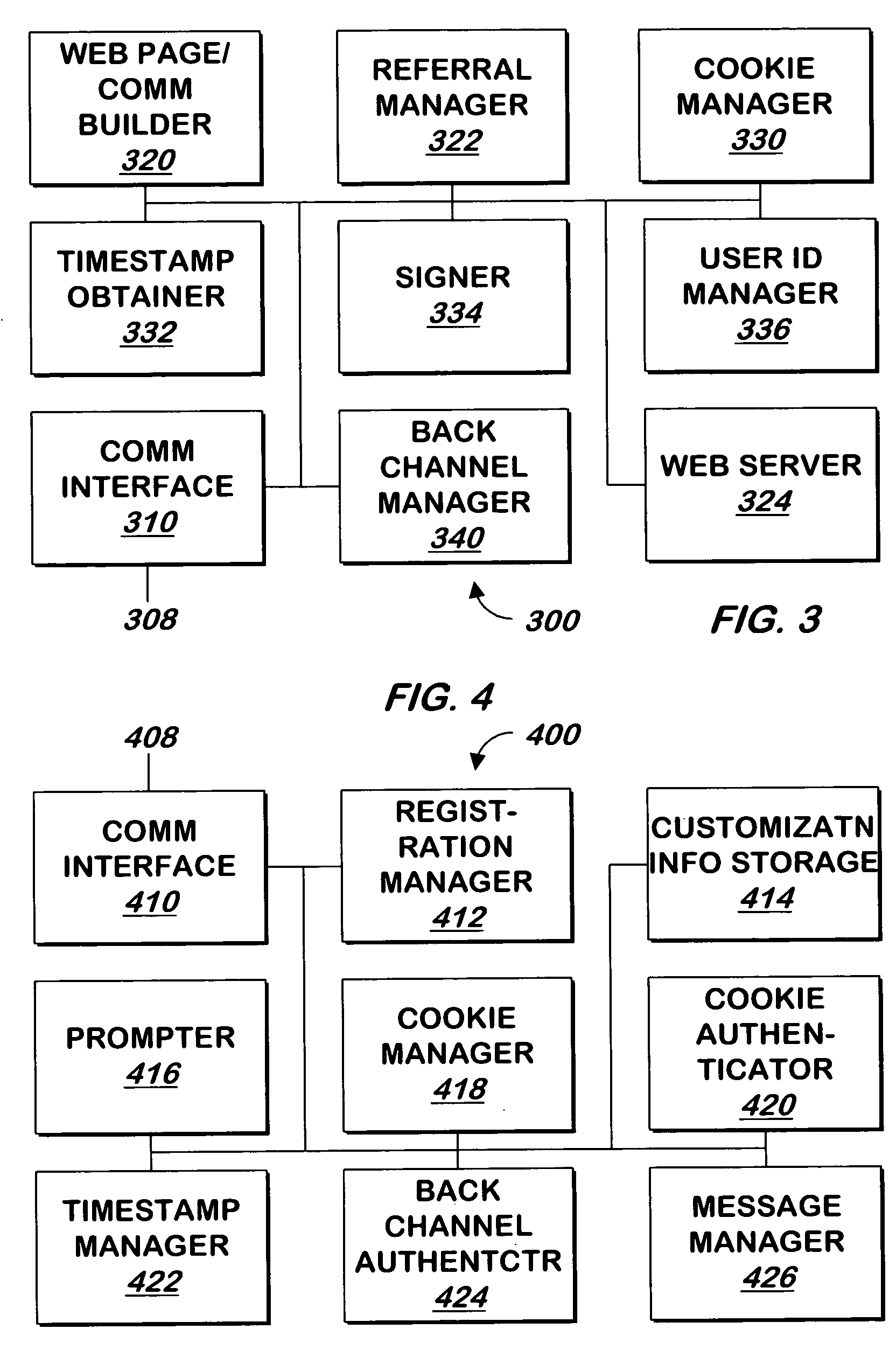
Patents
Literature
1408 results about "Shared secret" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
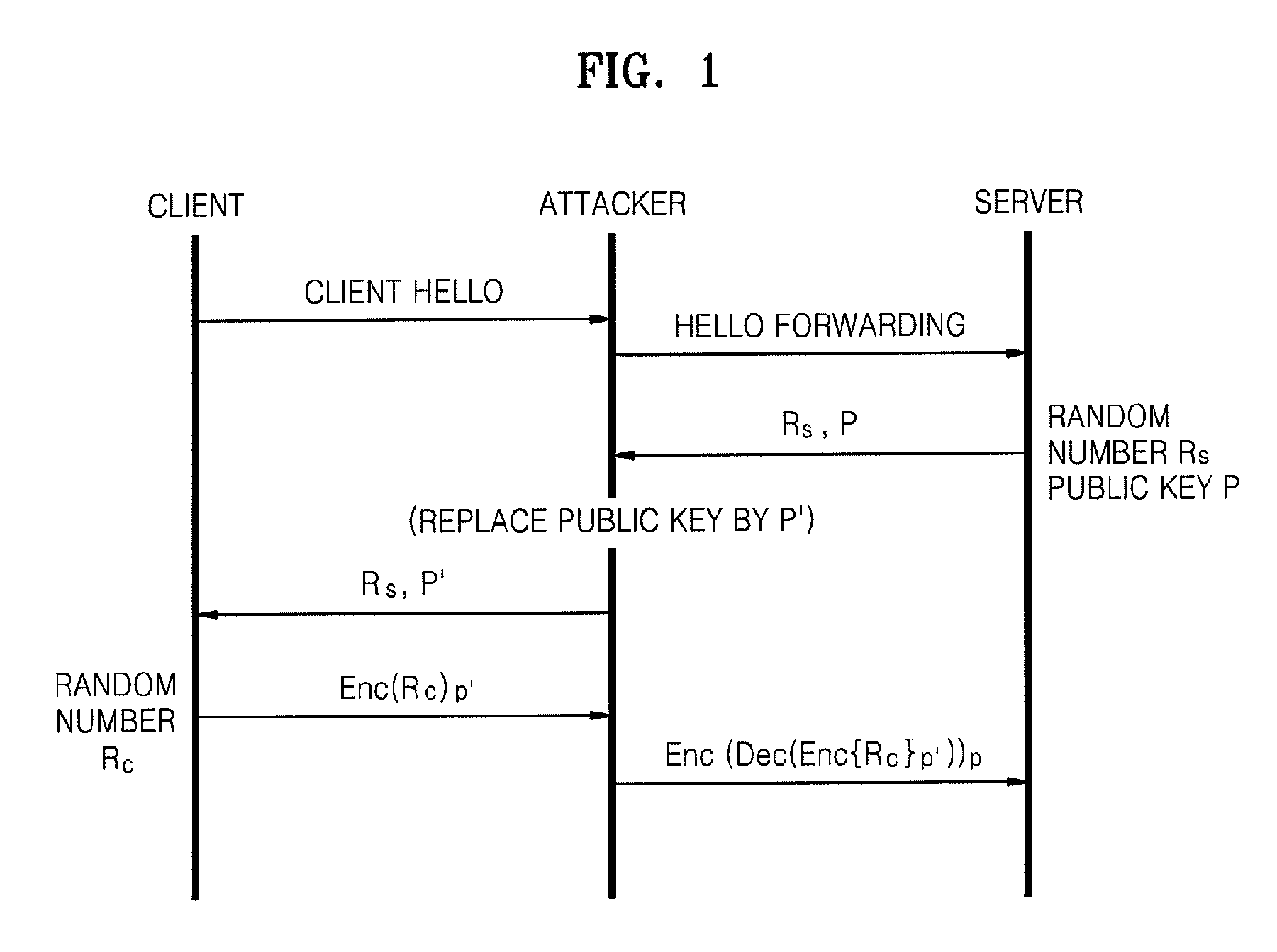
In cryptography, a shared secret is a piece of data, known only to the parties involved, in a secure communication. This usually refers to the key of a symmetric cryptosystem. The shared secret can be a password, a passphrase, a big number or an array of randomly chosen bytes.
Methods for secure cryptogram generation
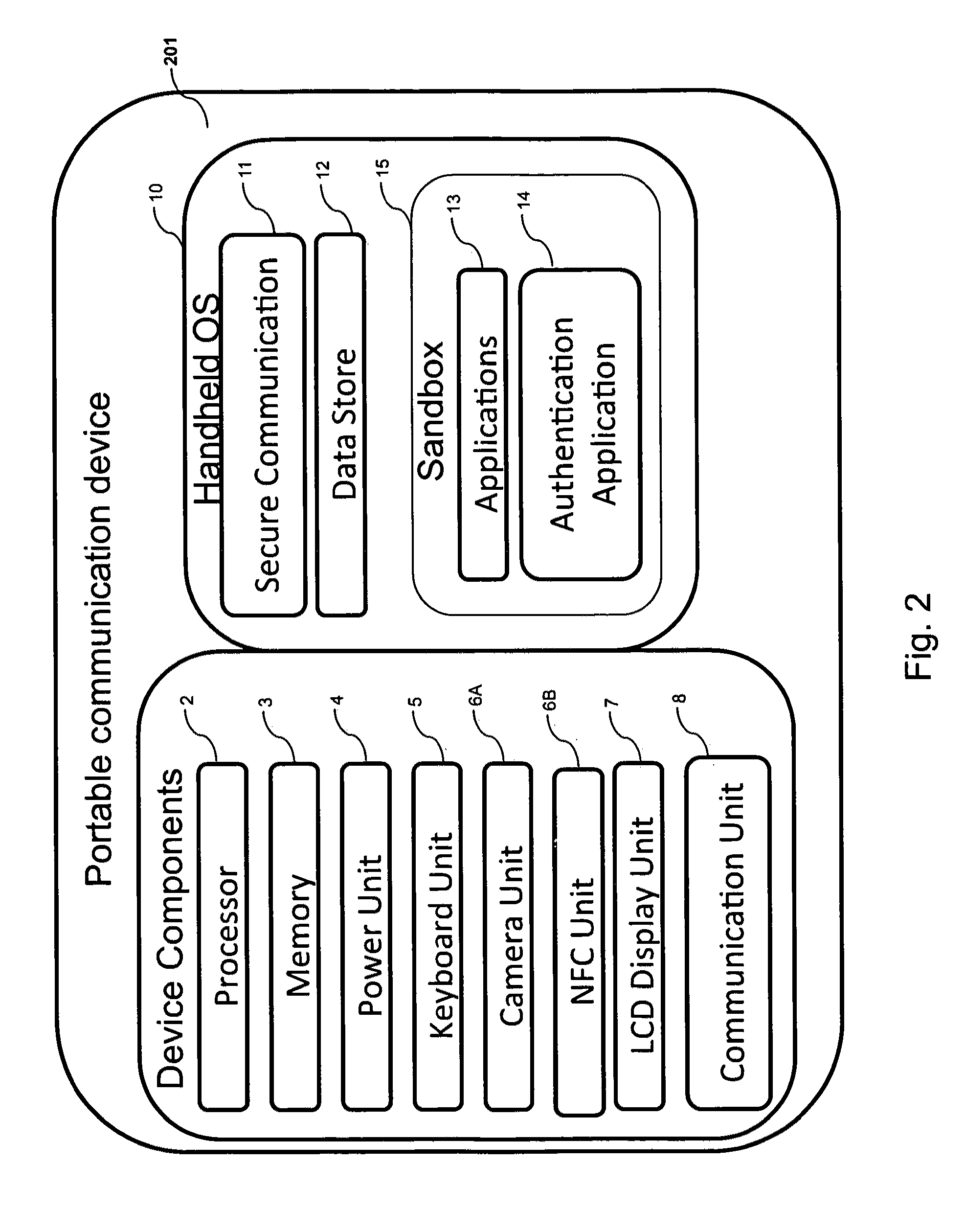
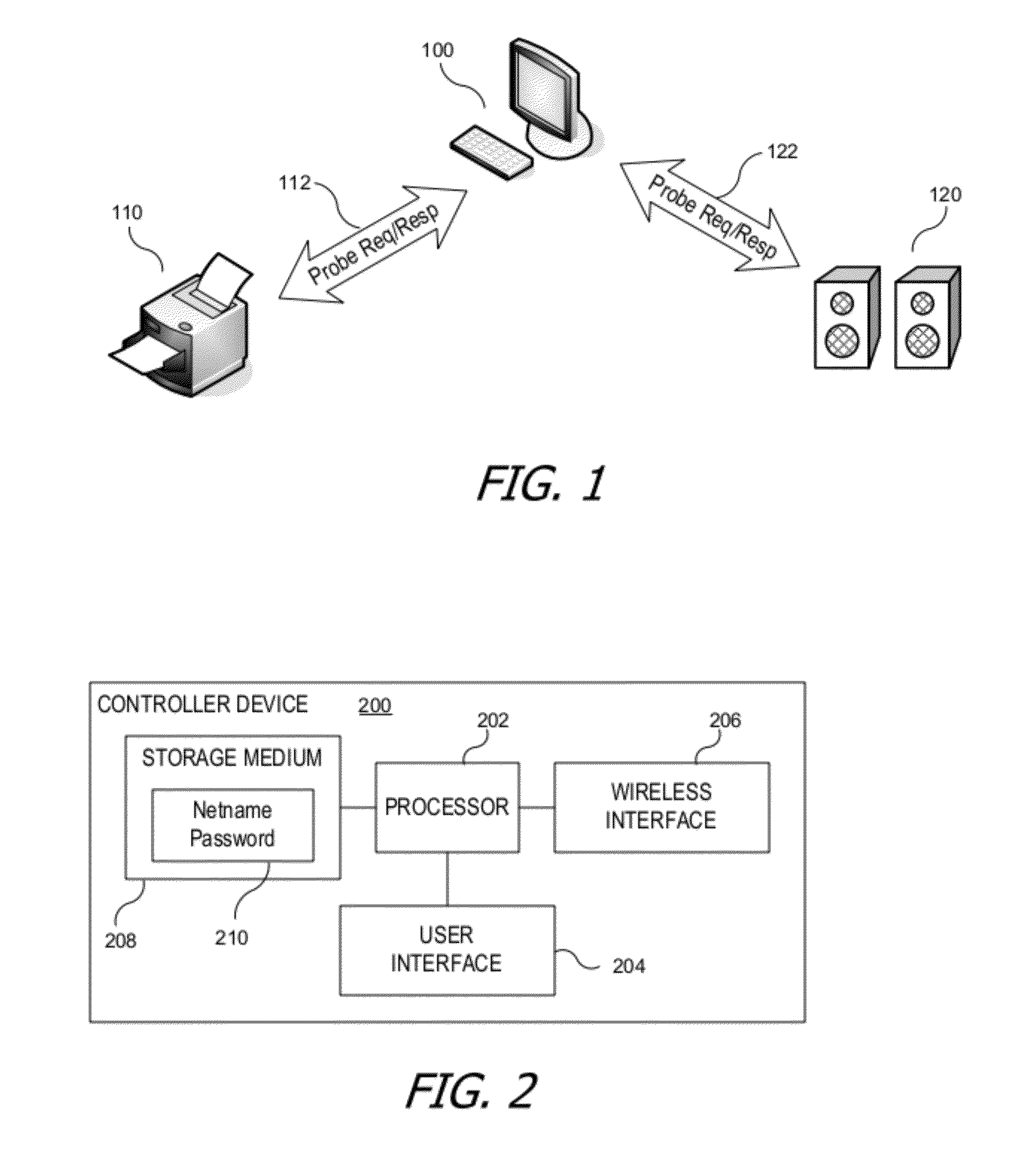
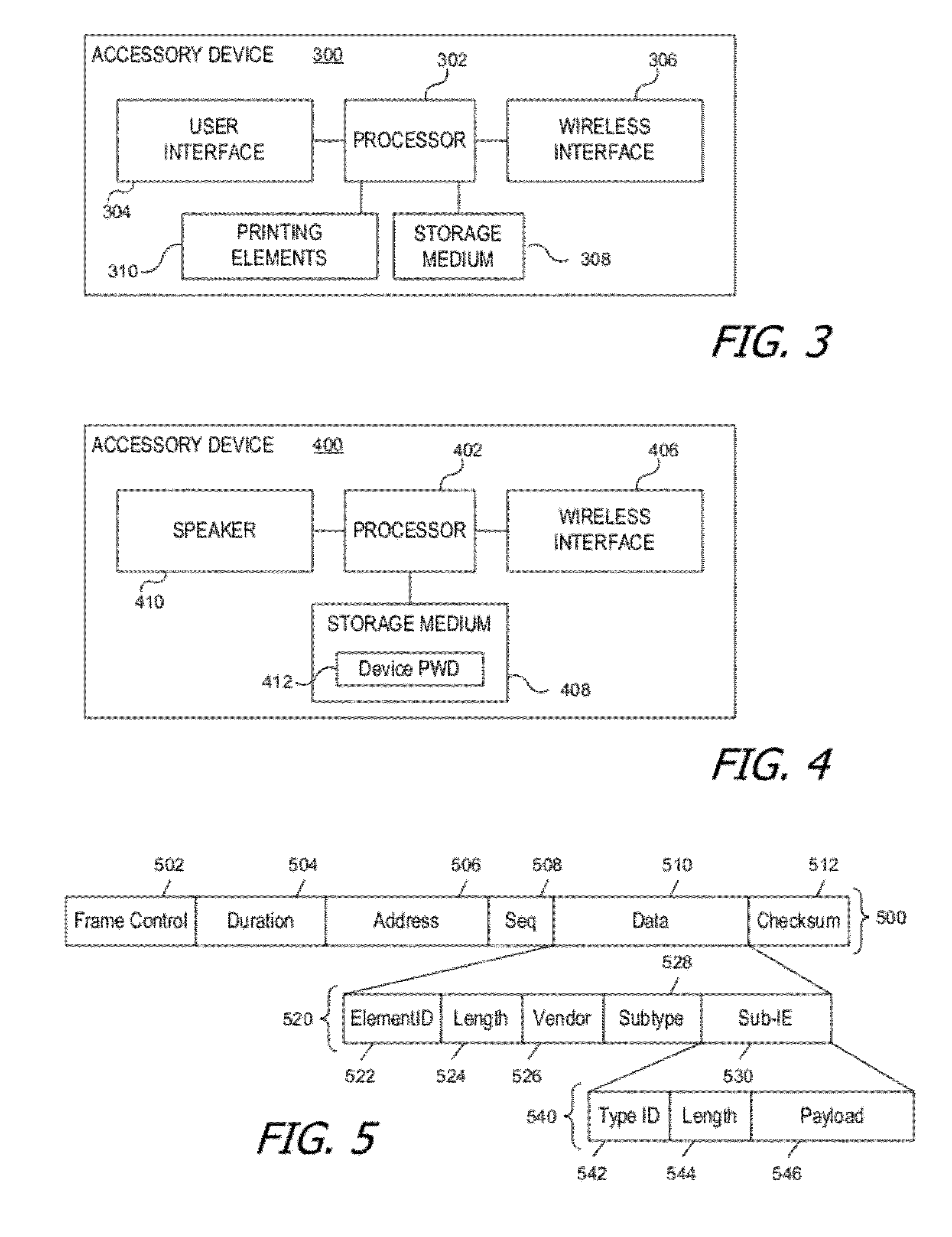
ActiveUS20160065370A1Avoid attackKey distribution for secure communicationMultiple keys/algorithms usageSecure communicationUser device
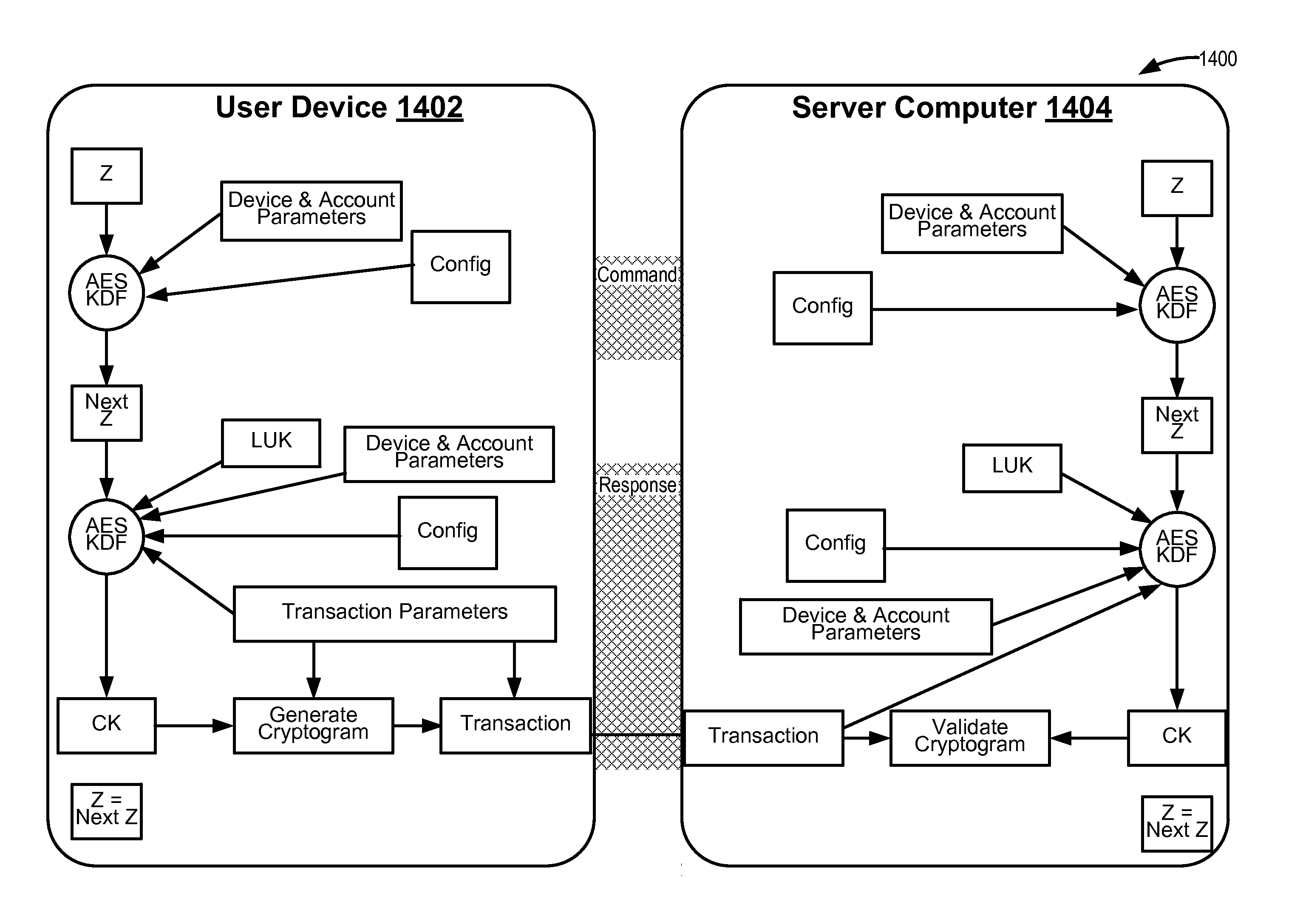
Embodiments of the invention introduce efficient methods for securely generating a cryptogram by a user device, and validating the cryptogram by a server computer. In some embodiments, a secure communication can be conducted whereby a user device provides a cryptogram without requiring the user device to persistently store an encryption key or other sensitive data used to generate the cryptogram. For example, the user device and server computer can mutually authenticate and establish a shared secret. Using the shared secret, the server computer can derive a session key and transmit key derivation parameters encrypted using the session key to the user device. The user device can also derive the session key using the shared secret, decrypt the encrypted key derivation parameters, and store the key derivation parameters. Key derivation parameters and the shared secret can be used to generate a single use cryptogram key. The cryptogram key can be used to generate a cryptogram for conducting secure communications.
Owner:VISA INT SERVICE ASSOC
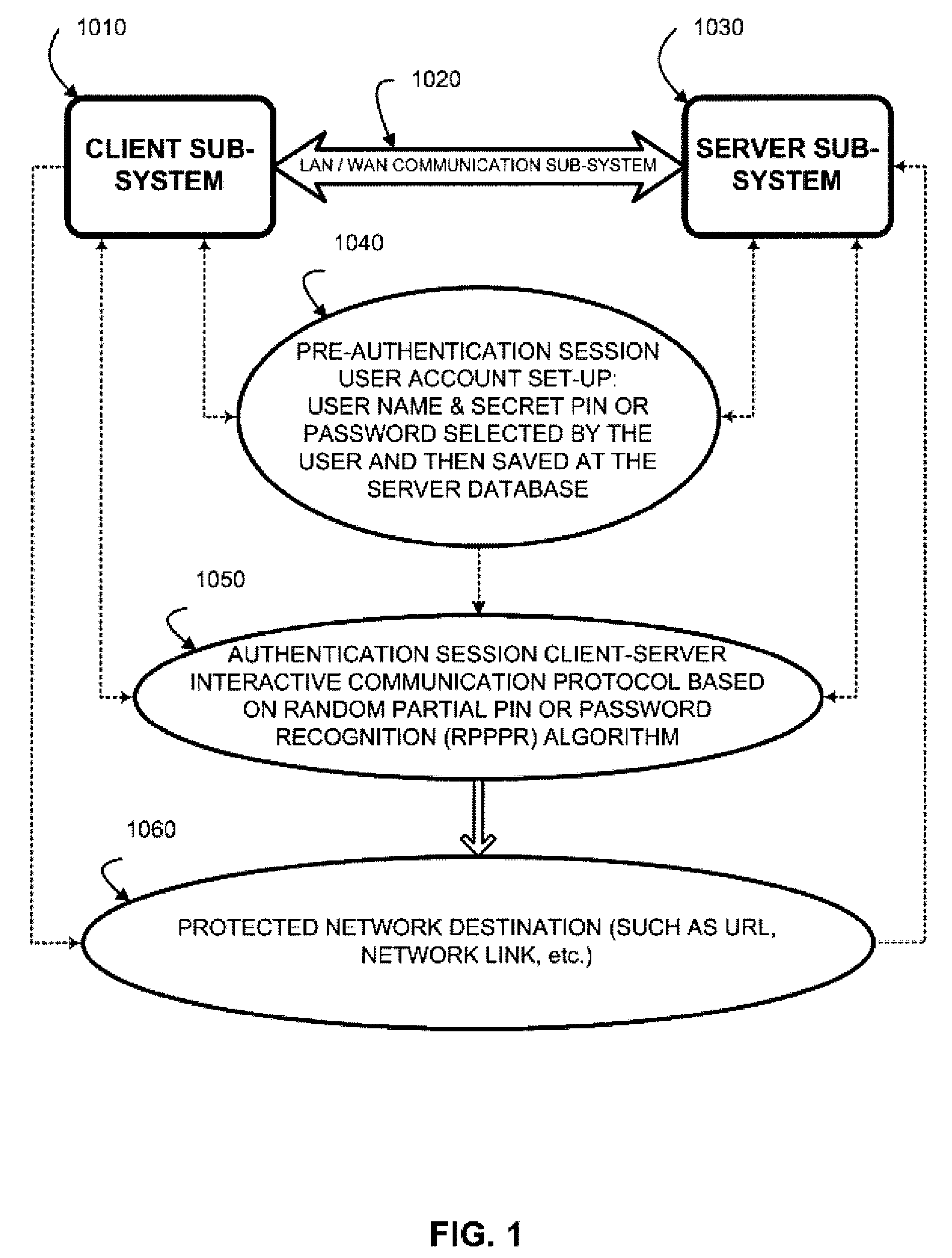
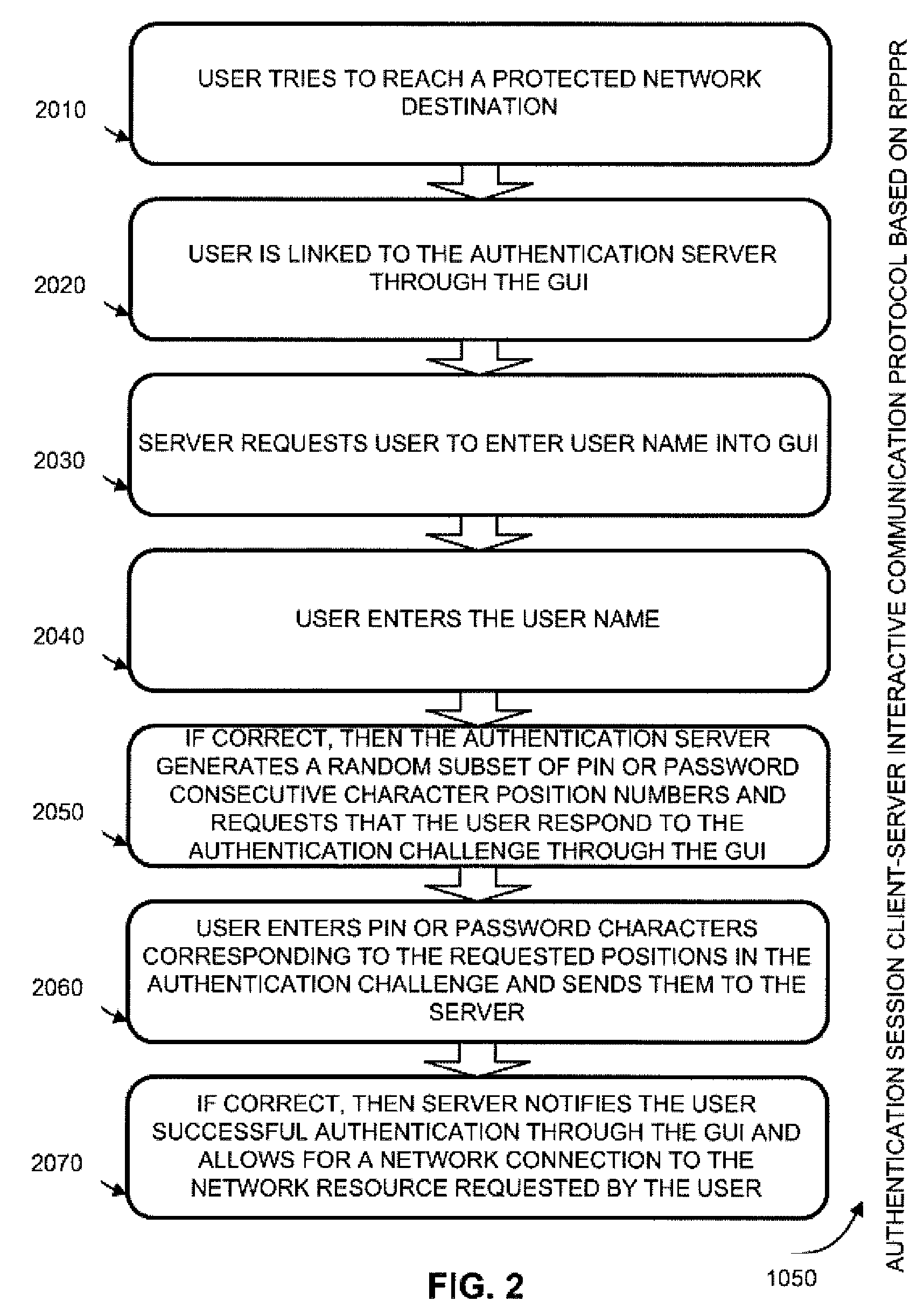
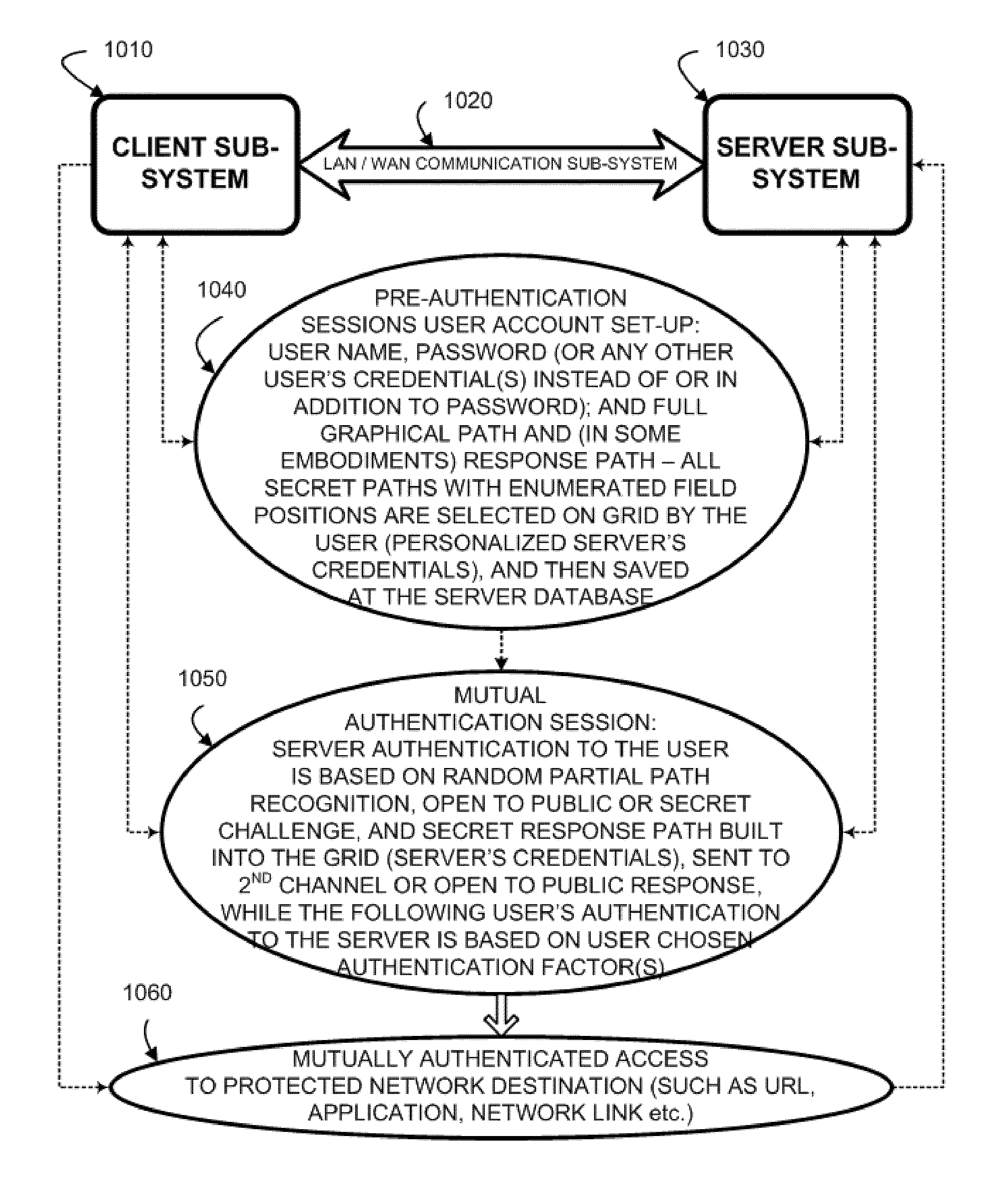
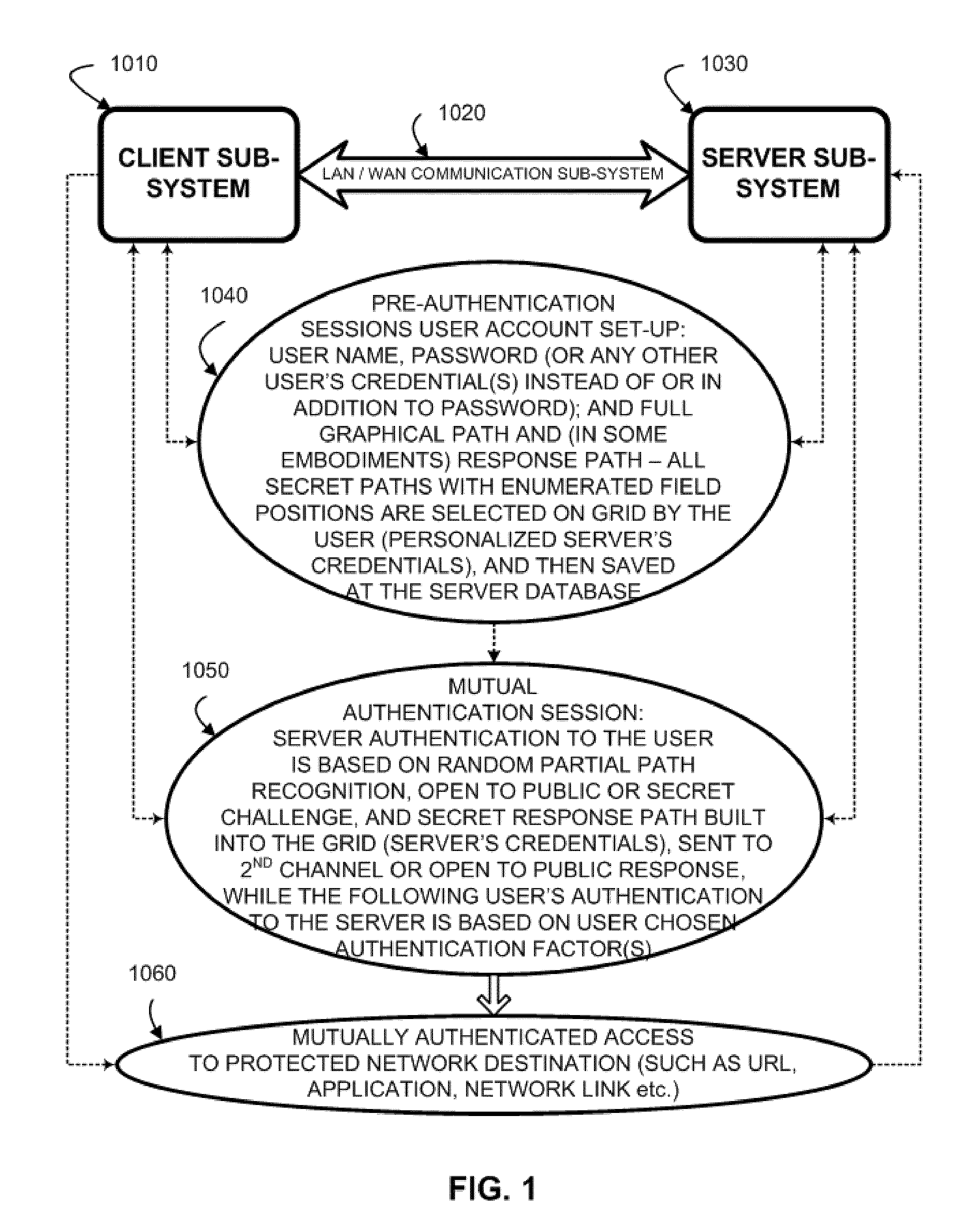
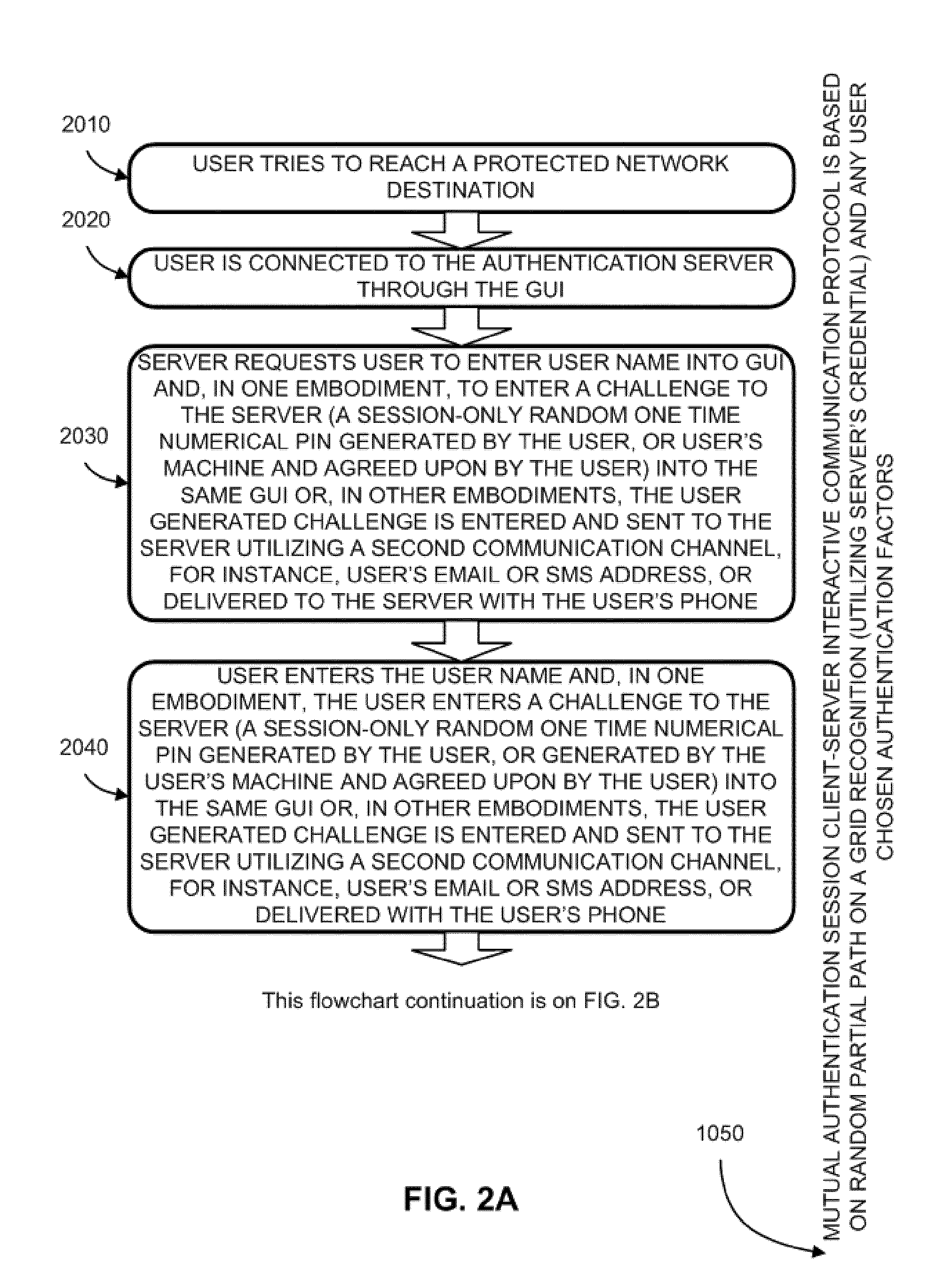
Two-channel challenge-response authentication method in random partial shared secret recognition system
ActiveUS20080098464A1Random number generatorsUser identity/authority verificationClient-sideServer-side
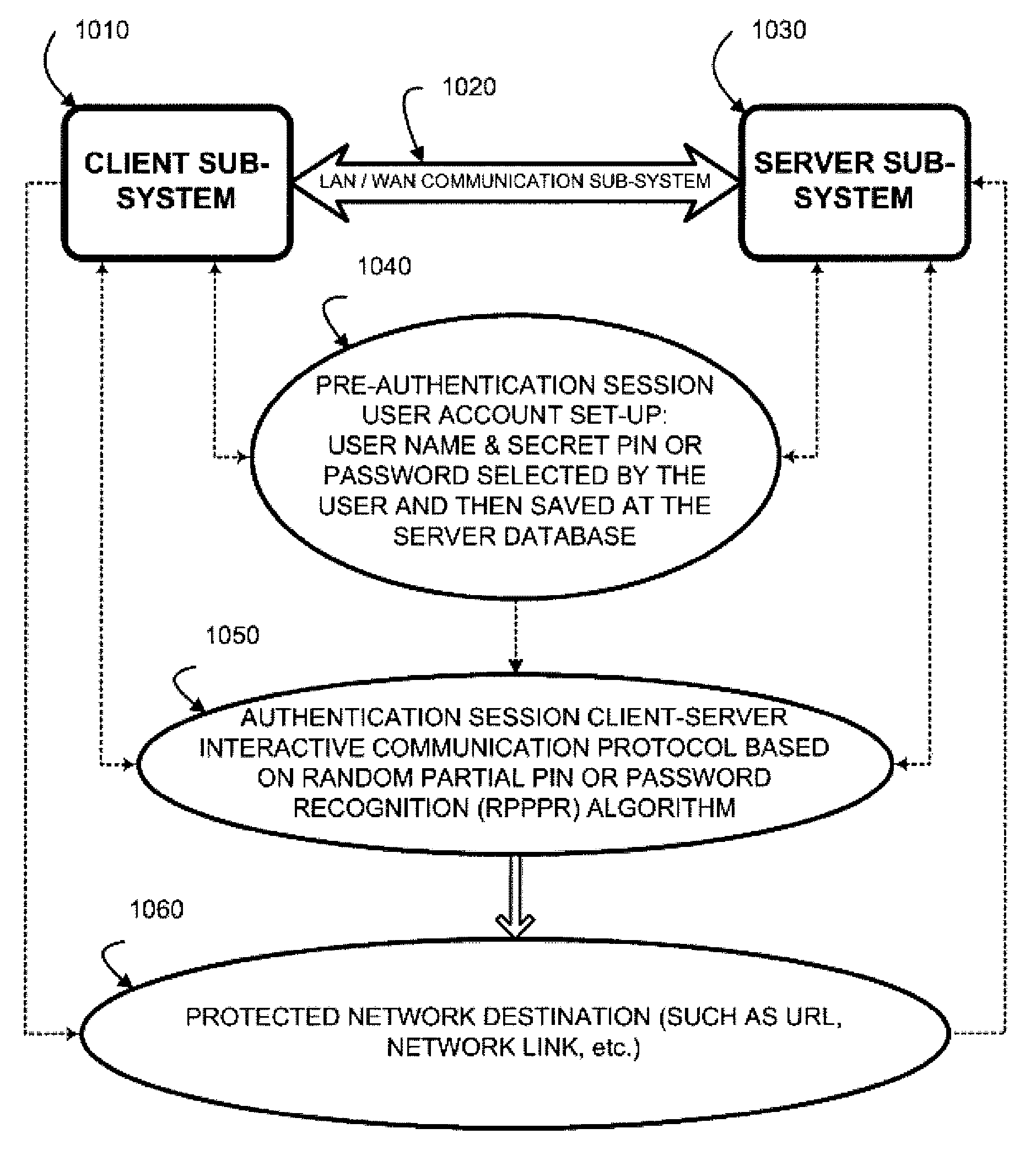
Random partial shared secret recognition is combined with using more than one communication channel between server-side resources and two logical or physical client-side data processing machines. After a first security tier, a first communication channel is opened to a first data processing machine on the client side. The session proceeds by delivering an authentication challenge, identifying a random subset of an authentication credential, to a second data processing machine on the client side using a second communication channel. Next, the user enters an authentication response in the first data processing machine, based on a random subset of the authentication credential. The authentication response is returned to the server side on the first communication channel for matching. The authentication credential can be a one-session-only credential delivered to the user for one session, or a static credential used many times.
Owner:AUTHERNATIVE INC
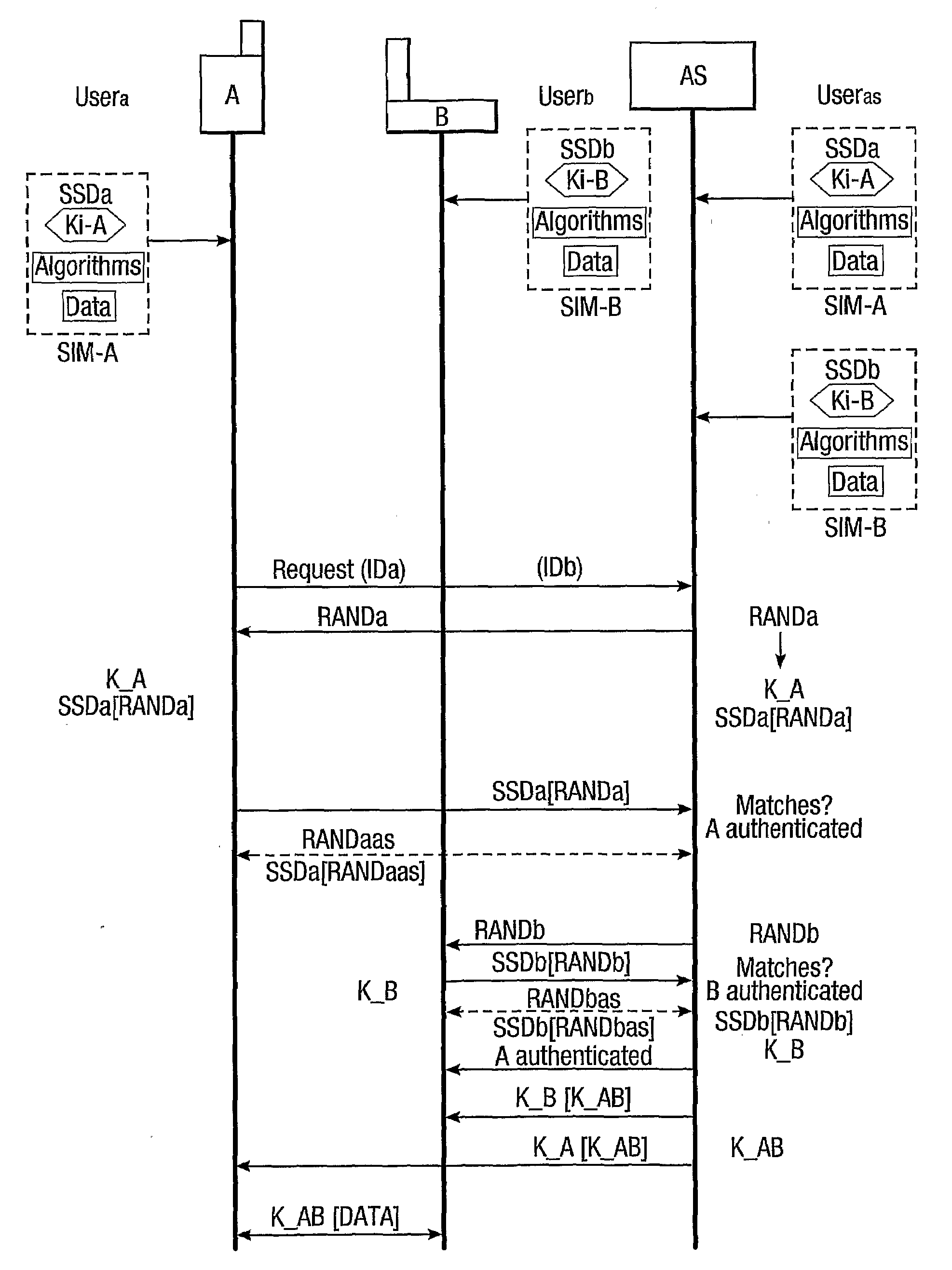
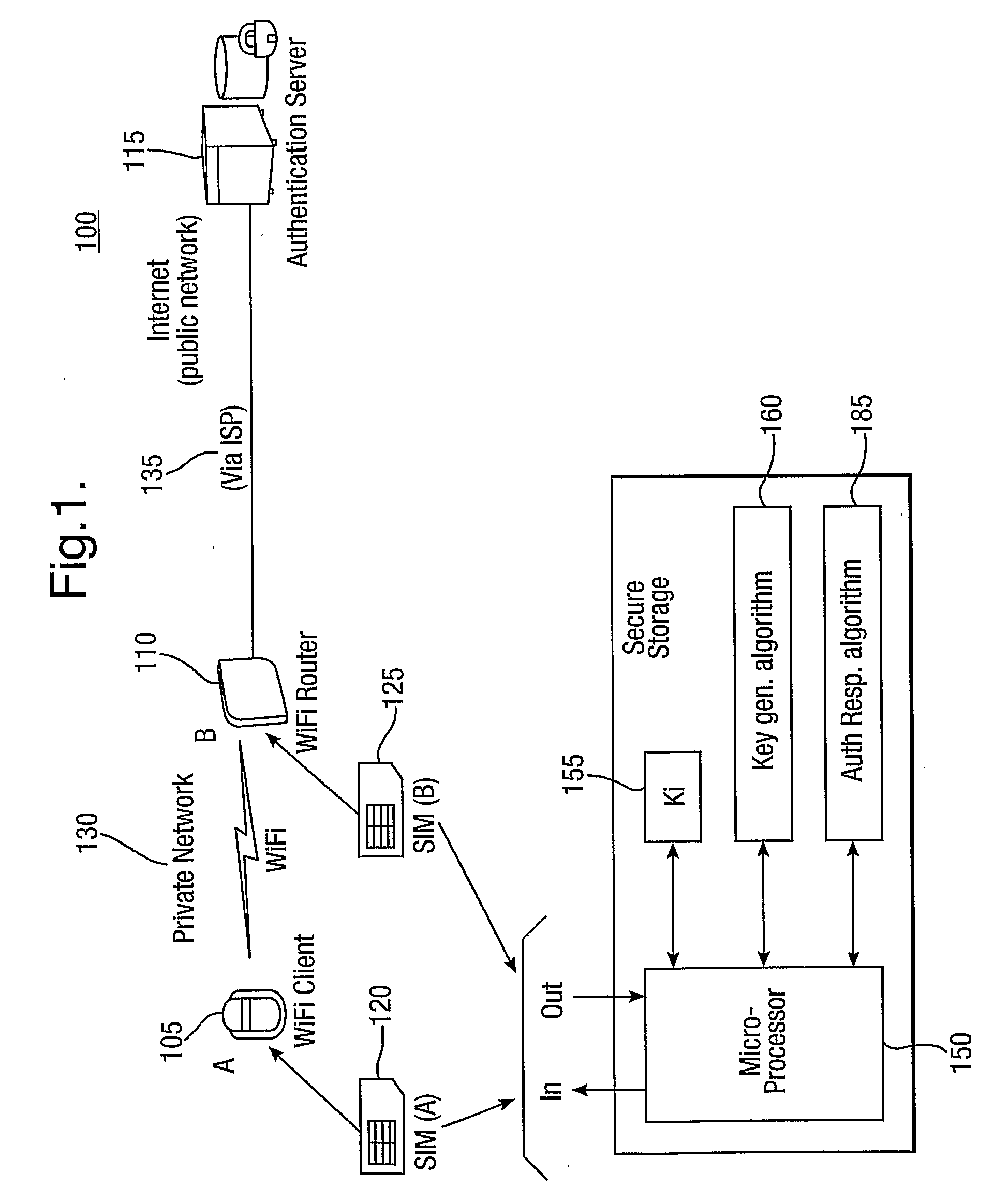
Provision of secure communications connection using third party authentication
