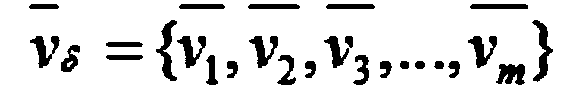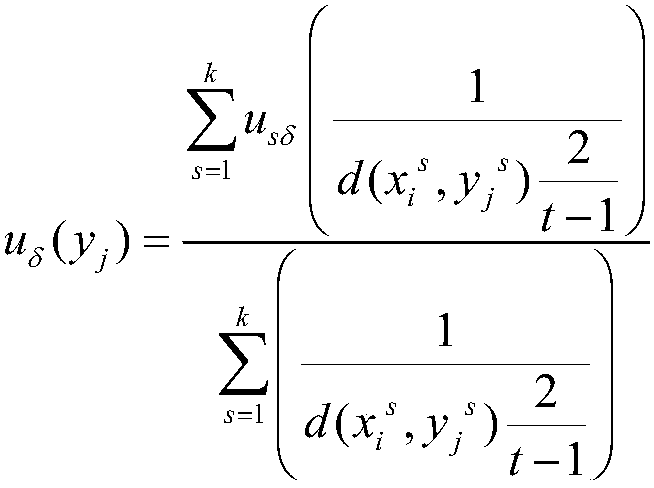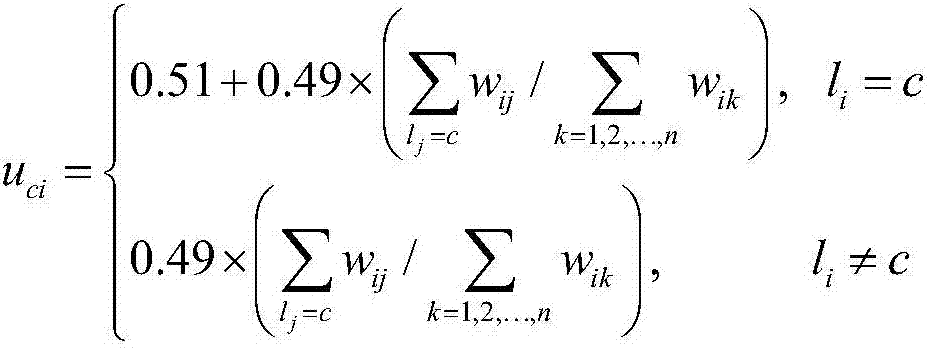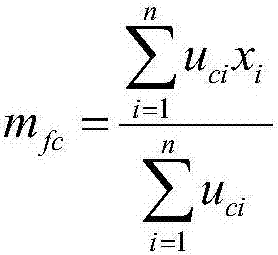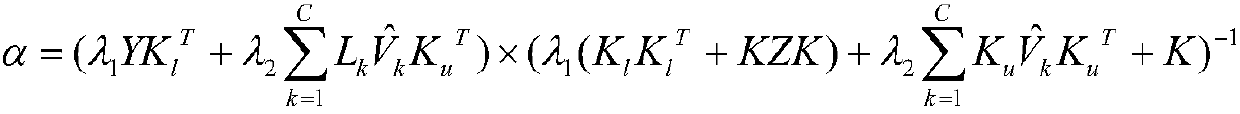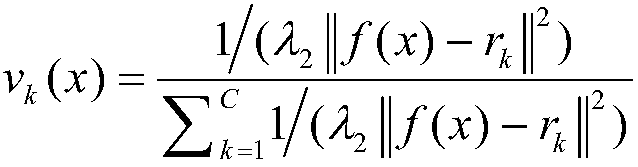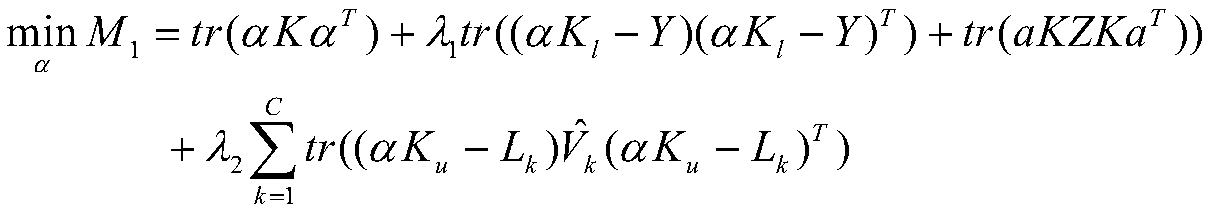Patents
Literature
32 results about "Class membership" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
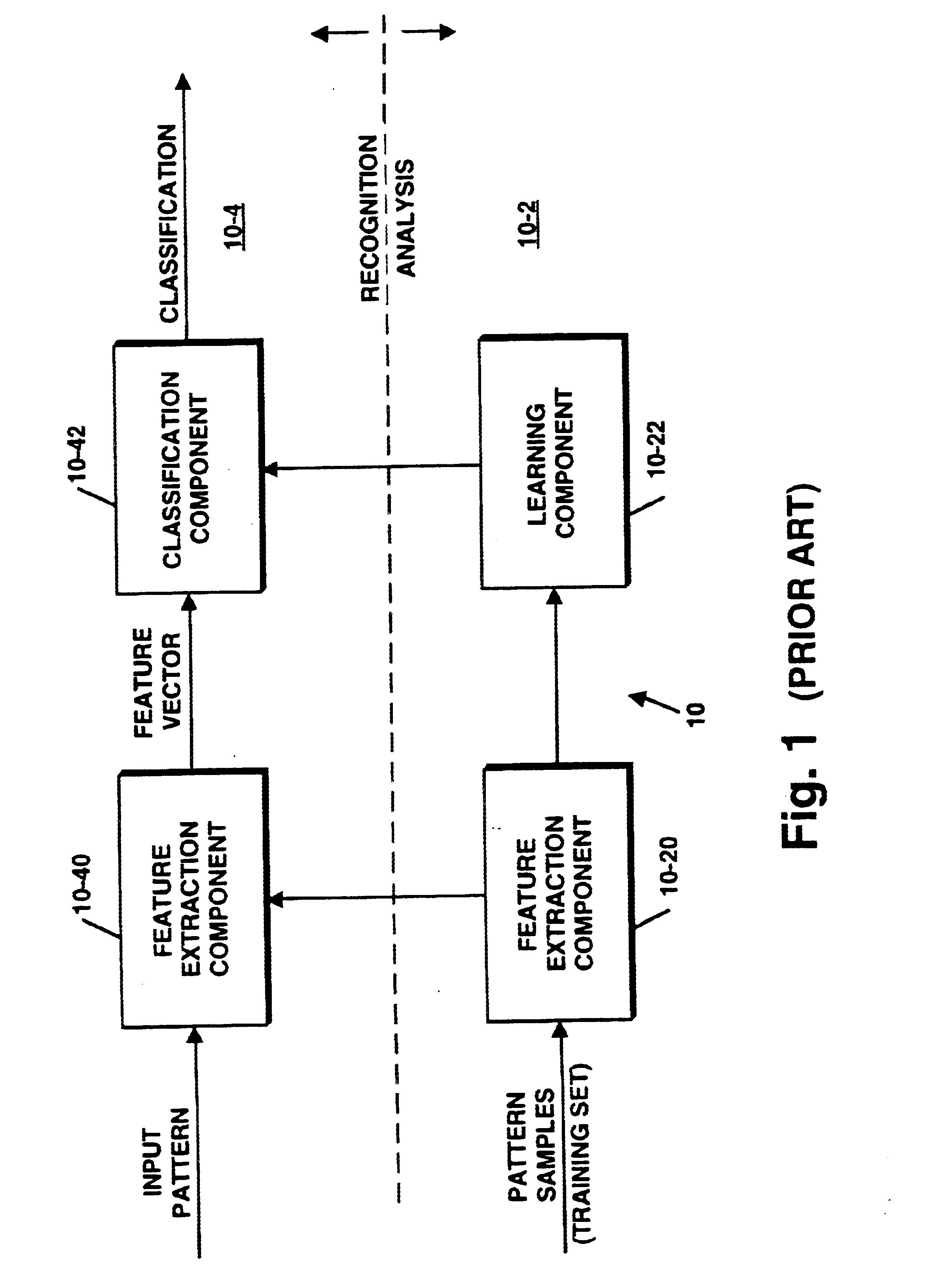
Class members, in C#, are the members of a class that represent the data and behavior of a class. Class members are members declared in the class and all those (excluding constructors and destructors) declared in all classes in its inheritance hierarchy. Class members can be of the following types:
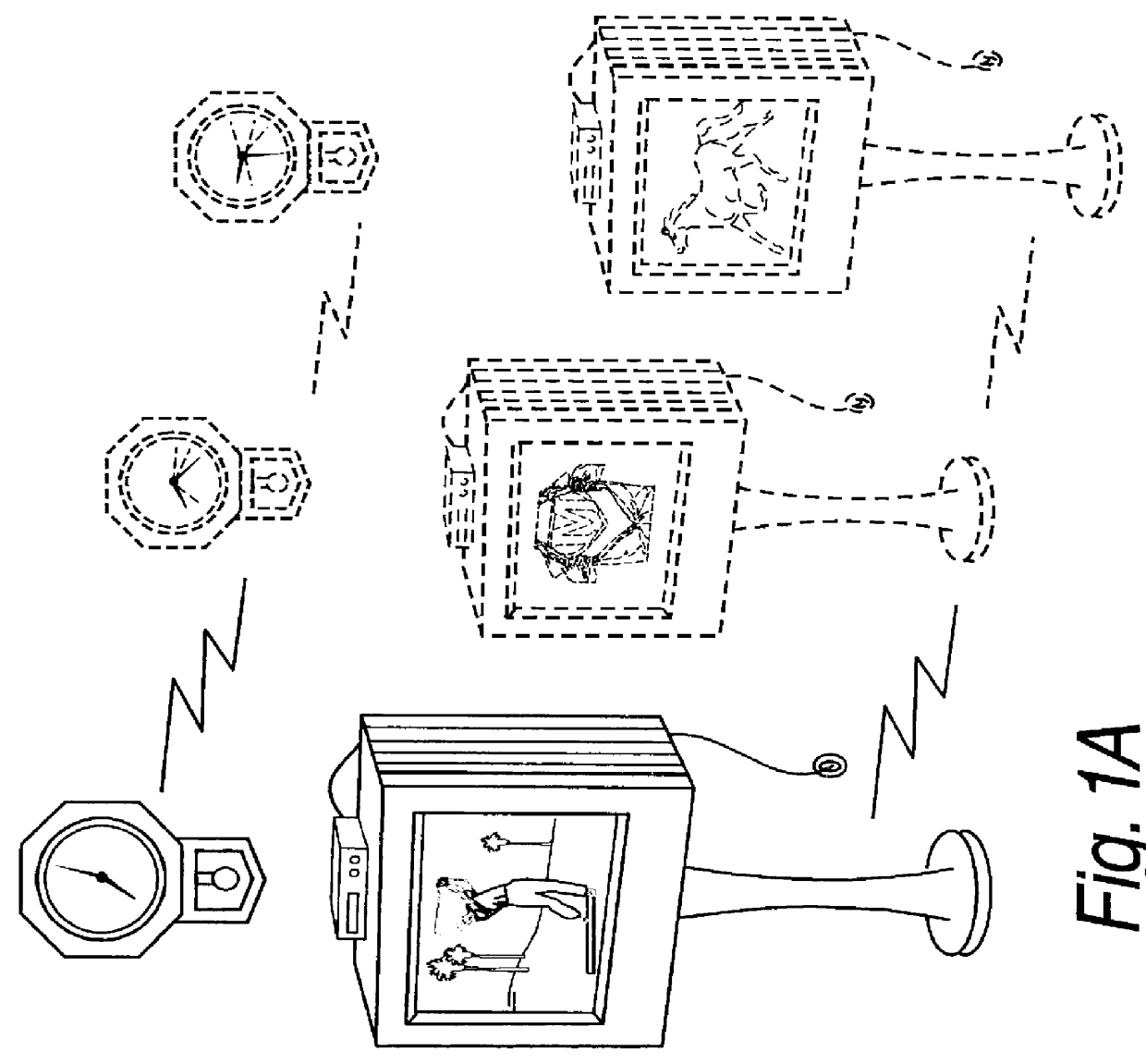
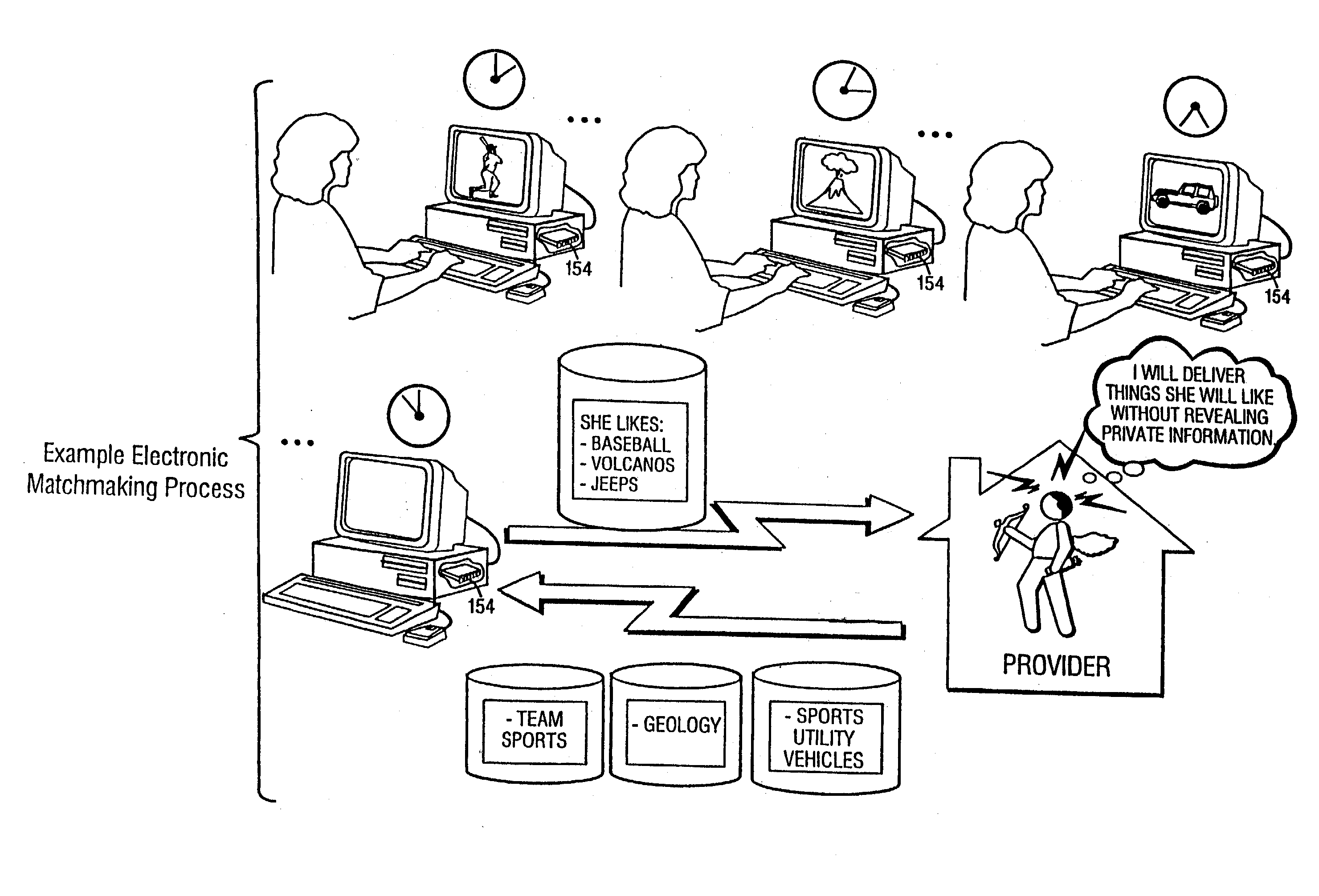
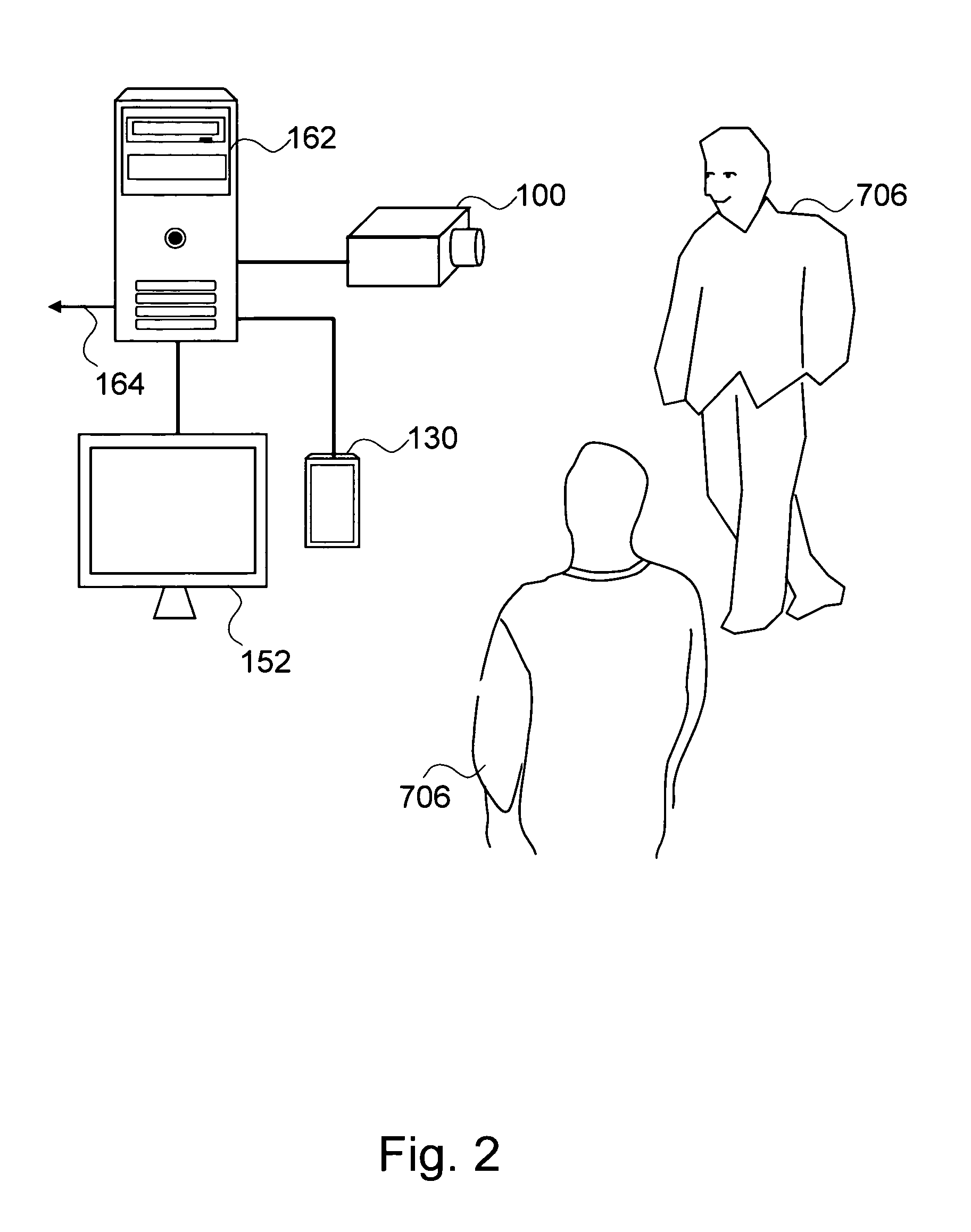
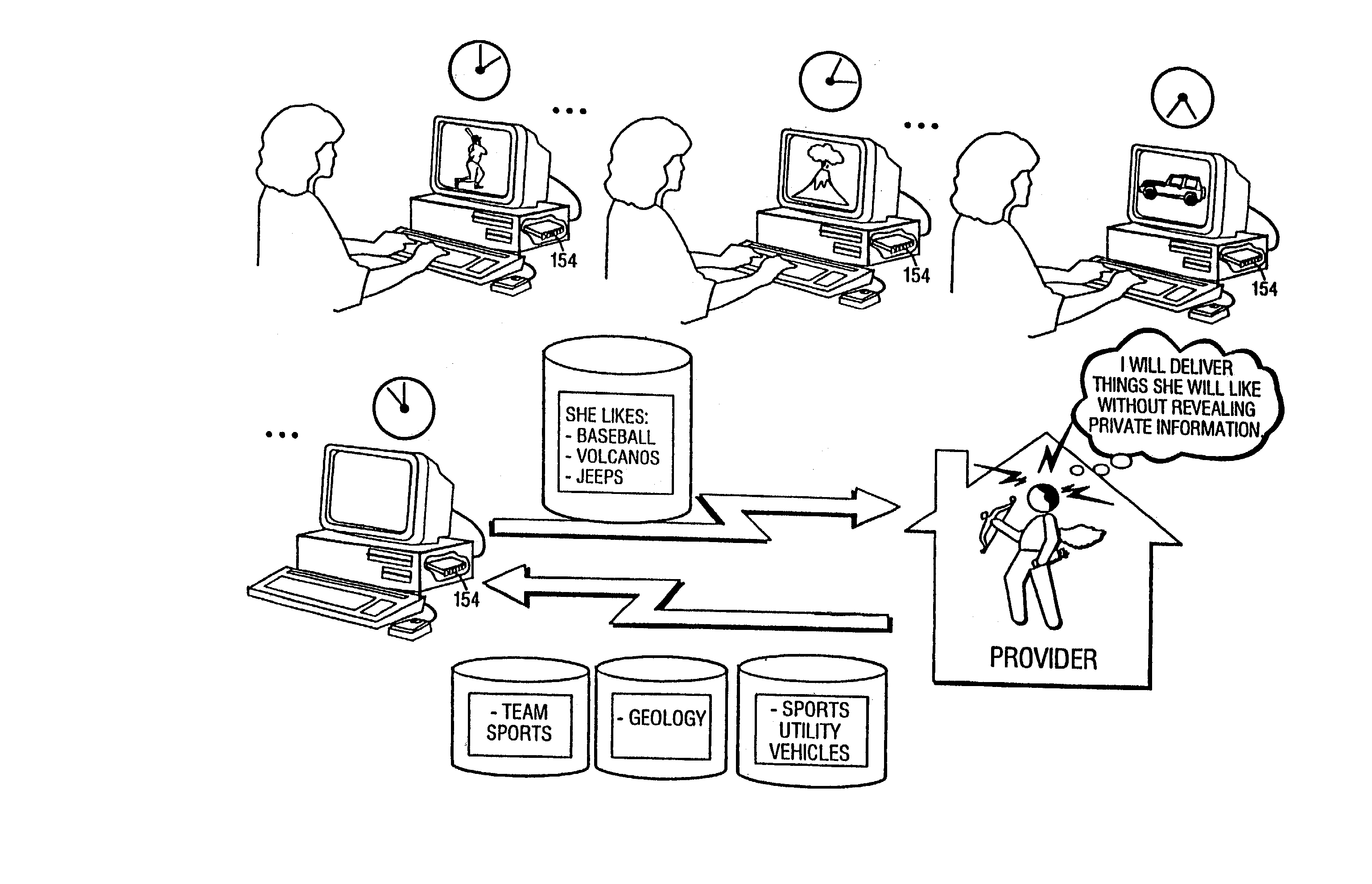
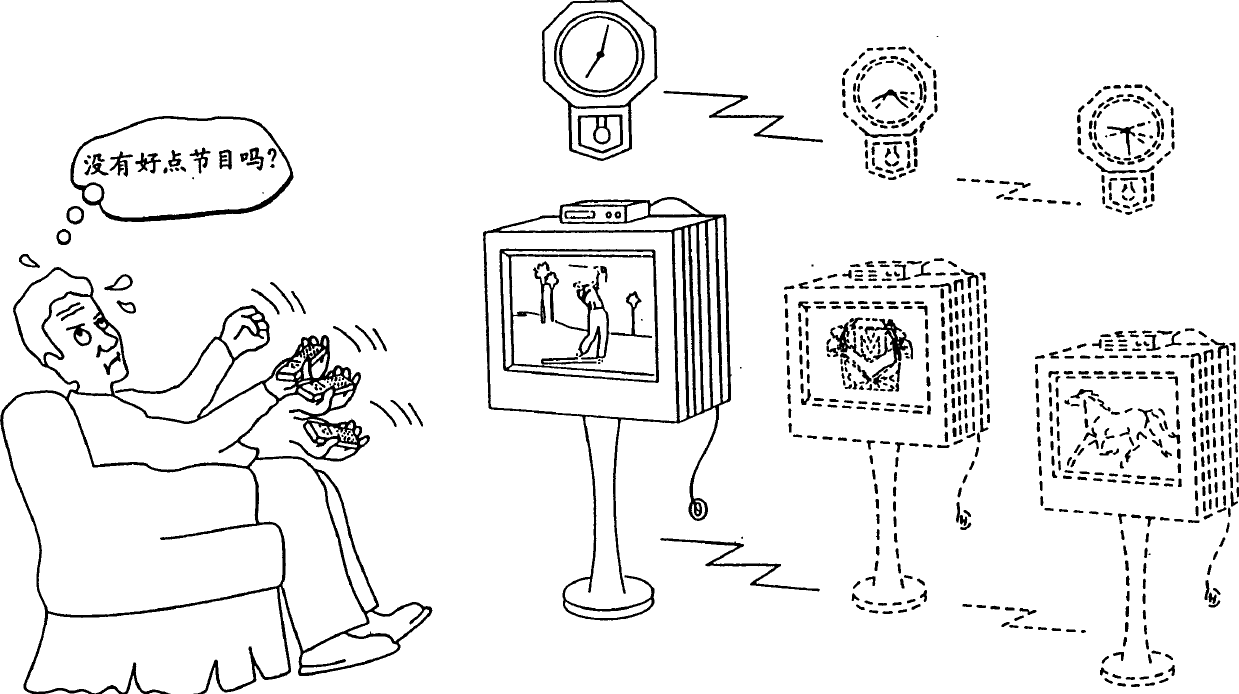
Systems and methods for matching, selecting, narrowcasting, and/or classifying based on rights management and/or other information
InactiveUS6112181AIncrease success rateCostly and inefficientUser identity/authority verificationSignalling system detailsRights managementUtility system
Rights management information is used at least in part in a matching, narrowcasting, classifying and / or selecting process. A matching and classification utility system comprising a kind of Commerce Utility System is used to perform the matching, narrowcasting, classifying and / or selecting. The matching and classification utility system may match, narrowcast, classify and / or select people and / or things, non-limiting examples of which include software objects. The Matching and Classification Utility system may use any pre-existing classification schemes, including at least some rights management information and / or other qualitative and / or parameter data indicating and / or defining classes, classification systems, class hierarchies, category schemes, class assignments, category assignments, and / or class membership. The Matching and Classification Utility may also use at least some rights management information together with any artificial intelligence, expert system, statistical, computational, manual, or any other means to define new classes, class hierarchies, classification systems, category schemes, and / or assign persons, things, and / or groups of persons and / or things to at least one class.
Owner:INTERTRUST TECH CORP
Methods for matching, selecting, narrowcasting, and/or classifying based on rights management and/or other information
InactiveUS20030069749A1Increase success rateCostly and inefficientAdvertisementsRelational databasesRights managementUtility system
Rights management information is used at least in part in a matching, narrowcasting, classifying and / or selecting process. A matching and classification utility system comprising a kind of Commerce Utility System is used to perform the matching, narrowcasting, classifying and / or selecting. The matching and classification utility system may match, narrowcast, classify and / or select people and / or things, non-limiting examples of which include software objects. The Matching and Classification Utility system may use any pre-existing classification schemes, including at least some rights management information and / or other qualitative and / or parameter data indicating and / or defining classes, classification systems, class hierarchies, category schemes, class assignments, category assignments, and / or class membership. The Matching and Classification Utility may also use at least some rights management information together with any artificial intelligence, expert system, statistical, computational, manual, or any other means to define new classes, class hierarchies, classification systems, category schemes, and / or assign persons, things, and / or groups of persons and / or things to at least one class.
