Patents
Literature
833 results about "Filter design" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
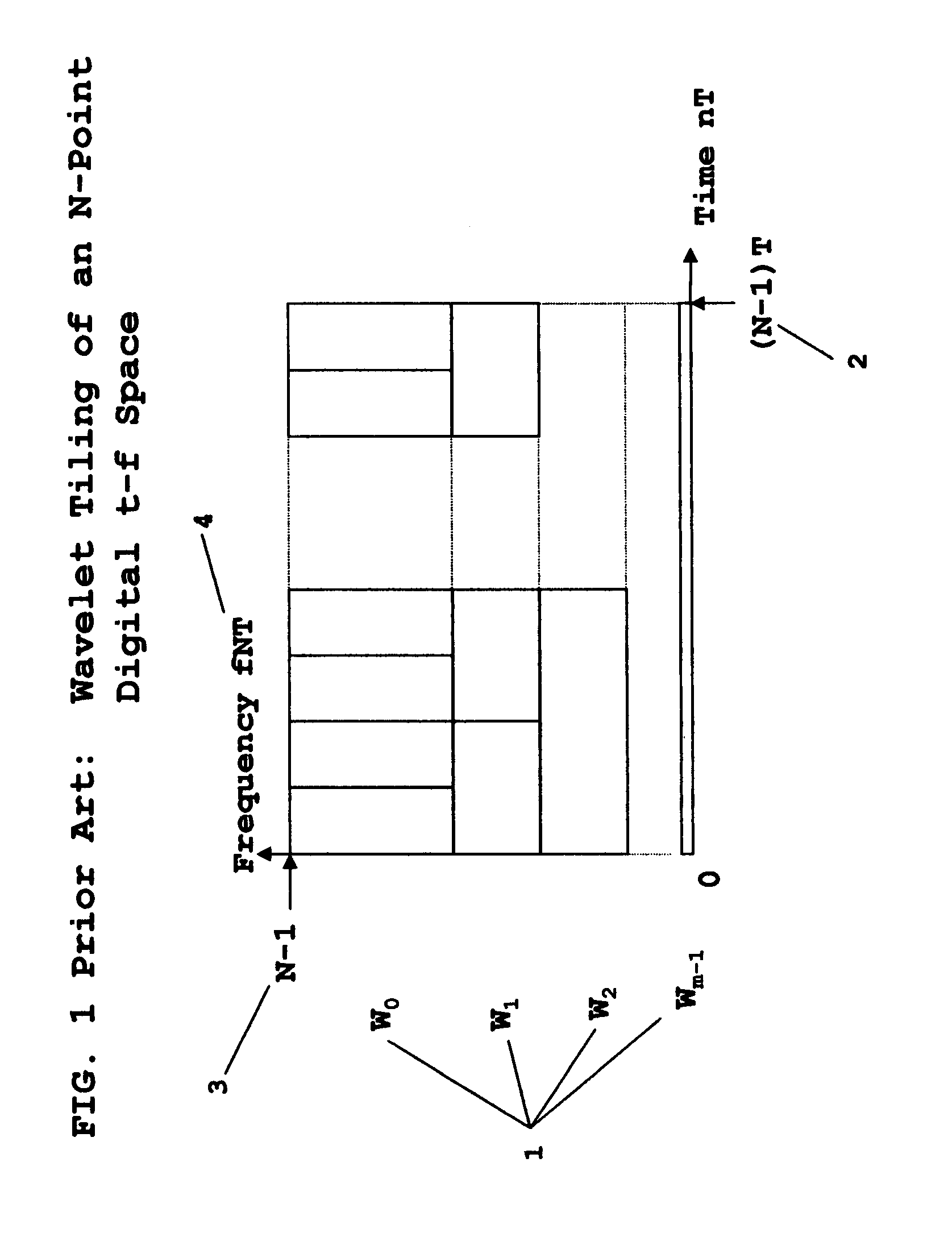
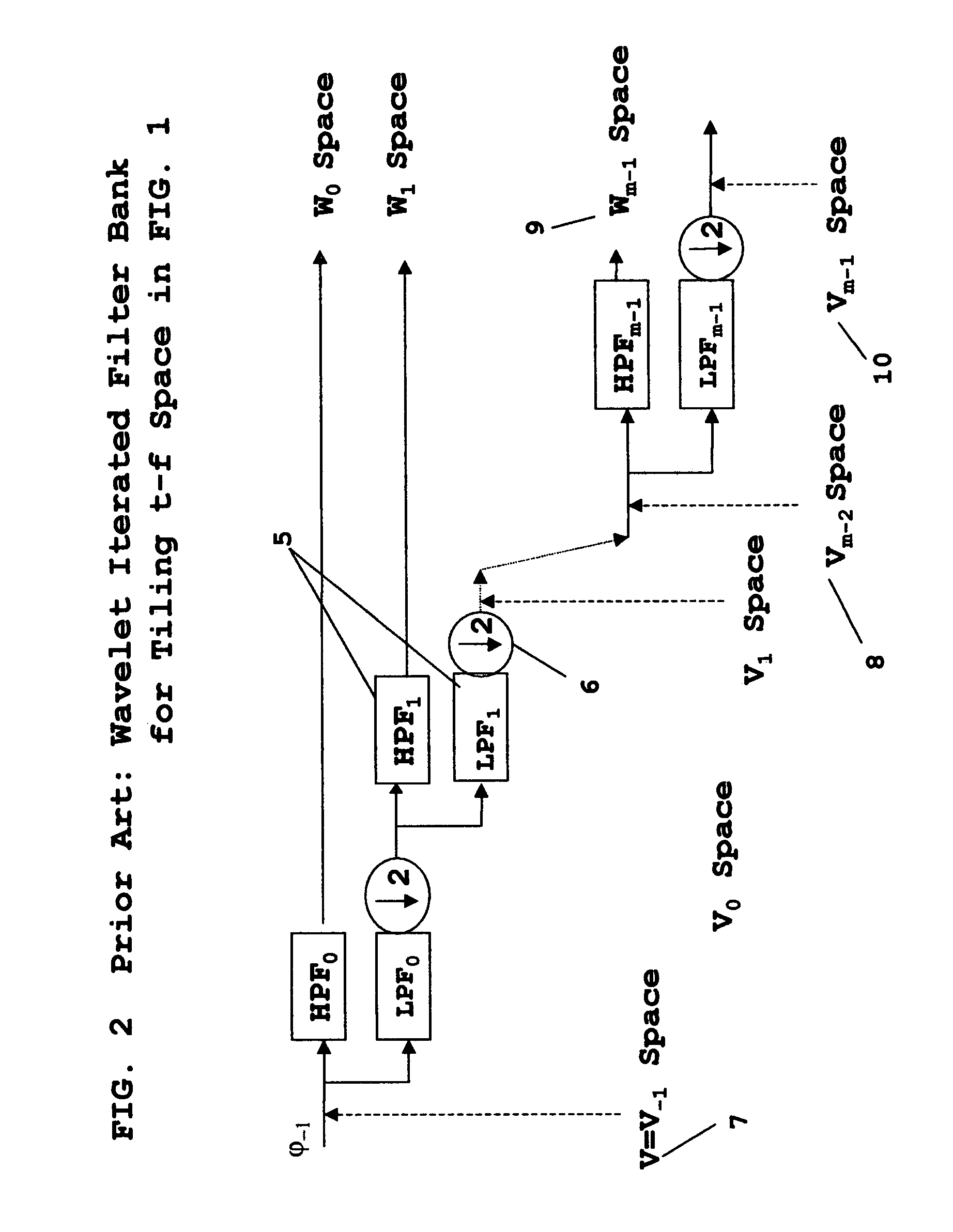
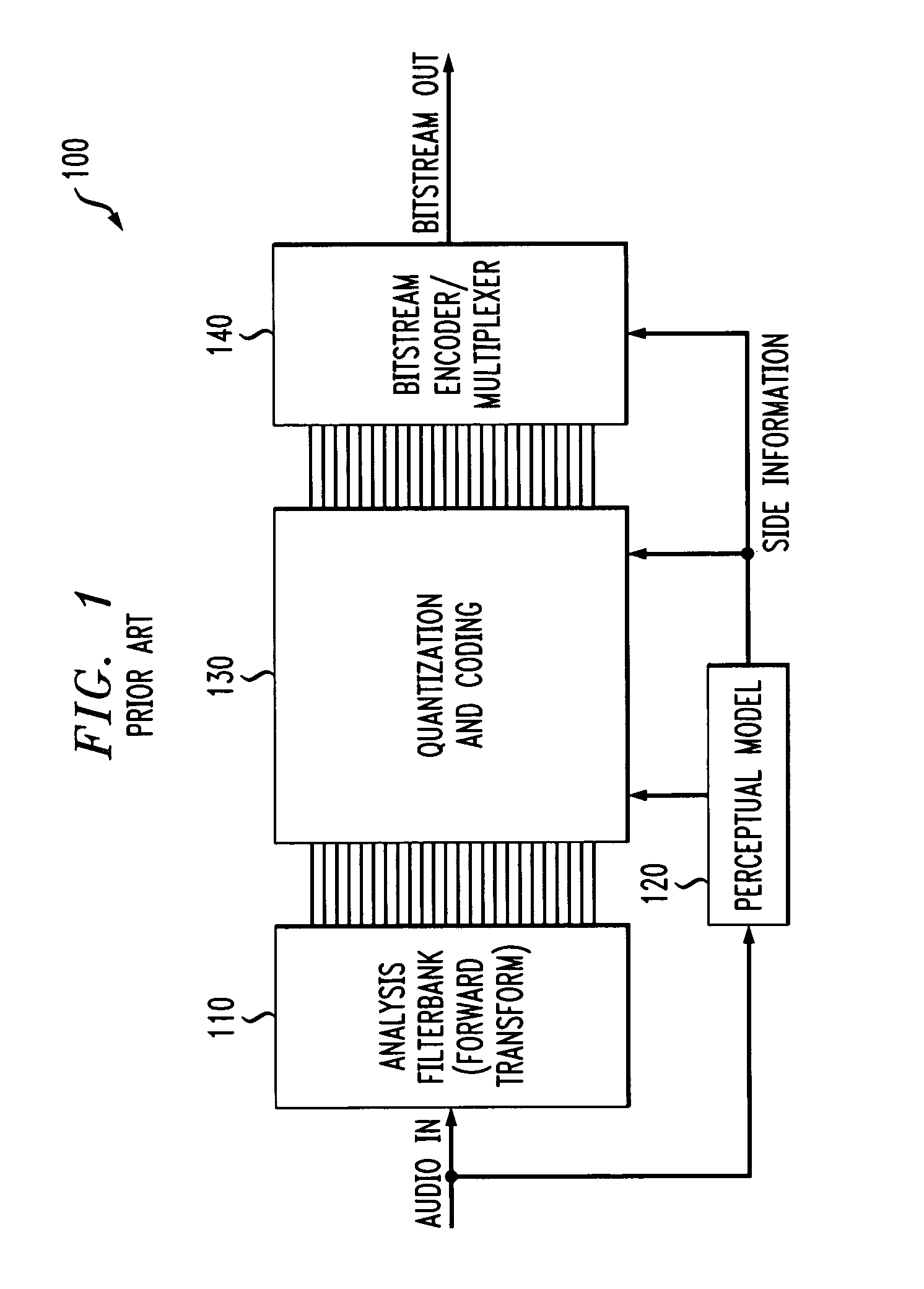
Filter design is the process of designing a signal processing filter that satisfies a set of requirements, some of which are contradictory. The purpose is to find a realization of the filter that meets each of the requirements to a sufficient degree to make it useful.
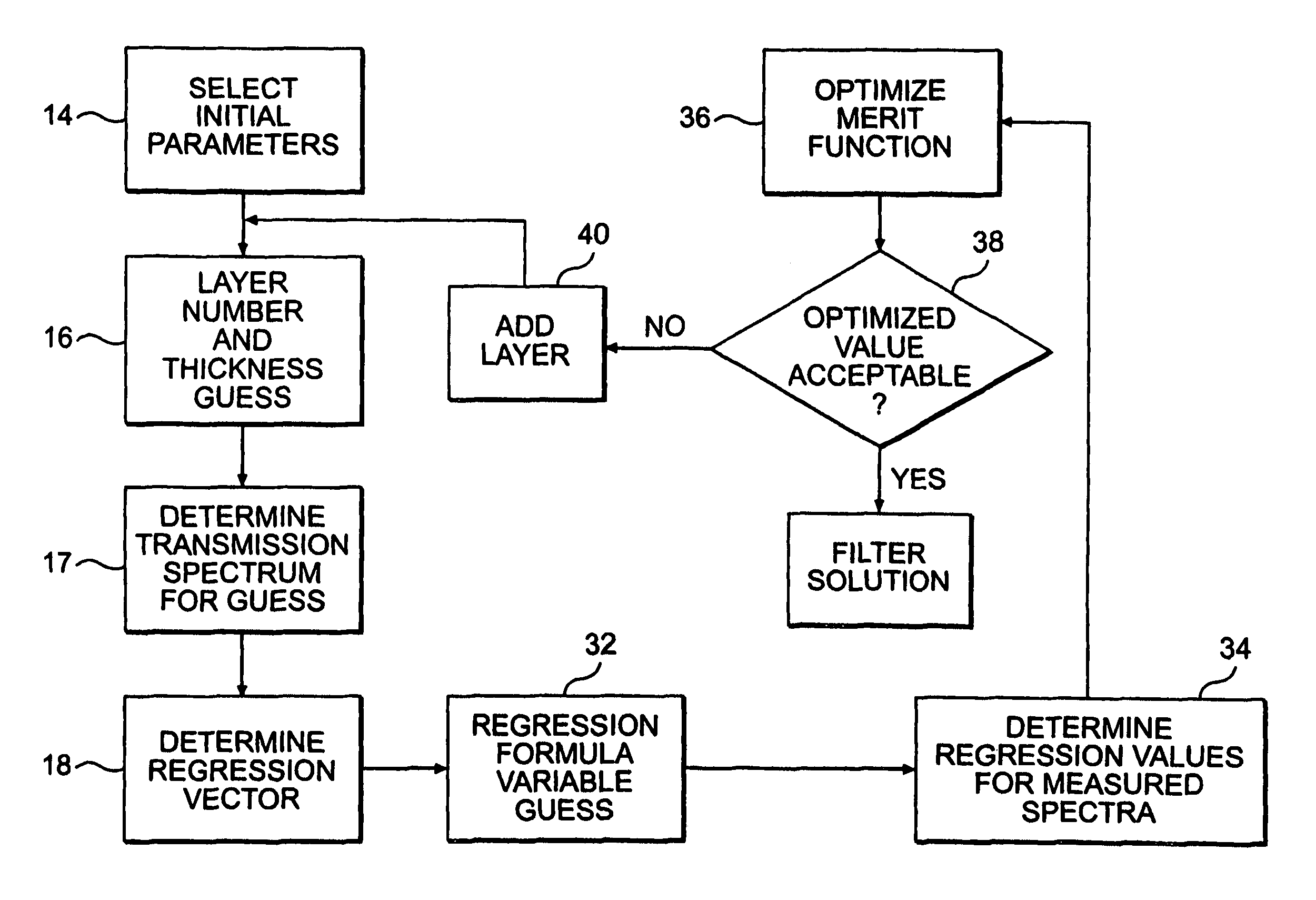
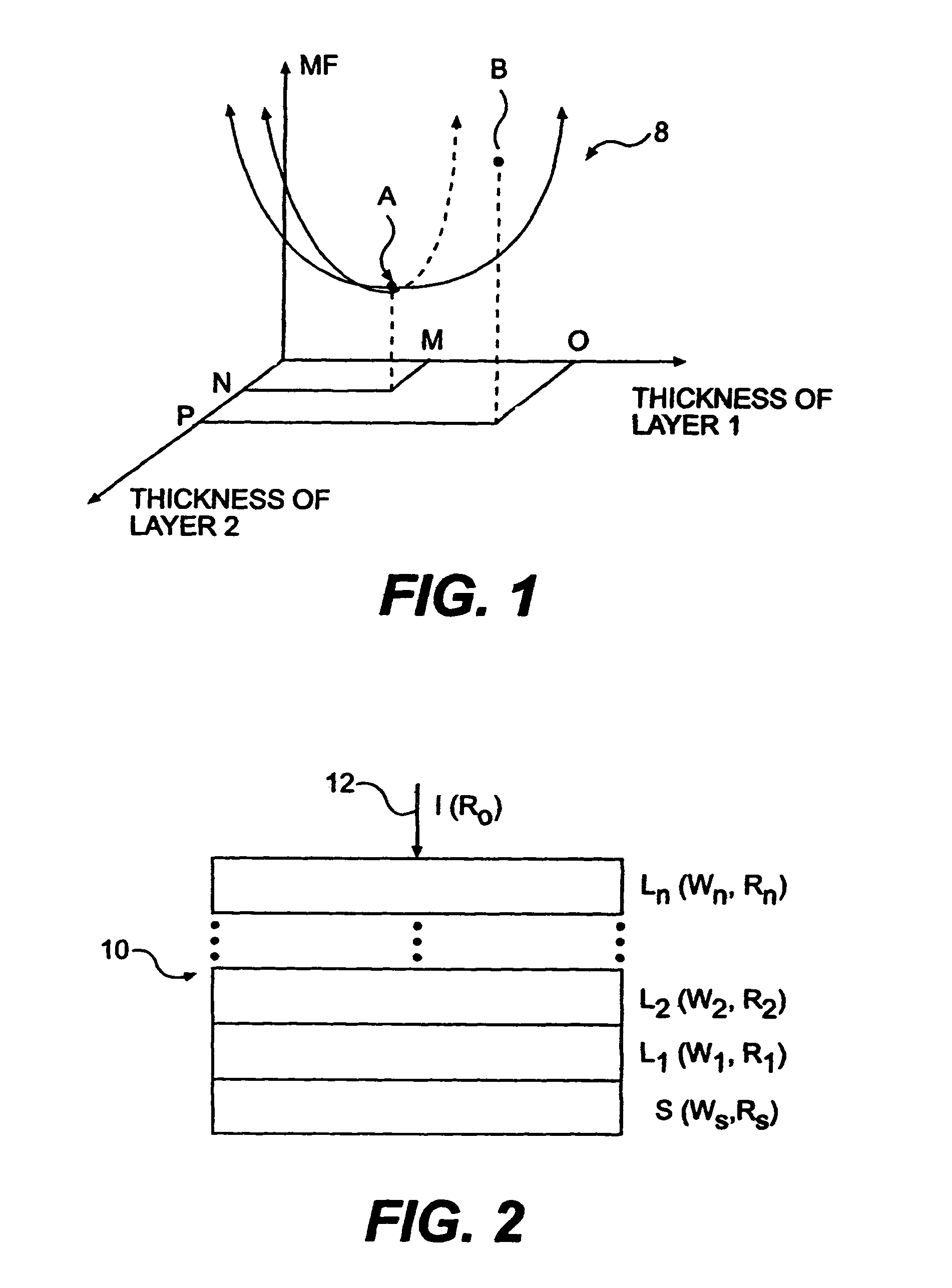
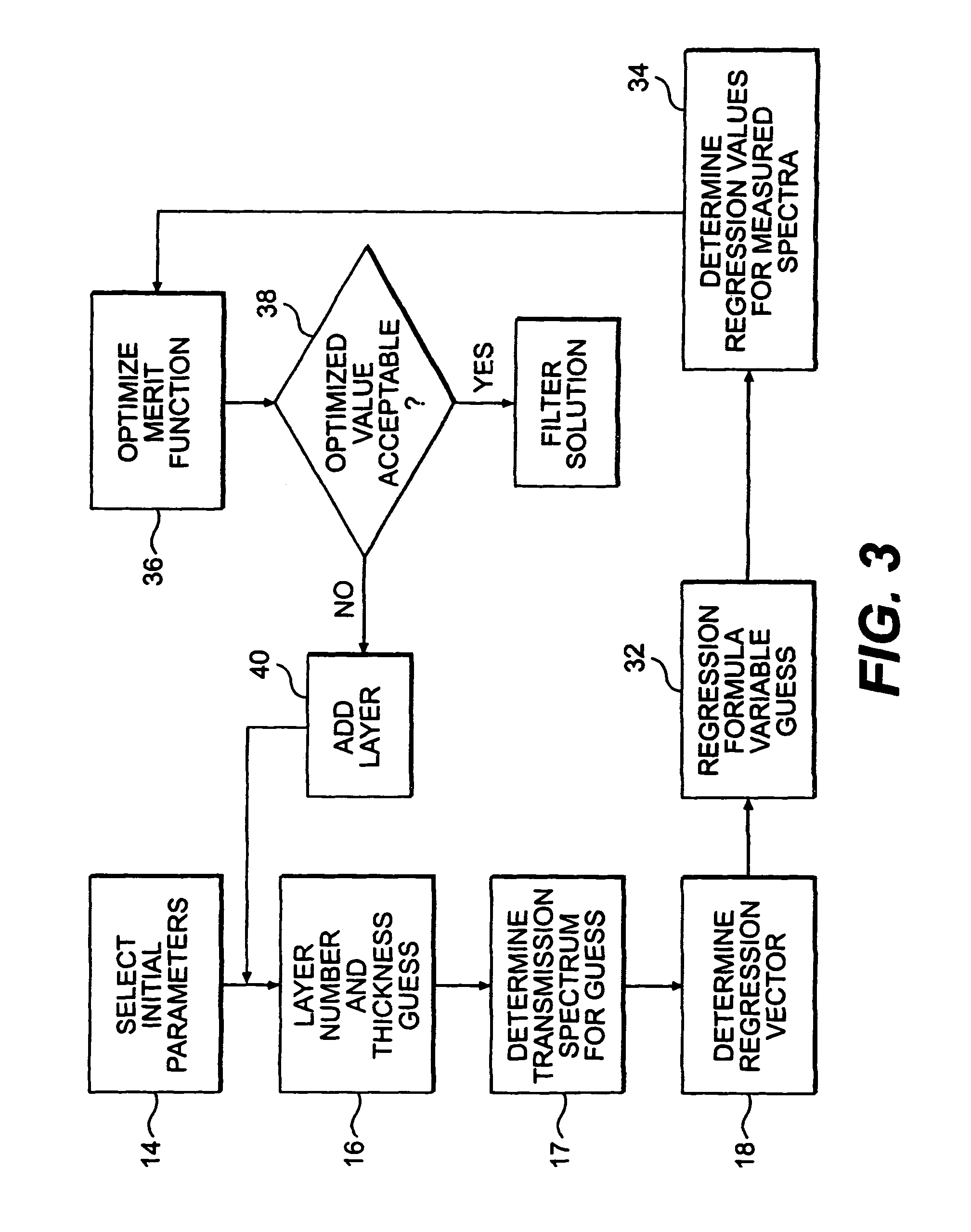
Filter design algorithm for multi-variate optical computing
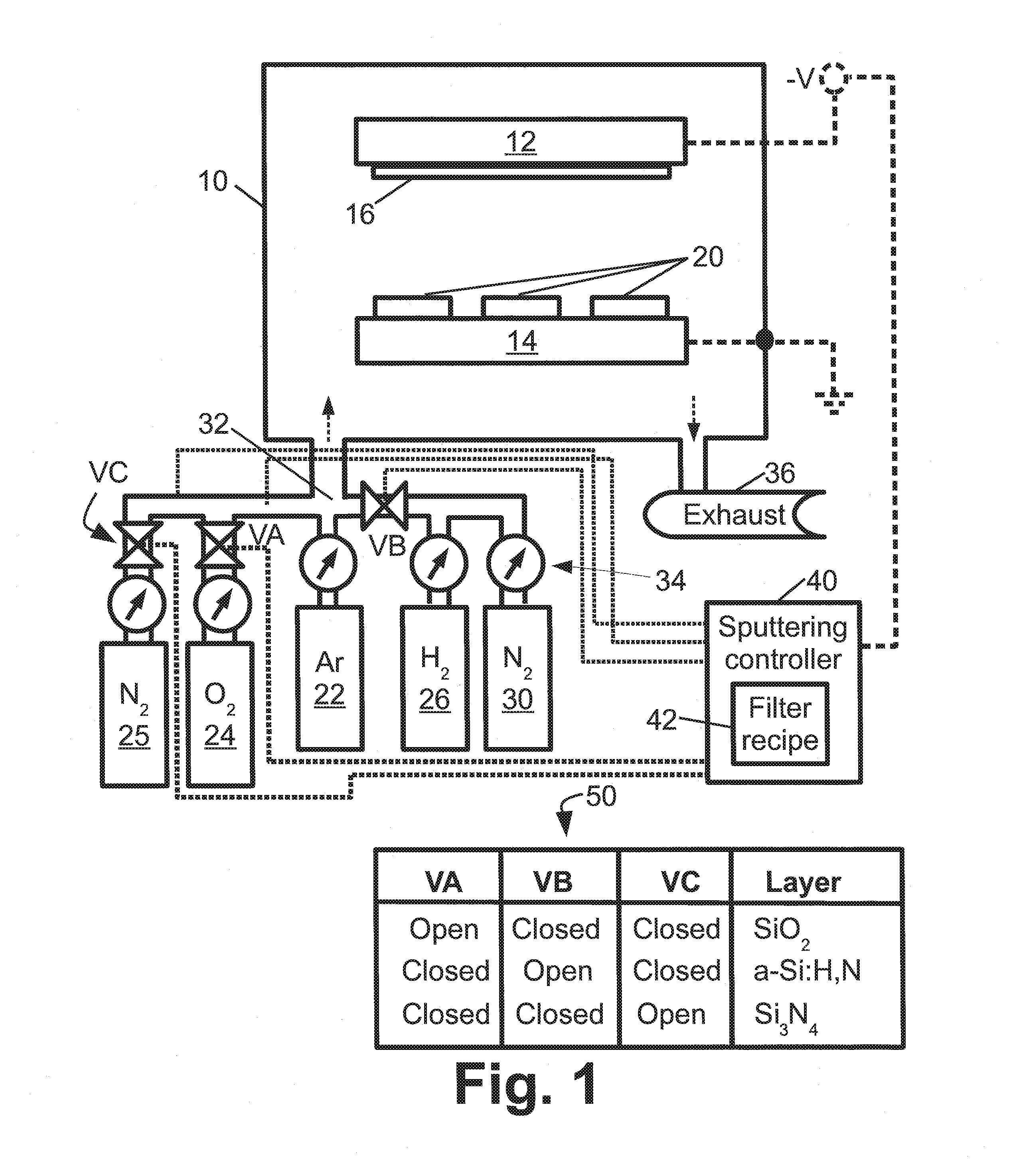
Within a method of making an optical interference filter, sample spectra and measurements of a predetermined characteristic associated with respective spectra are provided. Upon selection of an initial number of filter layers and a thickness for each layer, a transmission spectrum is determined. Each sample spectrum is applied to a regression formula that relates interaction of light with the transmission spectrum to a regression value. A comparison relationship between the calculated regression values and the sample measurements is defined and optimized, wherein thickness of each layer is an optimization variable.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
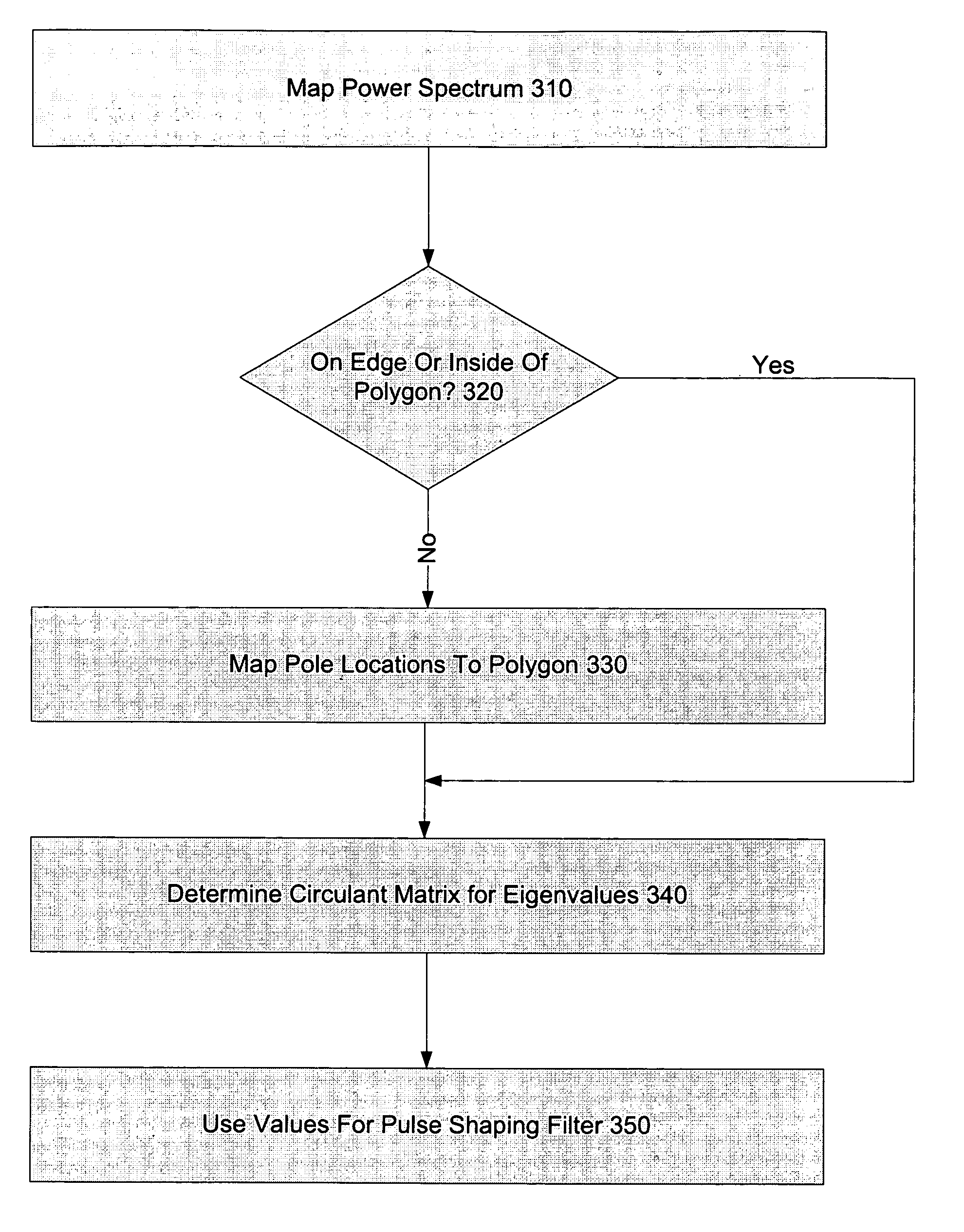
Method and system for statistical filters and design of statistical filters
InactiveUS7184938B1Less dataLess signalDigital variable displayNoise figure or signal-to-noise ratio measurementFrequency spectrumFilter system
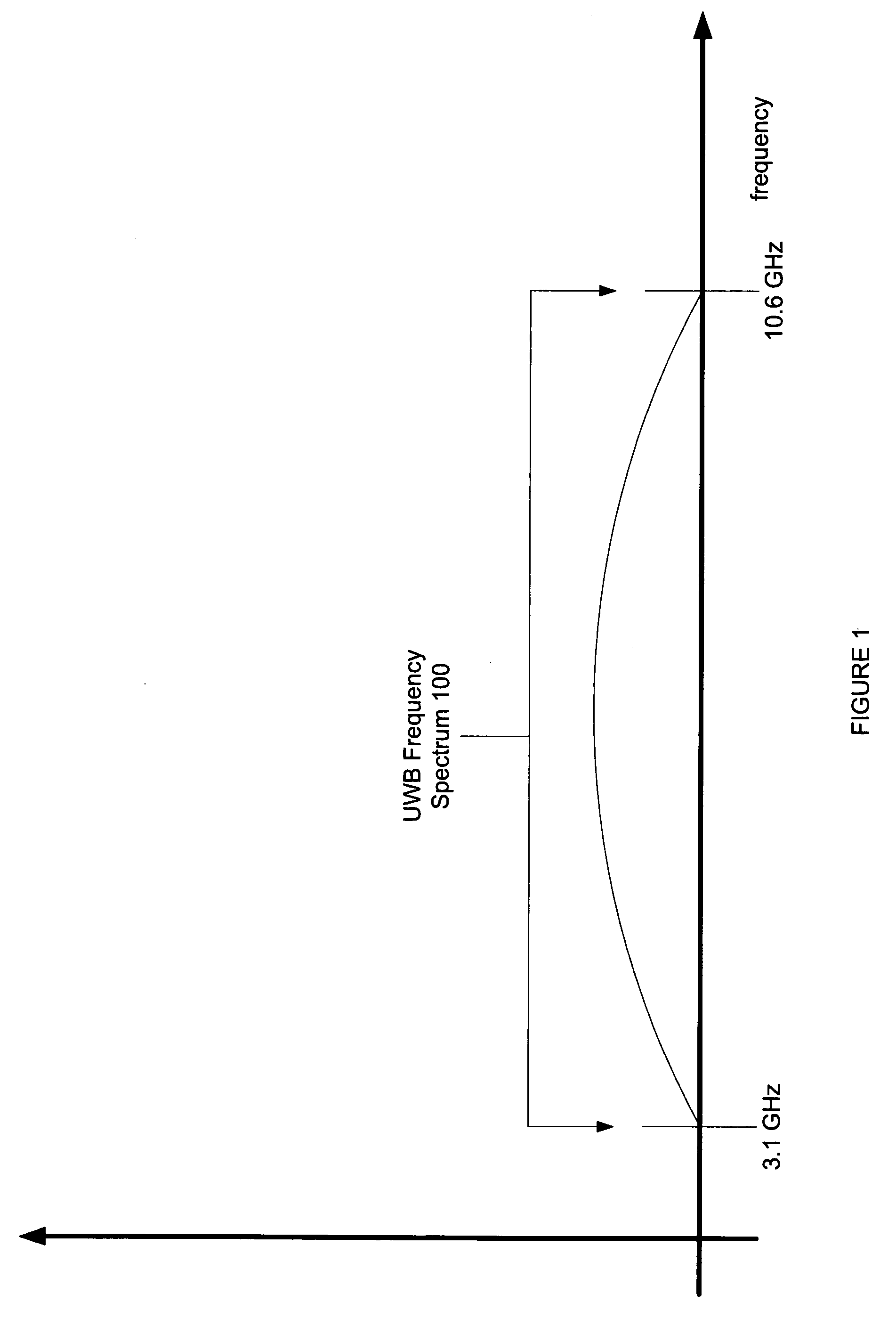
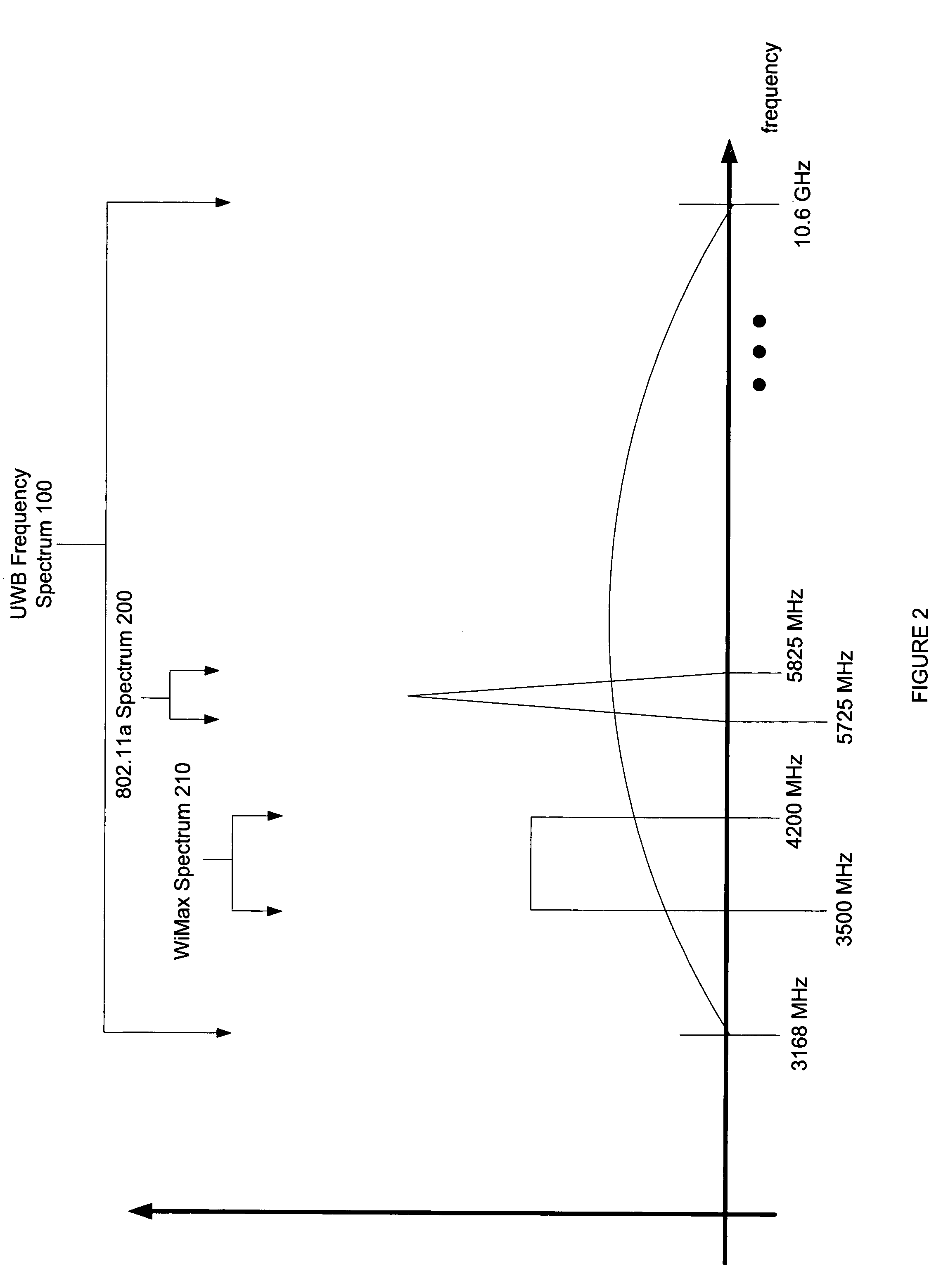
Systems and methods for the design or implementation of statistical filters for use in the spectral shaping of transmissions are disclosed. A desired power spectrum may be mapped to find pole locations that approximate the desired spectrum. These pole locations may then be mapped to the edge or inside of an equilateral polygon lying inside a unit circle, the equilateral polygon having the same number of sides as the order of the statistical filter desired and one vertex mapped to unity, to yield a set of eigenvalues. These eigenvalues may be the eigenvalues of a stochastic matrix the elements of which may be the Markov transition probabilities for use in a statistical filter designed to achieve the desired power spectrum. Use of a statistical filter employing these Markov transition values may be utilized to shape UWB or other signals to achieve the desired power spectrum.
Owner:ALEREON
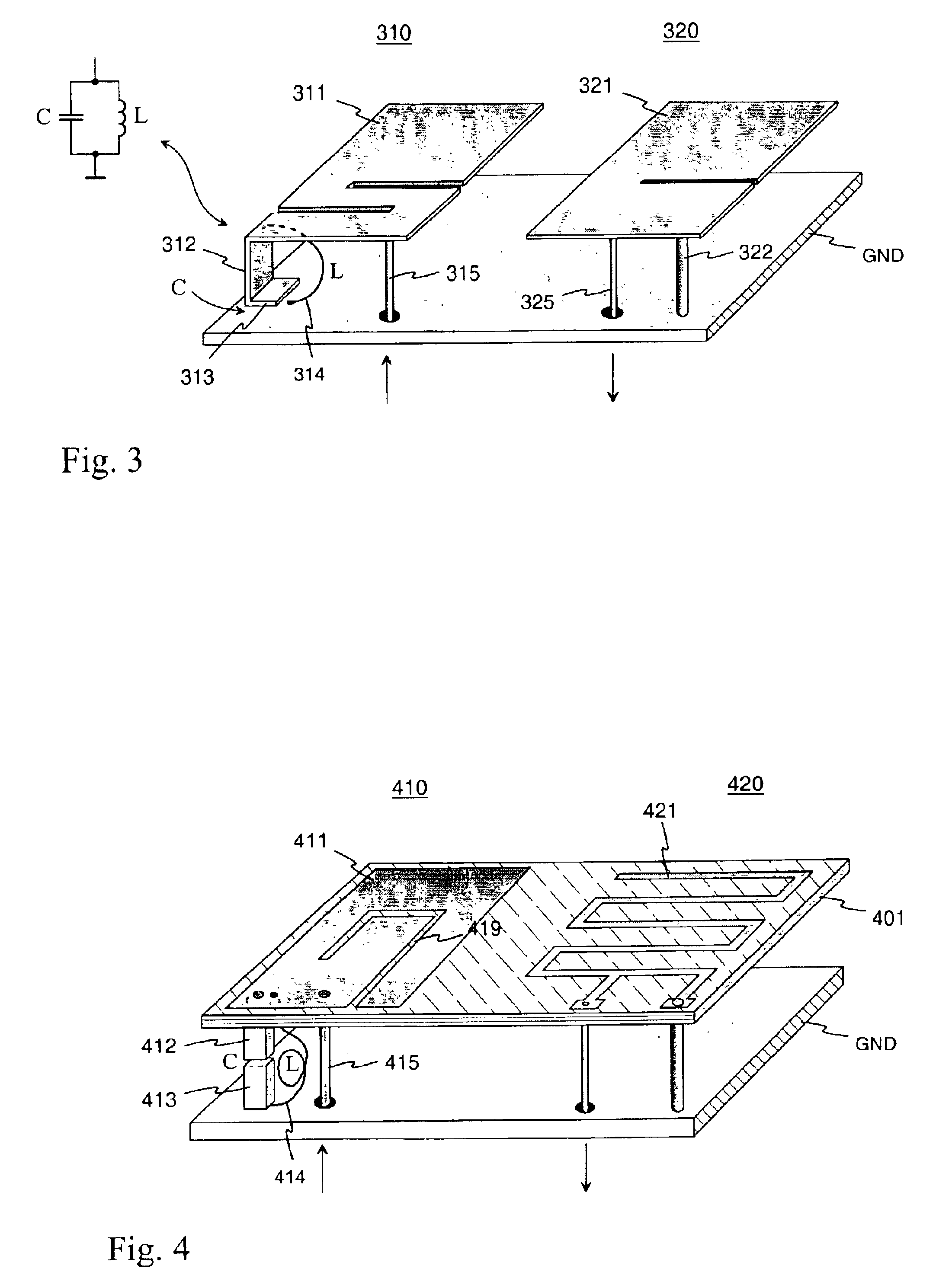
Dual antenna and radio device
InactiveUS6882317B2Reduce disadvantagesFilter design easyAntenna arraysSimultaneous aerial operationsElectricityRadio equipment