ActiveUS20090287922A1Connection securityCommunication securityKey distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationThird partySecure communication
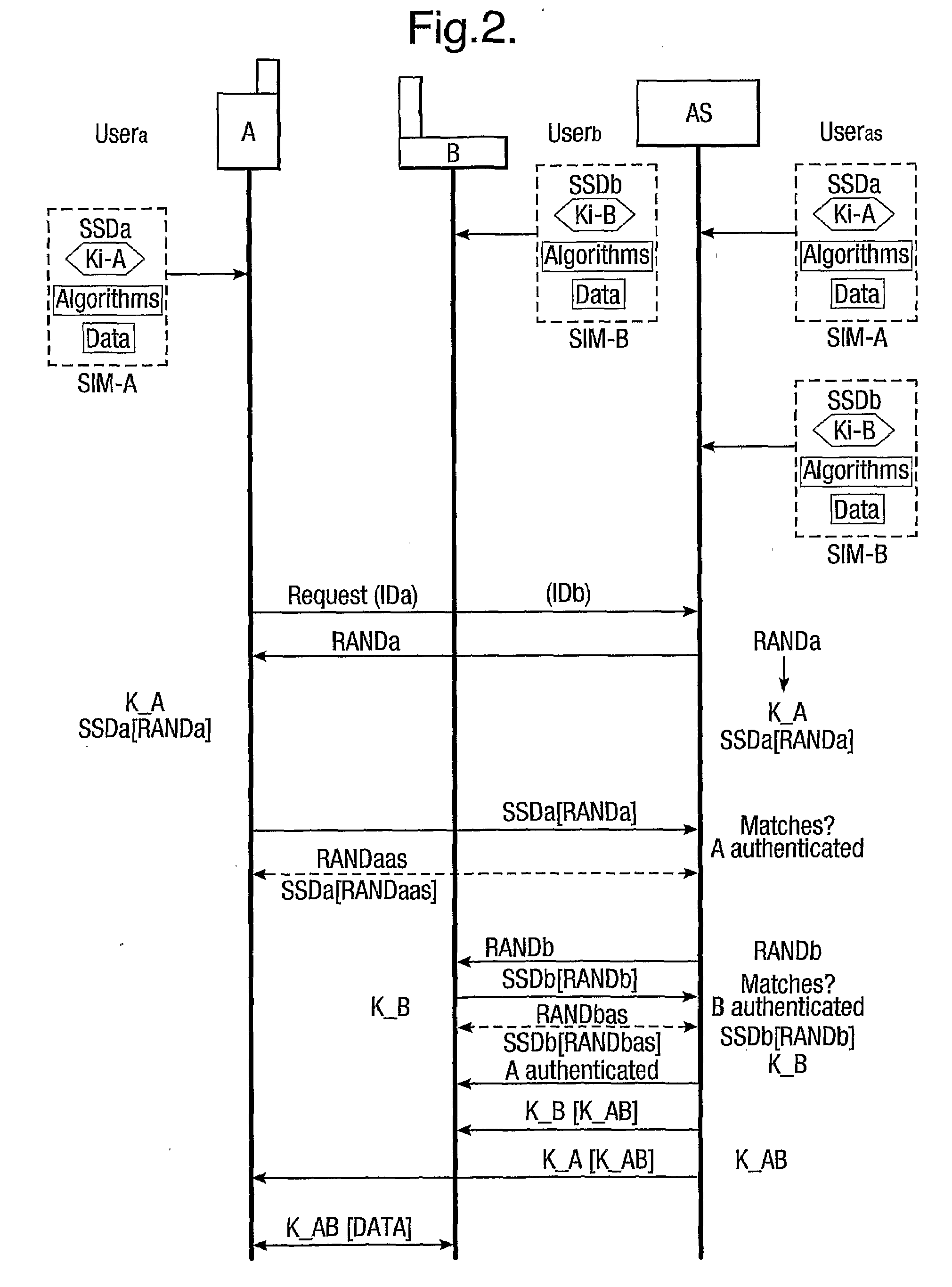
The present invention relates to communications, and in particular though not exclusively to forming a secure connection between two untrusted devices. The present invention provides a method of securely connecting a first device (A) to a second device (B) using a third party authentication server (AS) coupled to the second device, the first device and the authentication server both having first device shared secret data (SSDa) and the second device and the authentication server both having second device shared secret data (SSDb). The method comprises receiving a request from the first device at the authentication server; the authentication server and the first device both generating a first device key (K_A) using the first device shared secret data in response to a first device random number (RANDa) sent from the authentication server to the first device; the authentication server and the second device both generating a second device key (K_B) using the second device shared secret data in response to a second device random number (RANDb) sent from the authentication server to the second device; and the authentication server securely forwarding to the second device (B) and the first device (A) a common key (K_AB) using the second and first device keys (K_B, K_A).
Owner:BRITISH TELECOMM PLC
System, design and process for strong authentication using bidirectional OTP and out-of-band multichannel authentication
ActiveUS8763097B2Digital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsOutbound communicationBarcode
Owner:GCOM IP LLC
Methods, apparatus and computer programs performing a mutual challenge-response authentication protocol using operating system capabilities
InactiveUS20030093680A1Avoids security exposureMeet growth requirementsKey distribution for secure communicationDigital data processing detailsOperational systemCrypt
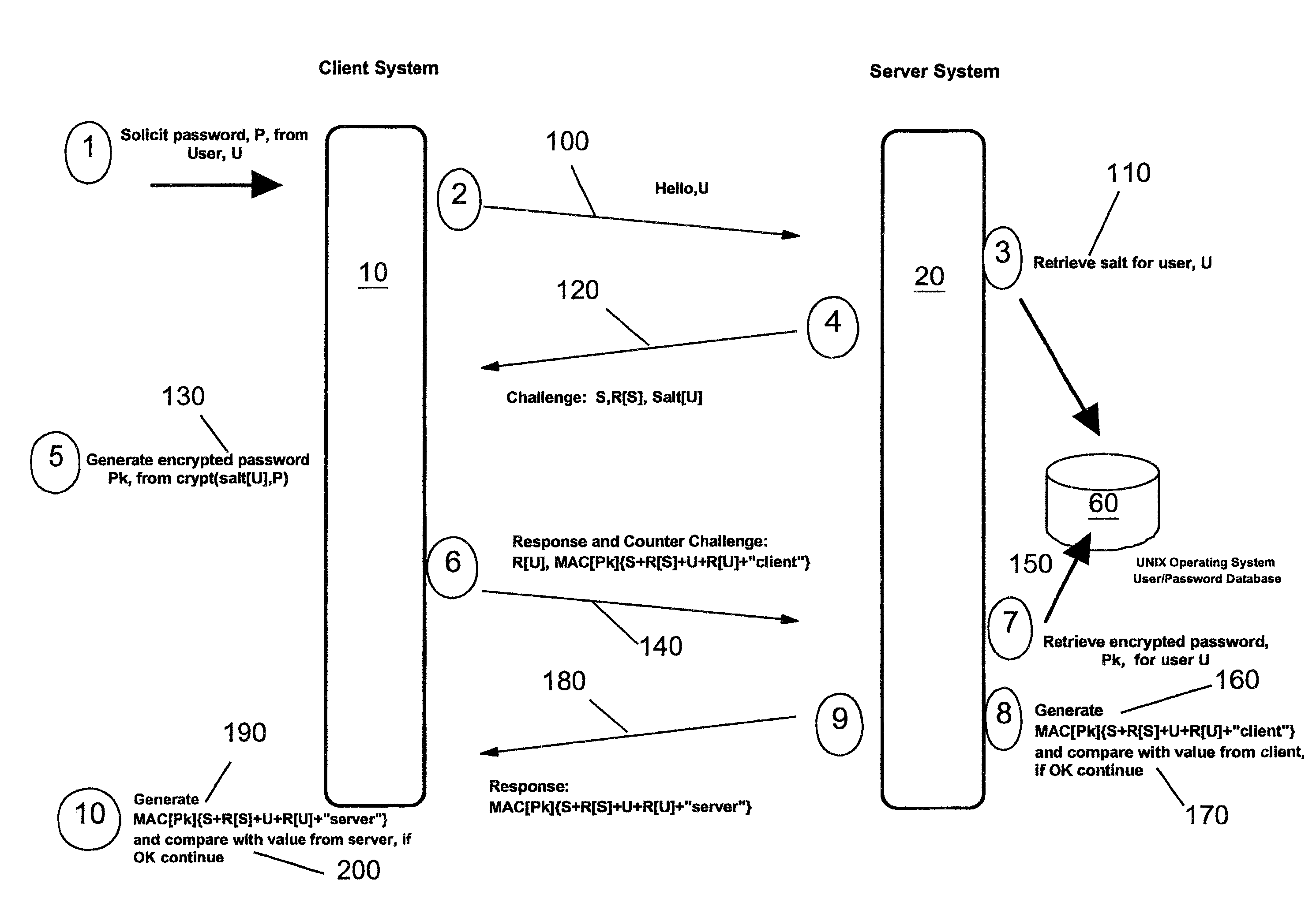
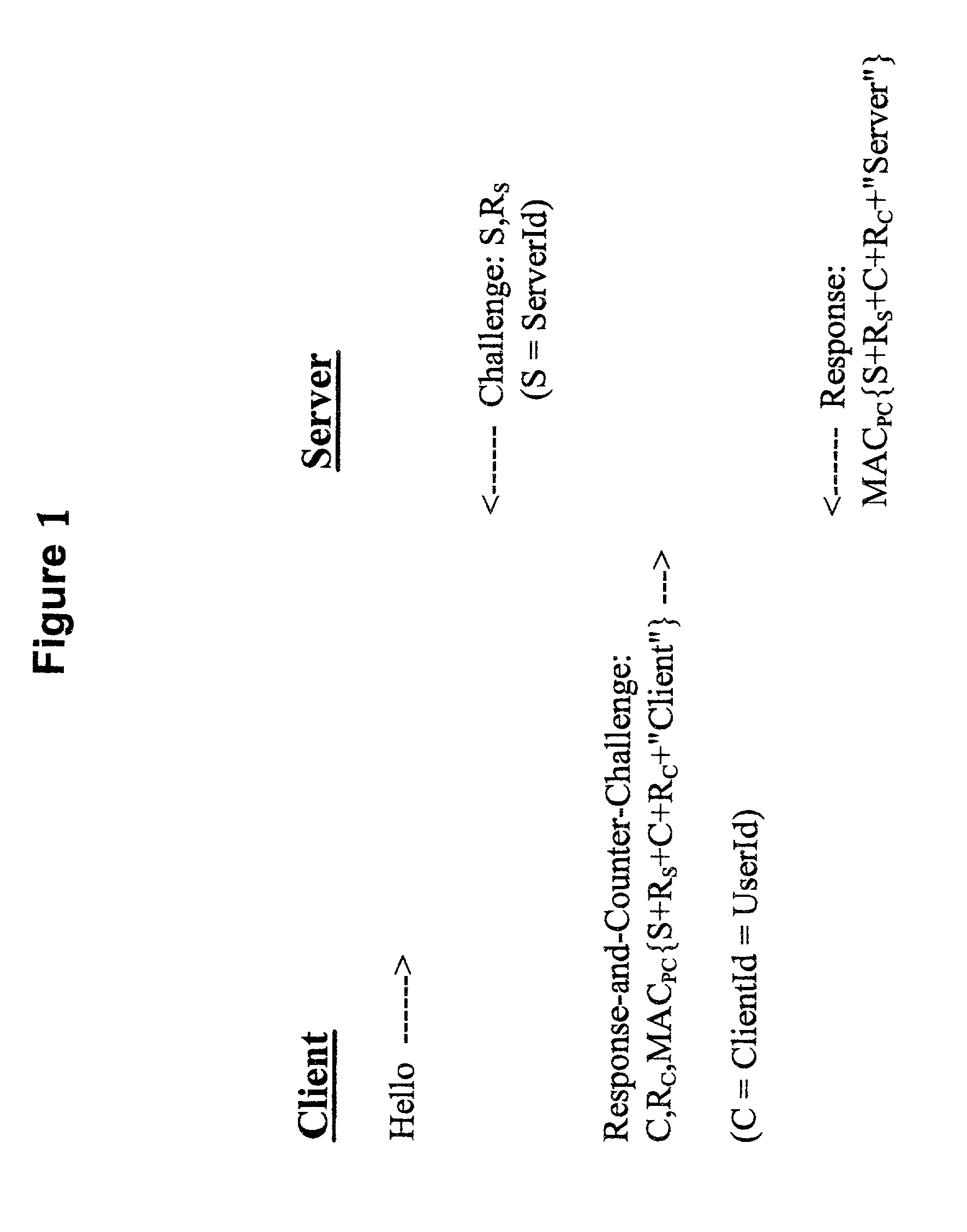
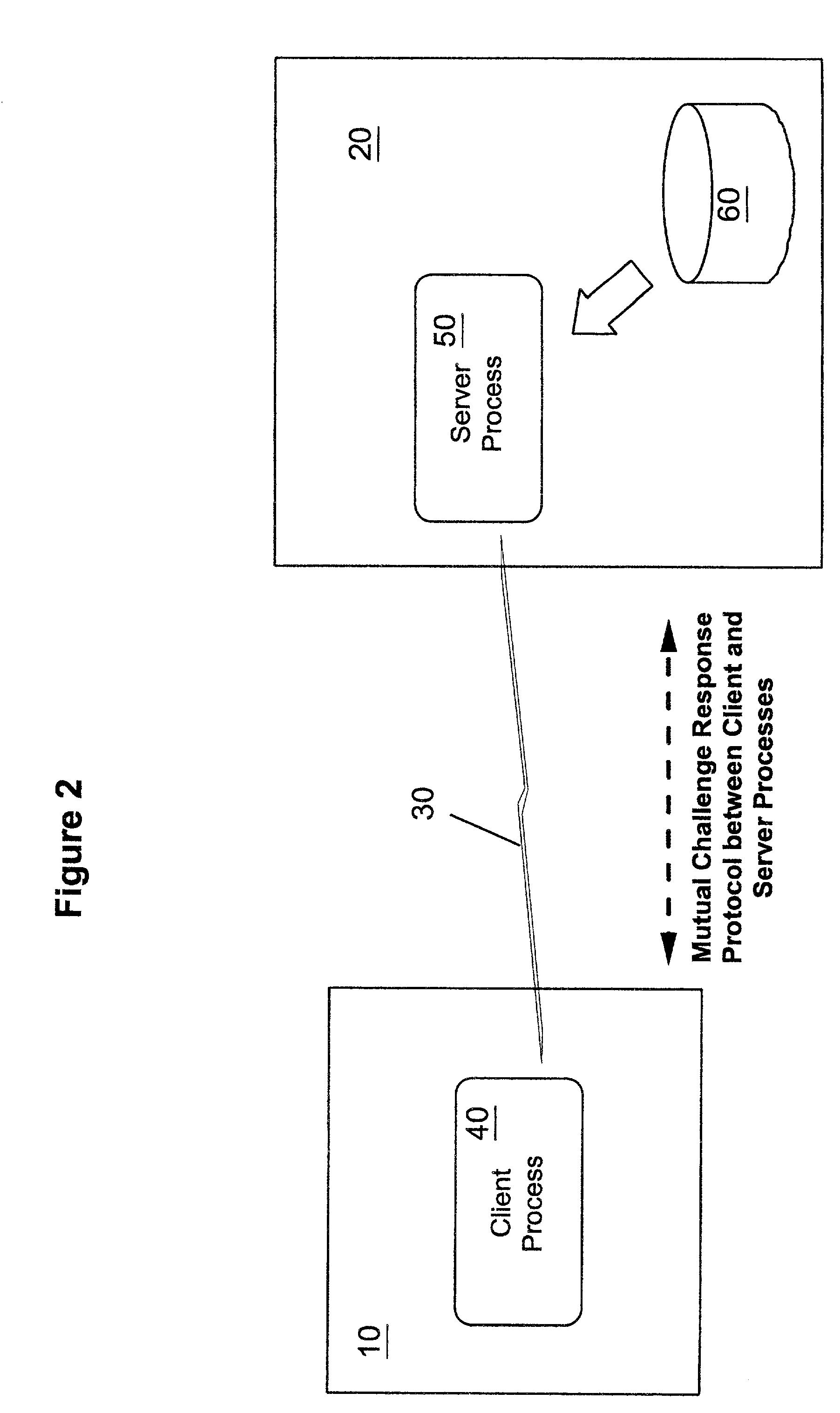
A client-server authentication method for use where a server process has access to a repository storing cipher-protected client passwords. The method includes applying the same cipher function to the client's copy of its password as was previously applied to generate the stored cipher-protected client passwords. This ensures that both the client and server have access to an equivalent cipher-protected client password-providing a shared secret for driving a mutual challenge-response authentication protocol without having to convert the password into cleartext at the server. The invention can be implemented without significant additional software infrastructure in a UNIX environment. Client passwords are typically stored in the UNIX password repository under the protection of the crypt( ) function applied to the combination of the password and a random number (a "salt'). By sending the salt to the client system together with the server's initial challenge of the authentication protocol, a process at the client is able to apply the crypt( ) function to the client password with the same salt such that the client and server have a shared secret for use as, or to generate, a common session key for the authentication.
