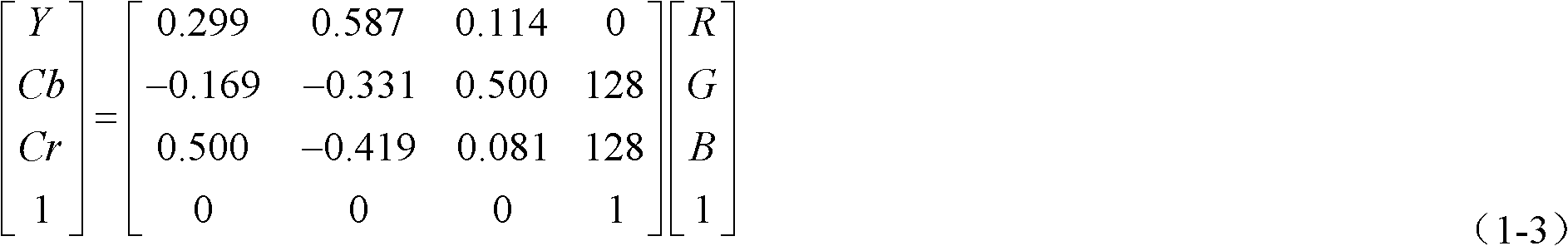Patents
Literature
1914 results about "Mean square" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
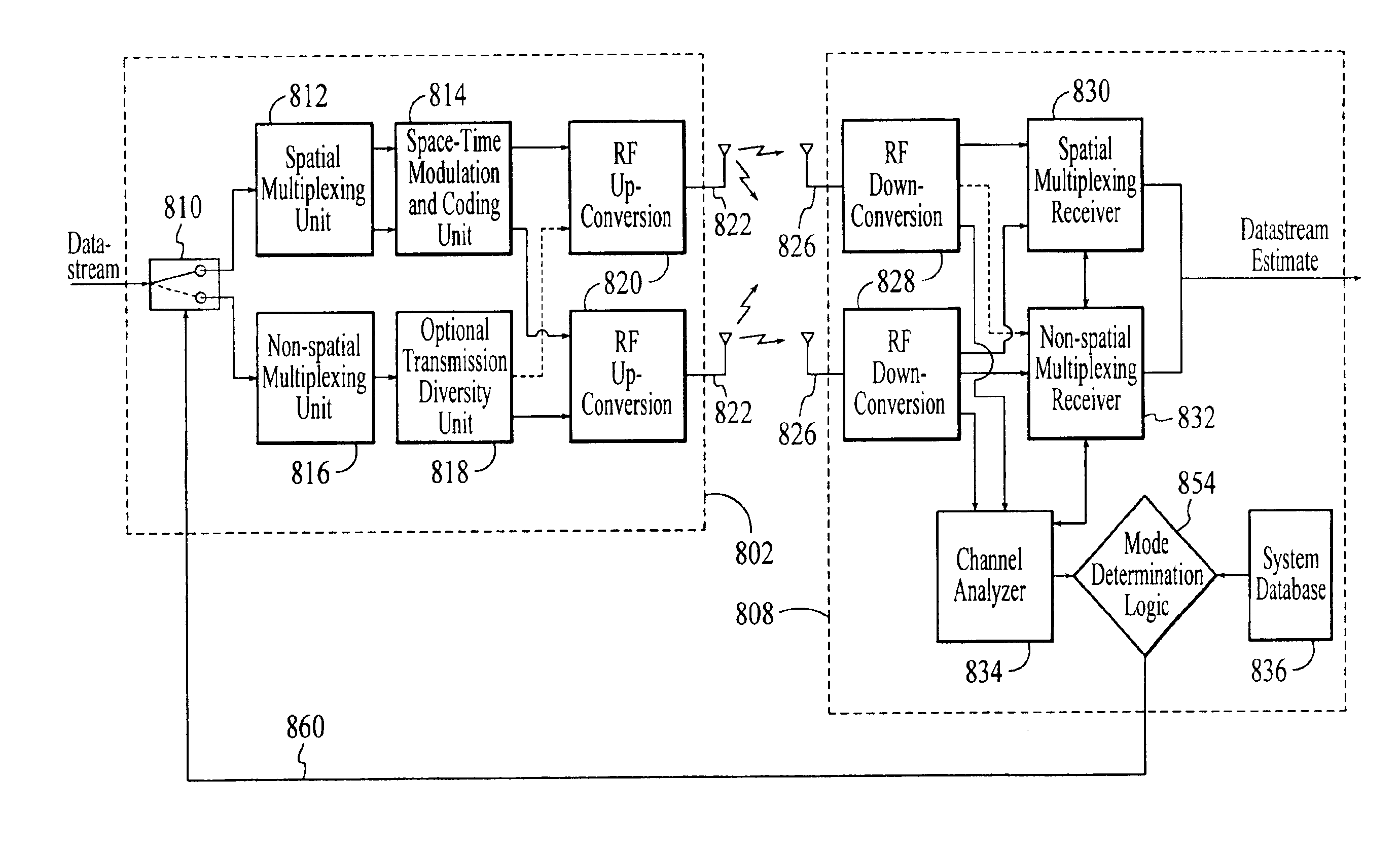
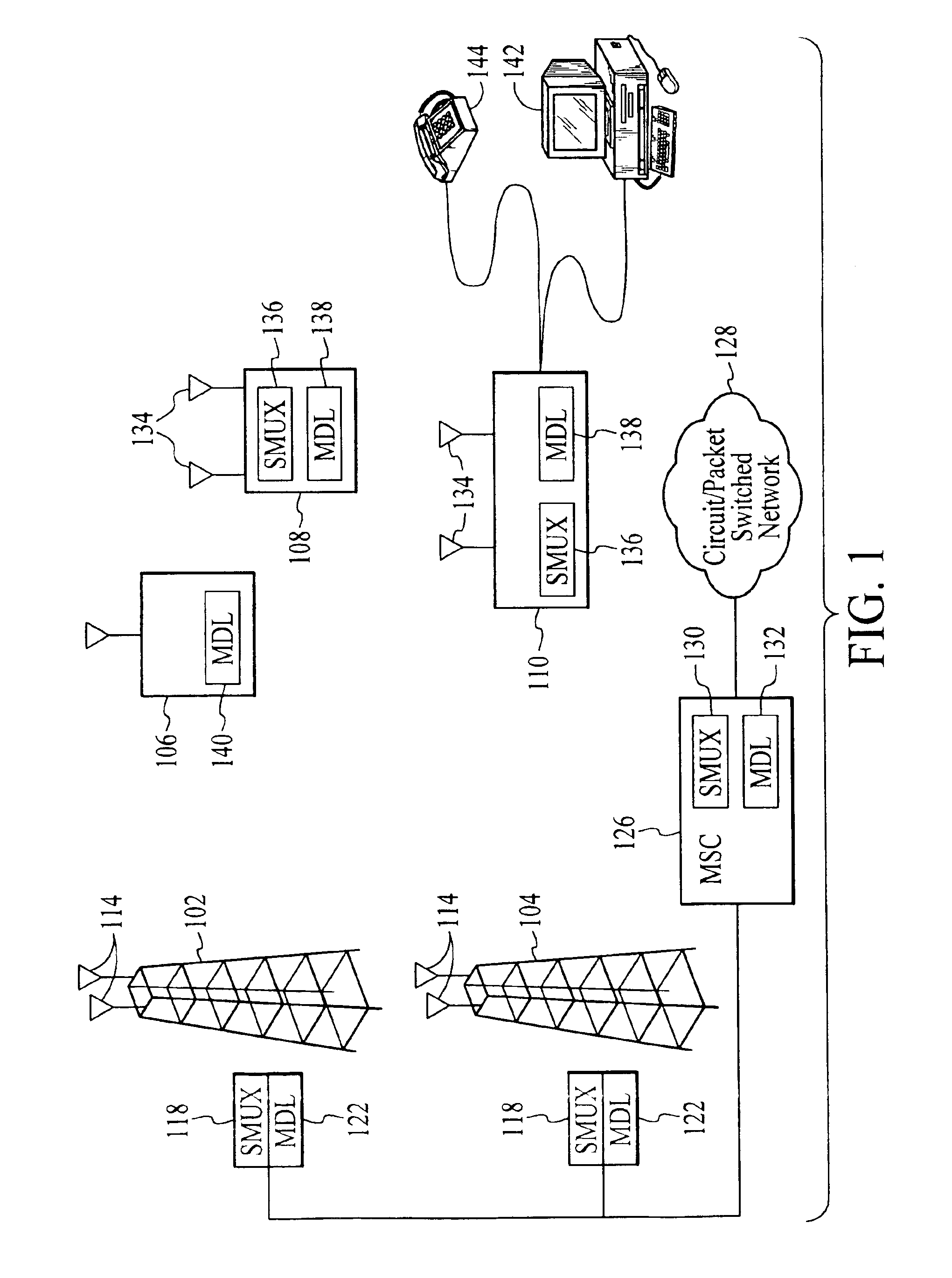
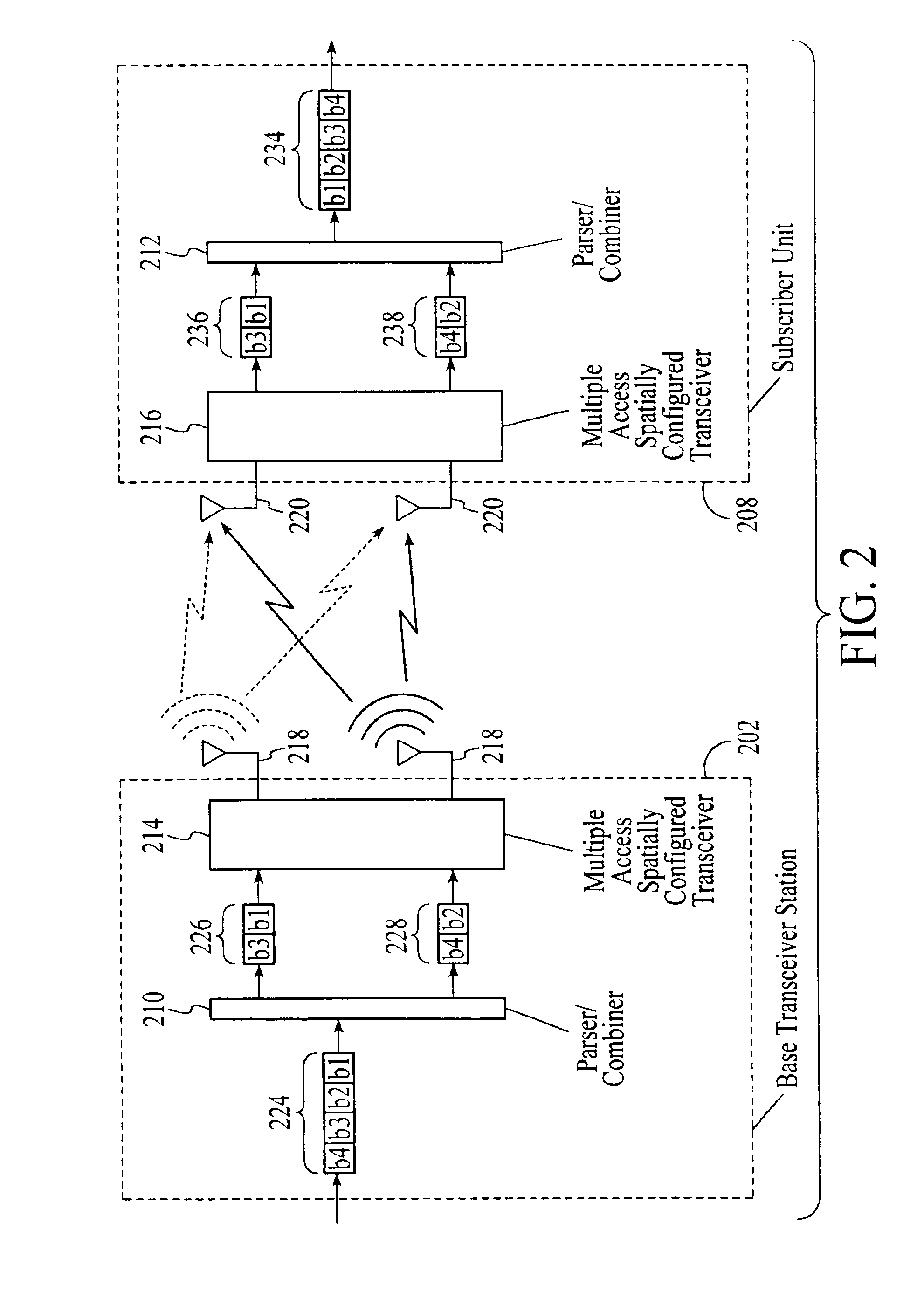
Wireless communications system that supports multiple modes of operation
InactiveUS20050174981A1Network traffic/resource managementAssess restrictionTransceiverMultiple modes
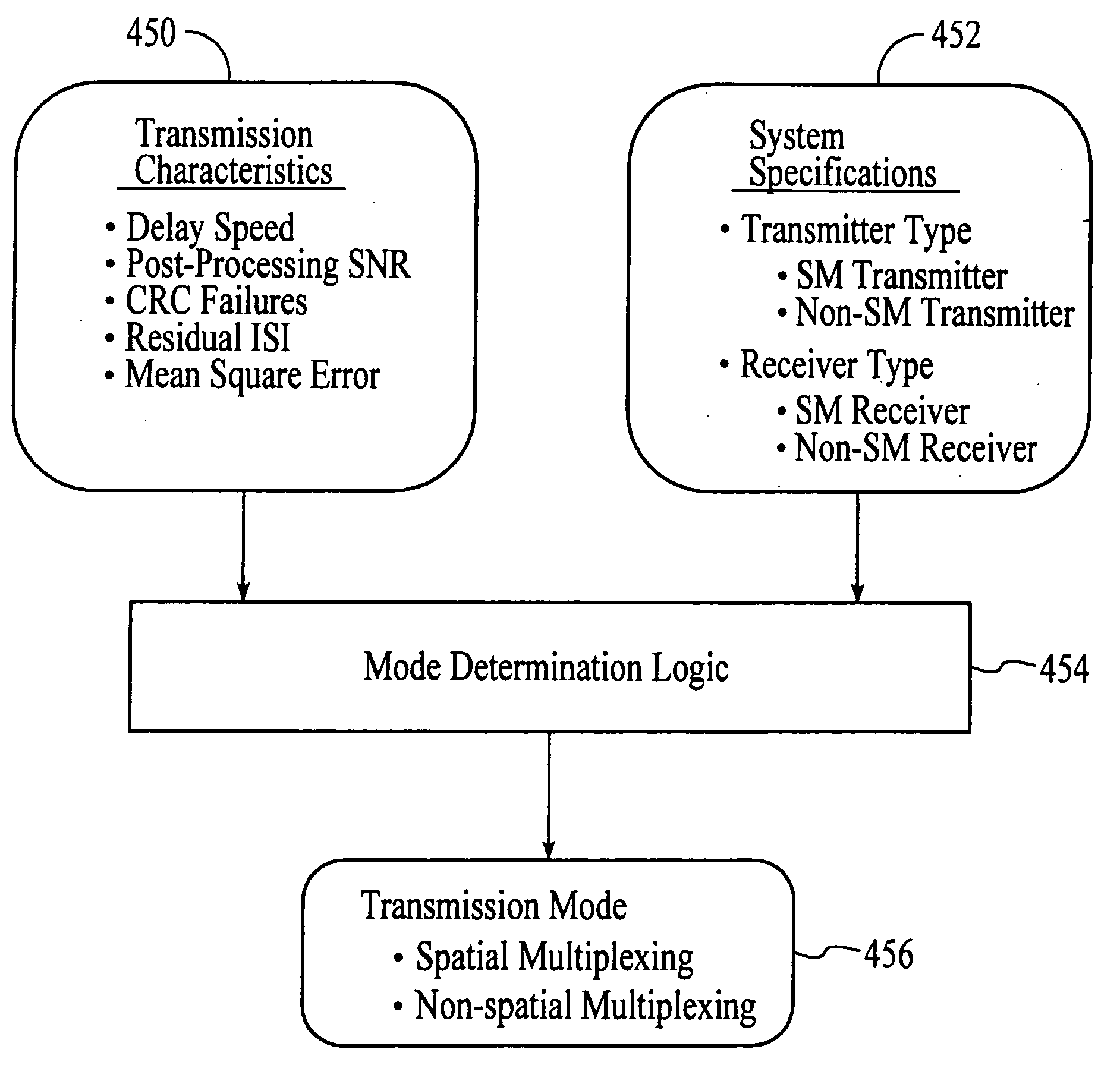
A wireless communications adapts its mode of operation between spatial multiplexing and non-spatial multiplexing in response to transmission-specific variables. An embodiment of a wireless communications system for transmitting information between a base transceiver station and a subscriber unit includes mode determination logic. The mode determination logic is in communication with the base transceiver station and the subscriber unit. The mode determination logic determines, in response to a received signal, if a subscriber datastream should be transmitted between the base transceiver station and the subscriber unit utilizing spatial multiplexing or non-spatial multiplexing. In an embodiment, the mode determination logic has an input for receiving a measure of a transmission characteristic related to the received signal. In an embodiment, the mode determination logic includes logic for comparing the measured transmission characteristic to a transmission characteristic threshold and for selecting one of spatial multiplexing and non-spatial multiplexing in response to the comparison of the measured transmission characteristic to the transmission characteristic threshold. In an embodiment, the transmission characteristic includes at least one of delay spread, post-processing signal-to-noise ratio, cyclical redundancy check (CRC) failure, residual inter-symbol interference, mean square error, coherence time, and path loss. By adapting the mode of operation in response to transmission-specific variables, the use of spatial multiplexing can be discontinued in unfavorable conditions. Additionally, because the wireless communications system can adapt its mode of operation between spatial multiplexing and non-spatial multiplexing, the communications system is compatible with both subscriber units that support spatial multiplexing and subscriber units that do not support spatial multiplexing.
Owner:APPLE INC
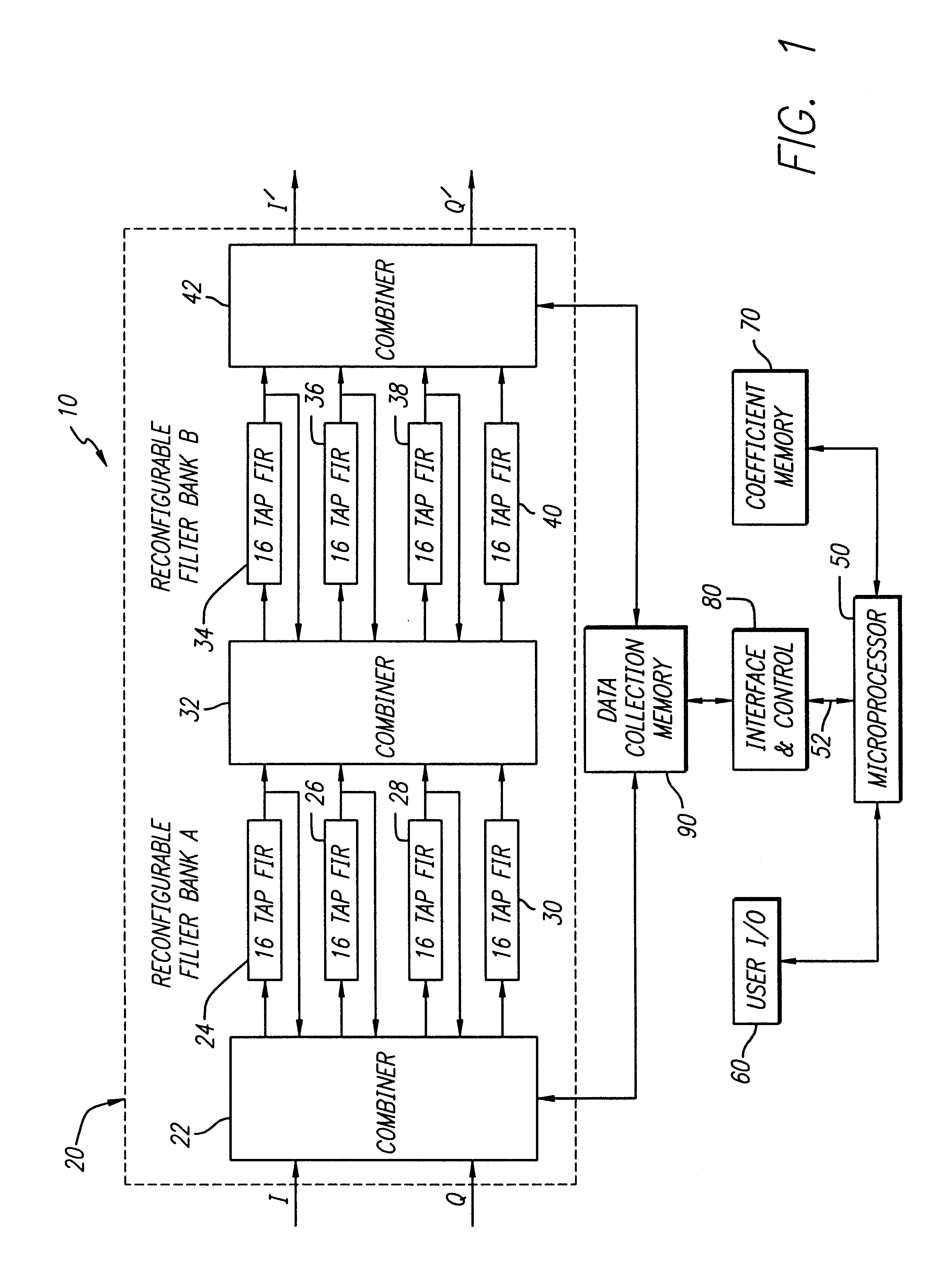
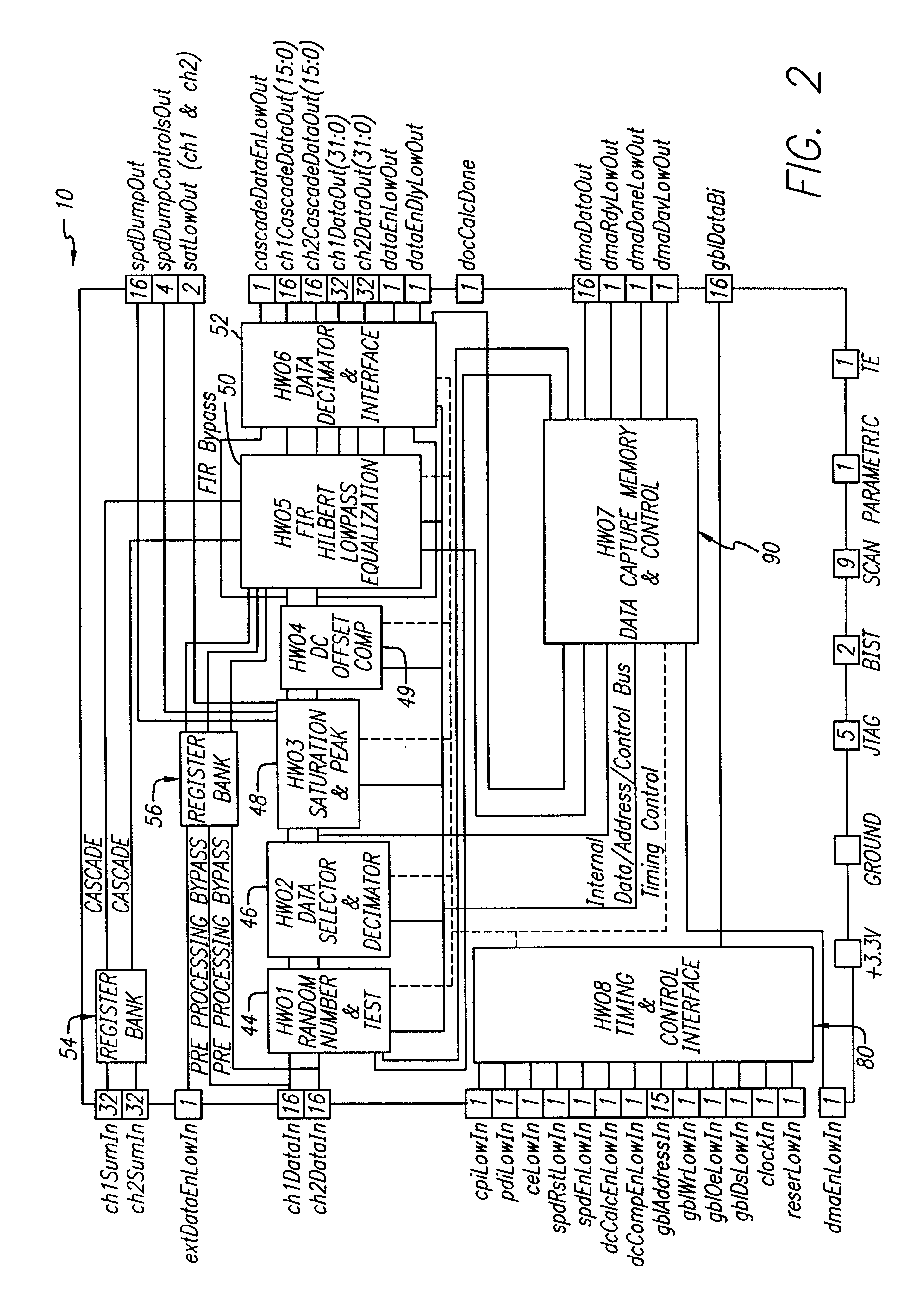
Equalization system using general purpose filter architecture
InactiveUS6411253B1Television system detailsDigital technique networkFinite impulse responseGeneral purpose
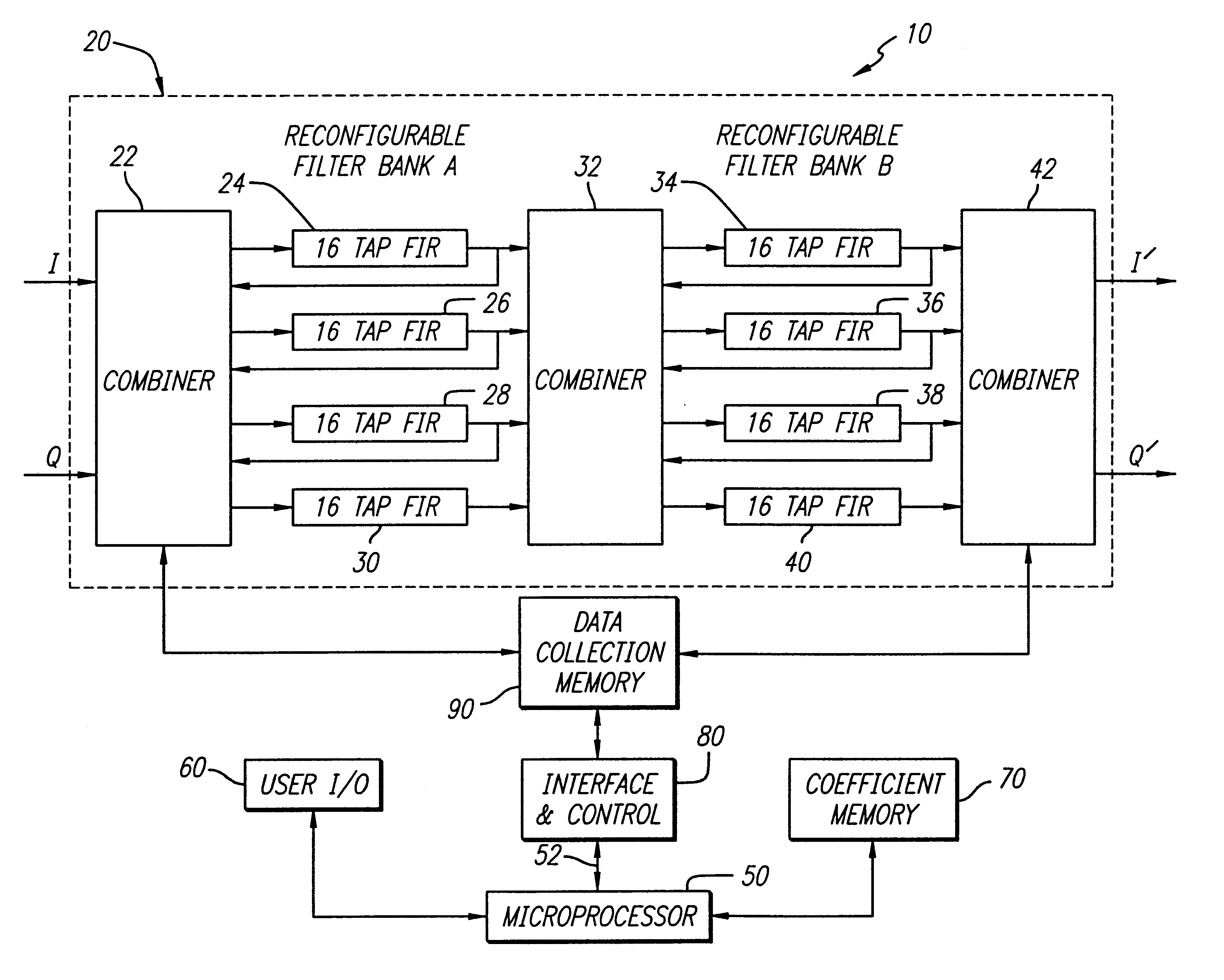
An equalization system and method. In a most general sense, the inventive equalization system includes first and second filters for filtering an in-phase component of a received signal in accordance with first and second sets of coefficients, respectively. The system includes third and fourth filters for filtering a quadrature component of the input signal in accordance with third and fourth sets of coefficients, respectively. The outputs of the first and third filters are subtracted to provide an equalized in-phase output signal and the outputs of the second and fourth filters are added to provide an equalized quadrature output signal. In the illustrative embodiment the filters are finite impulse response filters and the coefficients are provided by a microprocessor. In accordance with the present teachings, the filters are implemented in a general purpose filter. The delay elements of the filters are calculated in accordance with a mean square error algorithm. Accordingly, the coefficients are the product of the correlation between inputs to the delay elements and a cross correlation between the inputs and a set of values representative of a desired response.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Wireless communications system that supports multiple modes of operation
InactiveUS6937592B1Network traffic/resource managementAssess restrictionOperation modeMultiple modes
A wireless communications adapts its mode of operation between spatial multiplexing and non-spatial multiplexing in response to transmission-specific variables. An embodiment of a wireless communications system for transmitting information between a base transceiver station and a subscriber unit includes mode determination logic. The mode determination logic is in communication with the base transceiver station and the subscriber unit. The mode determination logic determines, in response to a received signal, if a subscriber datastream should be transmitted between the base transceiver station and the subscriber unit utilizing spatial multiplexing or non-spatial multiplexing. In an embodiment, the mode determination logic has an input for receiving a measure of a transmission characteristic related to the received signal. In an embodiment, the mode determination logic includes logic for comparing the measured transmission characteristic to a transmission characteristic threshold and for selecting one of spatial multiplexing and non-spatial multiplexing in response to the comparison of the measured transmission characteristic to the transmission characteristic threshold. In an embodiment, the transmission characteristic includes at least one of delay spread, post-processing signal-to-noise ratio, cyclical redundancy check (CRC) failure, residual inter-symbol interference, mean square error, coherence time, and path loss. By adapting the mode of operation in response to transmission-specific variables, the use of spatial multiplexing can be discontinued in unfavorable conditions. Additionally, because the wireless communications system can adapt its mode of operation between spatial multiplexing and non-spatial multiplexing, the communications system is compatible with both subscriber units that support spatial multiplexing and subscriber units that do not support spatial multiplexing.
