Patents
Literature
28752results about "Code conversion" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
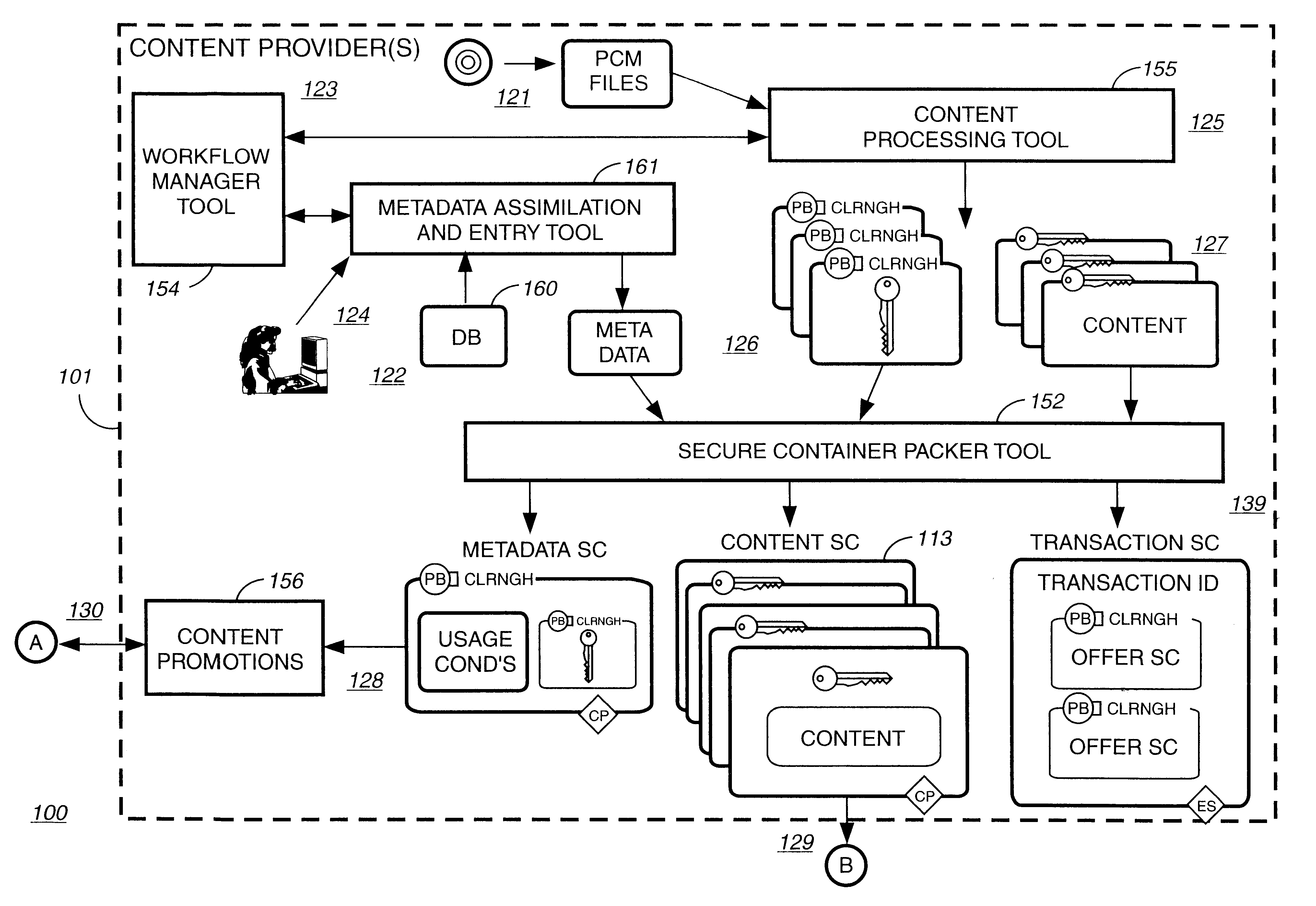
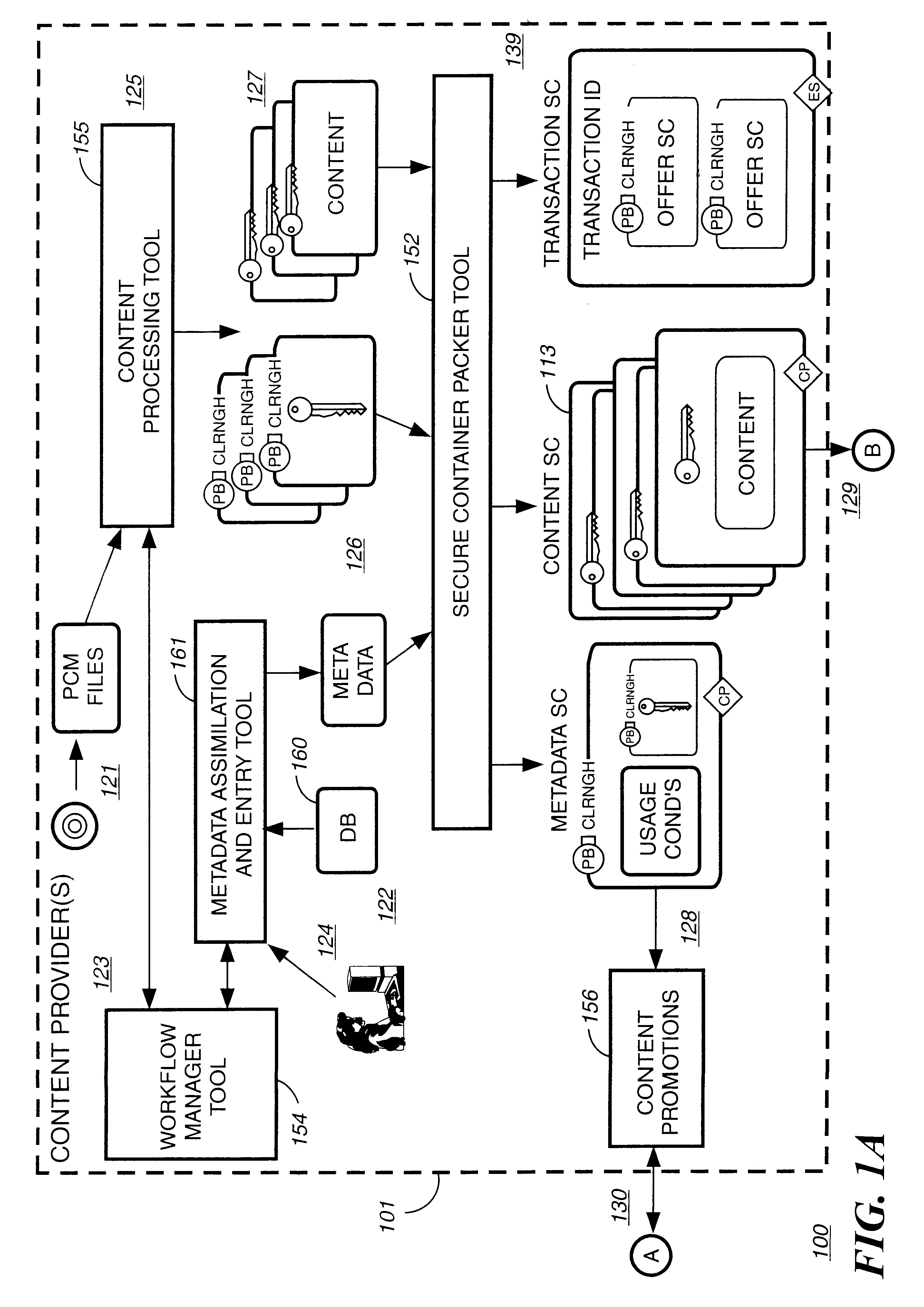
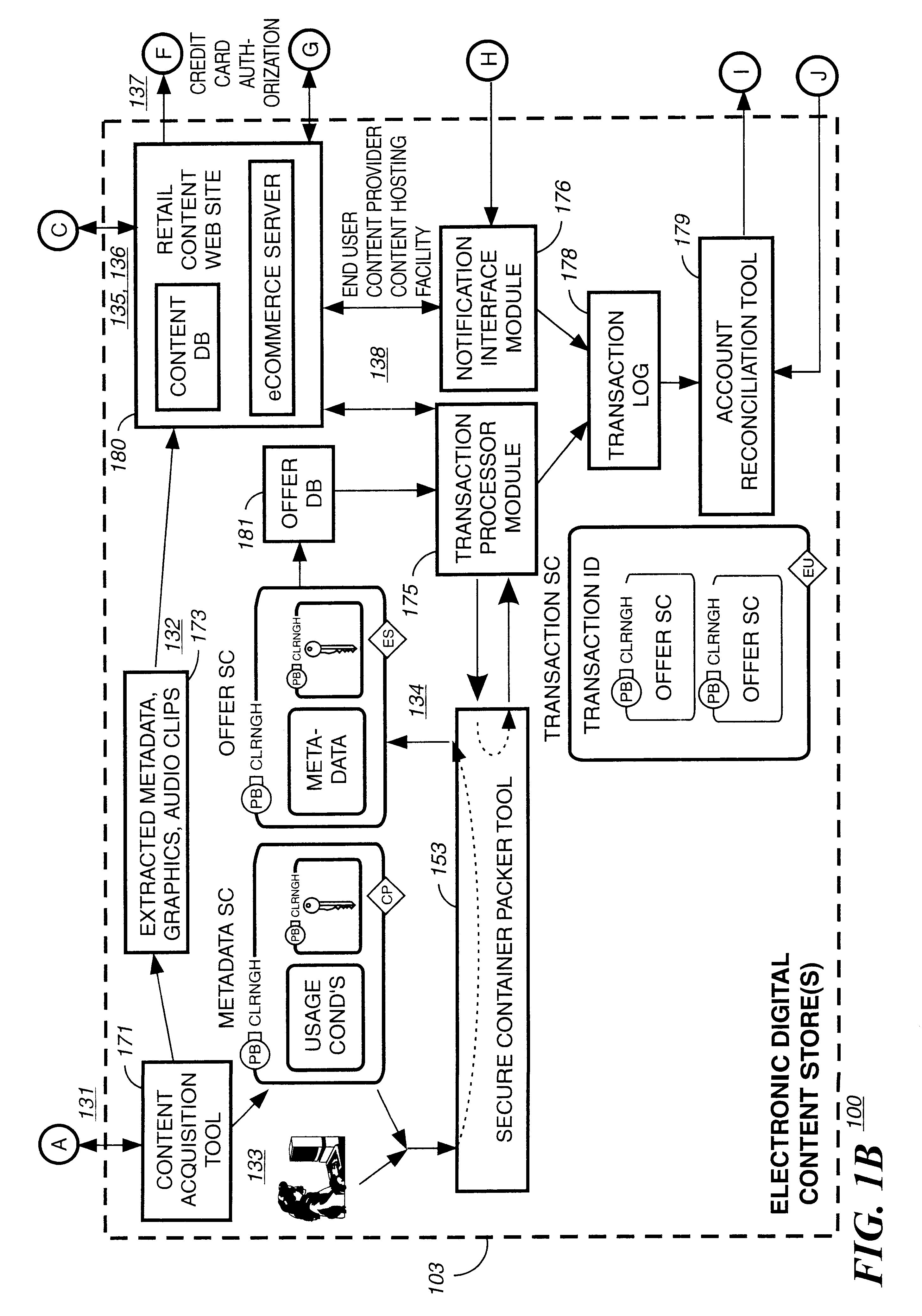
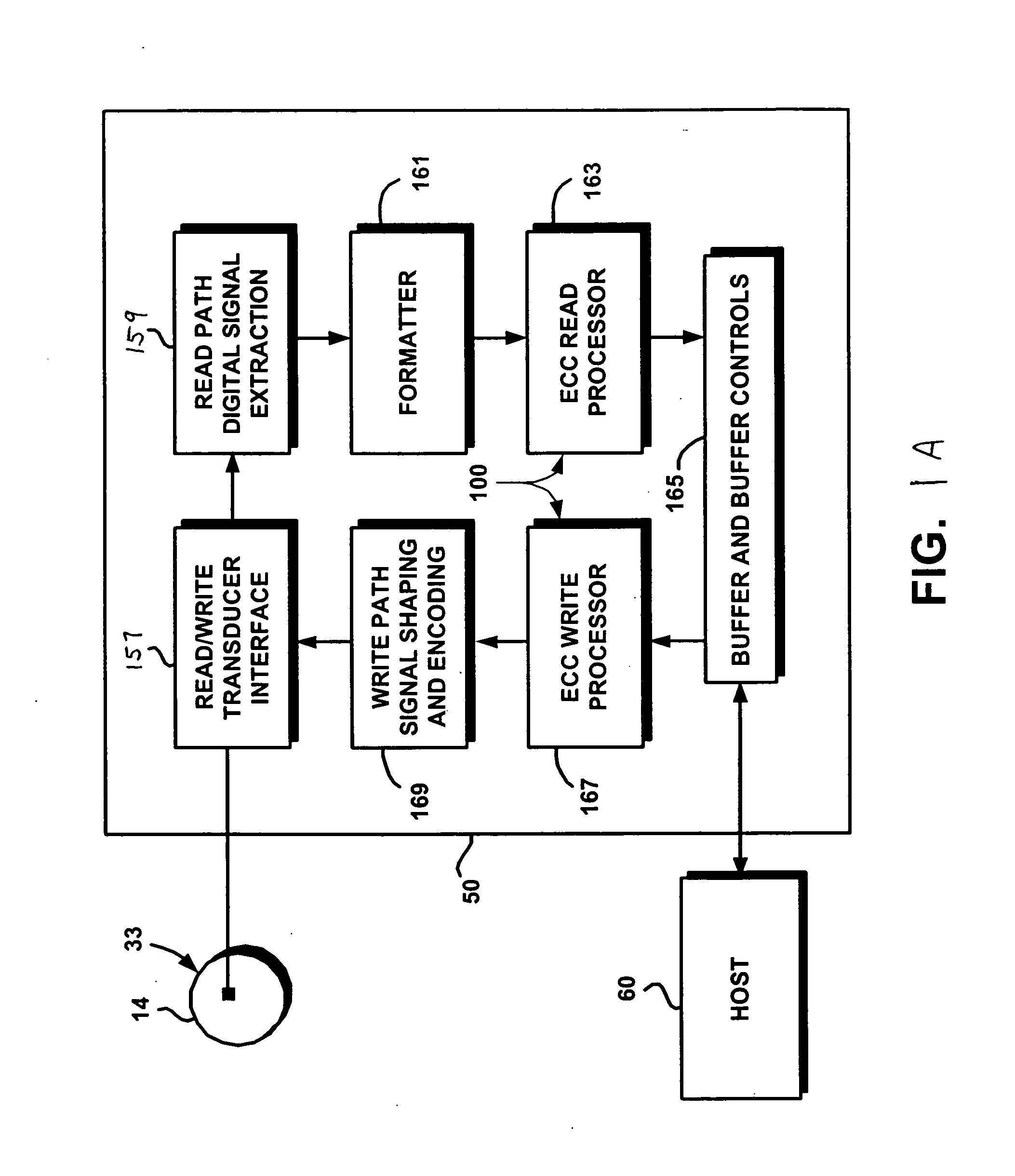
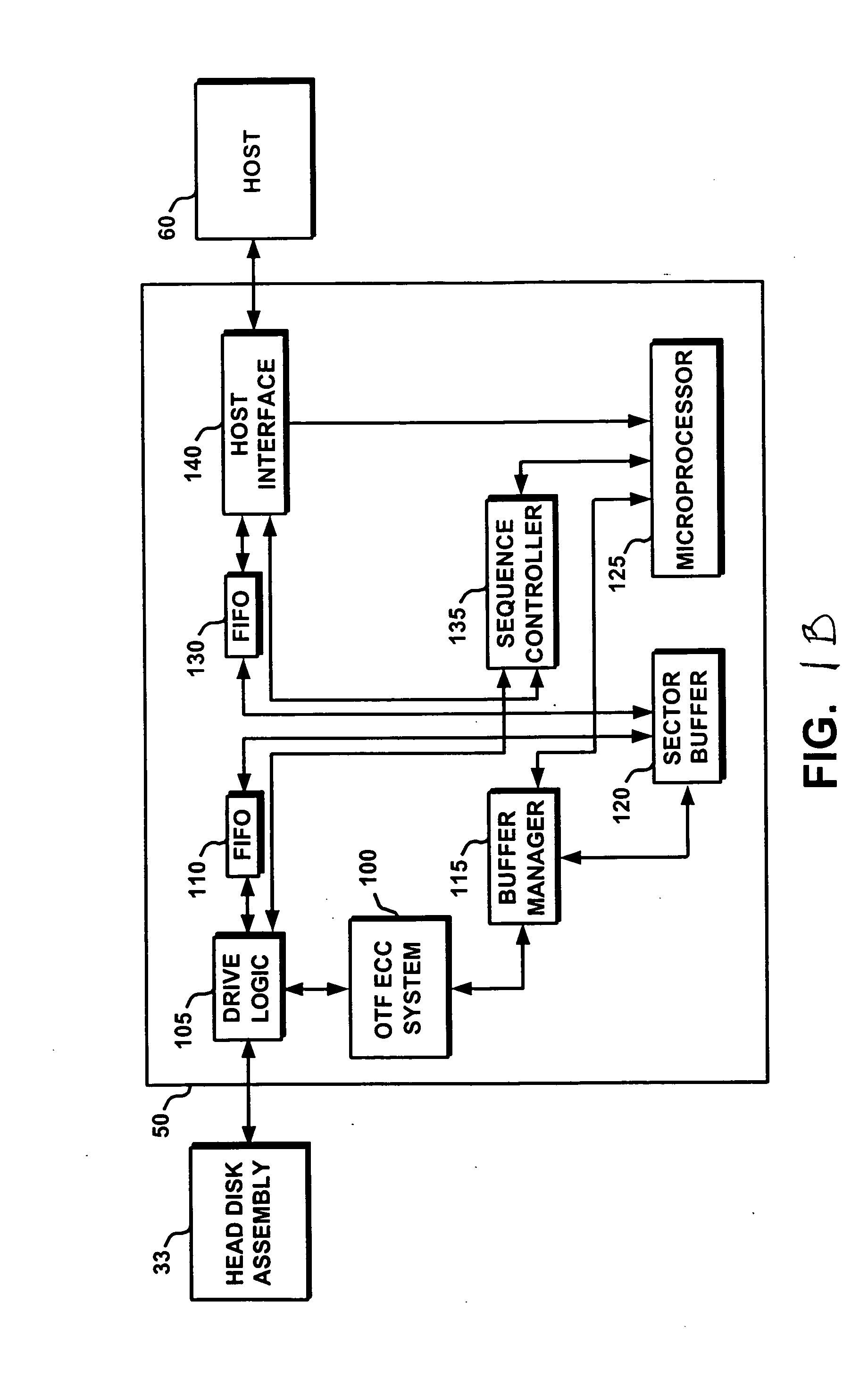
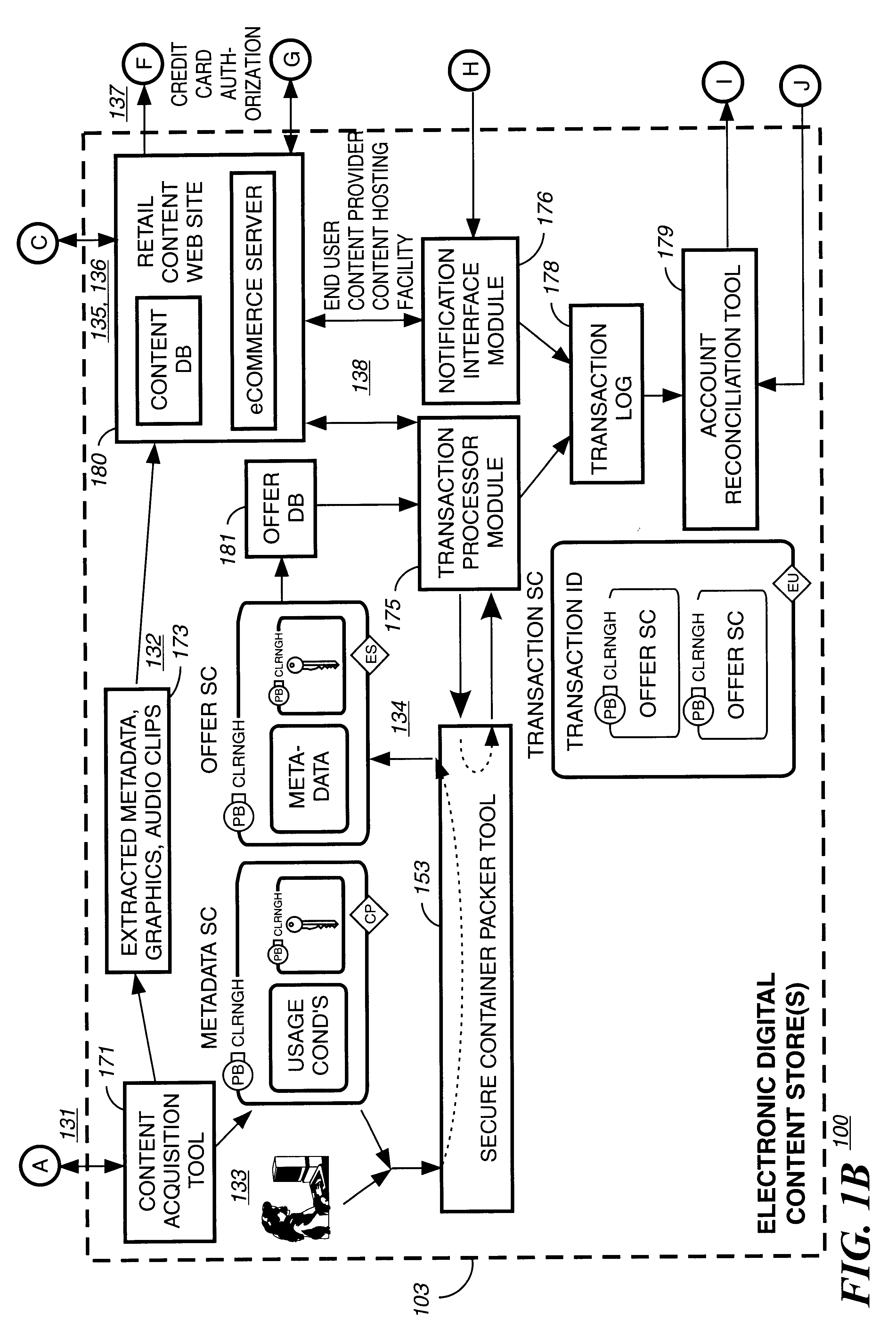
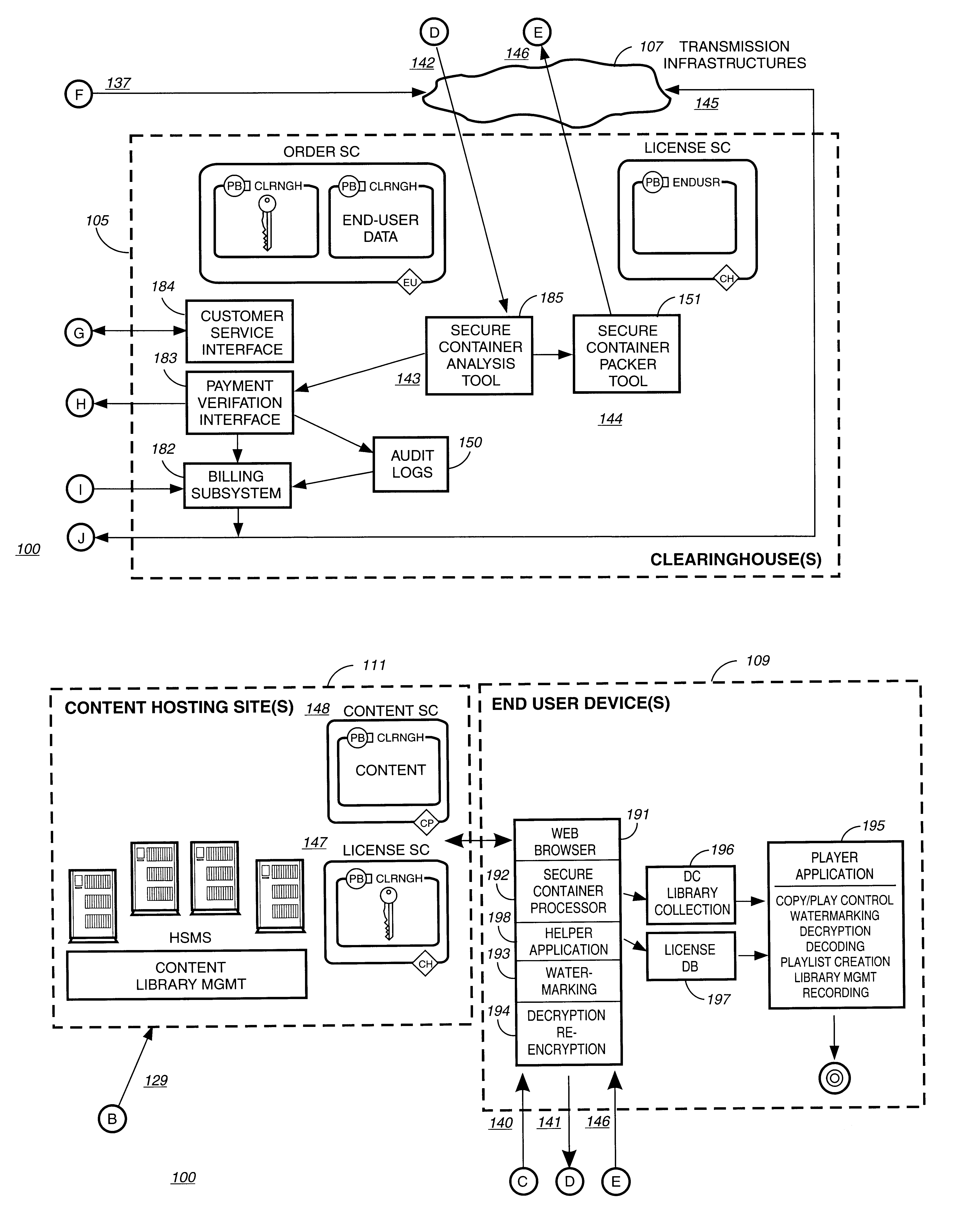
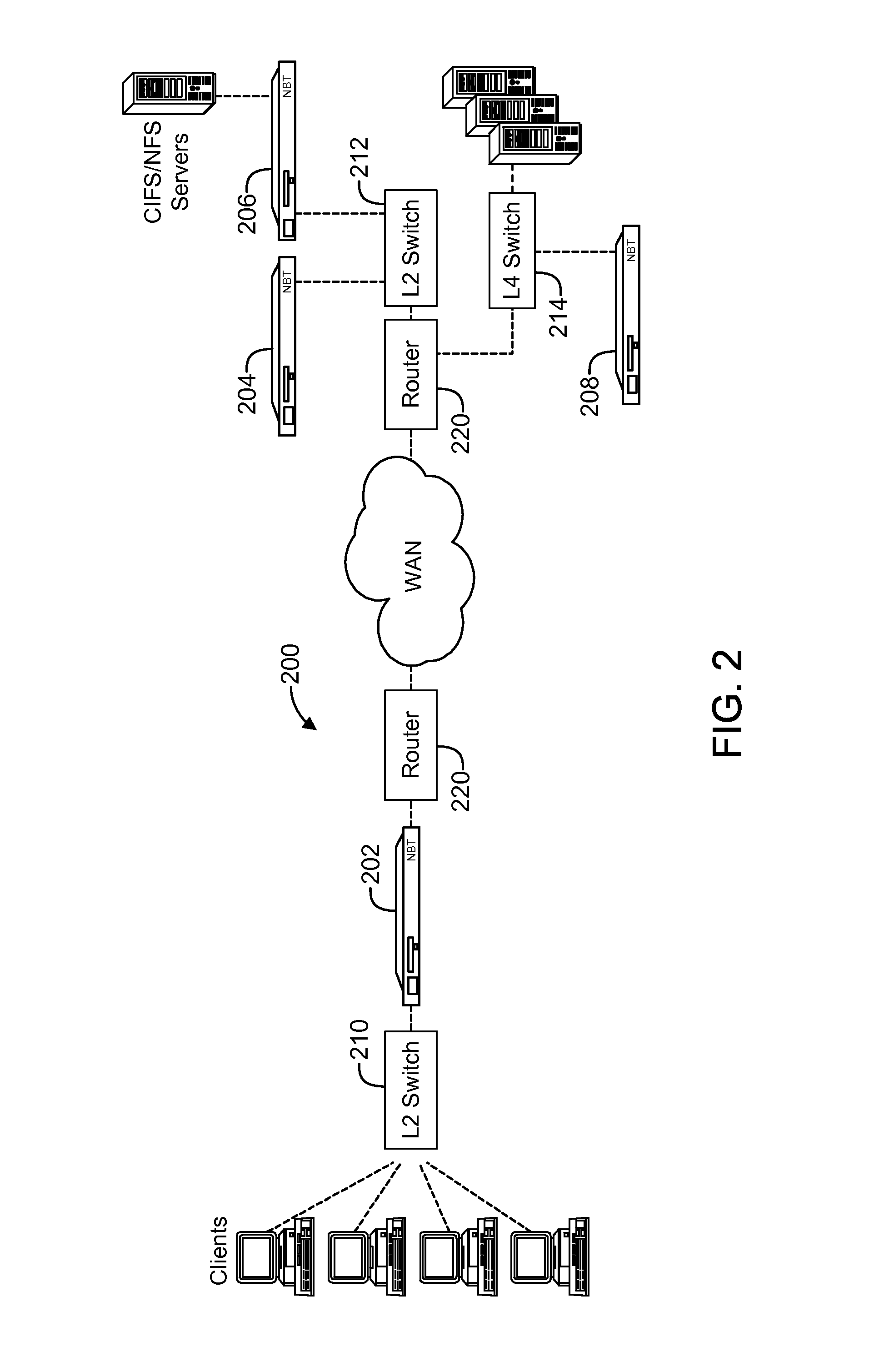
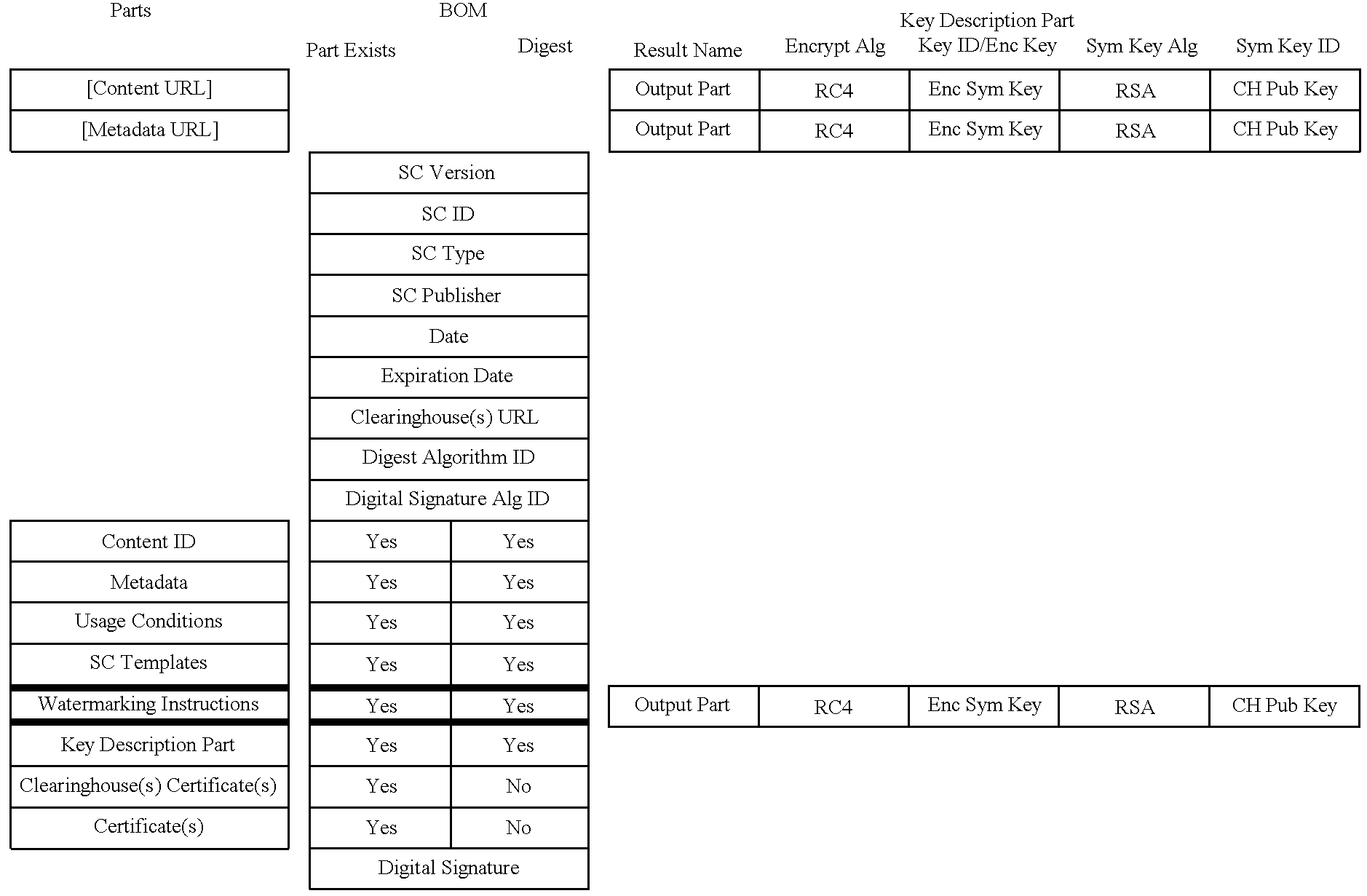
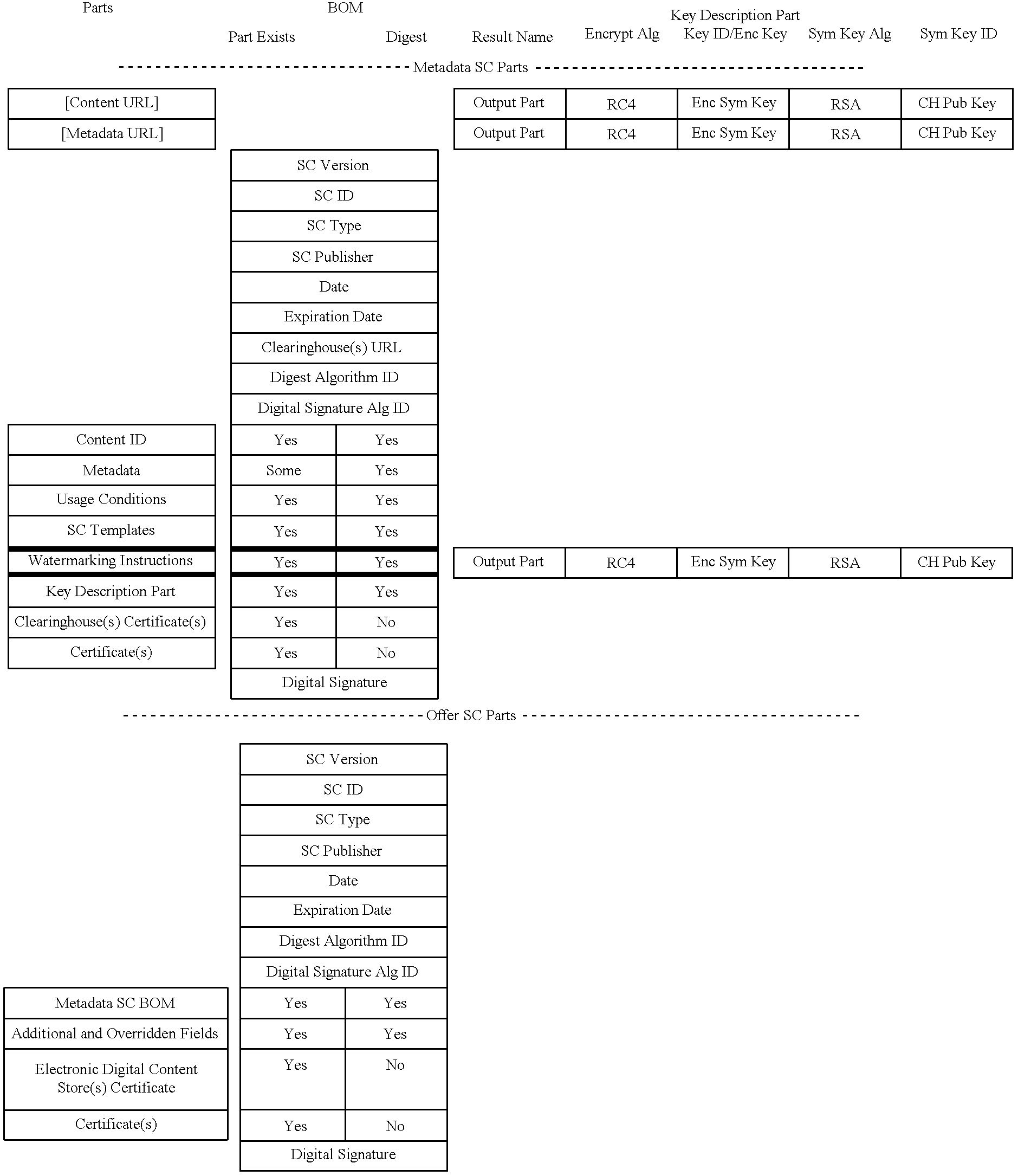
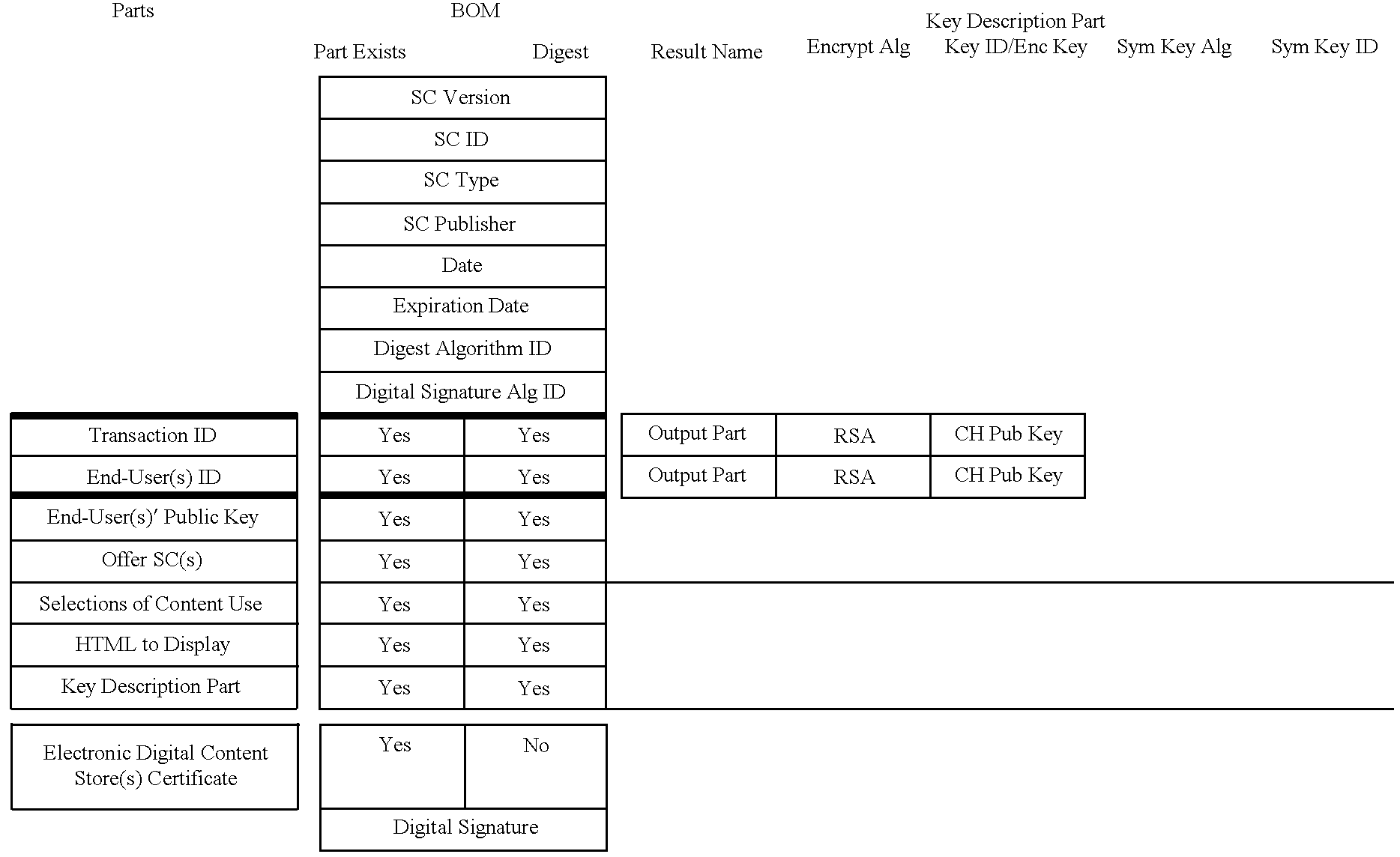
Electronic content delivery system
InactiveUS6226618B1Key distribution for secure communicationDigital data processing detailsDelivery systemSystem safety
Disclosed is a method and apparatus of securely providing data to a user's system. The data is encrypted so as to only be decryptable by a data decrypting key, the data decrypting key being encrypted using a first public key, and the encrypted data being accessible to the user's system, the method comprising the steps of: transferring the encrypted data decrypting key to a clearing house that possesses a first private key, which corresponds to the first public key; decrypting the data decrypting key using the first private key; re-encrypting the data decrypting key using a second public key; transferring the re-encrypted data decrypting key to the user's system, the user's system possessing a second private key, which corresponds to the second public key; and decrypting the re-encrypted data decrypting key using the second private key.