Owner:INTERTRUST TECH CORP
Method and system for determining the age category of people based on facial images
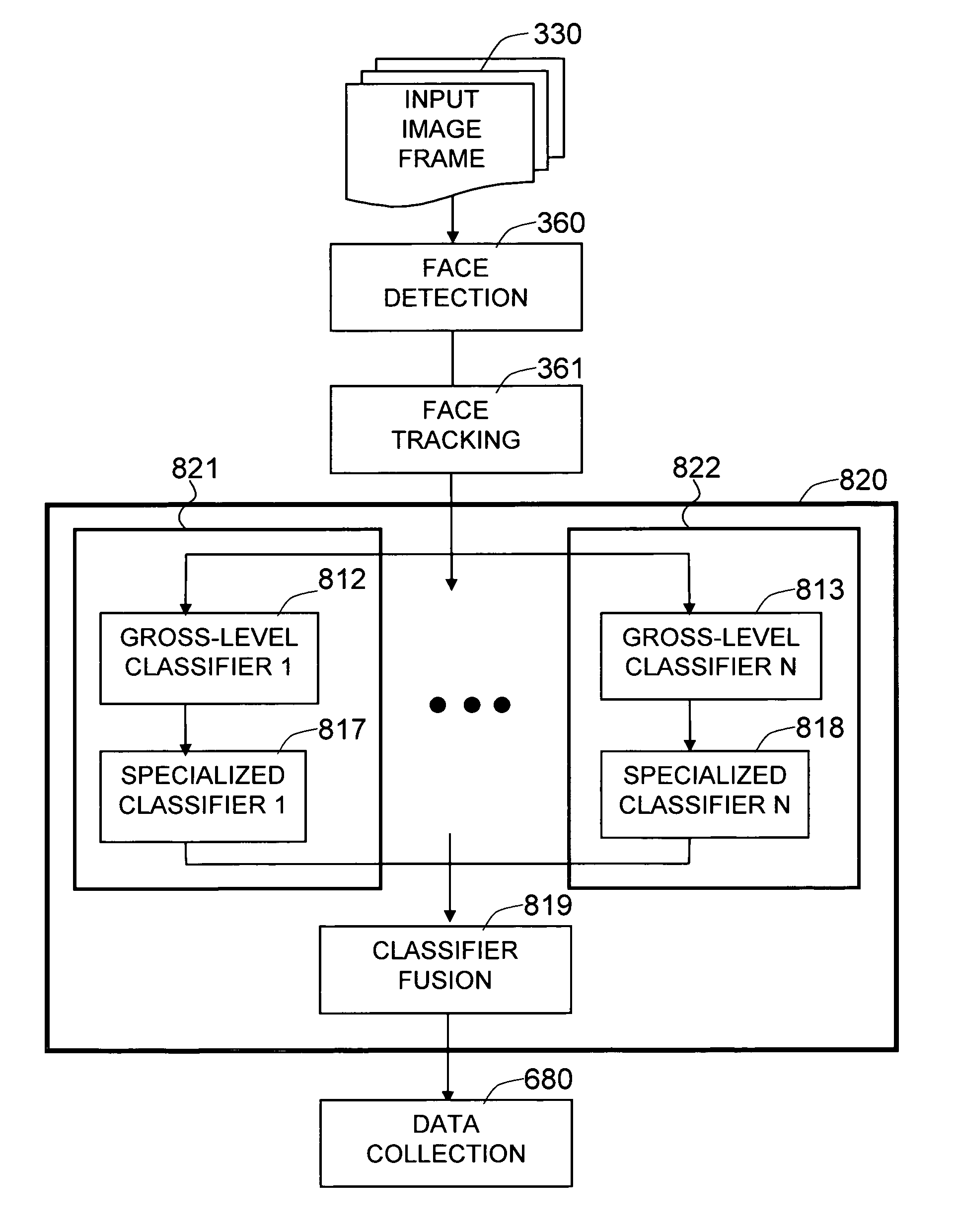
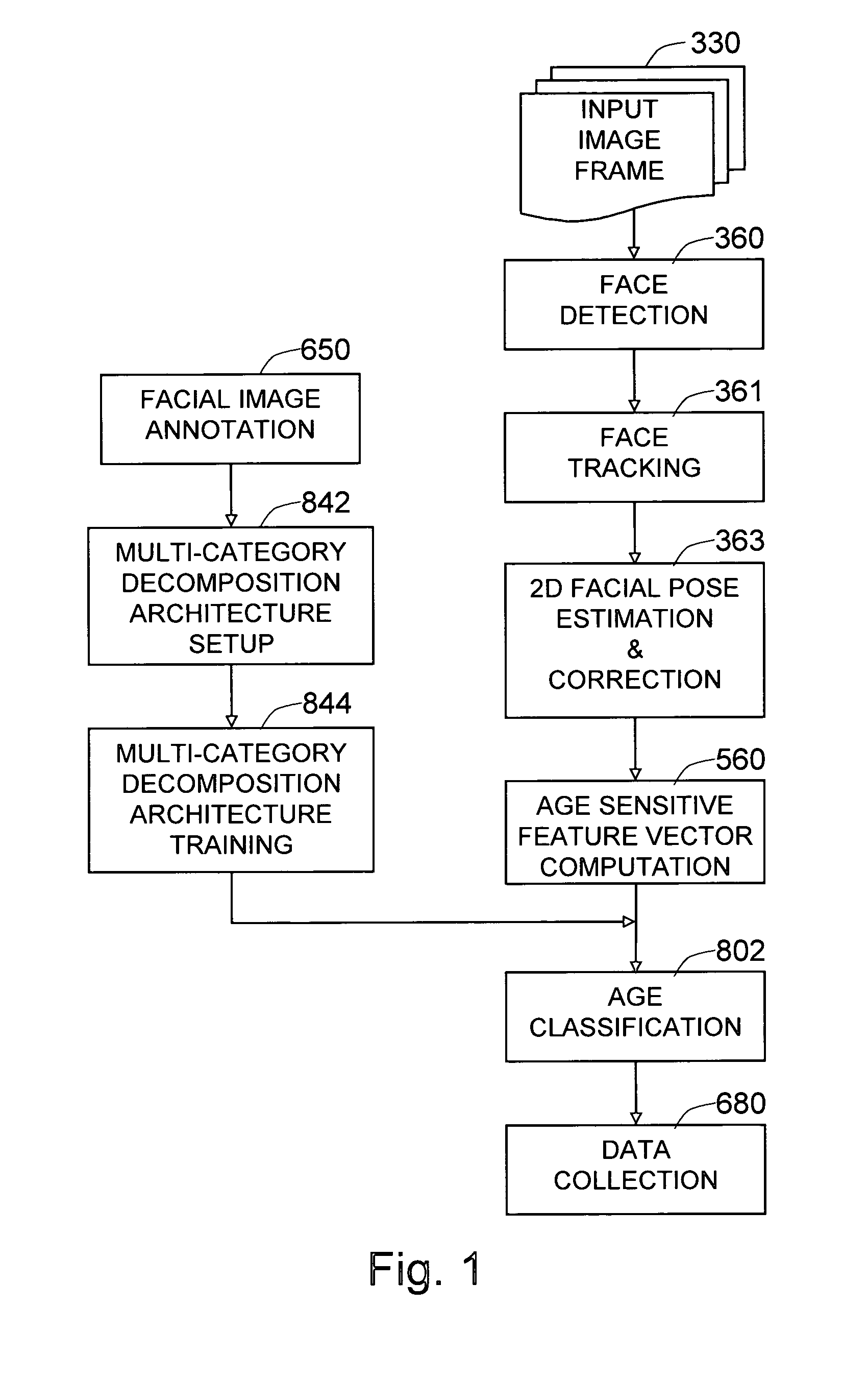
The present invention is a system and method for performing age classification or age estimation based on the facial images of people, using multi-category decomposition architecture of classifiers. In the multi-category decomposition architecture, which is a hybrid multi-classifier architecture specialized to age classification, the task of learning the concept of age against significant within-class variations, is handled by decomposing the set of facial images into auxiliary demographics classes, and the age classification is performed by an array of classifiers where each classifier, called an auxiliary class machine, is specialized to the given auxiliary class. The facial image data is annotated to assign the gender and ethnicity labels as well as the age labels. Each auxiliary class machine is trained to output both the given auxiliary class membership likelihood and the age group likelihoods. Faces are detected from the input image and individually tracked. Age sensitive feature vectors are extracted from the tracked faces and are fed to all of the auxiliary class machines to compute the desired likelihood outputs. The outputs from all of the auxiliary class machines are combined in a manner to make a final decision on the age of the given face.
Owner:VIDEOMINING CORP
Methods for matching, selecting, narrowcasting, and/or classifying based on rights management and/or other information
InactiveUS20030069748A1Difficult to navigateImprove privacyAdvertisementsRelational databasesRights managementUtility system
Rights management information is used at least in part in a matching, narrowcasting, classifying and / or selecting process. A matching and classification utility system comprising a kind of Commerce Utility System is used to perform the matching, narrowcasting, classifying and / or selecting. The matching and classification utility system may match, narrowcast, classify and / or select people and / or things, non-limiting examples of which include software objects. The Matching and Classification Utility system may use any pre-existing classification schemes, including at least some rights management information and / or other qualitative and / or parameter data indicating and / or defining classes, classification systems, class hierarchies, category schemes, class assignments, category assignments, and / or class membership. The Matching and Classification Utility may also use at least some rights management information together with any artificial intelligence, expert system, statistical, computational, manual, or any other means to define new classes, class hierarchies, classification systems, category schemes, and / or assign persons, things, and / or groups of persons and / or things to at least one class.
Owner:INTERTRUST TECH CORP
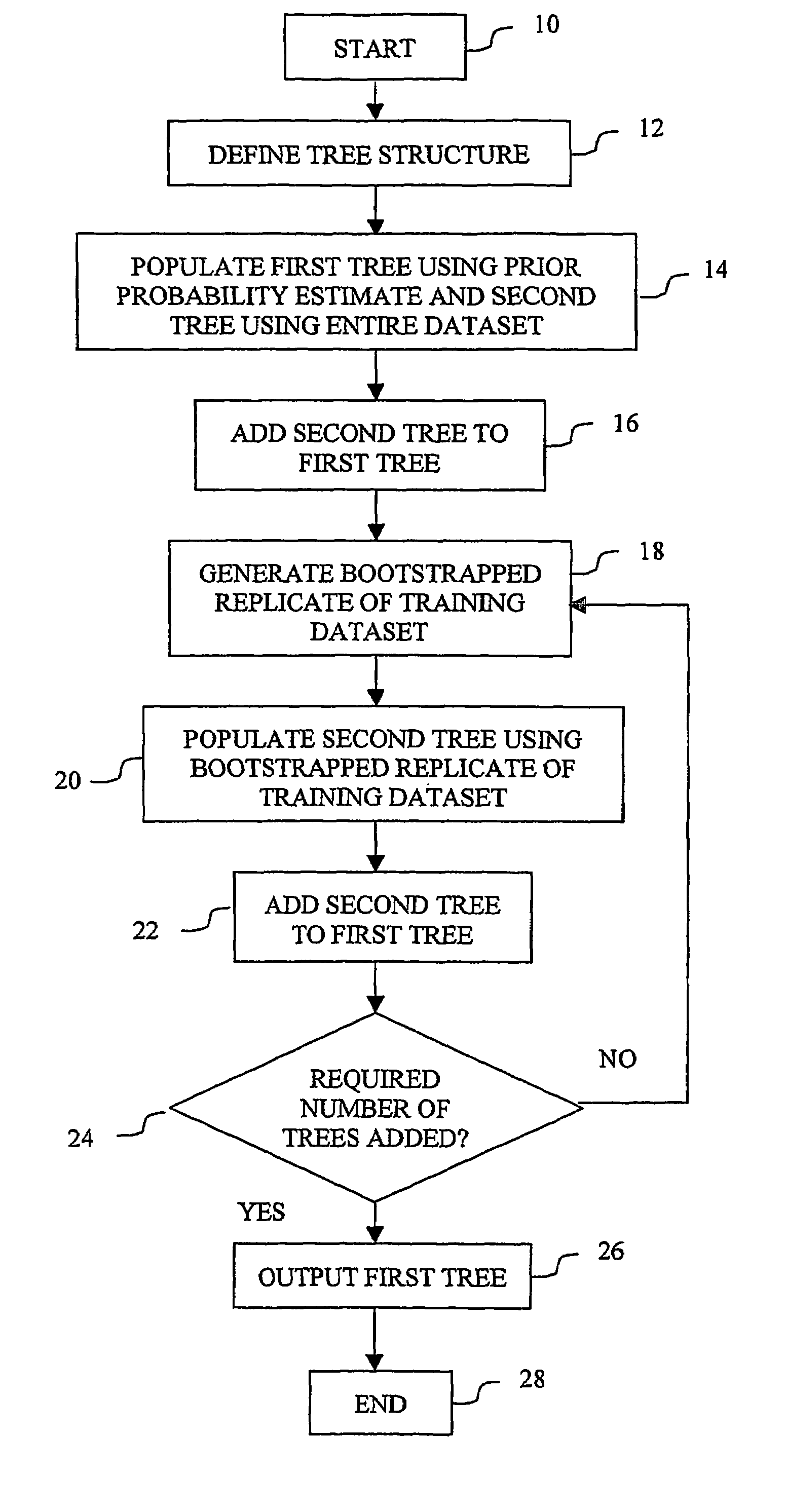
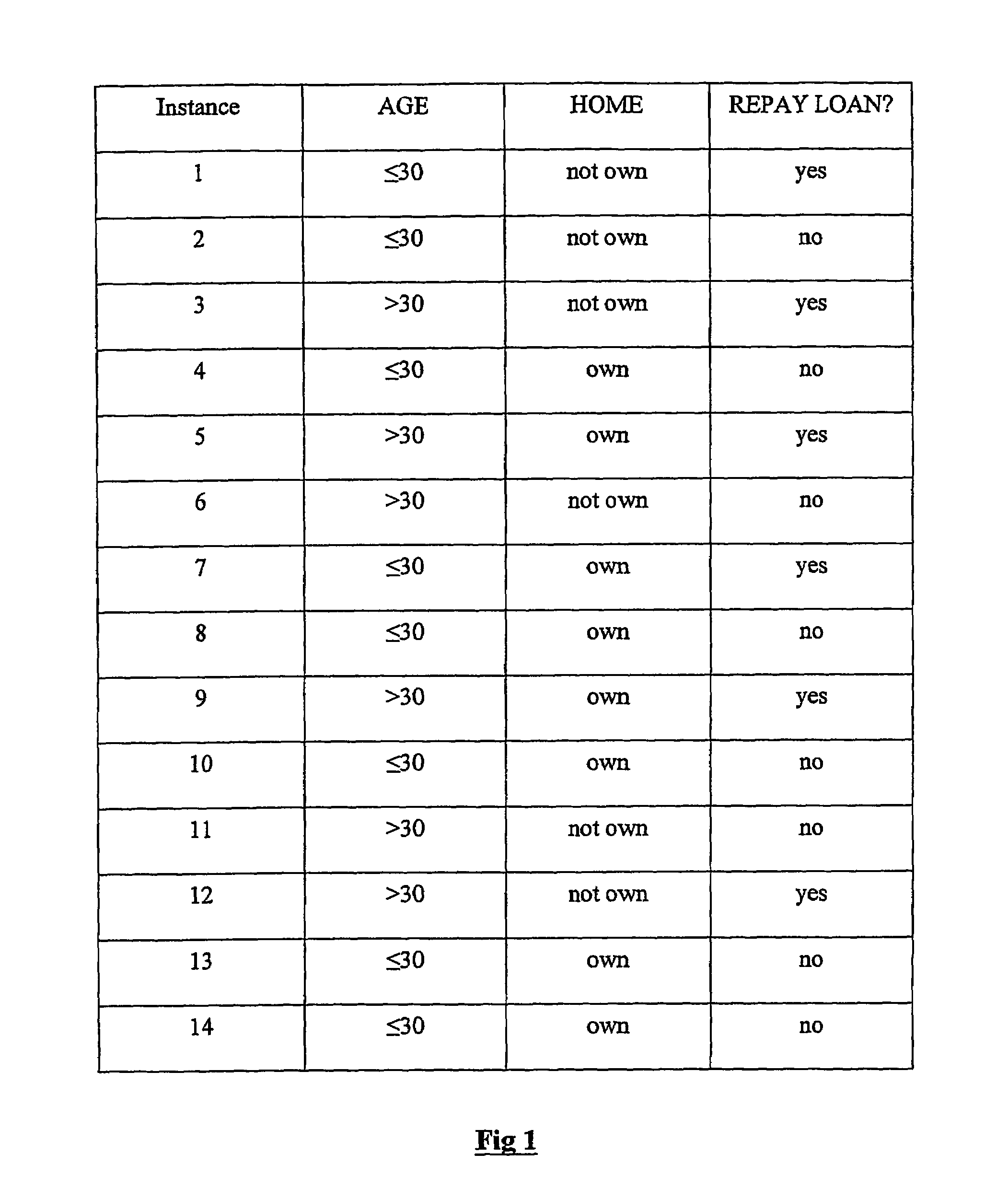
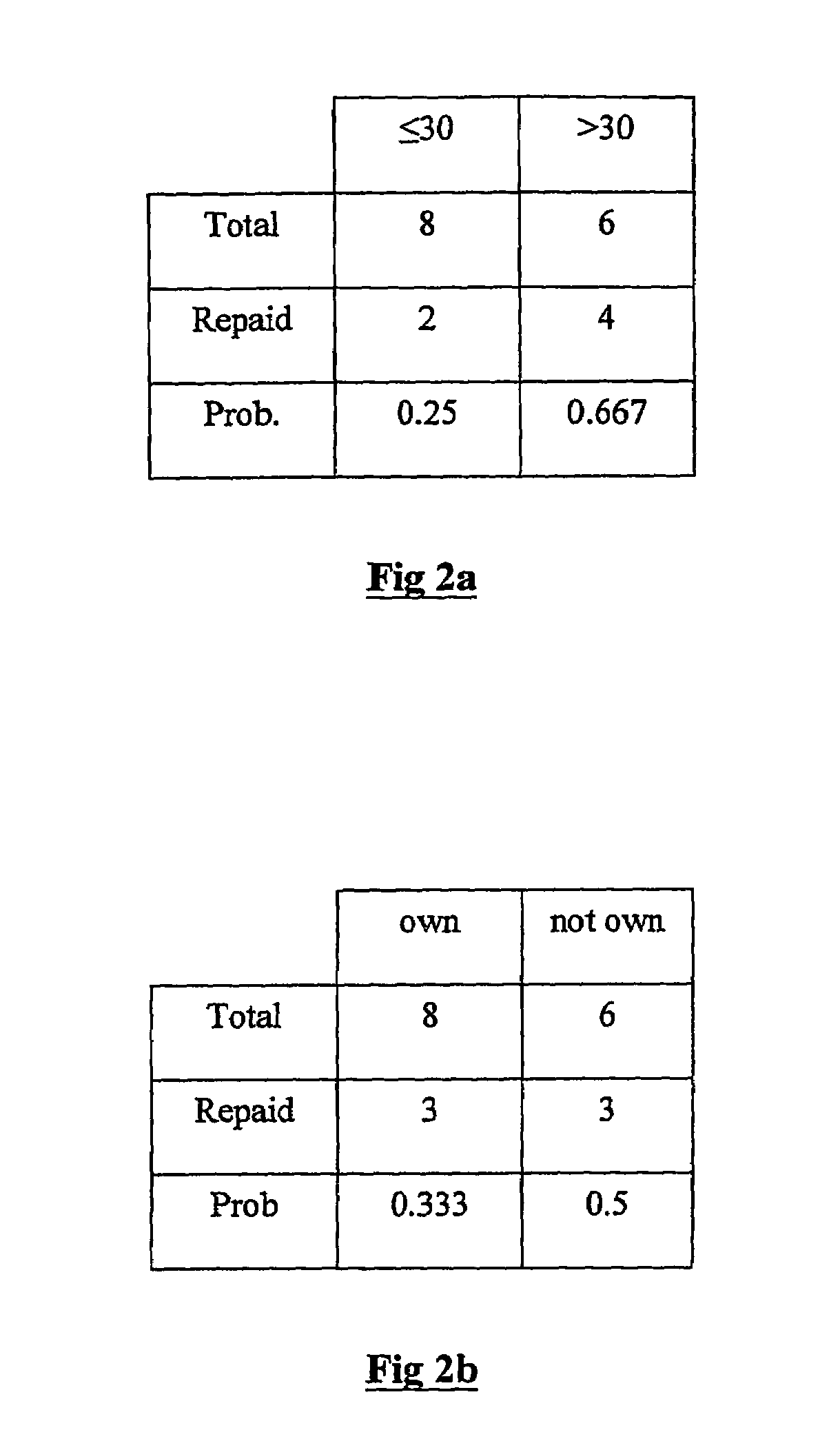
Classification using probability estimate re-sampling
ActiveUS7194380B2Improve fitEffective calculationMathematical modelsFinanceAlgorithmClass membership
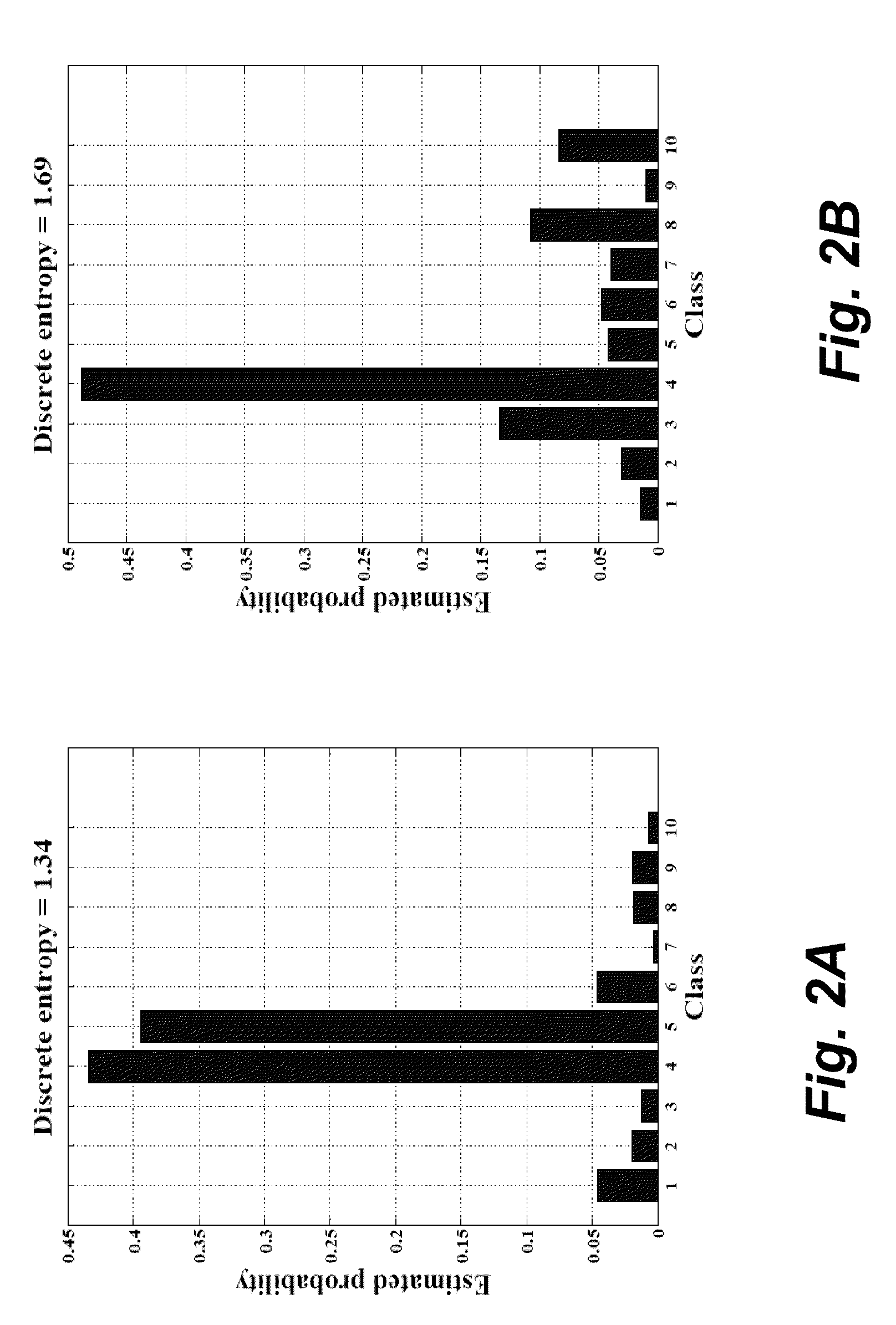
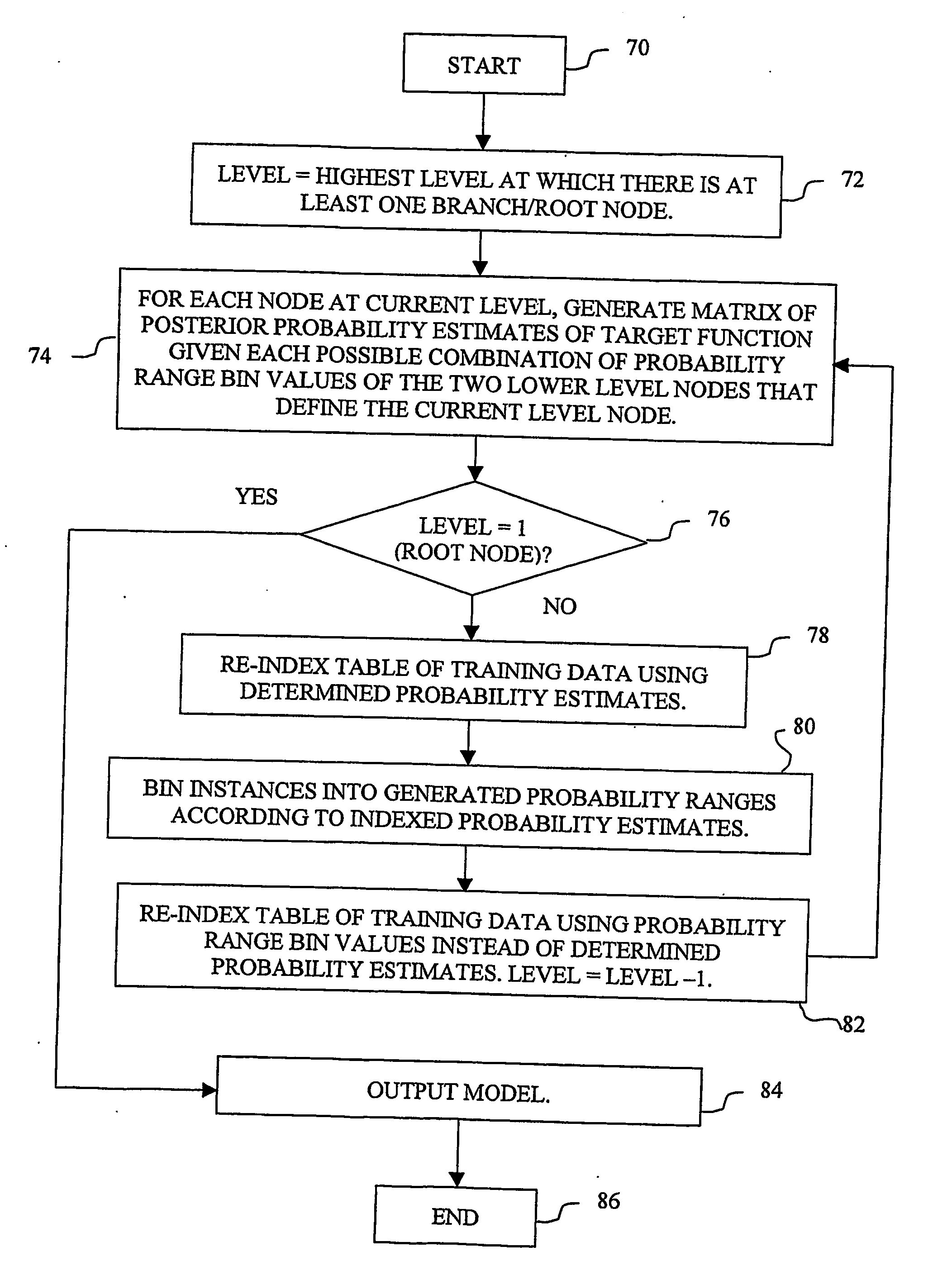
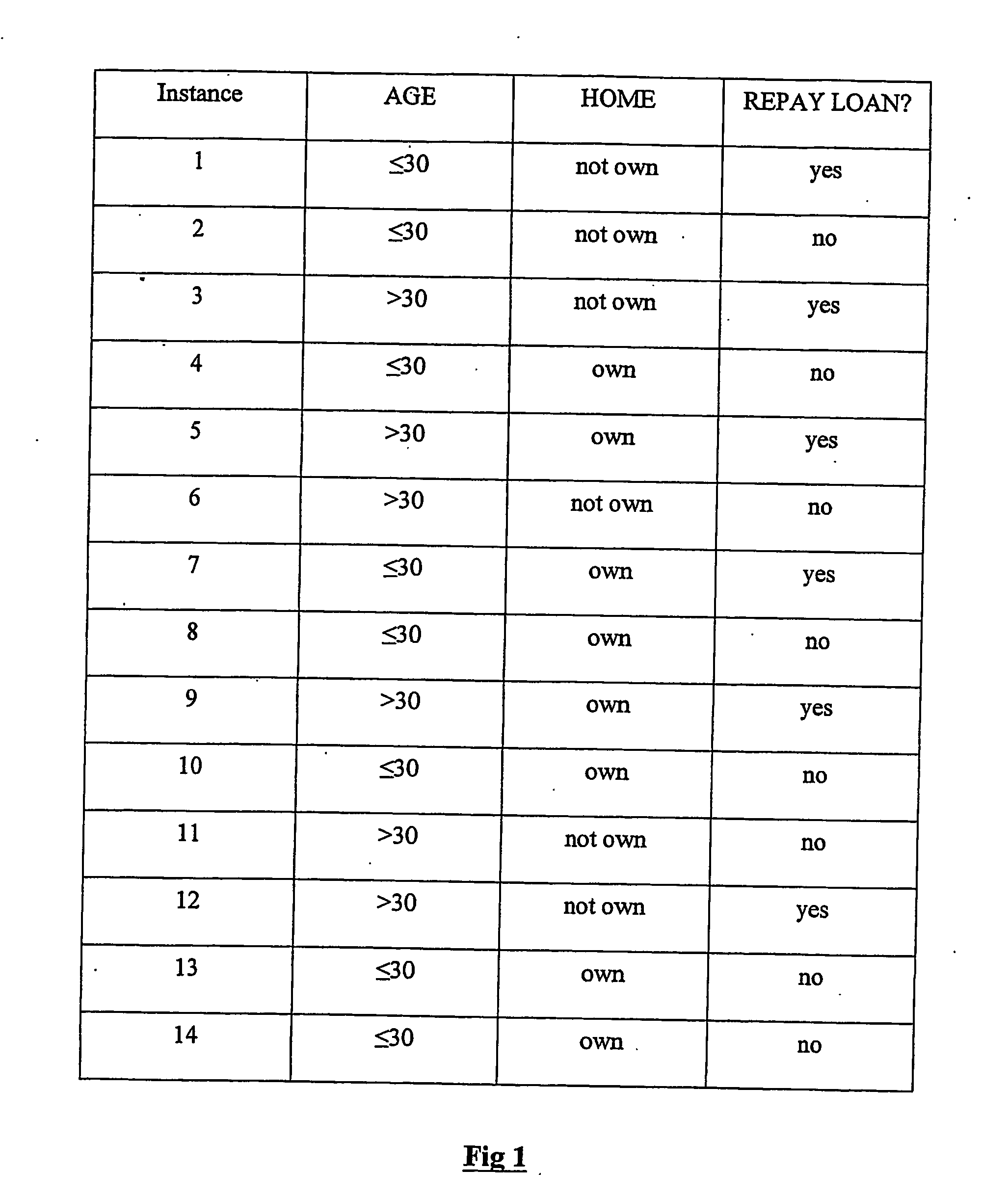
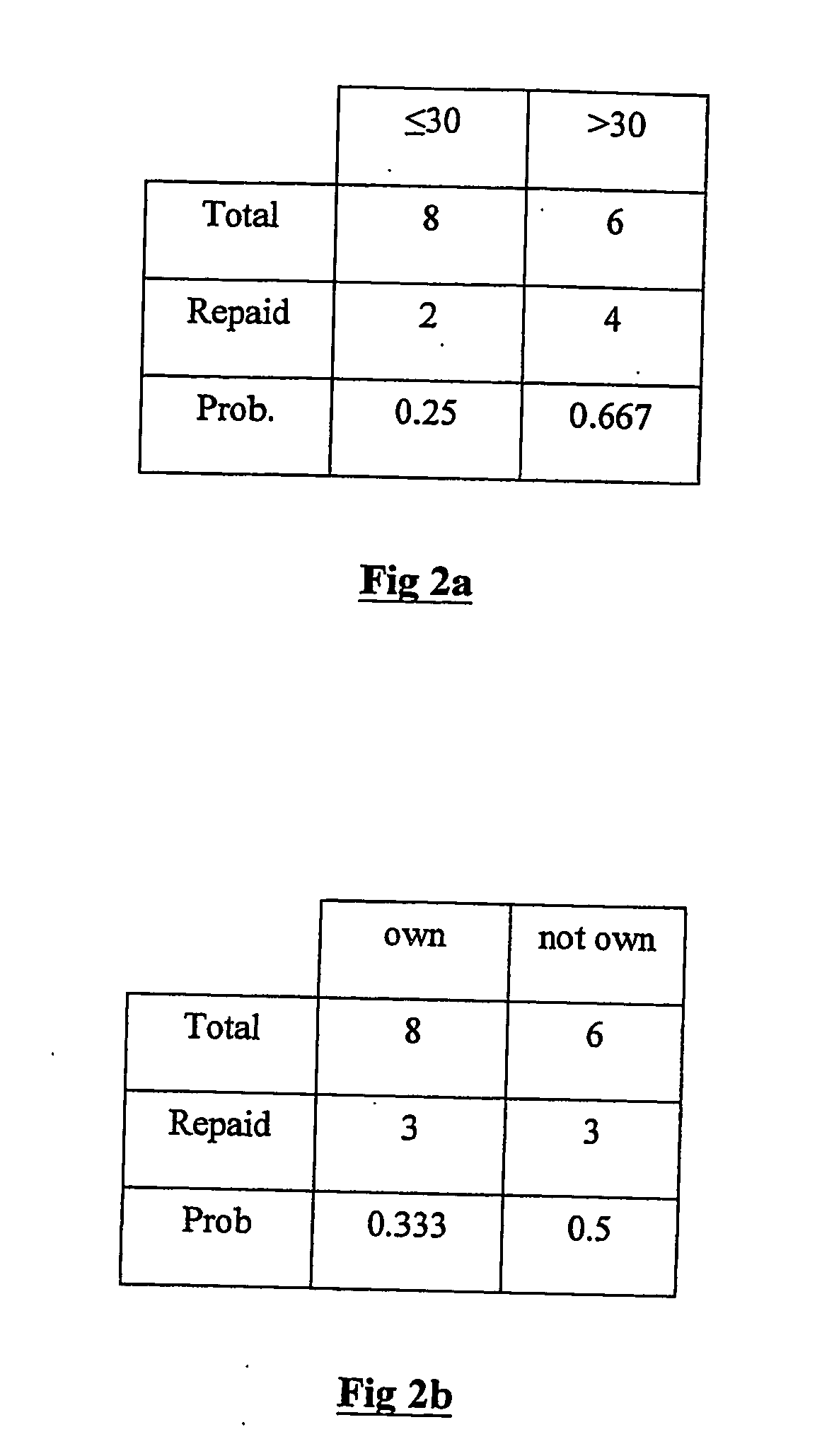
Embodiments of a computer-implemented method of calculating estimates of a joint posterior probability of class membership given combinations of attribute values of a pair of attributes are disclosed. The calculating is performed on the basis of data representing a training set of a plurality of instances defined by attribute values for a plurality of attributes together with a class membership outcome. Embodiments of the method comprise calculating first and second estimates of a posterior probability of class membership given attribute values of a first and second attribute of the pair, respectively, and binning the first and second estimates into a respective plurality of first and second probability range bins. Instances of the training set are mapped to combinations of one of each of the first and second pluralities of probability range bins, and on the basis of the mapping, calculating estimates of a joint posterior probability of class membership.
