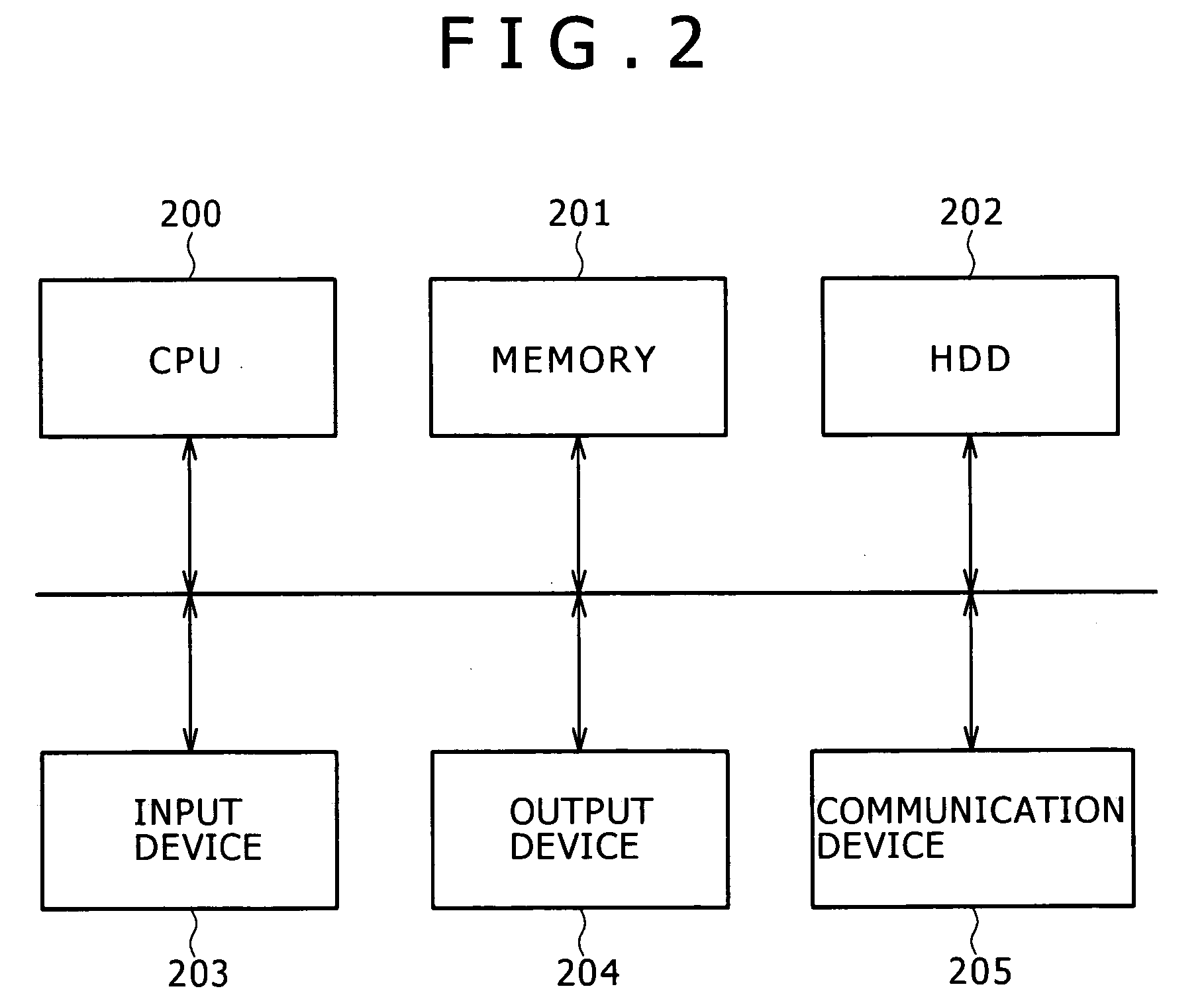
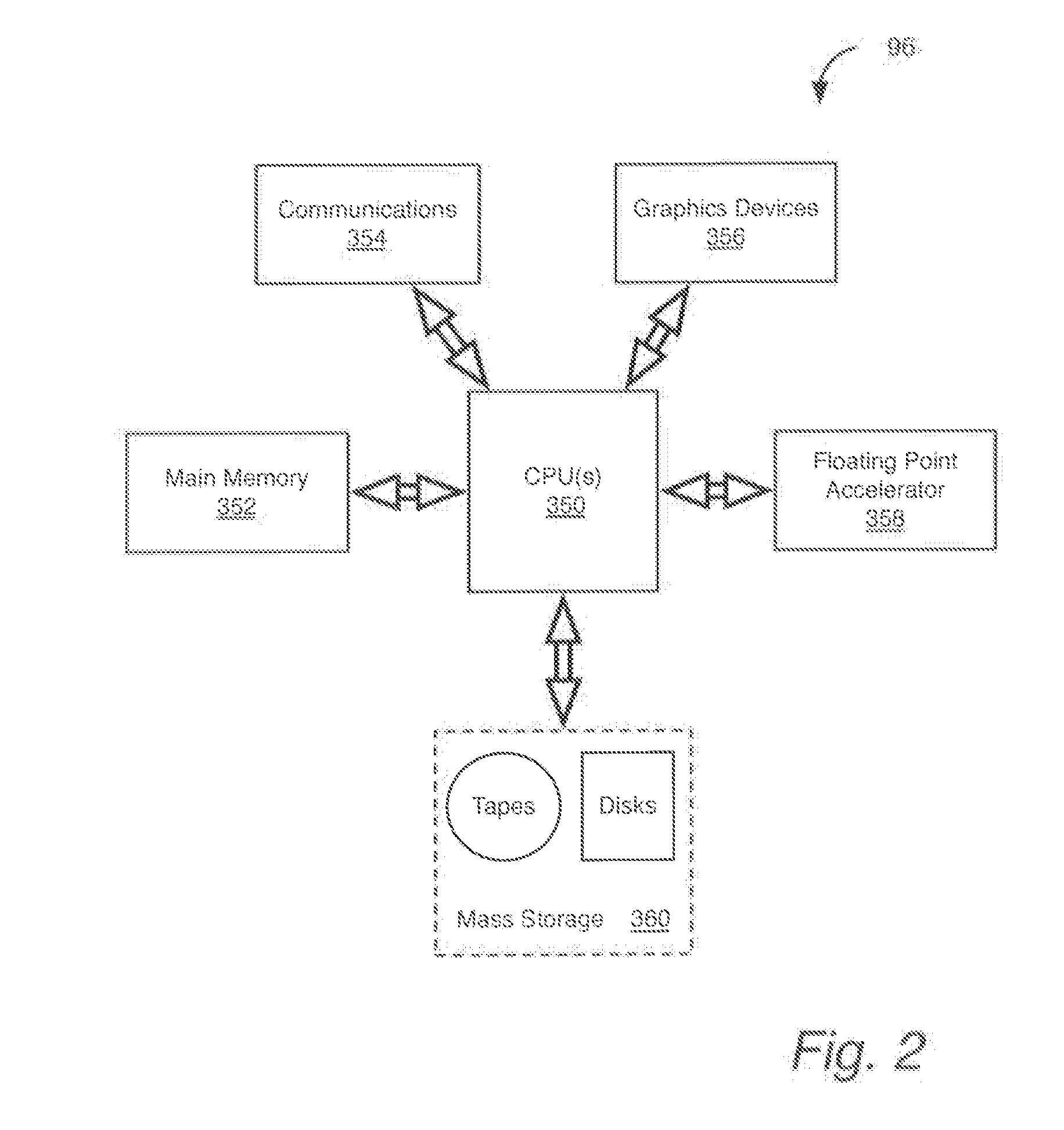
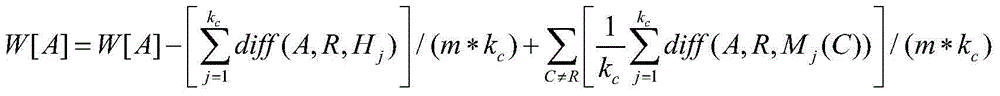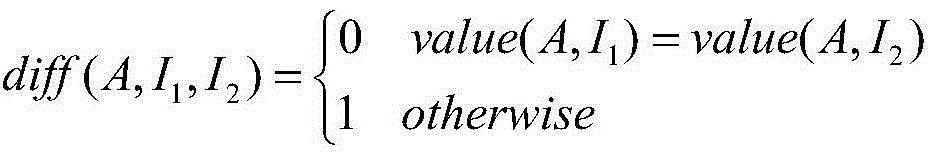Patents
Literature
742 results about "Probit" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
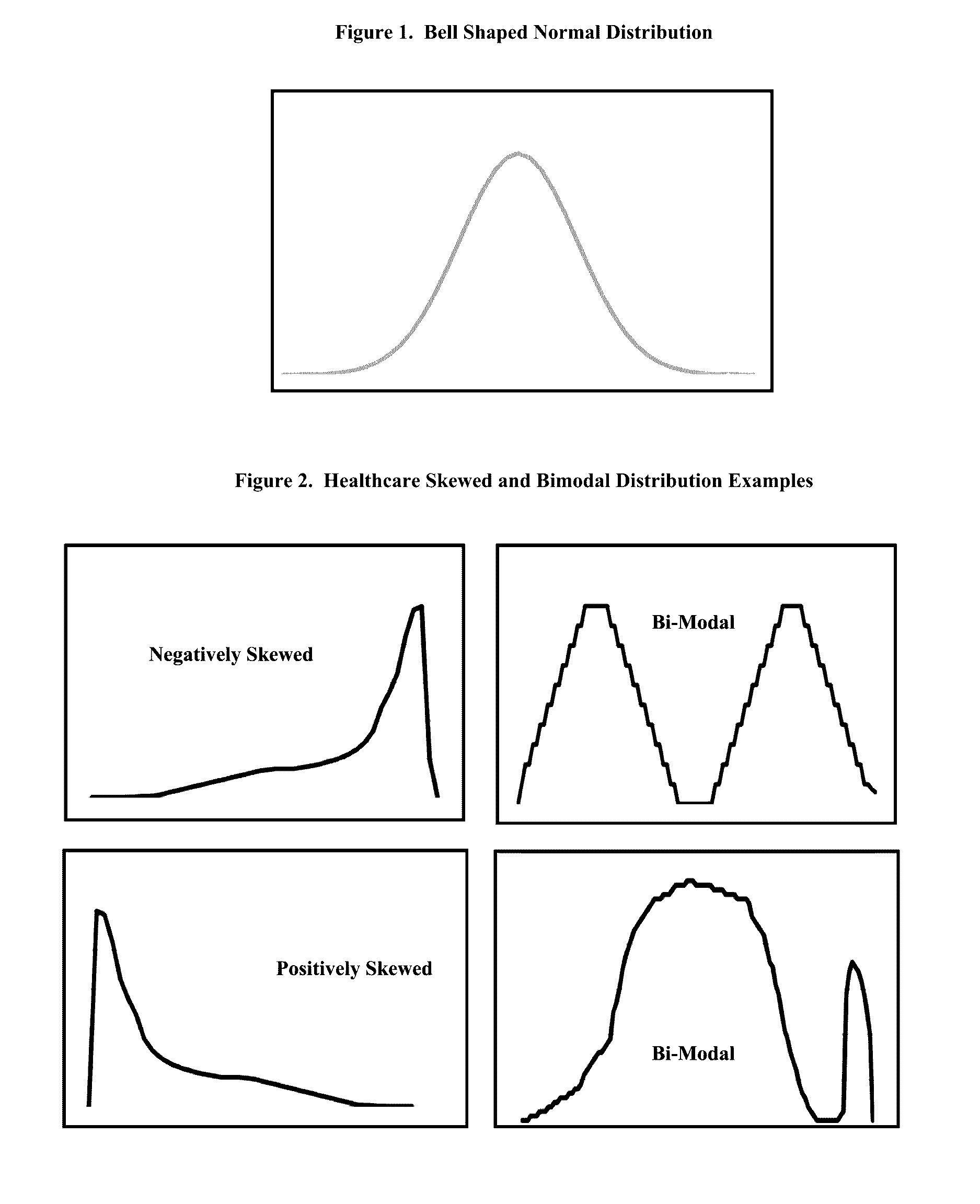
In probability theory and statistics, the probit function is the quantile function associated with the standard normal distribution, which is commonly denoted as N(0,1). Mathematically, it is the inverse of the cumulative distribution function of the standard normal distribution, which is denoted as Φ(z), so the probit is denoted as Φ⁻¹(p). It has applications in exploratory statistical graphics and specialized regression modeling of binary response variables.
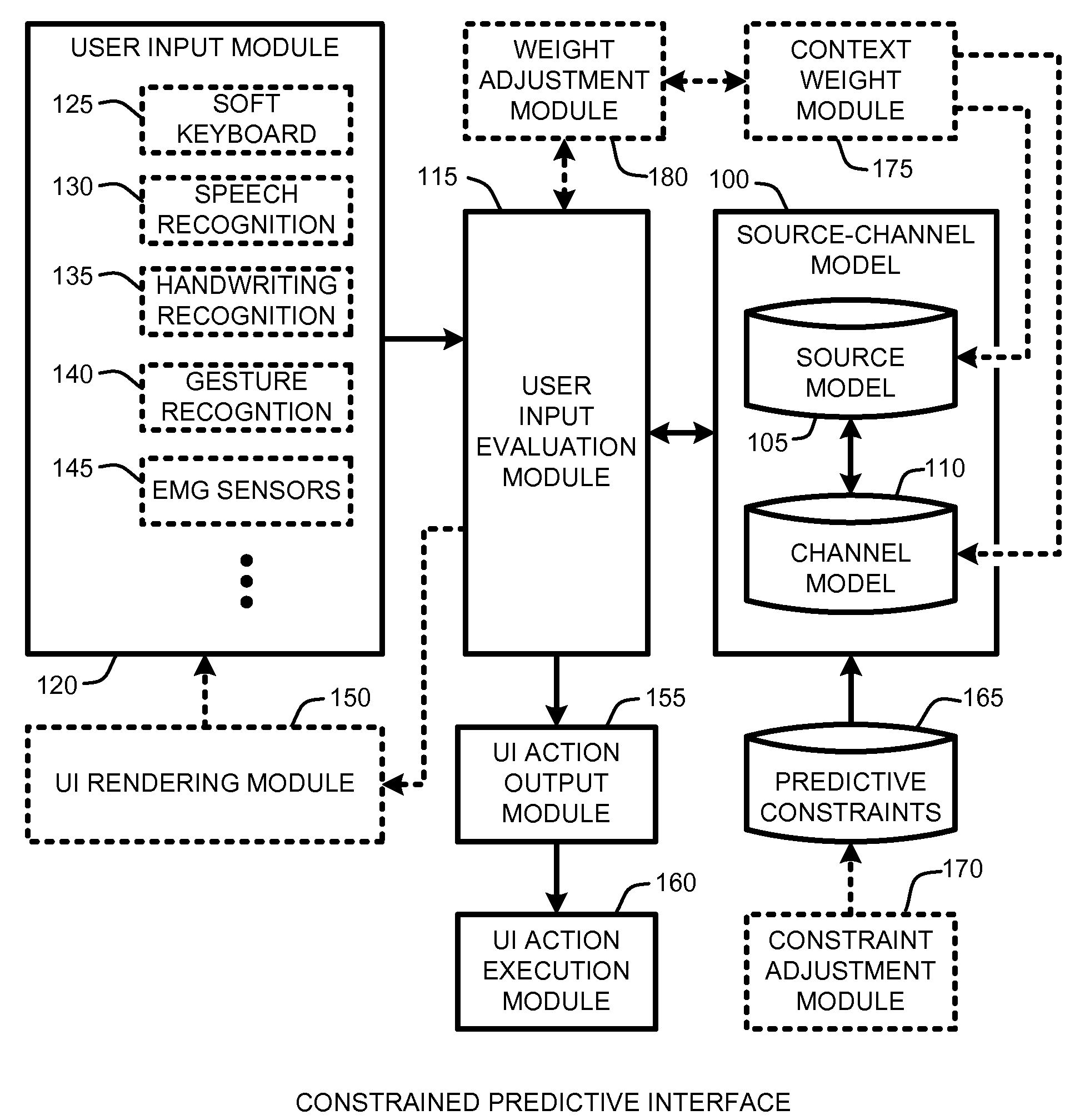
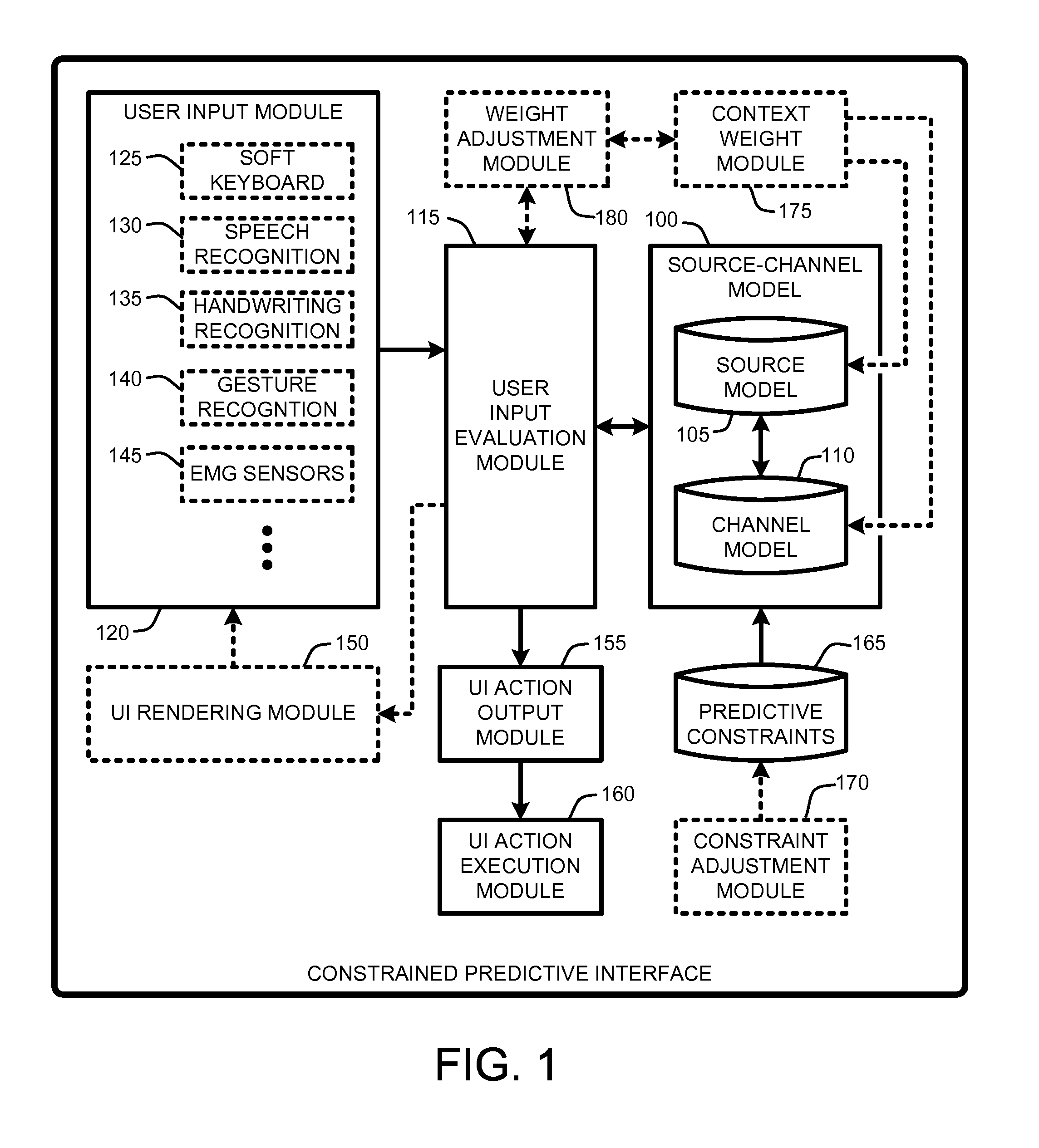
Predictive interfaces with usability constraints
InactiveUS20100315266A1Improve featuresGood user interfaceElectronic switchingInput/output processes for data processingMulti touch interfaceUsability
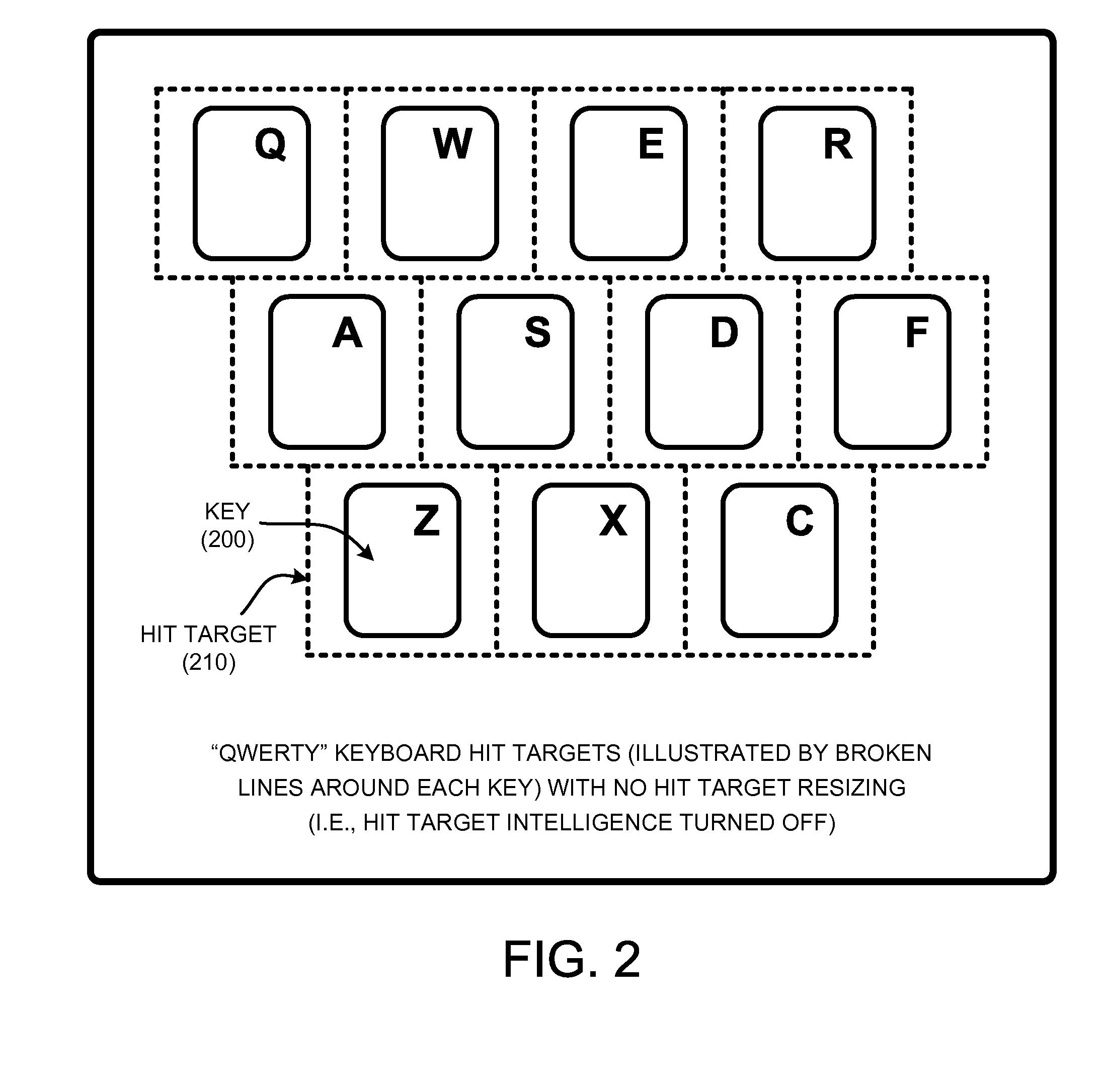
A “Constrained Predictive Interface” uses predictive constraints to improve accuracy in user interfaces such as soft keyboards, pen interfaces, multi-touch interfaces, 3D gesture interfaces, EMG based interfaces, etc. In various embodiments, the Constrained Predictive Interface allows users to take any desired action at any time by taking into account a likelihood of possible user actions in different contexts to determine intended user actions. For example, to enable a virtual keyboard interface, various embodiments of the Constrained Predictive Interface provide key “sweet spots” as predictive constraints that allow the user to select particular keys regardless of any probability associated with the selected or neighboring keys. In further embodiments, the Constrained Predictive Interface provides hit target resizing via various piecewise constant touch models in combination with various predictive constraints. In general, hit target resizing provides dynamic real-time virtual resizing of one or more particular keys based on various probabilistic criteria.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
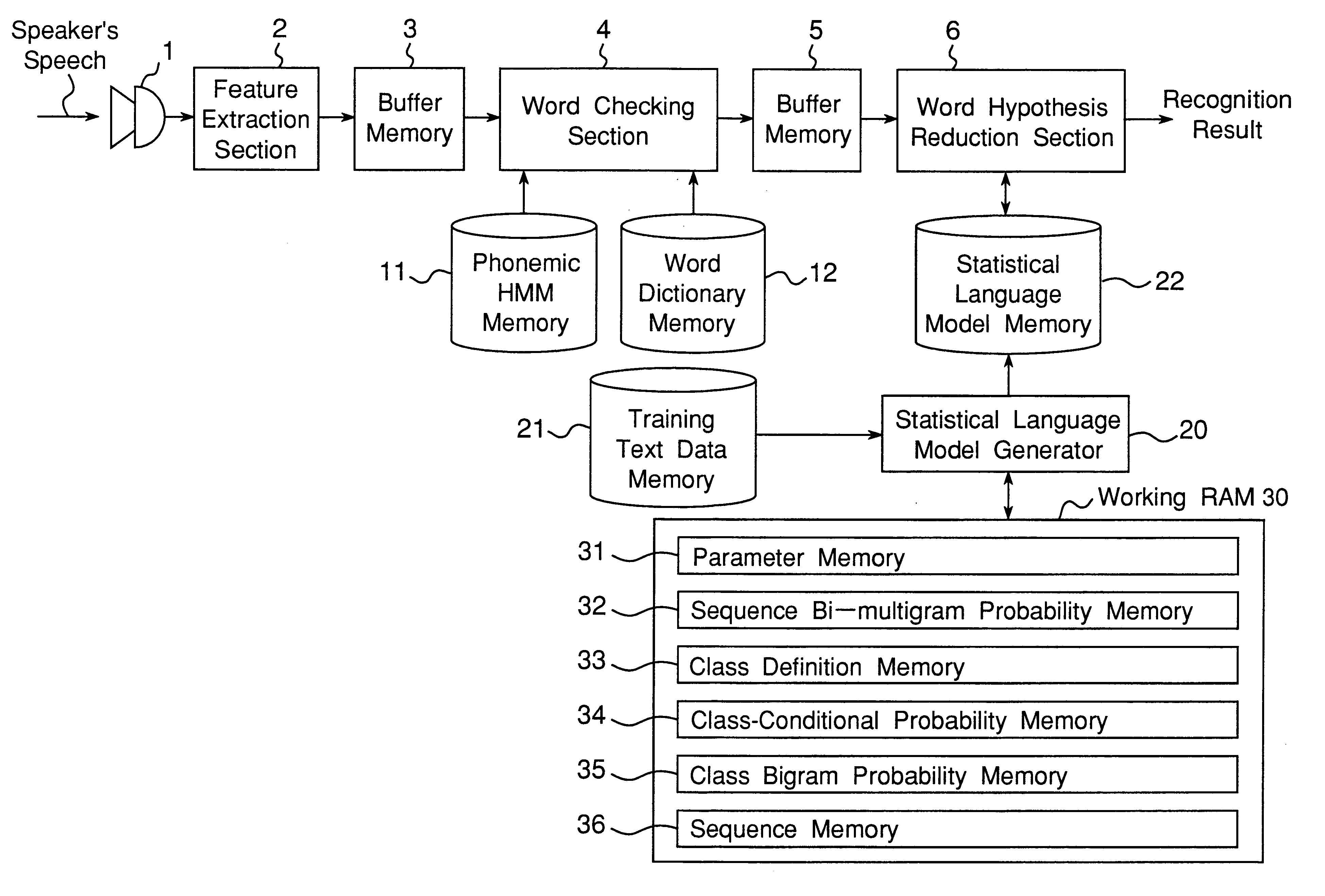
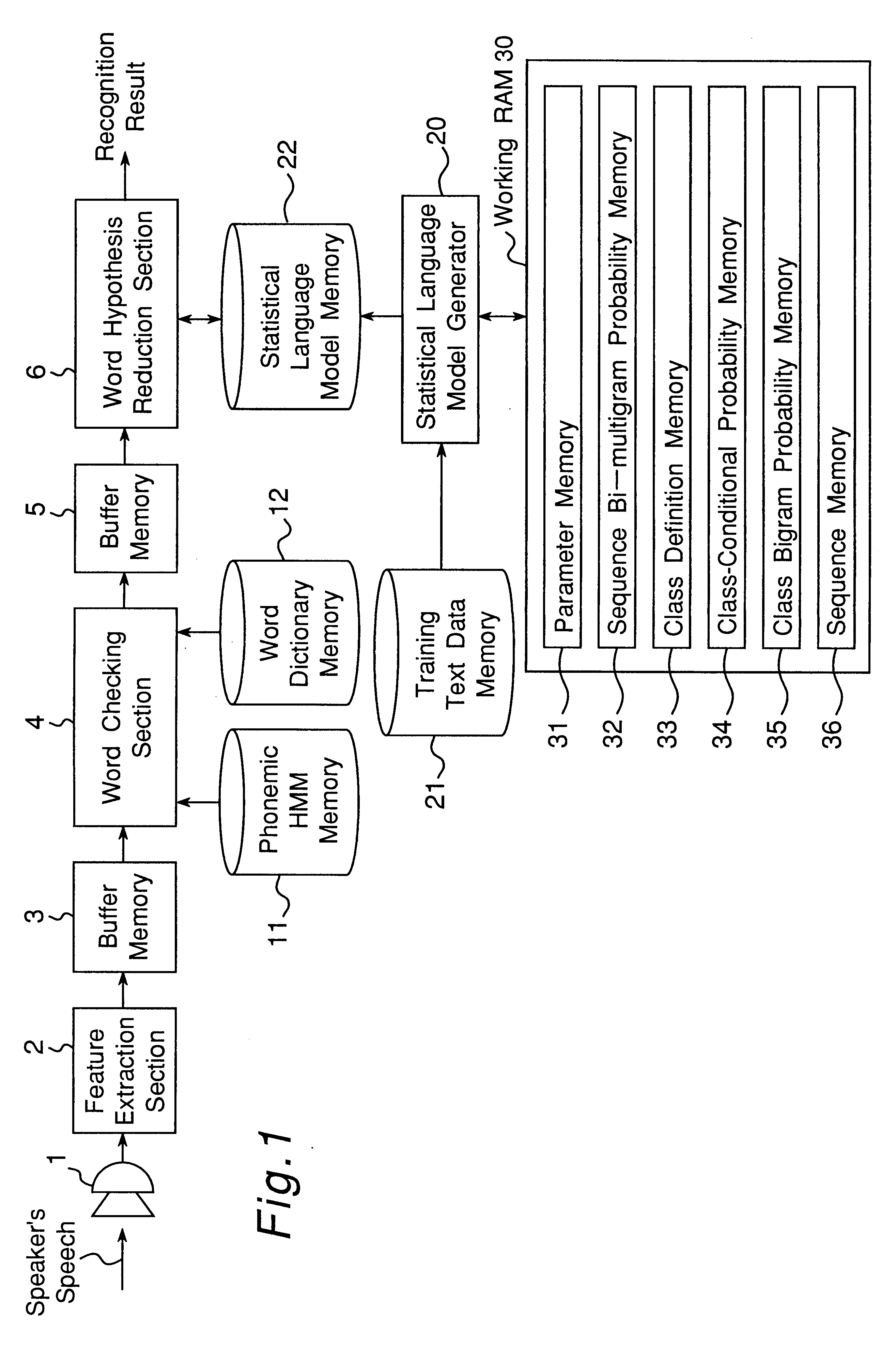
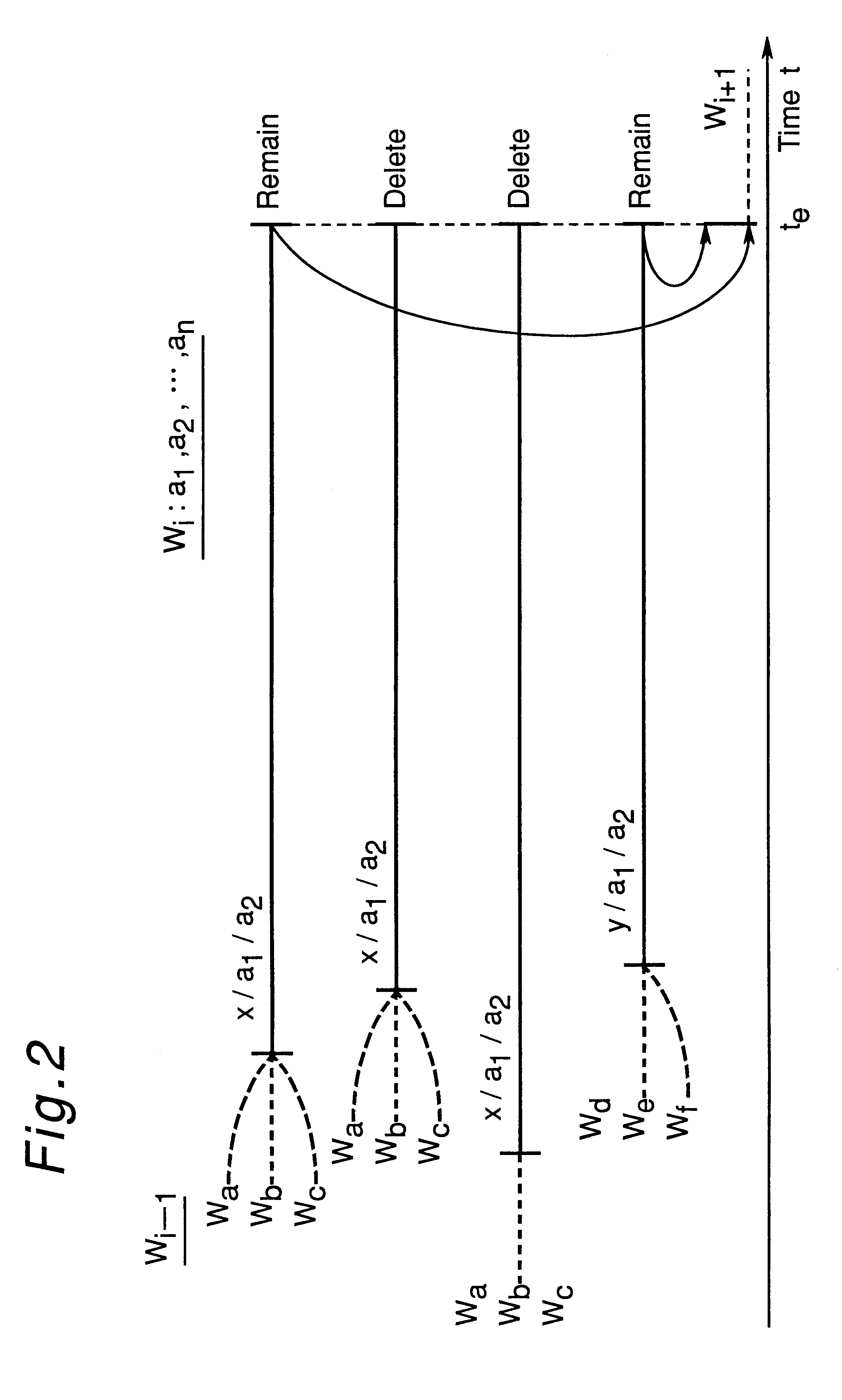
Apparatus for generating a statistical sequence model called class bi-multigram model with bigram dependencies assumed between adjacent sequences
InactiveUS6314399B1High speed machiningRecombinant DNA-technologySpeech recognitionSequence modelProbit
An apparatus generates a statistical class sequence model called A class bi-multigram model from input training strings of discrete-valued units, where bigram dependencies are assumed between adjacent variable length sequences of maximum length N units, and where class labels are assigned to the sequences. The number of times all sequences of units occur are counted, as well as the number of times all pairs of sequences of units co-occur in the input training strings. An initial bigram probability distribution of all the pairs of sequences is computed as the number of times the two sequences co-occur, divided by the number of times the first sequence occurs in the input training string. Then, the input sequences are classified into a pre-specified desired number of classes. Further, an estimate of the bigram probability distribution of the sequences is calculated by using an EM algorithm to maximize the likelihood of the input training string computed with the input probability distributions. The above processes are then iteratively performed to generate statistical class sequence model.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Automated operation of wellsite pumping equipment
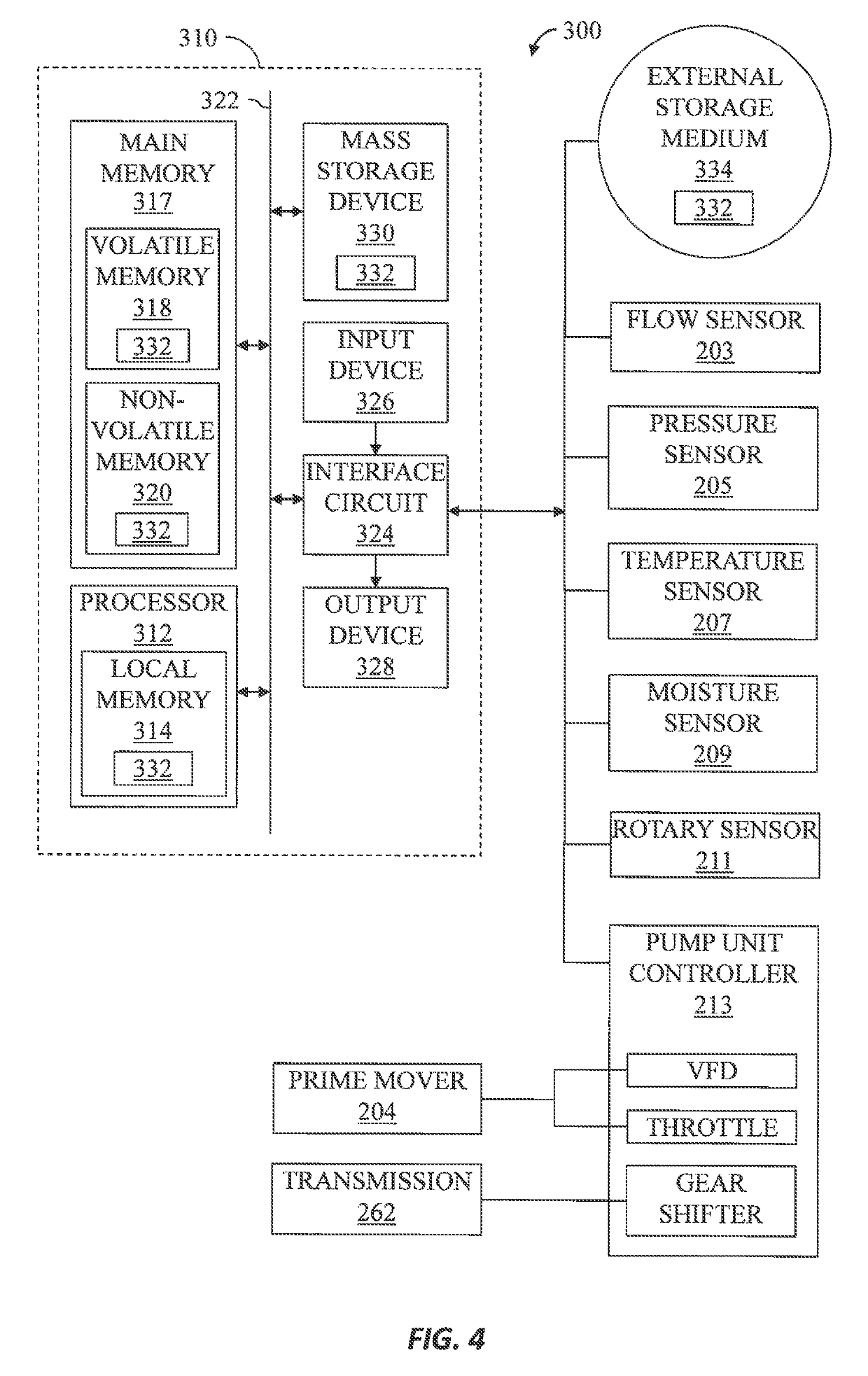
ActiveUS10415562B2Increase probabilityReduce probabilityComputer controlSimulator controlEngineeringProbit
Automated operation of well site pumping equipment, including generating a mathematical belief model for maintaining an interrelationship between flow rate achievable by a pump unit discharge pressure of the pump unit, and probability of achieving the flow rate at corresponding discharge pressure. Speed of the pump unit is controlled to achieve a target speed based on a flow rate set-point and the mathematical belief model and updating the mathematical belief model at least while the target speed is achieved. Updating the mathematical belief model may include increasing the probability of achieving the flow rate set-point when actual flow rate of the pump unit is not less than the flow rate set-point and decreasing the probability of achieving the flow rate set-point when the actual flow rate of the pump unit is less than the flow rate set-point.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Probabilistic Map Matching From A Plurality Of Observational And Contextual Factors
