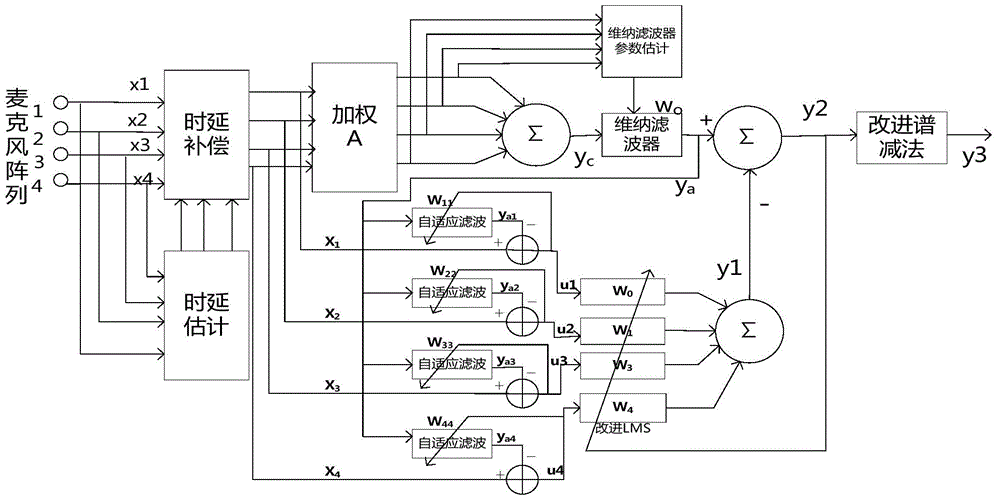
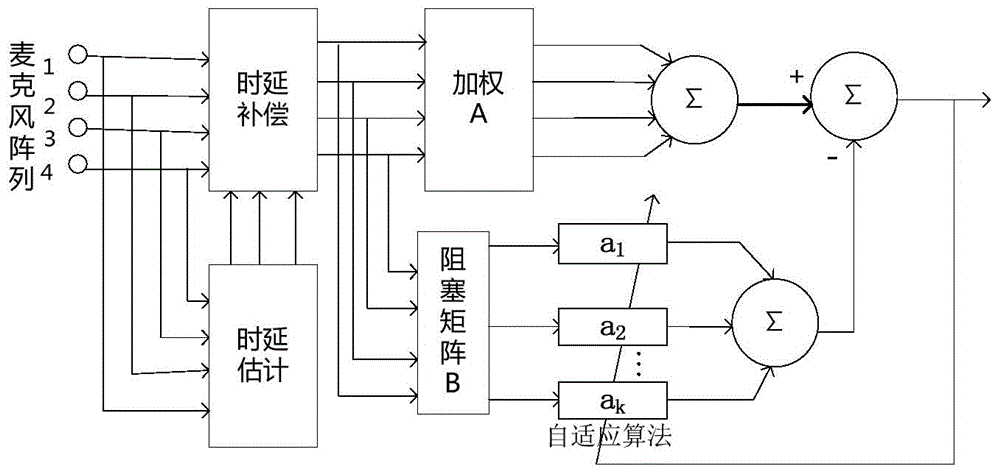
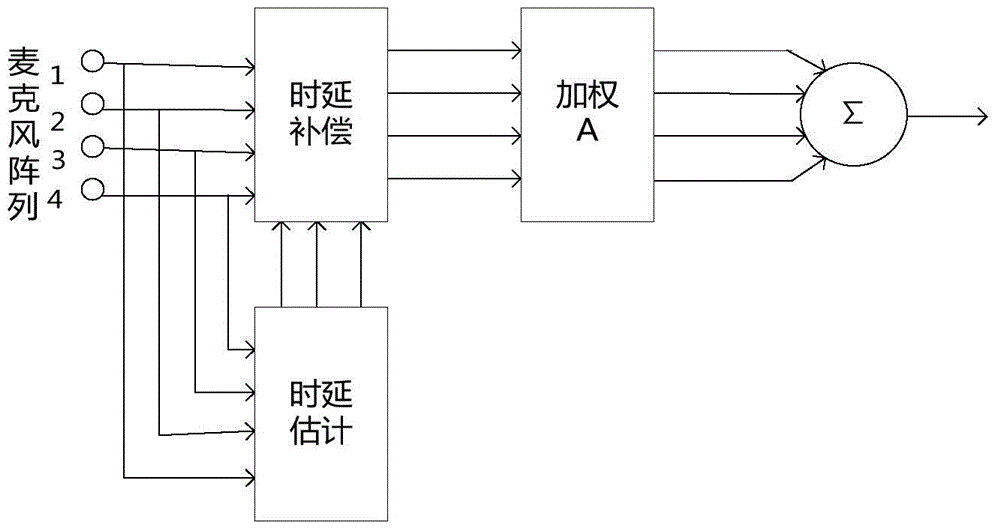
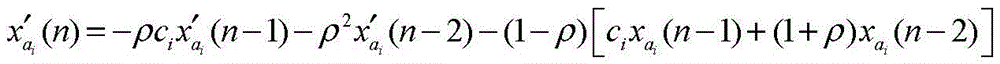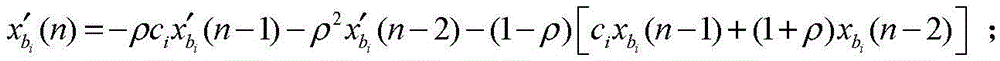Patents
Literature
280 results about "Residual noise" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
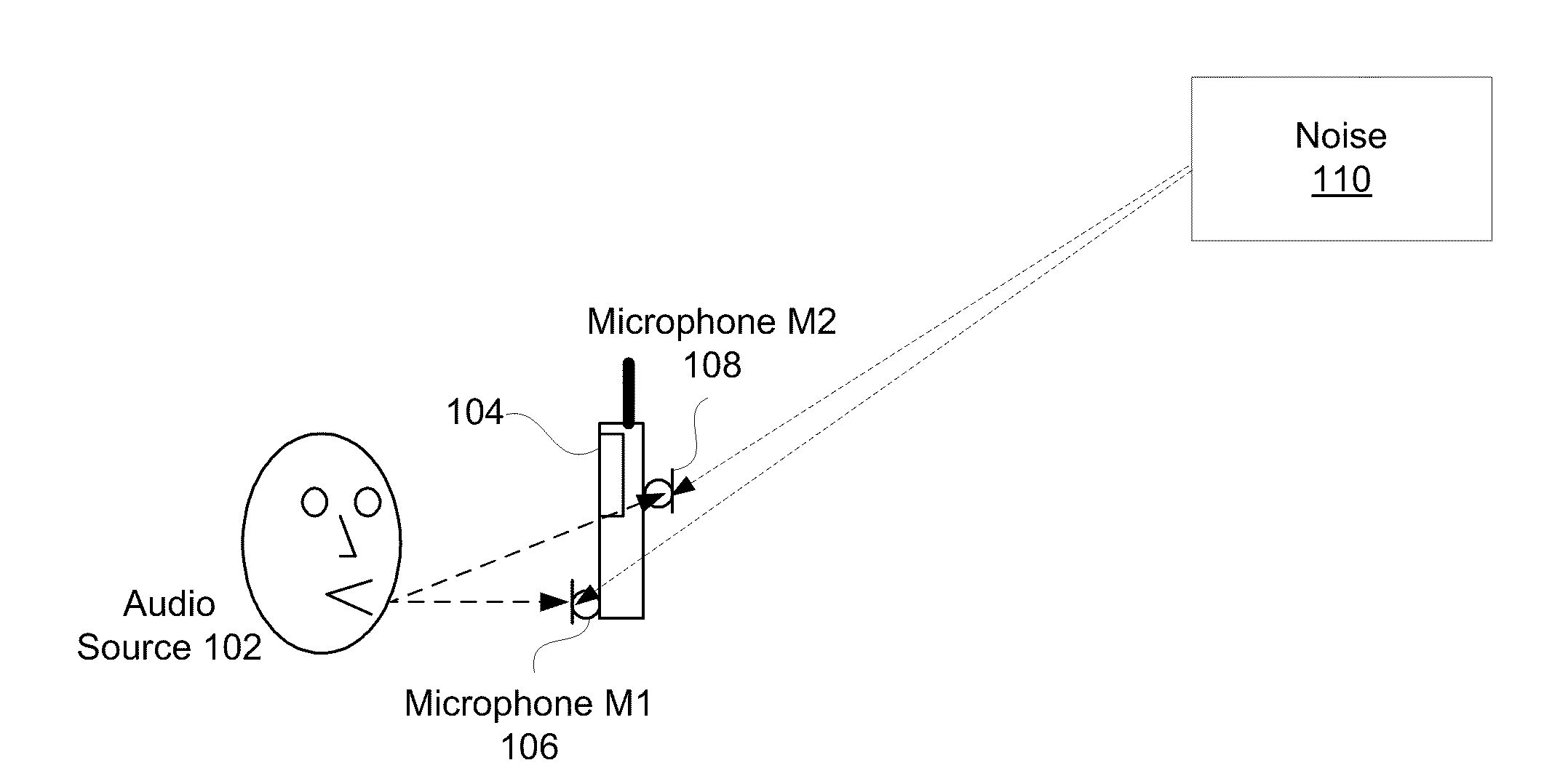
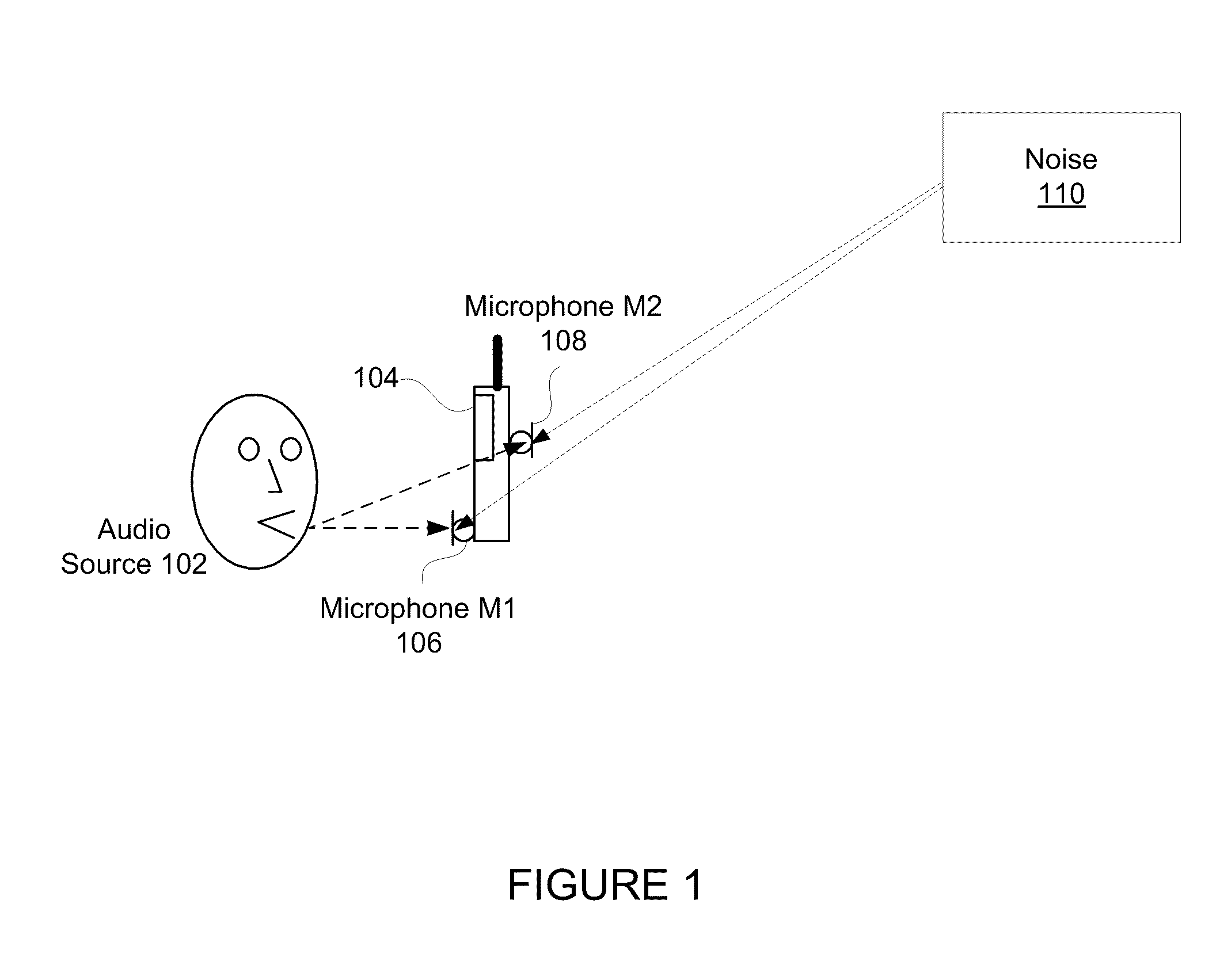
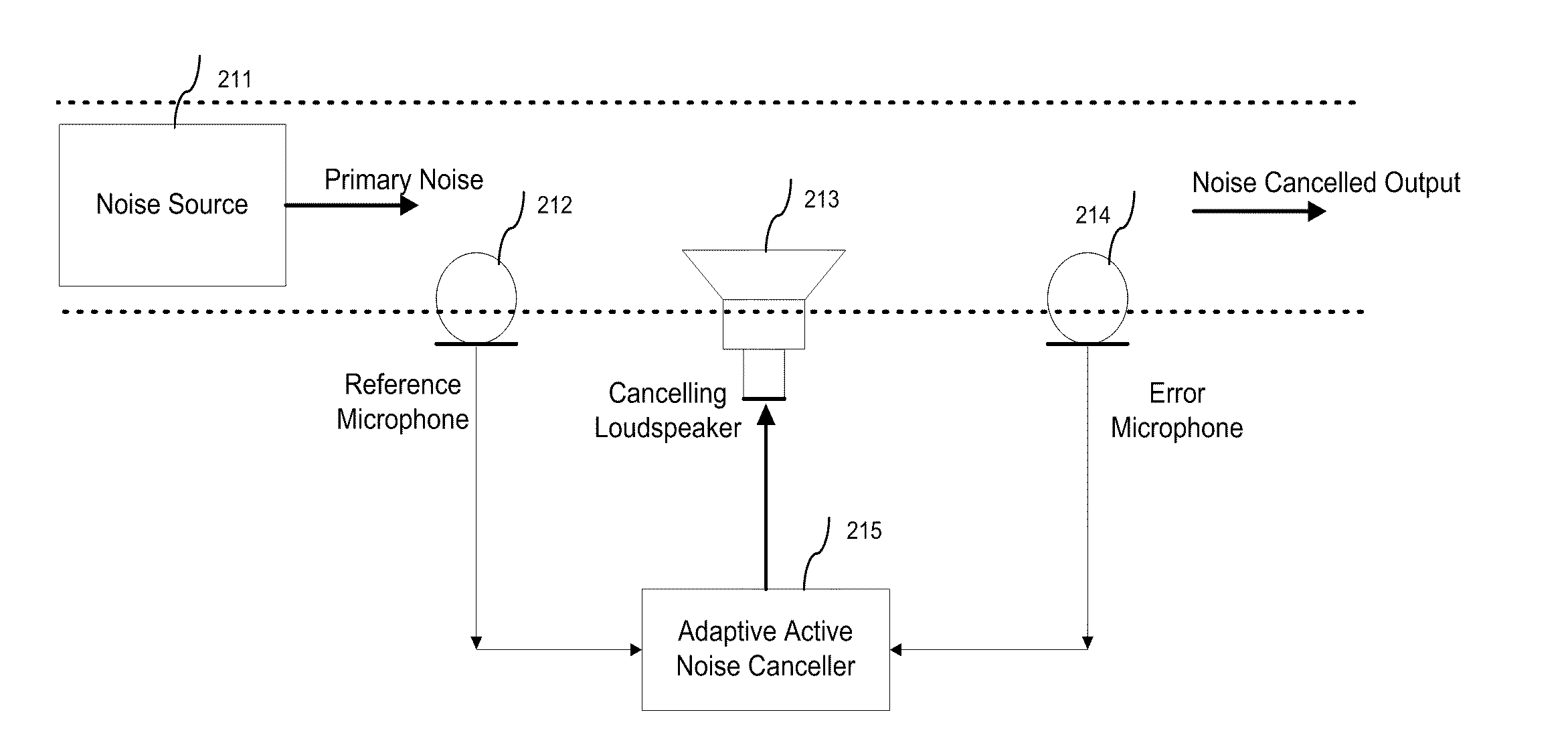
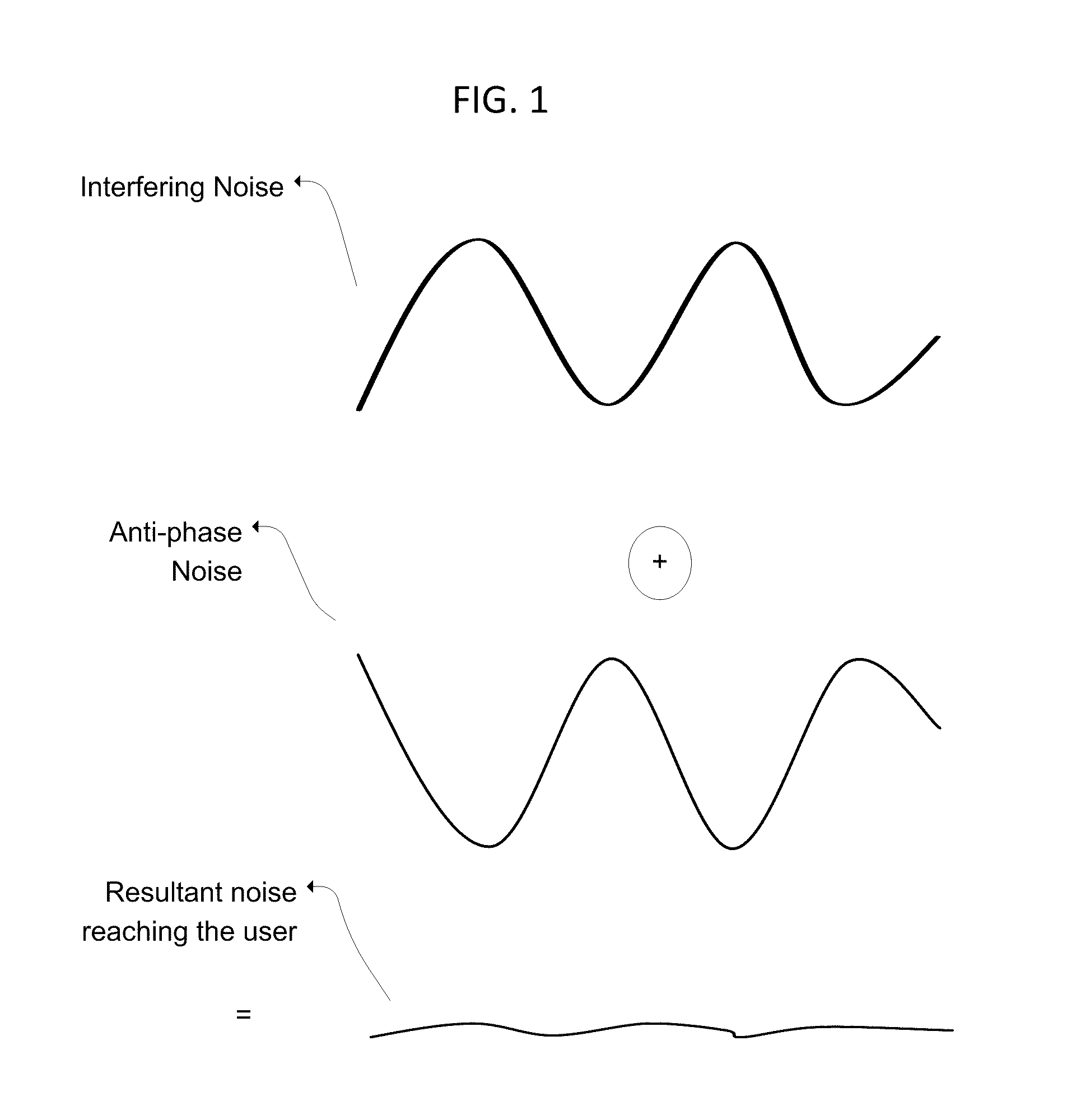
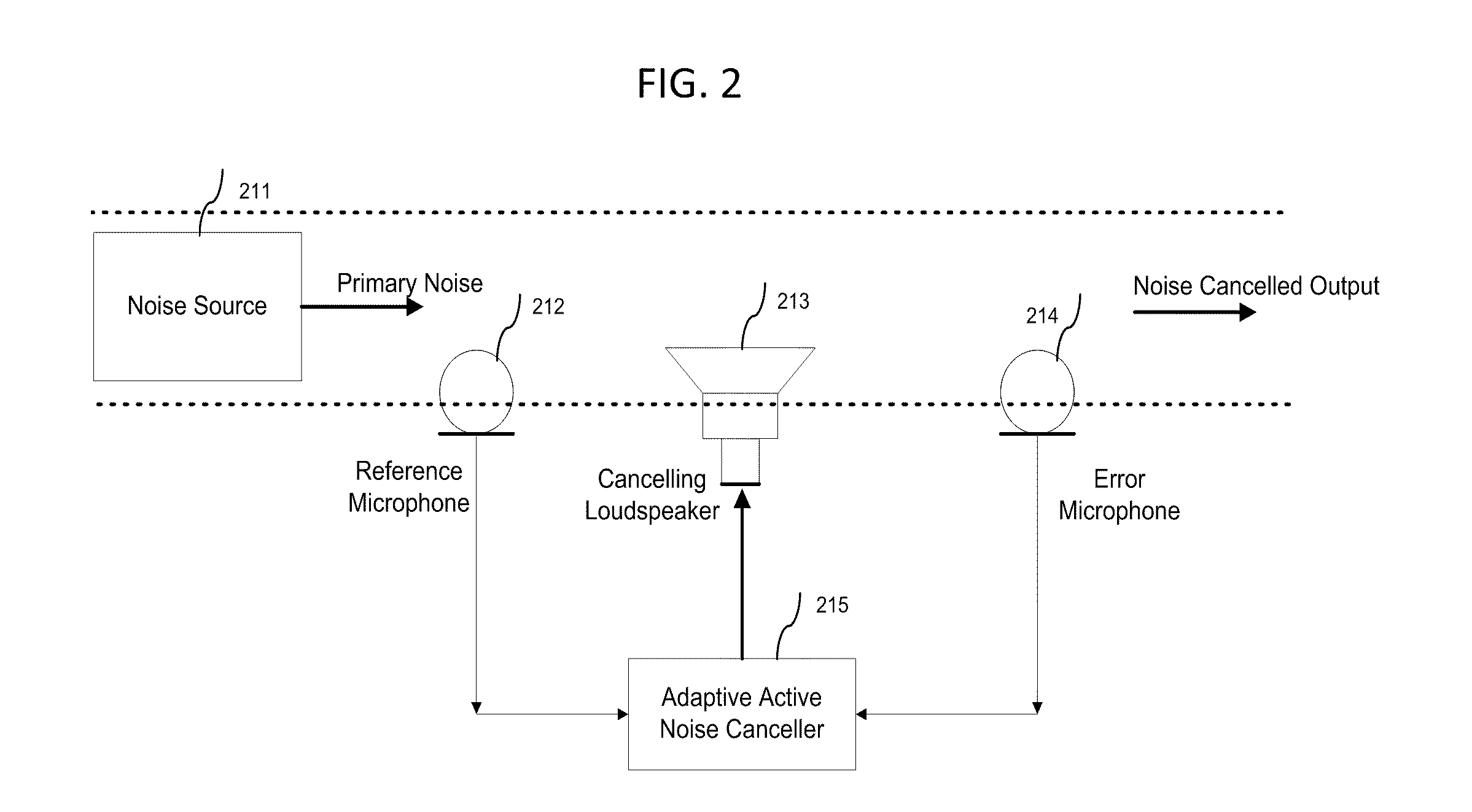
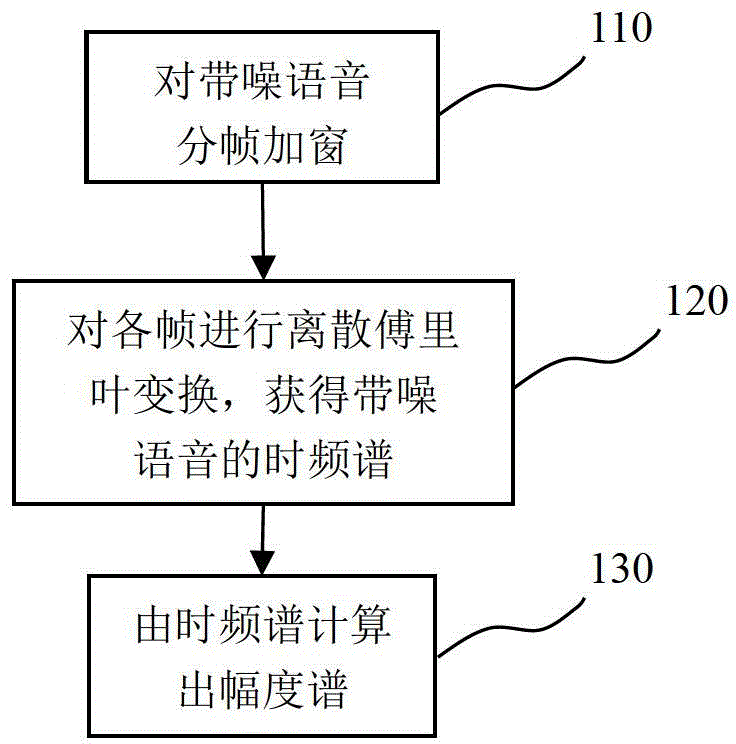
The residual noise is the noise remaining at a point under certain conditions when the noise from the specific source is suppressed.
