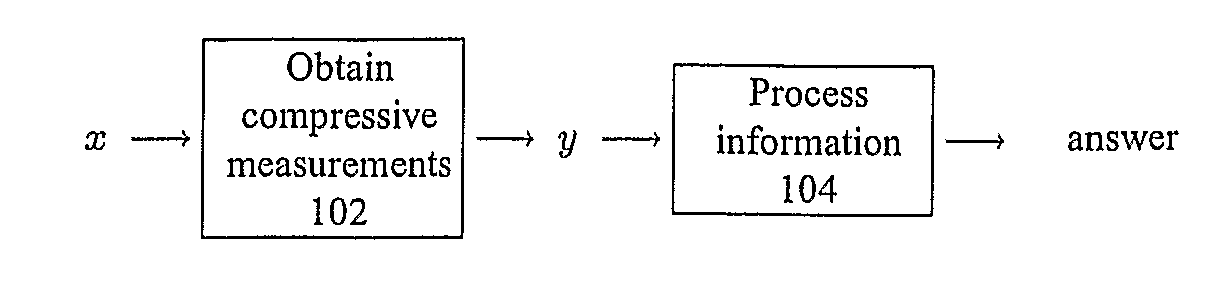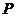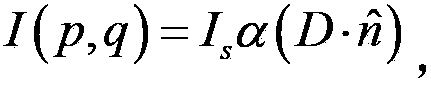Patents
Literature
2977 results about "Compressed sensing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
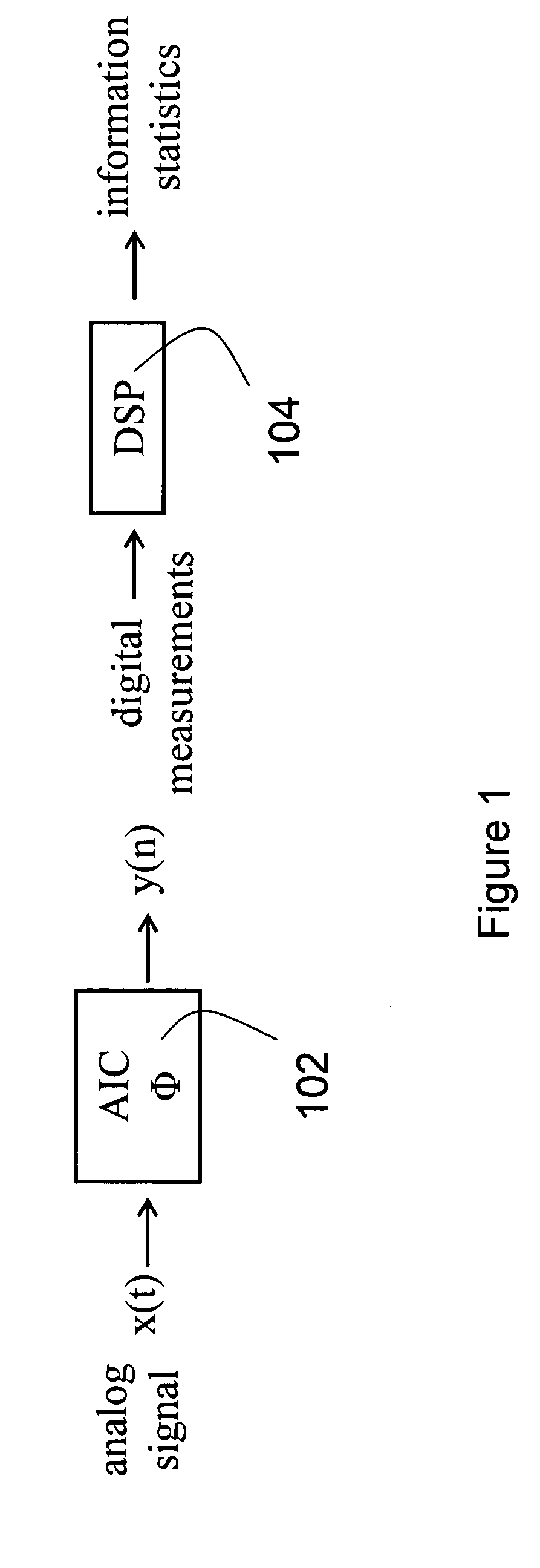
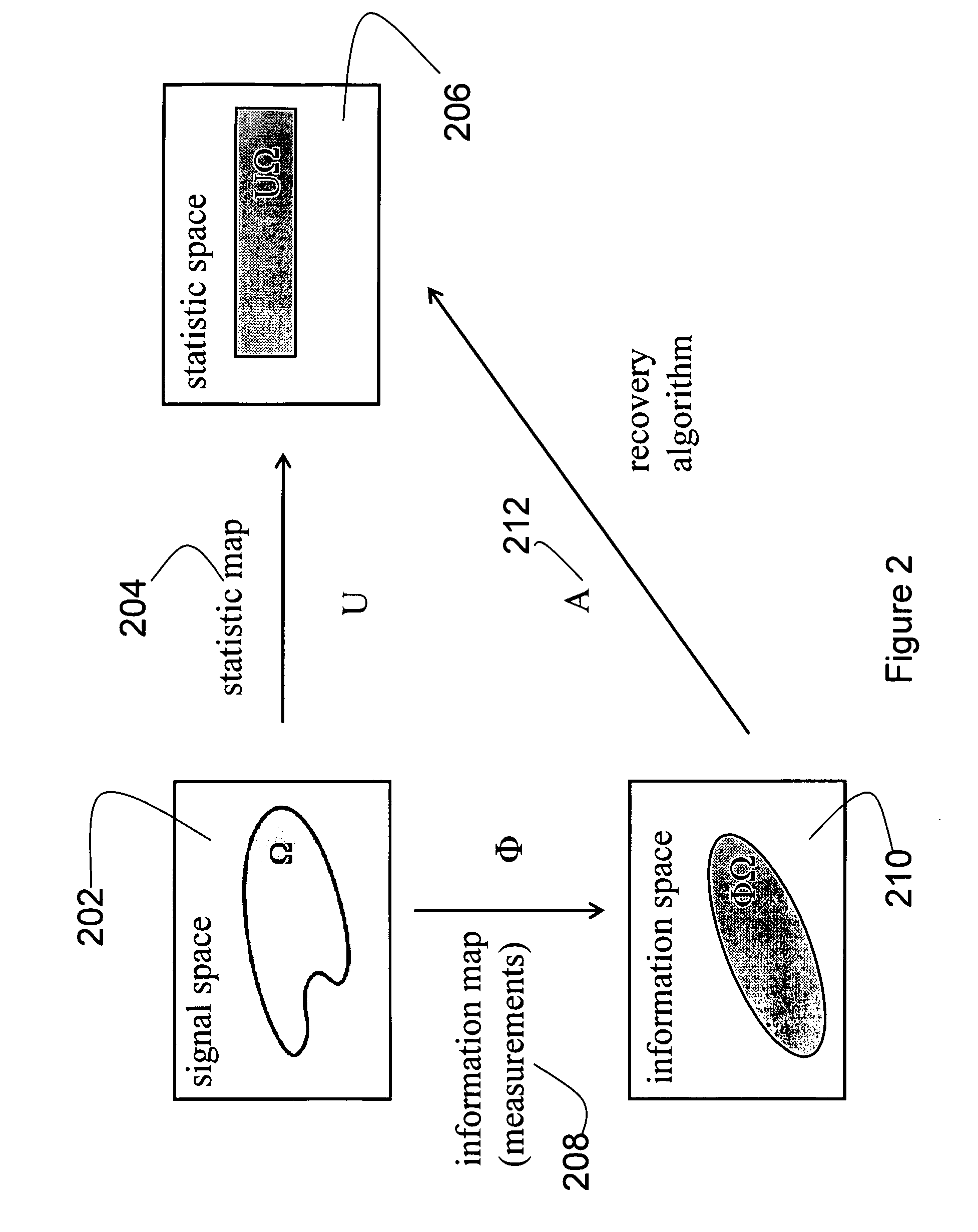
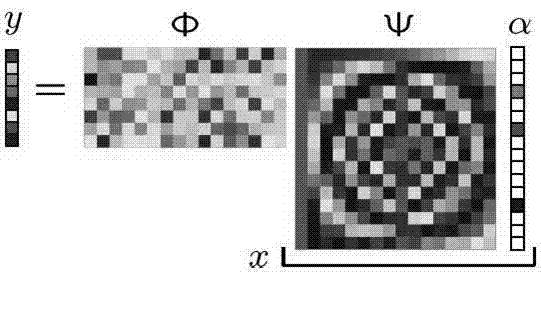
Compressed sensing (also known as compressive sensing, compressive sampling, or sparse sampling) is a signal processing technique for efficiently acquiring and reconstructing a signal, by finding solutions to underdetermined linear systems. This is based on the principle that, through optimization, the sparsity of a signal can be exploited to recover it from far fewer samples than required by the Nyquist–Shannon sampling theorem.
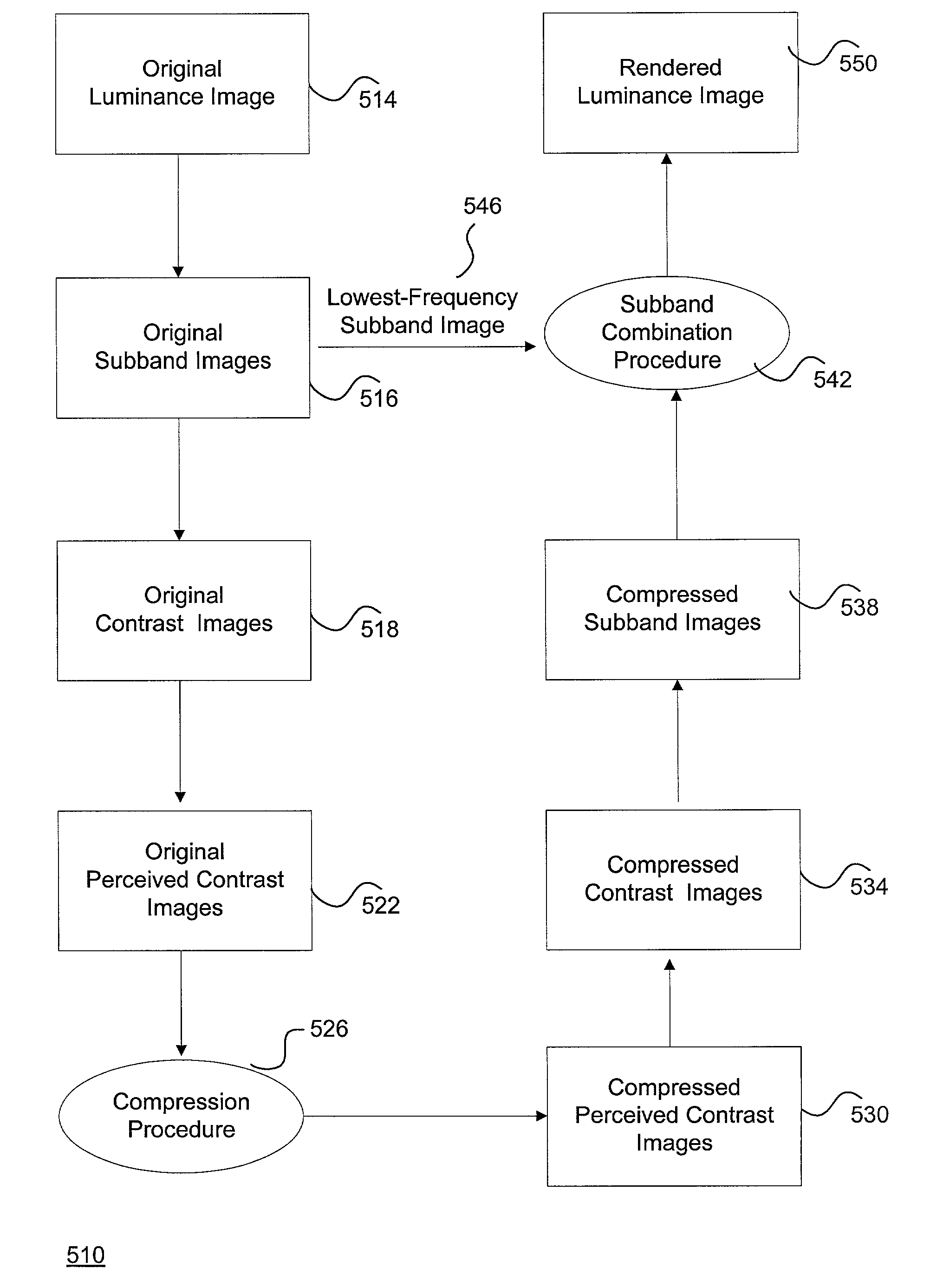
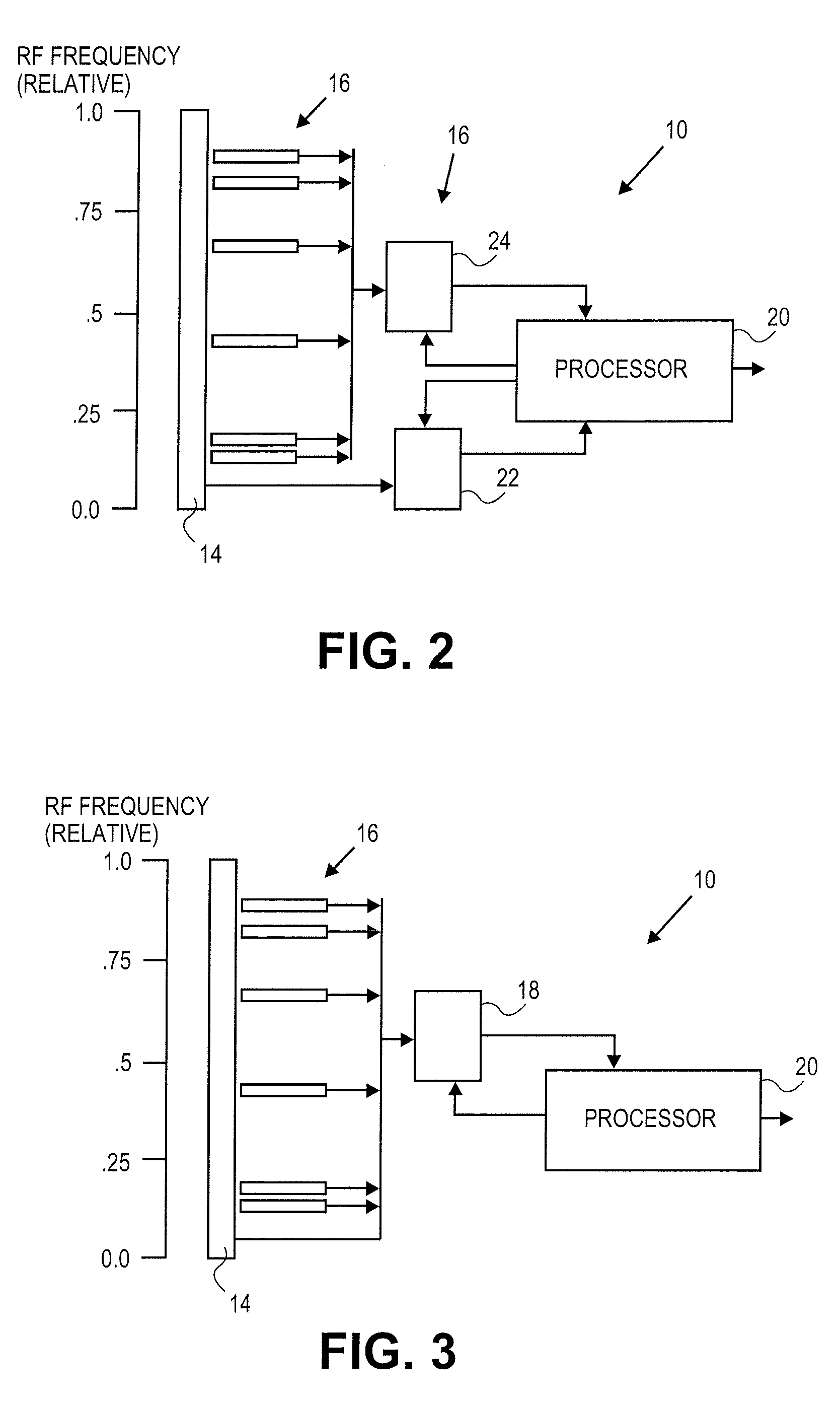
System and method for effectively rendering high dynamic range images
InactiveUS6993200B2High imagingEffectively renderingImage enhancementImage analysisComputer graphics (images)Image conversion
A system and method for rendering high dynamic range images includes a rendering manager that divides an original luminance image into a plurality of original subband images. The rendering manager converts the original subband images into original contrast images which are converted into original perceived contrast images. The rendering manager performs a compression procedure upon the original perceived contrast images to produce compressed perceived contrast images. The rendering manager converts the compressed perceived contrast images into compressed contrast images which are converted into compressed subband images. The rendering manager performs a subband combination procedure for combining the compressed subband images together with a lowest-frequency subband image to generate a rendered luminance image. The rendering manager may combines the rendered luminance image with corresponding chrominance information to generate a rendered composite image.
