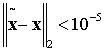Patents
Literature
76 results about "Block size" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
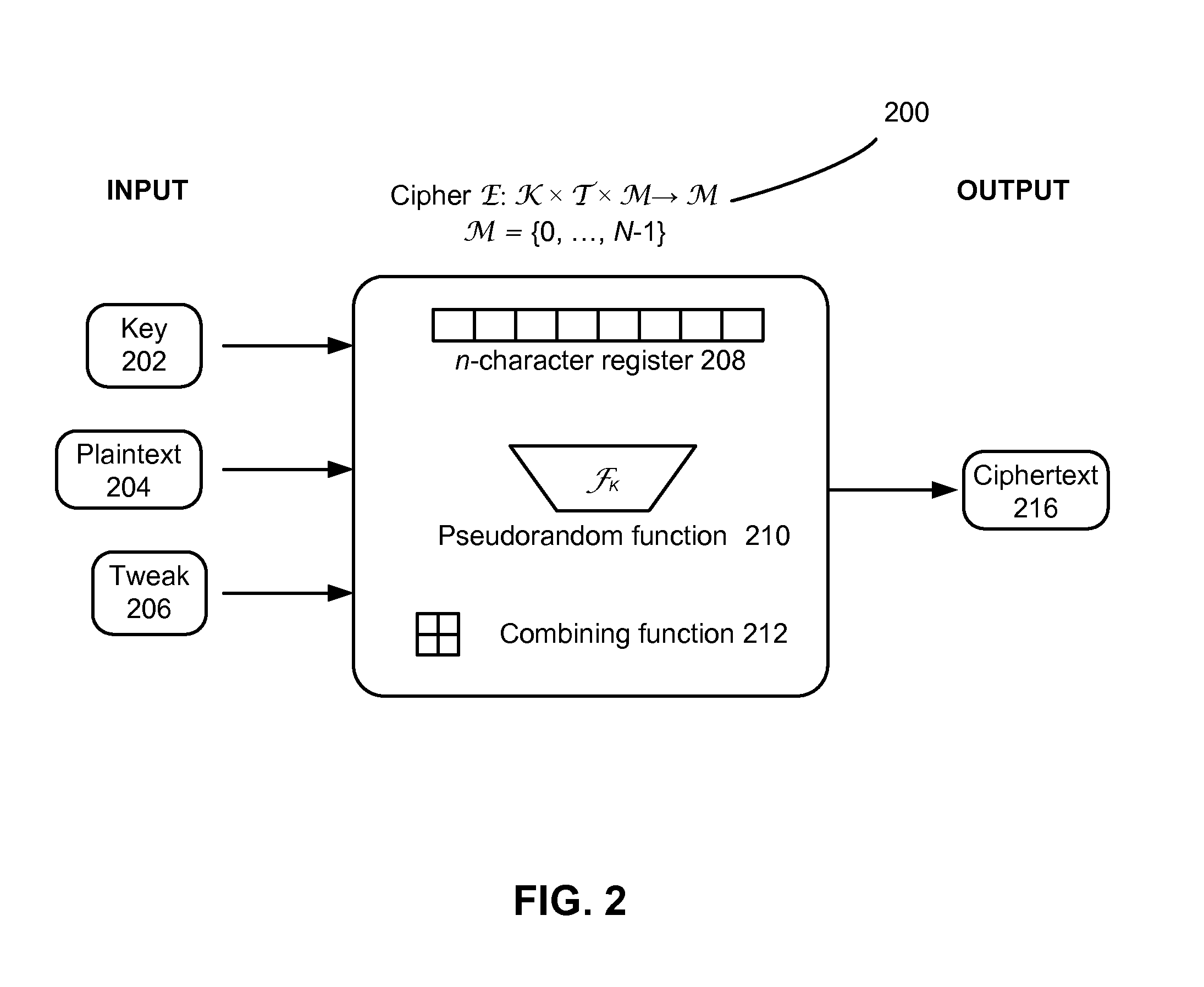
In modern cryptography, symmetric key ciphers are generally divided into stream ciphers and block ciphers. Block ciphers operate on a fixed length string of bits. The length of this bit string is the block size. Both the input (plaintext) and output (ciphertext) are the same length; the output cannot be shorter than the input – this follows logically from the pigeonhole principle and the fact that the cipher must be reversible – and it is undesirable for the output to be longer than the input.
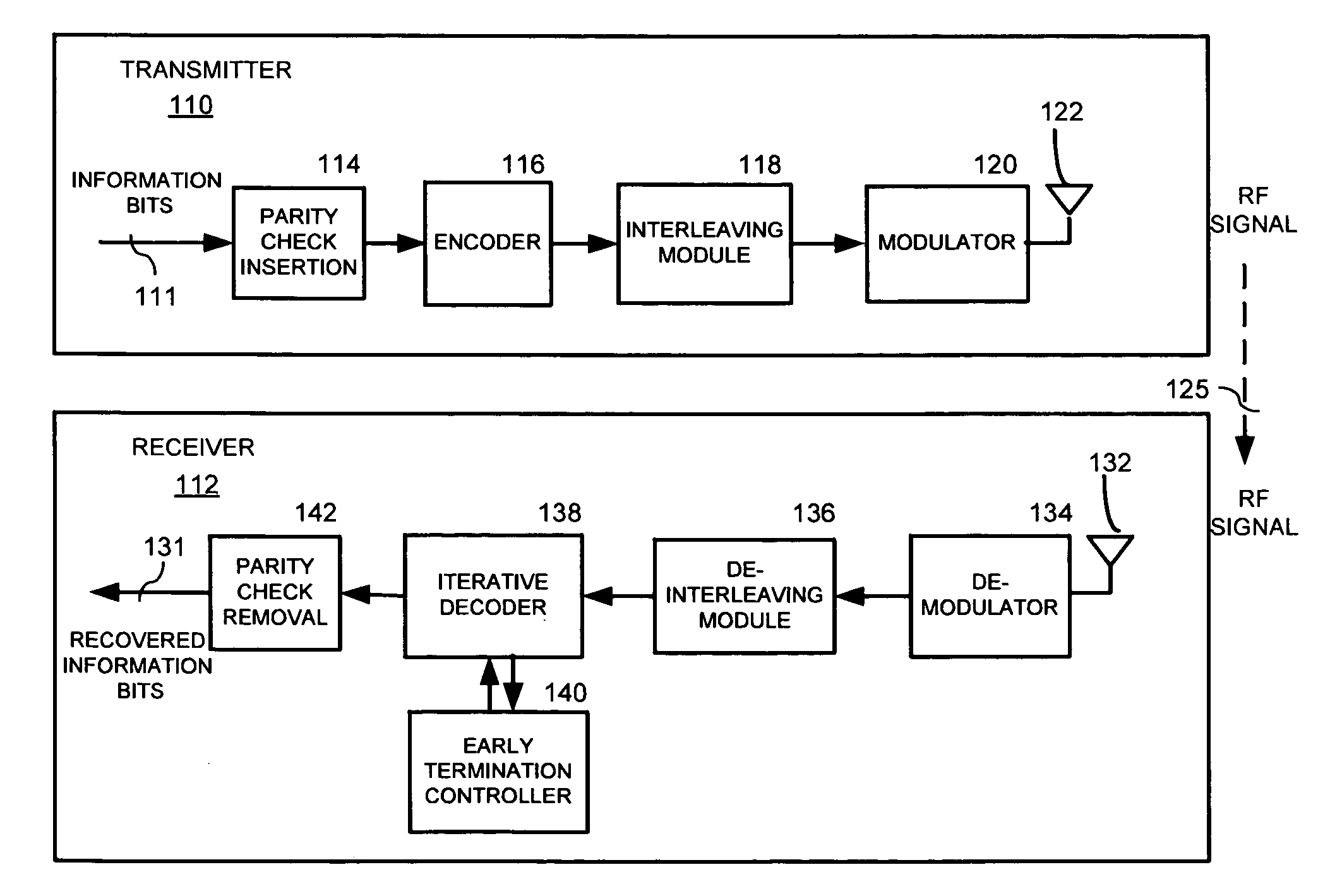
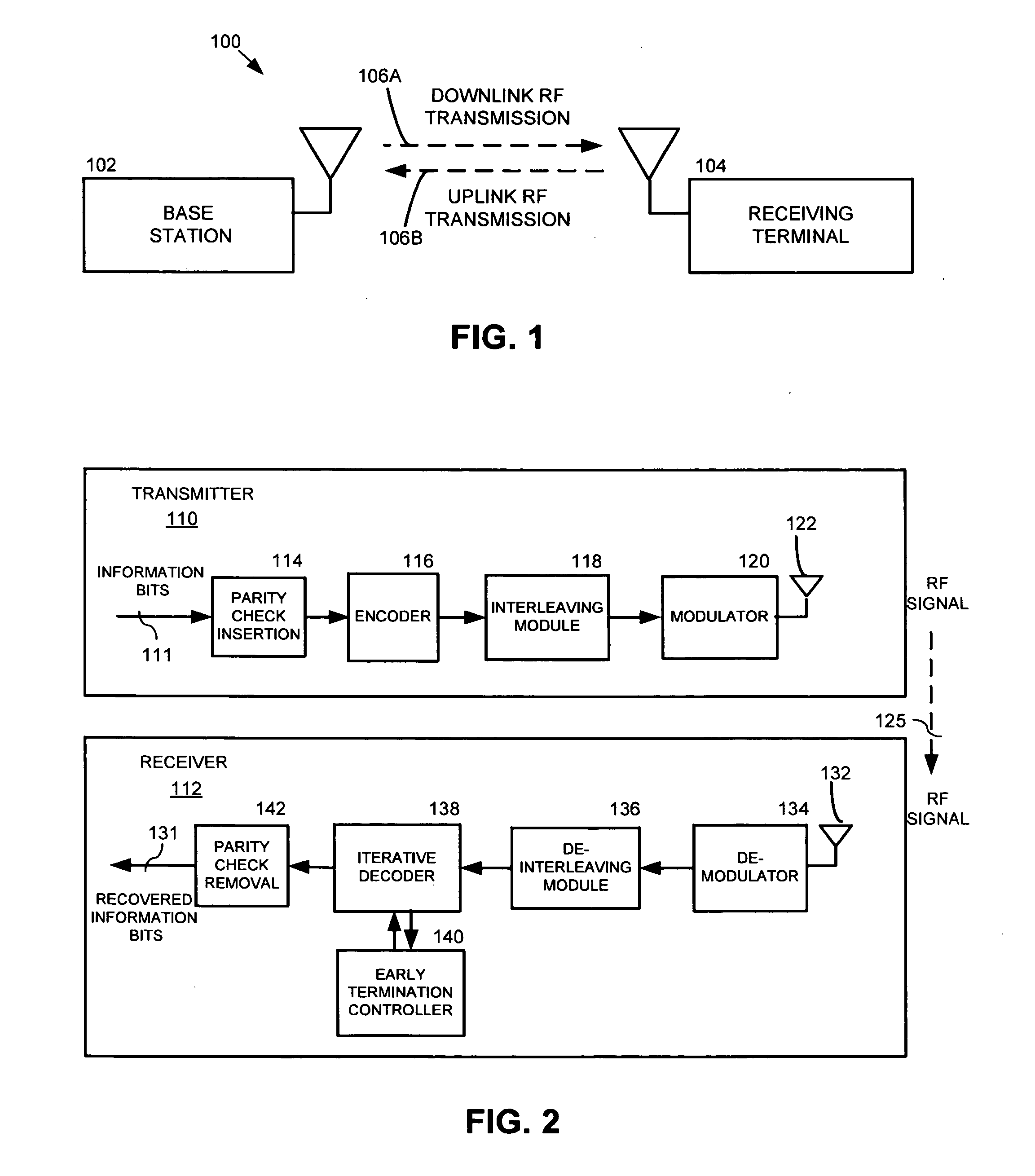
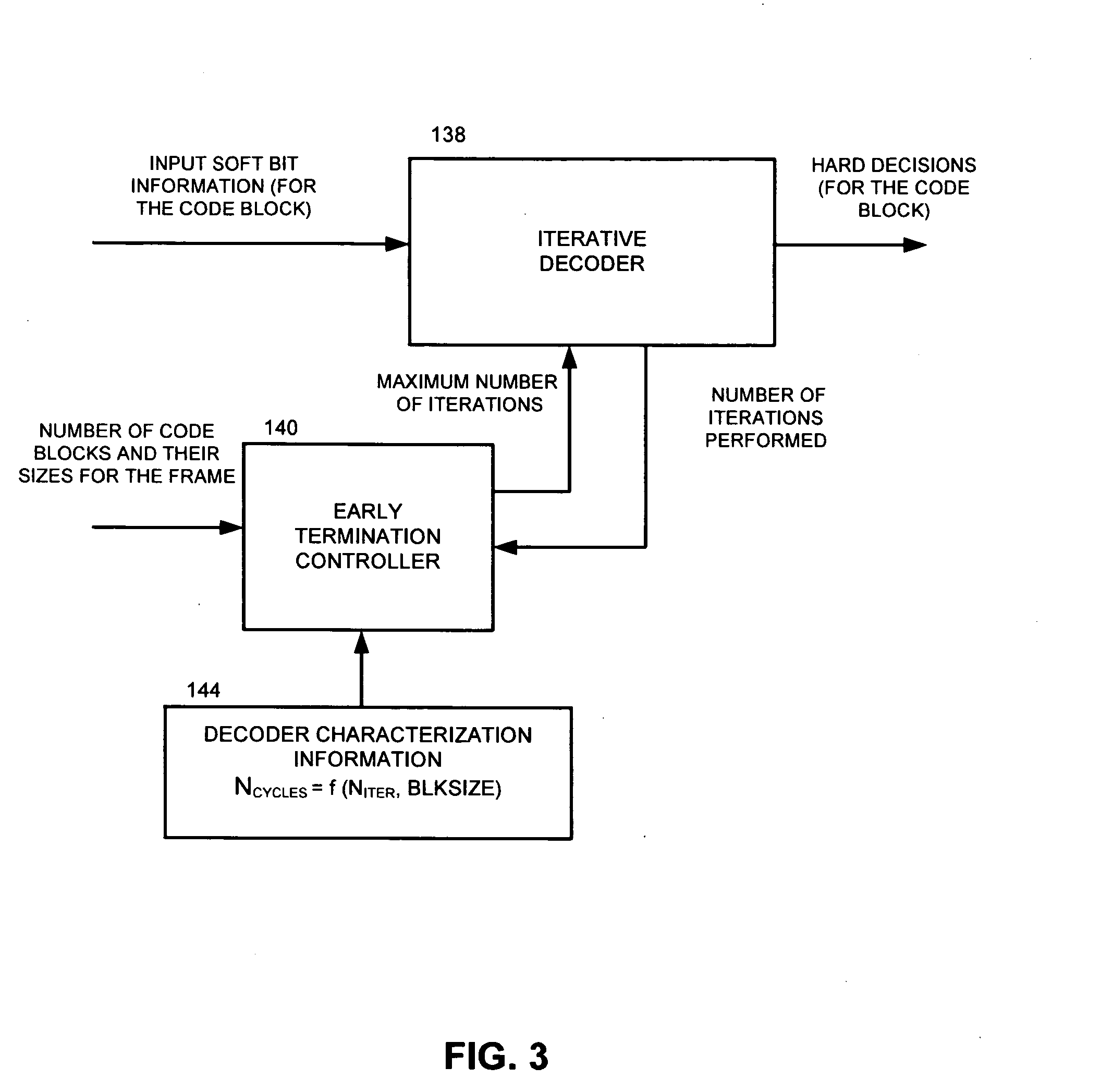
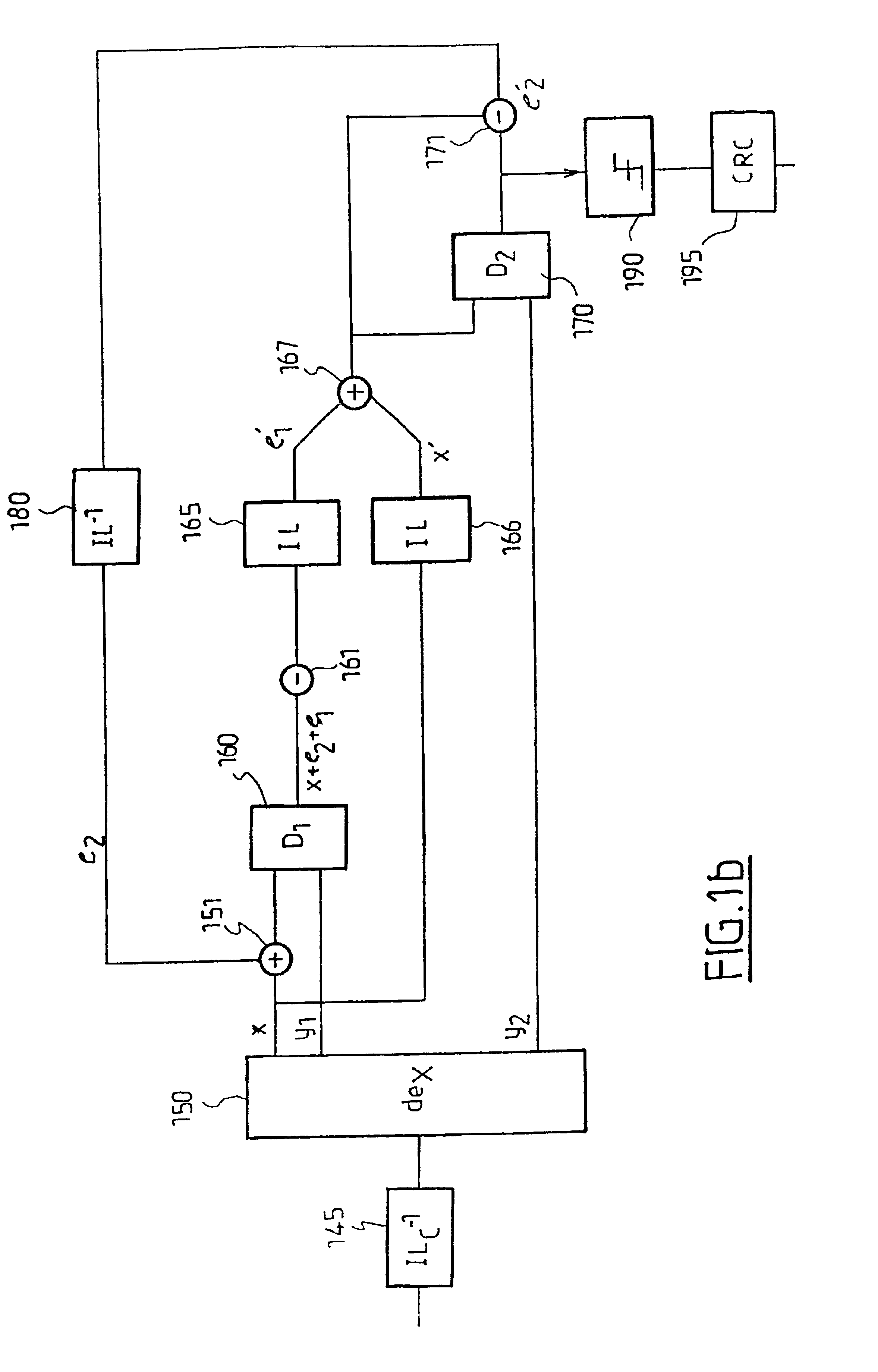
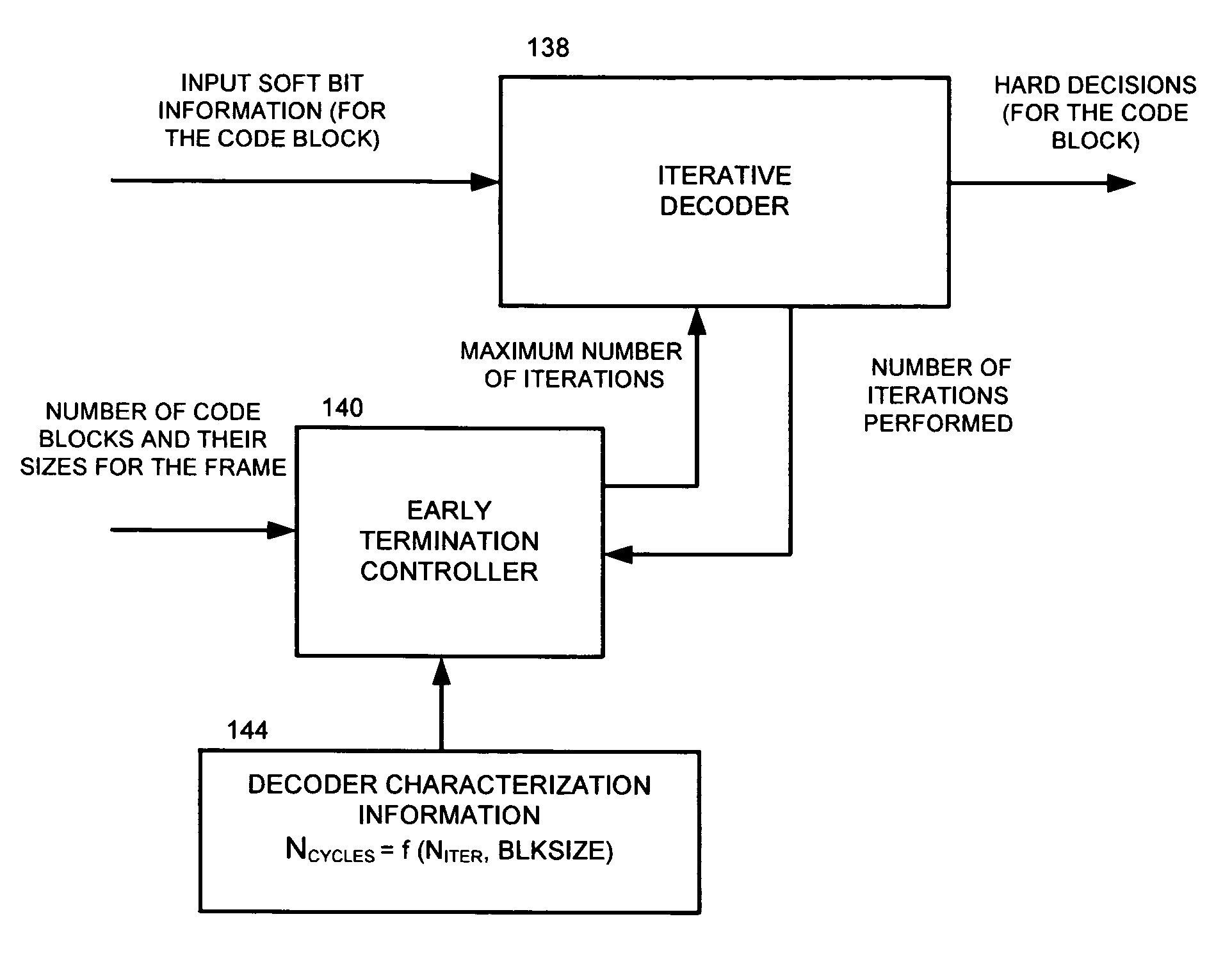
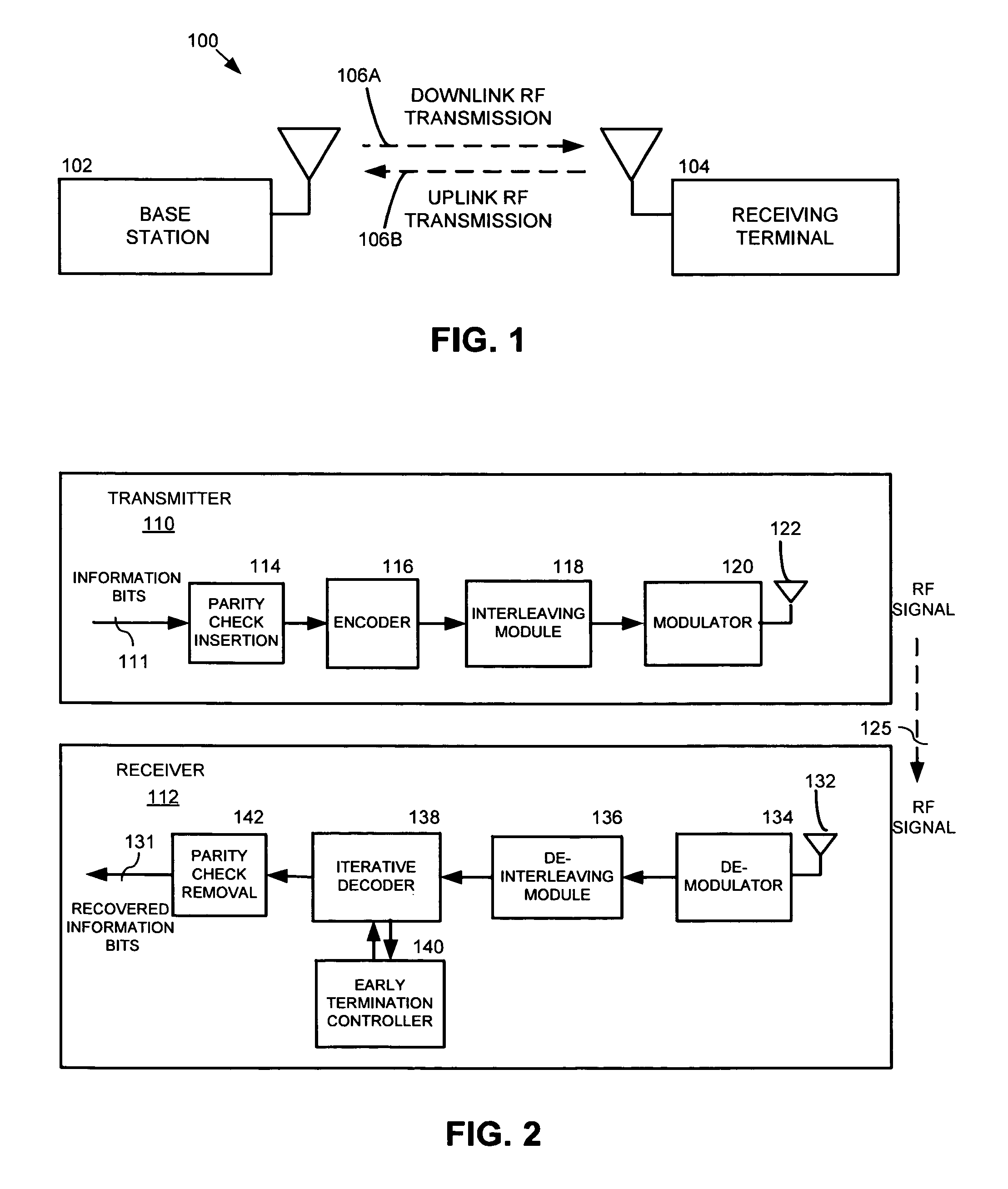
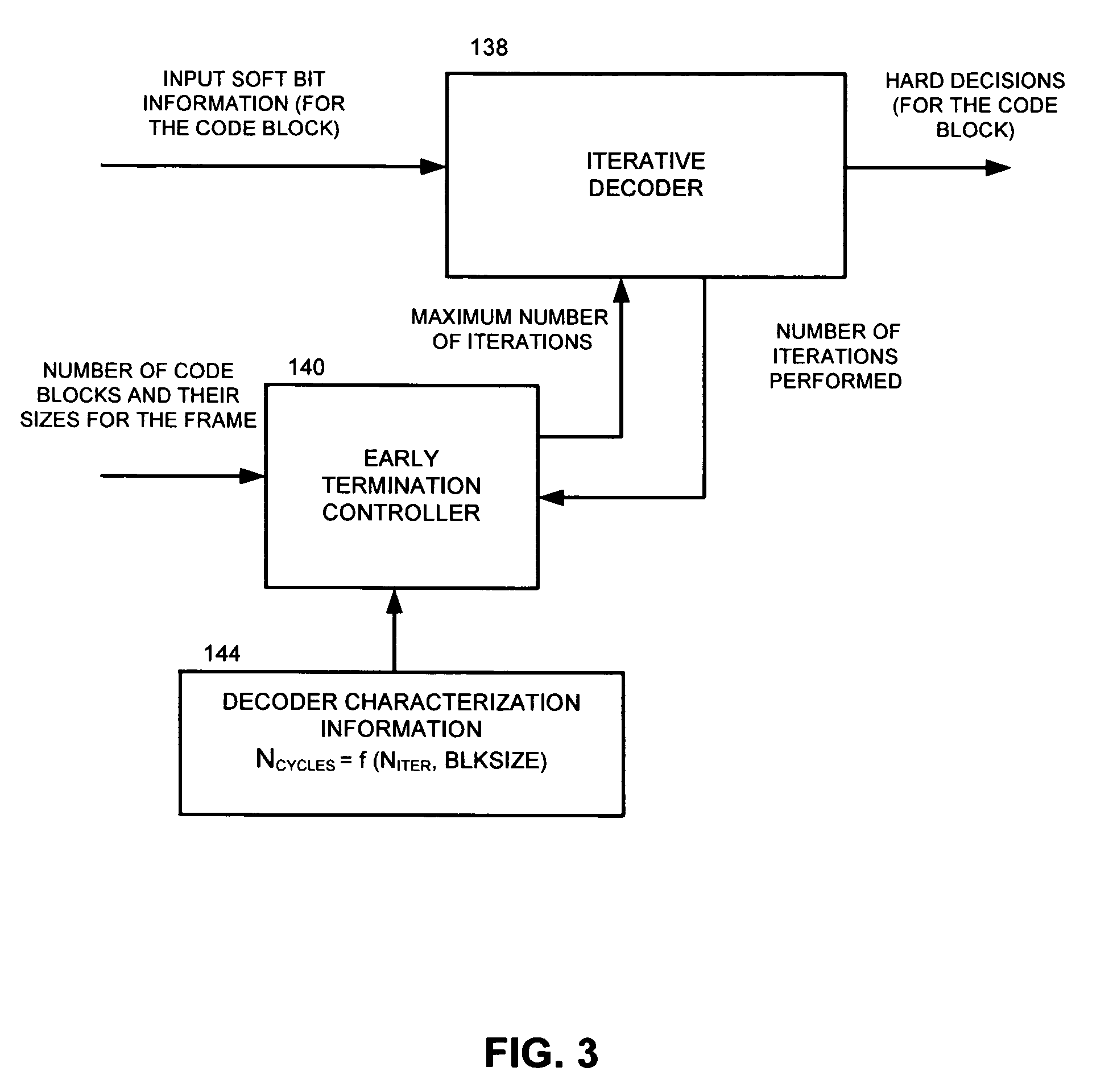
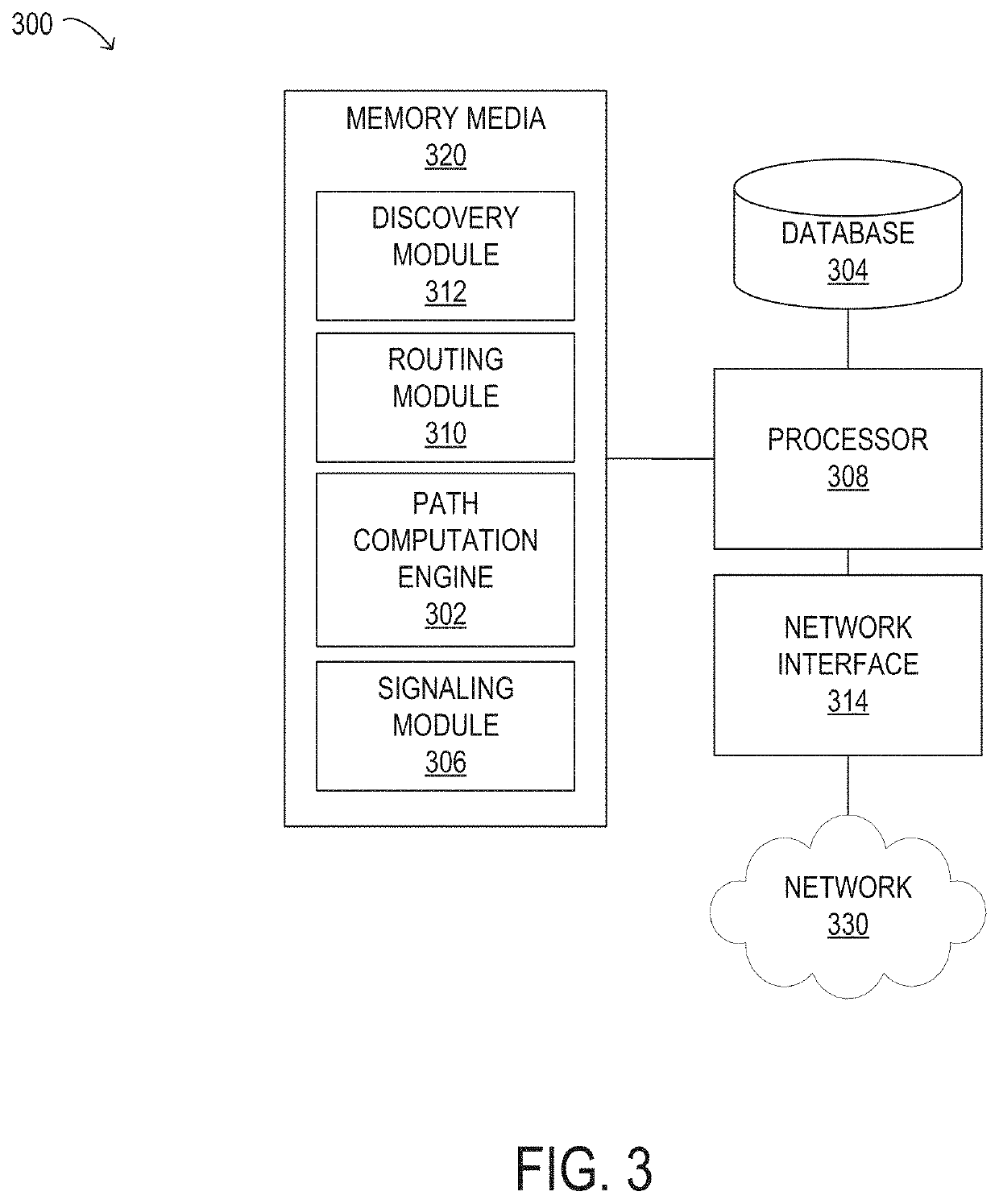
Early termination controller for iterative fec decoders and method therefor
InactiveUS20080148133A1Block error rate performanceMaximize capacityData representation error detection/correctionError preventionCoding blockCommunications system
A method, apparatus and system for improving block error rate performance of a receiver having an iterative decoder in a communication system, the method, apparatus and system includes receiving an encoded frame of data, the encoded frame of data includes a quantity of code blocks where each code block has a corresponding code block size, determining a first maximum number of iterations for each of the code blocks of the encoded frame of data iteratively performing a decoding operation on a first code block until the occurrence of one of (a) the first maximum number of iterations has been reached and (b) the first code block has converged, and determining a second maximum number of iterations for the remaining code blocks of the encoded frame of data based on the number of actual iterations used to decode the first code block.
Owner:APPLE INC
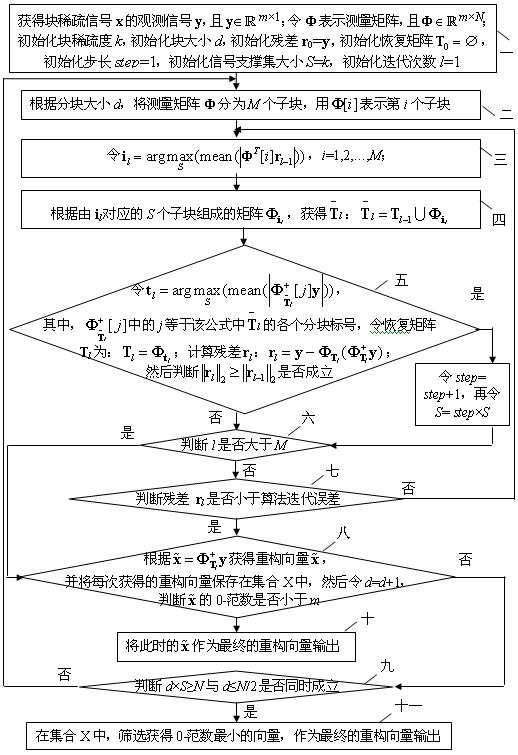
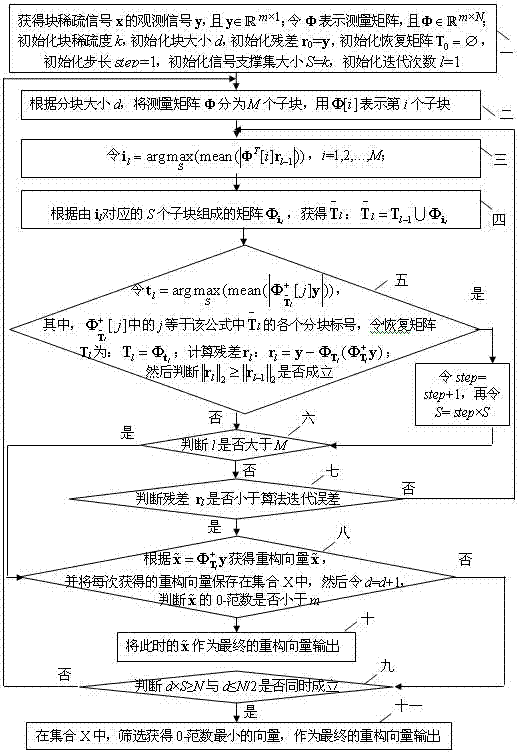
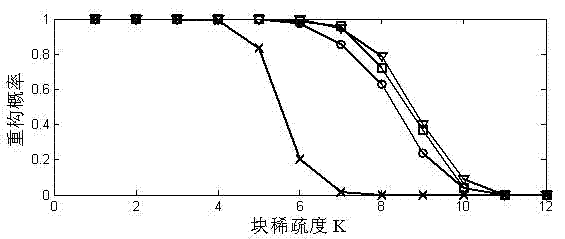
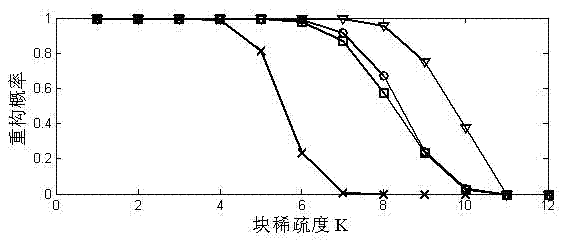
Blind reconstructing method of block sparse signal with unknown block size