ActiveUS20110313648A1Well formedInstruments for road network navigationRoad vehicles traffic controlProbit modelHide markov model
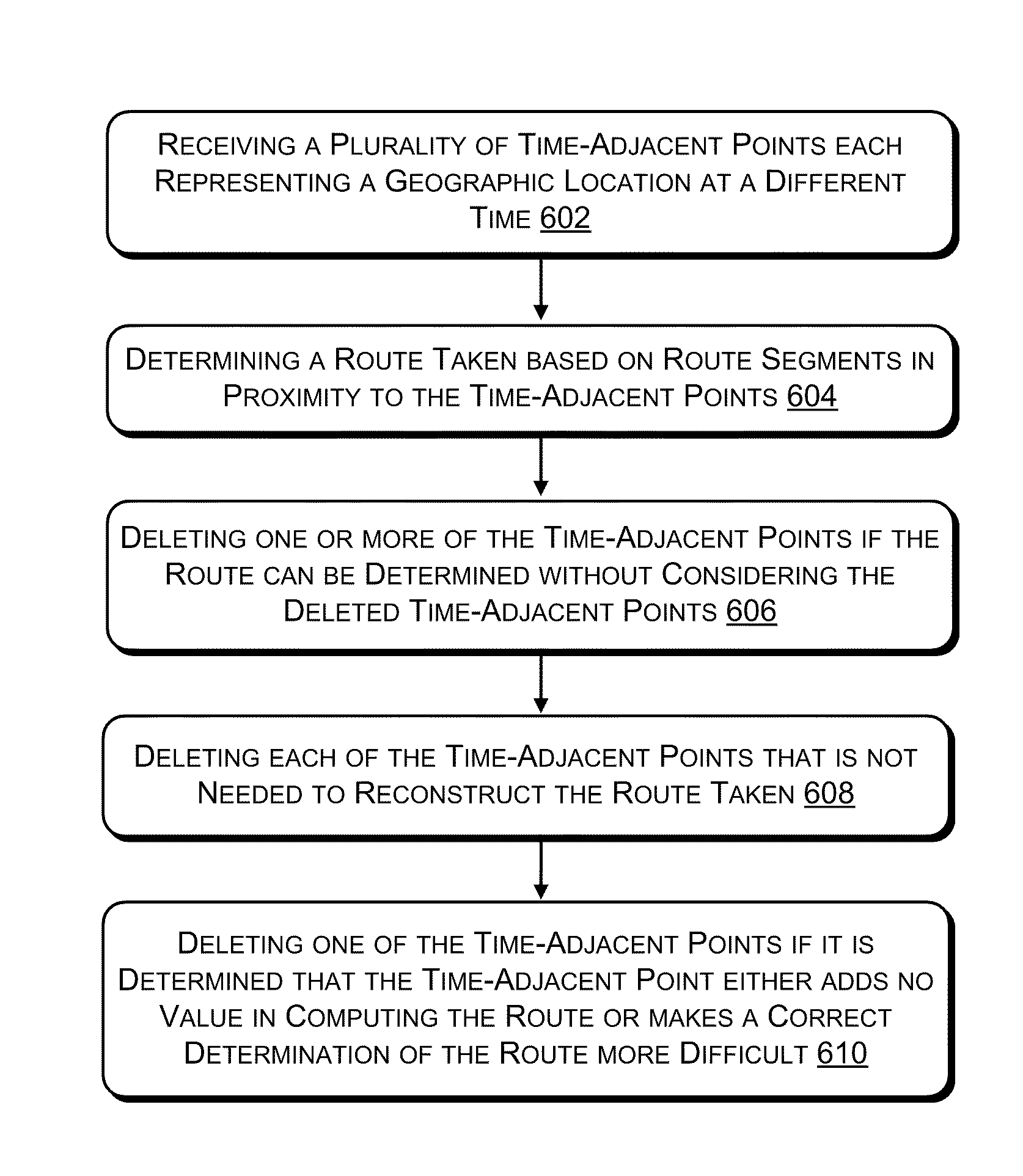
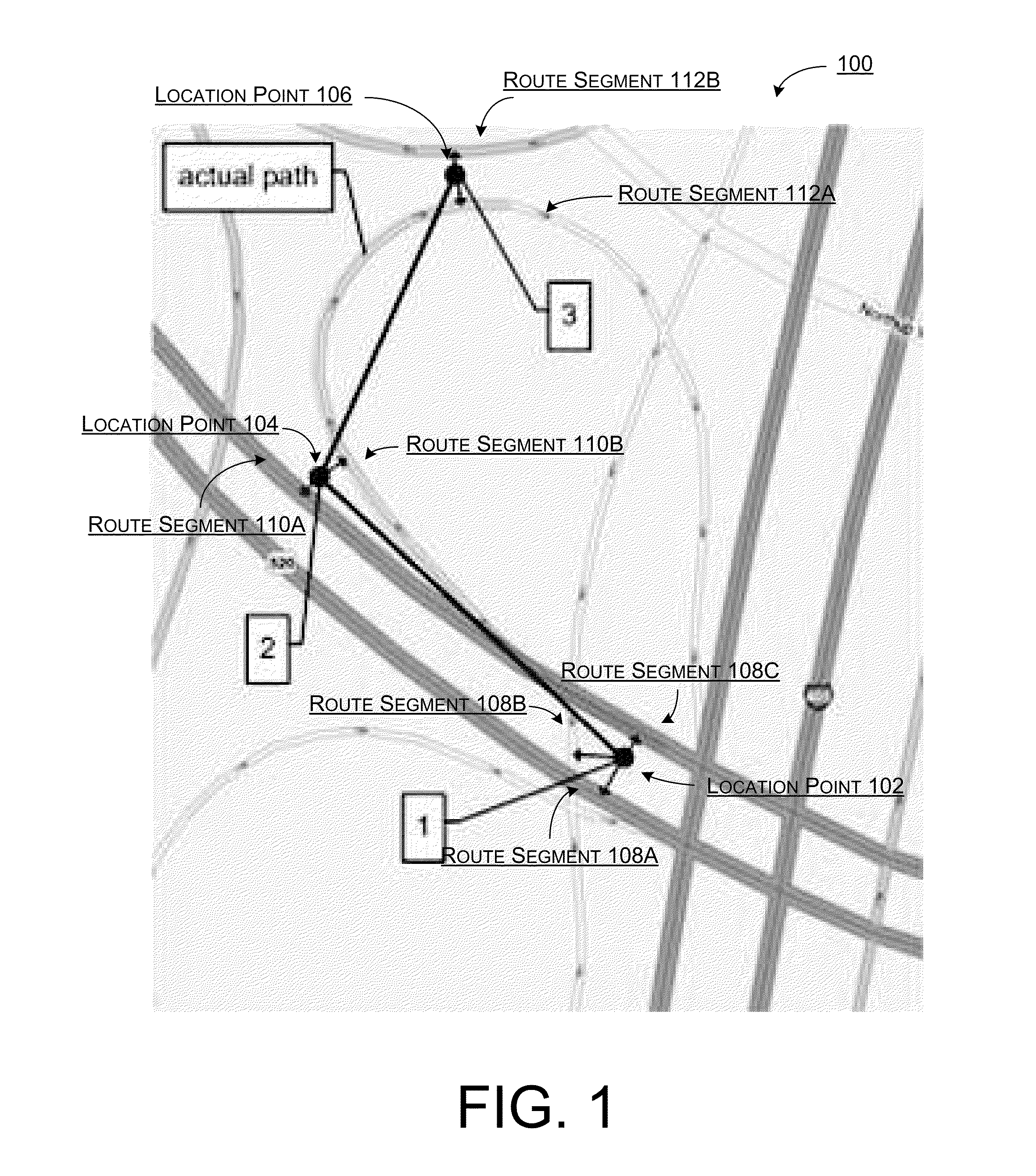
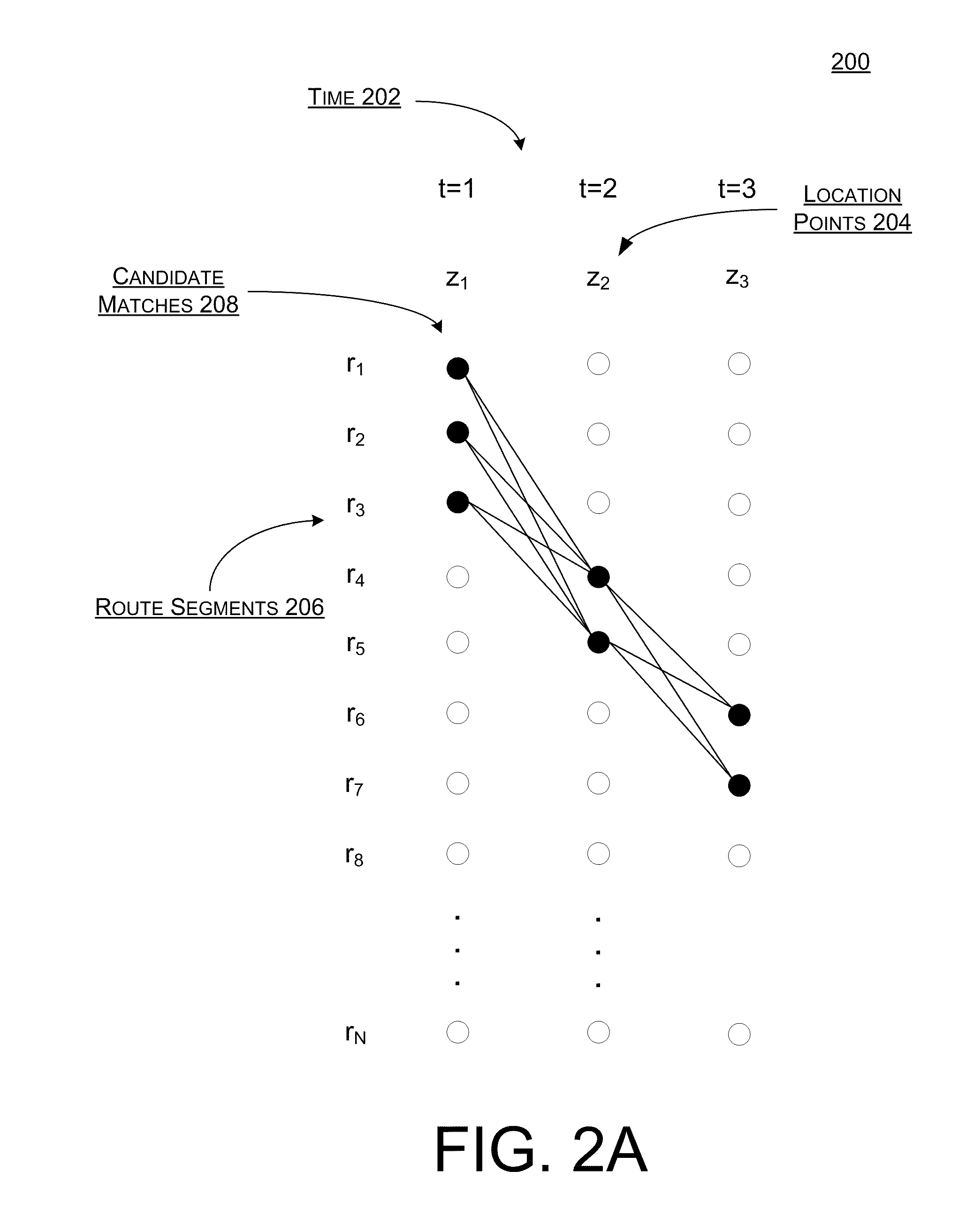
Systems, methods, and devices are described for implementing map matching techniques relating to measured location data. Probabilistic models, including temporal Bayesian network models and Hidden Markov Models, may be used for combining multiple classes of evidence relating to potential locations of points traversed on routes over time. Multiple route segments and overall routes may be maintained under relative uncertainty as candidates. The candidate route segments and overall routes may then be reduced into a smaller number of candidates or a single most likely route as a trip progresses. As the trip progresses, route segments in proximity to each location point are identified and candidate matches are determined. A probability of an entity traversing a candidate match at a given time and a probability of an entity traversing between a first candidate match at a first time and a second candidate match at a second time are determined based on a plurality of factors. Different modalities may be used to measure and transmit the location data.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
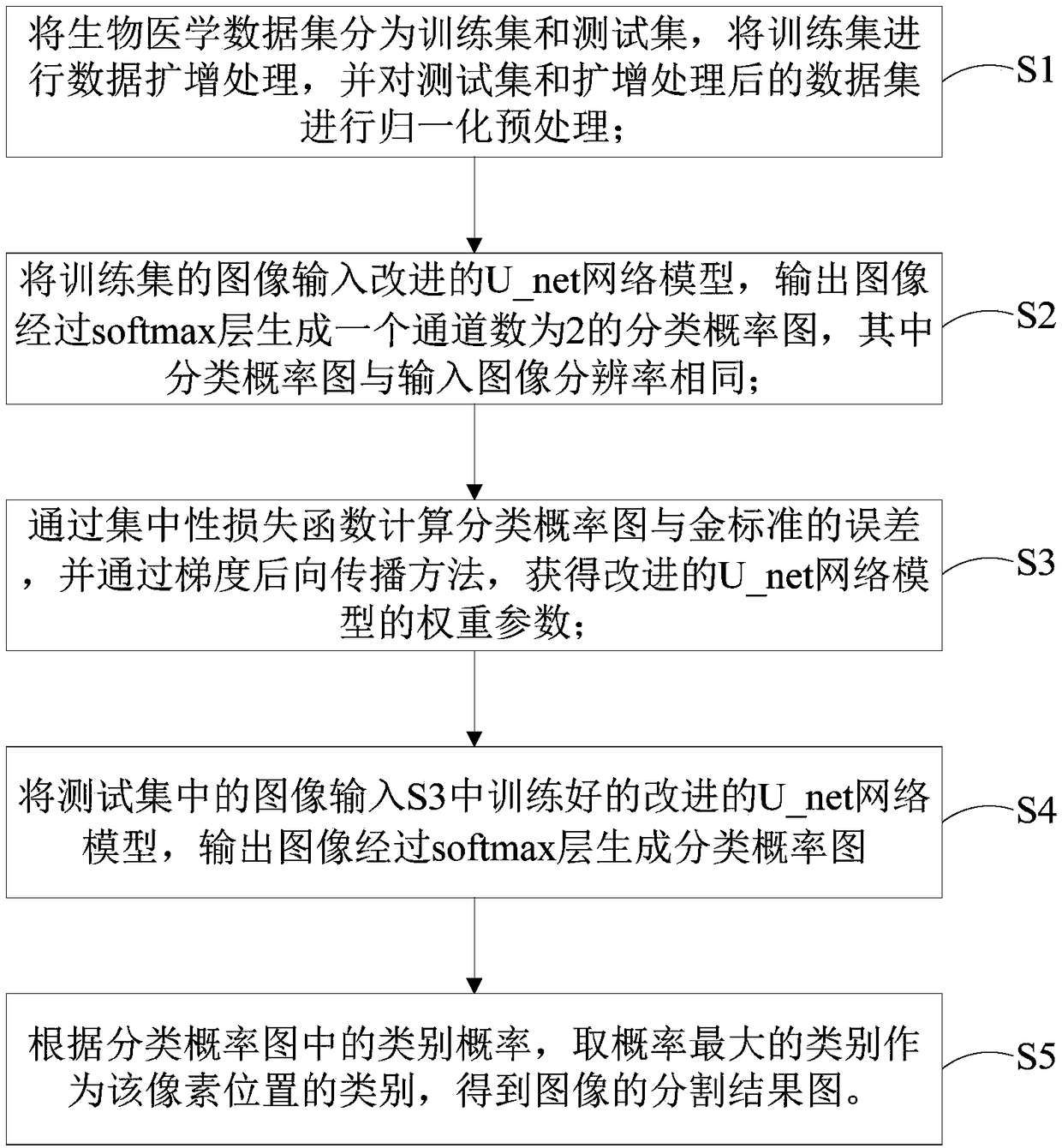
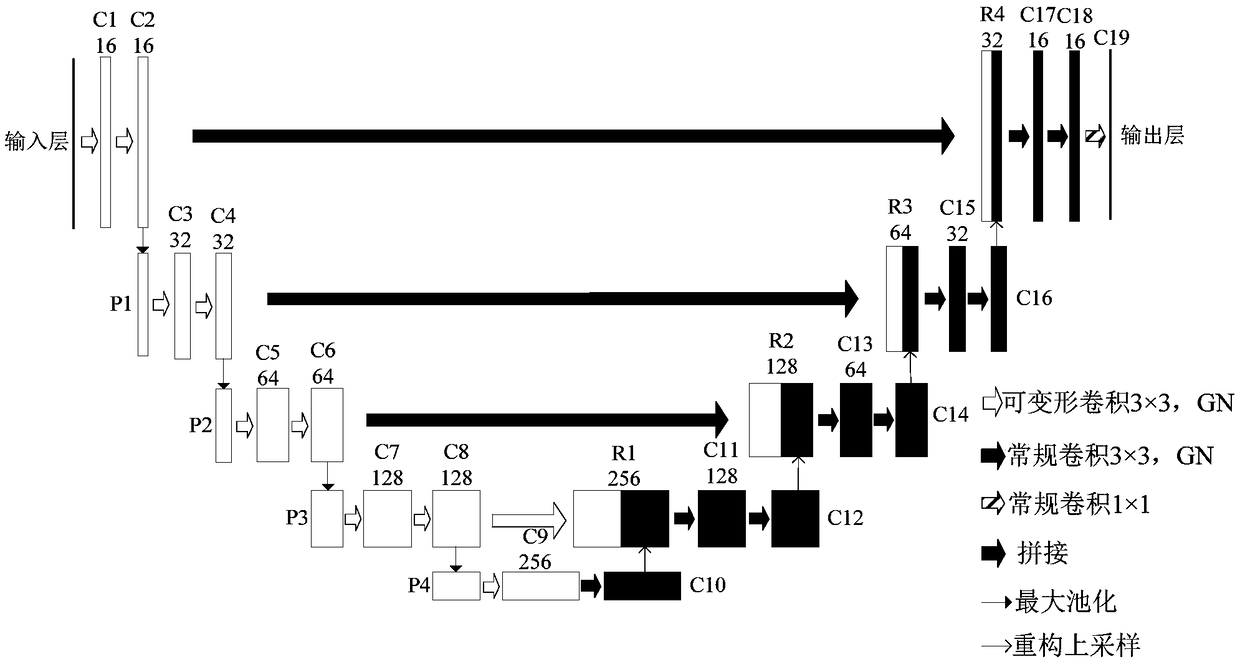
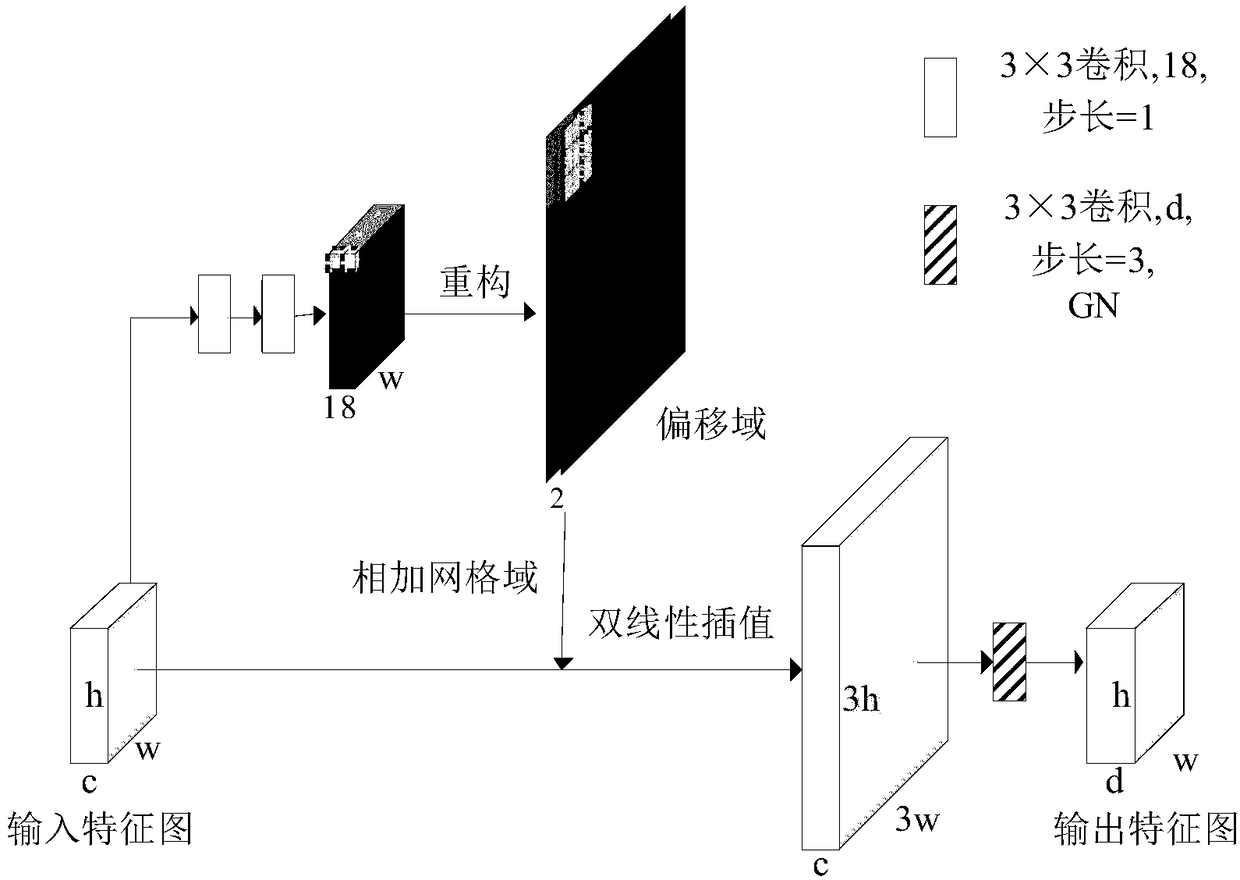
A novel biomedical image automatic segmentation method based on a U-net network structure
ActiveCN109191476AIncrease the number ofImprove segmentationImage enhancementImage analysisData setVisual technology
The invention belongs to the technical field of image processing and computer vision, and relates to a novel biomedical image automatic segmentation method based on a U-net network structure, including dividing a biomedical data set into a training set and a test set, and normalizing the test set and augmented test set; inputting the images of the training set into the improved U-net network model, and generating a classification probability map by output image passing through a softmax layer; calculating the error between classification probability diagram and gold standard by a centralized loss function, and obtaining the weight parameters of network model by a gradient backpropagation method; entering the images in the test set into the improved U-net network model, and outputting the image to generate a classification probability map through the softmax layer; according to the class probability in the classification probability graph, obtaining the segmentation result graph of theimage. The invention solves the problems that simple samples in the image segmentation process contribute too much to the loss function to learn difficult samples well.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
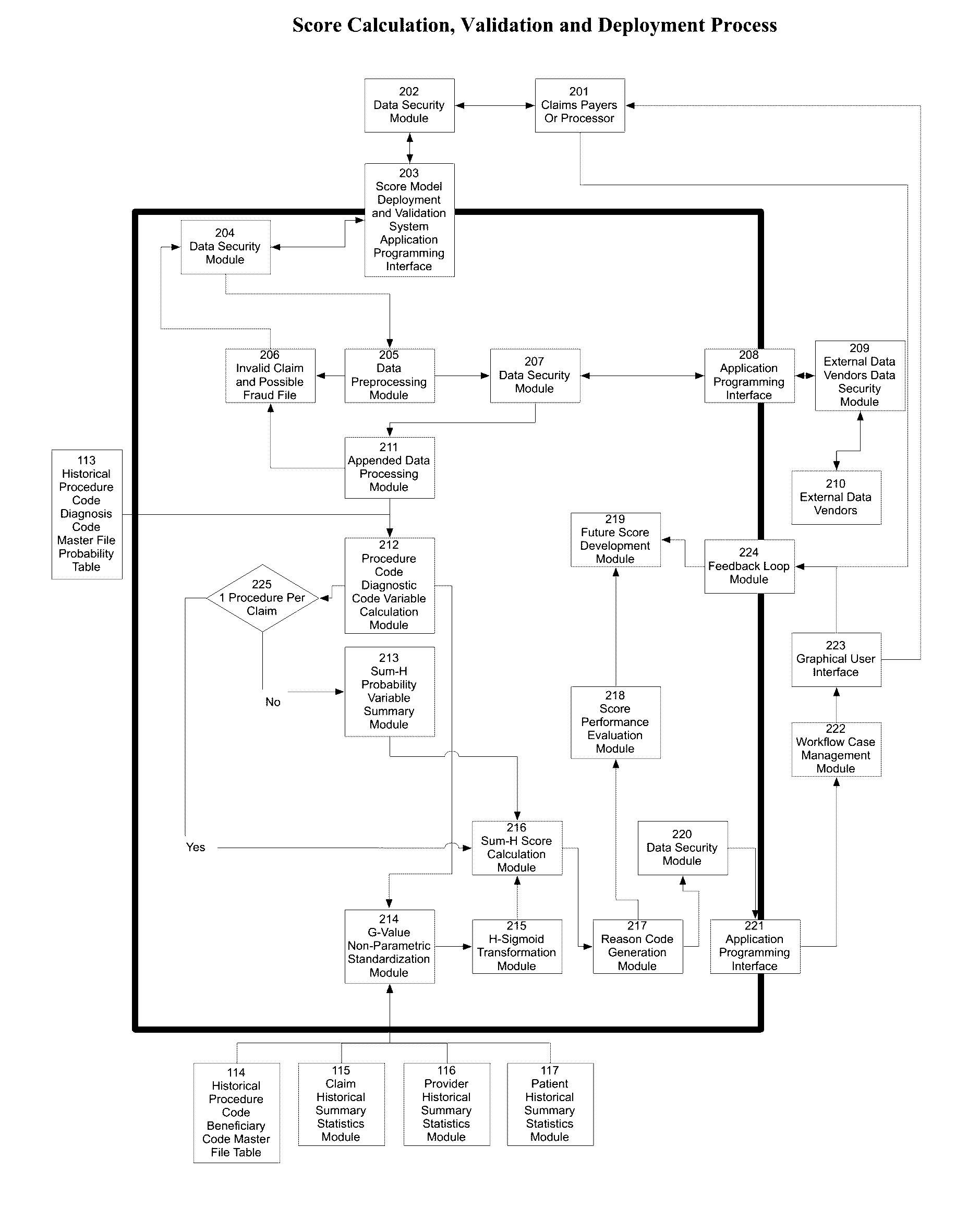
Healthcare claims fraud, waste and abuse detection system using non-parametric statistics and probability based scores
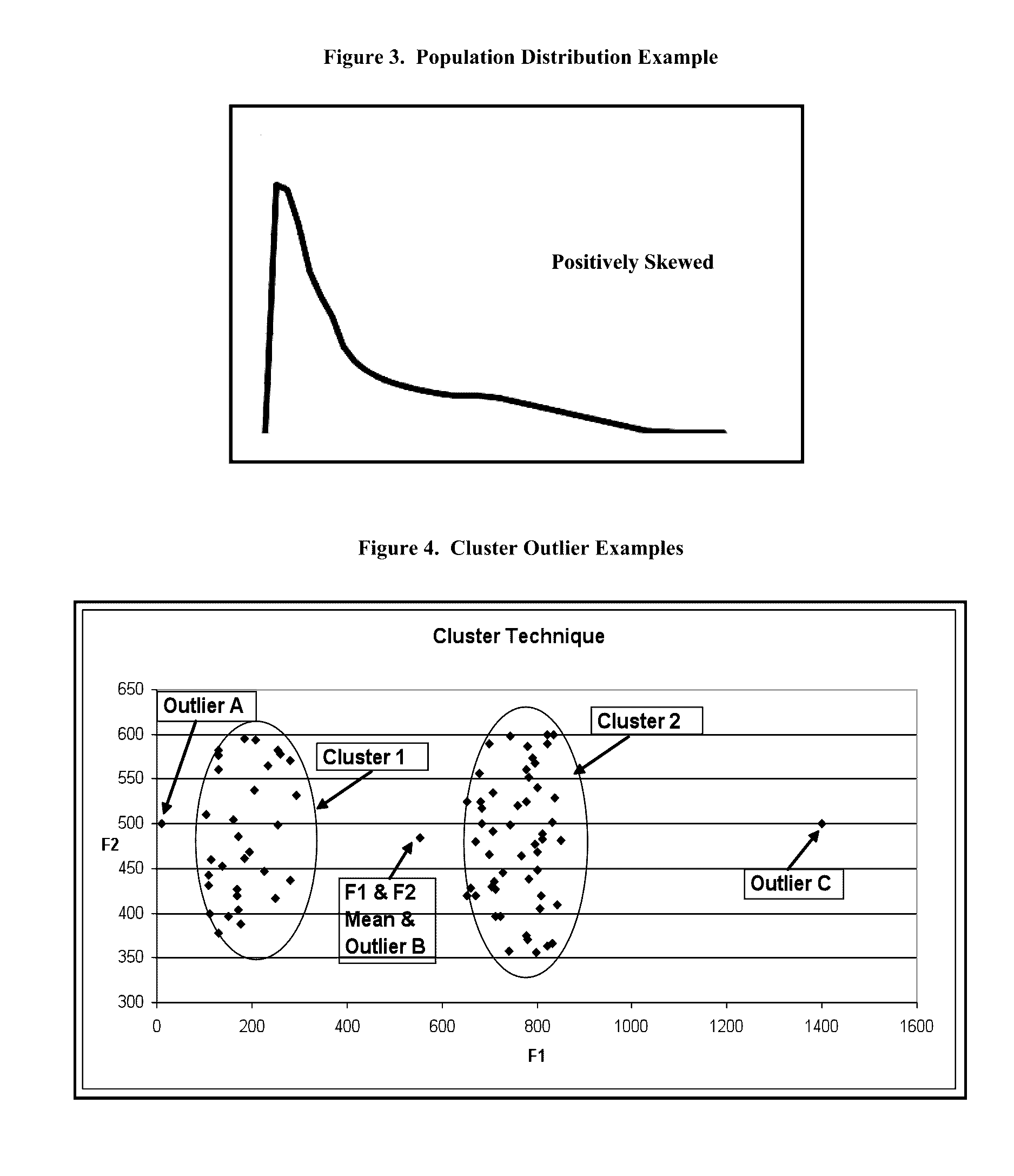
The present invention is in the field of Healthcare Claims Fraud Detection. Fraud is perpetrated across multiple healthcare payers. There are few labeled or “tagged” historical fraud examples needed to build “supervised”, traditional fraud models using multiple regression, logistic regression or neural networks. Current technology is to build “Unsupervised Fraud Outlier Detection Models”.Current techniques rely on parametric statistics that are based on assumptions such as outlier free and “normally distributed” data. Even some non-parametric statistics are adversely influenced by non-normality and the presence of outliers.Current technology cannot represent the combined variable values into one meaningful value that reflects the overall risk that this observation is an outlier. The single value, the “score”, must be capable of being measured on the same scale across different segments, such as geographies and specialty groups. Lastly, the score must substantially, monotonically rank the fraud risk and give reasons to substantiate the score.