Owner:CHORDIANT SOFTWARE INT
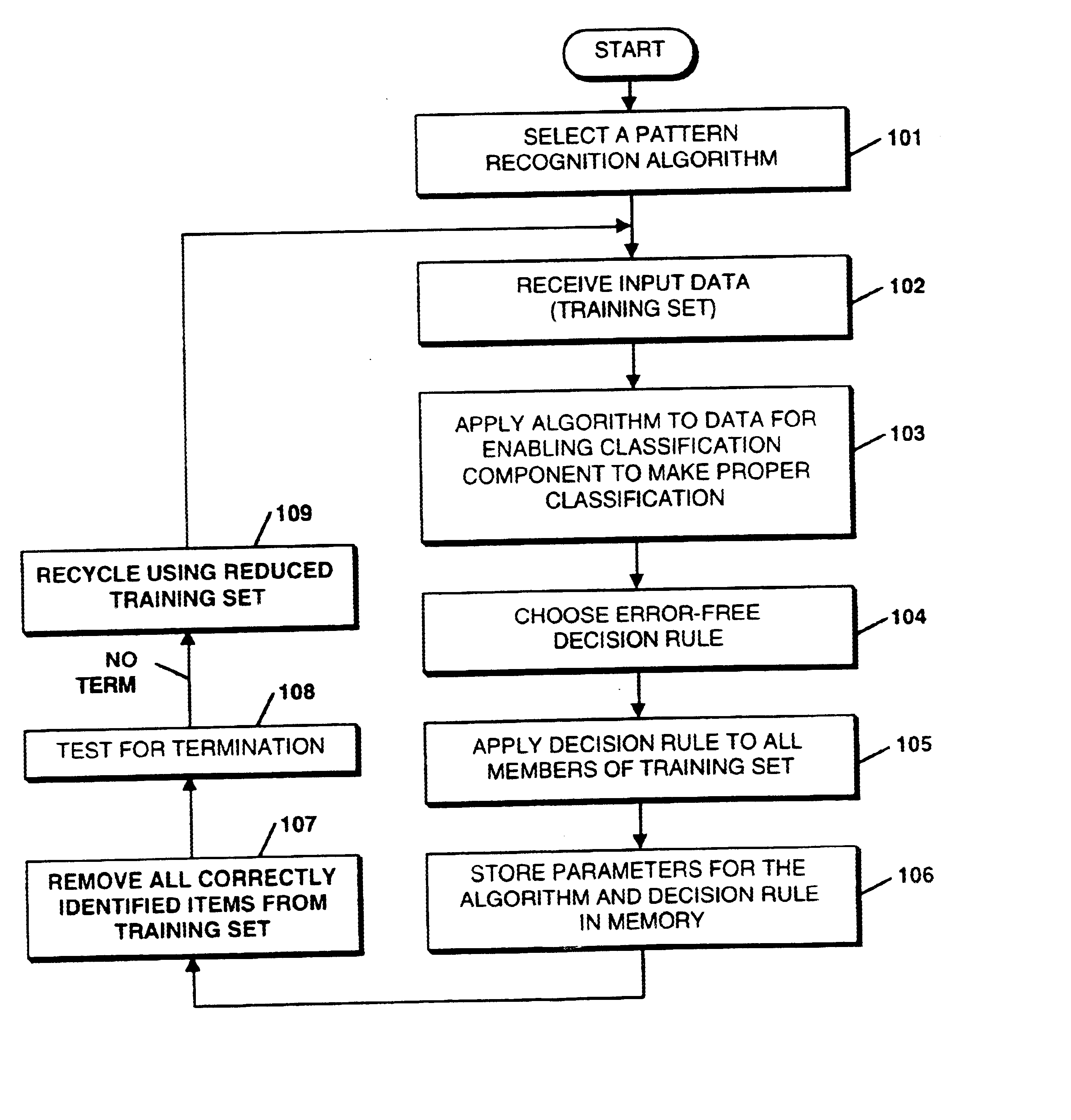
Method and system for improving pattern recognition system performance
InactiveUS6847731B1Improve robustnessMore system robustnessCharacter and pattern recognitionDiscriminantDecision boundary
Stand-alone or assistive pattern recognition system and process enabling error free classification of all objects in a training set and application to unclassified objects. Parameters and / or features of the data objects in a training set are selected and measured, from which discriminants are computed. The measured data is plotted in discriminant space and decision boundaries or thresholds determined, preferably such that at least one object from one class is isolated from the remaining objects, removed from the training set, and the process repeated until an acceptable number of unclassified objects remain. The system can be applied sequentially to classify all the members of the training set belonging to one class and then applied to objects in other classes. Fuzzy quantifiable determinations of an object's likelihood of class membership can be made. Objects' positions and classifications are obtainable in an optical system using Fourier techniques without limitation to linearly discriminable problems.
Owner:NORTHEAST PHOTOSCI
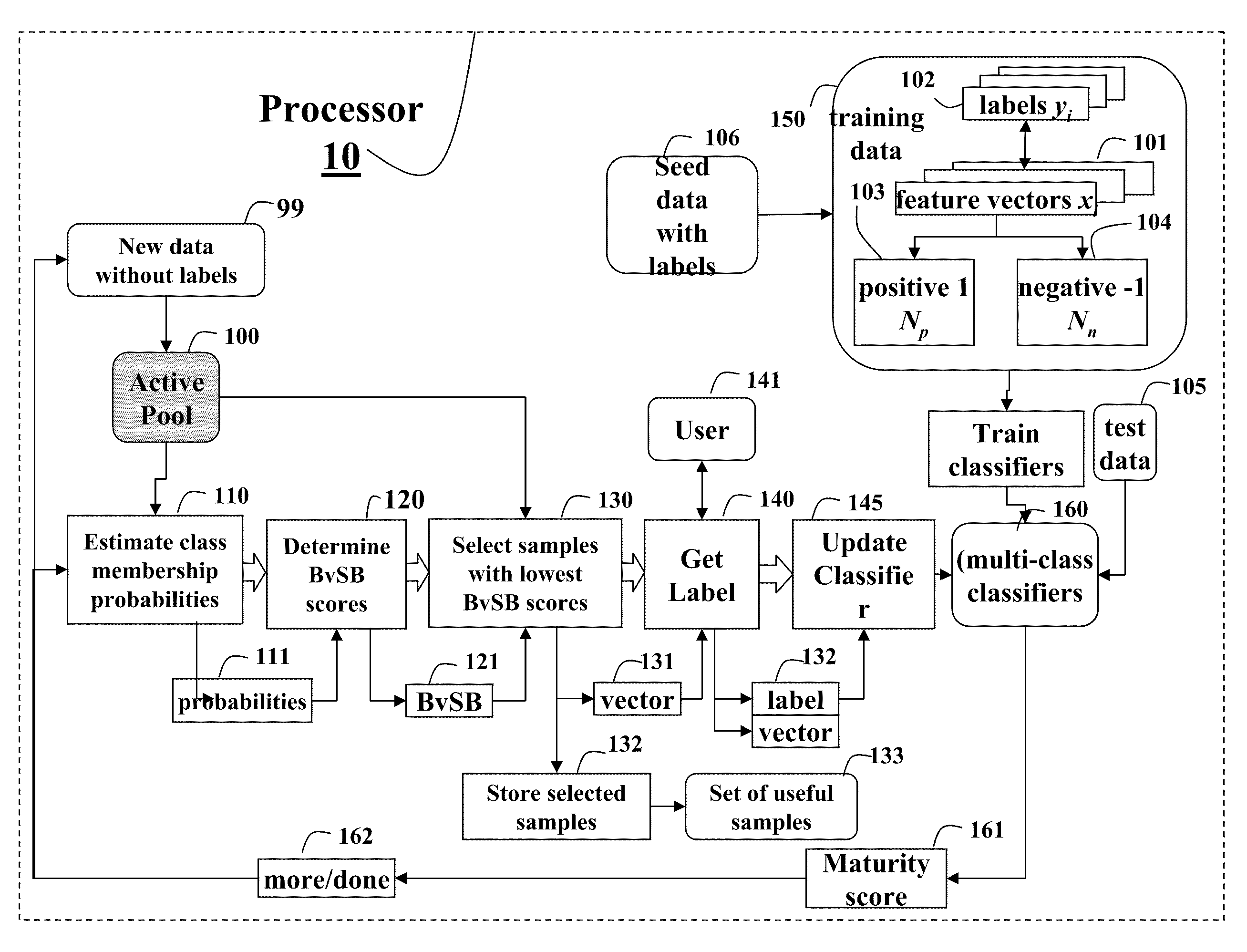
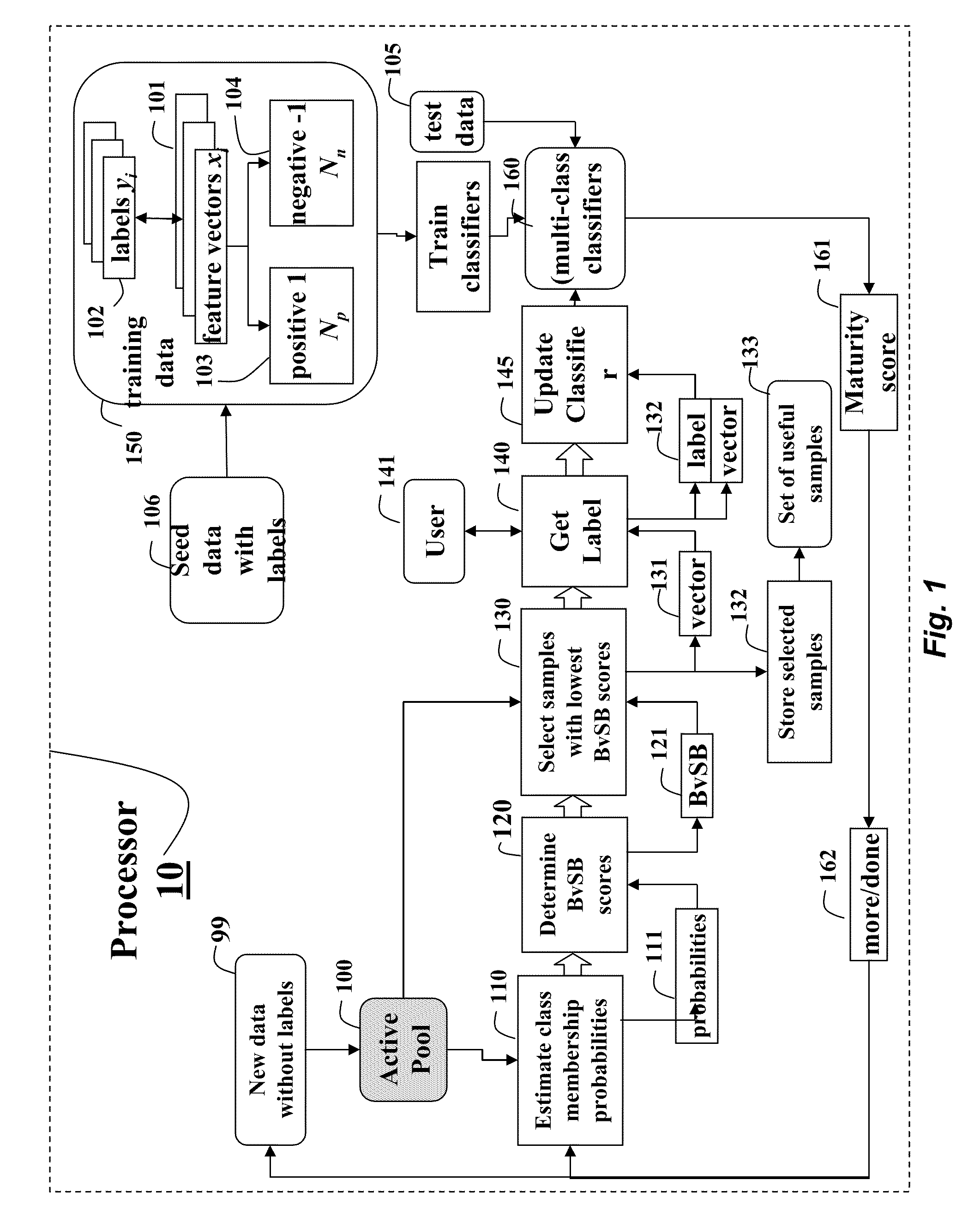
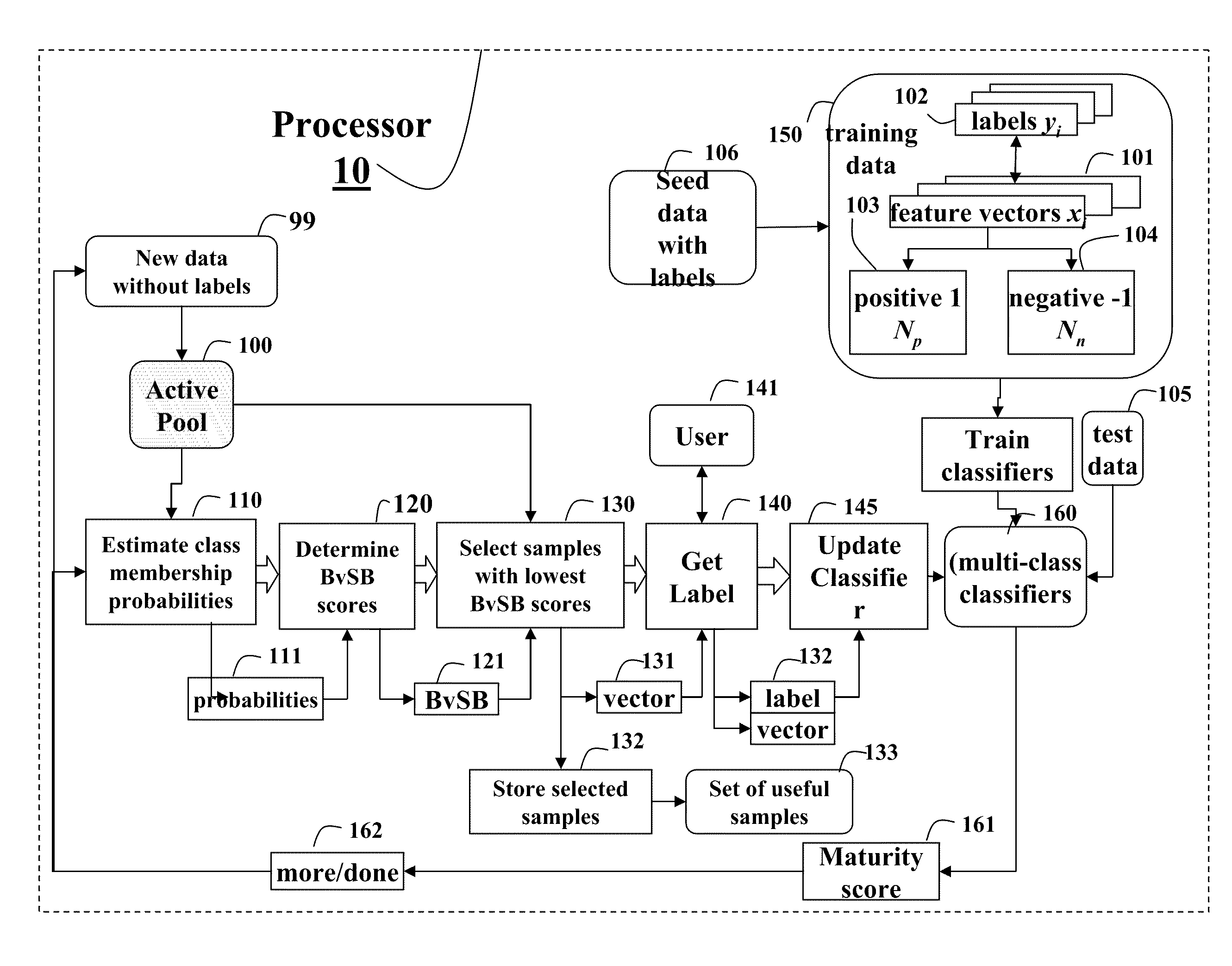
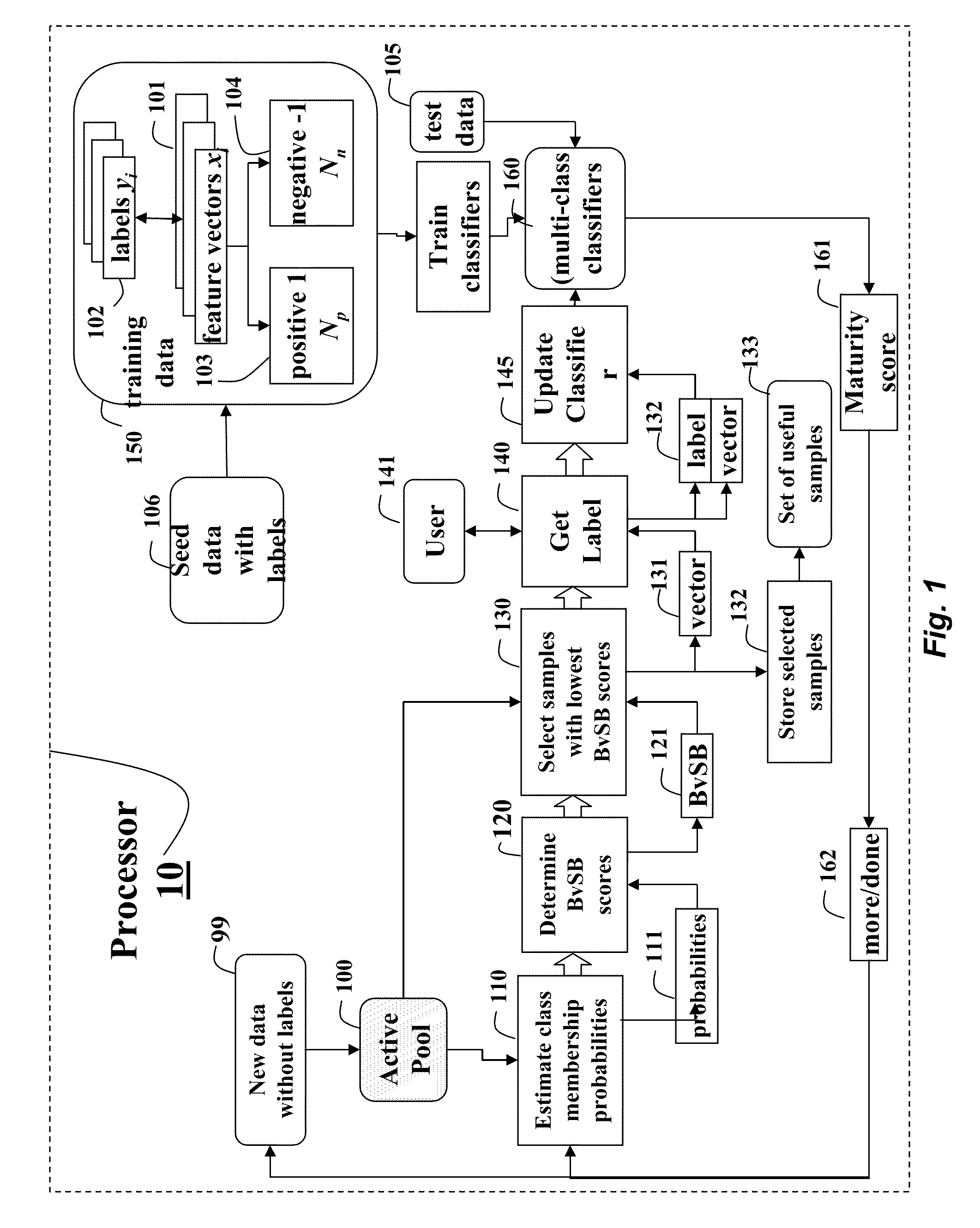
Active Learning Method for Multi-Class Classifiers
ActiveUS20100250473A1Easy to handleIncrease the number ofKernel methodsDigital computer detailsData setProactive learning
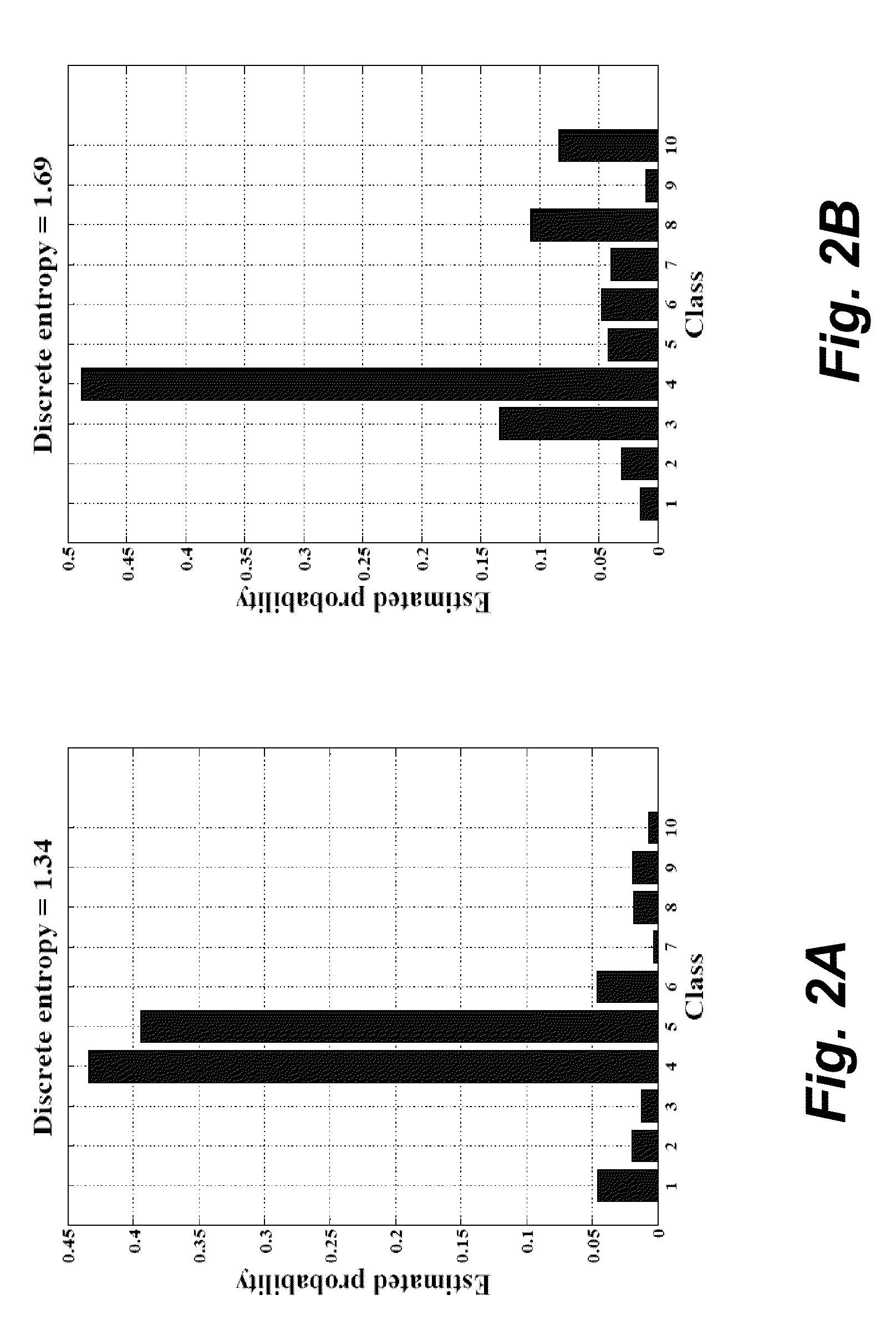
A method trains a multi-class classifier by iteratively performing the following steps until a termination condition is reached. The probabilities of class membership for unlabeled data obtained from an active pool of unlabeled data are estimated. A difference between a largest probability and a second largest probability is determined. The unlabeled data with the lowest difference is selected, labeled and then added to a training data set for training the classifier.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
Classification using probability estimate re-sampling
ActiveUS20060167655A1Effective calculationImprove fitMathematical modelsFinanceAlgorithmClass membership
Embodiments of a computer-implemented method of calculating estimates of a joint posterior probability of class membership given combinations of attribute values of a pair of attributes are disclosed. The calculating is performed on the basis of data representing a training set of a plurality of instances defined by attribute values for a plurality of attributes together with a class membership outcome. Embodiments of the method comprise calculating first and second estimates of a posterior probability of class membership given attribute values of a first and second attribute of the pair, respectively, and binning the first and second estimates into a respective plurality of first and second probability range bins. Instances of the training set are mapped to combinations of one of each of the first and second pluralities of probability range bins, and on the basis of the mapping, calculating estimates of a joint posterior probability of class membership.
