Patents
Literature
315 results about "Matrix estimation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
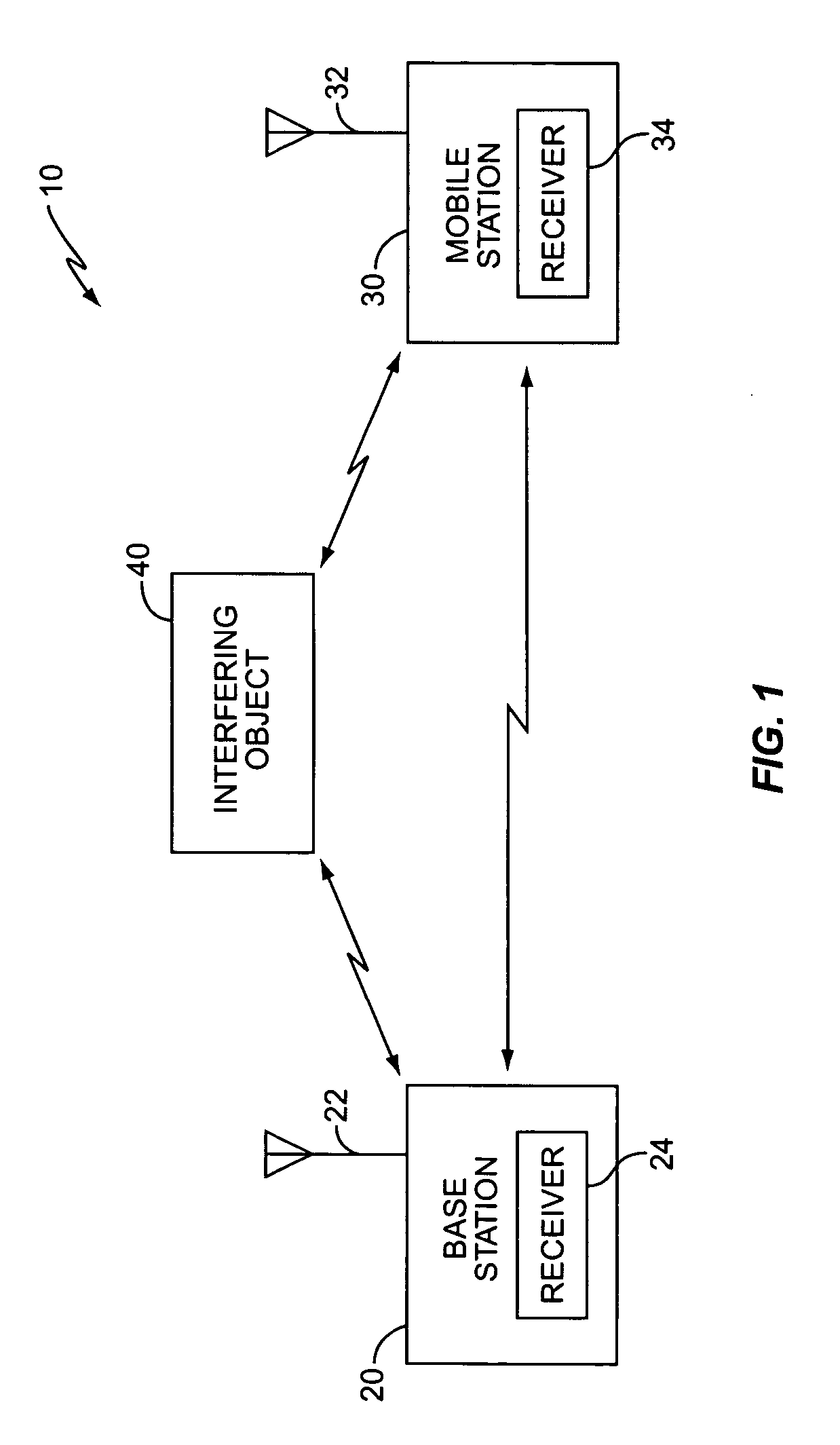
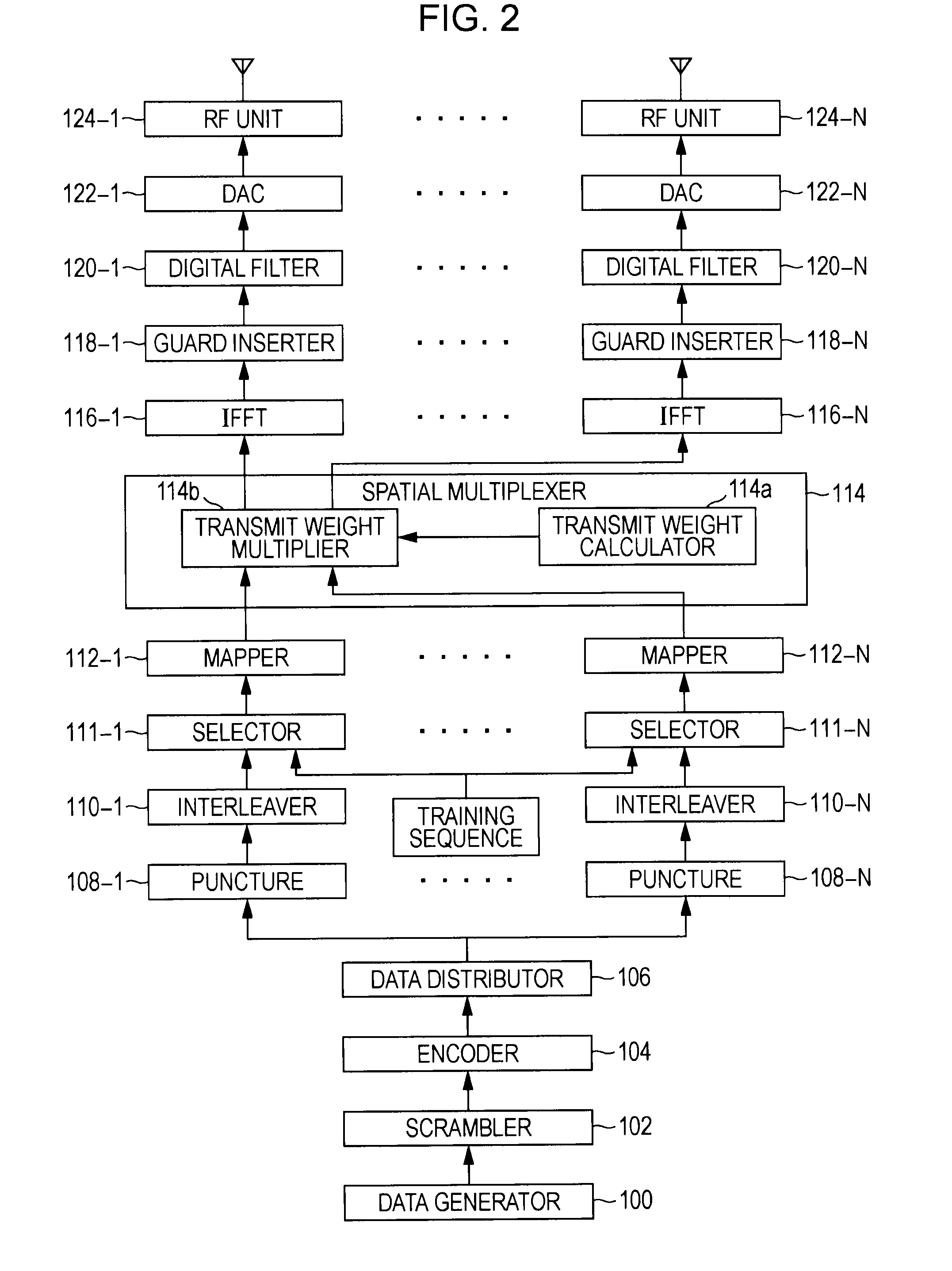
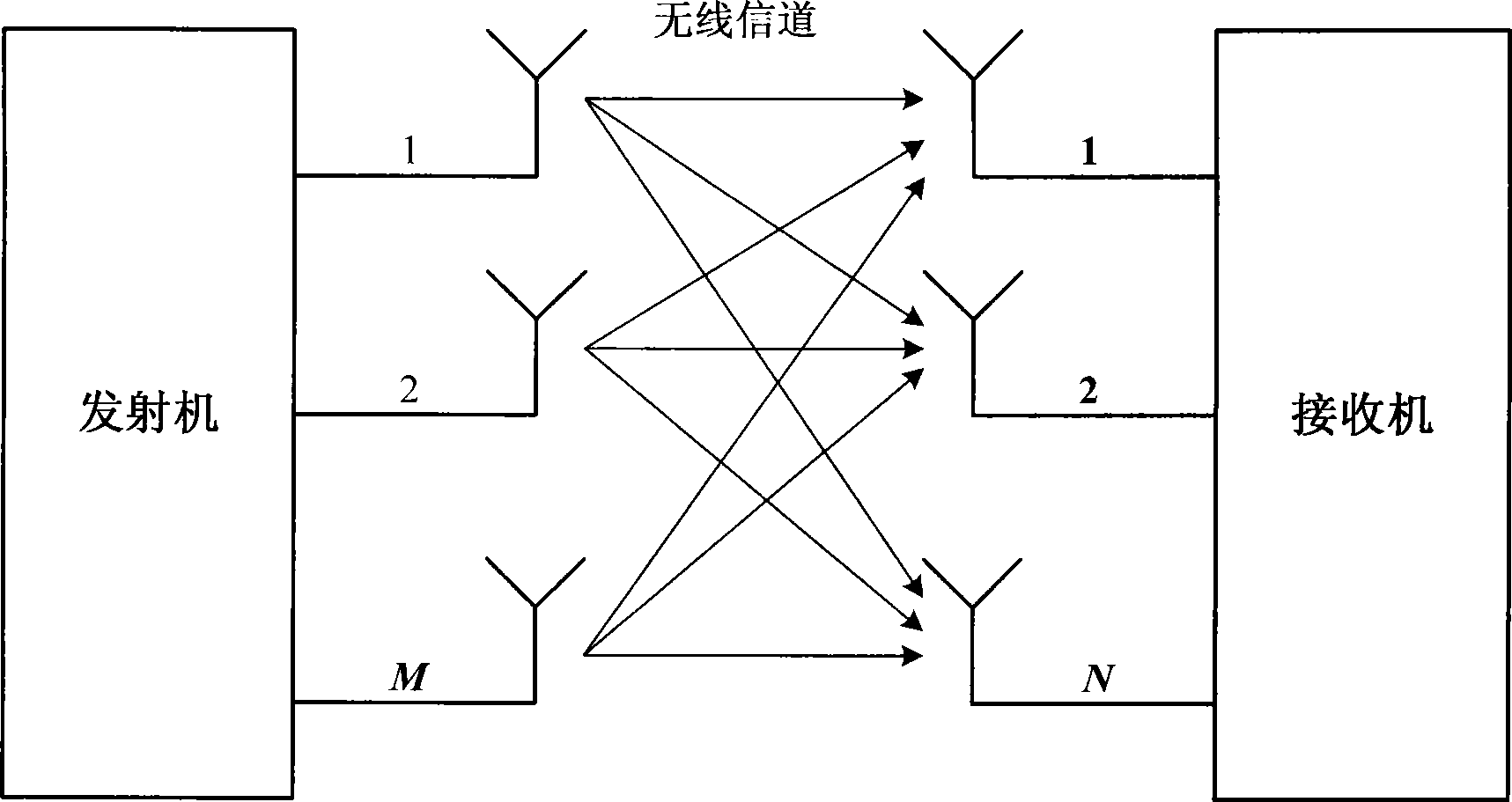
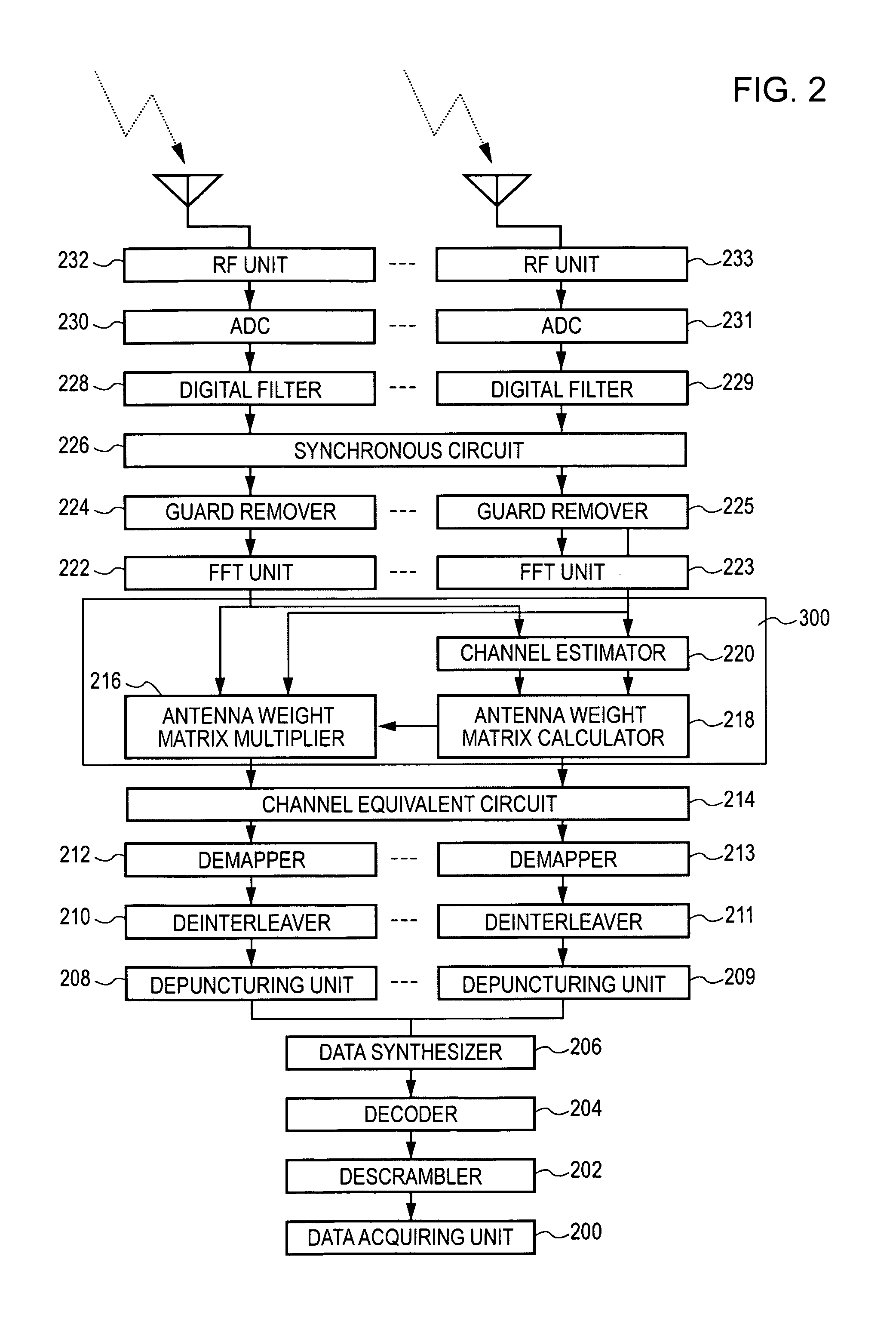
Space time encoded wireless communication system with multipath resolution receivers
ActiveUS7386076B2Modulated-carrier systemsPolarisation/directional diversityCommunications systemTransmitter antenna
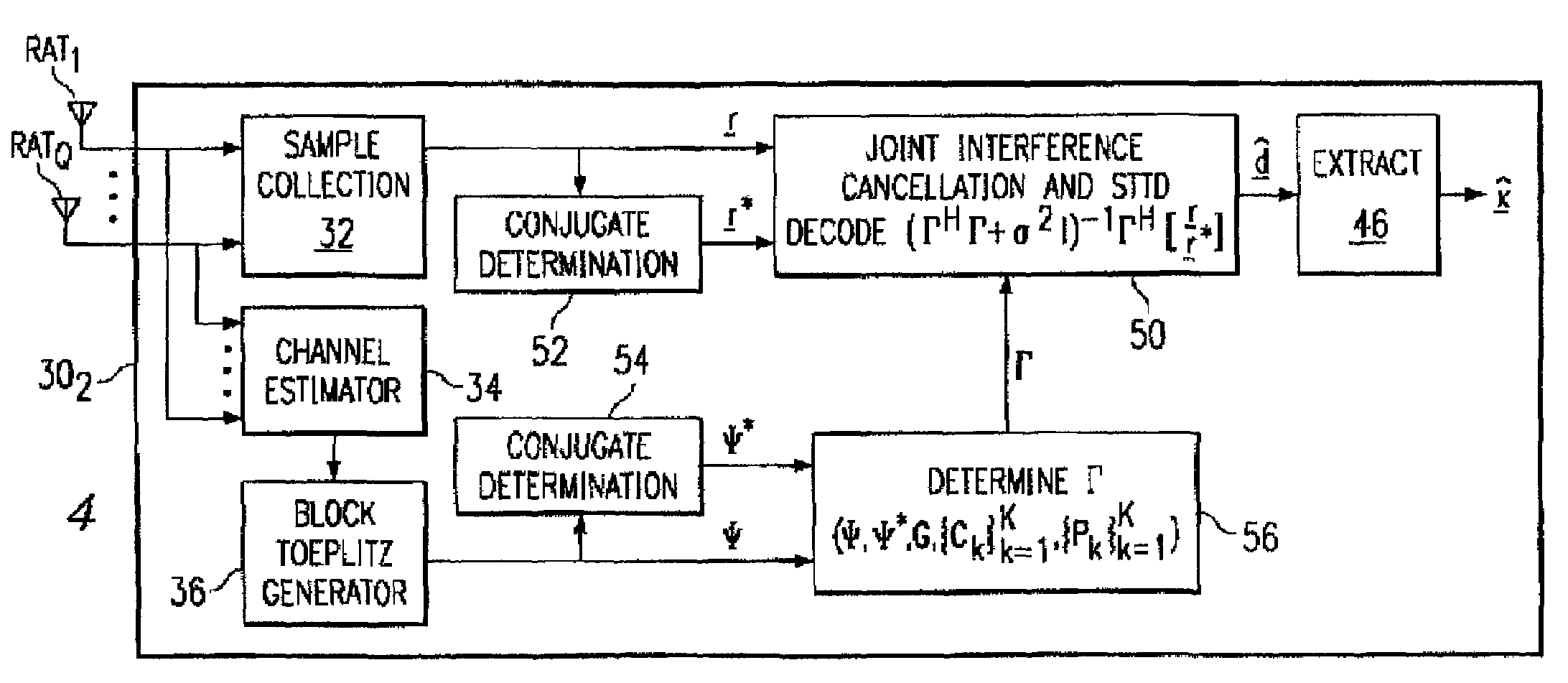
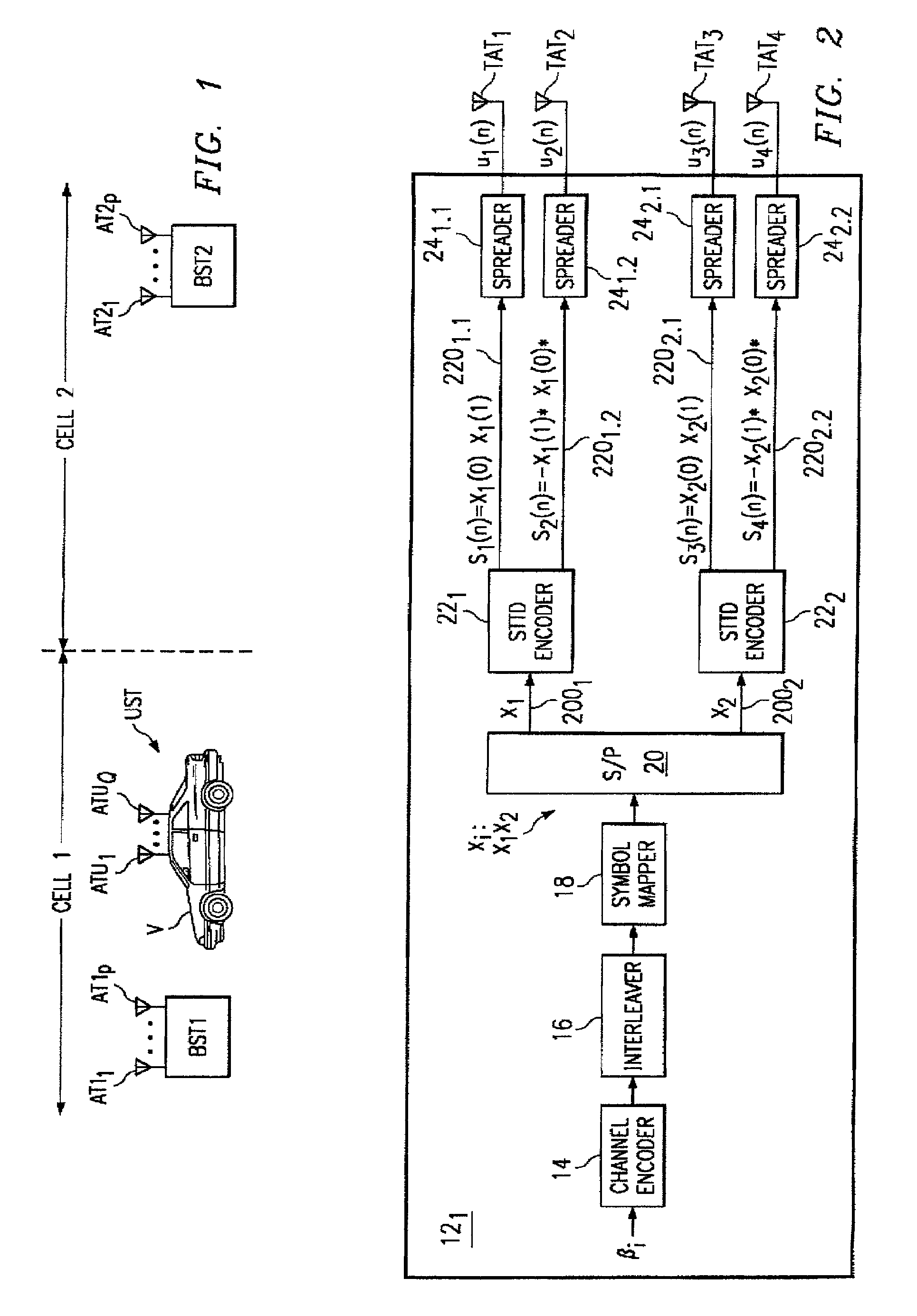
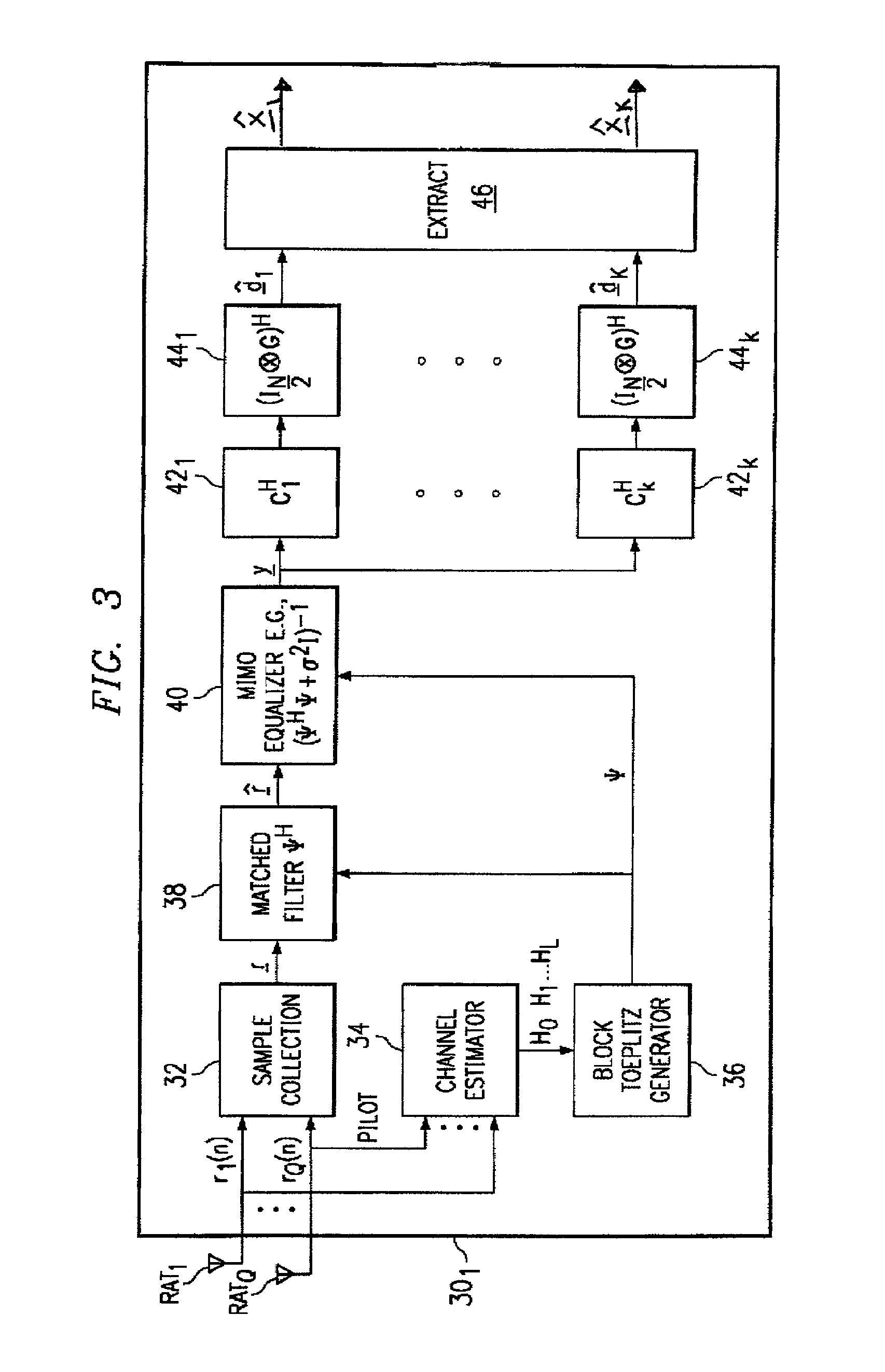
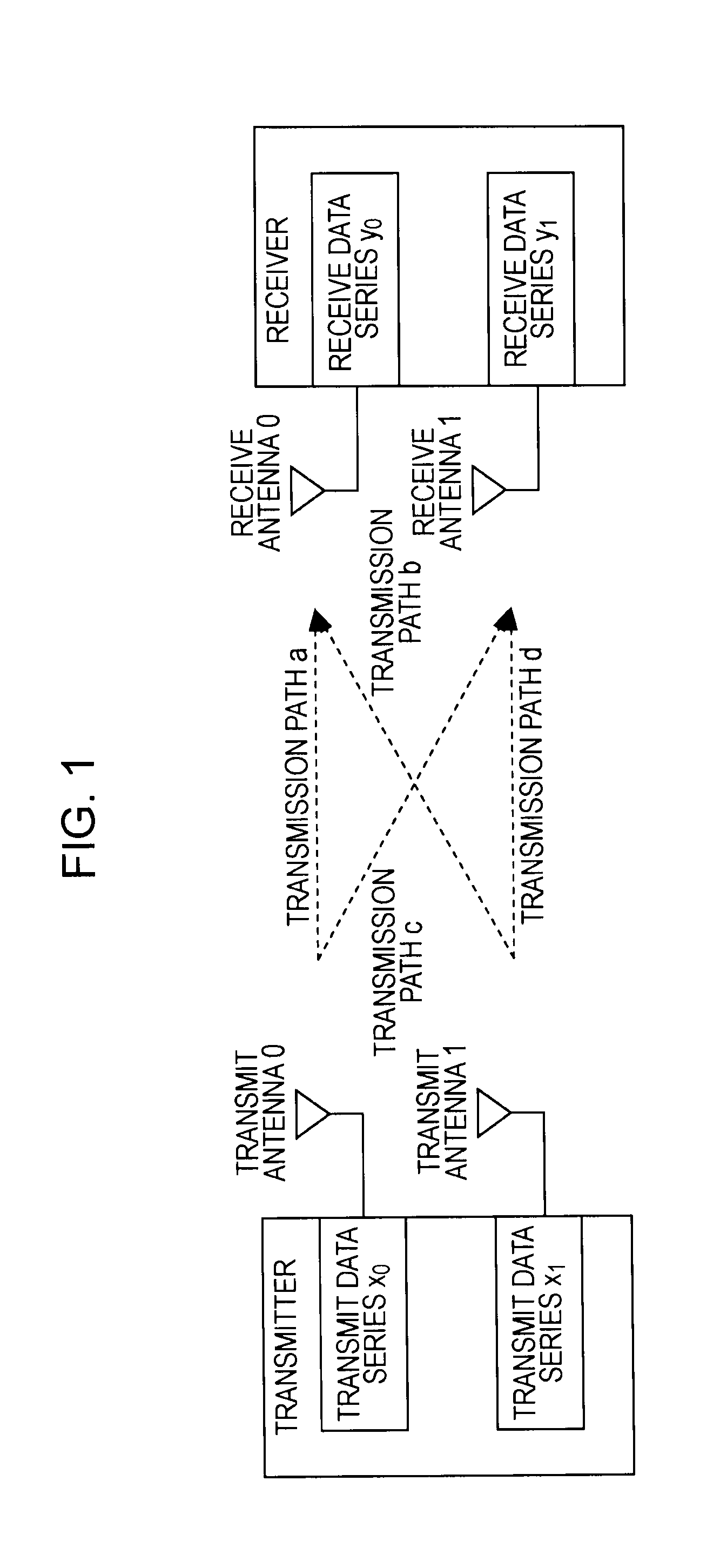
A wireless receiver (301) for receiving multiple space time encoded signals from a plurality of transmit antenna sets (TAT1 through TAT2, and TAT3 through TAT4), wherein the multiple space time encoded signals comprise a set of symbols and wherein each transmit antenna set is coupled to a corresponding encoder (221, 222) at a single transmitter (121). The receiver comprises a plurality of receive antennas (RAT1 through RATQ) and collection circuitry (32), coupled to the plurality of receive antennas, for collecting a plurality of signal samples for a plurality of successive time instances and from each of the plurality of receive antennas. The collected samples comprise samples of multipaths of the space time encoded signals. The receiver also comprises circuitry (34, 36), coupled to the plurality of receive antennas, for determining a linear time invariant multiple-input multiple-output matrix in response to pilot values in the received multiple space time encoded signals. Finally, the receiver comprise circuitry (40, 421, 441) for estimating at least selected ones of the symbols in response to the signal samples and the linear time invariant multiple-input multiple-output matrix.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Wireless communication system, wireless communication apparatus and wireless communication method
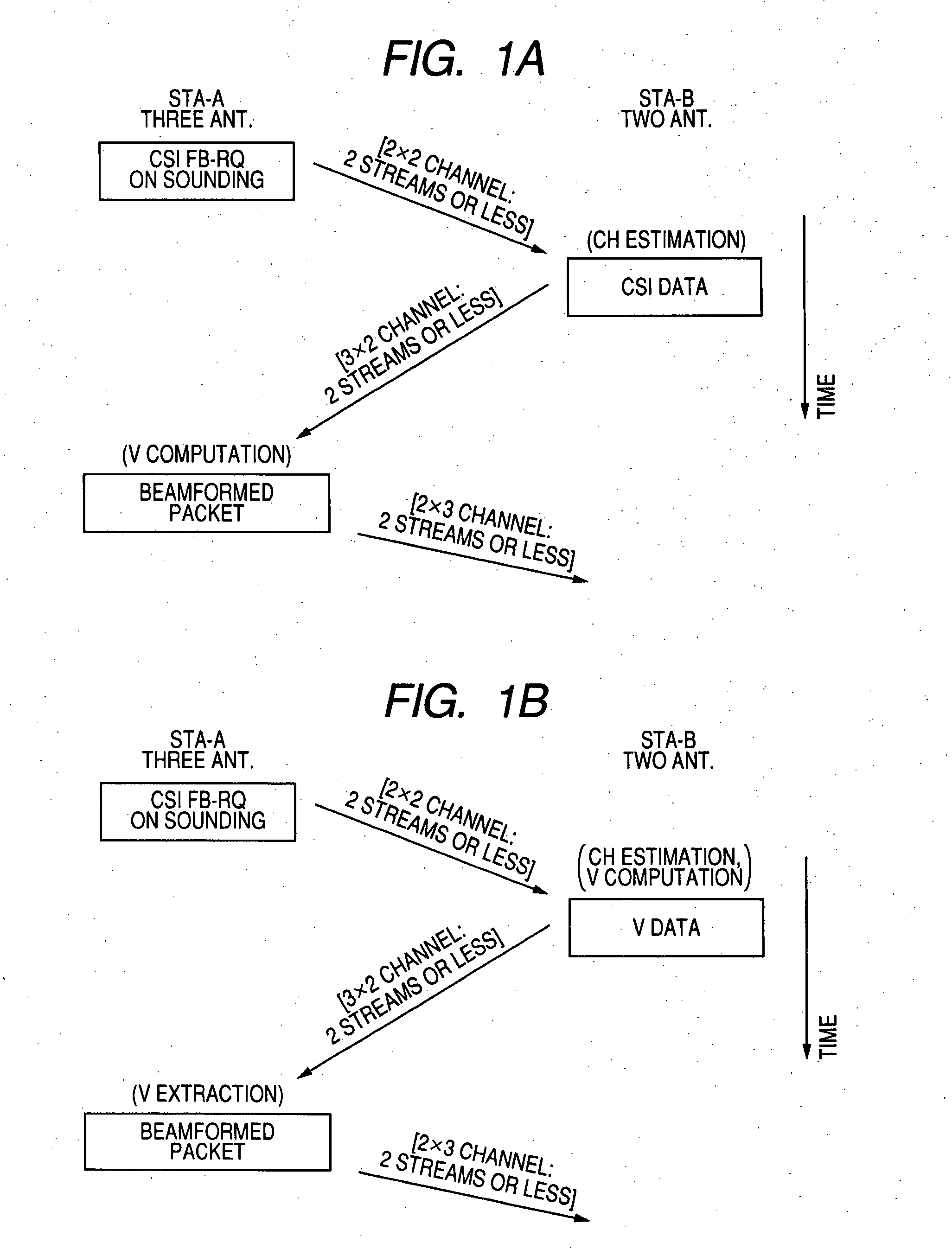
ActiveUS20070253501A1Improve transfer rateWithout deteriorating beamforming characteristicSpatial transmit diversityError preventionCommunications systemData transmission
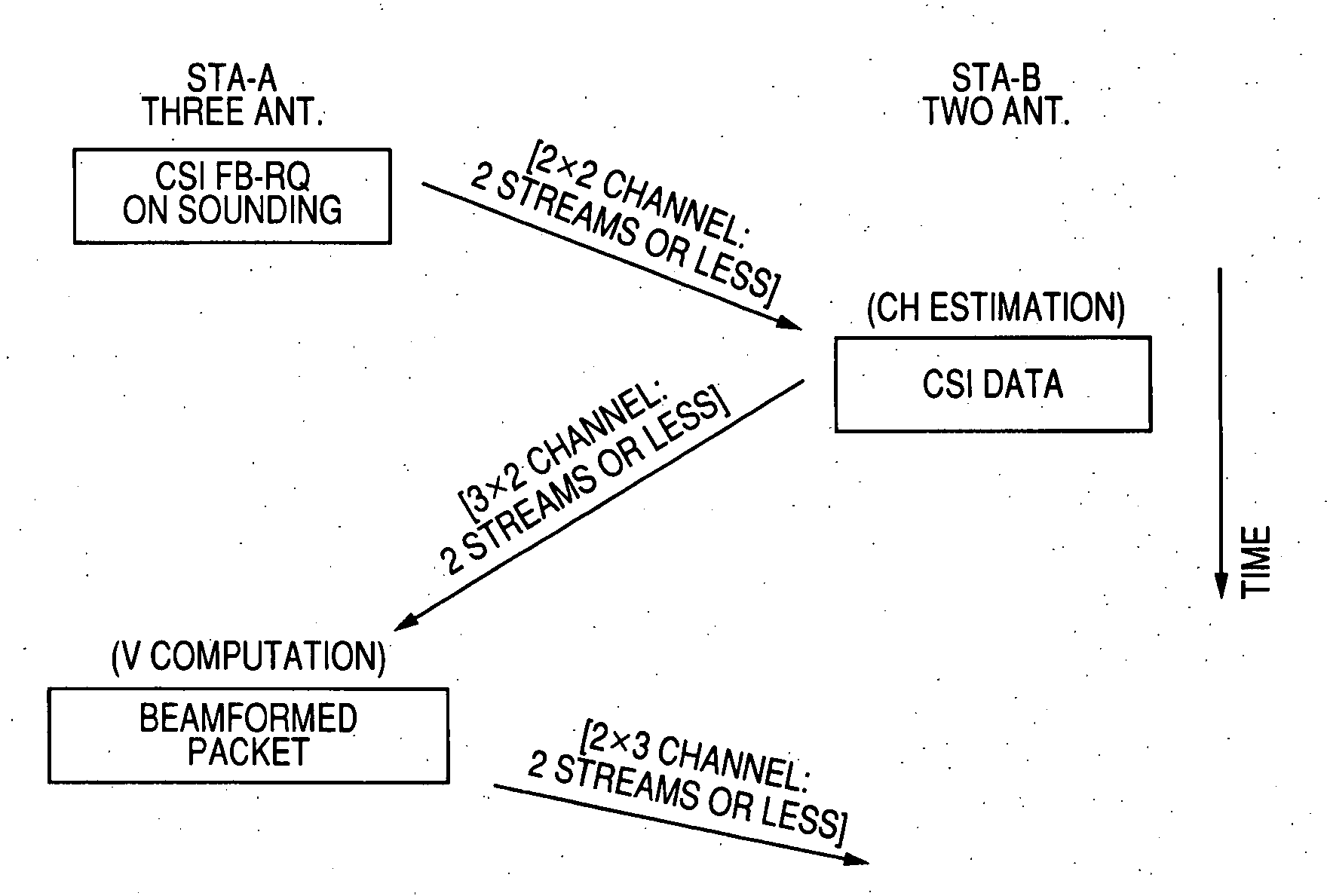
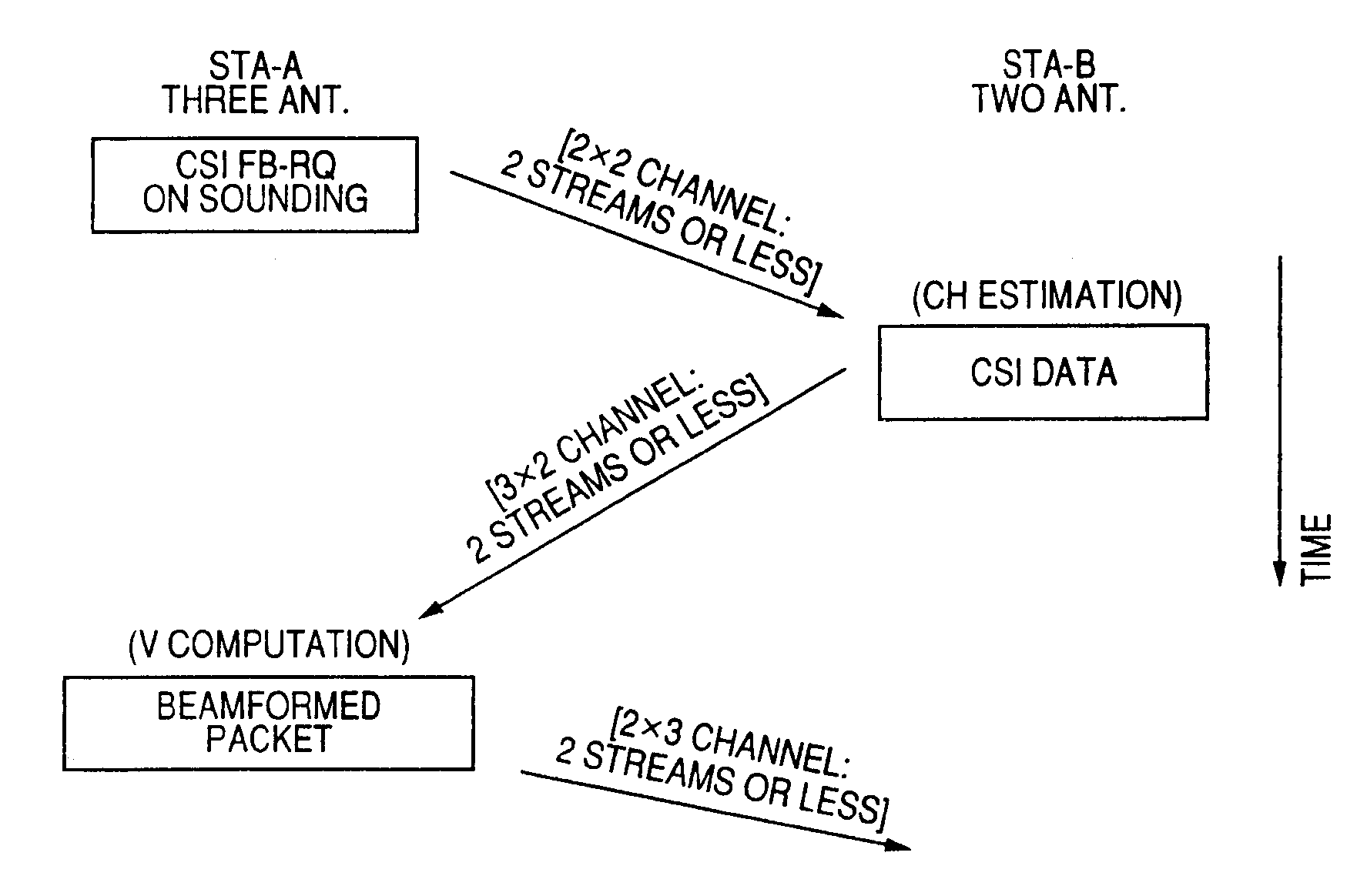
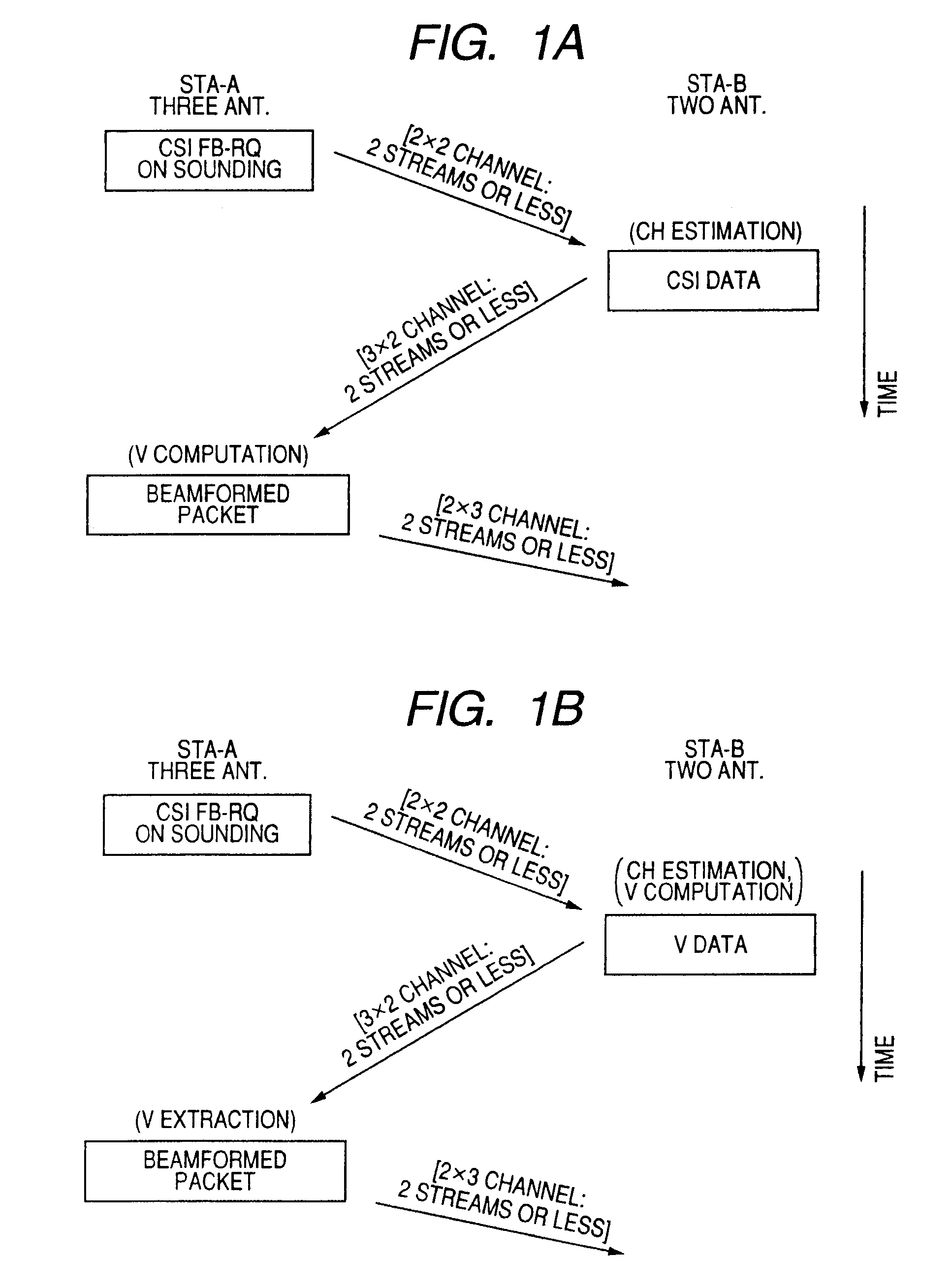
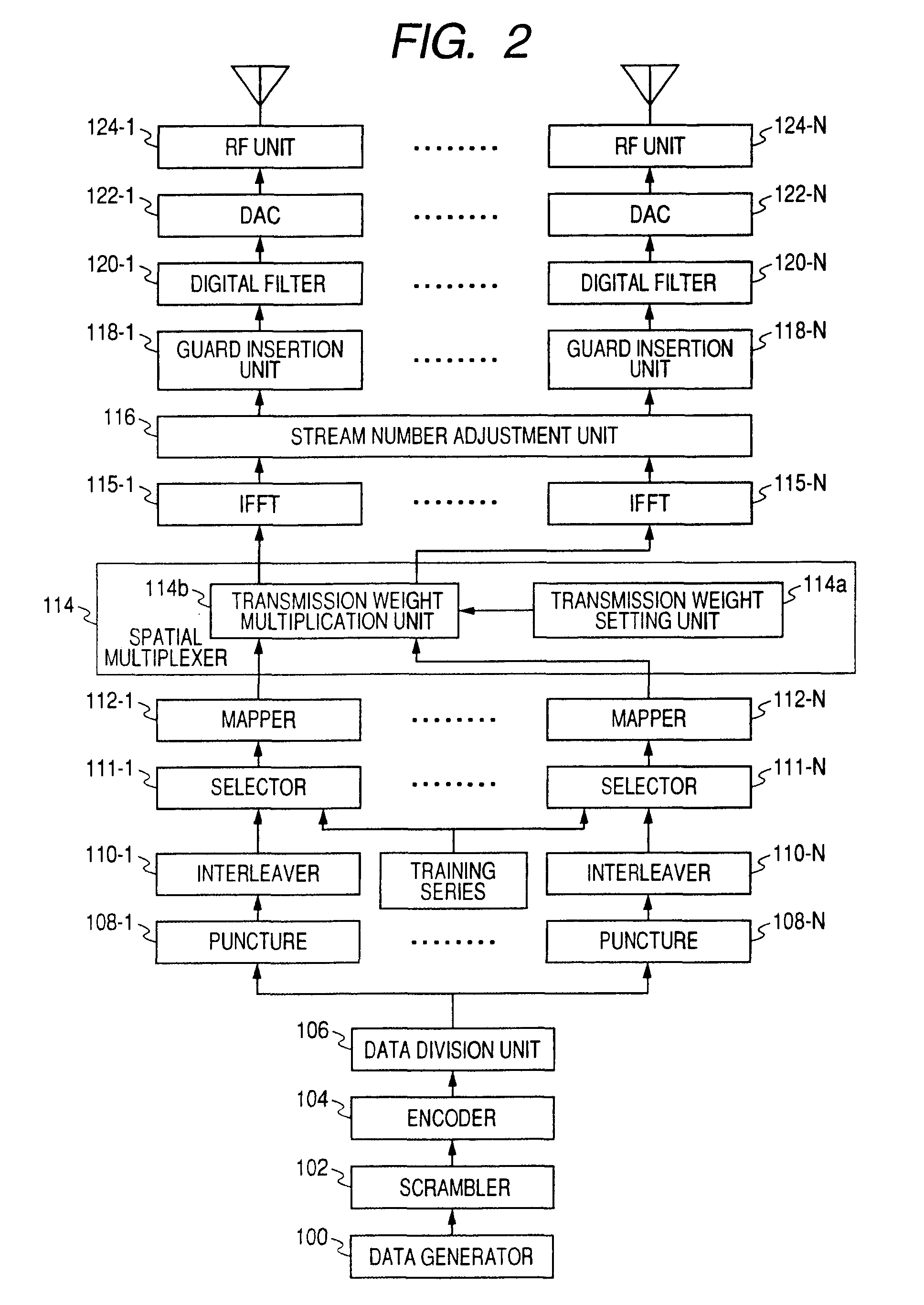
A wireless communication system which performs data transmission using spatially multiplexed streams from a first terminal including N antennas to a second terminal including M antennas (N is an integer of 2 or more and M is an integer of 1 or more) is disclosed. The system includes notifying means, training means, channel matrix estimation means, beamforming information feedback means, transmission weight matrix setting means, and beamforming means.
Owner:SONY CORP
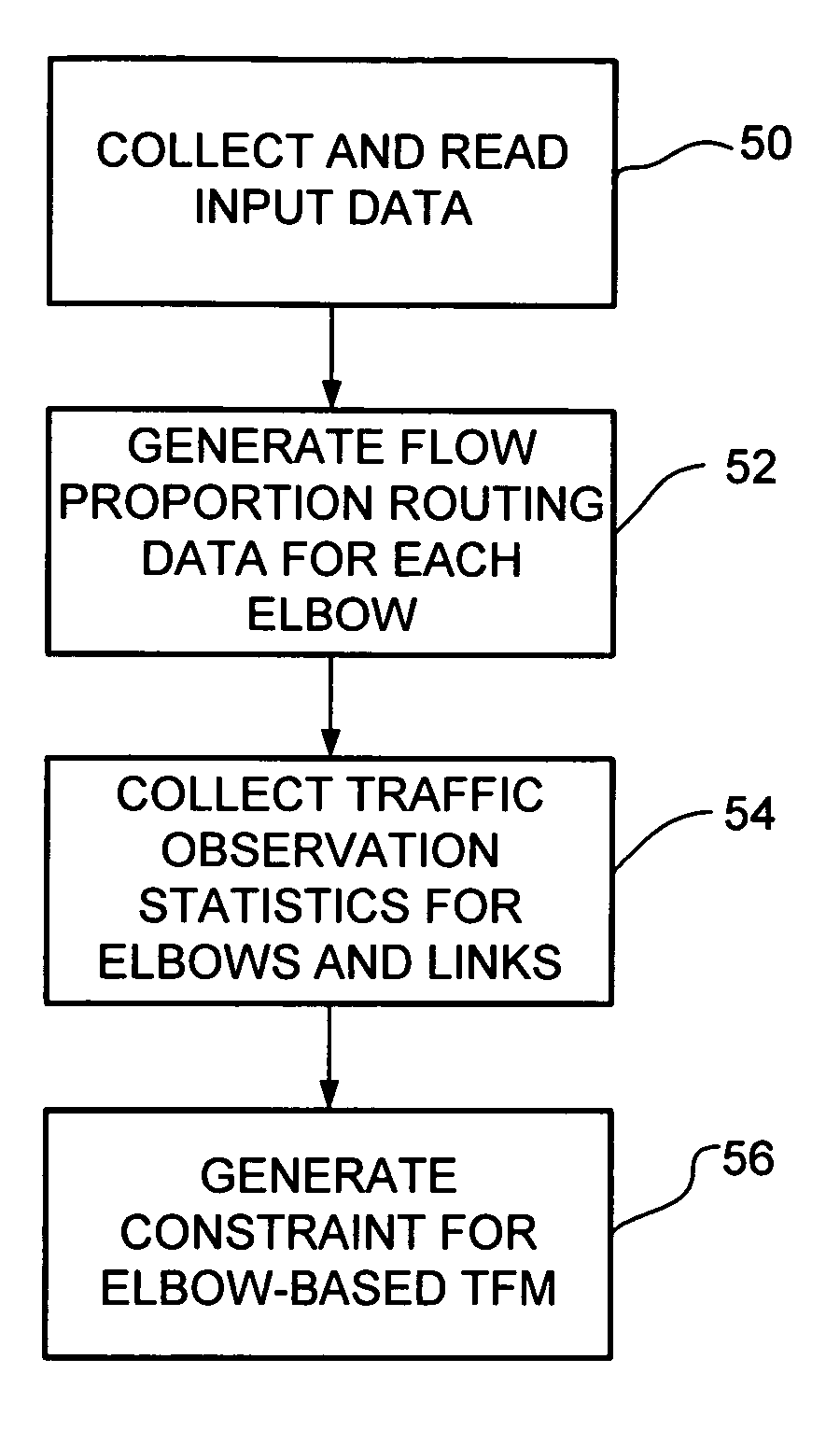
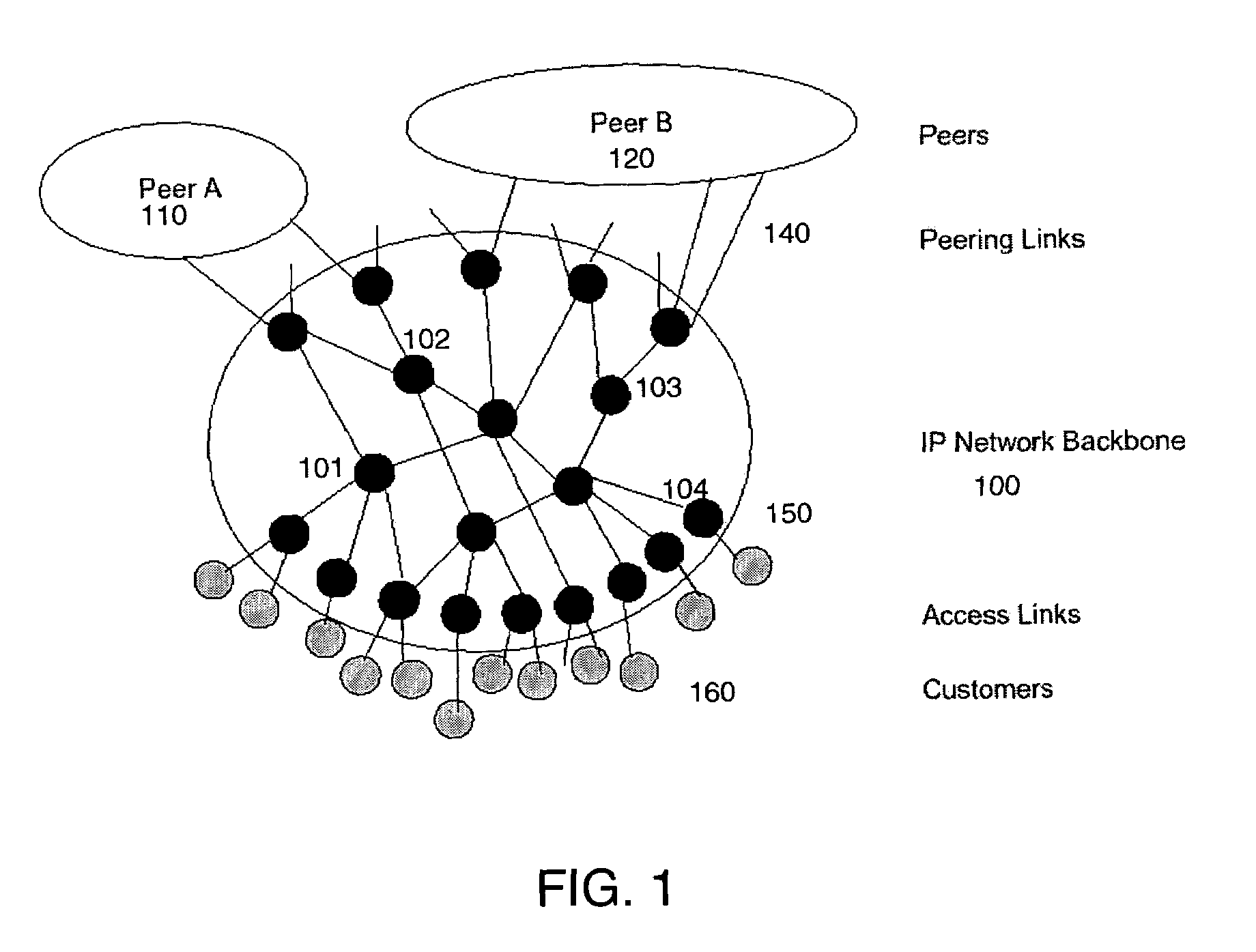
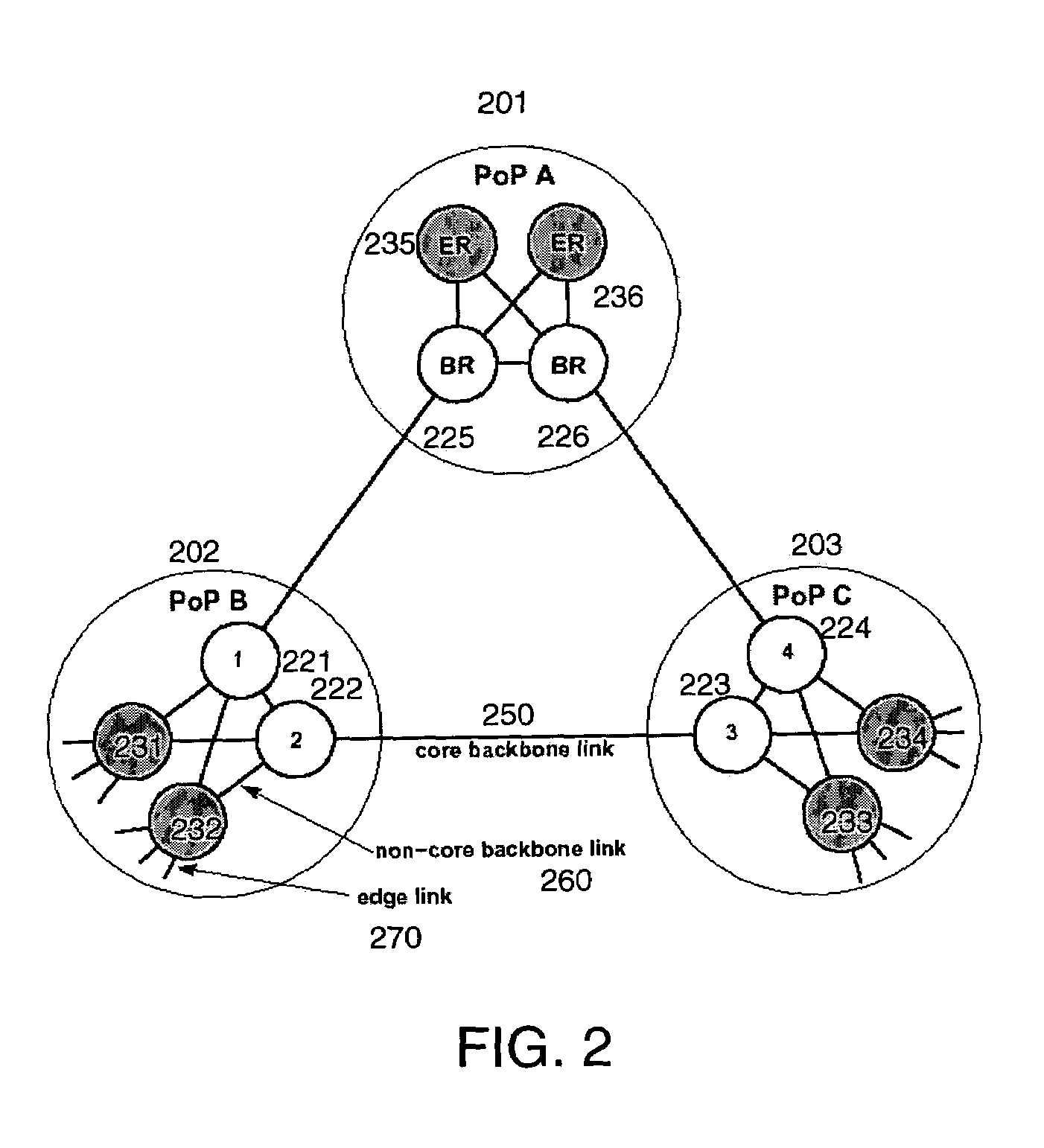
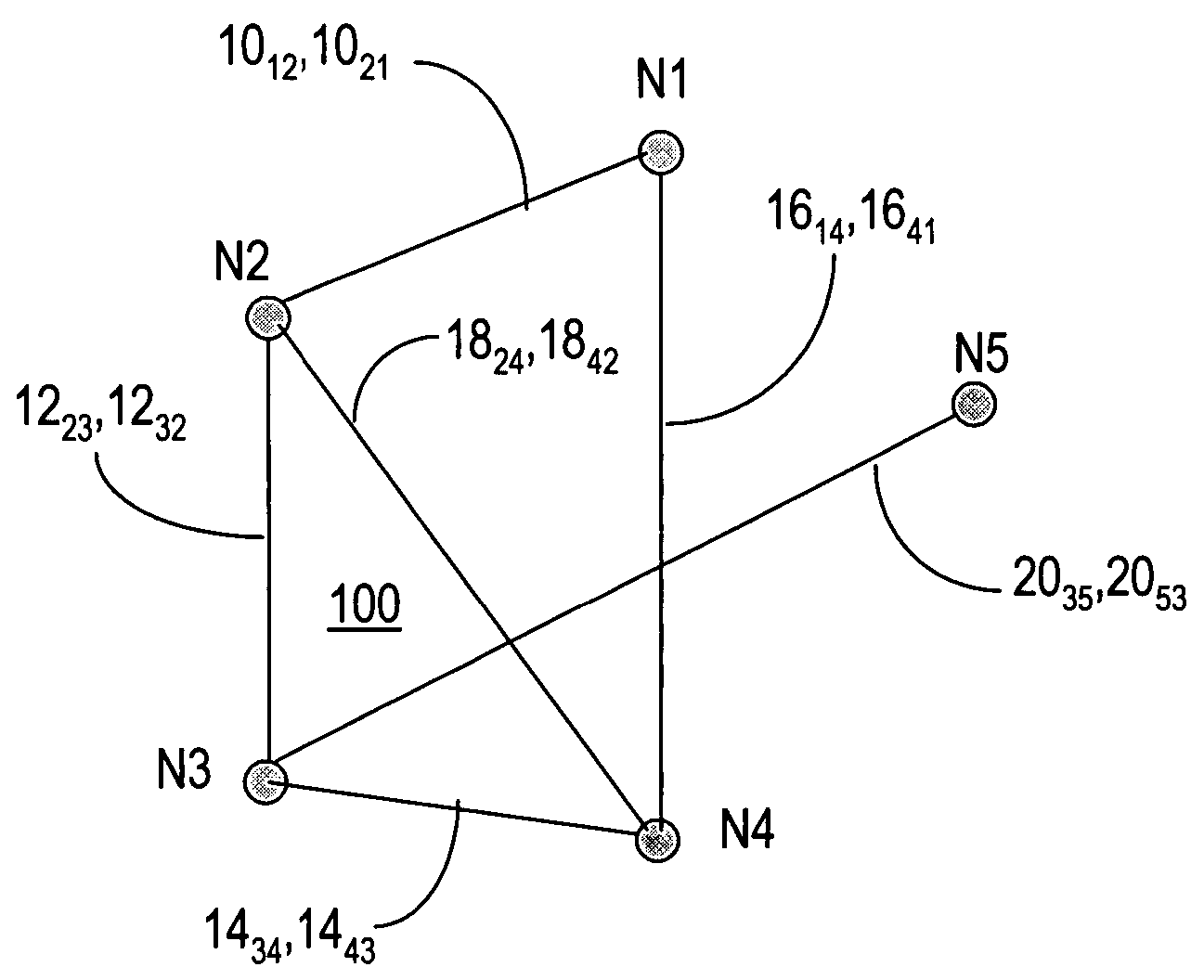
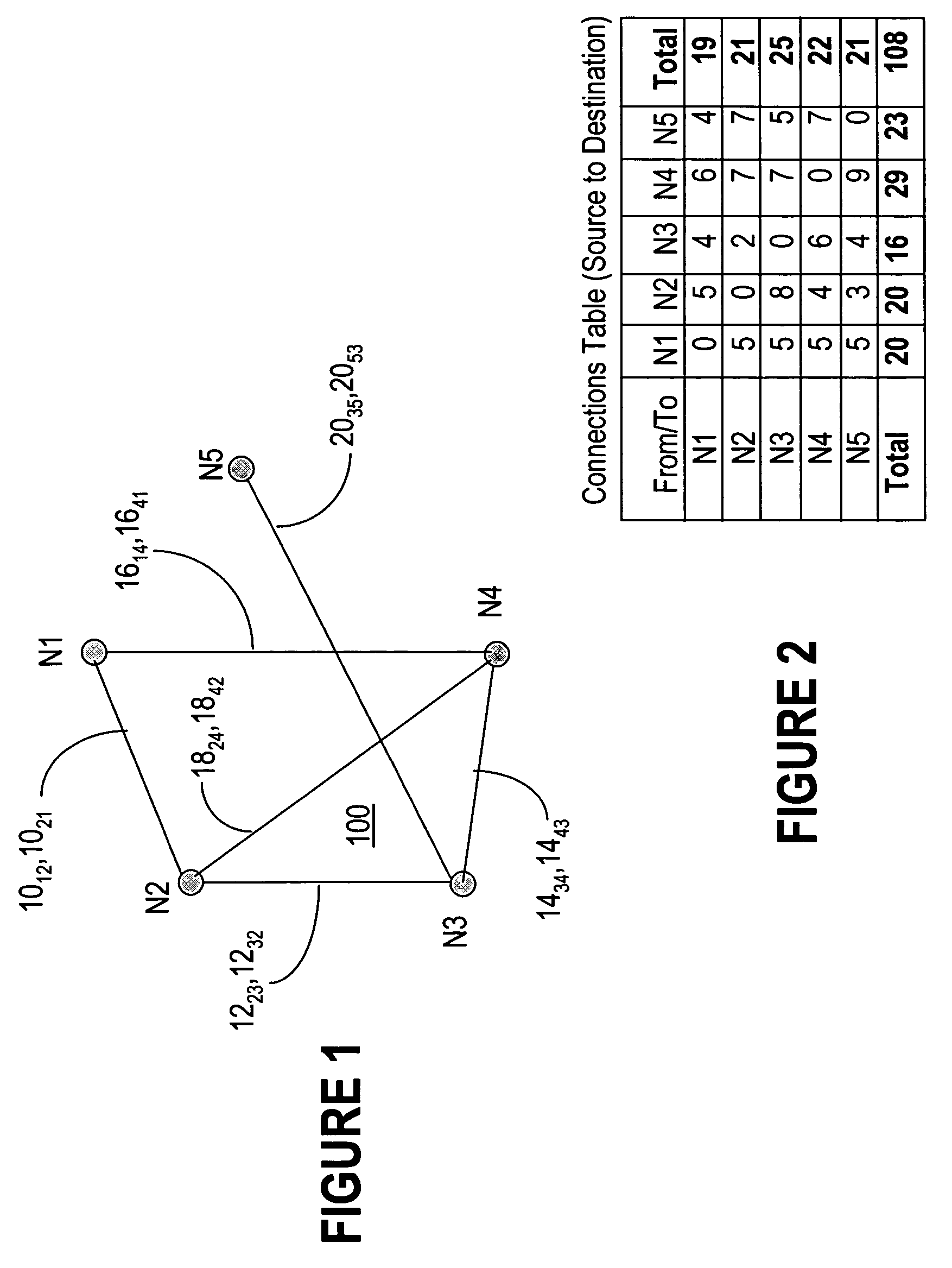
Method and system for network traffic matrix analysis
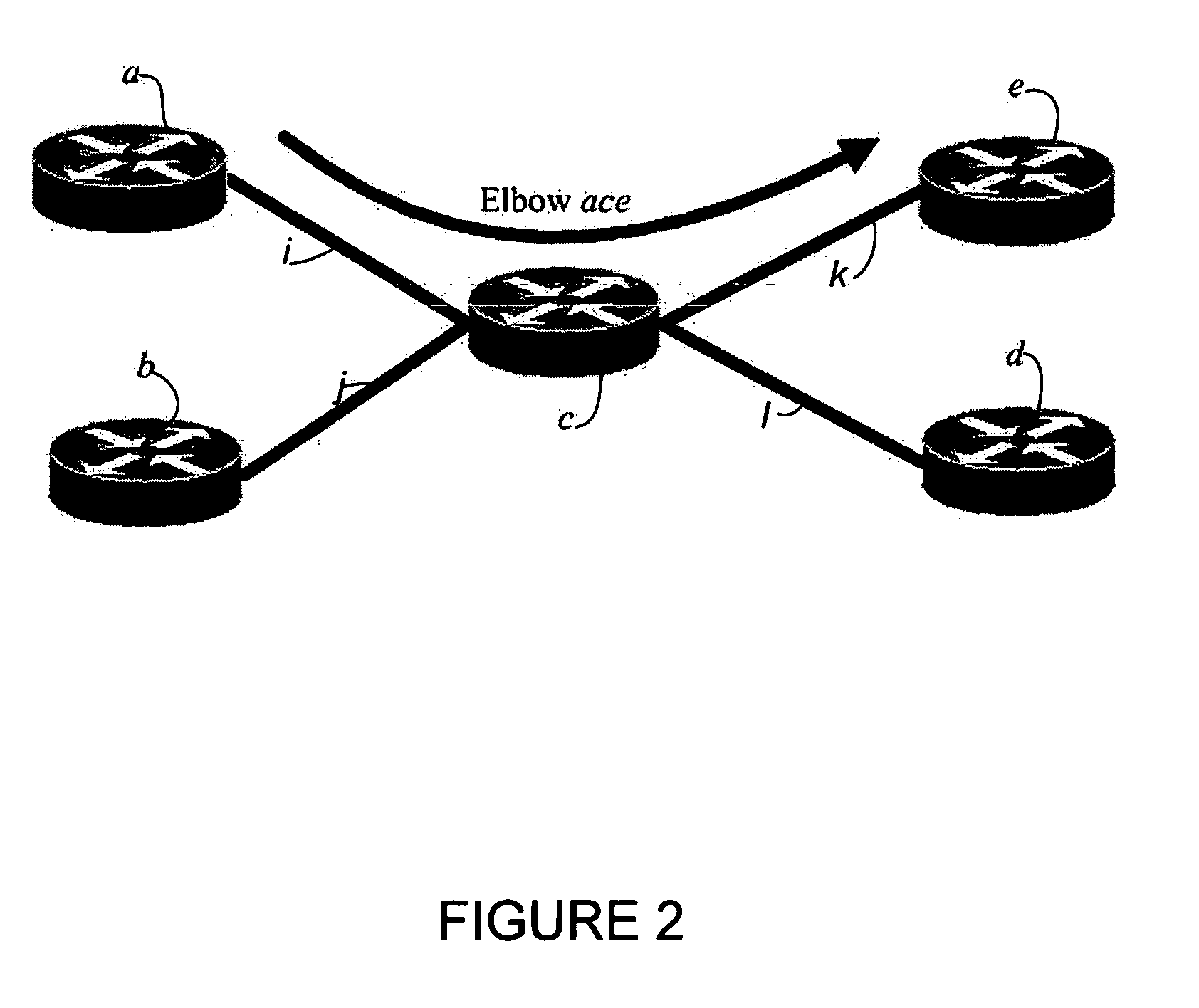