An arrangement for enhancing electrical isolation between antennas in antenna structures comprising at least two antennas, and a radio device applying the arrangement. The interfering antenna comprises components causing substantial degradation in radiation characteristics in the operating band of another antenna. For example, a PIFA (310) may comprise, instead of a short-circuit conductor, a conductive structure (312, 313, 314) having a parallel resonance in the operating band of another antenna (320). Mutual interference of radio parts using separate antennas can be made relatively small without electrical isolation arrangements between antenna elements. Moreover, the invention makes antenna filter design easier and reduces disadvantages caused by antenna filters.
Owner:PULSE FINLAND
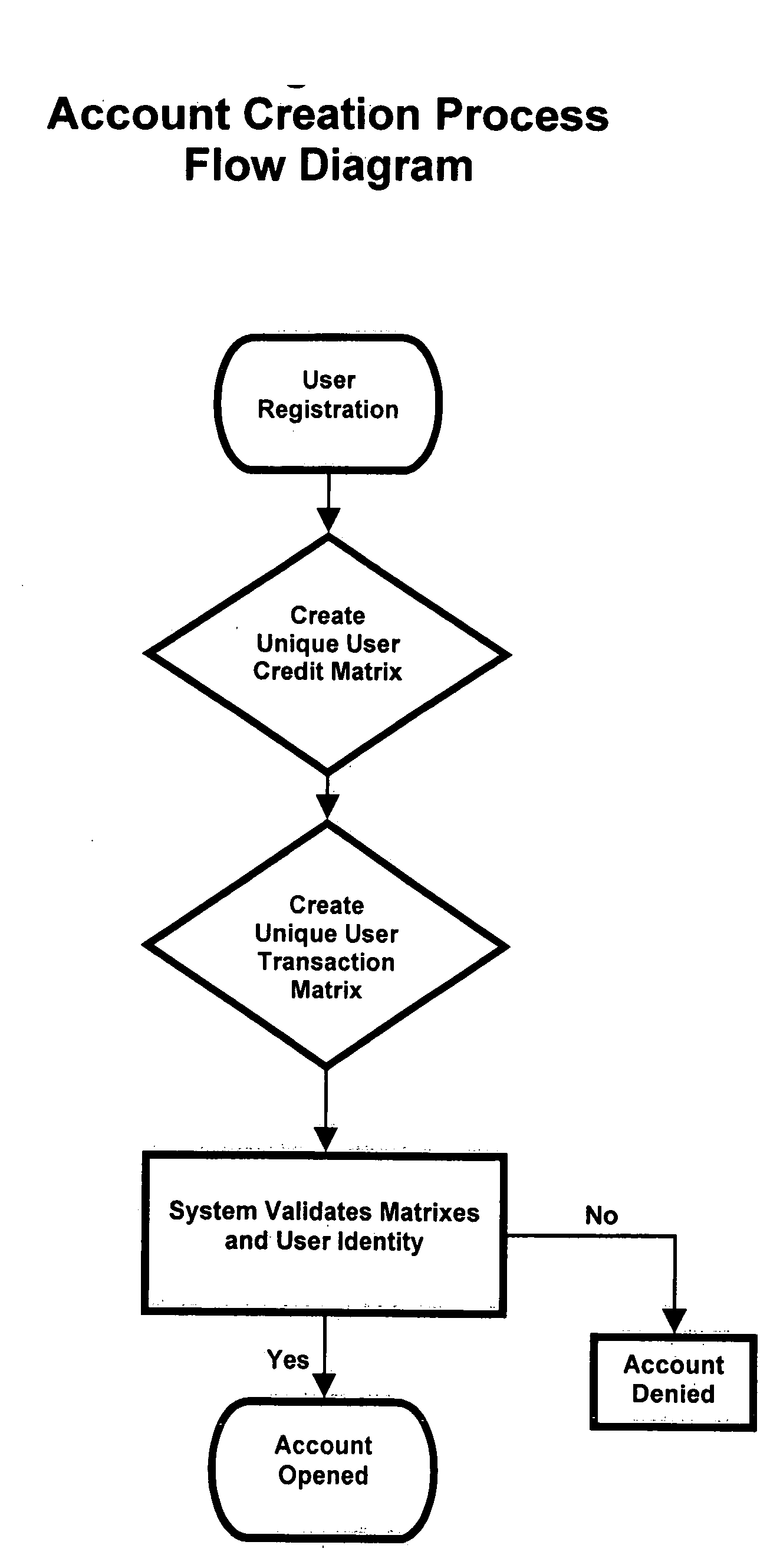
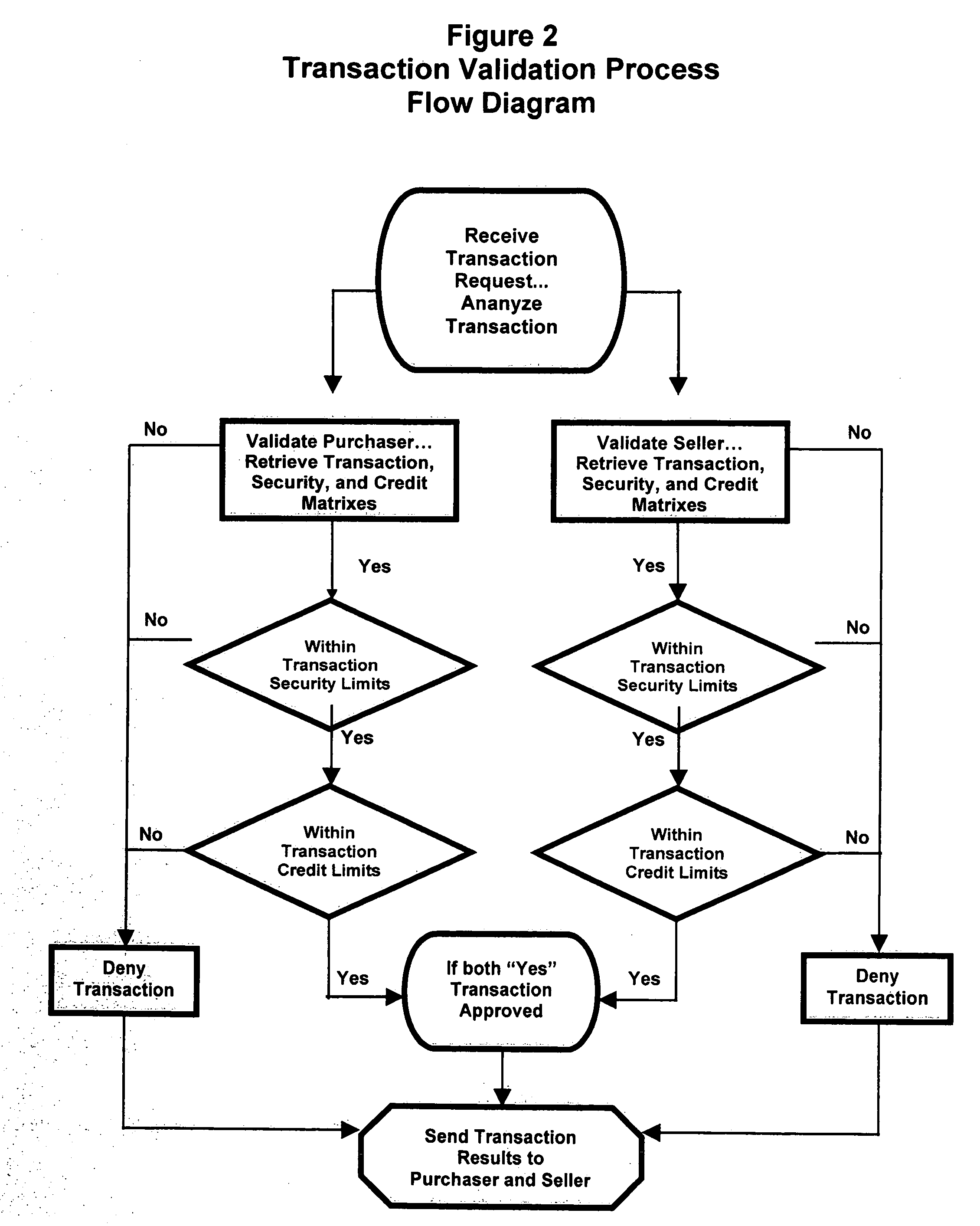
Mobile payment and accounting system with integrated user defined credit and security matrixes
InactiveUS20080255993A1Improve securityFinanceProtocol authorisationThe InternetFinancial transaction
A platform that accommodates financial transactions and is accessible via mobile phone networks, Internet and traditional methods is linked to user defined credit and security matrixes. Credit risk tolerance factors consider the qualifications, characteristics, and profile of counterparties. Security risk tolerance factors consider the user's willingness to use a particular financial platform in an environment where abuse, fraud, theft, and other security factors are of concern. In both cases the user creates matrixes that describe risk tolerance and financial transactions must successfully pass through the filters designed by the user. The system can be used alone or linked to bank accounts, credit and debit accounts, etc. This provides a higher level of security and risk control in a mobile or Web-based environment. By giving customers way to control risk, use of new electronic methods of payment and other financial transactions can be accommodated in a more comfortable, secure, and efficient manner.
Owner:BLINBAUM JACQUES
Push filter with floating key lock
ActiveUS8137551B1Simple replacement and removalMembrane filtersCartridge filtersFluid filtrationRefrigerated temperature
A filter assembly for fluid filtration having a push-activated lock and release mechanism. A push filter design activates a floating key lock upon insertion and extraction, where the filter key may be used simultaneously as a lock and as an identifier for particular filter attributes. The filter base may be situated inline, and in fluid communication, with influent and effluent piping, such as within a refrigerator. The filter housing assembly may be attached to, and removed from, the filter base by a push-actuated release. Upon insertion, the filter key shifts the filter lock longitudinally to receive interlocking segments. Upon extraction, the same axial push shifts the filter lock further to align the interlocking fingers within gaps that allow for easy extraction. The specific key lock design allows a user to identify and match certain filter configurations received by the mechanical support, and reject other filter configurations.