Owner:CHORDIANT SOFTWARE INT
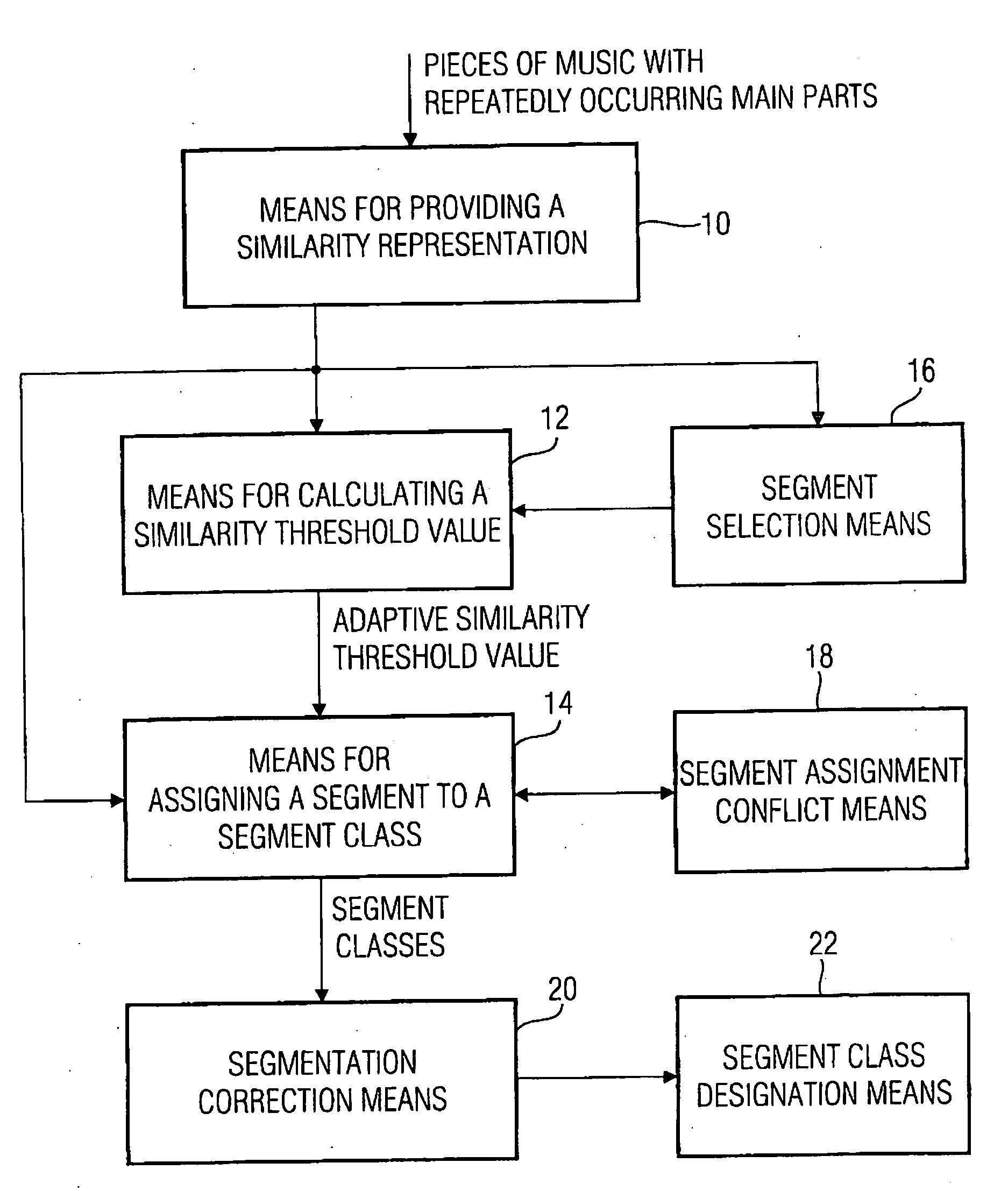
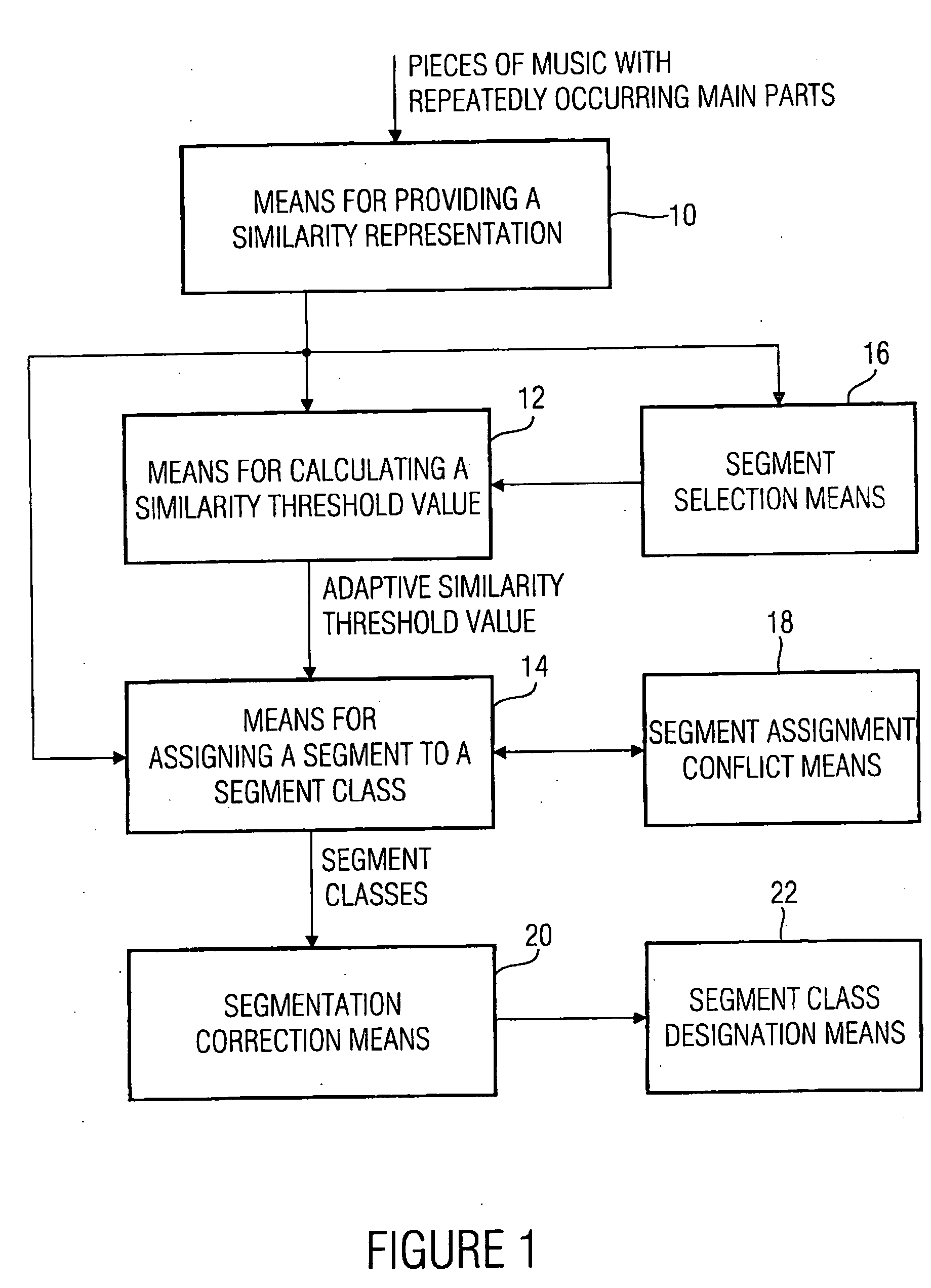
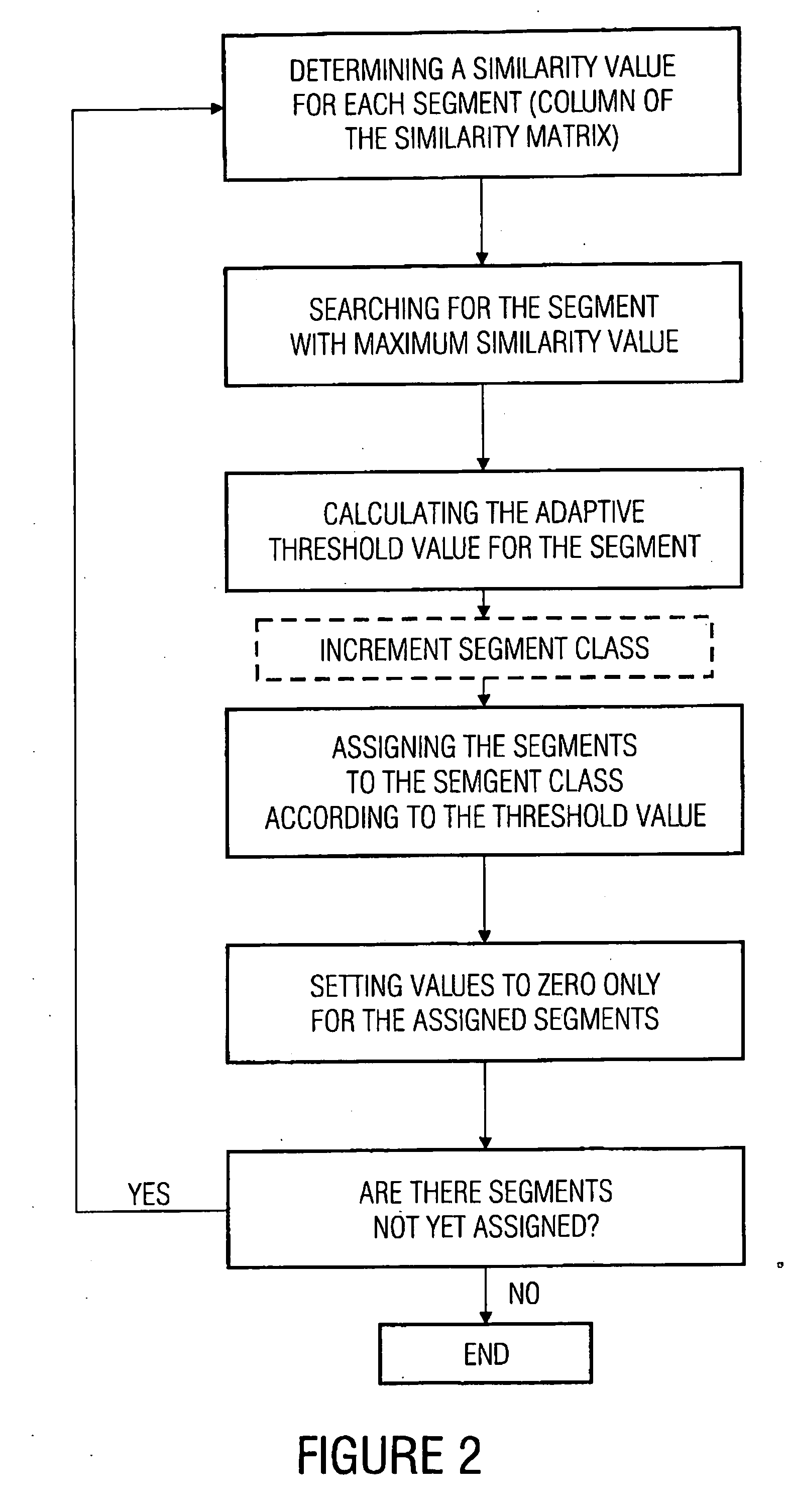
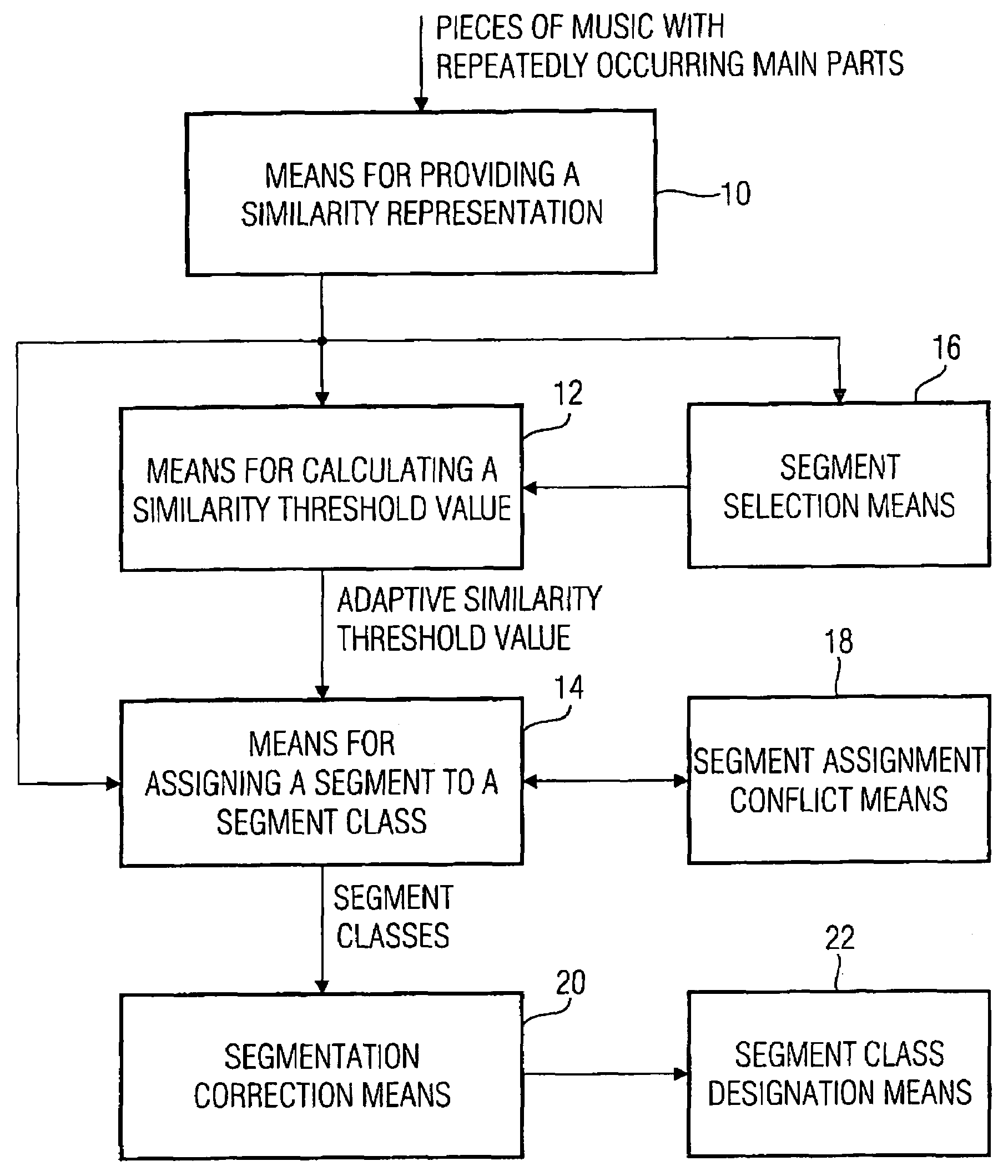
Apparatus and method for changing a segmentation of an audio piece
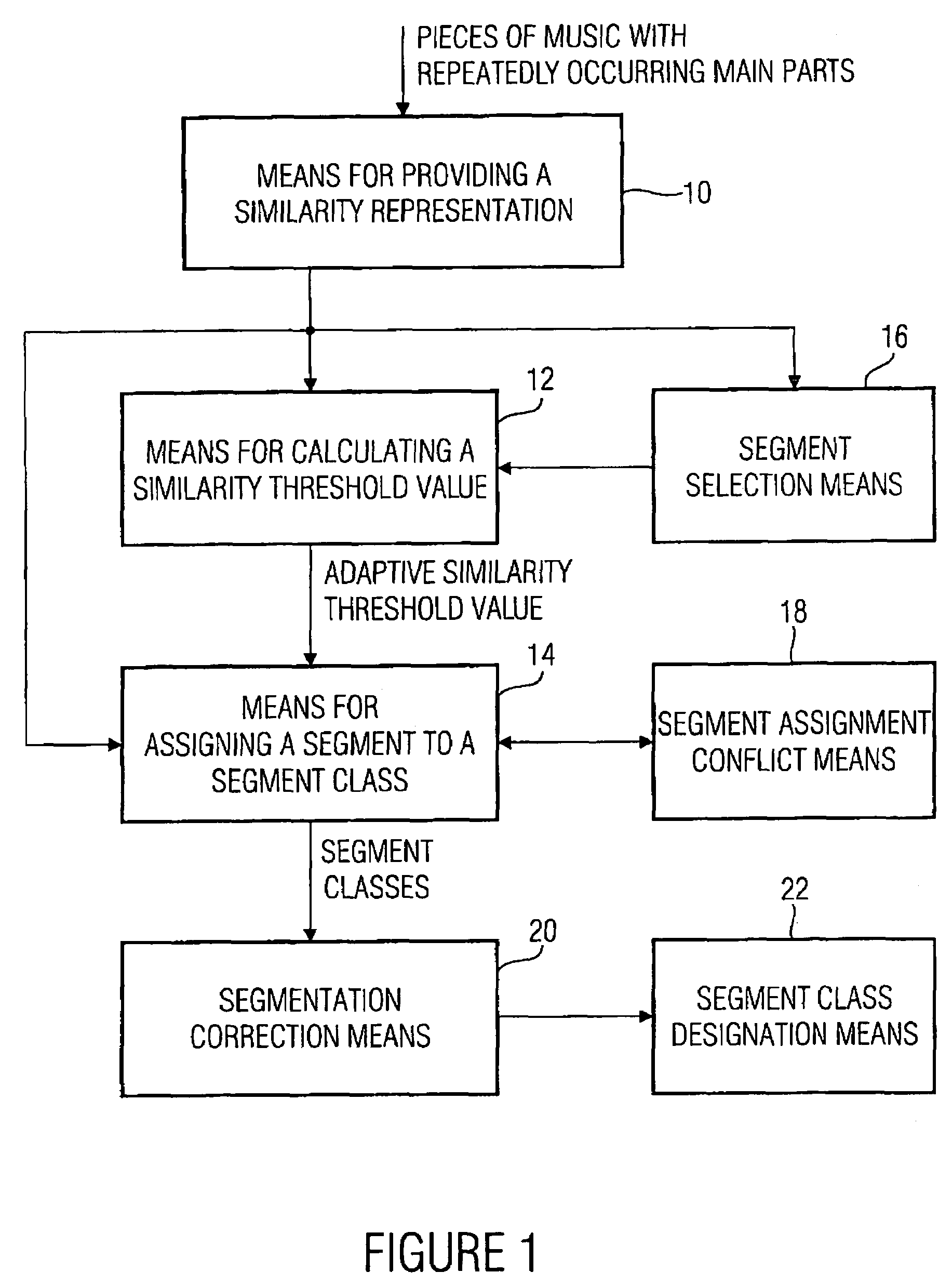
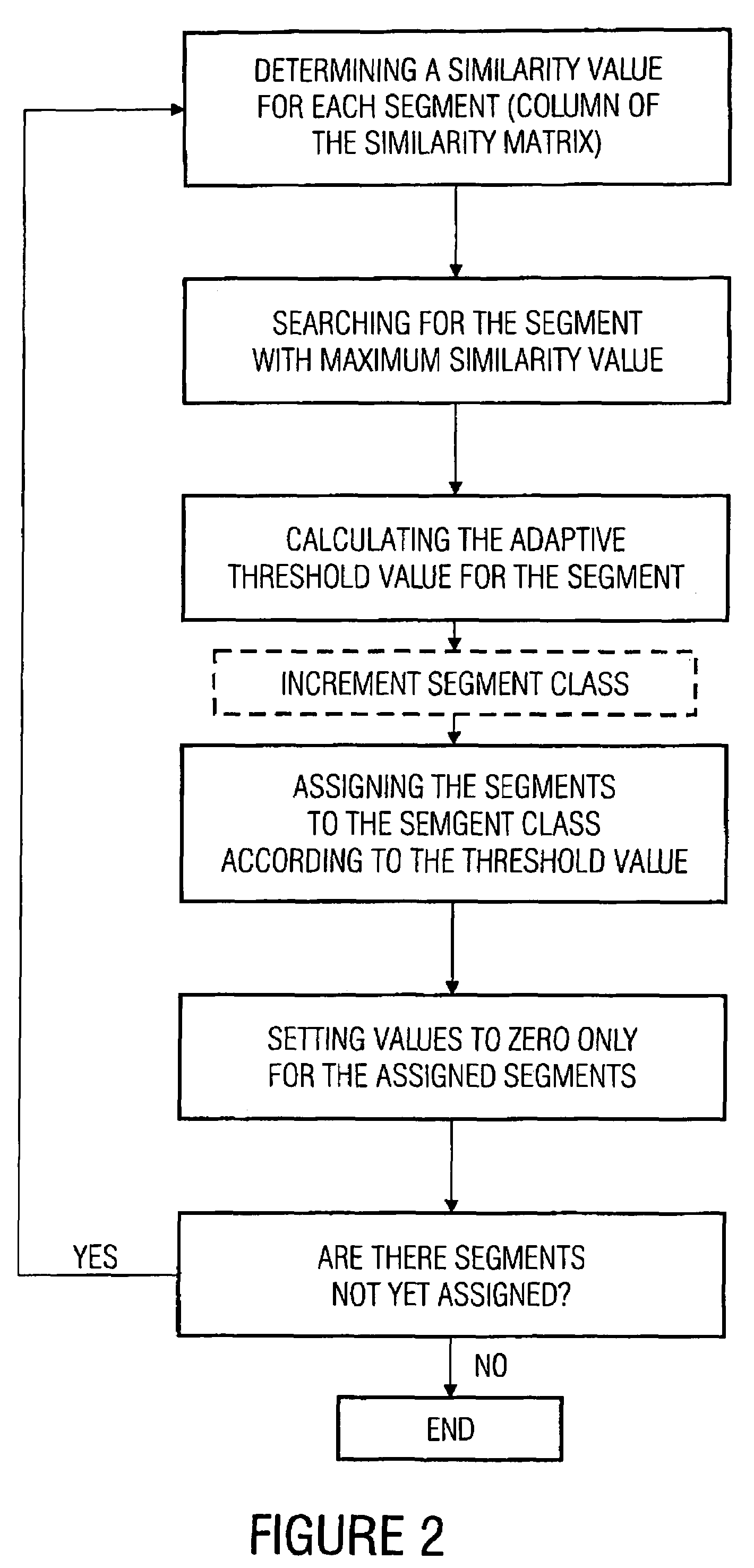
For changing a segmentation of an audio piece after a segment class assignment, at first a short segment is selected, which has a length shorter than a predetermined minimum length. This short segment is preferably merged with the corresponding successor segment or predecessor segment using information on a segment class membership of the short segment itself, but also the successor segment or the predecessor segment, in order to obtain a changed segmentation of the audio signal. With this, a not over-segmented segment representation of the audio signal is obtained, which further includes all audio information, i.e. is not a representation of the audio piece with holes.
Owner:SONY CORP
Pattern classification method
ActiveUS8346684B2Digital computer detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionConfidence intervalClassification methods
Owner:IEE INT ELECTRONICS & ENG SA
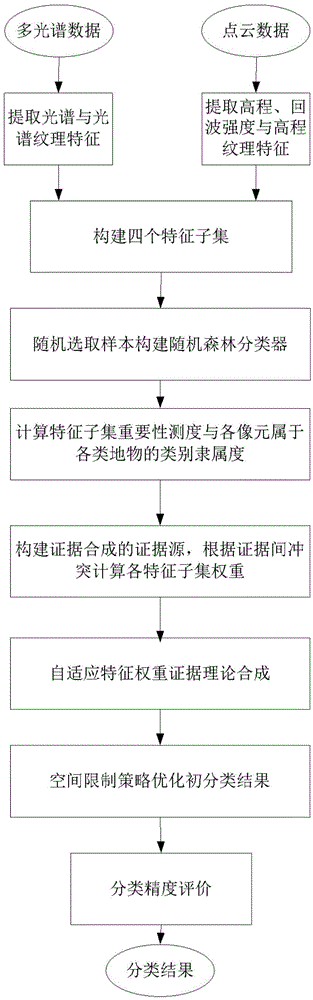
Precise LINDAR data ground object classification method based on adaptive characteristic weight synthesis
ActiveCN105469098AReduce lossesImprove classification accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisWeight coefficientClassification methods
Owner:ZHONGBEI UNIV
Interpreting a plurality of M-dimensional attribute vectors assigned to a plurality of locations in an N-dimensional interpretation space
ActiveUS8121969B2Character and pattern recognitionFuzzy logic based systemsAlgorithmComputerized system
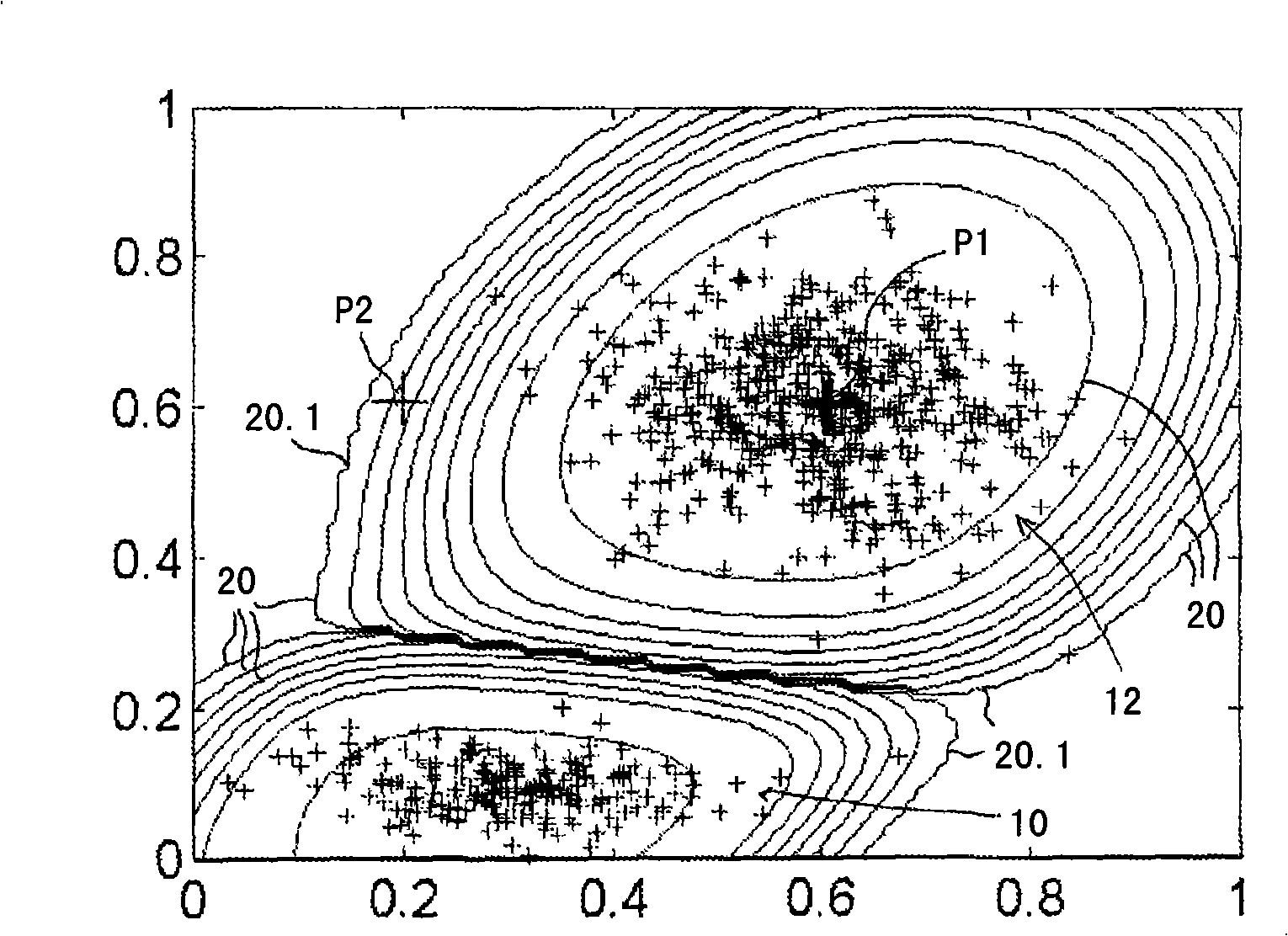
A method for interpreting a plurality of m-dimensional attribute vectors (m2) assigned to a plurality of locations in an n-dimensional interpretation space (n1), which method comprises arranging at least a subset of the attribute vectors as points in an m-dimensional attribute space; defining k classes (k2) of attribute vectors by identifying for each class at least one classification point in attribute space; postulating a classification rule for points in attribute space; determining a class-membership attribute of a point in attribute space using the classification points and the classification rule to obtain a classified point; and assigning a display parameter to the classified point which is related to the class-membership attribute. In one embodiment the display parameter is a mixed display parameter derived from probabilistic membership values each representing a probability that the classified point belongs to a selected class. In another embodiment classified points are displayed in attribute space and in interpretation space at the same time. The method can be used in a method of producing hydrocarbons from a subsurface formation. Also provided are corresponding computer program products and computer systems.