Owner:SONY CORP +1
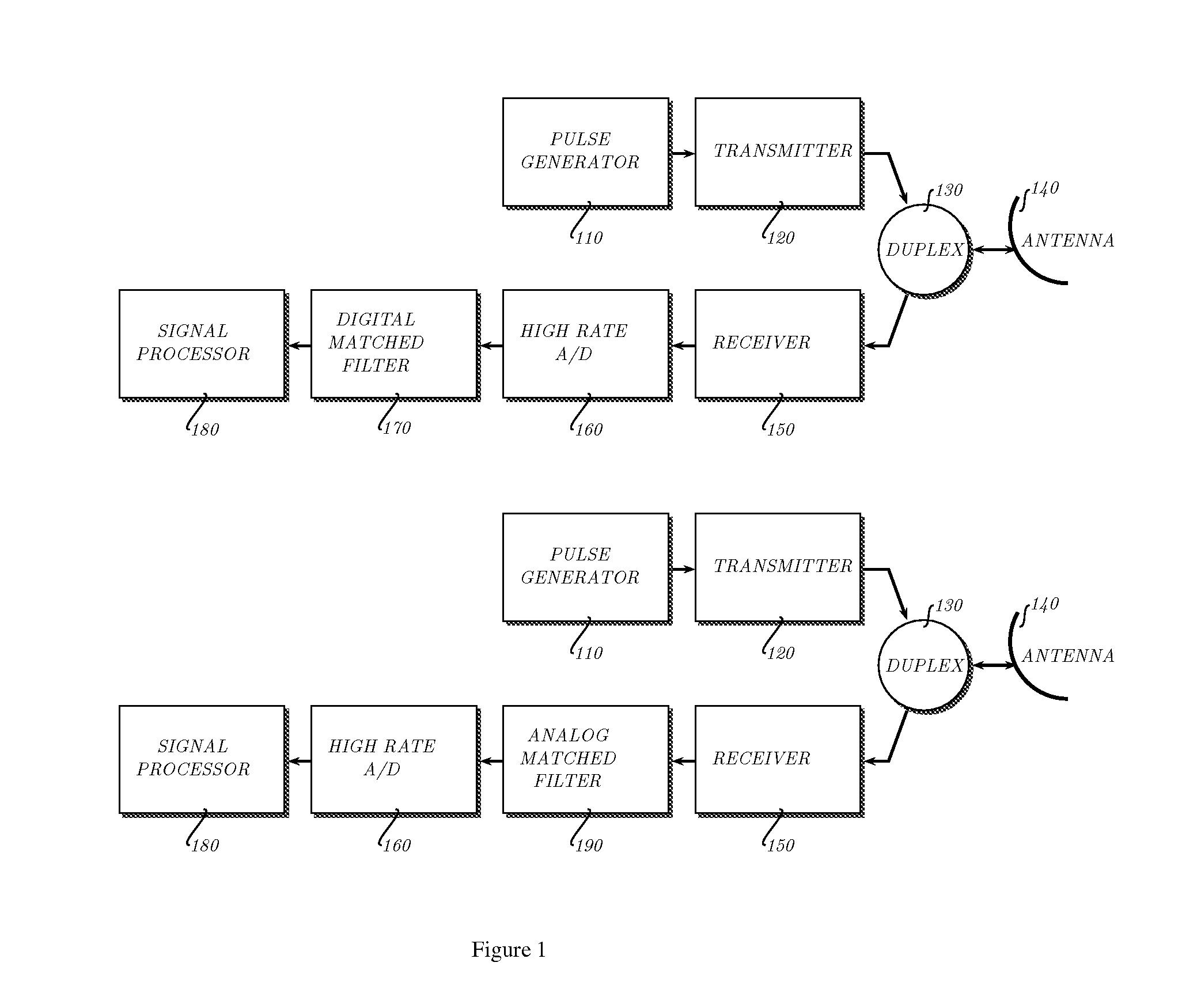
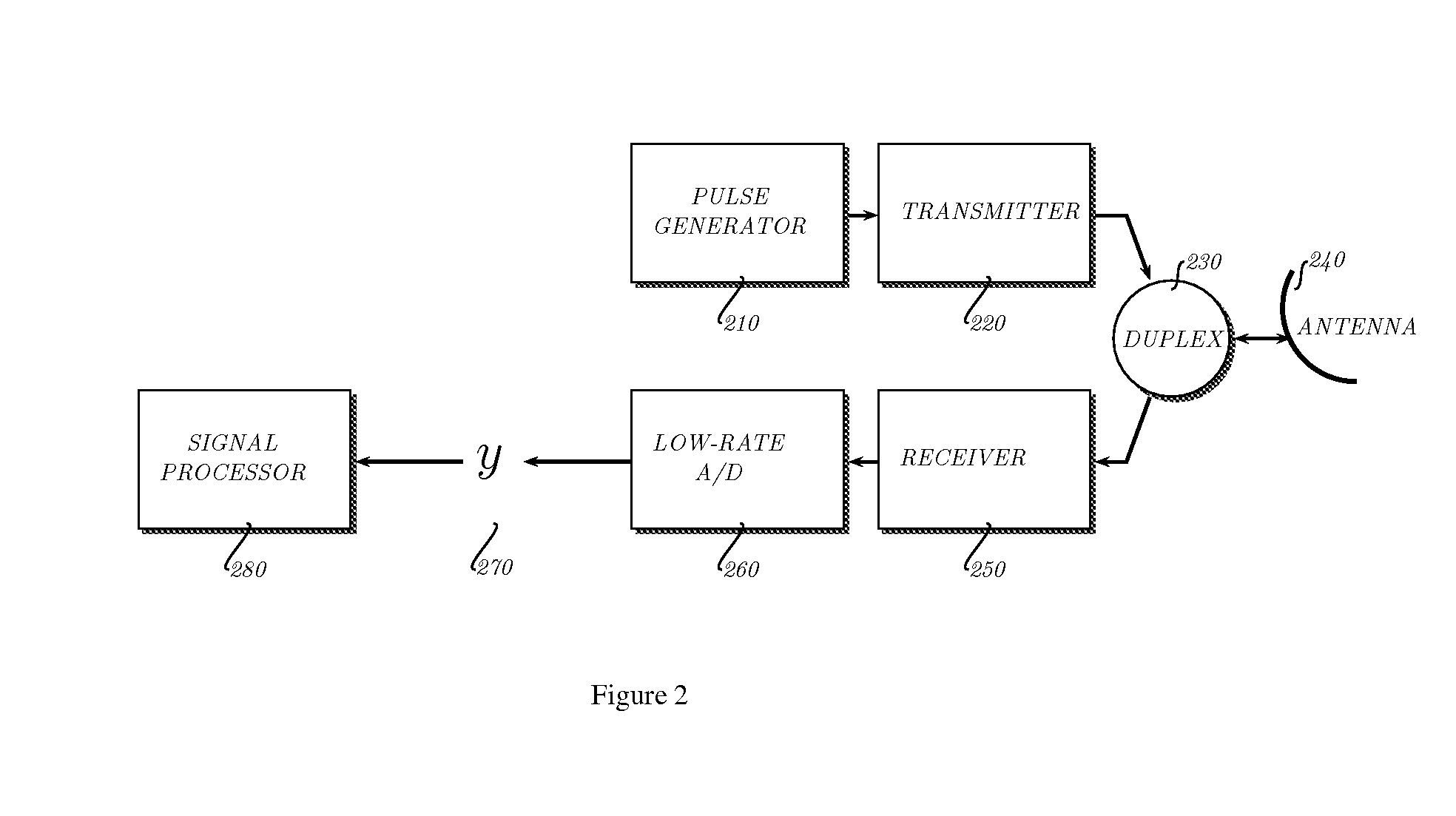
Method and Apparatus for On-Line Compressed Sensing
ActiveUS20090222226A1Improve system performanceAnalogue/digital conversionError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsHigh rateDiscrete-time signal
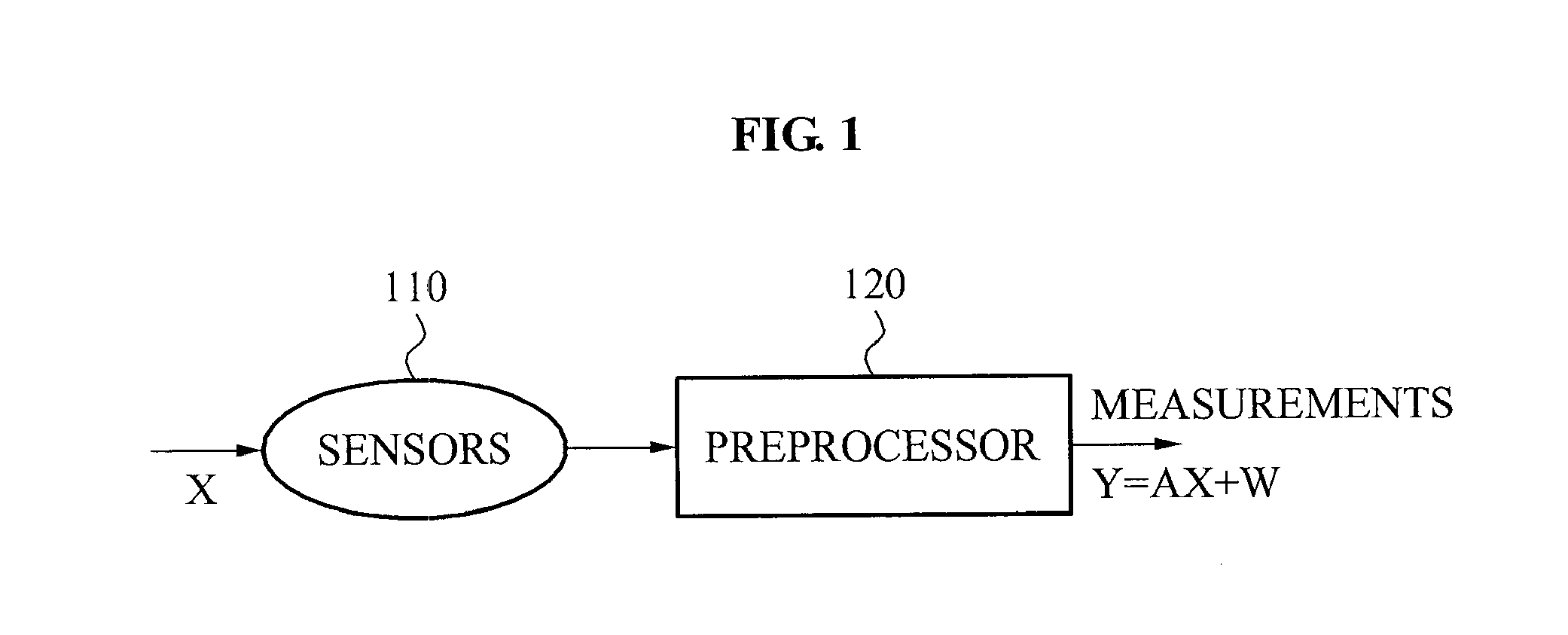
A typical data acquisition system takes periodic samples of a signal, image, or other data, often at the so-called Nyquist / Shannon sampling rate of two times the data bandwidth in order to ensure that no information is lost. In applications involving wideband signals, the Nyquist / Shannon sampling rate is very high, even though the signals may have a simple underlying structure. Recent developments in mathematics and signal processing have uncovered a solution to this Nyquist / Shannon sampling rate bottlenck for signals that are sparse or compressible in some representation. We demonstrate and reduce to practice methods to extract information directly from an analog or digital signal based on altering our notion of sampling to replace uniform time samples with more general linear functionals. One embodiment of our invention is a low-rate analog-to-information converter that can replace the high-rate analog-to-digital converter in certain applications involving wideband signals. Another embodiment is an encoding scheme for wideband discrete-time signals that condenses their information content.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN +1
Method and apparatus for distributed compressed sensing
ActiveUS7271747B2Efficient captureAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceCode conversionCompressed sensingComputer science
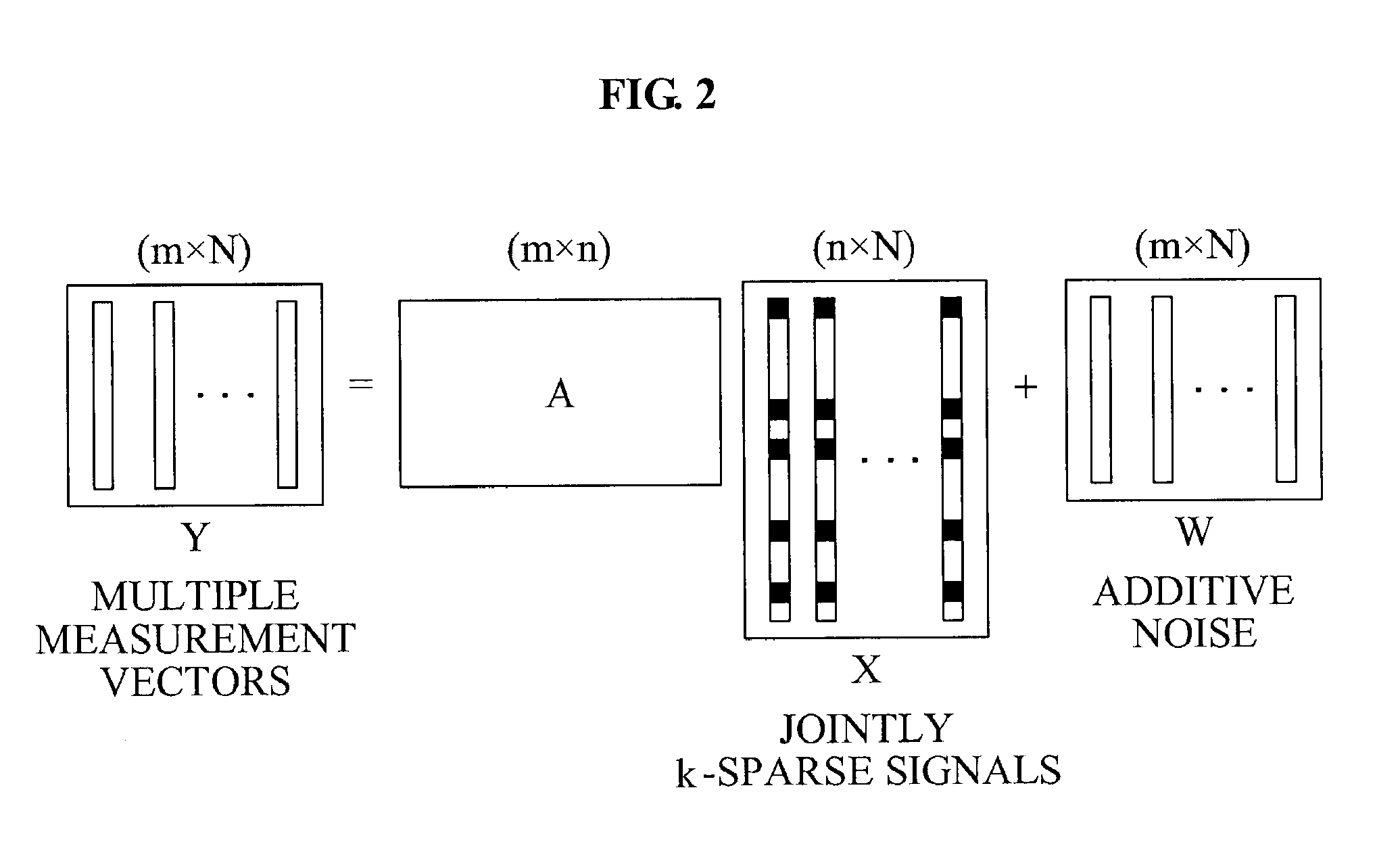
A method for approximating a plurality of digital signals or images using compressed sensing. In a scheme where a common component xc of said plurality of digital signals or images an innovative component xi of each of said plurality of digital signals each are represented as a vector with m entries, the method comprises the steps of making a measurement yc, where yc comprises a vector with only ni entries, where ni is less than m, making a measurement yi for each of said correlated digital signals, where yi comprises a vector with only ni entries, where ni is less than m, and from each said innovation components yi, producing an approximate reconstruction of each m-vector xi using said common component yc and said innovative component yi.
Owner:RICE UNIV
Method and apparatus for compressed sensing
ActiveUS20060029279A1Reduce in quantityImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionM-matrixCompressed sensing
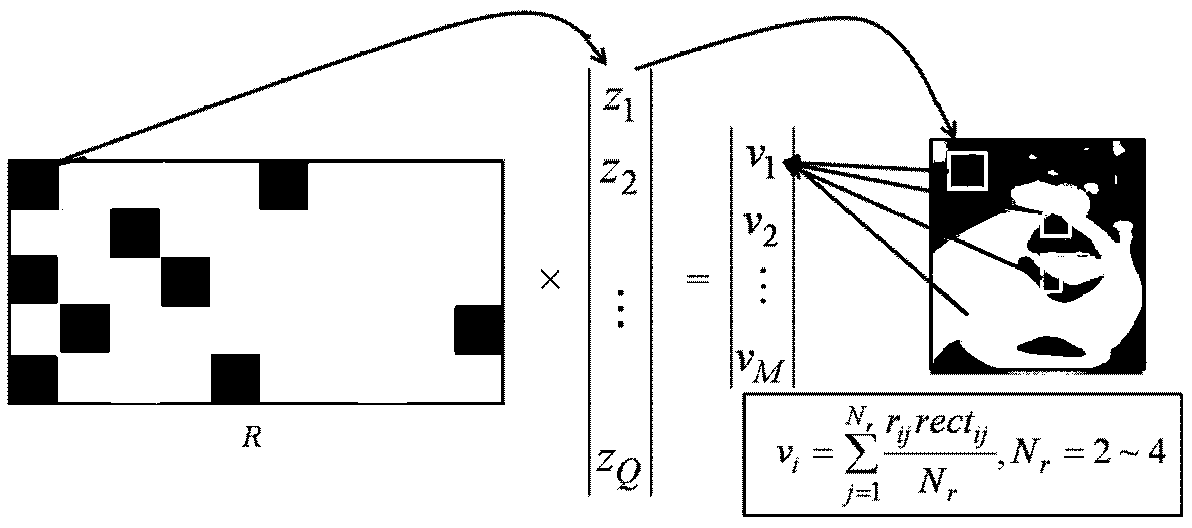
The invention provides a method and apparatus for making reduced numbers of measurements compared to current practice and still give acceptable quality reconstructions of the object of interest. In one embodiment, a digital signal or image is approximated using significantly fewer measurements than with traditional measurement schemes. A component x of the signal or image can be represented as a vector with m entries; traditional approaches would make m measurements to determine the m entries. The disclosed technique makes measurements y comprising a vector with only n entries, where n is less than m. From these n measurements, the disclosed invention delivers an approximate reconstruction of the m-vector x. In another embodiment, special measurement matrices called CS-matrices are designed for use in connection with the embodiment described above. Such measurement matrices are designed for use in settings where sensors can allow measurements y which can be represented as y=Ax+z, with y the measured m-vector, x the desired n-vector and z an m-vector representing noise. Here, A is an n by m matrix, i.e. an array with fewer rows than columns. A technique is disclosed to design matrices A which support delivery of an approximate reconstruction of the m-vector x, described above. Another embodiment of the invention discloses approximate reconstruction of the vector x from the reduced-dimensionality measurement y within the context of the embodiment described above. Given the measurements y, and the CS matrix A, the invention delivers an approximate reconstruction x# of the desired signal x. This embodiment is driven by the goal of promoting the approximate sparsity of x#.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Apparatus and Method for Compressive Sensing Radar Imaging
Method and apparatus for developing radar scene and target profiles based on Compressive Sensing concept. An outgoing radar waveform is transmitted in the direction of a radar target and the radar reflectivity profile is recovered from the received radar wave sequence using a compressible or sparse representation of the radar reflectivity profile in combination with knowledge of the outgoing wave form. In an exemplary embodiment the outgoing waveform is a pseudo noise sequence or a linear FM waveform.