Owner:LEVEL 3 COMM LLC
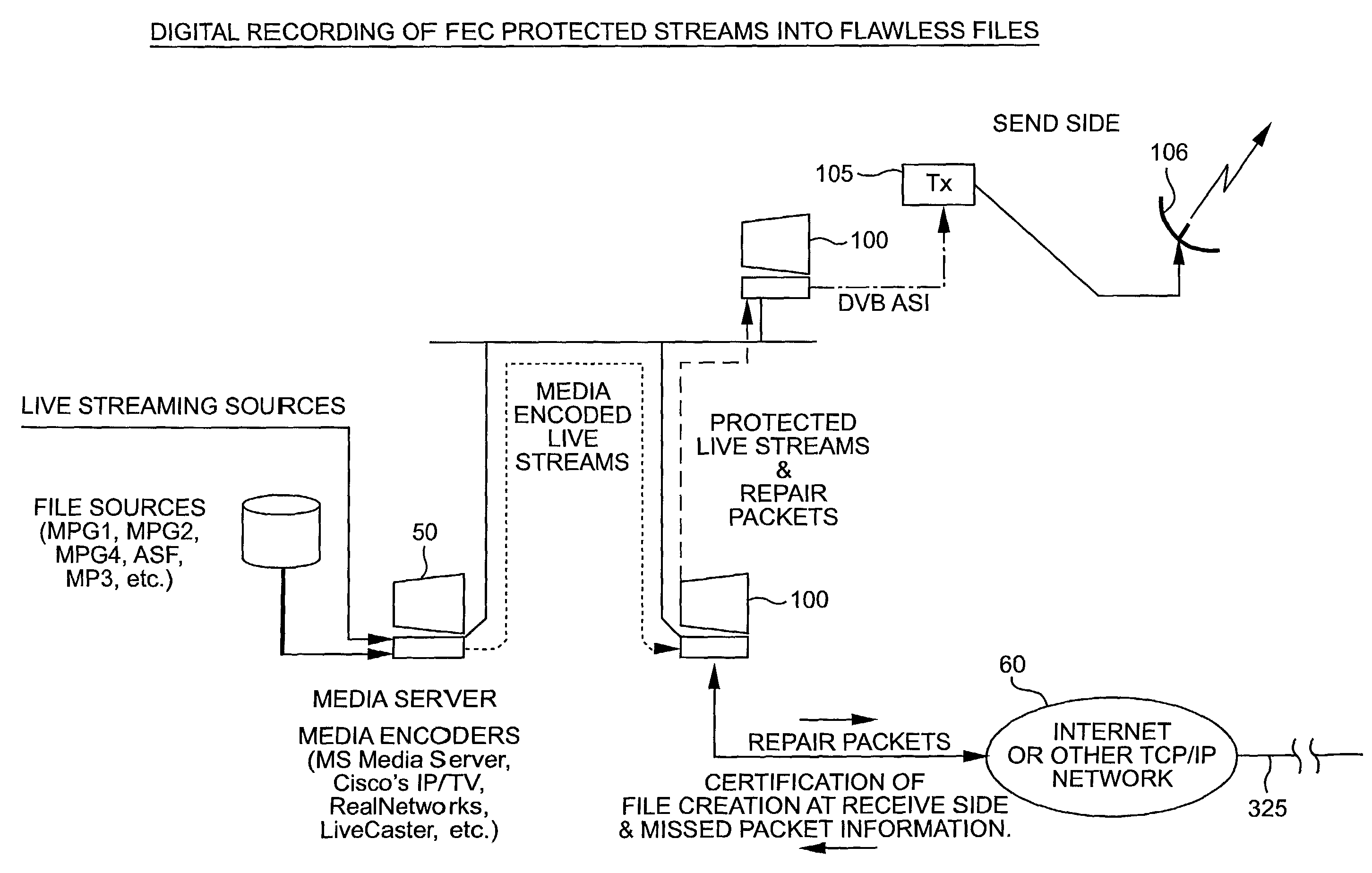
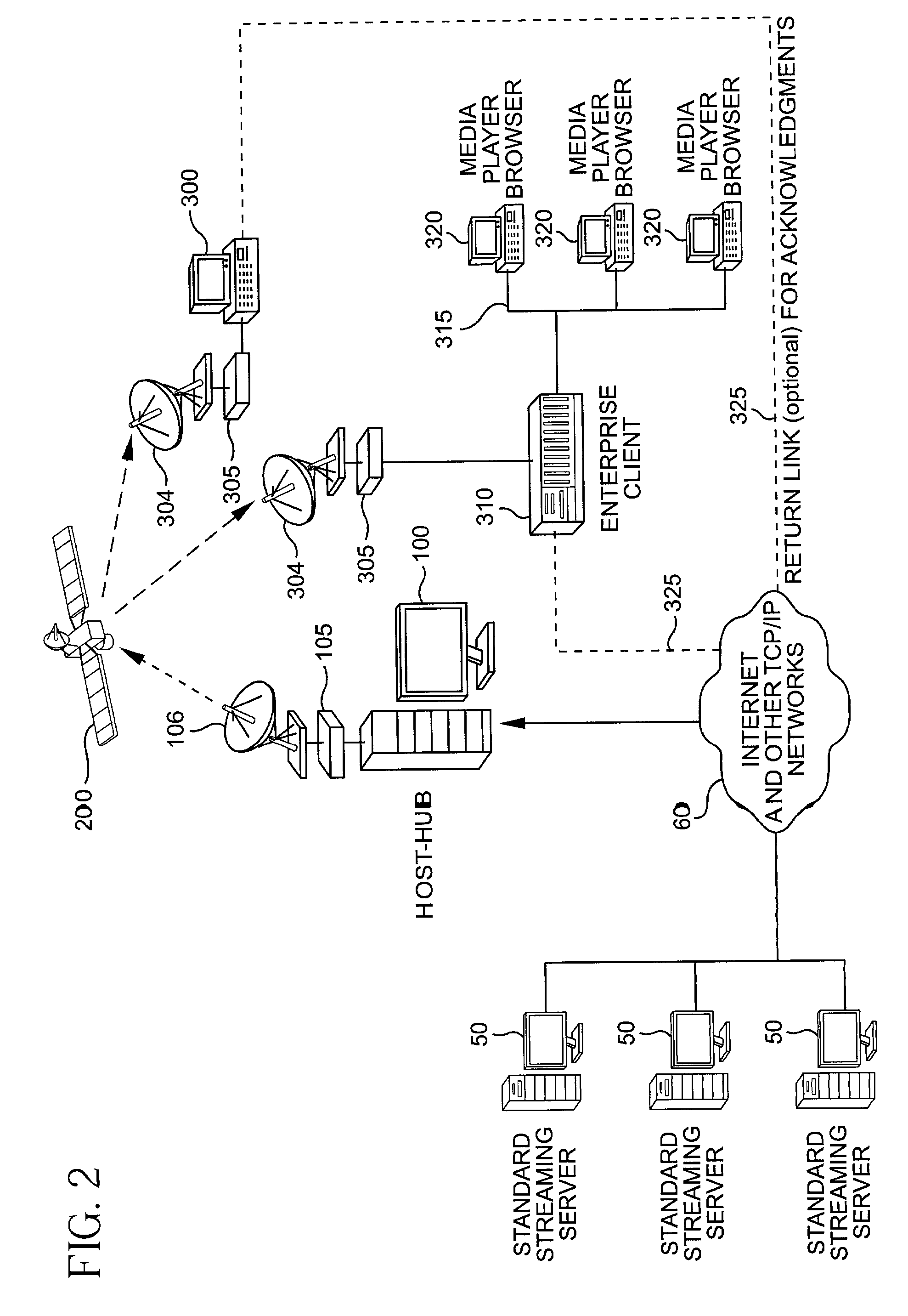
System for protecting the transmission of live data streams, and upon reception, for reconstructing the live data streams and recording them into files
ActiveUS7024609B2Error prevention/detection by using return channelTransmission systemsData streamReal-time data
The present invention relates to a system for (1) protecting the transmission of packet streams between a host computer and one or more client computers, and (2) upon reception, (a) reconstructing any outage damage caused during the transmission to the packet streams, and (b) digitally recording the reconstructed packet streams to a file. The present invention also relates to a method for dynamically generating a file index table as the packet stream is being digitally recorded.
Owner:KENCAST
Multi-dimensional data protection and mirroring method for micro level data
ActiveUS7103824B2Detection errorLow common data sizeCode conversionCyclic codesData validationData integrity
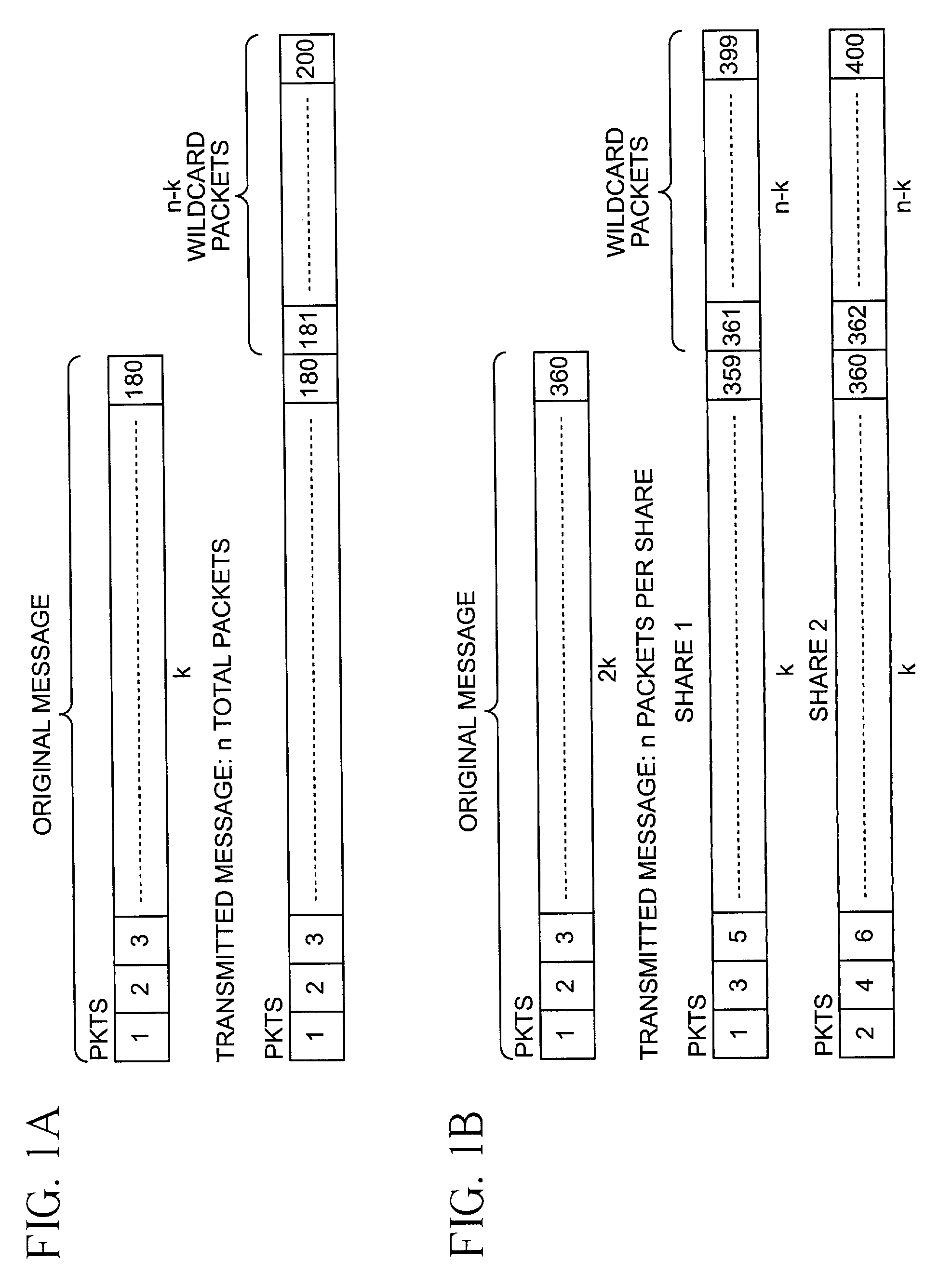
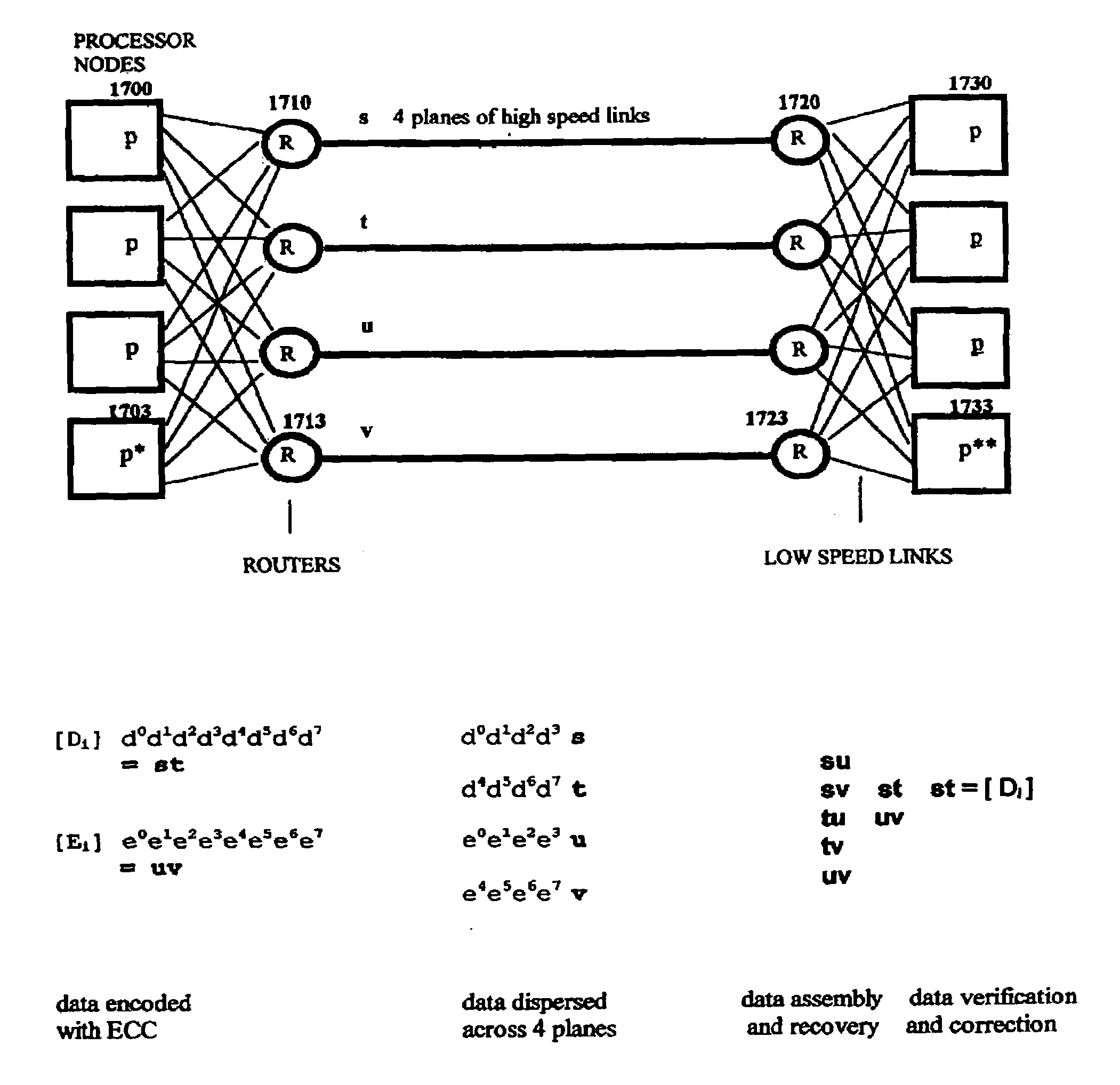
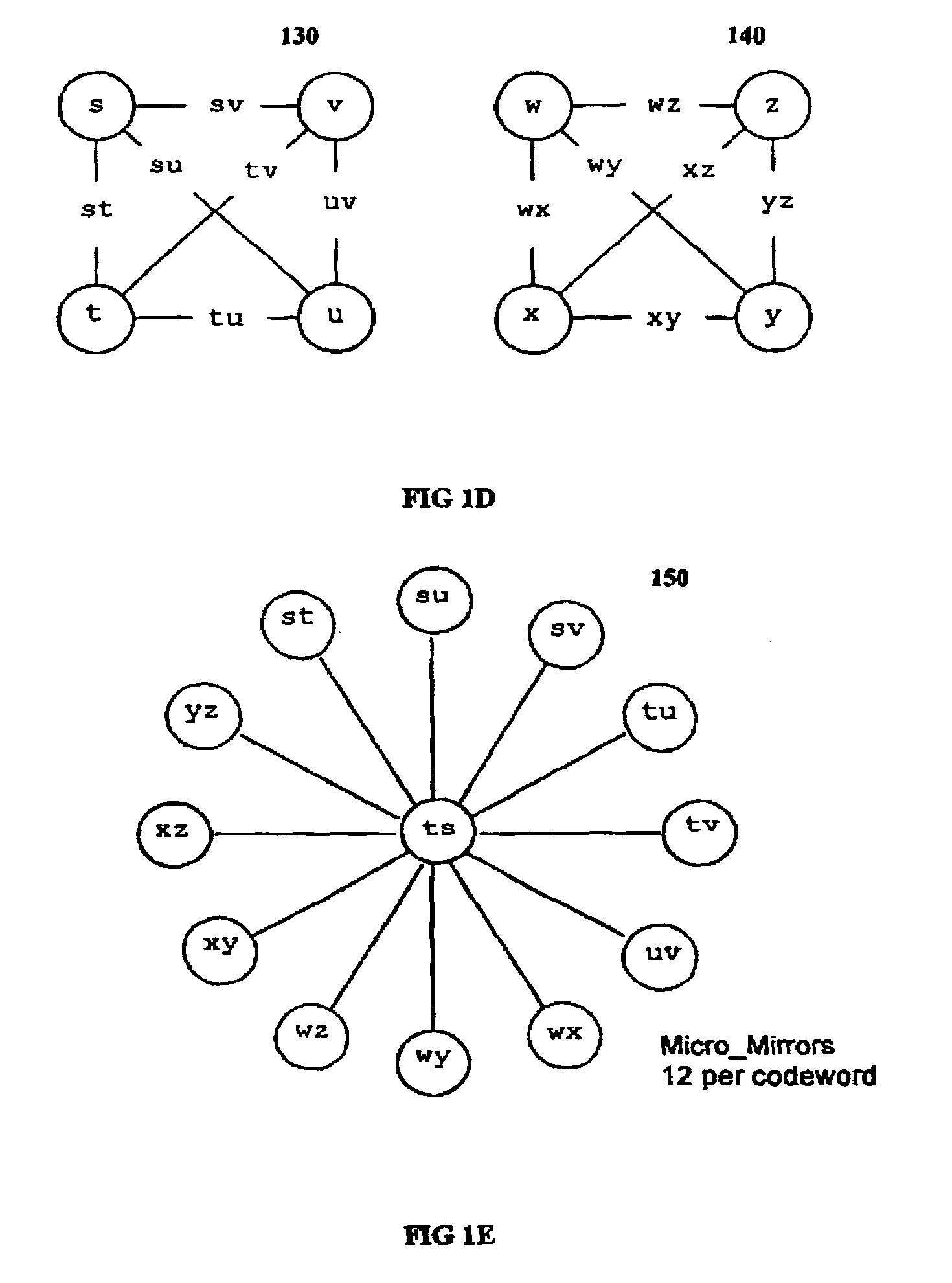
The invention discloses a data validation, mirroring and error / erasure correction method for the dispersal and protection of one and two-dimensional data at the micro level for computer, communication and storage systems. Each of 256 possible 8-bit data bytes are mirrored with a unique 8-bit ECC byte. The ECC enables 8-bit burst and 4-bit random error detection plus 2-bit random error correction for each encoded data byte. With the data byte and ECC byte configured into a 4 bit×4 bit codeword array and dispersed in either row, column or both dimensions the method can perform dual 4-bit row and column erasure recovery. It is shown that for each codeword there are 12 possible combinations of row and column elements called couplets capable of mirroring the data byte. These byte level micro-mirrors outperform conventional mirroring in that each byte and its ECC mirror can self-detect and self-correct random errors and can recover all dual erasure combinations over four elements. Encoding at the byte quanta level maximizes application flexibility. Also disclosed are fast encode, decode and reconstruction methods via boolean logic, processor instructions and software table look-up with the intent to run at line and application speeds. The new error control method can augment ARQ algorithms and bring resiliency to system fabrics including routers and links previously limited to the recovery of transient errors. Image storage and storage over arrays of static devices can benefit from the two-dimensional capabilities. Applications with critical data integrity requirements can utilize the method for end-to-end protection and validation. An extra ECC byte per codeword extends both the resiliency and dimensionality.
Owner:HALFORD ROBERT
Fixed content distributed data storage using permutation ring encoding
InactiveUS7240236B2Highly available and reliable and persistent storageError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsCode conversionCoding blockDatabase
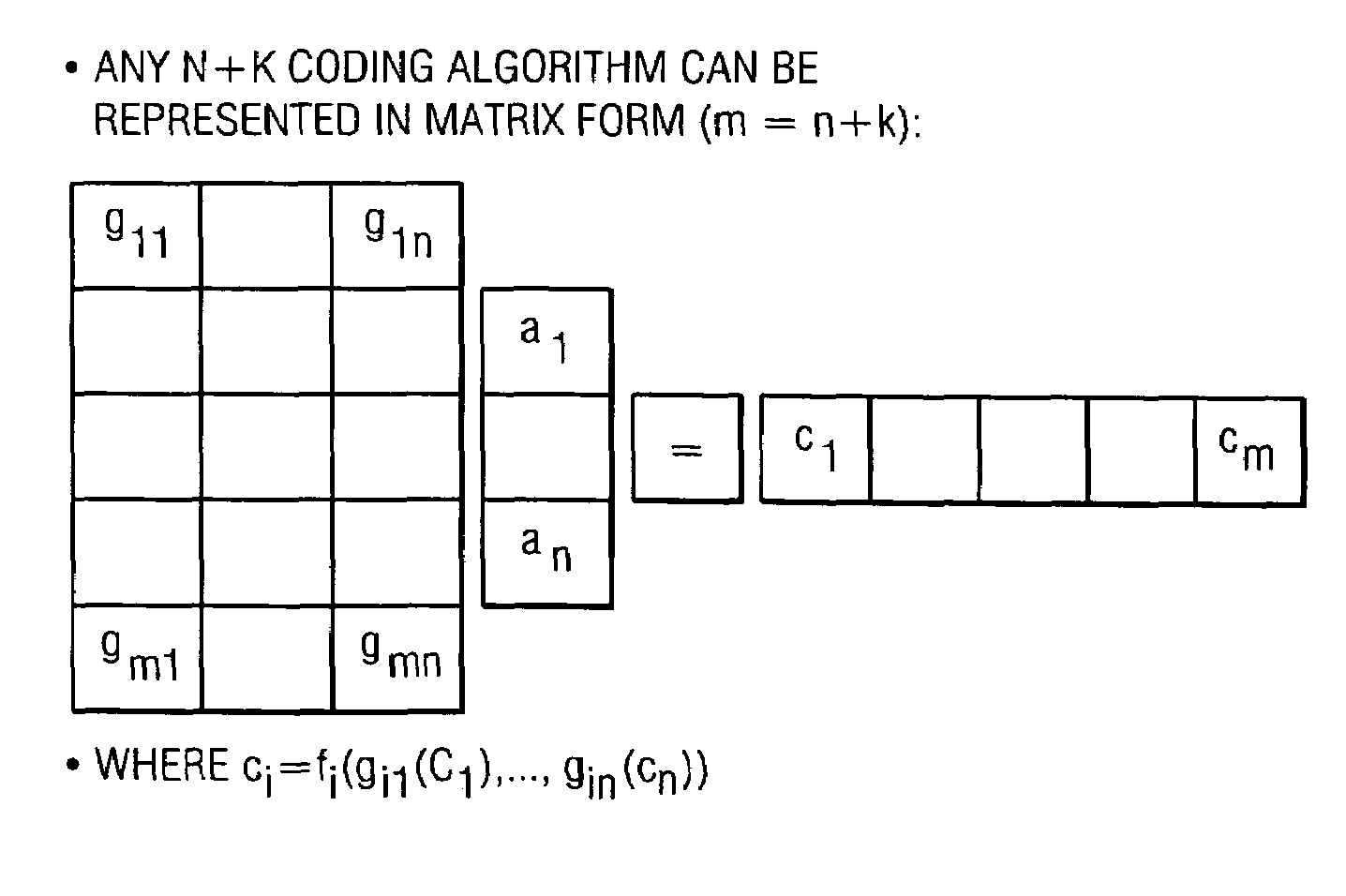
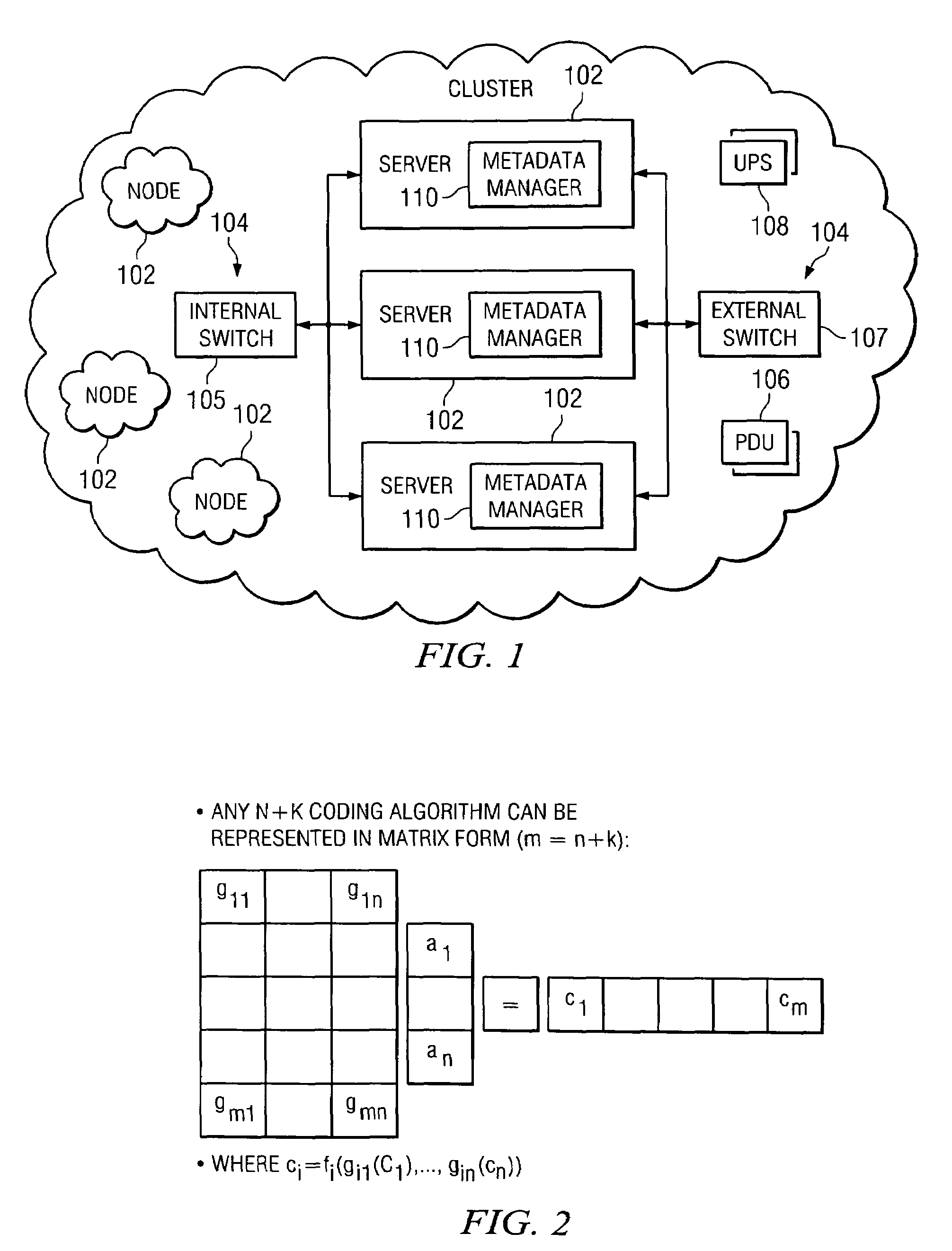
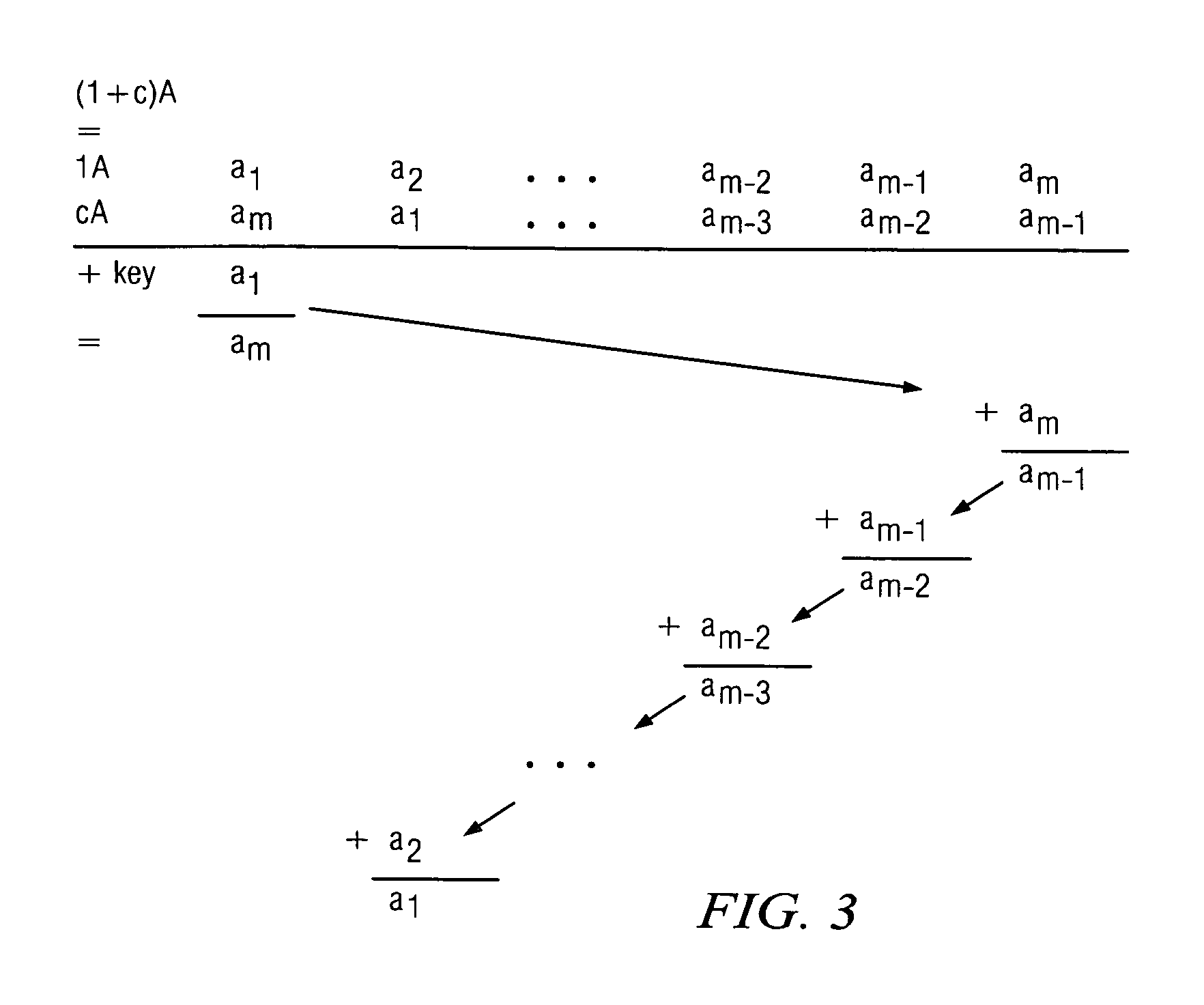
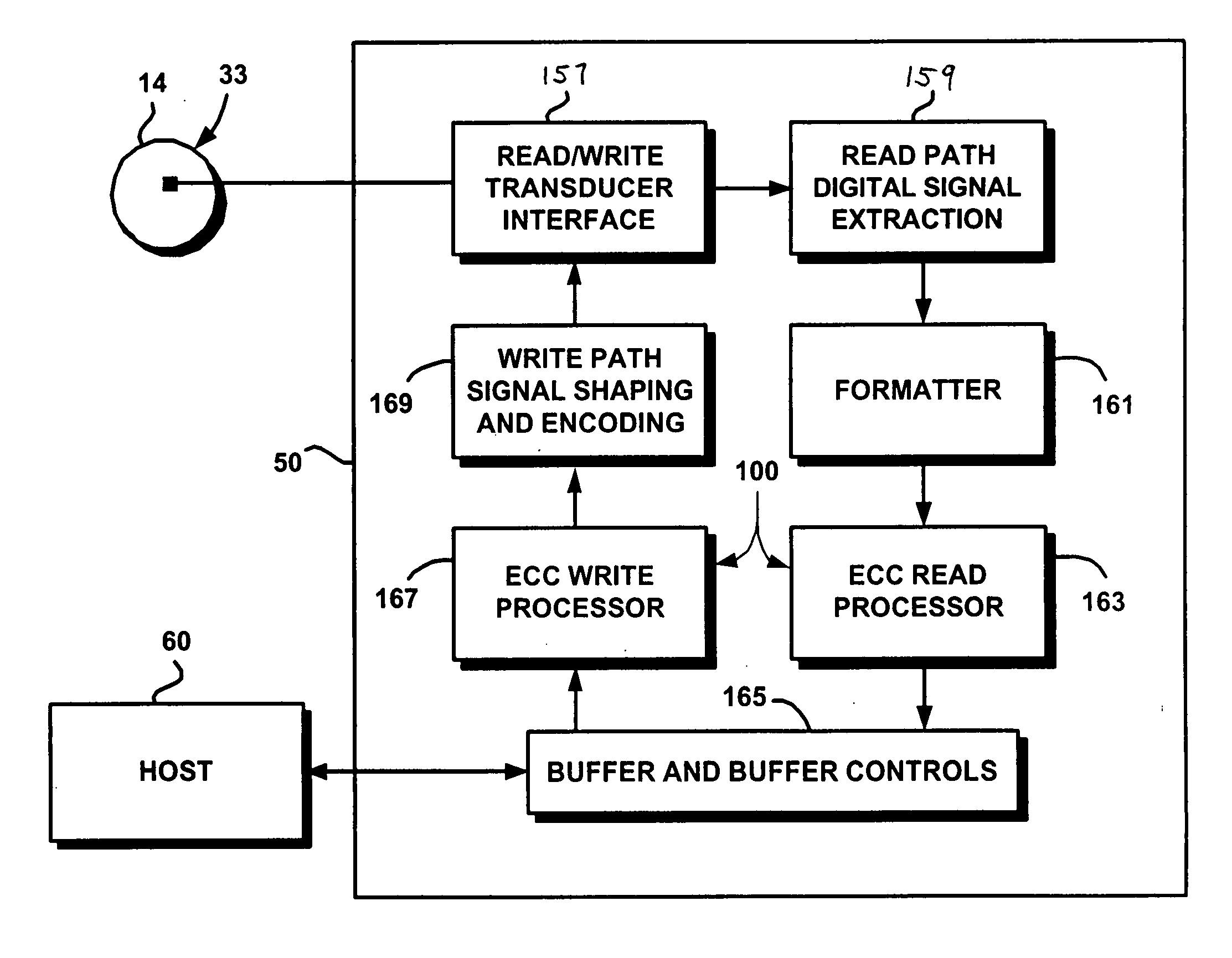
A file protection scheme for fixed content in a distributed data archive uses computations that leverage permutation operators of a cyclic code. In an illustrative embodiment, an N+K coding technique is described for use to protect data that is being distributed in a redundant array of independent nodes (RAIN). The data itself may be of any type, and it may also include system metadata. According to the invention, the data to be distributed is encoded by a dispersal operation that uses a group of permutation ring operators. In a preferred embodiment, the dispersal operation is carried out using a matrix of the form [IN<sub2>—< / sub2>C] where IN is an n×n identity sub-matrix and C is a k×n sub-matrix of code blocks. The identity sub-matrix is used to preserve the data blocks intact. The sub-matrix C preferably comprises a set of permutation ring operators that are used to generate the code blocks. The operators are preferably superpositions that are selected from a group ring of a permutation group with base ring Z2.
