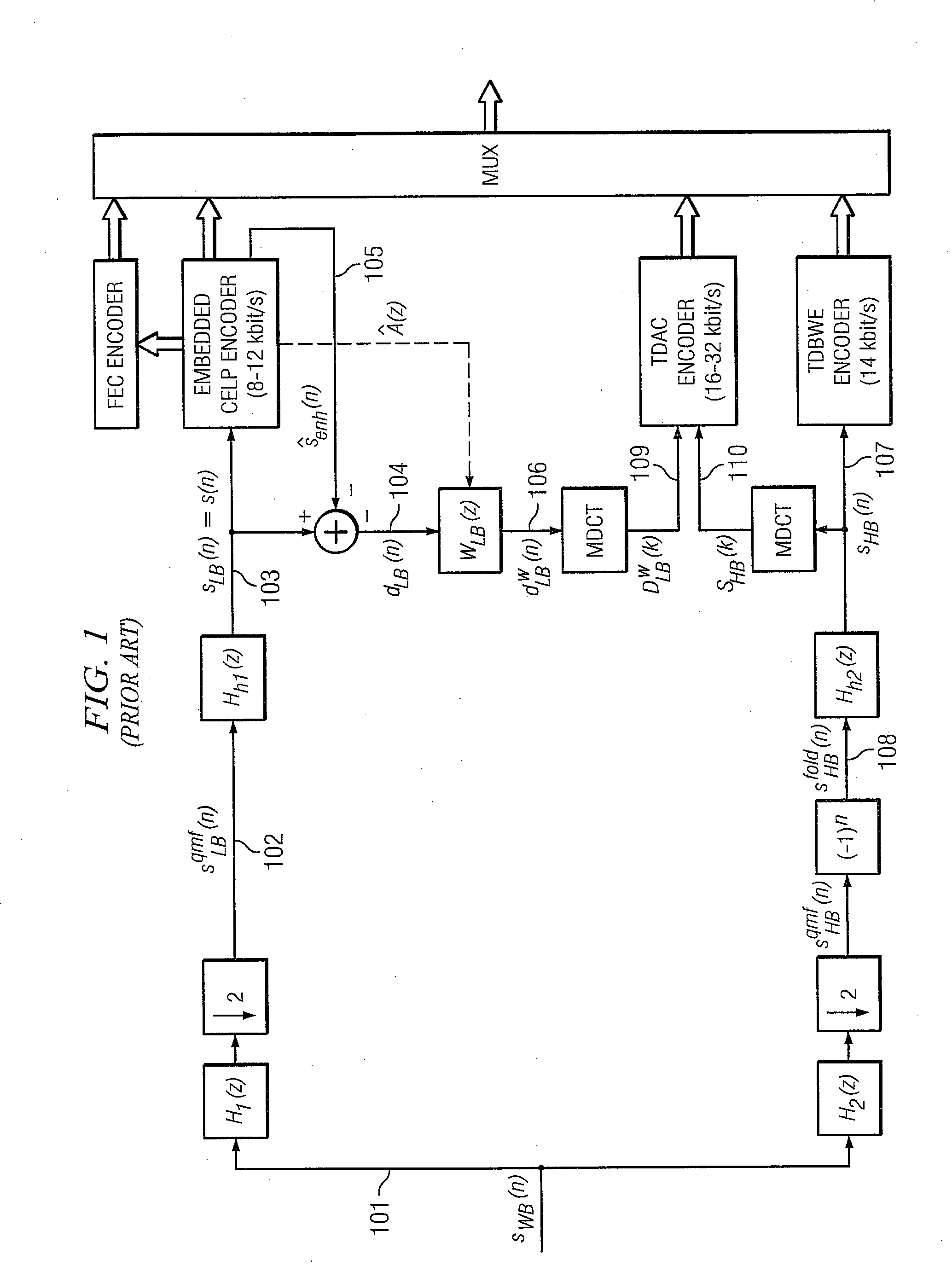
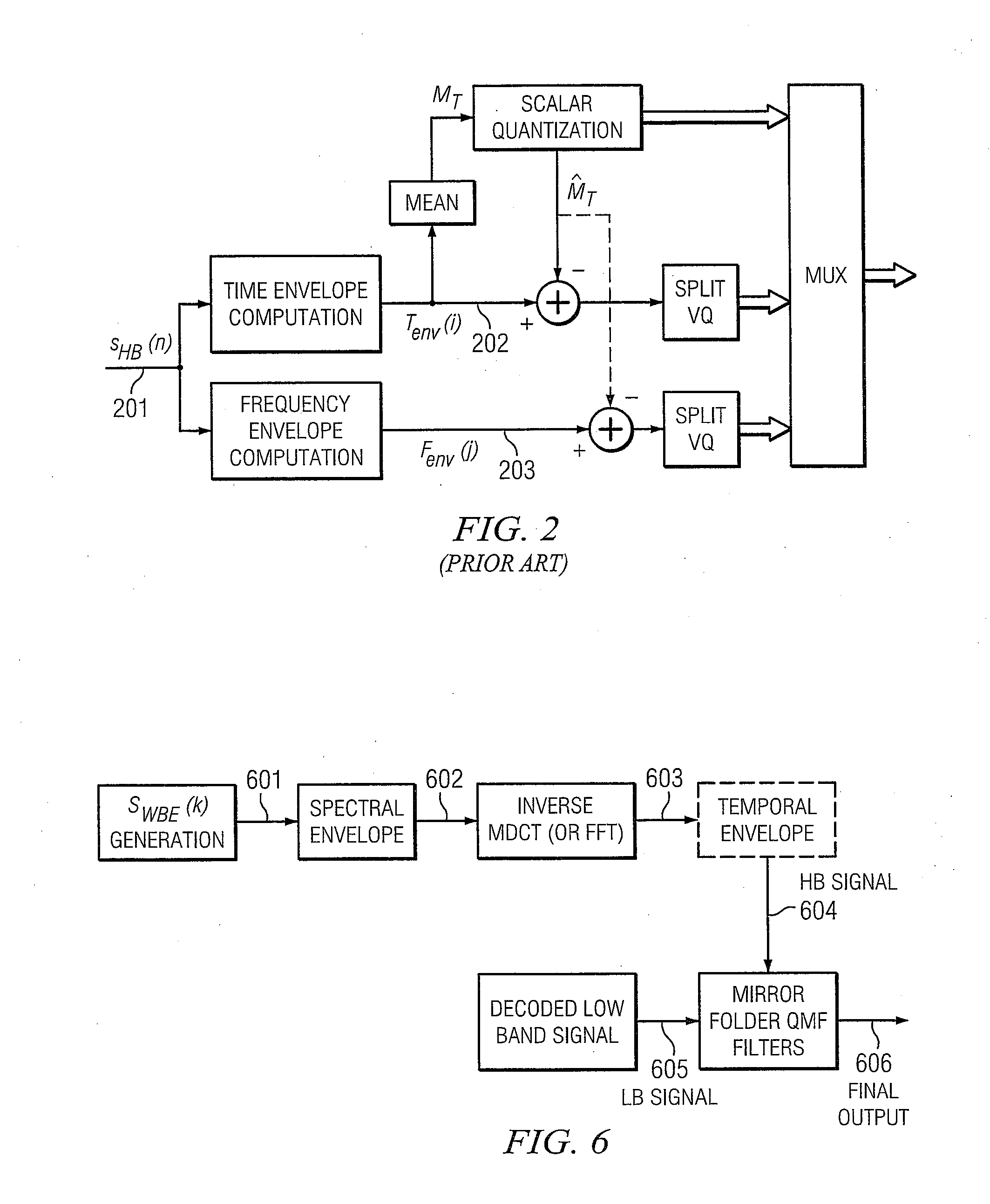
Patents
Literature
1688 results about "Noise component" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
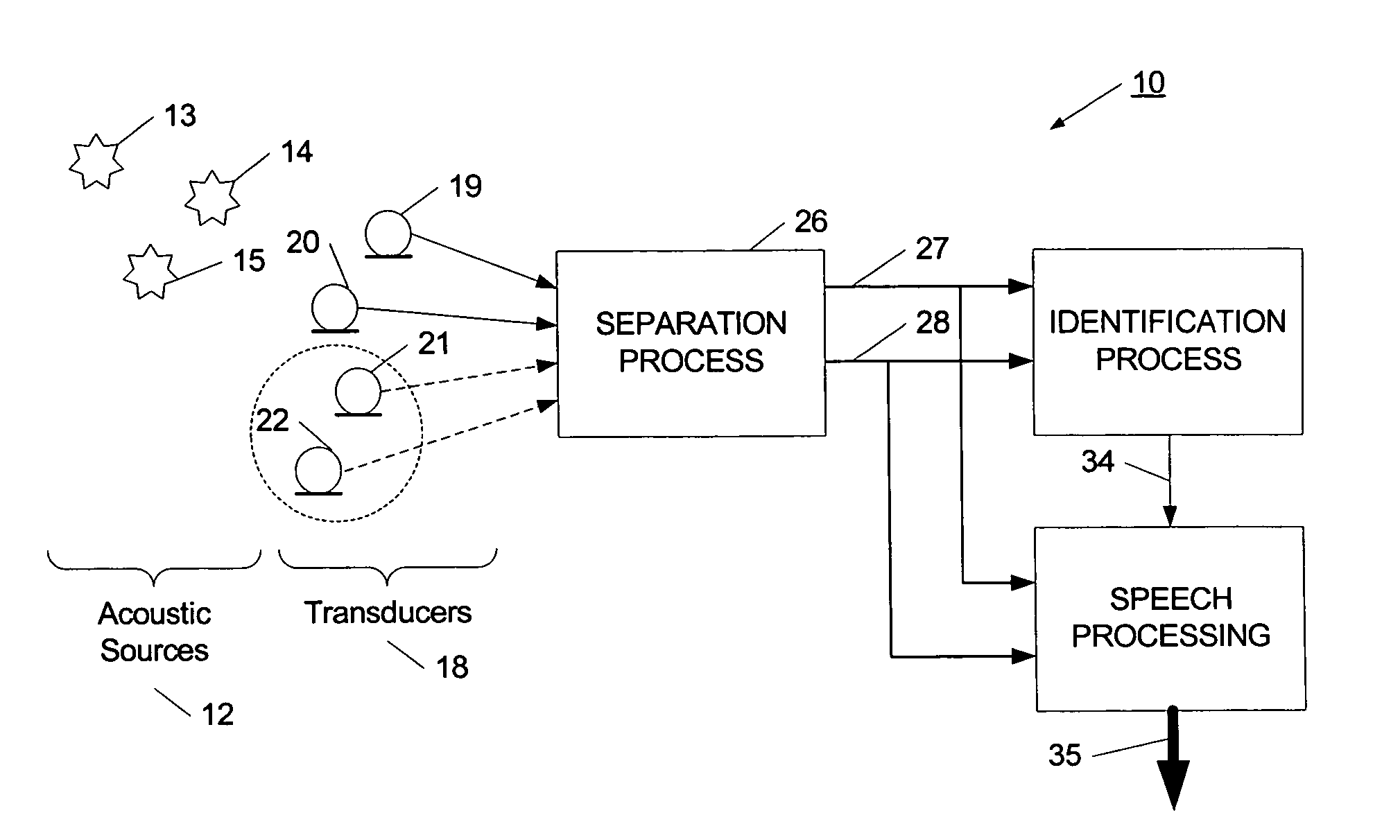
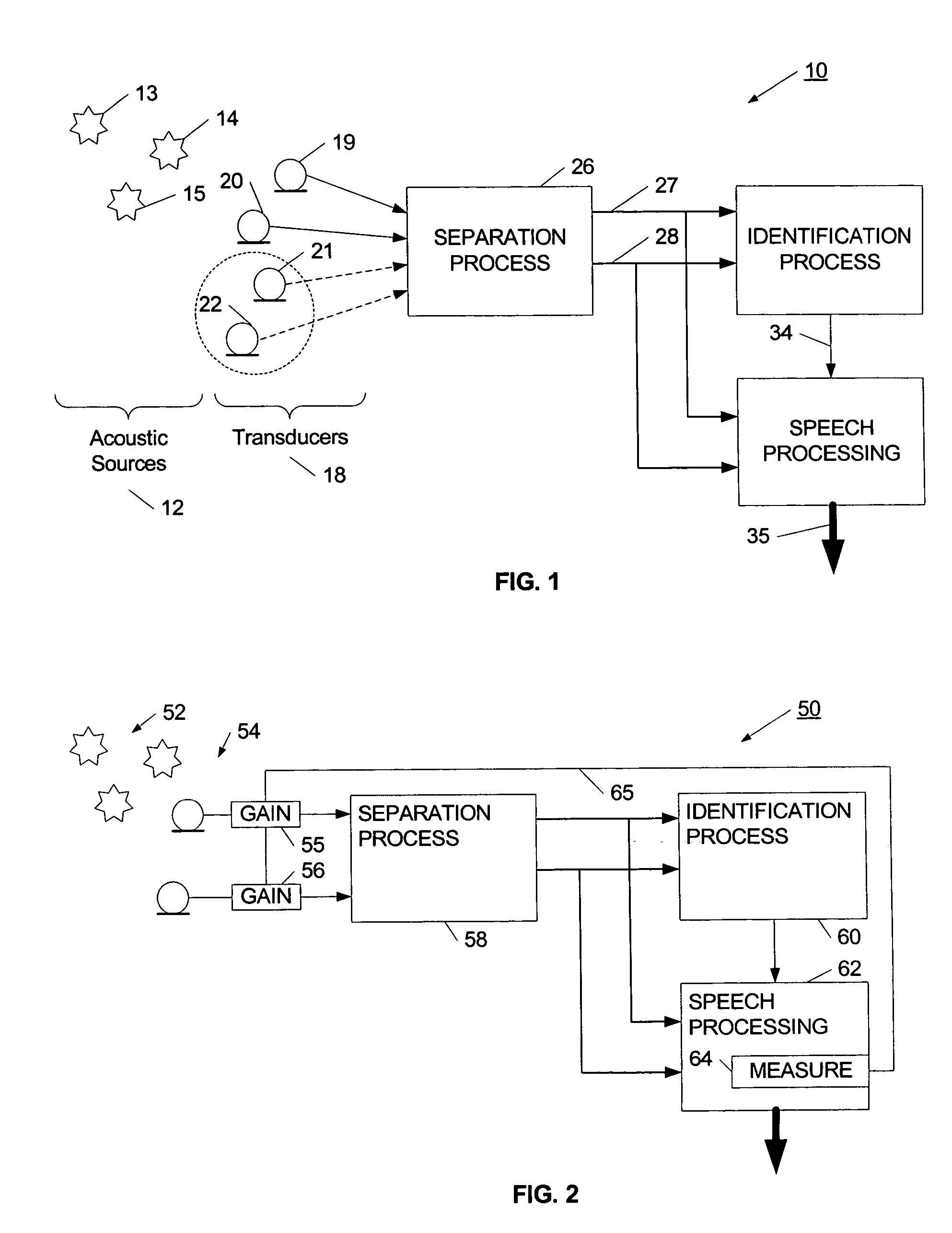
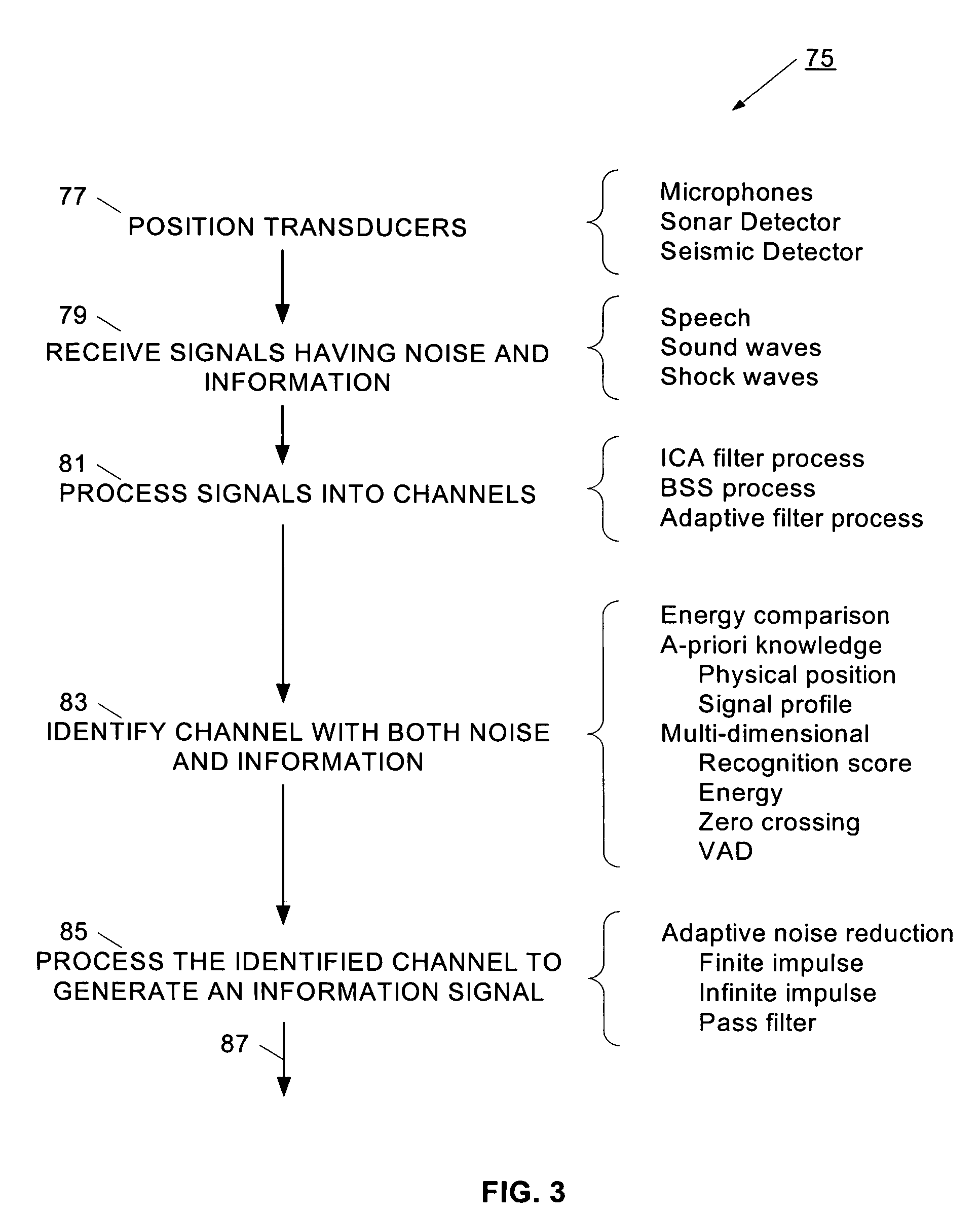
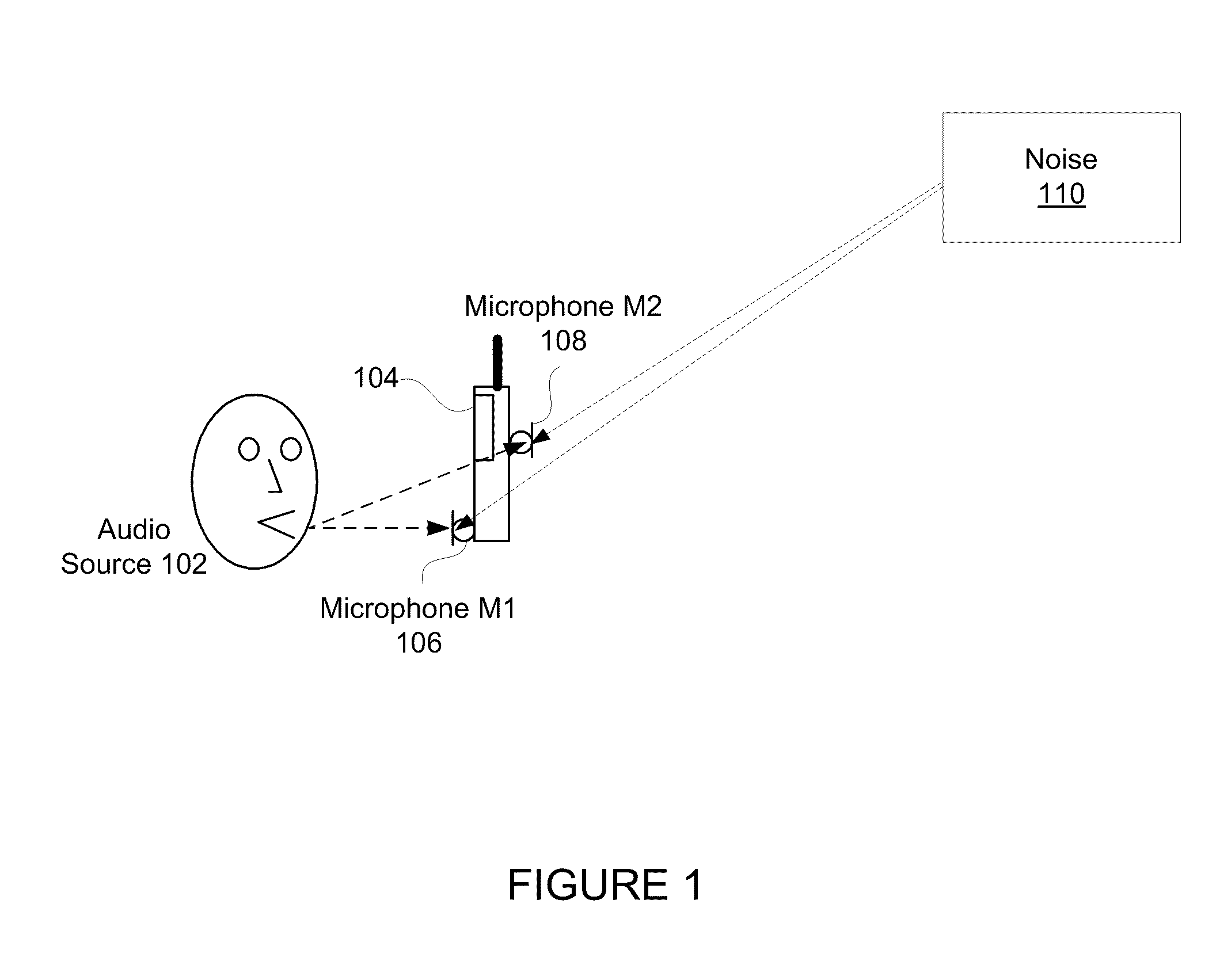
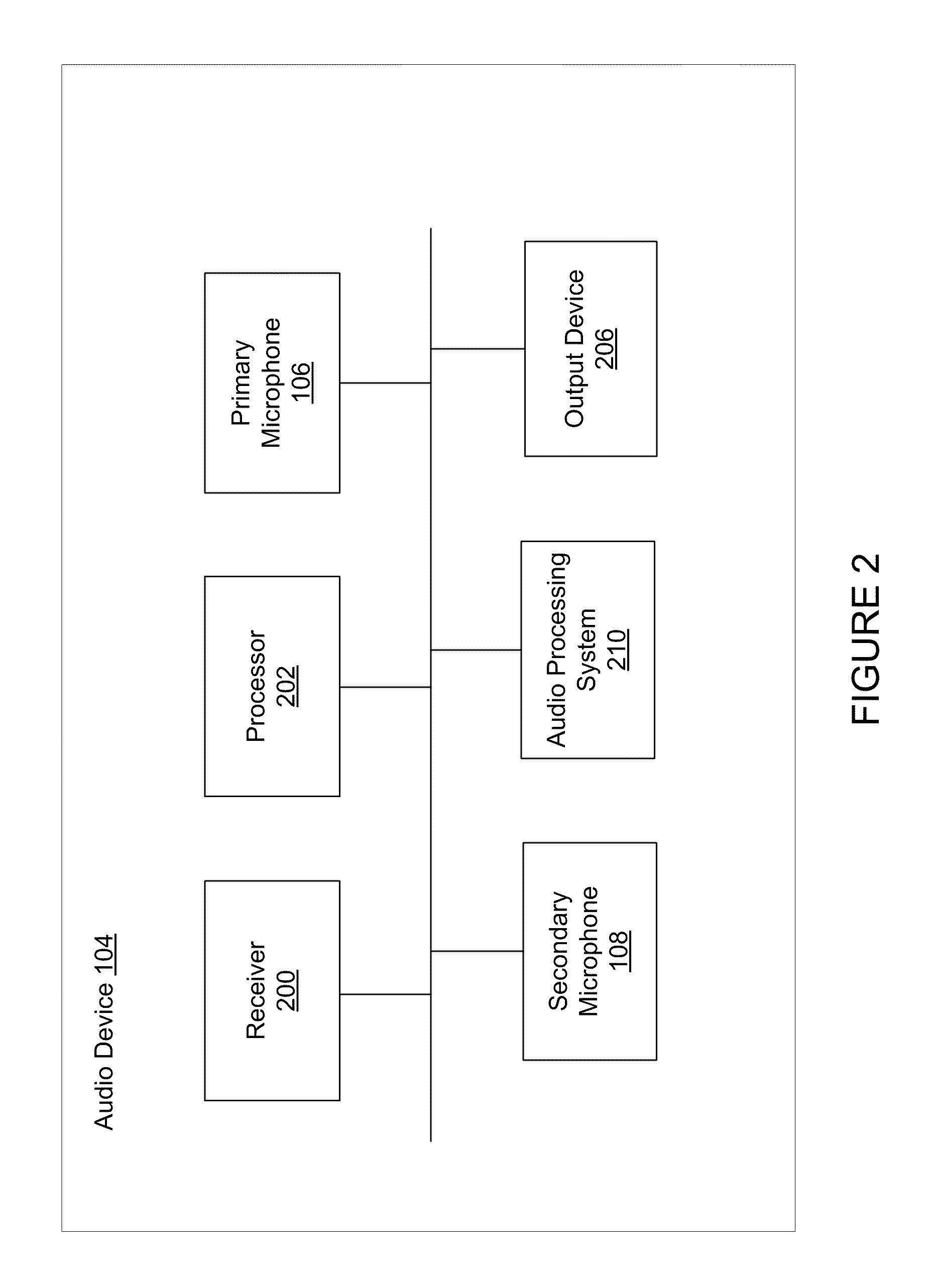
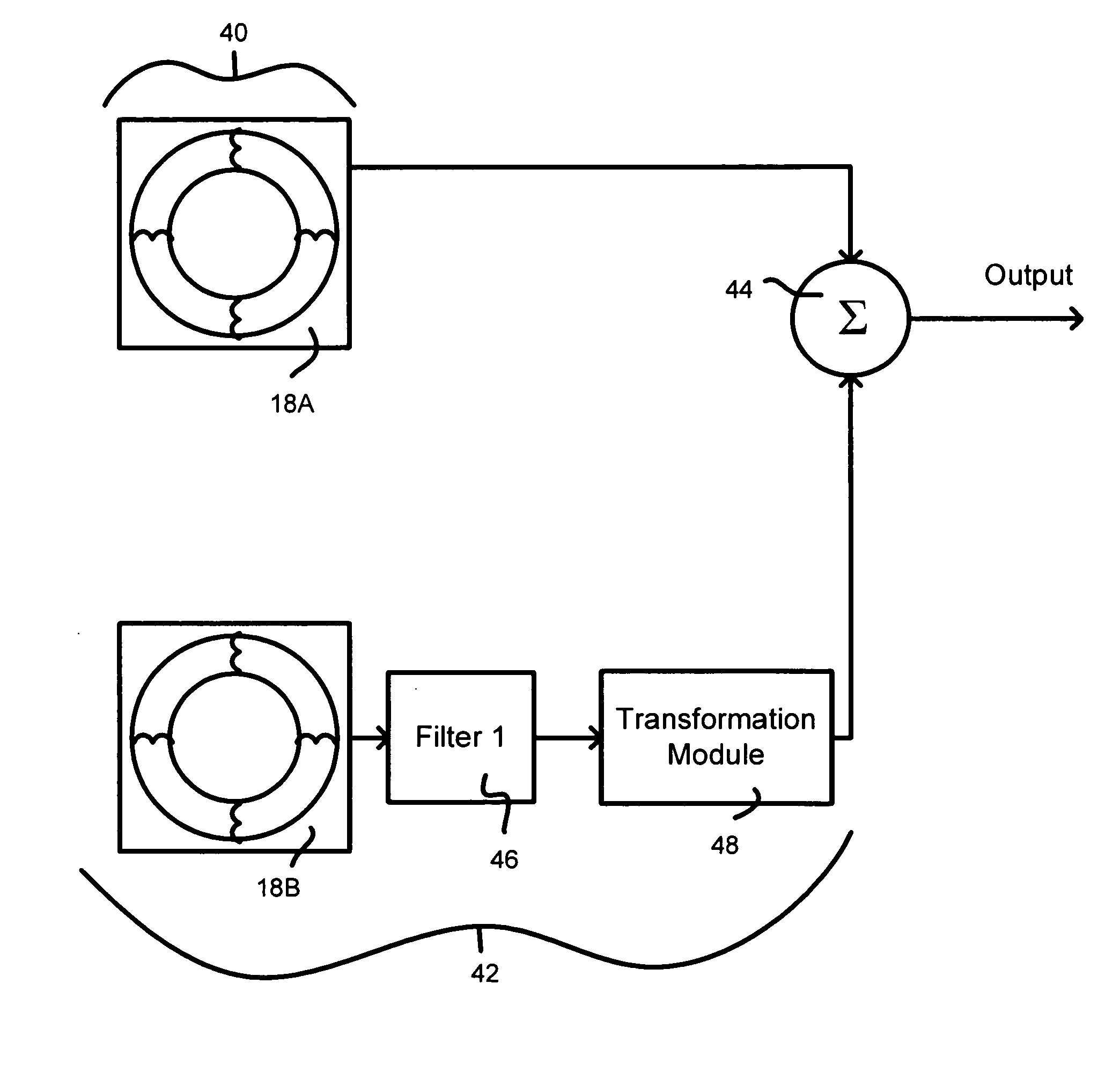
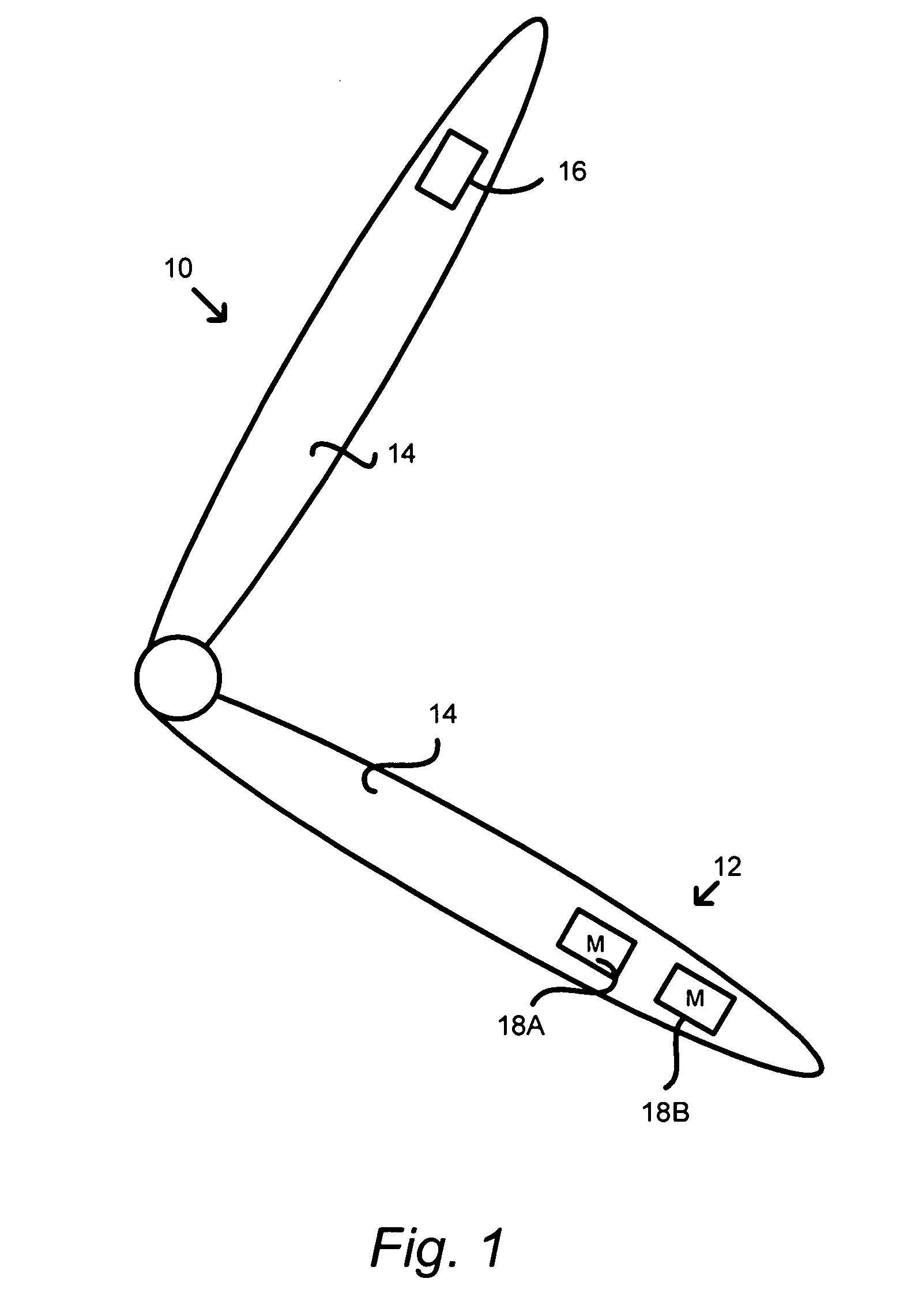
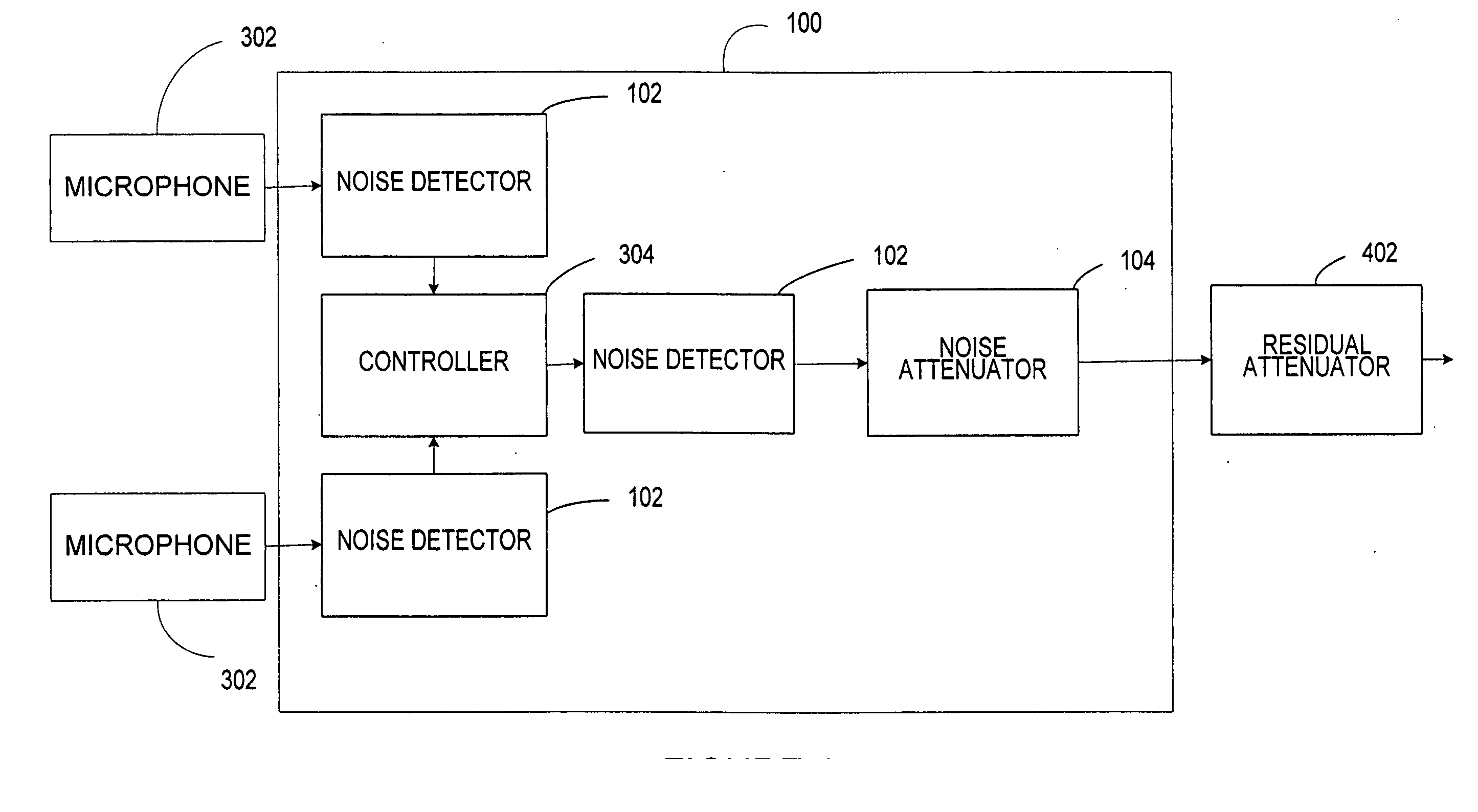
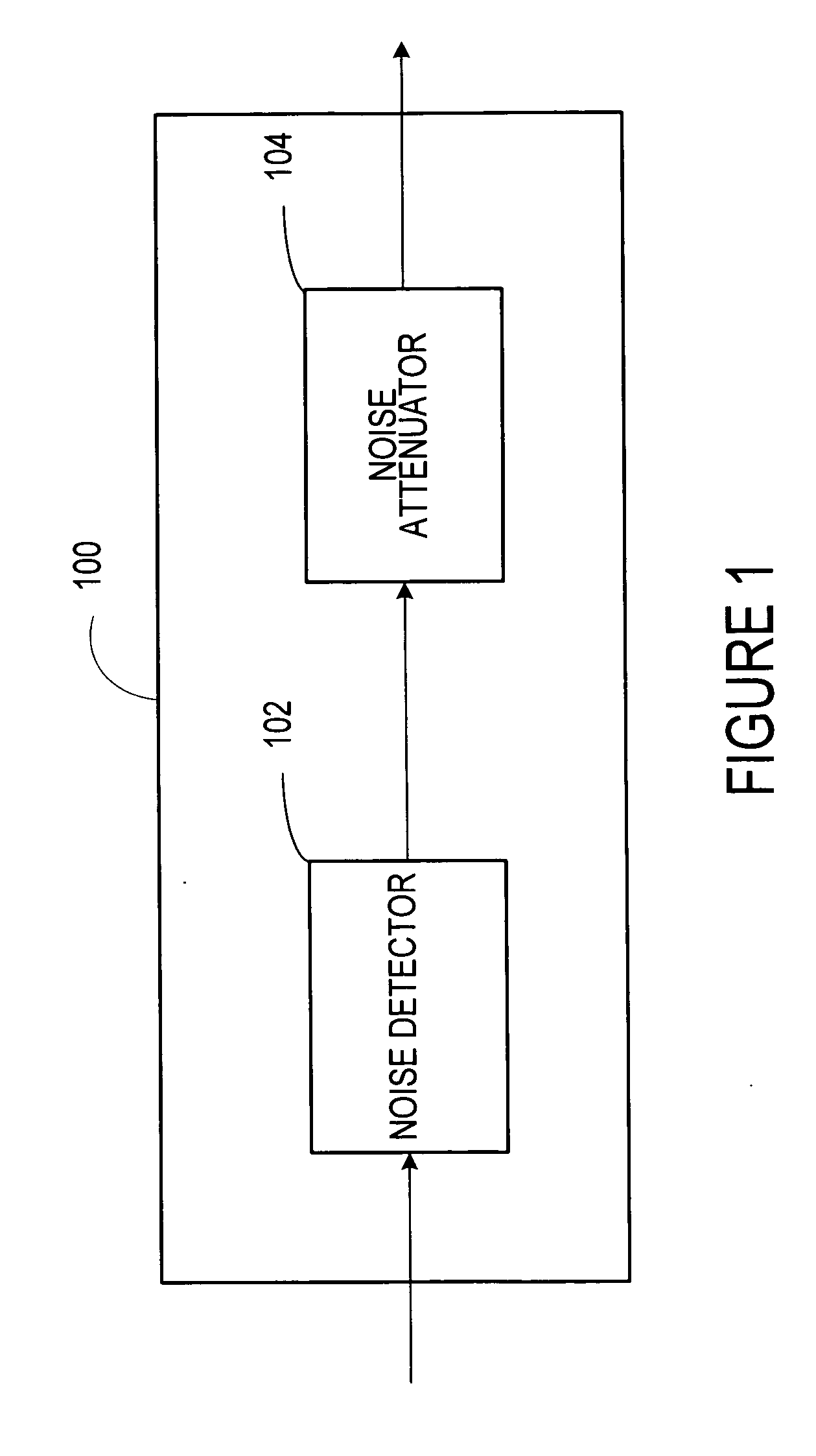
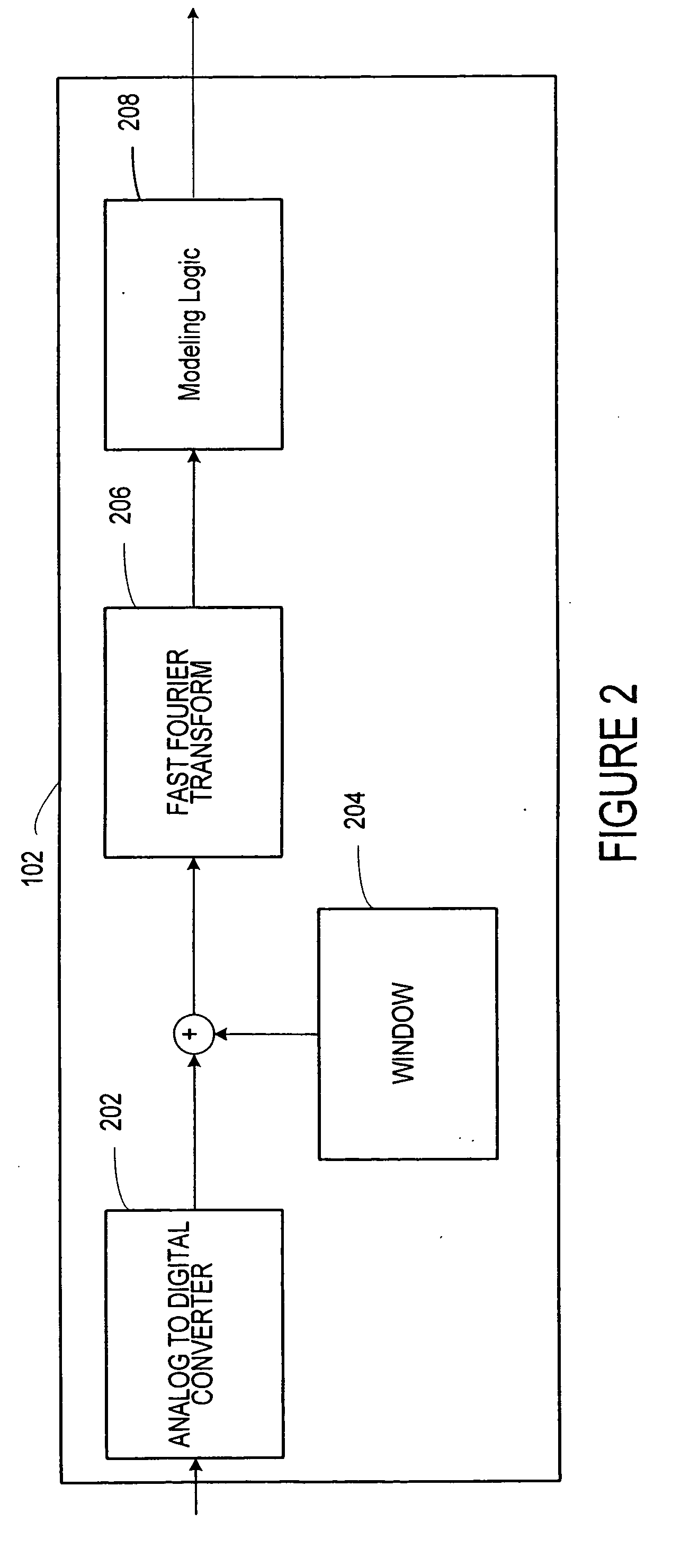
Separation of target acoustic signals in a multi-transducer arrangement
ActiveUS7099821B2Efficiently reduce or eliminate the noise componentEfficient removalTwo-way loud-speaking telephone systemsSignal processingTransducerEngineering
The present invention provides a process for separating a good quality information signal from a noisy acoustic environment. The separation process uses a set of at least two spaced-apart transducers to capture noise and information components. The transducer signals, which have both a noise and information component, are received into a separation process. The separation process generates one channel that is substantially only noise, and another channel that is a combination of noise and information. An identification process is used to identify which channel has the information component. The