The invention relates to a blind reconstructing method of a block sparse signal with unknown block size, relating to the technical field of compressed sensing and solving the problem that the traditional reconstructing method of the block sparse signal needs take the block size and block sparsity as priori knowledge. The blind reconstructing method comprises the following steps of: carrying out block sparsity self-adaptation iteration of an algorithm for each block size to find a reconstructed signal which corresponds to each block size by initializing the block sparsity and the block size; continuously iterate the algorithm and enlarging the block size accordingly, and finishing the algorithm till the 0-norm of the reconstructed signal obtained through the algorithm is less than the line number of a measurement matrix, outputting the reconstructed signal used as algorithm; if the condition is not met, operating the algorithm till: when block size is smaller than or equal to haft of the length of the reconstructed signal, the product of the block size and the block sparsity is larger than or equal to the length of the reconstructed signal, the iteration is completed, and a seriesof reconstructed signals are obtained; and finally screening the sparsest reconstructed signal as final algorithm output by utilizing 0-norm sparsity measurement criteria. The invention can be used for the technical field of compressed sensing of the block sparse signal.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Method for the optimization, under resource constraint, of the size of blocks of coded data
InactiveUS6892335B2Data representation error detection/correctionTransmission control/equlisationResource constraintsNormal sizes
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Early termination controller for iterative FEC decoders and method therefor
InactiveUS7765453B2Avoid performanceMaximize capacityData representation error detection/correctionError preventionCoding blockCommunications system
A method, apparatus and system for improving block error rate performance of a receiver having an iterative decoder in a communication system, the method, apparatus and system includes receiving an encoded frame of data, the encoded frame of data includes a quantity of code blocks where each code block has a corresponding code block size, determining a first maximum number of iterations for each of the code blocks of the encoded frame of data iteratively performing a decoding operation on a first code block until the occurrence of one of (a) the first maximum number of iterations has been reached and (b) the first code block has converged, and determining a second maximum number of iterations for the remaining code blocks of the encoded frame of data based on the number of actual iterations used to decode the first code block.