Owner:SHELL USA INC
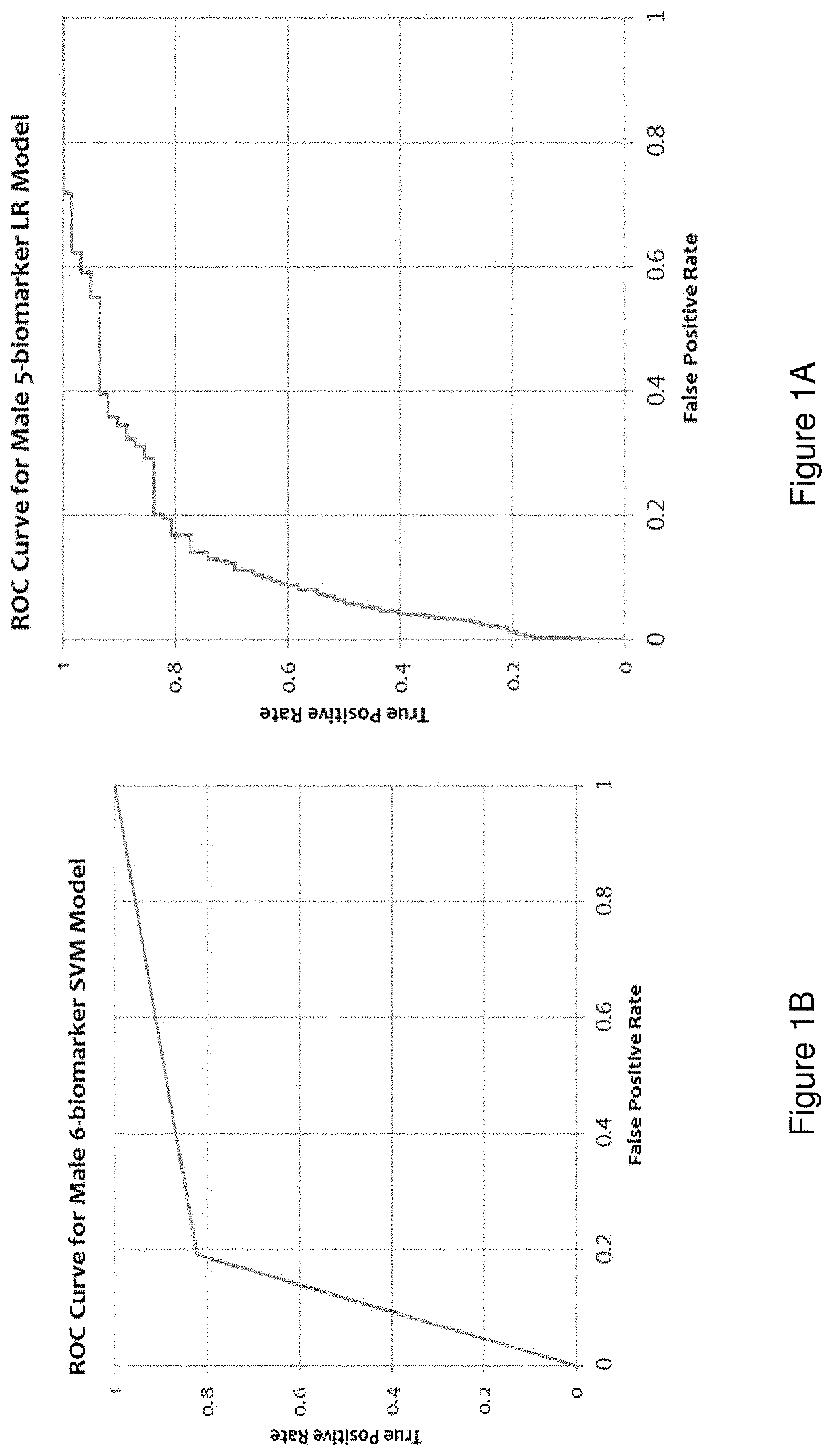
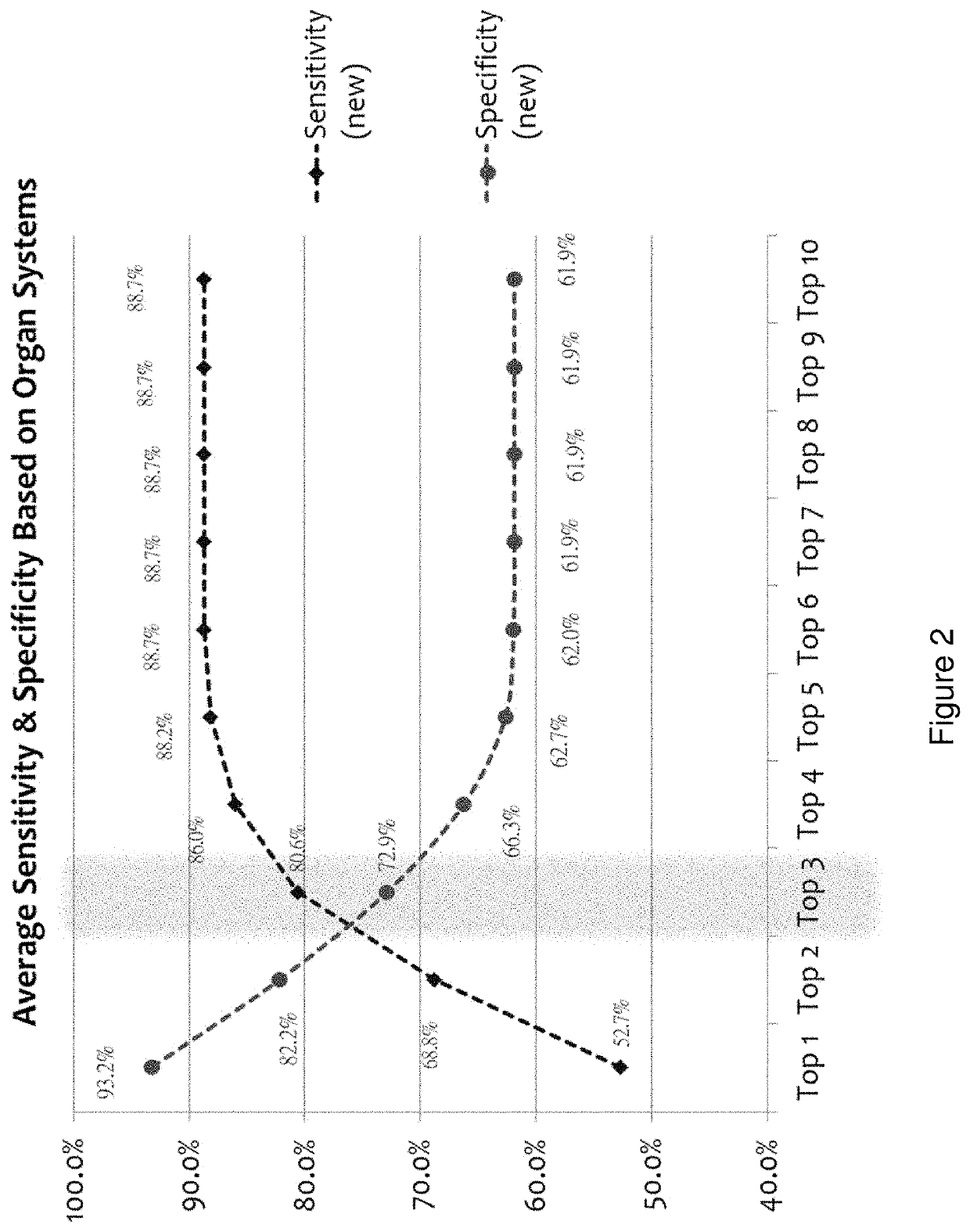
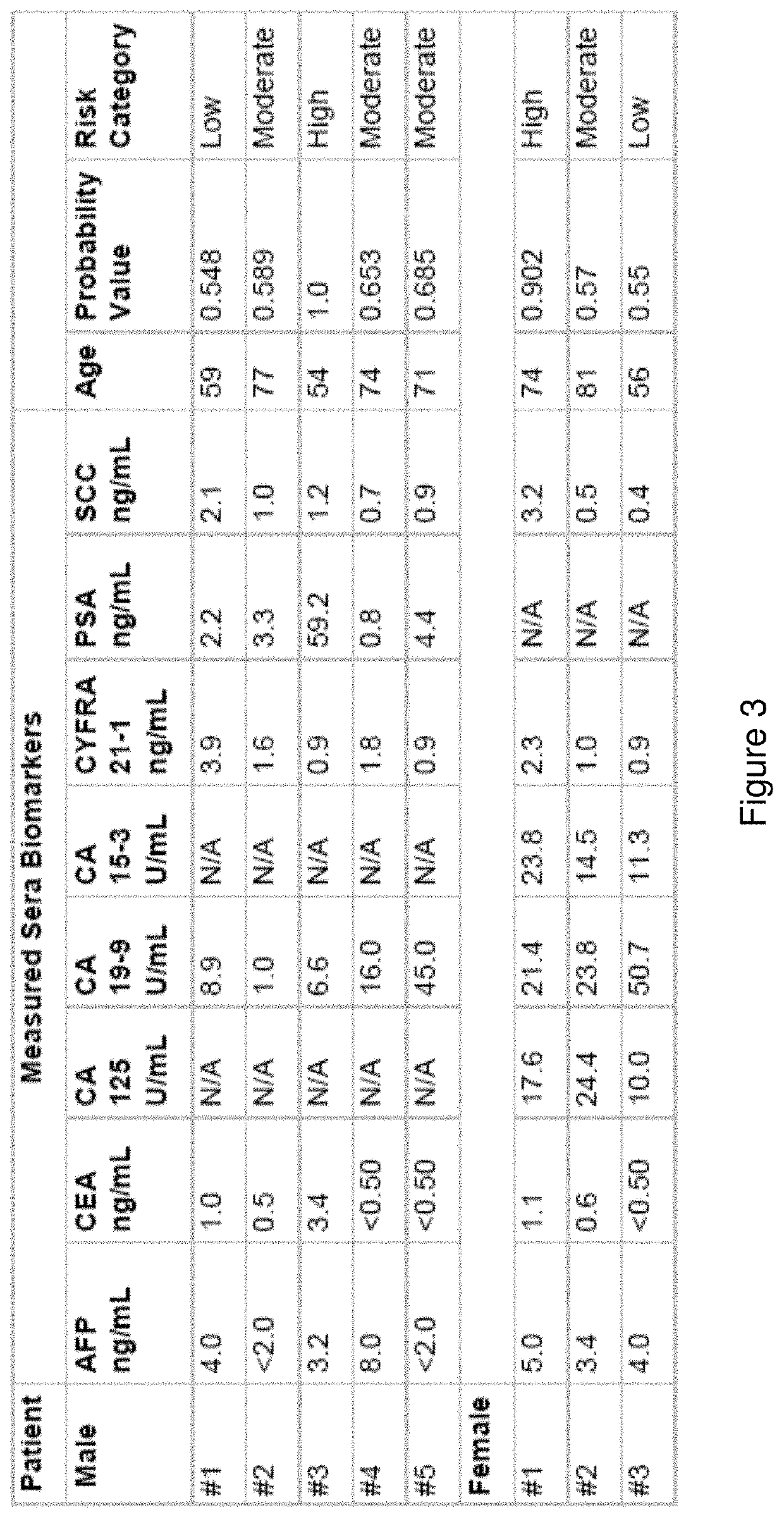
Cancer classifier models, machine learning systems and methods of use
PendingUS20200005901A1Increased riskImprove performanceMedical data miningEnsemble learningMedicineOrgan system
Disclosed herein are classifier models, computer implemented systems, machine learning systems and methods thereof for classifying asymptomatic patients into a risk category for having or developing cancer and / or classifying a patient with an increased risk of having or developing cancer into an organ system-based malignancy class membership and / or into a specific cancer class membership.
Owner:20 20 GENESYSTEMS INC
Active learning method for multi-class classifiers
ActiveUS8140450B2Easy to handleIncrease the number ofKernel methodsDigital computer detailsData setStudy methods
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
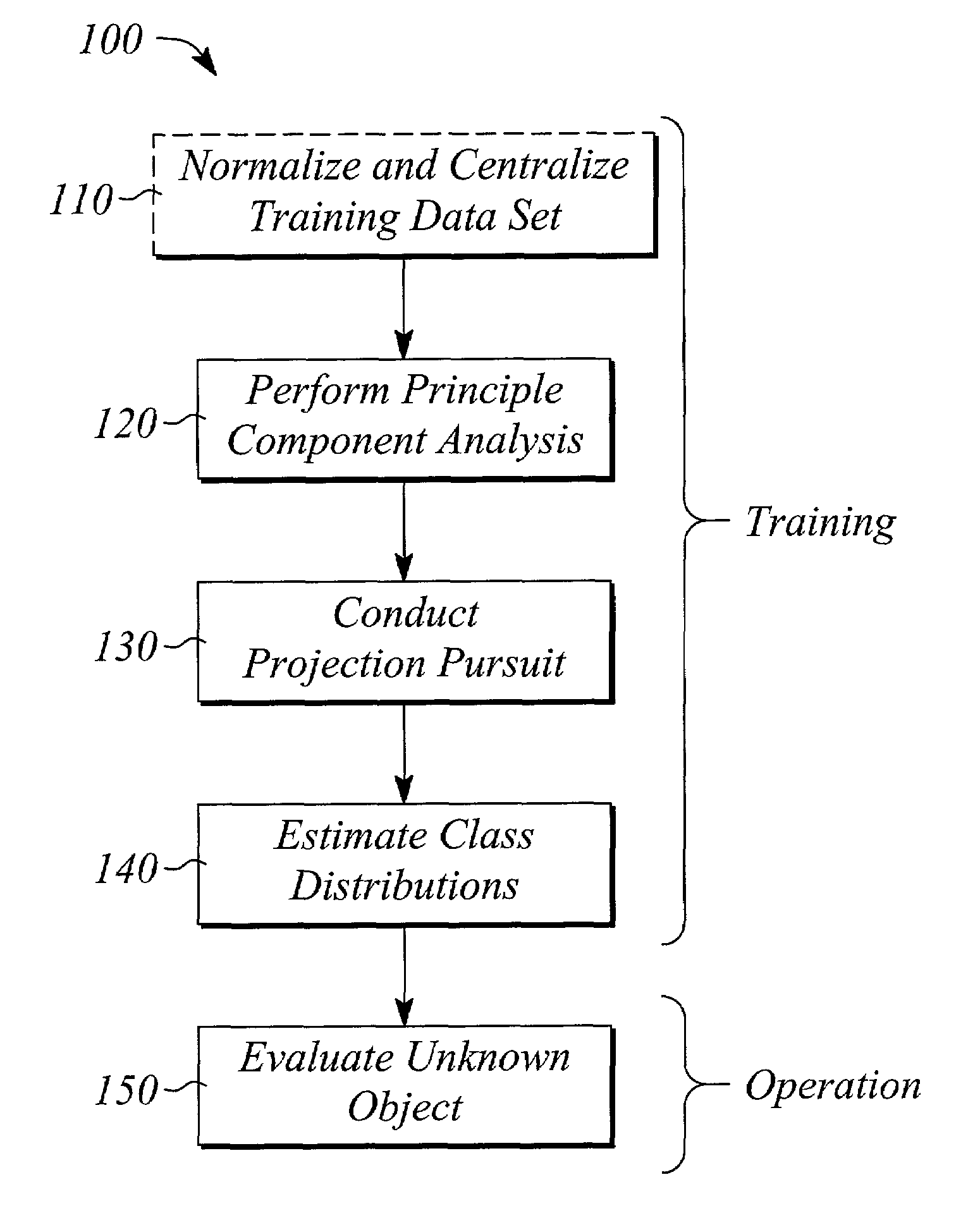
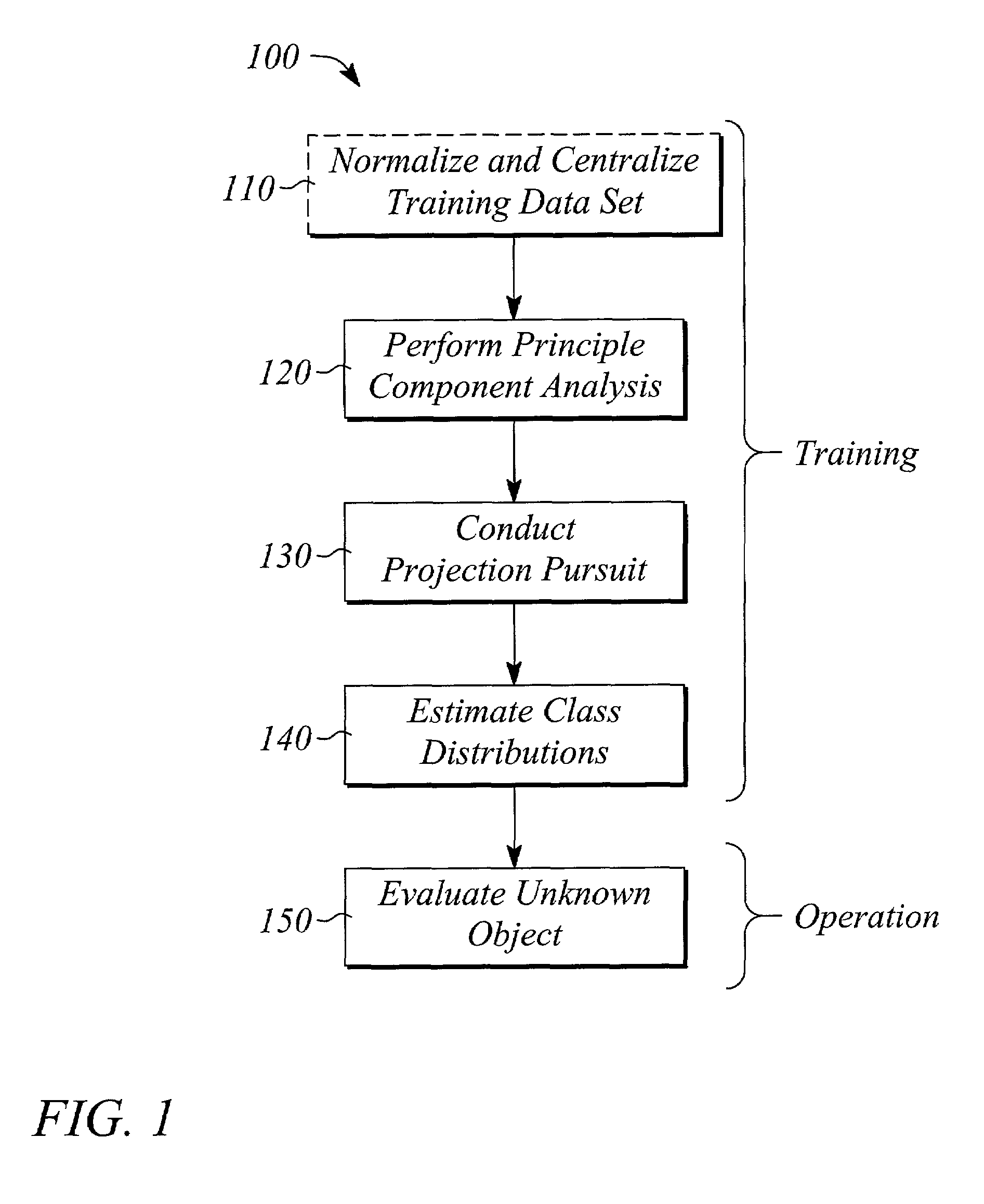
Method and system of object classification employing dimension reduction
InactiveUS6993193B2Minimizes problemReduce dimensionalityImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionDimensionality reductionPrincipal component analysis
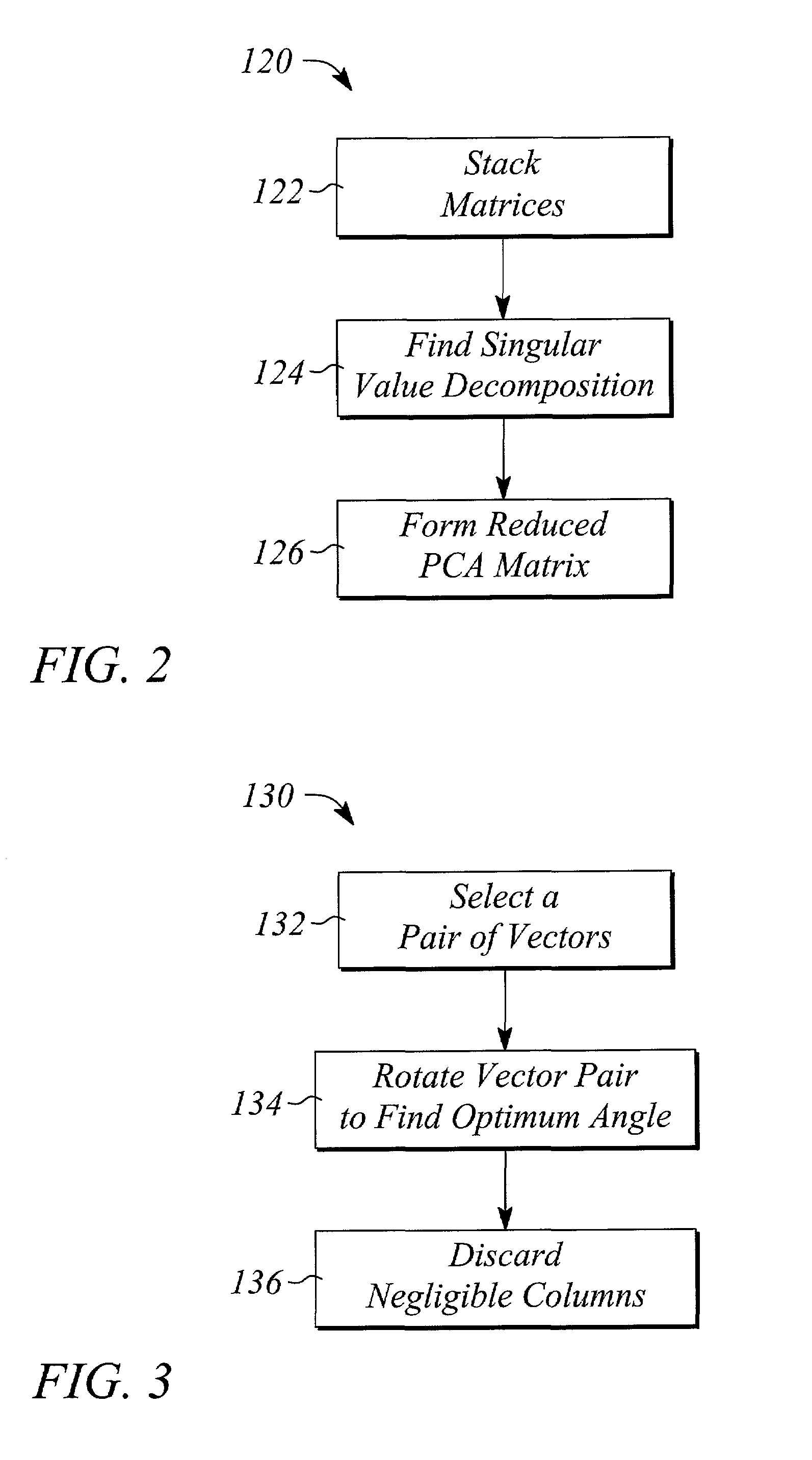
A method and system of object classification uses measurements for a training set of objects to classify an unknown object as being a member in one of several classes of the training set. The classes are defined by features of the training set, the objects of which have known class memberships. The method comprises performing principal component analysis on the training set measurements to discard features that have negligible information regarding class membership, conducting projection pursuit on the remaining training set measurements to accentuate differences between the classes, estimating a distribution of each accentuated class in the training set, and evaluating measurements of the unknown object to determine the membership of the unknown object in one of the accentuated classes. The system implements the method in a computer program stored in computer memory.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Picture region extraction method and device
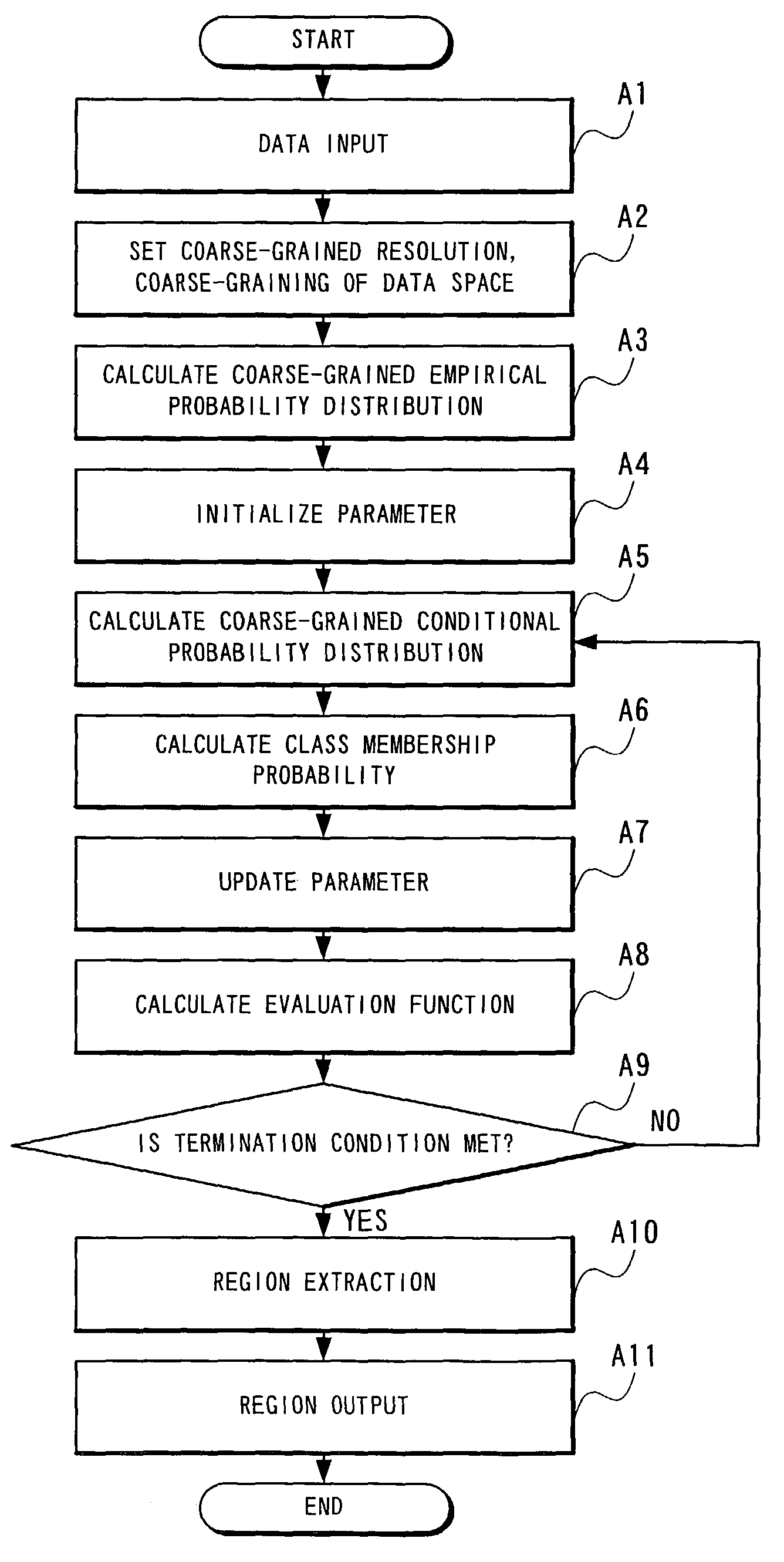
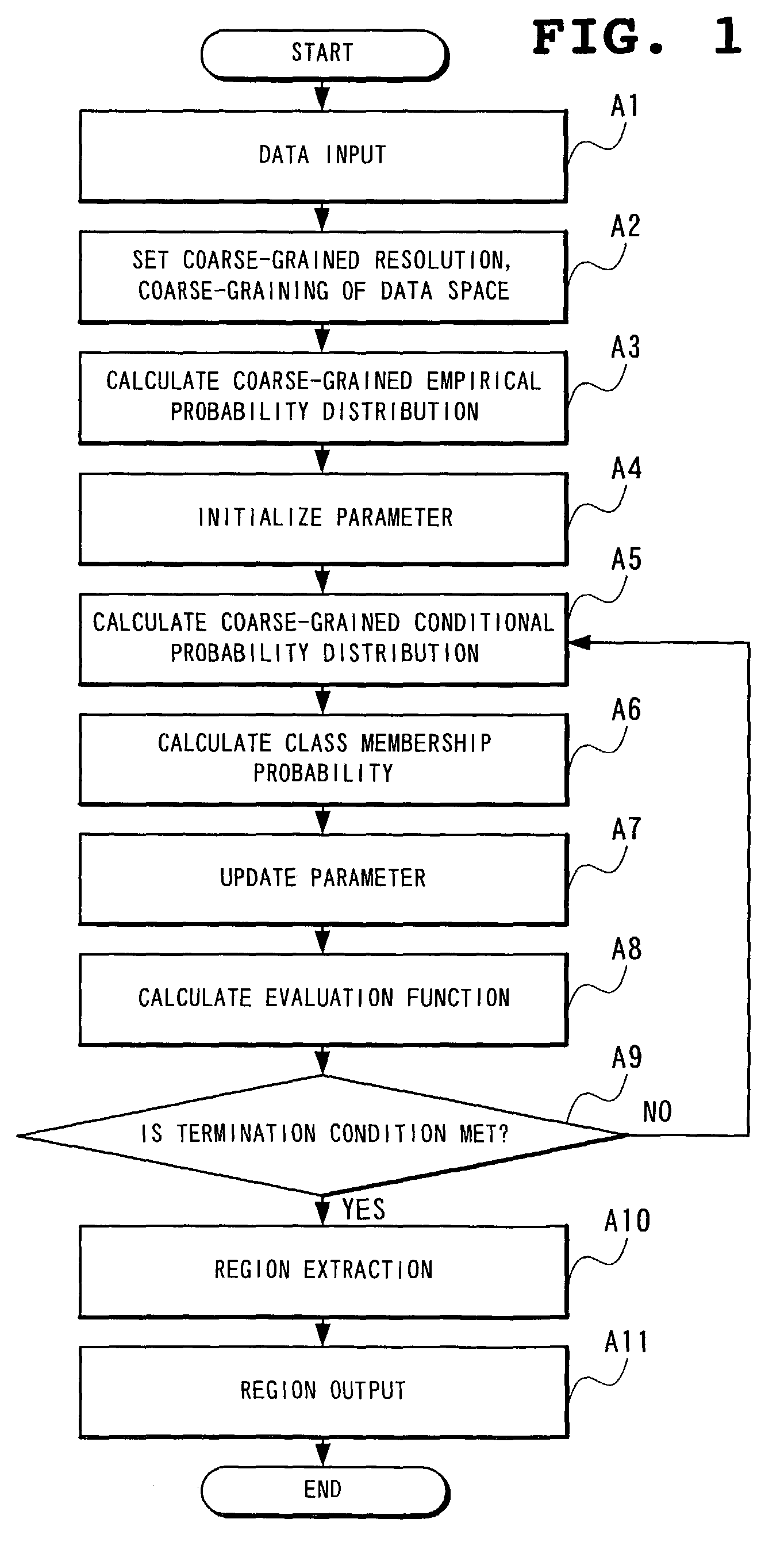
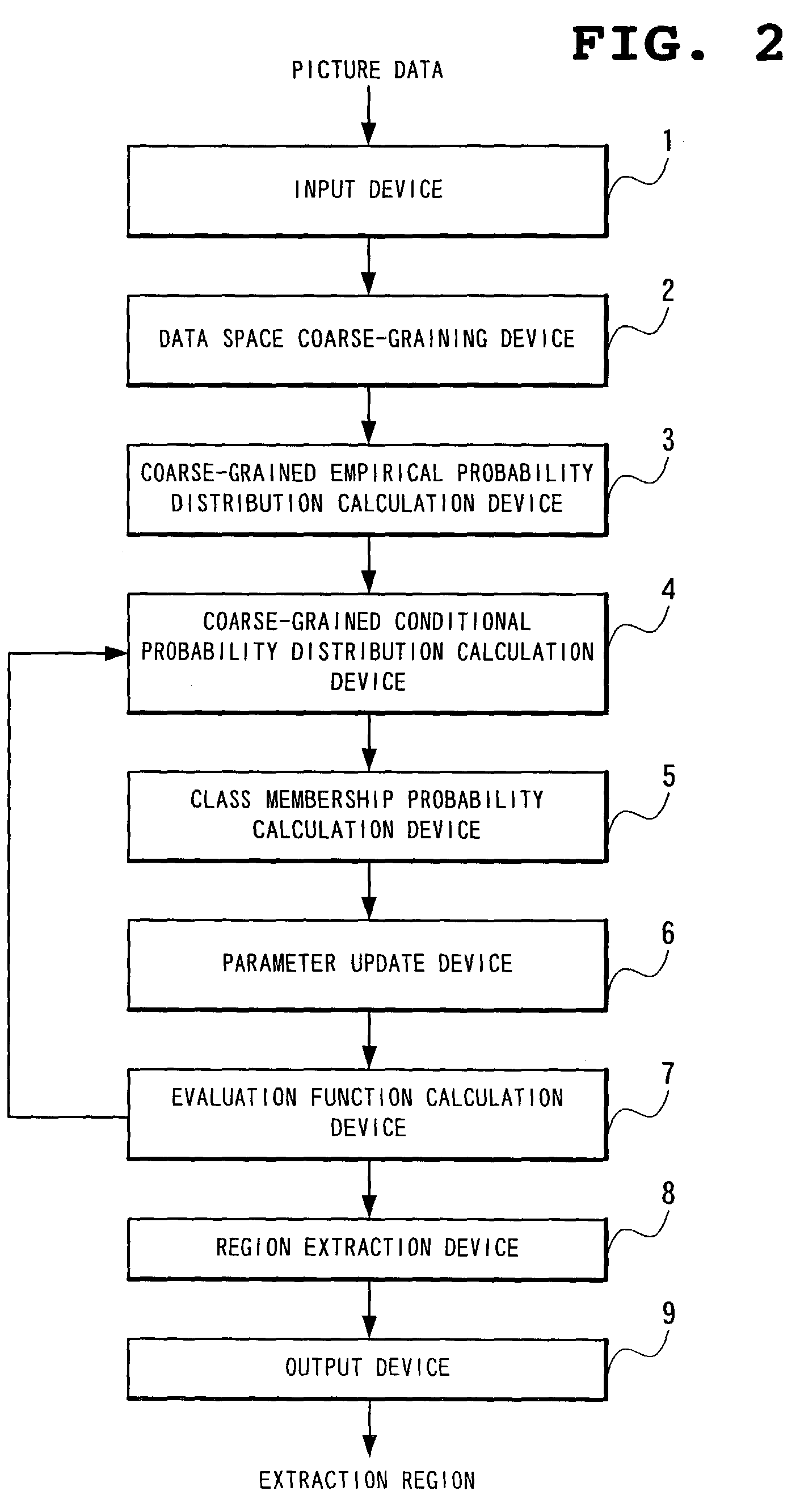
The picture region extraction method coarse-grains this picture data space, calculates a coarse-grained empirical probability distribution, initializes parameters, calculates a coarse-grained conditional probability distribution and a class membership probability, updates the parameters, and calculates an evaluation function, each process being repeated until there is no change in the evaluation function, at which point, a picture region is extracted based on the class membership probability.