noise signal is then used to set process characteristics that are applied to the combination signal to efficiently reduce or eliminate the noise component. In this way, the noise is effectively removed from the combination signal to generate a good qualify information signal. The information signal may be, for example, a speech signal, a seismic signal, a sonar signal, or other acoustic signal.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +1
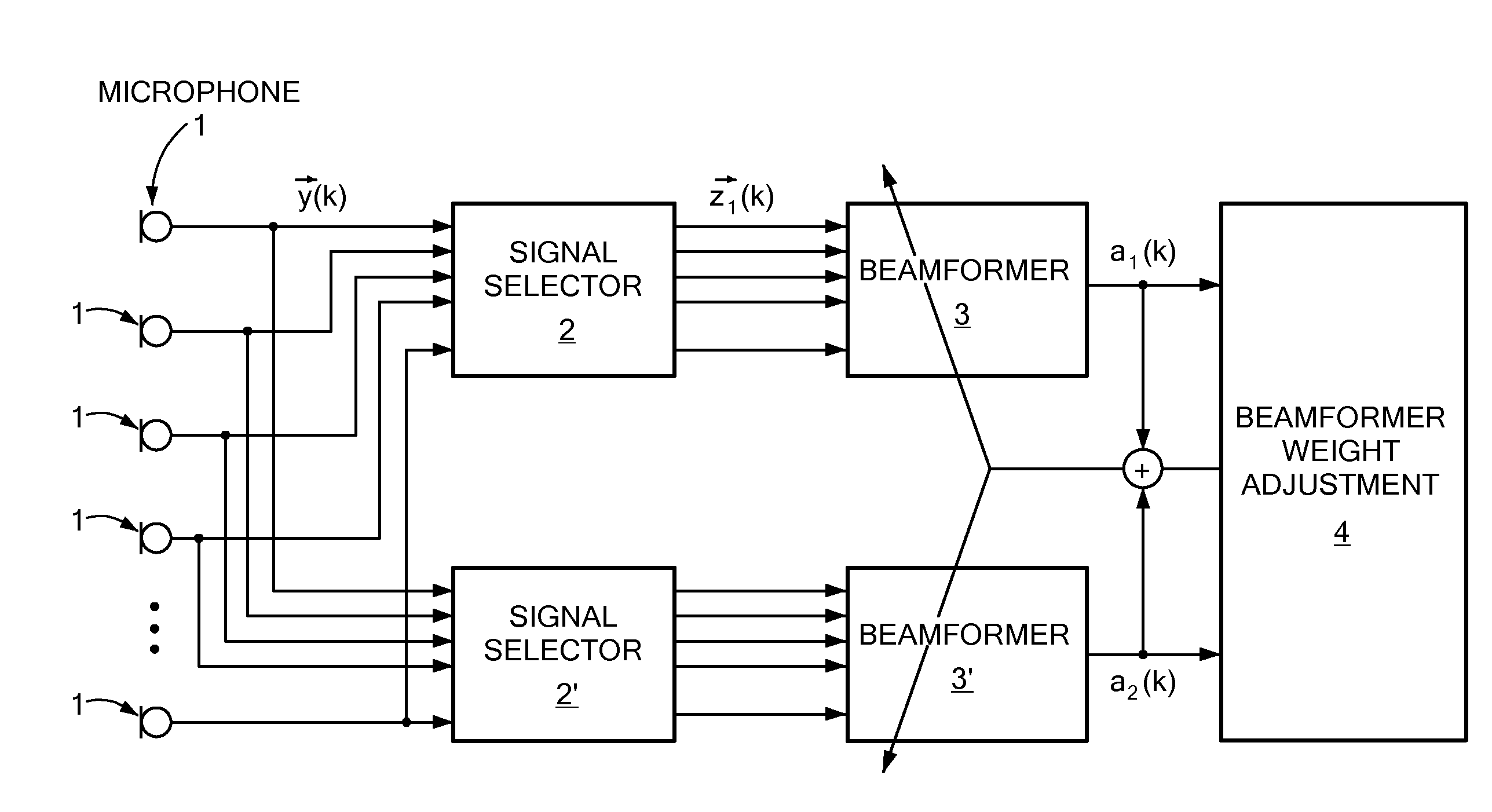
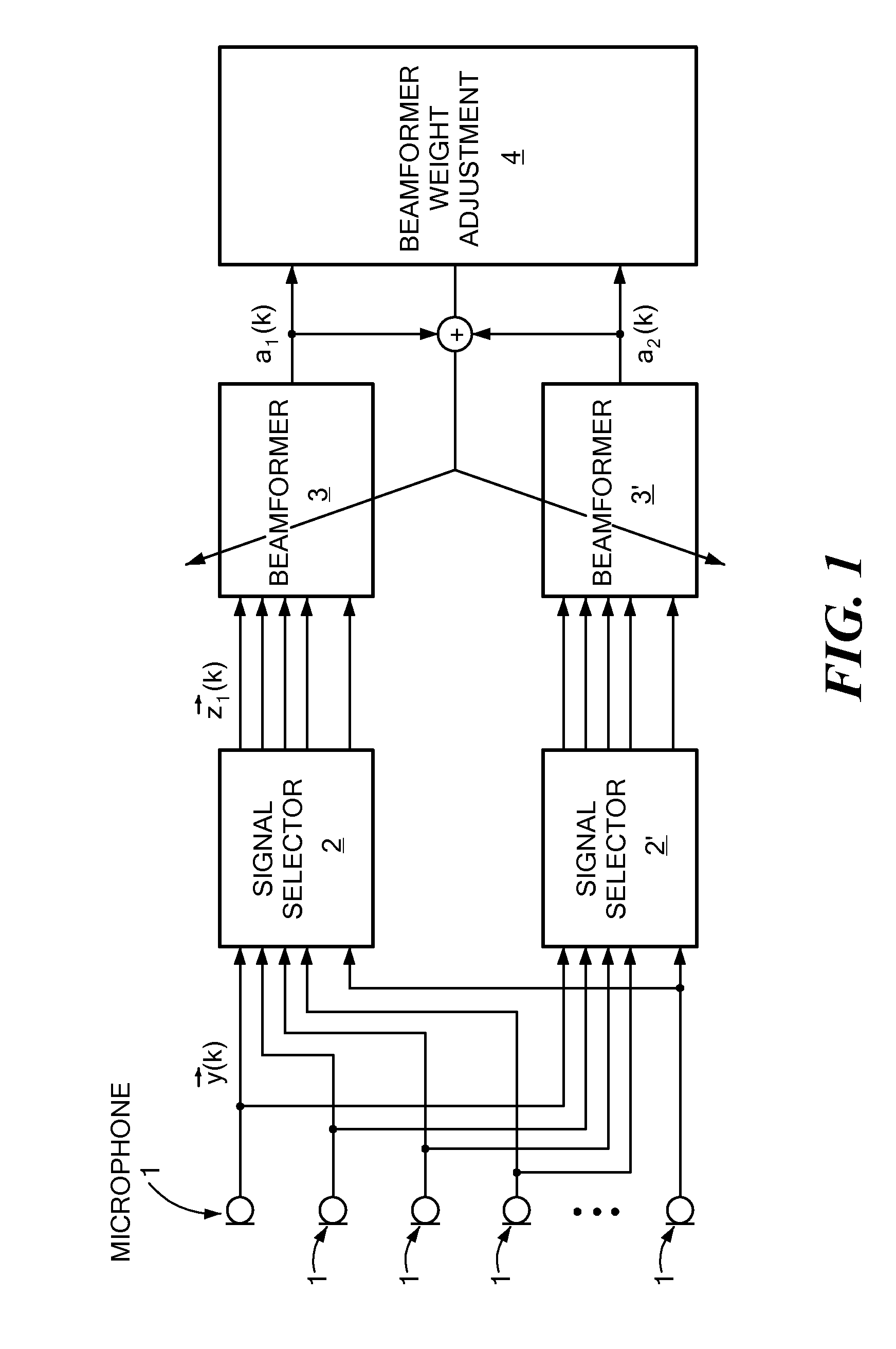
Beamforming Pre-Processing for Speaker Localization
Embodiments of the present invention relate to methods, systems, and computer program products for signal processing. A first plurality of microphone signals is obtained by a first microphone array. A second plurality of microphone signals is obtained by a second microphone array different from the first microphone array. The first plurality of microphone signals is beamformed by a first beamformer comprising beamforming weights to obtain a first beamformed signal. The second plurality of microphone signals is beamformed by a second beamformer comprising the same beamforming weights as the first beamformer to obtain a second beamformed signal. The beamforming weights are adjusted such that the power density of echo components and / or noise components present in the first and second plurality of microphone signals is substantially reduced.