Owner:APPLE INC
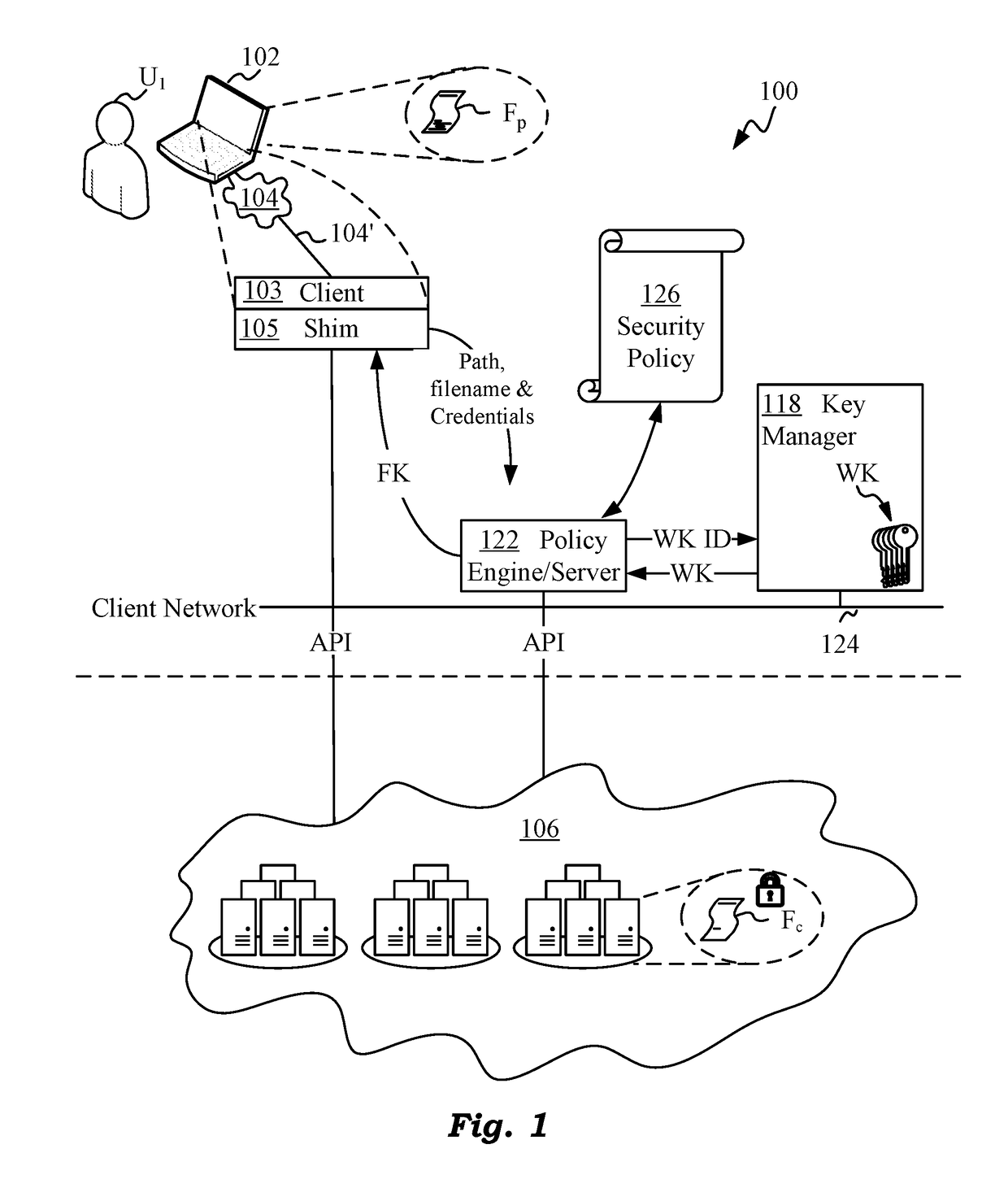
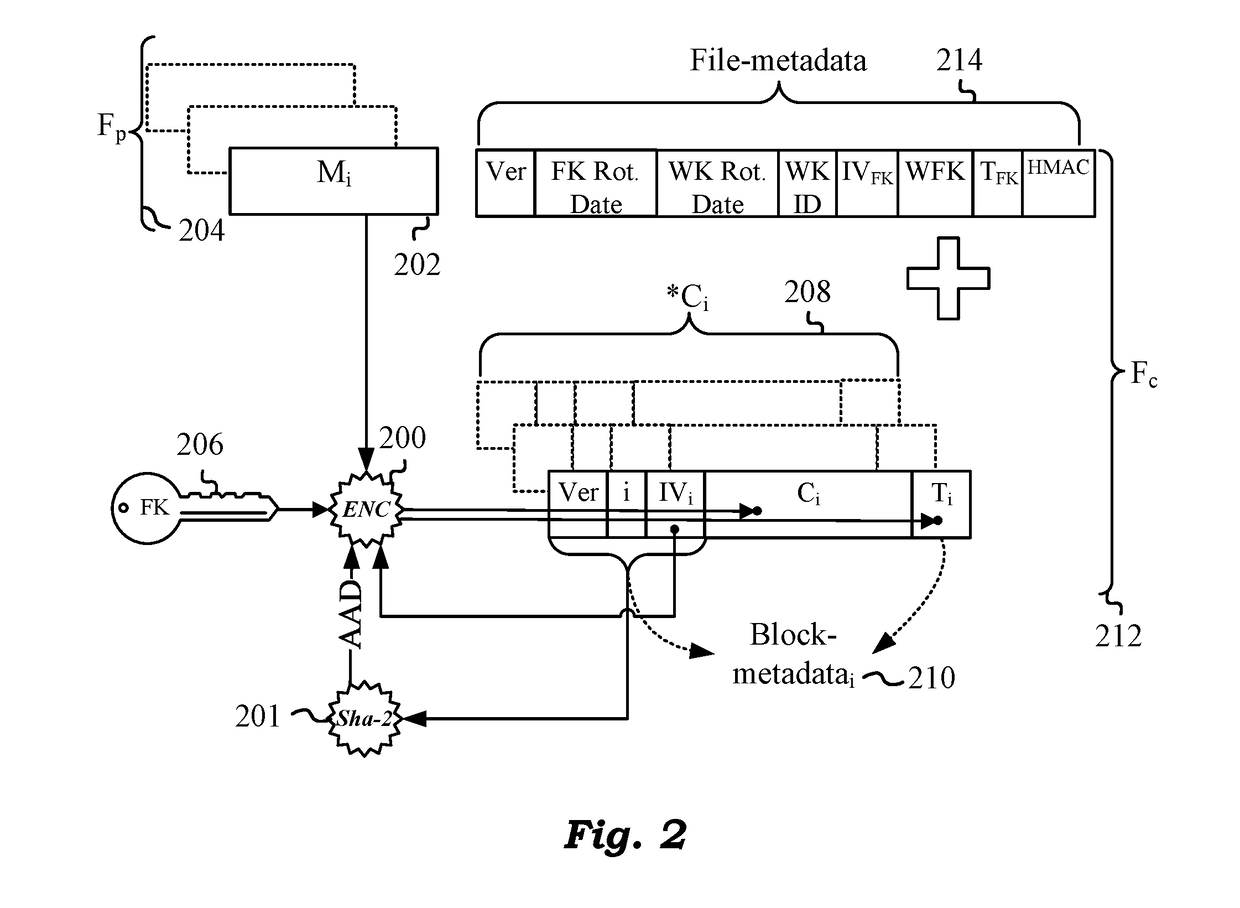
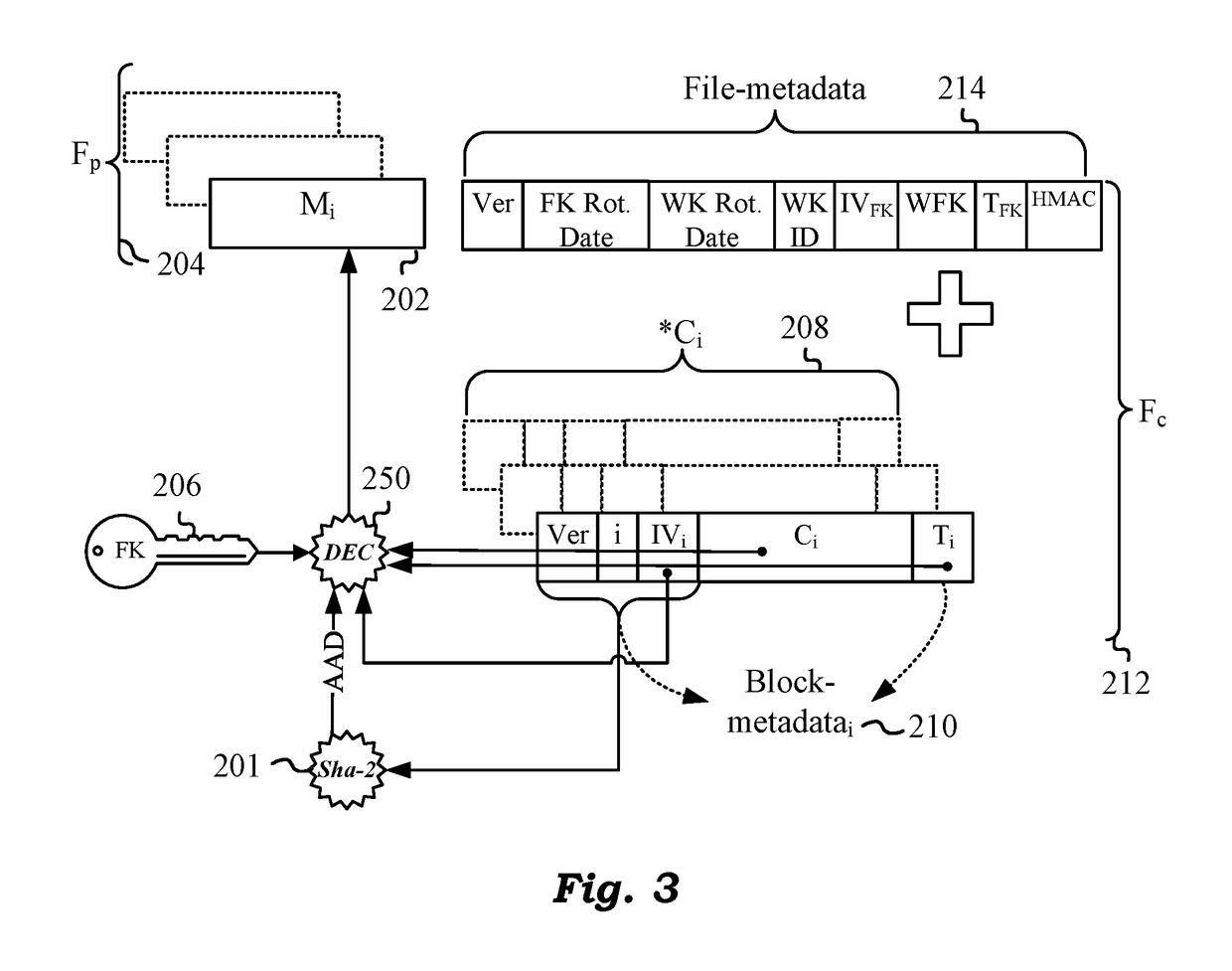
Cloud Storage Encryption With Variable Block Sizes
ActiveUS20190013936A1Key distribution for secure communicationDigital data protectionPlaintextManagement tool
Techniques are disclosed for securing data in a cloud storage. Plaintext files are stored as secured, encrypted files in the cloud. The ciphering scheme employs per-block authenticated encryption and decryption. A unique file-key is used to encrypt each file. The file-key is wrapped by authenticated encryption in a wrapping-key that may be shared between files. A centralized security policy contains policy definitions which determine which files will share the wrapping-key. Wrapping-keys are stored in a KMIP compliant key manager which may be backed by a hardware security module (HSM). File metadata is protected by a keyed-hash message authentication code (HMAC). A policy engine along with administrative tools enforce the security policy which also remains encrypted in the system. Various embodiments support blocks of fixed as well as variable sizes read / written from / to the cloud storage.
Owner:ZETTASET
Secret-key-controlled reversible circuit and corresponding method of data processing
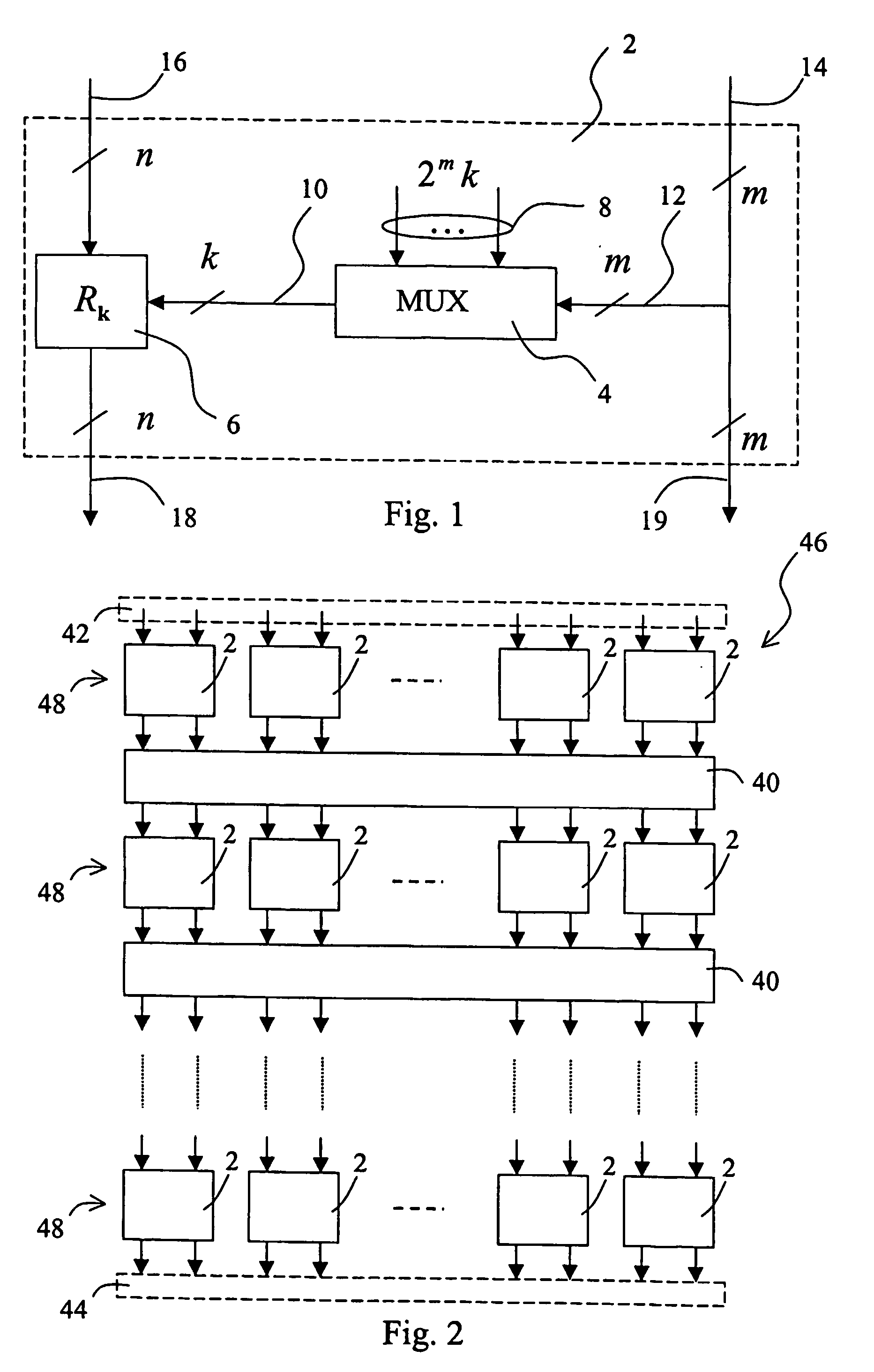
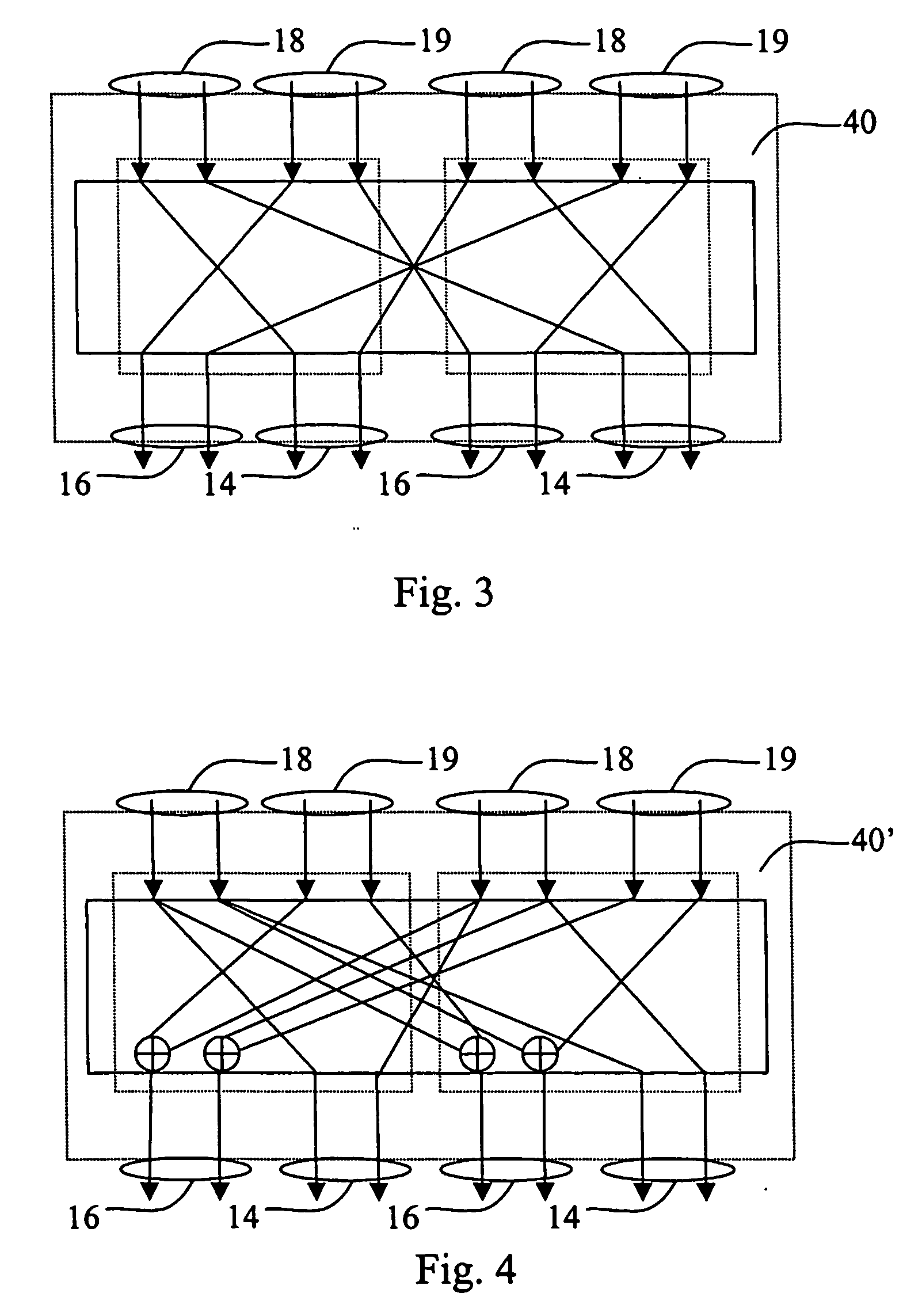
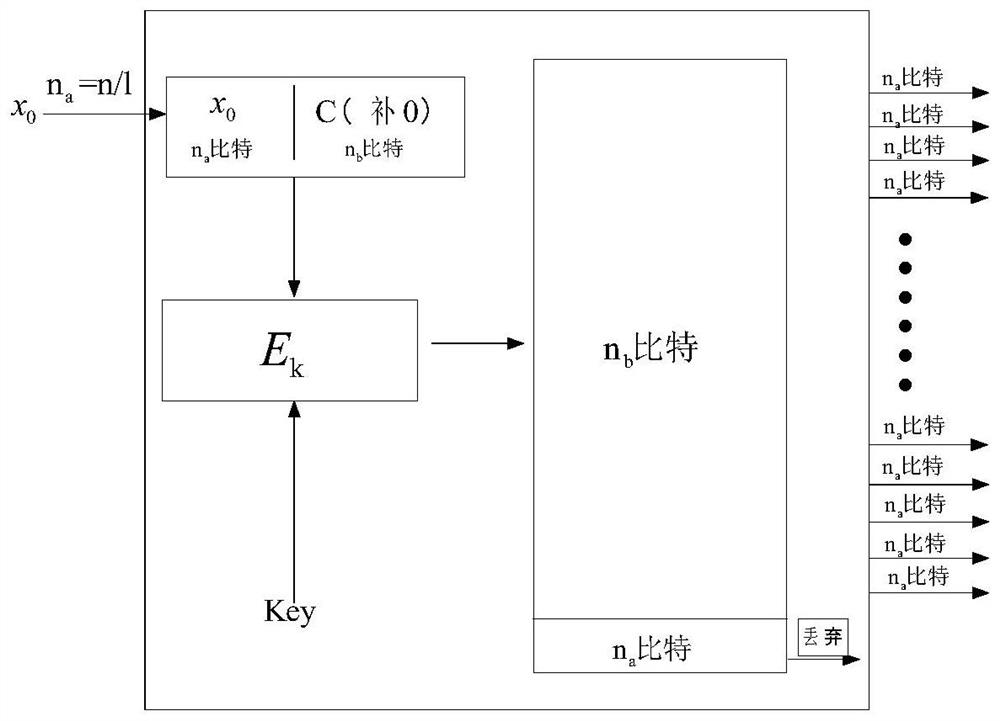
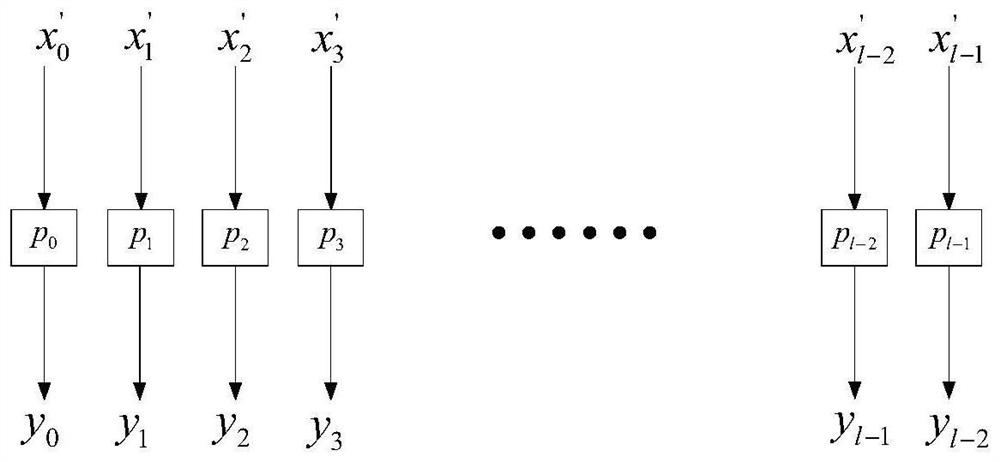
ActiveUS20060236102A1Make largeShorter delayEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesUser identity/authority verificationData bitsReversible circuits
A combinatorial key-dependent network suitable for the encryption / decryption of data on buses and in memories of data-processing devices, has a number of layers, where each layer has a number of elementary building blocks operating on very small block sizes. A generic building block acts on a small number of input data bits, which are divided into two groups of m and n bits, respectively. The m input bits, which are passed to the output intact, are used to select k out of 2mk key bits by a multiplexer circuit; the k bits are then used to select an (n×n)-bit reversible transformation acting on the remaining n input bits to produce the corresponding n output bits. The total number of the key bits in the building block is thus 2mk, which can easily he made larger that m+n. An inverse building block is the same except that the reversible transformations are replaced by their inverses.