Owner:HITACHI VANTARA CORP
Techniques for detecting and correcting errors using multiple interleave erasure pointers
InactiveUS20050229069A1Correction capabilityTransmission systemsCode conversionBlock codeError location
Techniques for detecting and correcting burst errors in data bytes formed in a two-level block code structure. A second level decoder uses block level check bytes to detect columns in a two-level block code structure that contain error bytes. The second level decoder generates erasure pointers that identify columns in the two-level block structure effected by burst errors. A first level decoder then uses codeword check bytes to correct all of the bytes in the columns identified by the erasure pointers. The first level decoder is freed to use all of the codeword check bytes only for error byte value calculations. The first level decoder does not need to use any of the codeword check bytes for error location calculations, because the erasure pointers generated by the second level decoder provide all of the necessary error locations. This techniques doubles the error correction capability of the first level decoder.
Owner:HITACHI GLOBAL STORAGE TECH NETHERLANDS BV +1
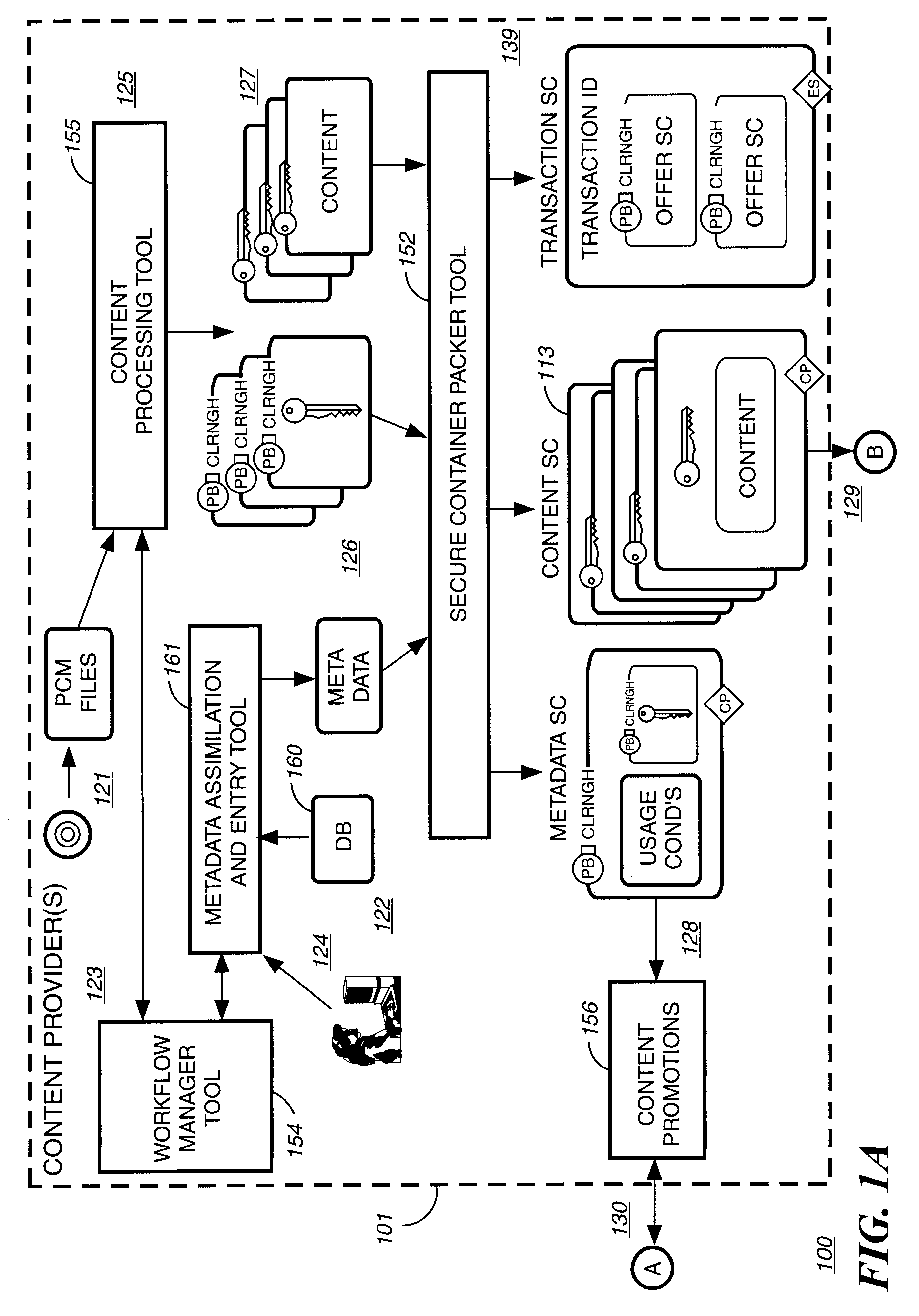
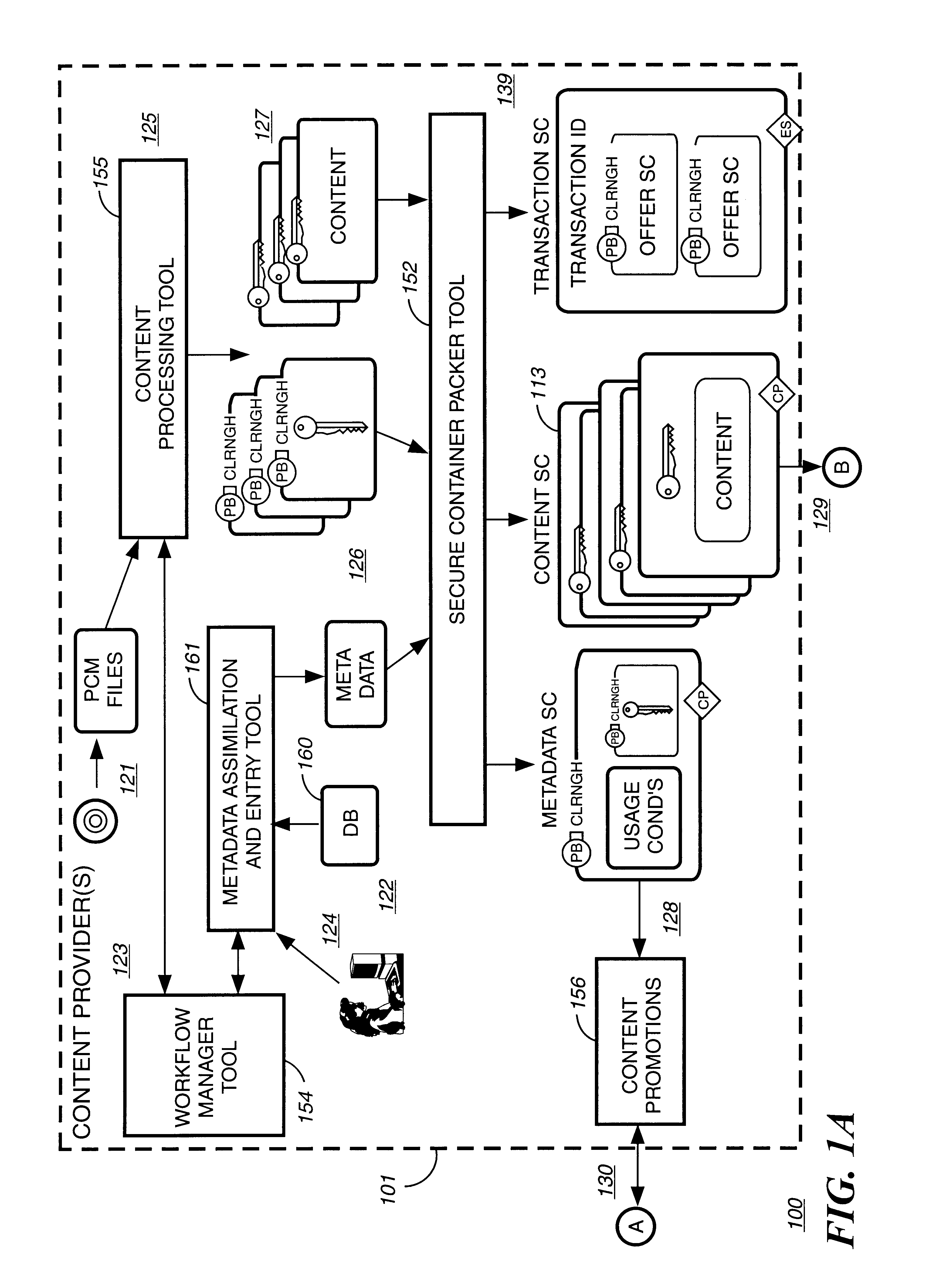
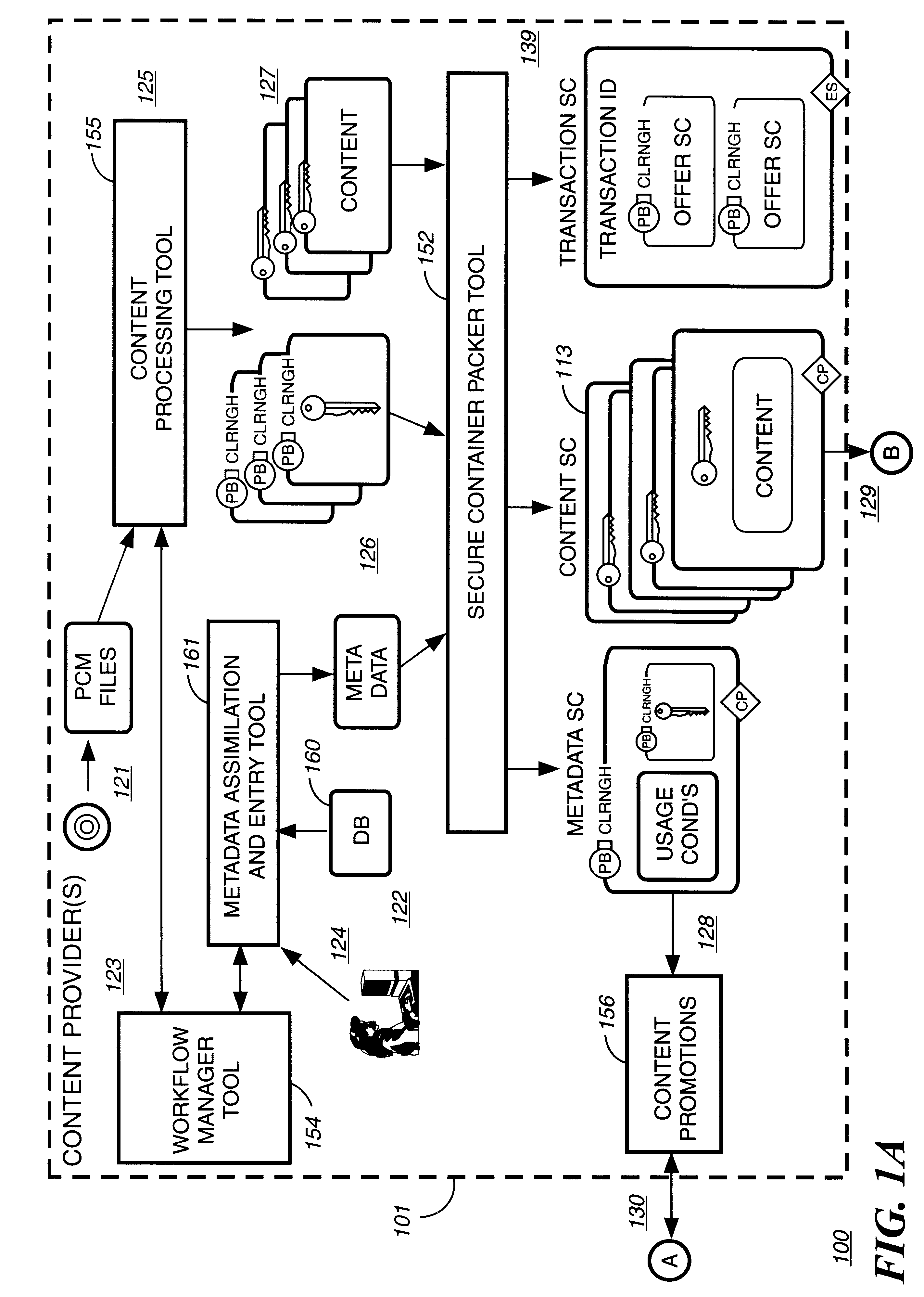
Automated method and apparatus to package digital content for electronic distribution using the identity of the source content
InactiveUS6345256B1Key distribution for secure communicationDigital data processing detailsDigital contentNumber content
A method to automatically retrieve data associated with content. An identifier is read that is stored on electronic readable medium storing content. The identifier is used to search a database for data associated with the content. Data that is associated with the content is retrieved as guided by the database. And the data retrieved is used to create a version of the content for electronic distribution. In accordance with another aspect of the invention, a computer readable medium is described to carry out the above method.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
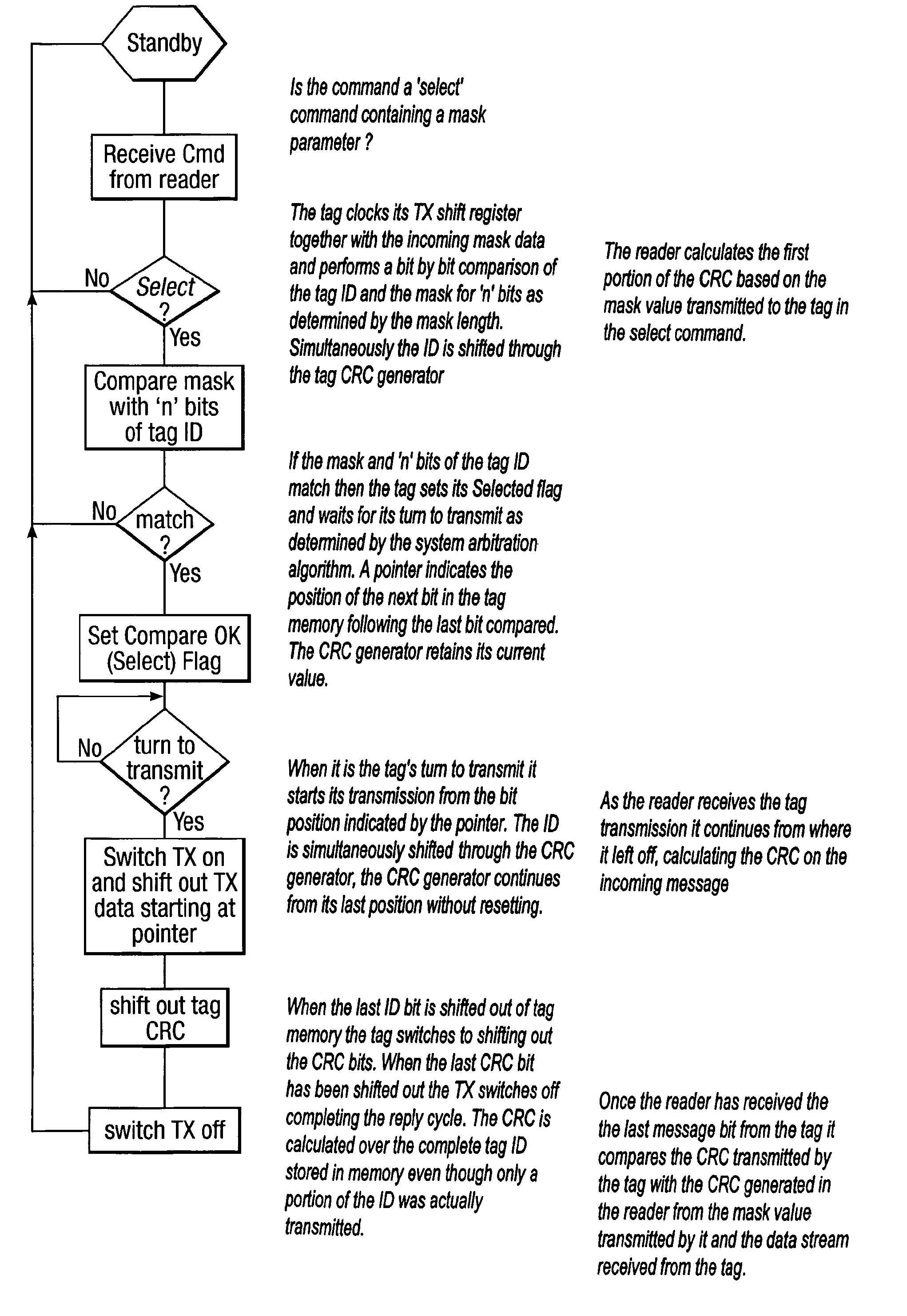
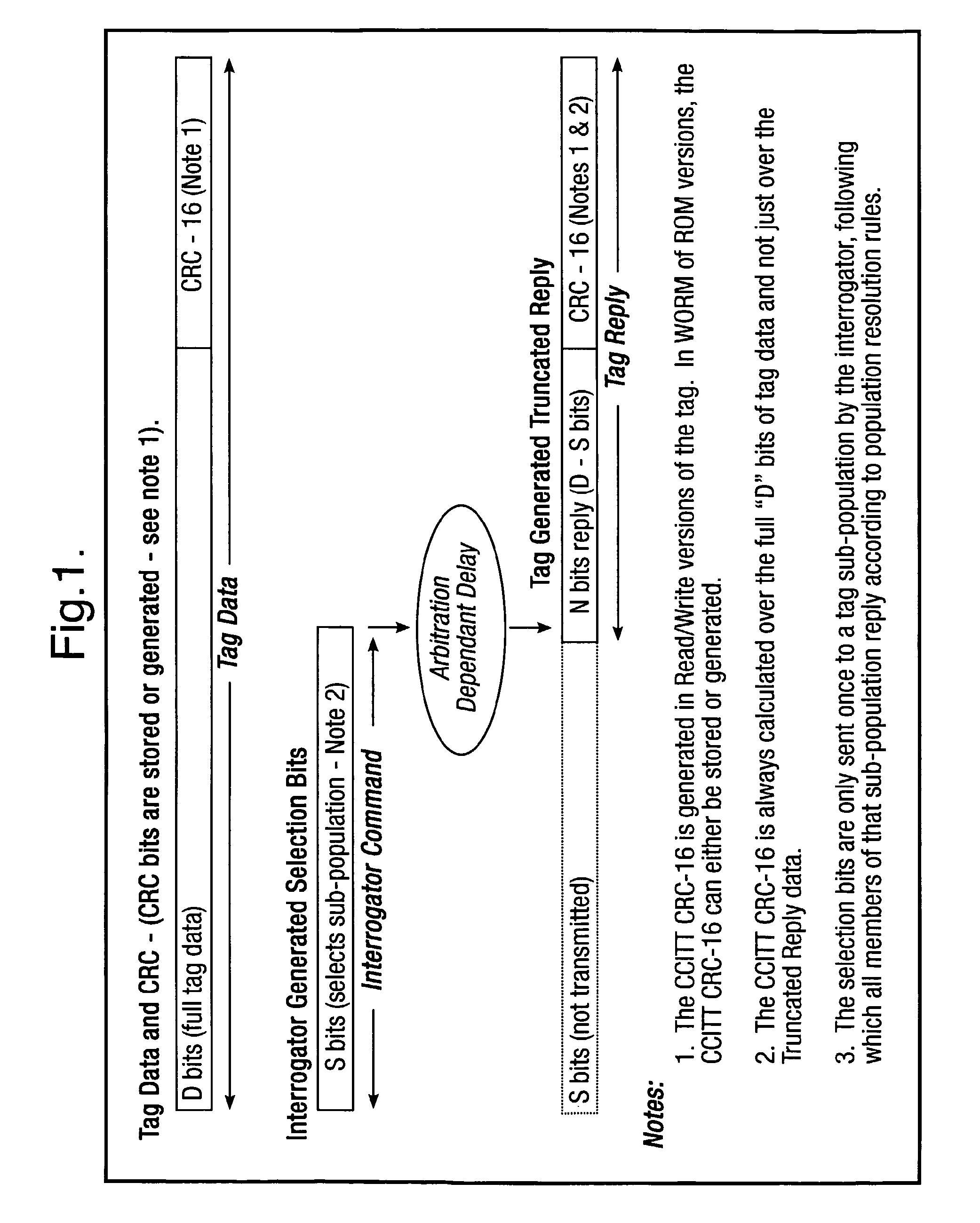
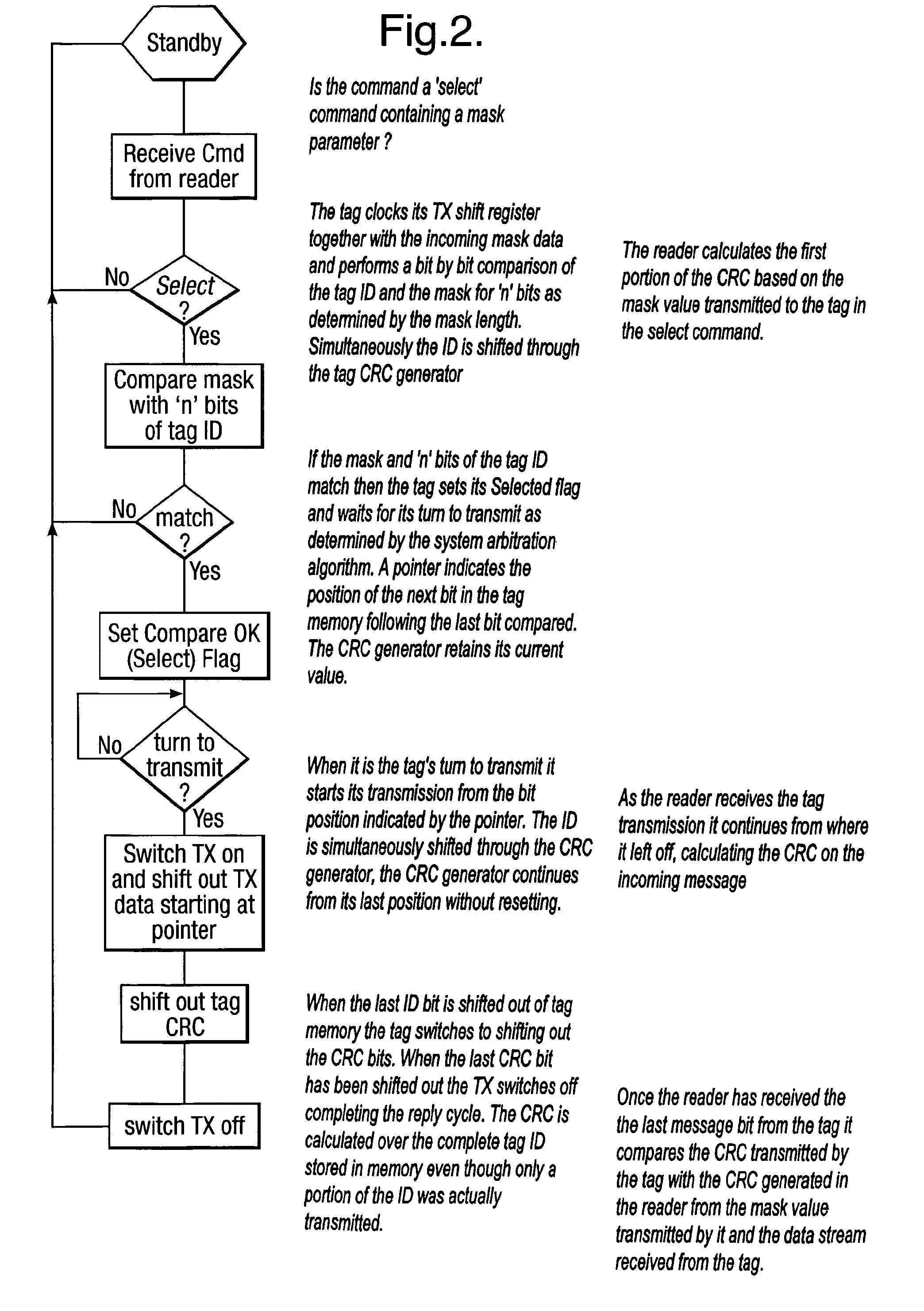
Method and system for calculating and verifying the integrity of data in a data transmission system
ActiveUS7987405B2Not having capability to accuratelyStay flexibleError preventionMemory record carrier reading problemsComputer hardwareData integrity
A method is described of calculating and verifying the integrity of data in a data communication system. The system comprises a base station and one or more remote stations, such as in an RFID system. The method includes transmitting a select instruction from the base station to the one or more remote stations, the select instruction containing a data field which matches a portion of an identity or other data field in one or more of the remote stations; transmitting from a selected remote station or stations a truncated reply containing identity data or other data of the remote station but omitting the portion transmitted by the base station; calculating in the base station a check sum or CRC from the data field originally sent and the truncated reply data received and comparing the calculated check sum or CRC with the check sum or CRC sent by the remote station.
Owner:ZEBRA TECH CORP
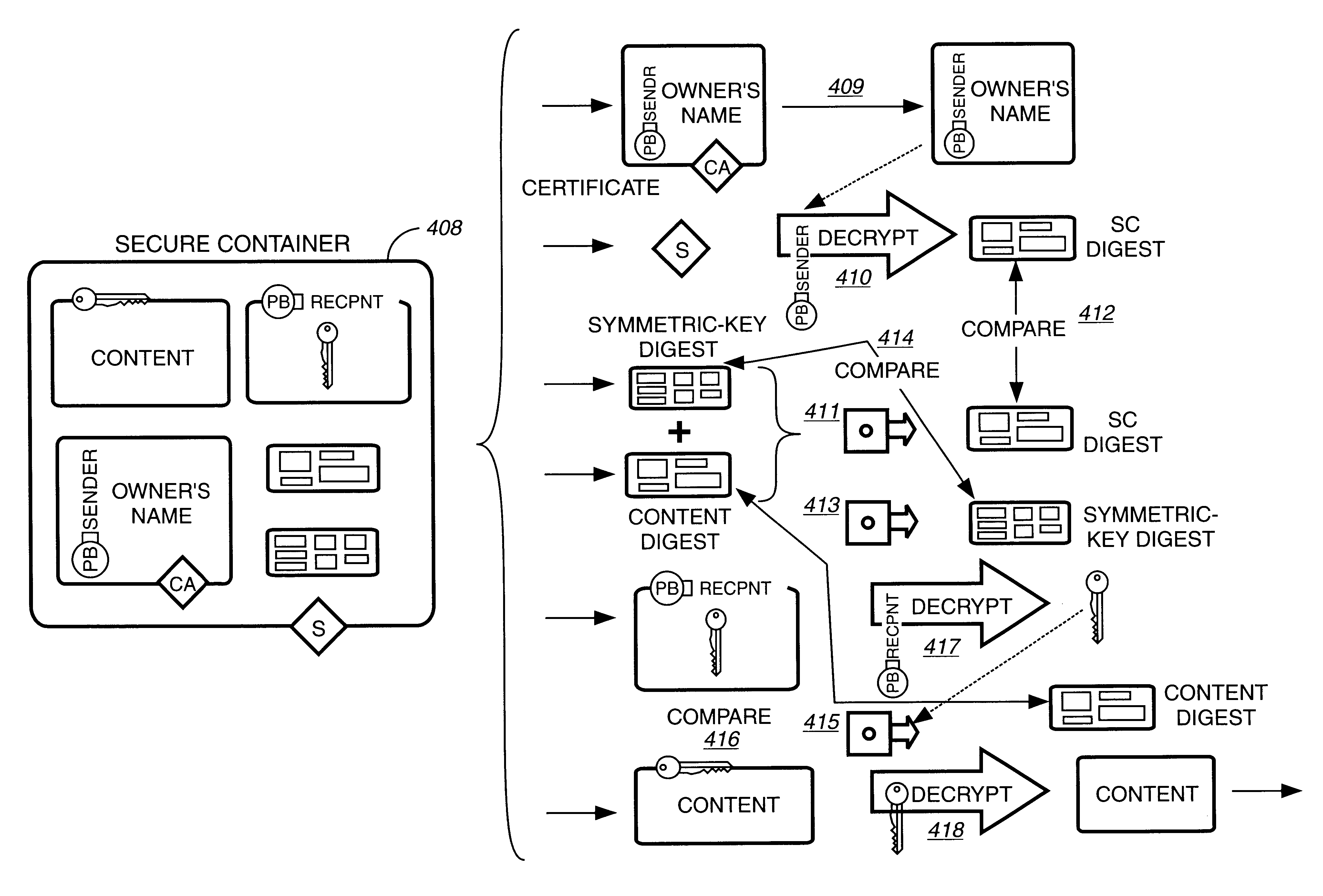
Secure electronic content distribution on CDS and DVDs
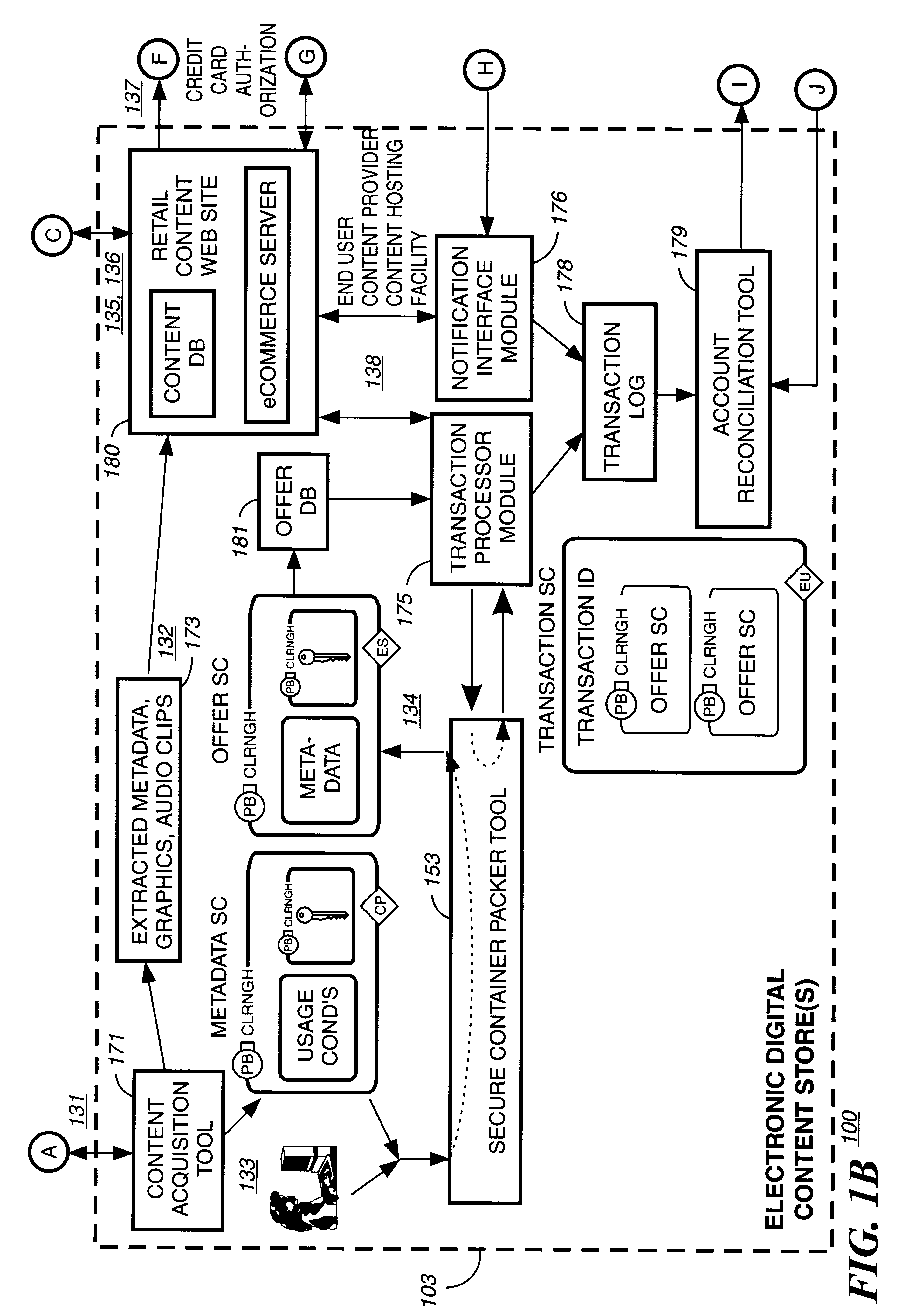
InactiveUS6611812B2Key distribution for secure communicationDigital data processing detailsDigital contentComputer terminal
A method to delivery encrypted digital content to a end user system for playing the content comprising the steps of: reading from a computer readable medium metadata which has previously associated with the content. A user selects from the metadata associated content to decrypt and the end user system establishes a secure connection with an authorization authority for decrypting the content. The end user system receives a secure container containing the decrypting key for decrypting at least part of the previously encrypted content as permitted. The system creates a secure container using the encrypting key from a clearing house, wherein the secure container has an encrypting key therein from the end user system; transferring the secure container to the clearing house for authentication of permission to decrypt the content. The system receives from the clearing house, a secure container encrypted using the encrypting key of the end user system containing the decrypting key for decrypting at least part of the previously encrypted content stored on the computer readable medium as permitted; and playing at least part of the previously encrypted content by decrypting the secure container using the encrypting key of the end user system to access the decrypting key for decrypting at least part of the encrypted content.