A method and system for calculating data traffic flow in a communications network are disclosed. The communications network comprises a plurality of nodes including a plurality of source nodes, a plurality of destination nodes, and a plurality of intermediate nodes. Each of the intermediate nodes includes at least one elbow comprising one ingress interface and one egress interface of the intermediate node. The method includes obtaining local data traffic measurements at each of the elbows, wherein the local data traffic measurements comprise data traffic arriving at the intermediate node via the ingress interface and leaving the intermediate node via the egress interface. The local data traffic measurements are used in calculation of the traffic flow and may be used, for example, to generate data traffic matrix information using data traffic matrix inference or data traffic matrix estimation.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
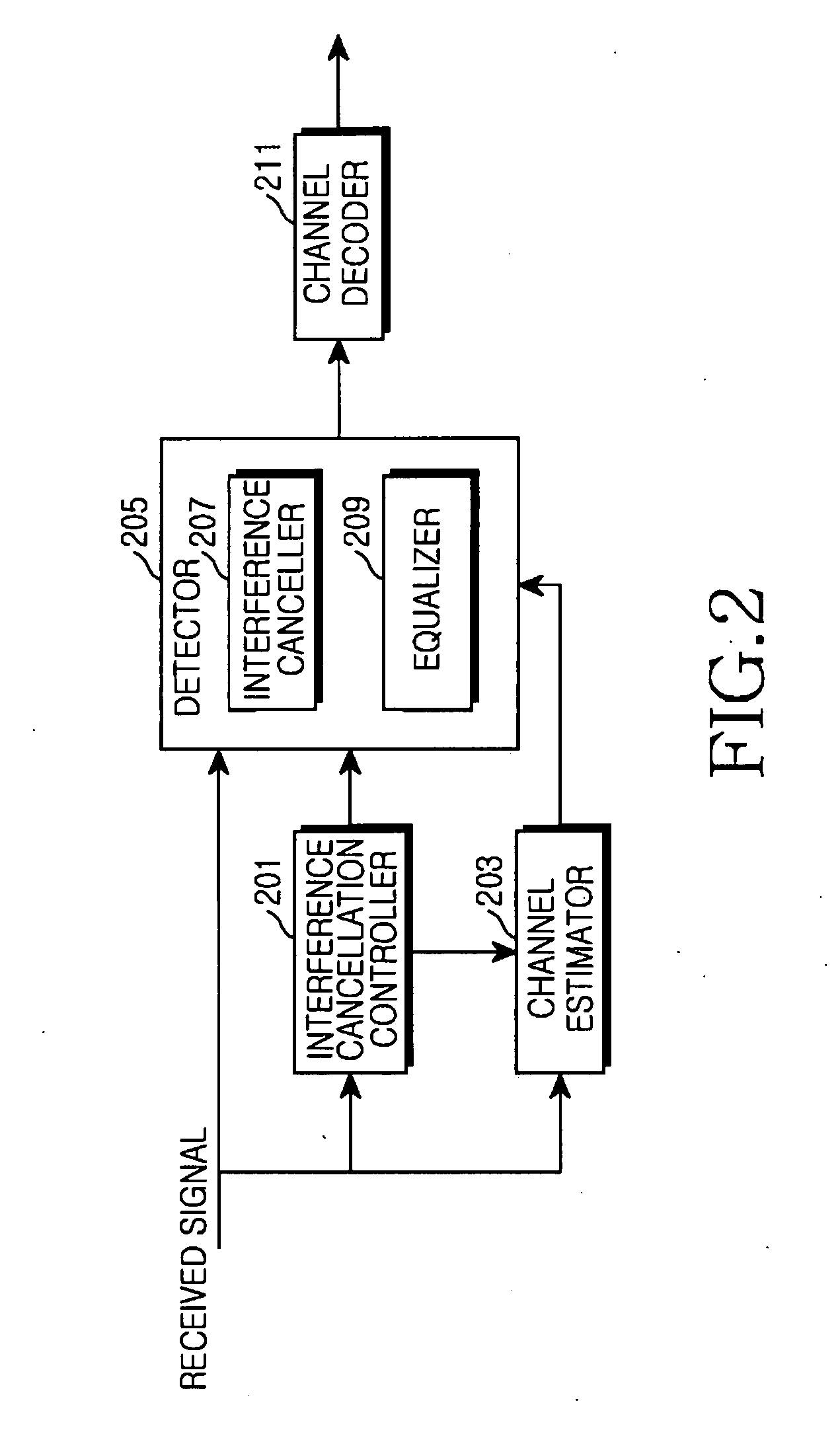
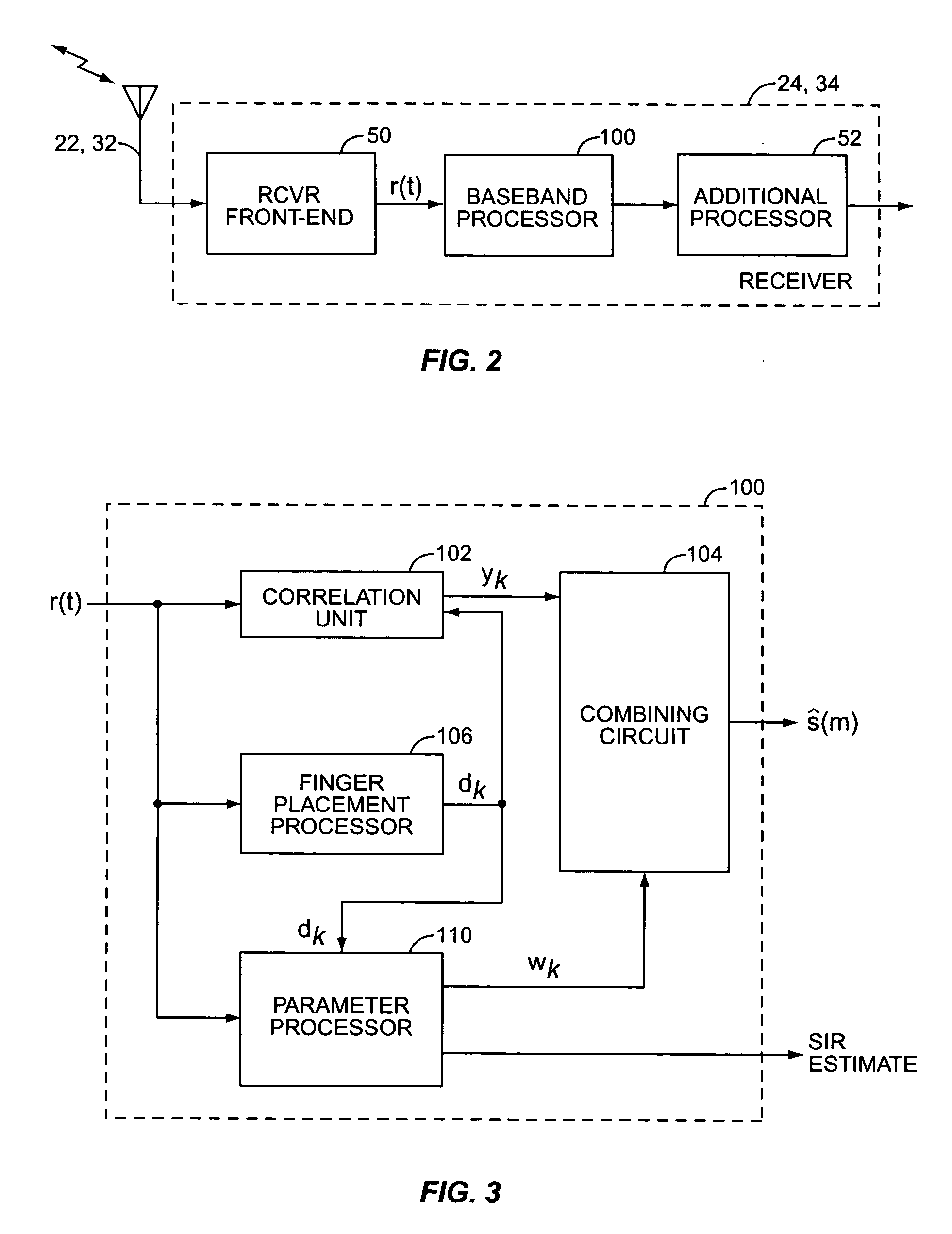
Channel estimation apparatus and method for interference cancellation in mobile communication system
InactiveUS20070242782A1Pipe supportsAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsEstimation methodsMobile communication systems
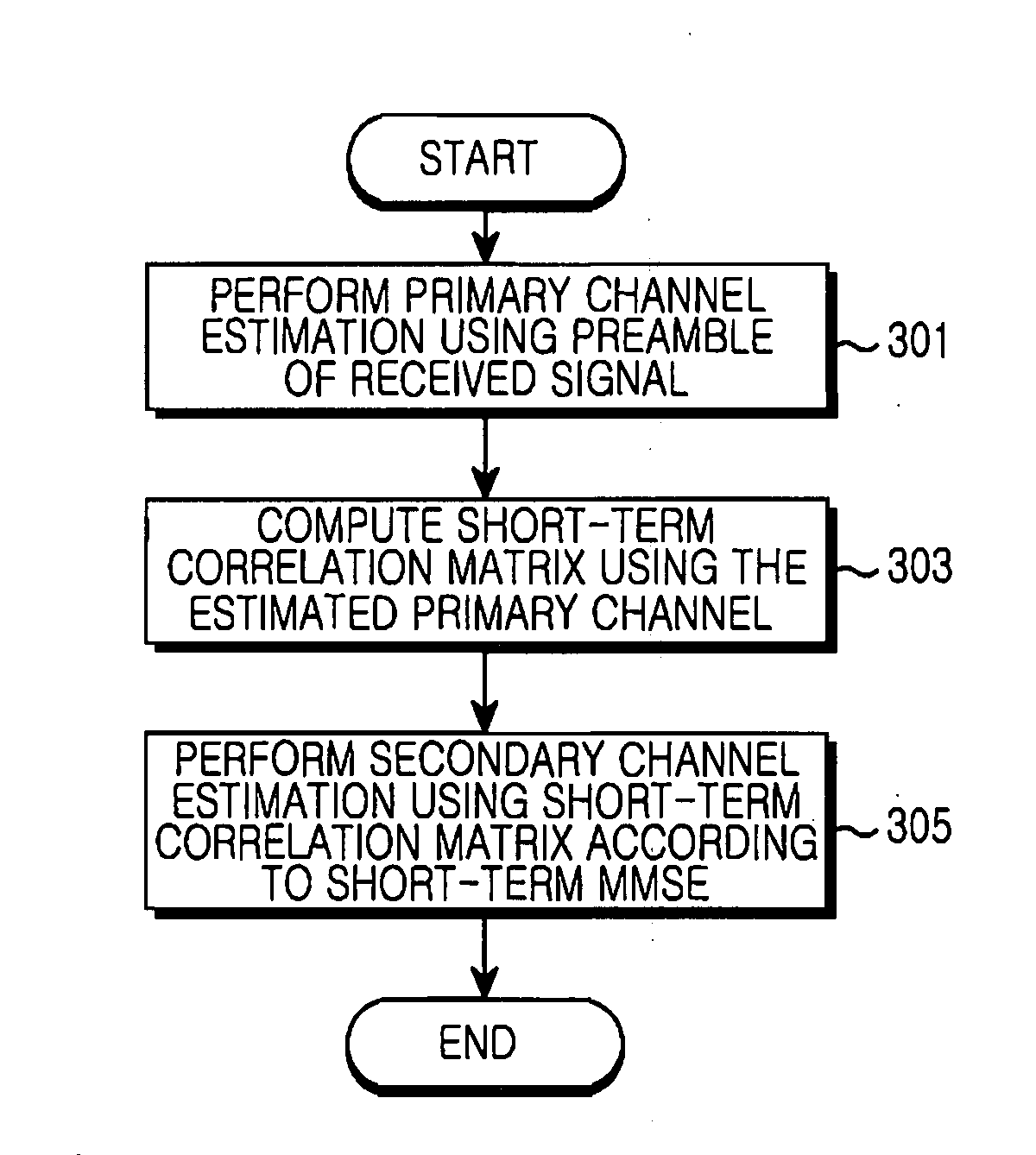
Channel estimation apparatus and method for interference cancellation in a mobile communication system are provided. The channel estimation method includes detecting a preamble from a received signal and estimating a primary channel using the detected preamble; calculating a short-term correlation matrix using the primary channel; and estimating a secondary channel using the calculated short-term correlation matrix according to a certain channel estimation scheme.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
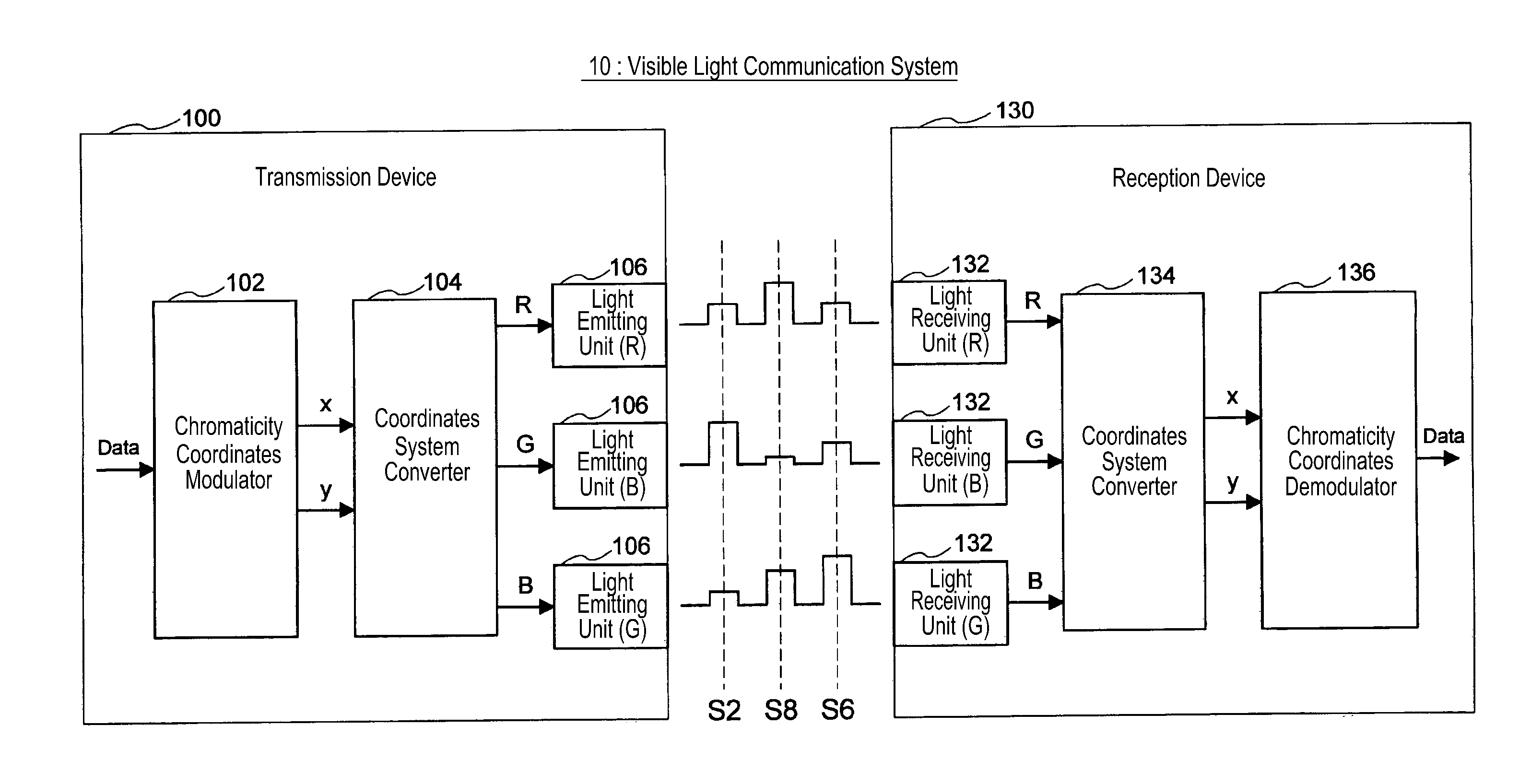
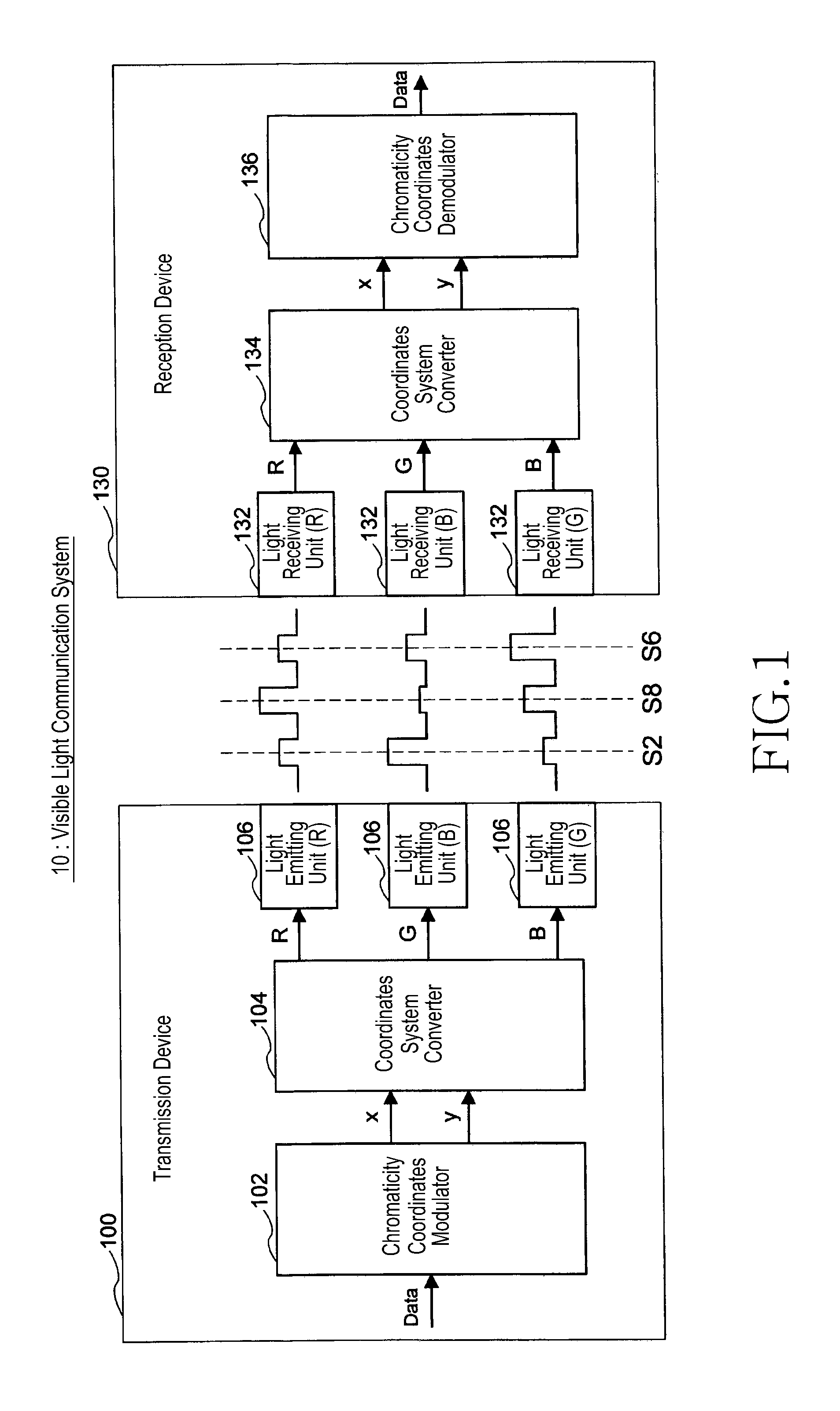
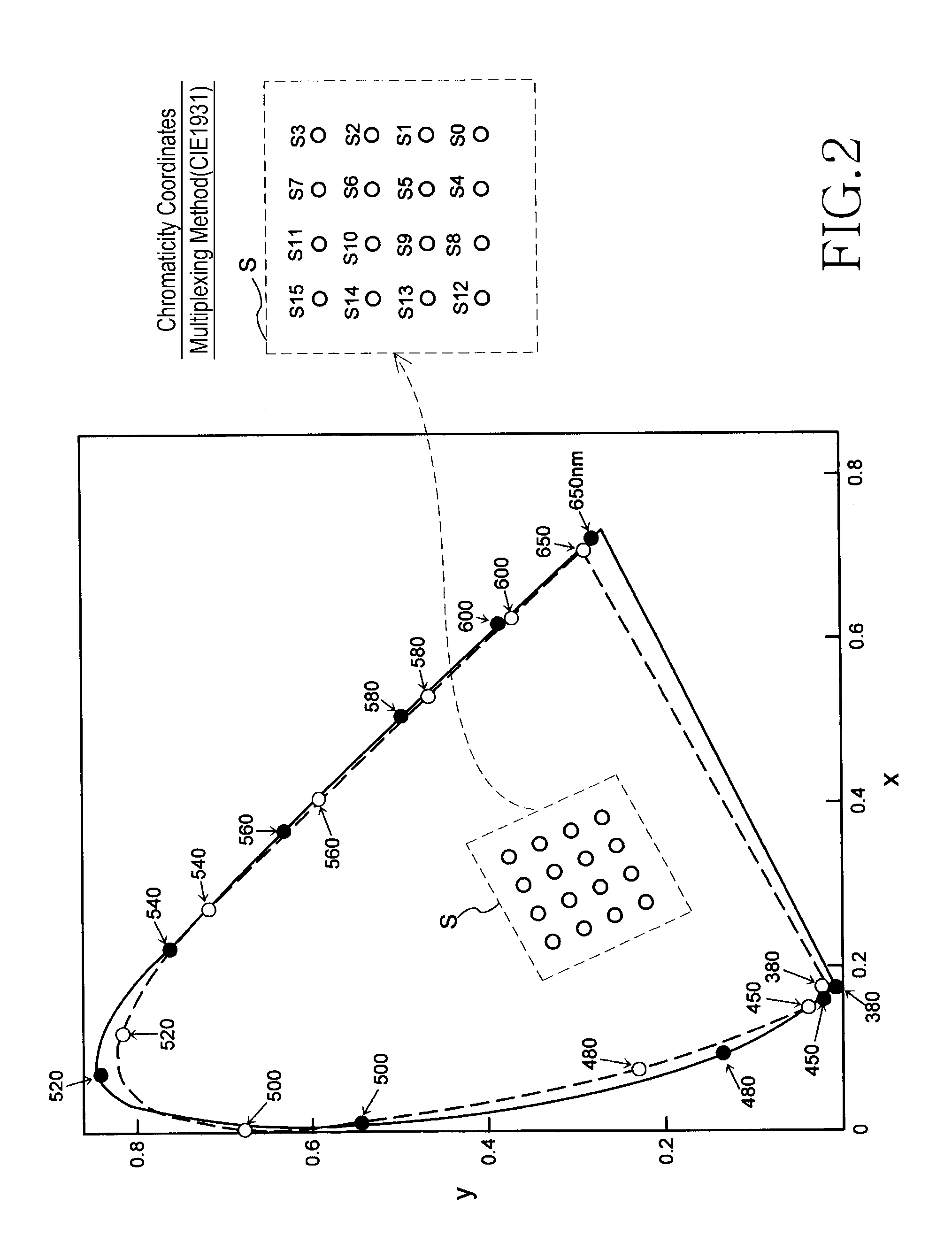
Visible-light communication system system and method
ActiveUS20110200338A1Deterioration of transmission qualityReduce computing loadWavelength-division multiplex systemsClose-range type systemsVisible light communicationLuminescence
Disclosed is a visible light communication system including a transmission device, including multiple light emitting units emitting light of different colors and mapping transmission data to a chromaticity point, calculating luminescence of each of the light emitting units, generating a preamble signal for channel matrix estimation, and emitting light based on the preamble signal and calculated luminescence amount. A reception device of the visible light communication system includes multiple light receiving units and estimates a channel matrix based on a corresponding optical signal when an optical signal corresponding to the preamble signal is received in each light receiving unit, compensates the optical signal corresponding to the chromaticity point for a propagation path based on the estimated channel matrix, detects a chromaticity point on the chromaticity coordinates based on a signal after the propagation path compensation, and demodulates the transmission data.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Impairment correlation estimation in a spread spectrum system
ActiveUS20050215218A1Suppress noiseSuppress interferenceRadio transmissionTransmitter/receiver shaping networksComputer scienceMulti path