Owner:FORTEL ANALYTICS LLC
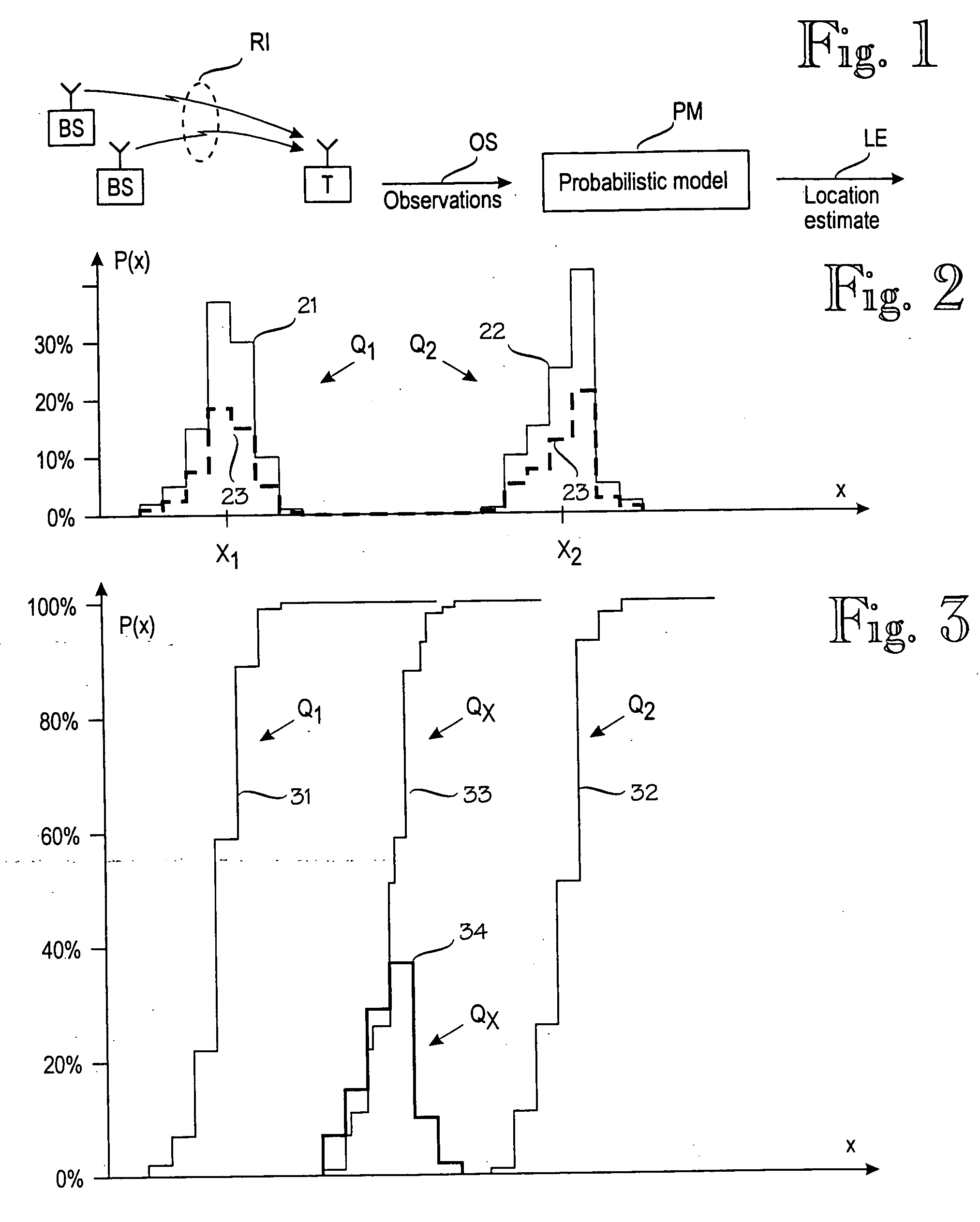
Probabilistic model for a positioning technique
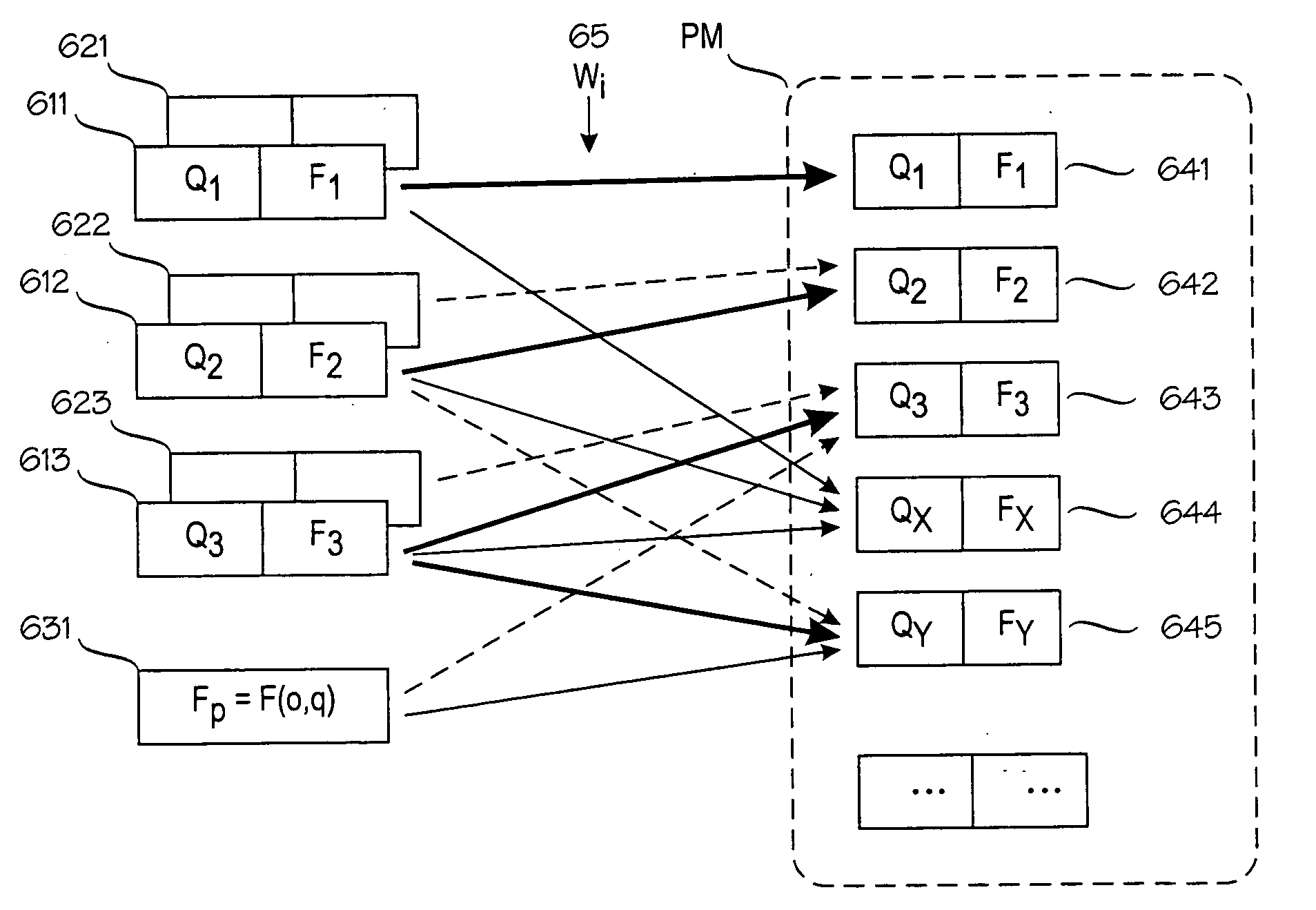
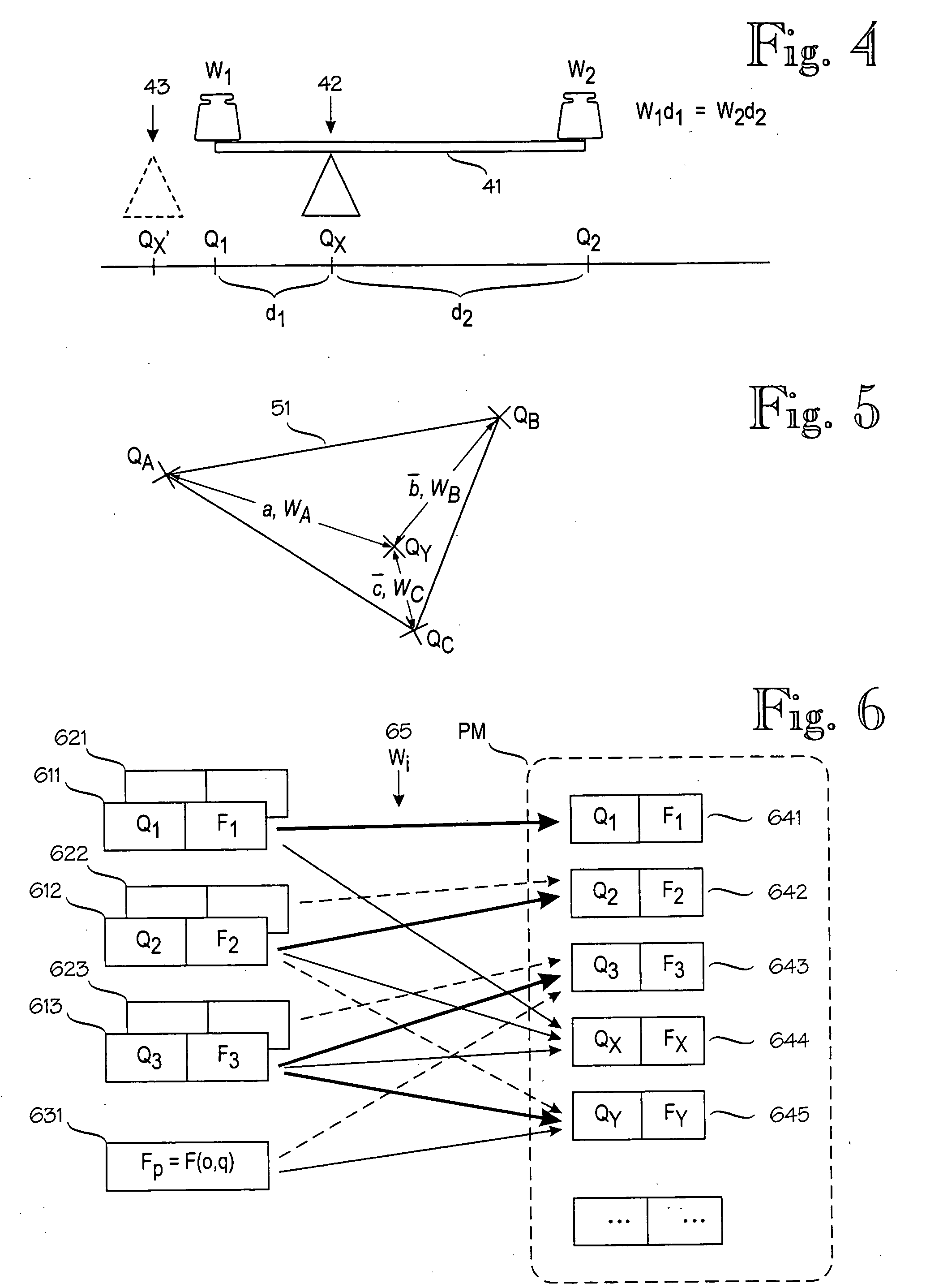
A model construction module (MCM) for constructing a probabilistic model (PM) of a wireless environment (RN) in which a target device (T) communicates using signals that have a measurable signal value (x), such as signal strength. The model construction module forms several submodels (611-631) of the wireless environment (RN). Each submodel indicates a probability distribution (F1-F3) for signal values at one or more locations (Q1-QY) in the wireless environment. The module combines the submodels to a probabilistic model (PM) of the wireless environment (RN), such that the probabilistic model indicates a probability distribution for signal values at several locations in the wireless environment. Alternatively, the model may insert new locations to a single model based on a combination of existing locations. The combination of submodels or existing locations comprises combining the inverse cumulative distribution functions of the submodels or existing locations.
Owner:AIRISTA FLOW INC +1
Auxiliary disease judgment method based on diagnostic element data association
InactiveCN102110192ASuitable for randomnessSuitable for complexitySpecial data processing applicationsDiseaseInformation analysis
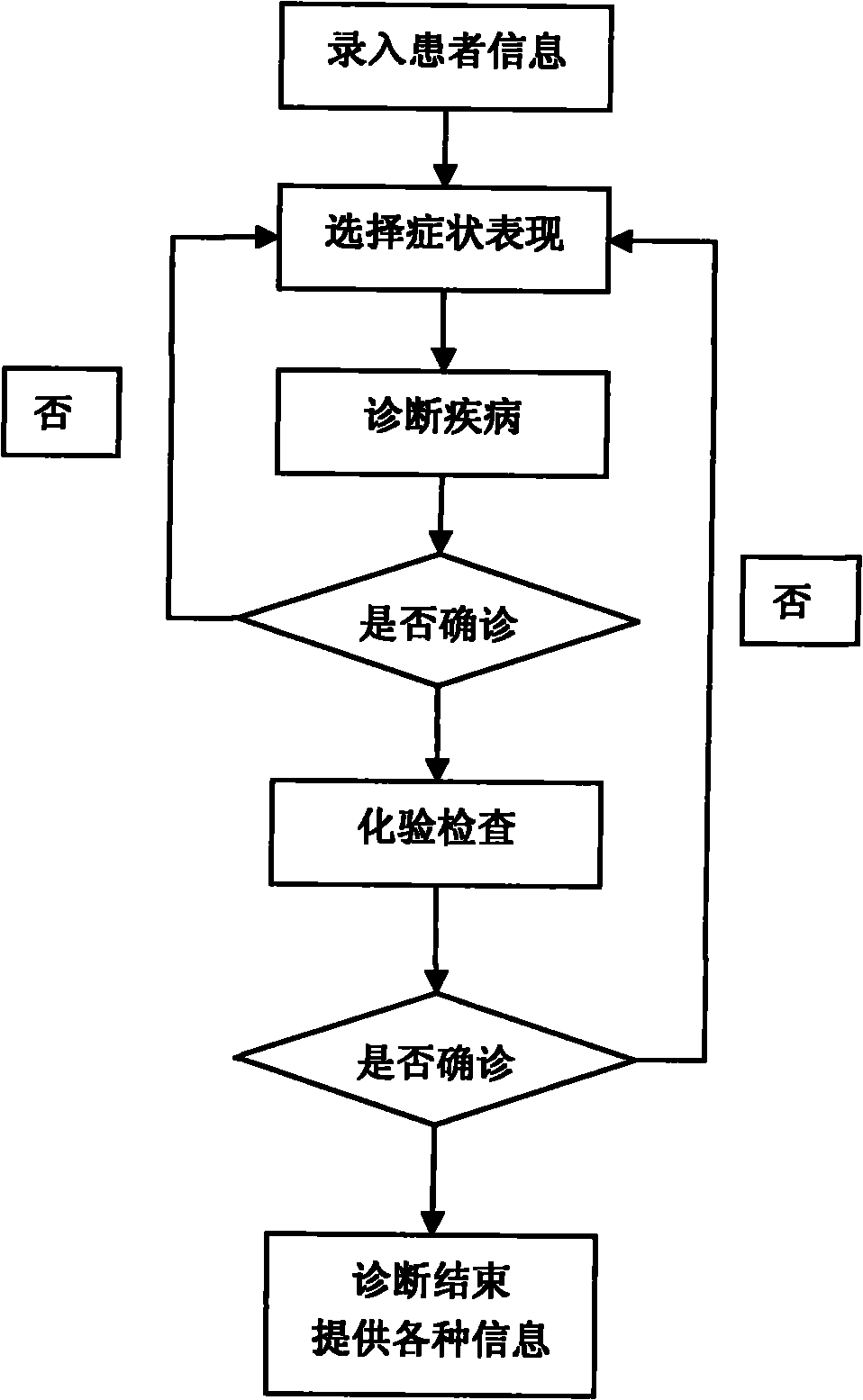
The invention discloses an auxiliary disease judgment method based on diagnostic element data association, belonging to the field of information analysis and aid decision making. The auxiliary disease judgment method comprises the following steps: establishing a disease library according to clinical experience and expert data; establishing a symptom library by taking symptoms to which each disease model relates in the disease library to serve as the constitution elements of the symptom library; according to the symptom information of a patient, selecting the symptoms in the symptom library to serve as the symptom set of the patient; according to the selected symptoms, finding all diseases with the symptoms from the preset disease library; and listing as a disease list according to the decreasing correlation degree or suspected probability. In the method, limited known information can be furthest utilized based on the practical requirement on diagnosis and treatment on patients by doctors according to the step of diagnosing patients for doctors in the practical work, and the information can be added and revised to furthest simulate the real situation. The obtained information (contents, such as symptoms and the like) is fully simulated by utilizing a self-forming rule, thus the method is suitable for the complex situation of the randomness and dynamics of the information resource of the disease.