Owner:IBM CORP
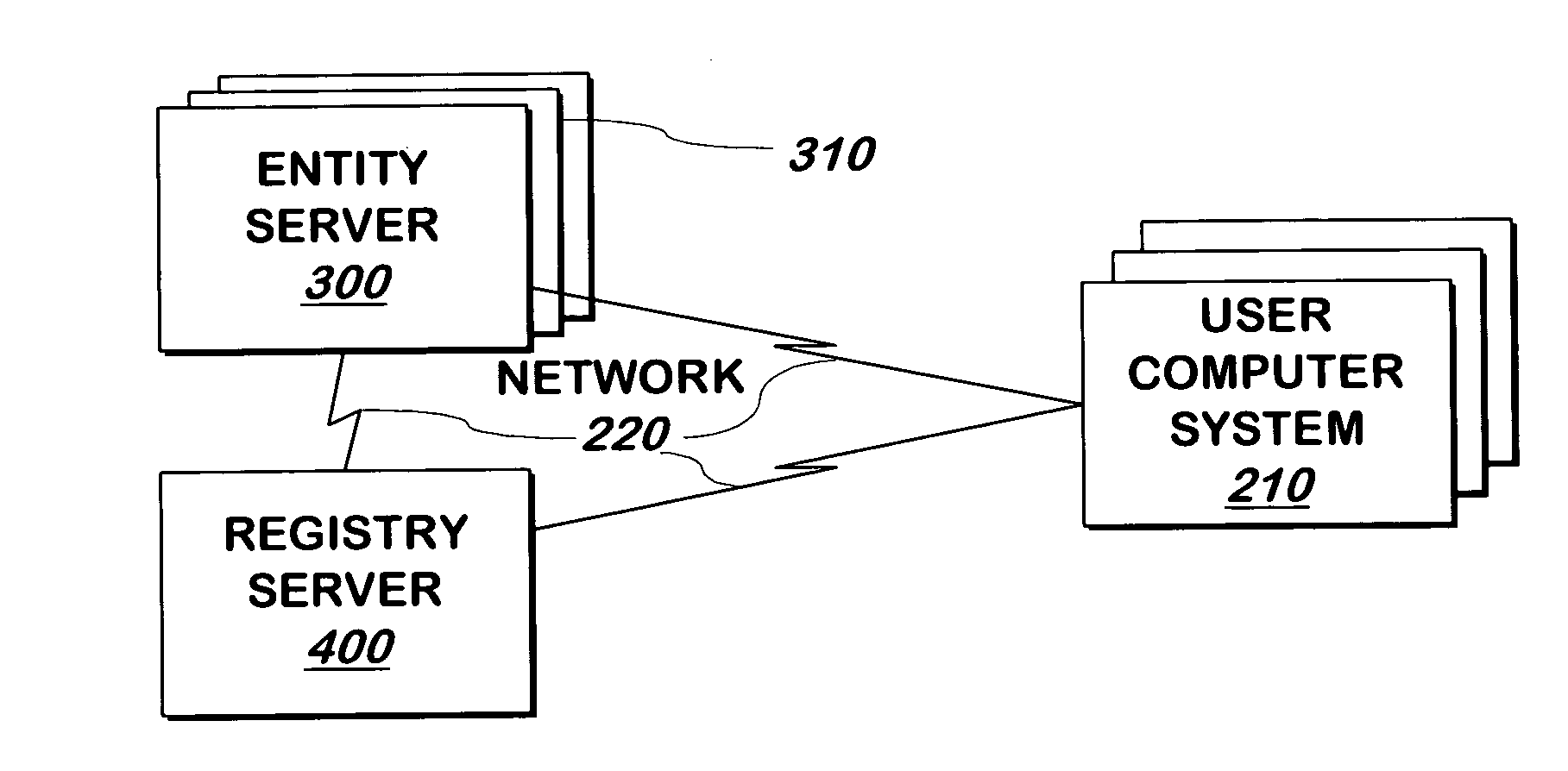
System and method for authenticating entities to users
InactiveUS7562222B2Digital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationUser verificationWindows Registry
A system and method communicates information from an entity that a registry can use to authenticate the entity to a user. If the registry authenticates the entity, it displays information that represents a shared secret between the registry and the user.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
System and method for authenticating entities to users
InactiveUS20050268100A1Digital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationUser verificationWindows Registry
A system and method communicates information from an entity that a registry can use to authenticate the entity to a user. If the registry authenticates the entity, it displays information that represents a shared secret between the registry and the user.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
Group key distribution
InactiveUS6038322AEfficient additionLow costKey distribution for secure communicationPublic key for secure communicationTimestampNetwork addressing
A method for distributing a secret key from a key holder H to intended group members M. The method assumes that during the distribution process each party, a group member M and the key holder H, can decrypt and encrypt exchanged information such that the encrypter knows that the decrypter will be the intended party. The method preferably uses a public key / private key encryption technique in which, for example, a trusted Certificate Authority in a public key infrastructure signs the certificates to provide the public keys involved in the encryption. Alternatively, the method, together with a symmetric cipher, uses a shared secret, established in an authenticated mechanism that is outside the information exchanges of the invention. Additionally, the method uses a strong mixing function that takes several items of data as input and produces a pseudo-random authentication (or digest). Inputs to the mixing function include identity stamps that are generated by each member M and key holder H. These inputs can be the identity of the stamp generator, such as a network address, port, or protocol, a timestamp, and / or a secret value that is known only to the stamp generator. The stamps include information to bind member M if generated by key holder H, and to bind key holder H if generated by member M. Consequently, the invention authenticates each communication exchange between member M and key holder H.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Methods and systems for secure user authentication
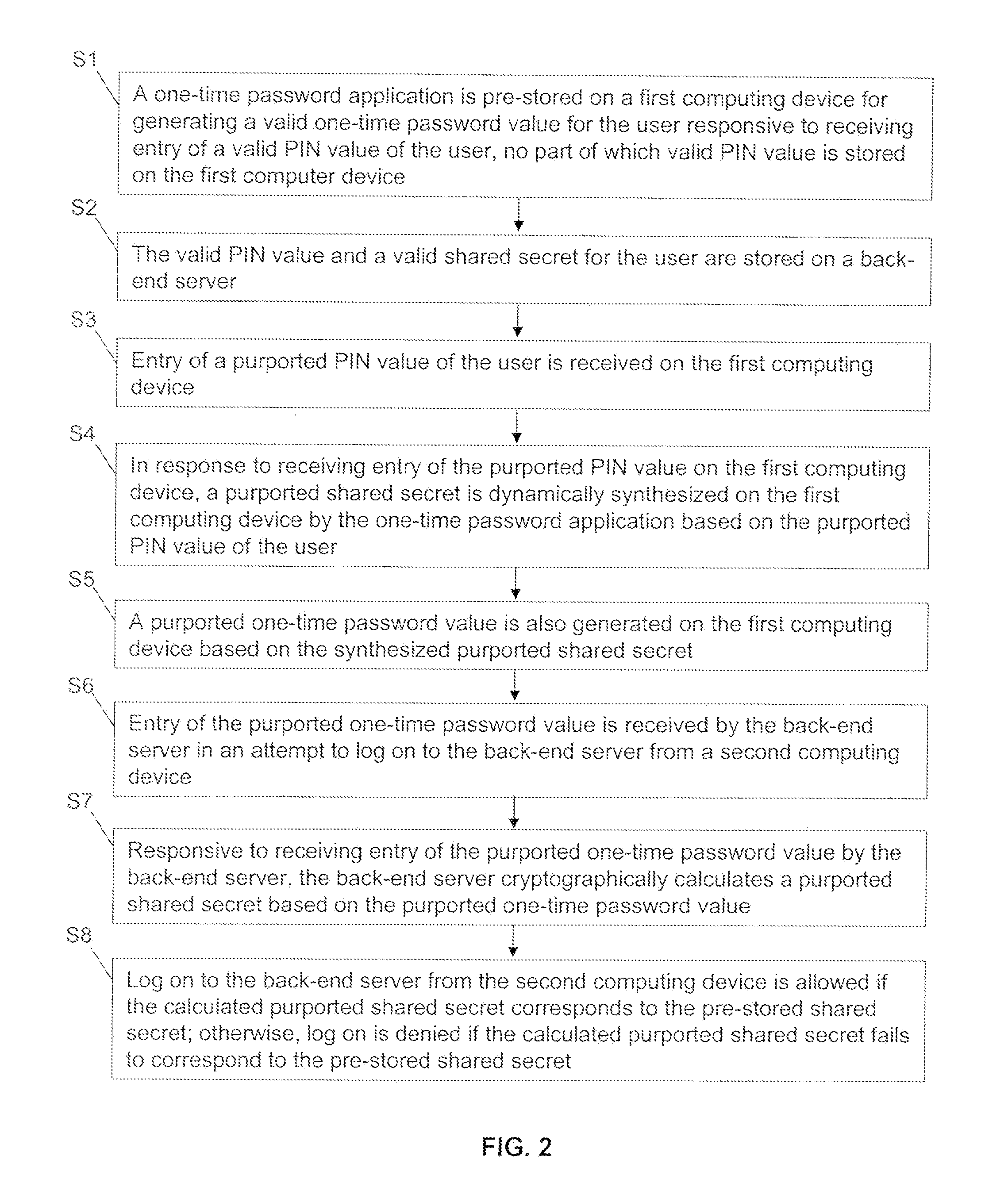
ActiveUS20110197266A1Reduce in quantityDigital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationUser authenticationBack end server
Methods and systems for secure user authentication using a OTP involve, for example, pre-storing a OTP application on a first computing device for generating a valid OTP value for the user responsive to receiving entry of a valid PIN value of the user, no part of the valid PIN value is stored on the first computing device and pre-storing on a back-end server the valid PIN value and a valid shared secret for the user. Upon receiving entry of a purported PIN value of the user, a purported shared secret is dynamically synthesized on the first computing device by the OTP application based on the purported PIN value of the user and a purported OTP value is generated on the first computing device. When entry of the purported OTP value is received by the back-end server in an attempt to log on the back-end server from a second computing device, the back-end server cryptographically calculates a window of OTP values, and log on to the back-end server from the second computing device is allowed if the calculated window of OTP values corresponds to the received OTP value.
Owner:CITICORP CREDIT SERVICES INC (USA)
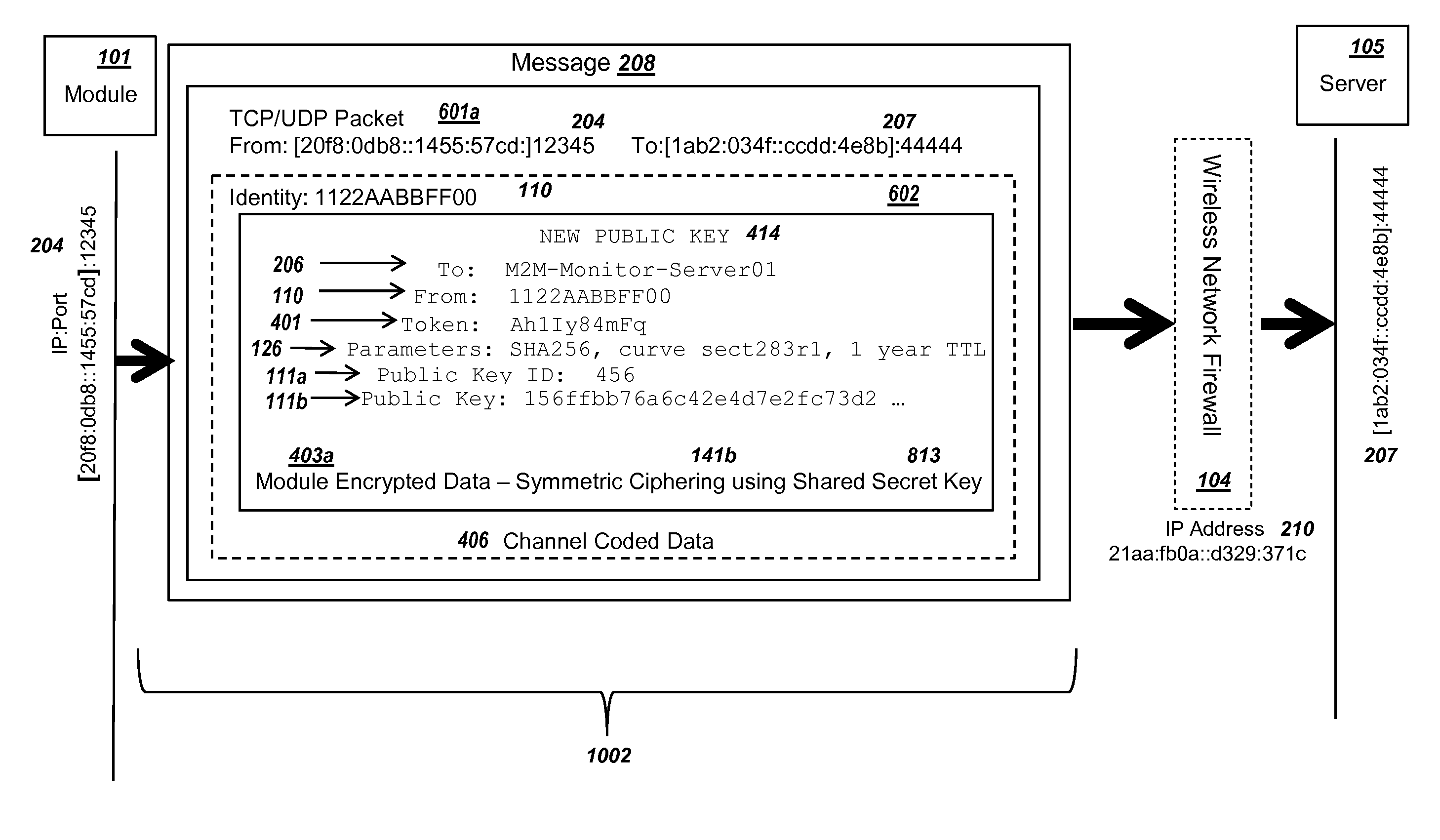
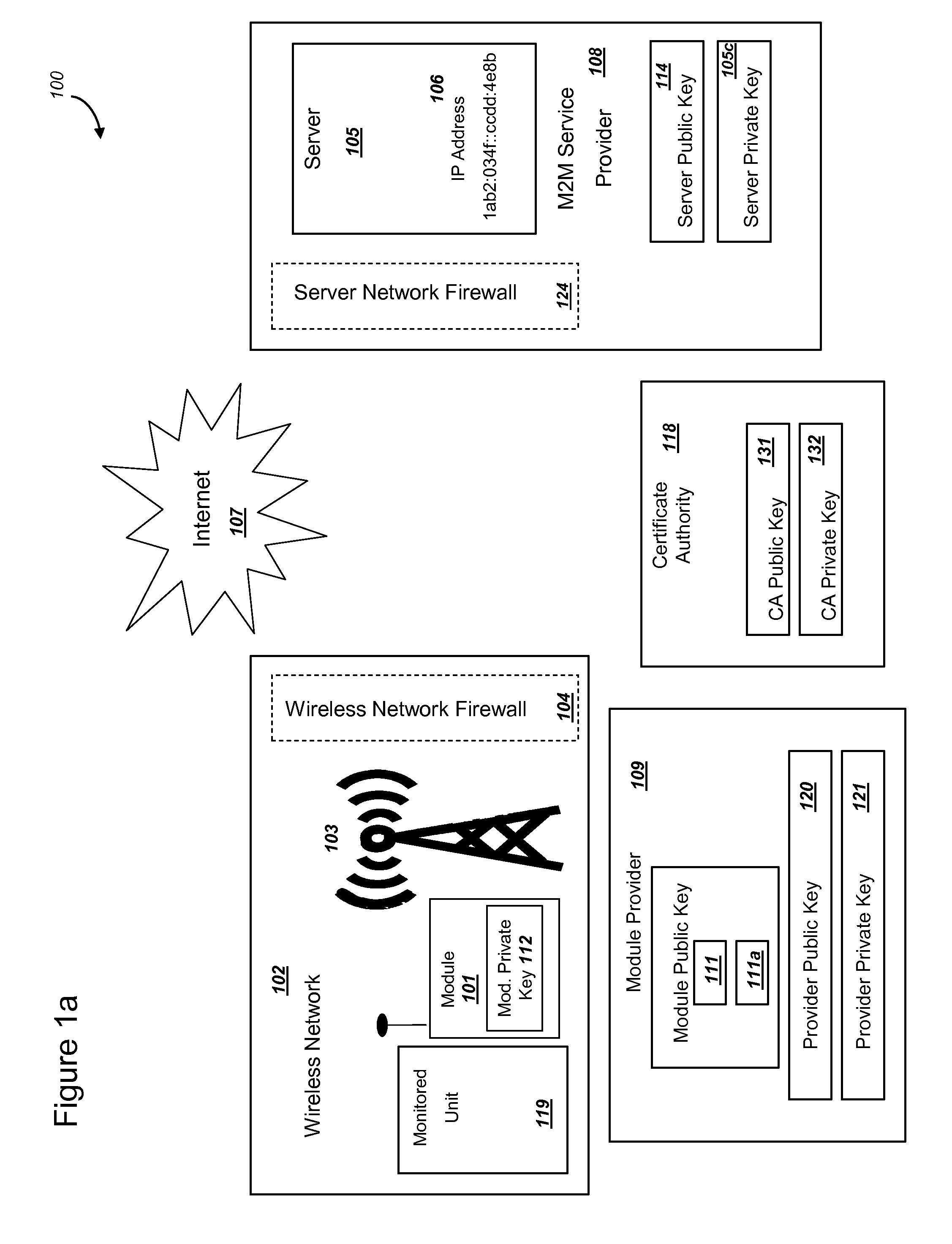
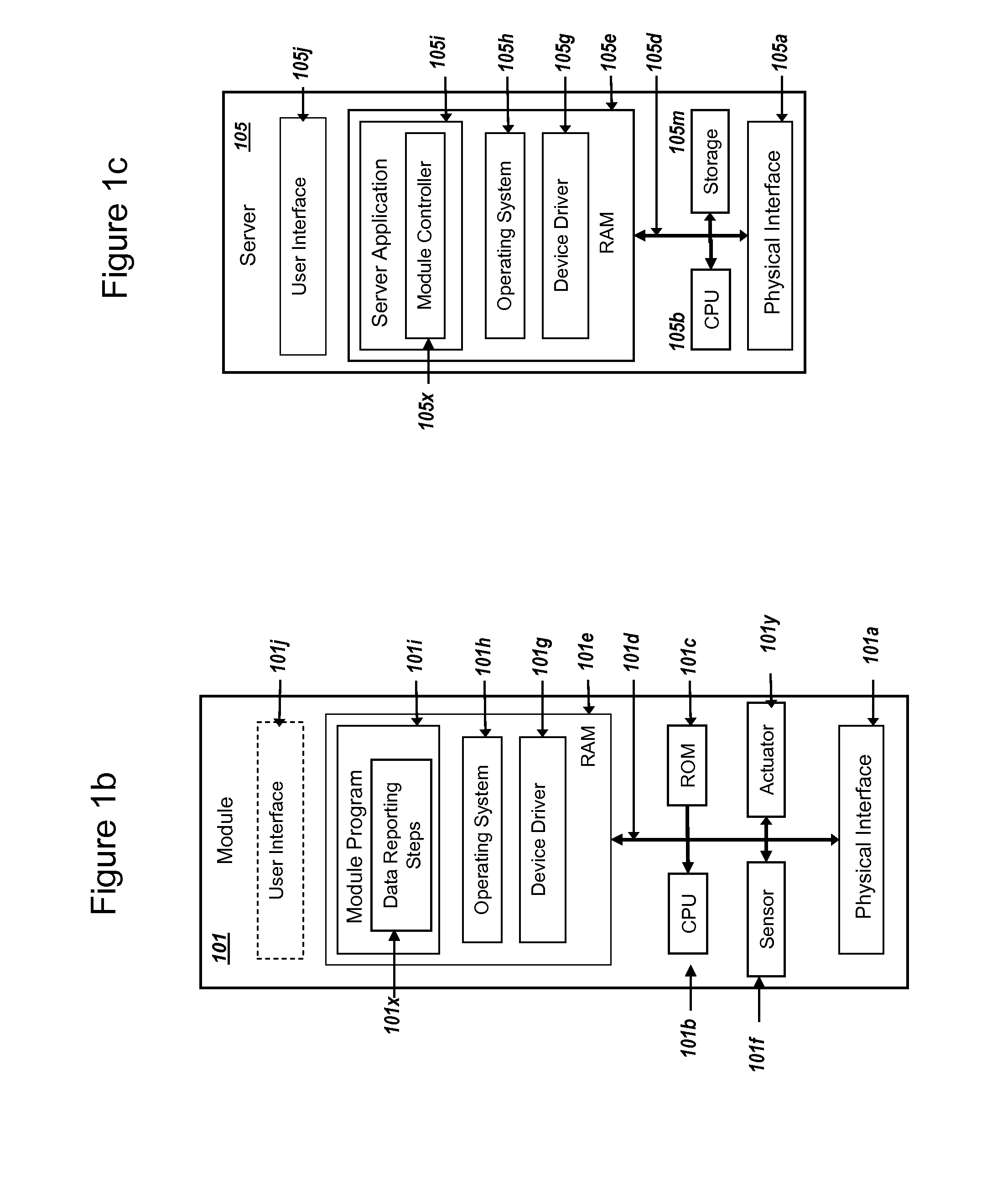
Secure PKI Communications for "Machine-to-Machine" Modules, including Key Derivation by Modules and Authenticating Public Keys
ActiveUS20150095648A1Extend battery lifeImprove efficiencyKey distribution for secure communicationMultiple keys/algorithms usageComputer hardwareDigital signature
Methods and systems are provided for efficient and secure “Machine-to-Machine” (M2M) between modules and servers. A module can communicate with a server by accessing the Internet, and the module can include a sensor and / or actuator. The module and server can utilize public key infrastructure (PKI) such as public keys to encrypt messages. The module and server can use private keys to generate digital signatures for datagrams sent and decrypt messages received. The module can internally derive pairs of private / public keys using cryptographic algorithms and a set of parameters. A server can use a shared secret key to authenticate the submission of derived public keys with an associated module identity. For the very first submission of a public key derived the module, the shared secret key can comprise a pre-shared secret key which can be loaded into the module using a pre-shared secret key code.
