Patents
Literature
336 results about "One-way function" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In computer science, a one-way function is a function that is easy to compute on every input, but hard to invert given the image of a random input. Here, "easy" and "hard" are to be understood in the sense of computational complexity theory, specifically the theory of polynomial time problems. Not being one-to-one is not considered sufficient of a function for it to be called one-way (see Theoretical definition, below).
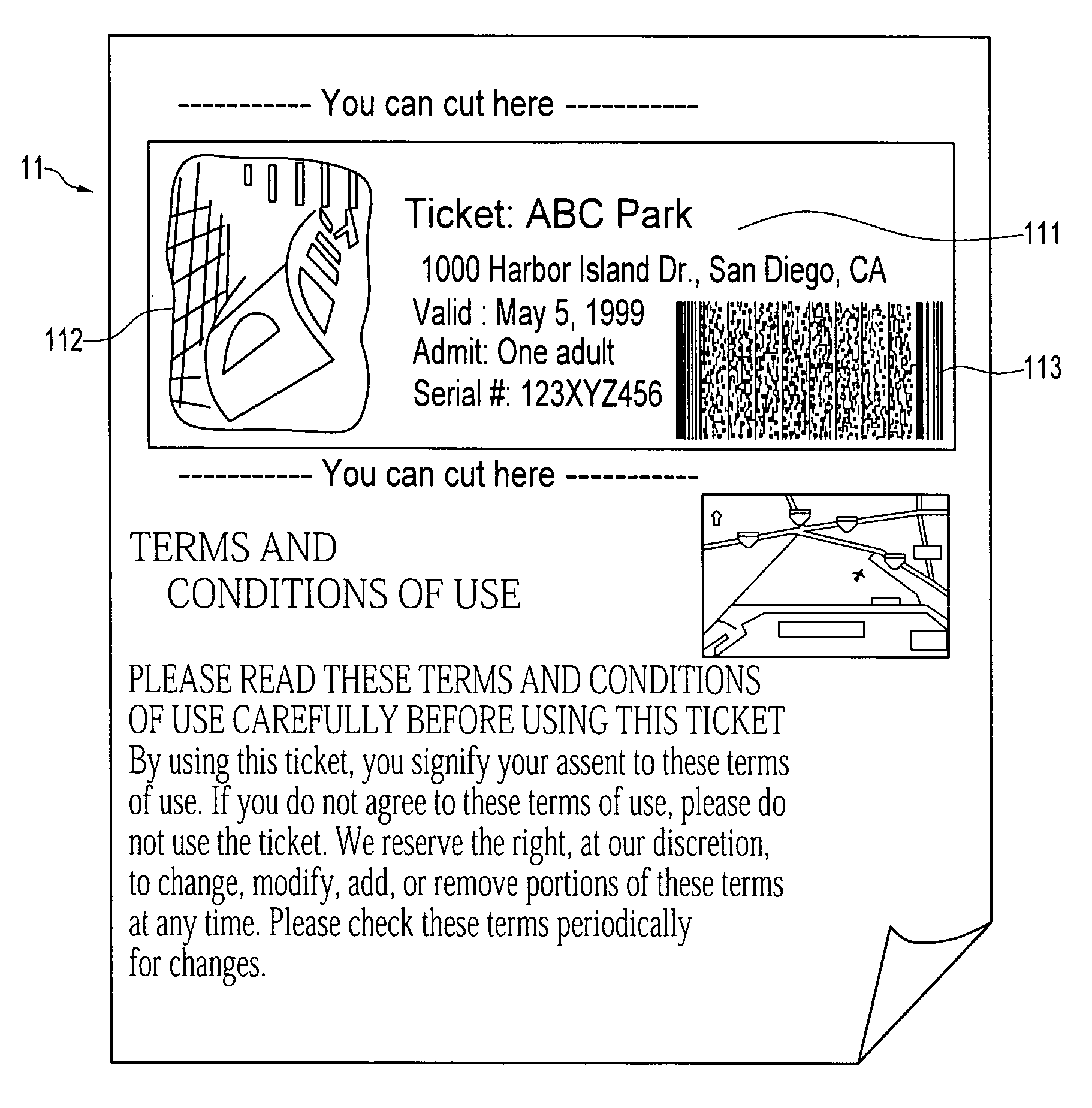
System and method for delivering and examining digital tickets
InactiveUS7093130B1Cost effectiveModest appearanceTicket-issuing apparatusUser identity/authority verificationTicketThe Internet
A digital ticket is procured by a client ticket consumer upon, preferably, the Internet from and by staged interaction with a ticket provider server. The digital ticket becomes embodied in a tangible transportable data storage medium, normally a 2-D bar code printed on paper by the consumer, or on the consumer's flexible disk or smart card, containing Sign(s,I||hash(R))||R where (1) R is a number having its origin in the computer of the ticket consumer, which number R is appended to (2) a number Sign(s,I||hash(R)). This number Sign(s,I||hash(R)) was earlier computed in the computer of the ticket provider as a digital signature using signature key s of a number hash(R) combined with event information I, and was subsequently communicated across the communications network to the computer of the ticket consumer. The number hash(R) was itself even earlier computed in the computer of the ticket consumer as a one-way function of random number R, which computed one-way function was subsequently communicated to the computer of the ticket provider. The number R is private to the ticket consumer and not public; the digital signature key s is private to the ticket provider.The digital ticket is redeemed by (1) transporting the transportable storage medium within which the Sign(s,I||hash(R))||R is written to the particular selected event; (2) tendering the digital ticket for verification and for admission; (3) reading the Sign(s,I||hash(R))||R to an event computer and extracting the number R; (4) decrypting the remaining Sign(s, I||hash(R)) with verification key v of the ticket producer to get hash(R) and I; (5) re-calculating from R, with the same one-way function previously used, a re-calculated hash(R); then, having this recalculated hash(R) to hand; (6) comparing the re-calculated hash(R) to the extracted hash(R). The (4) decrypting will work, producing a proper I for the selected event, and the (6) comparing will be equal, only for a legitimate ticket.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
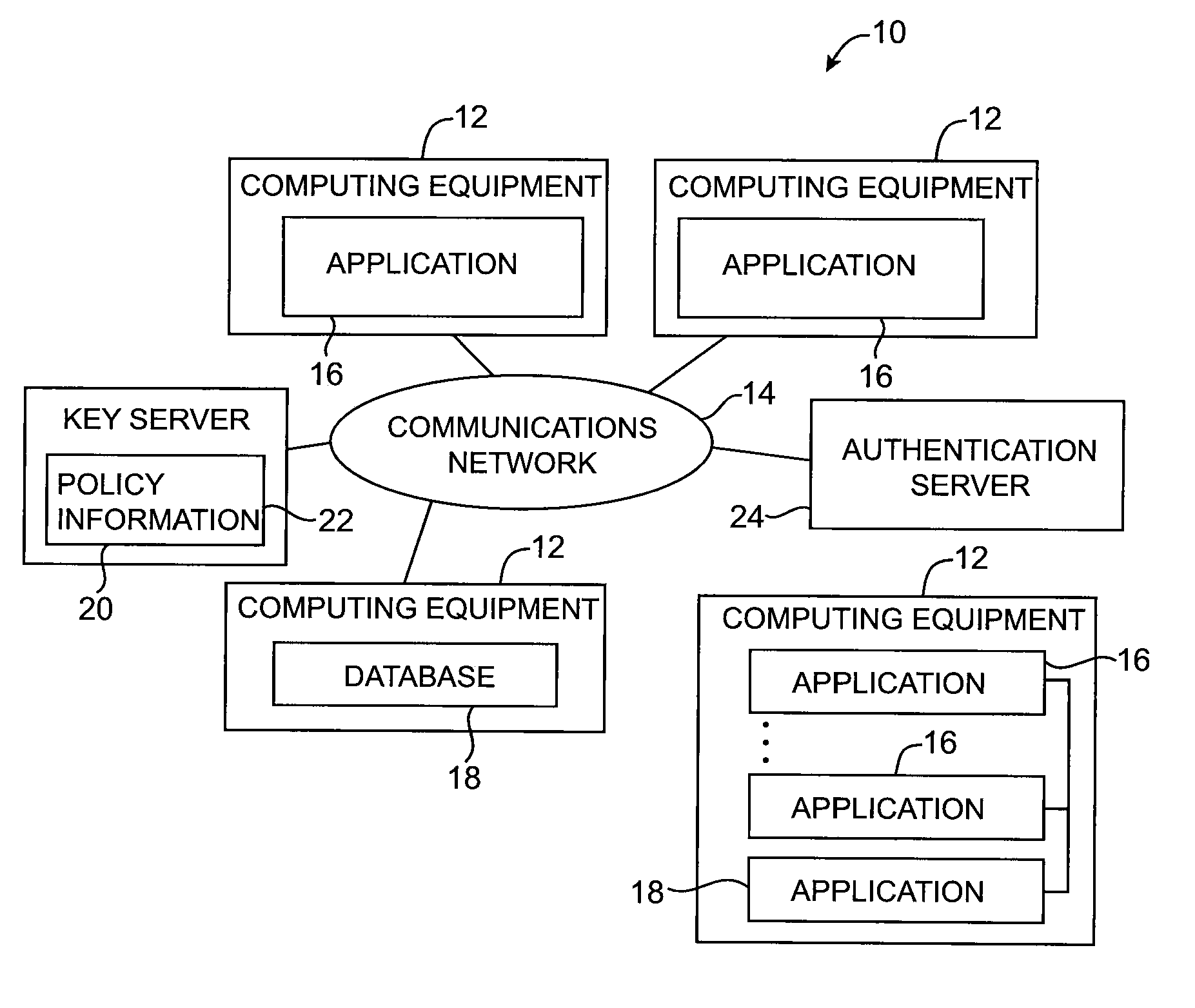
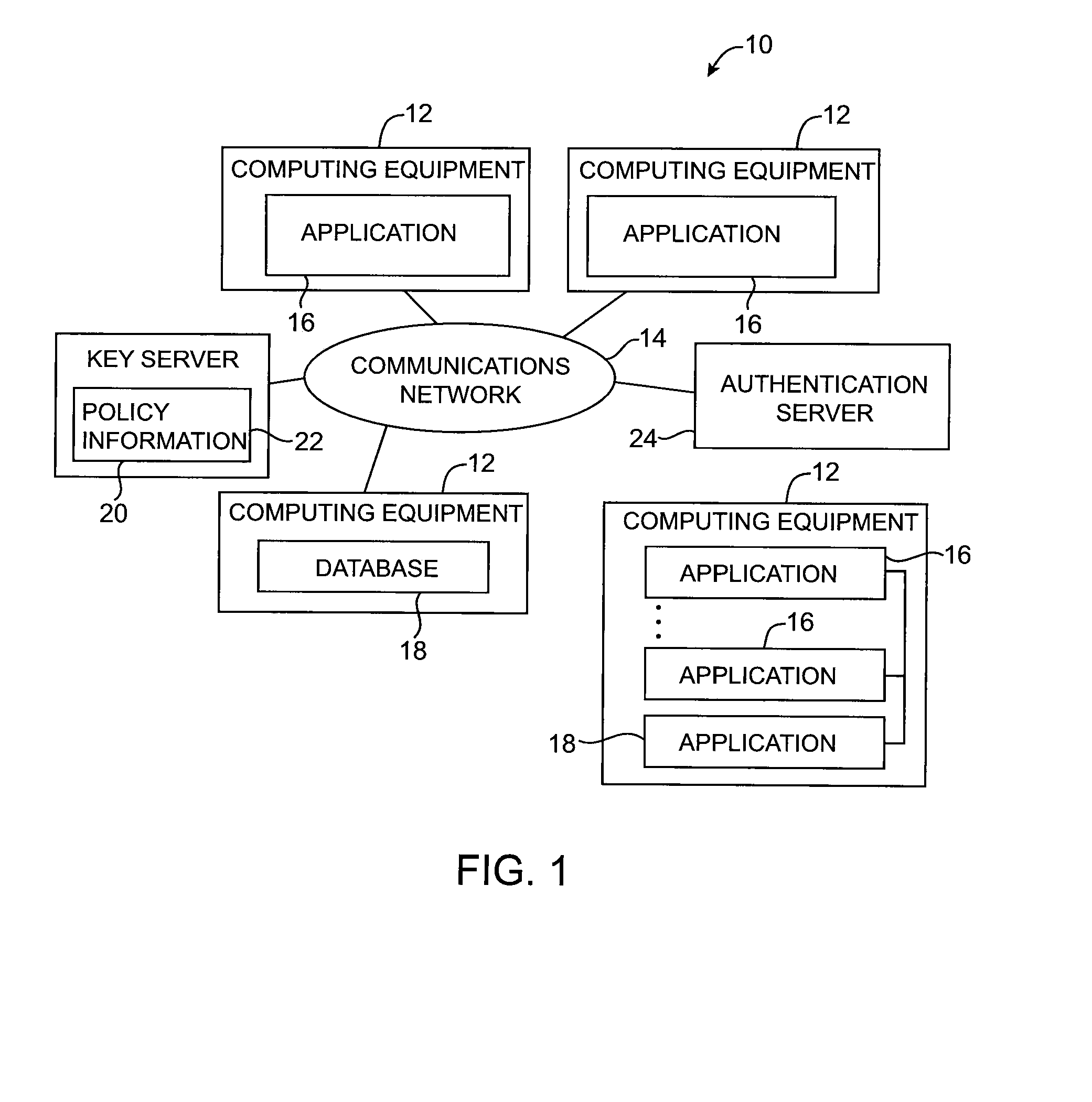
Format-preserving cryptographic systems
ActiveUS20080170693A1Error detection/correctionCryptography processingData processing systemOne-way function
Key requests in a data processing system may include identifiers such as user names, policy names, and application names. The identifiers may also include validity period information indicating when corresponding keys are valid. When fulfilling a key request, a key server may use identifier information from the key request in determining which key access policies to apply and may use the identifier in determining whether an applicable policy has been satisfied. When a key request is authorized, the key server may generate a key by applying a one-way function to a root secret and the identifier. Validity period information for use by a decryption engine may be embedded in data items that include redundant information. Application testing can be facilitated by populating a test database with data that has been encrypted using a format-preserving encryption algorithm. Parts of a data string may be selectively encrypted based on their sensitivity.
Owner:MICRO FOCUS LLC
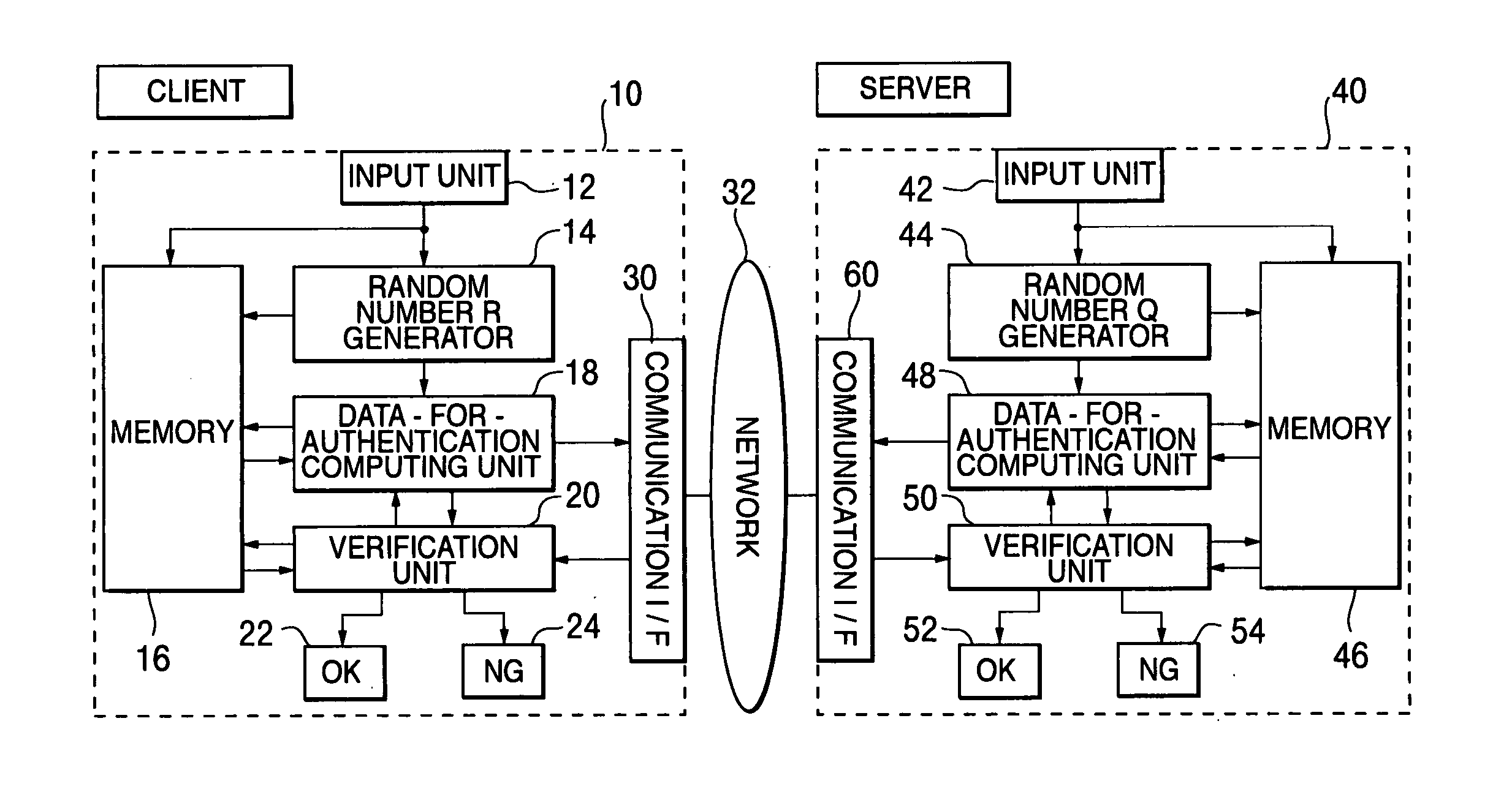
Inter-authentication method and device
InactiveUS20060143453A1Improve securityImprove convenienceUser identity/authority verificationCommunication unitOne-way function
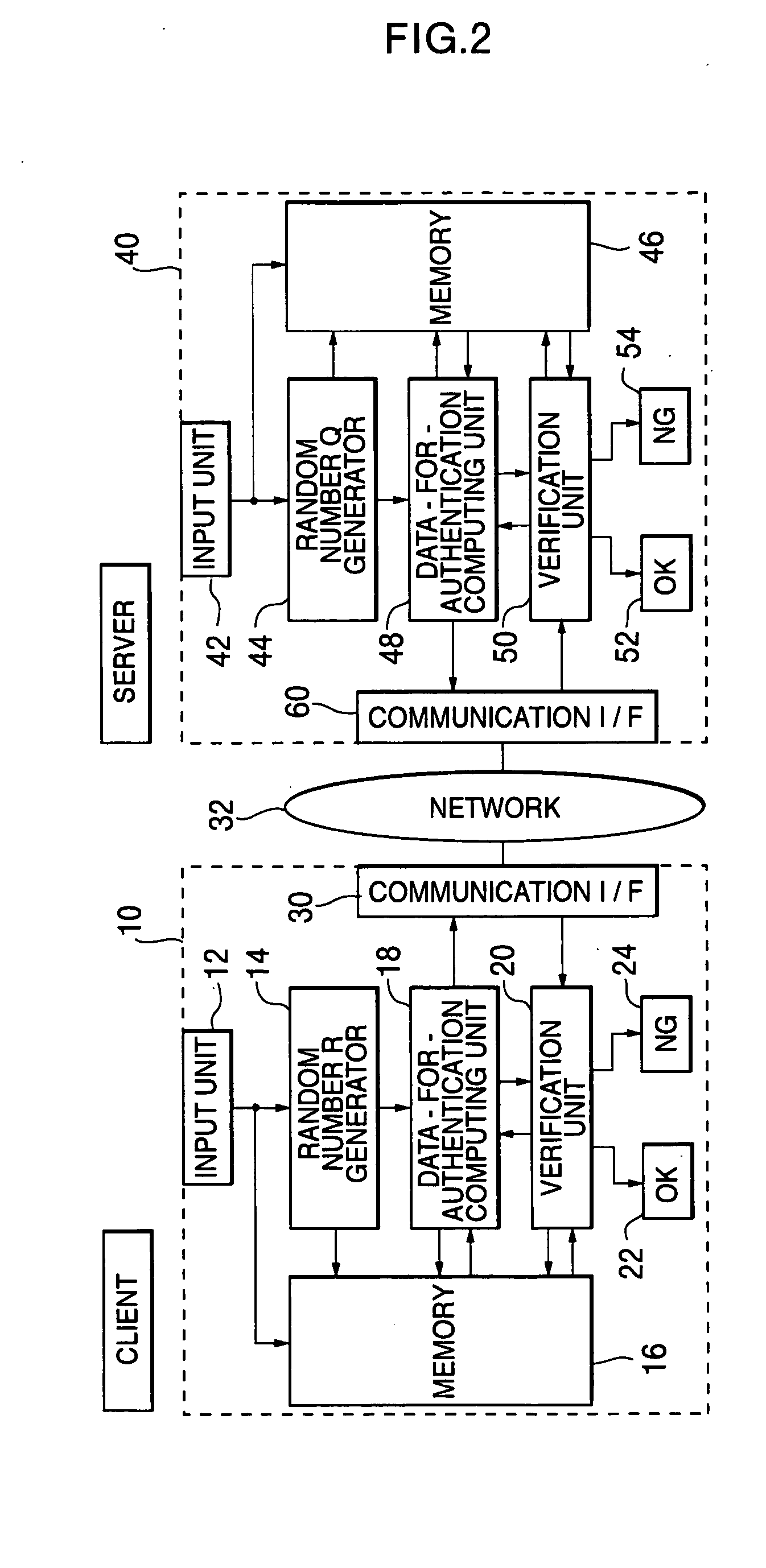
An objective of the present invention is to obtain a mutual authentication method in which mutual authentication is carried out securely and conveniently. In order to achieve the above objective, in the mutual authentication process, a private key K0, being an initial value, is stored in a client and a server (Pc0, Ps0). The client generates a random number R, calculates secret data C and authentication data A, and transmits the data items to the server (Pc1). The server receives the authentication data A and the secret data C from the client, and generates a random number Q, calculates secret data S, and authentication data B and returns the data items, as well as updating the private key K0 with a private key K1 (Ps1). The client receives from the server the authentication data B and the secret data S, generates the random number R, calculates secret data C2, authentication data A2, and returns the data items to the server, and updates the private key K0 with the private key K1(Pc2). The client and the server check whether or not validity is established (Psm+1, Pcm+1). Further in the authentication method above, there is a method for generating a onetime ID, assuming that the onetime ID is identification information usable just one time in the authentication between a plurality of devices or application. In each of the devices or applications which carries out the authentication, a variable shared key which changes per predefined communication unit requiring the authentication is generated, a function value of one-way function is obtained in which the variable shared key is used as an argument, a onetime ID hard to tap and superior in security is generated based on the function value, and the onetime ID is utilized.
Owner:PSD +1
Method and apparatus for secure identification of a mobile user in a communication network
InactiveUS6072875AKey distribution for secure communicationMultiple keys/algorithms usagePasswordOne-way function
A method and an apparatus are provided for securely identifying a mobile user while avoiding trackability of his / her movements, i.e. it provides a way for a secure user identification in secrecy. The gist is to encrypt the user's identifier, and / or his / her password, and a synchronization indication, preferably a fixed time interval, under a secret one-way function and sending the encrypted message, called a "dynamic user identifier", to the user's "home authority" where he / she is registered. The home authority comprises correspondence tables listing, pre-computed for every time interval (or another chosen synchronization), the dynamic user identifiers and the corresponding true identity of the user and can thus quickly decide whether the received encrypted message originates from a registered user. On the other hand, an intruder is neither able to detect from the encrypted messages the identity of the user nor can he / she track a user's moves.