A method and apparatus derives an impairment correlation matrix to process signals received at a wireless receiver over multiple paths of a multi-path channel. The receiver includes first and second impairment correlation estimators for estimating first and second impairment correlation matrices based on despread symbols received over multiple paths of a multi-path channel. The receiver then derives the impairment correlation matrix based on the estimated first and second impairment correlation matrices. The receiver may combine traffic despread values to suppress interference using weighting factors calculated based on the derived impairment correlation matrix. Further, the receiver may estimate a signal-to-interference ratio based on the derived impairment correlation matrix.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
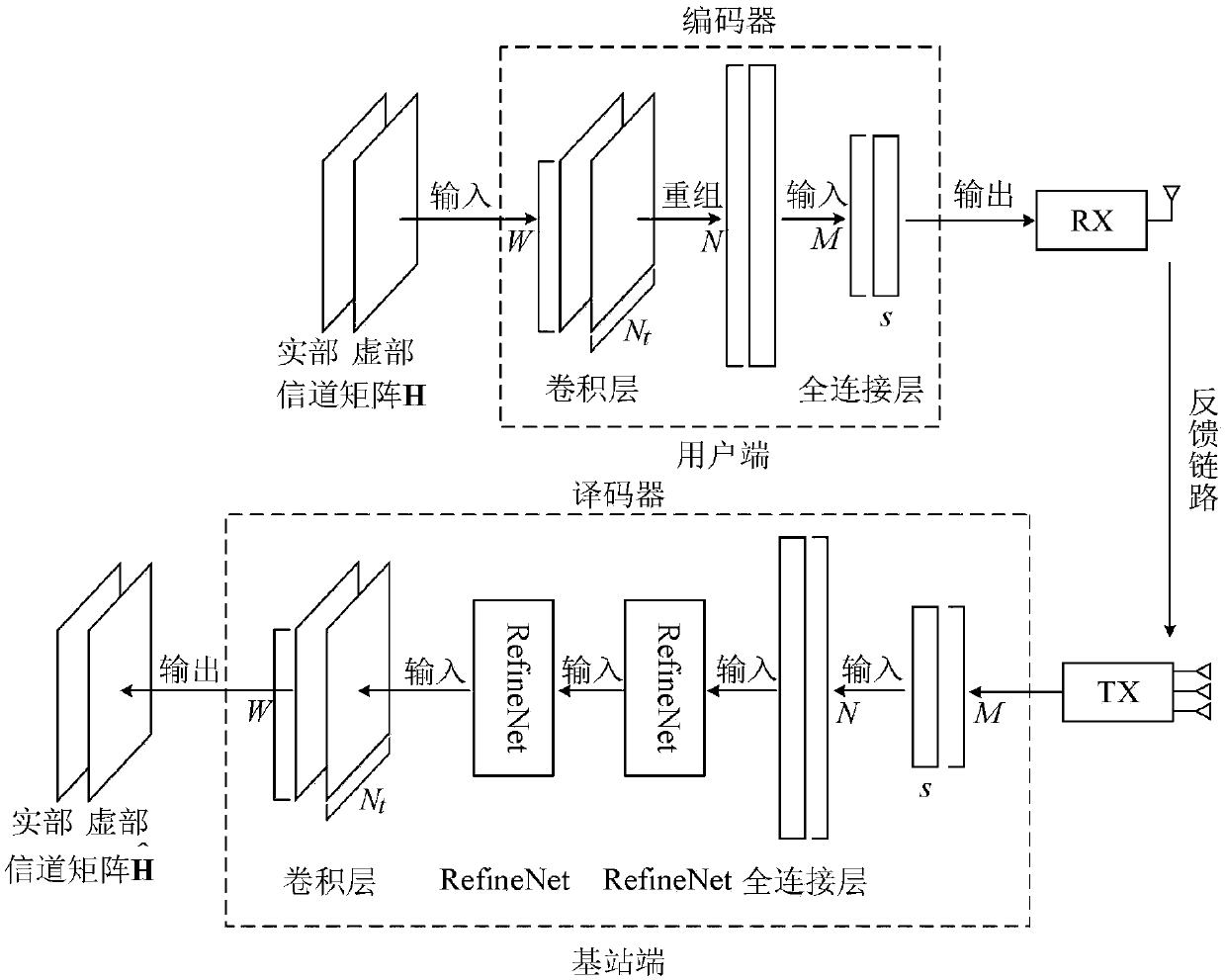
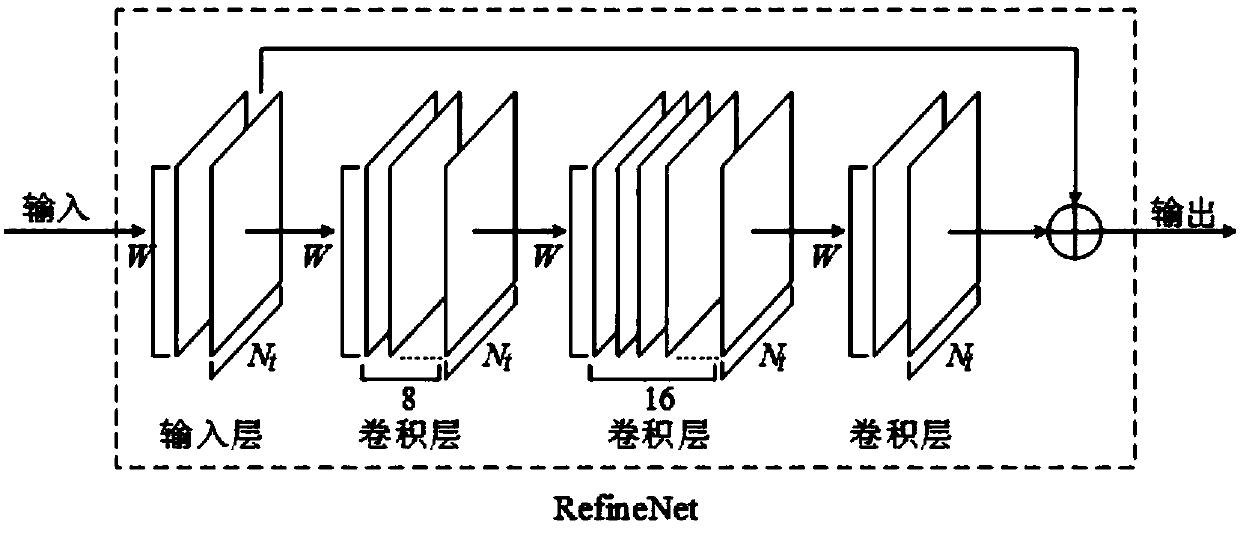
Large-scale MIMO channel state information feedback method based on deep learning
ActiveCN108390706AHigh speedImprove rebuild qualitySpatial transmit diversityFourier transform on finite groupsModel parameters
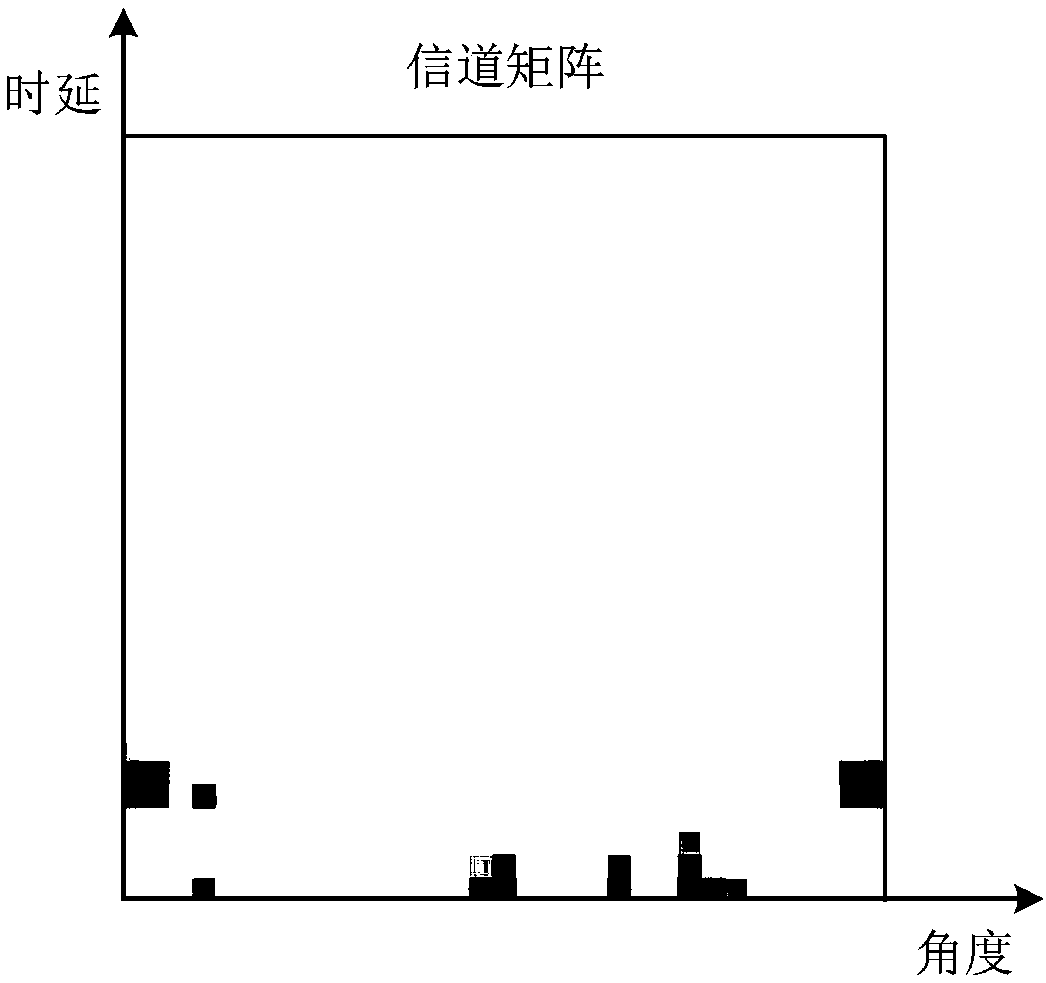
The invention discloses a large-scale MIMO channel state information feedback method based on deep learning. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, carrying out two-dimensional discrete Fourier transform (DFT) on a channel matrix H-wave of MIMO channel state information in a spatial frequency domain on a user side, so that a channel matrix H which is sparse in an angle delay domain isobtained; secondly, constructing a model CsiNet comprising a coder and a decoder, wherein the coder belongs to the user side and is used for coding the channel matrix H into codons with a lower dimension, and the decoder belongs to a base station side and is used for reconstructing an original channel matrix estimation value H-arrow from the codons; thirdly, training the model CsiNet to obtain model parameters; fourthly, carrying out two-dimensional inverse DFT on a reconstructed channel matrix H-arrow which is output by the CsiNet, so that a reconstructed value of the original channel matrixH-wave in the spatial frequency domain is recovered; and finally, using the trained model CsiNet for compressed sensing and reconstruction of channel information. The method provided by the inventionhas the advantages that large-scale MIMO channel state information feedback expenditures can be reduced, and an extremely high channel reconstruction quality and an extremely high channel reconstruction speed can be achieved.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Method and Arragement for Advanced Routing Metrics in Multihop Networks
ActiveUS20080232258A1Large capacityDetermine link costEnergy efficient ICTError preventionDistributed computingMatrix estimation
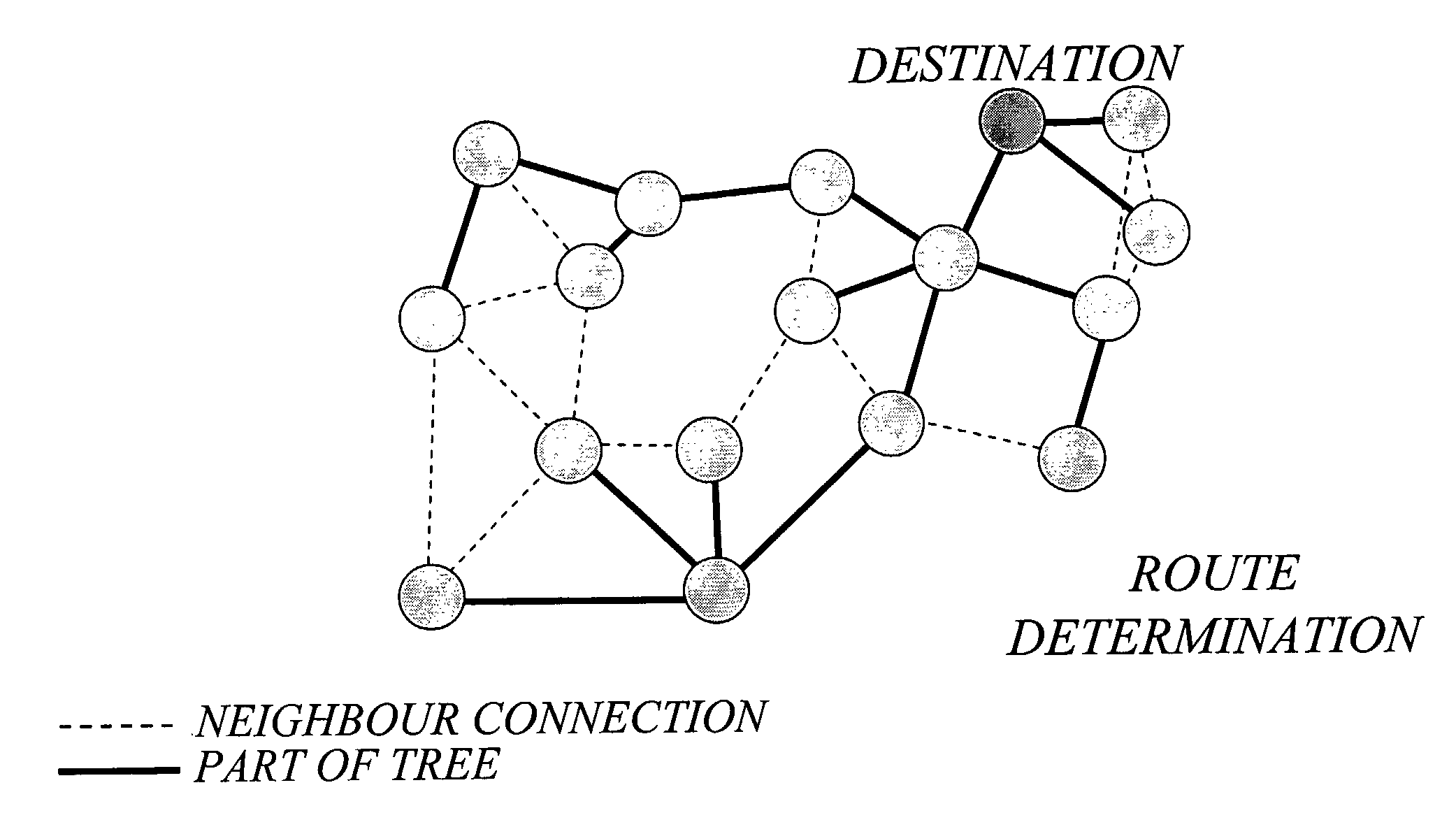
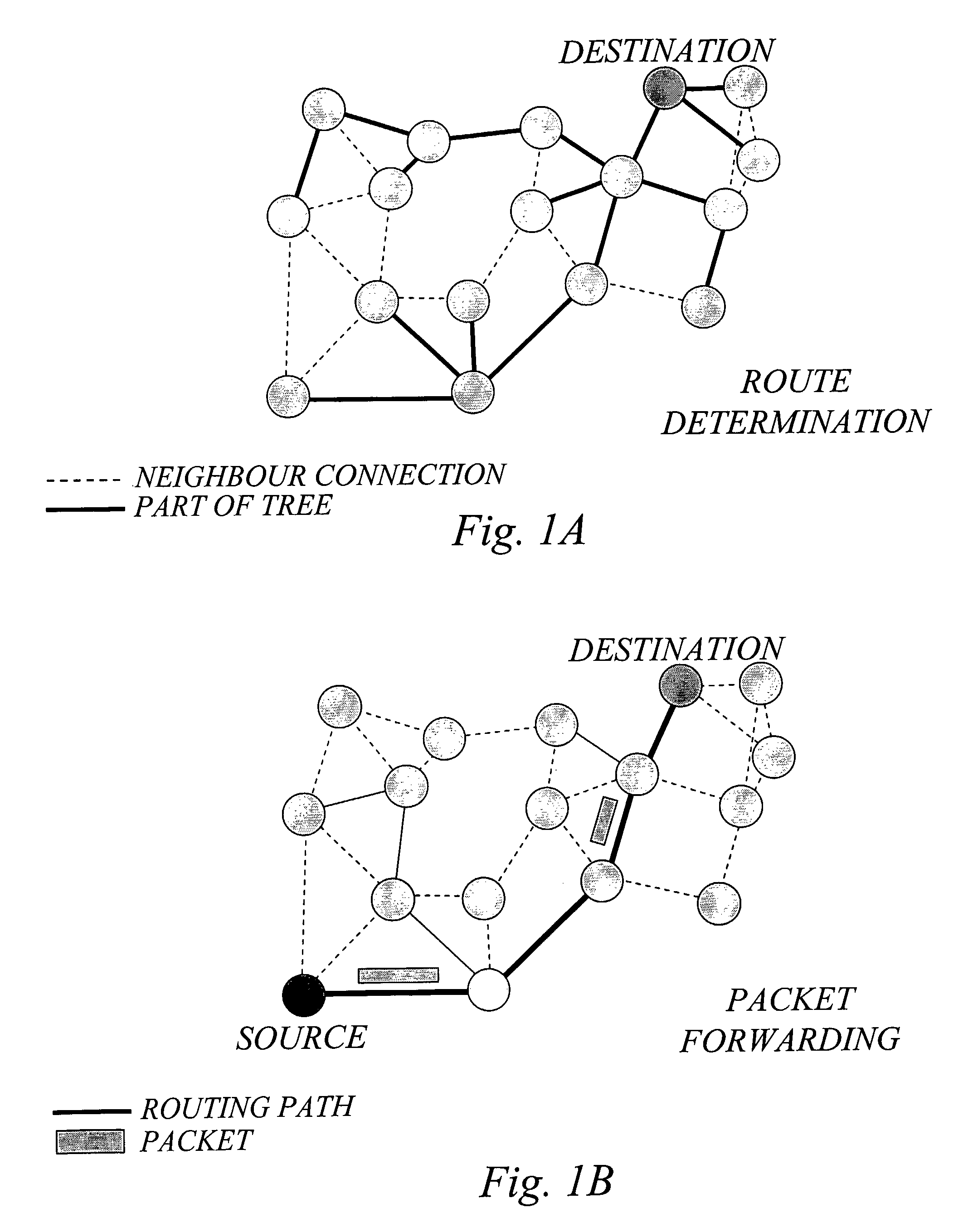
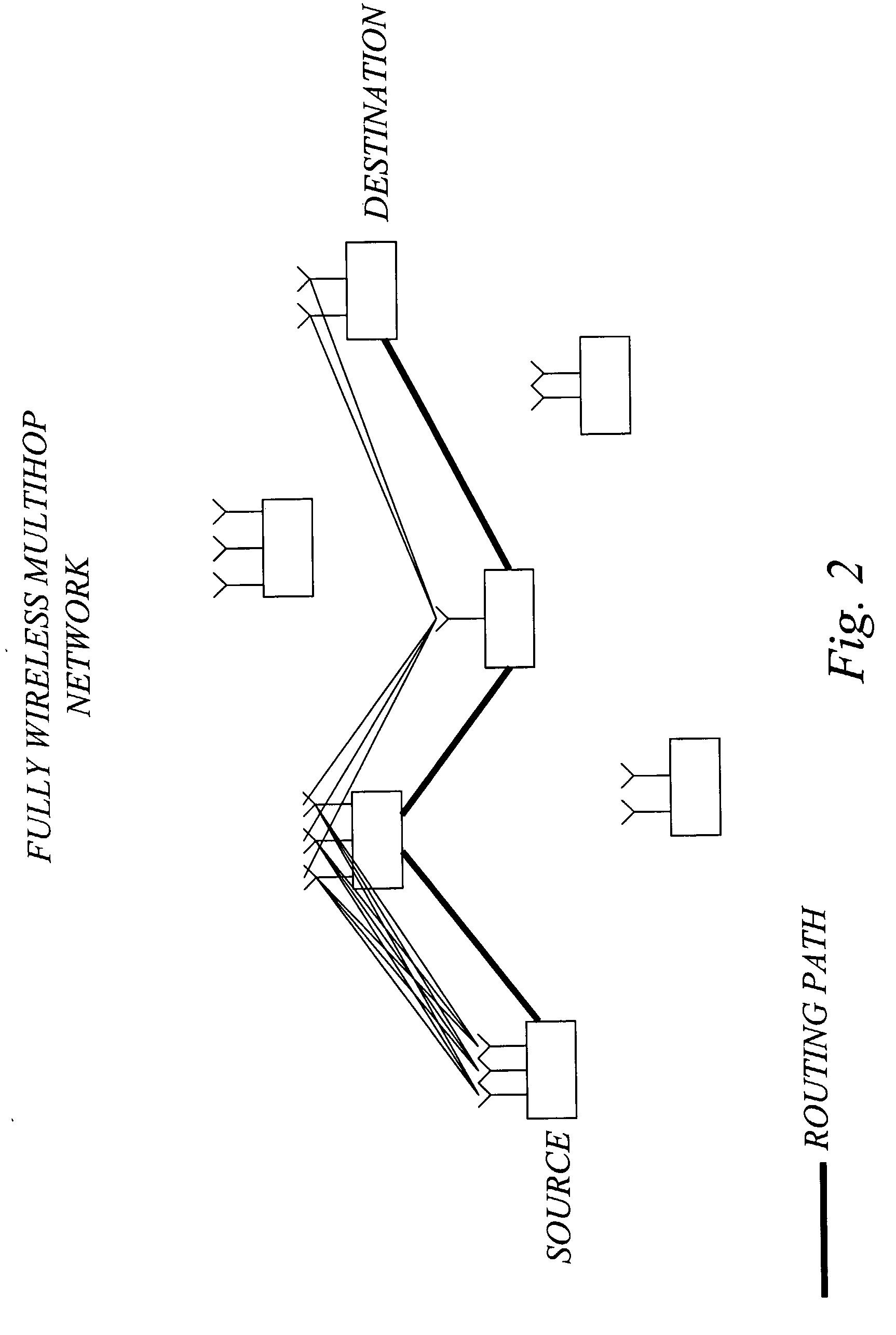