Owner:KX TECH LLC (DW US)
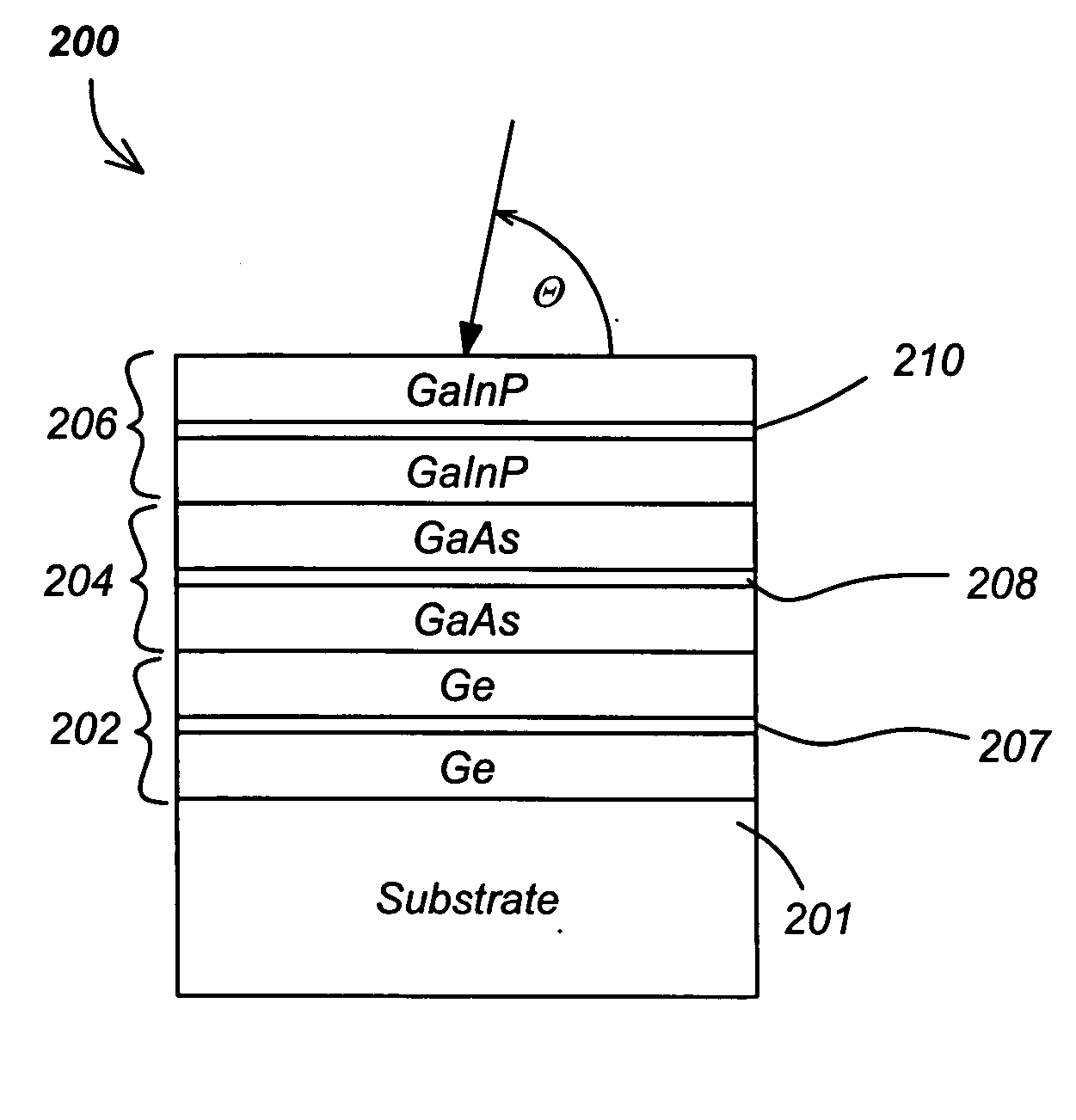
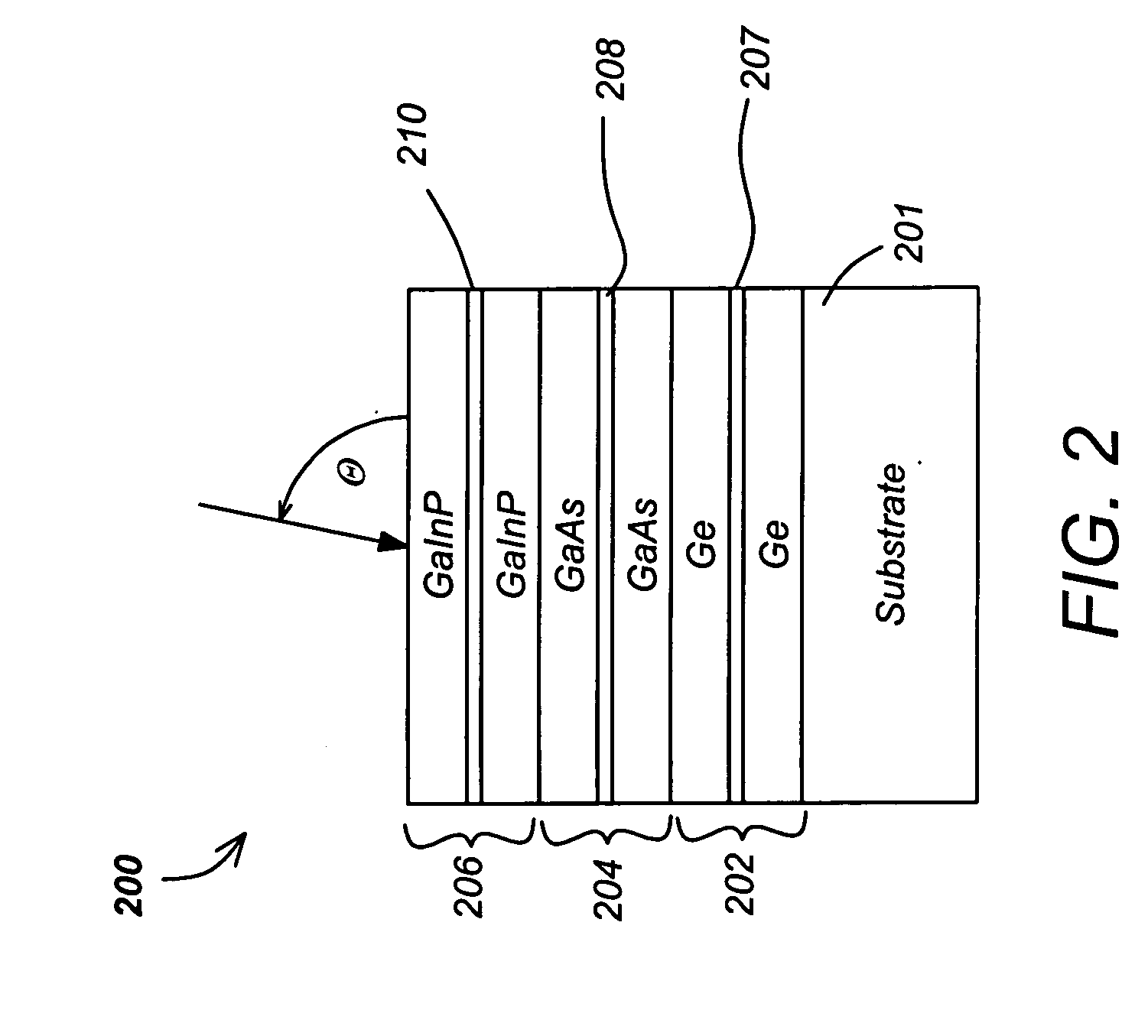
Notch filter for triple junction solar cells
ActiveUS20070137694A1High and low indexFinal product manufacturePhotovoltaic energy generationEngineeringSolar cell
A solar cell and method for producing same is disclosed. The solar cell includes a multijunction solar cell structure and a notch filter designed to reflect solar energy that does not contribute to the current output of the multijunction solar cell. By reflecting unused solar energy, the notch filter allows the solar cell to run cooler (and thus more efficiently) yet it still allows all junctions to fully realize their electrical current production capability.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Push filter with floating key lock
ActiveUS9233322B1Simple replacement and removalMembrane filtersStationary filtering element filtersFluid filtrationRefrigerated temperature
A filter assembly for fluid filtration having a push-activated lock and release mechanism. A push filter design activates a floating key lock upon insertion and extraction, where the filter key may be used simultaneously as a lock and as an identifier for particular filter attributes. The filter base may be situated inline, and in fluid communication, with influent and effluent piping, such as within a refrigerator. The filter housing assembly may be attached to, and removed from, the filter base by a push-actuated release. Upon insertion, the filter key shifts the filter lock longitudinally to receive interlocking segments. Upon extraction, the same axial push shifts the filter lock further to align the interlocking fingers within gaps that allow for easy extraction. The specific key lock design allows a user to identify and match certain filter configurations received by the mechanical support, and reject other filter configurations.
Owner:KX TECH LLC (DW US)
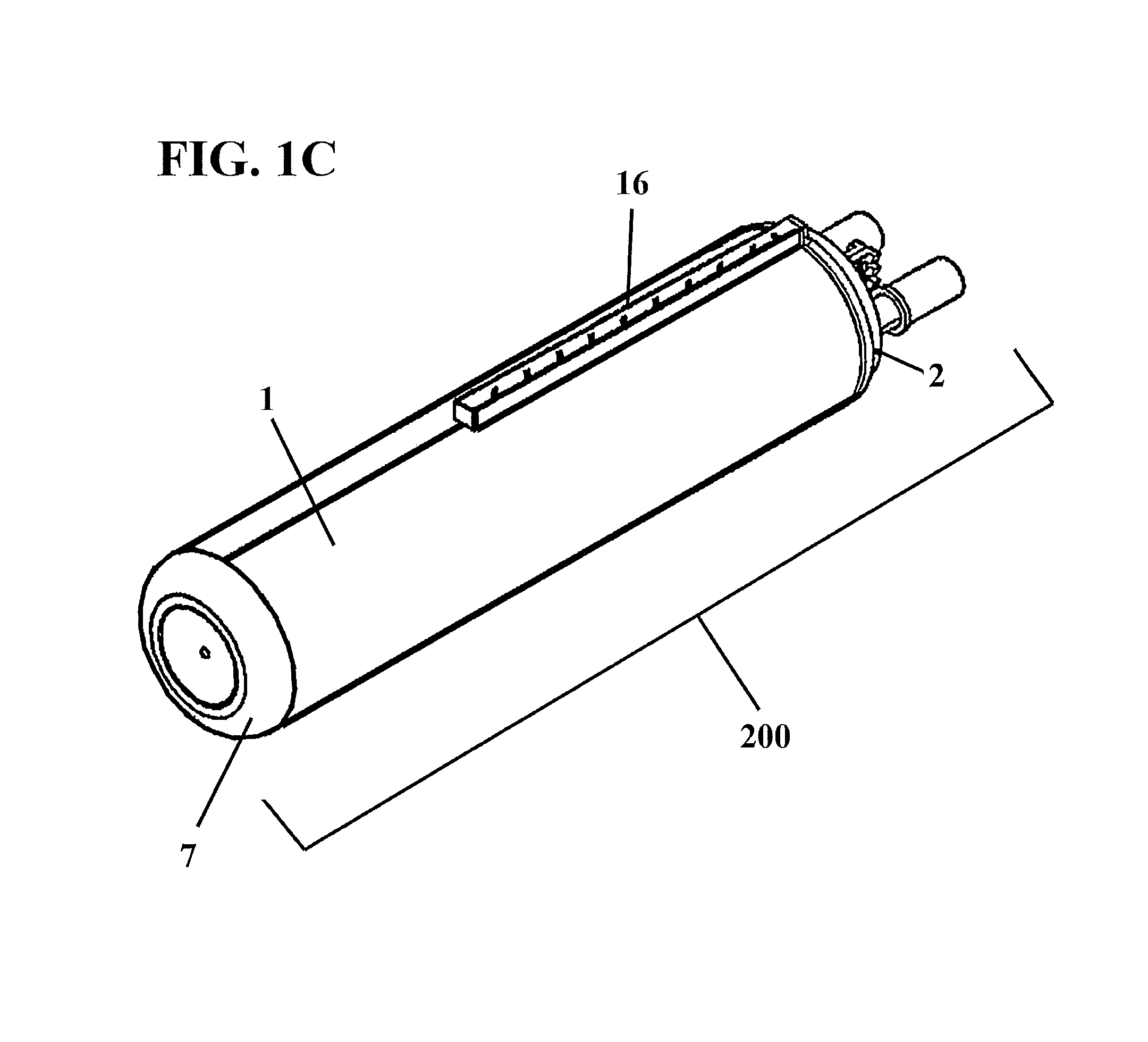
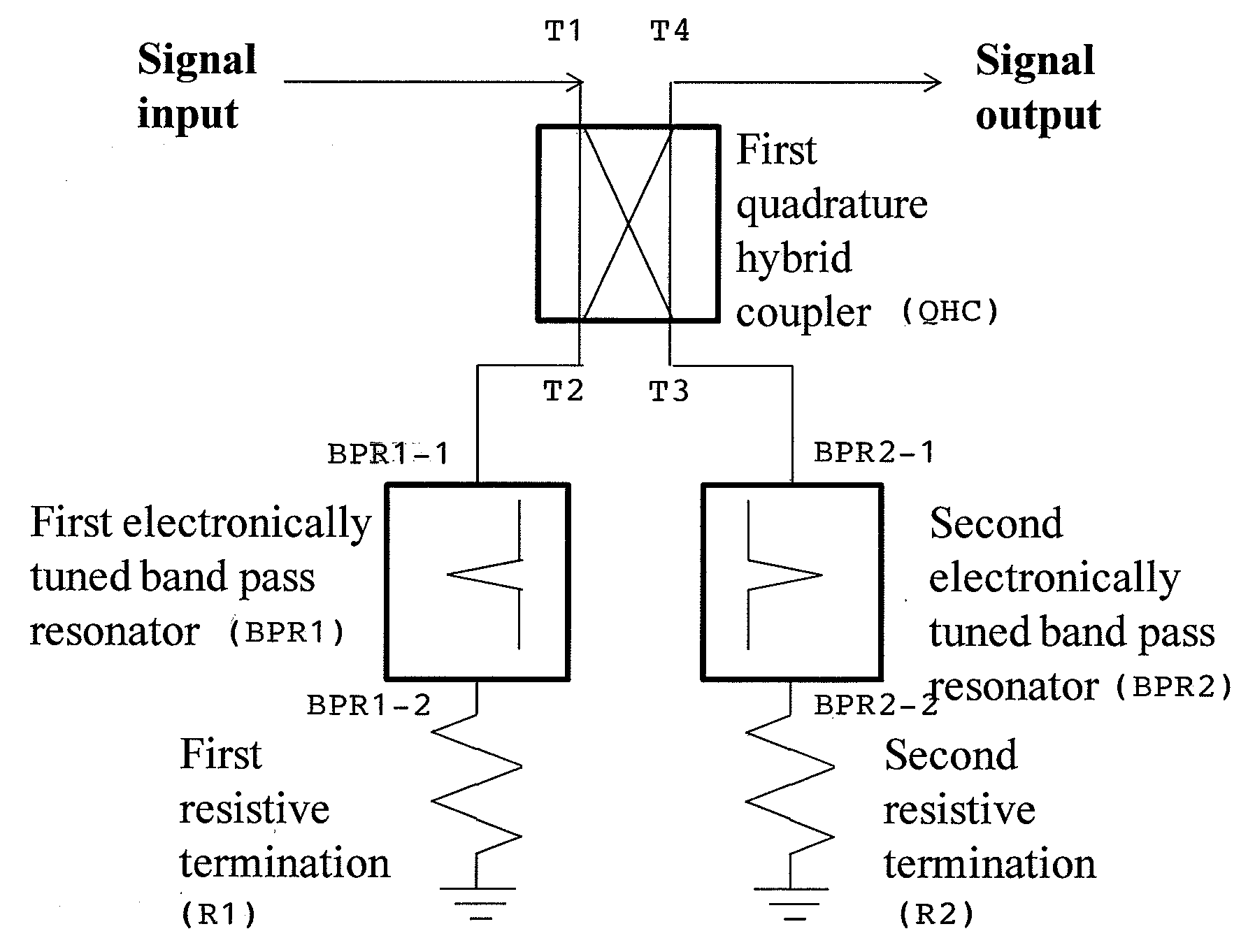
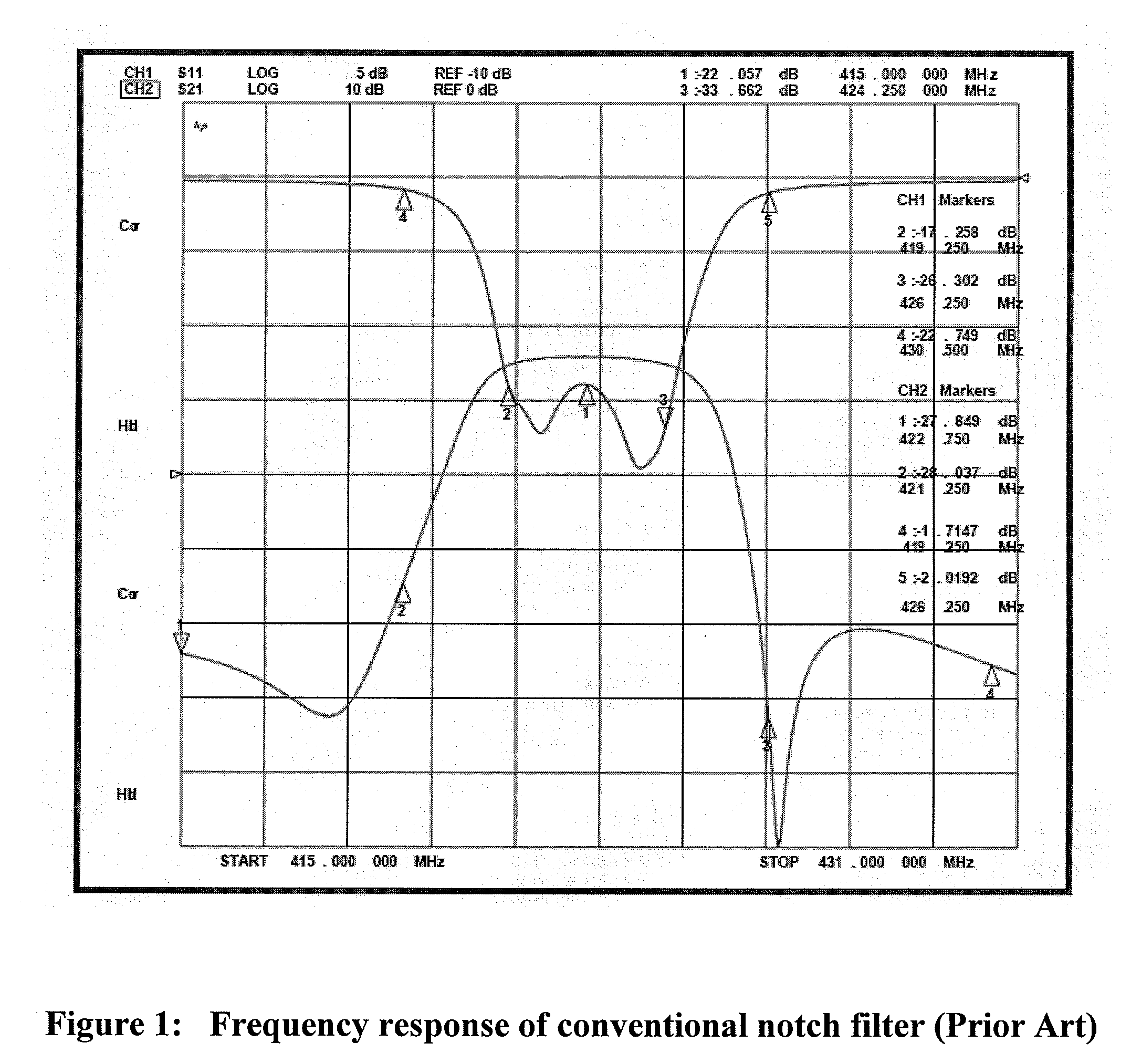
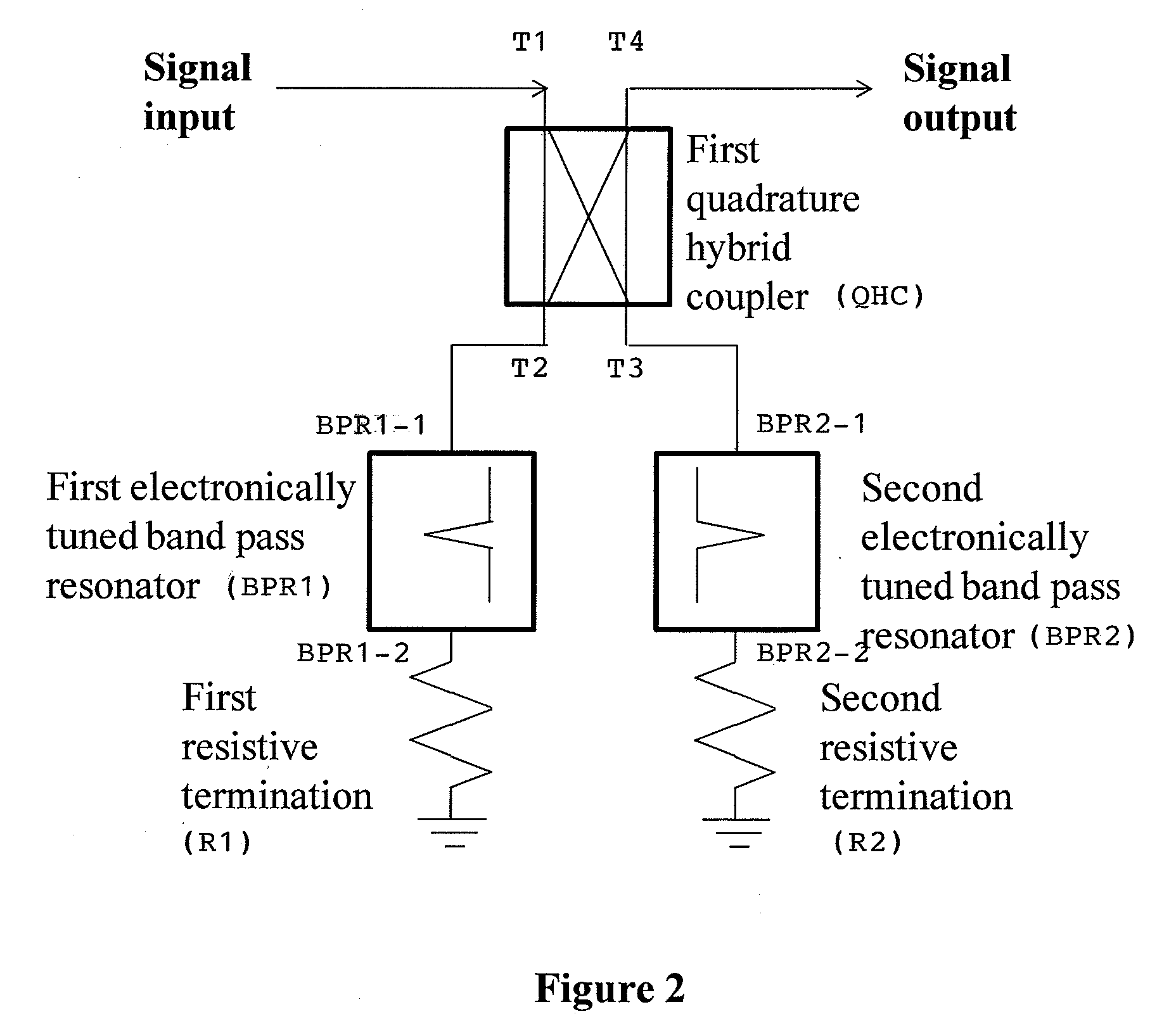
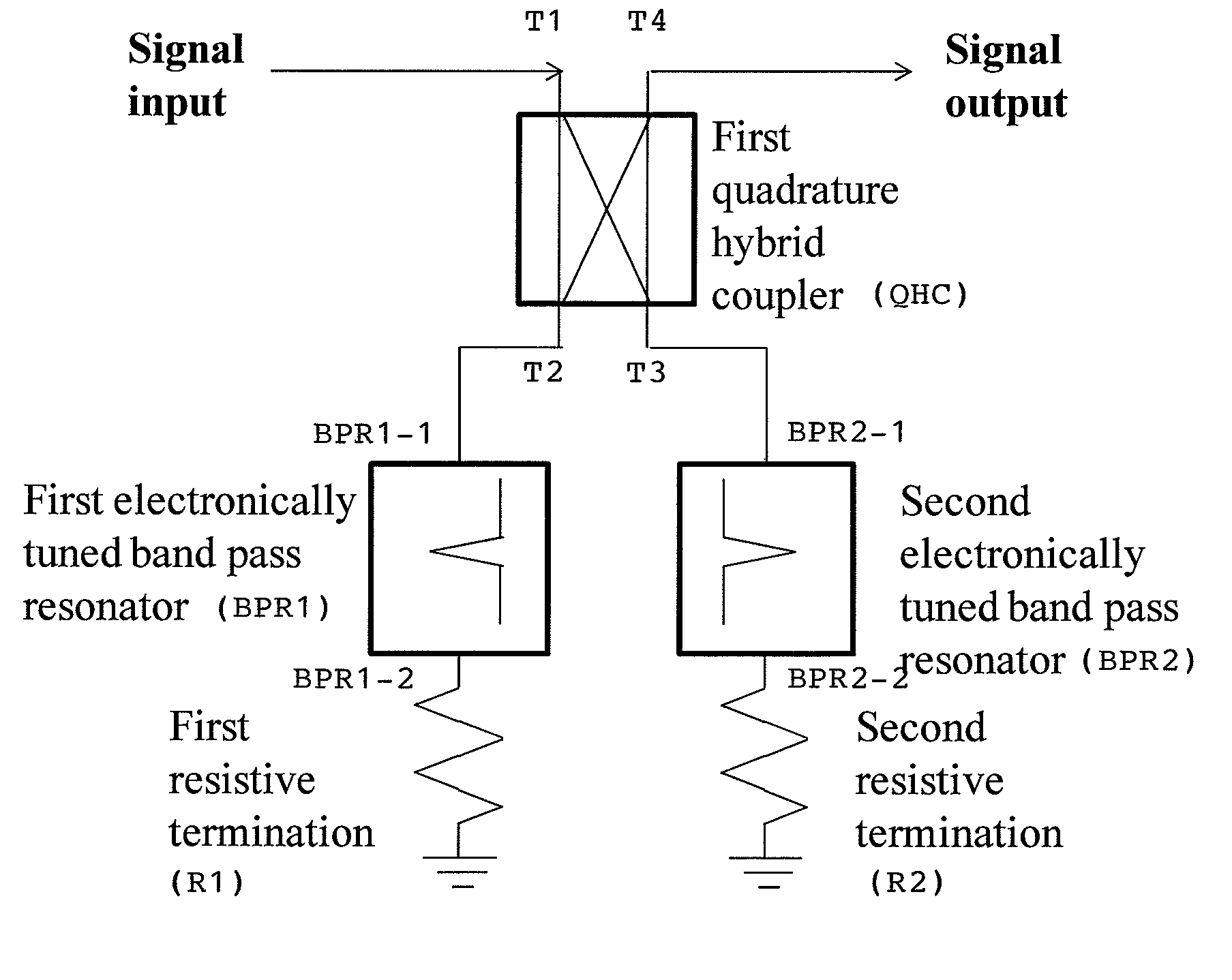
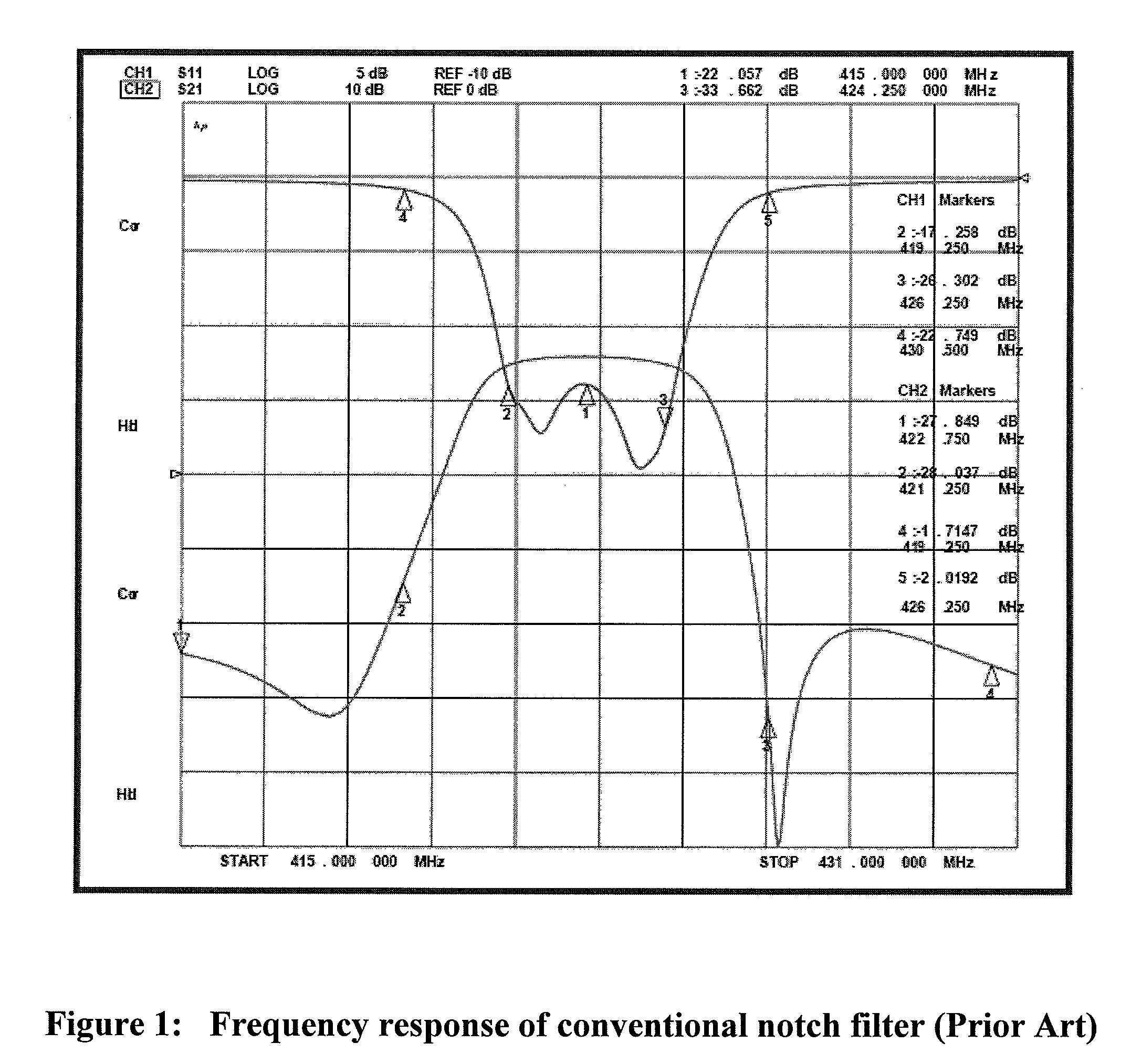
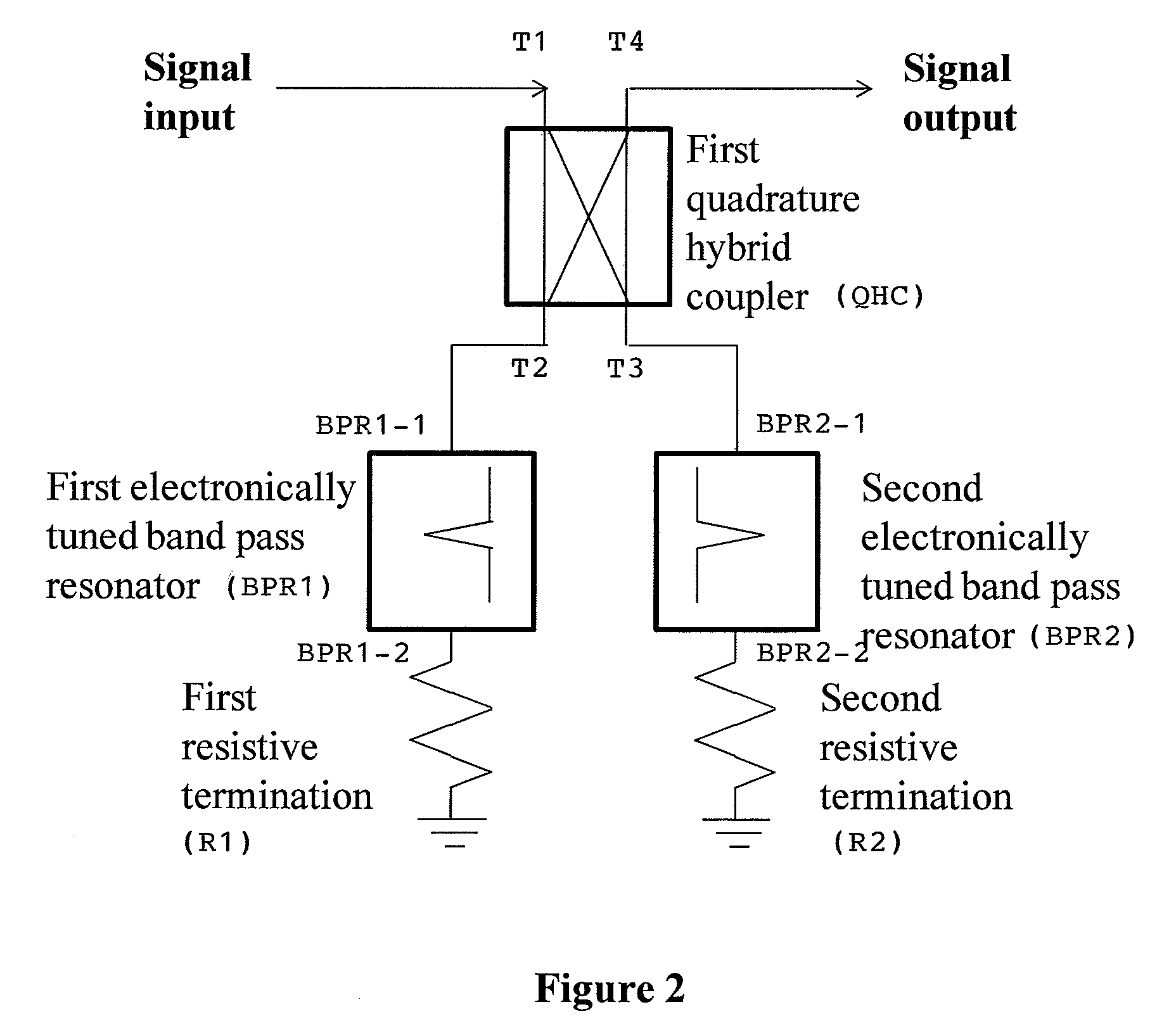
Electronically tunable, absorptive, low-loss notch filter
InactiveUS20090289744A1Little and no lossImproved power handlingMultiple-port networksTunable filtersWireless routerMatched pair
An electronically tuned, absorptive, low-loss notch filter with high RF power handling capability is obtained using a four-port quadrature hybrid coupler connected to a matched pair of band pass resonator devices and resistive terminations. The notch filter design uses series-only tuning elements for the band pass resonator devices to raise the RF power handling of the band pass resonators far above conventional techniques while also being tunable at high speeds. The notch filter architecture and method can be used for interference cancellation in a wide range of wireless technologies, such as cellular phone, wireless routers, hand-held radios, satellite communications, and any other environments where there are a number of wireless technologies in close signal proximity.