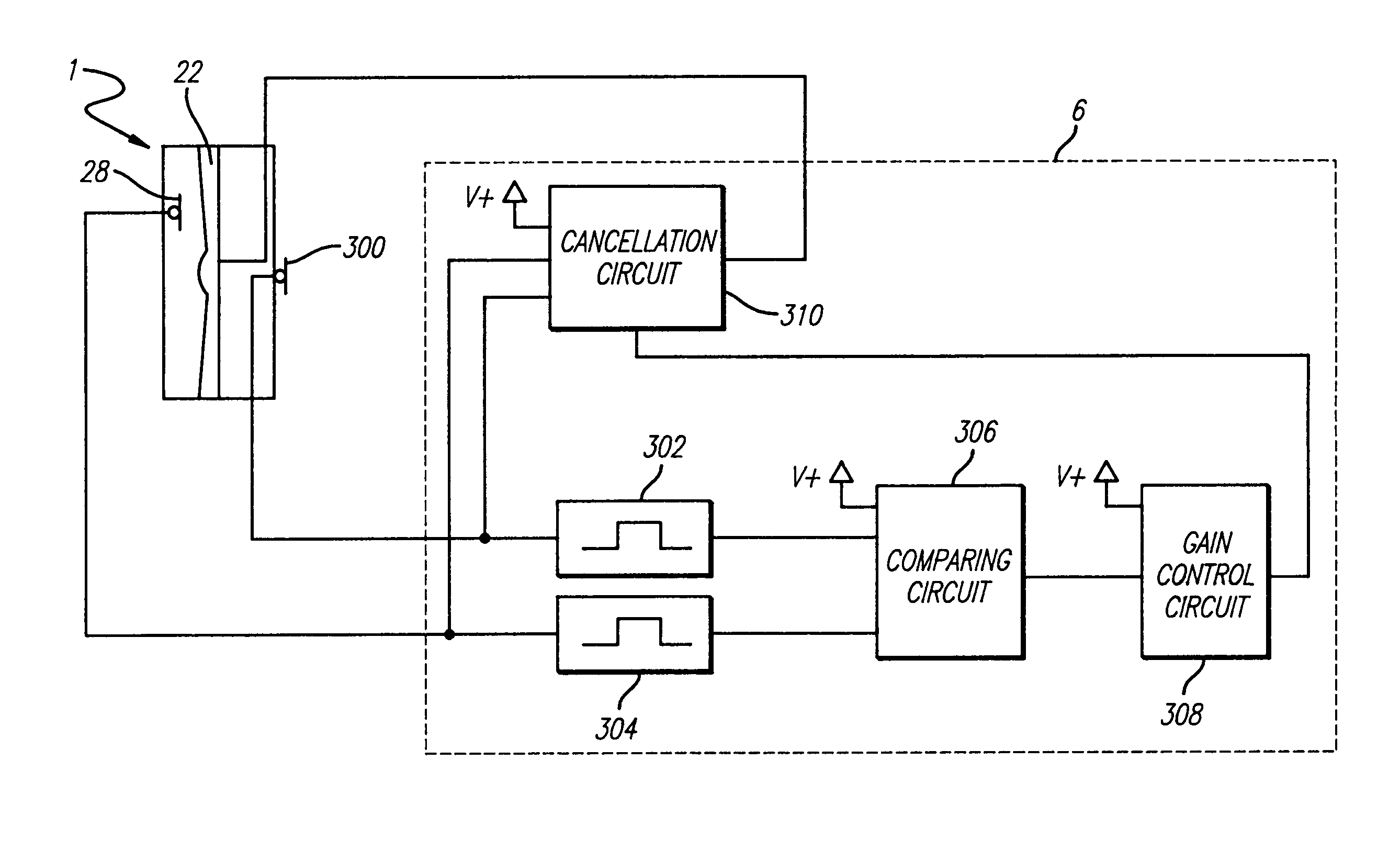
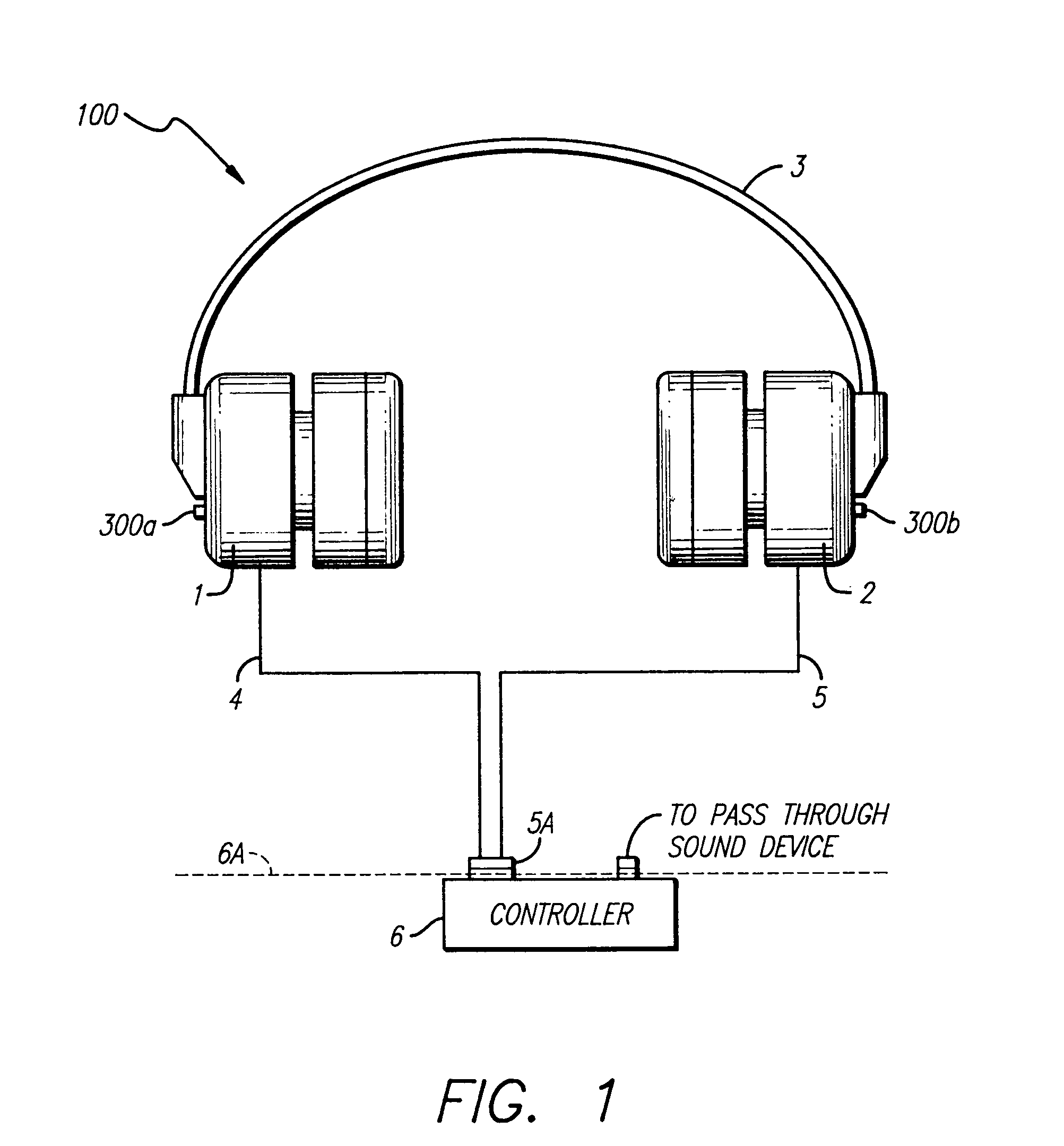
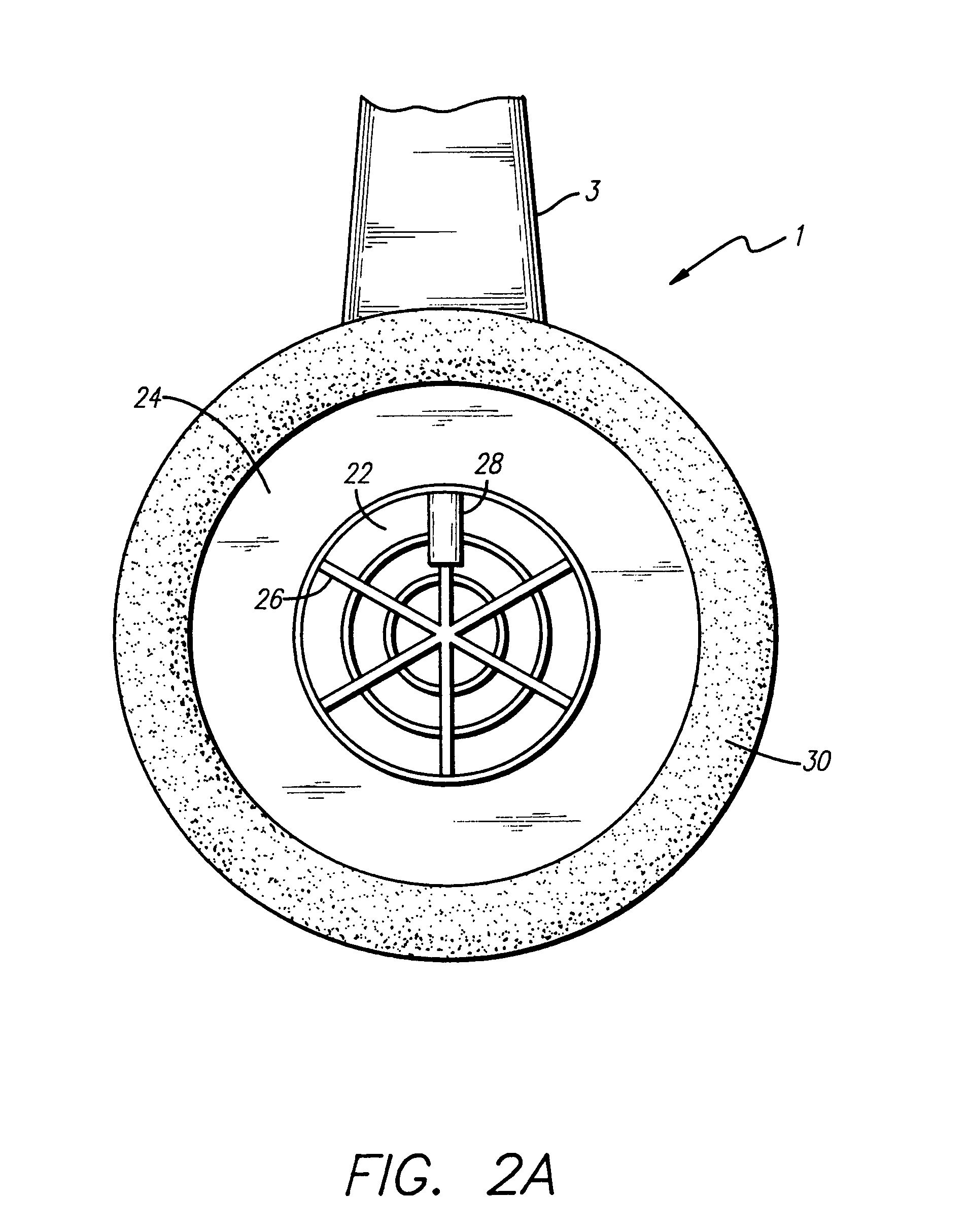
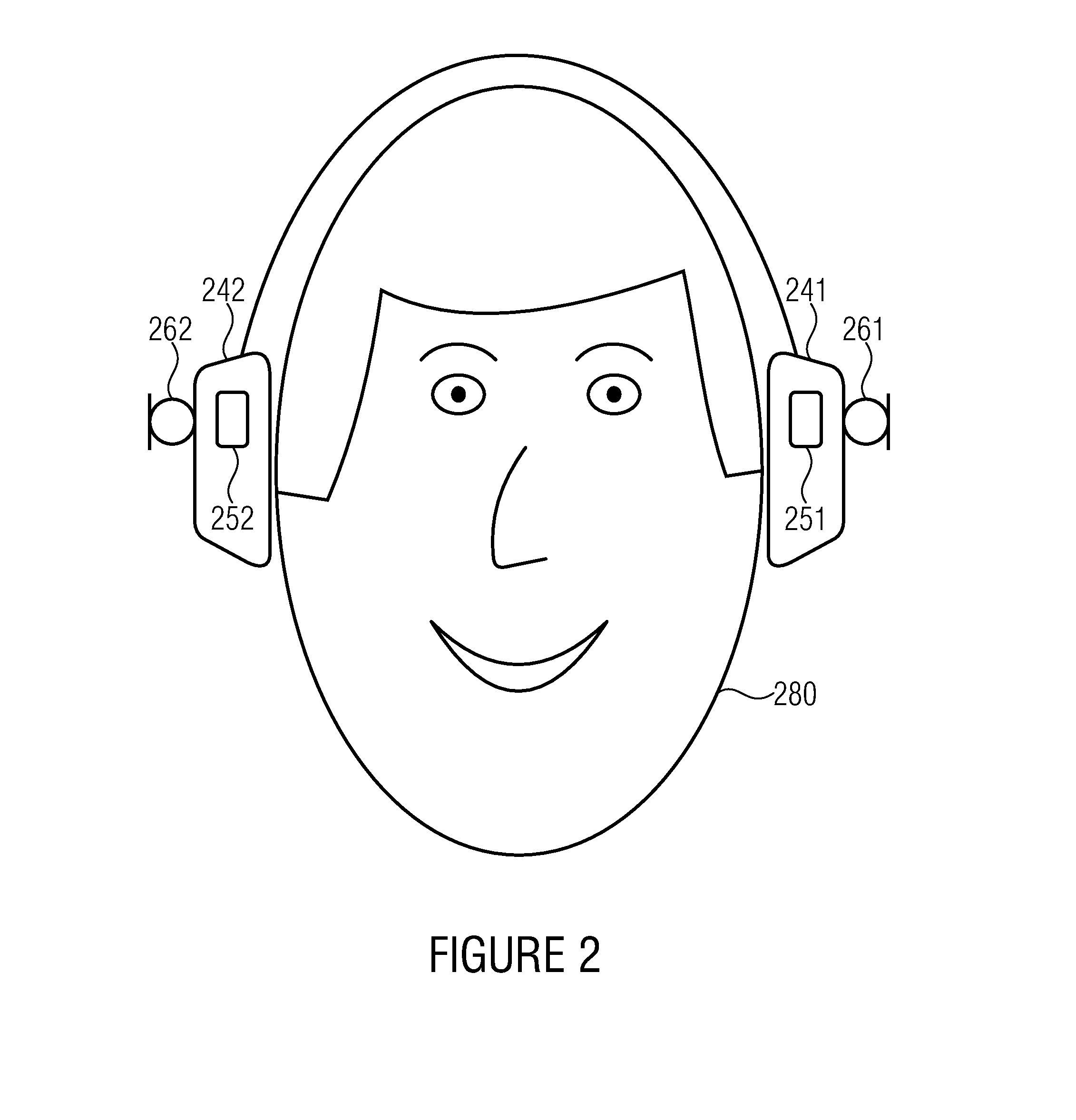
Variable gain active noise canceling system with improved residual noise sensing
InactiveUS6118878AReduce the possibilityCancellation system retains its effectiveness across its bandwidthNoise generationSound producing devicesInstabilityEngineering
An active noise cancellation system includes a series of features for more effective cancellation, greater reliability, and improved stability. A particular feature adapted for headset systems includes locating a residual microphone radially offset from the center of a sound generator to detect a signal more similar to that incident upon the eardrum of the user. In addition, an open back headset design includes perforations on the side of the headset instead of the back, so that the perforations are less susceptible to inadvertent blockage. The system also includes a mechanism for detecting changes in the acoustic characteristics of the environment that may be caused, for example, by pressure exerted upon the earpieces, and that may destabilize the cancellation system. The system automatically responds to such changes, for example, by reducing the gain or the frequency response of the system to preserve stability. The system further includes other methods for detecting imminent instability and compensating, such as detecting the onset of signals within enhancement frequencies characteristic of the onset of instability, and adjusting the gain or frequency response of the system or suppressing the enhanced signals. The system further includes a mechanism for conserving battery life by turning the system off when sound levels are low, or adjusting the power supply to the system to correspond to the current power requirements of the system.
Owner:NOISE CANCELLATION TECH
Variable gain active noise cancelling system with improved residual noise sensing
InactiveUS7103188B1Less instabilityImprove Noise CancellationEar treatmentHearing device active noise cancellationInstabilityEngineering
An active noise cancellation system includes a series of features for more effective cancellation, greater reliability, and improved stability. A particular feature adapted for headset systems includes locating a residual microphone radially offset from the center of a sound generator to detect a signal more similar to that incident upon the eardrum of the user. In addition, an open back headset design includes perforations on the side of the headset instead of the back, so that the perforations are less susceptible to inadvertent blockage. The system also includes a mechanism for detecting changes in the acoustic characteristics of the environment that may be caused, for example, by pressure exerted upon the earpieces, and that may destabilize the cancellation system. The system automatically responds to such changes, for example, by reducing the gain or the frequency response of the system to preserve stability. The system further includes other methods for detecting imminent instability and compensating, such as detecting the onset of signals within enhancement frequencies characteristic of the onset of instability, and adjusting the gain or frequency response of the system or suppressing the enhanced signals. The system further includes a mechanism for conserving battery life by turning the system off when sound levels are low, or adjusting the power supply to the system to correspond to the current power requirements of the system.
Owner:NCT GROUP
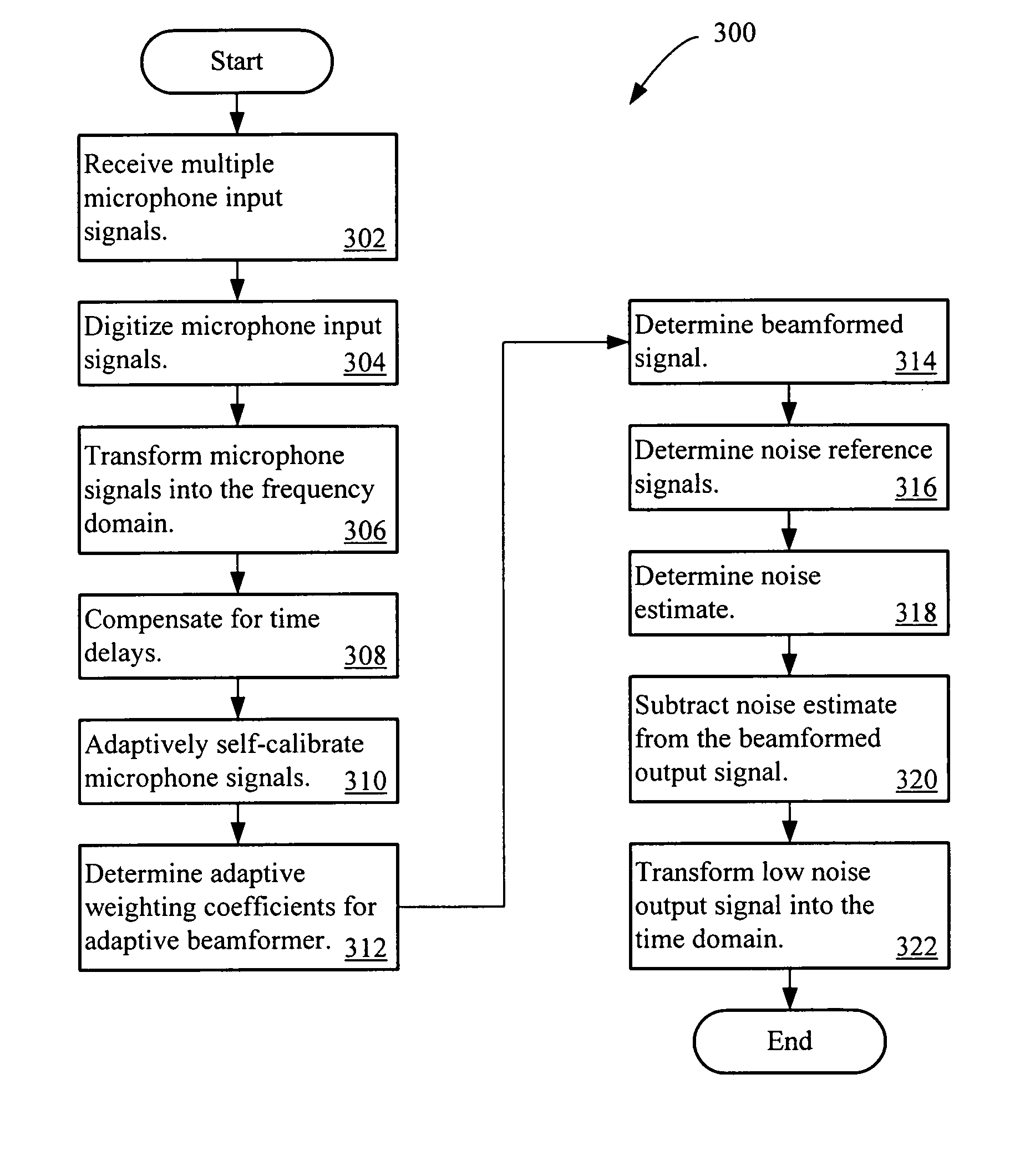
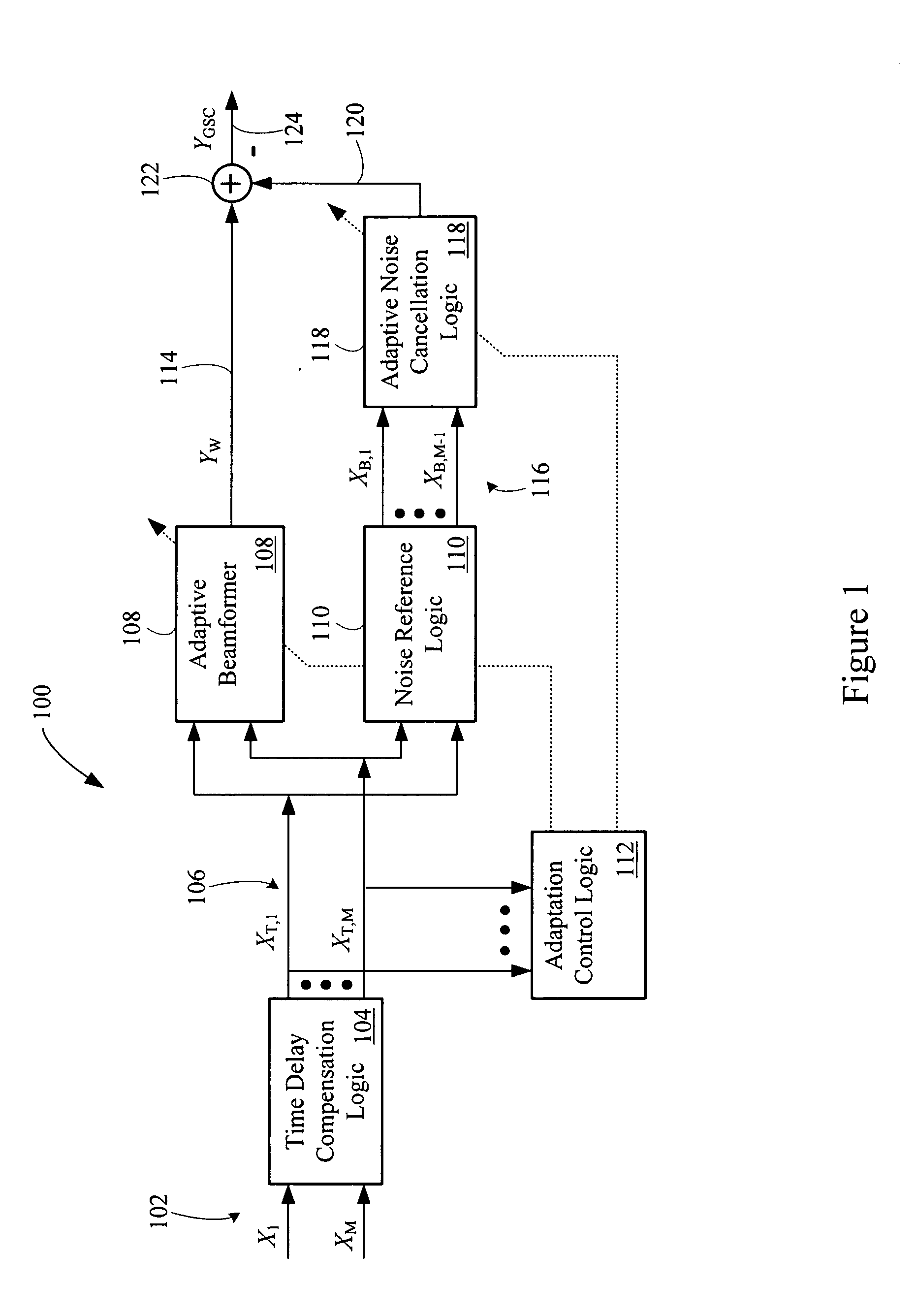
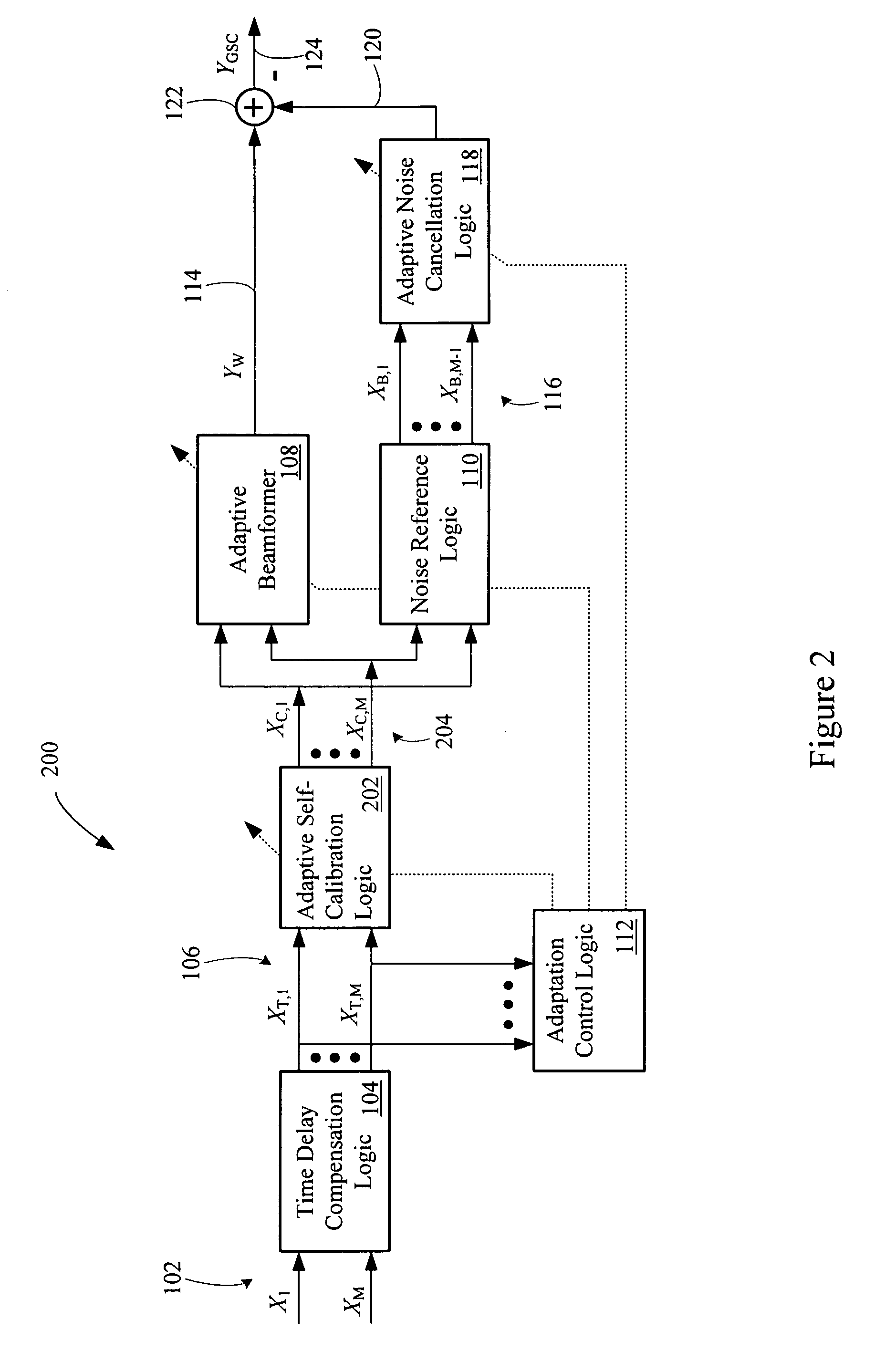
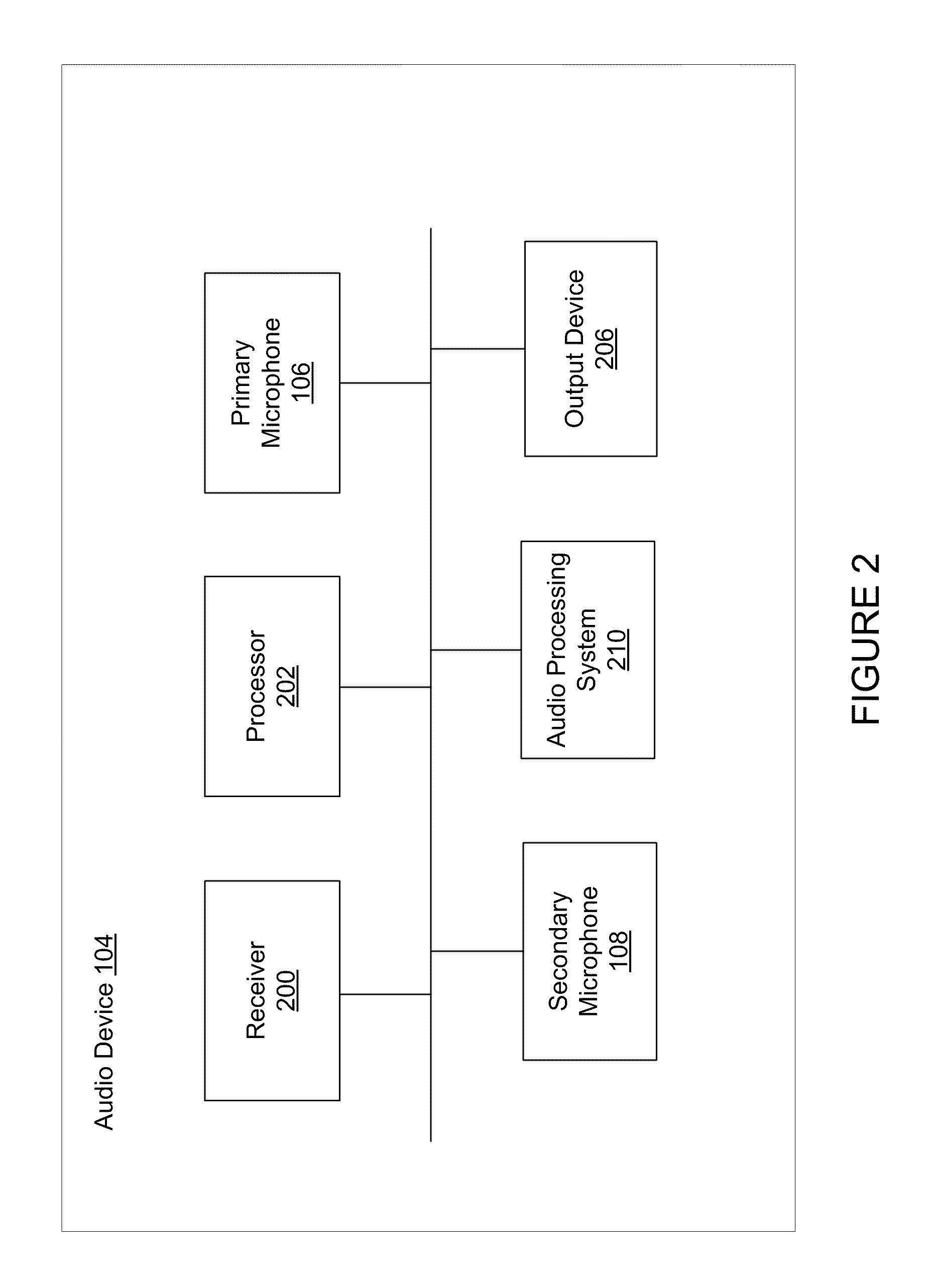
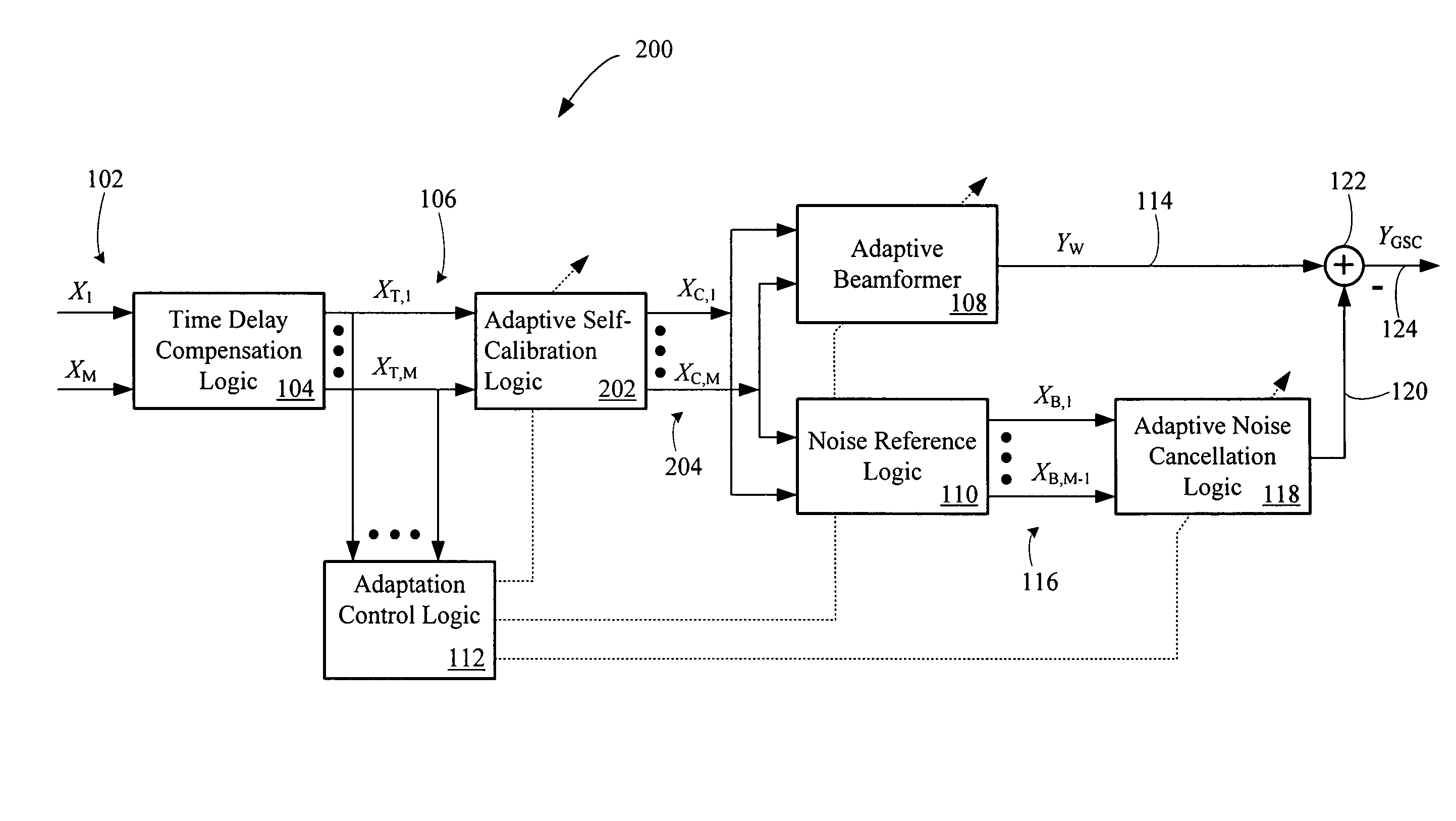
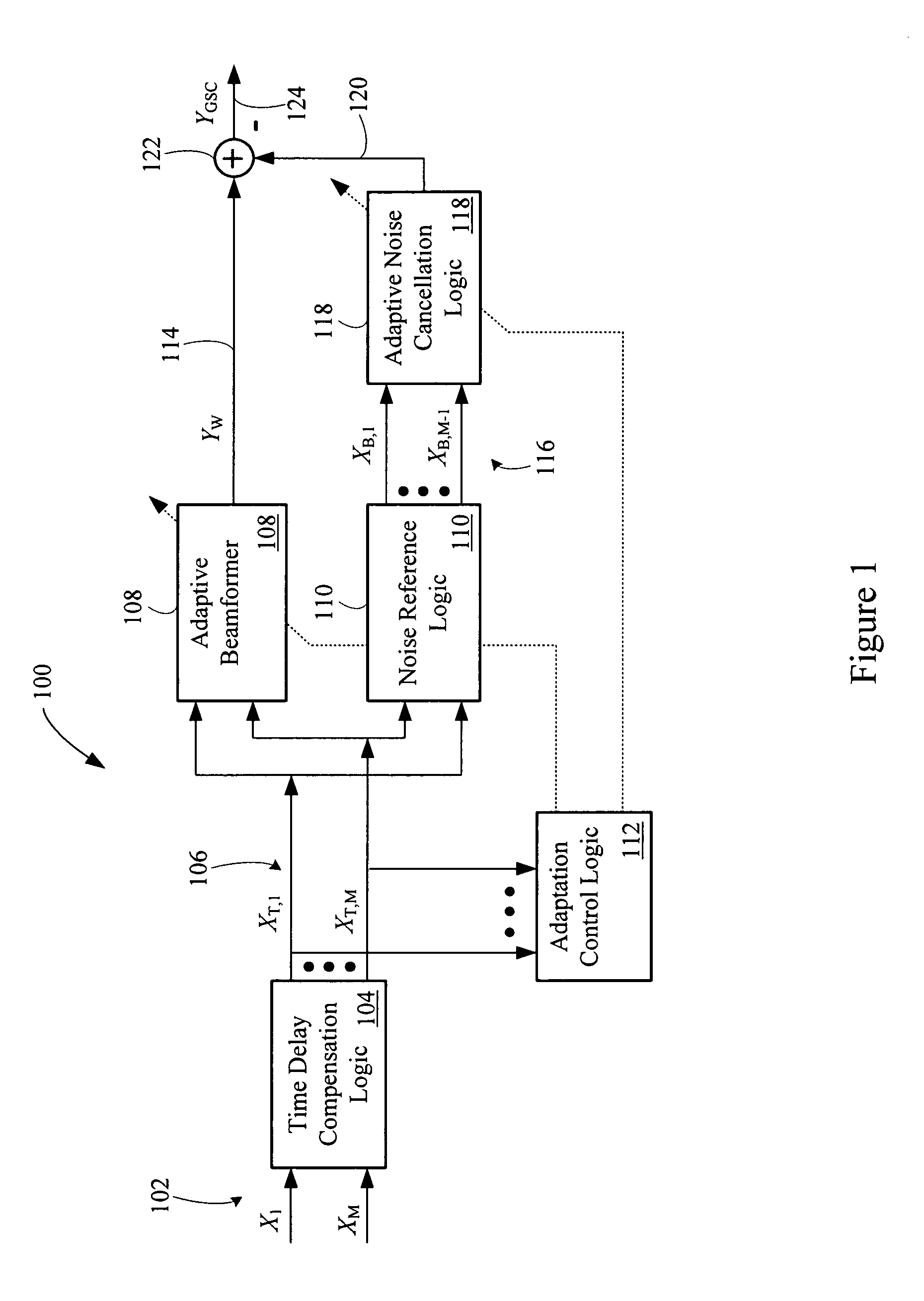
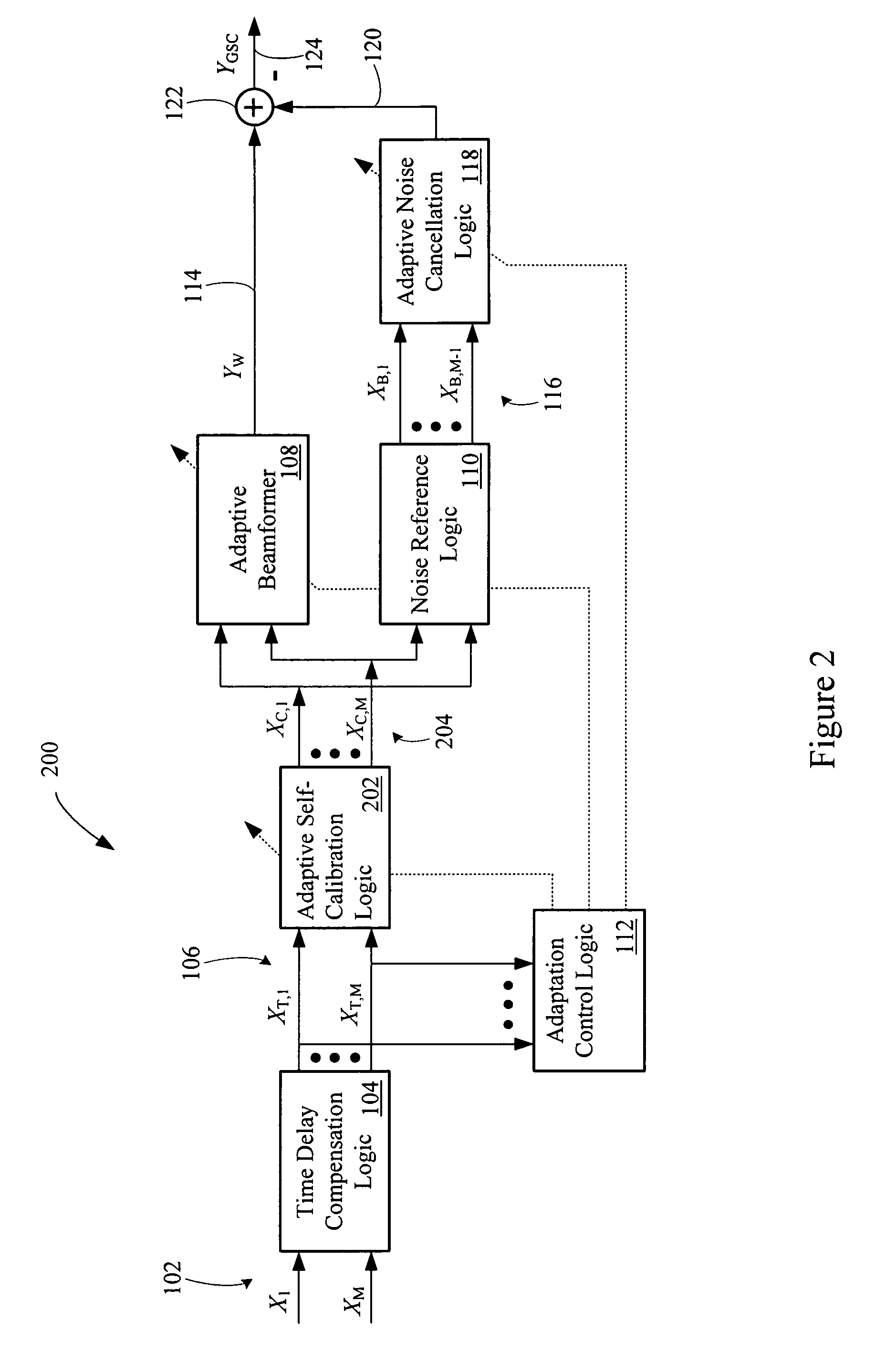
Multi-channel adaptive speech signal processing system with noise reduction
ActiveUS20060222184A1Improved speech signal clarityImprove intelligibilitySignal processingEar treatmentLow noiseHigh energy
An adaptive signal processing system eliminates noise from input signals while retaining desired signal content, such as speech. The resulting low noise output signal delivers improved clarity and intelligibility. The low noise output signal also improves the performance of subsequent signal processing systems, including speech recognition systems. An adaptive beamformer in the signal processing system consistently updates beamforming signal weights in response to changing microphone signal conditions. The adaptive weights emphasize the contribution of high energy microphone signals to the beamformed output signal. In addition, adaptive noise cancellation logic removes residual noise from the beamformed output signal based on a noise estimate derived from the microphone input signals.