The inventors have envisioned a multihop network scenario in which nodes are equipped with advanced multi-antenna arrangements, and recognized the advantage of exploring the presence of such advanced antenna arrangements in multihop network nodes for the specific purpose of determining link cost for routing in the network. A basic idea of the invention is therefore to determine link cost for a wireless link between a pair of nodes in the network based on multi-channel characteristics between the nodes, where at least one of the nodes is configured for operation with multiple antennas to provide for multiple channels. These multi-channel characteristics may for example be determined based on explicit channel matrix estimation and / or the number of transmit and receive antennas or other information on the antenna capabilities of the involved nodes. The determined link cost information may subsequently be used together with additional routing cost information for route determination, and packet forwarding.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Communication system and method using a relay node
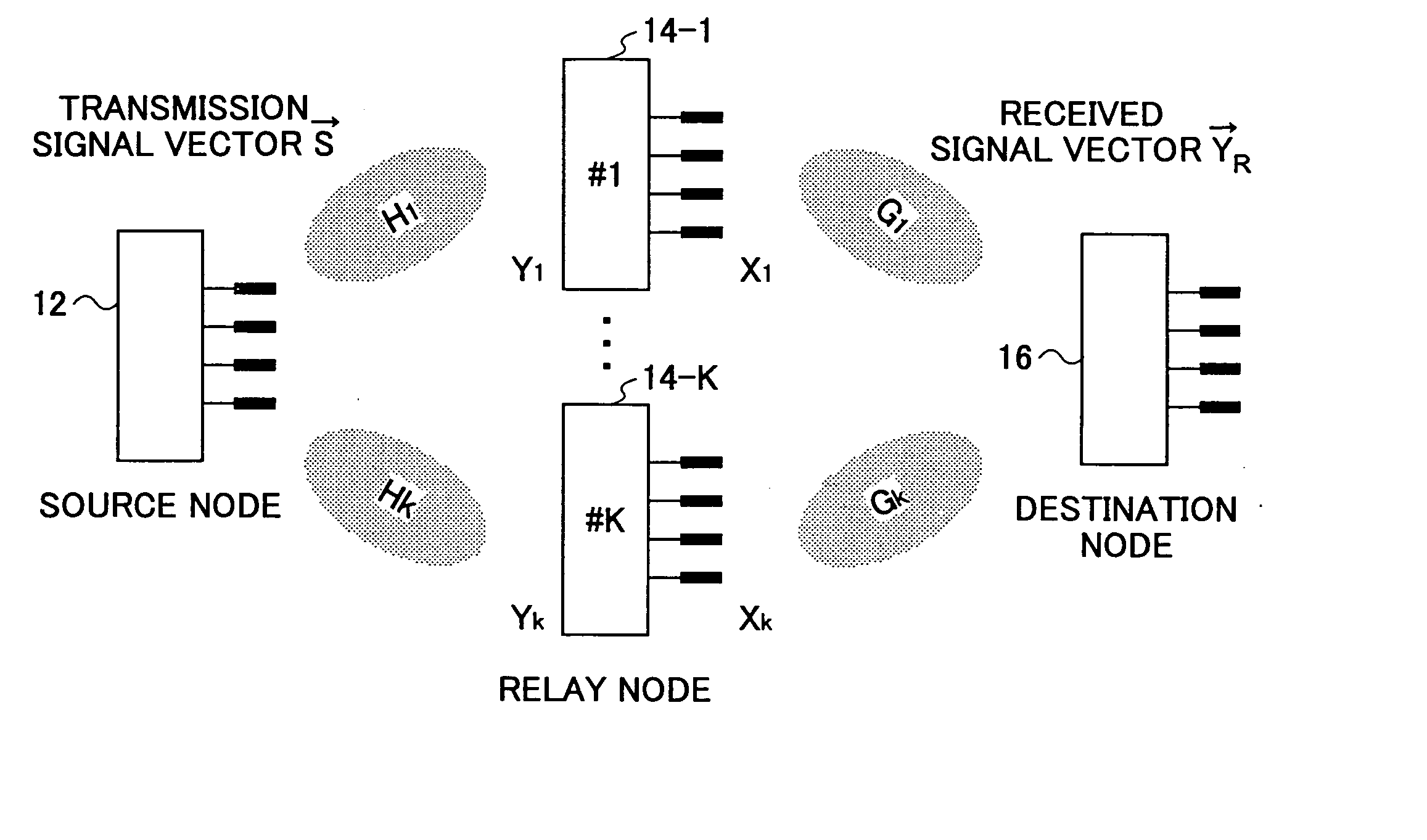
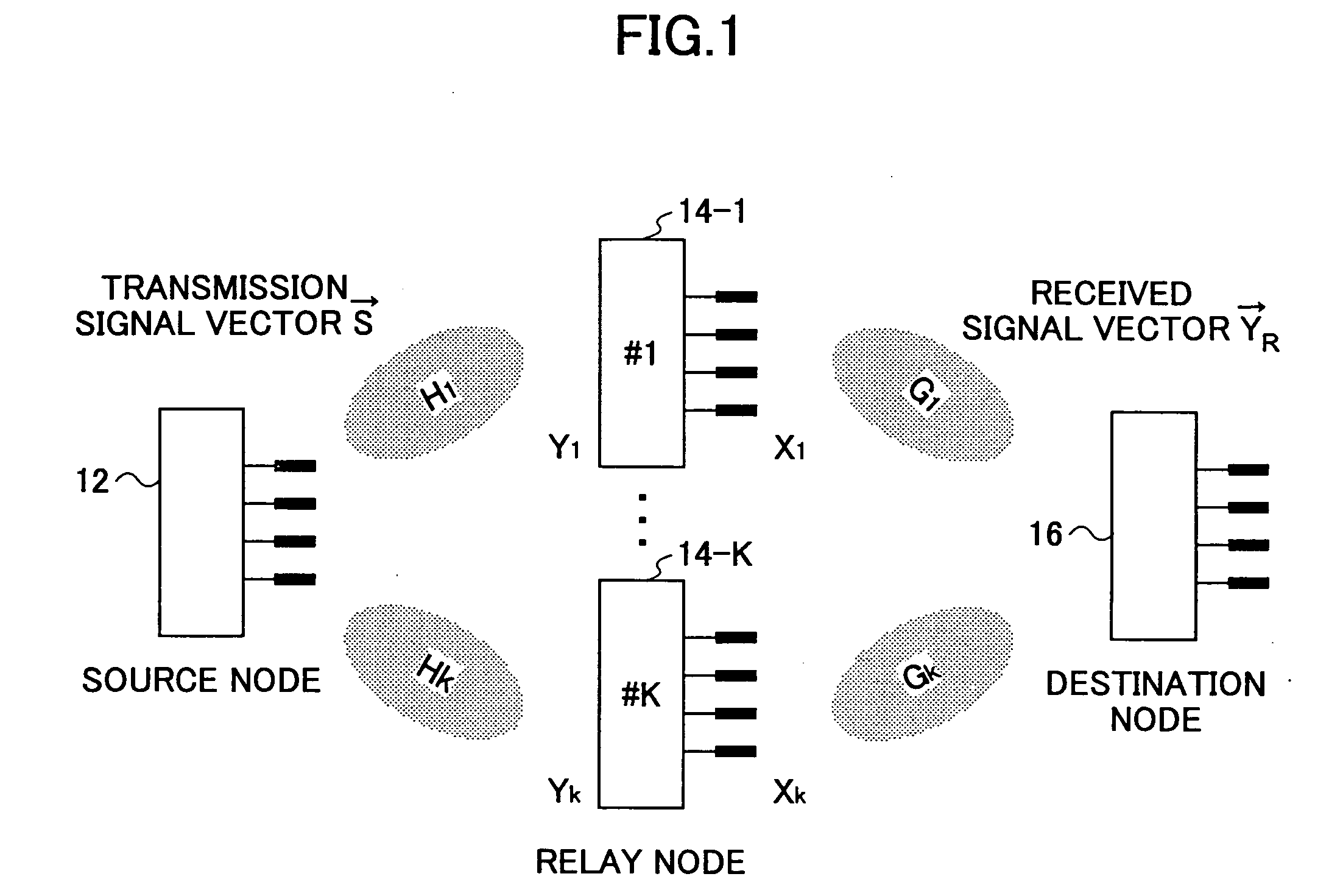
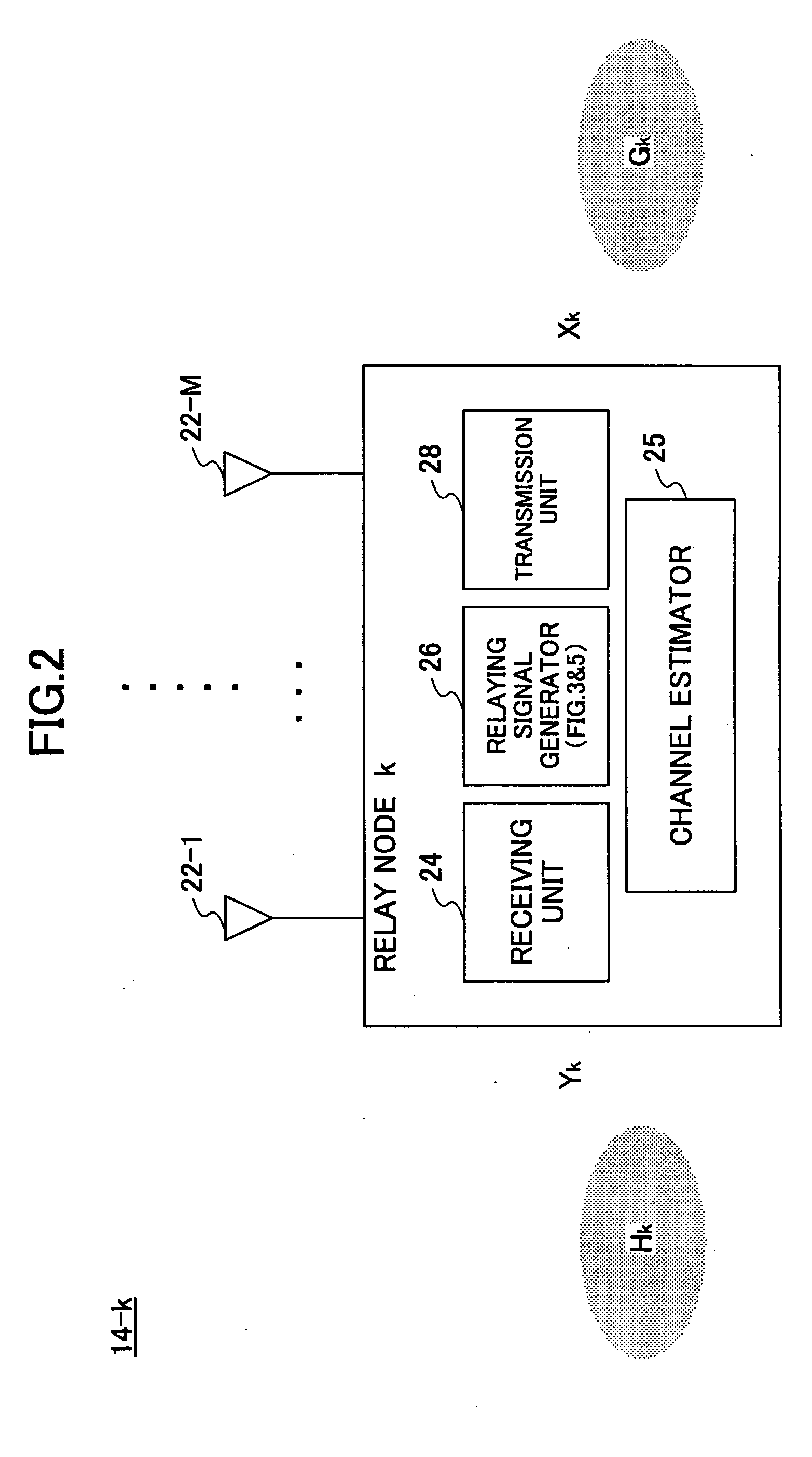
InactiveUS20060056338A1Quality improvementSite diversityFrequency-division multiplex detailsSingular value decompositionCommunications system
A communication node relays a transmission signal transmitted from a desired source node to a target destination node among multiple source nodes and multiple destination nodes. The communication node includes a first unitary matrix estimation unit that estimates a first unitary matrix by performing singular value decomposition involving one or more channel matrices between the relay node and the source nodes other than the desired source node; a second unitary matrix estimation unit that estimates a second unitary matrix by performing singular value decomposition involving one or more channel matrices between the relay node and the destination nodes other than the target destination node; and a transmission unit configured to transmit a relaying signal generated by multiplying a received signal by the first and second unitary matrices toward the target destination node.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
Self-adaptive tracking loop and implementation method
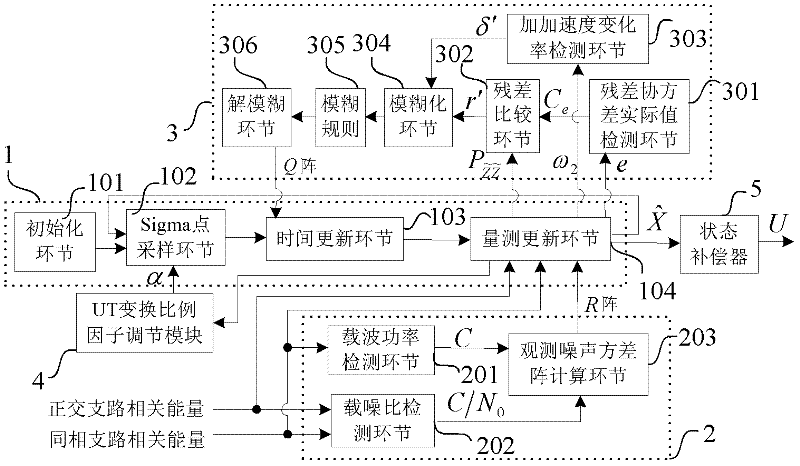
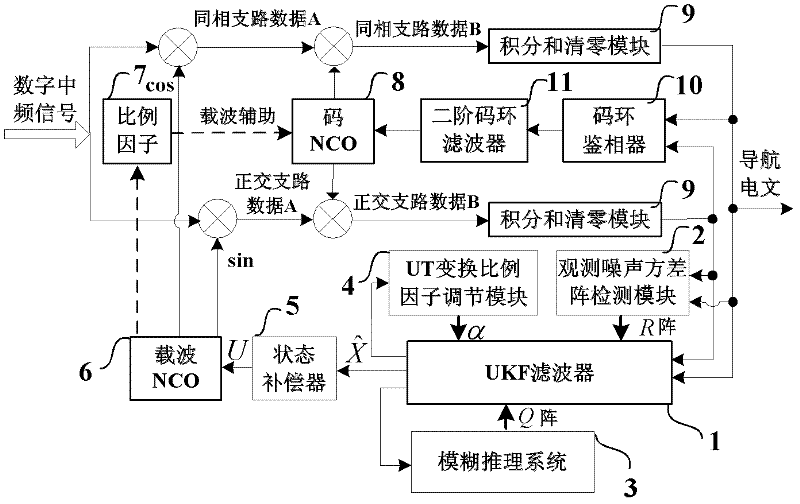
InactiveCN102540216AAccurate trackingSolve the noiseSatellite radio beaconingNumerical controlDiscriminator
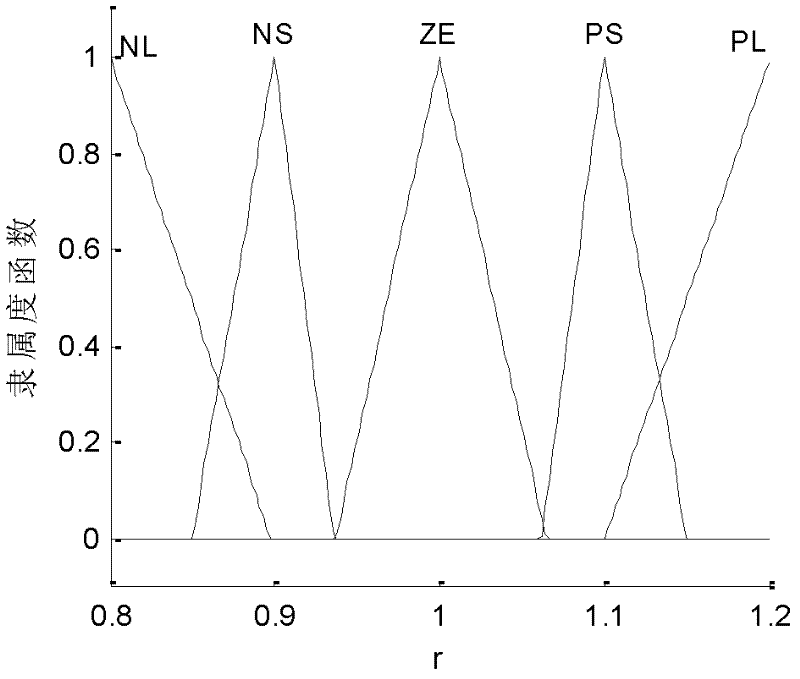
The invention discloses a self-adaptive tracking loop, which comprises an unscented Kalman filter (UKF), an observation noise variance matrix detection module, a fuzzy inference system, an unscented transformation (UT) scale factor regulation module, a state compensator, a carrier wave numerical controlled oscillator (NCO), scale factors, a code NCO, an integration and zero-clearing module, a code loop phase discriminator and a second order code loop filter, and additionally discloses an implementation method for the self-adaptive tracking loop. The implementation method comprises a step 1 ofsignal correlation, integration and zero clearing; a step 2 of code phase tracking; a step 3 of UKF modeling; a step 4 of observation noise variance matrix estimation; a step 5 of process noise variance matrix estimation; a step 6 of UT scale factor regulation; a step 7 of state estimation deviation compensation; and a step 8 of assistance of the carrier wave NCO in the code NCO. According to theself-adaptive tracking loop, the UKF, the observation noise variance matrix detection module and the fuzzy inference system are designed in the carrier tracking loop, so not only can a contradiction between thermal noise vibration in the tracking loop and a dynamic stress error be solved, but a process noise variance matrix and an observation noise variance matrix can be regulated in a self-adaptive manner according to changes of the external environment, and thereby the self-adaptive ability of the tracking loop under complex changeable environments of high dynamic, strong interference, and the like is effectively improved.