Owner:WISTRON CORP
Method and apparatus to create encoded digital content
InactiveUS6263313B1Electrophonic musical instrumentsKey distribution for secure communicationDigital contentNumber content
Owner:LEVEL 3 COMM LLC
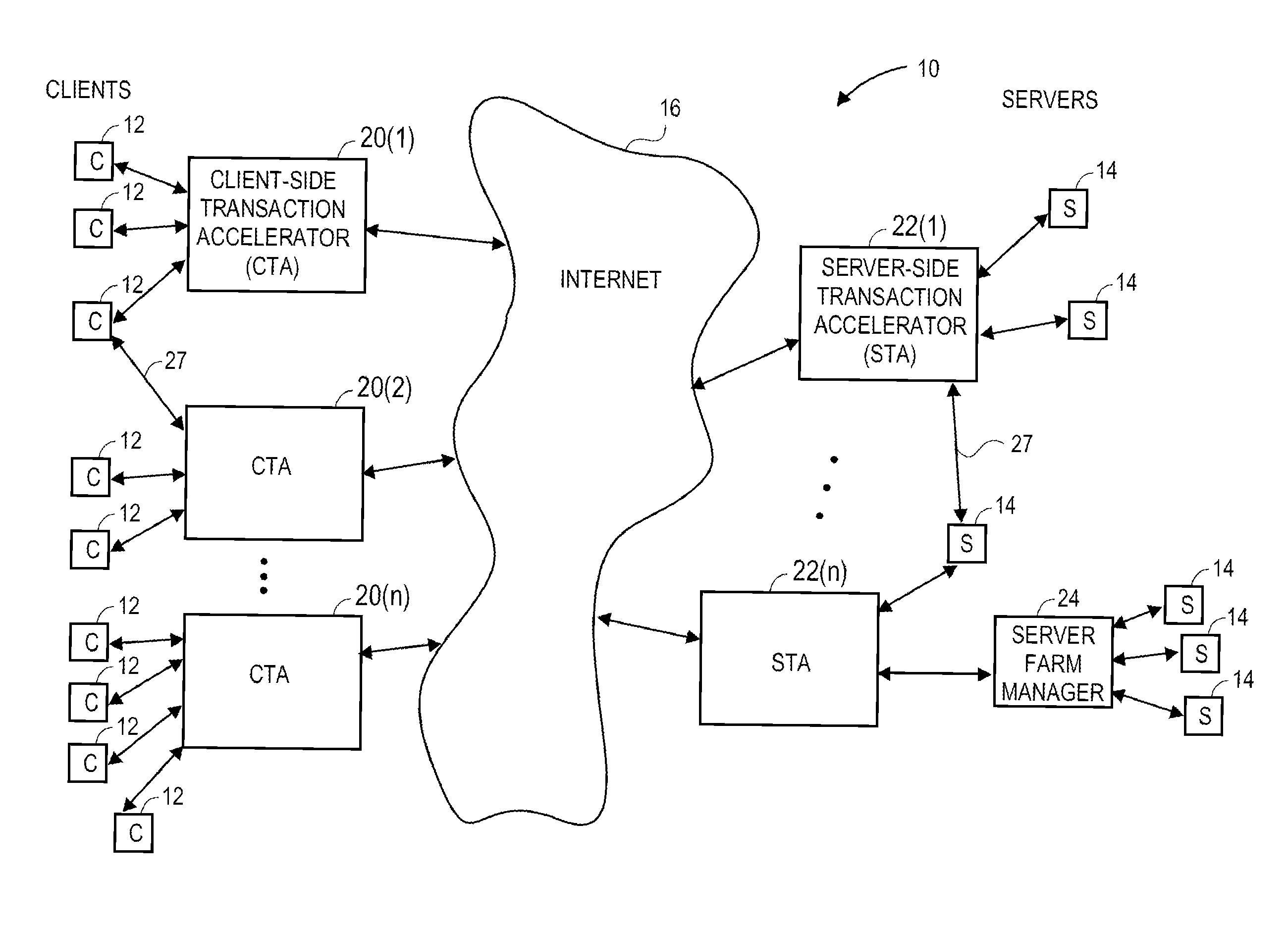
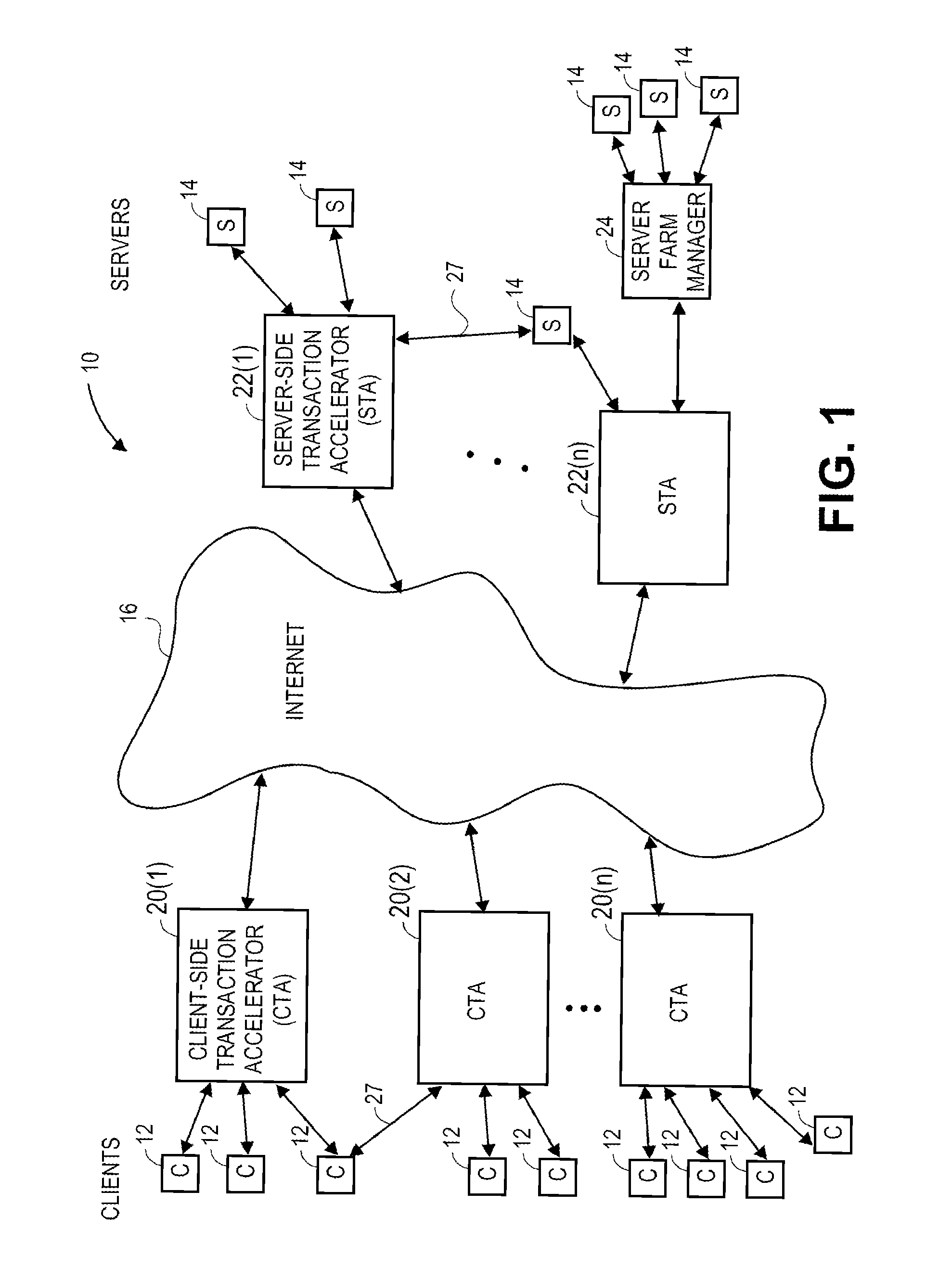
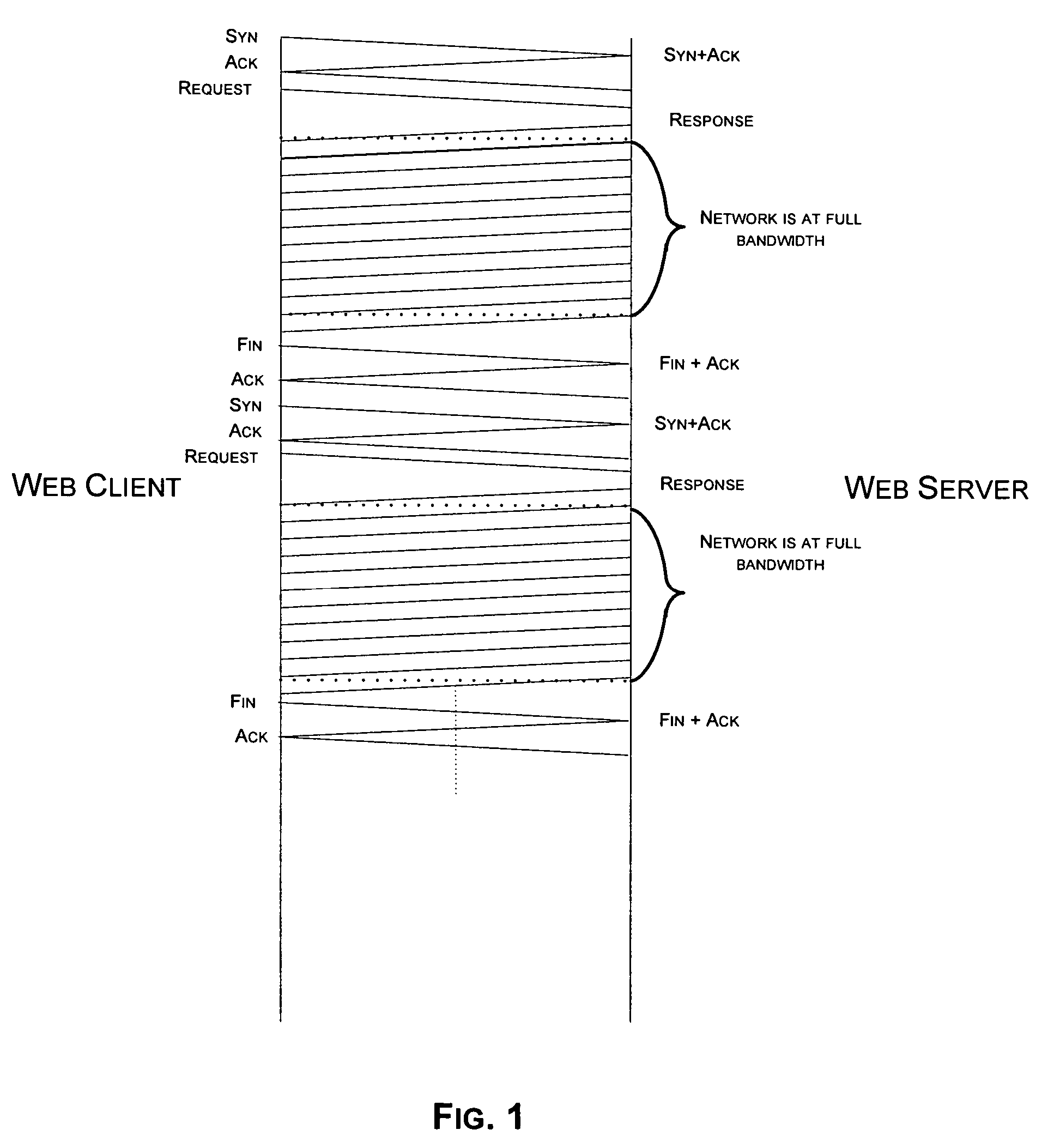
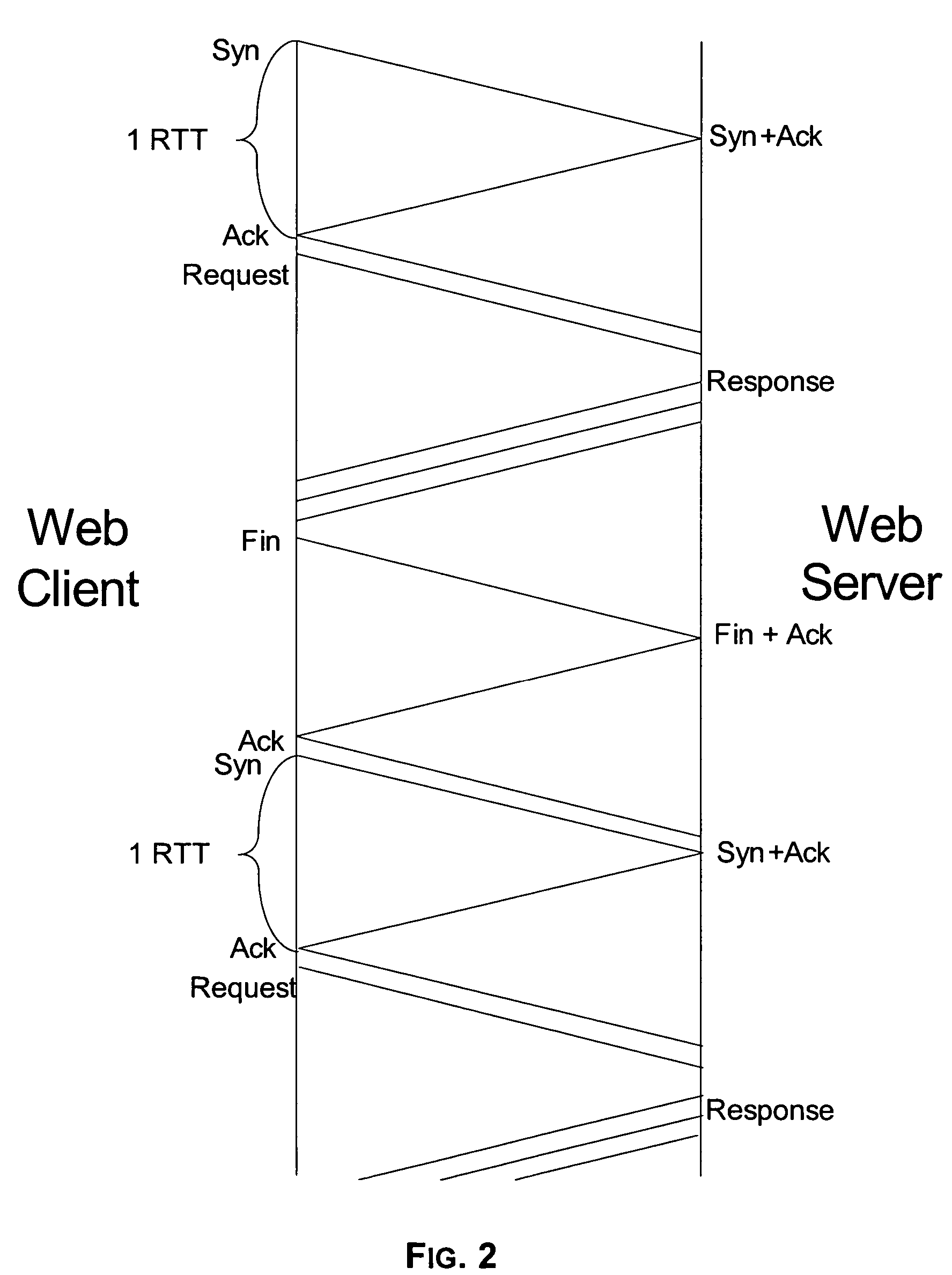
Transaction accelerator for client-server communications systems
ActiveUS20080320151A1Code conversionMultiple digital computer combinationsData segmentCommunications system
Self-discovering transaction accelerators improve communications between a client and a server. A client directs a message to a server. A client-side transaction accelerator intercepts the message, terminates the connection with the client, and accelerates the request by replacing segments of data with references. The accelerated request is forwarded to a server-side transaction accelerator through a new connection. The server-side transaction accelerator reconstructs the message by replacing the reference with segment data in a persistent segment store accessible to the server-side transaction accelerator. The reconstructed request is then provided to the server. Accelerations may occur in any direction of communication. Persistent segment stores can be pre-populated with segment data from other transaction accelerators and anticipated transactions. The persistent segment store can store segments that are data segmented based on content of the data and can be independent of transaction protocol, application, and device.
Owner:RIVERBED TECH LLC
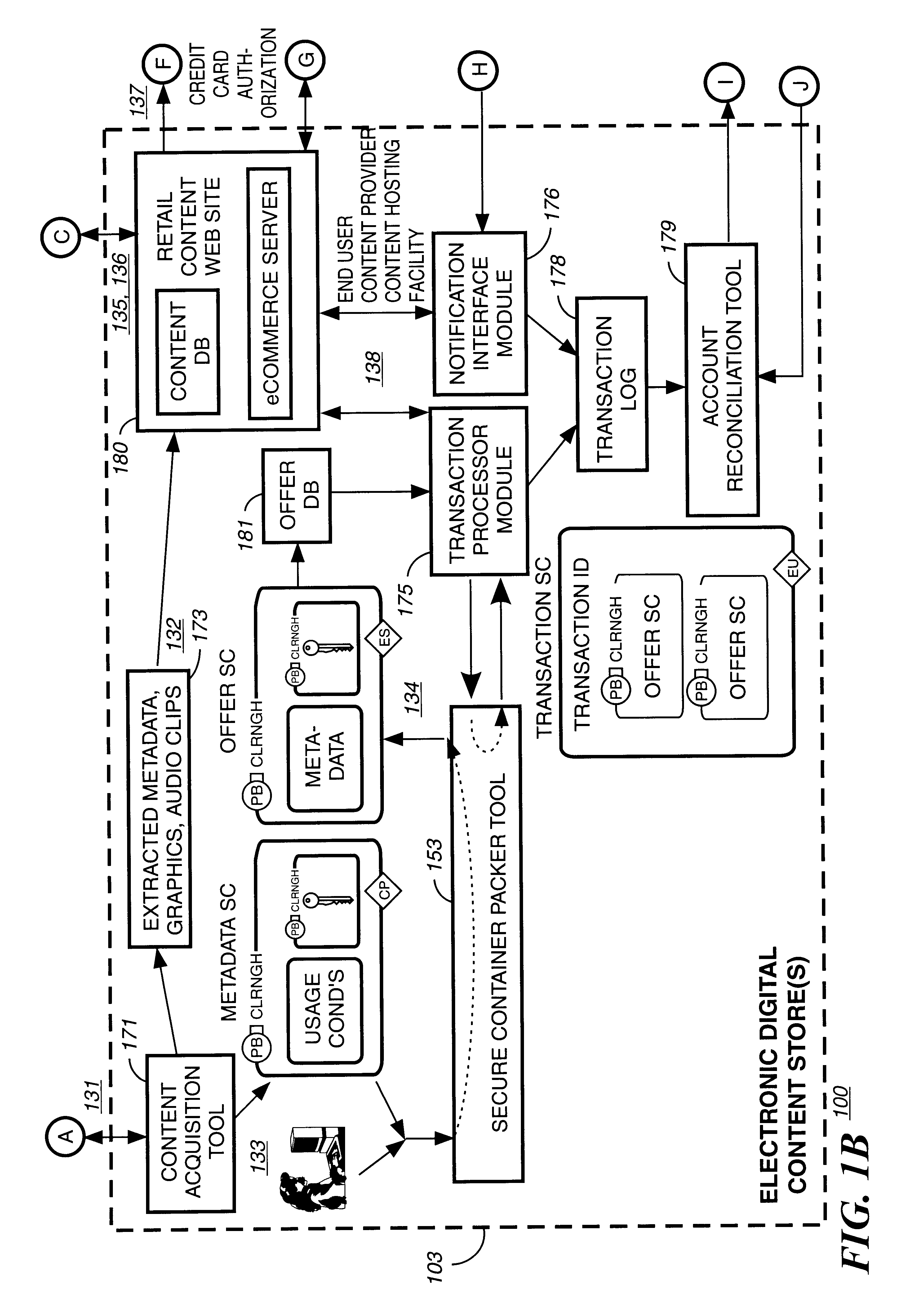
Method and apparatus for uniquely identifying a customer purchase in an electronic distribution system
InactiveUS6389403B1Key distribution for secure communicationDigital data processing detailsContent IdentifierUser device
A system for tracking usage of digital content on user devices. Content sites for distributing digital content over a computer readable medium to users. The content sites associate unique content identifier with the content associated. Electronic stores coupled to a network sell licenses to play digital content data to users. The licenses contain a unique transaction identifier for uniquely identifying the transaction, and the licenses contain a unique item identifier for uniquely identifying at least one item in the transaction. Content players, which receive from the network the licensed content data, are used to play the licensed content data. The content players produce a purchase identifier based upon the mathematical combination of the content identifier, the transaction identifier and the item identifier.
Owner:WISTRON CORP
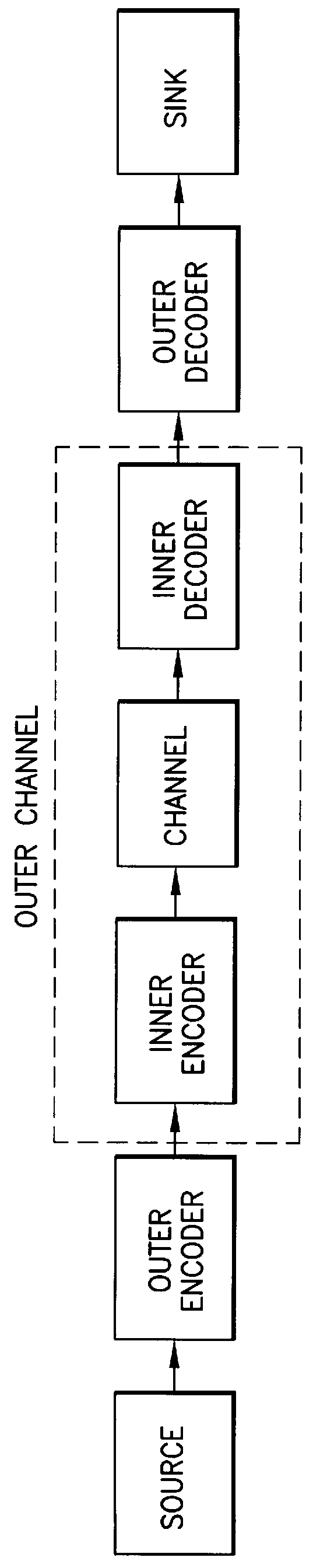
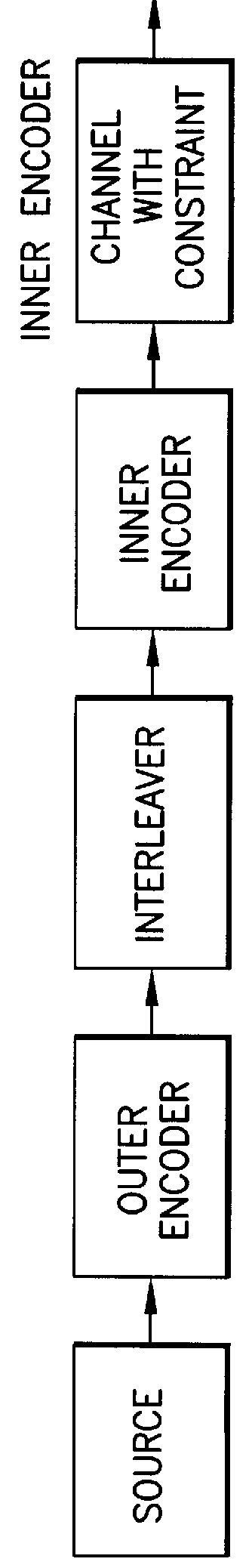
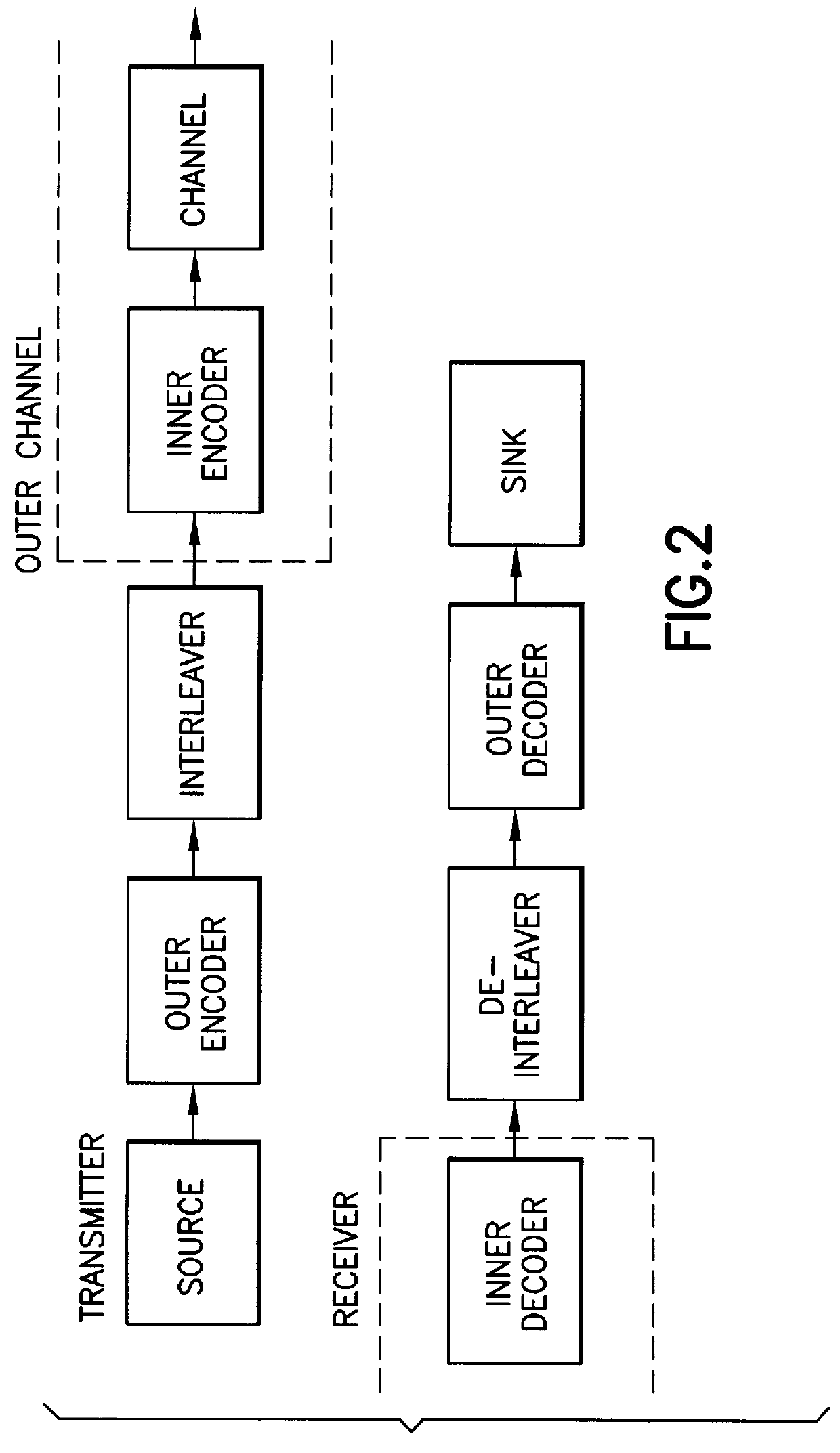
System and method for error correcting a received data stream in a concatenated system
A received signal is first converted into a digital sequence that may contain "erasures" (or ambiguity symbols) as well as errors. Then iterative decoding is applied in order to eliminate or reduce the erasures. This decoding procedure works effectively with the associated transmitter that adopts a concatenation of an outer coder, a permutation and an inner coder. The principal of the invention is also applicable to a system in which the inner coder is replaced by a "digital modulator" that introduces some constraint, or a channel that introduces some memory such as partial response signaling, intersymbol interference or multipath propagation. The invention can be applied to many existing systems while maintaining "backward compatibility" in the sense that the transmitter side need not be modified.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES FOR PRINCETON UNIV
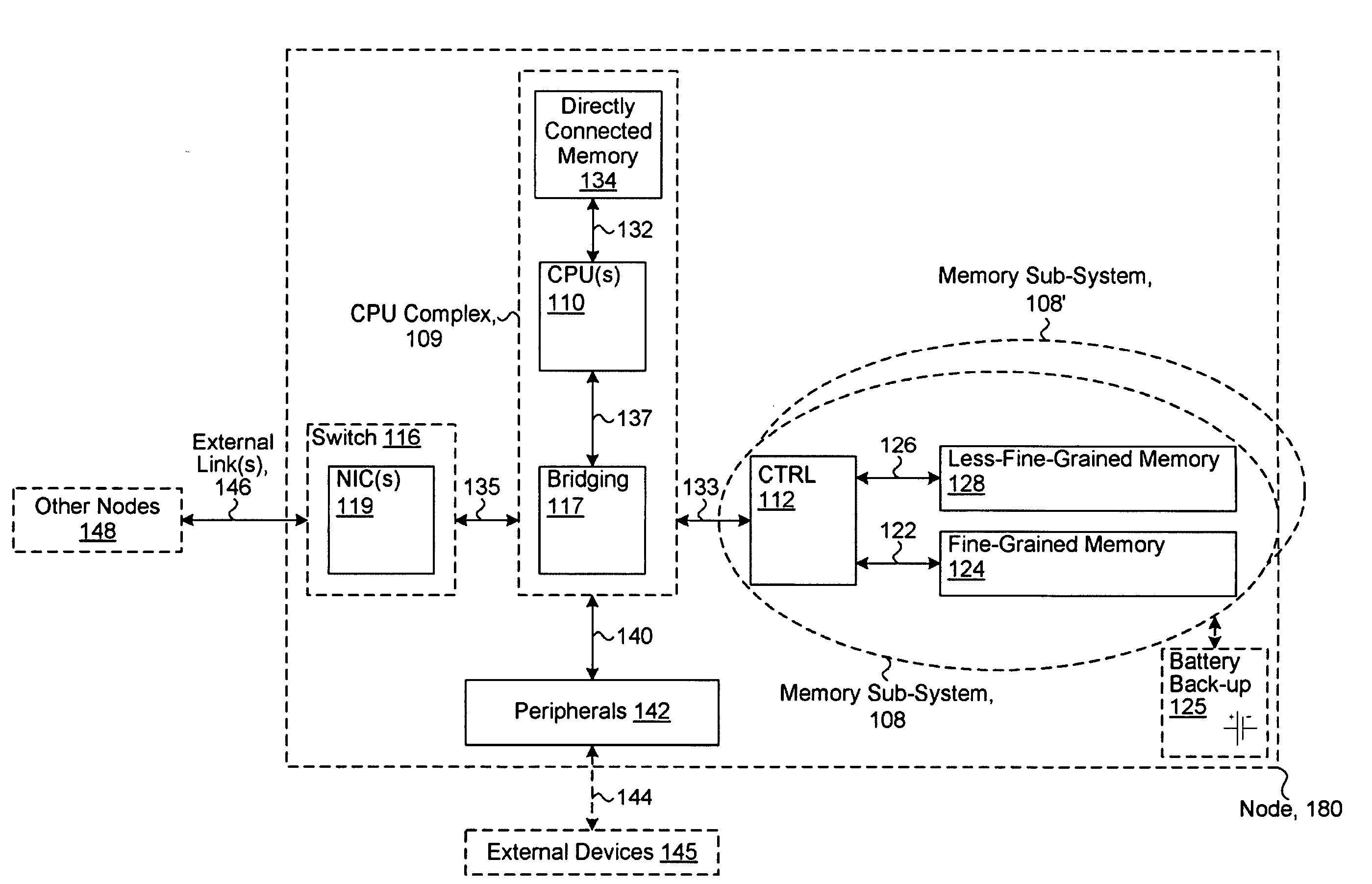
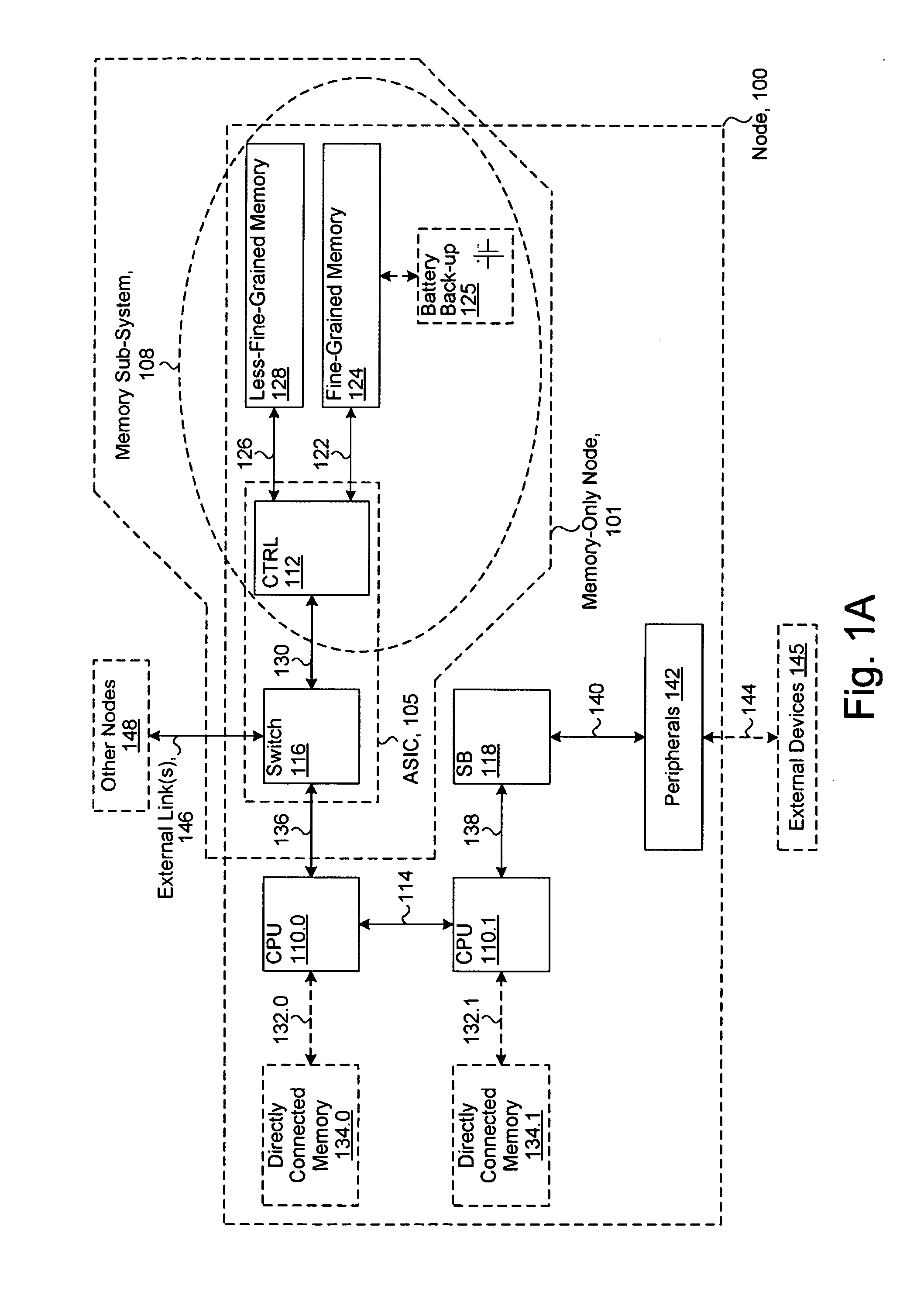
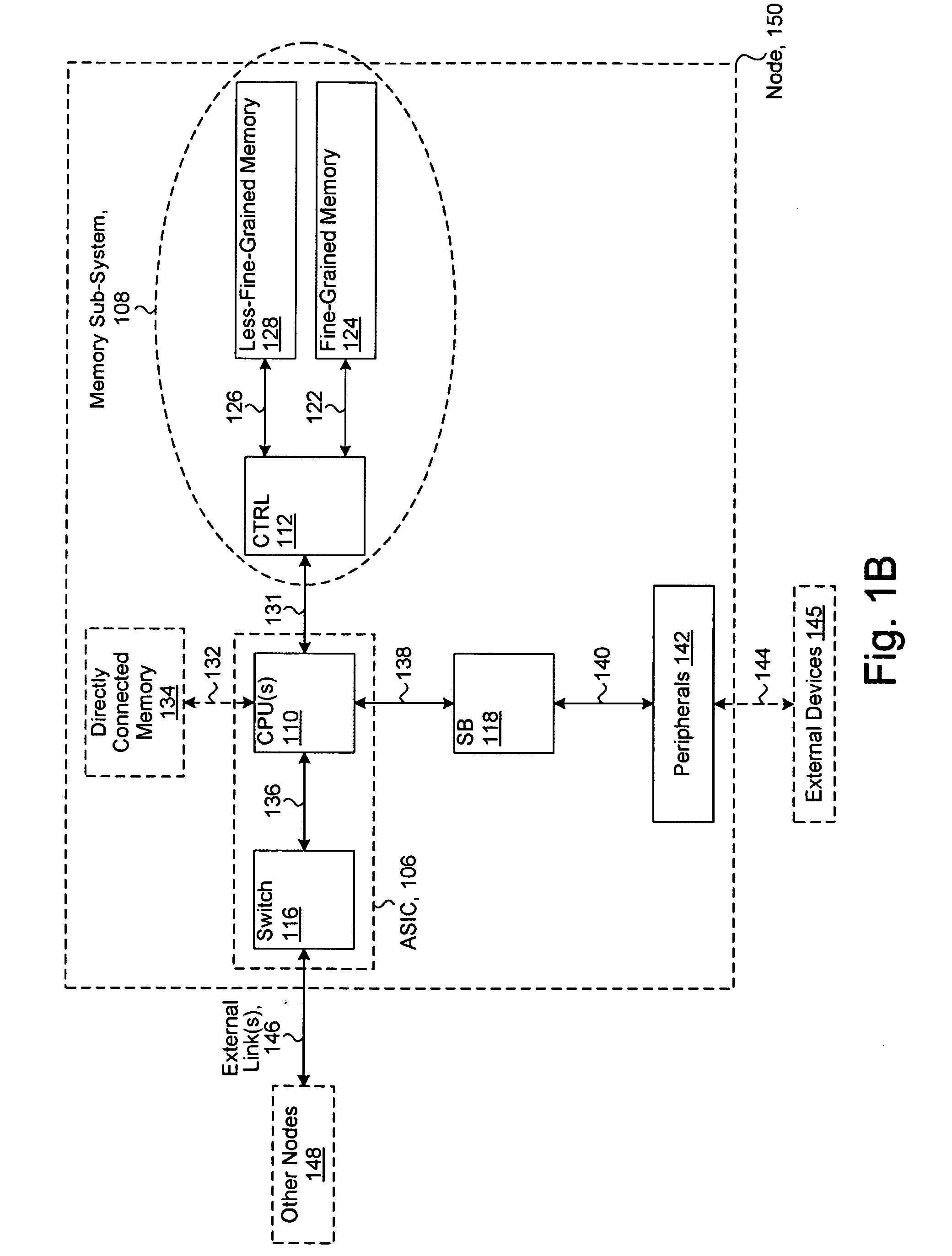
System including a fine-grained memory and a less-fine-grained memory
ActiveUS20080301256A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationEnergy efficient ICTData processing systemWrite buffer
A data processing system includes one or more nodes, each node including a memory sub-system. The sub-system includes a fine-grained, memory, and a less-fine-grained (e.g., page-based) memory. The fine-grained memory optionally serves as a cache and / or as a write buffer for the page-based memory. Software executing on the system uses n node address space which enables access to the page-based memories of all nodes. Each node optionally provides ACID memory properties for at least a portion of the space. In at least a portion of the space, memory elements are mapped to locations in the page-based memory. In various embodiments, some of the elements are compressed, the compressed elements are packed into pages, the pages are written into available locations in the page-based memory, and a map maintains an association between the some of the elements and the locations.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