Owner:TERASYS TECH
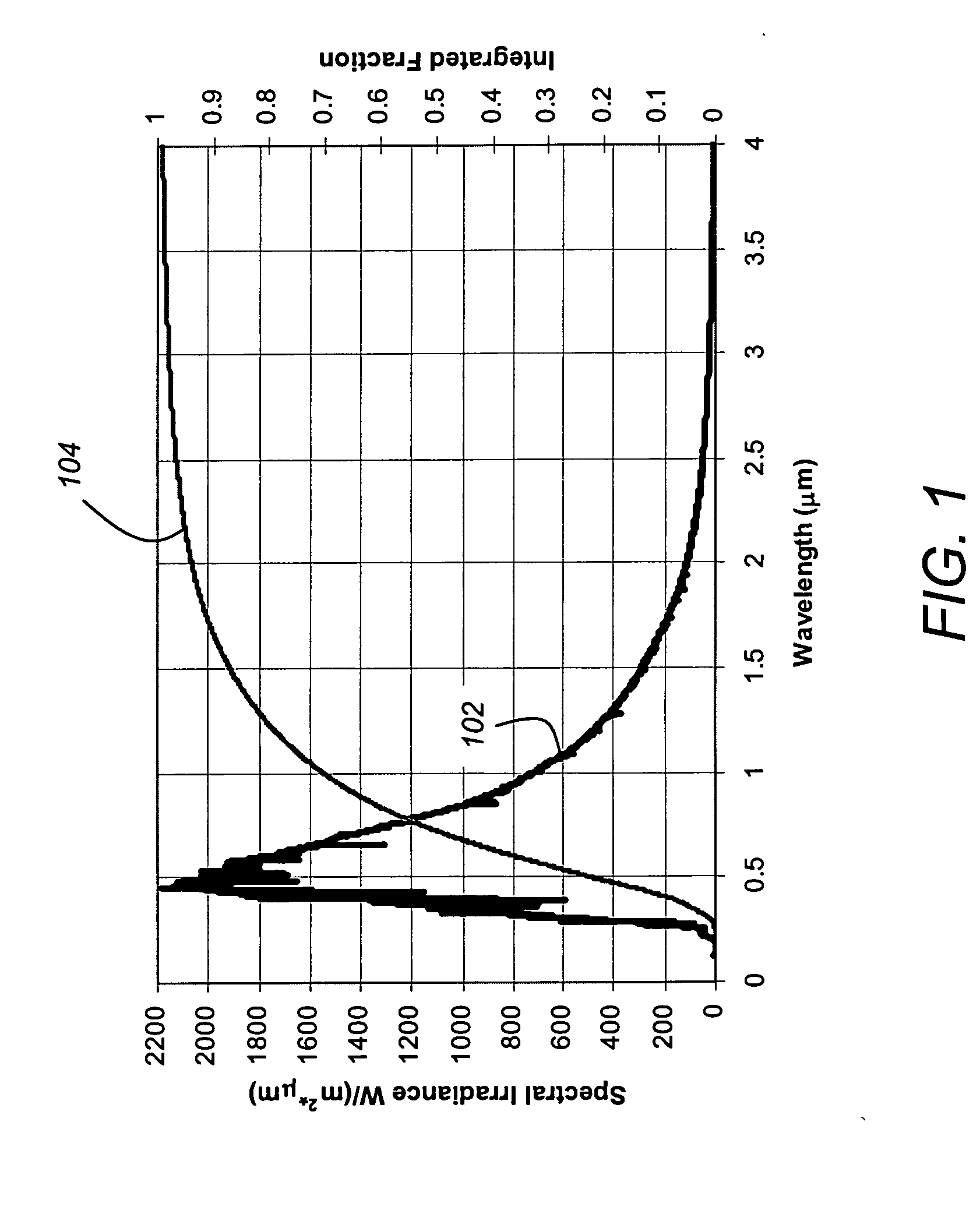
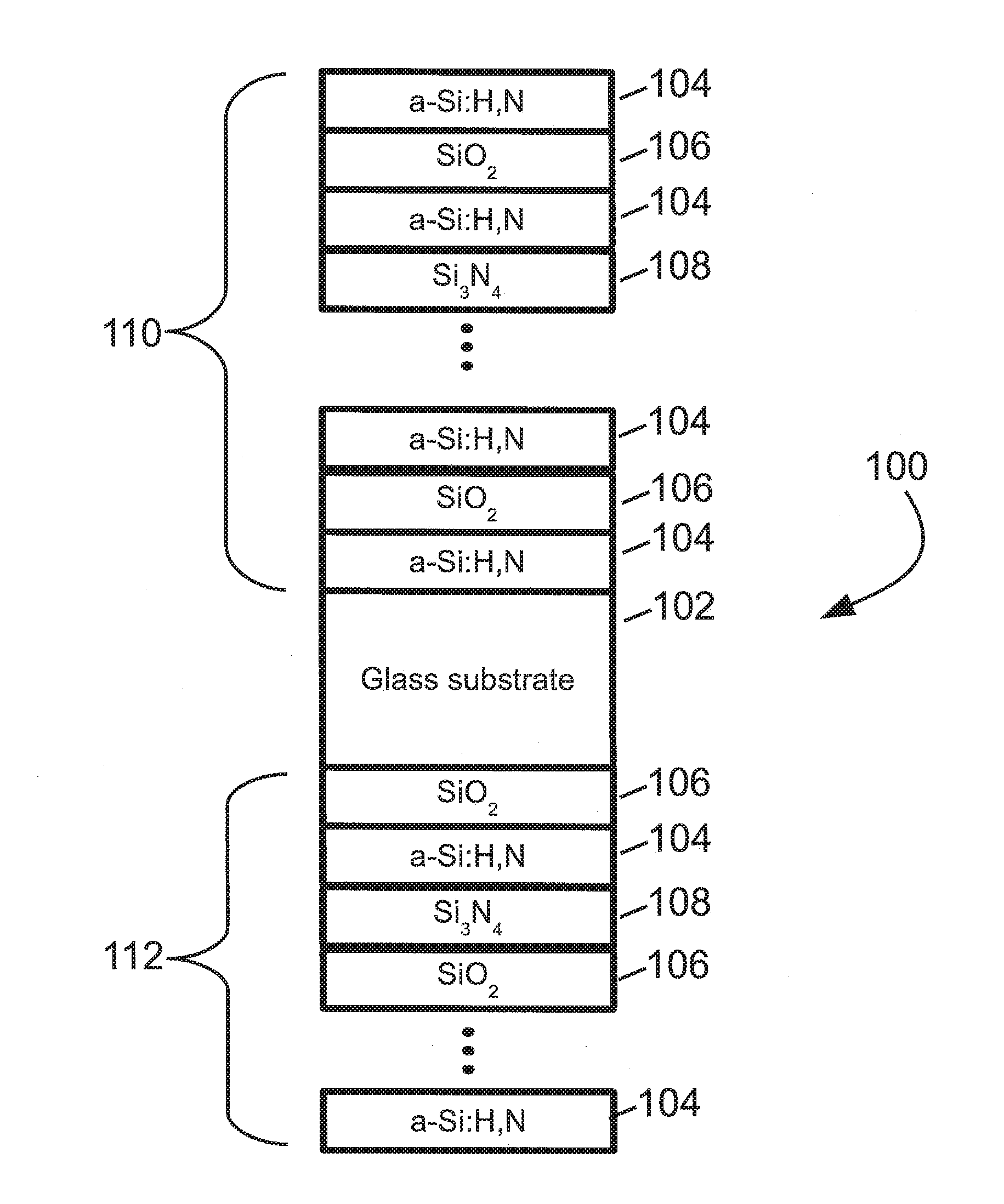
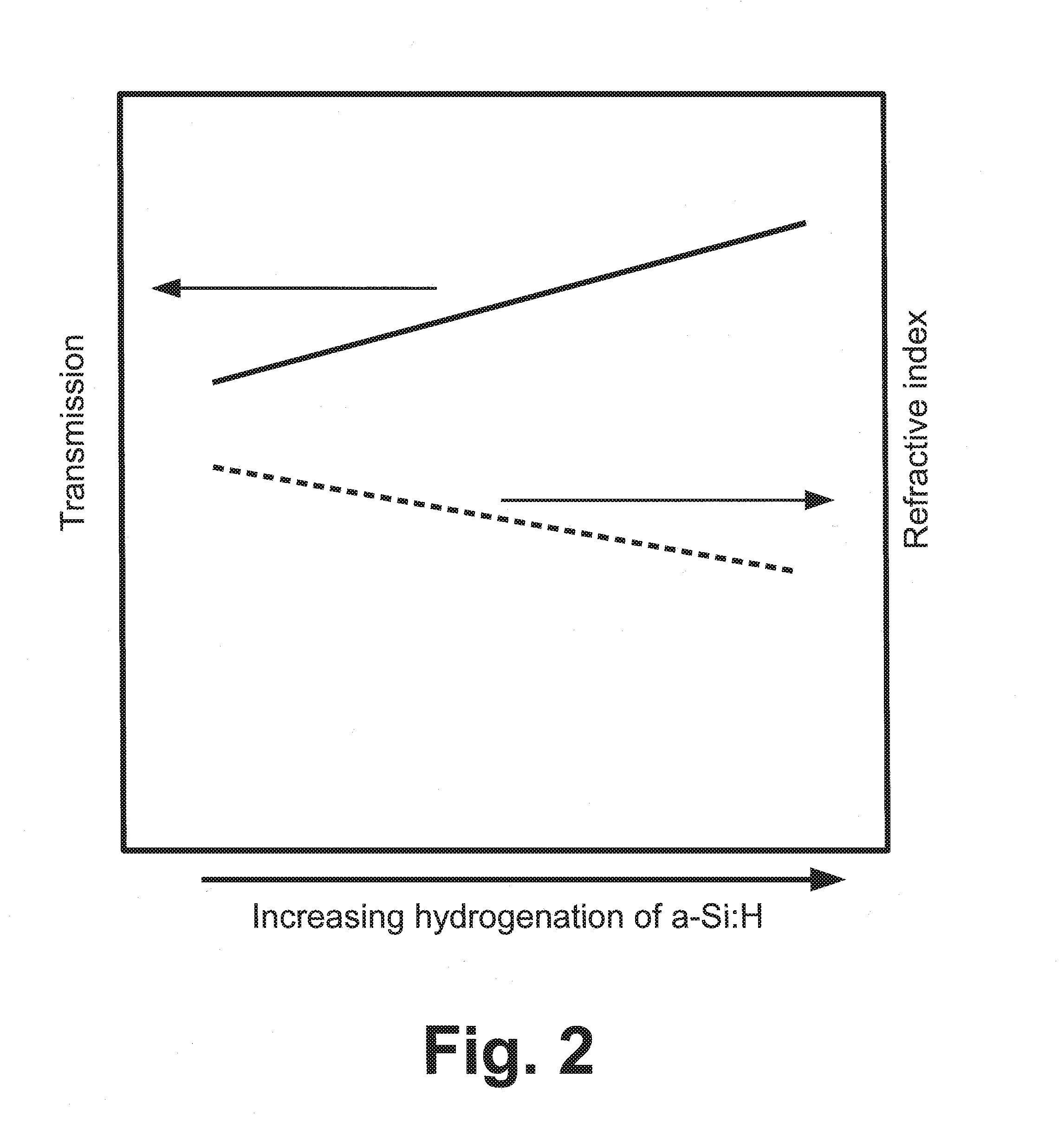
Near infrared optical interference filters with improved transmission
An interference filter includes a layers stack comprising a plurality of layers of at least: layers of amorphous hydrogenated silicon with added nitrogen (a-Si:H,N) and layers of one or more dielectric materials, such as SiO2, SiOx, SiOxNy, a dielectric material with a higher refractive index in the range 1.9 to 2.7 inclusive, or so forth. The interference filter is designed to have a passband center wavelength in the range 750-1000 nm inclusive. Added nitrogen in the a-Si:H,N layers provides improved transmission in the passband without a large decrease in refractive index observed in a-Si:H with comparable transmission. Layers of a dielectric material with a higher refractive index in the range 1.9 to 2.7 inclusive provide a smaller angle shift compared with a similar interference filter using SiO2 as the low index layers.
Owner:MATERION
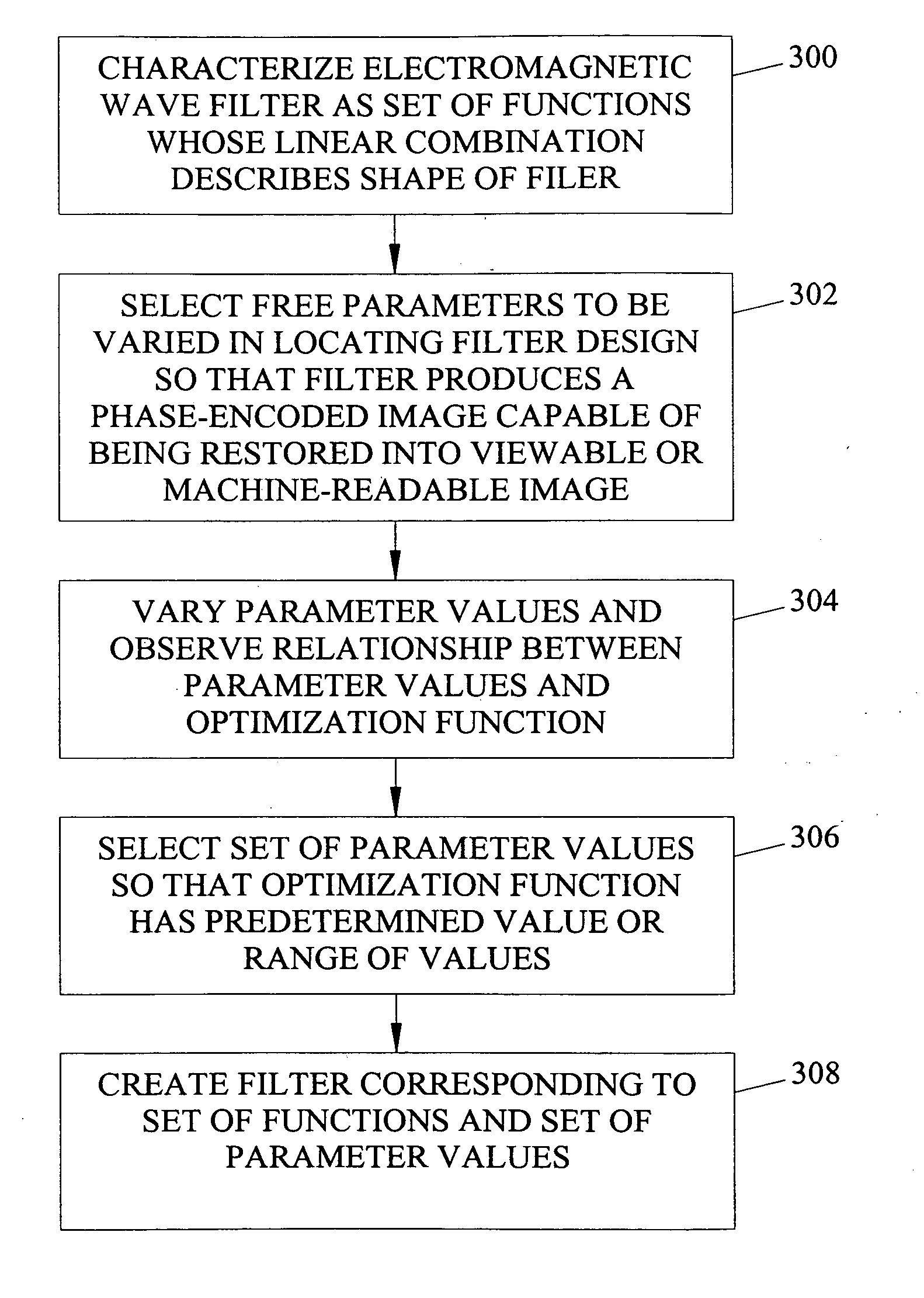
Methods and systems for designing electromagnetic wave filters and electromagnetic wave filters designed using same
InactiveUS20050204329A1Minimize spatially varying blurImage enhancementCharacter and pattern recognitionSystems designComputational physics
Methods and systems for designing electromagnetic wave filters and electromagnetic wave filters designed using the methods and systems are disclosed. In one method, functions are selected whose linear combination define the surface of a filter for producing a desired phase-encoded image. Free parameter values are selected for the function and are varied. The values of the free parameters are observed with regard to an optimization function. Final values of the free parameters are selected based on the optimization function having a specific value or range of values.