Owner:APPLE INC
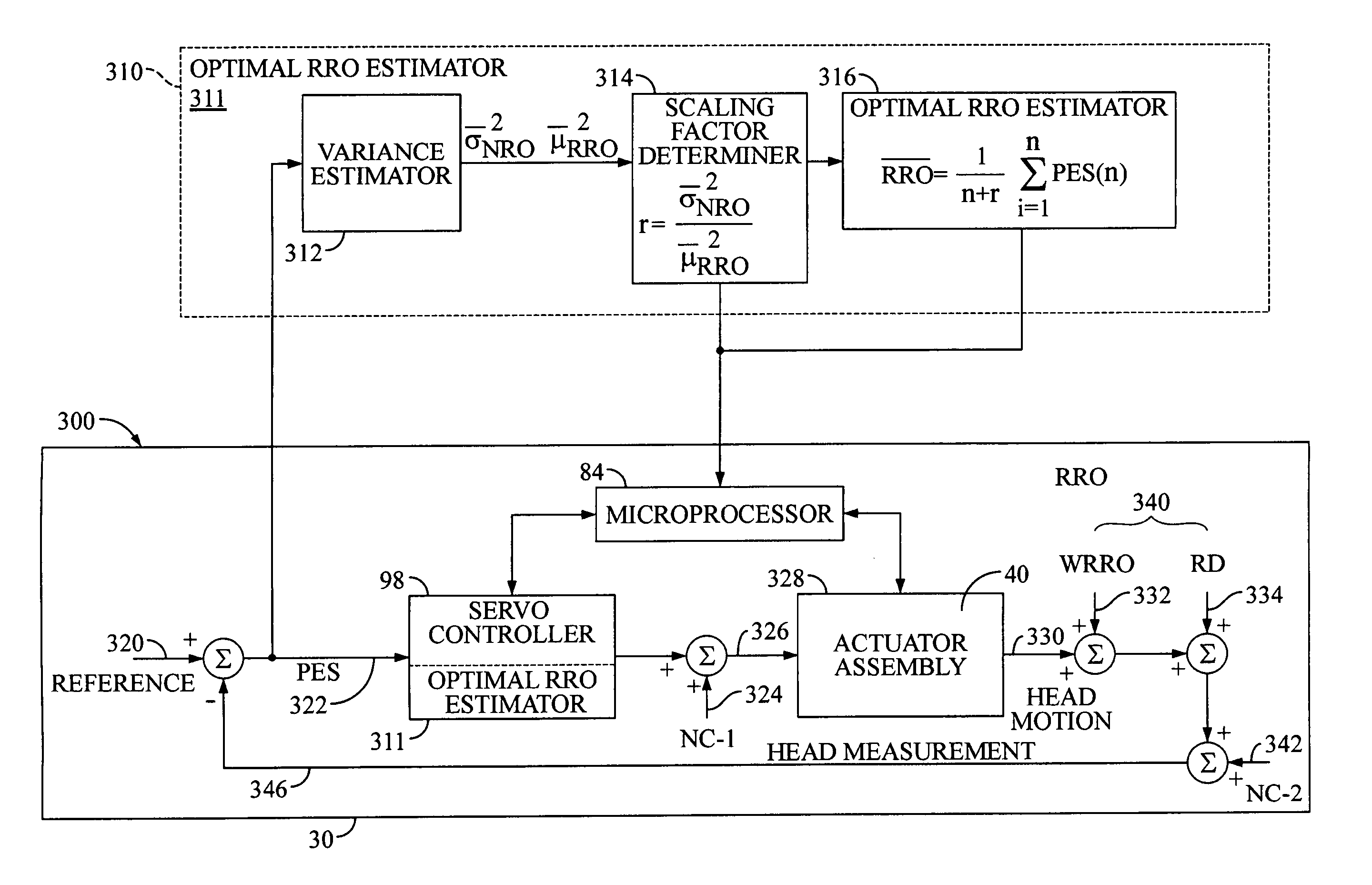
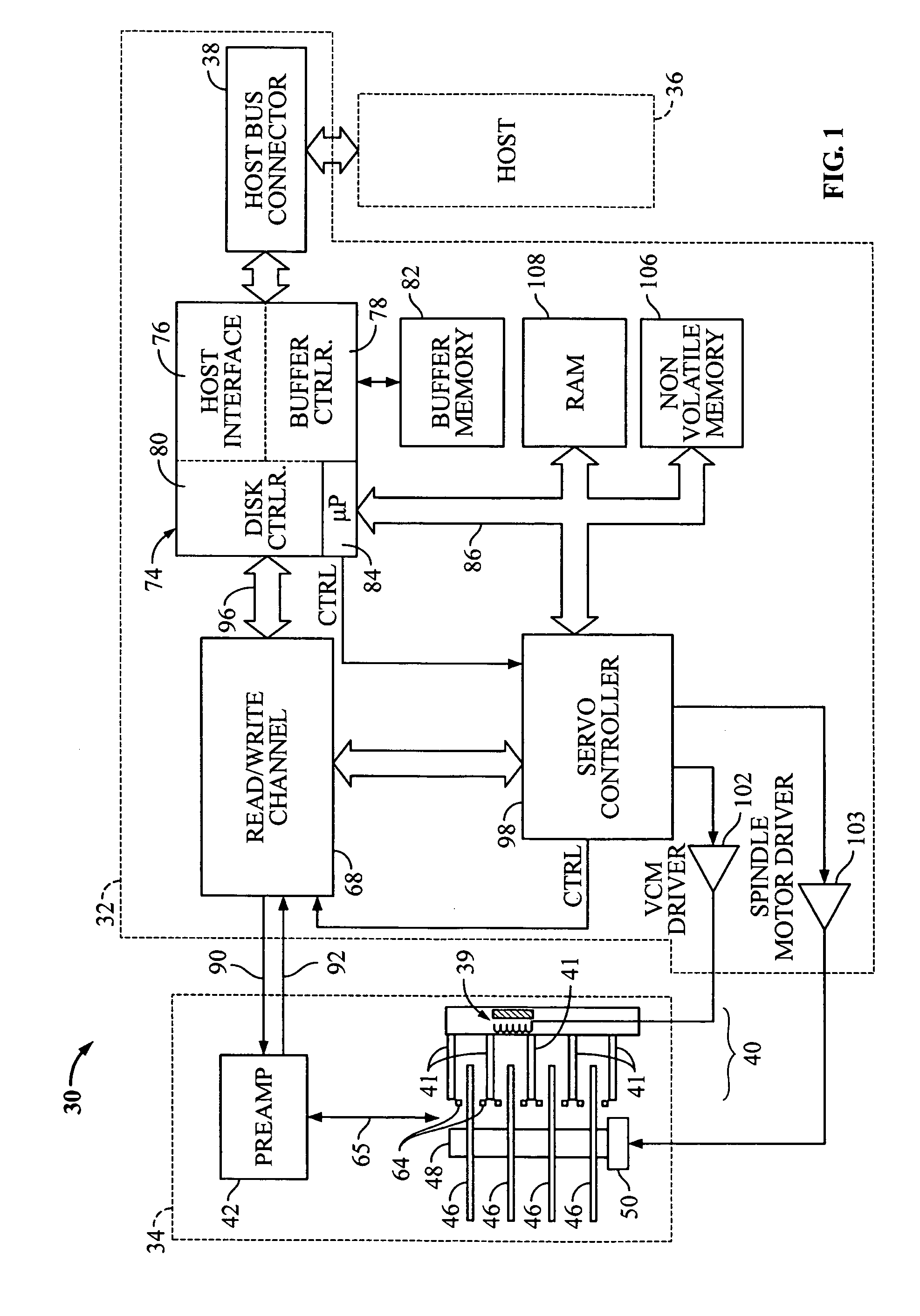
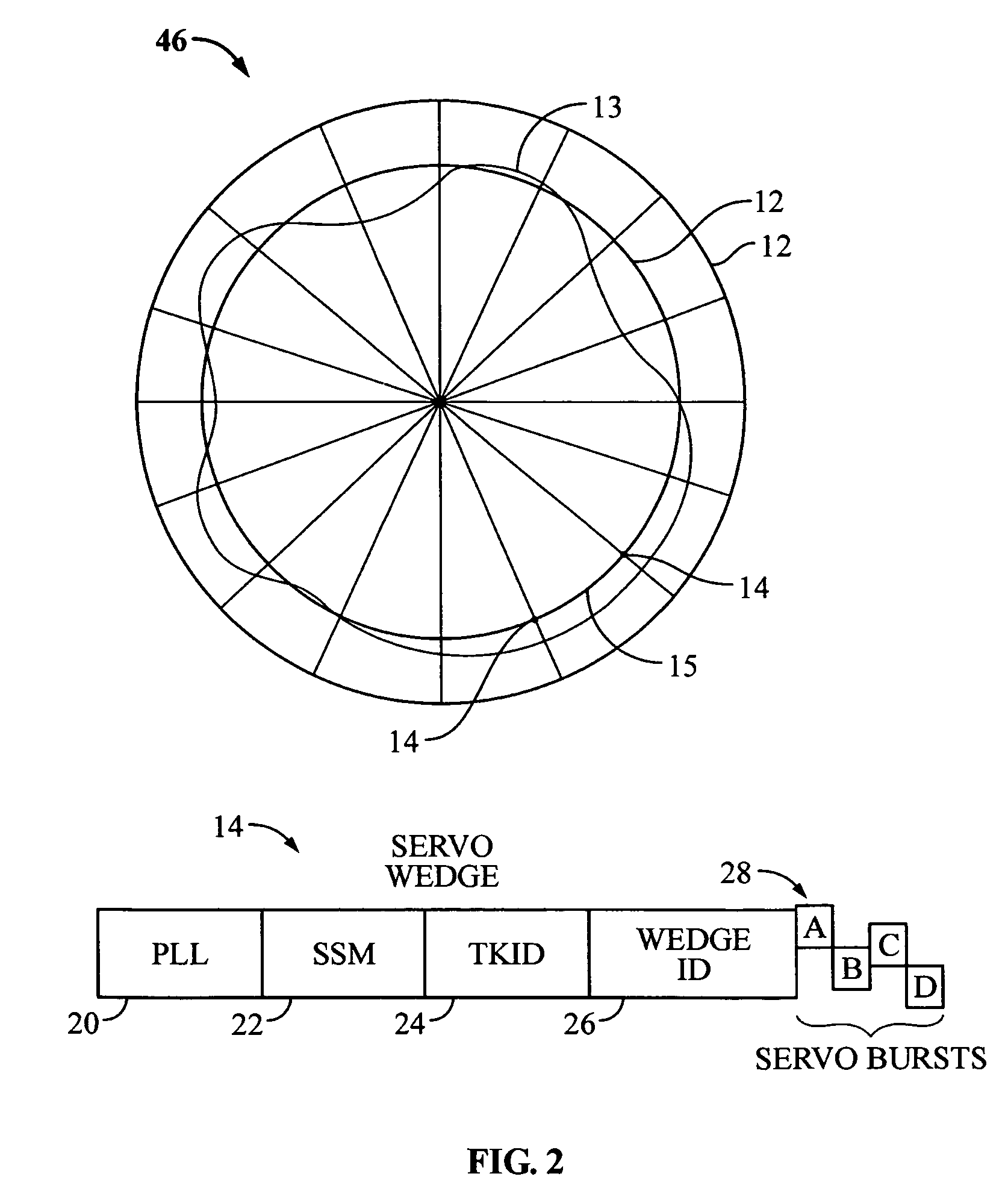
Disk drive to estimate repeatable runout (RRO) based upon on an optimal mean square estimation (MSE) learning method
InactiveUS7595954B1Record information storageAlignment for track following on disksMean squareStudy methods
Disclosed is a method of estimating repeatable runout (RRO) for a disk drive. The method includes: determining a plurality of position error signal (PES) values for a plurality of servo wedges of a track of a disk; and estimating repeatable runout (RRO) in the PES values for the servo wedges of the track by averaging determined PES values over a pre-determined number of revolutions of the disk of the disk drive and scaling the averaged PES values by a pre-determined ratio of the variance of non-repeatable runout (NRRO) to the variance of an optimal estimation of the RRO for the disk drive.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
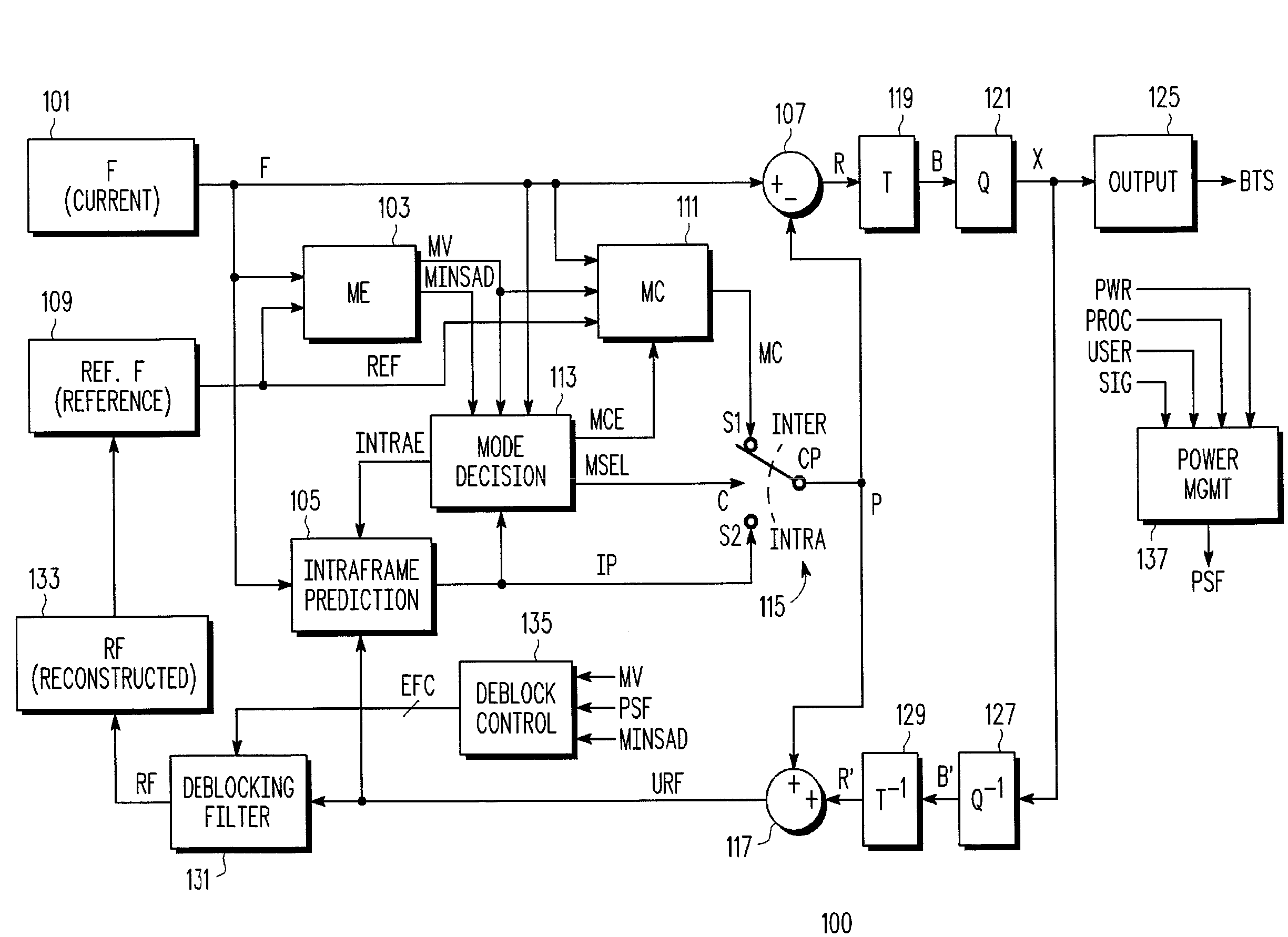
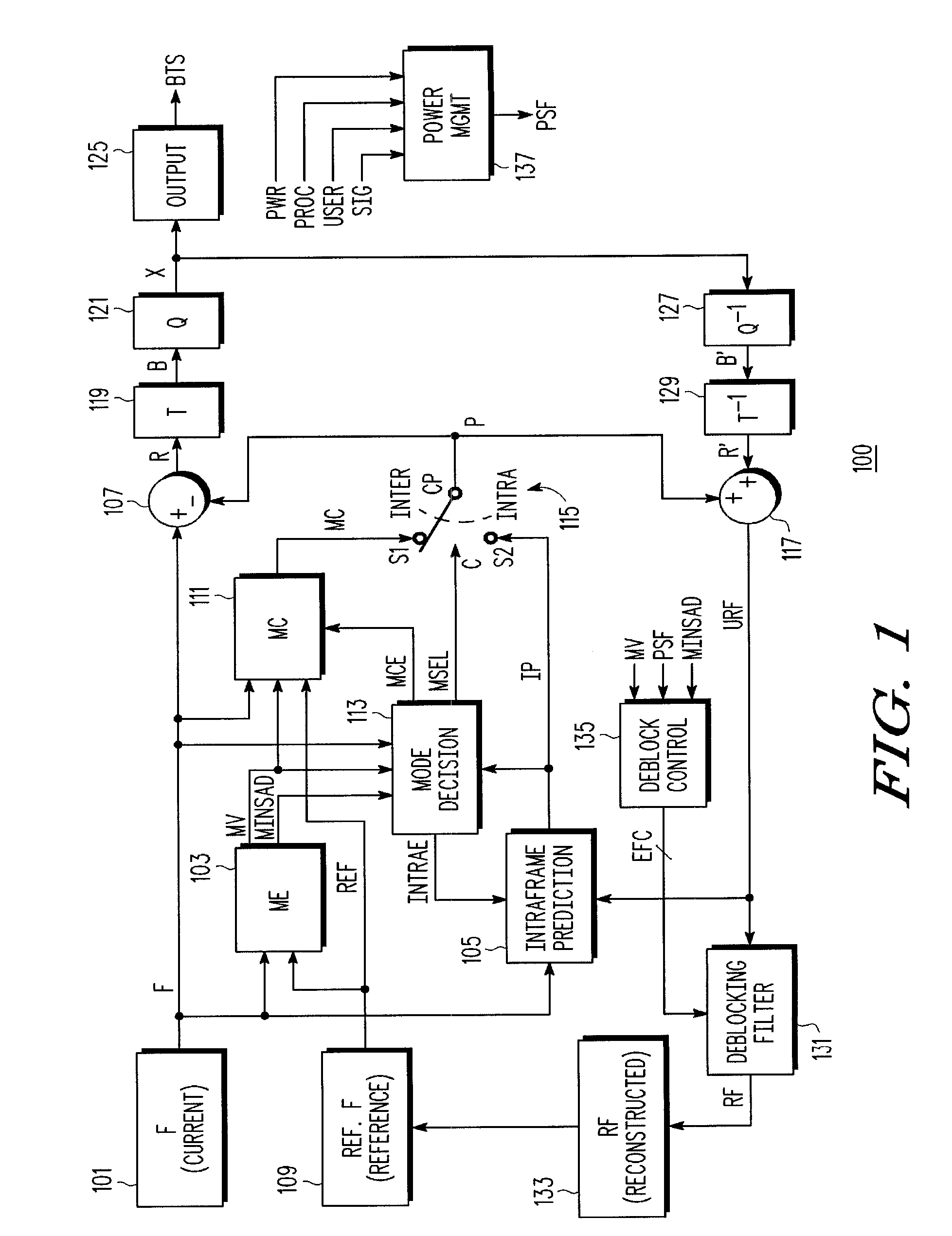
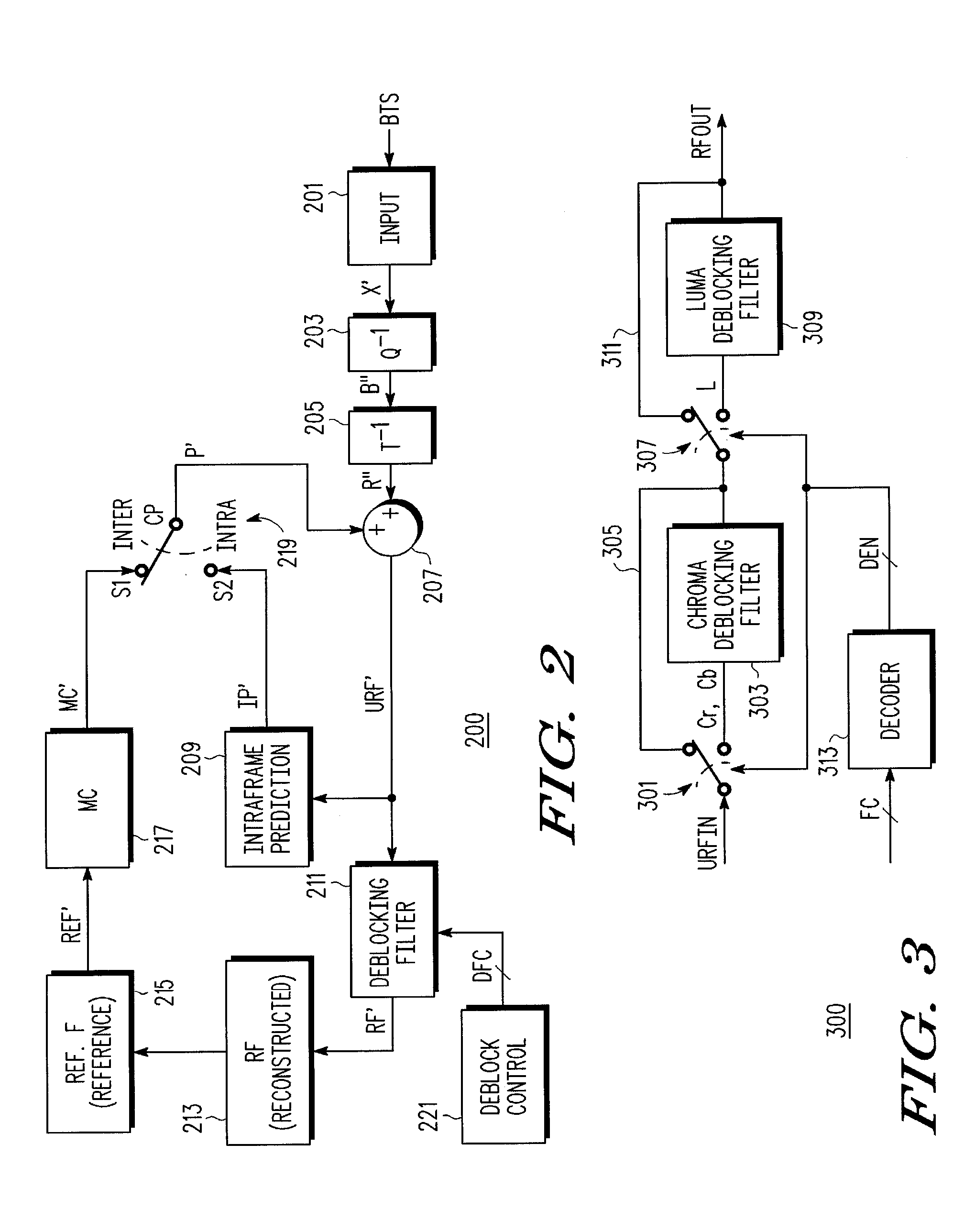
Adaptive disabling of deblock filtering based on a content characteristic of video information
ActiveUS20080137752A1Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionPattern recognitionInformation processing
A method of adaptively disabling deblock filtering of video information including determining a content characteristic of the video information, and adaptively disabling deblock filtering of the video information based on the content characteristic. The content characteristic may be a content complexity, such as an average of minimum sums of absolute differences of pixel values determined during motion estimation, or the mean square error of the video information, or the number of bits used for coding the video content. The content characteristic may be other than complexity, such as motion vector information. A video information processing system including a video processing circuit which processes video information and which determines a content characteristic of the video information, and a deblocking filter circuit which adaptively disables deblock filtering of the video information based on the content characteristic.
Owner:NXP USA INC
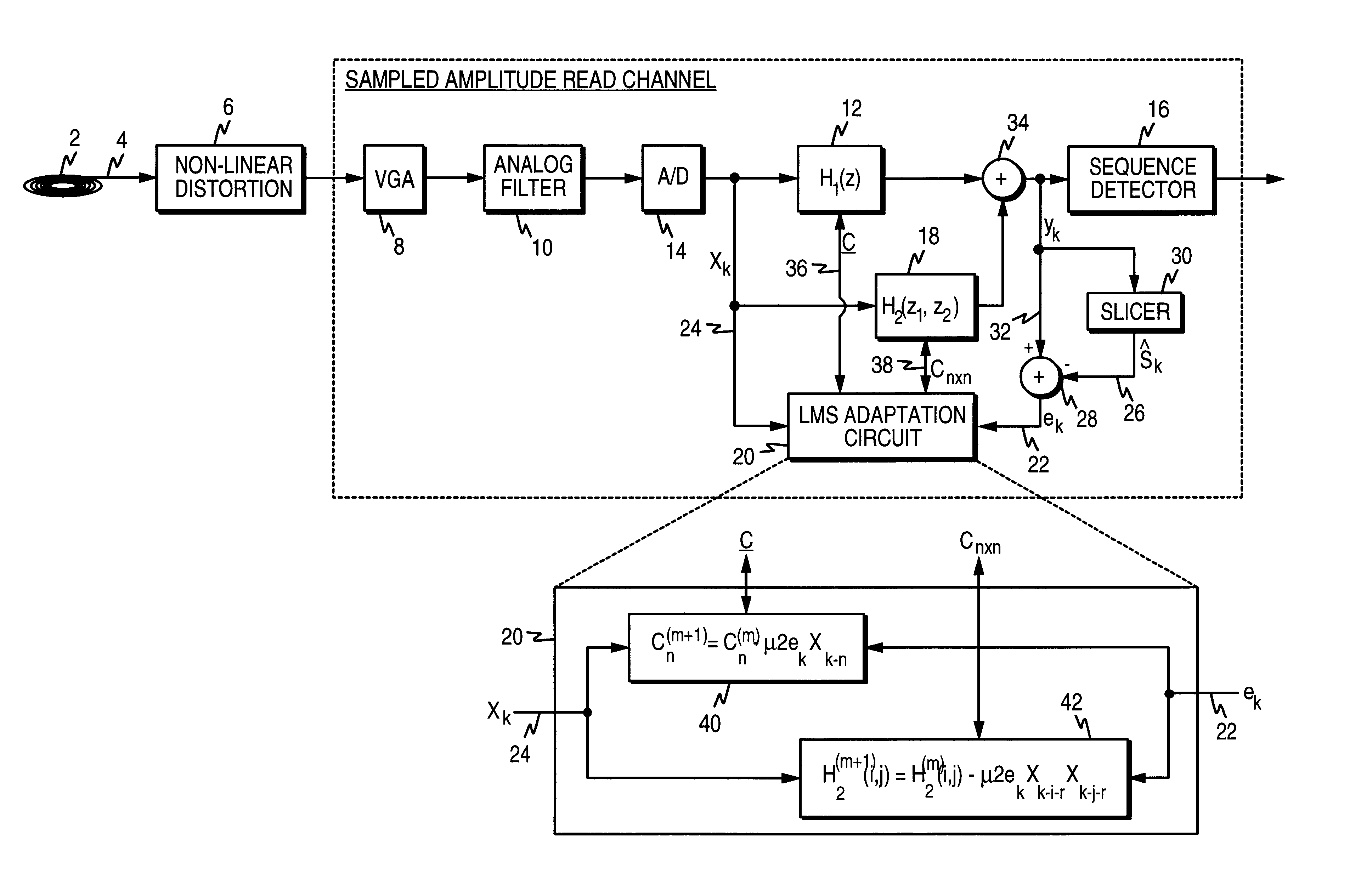
Sampled amplitude read channel employing an adaptive non-linear correction circuit for correcting non-linear distortions in a read signal
InactiveUS7012772B1Minimize complexityLow costMultiple-port networksModification of read/write signalsNonlinear distortionAsymmetric head
A sampled amplitude read channel is disclosed for magnetic disk storage systems comprising an adaptive non-linear correction circuit for correcting non-linear distortions in the read signal, such as asymmetry caused by the non-linear response of a magneto-resistive (MR) read head. The analog read signal is sampled and the discrete time sample values equalized into a desired partial response prior to sequence detection. The non-linear correction circuit is inserted into the read path prior to the sequence detector and adaptively tuned by a least-mean-square (LMS) adaptation circuit. In one embodiment, the non-linear correction circuit is a discrete-time Volterra filter comprising a linear response for implementing an equalizing filter, and a non-linear response for attenuating non-linear distortions in the read signal. The filter coefficients of both the linear and non-linear sections of the Volterra filter are adaptively adjusted by the LMS adaptation circuit. In an alternative embodiment, the non-linear correction circuit operates in the analog domain, prior to the sampling device, where the cost and complexity can be minimized. The analog correction circuit implements an inverse response to that of the non-linearity in the read signal, and the response is adaptively tuned using an LMS update value computed in discrete-time for a Volterra filter, without actually implementing a Volterra filter. Further, the LMS update value for the analog correction circuit can be implemented using a simple squaring circuit.