Owner:NUANCE COMM INC
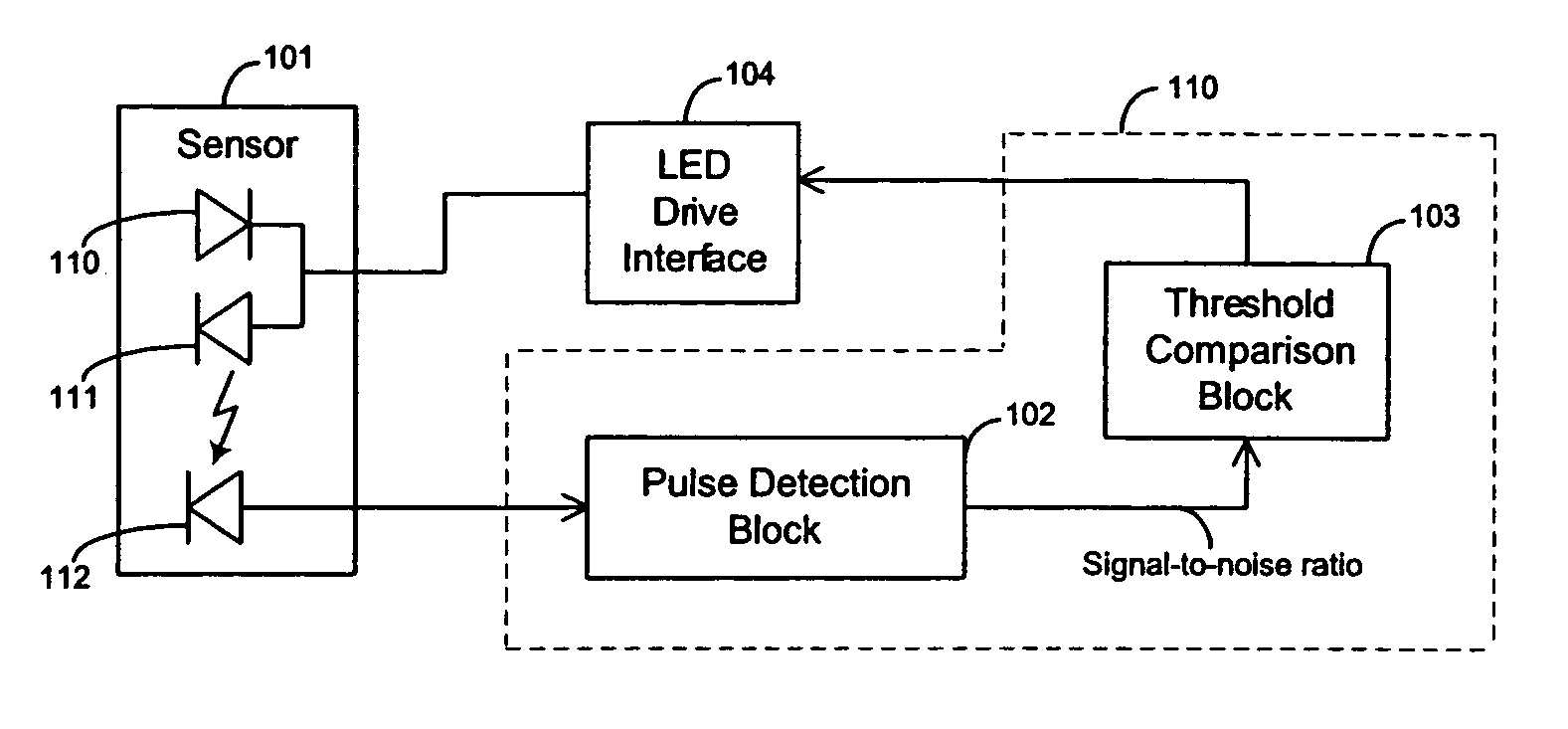
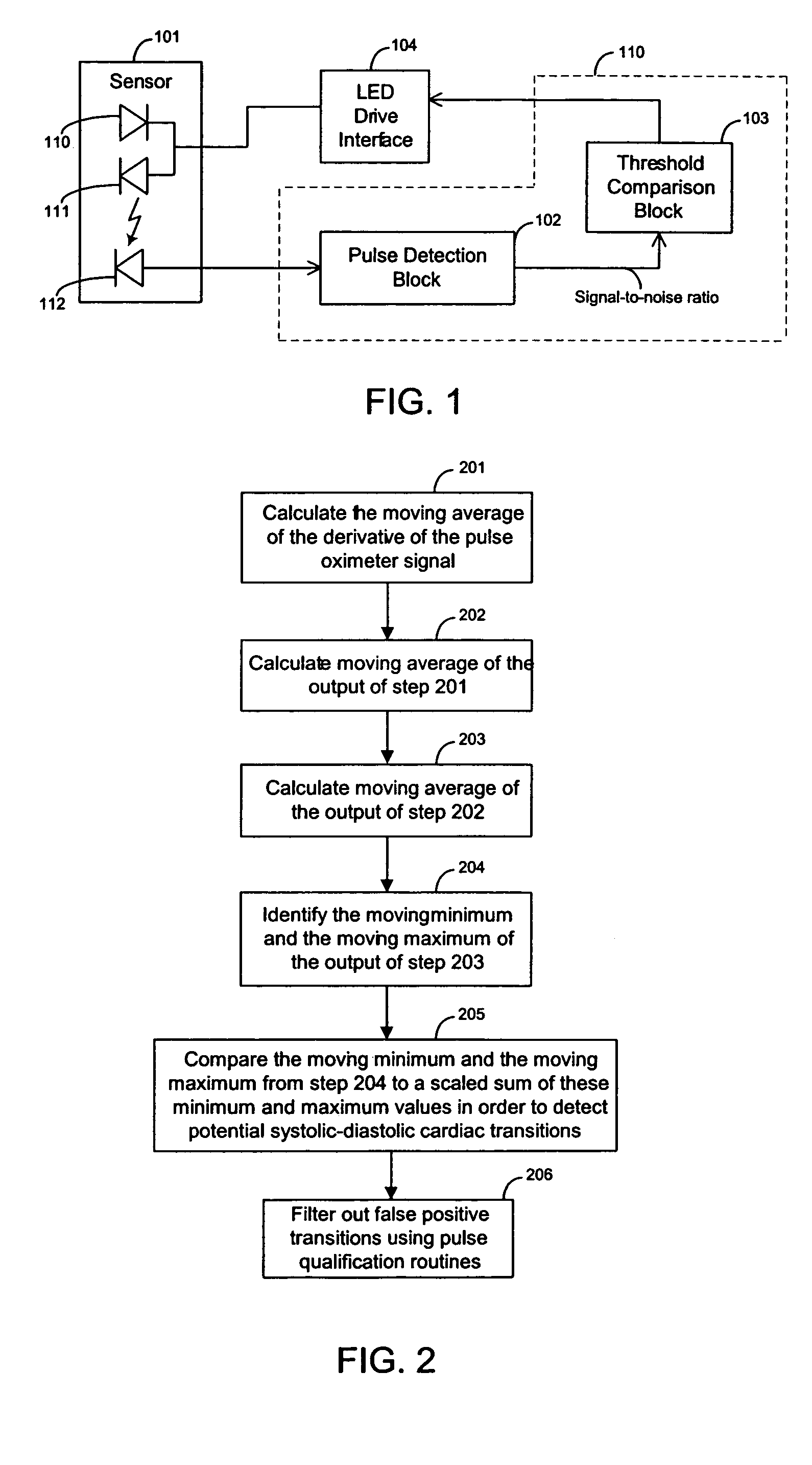
Techniques for detecting heart pulses and reducing power consumption in sensors
ActiveUS7162288B2Reduce power consumptionMaintain sufficiencySensorsMeasuring/recording heart/pulse rateDriving currentPower flow
Low power techniques for sensing cardiac pulses in a signal from a sensor are provided. A pulse detection block senses the sensor signal and determines its signal-to-noise ratio. After comparing the signal-to-noise ratio to a threshold, the drive current of light emitting elements in the sensor is dynamically adjusted to reduce power consumption while maintaining the signal-to-noise ratio at an adequate level. The signal component of the sensor signal can be measured by identifying systolic transitions. The systolic transitions are detected using a maximum and minimum derivative averaging scheme. The moving minimum and the moving maximum are compared to the scaled sum of the moving minimum and moving maximum to identify the systolic transitions. Once the signal component has been identified, the signal component is compared to a noise component to calculate the signal-to-noise ratio.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Signal processing method and device for signal-to-noise improvement
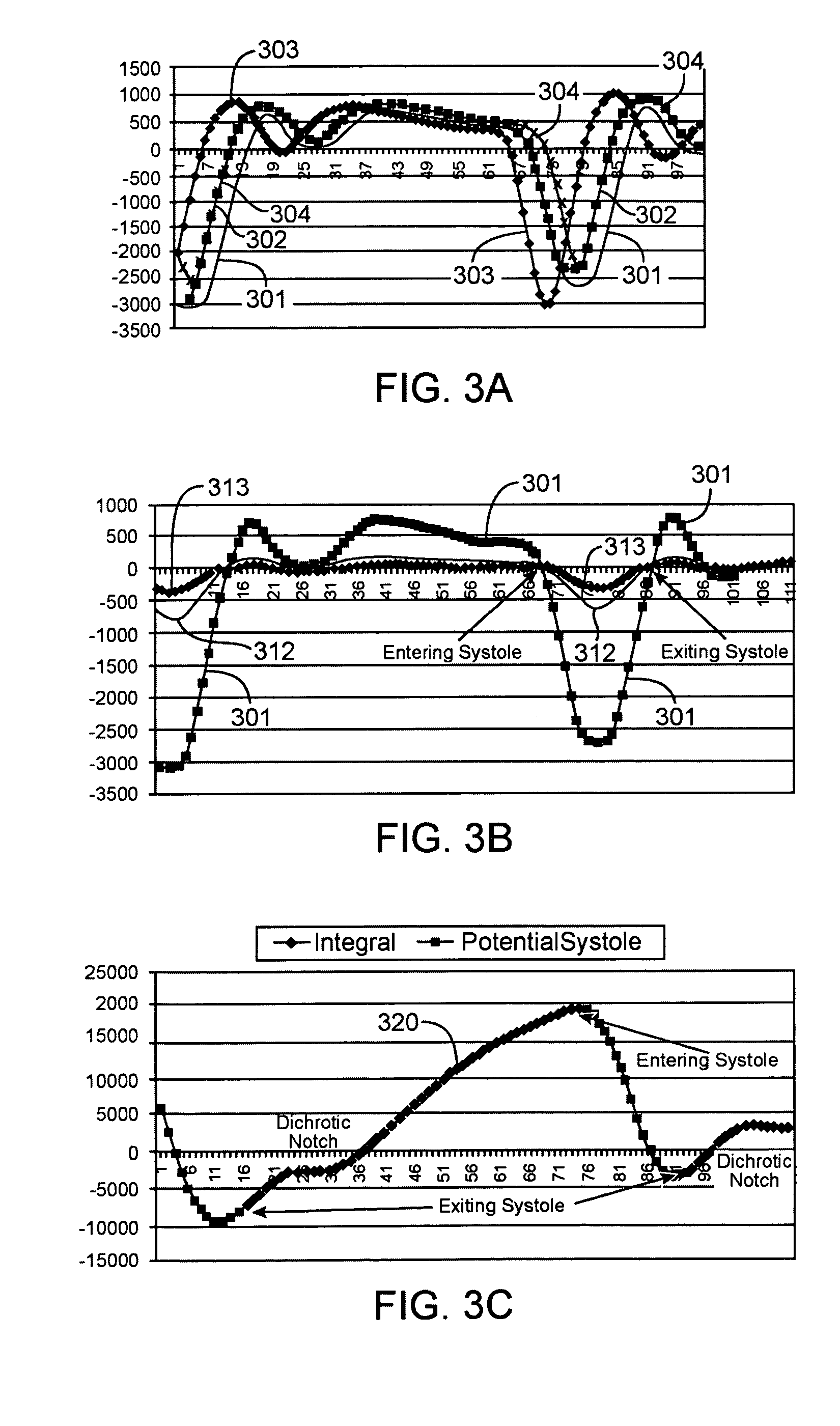
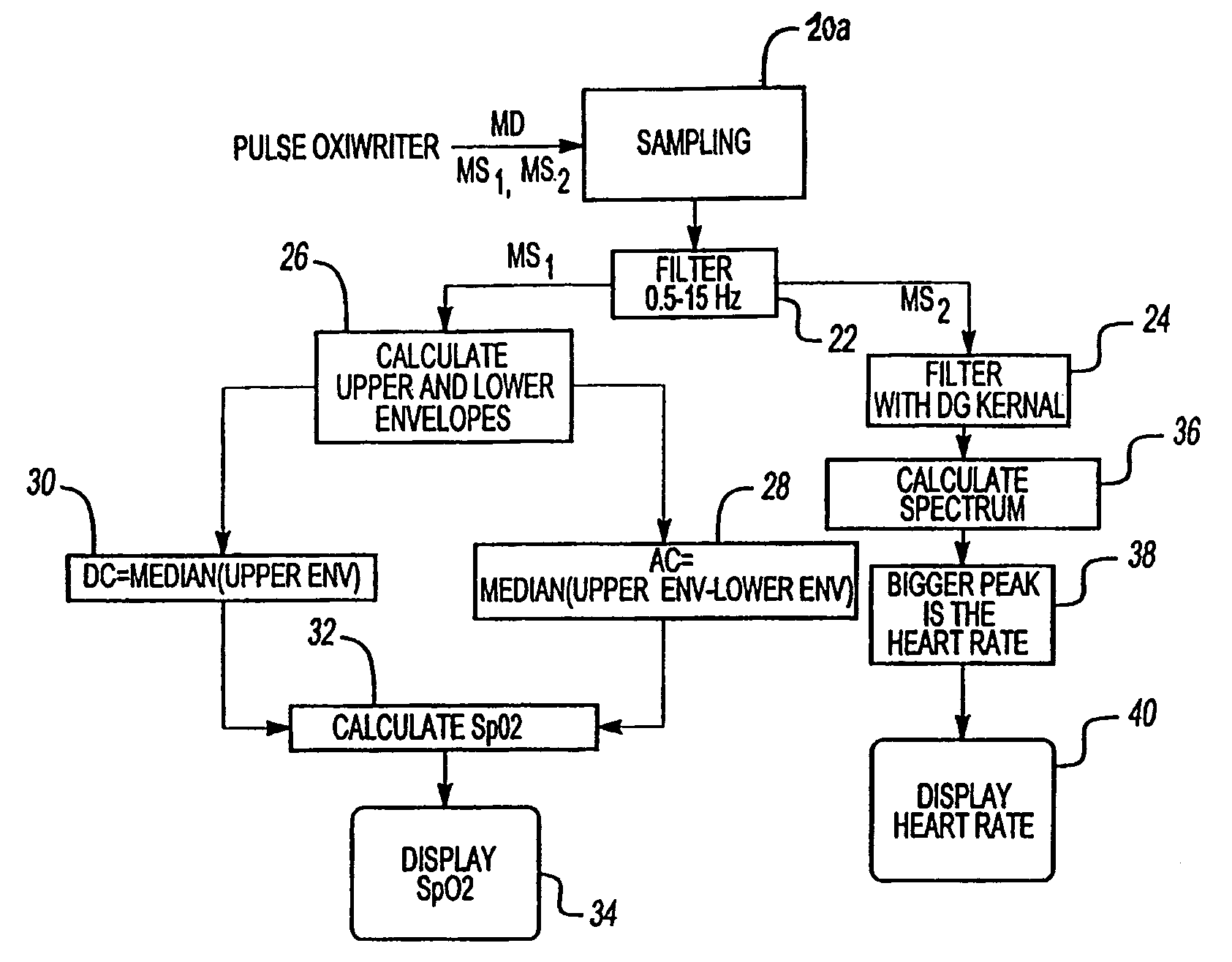
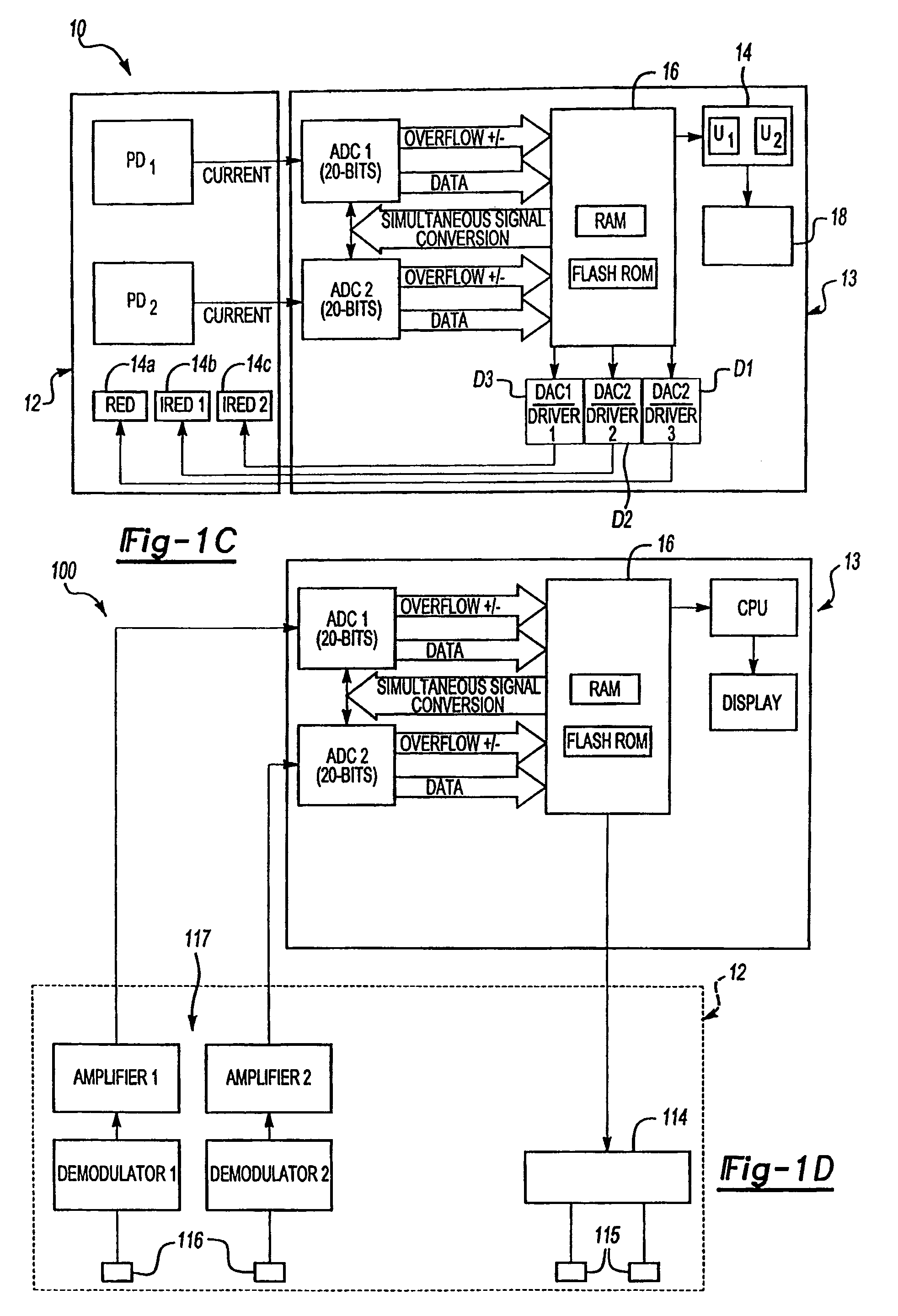
InactiveUS7027850B2Increase heightAdditional componentCatheterSensorsEngineeringSignal-to-quantization-noise ratio
A method and apparatus extract a signal component of a measured signal using one of two methods. If the signal component in the measured signal is a periodic signal with a certain well-defined peak-to-peak intensity value, upper and lower envelopes of the measured signal are determined and analyzed to extract said signal component of the measured signal. This signal component can further be used to calculate a desired parameter of the sample. The DC component of the signal is determined as the median value of the upper envelope, and the AC component is determined as the median value of the difference between the upper and lower envelopes. If the signal component of the measured signal is a periodic signal characterized by a specific asymmetric shape, a specific adaptive filtering is applied to the measured signal, resulting in the enhancement of the signal component relative to a noise component. This adaptive filtering is based on a derivative of the Gaussian Kernel having specific parameters matching the characteristics of the signal component.
Owner:CONMED CORP
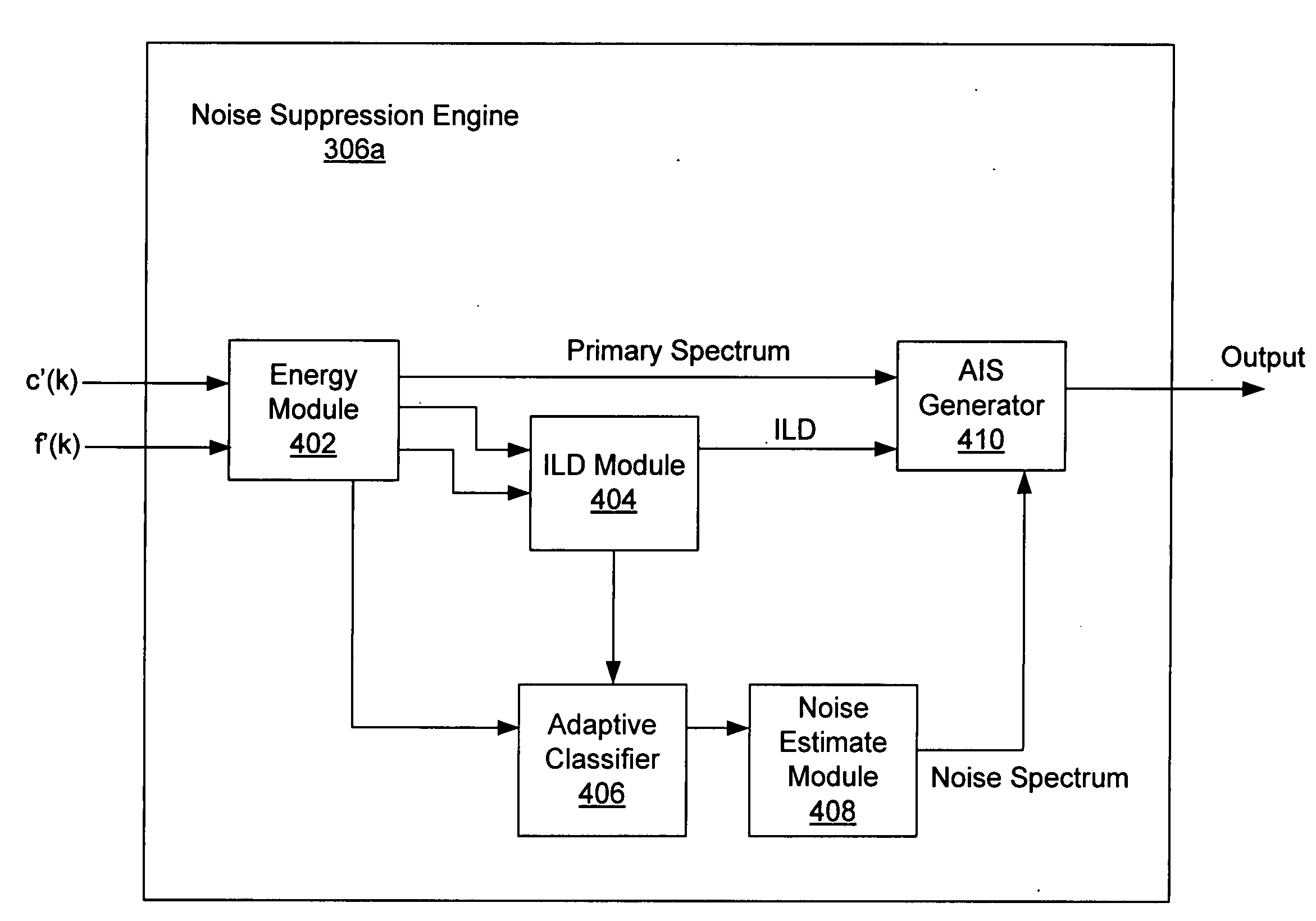
System and method for providing noise suppression utilizing null processing noise subtraction
Systems and methods for noise suppression using noise subtraction processing are provided. The noise subtraction processing comprises receiving at least a primary and a secondary acoustic signal. A desired signal component may be calculated and subtracted from the secondary acoustic signal to obtaining a noise component signal. A determination may be made of a reference energy ratio and a prediction energy ratio. A determination may be made as to whether to adjust the noise component signal based partially on the reference energy ratio and partially on the prediction energy ratio. The noise component signal may be adjusted or frozen based on the determination. The noise component signal may then be removed from the primary acoustic signal to generate a noise subtracted signal which may be outputted.
Owner:KNOWLES ELECTRONICS INC
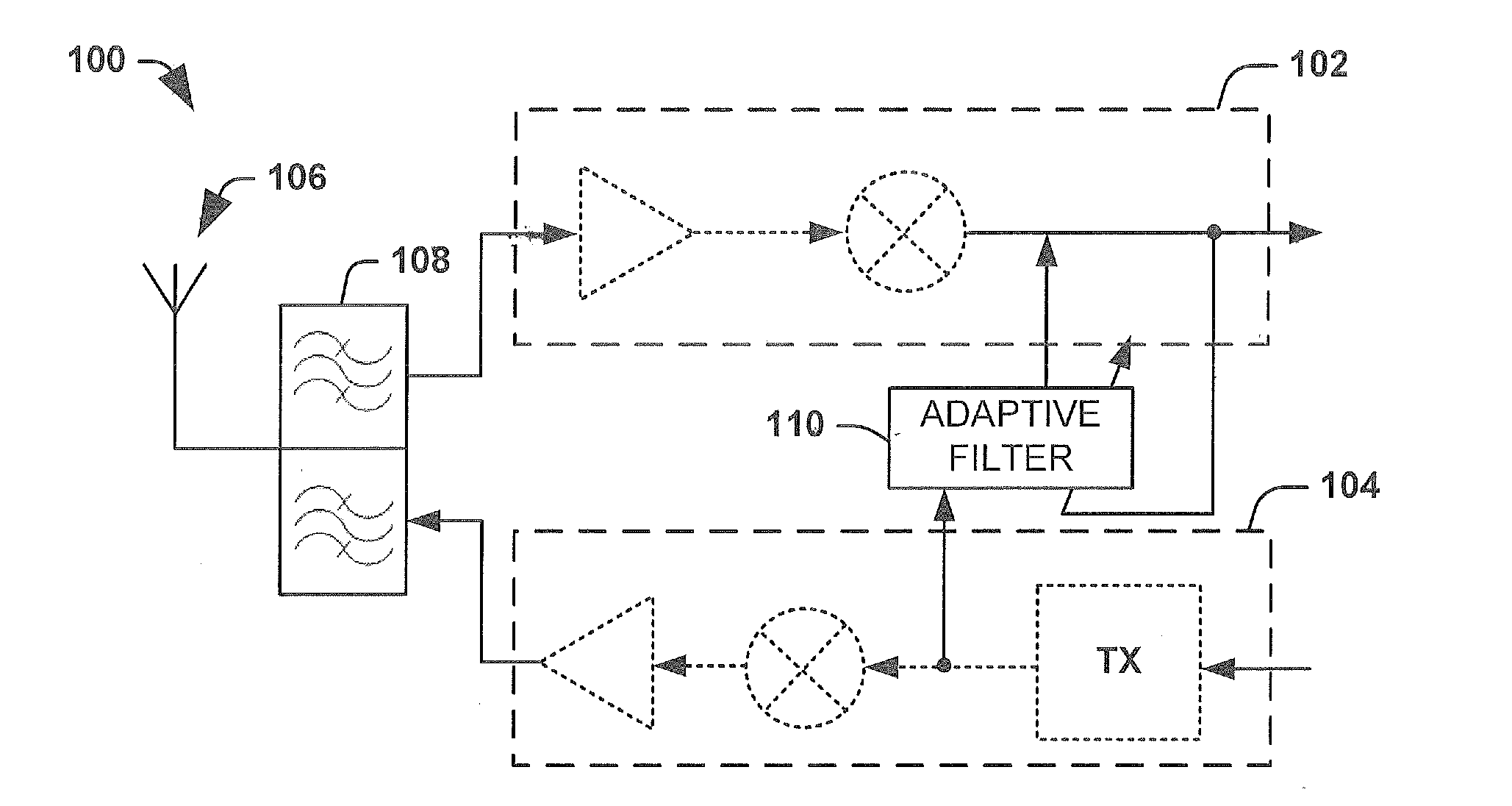
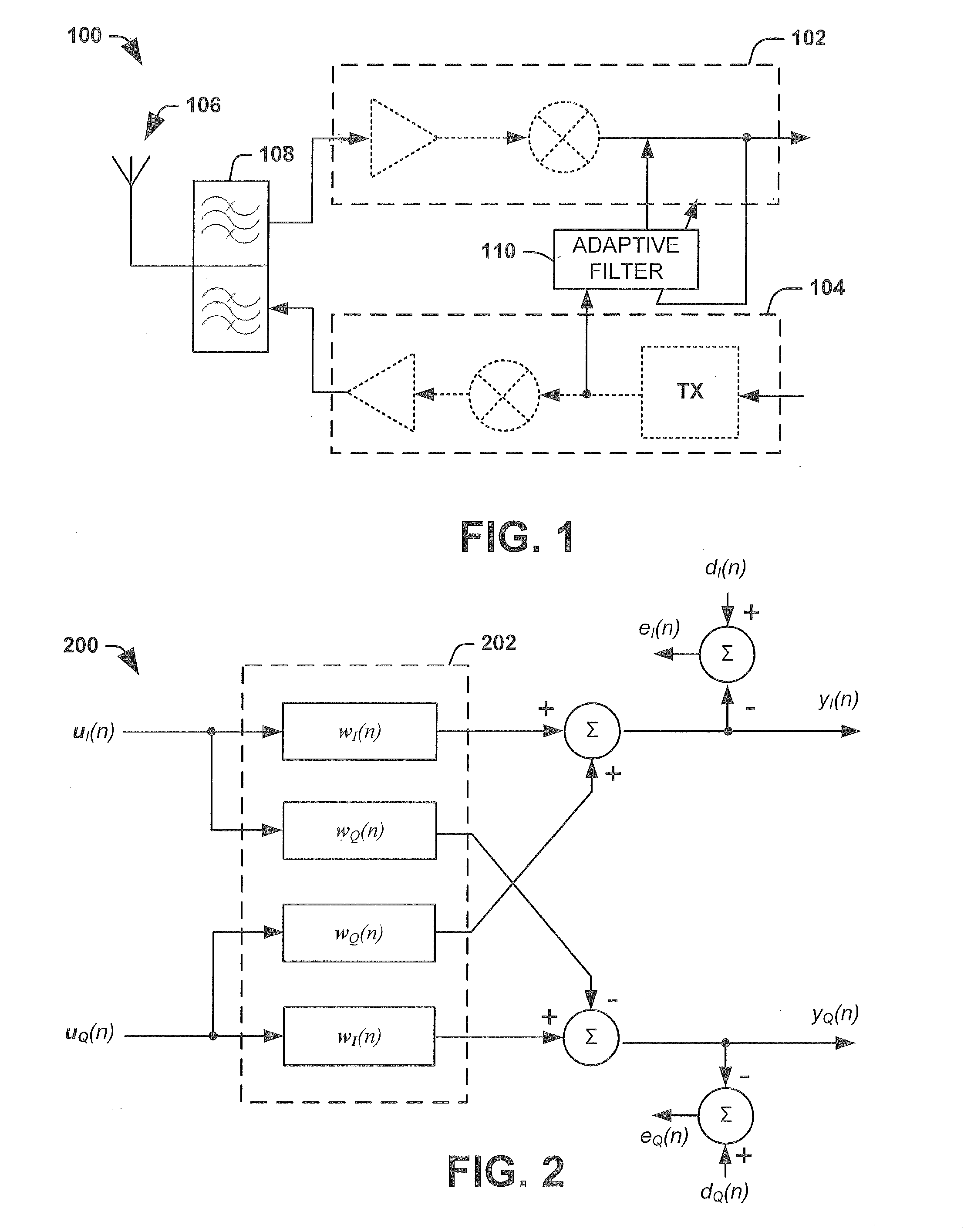
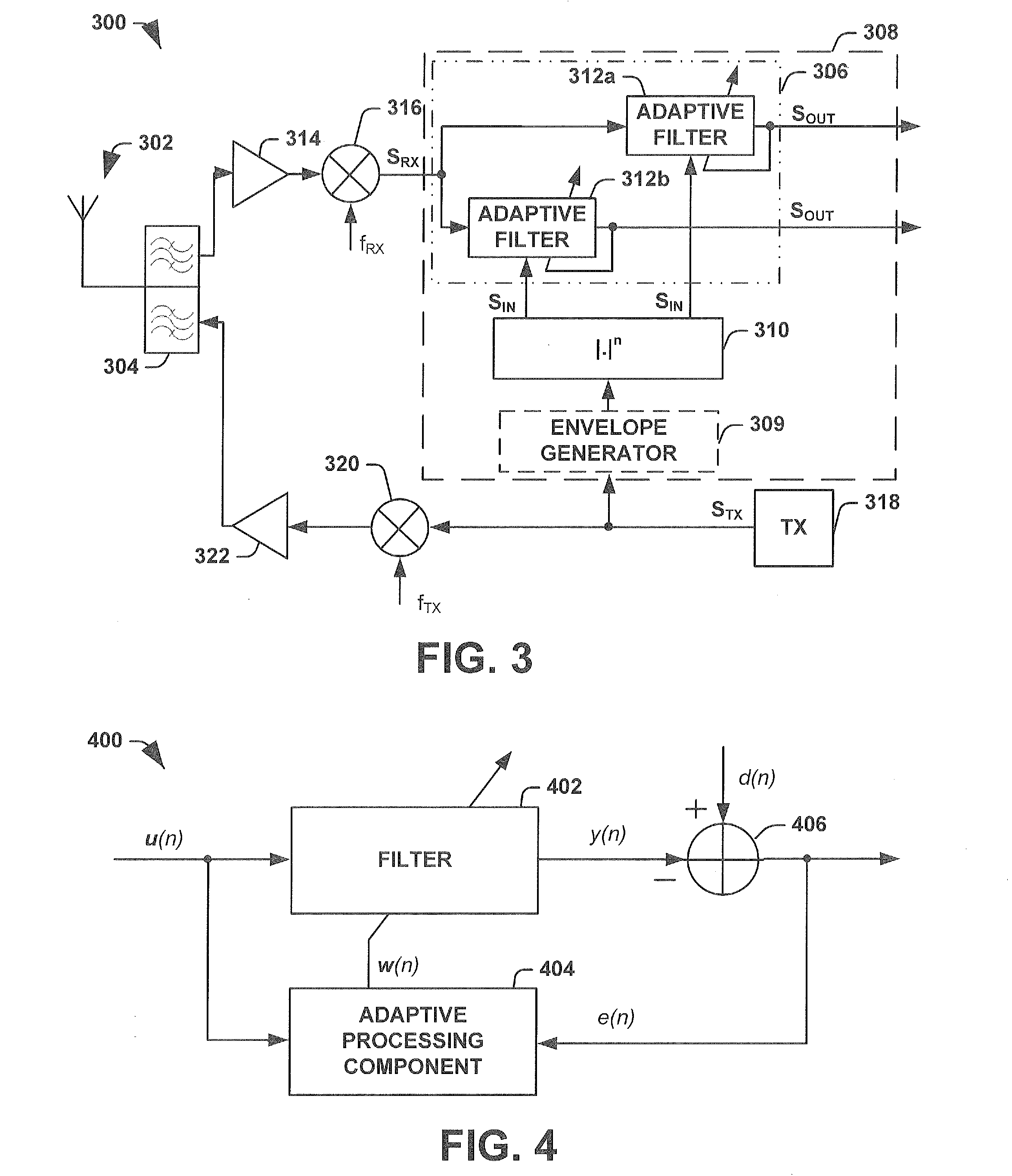
Simplified adaptive filter algorithm for the cancellation of tx-induced even order intermodulation products
InactiveUS20120140685A1Modulated-carrier systemsLine-transmissionAdaptive filtering algorithmAdaptive filter
One embodiment of the present invention relates to an adaptive filtering apparatus comprising first and second real valued adaptive filters, respectively configured to receive an adaptive filter input signal based upon a transmission signal in a transmission path. The first real valued adaptive filter is configured to operate a real valued adaptive filter algorithm on the input signal to estimate a first intermodulation noise component (e.g., an in-phase component) in a desired signal and to cancel the estimated noise. The second real valued adaptive filter is configured to operate a real valued adaptive filter algorithm on the input signal to estimate a second intermodulation noise component (e.g., a quadrature phase component) in the desired signal and to cancel the estimated noise. Accordingly, each filter operates a real valued adaptive algorithm to cancel a noise component, thereby removing complex cross terms between the components from the adaptive filtering process.