Owner:WAKE FOREST UNIV
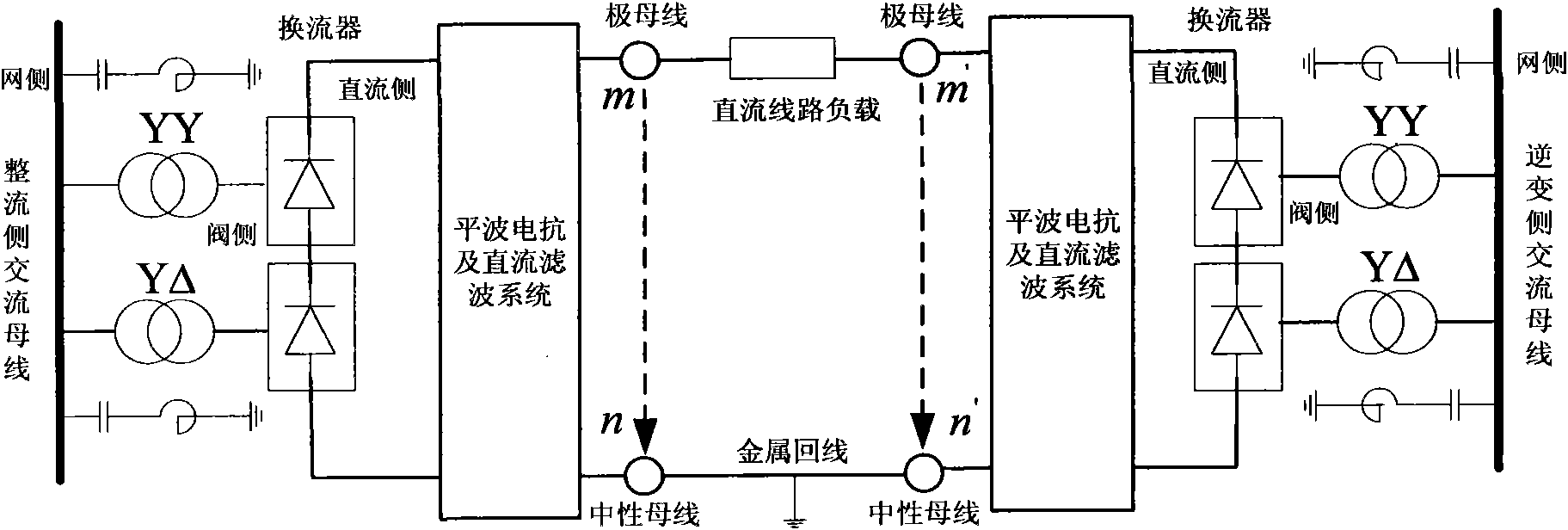
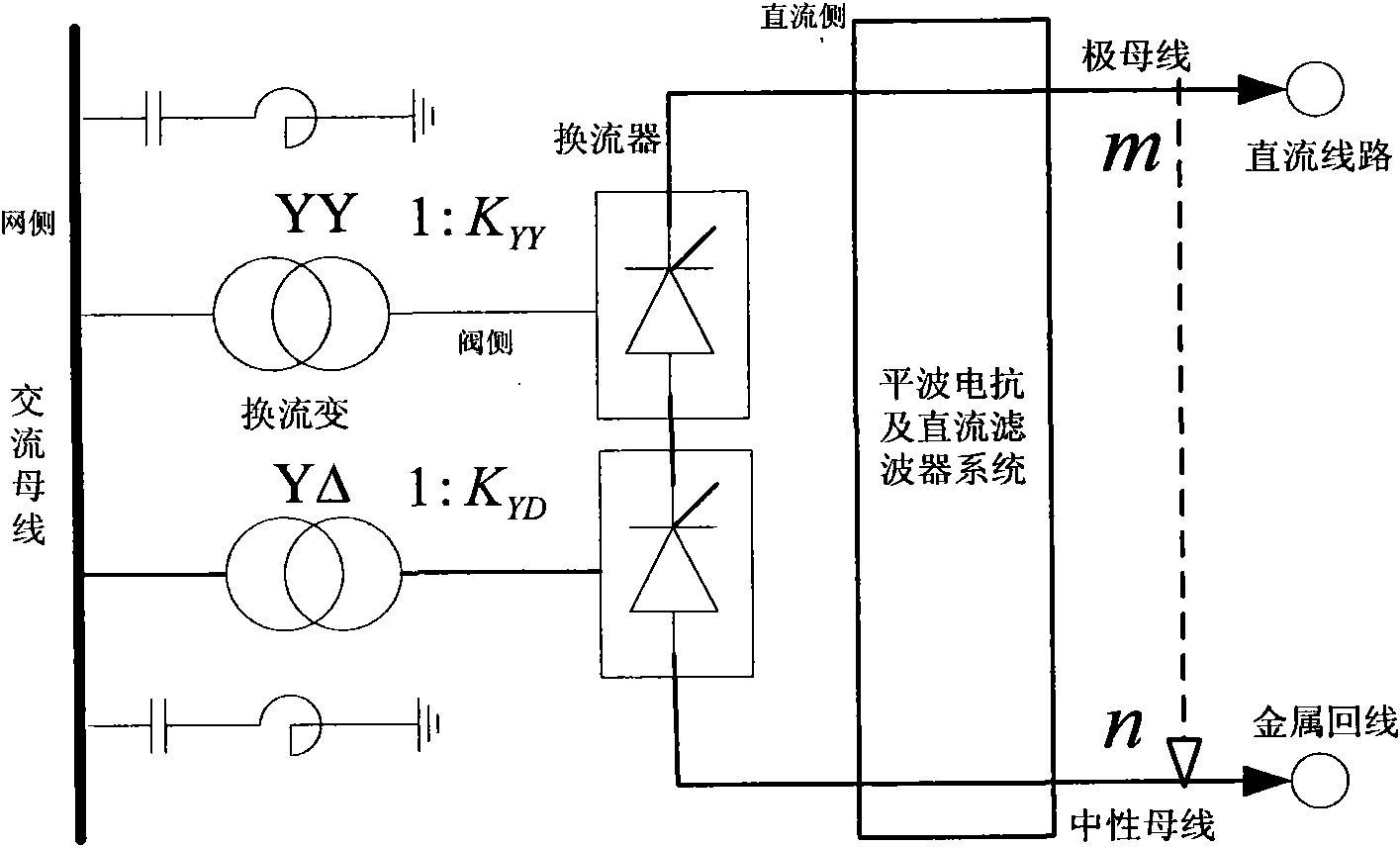
Determination method of network side harmonic current of high-voltage direct current power transmission system
InactiveCN101860037AAccelerate Design CycleImprove design qualityElectric power transfer ac networkHarmonic reduction arrangementTransformerInternal resistance
The invention discloses a determination method of network side harmonic current of a high-voltage direct current power transmission system. The determination method comprises the following steps: if the harmonic current voltage at a direct current power transmission line inlet is zero, decoupling and equalizing a rectifying side and an inverting side into a plurality of independent six-pulse moving bridge units; dividing a work period of the six-pulse moving bridge units into six phase converting sections and six non-phase converting sections; calculating a phase converting overlapping angle of each phase converting section; equalizing a current converter into a harmonic current voltage source containing internal resistance; calculating the direct current side harmonic current according to the concrete forms of a smoothing reactor and a direct current filter; obtaining valve side harmonic current according to an equivalent circuit of the current converter; and converting the valve side harmonic current to a network side according to a connecting structure of a transformer to obtain the network side harmonic current. The invention considers background harmonic current and other nonideal factors, and can quickly and accurately obtain the harmonic current at the network side of a converter transformer, accelerate the period for designing an alternating current filter in the high-voltage direct current power transmission engineering and improve the design quality and the design efficiency.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
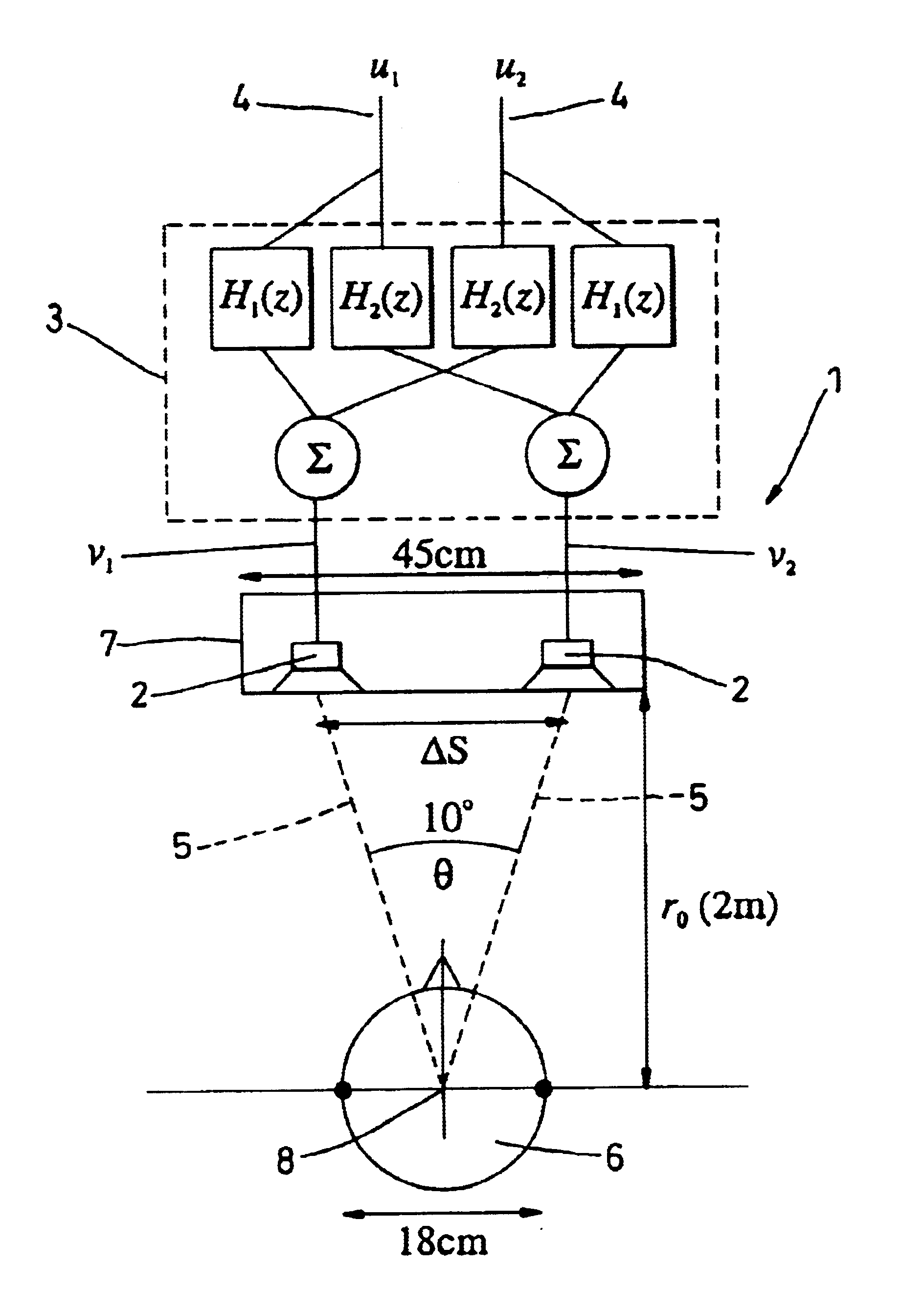
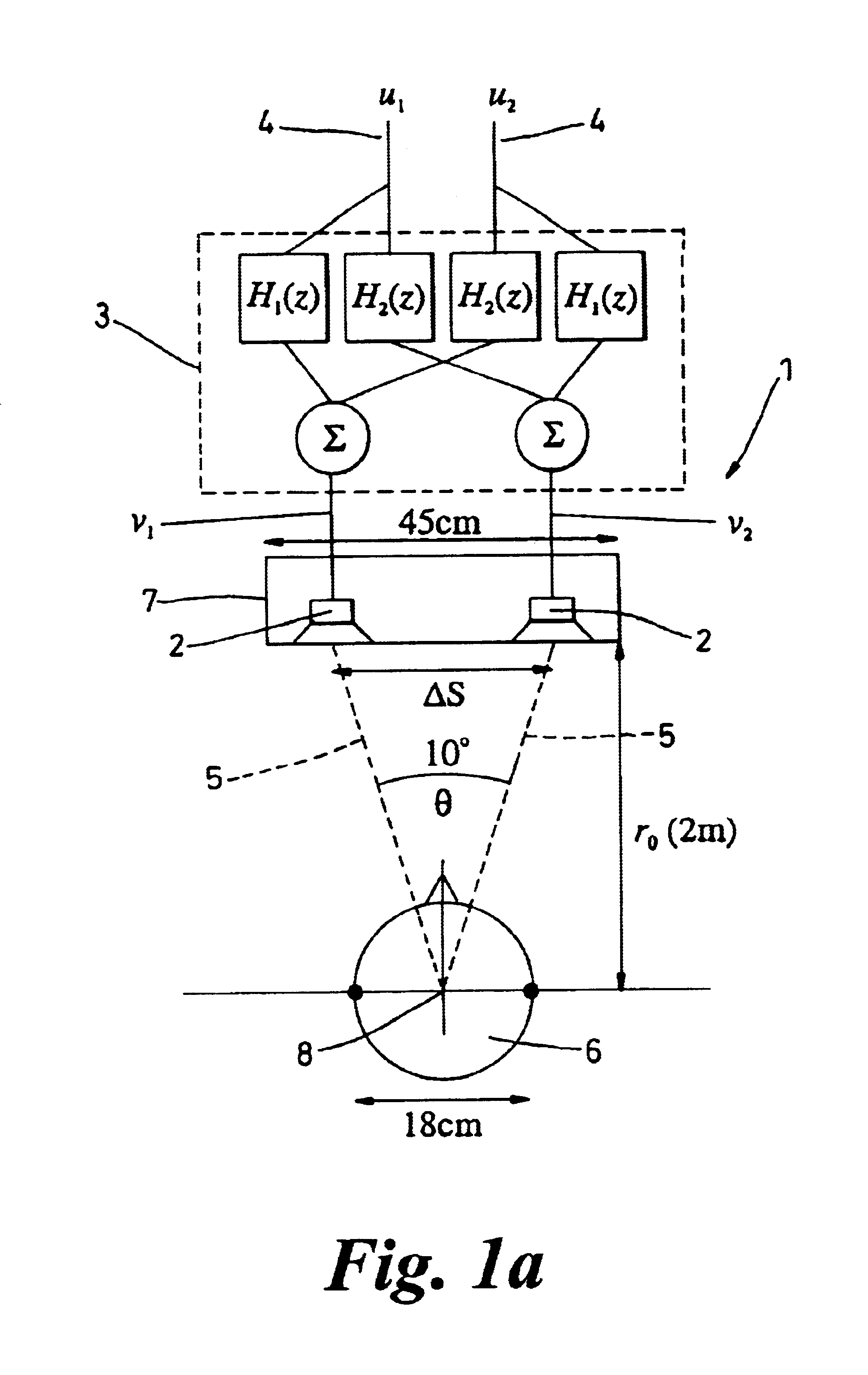
Loudspeaker array system
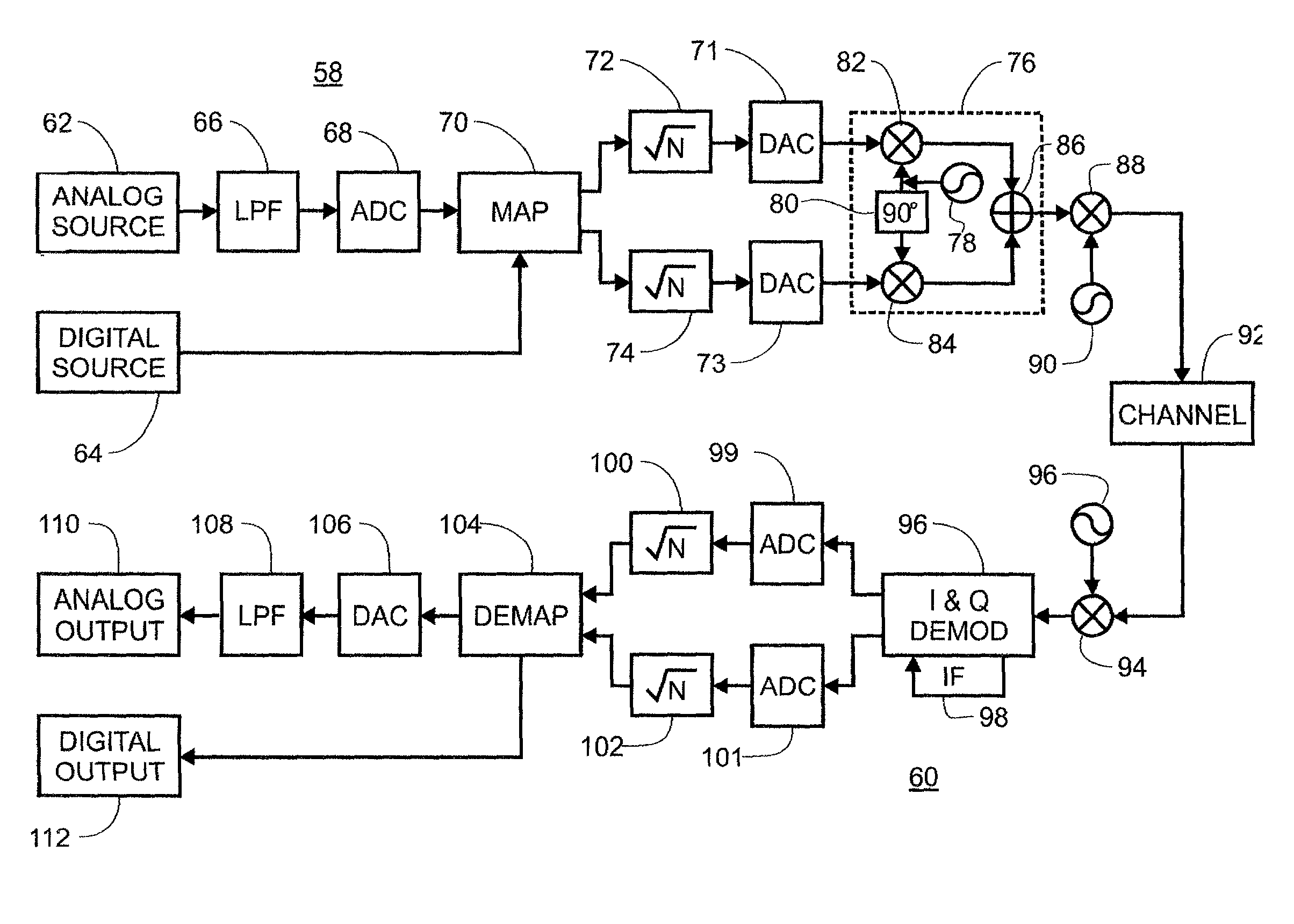
ActiveUS20050180577A1High-quality soundEasy to controlLoudspeaker signals distributionFrequency/directions obtaining arrangementsDigital signal processingEngineering
The invention is a multi-channel loudspeaker system that provides a compact loudspeaker configuration and filter design methodology that operates in the digital signal processing domain. Further, the loudspeaker system can be designed to include drivers of various physical dimensions and can achieve prescribed constant directivity over a large area in both the vertical and horizontal planes.
Owner:APPLE INC
Method and system for motion image digital processing
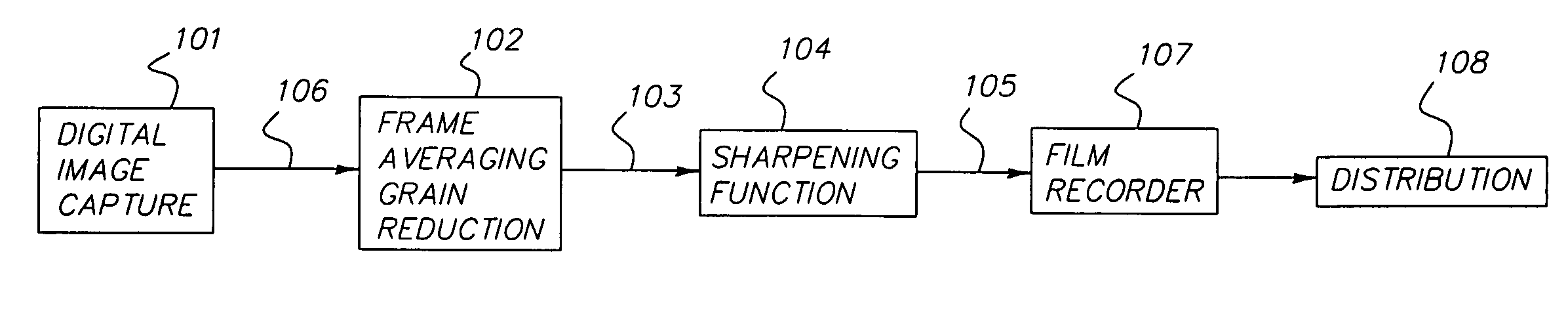
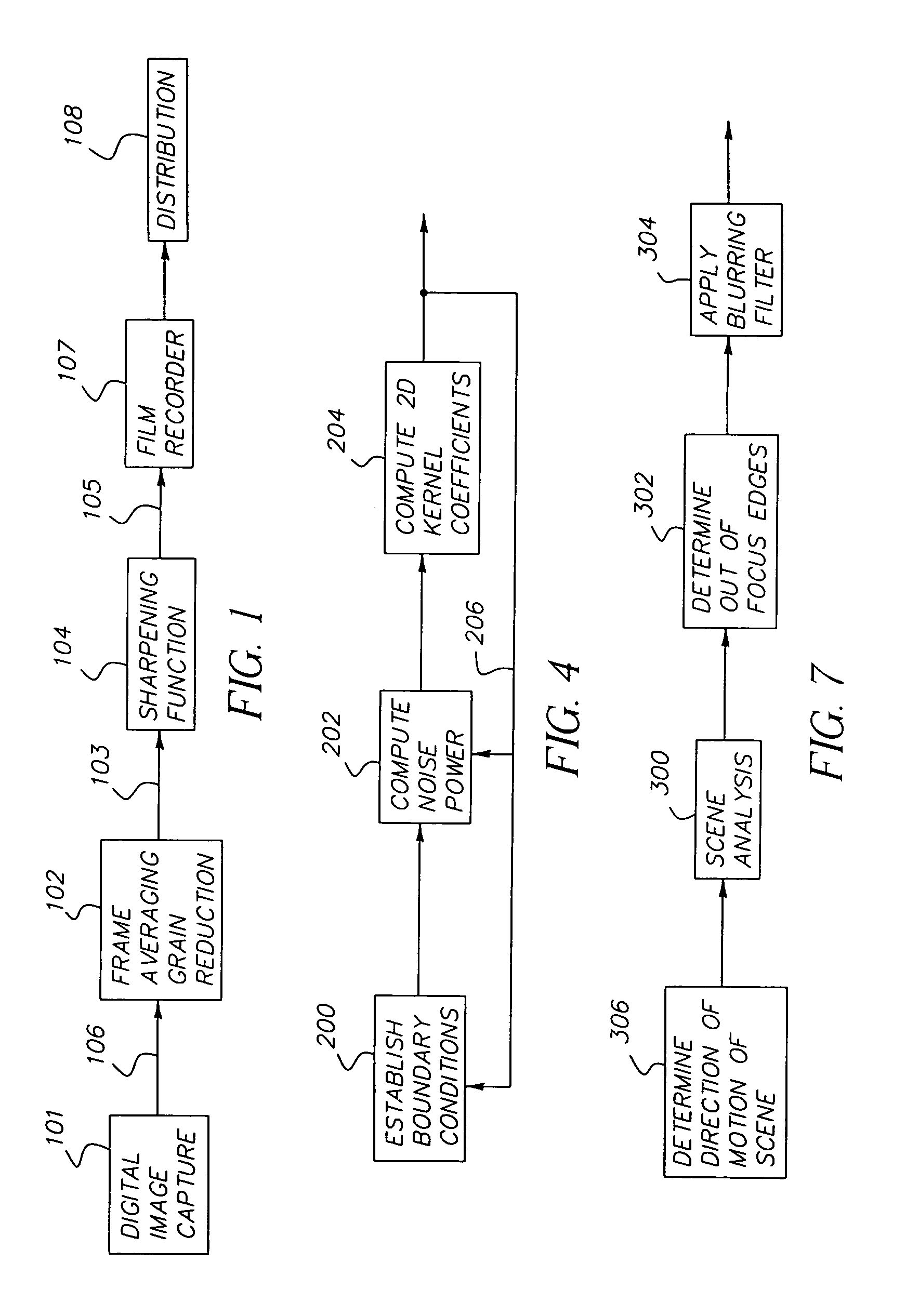
ActiveUS7092016B2Large format qualityPreserve noise characteristic and grain characteristicImage enhancementTelevision system detailsSharpeningImage signal
A method for digitally processing motion image signals comprises the steps of: (a) obtaining digital motion image signals that originated from a sequence of motion picture frames; (b) using a frame averaging technique to reduce noise in the digital motion image signals, thereby producing noise-processed motion image signals; and (c) producing output digital motion image signals by sharpening the noise-processed motion image signals with a sharpening filter designed in the spatial domain with a 2D kernel that increases the noise in order to provide a desired grain response.
Owner:MONUMENT PEAK VENTURES LLC
Synthetic aperture radar image target identification method based on depth model
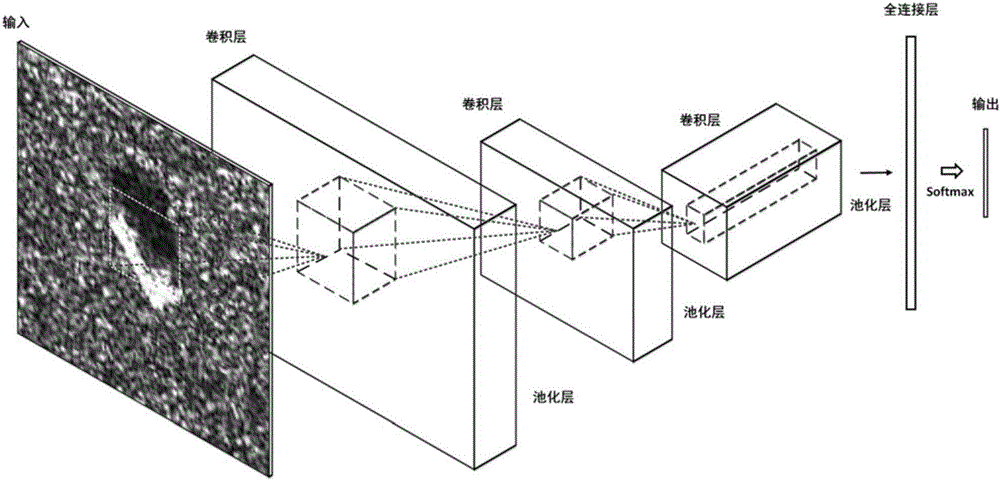
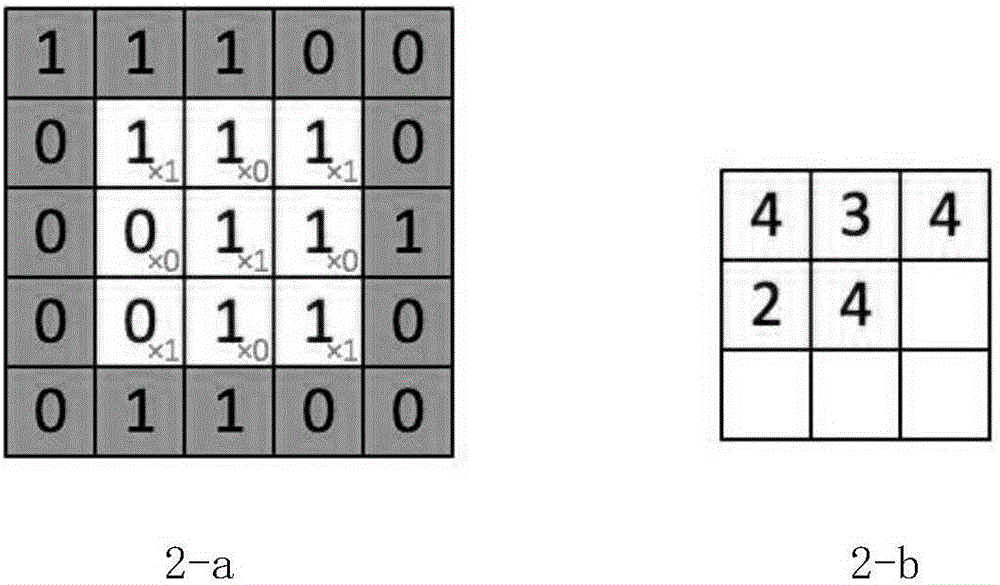
ActiveCN106407986AReduce overheadTarget recognition facilitatesCharacter and pattern recognitionFeature extractionLevel structure
The invention discloses a synthetic aperture radar image target identification method based on a depth model. The method comprises steps of image cutting; depth model level structure design, characteristic extraction filter design, parameter quantity control and overfitting prevention, function activation and non-linear lifting, identification classification and autonomous parameter correction update; depth model training; target identification. The method is advantaged in that filter parameters can realize autonomous iteration update in a training process, characteristic selection and extraction cost is greatly reduced, moreover, target different-level characteristics can be extracted through the depth model, the characteristics can be acquired through high-degree matching and training, so high-degree target representation can be realized, and target identification accuracy of SAR images is improved.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Sound recording and reproduction systems
InactiveUS6760447B1Avoid the needTransducers for sound channels pluralityTwo-channel systemsEngineeringLoudspeaker
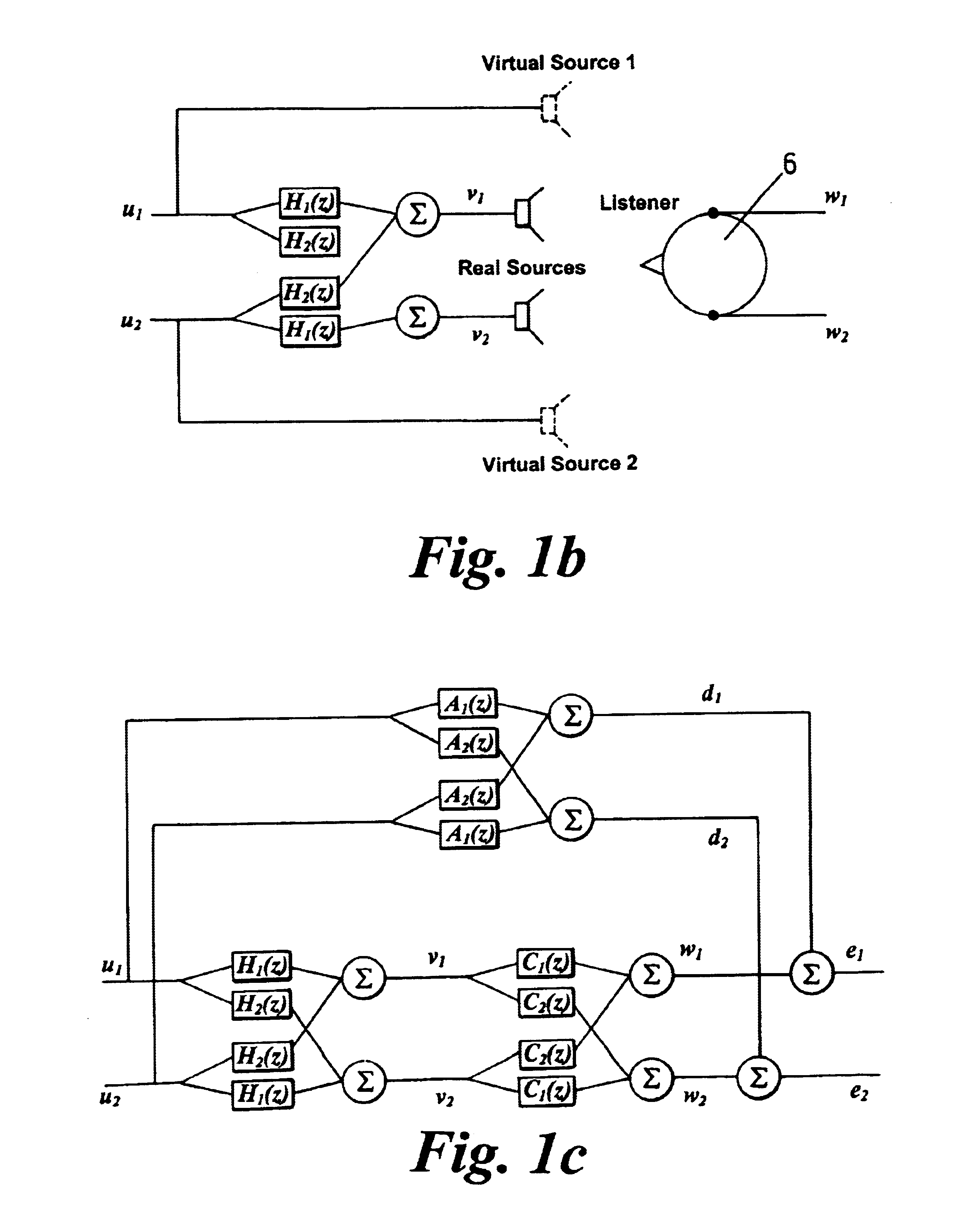
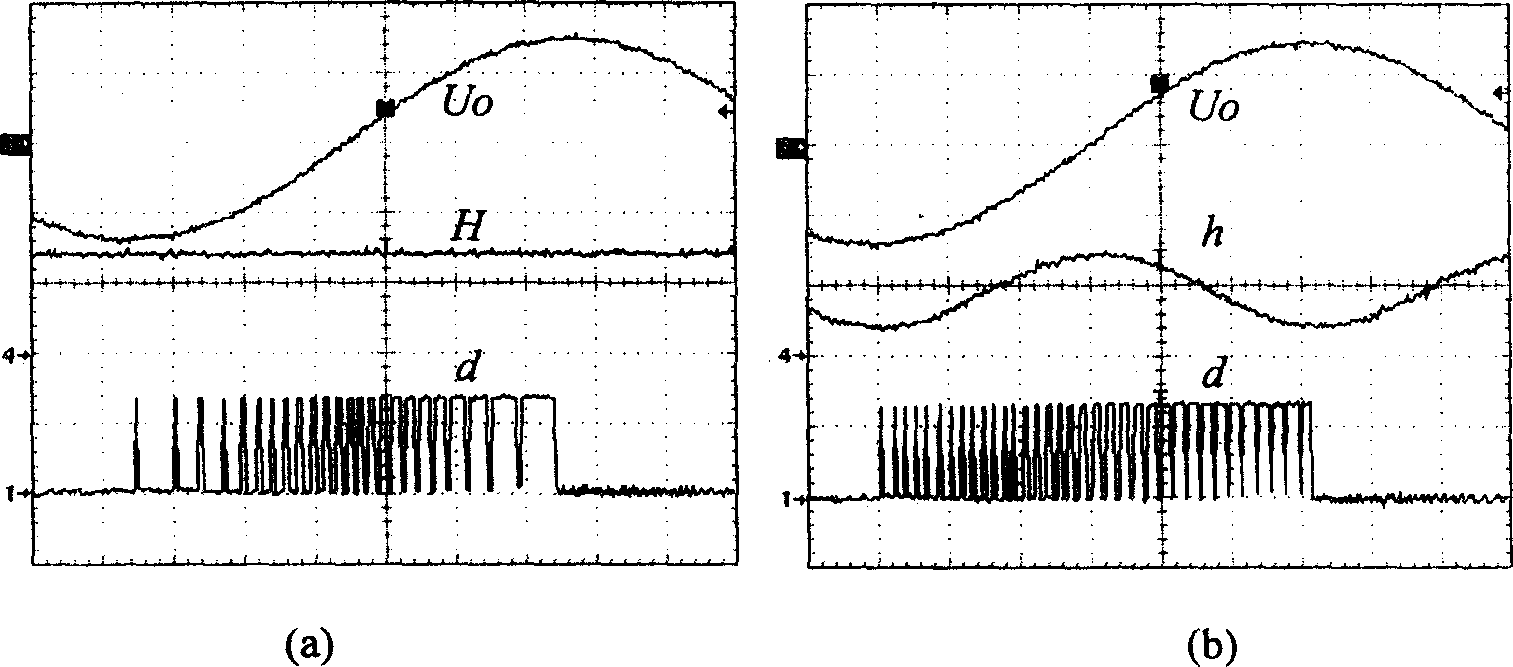
A method of recording sound for reproduction by a plurality of loudspeakers, or for processing sound for reproduction by a plurality of loudspeakers, is described in which some of the reproduced sound appears to a listener to emmanate from a virtual source which is spaced from the loudspeakers. A filter means (H) is used either in creating the recording, or in processing the recorded signals for supply to loudspeakers, the filter means (H) being created in a filter design step in which: a) a technique is employed to minimise error between the signals (w) reproduced at the intended position of a listener on playing the recording through the loudspeakers, and desired signals (d) at the intended position, wherein: b) said desired signals (d) to be produced at the listener are defined by signals (or an estimate of the signals) that would be produced at the ears of (or in the region of) the listener in said intended position by a source at the desired position of the virtual source. A least squares technique may be employed to minimise the time averaged error between signal reproduced at the intended position of a listener and the desired signal, or it may be applied to the frequency domain.
