Patents
Literature
295 results about "Spectral envelope" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
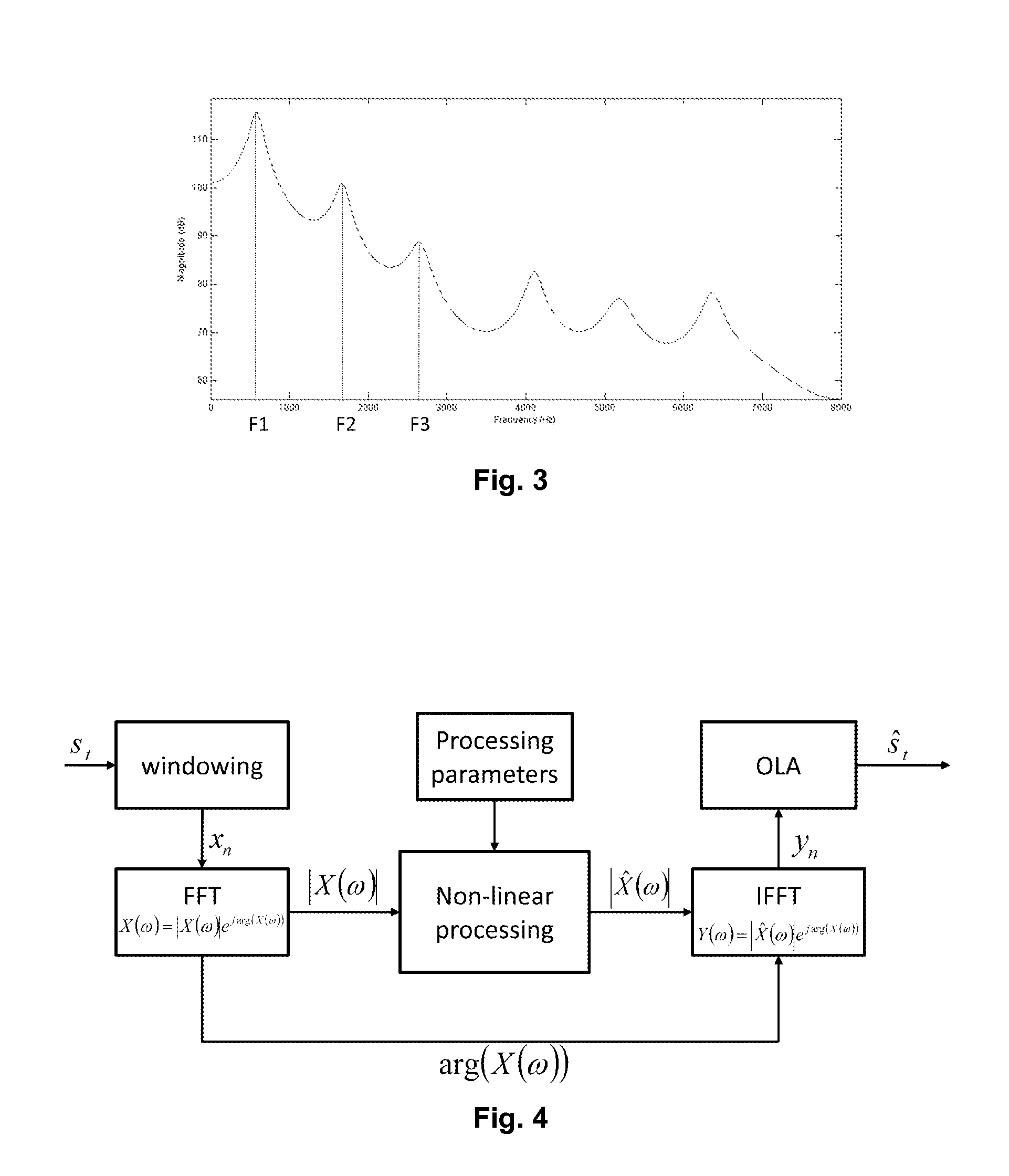
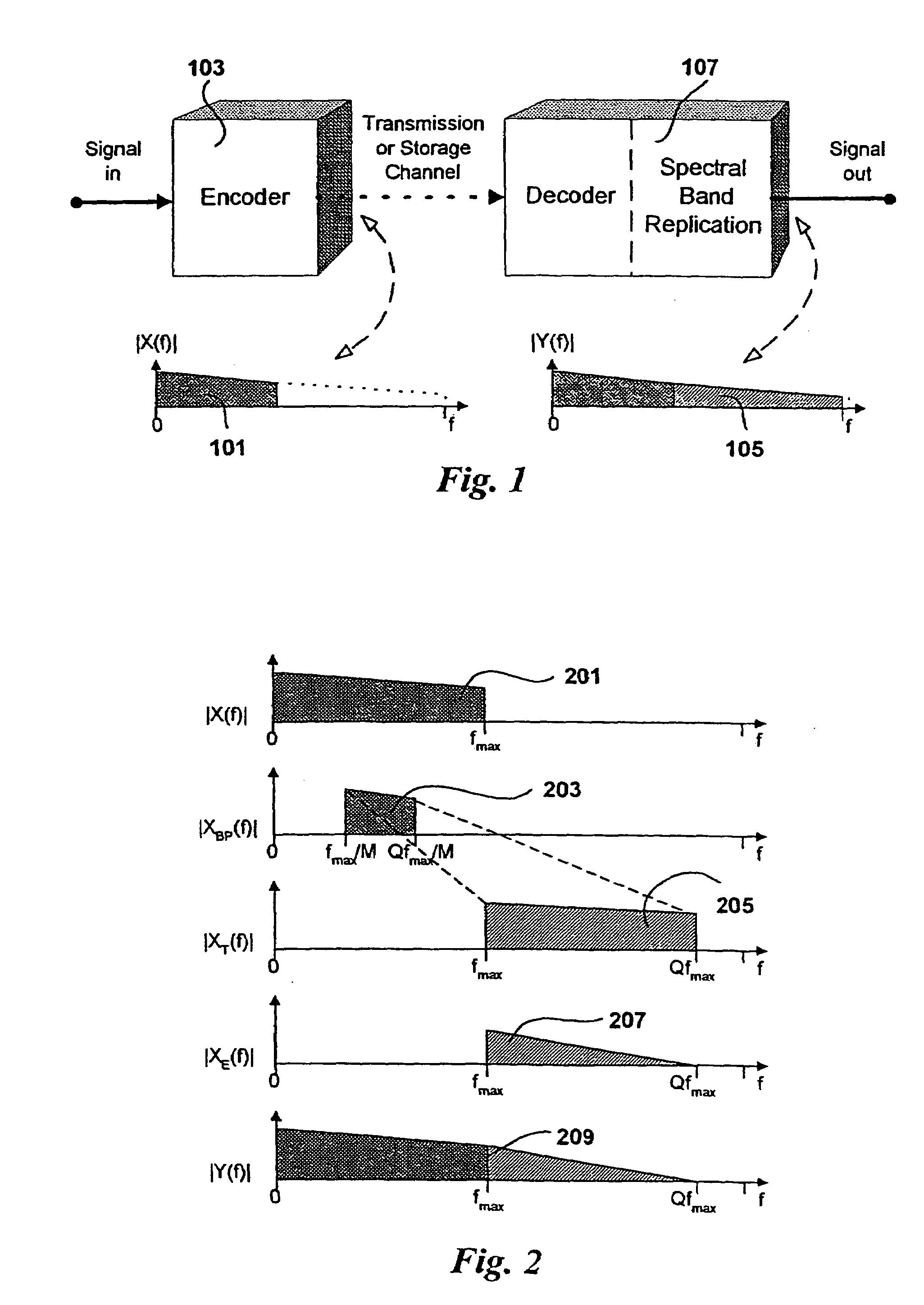
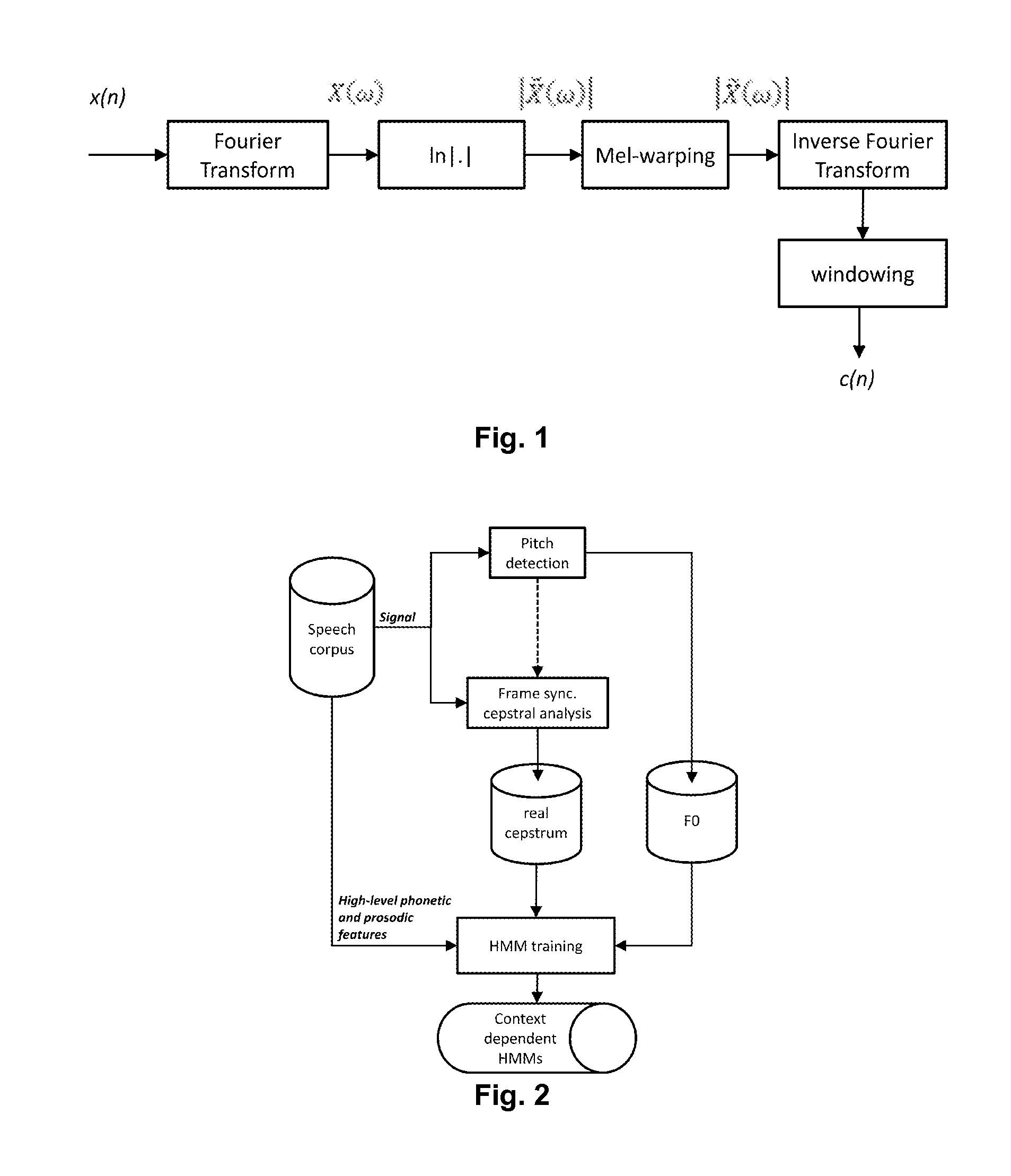
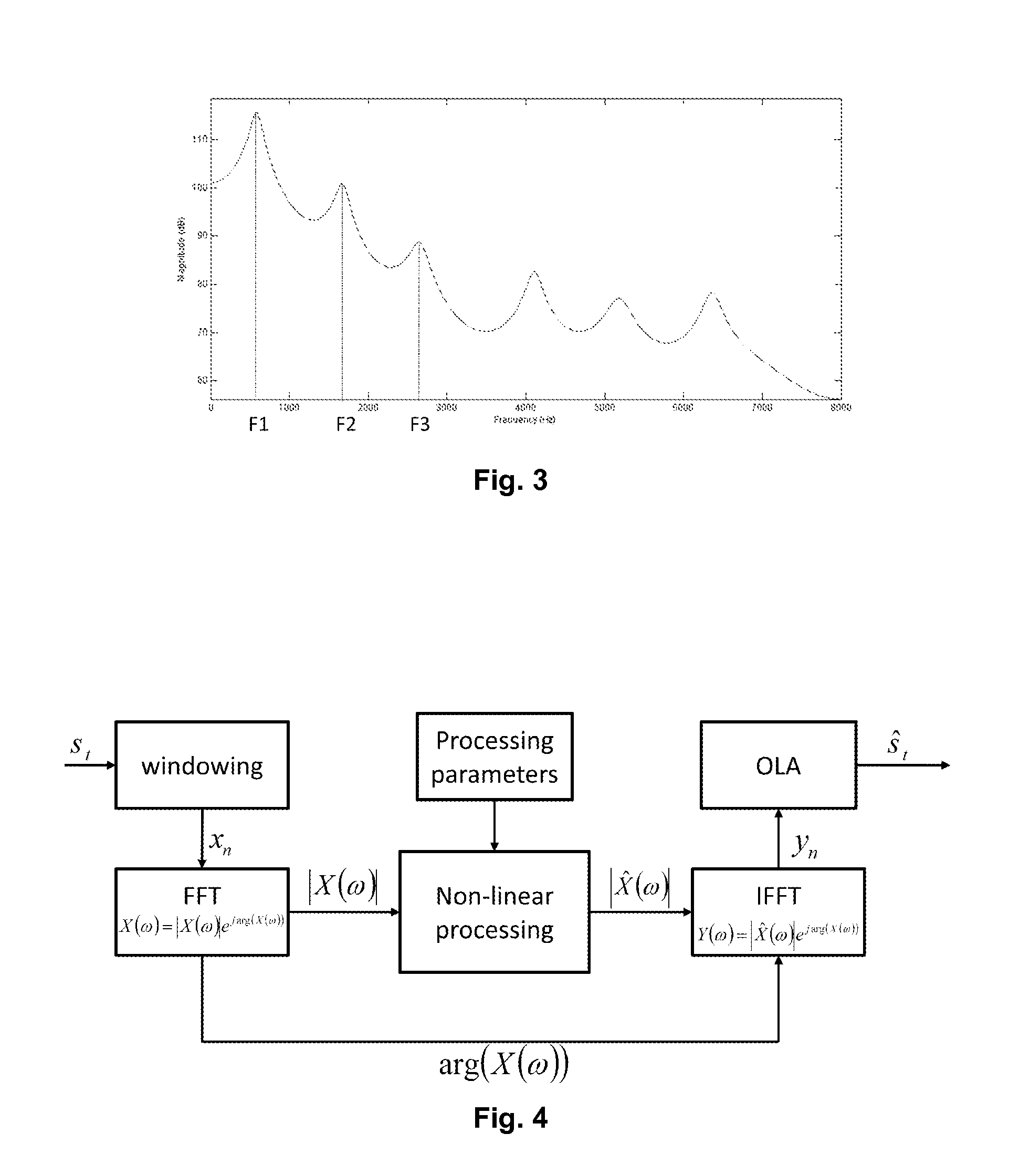
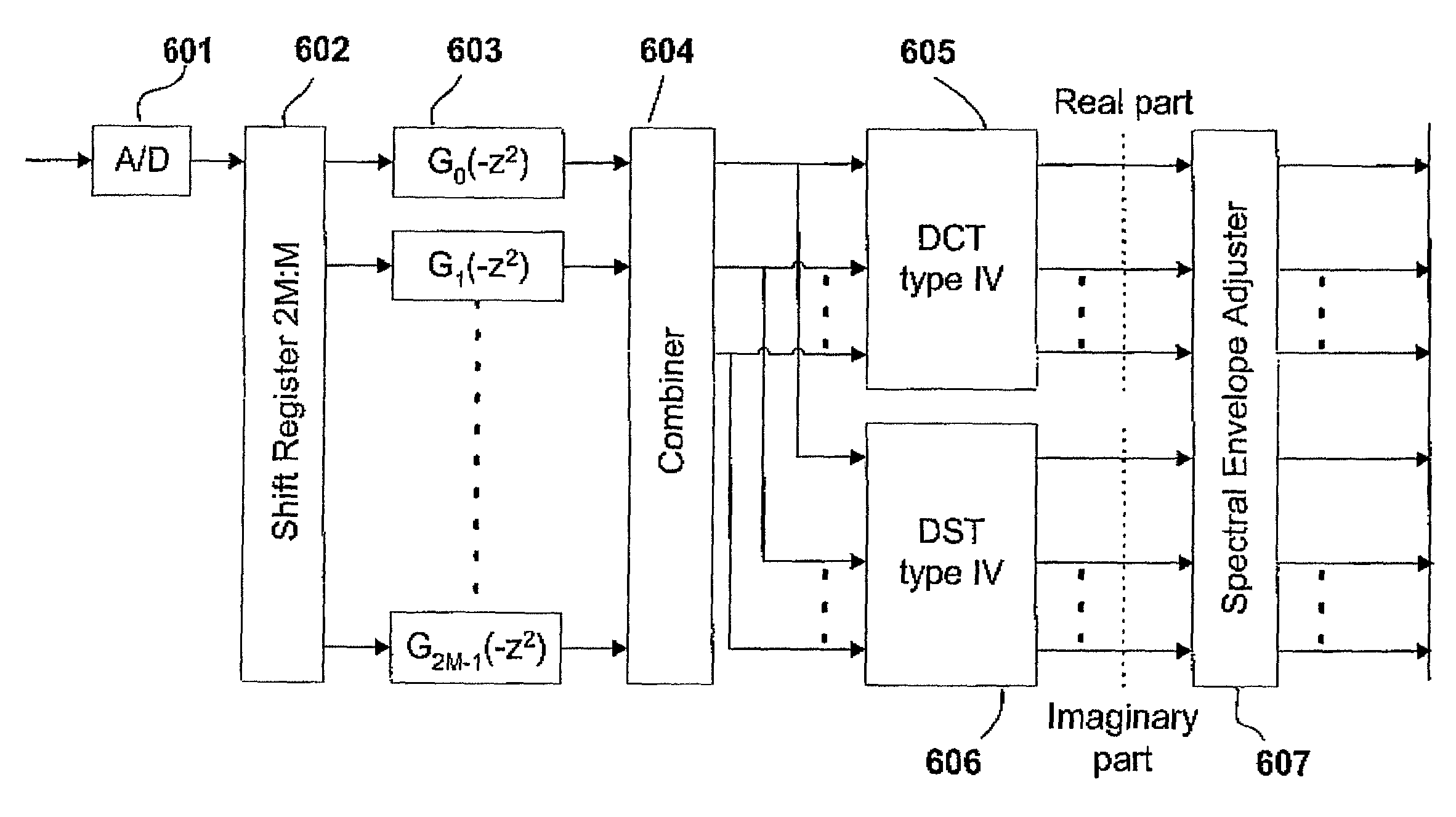
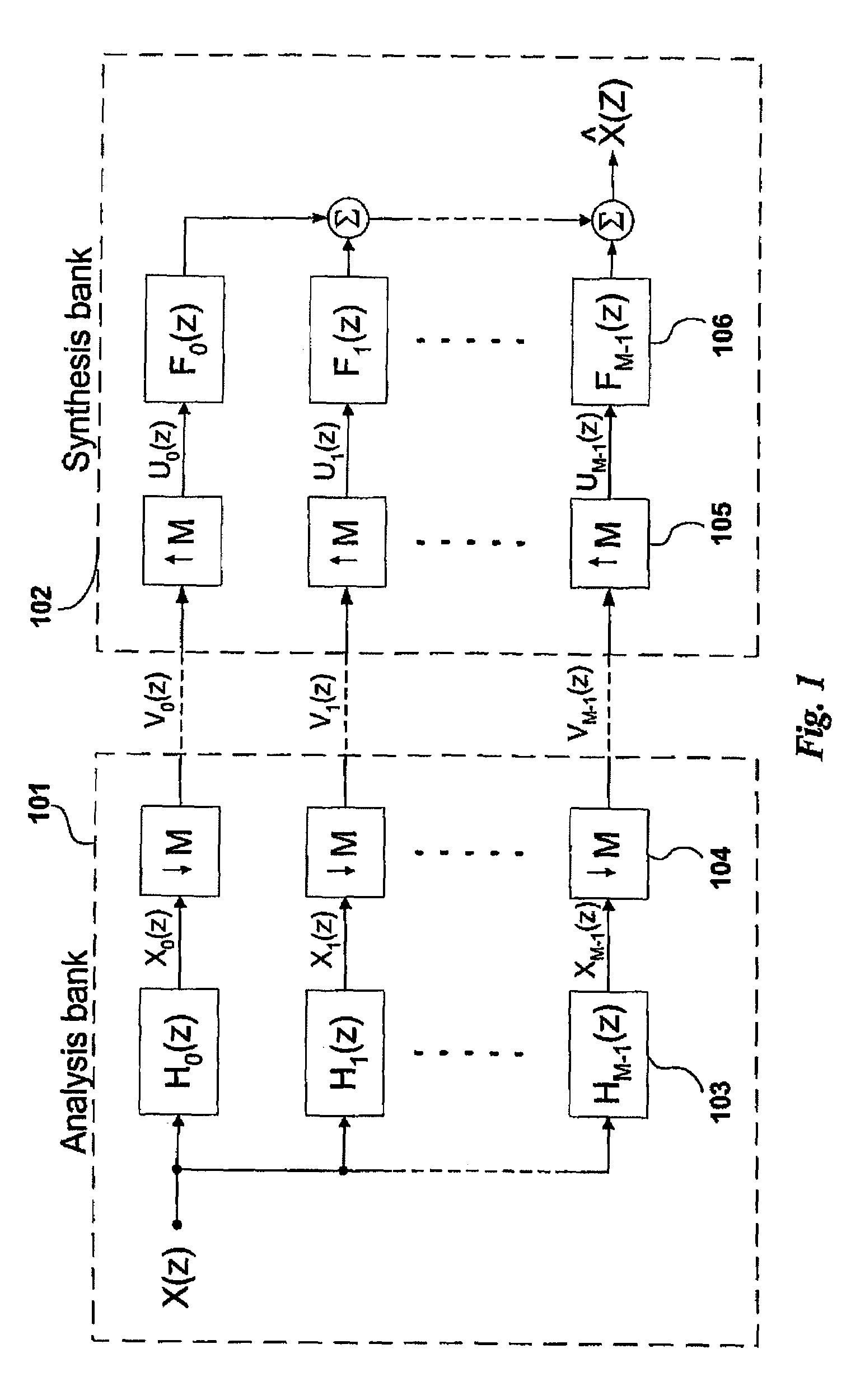
A spectral envelope is the envelope curve of the amplitude spectrum. It describes one point in time (one window, to be precise). In remote sensing using a spectrometer, the spectral envelope of a feature is the boundary of its spectral properties, as defined by the range of brightness levels in each of the spectral bands of interest.
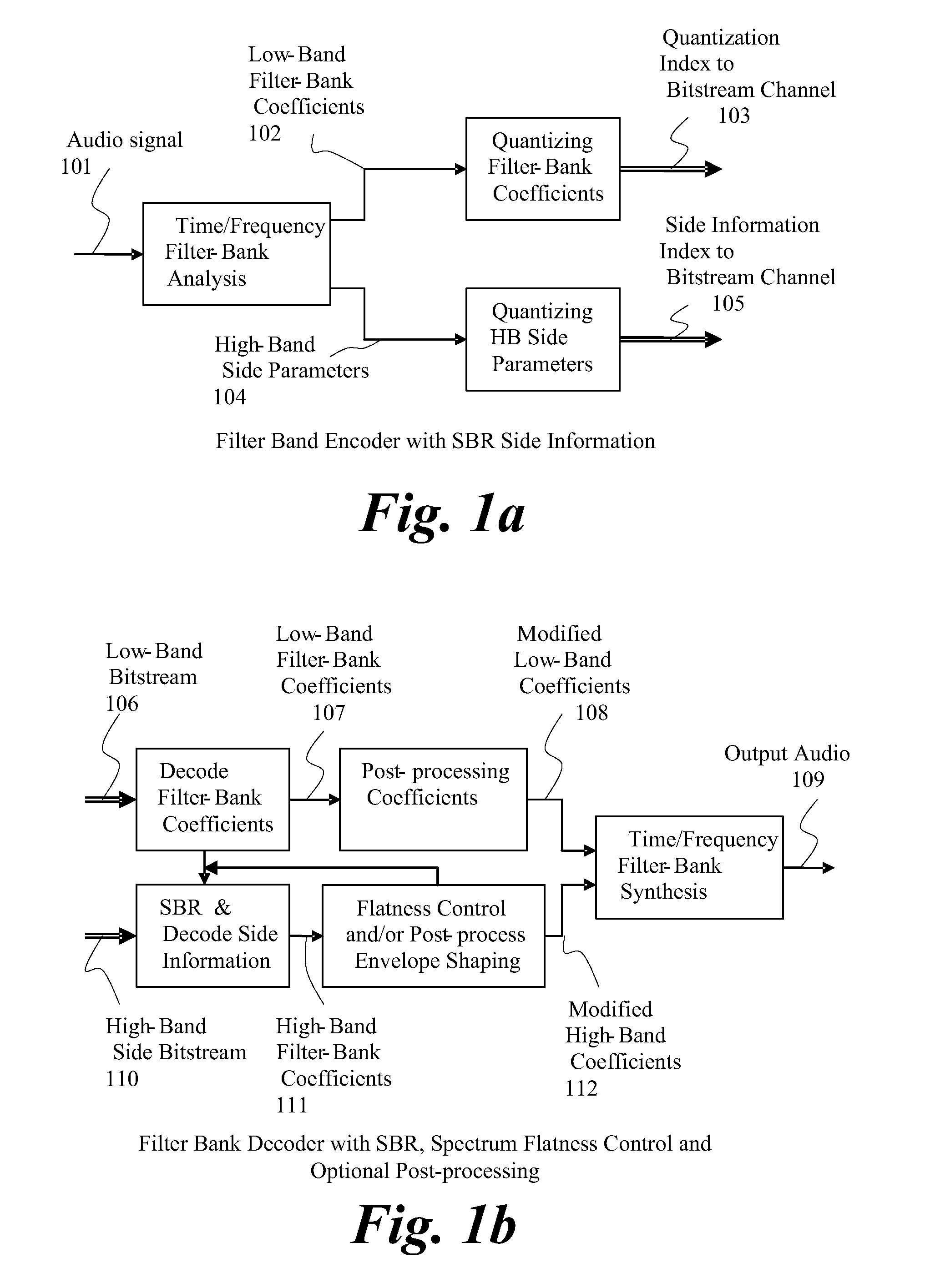
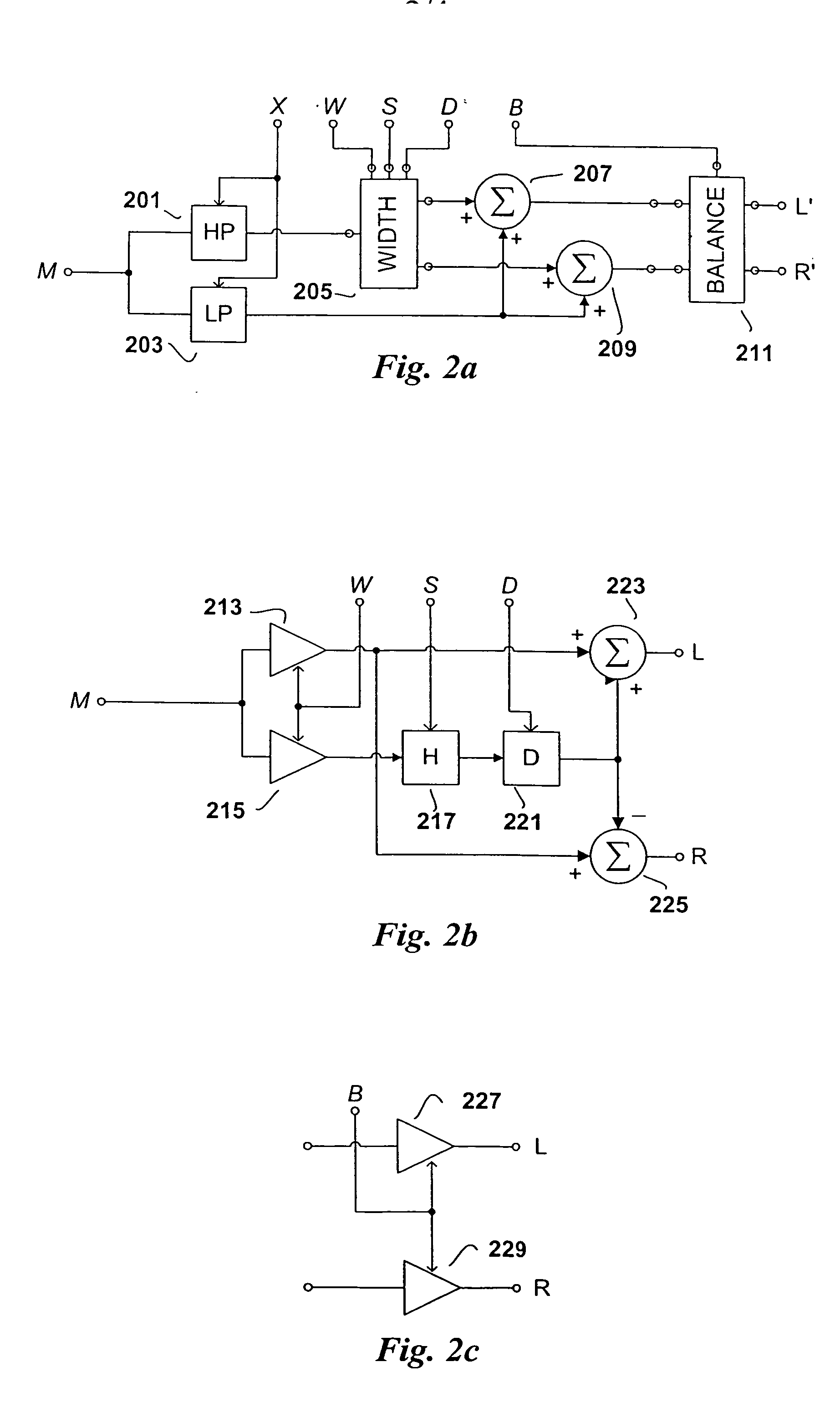
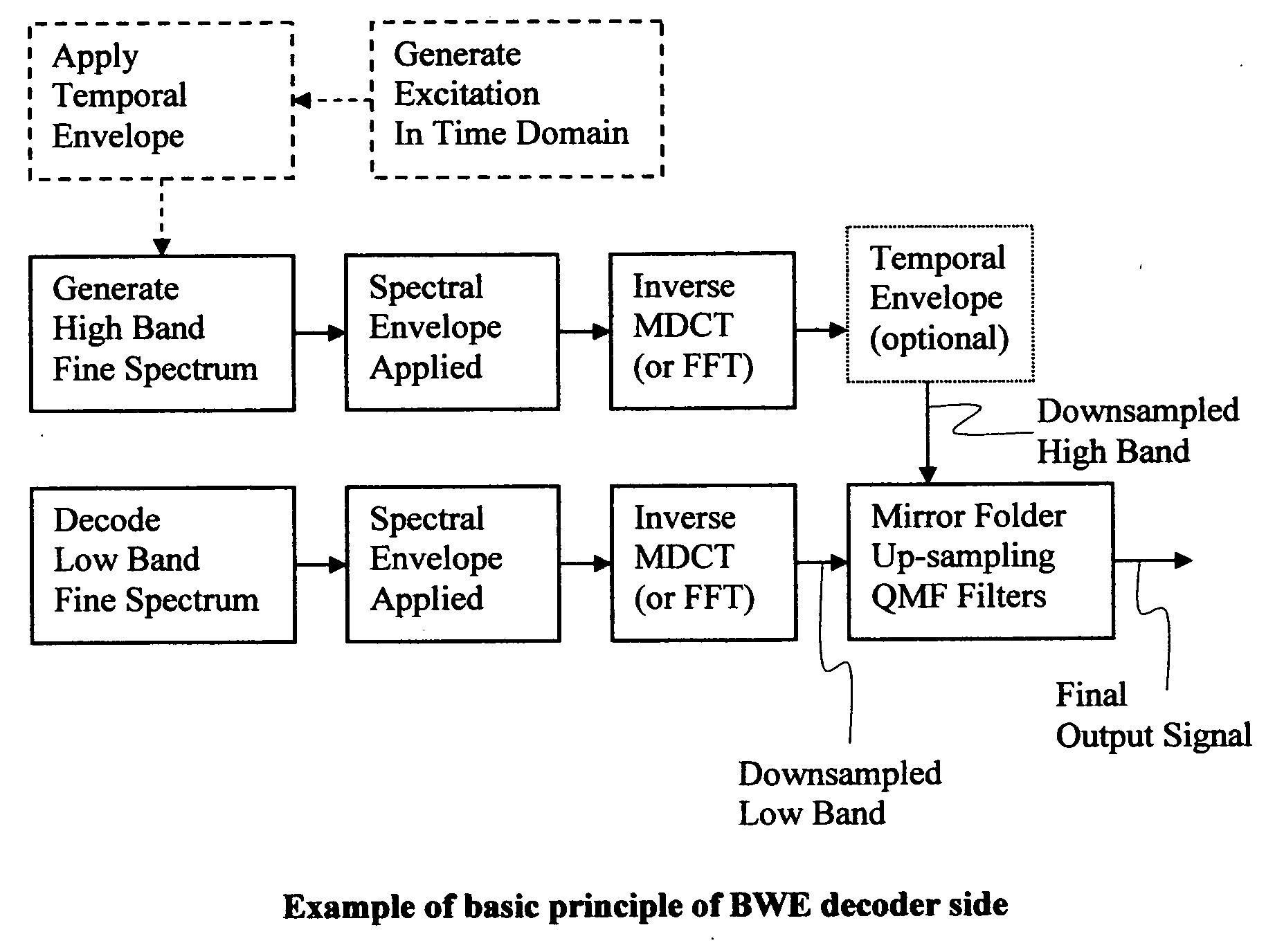
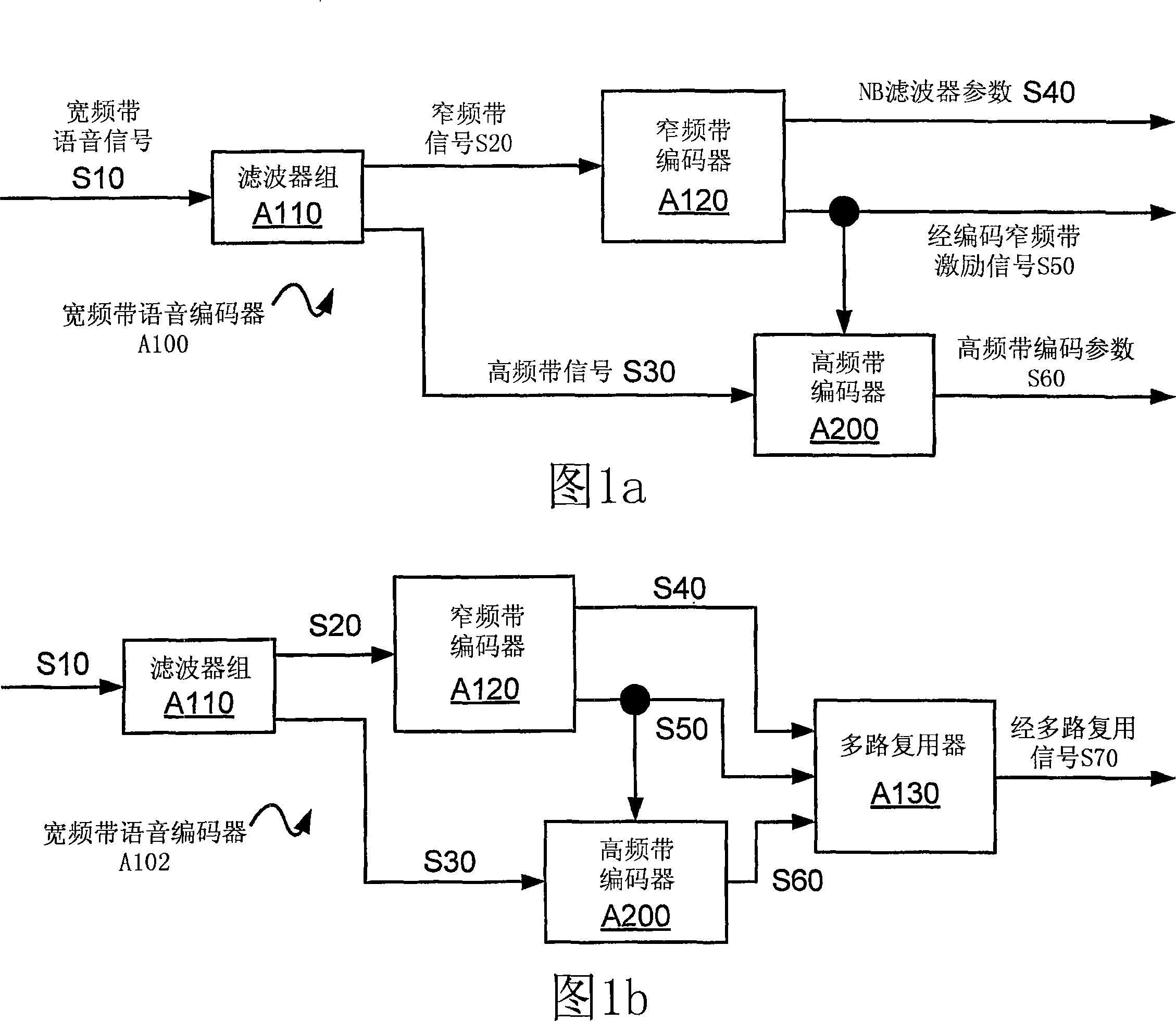
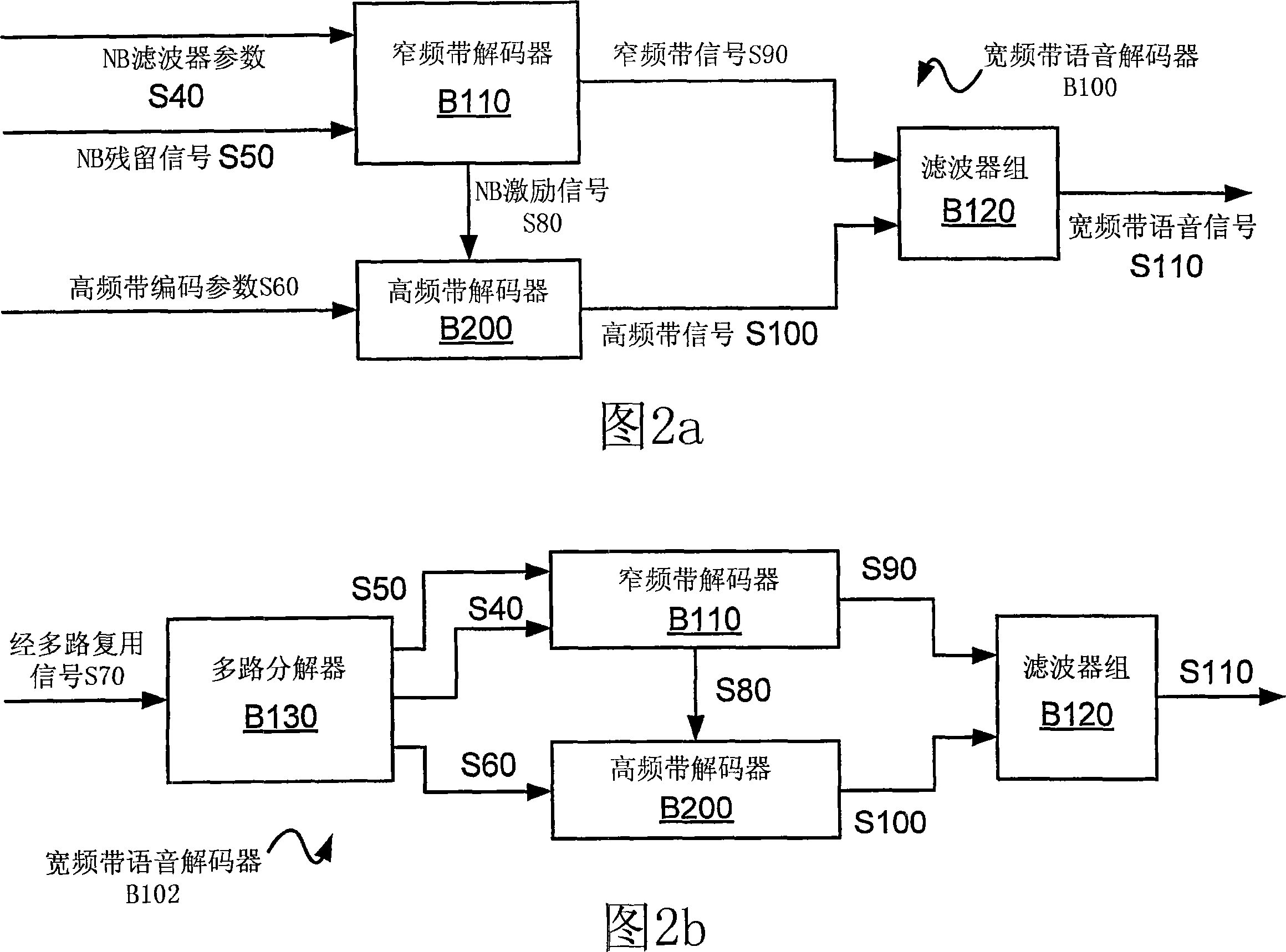
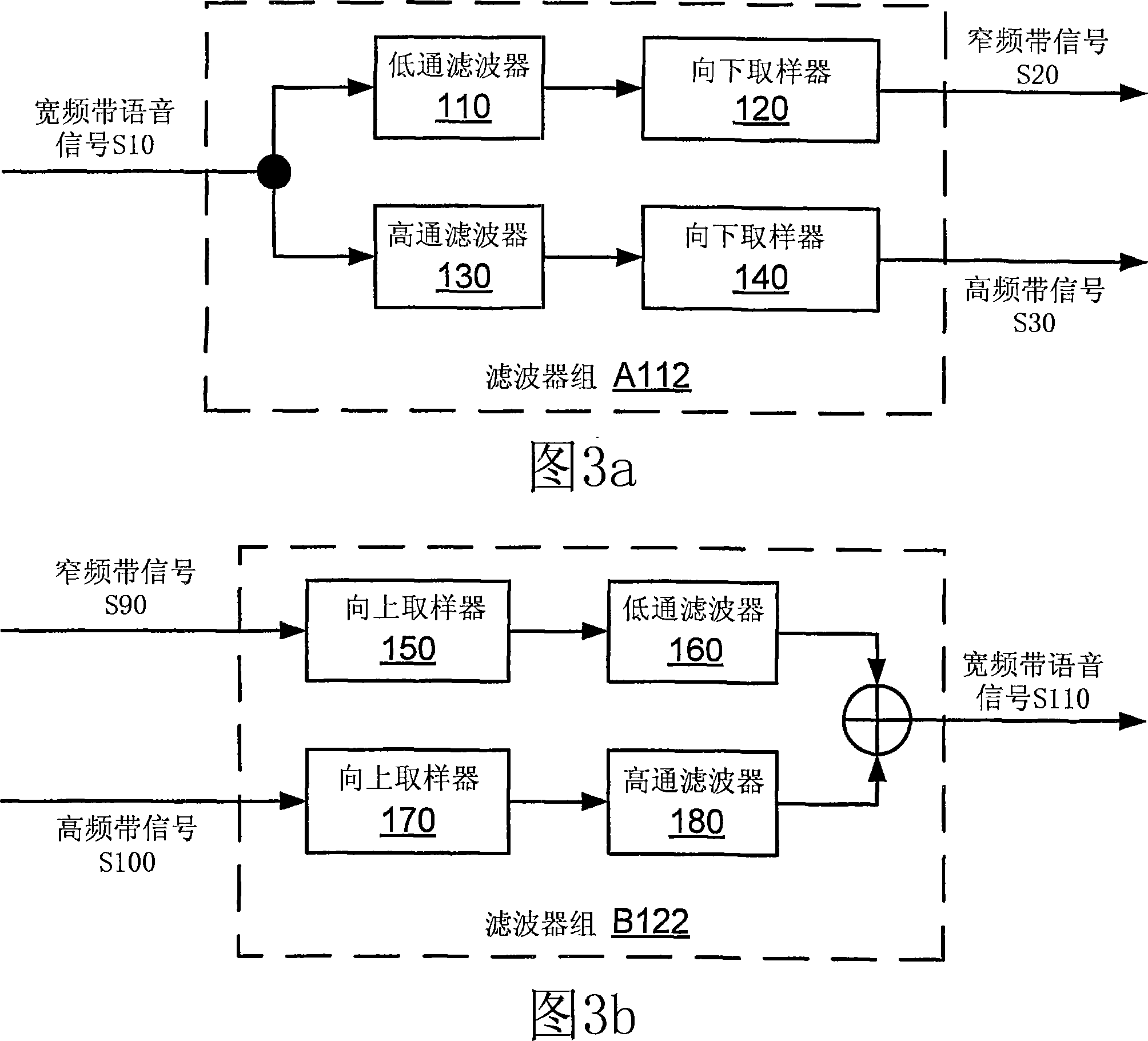
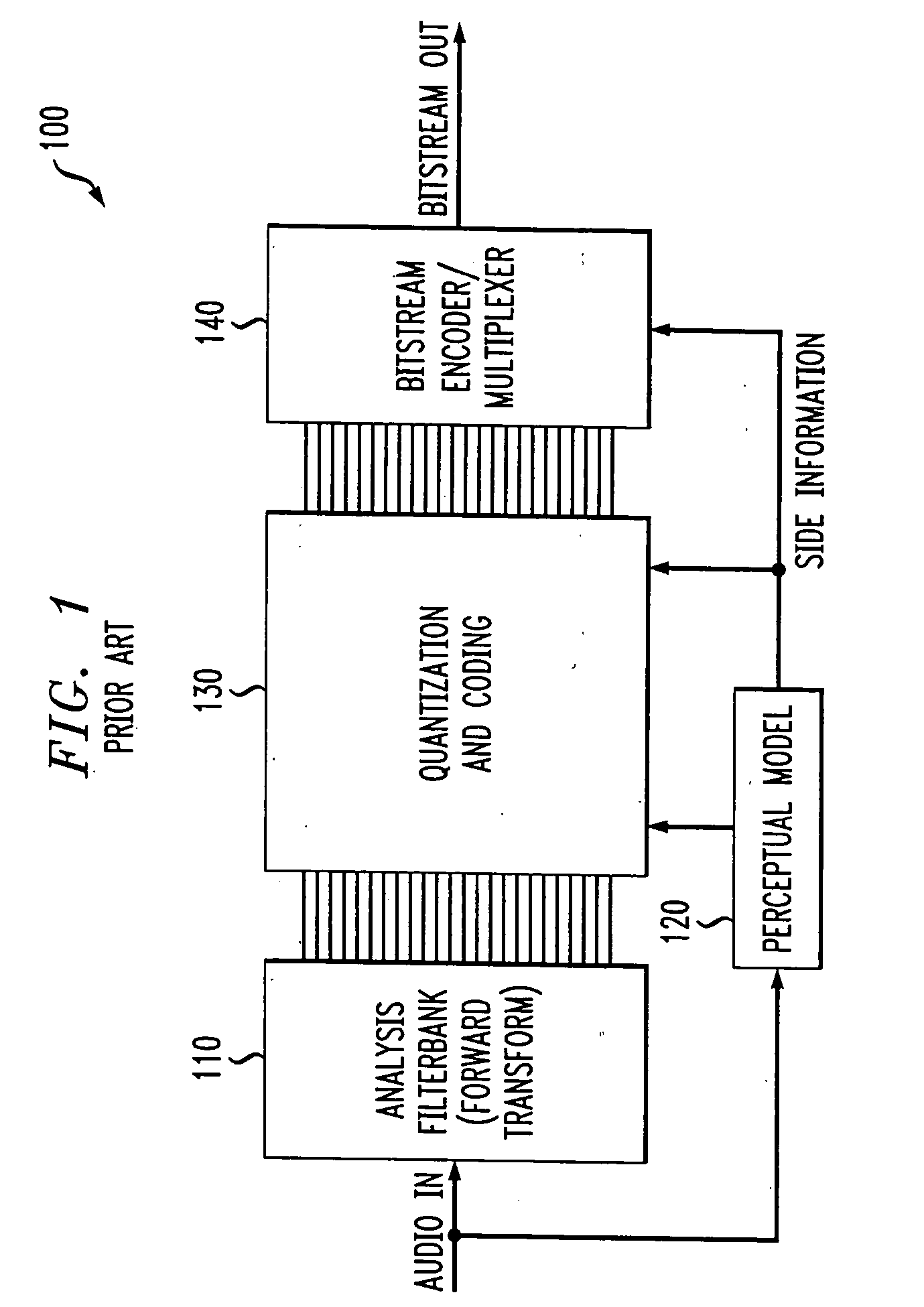
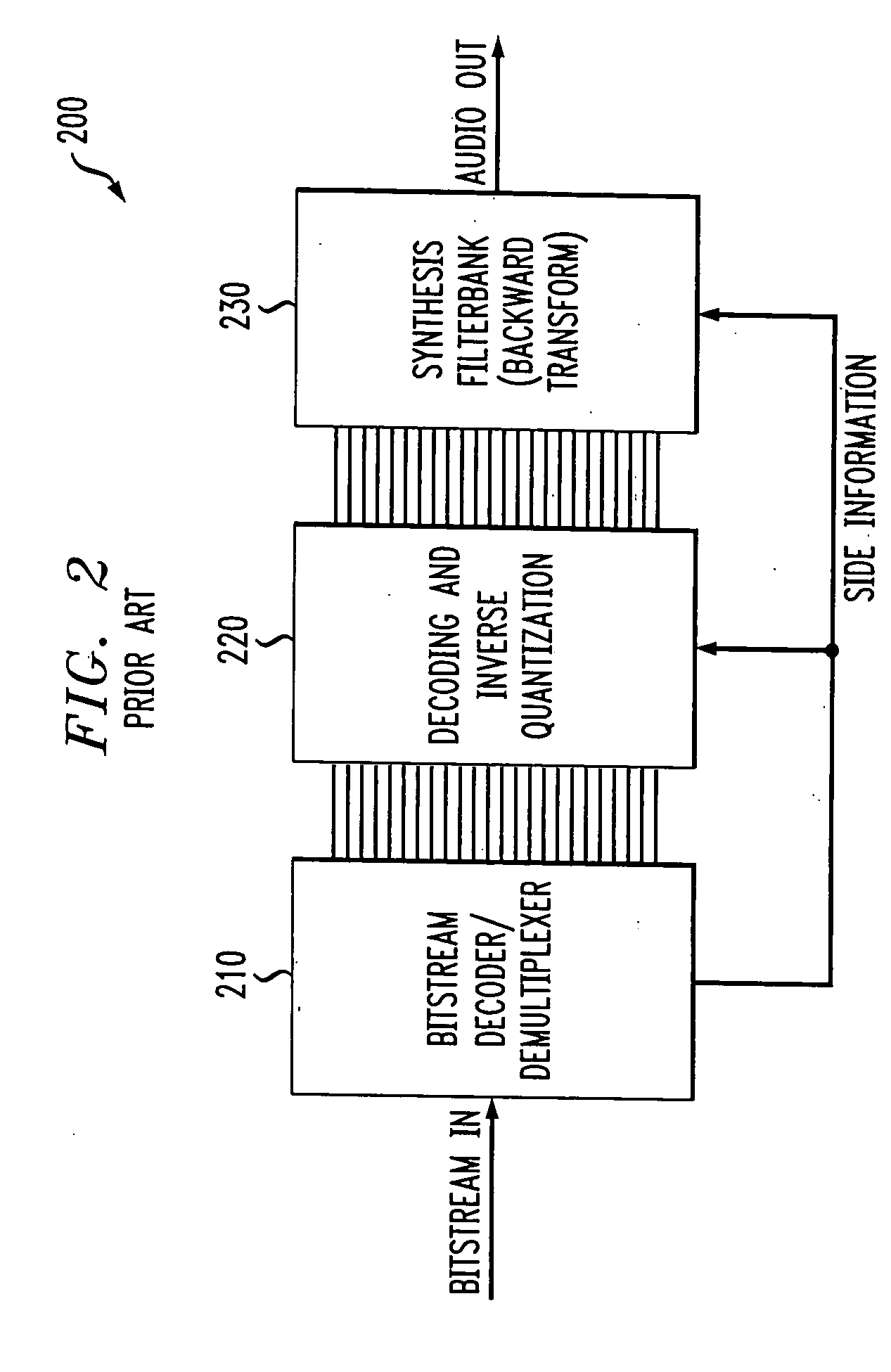
Broadband frequency translation for high frequency regeneration
InactiveUS20030187663A1Reduce in quantityMaintaining perceived qualitySpeech analysisFrequency spectrumAudio signal flow
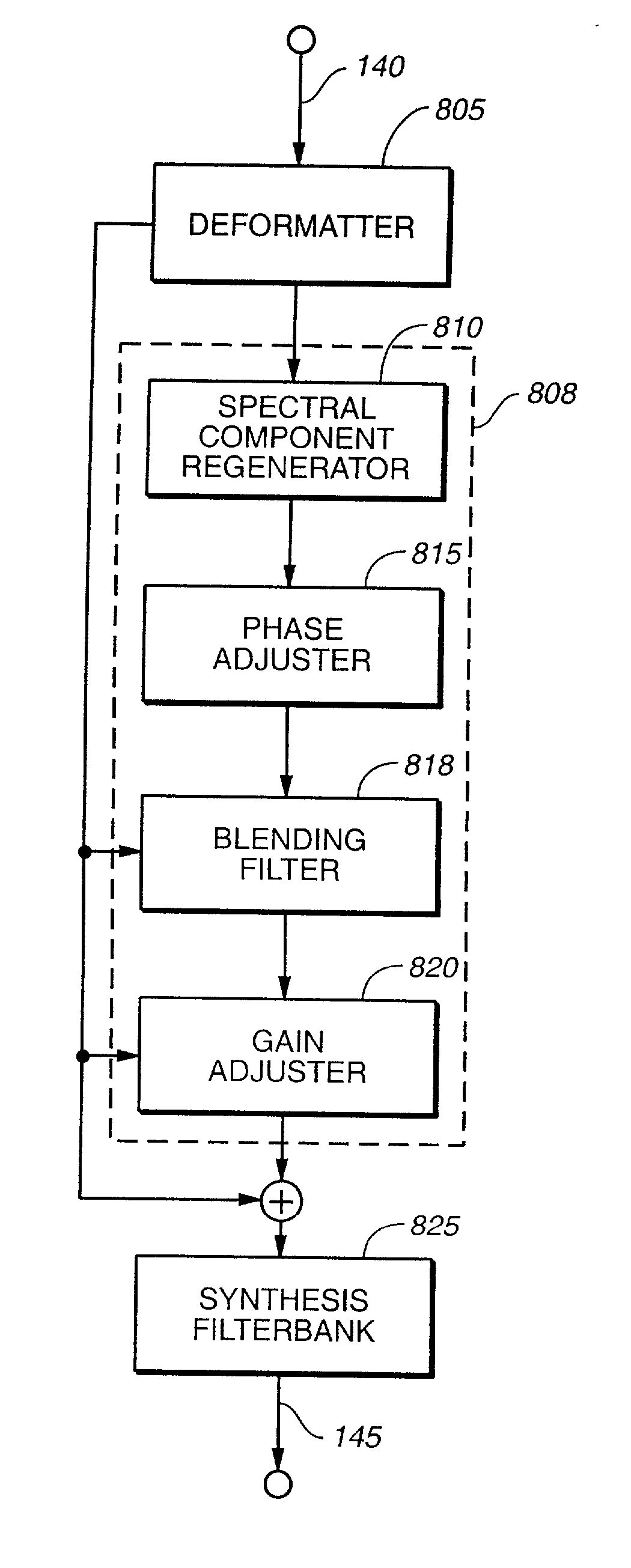
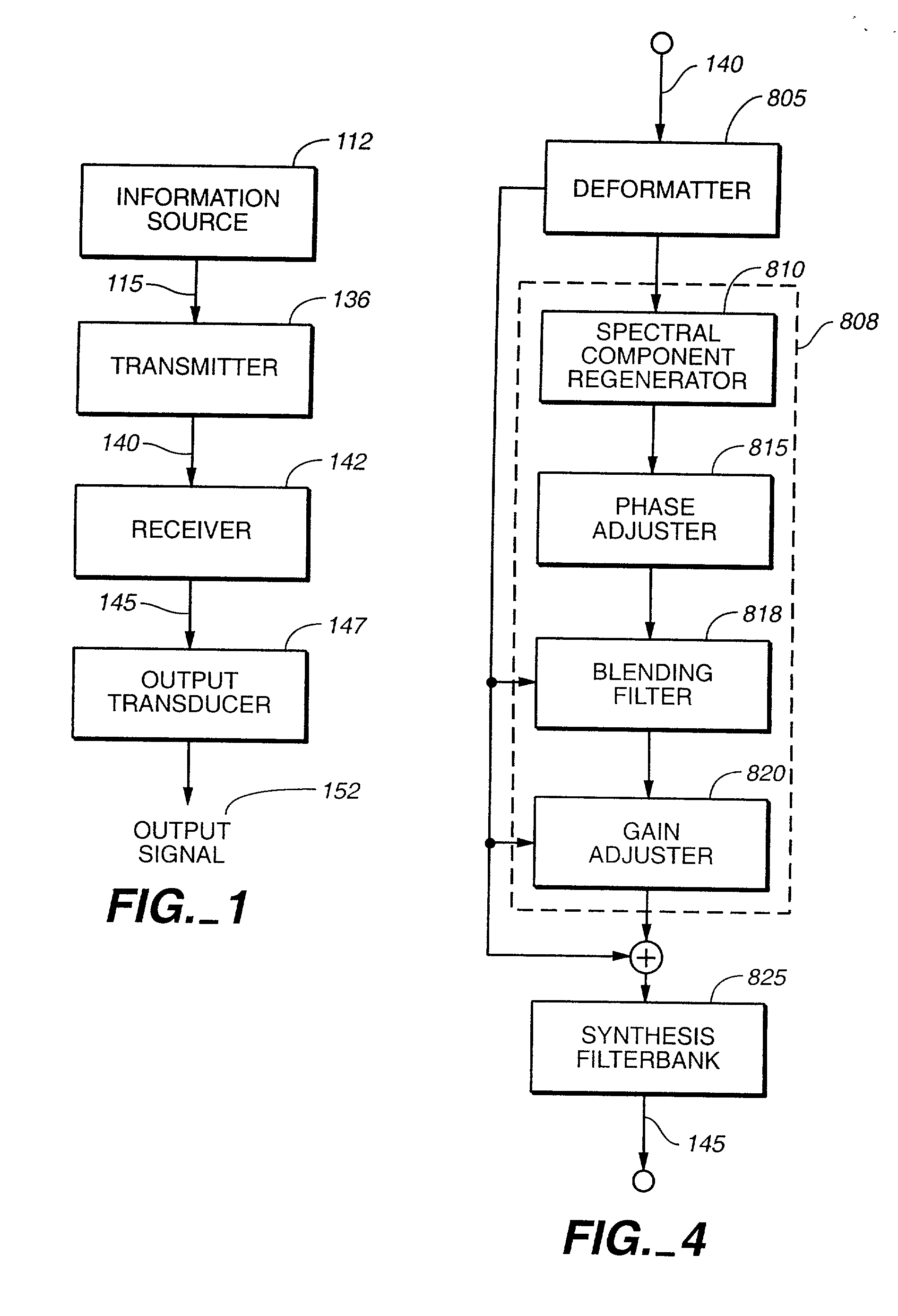
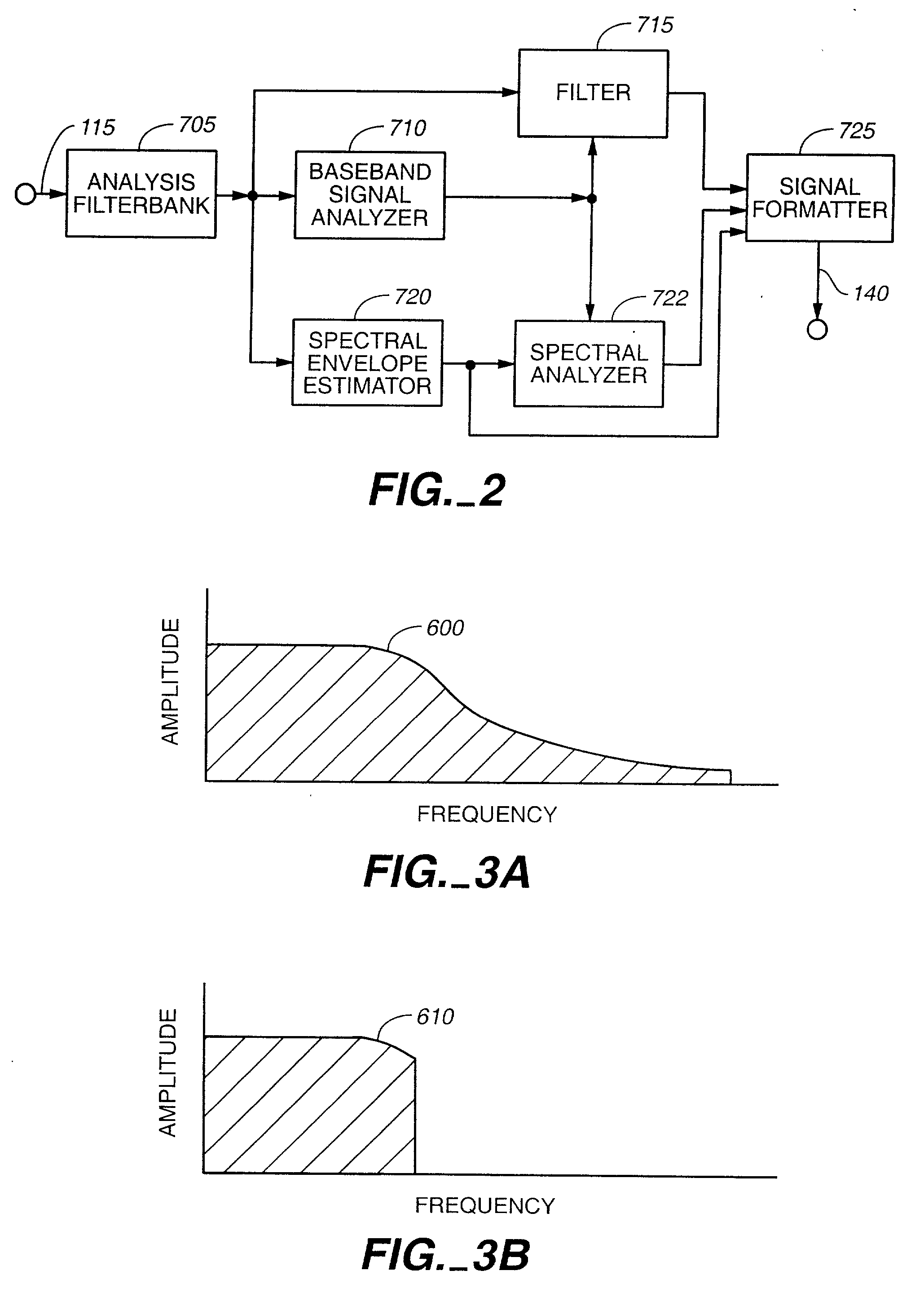
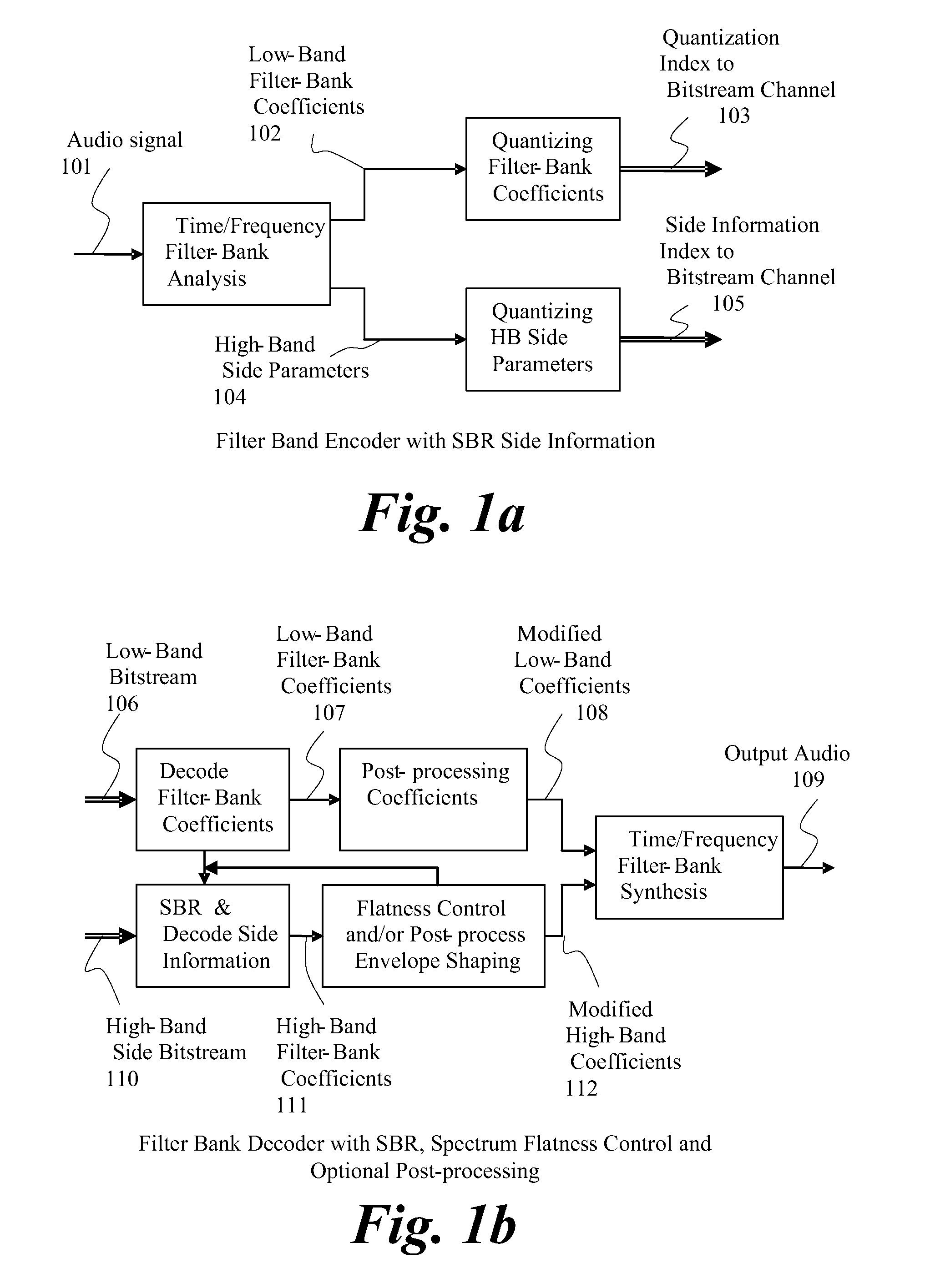
An audio signal is conveyed more efficiently by transmitting or recording a baseband of the signal with an estimated spectral envelope and a noise-blending parameter derived from a measure of the signal's noise-like quality. The signal is reconstructed by translating spectral components of the baseband signal to frequencies outside the baseband, adjusting phase of the regenerated components to maintain phase coherency, adjusting spectral shape according to the estimated spectral envelope, and adding noise according to the noise-blending parameter. Preferably, the transmitted or recorded signal also includes an estimated temporal envelope that is used to adjust the temporal shape of the reconstructed signal.