Owner:IBM CORP
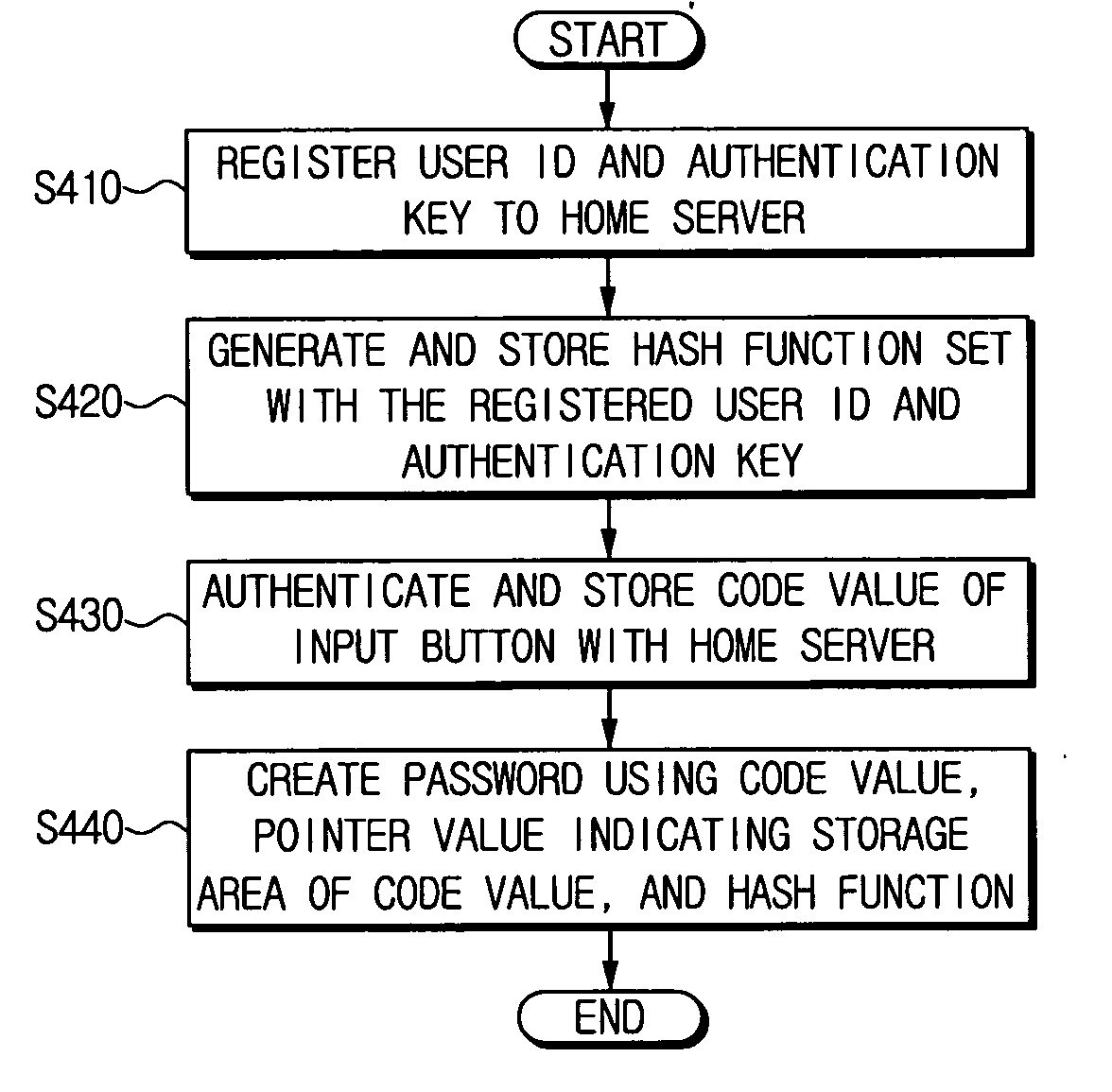
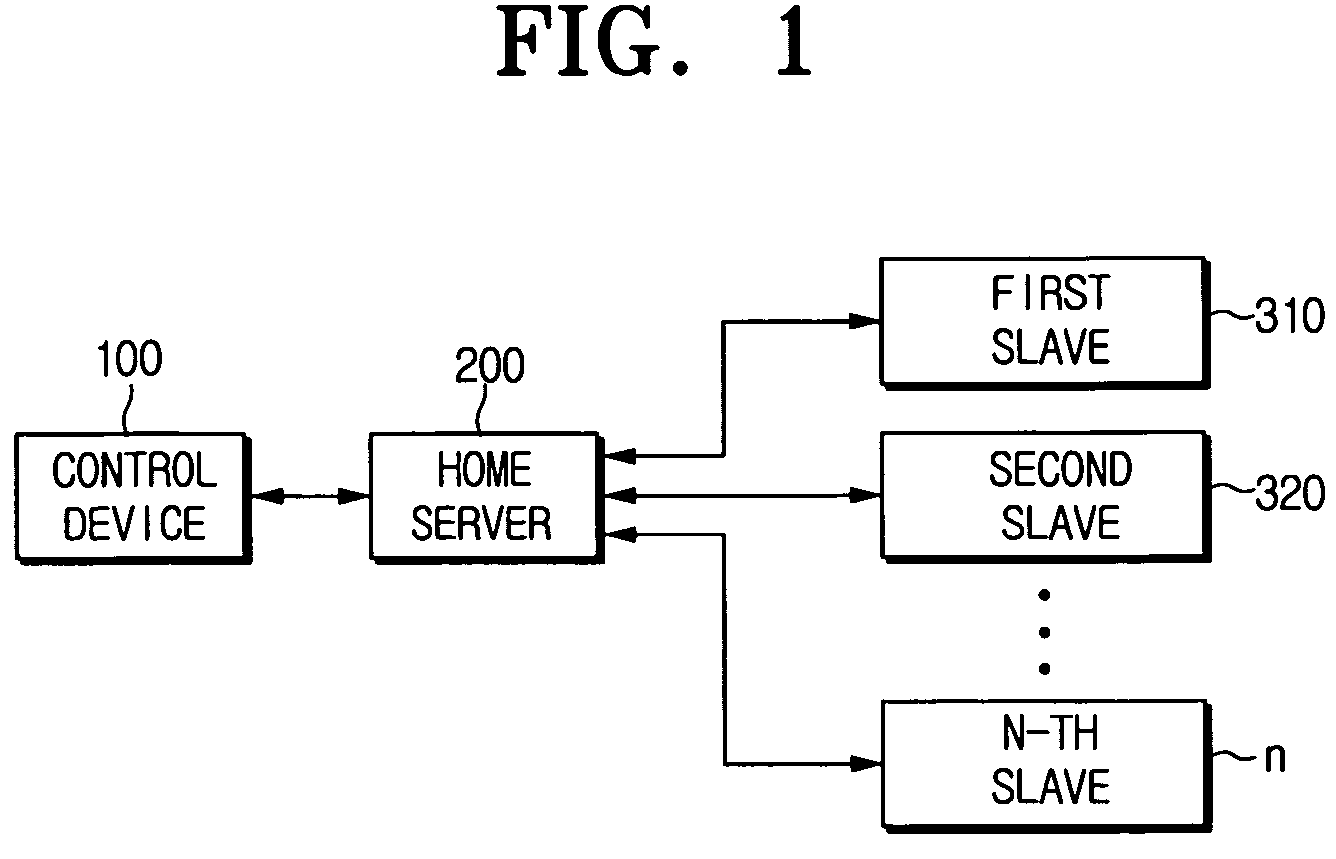
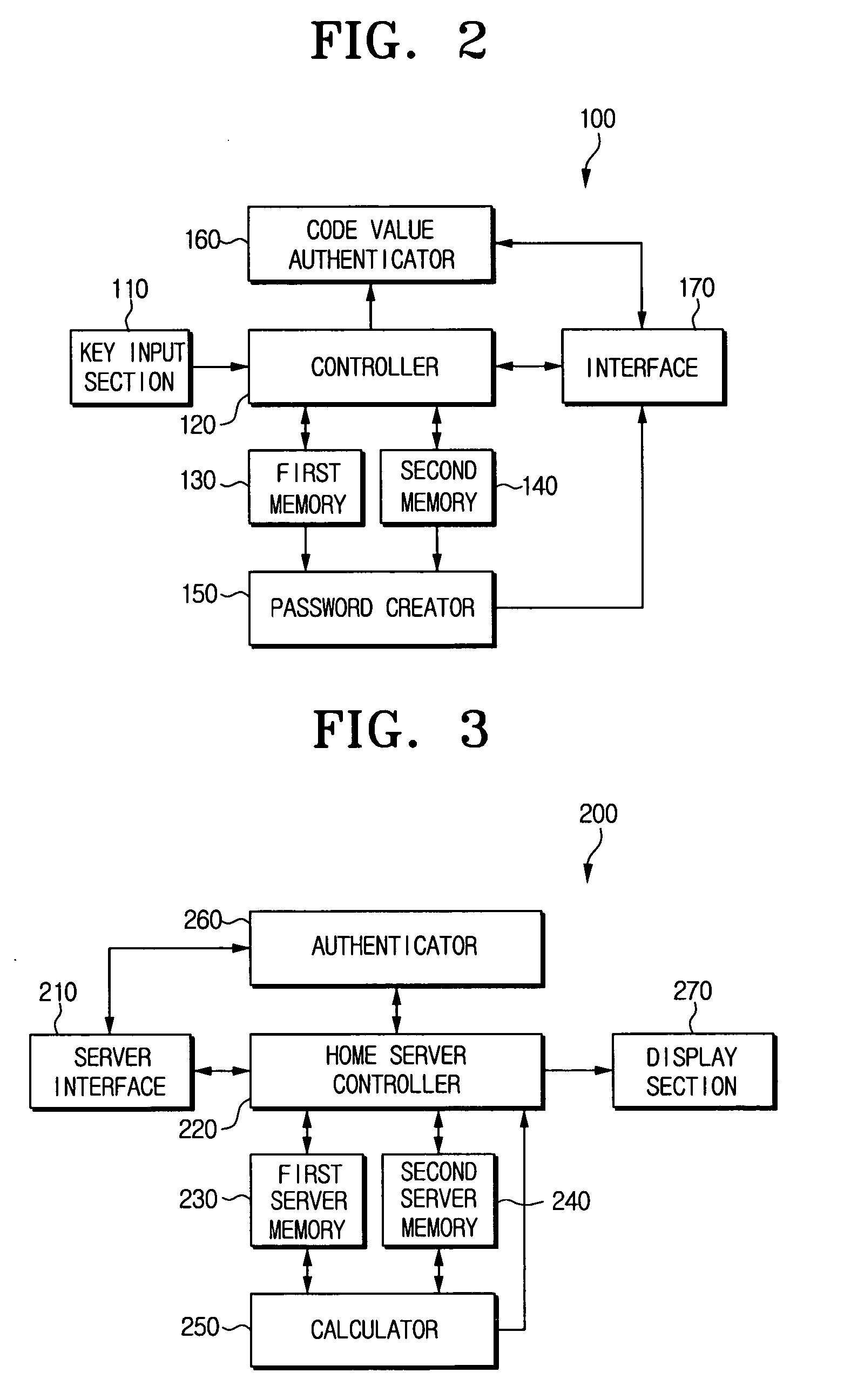
Control device for creating one-time password using pre-input button code, home server for authenticating control device using one-time password, and method for authenticating control device with one-time password
ActiveUS20060174105A1Telemetry/telecontrol selection arrangementsTransmission systemsRemote controlNetworked system
A control device authentication method in a home network system which includes a slave, a home server which controls the slave, and the control device which performs a remote control function to control the home server, includes registering the control device to the home server; generating and storing, by the control device and the home server, a one-way function set; storing, by the control device and the home server, a code value of a button pressed at the control device; creating, by the control device, a first password by performing an operation using a pointer value, the code value, and a one-way function number; requesting, by the control device, authentication by transferring the pointer value, the one-way function number, and the first password to the home server; and creating, by the home server, a second password.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
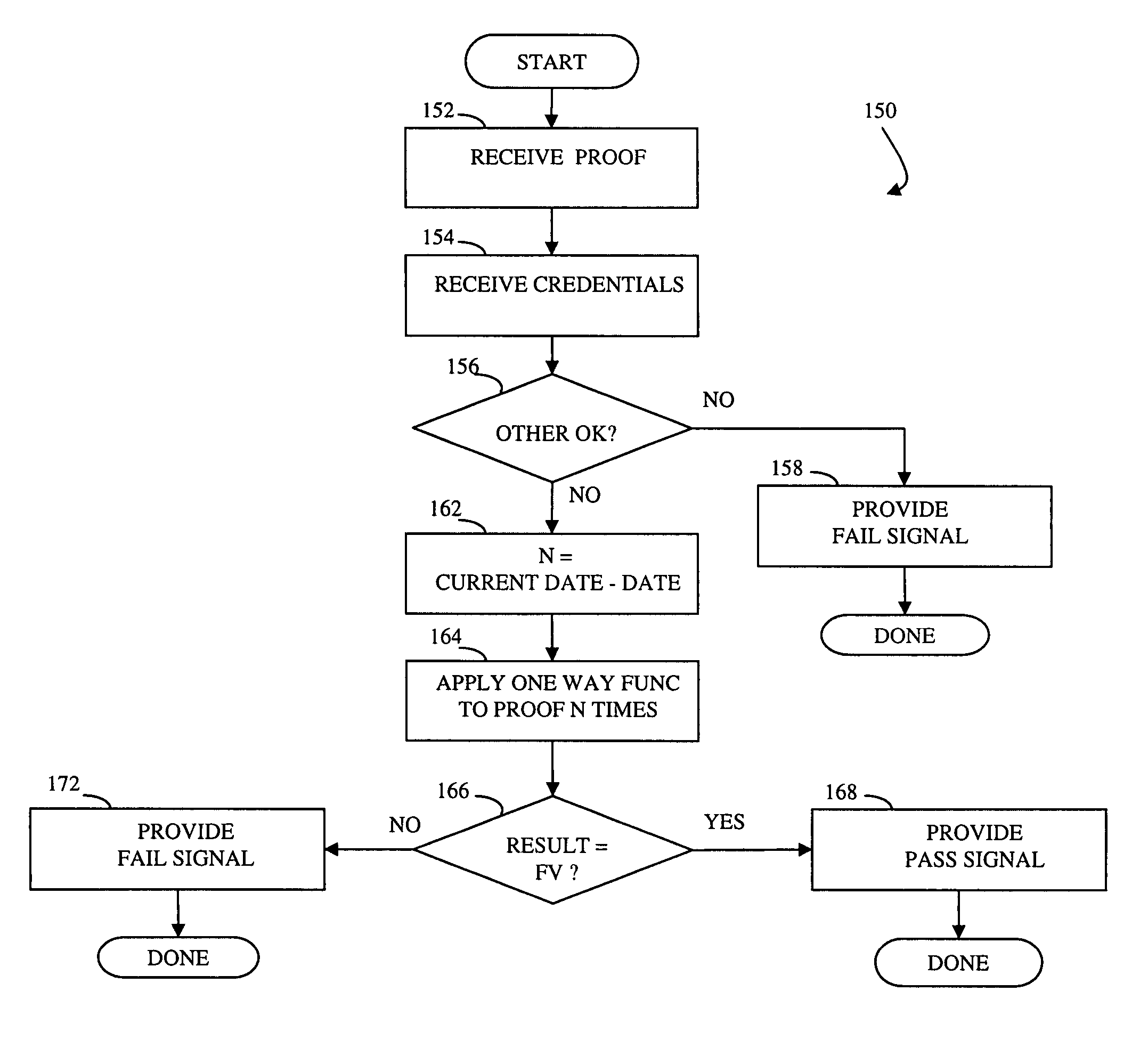
Controlling access to an area
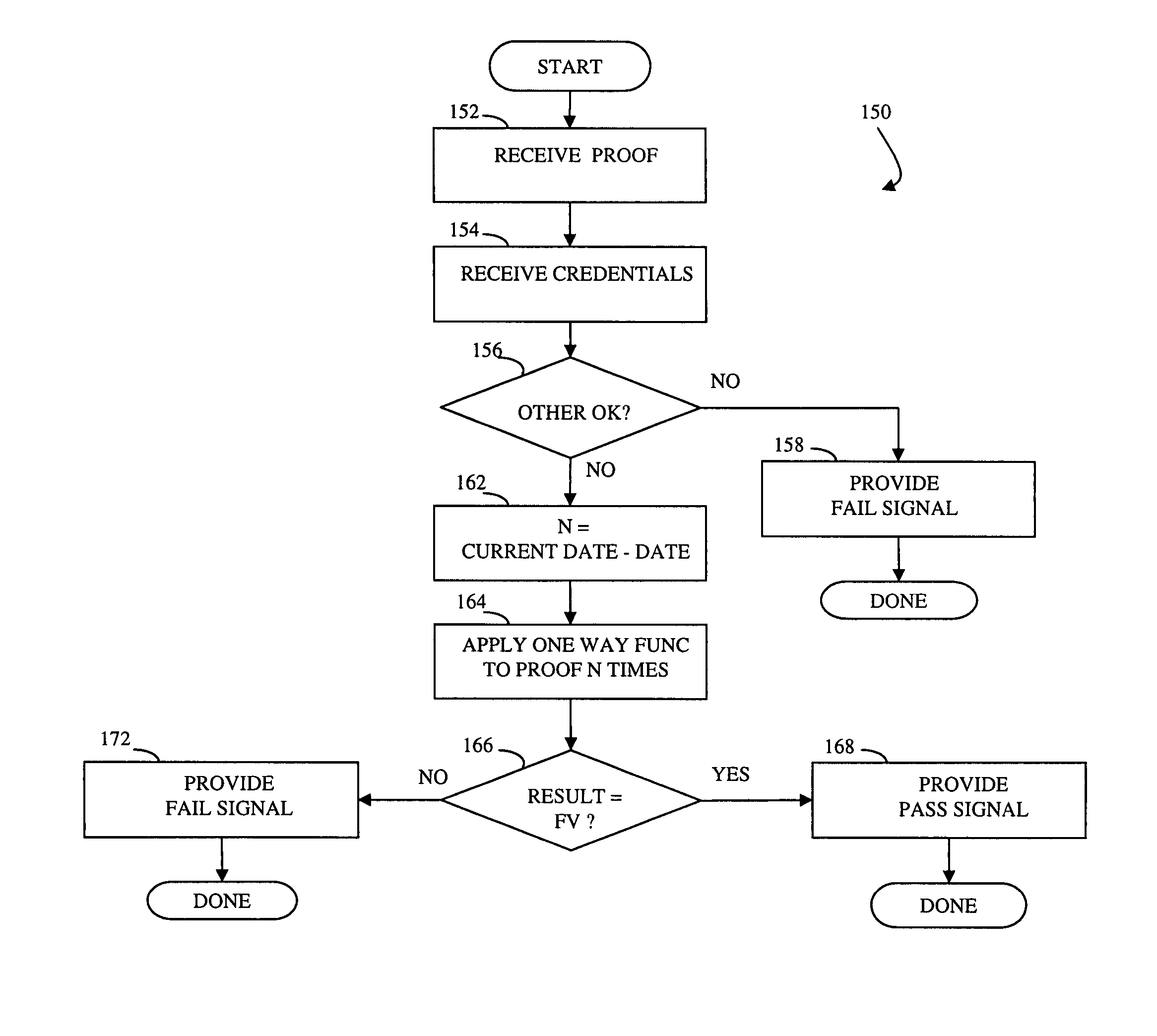
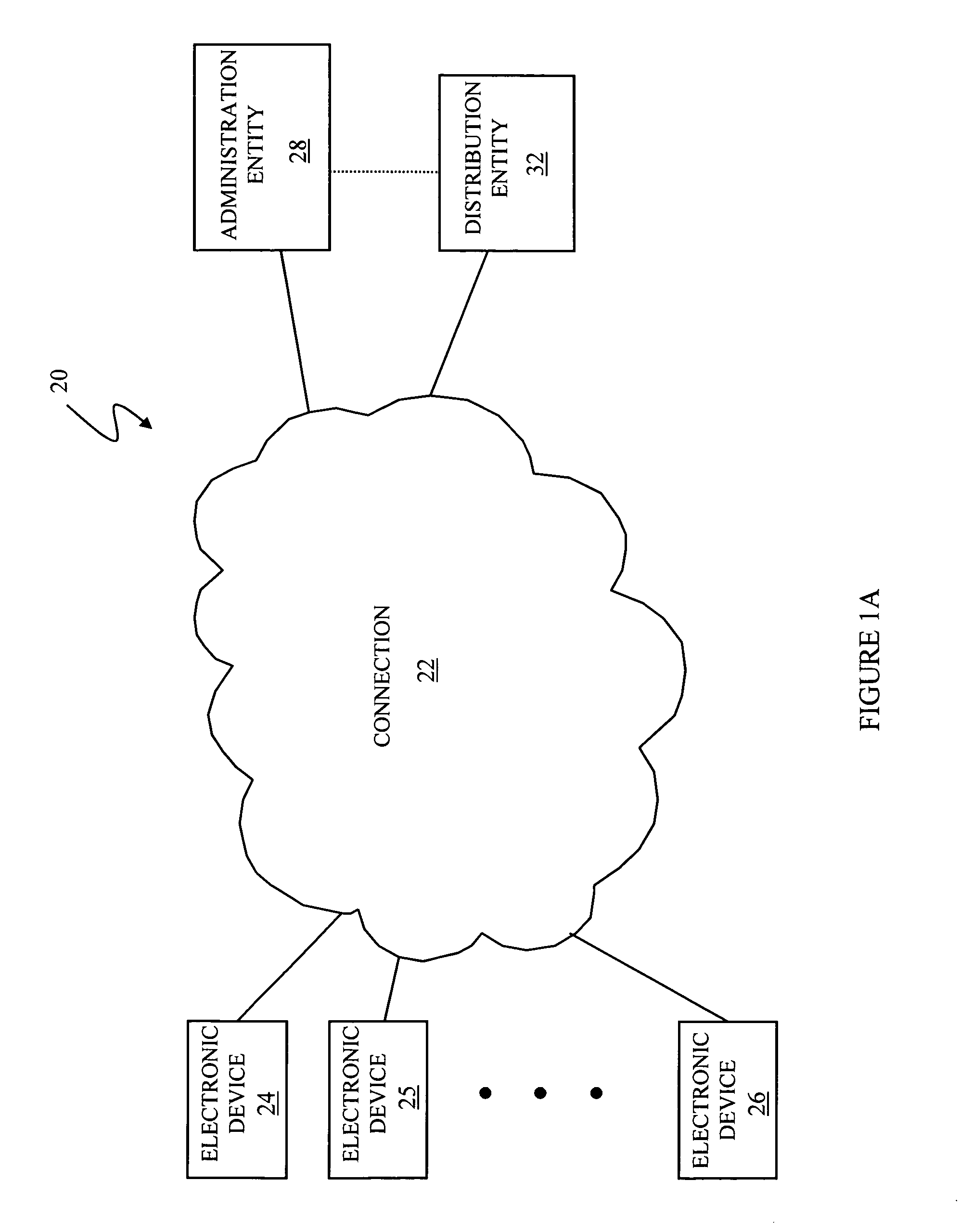
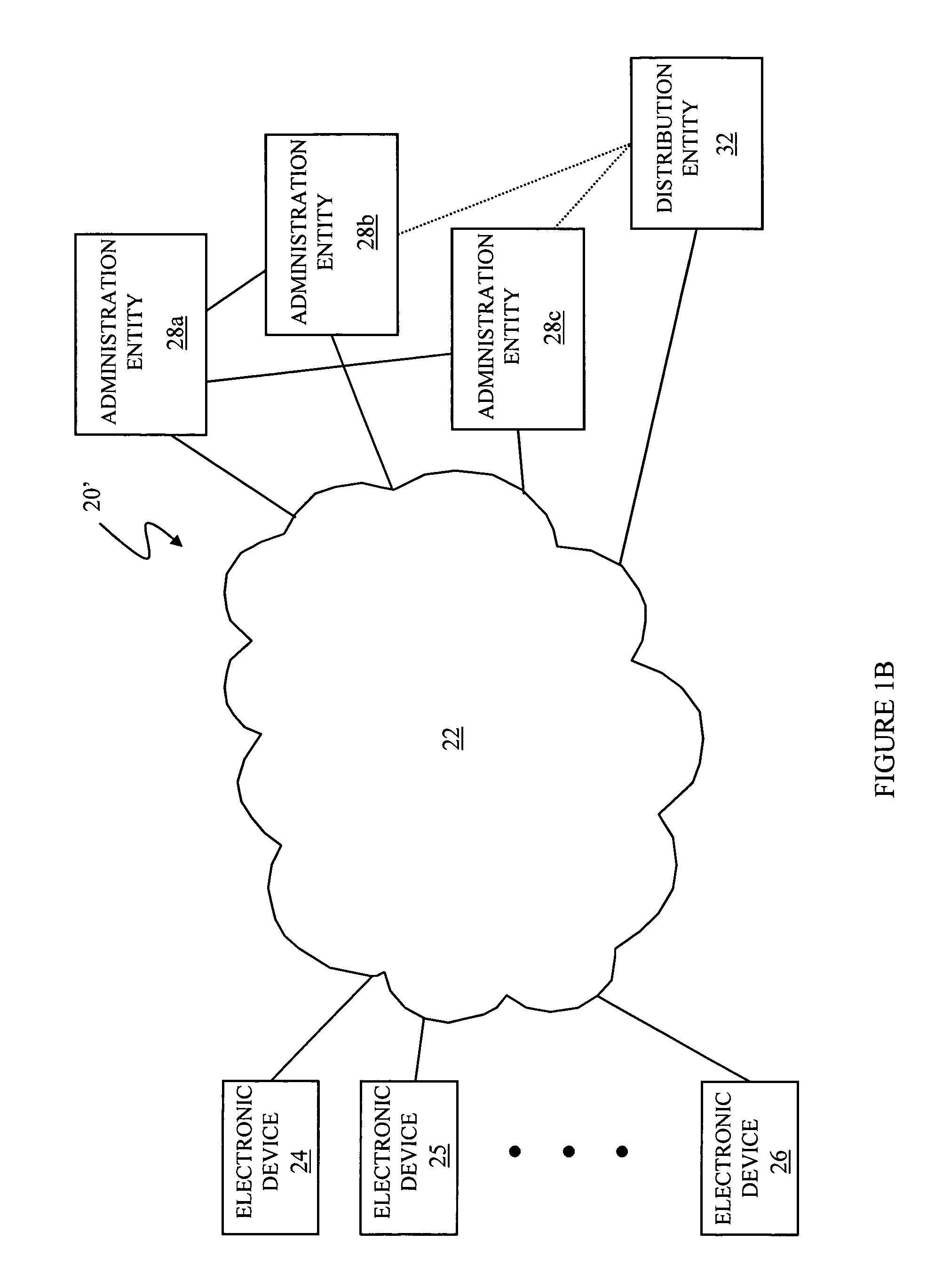
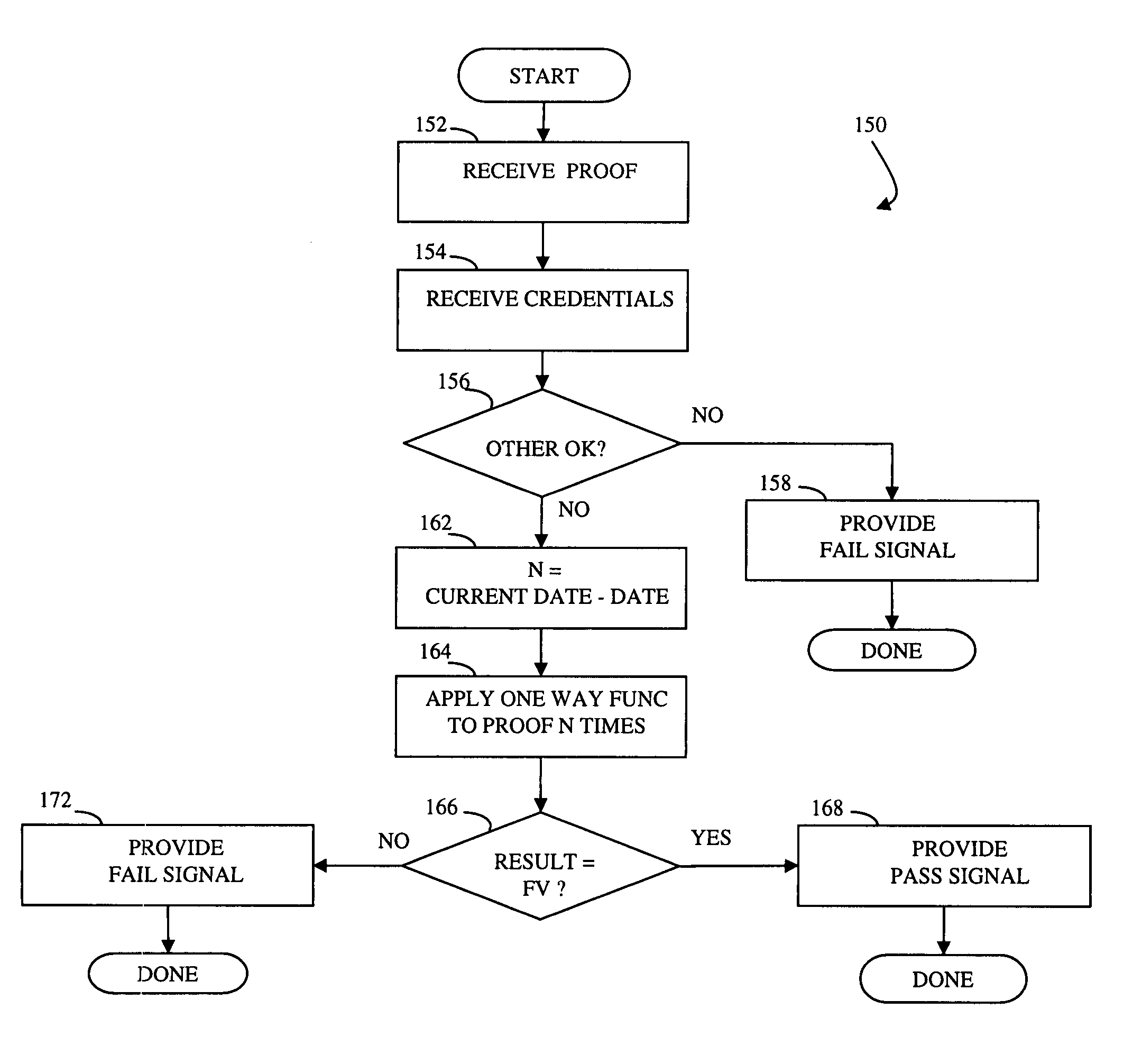
InactiveUS20050055567A1Digital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationOne-way functionComputer security
Controlling access includes providing a barrier to access that includes a controller that selectively allows access, at least one administration entity generating credentials / proofs, wherein no valid proofs are determinable given only the credentials and values for expired proofs, the controller receiving the credentials / proofs, the controller determining if access is presently authorized, and, if access is presently authorized, the controller allowing access. The credentials / proofs may be in one part or may be in separate parts. There may be a first administration entity that generates the credentials and other administration entities that generate proofs. The first administration entity may also generate proofs or the first administration entity may not generate proofs. The credentials may correspond to a digital certificate that includes a final value that is a result of applying a one way function to a first one of the proofs.