Owner:TELECOM ITALIA SPA
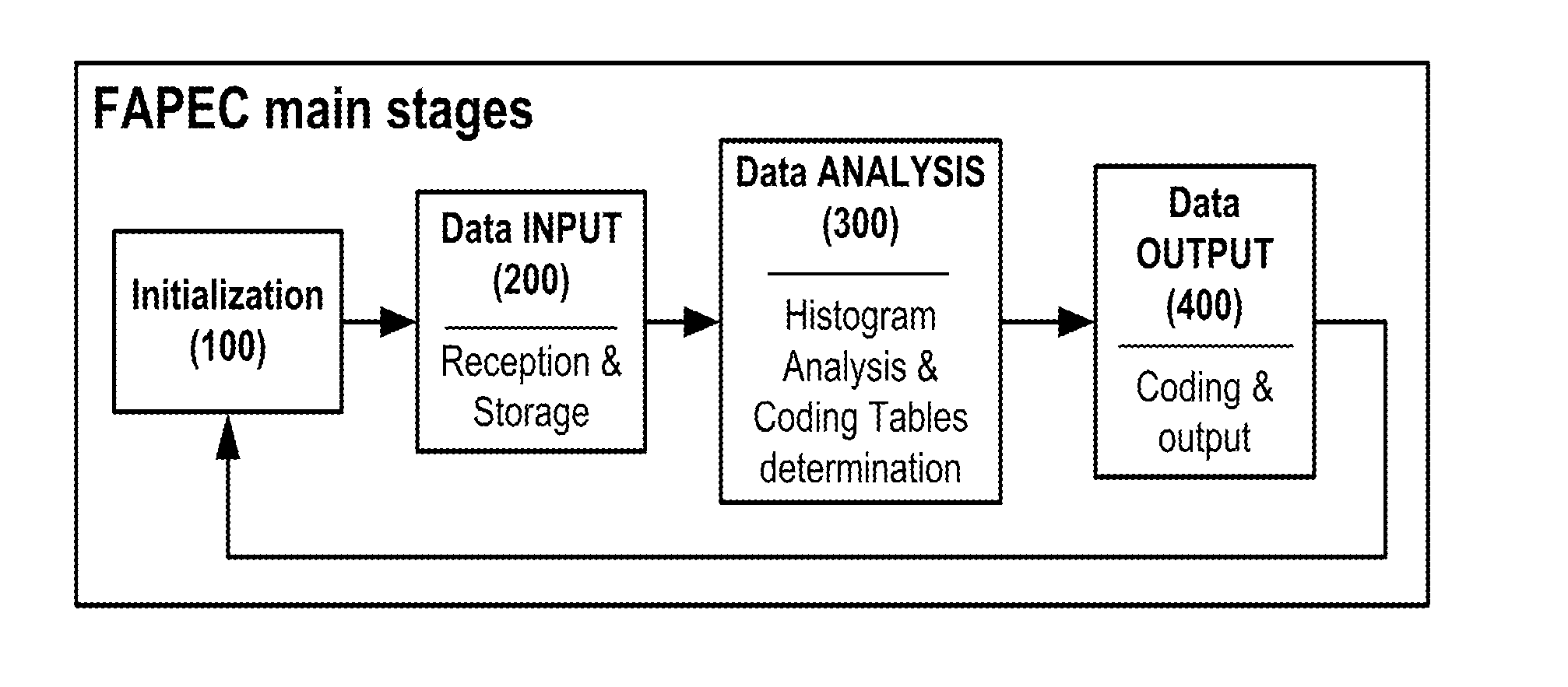
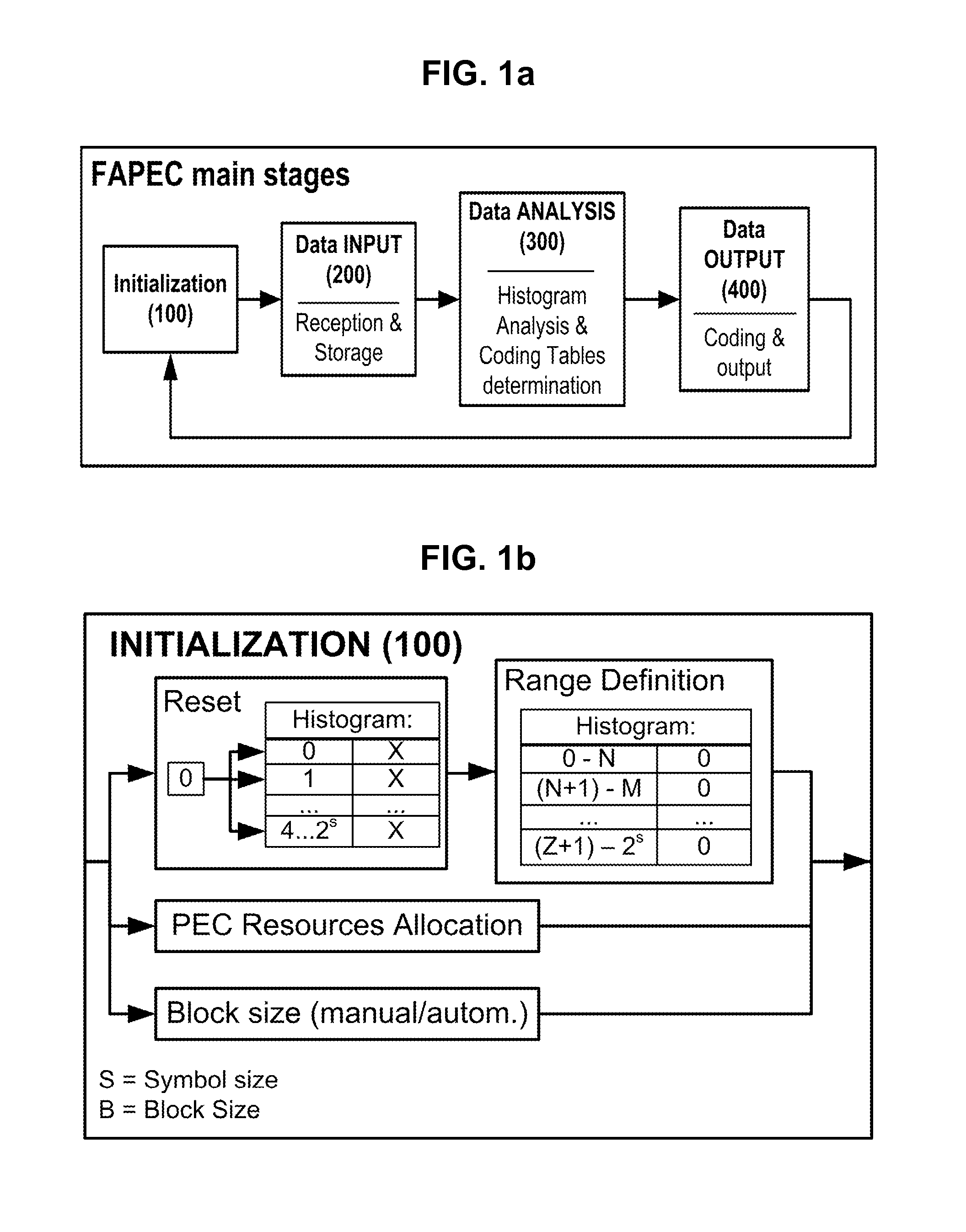
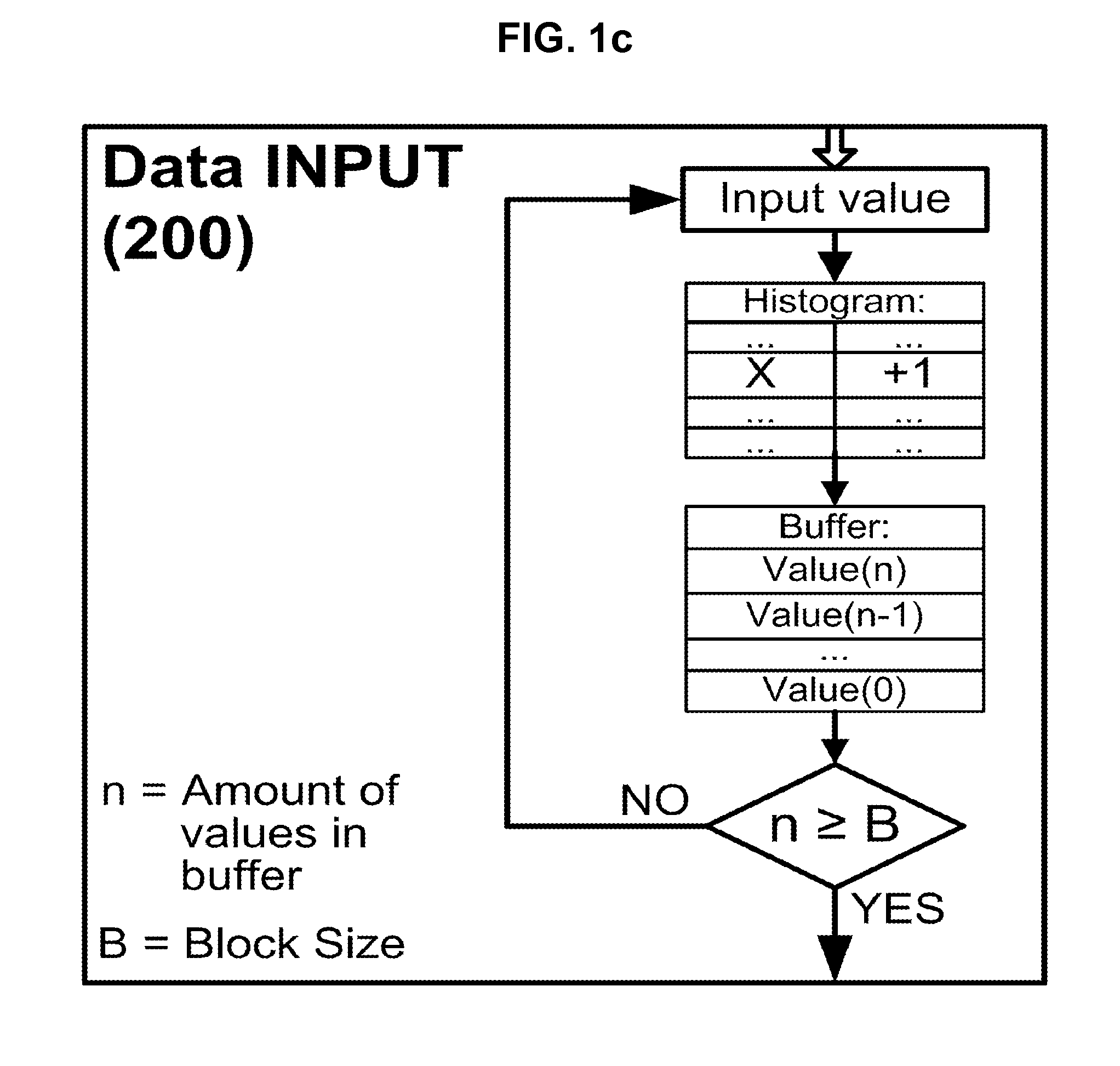
Method for fully adaptive calibration of a prediction error coder
ActiveUS20120166503A1Solve the lack of precisionQuick enoughDigital data processing detailsCode conversionCode tableLossless compression
Method for fully adaptive calibration of a prediction error coder, comprising a first step of initialization; a second step of reception and accumulation of block-size data samples wherein for each received value, it is added one to the histogram bin associated to that value; a third step of analysis of the histogram and determination of the coding option; a fourth step of analysis of the histogram and determination of a coding table; a fifth step of output a header with the prediction error coder coding table determined; and wherein previous steps are repeated if more samples need to be compressed. It is useful as a data compression technique, with the advantage of being faster and more robust than the current CCSDS lossless compression standard.
Owner:UNIV DE BARCELONA +1
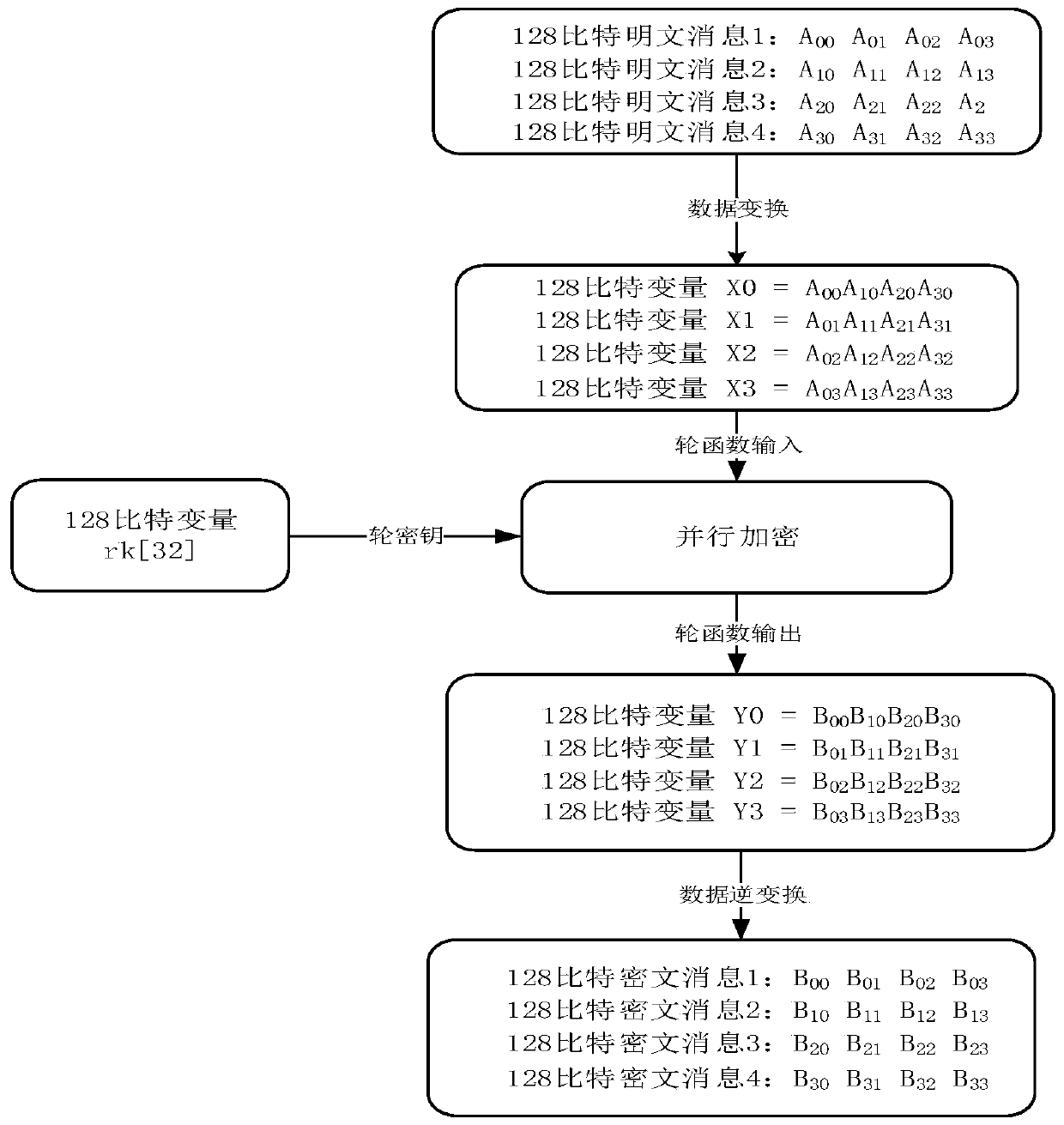
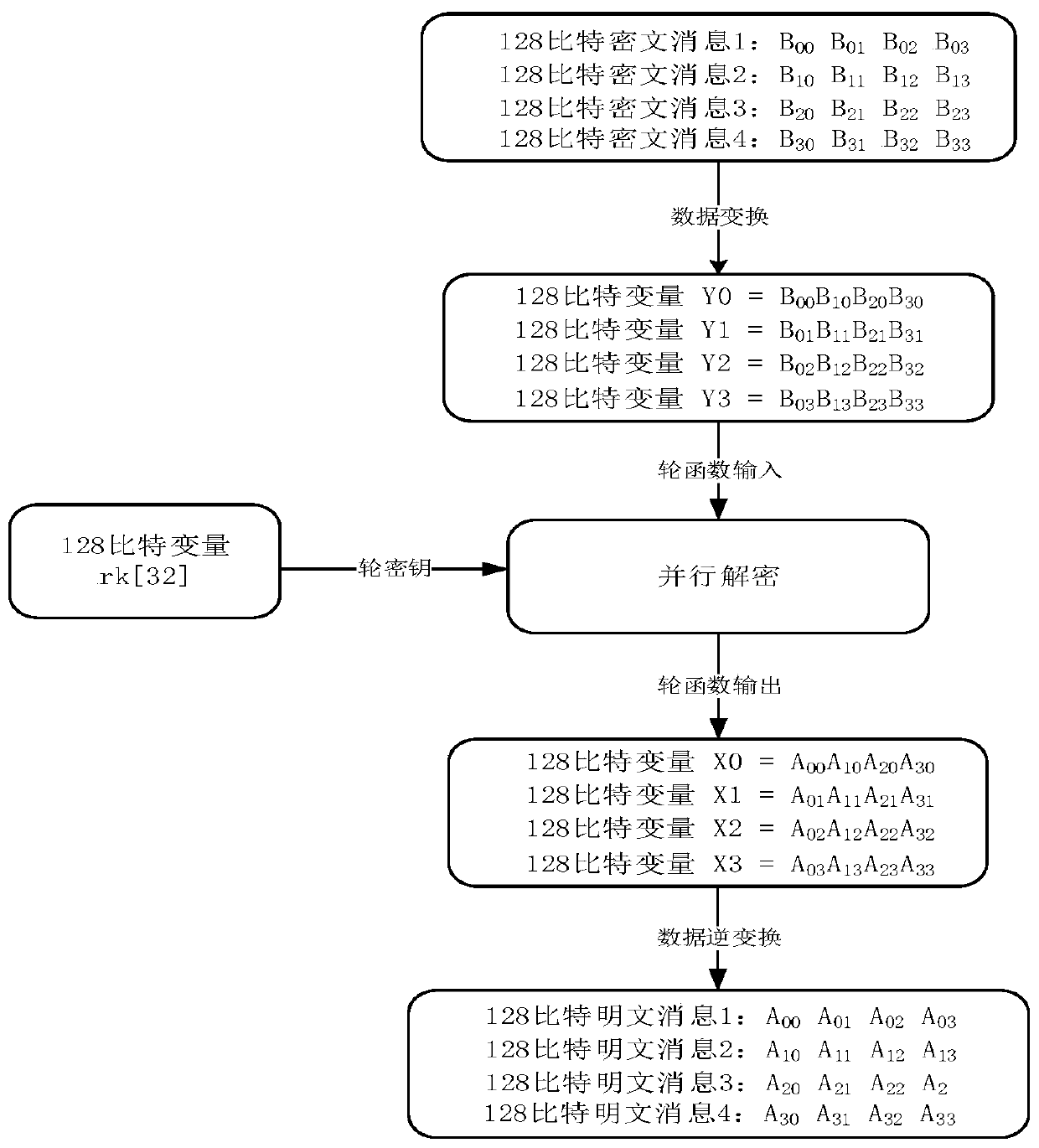
Method for encrypting and decrypting multiple messages in parallel by adopting grouping symmetric key algorithm
ActiveCN110880967AImprove throughputEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesParallel computingTheoretical computer science
The invention provides a method for encrypting and decrypting multiple messages in parallel by adopting a packet symmetric key algorithm, the size of a register is M, the size of a basic operation unit is N, and k = M / N pieces of data from different messages can be processed at the same time. The method comprises the following steps: respectively putting k pieces of data from different messages into k grouped data blocks, wherein the size of each grouped data block is the same as that of a register; dividing the data in each grouped data block into k sections, sequentially connecting the ith segments in the k grouped data in series and then putting the ith segments into the ith register variable, encrypting the ith register variable, dividing the encrypted data in the register variable into k segments, and connecting the jth segments in each register in series to obtain an encryption result of the jth group of plaintexts; the decryption method is similar to the encryption method. By parallelizing the data blocks of different messages, massive filling during short message processing in a current common parallel mode is avoided, and the throughput of a grouping algorithm is maximized.
Owner:BEIJING LIANSHI NETWORKS TECH CO LTD
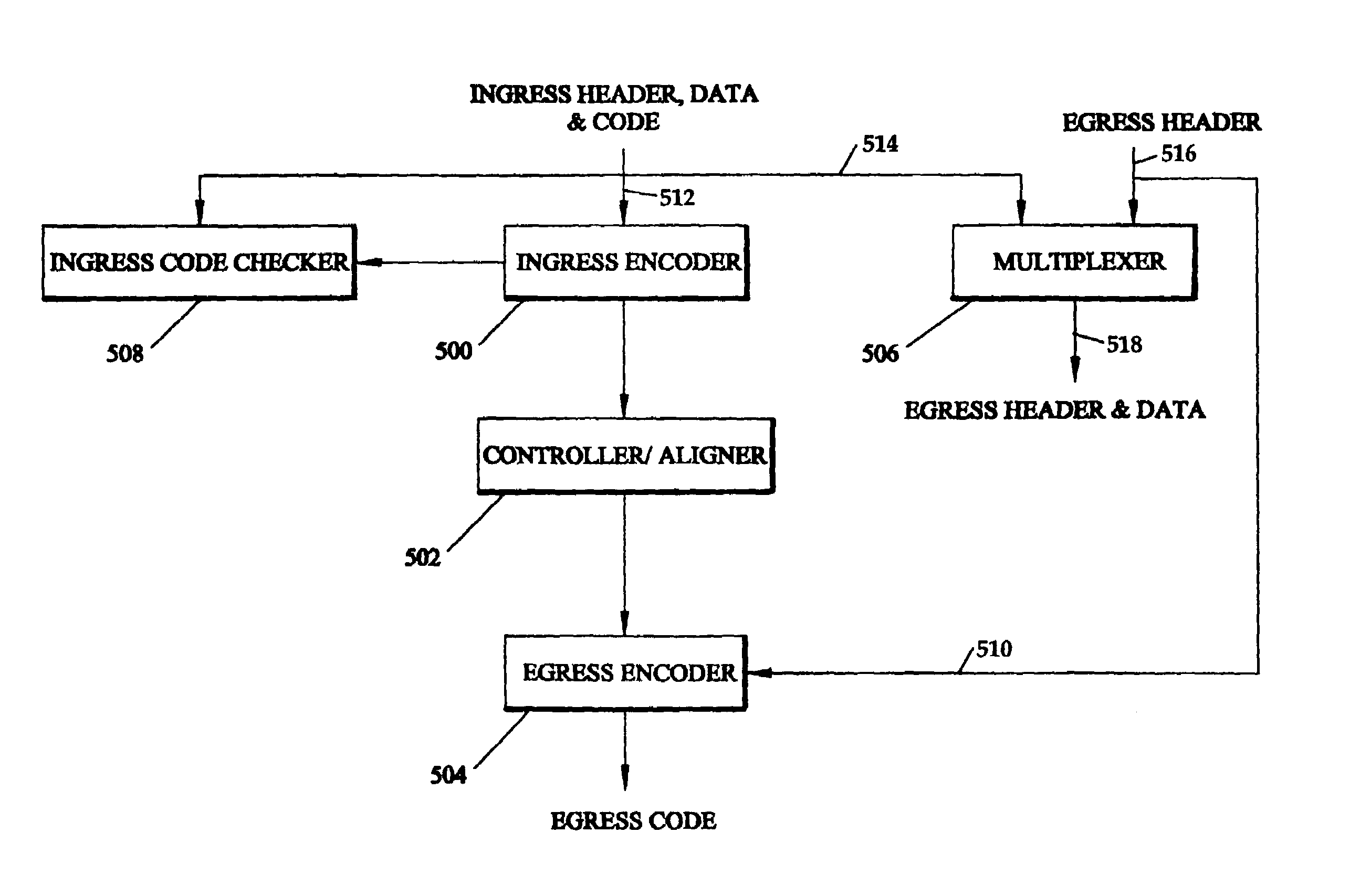
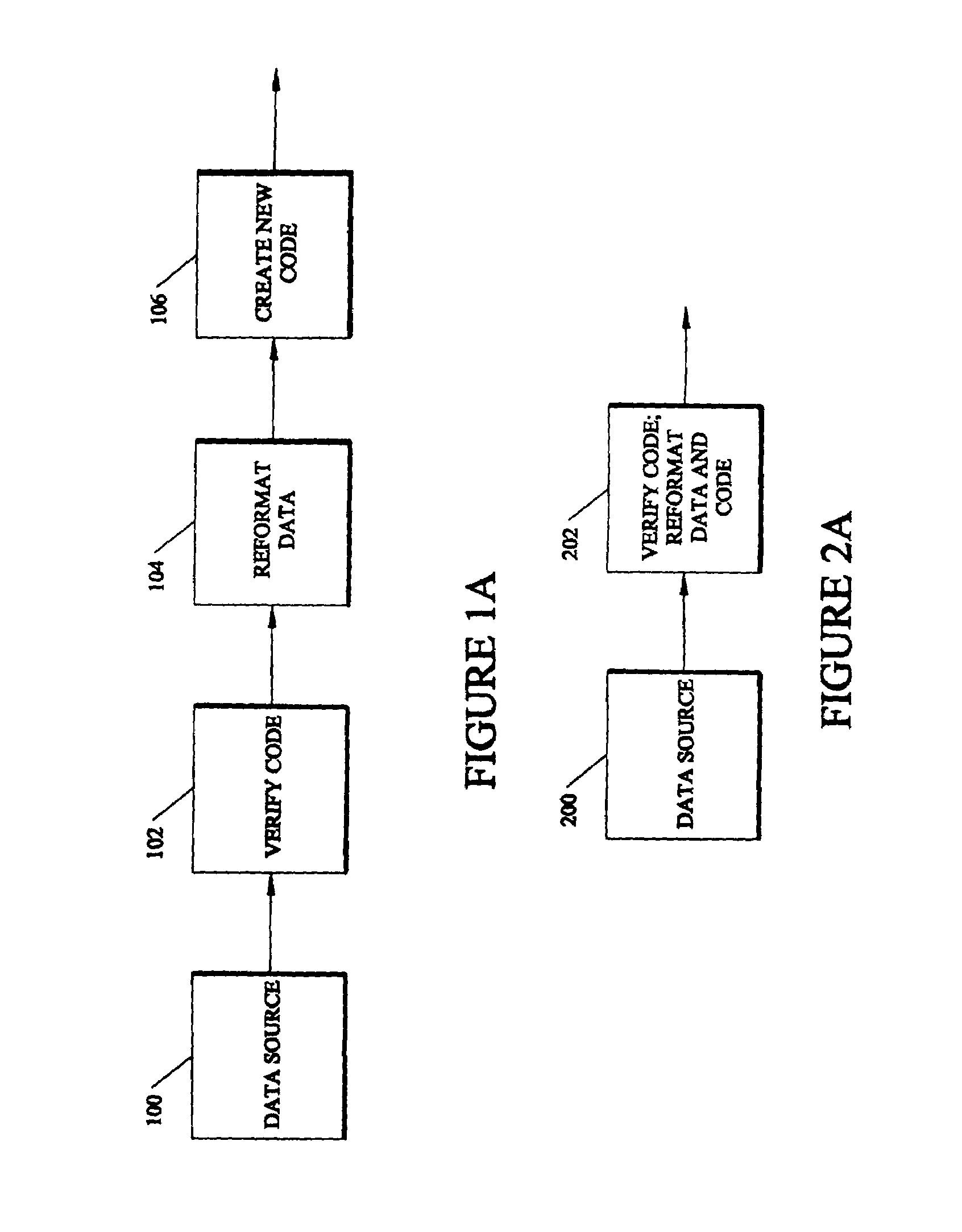
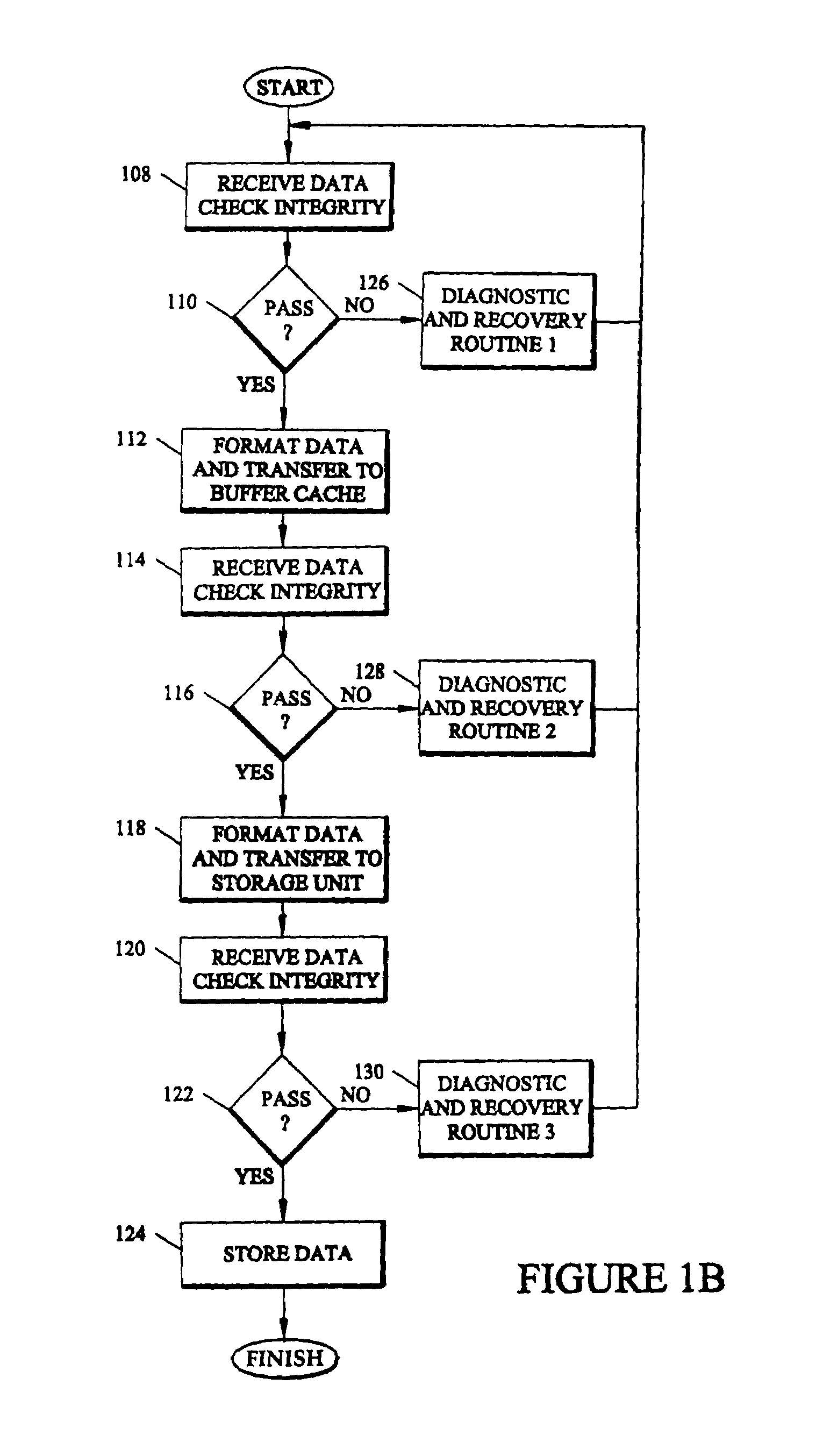
Method and apparatus for retaining error-control code protection across block-size discontinuities
InactiveUS6941503B1Other error detection/correction/protectionCode conversionOriginal dataTheoretical computer science
Each time data, in the form of data blocks protected by code checks, must be reformatted, the original data is broken into new data blocks and a new code check is calculated from, and combined with, each new data block, but the new data blocks and new code checks are both reconstituted versions of the original data blocks and the original code checks. Consequently, the data is never left without protection. In one embodiment, an ingress encoder recomputes an ingress code check from an original data block and its associated header. An egress encoder computes an egress code check from the egress header for an outgoing data block reformatted from the original data block and the ingress code check. The outgoing information is then assembled from the egress header, the outgoing data block and the newly computed egress code check.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
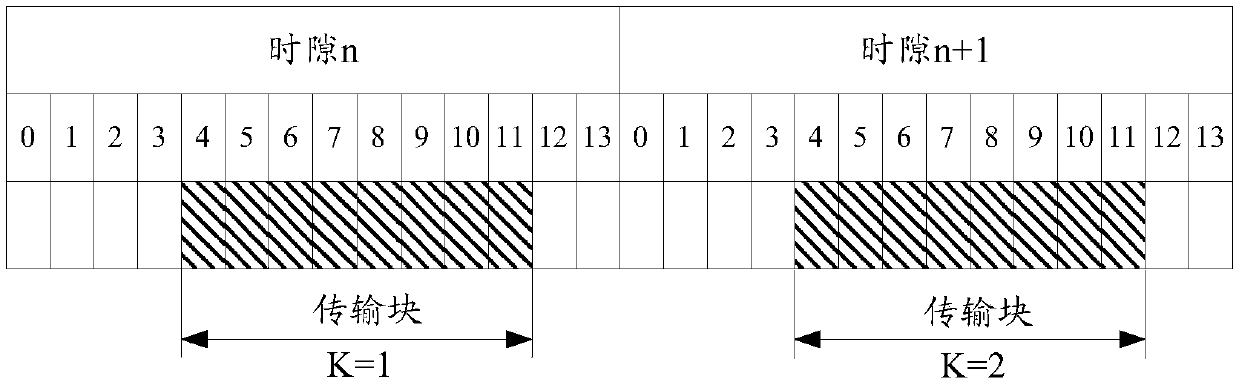
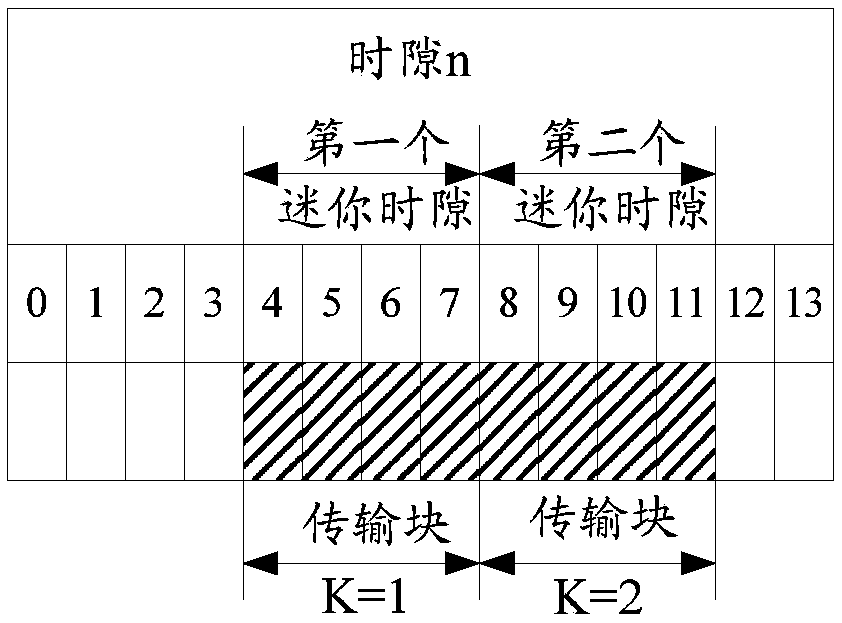
A method and apparatus for determining transport block size