Owner:NETWORK 1 TECH +1
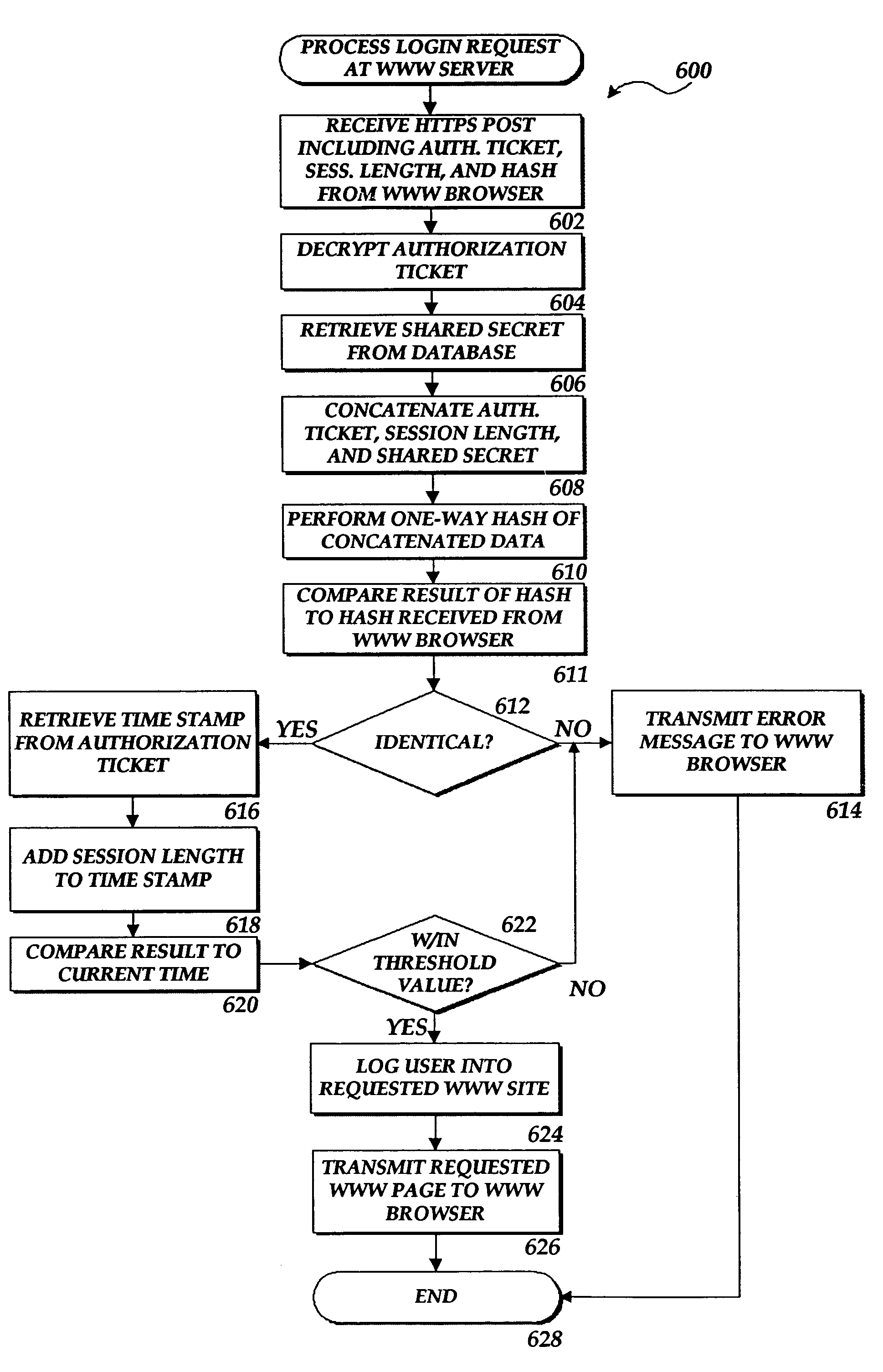
Method and system for authorizing a client computer to access a server computer
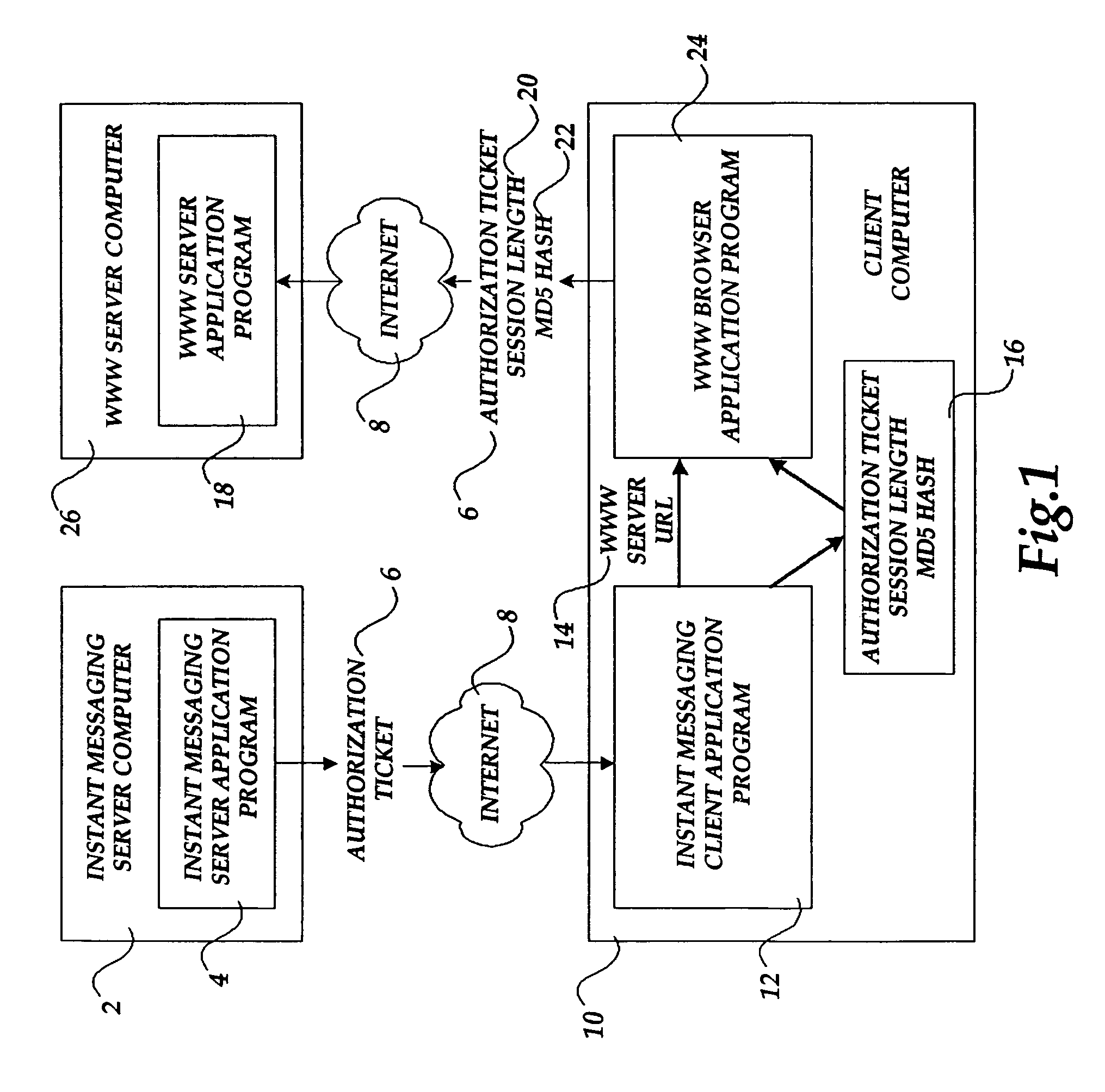
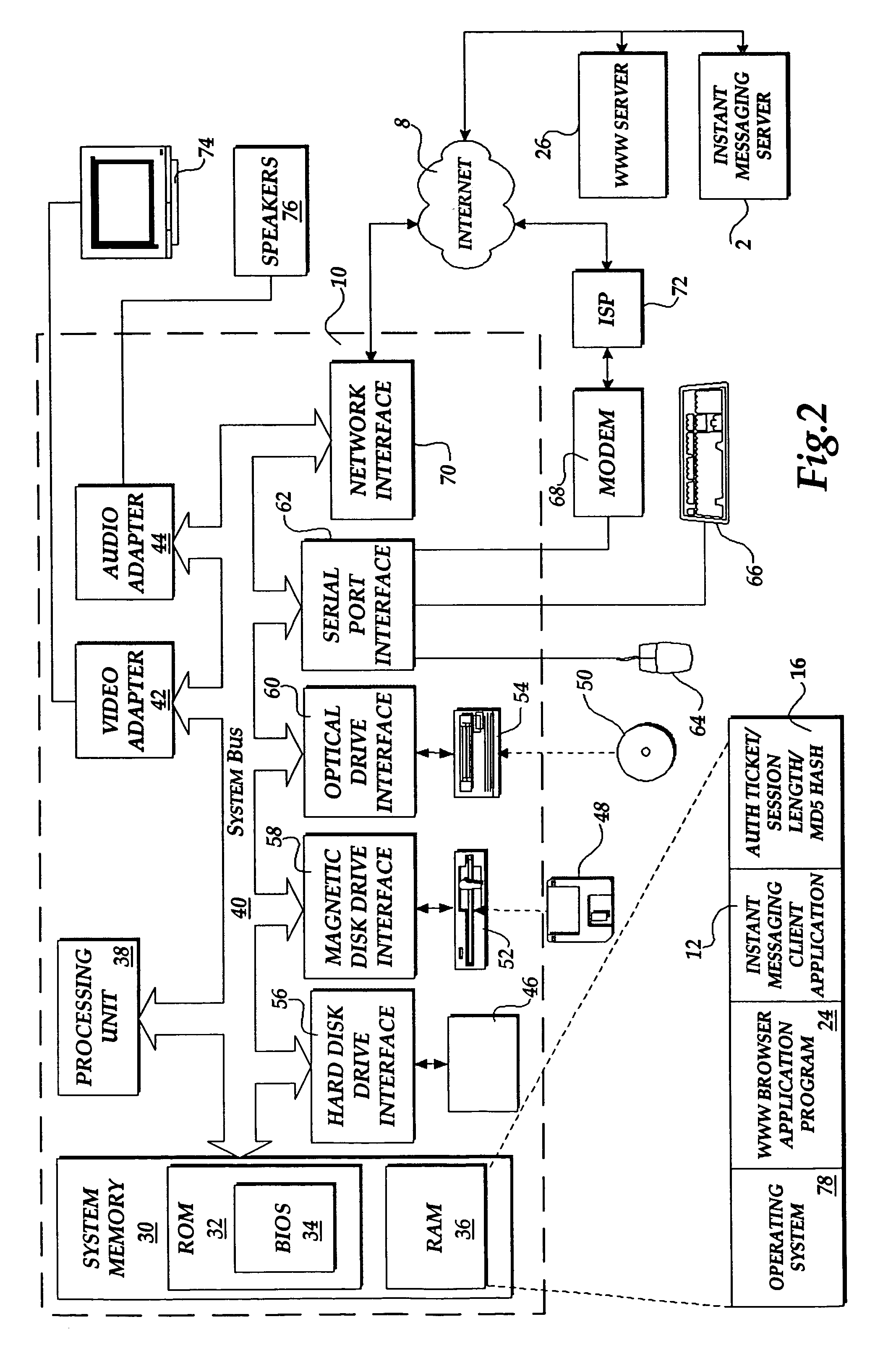
InactiveUS7089585B1Key distribution for secure communicationDigital data processing detailsAuthorization certificateHash function
The present invention includes a client computer, a first server computer, and a second server computer. The first server provides an authorization ticket containing a time stamp to the client computer when the client computer is authorized to access the first server. An elapsed time counter is started at the client computer when access is provided to the first server. When a request is received at the client computer to access the second server, the client computer determines the session length based upon the elapsed time counter. The client computer calculates a hash value for the authorization ticket, the session length, and a secret shared with the second server computer. The client computer transmits a login request to the second server including the authorization ticket, the session length, and the hash. The second server decrypts the authorization ticket and retrieves a copy of the shared secret. The second server executes a hash function on the authorization ticket, the session length, and the shared secret. The second server then compares the computed hash to the hash value received from the second client application. If the two hash values are identical, the second server retrieves the time stamp from the authorization ticket and adds the session length to the time stamp. The second server then compares the resulting value to the current time. If the resulting value and the current time are within a preset threshold value, the client computer is provided.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Authentication in a packet data network
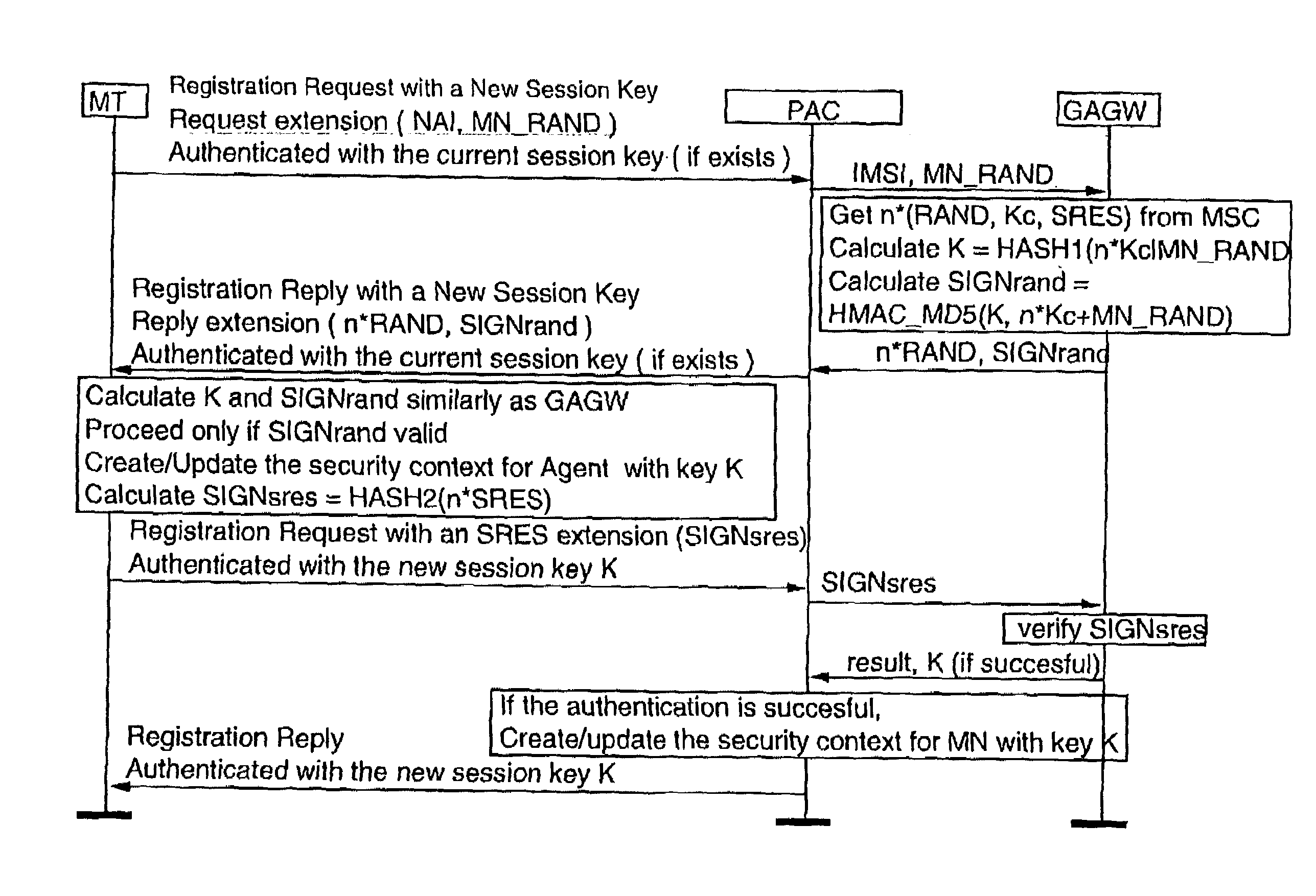
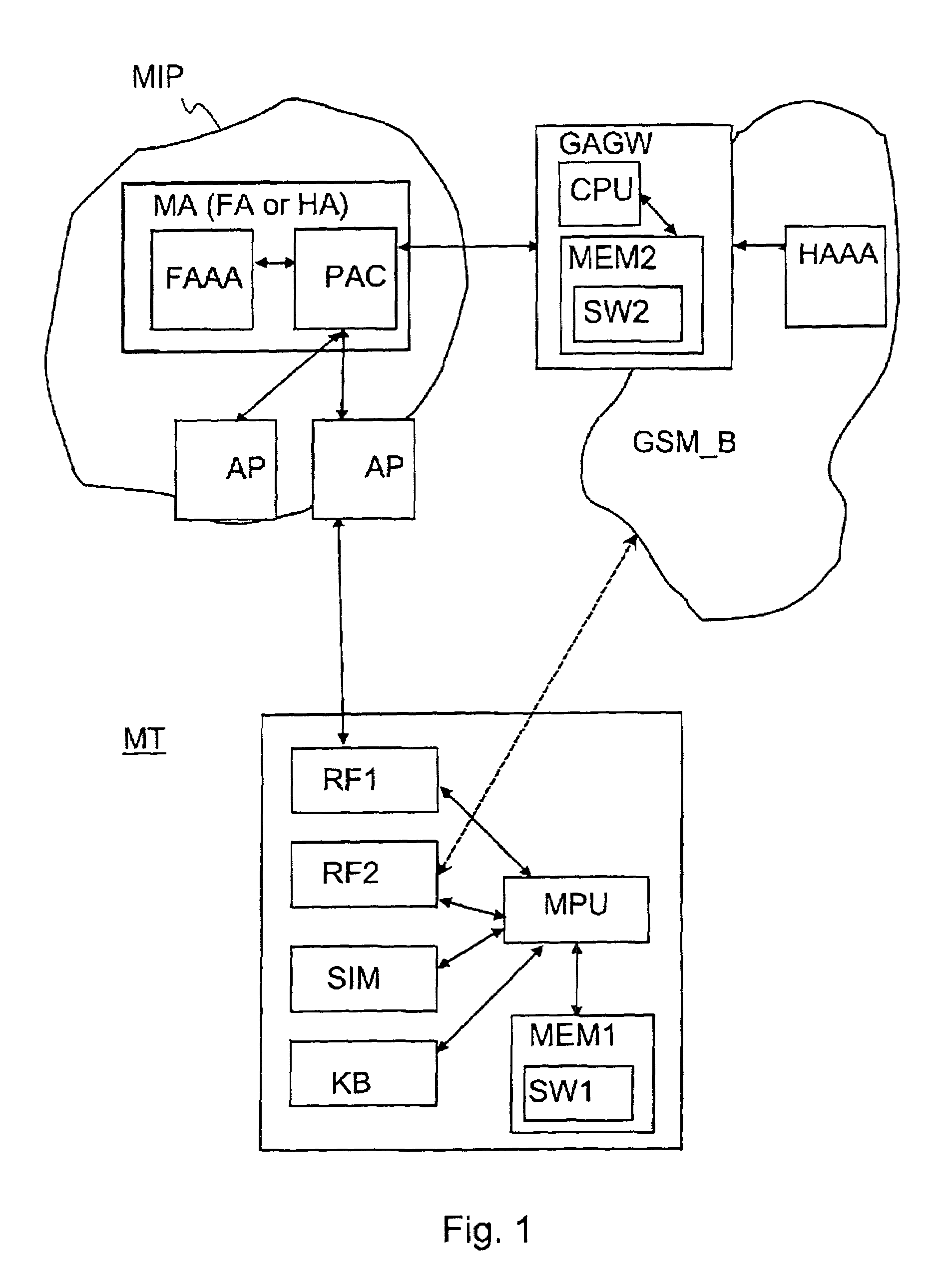
InactiveUS7107620B2Strong authenticationKey distribution for secure communicationUnauthorised/fraudulent call preventionTelecommunications networkComputer science
Authentication method for authenticating a mobile node to a packet data network, in which a shared secret for both the mobile node and the packet data network is arranged by using a shared secret of the mobile node and a telecommunications network authentication center. In the method, the mobile node sends its subscriber identity to the packet data network together with a replay attack protector. The packet data network obtains authentication triplets, forms a session key using them, and sends back to the mobile node challenges and a cryptographic authenticator made by using the session key. The mobile node can then form the rest of the authentication triplets using the challenges and then form the session key. With the session key, the mobile node can check the validity of the cryptographic authenticator. If the authenticator is correct, the mobile node sends a cryptographic response formed using the session key to the packet data network for authenticating itself to the packet data network.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
System and method for generating a strong multi factor personalized server key from a simple user password
ActiveUS20130124292A1Method securityEfficient consumptionPayment architectureDigital data authenticationPersonalizationPersonal identification number
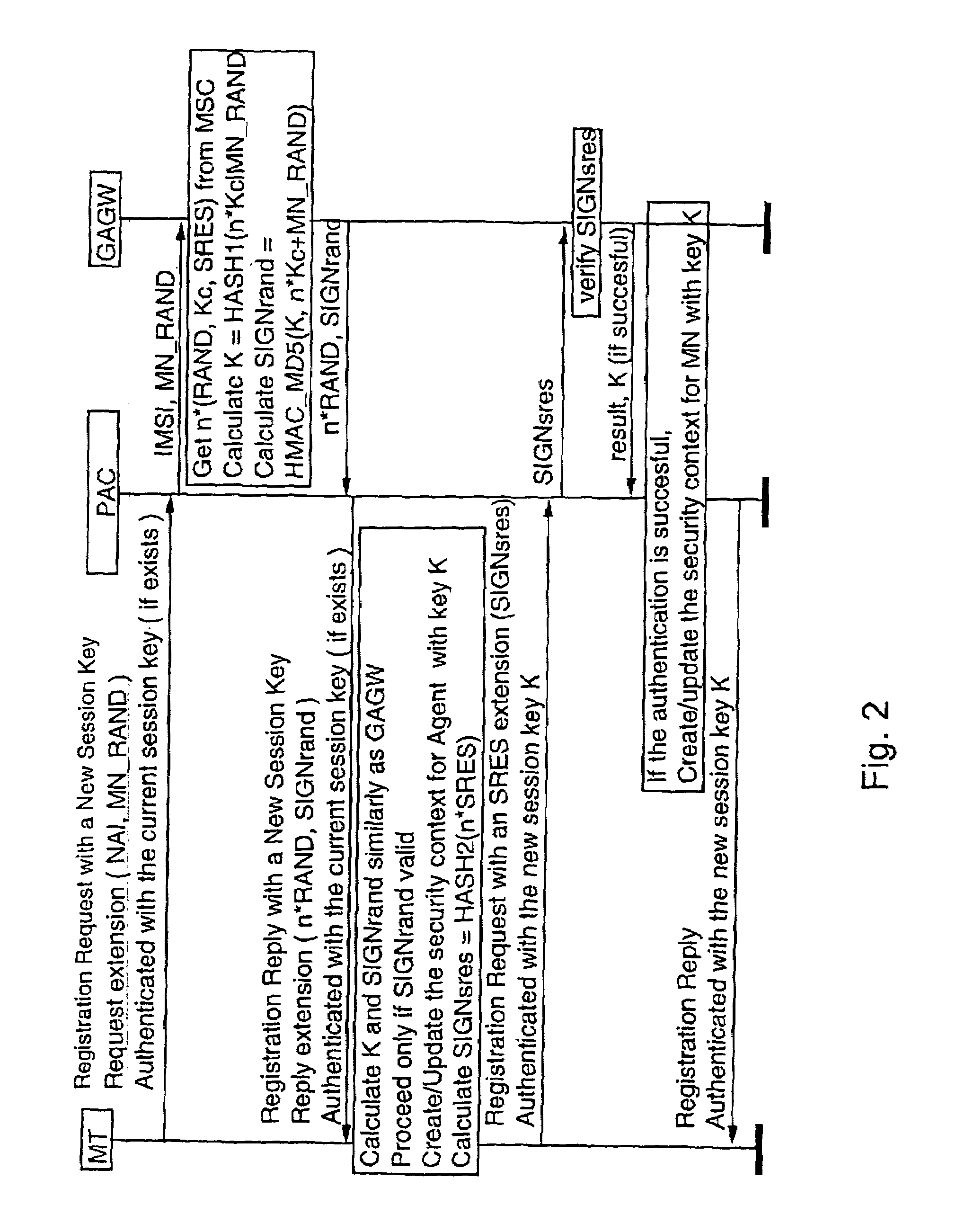
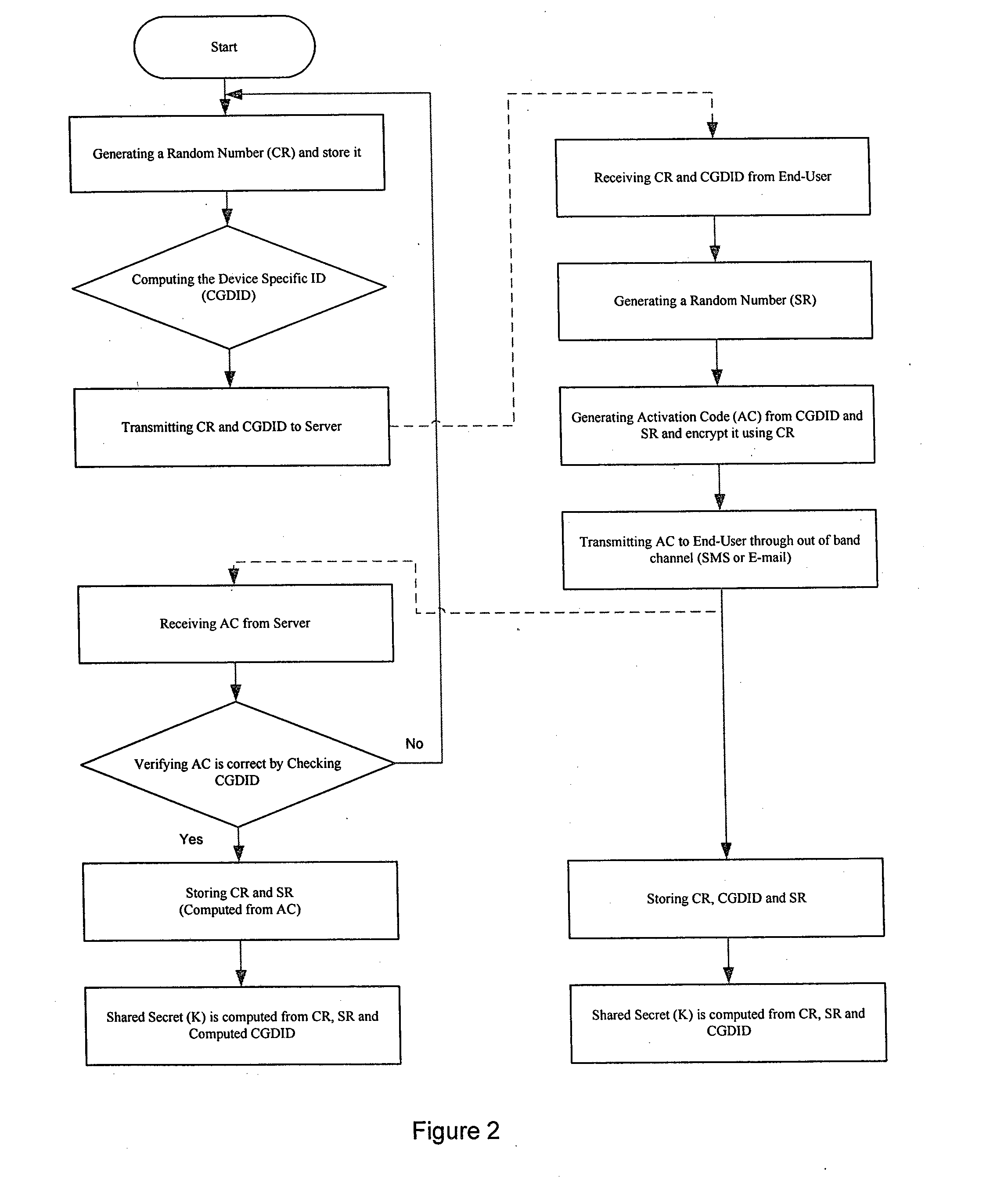
The present invention relates to a method of generating a multi-factor encryption key using a simple password in order to access control over information stored at a second entity from a first entity via at least one communication network. In one embodiment this is accomplished by, requesting to receive an application at the first entity from the second entity via the communication network, activating the first entity to generate a shared secret key, wherein the shared secret key is computed from a first entity specific ID and a random number generated at the first and second entity and allowing the user to register with the application of the second entity by the first entity, wherein the registration include entry of a personal PIN (personal identification number), a personal message etc.
Owner:JUTHANI NIRMAL
Authentication failure trigger method and apparatus
InactiveUS6236852B1Unauthorised/fraudulent call preventionEavesdropping prevention circuitsMobile stationService system
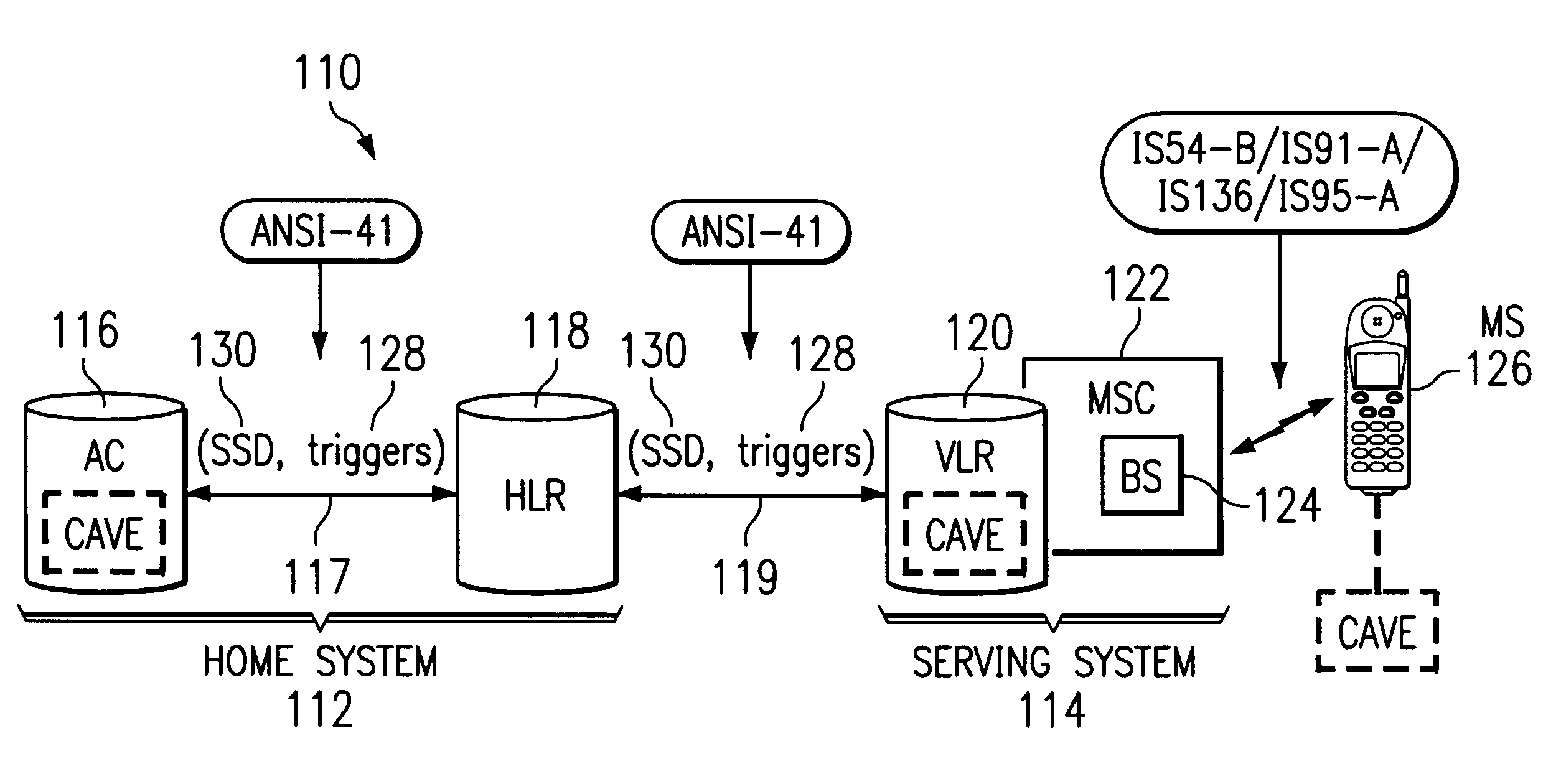
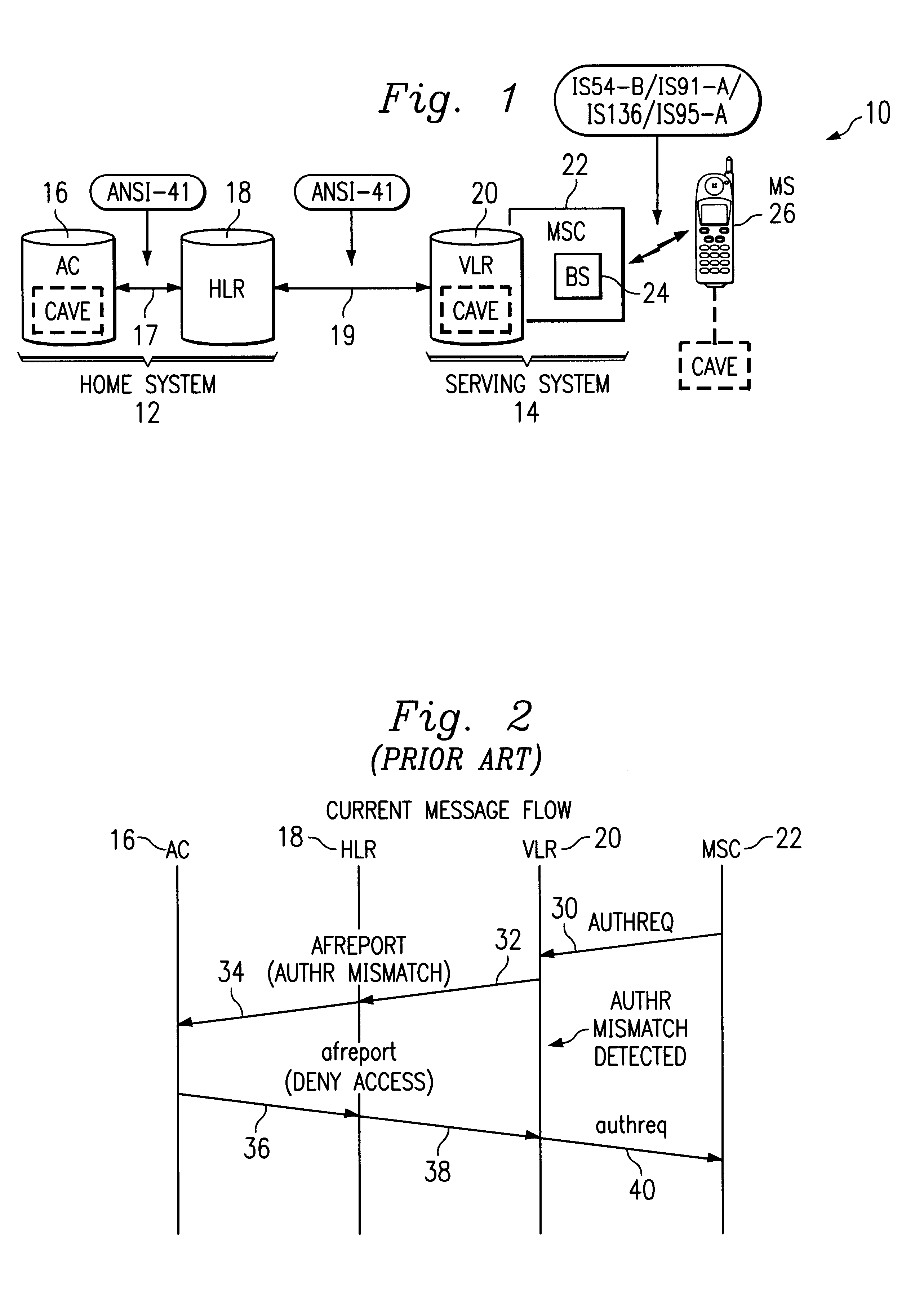
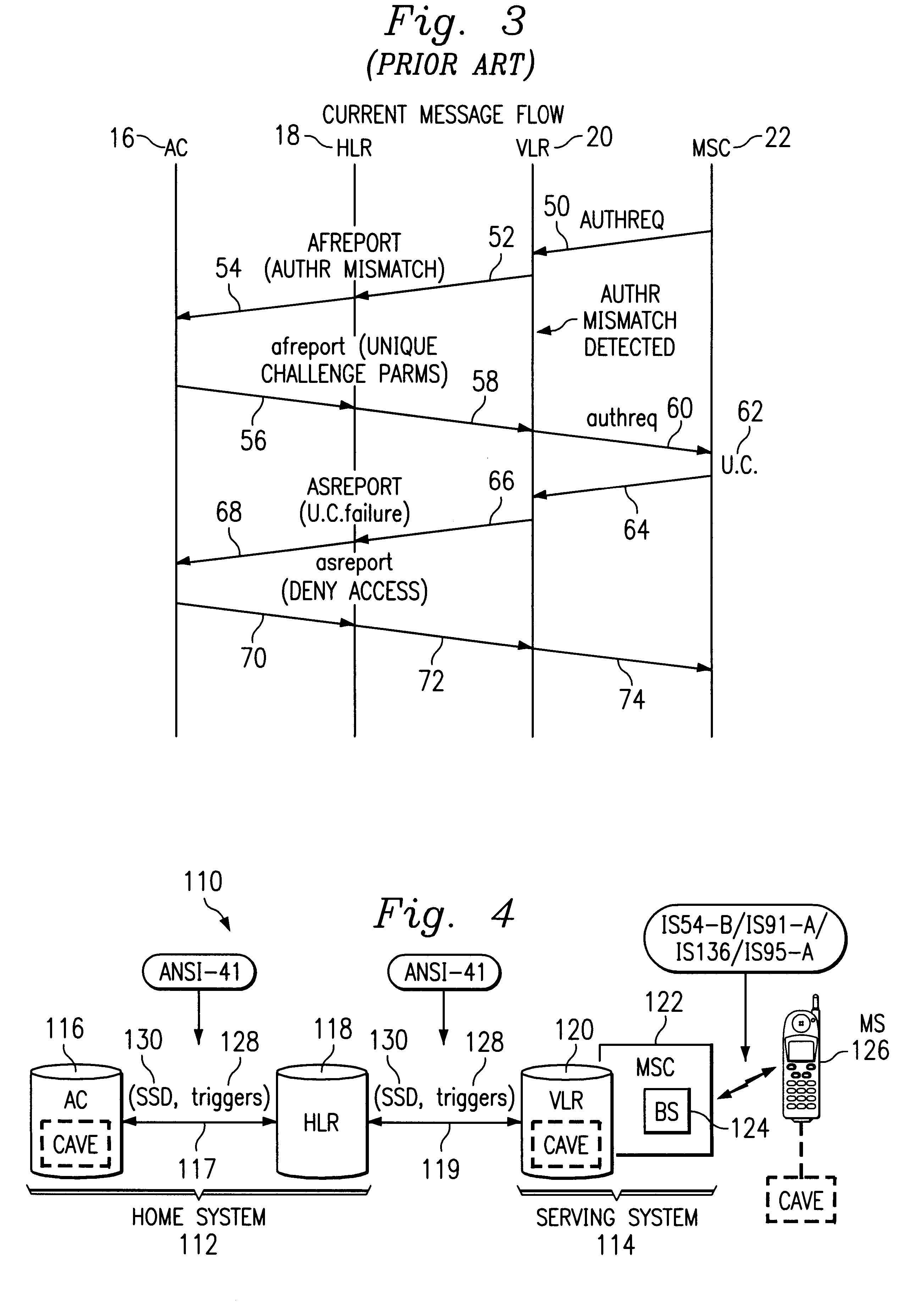
A wireless communications network and method include a home system, a serving system, and authentication failure triggers. The home system includes an authentication center, a network information element, and a prescribed authentication capable mobile station. The authentication center performs an authentication of the prescribed mobile station upon a network access by the mobile station. Authentication includes use of shared secret data particular to the prescribed mobile station. The serving system includes a network access element and a network information element associated therewith. The serving system is capable of performing authentication upon authentication capable mobile stations. Lastly, the authentication failure triggers and shared secret data are shared with the serving system by the authentication center of the home system upon the mobile station's initial system access. The authentication failure triggers include instructions for use by the serving system with respect to authentication failures which may occur during a subsequent serving system access. The authentication triggers direct the serving system to handle authentication failures according to the authentication policies of the home system's authentication center. Therefore, the requirement for the authentication failure report operation is advantageously reduced.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
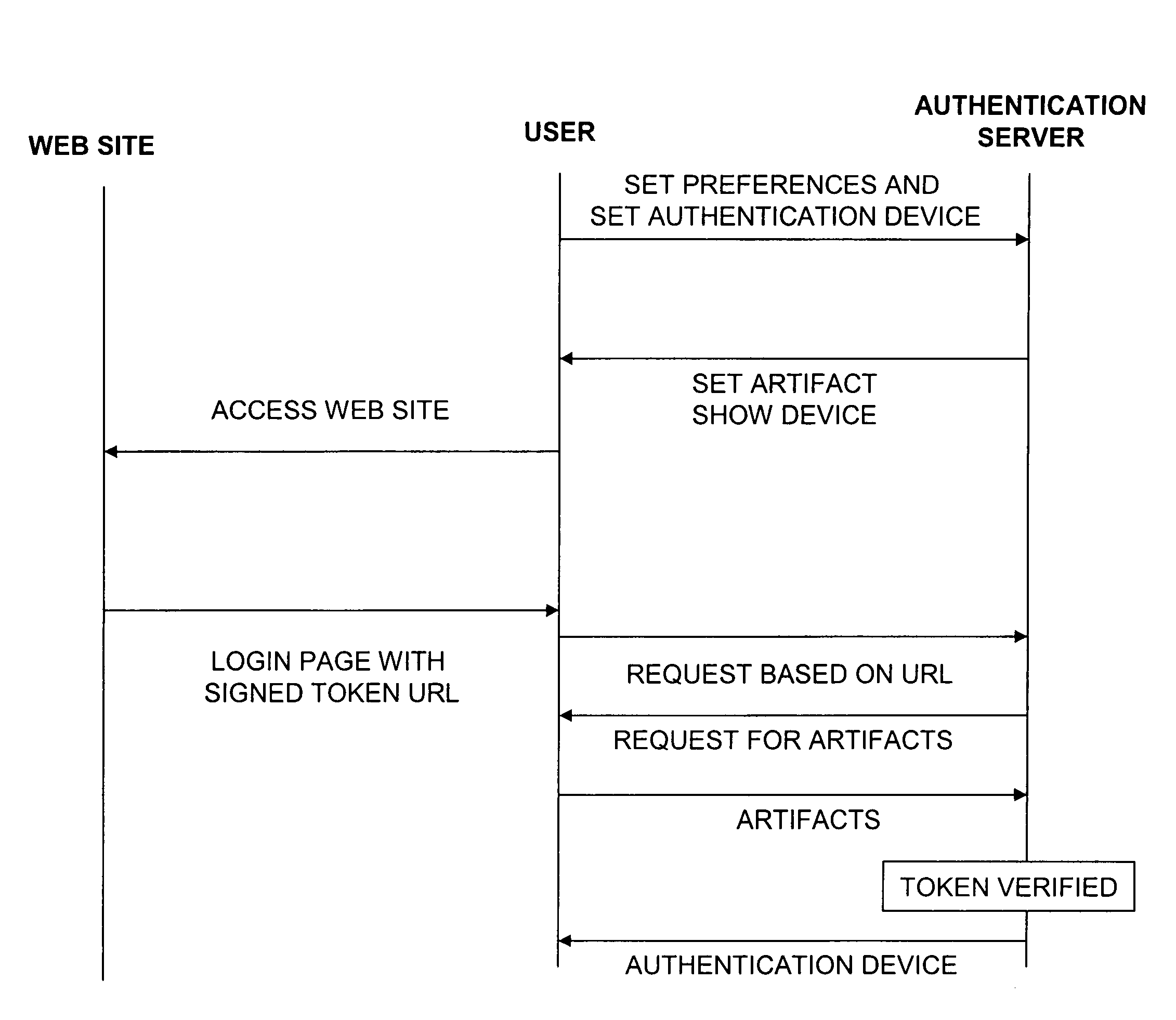
Web site authentication
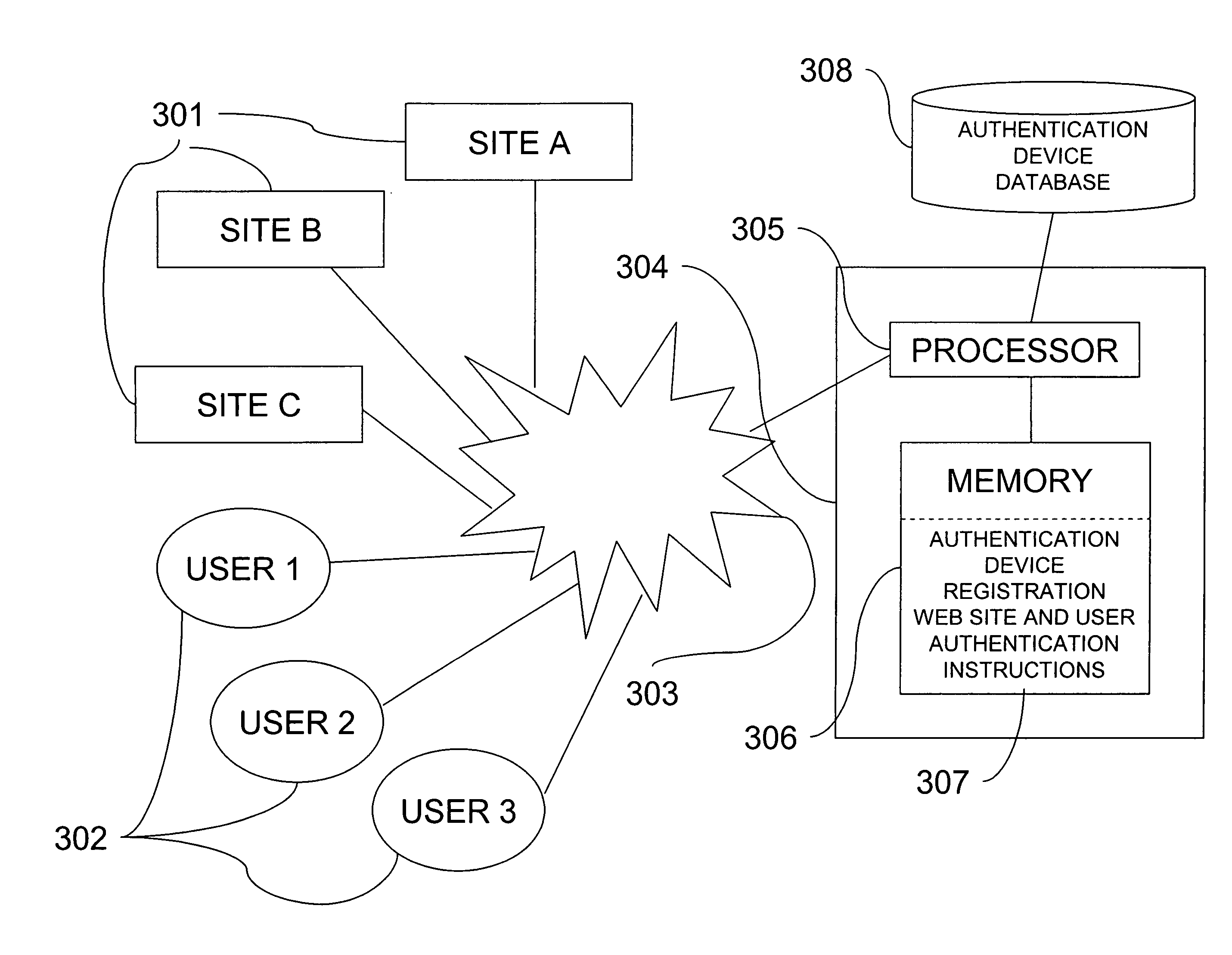
ActiveUS20080109657A1Digital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationWeb siteInternet Authentication Service
A web site can be authenticated by a third party authentication service. A user designates an authentication device that is a shared secret between the user and the authentication service. A web site page includes a URL that points to the authentication service. The URL includes a digital signature by the web site. When the user receives the page, the user's browser issues a request to the authentication service, which attempts to authenticate the digital signature. If the authentication is successful, it sends the authentication device to the user computer.