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
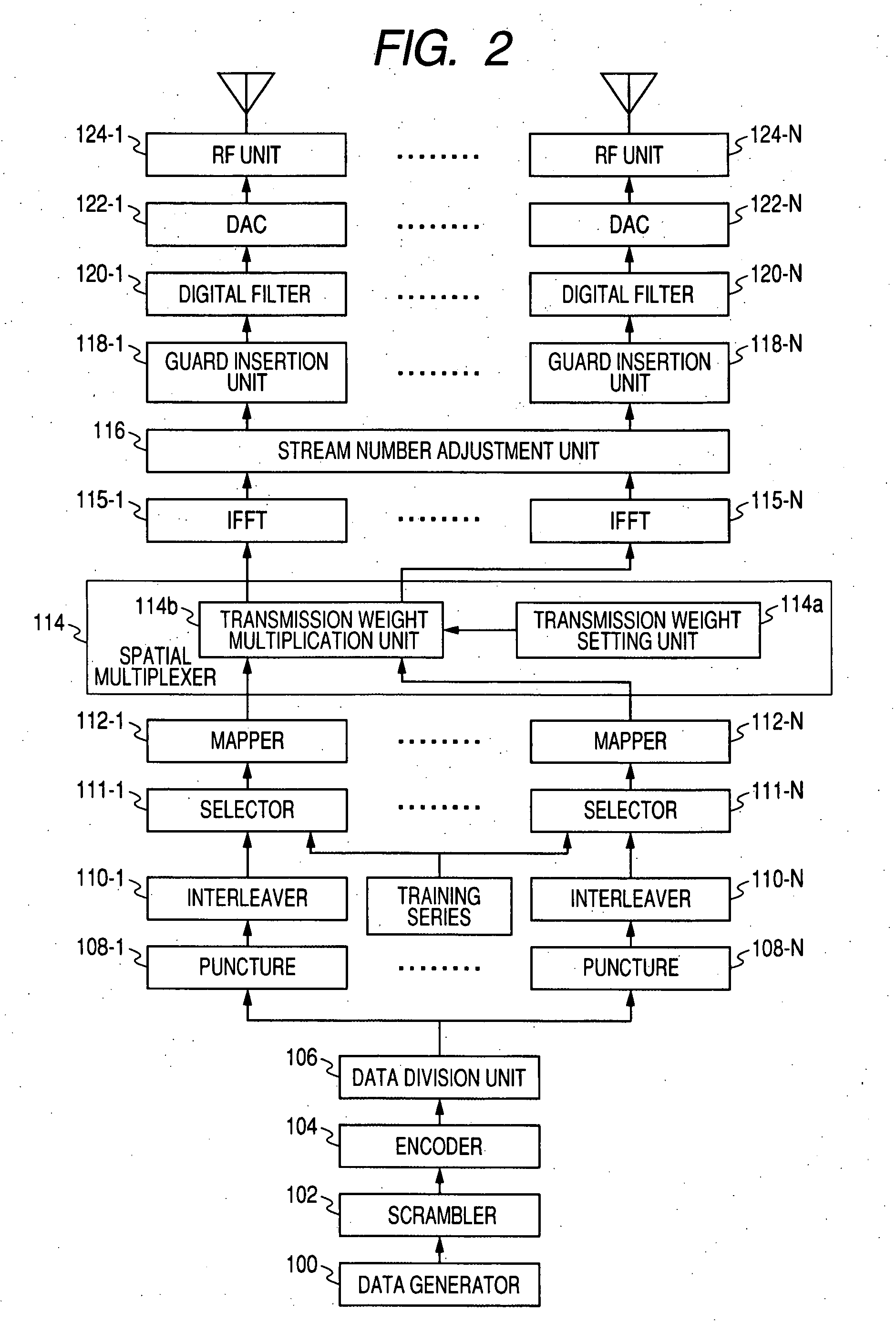
Wireless communication apparatus, wireless communication method, and computer program
InactiveUS8064502B2Avoid miscalculationsFast communicationTransmitters monitoringSpatial transmit diversityEqualizationComputer science
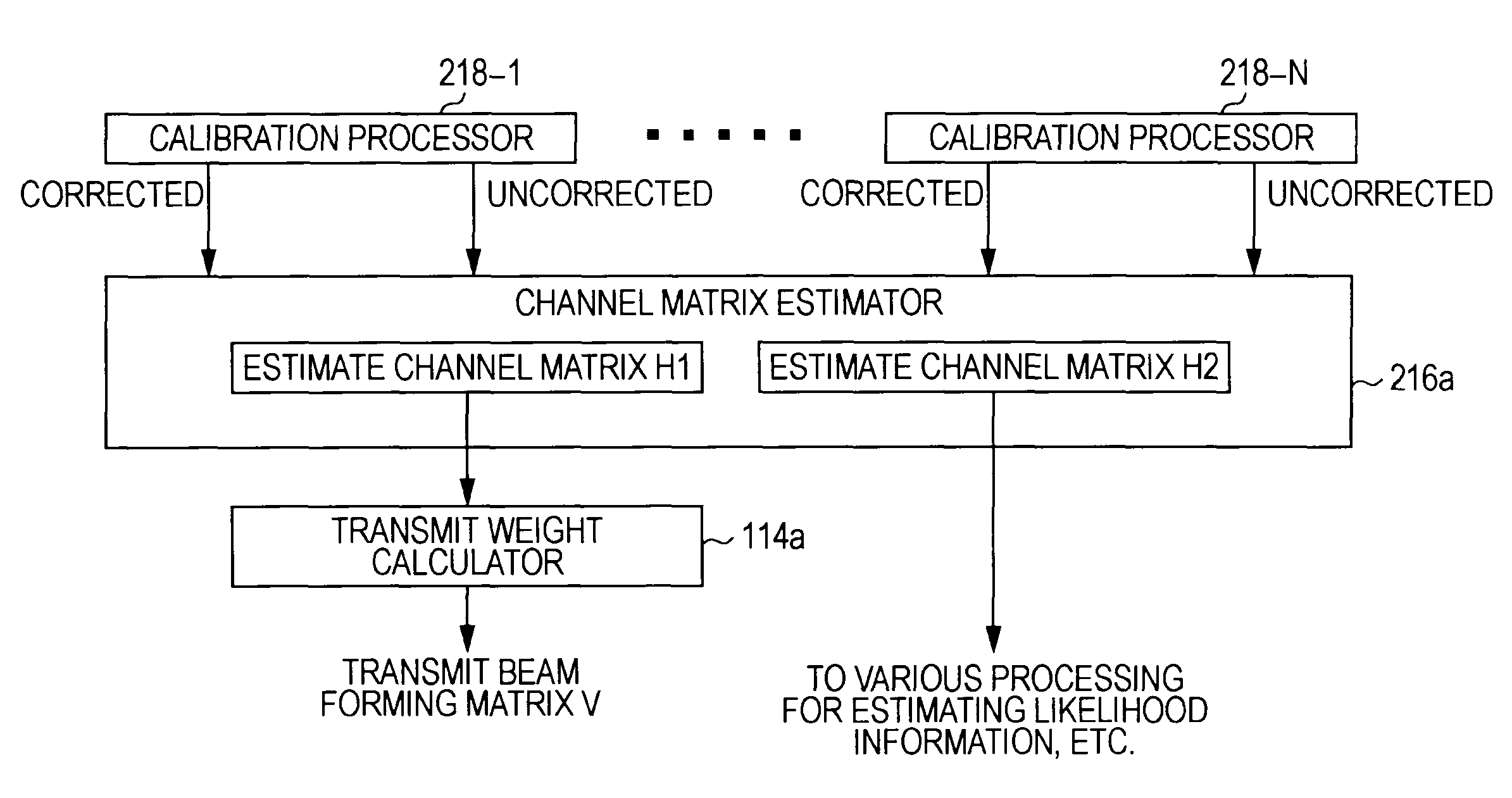
A wireless communication apparatus compensates for phase and amplitude imbalances existing among transmit and receive branches, while also preventing likelihood information and SNR estimation error produced by such imbalance compensation. In an apparatus having a plurality of transmit and receive antennas and respective branches for each antenna, a calibration processor multiplies receive signals in each receive branch by antenna calibration coefficients, in order to correct phase and amplitude imbalances existing among the receive branches. A transmit beamforming matrix estimator then estimates a transmit beamforming matrix by using the multiplied receive signals. An estimator then solves for estimated values such as the noise power, likelihood information, and channel waveform equalization values for each receive branch, and in addition, derives a final estimated value that takes the multiplication by correction coefficients into account when averaging the estimated values for each receive branch or when computing a weighted average according to likelihood.
Owner:SONY CORP
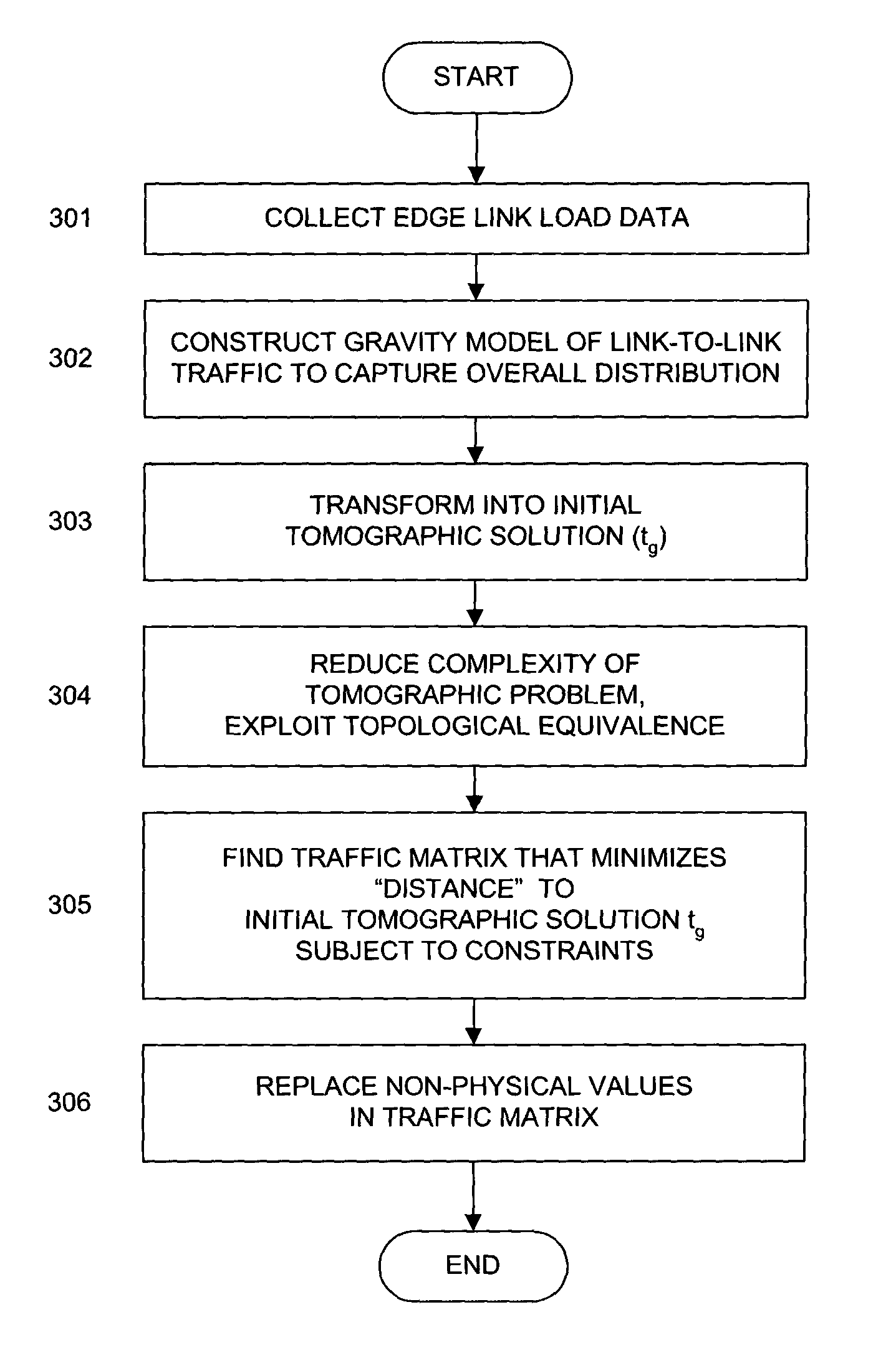
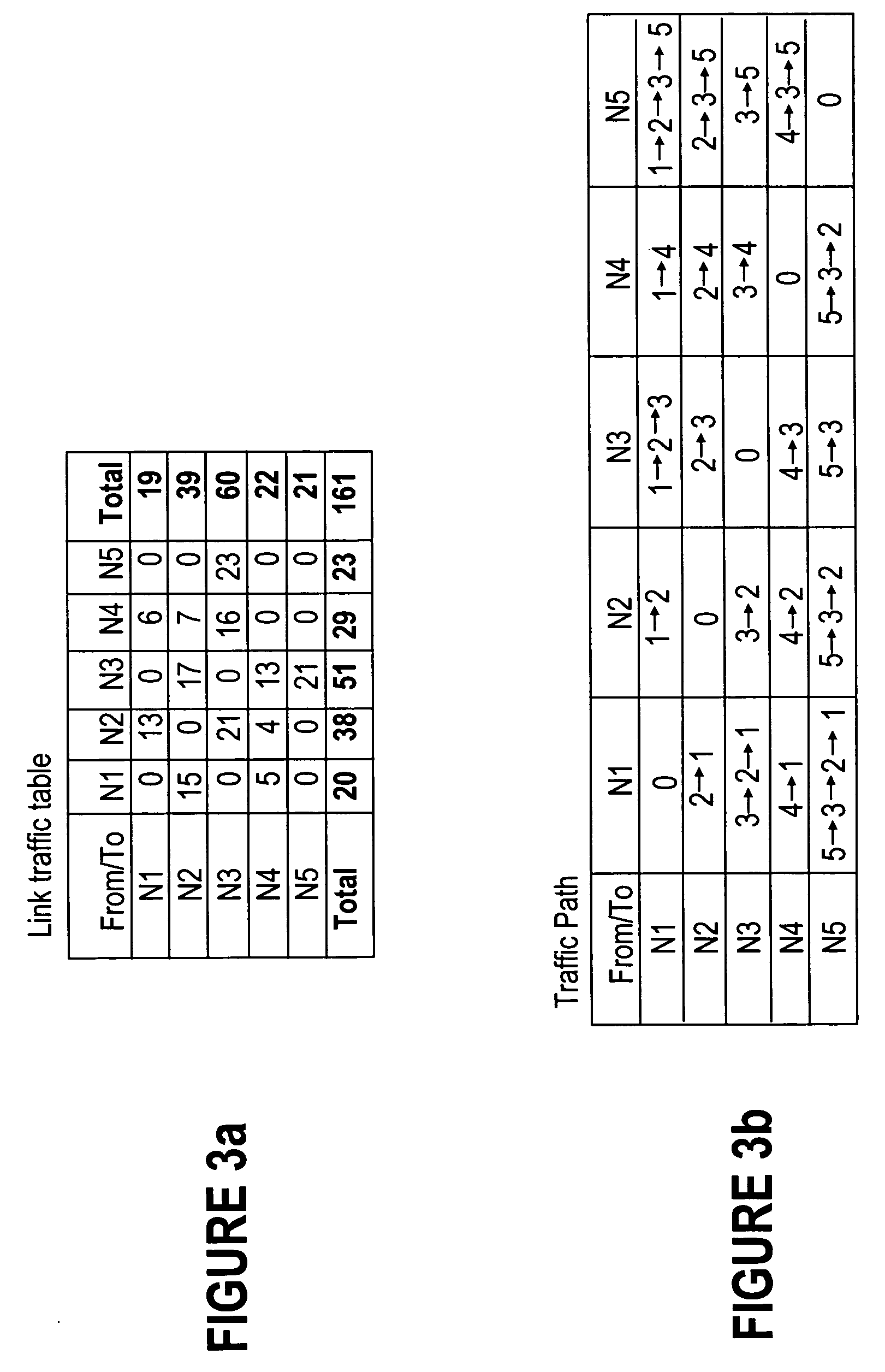
Traffic matrix estimation method and apparatus
InactiveUS7293086B1Reduce dimensionalityPromote resultsDigital computer detailsData switching networksTraffic capacityDistributed computing
A method and apparatus for the estimation of traffic matrices in a network are disclosed. Mechanisms are disclosed for measuring traffic volume from a plurality of ingress points to a plurality of egress points in a large scanl network, such as an IP backbone network. The traffic matrix is advantageously inferred from widely available link load measurements such as SNMP data.
Owner:AMERICAN TELEPHONE & TELEGRAPH CO
Wireless communication system, wireless communication apparatus and wireless communication method
ActiveUS8194720B2Improve transfer rateImprove process capabilitySpatial transmit diversityError preventionCommunications systemData transmission
A wireless communication system which performs data transmission using spatially multiplexed streams from a first terminal including N antennas to a second terminal including M antennas (N is an integer of 2 or more and M is an integer of 1 or more) is disclosed. The system includes notifying means, training means, channel matrix estimation means, beamforming information feedback means, transmission weight matrix setting means, and beamforming means.