The embodiment of the invention discloses a method and device for determining the size of a transmission block, relates to the field of communication, and solves the problem of how to determine a TBSbased on non-time slot repetition. According to the specific scheme, a sending device determines a TBS according to the number of REs included in M first time units and a modulation and coding mode, and sends data borne on symbols corresponding to the first time units for S times. And the receiving device receives the data borne on the symbols corresponding to the first time units for S times, determines the TBS according to the RE number and modulation and coding modes included in the M first time units, and decodes the data on the symbols corresponding to the first time units according to the TBS, wherein M is an integer greater than or equal to 1 and less than or equal to K, K is an integer greater than or equal to 2, K represents the number of times of pre-configured repeated sending of the data carried on the symbol corresponding to the first time unit, S is an integer, and S is greater than or equal to 1 and less than or equal to K. The embodiments of the present application areused in a process of determining a transport block size.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
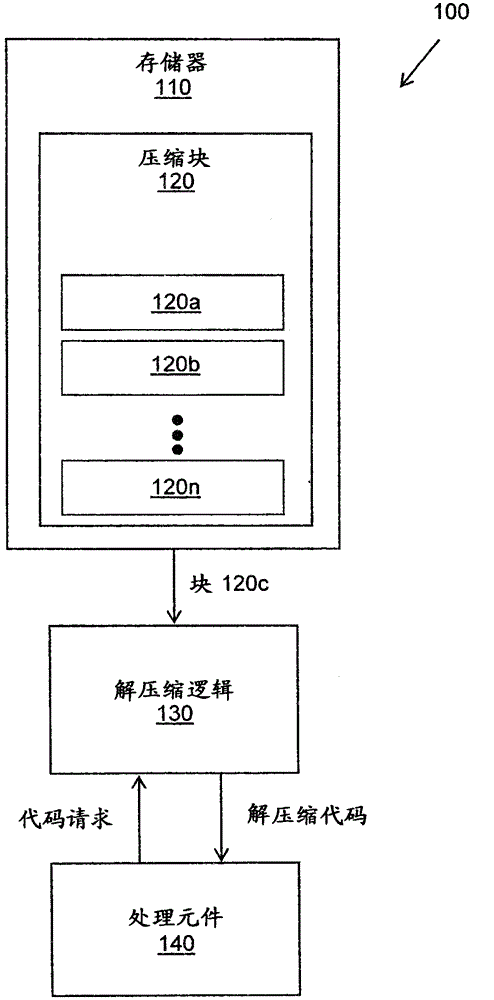
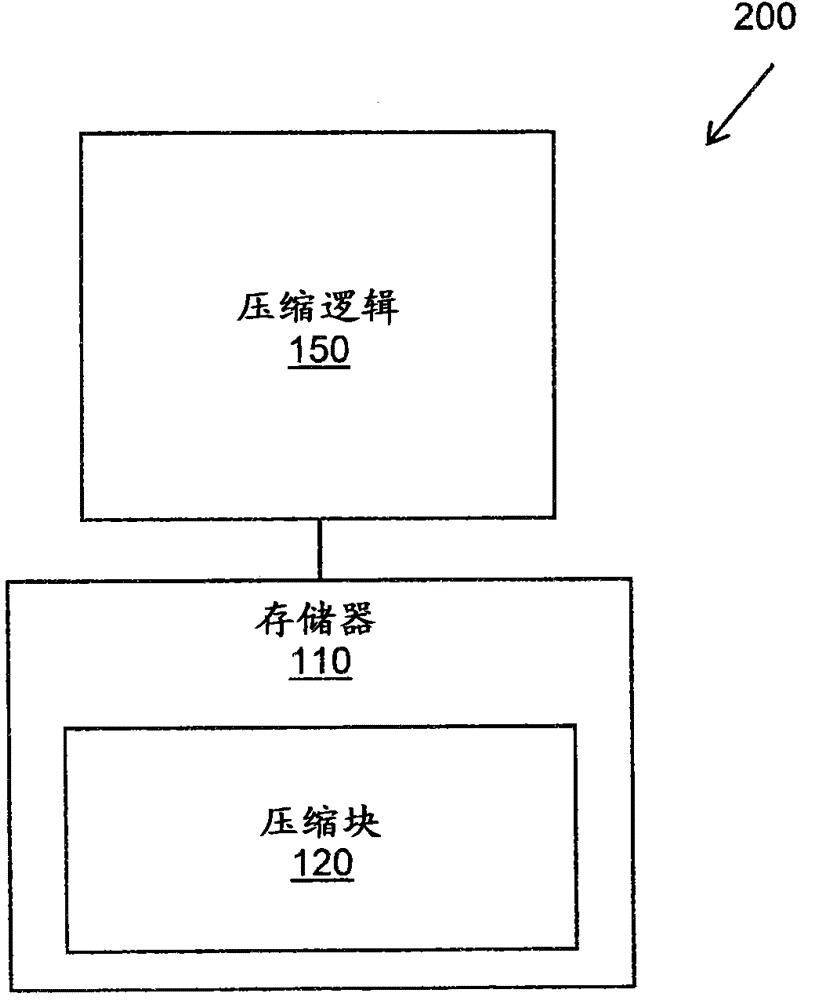
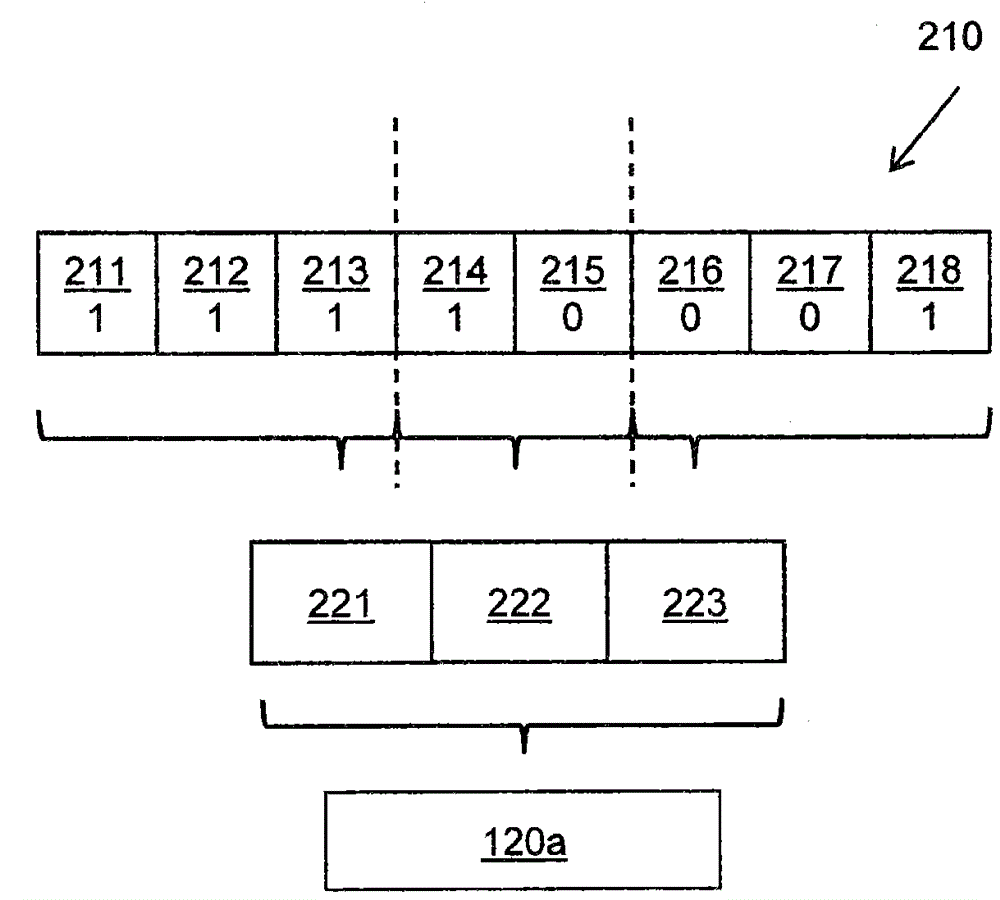
Method for compression and real-time decompression of executable code
Systems, methods, and other embodiments associated with compression and real-time decompression of executable code are described. According to one embodiment, an apparatus includes a memory that stores compressed blocks of data. The data is executable code for a processing element. The apparatus also includes a decompression logic. The decompression logic receives a request from the processing element for data and determines a compressed block that stores the data. The compressed block is decompressed to produce an uncompressed block. The decompression logic then provides the requested data to the processing element. In one embodiment an uncompressed block has a predetermined fixed block size. The predetermined fixed block size is selected based on at least one of an amount of uncompressed data, a desired compression ratio, and a desired access time.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
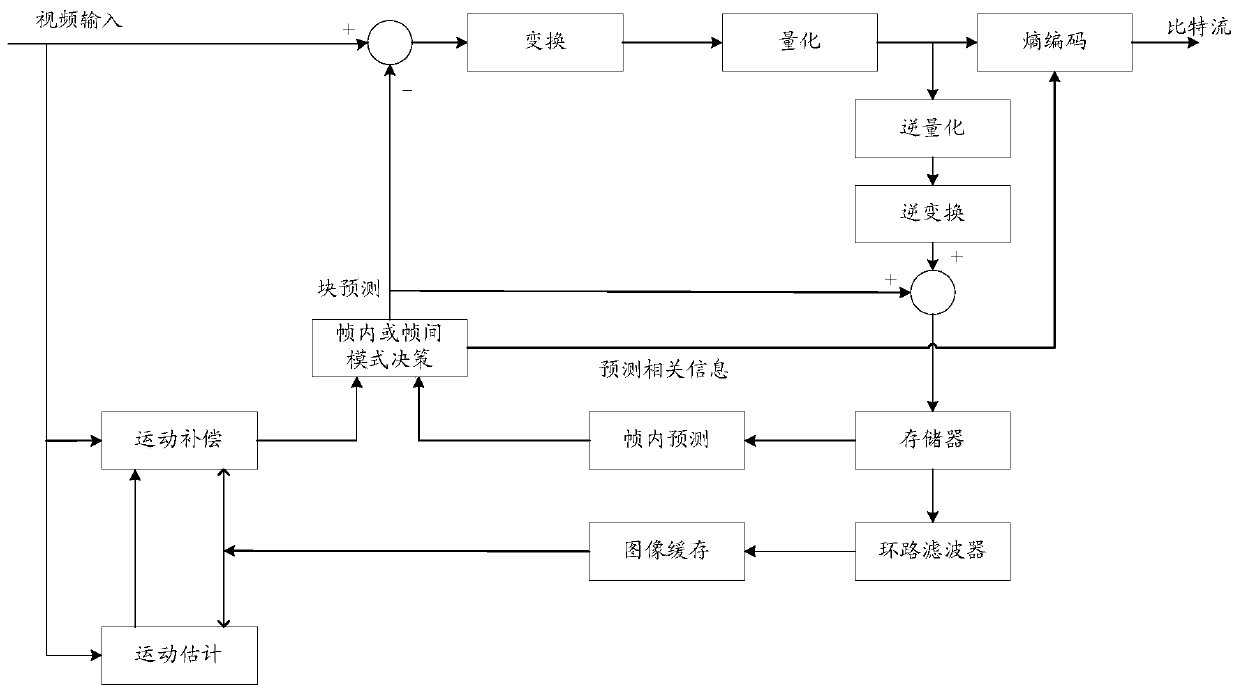
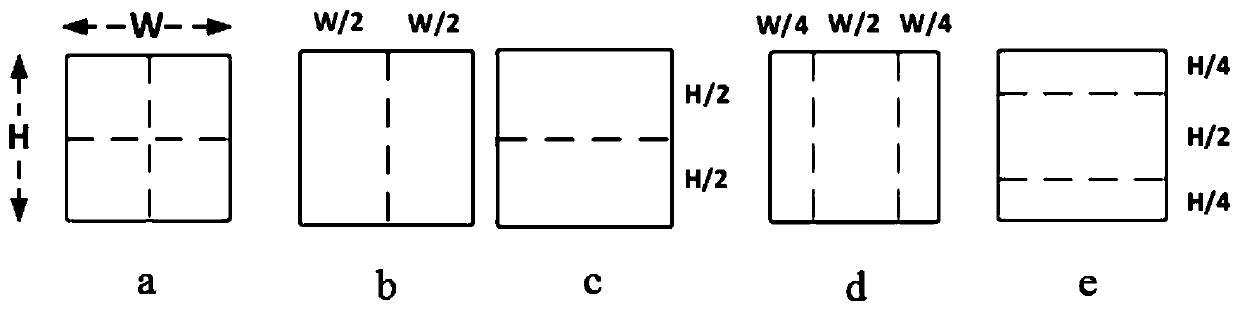
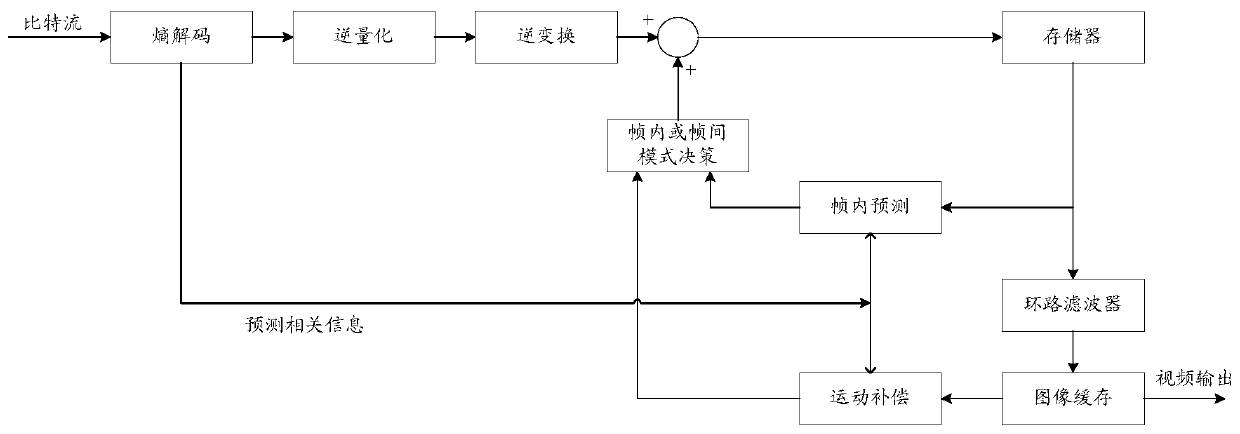
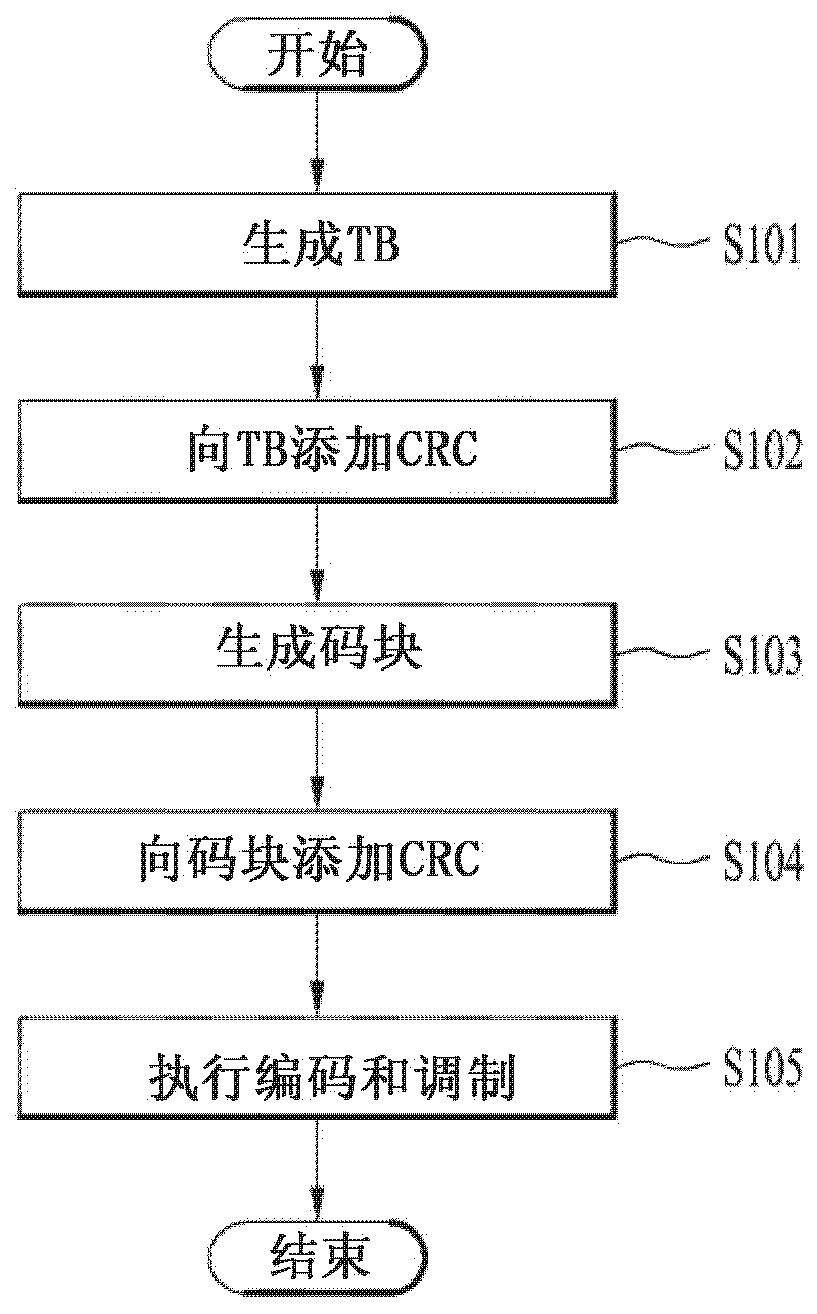
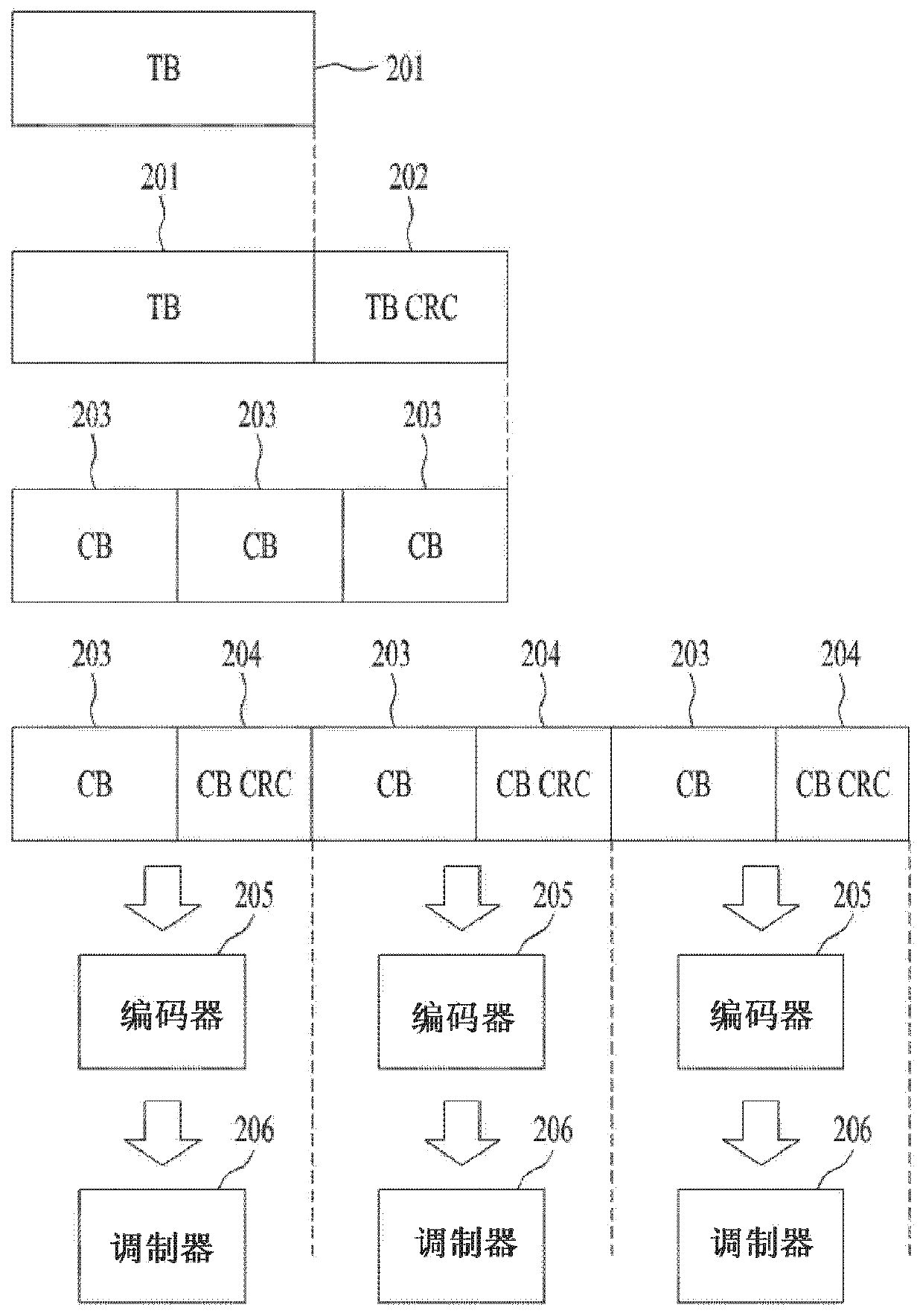
Video decoding method and device, and video encoding method and device
ActiveCN111294599AImprove encoding performanceDigital video signal modificationComputer hardwareCoding block
The disclosure relates to a video decoding method and device, and a video encoding method and device, and belongs to the technical field of video encoding and compression. The video decoding method comprises the following steps: receiving decoding information of an encoding block, wherein the decoding information at least comprises block size information, target division direction information, target prediction mode information, compressed error data and an ISP identifier for indicating that an ISP mode is configured to reconstruct the encoding block; performing sub-block division on the encoding block according to the block size information, the target division direction information and the sub-block division quantity of the configured block size information, predicting sub-blocks obtained by dividing the encoding block according to the target prediction mode information, acquiring a transformation skipping identifier of the encoding block according to the decoding information, determining prediction errors of the sub-blocks according to the transformation skipping identifier and the compressed error data, and decoding the encoding block according to the prediction results and theprediction errors of the sub-blocks. Thus, the ISP mode and the transformation skipping mode can be used in a combined mode, and the encoding effect of the ISP mode is favorably improved.