Owner:CIRRUS LOGIC INC
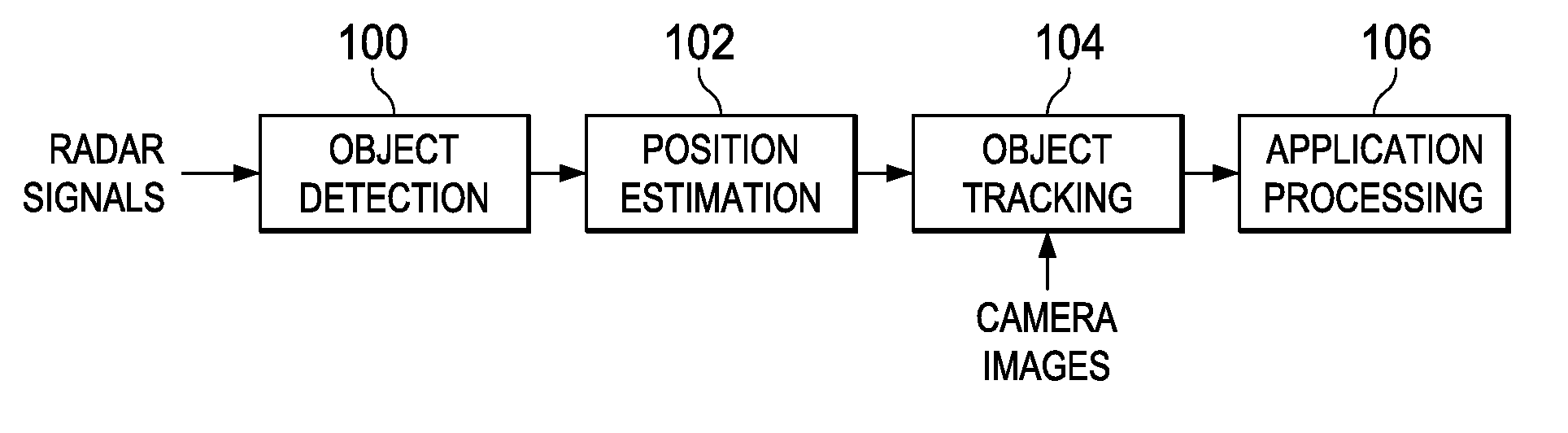
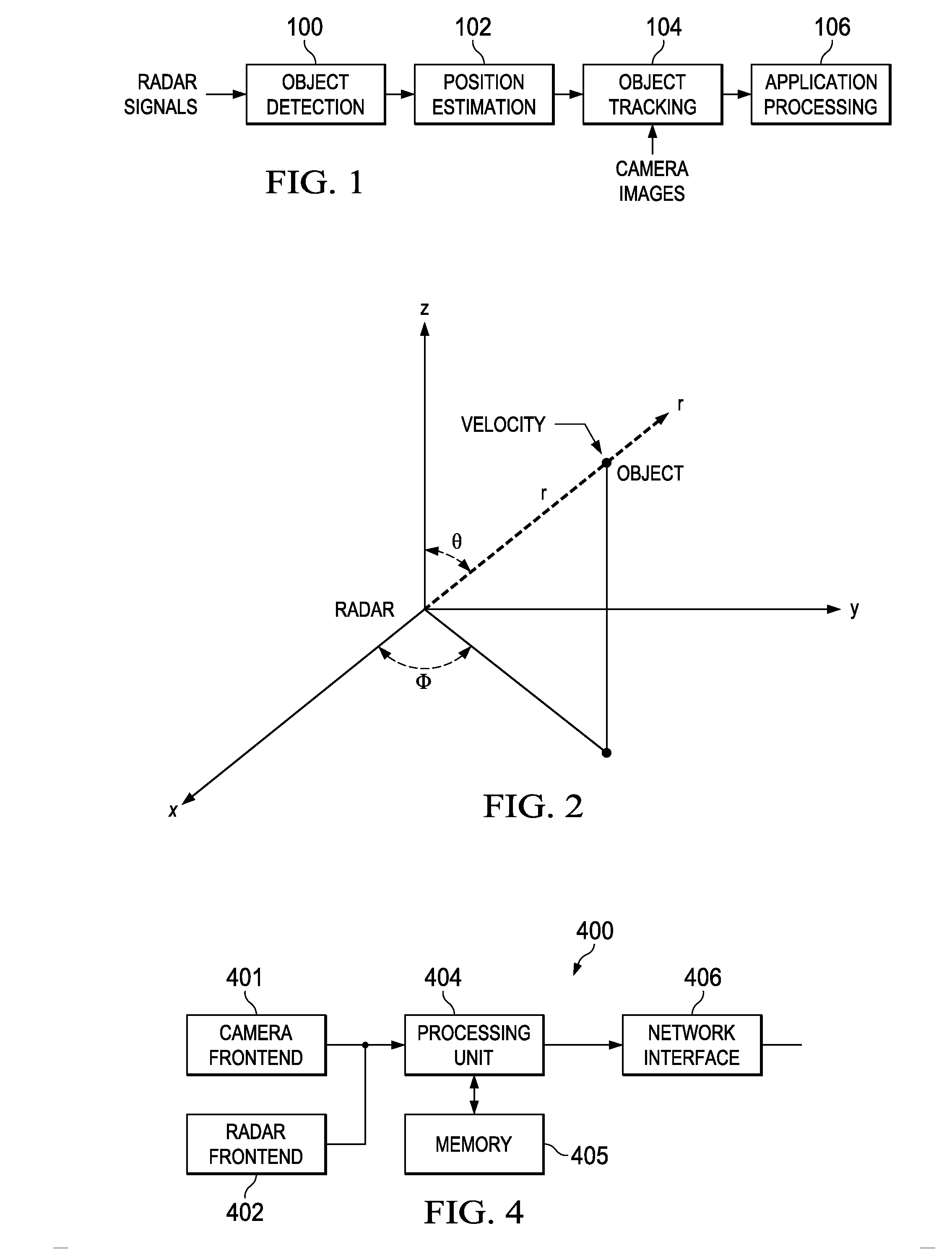
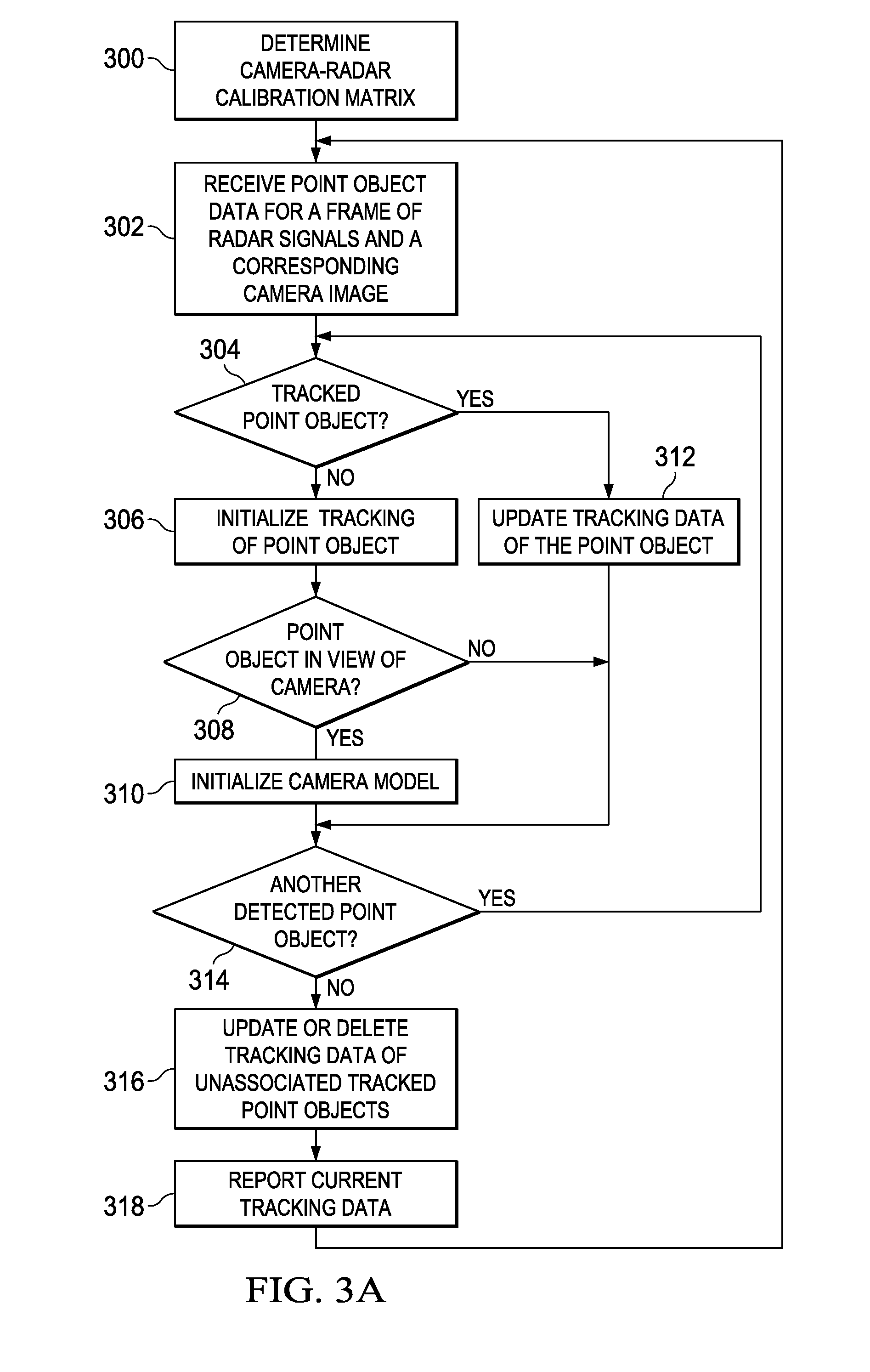
Camera Assisted Tracking of Objects in a Radar System
Camera-assisted tracking of point objects in a radar system is provided. An extended Kalman filter framework based on both radar and camera observations is used to track point objects detected in frames of radar signal data. This framework provides a minimum mean square estimation of the current state of a point object based on previous and current observations from both frames of radar signals and corresponding camera images.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
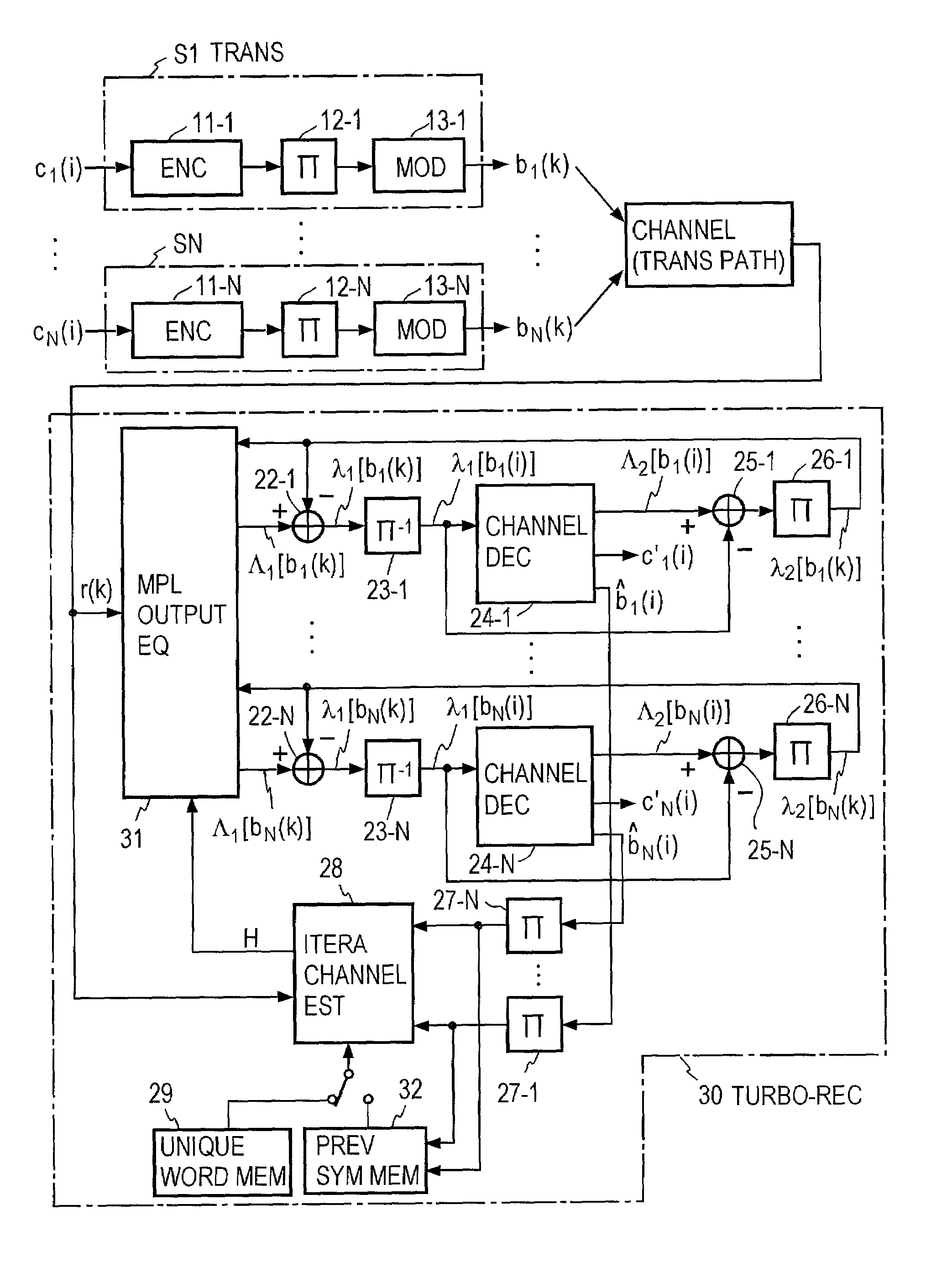
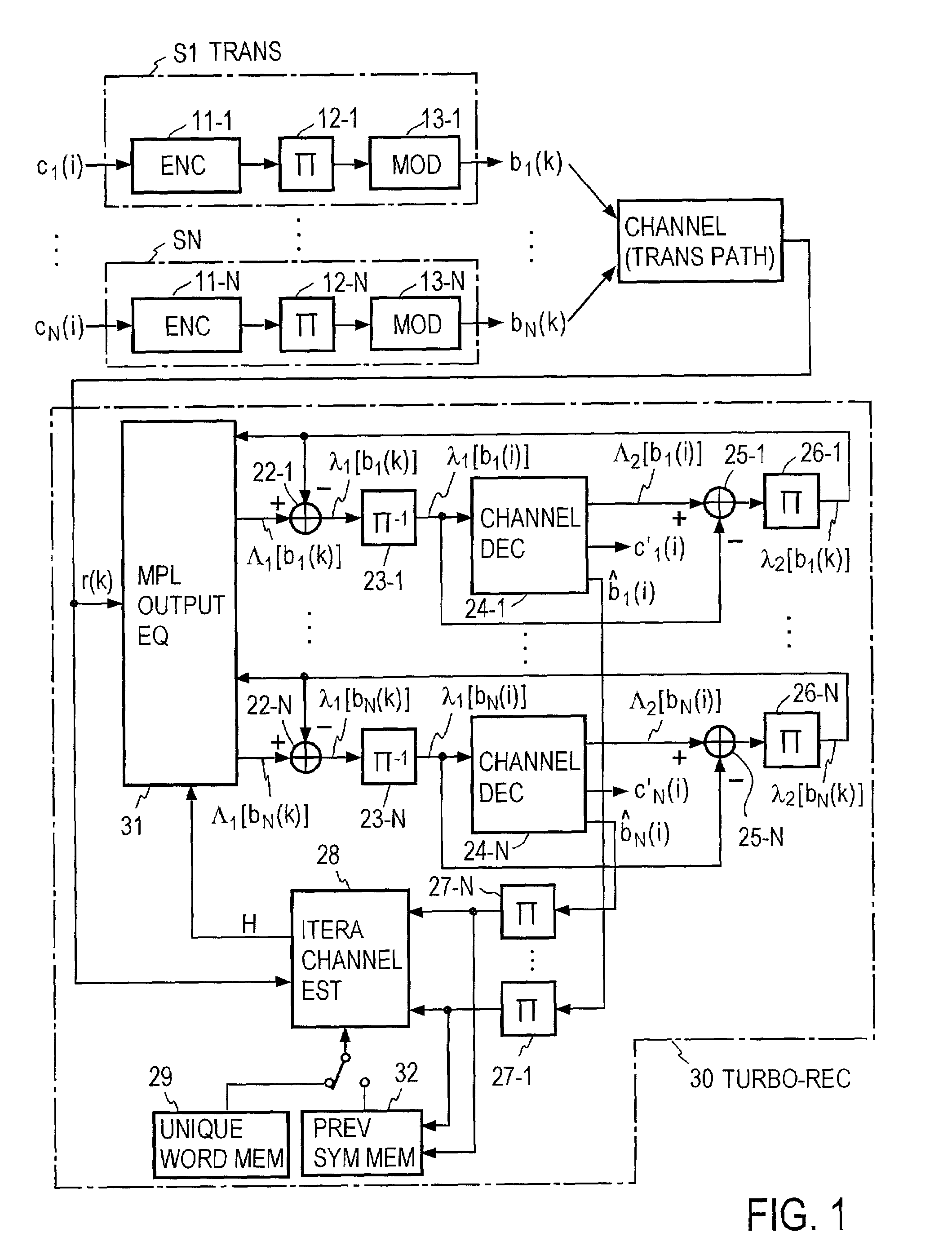
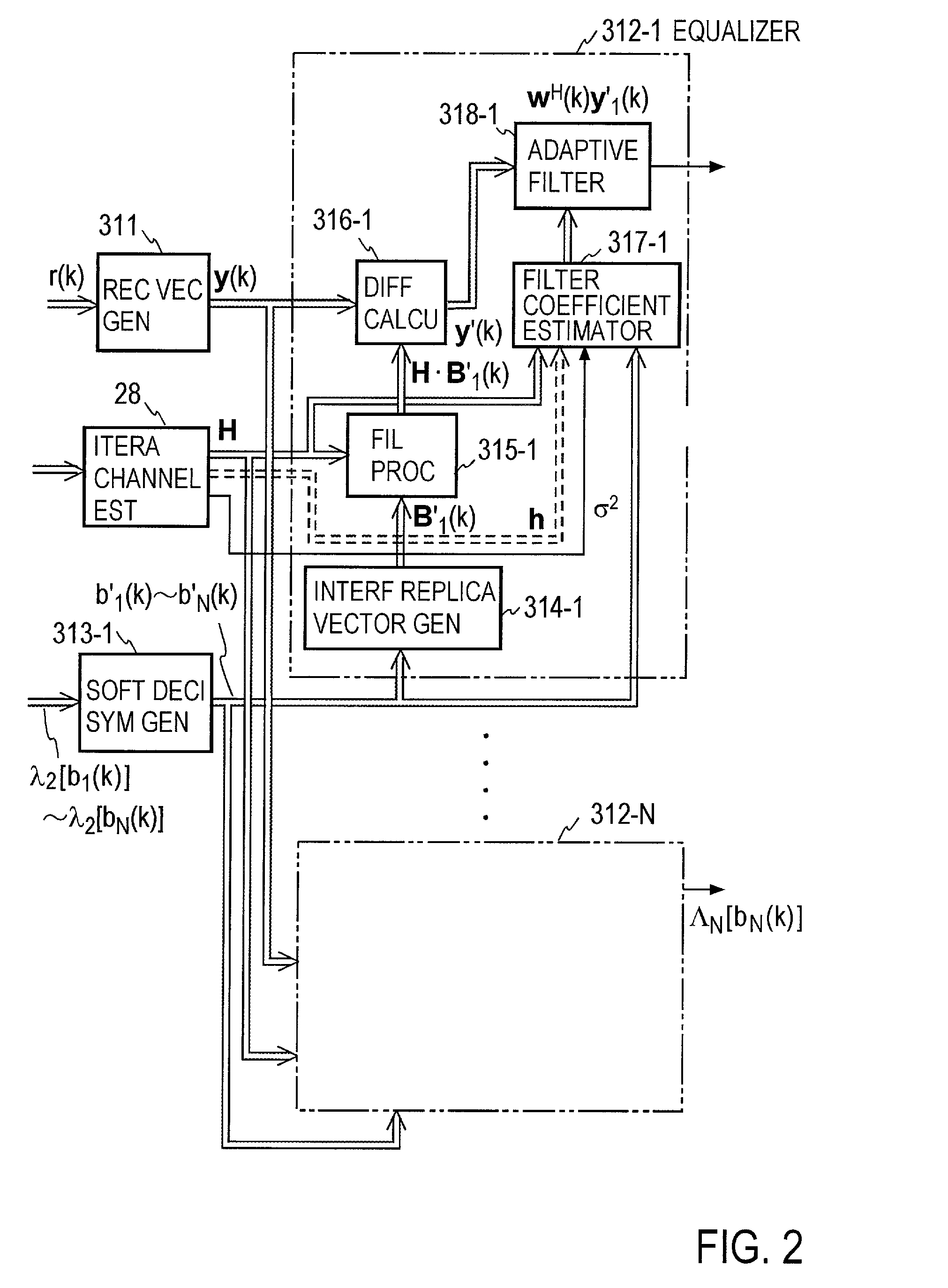
Turbo-reception method and turbo-receiver
InactiveUS7027533B2Improve accuracyData representation error detection/correctionCode conversionQ-matrixResidual interference
An impluse response hmn(q) of each transmission path is estimated from N received signals rm (m=1, . . . , M) and a known signal (for a number of users equal to N, n=1, . . . , N). M×N matrix H (q) having hmn(q) as an element and a Q×Q matrix H having H(q) as an element are determined (where Q represents a number of multipaths of each transmitted wave and q=0, . . . , Q−1). A soft decision value b′n(k) is determined from decoded λ2 [bn(k)], and this is used to generate an interference component matrix B′(k) to generate an interference replica H·B′(k). The interference replica H·B′(k) is subtracted from a received matrix y(k) to determine y′(k). y(k) and H are used to determine an adaptive filter coefficient wn(k) to be applied to an n-th user in order to eliminate residual interference components in y′(k) according to the minimum mean square error criteria. y(k) is passed through wn(k) to provide a log-likelihood ratio as a received signal from the user n from which interferences are eliminated.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
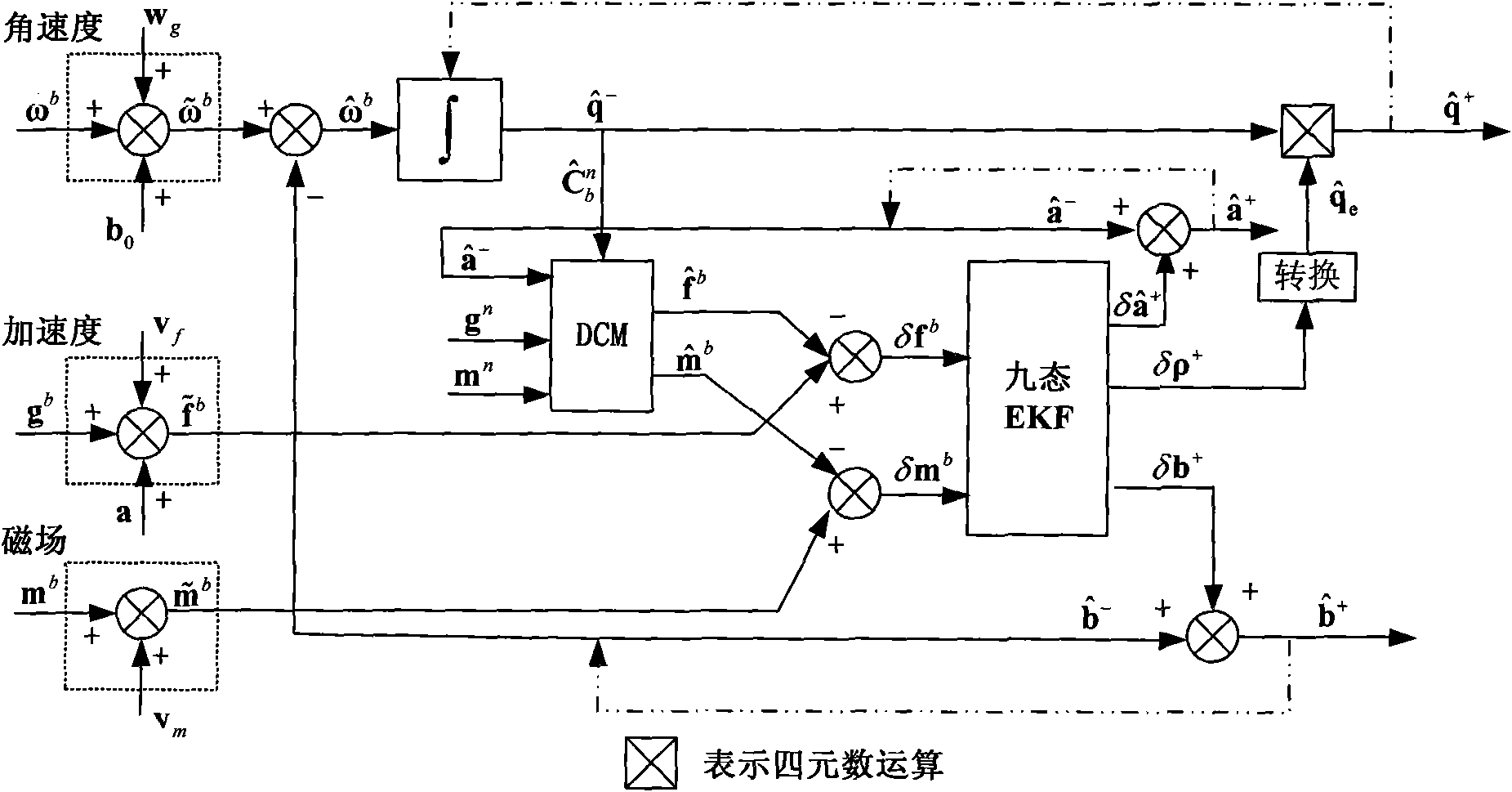
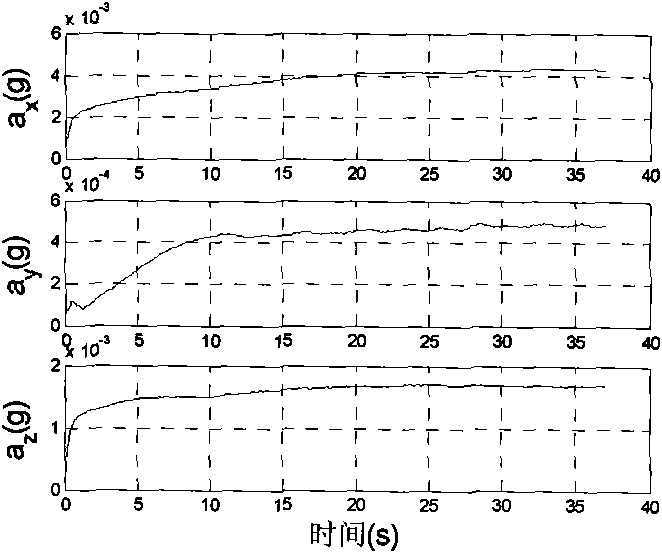
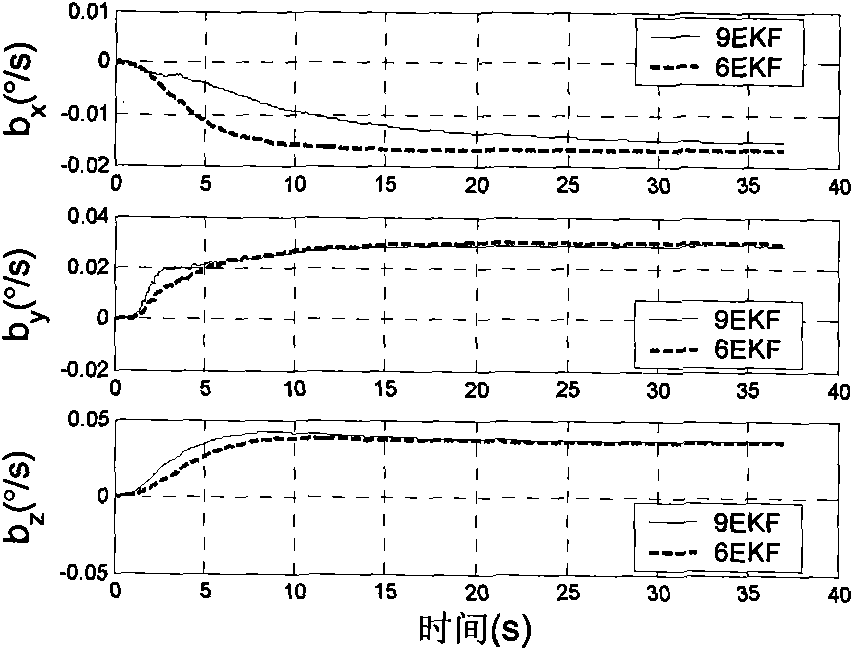
Attitude estimation method of maneuvering acceleration-assisted extended Kalman filter (EKF) attitude and heading reference system (AHRS)
InactiveCN101782391AReal-time correction of zero offsetNavigational calculation instrumentsNavigation by terrestrial meansAttitude and heading reference systemMean square
The invention provides an attitude estimation method of a maneuvering acceleration-assisted extended Kalman filter (EKF) attitude and heading reference system (AHRS). The state quantity of the EKF contains an error of three attitude angles, a null bias error of a three-axis gyroscope and a three-axis carrier maneuvering acceleration error of a carrier system, and the observed quantity of the EKF contains a three-axis acceleration error and a three-axis earth magnetic field error. A strapdown attitude algorithm and the nine-state EKF algorithm are subjected to data fusion to acquire attitude estimation of the AHRS. A single-axis turntable experiment, a vehicle-mounted dynamic experiment and a flight experiment prove that the maneuvering acceleration-assisted nine-state EKF data fusion algorithm has stable attitude angle accuracy under different maneuvering conditions, and the mean square deviation of the attitude angle can be limited within 2 degrees.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Control signalling and dynamic channel allocation in a wireless network
InactiveUS6977912B1Efficient reuseComplete informationNetwork traffic/resource managementData switching by path configurationDynamic channelSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
Owner:ADAPTIVE BROADBAND CORP
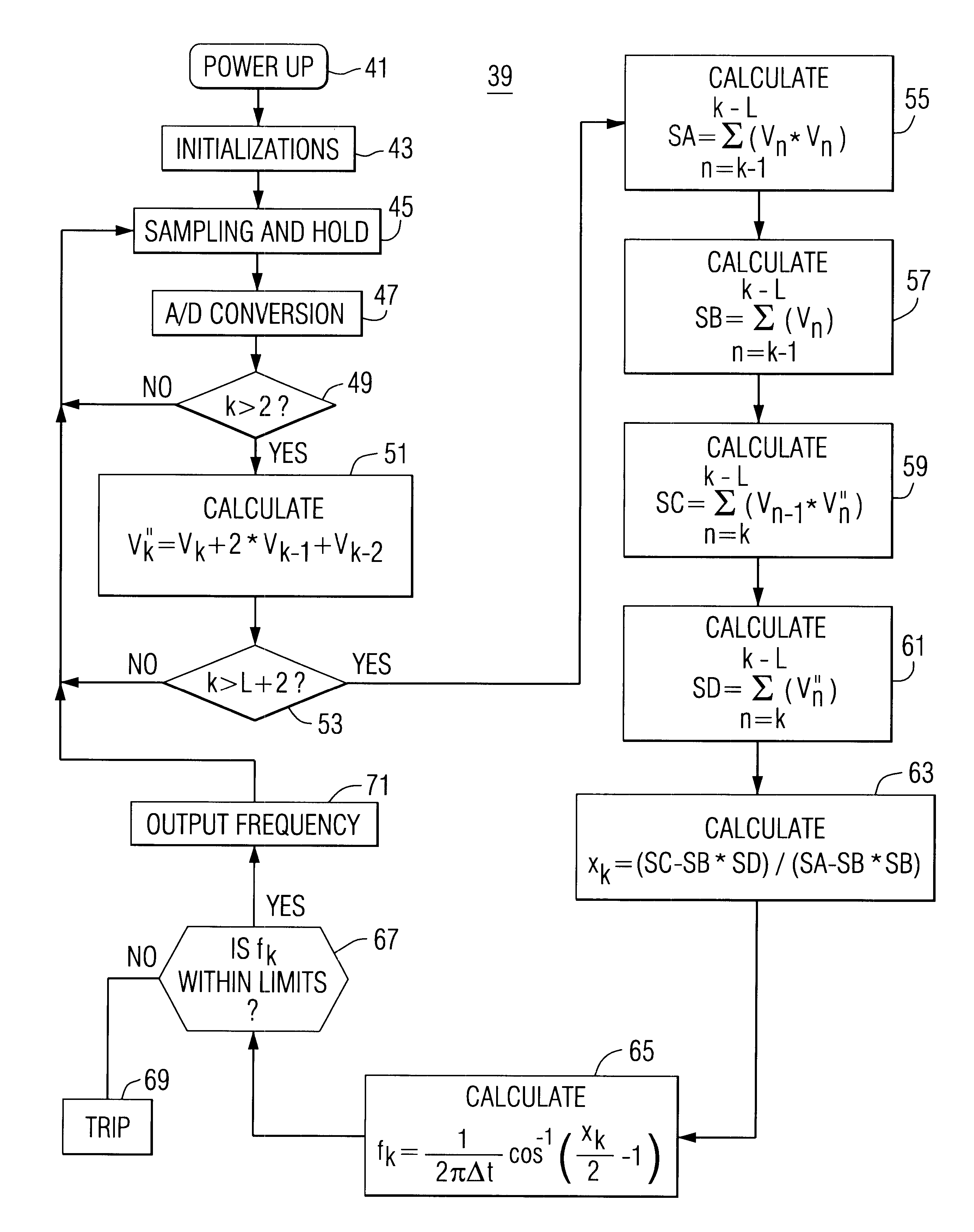
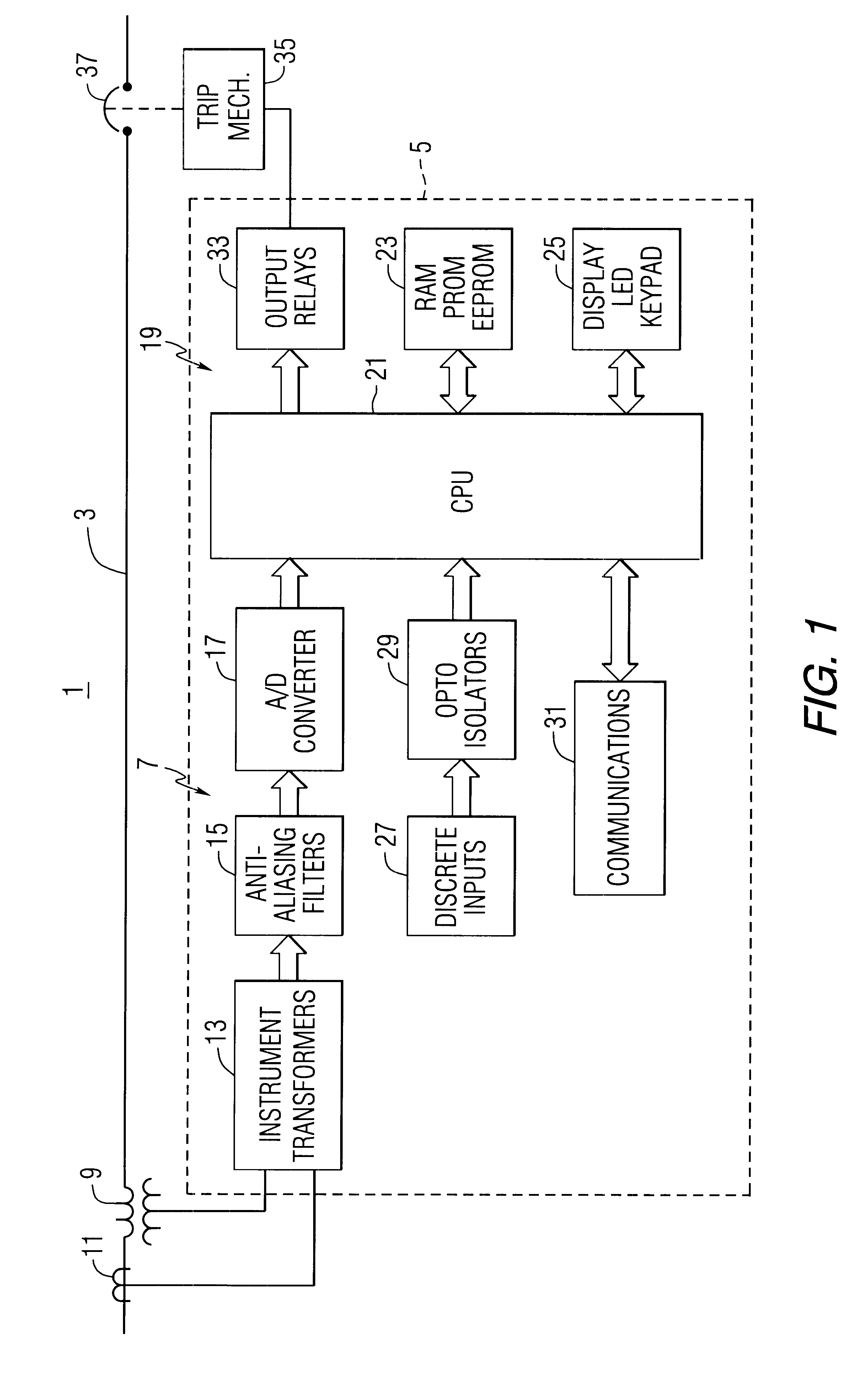
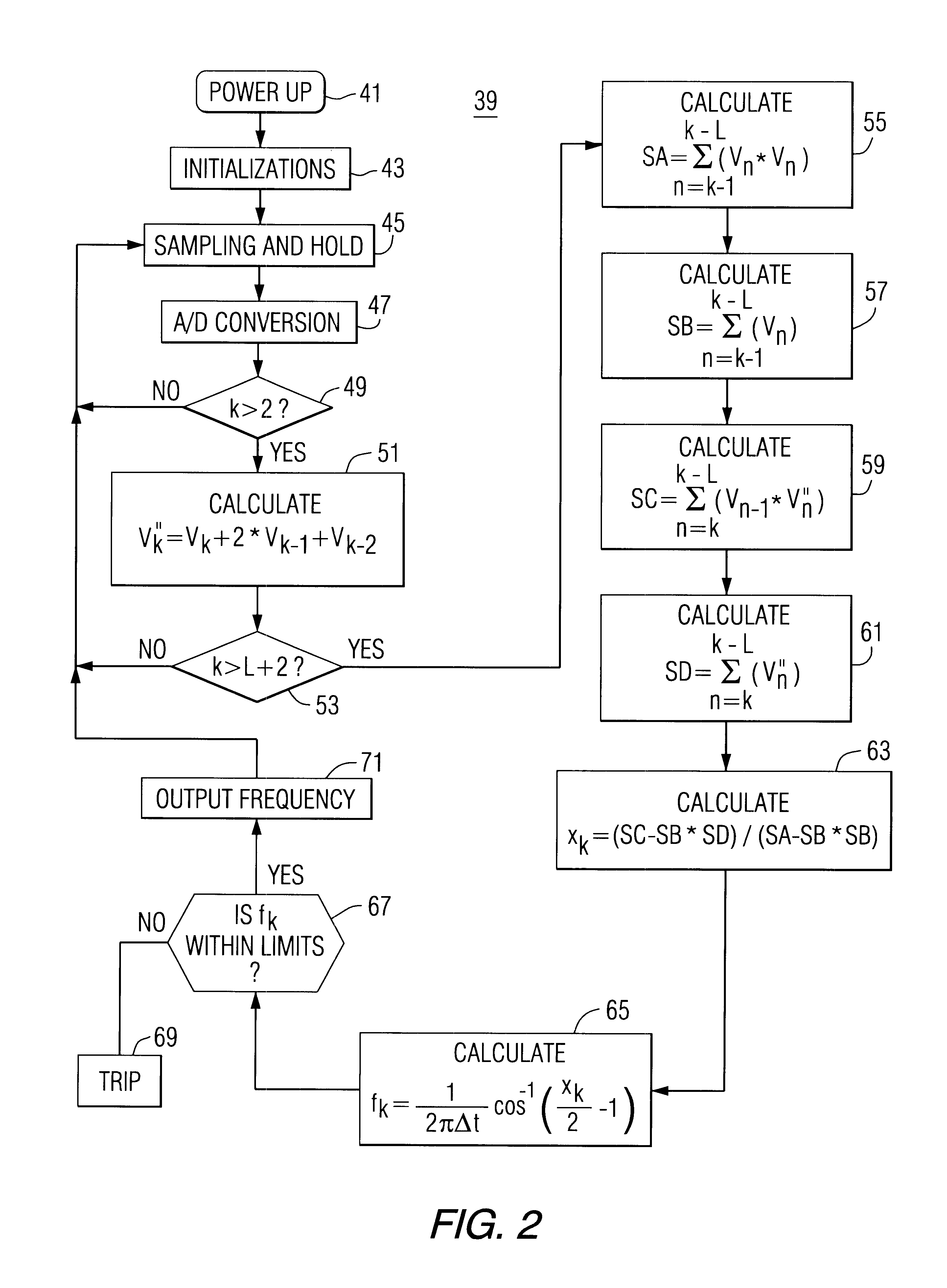