Owner:INTEL CORP
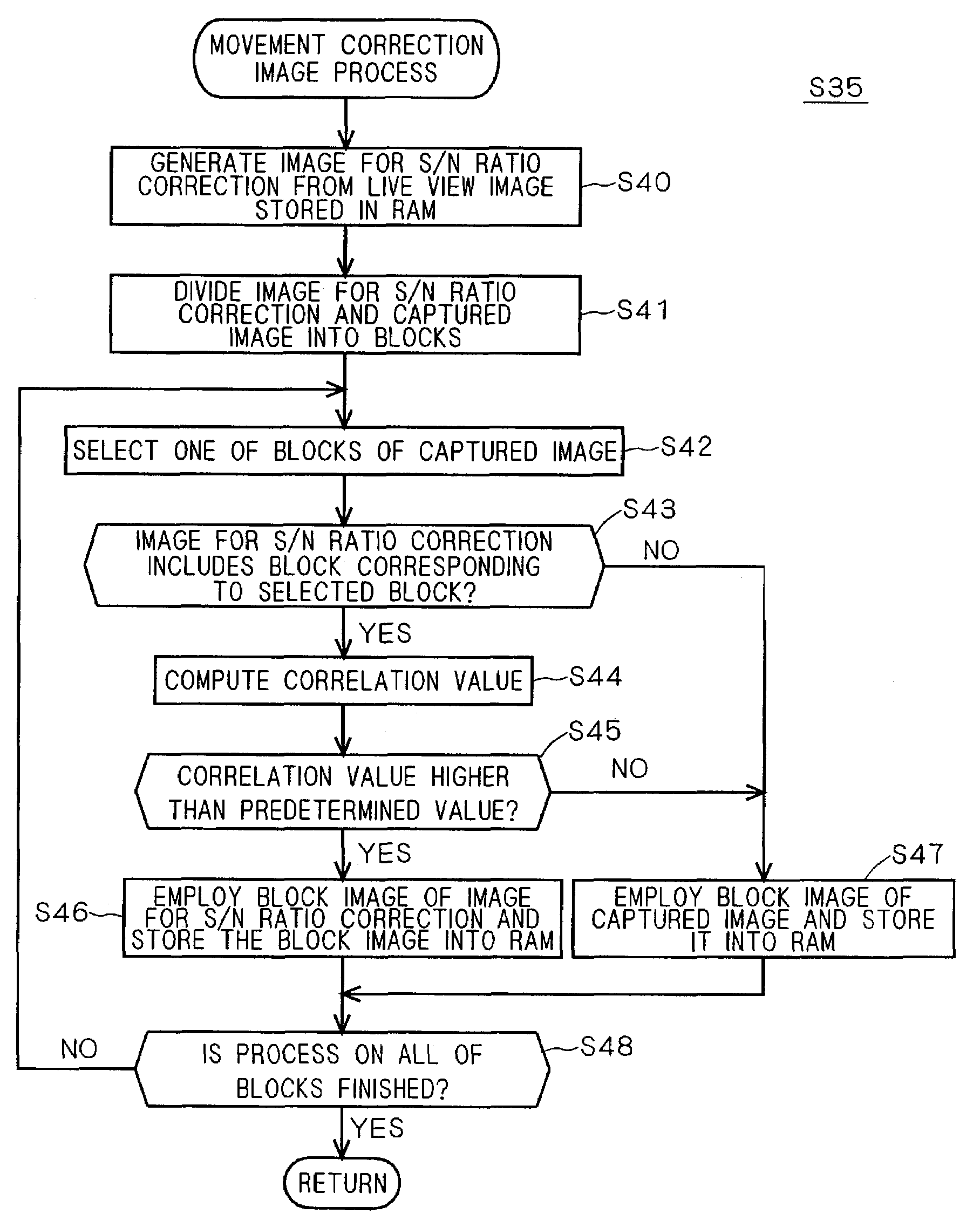
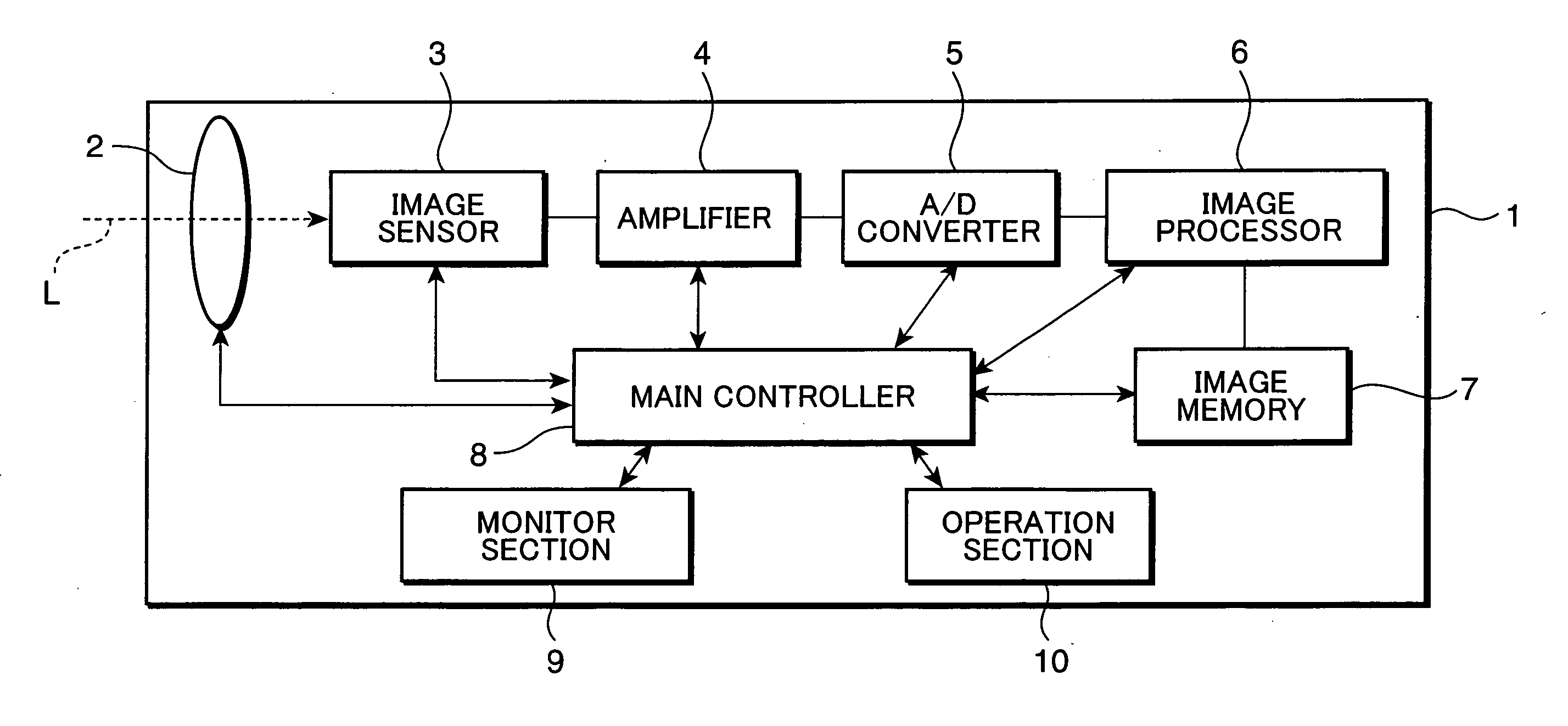
Image processing apparatus and method
InactiveUS7239342B2Solve the low matching degreeReduce time differenceTelevision system detailsPrintersImaging processingComputer science
An object of the present invention is to generate an image which is prevented from being influenced by a movement while suppressing increase in noise components. When a movement is detected during exposure of an image capturing device to light, an image capturing apparatus stops the exposure of the image capturing device and amplifies an image signal obtained with the exposure, thereby compensating exposure shortage. Luminance information is extracted from a captured image, and color information is extracted from a live view image obtained at a timing different from a timing at which the captured image is obtained. By synthesizing the luminance information of the captured image and the color information of the live view image, noise components included in color information are reduced.
Owner:MINOLTA CO LTD
Interference and noise estimation in an OFDM system
ActiveUS20050002324A1Quantity minimizationQuality improvementError detection/prevention using signal quality detectorTransmission monitoringMultiuser systemCarrier signal
Noise and interference can be independently measured in a multiple user Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM) system. Co-channel interference is measured in a frequency hopping, multiple user, OFDM system by tracking the sub-carriers assigned to all users in a particular service area or cell. The composite noise plus interference can be determined by measuring the amount of received power in a sub-carrier whenever it is not assigned to any user in the cell. A value is stored for each sub-carrier in the system and the value of noise plus interference can be a weighted average of the present value with previously stored values. The noise component can be independently determined in a synchronous system. In the synchronous system, all users in a system may periodically be prohibited from broadcasting over a sub-carrier and the received power in the sub-carrier measured during the period having no broadcasts.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Highly linear receiver front-end with thermal and phase noise cancellation
InactiveUS9148186B1Error preventionDc level restoring means or bias distort correctionPhase noiseRadio reception
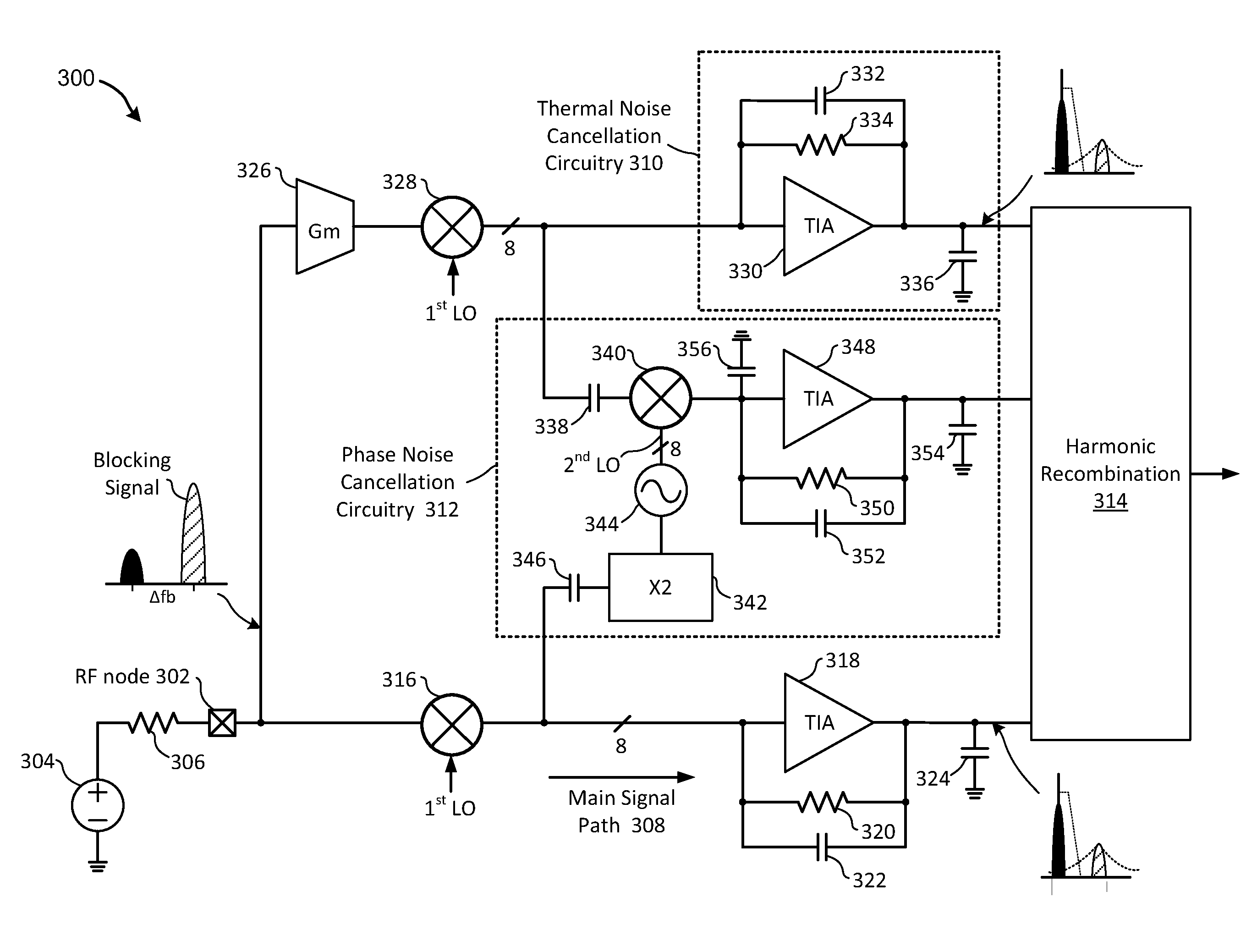
A radio receiver supporting cancellation of thermal and phase noise in a down-converted RF signal. An inbound RF signal and blocking signal are provided directly to a passive mixer for down-conversion into a first baseband signal having data, thermal noise, and reciprocal mixing (RM) noise components. The inbound signals are also provided to a transconductance circuit, the output of which is provided to a second passive mixer for conversion into a current signal having data and blocking signal components, and a RM image. The blocking signal component and the RM image are mixed with a second LO signal, derived from the blocking signal, to produce a RM noise cancellation signal. The data component of the current signal is converted into a second baseband signal having data and thermal noise components. The first baseband signal, second baseband signal and RM noise cancellation signal are then combined through harmonic recombination.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Noise suppressing device, mobile phone and noise suppressing method
InactiveCN101661753APrevent sound quality degradationSpeech analysisTelephone set constructionsEngineeringNoise component
A noise suppressing device receives sound signals through a plurality of sound-receiving units and suppresses noise components included in the input sound signals. The noise suppressing device includes a detecting unit which detects a usage pattern of the noise suppressing device from a plurality of usage patterns in which positional relationships of the plurality of sound-receiving units and / or positional relationships between the plurality of sound-receiving units and a target sound source are different from each other, a converting unit which converts using environment information used in anoise suppressing process to each of the sound signals inputted by the plurality of sound-receiving units into using environment information in accordance with a usage pattern detected by the detecting unit and a suppressing unit which performs the noise suppressing process using the using environment information converted by the converting unit to the sound signals.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
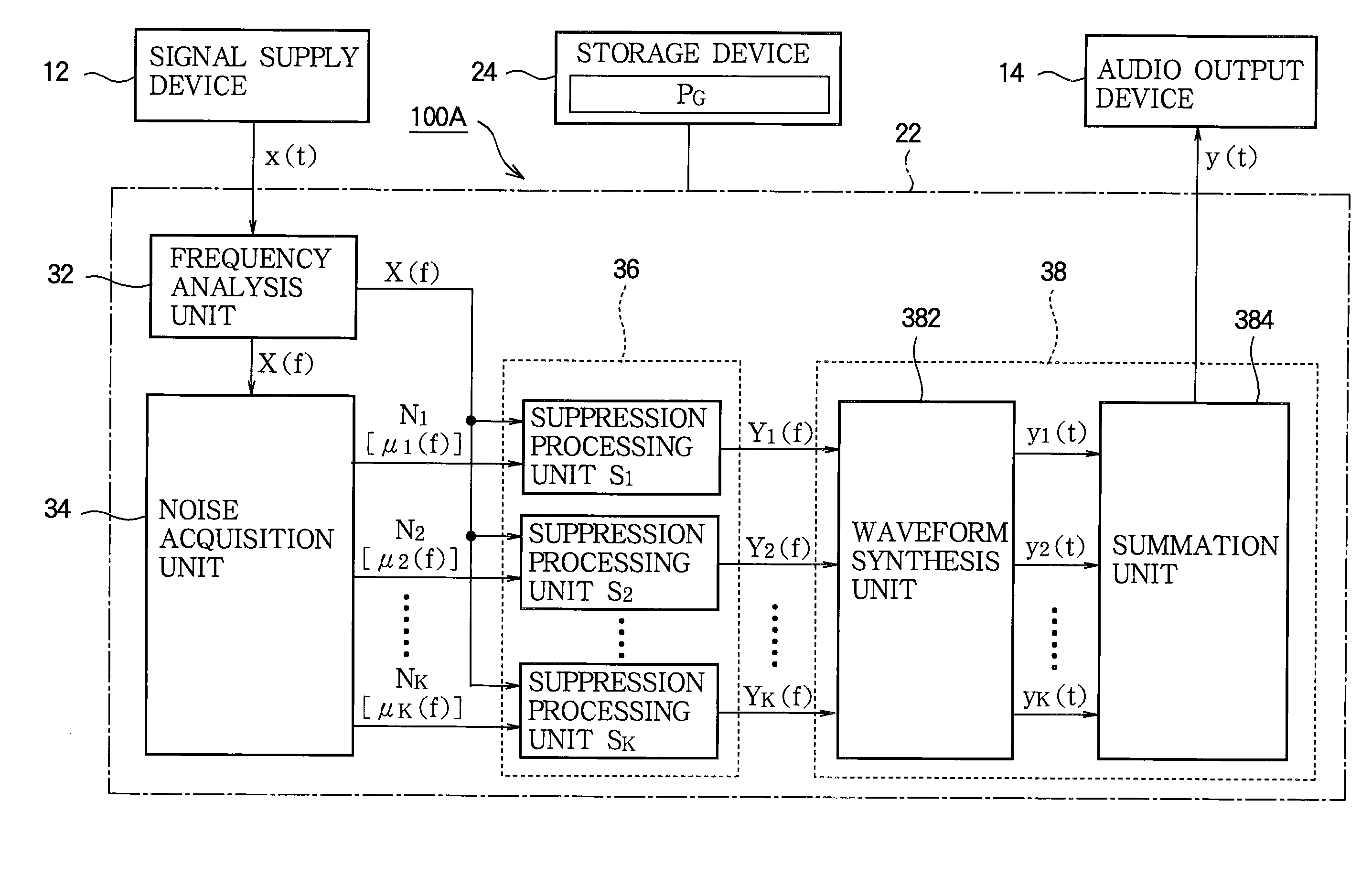
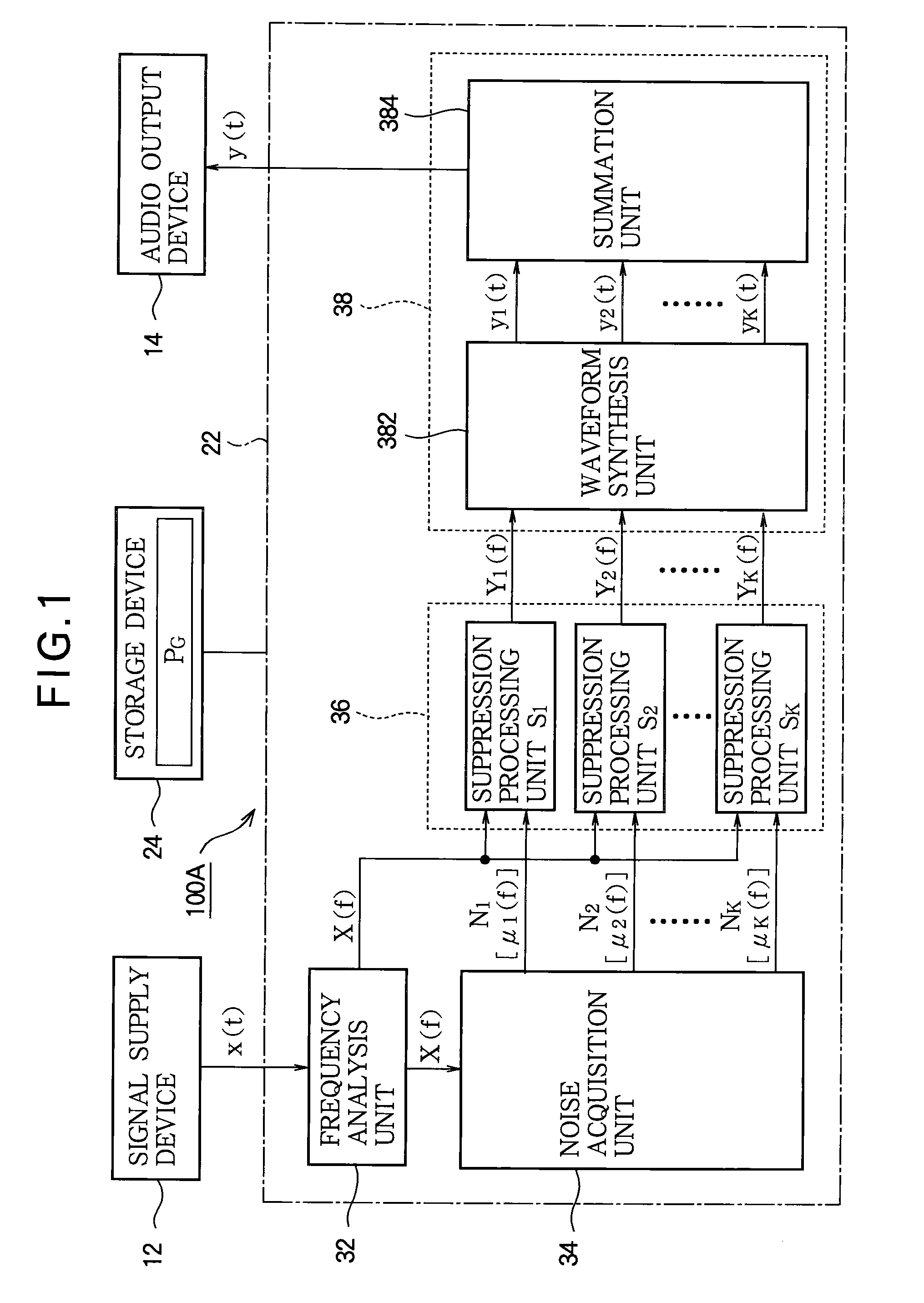
Noise suppressing device
InactiveUS20110170707A1Additional componentGood effectSpeech analysisTransmission noise suppressionEngineeringNoise suppression
A noise suppressing device is provided for suppressing noise of a first audio signal to generate a second audio signal. In the noise suppressing device, a noise acquisition unit acquires a plurality of noise components which are different from each other. A noise suppression unit generates each suppression component by suppressing each noise component from the first audio signal, thereby providing a plurality of suppression components different from each other in correspondence to the plurality of the noise components. A signal generation unit generates the second audio signal by summing the plurality of the suppression components that are provided from the noise suppression unit.
Owner:YAMAHA CORP
Image processing apparatus, image processing method, and image processing program
ActiveUS20060257047A1Quality improvementGood removal effectCharacter and pattern recognitionFace detectionImaging processing
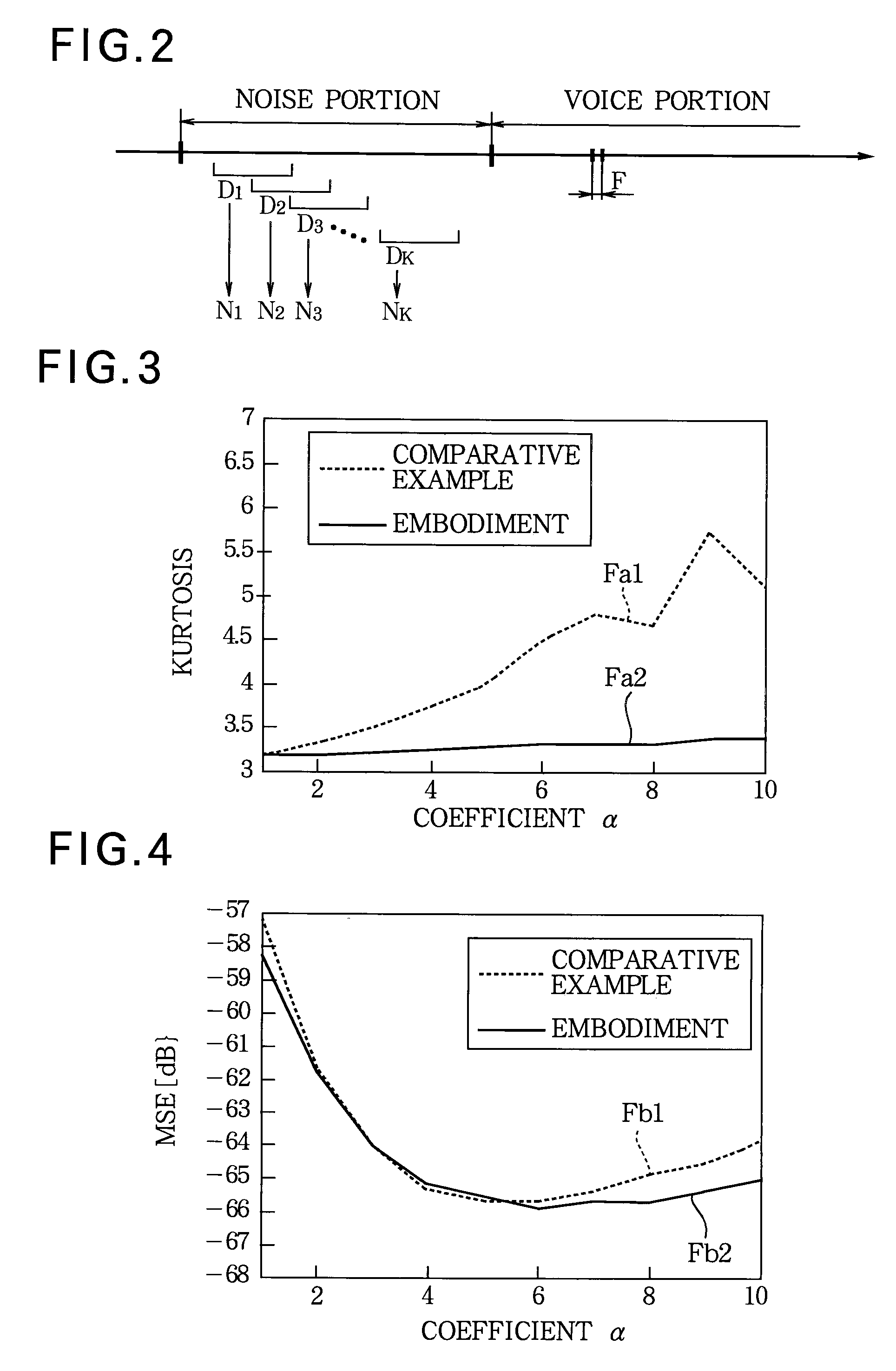
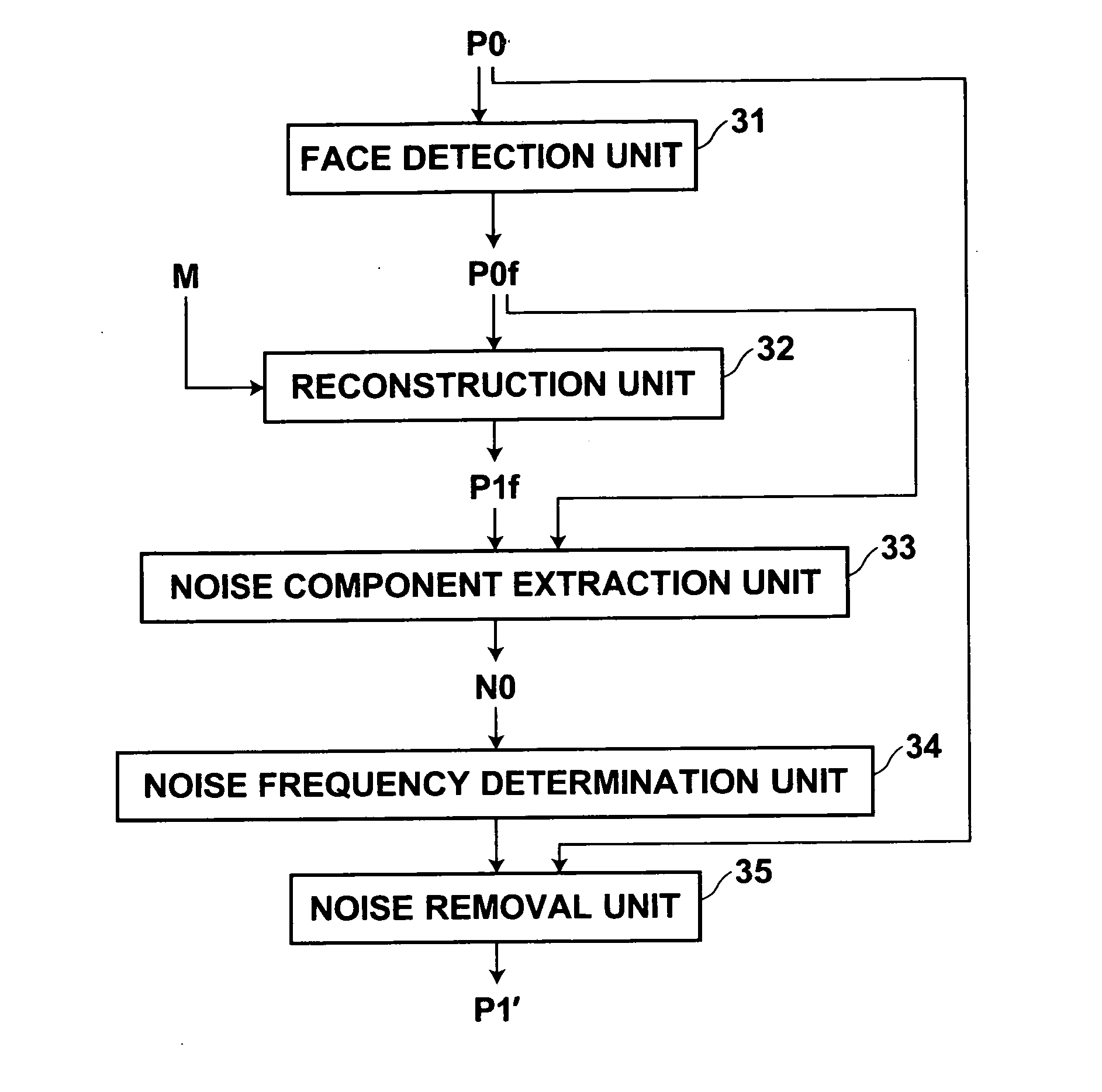
In order to accurately remove an unnecessary periodic noise component from an image, a reconstruction unit generates a reconstructed image without a periodic noise component by fitting to a face region detected in an image by a face detection unit a mathematical model generated according a method of AAM using a plurality of sample images representing human faces without a periodic noise component. The periodic noise component is extracted by a difference between the face region and the reconstructed image, and a frequency of the noise component is determined. The noise component of the determined frequency is then removed from the image.
Owner:FUJIFILM HLDG CORP +1
Active dry sensor module for measurement of bioelectricity
InactiveUS20090156925A1Component can be removedAvoid dangerElectroencephalographySensorsEngineeringReagent
An active dry sensor module for measurement of bioelectricity is disclosed. The active dry sensor module of the present invention excludes the use of a conductive gel, thereby not supplying unpleasantness and discomfort to a reagent and preventing the interference of the signal due to a noise component. Further, the active dry sensor module of the present invention amplifies the biomedical signal to a desired level, thereby precisely and easily measuring the biomedical signal.