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
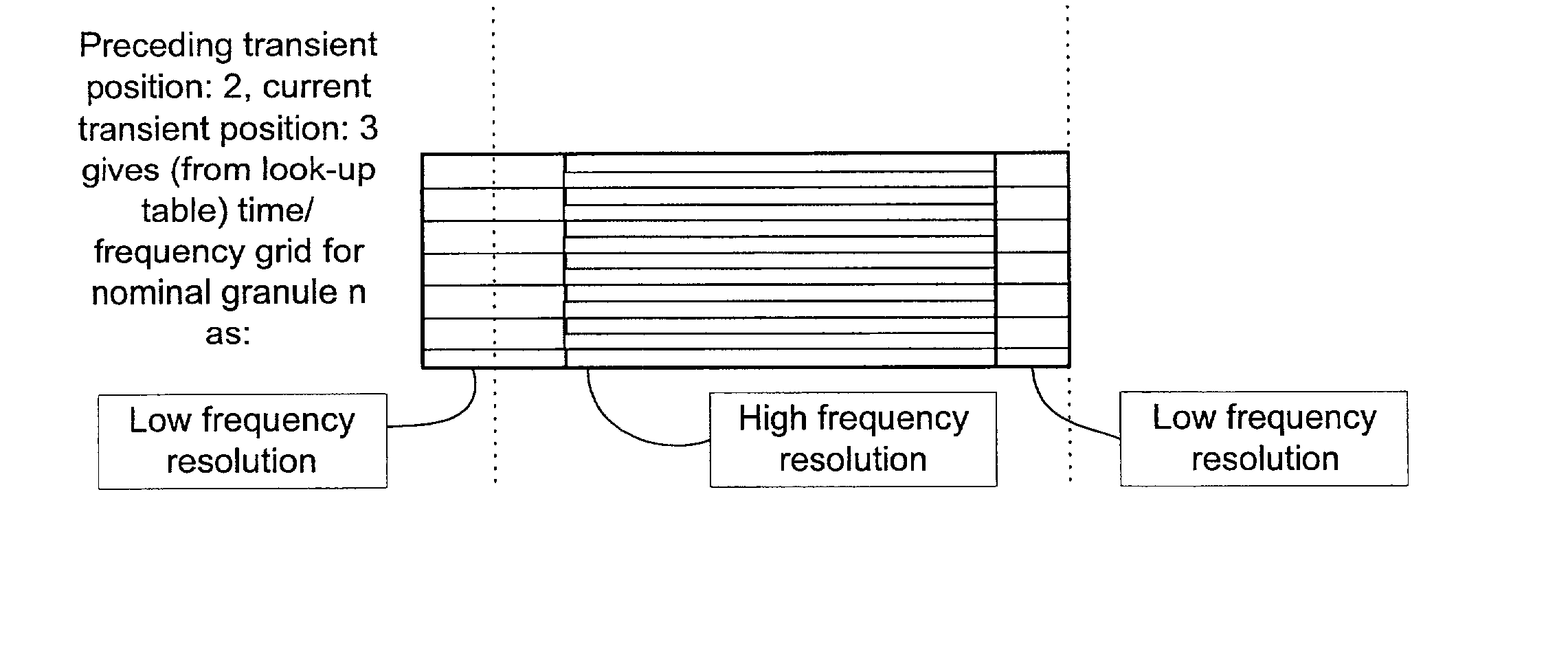
Efficient spectral envelope coding using variable time/frequency resolution and time/frequency switching
InactiveUS6978236B1Less variationImprove coding efficiencySpeech analysisDigital computer detailsSpectral envelopeImage resolution
The present invention provides a new method and an apparatus for spectral envelope encoding. The invention teaches how to perform and signal compactly a time / frequency mapping of the envelope representation, and further, encode the spectral envelope data efficiently using adaptive time / frequency directional coding. The method is applicable to both natural audio coding and speech coding systems and is especially suited for coders using SBR [WO 98 / 57436] or other high frequency reconstruction methods.
Owner:DOLBY INT AB
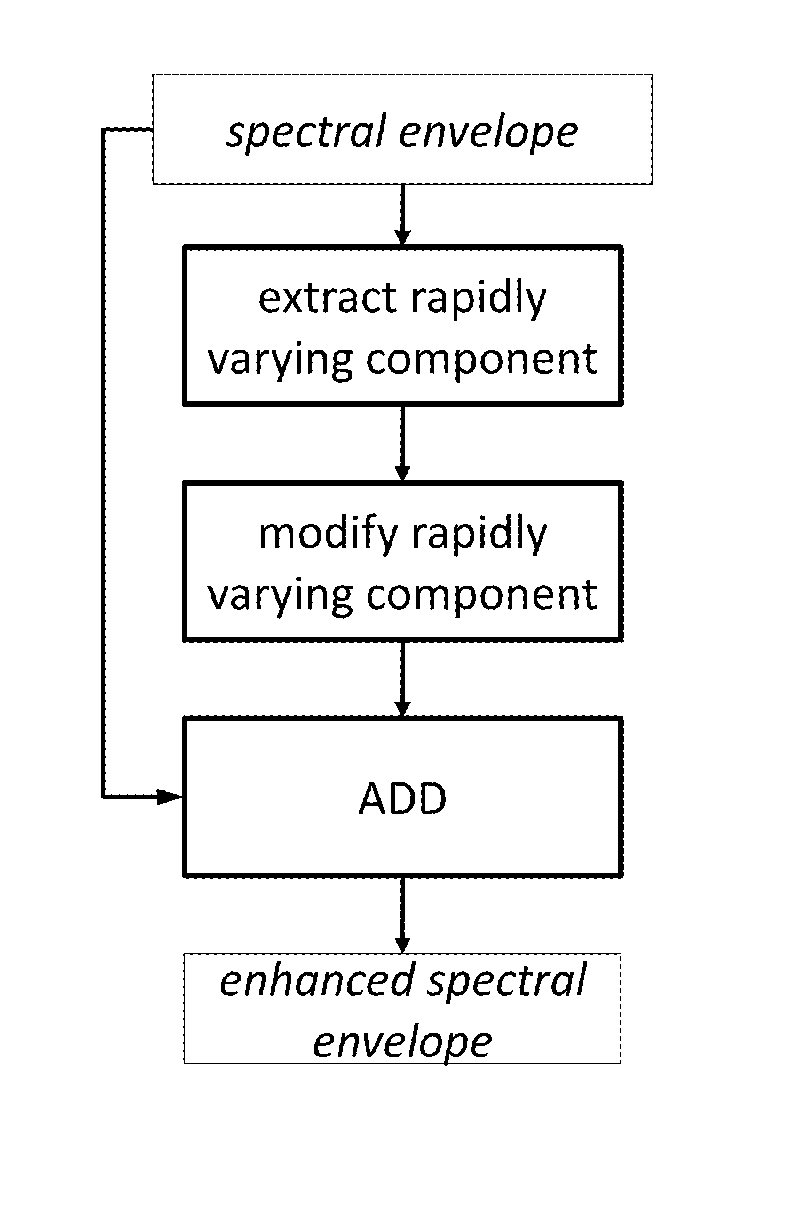
Speech enhancement techniques on the power spectrum
The method provides a spectral speech description to be used for synthesis of a speech utterance, where at least one spectral envelope input representation is received. In one solution the improvement is made by manipulation an extremum, i.e. a peak or a valley, in the rapidly varying component of the spectral envelope representation. The rapidly varying component of the spectral envelope representation is manipulated to sharpen and / or accentuate extrema after which it is merged back with the slowly varying component or the spectral envelope input representation to create an enhanced spectral envelope final representation. In other solutions a complex spectrum envelope final representation is created with phase information derived from one of the group delay representation of a real spectral envelope input representation corresponding to a short-time speech signal and a transformed phase component of the discrete complex frequency domain input representation corresponding to the speech utterance.