Owner:HARMAN BECKER AUTOMOTIVE SYST WAVEMAKERS
Active noise control algorithm that requires no secondary path identification based on the SPR property
InactiveUS20100284546A1Reduce vibration and noiseReduce residual noise powerEar treatmentNoise generationNoise controlControl system
A control system for reducing noise or vibration in a target zone. The noise or vibration is produced by a source and transferred to the target zone by a main path. The control system is provided with an actuator, at least one error sensor and a controller. The actuator is positioned to deliver actuated signals into at least a portion of the target zone. The at least one error sensor monitors the residual noise or vibration power in the target zone and produces an error signal representative thereof. The controller receives a reference signal representative of noise or vibration produced by the source, and the error signal representative of the residual noise power in the target zone. The controller analyzes sub-bands of the reference signal and the error signal without identification of a secondary path, and provides drive signals to the actuator to cause the actuator to deliver the actuated signals into the target zone so as to reduce the residual noise power in the target zone.
Owner:THE BOARD OF RGT UNIV OF OKLAHOMA
Active noise control apparatus
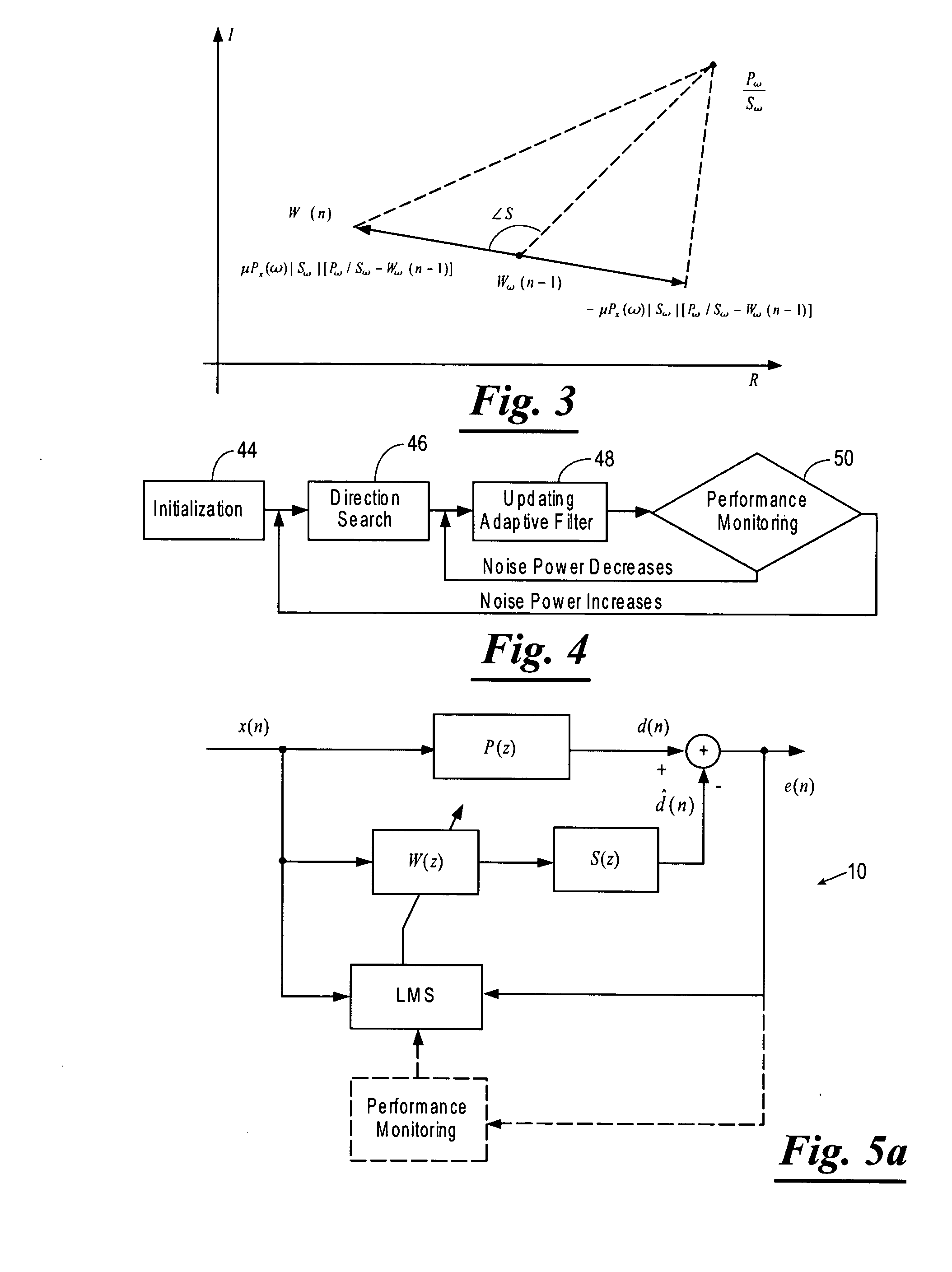
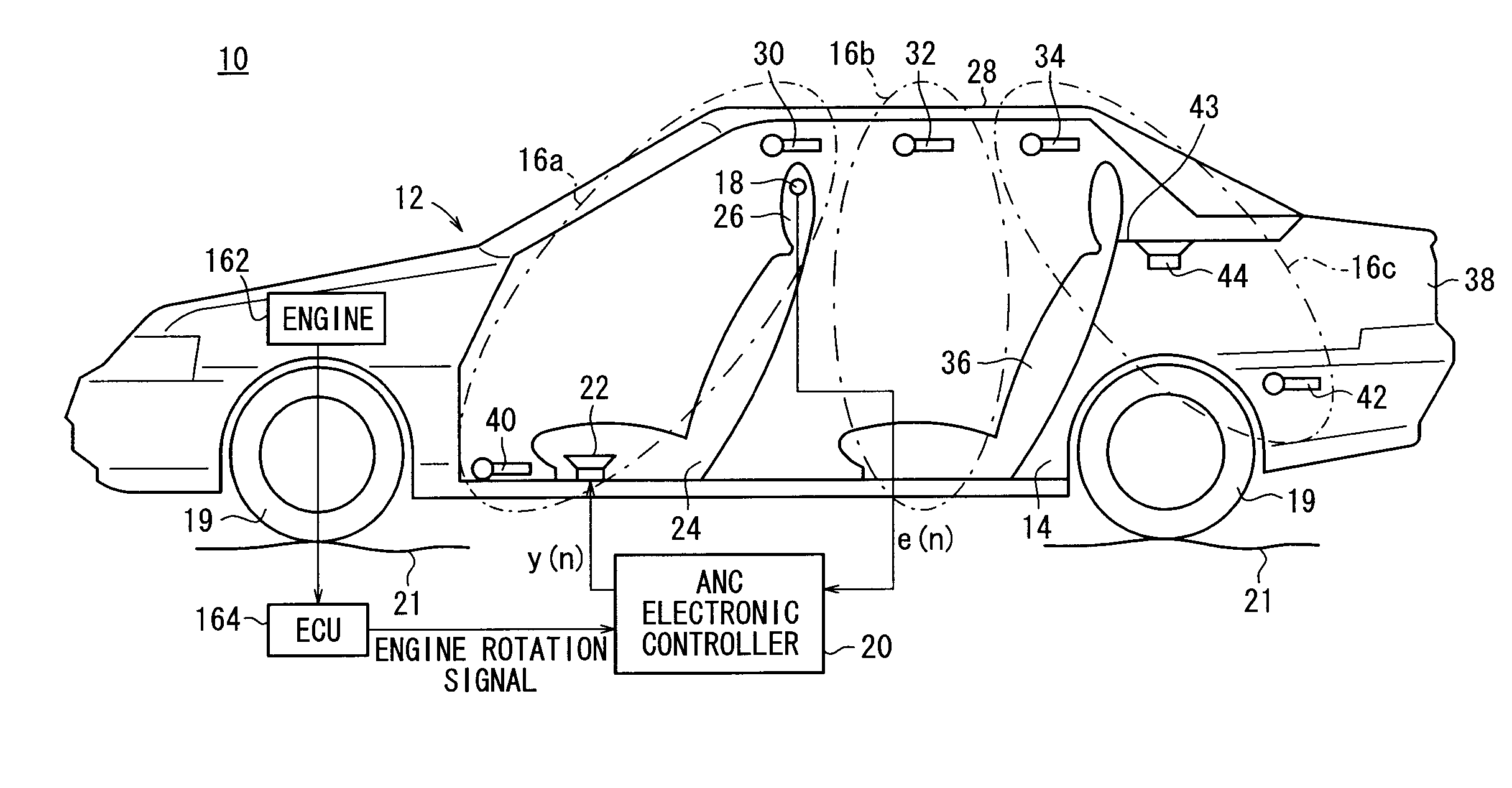
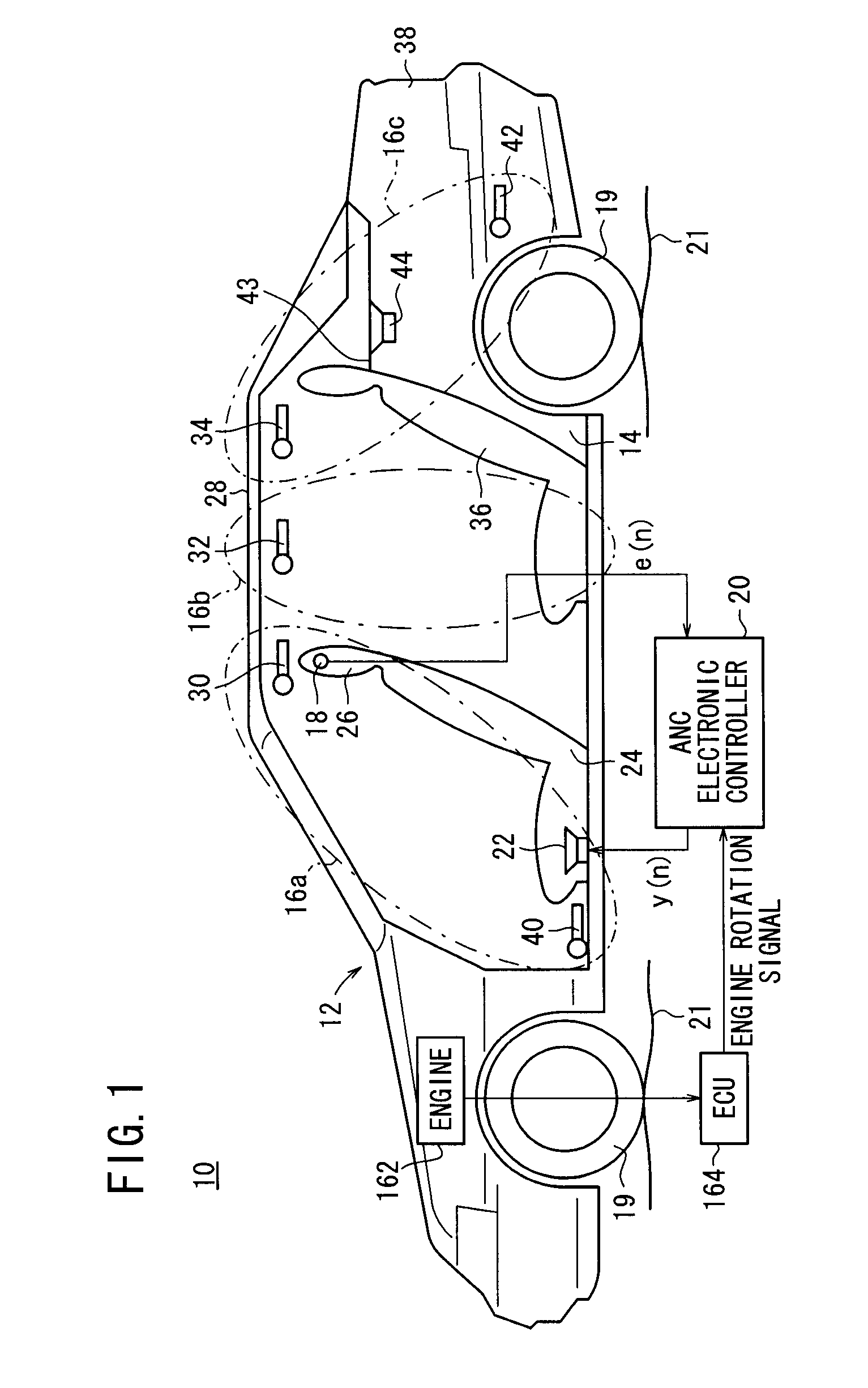
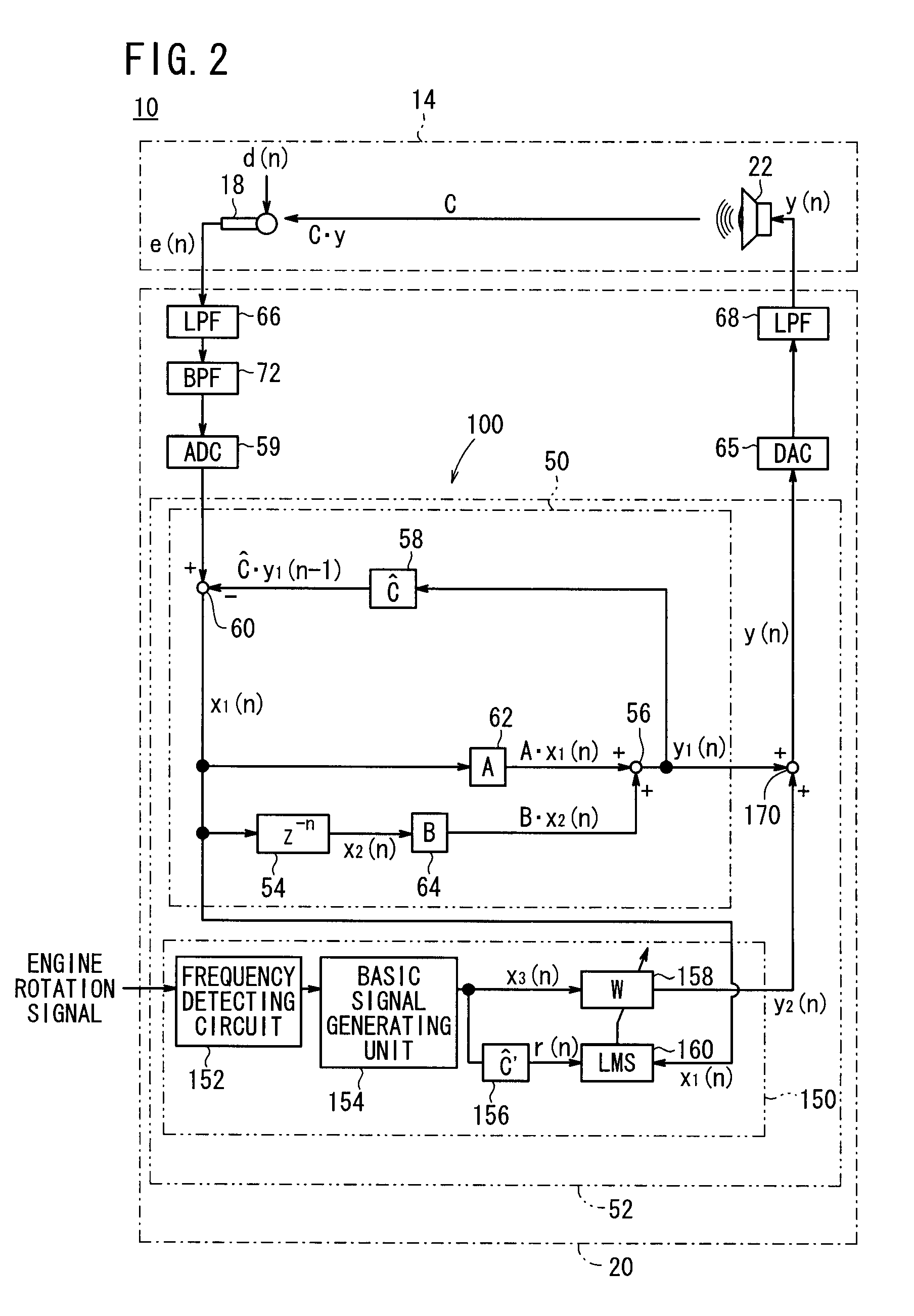
InactiveUS20080240457A1Lighten the computational burdenReduce manufacturing costEar treatmentNoise generationNoise controlControl signal
A subtractor subtracts an echo canceling signal Ĉ·yl(n−1) from a canceling error signal e(n) to estimate a residual noise to be silenced at the position of a microphone, and outputs a first basic signal x1(n) representing the residual noise. A first control circuit section generates a first control signal y1(n) based on the first basic signal x1(n) and a second basic signal x2(n) that is generated by delaying the first basic signal x1(n) by a time Z−n. A second circuit section generates a second control signal y2(n) based on the first basic signal x1(n) and an engine rotation signal.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Method for Jointly Optimizing Noise Reduction and Voice Quality in a Mono or Multi-Microphone System
ActiveUS20110257967A1Reduce noiseDecreased energy levelSpeech analysisTransducer circuit dampingAdaptive denoisingEngineering
The present technology provides adaptive noise reduction of an acoustic signal using a sophisticated level of control to balance the tradeoff between speech loss distortion and noise reduction. The energy level of a noise component in a sub-band signal of the acoustic signal is reduced based on an estimated signal-to-noise ratio of the sub-band signal, and further on an estimated threshold level of speech distortion in the sub-band signal. In embodiments, the energy level of the noise component in the sub-band signal may be reduced to no less than a residual noise target level. Such a target level may be defined as a level at which the noise component ceases to be perceptible.