Owner:RICE UNIV
Method and apparatus for compressed sensing
ActiveUS7646924B2Image enhancementReconstruction from projectionArray data structureComputer science
Method and apparatus for compressed sensing yields acceptable quality reconstructions of an object from reduced numbers of measurements. A component x of a signal or image is represented as a vector having m entries. Measurements y, comprising a vector with n entries, where n is less than m, are made. An approximate reconstruction of the m-vector x is made from y. Special measurement matrices allow measurements y=Ax+z, where y is the measured m-vector, x the desired n-vector and z an m-vector representing noise. “A” is an n by m matrix, i.e. an array with fewer rows than columns. “A” enables delivery of an approximate reconstruction, x#, of x. An embodiment discloses approximate reconstruction of x from the reduced-dimensionality measurement y. Given y, and the matrix A, x# of x is possible. This embodiment is driven by the goal of promoting the approximate sparsity of x#.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
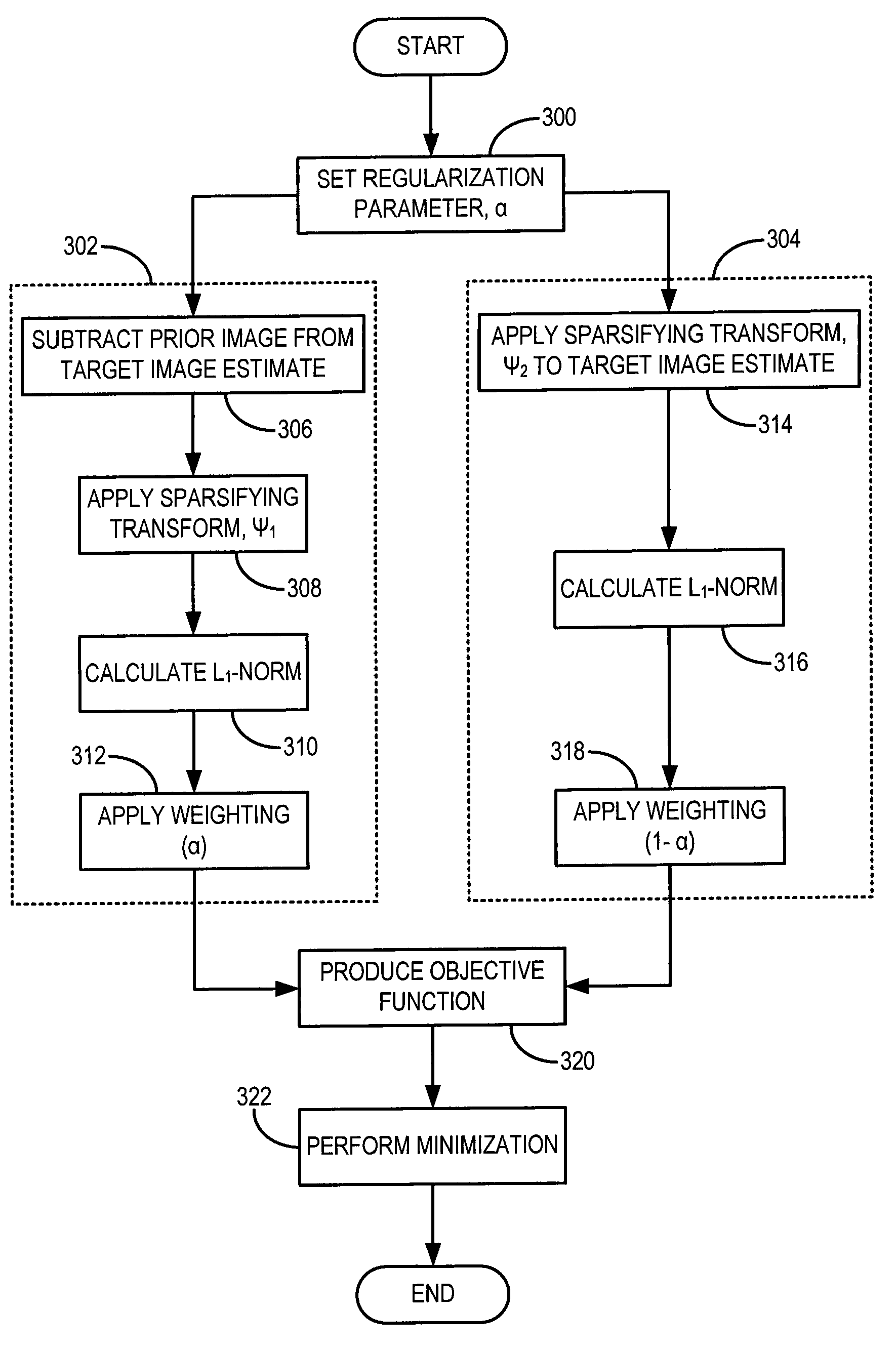
Method for dynamic prior image constrained image reconstruction
ActiveUS20090161933A1Improve signal-to-noise ratioHigh resolutionReconstruction from projectionCharacter and pattern recognitionDiagnostic Radiology ModalityTemporal resolution
A method for reconstructing a high quality image from undersampled image data is provided. The image reconstruction method is applicable to a number of different imaging modalities. Specifically, the present invention provides an image reconstruction method that incorporates an appropriate prior image into the image reconstruction process. Thus, one aspect of the present invention is to provide an image reconstruction method that requires less number of data samples to reconstruct an accurate reconstruction of a desired image than previous methods, such as, compressed sensing. Another aspect of the invention is to provide an image reconstruction method that produces a time series of desired images indicative of a higher temporal resolution than is ordinarily achievable with the imaging system. For example, cardiac phase images can be produced with high temporal resolution (e.g., 20 milliseconds) using a CT imaging system with a slow gantry rotation speed.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
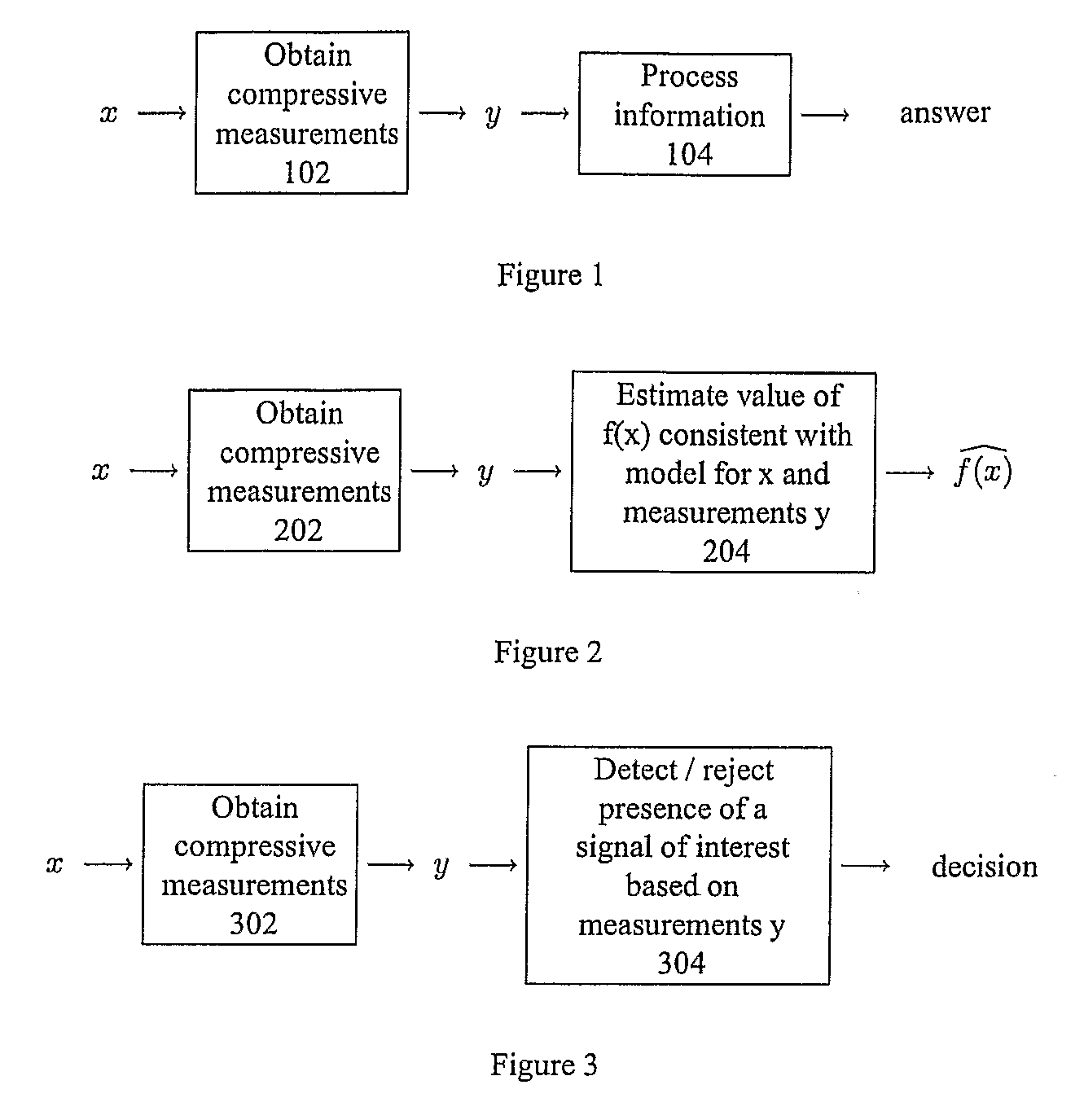
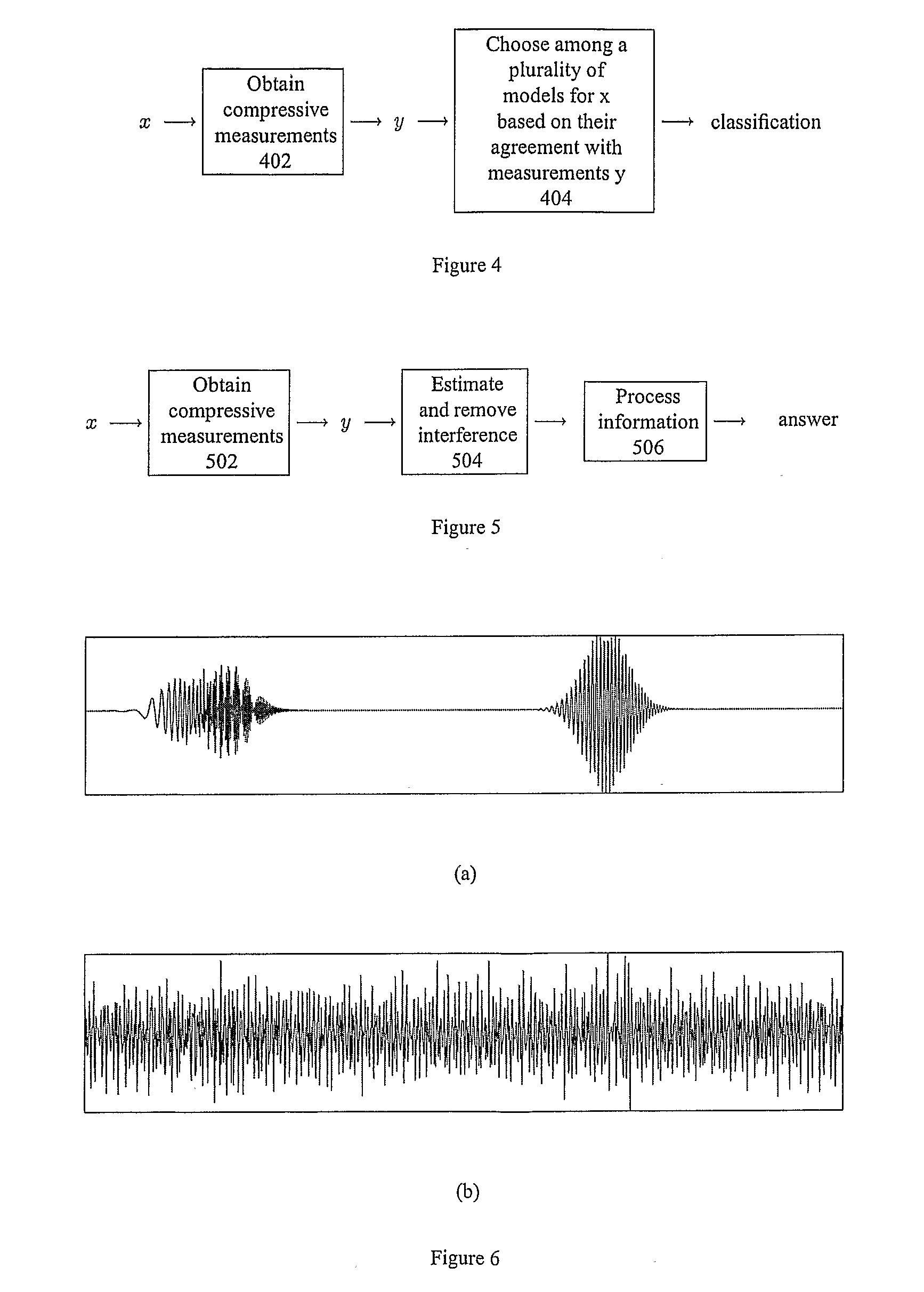
Method and Apparatus for Signal Detection, Classification and Estimation from Compressive Measurements
ActiveUS20080228446A1Amplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceDigital computer detailsDecision takingSignal restoration
The recently introduced theory of Compressive Sensing (CS) enables a new method for signal recovery from incomplete information (a reduced set of “compressive” linear measurements), based on the assumption that the signal is sparse in some dictionary. Such compressive measurement schemes are desirable in practice for reducing the costs of signal acquisition, storage, and processing. However, the current CS framework considers only a certain task (signal recovery) and only in a certain model setting (sparsity).We show that compressive measurements are in fact information scalable, allowing one to answer a broad spectrum of questions about a signal when provided only with a reduced set of compressive measurements. These questions range from complete signal recovery at one extreme down to a simple binary detection decision at the other. (Questions in between include, for example, estimation and classification.) We provide techniques such as a “compressive matched filter” for answering several of these questions given the available measurements, often without needing to first reconstruct the signal. In many cases, these techniques can succeed with far fewer measurements than would be required for full signal recovery, and such techniques can also be computationally more efficient. Based on additional mathematical insight, we discuss information scalable algorithms in several model settings, including sparsity (as in CS), but also in parametric or manifold-based settings and in model-free settings for generic statements of detection, classification, and estimation problems.
Owner:RICE UNIV
Recursive sparse reconstruction
A method for real-time reconstruction is provided. The method includes receiving a sparse signal sequence one at a time and performing compressed sensing on the sparse signal sequence in a manner which causally estimates a time sequence of spatially sparse signals and generates a real-time reconstructed signal. Recursive algorithms provide for causally reconstructing a time sequence of sparse signals from a greatly reduced number of linear projection measurements.
Owner:IOWA STATE UNIV RES FOUND
Method and apparatus for compressed sensing
InactiveUS7289049B1Electric signal transmission systemsCurrent/voltage measurementComputer scienceCompressed sensing
Embodiments of the present invention provide a method and apparatus for compressed sensing. The method generally comprises forming a first compressed sensing matrix utilizing a first set of time indices corresponding to a first sampling rate, forming a second compressed sensing matrix utilizing a plurality of frequencies and a second set of time indices corresponding to a second sampling rate, forming a combined compressed sensing matrix from the first compressed sensing matrix and the second compressed sensing matrix, and reconstructing at least a portion of the input signal utilizing the combined compressed sensing matrix. The first and second sampling rates are each less than the Nyquist sampling rate for the input signal.
Owner:L 3 COMM CORP
Method for estimating discontinuous orthogonal frequency division multiplying channel based on compressed sensing
InactiveCN101984612AFlexible placementEasy to chooseBaseband system detailsMulti-frequency code systemsCarrier signalEngineering
The invention discloses a method for estimating a discontinuous orthogonal frequency division multiplying channel based on compressed sensing. The method comprises the steps of: designing a channel estimating pilot pattern, selecting a pilot pattern and estimating a channel frequency domain response. The pilot pattern is selected by using two schemes. The first scheme is to maintain a traditional uniform pilot pattern and automatically disable a pilot at a disabled sub-carrier in order that an available pilot presents a natural non-homogeneity. The second scheme is to fix the quantity of the pilots and utilize the following optimized problems to search P sub-carrier transporting pilot marks in the available sub-carrier based on a criterion of recovering matrixes correlation minimization, wherein L is the channel length, P is the number of pilots, and N is the total number of OFDM system sub-carriers. The method of the invention can be applied to various scenes of the disabled sub-carrier. Through the method of the invention with fewer pilots, the acquired channel estimating property and system error ratio property are better than those acquired by using the other methods in prior art.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
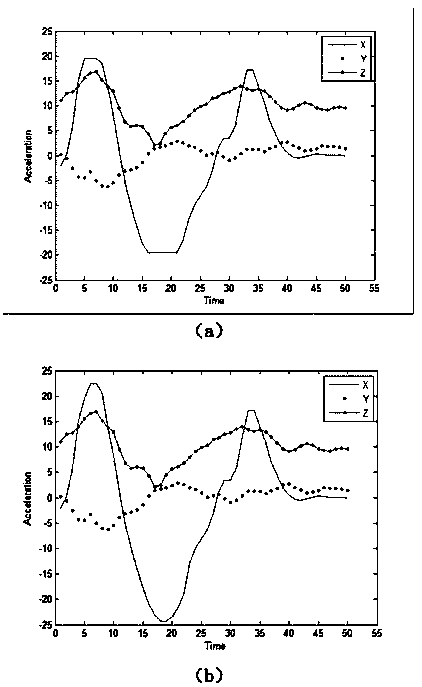
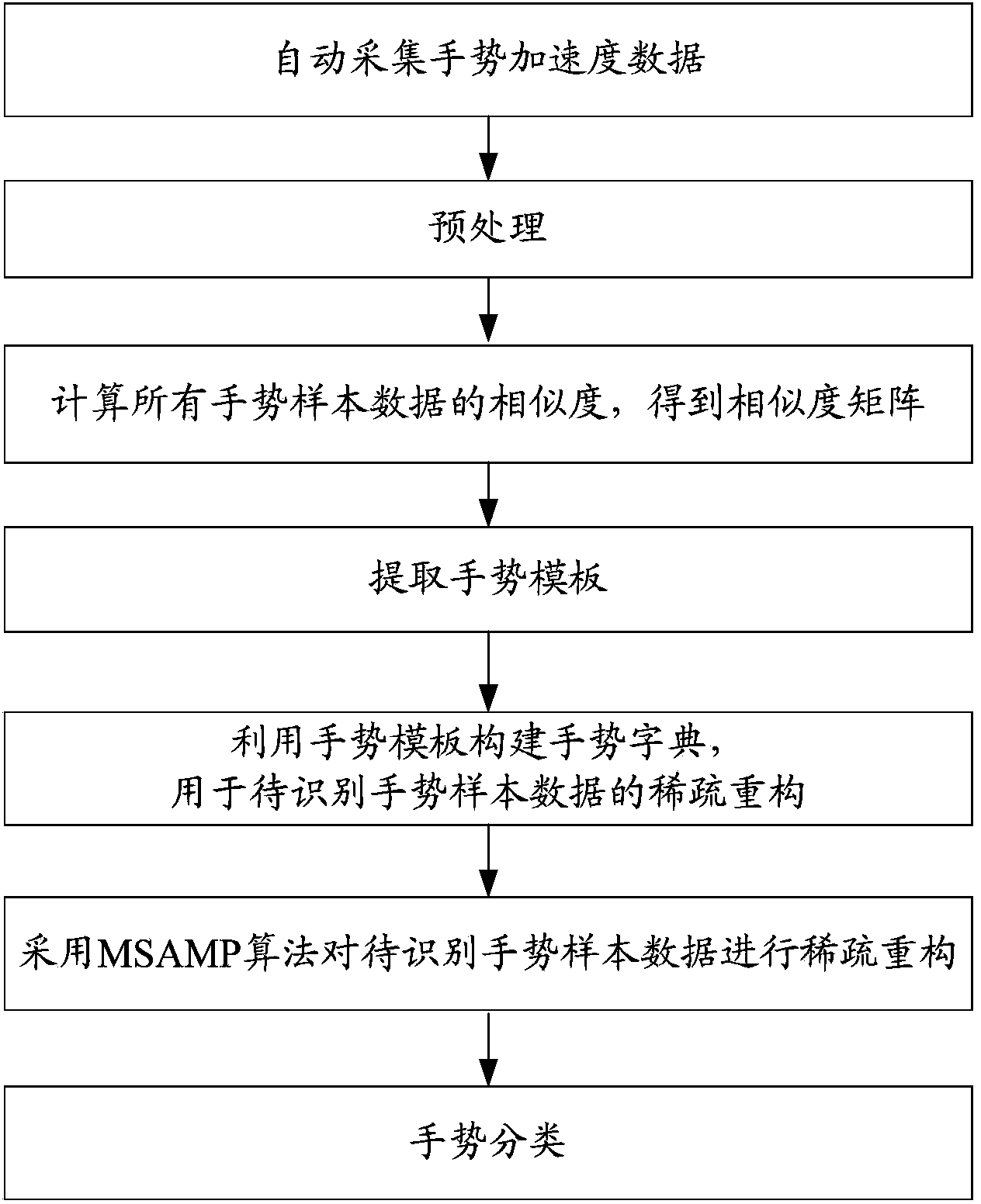
Gesture recognition method based on acceleration sensor
InactiveCN103984416ASmooth waveformWaveform Regularization and UnificationInput/output for user-computer interactionCharacter and pattern recognitionAdaptive matchingCompressed sensing
The invention discloses a gesture recognition method based on an acceleration sensor. The gesture recognition method based on an acceleration sensor comprises the following steps: automatically collecting gesture acceleration data, preprocessing, calculating the similarity of all gesture sample data so as to obtain a similarity matrix, extracting a gesture template, constructing a gesture dictionary by utilizing the gesture template, and carrying out sparse reconstruction and gesture classification on the gesture sample data to be recognized by adopting an MSAMP (modified sparsity algorithm adaptive matching pursuit) algorithm. According to the invention, the compressed sensing technique and a traditional DTW (dynamic time warping) algorithm are combined, and the adaptability of the gesture recognition to different gesture habits is improved, and by adopting multiple preprocessing methods, the practicability of the gesture recognition method is improved. Additionally, the invention also discloses an automatic collecting algorithm of the gesture acceleration data; the additional operation of traditional gesture collection is eliminated; the user experience is improved; according to the invention, a special sensor is not required, the gesture recognition method based on the acceleration sensor can be used for terminals carried with the acceleration sensor; the hardware adaptability is favorable, and the practicability of the recognition method is enhanced. The coordinate system is uniform, and can be adaptive to different multiple gesture habits.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Method and apparatus for compressed sensing with joint sparsity
InactiveUS20120259590A1Amplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceCode conversionRobustificationEngineering
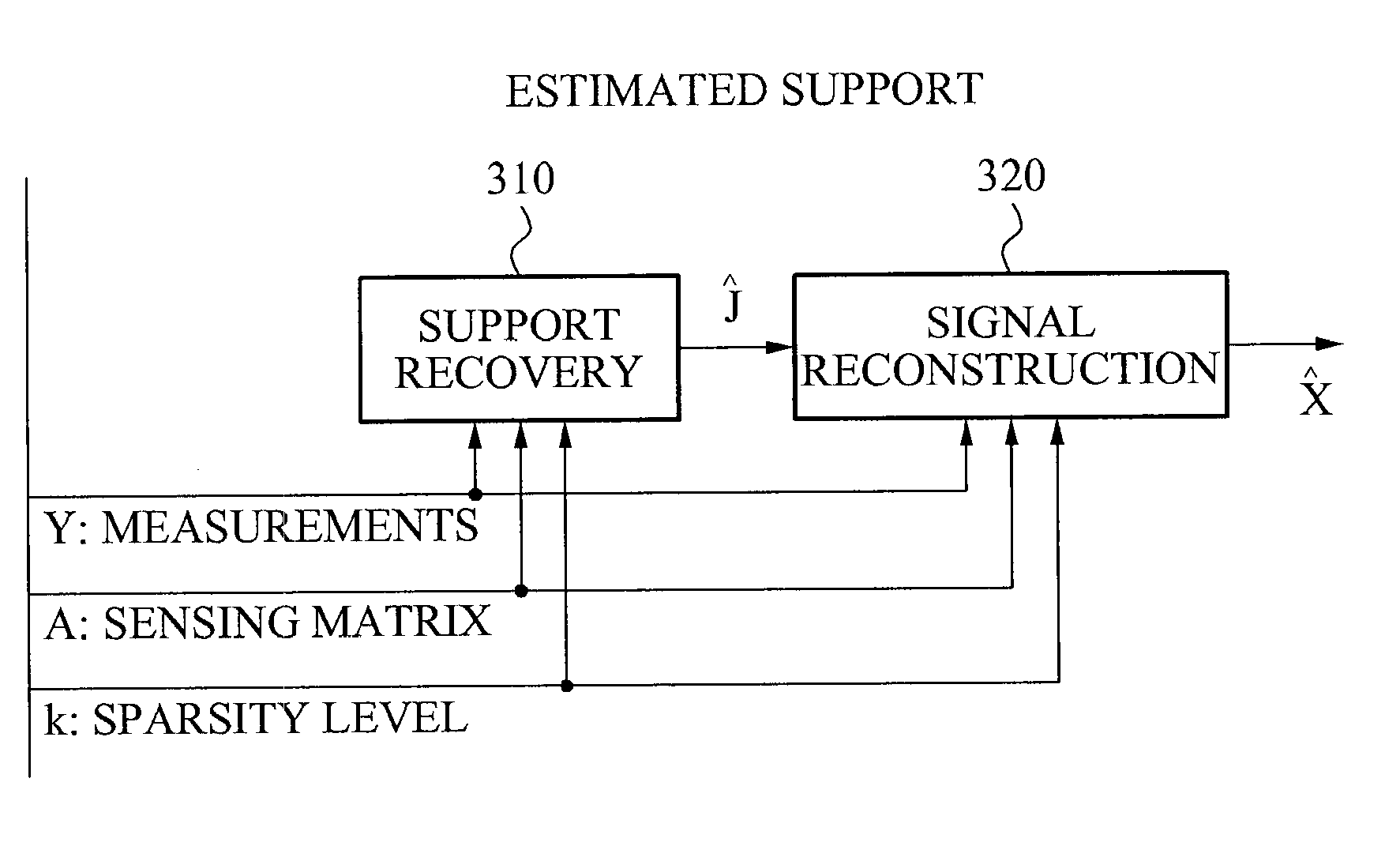
Provided is a method and apparatus for support recovery of jointly sparse signals from a plurality of snapshots, thereby enhancing a capability for reconstructing a support in a variety of circumstances, by providing enhanced robustness against noise and perturbation, and / or enhanced computational efficiency. The method may include partial support recovery using a compressed sensing-multiple measurement vector (CS-MMV) scheme; and a complementary support recovery and sparsity level estimation. The complementary support recovery may use subspace information extracted from the plurality of snapshots and partial support information. The total number of elements in the partial support and in the complementary support may be equal to the sparsity level.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
Rapid magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) method based on CS ( compressed sensing ) technique
InactiveCN101975936AReduce acquisition timeSolve the inconsistency that full random sampling does not work on real hardwareMagnetic measurementsLow speedData acquisition
The invention discloses a rapid magnetic resonance imaging method based on a CS (compressed sensing) technique. The traditional imaging method has relatively low speed and high hardware cost. The method comprises the following steps of: firstly, acquiring variable-density random k spatial data; specifically, determining under sampling rate according to the structural sparsity of an image; carrying out sparse acquisition in a k-space central area and carrying out random sparse acquisition in a k-space peripheral area according to the under sampling rate by combining with the k-space energy distribution rule to generate a variable-density random data acquisition path; acquiring the data according to the determined data acquisition path; then carrying out sparse conversion on an MRI image; and finally, nonlinearly optimizing and reconstructing the image based on Li norm minimum. The method breaks through the limit of the classical Nyguist sampling theorem, accurately reconstructs the signal of the MRI image through randomly acquiring few data points by utilizing a nonlinear optimization algorithm and greatly shortens the data acquisition time.