Owner:ASSA ABLOY AB
Encryption method and apparatus with forward secrecy and random-access key updating method
InactiveUS7095850B1Generate efficientlyComputationally efficientData stream serial/continuous modificationSecret communicationOne-way functionRekeying
An encryption method and apparatus that provides forward secrecy, by updating the key using a one-way function after each encryption. By providing forward secrecy within a cipher, rather than through a key management system, forward secrecy may be added to cryptographic systems and protocols by using the cipher within an existing framework. A random-access key updating method can efficiently generate one or more future keys in any order. Embodiments are applicable to forward secret ciphers that are used to protect protocols with unreliable transport, to ciphers that are used in multicast or other group settings, and to protection of packets using the IPSec protocols.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Validation protocol and system
InactiveUS7249108B1Reducing possible errorSimple designTelevision system detailsPublic key for secure communicationOne-way functionAuthentication
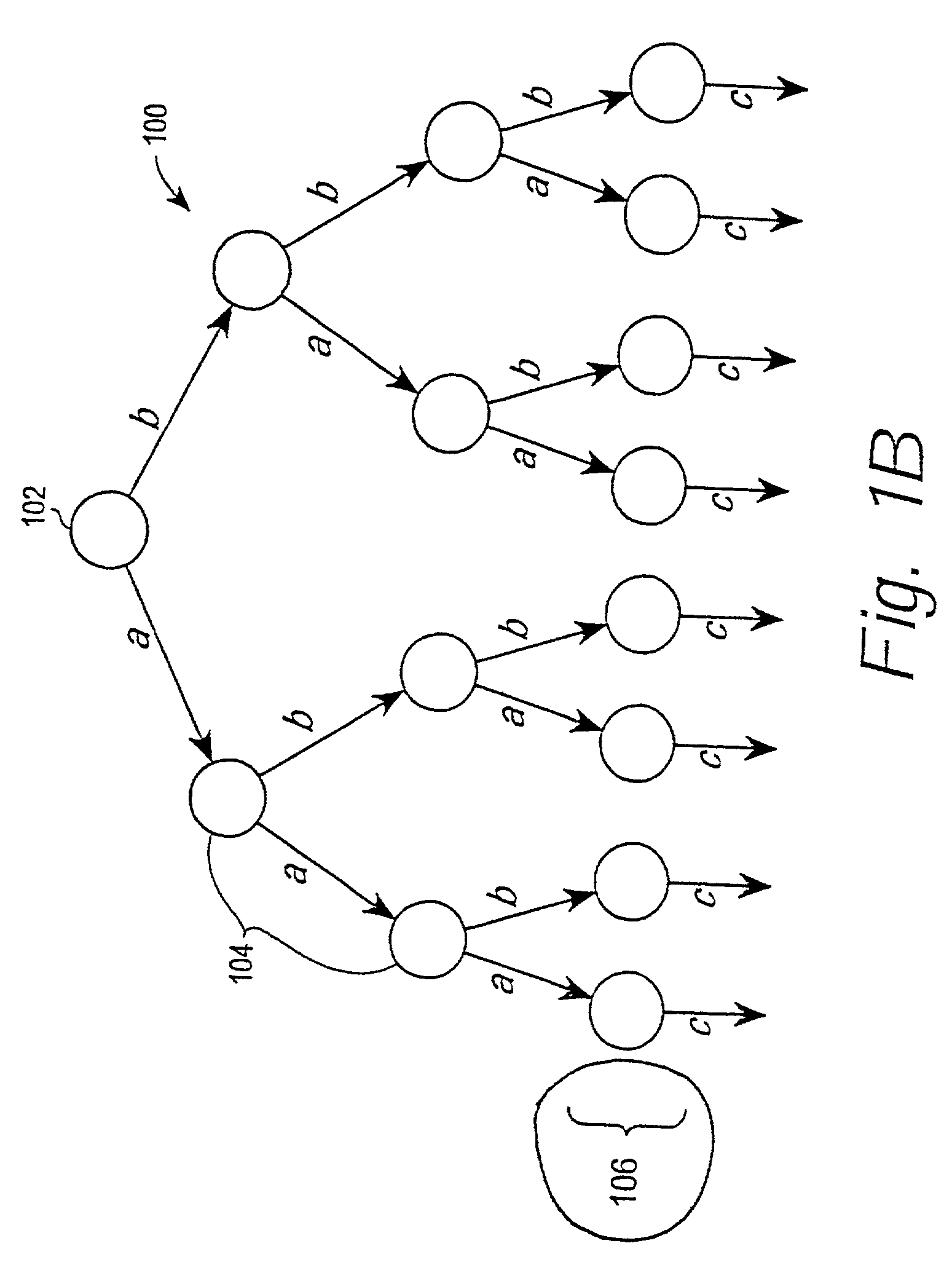
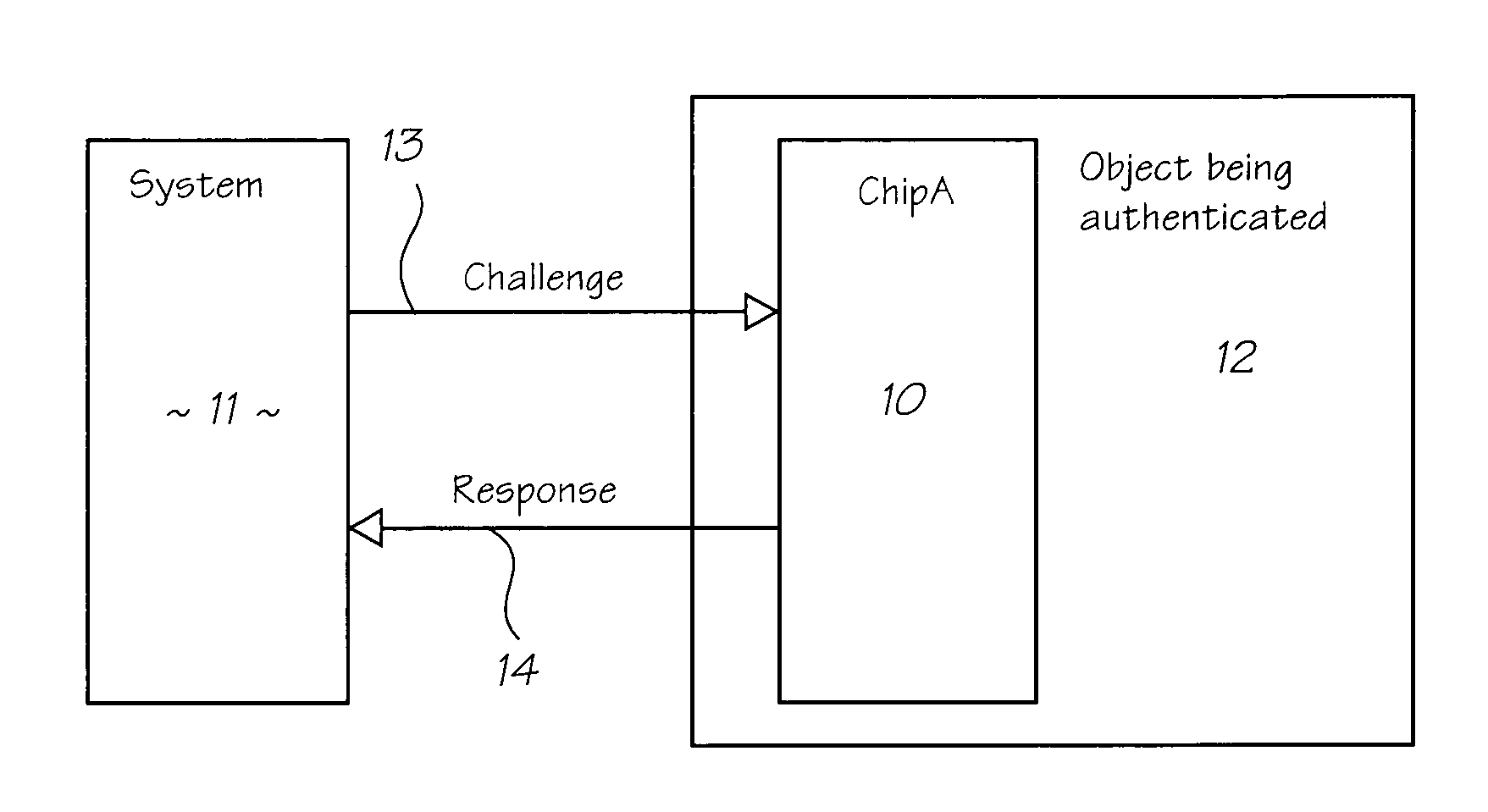
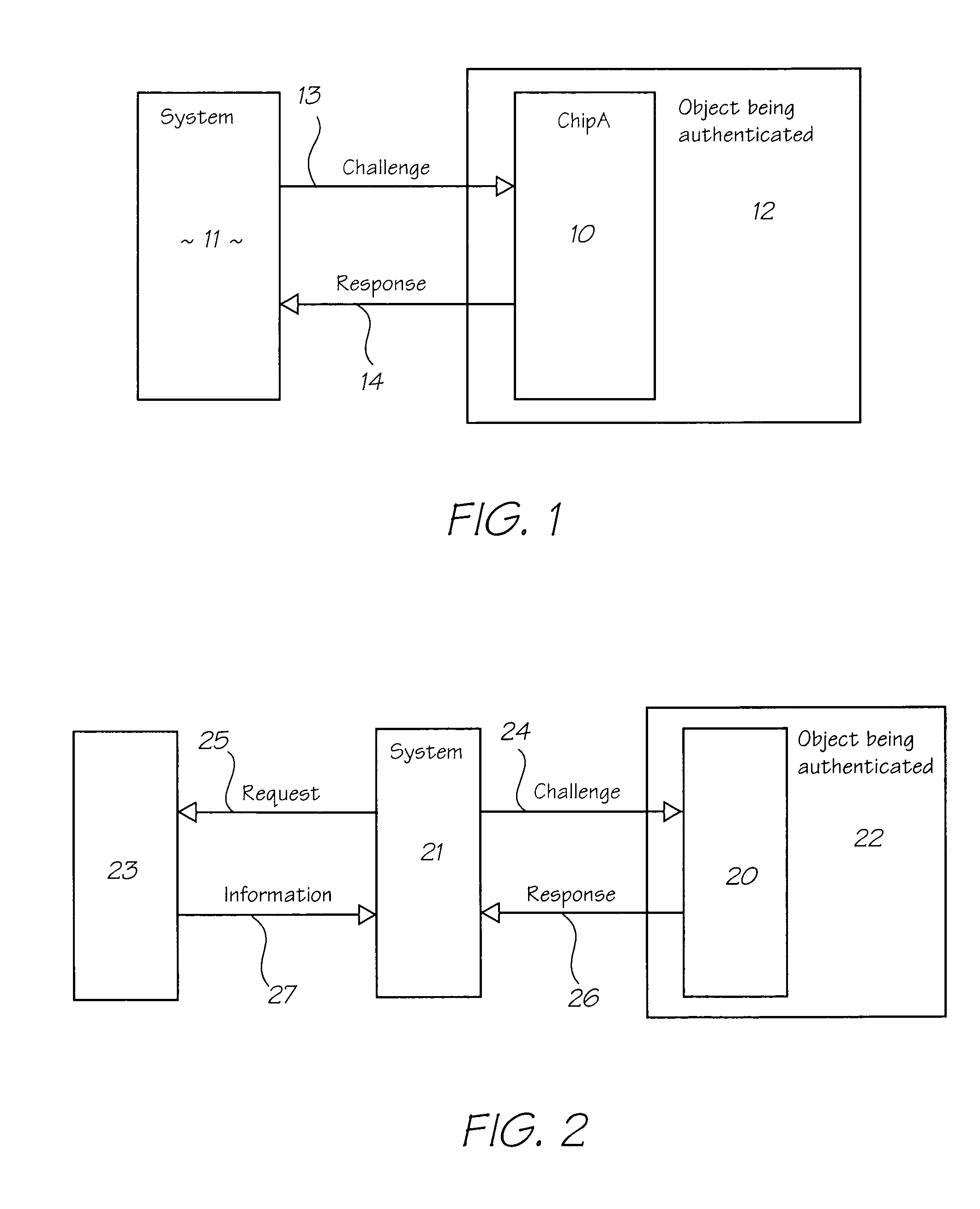
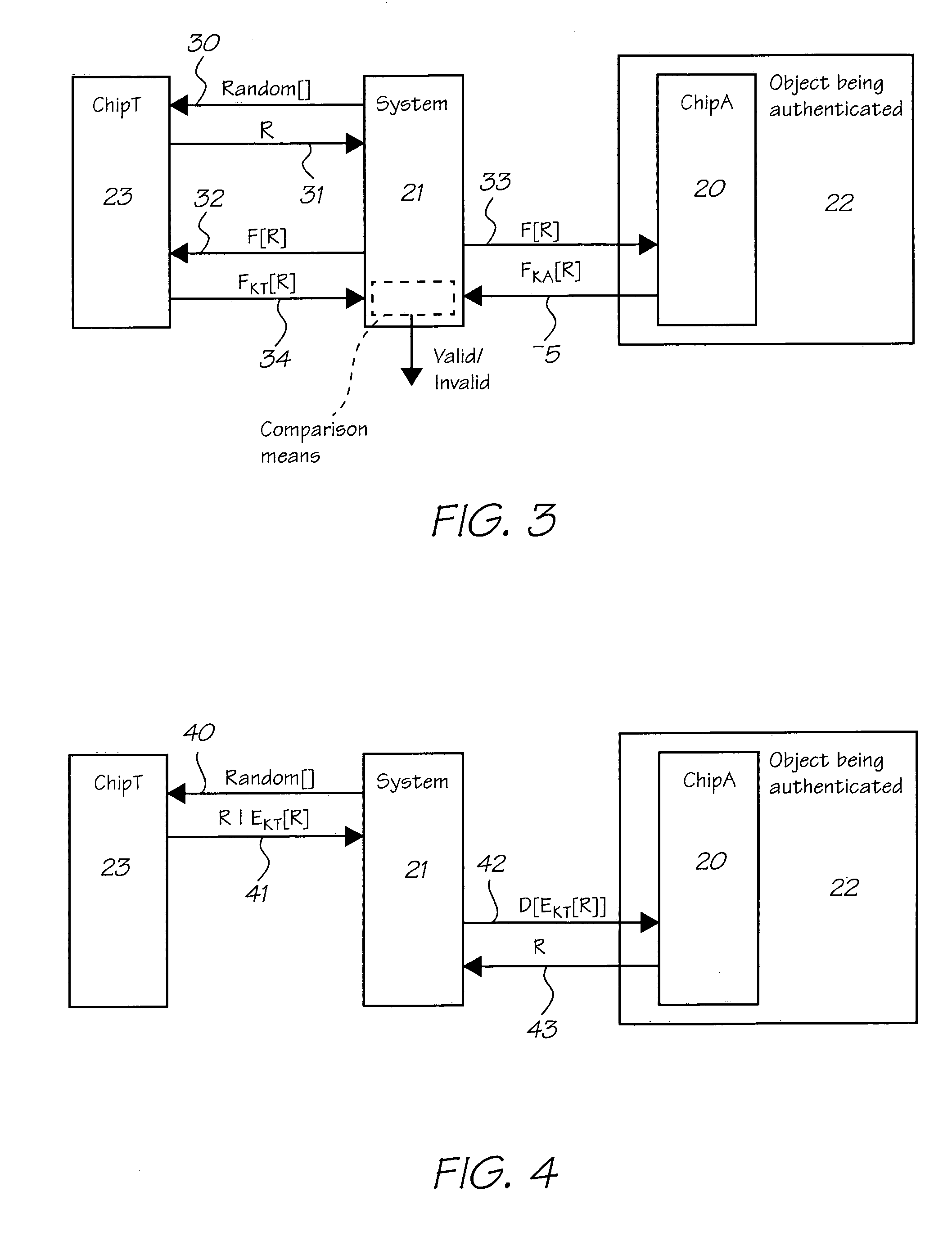
This invention concerns a validation protocol for determining whether an untrusted authentication chip is valid, or not. The protocol may be used to determine the physical presence of a valid authentication chip and from that determine whether a consumable containing the chip is valid. In another aspect the invention also concerns a system for validating the chip. The invention involves generating a random number in a trusted authentication chip, then applying a keyed one way function to the random number in both the trusted authentication chip and an untrusted authentication chip and comparing the outcomes. A match indicates that the untrusted chip is valid.
Owner:MEMJET TECH LTD
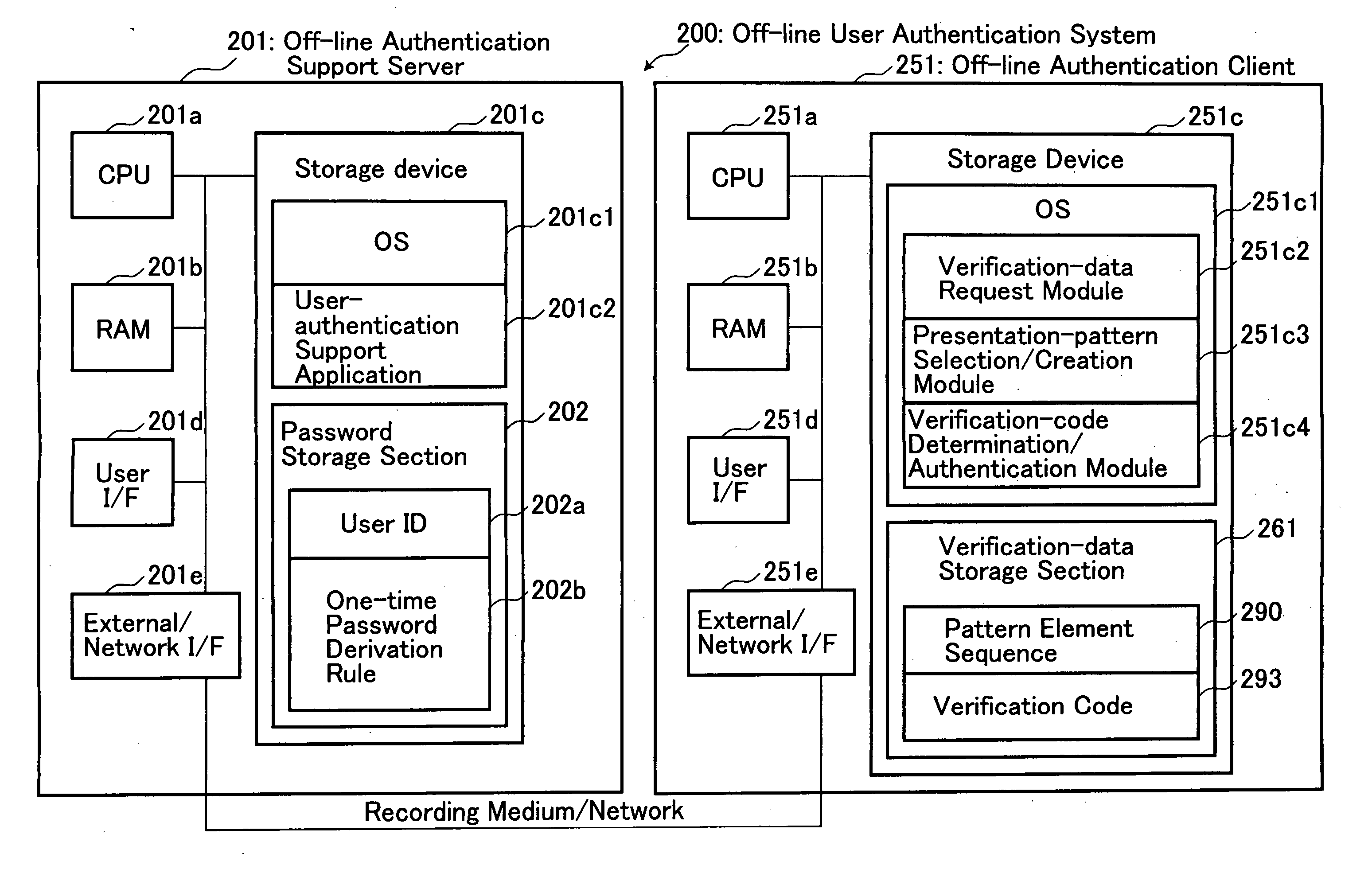
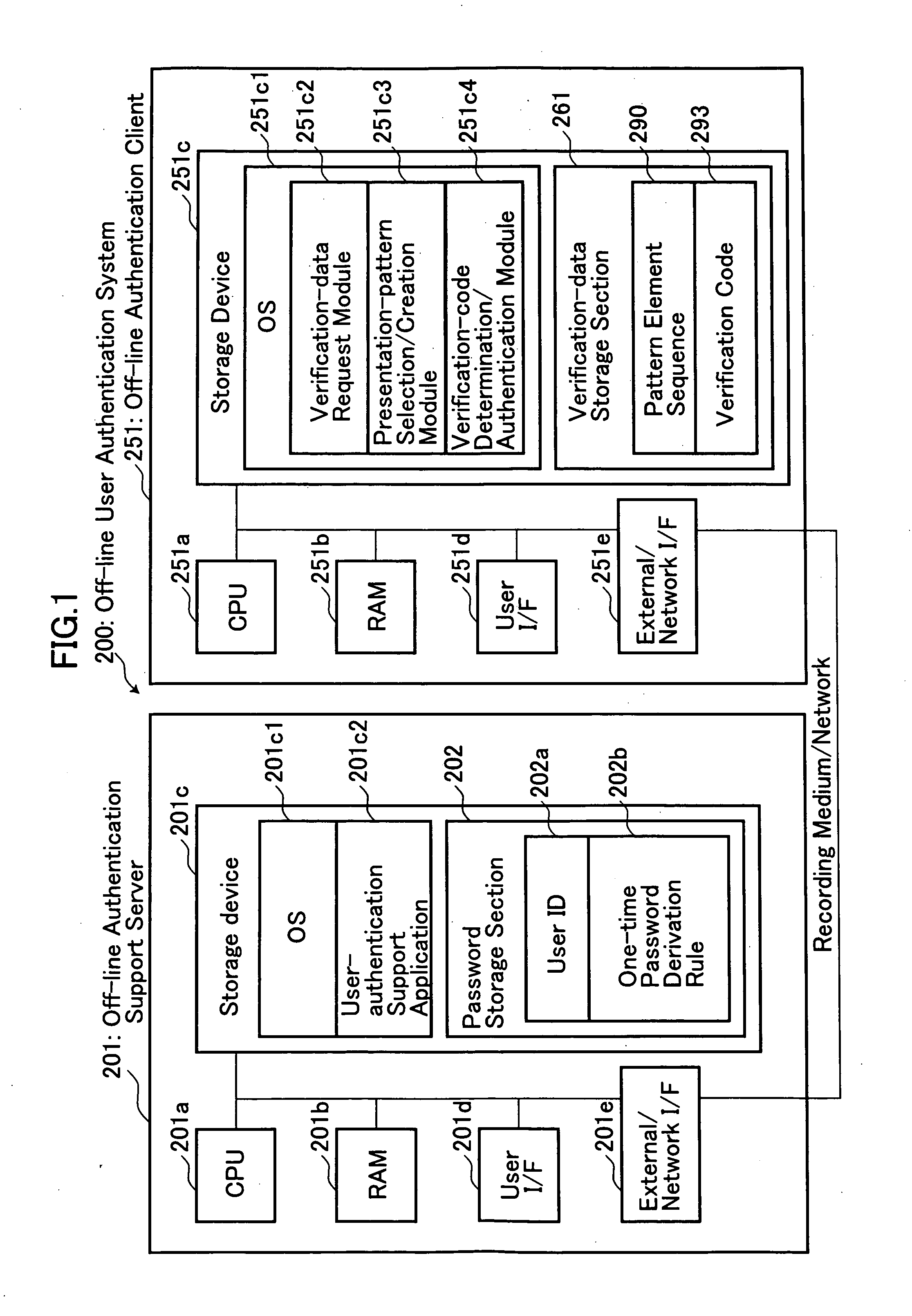
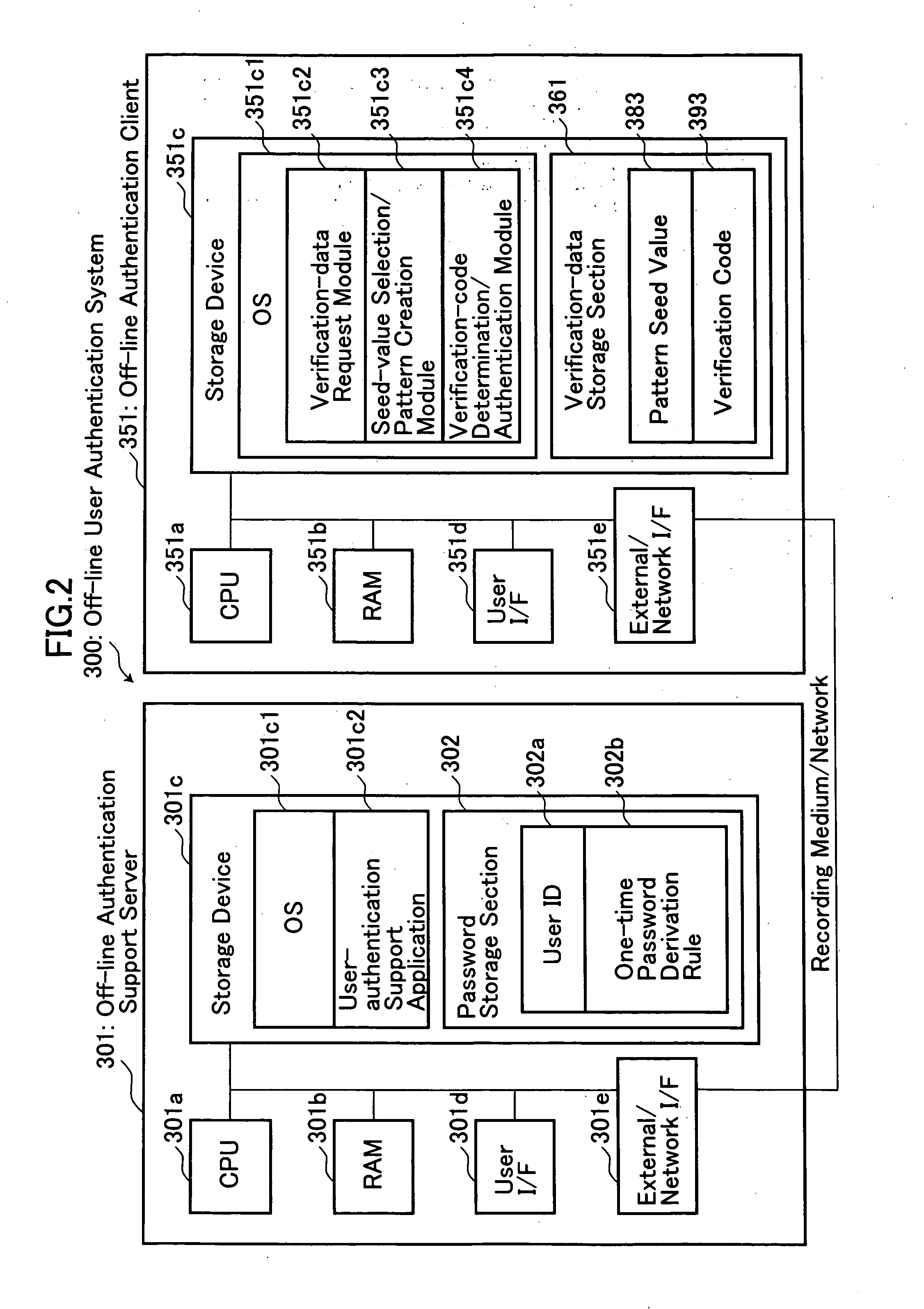
System, method and program for off-line user authentication
ActiveUS20070234063A1Prevent leakageImprove securityRandom number generatorsUser identity/authority verificationUser inputUser authentication
Disclosed is an off-line user authentication system, which is designed to present a presentation pattern to a user subject to authentication, and apply a one-time-password derivation rule serving as a password to certain pattern elements included in the presentation pattern at specific positions so as to create a one-time password. An off-line authentication client pre-stores a plurality of pattern element sequences each adapted to form a presentation pattern, and a plurality of verification codes created by applying a one-time-password derivation rule to the respective presentation patterns and subjecting the obtained results to a one-way function algorism. A presentation pattern is created using one selected from the stored pattern element sequences, and presented to a user. A one-time password entered from the user is verified based on a corresponding verification code to perform user authentication. The present invention provides an off-line matrix authentication scheme with enhanced security.