Owner:CERENCE OPERATING CO
Spectrum Flatness Control for Bandwidth Extension
ActiveUS20120016667A1Improvement factorImproving spectrum flatness of high-frequencySpeech analysisFrequency spectrumBand width
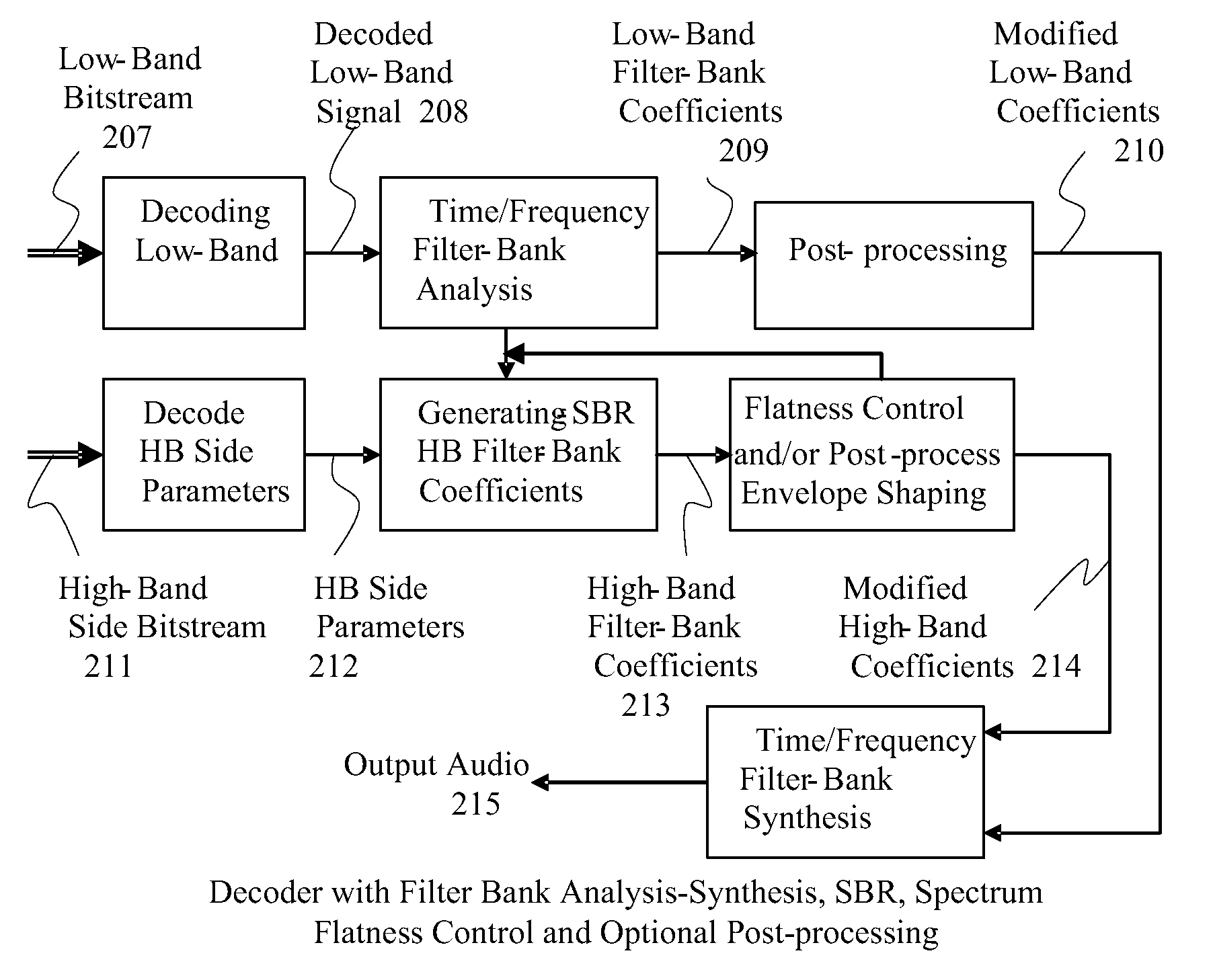
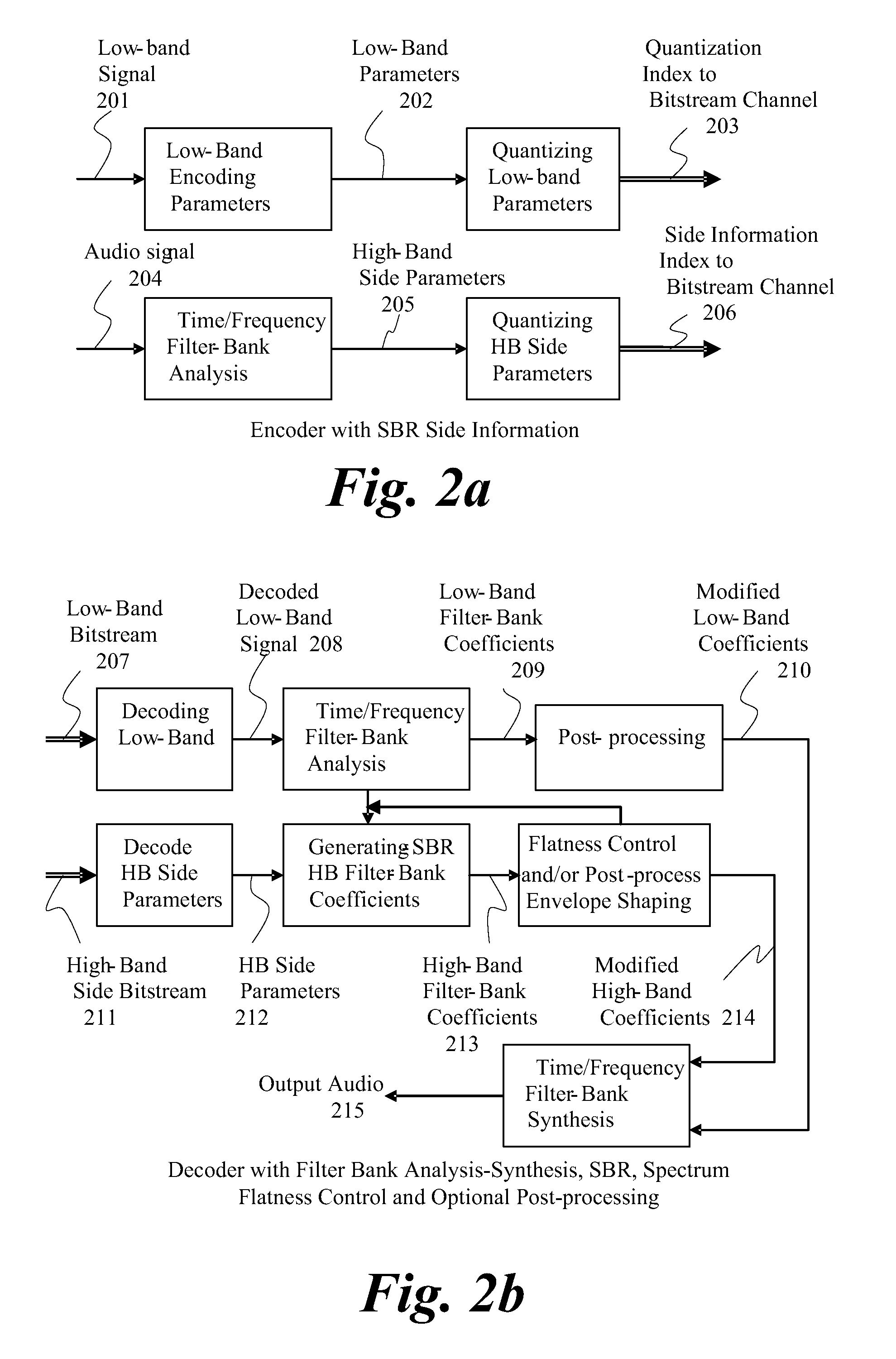
In accordance with an embodiment, a method of decoding an encoded audio bitstream at a decoder includes receiving the audio bitstream, decoding a low band bitstream of the audio bitstream to get low band coefficients in a frequency domain, and copying a plurality of the low band coefficients to a high frequency band location to generate high band coefficients. The method further includes processing the high band coefficients to form processed high band coefficients. Processing includes modifying an energy envelope of the high band coefficients by multiplying modification gains to flatten or smooth the high band coefficients, and applying a received spectral envelope decoded from the received audio bitstream to the high band coefficients. The low band coefficients and the processed high band coefficients are then inverse-transformed to the time domain to obtain a time domain output signal.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
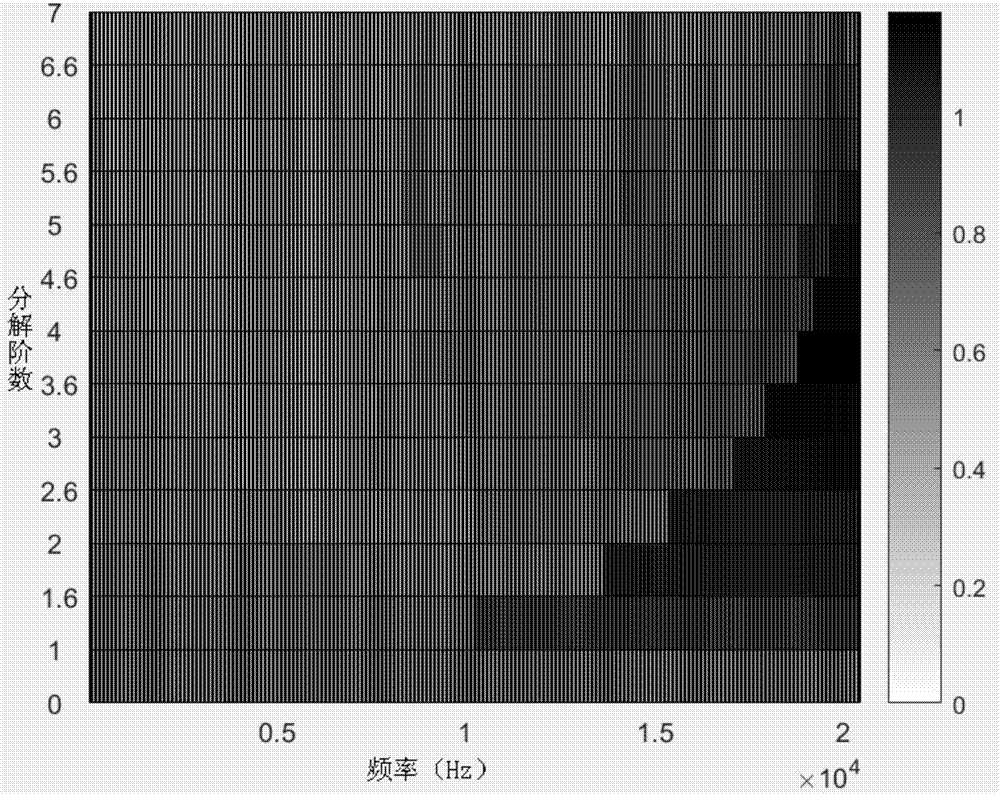
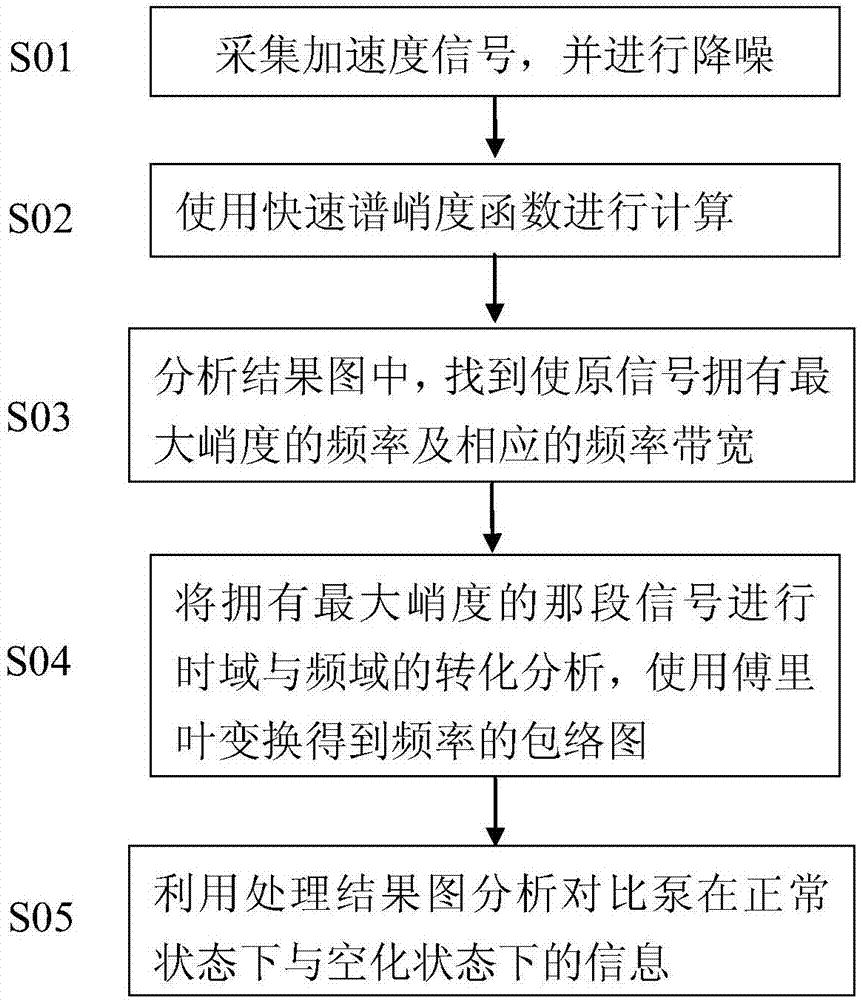
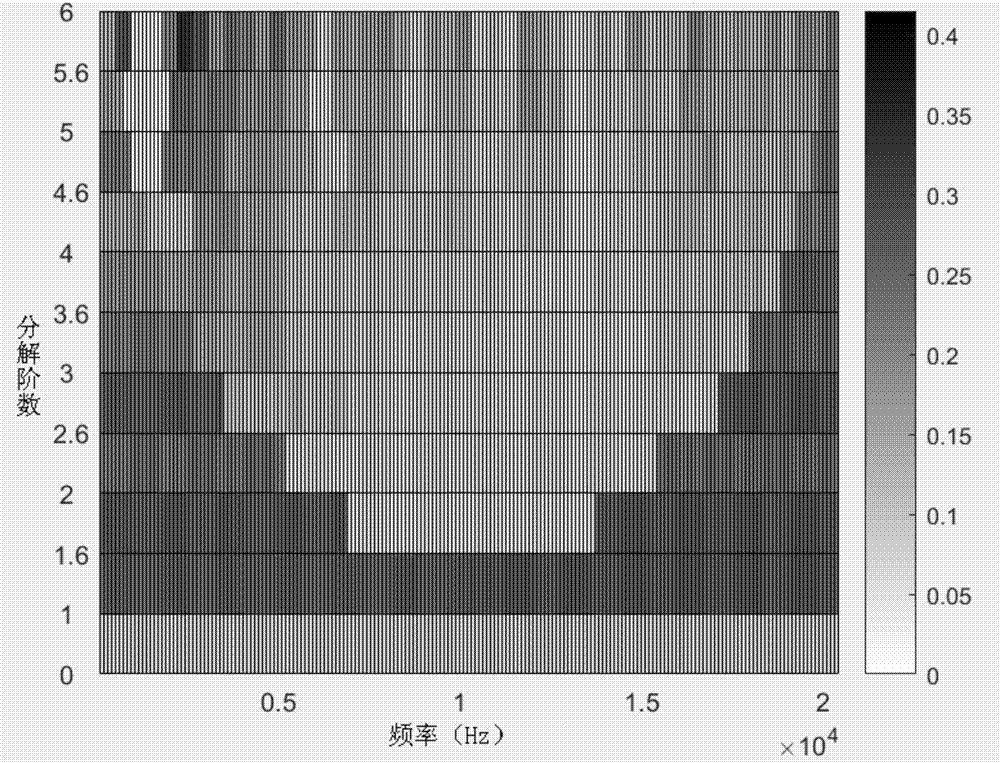
Pump potential cavitation fault detecting method based on quick spectrum kurtosis analysis
ActiveCN107956708AImprove acceleration performanceClear resolutionPump controlNon-positive displacement fluid enginesVibration accelerationCavitation
The invention discloses a pump potential cavitation fault detecting method based on quick spectrum kurtosis analysis. The pump potential cavitation fault detecting method comprises the steps that 1, vibration acceleration signals are collected to be subject to noise reduction to serve as to-be-processed signals; 2, according to the data size of the signals, the resolving order of signal processingis determined; 3, according to the quick spectrum kurtosis algorithm computation result, the optimal carrier frequency and bandwidth are selected; 4, the selected signals within the carrier frequencyand bandwidth are subject to Fourier transformation, and a frequency spectrum envelope diagram is obtained; and 5, an original signal time domain figure, a signal time domain figure treated through quick spectrum kurtosis filtering processing and the frequency spectrum envelope diagram obtained after selected zone Fourier transformation are compared, and cavitation trouble signal time and frequency characteristics are analyzed. By means of the method, more cavitation instant signals can be detected, information in the aspects of time domain and frequency domain is seen more clearly, and the normal state and the cavitation state of a pump can be distinguished obviously.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
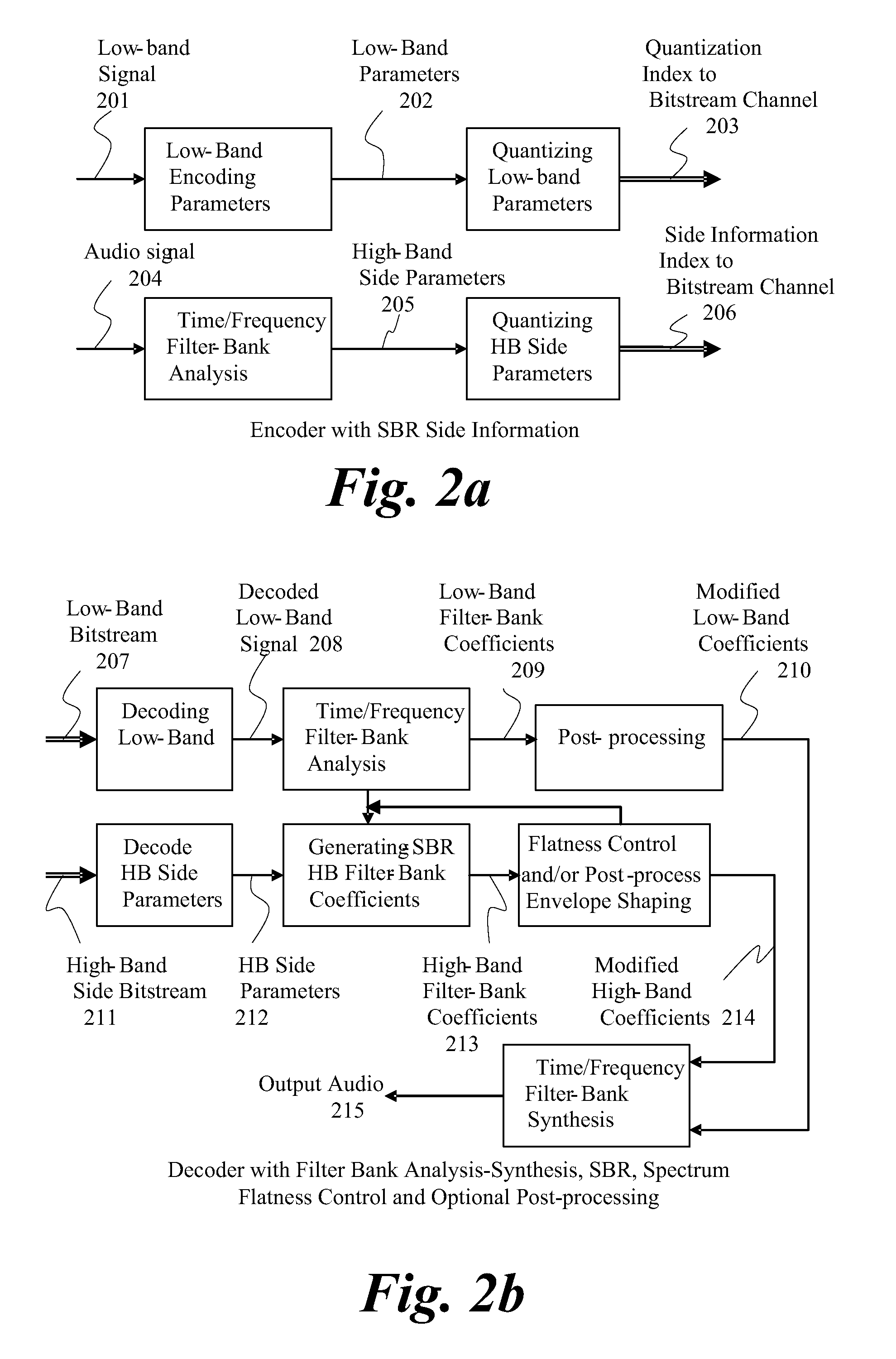
Source coding enhancement using spectral-band replication
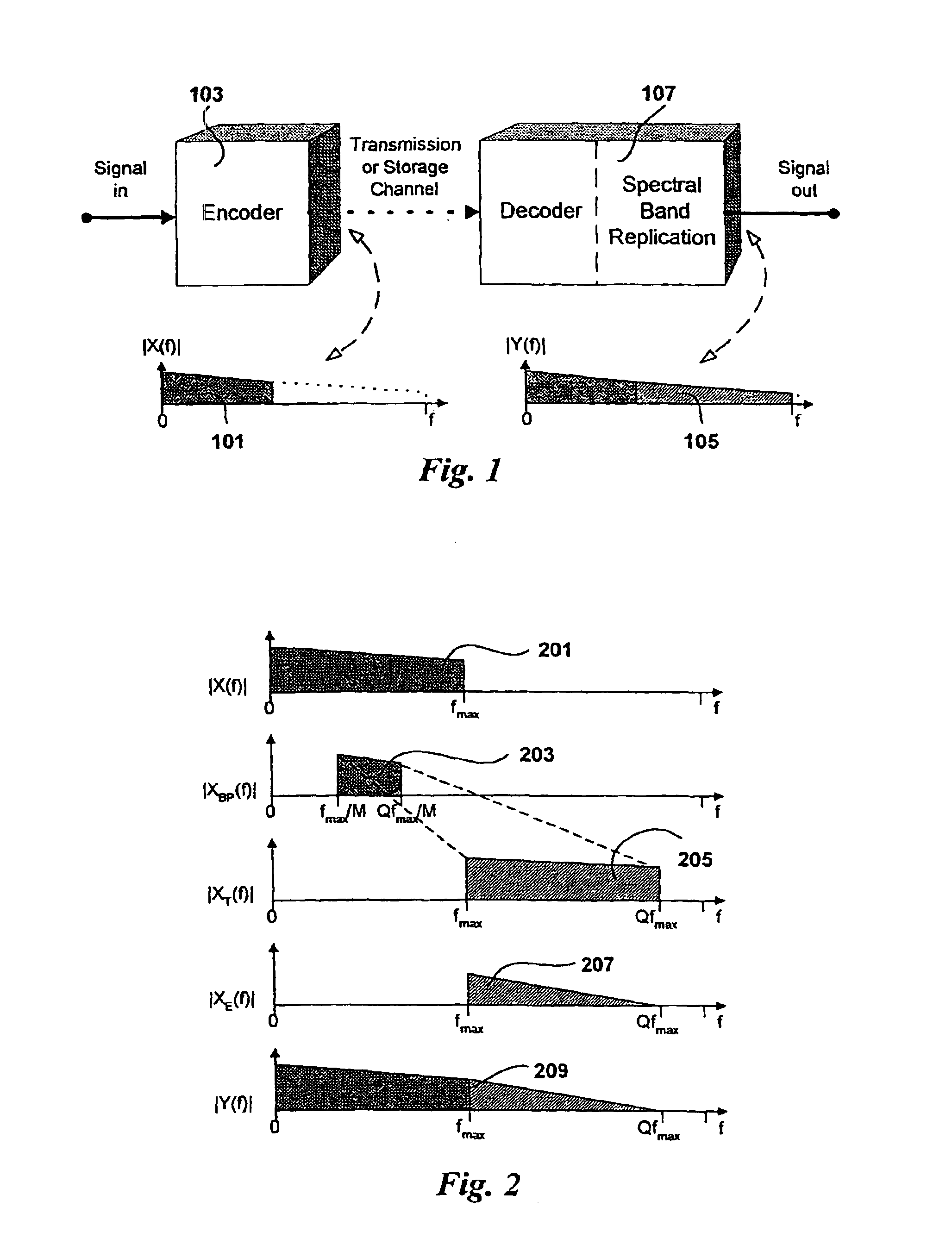
InactiveUS7283955B2Improvements of audio codecsImprove perceived qualitySpeech analysisCode conversionFrequency spectrumComputer science
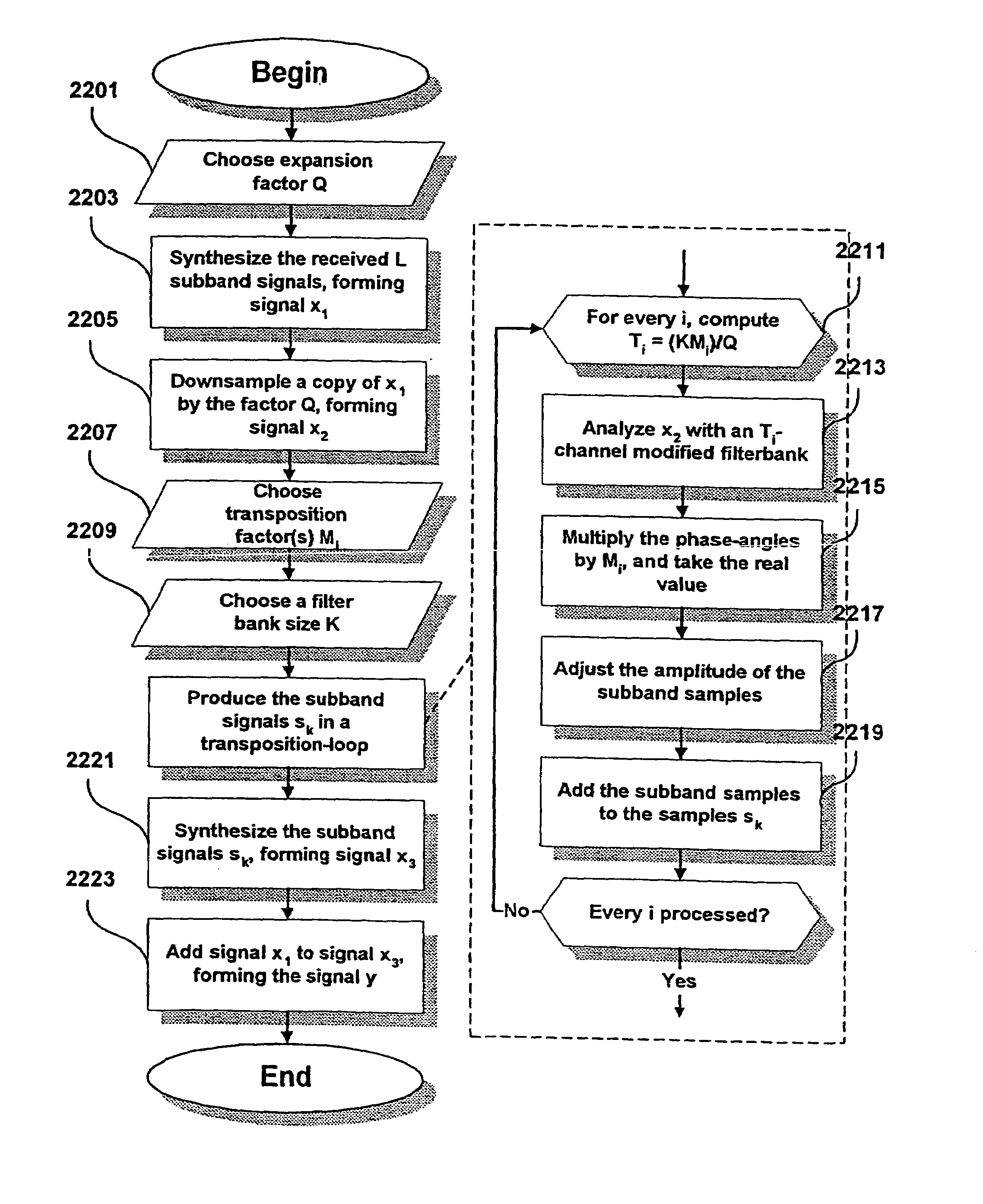
The present invention proposes a new method and apparatus for the enhancement of source coding systems. The invention employs bandwidth reduction (101) prior to or in the encoder (103), followed by spectral-band replication (105) at the decoder (107). This is accomplished by the use of new transposition methods, in combination with spectral envelope adjustments. Reduced bitrate at a given perceptual quality or an improved perceptual quality at a given bitrate is offered. The invention is preferably integrated in a hardware or software codec, but can also be implemented as a separate processor in combination with a codec. The invention offers substantial improvements practically independent f codec type and technological progress.
Owner:DOLBY INT AB
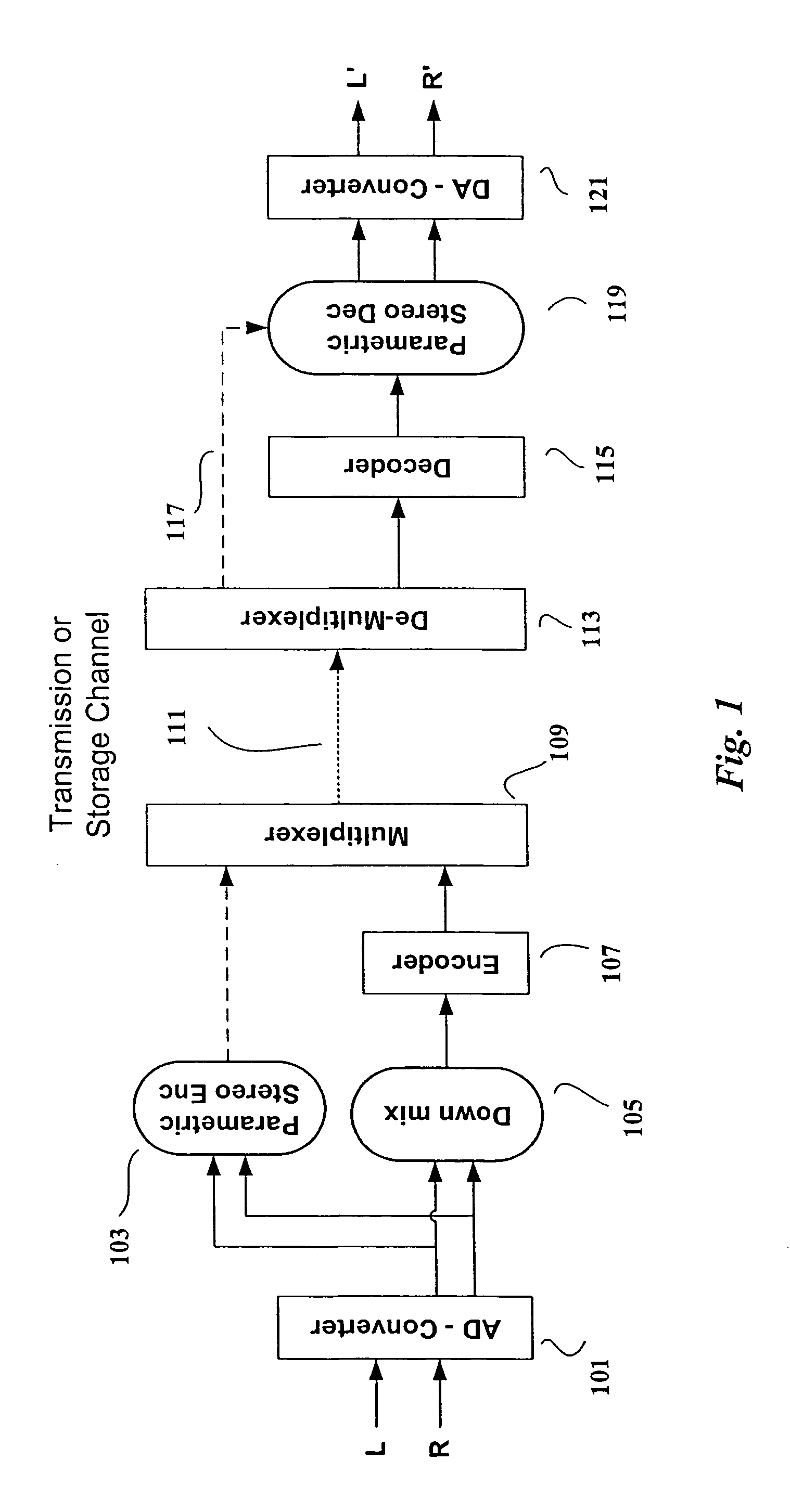
Efficient and scalable parametric stereo coding for low bitrate applications
ActiveUS20050053242A1Reduce riskGuaranteed normal transmissionSpeech analysisPseudo-stereo systemsVocal tractStereo image
The present invention provides improvements to prior art audio codecs that generate a stereo-illusion through post-processing of a received mono signal. These improvements are accomplished by extraction of stereo-image describing parameters at the encoder side, which are transmitted and subsequently used for control of a stereo generator at the decoder side. Furthermore, the invention bridges the gap between simple pseudo-stereo methods, and current methods of true stereo-coding, by using a new form of parametric stereo coding. A stereo-balance parameter is introduced, which enables more advanced stereo modes, and in addition forms the basis of a new method of stereo-coding of spectral envelopes, of particular use in systems where guided HFR (High Frequency Reconstruction) is employed. As a special case, the application of this stereo-coding scheme in scalable HFR-based codecs is described.
Owner:DOLBY INT AB
Band-width spreading method and system for voice or audio signal
The invention discloses a method and system for speech or audio signal bandwidth expansion, which comprises: A. to simulate spectral envelope of the high-frequency signal components in the speech or audio signal. B. to make a synthesis of the said spectrum envelope and the low-frequency signal components corresponding to the high-frequency signal components in the frequency and spatial domain to obtain the reset high-frequency signal components. The invention also discloses the method and system to realize the said bandwidth expansion, the technical scheme offered by which has the advantage of less bit number of coding that can be adaptively adjusted based on the type features of the signals. Besides, by extracting spectrum envelope of the high-frequency signal components, the invention makes the fine structure acted on the low-frequency signal components corresponding frequency and spatial domain to guarantee the correlation between the reset high-frequency signal spectrum and the harmonization of the high-frequency signal spectrum lopped during coding.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD +1
Speech Enhancement Techniques on the Power Spectrum
ActiveUS20120265534A1Improved spectral magnitudeImproved phase processing techniqueSpeech synthesisFrequency spectrumSpeech sound
The method provides a spectral speech description to be used for synthesis of a speech utterance, where at least one spectral envelope input representation is received. In one solution the improvement is made by manipulation an extremum, i.e. a peak or a valley, in the rapidly varying component of the spectral envelope representation. The rapidly varying component of the spectral envelope representation is manipulated to sharpen and / or accentuate extrema after which it is merged back with the slowly varying component or the spectral envelope input representation to create an enhanced spectral envelope final representation. In other solutions a complex spectrum envelope final representation is created with phase information derived from one of the group delay representation of a real spectral envelope input representation corresponding to a short-time speech signal and a transformed phase component of the discrete complex frequency domain input representation corresponding to the speech utterance.
Owner:CERENCE OPERATING CO
Aliasing reduction using complex-exponential modulated filterbanks
ActiveUS7242710B2Signal can be impairedMitigation of impairmentMultiple-port networksAdaptive networkFrequency spectrumComputer science
The present invention proposes a new method and apparatus for the improvement of digital filterbanks, by a complex extension of cosine modulated digital filterbanks. The invention employs complex-exponential modulation of a low-pass prototype filter and a new method for optimizing the characteristics of this filter. The invention substantially reduces artifacts due to aliasing emerging from independent modifications of subband signals, for example when using a filterbank as an spectral equalizer. The invention is preferably implemented in software, running on a standard PC or a digital signal processor (DSP), but can also be hardcoded on a custom chip. The invention offers essential improvements for various types of digital equalizers, adaptive filters, multiband companders and spectral envelope adjusting filterbanks used in high frequency reconstruction (HFR) systems.