Apparatus providing on-line indication of frequency of an AC electric power system
InactiveUS6519537B1Noise figure or signal-to-noise ratio measurementElectrical testingMean squareEngineering
Apparatus for determining the frequency of an ac power signal, includes sensing circuitry to sense the ac signal. In a digital implementation of the invention, a double average of the samples is generated by a processor as the sum of the most recent sample, twice the next most recent sample plus the third most recent sample. The least mean square of a running window of the most recent double average signals is generated to avoid discontinuities at the zero crossings and to reduce the effects of noise. The frequency is determined from this least mean square value of the window of double average signals. As implemented in a protective relay, a trip signal is generated if the frequency is out of limits.
Owner:EATON CORP
Video compression method based on deep neural network
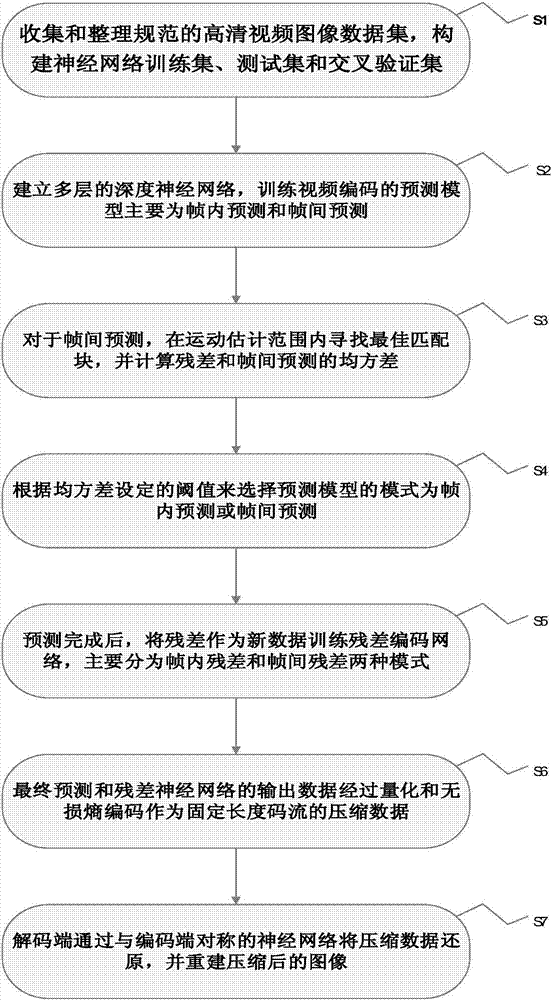
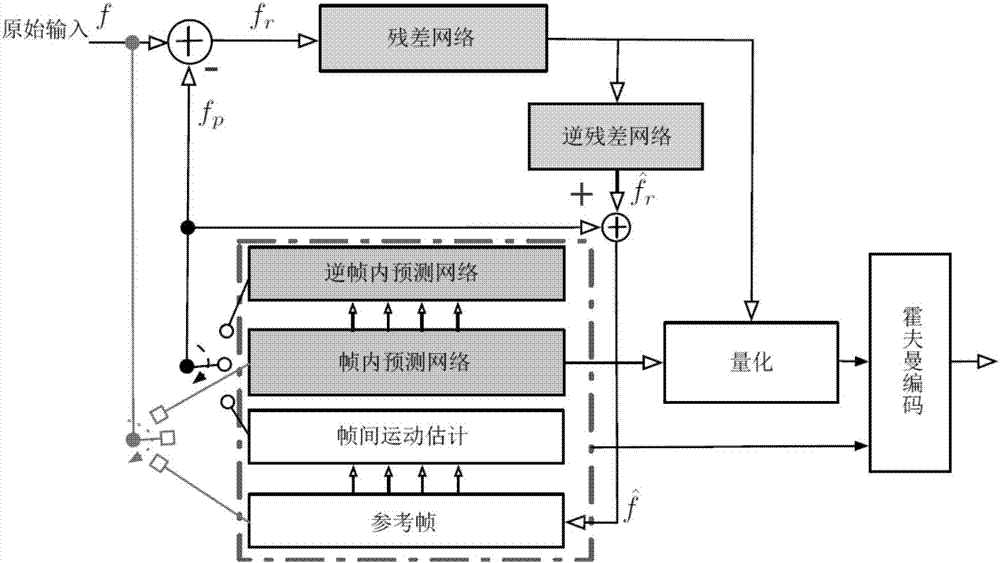
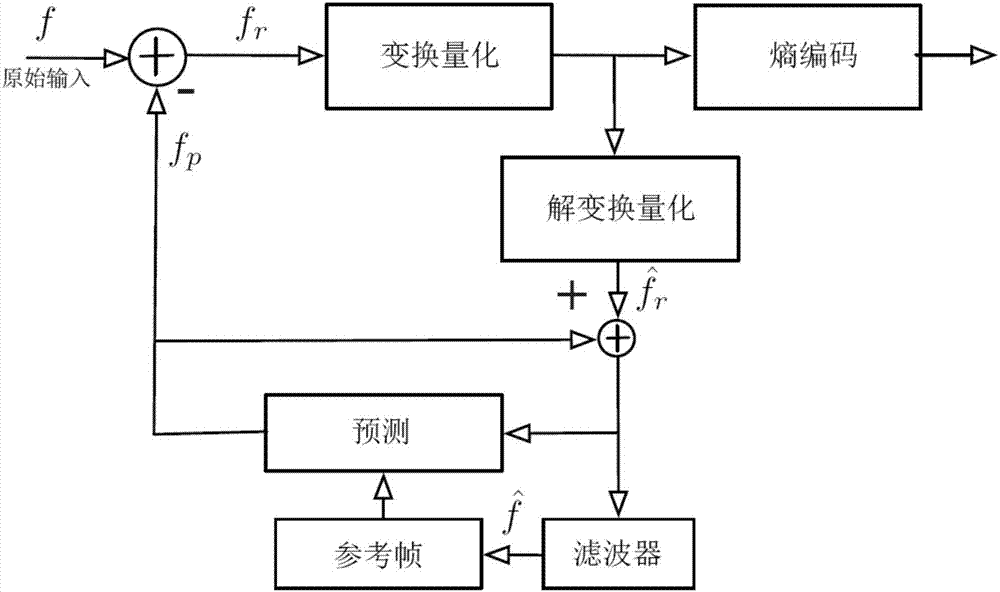
ActiveCN107396124AReduce bit rateImprove scalabilityDigital video signal modificationNeural architecturesData setResidual neural network
The invention discloses a video compression method based on the deep neural network. The method includes the following steps that a video image data set is collected and organized, and a neural network training set, a test set and a cross validation set are constructed; the multi-layer deep neural network is set up; for inter-frame prediction, a motion estimation algorithm is used for searching for the optimal matching block, and residuals and the mean square error of inter-frame prediction are calculated; the residuals obtained after prediction are used as new training data to train a residual code network, and a residual network model comprises an intra-frame residual and an inter-frame residual; compression data serving as fixed-length code streams together with output data, obtained after quantization and lossless entropy coding, of the residual neural network is predicted; a decoding terminal restores the compression data through a neutral network symmetric with a coding terminal, and a compressed image is obtained through reestablishment and recovery. Compared with a traditional H.264 video coding method in equality comparison of plenty of test video sequences, the video compression method can save about 26% code rate on the premise of equal quality.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
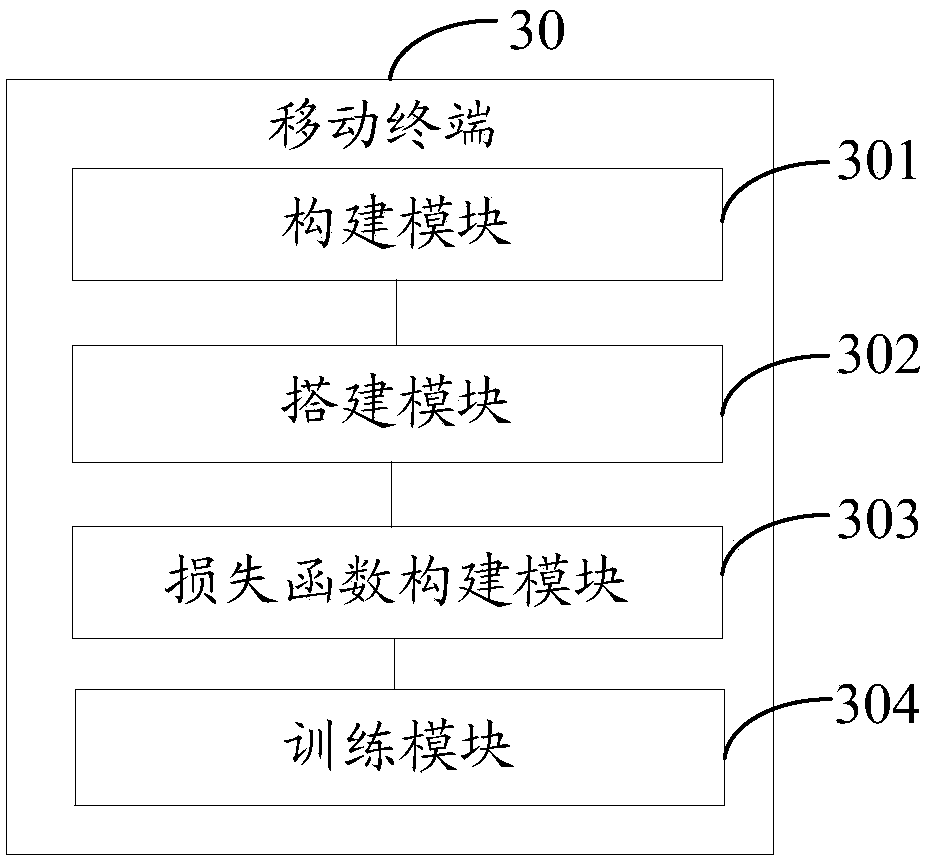
Image style migration model generation method and mobile terminal
PendingCN108537776ASmall workloadAvoid distortionImage enhancementImage analysisMean squareComputer graphics (images)
The embodiments of the invention provide an image style migration model generation method and a mobile terminal. The image style migration model generation method includes the steps: constructing a style training data pair; establishing a neural network according to the structural sequence: an input layer, a preposition layer, at least one residual error characteristic construction layer, a postposition layer and an output layer in order; constructing a loss function based on the mean square error loss of a training original image and a style image and the mean square error of the depth perception feature; and according to the style training data pair and the loss function, training the neural network to generate an image style migration model. By means of the image style migration model generated by the image style migration model generation method, a high-fidelity image after style migration can be quickly obtained by inputting the image to be processed into the image style migrationmodel, without performing cumbersome iterative operations, so that the consumed time is short, and the processor has a light workload, and space distortion of the style migration image can be avoided.