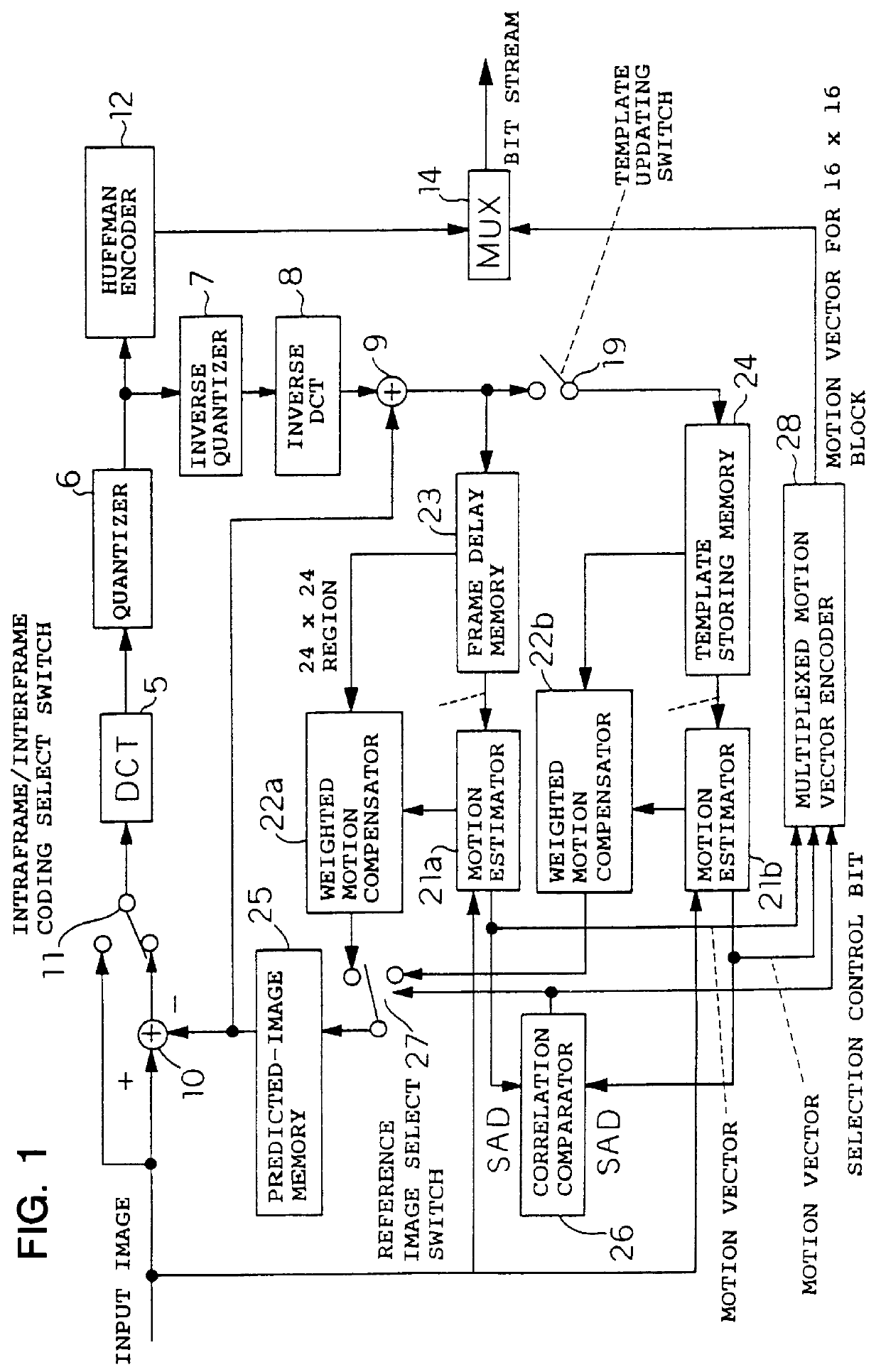
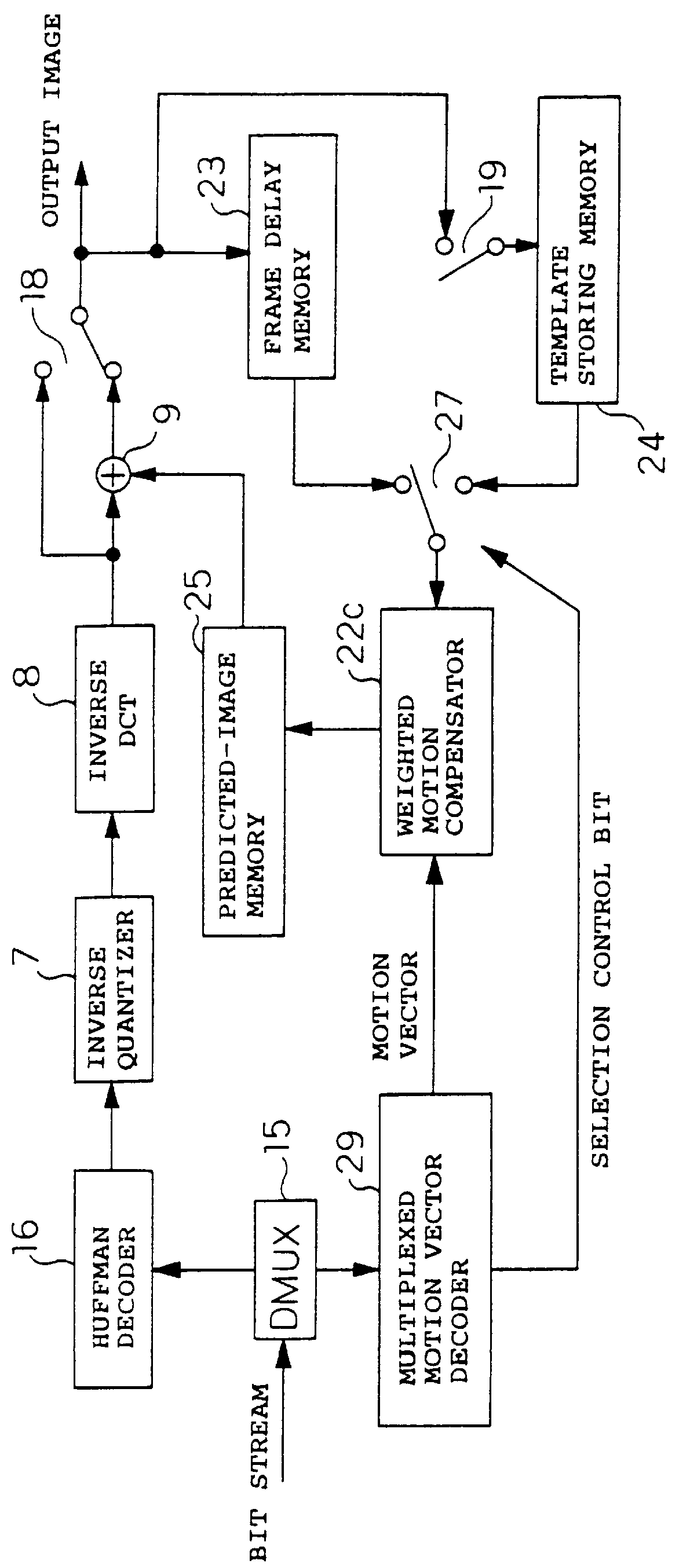
Image coding and decoding apparatus and methods thereof
InactiveUS6081551APicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesCode conversionExtensibilityMotion vector
To achieve an image encoding apparatus that has extensibility by not limiting an image to be referenced, and that can reduce processing time satisfactorily if the processing of an ordinary frame is skipped, the apparatus of the present invention comprises: motion detecting means for detecting a motion vector for each block of a prescribed size from a reference image and an input image; weighted motion-compensation means for, based on the detected motion vector, extracting from the reference image an area of a prescribed size which is wider than the prescribed block size and which contains an area corresponding to each block of the input image, and for creating a predicted image for the input image by applying a predetermined weight to each of pixels in the wider area and by using the weighted pixels of the wider area; a predicted-image memory for storing the predicted image; encoding means for taking a residual between the stored predicted image and the input image, and for encoding the residual; and decoding means for decoding the encoded image data and thereby obtaining a reference image.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
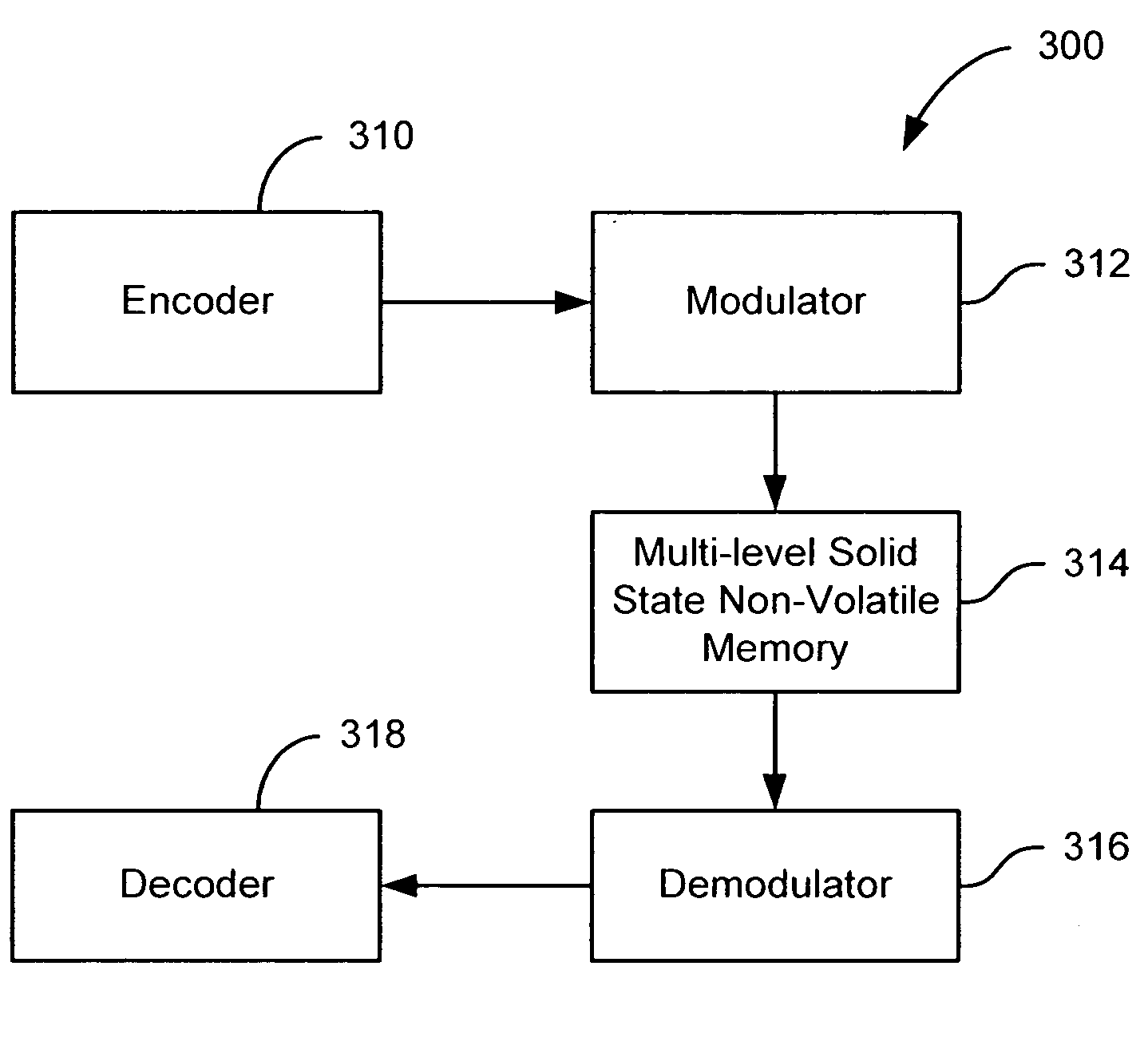
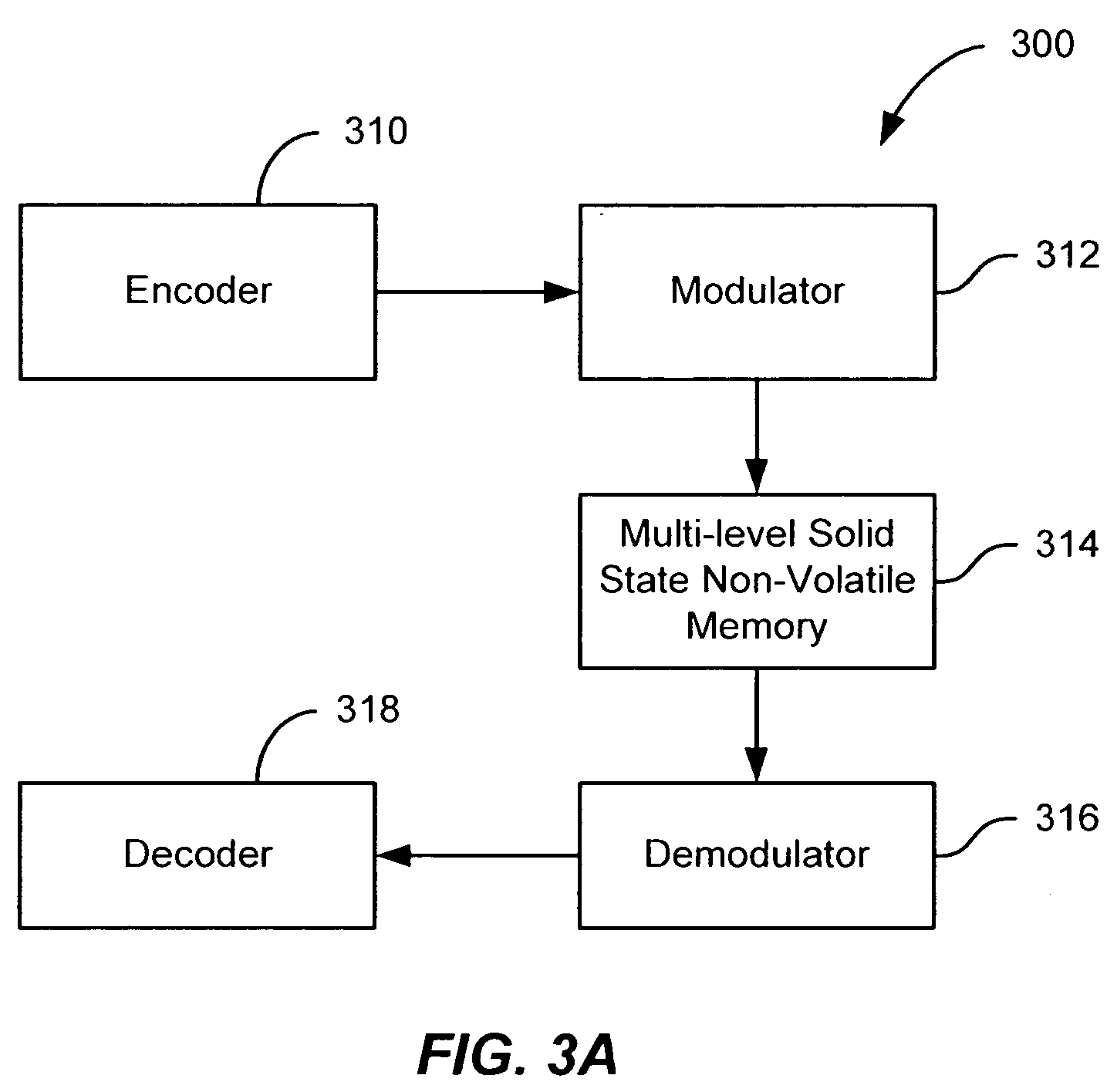
Flash memory with coding and signal processing
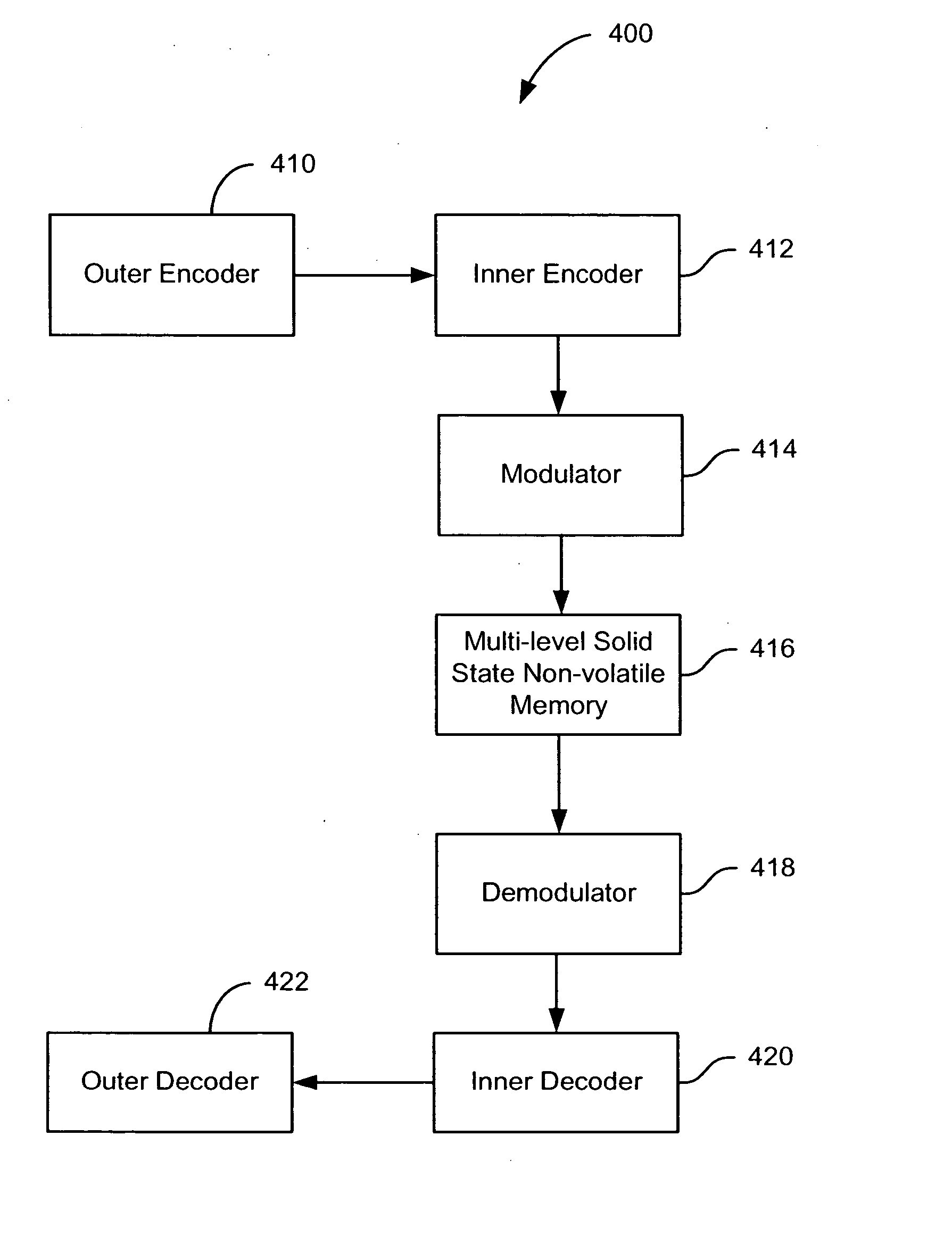
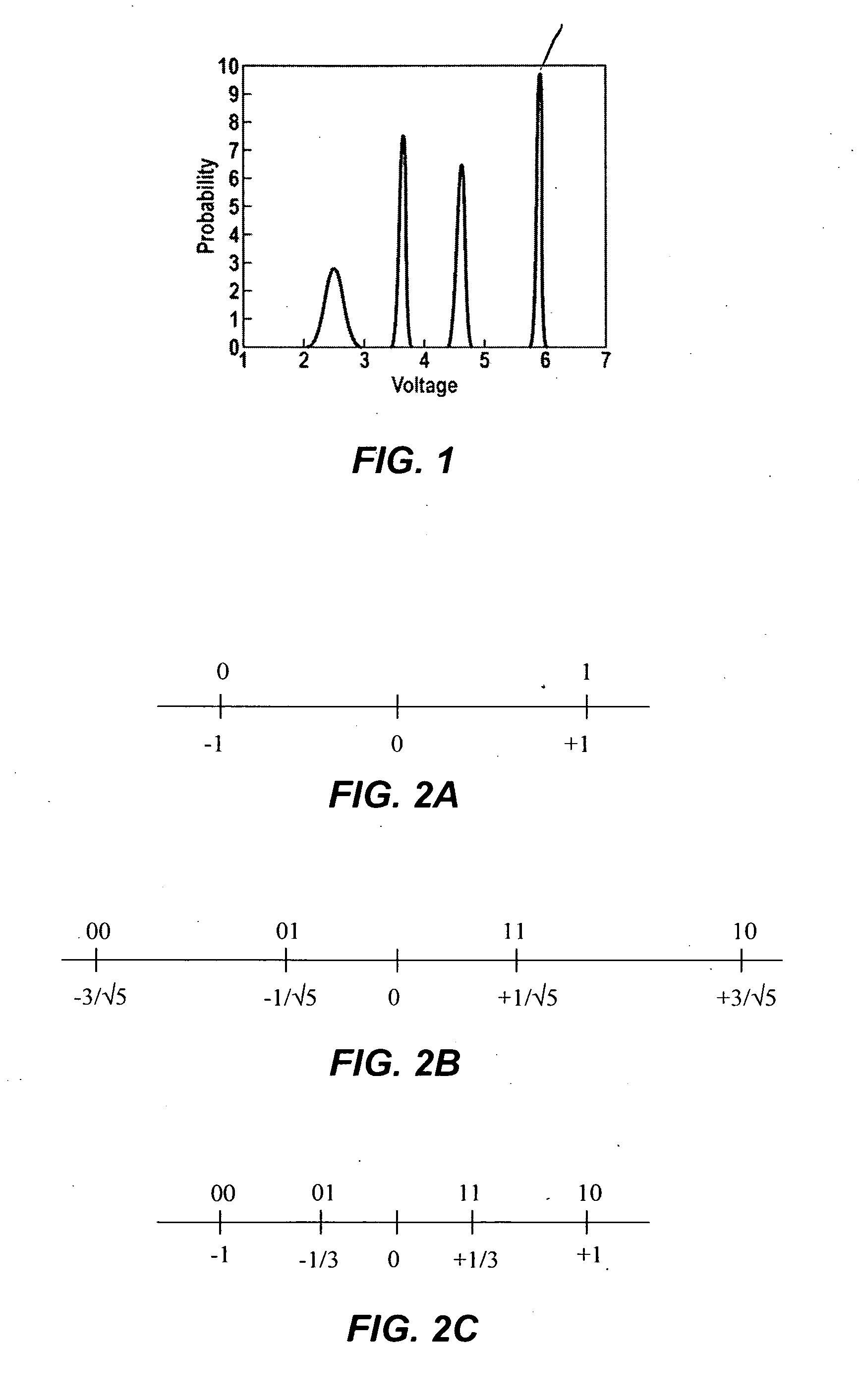
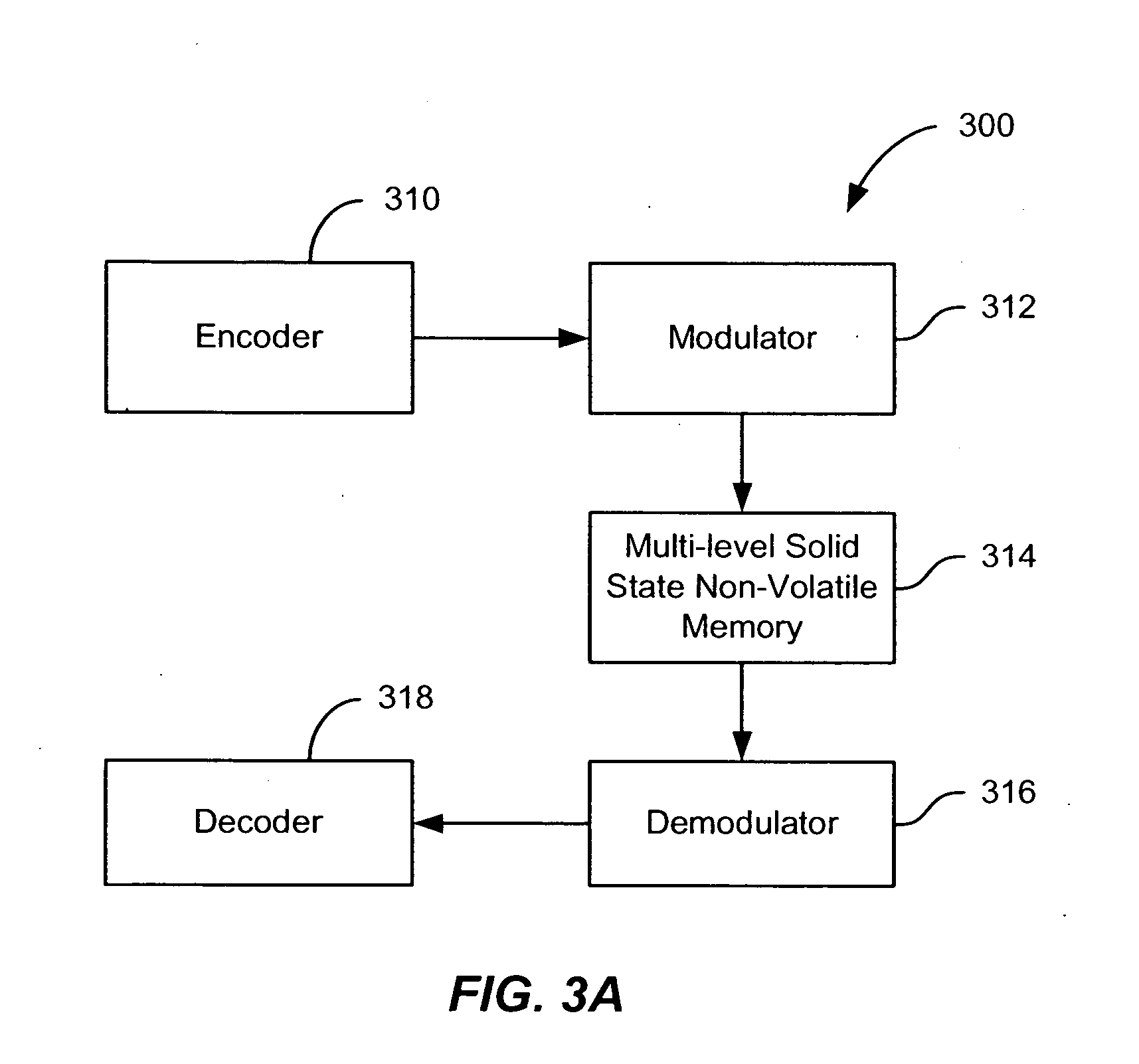
A solid state non-volatile memory unit includes, in part, an encoder, a multi-level solid state non-volatile memory array adapted to store data encoded by the encoder, and a decoder adapted to decode the data retrieved from the memory array. The memory array may be a flash EEPROM array. The memory unit optionally includes a modulator and a demodulator. The data modulated by the modulator is stored in the memory array. The demodulator demodulates the modulated data retrieved from the memory array.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
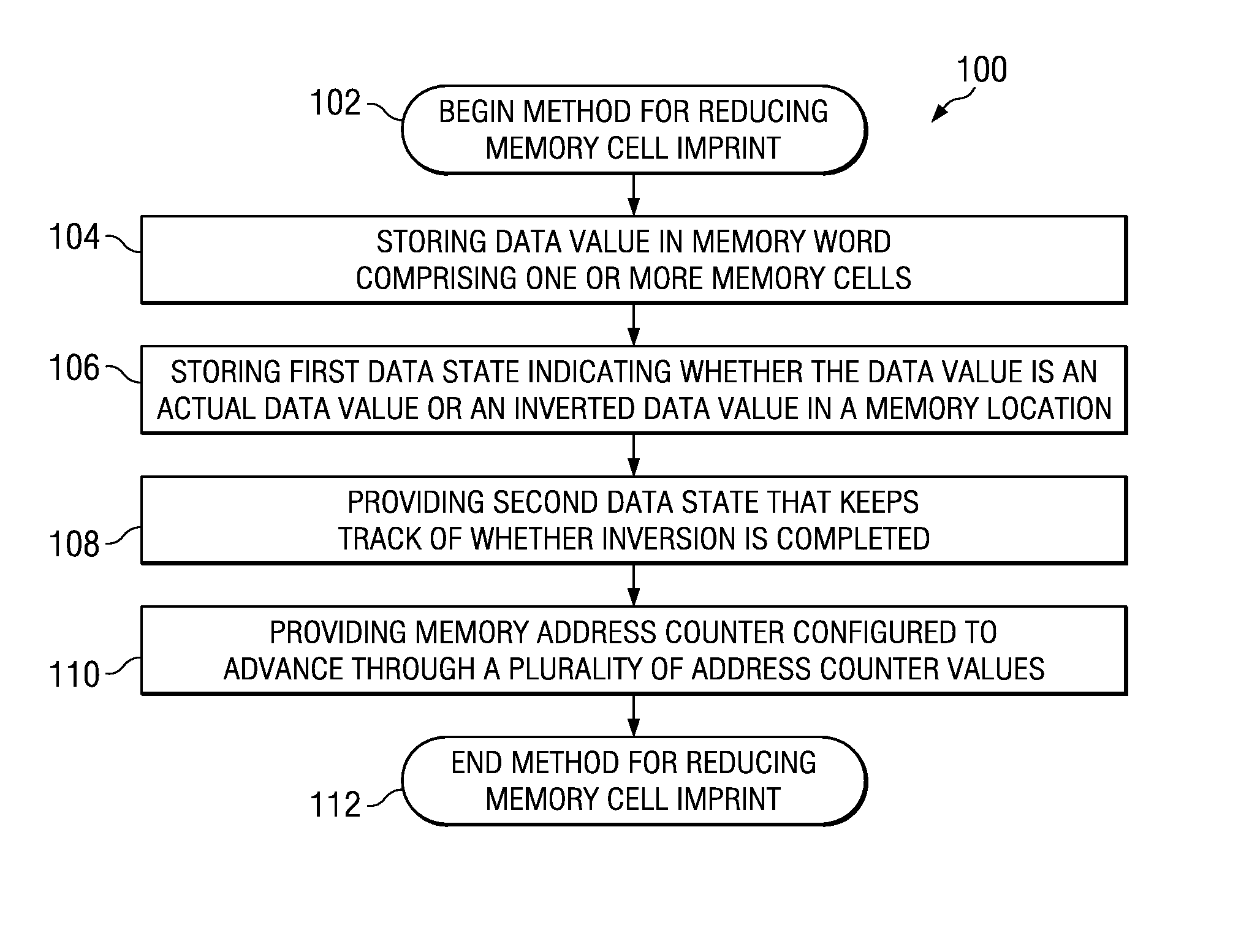
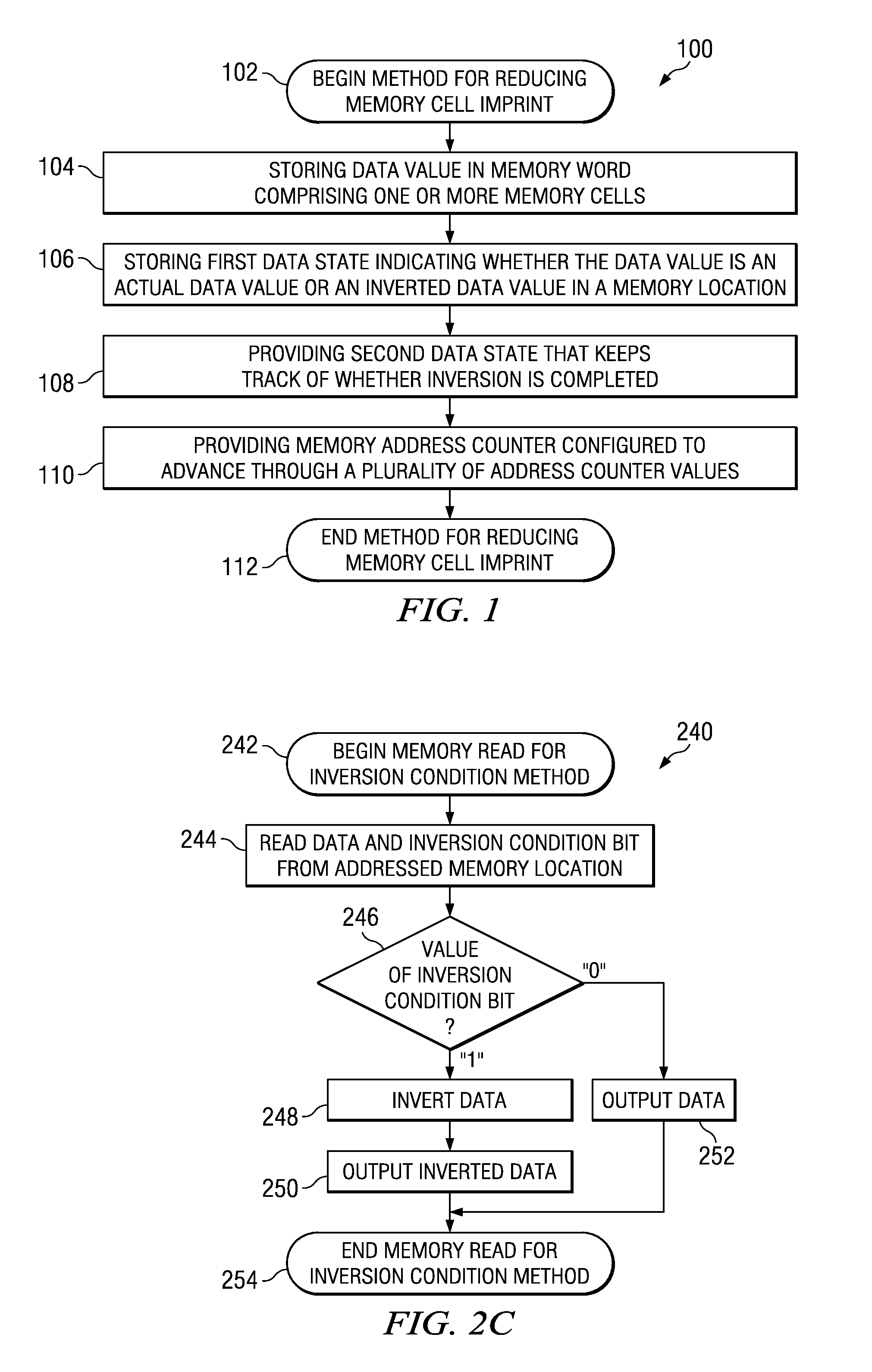
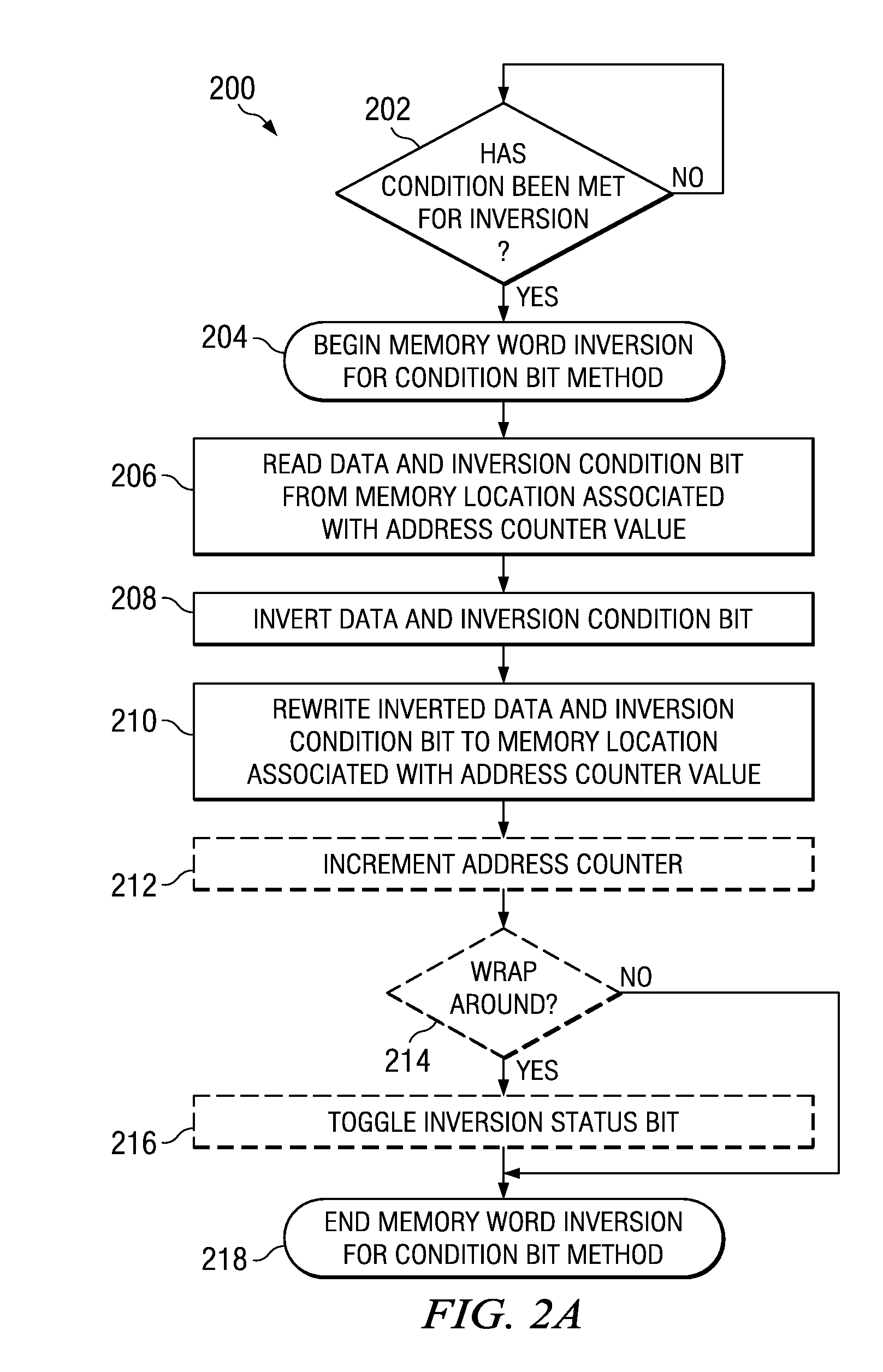
Technique for memory imprint reliability improvement
One embodiment of the present invention relates to a method of reducing imprint of a memory cell. The method comprises adding an inversion condition bit operably associated with one or more memory cells storing a memory word. The inversion condition bit indicates whether the memory word represents an actual payload or an inversion of the actual payload. The inversion condition bit and memory word are selectively toggled by a control circuitry. Inversion is performed by reading the inversion condition bit and memory word and rewriting the memory word back to the one or more memory cells in an inverted or non-inverted state, depending on an inversion condition bit. The inversion condition bit is then written to the inversion status bit value. The memory address is incremented, and the inversion status data state is toggled once the address counter addresses the entire memory array. Other methods and circuits are also disclosed.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Multi-Level Striping and Truncation Channel-Equalization for Flash-Memory System
InactiveUS20090240873A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationError preventionLogical block addressingData access
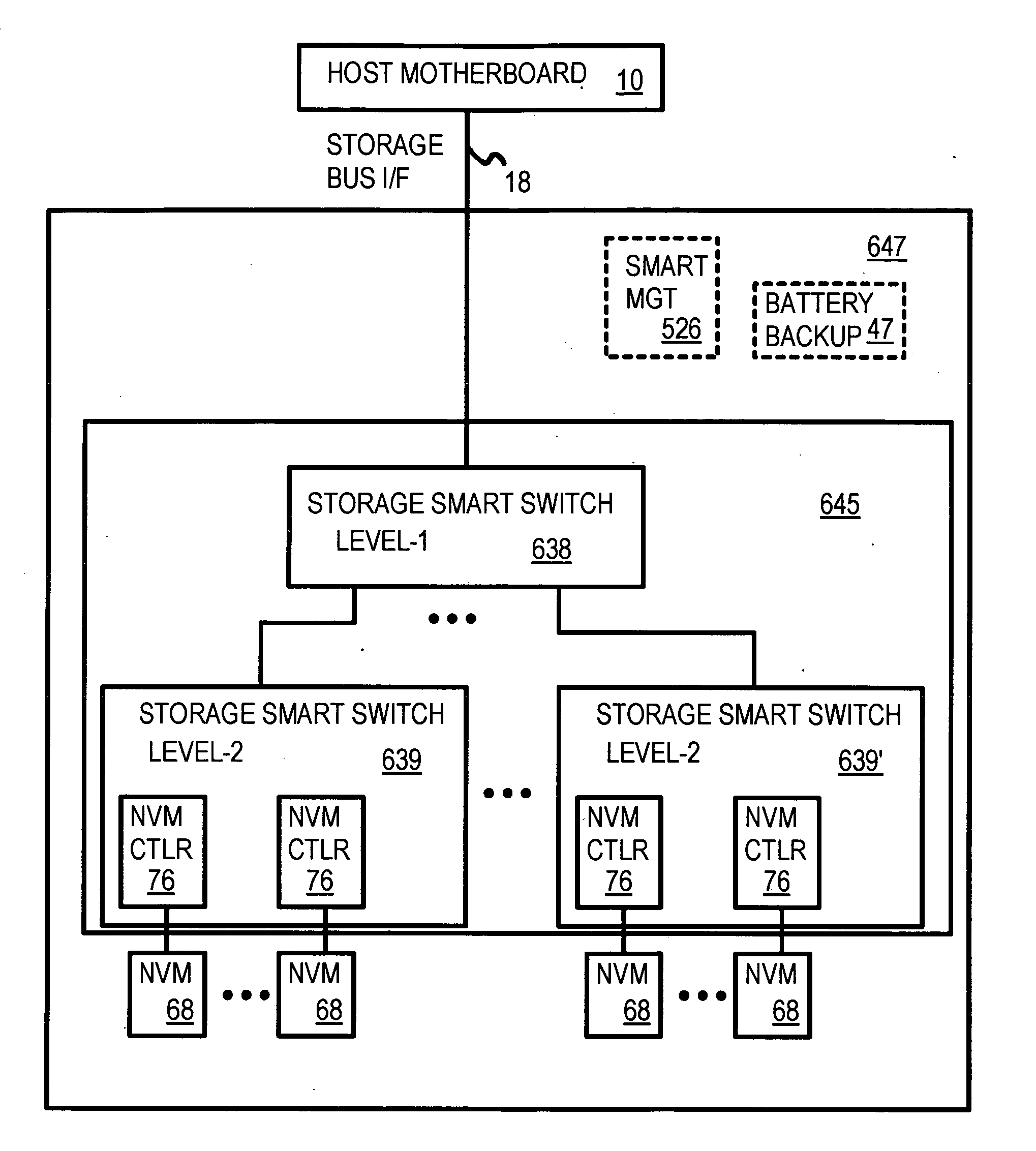
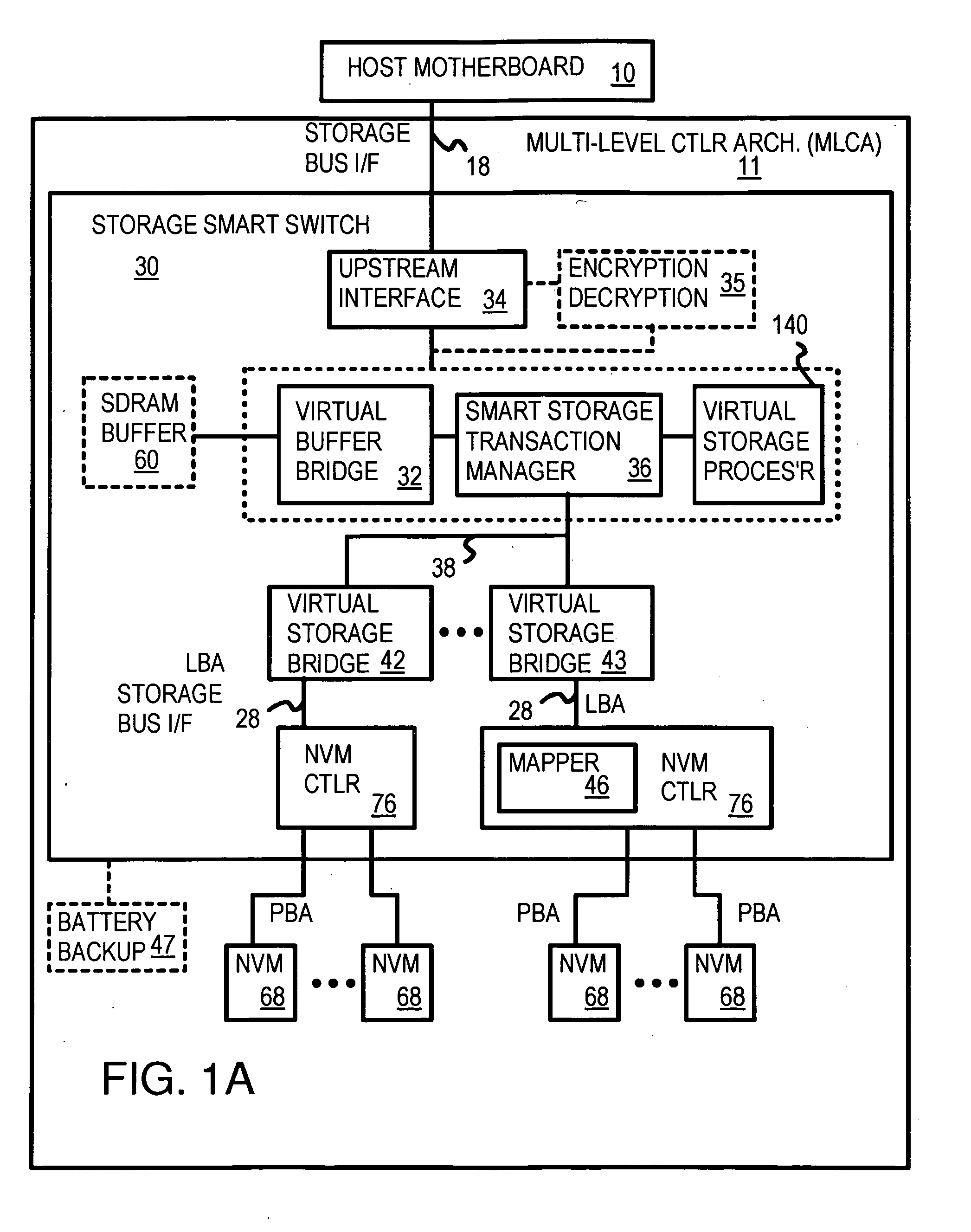
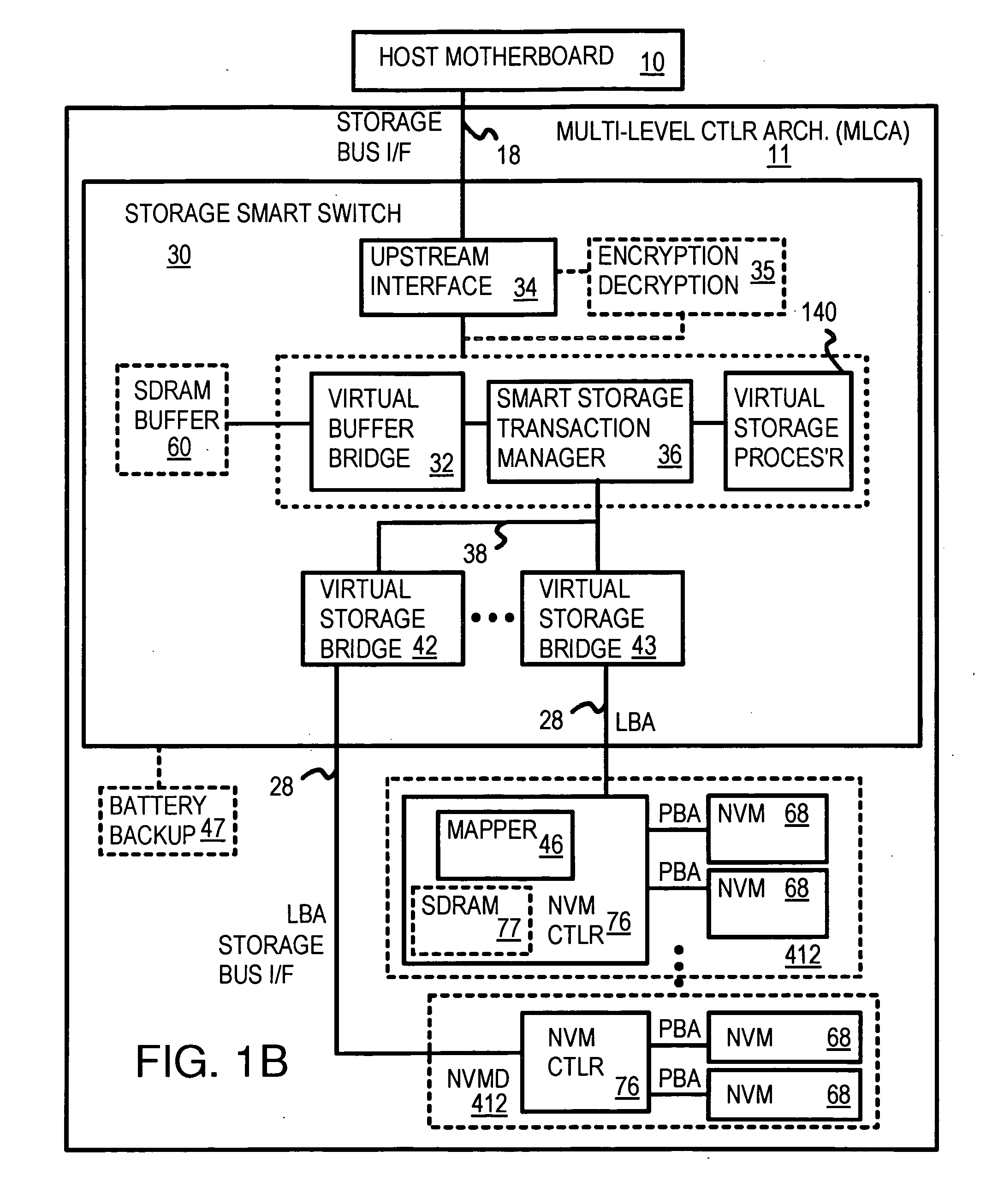
Truncation reduces the available striped data capacity of all flash channels to the capacity of the smallest flash channel. A solid-state disk (SSD) has a smart storage switch salvages flash storage removed from the striped data capacity by truncation. Extra storage beyond the striped data capacity is accessed as scattered data that is not striped. The size of the striped data capacity is reduced over time as more bad blocks appear. A first-level striping map stores striped and scattered capacities of all flash channels and maps scattered and striped data. Each flash channel has a Non-Volatile Memory Device (NVMD) with a lower-level controller that converts logical block addresses (LBA) to physical block addresses (PBA) that access flash memory in the NVMD. Wear-leveling and bad block remapping are preformed by each NVMD. Source and shadow flash blocks are recycled by the NVMD. Two levels of smart storage switches enable three-level controllers.