Owner:DOLBY INT AB
Audio bandwidth expansion coding and decoding devices
ActiveCN101521014AImprove decoding qualityQuality improvementSpeech analysisFrequency spectrumAudio signal
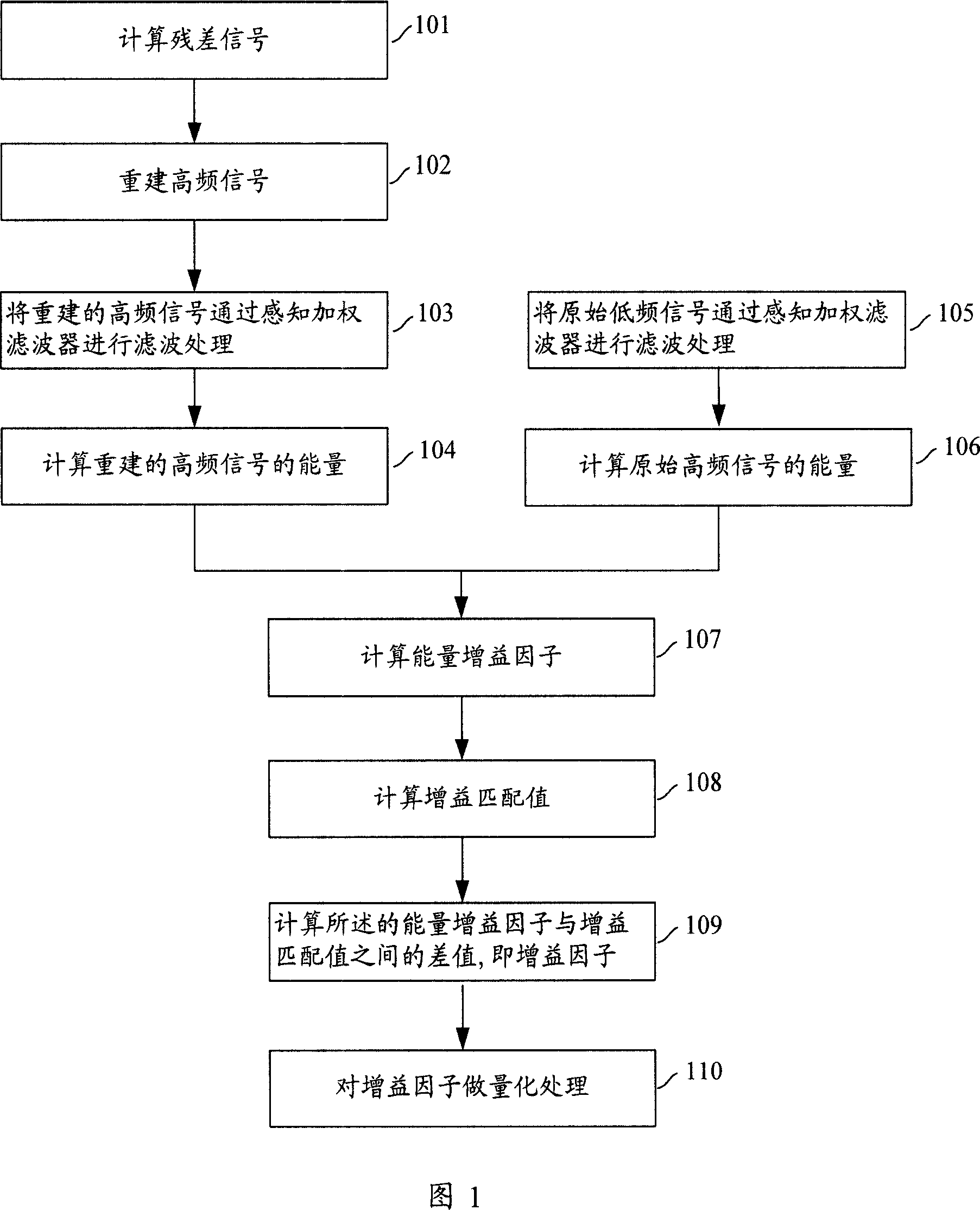
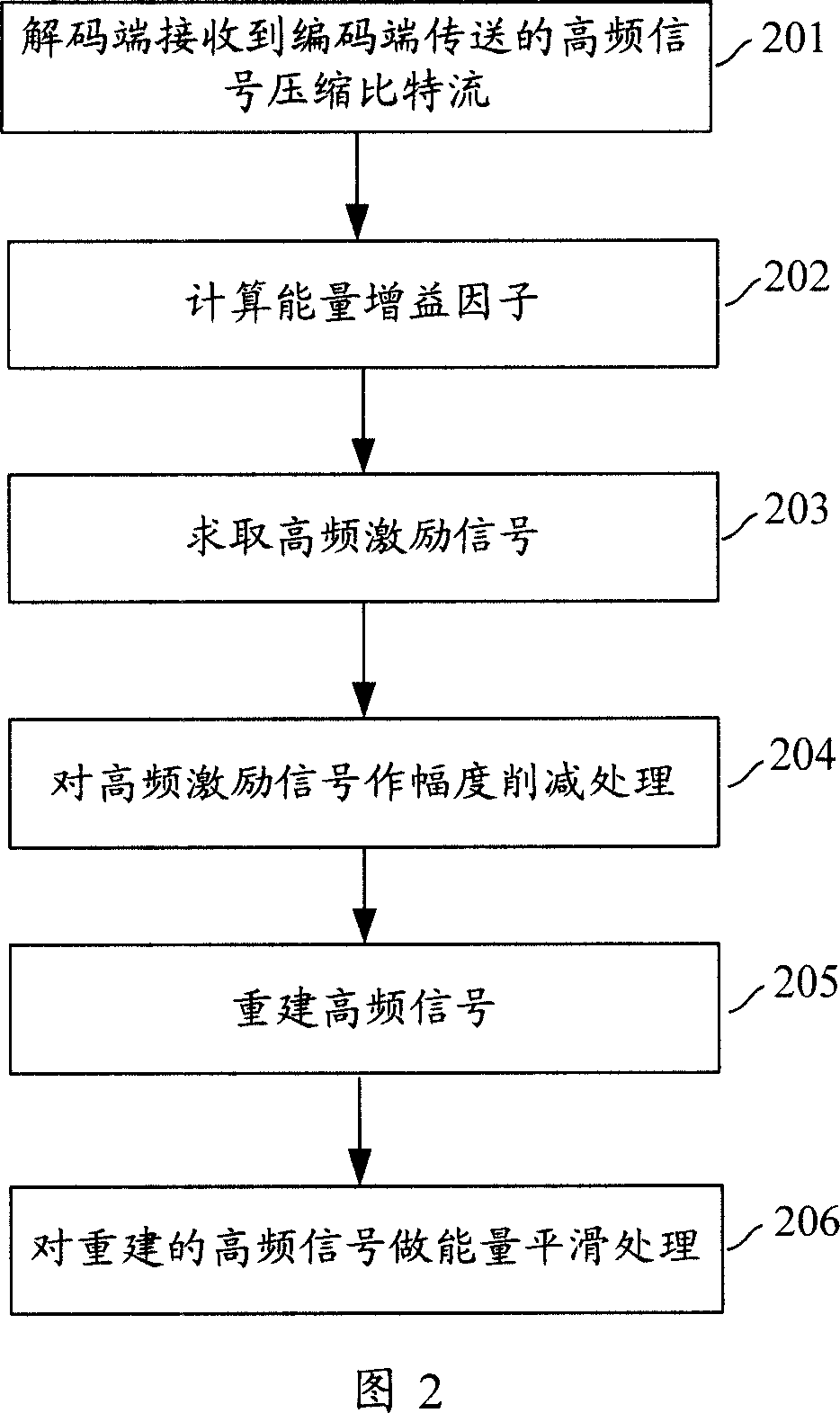
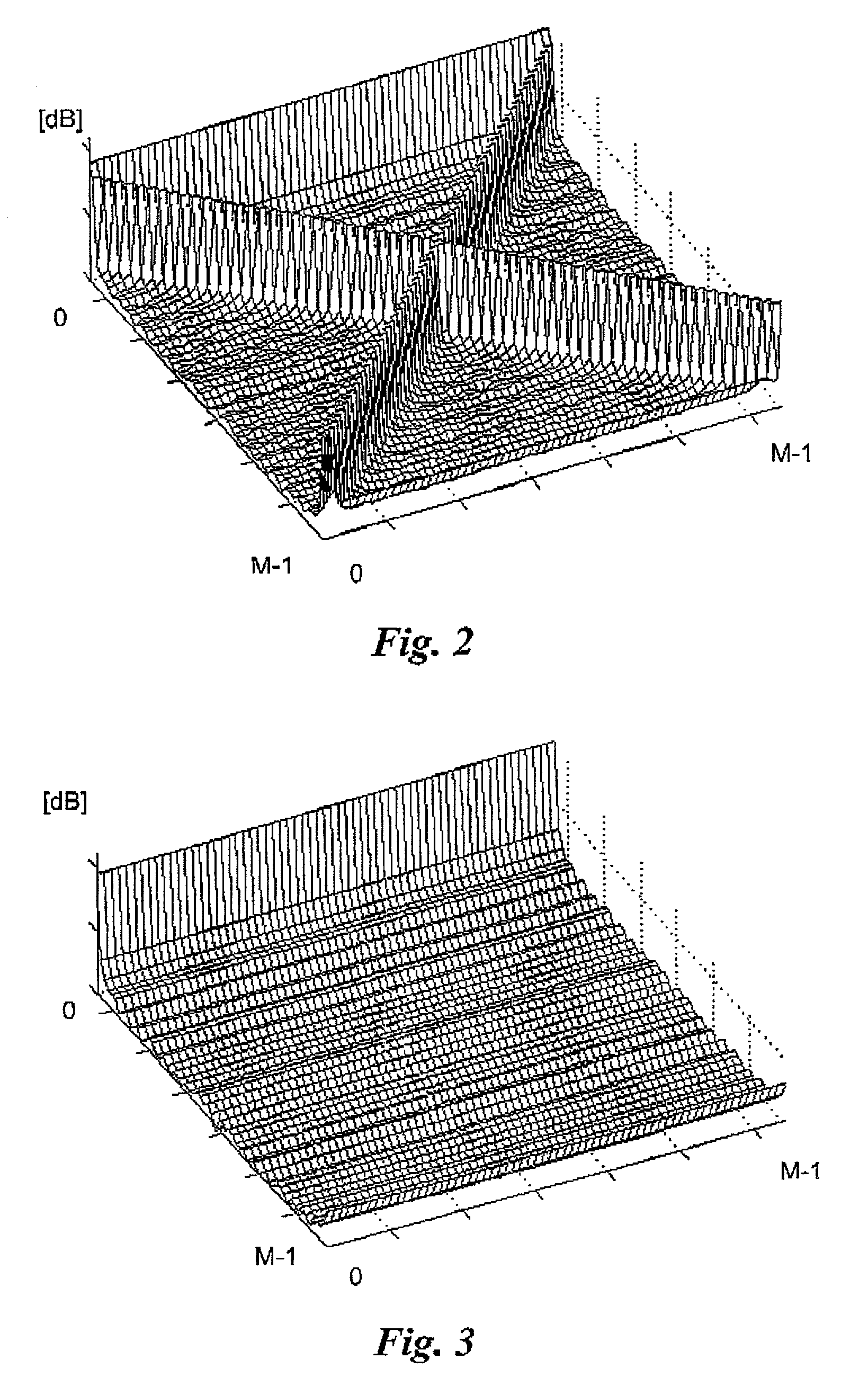
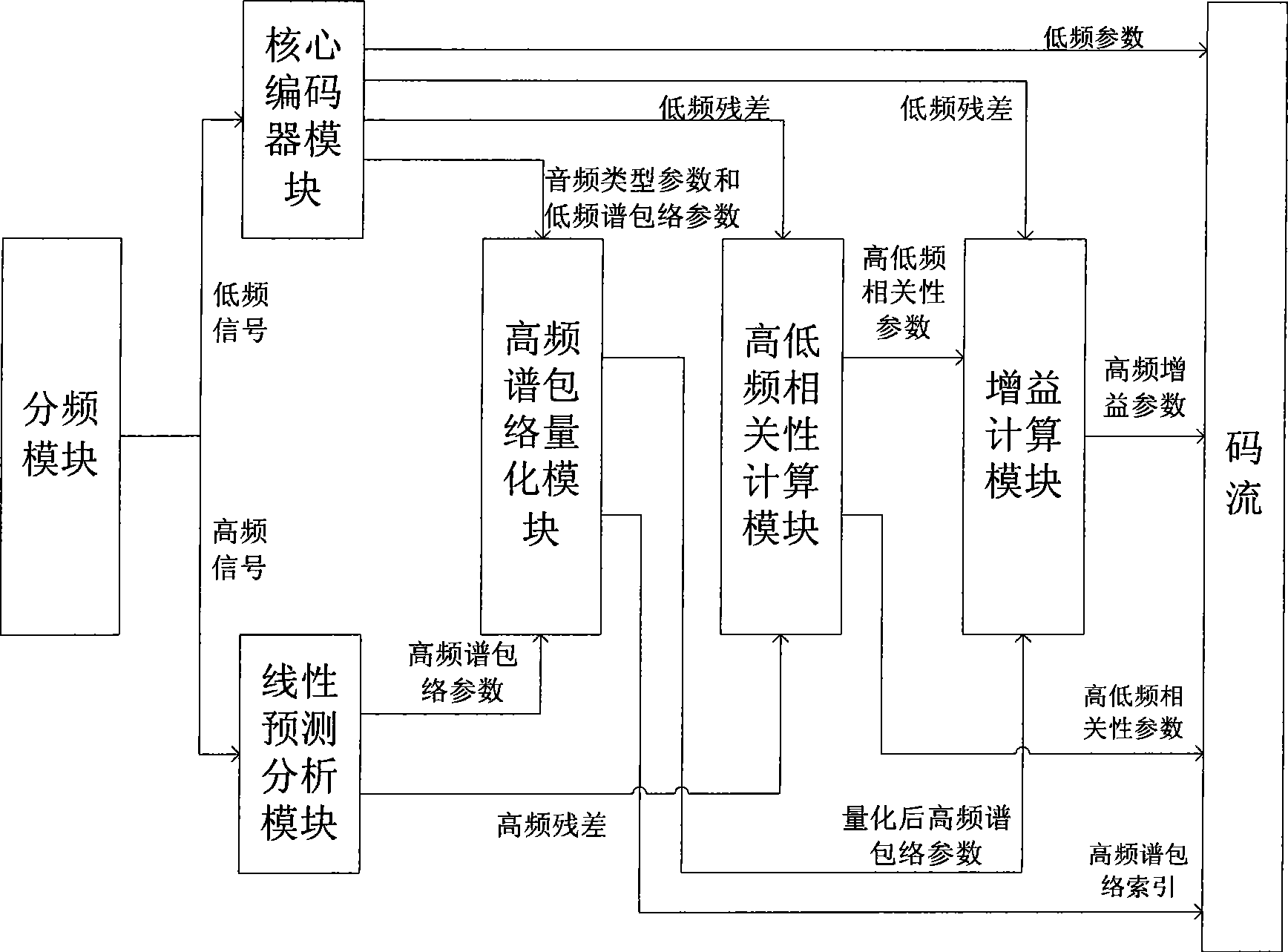
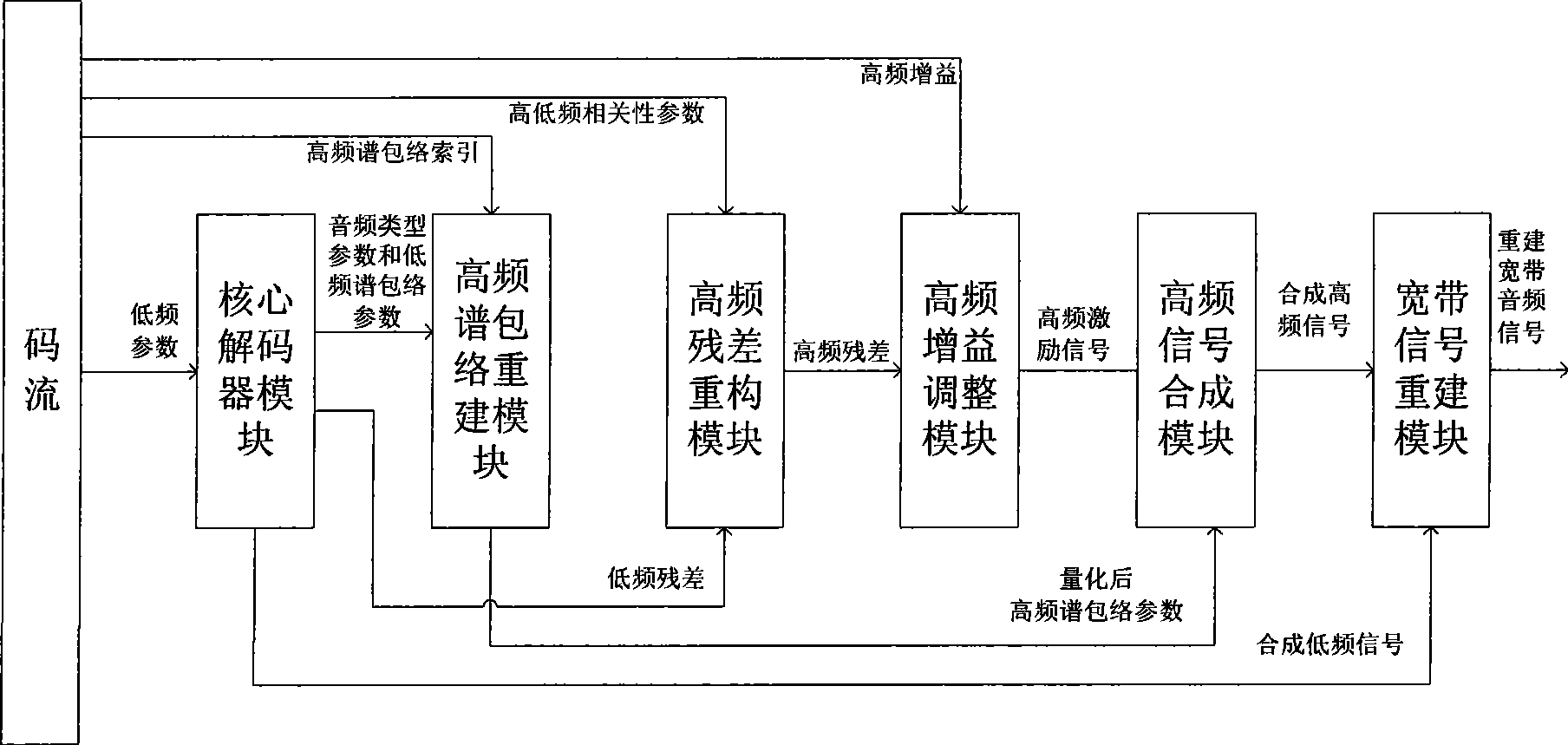
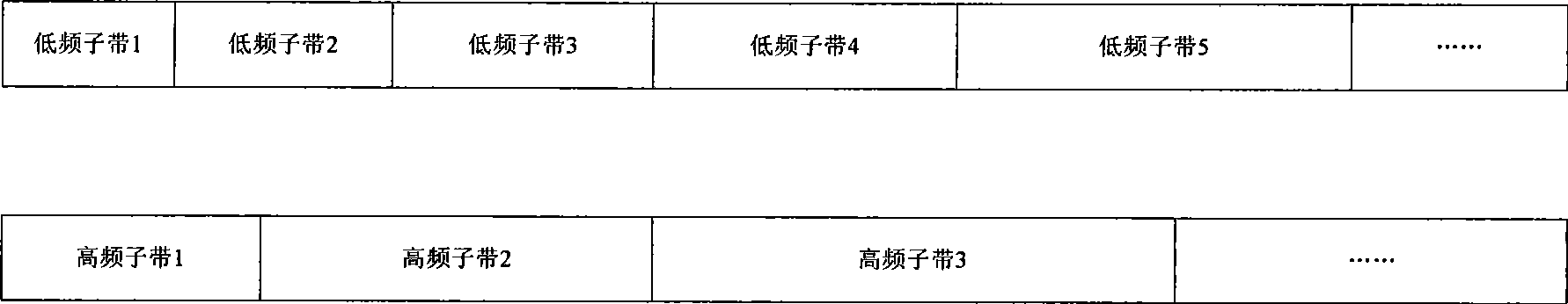
The invention provides audio bandwidth expansion coding and decoding devices which can reconstruct a high frequency signal by using the lower code rate so as to improve the quality of the output audio signal. The audio bandwidth expansion coding device comprises a frequency division module, a core coder module, a linear prediction analysis module, a spectrum envelope quantization module, a high and low frequency correlation computation module and a gain computation module; and the audio bandwidth expansion decoding device comprises a core decoder module, a high-frequency spectrum envelope reconstruction module, a high-frequency residual error reconstruction module, a high-frequency gain adjustment module, a high-frequency signal synthesis module and a wideband signal reconstruction module.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Selective Bandwidth Extension
ActiveUS20100063827A1Maximize perceived qualityQuality improvementSpeech analysisDigital computer detailsFrequency spectrumBandwidth extension
A method of receiving an audio signal includes measuring a periodicity of the audio signal to determine a checked periodicity. At least one best available subband is determined. At least one extended subband is composed, wherein composing includes reducing a ratio of composed harmonic components to composed noise components if the checked periodicity is lower than a threshold, and scaling a magnitude of the at least one extended subband based on a spectral envelope on the audio signal.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
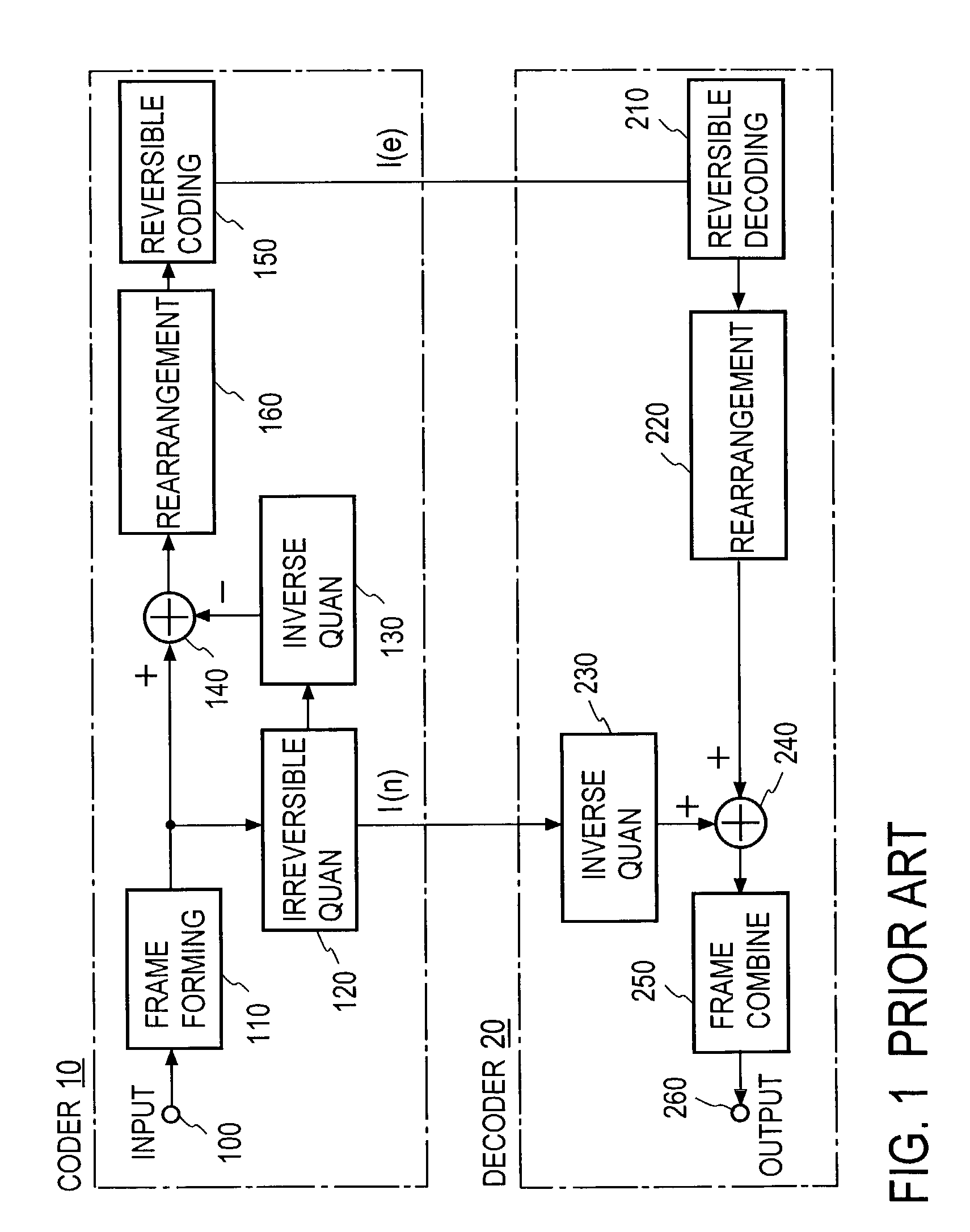
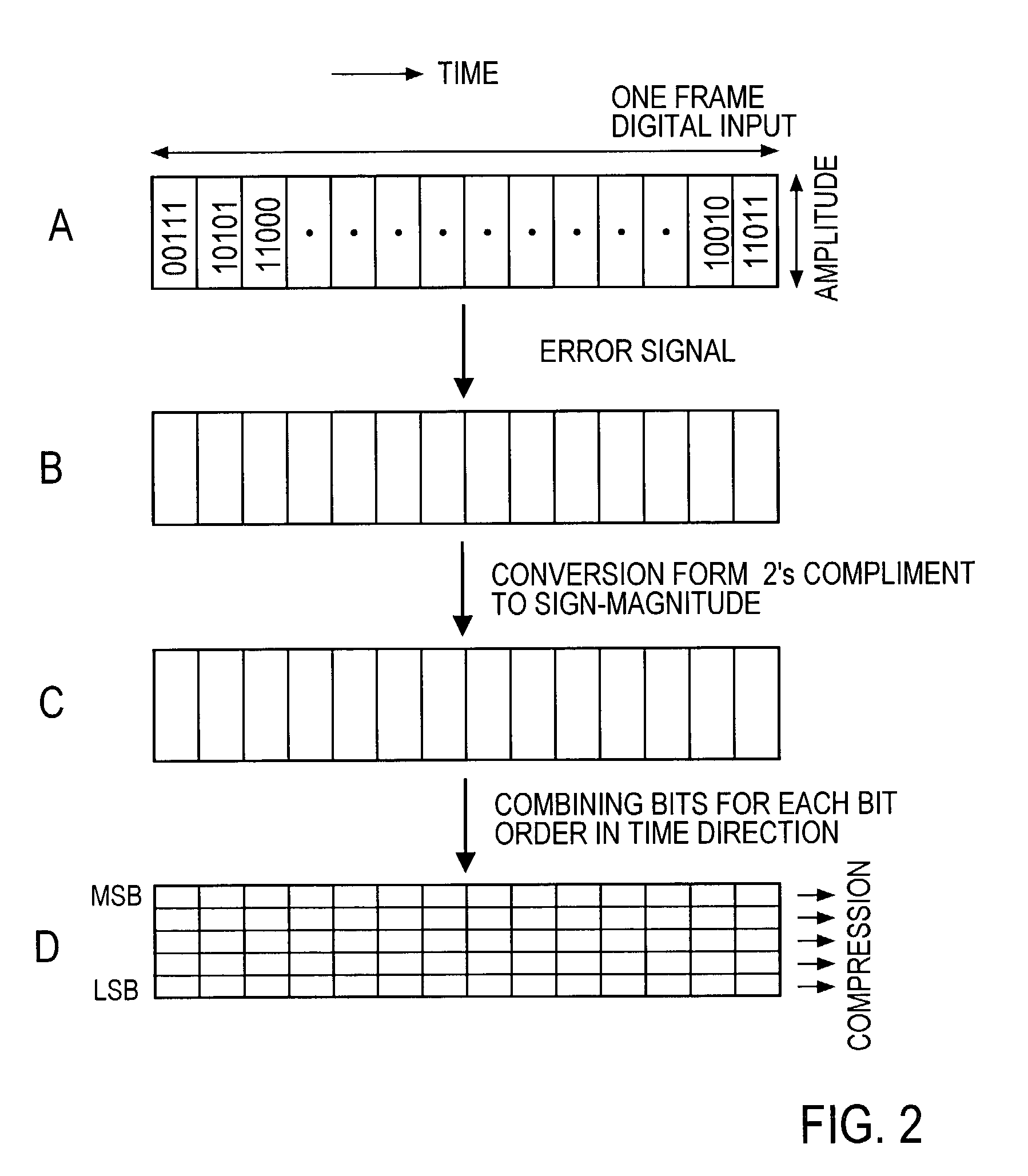
Digital signal coding and decoding methods and apparatuses and programs therefor
ActiveUS7200561B2Reduce the amount of informationSpeech analysisCode conversionDecoding methodsFrequency spectrum
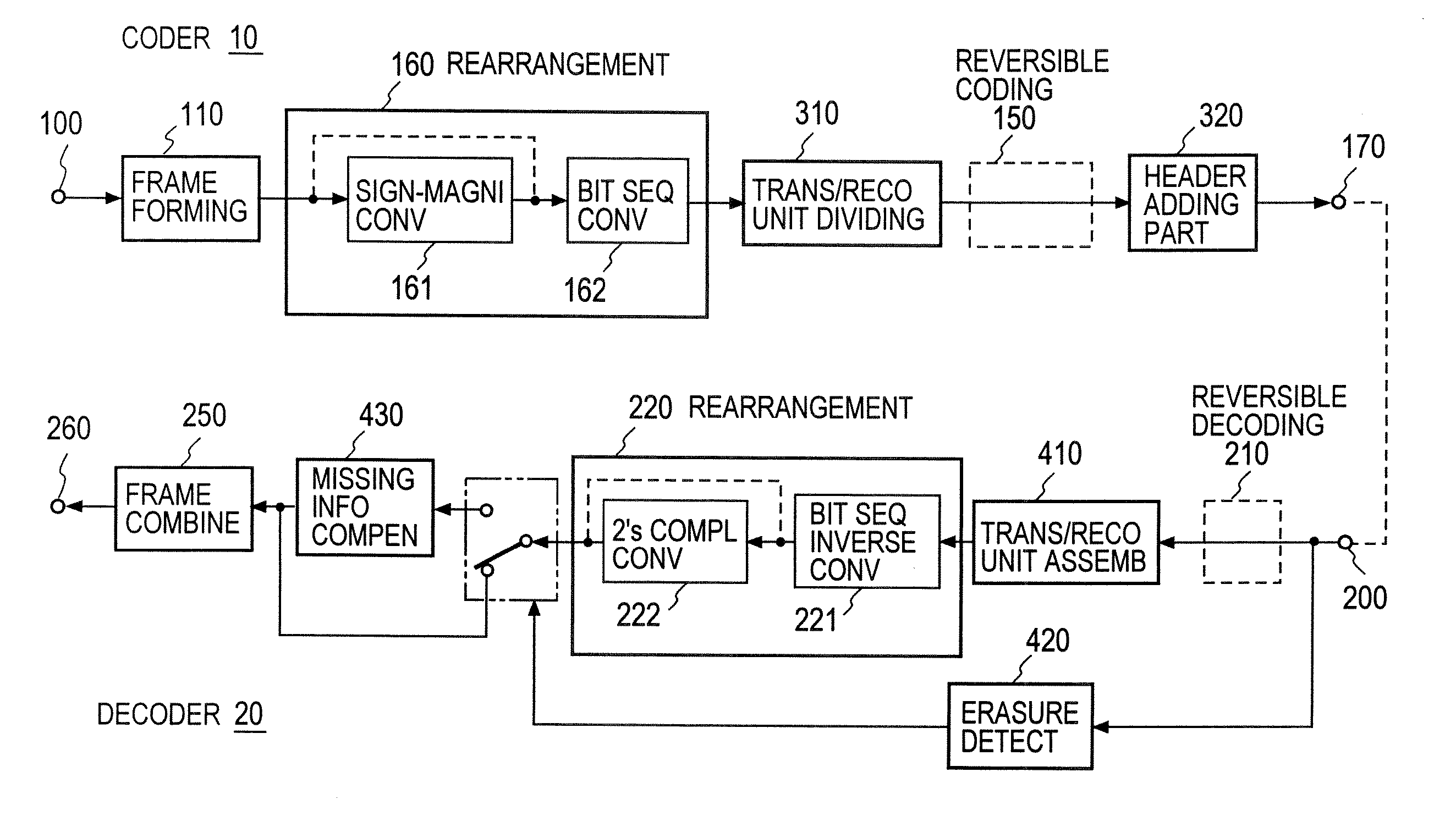
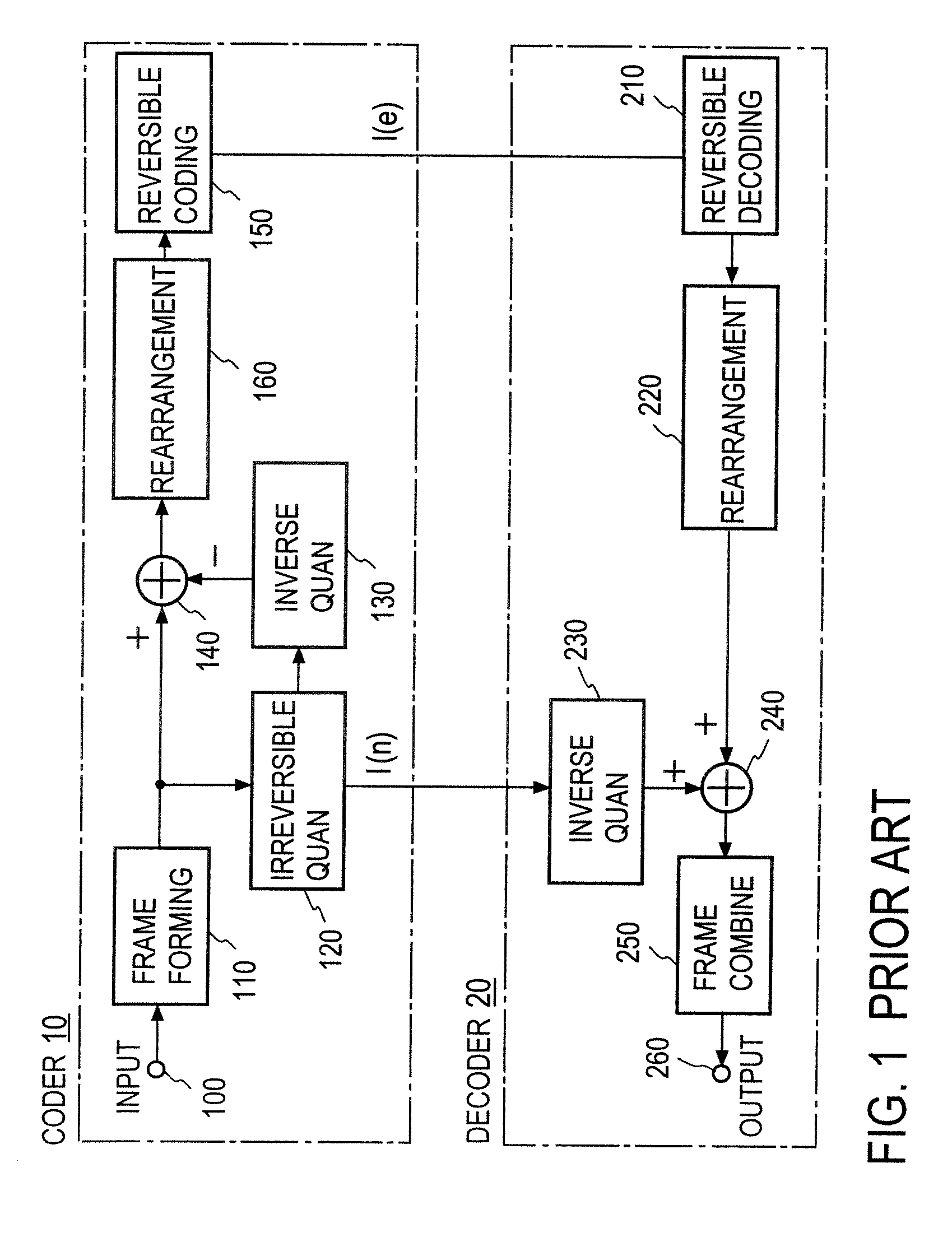
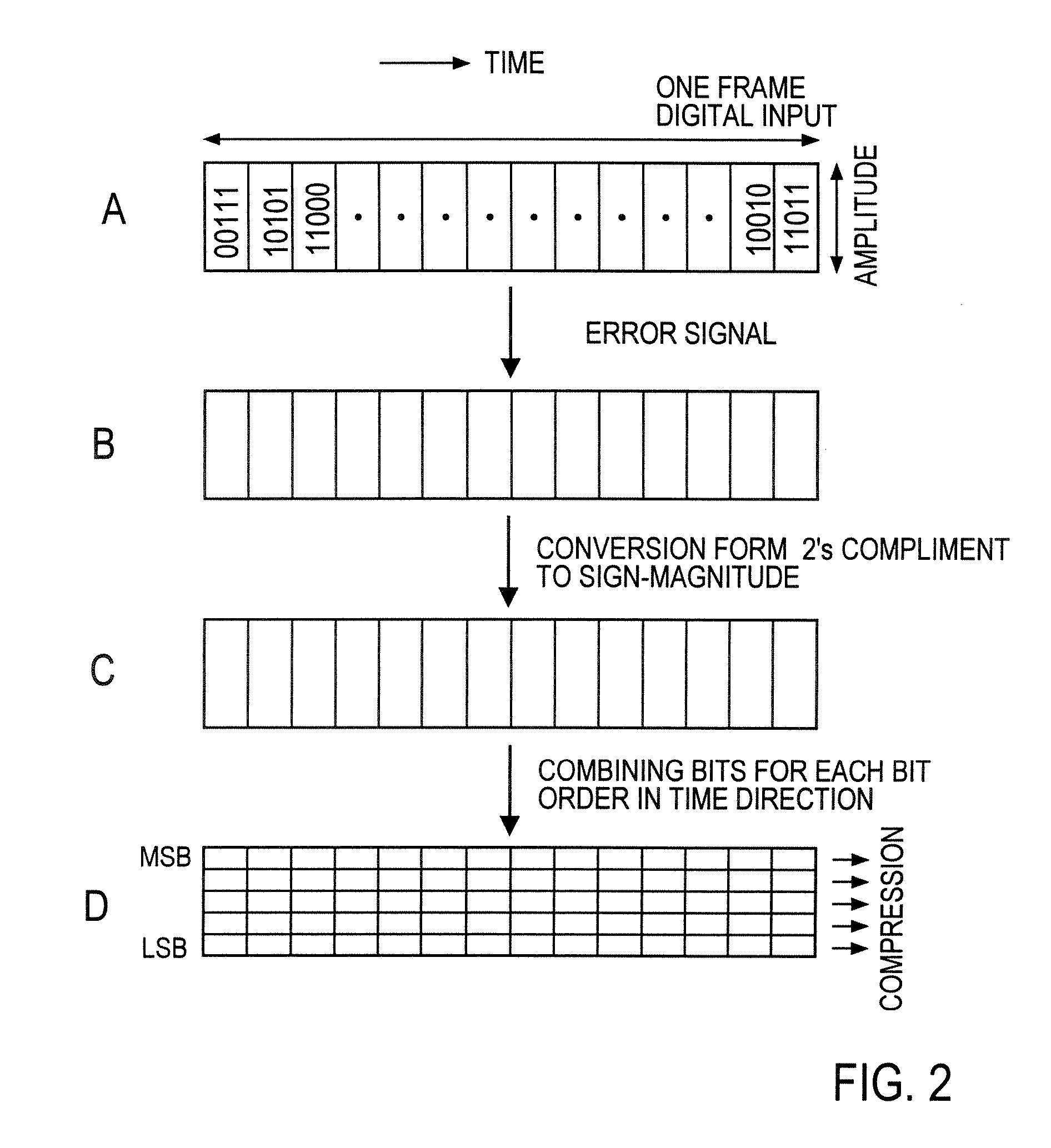
At the coder side, bits of samples of each frame of an input digital signal are concatenated every digit common to the samples across each frame to generate equi-order bit sequences, which are output as packets. At the decoding side, the input equi-order sequences are arranged inversely to their arrangement at the coder side to reconstruct sample sequences. When a packet dropout occurs, a missing information compensating part 430 correct the reconstructed sample sequences in a manner to reduce an error between the spectral envelope of the reconstructed sample sequence concerned and a known spectral envelope.
Owner:NIPPON TELEGRAPH & TELEPHONE CORP
Classification of Fast and Slow Signal
ActiveUS20100063806A1Convenient timeQuality improvementSpeech analysisFrequency spectrumImage resolution
Low bit rate audio coding such as BWE algorithm often encounters conflict goal of achieving high time resolution and high frequency resolution at the same time. In order to achieve best possible quality, input signal can be first classified into fast signal and slow signal. This invention focuses on classifying signal into fast signal and slow signal, based on at least one of the following parameters or a combination of the following parameters: spectral sharpness, temporal sharpness, pitch correlation (pitch gain), and / or spectral envelope variation. This classification information can help to choose different BWE algorithms, different coding algorithms, and different postprocessing algorithms respectively for fast signal and slow signal.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Source coding enhancement using spectral-band replication
InactiveUS6925116B2Improvements of audio codecsImprove perceived qualitySpeech analysisCode conversionFrequency spectrumComputer science
The present invention proposes a new method and apparatus for the enhancement of source coding systems. The invention employs bandwidth reduction (101) prior to or in the encoder (103), followed by spectral-band replication (105) at the decoder (107). This is accomplished by the use of new transposition methods, in combination with spectral envelope adjustments. Reduced bitrate at a given perceptual quality or an improved perceptual quality at a given bitrate is offered. The invention is preferably integrated in a hardware or software codec, but can also be implemented as a separate processor in combination with a codec. The invention offers substantial improvements practically independent of codec type and technological progress.