Owner:VIVO MOBILE COMM CO LTD
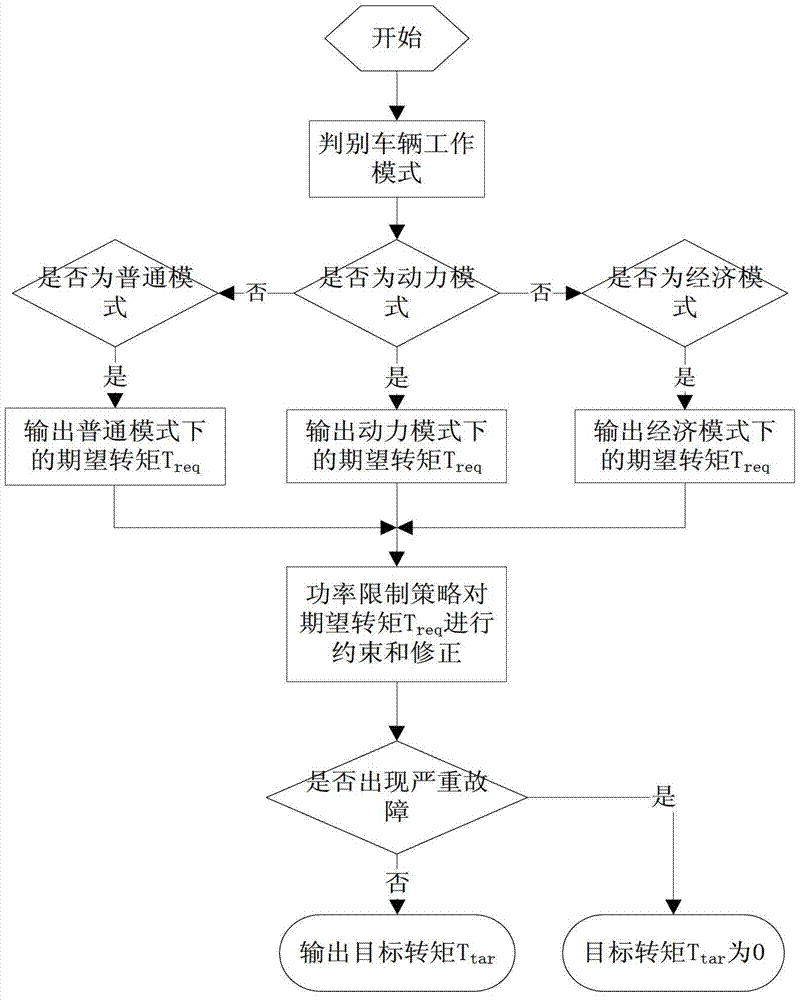
Drive control method for all-electric car
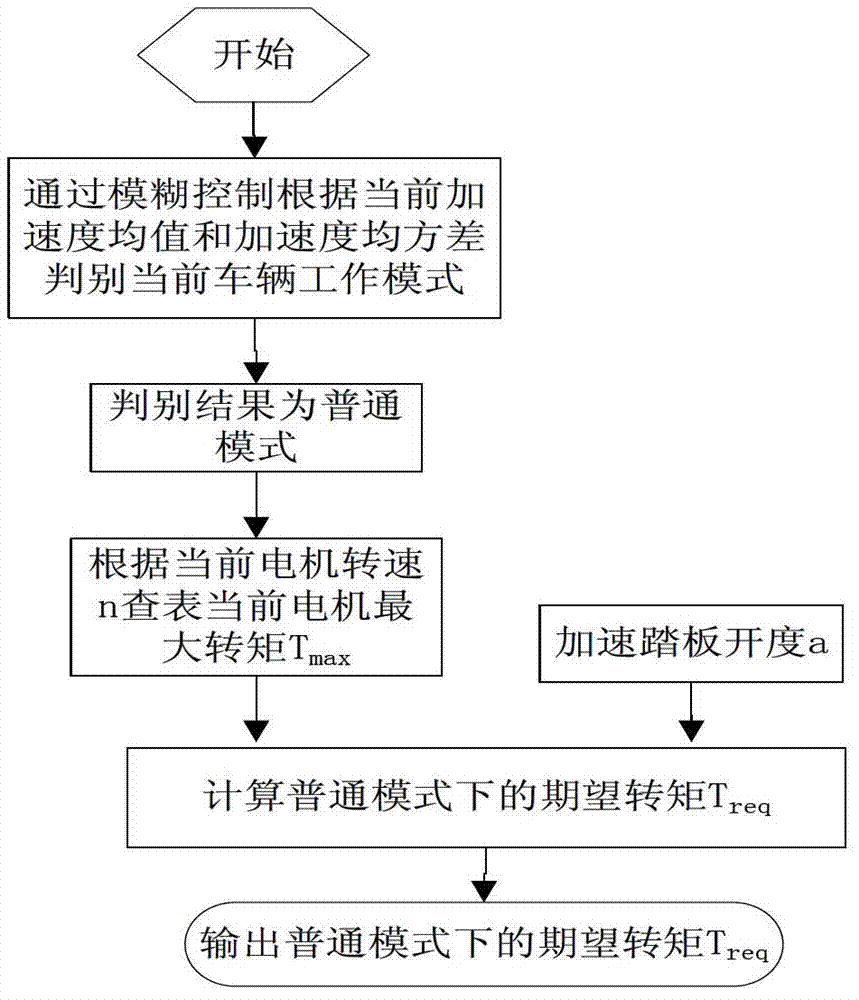
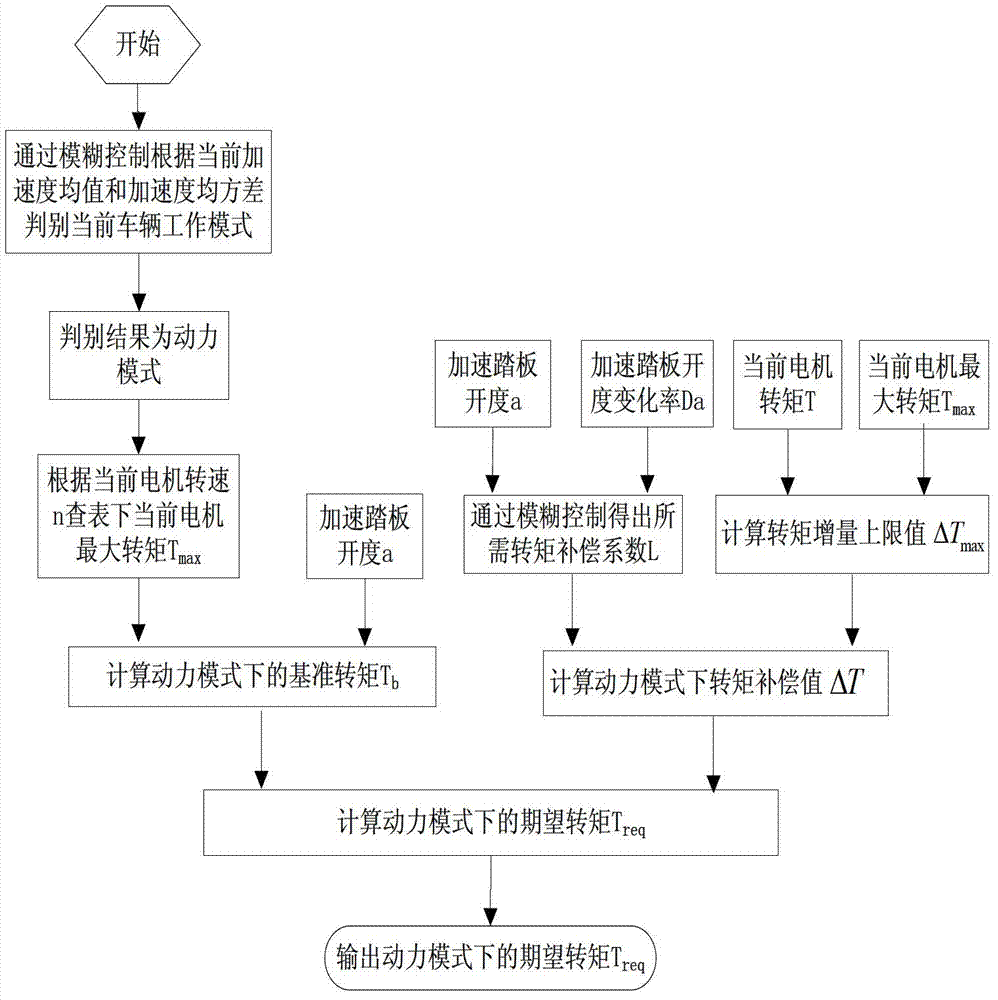
InactiveCN103192737AImprove powerImprove economySpeed controllerElectric energy managementPower modeMean square
The invention discloses a drive control method for an all-electric car. The drive control method aim at solving the problems that division of working modes during a finished automobile driving running is not considered, a torque compensation function is not considered in the running process of other vehicles except flooring of an accelerator pedal, and united efficiency of a power component is not considered in goal torque setting. The drive control method for the all-electric car comprises the steps of utilizing a finished automobile controller to automatically identify a finished automobile working mode according to current finished automobile acceleration mean values and an acceleration mean square errors, and enabling the finished automobile working mode to be one of a common mode, a power mode and an economic mode; working out an expected torque Treq under the corresponding mode according to a goal working mode control strategy in the finished automobile controller after the working mode identification is finished; restraining and correcting the expected torque Treq according to a power limiting value strategy in the finished automobile controller after the expected torque Treq under the goal working mode is obtained, and if a finished automobile has no major failure at the time, outputting ultimate goal torque commands to a motor.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
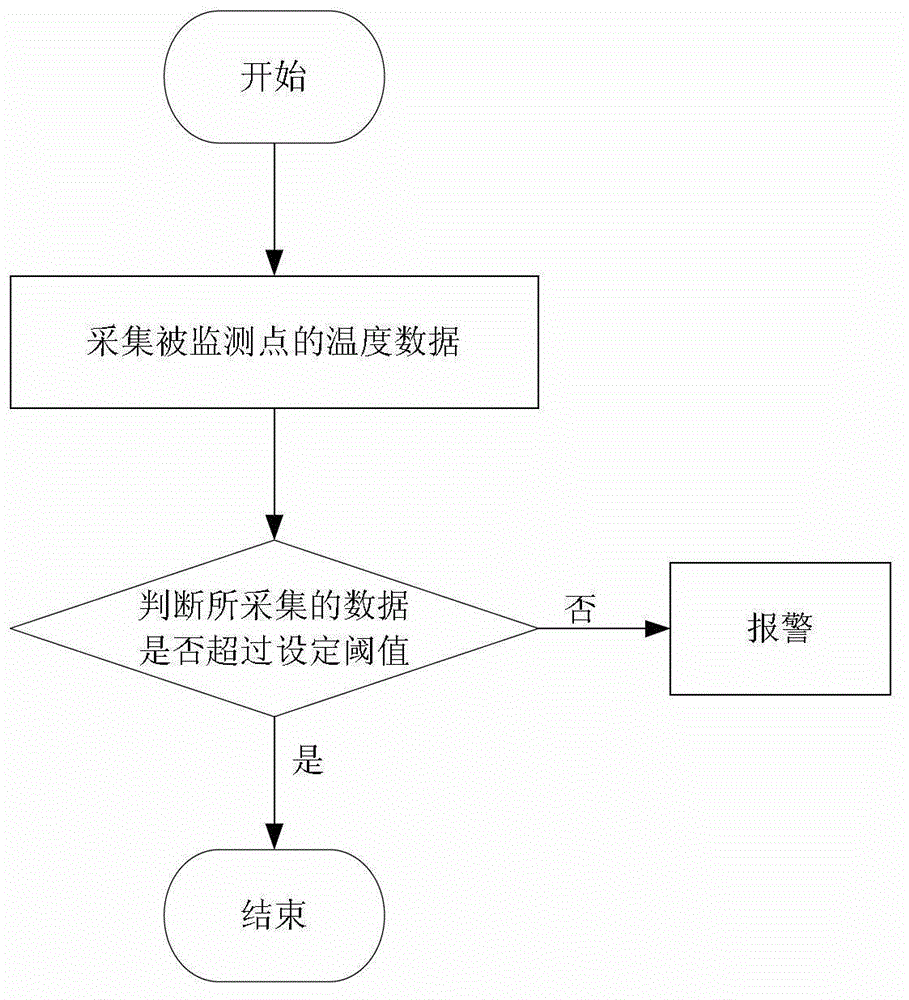
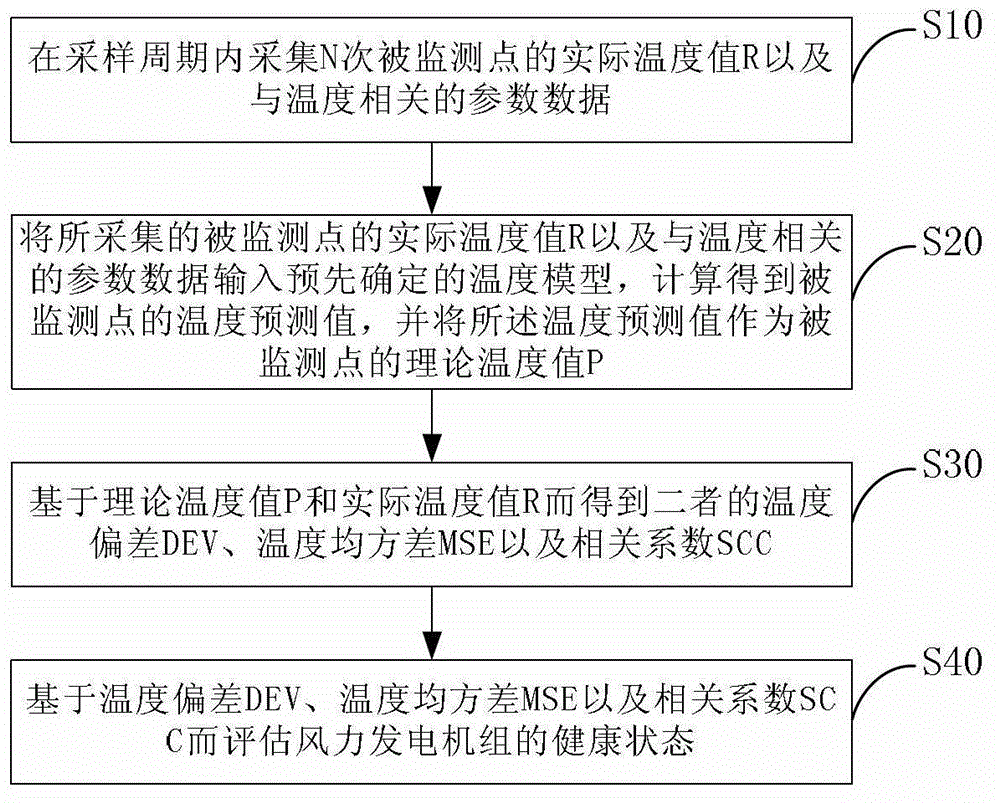
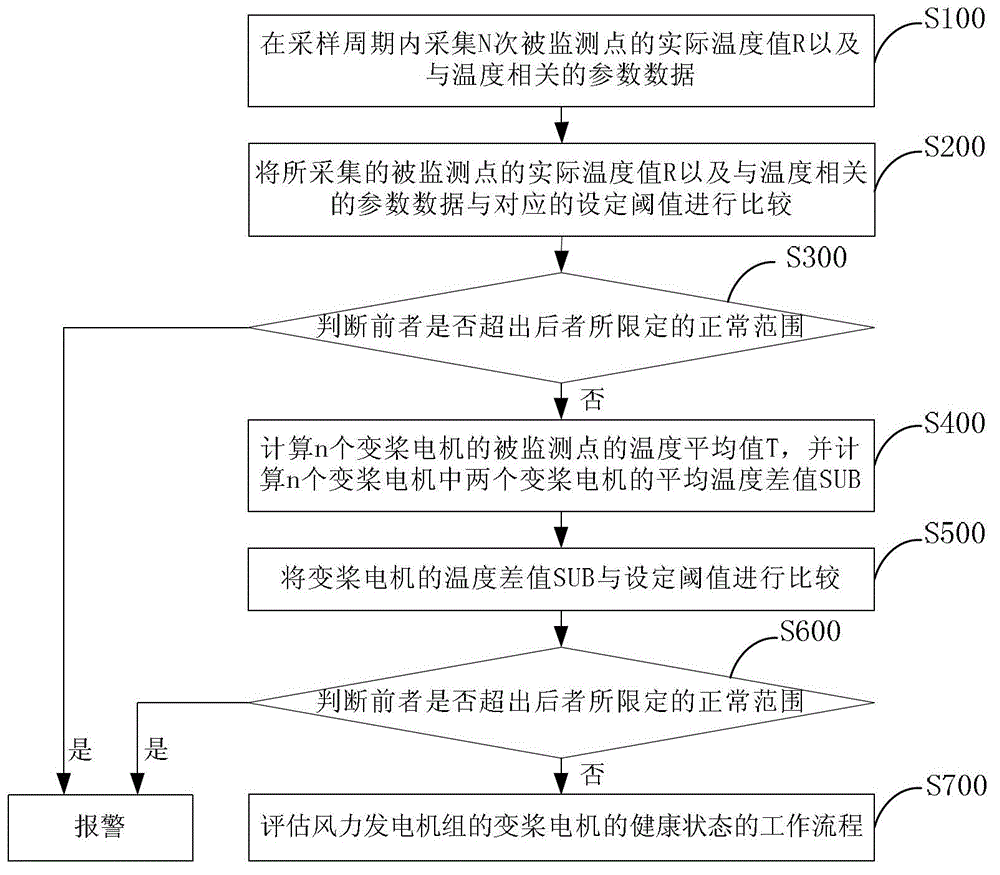
Fault early warning method of wind generating set
ActiveCN102721924ARefined health status levelHigh precisionEngine testingDynamo-electric machine testingMean squareHealth condition
The invention provides a fault early warning method of a wind generating set. The fault early warning method comprises the following steps of: 10) collecting the actual temperature value R and temperature related parameter data of a monitored point for N times in a sampling period; 20) inputting the collected actual temperature value R and the temperature related parameter data of the monitored point into a predetermined temperature mould, computing to obtain a temperature predicted value of the monitored point and taking the temperature predicted value as the theoretical temperature value P of the monitored point; 30) obtaining a temperature deviation DEV, a temperature mean-square deviation MSE and related coefficients SCC of the theoretical temperature value P and the actual temperature value; and 40) estimating the health condition of the wind generating set on the basis of the temperature deviation DEV, the temperature mean-square deviation MSE and related coefficients SCC. By means of the fault early warning method, the accuracy of estimating the health condition of the wind generating set can be improved.
Owner:XINJIANG GOLDWIND SCI & TECH
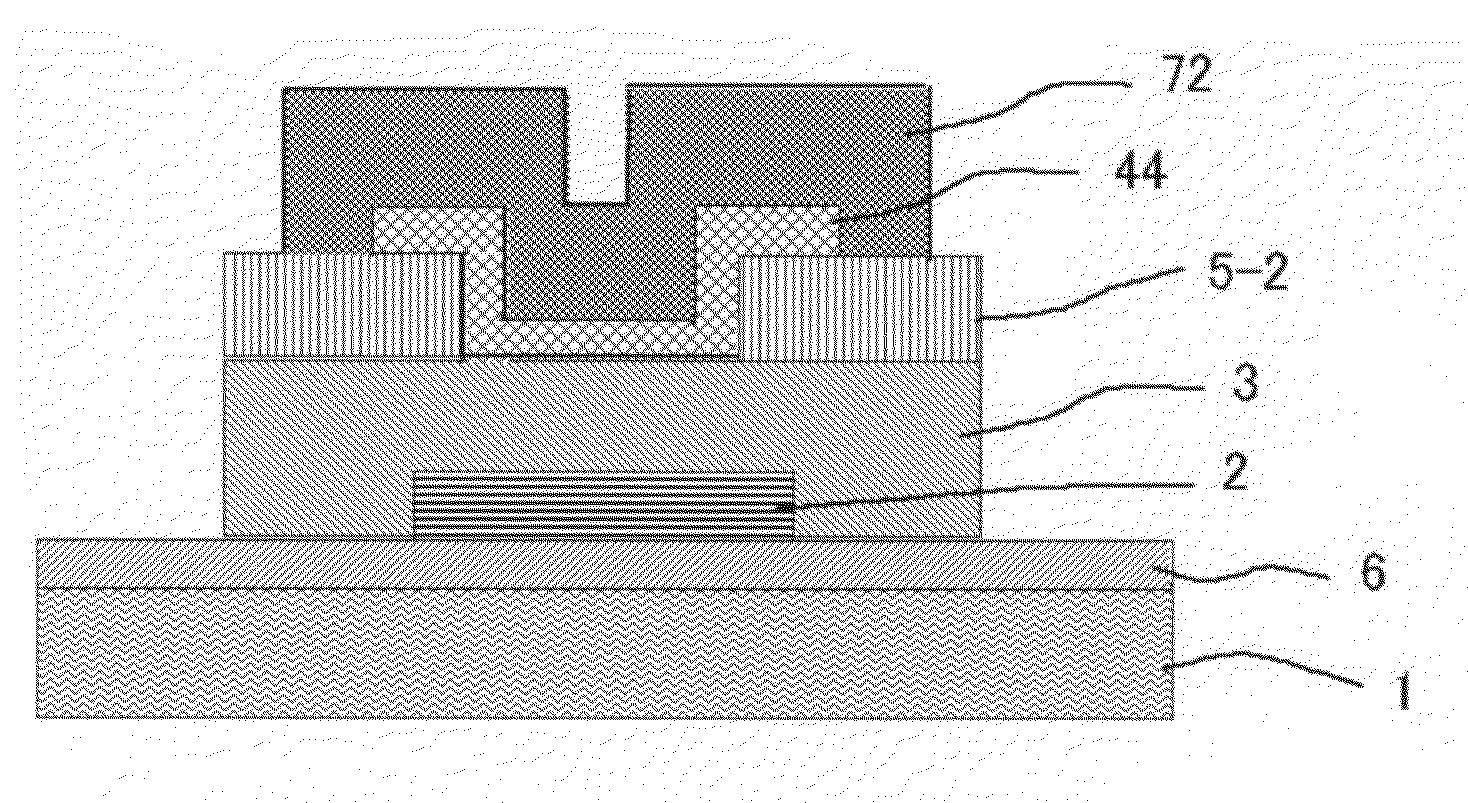
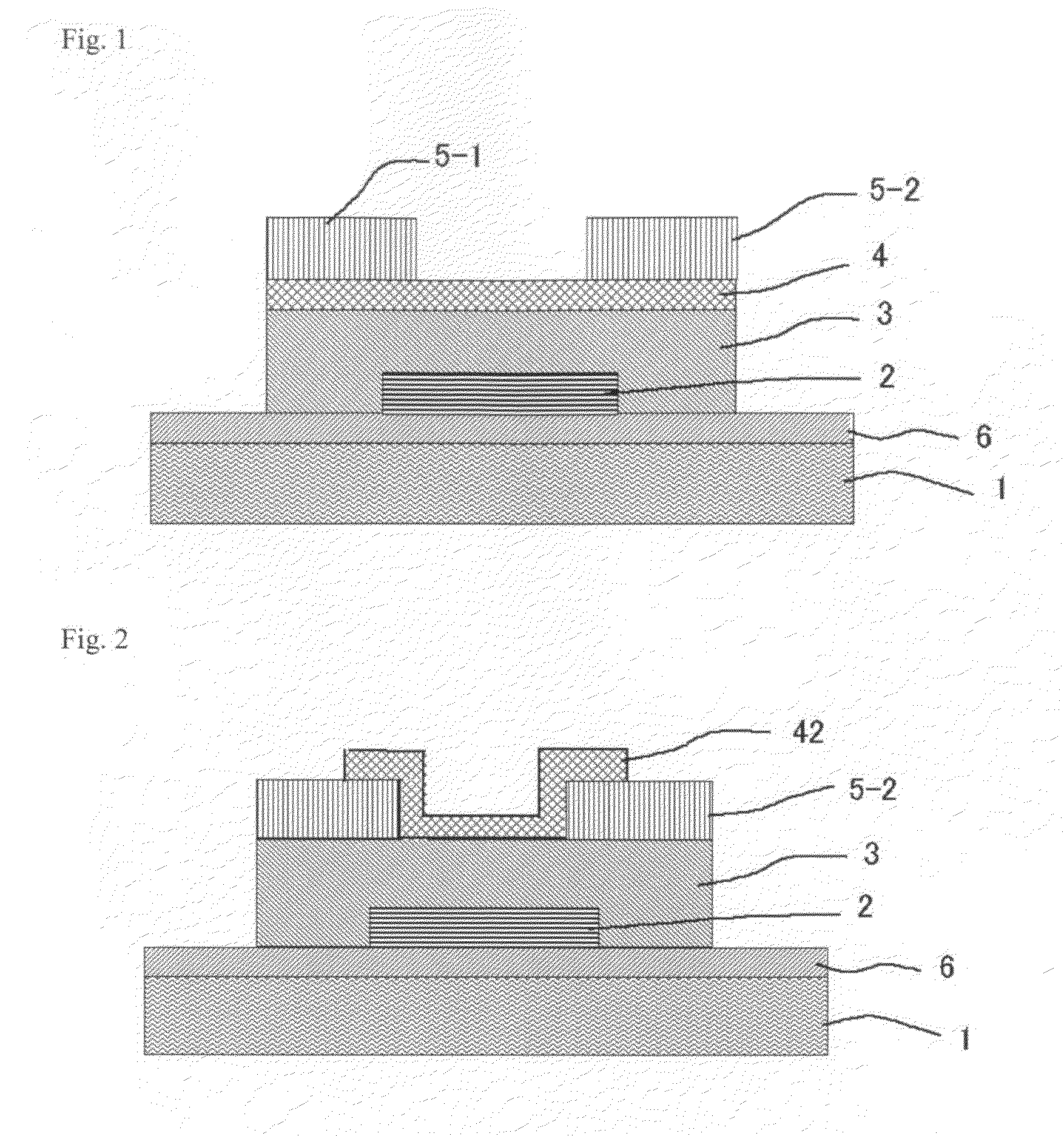
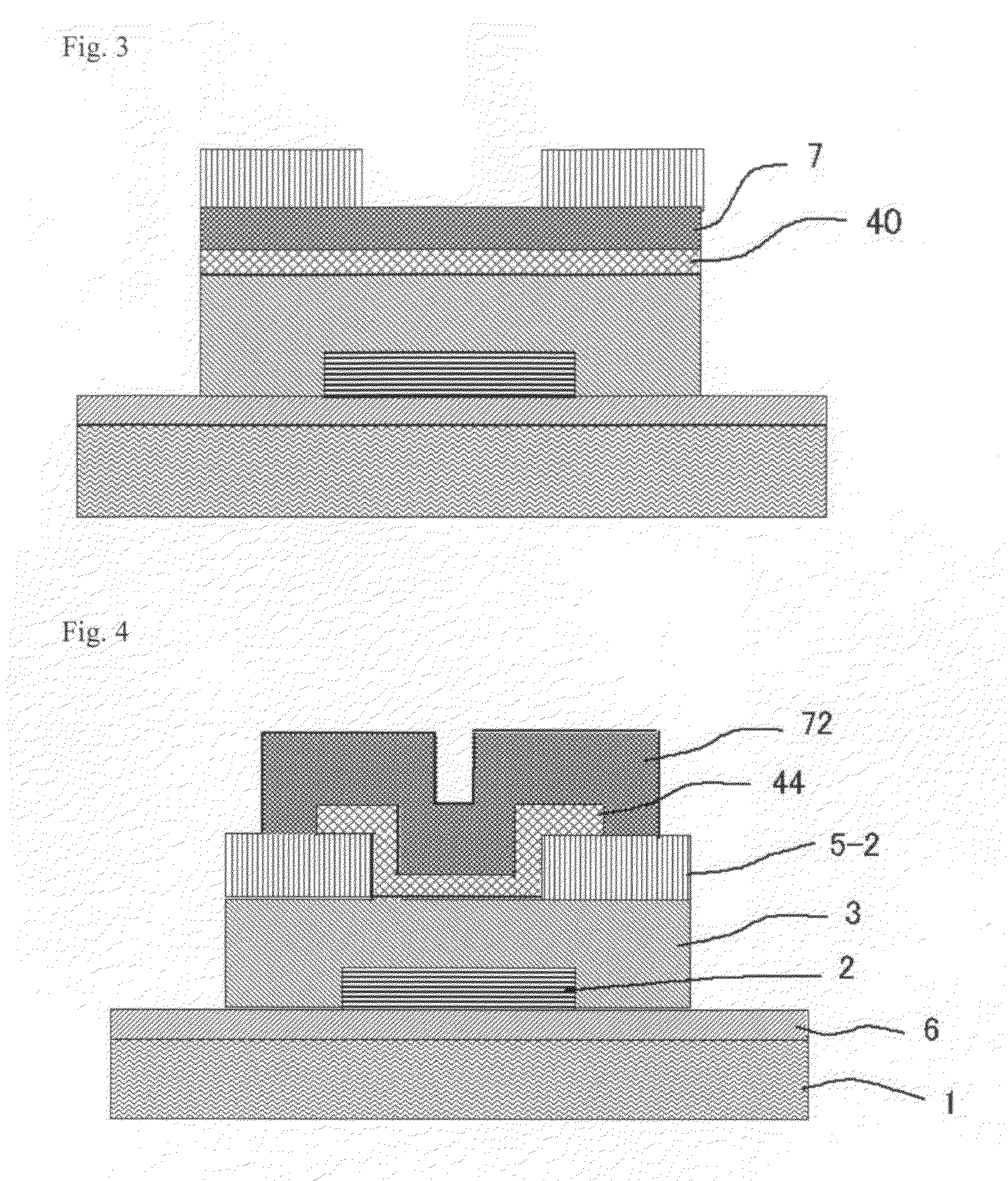
Thin film field effect transistor and display using the same
A TFT is provided which includes on a substrate, at least a gate electrode, a gate insulating layer, an active layer containing an amorphous oxide semiconductor, a source electrode, and a drain electrode, wherein a mean square interface roughness between the gate insulating layer and the active layer is less than 2 nm, a carrier concentration of the active layer is 1×1015 cm−3 or more, and a film thickness of the active layer is 0.5 nm or more and less than 20 nm. A TFT is provided which has high field effect mobility and a high ON-OFF ratio, and is improved in environmental temperature dependency. Also, a display using the TFT is provided.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
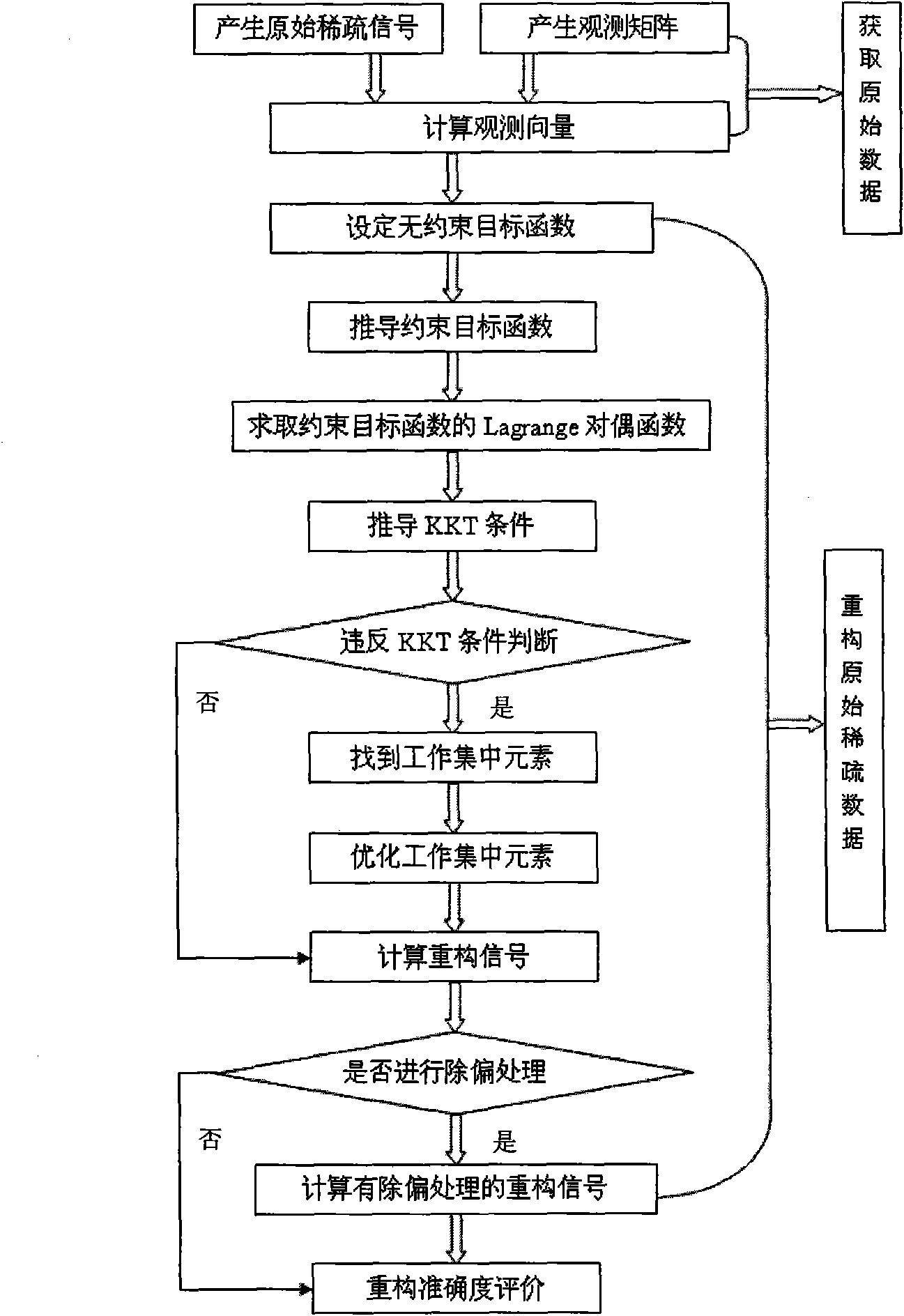
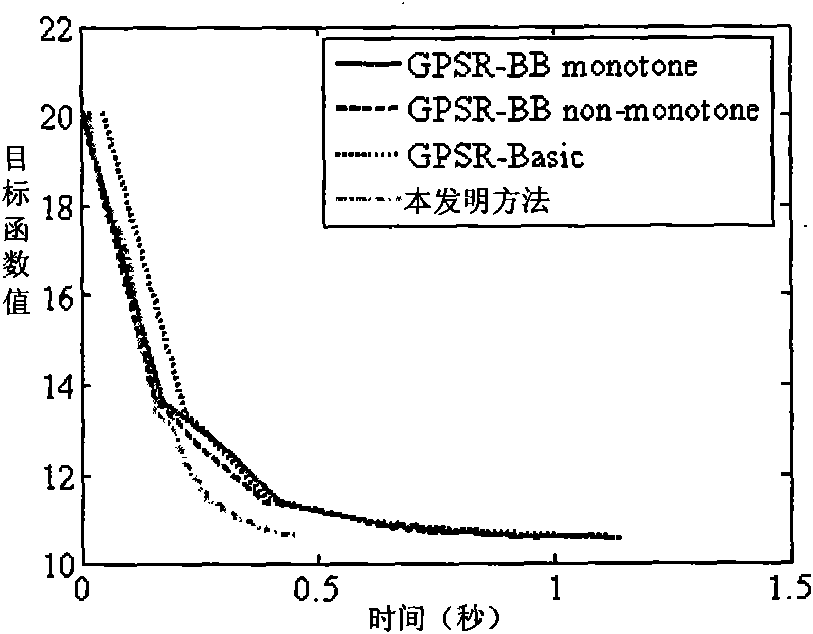
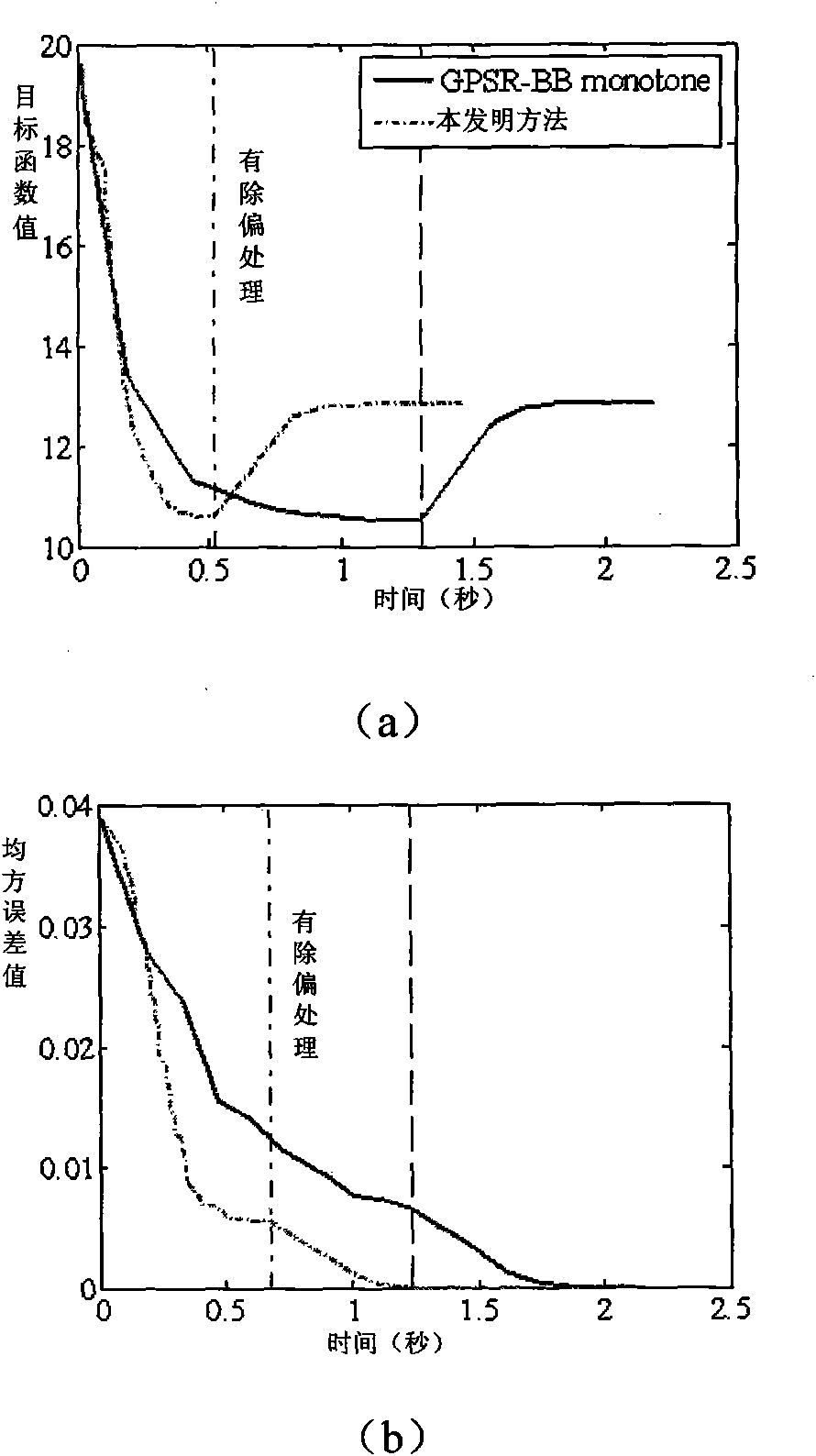
Reconstruction method of sparse signal
InactiveCN101640541ASave storage spaceFast convergenceCode conversionComplex mathematical operationsMean squareSequential minimal optimization