Owner:NEUROSKY
Parallel data interface and method for high-speed timing adjustment
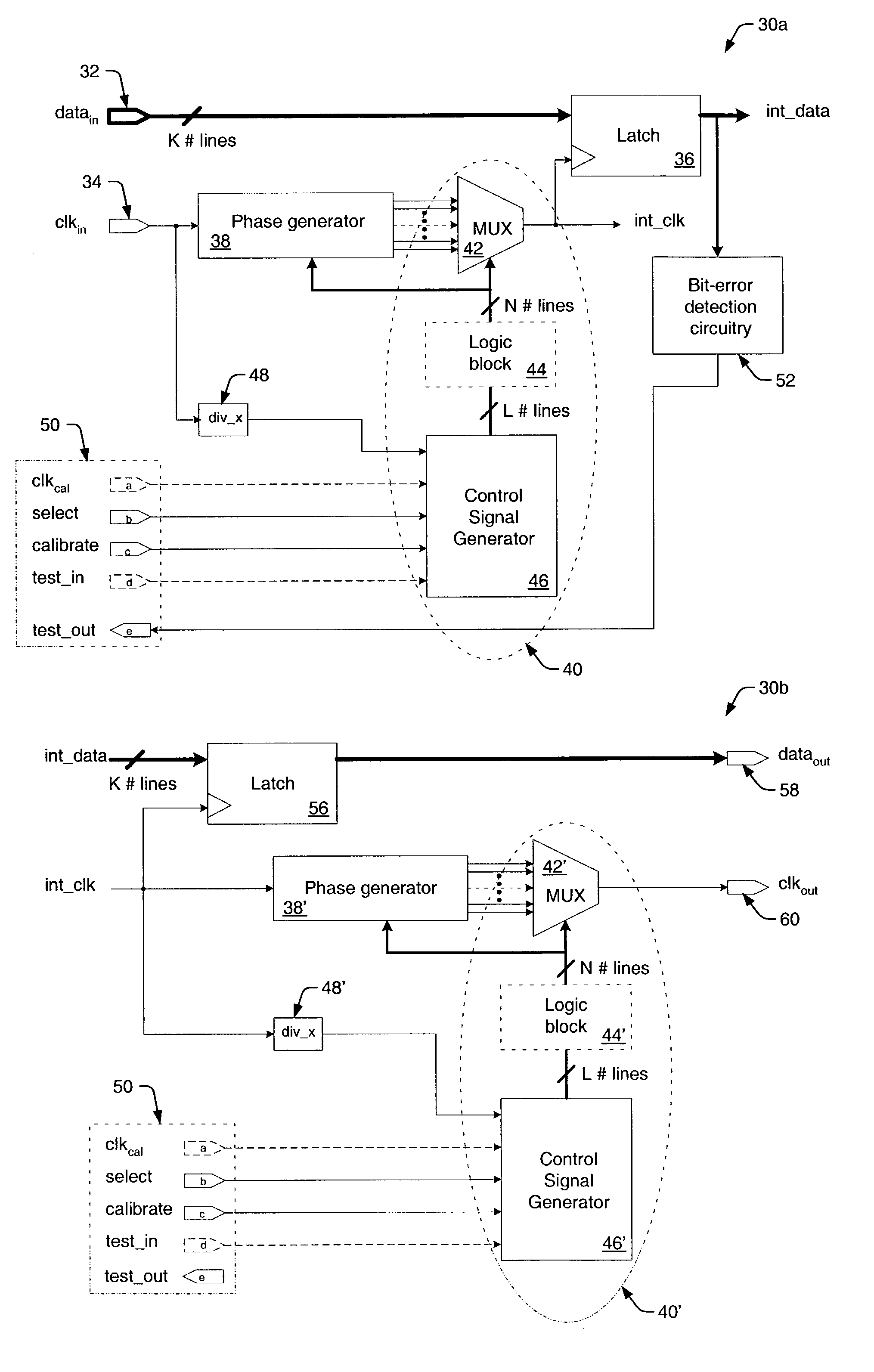
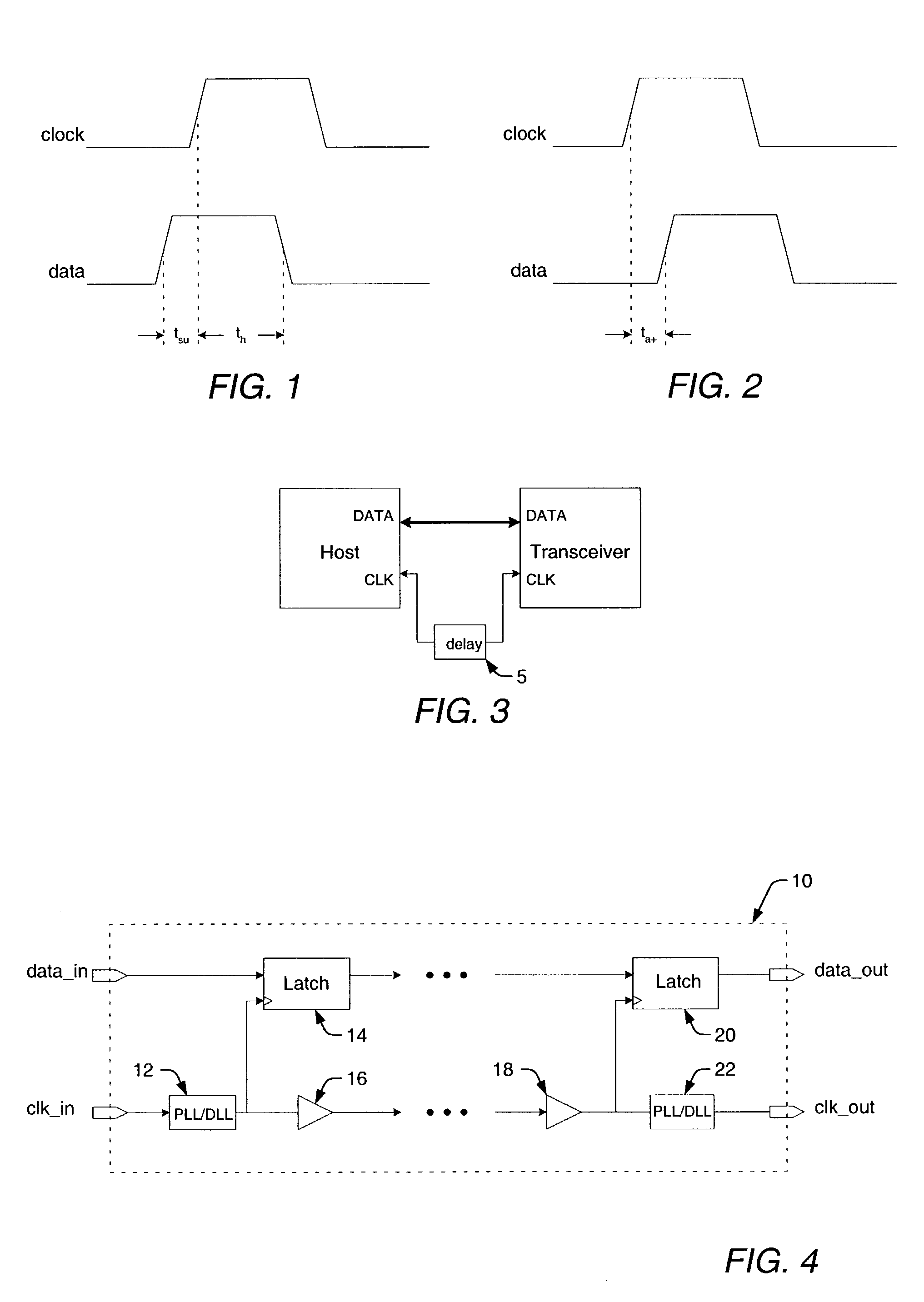
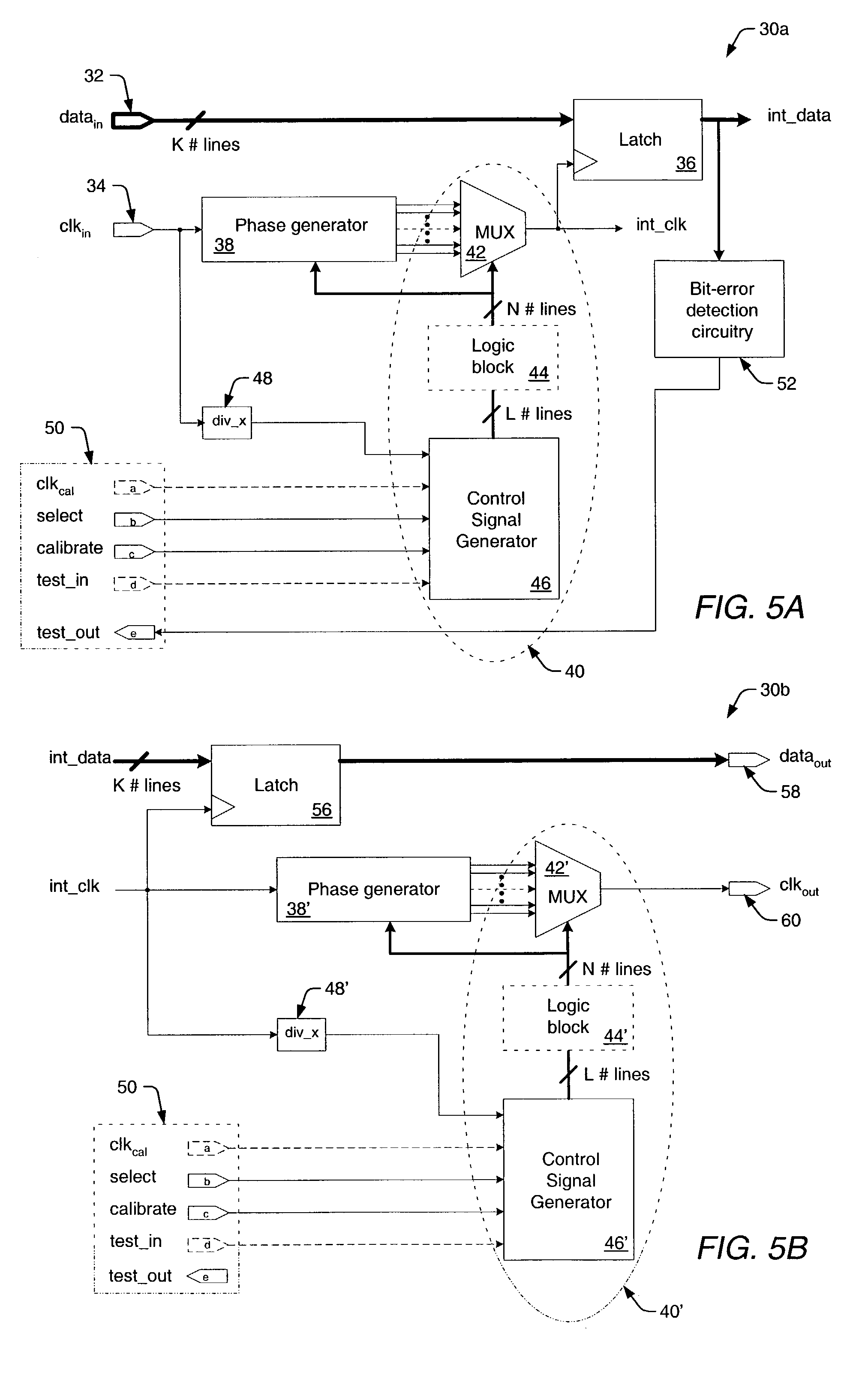
InactiveUS7069458B1Accurate samplingMinimize clock skewPulse automatic controlElectronic circuit testingAccess timeTime delays
A parallel data interface and method is provided herein, which adjusts a timing relationship of a clock signal to not only minimize clock skew, but to also compensate for noise components that may affect one or more paths of a parallel data bus. In some embodiments, the parallel data interface includes a first phase generator coupled to generate a first plurality of time delay pulses, and a first phase selector adapted to select one of the first plurality of time delay pulses to adjust the timing of a clock signal to sample each and every one of the plurality of data signals between minimum setup and hold time thresholds. In some embodiments, the parallel data interface includes a second phase generator coupled to generate a second plurality of time delay pulses, and a second phase selector adapted to select one of the second plurality of time delay pulses to adjust the timing of the clock signal to output the plurality of data signals from the data interface at least an amount of time (i.e., an access time) after the adjusted clock transition is output from the data interface.
Owner:RPX CORP
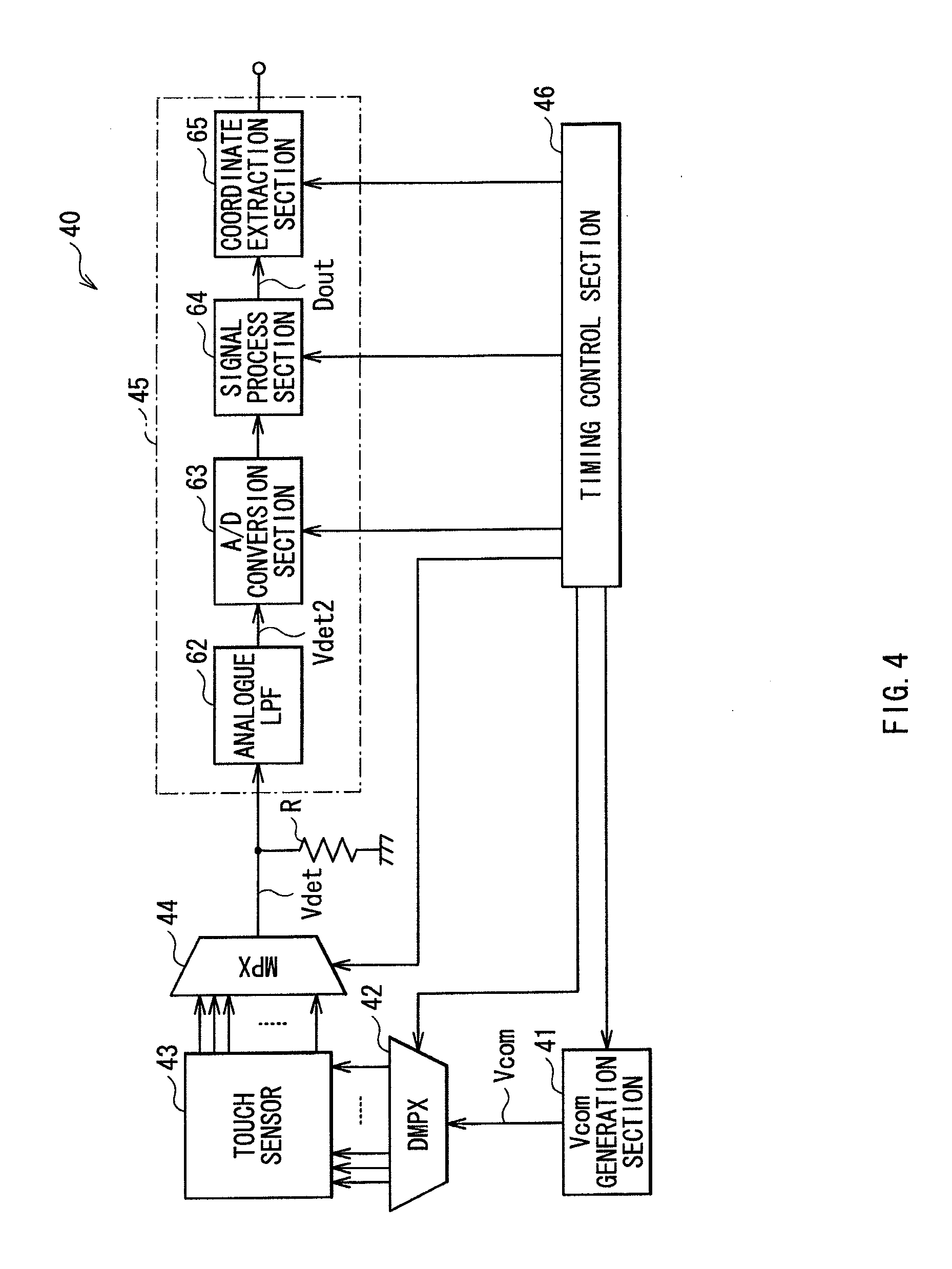
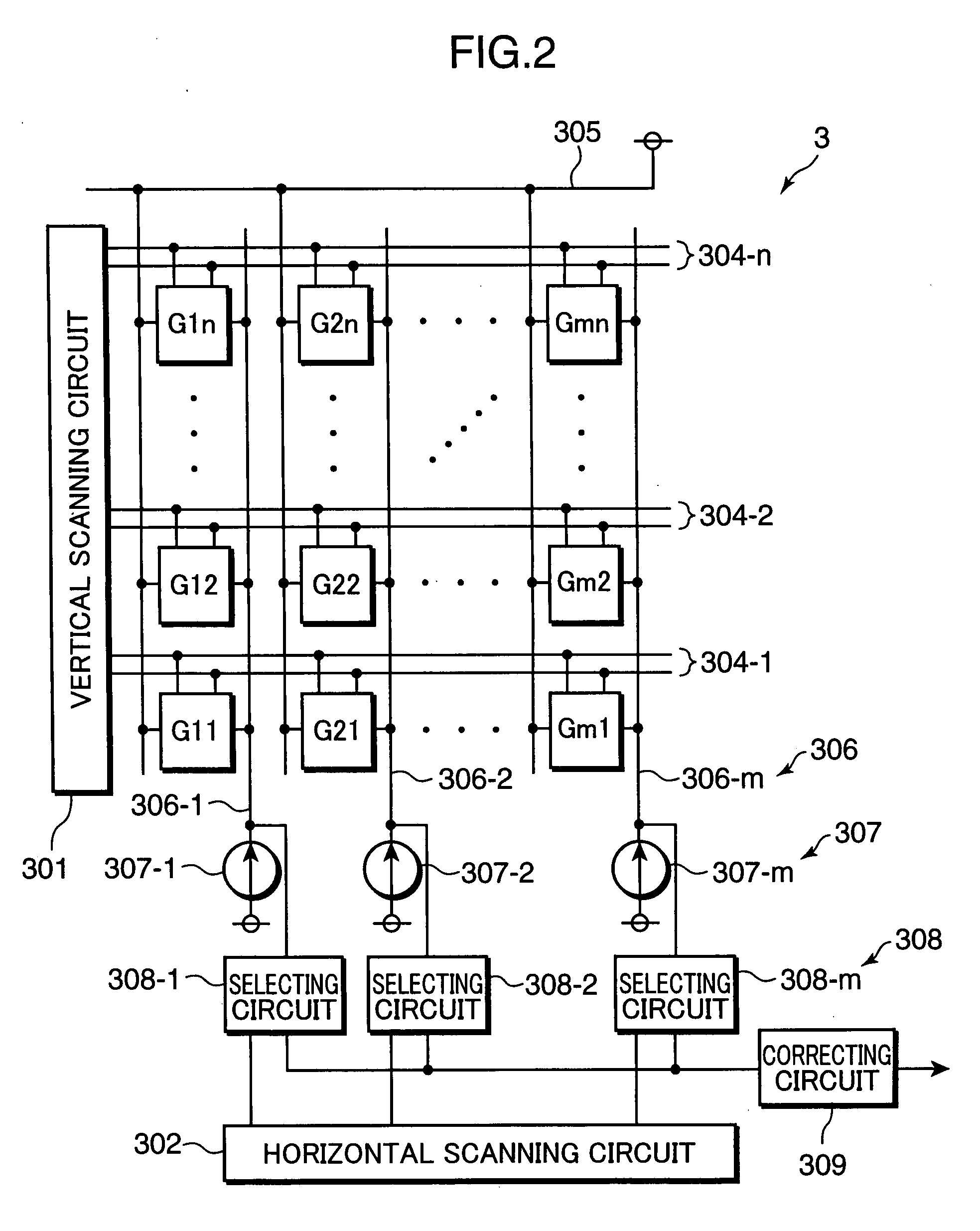
Capacitive touch panel and display device with touch detection function
InactiveUS20110134076A1Reduce the necessary timeImprove performanceInput/output processes for data processingDisplay deviceTouch panel
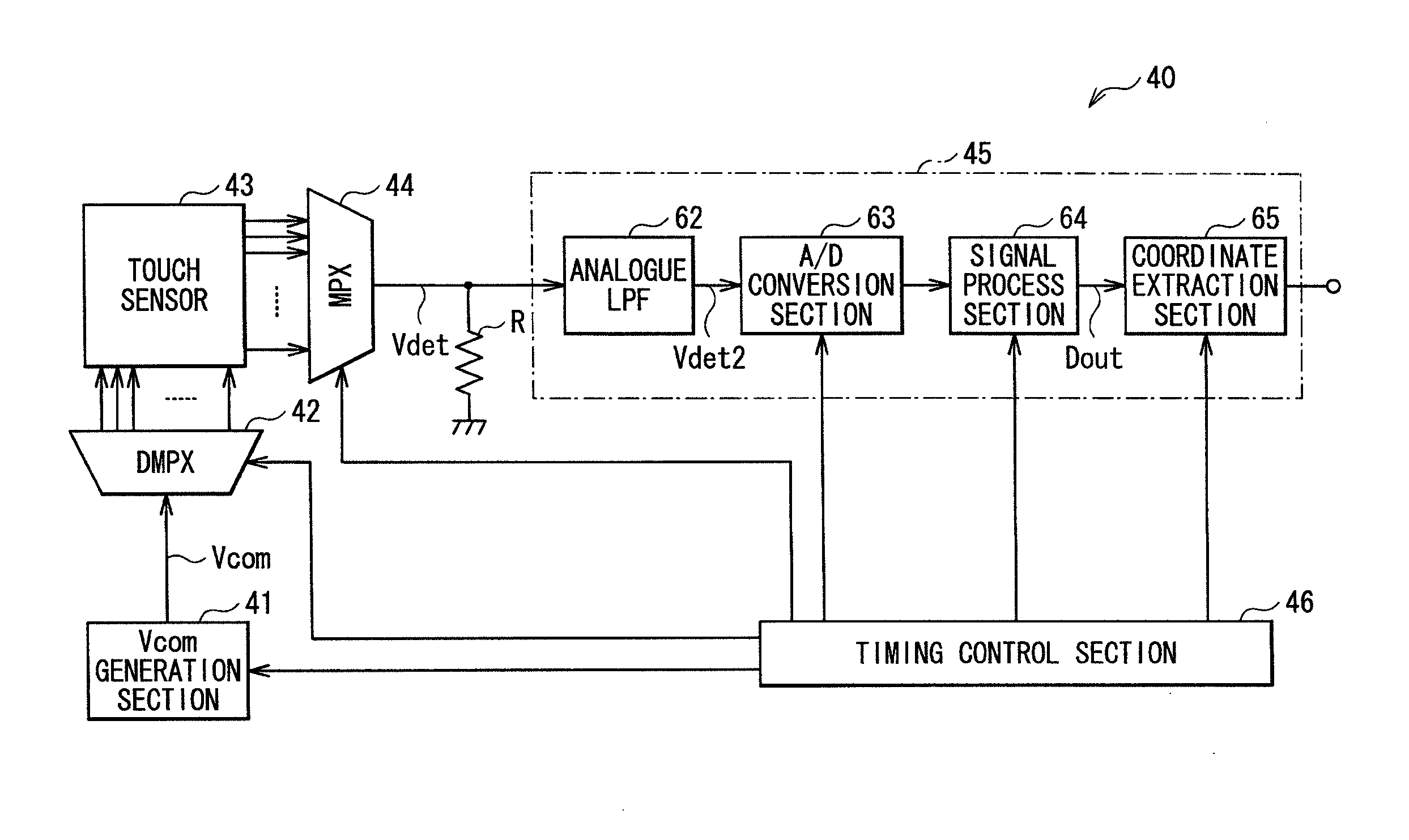
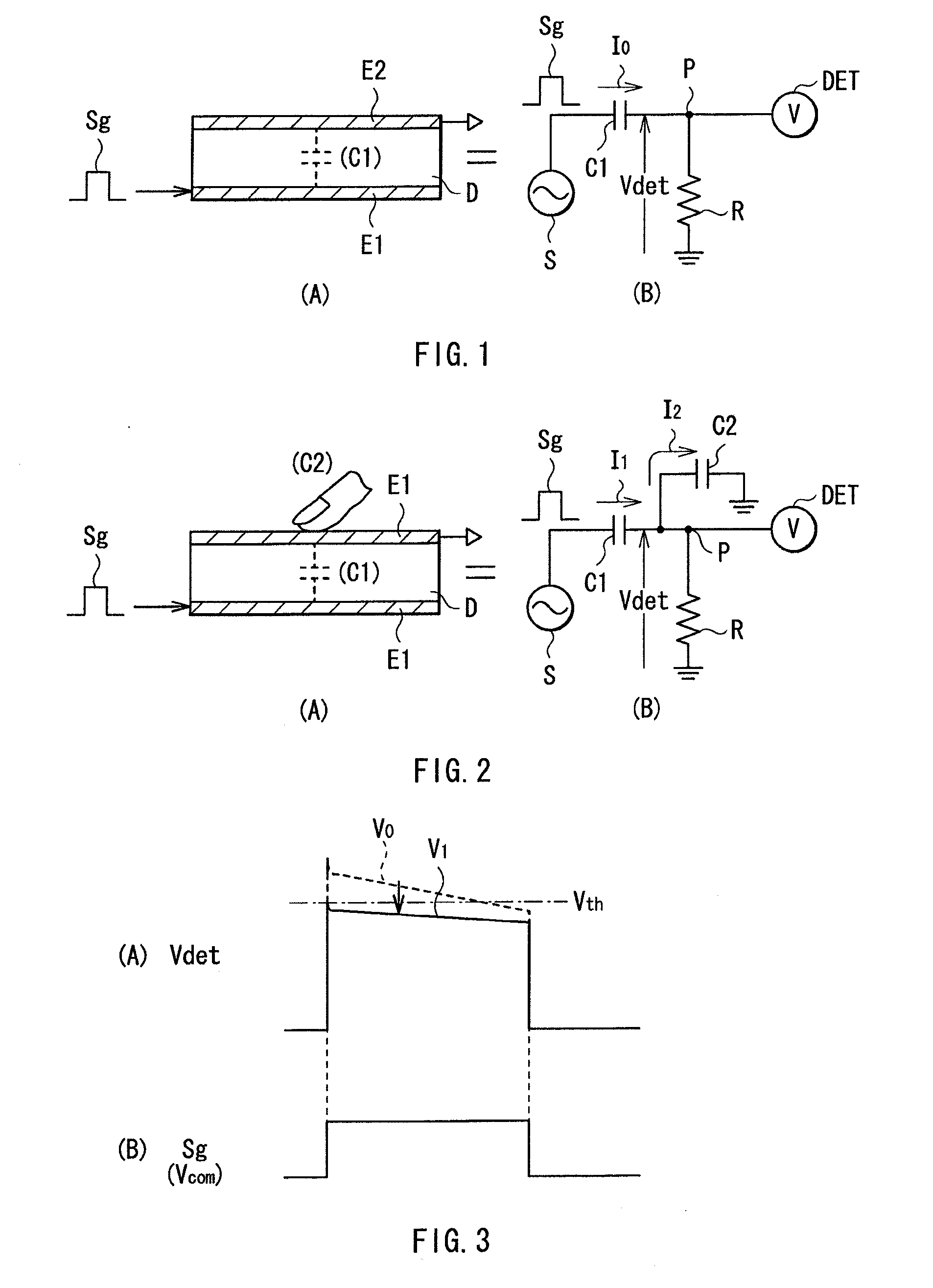
A capacitive touch panel capable of reducing a disturbance noise and reducing touch detection time with a simple structure is obtained. The capacitive touch panel includes: a plurality of drive electrodes each to which a drive signal for touch detection is applied; a plurality of touch detection electrodes arranged to intersect the plurality of drive electrodes, and each outputting a detection signal synchronized with the drive signal; a first sampling circuit (A / D conversion circuits 72 and 73) extracting a first series of sampling signal including a signal component with first level and a noise component, from the detection signal; a second sampling circuit (A / D conversion circuits 75 and 76) extracting a second series of sampling signal including a signal component with second level different from the first level and the noise component, from the detection signal; a filter circuit (digital LPFs 81 and 82) performing a high range cut process on the first series of sampling signal and the second series of sampling signal; and a computation circuit (a subtraction circuit 90) determining a signal for touch detection based on an output of the filter circuit.