Owner:中国医学科学院医学信息研究所
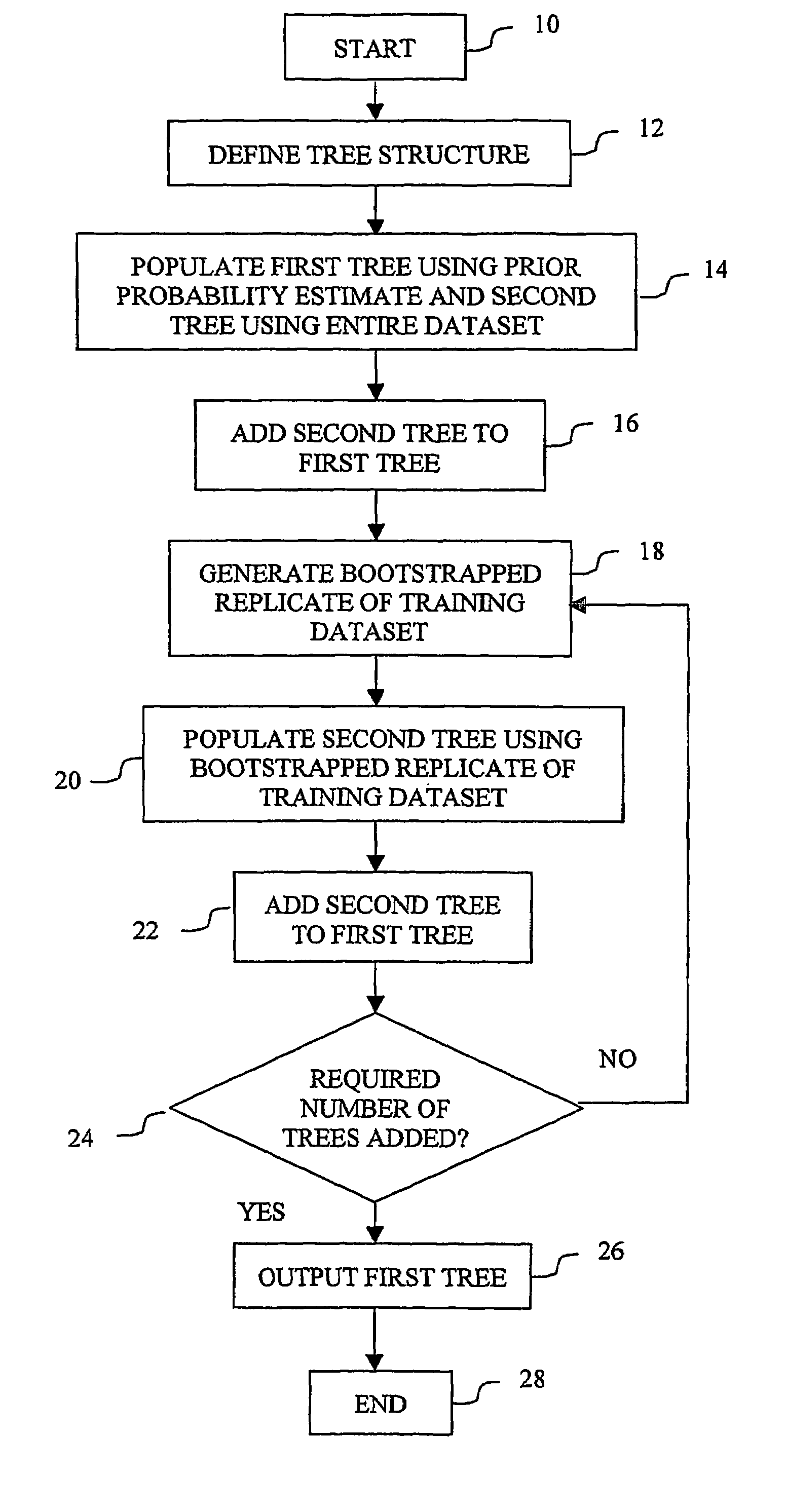
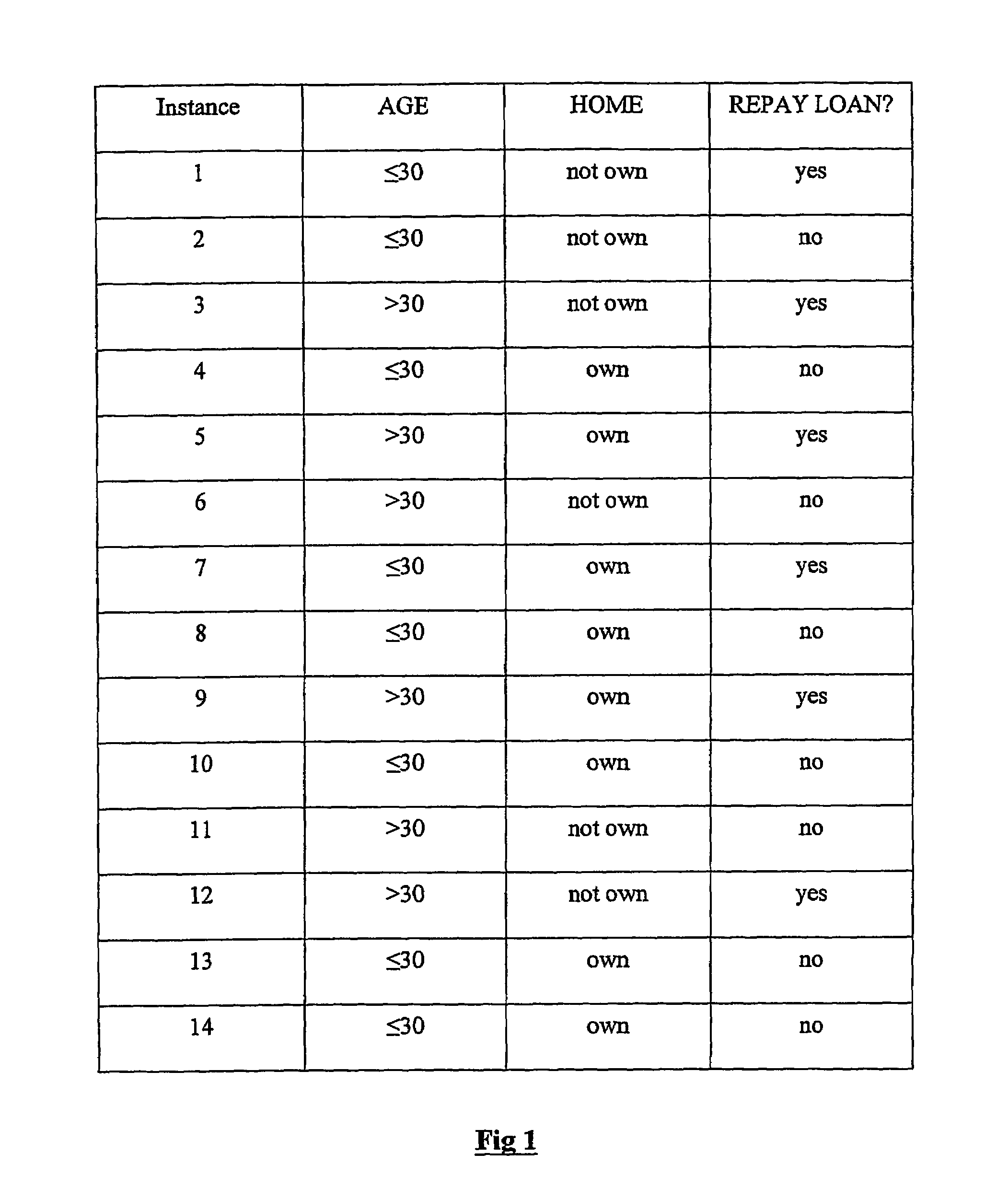
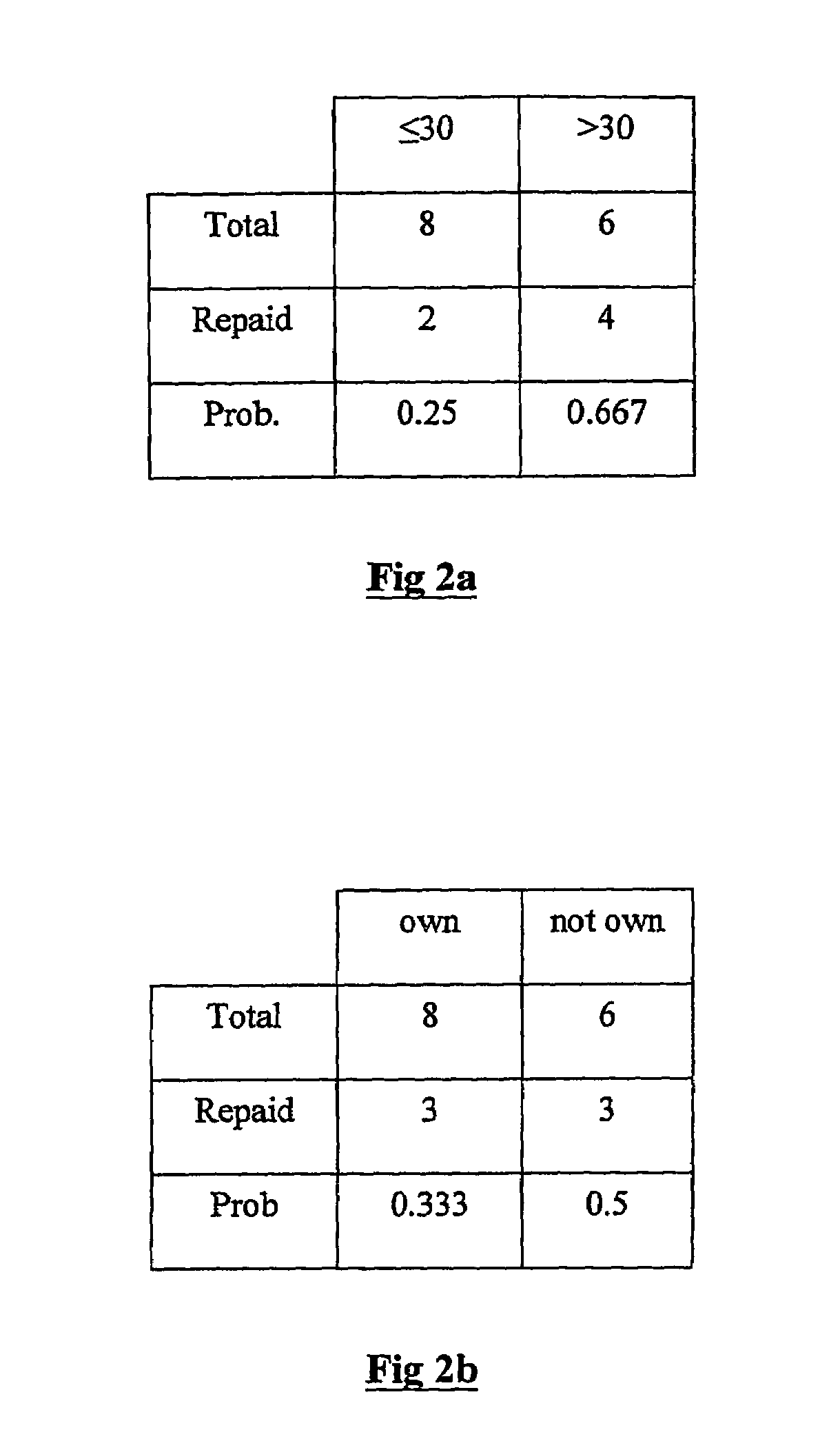
Classification using probability estimate re-sampling
ActiveUS7194380B2Improve fitEffective calculationMathematical modelsFinanceAlgorithmClass membership
Embodiments of a computer-implemented method of calculating estimates of a joint posterior probability of class membership given combinations of attribute values of a pair of attributes are disclosed. The calculating is performed on the basis of data representing a training set of a plurality of instances defined by attribute values for a plurality of attributes together with a class membership outcome. Embodiments of the method comprise calculating first and second estimates of a posterior probability of class membership given attribute values of a first and second attribute of the pair, respectively, and binning the first and second estimates into a respective plurality of first and second probability range bins. Instances of the training set are mapped to combinations of one of each of the first and second pluralities of probability range bins, and on the basis of the mapping, calculating estimates of a joint posterior probability of class membership.
Owner:CHORDIANT SOFTWARE INT
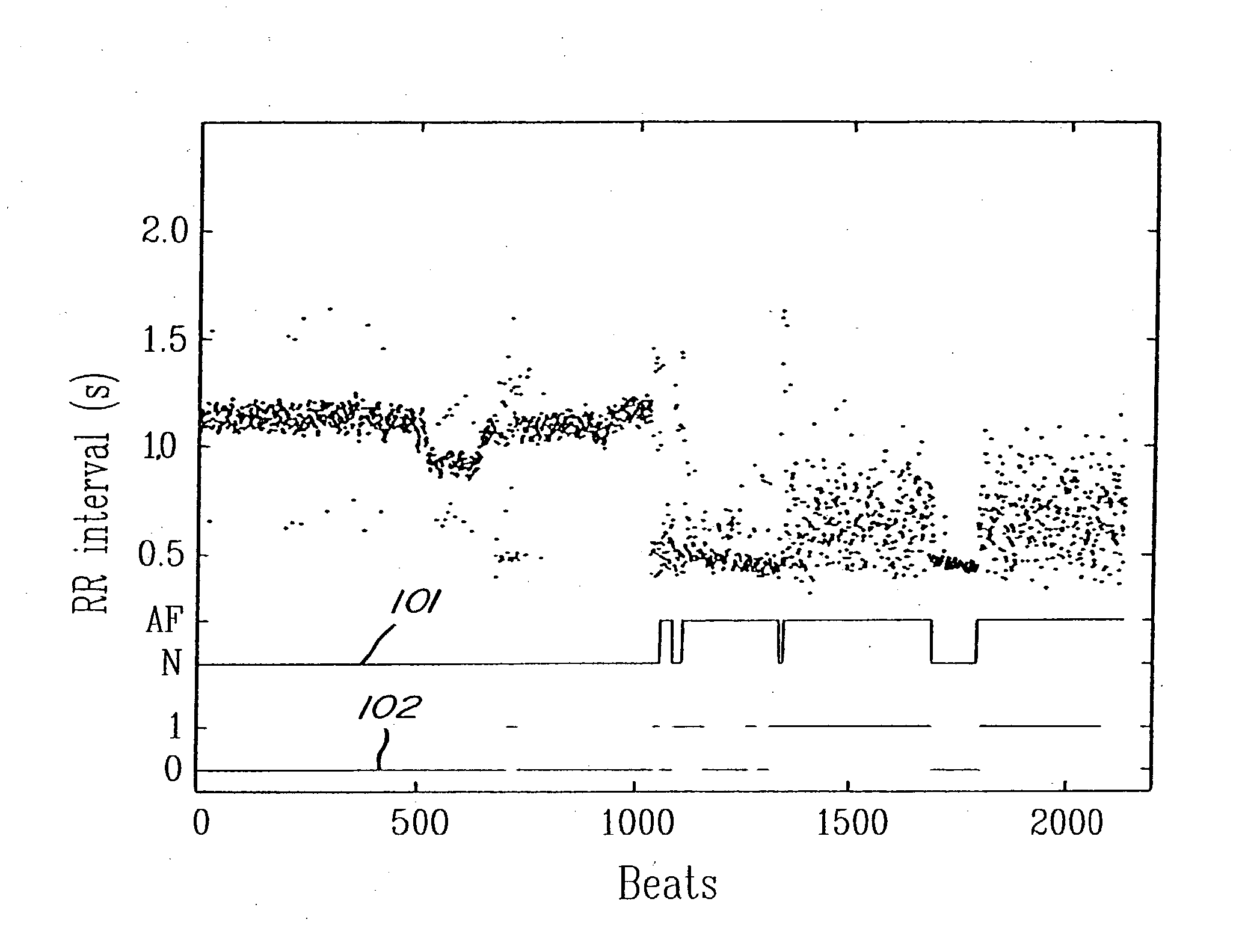
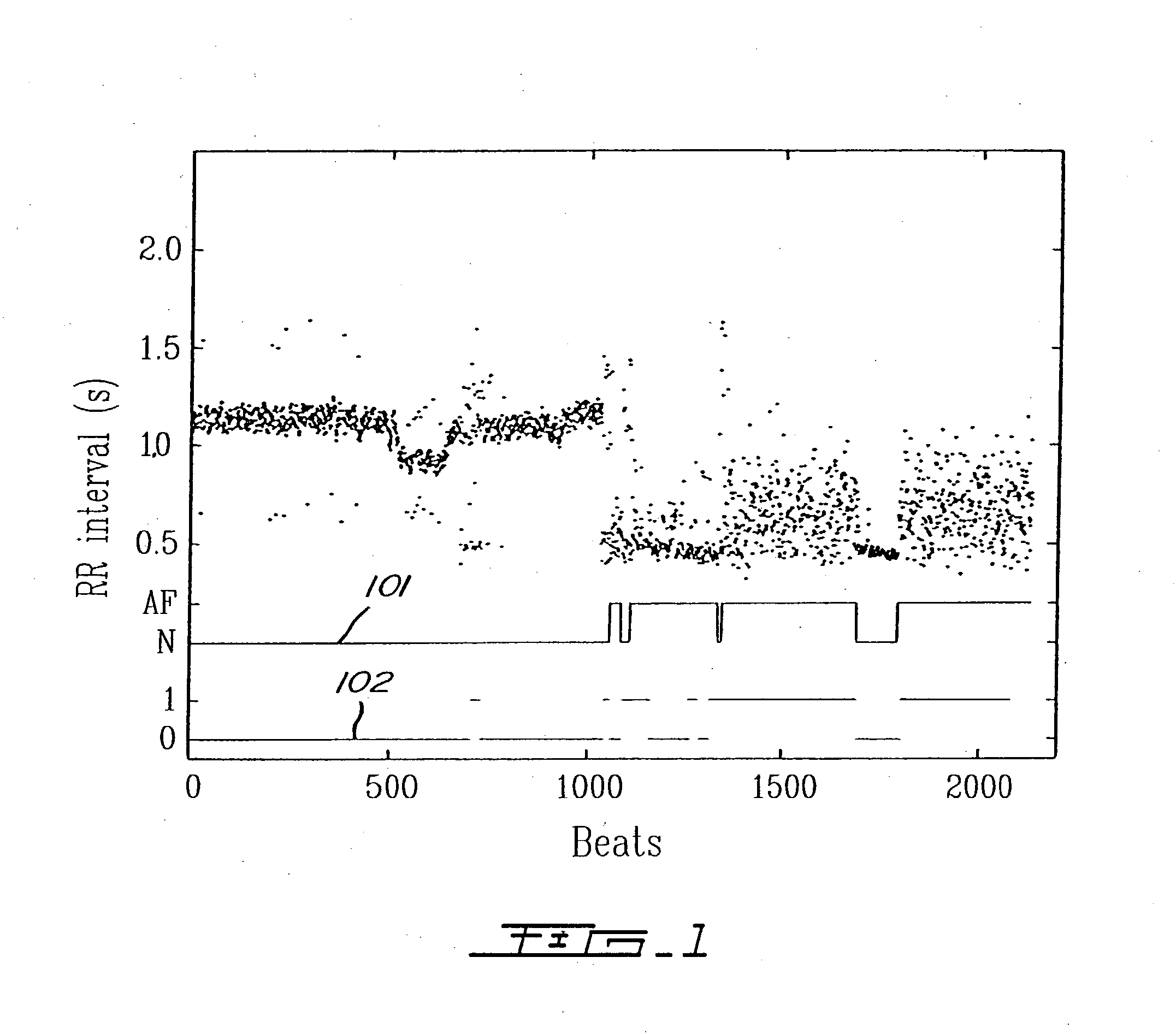
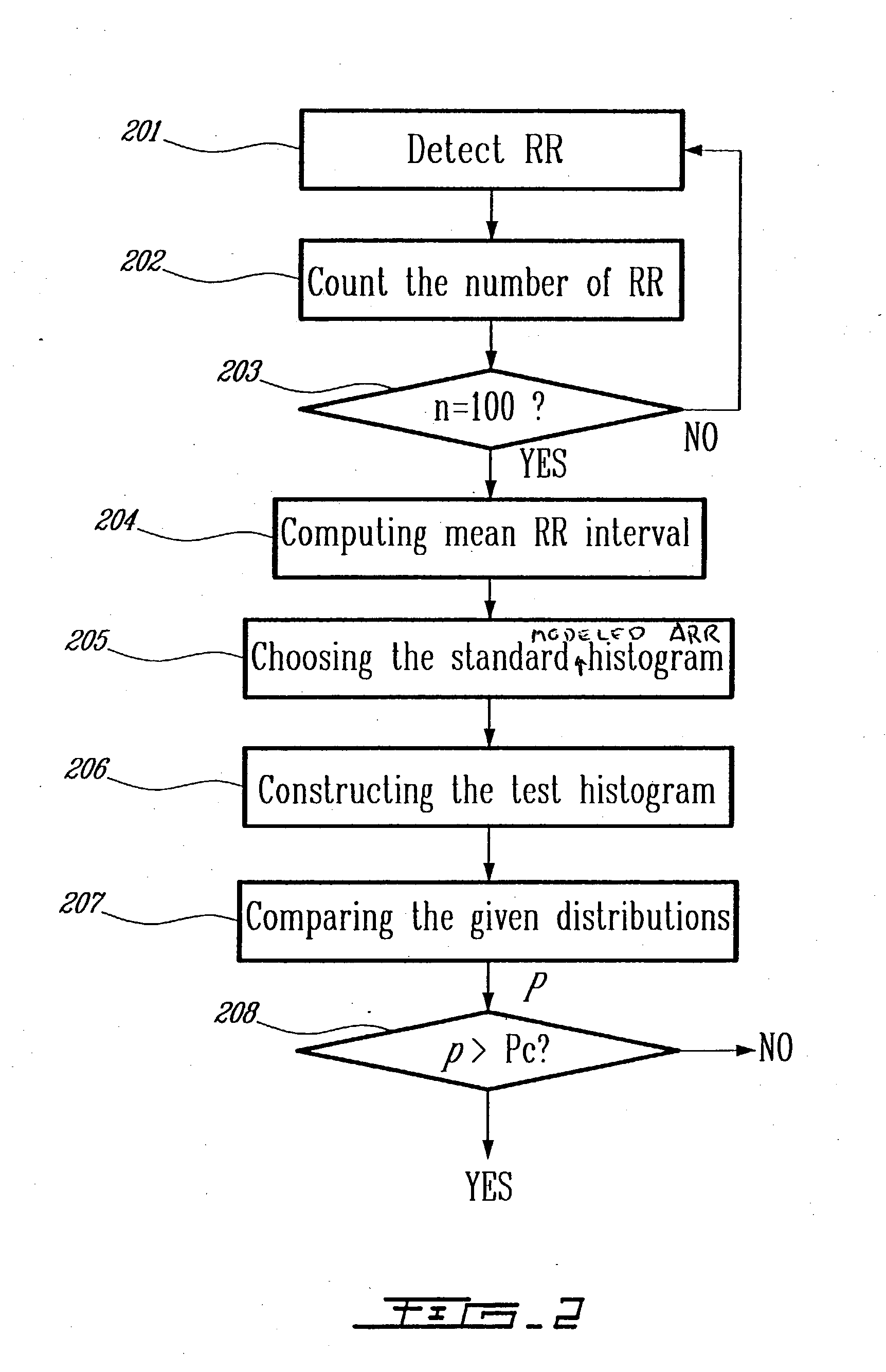
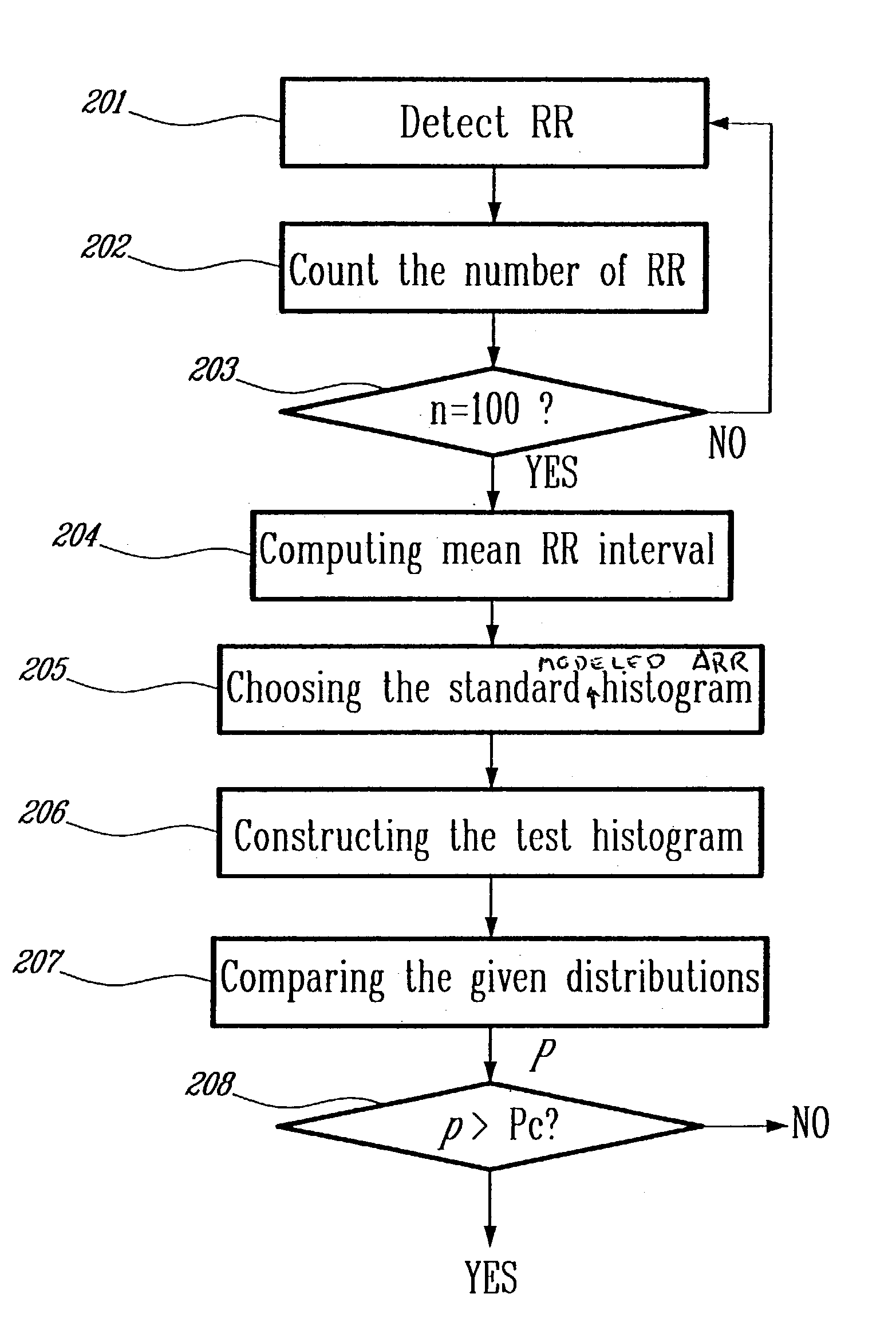
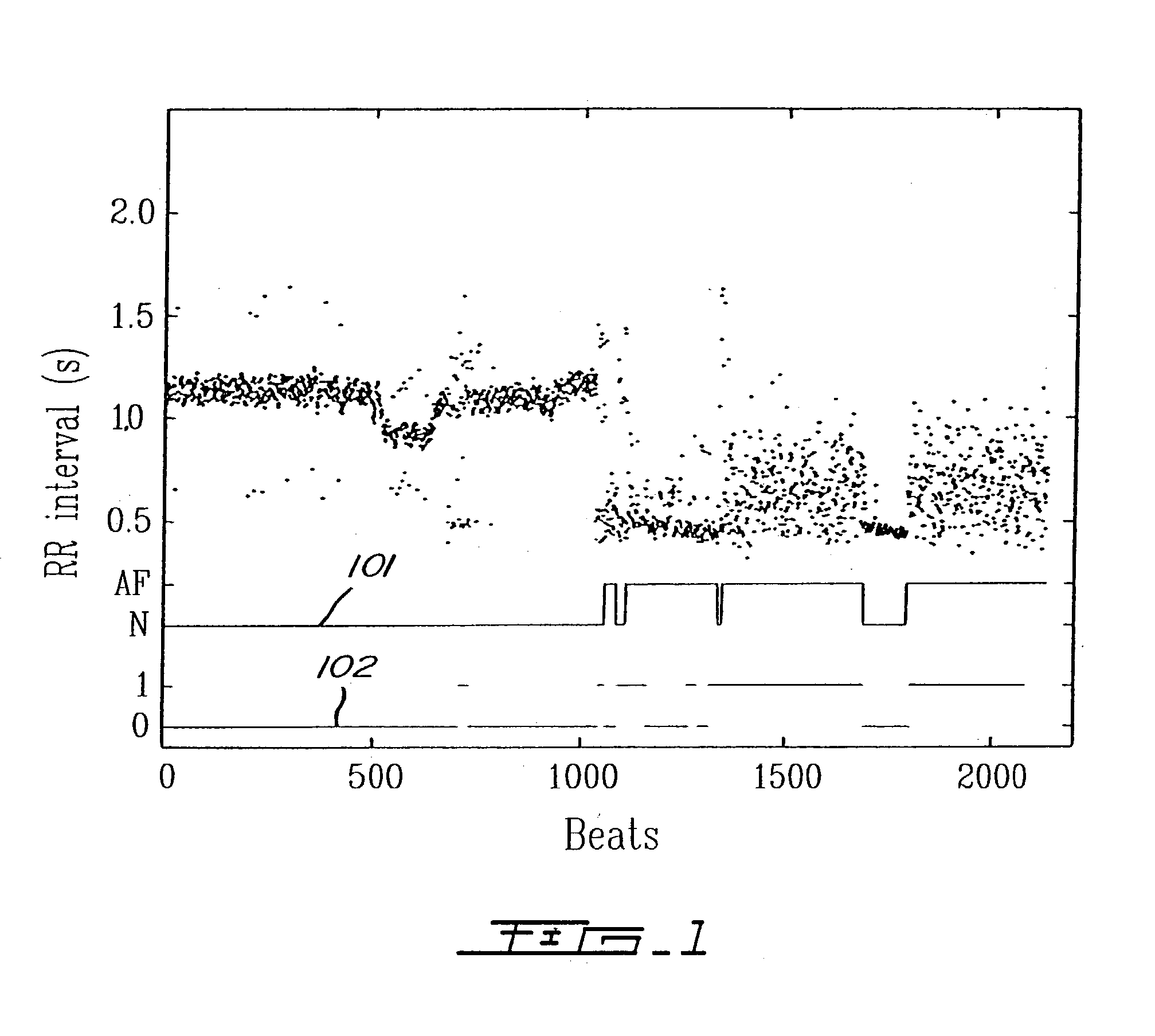
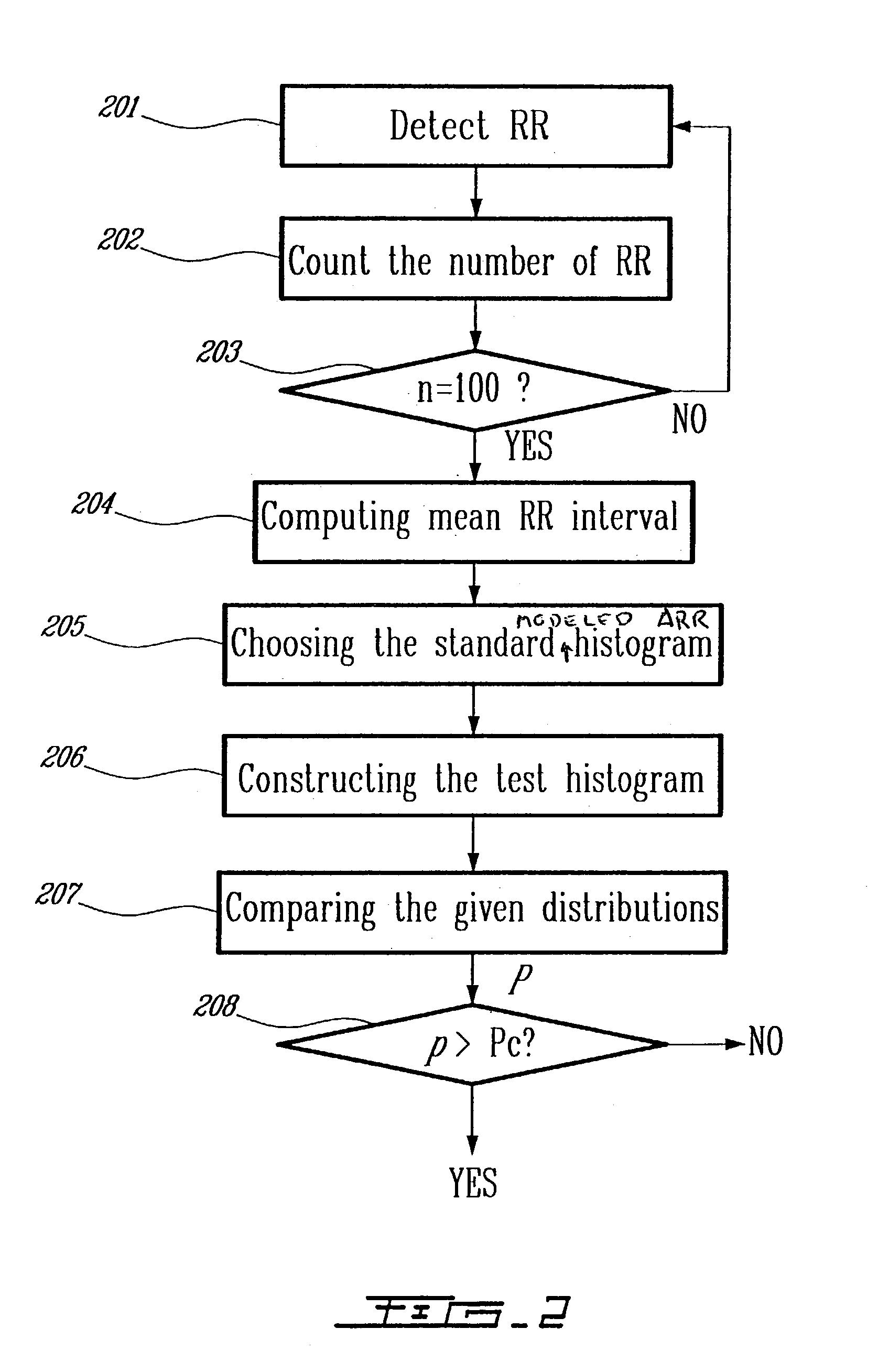
Detection of cardiac arrhythmia using mathematical representation of standard deltaRR probability density histograms
ActiveUS20050004486A1Improve accuracyReduce storage requirementsElectrocardiographySensorsRR intervalMedicine
A method and a system for detecting cardiac arrhythmias that includes detecting RR intervals of the patient wherein each RR interval is an interval between two heart beats, and simulating standard probability density histograms of ΔRRs by means of a suitable probability distribution calculated through at least one mathematical formulae, wherein ΔRR is a difference between two successive RR intervals. Test probability density histograms of ΔRRs of the patient are constructed from the detected RR intervals. Finally, the standard and test histograms are compared to detect whether the patient suffers from cardiac arrhythmia. As non limiting examples, the standard probability density histograms of ΔRRs are modeled by a mathematical equation selected from the group consisting of: the Lorentzian distribution, the Gaussian distribution, the Student's t-distribution, and a probability distribution including a linear combination of the Lorentzian and Gaussian distribution.