Owner:DOLBY INT AB
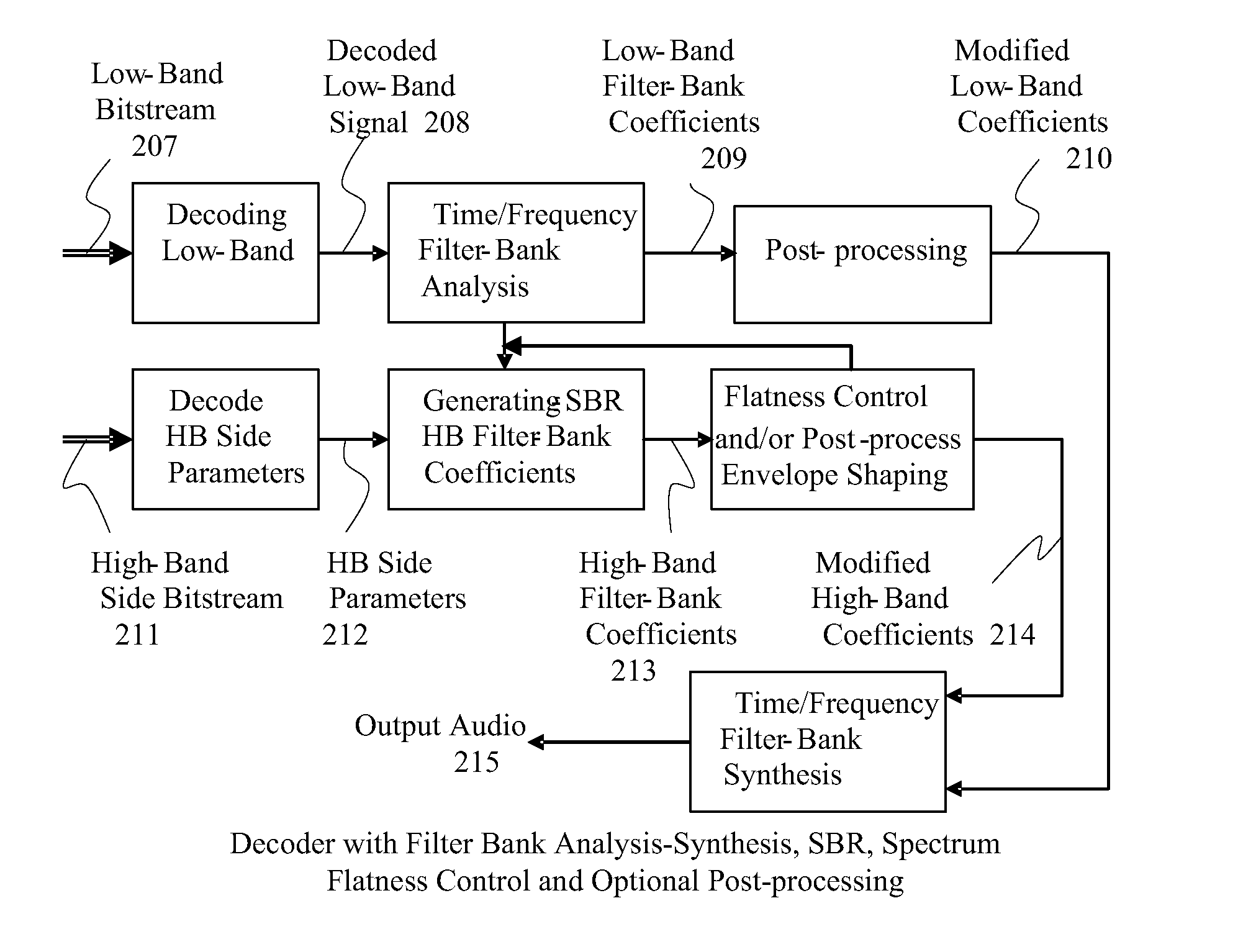
Spectrum flatness control for bandwidth extension
In accordance with an embodiment, a method of decoding an encoded audio bitstream at a decoder includes receiving the audio bitstream, decoding a low band bitstream of the audio bitstream to get low band coefficients in a frequency domain, and copying a plurality of the low band coefficients to a high frequency band location to generate high band coefficients. The method further includes processing the high band coefficients to form processed high band coefficients. Processing includes modifying an energy envelope of the high band coefficients by multiplying modification gains to flatten or smooth the high band coefficients, and applying a received spectral envelope decoded from the received audio bitstream to the high band coefficients. The low band coefficients and the processed high band coefficients are then inverse-transformed to the time domain to obtain a time domain output signal.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
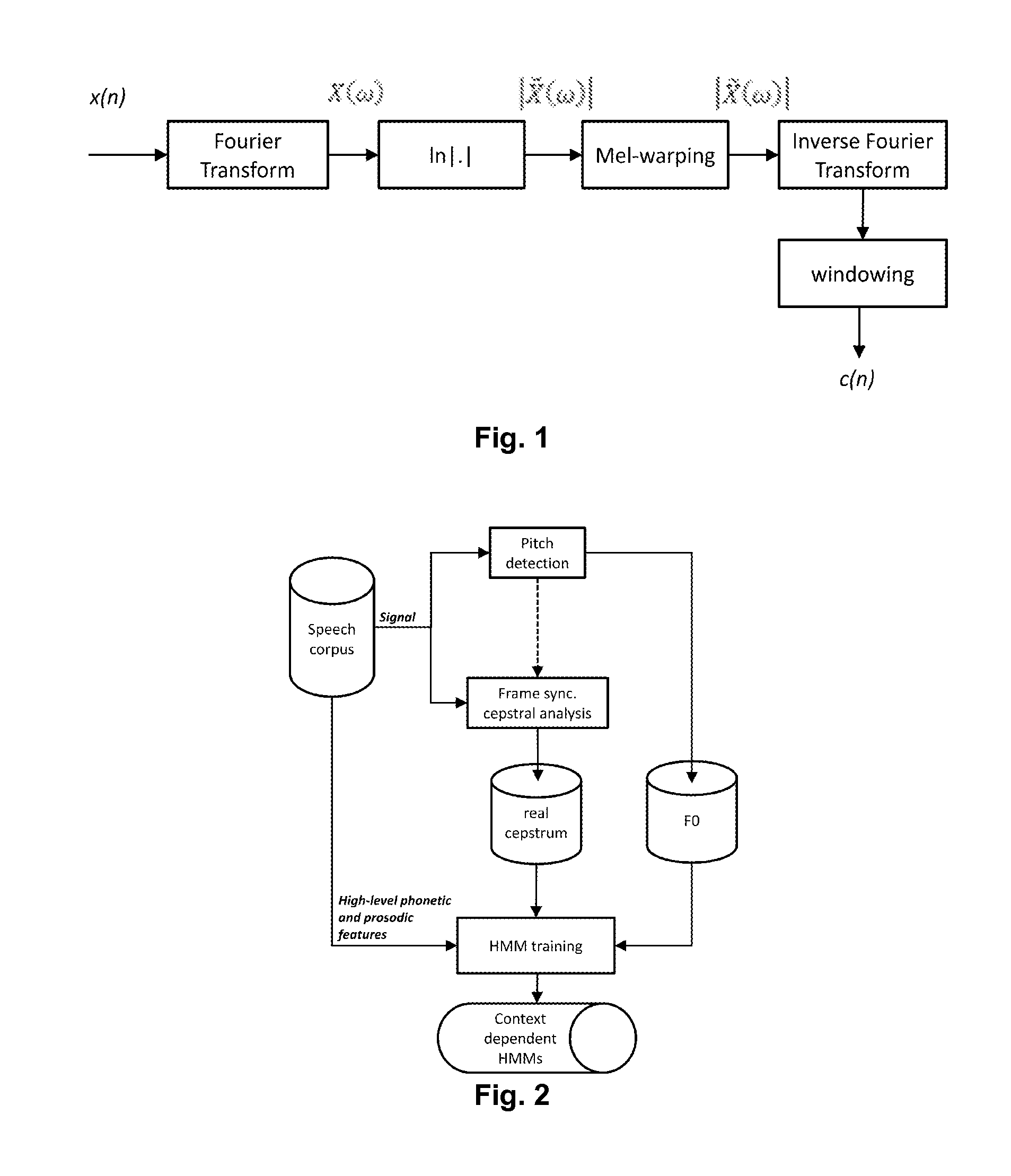
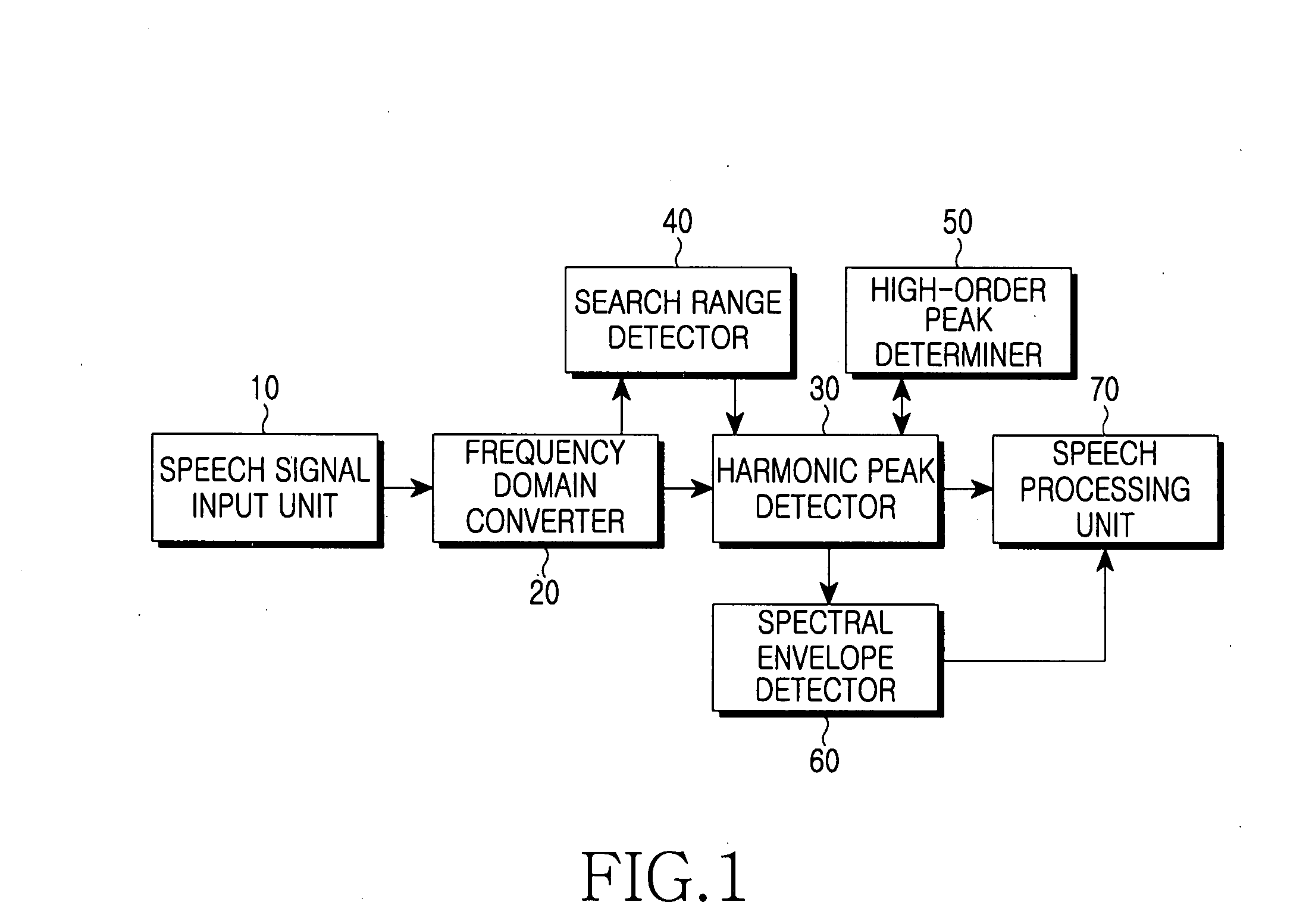
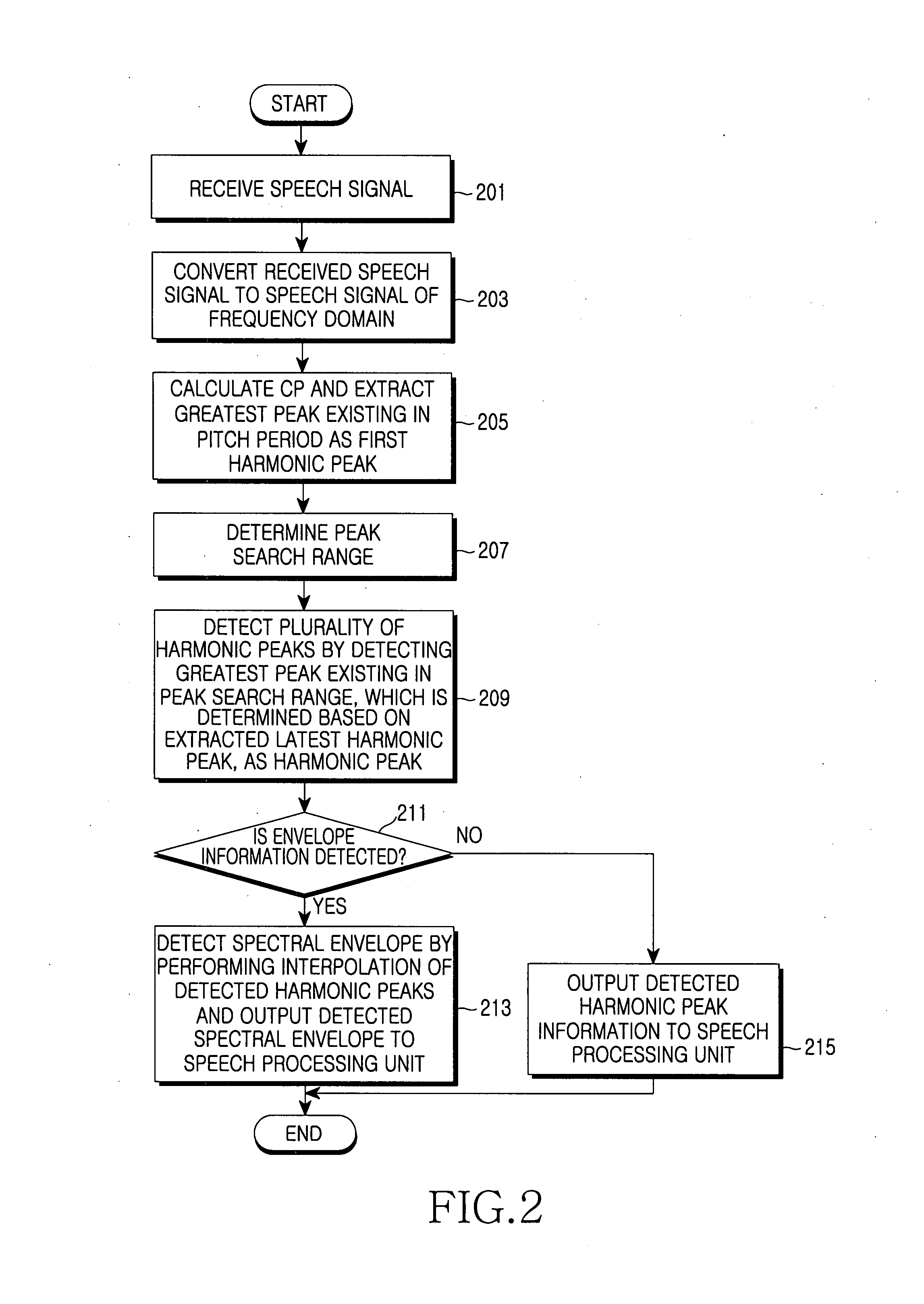
Method and apparatus for estimating harmonic information, spectral envelope information, and degree of voicing of speech signal
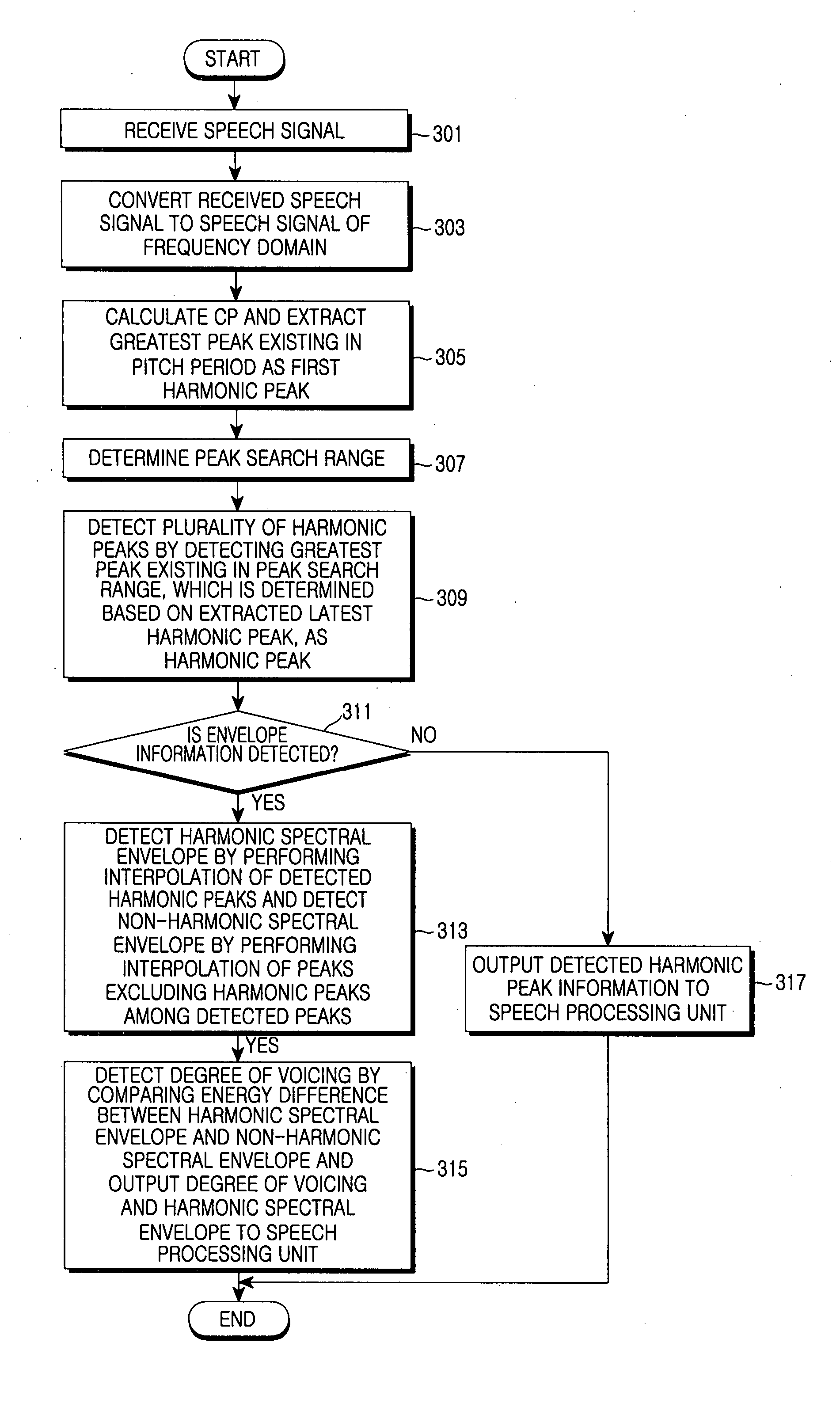
A degree of voicing is extracted using the characteristic of harmonic peaks existing in a constant period by converting an input speech or audio signal to a speech signal of the frequency domain, selecting the greatest peak in a first pitch period of the converted speech signal as a harmonic peak, thereafter selecting a peak having the greatest spectral value among peaks existing in each peak search range of the speech signal as a harmonic peak, extracting harmonic spectral envelope information by performing interpolation of the selected harmonic peaks, extracting non-harmonic spectral envelope information by performing interpolation of the non-harmonic peaks, and comparing the two pieces of envelope information to each other.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Speech processing apparatus and speech synthesis apparatus
ActiveUS20090144053A1Quality improvementEasy execution of processingSpeech synthesisFine structureFrequency spectrum
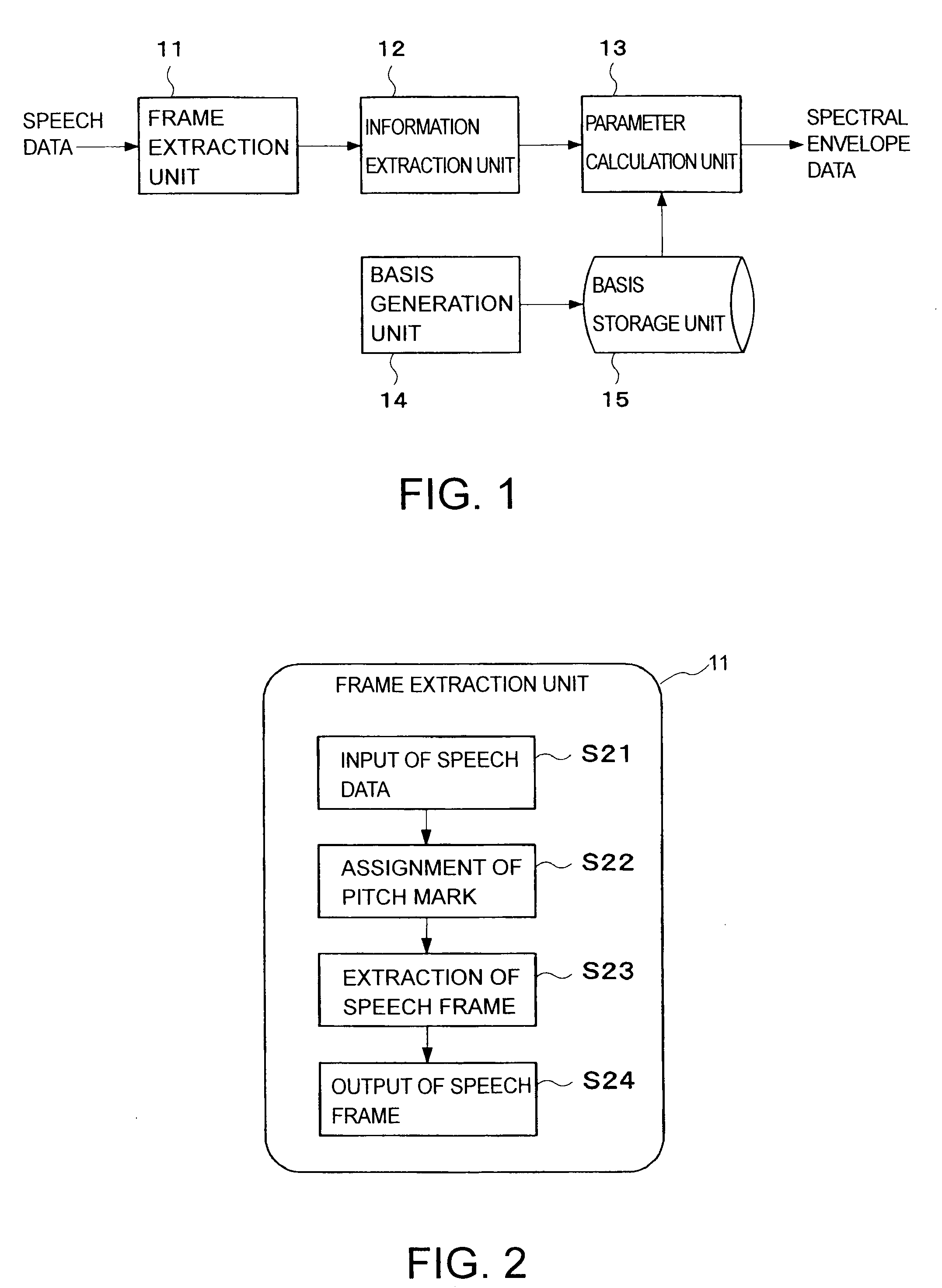
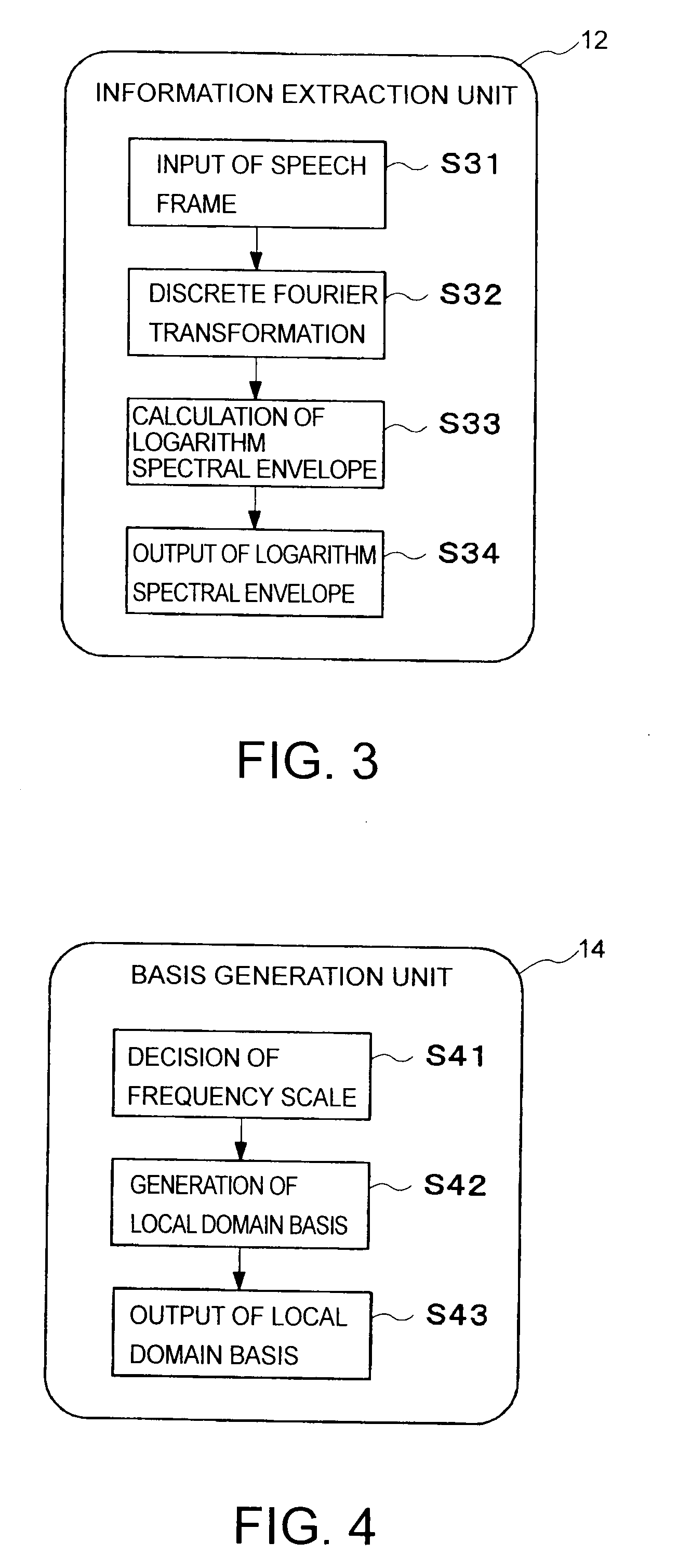
An information extraction unit extracts spectral envelope information of L-dimension from each frame of speech data. The spectral envelope information does not have a spectral fine structure. A basis storage unit stores N bases (L>N>1). Each basis is differently a frequency band having a maximum as a peak frequency in a spectral domain having L-dimension. A value corresponding to a frequency outside the frequency band along a frequency axis of the spectral domain is zero. Two frequency bands of which two peak frequencies are adjacent along the frequency axis partially overlap. A parameter calculation unit minimizes a distortion between the spectral envelope information and a linear combination of each basis with a coefficient by changing the coefficient, and sets the coefficient of each basis from which the distortion is minimized to a spectral envelope parameter of the spectral envelope information.
Owner:TOSHIBA DIGITAL SOLUTIONS CORP
Wideband signal encoding, decoding and transmission
InactiveUS20070296614A1Code conversionDigital video signal modificationFrequency spectrumLow frequency band
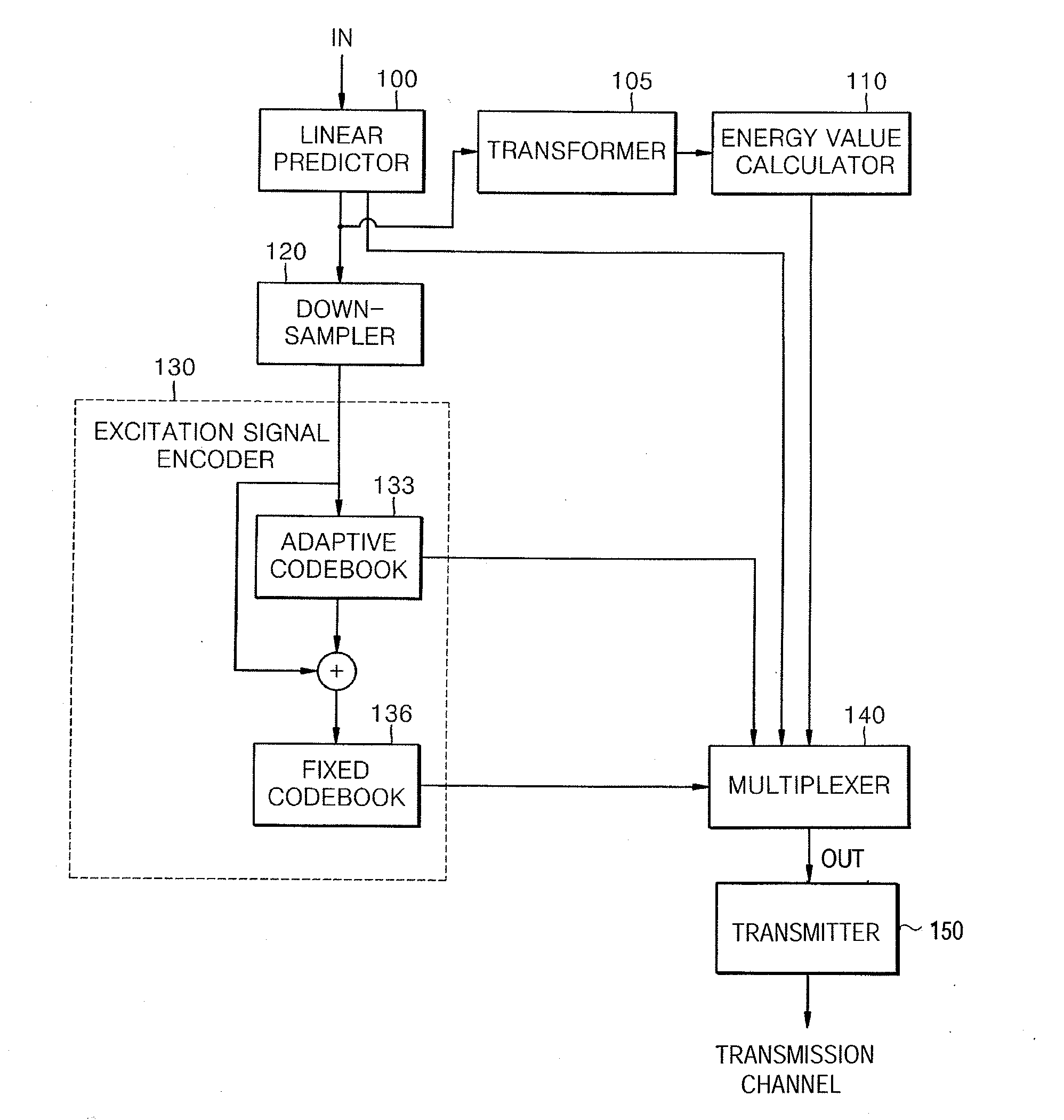
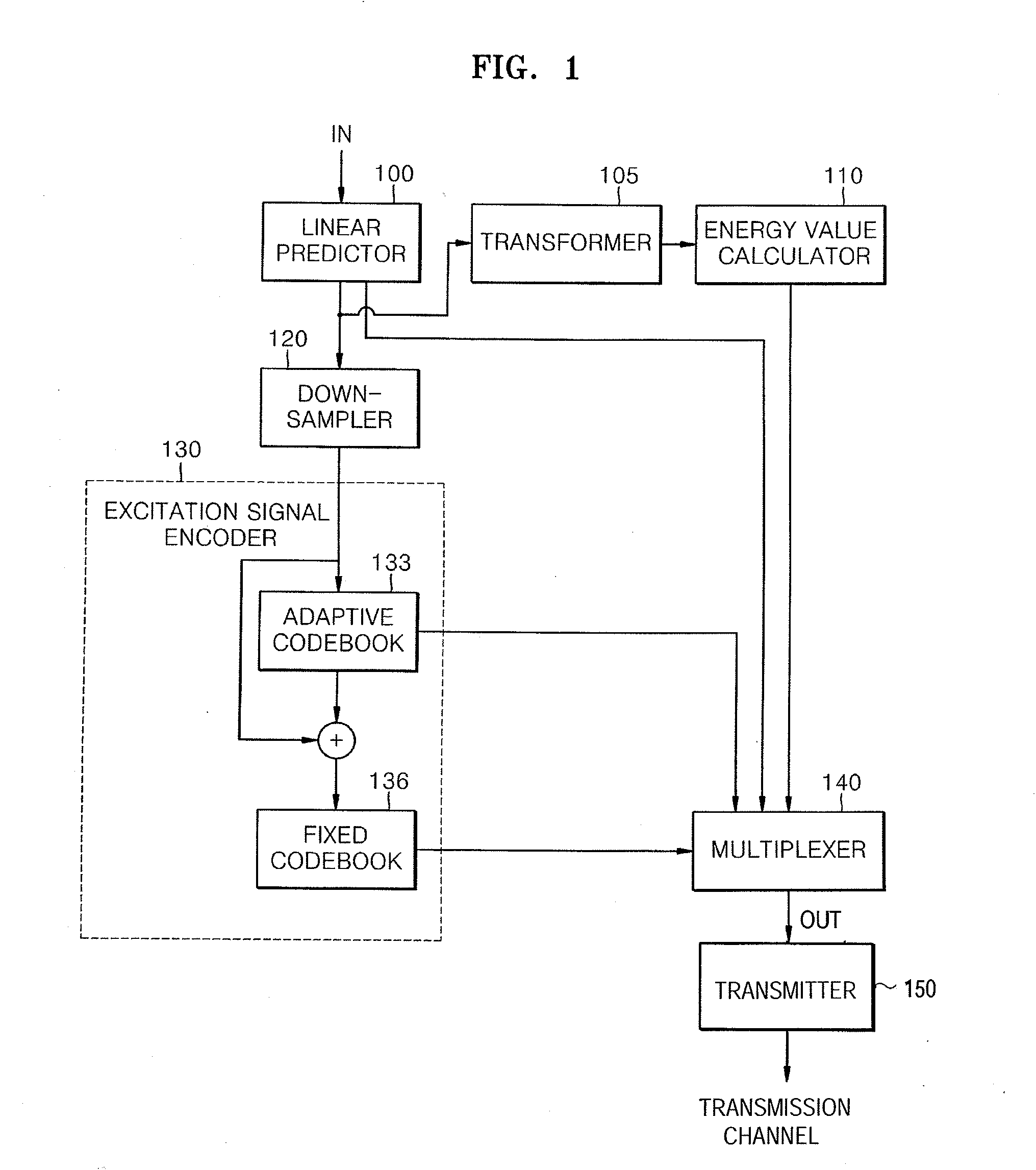
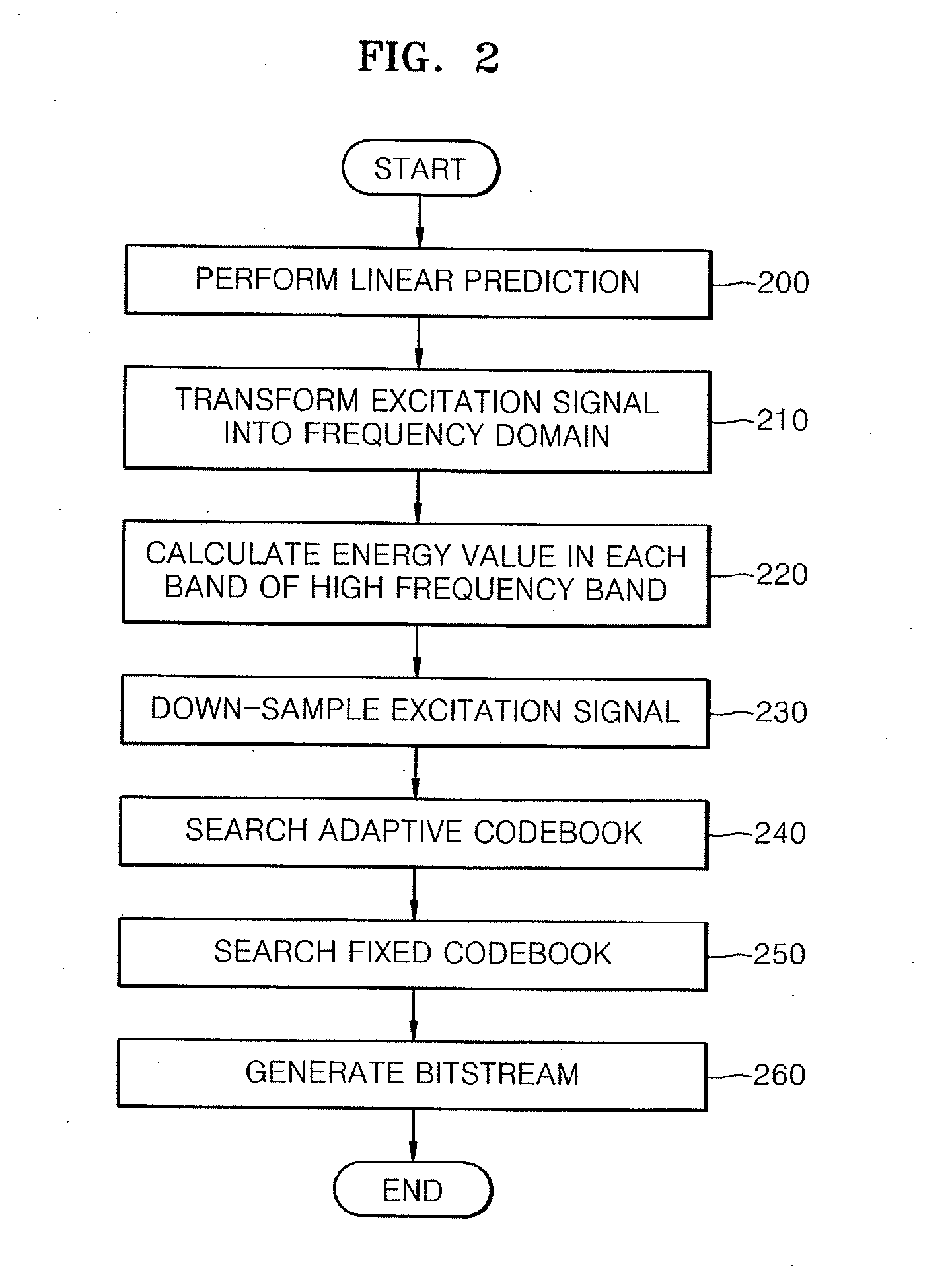
Encoding and / or decoding a wideband signal produces high frequency band spectra from low frequency band spectral information. Linear prediction filter coefficients are determined for the entire wideband spectrum of an input signal. An energy value in each of a plurality of sub-bands in the high frequency band is determined and encoded. The short-term correlation removed input signal is then down-sampled to form a low frequency band signal. At a decoder, the high frequency band signal is generated using the encoded low frequency band signal. The energy in each sub-band of the high frequency band is adjusted using the encoded energy value. Thus, the spectral envelope for the entire wideband signal is synthesized and decoded using linear predictive synthesis.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Digital signal coding and decoding methods and apparatuses and programs therefor
InactiveUS20070083362A1Reduce the amount of informationSpeech analysisCode conversionDecoding methodsSample sequence
At the coder side, bits of samples of each frame of an input digital signal are concatenated every digit common to the samples across each frame to generate equi-order bit sequences, which are output as packets. At the decoding side, the input equi-order sequences are arranged inversely to their arrangement at the coder side to reconstruct sample sequences. When a packet dropout occurs, a missing information compensating part 430 correct the reconstructed sample sequences in a manner to reduce an error between the spectral envelope of the reconstructed sample sequence concerned and a known spectral envelope.