Owner:SYMANTEC CORP
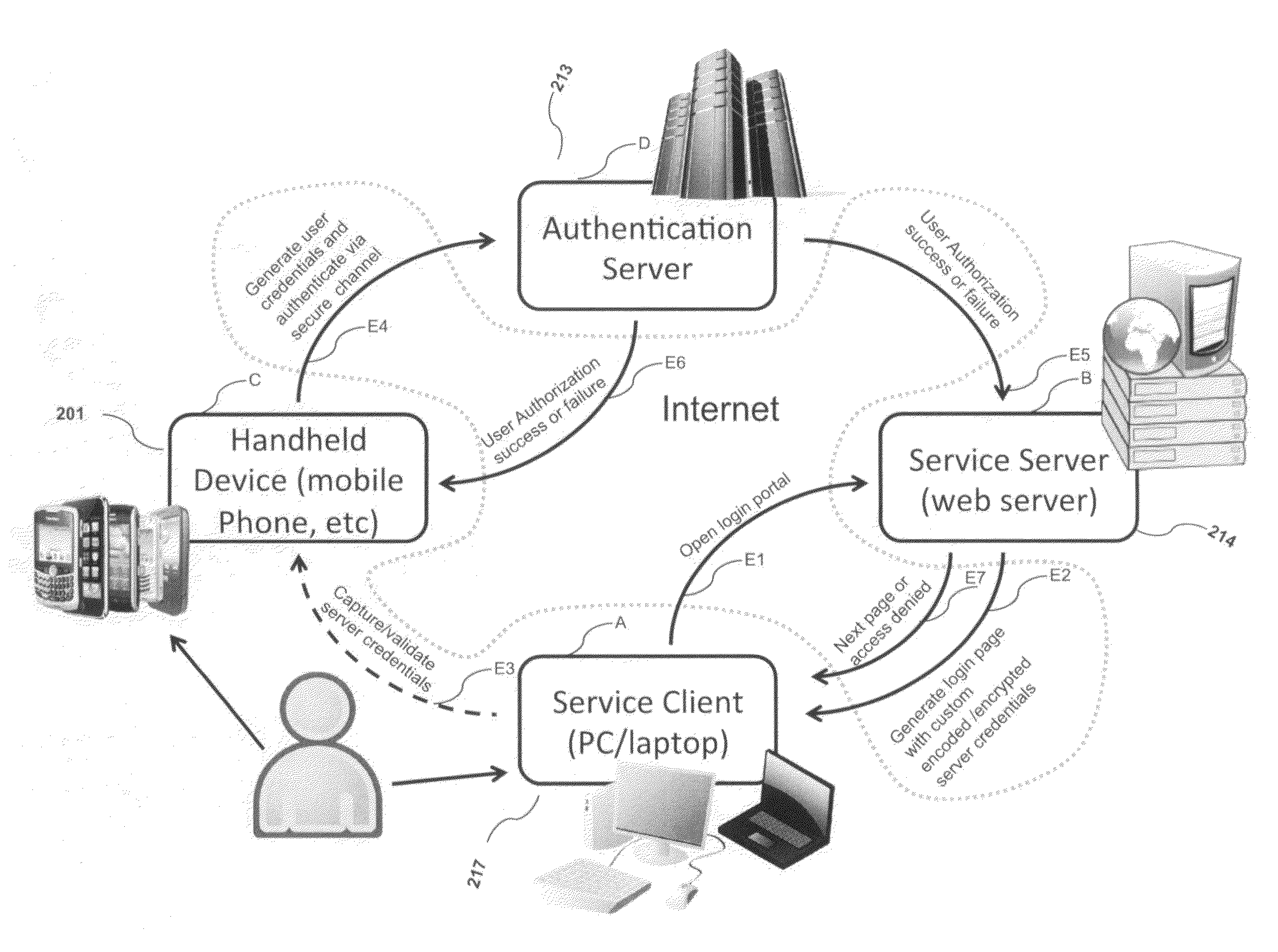
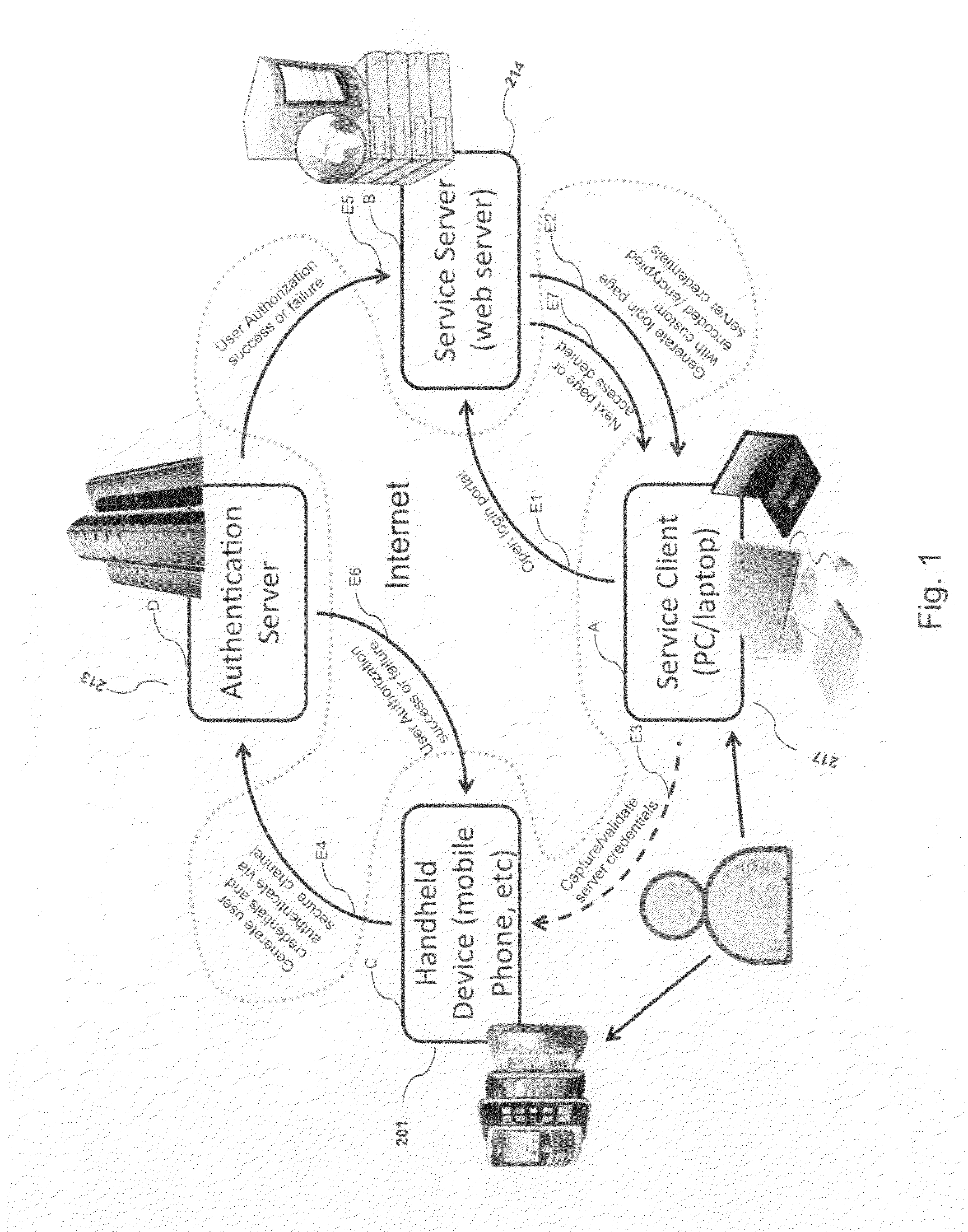
System, design and process for strong authentication using bidirectional OTP and out-of-band multichannel authentication
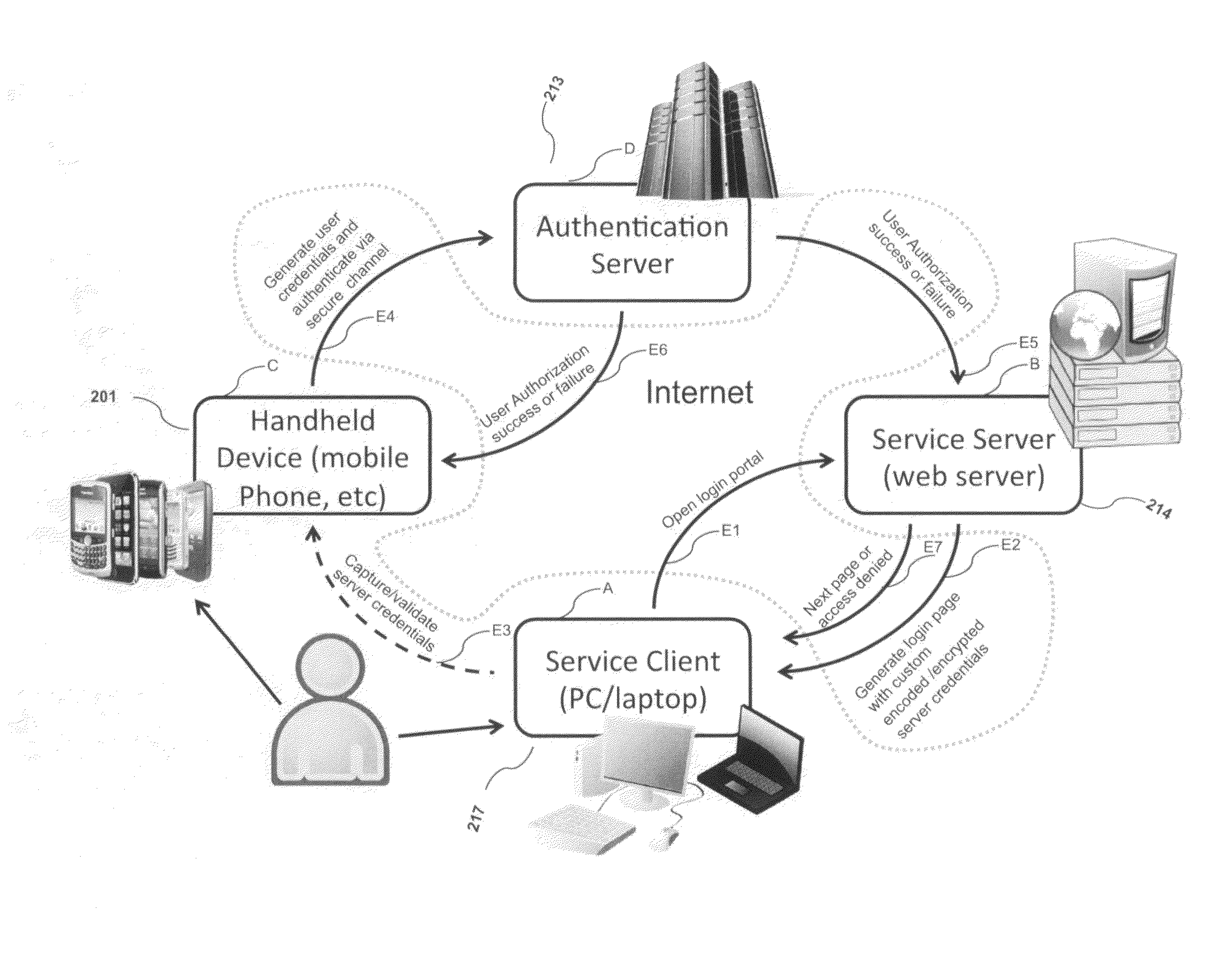
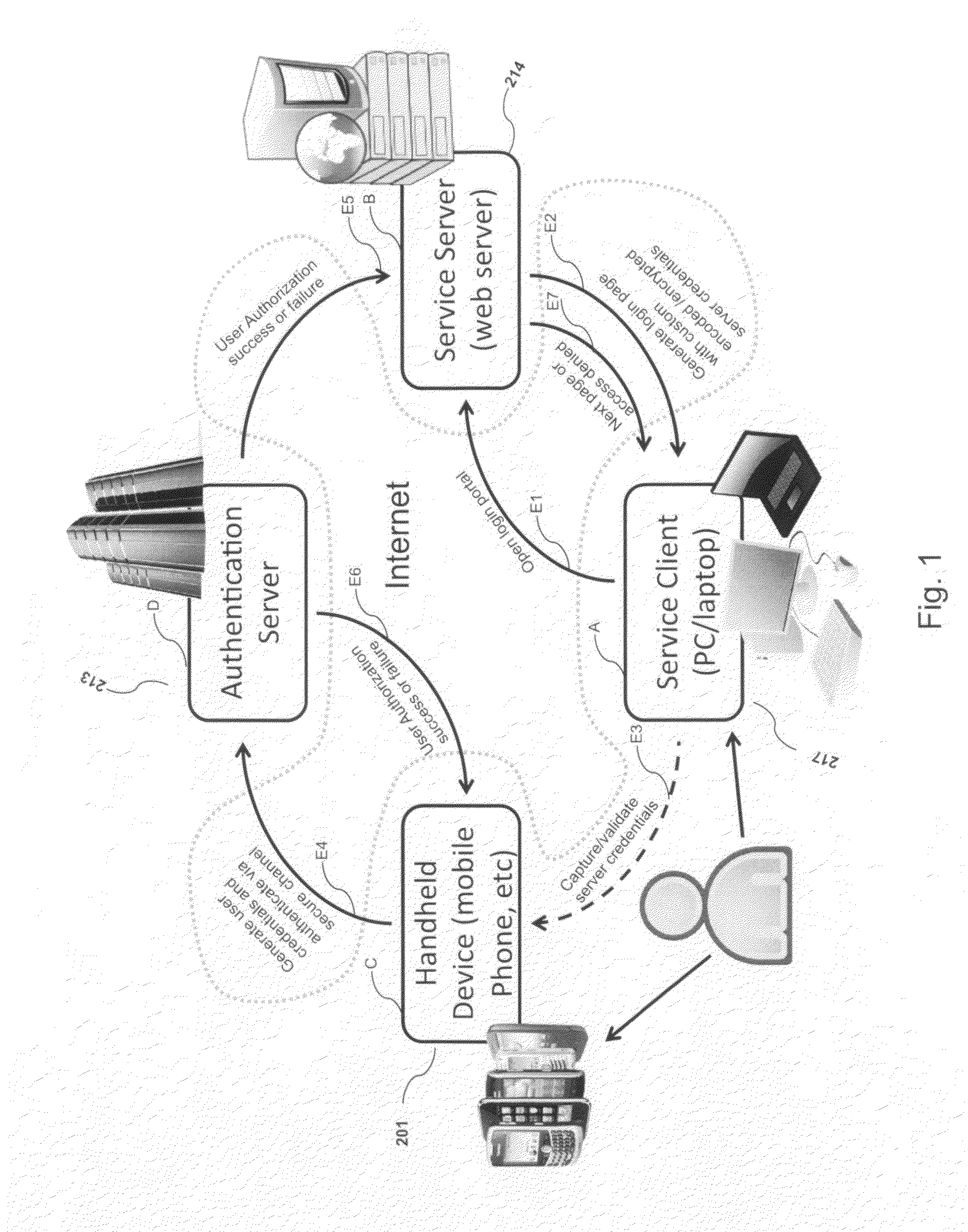
ActiveUS20120240204A1Digital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsOutbound communicationBarcode
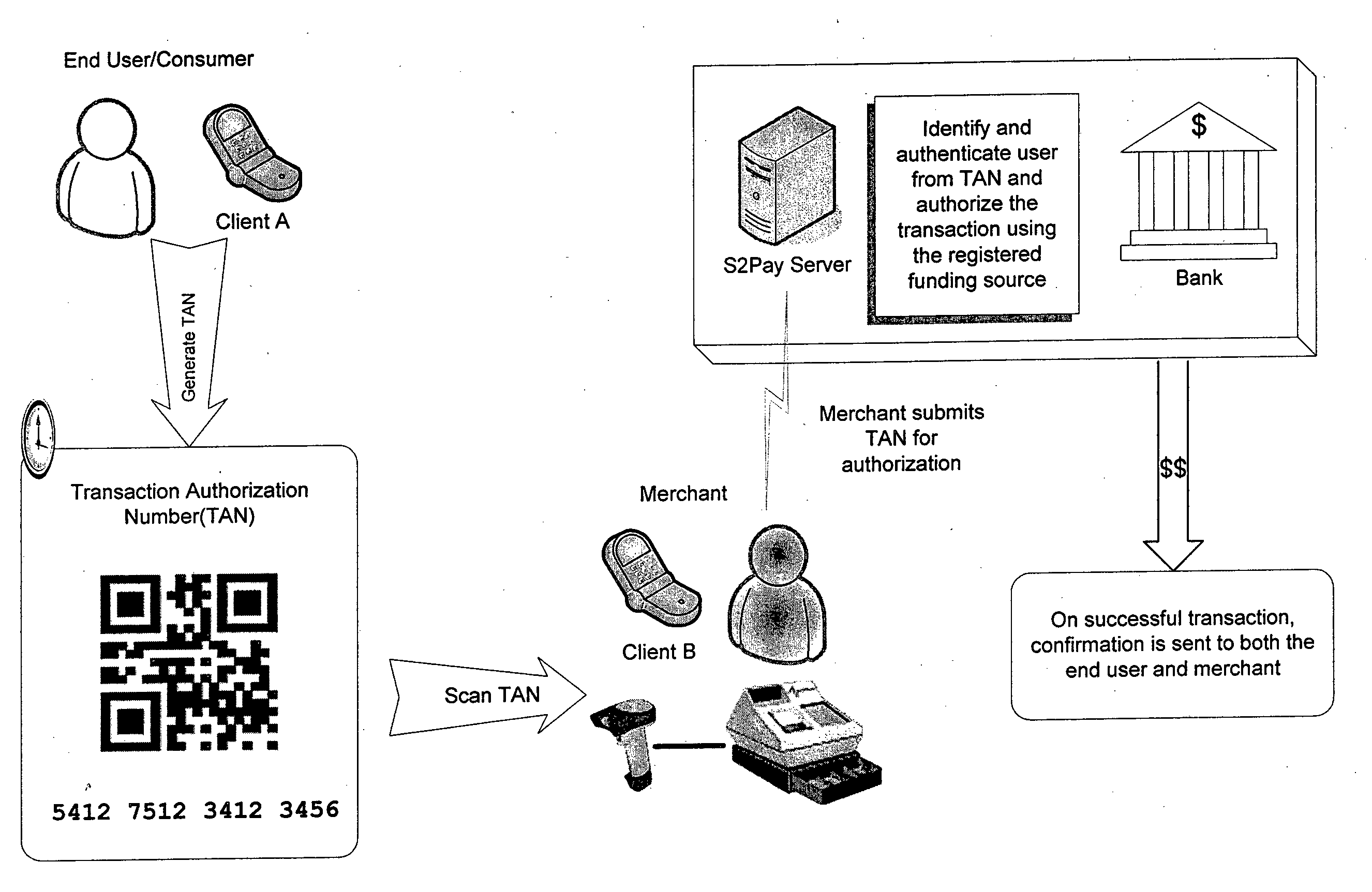
Systems and methods of authentication according to the invention are provided comprising a user, a service client, a service server, a portable communications device and an authentication server, wherein the method comprises use of one time passwords and out-of-band outbound communication channels. This system gives access to authentication seekers based on OTP out of band outbound authentication mechanism. The authentication seeker or system user scans a multi-dimensional barcode or another like encoding mechanism and validates the client and triggers the out of band outbound mechanism. The portable mobile device invokes the client server to request authentication. The client server authenticates the user based on a shared secret key and the user is automatically traversed to the next page.
Owner:GCOM IP LLC
Inter-authentication method and device
InactiveUS20060143453A1Improve securityImprove convenienceUser identity/authority verificationCommunication unitOne-way function
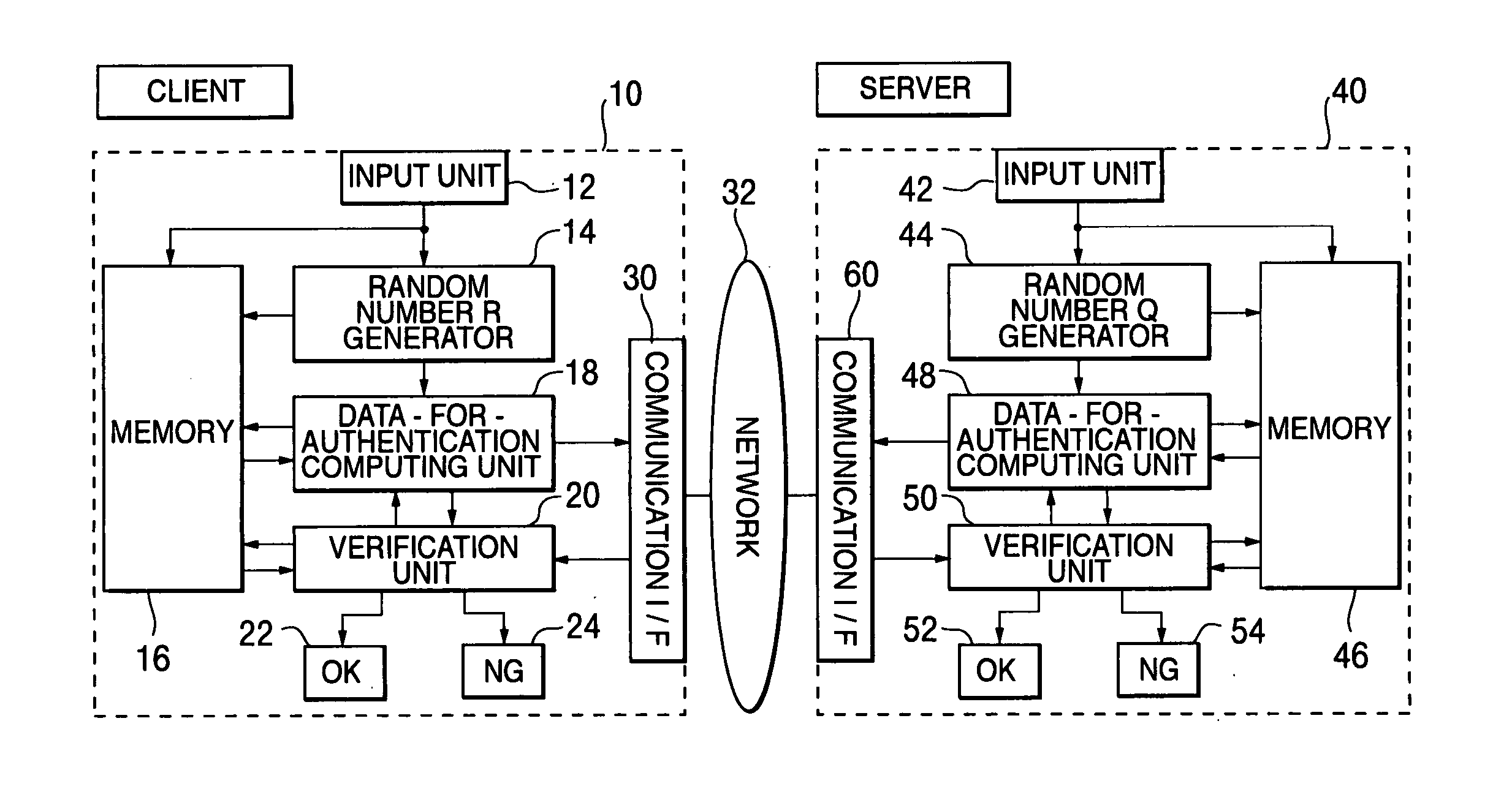
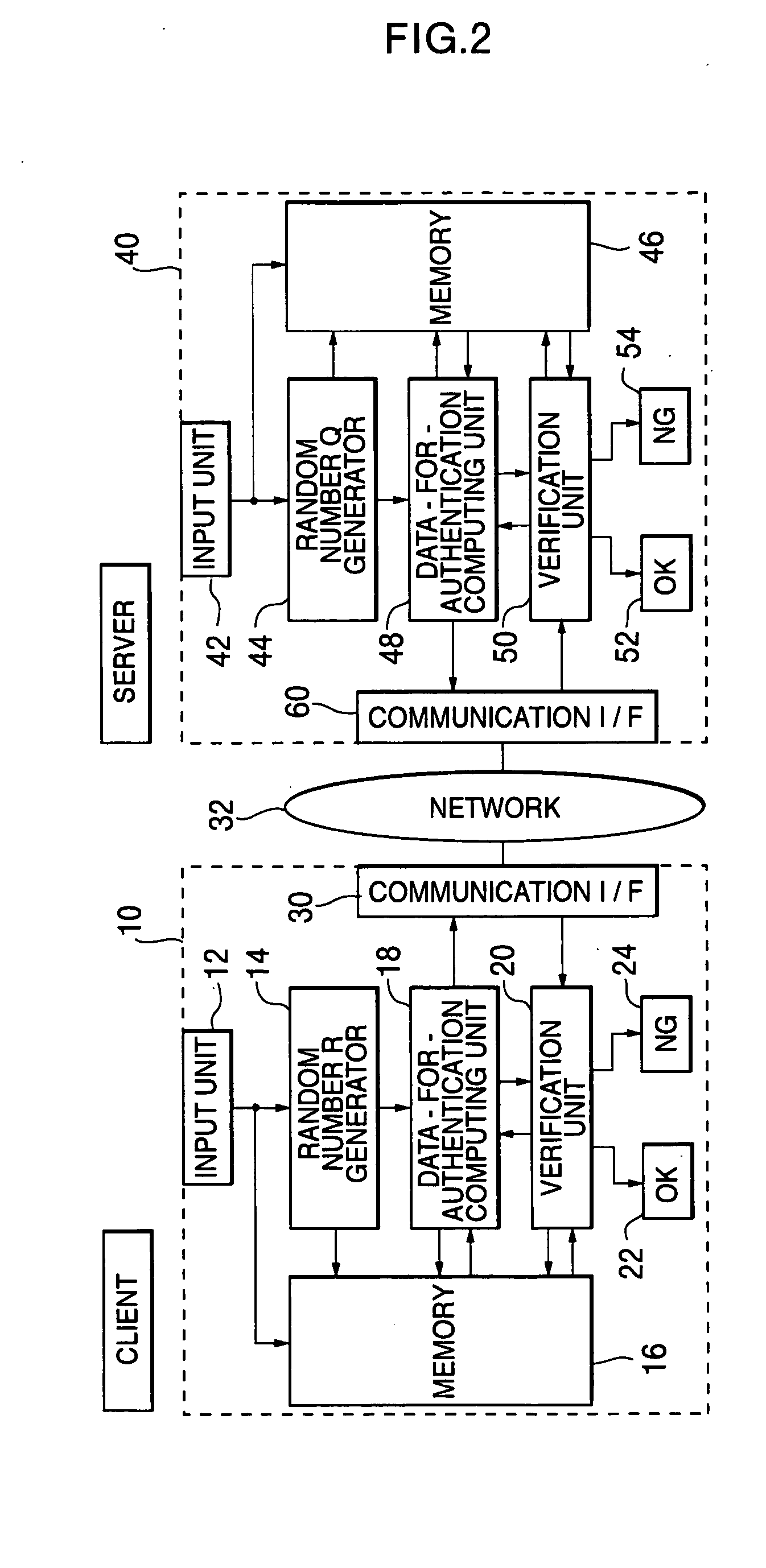
An objective of the present invention is to obtain a mutual authentication method in which mutual authentication is carried out securely and conveniently. In order to achieve the above objective, in the mutual authentication process, a private key K0, being an initial value, is stored in a client and a server (Pc0, Ps0). The client generates a random number R, calculates secret data C and authentication data A, and transmits the data items to the server (Pc1). The server receives the authentication data A and the secret data C from the client, and generates a random number Q, calculates secret data S, and authentication data B and returns the data items, as well as updating the private key K0 with a private key K1 (Ps1). The client receives from the server the authentication data B and the secret data S, generates the random number R, calculates secret data C2, authentication data A2, and returns the data items to the server, and updates the private key K0 with the private key K1(Pc2). The client and the server check whether or not validity is established (Psm+1, Pcm+1). Further in the authentication method above, there is a method for generating a onetime ID, assuming that the onetime ID is identification information usable just one time in the authentication between a plurality of devices or application. In each of the devices or applications which carries out the authentication, a variable shared key which changes per predefined communication unit requiring the authentication is generated, a function value of one-way function is obtained in which the variable shared key is used as an argument, a onetime ID hard to tap and superior in security is generated based on the function value, and the onetime ID is utilized.