Owner:JAPAN DISPLAY WEST
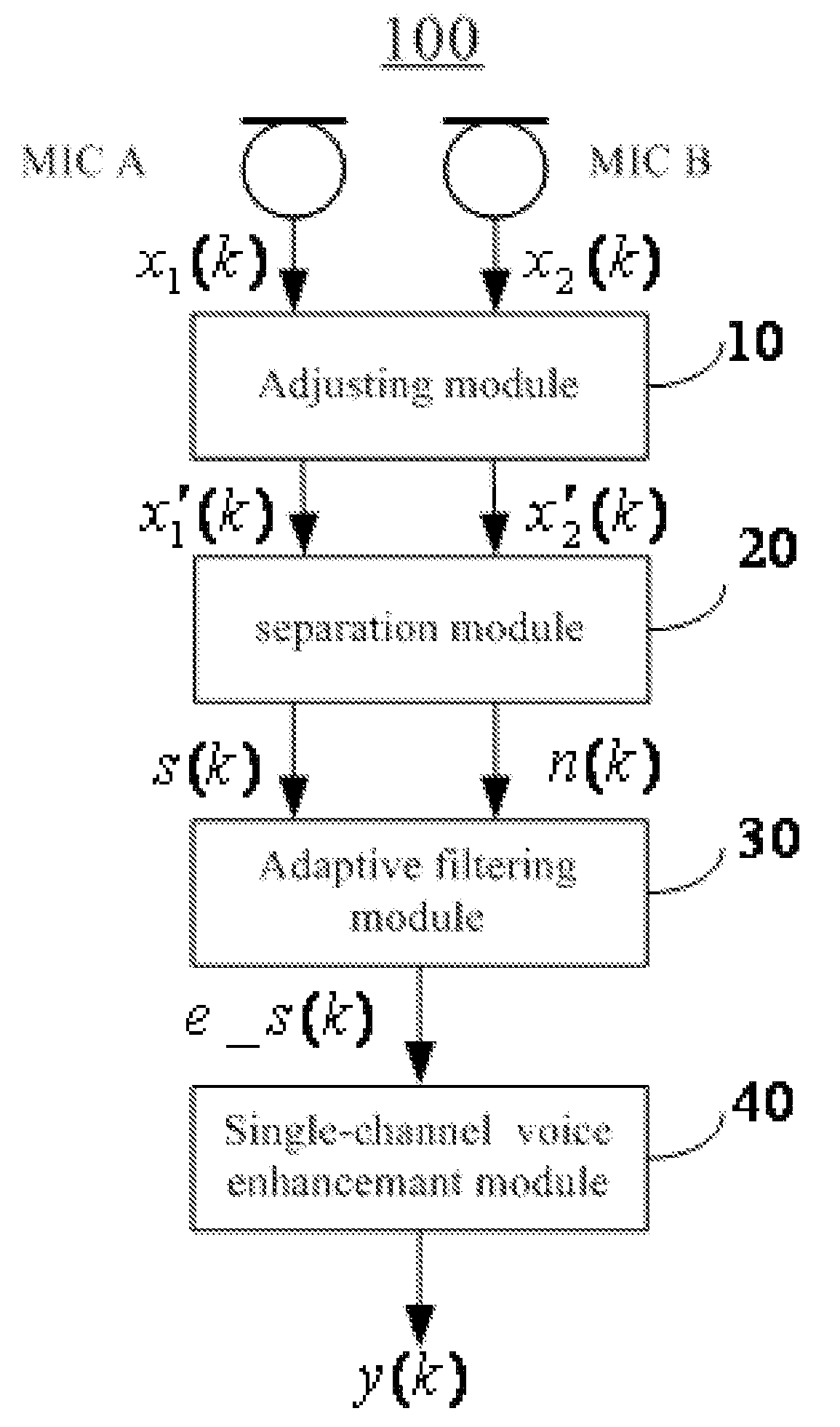
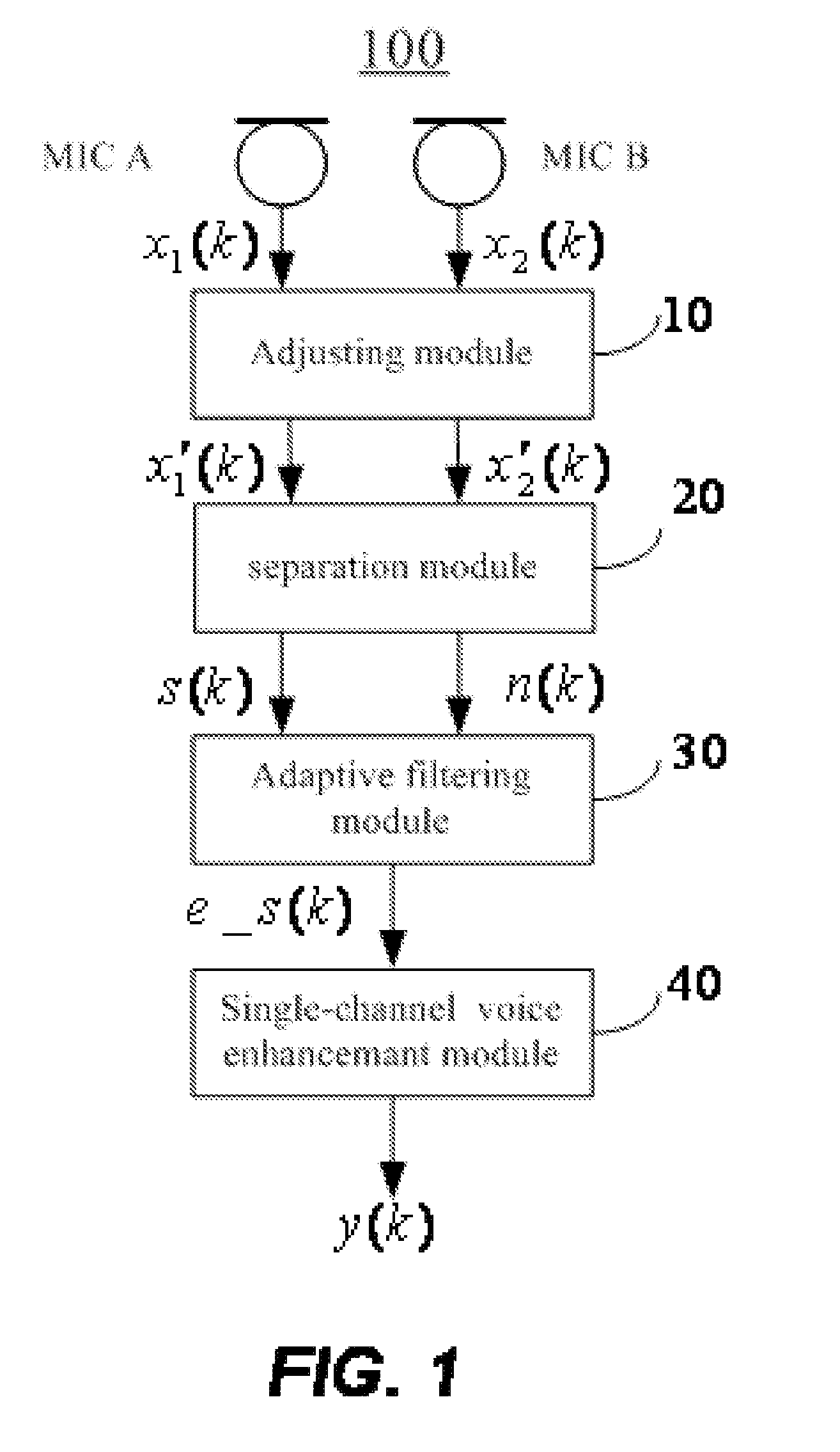
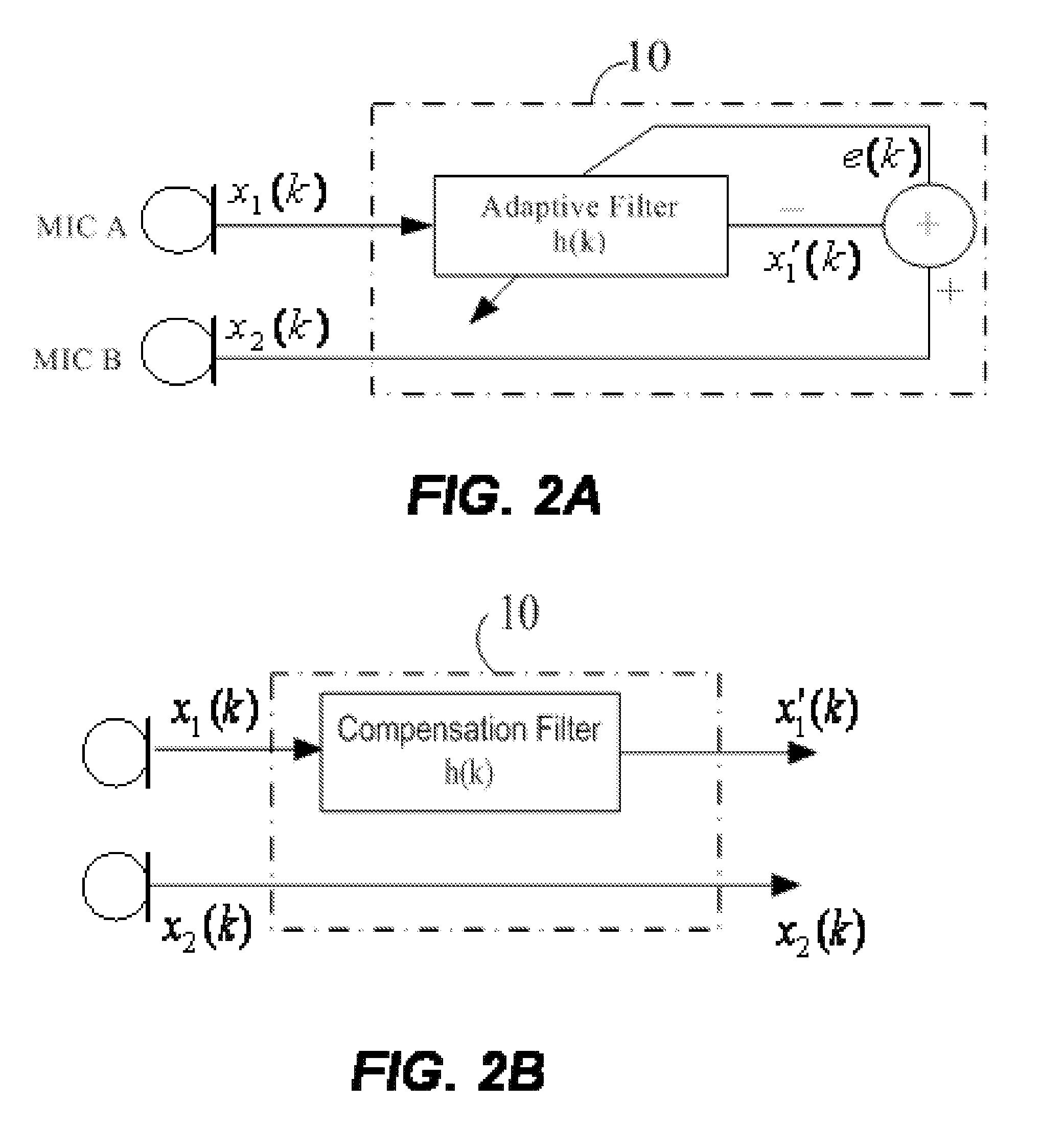
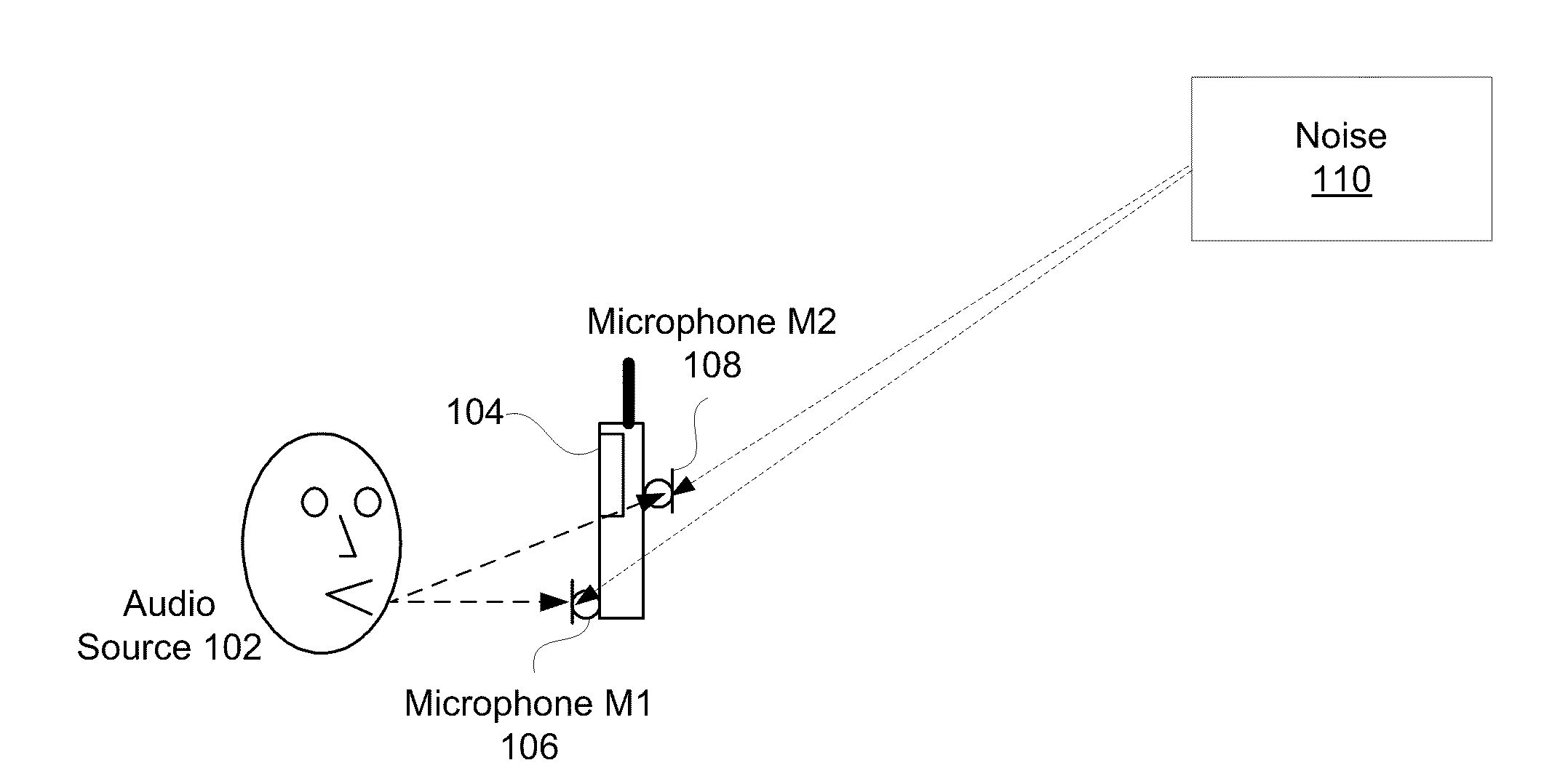
Dual Microphone System and Method for Enhancing Voice Quality
InactiveUS20070165879A1Enhanced signalMinimize the differenceMicrophonesSignal processingTime domainAdaptive filter
Techniques to enhance voice signals in a dual microphone system are disclosed. According to one aspect of the present invention, there are at least two microphones that are positioned in a pre-configured array. Two audio signals x1(k) and x2(k) are received and coupled to an adjusting module that is provided to control the gain of each of the audio signals x1(k) and x2(k) to minimize signal differences between the two signals. A separation module is provided to receive matched audio signals x′1(k) and x′2(k) from the adjusting module. The separation module separates the audio signals x′1(k) and x′2(k) to obtain a first audio signal s(k) containing mainly the voice and a second audio signal n(k) containing mainly the noise. An adaptive filtering module is provided to eliminate the noise component in the audio signal s(k) to obtain an estimated voice signal e_s(k) with a higher S / N ratio. Furthermore, the adaptive filtering module can be also configured to suppress echo in the audio signal s(k) at same time. The voice signal e_s(k) may be further coupled to a single-channel voice enhancement module that is configured to eliminate any residual of the noise component in the voice signal e_s(k) according to the differences between the voice signal and the noise signal in time domain and frequency domain, whereby, the S / N ratio is further enhanced.
Owner:VIMICRO CORP
Image processing device, image processing method, and image sensing apparatus
ActiveUS20080122953A1Good removal effectLess and influenceImage enhancementTelevision system detailsImaging processingFrequency synthesizer
An image processing device includes: a frequency divider for performing a frequency division processing of dividing an input image into a plurality of frequency components each having a frequency band; a noise remover for performing a noise component removal processing of removing a noise component from a high frequency component in the frequency components each having the frequency band obtained by the frequency division processing by the frequency divider; an edge preservation information calculator for detecting an edge intensity based on a low frequency component in the frequency components each having the frequency band obtained by the frequency division processing by the frequency divider, and calculating edge preservation information relating to a degree of preserving an edge component based on the detected edge intensity; an edge preserving section for preserving the edge component in the high frequency component, based on the edge preservation information calculated by the edge preservation information calculator; and a frequency synthesizer for synthesizing the high frequency component whose noise component is removed by the noise remover and whose edge component is preserved by the edge preserving section, and the low frequency component, in each of the frequency bands.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA INC
Method for Jointly Optimizing Noise Reduction and Voice Quality in a Mono or Multi-Microphone System
ActiveUS20110257967A1Reduce noiseDecreased energy levelSpeech analysisTransducer circuit dampingAdaptive denoisingEngineering
The present technology provides adaptive noise reduction of an acoustic signal using a sophisticated level of control to balance the tradeoff between speech loss distortion and noise reduction. The energy level of a noise component in a sub-band signal of the acoustic signal is reduced based on an estimated signal-to-noise ratio of the sub-band signal, and further on an estimated threshold level of speech distortion in the sub-band signal. In embodiments, the energy level of the noise component in the sub-band signal may be reduced to no less than a residual noise target level. Such a target level may be defined as a level at which the noise component ceases to be perceptible.
Owner:KNOWLES ELECTRONICS INC
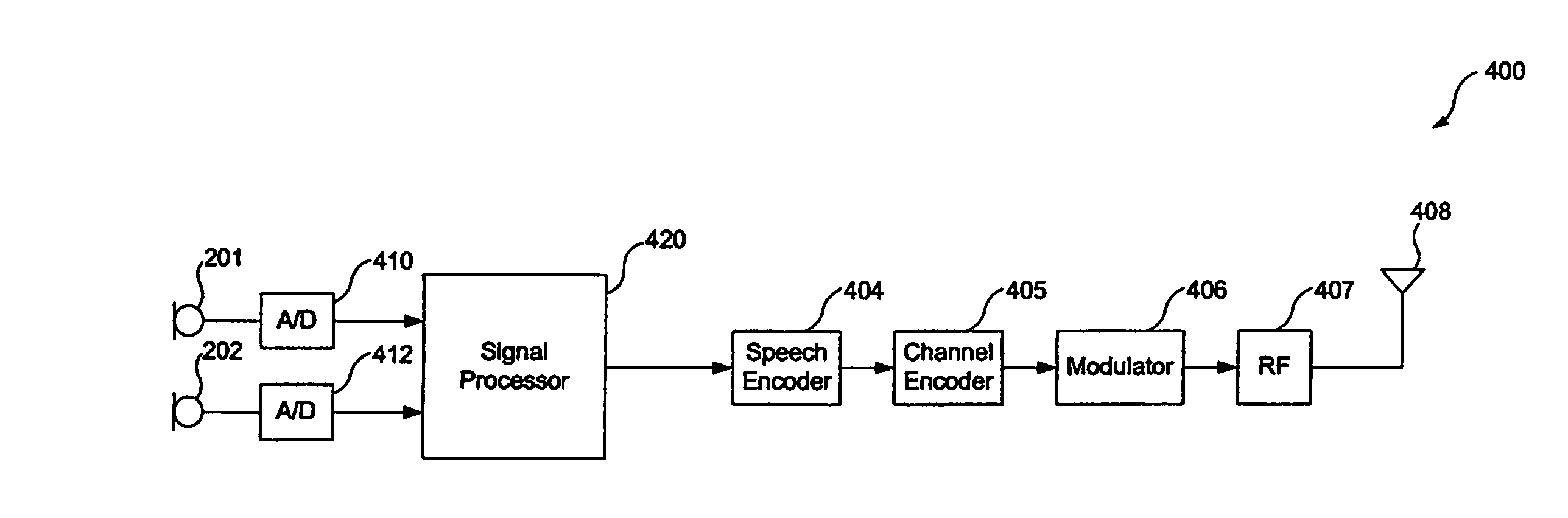
Wireless telephone having multiple microphones
InactiveUS20060133621A1Improved noise suppressionNoise suppression and VAD functionalityGain controlSpeech analysisBackground noiseAudio frequency
The present invention is directed to a wireless telephone having a first microphone and a second microphone and a method for processing audio signal in a wireless telephone having a first microphone and a second microphone. The wireless telephone includes a first microphone, a second microphone, and a signal processor. The first microphone outputs a first audio signal, the first audio signal comprising a voice component and a background noise component. The second microphone outputs a second audio signal. The signal processor increases a ratio of the voice component to the noise component of the first audio signal based on the content of at least one of the first audio signal and the second audio signal to produce a third audio signal.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
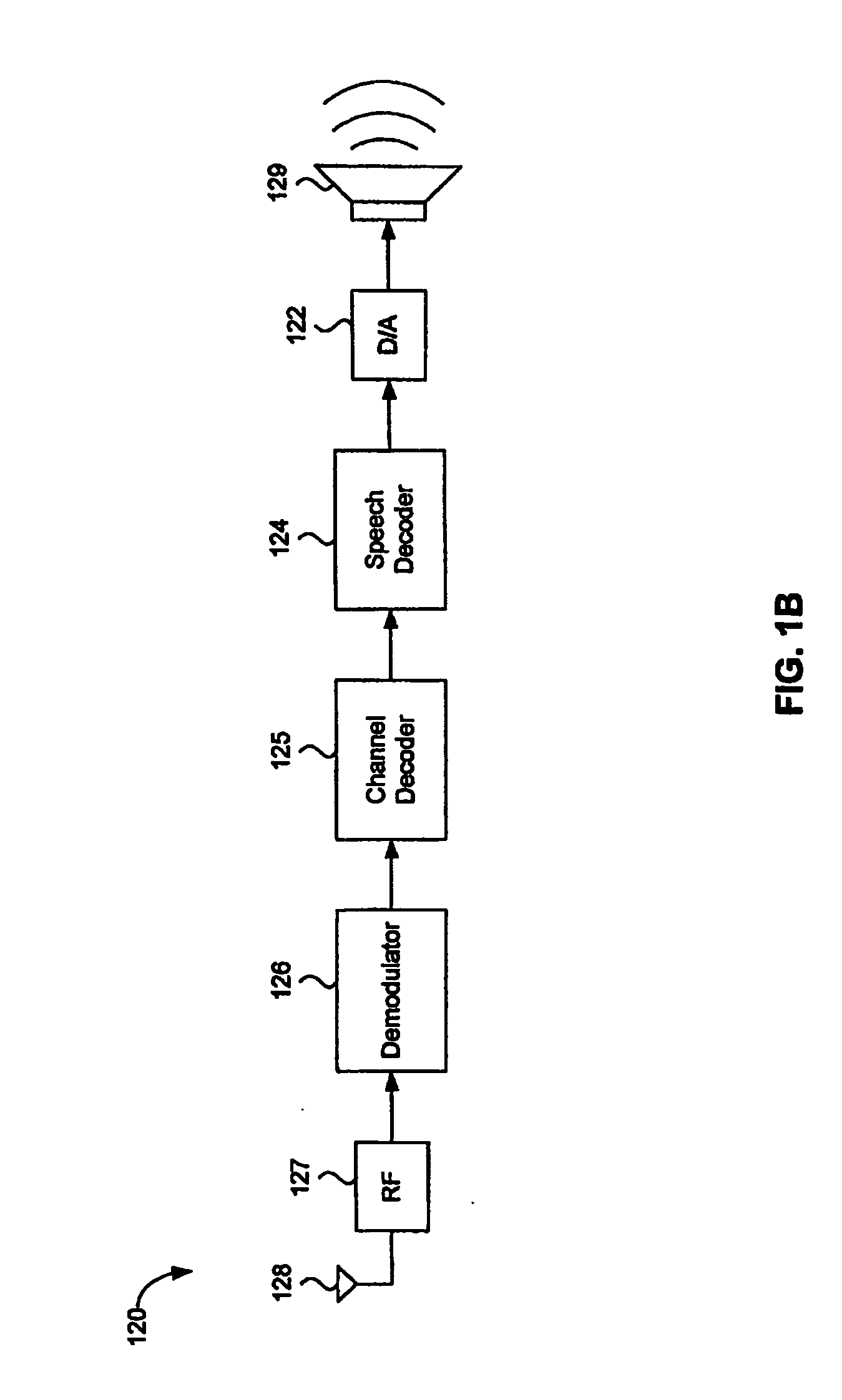
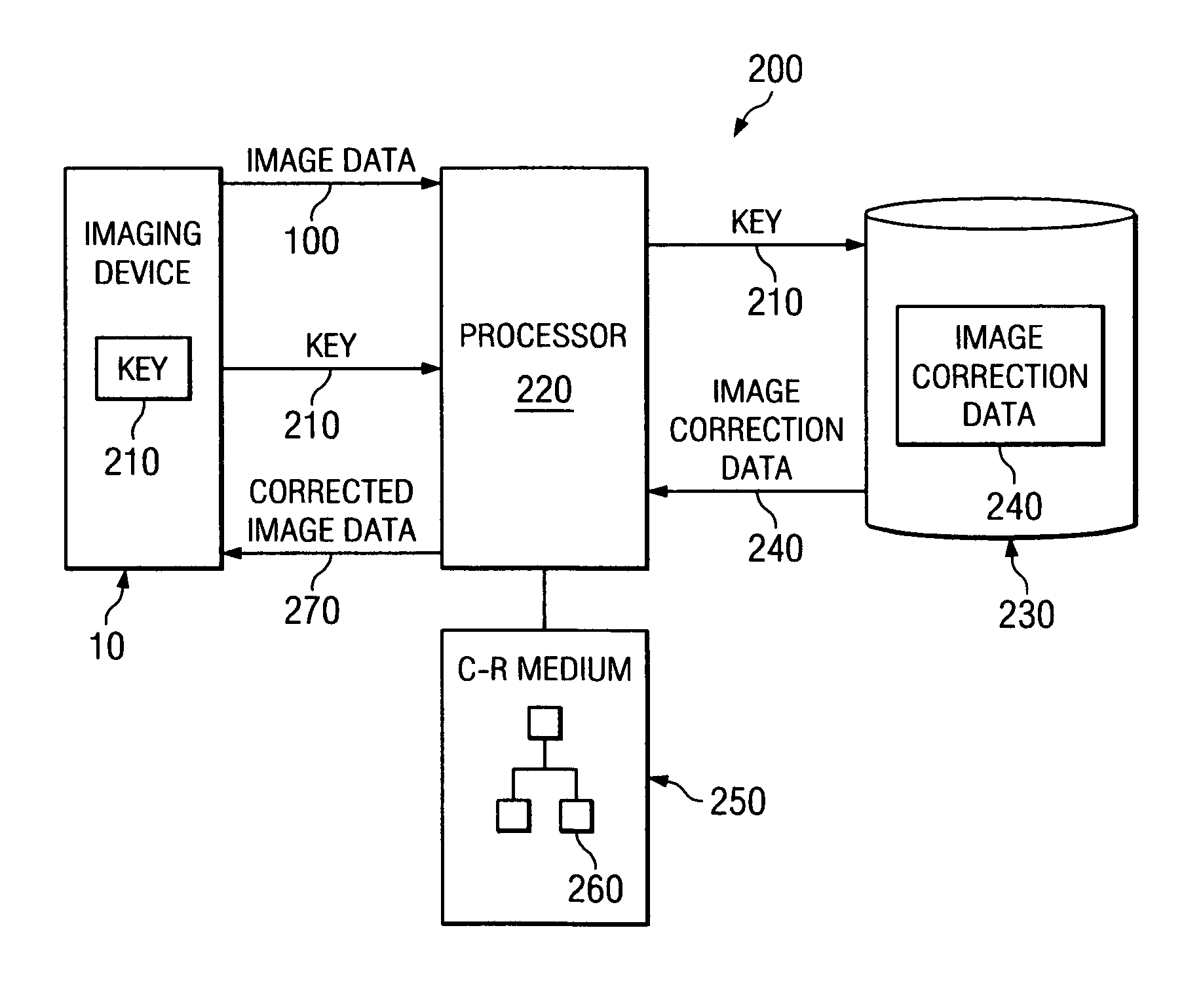
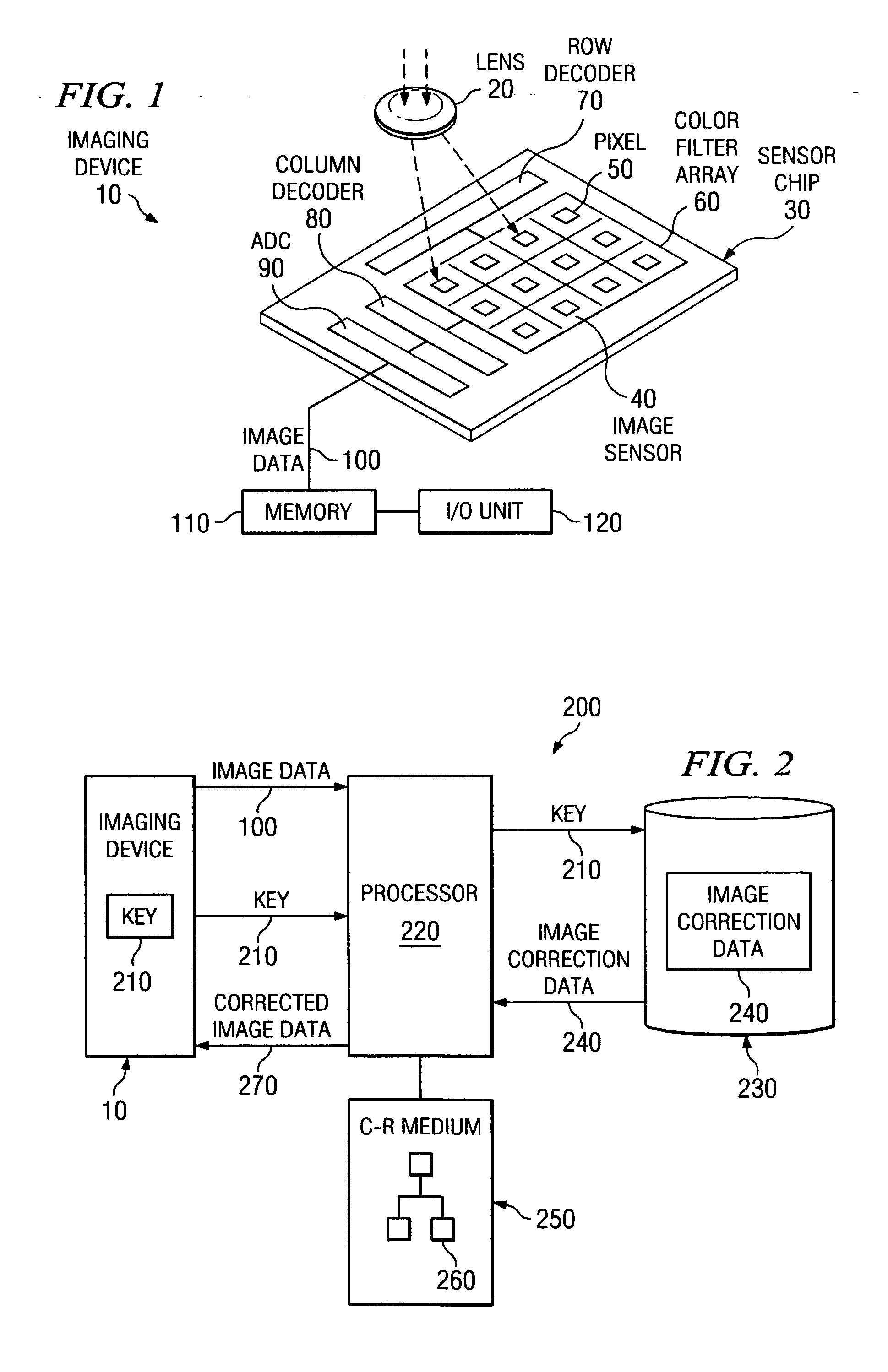
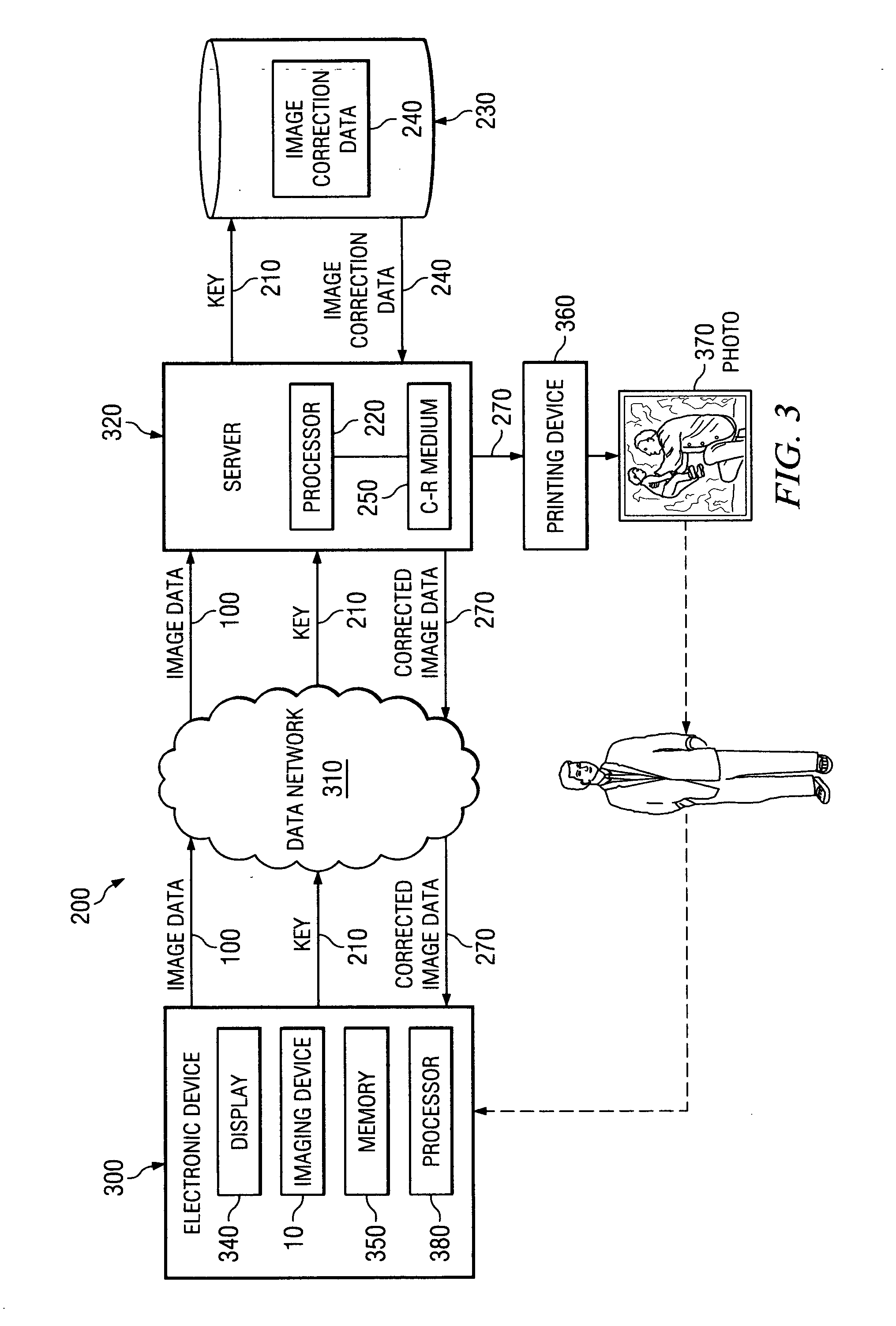
System and method for processing images using centralized image correction data
InactiveUS20060268357A1Cost-effectiveTelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsImaging processingImage correction
An image processing system uses centralized image correction data to process digital images. The image processing system includes a centralized database for storing image correction data for imaging devices. An image processor that receives image data representing an image captured by one of the imaging devices accesses the centralized database with a key associated with the imaging device to retrieve the image correction data for the imaging device. The image processor processes the image data using the retrieved image correction data to correct the image data by reducing various noise components in the image.