Owner:SONY CORP
System and method for robust 2d-3d image registration
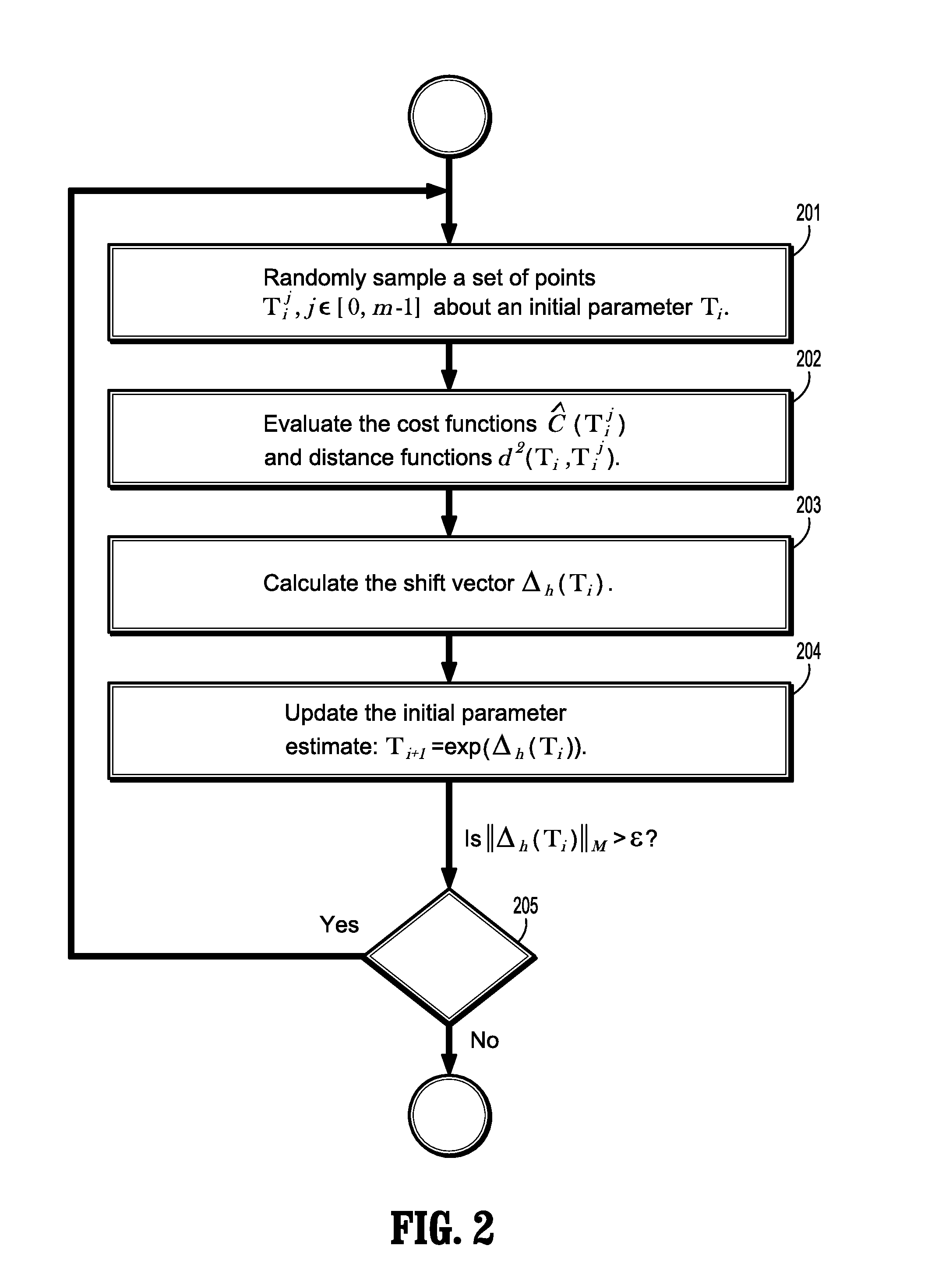
ActiveUS20110122226A1Expand the capture rangeRobust solutionImage enhancementImage analysis3d imageMean-shift
A method for registering 2-dimensional (2D) images with 3-dimensional (3D) images includes receiving a 2D reference image and a 3D moving image, initializing a registration parameter matrix that rigidly transforms the domain of the moving image, randomly sampling a set of registration parameter matrices in a neighborhood of the initial registration parameters, estimating a cost function for each of the randomly sampled parameter matrices, calculating a distance from each randomly sampled parameter matrix to the initial registration parameter matrix, calculating a mean shift vector from the estimated cost functions and distance, and updating the initial registration parameter matrix from the mean shift vector.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
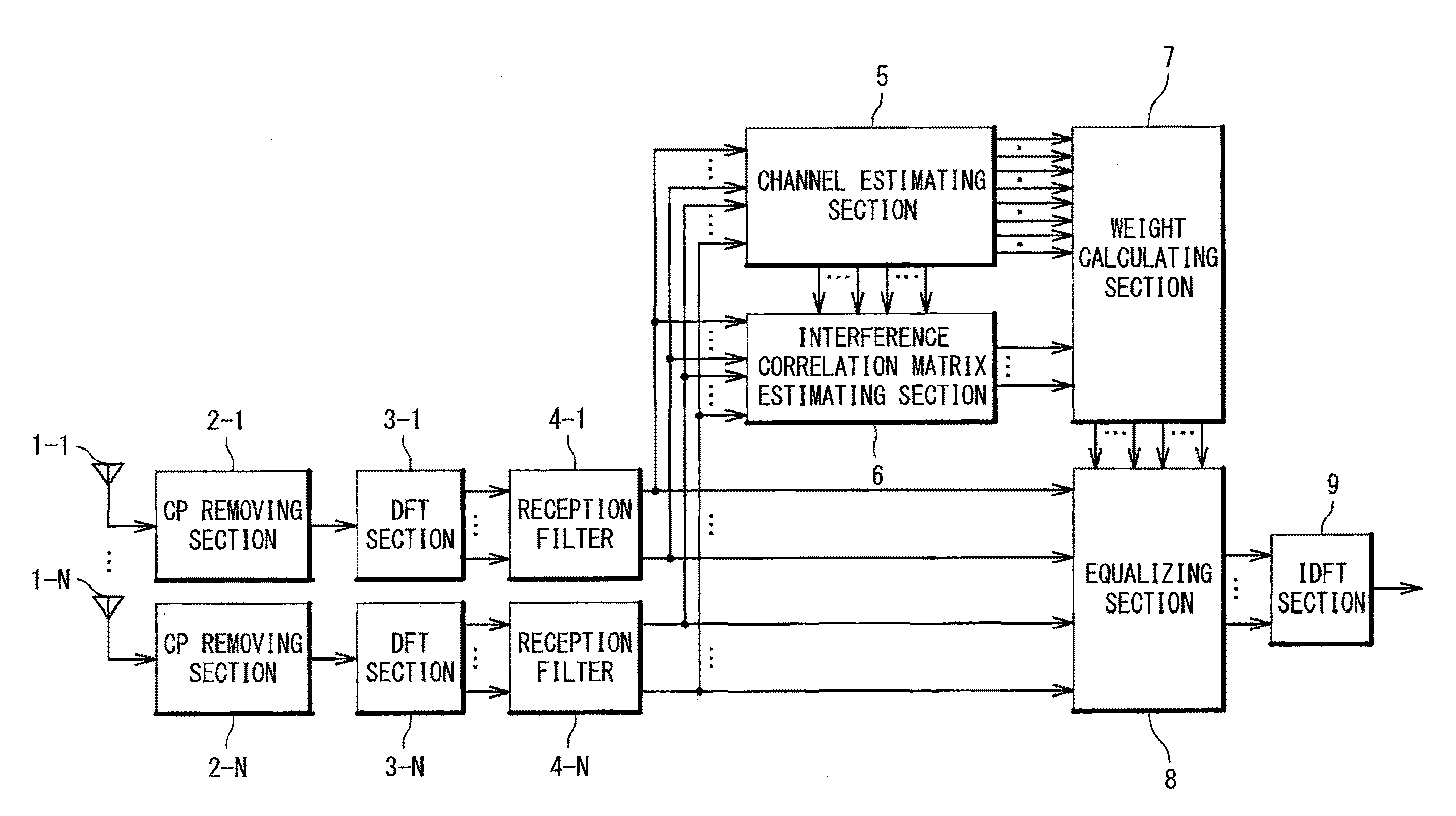
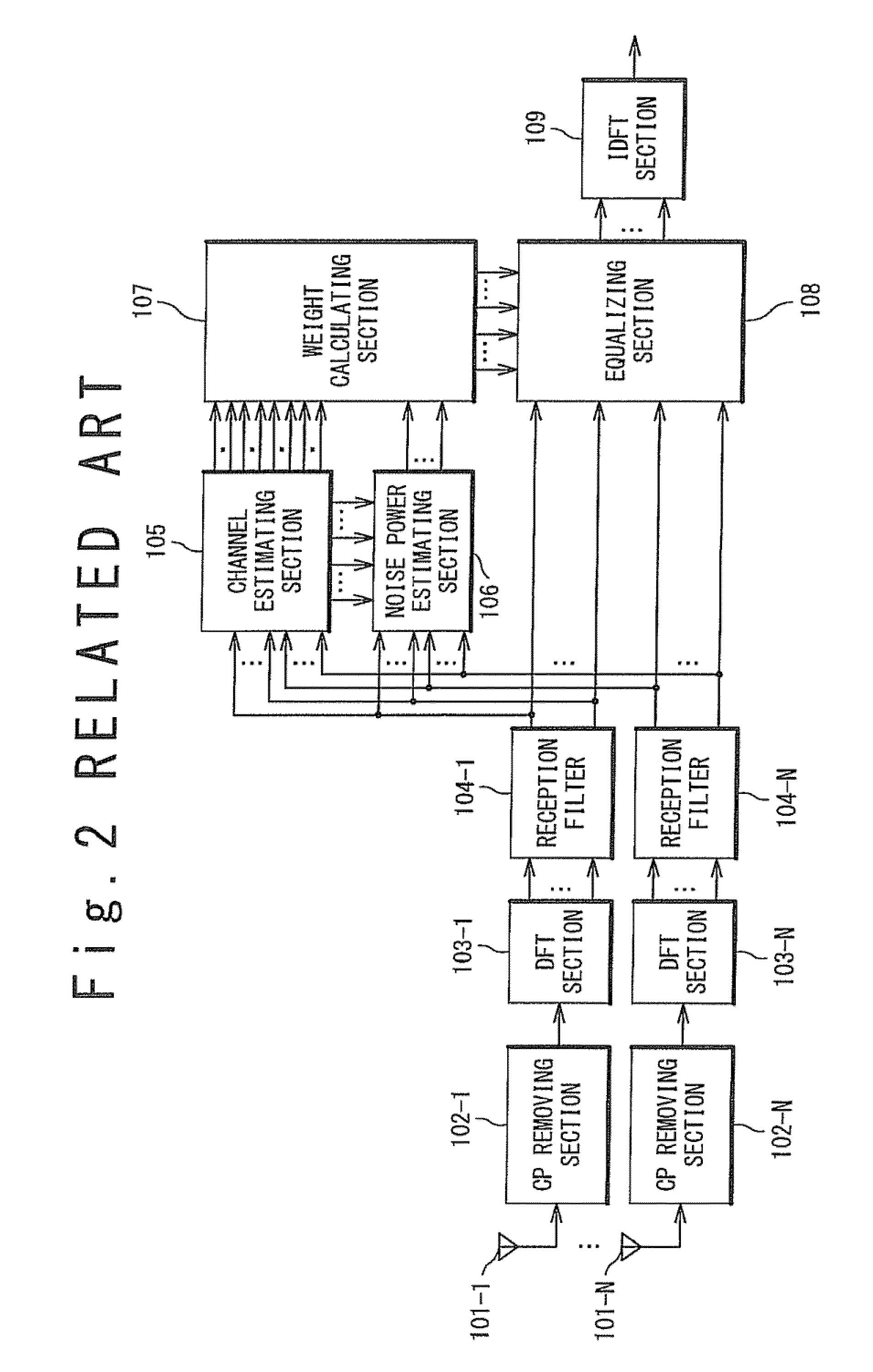
Receiving apparatus and mobile communication system
A receiving apparatus is provided in which a single carrier signal is received by a plurality of receiving antennas, and multipath equalization and other cell interference suppression are carried out in a frequency domain at a same time. A plurality of antennas 1-1 to 1-N receives the single carrier signal. The DFT sections 3-1 to 3-N converts the reception signals into frequency domain signals. A channel estimating section 5 estimates a channel gain of a desired user signal by using pilot reception signals. An interference correlation matrix estimating section 6 estimates an interference correlation matrix from the pilot reception signals and a channel estimation value. A weight, calculating section. A weight calculating section 7 receives the channel estimates and the interference correlation matrix and calculates equalization weights. An equalising section 8 performs multipath equalization and other cell interference suppression to the desired user signal in a frequency domain. An IDFT section 9 converts an equalization signal into a signal in a time domain.
Owner:NEC CORP
Method for predicting suburban rail transit passenger flow
InactiveCN102024206AOvercome the resultOvercome the defect that there is a large gap with the actual data after the eventData processing applicationsSimulationRail transit
The invention relates to a method for predicting suburban rail transit passenger flow, which comprises the following steps: (1) constructing a prediction model basic data base through OD (Origin and Destination) matrix estimation and station attraction; (2) conducting the distribution network of the rail transit passenger flow according to the functional localization of suburban rail transit and by combining an operation connection mode; (3) conducting a prediction model respectively aiming at the operation connection mode between the suburban rail transit and the urban rail transit; (4) distributing suburban rail transit passenger flow on a corresponding rail transit distribution network by combining the prediction model and the basal data so as to obtain the whole line passenger flow, the station passenger flow, the branch passenger flow and the transferring passenger flow of the suburban rail transit; (5) and recommending a best operation planning scheme by comparing the passenger flow prediction results of different operation organization schemes, and performing the passenger flow prediction of a final scheme according to the recommended operation planning scheme. The invention overcomes the defect in the prior art that the prediction results are unsatisfactory and have lager difference with the ex-post real data, and further improves the accuracy of predicting.
Owner:JIANGSU TRANSPORTATION RES INST CO LTD
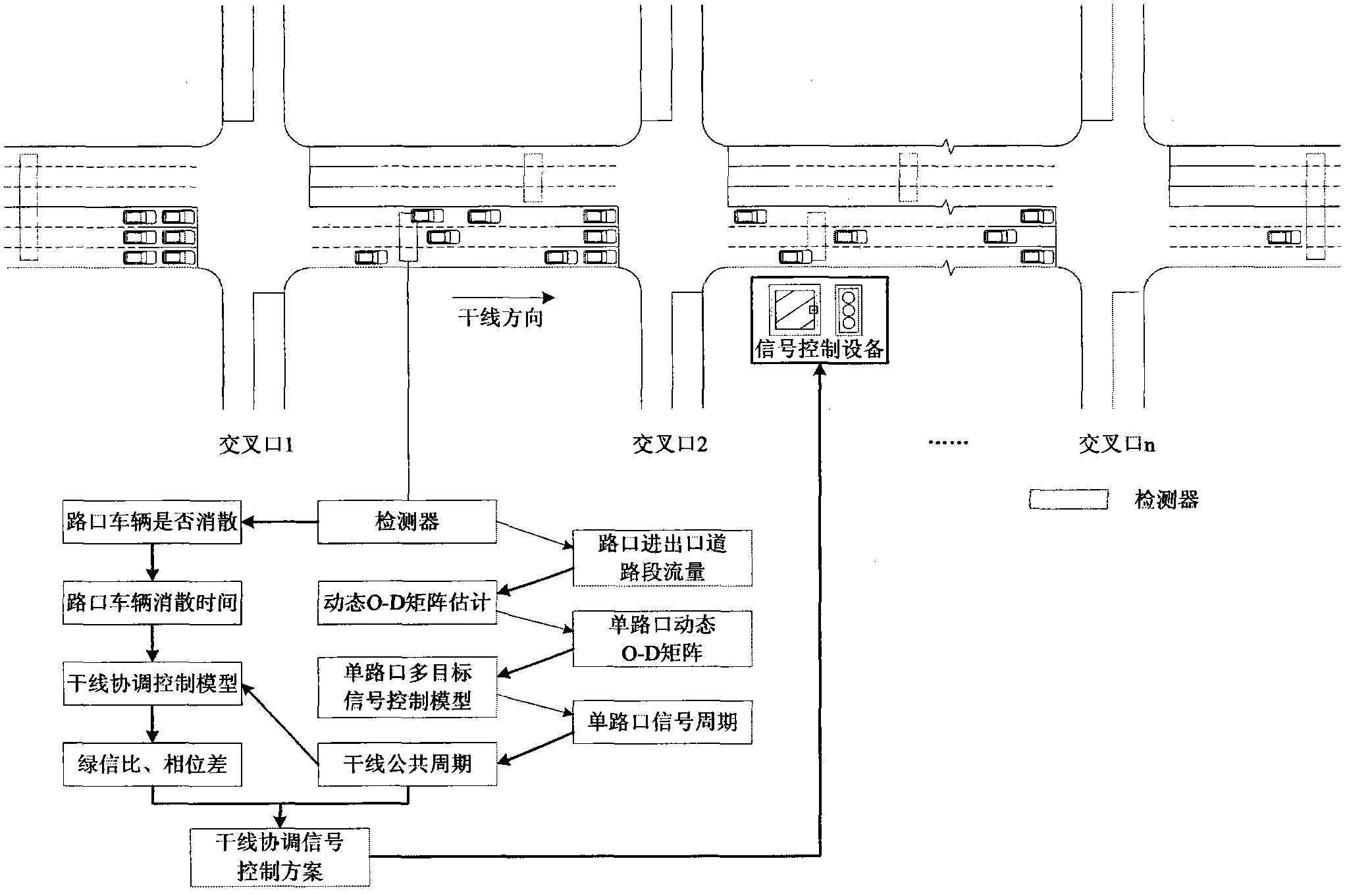
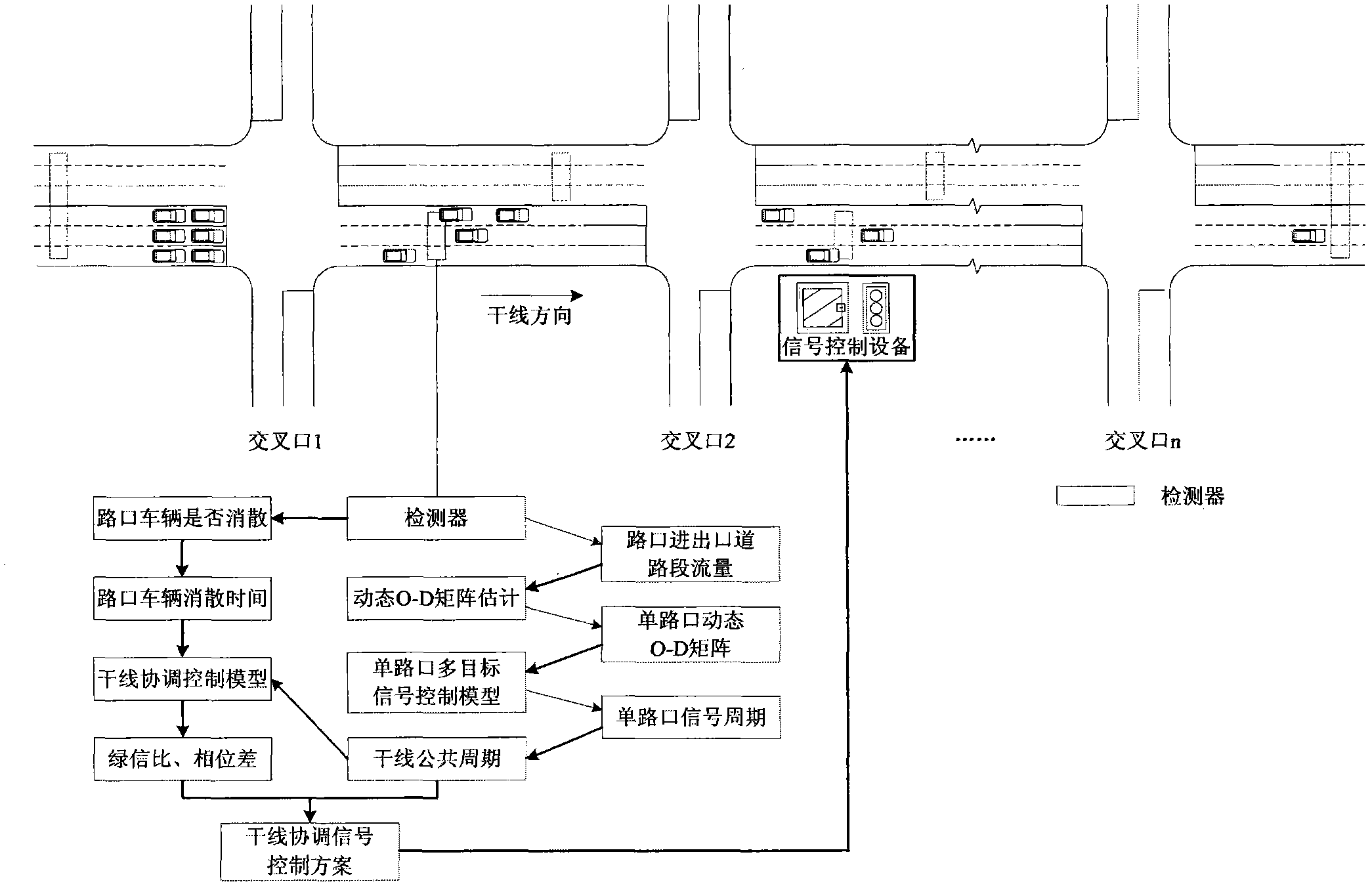
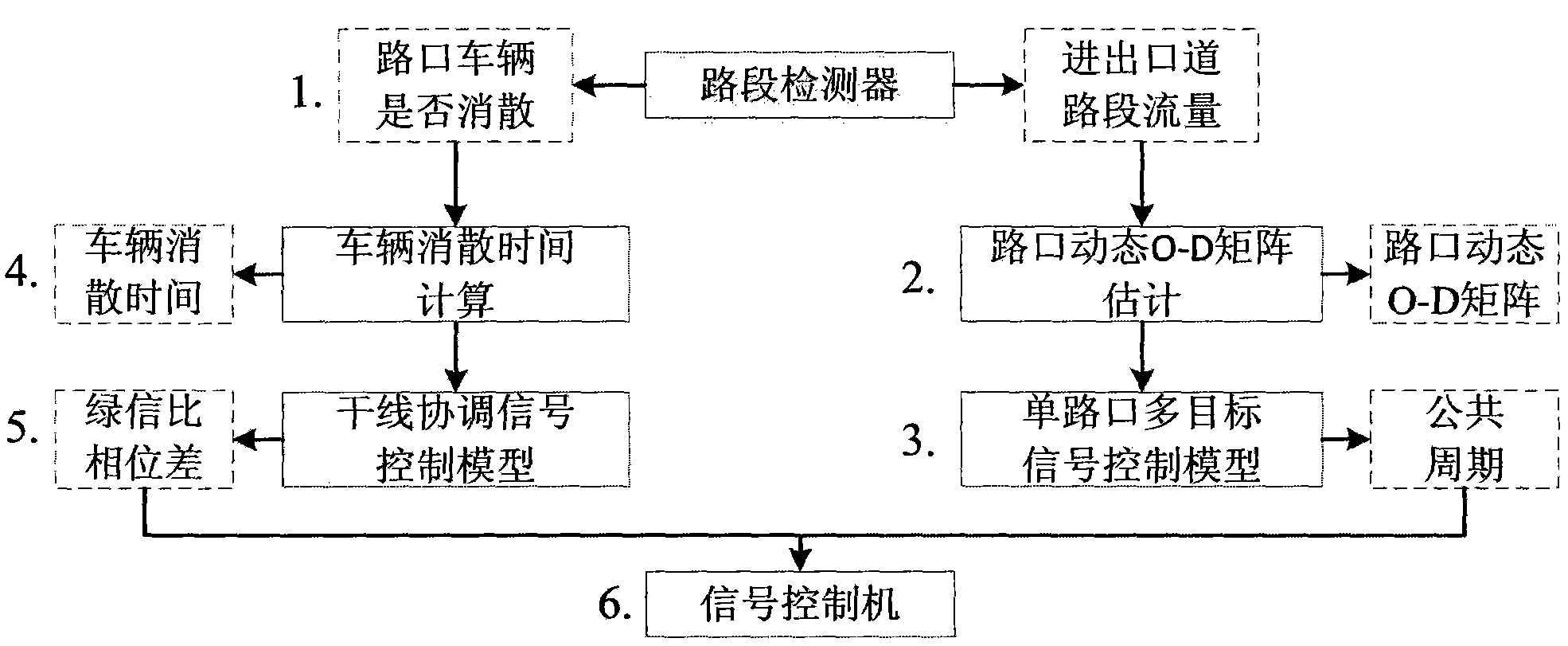
Artery coordination signal control method based on dynamic O-D matrix estimation
ActiveCN103927890AHigh precisionImprove stabilityControlling traffic signalsPhase differenceTarget signal
Owner:BEIJING UNIVERSITY OF CIVIL ENGINEERING AND ARCHITECTURE
Signal detection method and apparatus for MIMO system
InactiveCN101383652AEasy to detectReduce complexitySpatial transmit diversityBaseband system detailsMulti inputCurrent channel
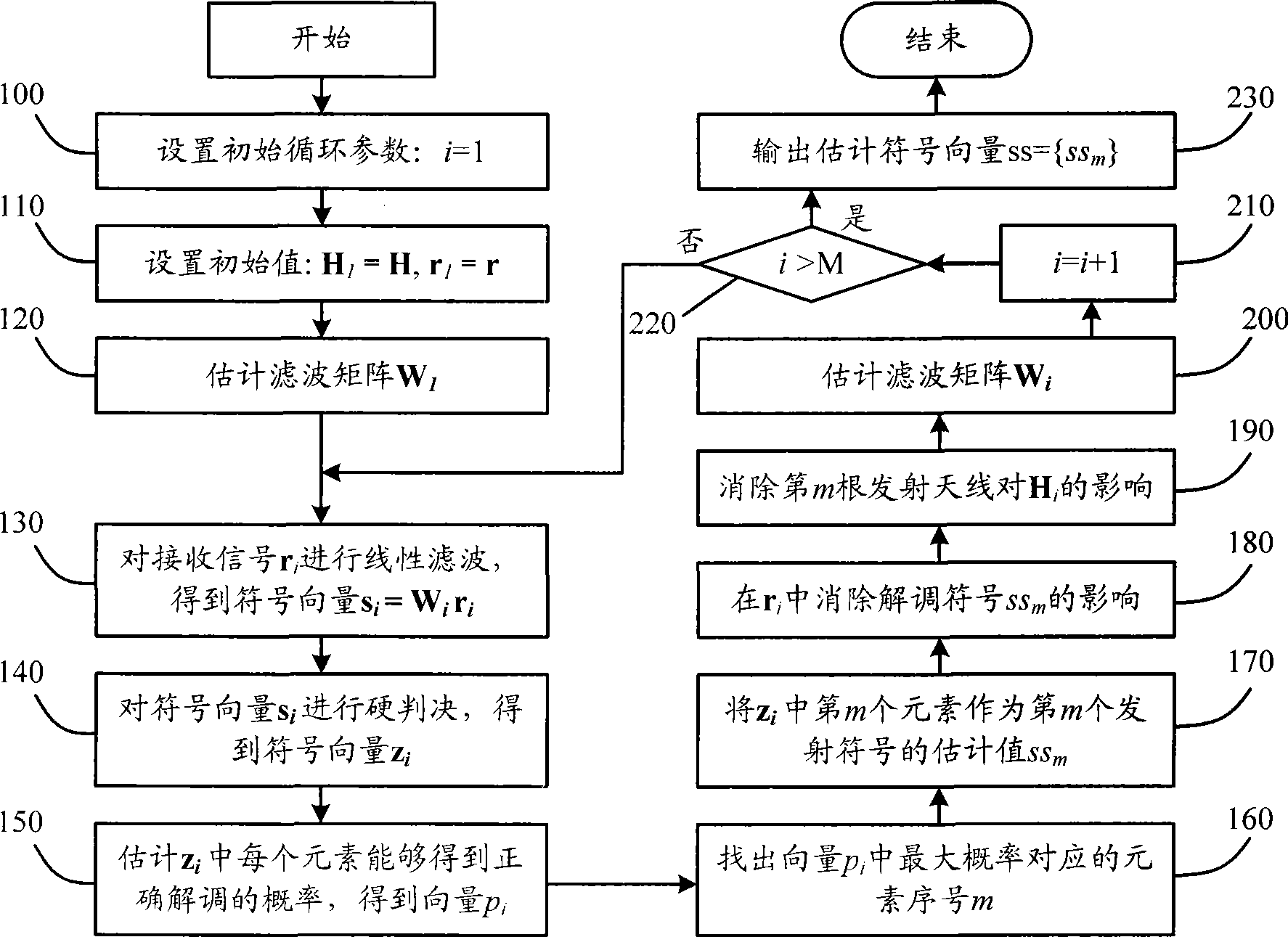
The invention relates to a signal detection method of a multi-input multi-output system and a device thereof. The system is provided with m sending antennae and n receiving antennae. The method comprises the following steps: a current channel response matrix is utilized to estimate and obtain a linear filtering matrix which performs the linear filtration to a current receiving signal, so an estimation sending symbol vector is obtained; each symbol in the estimation sending symbol vector is performed the hard decision to obtain a symbol vector described by constellation points, a symbol of the maximum probability value accurately demodulated can be found in the symbol vector, and the symbol is used as the estimation value of symbols having the same sequence number in the sending symbol vector; the current receiving signal and the current channel response matrix are updated for eliminating the influences of the symbols obtained the estimation value to the receiving signal and the corresponding antennae to the channel response matrix; the three steps are performed circularly until the estimation values of all symbols in the sending symbol vector are obtained. The detection algorithm and the device cause the detection performance of an MIMO signal to approach the ML detection algorithm, and the complexity is nearly less one order of magnitude than the ML.