Owner:PSD +1
Method for secure user and transaction authentication and risk management
ActiveUS8806592B2Compromising usabilityCompromising costDigital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationSecret shareOne-time password
To provide a user signature on a network transaction, a security server receives transaction information representing a transaction between a network user and a network site, such as a website, directly from the network site. The security server calculates a one-time-password based on the received transaction information and a secret shared by the security server and the network site, but not by the user. The security server transmits the calculated one-time-password for application as the user's signature on the transaction. The one-time-password is independently calculable by the network site based on the shared secret.
Owner:PAYFONE
System and method for in- and out-of-band multi-factor server-to-user authentication
ActiveUS20110197070A1More versatile security requirementPracticalDigital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationUser authenticationClient-side
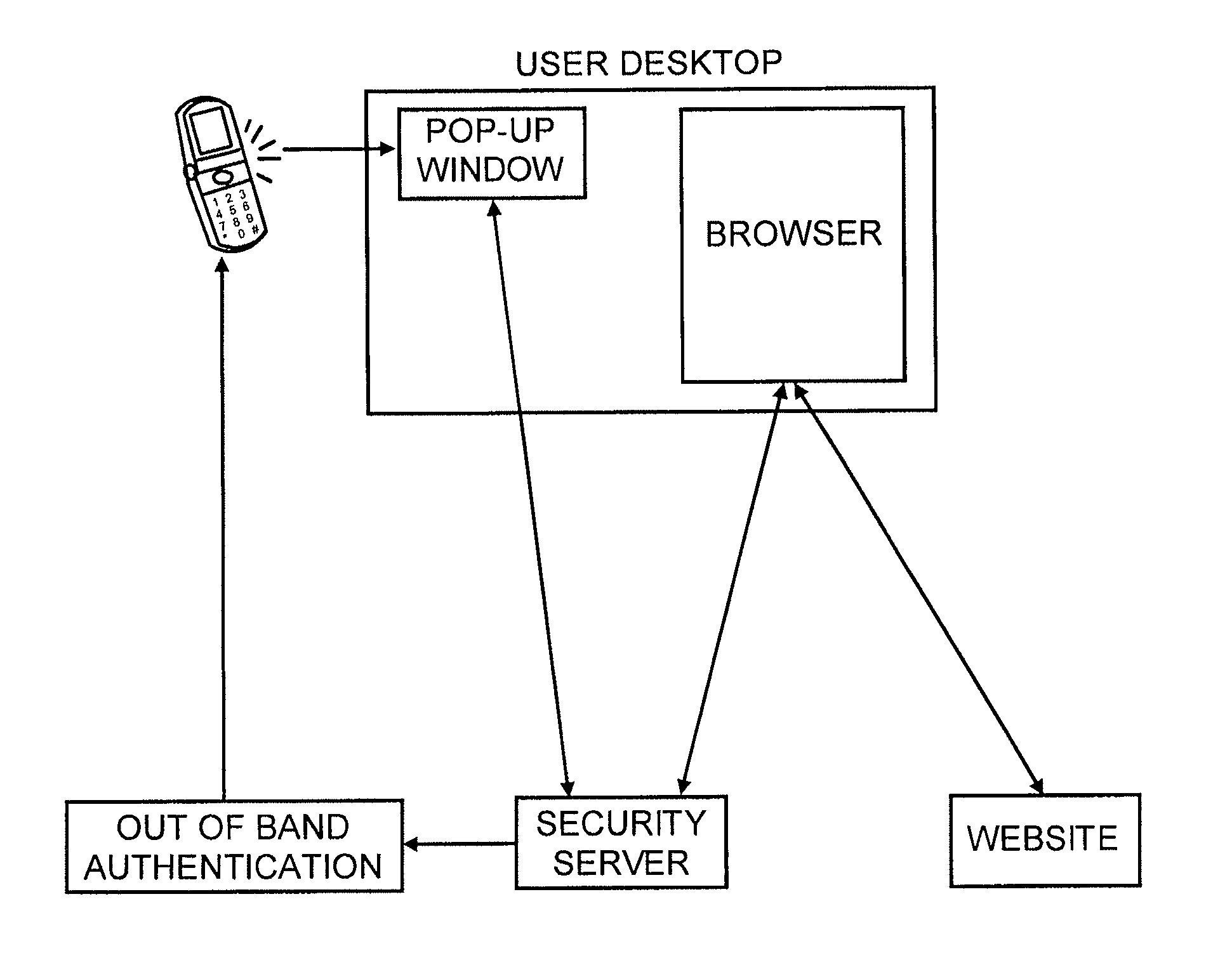
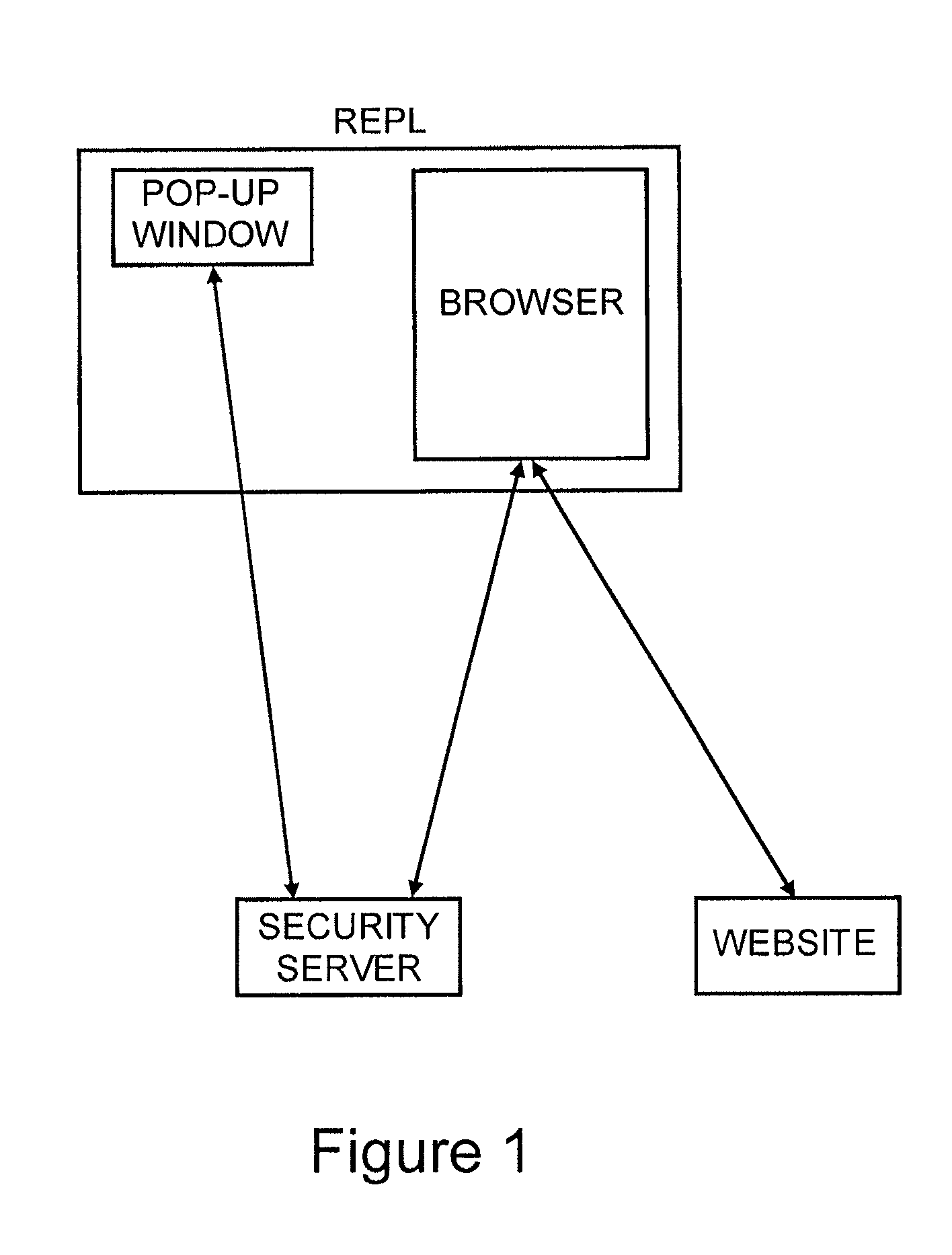
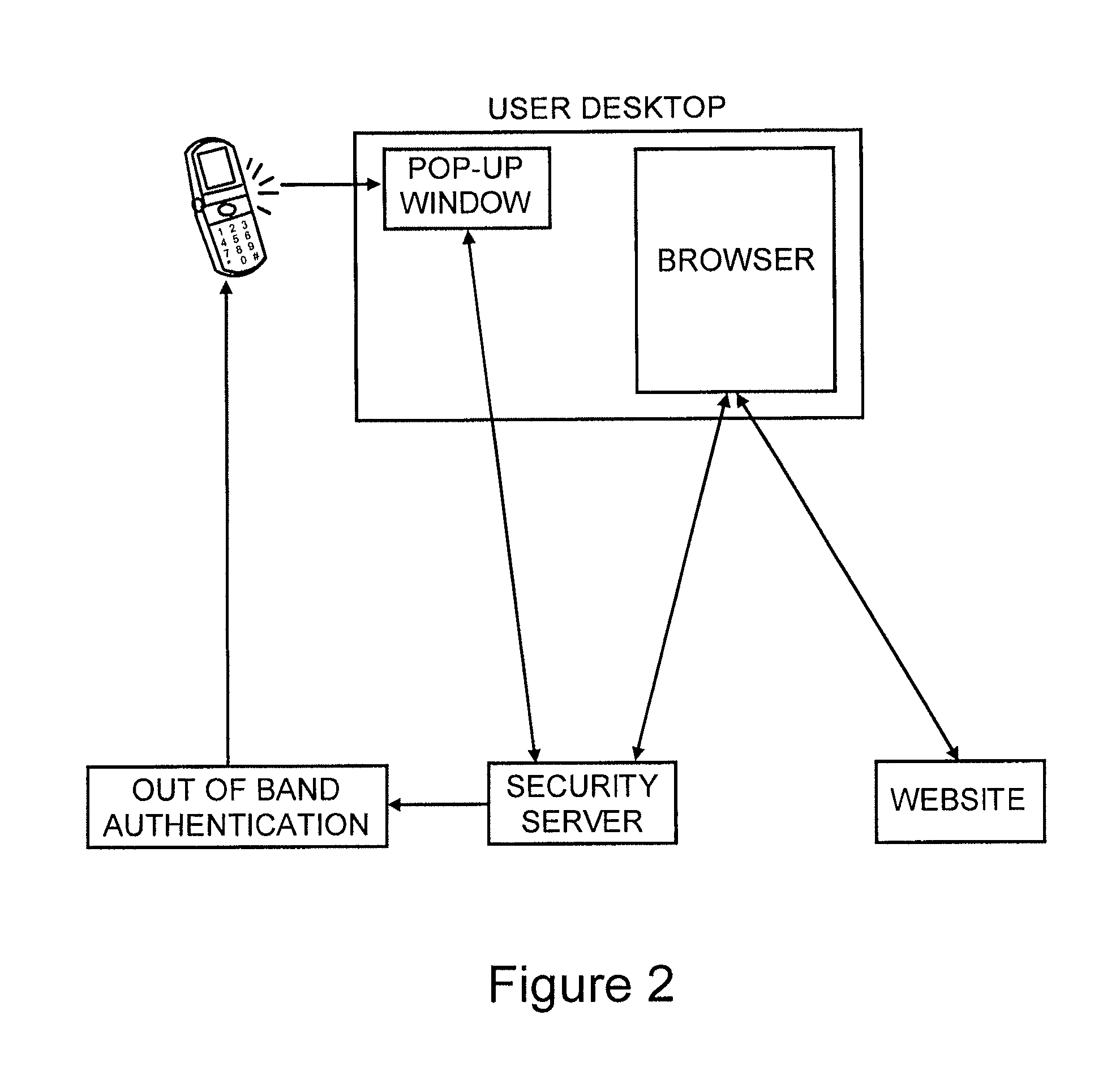
A method to authenticate a server to a client is provided, including in-band and out-of-band techniques. At least a first shared secret identifies a server path, including a plurality of pre-defined locations on a frame of reference (e.g. a grid). An authentication session is initiated upon receiving a client identifier at the server-side resources. A current session instance of the grid is presented to the client, populated with characters. The process includes sharing between the client and the server a challenge identifying a random subset of the plurality of predefined locations in the server path, and a response including characters that match the characters in the locations on the server path identified by the challenge. As a result, client is capable of verifying that the server has access to the first shared secret. Then a protocol is executed to authenticate the client to the server.
Owner:AUTHERNATIVE INC
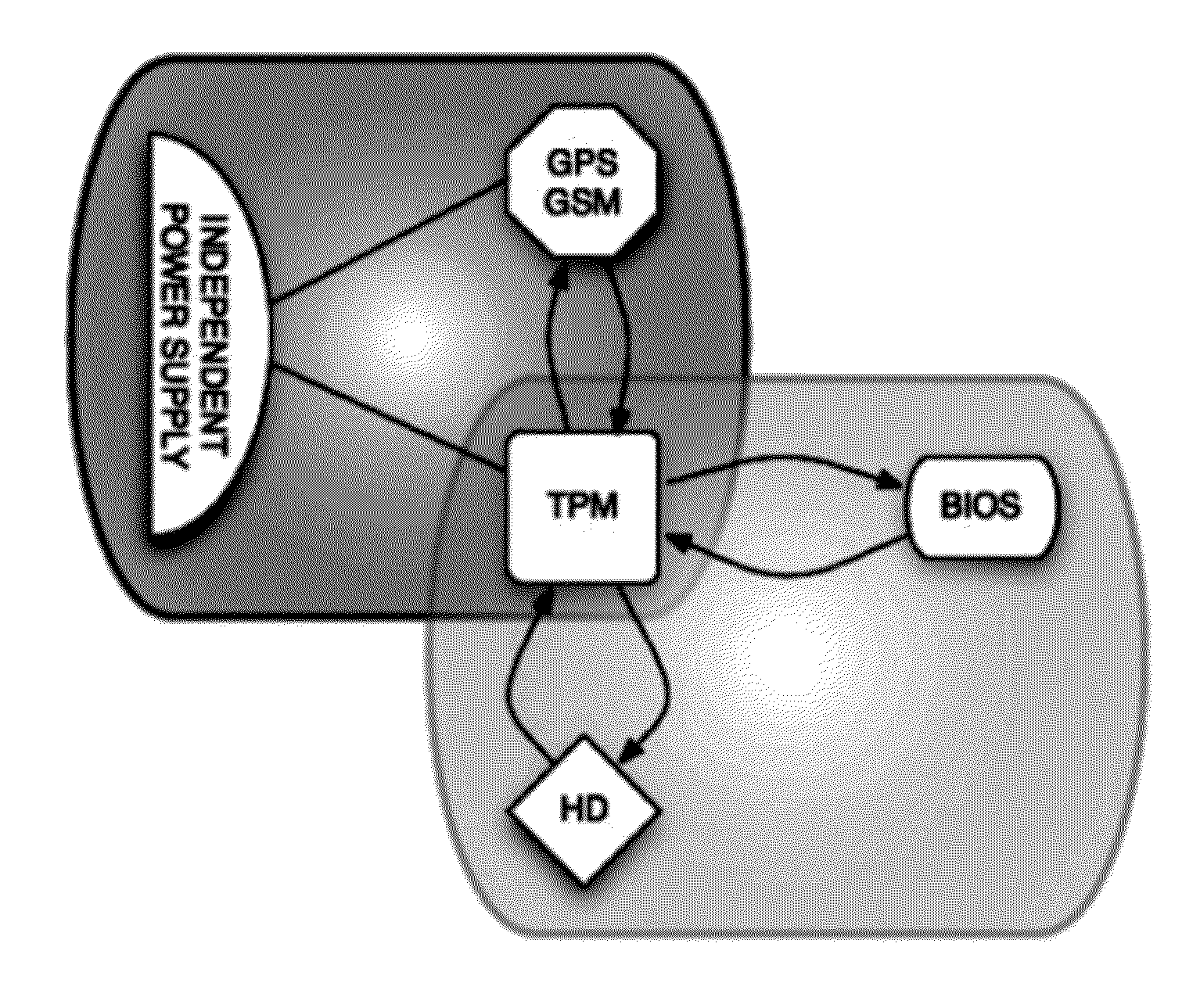
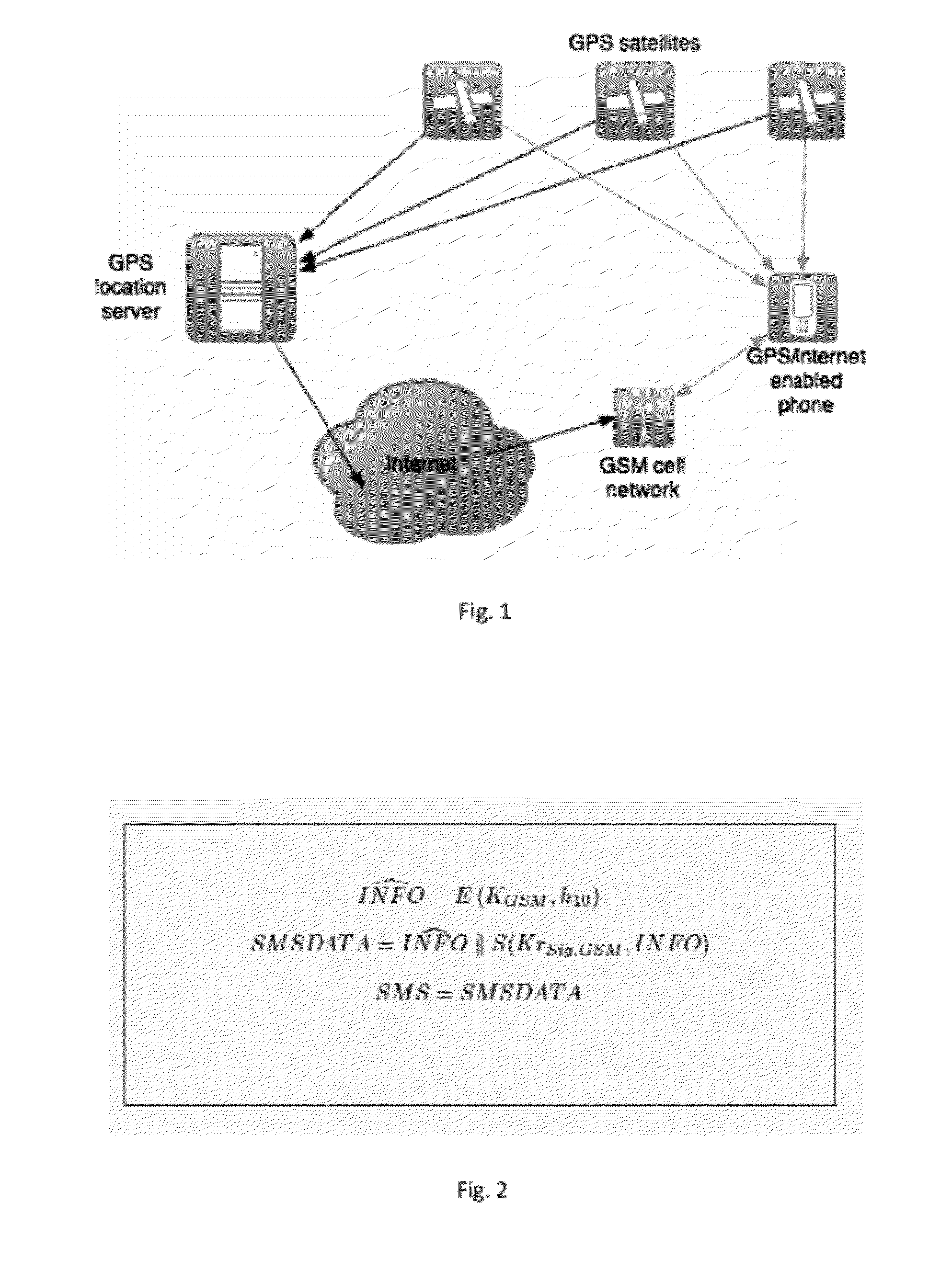
Method for securing a computing device with a trusted platform module-tpm
InactiveUS20120151223A1Unauthorized memory use protectionHardware monitoringExternal storageHash-based message authentication code
Methods, systems and computer program products for securing a computing device with data storage, power-on firmware—BIOS, geolocation and mobile data module—GPS / GSM, and a Trusted Platform Module—TPM, including establishing a shared-secret between the BIOS and the TPM, requesting the TPM to generate suitable encryption keys, namely for encrypting the data storage, supplying the user of the computing device suitable keys for external storage, calculating a hash-based message authentication codes over the BIOS, MBR, unique ID of the TPM, unique ID of the GPS / GSM module and unique ID of the BIOS; using user provided password and / or token device; using mobile data messages to secure the device if misplaced.
Owner:UNIV DE LISBOA
Method of and apparatus for sharing secret information between device in home network
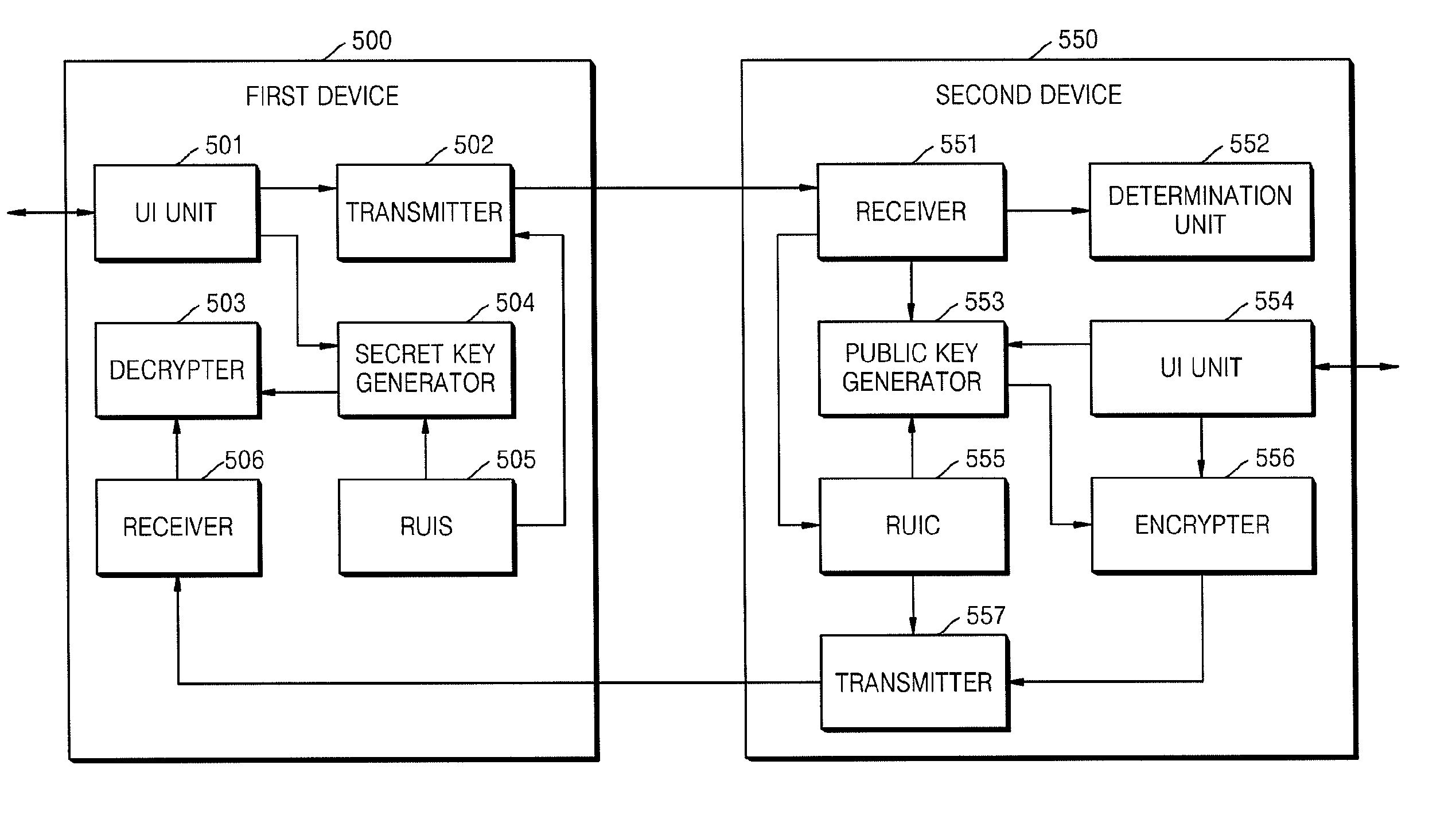
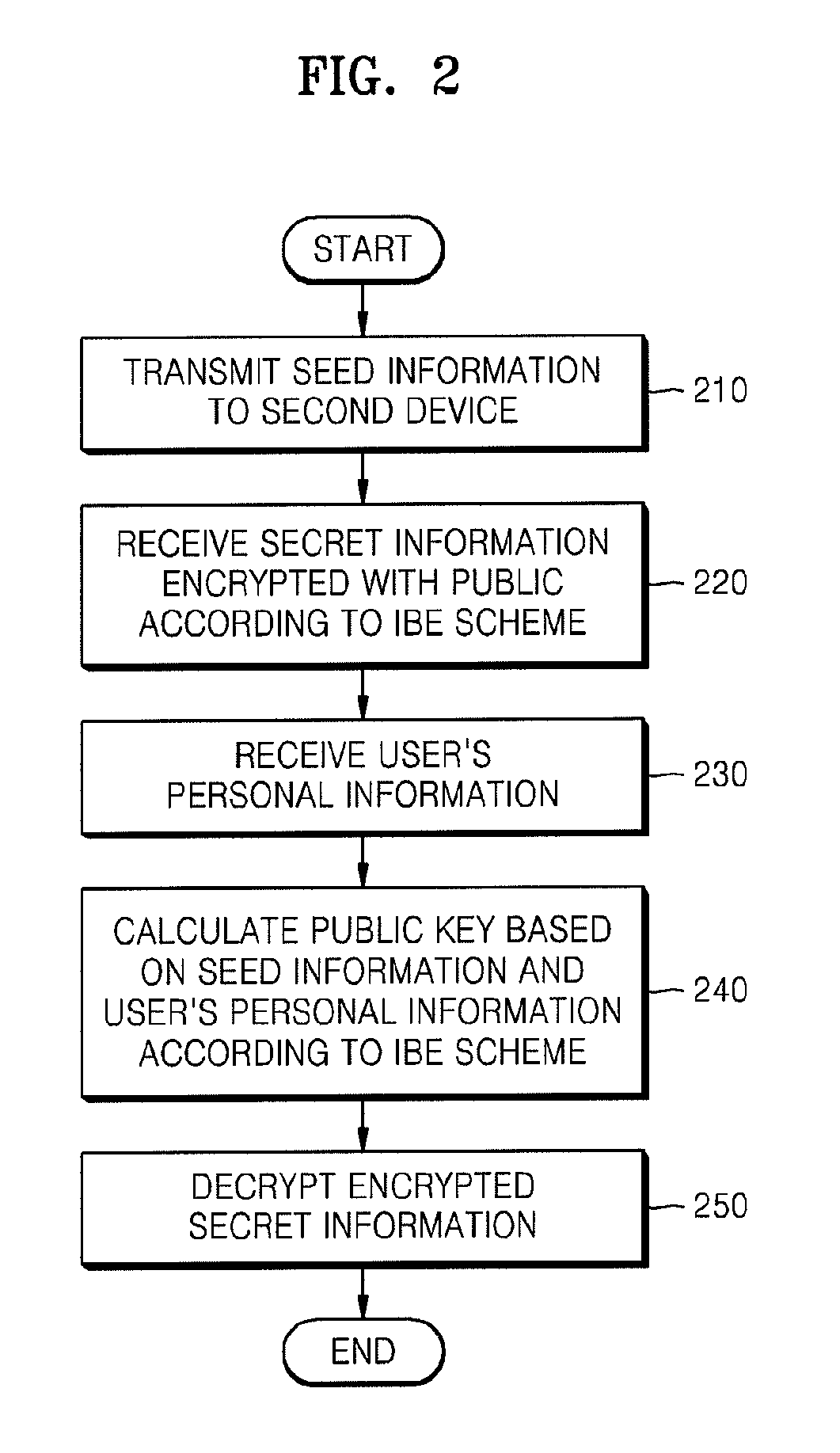
InactiveUS20090055648A1Reduce traffic problemsAvoid complex calculationsKey distribution for secure communicationPublic key for secure communicationID-based encryptionPassword
A method and apparatus for sharing secret information between devices in a home network are provided. In the method and apparatus, home network devices receive a password (credential) input by a user and encrypt secret information based on the credential by using keys generated according to a predetermined identity-based encryption (IBE) scheme. Accordingly, it is possible to securely share the secret information between home network devices without any certificate authority or certificate.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Secure wireless link between two devices using probes
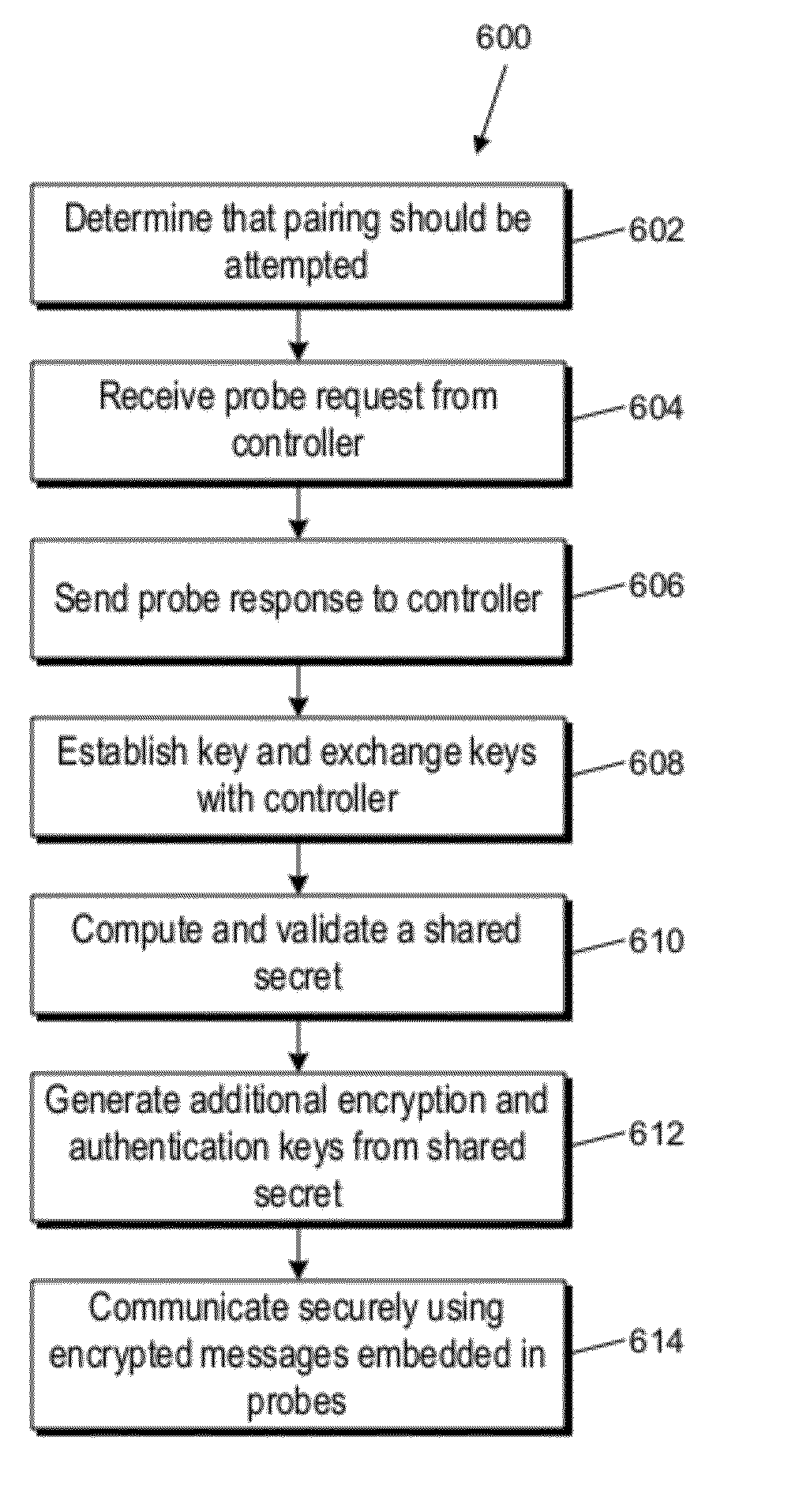
ActiveUS20120054493A1Simple interventionKey distribution for secure communicationPublic key for secure communicationComputer hardwareTelecommunications link
A secure wireless communication link (pairing) between two devices can be established using cleartext wireless transmissions between devices not joined to a network (“probes”). One device can broadcast a first probe indicating that it is seeking to establish a pairing. The other device can respond with a second probe, and the two devices can establish a shared secret, e.g., by exchanging further information using additional probes. Thereafter, either device can send a message to the other by encrypting the message using a cryptographic key derived from the shared secret; encrypted messages can also be sent within probes. The receiving device can extract an encrypted message from a probe and decrypt it using the cryptographic key. The encrypted message can include credentials usable by the receiving device to join a wireless network.