Owner:THE ROYAL INSTION FOR THE ADVANCEMENT OF LEARNING MCGILL UNIV A UNIV
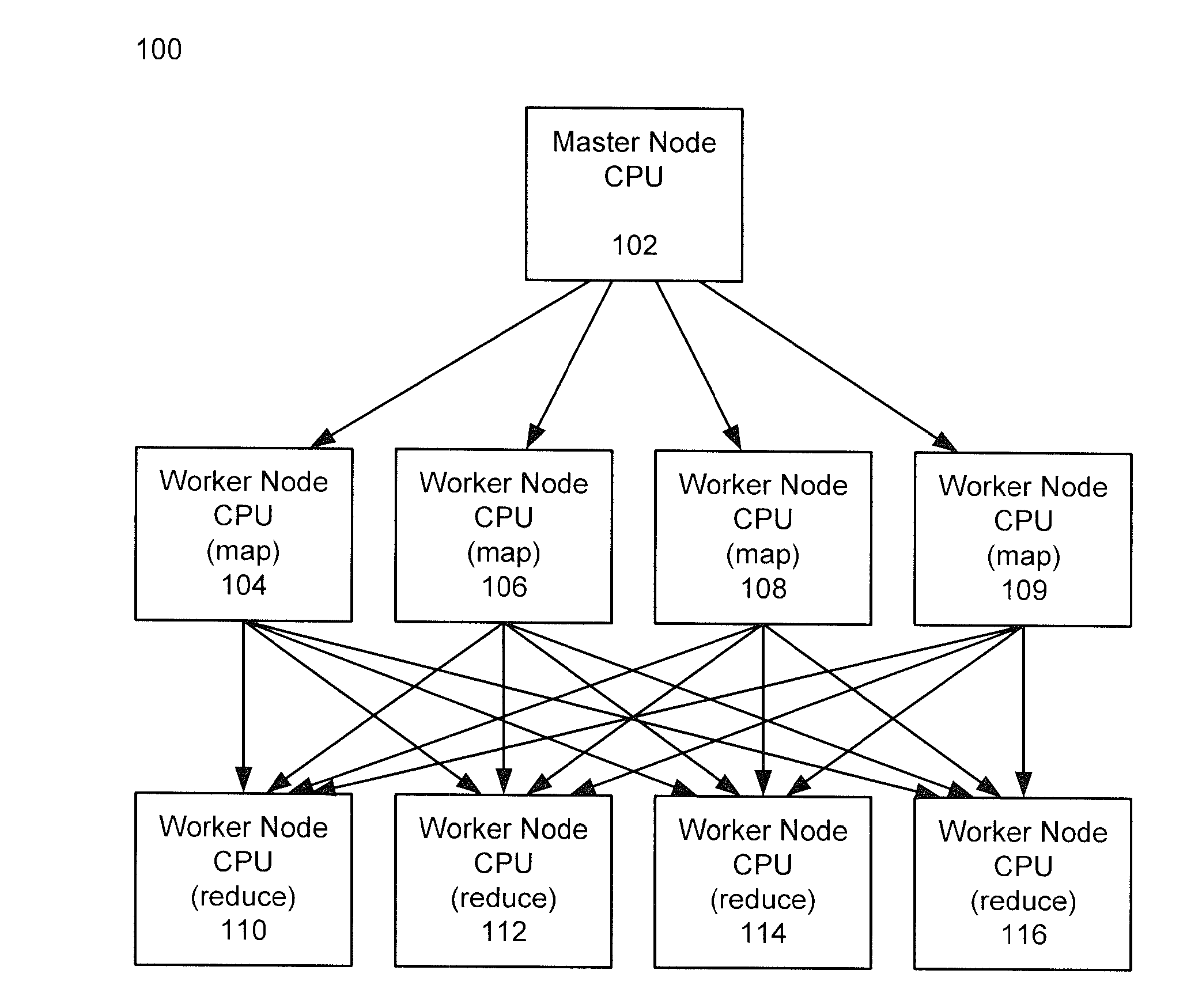
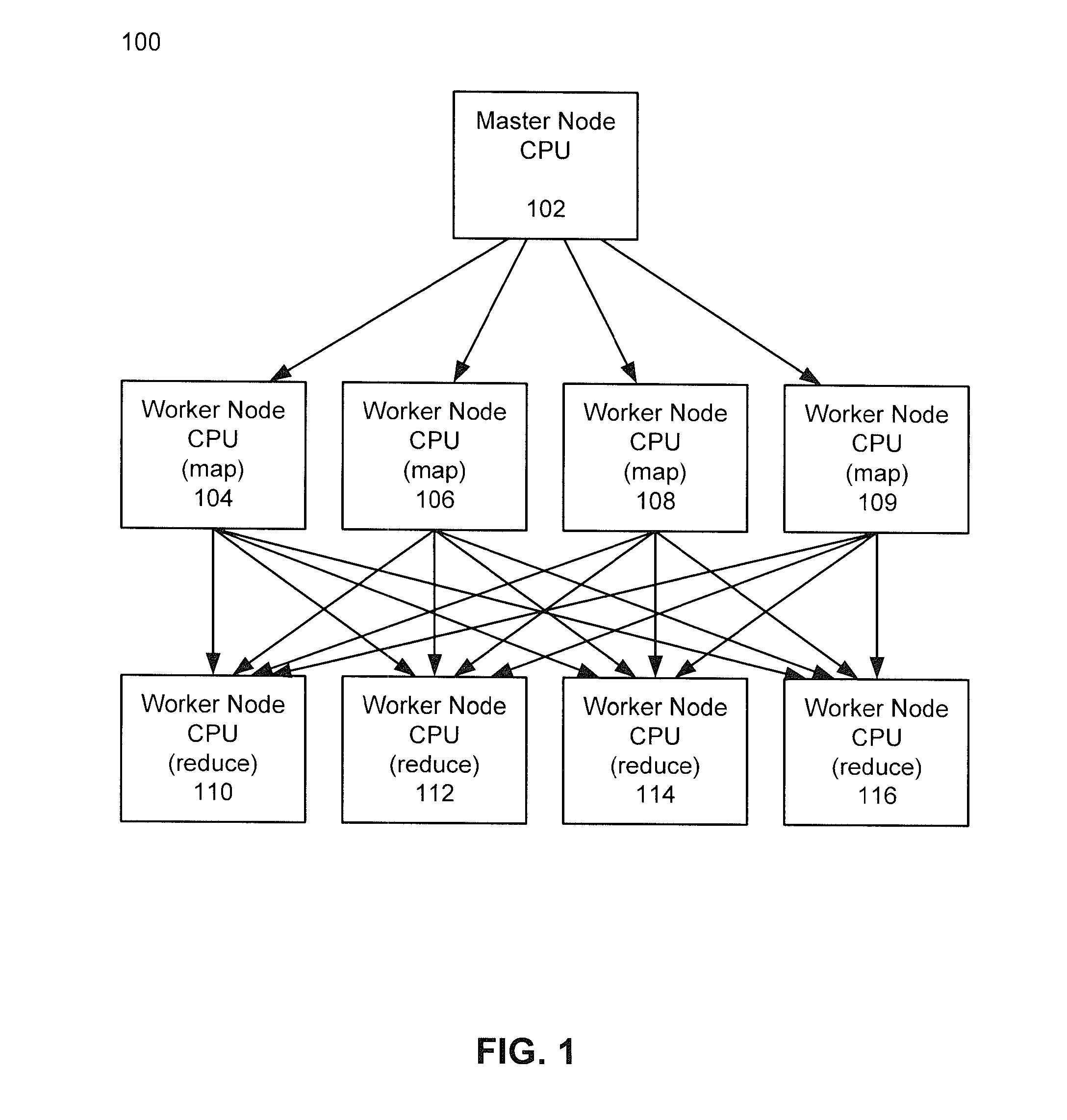
Methods and systems for using map-reduce for large-scale analysis of graph-based data
ActiveUS20130024412A1Improve memory usageEasy to implementKnowledge representationSpecial data processing applicationsCluster algorithmMarkov clustering
Embodiments are described for a method for processing graph data by executing a Markov Clustering algorithm (MCL) to find clusters of vertices of the graph data, organizing the graph data by column by calculating a probability percentage for each column of a similarity matrix of the graph data to produce column data, generating a probability matrix of states of the column data, performing an expansion of the probability matrix by computing a power of the matrix using a Map-Reduce model executed in a processor-based computing device; and organizing the probability matrix into a set of sub-matrices to find the least amount of data needed for the Map-Reduce model given that two lines of data in the matrix are required to compute a single value for the power of the matrix. One of at least two strategies may be used to computing the power of the matrix (matrix square, M2) based on simplicity of execution or improved memory usage.
Owner:SALESFORCE COM INC
Using Linear and Log-Linear Model Combinations for Estimating Probabilities of Events
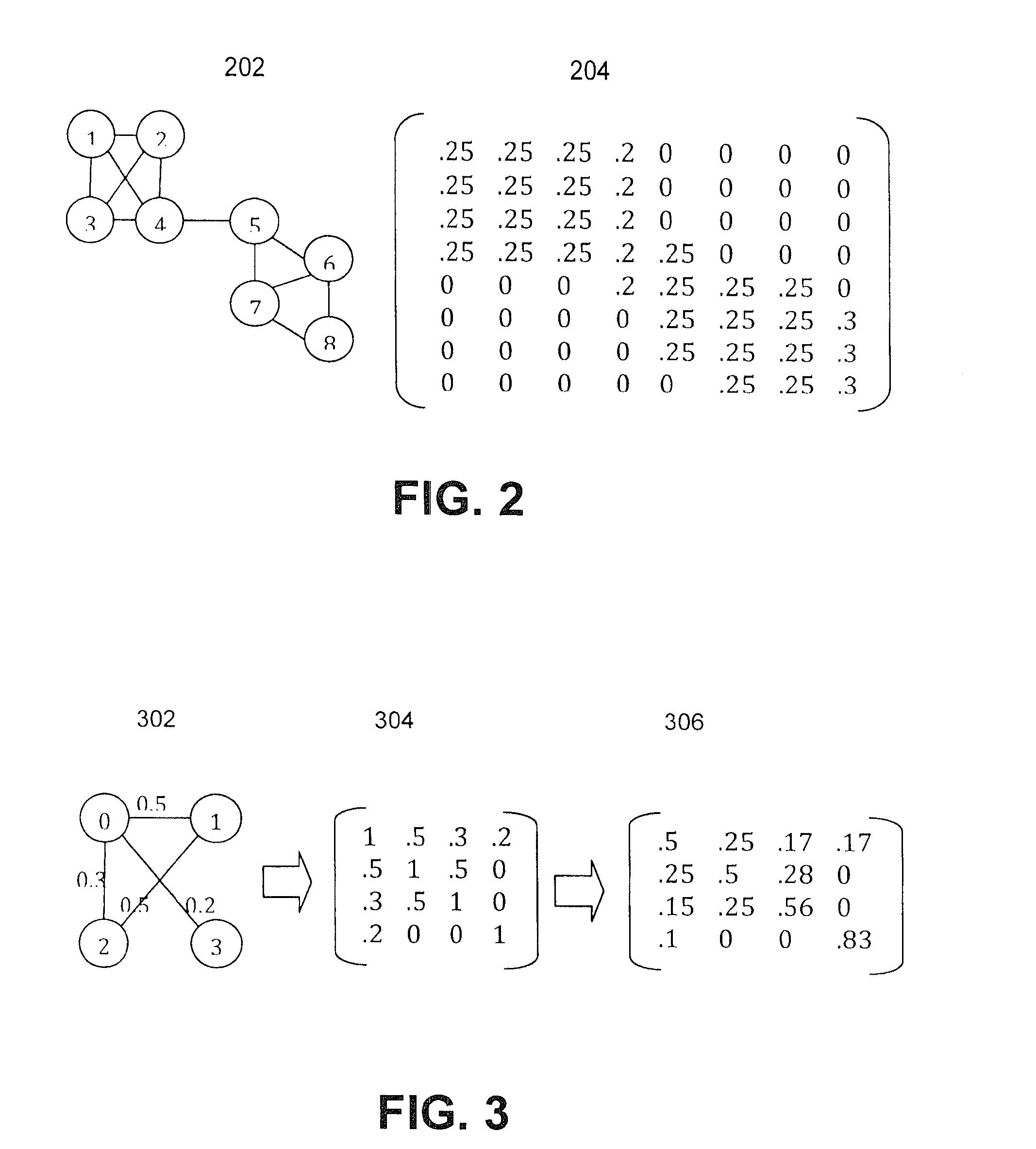
A method for combining multiple probability of click models in an online advertising system into a combined predictive model, the method commencing by receiving a feature set slice (e.g. corresponding to demographics or taxonomies or clusters), and using the sliced data for training multiple slice-wise predictive models. The trained slice-wise predictive models are combined by overlaying a weighted distribution model over the trained slice-wise predictive models. The combined predictive model then is used in predicting the probability of a click given a query-advertisement pair in online advertising. The method can flexibly receive slice specifications, and can overlay any one or more of a variety of distribution models, such as a linear combination or a log-linear combination. Using an appropriate weighted distribution model, the combined predictive model reliably yields predictive estimates of occurrence of click events that are at least as good as the best predictive model in the slice-wise predictive model set.
Owner:TWITTER INC
Driving assistance system
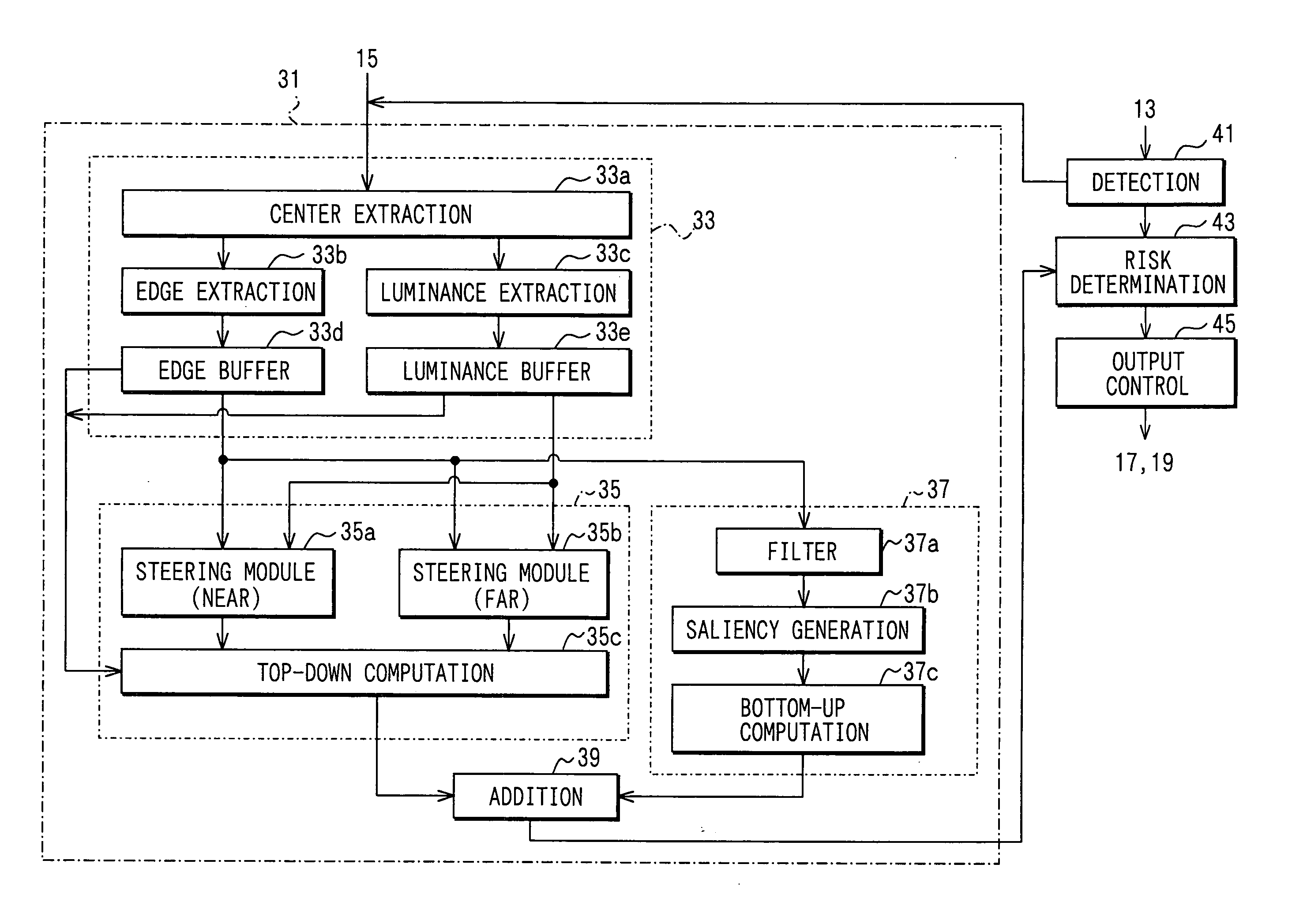
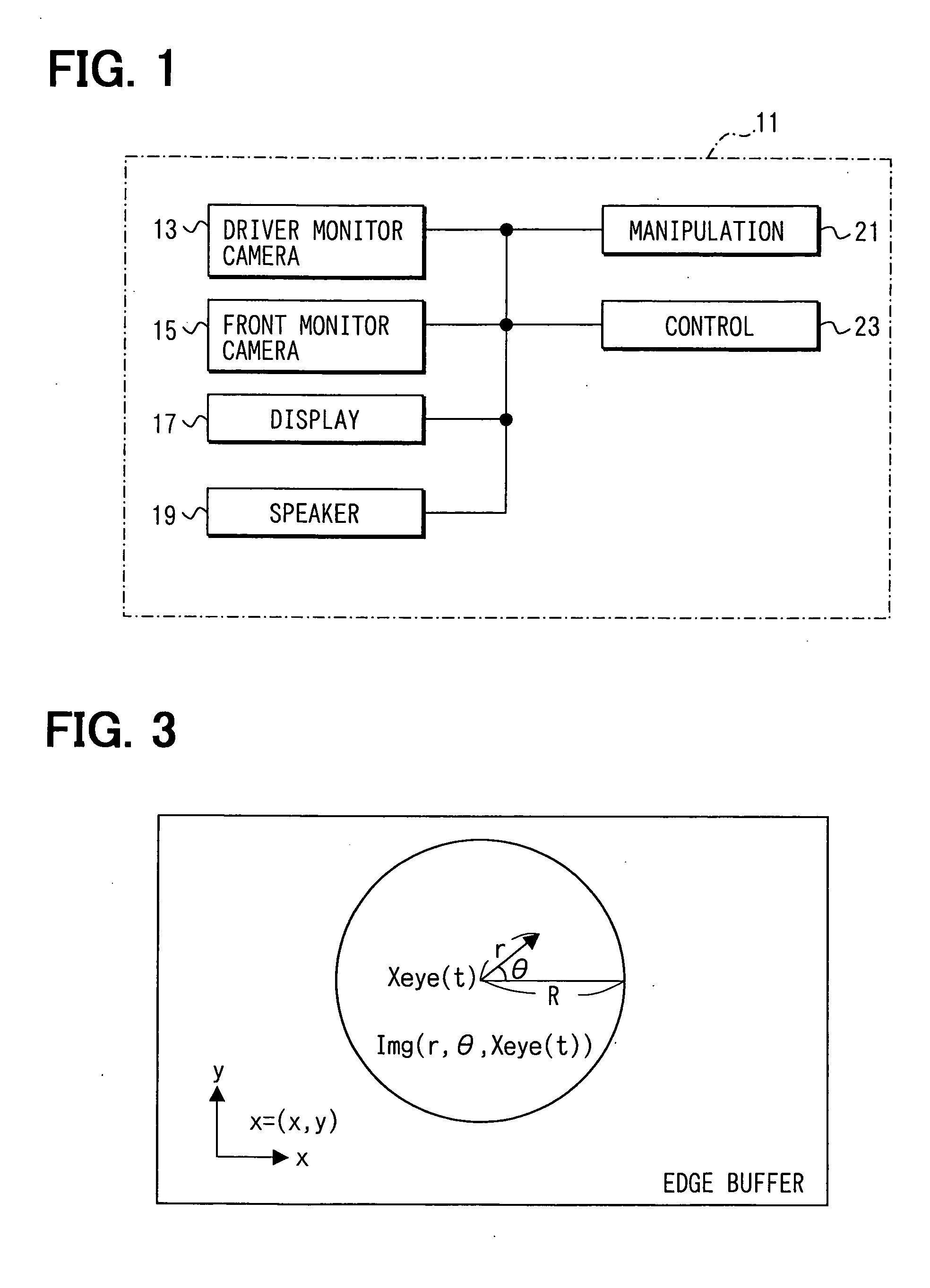
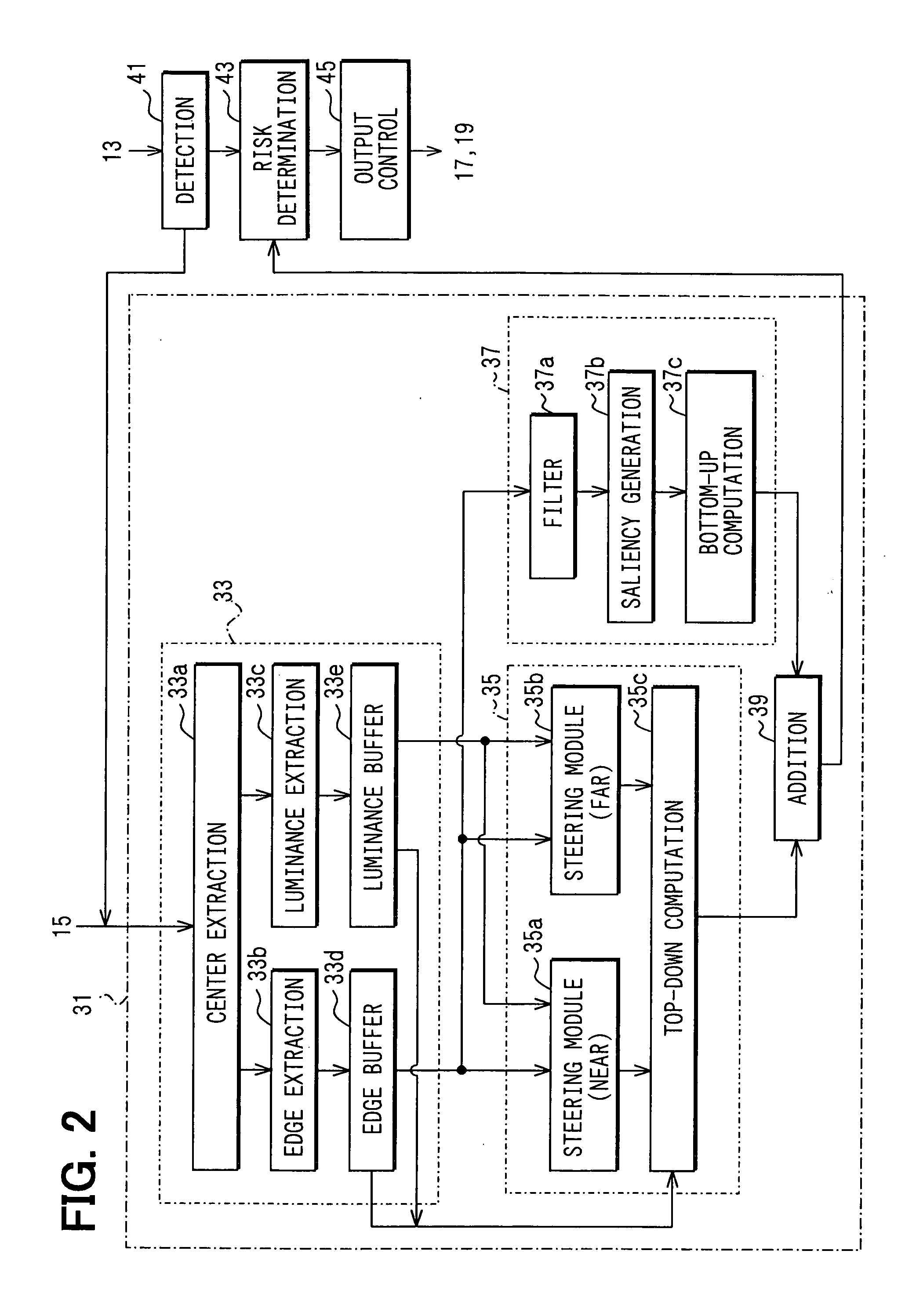
InactiveUS20050209749A1Avoid secondary riskEnsure correct executionDigital data processing detailsPedestrian/occupant safety arrangementVisual field lossPattern recognition
A driver's gaze distribution is detected. Based on the detected distribution, an image corresponding to a driver's visual-field is extracted from images photographed by a front monitor camera and is accumulated. A first driver's gaze probability distribution necessary for steering operation is computed based on the accumulated images, and a second driver's gaze probability distribution that is expected is computed based on visual characteristics within the images. An ideal gaze probability distribution is obtained by adding up the first and the second probability distributions. Presence of a risk is determined when the difference between the driver's gaze and the ideal gaze probability distribution becomes a given threshold. A windshield display or a speaker outputs the determined result.
Owner:DENSO CORP +1
Systems and methods for the diagnosis and treatment of neurological disorders
Systems and methods for data compression which facilitate the diagnosis and treatment of neurodevelopmental and neurodegenerative disorders. The methods comprise performing the following operations by a computing device: generating Normalized Data ("ND") from Original Data ("OD") that defines a Normalized Waveform ("NW") that is unitless and scaled from zero to one; processing ND to extract Micro-Movement Data ("MMD") defining a Micro-Movement Waveform ("MMW") comprising a plurality of MMD points; and generating compressed data comprising a stochastic signature of MMW. Each MMD point determined based on a value of a peak of NW and a value representing an average of all data point values between a first valley of NW immediately preceding the peak and a second valley of NW immediately following the peak. The stochastic signature is defined by empirically estimated values of at least one parameter representing a Probability Distribution Function ("PDF") of a continuous family of PDFs.