Owner:APTINA IMAGING CORP
Noise reduction device, program and method
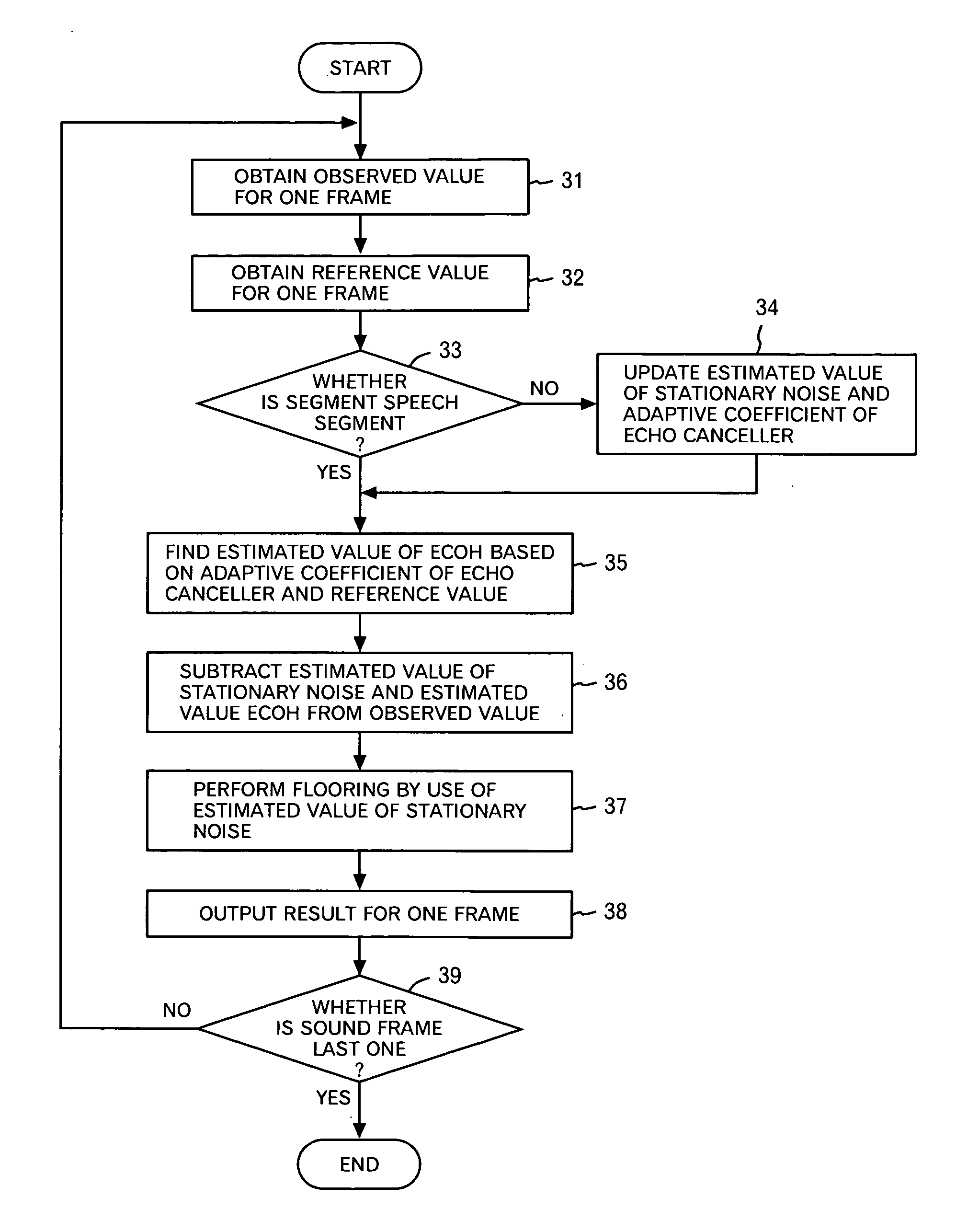
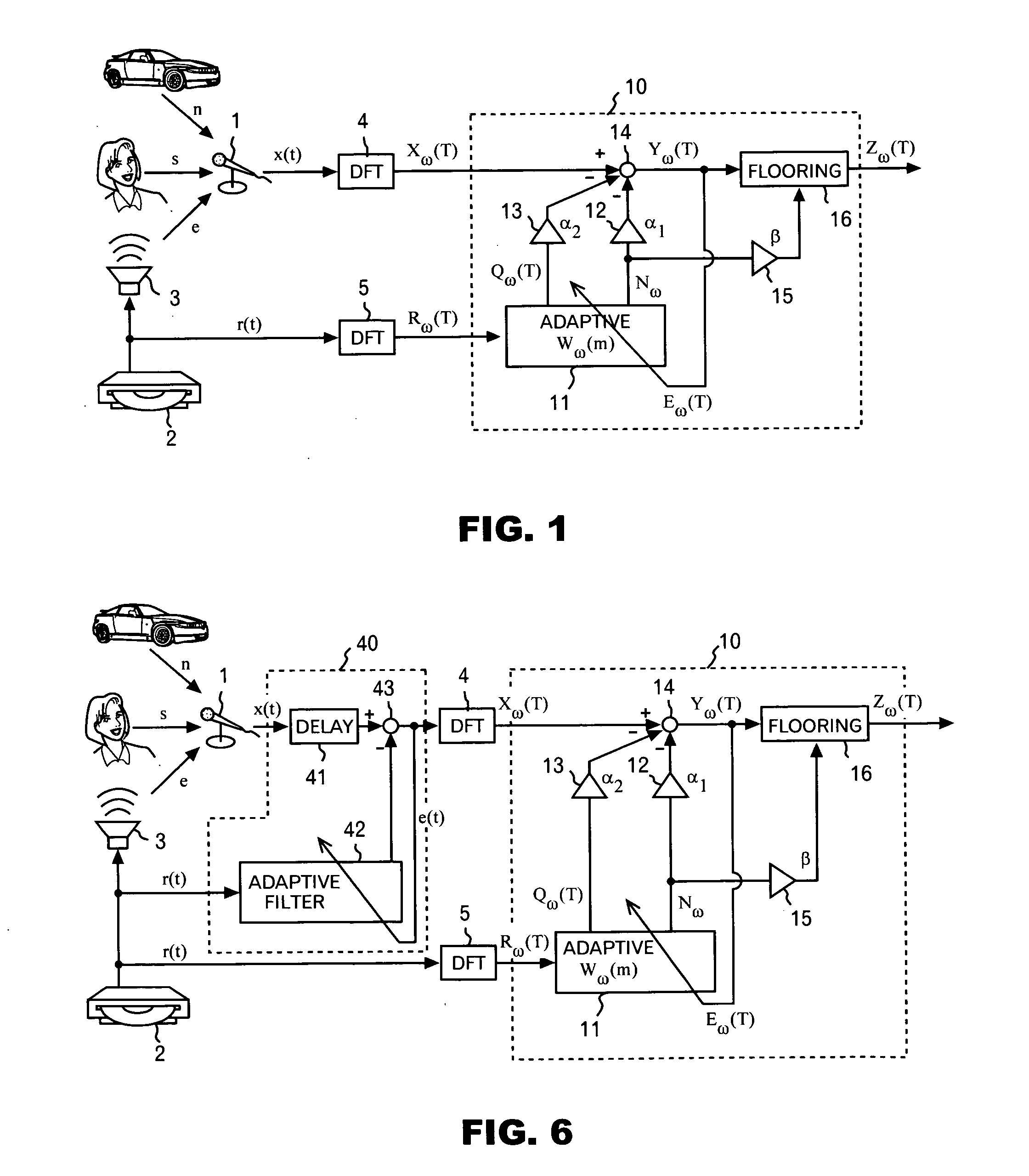
InactiveUS20060136203A1Improve Noise RobustnessMaintain compatibilitySpeech analysisStationary noiseAdaptive learning
A noise reduction device is configured by use of: means for calculating a predetermined constant, and a predetermined reference signal Rω(T) in the frequency domain, respectively by use of adaptive coefficients Wω(m), and for thereby obtaining estimated values Nω and Qω(T) respectively of stationary noise components, and non-stationary noise components corresponding to the reference signal, which are included in a predetermined observed signal Xω(T) in the frequency domain; means and for applying a noise reduction process to the observed signal on the basis of each of the estimated values, and for updating each of the adaptive coefficients on the basis of a result of the process; and an adaptive learning means and for repeating the obtaining of the estimated values and the updating of the adaptive coefficients, and for thereby learning each of the adaptive coefficients.
Owner:IBM CORP
Selective Bandwidth Extension
ActiveUS20100063827A1Maximize perceived qualityQuality improvementSpeech analysisDigital computer detailsFrequency spectrumBandwidth extension
A method of receiving an audio signal includes measuring a periodicity of the audio signal to determine a checked periodicity. At least one best available subband is determined. At least one extended subband is composed, wherein composing includes reducing a ratio of composed harmonic components to composed noise components if the checked periodicity is lower than a threshold, and scaling a magnitude of the at least one extended subband based on a spectral envelope on the audio signal.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
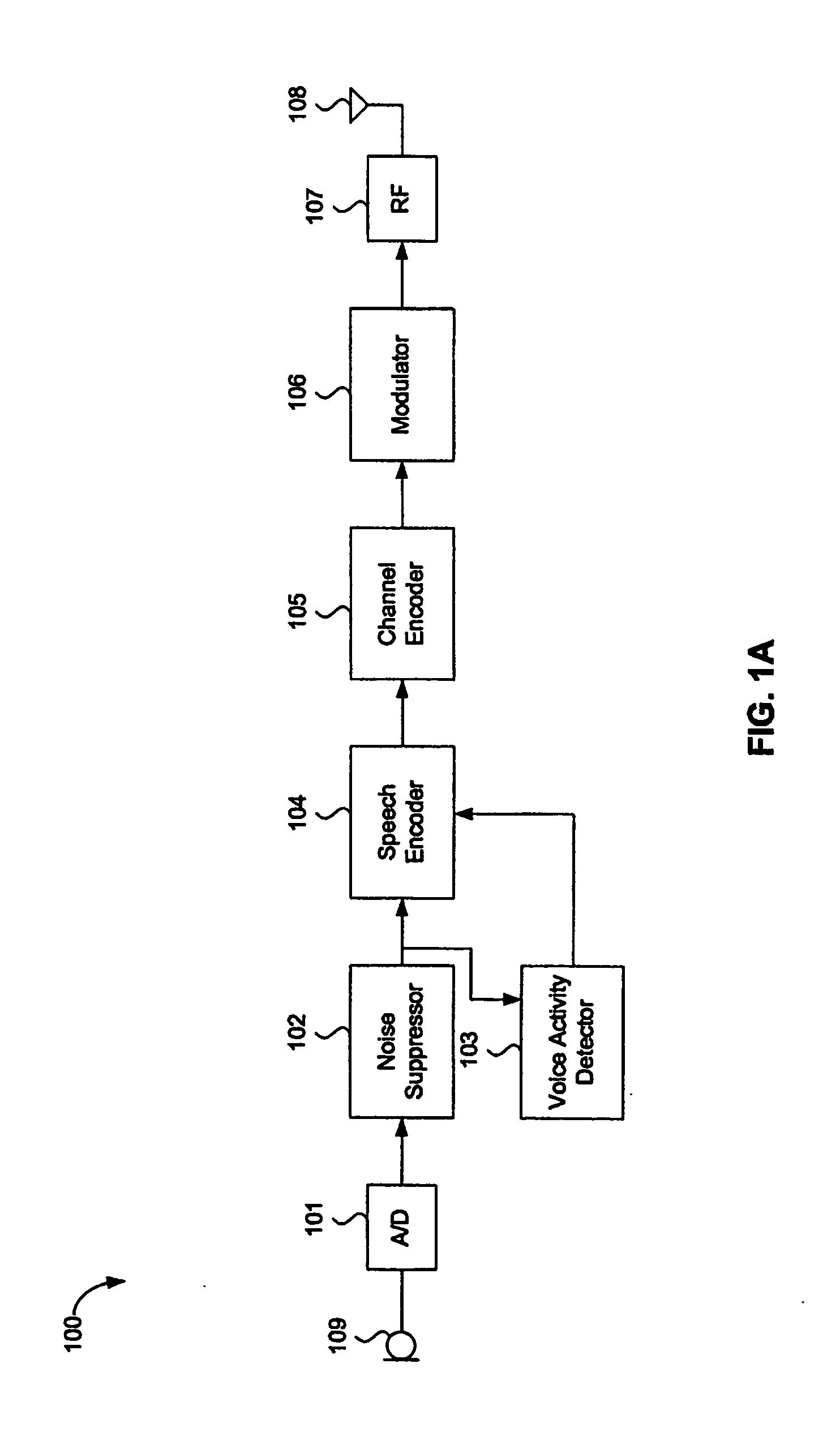
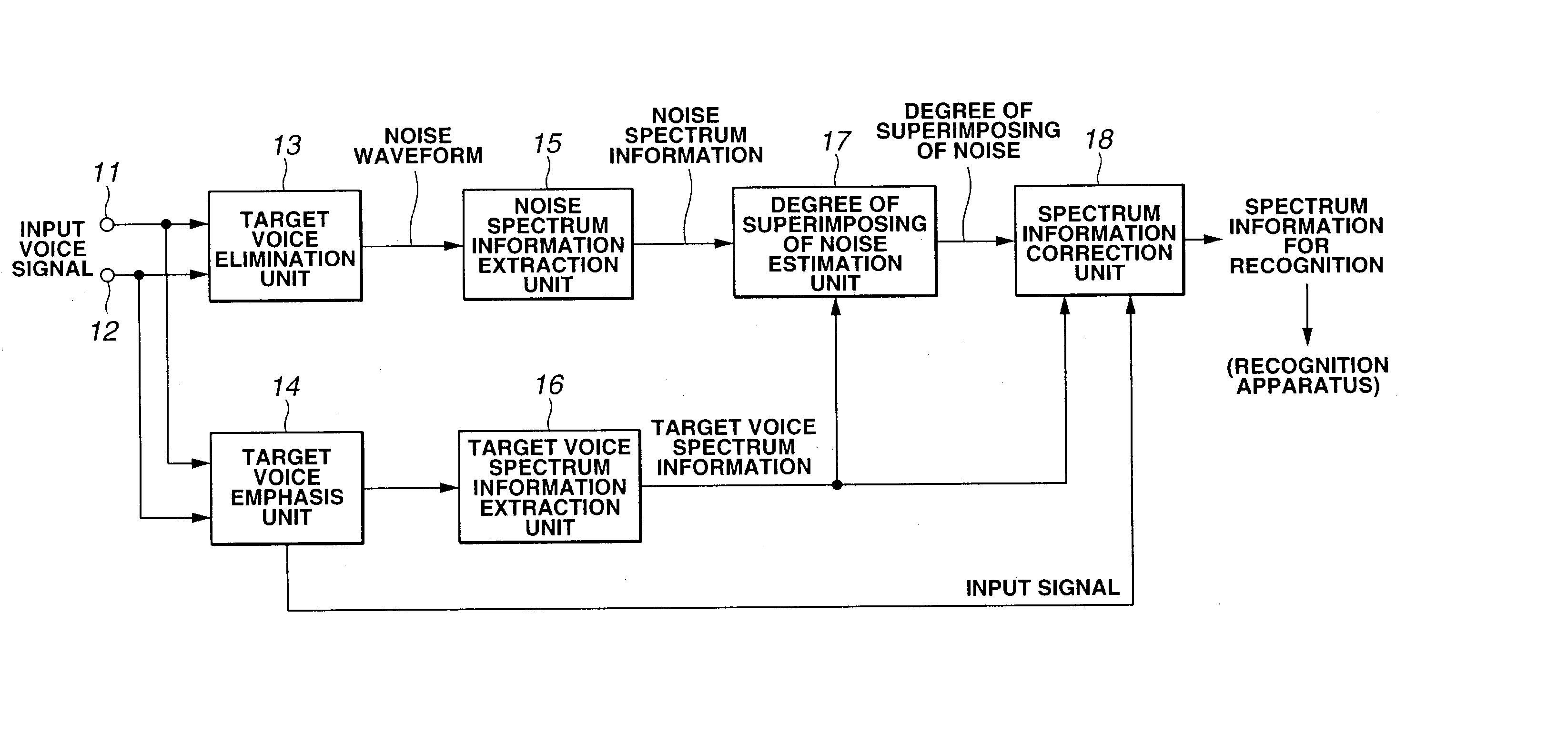
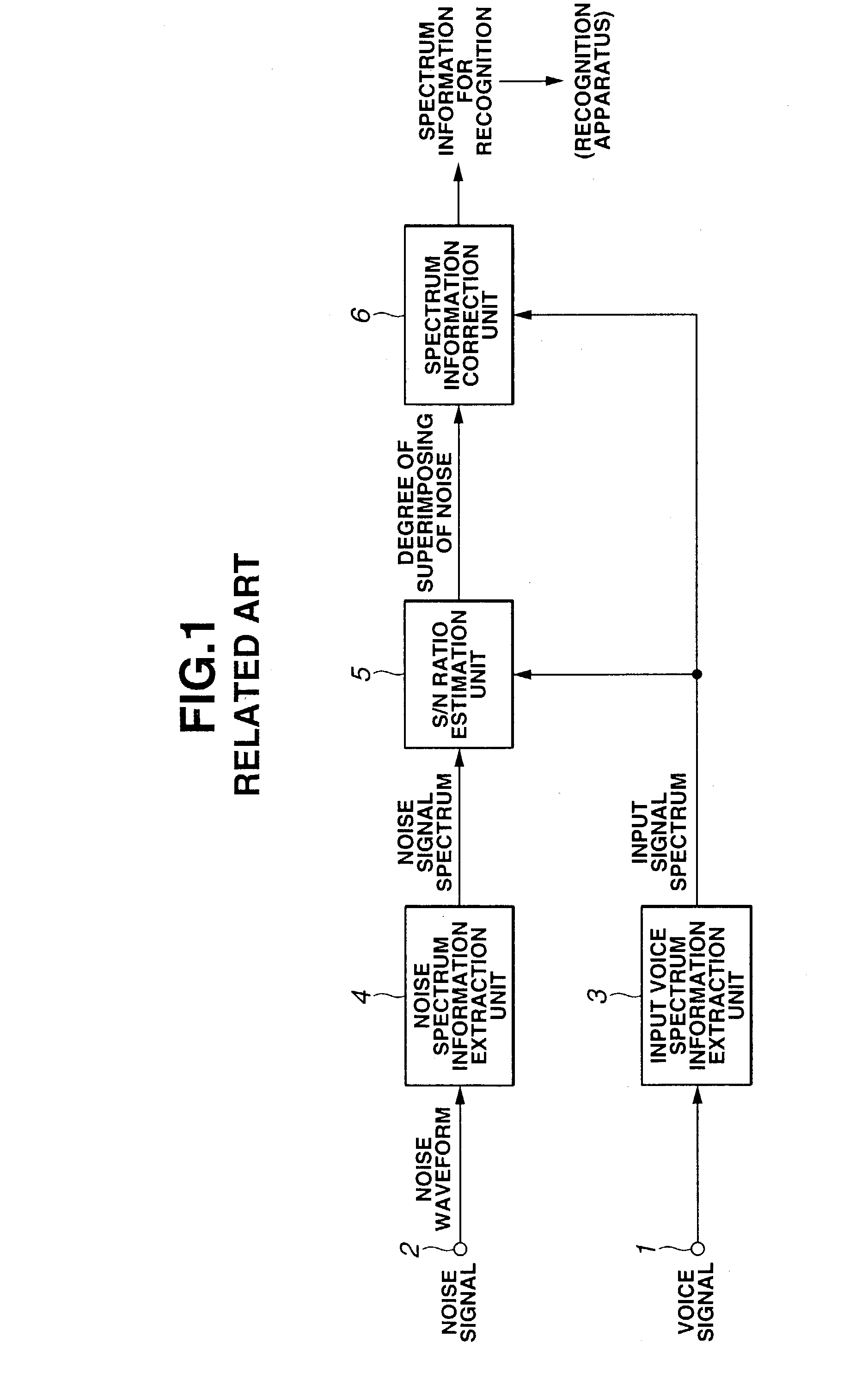
Noise suppression apparatus and method for speech recognition, and speech recognition apparatus and method
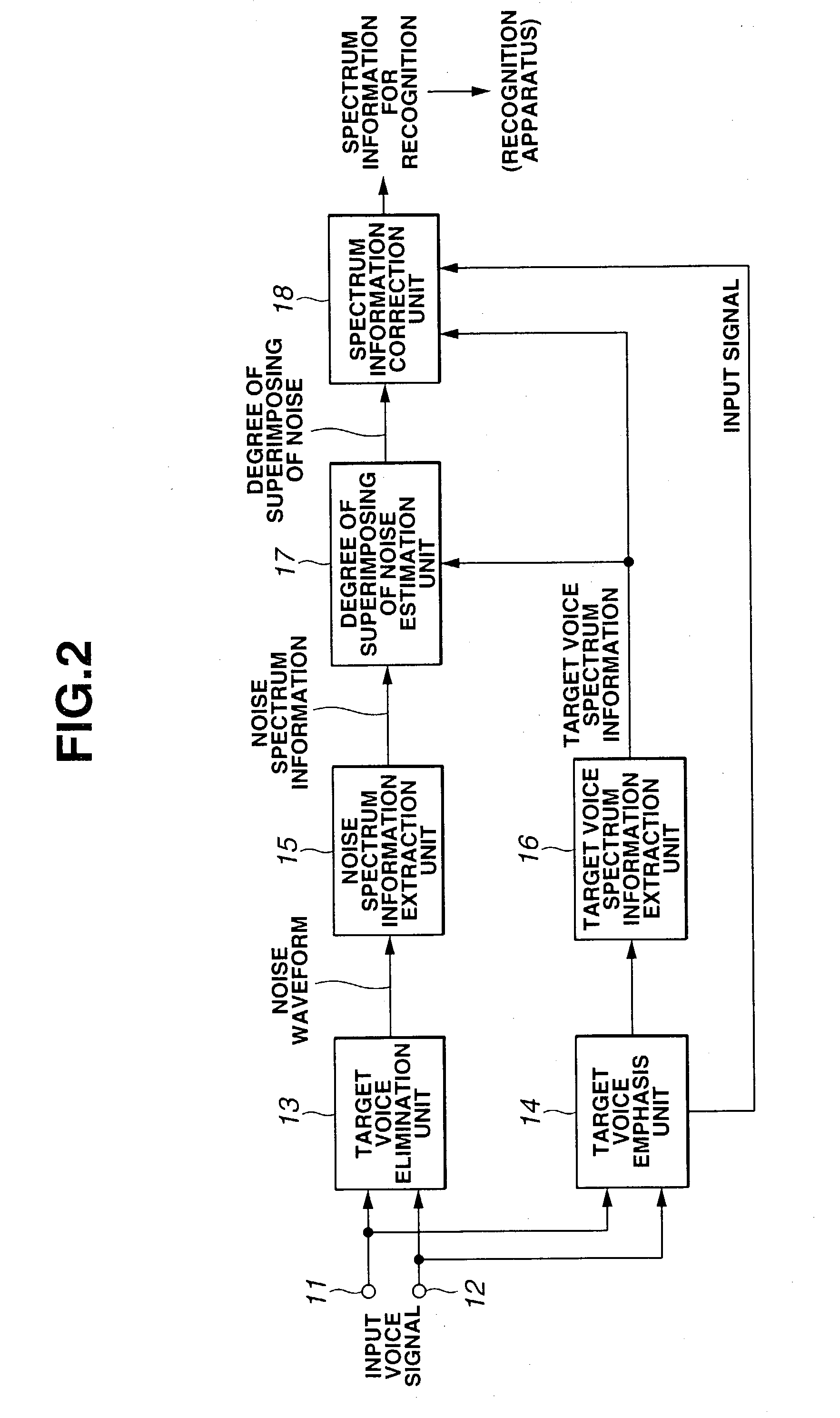
A target voice elimination unit reliably eliminates a target voice and outputs a target voice elimination signal including only a noise component. A target voice emphasis unit outputs a target voice emphasis signal from which a noise component is eliminated to some extent. A noise spectrum information extraction unit extracts noise spectrum information from the target voice elimination signal, and a target voice spectrum information extraction unit extracts target voice spectrum information from the target voice emphasis signal. A degree of multiplexing of noise estimation unit reliably detects the position where noise is superimposed and the magnitude of the noise from the noise spectrum information and the target voice spectrum information and obtains a degree of multiplexing of noise. A spectrum information correction unit reliably corrects the target voice spectrum information using the information of the degree of multiplexing of noise indicating the position and magnitude of the noise detected correctly. The influence of noise is greatly reduced in the spectrum information, thereby the accuracy of speech recognition can be improved.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Adjusting manufacturing process control parameter using updated process threshold derived from uncontrollable error
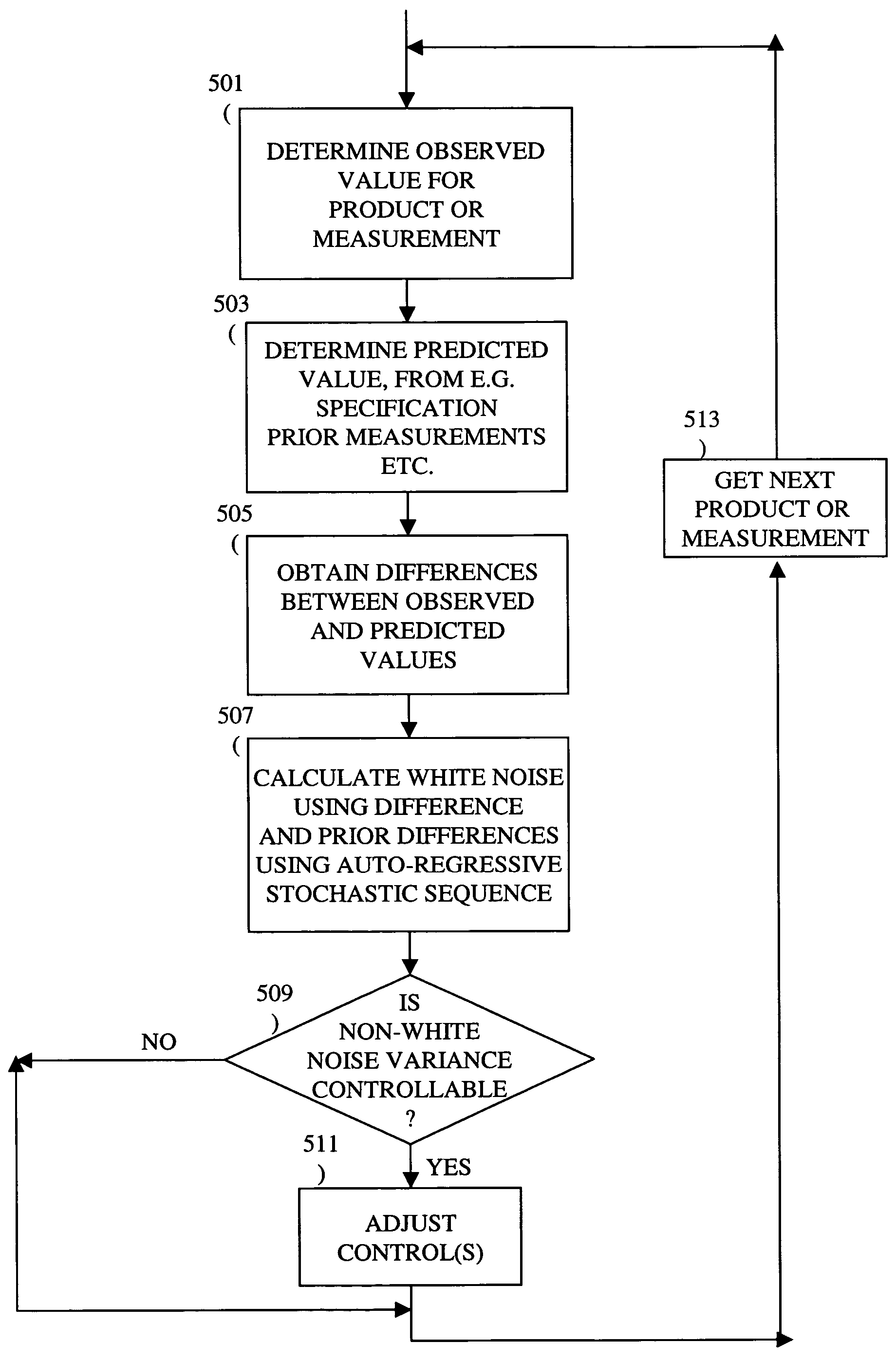
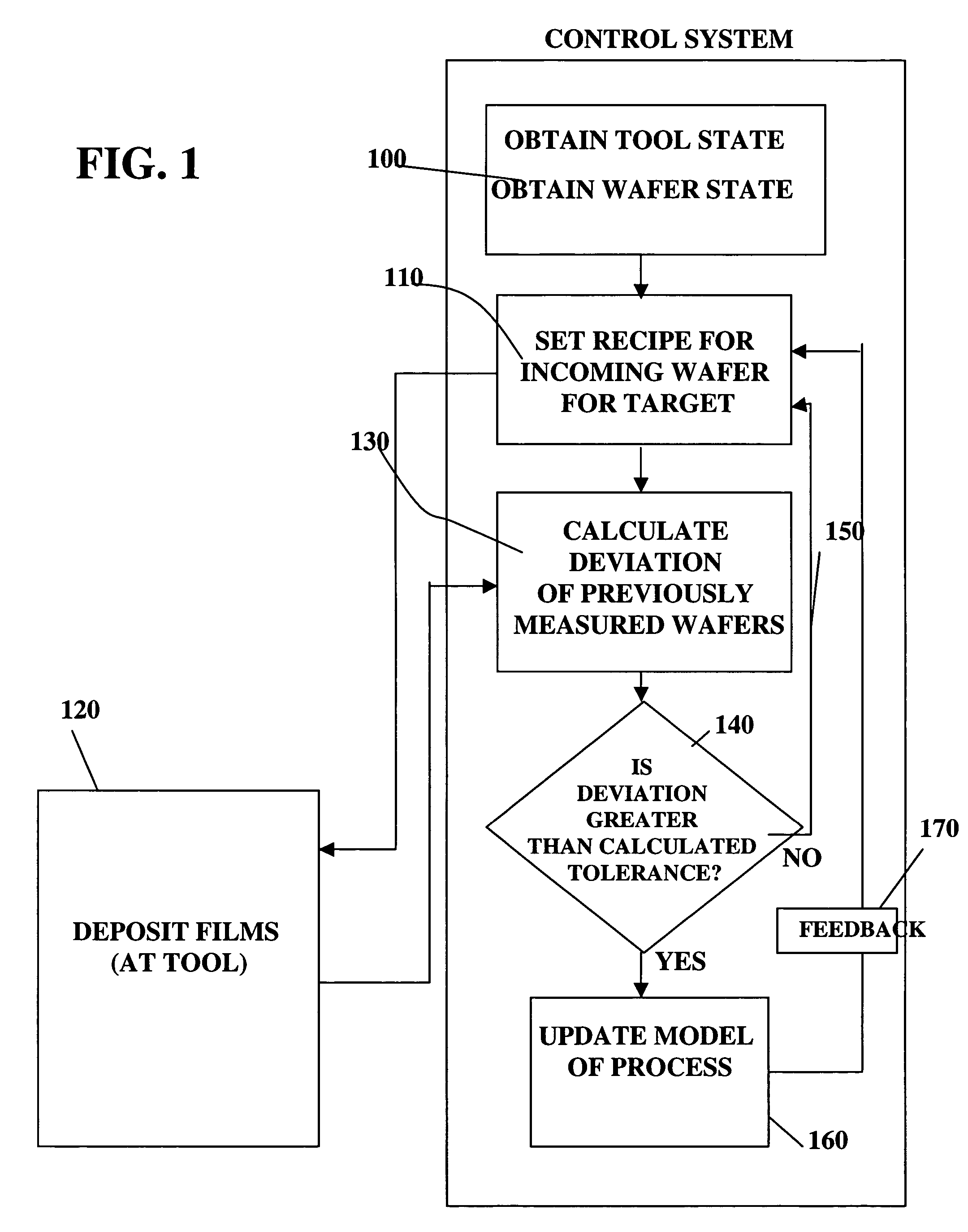
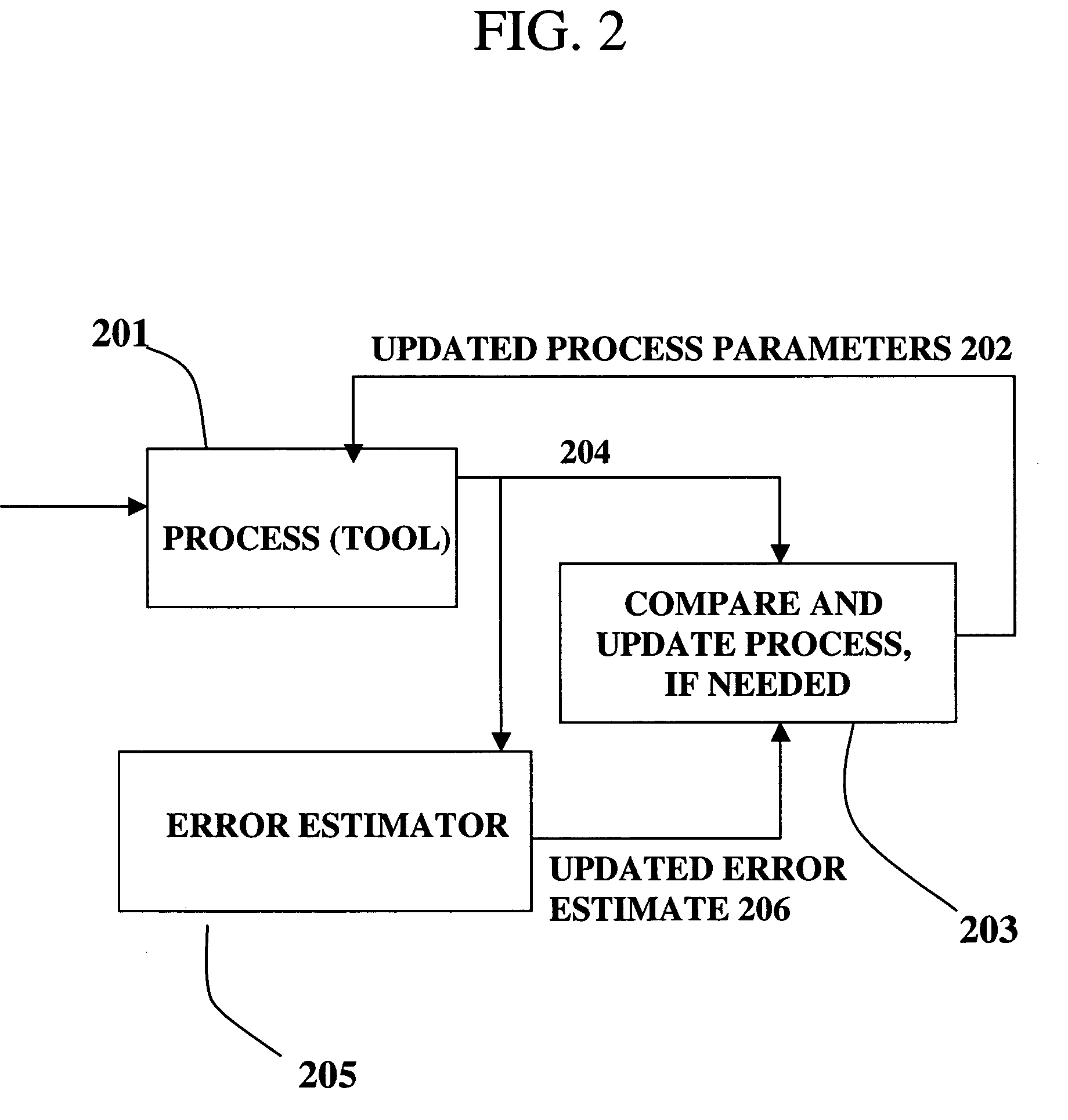
InactiveUS7349753B2Strict controlNon-controllableTotal factory controlSpecial data processing applicationsSemiconductor chipRandom noise
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Noise mitigating microphone system and method
ActiveUS20070047744A1Effectively mitigatedRemove and mitigatesMicrophonesMicrophones signal combinationEngineeringCombinational logic
A microphone system has a base coupled with first and second microphone apparatuses. The first microphone apparatus is capable of producing a first output signal having a noise component, while the second microphone apparatus is capable of producing a second output signal. The system also has combining logic operatively coupled with the first microphone apparatus and the second microphone apparatus. The combining logic uses the second output signal to remove at least a portion of the noise component from the first output signal.