Owner:SUPER TALENT TECH CORP
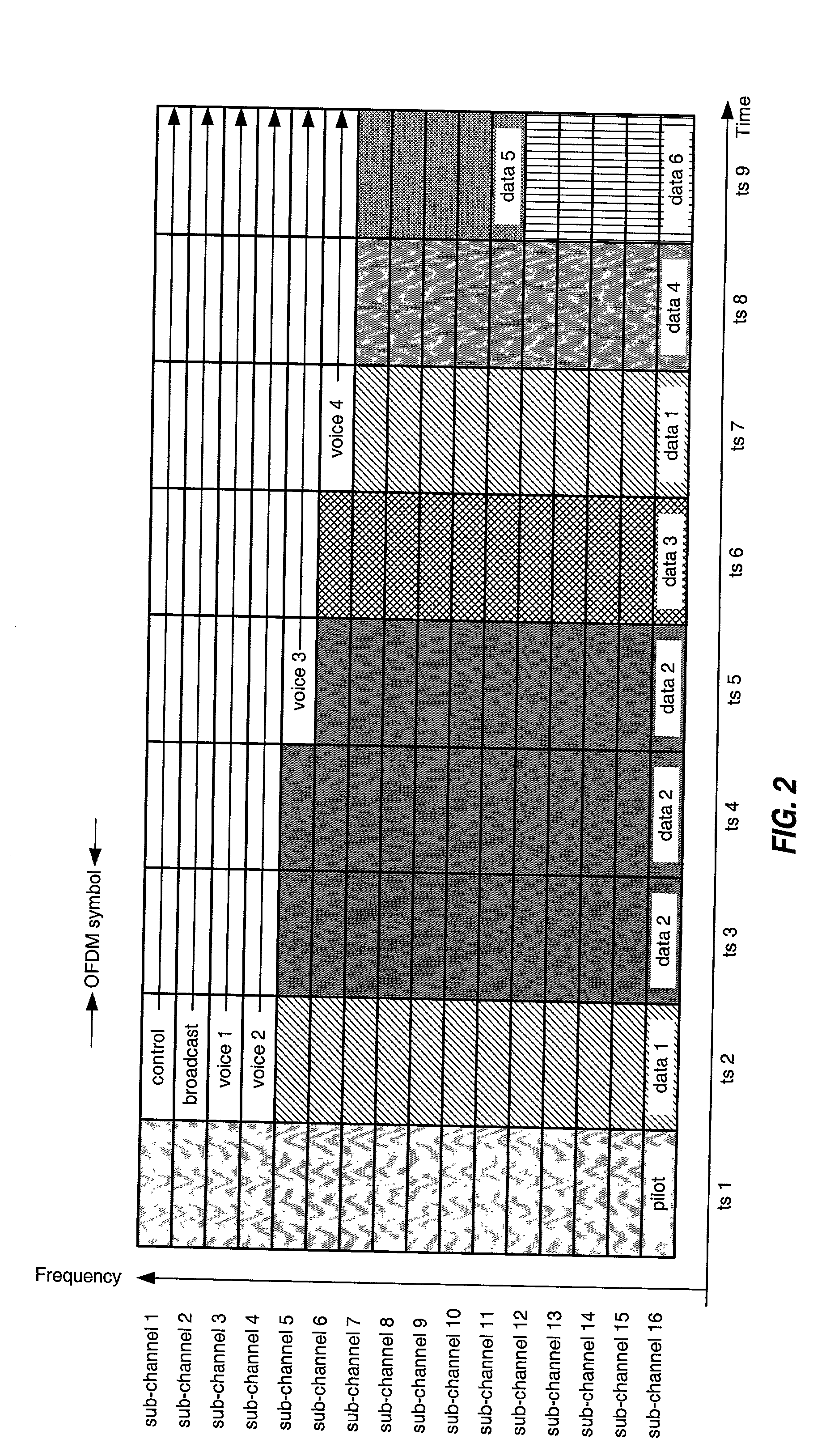
Coding scheme for a wireless communication system
InactiveUS20030043928A1High data transmission reliabilityRemove correlationData representation error detection/correctionColor television with pulse code modulationBase codePre-condition
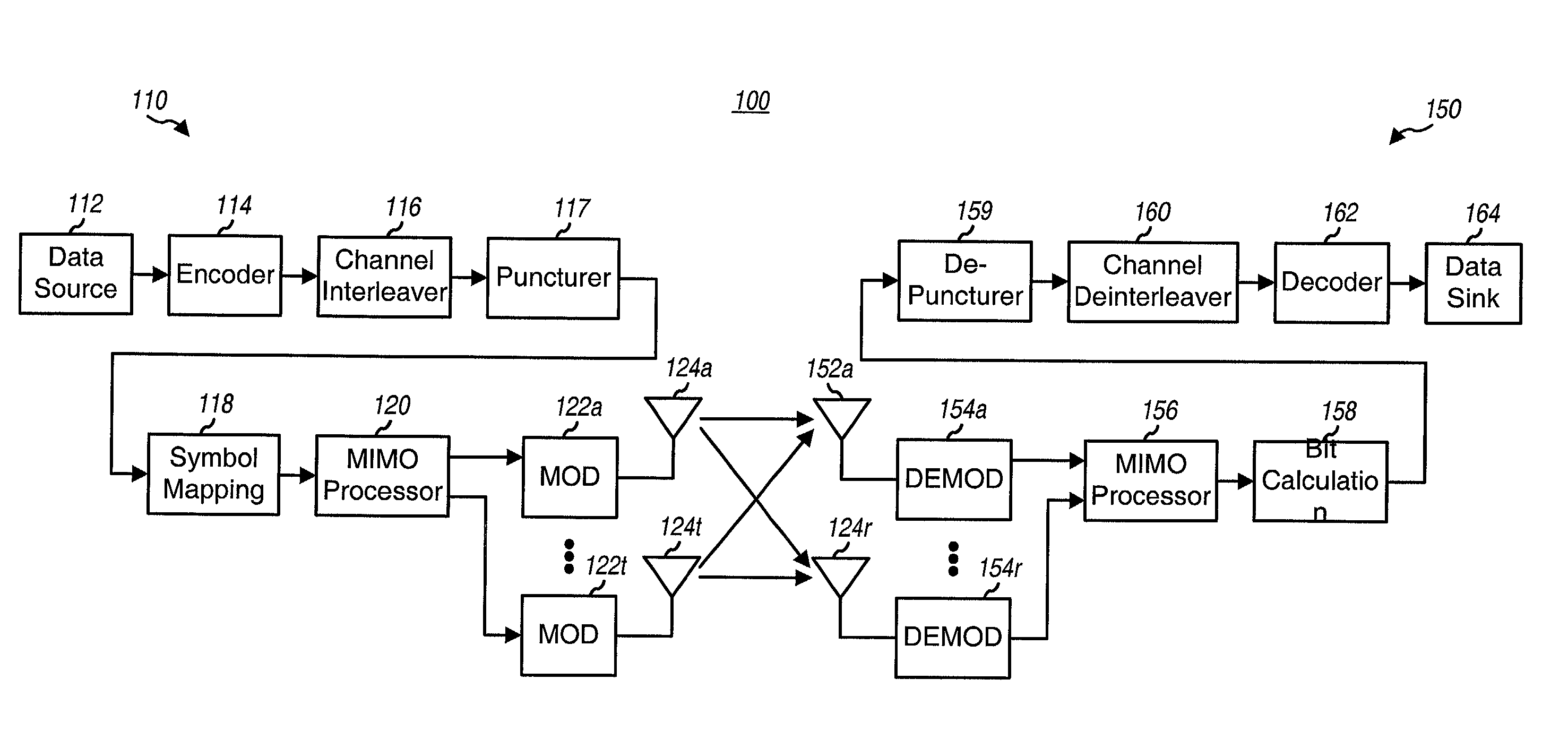
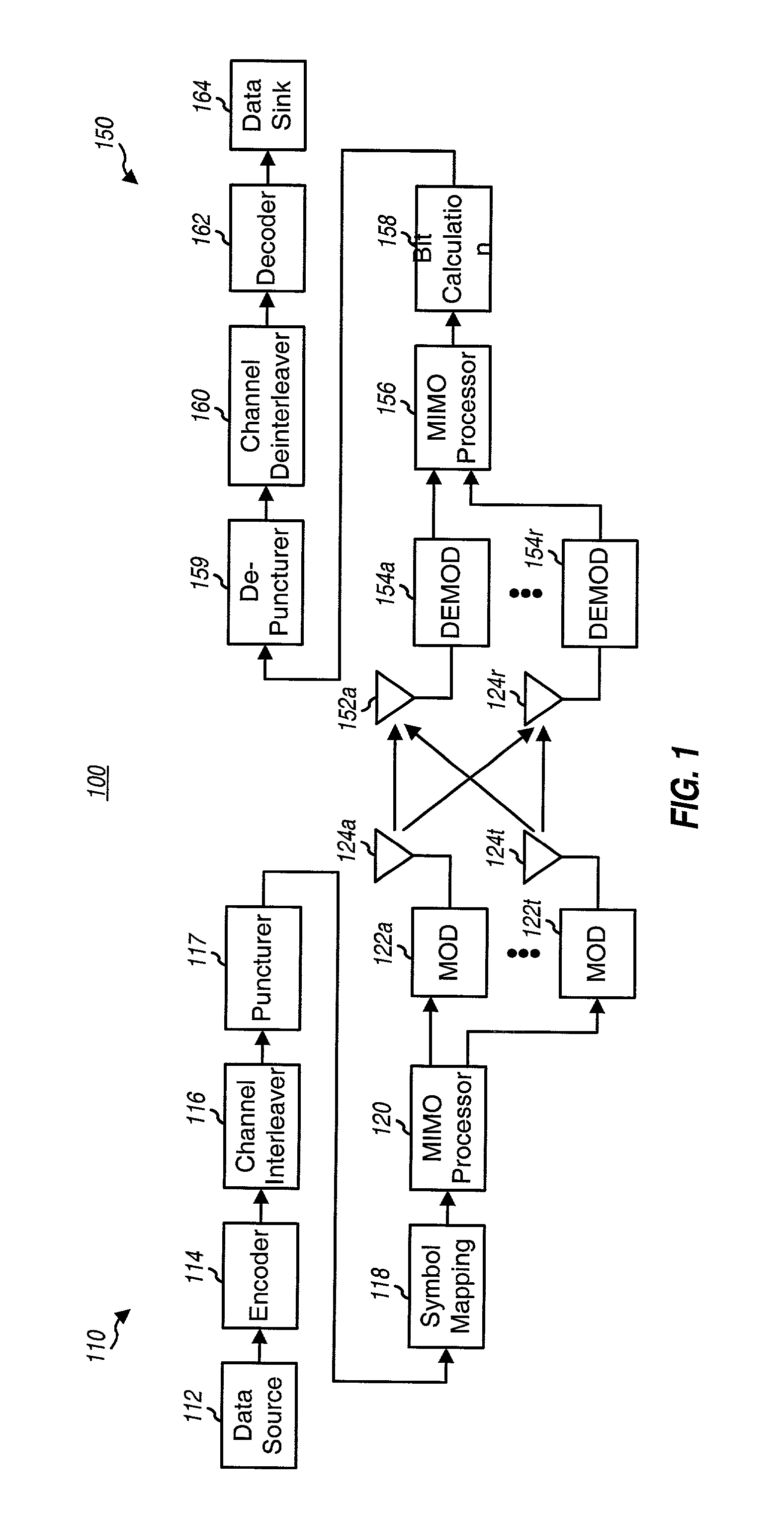
Coding techniques for a (e.g., OFDM) communication system capable of transmitting data on a number of "transmission channels" at different information bit rates based on the channels' achieved SNR. A base code is used in combination with common or variable puncturing to achieve different coding rates required by the transmission channels. The data (i.e., information bits) for a data transmission is encoded with the base code, and the coded bits for each channel (or group of channels with the similar transmission capabilities) are punctured to achieve the required coding rate. The coded bits may be interleaved (e.g., to combat fading and remove correlation between coded bits in each modulation symbol) prior to puncturing. The unpunctured coded bits are grouped into non-binary symbols and mapped to modulation symbols (e.g., using Gray mapping). The modulation symbol may be "pre-conditioned" and prior to transmission.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
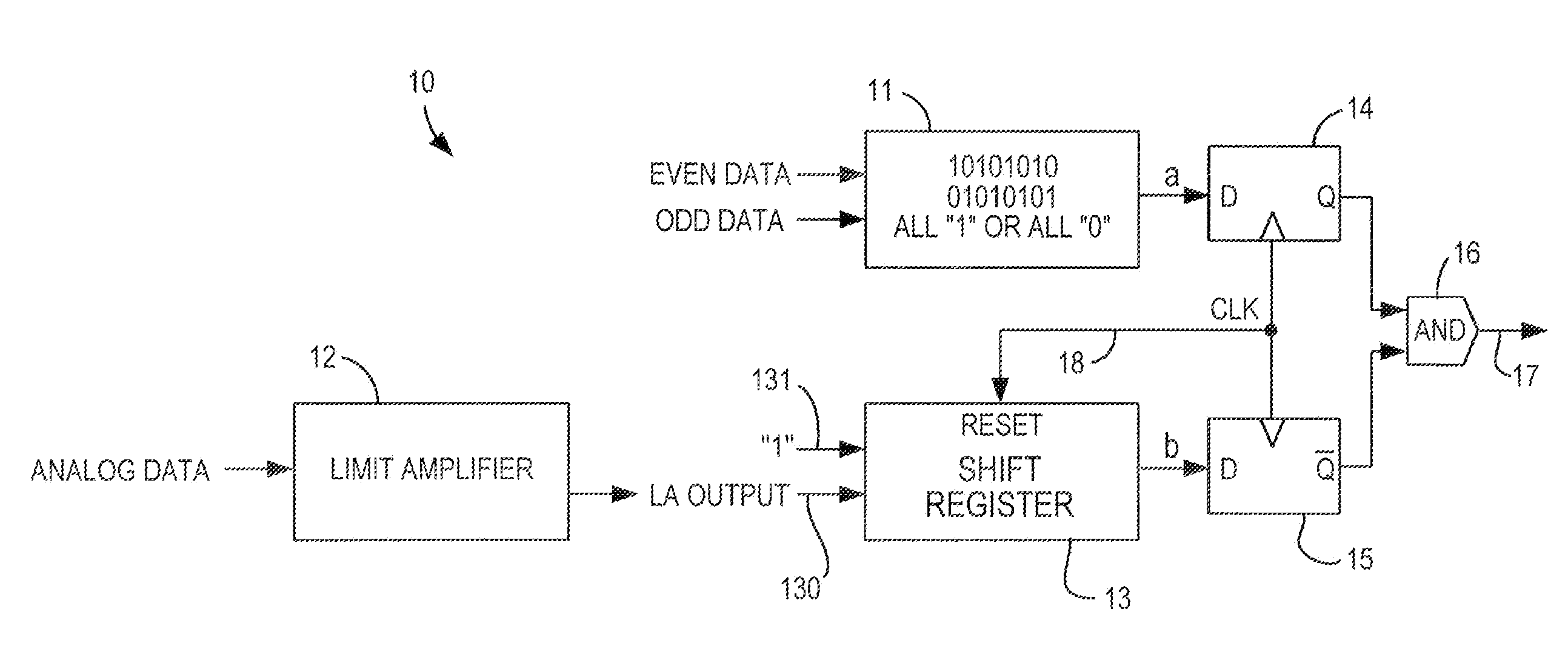
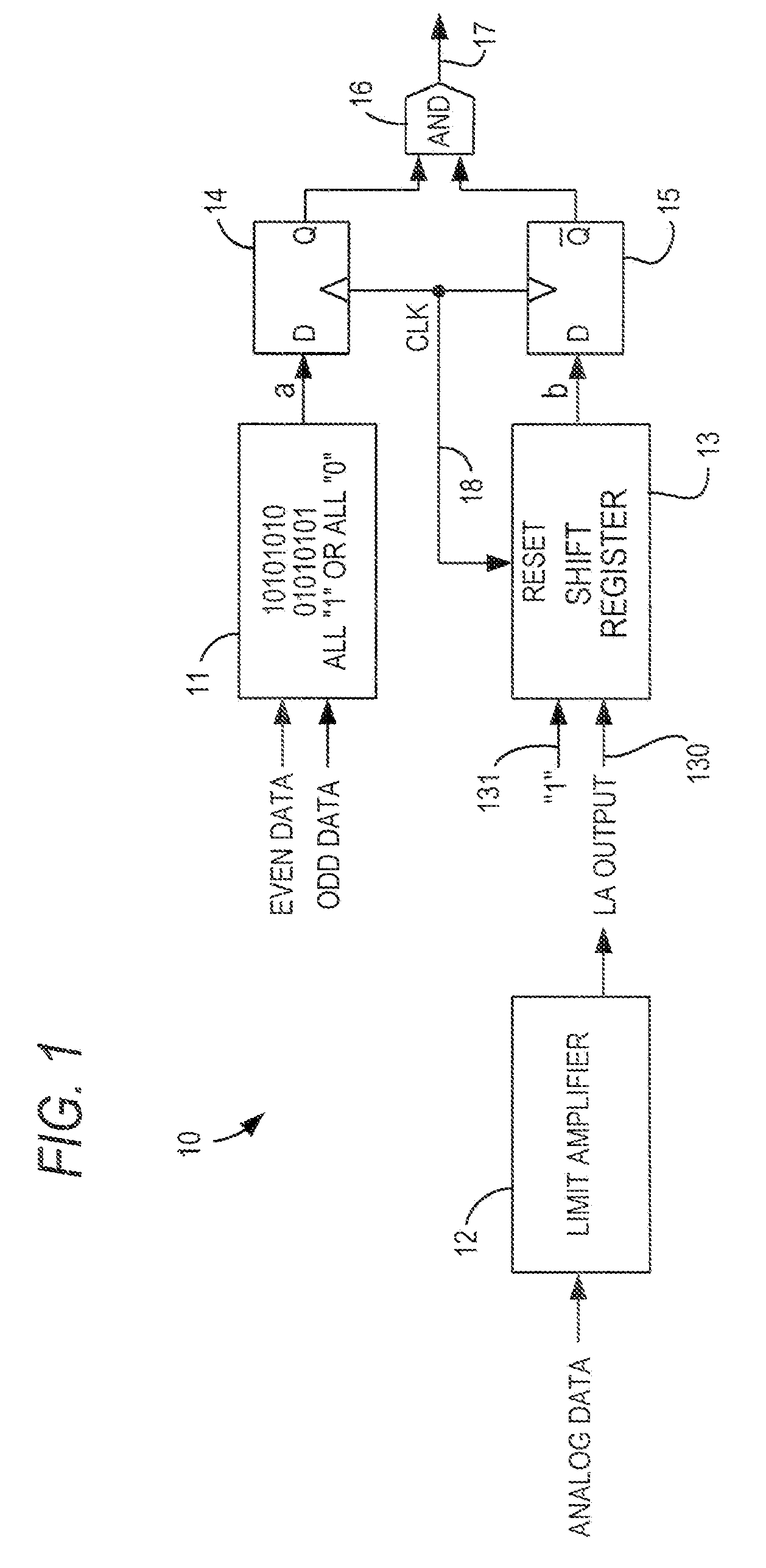
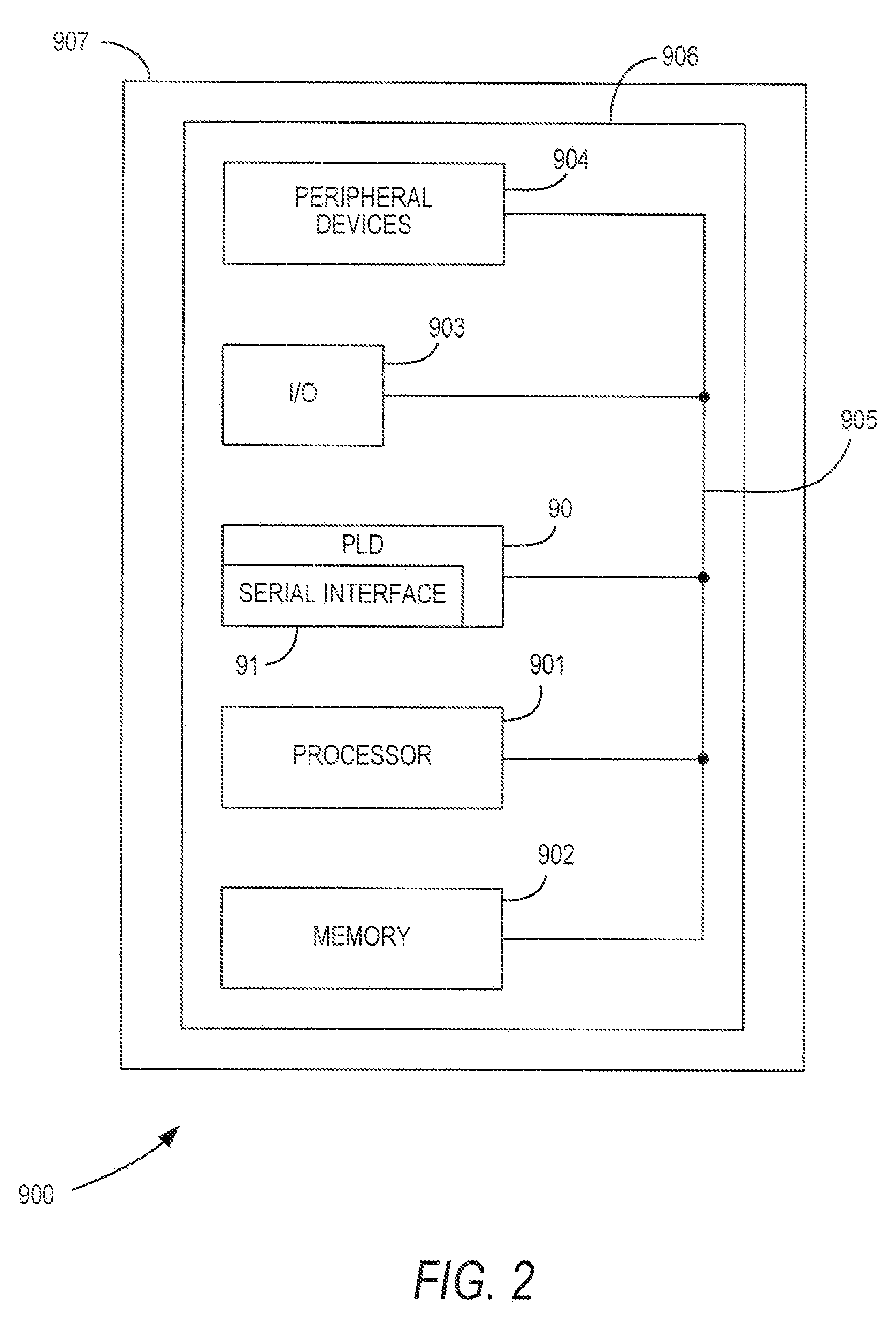
Signal loss detector for high-speed serial interface of a programmable logic device
InactiveUS7996749B2Multiple-port networksData representation error detection/correctionPattern matchingProgrammable logic device
Owner:ALTERA CORP
Generating and matching hashes of multimedia content
ActiveUS20020178410A1RobustRobust hashingElectrophonic musical instrumentsCode conversionFrequency spectrumAlgorithm
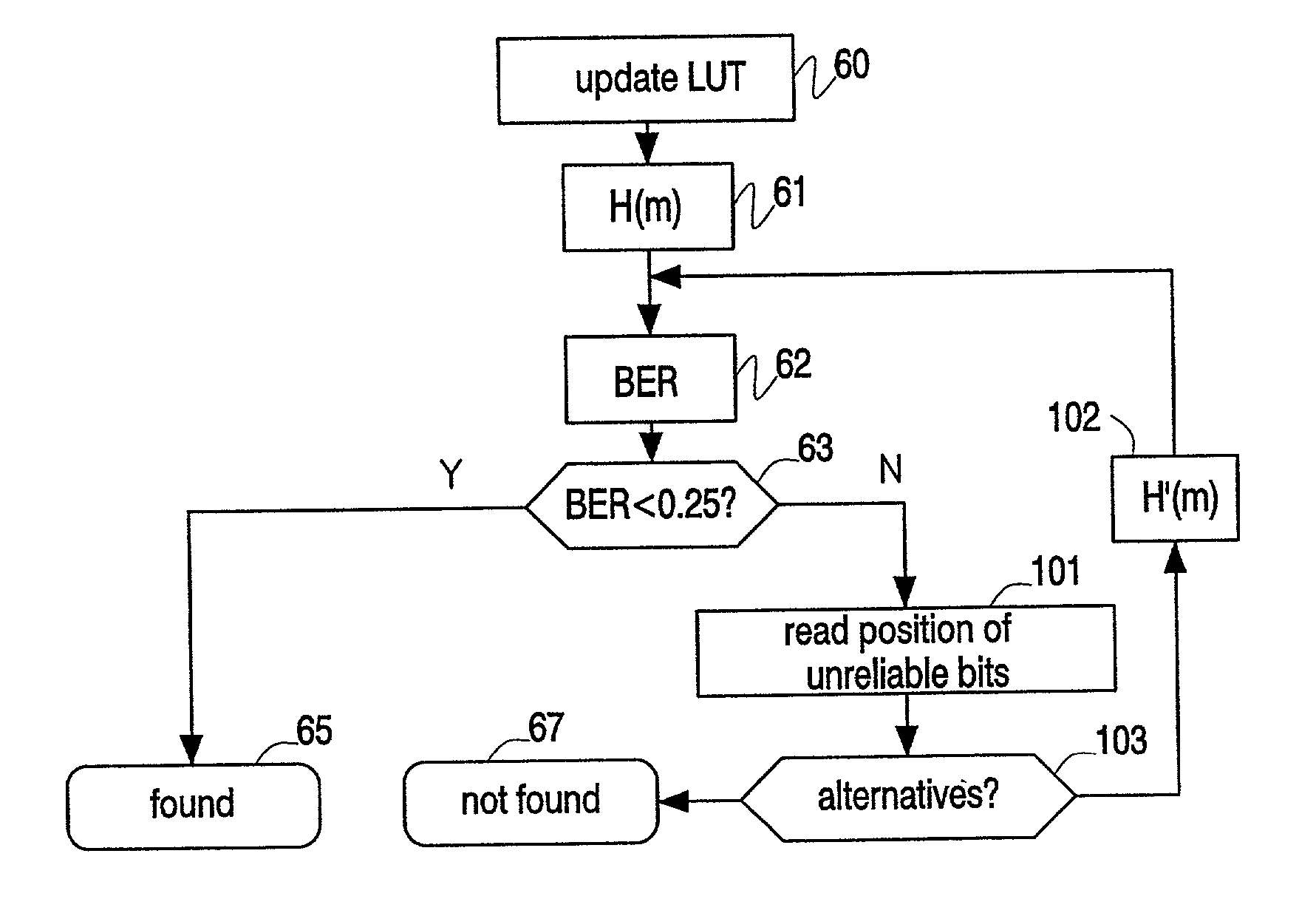
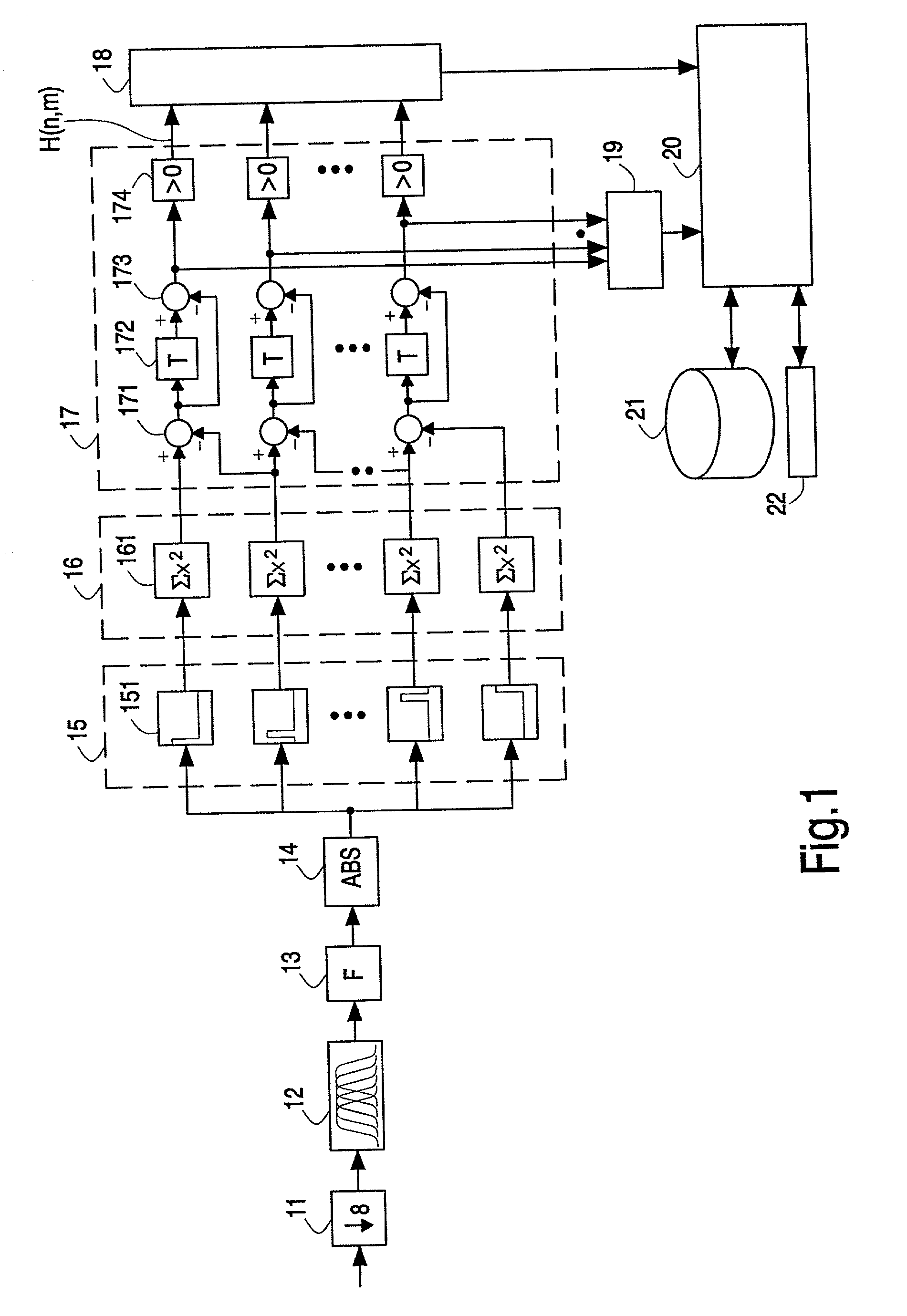
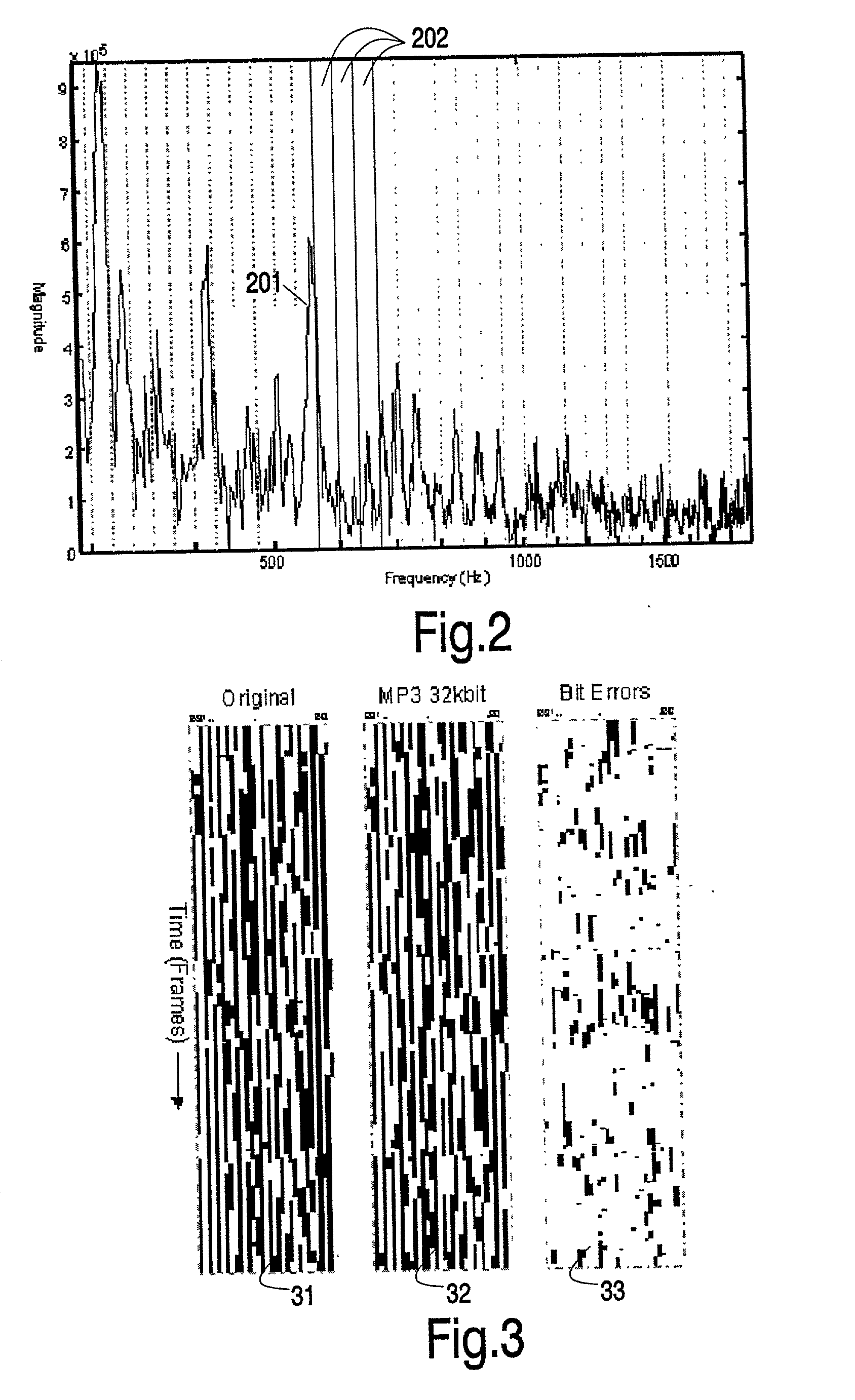
Hashes are short summaries or signatures of data files which can be used to identify the file. Hashing multimedia content (audio, video, images) is difficult because the hash of original content and processed (e.g. compressed) content may differ significantly. The disclosed method generates robust hashes for multimedia content, for example, audio clips. The audio clip is divided (12) into successive (preferably overlapping) frames. For each frame, the frequency spectrum is divided (15) into bands. A robust property of each band (e.g. energy) is computed (16) and represented (17) by a respective hash bit. An audio clip is thus represented by a concatenation of binary hash words, one for each frame. To identify a possibly compressed audio signal, a block of hash words derived therefrom is matched by a computer (20) with a large database (21). Such matching strategies are also disclosed. In an advantageous embodiment, the extraction process also provides information (19) as to which of the hash bits are the least reliable. Flipping these bits considerably improves the speed and performance of the matching process.