Owner:HANGZHOU DIANZI UNIV
Autocalibrating parallel imaging reconstruction method from arbitrary k-space sampling with reduced noise
ActiveUS20120092009A1Measurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionParallel imagingReconstruction method
A computer implemented method for magnetic resonance imaging is provided. A 3D Fourier Transform acquisition is performed with two phase encode directions, wherein phase code locations are chosen so that a total number of phase encodes is less than a Nyquist rate, and closest distances between phase encode locations takes on a multiplicity of values. Readout signals are received through a multi-channel array of a plurality of receivers. An autocalibrating parallel imaging interpolation is performed and a noise correlation is generated. The noise correlation is used to weight a data consistency term of a compressed sensing iterative reconstruction. An image is created from the autocalibration parallel imaging using the weighted data consistency term. The image is displayed.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Compression sensing technology-based method for distributed type information source coding
InactiveCN101742313AEasy to operateReduce complexityTelevision systemsDigital video signal modificationPattern recognitionWorkload
The invention provides a compression sensing technology-based method for distributed type information source coding. The advantages of the CS technology and the sparse characteristics of video images are adopted in a process of realizing the distributed type information source coding DSC to form a novel distributed type information source coding method, namely in the corresponding operational steps of the DSC process, the CS technology is adopted to process the video image data and execute the corresponding recovery processing which comprises using the CS operation and the sparse reconstruction of the CS to replace the data sampling and the DCT transformation operation and the DCT inverse transformation in the conventional information source coding respectively so as to use much less measuring data to reconstruct a video image source, reduce a sampling speed ratio and memory burden of the system, reinforce the robustness of the system and realize the construction of the distributed type information source coding in three different structures. The method has the advantages of reducing the sampling rate and the operating complexity of the system, obviously reducing the workload of the data sampling and relative processing and the necessary memory space, improving the robustness of the system and reducing the speed rate of data transmission.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Method and Apparatus for Distributed Compressed Sensing
ActiveUS20070027656A1Efficient captureAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceDigital computer detailsComputer scienceCompressed sensing
A method for approximating a plurality of digital signals or images using compressed sensing. In a scheme where a common component xc of said plurality of digital signals or images an innovative component xi of each of said plurality of digital signals each are represented as a vector with m entries, the method comprises the steps of making a measurement yc, where yc comprises a vector with only ni entries, where ni is less than m, making a measurement yi for each of said correlated digital signals, where yi comprises a vector with only ni entries, where ni is less than m, and from each said innovation components yi, producing an approximate reconstruction of each m-vector xi using said common component yc and said innovative component yi.
Owner:RICE UNIV
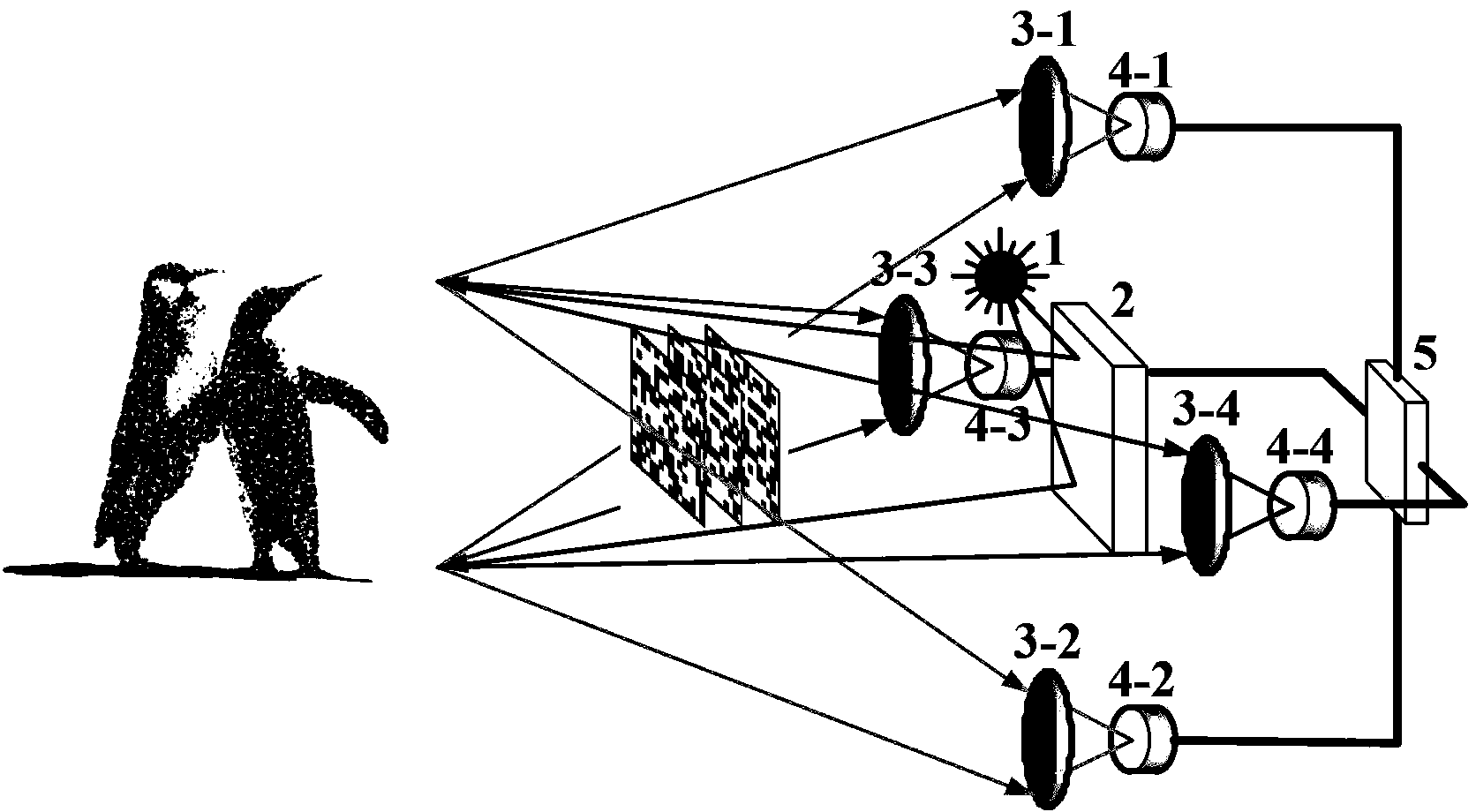
Compressing three-dimension calculation ghost imaging system and method
ActiveCN103363924AReduce redundancyReduce complexityUsing optical meansOptical elementsSpatial light modulatorSurface gradient
The invention relates to a compressing three-dimension calculation ghost imaging system. The system comprises a light source, a spatial light modulator, at least four sets of convergence light receiving lenses, at least four sets of point detectors corresponding to the convergence light receiving lenses and an algorithm module. Light emitted by the light source is projected on the spatial light modulator, the spatial light modulator modulates the light randomly, the modulated light is projected on an object, the object reflects the light in different directions, and one set of convergence light receiving lens and point detector are arranged in each of at least four reflecting directions. Total light intensity in all the directions are compressed and sampled by the point detectors, a compressing and sampling result is input into the algorithm module, the processes of the compression and sampling of the total light intensity and the input of the result are repeated for many times, the spatial light modulator modulates different patterns every time, the algorithm module inverts a two-dimension image corresponding to the direction of each point detector by the application of the compressed sensing algorithm according to a measurement matrix and the measurement results obtained by the repeated compression and sampling, the information of shadow parts of the images is compared to construct a three-dimension surface gradient, and finally a three-dimension object shape is reconstructed.
Owner:NAT SPACE SCI CENT CAS
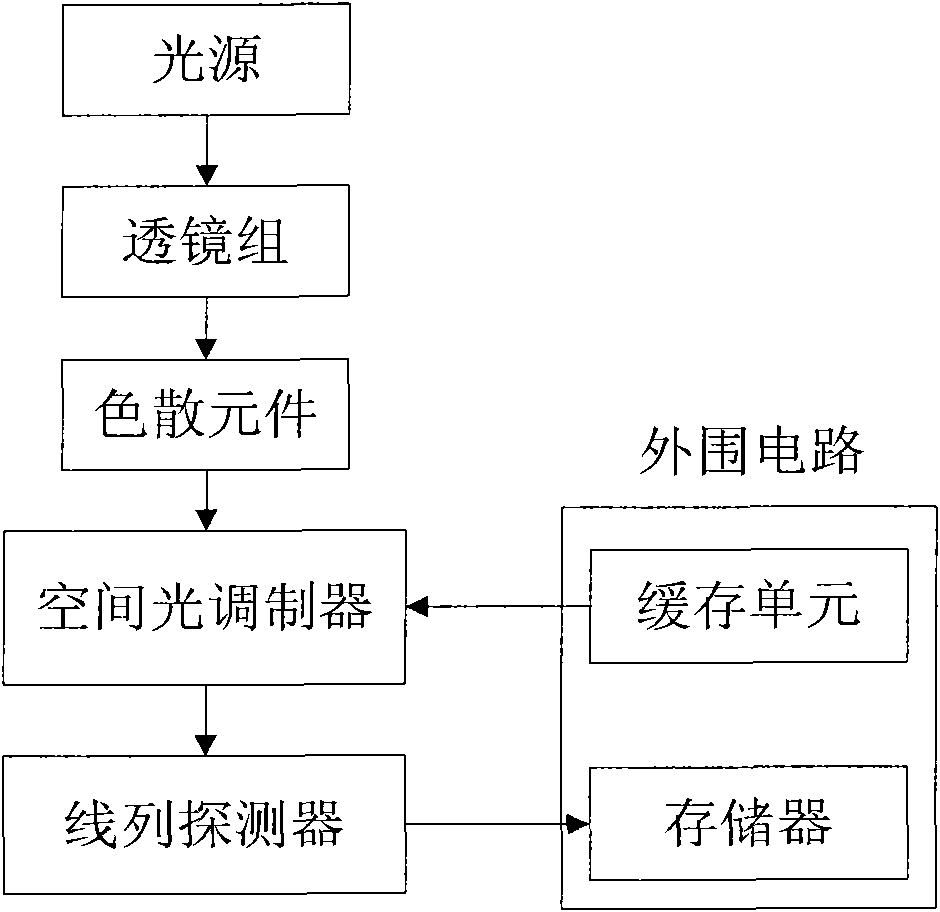
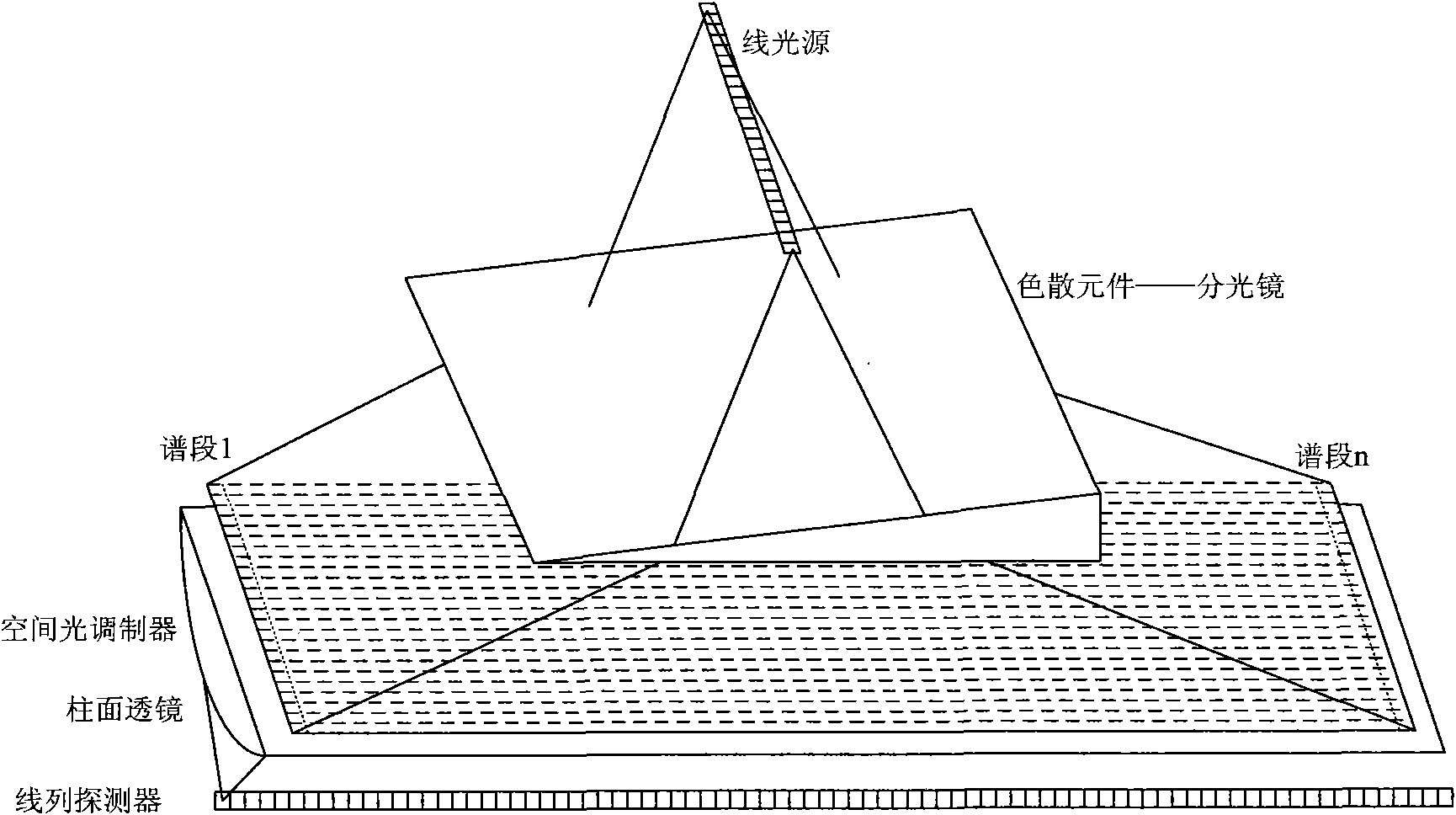
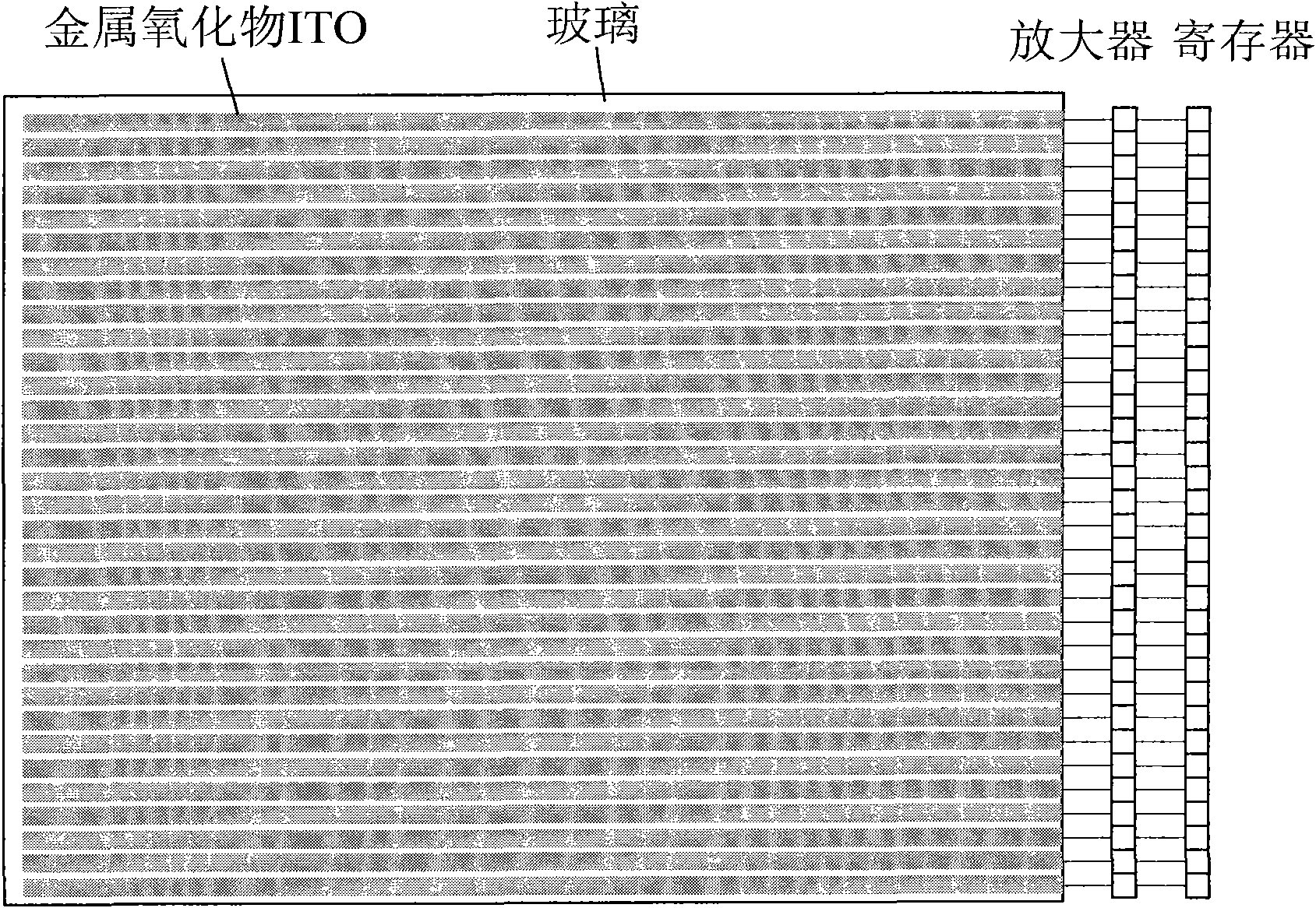
Hyperspectral imager and imaging method based on compressive sensing
InactiveCN101893552AReduce sampling costsReduce computing costSpectrum investigationColor/spectral properties measurementsSpatial light modulatorSpectral dimension
The invention discloses a hyperspectral imager and an imaging method based on compressive sensing, mainly solving the problem that the existing hyperspectral imager has high sampling rate and high sensor realization difficulty. The imager comprises a battery of lens, a dispersive device, a spatial light modulator, a linear detector and a peripheral circuit. The acquired linear light source is split in the space through the dispersive device to form the plane light source formed by spatial dimension and spectral dimension. The plane light source converges again in the direction of spatial dimension after being modulated by the spatial light modulator to form the linear light source formed by spectral dimension. The linear detector completes sampling and quantizing. The imaging method is characterized by utilizing the obtained hyperspectral compressive observation vector to obtain the hyperspectral images through grouping and reconstitution. The hyperspectral imager improves the average reconstitution accuracy of each spectrum by utilizing the joint sparse characteristic among the hyperspectral spectra, has the advantages of simple structure and low cost and is suitable for compressive sensing and imaging of hyperspectra.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Sparse OFDM channel estimation method based on generalized orthogonal matching tracking algorithm
ActiveCN108322409AImprove estimation accuracyTake full advantage of the coefficient characteristicsBaseband system detailsMulti-frequency code systemsOfdm channel estimationRunning time
The invention discloses a sparse OFDM channel estimation method based on a generalized orthogonal matching tracking algorithm. The method comprises the following steps: step one, translating a channelestimation problem into a problem for reconstructing original signal based on the compressed sensing theory; step two, designing a measurement matrix; and step three, reconstructing the original signal by using the generalized orthogonal matching tracking method so as to finish the channel estimation. The sparse OFDM channel estimation method based on the generalized orthogonal matching trackingalgorithm in the compressed sensing disclosed by the invention comprises the steps of translating the channel estimation problem into the problem for reconstructing original signal based on the compressed sensing theory, designing the measurement matrix and reconstructing the original signal by using the generalized orthogonal matching tracking algorithm. The operation complexity, namely the running time, are greatly reduced, the impulse response of the channel is precisely estimated, the system performance of the OFDM sparse channel estimation is improved so as to improve the signal demodulation quality, and the method has high application value.