Owner:ADAPTIVE AUDIO
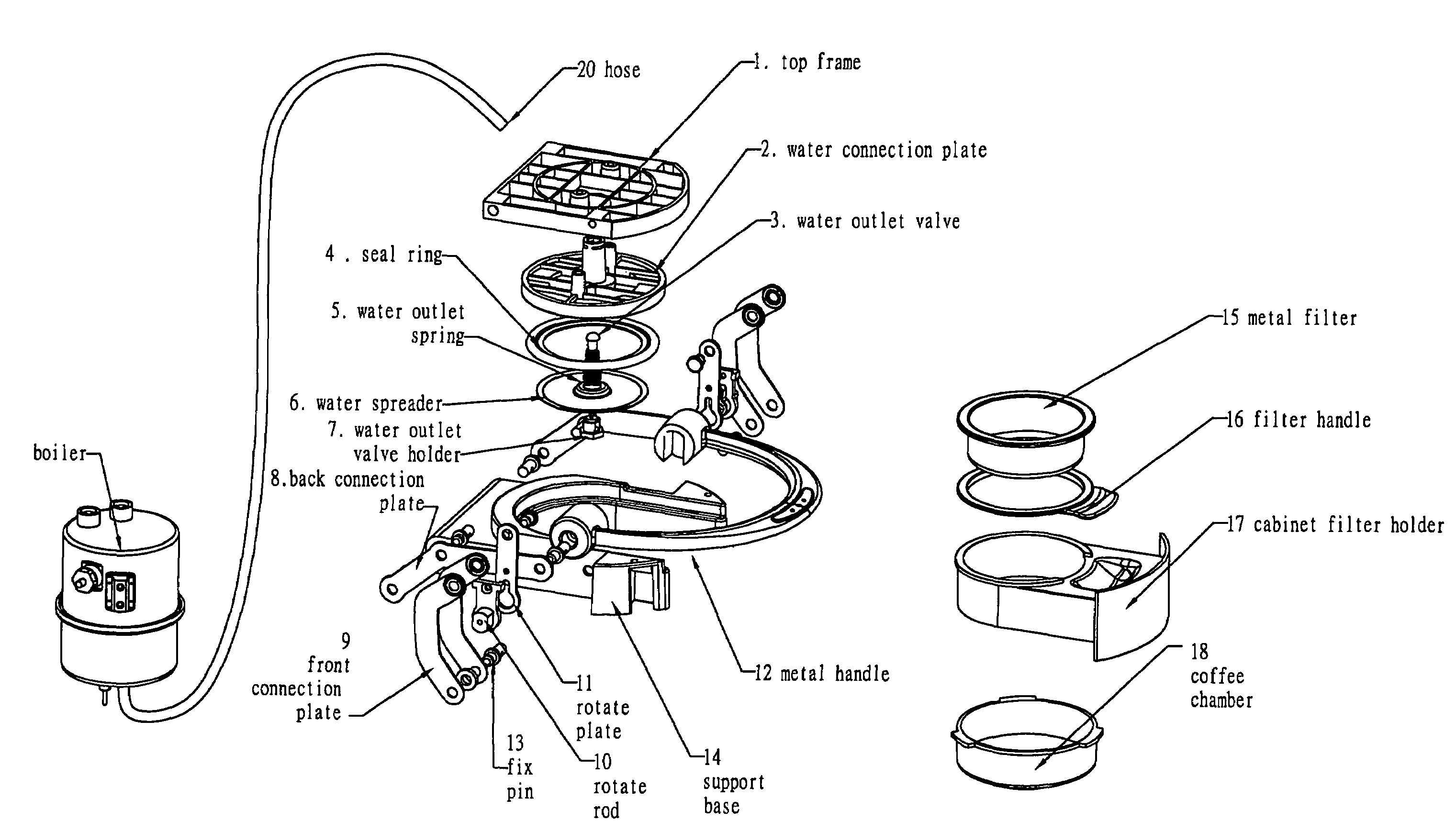
Cabinet design of filter holder for pressurized espresso machines
Owner:ELECTRICAL & ELECTRONICS LTD
Video encoding/decoding apparatus
InactiveUS20100303149A1Reduce errorsColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionVideo encodingEncoder
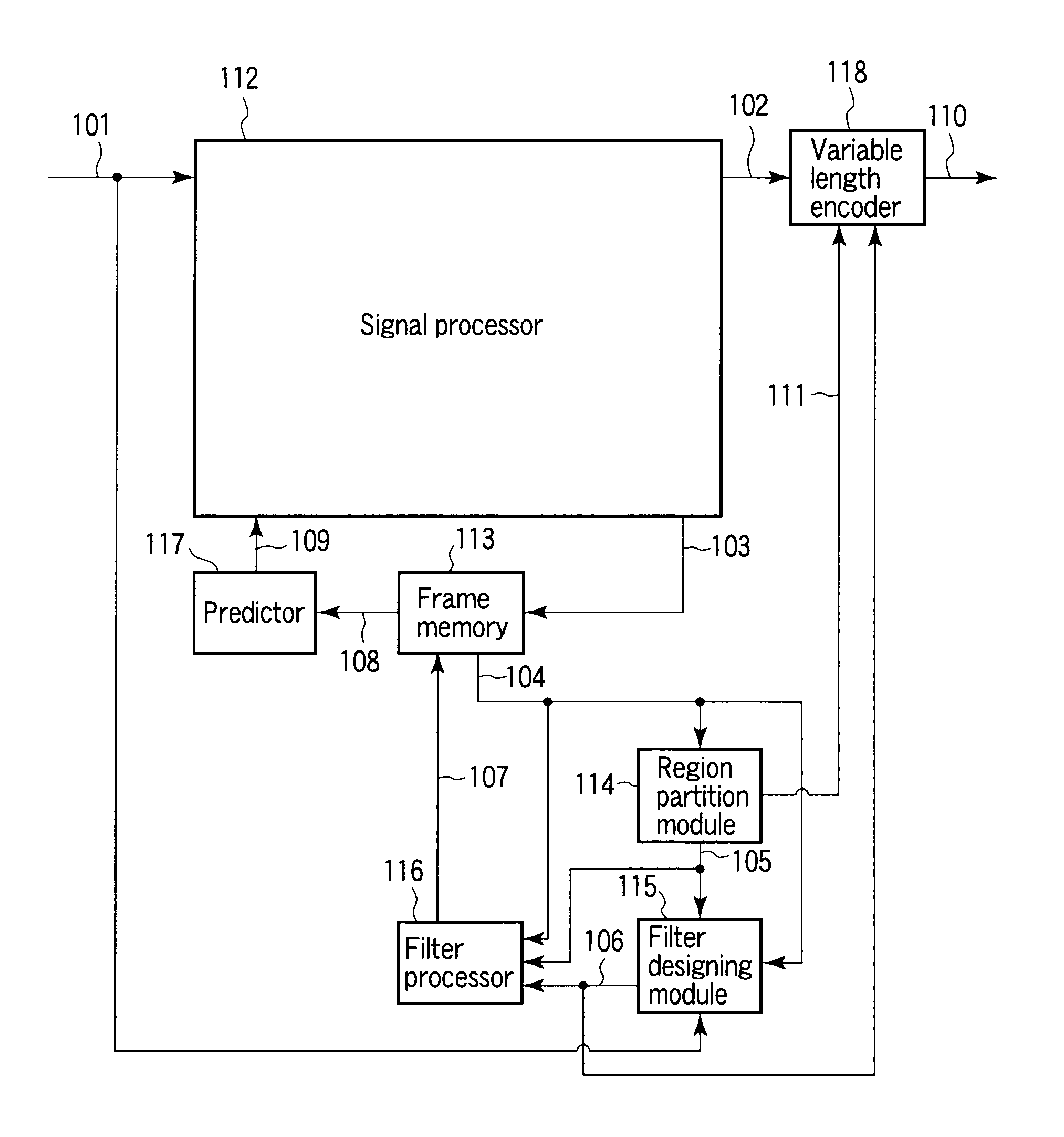
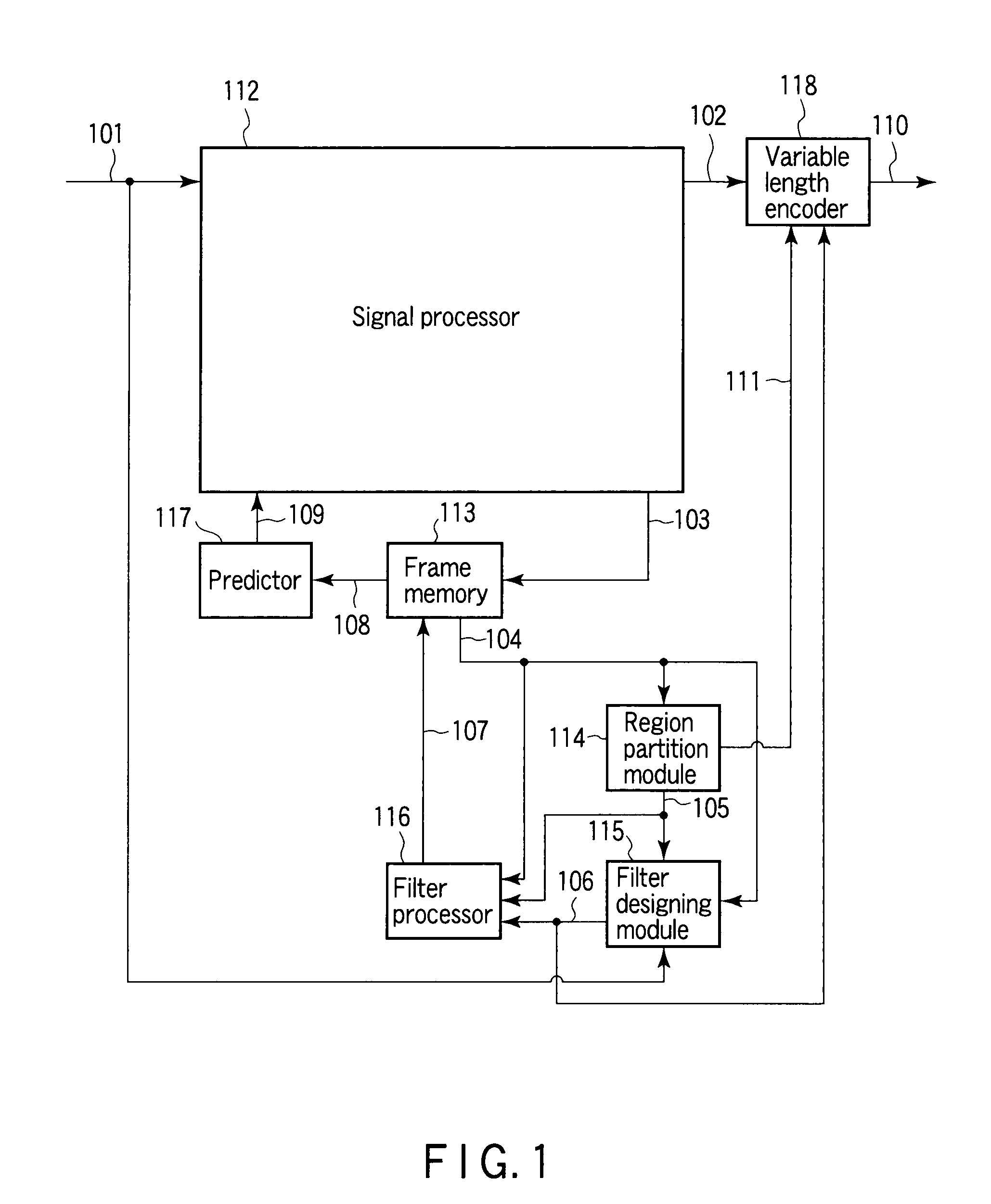
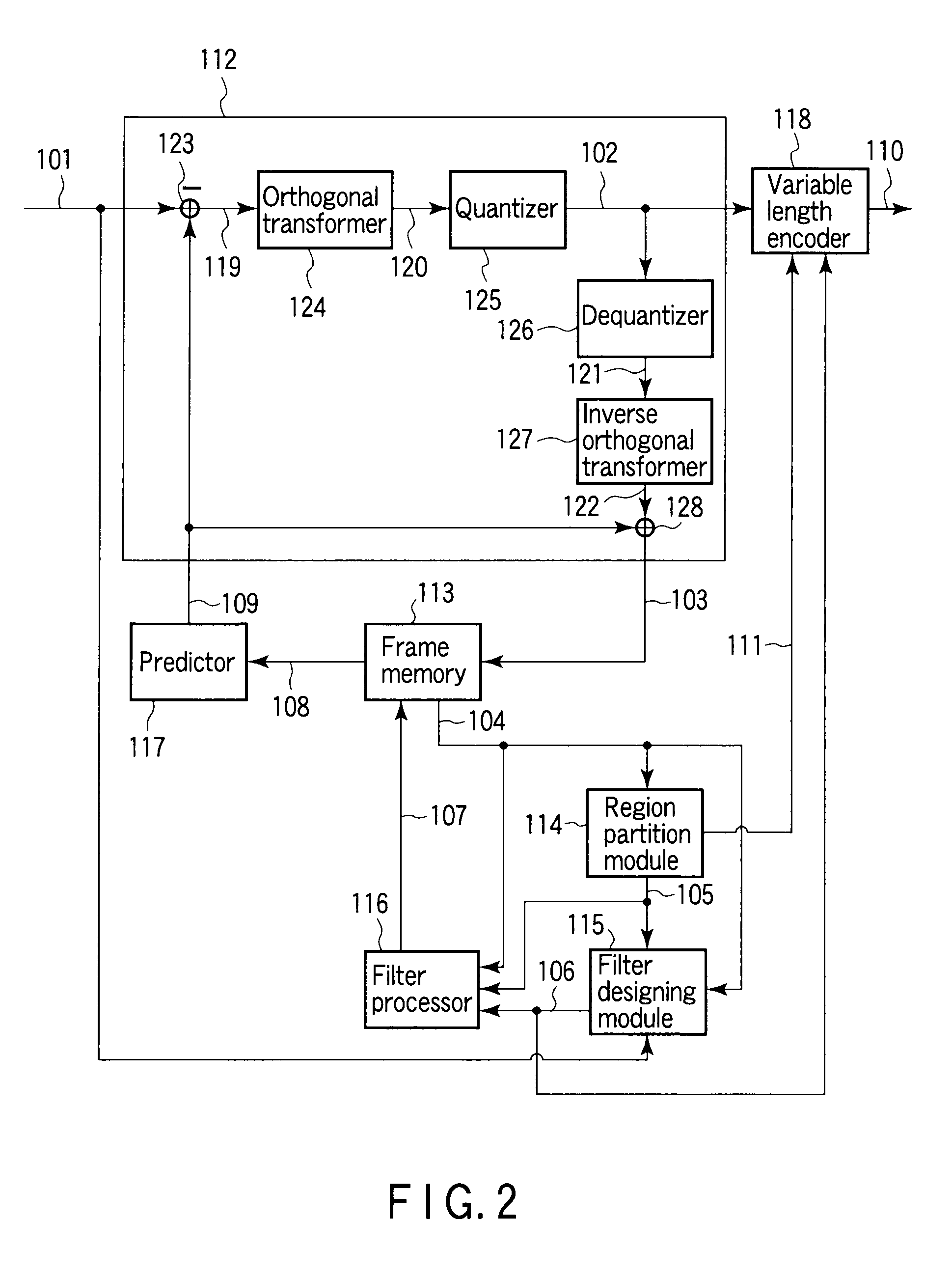
An image processor to produce a local decoded image corresponding to an input image, a region partitioning module to classify the local decoded image into a plurality of regions using a given parameter, a filter designing module to design a filter coefficient for every classified region, a filter processor to filter the local decoded image according to a corresponding filter coefficient for every classified region, a frame memory to store a filtered image, a predictor to produce a prediction image using a stored image, and an encoder to output a parameter used for classification of the region and information of a filter coefficient every classified region as encoded data are provided.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Data adaptive ramp in a digital filter
InactiveUS20020136288A1Analogue/digital conversionMultiple-port networksFrequency spectrumData stream
A system and method for improving the performance of digital filters is disclosed. The data bandwidth and spectral control are improved by adaptively selecting ramp-up and ramp-down symbols based on the actual filtered data. Thus, the energy in the truncated tail of the filter is minimized for a given filter design. The invention is of particular utility in systems that filters intermittent data streams, thus requiring the filter to energize and deenergize repeatedly.
Owner:SOAR S K LIABILITY
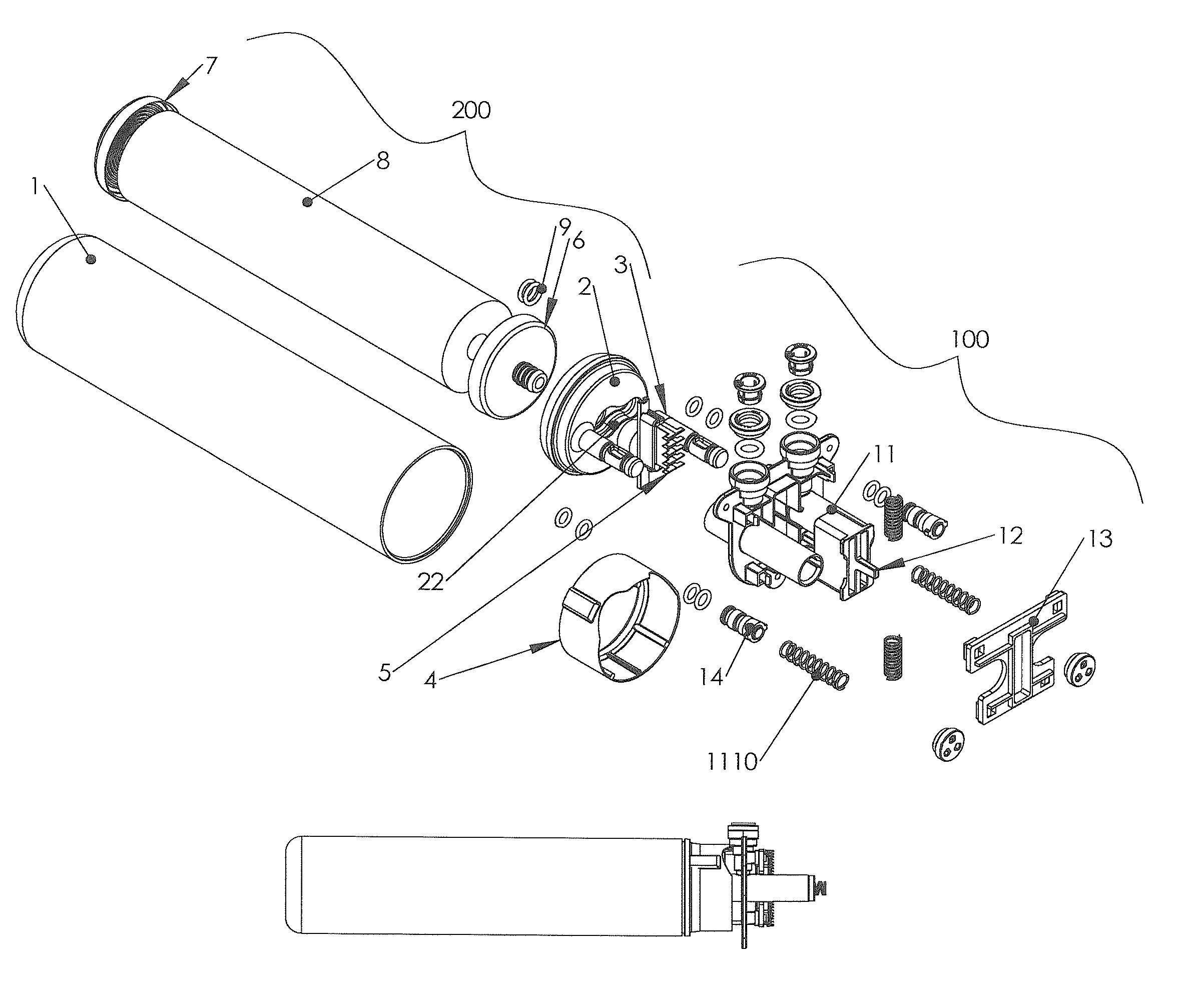
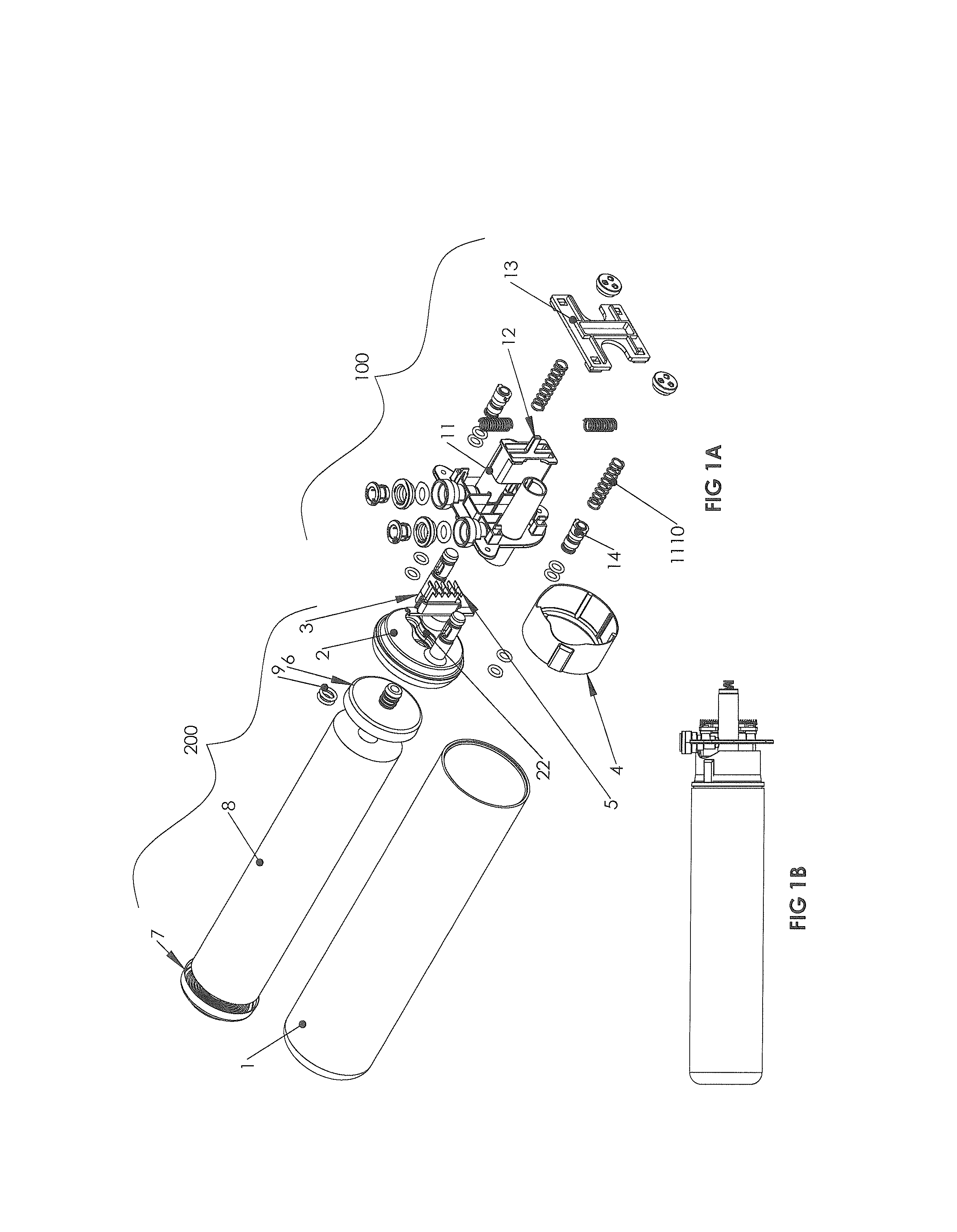
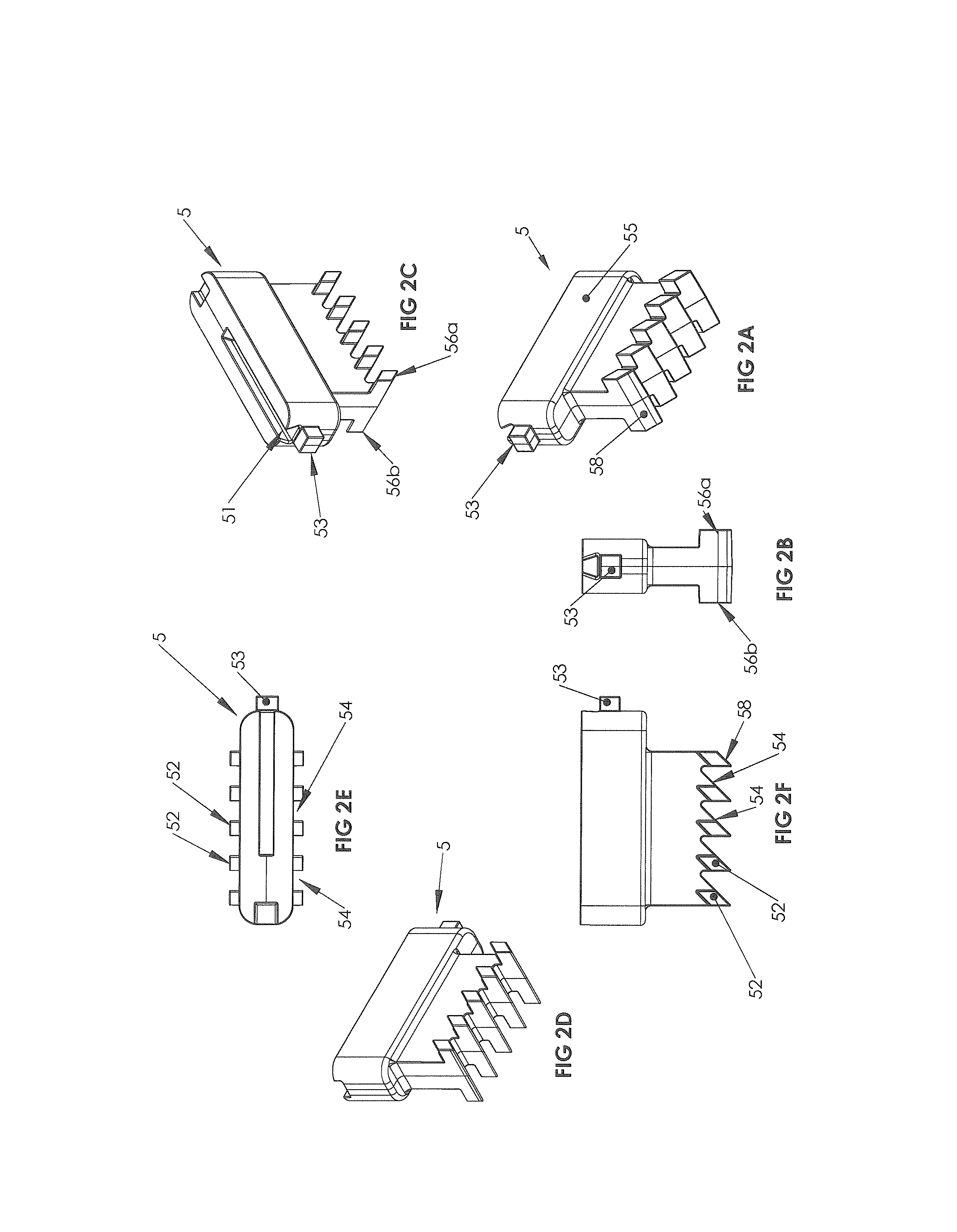
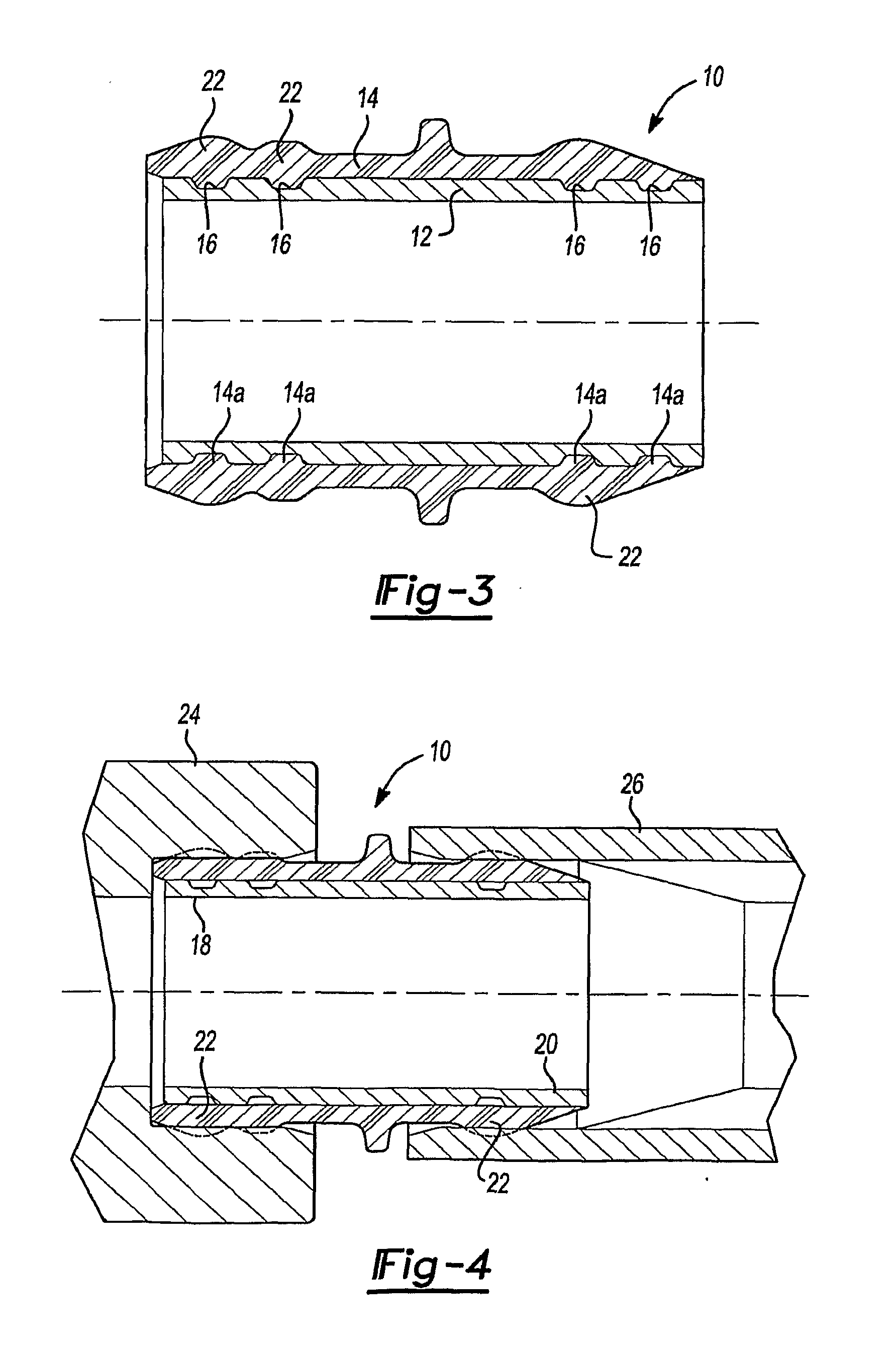
Tube Seal Components
ActiveUS20090072494A1Acceptable performanceExtra interferenceSleeve/socket jointsEngine sealsEngineeringMechanical engineering
A tube seal is provided including a rigid cylindrical tube and an elastomeric seal body molded to the outer surface of the cylindrical tube. The rigid cylindrical tube includes a recessed annular groove at each end thereof for receiving the elastomeric seal body therein to create a mechanical connection to resist the seal body from being pulled away from the cylindrical tube. The tube seal is also incorporated into a diameter reducing tube seal, an integrated tube seal and filter design and an integrated tube seal and valve design.