Owner:GRACENOTE
Robust visual passwords
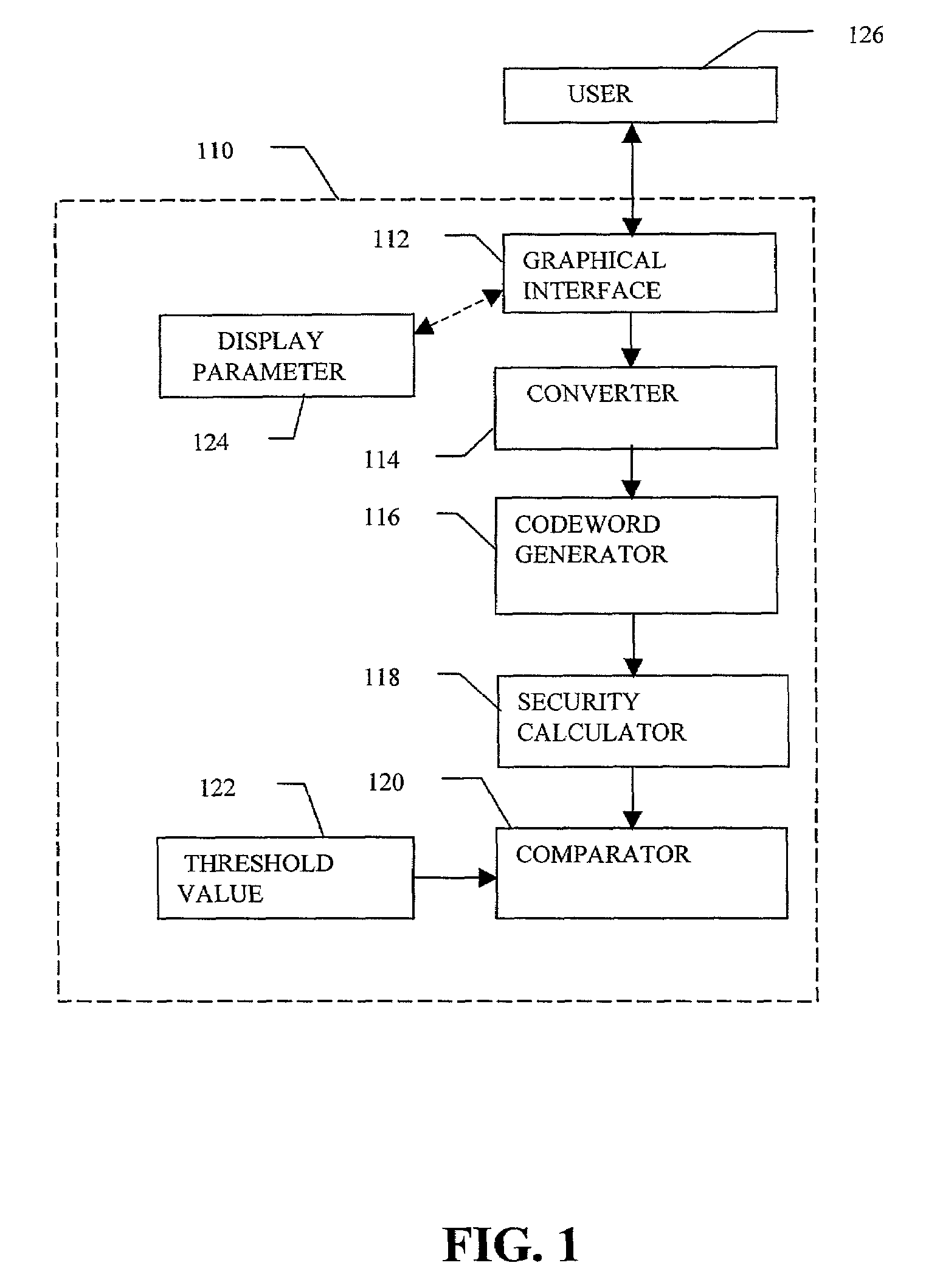
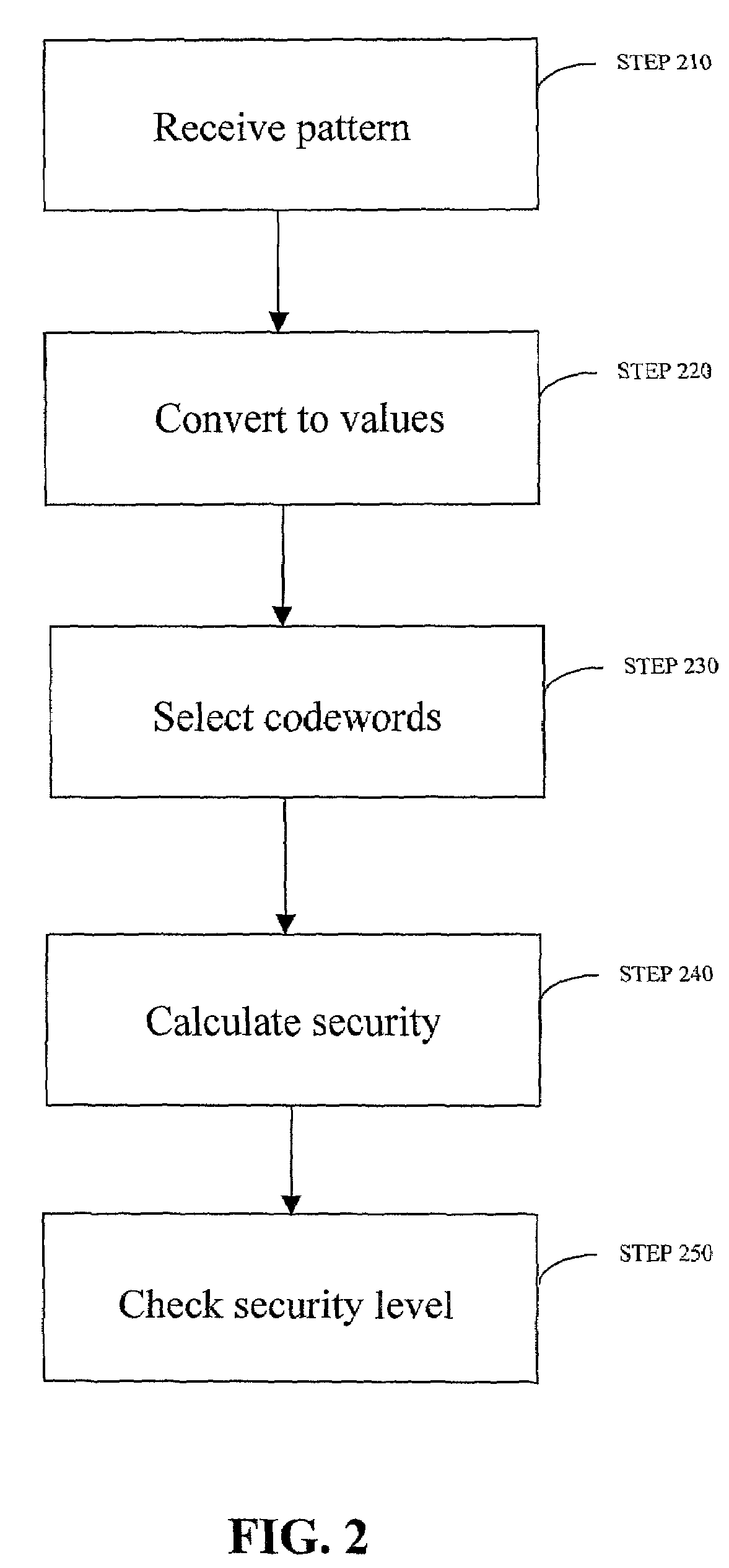
InactiveUS7219368B2Easy to rememberKey distribution for secure communicationPublic key for secure communicationGraphicsUser input
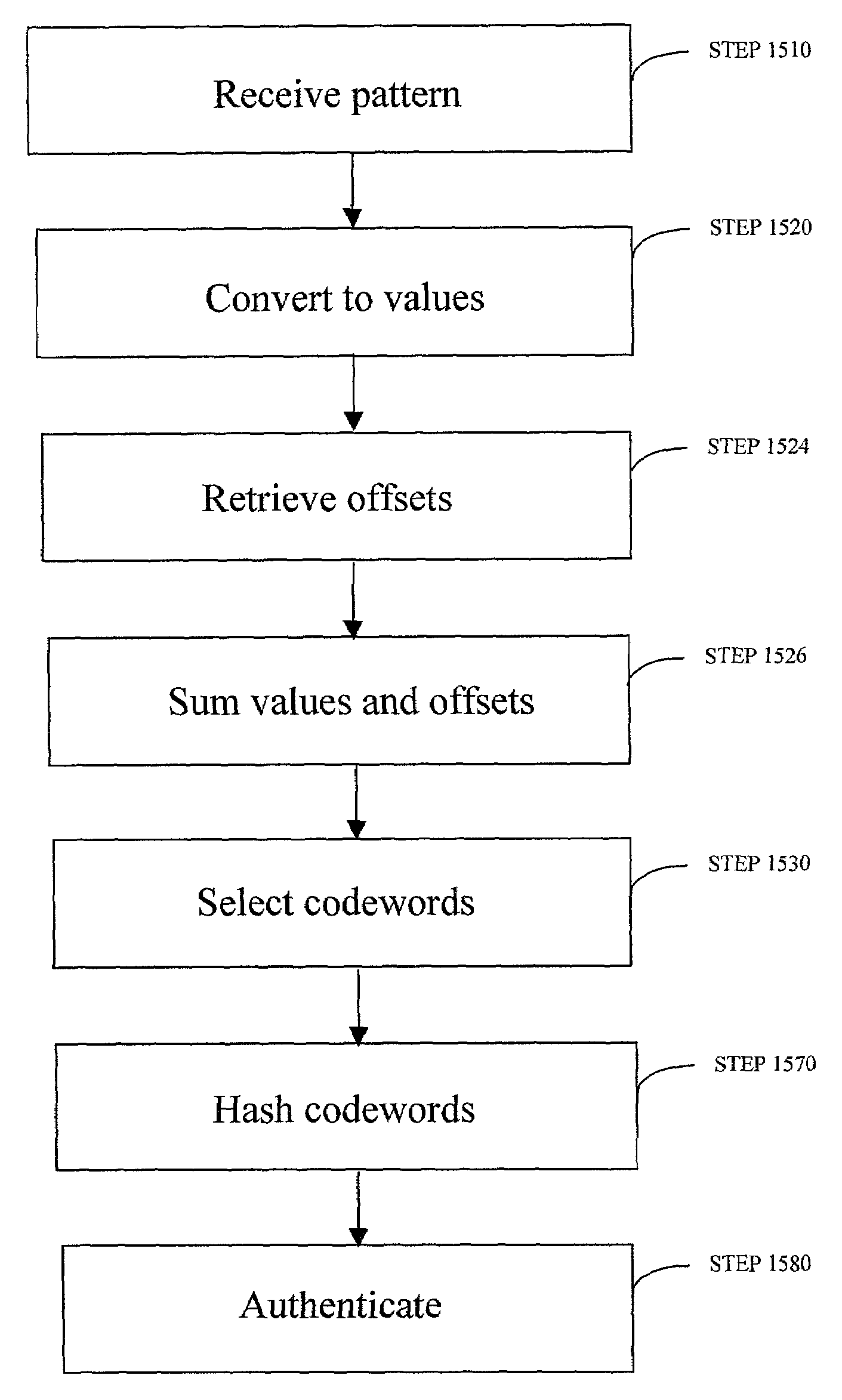
Enrollment and authentication of a user based on a sequence of discrete graphical choices is described. A graphical interface presents various images and memory cues that a user may associate with their original graphical choices. Enrollment may require the input to have a security parameter value that meets or exceeds a threshold. An acceptable sequence of graphical choices is converted to a sequence of values and mapped to a sequence of codewords. Both a hash of the sequence of codewords and a sequence of offsets are stored for use in authenticating the user. An offset is the difference between a value and its corresponding codeword. Authentication requires the user to enter another sequence of discrete graphical choices that is approximately the same as original. The offsets are summed with the corresponding values before mapping to codewords. Authentication requires the sequence of codewords, or a hash thereof, to match.
Owner:RSA
Method and System for Accelerated Stream Processing
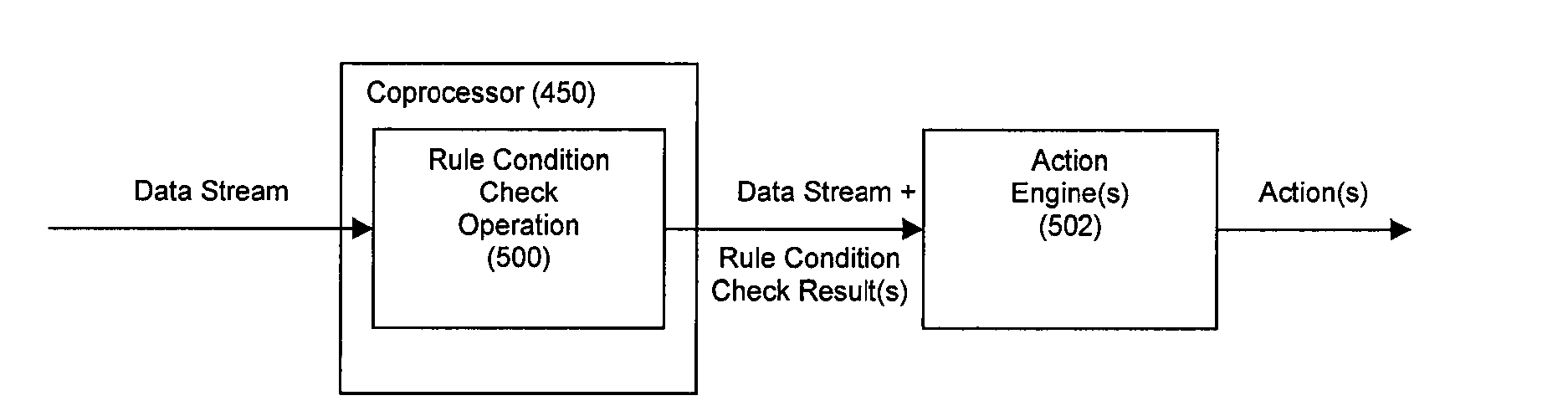
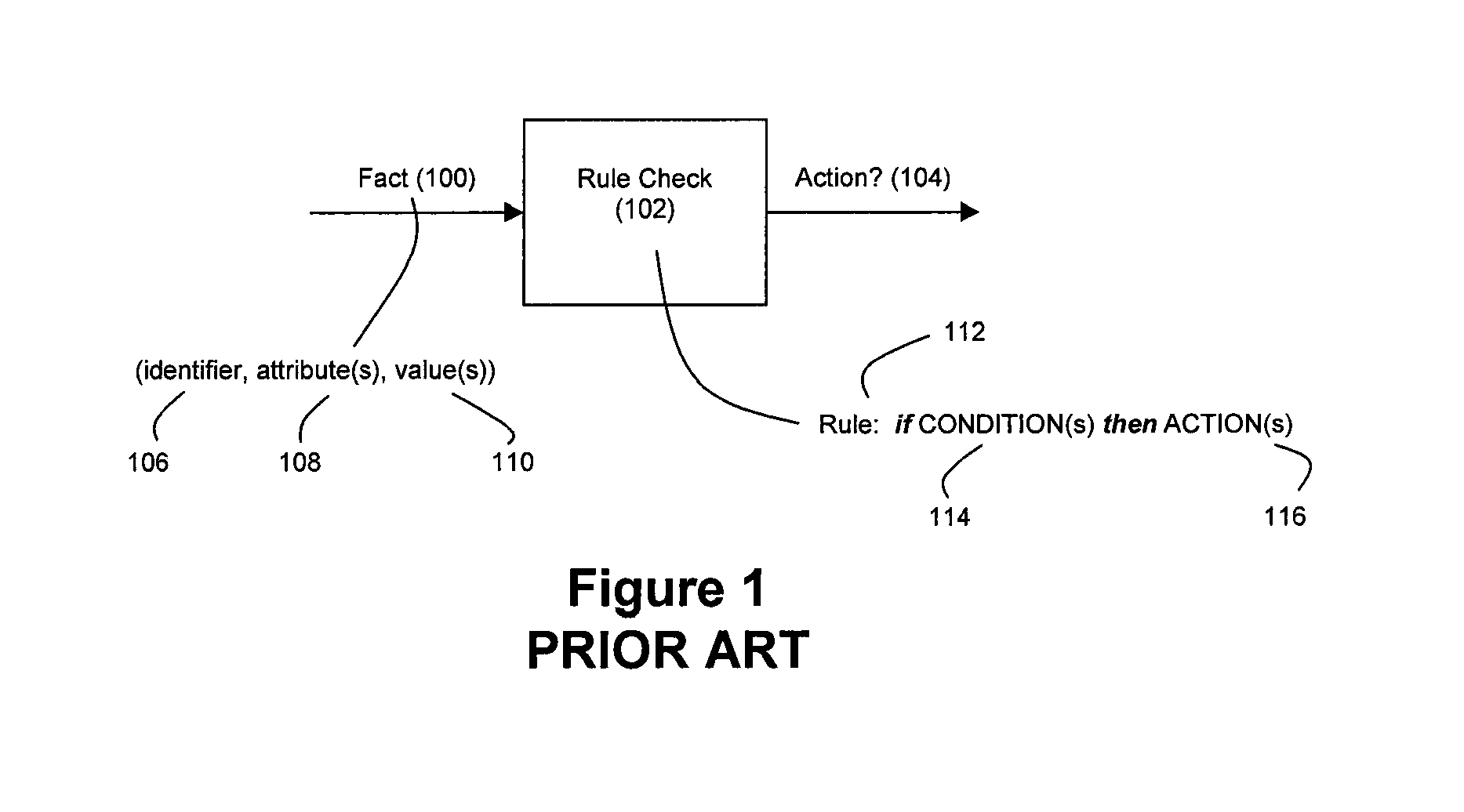
ActiveUS20090287628A1Lower latencyImprove latencyDigital computer detailsCode conversionBusiness ruleEvent stream
Disclosed herein is a method and system for hardware-accelerating various data processing operations in a rule-based decision-making system such as a business rules engine, an event stream processor, and a complex event stream processor. Preferably, incoming data streams are checked against a plurality of rule conditions. Among the data processing operations that are hardware-accelerated include rule condition check operations, filtering operations, and path merging operations. The rule condition check operations generate rule condition check results for the processed data streams, wherein the rule condition check results are indicative of any rule conditions which have been satisfied by the data streams. The generation of such results with a low degree of latency provides enterprises with the ability to perform timely decision-making based on the data present in received data streams.
Owner:IP RESERVOIR
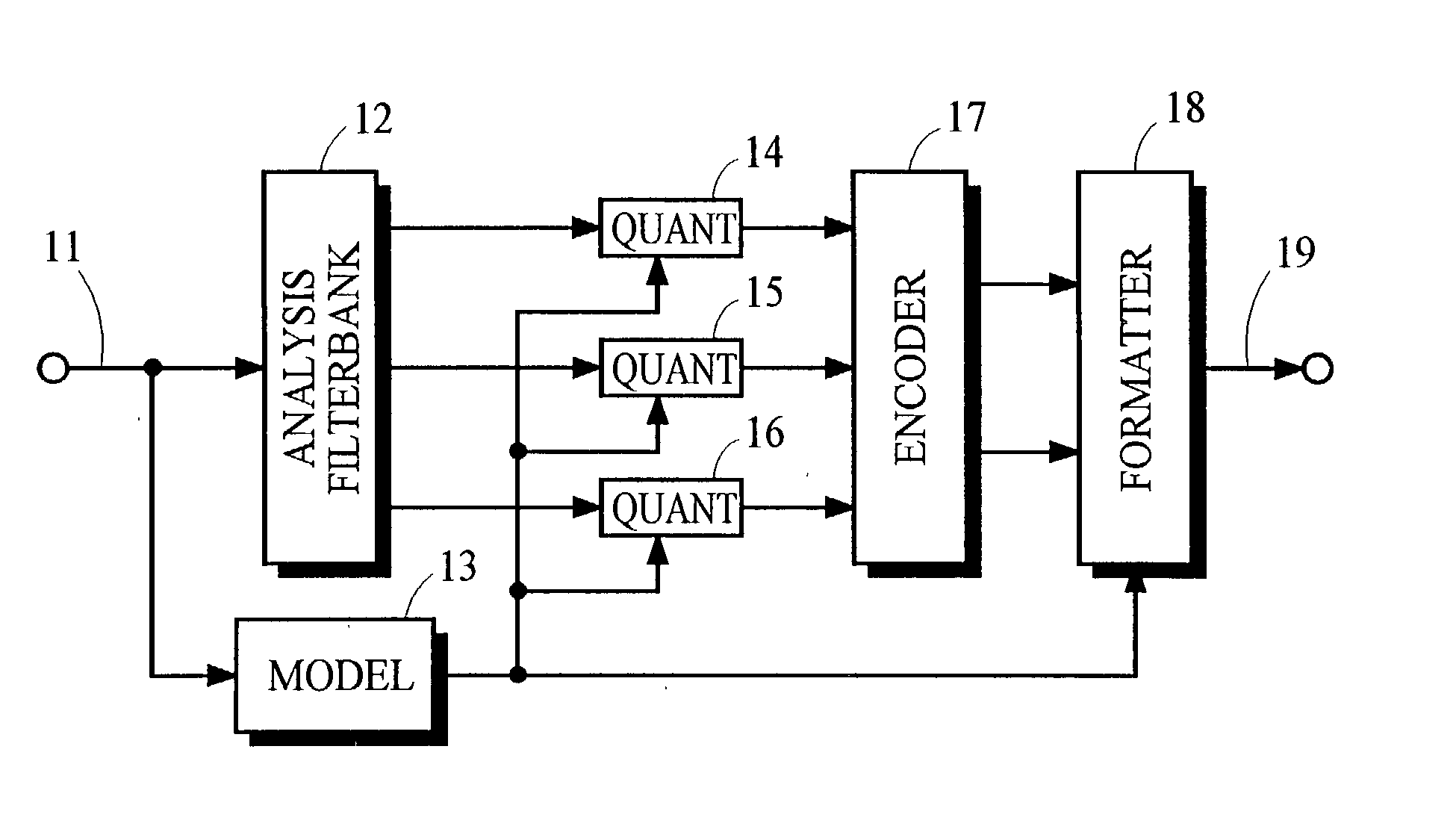
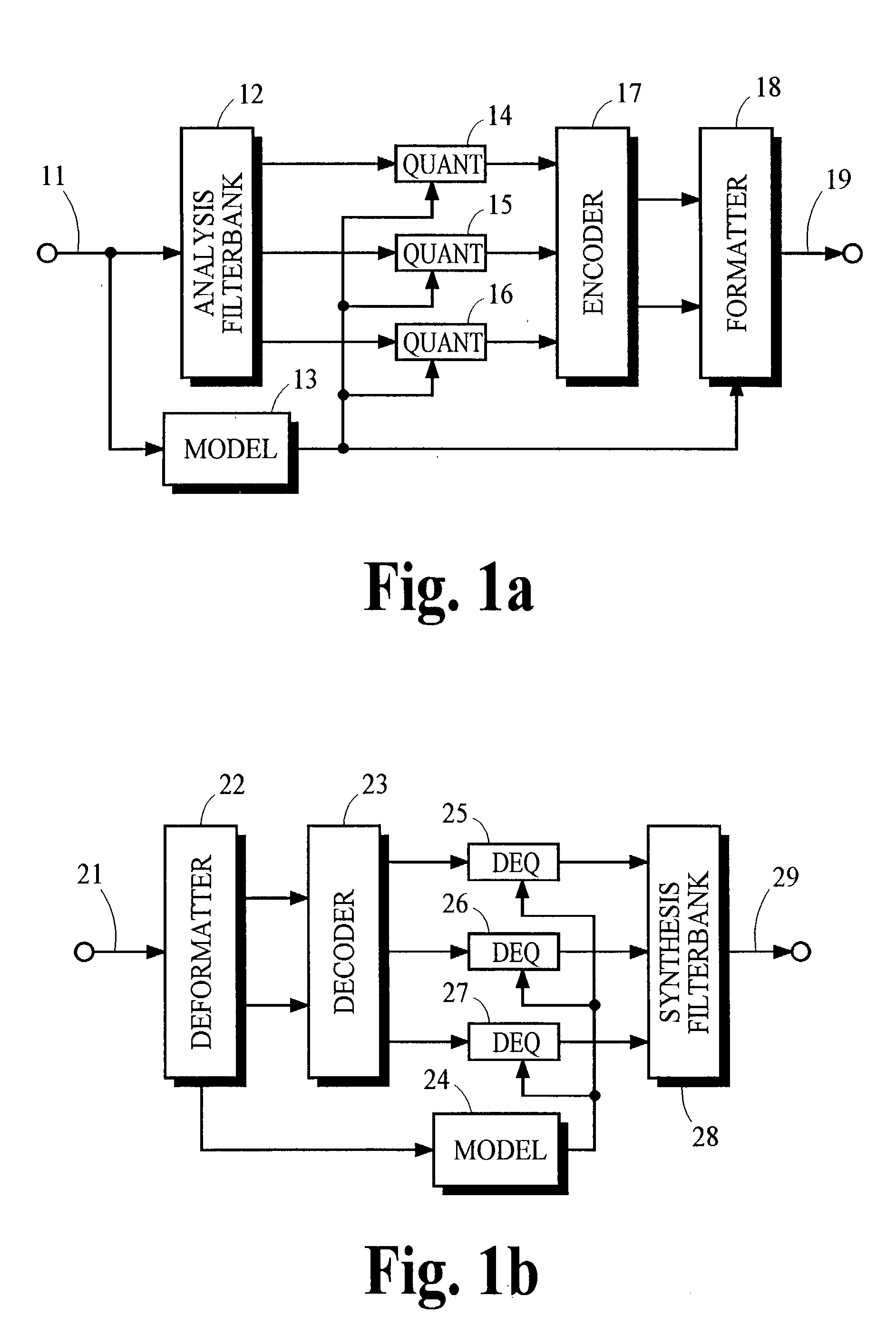
Method and apparatus for low density parity check encoding of data
InactiveUS6895547B2Improve performanceError preventionError detection/correctionTheoretical computer scienceParity-check matrix
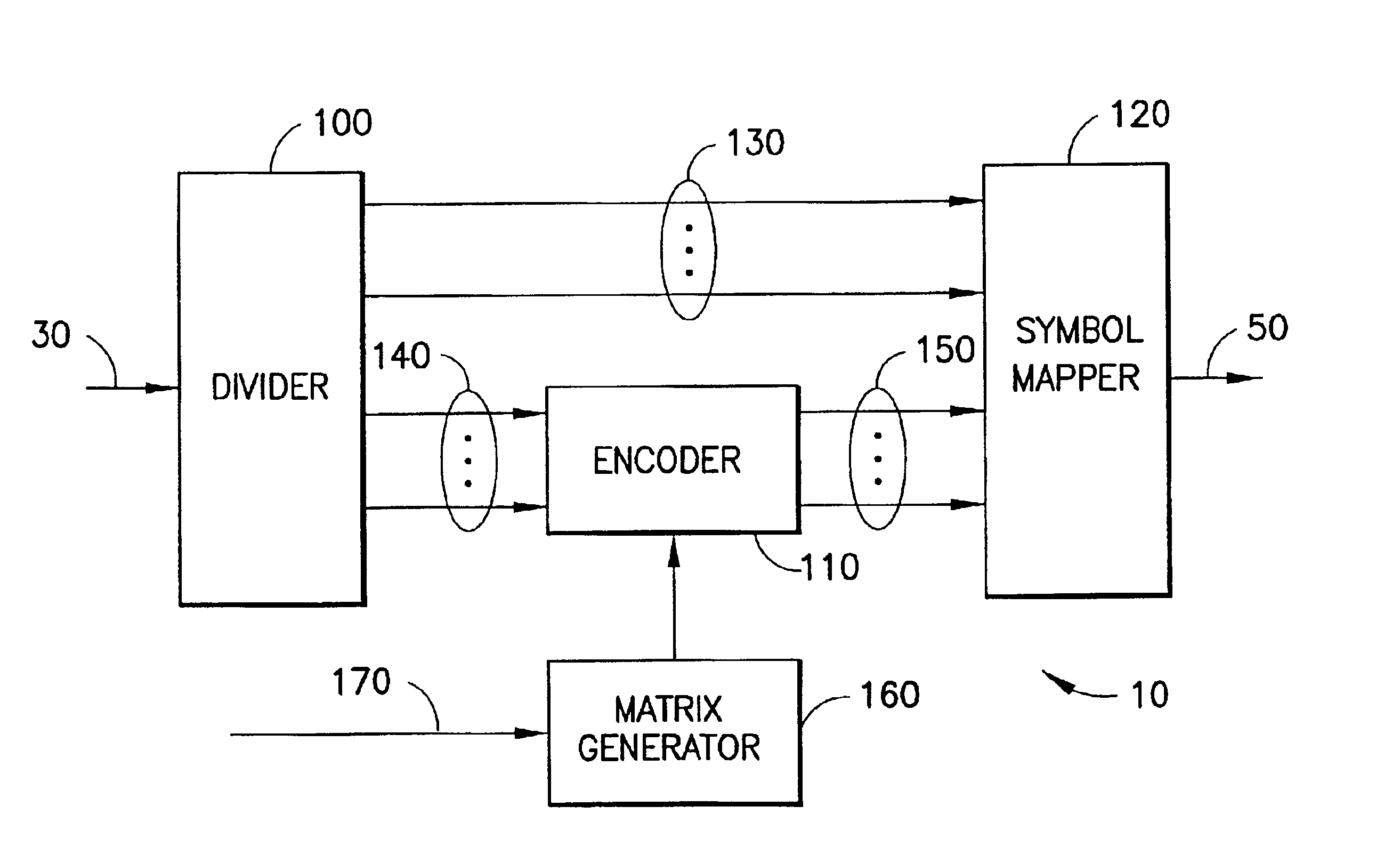
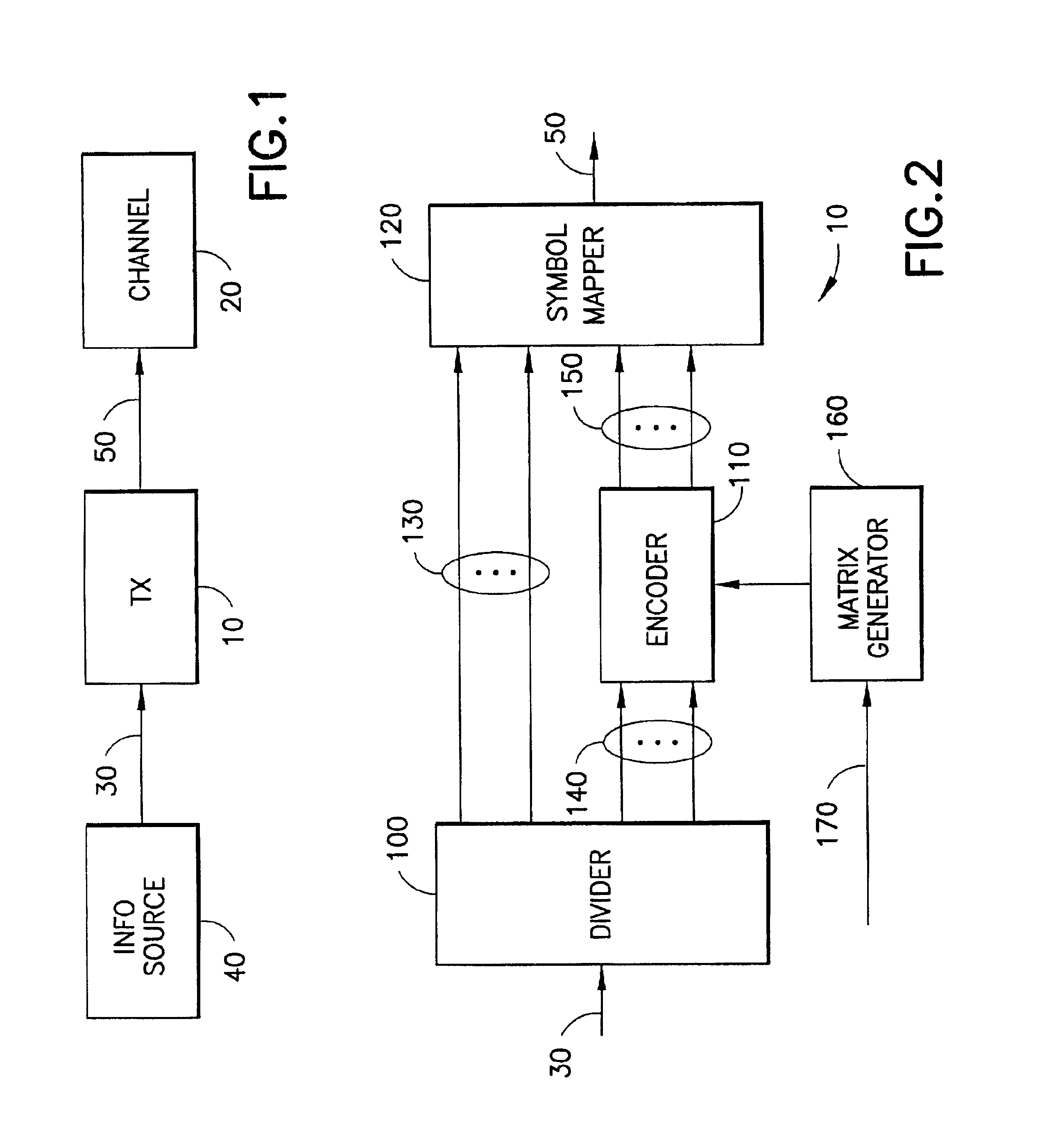
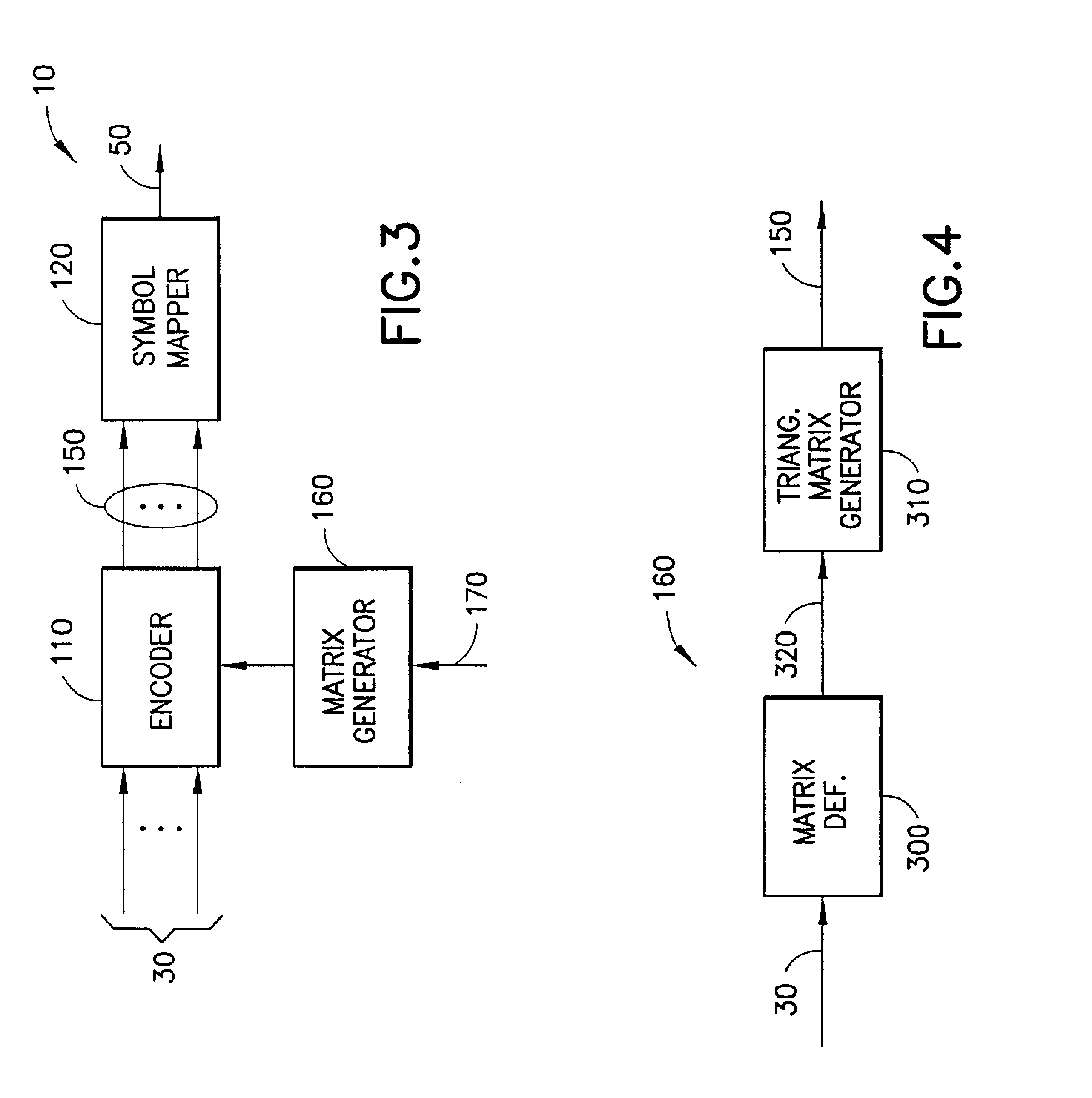
A method for low-density parity-check (LDPC) encoding of data comprises defining a first M×N parity check matrix; generating, based on the first parity check matrix, a second parity check matrix having an M×M triangular sub-matrix; and, mapping the data into an LDPC code word based on the second parity check matrix. The method is particularly useful for data communications applications, but may also be employed in other applications such as, for example, data storage.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
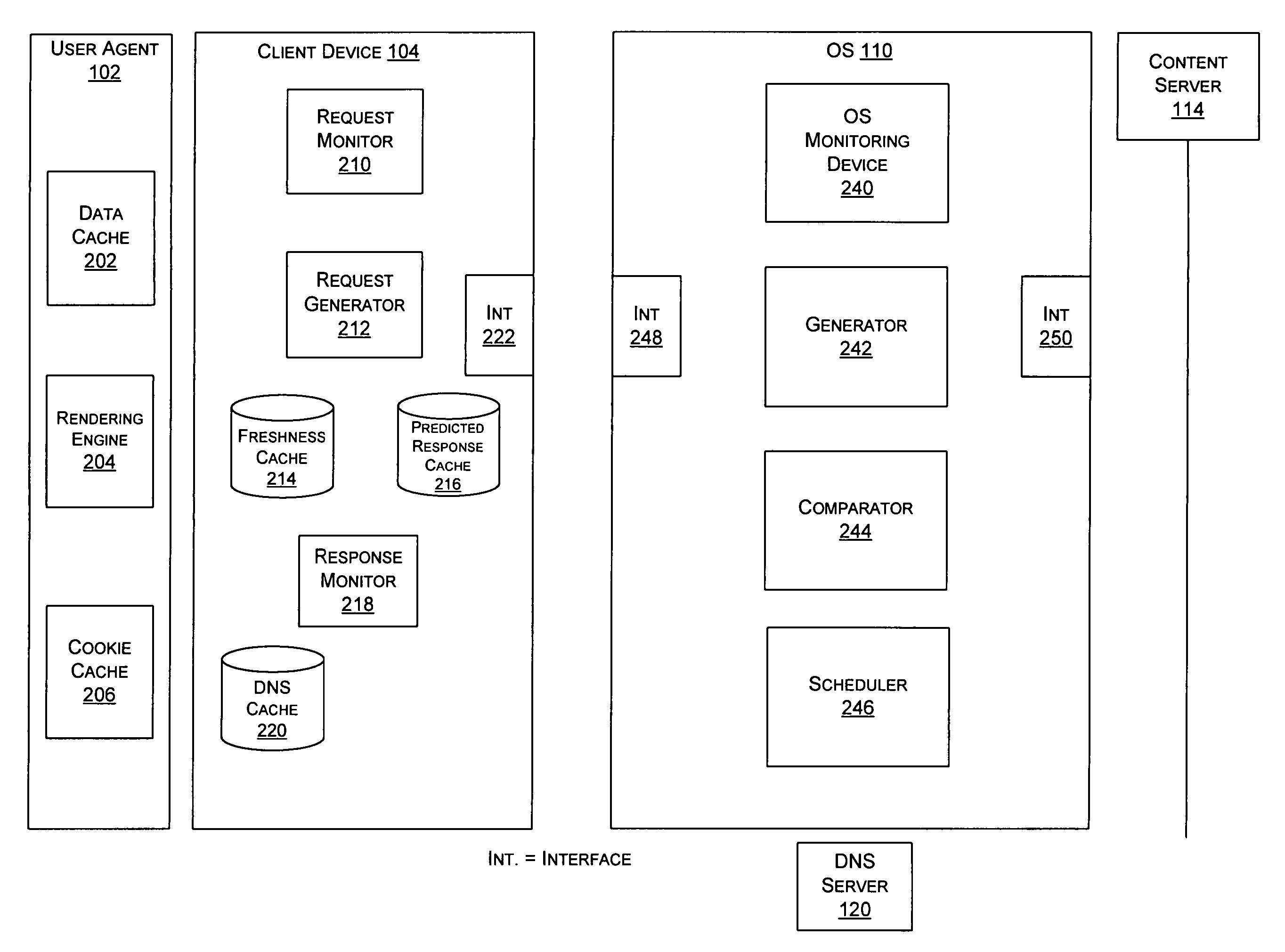
Method and system for object prediction
A method including communicating with a content server, wherein the communication includes transmitting request data to the content server and receiving first response data associated with the request data; identifying response object data within the first response data; determining whether the response object data is to be downloaded; querying the content server for second response data that corresponds to the response object data based on the determination; transmitting the first response data to a user agent; and storing the second response data, wherein the second response data can be provided to the user agent in a subsequent request.