Owner:BEIJING DAJIA INTERNET INFORMATION TECH CO LTD
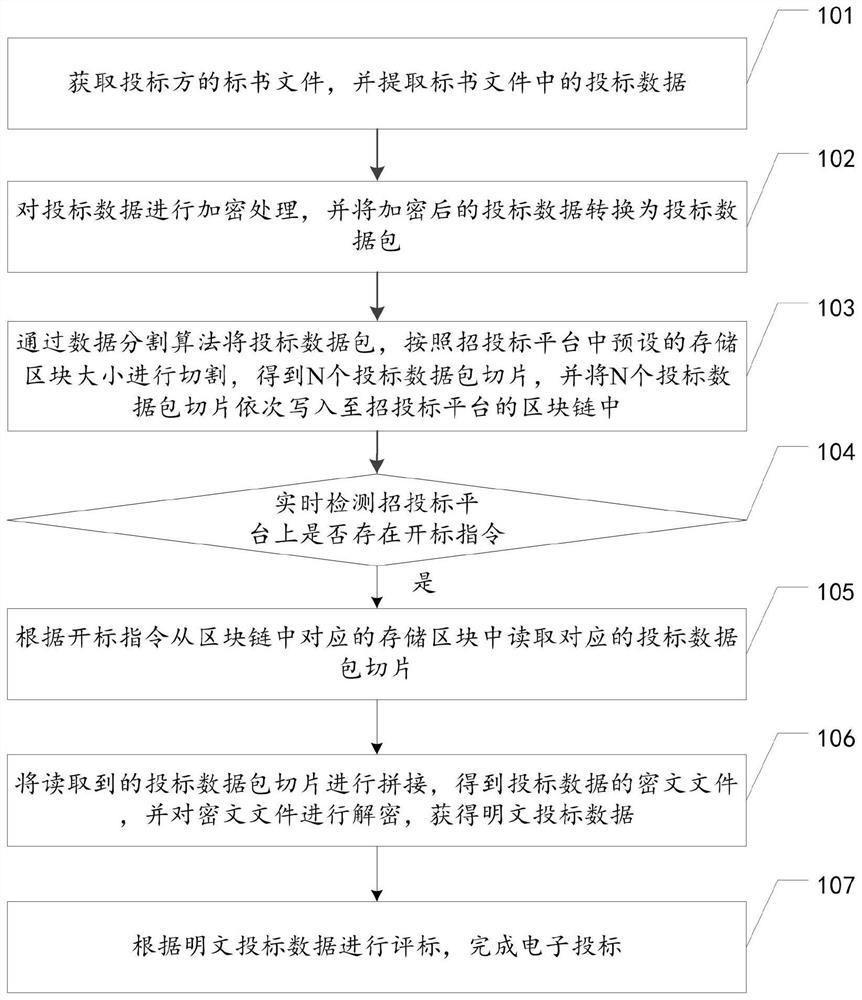
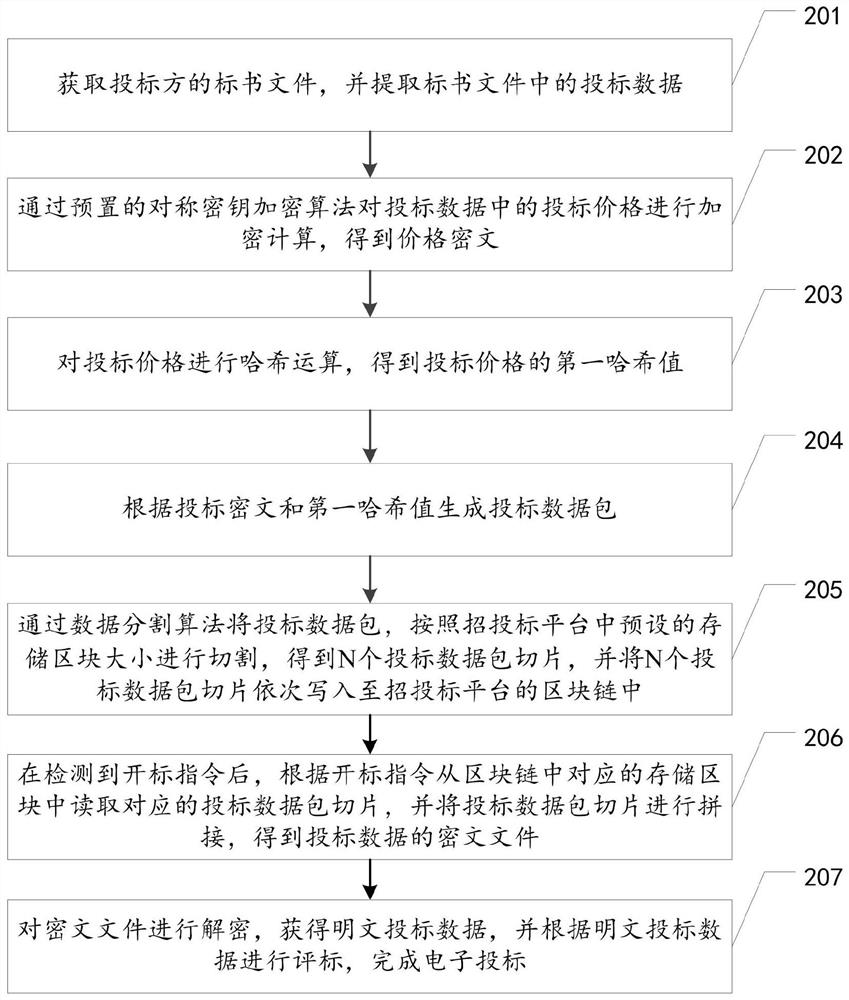
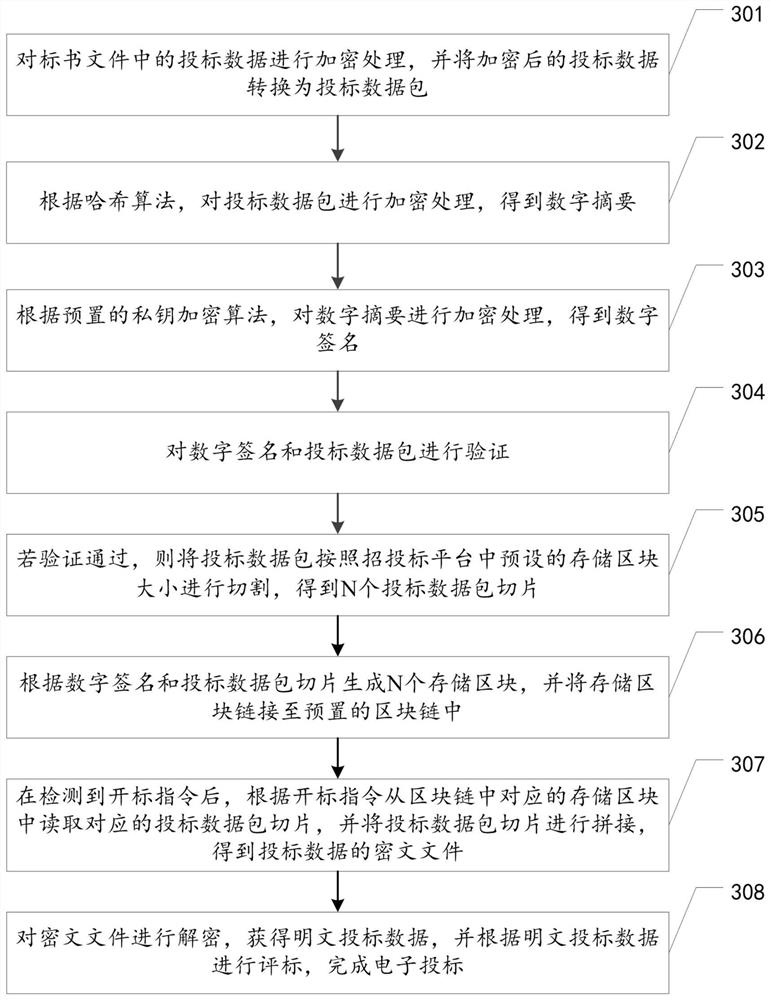
Electronic bidding method, device and equipment based on block chain, and storage medium
PendingCN111767582AAvoid modificationDatabase distribution/replicationDigital data protectionPlaintextData pack
The invention relates to the technical field of block chains, and discloses an electronic bidding method, device and equipment based on a block chain and a storage medium, which are used for data security in the field of electronic bidding. The method comprises the steps of encrypting bidding data in a bidding document file, converting the bidding data into bidding data packets, cutting the bidding data packets according to a preset storage block size through a data cutting algorithm, and writing the bidding data packets into a block chain; detecting whether a bid opening instruction exists ornot in real time, and when the bid opening instruction is detected, obtaining bid data packet slices from a storage block of the block chain according to the bid opening instruction, and splicing thebid data packet slices to obtain a ciphertext file; and decrypting the ciphertext file to obtain plaintext bidding data, and evaluating bids according to the plaintext bidding data. According to themethod, the bidding data is stored in the block chain, in the bidding process, all participants can supervise the encrypted bidding data at low cost, and it can be effectively avoided that in the bidding process, a bidding platform and a bidder modify the data.
Owner:深圳赛安特技术服务有限公司
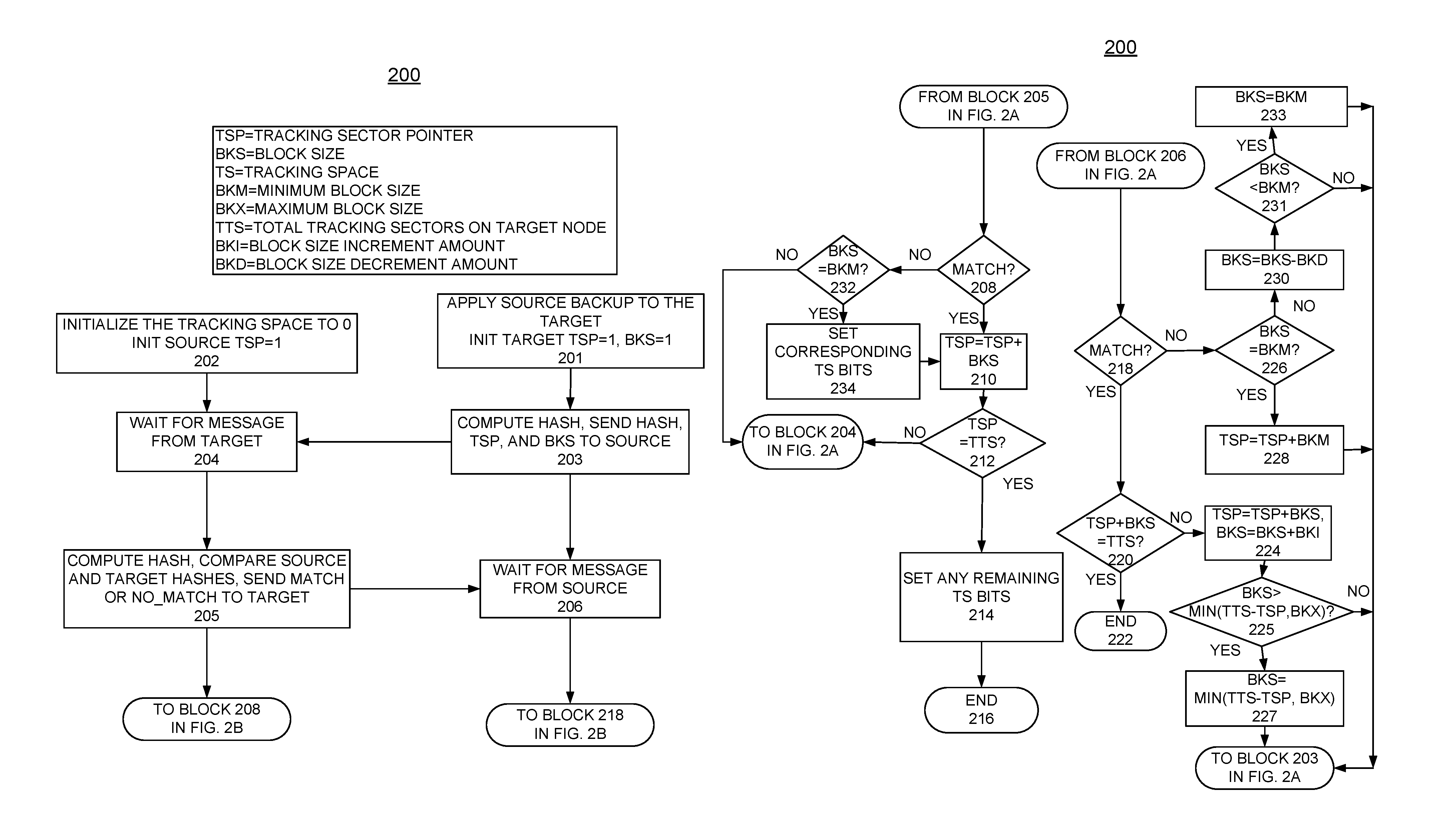
Implementing synchronization for remote disk mirroring
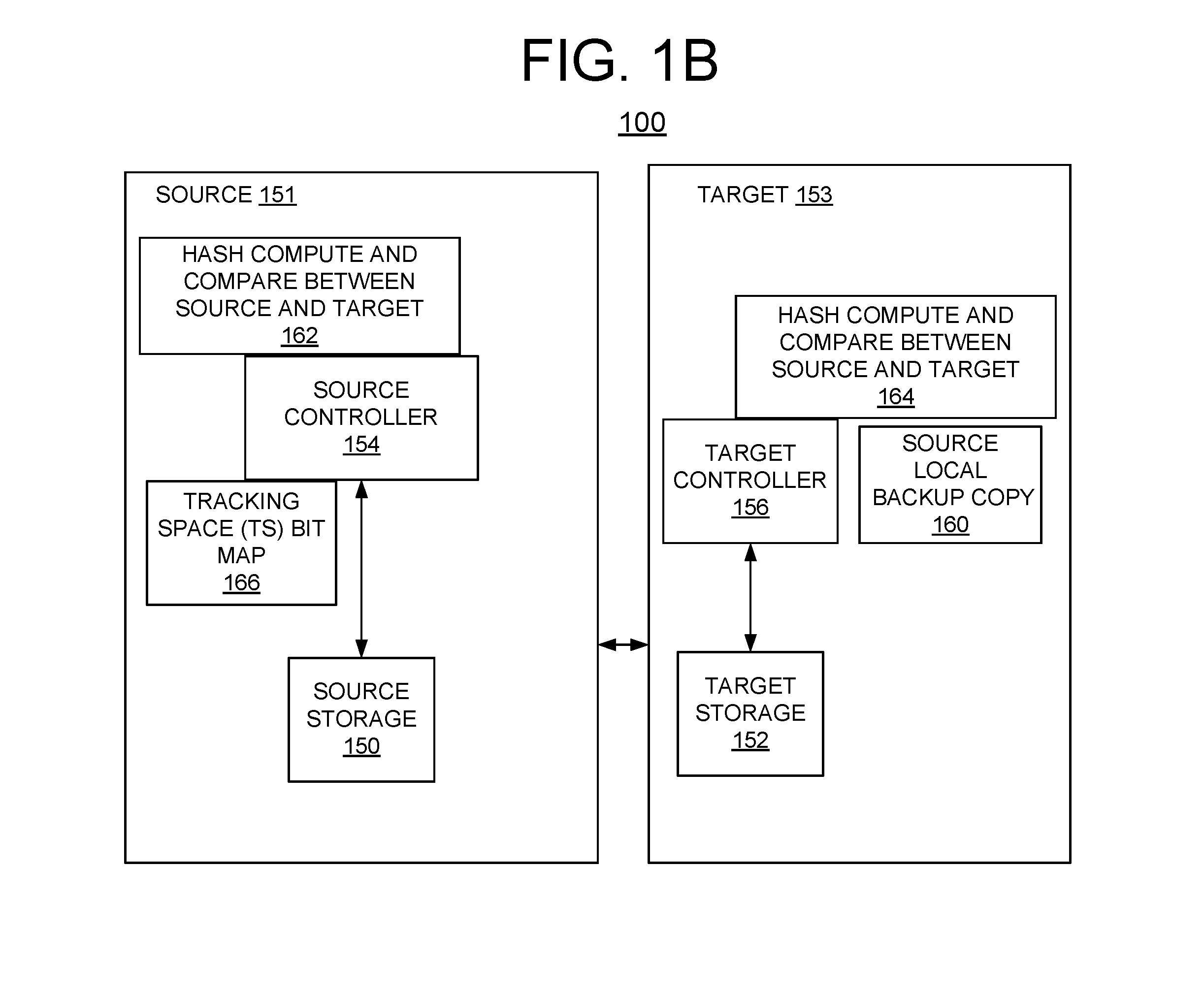
InactiveUS9430163B1Sync fastWithout negative effectMemory architecture accessing/allocationInput/output to record carriersHash functionComputerized system
A method, and system for implementing enhanced fast full synchronization for remote disk mirroring in a computer system. A source backup copy is made locally available to a target for remote disk mirroring. Sectors are identified that are different between the source and target. A hash function is used over a block to be compared, with an adaptive number of tracking sectors per block, starting with a minimum block size.