Owner:RUTGERS THE STATE UNIV +1
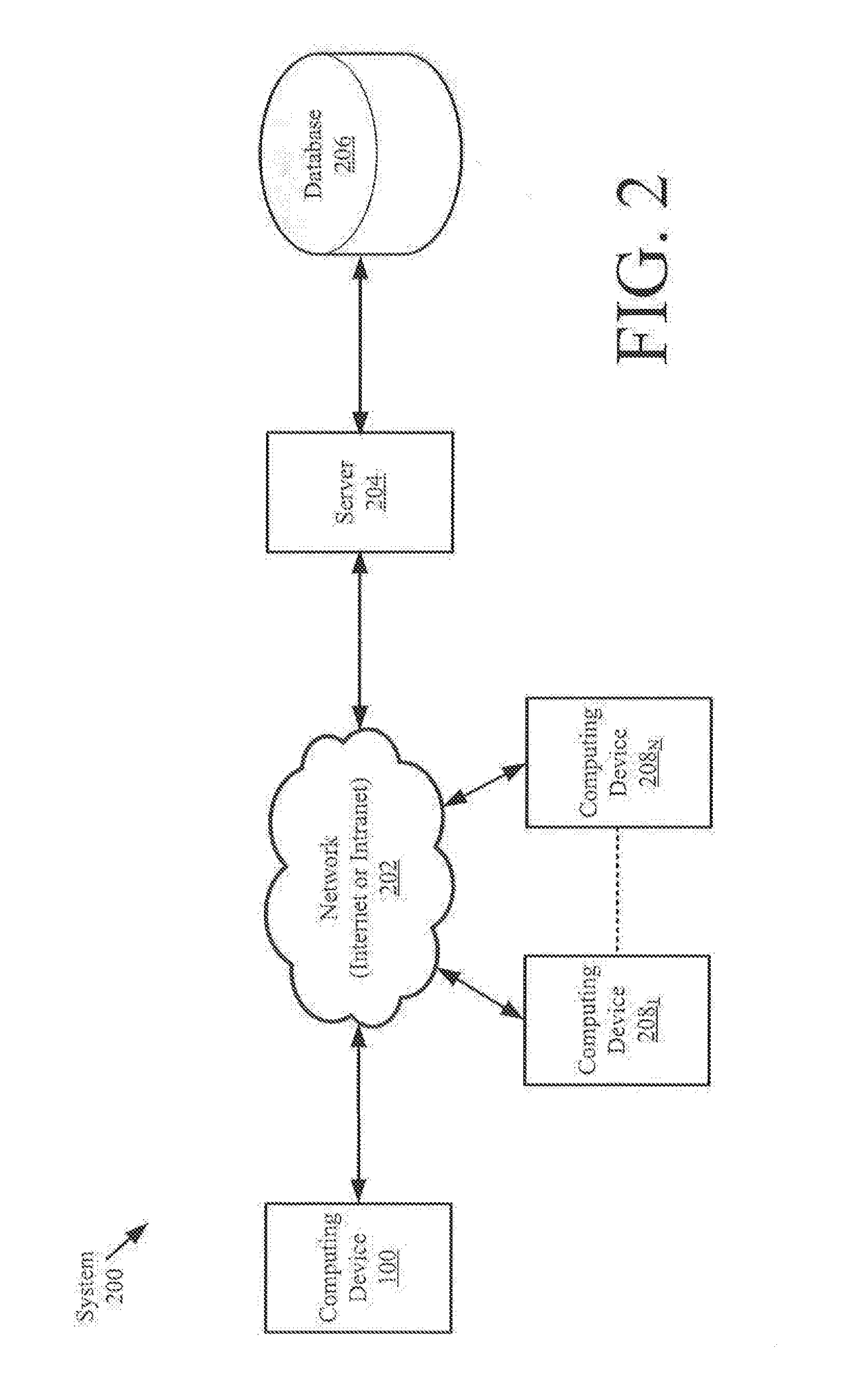
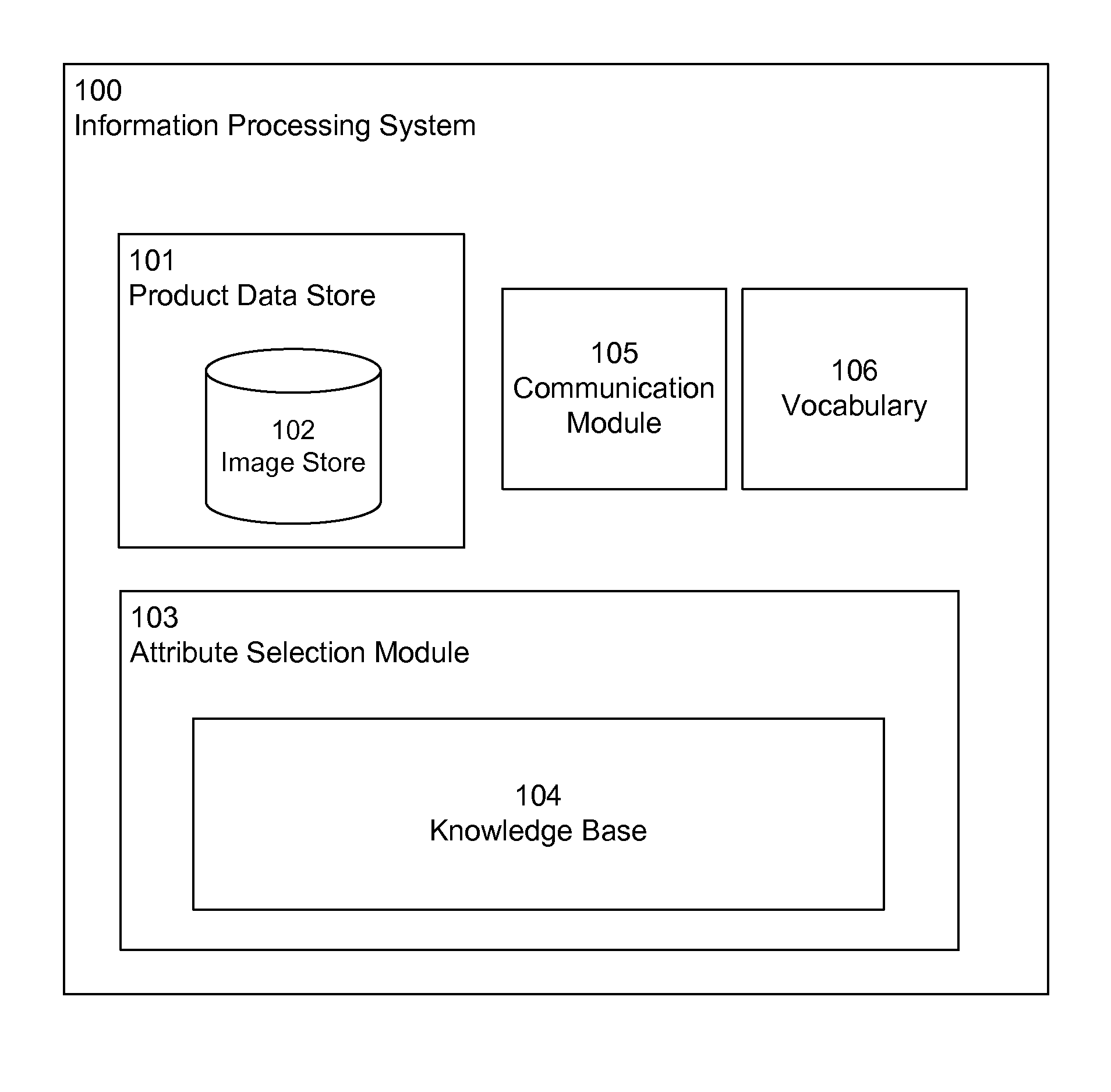
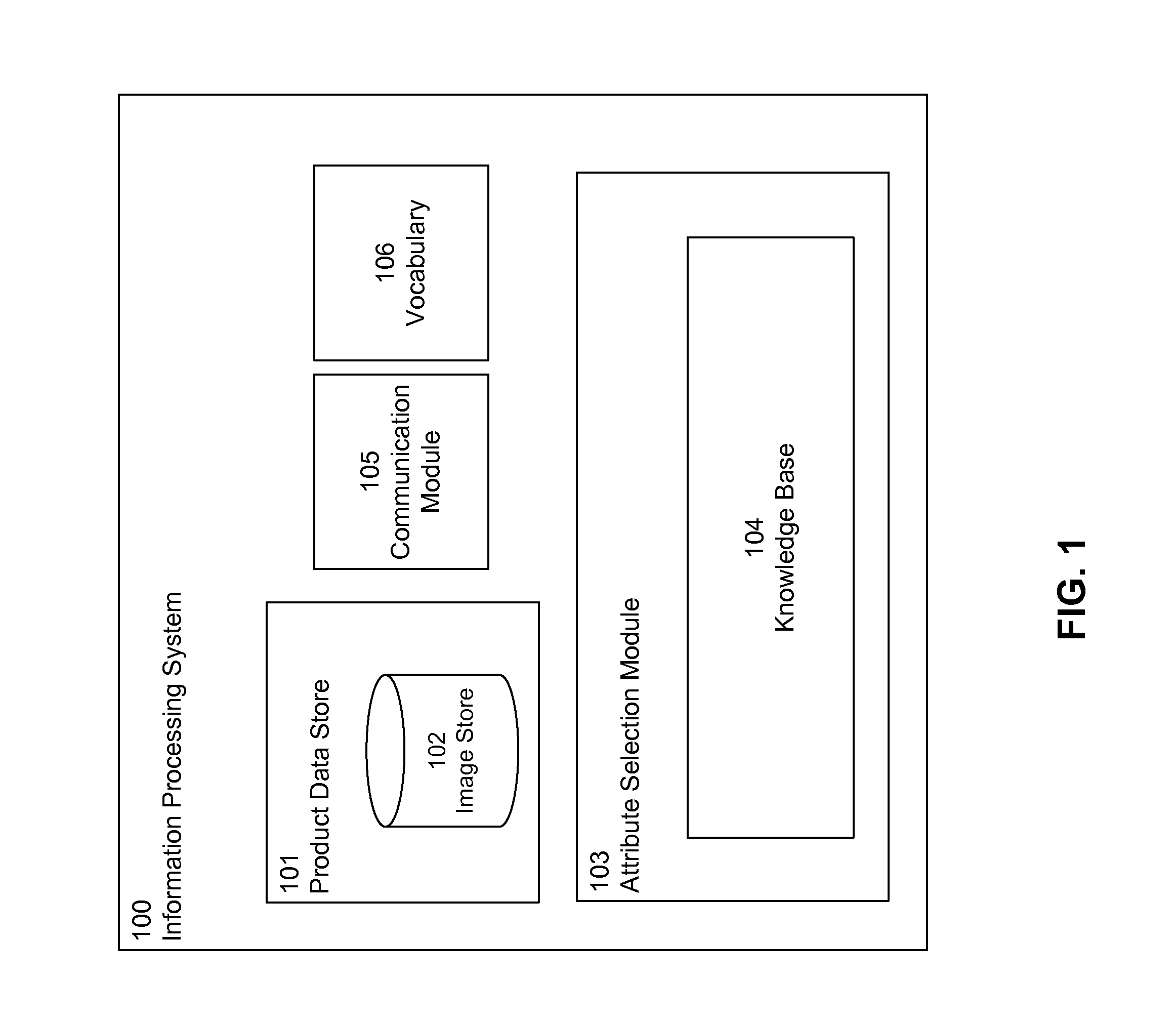
Automated Product Attribute Selection
Product data for a product is received by an attribute selection module. The product data includes product image data and product text data. This product data is used to generate a plurality of probability distributions for a category. The category includes a plurality of attributes, and the probability distribution includes a plurality of probabilities indicating the likelihoods that attributes of the category are applicable to the product. The plurality of probability distributions for the category are weighted and summed to generate a combined probability distribution for the category. An attribute label is determined by selecting an attribute from the category that is indicated to be most likely applicable to the product based on the combined probability distribution for the category. The attribute label is associated with the product. The attribute label enables other services to search for and retrieve the product based on the attribute.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
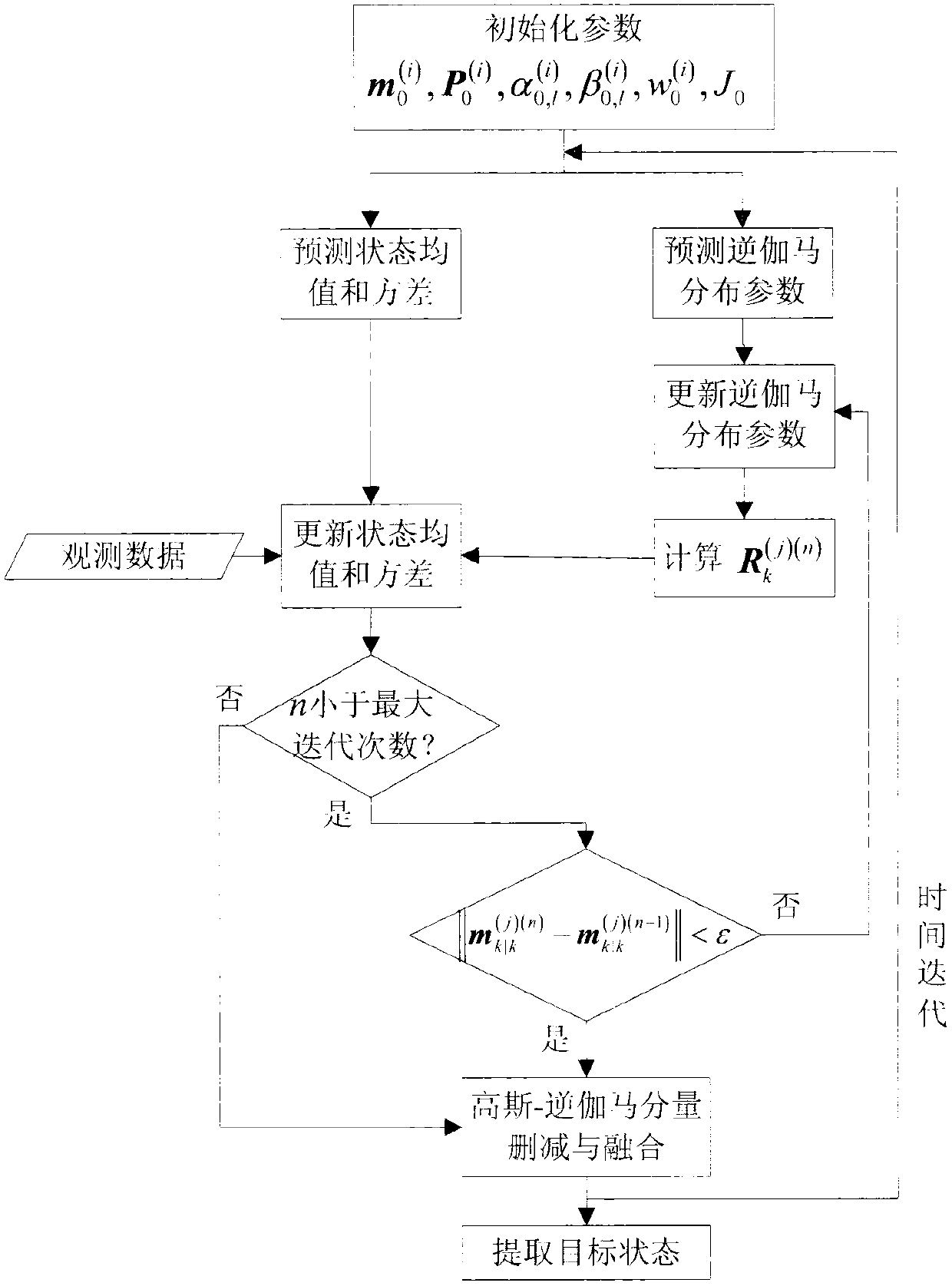
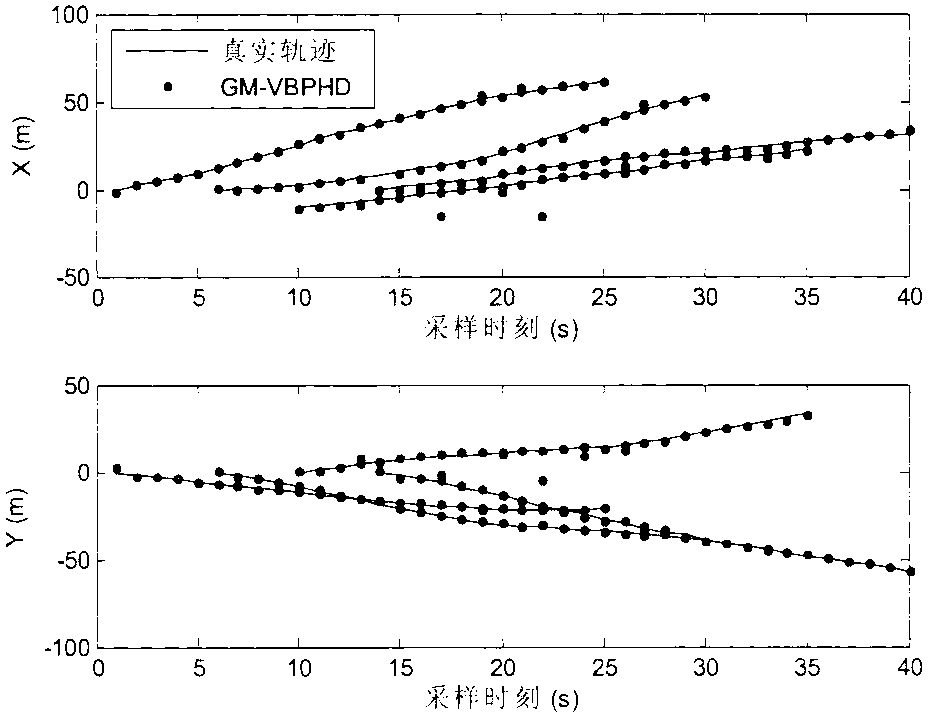
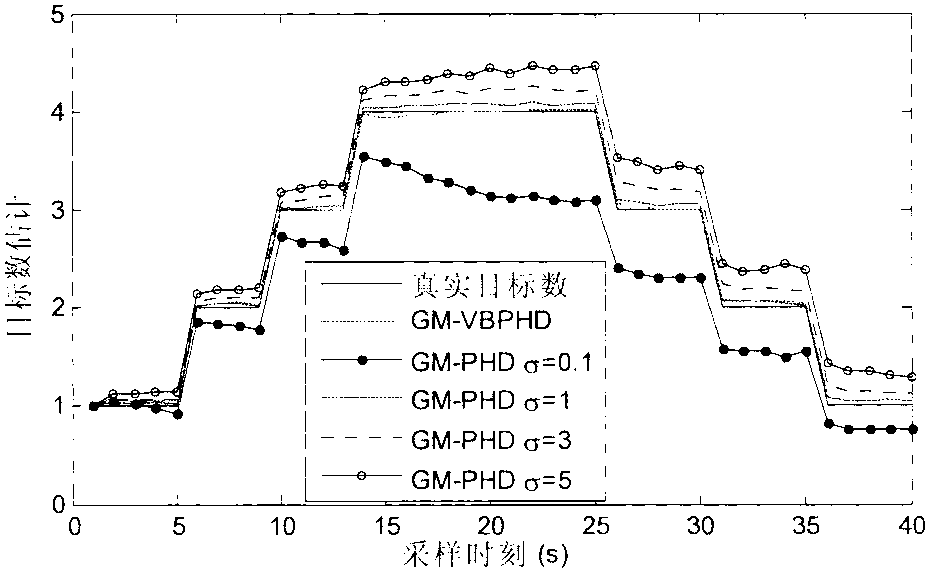
Probability hypothesis density multi-target tracking method based on variational Bayesian approximation technology
ActiveCN103345577AEfficient estimation of true measurement noiseAchieve goal trackingSpecial data processing applicationsInformation processingHypothesis
The invention discloses a probability hypothesis density multi-target tracking method based on a variational Bayesian approximation technology, and belongs to the technical field of guidance and intelligent information processing. The probability hypothesis density multi-target tracking method based on the variational Bayesian approximation technology mainly solves the problem that an existing random set filtering method can not achieved varied number multi-target tracking under an unknown quantity measurement noise environment. According to the method, the variational Bayesian approximation technology is introduced, posterior probability hypothesis density of target states and measurement noise covariance is estimated in a combination mode, a Gaussian mixture inverse gamma distribution recurrence closed solution is adopted, and thus the varied number multi-target tracking under the unknown quantity measurement noise environment is achieved. The probability hypothesis density multi-target tracking method based on the variational Bayesian has a good tracking effect and robustness, is capable of meeting the design demands on practical engineering systems and has good engineering application value.
Owner:江苏华文医疗器械有限公司
Detection of cardiac arrhythmia using mathematical representation of standard DeltaRR probability density histograms
ActiveUS7146206B2Improve accuracyStorage requirements is greatly reducedElectrocardiographySensorsRR intervalMedicine
Owner:THE ROYAL INSTION FOR THE ADVANCEMENT OF LEARNING MCGILL UNIV A UNIV
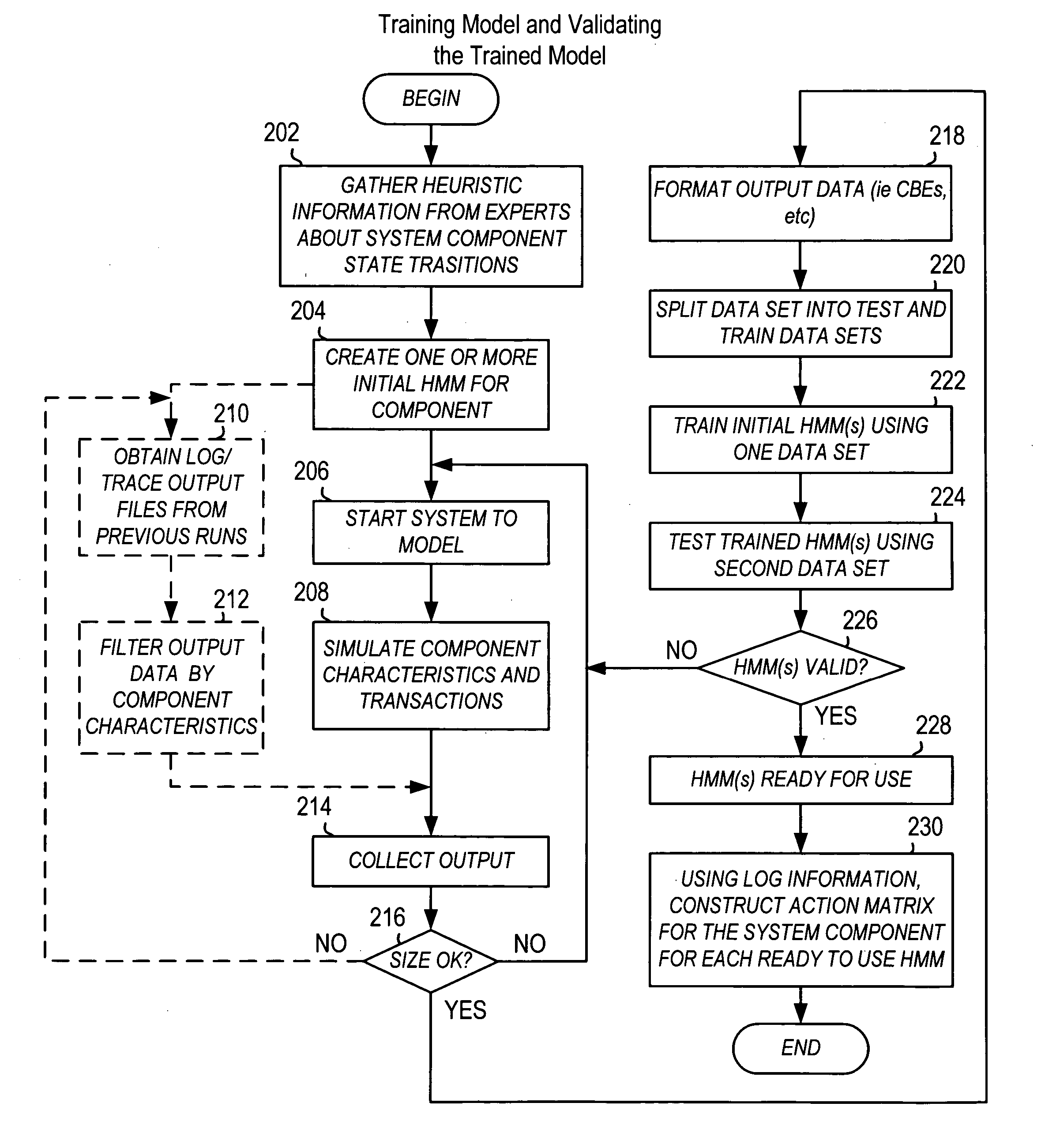
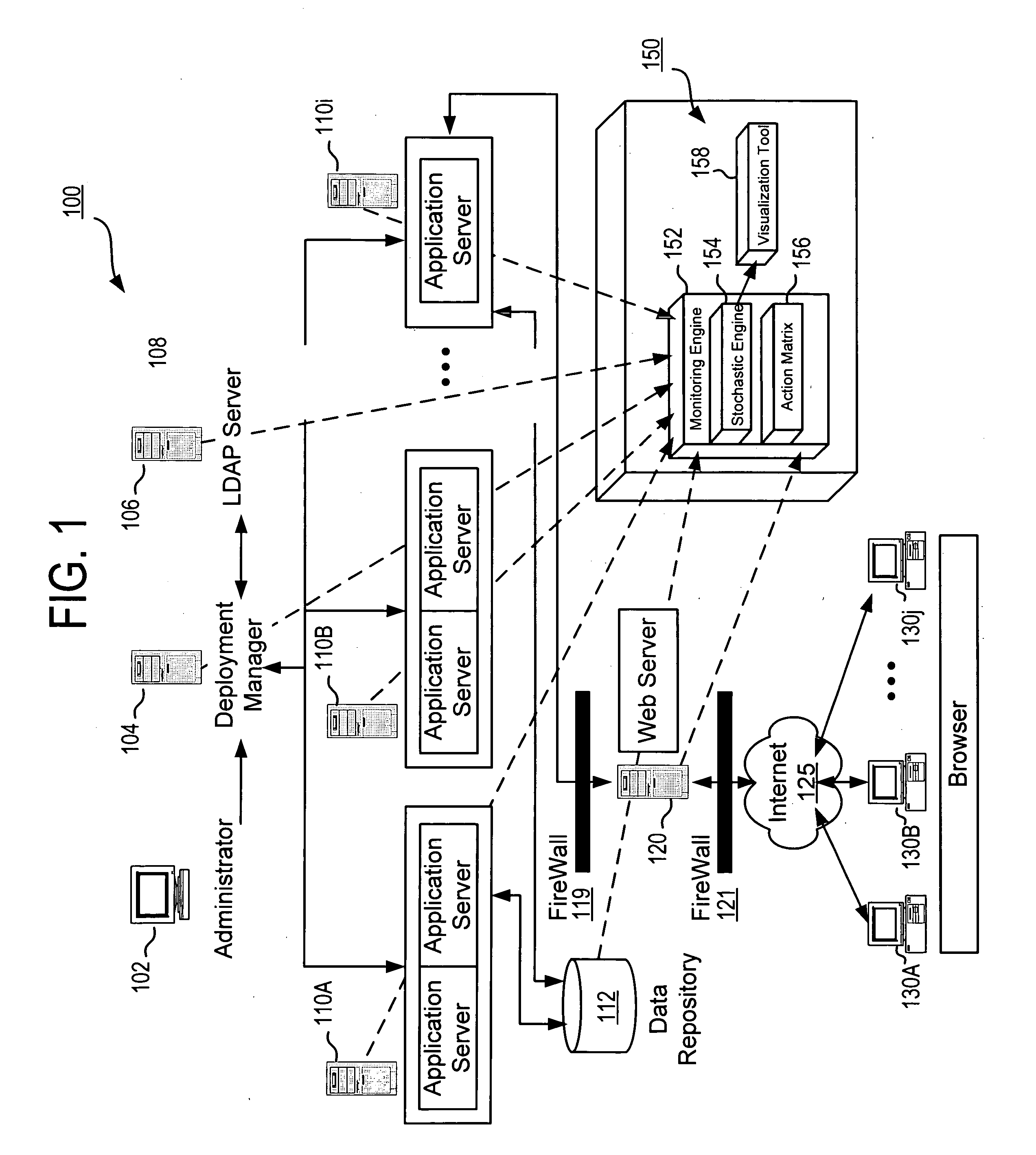
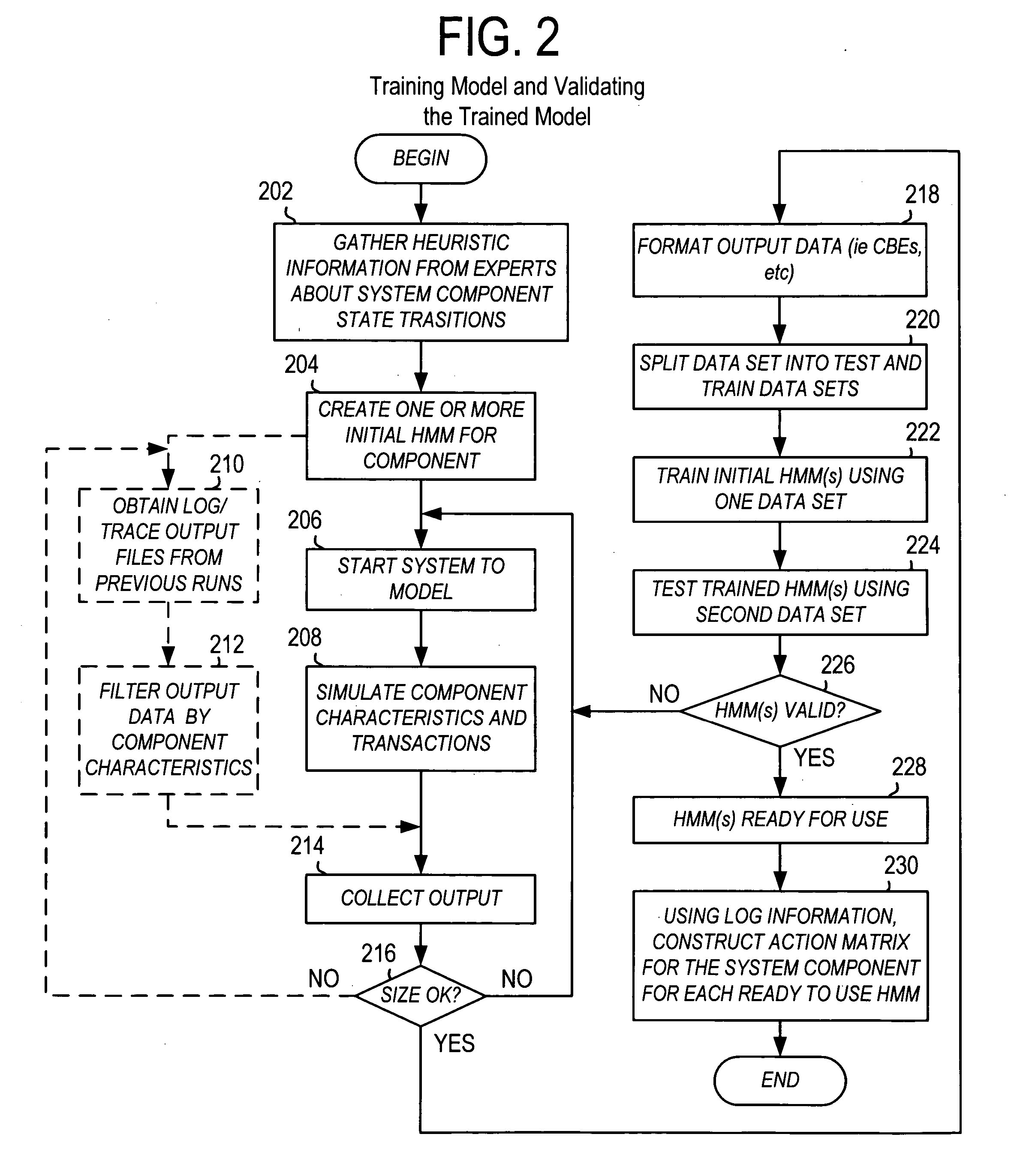
Using stochastic models to diagnose and predict complex system problems
InactiveUS20070265811A1ForecastingComputation using non-denominational number representationHealth conditionState switching
A plurality of stochastic models is built that predict the probabilities of state transitions for components in a complex system. The models are trained using output observations from the system at runtime. The overall state and health of the system can be determined at runtime by analyzing the distribution of current component states among the possible states. Subsequent to a low level component failure, the state transition probability stochastic model for the failed component can be analyzed by uncovering the previous states at N time intervals prior to the failure. The resulting state transition path for the component can be analyzed for the causes of the failure. Additionally, component failures resulting from the failure, or worsening state transition, in other components can be diagnosed by uncovering the previous states at the N times prior to the failure for multiple components in the system and then analyzing the state transition paths for correlations to the failed component. Additionally, transitions to worsening states can be predicted using an action matrix. The action matrix is created beforehand using state information and transition probabilities derived from a component's stochastic model. The action matrix is populated probabilities of state transitions at a current state for given actions. At runtime, when an action is requested of a component, the probability of the component transitioning to a worsening state by performing the action can be assessed from the action matrix by using the current state of the component (available from the stochastic model).