Owner:KNOWLES ELECTRONICS INC
Method and an apparatus for estimating residual noise in a signal and an apparatus utilizing the method
InactiveUS6871066B1Improve performanceReduce equipment production costsTwo-way loud-speaking telephone systemsError detection/prevention using signal quality detectorCommunications systemDigital radio
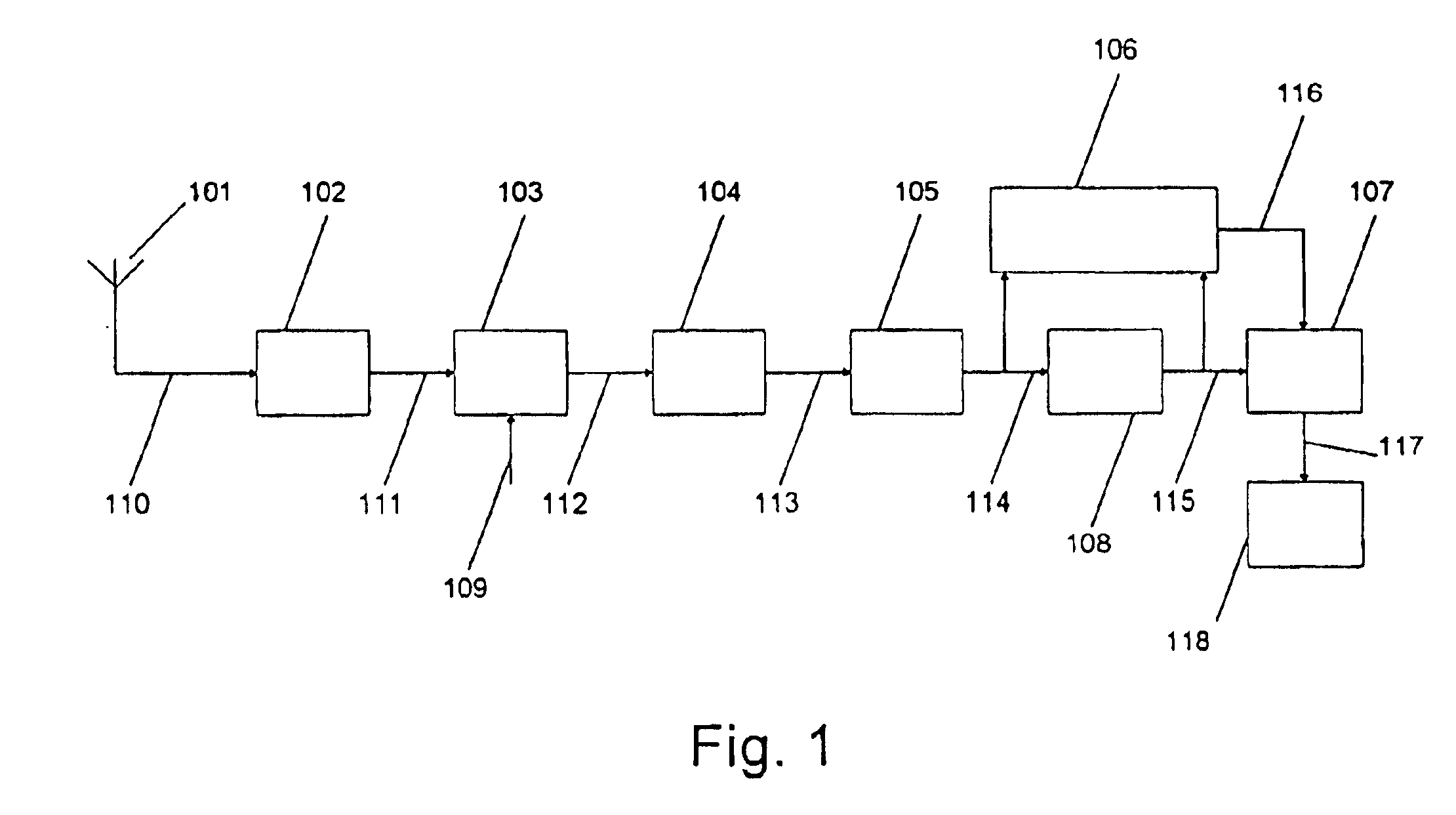
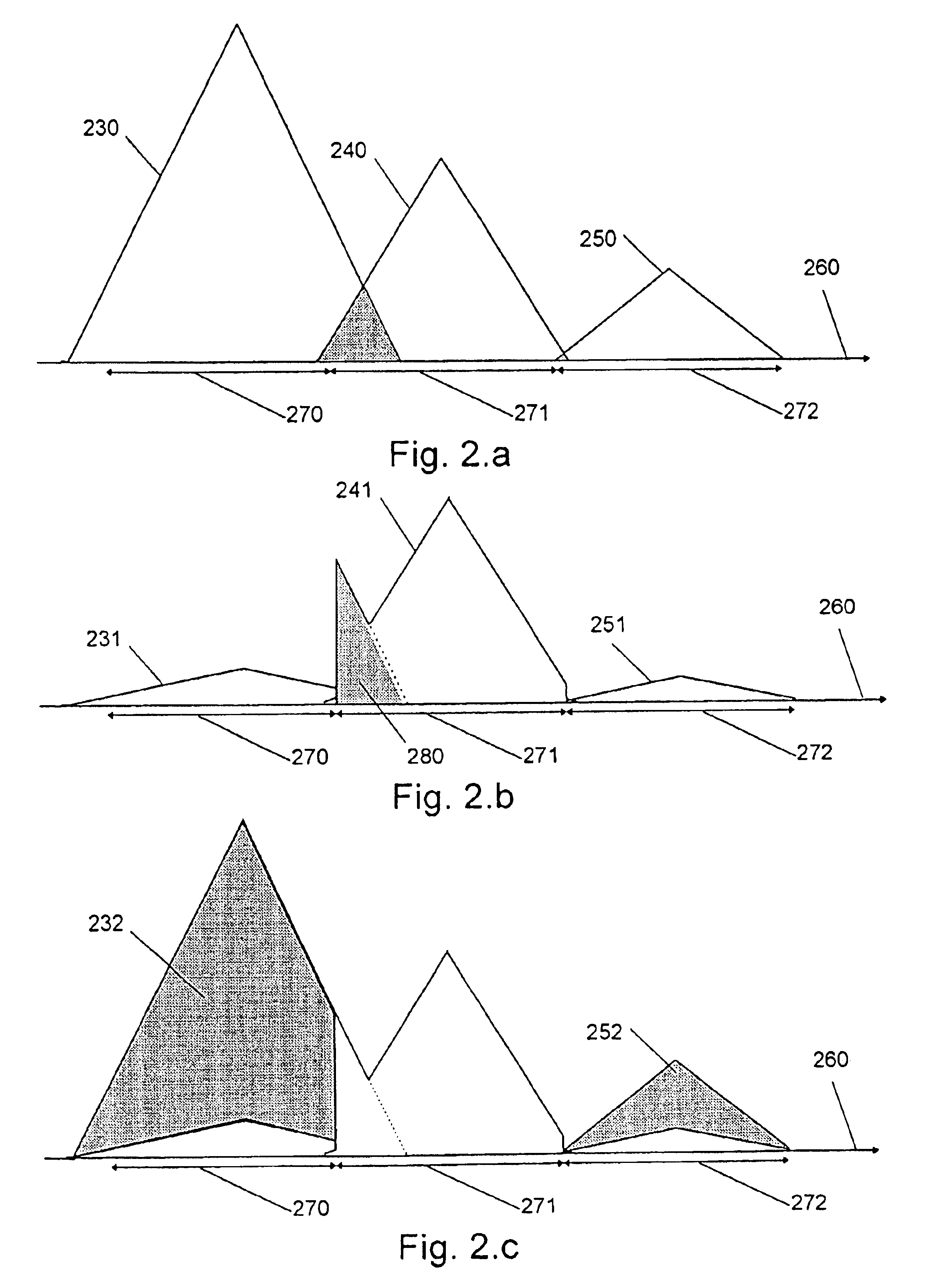
The invention relates to: A method for estimating residual noise in the frequency range (271) of a desired part (240) of a signal to a corresponding apparatus and to a mobile telephone utilizing the method.The object of the present invention is to generate a measure for the residual noise in a signal.The problem is solved in that the amplitude of the signal (114) comprising the noise is modified, and the signal (114) is combined with the modified signal (115) to create a noise estimation measure (116).The invention may e.g. be used in digital radio communications systems to contribute to the monitoring of link quality and therefore to improve payload throughput. One of the advantages of the invention is that an indication of link quality at an early stage in the receiver is provided.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Apparatus and method for improving the perceived quality of sound reproduction by combining active noise cancellation and a perceptual noise compensation
ActiveUS20150003625A1Improve sound qualityEar treatmentHearing device active noise cancellationEnvironmental noiseTarget signal
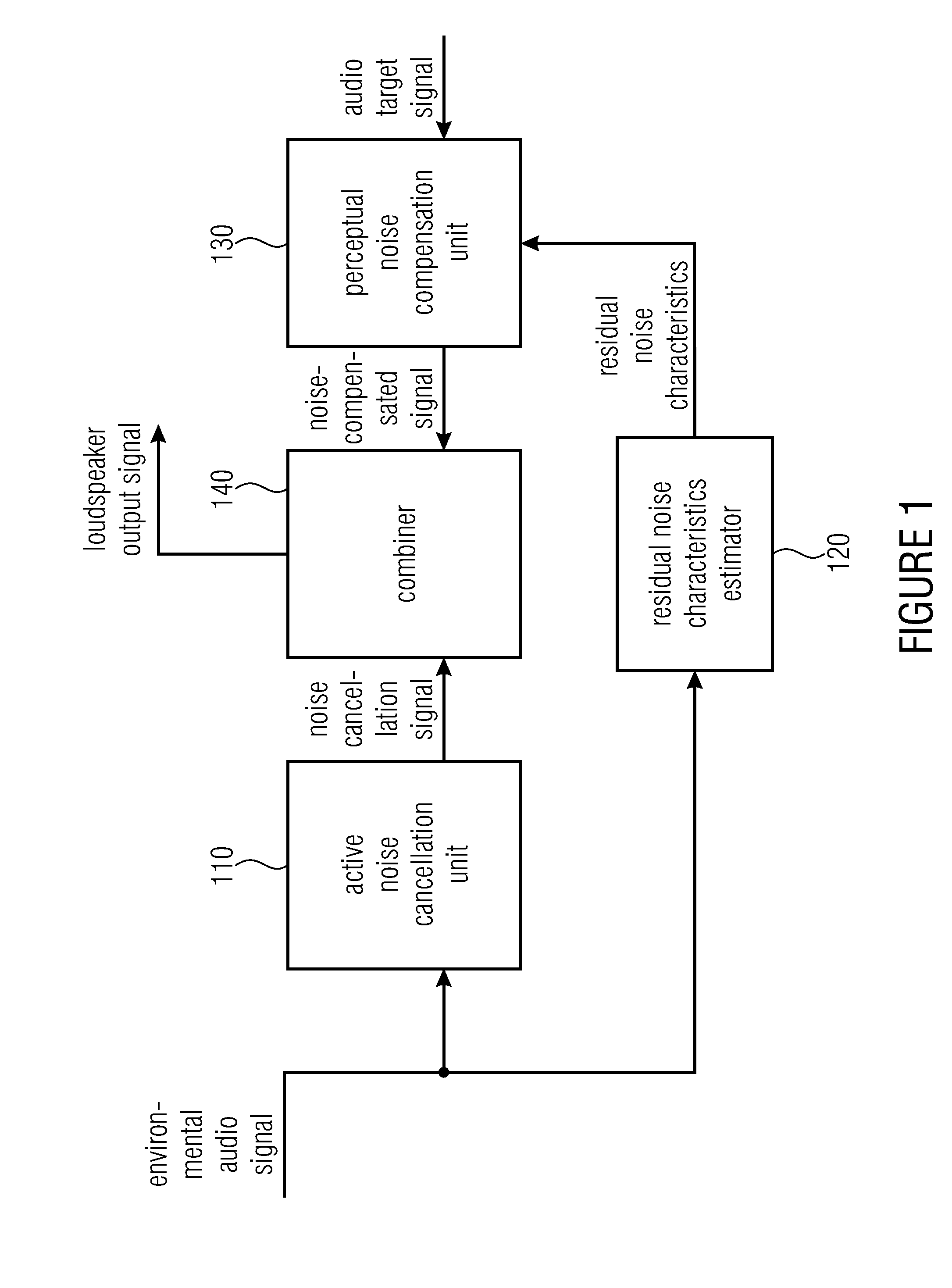
An apparatus for improving a perceived quality of sound reproduction of an audio output signal is provided. The apparatus has an active noise cancellation unit for generating a noise cancellation signal based on an environmental audio signal, wherein the environmental audio signal has noise signal portions, the noise signal portions resulting from recording environmental noise. Moreover, the apparatus has a residual noise characteristics estimator for determining a residual noise characteristic depending on the environmental noise and the noise cancellation signal. Furthermore, the apparatus has a perceptual noise compensation unit for generating a noise-compensated signal based on an audio target signal and based on the residual noise characteristic. Moreover, the apparatus has a combiner for combining the noise cancellation signal and the noise-compensated signal to obtain the audio output signal.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
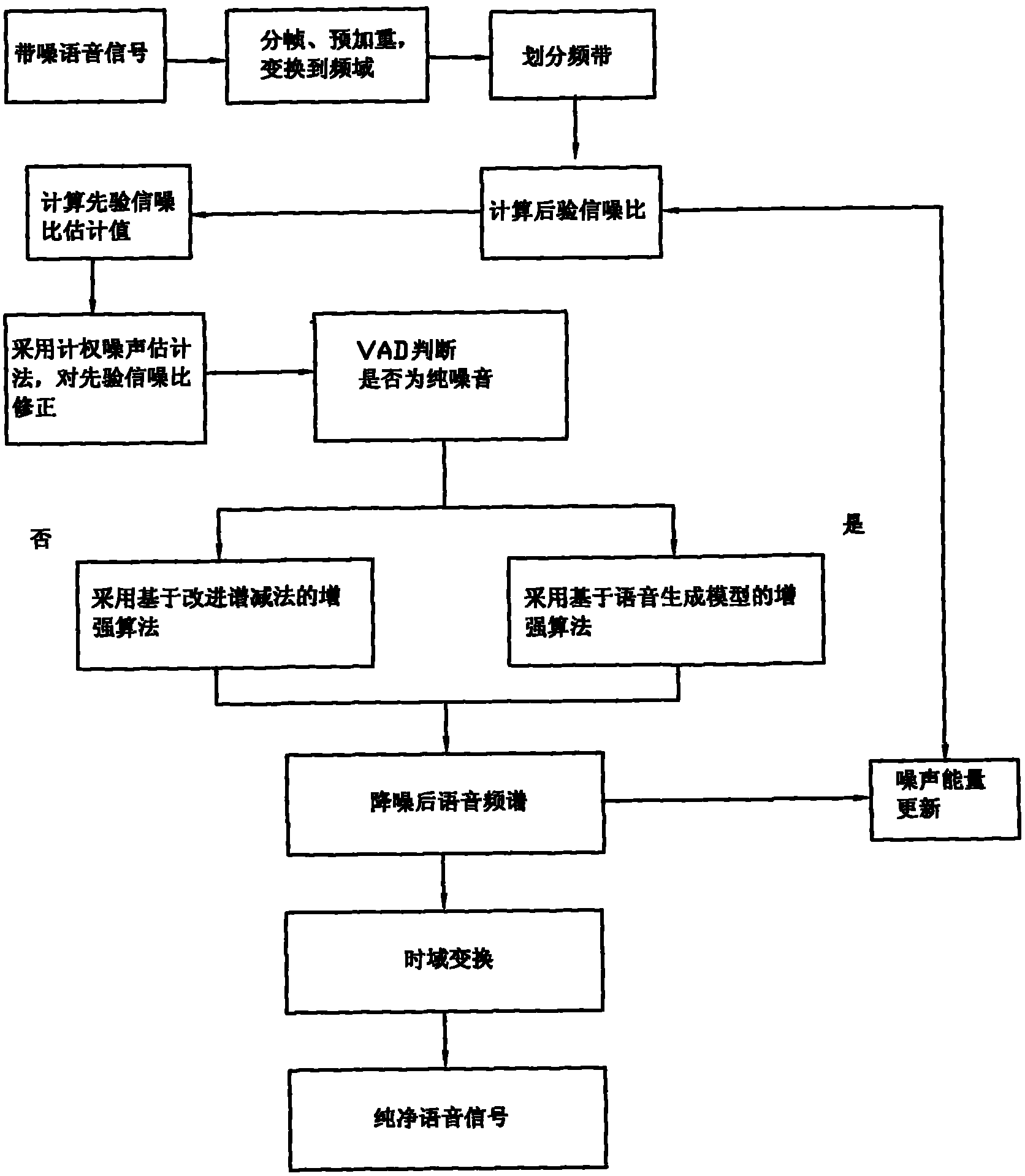
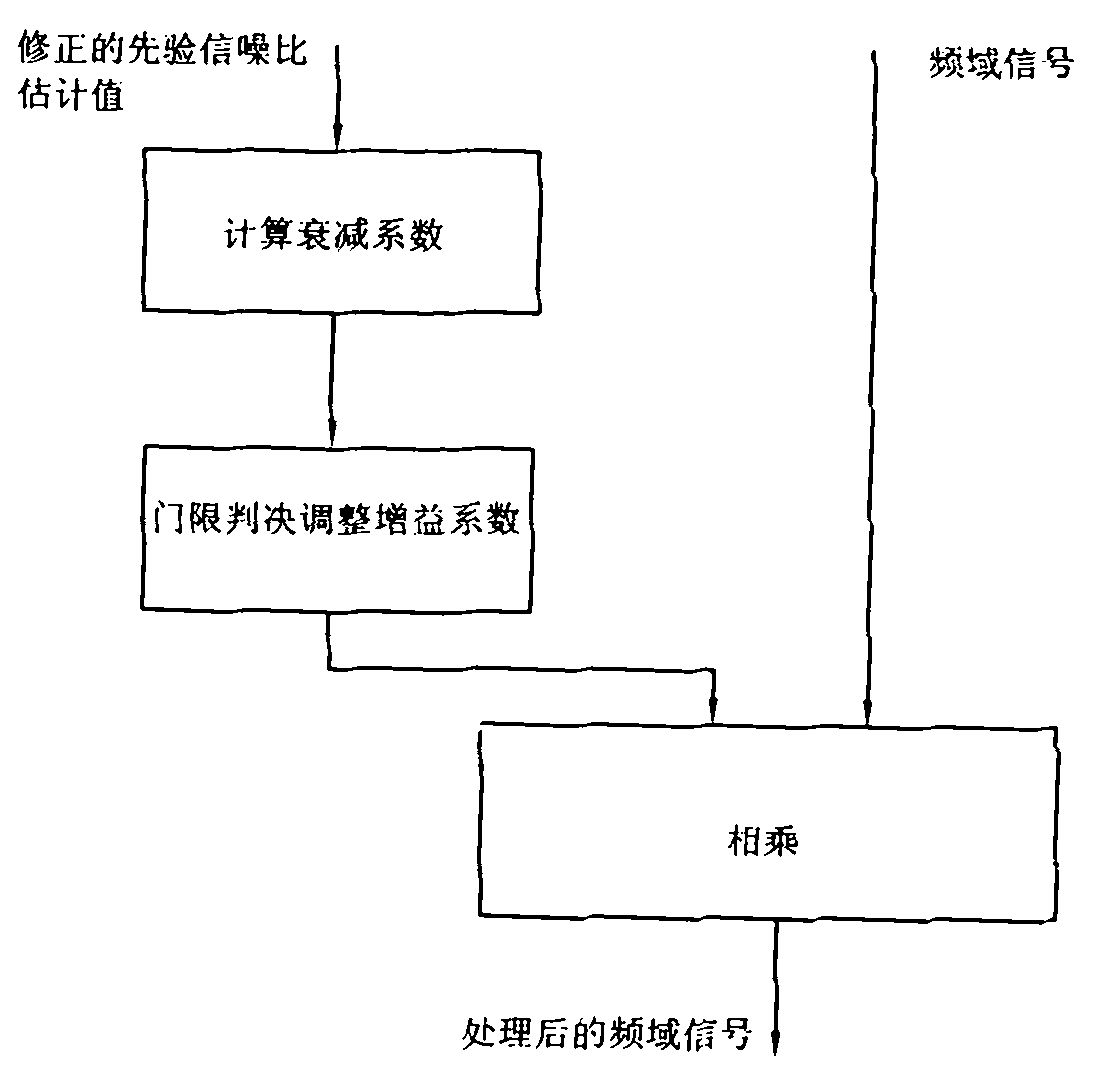
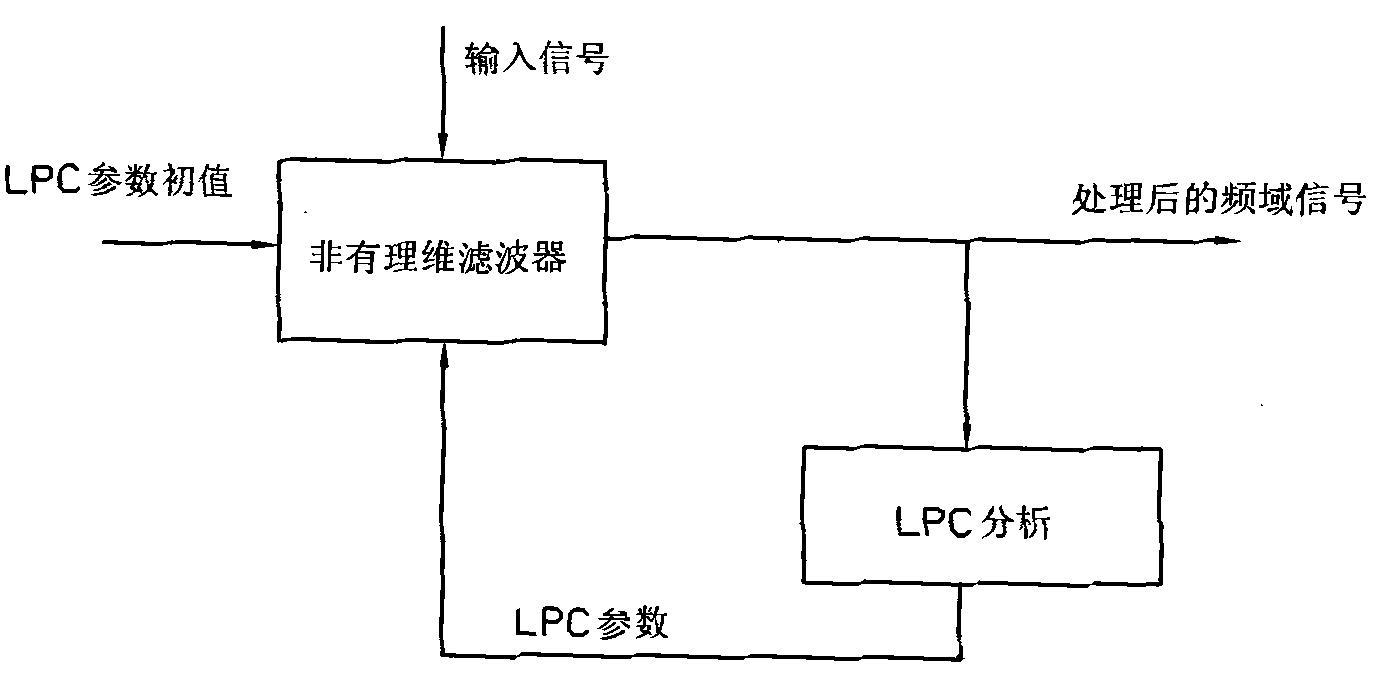
Voice enhancement method and device using same
ActiveCN101976566AGuaranteed intelligibilitySuppress background noiseSpeech analysisTime domainUltrasound attenuation
The invention provides a voice enhancement method. The method comprises the following steps of: judging whether the current frame has pure noise by using a judgment device; if the current frame has pure noise and a plurality of previous frames of the current frame have pure noise, improving frequency domain signals by using a voice enhancement algorithm of an improved spectral subtraction method, otherwise, improving the frequency domain signals by using an enhancement algorithm of a voice generating model; and transforming the processed frequency domain signals to a time domain, performing de-emphasis processing and acquiring output signals. The invention also provides a device using the method. The voice enhancement method greatly improves the attenuation of residual noise, and ensures the voice intelligibility.
Owner:AAC TECH PTE LTD
Active Noise Control in Mobile Devices
InactiveUS20110091047A1Ability to detect and reduce different level of background noiseComputationally inexpensiveEar treatmentNoise generationNoise controlMean square
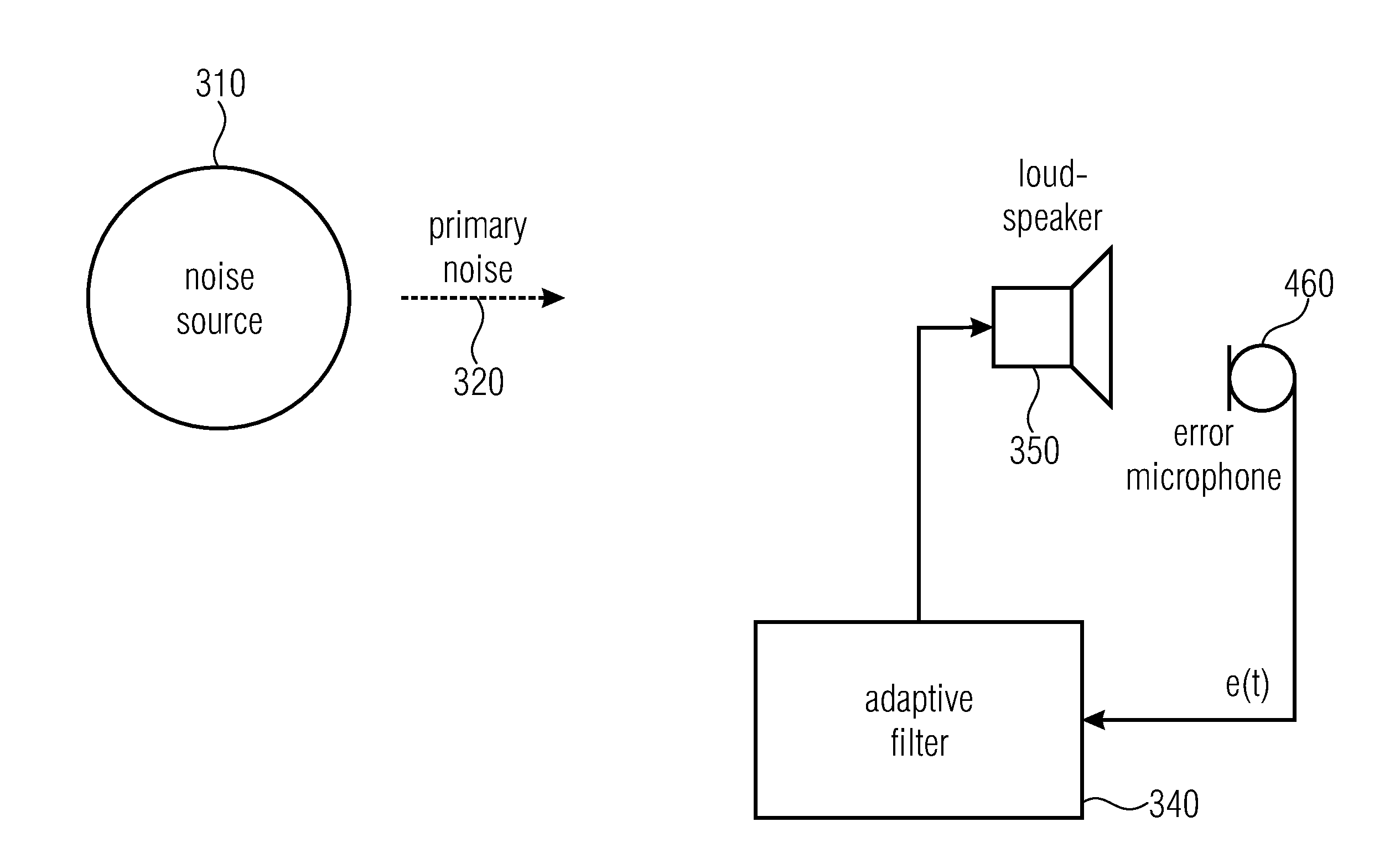
A three dimensional area of quiet is created by an active noise cancellation system comprising a reference microphone receiving background noise and sending the noise signal to an adaptive active noise canceller. An adaptive filter system using weights updated by a least mean squares method or other method generates an anti-phase signal which is broadcasted to counteract the background noise. The resulting residual noise or residual signal is sent back to the adaptive active noise canceller to reset the weights of the adaptive filter.
Owner:NOISE FREE WIRELESS
Noise analysis in a communication system
InactiveUS7492703B2Improve noiseError detection/prevention using signal quality detectorTransmission systemsCommunications systemEngineering
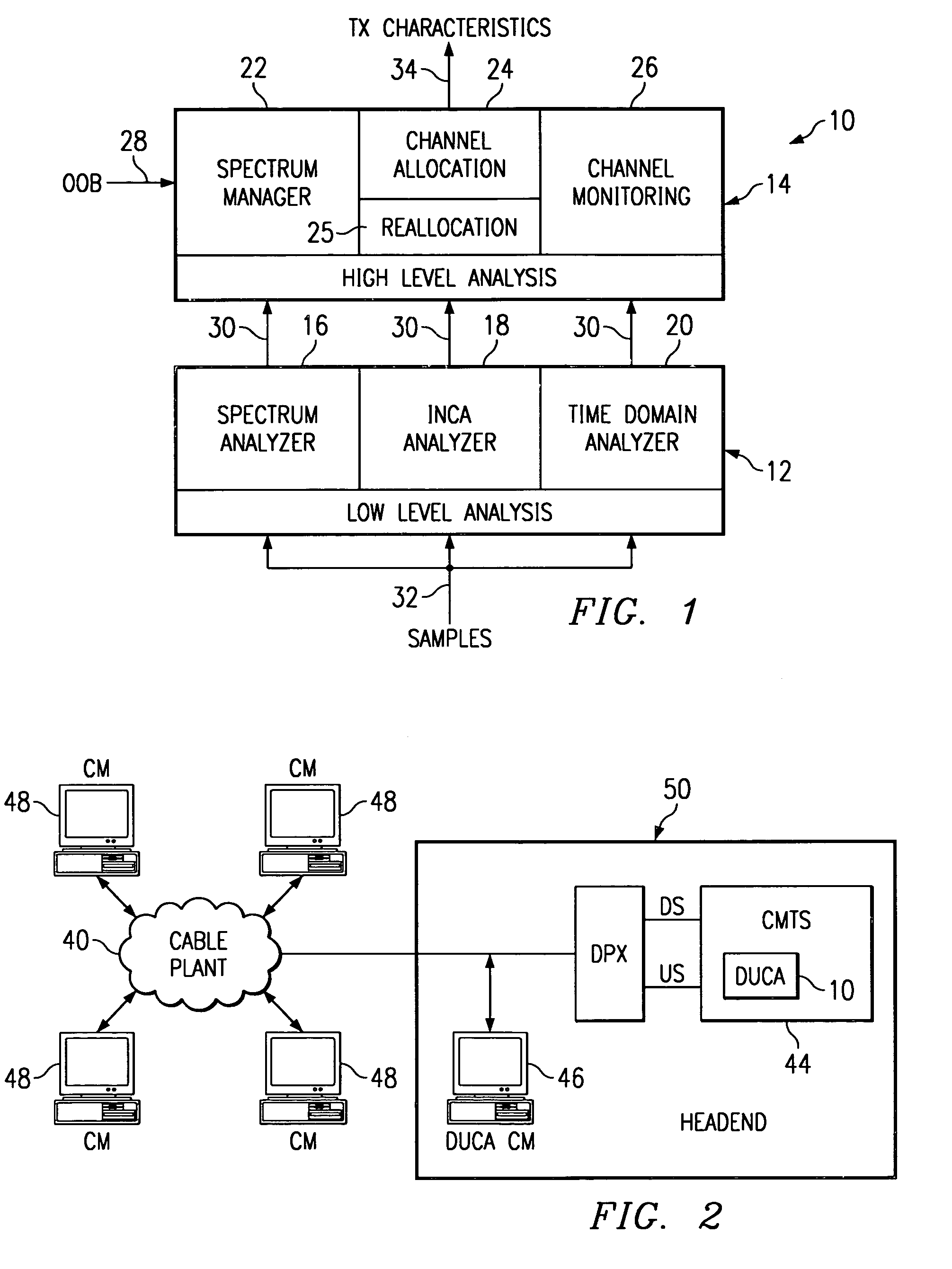
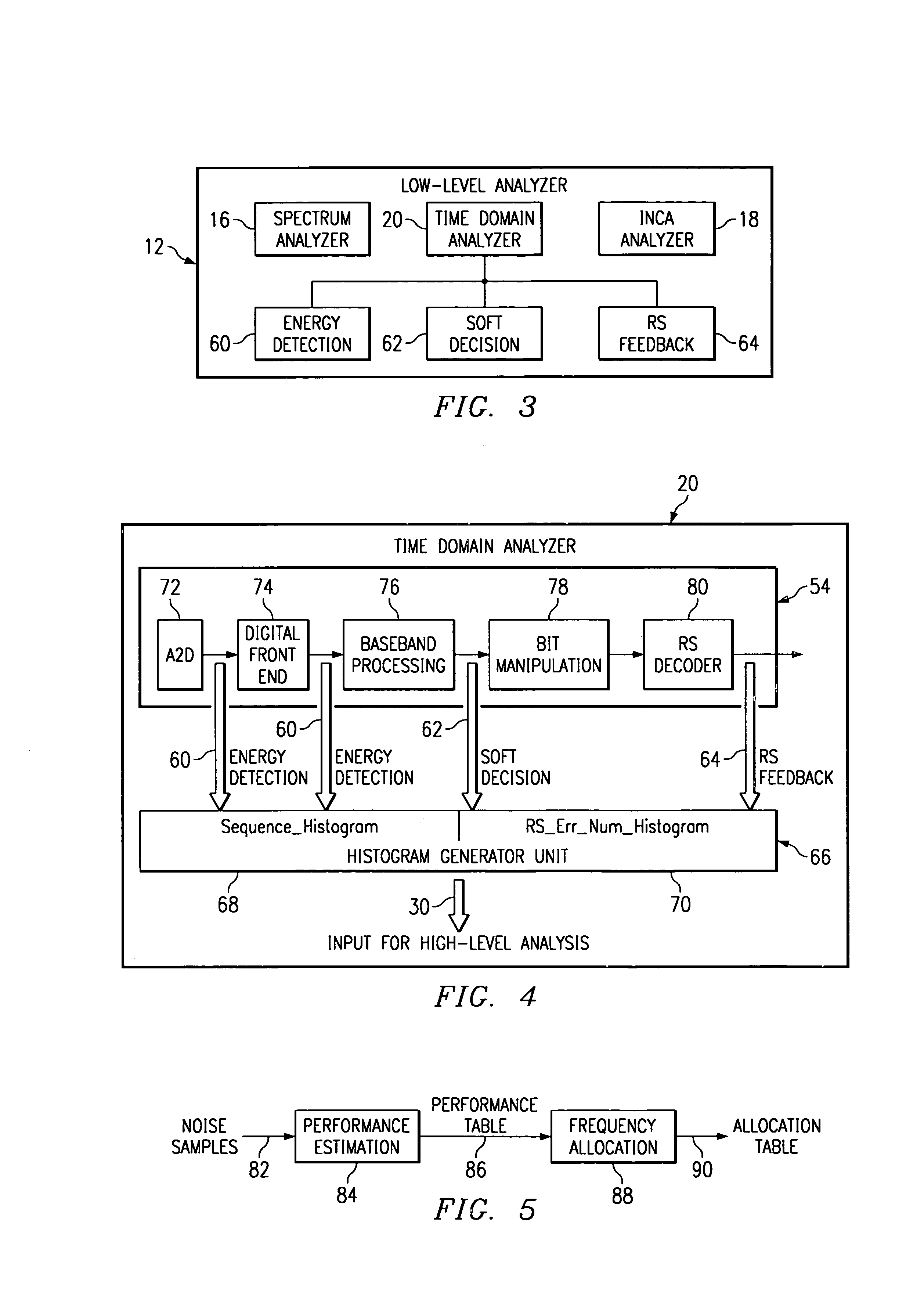
A system is provided to automatically estimate performance of a receiver for receiving input signals, the input signals having a carrier frequency and a baud rate, from a channel in a communication system and the effect of highly correlated noise cancellation on performance of the receiver, while no active transmission is occurring on the channel, comprising: a digital front end in the receiver for receiving samples of the input signals; a predictor coupled to the digital front end for predicting highly correlated noise in a second sample of the input signal; and a subtraction unit coupled to the predictor for subtracting the predictor output from the second sample to determine residual noise in the second sample. Other systems and methods are disclosed.
Owner:MAXLINEAR INC
Time-space methods and systems for the reduction of video noise
A time-space domain video denoising method is provided which reduces video noise of different types. Noise is assumed to be real-world camera noise such as white Gaussian noise (signal-independent), mixed Poissonian-Gaussian (signal-dependent) noise, or processed (non-white) signal-dependent noise. This method comprises the following processing steps: 1) time-domain filtering on current frame using motion-compensated previous and subsequent frames; 2) restoration of possibly blurred contents due to faulty motion compensation and noise estimation; 3) spatial filtering to remove residual noise left from temporal filtering. To reduce the blocking effect, a method is applied to detect and remove blocking in the motion compensated frames. To perform time-domain filtering weighted motion-compensated frame averaging is used. To decrease the chance of blurring, two levels of reliability are used to accurately estimate the weights.