Owner:CSE CO LTD
Controlling access to an area
InactiveUS7822989B2Digital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationOne-way functionComputer security
Controlling access includes providing a barrier to access that includes a controller that selectively allows access, at least one administration entity generating credentials / proofs, wherein no valid proofs are determinable given only the credentials and values for expired proofs, the controller receiving the credentials / proofs, the controller determining if access is presently authorized, and, if access is presently authorized, the controller allowing access. The credentials / proofs may be in one part or may be in separate parts. There may be a first administration entity that generates the credentials and other administration entities that generate proofs. The first administration entity may also generate proofs or the first administration entity may not generate proofs. The credentials may correspond to a digital certificate that includes a final value that is a result of applying a one way function to a first one of the proofs.
Owner:ASSA ABLOY AB
Controlling access using additional data
InactiveUS7600129B2Key distribution for secure communicationDigital data processing detailsData controlOne-way function
Determining access includes determining if particular credentials / proofs indicate that access is allowed, determining if there is additional data associated with the credentials / proofs, wherein the additional data is separate from the credentials / proofs, and, if the particular credentials / proofs indicate that access is allowed and if there is additional data associated with the particular credentials / proofs, then deciding whether to deny access according to information provided by the additional data. The credentials / proofs may be in one part or in separate parts. There may be a first administration entity that generates the credentials and other administration entities that generate proofs. The first administration entity may also generate proofs or may not generate proofs. The credentials may correspond to a digital certificate that includes a final value that is a result of applying a one way function to a first one of the proofs.
Owner:ASSA ABLOY AB
Signature System and Signature Method
InactiveUS20080095360A1Improve securitySmall data sizePublic key for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationSmart cardOne-way function
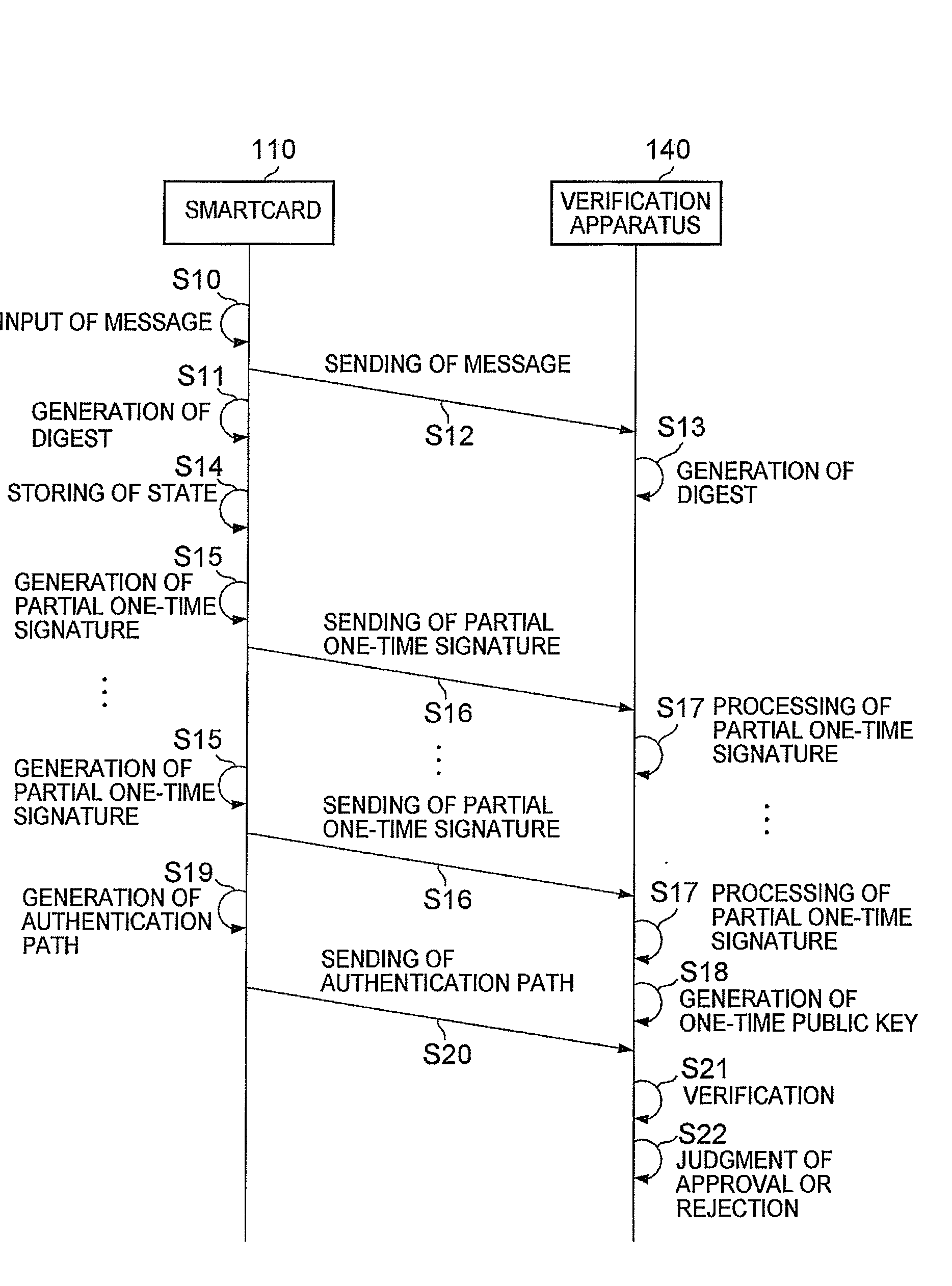
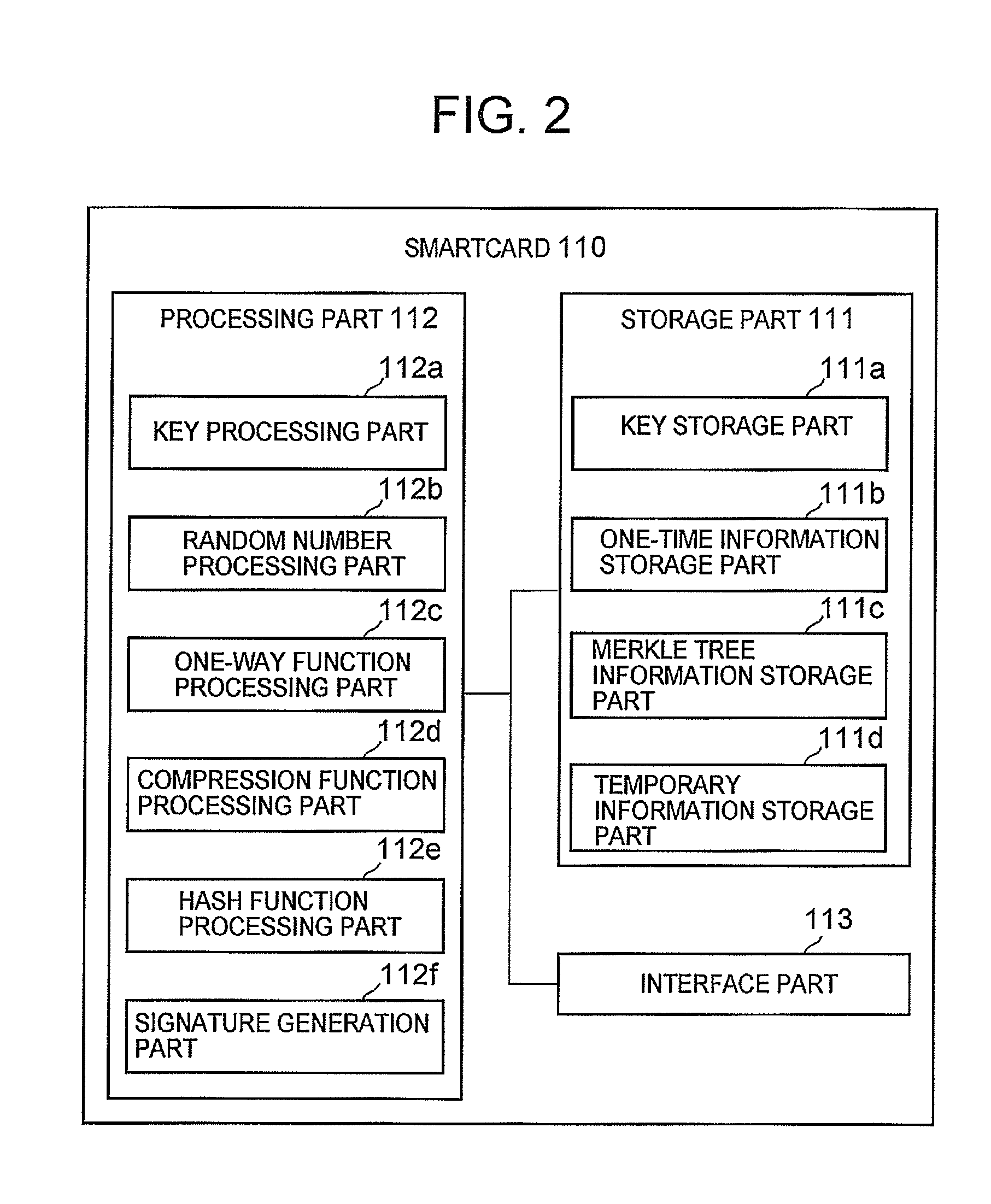
A signature system in which size of data to be transmitted is small and data can be processed efficiently in a Merkle signature system having high security. A processing part 112 of a smartcard 110 divides a message to be signed into groups of specific numbers of bits, starting from the first bit of the message. Then, respective partial one-time signatures of the groups are generated by encrypting each group by a one-way function processing part 112c. The partial one-time signatures are sequentially outputted to a verification apparatus through a interface part 113.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Access to authorized domains
InactiveUS20090132811A1Easy to controlKey distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationA domainOne-way function
In a domain comprising a plurality of devices, the devices in the domain sharing a common domain key, a method of enabling a entity that is not a member of the domain to create an object that can be authenticated and / or decrypted using the common domain key, the method comprising providing to the entity that is not a member of the domain a diversified key that is derived using a one-way function from at least the common domain key for creating authentication data related to said object and / or for encrypting said object, the devices in the domain being configured to authenticate and / or decrypt said object using the diversified key.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Access control
InactiveUS20050010783A1Promote recoveryLimited accessData processing applicationsDigital data authenticationOne-way functionSingle administration
At least one administration entity controls access to an electronic device by the at least one administration entity generating credentials and a plurality of corresponding proofs for the electronic device, wherein no valid proofs are determinable given only the credentials and values for expired proofs, the electronic device receiving the credentials, if access is authorized at a particular time, the electronic device receiving a proof corresponding to the particular time, and the electronic device confirming the proof using the credentials. The at least one administration entity may generate proofs after generating the credentials. A single administration entity may generate the credentials and generate the proofs. There may be a first administration entity that generates the credentials and other administration entities that generate proofs. The first administration entity may also generate proofs or may not. The credentials may be a digital certificate that includes a final value that is a result of applying a one way function to a first one of the proofs. Each of the proofs may be a result of applying a one way function to a future one of the proofs. The digital certificate may include an identifier for the electronic device.
Owner:ASSA ABLOY AB
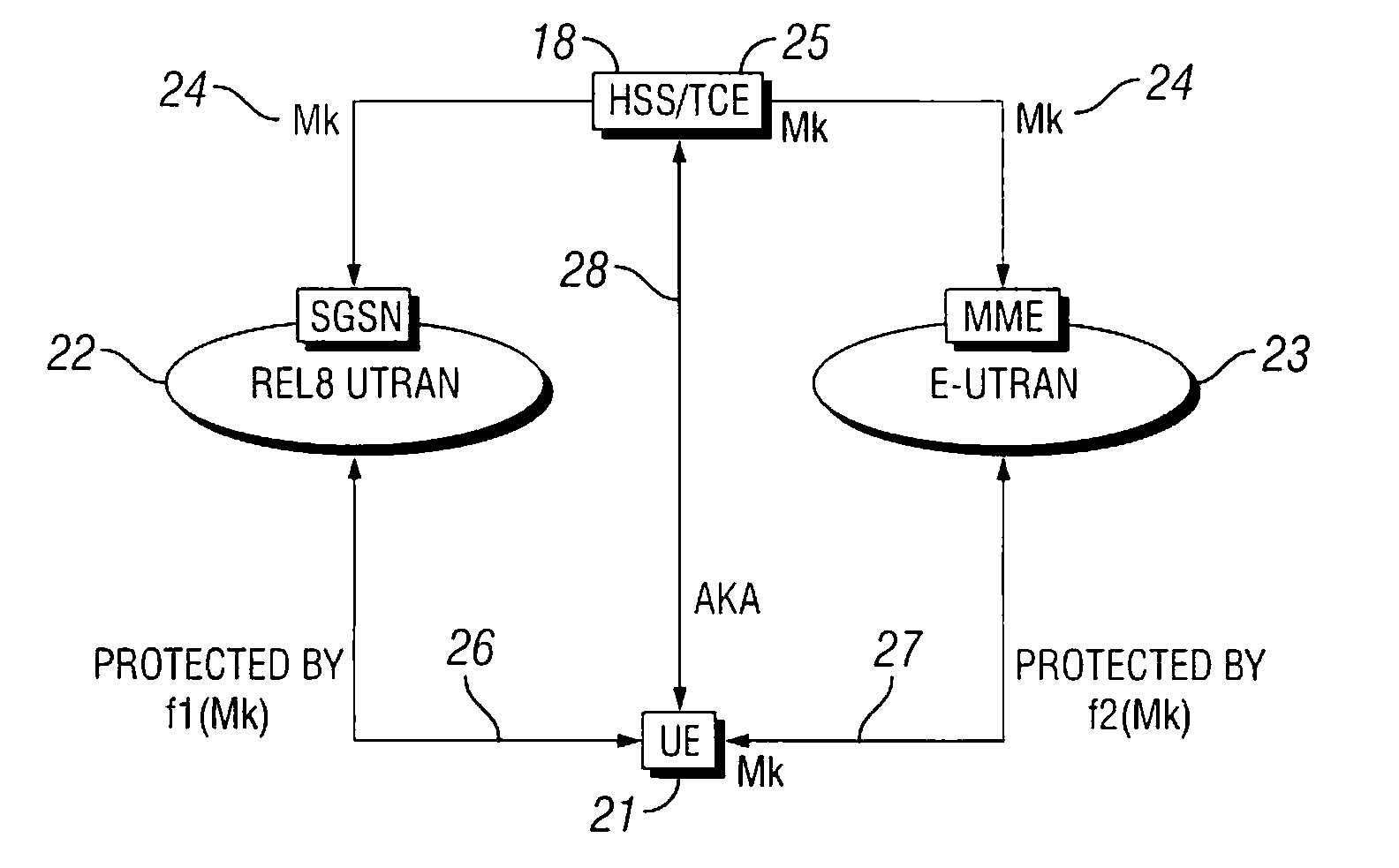
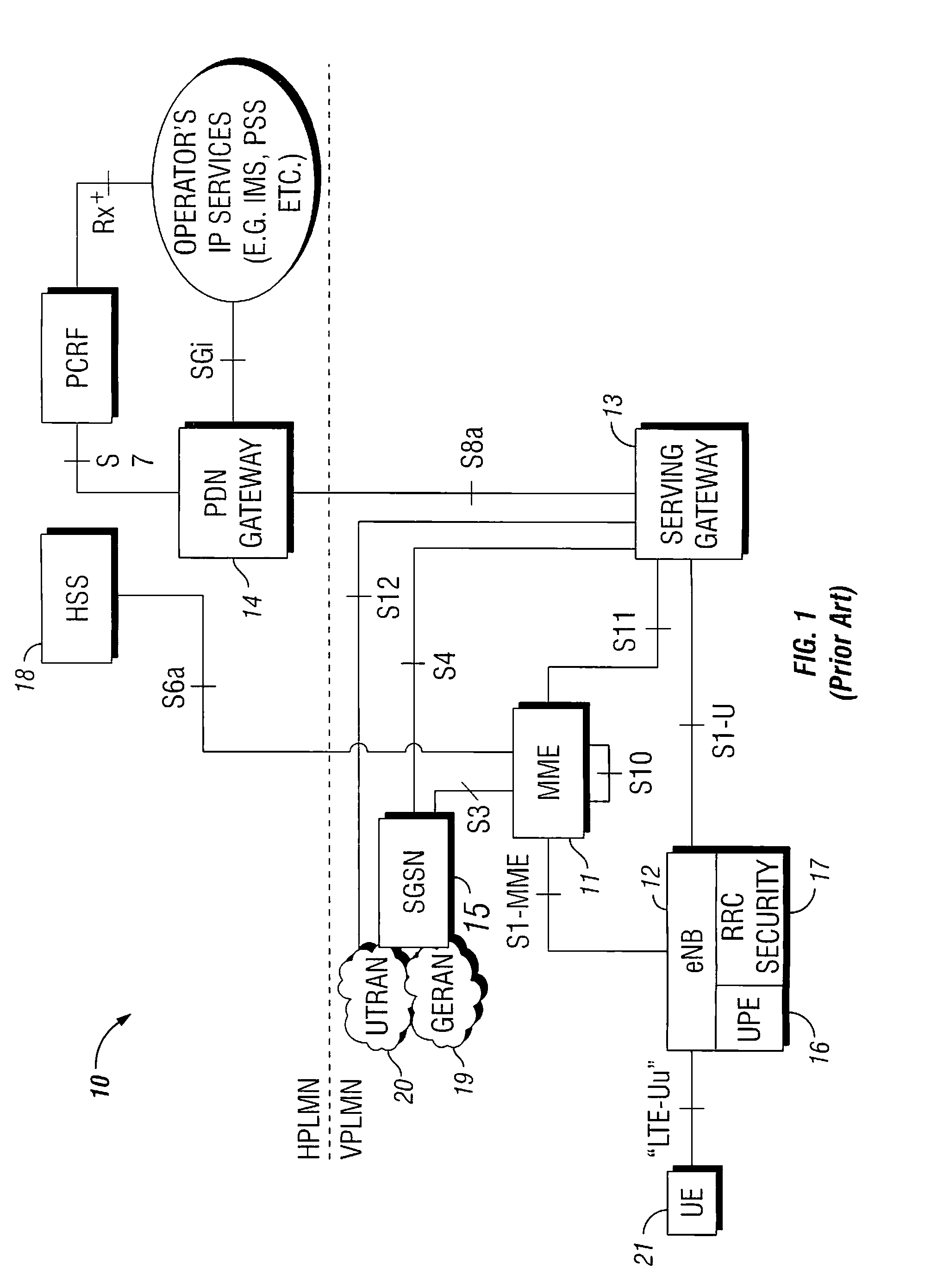
Cryptographic key management in communication networks
InactiveUS20080095362A1Key distribution for secure communicationMultiple keys/algorithms usageAccess networkCryptographic nonce
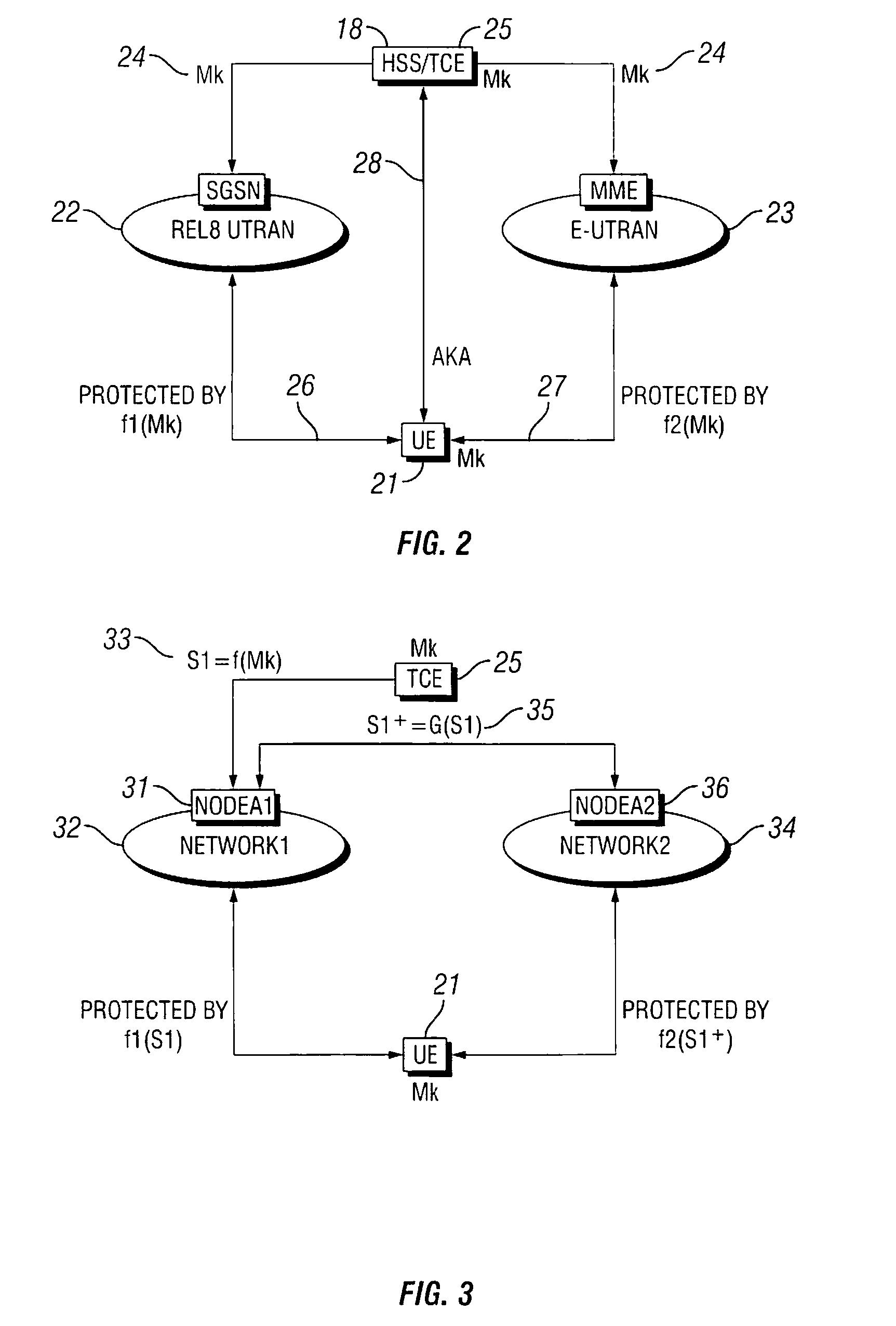
An authentication server and a system and method for managing cryptographic keys across different combinations of user terminals, access networks, and core networks. A Transformation Coder Entity (TCE) creates a master key (Mk), which is used to derive keys during the authentication procedure. During handover between the different access types, the Mk or a transformed Mk is passed between two nodes that hold the key in the respective access networks when a User Equipment (UE) terminal changes access. The transformation of the Mk is performed via a one-way function, and has the effect that if the Mk is somehow compromised, it is not possible to automatically obtain access to previously used master keys. The transformation is performed based on the type of authenticator node and type of UE / identity module with which the transformed key is to be utilized. The Mk is never used directly, but is only used to derive the keys that are directly used to protect the access link.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Method for effective tamper resistance
InactiveUS20080148061A1Inhibitory contentEliminate needUnauthorized memory use protectionHardware monitoringTamper resistanceTheoretical computer science
A system, method, and computer program product for preventing a malicious user from analyzing and modifying software content. The one-way functions used in prior art systems using dynamically evolving audit logs or self-modifying applications are replaced with a one-way function based on group theory. With this modification, untampered key evolution will occur inside a defined mathematical group such that all valid key values form a subgroup. However, if the program is altered, the key will evolve incorrectly and will no longer be a member of the subgroup. Once the key value is outside of the subgroup, it is not possible to return it to the subgroup. The present invention provides a limited total number of valid keys. The key evolution points are not restricted to locations along the deterministic path, so the key can be used in various novel ways to regulate the program's behavior, including in non-deterministic execution paths.
Owner:IBM CORP
Apparatus and method for secure delivery of data utilizing encryption key management
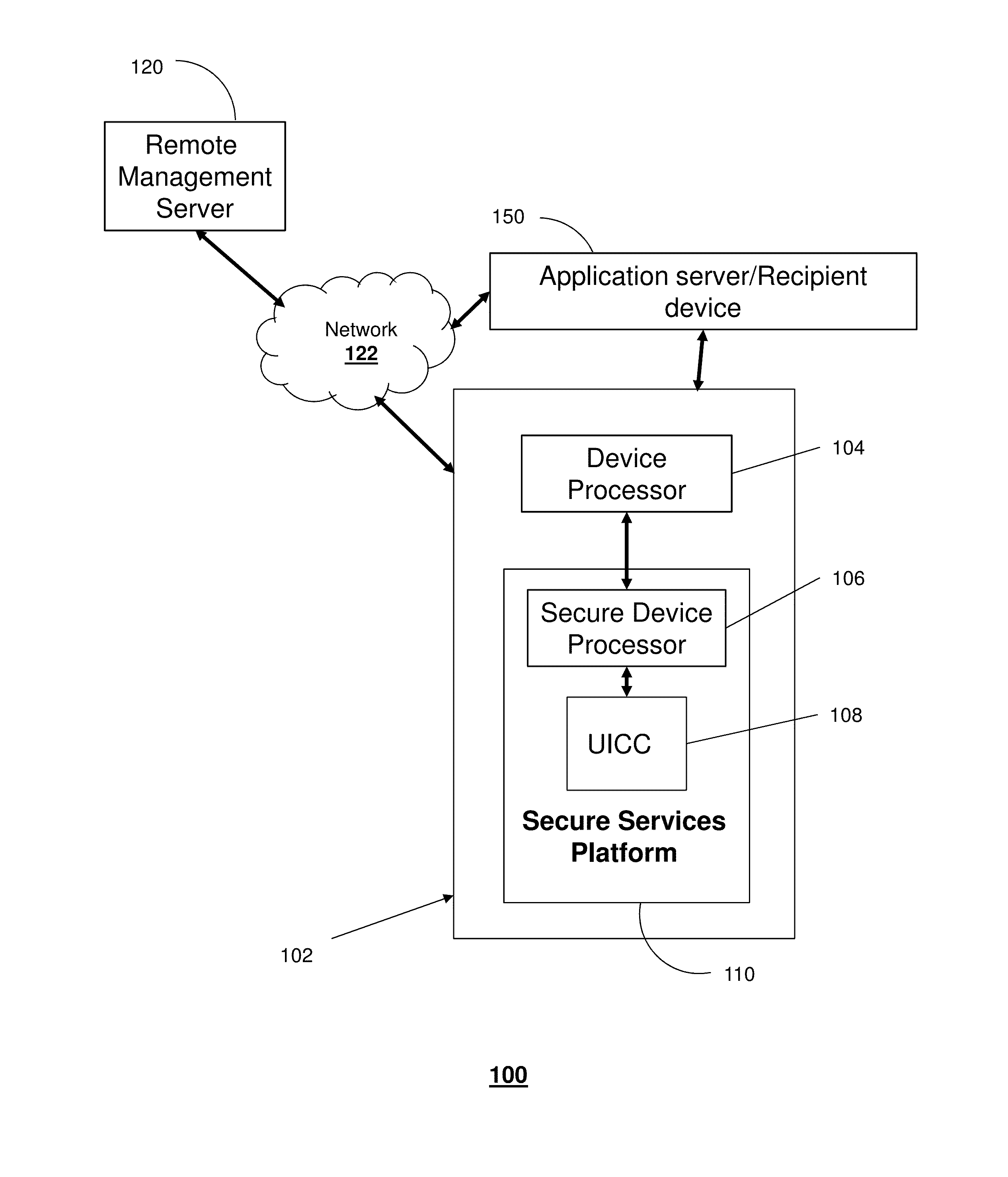
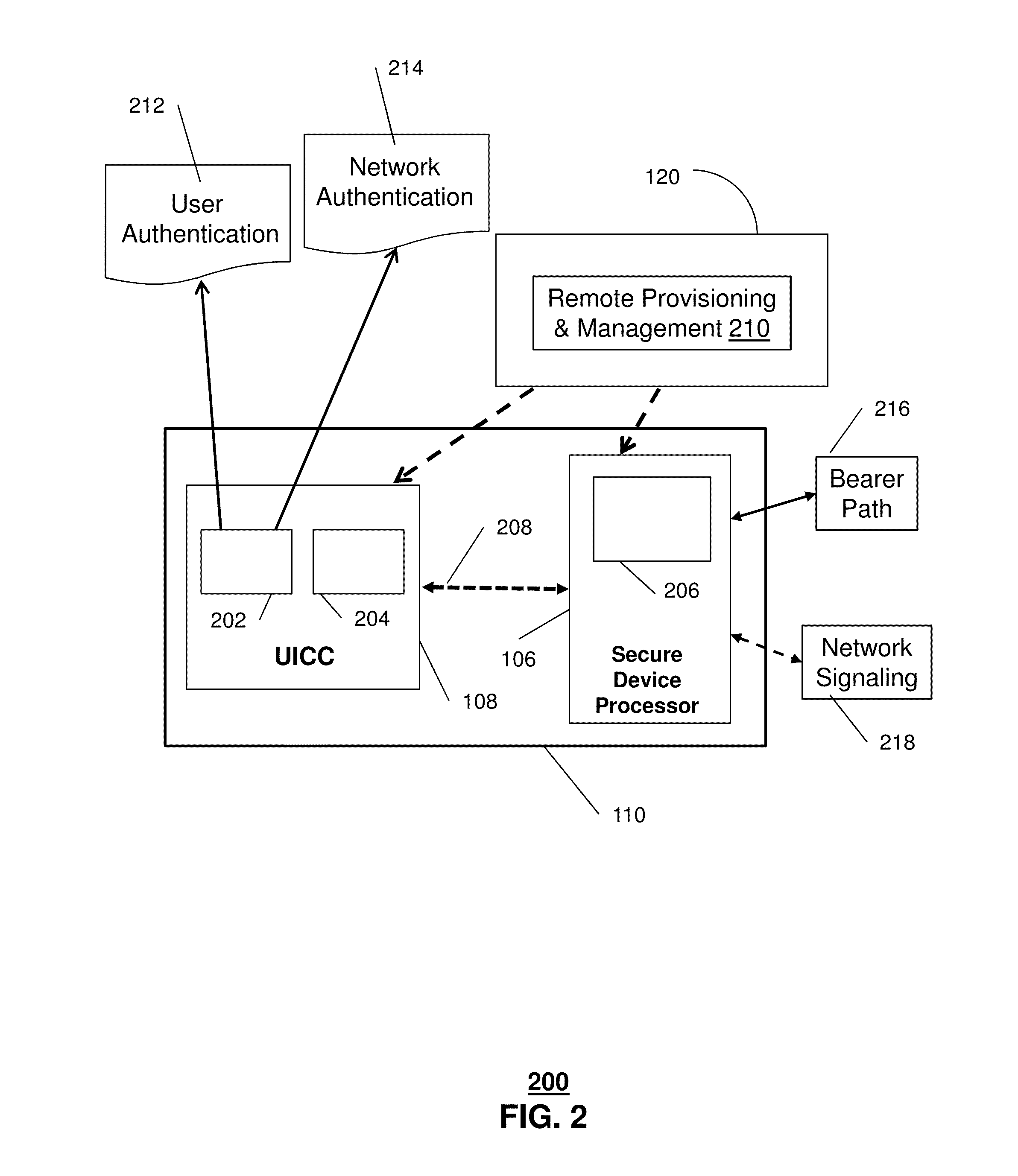
ActiveUS20150319151A1User identity/authority verificationComputer security arrangementsOne-way functionMaster key
A device that incorporates the subject disclosure may perform, for example, receiving a derived encryption key from a remote management server without receiving a master key from which the derived encryption key was generated, applying a one-way function to the derived encryption key and a nonce to generate a temporary encryption key, obtaining data for transmission to a recipient device, encrypting the data using the temporary encryption key to generate encrypted data, and providing the encrypted data over a network to the recipient device. Other embodiments are disclosed.