Owner:NIPPON TELEGRAPH & TELEPHONE CORP
Sound signal processing method, sound signal processing apparatus and computer program
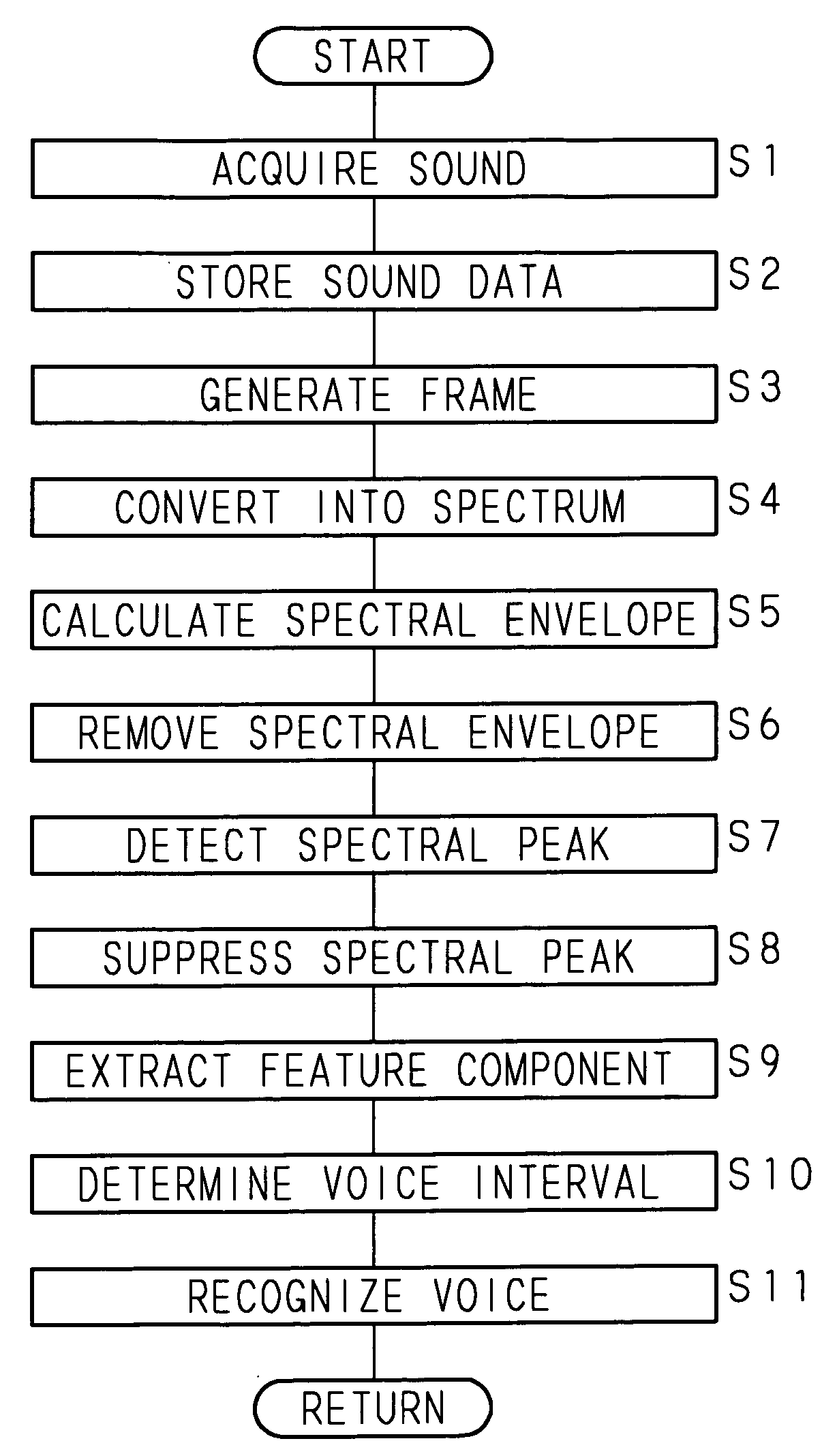
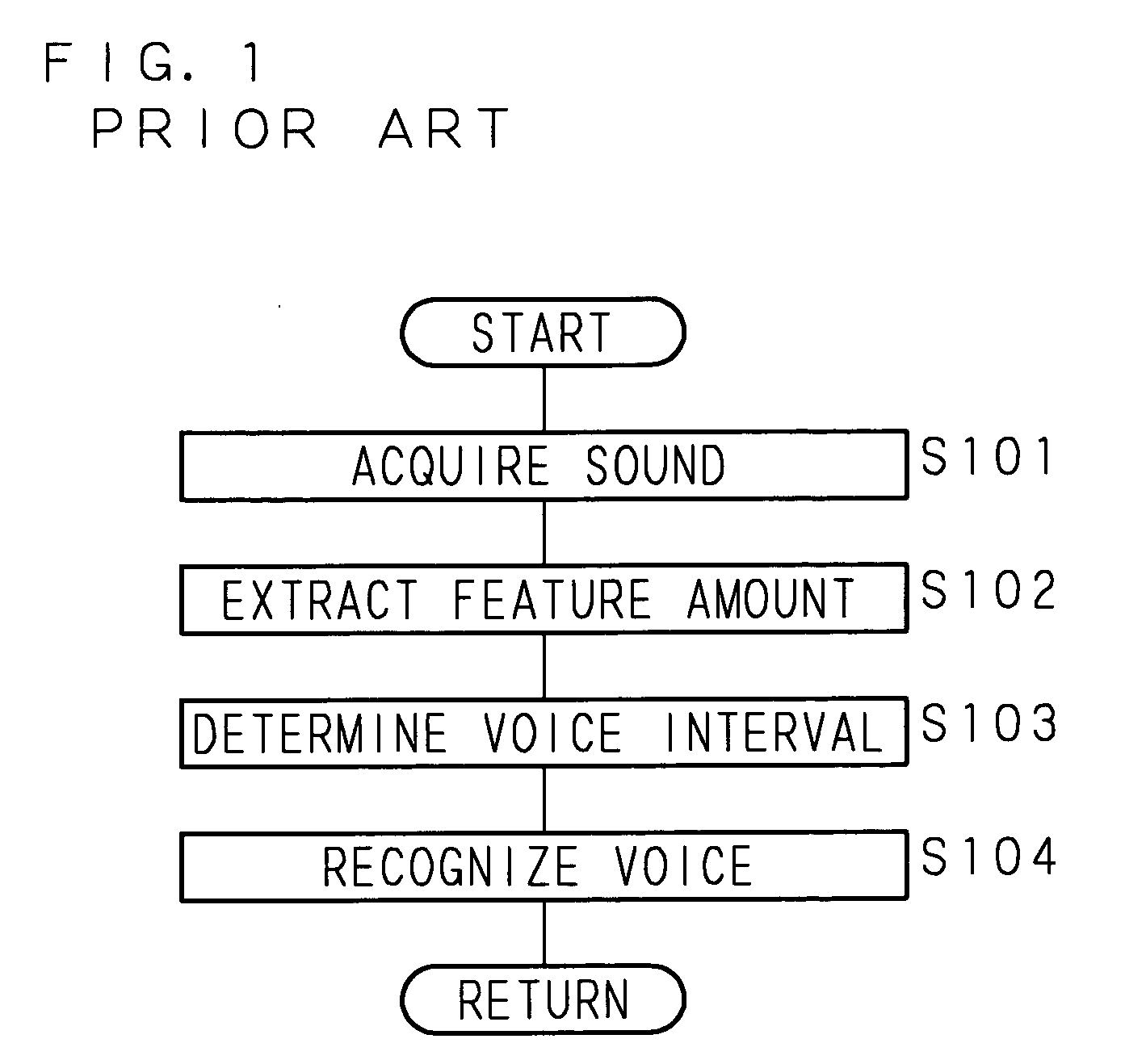
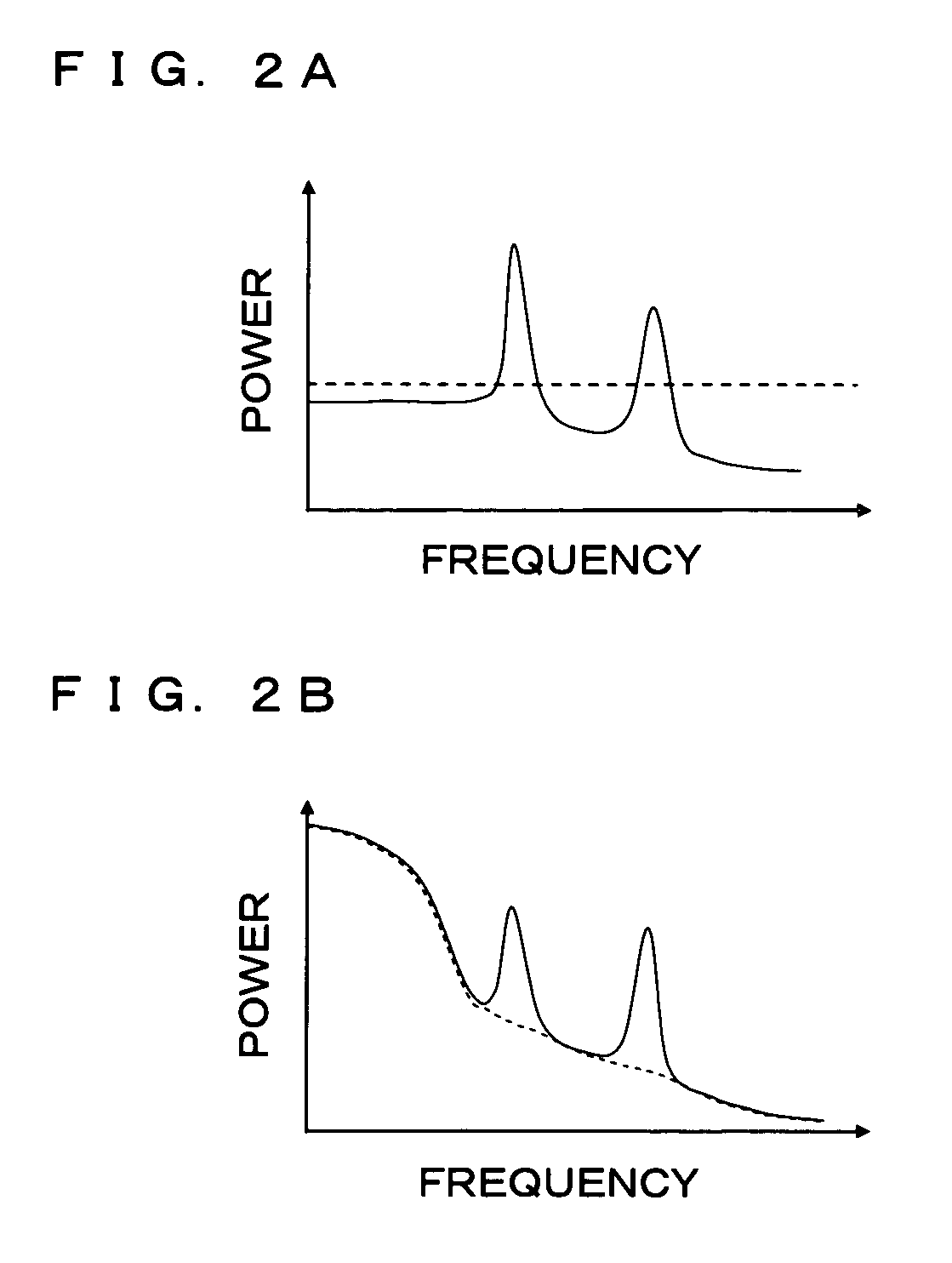
InactiveUS20080069364A1Improve accuracyAccurate detectionStereophonic circuit arrangementsSpeech recognitionFrequency spectrumPeak value
A sound signal processing apparatus creates frames from acquired sound data, and converts a sound signal into a spectrum on a frame-by-frame basis. Then, the sound signal processing apparatus calculates a spectral envelope based on the spectrum, removes the spectral envelope from the spectrum, detects a spectral peak in the spectrum obtained by the removal of the spectral envelope, and suppresses the detected spectral peak. The sound signal processing apparatus determines a voice interval from the spectrum with the suppressed spectral peak, and executes voice recognition processing based on the spectrum with the suppressed spectral peak in a frame determined to be a voice interval.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Noise-Reduction Processing of Speech Signals
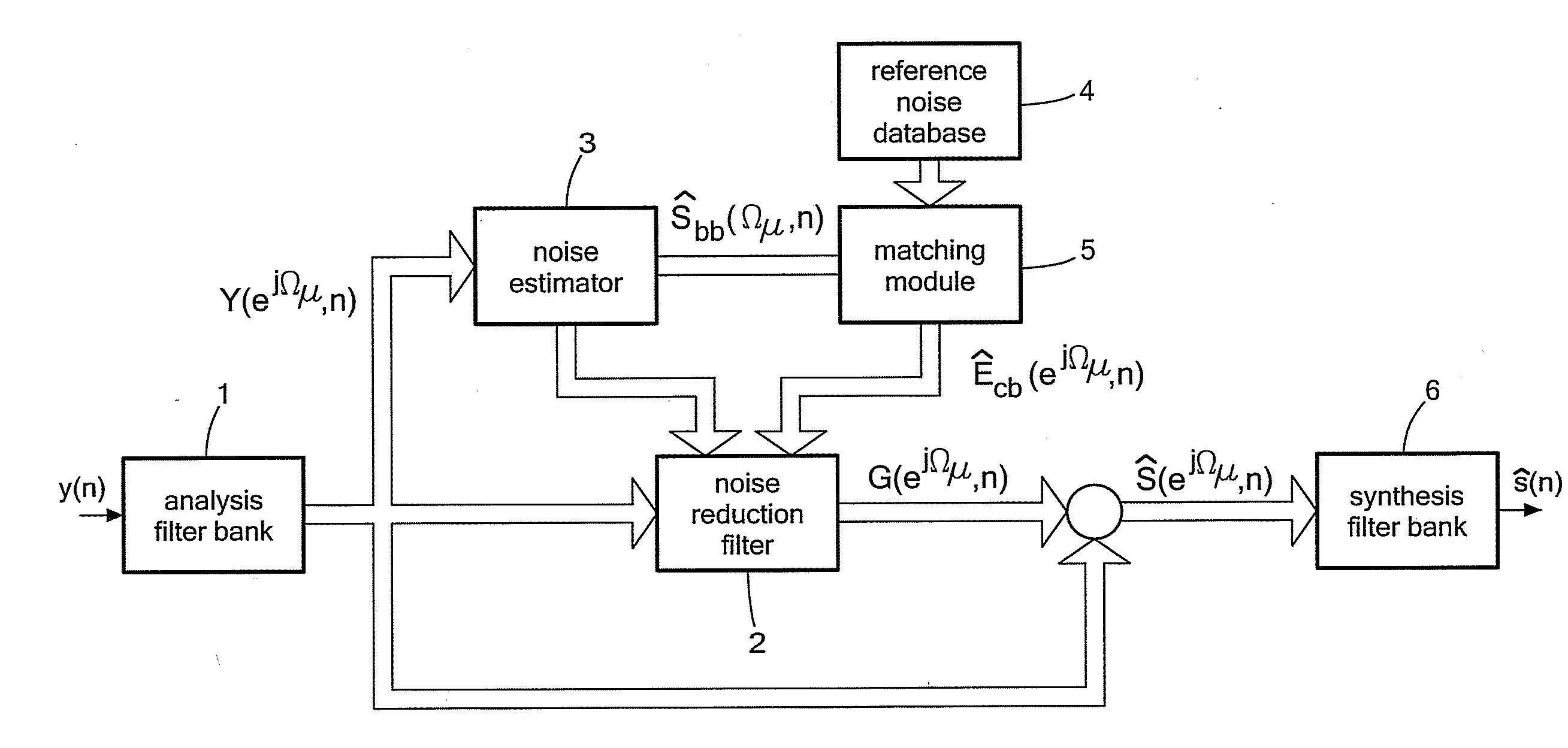
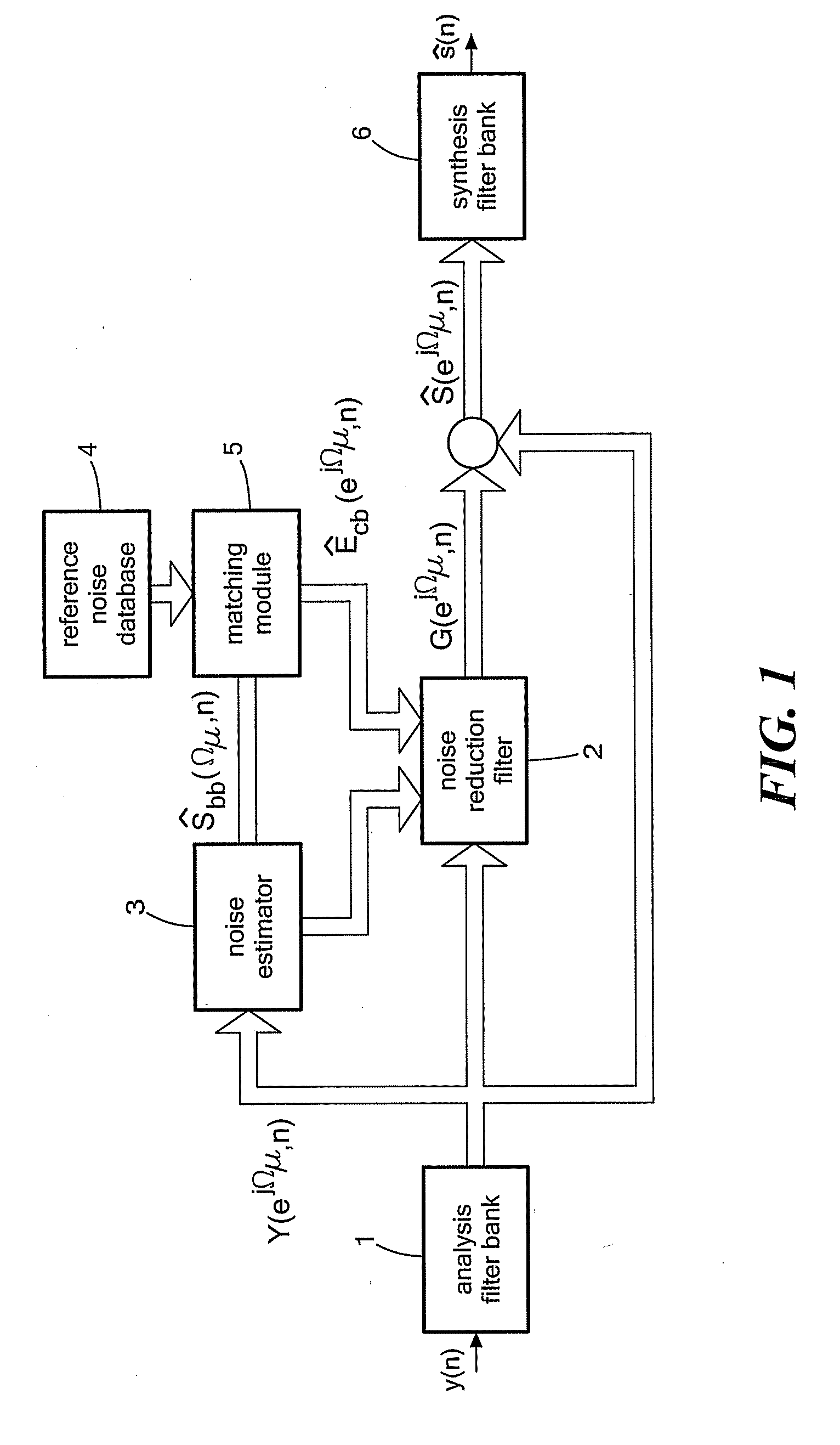
ActiveUS20100036659A1Quality improvementEfficiently be suppressedSpeech recognitionTransmission noise suppressionFrequency spectrumMicrophone signal
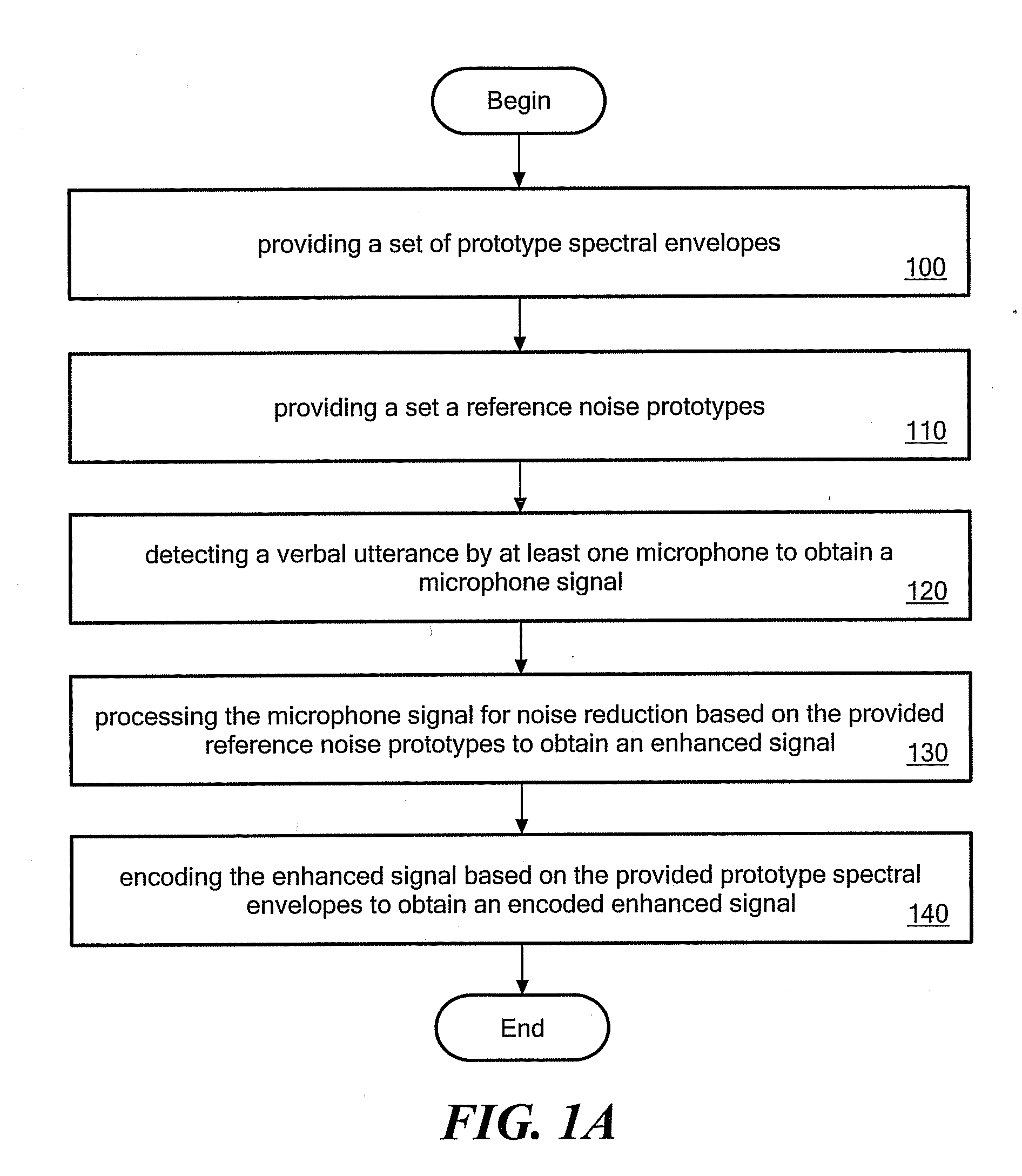
The present invention relates to a method for signal processing comprising the steps of providing a set of prototype spectral envelopes, providing a set of reference noise prototypes, wherein the reference noise prototypes are obtained from at least a sub-set of the provided set of prototype spectral envelopes, detecting a verbal utterance by at least one microphone to obtain a microphone signal, processing the microphone signal for noise reduction based on the provided reference noise prototypes to obtain an enhanced signal and encoding the enhanced signal based on the provided prototype spectral envelopes to obtain an encoded enhanced signal.
Owner:CERENCE OPERATING CO
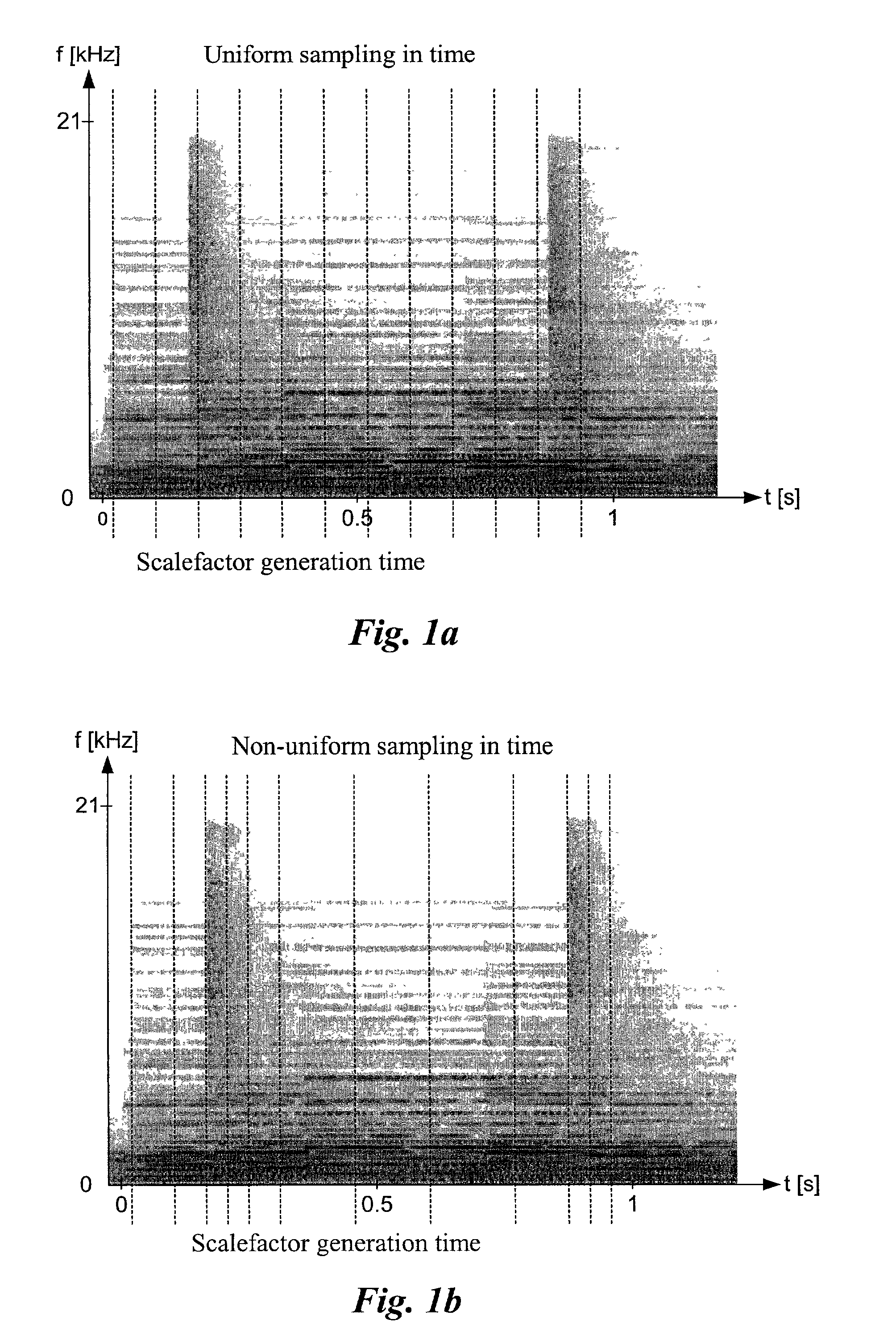
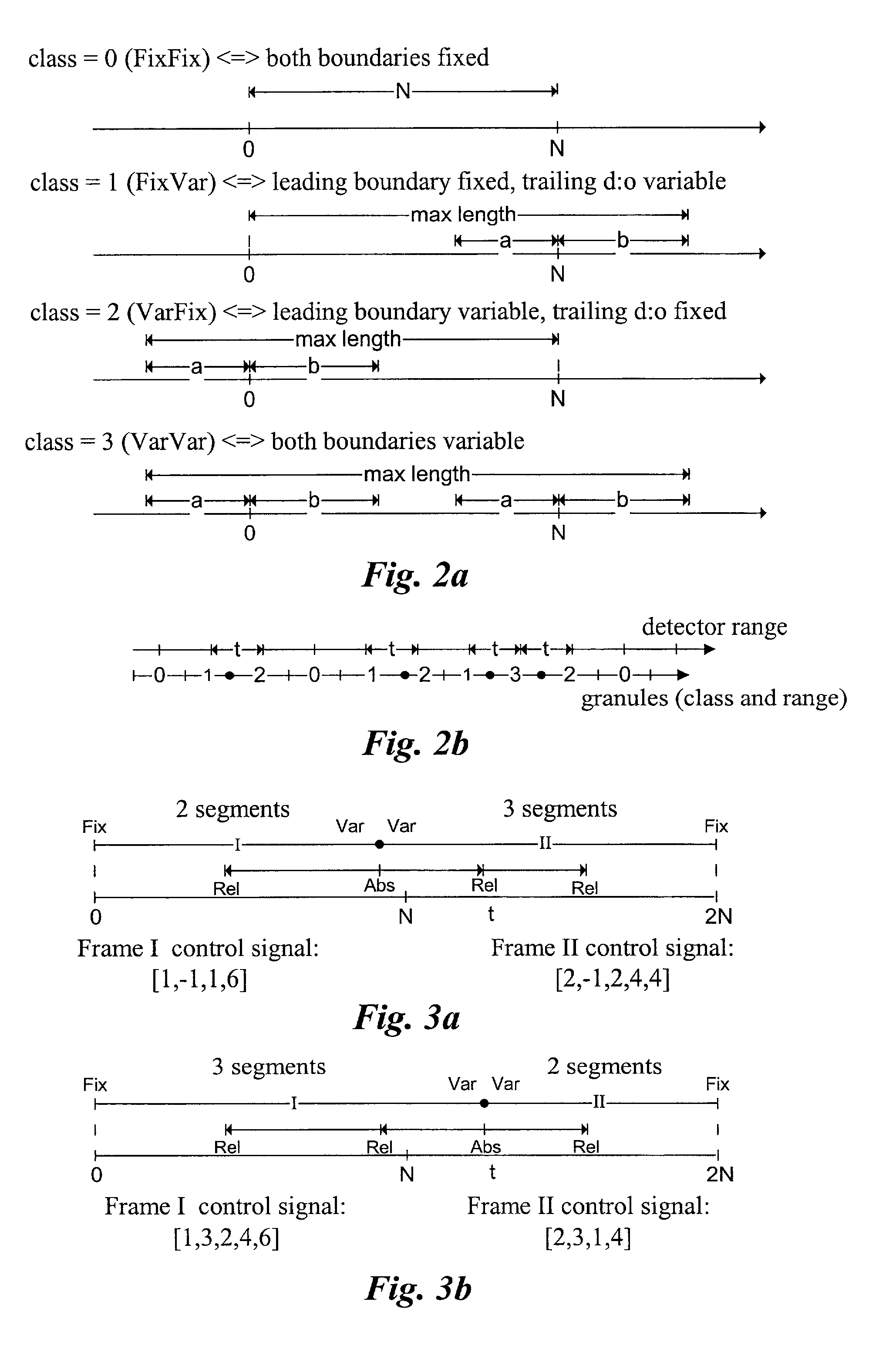
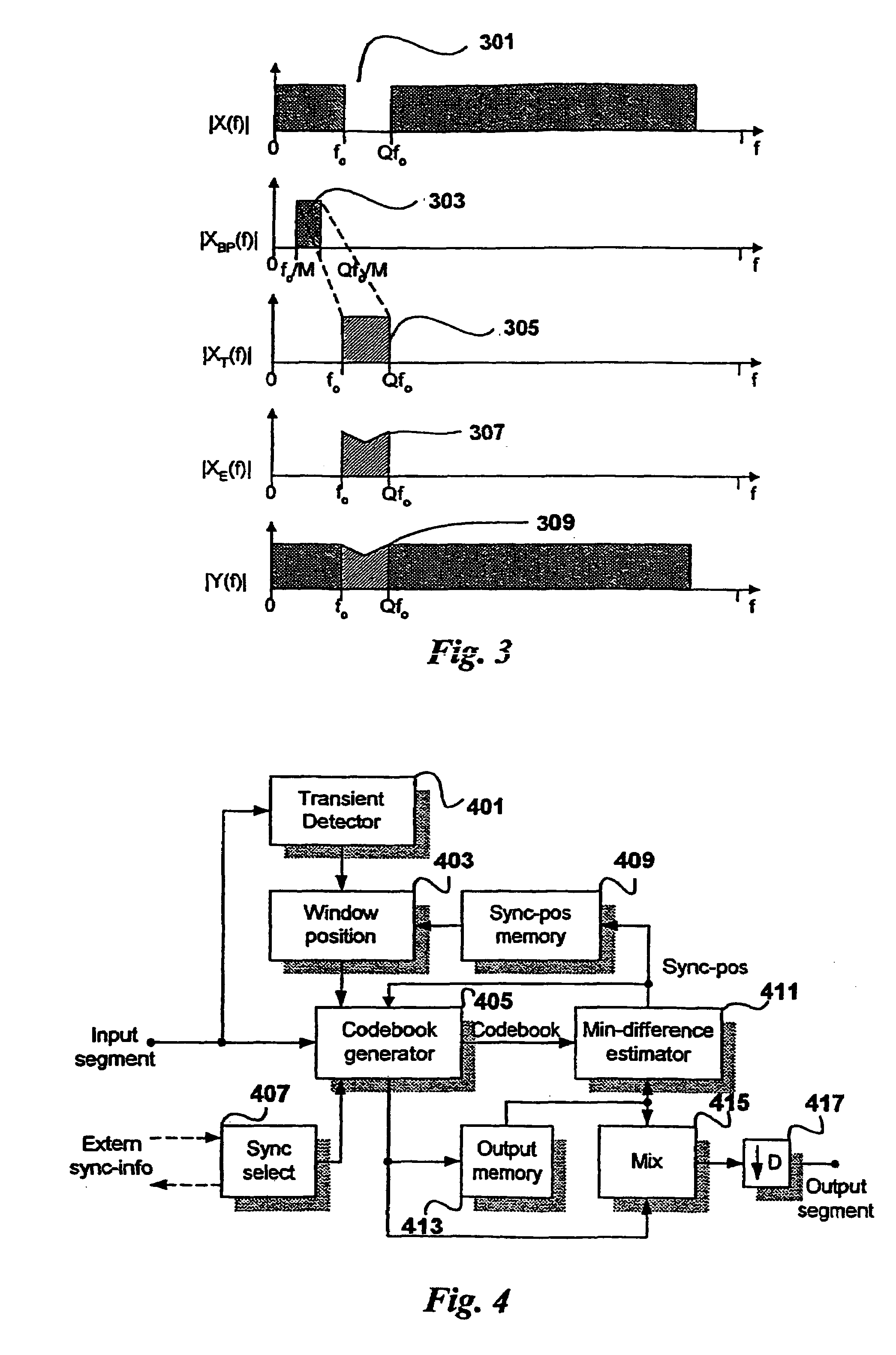
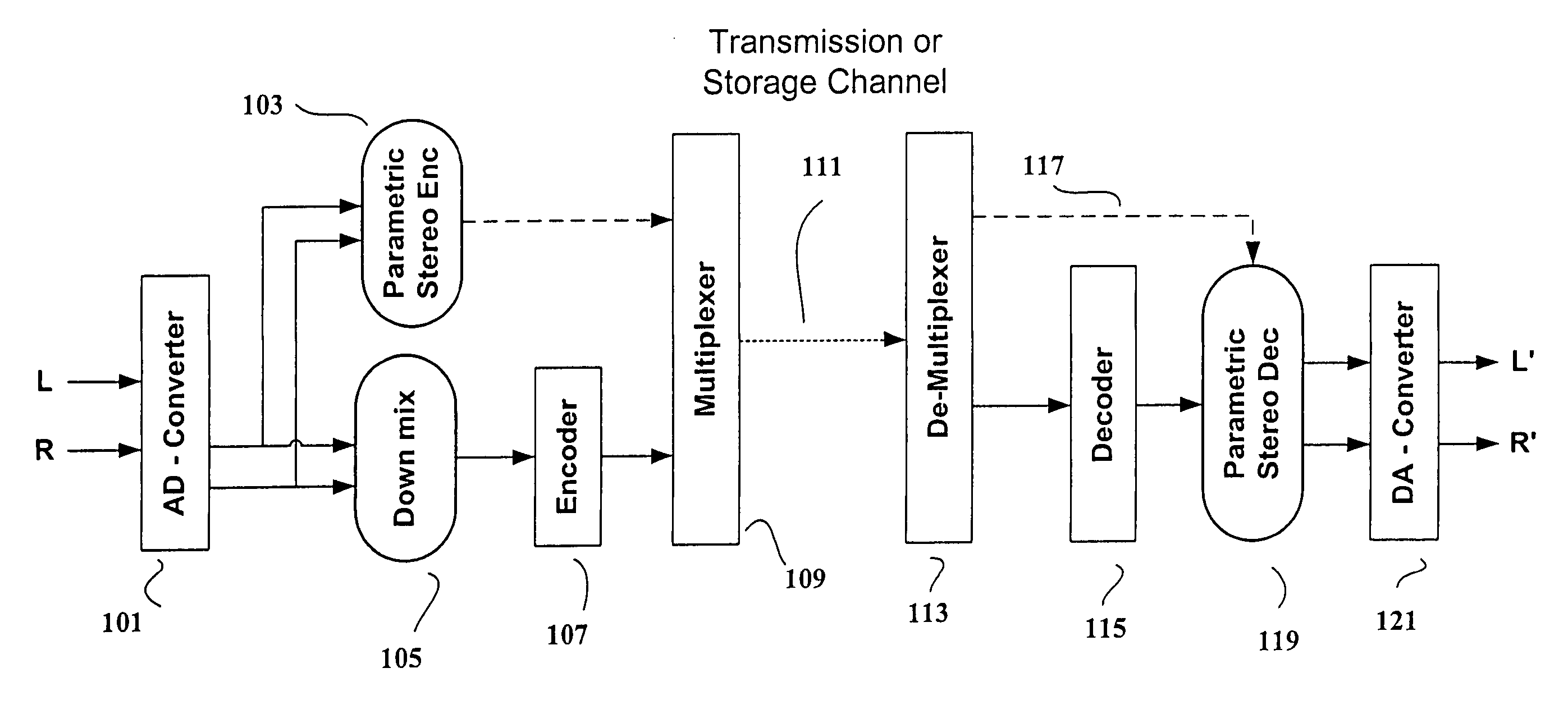
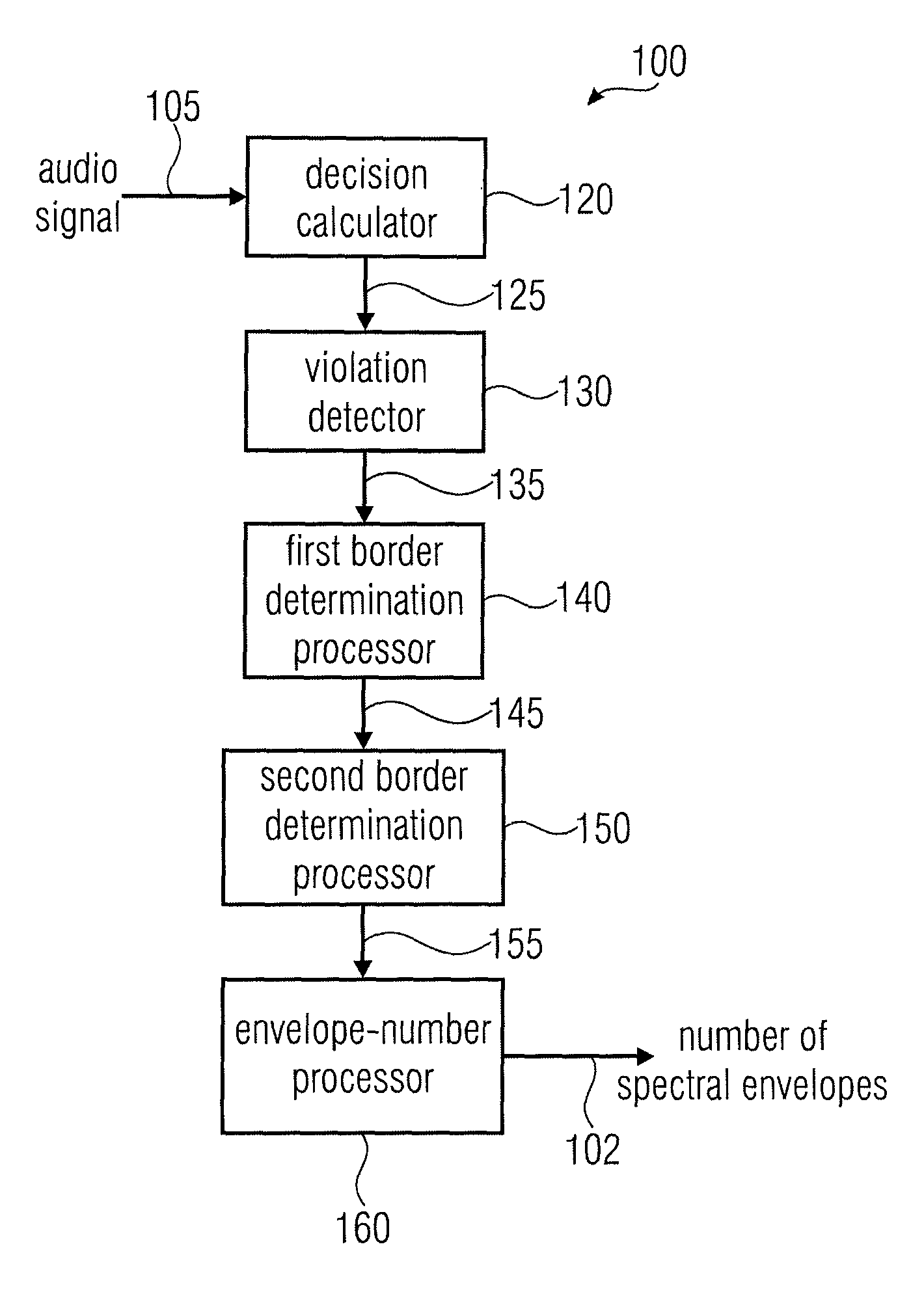
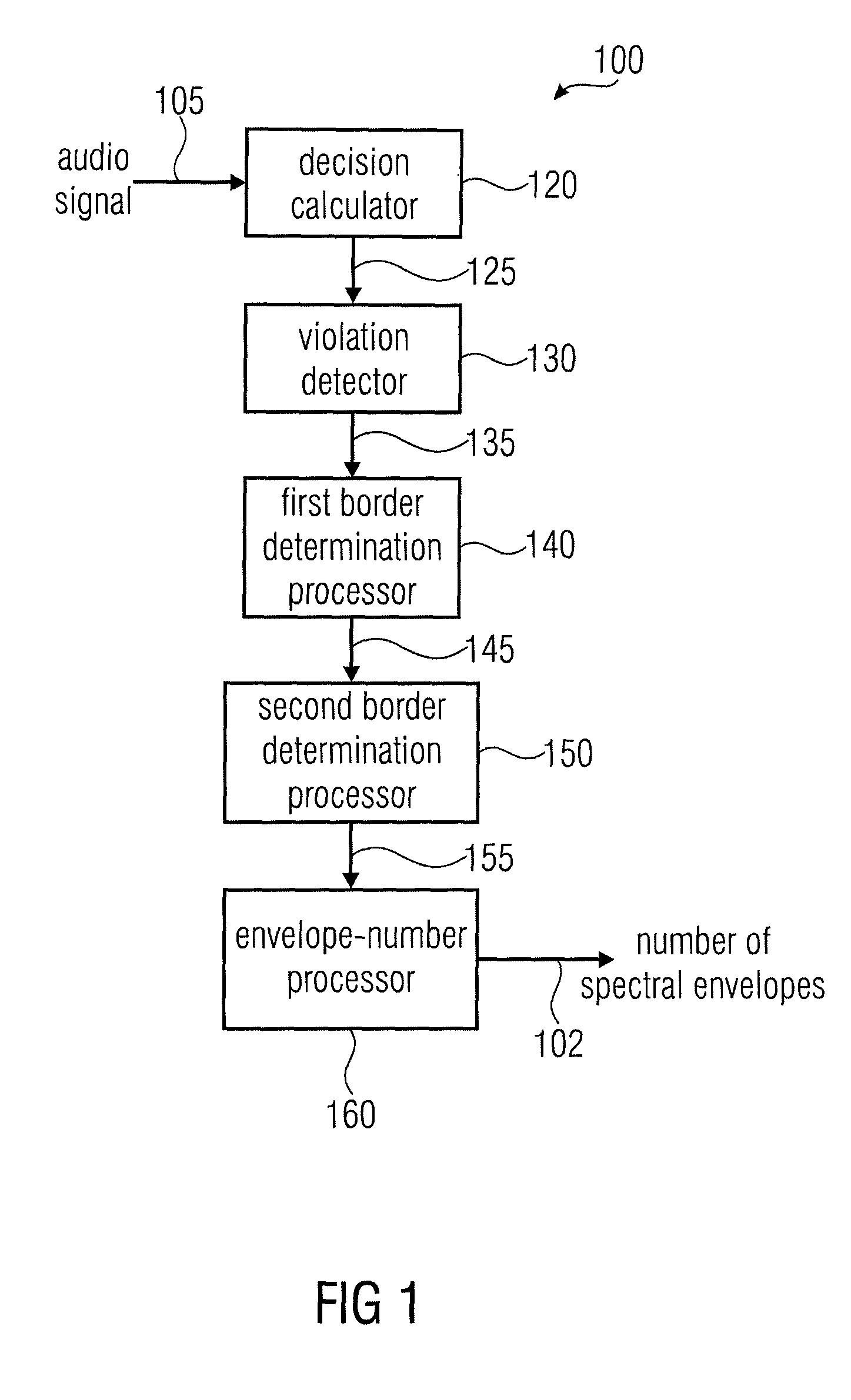
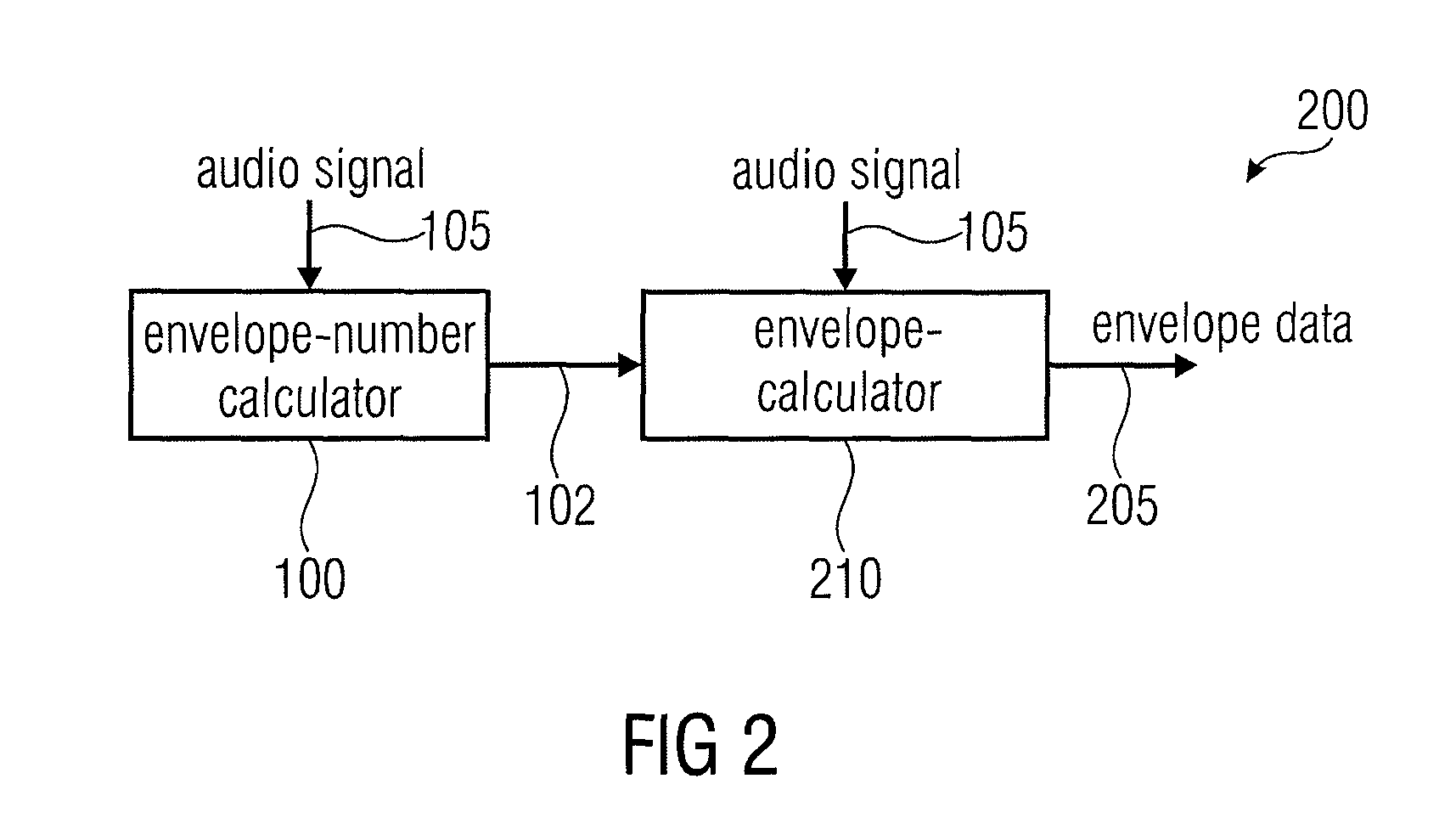
Apparatus and a Method for Calculating a Number of Spectral Envelopes
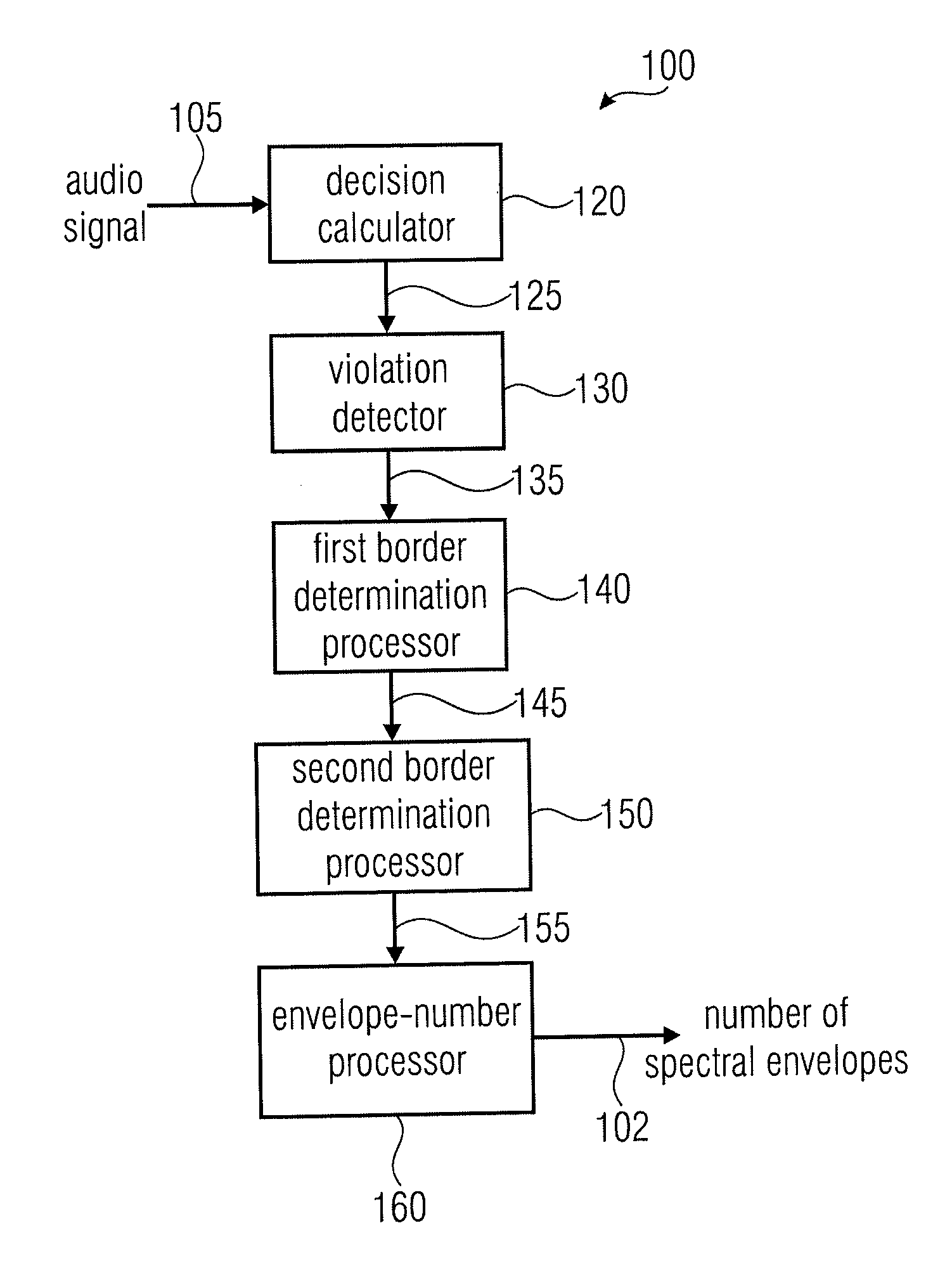
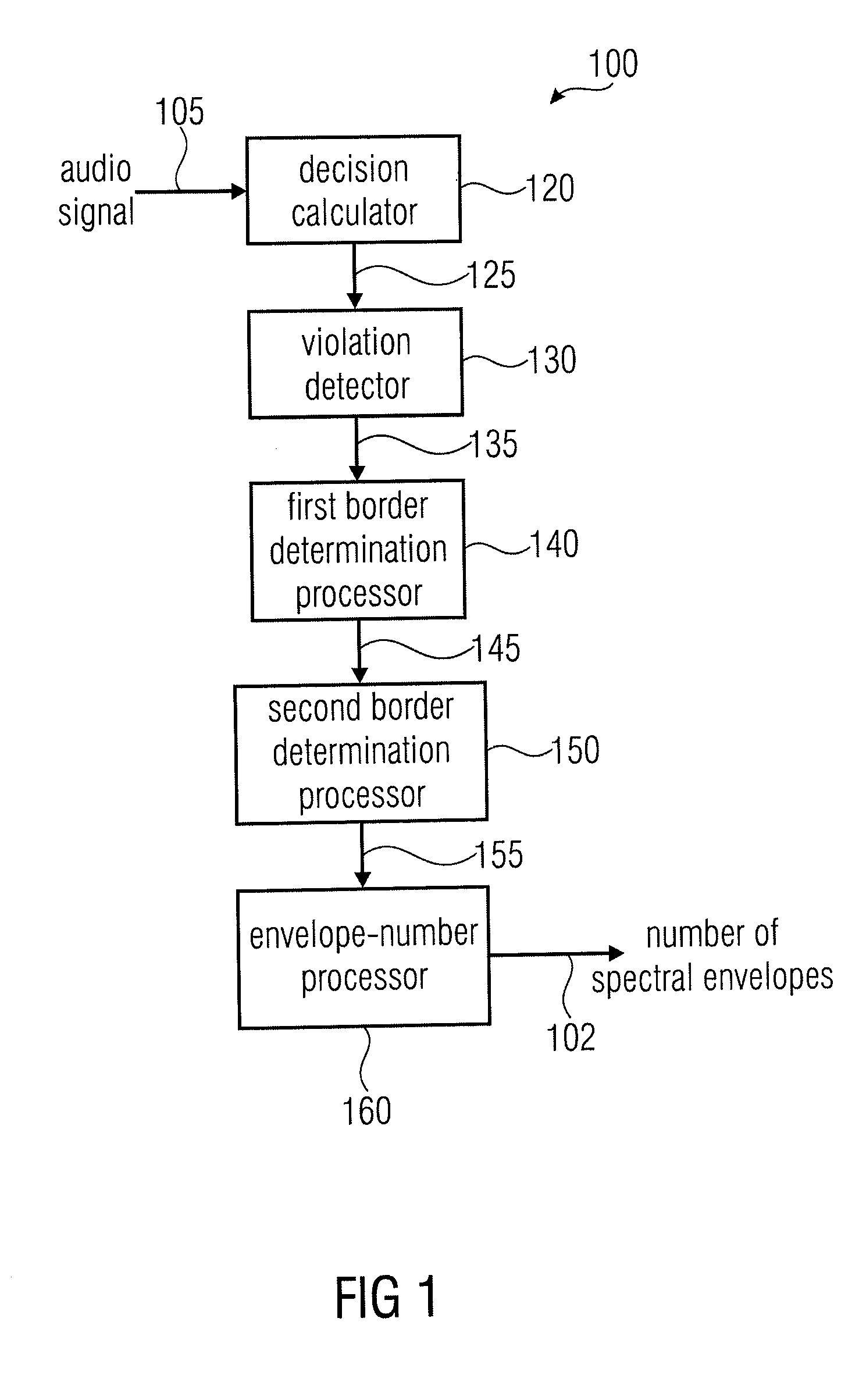
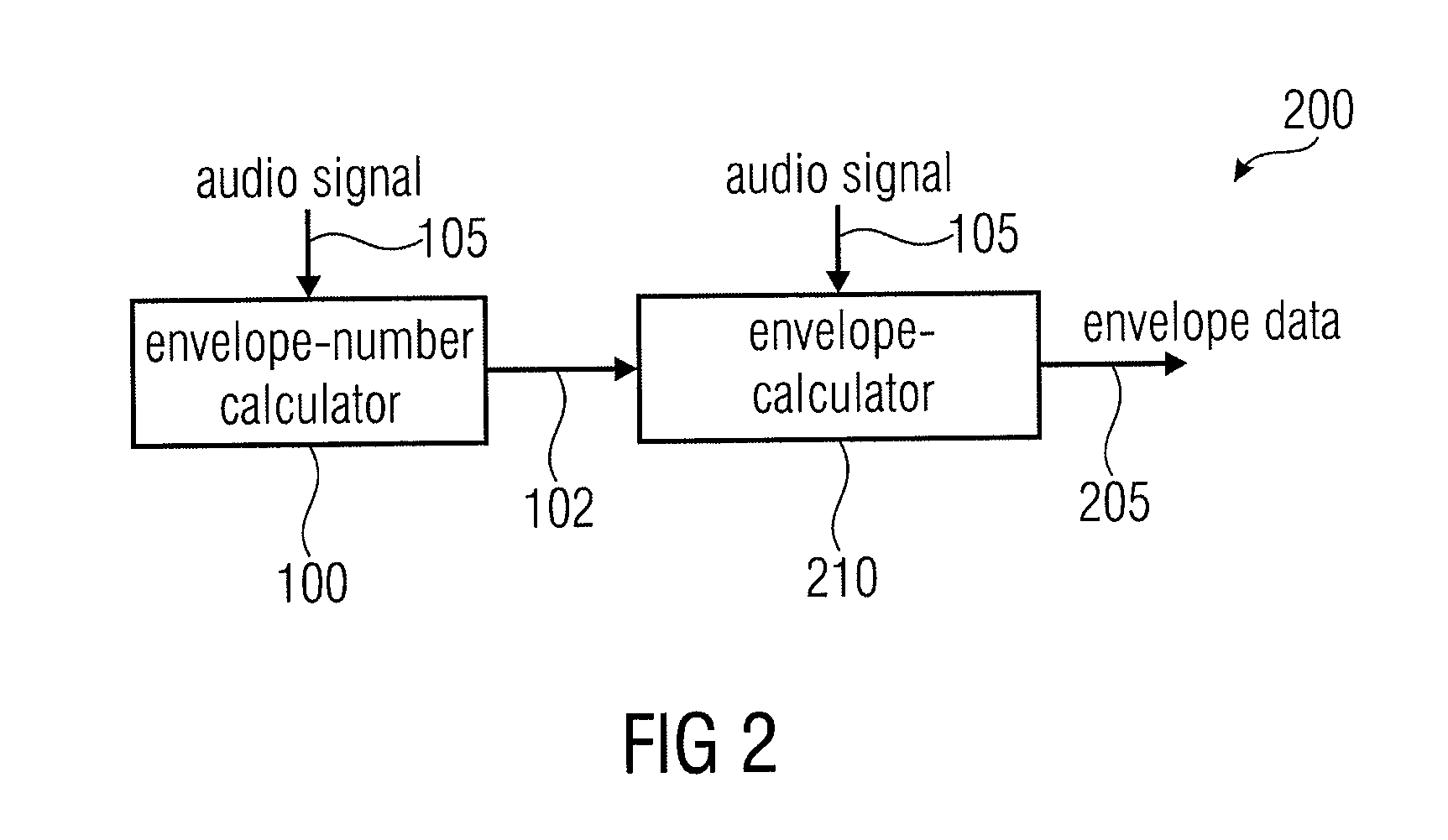
ActiveUS20110202358A1Easy to shapeFast enough to causeSpeech analysisDigital computer detailsFrequency spectrumChronological time