Owner:WRNCH INC
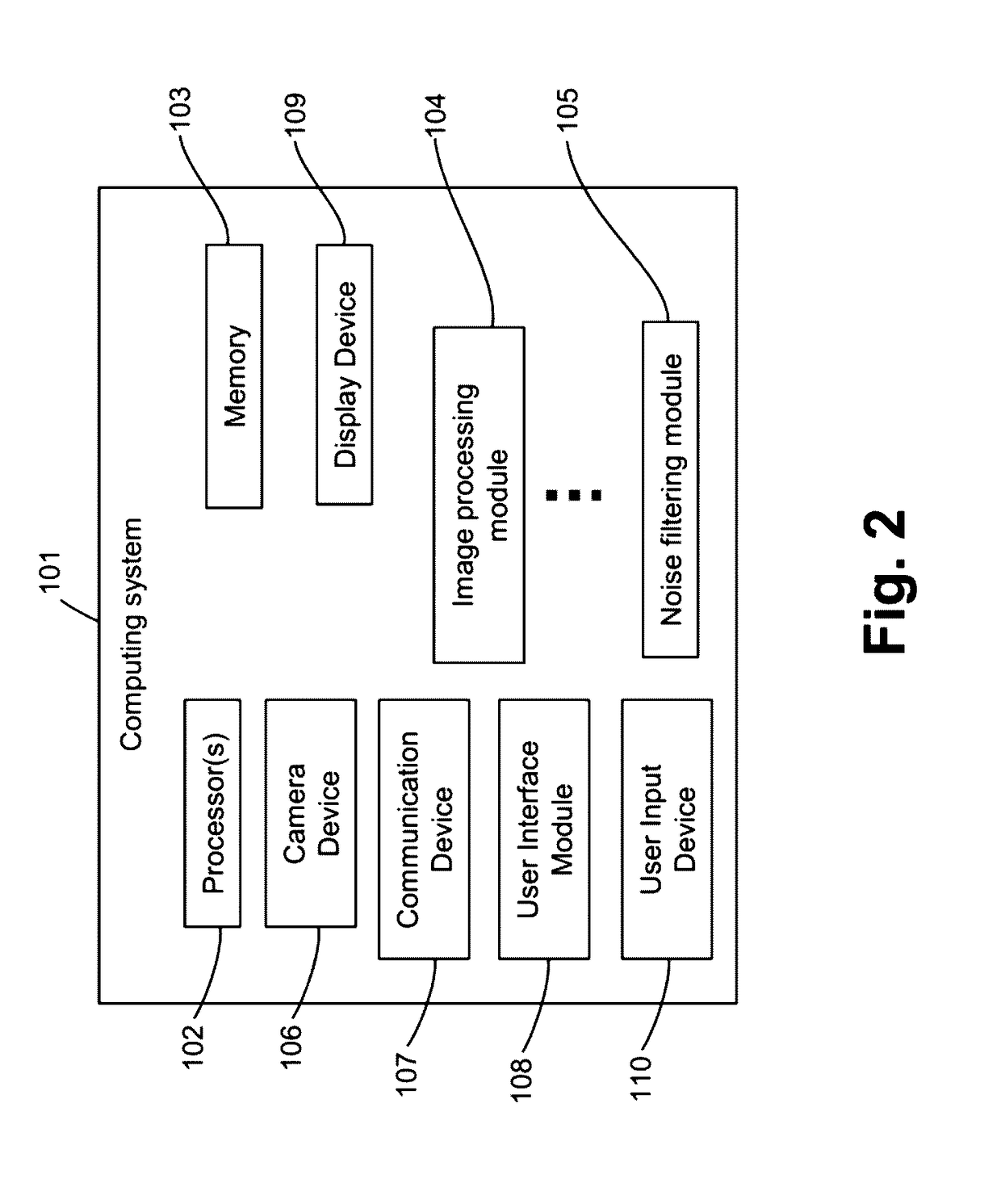
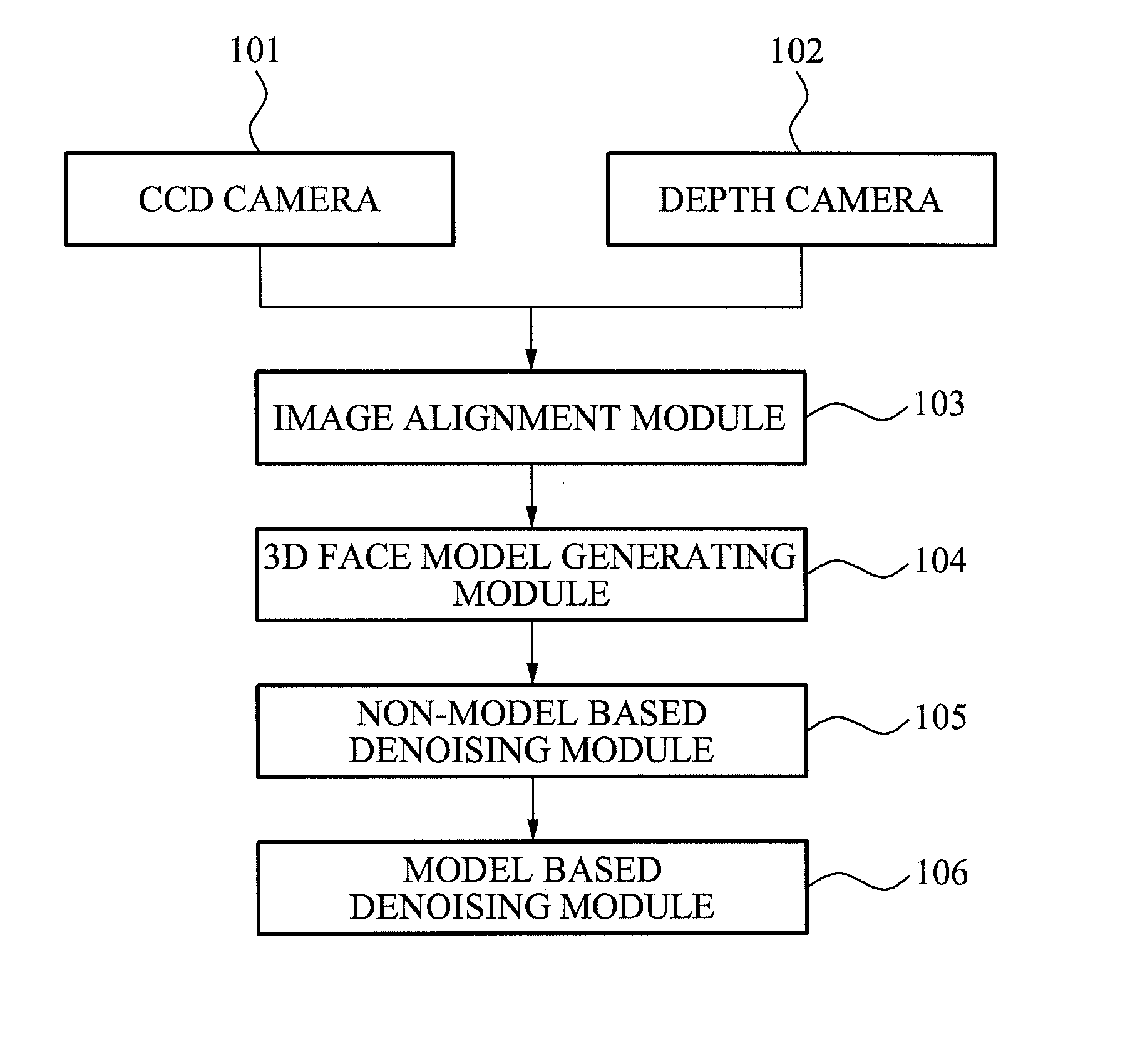
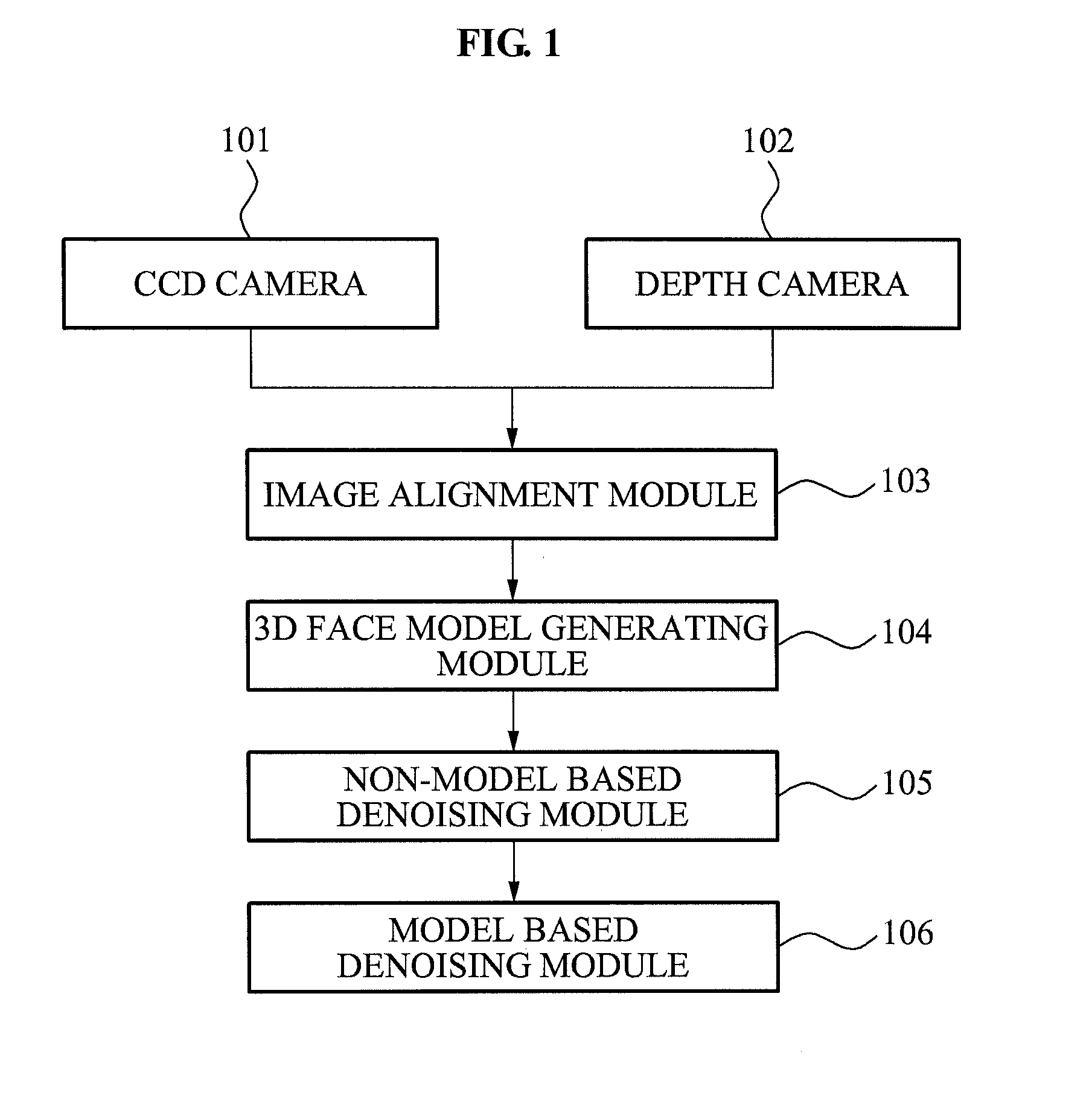
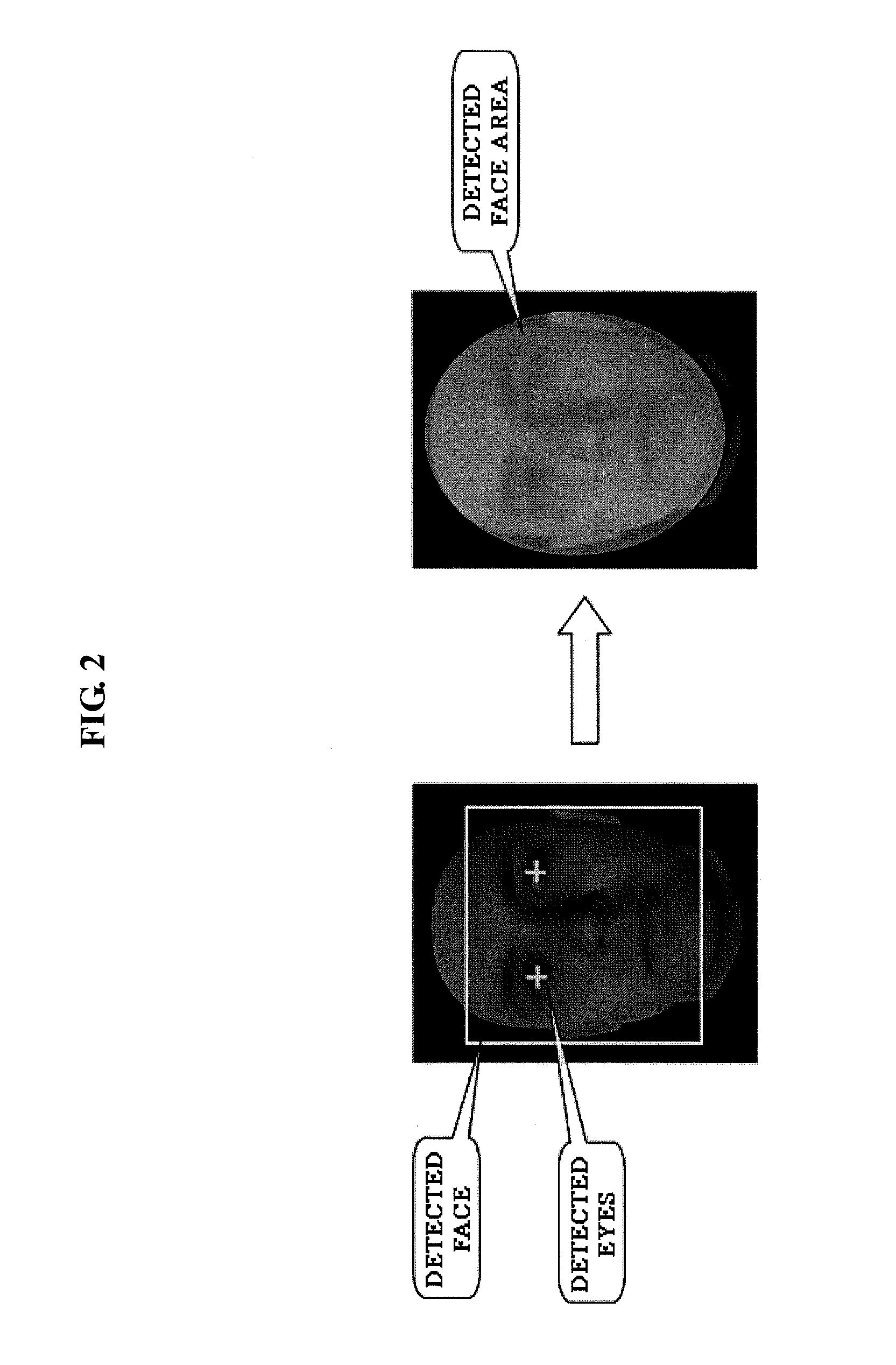
Three-dimensional face capturing apparatus and method and computer-readable medium thereof
ActiveUS20110043610A1Details involving processing stepsTelevision system detailsPattern recognitionColor image
Disclosed is a 3D face capturing apparatus, method and computer-readable medium. As an example, the 3D face capturing method includes obtaining a face color image, obtaining a face depth image, aligning, by a computer, the face color image and the face depth image, obtaining, by the computer, a 3D face model by 2D modeling of the face color image and covering a modeled 2D face area on an image output by an image alignment module, removing by the computer, depth noise of the 3D face model, and obtaining, by the computer, an accurate 3D face model by aligning the 3D face model and a 3D face template, and removing residual noise based on a registration between the 3D face model and the 3D face template.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method for improving performance of feedforward narrow-band active noise control system
InactiveCN101976560AImprove performanceReduce residual noise energy impactSpeech analysisSound producing devicesNoise controlSteady state
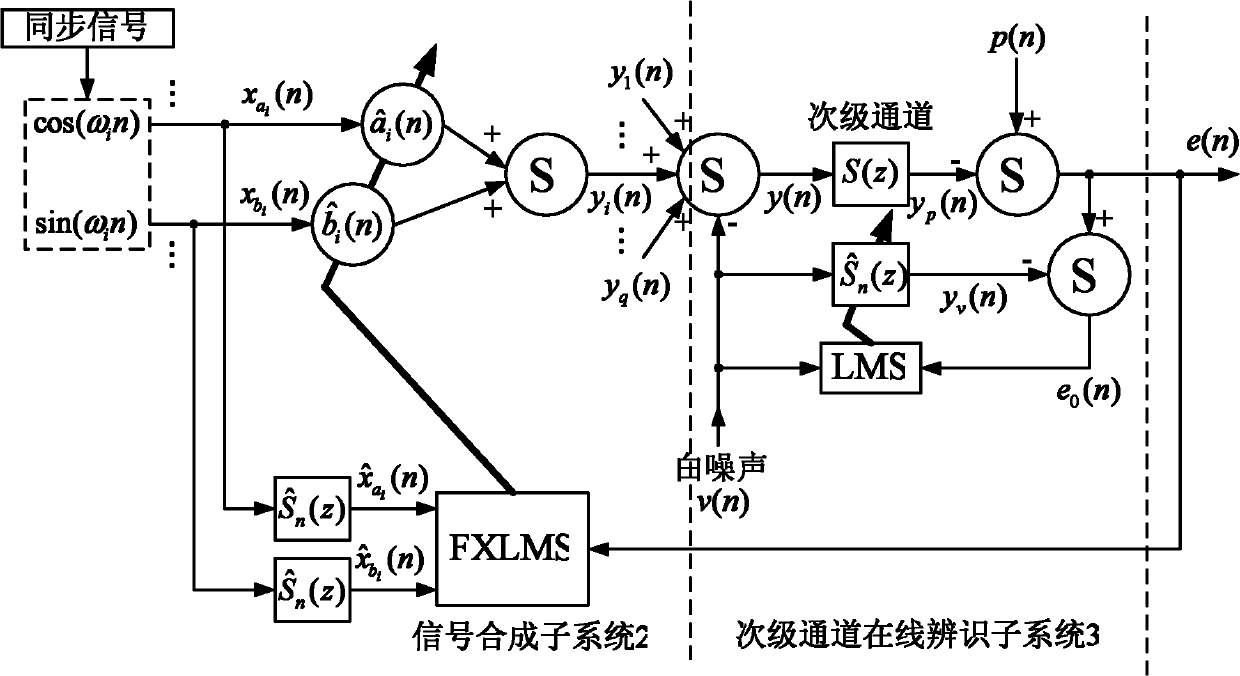
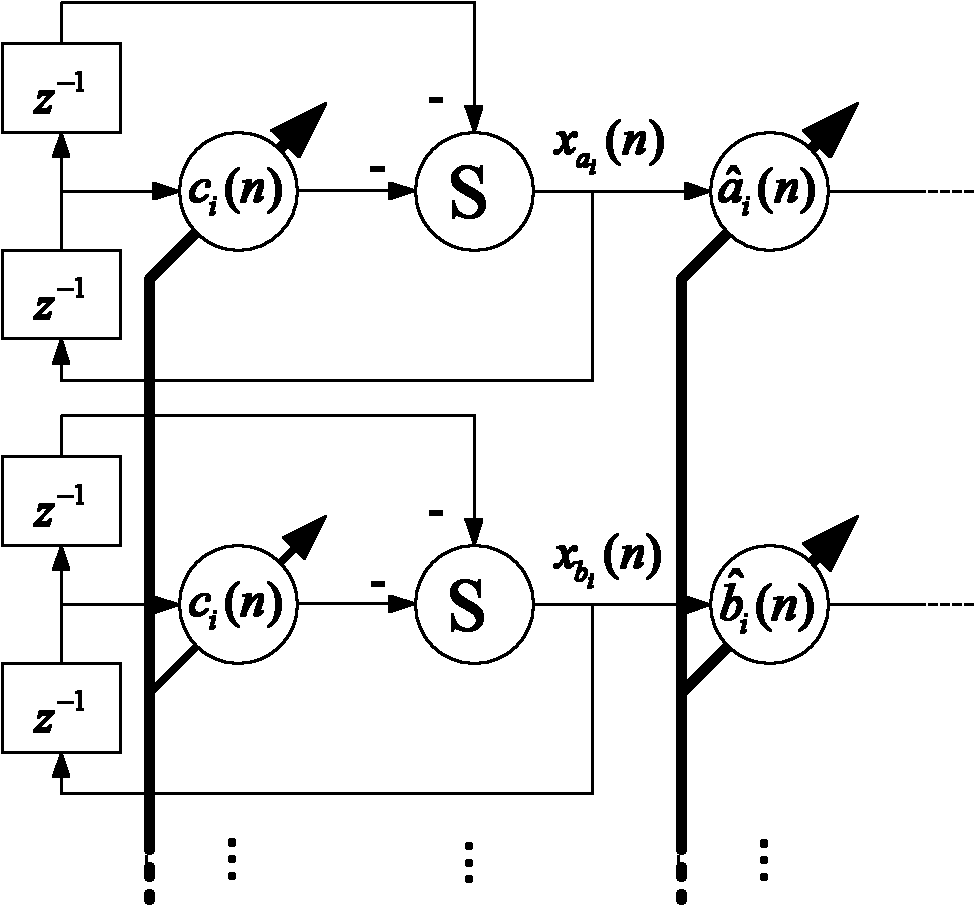
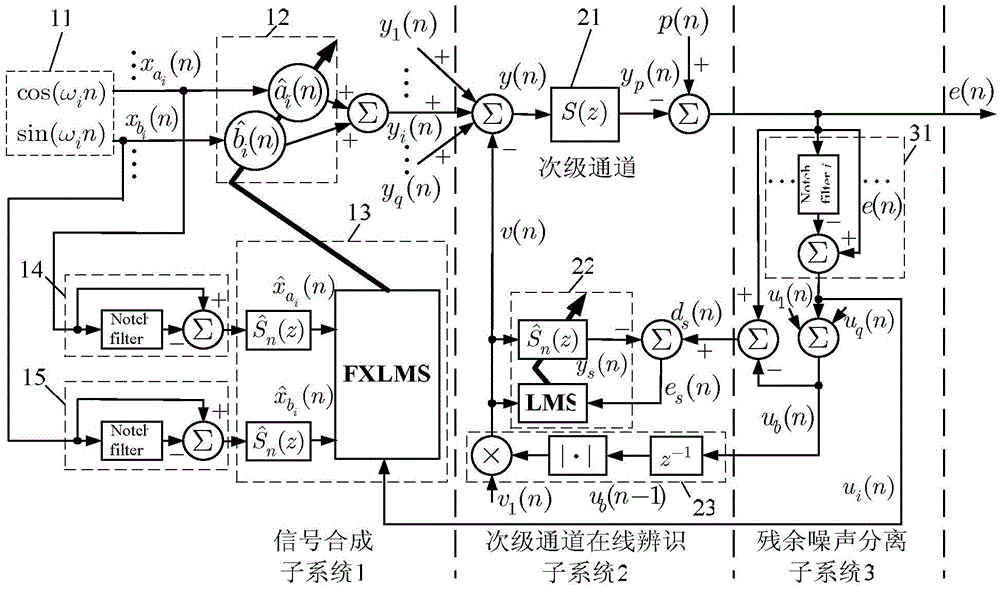
The invention discloses a method for improving the performance of a feedforward narrow-band active noise control system, which relates to the field of active noise control, and aims at the situation that the reference signal frequency acquired by a non-acoustic sensor in the feedforward narrow-band active noise control system with a minor access road on-line identification function and the target noise actual frequency are imbalanced and the problem the auxiliary noise brought by the minor access road on-line identification seriously hinders the reduction of the residual noise energy of the system. The control system comprises a frequency compensation subsystem, a signal synthesis subsystem and a minor access road on-line identification subsystem; the frequency compensation subsystem comprises a second-order autoregression module and a least mean square (LMS) algorithm module; the frequency compensation subsystem transmits the cosine component and sinusoidal component of the adjusted reference signal of an ith frequency channel to the signal synthesis; when the frequency imbalance reaches above 50%, the target noise can still be effectively restrained; and when in a steady state, the residual noise energy of the system is reduced to an ideal level, so that the performance of the control system can be further improved and is closer to the practice.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Multi-channel adaptive speech signal processing system with noise reduction
ActiveUS8194872B2Improve clarityImprove intelligibilitySignal processingEar treatmentLow noiseHigh energy
An adaptive signal processing system eliminates noise from input signals while retaining desired signal content, such as speech. The resulting low noise output signal delivers improved clarity and intelligibility. The low noise output signal also improves the performance of subsequent signal processing systems, including speech recognition systems. An adaptive beamformer in the signal processing system consistently updates beamforming signal weights in response to changing microphone signal conditions. The adaptive weights emphasize the contribution of high energy microphone signals to the beamformed output signal. In addition, adaptive noise cancellation logic removes residual noise from the beamformed output signal based on a noise estimate derived from the microphone input signals.
Owner:HARMAN BECKER AUTOMOTIVE SYST WAVEMAKERS
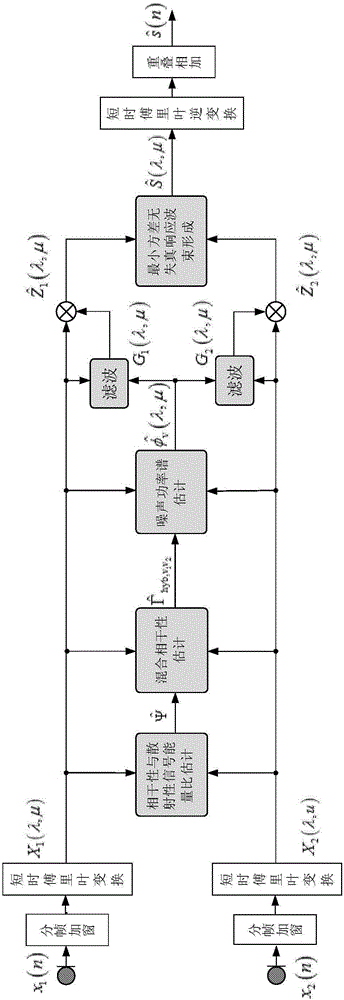
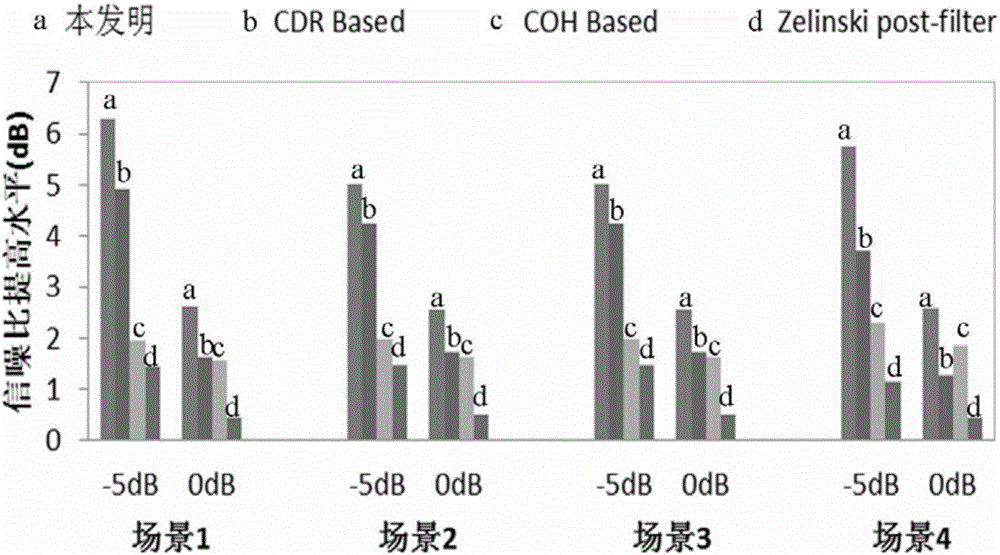
Two-channel beam forming speech enhancement method based on noise mixed coherence
ActiveCN105869651AGood effectImprove voice enhancementSpeech analysisNoise power spectrumMixed noise
The invention discloses a two-channel beam forming speech enhancement method based on noise mixed coherence. Adaptive beam forming can effectively inhibit directional noise signals under the reverberation-free condition, but the inhibiting effect of the adaptive beam forming is greatly reduced in the presence of reverberation. Aiming at the problem, the invention provides the two-channel beam forming method based on noise mixed coherence. Considering that coherence and scattering noises exist simultaneously in a sound field, in the method provided by the invention, the hypothesis of replacing the traditional scattering sound field with a mixed noise field is provided, specifically, the method comprises the following steps: firstly, estimating the noise coherence in the mixed noise field, estimating a power spectrum of the noises by utilizing the noise coherence, and calculating a gain function of a frequency domain filtering by using the estimated result for the power spectrum of the noises; and carrying out frequency domain filtering processing on the noises and reverberant signals, and carrying out further processing on the residual noises by adopting a minimum variance distortionless response beam forming device. The experiment proves that the quality of the speech enhanced by adopting the method provided by the invention is obviously improved compared with that enhanced by adopting the traditional method.
Owner:PEKING UNIV SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL
Multi-band integrated speech separating microphone array processor with adaptive beamforming
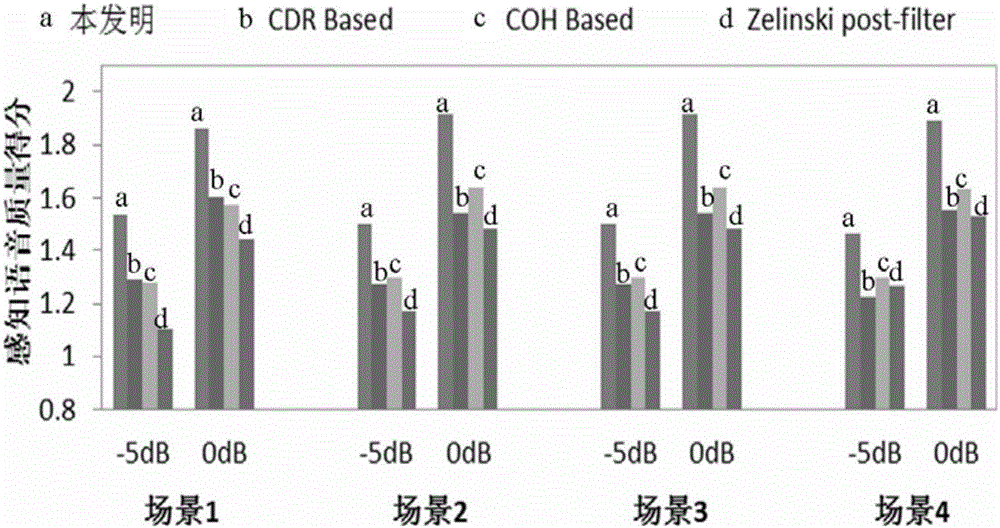
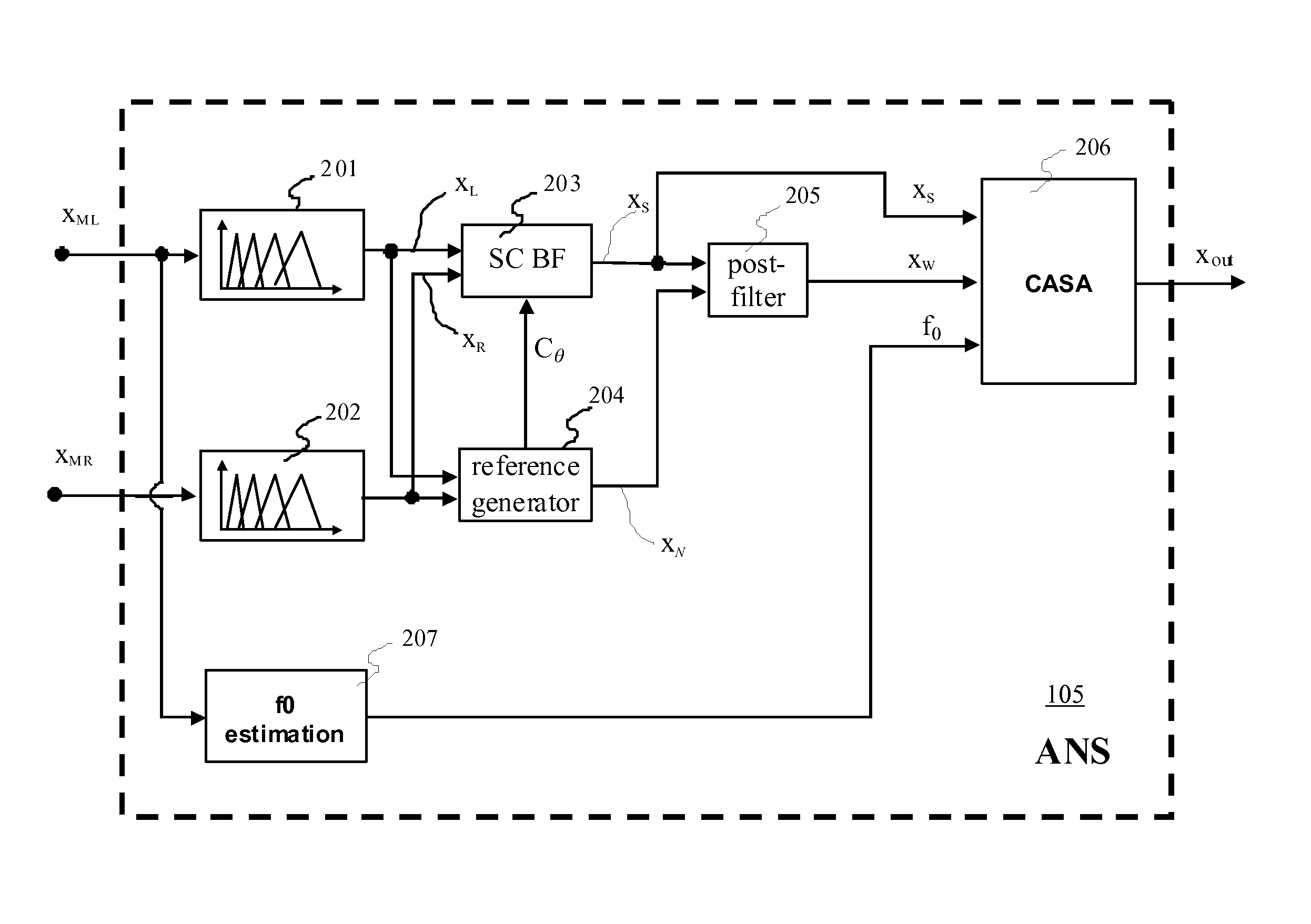
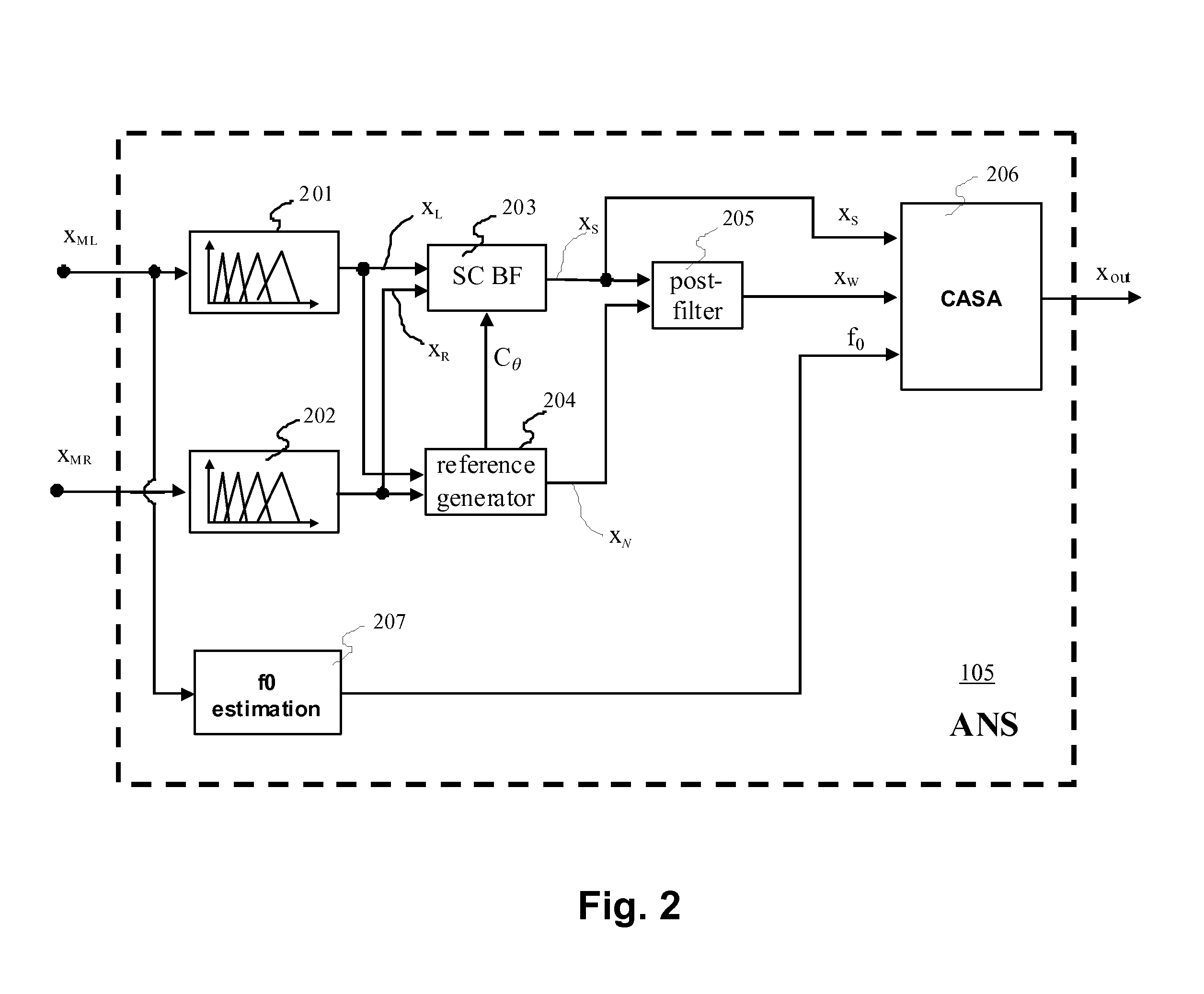
A speech separating digital signal processing system and algorithms for implementing speech separation combine beam-forming with residual noise suppression, such as computational auditory scene analysis (CASA) using a beam-former that has a primary lobe steered toward the source of speech by a control value generated from an adaptive filter. An estimator estimates the ambient noise and provides an input to the residual noise suppressor, and a post-filter may be used to noise-reduce the output of the estimator using a time-varying filter that compares two or more outputs of the beam-former with a quasi-stationary model of the speech and ambient noise.