Owner:NEC CORP
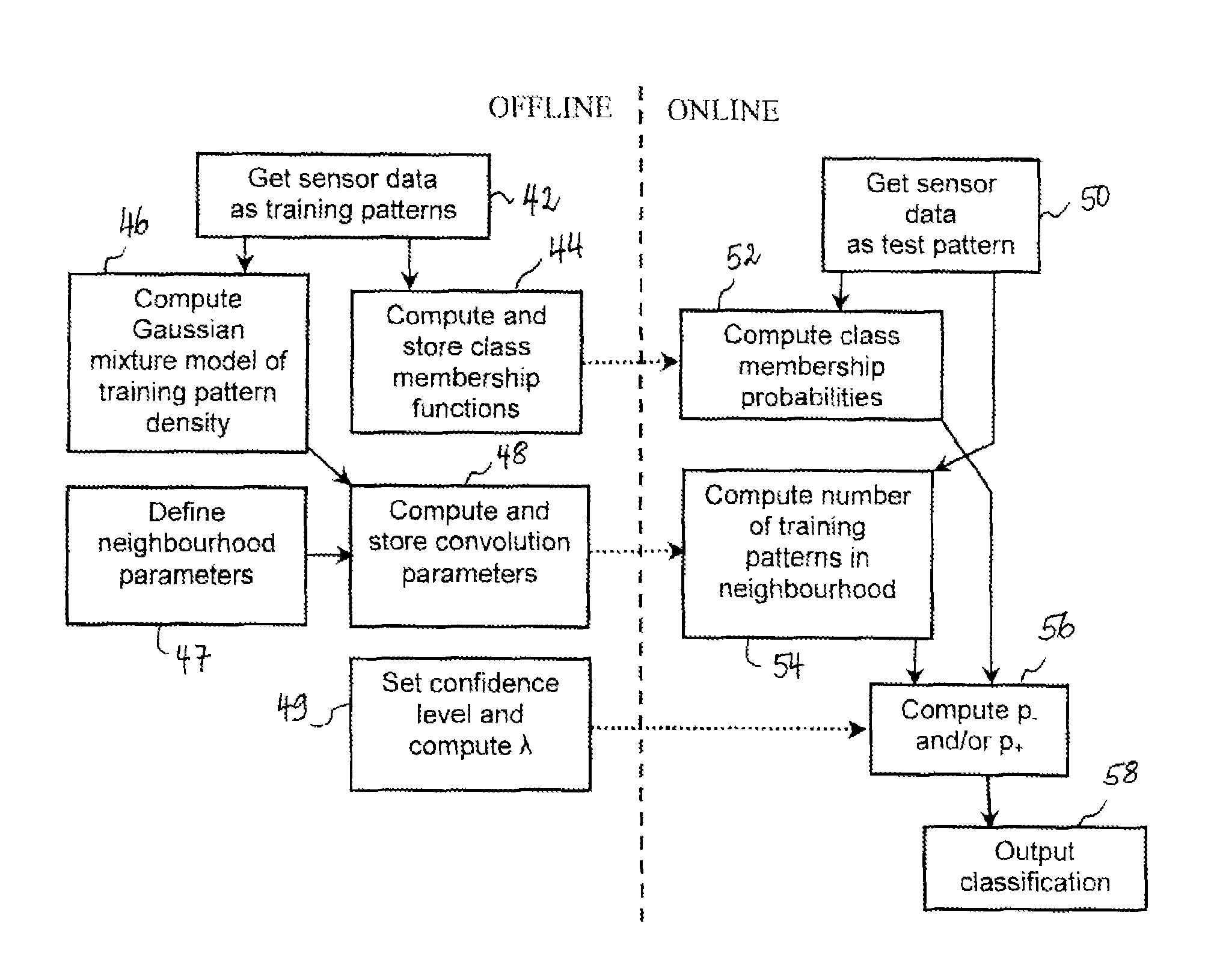
Pattern classification method
ActiveUS20090319451A1Digital computer detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionConfidence intervalClassification methods
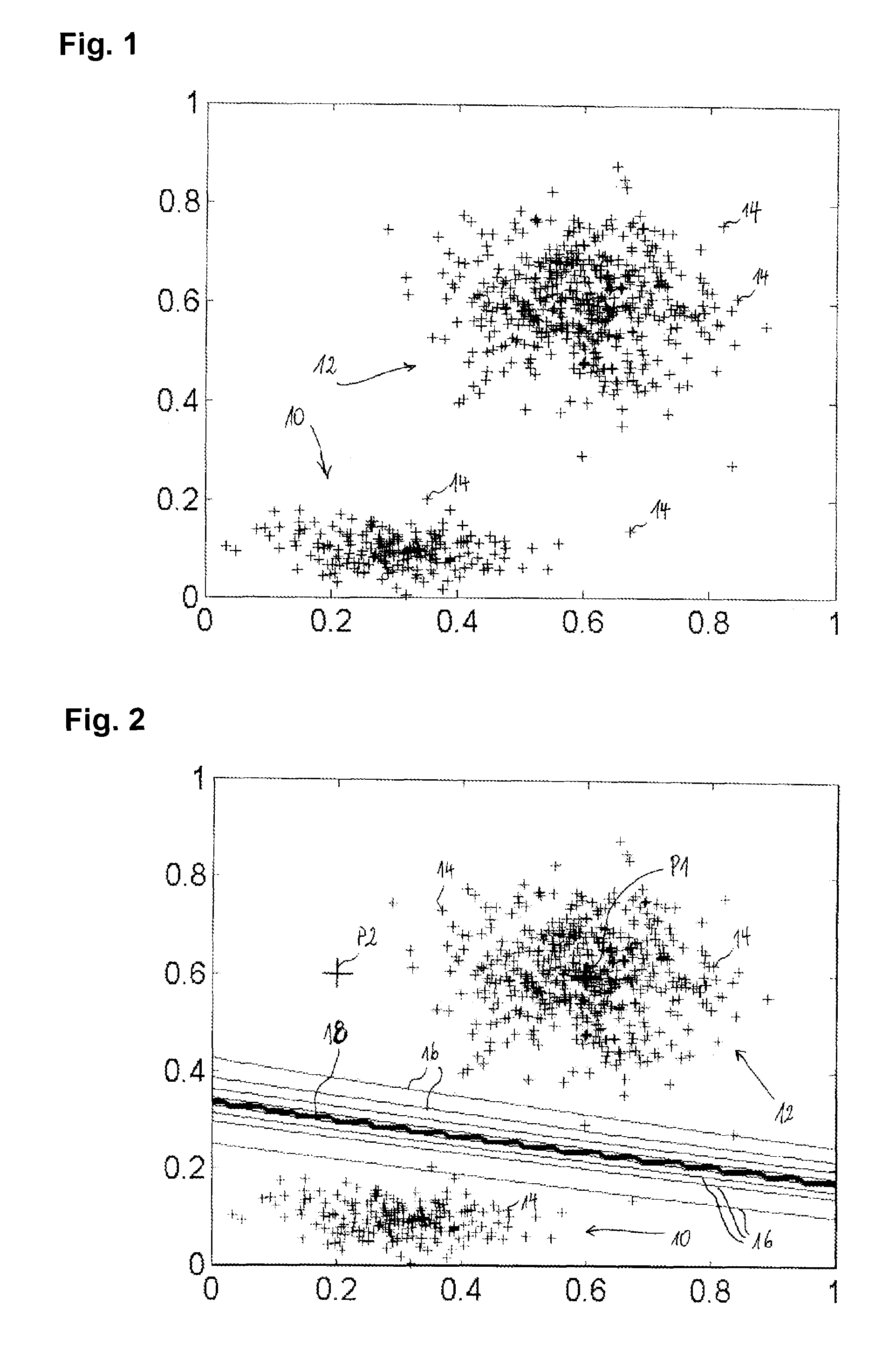
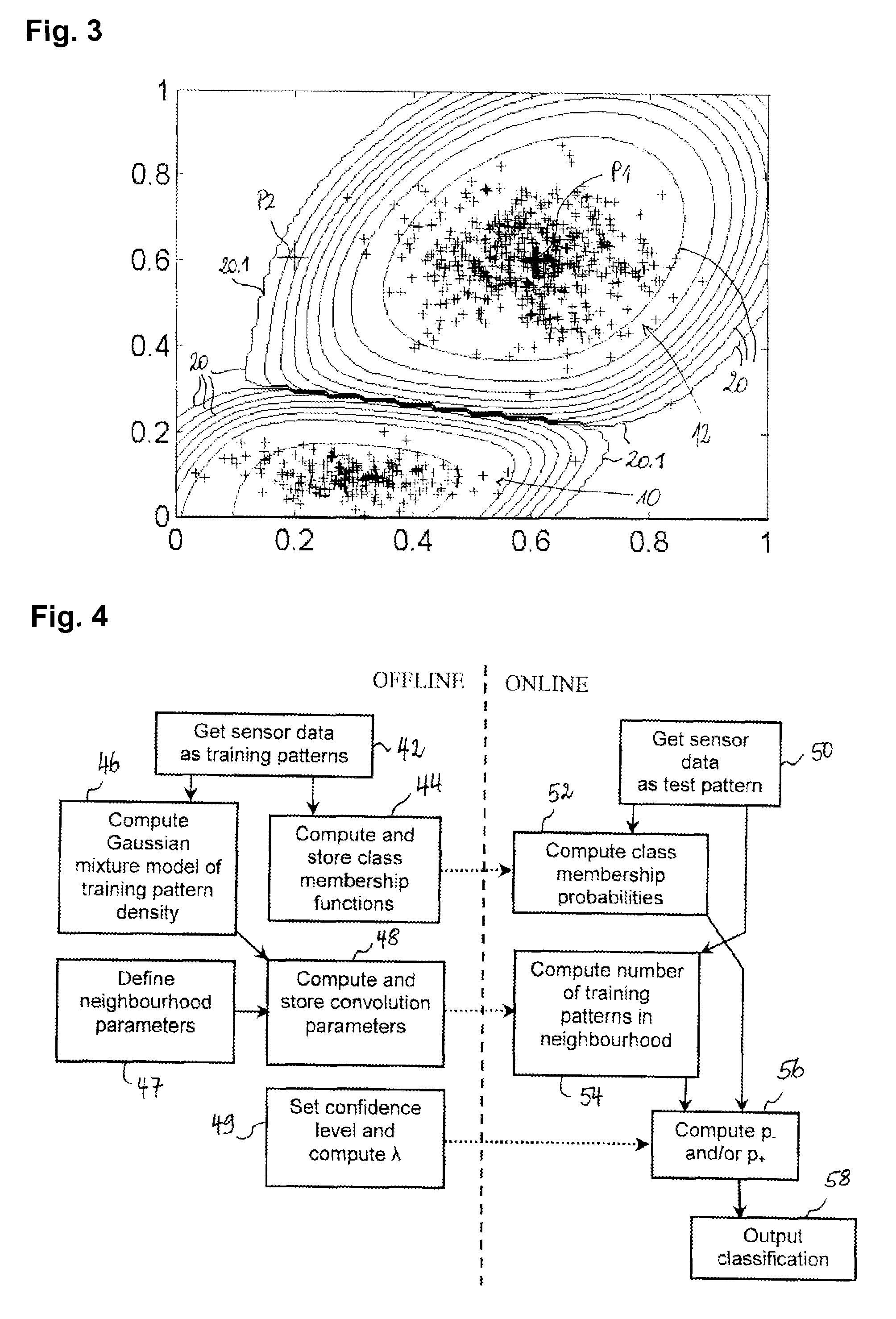
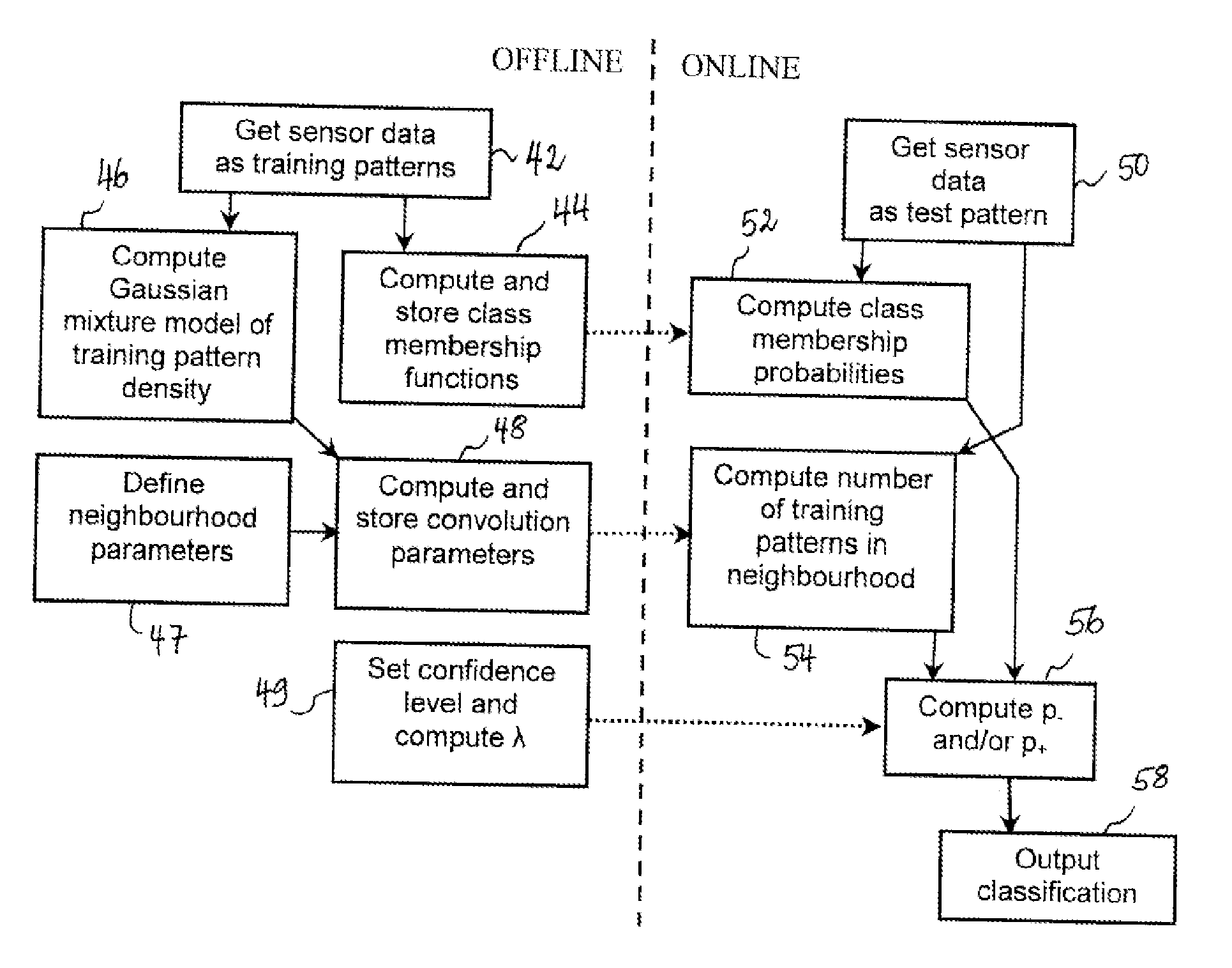
For assigning a test pattern to a class chosen from a predefined set of classes, the class membership probability for the test pattern is calculated as well as the confidence interval for the class membership probability based upon a number of training patterns in a neighbourhood of the test pattern in the feature space. The number of training patterns in the neighbourhood of the test pattern is obtained from computing a convolution of a density function of the training patterns with a Gaussian smoothing function centred on the test pattern, where the density function of the training patterns is represented as a mixture of Gaussian functions. The convolution of the smoothing function and the mixture of Gaussian functions can be expressed analytically.
Owner:IEE INT ELECTRONICS & ENG SA
Enhanced relationship classifier based on representative samples
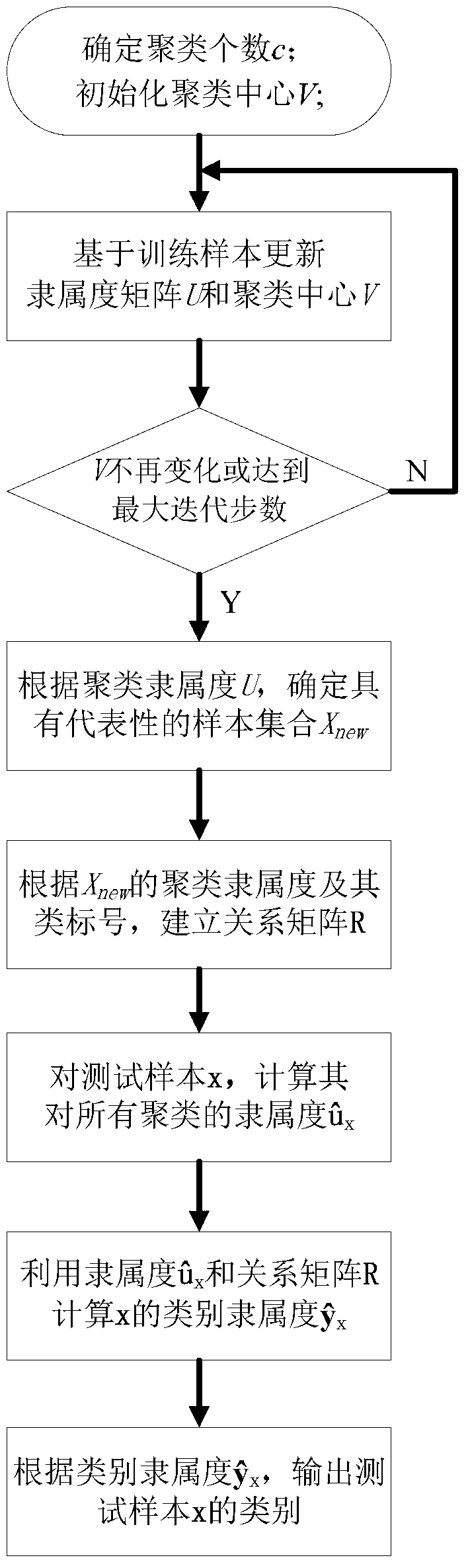
InactiveCN102799902AImplement category predictionImprove effectivenessCharacter and pattern recognitionComputation complexityTest sample
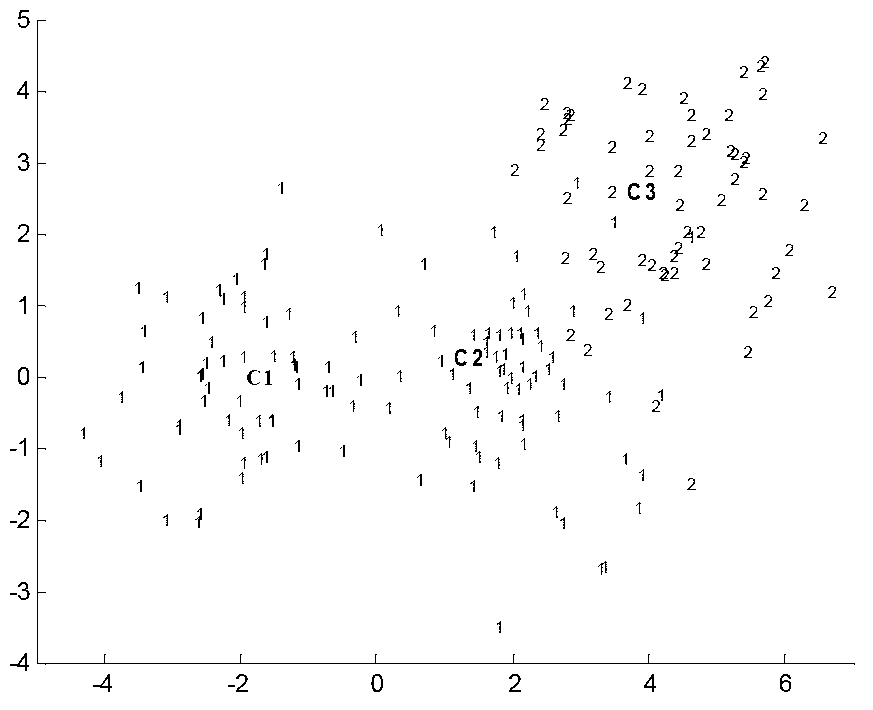
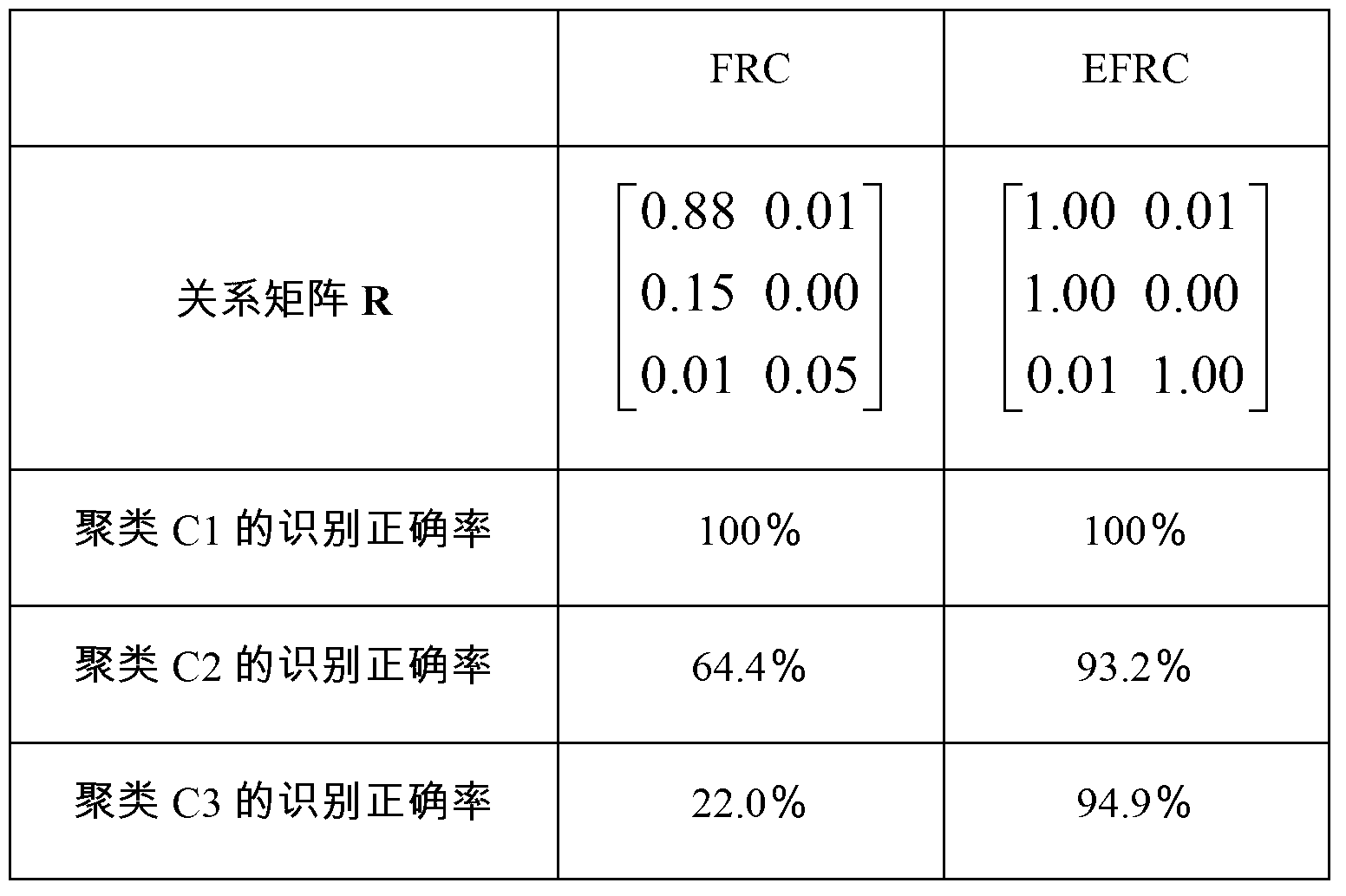
The invention relates to an enhanced relationship classifier based on representative samples. The method mainly comprises two steps: first, selecting representative samples to form a new training sample set Xnew according to the clustering membership of samples; and then, constructing a fuzzy relationship matrix R with a Phi composite operator about the clustering membership and the class membership of Xnew. The enhanced relationship classifier is mainly characterized in that (1) the matrix R can reveal the inherent logic relationship between a cluster and a class; (2) the computation complexity of the matrix R decreases from O(NLc) to O(MLc), wherein L is the number of classes, c is the number of clusters, N is the number of samples of the original dataset X, M is the number of samples of Xnew, and N is greater than M; and (3) when sufficient judgment information cannot be found in certain areas in the sample space, the classifier rejects to make strategies for test samples falling into the areas, so as to guarantee the confidence level of classification results.