The invention discloses a reconstruction method of sparse signal, mainly solving the problem of low rate of raw sparse signal reconstructed from observation vectors. Utilizing the decomposability of aconstrained object function, the method decomposes the problem of optimizing the constrained object function into a series of small constrained object functions for optimization to improve the reconstruction rate, comprising a raw data acquisition part, a raw sparse signal reconstruction part and a reconstruction accuracy evaluation part, wherein the raw data acquisition part comprises raw sparsesignal generation, matrix observation and vector observation; the raw sparse signal reconstruction part mainly comprises setting unconstrained object function, deducing constrained object function, decomposing the constrained object function by a sequential minimal optimization method, calculating reconstruction signal and debiasing reconstruction signal; the reconstruction accuracy evaluation isto compare the magnitude of the error of mean square. The reconstruction method can improve the reconstruction rate on the premise of ensuring reconstruction accuracy rate and be used for solving theproblem of sparse signal reconstruction in the fields of compressed sensing and the like.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
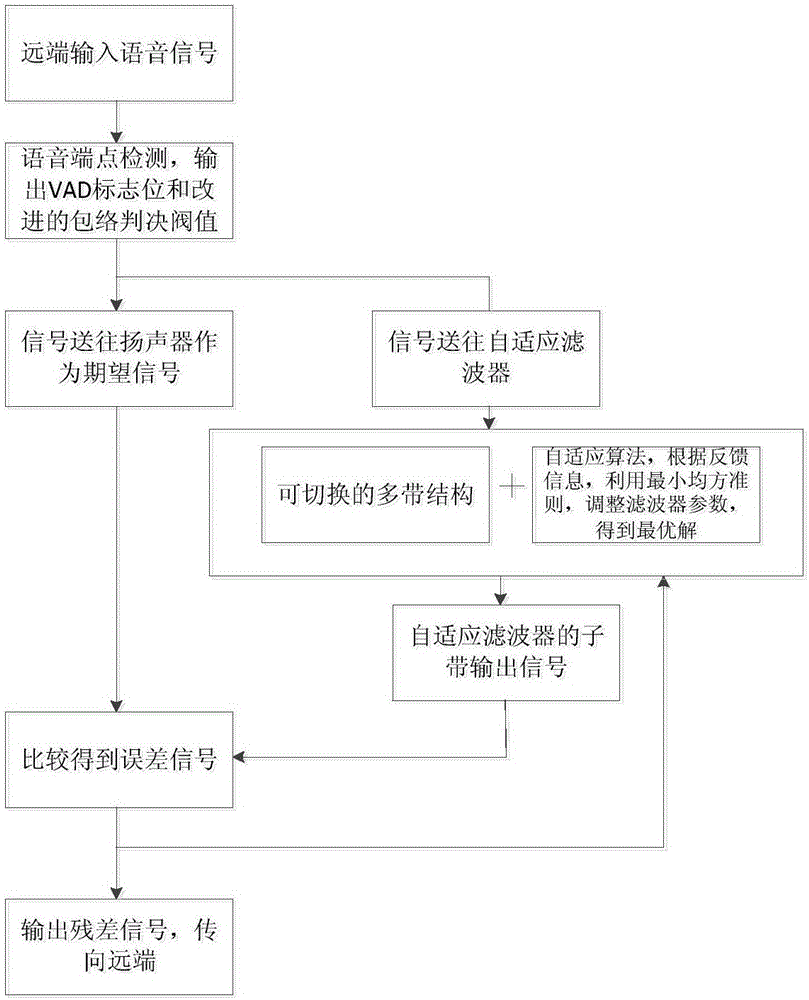
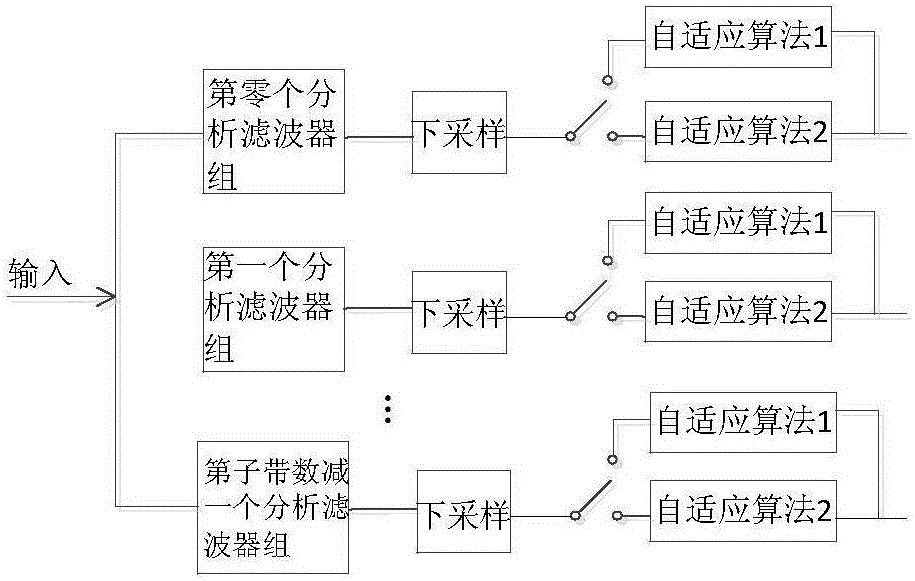
Multi-band structure self-adaptive filter switching method for AEC (acoustic echo cancellation)
ActiveCN106782593AAchieving Convergence Speed AdvantageOvercome speedSpeech analysisMulti bandAdaptive filter
The invention discloses a multi-band structure self-adaptive filter switching method for AEC (acoustic echo cancellation). Firstly, a far-end voice signal is acquired; a voice endpoint is detected, and a VAD (voice activity detection) flag bit and an improved envelope decision threshold are output; the voice signal is fed into a loudspeaker to serve as a desired signal and also input into a self-adaptive filter; the self-adaptive filter adopts a switchable multi-band structure and a corresponding self-adaptive algorithm, parameters of the filter are adjusted by use of the least mean square criterion according to feedback information, and the optimal solution is obtained. According to the provided switching method, voice characteristics are considered sufficiently under the condition that steady maladjustment is guaranteed, and optimized configuration of the convergence rate and the algorithm complexity is realized while advantages of the algorithm in the convergence rate are utilized. During actual application of echo cancellation, a single algorithm does not easily meet various variable demands. The variable switching algorithm provides more probability for a user and has great significance in application of self-adaptive echo cancellation.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
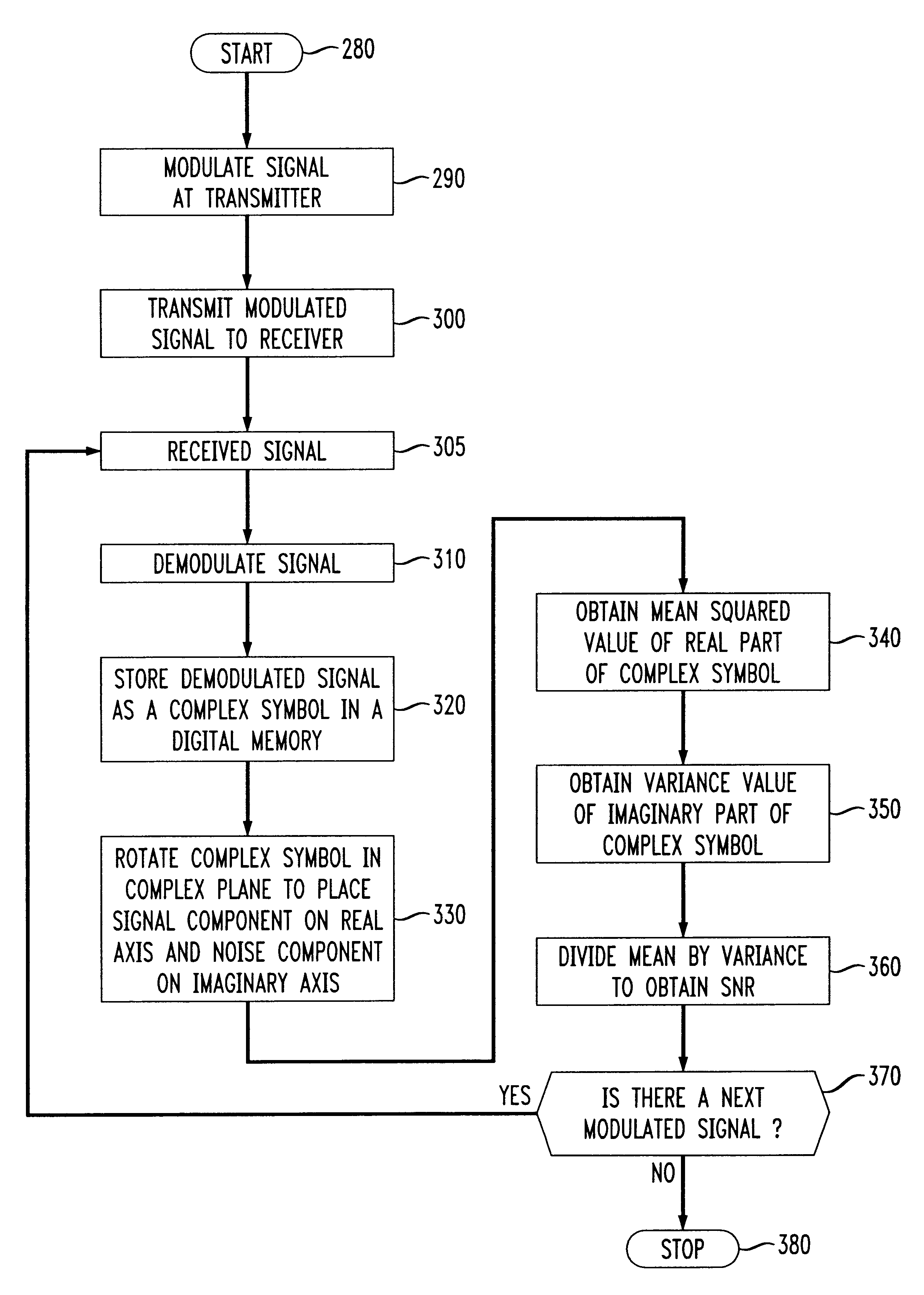
Methods of estimating signal-to-noise ratios
InactiveUS6317456B1Transmission monitoringPhase-modulated carrier systemsMean squareSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
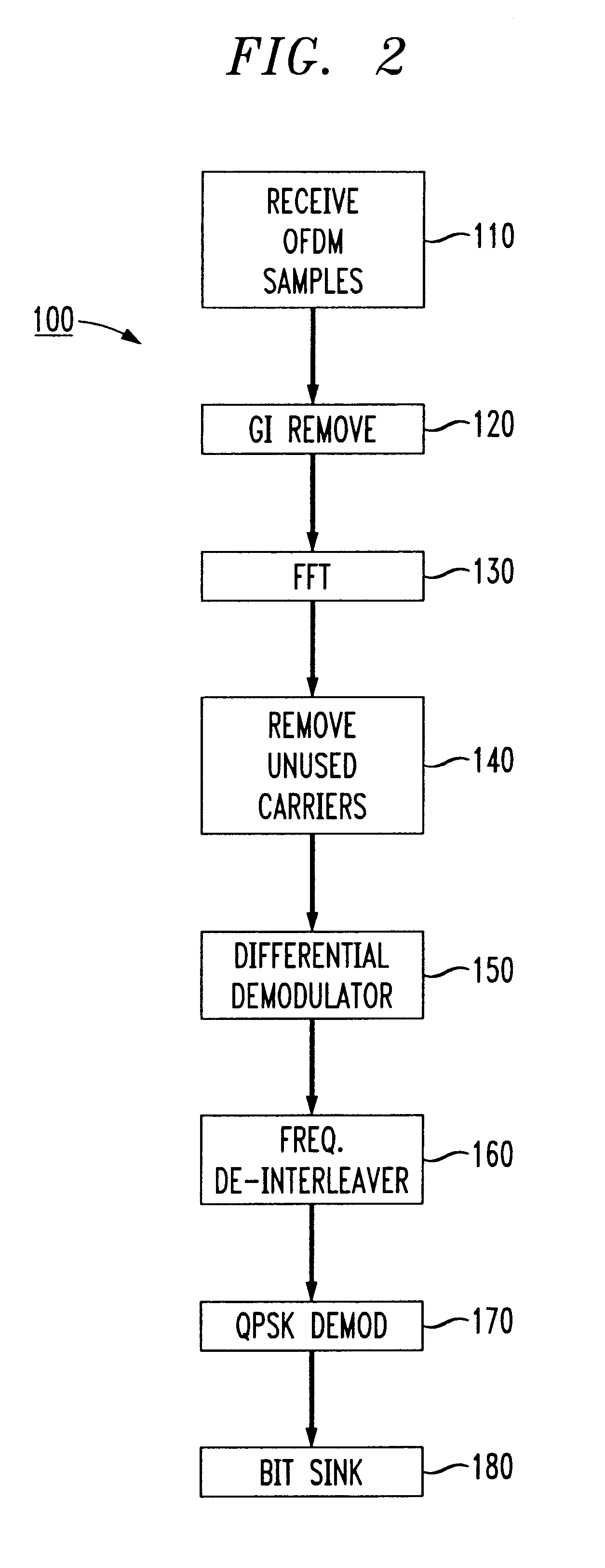
Methods of estimating the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) of a signal in an orthogonal frequency division multiplexed (OFDM) system include the steps of representing the signal as a complex symbol and rotating the complex symbol in a complex plane so that the signal component of the function lies substantially on the real axis of the complex plane and the noise function lies substantially on the imaginary axis of the complex plane. By obtaining the means squared value of the complex symbol and the variance of the complex symbol and dividing them, an estimate for the SNR of the signal is obtained.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC +1
Active Noise Control in Mobile Devices
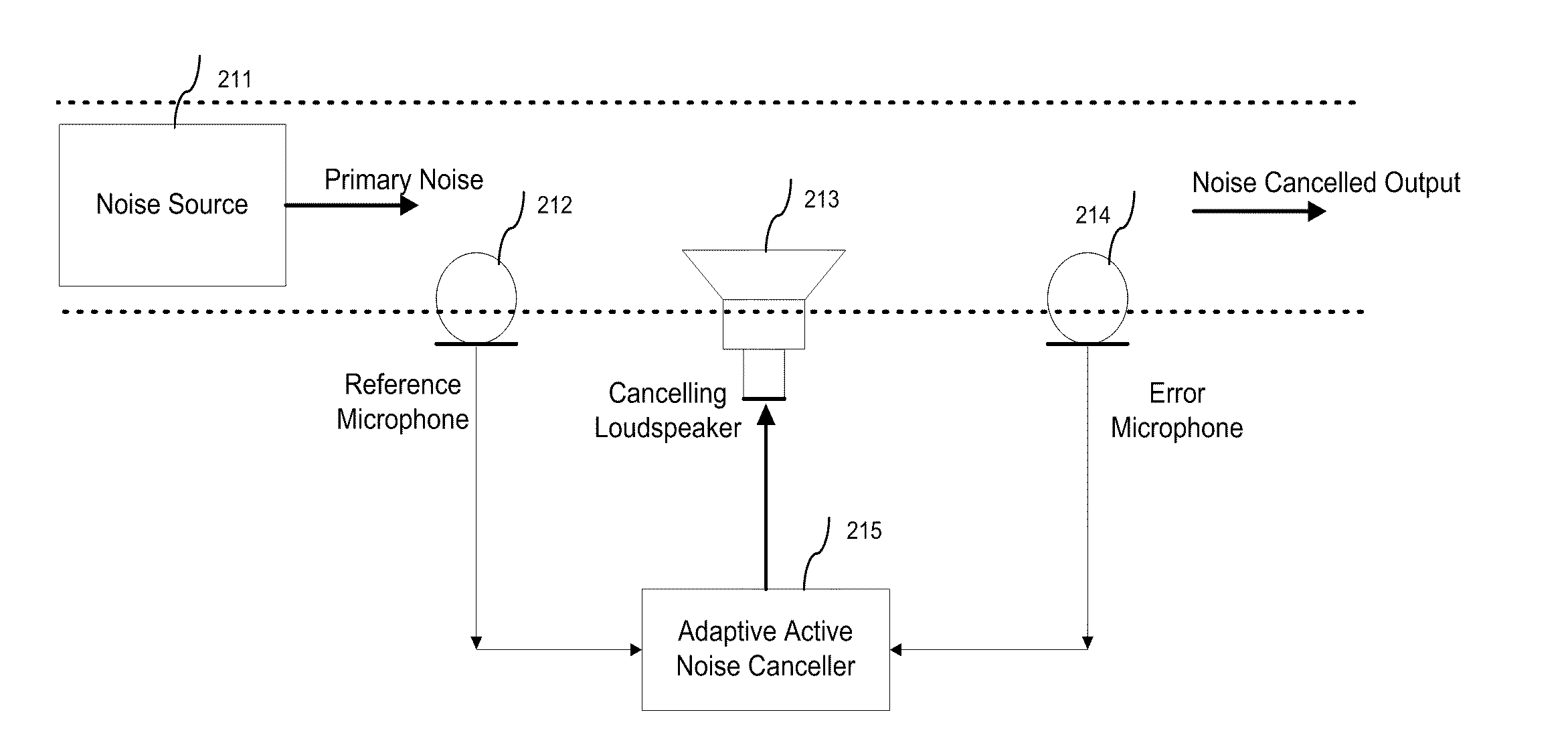
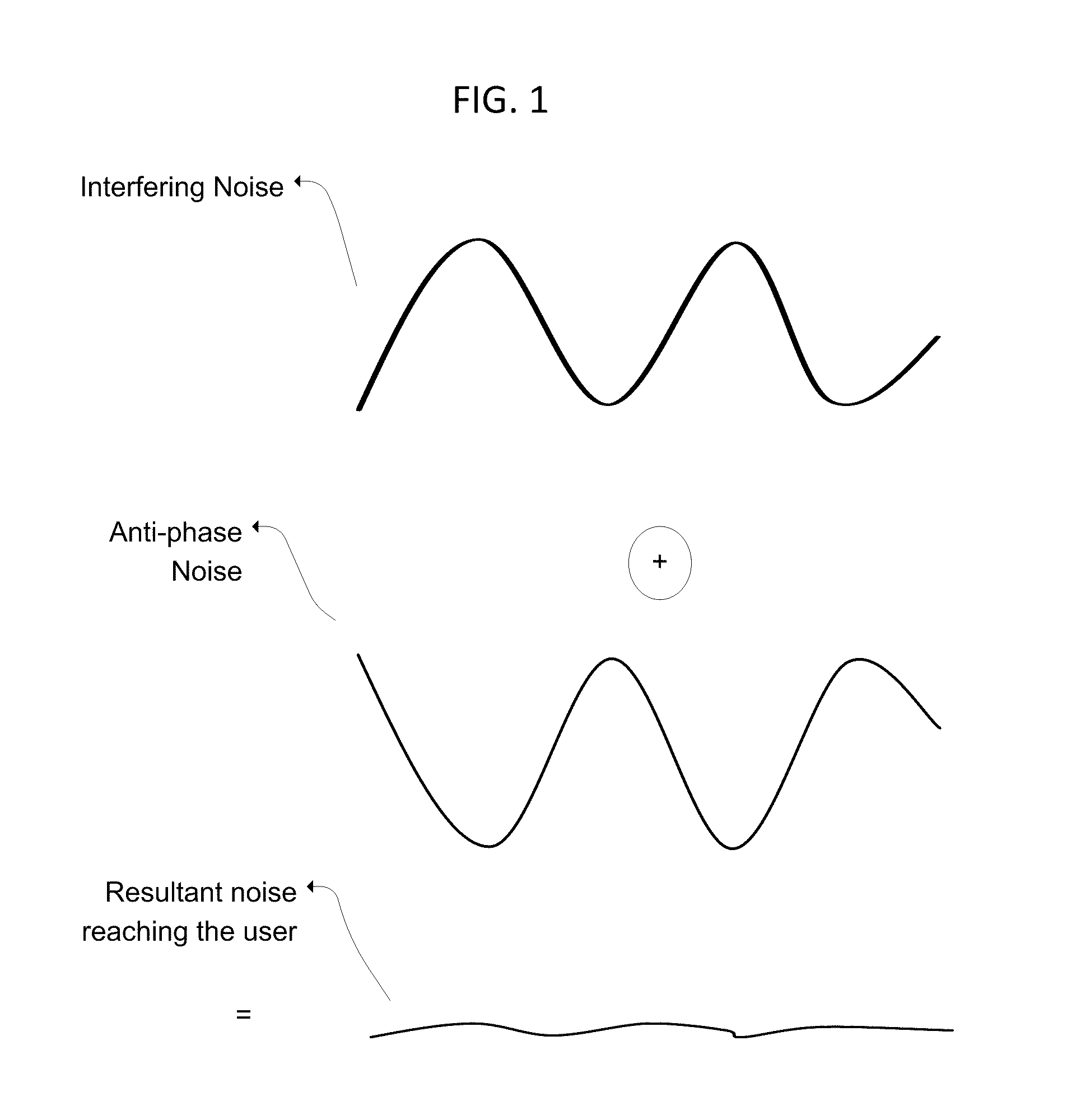
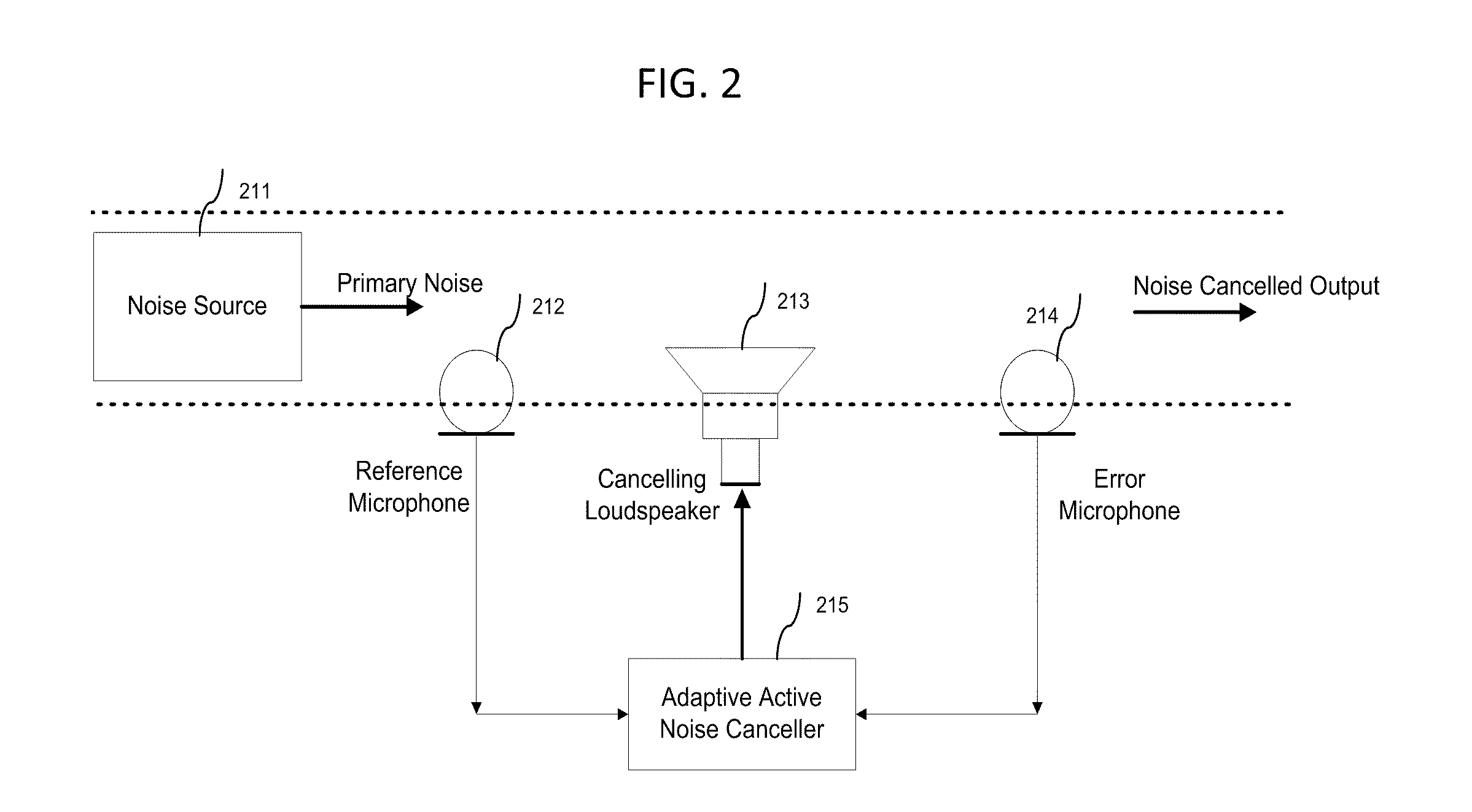
InactiveUS20110091047A1Ability to detect and reduce different level of background noiseComputationally inexpensiveEar treatmentNoise generationNoise controlMean square
A three dimensional area of quiet is created by an active noise cancellation system comprising a reference microphone receiving background noise and sending the noise signal to an adaptive active noise canceller. An adaptive filter system using weights updated by a least mean squares method or other method generates an anti-phase signal which is broadcasted to counteract the background noise. The resulting residual noise or residual signal is sent back to the adaptive active noise canceller to reset the weights of the adaptive filter.