Owner:HANGZHOU DIANZI UNIV
Channel estimation method for reducing pilot number by using compression perception in wideband mobile communication
InactiveCN101494627AEffective estimateReduce the number of pilot symbolsMulti-frequency code systemsTransmitter/receiver shaping networksCommunications systemEstimation methods
The invention discloses a signal channel estimating method, which is used for reducing the number of pilot frequencies through compressive sensing in a mobile broadband communicating system, is realized by reducing the required number of pilot frequency symbols in the signal channel estimation of the system as well as on the basis of the principle that the compressive sensing technique can recover sparse signals with less measuring values and the sparse characteristic of the signal channel of the mobile broadband communicating system, and can ensure the signal channel estimation performance of the system. The signal channel estimating method can well solve the defect in the prior art that the sparse characteristic of the signal channel is not considered in the signal channel estimating ways of the prior art and consequently more pilot frequencies consumption is required, and improves the traditional methods as follows: by utilizing the sparse signal channel characteristic, a new signal channel estimating method is designed to reduce the number of pilot frequencies, greatly reduce the energy consumption of the system and ensure effective signal channel estimation. The signal channel estimating method has well popularization and application prospect.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
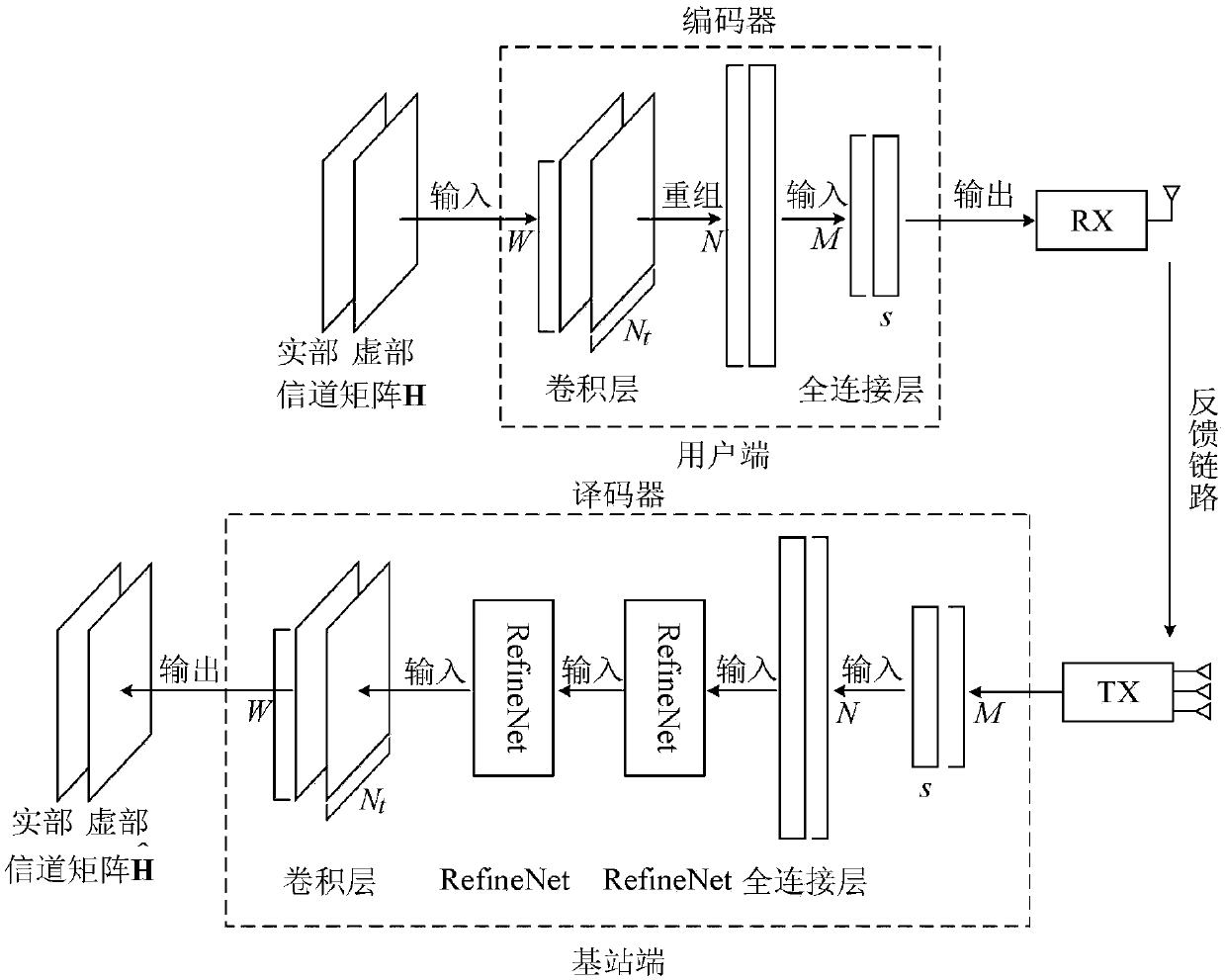
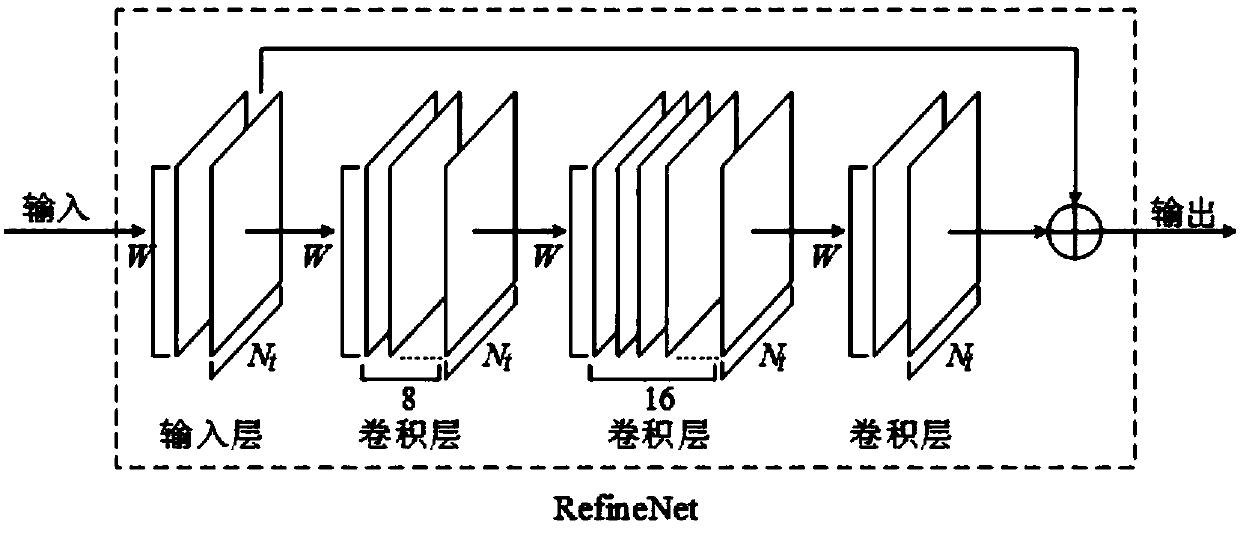
Large-scale MIMO channel state information feedback method based on deep learning
ActiveCN108390706AHigh speedImprove rebuild qualitySpatial transmit diversityFourier transform on finite groupsModel parameters
The invention discloses a large-scale MIMO channel state information feedback method based on deep learning. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, carrying out two-dimensional discrete Fourier transform (DFT) on a channel matrix H-wave of MIMO channel state information in a spatial frequency domain on a user side, so that a channel matrix H which is sparse in an angle delay domain isobtained; secondly, constructing a model CsiNet comprising a coder and a decoder, wherein the coder belongs to the user side and is used for coding the channel matrix H into codons with a lower dimension, and the decoder belongs to a base station side and is used for reconstructing an original channel matrix estimation value H-arrow from the codons; thirdly, training the model CsiNet to obtain model parameters; fourthly, carrying out two-dimensional inverse DFT on a reconstructed channel matrix H-arrow which is output by the CsiNet, so that a reconstructed value of the original channel matrixH-wave in the spatial frequency domain is recovered; and finally, using the trained model CsiNet for compressed sensing and reconstruction of channel information. The method provided by the inventionhas the advantages that large-scale MIMO channel state information feedback expenditures can be reduced, and an extremely high channel reconstruction quality and an extremely high channel reconstruction speed can be achieved.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
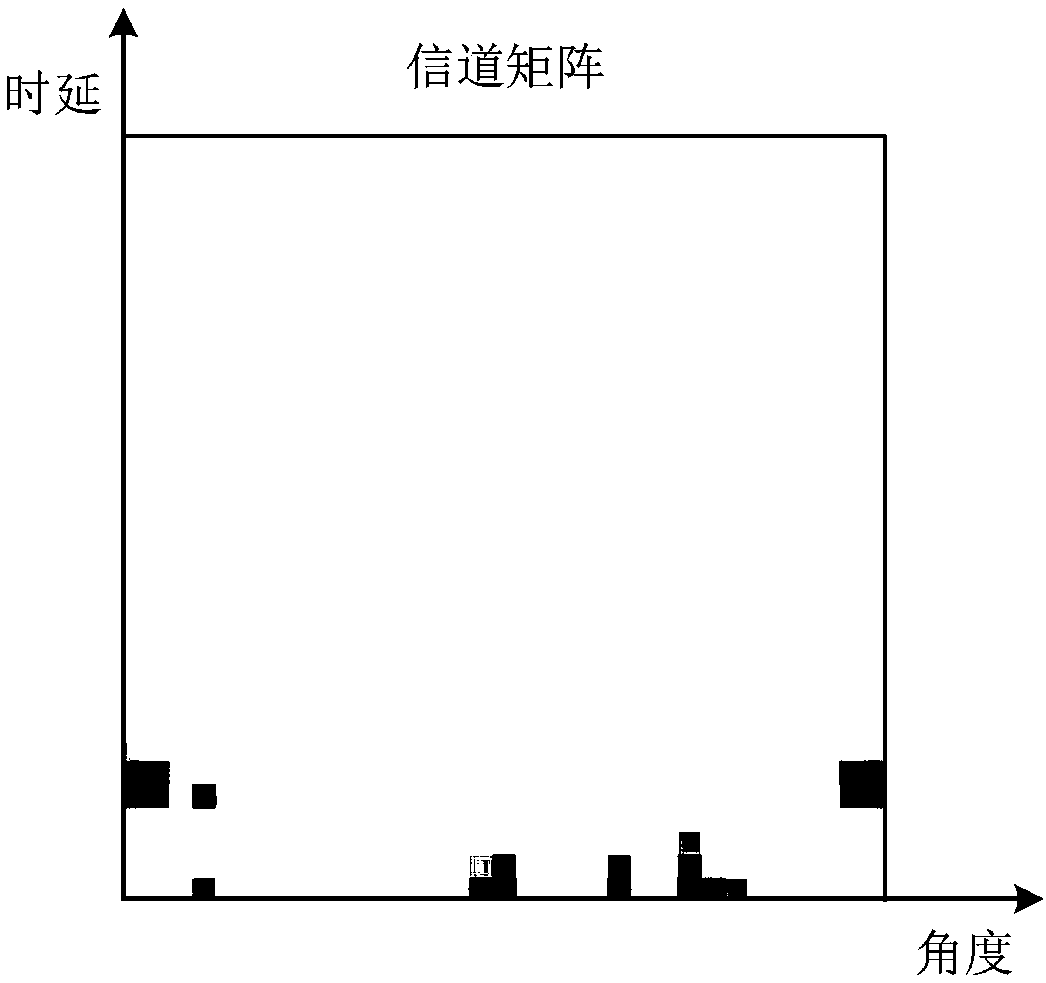
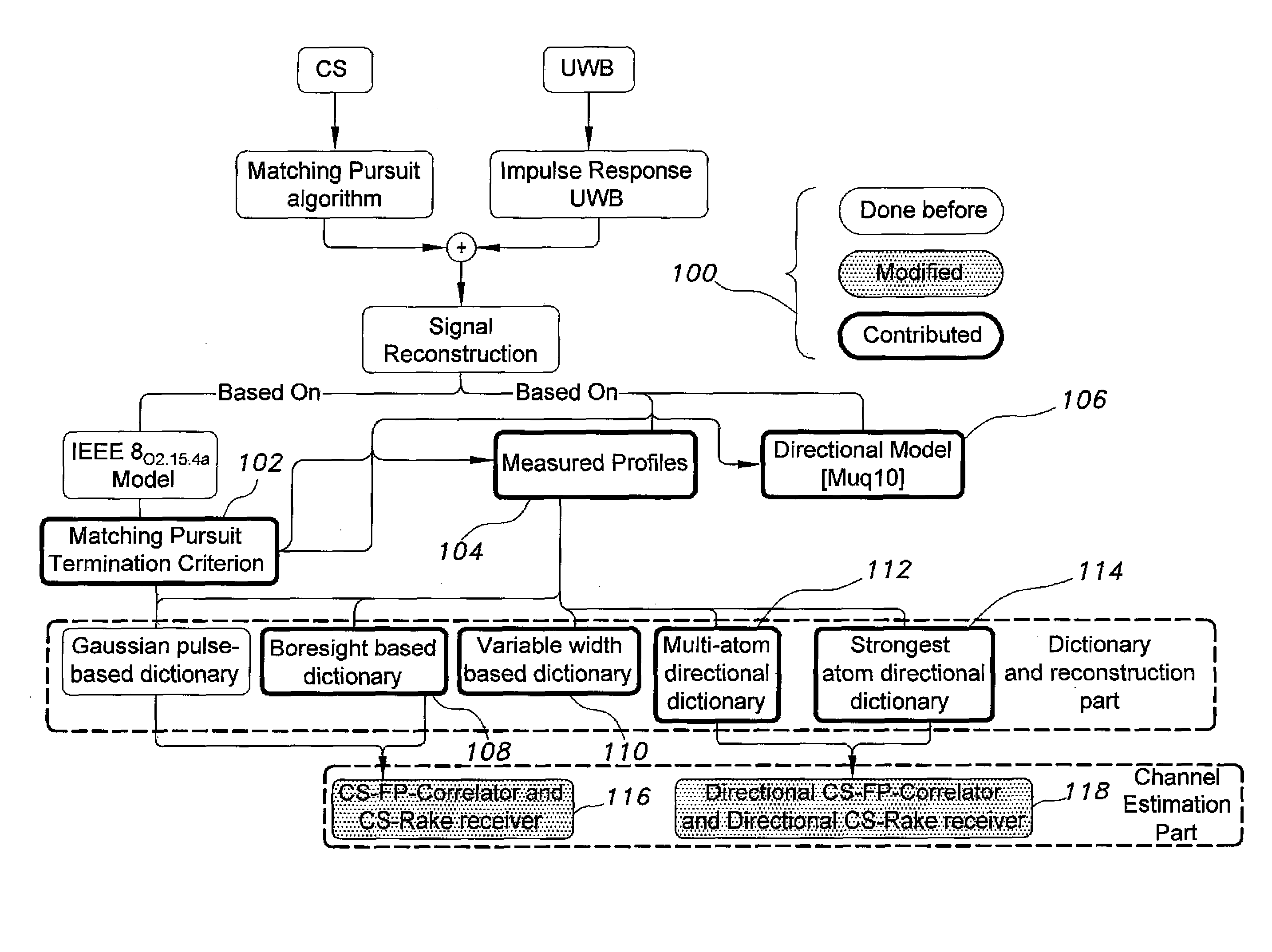
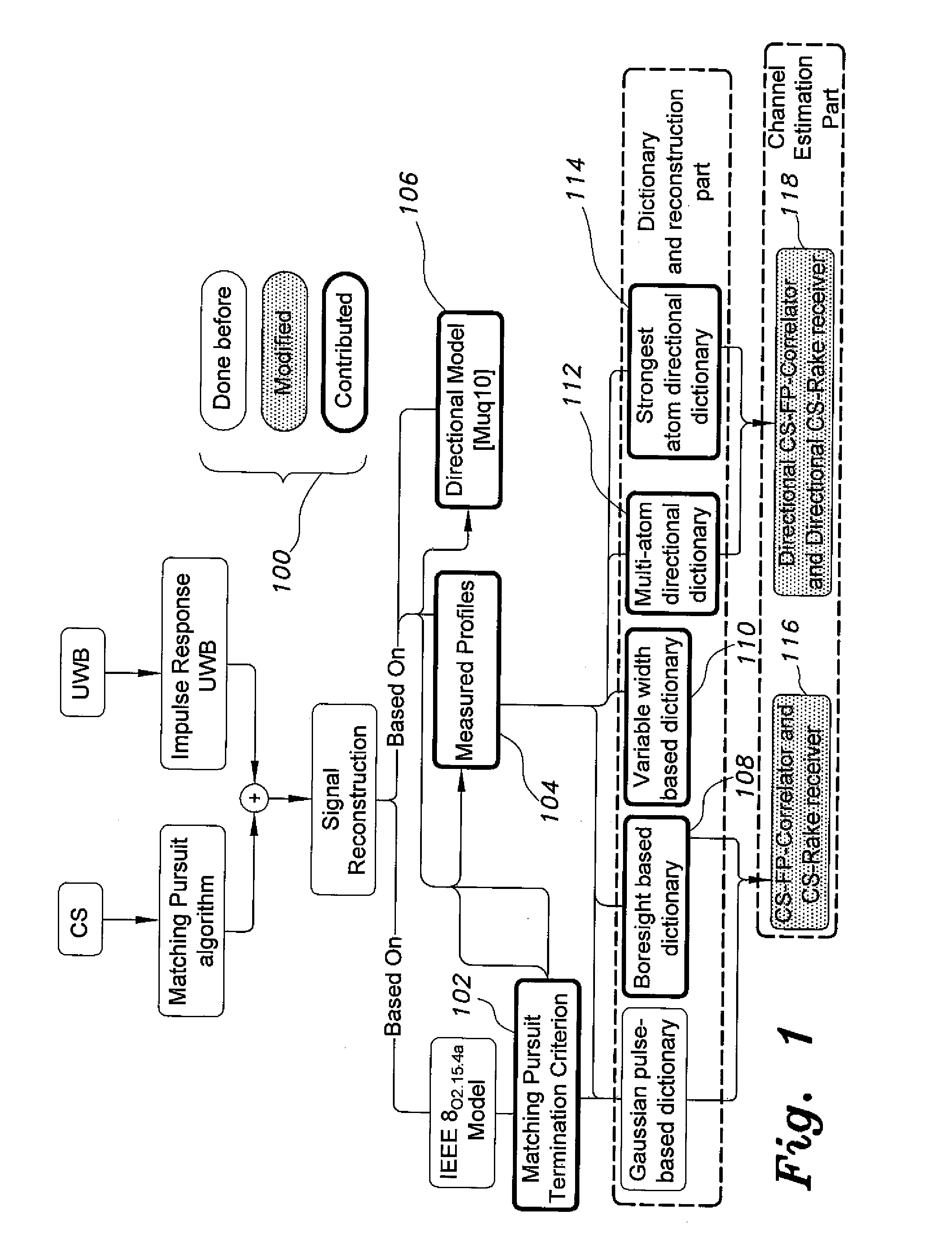
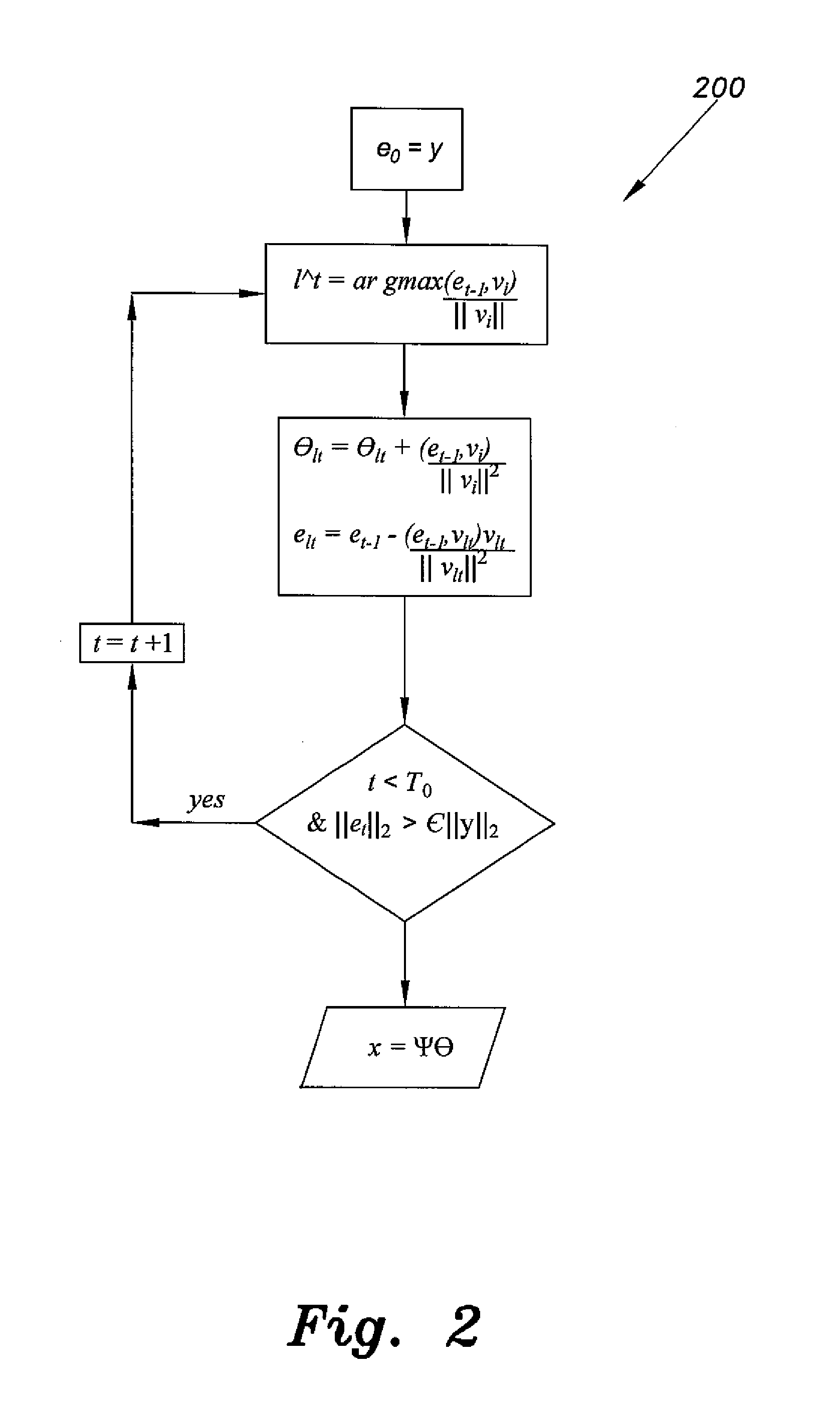
Method for compressive sensing , reconstruction, and estimation of ultra-wideband channels
InactiveUS20140140375A1Improve sparsityReasonable complexityTransmissionUltra-widebandRound complexity
The method for compressive sensing (CS) and reconstruction of ultra-wideband (UWB) channels includes building four practically-based dictionaries related to the antenna angles of transmission and angles of arrival that enhance the sparsity of UWB signals. The dictionaries account for the practical effects of the channel, such as pulse dispersion and the unavoidable effects of the antenna. Utilizing the practically-based dictionaries CS is able to reconstruct the UWB signals more efficiently with reasonable complexity. In addition to waveform reconstruction, the dictionaries are used for channel estimation. The CS method can be used with either a single-shot full profile correlator or a Rake receiver. The Rake receiver employs CS in adjusting its parameters to take advantage of the energy available in the strongest propagation paths.