Owner:江苏久泰电缆有限公司
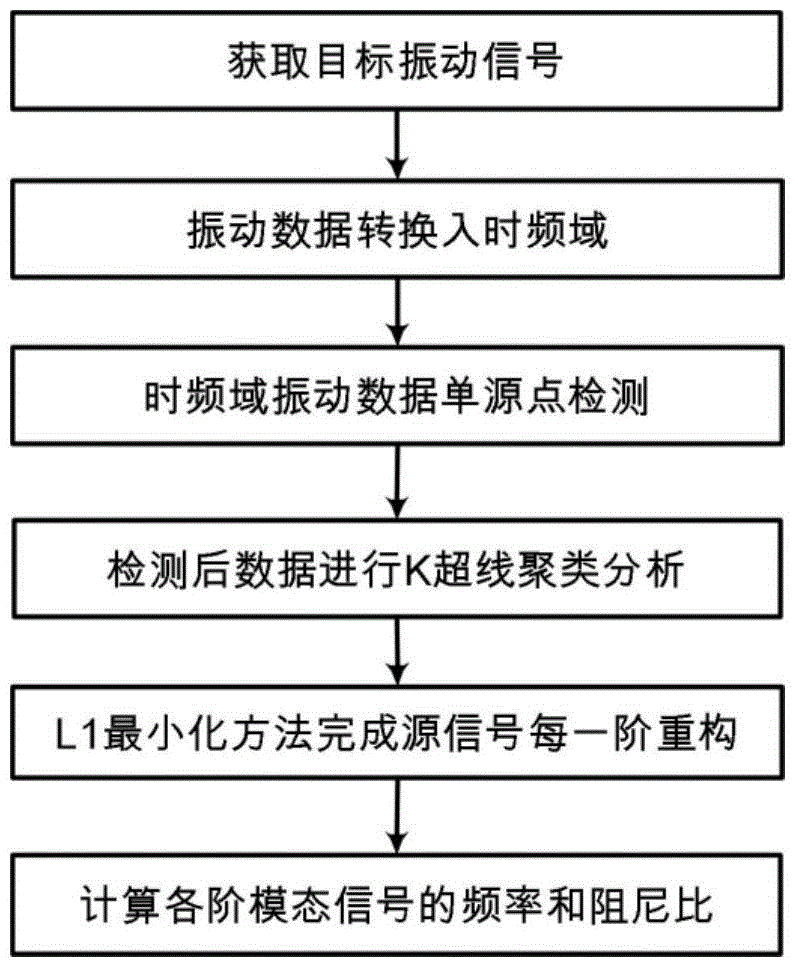
Working modal identification method based on time-frequency domain single-source-point sparse component analysis
ActiveCN104166804ASmall amount of calculationEfficient identificationSpecial data processing applicationsL1 minimizationMeasurement point
The invention provides a working modal identification method based on time-frequency domain single-source-point sparse component analysis. The working modal identification method specifically includes the following steps that vibration signals of an equipment target position under the working state are obtained through measurement; time-frequency domain conversion is conducted on the mixed vibration signals; a single-source-point method is used for extracting the mixed vibration signals used for estimating a hybrid matrix in a time-frequency domain; a hybrid matrix estimation method based on K hyperline clustering sparse component analysis is used for estimating the hybrid matrix; after the hybrid matrix is solved, the time-frequency domain is returned, the l1 minimization method is used for reconstructing each order of source signals, and modal vectors of a structure are extracted; then the working modal frequency and the damping ratio are obtained through signal index expression. According to the method, the calculation amount in the hybrid matrix estimation process is reduced, under the poor condition that the number of measuring points is less than that of the source signals, modal parameters are identified effectively, and the method has good anti-interference capacity for incomplete sparsity of noise, abnormal values and the source signals.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Self-adaptive channel estimation method based on compressed sensing and large-scale MIMO
InactiveCN105656819ANarrow searchThe estimate is accurateSite diversityChannel estimationSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Decomposition
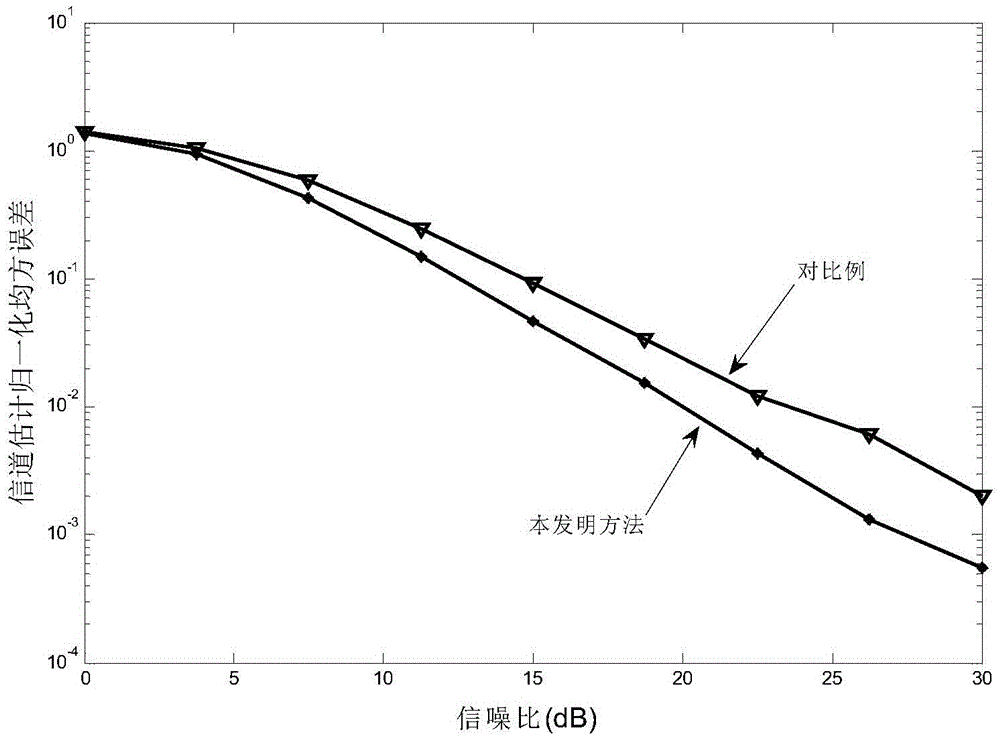
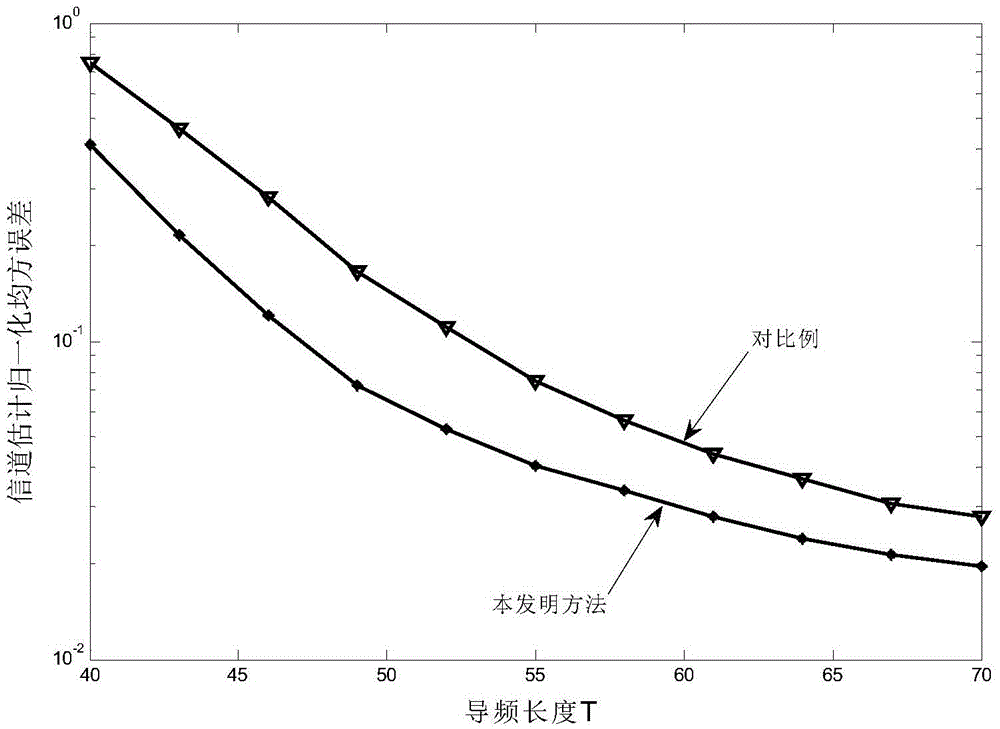
The invention discloses a self-adaptive channel estimation method based on compressed sensing and large-scale MIMO and belongs to the technical field of wireless communication. The self-adaptive channel estimation method includes the steps that decomposition values Ur and Ut of a channel matrix in an angle domain are obtained, and a corresponding measurement matrix phi and a corresponding perceptual measurement value Y are calculated; iterative computation is conducted on a shared channel parameter estimation value (shown in the description) based on an index set Gamma n-1 at a previous moment of a system, the measurement matrix phi and the perceptual measurement value Y; a sparse signal estimation value (shown in the description) is calculated through iteration of the shared channel parameter estimation value (shown in the description), the phi and the Y; finally, a channel matrix estimation value (shown in the description) is obtained according to a formula (shown in the description) based on the number M of transmitting antennas, the signal-to-noise ratio P of the transmitting antennas and the pilot frequency length T of the transmitting antennas. The self-adaptive channel estimation method does not need knowing shared channel information for channel estimation, utilizes the index set at the previous moment in a self-adaptive mode and produces smaller errors compared with a traditional subspace tracking algorithm.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Wireless communication apparatus and wireless communication method
ActiveUS20060269006A1Avoid performance degradationHighly reliable likelihood estimationMultiplex communicationDiversity/multi-antenna systemsSignal onEngineering
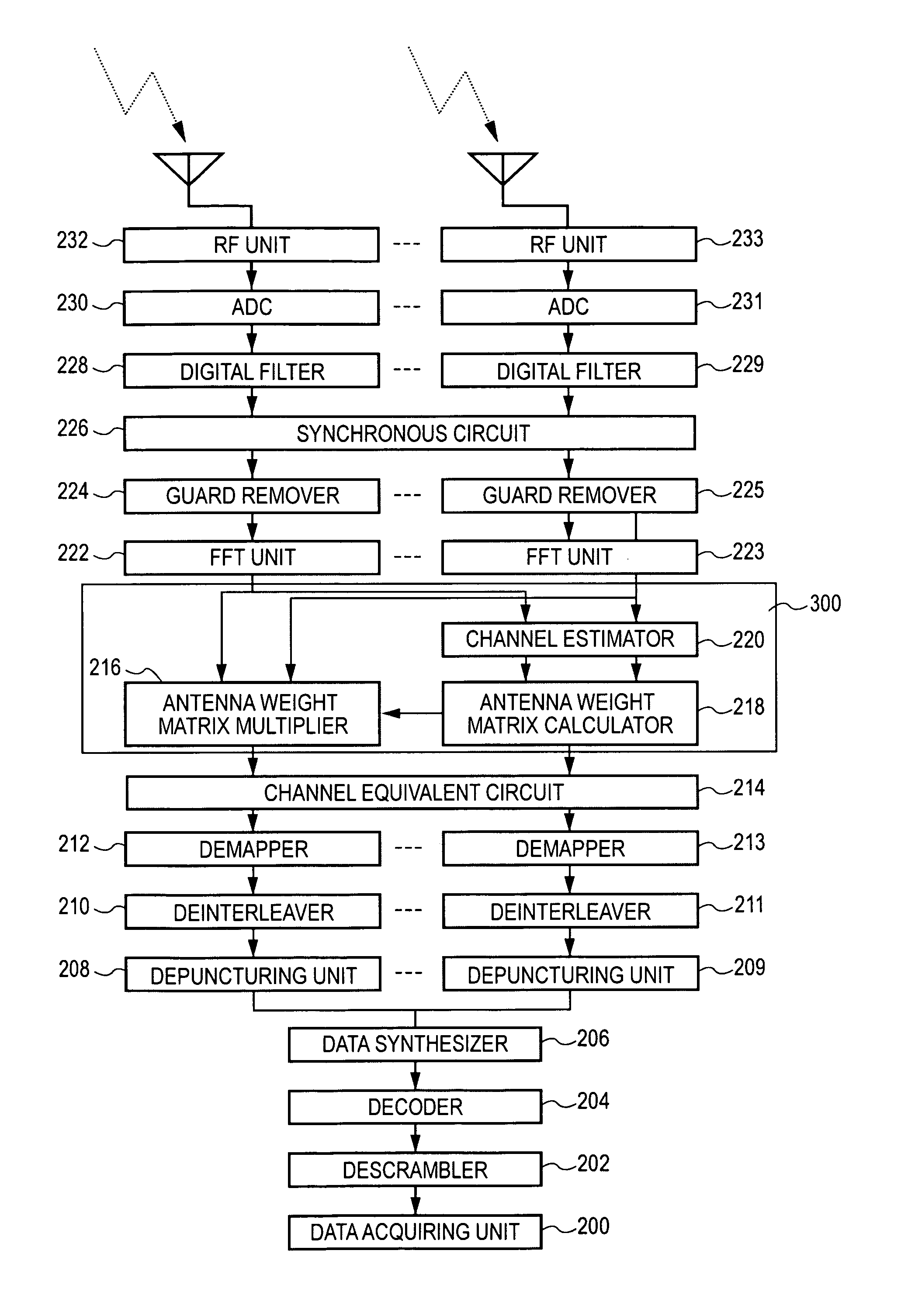
A wireless communication apparatus for receiving spatially multiplexed signals in which a plurality of streams are spatially multiplexed, using a plurality of antennas, includes the following elements: a channel matrix estimator for estimating a channel matrix for multiplexed channels; a spatial decoder for spatially decoding received signals each of which has been received by a corresponding antenna so as to separate the received signals into individual stream signals by obtaining an antenna weight matrix from the estimated channel matrix, and then multiplying each received signal by the antenna weight matrix; a likelihood information estimator for estimating likelihood information using the estimated channel matrix, the antenna weight matrix, and estimated noise power; and a soft decision decoder for performing soft decision decoding on each stream signal on the basis of the estimated likelihood information.
Owner:REDWOOD TECHNOLOGIES LLC
Image mosaicing apparatus for mitigating curling effect
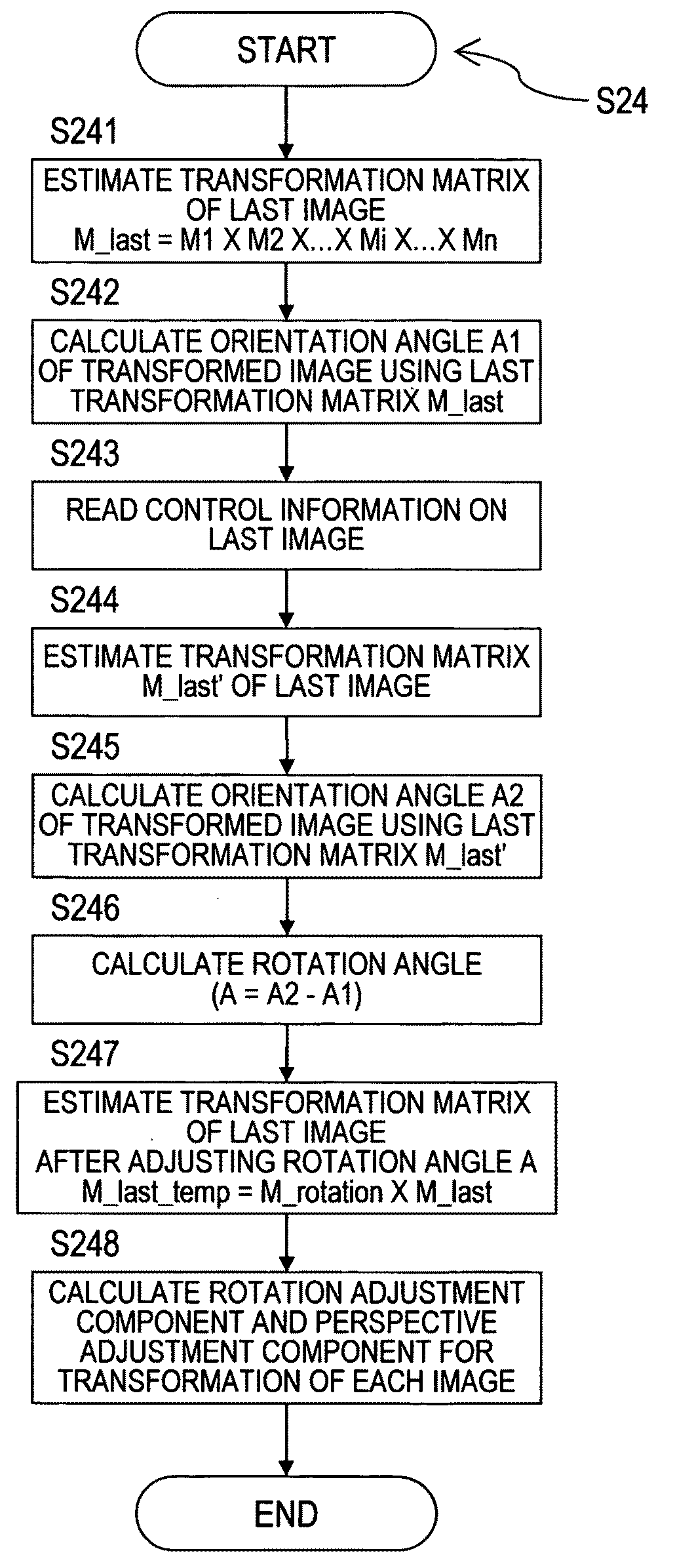
InactiveUS20090141043A1Effectively mitigate curlingGeometric image transformationCathode-ray tube indicatorsComputer scienceMatrix estimation
The mosaicing curling effect which causes a mosaic strip to curl is effectively mitigated in a system for generating a mosaic image from sequential images which partially overlap with one another. The system has a matrix estimating unit, an adjustment element calculating unit, and an image projecting unit. The matrix estimating unit estimates a transformation matrix for transformation between two adjacent images taken out from among the sequential images. The adjustment element calculating unit calculates an adjustment element of the estimated transformation matrix by decomposing the transformation matrix into a rotational component and a perspective component. The image projecting unit projects each image on the mosaic plane using the transformation matrix to which the calculated adjustment element has been applied.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Video segmentation method based on depth recovery and motion estimation
The invention discloses a video segmentation method based on depth recovery and motion estimation. The video segmentation method based on the depth recovery and motion estimation comprises the following steps of: (1) working out a background subtraction measure by using homography matrix estimation or using a camera motion and dense depth map recovered by a video sequence consistent depth recovery method; (2) performing dense motion estimation, and estimating dense motion fields d and occlusion maps o of continuous two frames of images; (3) calculating a video segmentation result according to an interactively generated combination strategy of multiple measures; and (4) repeating the step (3) for at least two times, and then, ending. Firstly, according to the video segmentation method based on the depth recovery and motion estimation disclosed by the invention, videos can be segmented by iterative optimization of motion, depth and segmentation information. Secondly, according to the video segmentation method based on the depth recovery and motion estimation disclosed by the invention videos of which the backgrounds do a planar motion can be segmented without estimating camera parameters and the depth information. Finally, the video segmentation method based on the depth recovery and motion estimation disclosed by the invention is a video segmentation method of combining multiple measures, the accuracy of various measures can be measured, and reliable measures are screened out to involve in video segmentation calculation.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV +1
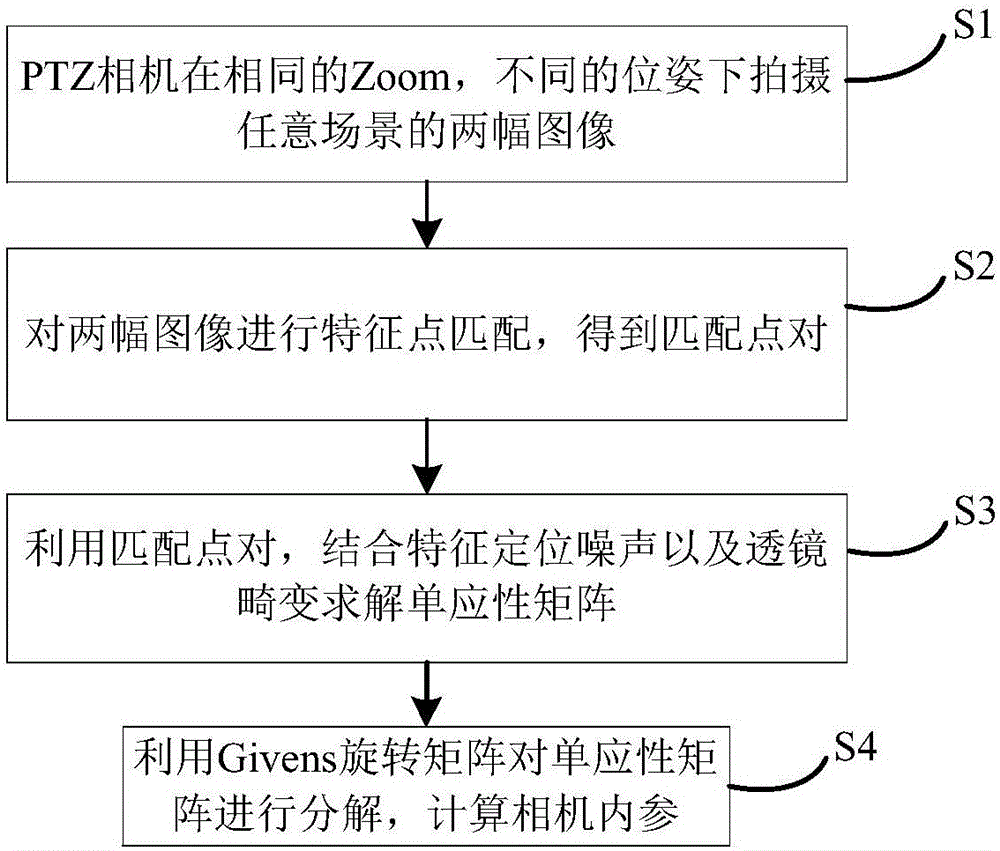
Method for calibrating PTZ camera by using only two scene images
InactiveCN106530358ASimplify the internal calibration processHigh precisionImage analysisCamera lensPrincipal point
The present invention discloses a method for calibrating a PTZ camera by using only two scene images. Firstly, two images with overlapped areas of any scene in a same focal length and different Pan-Tilt angles relative to the PTZ camera are photographed, the two images are subjected to feature point matching, a matching feature point pair between the two images is obtained, the influences of the uncertainty of matching feature point positioning and camera lens distortion are considered, a homography matrix estimation method with the combination of feature point positioning noise and lens distortion is created, the homography matrix between the two images and the radial distortion coefficient of the PTZ camera under the focal length are obtained, finally a Givens rotation matrix is constructed to decompose the obtained homography matrix, and thus the four internal references (focal length, principal point coordinate, and aspect ratio) of the camera is resolved and obtained. According to the method, the online calibration of five parameters of the PTZ camera can be realized.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Wireless communication device, wireless communication method, signal processing device, signal processing method, and computer program
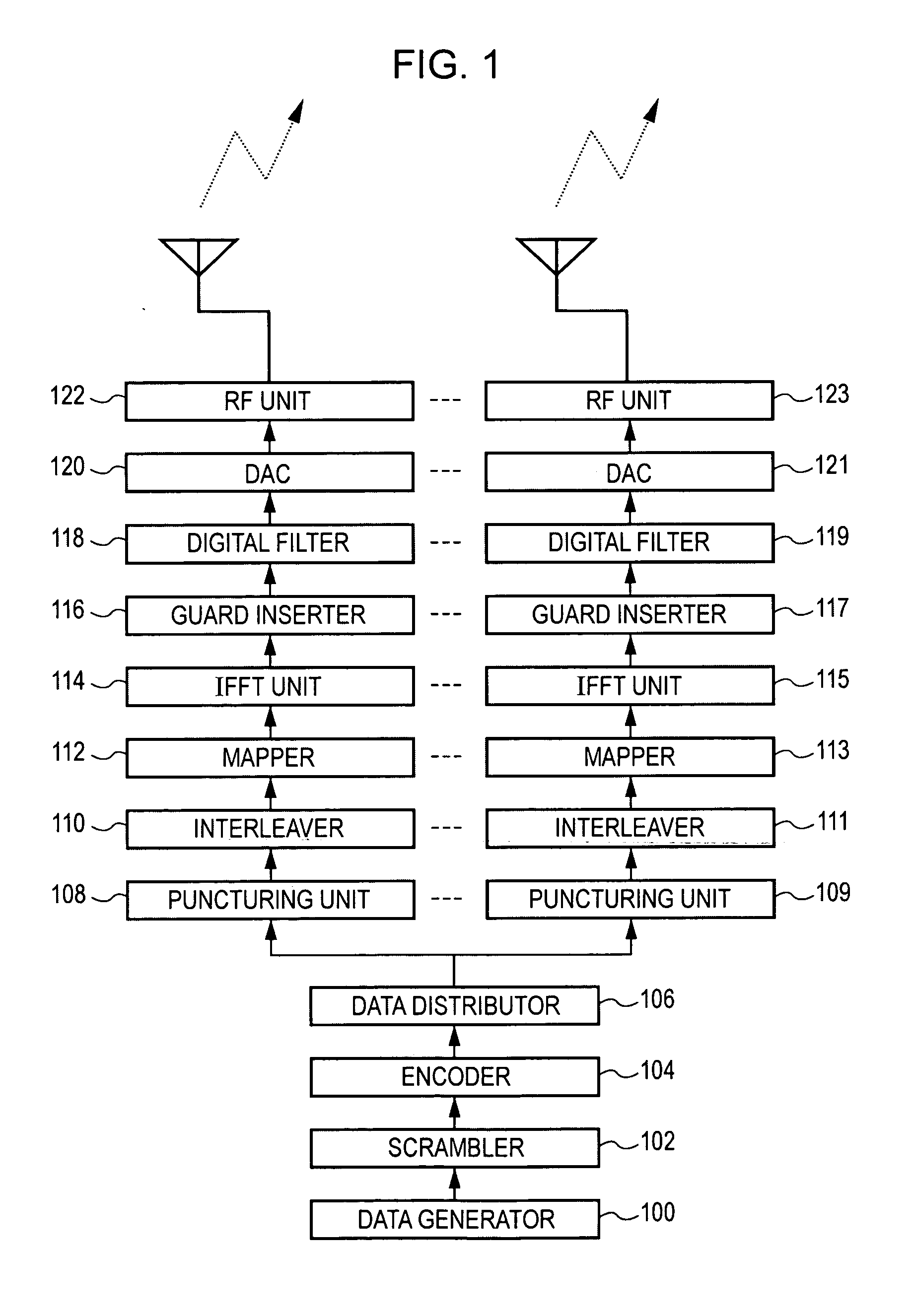
InactiveUS20100111157A1Prevent deterioration in decoding characteristicPrecise cuttingMultiple-port networksError preventionSignal onComputer science
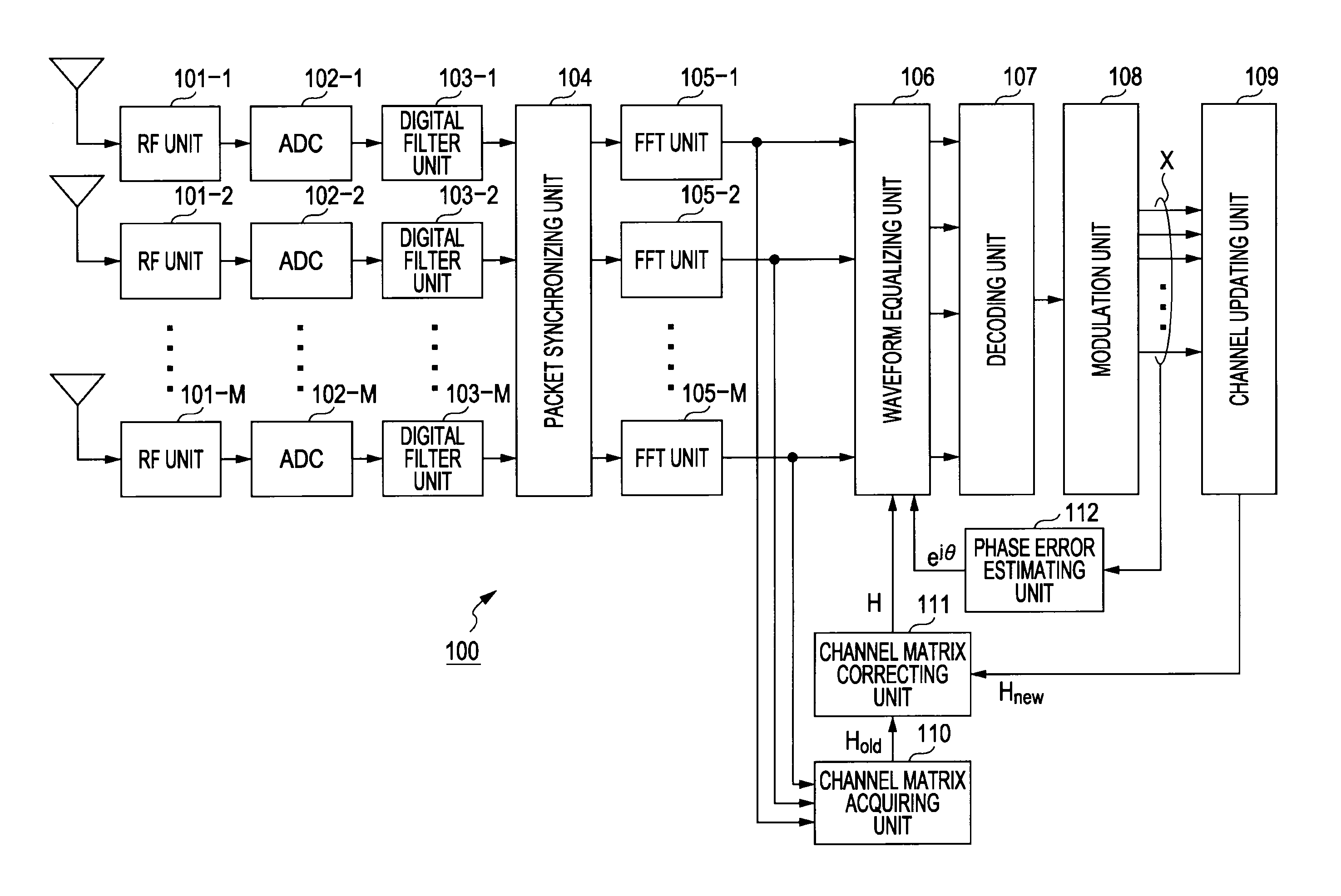
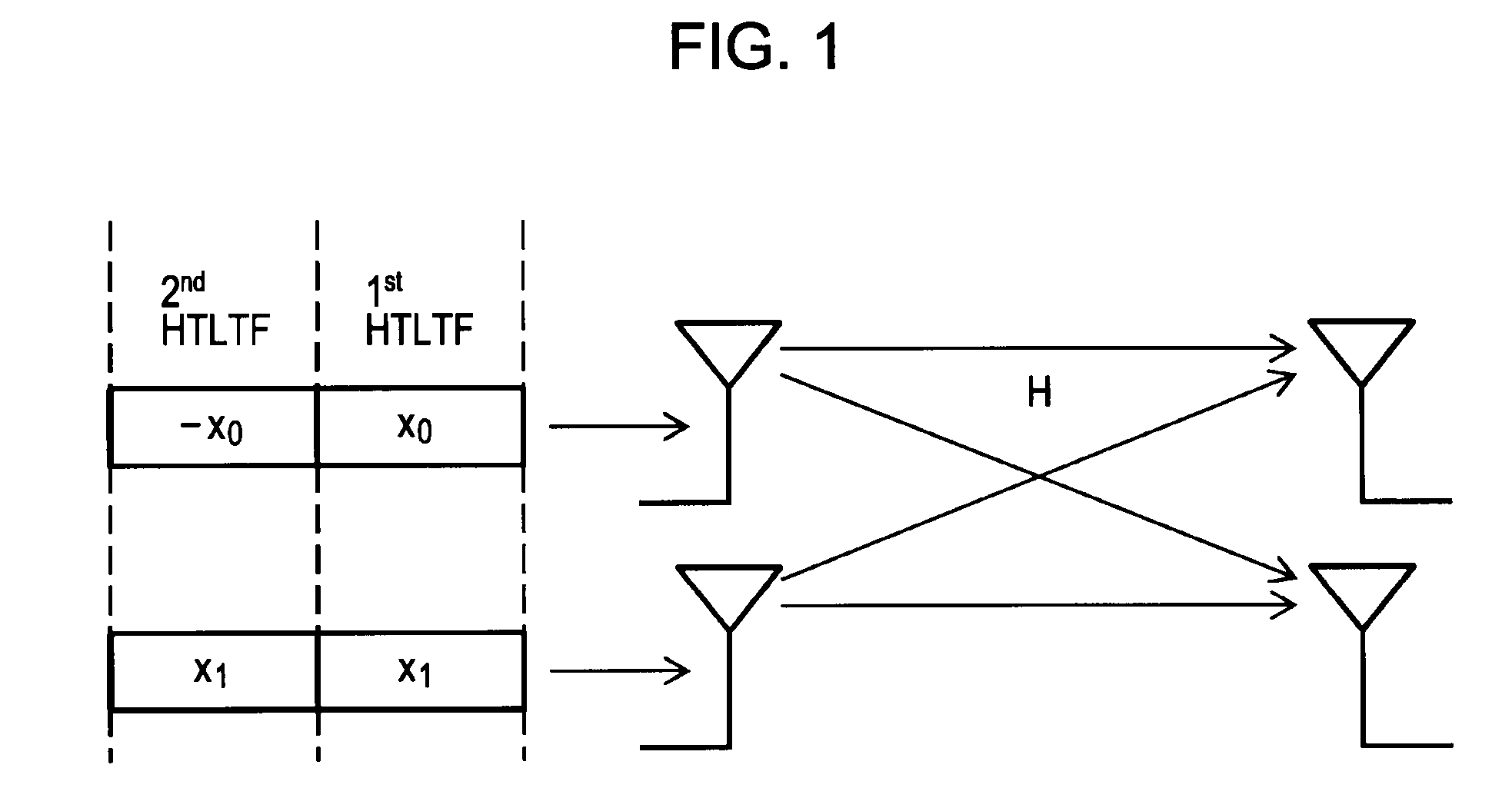
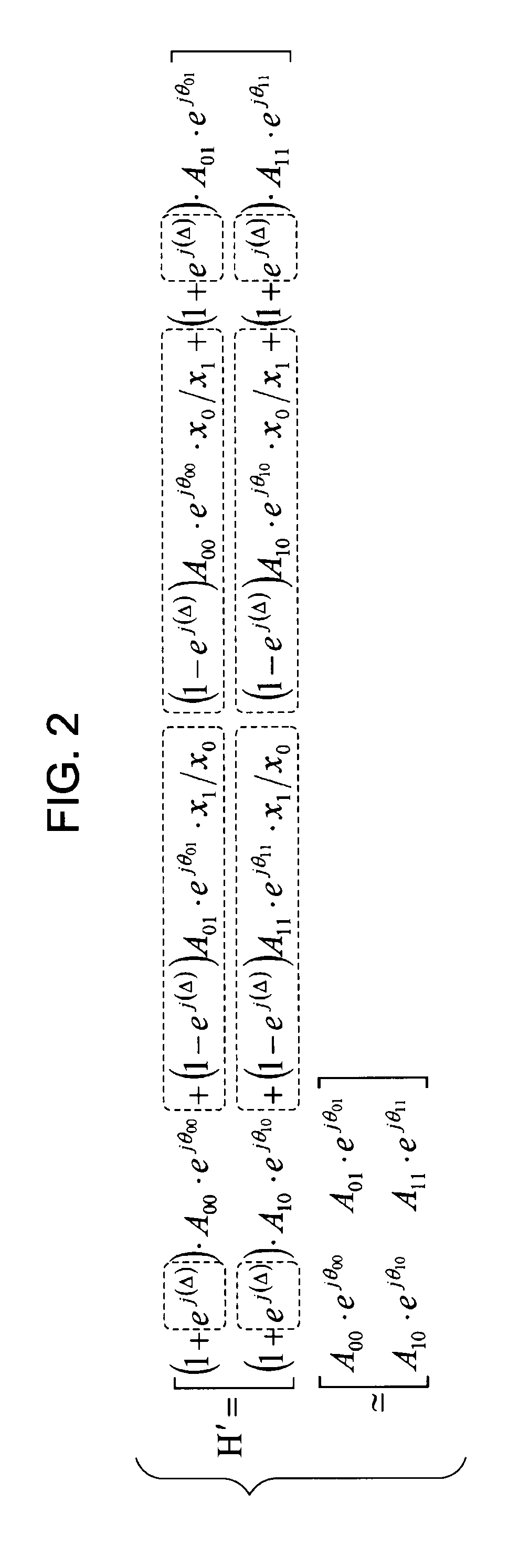
A wireless communication device includes: a channel matrix estimating unit estimating a channel matrix including channel response elements between antennas; a phase error estimating unit estimating a phase error in a received signal on the basis of a decoding result of encoded and transmitted information symbols of a preamble of a received packet; and a waveform equalizing unit equalizing a waveform of data symbols of the received packet using the channel matrix. Original channel response elements are derived by removing an error of an estimated channel value due to the phase error estimated by the phase error estimating unit from the channel response elements of the channel matrix supplied from the channel matrix estimating unit, and the waveform equalizing unit equalizes the waveform of the data symbols using the channel matrix including the original channel response elements.