Owner:IBM CORP
Systems and methods for mitigating decoding errors due to puncturing of symbols
ActiveUS10560220B2Error minimizationReduce decoding errorError prevention/detection by using return channelError correction/detection using convolutional codesResource blockEngineering
Aspects of the disclosure relate to techniques for mitigating the decoding errors observed at the receiver as a result of puncturing symbols between consecutive subframes having the same transmission direction. To reduce the decoding errors, a plurality of transmission options, each including a number of resource blocks and a modulation and coding scheme (MCS), may be identified. In addition, each transmission option may be associated with one or more puncturing patterns that hinder decoding of a codeword at the receiver. The base station or user equipment (UE) may then select or modify at least one aspect of a scheduling decision involving the communication of the codeword in a given subframe of at least two consecutive subframes to minimize decoding errors. For example, a selected puncturing pattern or a transport block size associated with a selected transmission option may be modified.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Blind reconstructing method of block sparse signal with unknown block size
The invention relates to a blind reconstructing method of a block sparse signal with unknown block size, relating to the technical field of compressed sensing and solving the problem that the traditional reconstructing method of the block sparse signal needs take the block size and block sparsity as priori knowledge. The blind reconstructing method comprises the following steps of: carrying out block sparsity self-adaptation iteration of an algorithm for each block size to find a reconstructed signal which corresponds to each block size by initializing the block sparsity and the block size; continuously iterate the algorithm and enlarging the block size accordingly, and finishing the algorithm till the 0-norm of the reconstructed signal obtained through the algorithm is less than the line number of a measurement matrix, outputting the reconstructed signal used as algorithm; if the condition is not met, operating the algorithm till: when block size is smaller than or equal to haft of the length of the reconstructed signal, the product of the block size and the block sparsity is larger than or equal to the length of the reconstructed signal, the iteration is completed, and a series of reconstructed signals are obtained; and finally screening the sparsest reconstructed signal as final algorithm output by utilizing 0-norm sparsity measurement criteria. The invention can be used for the technical field of compressed sensing of the block sparse signal.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Method for optimizing code data-block size under performance constraint condition
InactiveCN1375939AReduce resource consumptionPulse modulation television signal transmissionError preventionMaximum errorBlock size
A method of optimizing the size of blocks of coded data intended to be subjected to an iterative decoding process, a maximum error rate of the iterative decoding process being fixed in advance, in which there are sought, among a plurality of block sizes (N / k) which are submultiples of the normal block size by an integer factor (k) greater than or equal to 1 and a plurality of integers giving the maximum number of iterations that can be effected by the said iterative decoding on a block, (1) a submultiple size, and (2) a maximum number of iterations such that they are compatible with the maximum error rate, and such that the mean number of iterations that will be applied by the iterative decoding process on a block of submultiple size is minimized.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Low rate loss bit-level distribution matcher for constellation shaping
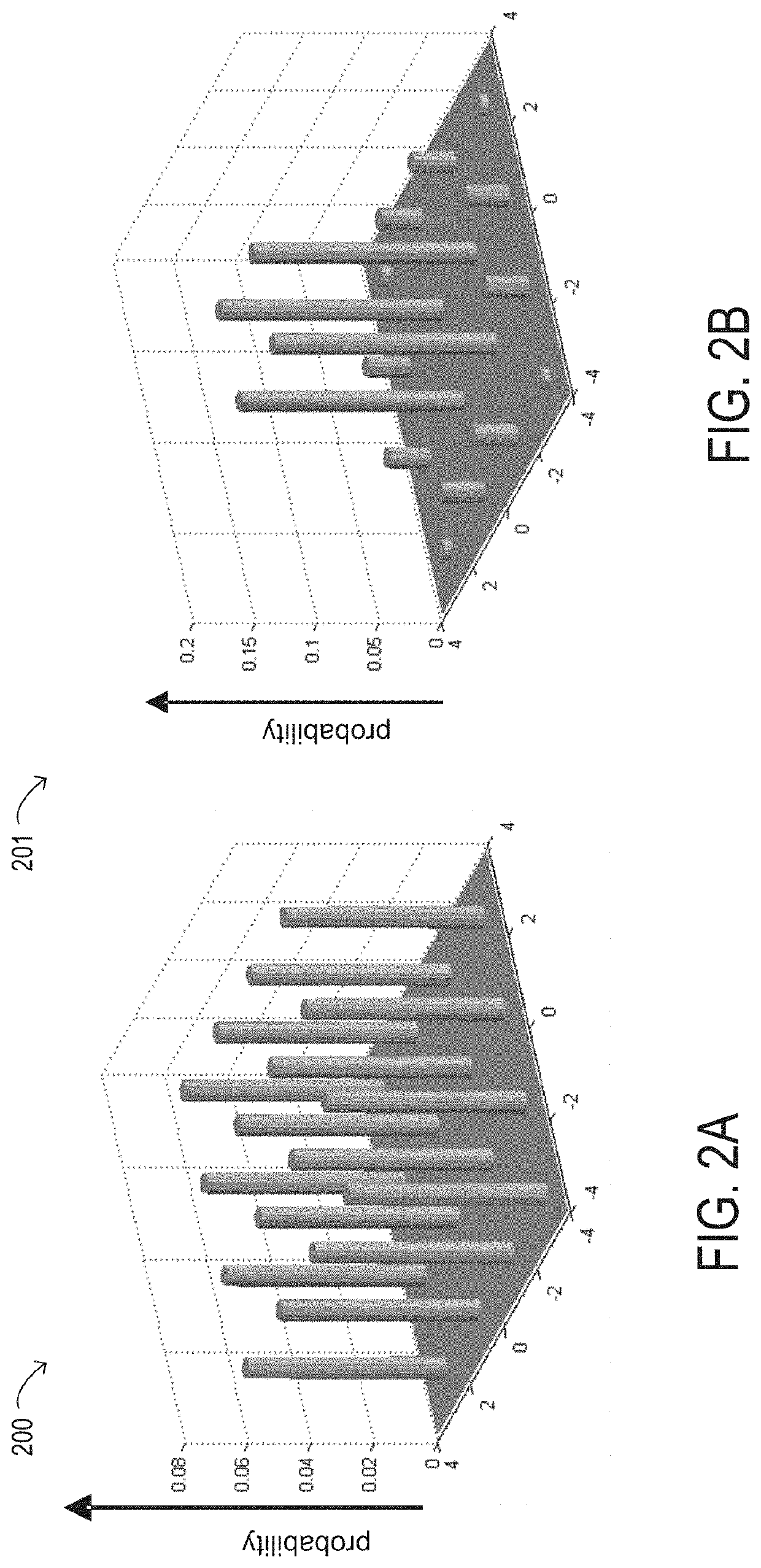
ActiveUS20210194596A1Wavelength-division multiplex systemsElectromagnetic receiversBlock sizeComputer engineering
Systems and methods for constellation shaping using low rate loss bit-level distribution matchers include receiving blocks of input bits and, for each input block of a predetermined size, assigning a respective codeword of a predetermined output block size. The number of bits of a given bit value in the codeword is dependent on a predetermined target probability distribution. A one-to-one mapping exists between each possible combination of input bits and a codeword for input blocks containing the combination. Some codewords include a number of bits having the given bit value that is different than the predetermined target probability distribution, but an average number of bits having the given bit value in the available codewords meets the predetermined target probability distribution. The disclosed methods result in more available codewords and a lower rate loss than in bit-level distribution matchers with a constant modulus, while achieving similar shaping.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Decoding device, decoding method, encoding device, and encoding method
ActiveUS10687060B2Efficient codingGuaranteed effective sizeDigital video signal modificationBlock sizeDecodes
A decoding device, including circuitry configured to decode a bit stream and generate a quantized value, and inversely quantize the generated quantized value by using a flat scaling list, in a case where a block size of a transform block to which a transform skip is applied is larger than a 4 by 4 block size.
Owner:SONY CORP
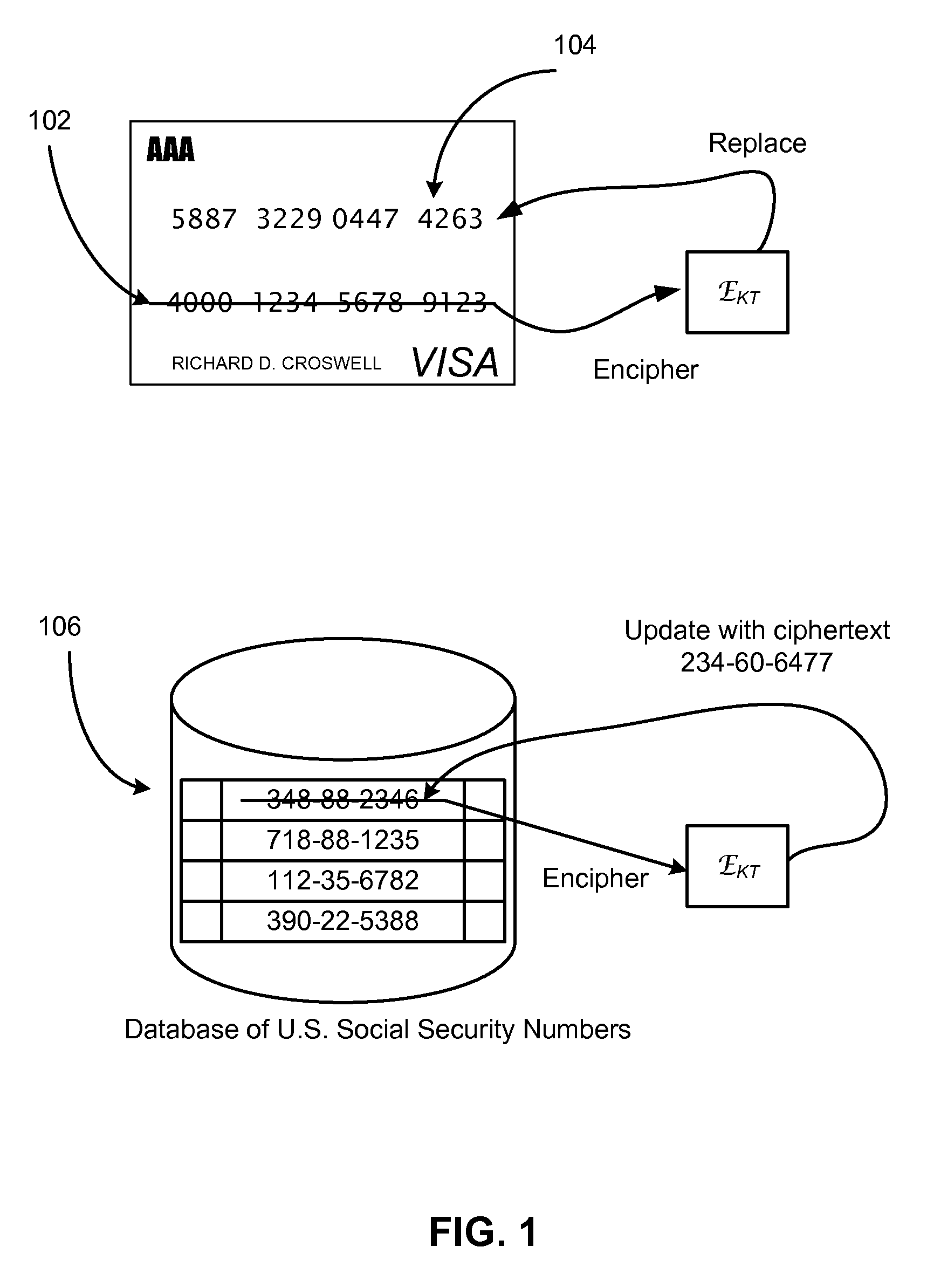
Method and system for accelerating the deterministic enciphering of data in a small domain
ActiveUS8687802B2Processing speedReduce in quantityUnauthorized memory use protectionHardware monitoringCredit cardDeterministic encryption
Conventional block ciphers that traffic in 128-bit block sizes are ill-suited for operating in small domains like credit card numbers. Some embodiments relate to techniques for constructing and speeding up practical and provably secure schemes for deterministically enciphering data from a small domain like credit card numbers using a conventional block cipher or other pseudorandom function.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Low rate loss bit-level distribution matcher for constellation shaping
ActiveUS11265086B2Wavelength-division multiplex systemsElectromagnetic receiversBlock sizeComputer engineering
Systems and methods for constellation shaping using low rate loss bit-level distribution matchers include receiving blocks of input bits and, for each input block of a predetermined size, assigning a respective codeword of a predetermined output block size. The number of bits of a given bit value in the codeword is dependent on a predetermined target probability distribution. A one-to-one mapping exists between each possible combination of input bits and a codeword for input blocks containing the combination. Some codewords include a number of bits having the given bit value that is different than the predetermined target probability distribution, but an average number of bits having the given bit value in the available codewords meets the predetermined target probability distribution. The disclosed methods result in more available codewords and a lower rate loss than in bit-level distribution matchers with a constant modulus, while achieving similar shaping.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Method for selecting LDPC base code in multi-lpdc code, and device therefor
A method for encoding a quasi-cyclic low-density parity-check (LDPC) code which supports a multi-base code according to an embodiment of the present invention includes: a step for selecting a base code for generating a parity-check matrix from among a first base code and a second base code; a step for selecting a lifting value for generating the parity-check matrix from among a plurality of lifting values; and a step for generating the parity-check matrix using the selected base code and lifting value, wherein the base code can be determined on the basis of the code block size and a code rate,and the lifting value can be determined on the basis of a parameter of the base code and the code block size.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Adaptive retrieval of objects from remote storage
ActiveUS20200272568A1Effective installationQuick searchInput/output to record carriersResource allocationEngineeringByte
Various embodiments of the present application set forth a computer-implemented method for accessing data comprising identifying a first set of read operations occurring during a first time period, where each read operation included in the set of read operations is associated with retrieving a different portion of at least one object from a storage system, determining a byte density associated with the set of read operations, where the byte density indicates a size of contiguous portions of the at least one object that were retrieved during the first time period, and determining, based on the byte density, a pre-buffering block size for a read operation during a second period, where the pre-buffering block size specifies a size of a portion of at least one object that is to be retrieved from the storage system.
Owner:NETFLIX
Storage access interface to an encoded storage system
ActiveUS10972125B2Input/output to record carriersInterprogram communicationComputer hardwareCoding block
A combination of a block-oriented encoder and decoder with a modified dataset identifier that is associated with an encoded block size are used to perform block-based encoding and decoding operations. The encoding process may generate optional metadata that includes an array of encoded block sizes to support random access into the stream or group of encoded blocks during the decoding process. The modified dataset identifier associates the original dataset identifier with the block size used by the encoder.
Owner:ANACODE LABS INC
Construction method and system of white-box block cipher based on feistelbox structure
ActiveCN109981256BImprove securityAffine Transform EliminationKey distribution for secure communicationEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesCiphertextPassword
Owner:SOUTH CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY
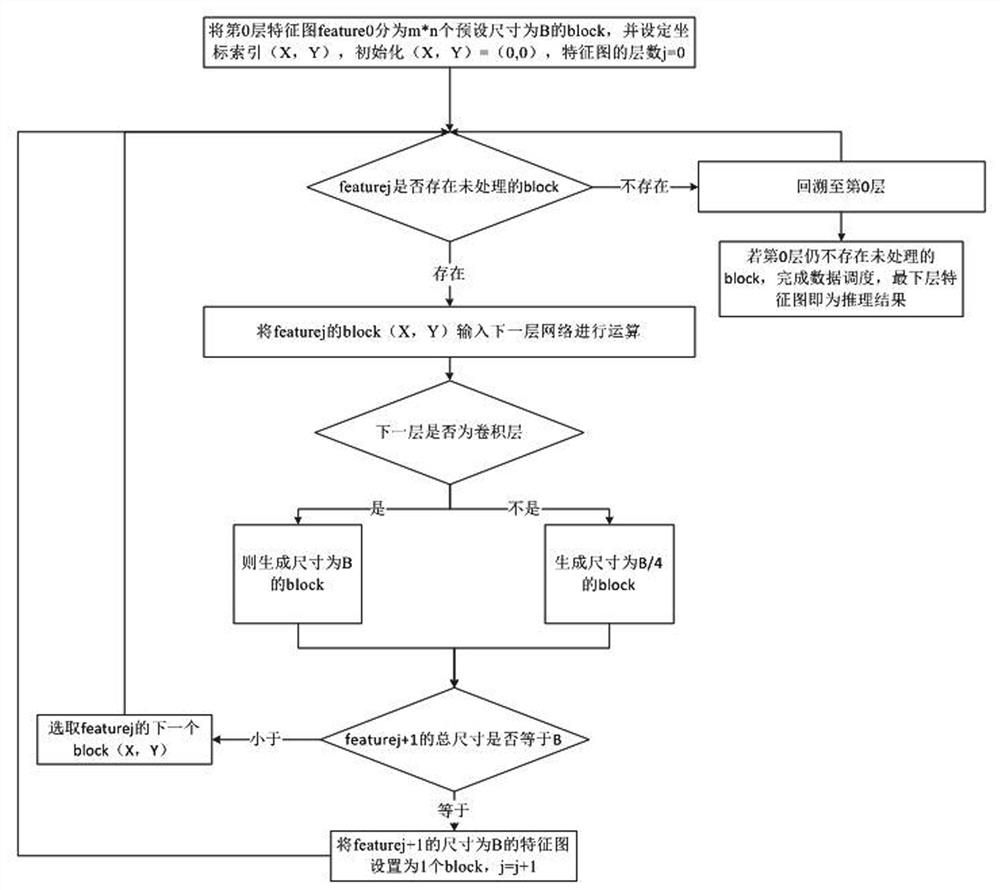
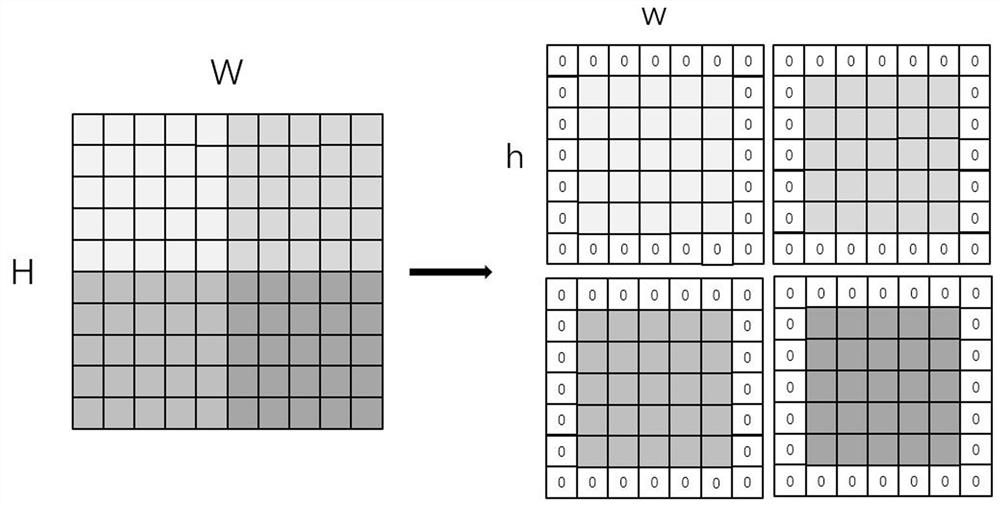
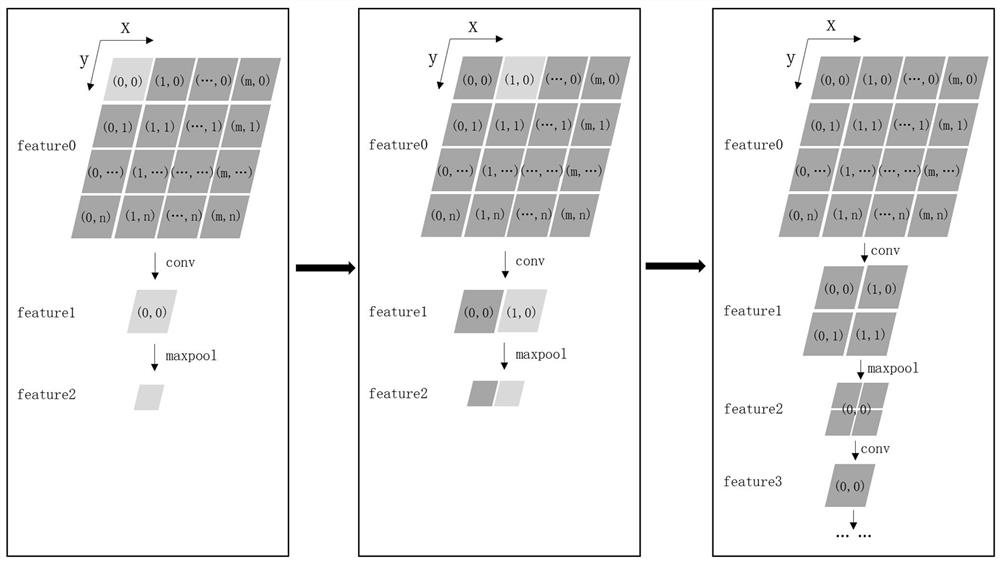
Depth-first data scheduling method, system and equipment based on block convolution
ActiveCN112949831AImprove reasoning efficiencyAvoid memory consumptionNeural architecturesPhysical realisationTheoretical computer scienceTerm memory
The invention belongs to the field of convolutional neural networks, particularly relates to a depth-first data scheduling method, system and equipment based on block convolution, and aims to solve the problems that an existing convolution model calculation method needs to perform calculation layer by layer, and storage of an intermediate result feature map needs to occupy a large amount of memory and is not suitable for being deployed in full-hardware equipment. The method comprises the following steps: dividing an input feature image into a plurality of blocks, calling the blocks one by one to carry out convolution or maximum pooling to generate a next-layer feature map, if the next-layer feature map reaches a preset block size, continuing to call to the next layer to obtain a deeper feature map, and if the next-layer feature map is smaller than the preset block size, returning to the 0-th layer to call until the reasoning process is completed. According to the method, memory consumption caused by storage of a large number of convolution layer intermediate results is avoided, and the reasoning efficiency of the convolution model on full hardware equipment is improved.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
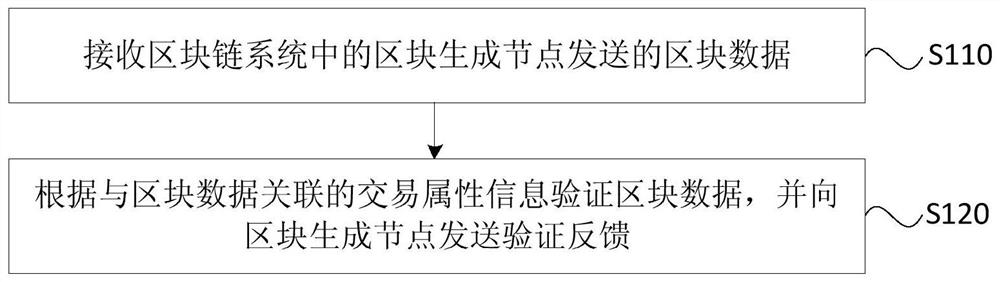
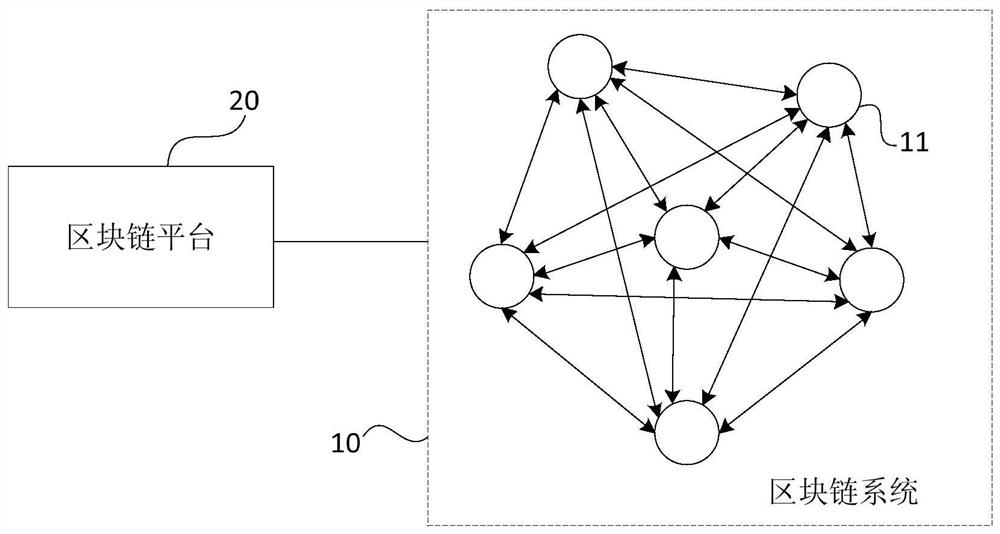
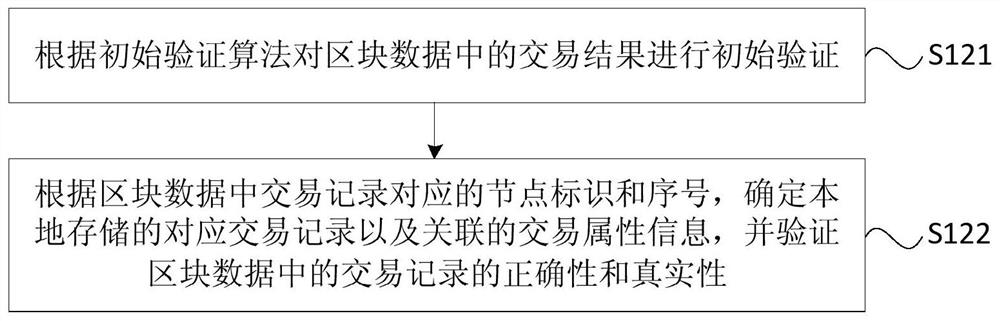
A verification method, device, equipment and storage medium for block data
ActiveCN108924130BRealize authenticity verificationIncrease authenticityEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesOther databases indexingComputer hardwareSource Data Verification
The embodiment of the invention discloses a block data verification method, device, equipment and storage medium. Wherein, the method includes: receiving the block data sent by the block generation node in the block chain system; verifying the block data according to the transaction attribute information associated with the block data, and sending the block data to the block generation node Send verification feedback. The technical solution of the embodiment of the present invention realizes the authenticity verification of the block data through the transaction attribute information associated with the block data in the node, increases the diversity of the block data verification in the block chain system, and reduces the The possibility of generation nodes maliciously generating transaction records in block data improves the authenticity of block data recorded in the blockchain.