An apparatus calculates a number of spectral envelopes to be derived by a spectral band replication (SBR) encoder, wherein the SBR encoder is adapted to encode an audio signal using a plurality of sample values within a predetermined number of subsequent time portions in an SBR frame extending from an initial time to a final time, the predetermined number of subsequent time portions being arranged in a time sequence given by the audio signal. The apparatus has a decision value calculator for determining a decision value, the decision value measuring a deviation in spectral energy distributions of a pair of neighboring time portions. The apparatus further has a detector for detecting a violation of a threshold by the decision value and a processor for determining a first envelope border between the pair of neighboring time portions when the violation of the threshold is detected.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
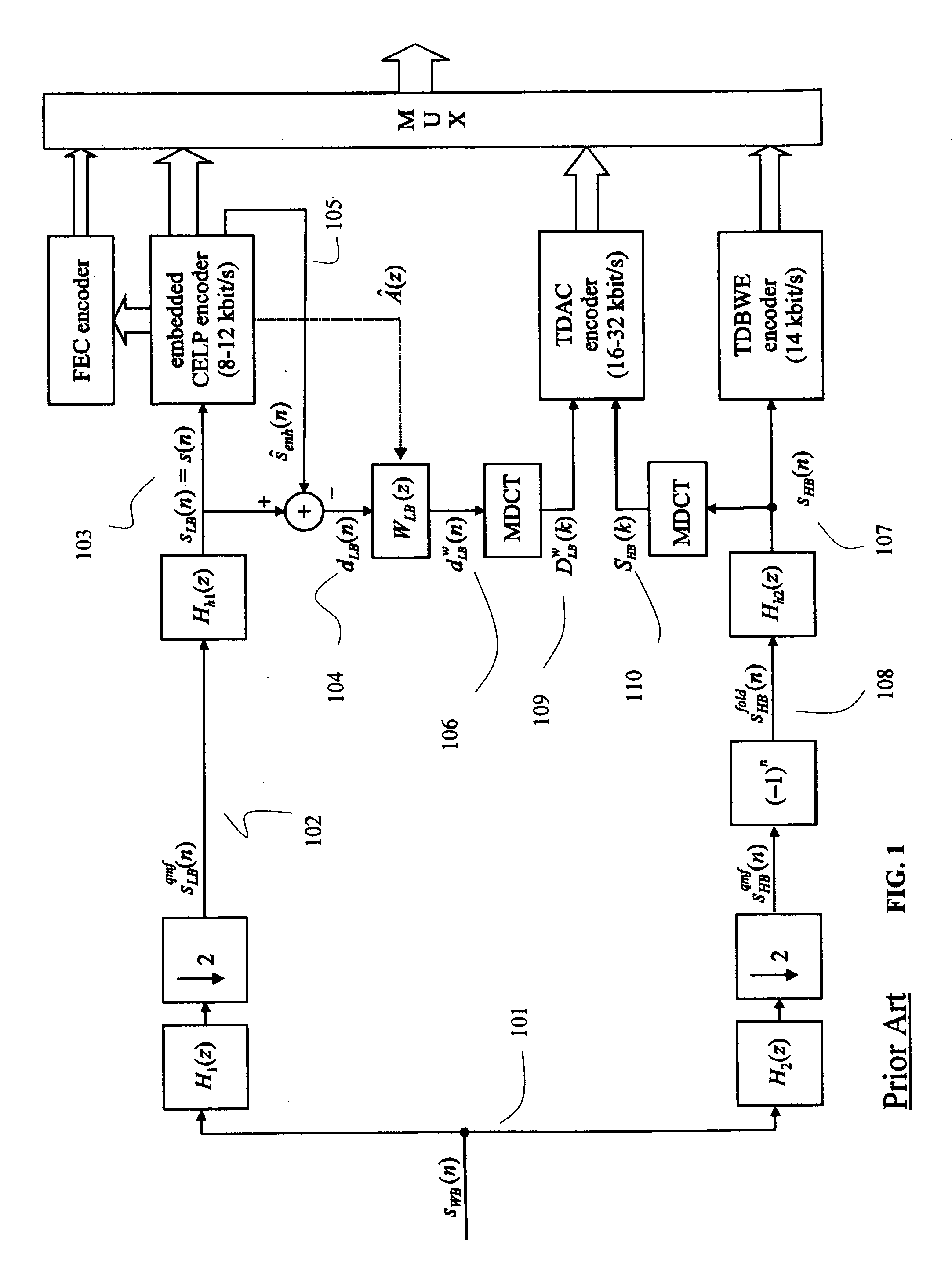
Methods and apparatus for coding and decoding highband part of voice signal
A wideband speech encoder according to one embodiment includes a lowband encoder and a highband encoder. The lowband encoder is configured to encode a lowband portion of a wideband speech signal as a set of filter parameters and an encoded excitation signal. The highband encoder is configured to calculate values for coding parameters that specify a spectral envelope and a temporal envelope of a highband portion of the wideband speech signal. The temporal envelope is based on a highband excitation signal that is derived from the encoded excitation signal. In one such example, the temporal envelope is based on a difference in levels between the highband portion and a synthesized highband signal, wherein the synthesized highband signal is generated according to the highband excitation signal and a set of highband filter parameters.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
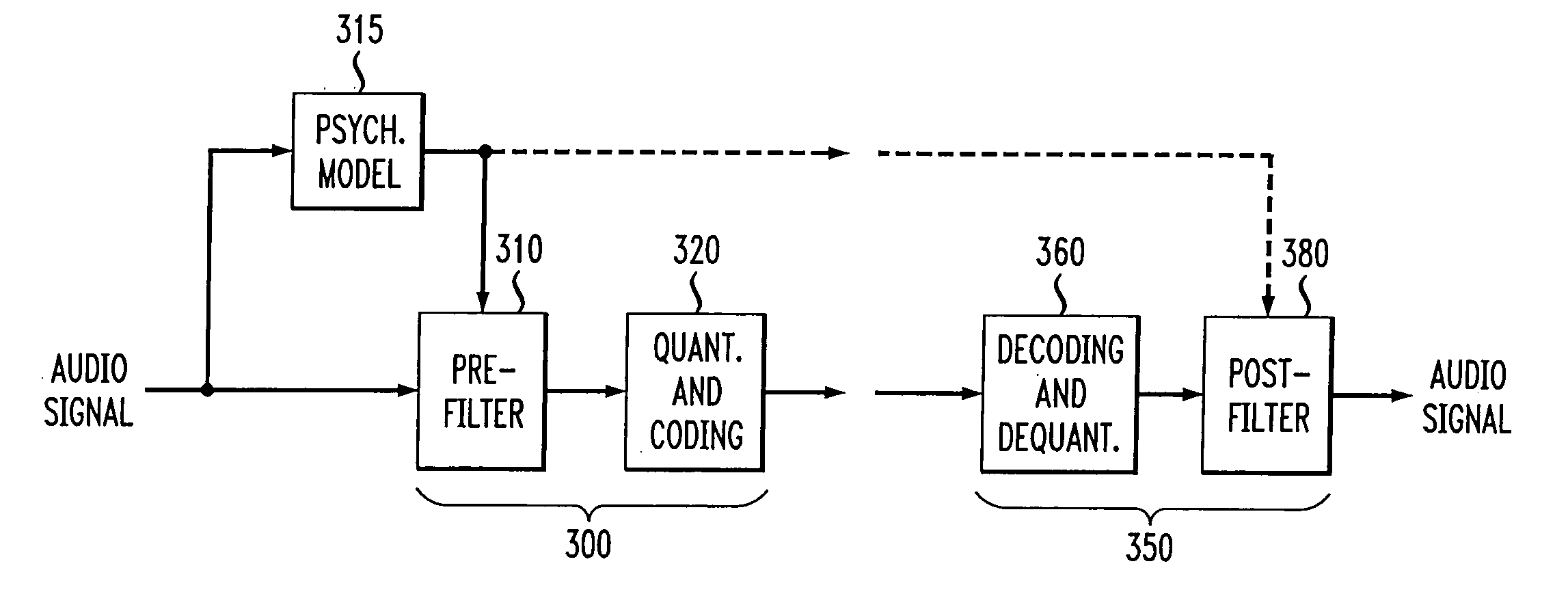
Perceptual coding of image signals using separated irrelevancy reduction and redundancy reduction
InactiveUS20060147124A1Guaranteed normal transmissionConserving transmitted bitsSpeech analysisCode conversionFrequency spectrumTemporal resolution
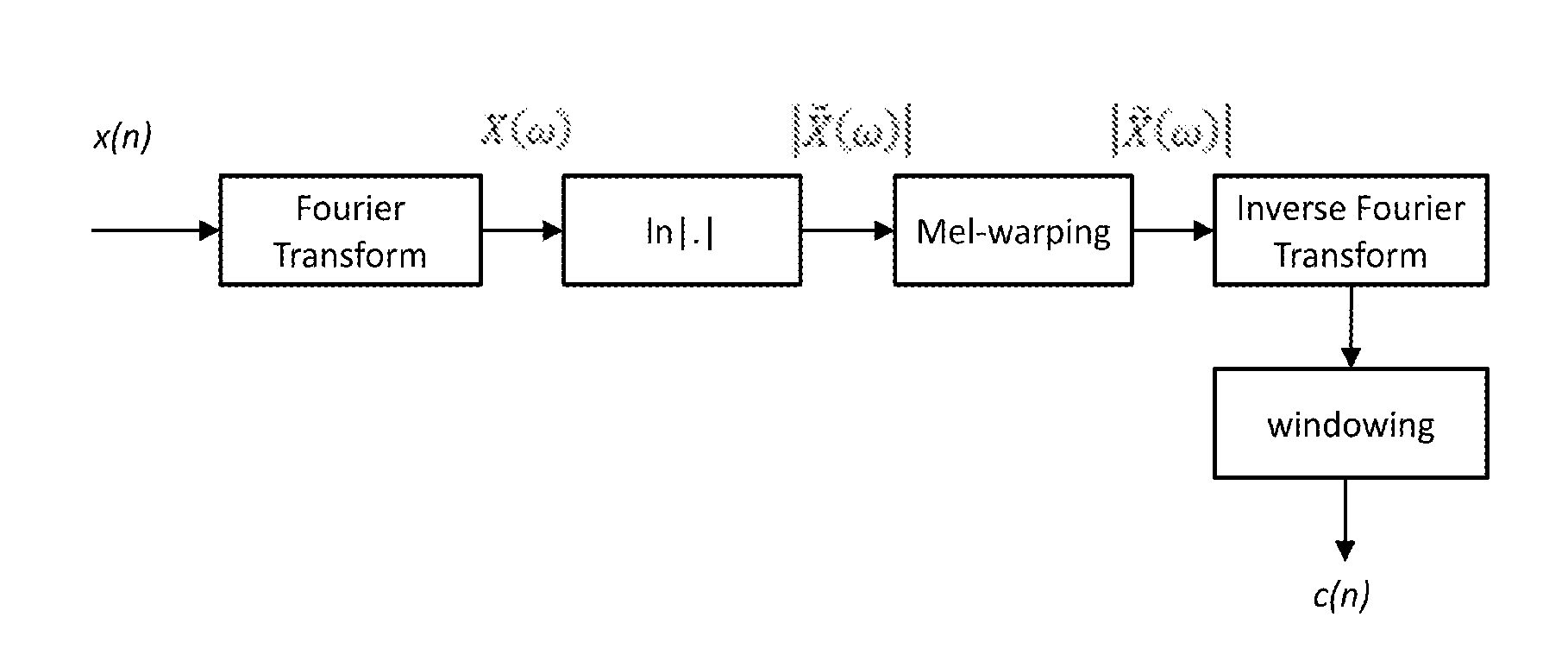
A perceptual coder is disclosed for encoding image signals, such as speech or music, with different spectral and temporal resolutions for redundancy reduction and irrelevancy reduction. The image signal is initially spectrally shaped using a prefilter. The prefilter output samples are thereafter quantized and coded to minimize the mean square error (MSE) across the spectrum. The disclosed perceptual image coder can use fixed quantizer step-sizes, since spectral shaping is performed by the pre-filter prior to quantization and coding. The disclosed pre-filter and post-filter support the appropriate frequency dependent temporal and spectral resolution for irrelevancy reduction. A filter structure based on a frequency-warping technique is used that allows filter design based on a non-linear frequency scale. The characteristics of the pre-filter may be adapted to the masked thresholds, using techniques known from speech coding, where linear-predictive coefficient (LPC) filter parameters are used to model the spectral envelope of the speech signal. Likewise, the filter coefficients may be efficiently transmitted to the decoder for use by the post-filter using well-established techniques from speech coding, such as an LSP (line spectral pairs) representation, temporal interpolation, or vector quantization.