Owner:KING FAHD UNIVERSITY OF PETROLEUM AND MINERALS
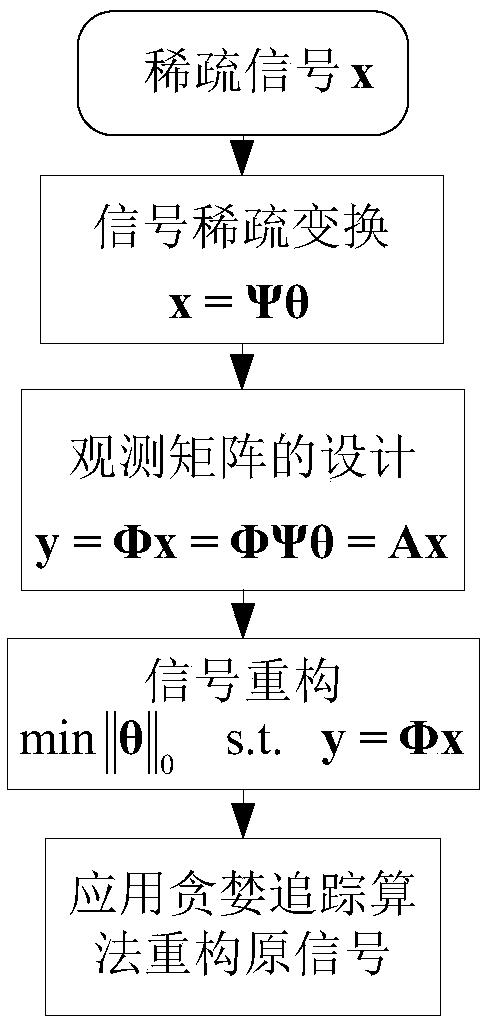
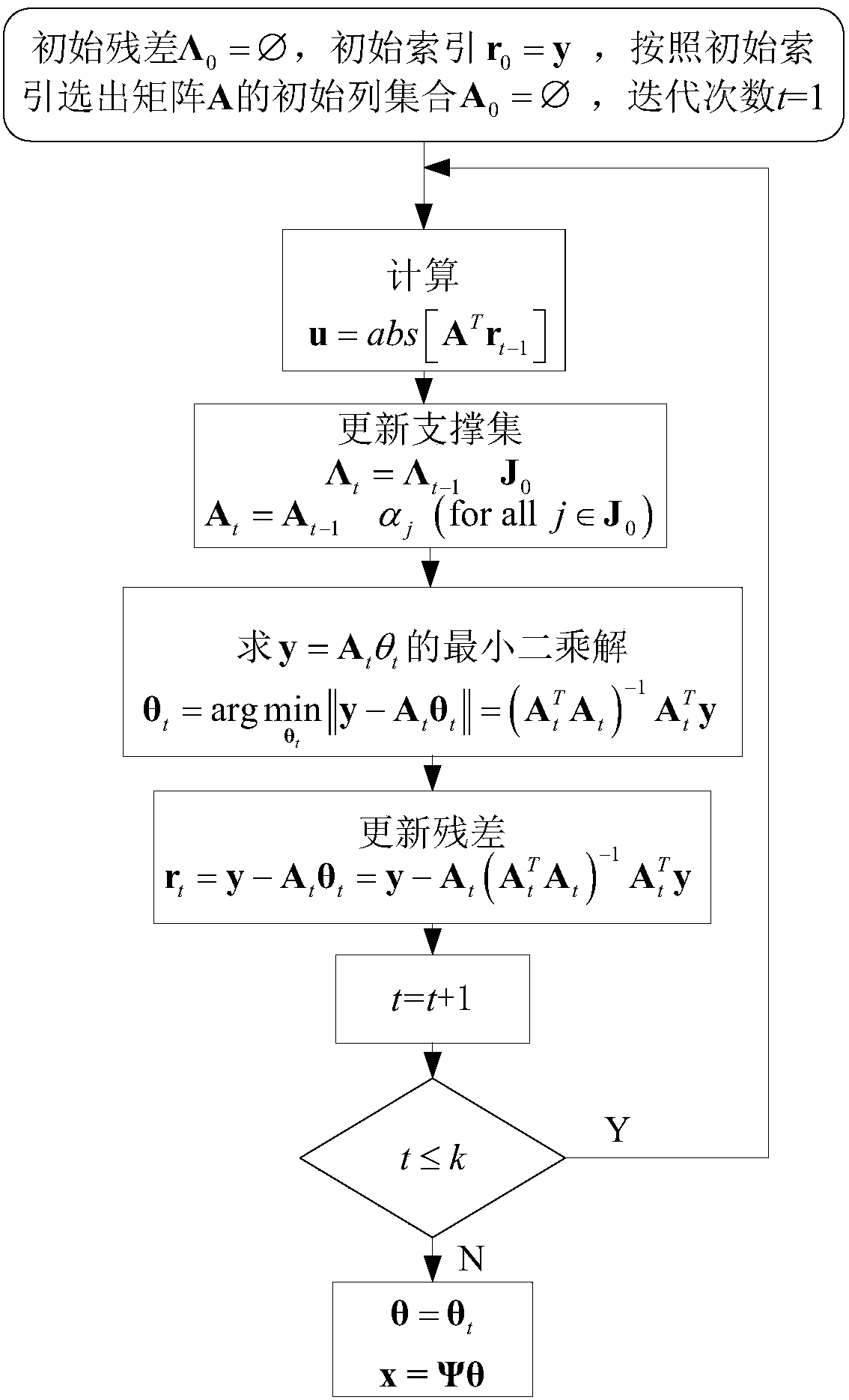
Sparse sampling and signal compressive sensing reconstruction method
InactiveCN103595414AFew samplesReduce the number of samplesCode conversionNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceReconstruction method
The invention discloses a sparse sampling and signal compressive sensing reconstruction method. The method comprises: establishing a signal sampling interval of each time, sampling point number, and the number of points recovering, establishing random sparse sampling lower than a Nyquist sampling theorem value; and designing a measurement matrix by random sampling timing sequence values, designing a transformation matrix of a sparse expression domain of signals, determining a compressive sensing matrix, and separated compressive sensing optimizing signal reconstruction in a nonlinear manner. The method is based on rationality of objective world rules, and makes full use of signal sparsity, uses transformation space to describe the signals, and establishes theoretical framework of new signal description and processing, so under the condition that information is not lost is ensured, signals are sampled by speed much lower than required speed of a Shannon's sampling theorem. Simultaneously, signals can be recovered completely, that is, sampling of signals is converted into sampling of information. The invention provides a whole set of complete method. The method can be used in one-dimensional and multidimensional signals, and can process audio frequency, videos, nuclear magnetic resonance, and other signals.
Owner:HUNAN INT ECONOMICS UNIV
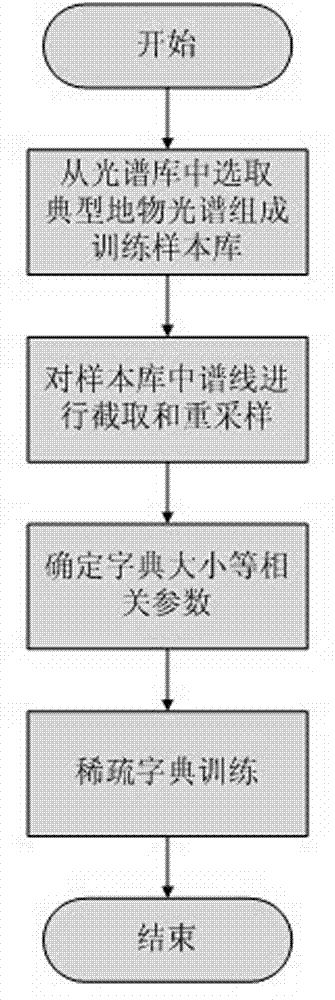
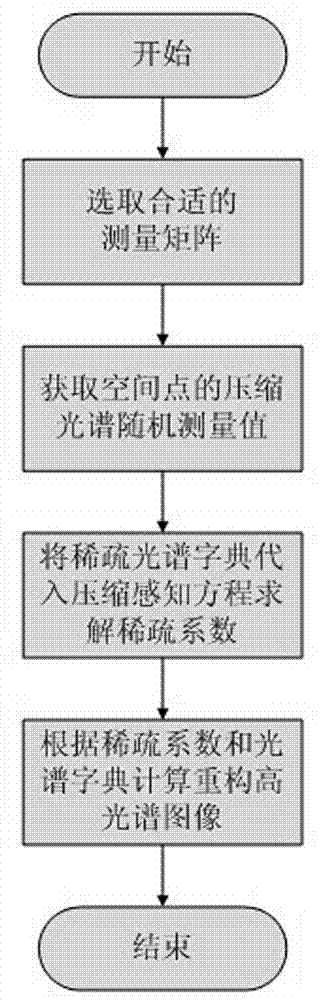
Sparse-spectrum-dictionary hyperspectral image reconstruction method by using compressed sensing
ActiveCN103247034AGood thinning effectHigh precisionImage enhancementDecompositionReconstruction method
The invention relates to a sparse-spectrum-dictionary hyperspectral image reconstruction method by using compressed sensing, belongs to the technical field of remote sensing, and aims to solve the problems of large data amount, complex system and high cost in a current hyperspectral imaging system. The method is based on a current ground-object spectrum library, and comprises the following steps: selecting curves of typical spectrums to form a sampling library in a classified manner, adopting related algorithms in a signal sparse decomposition field to train the sampling library to obtain a sparse dictionary, combining a compressed measured value and a random measurement matrix to perform high-spectrum reconstruction, and adjusting related parameters of the algorithm according to a reconstruction effect till to be the best. The sparse dictionary obtained by the method has a better sparsification effect on ground-object spectrums; the precision of spectrum reconstruction is higher; and unlike decomposition and reconstruction of a conventional signal under the sparse dictionary, the method does not need priori information of a target, and has a wide application range.
