
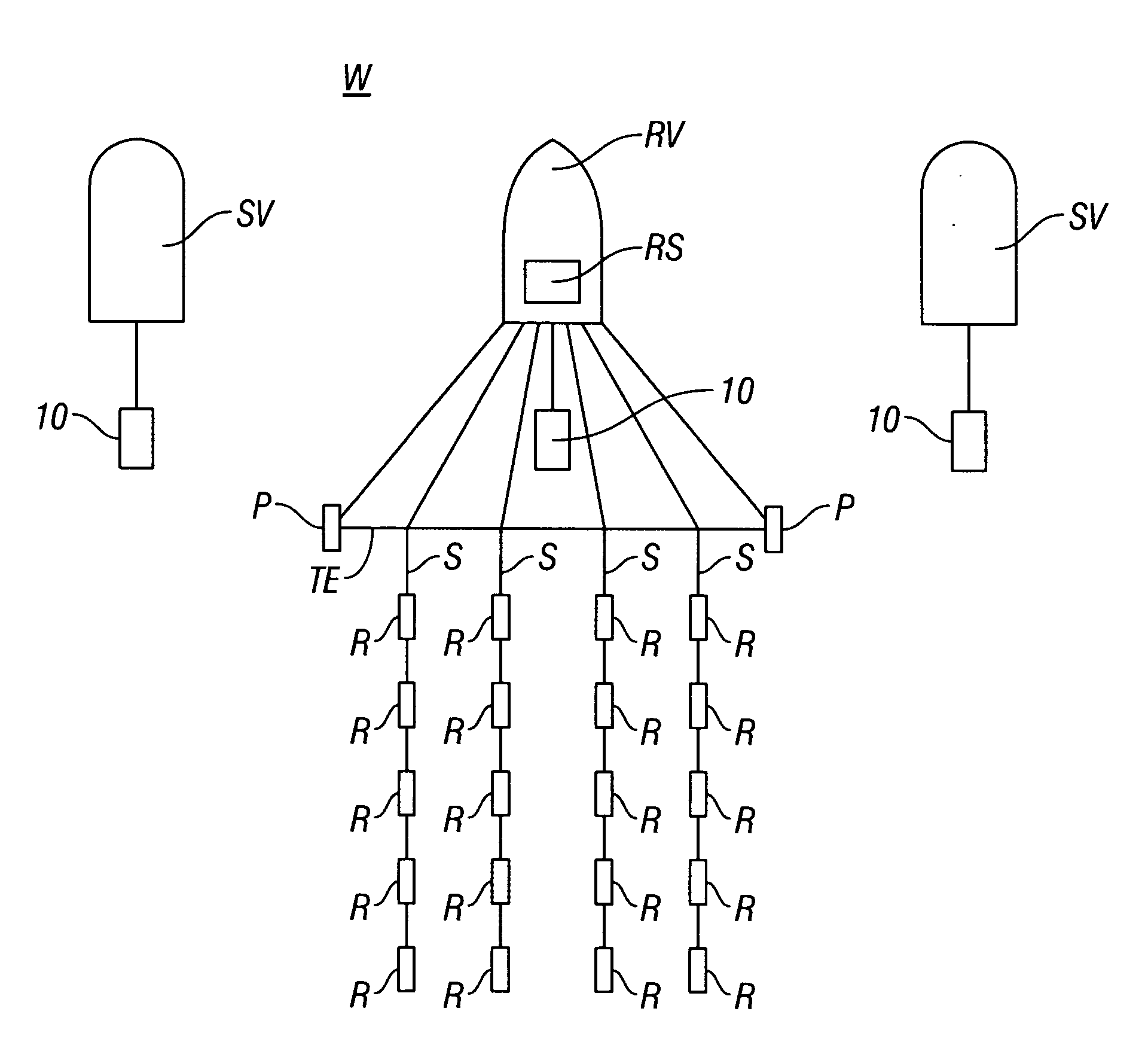
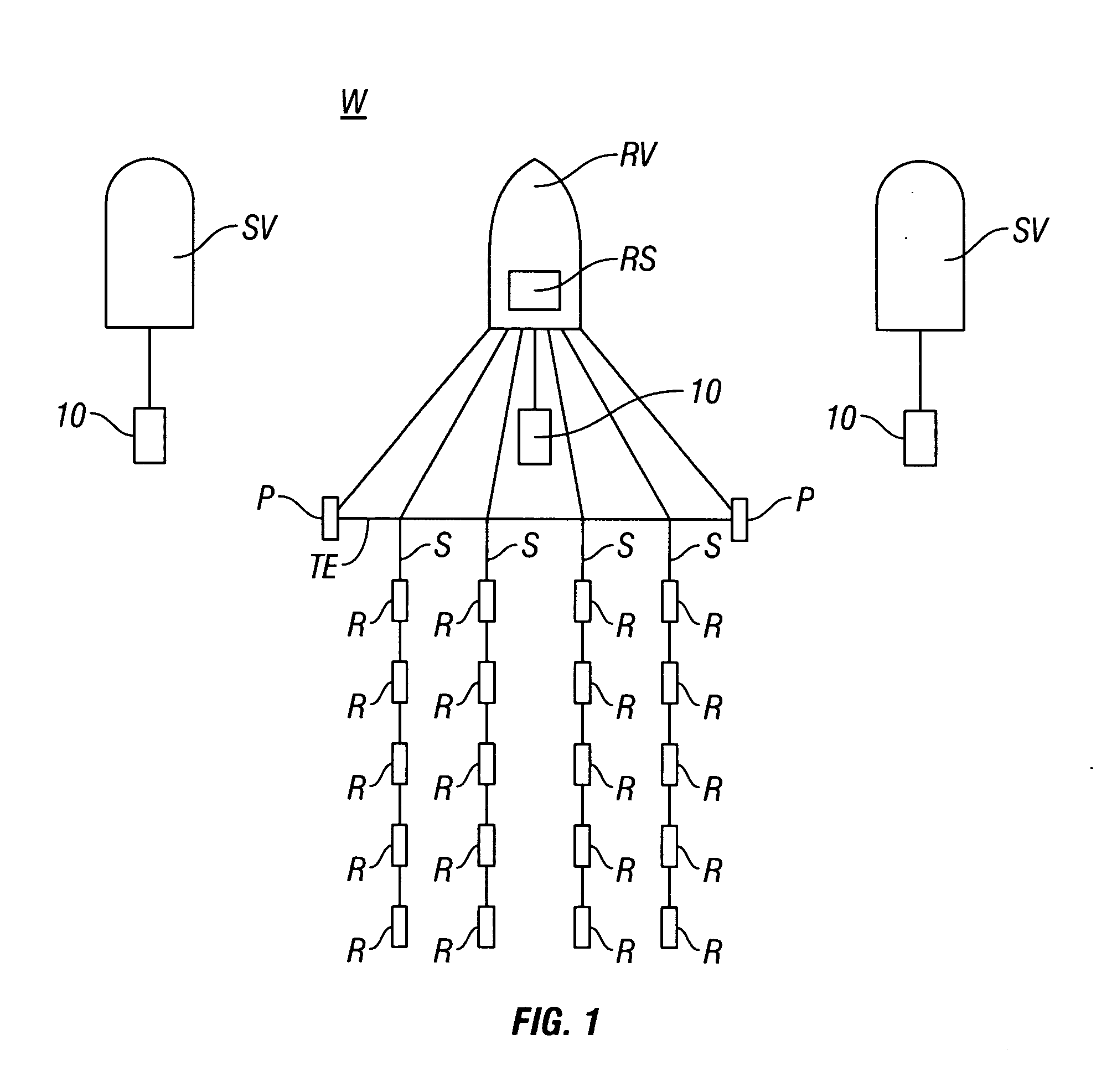
A radar system (22) includes a transmitter (45), a receiver (59), and a software defined radio (SDR) peripheral (40). Methodology (80) for investigating a target zone (26) utilizing the system (22) entails generating (106) a direct sequence spread spectrum (DSSS) code (120) having a code length (122) corresponding to a time duration of radio wave travel between the transmitter (45), the target zone (26), and the receiver (59) at a carrier frequency (112). A beacon signal (34), modulated (108) by the DSSS code (120), is transmitted (152) from the transmitter (45) toward the target zone (26) and a return signal (38) is received (156) at the receiver (56). The return signal (38) is compared (170) to a replica signal (168) characterized by the DSSS code (120), and presence of an object (32) in the target zone (26) is ascertained (178) when the return signal (38) matches the replica signal (168).
Owner:SANDIA RES CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com