Owner:CIRRUS LOGIC INC
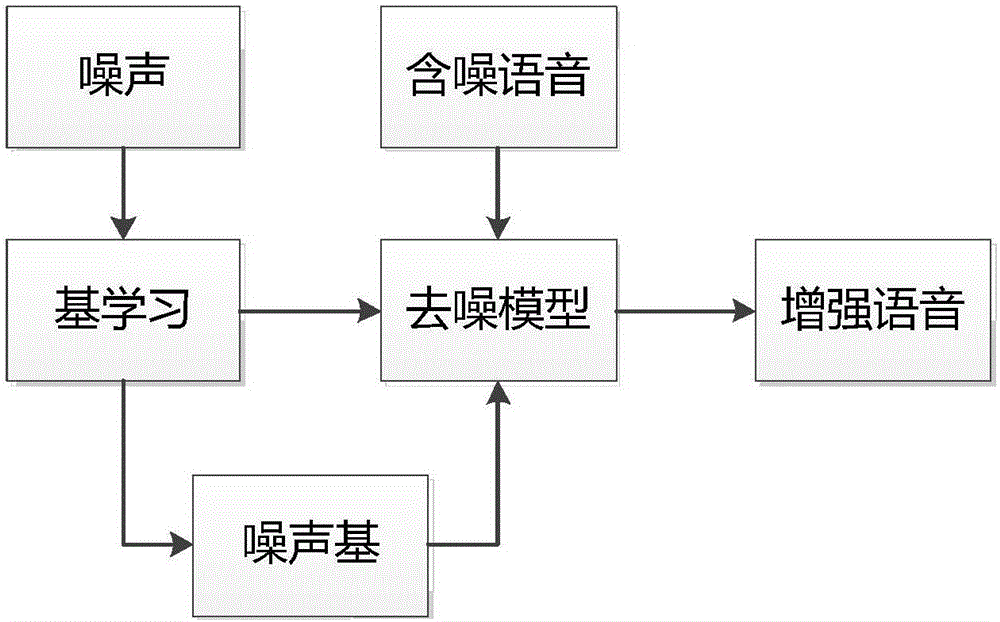
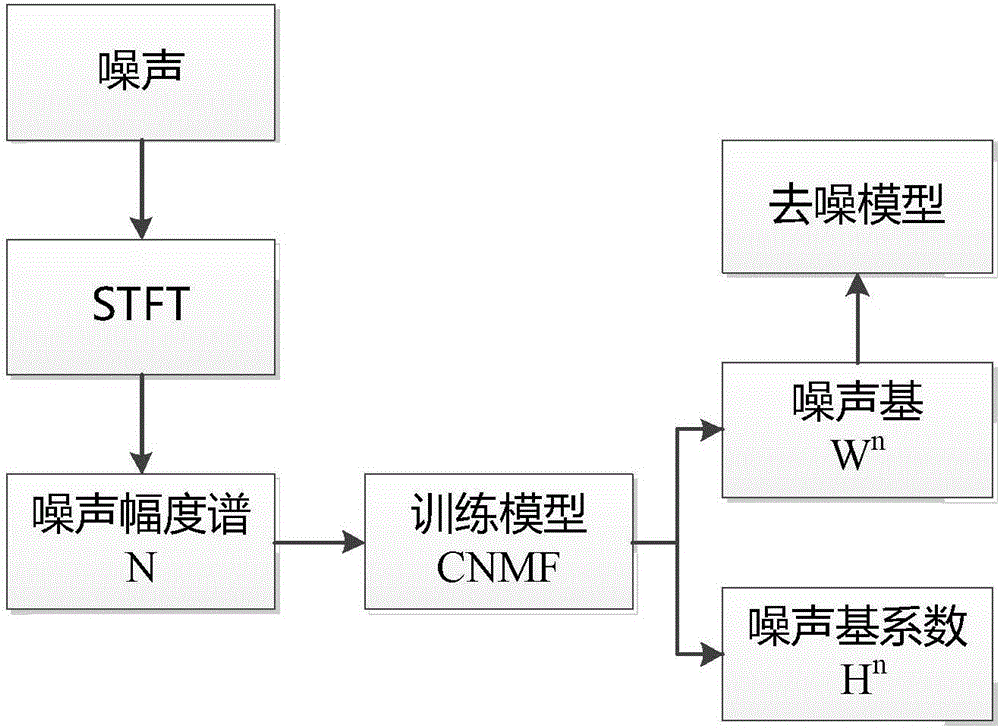
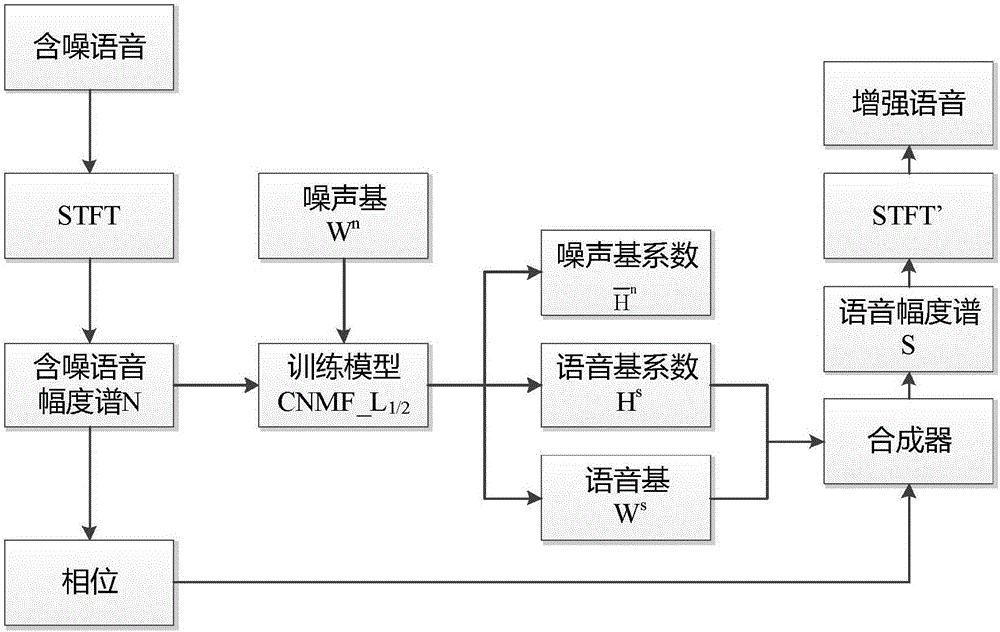
Voice denoising method and system based on L1/2 sparse constraint convolution non-negative matrix decomposition
ActiveCN105957537ALess residual noiseImprove intelligibilitySpeech analysisMatrix decompositionSpectral subtraction
The invention discloses a voice denoising method and system based on L1 / 2 sparse constraint convolution non-negative matrix decomposition. In single-channel voice enhancement, it is assumed that noised voice signals v(i) are additively relevant to noise signals n(i) and voice signals s(i), i.e., v(i)=n(i)+s(i), and noise-base information is obtained by training specific noise by use of a CNMF method; and then by taking a noise base as prior information, a voice base is obtained by decomposing noised voice by use of a CNMF_L1 / 2 method, and finally, voice after denoising is synthesized. According to the method, correlation of voice between frames can be better described; and strong-sparse constraining is performed on a voice-base coefficient matrix by use of L1 / 2 regular item, and the voice after separation comprises less residual noise. Compared to conventional methods such as a spectral subtraction method, a wiener filtering method and a minimum mean square deviation logarithm domain spectrum estimation method and the like, the voice after enhancement can be understood more easily.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY
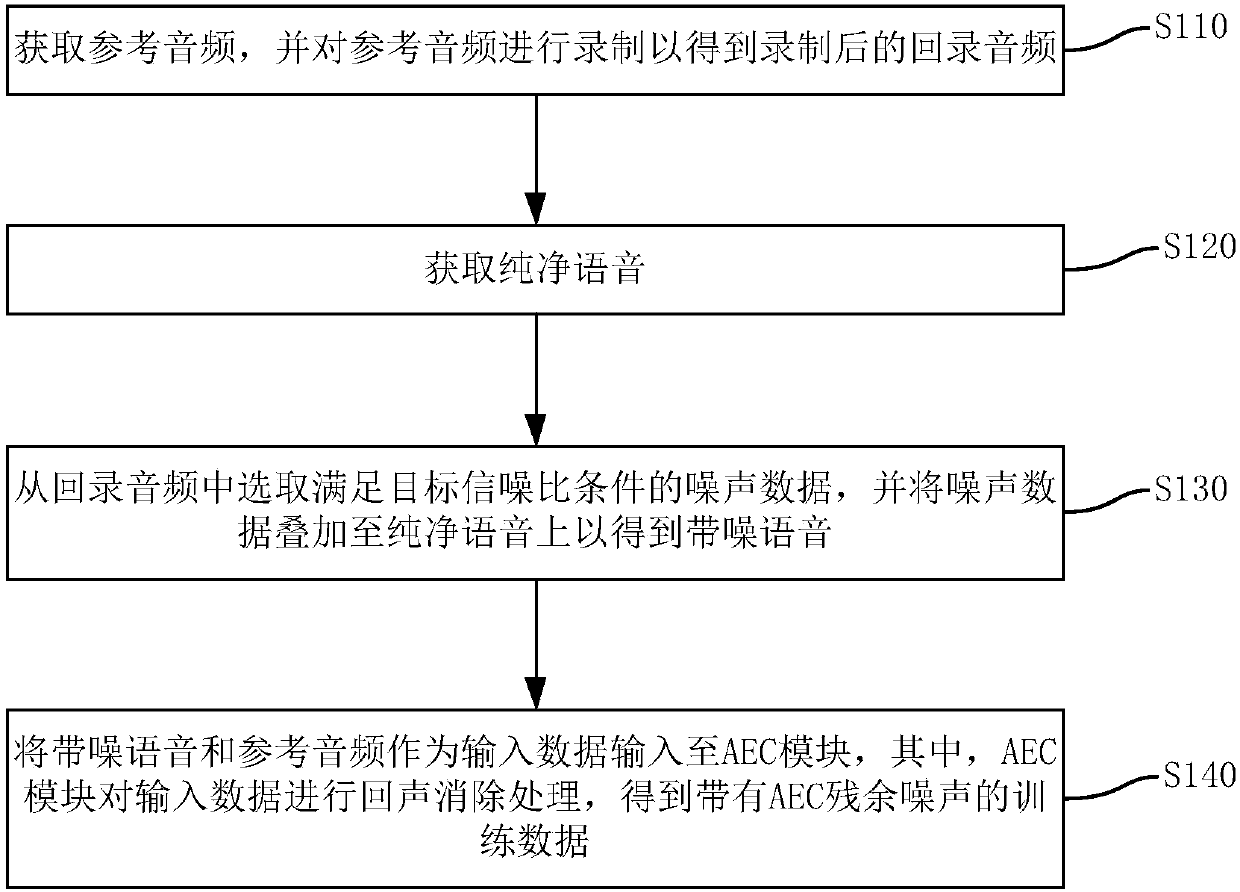
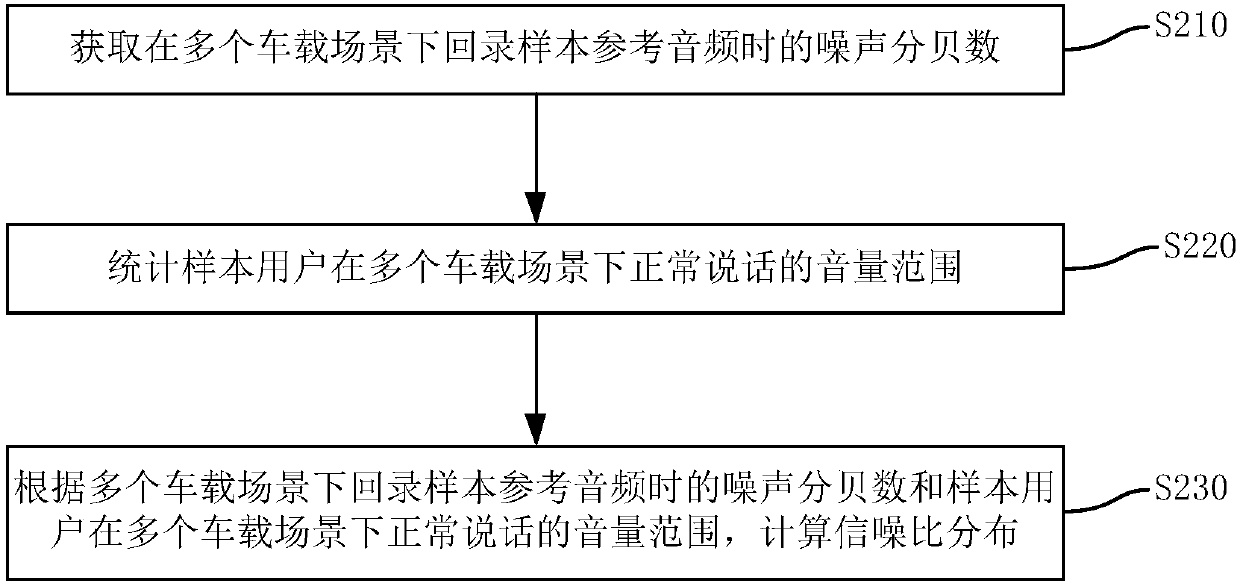
Processing method and device for voice recognition in vehicle and electronic equipment
ActiveCN108022591AImprove experienceImprove speech recognition performanceSpeech recognitionSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)In vehicle
The invention discloses a processing method and device for voice recognition in a vehicle, electronic equipment and a storage medium. The method comprises the following steps: reference audio is obtained and recorded, and therefore recorded play-back audio is obtained; pure voice is obtained, noise data satisfying object signal to noise ratio conditions is chosen from the play-back audio, noisy voice is obtained after the noise data is superposed on the pure voice, the noisy voice and the reference audio are input as input data into an AEC module, echo cancellation processing operation is performed on the input data via the AEC module, and training data containing AEC residual noise can be obtained. Thus, in actual online application, voice in the vehicle can be trained and recognized viathe training data containing the residual noise, voice recognition effects are improved, recognition performance and recognition stability are improved, and user experience is enhanced.
Owner:BEIJING BAIDU NETCOM SCI & TECH CO LTD
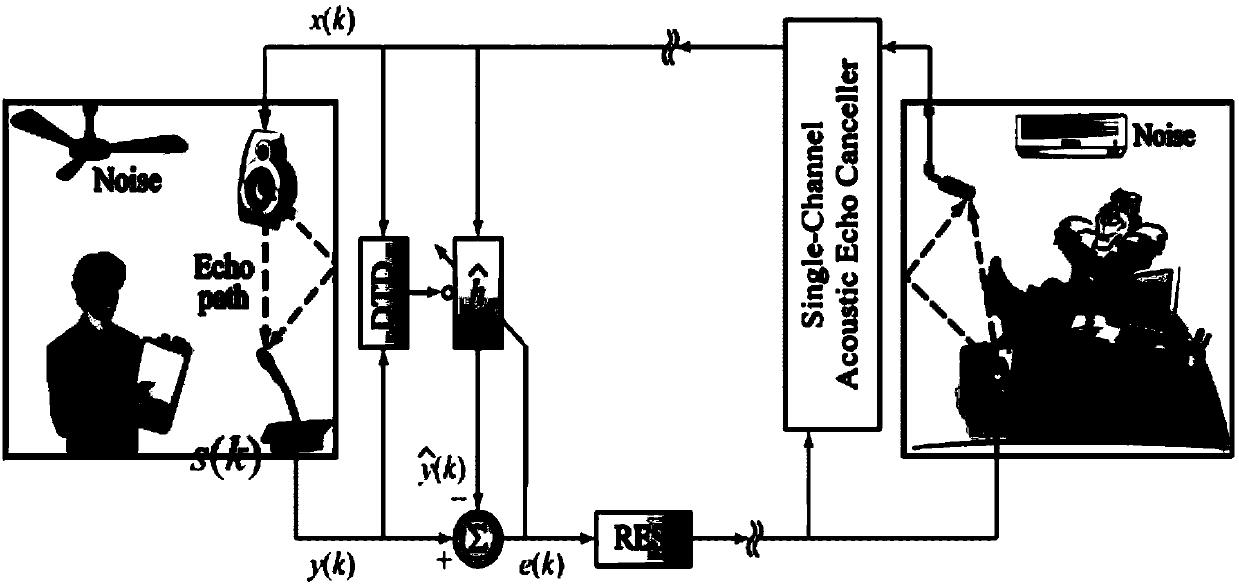
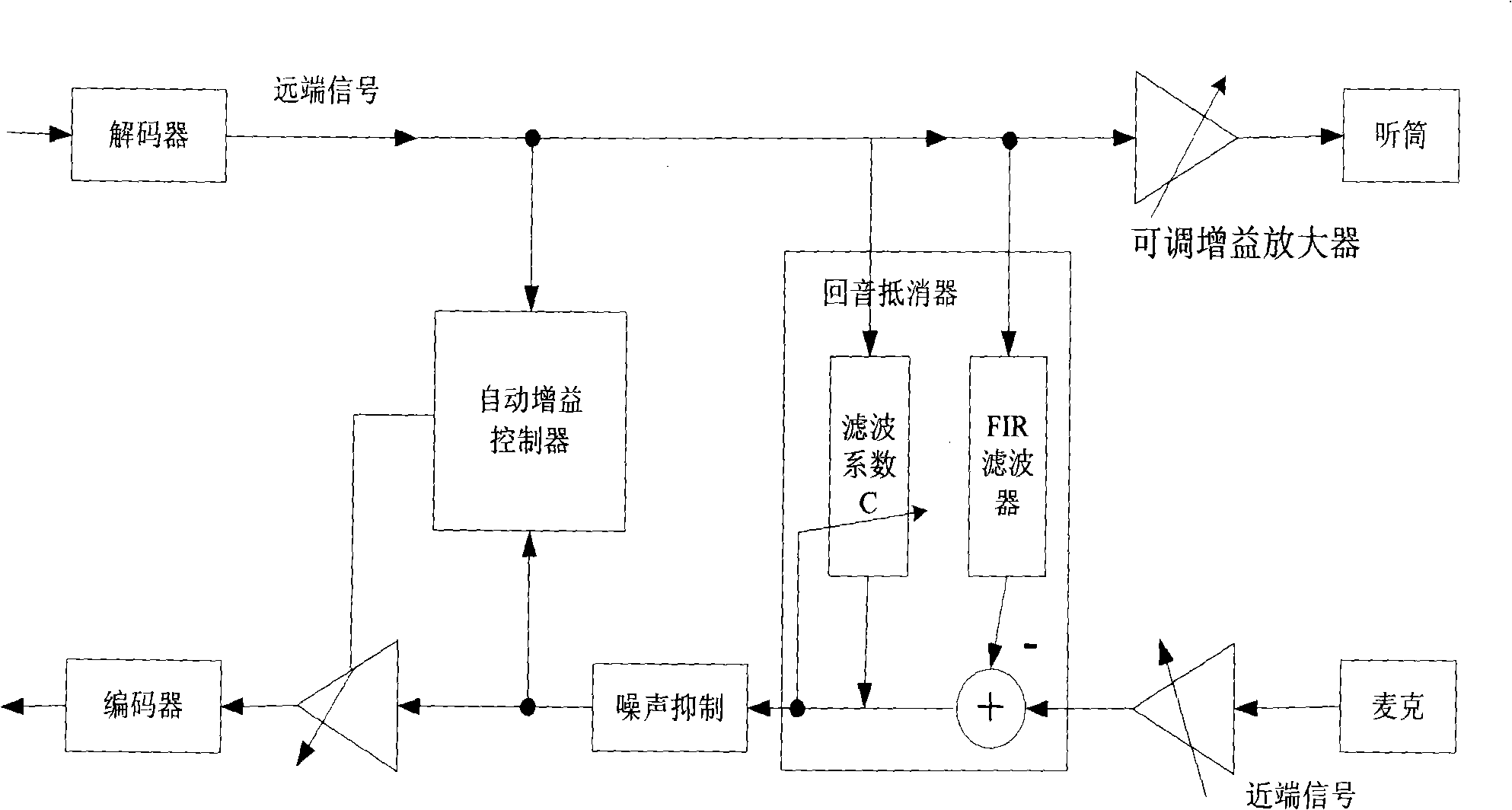
A device for eliminating echo of mobile terminal
InactiveCN101262530AContinuous transmissionTransmission distortionTwo-way loud-speaking telephone systemsSpeech analysisUltrasound attenuationOperation mode
The invention discloses a device for eliminating echoes of mobile terminals, which comprises an echo canceller, an automatic gain controller and a noise suppression module, wherein the echo canceller is used for eliminating part of echo signals thereof according to the correlation between upstream signals and downstream signals and then sending output signals to the noise suppression module; the noise suppression module is used for receiving the output signals sent by the echo canceller, filtering noises of environment and residual noises not eliminated by the echo canceller and sending the output signals to the automatic gain controller; the automatic gain controller is used for comparing the downstream signals with the output signals sent by the noise suppression module in real time to conclude a decrement and adding the decrement to the upstream signals to eliminate the residual echoes thereof. The device for eliminating echoes of mobile terminals of the invention solves the problem of destroying normal voice signals when eliminating echoes, such as too great voice attenuation, changes of operation mode into simplex, discontinuous voices, distortion and so on.
Owner:ZTE CORP
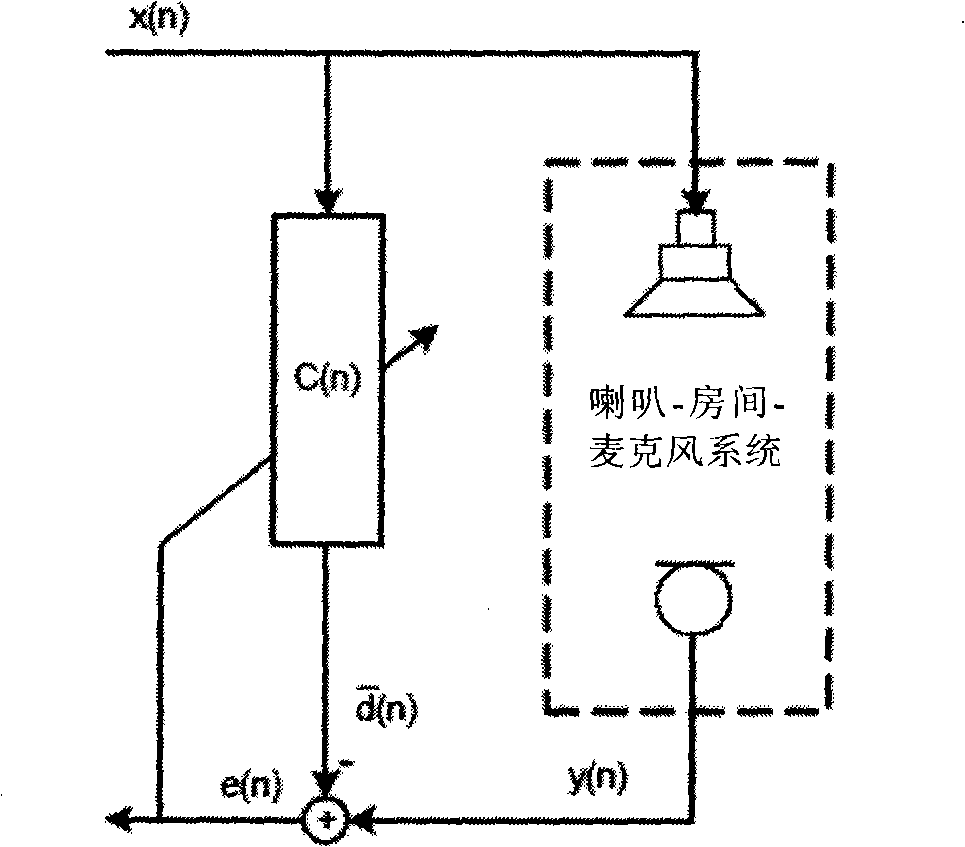
Automobile active noise reduction method
PendingCN106128449ACorrect noise reduction amount fluctuationsImprove stabilitySound producing devicesActive noise controlAdaptive filterEngineering
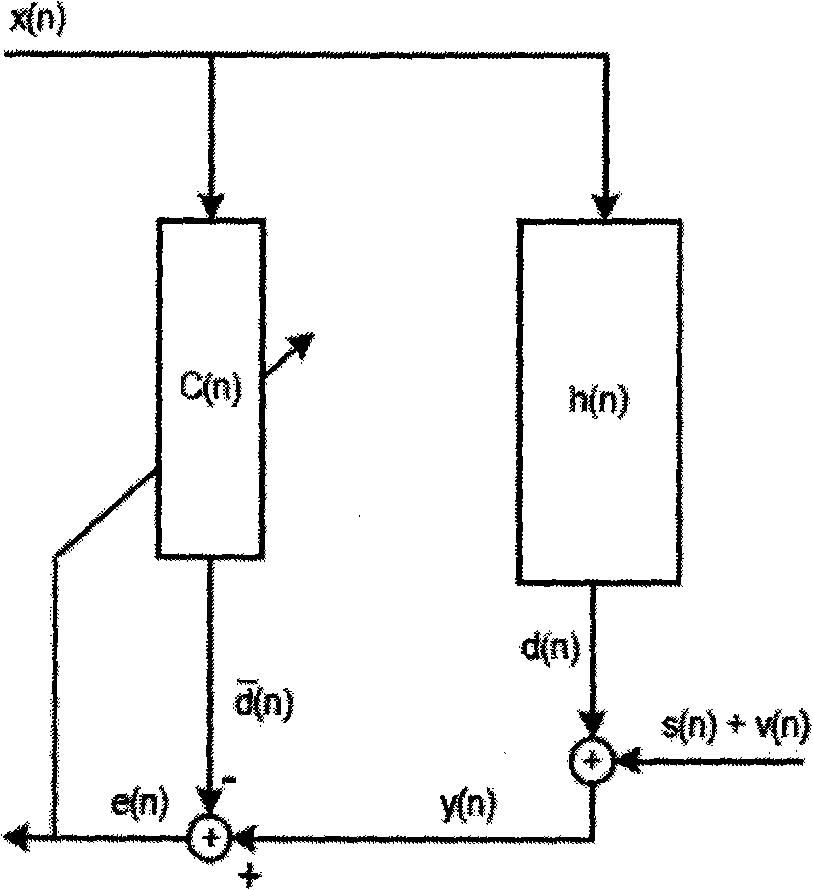
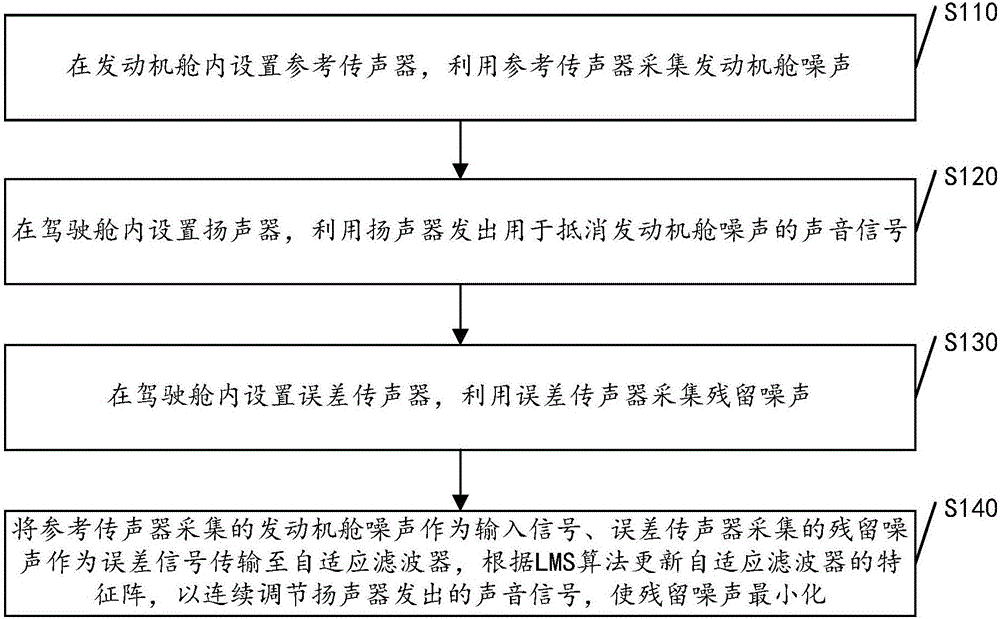
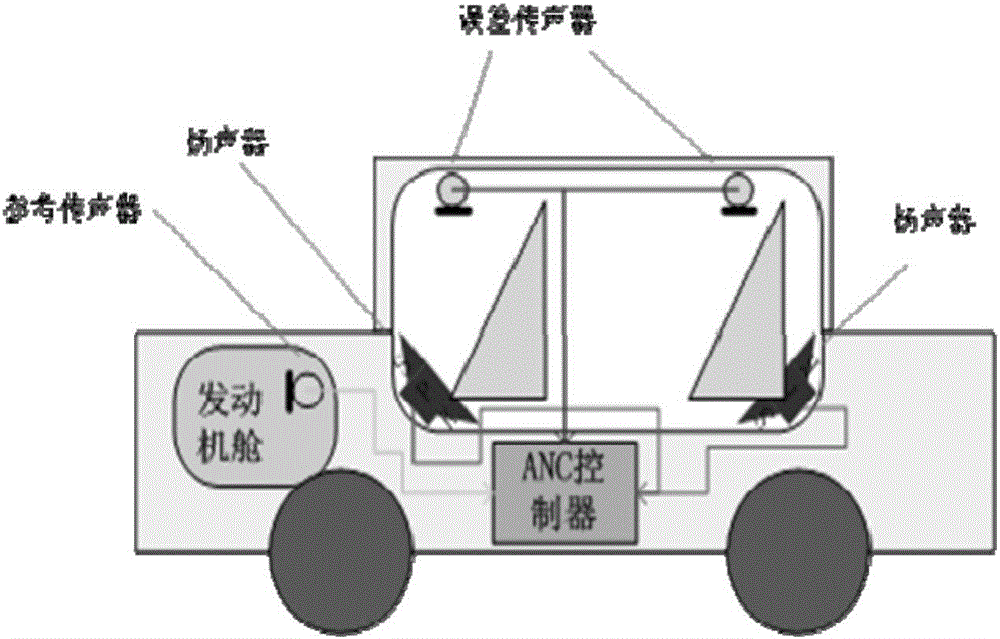
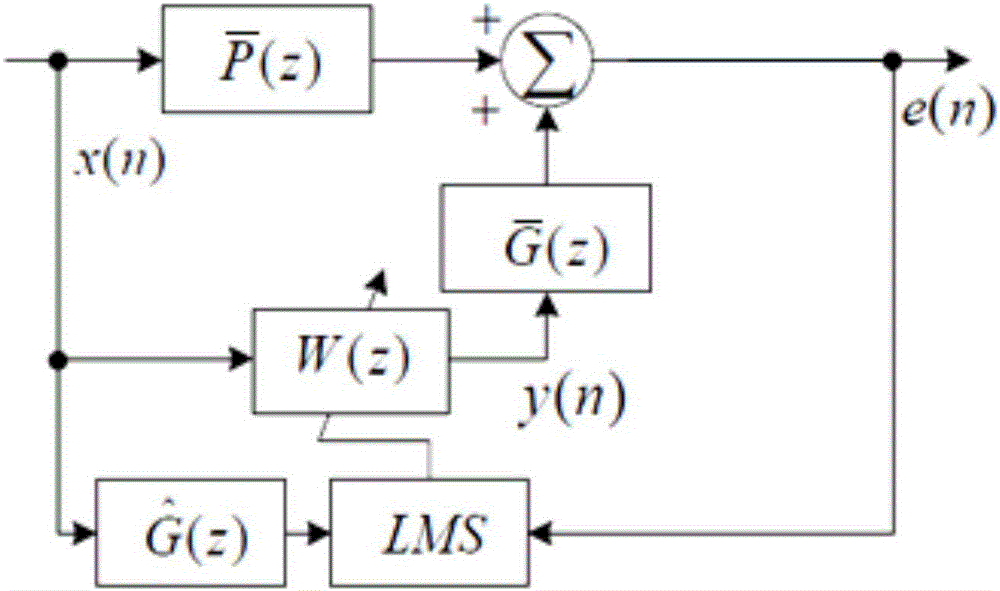
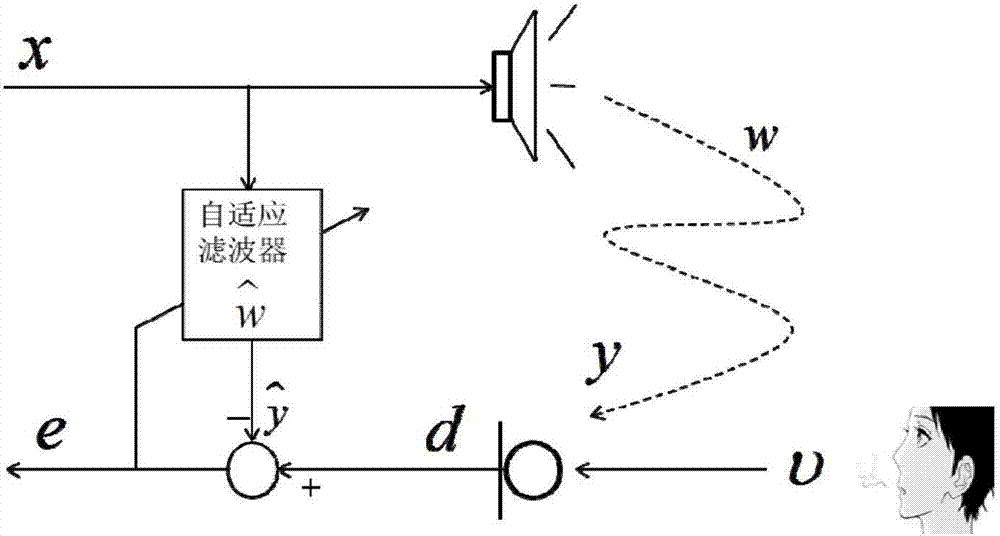
The invention discloses an automobile active noise reduction method. The method comprises steps: a reference microphone is arranged in an engine compartment, and the reference microphone is used for acquiring engine compartment noise x(n); a loudspeaker is arranged in a driving compartment, and the loudspeaker is used for producing a sound signal y(n) for cancelling the engine compartment noise x(n); an error microphone is arranged in the driving compartment, and the error microphone is used for acquiring residual noise e(n); the engine compartment noise x(n) acquired by the reference microphone serves as an input signal, the residual noise e(n) acquired by the error microphone serves as an error signal, the signals are transmitted to an adaptive filter, a characteristic matrix W of the adaptive filter is updated according to an LMS algorithm, the sound signal y(n) produced by the loudspeaker is continuously adjusted, and the residual noise e(n) is made to be minimum. When the acoustic environment in the driving compartment changes, good noise reduction can still achieved, and thus, the method is not limited to specific automobile models, and the application range is large.