Owner:ACAD OF OPTO ELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
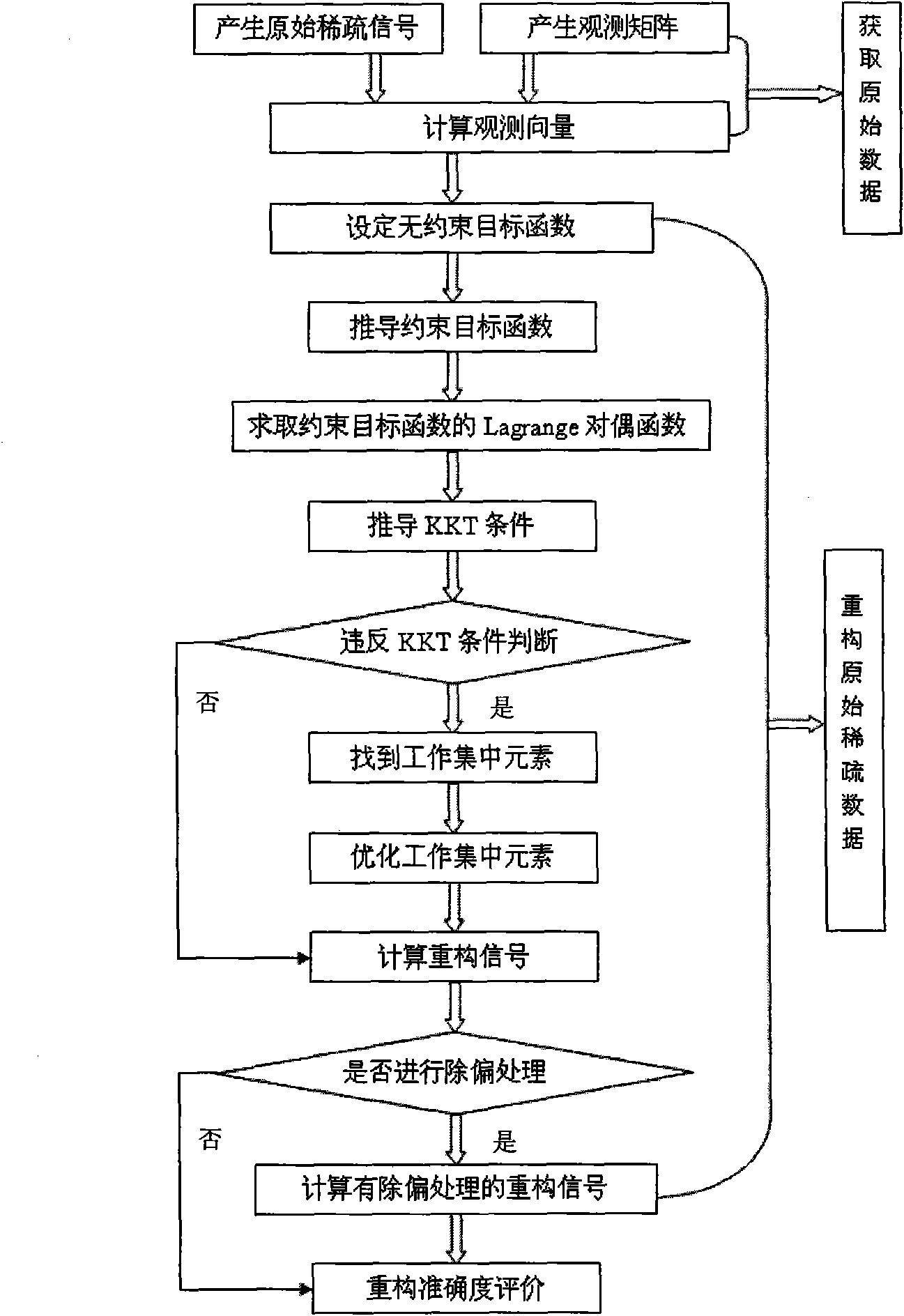
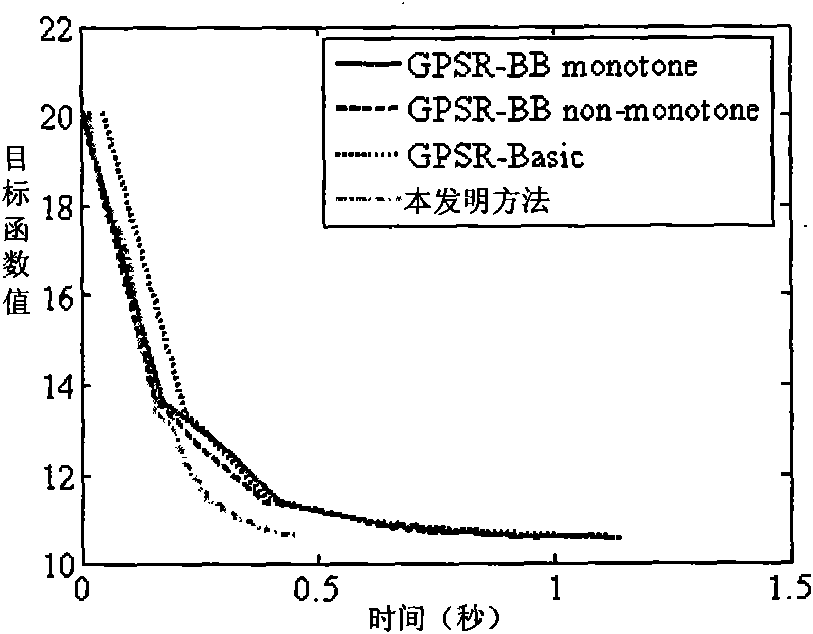
Reconstruction method of sparse signal
InactiveCN101640541ASave storage spaceFast convergenceCode conversionComplex mathematical operationsMean squareSequential minimal optimization
The invention discloses a reconstruction method of sparse signal, mainly solving the problem of low rate of raw sparse signal reconstructed from observation vectors. Utilizing the decomposability of aconstrained object function, the method decomposes the problem of optimizing the constrained object function into a series of small constrained object functions for optimization to improve the reconstruction rate, comprising a raw data acquisition part, a raw sparse signal reconstruction part and a reconstruction accuracy evaluation part, wherein the raw data acquisition part comprises raw sparsesignal generation, matrix observation and vector observation; the raw sparse signal reconstruction part mainly comprises setting unconstrained object function, deducing constrained object function, decomposing the constrained object function by a sequential minimal optimization method, calculating reconstruction signal and debiasing reconstruction signal; the reconstruction accuracy evaluation isto compare the magnitude of the error of mean square. The reconstruction method can improve the reconstruction rate on the premise of ensuring reconstruction accuracy rate and be used for solving theproblem of sparse signal reconstruction in the fields of compressed sensing and the like.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
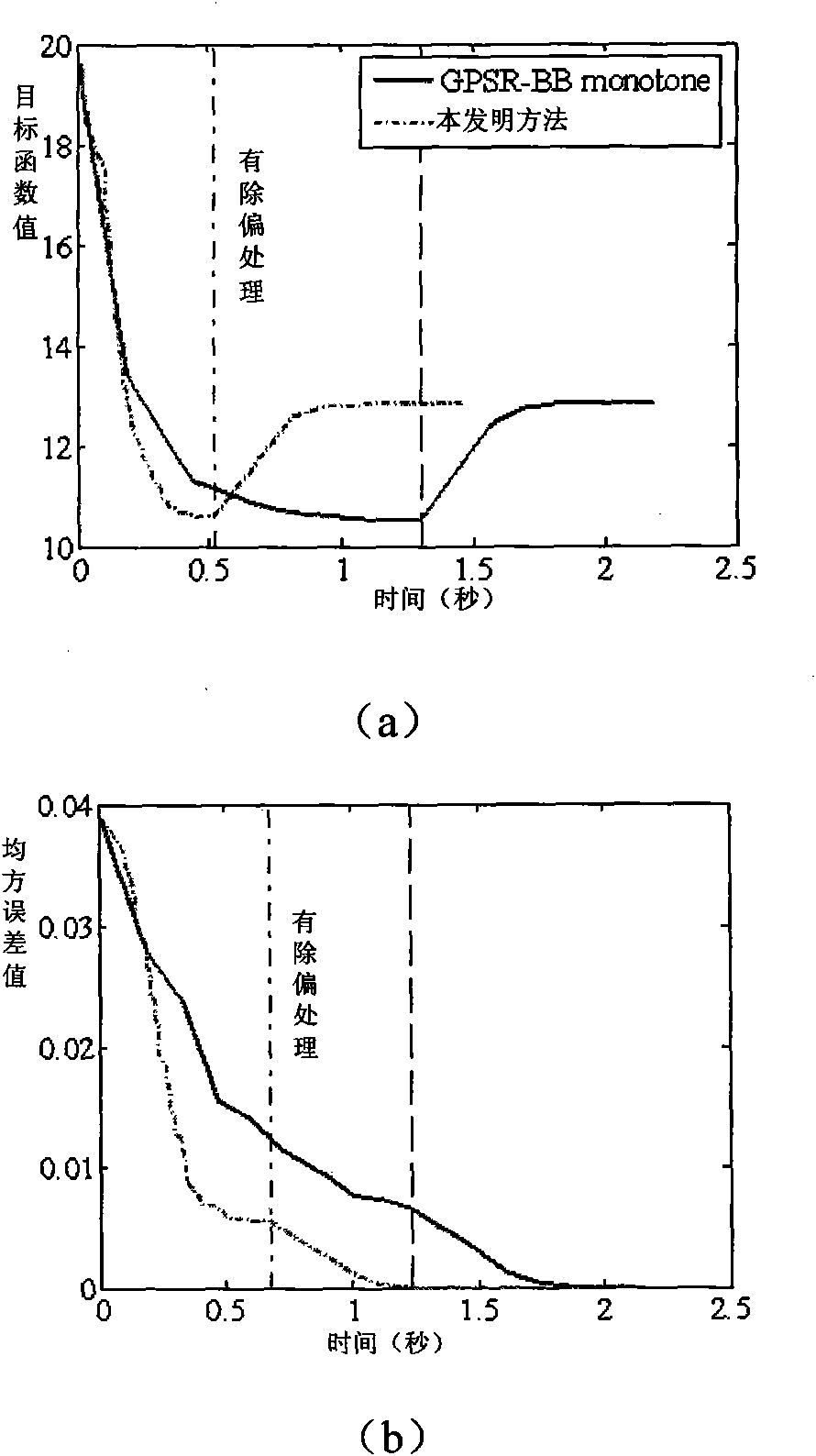
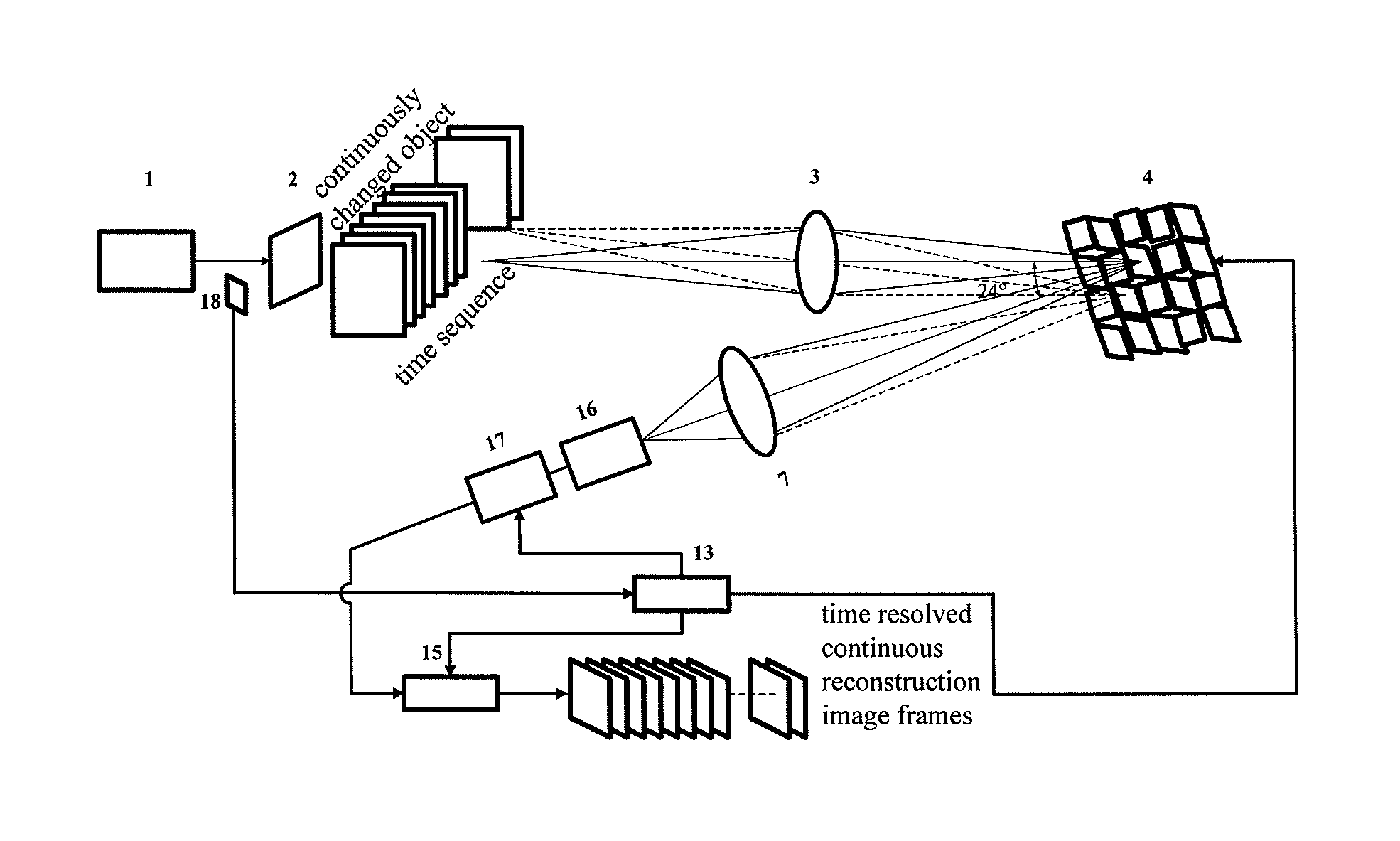
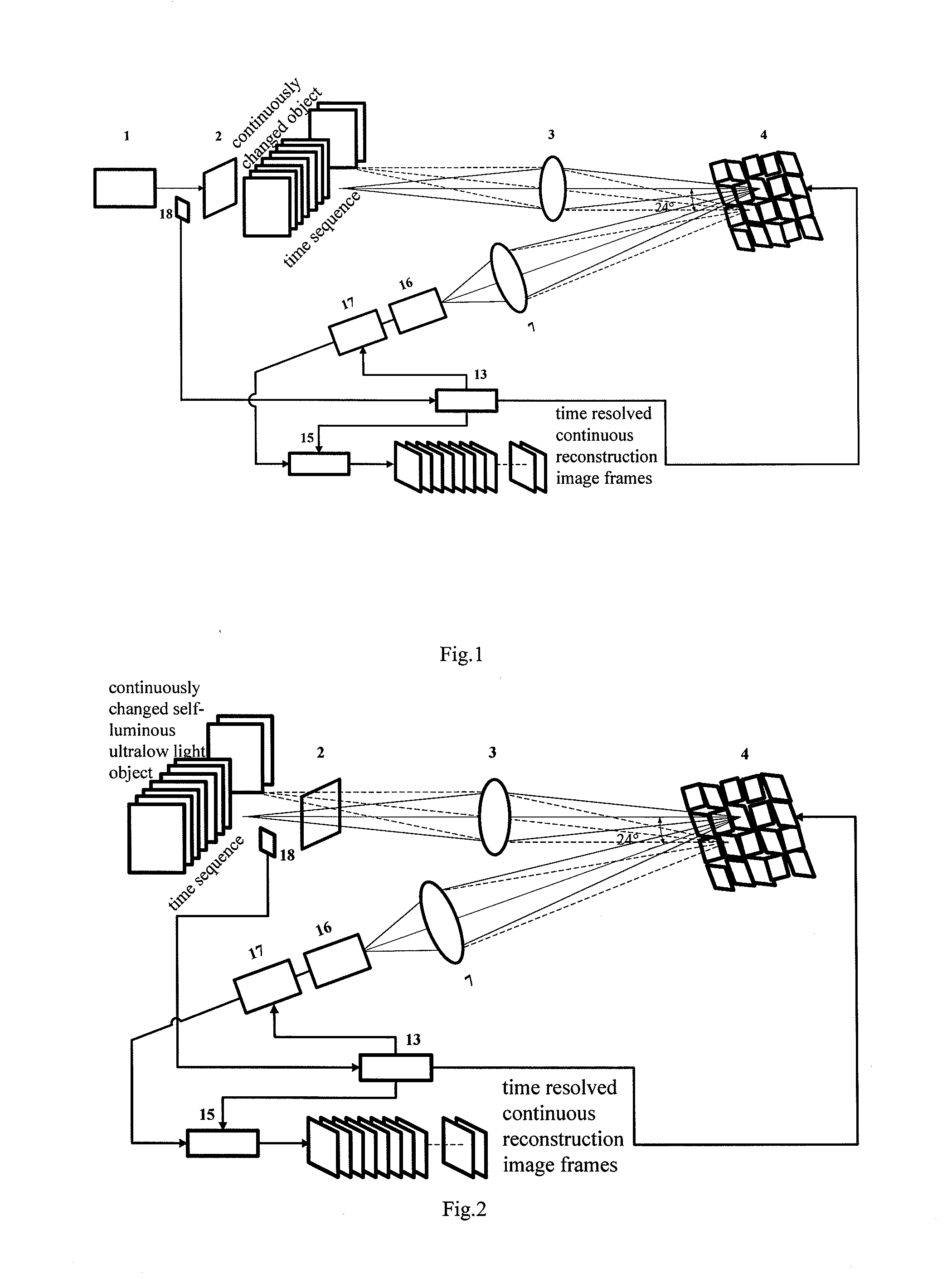
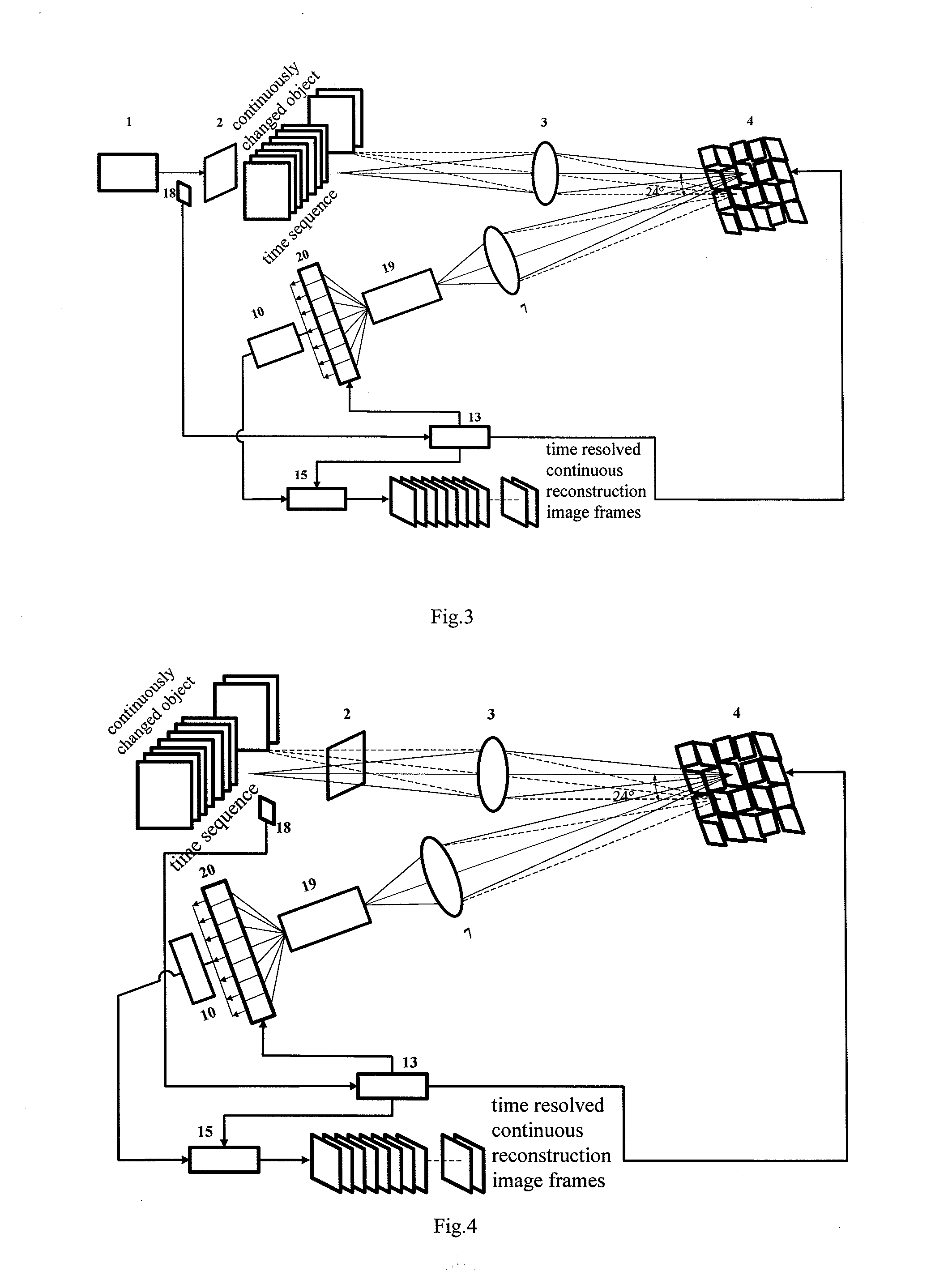
Time-Resolved Single-Photon or Ultra-Weak Light Multi-Dimensional Imaging Spectrum System and Method
InactiveUS20140253713A1Improve reconstruction qualityShorten recovery timeColor television detailsClosed circuit television systemsSpatial light modulatorGrating
A single-photon or ultra-weak light multi-D imaging spectral system and method. In order to realize rough time resolution, a time-resolved single-photon counting 2D imaging system for forming color or grey imaging is provided. Moreover, in order to realize high-precision time resolution, the system comprises a light source, an imaging spectral measurement unit, an electric detection unit, a system control unit and an algorithm unit. The light carrying information of an object is imaged on a spatial light modulator and randomly modulated according to compressed sensing theory, emergent light of a grating is collected using a point or array single-photon detector, the number of photons and photon arrival time are recorded, and reconstruction is carried out using the compressed sensing algorithm and related algorithm of the spectral imaging. The system provides single-photon detection sensitivity, high time resolution and wide spectral range, and can be applied in numerous new high-tech industries.