Owner:FREUDENBERG NOK GEN PARTNERSHIP
Electronically tunable, absorptive, low-loss notch filter
InactiveUS8013690B2Fast tuningHigh levelMultiple-port networksCoupling devicesWireless routerHybrid coupler
Owner:TERASYS TECH
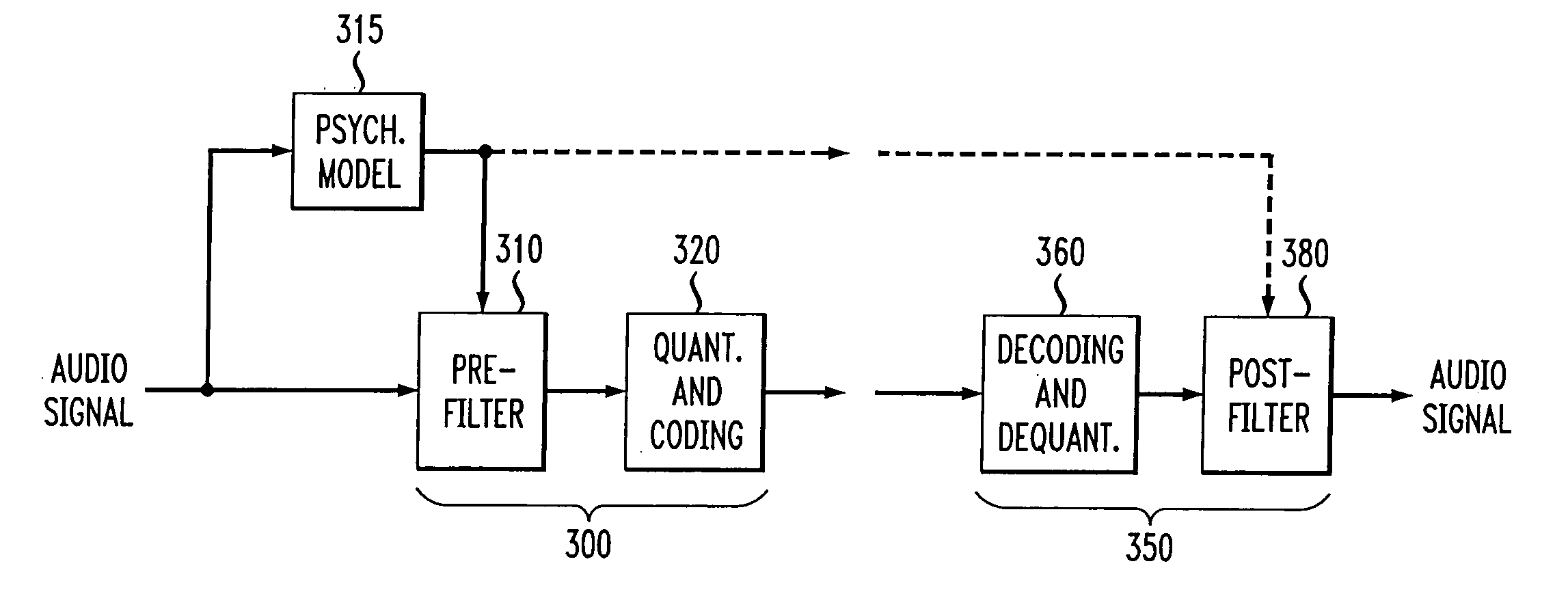
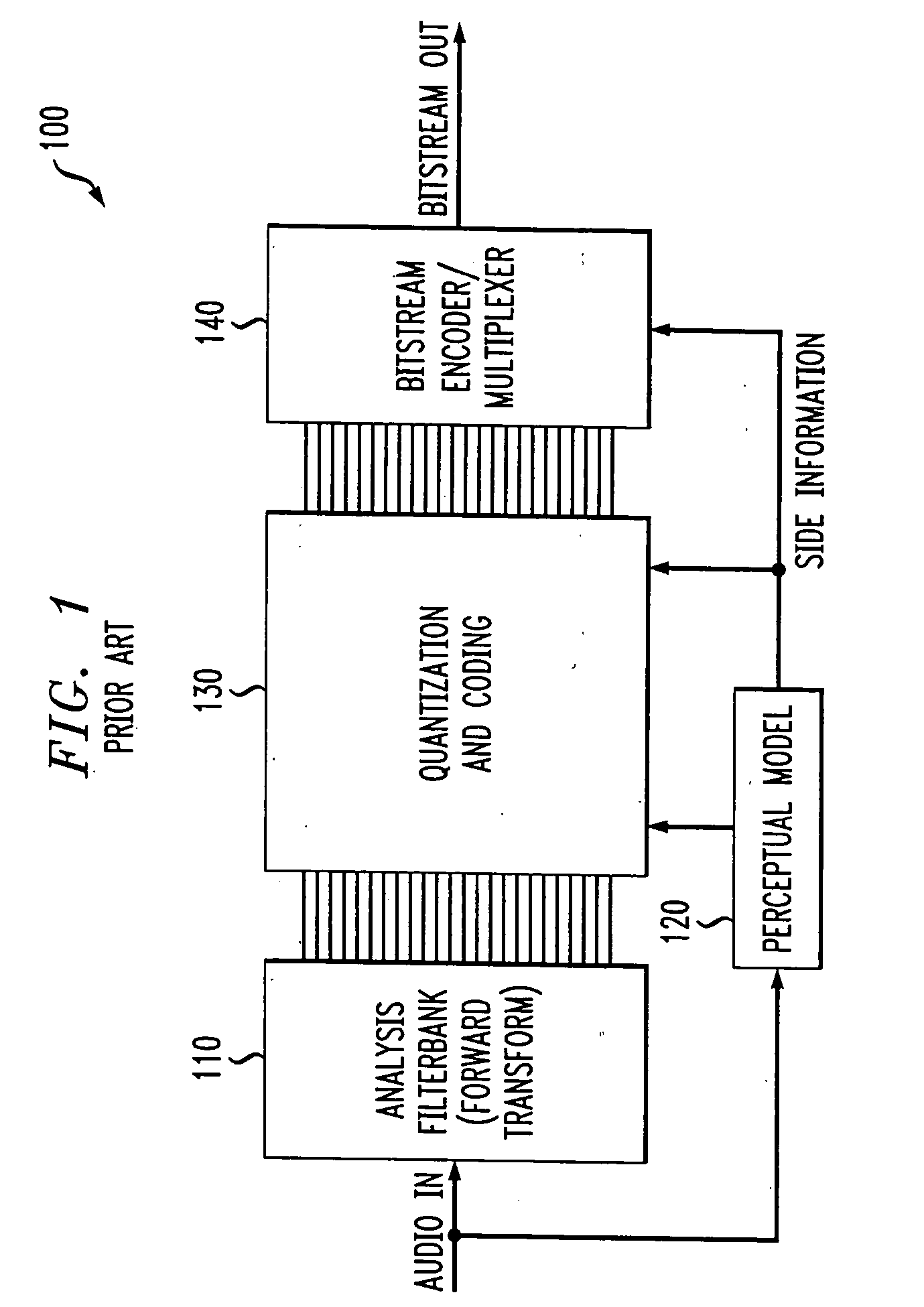
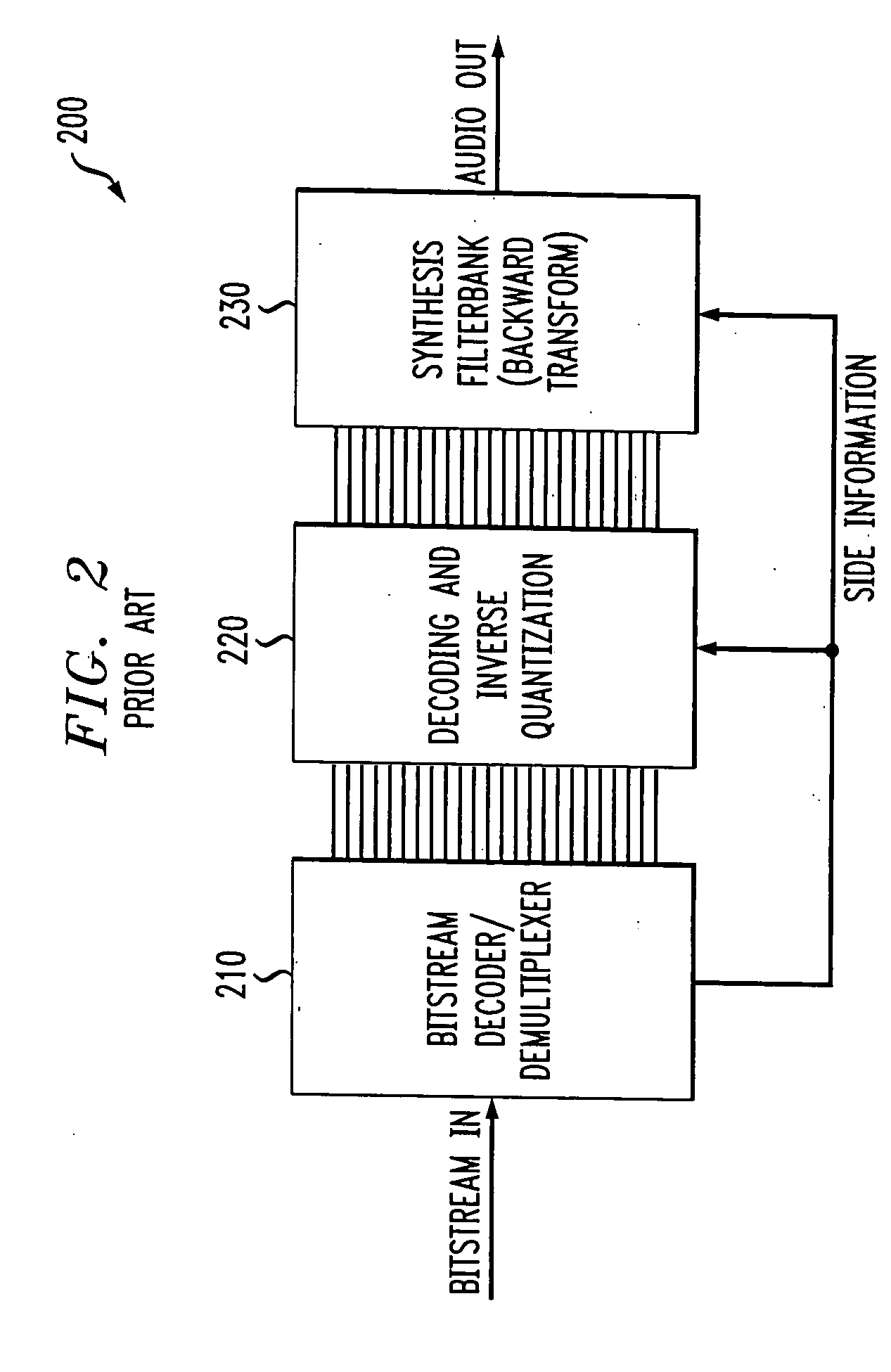
Perceptual coding of image signals using separated irrelevancy reduction and redundancy reduction
InactiveUS20060147124A1Guaranteed normal transmissionConserving transmitted bitsSpeech analysisCode conversionFrequency spectrumTemporal resolution
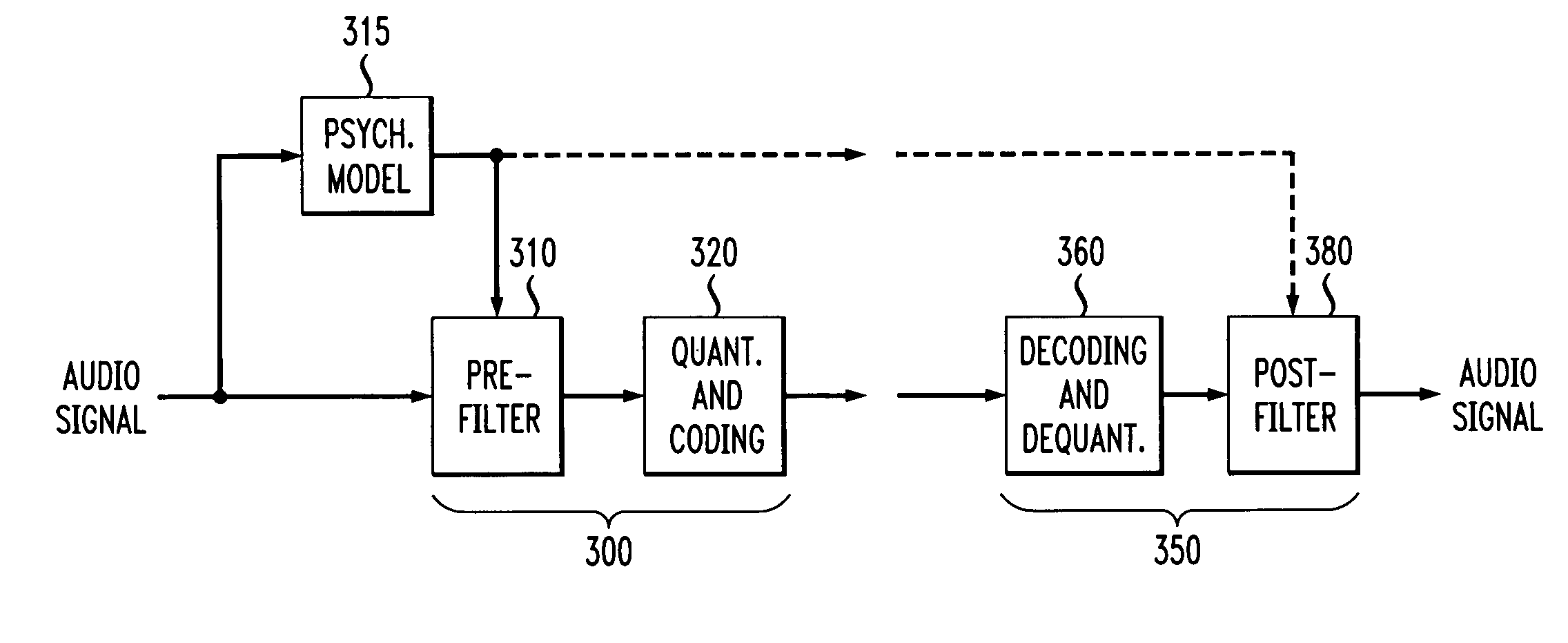
A perceptual coder is disclosed for encoding image signals, such as speech or music, with different spectral and temporal resolutions for redundancy reduction and irrelevancy reduction. The image signal is initially spectrally shaped using a prefilter. The prefilter output samples are thereafter quantized and coded to minimize the mean square error (MSE) across the spectrum. The disclosed perceptual image coder can use fixed quantizer step-sizes, since spectral shaping is performed by the pre-filter prior to quantization and coding. The disclosed pre-filter and post-filter support the appropriate frequency dependent temporal and spectral resolution for irrelevancy reduction. A filter structure based on a frequency-warping technique is used that allows filter design based on a non-linear frequency scale. The characteristics of the pre-filter may be adapted to the masked thresholds, using techniques known from speech coding, where linear-predictive coefficient (LPC) filter parameters are used to model the spectral envelope of the speech signal. Likewise, the filter coefficients may be efficiently transmitted to the decoder for use by the post-filter using well-established techniques from speech coding, such as an LSP (line spectral pairs) representation, temporal interpolation, or vector quantization.
Owner:AGERE SYST INC
Wavelet multi-resolution waveforms
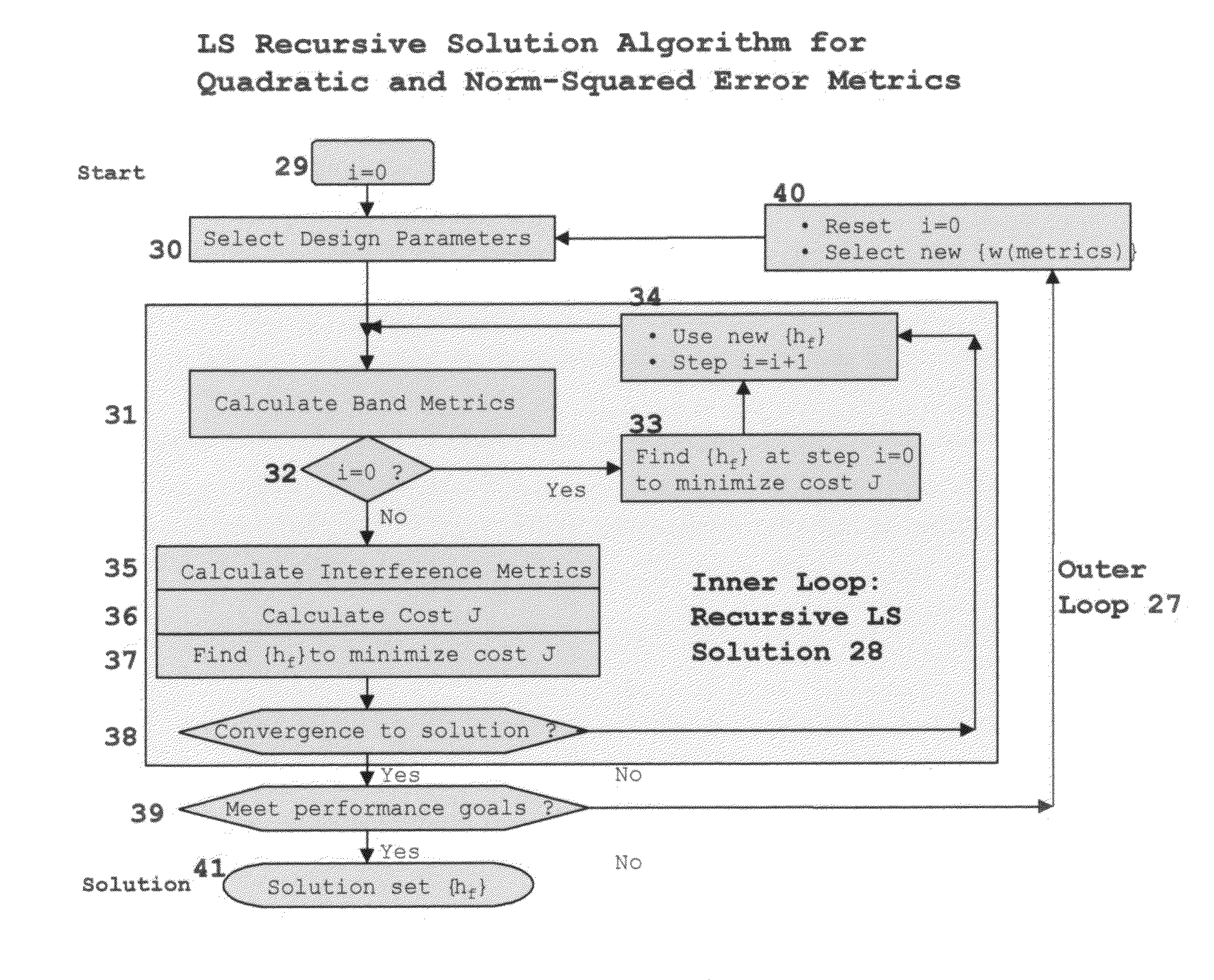
InactiveUS7376688B1Improve performanceModulated carrier system with waveletsComplex mathematical operationsFinite impulse responseSynthetic aperture radar
A method for designing Wavelets for communications and radar which combines requirements for Wavelets and finite impulse response FIR filters including no excess bandwidth, linear performance metrics for passband, stopband, quadrature mirror filter QMF properties, intersymbol interference, and adjacent channel interference, polystatic filter design requirements, and non-linear metrics for bandwidth efficient modulation BEM and synthetic aperture radar SAR. Demonstrated linear design methodology finds the best design coordinates to minimize the weighted sum of the contributing least-squares LS error metrics for the respective performance requirements. Design coordinates are mapped into the optimum FIR symbol time response. Harmonic design coordinates provide multi-resolution properties and enable a single design to generate Wavelets for arbitrary parameters which include dilation, down-sampling, up-sampling, time translation, frequency translation, sample rate, symbol rate, symbol length, and set of design harmonics. Non-linear applications introduce additional constraints. Performance examples are linear communications, BEM, and SAR.