Owner:NOISE FREE WIRELESS
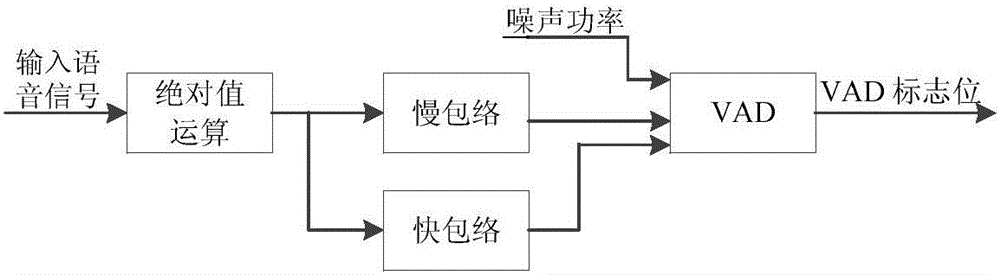
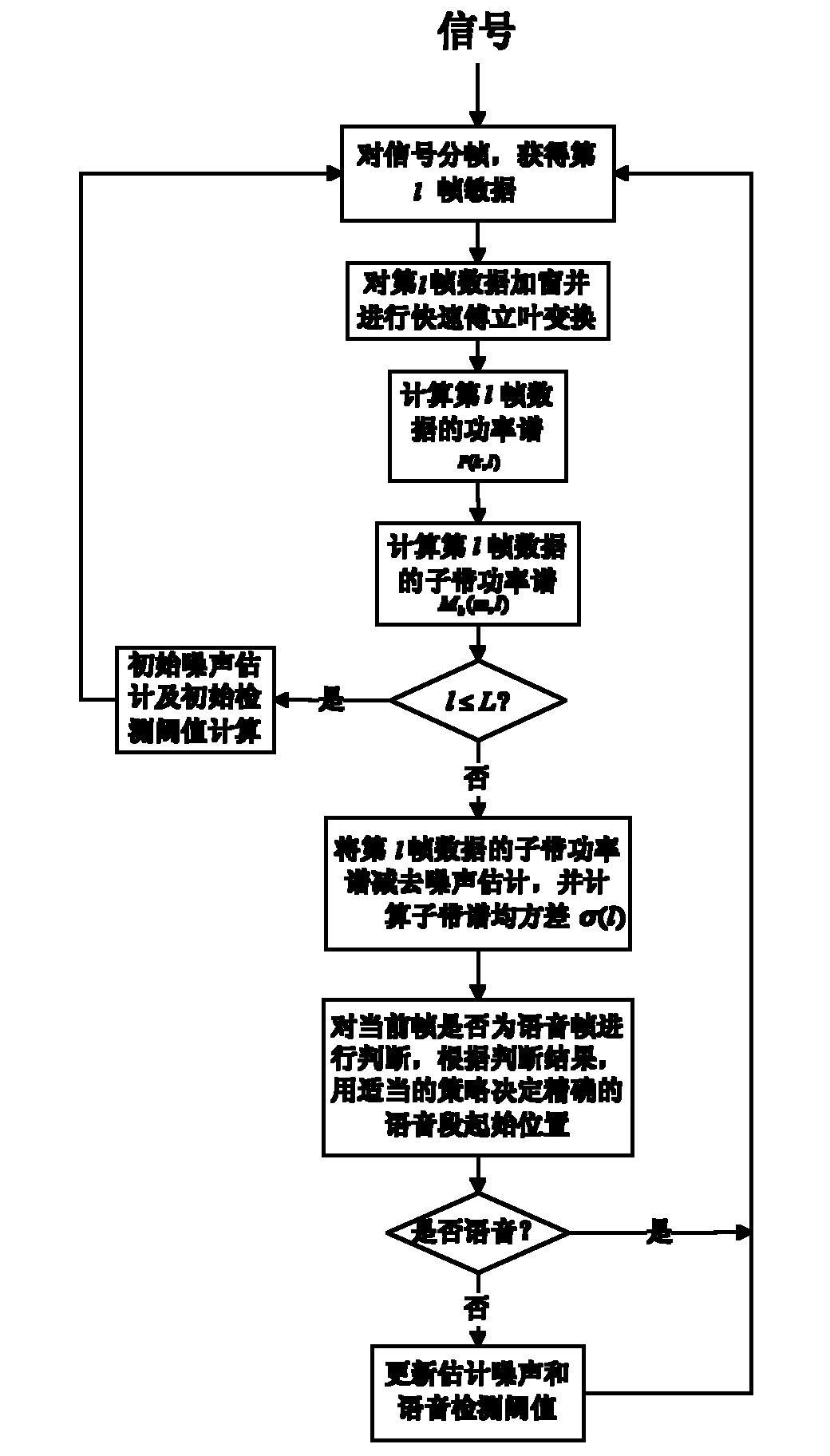
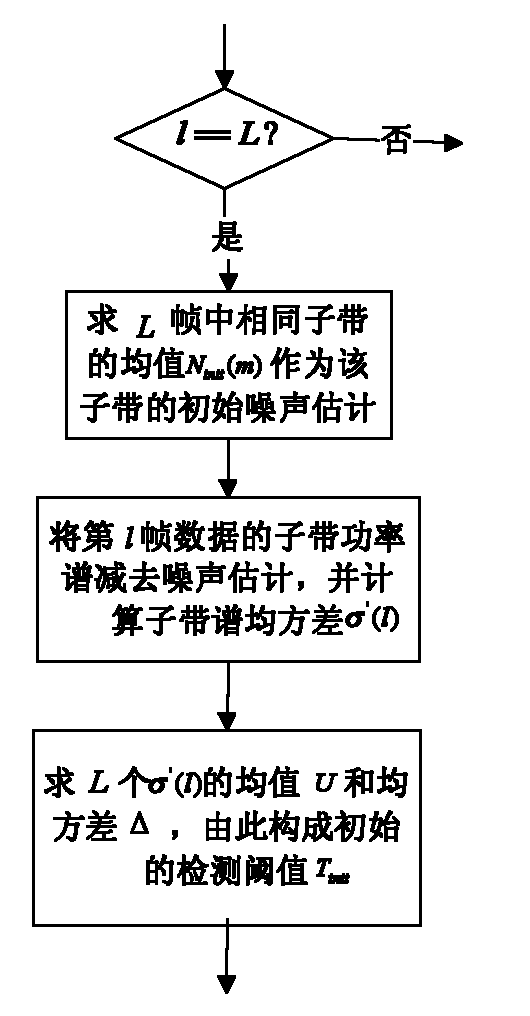
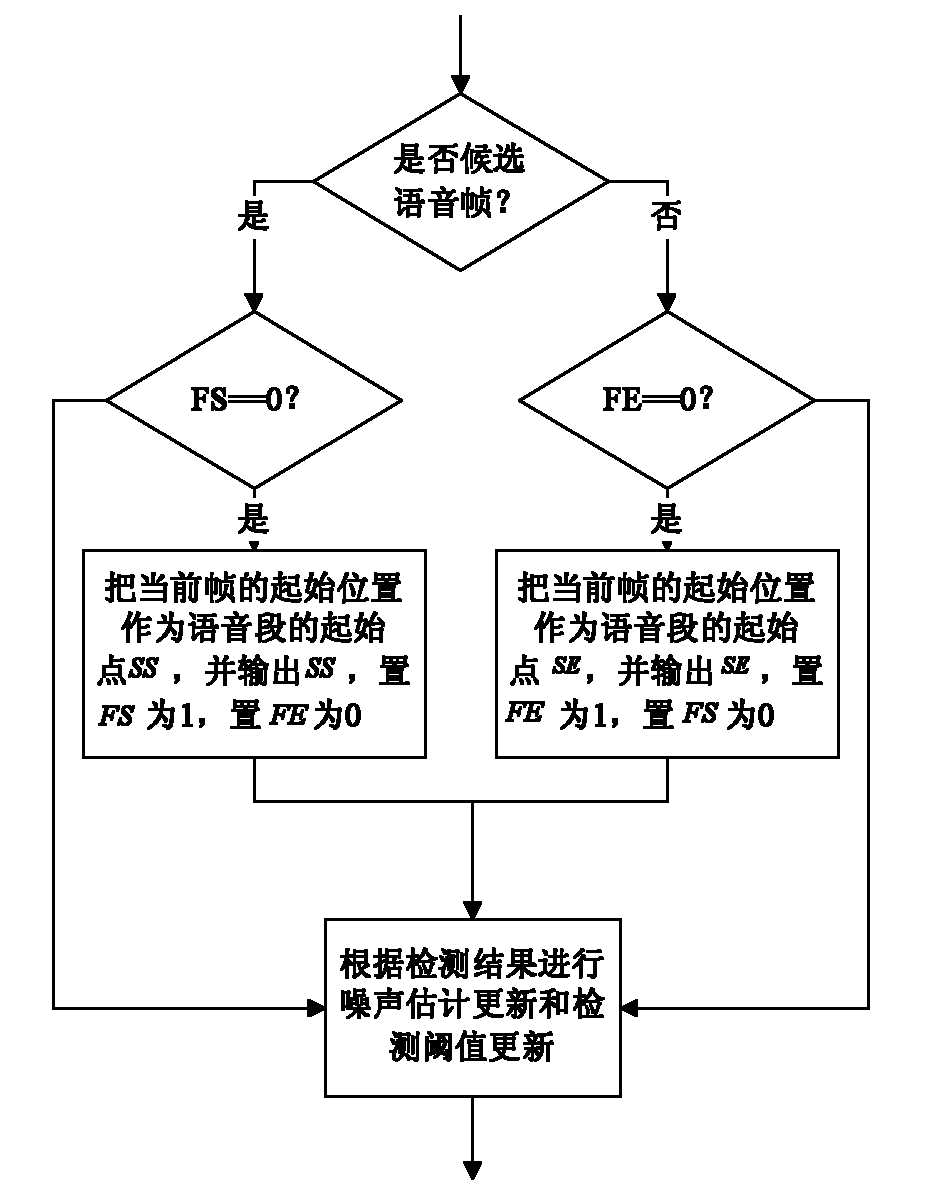
Voice detection method under noise condition
The invention provides a voice detection method under noise condition, and belongs to the technical fields of digital signal processing, computer artificial intelligence and pattern recognition. The method comprises the following steps of: converting input signals to a frequency domain, and dividing into subbands; calculating a power spectrum of each subband to form a subband power spectrum; calculating mean-square deviation of the subband power spectrum of each frame, and comparing the mean-square deviation serving as a detection characteristic with an adaptive voice detection threshold to determine whether the current frame contains voice signals; and according to a detection result, adopting a certain endpoint determination strategy to determine an initial position and an ending position of a voice segment.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Model-based tomographic reconstruction
InactiveUS20100060509A1Reduce complexityReduce dimensionalityRadio wave reradiation/reflectionMean squareTime gate
A model-based approach to estimating wall positions for a building is developed and tested using simulated data. It borrows two techniques from geophysical inversion problems, layer stripping and stacking, and combines them with a model-based estimation algorithm that minimizes the mean-square error between the predicted signal and the data. The technique is designed to process multiple looks from an ultra wideband radar array. The processed signal is time-gated and each section processed to detect the presence of a wall and estimate its position, thickness, and material parameters. The floor plan of a building is determined by moving the array around the outside of the building. In this paper we describe how the stacking and layer stripping algorithms are combined and show the results from a simple numerical example of three parallel walls.
Owner:LAWRENCE LIVERMORE NAT SECURITY LLC
Forward and reverse calibration for ground-based beamforming
ActiveUS8331329B2Frequency-division multiplex detailsTransmission path divisionCommunications systemMean square
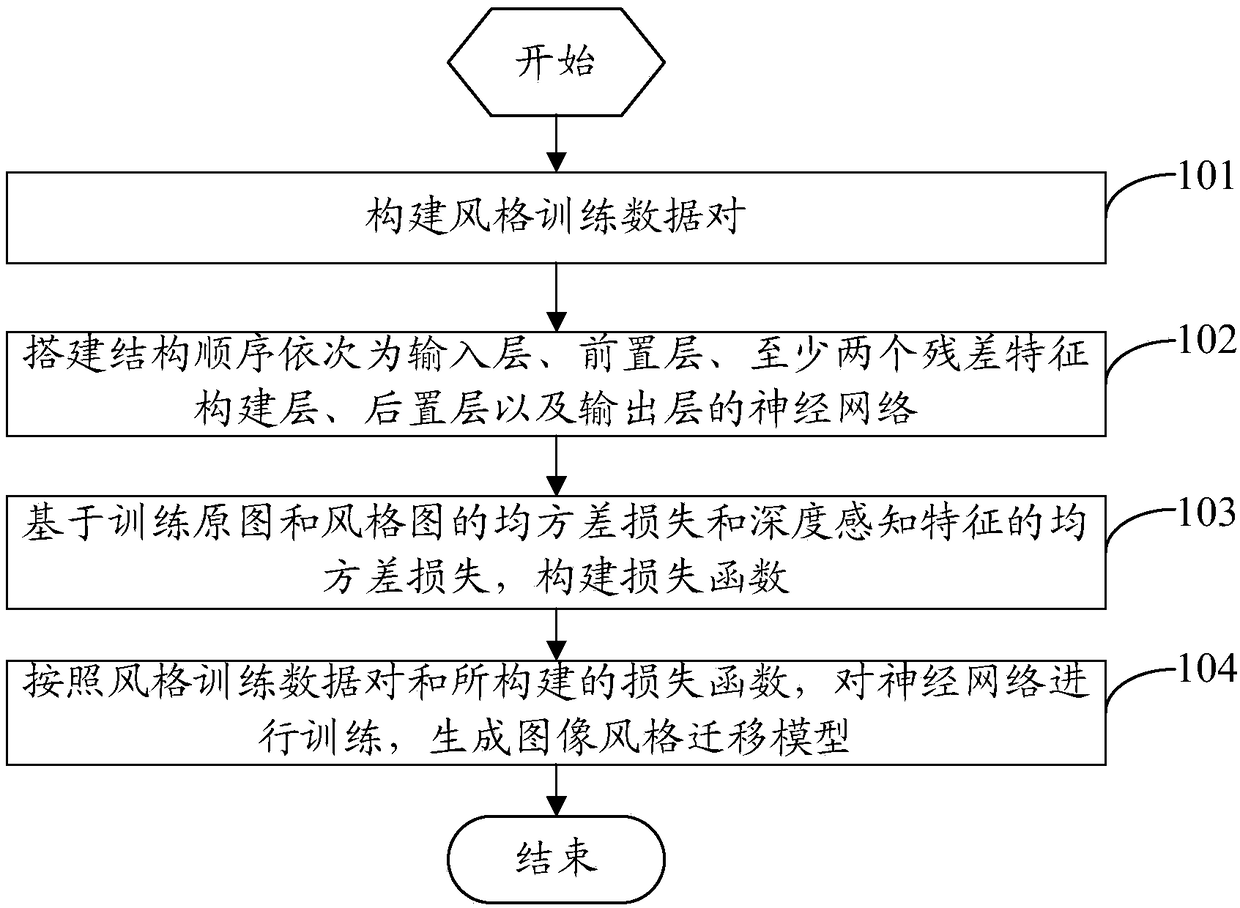
Owner:VIASAT INC
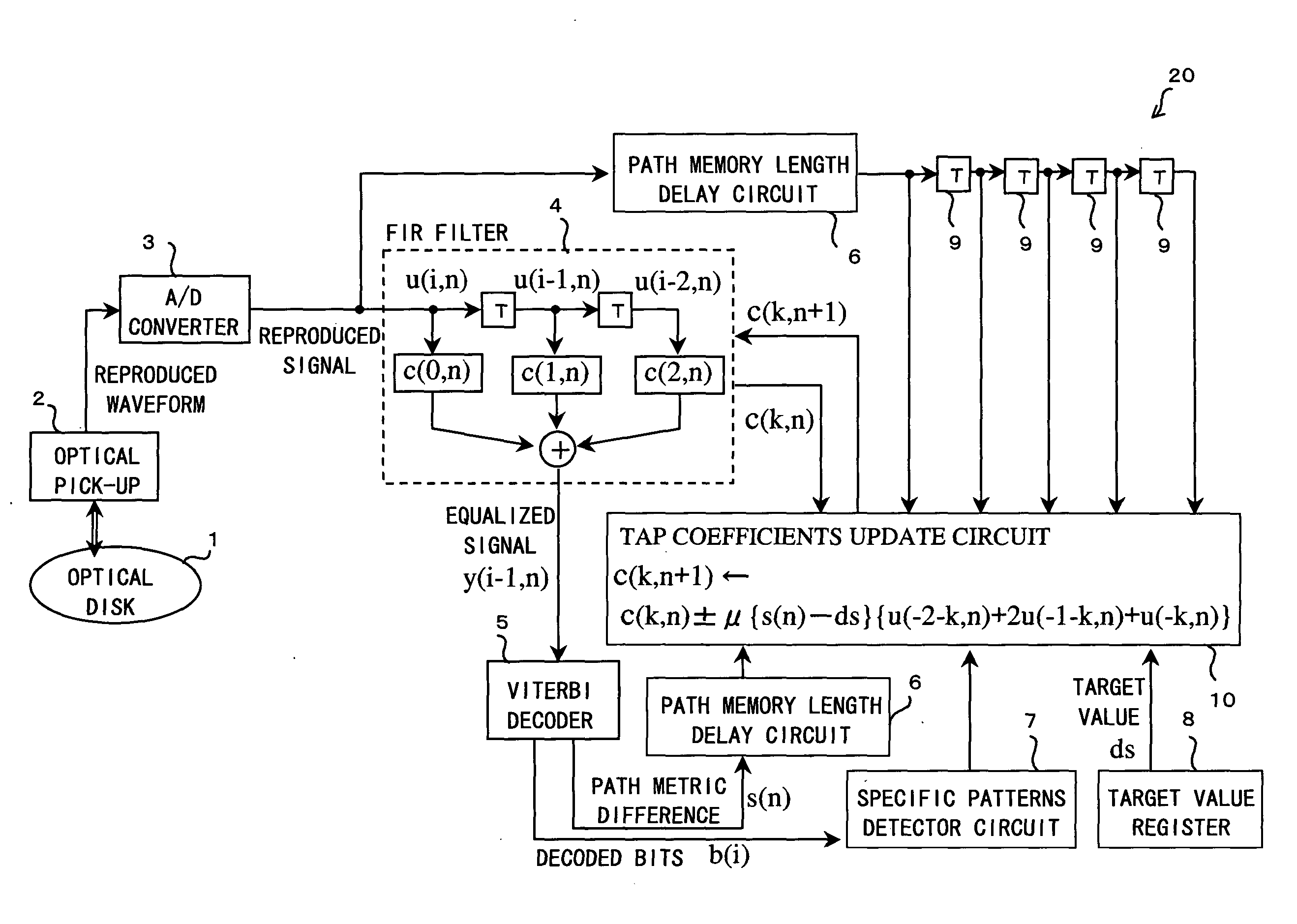
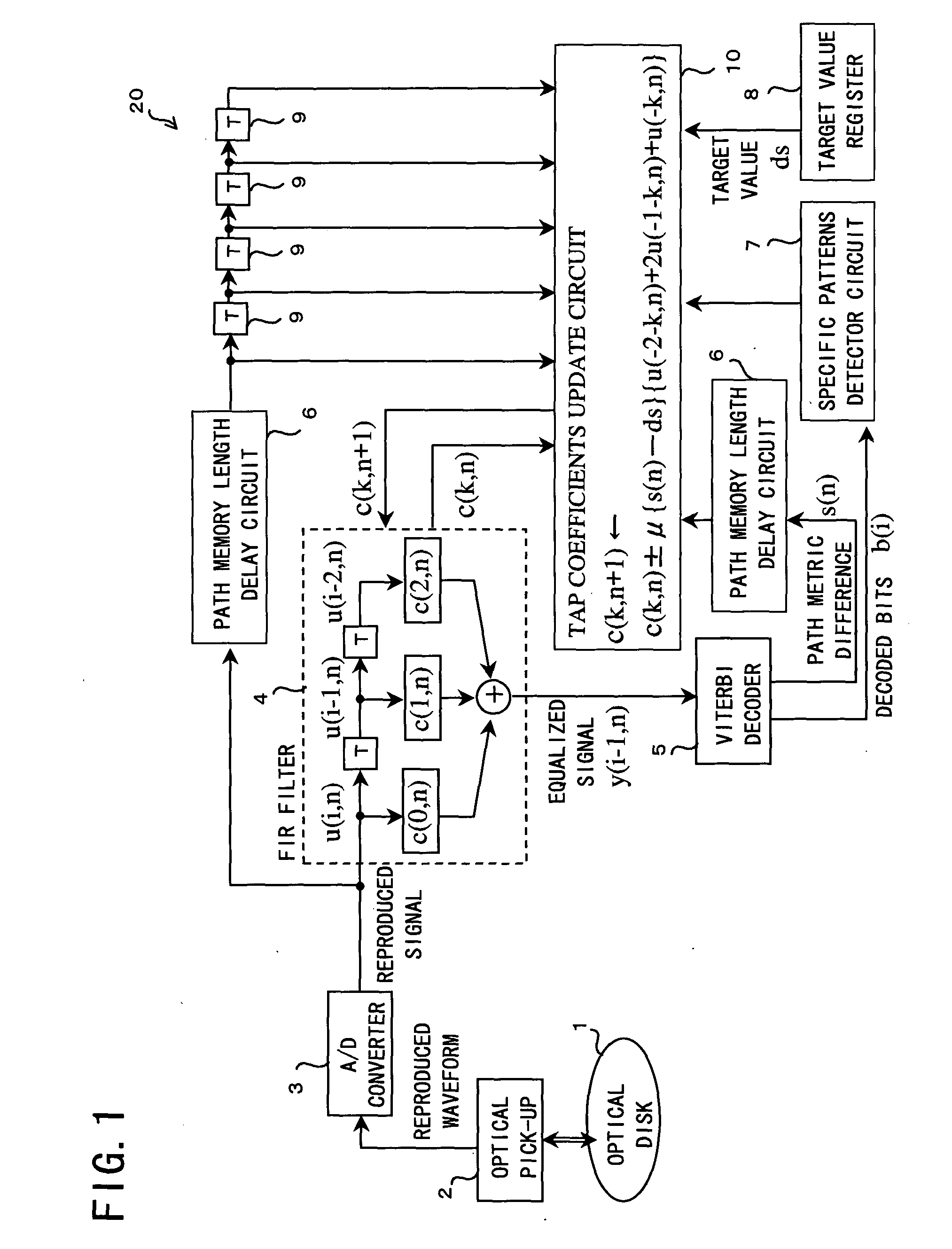
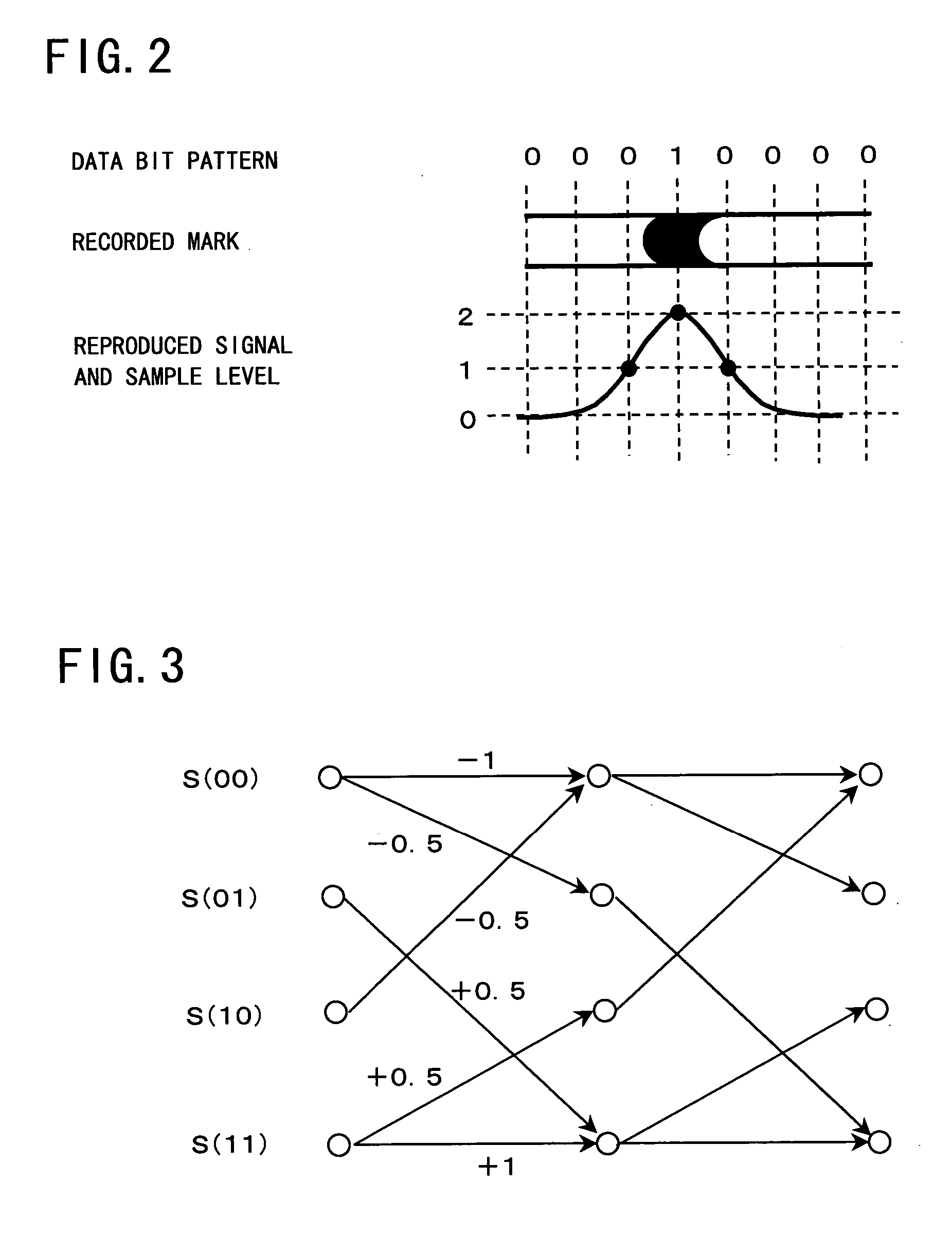
Adaptive waveform equalization for viterbi-decodable signal and signal quality evaluation of viterbi-decodable signal
InactiveUS20050193318A1Convenient ArrangementEvaluate qualityMultiple-port networksData representation error detection/correctionMean squareSignal quality
The waveform equalizing device includes: an FIR filter for generating an equalized signal pattern y(i, n) on the basis of equalization of a waveform of the reproduced signal pattern u(i, n); a Viterbi decoding circuit for detecting a path metric difference s(n) between a correct path determined as a survivor path and an error path which fails to survive the correct path in Viterbi decoding based on the equalized signal pattern y(i, n); a target register for setting a target value ds for the path metric difference s(n); and a tap coefficients update circuit for adapting the equalization according to an error of the detected path metric difference from the target value. The tap coefficients update circuit adapts equalization properties so that the mean square error is minimized, thereby achieving a satisfactory result in lowering the error rate.
Owner:SHARP KK
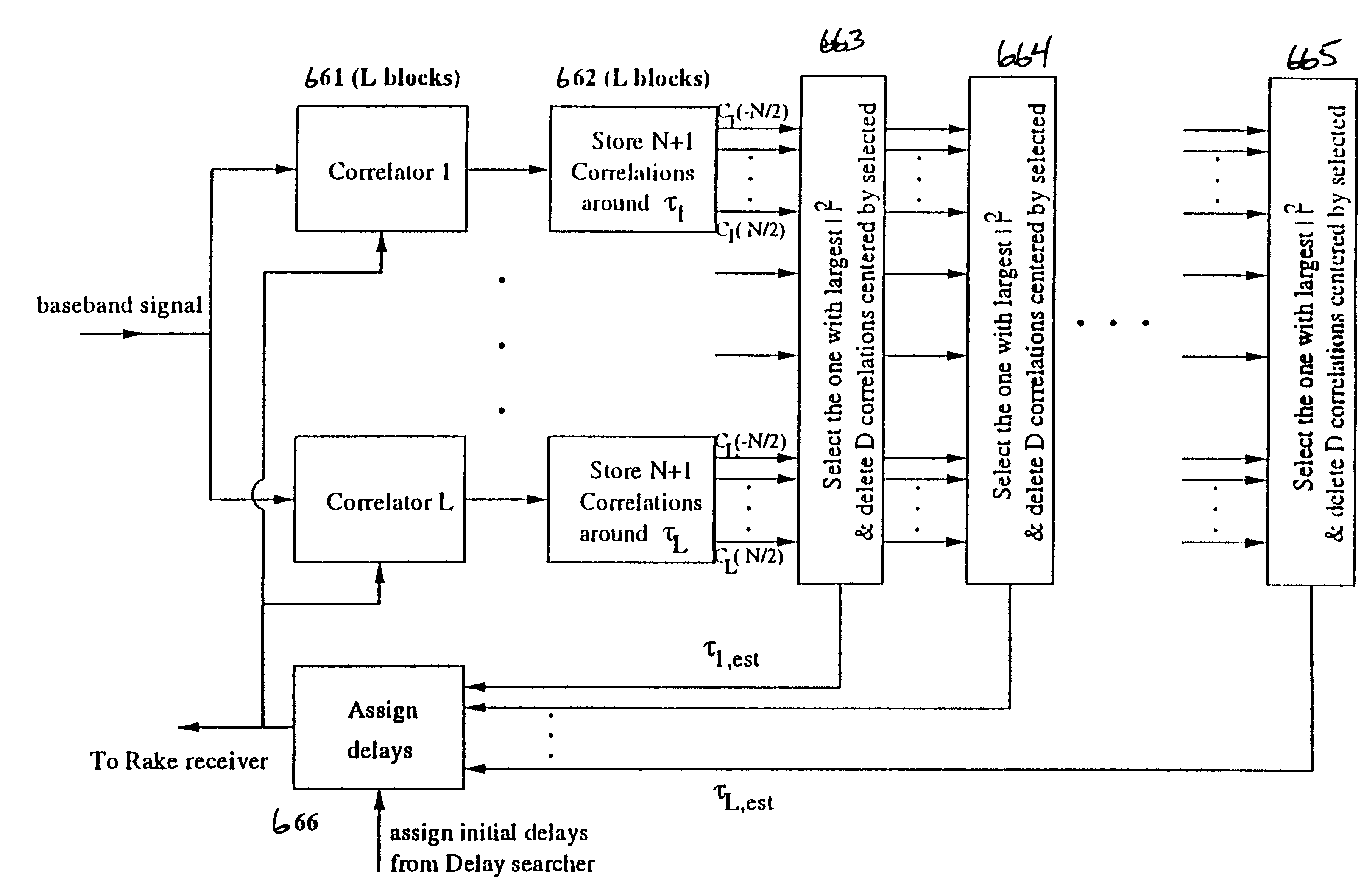
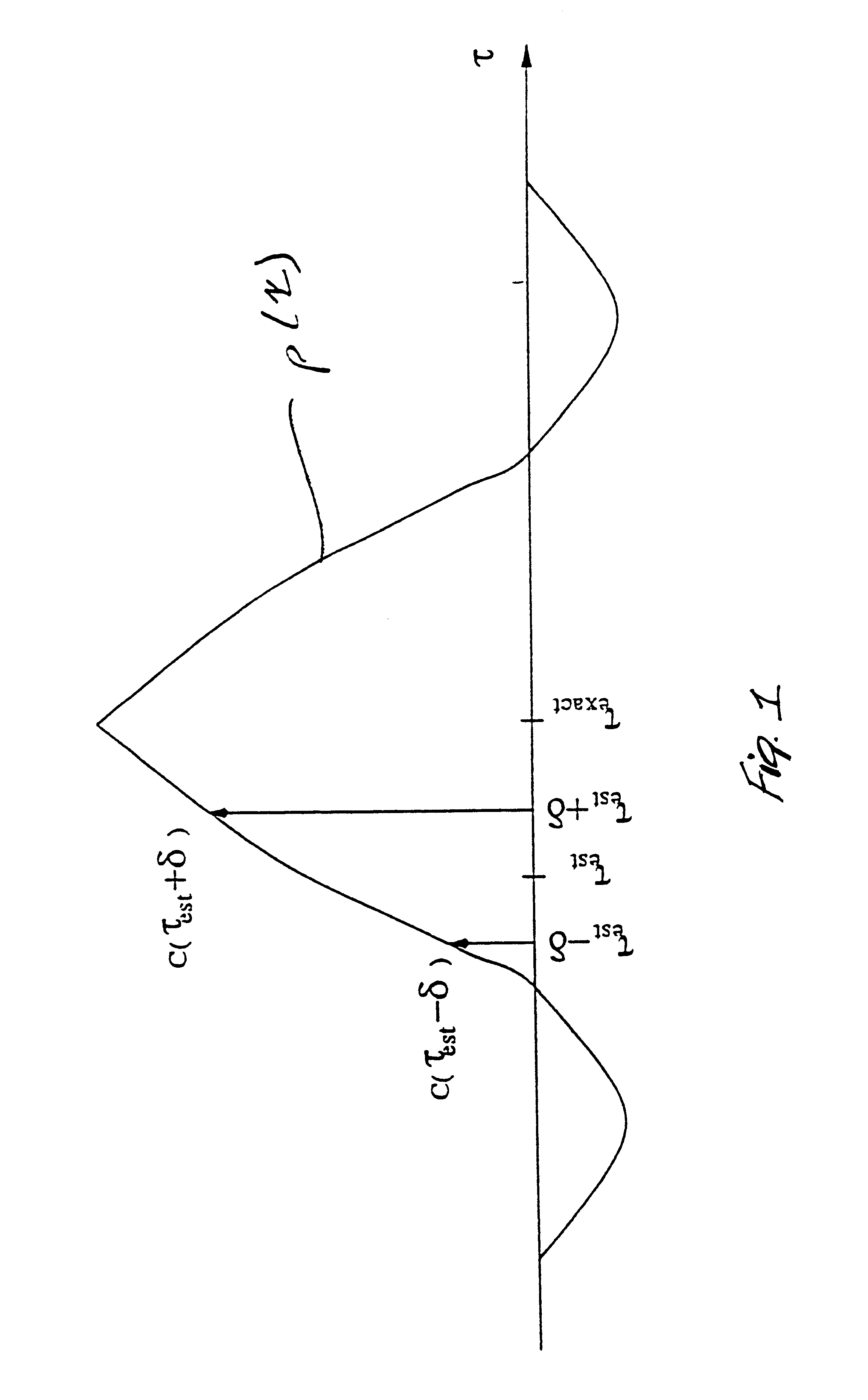
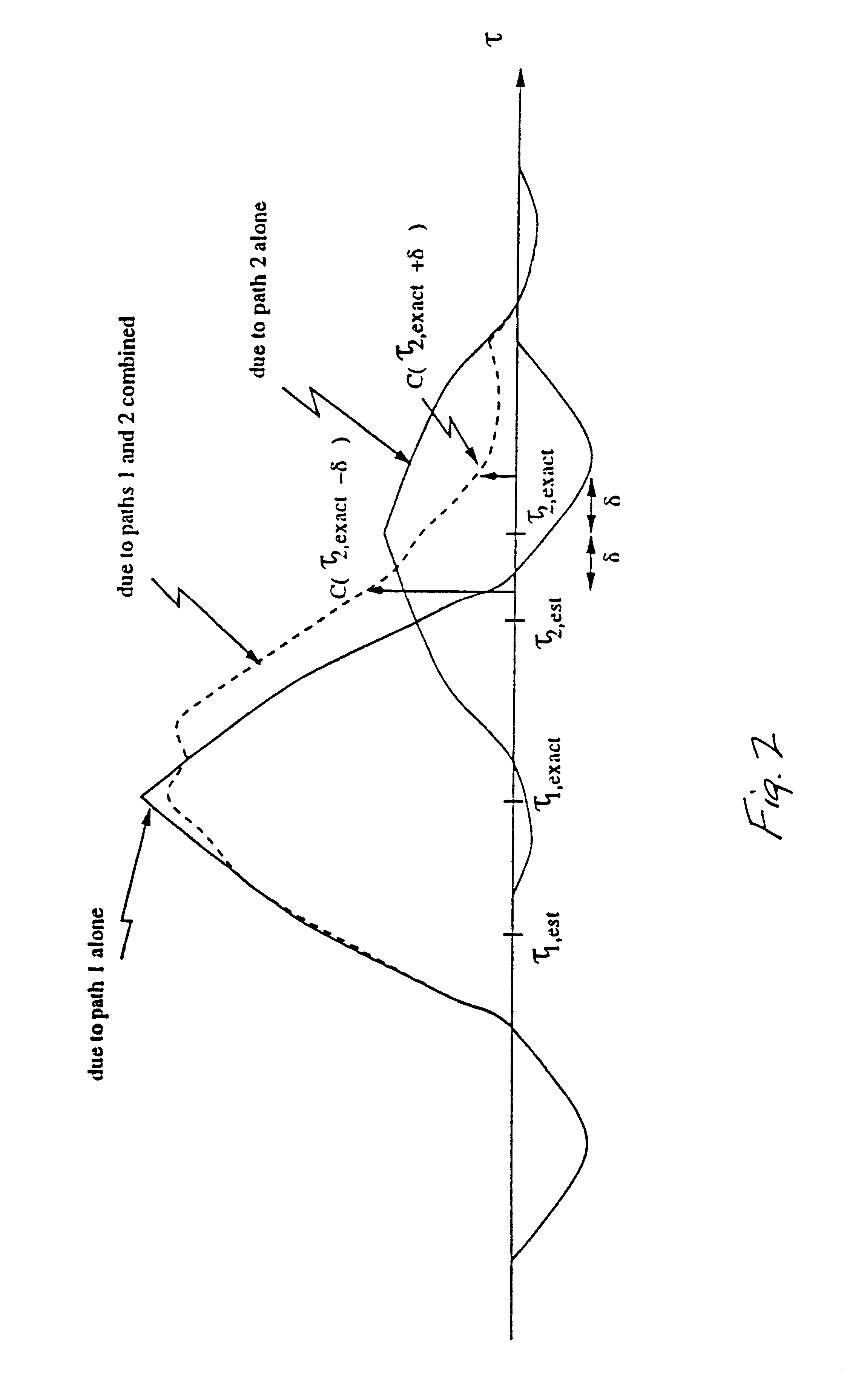
Method and apparatus for multipath delay estimation in direct sequence spread spectrum communication systems
InactiveUS6839378B1Solve the real problemRadio transmission for post communicationMean squareSide information
Multipath delay estimation of a direct sequence spread spectrum (DS-SS) signal transmitted in a multipath fading channel is accomplished by measuring the envelope of the signal to determine a new delay estimate. Delay estimates are also obtained in ray strength order, by subtracting out the influence of the stronger rays on the weaker ones. This subtraction approach can be performed iteratively, allowing further refinement of the delay estimates. Delay estimates can also be determined by minimizing the mean square error (MSE) between a measured correlation function and a modeled correlation function. The minimum mean square error (MMSE) approach can performed iteratively, to further refine the delay estimates. Maximum likelihood (ML) delay estimates can also be obtained by exploiting side information regarding the transmit and receive pulse shapes.