Owner:NANJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
A fuzzy K-nearest neighbor classification method and system based on weighted chi-square distance metric
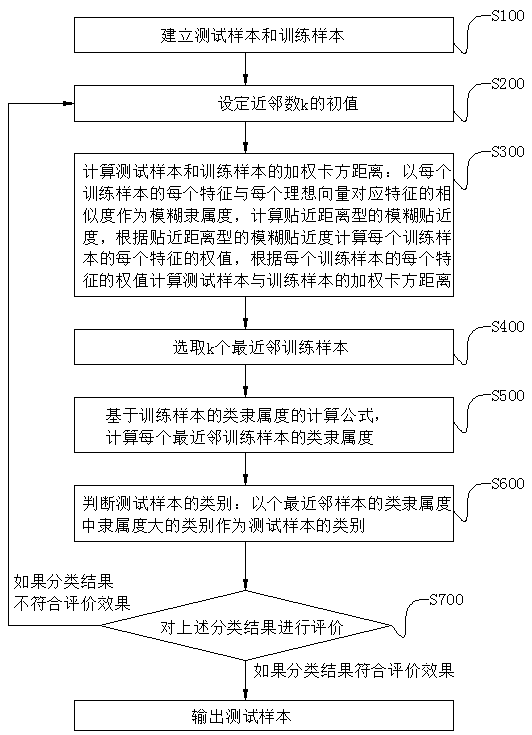
InactiveCN109255363AThe recall rate is obviousMaintain stabilityCharacter and pattern recognitionFuzzy k nearest neighborAlgorithm
The invention discloses a fuzzy K-nearest neighbor classification method and system based on weighted chi-square distance metric, belonging to the field of fuzzy K-nearest neighbor algorithm. The technical problem to be solved is that the classification accuracy of the existing fuzzy K-nearest neighbor algorithm is low, and the classification accuracy is influenced by noise, irrelevant data and unweighted data. The method comprises the following steps: establishing a training sample and a test sample, and setting a value of a nearest neighbor number k; Calculating weighted chi-square distance;with weighted chi-square distance between the training sample and the test sample as the distance measure, by using the class membership degree of k nearest neighbor training samples,determining theclass of the test sample; evaluating the class. The system includes a sample building module, a nearest neighbor number setting module, a weighted chi-square distance calculation module, a sample category determination module and a sample evaluation module. The classification time is short, the classification accuracy is not affected by noise, relative data and unweighted data, and the stability of the method is high.
Owner:QILU UNIV OF TECH
Pattern classification method
For assigning a test pattern to a class chosen from a predefined set of classes, the class membership probability for the test pattern is calculated as well as the confidence interval for the class membership probability based upon a number of training patterns in a neighbourhood of the test pattern in the feature space. The number of training patterns in the neighbourhood of the test pattern is obtained from computing a convolution of a density function of the training patterns with a Gaussian smoothing function centred on the test pattern, where the density function of the training patterns is represented as a mixture of Gaussian functions. The convolution of the smoothing function and the mixture of Gaussian functions can be expressed analytically.
Owner:IEE INT ELECTRONICS & ENG SA
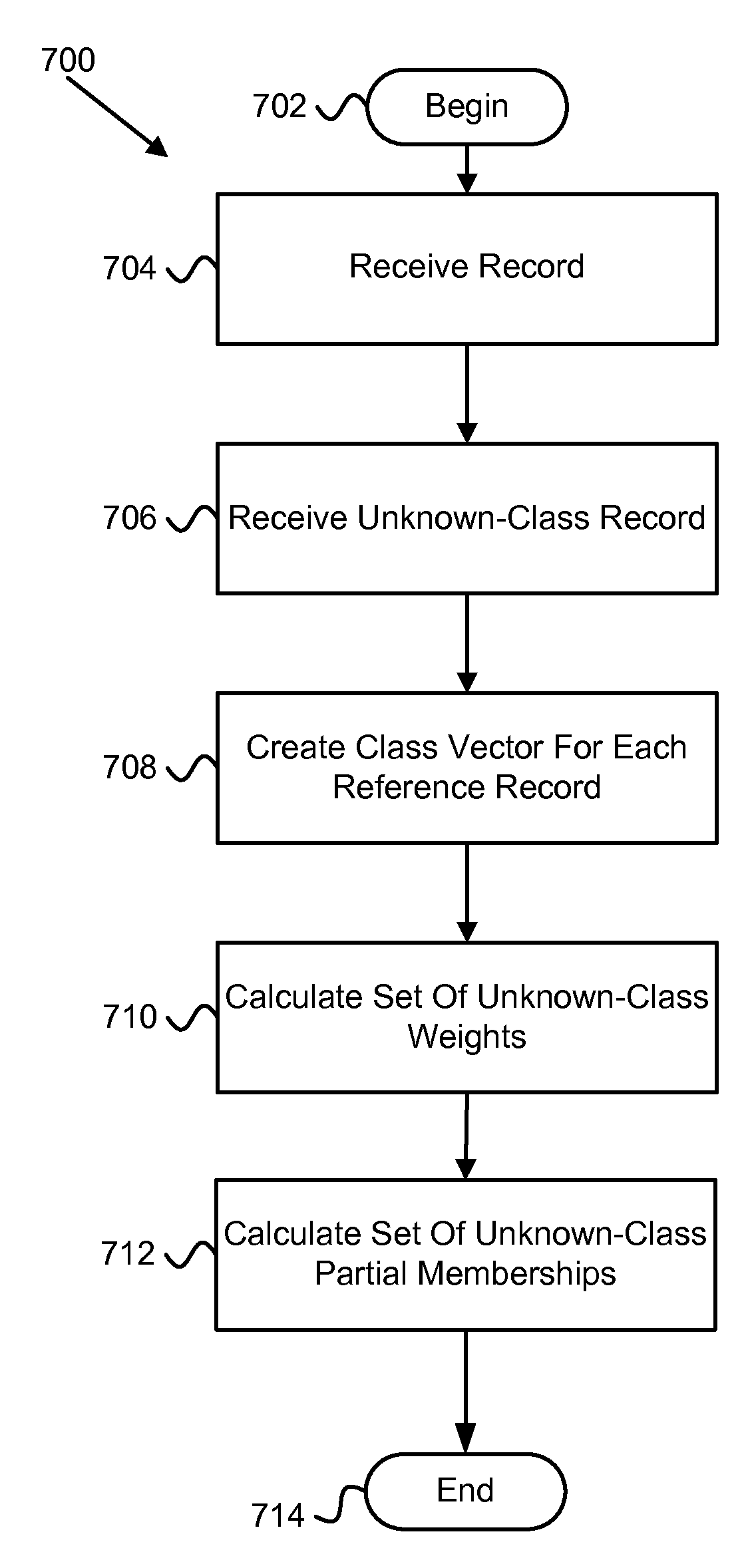
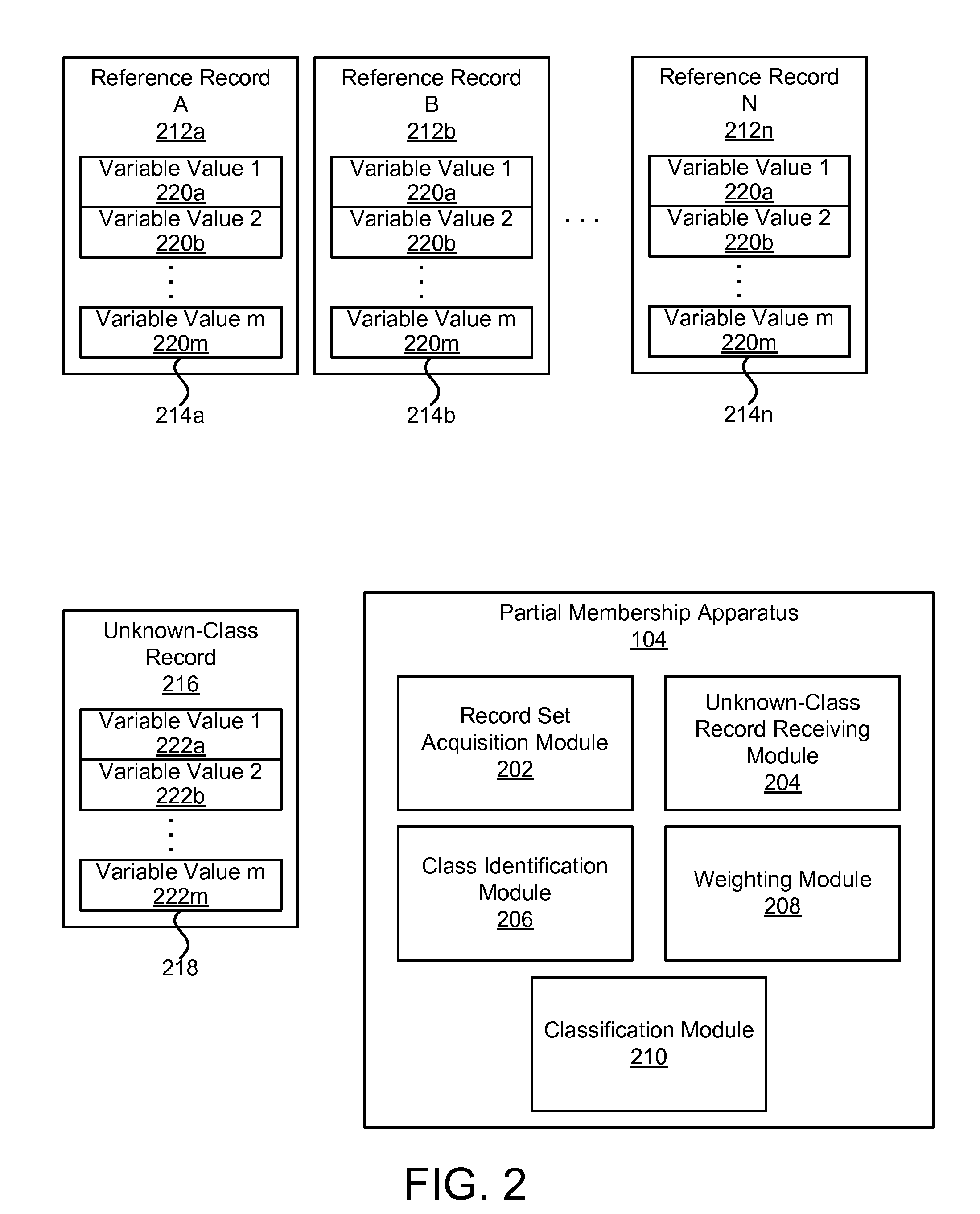
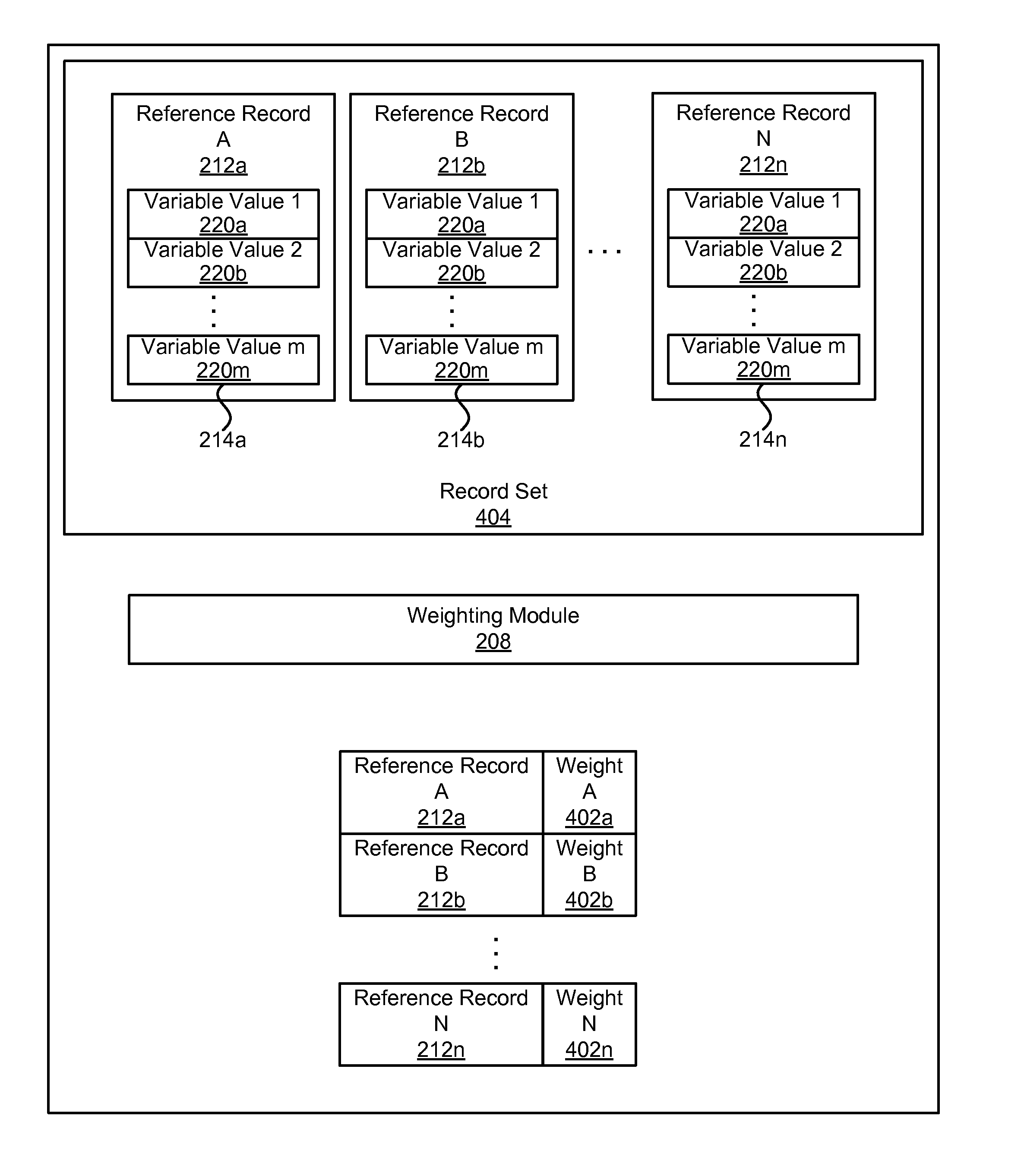
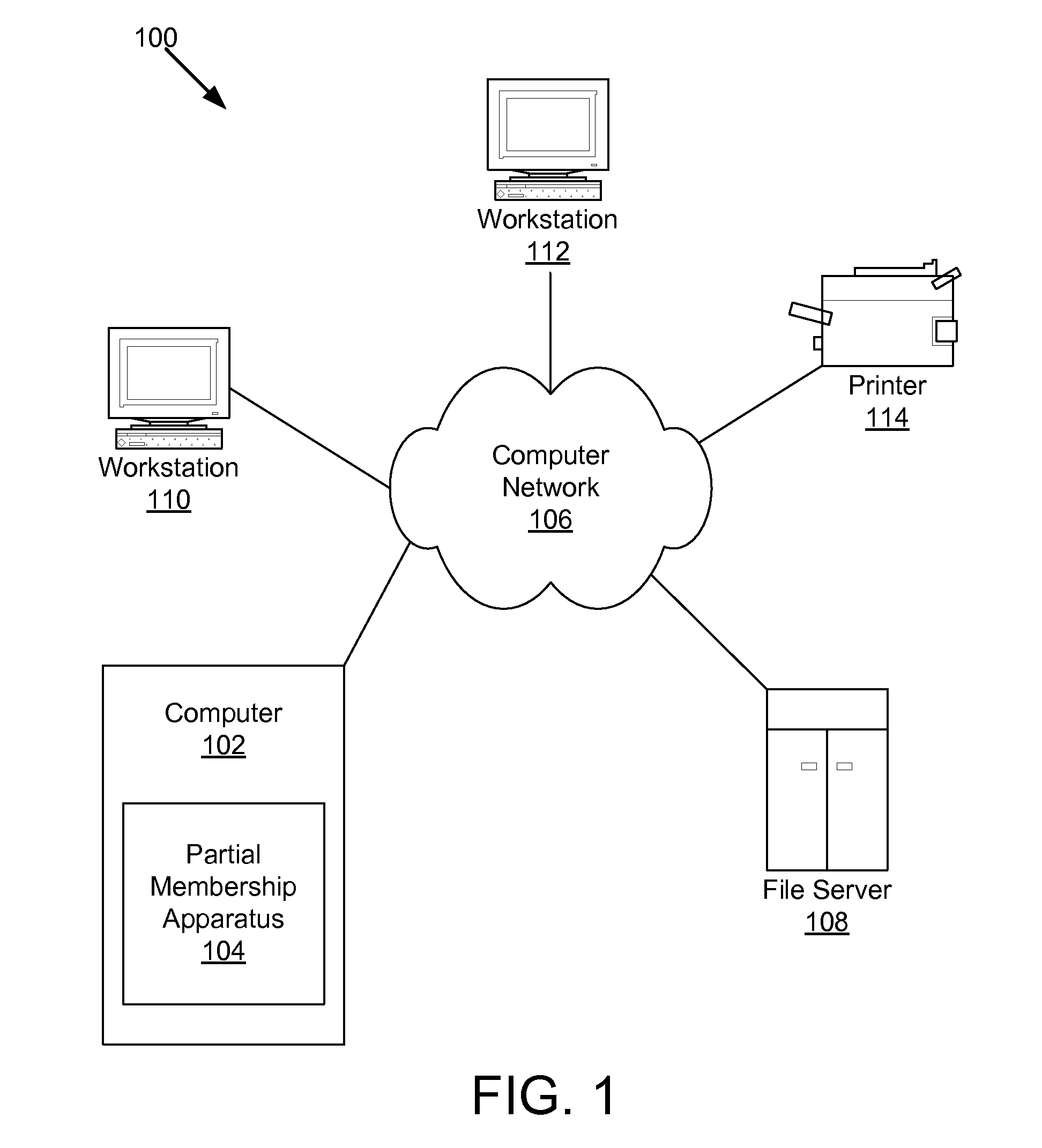
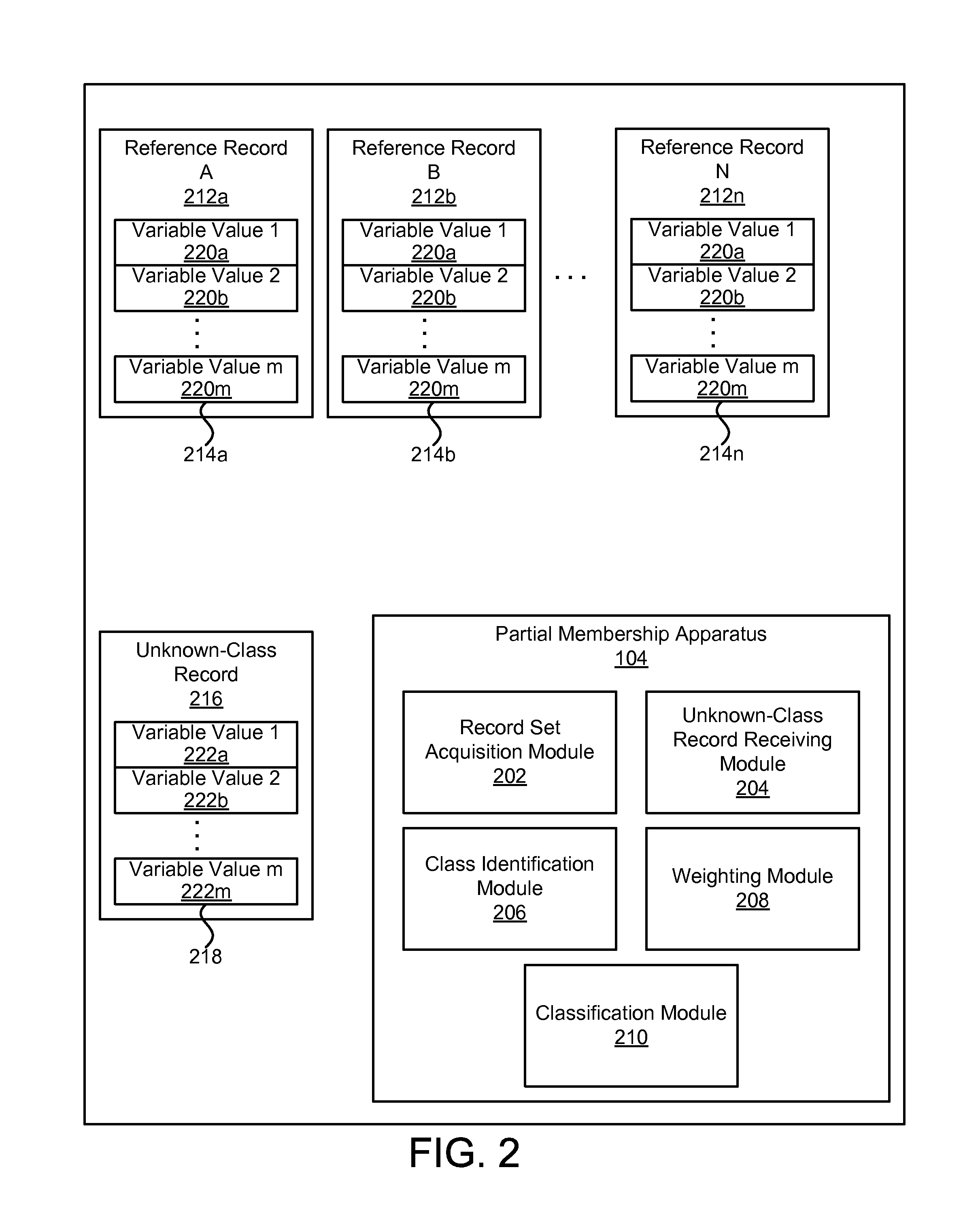
Apparatus, system, and method for determining a partial class membership of a data record in a class
ActiveUS20100299294A1Data processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsData recordingData mining
An apparatus, system, and method are disclosed for determining a partial class membership of a data record in a class. The apparatus includes a record set acquisition module that receives a set of reference records having the same independent variables and belonging to a known class within a group of classes. An unknown-class record receiving module receives an unknown-class record having same independent variables as reference records. A class identification module creates a class vector for each reference record identifying whether the record is in a class. A weighting module calculates a set of unknown-class record weights for the unknown-class record. A classification module determines a partial class membership for the unknown-class record for each class in the group of classes using the set of unknown-class record weights. Each partial class membership identifies a probability that the unknown-class record belongs to a corresponding class in the group of classes.
Owner:ITRON NETWORKED SOLUTIONS INC
Apparatus and method for changing a segmentation of an audio piece
For changing a segmentation of an audio piece after a segment class assignment, at first a short segment is selected, which has a length shorter than a predetermined minimum length. This short segment is preferably merged with the corresponding successor segment or predecessor segment using information on a segment class membership of the short segment itself, but also the successor segment or the predecessor segment, in order to obtain a changed segmentation of the audio signal. With this, a not over-segmented segment representation of the audio signal is obtained, which further includes all audio information, i.e. is not a representation of the audio piece with holes.