Owner:VON DER EMBSE URBAIN A
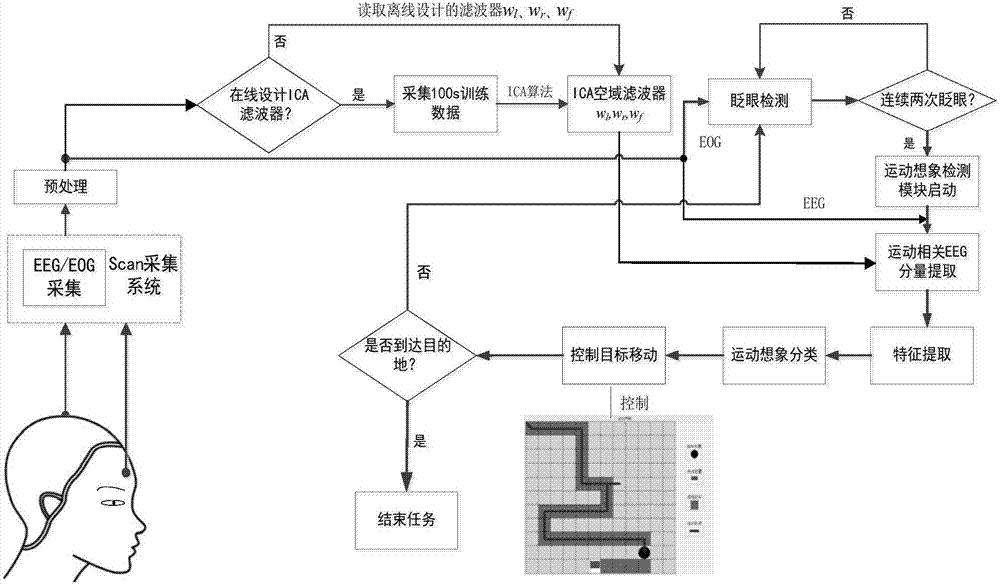
Hybrid brain-computer interface system and method based on movement imagination
InactiveCN107037883AImprove interactivityImprove practicalityInput/output for user-computer interactionGraph readingSystems designOperability
The invention discloses a hybrid brain-computer interface system and method based on movement imagination. The system comprises an electroencephalography and electrooculogram collection / processing module, an ICA filter design module, a zero-training MI classification module, a target movement control and path display module and an information feedback module. An ICA filter and a BCI system can be designed on line or off line; and after system design is completed, an eye movement detection module judges whether to get into a electroencephalography processing and classifying mode through analysis of the number of blinks of a user, and the classification result is converted into a command used for controlling a target on a system main interface to move along a specified path. The user can observe the difference between a true movement trace of the target and a planned path, adjust the MI mode in time and control the target to return to the planned path. By aid of the advantages of ICA unsupervised learning, the collection amount of BCI training data is effectively reduced, and through reasonable algorithm module design, the designed hybrid BCI system has good stability and operability.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY
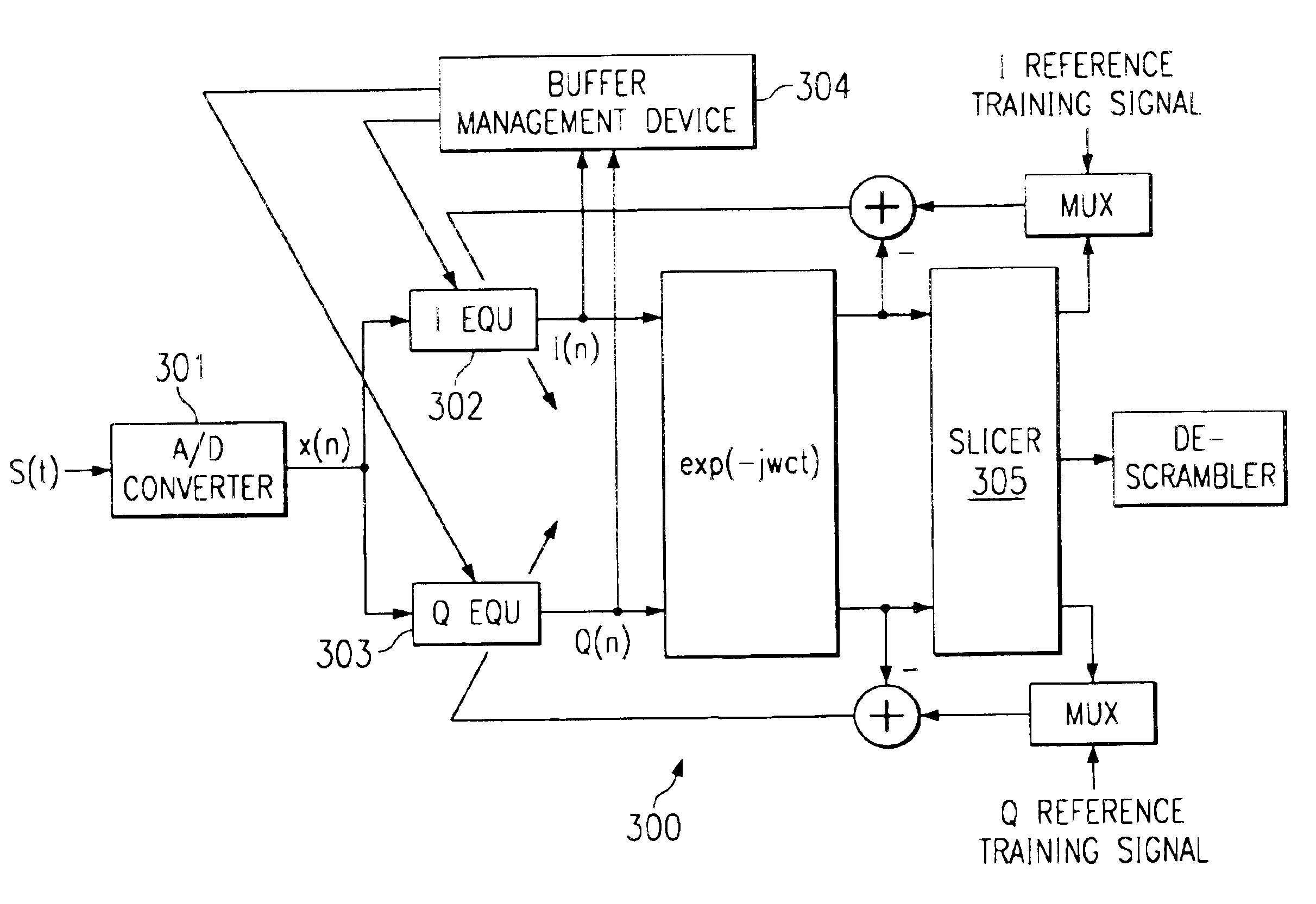
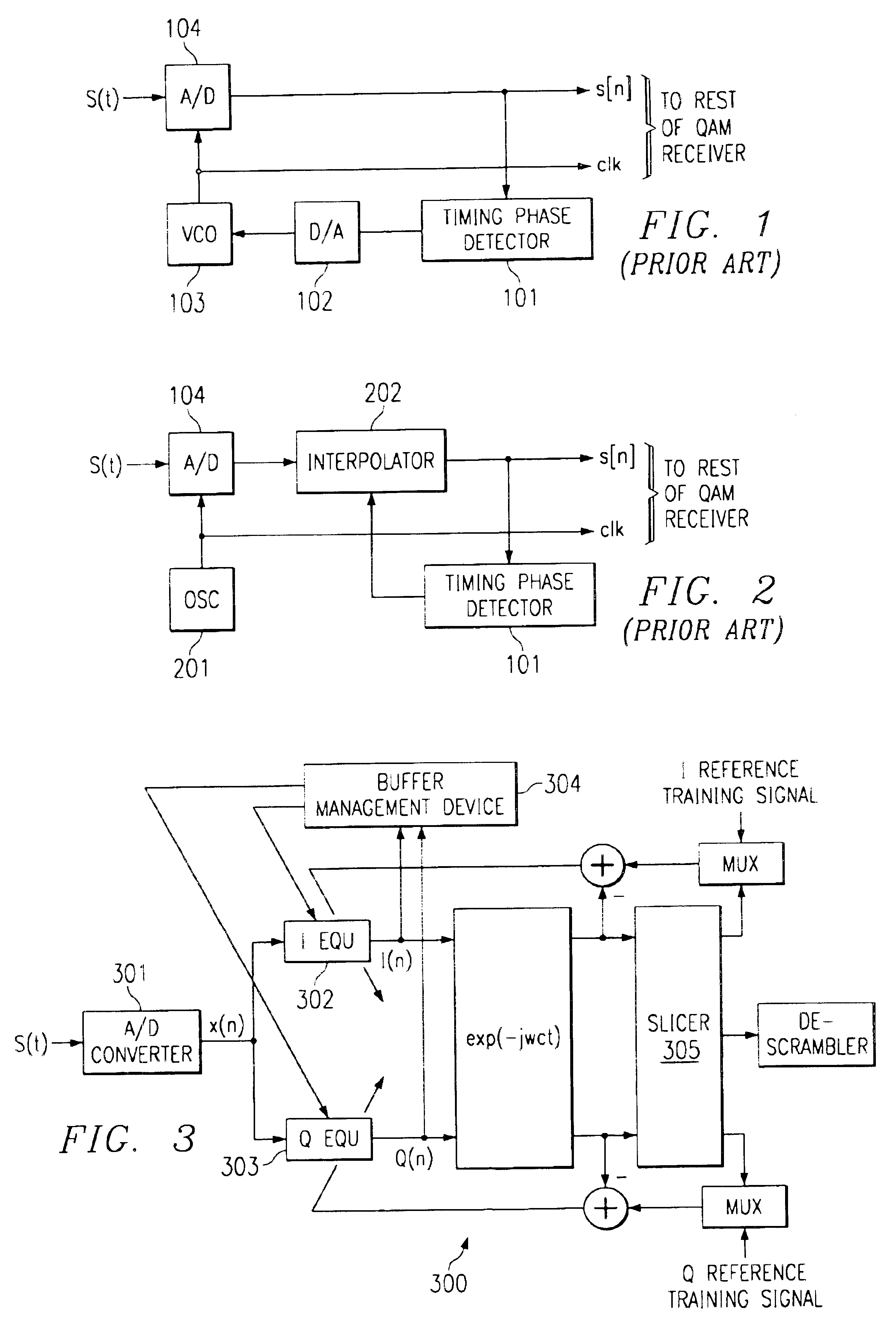
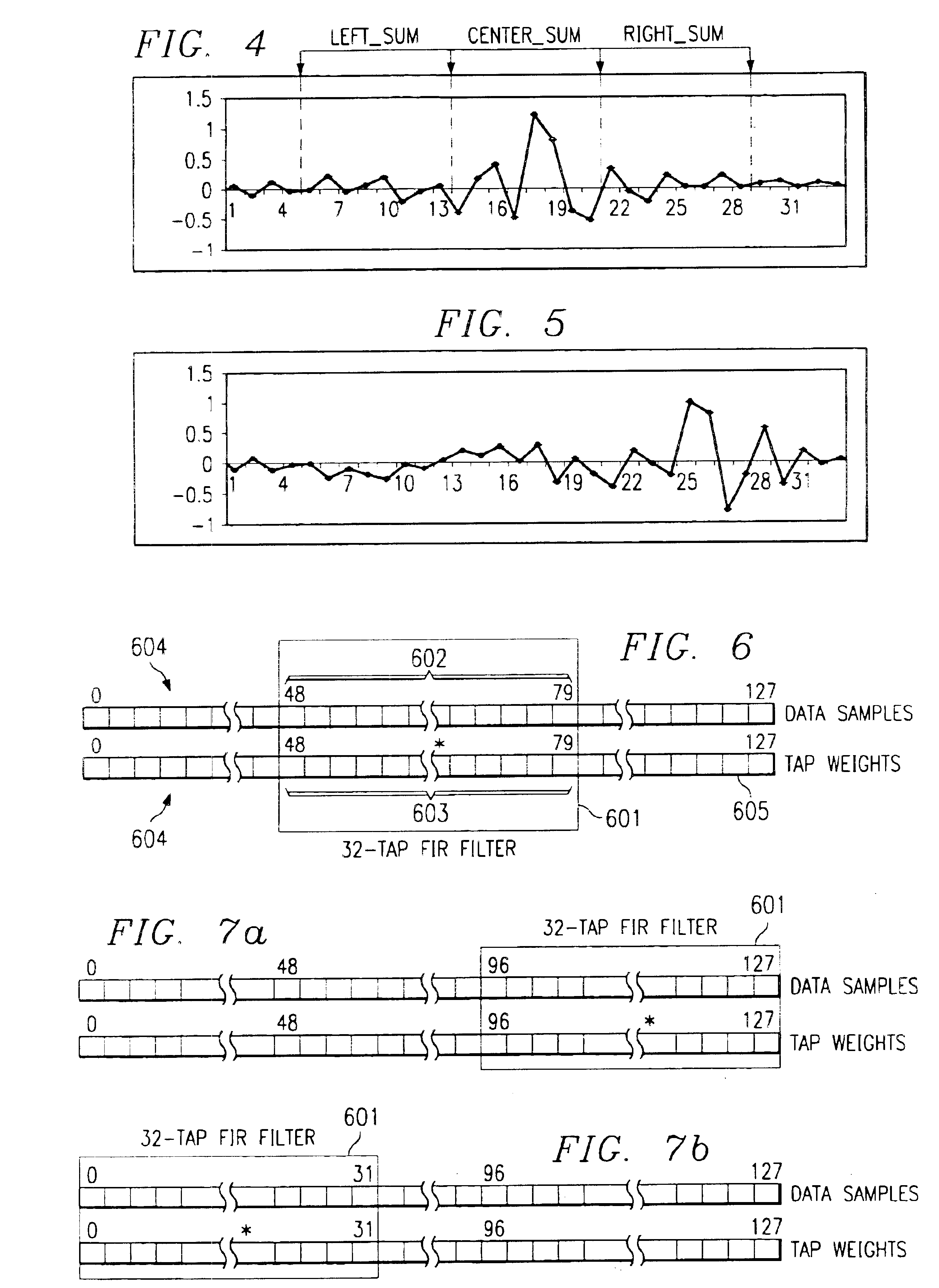
Timing recovery device and method for telecommunications systems
InactiveUS6856655B1Avoid driftingModulated-carrier systemsSynchronisation error detectionQam modulationComputer science
A timing recovery device for CAP / QAM modems includes an equalizer filter designed to monitor the movement of the filter coefficients within a memory buffer and to adjust the relative position of the filter coefficients within the memory buffer so that the coefficients remain substantially centered within the buffer.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Multi-feed antenna for path optimization
ActiveUS8648756B1Optimal component selectionImprove antenna performanceSimultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsTransceiverActive component
An antenna comprised of multiple feed ports with independent tuning of the antenna at each feed port to optimize the impedance match between the antenna and transceivers connected to the ports. Filters designed into one or several of the feed ports to provide isolation between the multiple ports and to adjust the frequency response at each port. One or multiple active components connected to the feed ports to provide dynamic tuning of the coupled or driven elements.
Owner:KYOCERA AVX COMPONENTS (SAN DIEGO) INC
Method and circuit for controlling changing cyclic width lag cyclic current of inventer
InactiveCN1858982AImprove stabilityFast dynamic performanceAc-dc conversionPower inverterFrequency spectrum
This invention discloses a controlling method to inverters of width sluggish loop current by changing the loop width and a circuit, in which, the method includes: 1, computing loop width to get a signal of the width of a sluggish loop, 2, sending said signal to a comparison segment of a changed loop width and the sluggish loop, the other input volume of which is the current error signal of the inverter, the comparison segment carries logic operation to get a pulse width modulation waveform to drive the operation of the master circuit switch of the inverter, its circuit is a loop width adjusting circuit and a changed loop width and sluggish loop comparator, which maintains the character of the traditional fixed loop width sluggish loop current control and realizes the constant switch frequency of the inverter controlled by the sluggish loop current.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Perceptual coding of audio signals using separated irrelevancy reduction and redundancy reduction
InactiveUS7110953B1Conserving transmitted bitsGuaranteed normal transmissionSpeech analysisCode conversionFrequency spectrumTemporal resolution
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
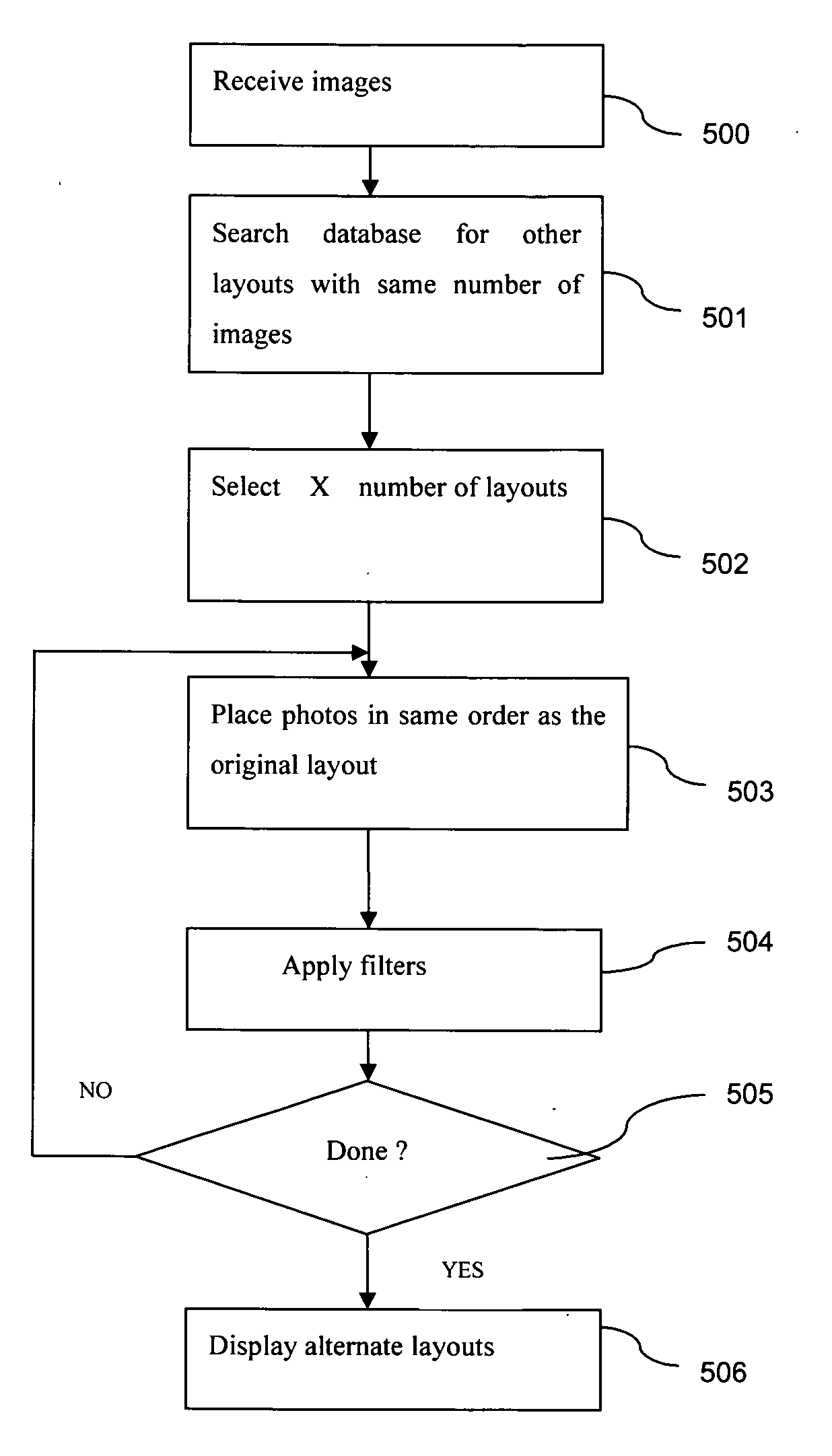
Automatic creation of alternative layouts using the same selected photos by applying special filters and/or changing photo locations in relation to creating the photobook
InactiveUS20110213795A1Still image data indexingSpecial data processing applicationsComputer graphics (images)Digital image
A system and a method are disclosed for generating photo books using digital images by using pre-assigned templates and pre-assigned filters designed for a particular type of an event, such as weddings and portraits. The placement of the photos and subsequent processing of the photos using pre-defined templates and filters wherein by intelligently selecting and creating page spreads based on limited user information of a number of photos in a single page layout. Based on an original layout, present system and method provides alternate layouts wherein the same images are filtered and / or locations of the images are changed.
Owner:LEE KENNETH KUN +1
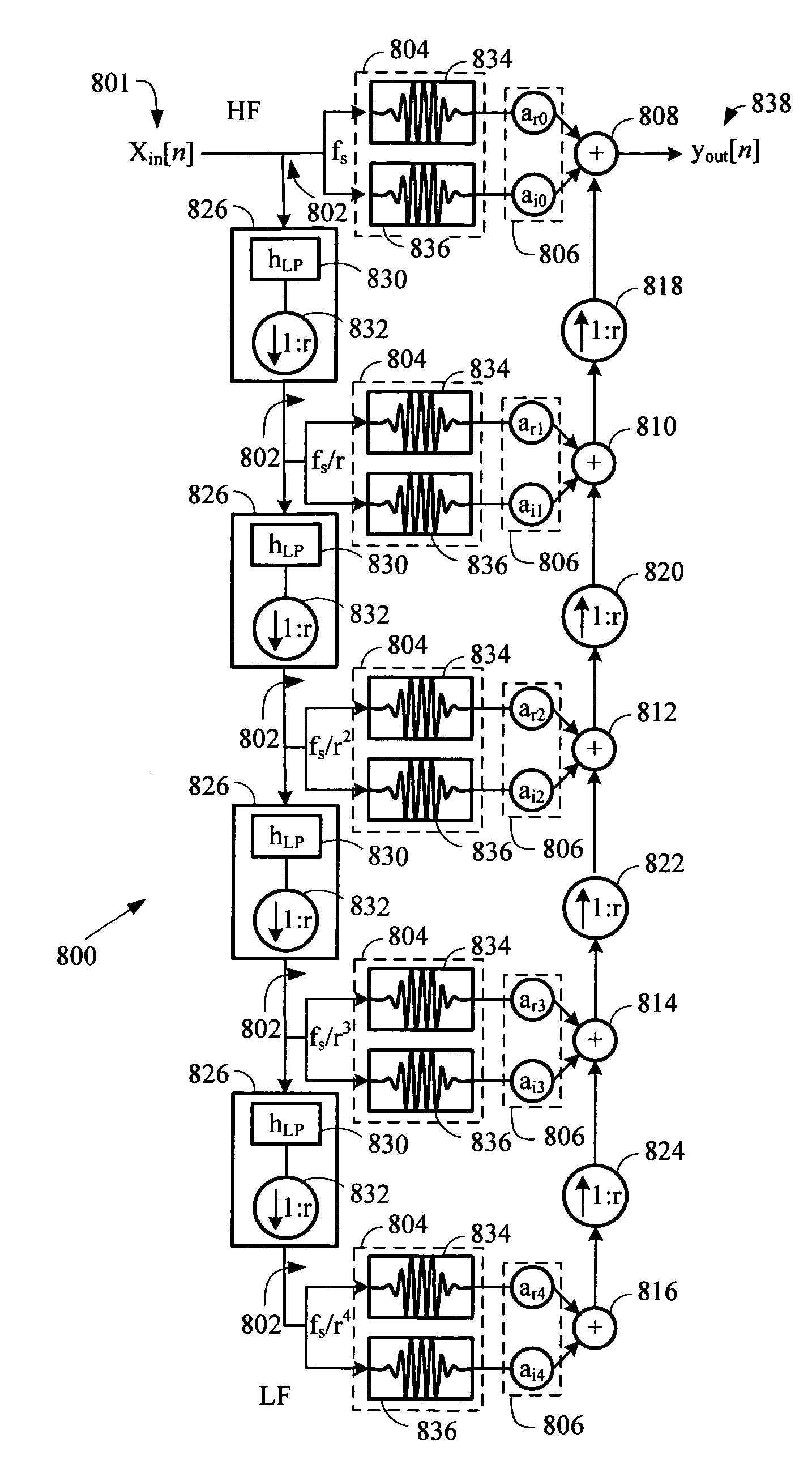
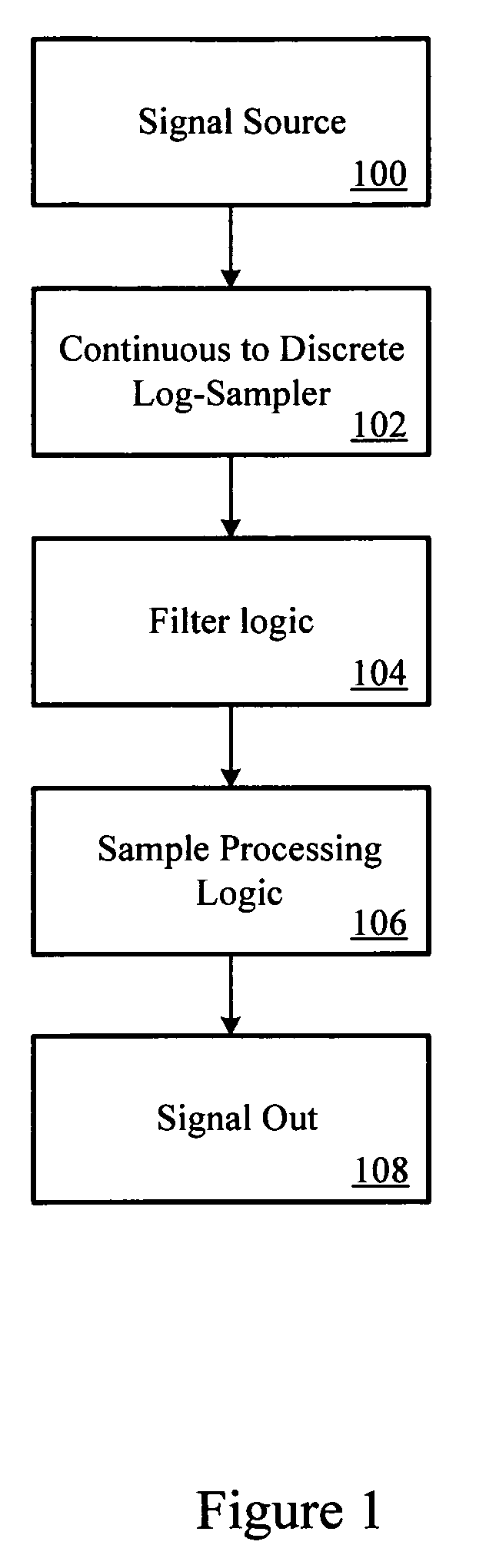
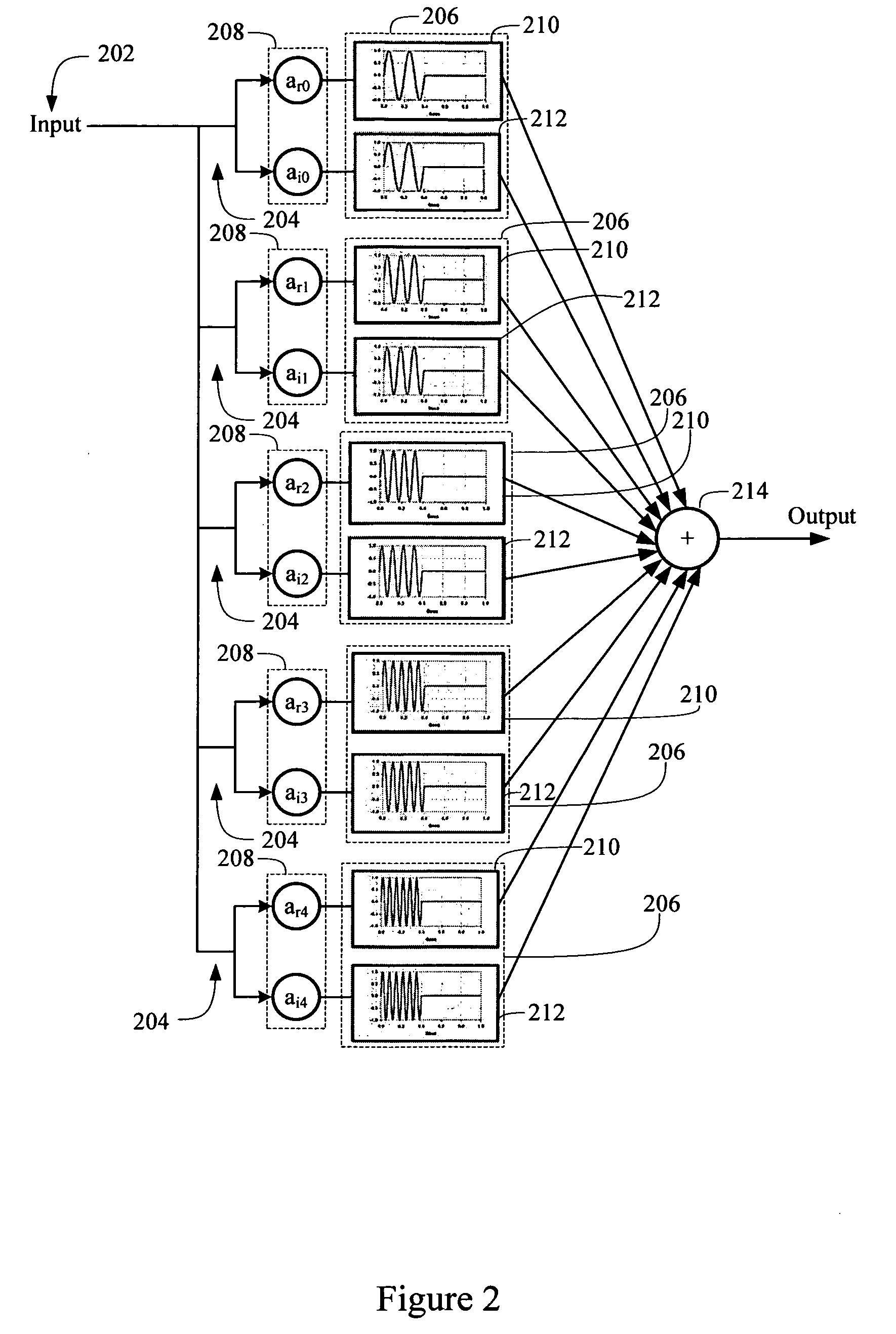
Log-sampled filter system
Owner:HARMAN INT IND INC
Cabinet design of filter holder for pressurized coffee machines
This invention provides a brewing head unit of a coffee machine for inserting and locking the filter and the filter holder into the brewing head of a coffee machine. The filter and the filter holder can be inserted into the coffee machine visually. This invention further provides a simpler and easier method for inserting filter holder into a pressurized coffee machine. This invention also provides a cabinet filter holder which can be inserted or placed into the brewing head assembly / unit of a coffee machine by sliding the filter holder into the brewing head unit from front or side; by swinging the filter holder into the brewing head assembly / unit on a pivot; or by inserting the filter holder from the top. This invention further provides a brewing head assembly / unit wherein the locking mechanism is motor-driven. In one aspect of this invention, the method for opening and closing the brewing head assembly / unit of the coffee machine can be operated by remote control. This invention further provides a cabinet filter design wherein the boiler or heating system is separated from the brewing head assembly / unit.
Owner:ELECTRICAL & ELECTRONICS LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com