Owner:AGERE SYST INC
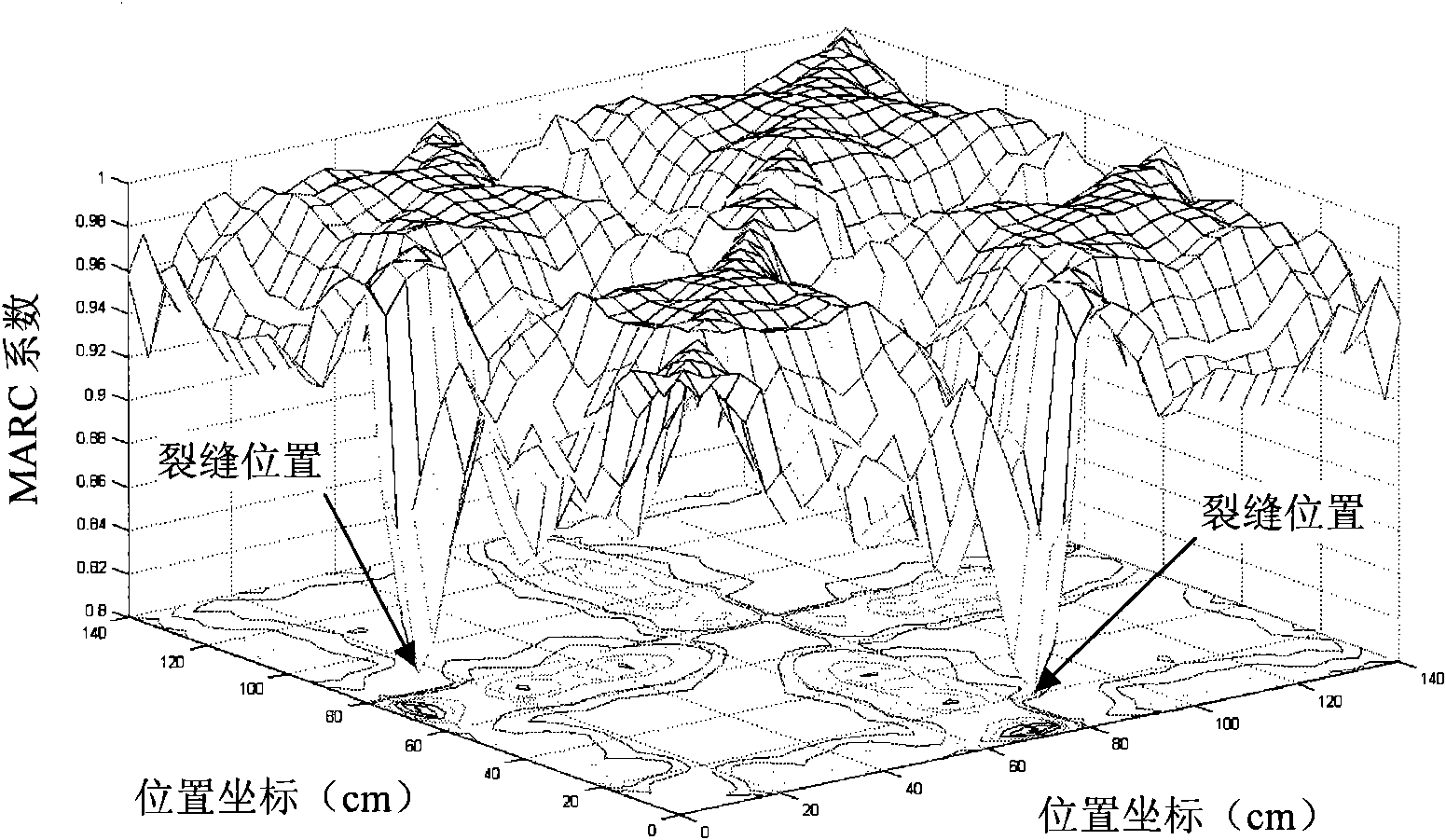
Tap-scanning method for detecting structural damages
ActiveCN101561379AAvoid distractionsHigh precisionMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesMaterial strength using repeated/pulsating forcesSpectral envelopeFrequency band
The invention belongs to the technical field of structural nondestructive detection and in particular relates to a tap-scanning method for detecting structural damages. The method comprises the following steps: scanning along the surface of a structure to be detected by using a tapping device provided with an acceleration transducer and describing the relations between the acceleration a of the tapping device and structural displacement response b, a structural local impedance Z and a tapping force F by using an approximate formula (shown above); segmenting an acceleration signal and subjecting the acceleration signal to transform processing to obtain a spectrogram of the acceleration signal; intercepting a spectrum envelope corresponding to a frequency band covered by a preset tapping force and recording the spectrum envelope by using vectors; and obtaining an MAC coefficient matrix. A curved line is drawn by using the values of a row of elements selected from the MAC coefficient array as the elements of a vertical axis and using corresponding structural positions to form a horizontal axis, and if a structure has no damage, the curved line is smooth; and if the curved line declines suddenly at a certain position, a damage occurs at the position, and a greater the declination represents a more serious damage.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
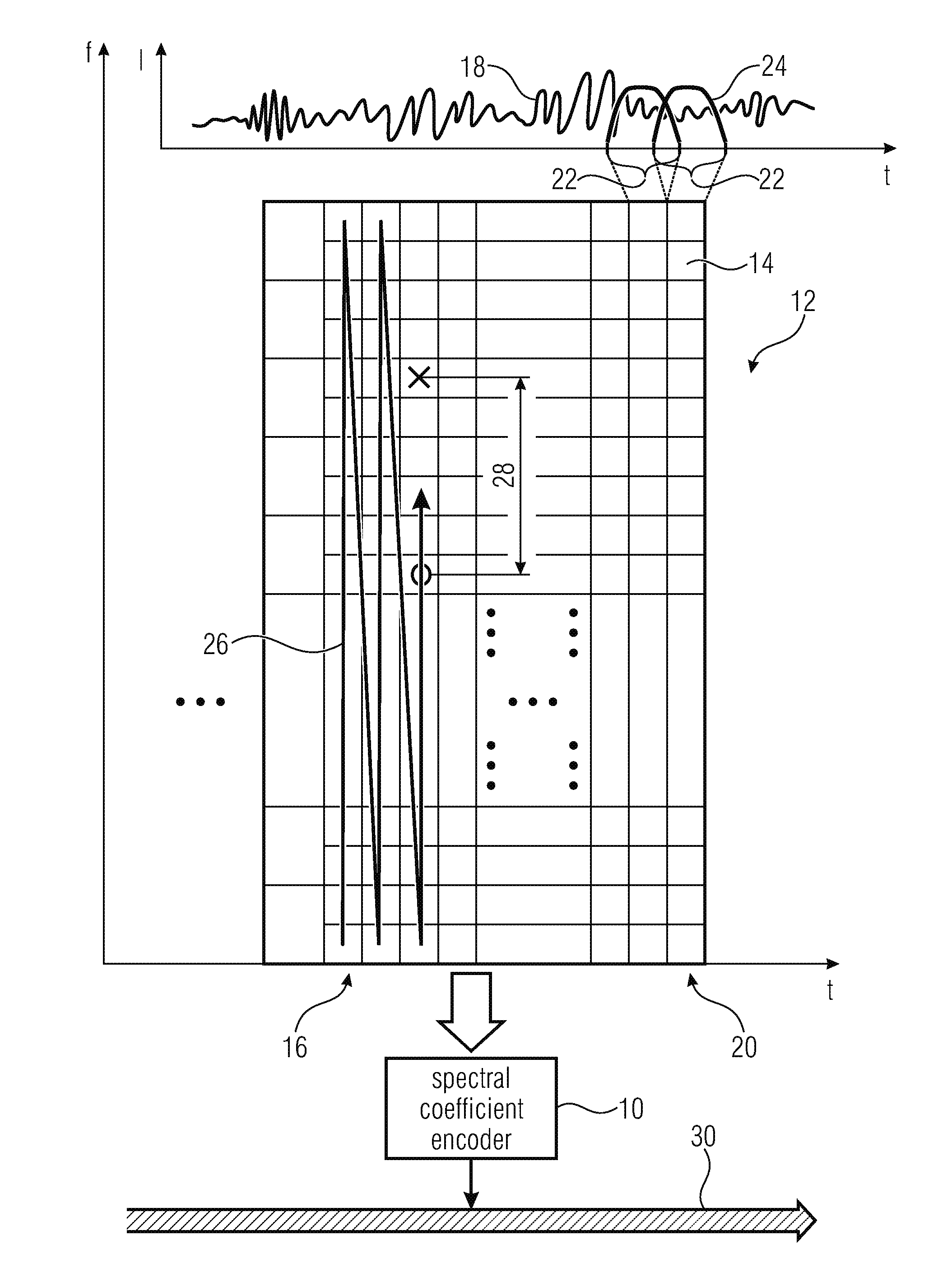
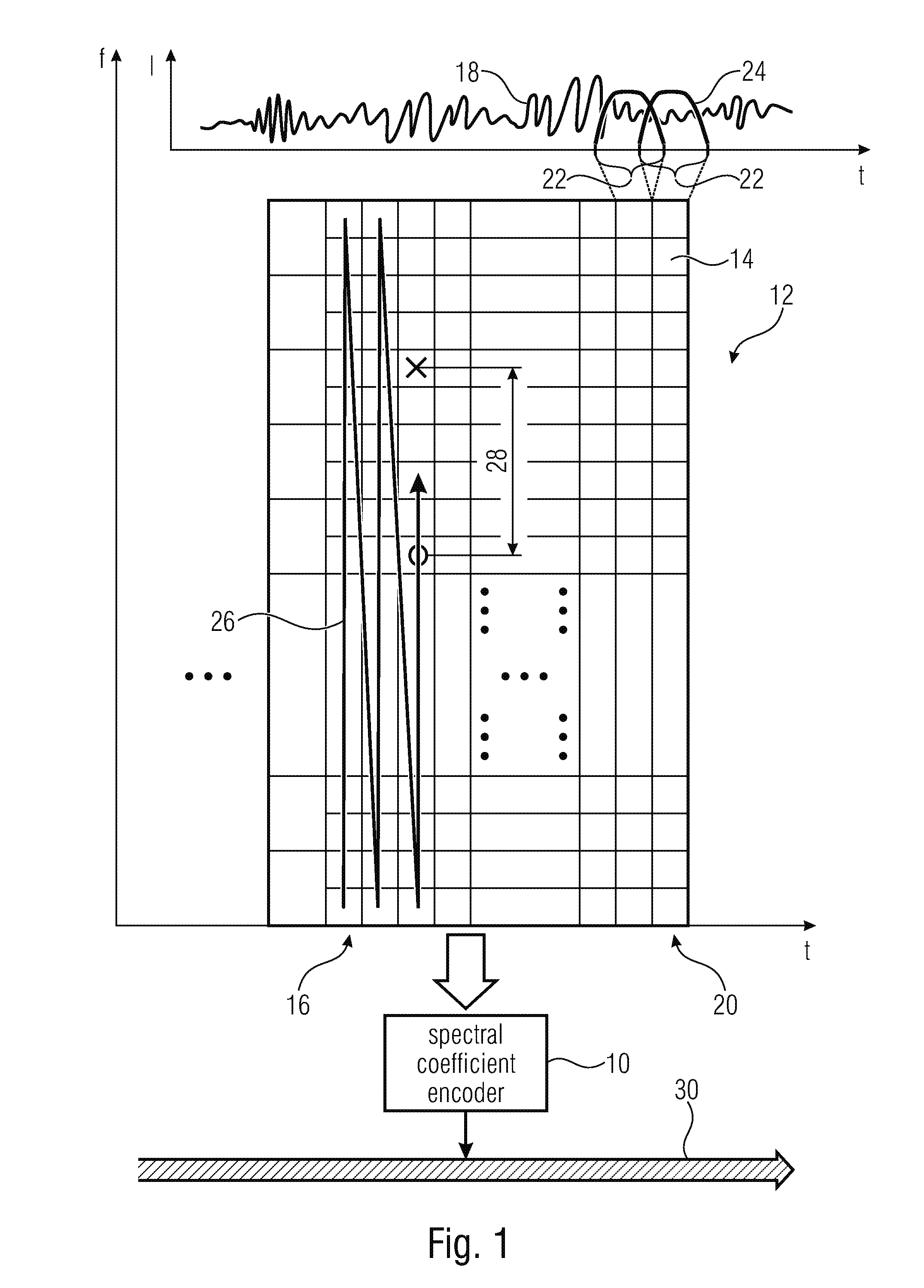
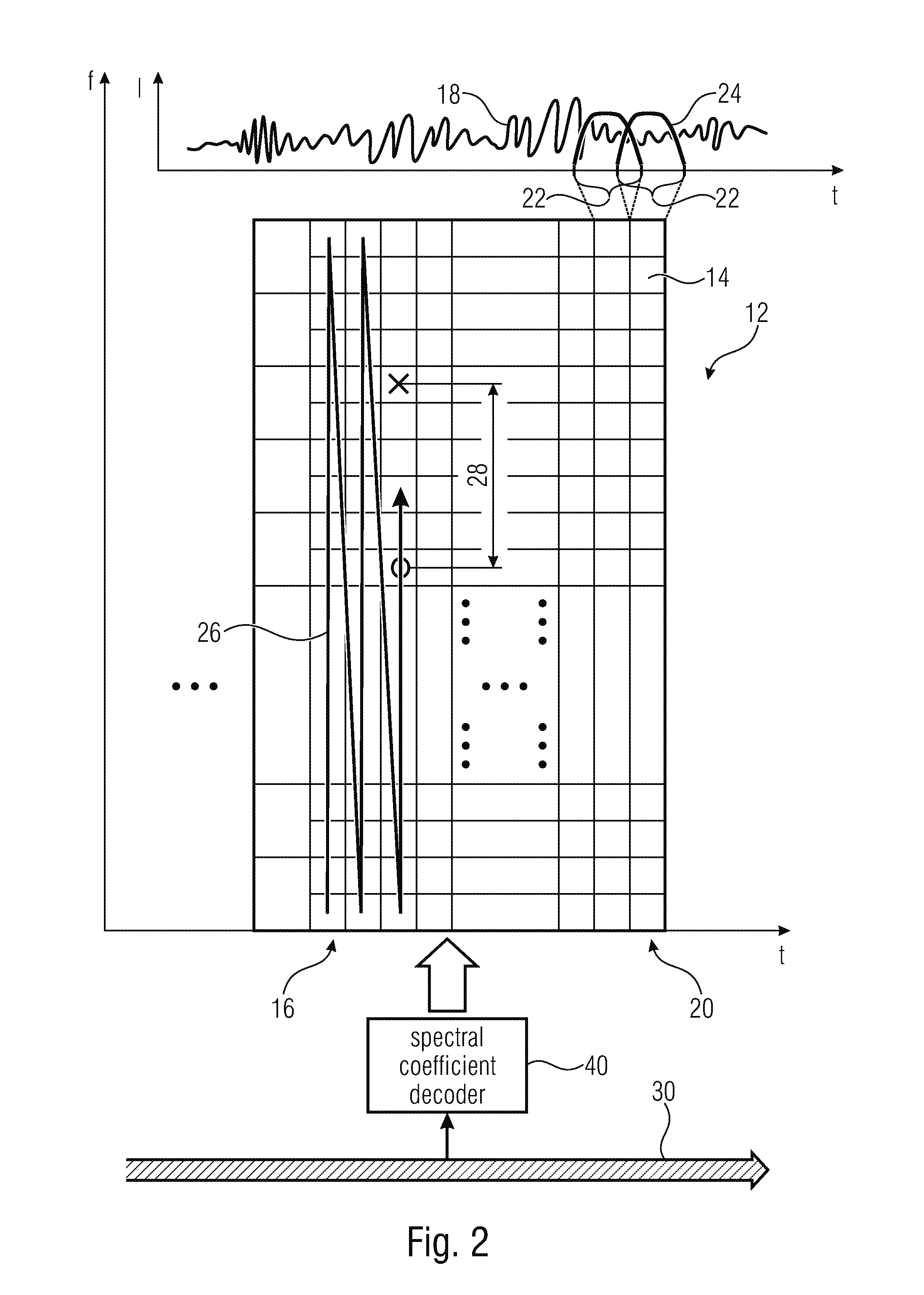
Coding of spectral coefficients of a spectrum of an audio signal
ActiveUS20160307576A1Enhancing entropy coding efficiencyImprove coding efficiencySpeech analysisCode conversionFrequency spectrumHarmonic
A coding efficiency of coding spectral coefficients of a spectrum of an audio signal is increased by en / decoding a currently to be en / decoded spectral coefficient by entropy en / decoding and, in doing so, performing the entropy en / decoding depending, in a context-adaptive manner, on a previously en / decoded spectral coefficient, while adjusting a relative spectral distance between the previously en / decoded spectral coefficient and the currently en / decoded spectral coefficient depending on an information concerning a shape of the spectrum. The information concerning the shape of the spectrum may have a measure of a pitch or periodicity of the audio signal, a measure of an inter-harmonic distance of the audio signal's spectrum and / or relative locations of formants and / or valleys of a spectral envelope of the spectrum, and on the basis of this knowledge, the spectral neighborhood which is exploited in order to form the context of the currently to be en / decoded spectral coefficients may be adapted to the thus determined shape of the spectrum, thereby enhancing the entropy coding efficiency.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
Method and system for encoding and synthesizing speech based on speech primitive
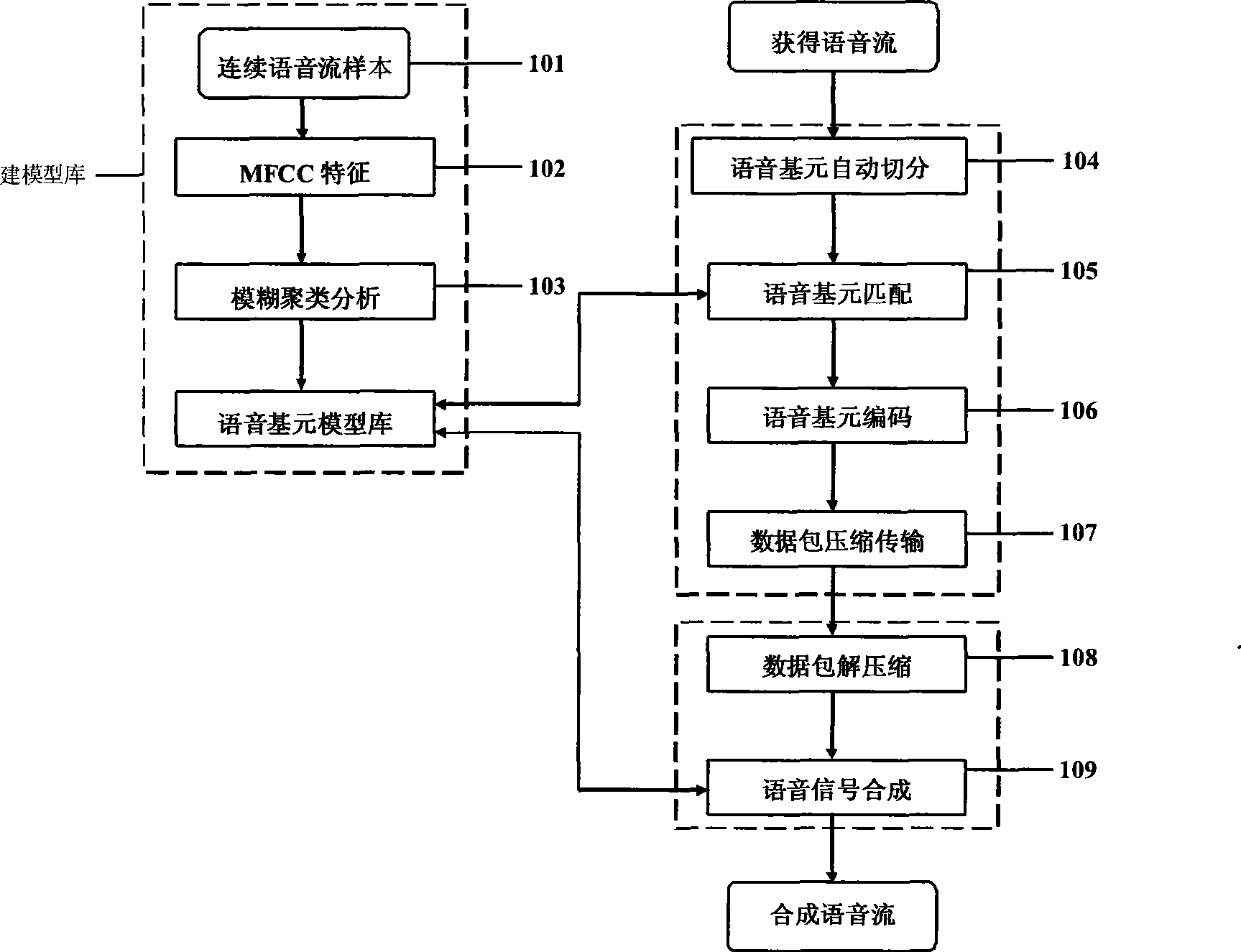
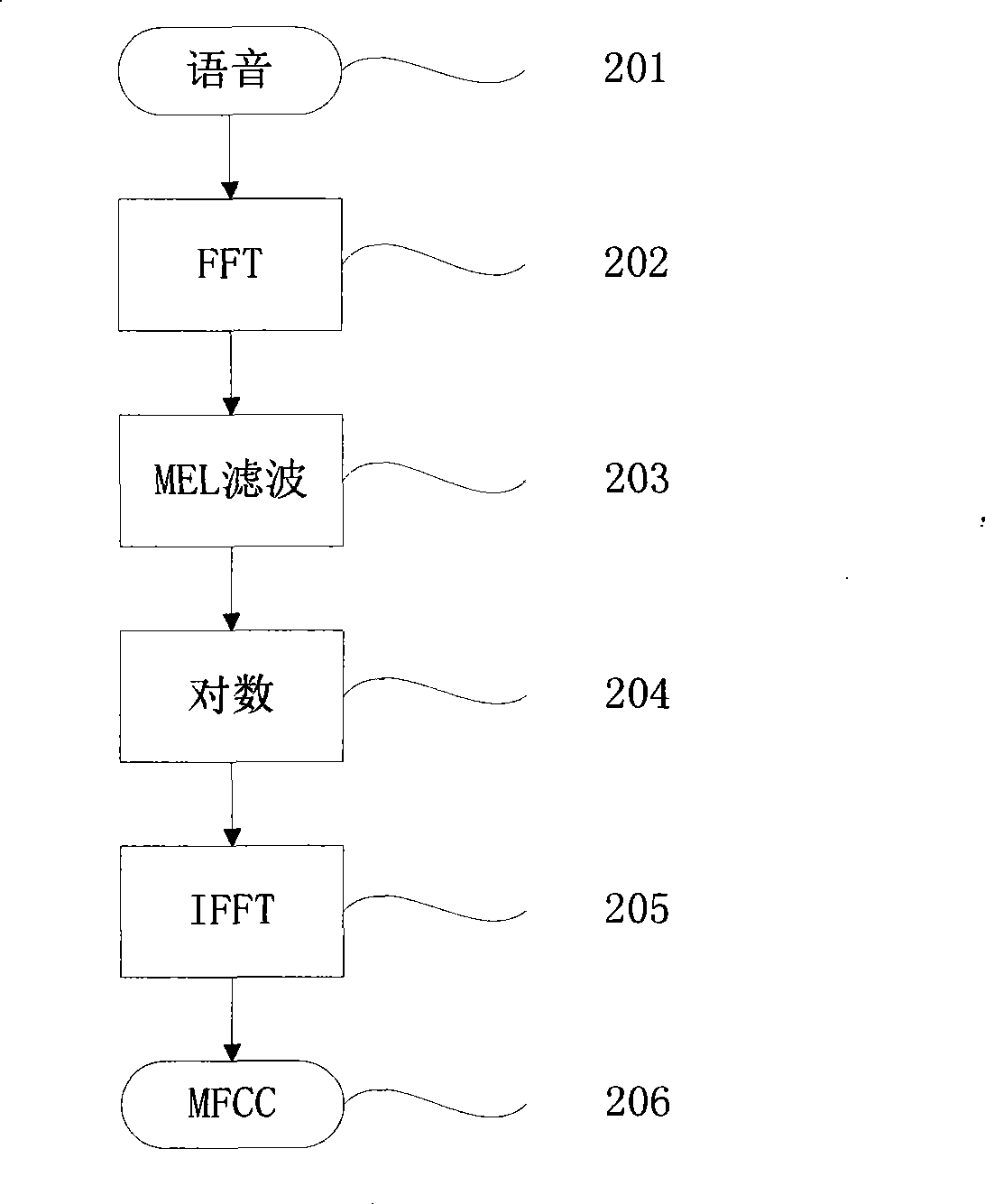
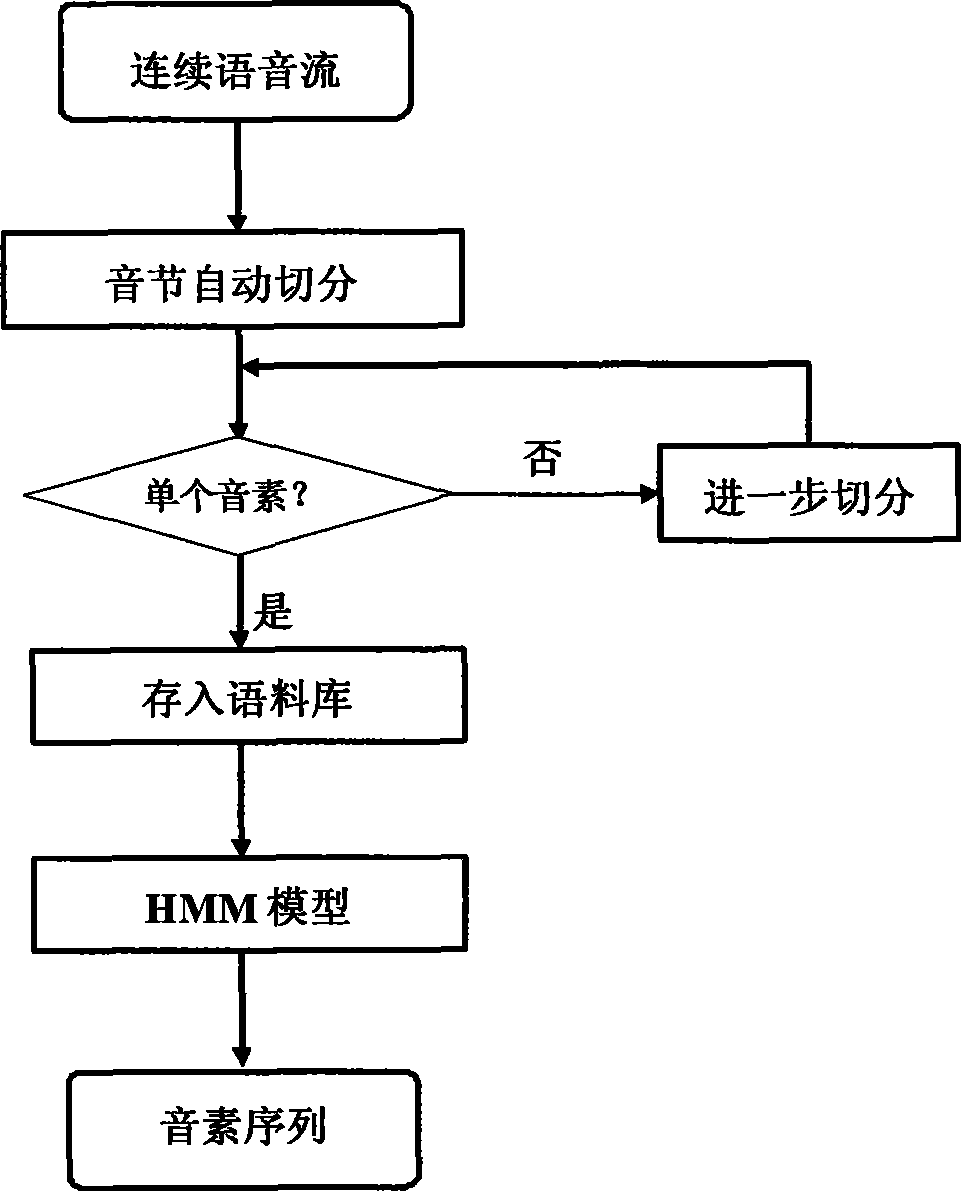
ActiveCN101510424AReduce coding spaceShorten the lengthSpeech recognitionFrequency spectrumSpeech code
The invention discloses a speech coding and synthesizing method and a system thereof, which are based on a speech primitive and can be applied to low-bandwidth and high-tone quality speech transmission. On the basis of digital speech transmission, the constructed speech primitive is taken as a coding object and a clustering algorithm is adopted to construct a speech primitive model base by analysis on daily speech; then, a speech primitive automatic cut algorithm is utilized to carry out automatic speech primitive cutting to the obtained continuous speech stream and extract the MFCC characteristics of the speech primitive; a number corresponding to the speech primitive is obtained by carrying out matching identification to the speech primitive in the speech primitive model base, and the number carries out coding by replacing the speech primitive. During the process of speech synthesizing, the speech primitive corresponding to the number is taken out from the speech primitive model base according to the number, and processing such as interpretation fitting and the like is carried out to the spectra enveloping of the speech primitive by mathematical manipulation so as to form smooth transited speech.
Owner:孟智平
Apparatus and a method for calculating a number of spectral envelopes
ActiveUS8296159B2Quality improvementLimits the core coder bandwidth—itSpeech analysisDigital computer detailsFrequency spectrumChronological time
An apparatus calculates a number of spectral envelopes to be derived by a spectral band replication (SBR) encoder, wherein the SBR encoder is adapted to encode an audio signal using a plurality of sample values within a predetermined number of subsequent time portions in an SBR frame extending from an initial time to a final time, the predetermined number of subsequent time portions being arranged in a time sequence given by the audio signal. The apparatus has a decision value calculator for determining a decision value, the decision value measuring a deviation in spectral energy distributions of a pair of neighboring time portions. The apparatus further has a detector for detecting a violation of a threshold by the decision value and a processor for determining a first envelope border between the pair of neighboring time portions when the violation of the threshold is detected.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
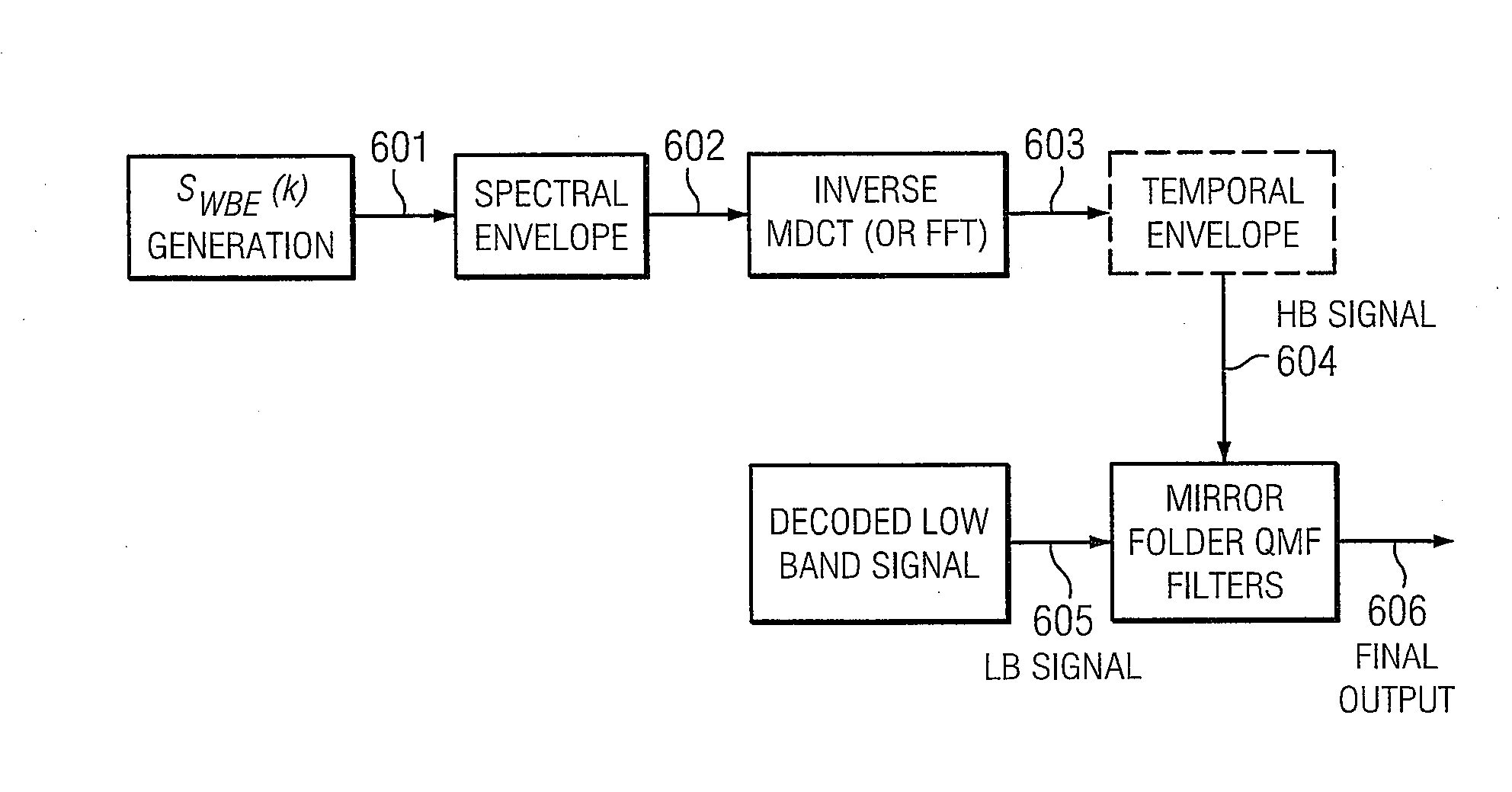
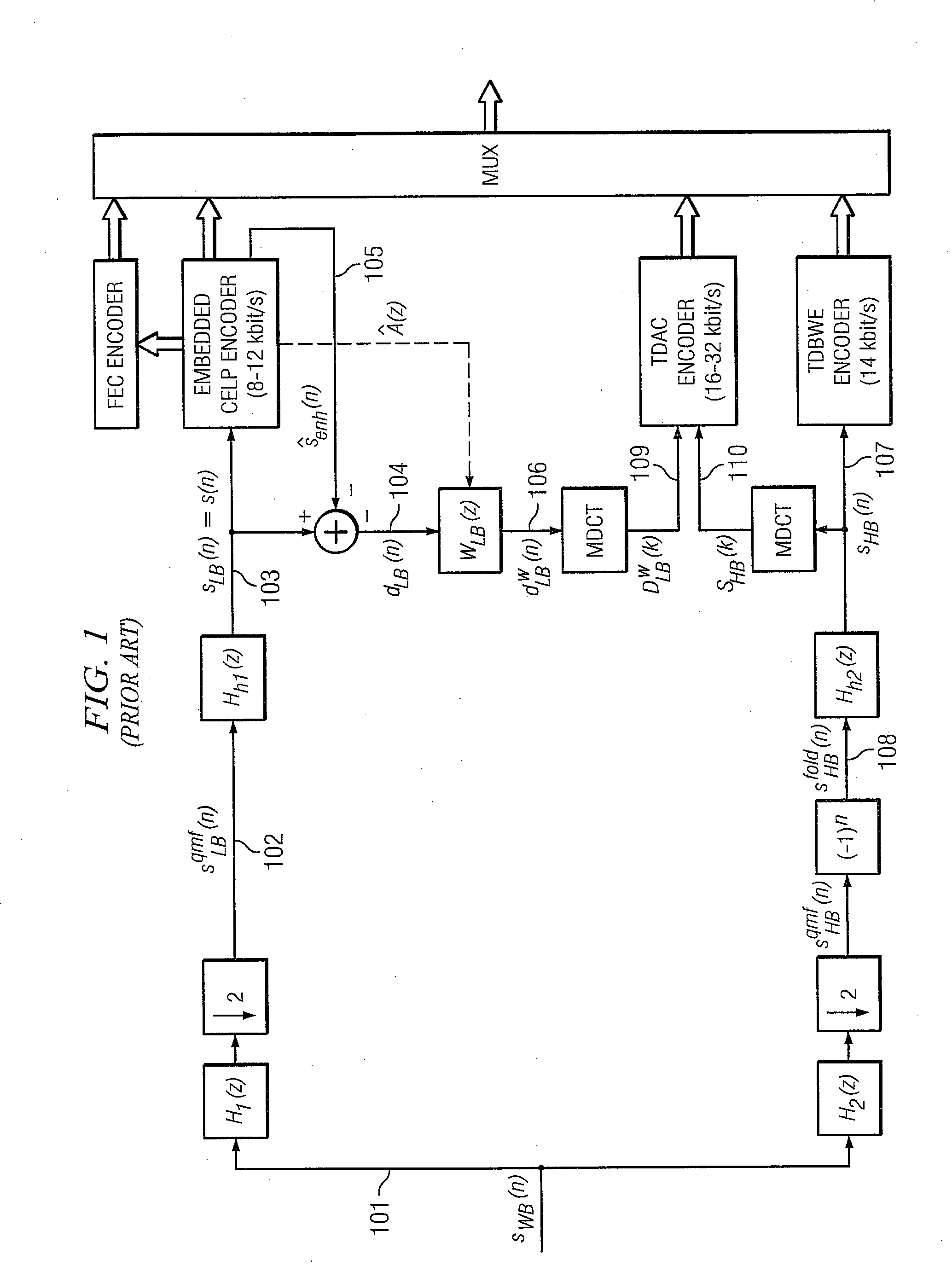
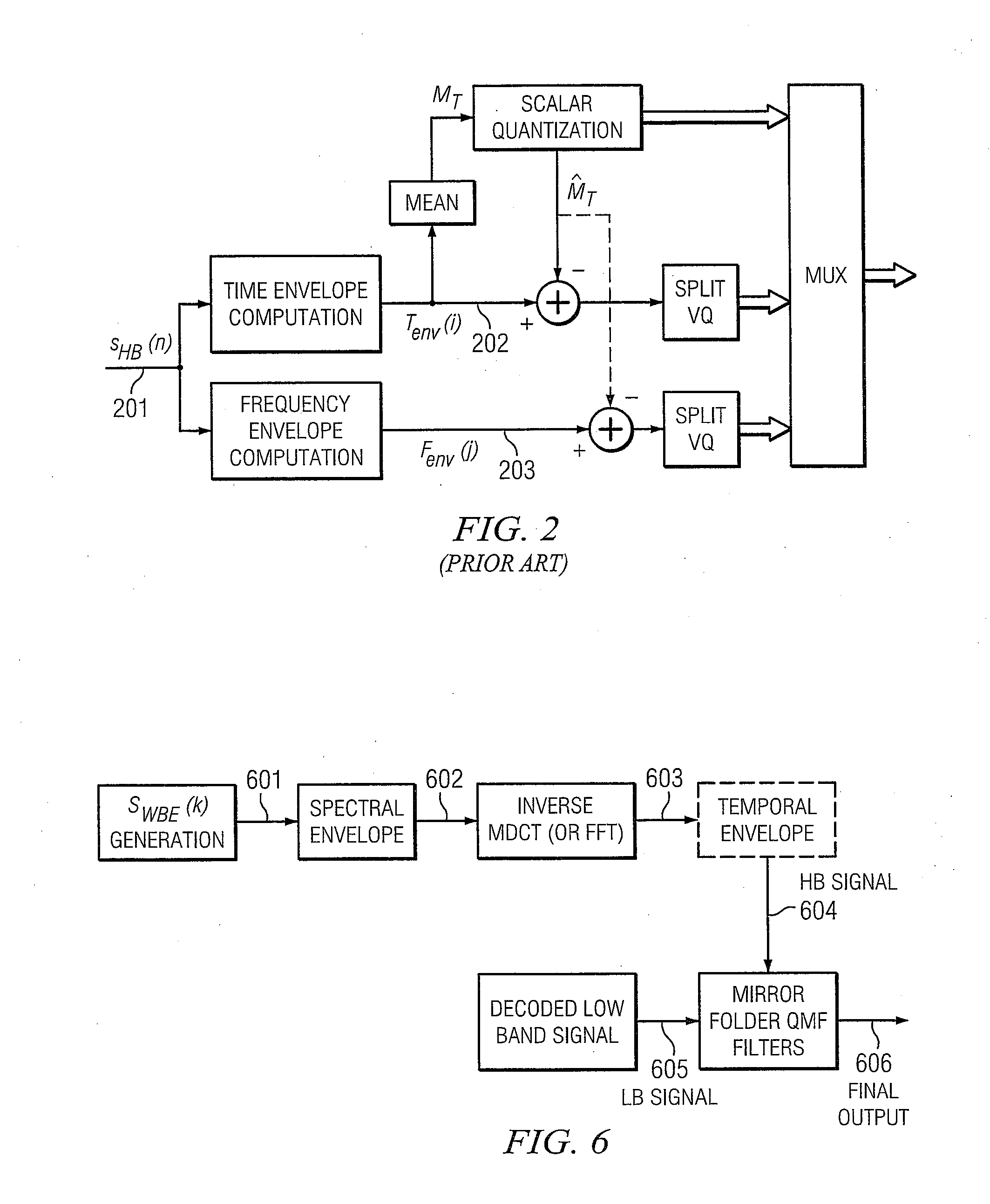
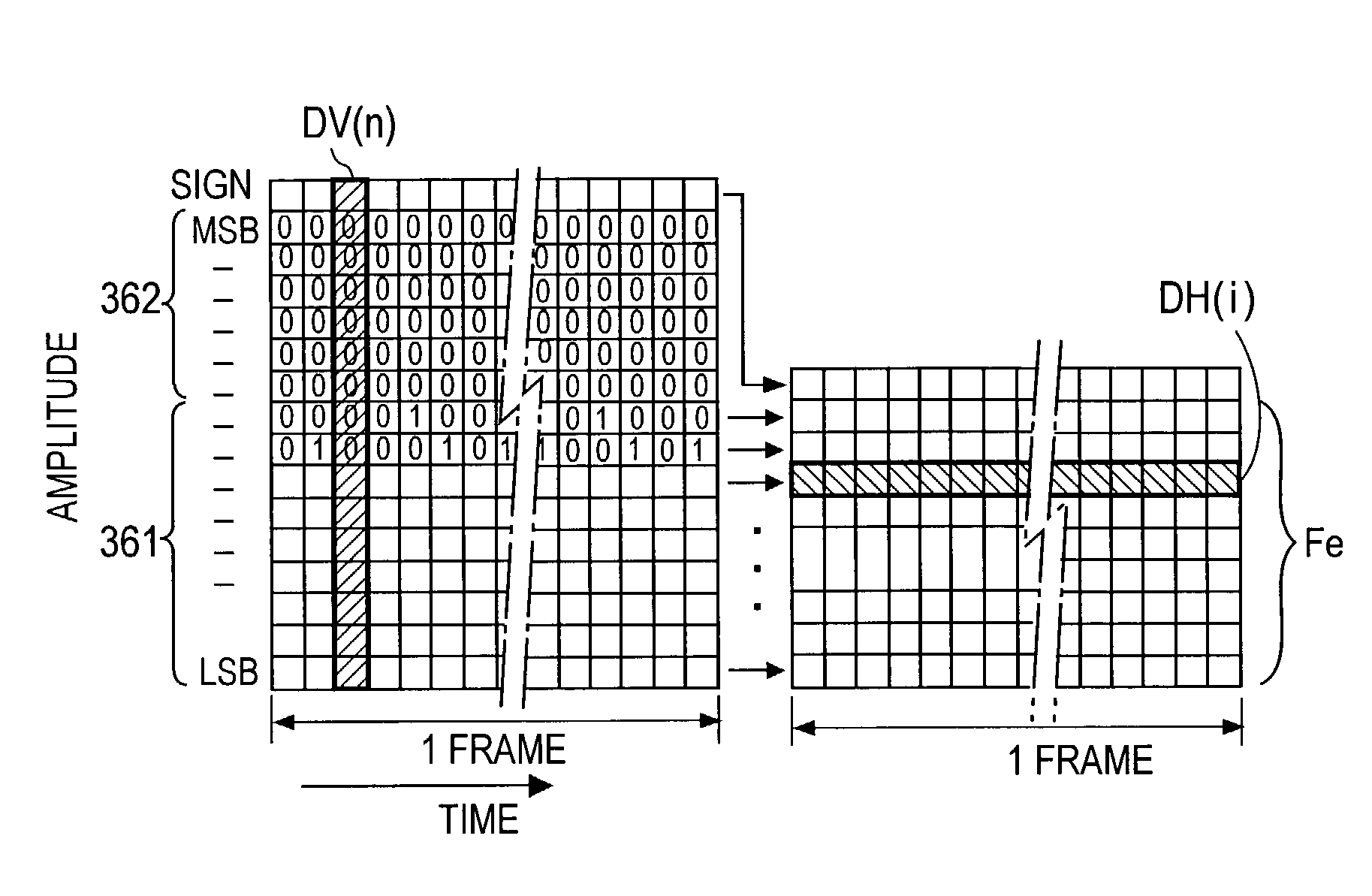
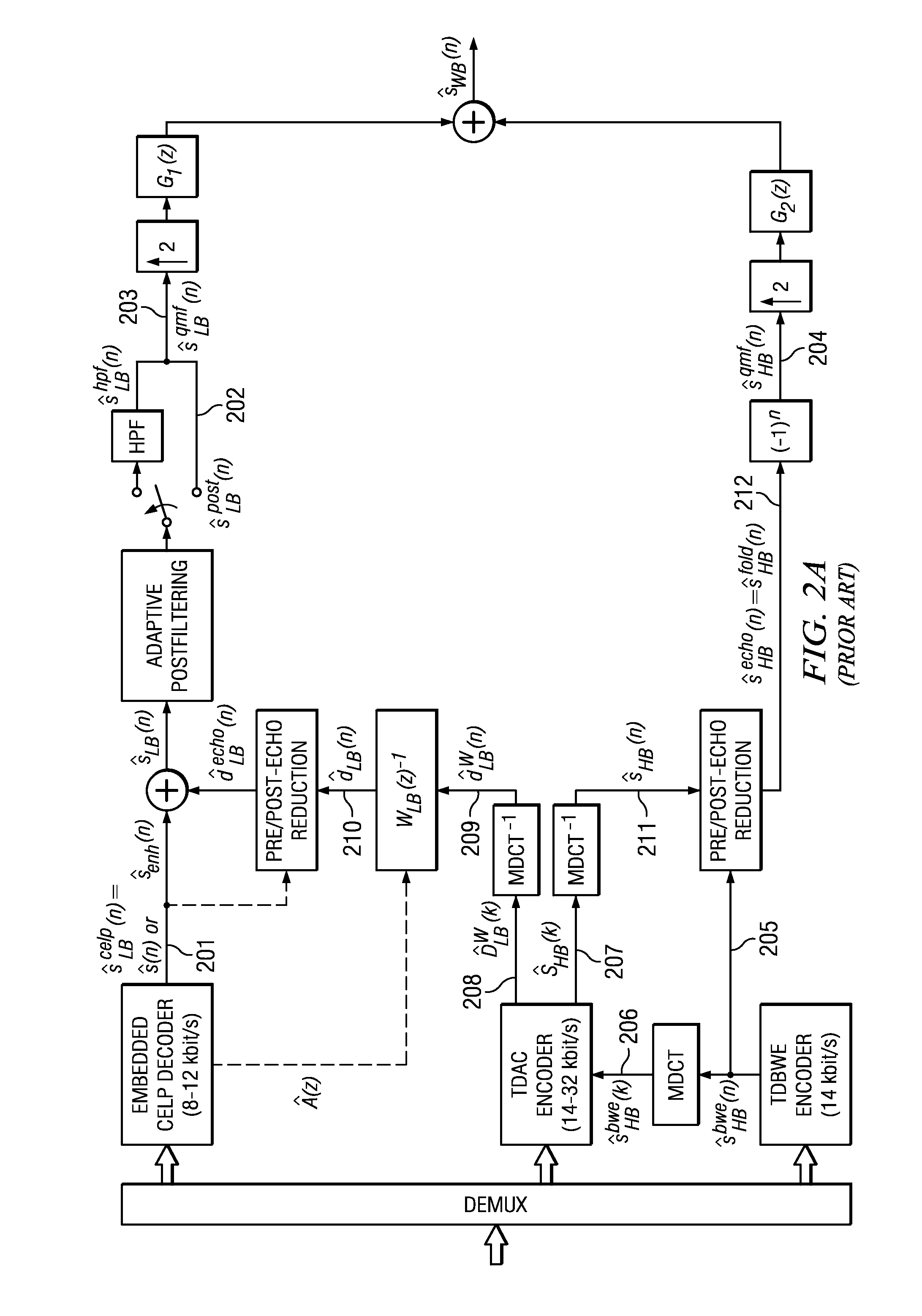
Adding Second Enhancement Layer to CELP Based Core Layer
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com