Owner:IBM CORP
Multi-class image semi-supervised classifying method and system
ActiveCN104463202ASufficient sparsityImprove applicabilityCharacter and pattern recognitionAlgorithmSignal on
The invention discloses a multi-class image semi-supervised classifying method and system. The method comprises the steps that firstly, similarity learning is conducted on image samples with tags and image samples without tags in a training set, and similar neighbor images and normalized weights are constructed and used for representing sample similarities; secondly, a class tag matrix is initialized, L2,1-norm regularization is introduced to effectively reduce the influence of mixed signals in prediction tags F of flexible class tags on results, constrains which are not negative and are one in column sum are applied to F at the same time, and thus it is ensured that estimated flexible tags meet the probability definition and non-negativity; finally, parameters are used for balancing the influences of similarity measurement, initial class tags and L2,1-norm regularization on classification, semi-supervised learning modeling is completed, the maximum value of similarity probabilities is taken to be used for image class identification, and classification results are obtained. Due to the fact that the L2,1-norm regularization is introduced, the influence of the mixed signals on the classification is reduced, and thus the classification accuracy is improved. In addition, data outside the training set can be effectively classified, and the expansibility is good.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
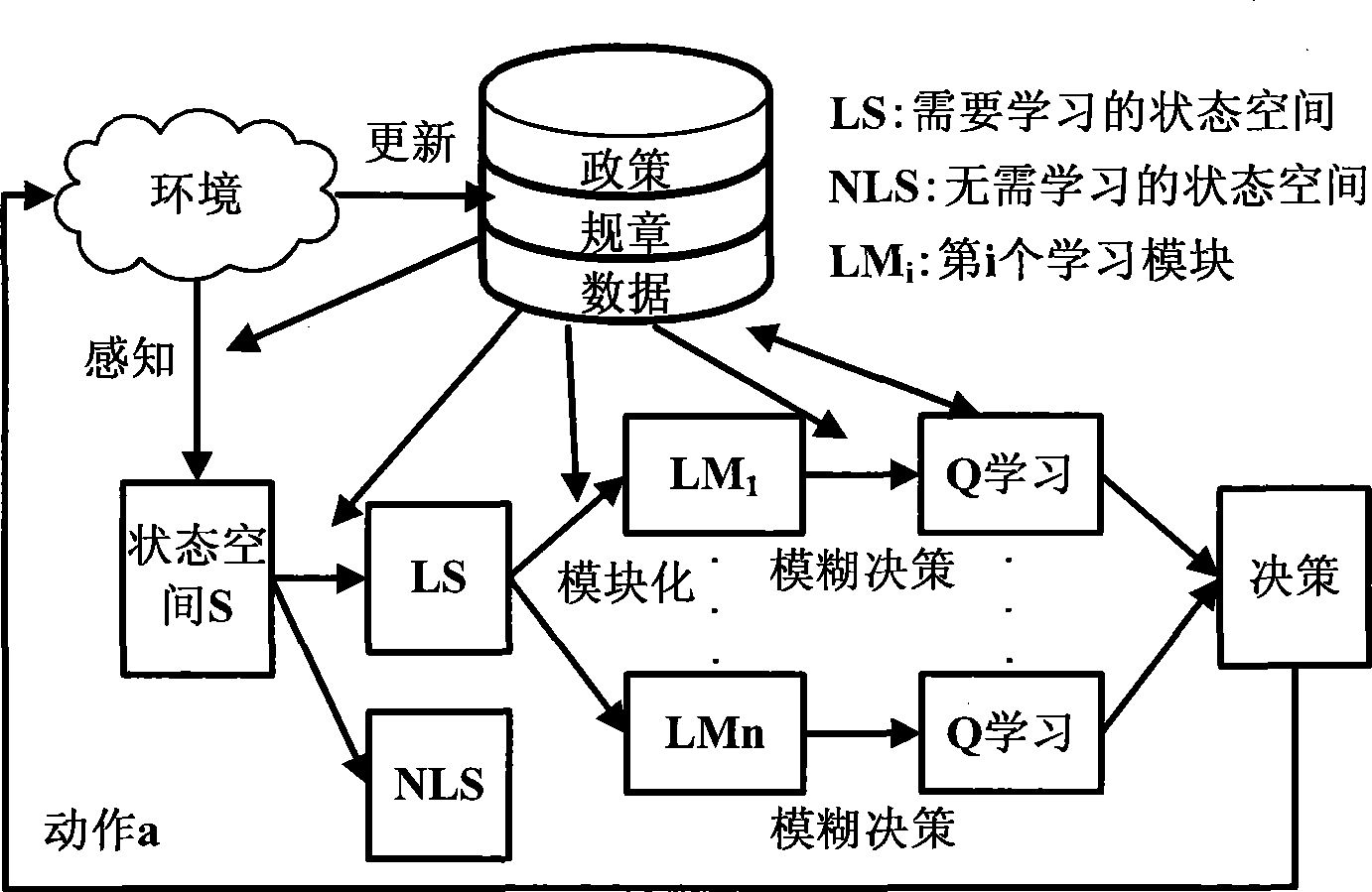
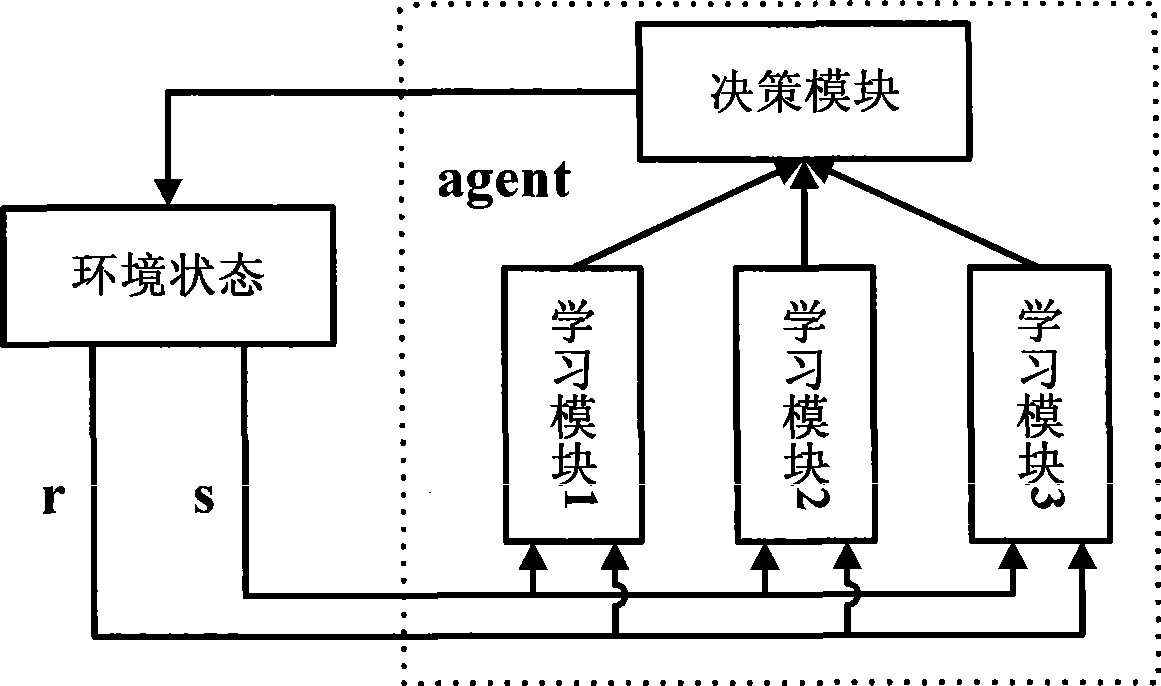
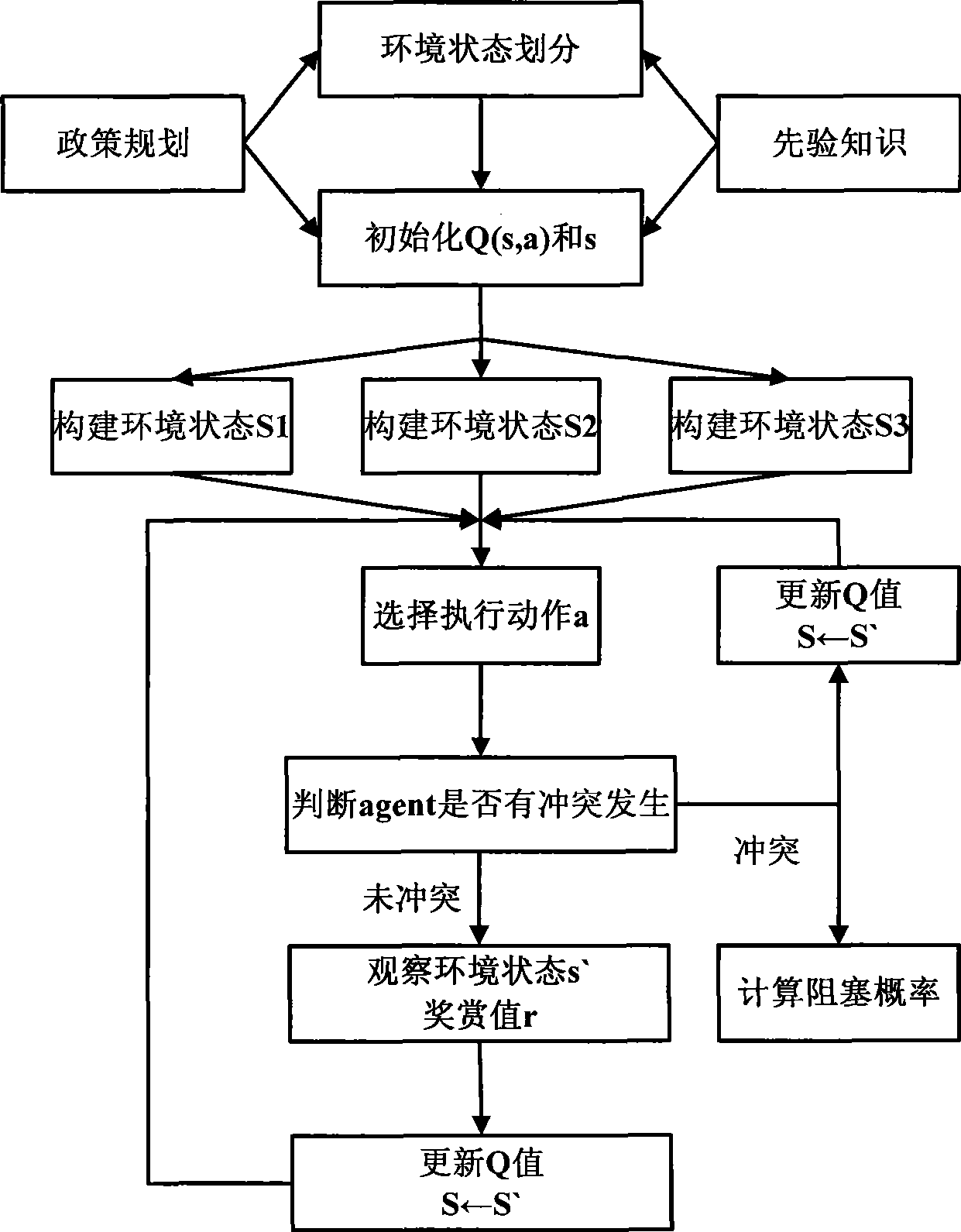
Dynamic spectrum access method based on policy planning constrain Q study
InactiveCN101466111AAvoid blindnessImprove learning efficiencyWireless communicationPropogation channels monitoringCognitive userFrequency spectrum
The invention provides a dynamic spectrum access method on the basis that the policy planning restricts Q learning, which comprises the following steps: cognitive users can divide the frequency spectrum state space, and select out the reasonable and legal state space; the state space can be ranked and modularized; each ranked module can finish the Q form initialization operation before finishing the Q learning; each module can individually execute the Q learning algorithm; the algorithm can be selected according to the learning rule and actions; the actions finally adopted by the cognitive users can be obtained by making the strategic decisions by comprehensively considering all the learning modules; whether the selected access frequency spectrum is in conflict with the authorized users is determined; if so, the collision probability is worked out; otherwise, the next step is executed; whether an environmental policy planning knowledge base is changed is determined; if so, the environmental policy planning knowledge base is updated, and the learning Q value is adjusted; the above part steps are repeatedly executed till the learning convergence. The method can improve the whole system performance, and overcome the learning blindness of the intelligent body, enhance the learning efficiency, and speed up the convergence speed.
Owner:COMM ENG COLLEGE SCI & ENGINEEIRNG UNIV PLA
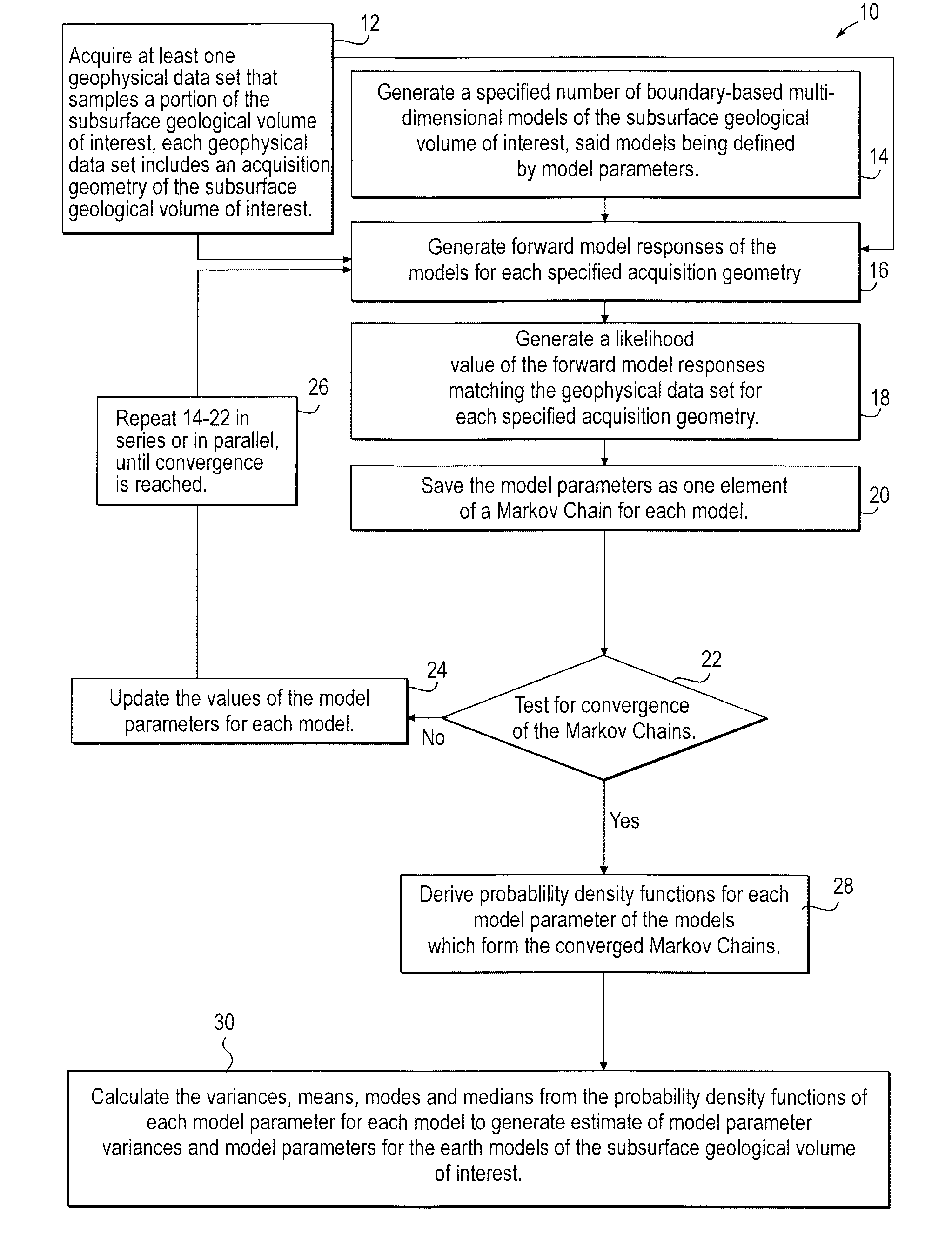
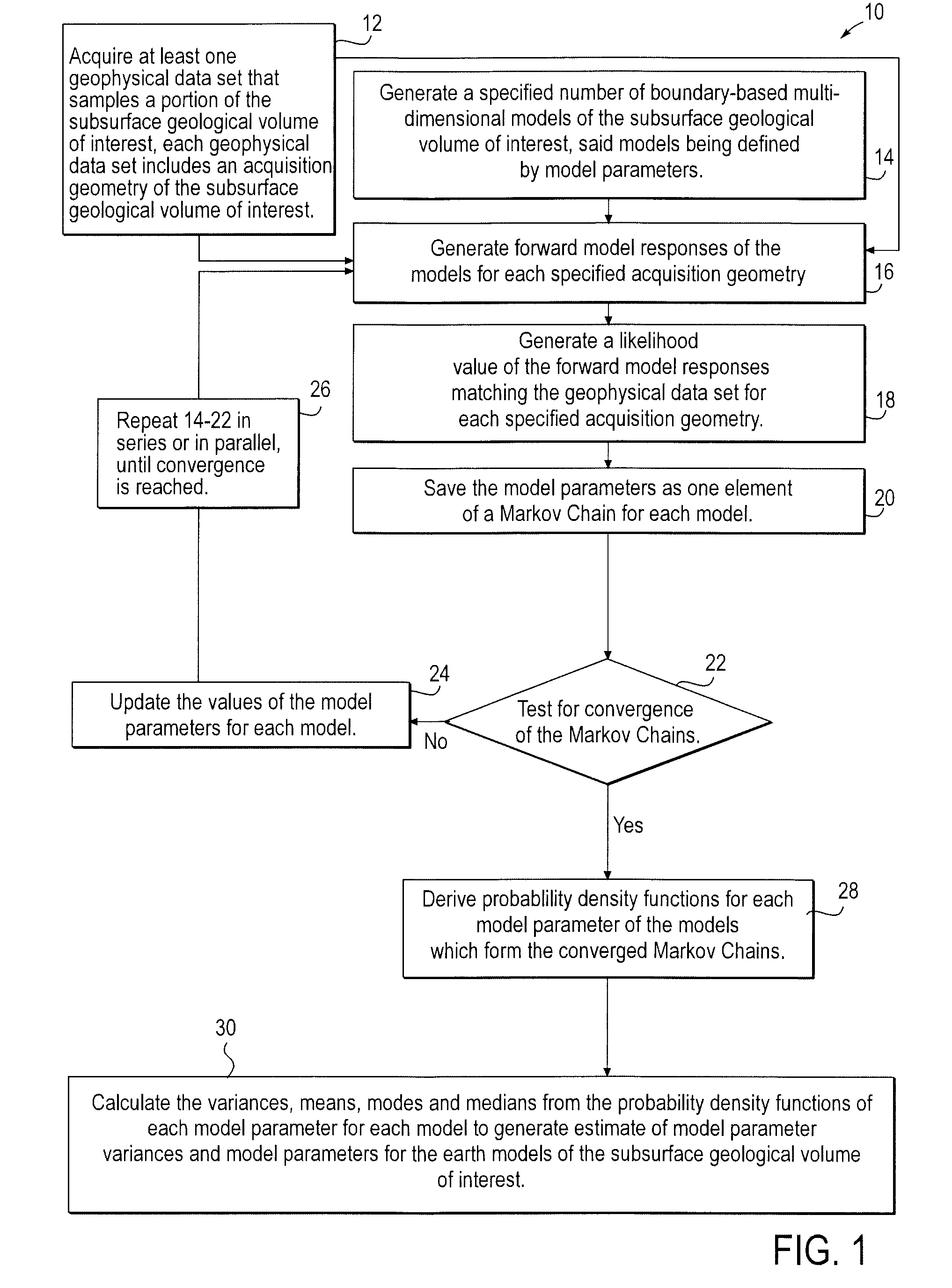
Stochastic inversion of geophysical data for estimating earth model parameters
A computer implemented stochastic inversion method for estimating model parameters of an earth model. In an embodiment, the method utilizes a sampling-based stochastic technique to determine the probability density functions (PDF) of the model parameters that define a boundary-based multi-dimensional model of the subsurface. In some embodiments a sampling technique known as Markov Chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) is utilized. MCMC techniques fall into the class of “importance sampling” techniques, in which the posterior probability distribution is sampled in proportion to the model's ability to fit or match the specified acquisition geometry. In another embodiment, the inversion includes the joint inversion of multiple geophysical data sets. Embodiments of the invention also relate to a computer system configured to perform a method for estimating model parameters for accurate interpretation of the earth's subsurface.
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC
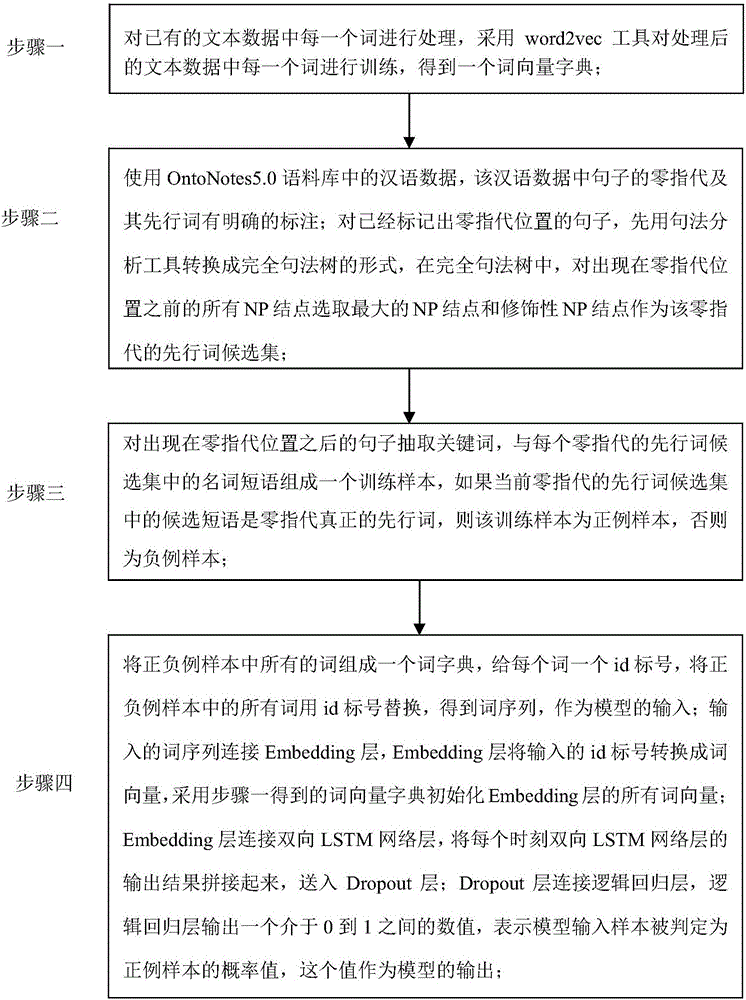
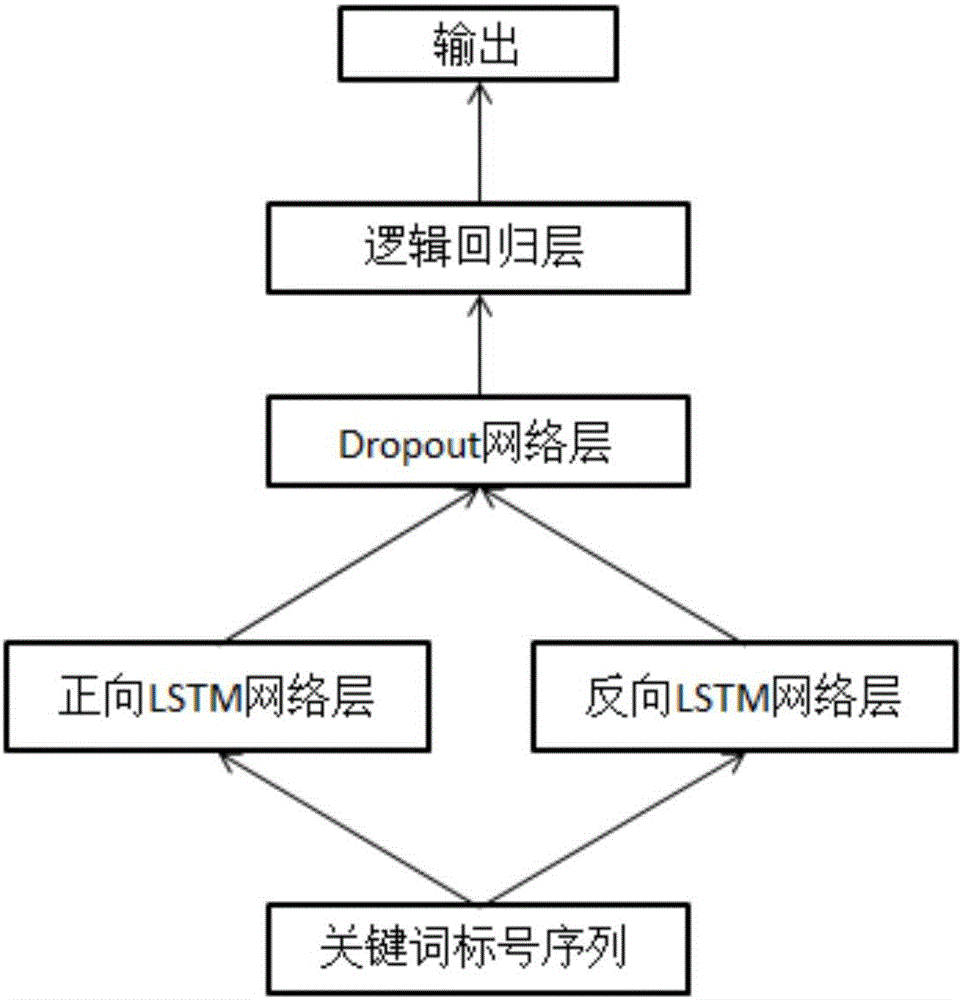
Chinese zero anaphora resolution method based on LSTM
InactiveCN106294322AImprove accuracySemantic analysisSpecial data processing applicationsAlgorithmEuclidean vector
The invention relates to a Chinese zero anaphora resolution method based on LSTM and aims at solving the problem that according to an existing method, a Chinese zero anaphora resolution task is low in accuracy and the accuracy of understanding semantic information is low. The method comprises the steps of 1, processing each word in existing text data, and training each word in the processed text data by employing a word2vec tool, thereby obtaining a word vector dictionary; 2, selecting an antecedent candidate set of zero anaphora; 3, if candidate phrases in the current antecedent candidate set of the zero anaphora is true antecedents of the zero anaphora, determining that the training samples are positive example samples, otherwise determining that the training samples are negative example samples; and 4, connecting a Dropout layer with a logistic regression layer, representing probability value that model input samples are judged as the positive example samples, and outputting the value as a model. The method is applicable to the field of natural language processing.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
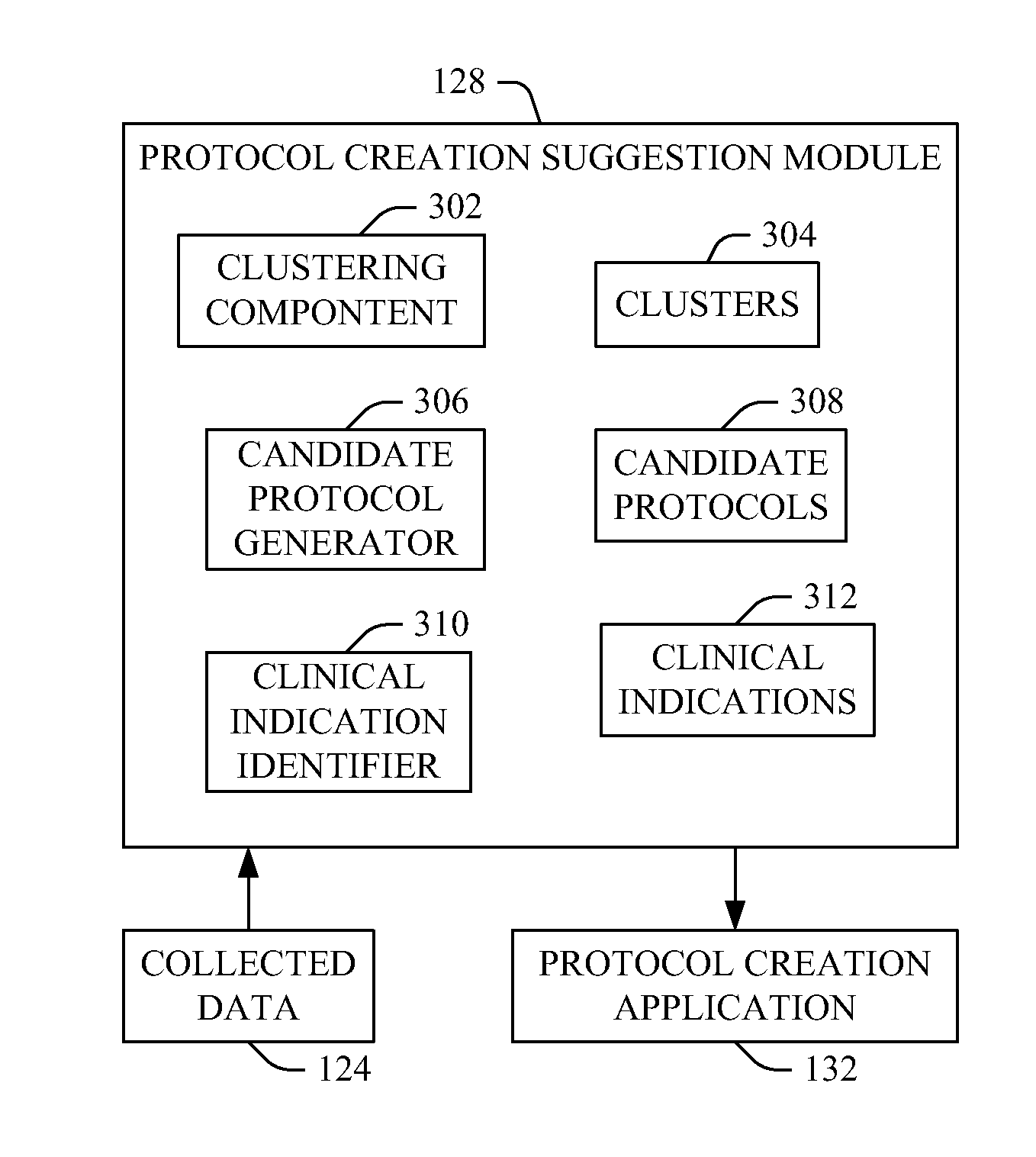
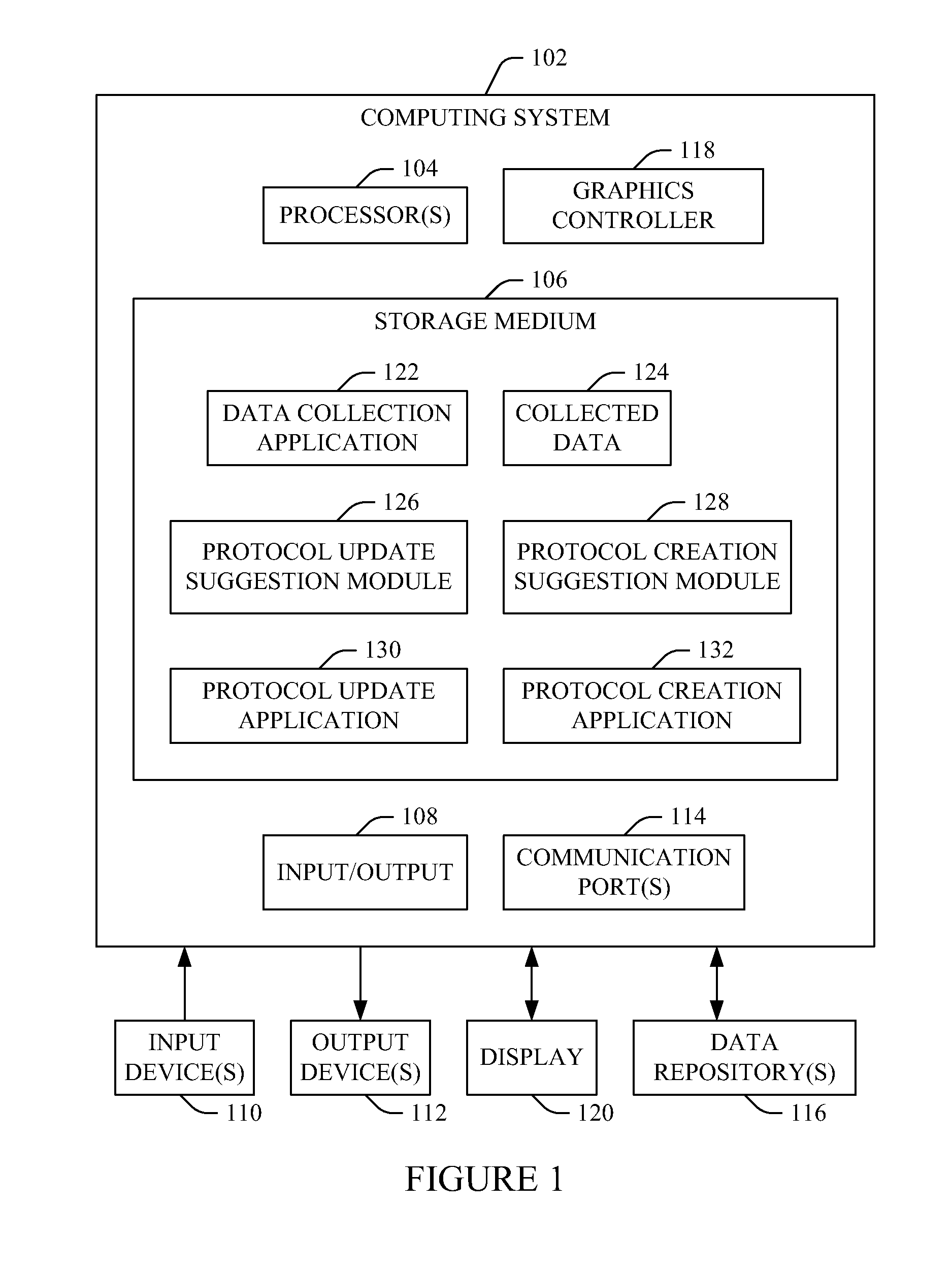
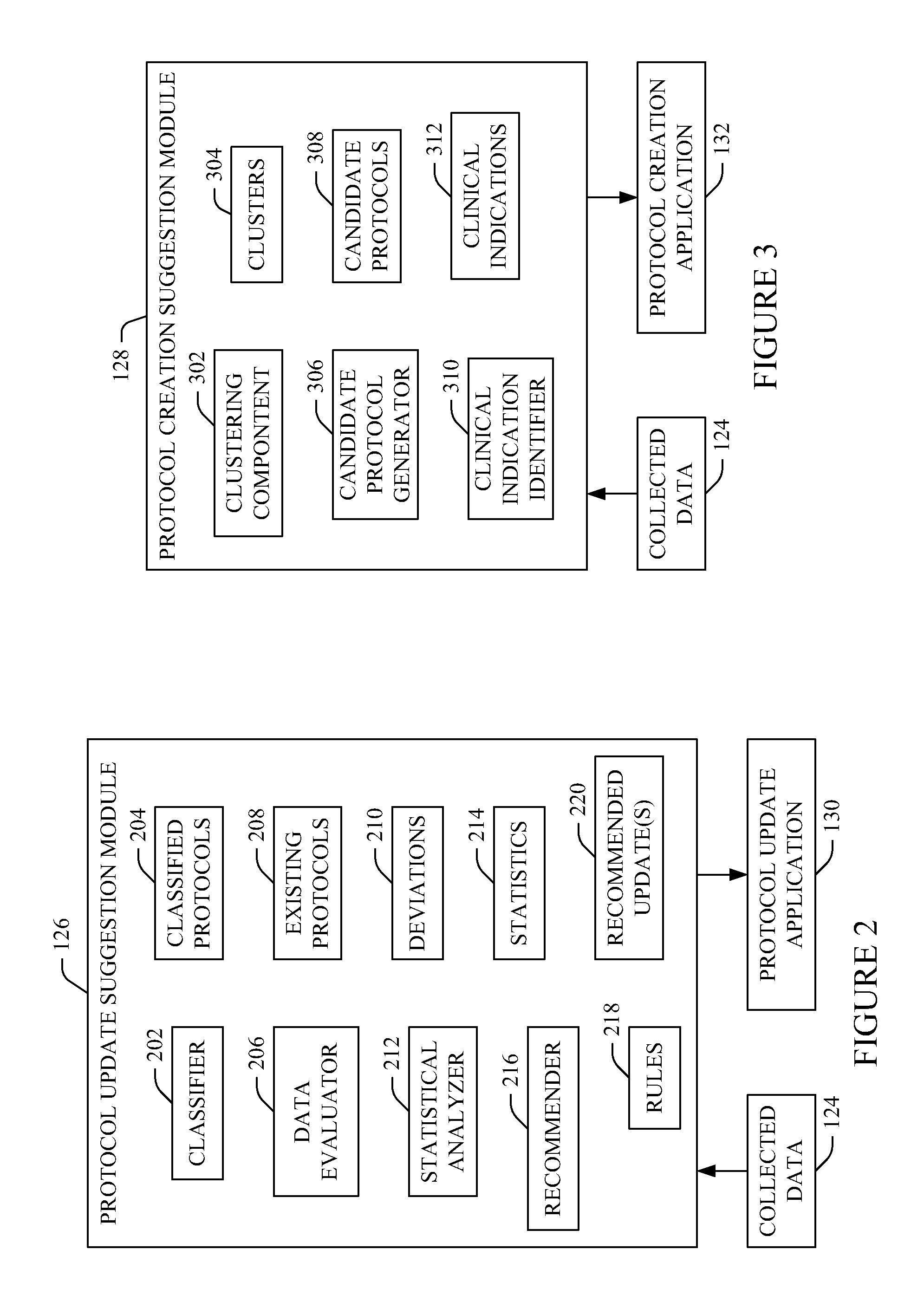
Imaging protocol update and/or recommender
A method includes obtaining electronically formatted information about previously performed imaging procedures, classifying the information into groups of protocols based on initially selected protocols for the previously performed imaging procedures and generating data indicative thereof, identifying deviations between the classified information and the corresponding initially selected protocols for the previously performed imaging procedures, and generating a signal indicative of the deviations. A method includes recommending at least one of a plurality of protocols for an imaging procedure based on at least one of a score, a probability, or a pre-determined rule, which is based on extracted medical concepts from patient information and extracted medical concepts from previously imaged patient information, and generating a signal indicative of the recommendation.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
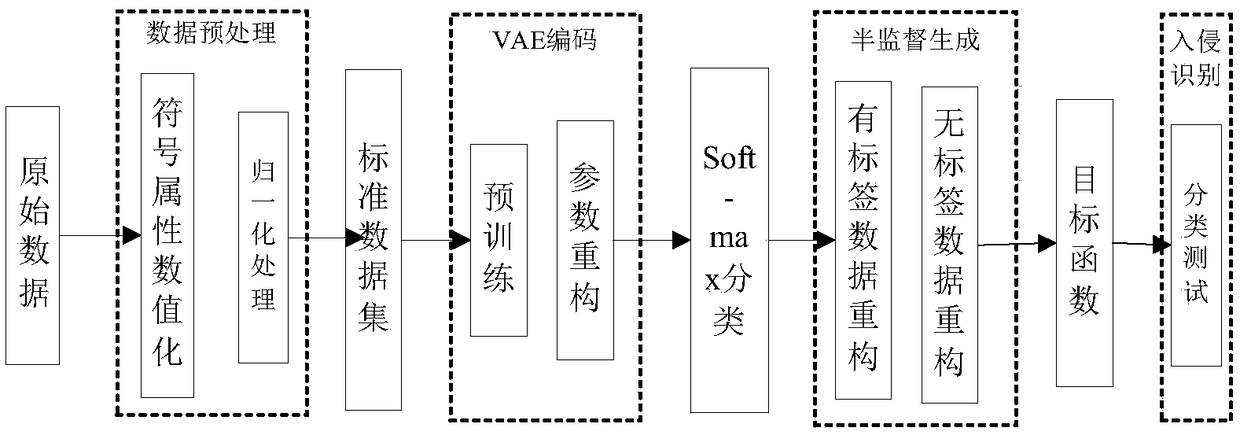
Semi-supervised intrusion detection method based on depth generation model
ActiveCN108881196AImprove classification accuracyReduce demandCharacter and pattern recognitionTransmissionFeature vectorComputational model
The invention discloses a semi-supervised intrusion detection method based on a depth generation model. The method comprises the steps of: 1, preprocessing data: converting symbol attributes in a dataset into numerical attributes, and then normalizing all the numerical attributes; 2, converting high-dimensional feature representations of labeled and unlabeled data into low-dimensional representations of a new feature space by using the variational self-encoding technology in the generation model, adding a constraint to low-dimensional feature vectors to obey Gaussian positive distribution soas to obtain a hidden variable z, and training a classifier by using the hidden variable z in combination with a labeled sample; 3, reconstructing labeled sample data: jointly generating a new labeledsample by using the hidden variable z in combination with label class information; 4, reconstructing an unlabeled sample: predicting the probability of each class of an unlabeled sample by using thehidden variable z, and then generating a new unlabeled sample in combination with the hidden variable z; and 5, calculating a reconstruction error of the model with the newly generated labeled and unlabeled samples, and training and optimizing model parameters in combination with a classification error till convergence.