Owner:AT&T INTPROP I L P
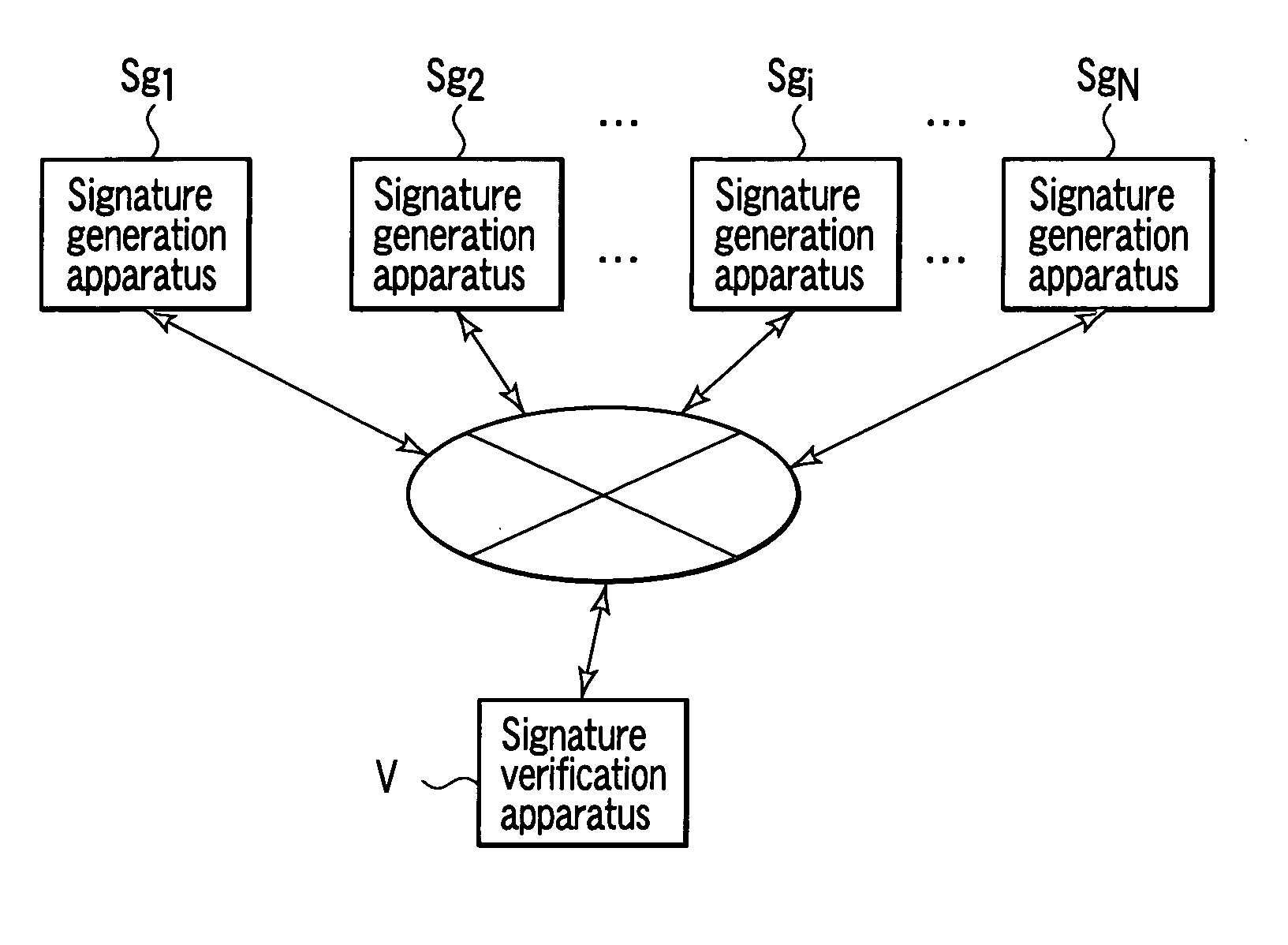
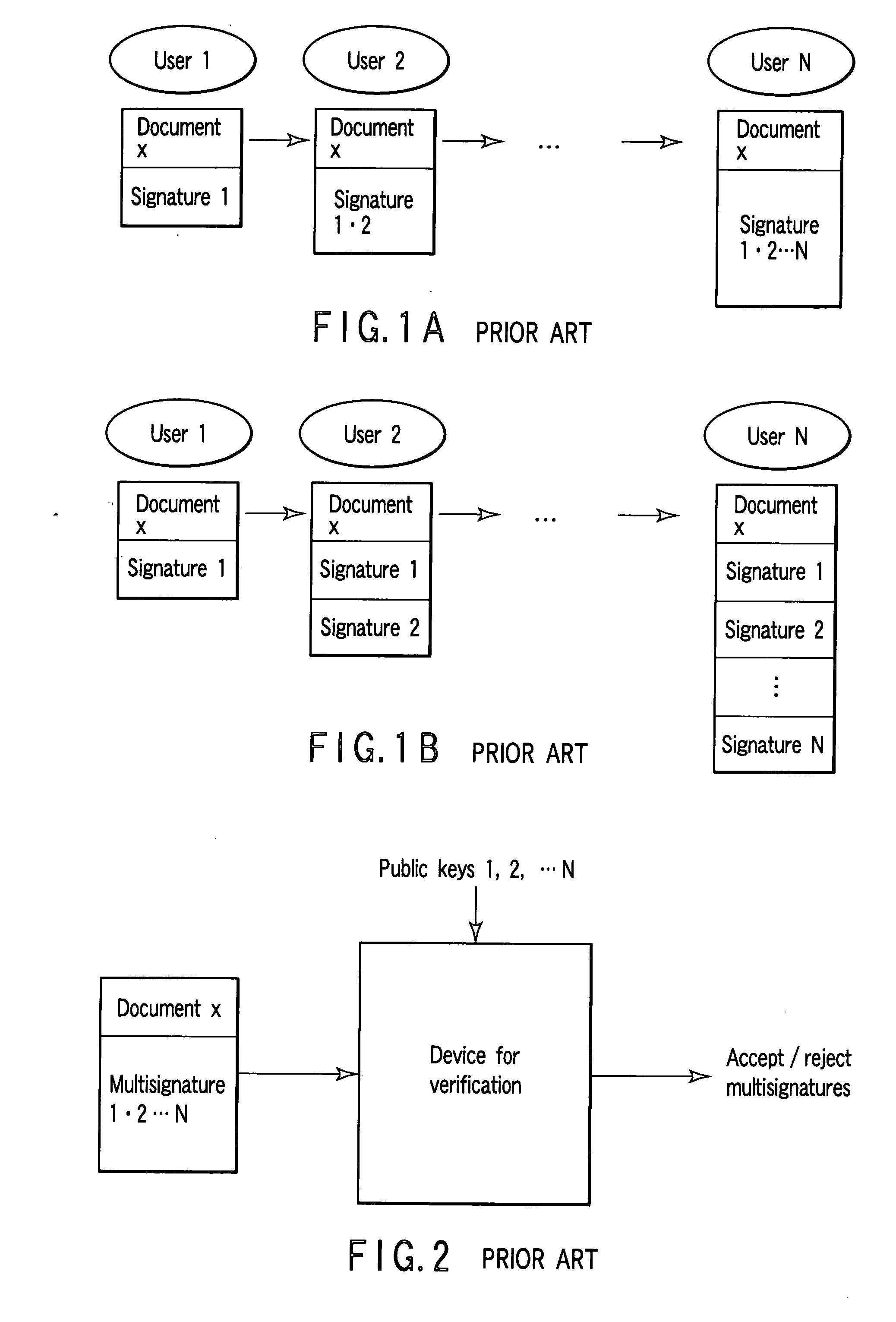
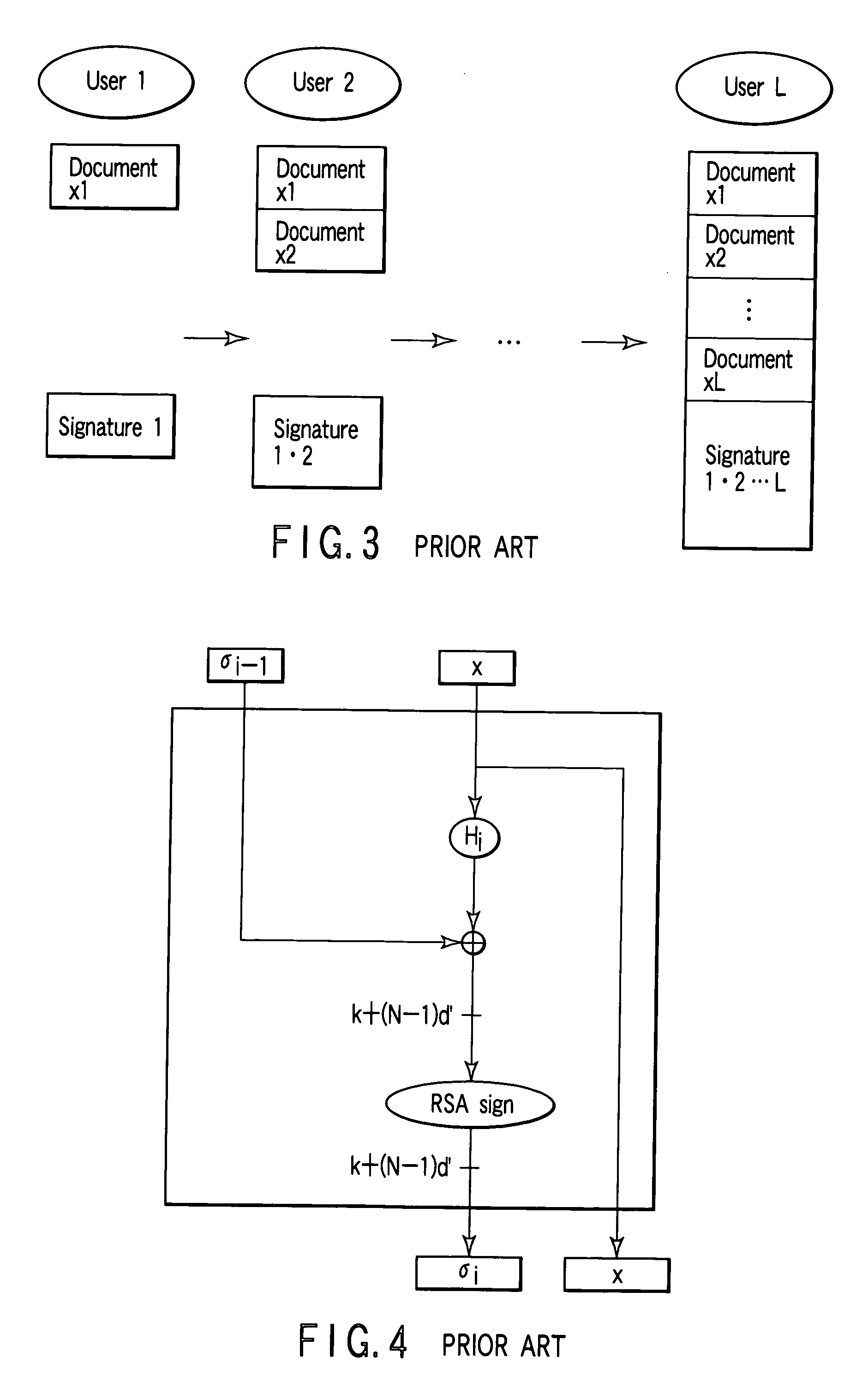
Multisignature method, apparatus, program, and system
InactiveUS20050201561A1Overall small sizeUser identity/authority verificationSecret communicationTheoretical computer scienceRSA problem
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
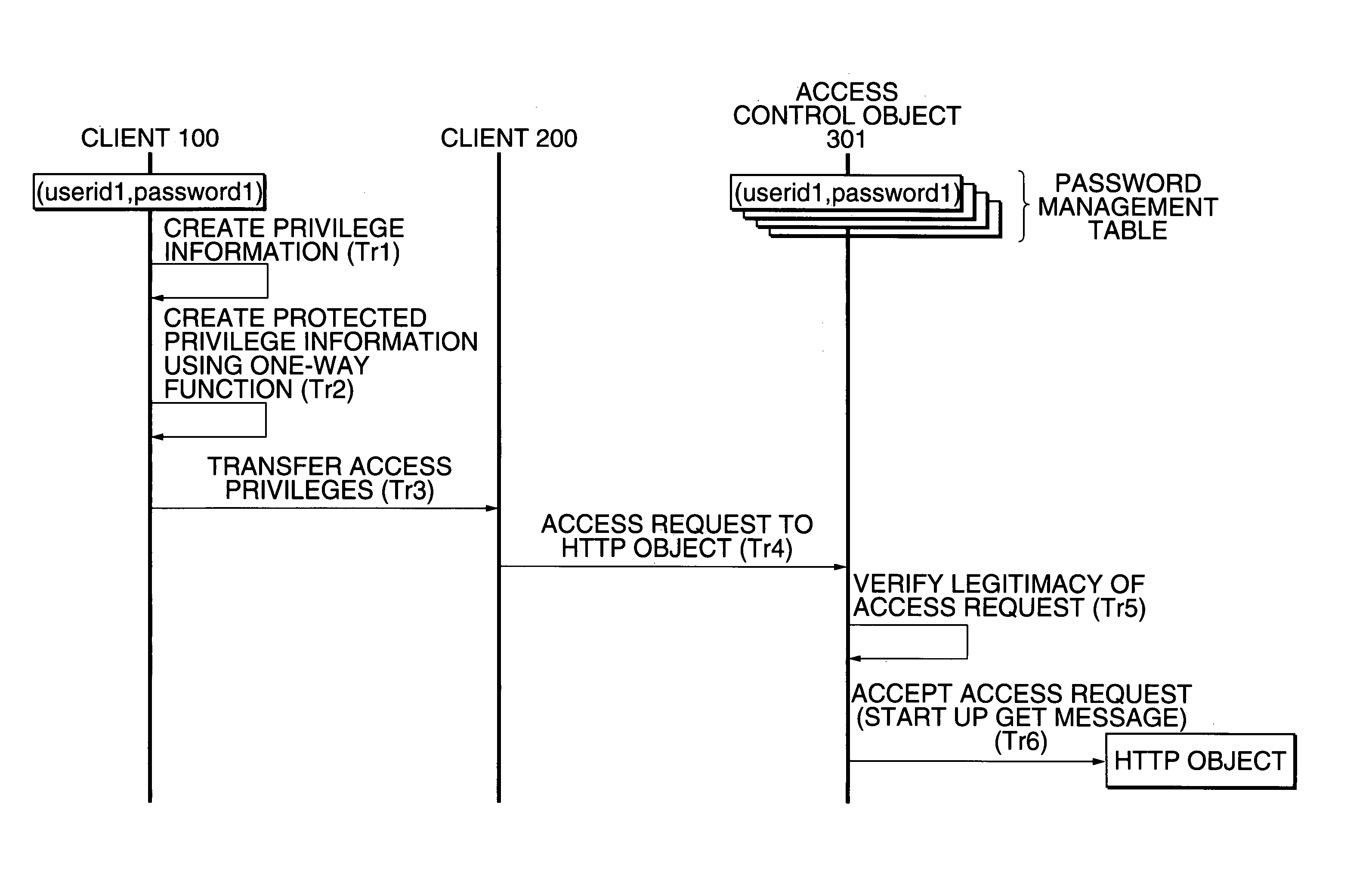
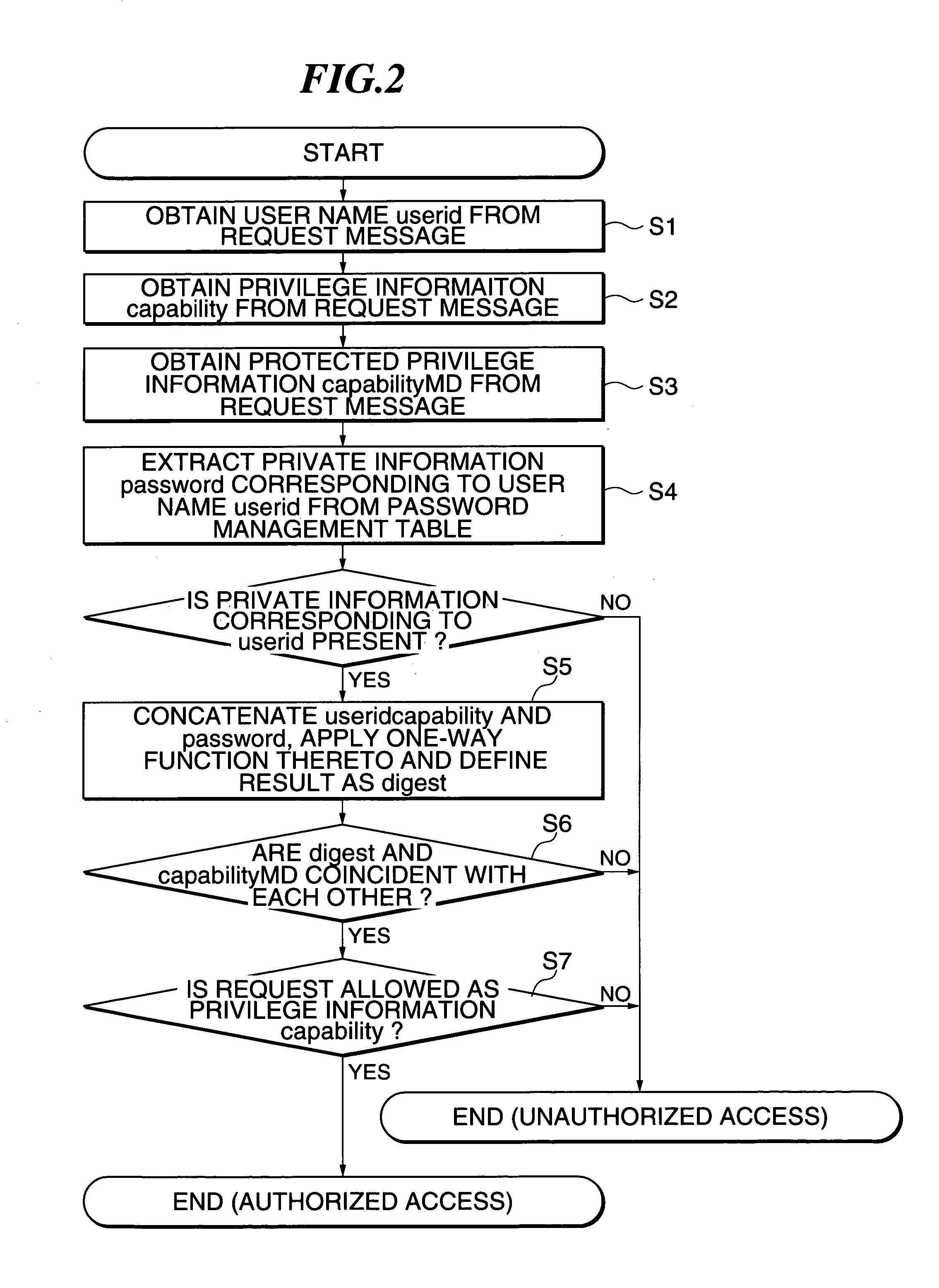
Access privilege transferring method
InactiveUS7058971B1Simple methodSafely transmitting “capabilityDigital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationThird partyClient-side
Disclosed herein is an access privilege transferring method for safely transmitting privilege information about each object between subjects (users) over an object space in which service objects are scattered. User information and secret information of clients are shared between the clients and servers. A client that transfers privilege information generates privilege information weakened in its own contents of privilege. Further, the client applies a one-way function or an encryption function to a bit string obtained by joining the generated privilege information and the secret information to each other, thereby generating protected privilege information with which a third party who does not know the secret information is not capable of tampering. Utilizing the protected privilege information makes it possible to safely transfer access privileges. Further, the server analyzes the protected privilege information by using the secret information to thereby make it possible to safely confirm whether a client that makes an object request is authorized.