Owner:SONY CORP
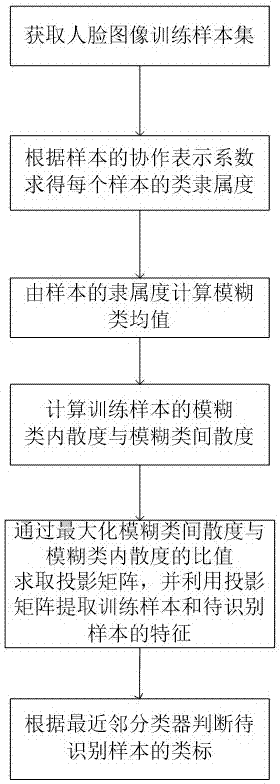
Multi-pose face recognition method based on collaborative fuzzy mean discriminant analysis
ActiveCN107220627AImprove robustnessRobustCharacter and pattern recognitionHat matrixNearest neighbor classifier
The invention discloses a multi-pose face recognition method based on collaborative fuzzy mean discriminant analysis, which comprises the steps of acquiring a multi-pose face image training sample set comprising a plurality of different classes, performing normalization on each training sample and a sample to be recognized, and performing dimension reduction by using PCA; calculating the class membership degree of each training sample by using a collaboration representation coefficient of the training samples; calculating a fuzzy class mean; calculating the fuzzy intra-class divergence and the fuzzy inter-class divergence of the training samples; solving a projection matrix through maximizing a ratio of the fuzzy inter-class divergence and the fuzzy intra-class divergence of the training samples, and extracting features of the training samples and the sample to be recognized by using the projection matrix; and judging and determining a class label of the sample to be recognized according to a nearest neighbor classifier. According to the invention, class information of the samples are sufficiently utilized, the similarity of the same class of samples and the difference of different classes of samples are considered, and the robustness for noise and wild points is enhanced through introducing membership degree information when a sample has various changes in illumination, pose and expression.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
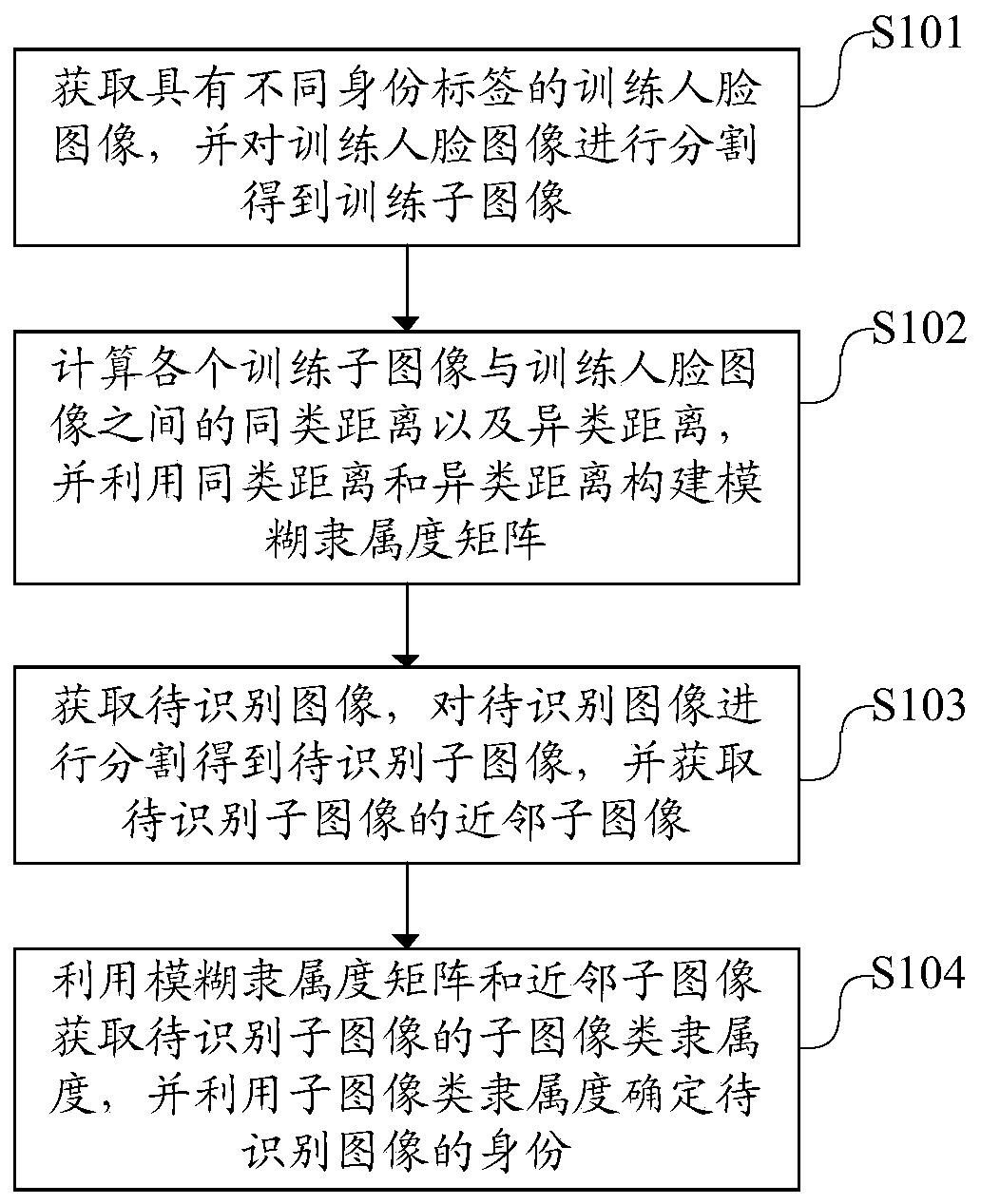
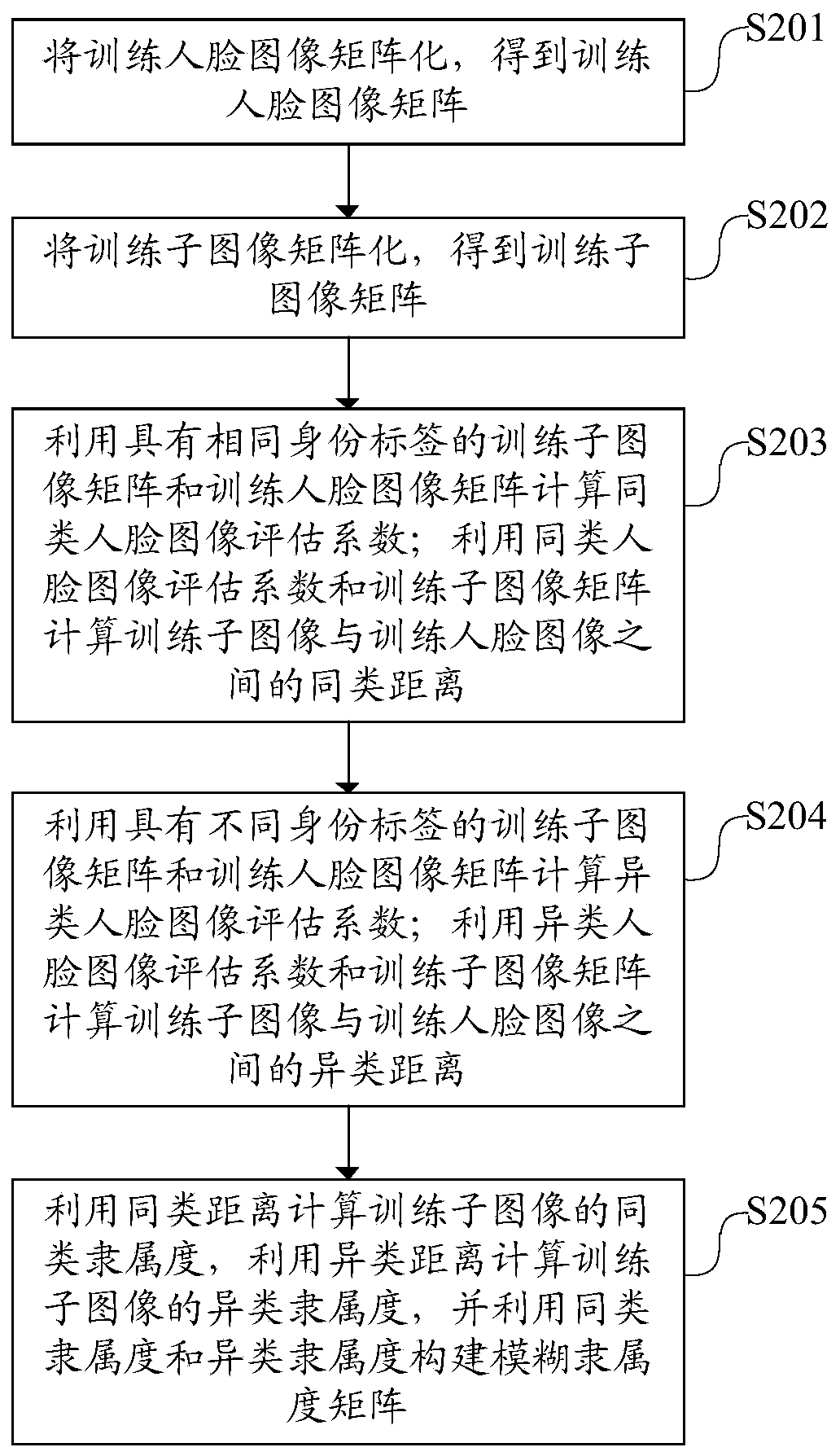
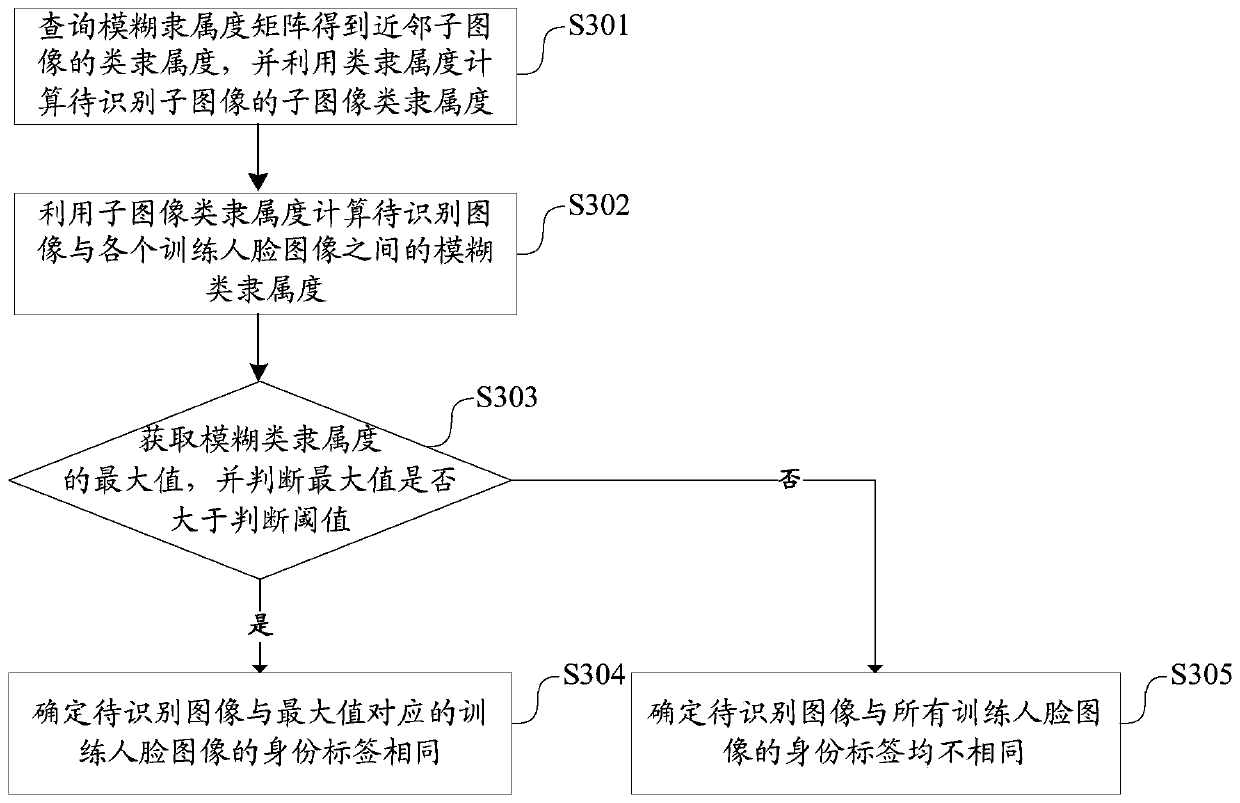
Face image recognition method, device and equipment based on fuzzy theory
ActiveCN110348386ALower quality requirementsEase congestionCharacter and pattern recognitionRecognition algorithmComputer science
The invention discloses a face image recognition method based on a fuzzy theory, and the method comprises the steps: obtaining training face images with different identity labels, and carrying out thesegmentation of the training face images to obtain training sub-images; calculating a similar distance and a heterogeneous distance between each training sub-image and the training face image, and constructing a fuzzy membership matrix by using the similar distance and the heterogeneous distance; obtaining a to-be-recognized image, segmenting the to-be-recognized image to obtain to-be-recognizedsub-images, and obtaining neighbor sub-images of the to-be-recognized sub-images; obtaining subimage class membership of the to-be-identified subimage by using the fuzzy membership matrix and the neighbor subimage, and determining the identity of the to-be-identified subimage by using the subimage class membership. According to the method, the robustness of a face recognition algorithm is improved, so that the recognition speed is increased, and the problem of low recognition speed in the prior art is solved. The invention also provides a face image recognition device and equipment based on the fuzzy theory, and a computer readable storage medium, which also have the above beneficial effects.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
Multi-spectral remote sensing image terrain classification method
ActiveCN108830297AResolve ill-posedSolve ill-posed problemsCharacter and pattern recognitionData dredgingClassification methods
The invention, which belongs to the crossing field of data mining and remote sensing image processing, discloses a multi-spectral remote sensing image terrain classification method. A new membership degree calculation formula is designed and a weighted index is reduced appropriately; a marked sample set for some data is obtained based on the expert knowledge and the centroid is initialized by using the marked sample set; restraining is carried out by using marked samples during the iterative calculation of the centroid and the effect of the marked samples is maximized by using a marker trust factor; and a membership interval is constructed by a fuzzy distance measure, an adaptive factor is constructed by using an intra-class mean square error, and the interval length of the membership function is dynamically adjusted to explore an equivalent I-class membership, and the membership is normalized. With the method provided by the invention, a good classification result is obtained; the robustness and well-posedness to large-scale remote sensing image data are high; and compared with the existing fuzzy C-means method, the provided method has the improved precision.
Owner:YANTAI UNIV
Semi-supervised classification method of modified clustering assumption combined with pairwise constraints
InactiveCN108038511AOvercoming the problem of hard partitioningGood fuzzy division abilityCharacter and pattern recognitionAlgorithmClassification methods
The invention discloses semi-supervised classification method of modified clustering assumption combined with pairwise constraints. The method relates to a semi-supervised learning algorithm, and includes the steps of: initializing class membership degrees of unlabeled samples through an FCM method; selecting appropriate parameters of lambda1 and lambda2, and calculating initialized alpha, a membership degree function of v(x) and a new objective function of M according to formulas; judging whether an iteration termination condition is reached; if yes, returning the membership degree function v(x), and obtaining a classification decision function of f(x) according to the alpha; and otherwise, re-calculating the initialized alpha, the membership degree function of v(x) and the new objectivefunction of M, and carrying out judgement. According to the method, exploration of modified clustering assumption on the unlabeled samples and utilization of the pairwise constraints on supervisory information are combined to jointly form more completed empirical risk terms, thus knowledge contained by the supervisory information is further mined, and the purpose of algorithm performance improvement is achieved. The method has higher validity and correctness.
Owner:江苏江大智慧科技有限公司
Method of selecting at least one of a collection of content items
InactiveUS8843842B2Valid choiceDigital data information retrievalSpecial data processing applicationsA domainClass membership
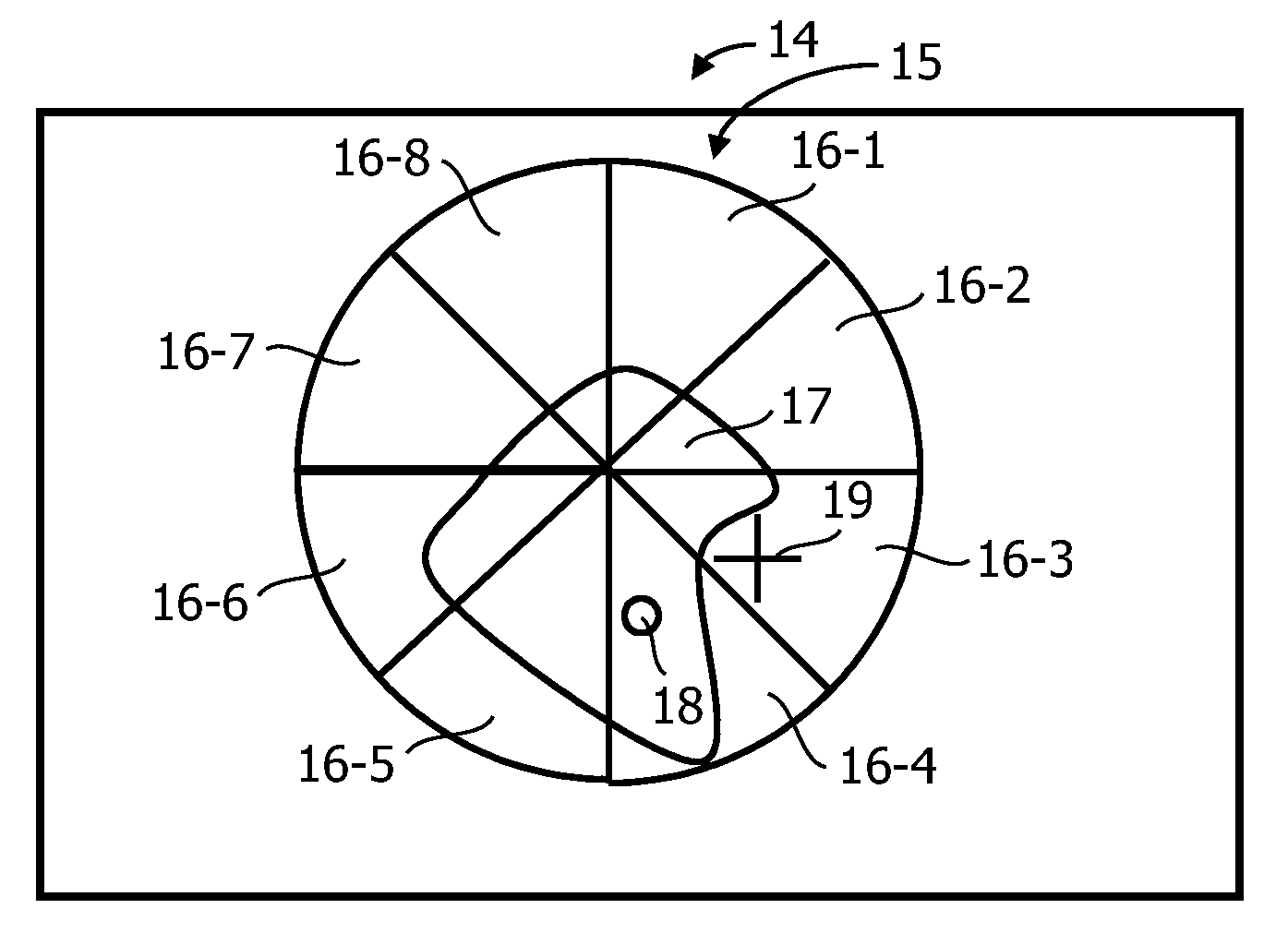
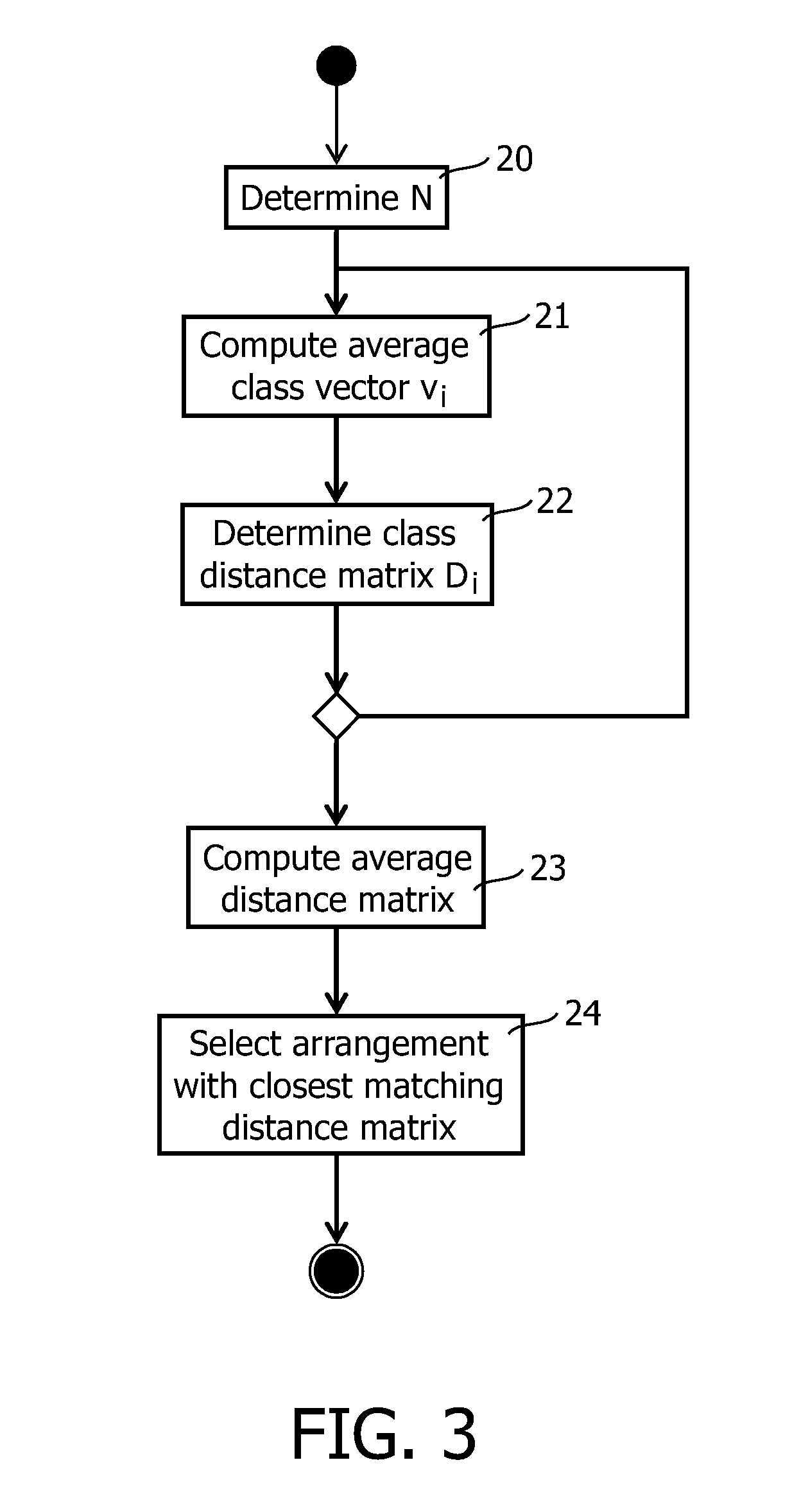
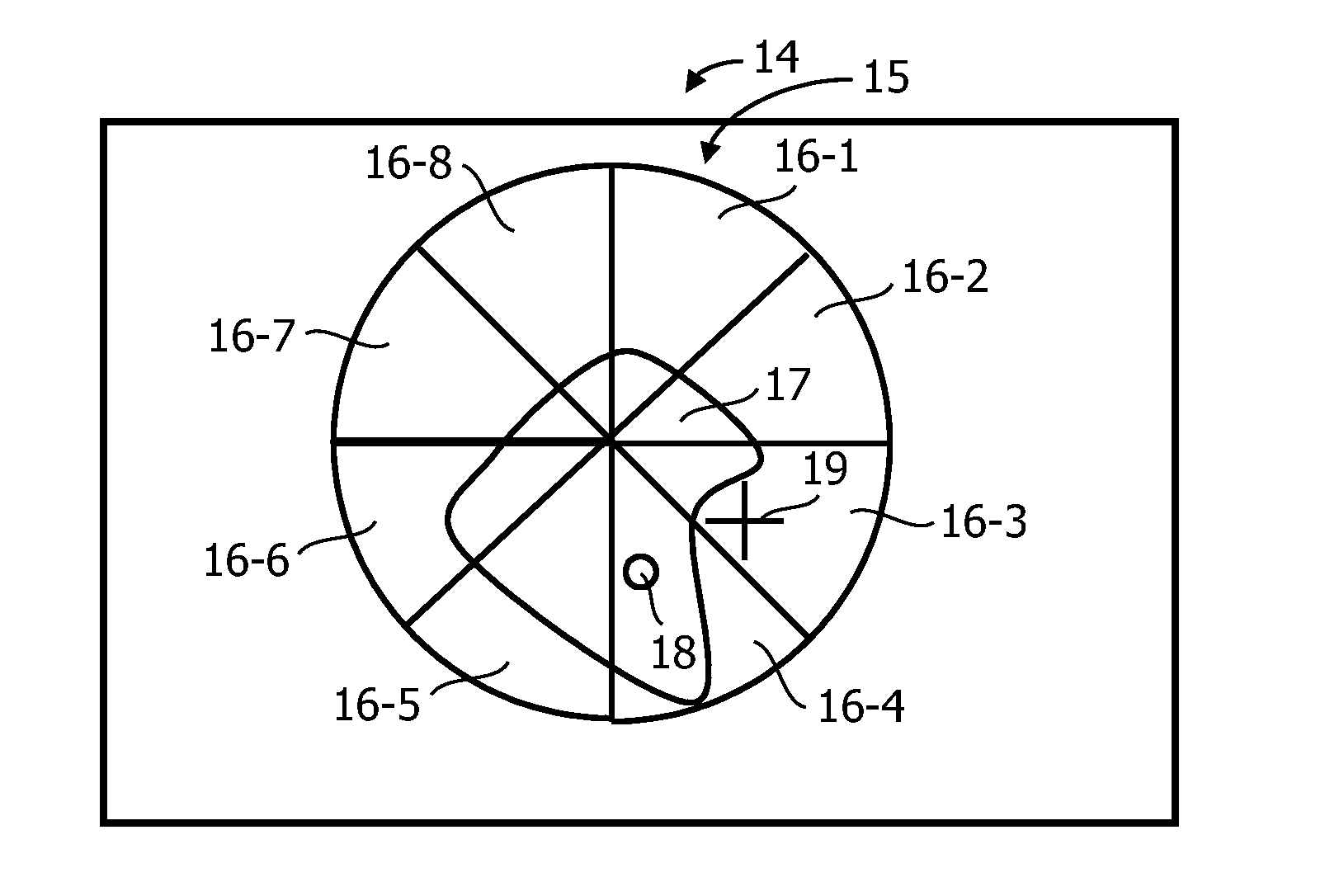
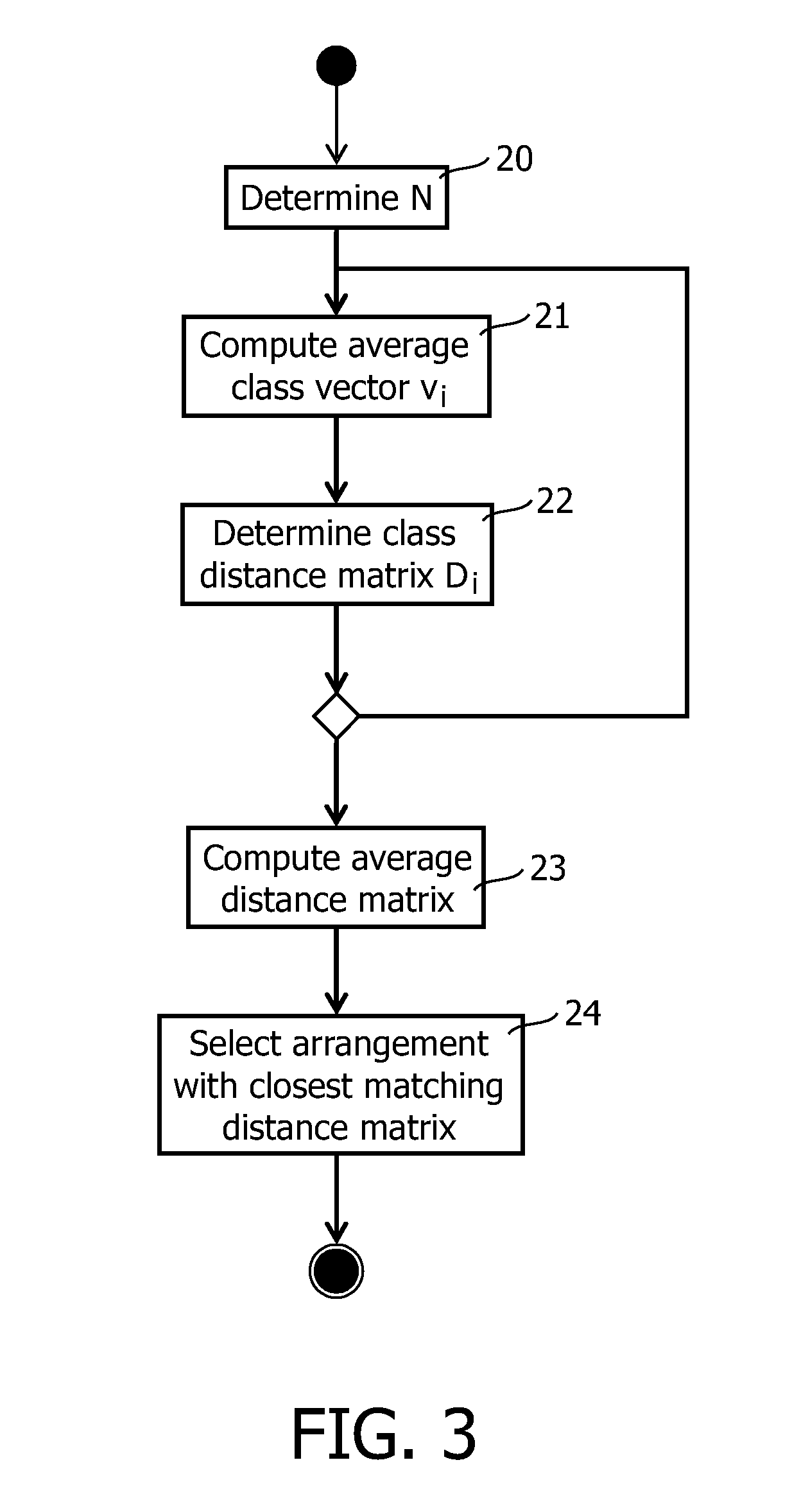
Data indicative of membership of at least one of a plurality of content classes is made available for each one of a collection of content items. A method of selecting at least one item includes displaying a representation of sections of a geo-metrical construct occupying an at least one-dimensional space. The geometrical construct is partitioned into sections in accordance with a mapping between the at least one-dimensional space and a domain of the data indicative of class membership, such that each section represents a class. A signal defining a sub-space within the space is received, and the mapping is used to effect a selection of at least one item of content data commensurate with the defined sub-space.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Method of selecting at least one of a collection of content items
InactiveUS20100218133A1Valid choiceDigital data information retrievalSpecial data processing applicationsA domainComputer science
Data indicative of membership of at least one of a plurality of content classes is made available for each one of a collection of content items. A method of selecting at least one item includes displaying a representation of sections (16) of a geo-metrical construct (15) occupying an at least one-dimensional space. The geometrical construct (15) is partitioned into sections (16) in accordance with a mapping between the at least one-dimensional space and a domain of the data indicative of class membership, such that each section (16) represents a class. A signal defining a sub-space within the space is received, and the mapping is used to effect a selection of at least one item of content data commensurate with the defined sub-space.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Method for operating theme exchange system
InactiveCN1607531AUser identity/authority verificationSignalling system detailsEngineeringRights management
The present application relates to a method of operating a subject exchange system. Rights management information is used, at least in part, in matching, narrowcasting, classification and / or selection processes. A matching and sorting utility system including a business application system is used to complete matching, narrowband broadcasting, sorting and selection. Such matching and classification utility systems may match, narrowcast, classify, and / or select people and / or things (non-limiting examples of which include software objects). Such matching and classification utility systems may use pre-existing classification tables that include at least some rights management information, and / or other qualitative and / or parametric data that specifies and / or defines classes, classification systems, Class hierarchy, class table, class assignment results, class assignment results, and / or class membership.
Owner:INTERTRUST TECH CORP
Apparatus, system, and method for determining a partial class membership of a data record in a class
ActiveUS8103672B2Data processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsData recordingData mining
An apparatus, system, and method are disclosed for determining a partial class membership of a data record in a class. The apparatus includes a record set acquisition module that receives a set of reference records having the same independent variables and belonging to a known class within a group of classes. An unknown-class record receiving module receives an unknown-class record having same independent variables as reference records. A class identification module creates a class vector for each reference record identifying whether the record is in a class. A weighting module calculates a set of unknown-class record weights for the unknown-class record. A classification module determines a partial class membership for the unknown-class record for each class in the group of classes using the set of unknown-class record weights. Each partial class membership identifies a probability that the unknown-class record belongs to a corresponding class in the group of classes.
Owner:ITRON NETWORKED SOLUTIONS INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com