Owner:SHANGHAI DAJIAYING INFORMATION TECH CO LTD
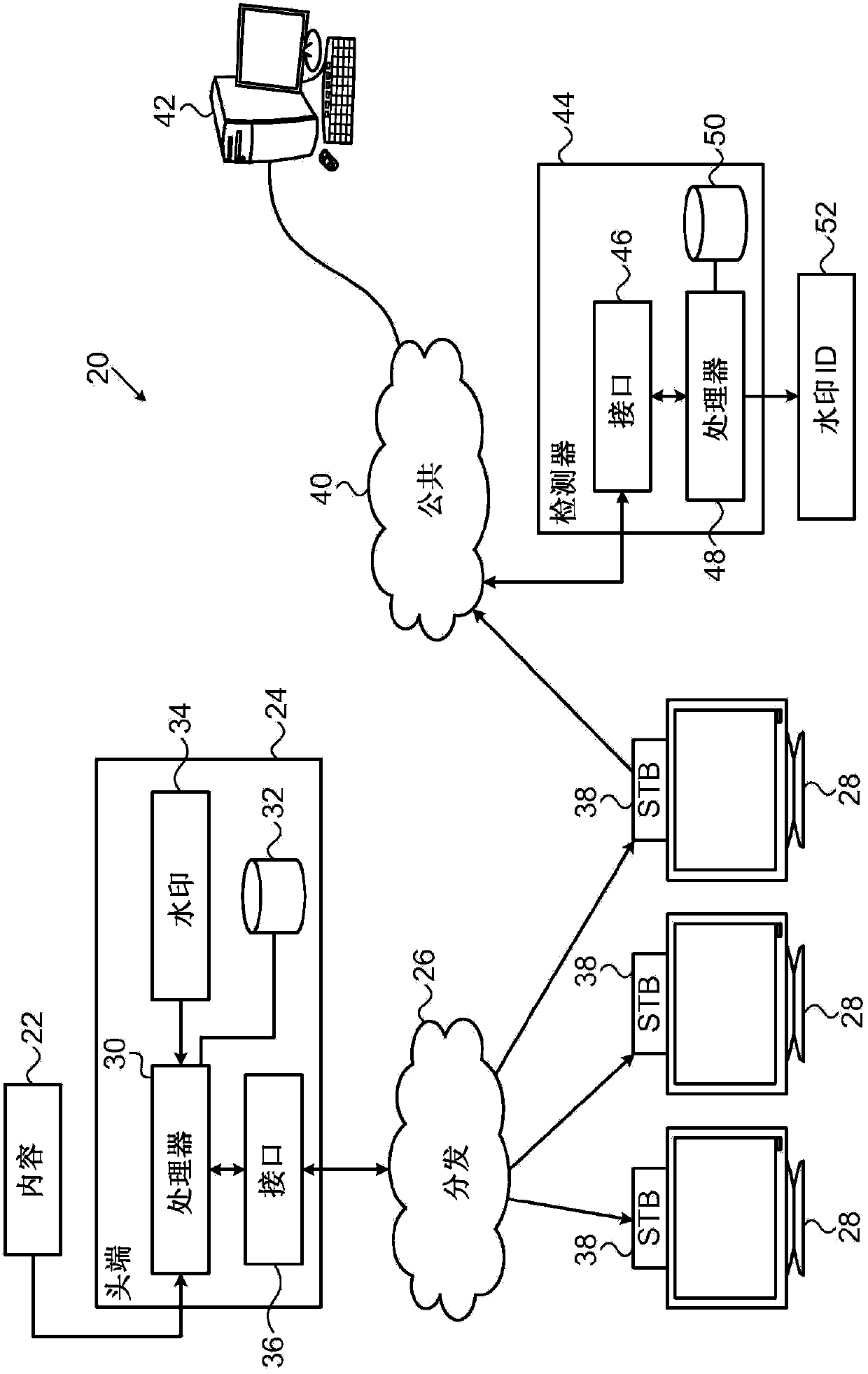
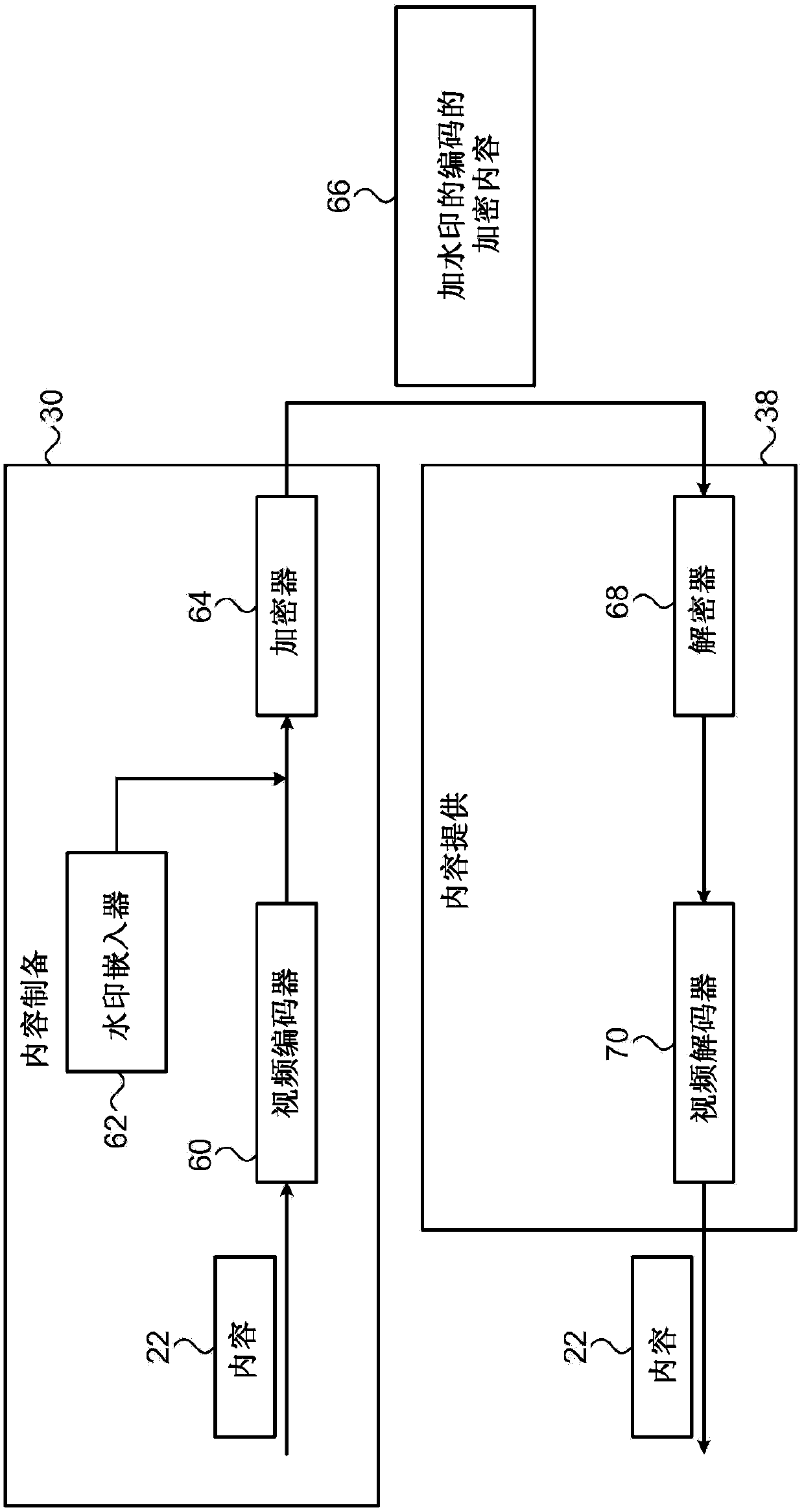
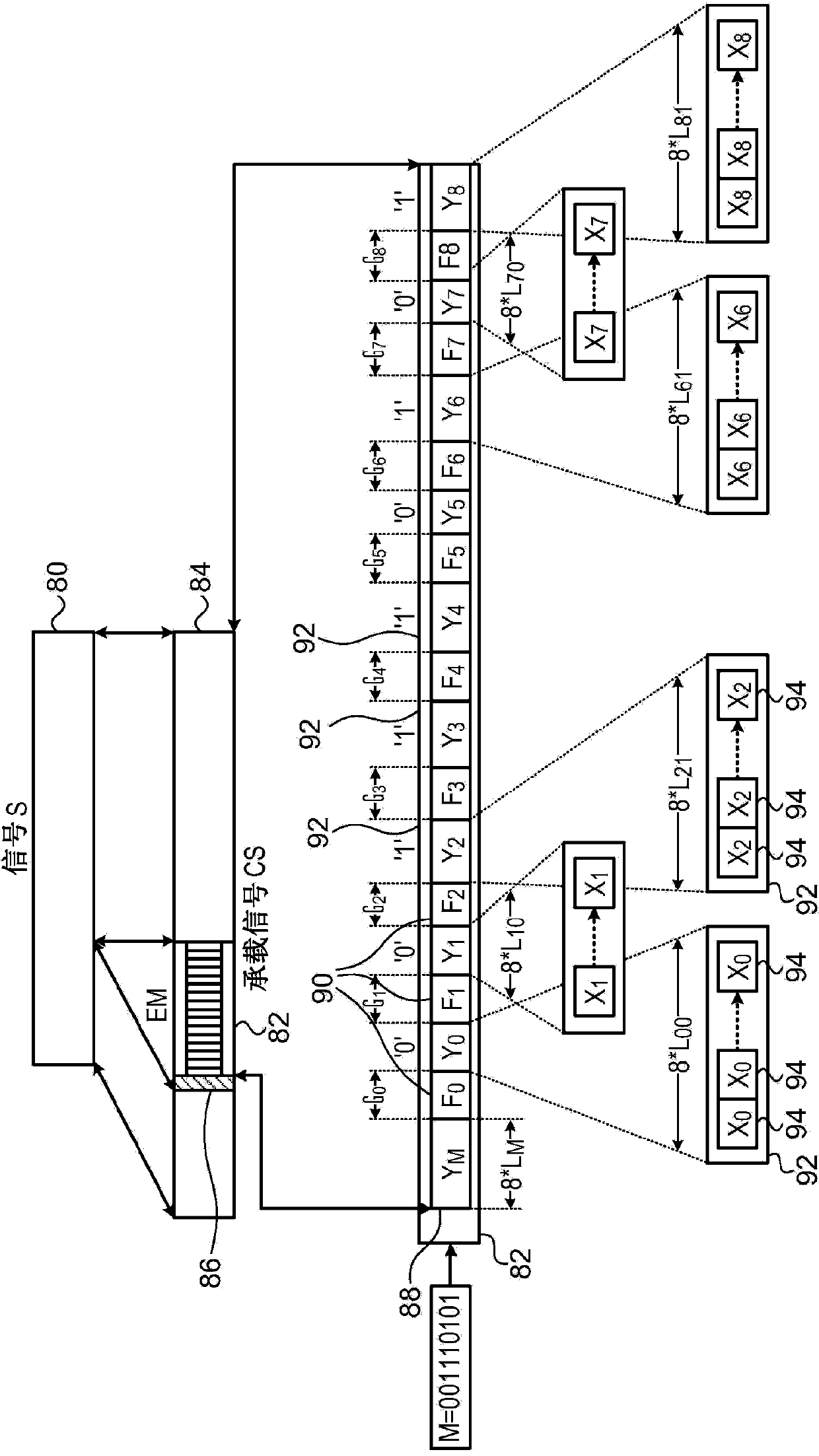
Encryption-resistant watermarking
ActiveCN104272748AImage data processing detailsSelective content distributionDigital dataSequence Insertions
A method and system for providing encryption resistant watermarking of data is described. The method and system comprises encoding a string of symbols, each having a respective symbol value, as a sequence of vectors where each vector includes a respective number of repetitions of a sub-vector of a predefined length, such that the respective number of the repetitions in each vector in the sequence is indicative of the respective symbol value of a corresponding symbol in the string. This sequence of vectors is then inserted into the item of content including digital data to apply a watermark to the item of content. This insertion process may involve interleaving the vectors with gaps of known lengths containing arbitrary data and may involve insertion prior to the vector sequence a marker comprising a concatenation of a number of copies of a marker vector. The length of the sub-vector may be chosen to be an integer divisor of a block size of a block cipher that is to be applied to the item of content after application of the watermark thereto.
Owner:SYNAMEDIA LTD
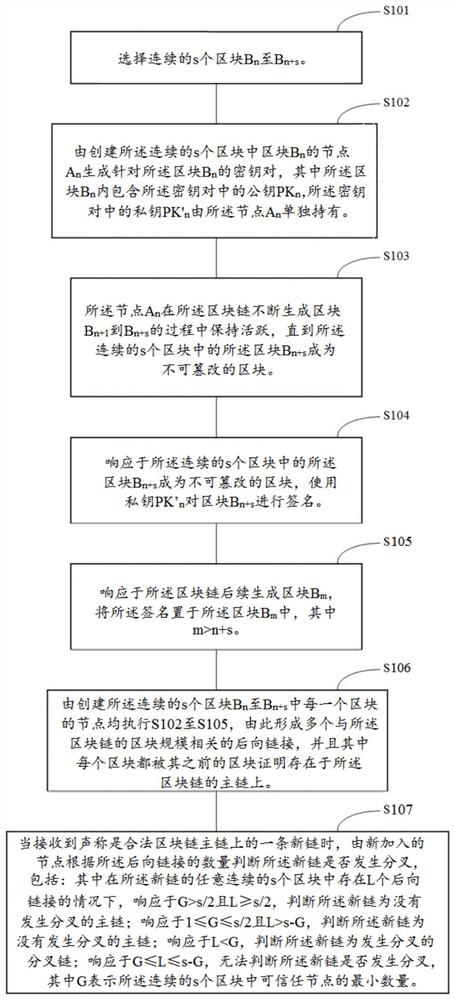
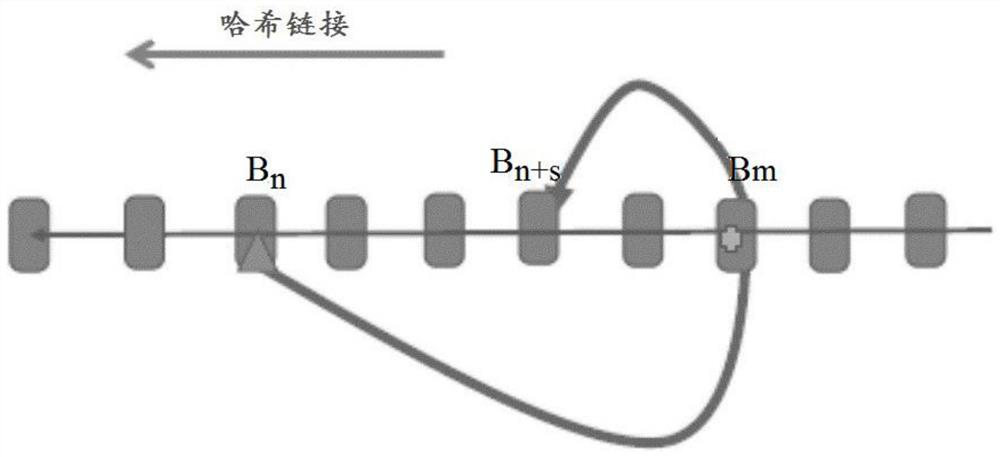
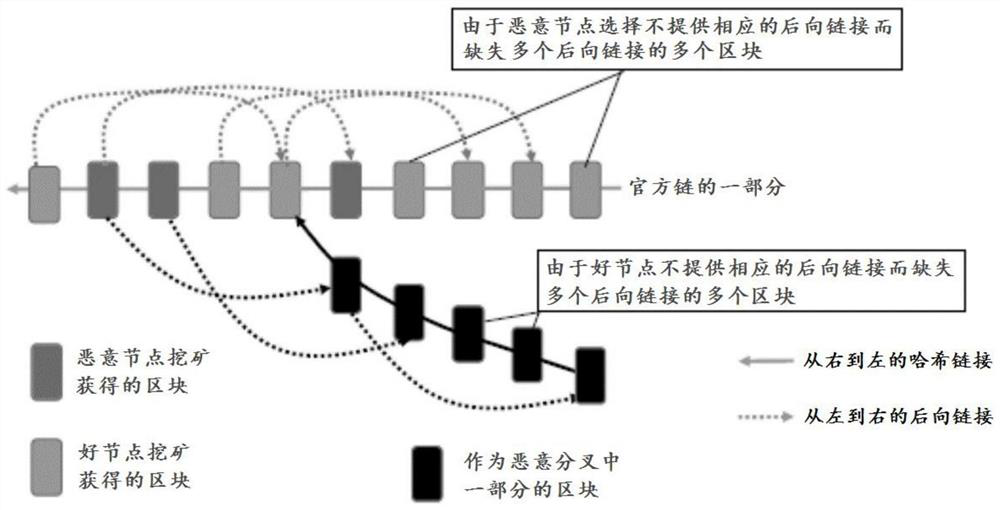
Method and apparatus for preventing blockchain forks
ActiveCN111445247BMake sure to generateSafe generationPayment protocolsSpecial data processing applicationsSoftware engineeringBlock size
Owner:THE BLOCKHOUSE TECH LTD
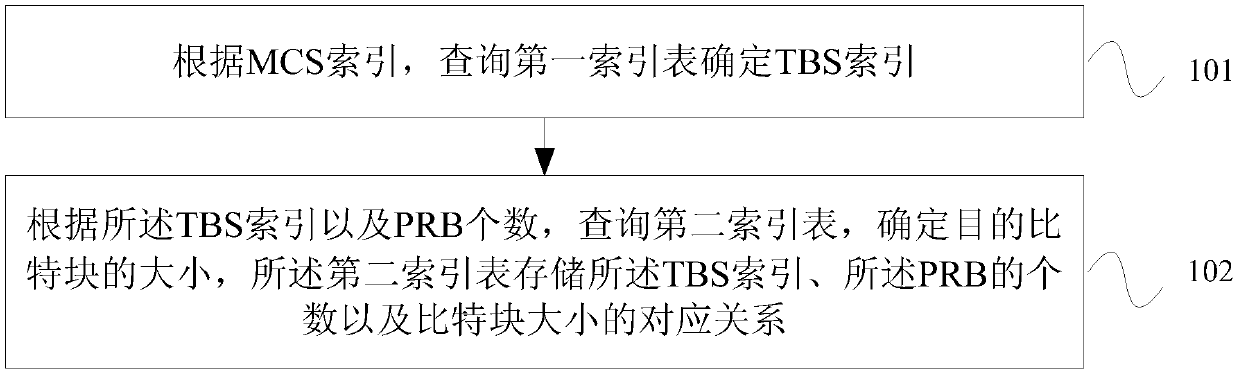
Method and device for determining bit block size
ActiveCN108781454BReduce lossesIncrease the uplink code rateWireless communicationFrequency spectrumData transmission
Embodiments of the present invention provide a method and device for determining the size of a bit block. The TBS index is determined by querying the first index table according to the MCS index, and the target bit block size is determined by querying the second index table according to the TBS index and the number of PRBs. In this process, since the TBS index corresponding to each MCS index in the first index table increases, the bit block size corresponding to the newly added TBS index is expanded in the second index table, and the larger the TBS index, the corresponding bit block bigger. Therefore, the first index table and the second index table are adapted to the uplink 256AQM. In the process of sending uplink data, the available REs in the RB can be used as much as possible to increase the uplink code rate and reduce the loss caused by the uplink peak rate, thereby improving the uplink data rate. Peak throughput and spectral efficiency.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com