Owner:INVENSENSE
Speech intelligibility in telephones with multiple microphones
ActiveUS20090111507A1Improve speech clarityMicrophones signal combinationSubstation equipmentVoice activityAudio frequency
The present invention is directed to improved speech intelligibility in telephones with multiple microphones. Such a telephone includes a first microphone, a second microphone, a voice activity detector (VAD), a receiver module, and a signal processor. The first microphone outputs a first audio signal, which comprises a voice component when a near-end user talks and a background noise component. The second microphone outputs a second audio signal. The VAD generates a voice activity signal responsive to a ratio between the first audio signal and the second audio signal. The voice activity signal identifies time intervals in which the voice component of the near-end user is present in the first audio signal. The receiver module receives a third audio signal, which comprises a voice component of a far-end user. The signal processor modifies the third audio signal responsive to the voice activity signal.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
CMOS APS readout scheme that combines reset drain current and the source follower output
InactiveUS7317484B2Reduce low frequency noiseReduce noiseTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsMultiplexingEngineering
A circuit and method for reducing noise in video imagers which takes advantage of the fact that the same image information is present in the drain current in a reset transistor used to reset a photodiode in a pixel as is present in the readout current. The noise is reduced by passing the multiplexed output voltage from the source follower output transistor in an APS imager system through a high pass filter to reduce the low frequency noise from the source follower. The drain current in the reset transistor used to reset the APS is passed through a low pass filter. The low pass filter output and the high pass filter output are then combined. Since the drain current in the reset transistor contains the same image information as the voltage output of the source follower output transistor the image information can be obtained by combining the output of the low pass filter and the output of the high pass filter. Since the low frequency noise components of the source follower output transistor have been suppressed combined outputs of the low pass filter and high pass filter will provide the image information with greatly suppressed low frequency noise.
Owner:RPX CORP
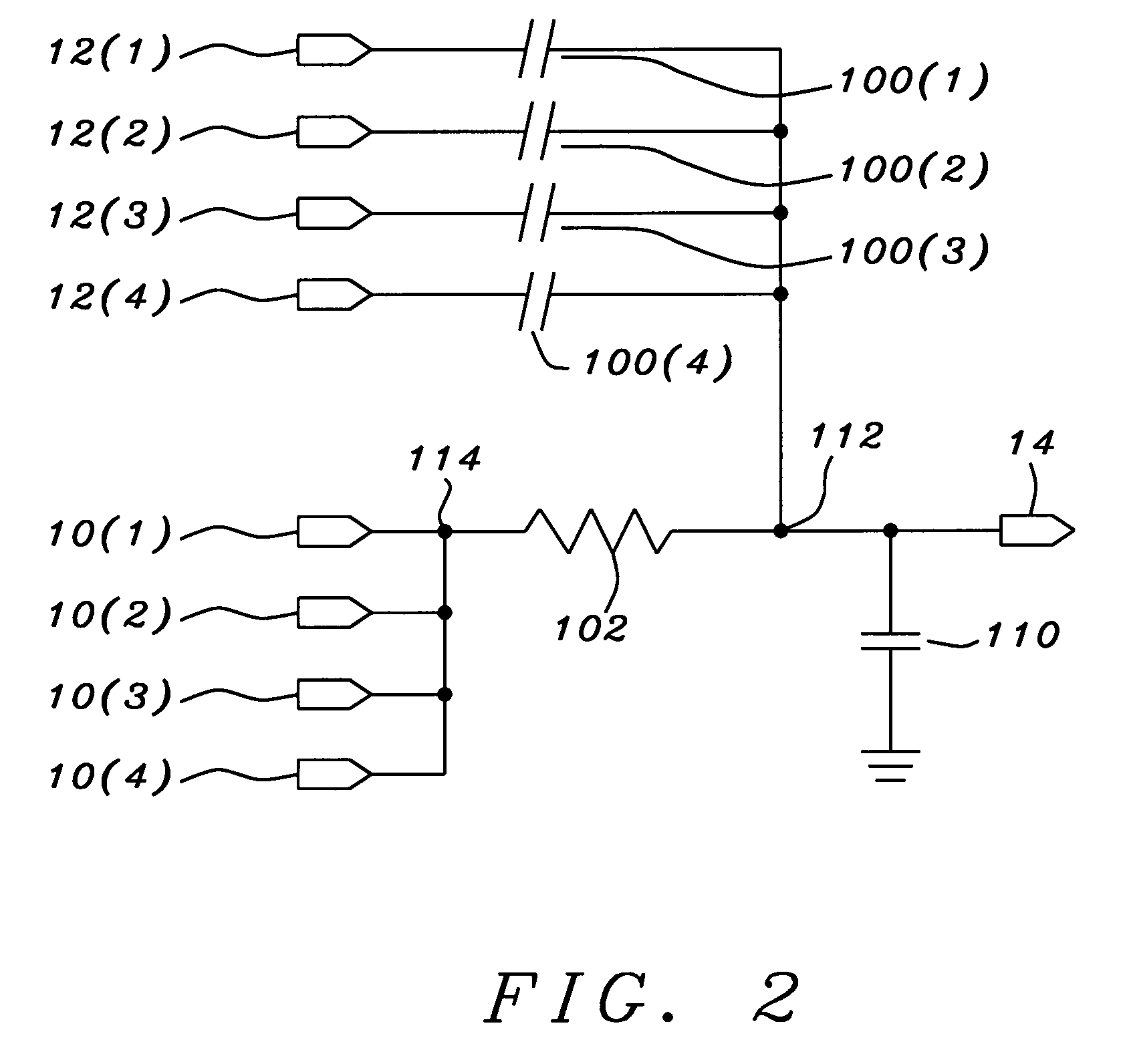
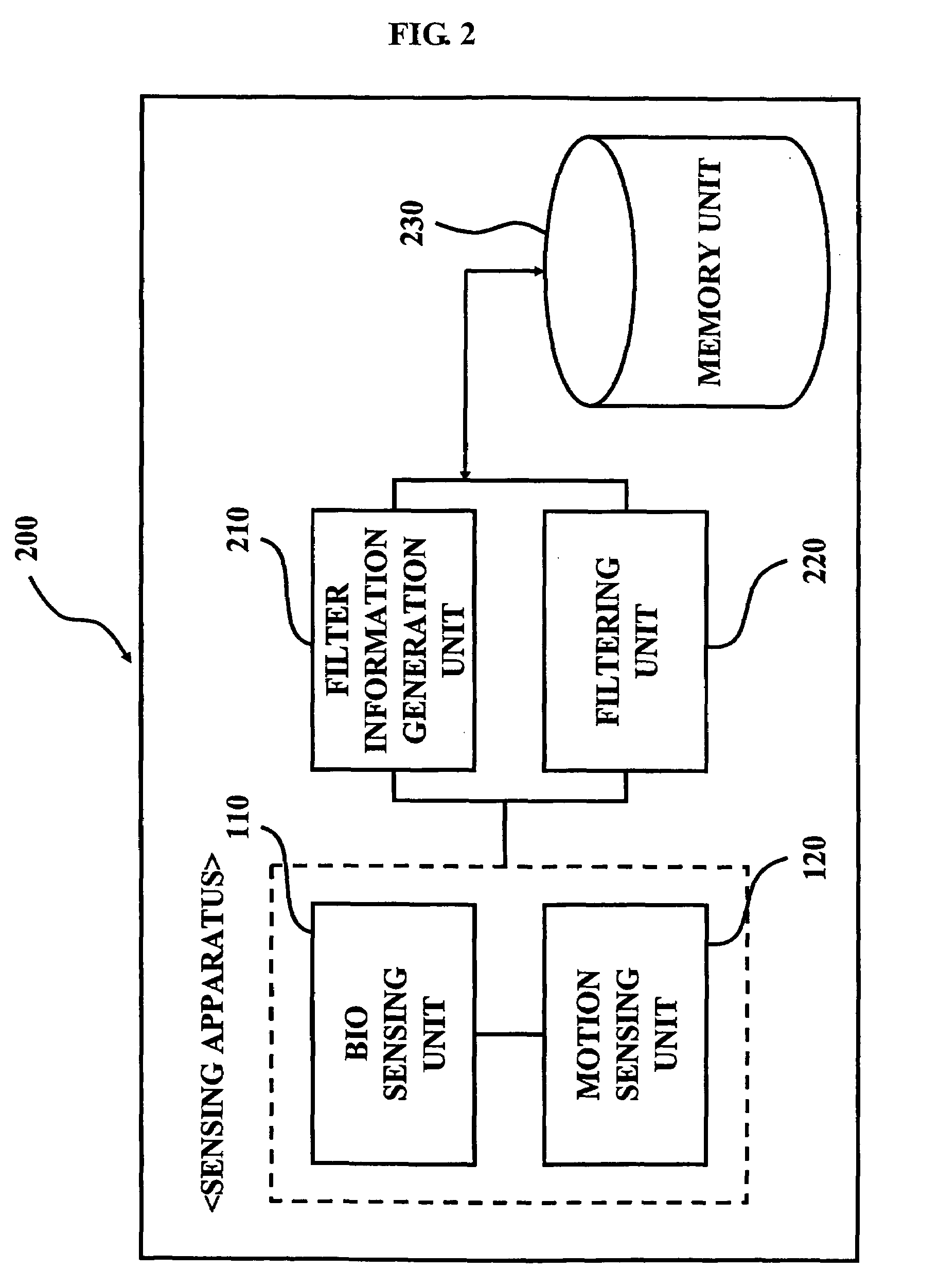
Method and system for removing noise by using change in activity pattern
ActiveUS7620450B2Fast noiseSure easyElectrocardiographyElectromyographyNoise generationNoise removal
A noise removal method and system using a change in activity pattern, in which it is recognized that noise components exist in different frequency bands and different filters for removing noise are stored according to each activity pattern, thereby optimally removing the noise components. A method of removing noise by using a change in an activity pattern includes: recognizing an activity pattern of the subject using an activity sensor; sensing a first bio signal corresponding to the activity pattern from the subject using an electric potential sensor; recognizing a noise generation pattern according to the activity pattern by analyzing a noise component for each section of the first bio signal; selecting filter information for each section according to the noise generation pattern; storing the filter information selected for each section in association with the activity pattern; and removing noise from a second bio signal sensed from the subject by applying the stored filter information.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Signature noise removal
ActiveUS20070078649A1Improve processing qualityImprove reception qualitySpeech recognitionNoise removalSpeech sound
A speech enhancement system improves the perceptual quality of a processed voice signal. The system improves the perceptual quality of a voice signal by removing unwanted noise components from a voice signal. The system removes undesirable signals that may result in the loss of information. The system receives and analyzes signals to determine whether an undesired random or persistent signal corresponds to one or more modeled noises. When one or more noise components are detected, the noise components are substantially removed or dampened from the signal to provide a less noisy voice signal.
Owner:MALIKIE INNOVATIONS LTD
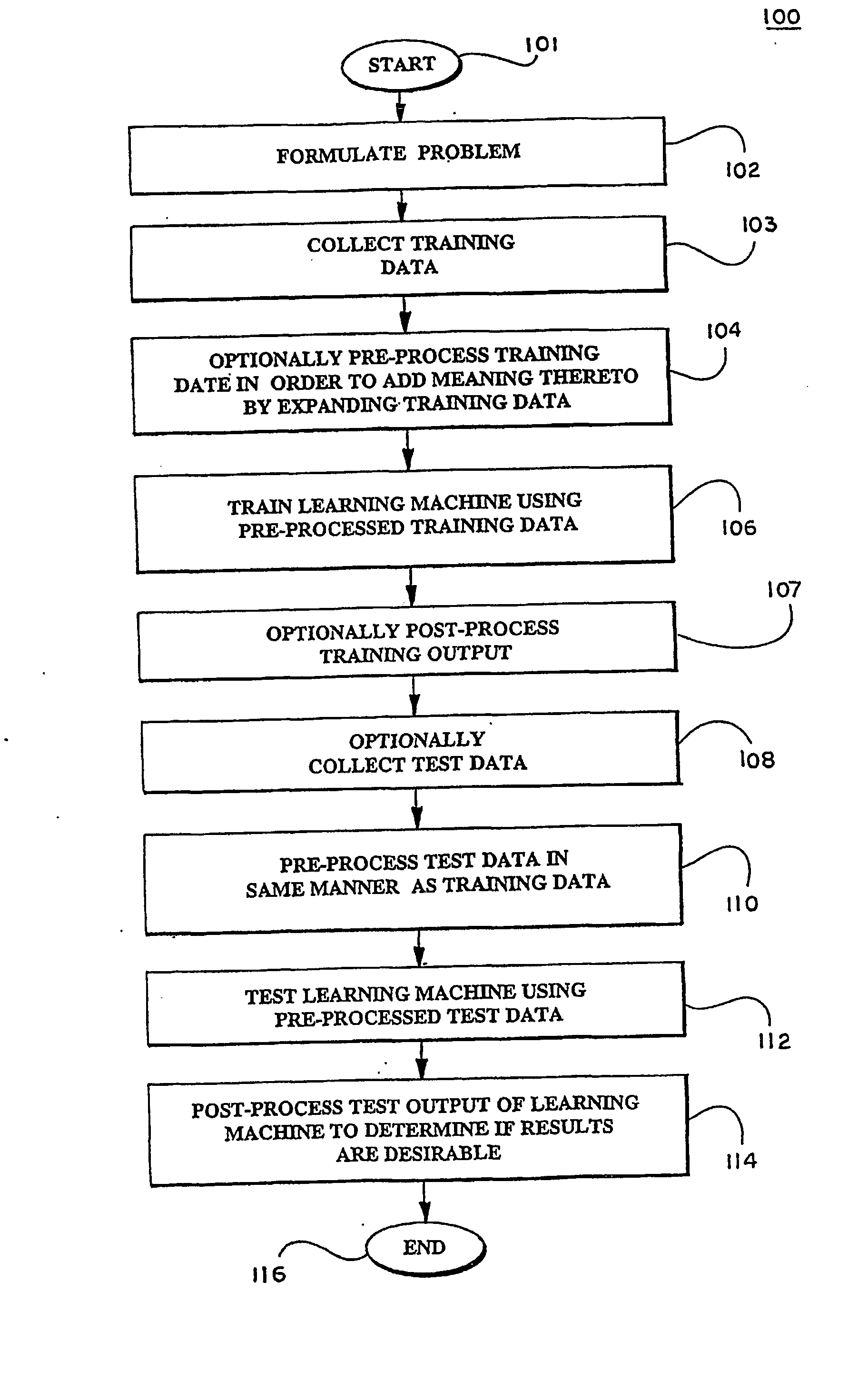
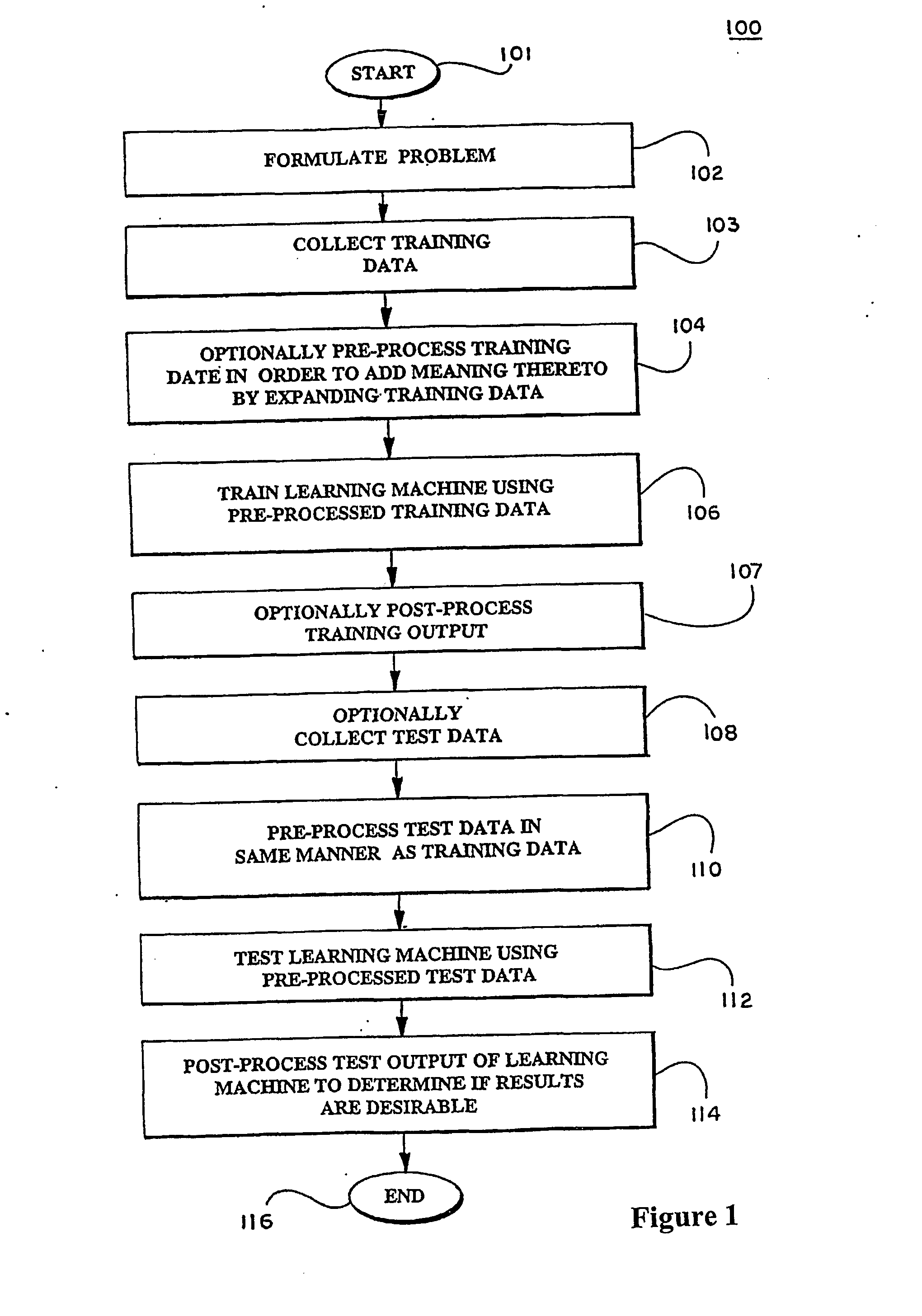
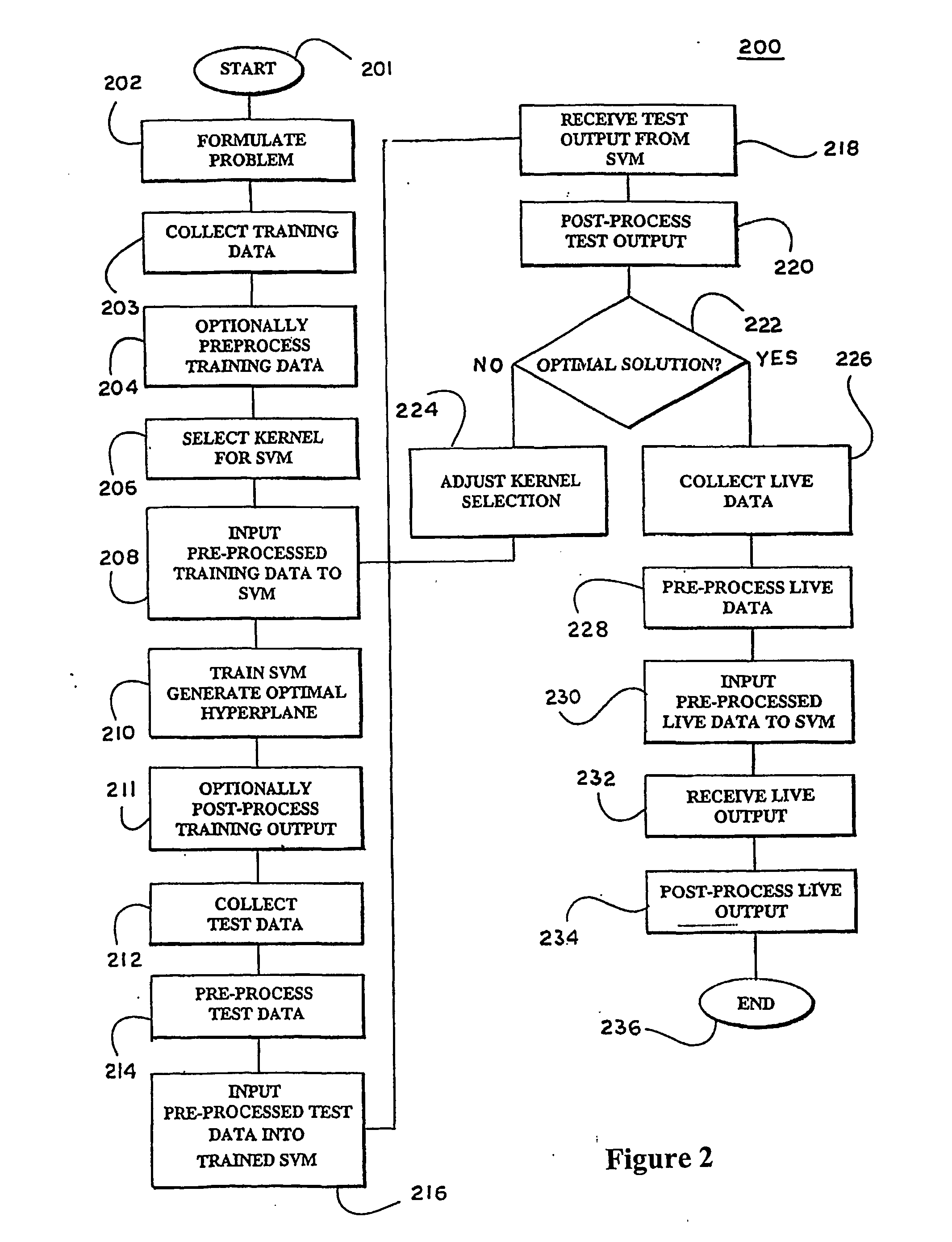
Kernels and methods for selecting kernels for use in learning machines
InactiveUS20050071300A1Enhancing knowledge discoveryDigital data processing detailsKernel methodsLearning machineEcg signal
Kernels (206) for use in learning machines, such as support vector machines, and methods are provided for selection and construction of such kernels are controlled by the nature of the data to be analyzed (203). In particular, data which may possess characteristics such as structure, for example DNA sequences, documents; graphs, signals, such as ECG signals and microarray expression profiles; spectra; images; spatio-temporal data; and relational data, and which may possess invariances or noise components that can interfere with the ability to accurately extract the desired information. Where structured datasets are analyzed, locational kernels are defined to provide measures of similarity among data points (210). The locational kernels are then combined to generate the decision function, or kernel. Where invariance transformations or noise is present, tangent vectors are defined to identify relationships between the invariance or noise and the data points (222). A covariance matrix is formed using the tangent vectors, then used in generation of the kernel.
Owner:BIOWULF TECH +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com