Owner:APPLE INC
Systems and methods to securely generate shared keys
ActiveUS20050251680A1Key distribution for secure communicationPublic key for secure communicationMaster keyRe keying
A method for secure bidirectional communication between two systems is described. A first key pair and a second key pair are generated, the latter including a second public key that is generated based upon a shared secret. First and second public keys are sent to a second system, and third and fourth public keys are received from the second system. The fourth public key is generated based upon the shared secret. A master key for encrypting messages is calculated based upon a first private key, a second private key, the third public key and the fourth public key. For re-keying, a new second key pair having a new second public key and a new second private key is generated, and a new fourth public key is received. A new master key is calculated using elliptic curve calculations using the new second private key and the new fourth public key.
Owner:MALIKIE INNOVATIONS LTD
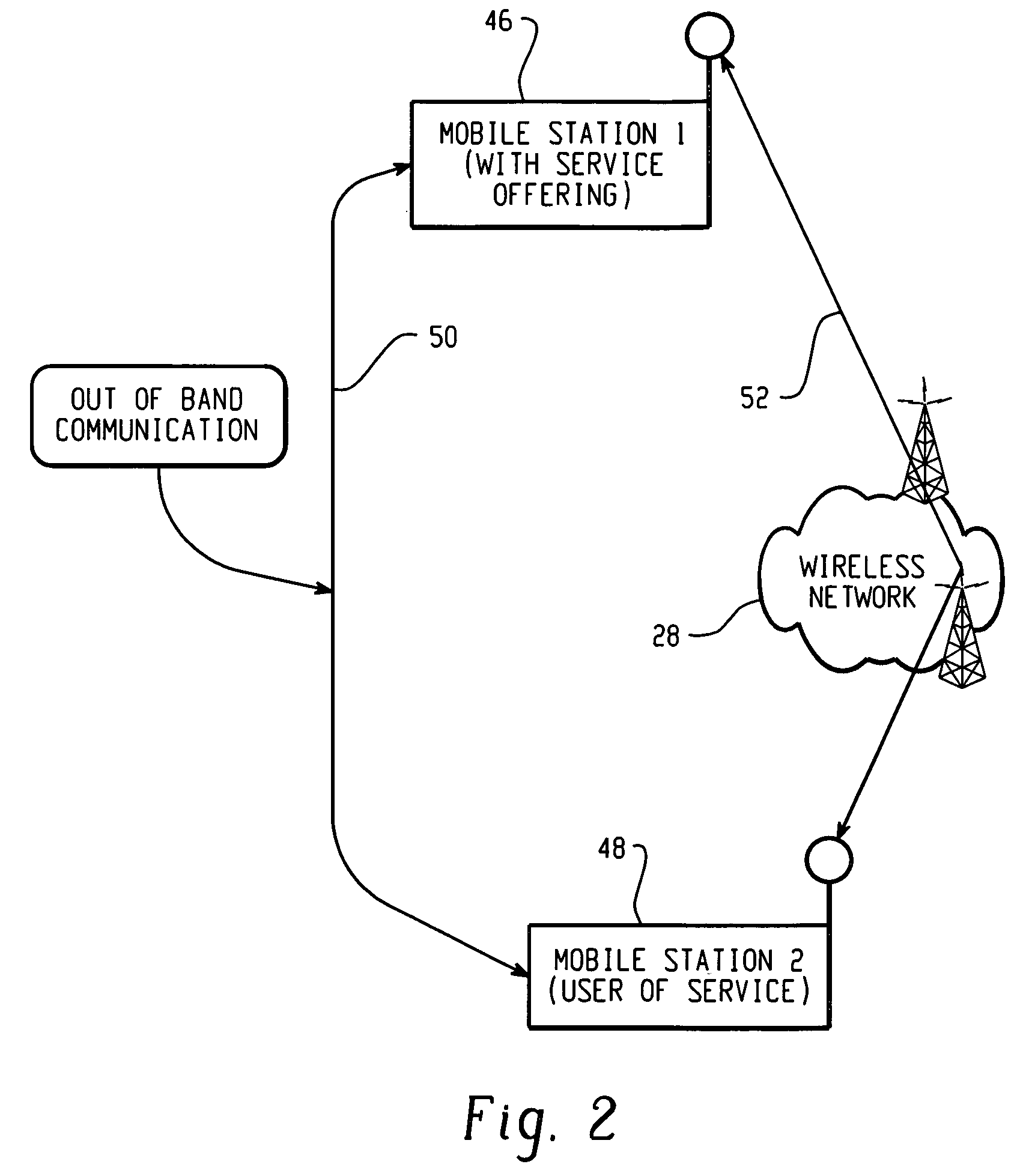
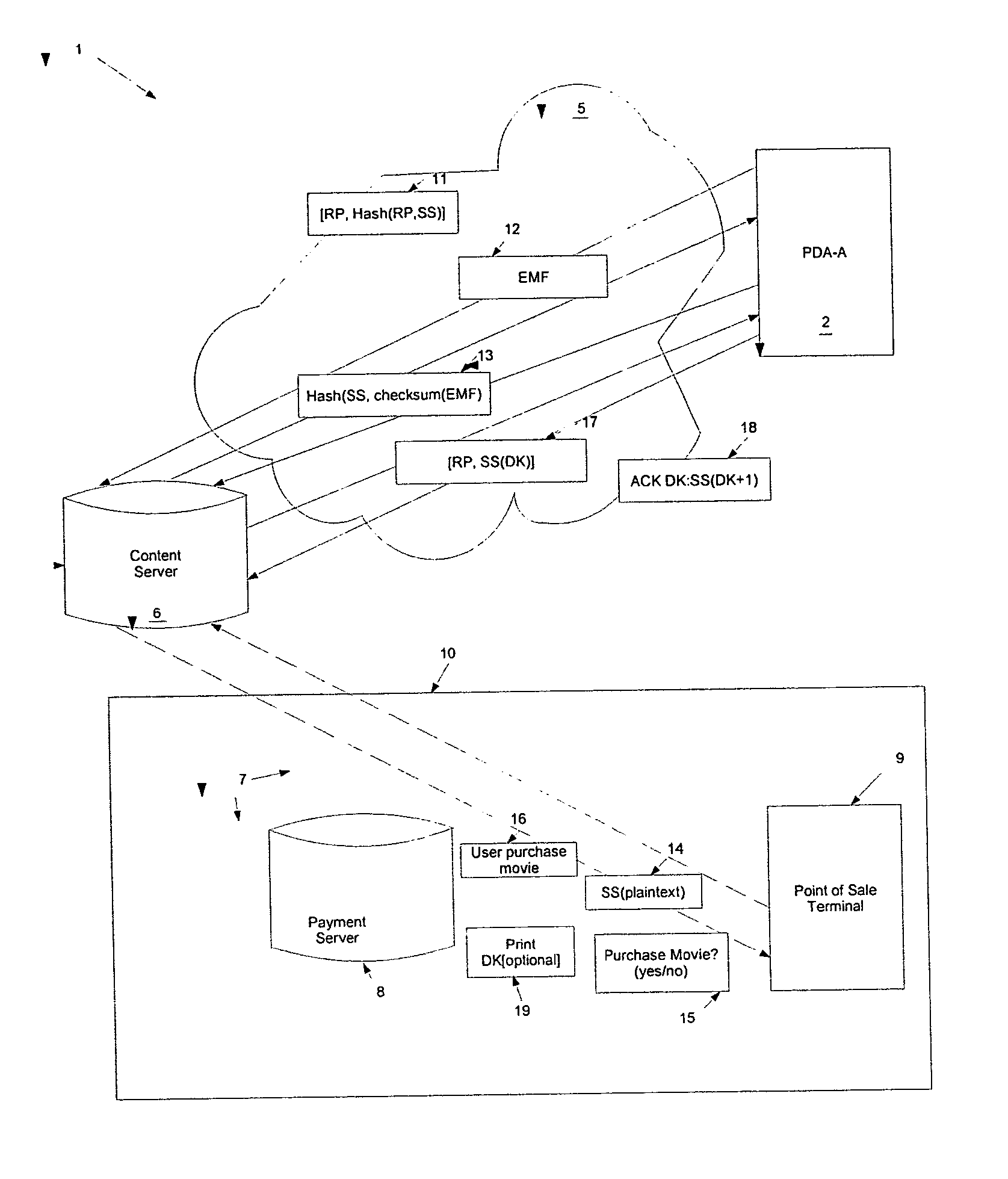
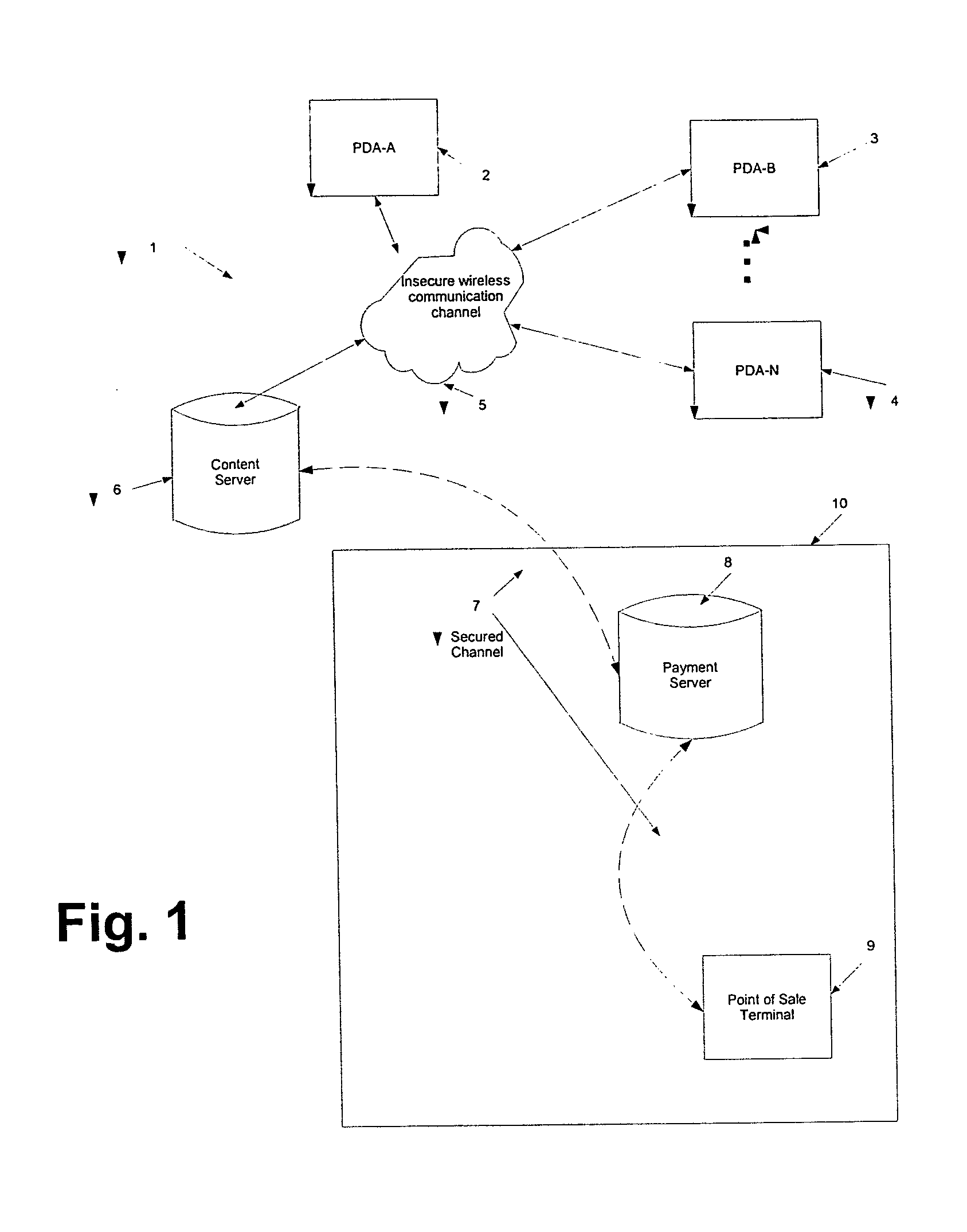
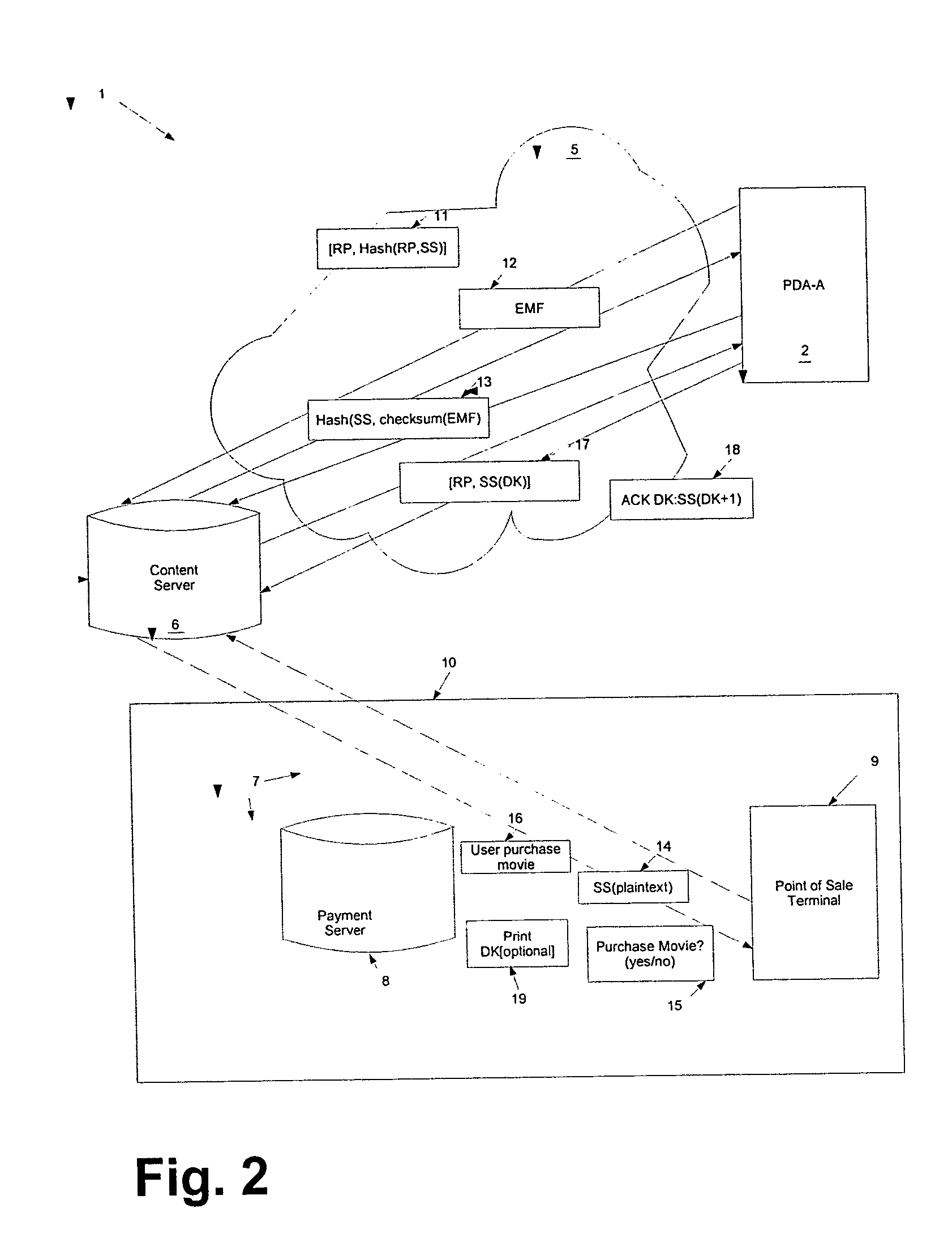
Method and system for content downloads via an insecure communications channel to devices
ActiveUS20050076210A1Easy to downloadKey distribution for secure communicationDigital data processing detailsPlaintextSecure communication
The present teachings provide for a method and system for facilitating content download to one or more remote devices via an insecure communication channel. The method comprises the steps of receiving at least one shared secret from a device via an insecure communications channel, each shared secret encoded and functioning as an identifier for the device, transmitting an encrypted file, from a file server, to the device associated with the encoded shared secret, receiving the shared secret in a plaintext form a via a secure communications channel, receiving a confirmation authorizing the release of a decryption key, and sending a decryption key corresponding to the transmitted file, for which the authorization for the release of the decryption key has been received. The decryption key is encrypted using the shared secret if transmission is via the insecure channel.
Owner:MARQETA
Efficient and secure authentication of computing systems
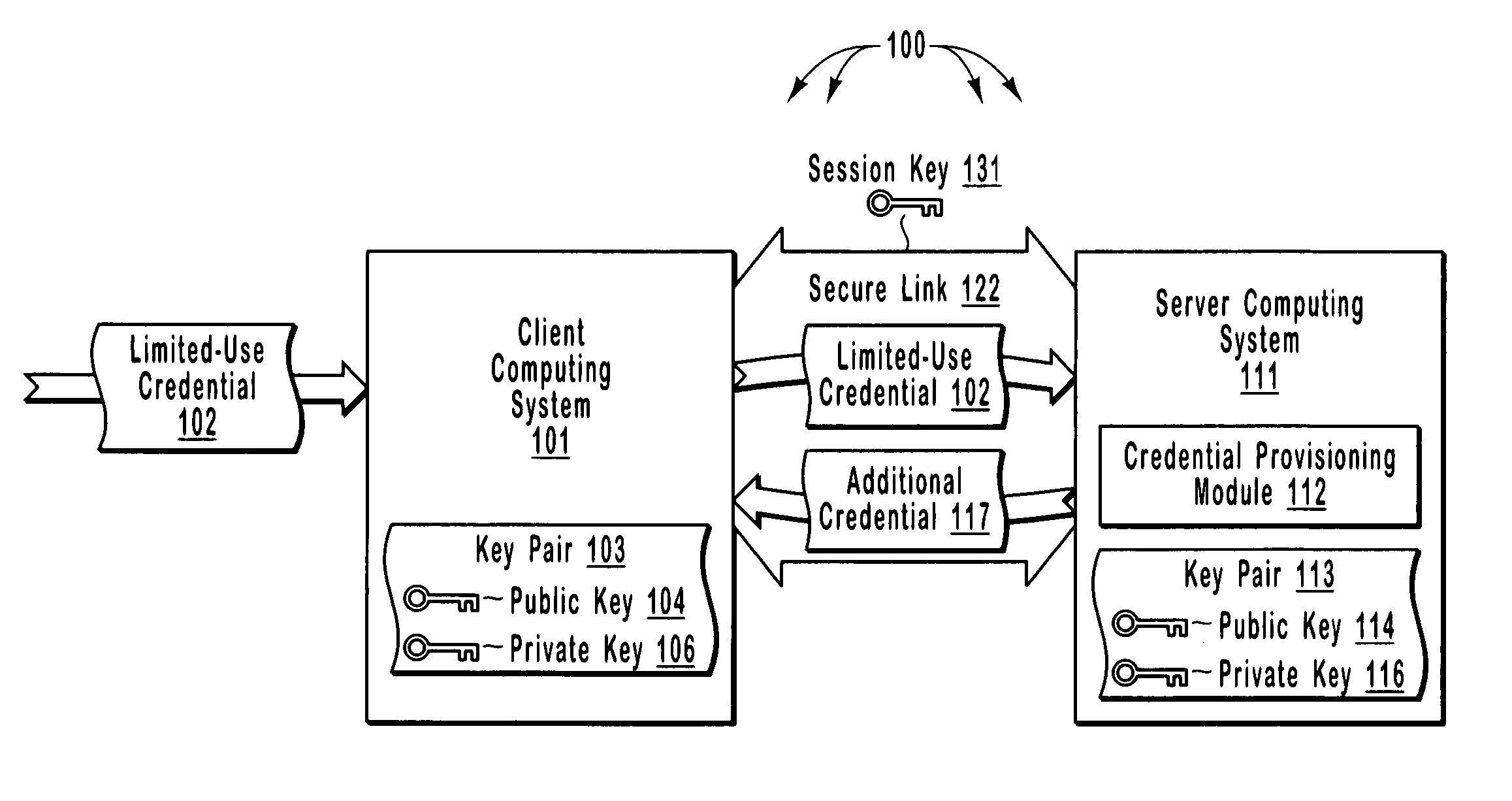
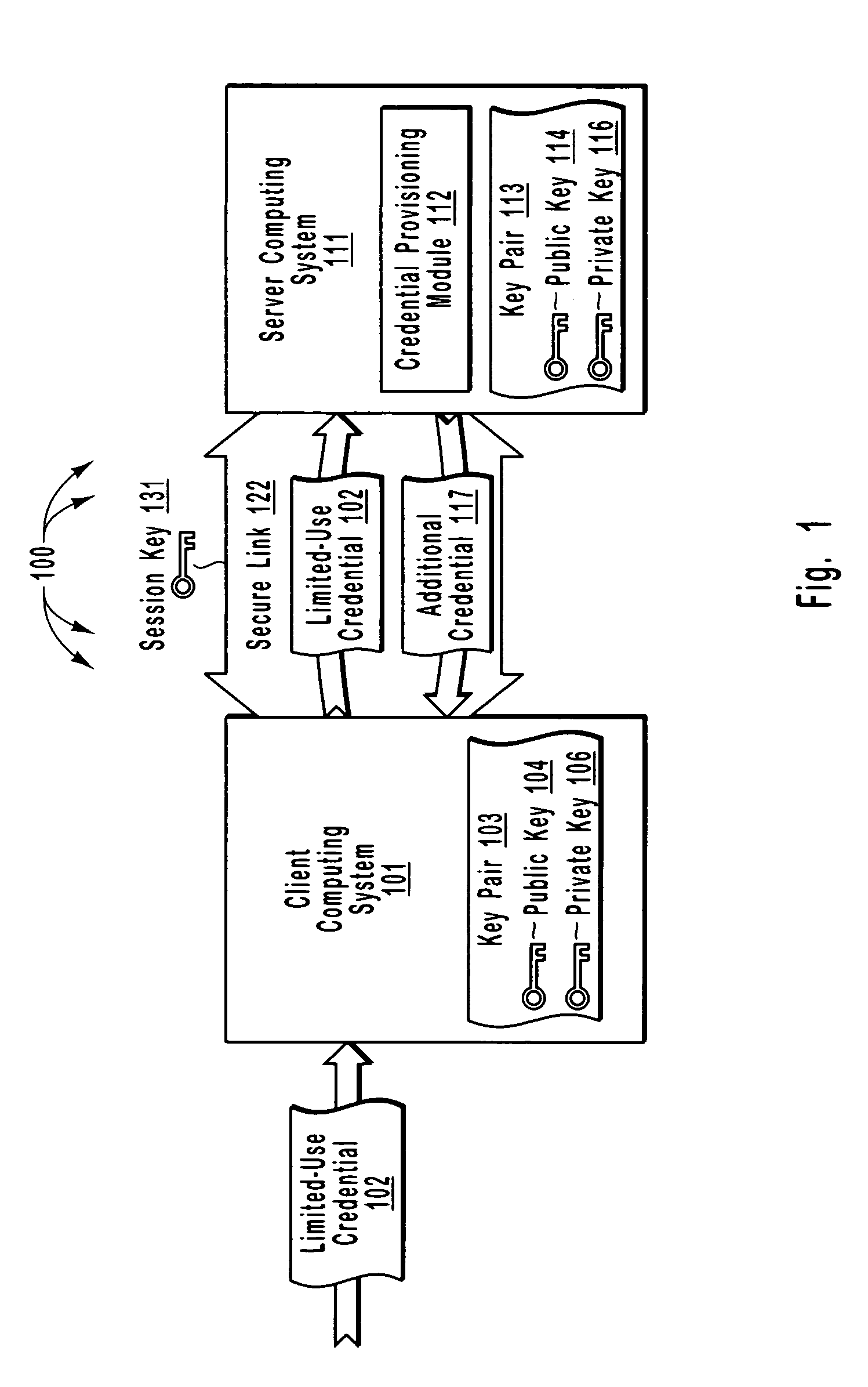
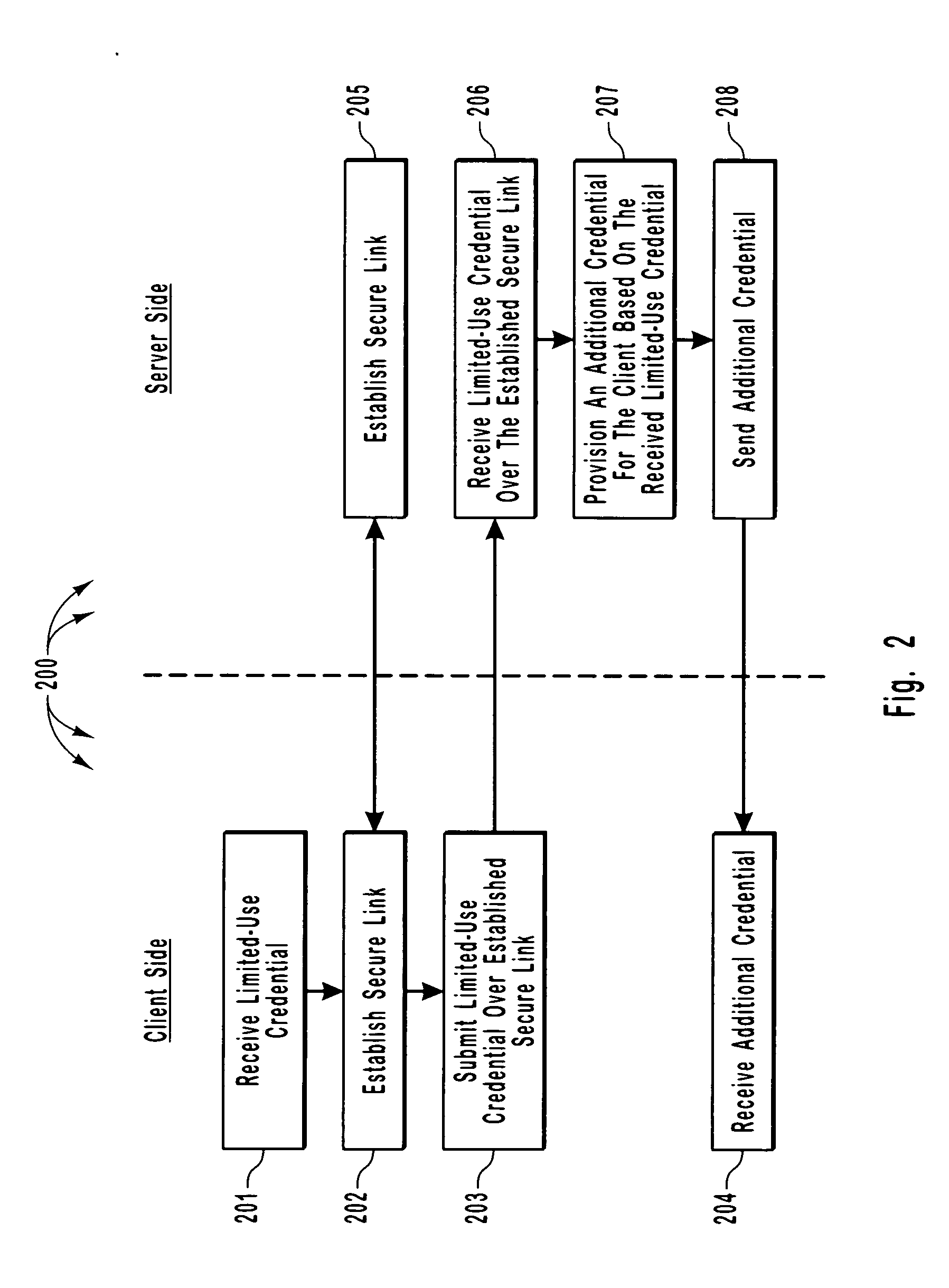
ActiveUS20050210252A1Efficiently and securely authenticatingKey distribution for secure communicationDigital data processing detailsClient-sideProtocol for Carrying Authentication for Network Access
The principles of the present invention relate to systems, methods, and computer program products for more efficiently and securely authenticating computing systems. In some embodiments, a limited use credential is used to provision more permanent credentials. A client receives a limited-use (e.g., a single-use) credential and submits the limited-use credential over a secure link to a server. The server provisions an additional credential (for subsequent authentication) and sends the additional credential to the client over the secure link. In other embodiments, computing systems automatically negotiate authentication methods using an extensible protocol. A mutually deployed authentication method is selected and secure authentication is facilitated with a tunnel key that is used encrypt (and subsequently decrypt) authentication content transferred between a client and a server. The tunnel key is derived from a shared secret (e.g., a session key) and nonces.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
System and method for website authentication using a shared secret
ActiveUS8060916B2Digital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationThird partyInternet privacy
Owner:SYMANTEC CORP
Hardware trust anchors in sp-enabled processors
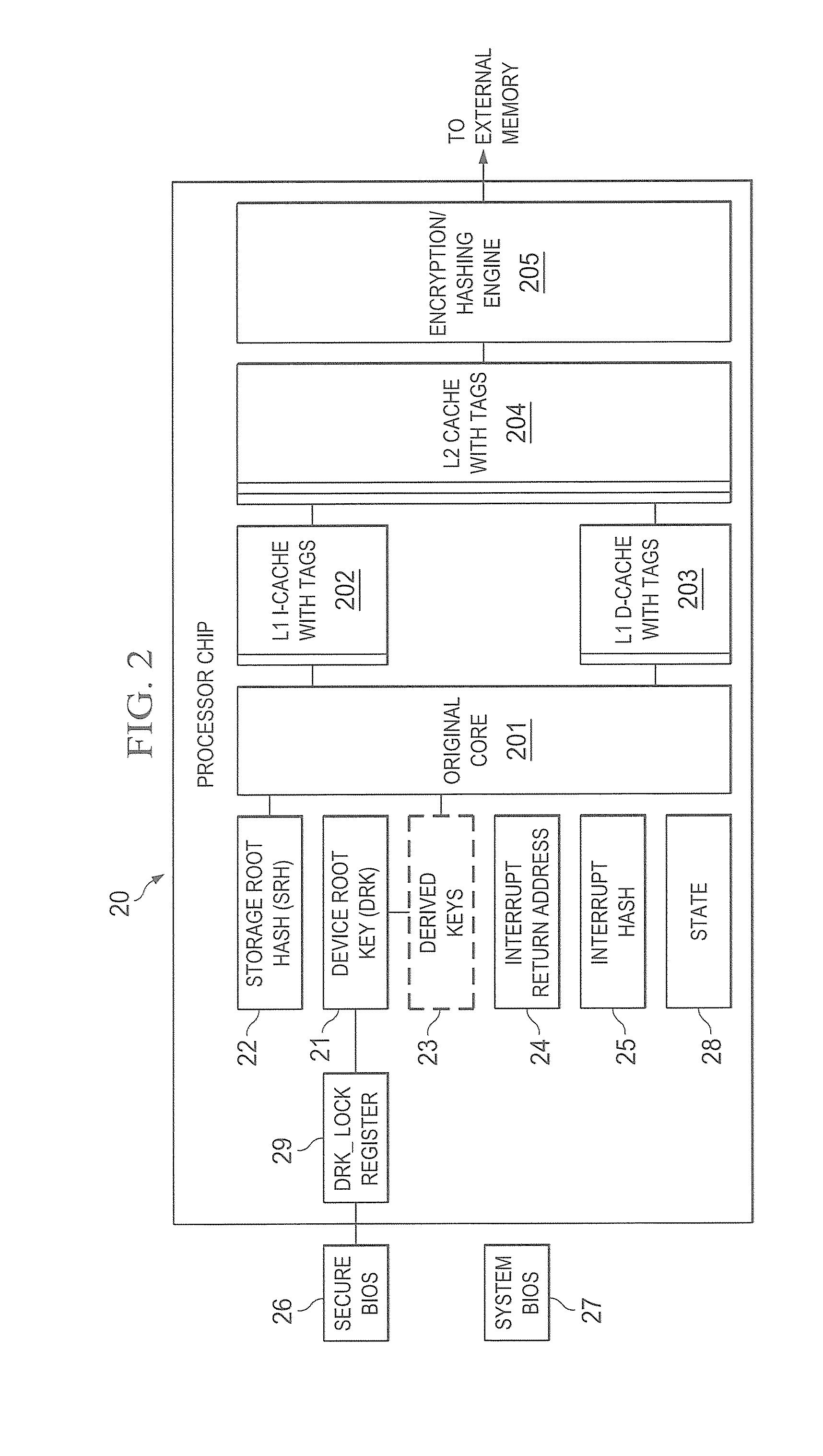
ActiveUS20100042824A1User identity/authority verificationDigital computer detailsOperational systemConfidentiality
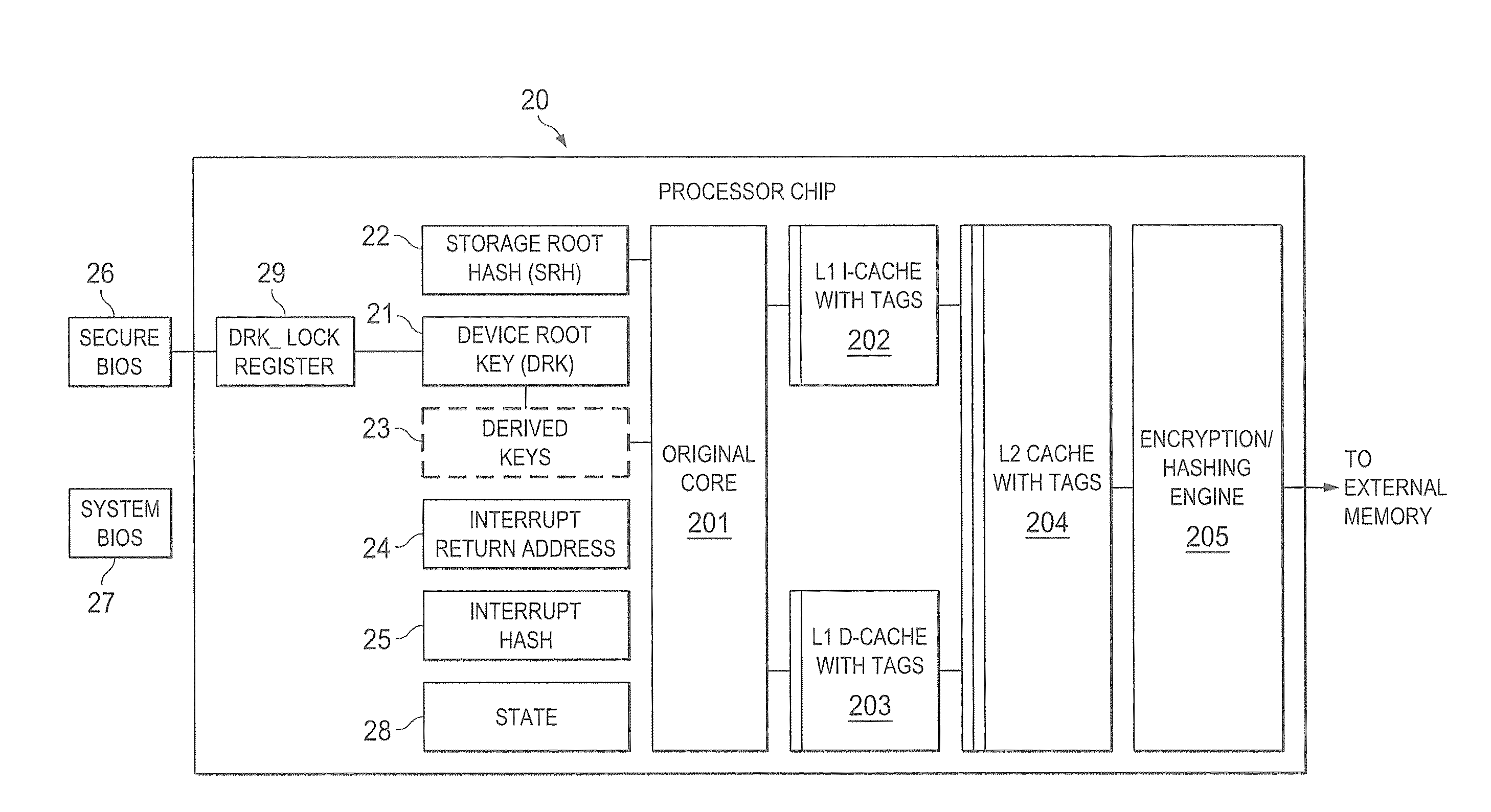
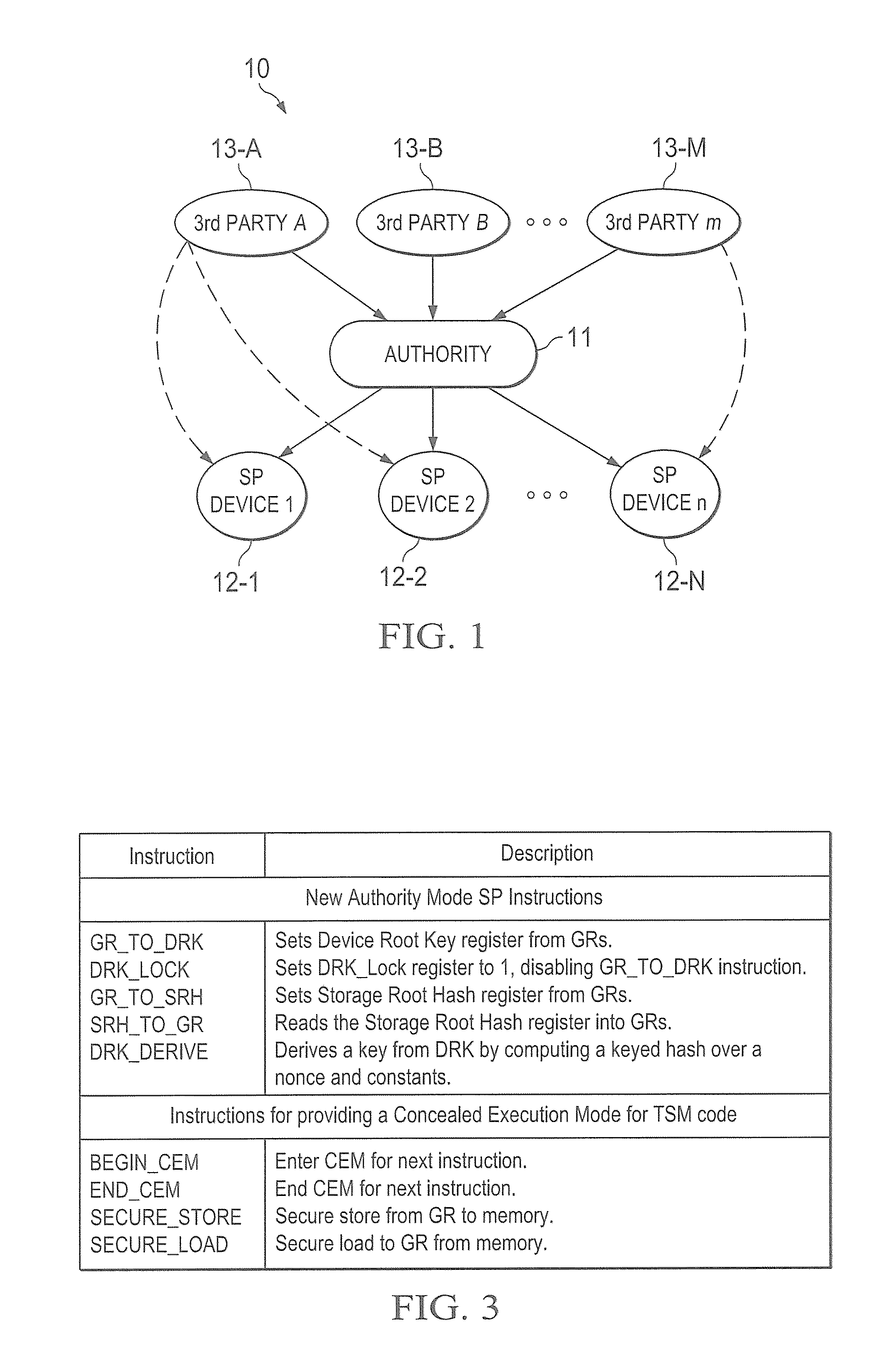
A trust system and method is disclosed for use in computing devices, particularly portable devices, in which a central Authority shares secrets and sensitive data with users of the respective devices. The central Authority maintains control over how and when shared secrets and data are used. In one embodiment, the secrets and data are protected by hardware-rooted encryption and cryptographic hashing, and can be stored securely in untrusted storage. The problem of transient trust and revocation of data is reduced to that of secure key management and keeping a runtime check of the integrity of the secure storage areas containing these keys (and other secrets). These hardware-protected keys and other secrets can further protect the confidentiality