Owner:ERICSSON INC
Wireless sensor network topology control method based on non-uniform sections
InactiveCN101267391ABalanced energy consumptionIncrease data transfer volumeEnergy efficient ICTData switching networksWireless transmissionMean square
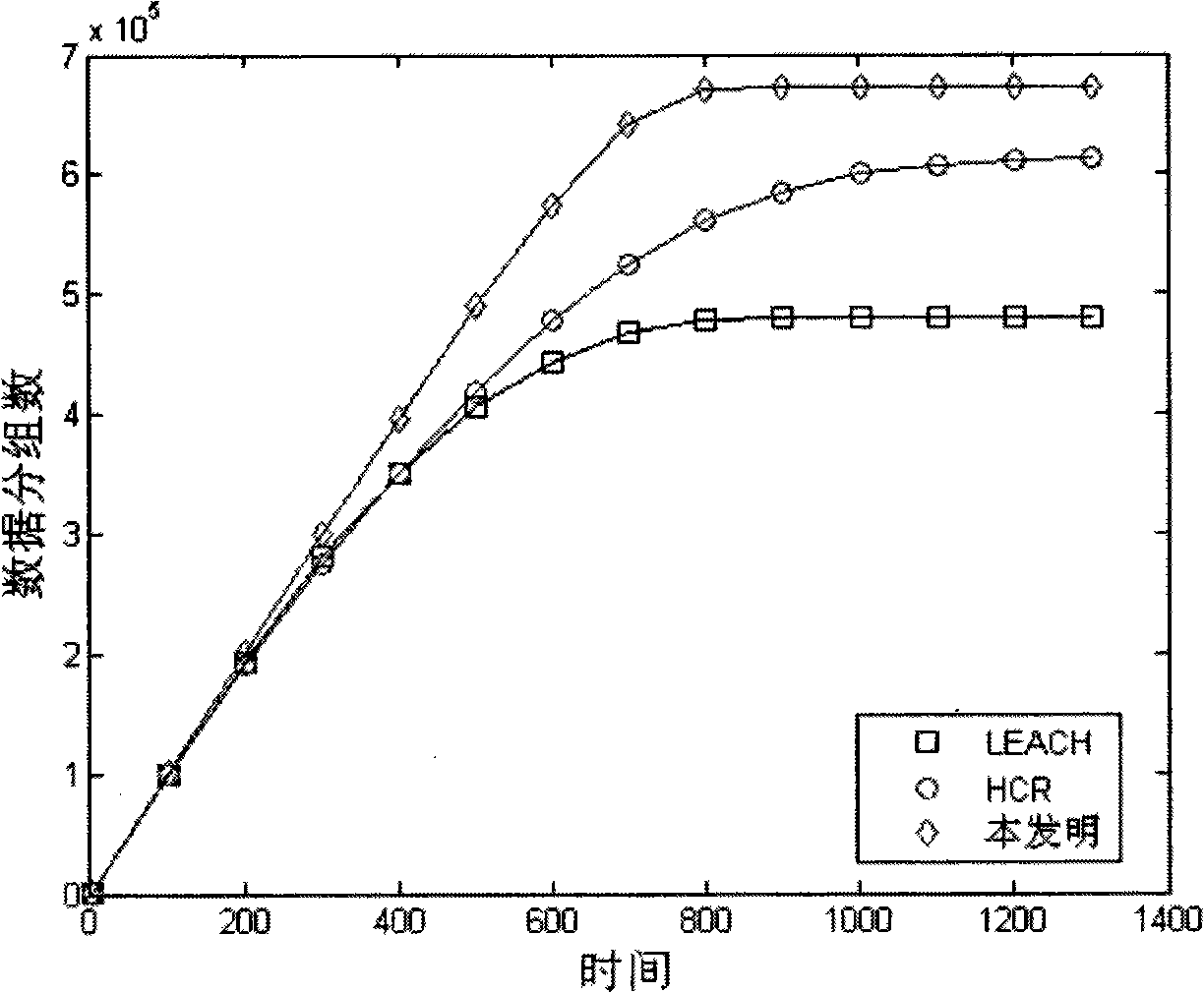
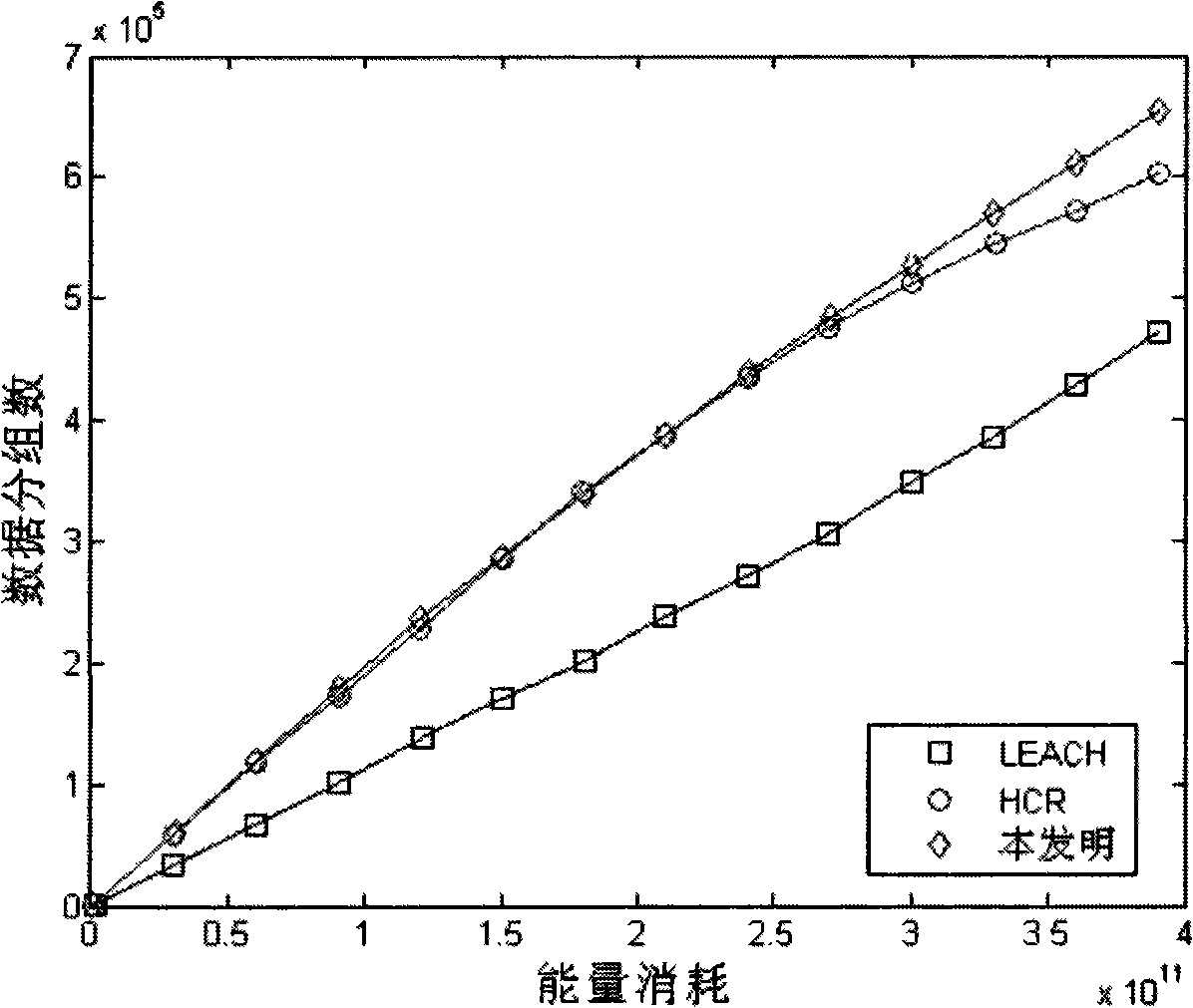
The invention relates to a topology control method for wireless sensor network based on uneven cluster, belong to sensor technical field, comprising: during the topology generating stage, introducing an uneven minimum mean square subtraction clustering mechanism on a finished cluster in order to reduce energy consumption of in-cluster node; using a strategy based on cluster head energy consumption for setting cluster head changing time, in order to equalize energy consumption on each cluster head node in the network; establishing a cluster head-cluster head energy sensing route, in order to avoid remote wireless transmission; during topology maintenance stage, using a cluster head selection scheme based on node surplus energy and in-cluster node distribution, and using the same strategy to set cluster changing time. With the realization of the method, it can reduce total network energy consumption and equalize energy consumption on each node, in order to prolong cooperative working time of most nodes in the network.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Face detection method based on Gaussian model and minimum mean-square deviation
InactiveCN102096823AAccurate segmentationQuick splitCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionFace detection
The invention provides a face detection method based on a Gaussian model and a minimum mean-square deviation, and relates to a face recognition technology. A face detection method based on the Gaussian model and the minimum mean-square deviation under the premise of a complicated background, a side face, a stopper and a plurality of faces. The method comprises the following steps of: building a YCbCr Gaussian model: building the YCbCr Gaussian model for face skin color distribution according to collected skin color sample data, and performing lighting compensation on the image, wherein in the YCbCr, Y is a brightness component, Cb is a blue chroma component, and Cr is a red chroma; performing skin color segmentation on the image by using the built YCbCr Gaussian model and the minimum mean-square deviation; performing binaryzation on a skin color region, and processing a binary image by opening to eliminate a small bridge and discrete points; rejecting detected non-face regions in the similar skin color or skin color according to future knowledge of a face; and finally marking a face position by using a rectangular frame.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
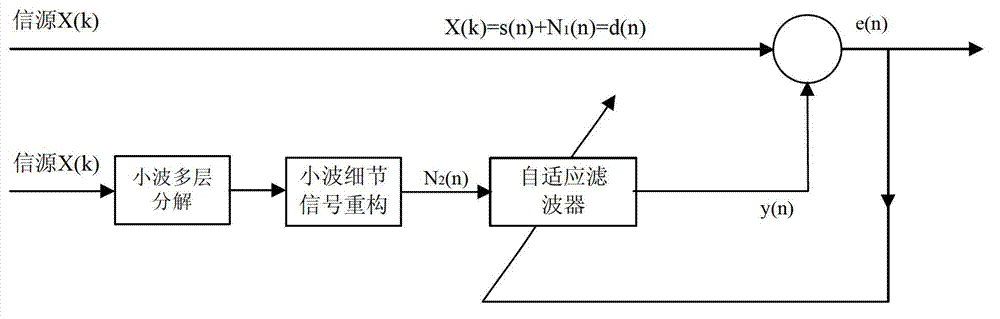
Wavelet transform and variable-step-size LMS (least mean square) adaptive filtering based signal denoising method
ActiveCN102832908ASimple stepsReasonable designAdaptive networkDigital technique networkPattern recognitionAdaptive filter
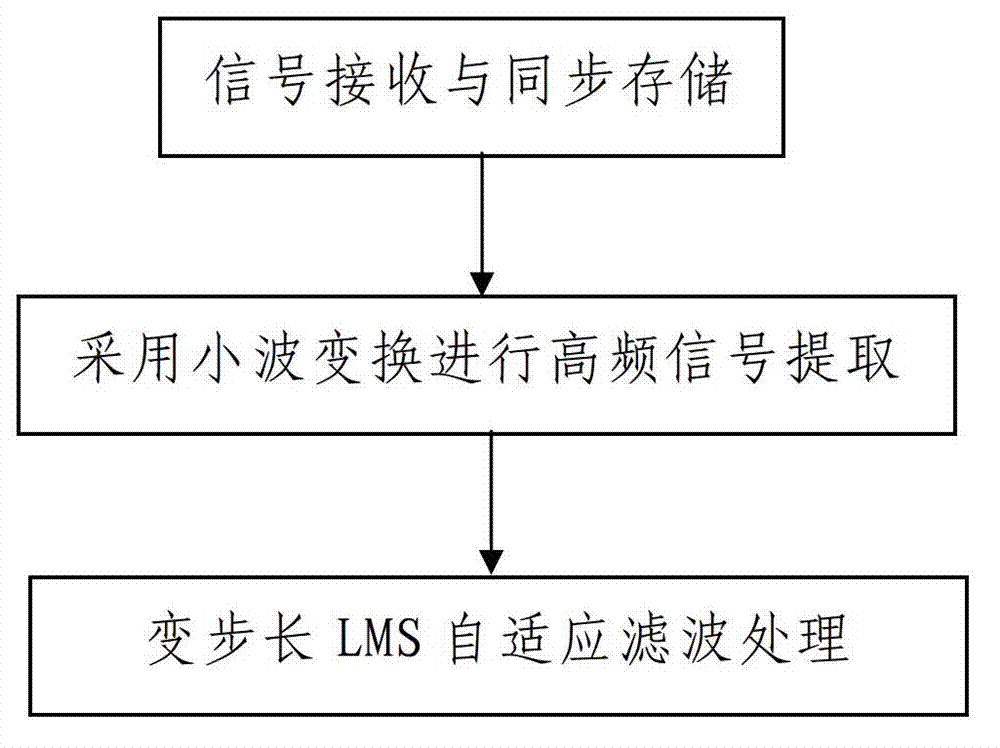
The invention discloses a wavelet transform and variable-step-size LMS (least mean square) adaptive filtering based signal denoising method which comprises the following steps that: 1, signal receiving and synchronous storage: a data processor synchronously stores received signals into a data memory so as to obtain a sampling sequence X (k) which is a one-dimensional signal; 2, high-frequency signal extraction: the data processor carries out wavelet transform on the currently received one-dimensional signal X (k) and extracts high-frequency signals; and 3, LMS adaptive filtering: the data processor invokes the high-frequency signals extracted by an LMS adaptive filter to carry out LMS error calculation so as to obtain output signals subjected to filtering, and carries out adjustment on the parameters of the filter according to error signals, so that the output signals tend to interference signals. The method disclosed by the invention is simple in steps, reasonable in design, convenient to realize, and good in denoising effect; and the denoising process is performed through the combination of wavelet transform and variable-step-size LMS adaptive filtering, so that the filtering effect and the tracking speed are effectively increased.
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
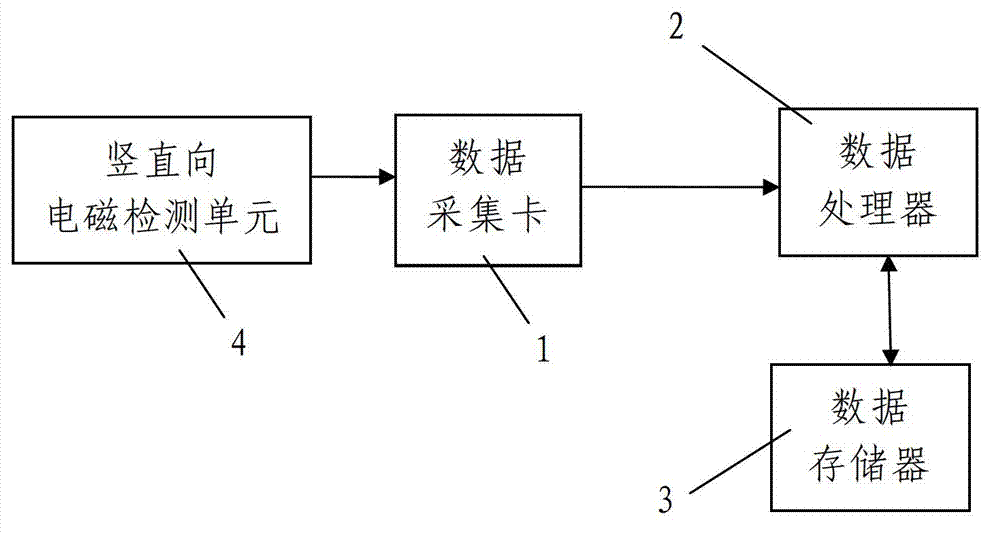
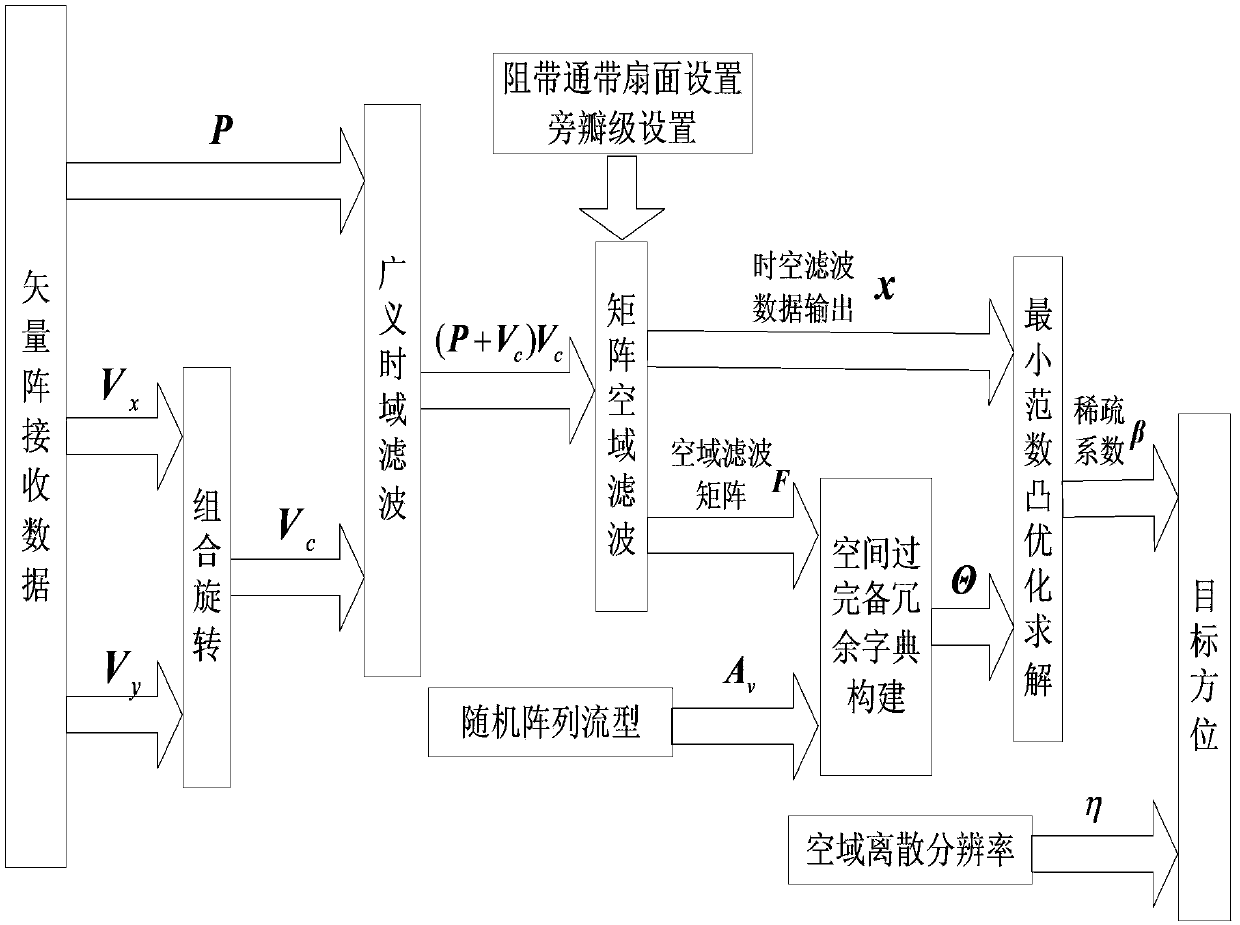
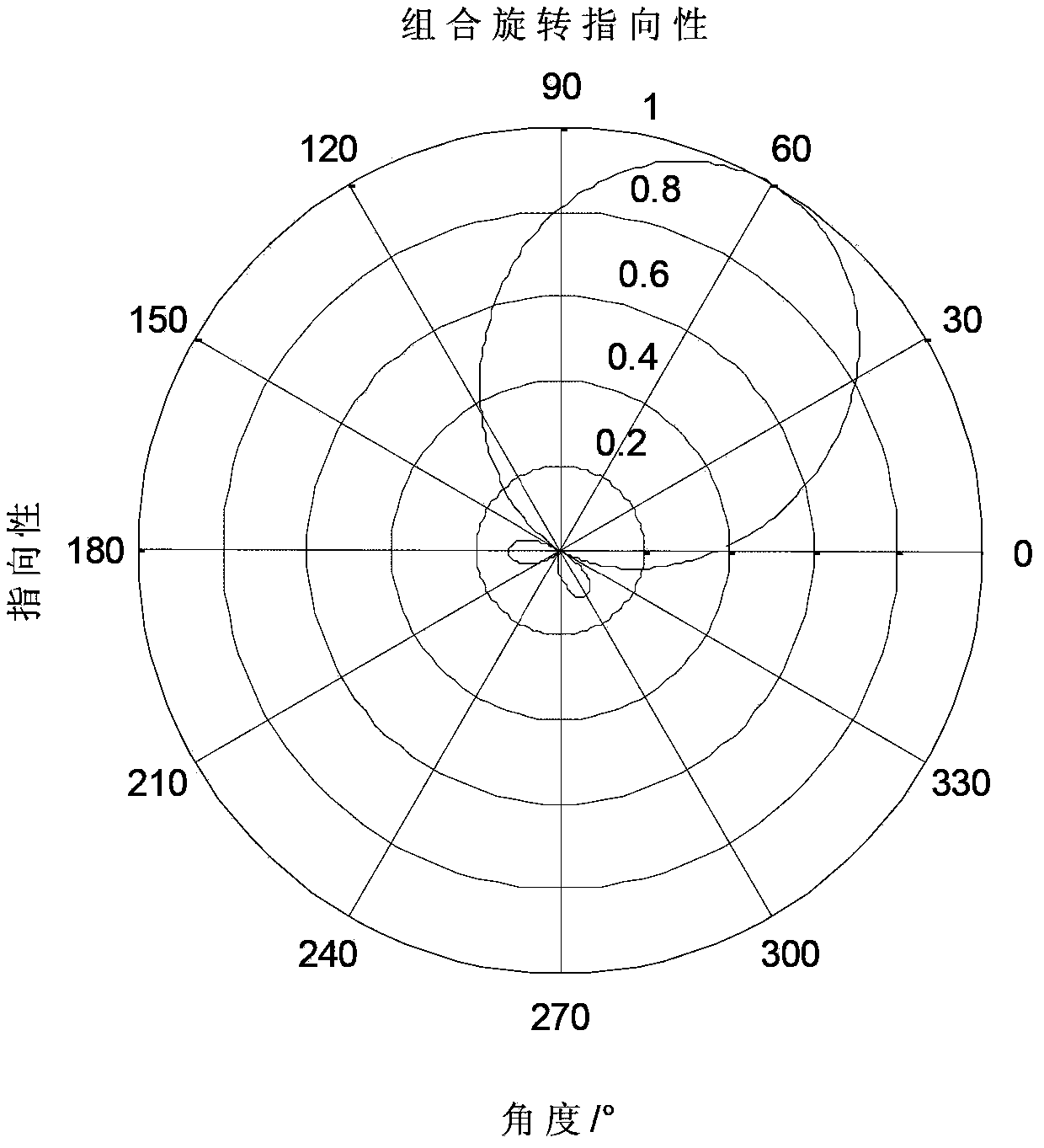
Temporal-spatial joint filtering high-resolution DOA (Direction of Arrival) estimation method based on compressed sensing technology
InactiveCN103399312ALower the input SNR thresholdEffective estimateWave based measurement systemsCompressed sensingNarrowband
The invention provides a temporal-spatial joint filtering high-resolution DOA (Direction of Arrival) estimation method based on a compressed sensing technology. The method comprises the following steps: (1) acoustic pressure vibration velocity joint temporal filtering, to be specific, carrying out rotating combination on the data of an acoustic vector sensor, and utilizing differences in the corresponding properties of a signal and noise to carry out denoising processing; (2) matrix spatial filtering, to be specific, carrying out spatial filtering on the temporally filtered data by a matrix spatial filter of which the maximum value of the mean square error of attenuation in a stop-band and a passband is minimum; and (3) compressed sensing DOA estimation by the array of the acoustic vector sensor, to be specific, receiving data and a manually formed spatial over-complete redundance dictionary via an input array preprocessed by temporal filtering, and seeking the sparse representation of the signal to carry out vector spatial spectrum estimation. The method has great spectral resolution capability in the high-resolution DOA estimation problem of a high-speed motion target under single snapshot conditions and is insensitive to the wideband and narrowband properties and coherent properties of the signal.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Rolling bearing fault feature extraction method based on signal sparse representation theory
InactiveCN105241666AWide versatilityReduce pointsMachine bearings testingDamping ratioAdaptive method
The invention discloses a rolling bearing fault feature extraction method based on the signal sparse representation theory, and the method comprises the following steps: constructing an over-complete dictionary representing local damages of a rolling bearing through employing a multi-stage inherent frequency unit impulse response function; recognizing the multi-stage inherent frequency and damping ratio of the rolling bearing and a sensor system from a vibration response signal through a related filtering method, and obtaining an optimized dictionary; solving a sparse coefficient through employing a matching tracking algorithm, and improving the solving speed and precision through reasonable segmentation; reconstructing an impact response signal of each segment, and obtaining the sparse representation of a fault feature signal; carrying out time domain index statistic characteristic analysis of time intervals of adjacent impact response components in a sparse signal, and diagnosing the type of a fault through combining a mean value and a mean square deviation value. The method has the advantages of an analytical method and an adaptive method, improves the precision of waveform features, and can iron out the defects that a conventional method based on Fourier transform is not suitable for rotating speed fluctuation.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com