Owner:FUJIFILM BUSINESS INNOVATION CORP
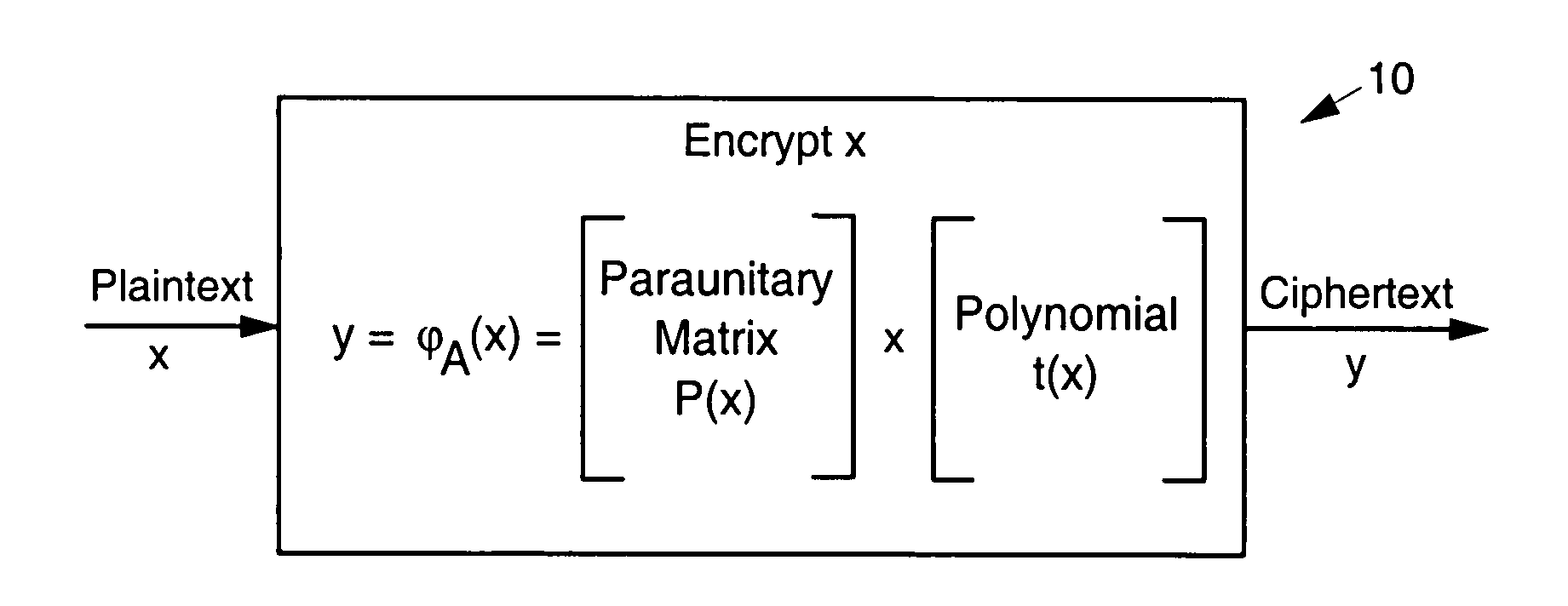
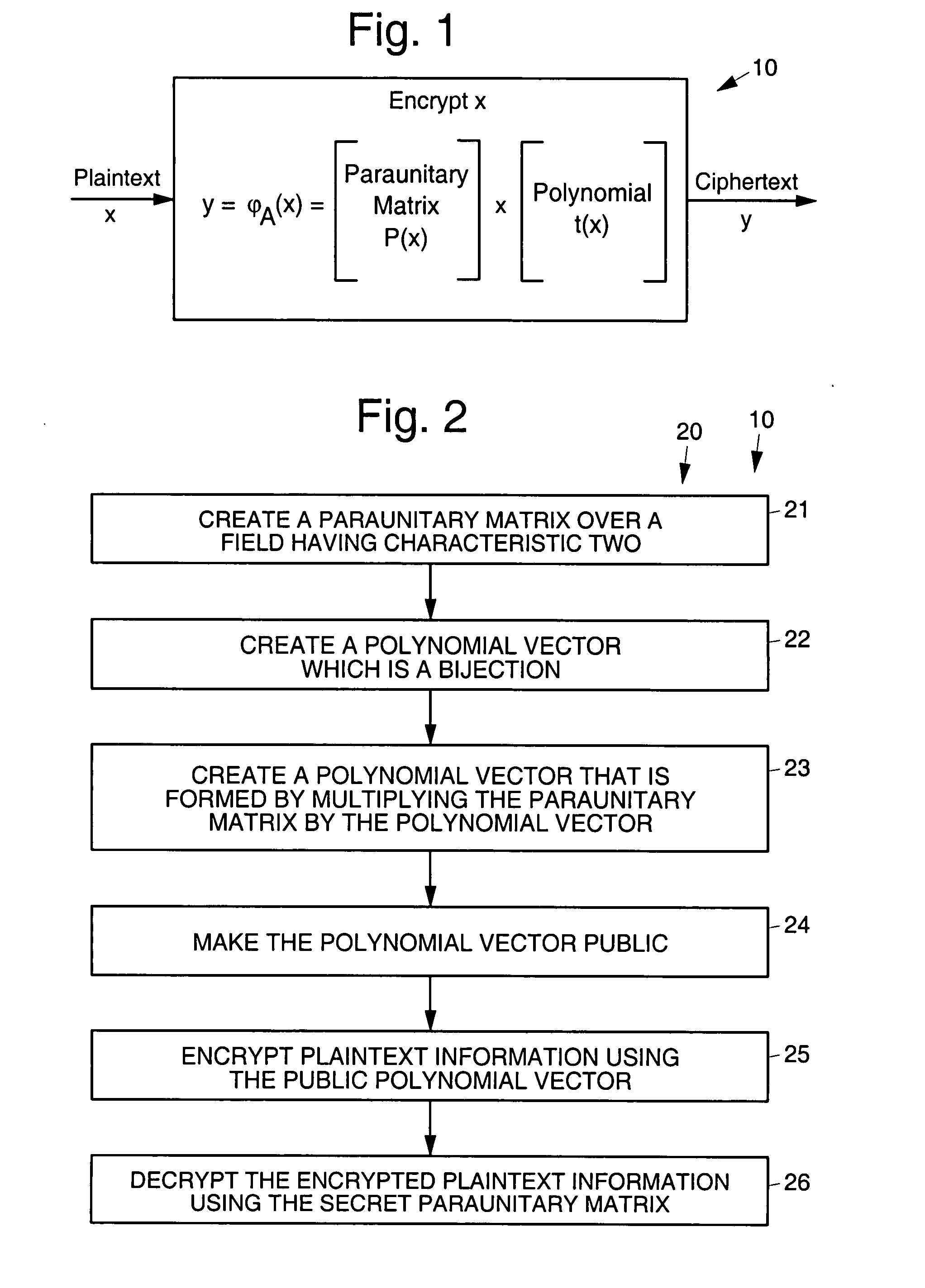
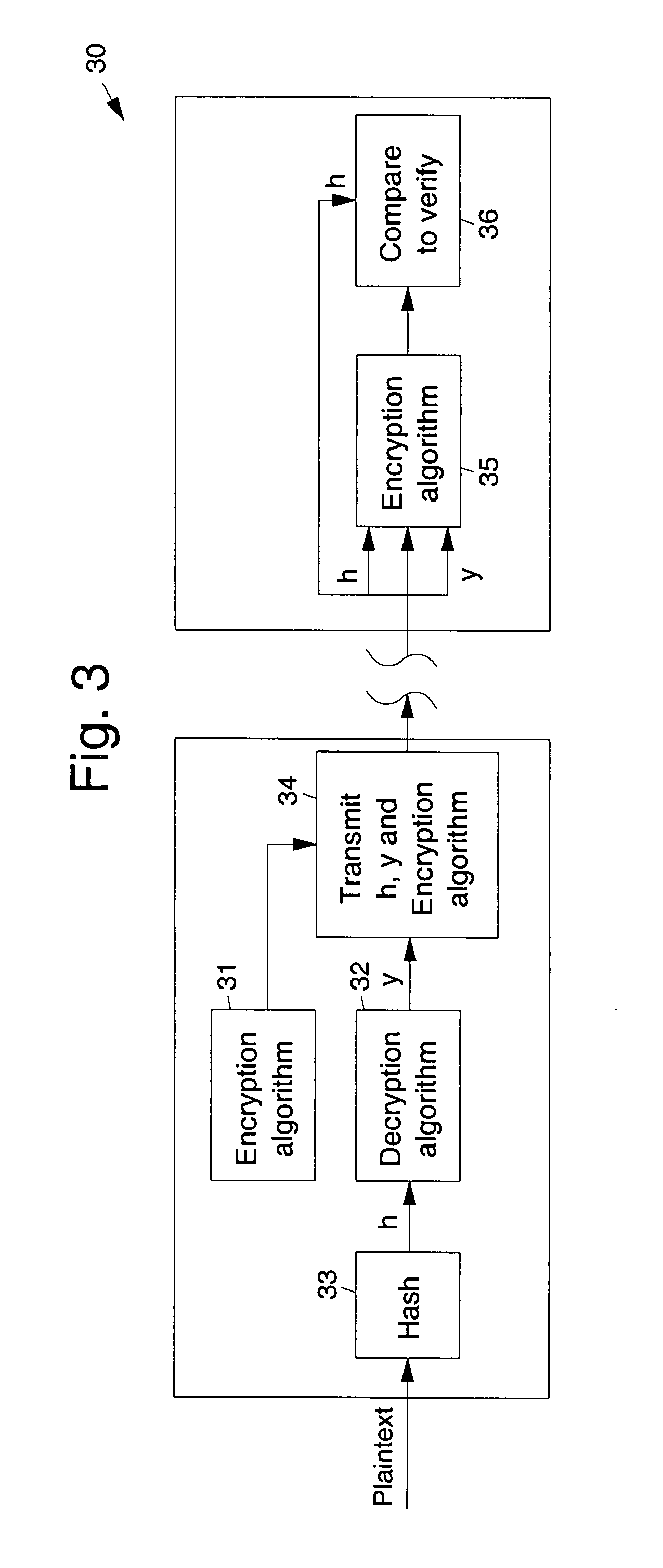
Asymmetric cryptosystem employing paraunitary matrices
InactiveUS20090010428A1Public key for secure communicationSecret communicationNon symmetricCiphertext
Disclosed are multivariate paraunitary asymmetric cryptographic systems and methods that are based on paraunitary matrices. An algebraic approach is employed in designing the multivariate cryptographic systems and methods. The cryptographic systems and methods are based on formulating a general system of multivariate polynomial equations by paraunitary matrices. These matrices are a family of invertible polynomial matrices that can be completely parameterized and efficiently generated by primitive building blocks. Using a general formulation that involves paraunitary matrices, a one-way function is designed that operates over the fields of characteristic two. To include a trapdoor, approximations are made to the paraunitary matrix. The result is a trapdoor one-way function that is efficient to evaluate, but hard to invert unless secret information about the trapdoor is known. An exemplary implementation operates on the finite field GF(256). In this example, the message block includes 16 to 32 symbols from GF(256), i.e., the block size n is an integer between 16 and 32. The ciphertext block takes its elements from the same field and has at least 10 extra symbols.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
Double factor combined public key generating and authenticating method
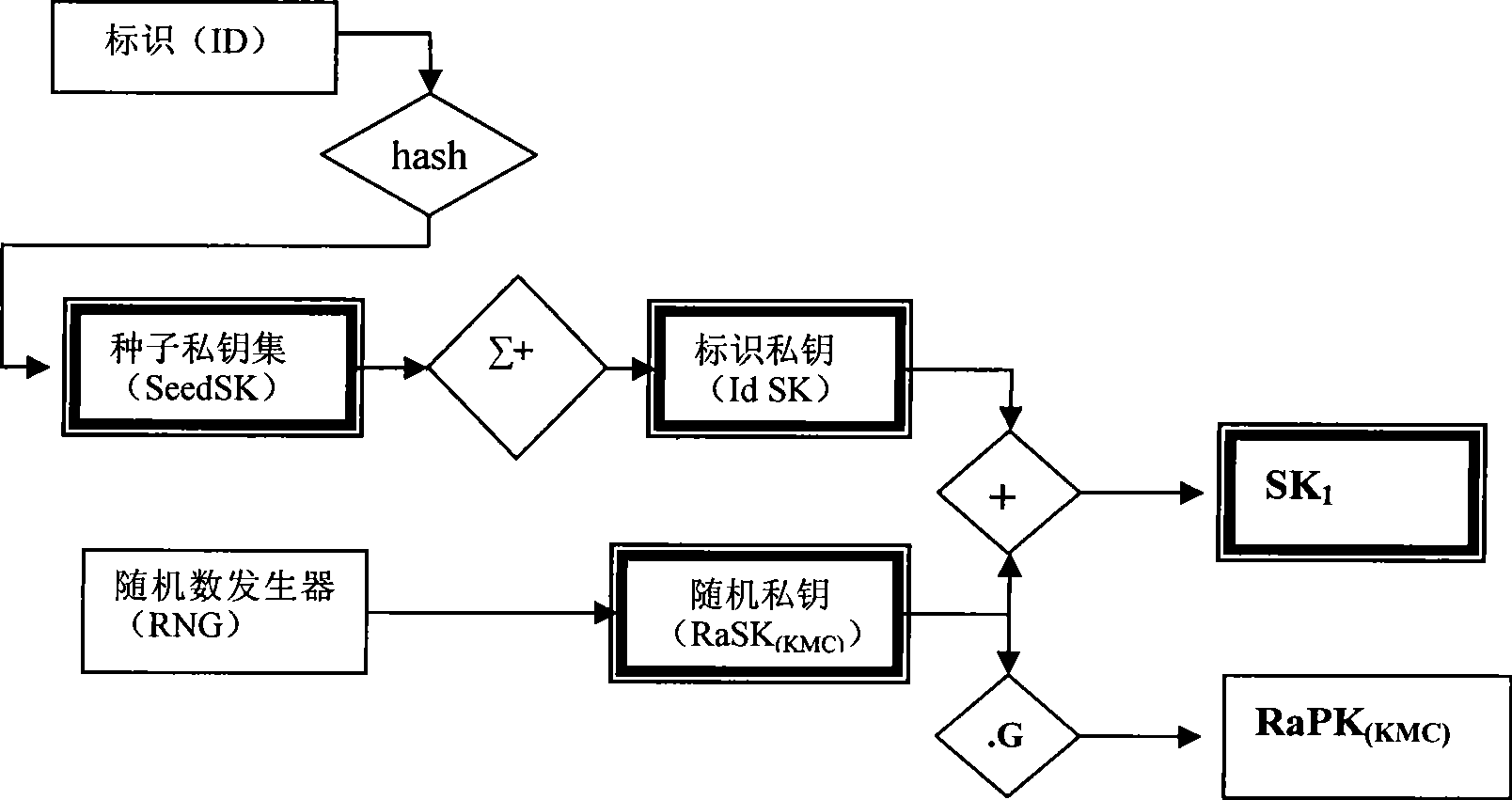
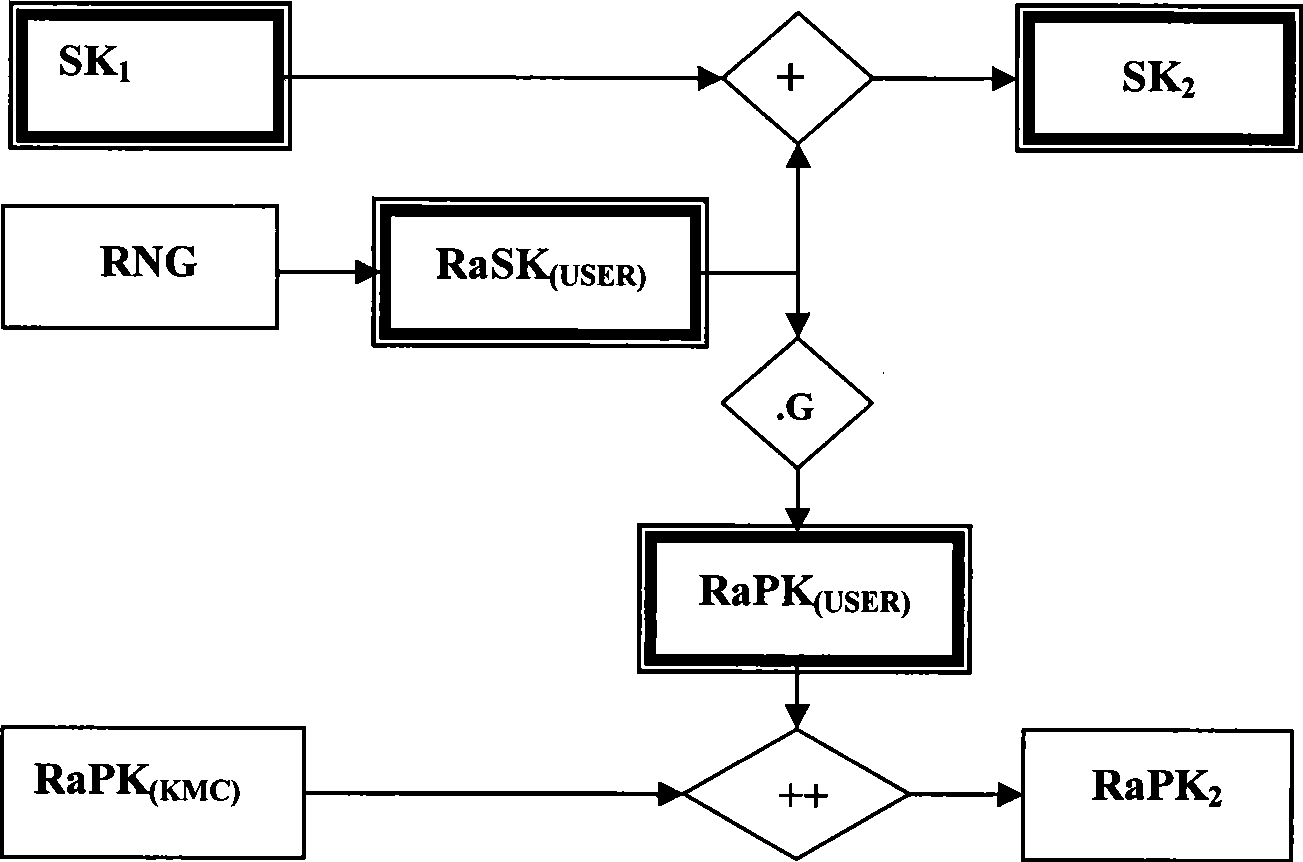
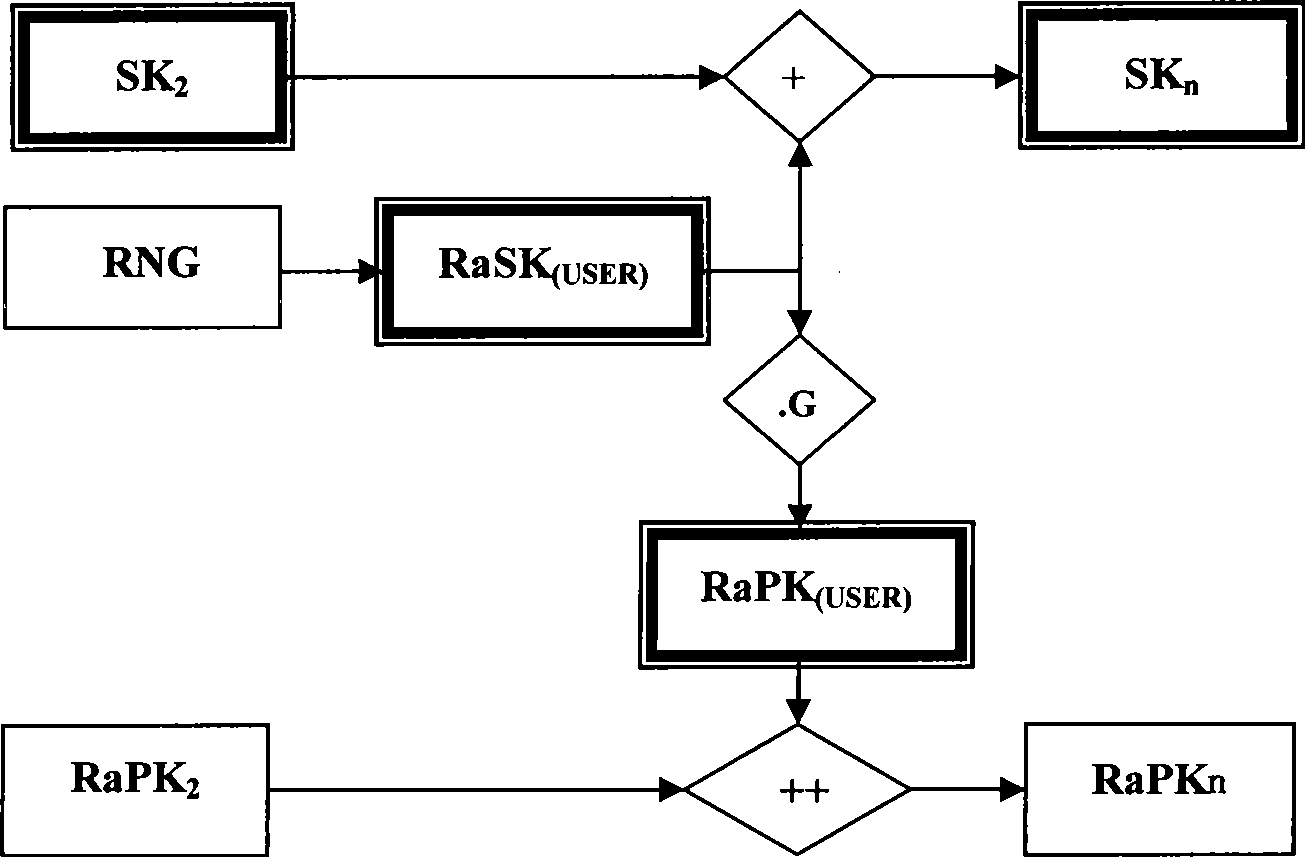
InactiveCN101420300AMeet the needs of centralized managementImprove securityKey distribution for secure communicationPublic key for secure communicationIdentification keyLogistics management
The present invention provides an identification key and random key complicated two-factor combined public key system and an authentication method. The identification keys are generated by selecting and combining seed key sets by the user identification generated sequence; the random keys are generated on the basis of one-way function principle which is also the basis of general public key ciphers. Multiple complication modes of the random key and the identification key can not only satisfy the requirement of centralized management, but also provide the proprietary right of private keys for users. An authentication system based on the key generating method has the characteristics of the identification authentication which does not need a third part certificate to prove and high randomization and privacy of general public key cipher and random private key. The present invention can be widely applied to authentication of systems with various scales, especially the authentication of public systems with enormous scale, and the applicable fields comprises reliable access, reliable load, electronic bank, reliable transaction, reliable logistics and the like.
Owner:BEIJING E HENXEN AUTHENTICATION TECH
Data holding proving method and device based on block chain and readable storage medium
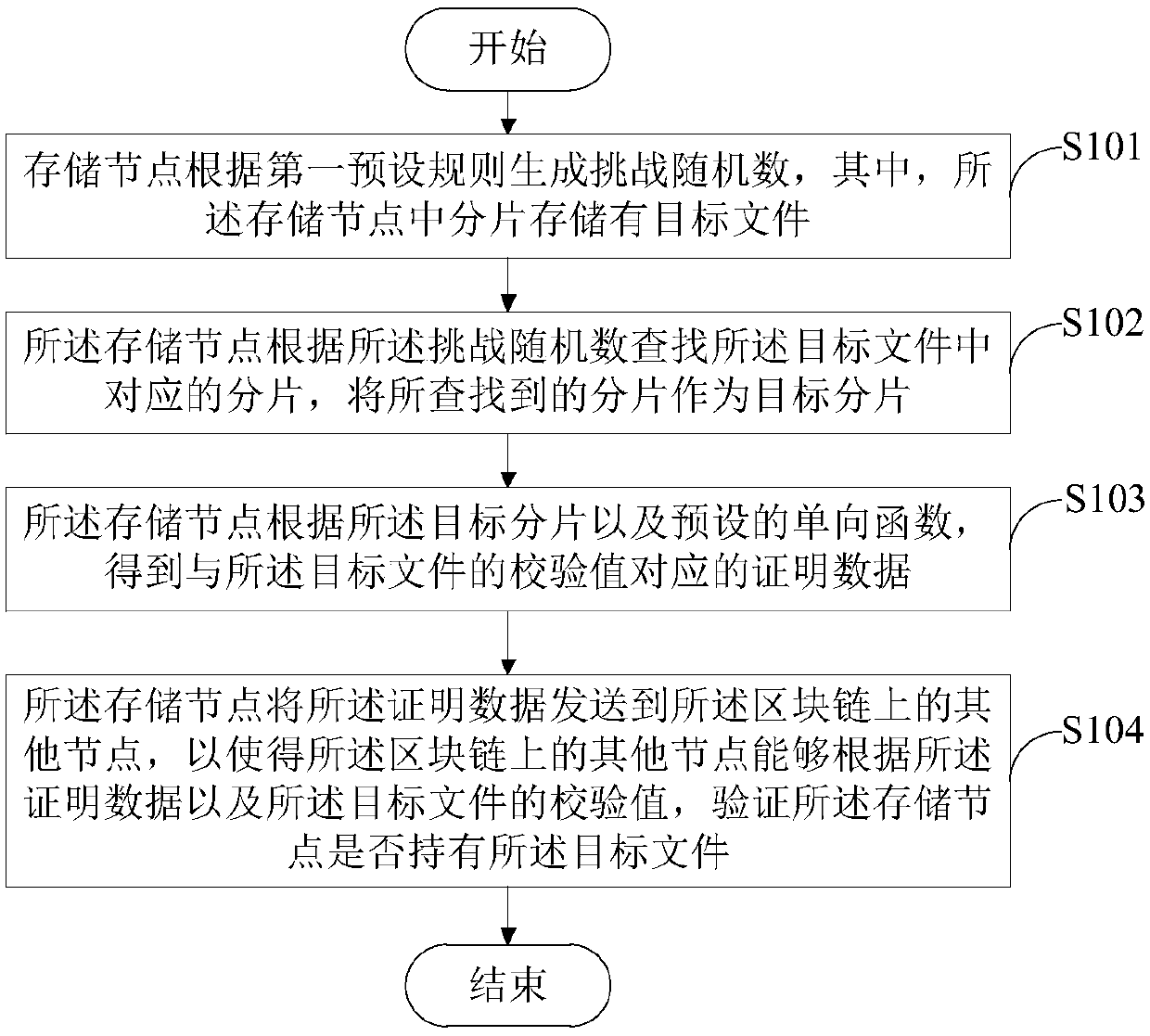
InactiveCN108681583AProblems preventing workload cheatingSpecial data processing applicationsThe InternetOne-way function
The invention discloses a data holding proving method based on a block chain, a device and a readable storage medium, belonging to the technical field of the Internet. The method comprises: a memory node generates a challenge random number according to a first preset rule, wherein a target file is stored in pieces in the memory node; then the corresponding pieces in the target file are searched according to the challenge random number, the searched pieces are taken as the target pieces, and the proving data corresponding to the check value of the target file is obtained according to the targetpieces and a preset one-way function, and the obtained proving data is broadcasted to the block chain as the workload proof of the memory node. In this way, other nodes in the block chain can verifywhether the memory node actually holds the target file according to the proving data and the check value of the target file, thereby preventing the memory node in the block chain system from cheatingin workload.
Owner:BEIJING QIHOO TECH CO LTD
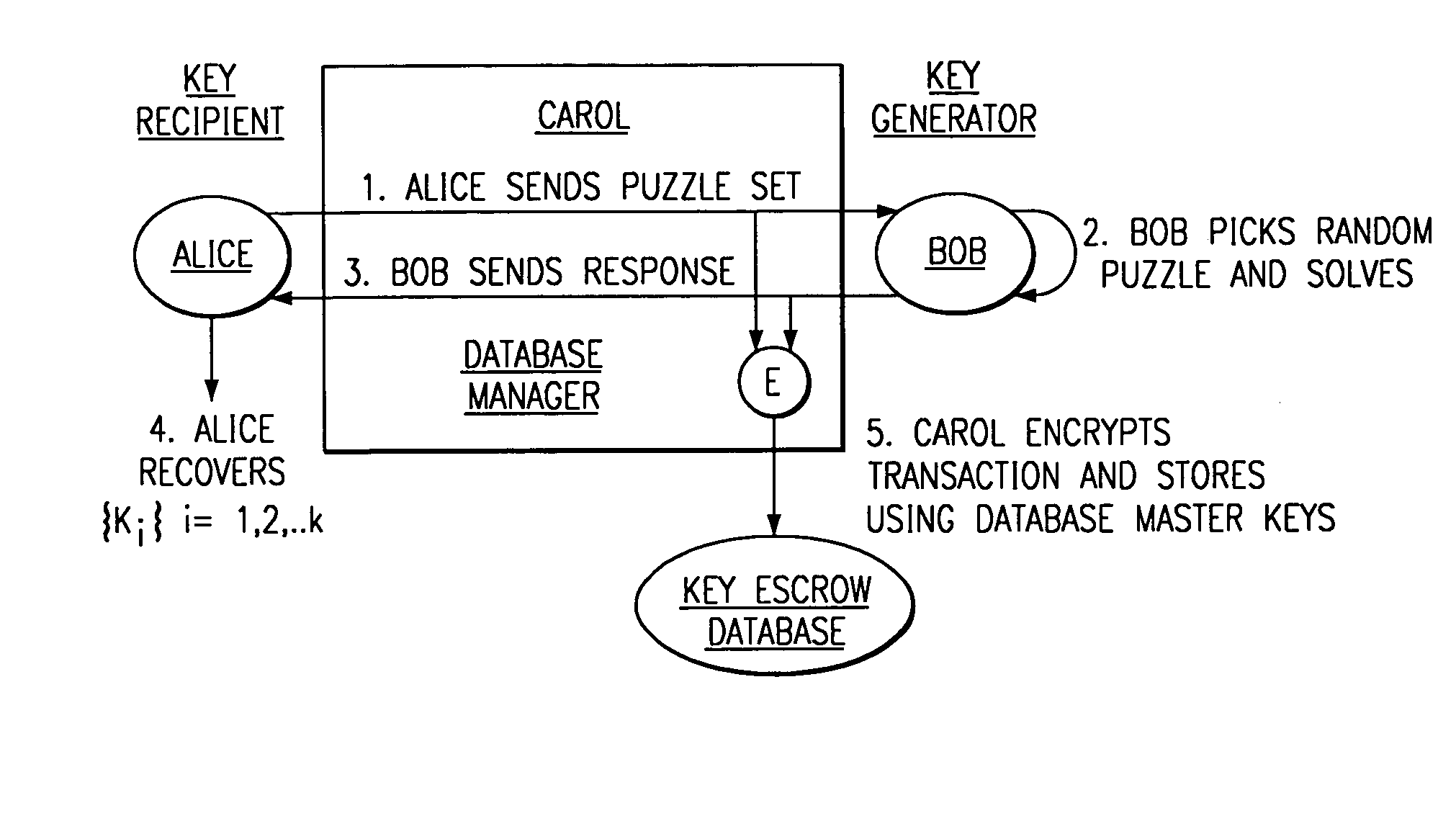
Key escrow systems
ActiveUS7269261B1Easy to changePermit multiplicationKey distribution for secure communicationComputer hardwareKey escrow
The storage and retrieval of cryptographic key materials from a storage database utilizes a limited one-way function to create computational barriers. The limited one-way function is asymmetric in nature, in terms of work to compute and work to invert, to store and retrieve encryption keys. The limited one-way function is not intractable, but alternatively, there is some measurable difference in the amount of work required to invert a stored encryption key, compared to the work required for a calculation of the output of the one-way function for storage of an encryption key in a database.