Owner:QINGDAO GOERTEK
Method of noise reduction in digital x-rayograms
InactiveUS20130216117A1Reduce the amount requiredReduce noise levelImage enhancementTelevision system detailsX ray imageResidual noise
The invention relates to the field of digital image processing and can find use in suppression of noise in digital images, formed by high-energy radiation, including X-ray radiation. Specifically, the invention relates to a method for suppression of noise in digital x-ray images. The objective of the invention is to provide a method for noise suppression in digital X-ray images that has extended functionality, specifically, a method that makes it possible to reduce residual noise level and amount of artifacts in the form of discontinuities, directed along local orientation of object borders in textured image areas, to reduce residual LF noise level, and to eliminate over-smoothing (excessive filtering) of fine details. The technical innovation achieved is the improvement of digital image processing quality.
Owner:ZAKRYTOE AKCIONERNOE OBSHCHESTVO IMPULS
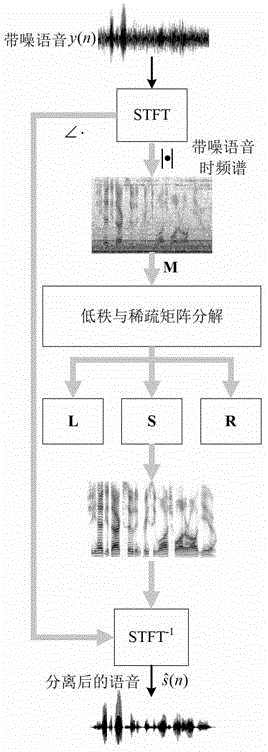
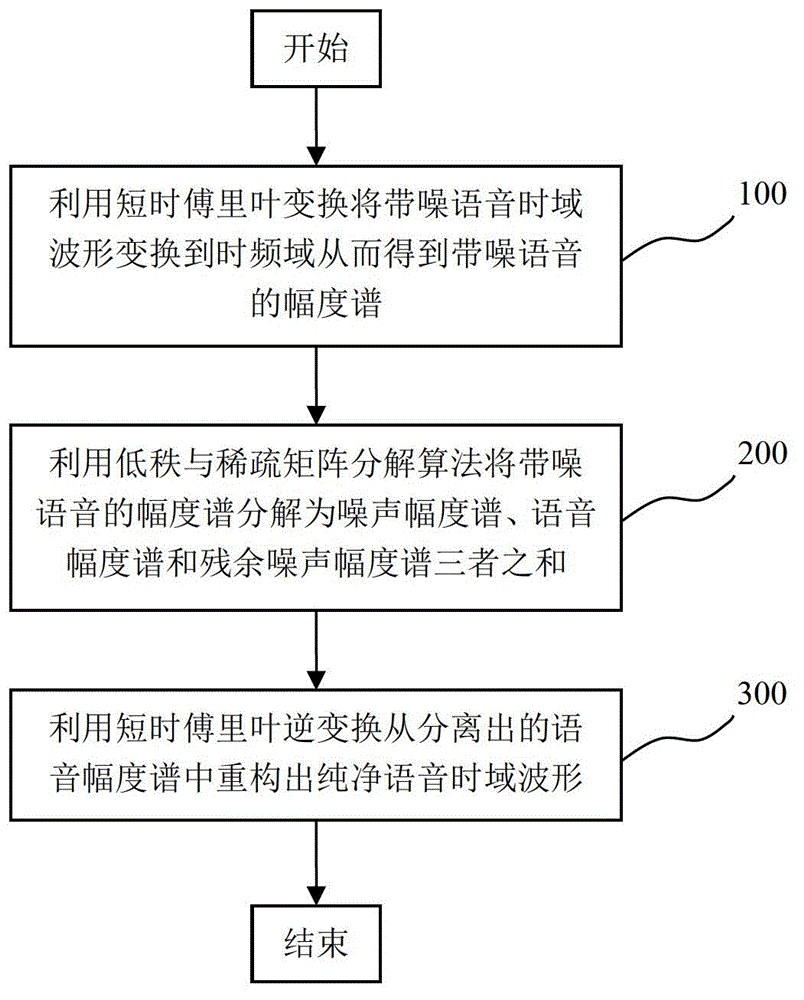
Single-channel monitor-free voice and noise separating method based on low-rank and sparse matrix decomposition
ActiveCN102915742AReduce reconstruction errorAvoid decompositionSpeech analysisDecompositionTime domain waveforms
The invention discloses a single-channel monitor-free voice and noise separating method based on low-rank and sparse matrix decomposition. The method includes the steps of converting a time domain waveform of noise-contained voice to a time frequency domain via short-time Fourier transform to obtain a magnitude spectra with noises; decomposing the magnitude spectra with the noises into a sum of a noise magnitude spectra, a voice magnitude spectra and a residual noise magnitude spectra by a low-rank and sparse matrix decomposition algorithm; and finally reconstructing a voice time-domain waveform from the voice magnitude spectra via short-time Fourier transform. Without any priori information about voice and noise, the method is the single-channel monitor-free voice and noise separating method, pure voice can be separated from noise-contained voice by the aid of an algorithm, and the single-channel monitor-free voice and noise separating method is simple, effective, and particularly suitable for voice extraction in strong-noise environment.
Owner:PLA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
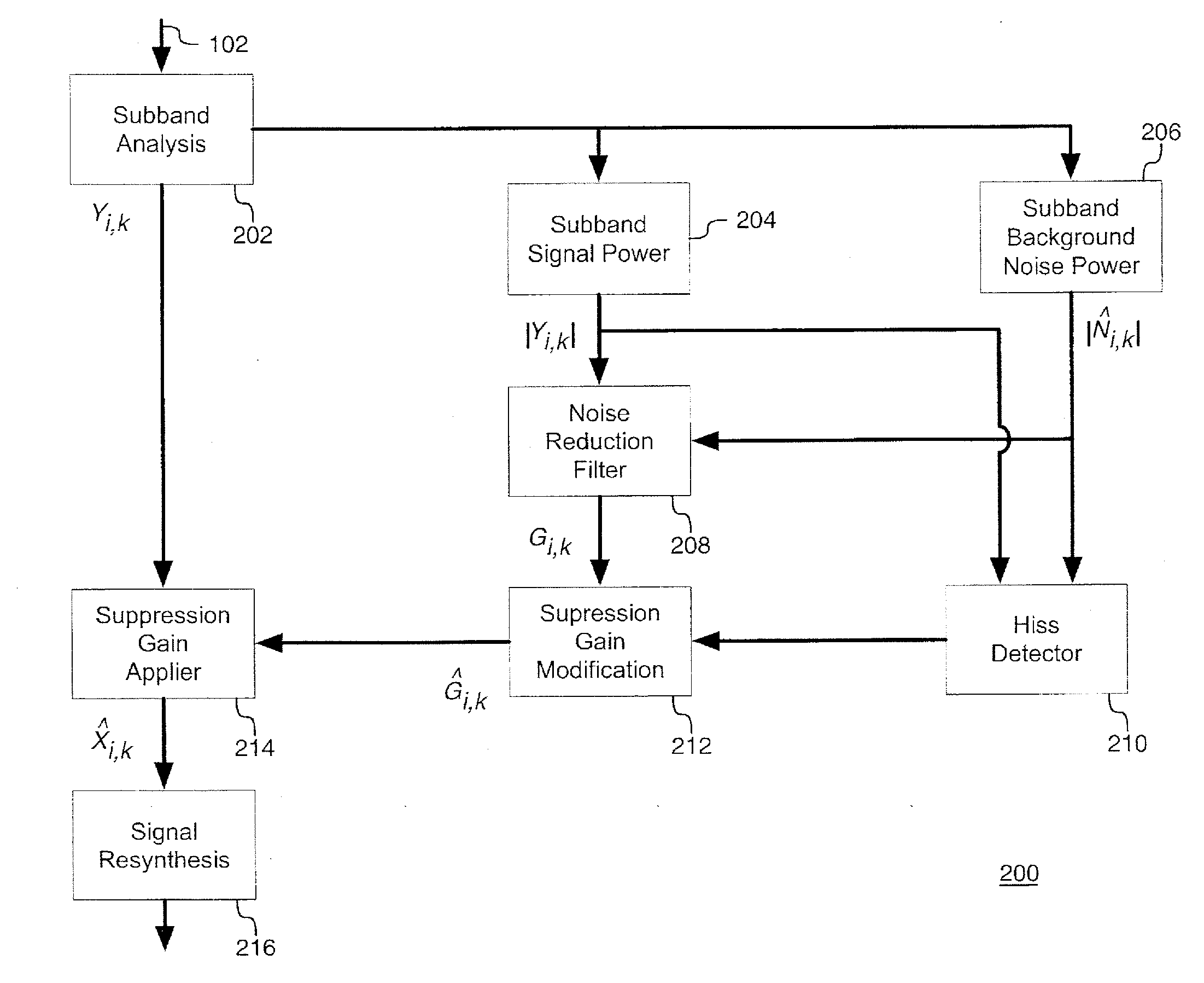
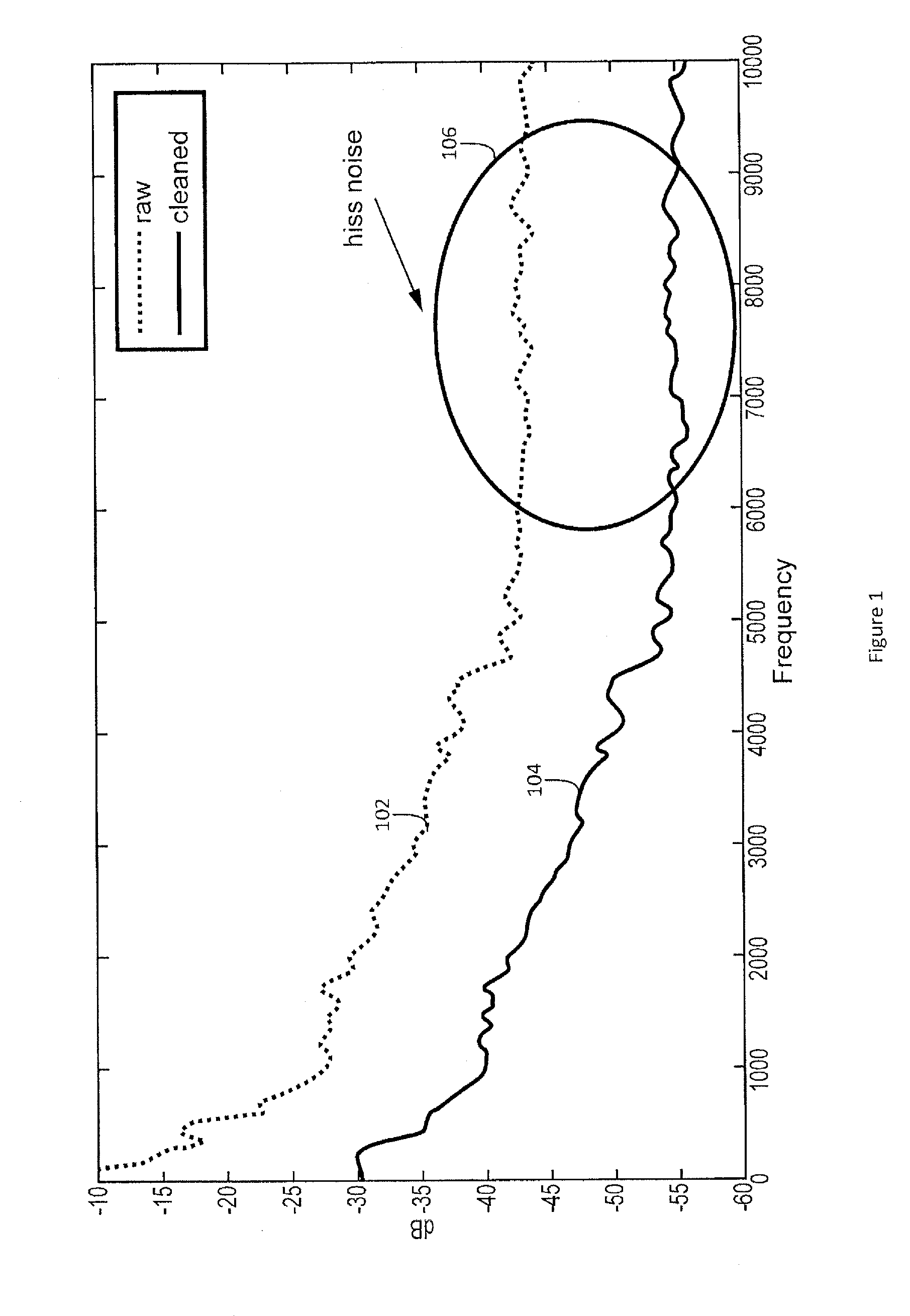
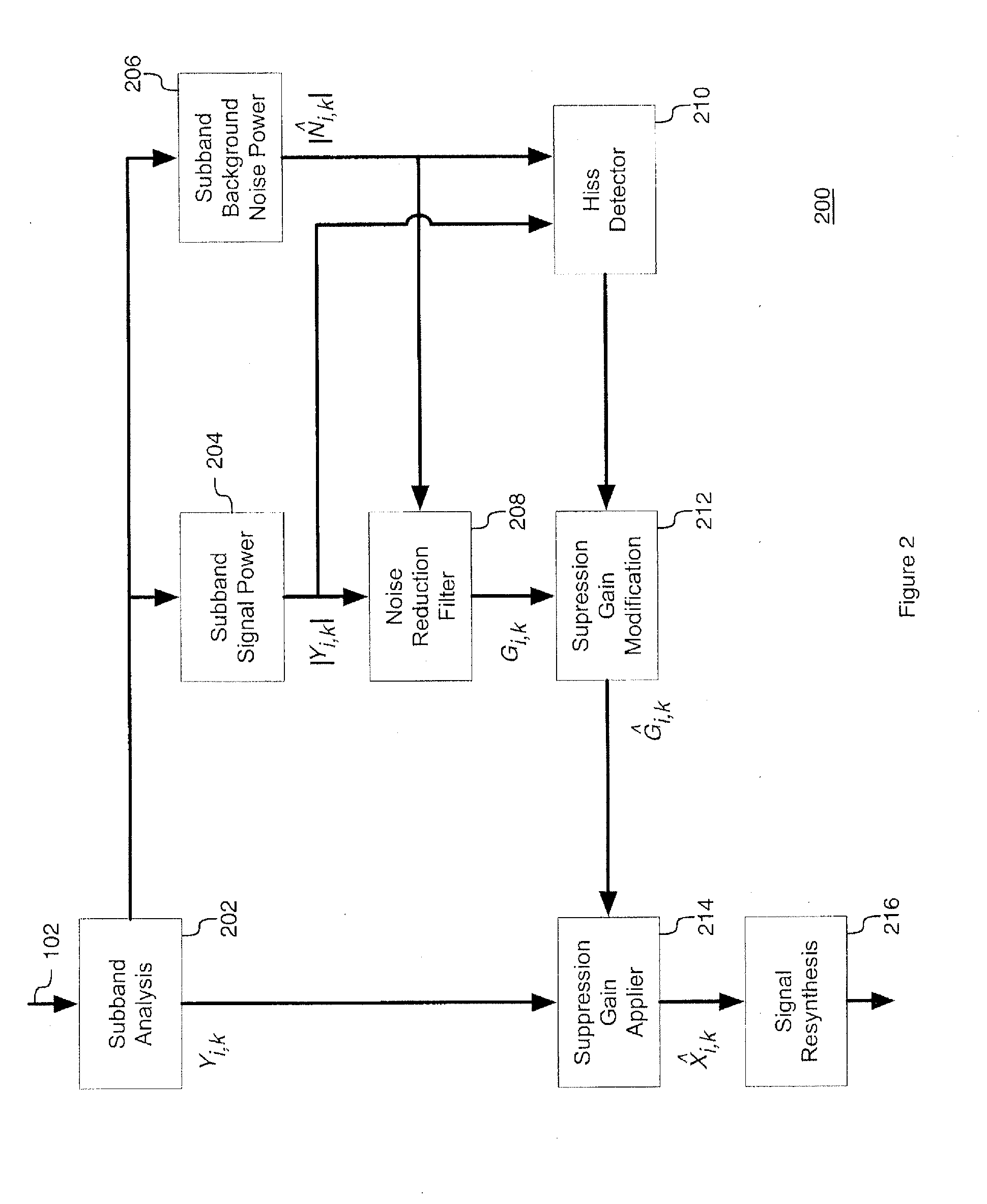
System and method for dynamic residual noise shaping
A system and method for dynamic residual noise shaping configured to reduce hiss noise in an audio signal. The system and method may detect an amount and type of hiss noise. The system and method may limit calculated noise suppression gains responsive to the detected amount and type of hiss noise. The limited noise suppression gains may be applied to the audio signal and may reduce the hiss noise.
Owner:MALIKIE INNOVATIONS LTD
Audio signal processing method and system, audio interaction device and computer equipment
ActiveCN106898359AEasy to detectImprove filtering effectInterconnection arrangementsSpeech analysisEnvironmental noiseInteraction device
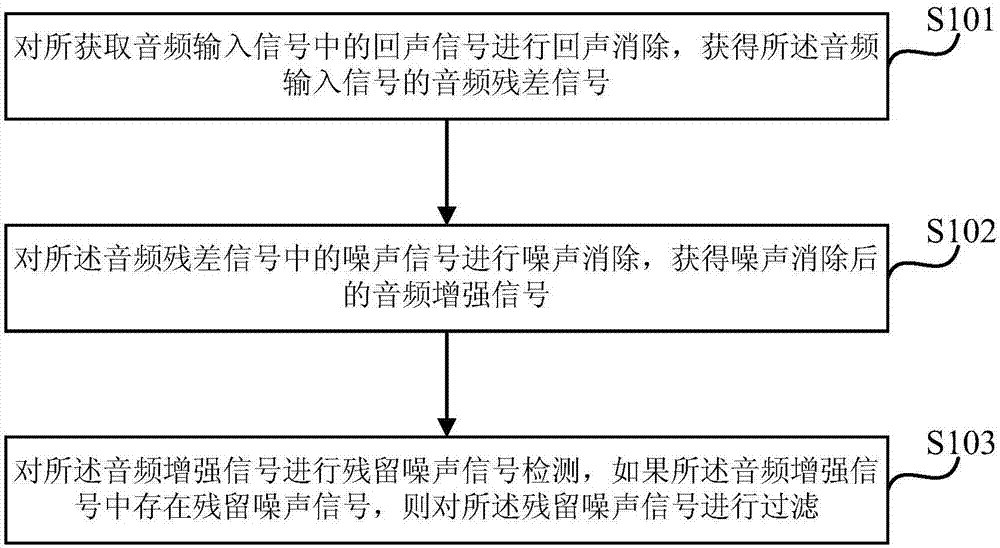
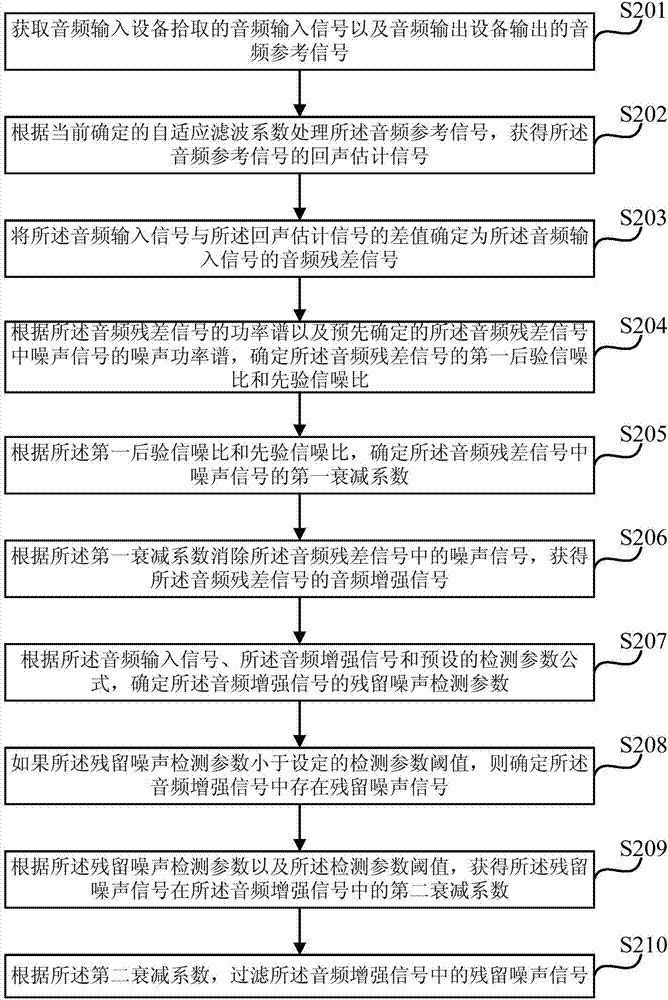
The embodiment of the invention discloses an audio signal processing method and system, an audio interaction device and computer equipment. The method includes the following steps: performing echo cancellation on an echo signal in an acquired audio input signal to obtain an audio residual error signal of the audio input signal; performing noise cancellation on a noise signal in the audio residual error signal to obtain an audio enhancing signal after noise cancellation; and performing residual noise signal detection on the audio enhancing signal, and if a residual noise signal exists in the audio enhancing signal, filtering out the residual noise signal. By utilization of the method, the echo signal and the environmental noise signal in the audio input signal during audio interaction can be removed, detection and filtering of residual noise are realized at the same time, influence of environmental noise on an audio interaction process is effectively suppressed, and an effect of cancelling echoes and noise in the audio interaction process is improved, thereby improving the performance of an audio interaction device in cancelling echoes and noise.