Owner:CENT FOR SPACE SCI & APPLIED RES
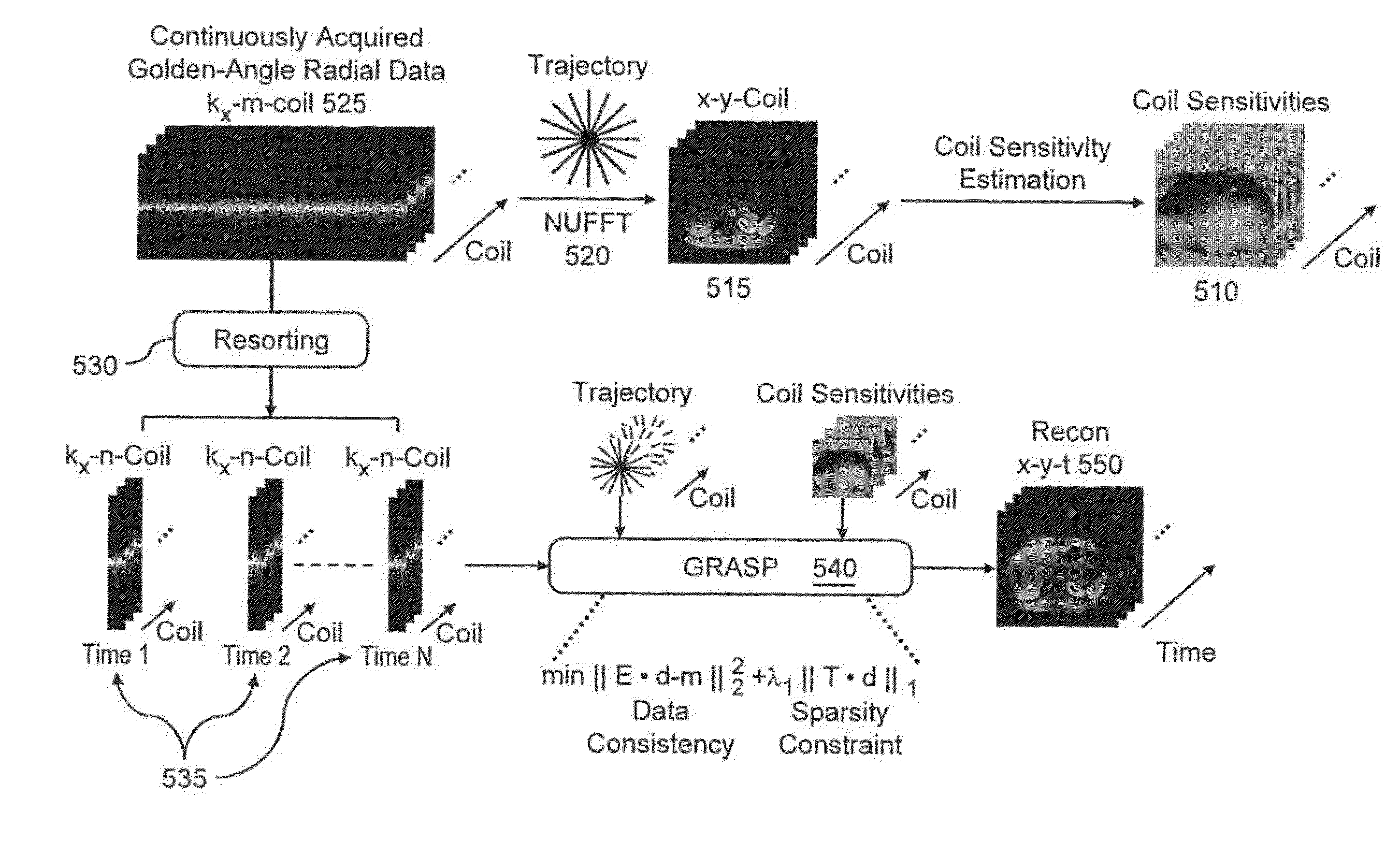
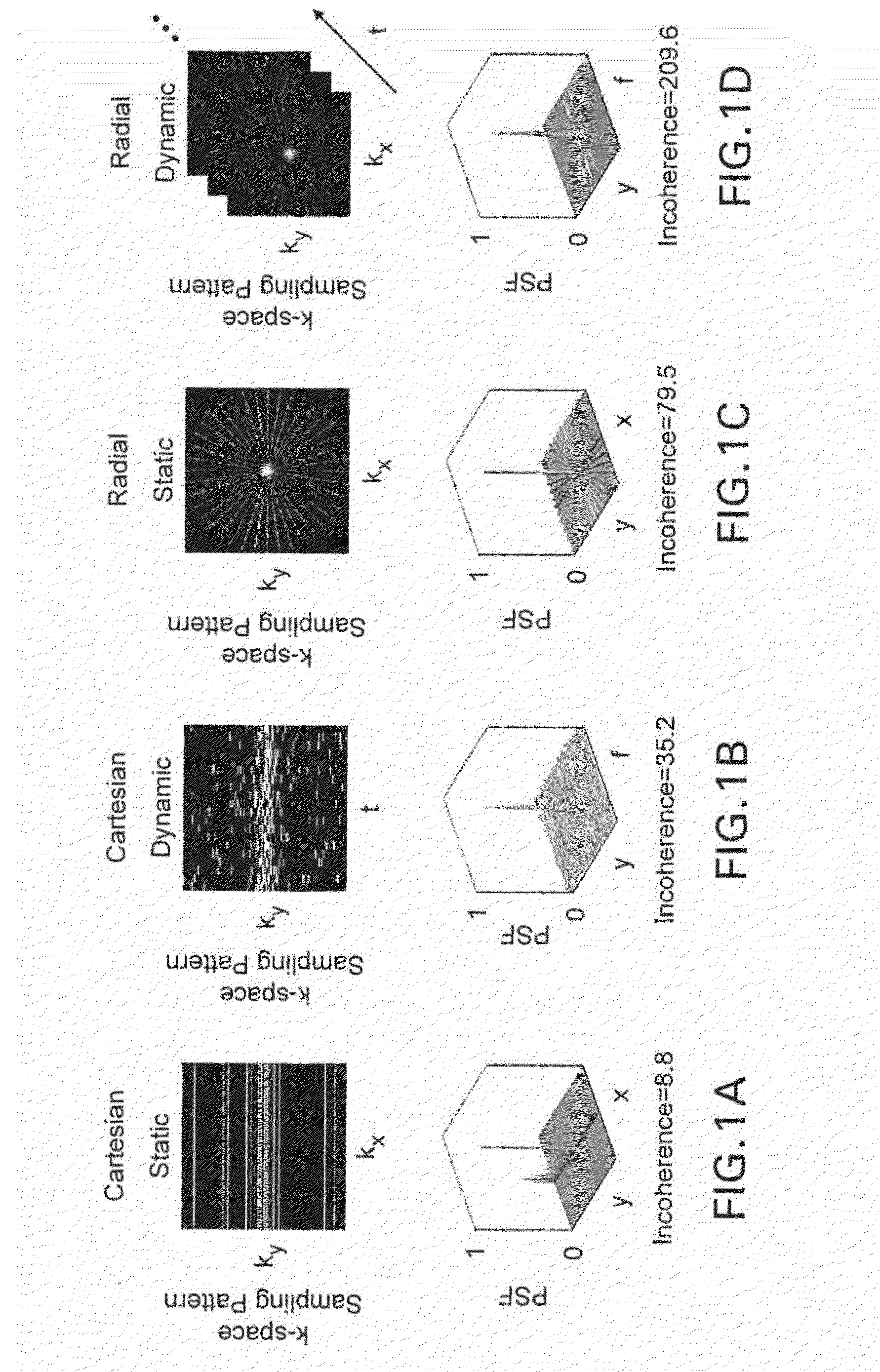
System, method and computer-accessible medium for highly-accelerated dynamic magnetic resonance imaging using golden-angle radial sampling and compressed sensing
ActiveUS20150077112A1Promote reconstructionDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsTemporal resolutionImage resolution
Exemplary method, system and computer-accessible medium can be provided which facilitates an acquisition of radial data, which can be continuous, with an exemplary golden-angle procedure and reconstruction with arbitrary temporal resolution at arbitrary time points. According to such exemplary embodiment, such procedure can be performed with a combination of compressed sensing and parallel imaging to offer a significant improvement, for example in the reconstruction of highly undersampled data. It is also possible to provide an exemplary procedure for highly-accelerated dynamic magnetic resonance imaging using Golden-Angle radial sampling and multicoil compressed sensing reconstruction, called Golden-angle Radial Sparse Parallel MRI (GRASP).
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
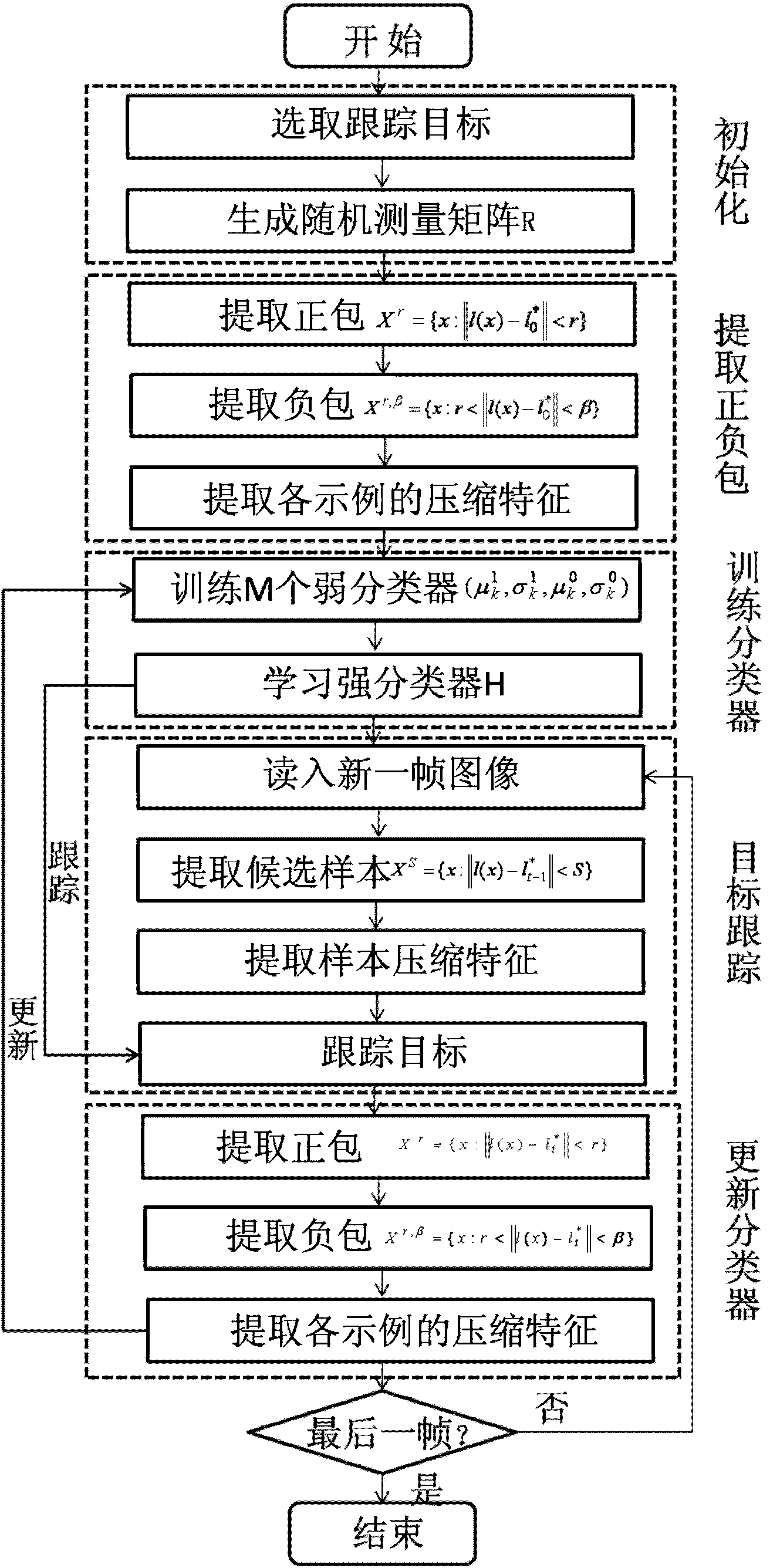
Moving target tracking method based on improved multi-example learning algorithm
InactiveCN103325125AValid descriptionImprove robustnessImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionDimensionality reductionPattern perception
The invention belongs to the field of computer vision and pattern recognition and discloses a moving target tracking method based on an improved multi-example learning algorithm. Firstly, a random measurement matrix is designed according to the compression perception theory. Then a multi-example learning algorithm is used to sample an example in a current tracking result small neighborhood to form a positive package, and at the same time, sampling an example is carried out in a large neighborhood ring to obtain a negative package. For each example, the characteristic of a character target is extracted at an image surface, and the random measurement matrix is utilized to carry out dimensionality reduction on the characteristic. According to the extracted example characteristic, online learning weak classifiers are utilized, and weak classifiers with strong discrimination ability are selected from a weak classification pool to form a strong classifier. Finally, when a new target position is tracked, according to a similarity score of the current tracking result and a target template, the online adaptive adjustment of classifier update degree parameters is carried out. According to the method, a problem that a tracking result in the existing algorithm is easily affected by an illumination change, an attitude change, the interference of a complex background, target fast motion and the like is solved.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
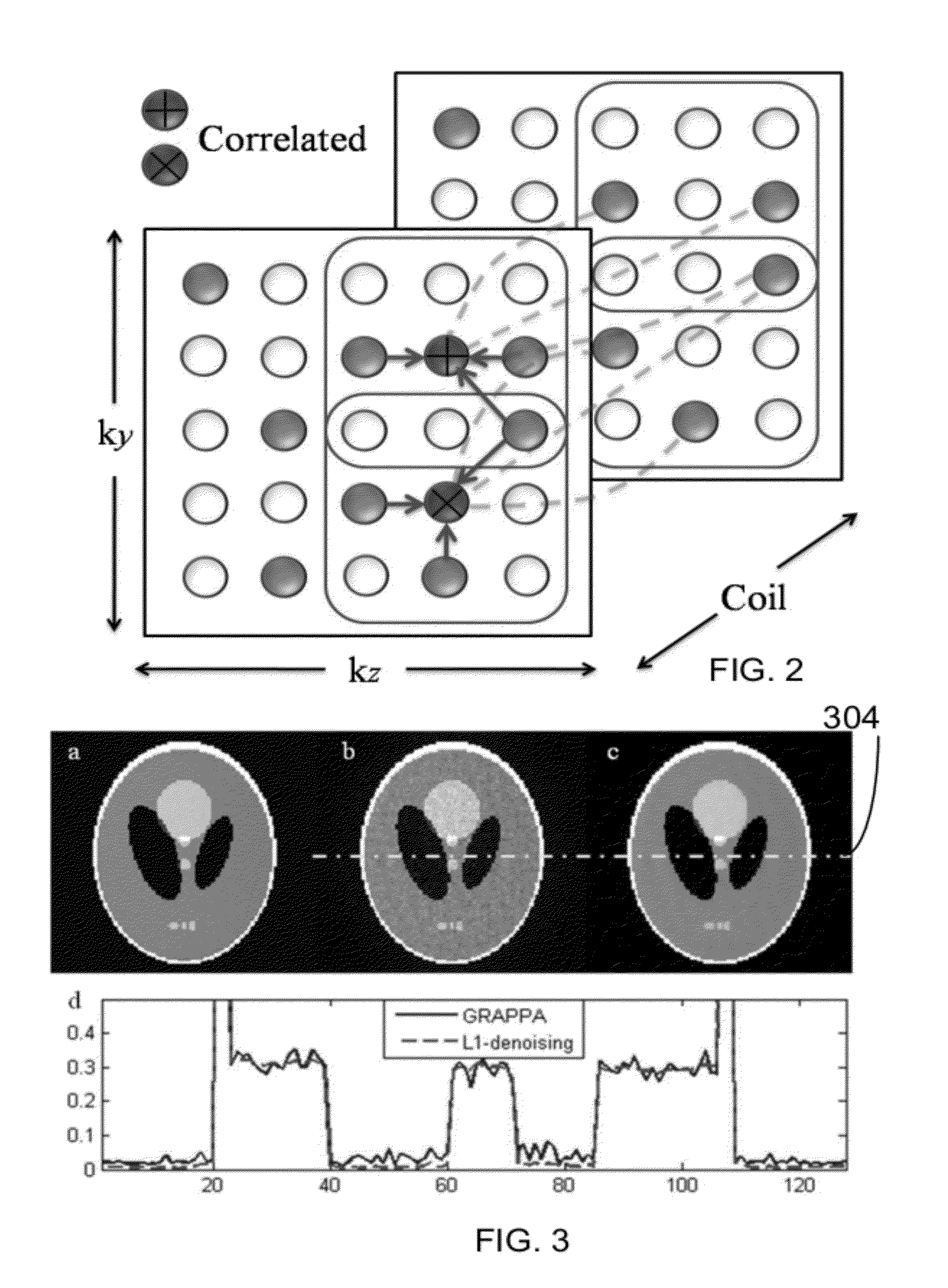
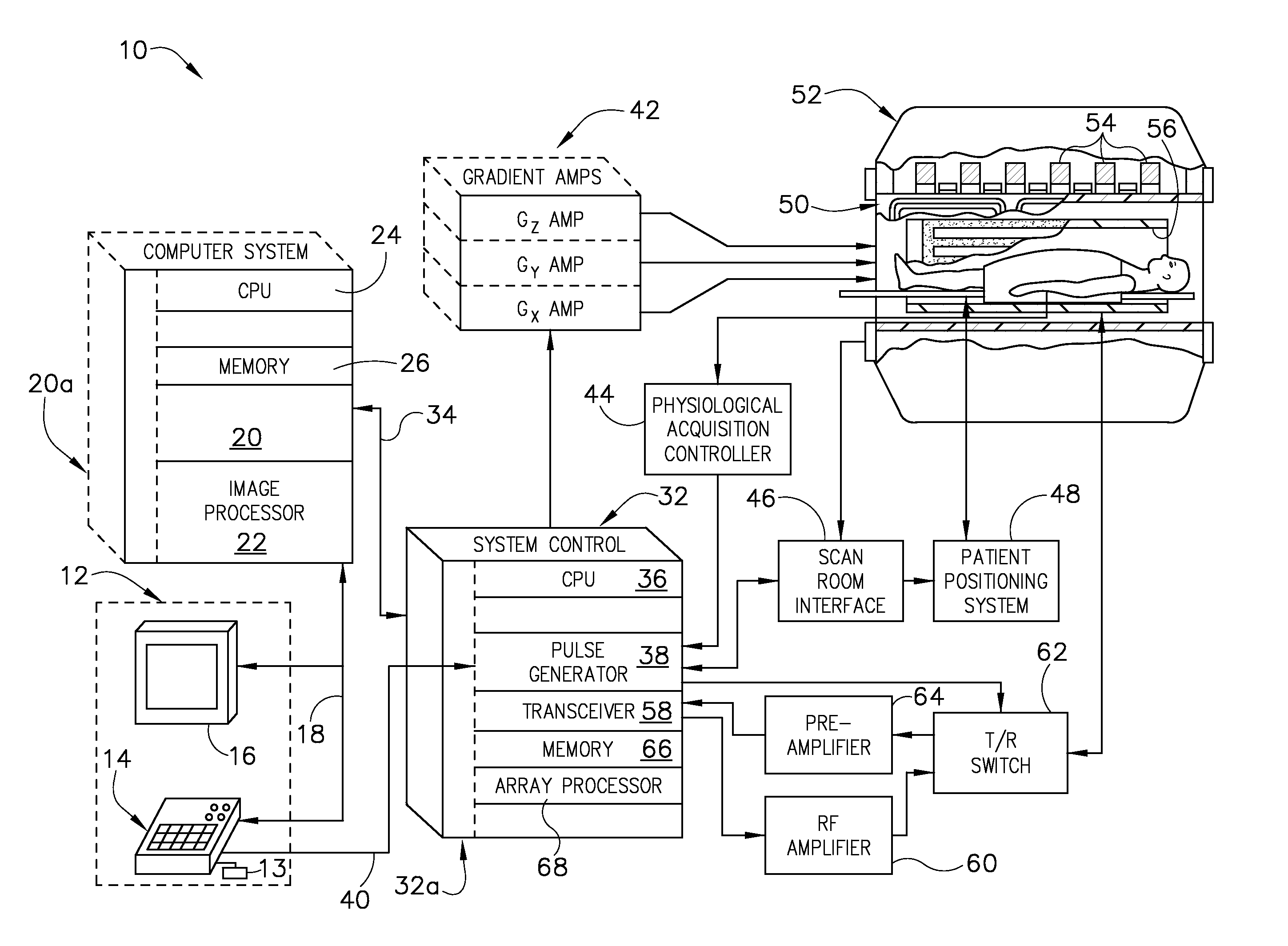
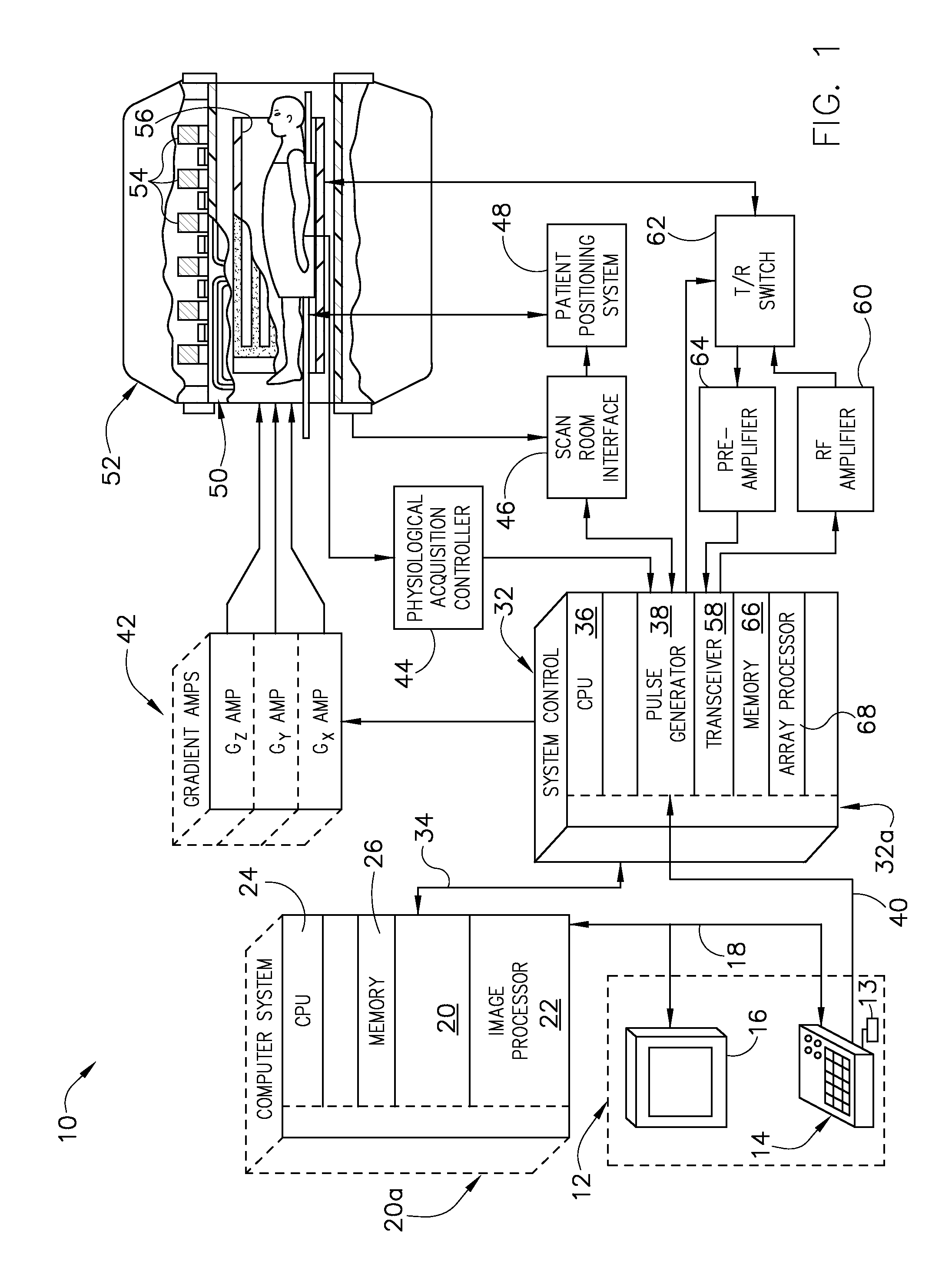
System and method for using parallel imaging with compressed sensing
ActiveUS7688068B2Magnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringParallel imagingComputer science
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com