Owner:FORCEPOINT FEDERAL
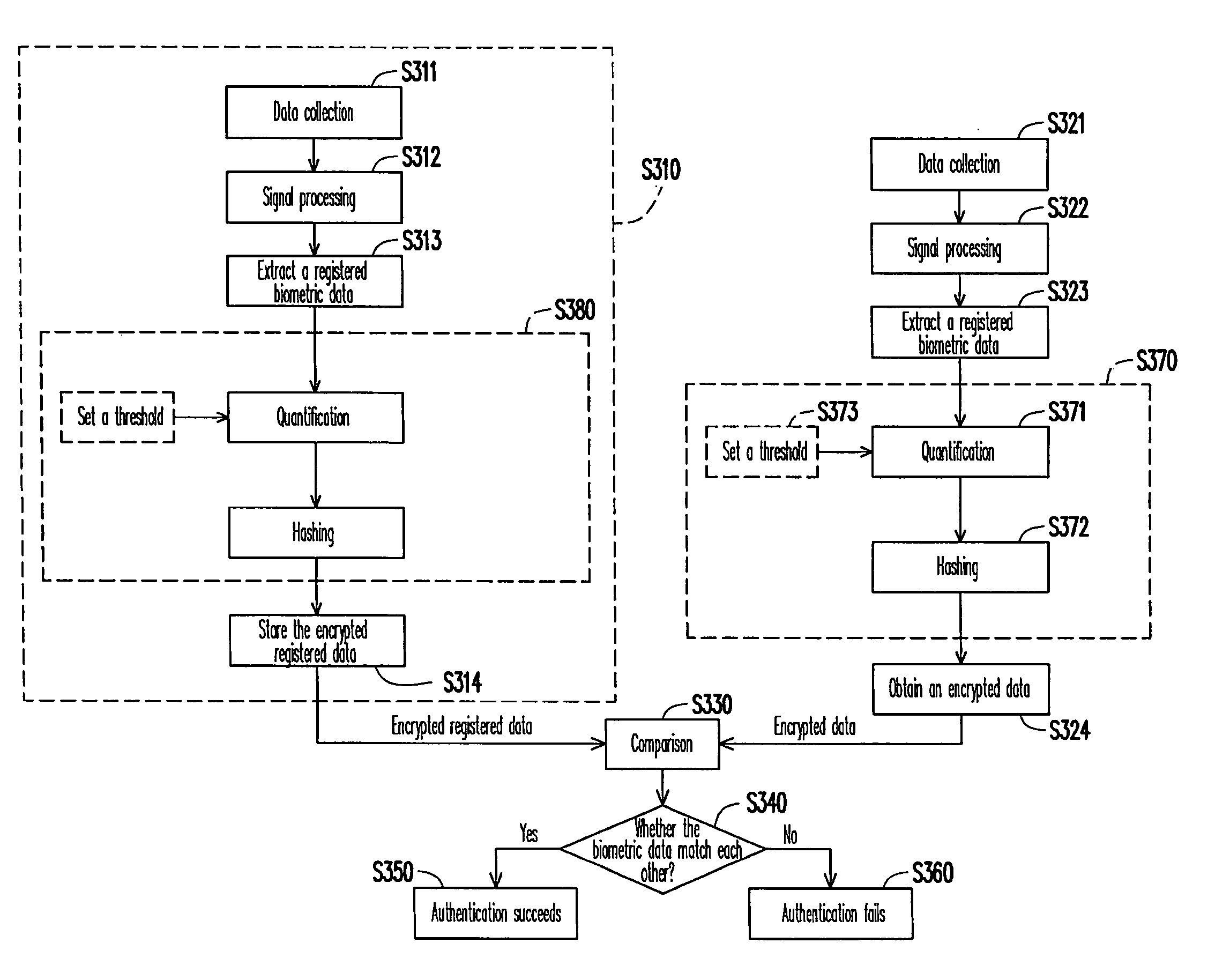
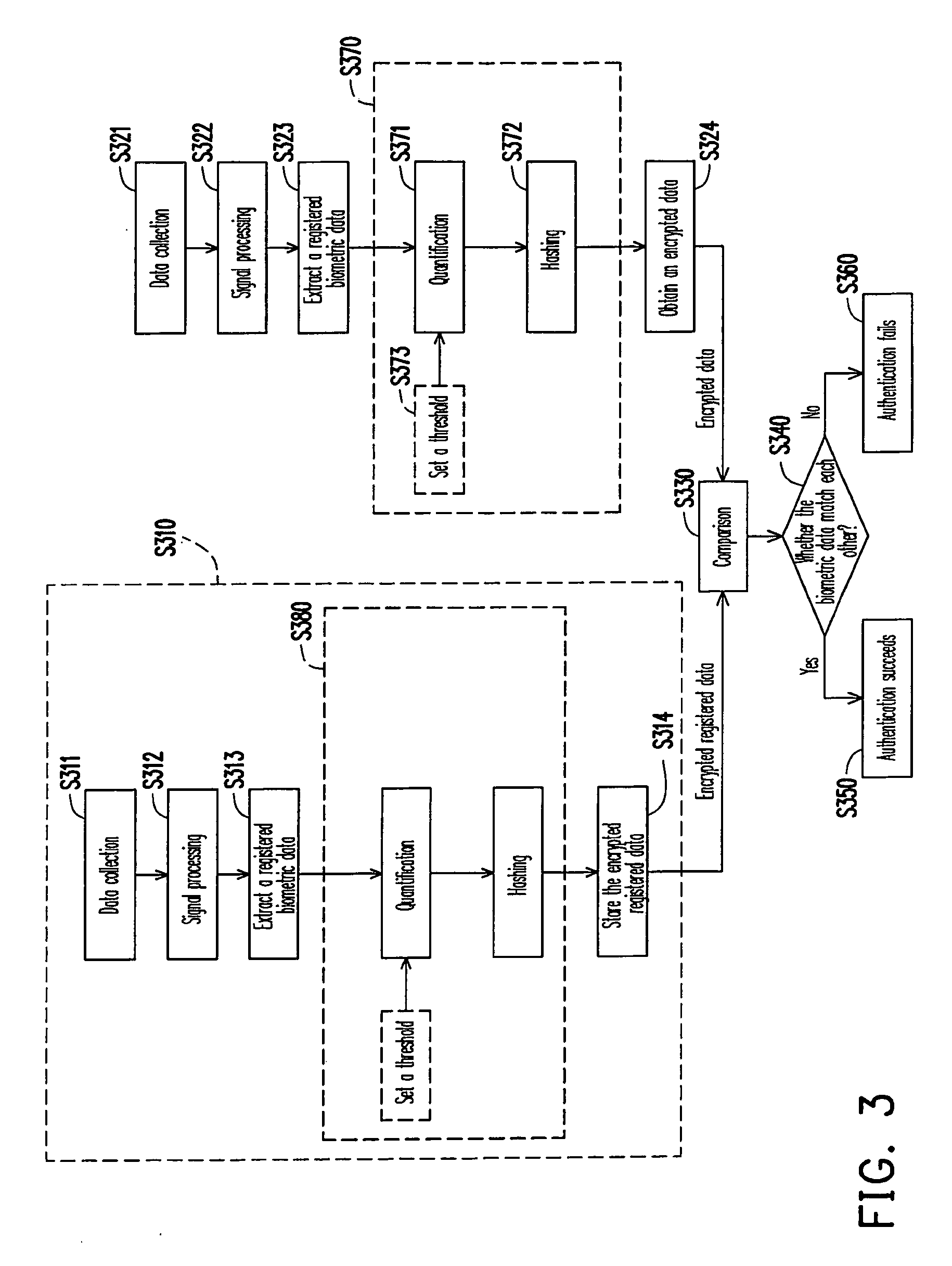
Biometric method and apparatus and biometric data encryption method thereof
ActiveUS20090138724A1Improve securityRealize functionUser identity/authority verificationCharacter and pattern recognitionBiometric dataFeature data
A biometric method, a biometric apparatus, and a biometric data encryption method thereof are disclosed. In the biometric method and the biometric apparatus, a biometric data is quantified to obtain a quantified data. A one-way function is then performed to convert the quantified data into an encrypted data. In the present invention, the biometric data is protected through a cryptography system so as to prevent the biometric features from being stolen or misappropriated. Moreover, in the present invention, a biometric technique can be integrated with a cryptography technique.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
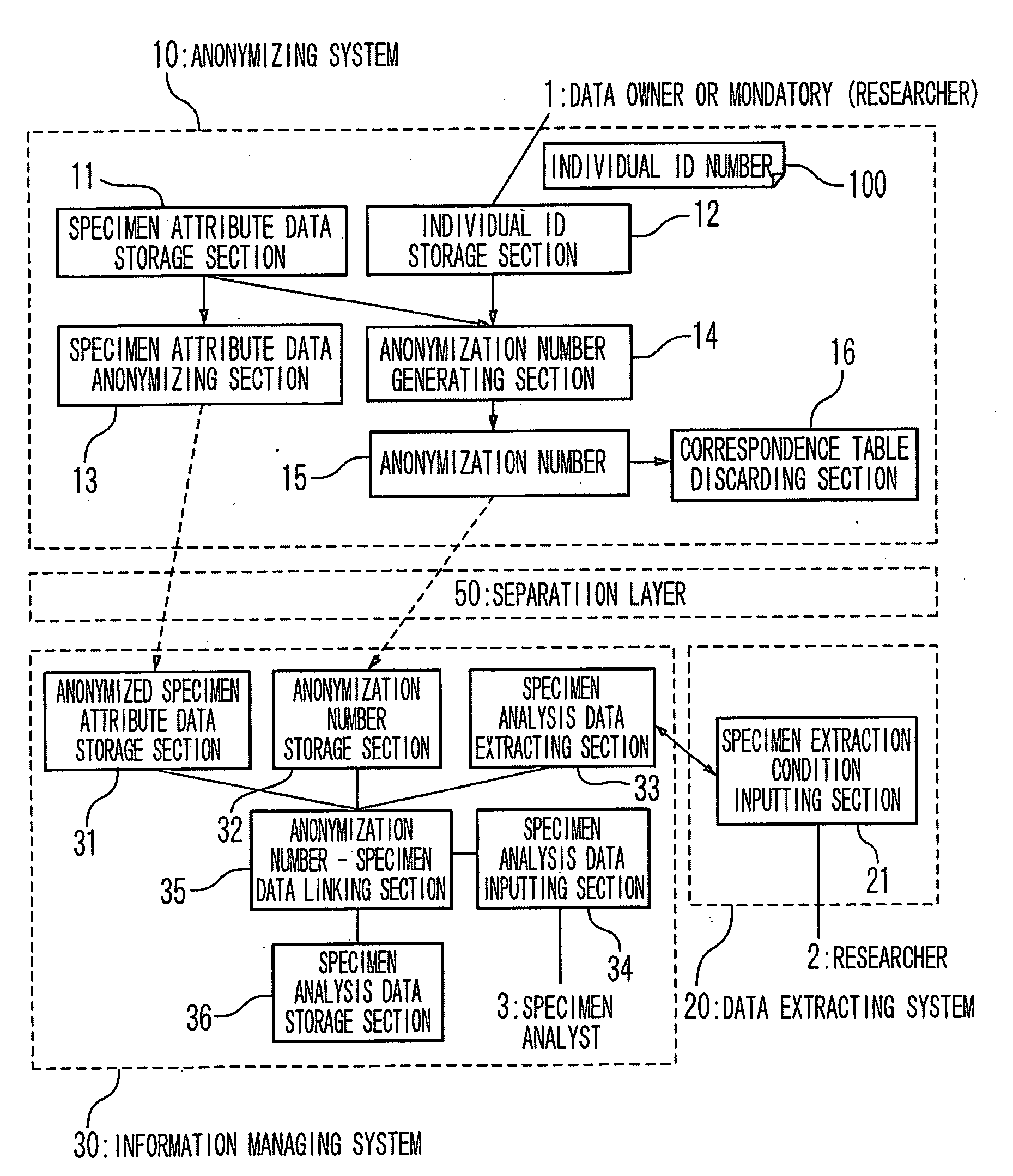
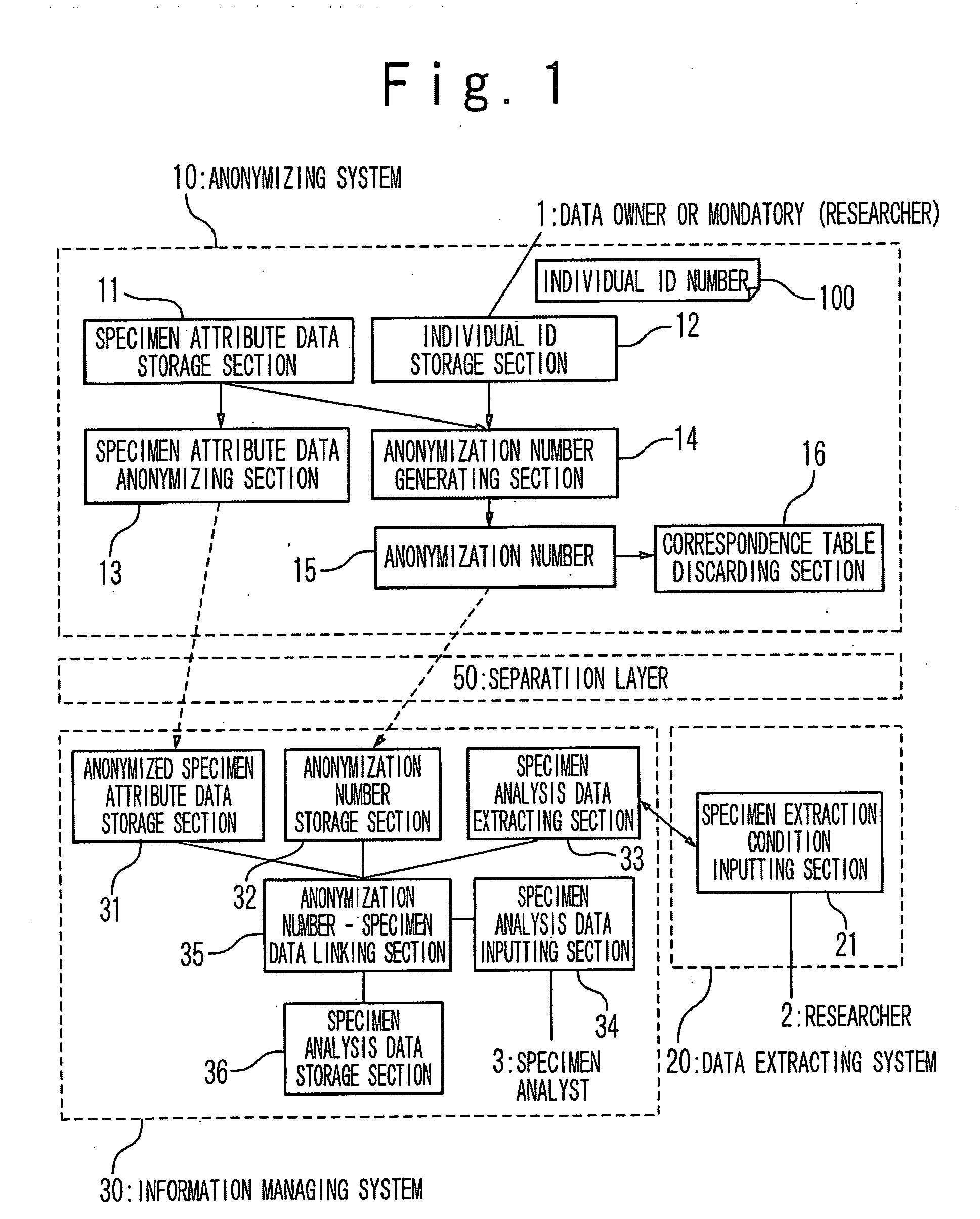
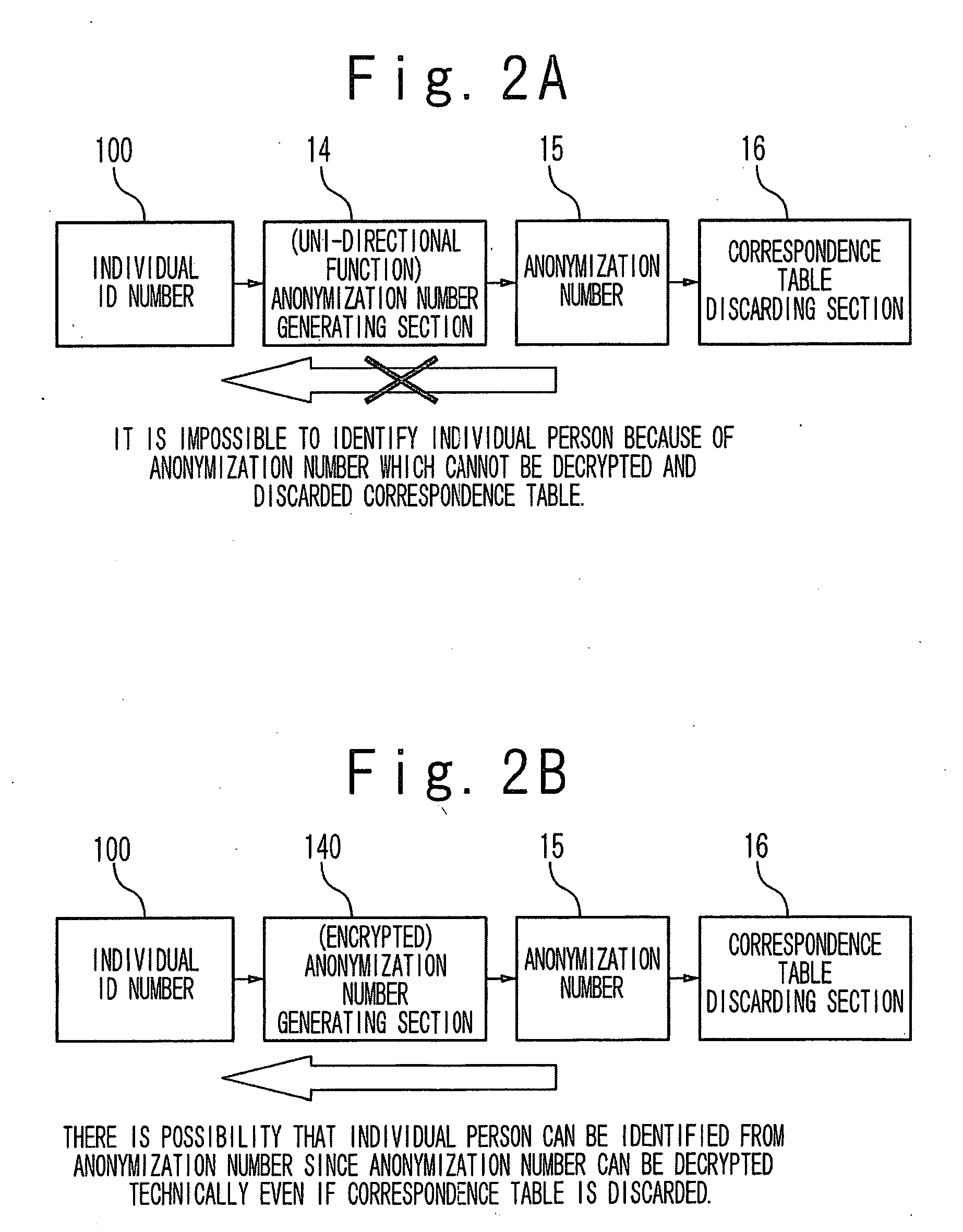
Information managing system, anonymizing method and storage medium
InactiveUS20100034376A1Build securityUser identity/authority verificationDigital data protectionRelevant informationData storing
After anonymization of individual information such as clinical data, only the owner of a specimen data or the owner of a browsing right can identify data stored or related to it after the anonymization. Therefore, in an unlinkable anonymizing method, a uni-directional function such as a hash value calculation is applied to a combination data of related information such as an individual identifiable ID number or data, ID information and a key symbol in case of the anonymization, or a relational data such as a specimen number from only which an individual cannot be identified. A correspondence table of the anonymization number and the individual information is deleted. An estimation of an original individual or a specimen number from the anonymization number is prevented by use of uni-directional function. The access to the data after the anonymization is limited only to the owner who knows anonymization key data or the mandatory of the information.
Owner:NEC CORP
Encryption/signature method, apparatus, and program
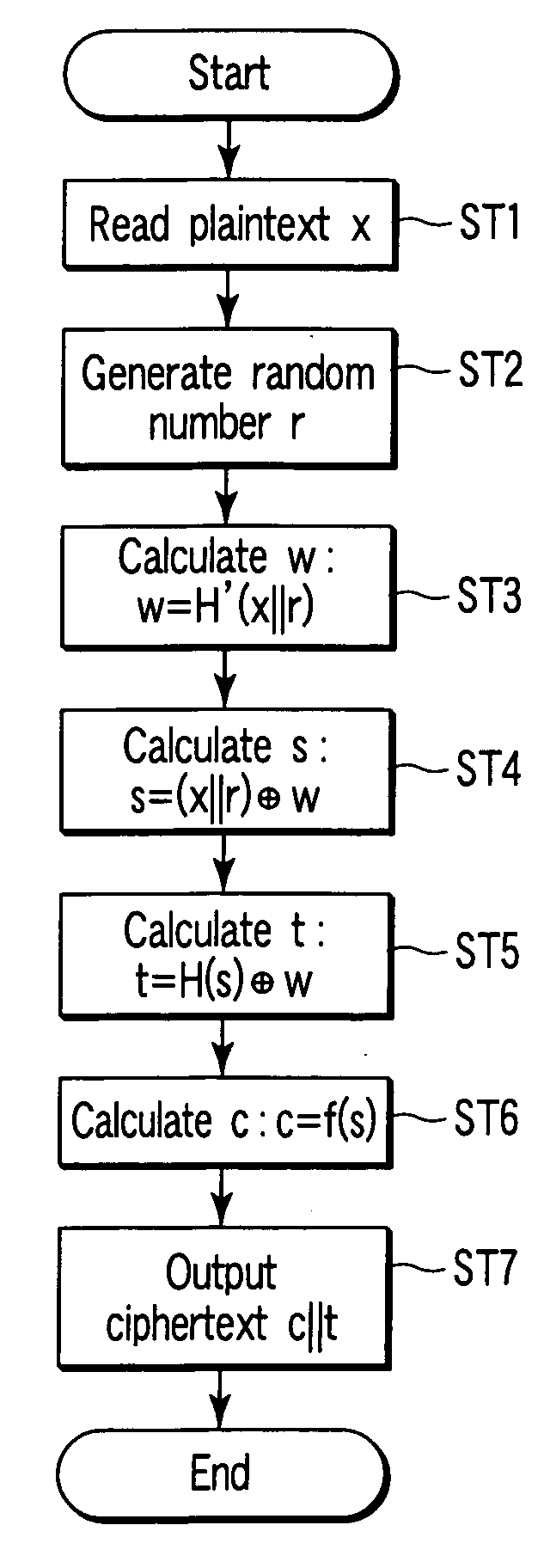
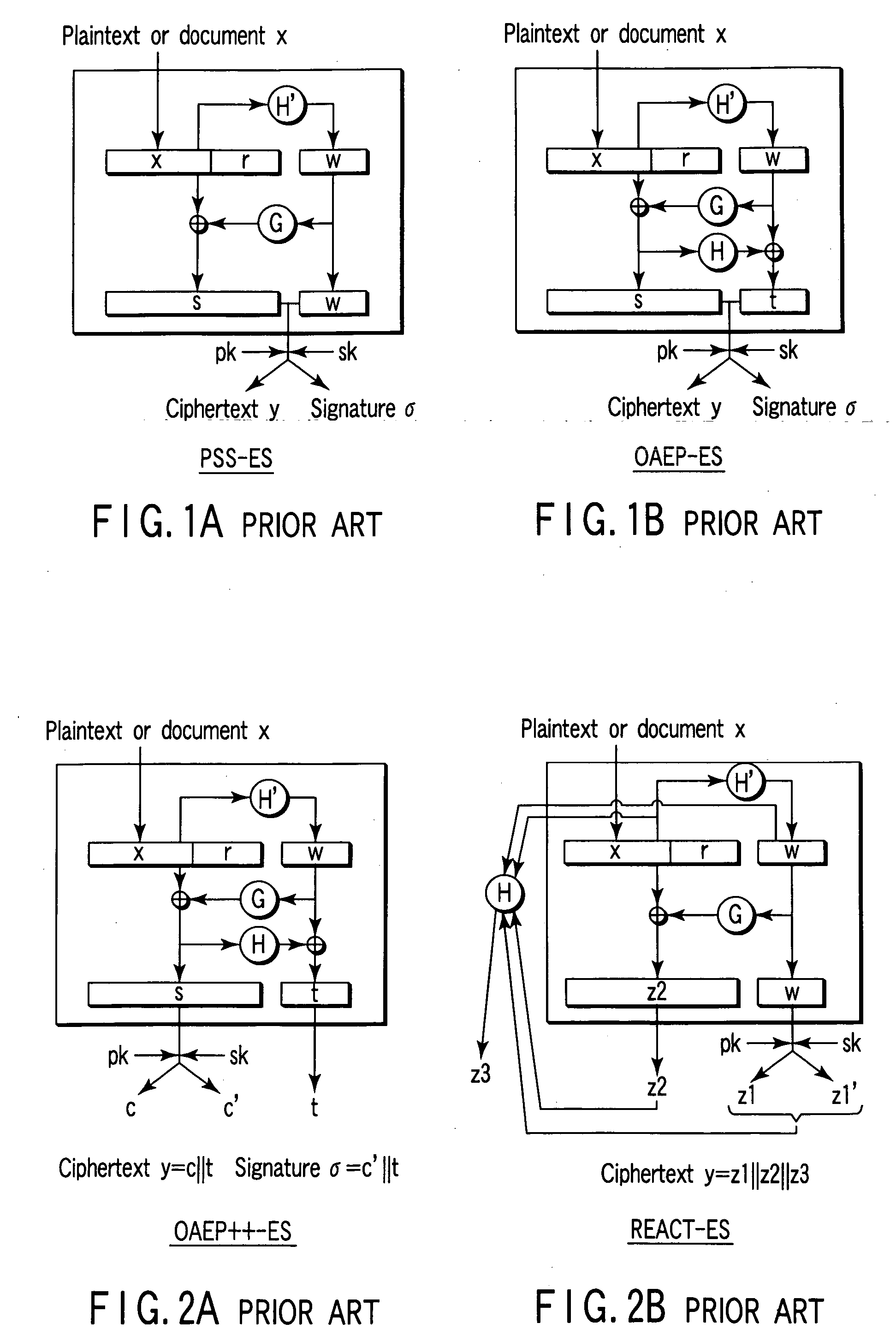
InactiveUS20050157871A1Public key for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationCiphertextTime of use
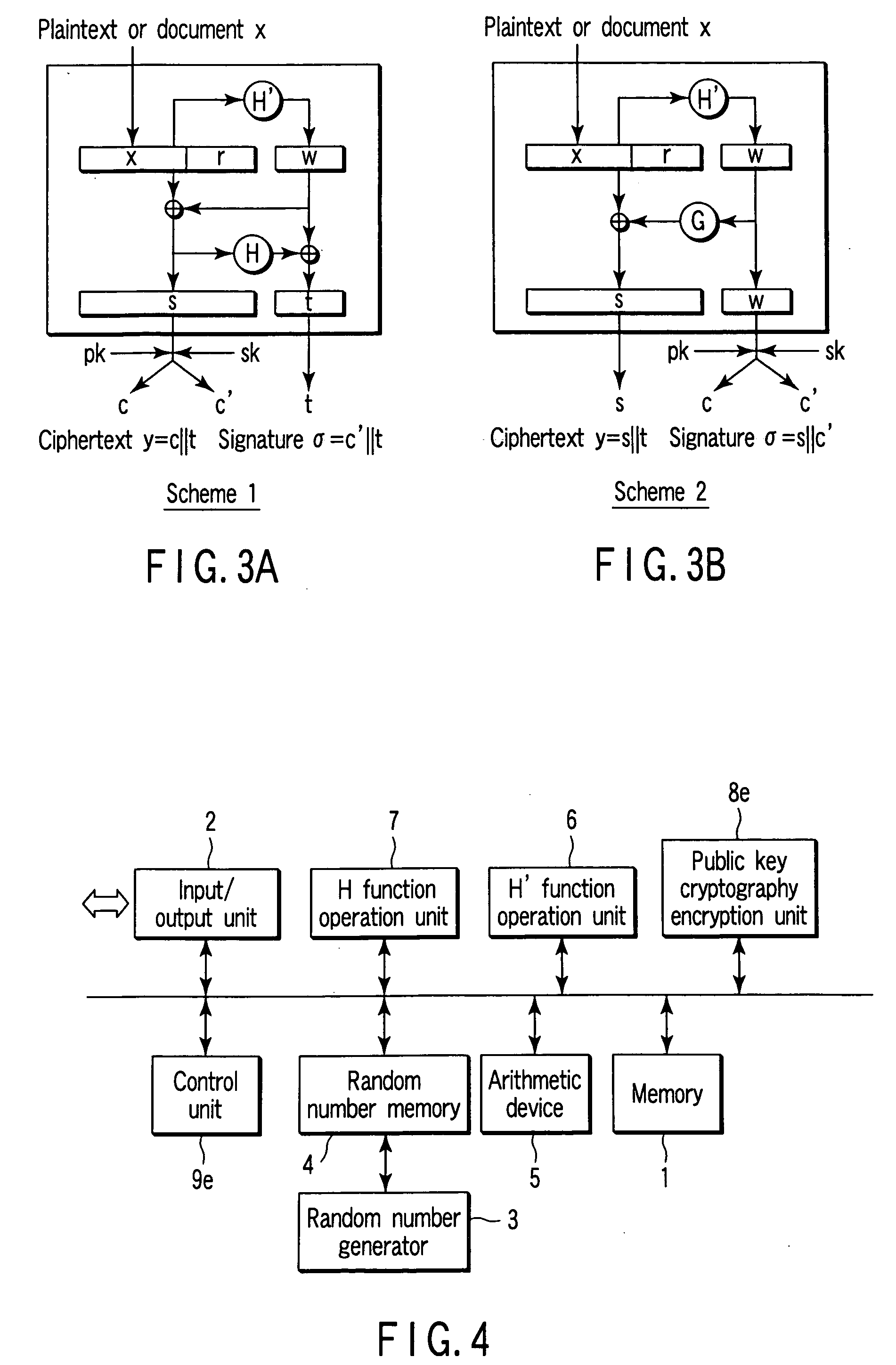
According to each embodiment of the present invention, random function operations less than three times and tight security can simultaneously be implemented. More specifically, a ciphertext y=c∥t or a signature σ=c′∥t is created as concatenated data of two data. The concatenated data is created by using a public key encryption scheme for only one (necessary part s) of the data. For this reason, tight security for the one-way characteristic of a trapdoor one-way function of the public key encryption scheme can be implemented. In addition, the output size of a first random function H′ is limited. Accordingly, a random function G for bit expansion in the conventional. OAEP++-ES scheme can be omitted. Hence, the number of times of use of random functions can be reduced to two.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Pseudo public key encryption
InactiveUS20070189517A1Low costCheap to achievePublic key for secure communicationSecret communicationComputer hardwareTamper proof hardware
According to the present invention, a secret key cryptosystem and tamper-proof hardware are used to realize a pseudo public key cryptosystem at a low cost. A trap-door one-way function is substantially realized with the use of tamper-proof hardware. Each user performs communication using equipment provided with hardware having the same capabilities described below. Such hardware retains association between an ID and a key. In response to a request from a user, the hardware issues and stores an ID, and it can perform decryption and generation of a MAC (message authentication code) with a key associated with the ID. A user publishes his ID. When performing encryption, a message sender encrypts a message using the published ID. A third person can perform decryption with the ID only by analyzing the mechanism in the hardware. However, the hardware has a capability of destroying itself when such an act is attempted.