Owner:SONY CORP
Detection method of interference target for space-time adaptive processing
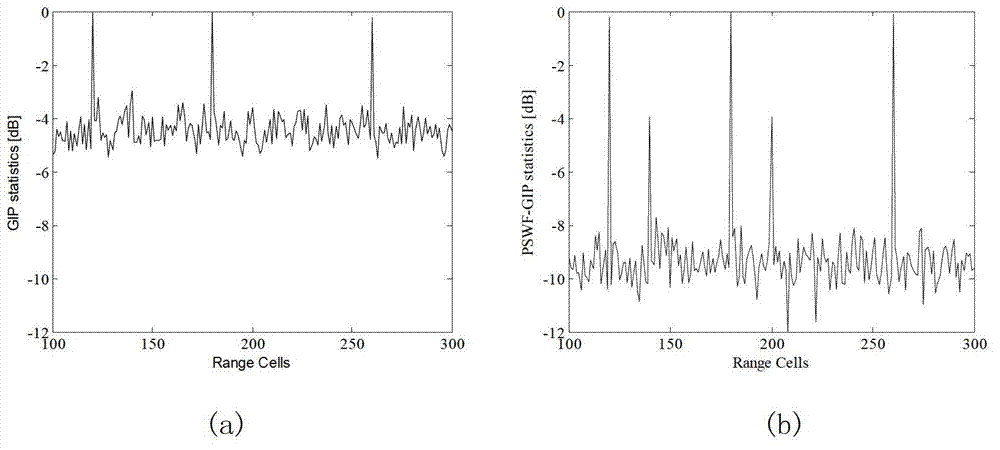
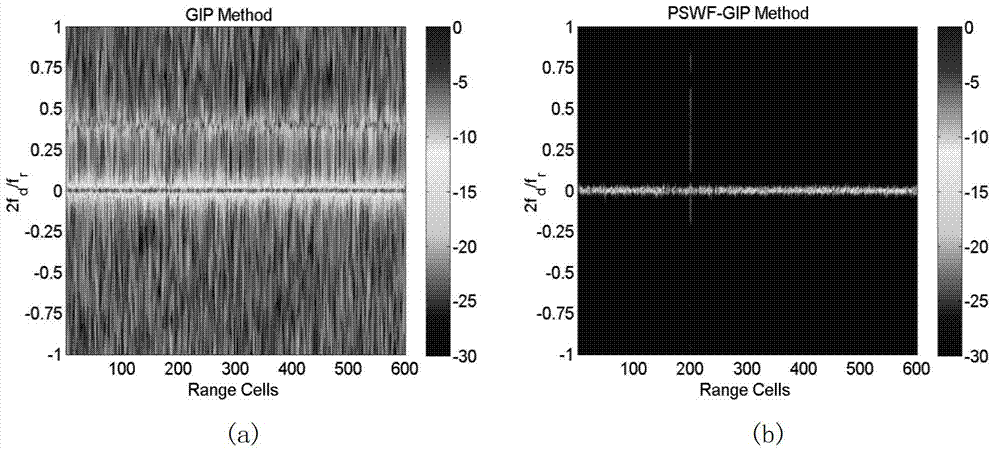
InactiveCN102879767AAccurate removalImprove object detection performanceWave based measurement systemsAlgorithmGeneralized inner product
The invention provides a detection method of an interference target for space-time adaptive processing, which solves the problem that the performance is influenced by the interference target when the traditional non-uniform detector NHD (nonhmogeneity detection) is used for removing non-uniform training samples. The detection method comprises the steps as follows: step I, estimation of a clutter covariance matrix based on an elliptical long ball wave function: firstly receiving a space-time clutter data model, then determining the relationship of the elliptical long ball wave function and clutter data, and finally estimating the clutter covariance matrix based on the elliptical long ball wave function; step II, calculating the detection statistic of the interference target of GIP (generalized inner products); and step III, removing the non-uniform training samples influenced by the interference target according to a set threshold value.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
MIMO radio communication apparatus and method
ActiveUS8102830B2Maximize channel capacityMaximize capacityMultiple-port networksDelay line applicationsMulti inputSelf adaptive
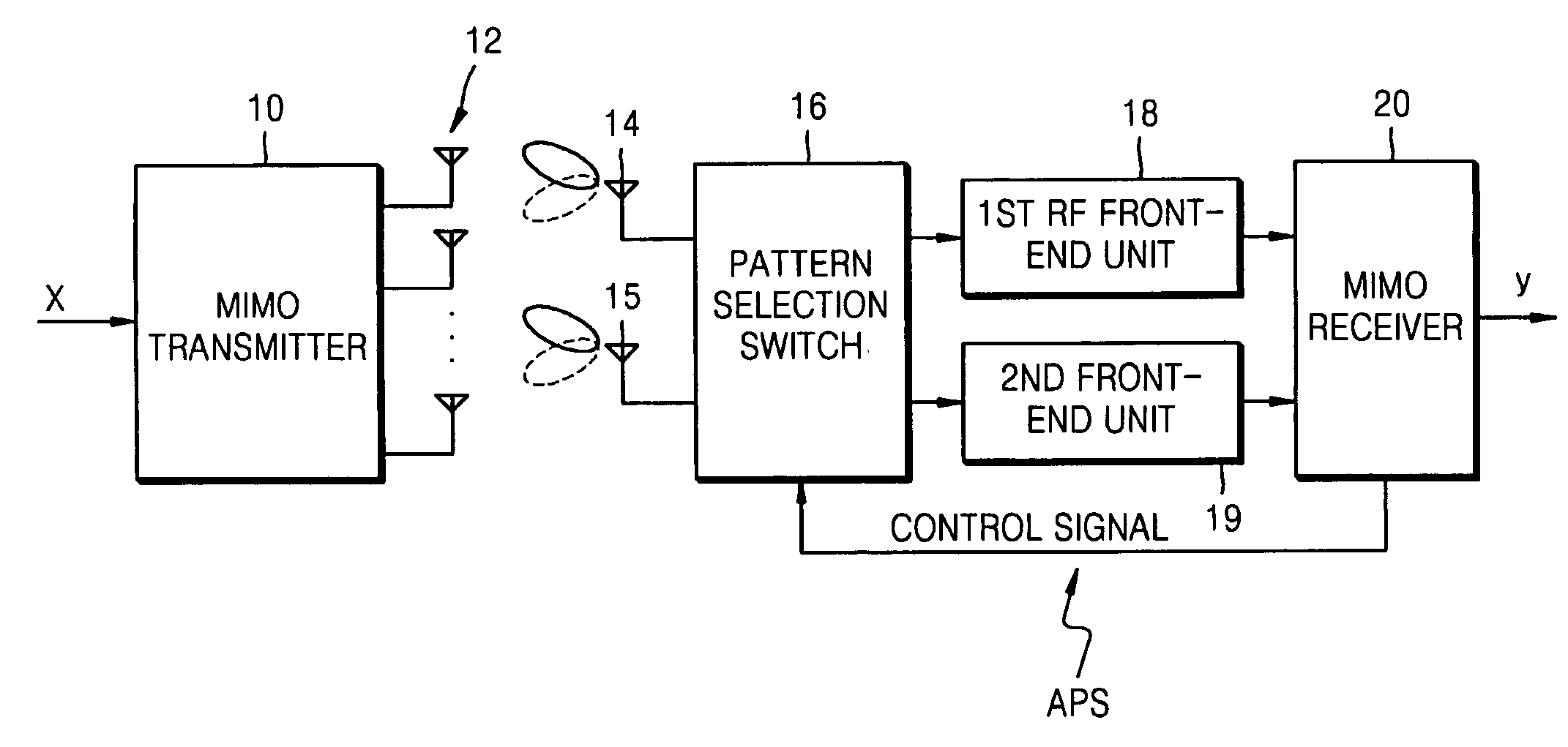
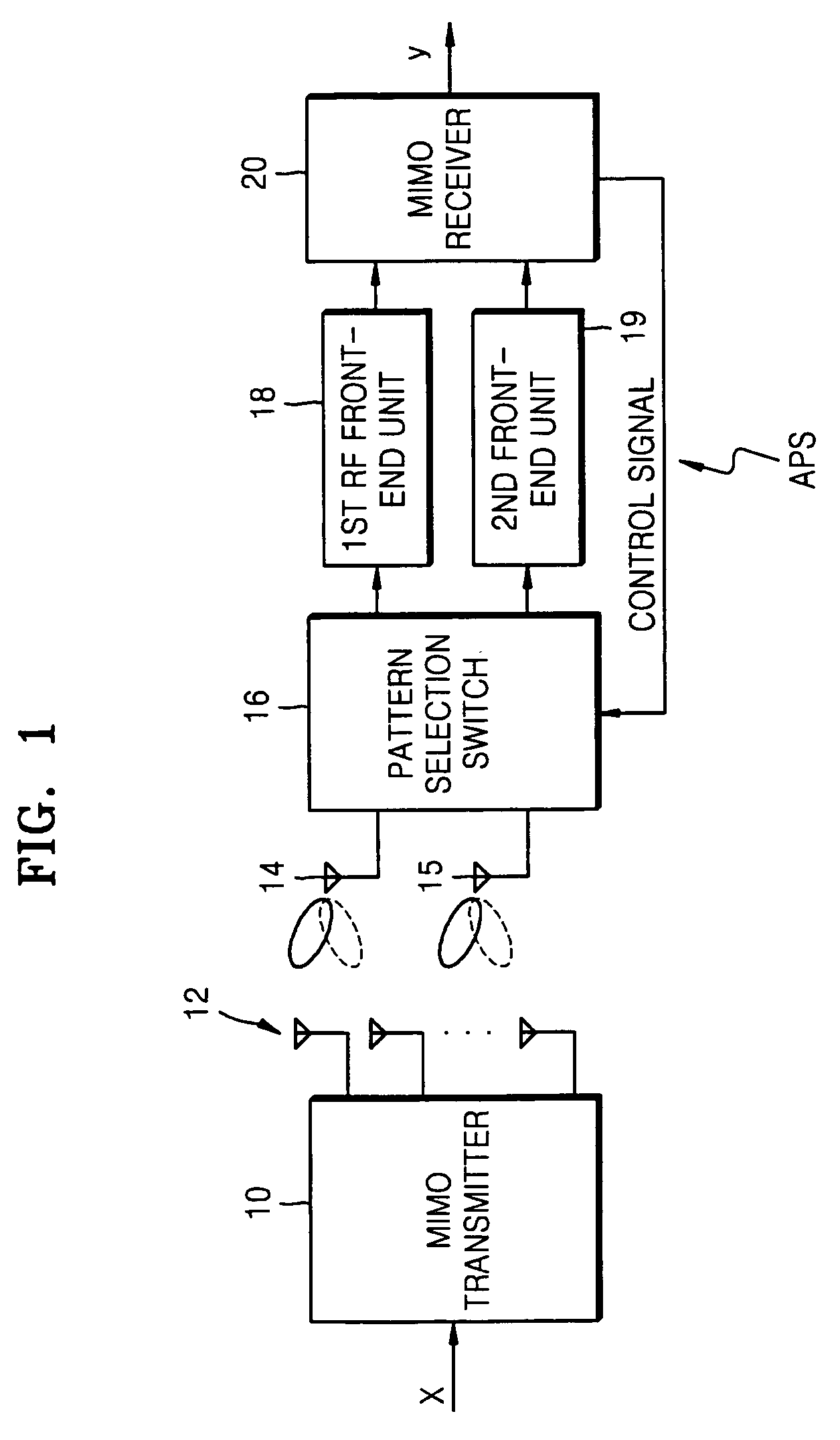
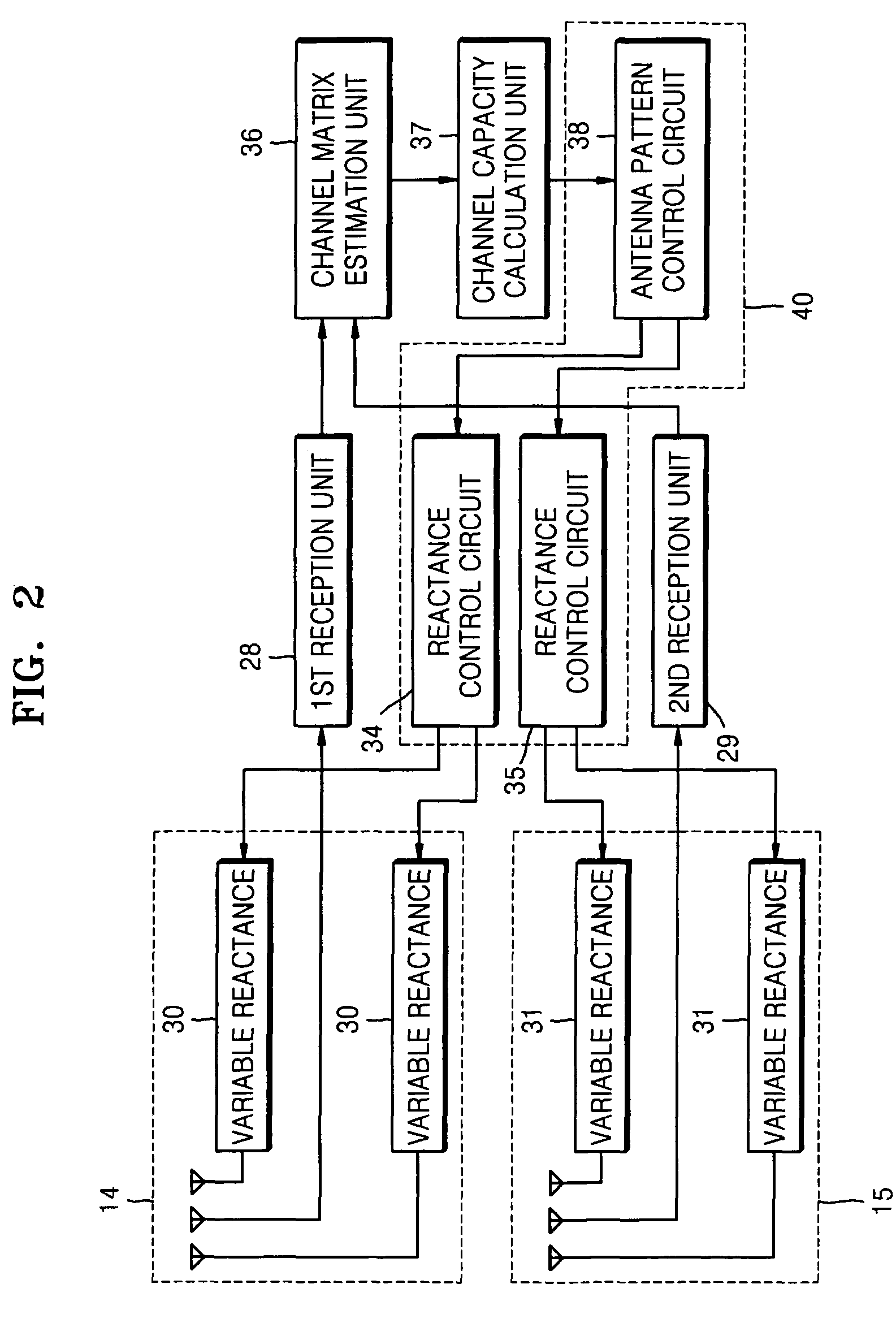
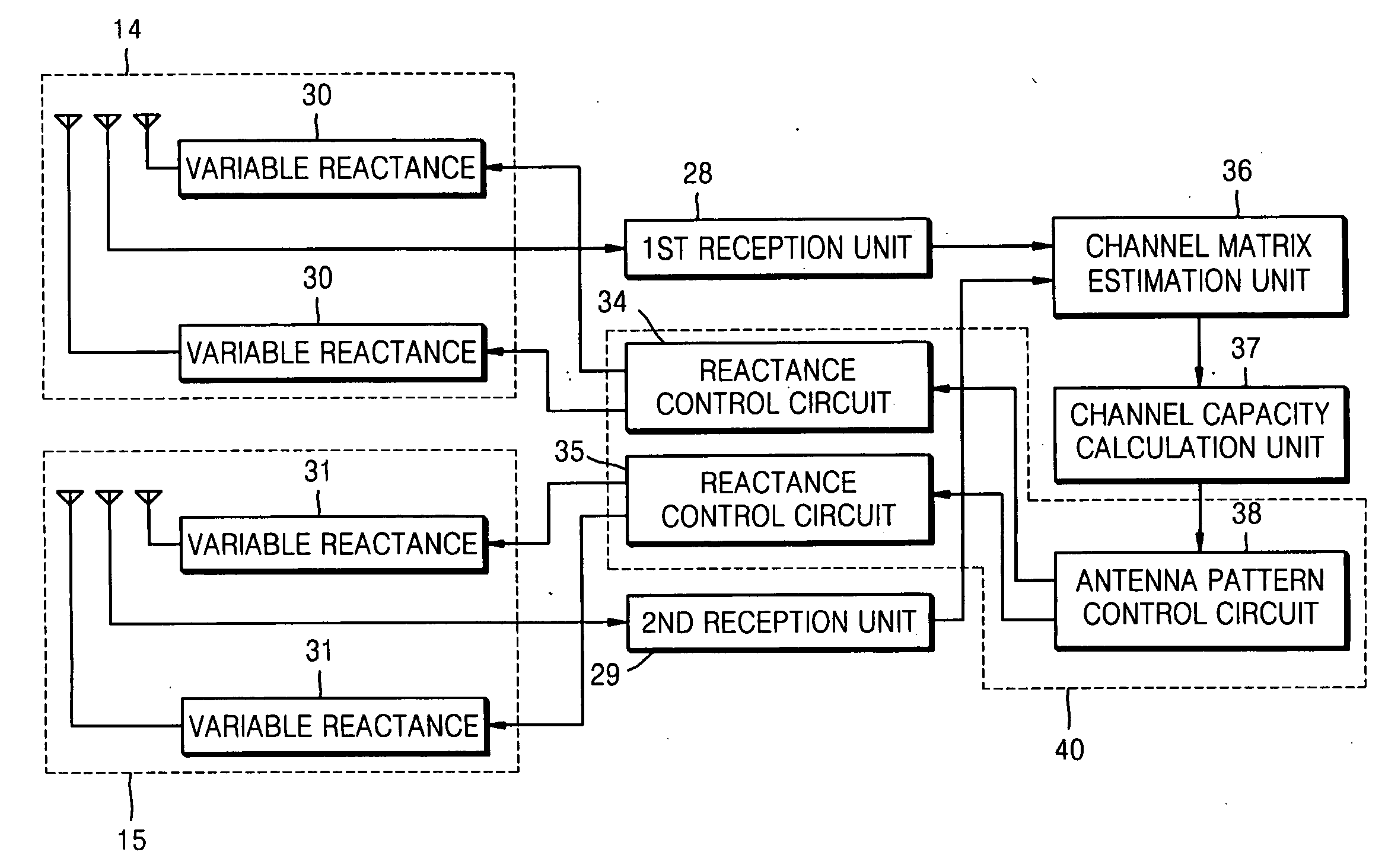
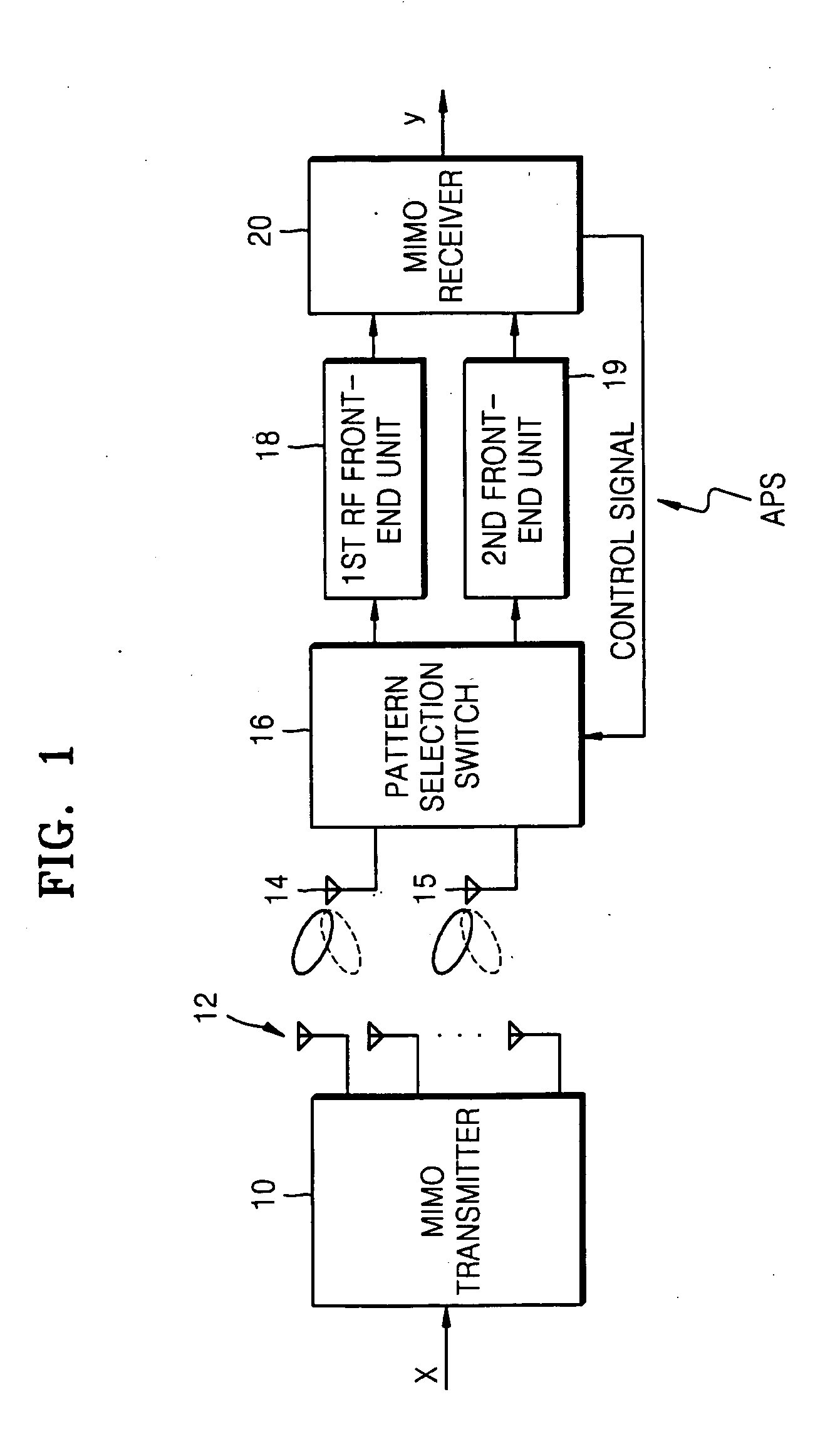
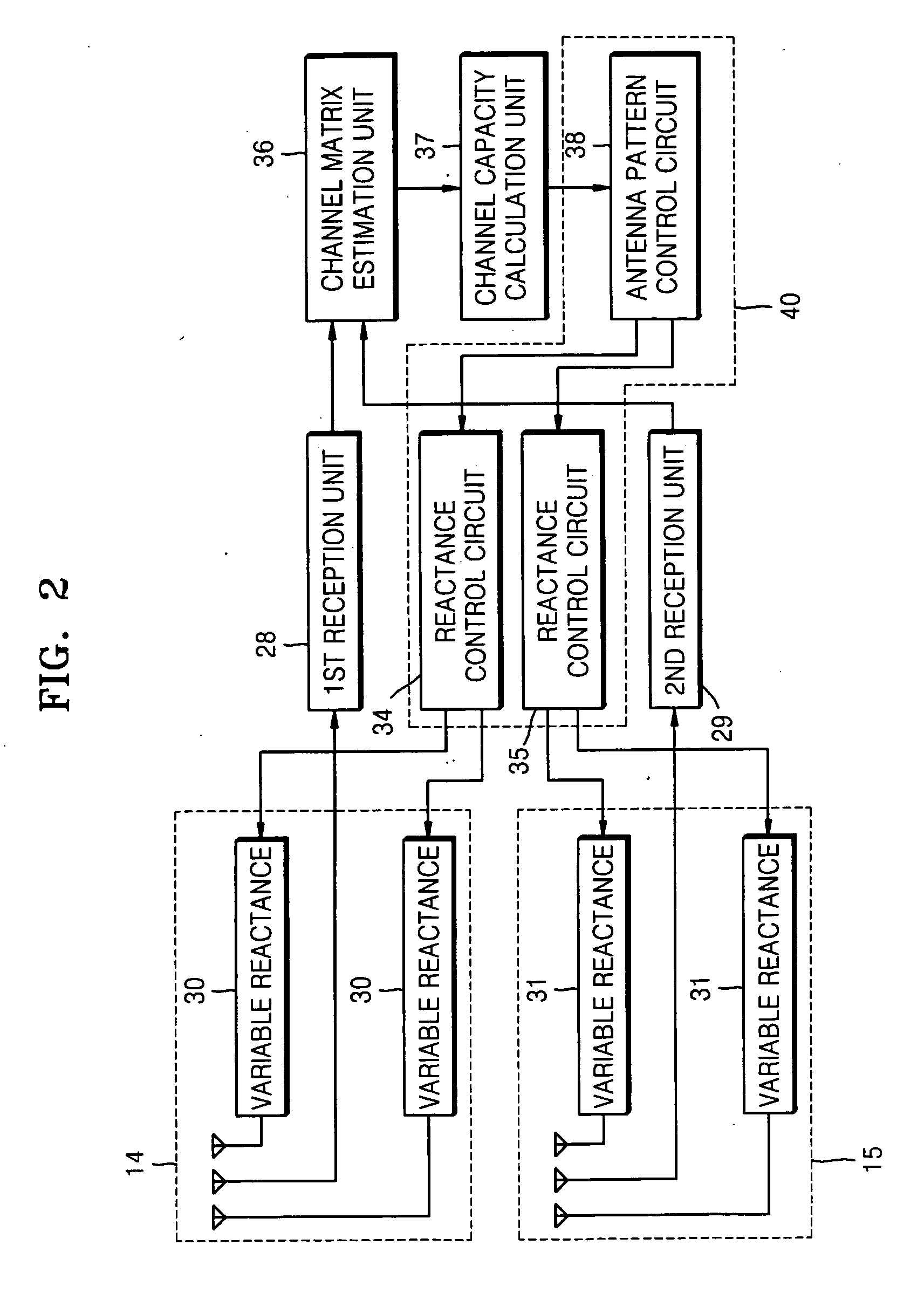
A multi-input multi-output (MIMO) radio communication apparatus and method are provided. The MIMO apparatus includes a plurality of reception antennas each having a plurality of antenna patterns; a channel matrix estimation unit for estimating a channel matrix between a plurality of transmission antennas and the plurality of reception antennas; a channel capacity calculation unit for calculating a channel capacity corresponding to a combination of antenna patterns of the plurality of reception antennas by using the estimated channel matrix; and an antenna pattern control unit for changing the antenna patterns of the plurality of reception antennas to maximize the channel capacity. According to the MIMO radio communication apparatus and method, direction can be controlled adaptively to a propagation environment.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Radio communication apparatus and method
ActiveUS20070142004A1Maximize channel capacityMaximize capacityMultiple-port networksResonant long antennasMulti inputEngineering
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Simulated annealing for traffic matrix estimation
The SATME method and system estimates source-to-destination traffic matrices using a simulated annealing algorithm, the traffic matrix estimation being represented as a probability distribution over the set of all possible matrices that satisfy a set of given constraints. The constraints explicitly encode information that the user knows about the network traffic as components of an objective function (a fitness function), that is then minimized using simulated annealing. With the method according to the invention, arbitrary constraints of any form can be included, and the case where there are no feasible solutions can be diagnosed by the objective function not converging to zero.
Owner:RPX CORP
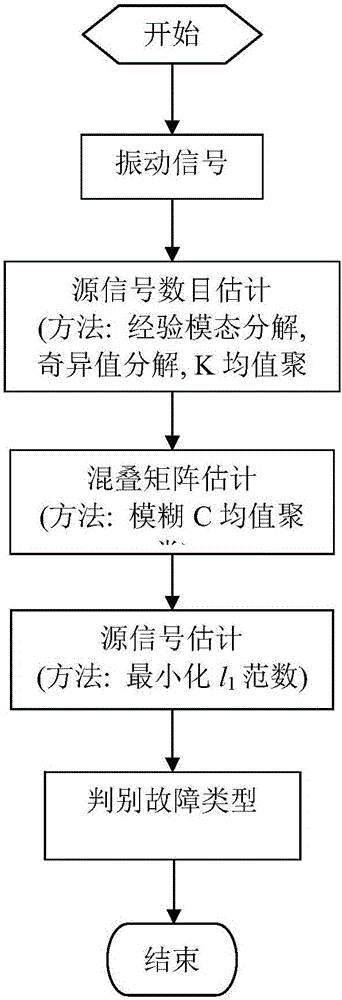
Wind turbine generator gearbox fault diagnosis method based on vibration signal blind source separation and sparse component analysis
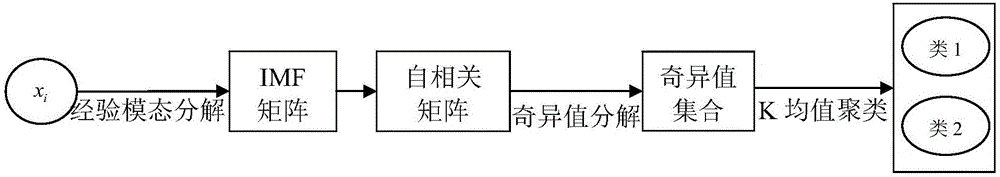
ActiveCN106096562AReduce aliasingReduce maintenance costsData processing applicationsCharacter and pattern recognitionSingular value decompositionElectricity
The invention discloses a wind turbine generator gearbox fault diagnosis method based on vibration signal blind source separation and sparse component analysis. The wind turbine generator gearbox fault diagnosis method mainly comprises three algorithms, which are an empirical mode decomposition (EMD), singular value decomposition (SVD) and K-means clustering (K-Means) based source signal number estimation algorithm, a fuzzy C-means clustering (FCM) based aliasing matrix estimation method, and a minimized l1-norm based source signal estimation and diagnosis algorithm. An idea of blind source separation (BSS) and sparse component analysis (SCA) is introduced into the whole algorithm process. The wind turbine generation gearbox fault diagnosis method takes simulated signals and actual vibration signals as a test object, detailed algorithm description is provided, and the effectiveness of the algorithms in the aspects of signal processing and fault analysis is verified through a series of experiments.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com