Owner:CITRIX SYST INC
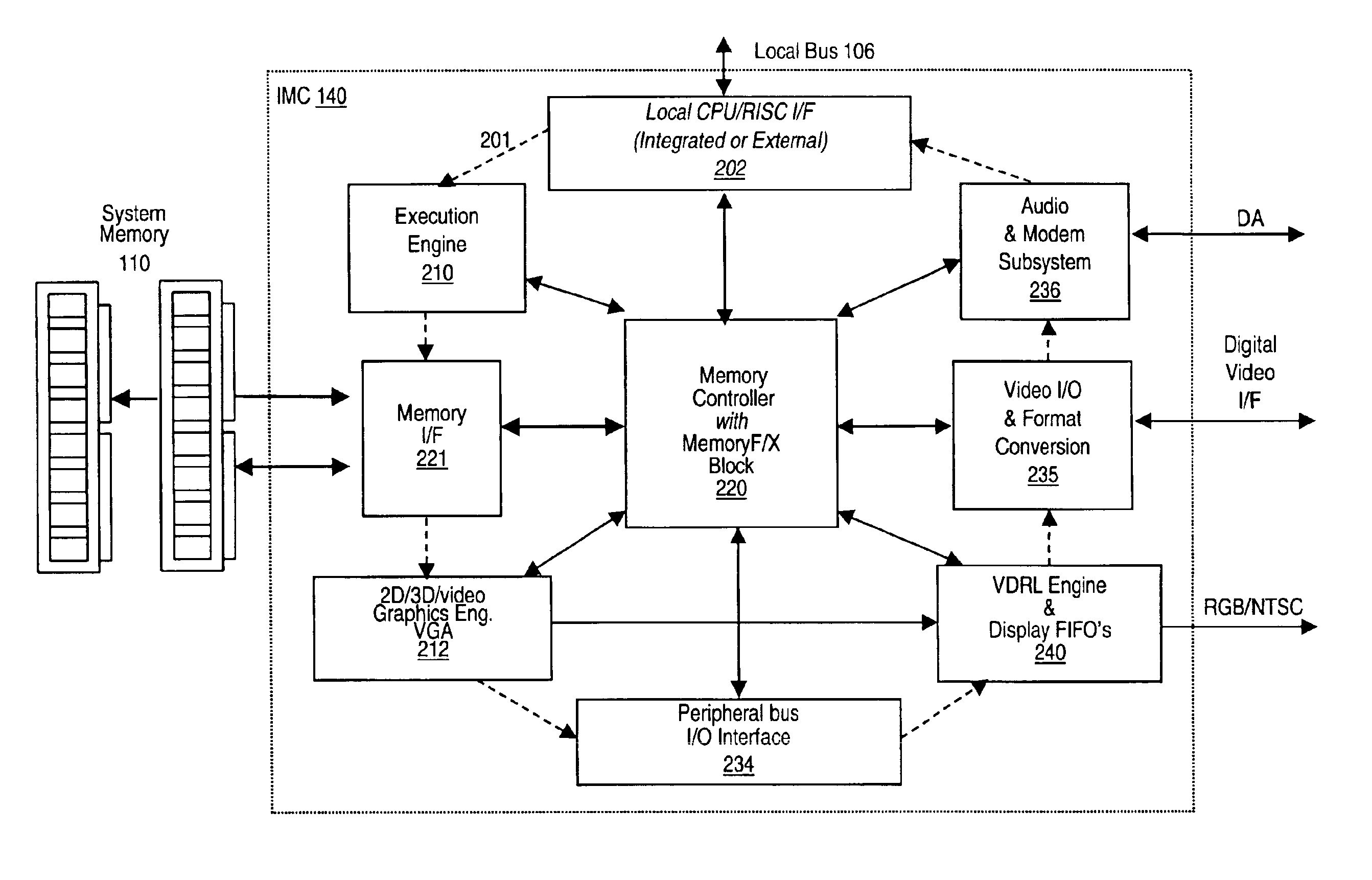
Memory module including scalable embedded parallel data compression and decompression engines
InactiveUS6879266B1Low costSmall data storage requirementMemory architecture accessing/allocationEnergy efficient ICTParallel compressionParallel computing
An memory module including parallel data compression and decompression engines for improved performance. The memory module includes MemoryF / X Technology. To improve latency and reduce performance degradations normally associated with compression and decompression techniques, the MemoryF / X Technology encompasses multiple novel techniques such as: 1) parallel lossless compression / decompression; 2) selectable compression modes such as lossless, lossy or no compression; 3) priority compression mode; 4) data cache techniques; 5) variable compression block sizes; 6) compression reordering; and 7) unique address translation, attribute, and address caches. The parallel compression and decompression algorithm allows high-speed parallel compression and high-speed parallel decompression operation. The memory module-integrated data compression and decompression capabilities remove system bottlenecks and increase performance. This allows lower cost systems due to smaller data storage, reduced bandwidth requirements, reduced power and noise.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL VENTURES I LLC
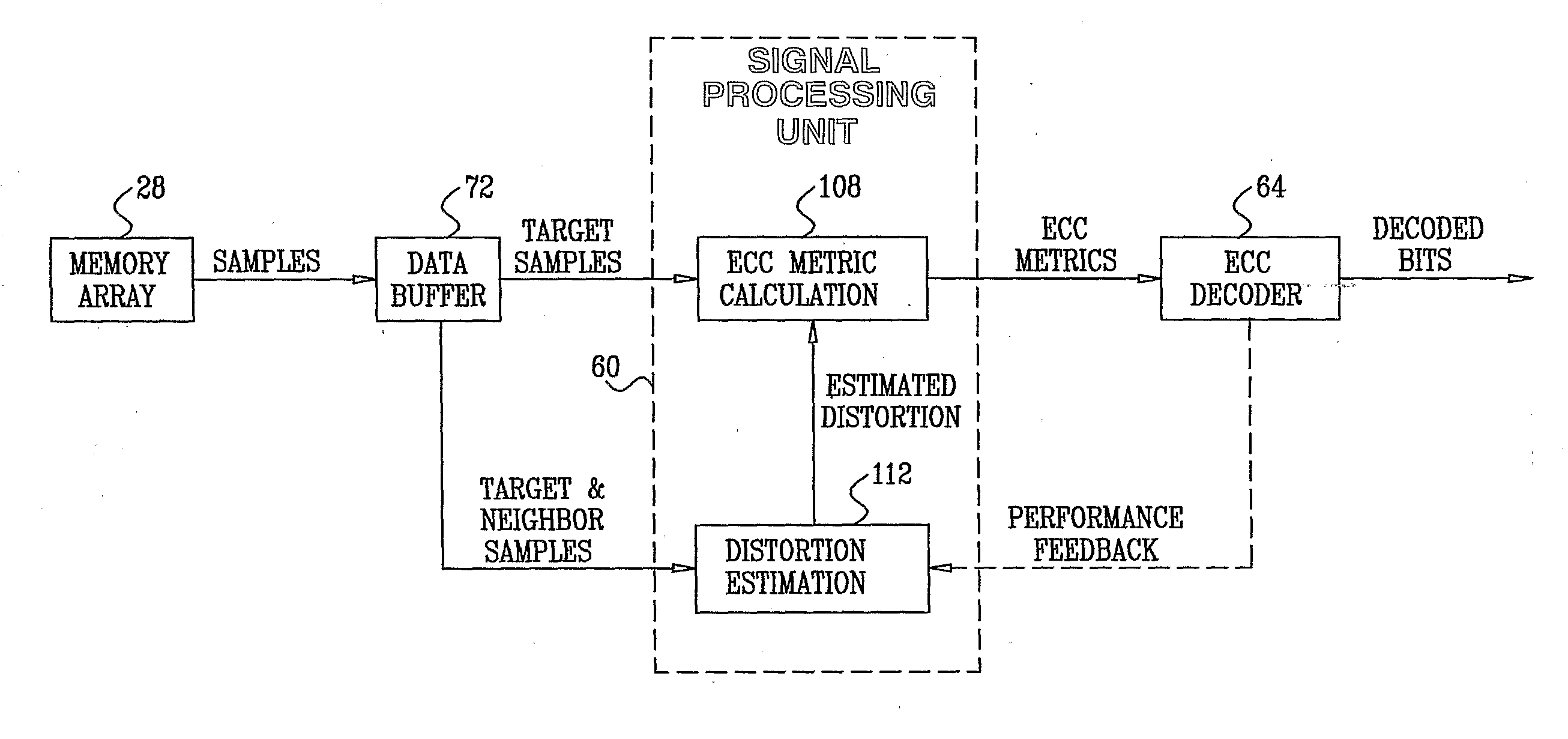
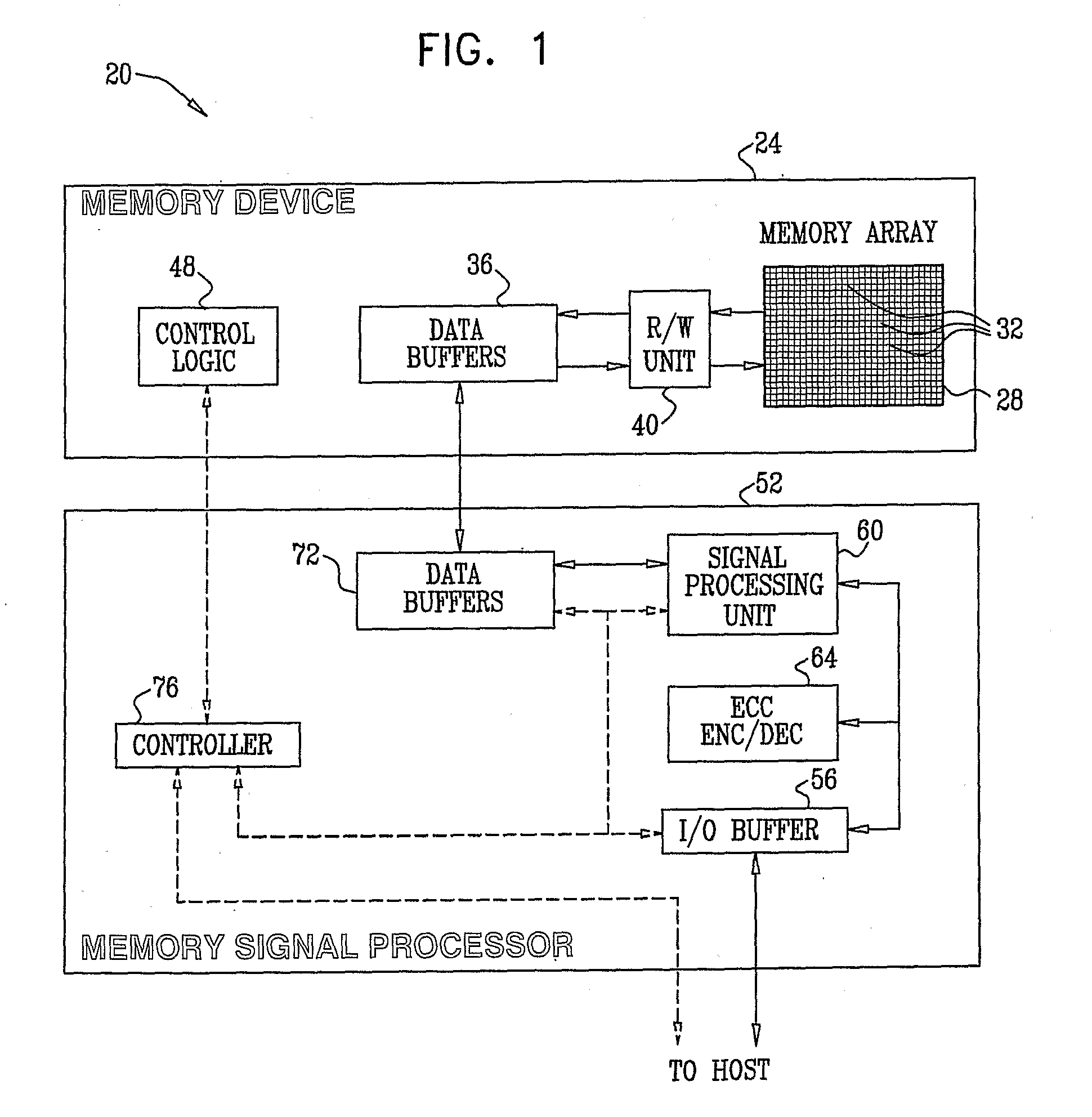
Combined distortion estimation and error correction coding for memory devices
ActiveUS20090024905A1Improve performanceData representation error detection/correctionError detection/correctionCalculation errorDistortion
A method for operating a memory device (24) includes encoding data using an Error Correction Code (ECC) and storing the encoded data as first analog values in respective analog memory cells (32) of the memory device. After storing the encoded data, second analog values are read from the respective memory cells of the memory device in which the encoded data were stored. At least some of the second analog values differ from the respective first analog values. A distortion that is present in the second analog values is estimated. Error correction metrics are computed with respect to the second analog values responsively to the estimated distortion. The second analog values are processed using the error correction metrics in an ECC decoding process, so as to reconstruct the data.
Owner:APPLE INC
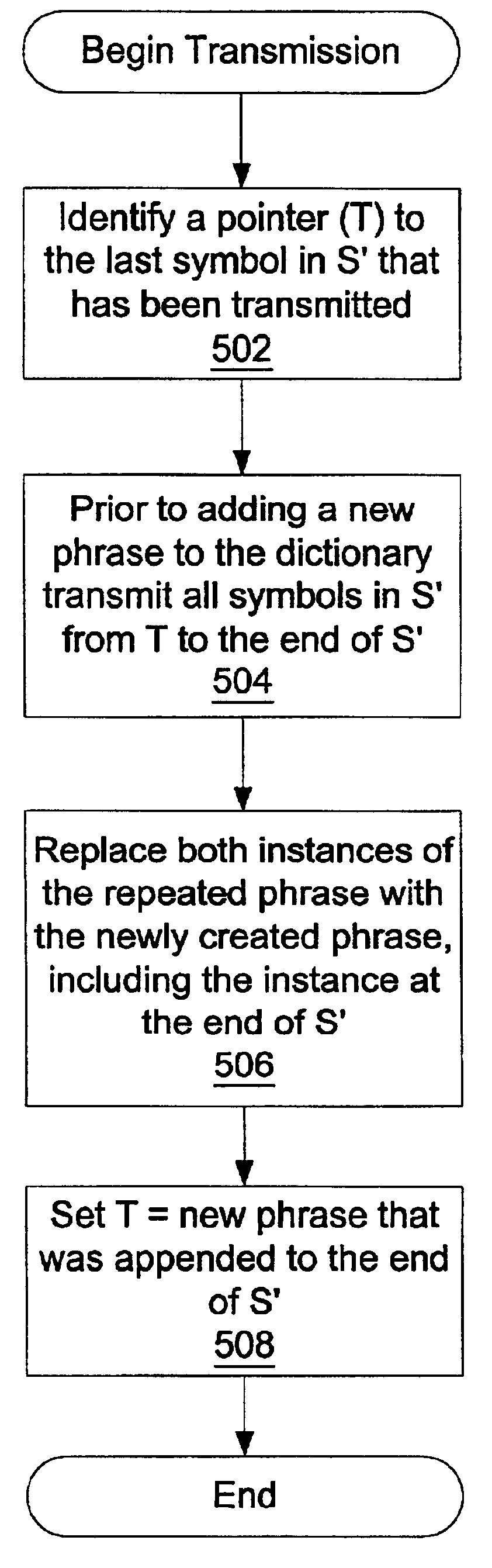
System and method for incremental and continuous data compression
ActiveUS6856651B2Not affect speedEfficient compressionColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionData compressionVariable length
A data compression system and method for that is capable of detecting and eliminating repeated phrases of variable length within a window of virtually unlimited size.
Owner:RIVERBED TECH LLC
Method and system for error correction in flash memory
ActiveUS20070171730A1Improve storage densityImprove reliabilityMemory architecture accessing/allocationError detection/correctionA d converterData memory
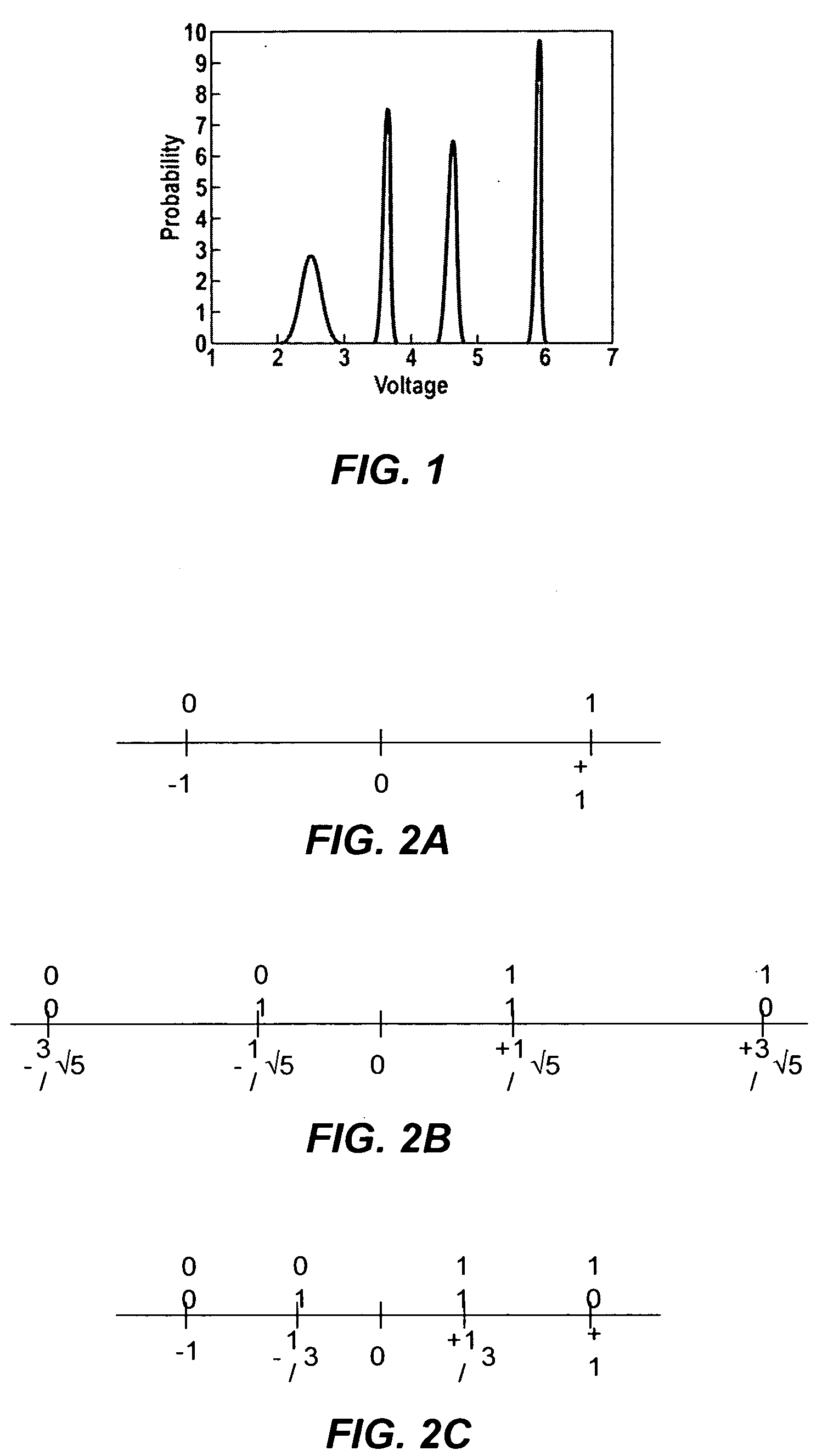
A solid state non-volatile memory unit. The memory unit includes a multi-level solid state non-volatile memory array adapted to store data characterized by a first number of digital levels. The memory unit also includes an analog-to-digital converter having an input and an output. The input of the analog-to-digital converter is adapted to receive data from the multi-level solid state non-volatile memory array. The output of the analog-to-digital converter is adapted to output a digital signal characterized by a second number of digital levels greater than the first number of digital levels.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
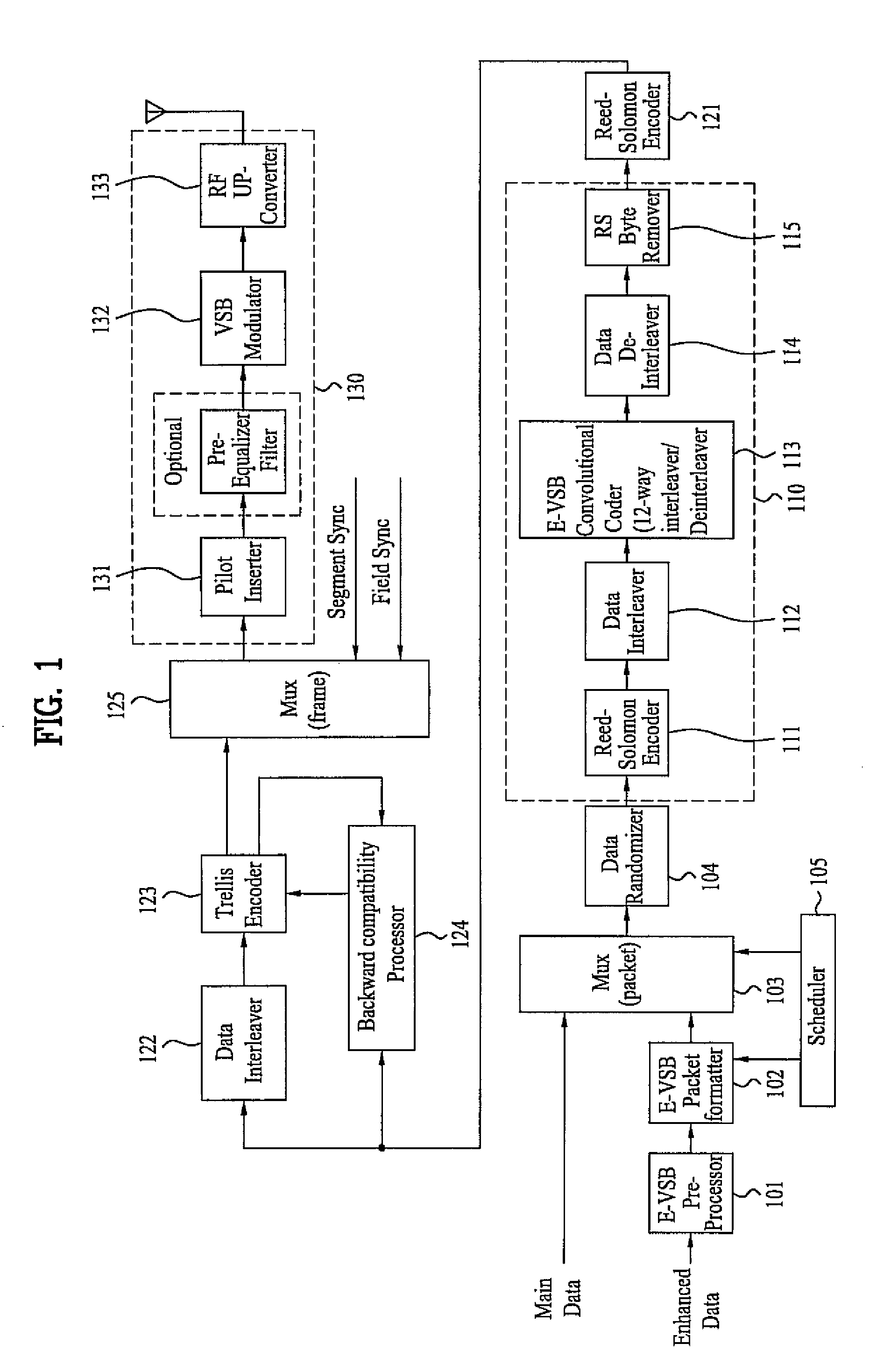
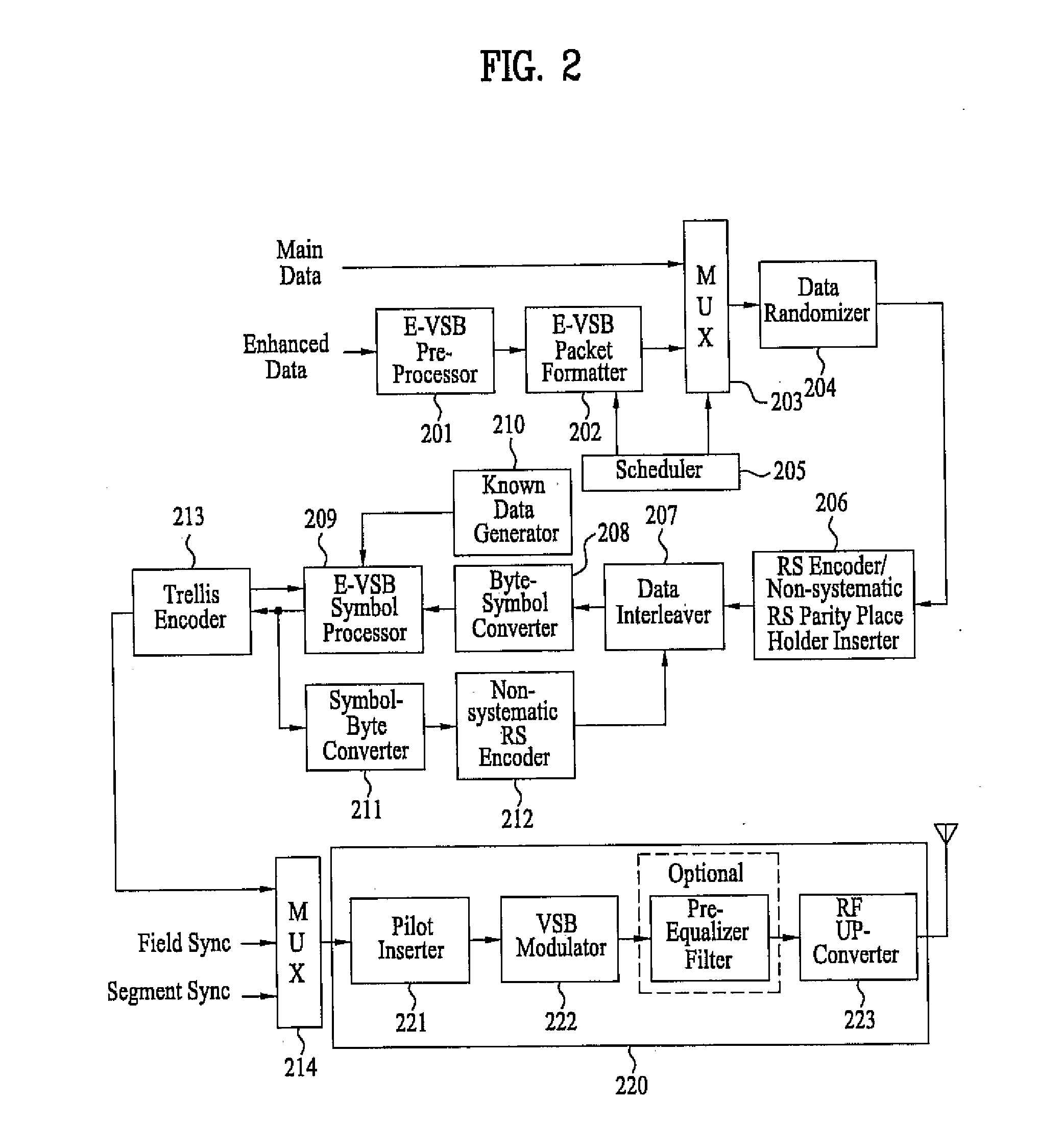
Digital television transmitter/receiver and method of processing data in digital television transmitter/receiver
InactiveUS20070121681A1Robust against noiseTransmit dataData representation error detection/correctionPulse modulation television signal transmissionTime informationMultiplexing
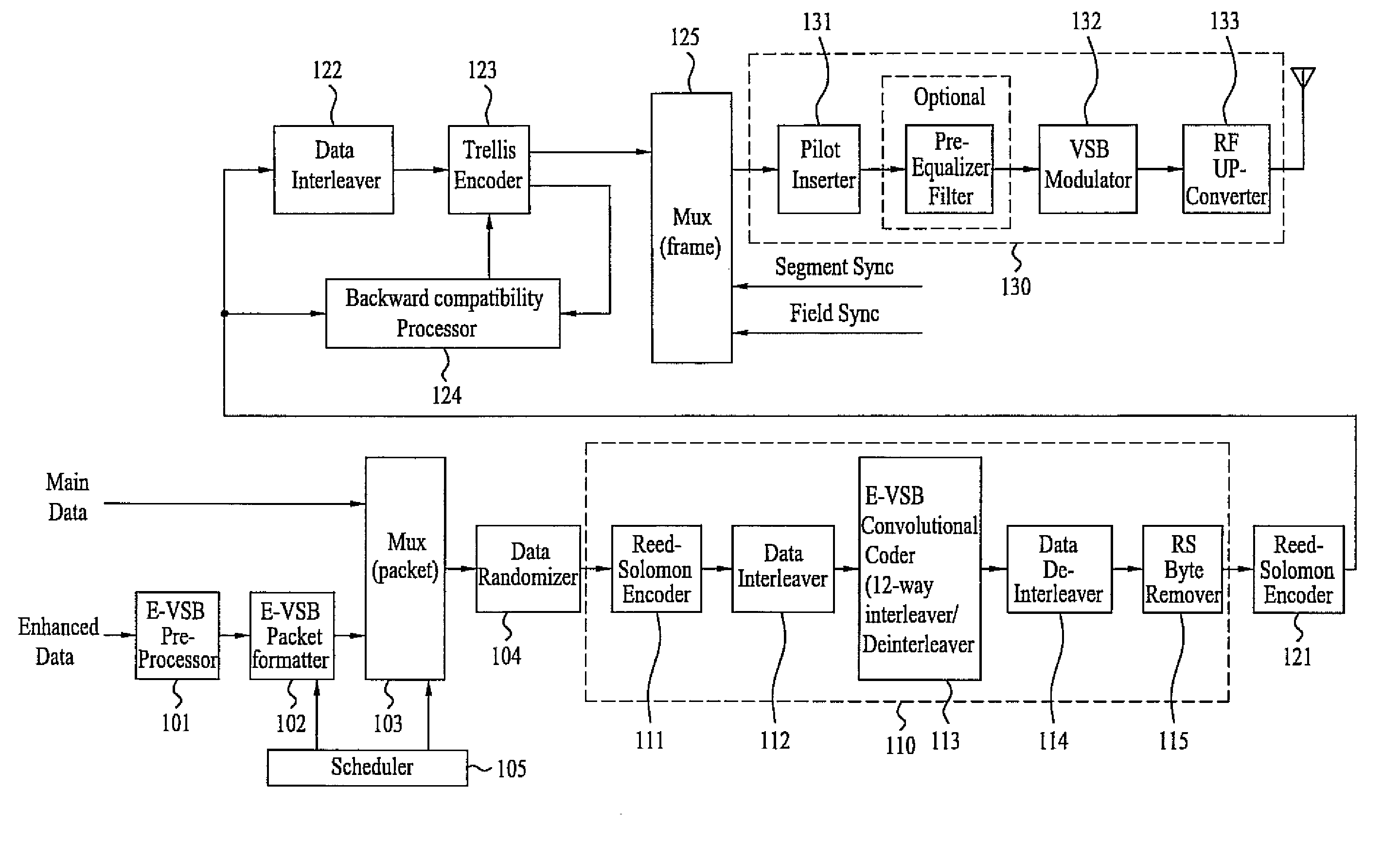
A digital television (DTV) transmitter and a method of processing data in the DTV transmitter / receiver are disclosed. In the DTV transmitter, a pre-processor pre-processes the enhanced data by coding the enhanced data for forward error correction (FEC) and expanding the FEC-coded data. A packet formatter generates one or more groups of enhanced data packets, each enhanced data packet including the pre-processed enhanced data and known data, wherein the data formatter adds burst time information into each group of enhanced data packets. And, a packet multiplexer generates at least one burst of enhanced data by multiplexing the one or more groups of enhanced data packets with at least one main data packet including the main data, each burst of enhanced data including at least one group of enhanced data packets.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
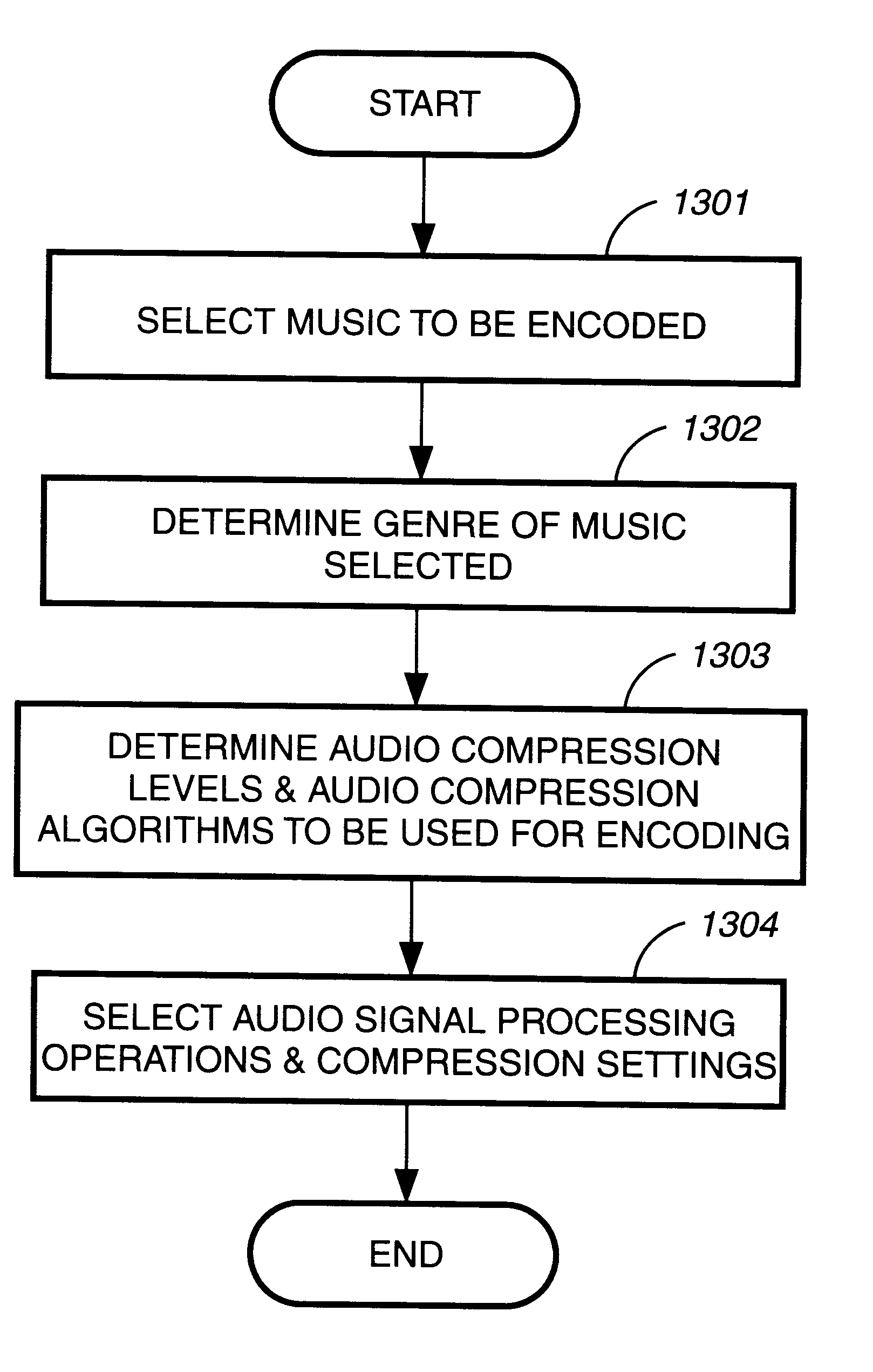
Audio coding system using spectral hole filling
ActiveUS20030233234A1Improve perceived qualityReducing and avoiding degradationCode conversionSpeech recognitionFrequency spectrumAudio frequency
Audio coding processes like quantization can cause spectral components of an encoded audio signal to be set to zero, creating spectral holes in the signal. These spectral holes can degrade the perceived quality of audio signals that are reproduced by audio coding systems. An improved decoder avoids or reduces the degradation by filling the spectral holes with synthesized spectral components. An improved encoder may also be used to realize further improvements in the decoder.
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com