Owner:SHANGHAI XIAOI ROBOT TECH CO LTD
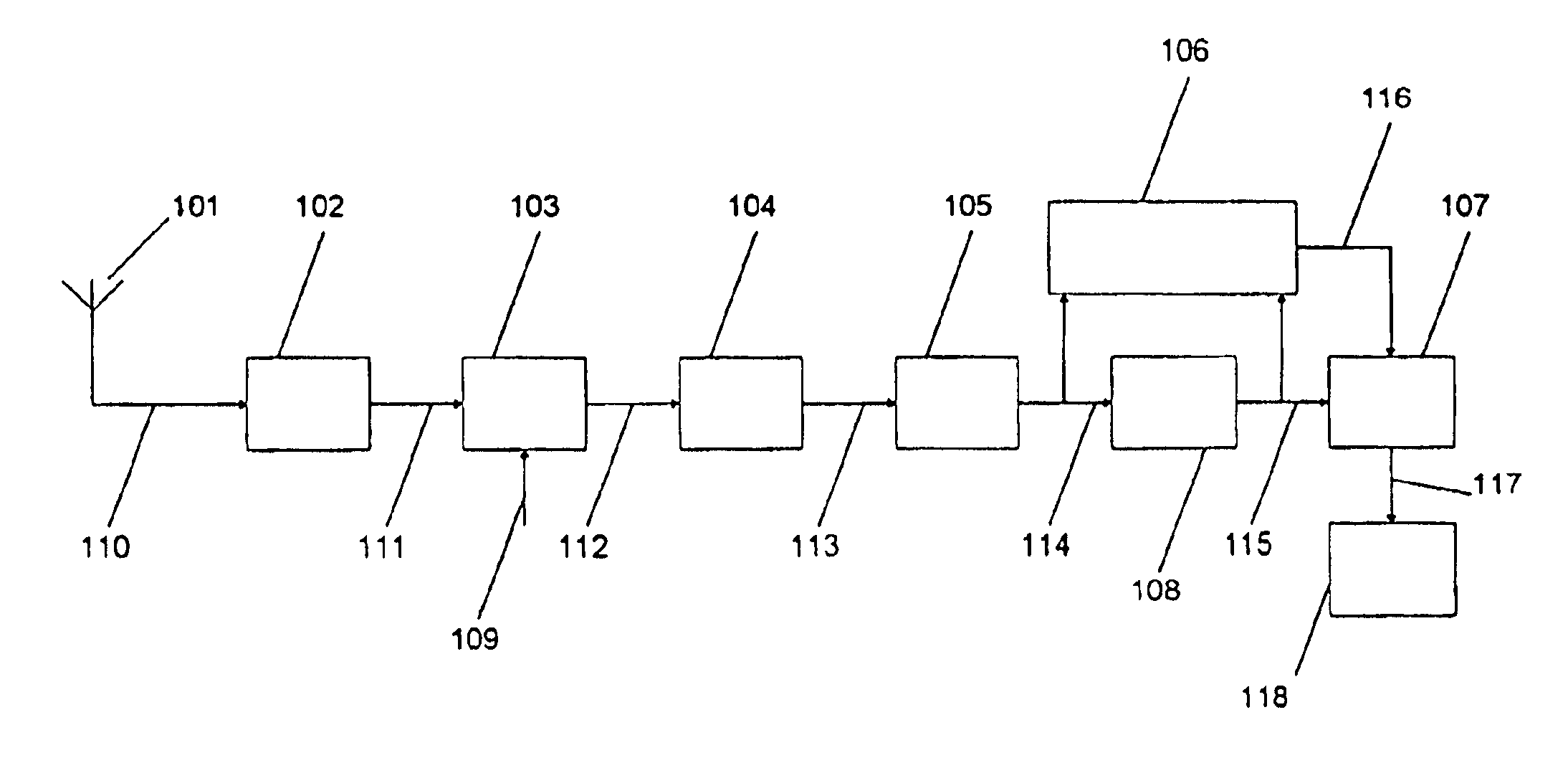
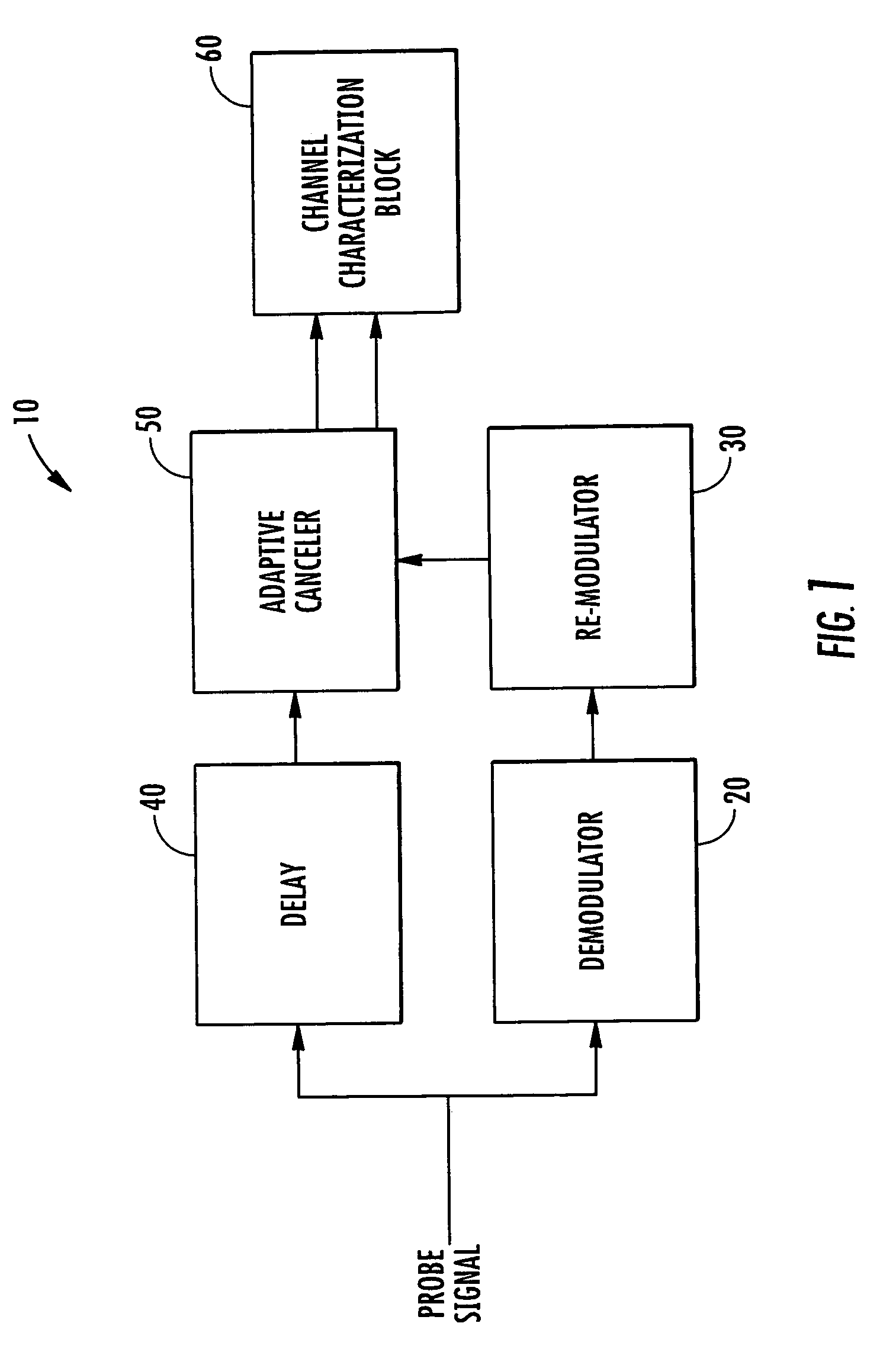
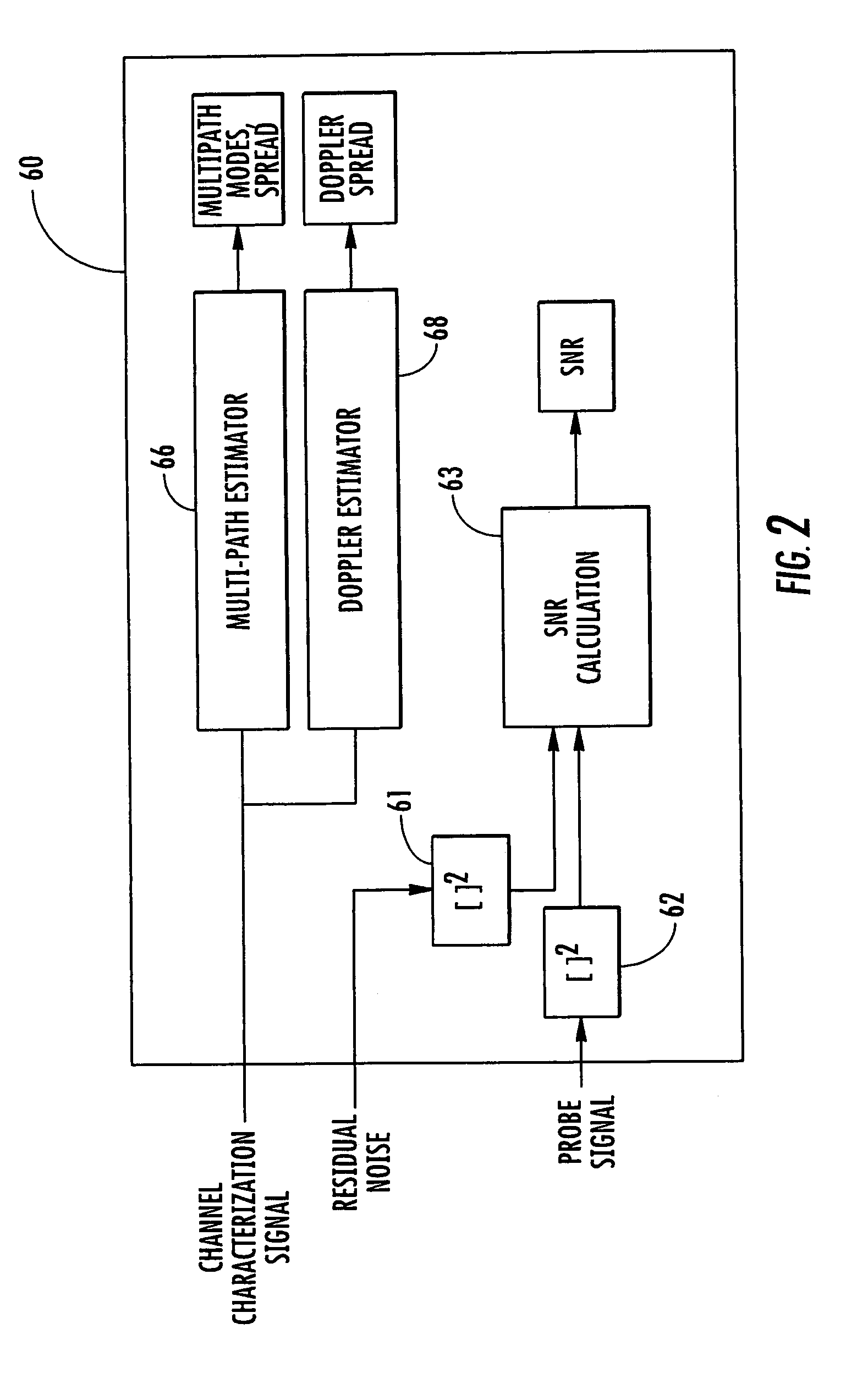
Communications channel characterization device and associated methods
ActiveUS7085539B2Error detection/prevention using signal quality detectorTransmission monitoringDoppler spreadSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
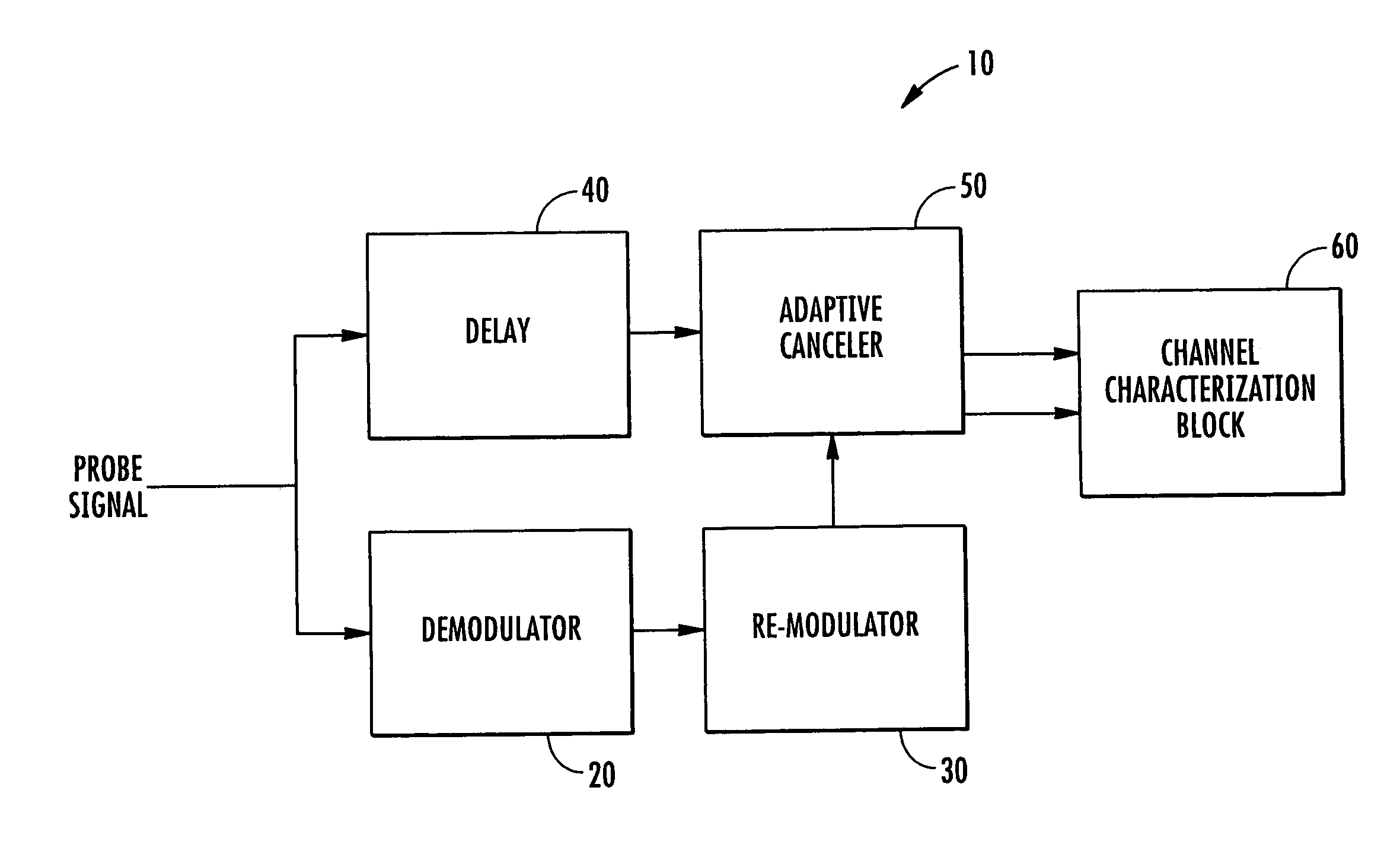
The system and method characterize a communications channel with respect to signal-to-noise ratio (SNR), time dispersion or multi-path, and frequency dispersion or Doppler spread. A probe signal demodulator receives a probe signal transmitted on a wireless communication channel and generates a demodulated probe signal, and a probe signal re-modulator generates a replica probe signal. A delay unit generates a delayed probe signal, and an adaptive canceller receives the delayed probe signal and the replica probe signal, and generates a residual noise signal and a channel characterization signal. A channel characterization block receives the channel characterization signal and the residual noise signal to generate channel measurements of the wireless communication channel.
Owner:HARRIS GLOBAL COMM INC
Feedforward narrow band active noise control system with online secondary path identification
InactiveCN105489225AHigh precisionHigh speedSpeech analysisSound producing devicesNoise controlControl system
The invention belongs to the field of active noise control and discloses a feedforward narrow band active noise control system with online secondary path identification. The feedforward narrow band active noise control system aims to solve the problem that system residual noise inhibition performance is seriously affected by auxiliary noise introduced into online secondary path identification in the feedforward narrow band active noise control system. The feedforward narrow band active noise control system comprises a signal synthesis subsystem, an online secondary path identification subsystem and a residual noise separation subsystem. The signal synthesis subsystem is used for generating secondary noise source signals with same frequency as sound signals in target noise. The online secondary path identification subsystem is capable of completing online secondary path identification in real time along with running of the narrow band active noise control system and used for inhibiting the target noise. The residual noise separation subsystem is capable of separating sound signals with frequencies in limited quantity from the residual noise. Energy of the introduced auxiliary noise is regulated by the separated residual sound signals, and consequently precision and quickness in online secondary path identification are improved, and influences of the introduced auxiliary noise on the residual noise are remarkably reduced.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Improved GSC self-adaptive speech enhancement method
InactiveCN104835503AImprove blockageReduce cancellationSpeech analysisTarget signalWeight coefficient
The invention relates to an improved GSC self-adaptive speech enhancement method. An improved GSC self-adaptive speech enhancement system is used, a weight coefficient of a post filter is estimated based on the signal received by a microphone, incoherent noises in the signal are removed by using the post wiener filter, a self-adaptive blocking matrix is used for replacing a fixed blocking matrix in a conventional GSC structure so as to better block target signals and reduce cancellation of the target signals, the iterative mode of a self-adaptive algorithm is improved, the convergence rate and steady-state misadjustment signals and filter noise interference signals are balanced, and based on the characteristics of easy noise removal, small amount of calculation and the like of a spectral subtraction method, the possible residual noise signals can be further removed by using an improved spectral subtraction method. According to the invention, the method is capable of self-adaptive speech enhancement of signals at any angle and has a certain robustness for speech signal enhancement under a random environment, and the subsequent spectral subtraction method can be used for further removing the residual noises and improving the denoising capability of the entire system.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF INFORMATION SCI & TECH
Speech enhancement processing method
ActiveCN109524020AFix stability issuesSolve the problem of mode crashSpeech analysisInternal combustion piston enginesLower limitSpectral subtraction
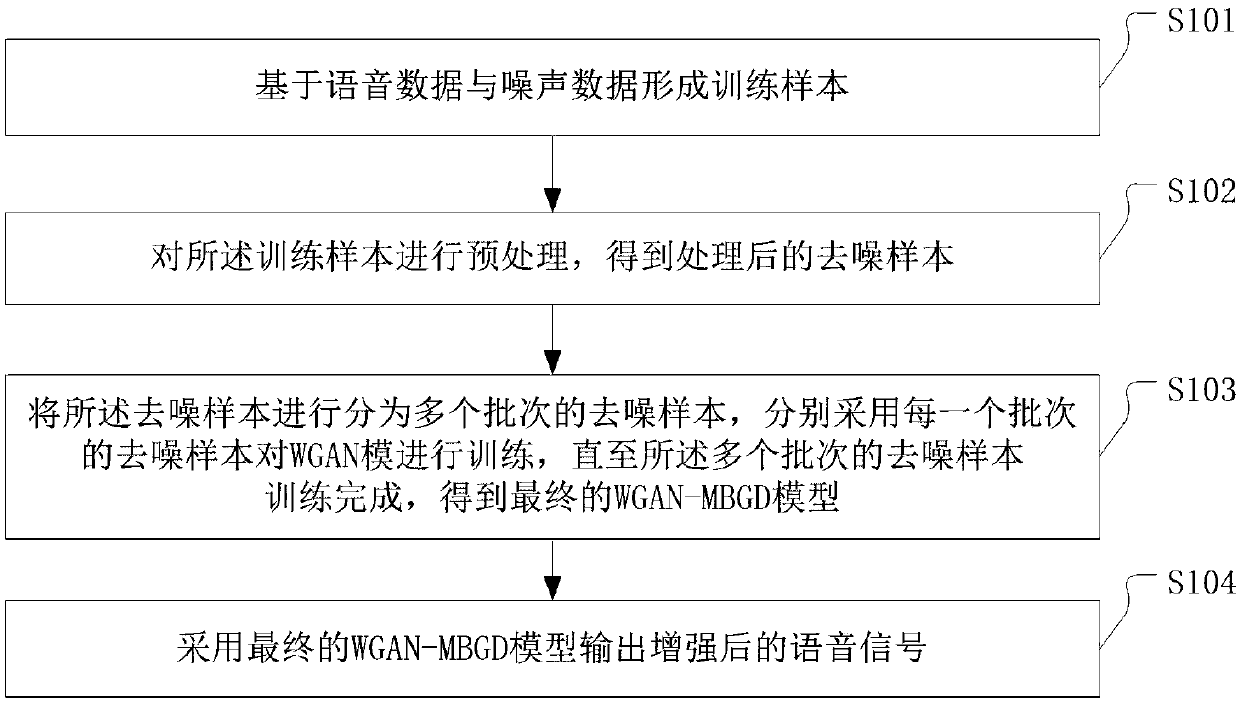
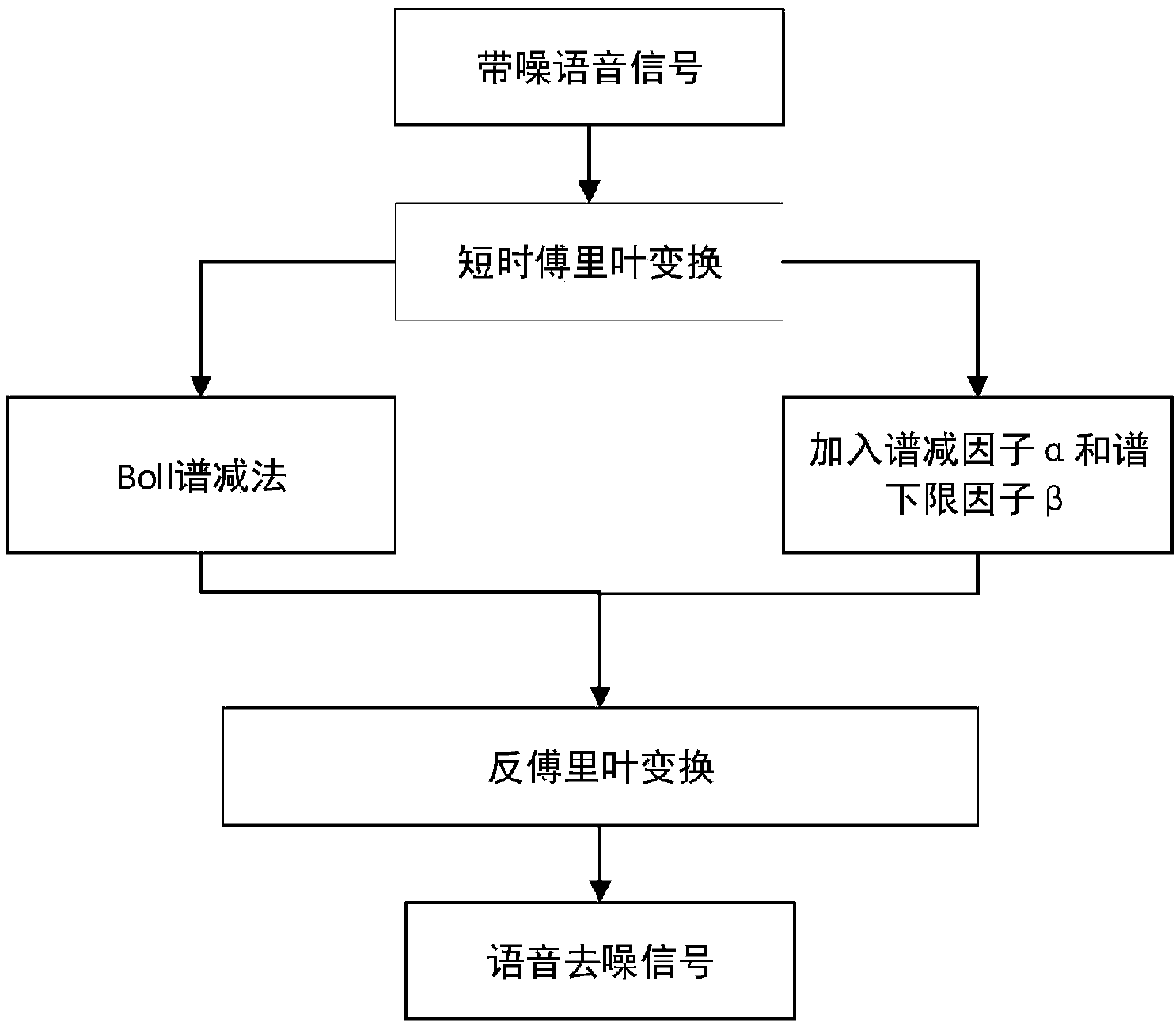
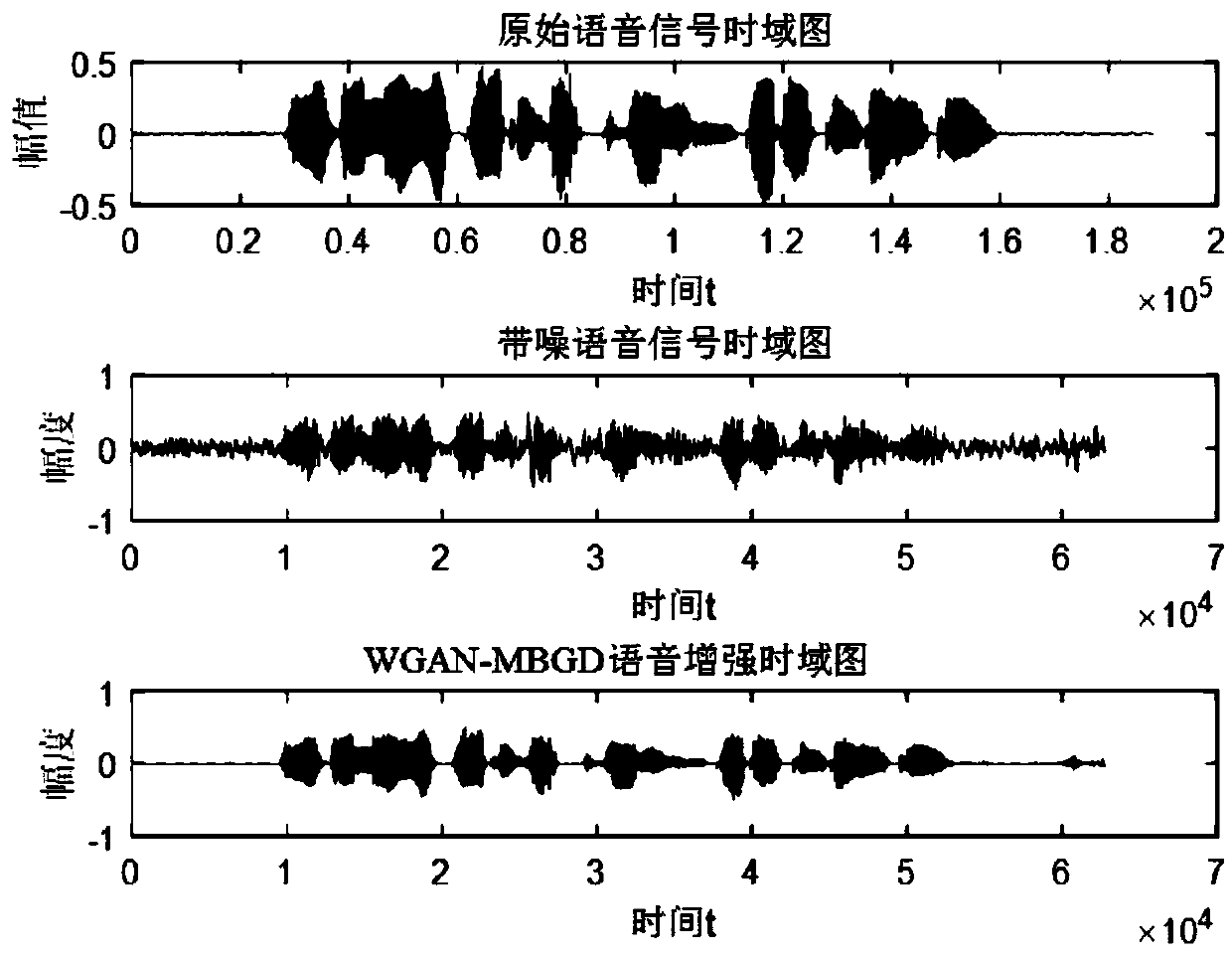
The invention discloses a speech enhancement processing method. The method comprises the steps that a training sample is formed based on speech data and noise data; the training sample is preprocessedto obtain a processed denoising sample; the denoising sample is divided into multiple batches of denoising samples, a WGAN model is trained by adopting each batch of the denoising sample until training of multiple batches of the denoising samples is completed, and a final WGAN-MBGD model is obtained; an enhanced speech signal is output by adopting the final WGAN-MBGD model. The speech enhancementprocessing method has the advantages that the unstable adversarial network gradient is generated, the rate of convergence is quicker, the small-batch calculation is applied, the calculated amount isalso reduced, spectral subtraction factors and spectral lower limit factors are introduced, and the residual noise is reduced by reducing the error among frequency spectrums.
Owner:SHANGHAI MARITIME UNIVERSITY
Method for recovering target speech based on speech segment detection under a stationary noise
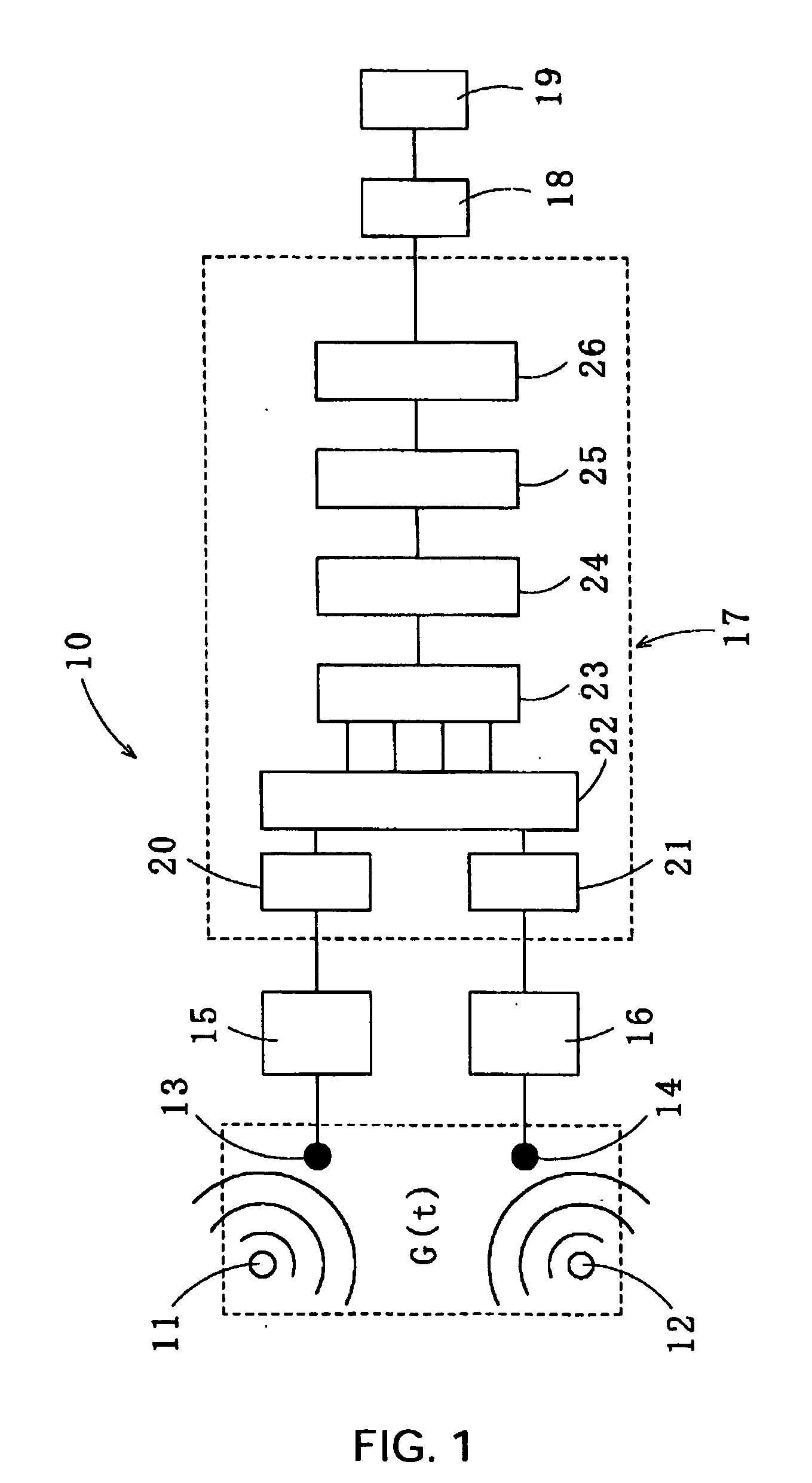
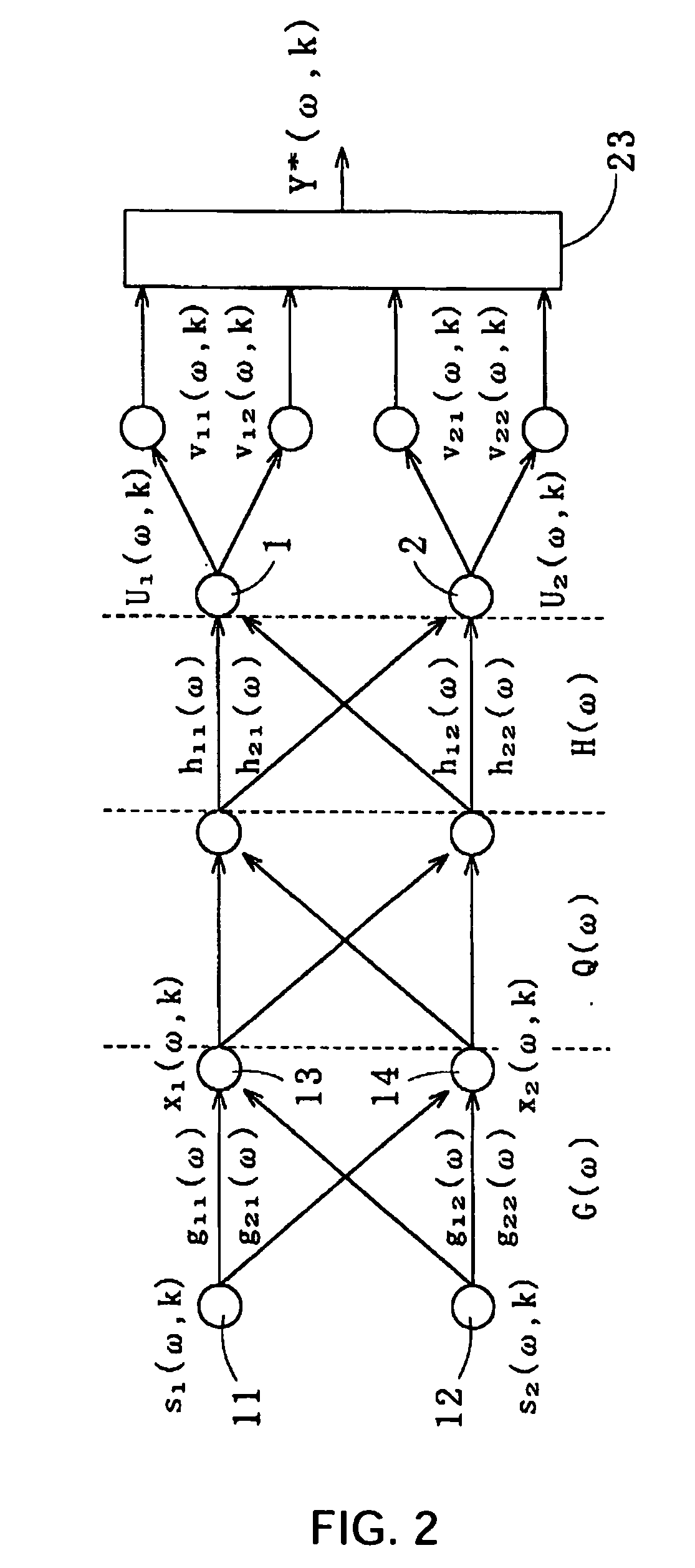
InactiveUS20070055511A1Minimizing residual noiseNoise minimizationSpeech recognitionFrequency spectrumPresent method
Method for recovering target speech by extracting signal components falling in a speech segment, which is determined based on separated signals obtained through the Independent Component Analysis, thereby minimizing the residual noise in the recovered target speech. The present method comprises: the first step of receiving target speech emitted from a sound source and a noise emitted from another sound source and extracting estimated spectra Y* corresponding to the target speech by use of the Independent Component Analysis; the second step of separating from the estimated spectra Y* an estimated spectrum series group y* in which the noise is removed by applying separation judgment criteria based on the kurtosis of the amplitude distribution of each of estimated spectrum series in Y*; the third step of detecting a speech segment and a noise segment of the total sum F of all the estimated spectrum series in y* by applying detection judgment criteria based on a predetermined threshold value T that is determined by the maximum value of F; and the fourth step of extracting components falling in the speech segment from the estimated spectra Y* to generate a recovered spectrum group of the target speech for recovering the target speech.
Owner:KITAKYUSHU FOUND FOR THE ADVANCEMENT OF IND SCI & TECH +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com