Owner:CIVIL AVIATION UNIV OF CHINA
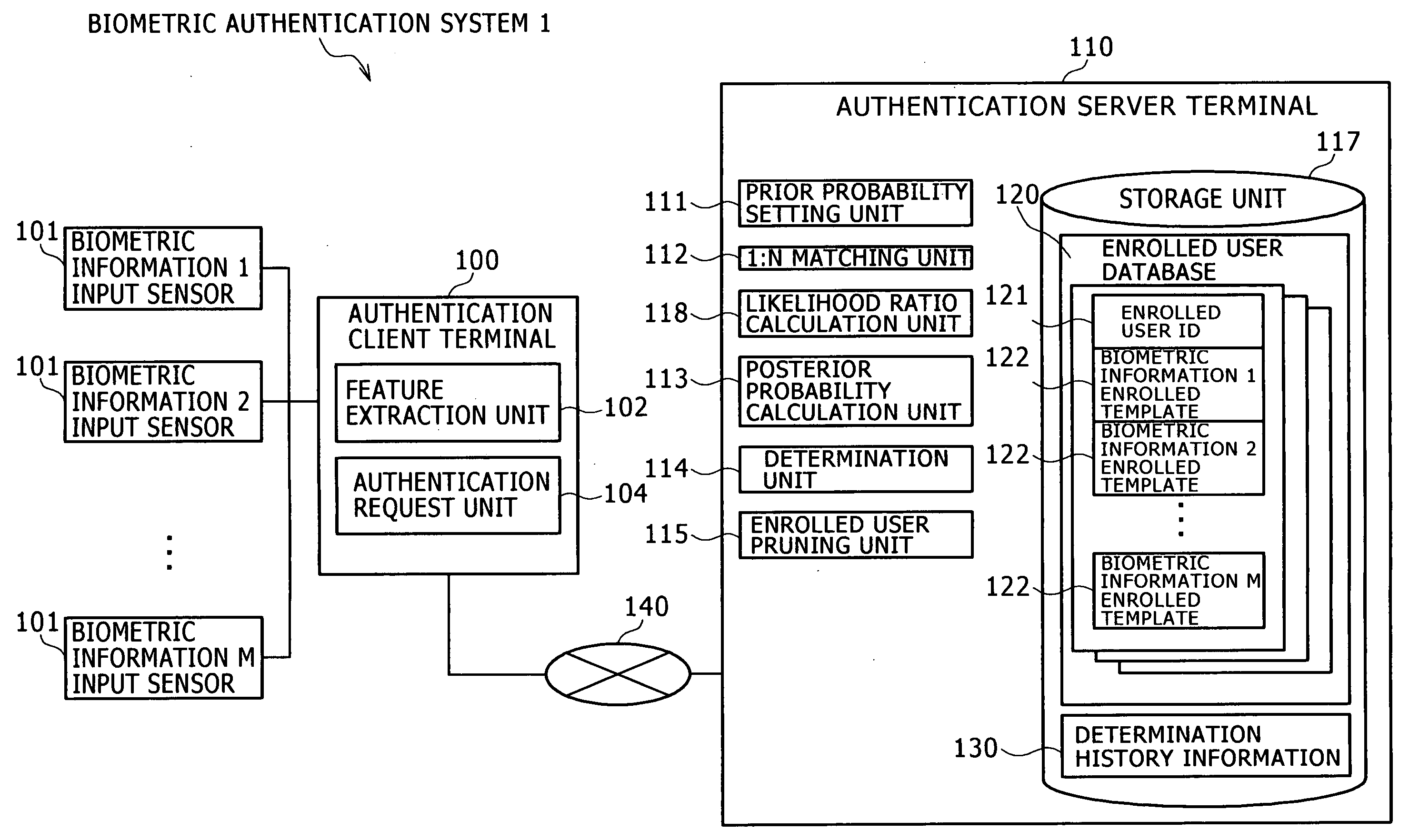
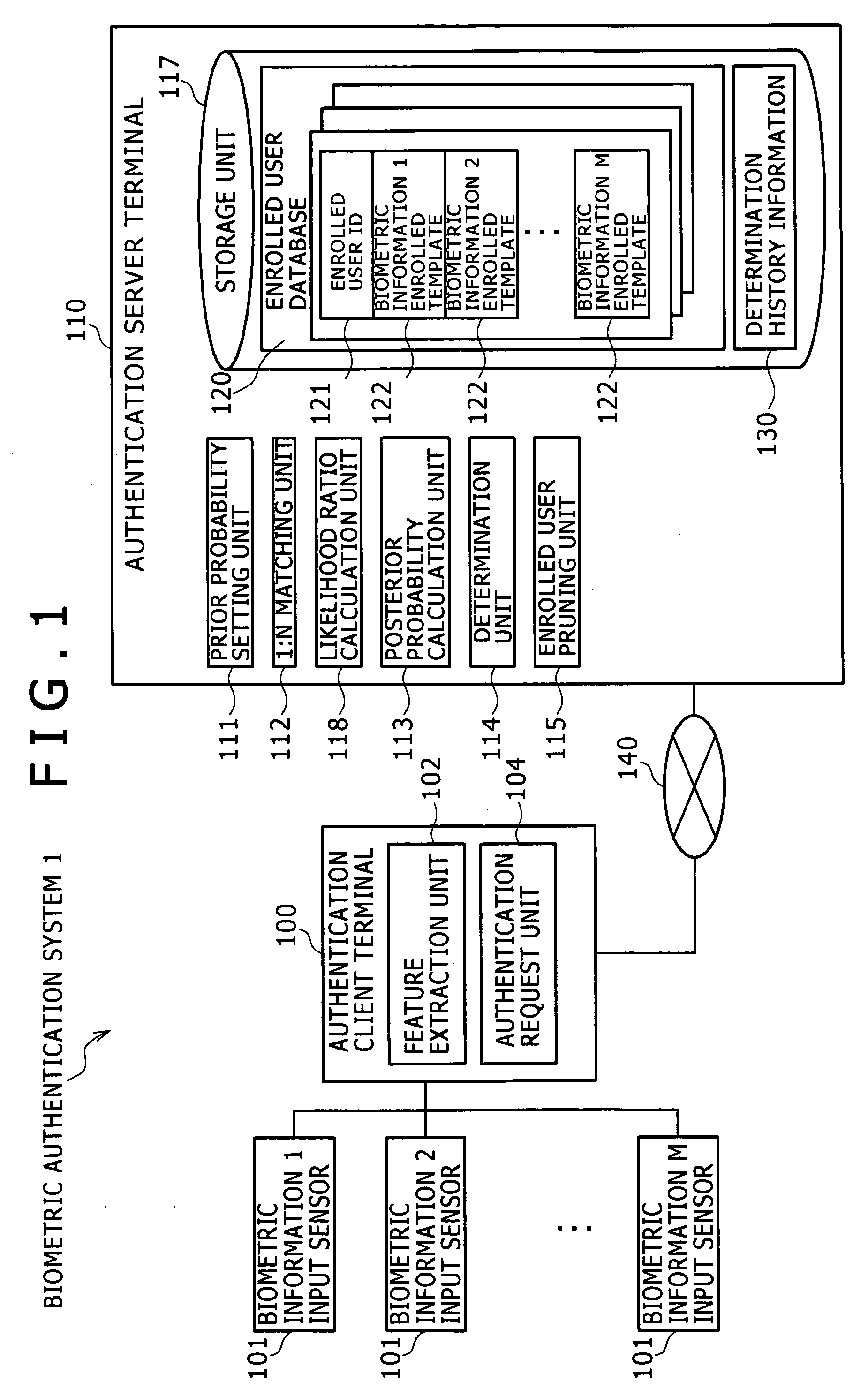
Biometric authentication system, authentication client terminal, and biometric authentication method
ActiveUS20090289760A1Reduce the number of inputsReduce additionalProgramme controlElectric signal transmission systemsBiometric dataFeature data
A biometric authentication system, authentication client terminal, and biometric authentication method are provided to reduce an expected value of the number of inputs of biometric data for authentication, while effectively preventing forgery. In a biometric authentication system, prior probabilities of enrolled users un and non-enrolled user u0 are previously set. 1:N matching is performed between feature data of a claimant v and matching feature data. The matching score is calculated for each enrolled user un. A ratio of the likelihood v=un to the likelihood v≠un is calculated for each enrolled user un using the calculated matching scores. Posterior probabilities of the enrolled users un and non-enrolled user u0 are calculated, using the likelihood ratios, and the prior probabilities of both the enrolled users un and the non-enrolled user u0. Then, determination is made by comparing each posterior probability with a first threshold.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
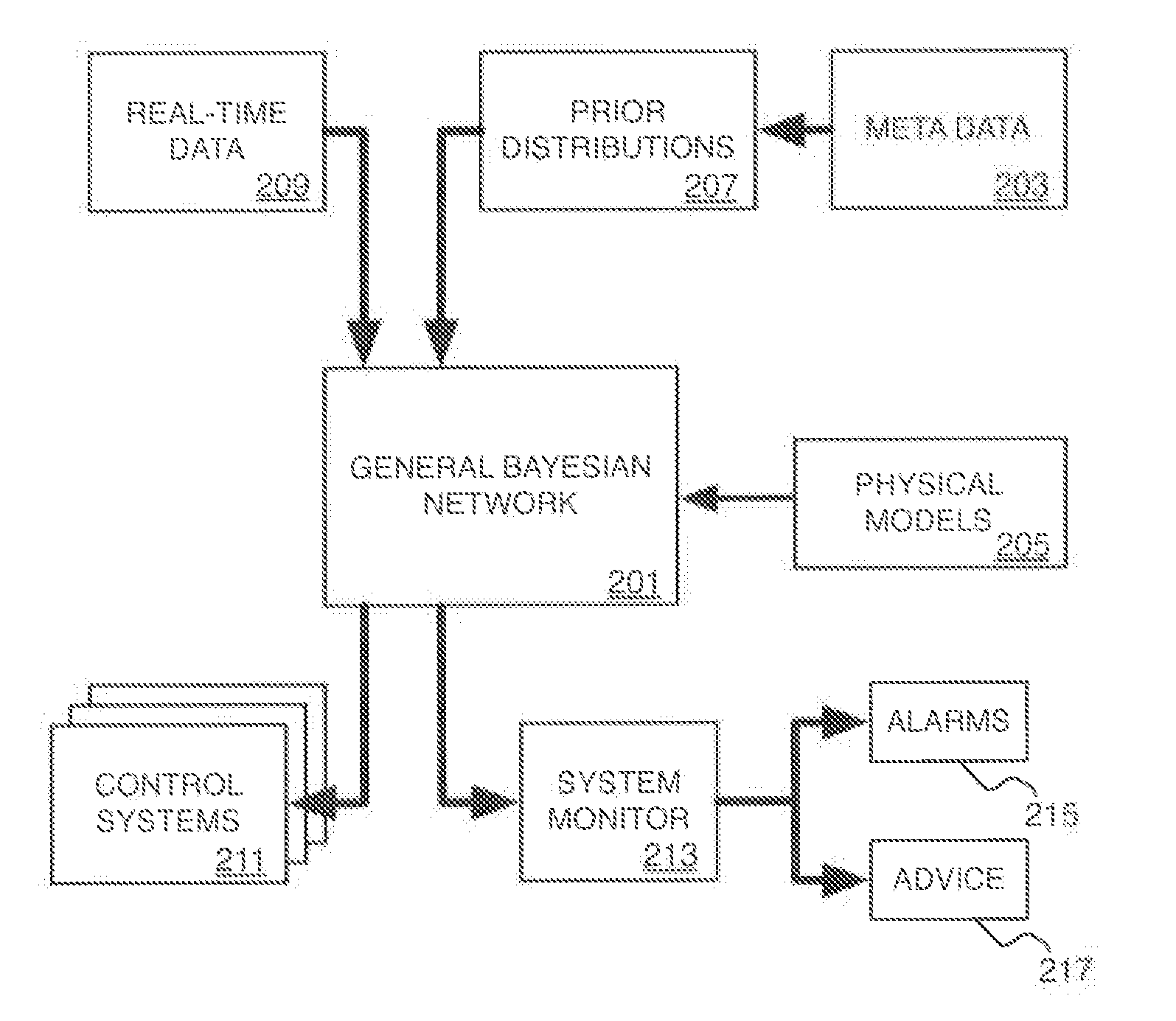
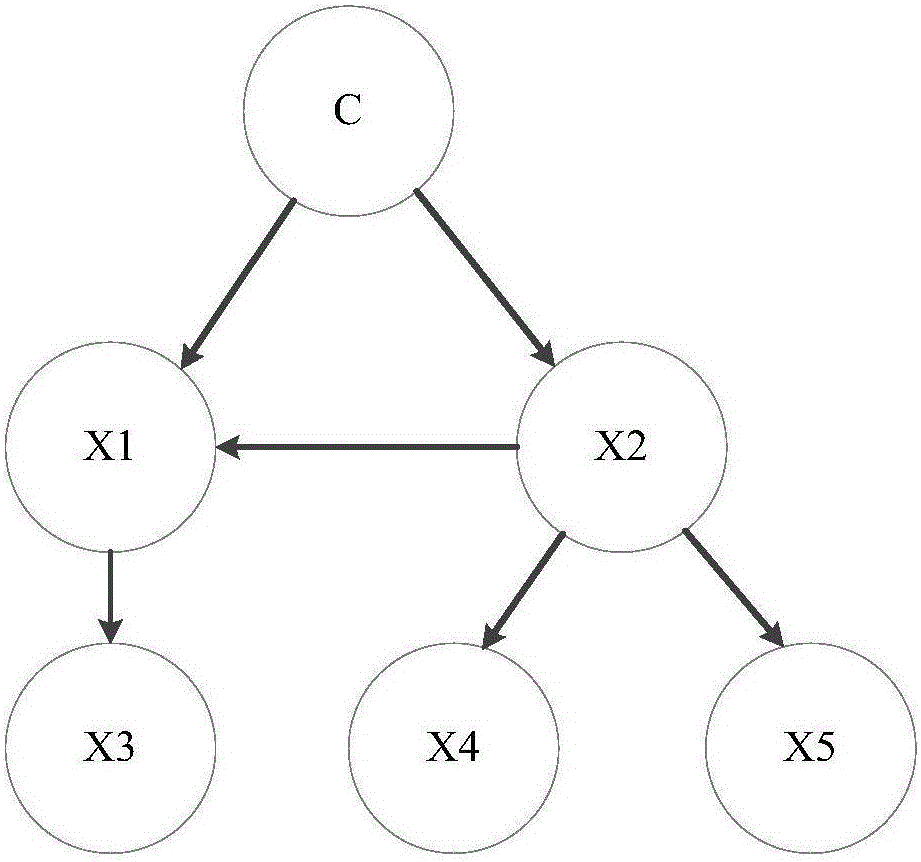
Use of general bayesian networks in oilfield operations
Embodiments of the present invention provide methods of using General Bayesian Networks to automate oilfield operations. In certain aspects, a Monte-Carlo method is used to propagate probability density functions for root-variables to continuous-valued hidden variables reflecting some oilfield operation properties. Evidence in the form of observed properties are used to weight samples used in the Monte-Carlo process thereby propagating the observed values onto other variables. The inferred probability distributions are provided to an oilfield control system or monitoring system.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Android malicious act detection method based on Bayesian network
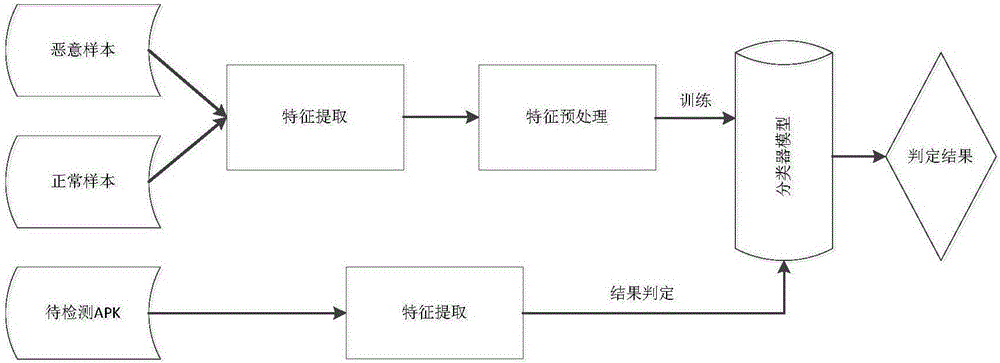
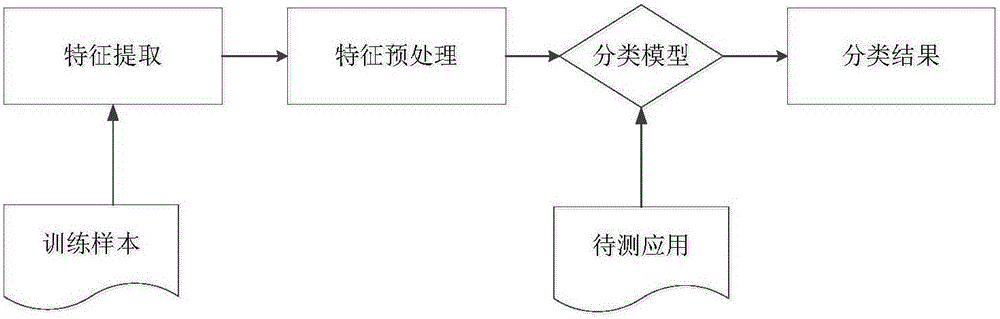
ActiveCN105740712APredicting the Impact of ClassificationEasy to usePlatform integrity maintainanceFeature extractionProbit
The invention discloses an Android malicious act detection method based on the Bayesian network.The method specifically comprises the steps of 1, conducting static feature extraction on an Android application training sample; 2, conducting feature processing, and calculating the correlation degree between feature and category with the chi-squared statistic feature selection approach; 3, establishing an Android software malicious act detection model based on the Bayesian network classification algorithm; 4, inputting an APK extraction feature to be detected into a well trained Bayesian network virus detection model, and calculating the posterior probability of the category of the feature; 5, comparing the two data obtained from the step 4 representing the posterior probability that the APK extraction feature to be detected belongs to the virus category and representing the posterior probability that the APK extraction feature to be detected belongs to the normal category respectively, and taking the category with larger posterior probability as the classification result of the application.The method can effectively detect Android malice applications and reduce the learning time of the Bayesian network to a certain degree.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Complex object automatic recognition method based on multi-category primitive self-learning
ActiveCN102436589AStrengthen the spatial constraintsImprove training efficiencyCharacter and pattern recognitionImaging interpretationAutodidacticism
The invention relates to a complex object automatic recognition method based on multi-category primitive self-learning, which comprises the steps of: a) establishing a representational set of multi-category object images; b) preprocessing images in a training set and respectively extracting point, linear and planar primitives; c) conducting concentrated matching calculation, screening and merging to the obtained numerous primitives in a confirmation image set, and respectively constructing point, linear and planar primitive dictionaries; and d) selecting a certain quantity of primitives from the dictionaries, using the primitives as a weak classifier after the primitives are mated and combined, and respectively training the strong classifiers of the three categories of primitives through self-learning; and e) combining the strong classifiers of the three categories of primitives in a probabilistic polling space to realize the accurate positioning, contour extraction and categorical recognition of multi-category complex objects. The method provided by the invention has the advantages that the intelligent level is high and the demands for the recognition and image interpretation of multi-category complex objects can be met.
Owner:济钢防务技术有限公司
Source node loophole detection method based on integrated neural network
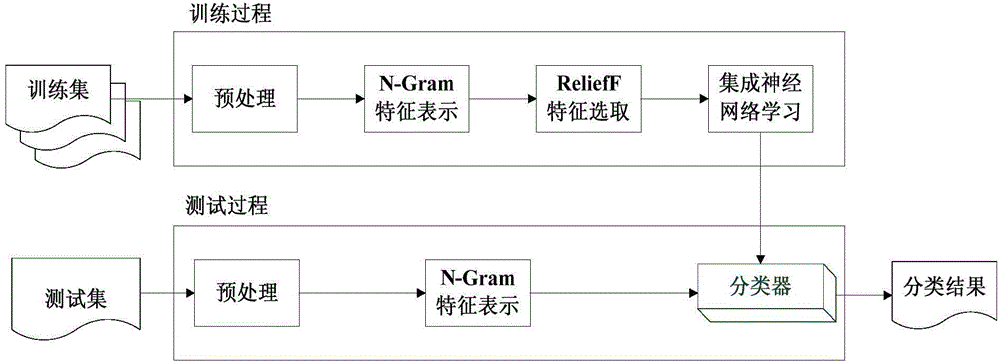
InactiveCN104809069AAccurate and effective vulnerability detectionGuaranteed propertyBiological neural network modelsSoftware testing/debuggingSmall sampleAlgorithm
The invention provides a source node loophole detection method based on an integrated neural network. Source nodes are processed with an N-Gram algorithm, and a represented by an N-Gram set; implicit characteristics are mined from the N-Gram set with a probability statistics method, so that the attribute of code content is ensured, and the sequence correlation property among the codes is kept; characteristic selection is performed with a ReliefF algorithm to calculate a characteristic weight; specific to the aim of solving extreme imbalance of sample data, the functions of small type samples need to be fully considered during calculation, and different neighbor values are set for different types so that the characteristics of the small sample data can play certain roles in calculation; a multilayer feed-forward network is trained with a BP algorithm in the neural network for serving as individual networks, the trust scope of each individual network is learned through a series of parameter learning of identification rate, reject rate and the like with a DS evidence theory, and a final detection result is summarized according to different trust values of each network, so that accurate and effective source node loophole detection is realized.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRIC POWER RES INST +3
Relevance vector machine-based multi-class data classifying method
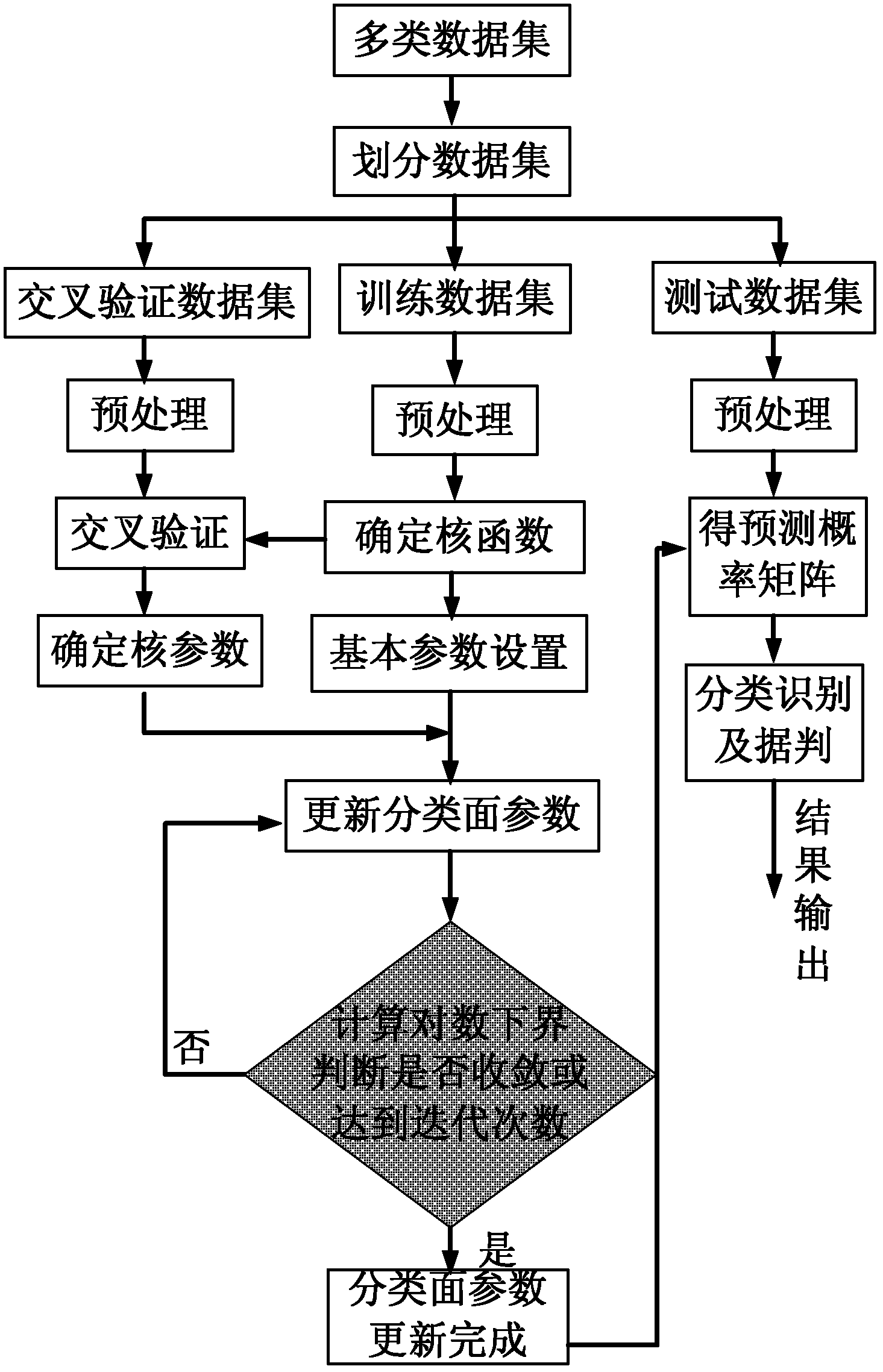
InactiveCN102254193AAvoid Category OverlapAvoid approximationCharacter and pattern recognitionValue setData set
The invention provides a relevance vector machine-based multi-class data classifying method, which mainly solves the problem that the traditional multi-class data classifying method cannot integrally solve classifying face parameters and needs proximate calculation. The relevance vector machine-based multi-class data classifying method comprises a realizing process comprising the following steps of: partitioning a plurality of multi-class data sets and carrying out a normalizing pretreatment; determining a kernel function type and kernel parameters; setting basic parameters; calculating the classifying face parameters; calculating lower bounds of logarithms and solving variant values of the lower bounds of the logarithms and adding 1 to an iterative number; if the variant values of the lower bounds of the logarithms are converged or the iterative number reaches iterating times, finishing updating the classifying face parameters, and otherwise, continuing to updating; and obtaining a prediction probability matrix according to the updated classifying face parameters, wherein column numbers corresponding to a maximum value of each row of the matrix compose classifying classes for testing the data sets, and samples which have the prediction probability less than a false-alarm probability and the detection probability corresponding to a false-alarm probability value set in a curve are rejected. The relevance vector machine-based multi-class data classifying method has the advantages of obtaining classification which is comparable to that of an SVM (Support Vector Machine) by using less relevant vectors and rejecting performance and can be used for target recognition.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com