and / or integrity of any amount of other information of arbitrary size (e.g., files, programs, data) by the use of strong encryption and / or keyed-hashing, respectively. In addition to secrets the Authority owns, the system provides access to third party secrets from the computing devices. In one embodiment, the hardware-rooted encryption and hashing each use a single hardware register fabricated as part of the computing device's processor or System-on-Chip (SoC) and protected from external probing. The secret data is protected while in the device even during operating system malfunctions and becomes non-accessible from storage according to various rules, one of the rules being the passage of a certain time period. The use of the keys (or other secrets) can be bound to security policies that cannot be separated from the keys (or other secrets). The Authority is also able to establish remote trust and secure communications to the devices after deployment in the field using a special tamper-resistant hardware register in the device, to enable, disable or update the keys or secrets stored securely by the device.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES FOR PRINCETON UNIV +1
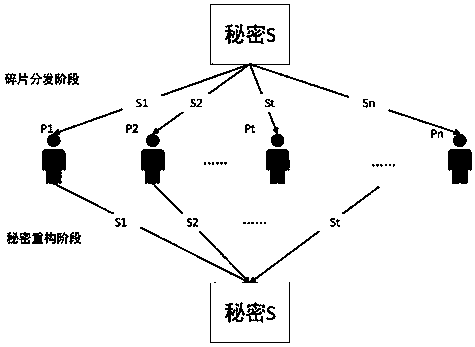
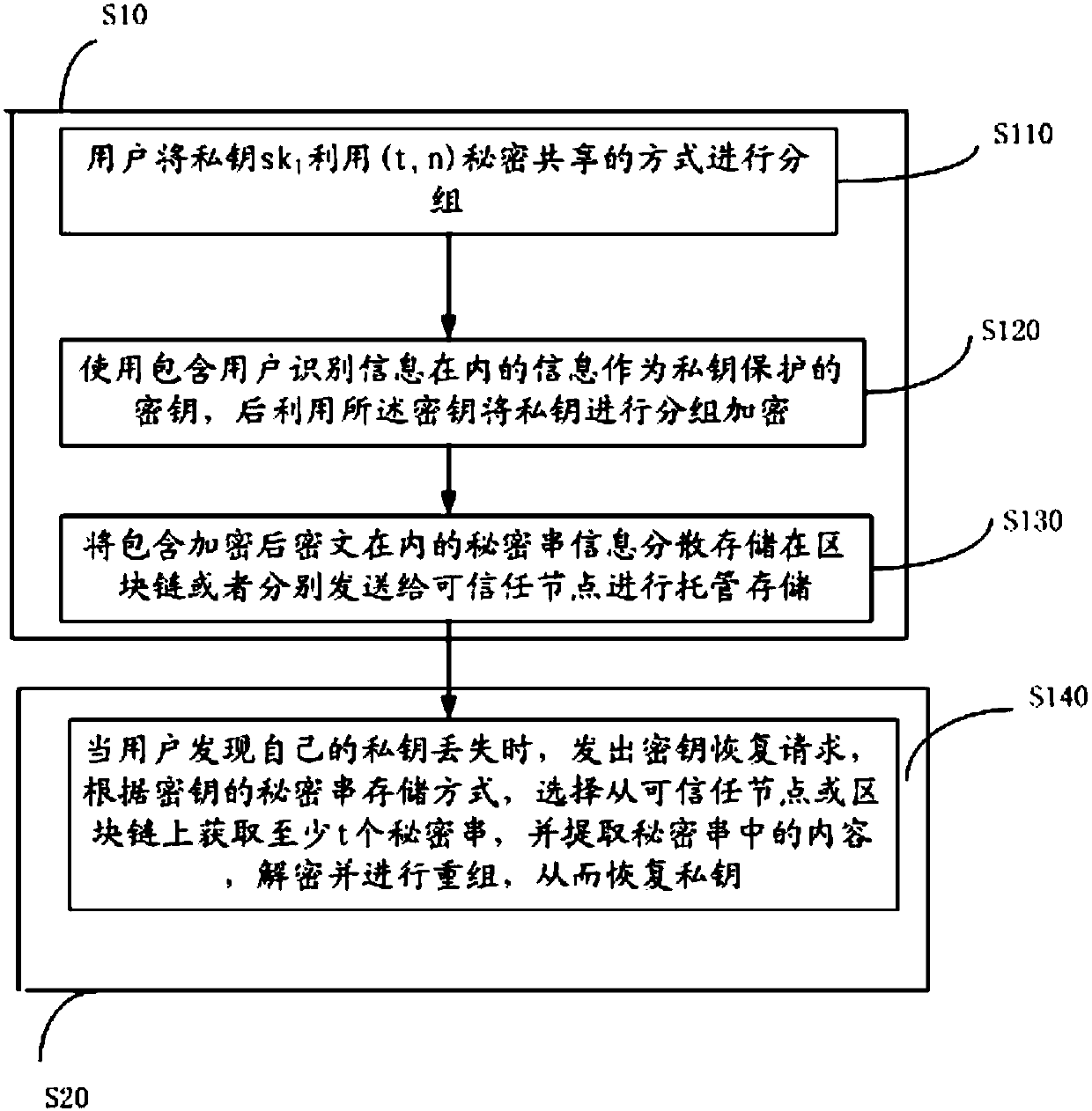
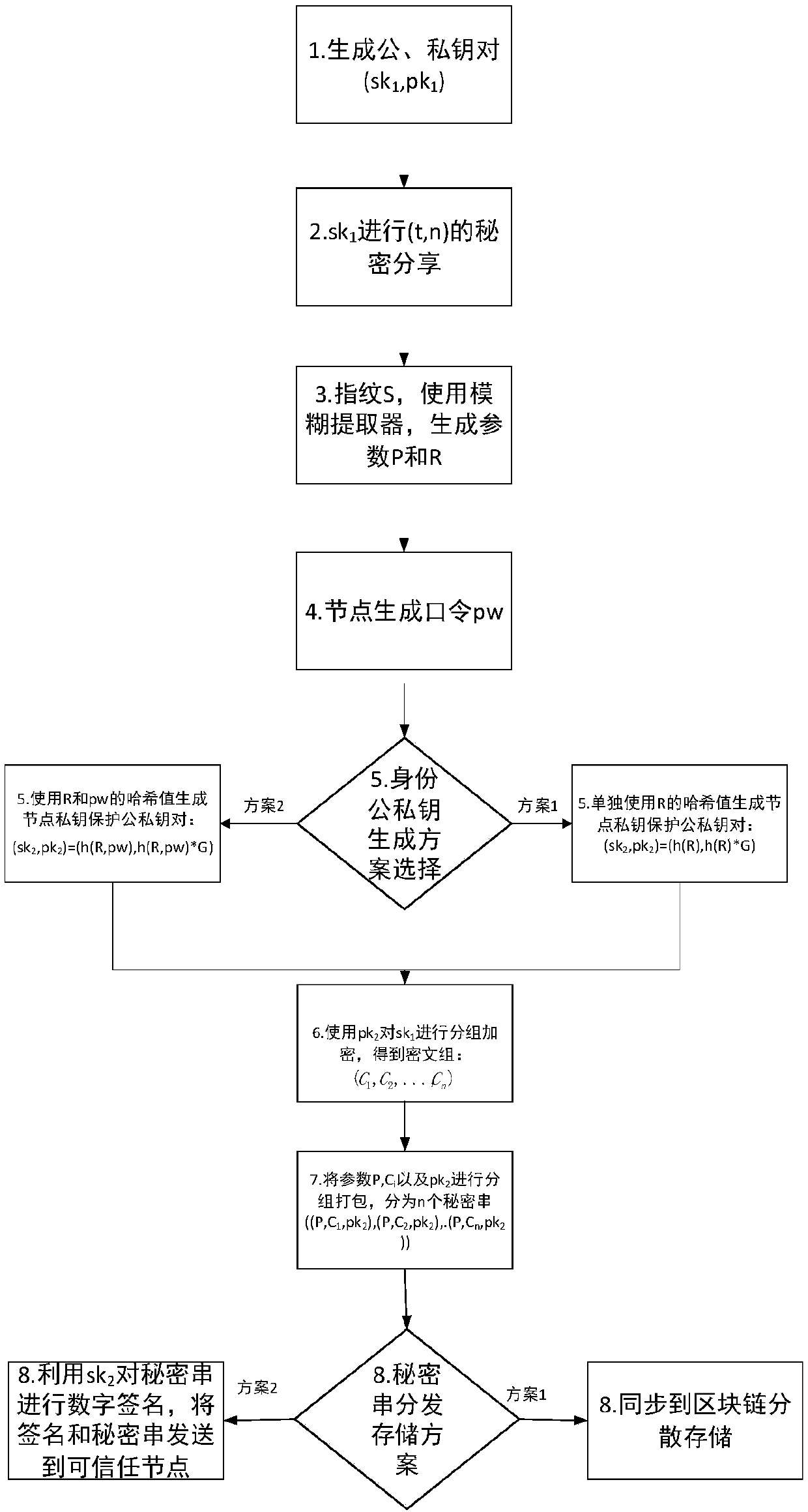
Block chain key trusteeship and recovery method and device based on secrecy sharing technology
InactiveCN107623569ASafekeepingSafe recoveryKey distribution for secure communicationRecovery methodRestoration method
The invention discloses a block chain key trusteeship and recovery method and device based on a secrecy sharing technology. The method comprises the steps that A1, a user groups a private key sk1 in a(t, n) secrecy sharing mode, wherein the n is the number of fragments of shared secrecies obtained by splitting the private key, the t is the minimum number of the fragments for recovery of the private key, and the t is greater than or equal to 2 and is smaller than or equal to the n; A2, information containing user identification information is taken as a private key protection key, and then grouping encryption is carried out on the private key through utilization of the key; and A3, secrecy string information containing encrypted ciphertexts is dispersely stored to a block chain or is sentto trusted nodes for trusteeship and storage, when the user discovers that own private key is lost, a key recovery request is generated, at least t secrecy strings are obtained from the trusted nodesor the block chain in a secrecy string storage mode of the key, and the content in the secrecy strings is extracted, decrypted and recombined, so the private key is recovered. According to the methodand the device, the secrecy sharing technology is applied to a block chain scene for the first time, thereby solving the private key trusteeship and recovery security problem.
Owner:JUZIX TECH SHENZHEN CO LTD
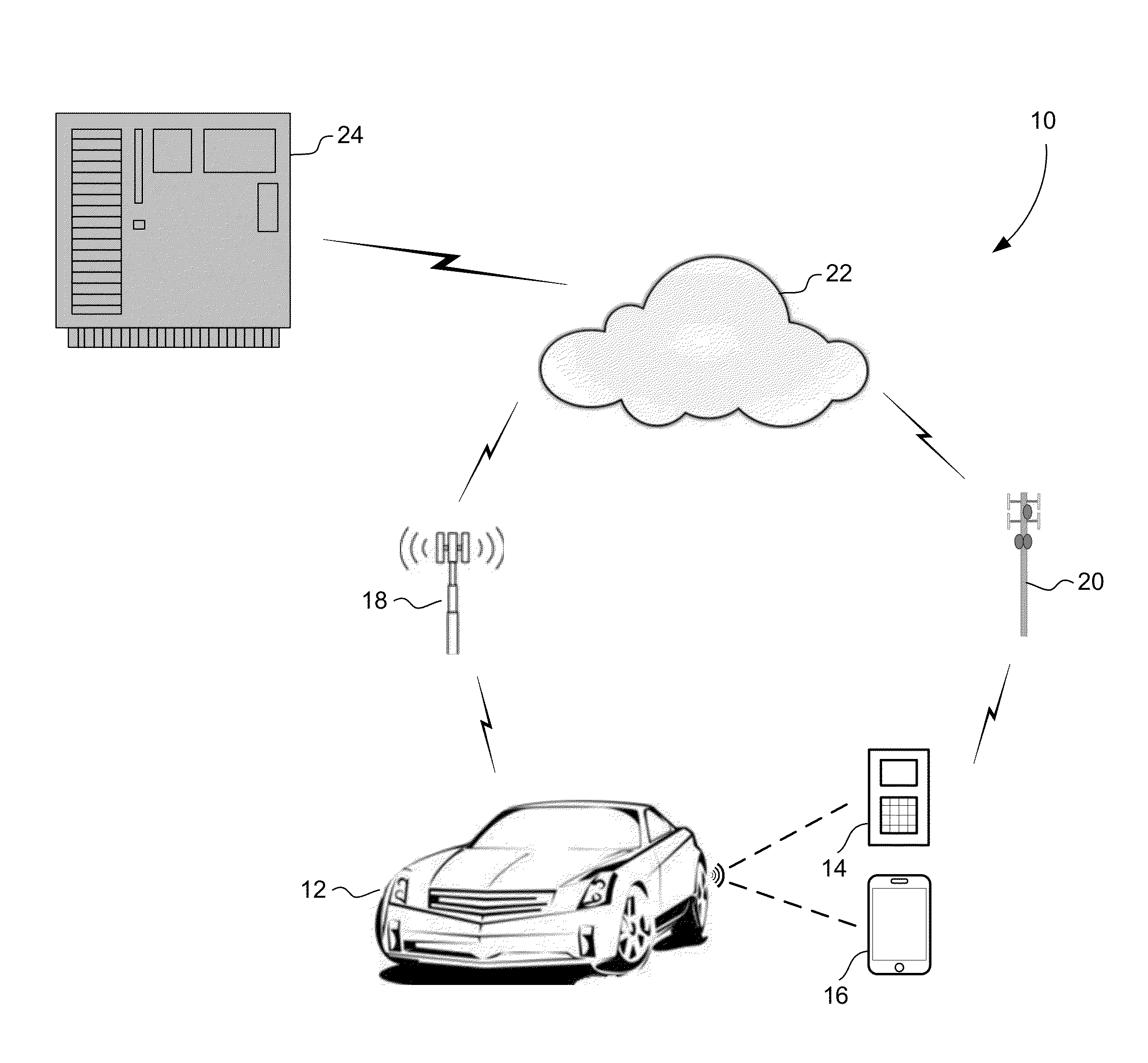
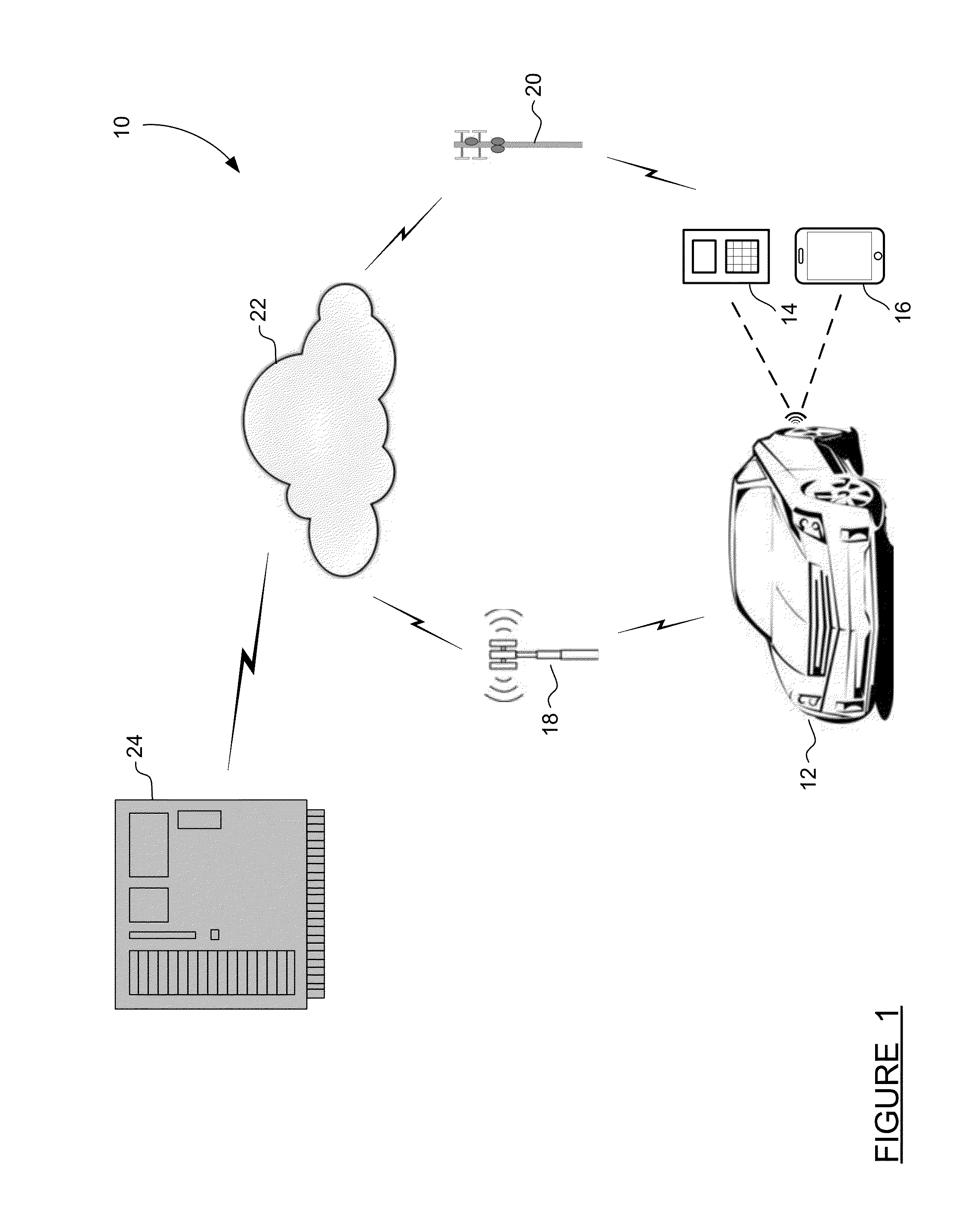
Method and apparatus for secure pairing of mobile devices with vehicles using telematics system
A method for establishing secure wireless communications between a mobile device and a vehicle, where a user is not required to enter a password, but instead the telematics system is used to bootstrap the trust between the mobile device and the vehicle. The user initiates the process by pressing a button on the mobile device to request pairing. The vehicle uses its secure OnStar cellular communication link to verify the mobile device with the OnStar server, which generates and sends a session key to the vehicle via the vehicle-OnStar cellular connection, and also sends the session key to the mobile device via the device's own cellular connection. The session key serves as a shared secret, such that the vehicle can issue a secrecy challenge to the mobile device. When the mobile device responds appropriately, a trusted wireless communications link can be established between the mobile device and the vehicle.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
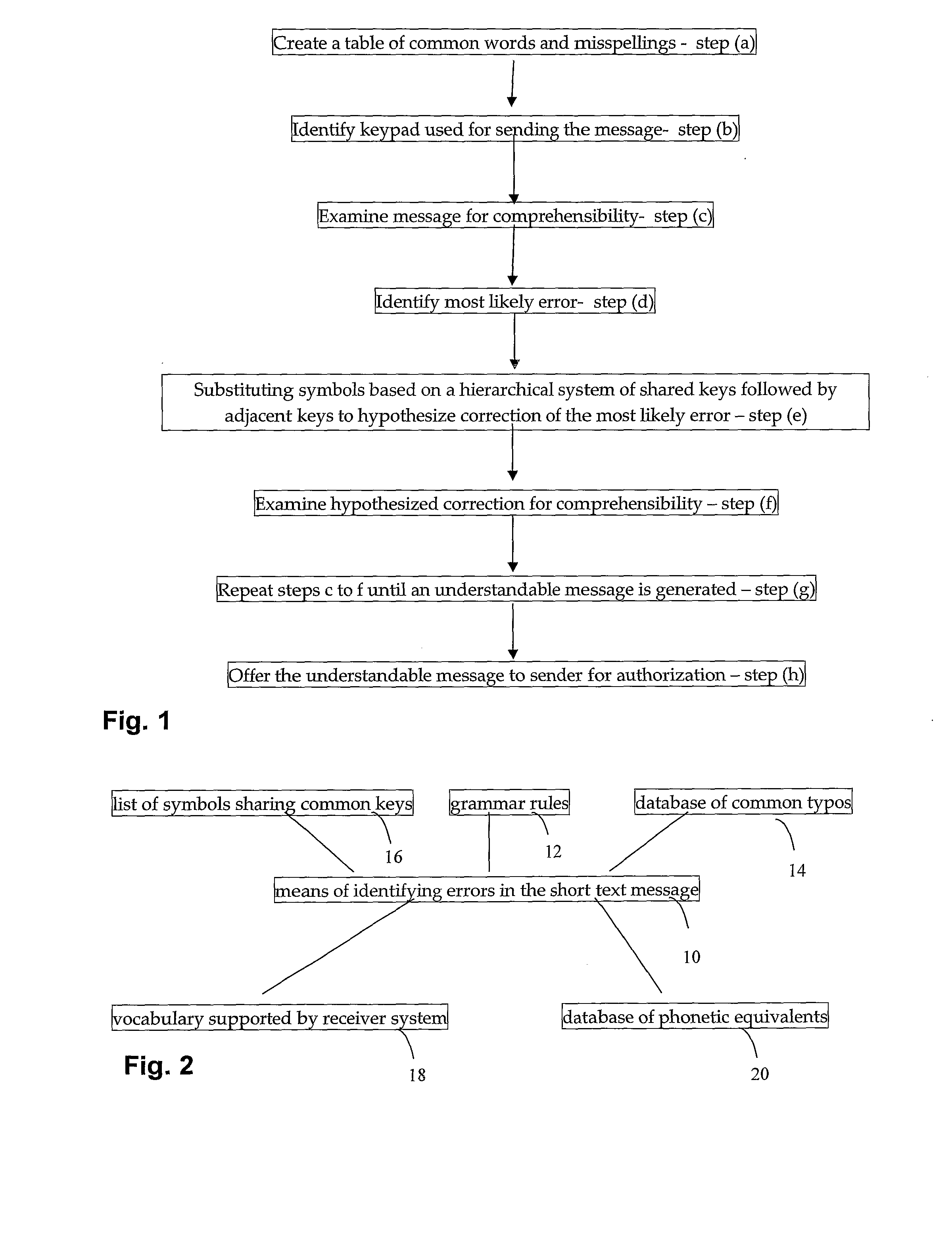
Context sensitive, error correction of short text messages
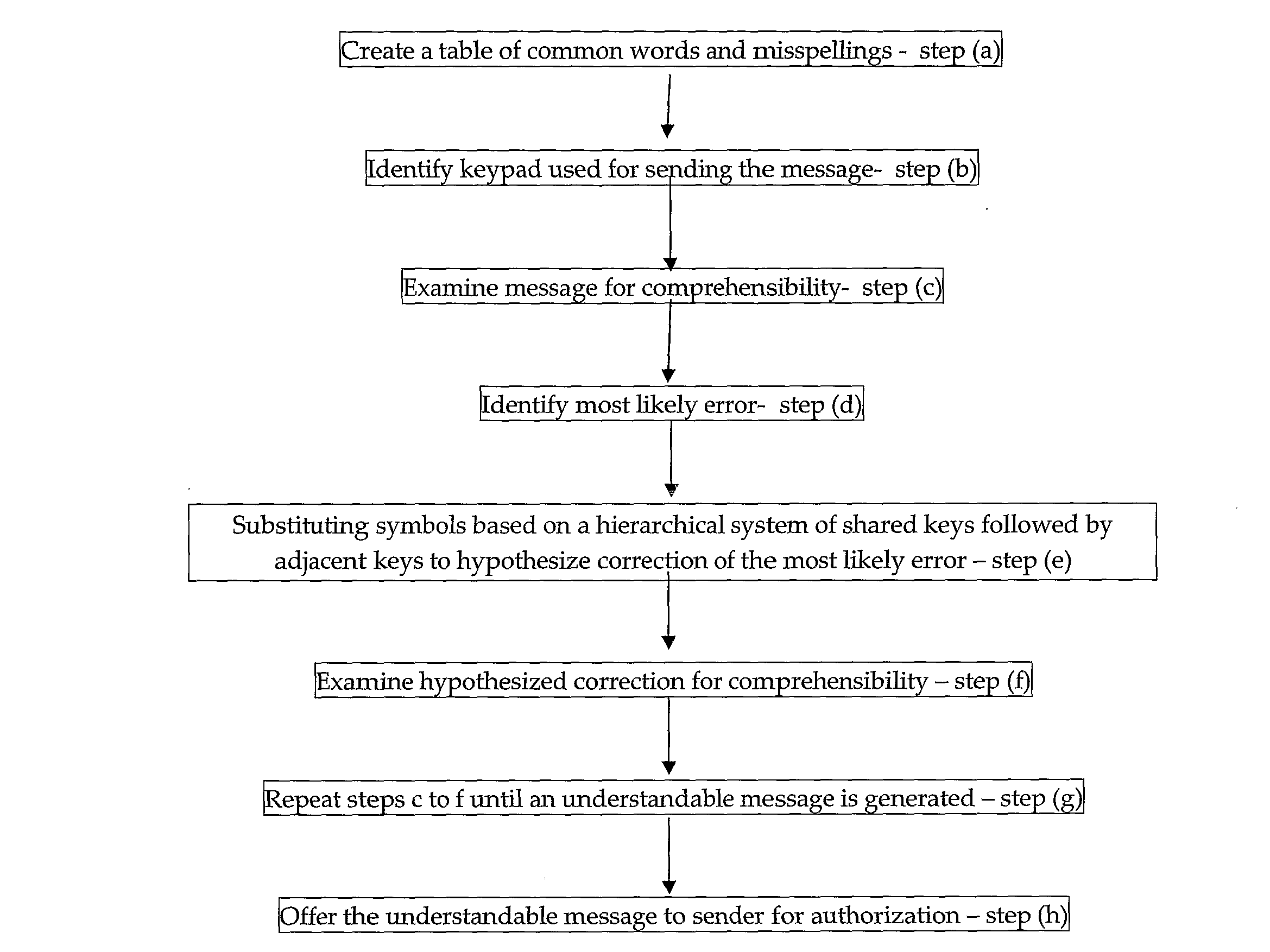
InactiveUS20100050074A1Efficient deploymentNatural language data processingSpecial data processing applicationsForward error correctionCommon word
A method for correcting a short text message comprising the steps of: creating a table of common words and misspellings; identifying keypad used for sending the message, examining message for comprehensibility; identifying most likely error, substituting symbols based on a hierarchical system of shared keys followed by adjacent keys to hypothesize correction of the most likely error; examining hypothesized correction for comprehensibility, and repeating steps (c) to (f) until an understandable message is generated.
Owner:CELLESENSE TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com