Owner:IBM CORP
Method to generate, verify and deny an undeniable signature
ActiveUS20050193048A1User identity/authority verificationSecret communicationUndeniable signatureTheoretical computer science
The aim of the invention is to propose the generation, verification and denial of an undeniable signature which has a size smaller than the currently available undeniable signatures, i.e. less than 80 bits. This aim is achieved by the method to generate an undeniable signature (y1, . . . , yt) on a set of data, this method comprising the following steps: transforming the set of data (m) to a sequence of a predetermined number (t) of blocks (x1, . . . , xt), these blocks being members of an Abelian group, this transformation being a one way function, applying to each block (xi) a group homomorphism (f) to obtain a resulting value (yi), in which the number of elements of the initial group (G) is larger than the number of elements (d) of the destination group (H).
Owner:ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE FEDERALE DE LAUSANNE (EPFL)
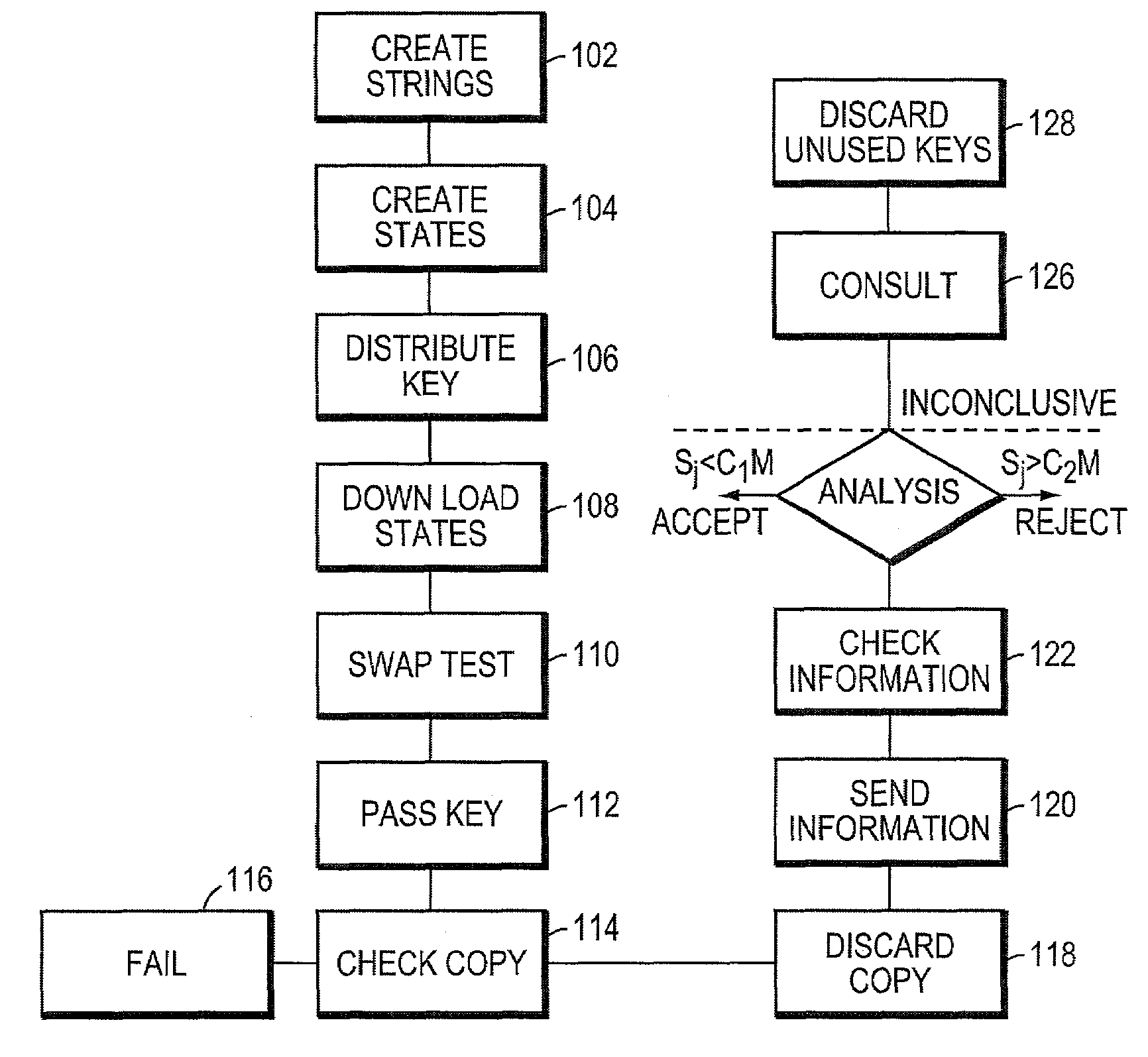
Quantum digital signatures
ActiveUS7246240B2User identity/authority verificationSecret communicationDigital signatureDigital signature forgery
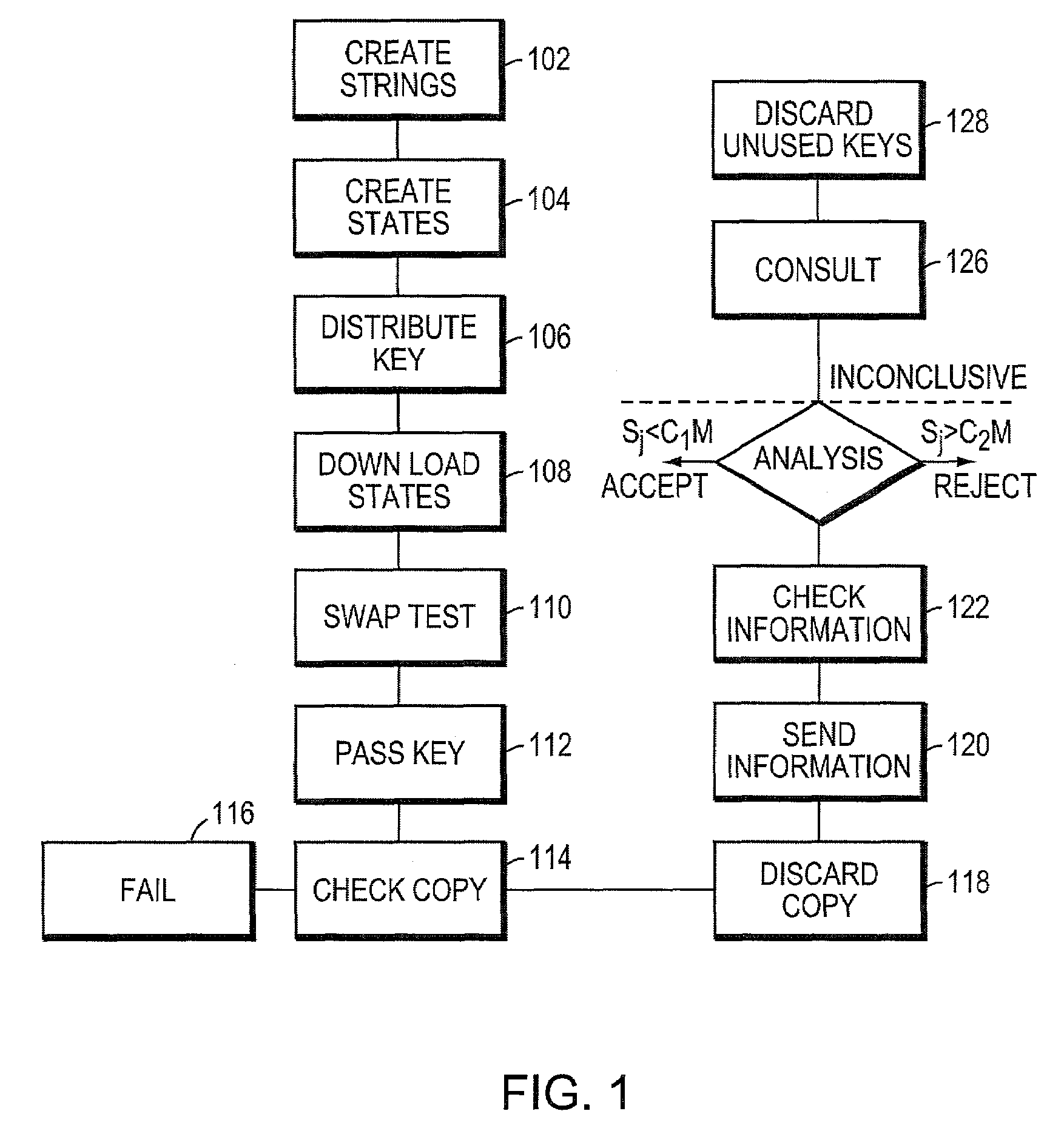
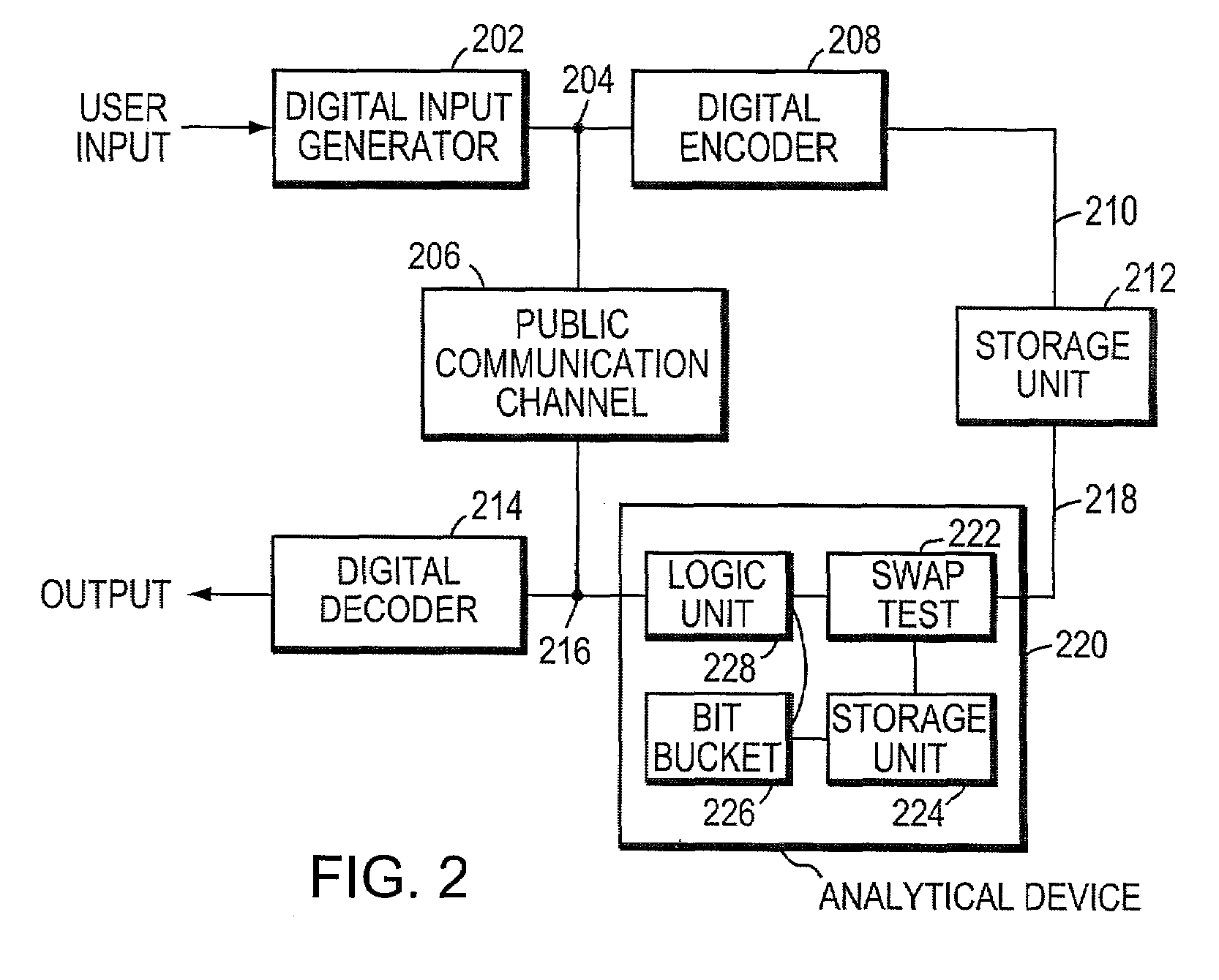
Systems and methods for providing secure quantum digital signatures. In one embodiment, a digital signature user creates a plurality of identical “public” keys having one or more bits and a corresponding quantum mechanical one-way function. Quantum digital signature recipients use a “swap test” to check the validity of a copy of the key, and compare the test results with others. The quantum digital signature user sends a signed message over any channel, including an insecure channel. The recipients evaluate the signed message, and quantify the number of incorrect keys. The message is deemed valid and original, or forged and / or tampered with, when the number of incorrect keys is less than a lower threshold, or exceeds an upper threshold, respectively. For an intermediate number of incorrect keys, the recipients determine message authenticity by comparing observations. Hardware useful for application of the method is disclosed.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Method and apparatus for generating cryptographic key using biometric data
InactiveUS20100014655A1Digital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationThird partyBiometric data
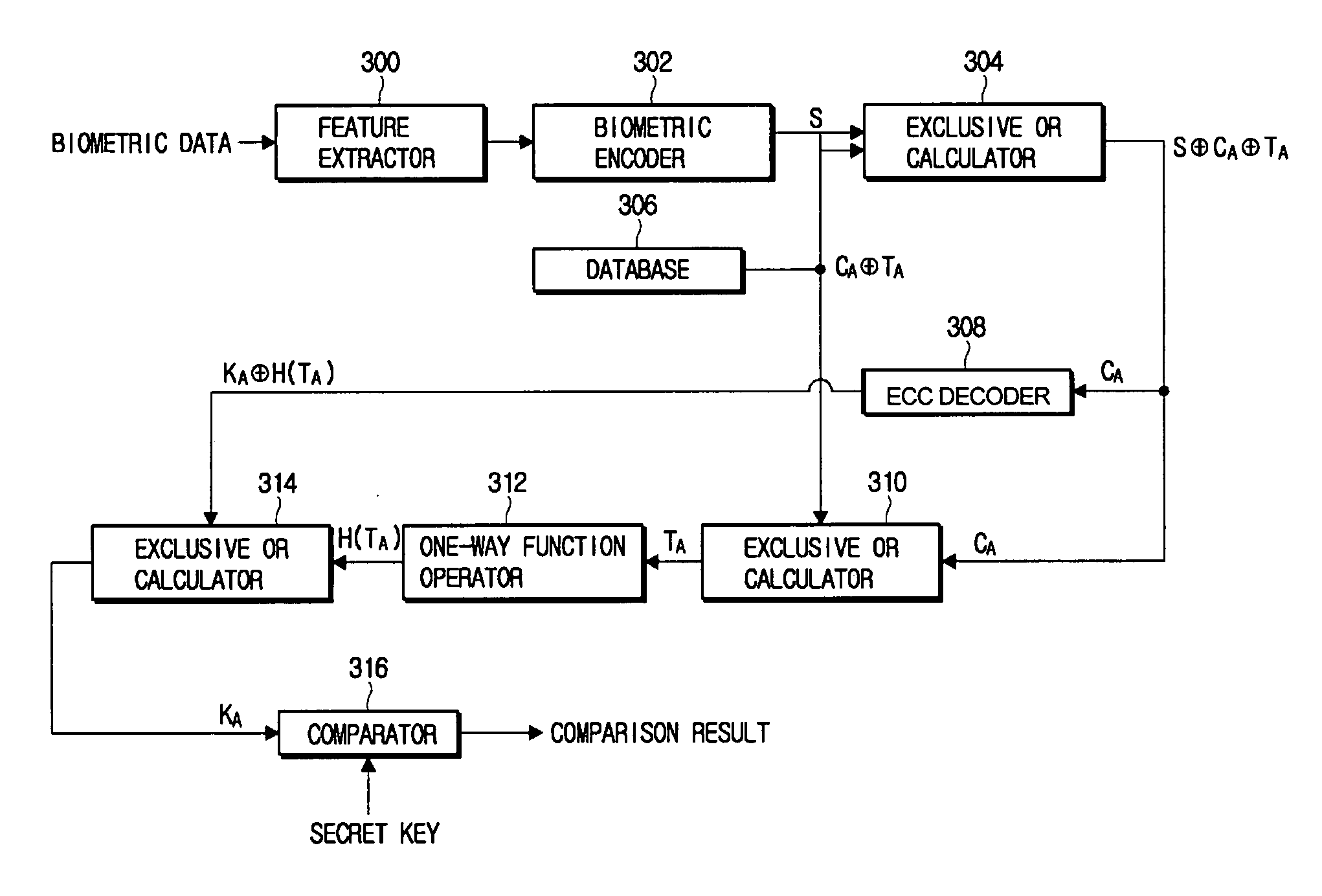
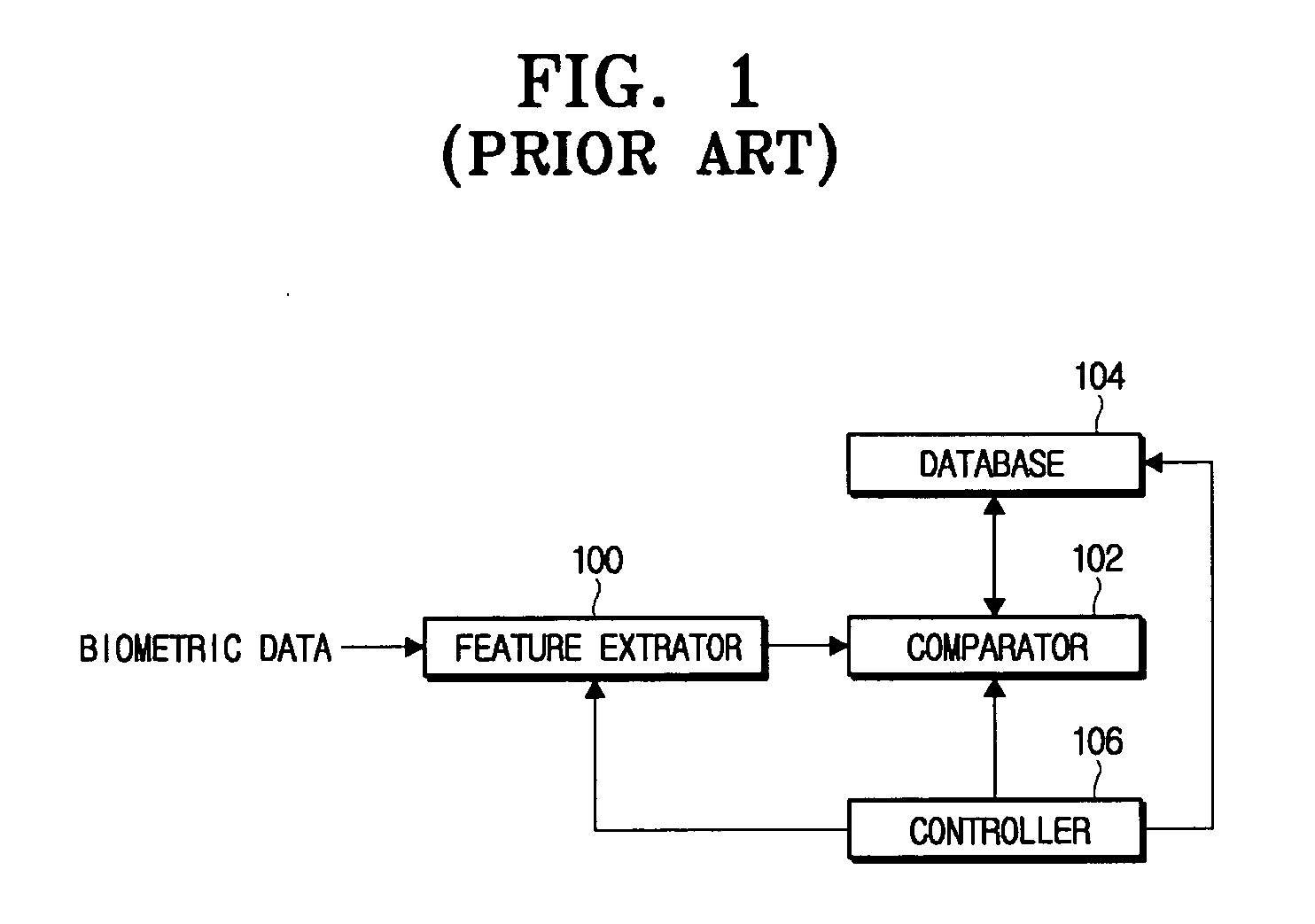
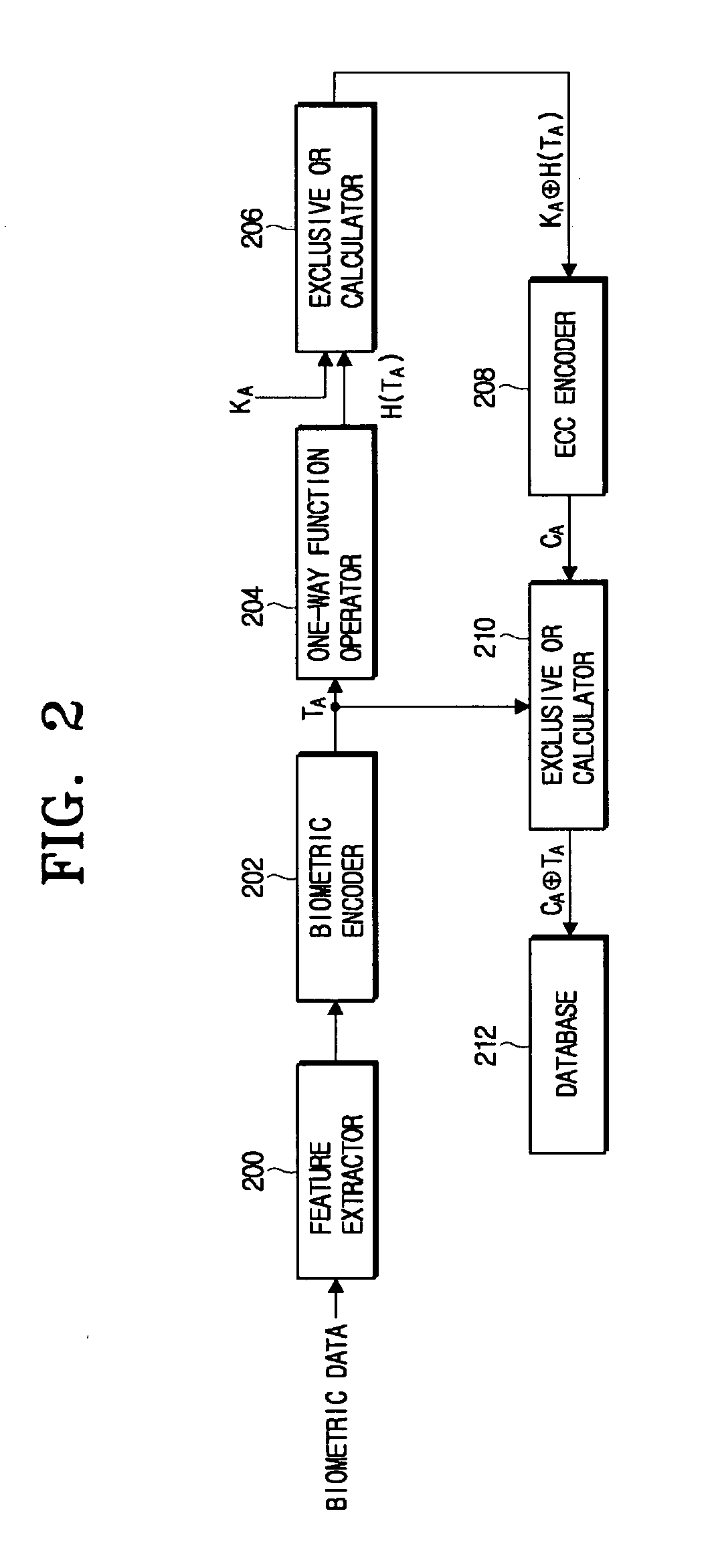
A method of securely storing and authenticating biometric data against attacks of a third party includes encoding input biometric data, and applying a one-way function to the encoded biometric data. A first exclusive OR operation is performed to the result of the one-way function and a selected secret key. The result of the first exclusive OR operation is encoded, and a second exclusive OR operation is performed to the encoded result of the first exclusive OR operation and the encoded biometric data. The result of the second exclusive OR operation is stored. In the same manner, the biometric data is authenticated. Accordingly, the biometric data can be securely stored against the attacks of a third party by processing and storing the biometric data according to a predetermined procedure.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com