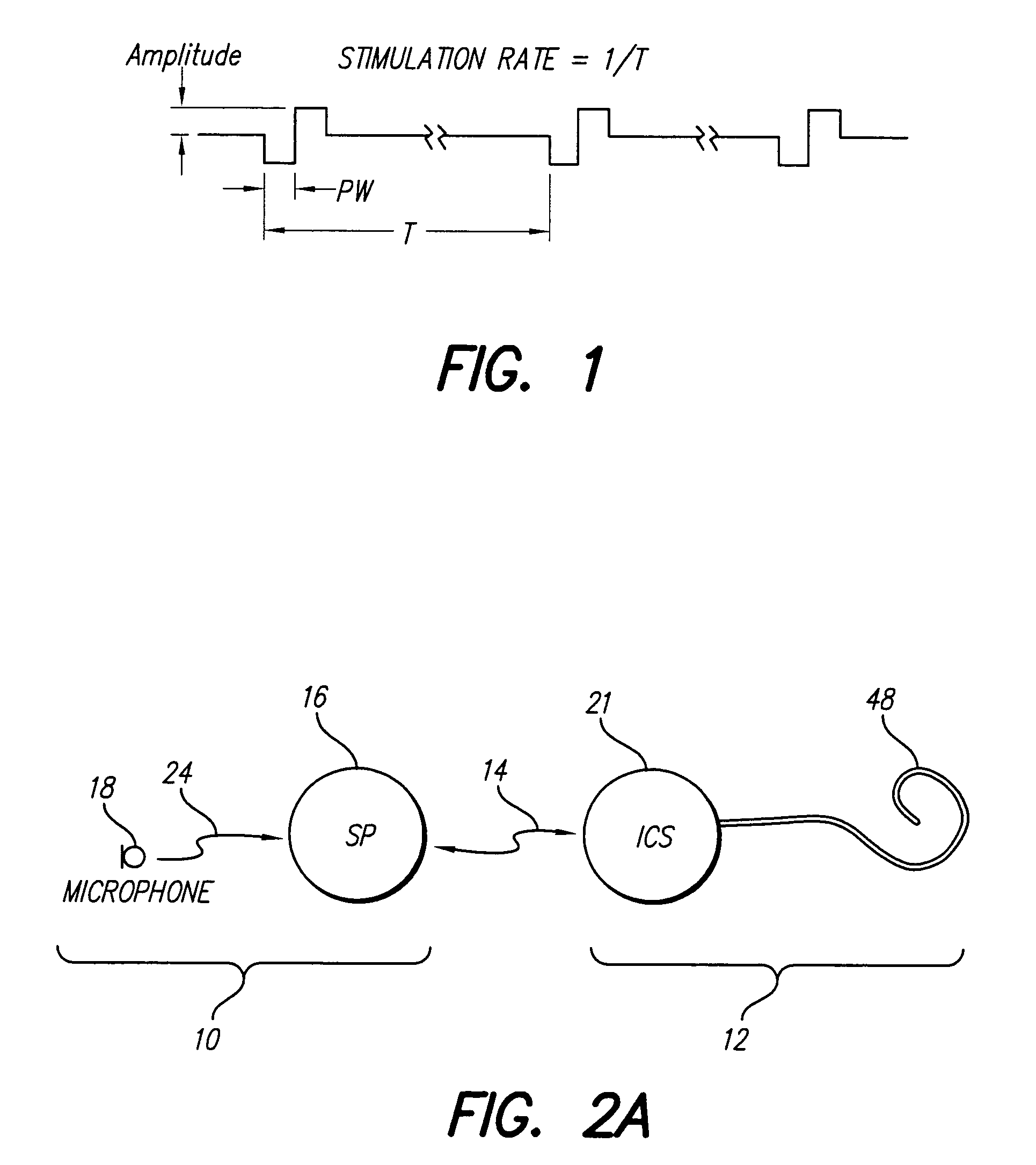
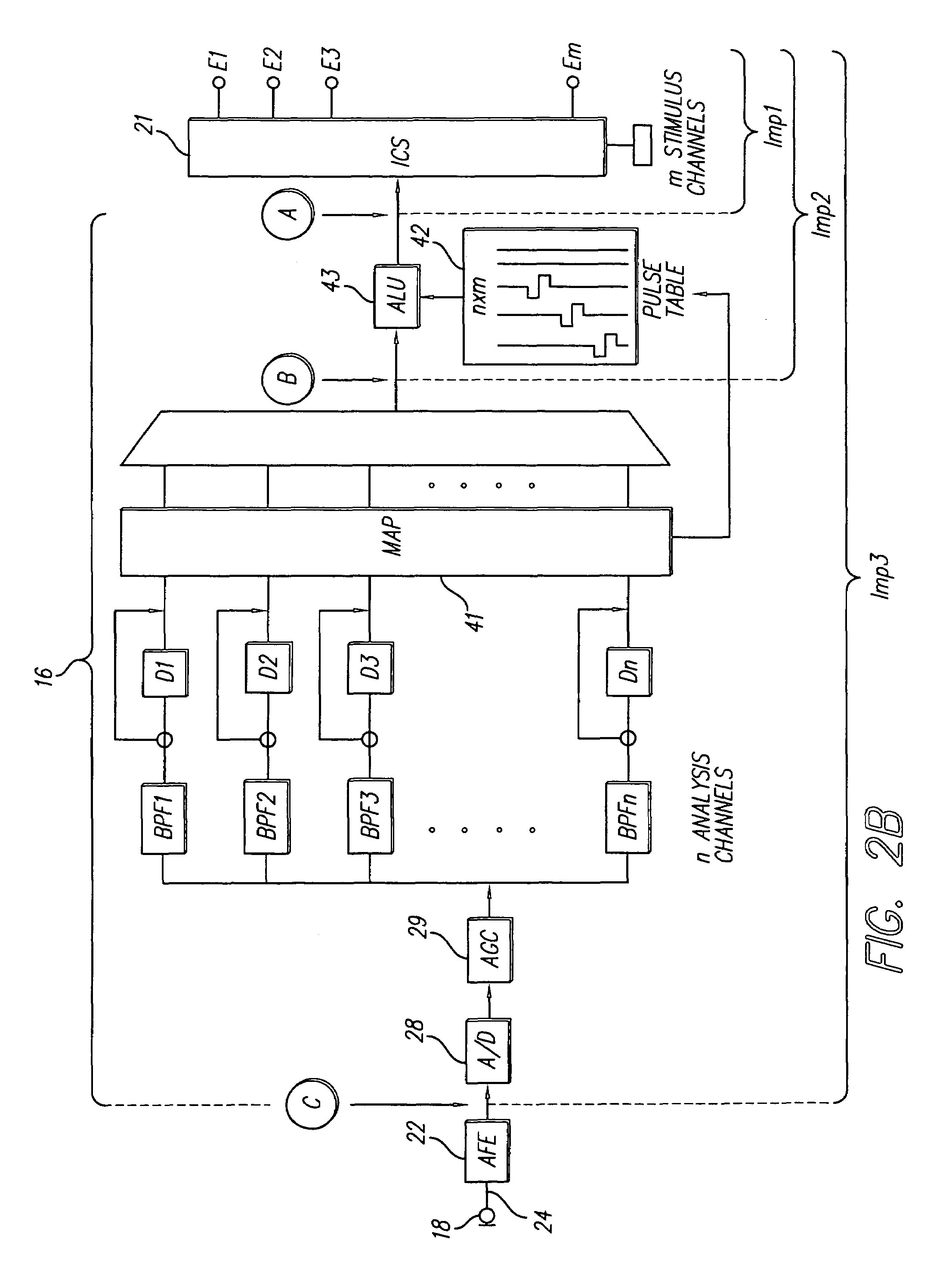
Patents
Literature
272results about How to "Improve perceived quality" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
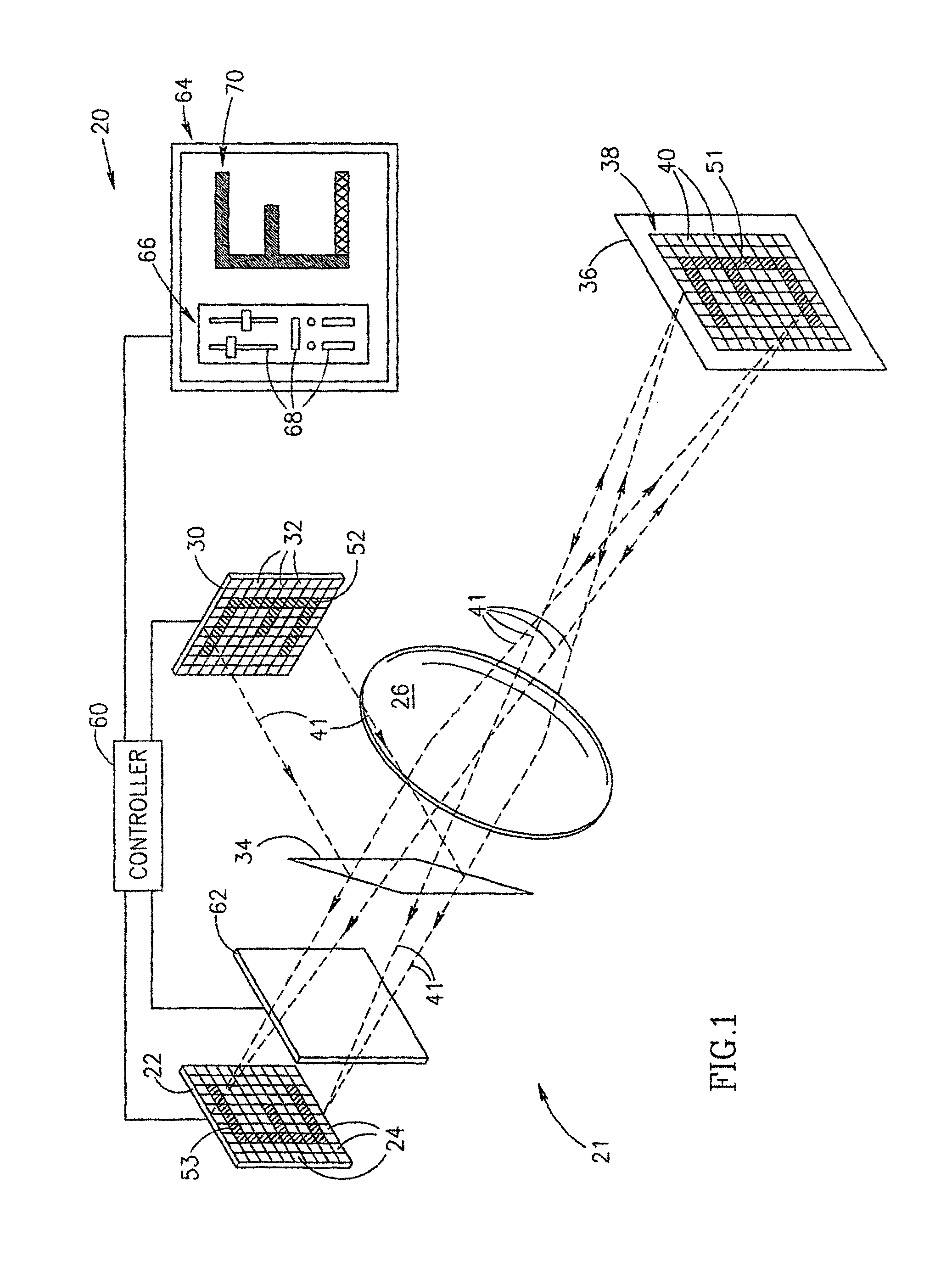
Quality of displayed images with user preference information
InactiveUS20040008208A1Improve perceived qualityImprove image qualityCathode-ray tube indicatorsHousing of computer displaysImaging qualityDisplay device
The present invention relates to methods and apparatus for increasing the perceived quality of displayed images. This is achieved in a variety of ways including the use of a plurality of device specific display characteristics when preparing images for display. It is also achieved through the monitoring of display device and / or ambient light conditions, e.g., on a periodic basis, and using the obtained information when controlling display output. Another approach to improving the perceived quality of displayed images involves the use of information relating to a specific user's ability to perceive image characteristics such as color. By customizing display output to an individual user's own physical perception capabilities and / or viewing characteristics it is possible to enhance the image quality perceived by the individual viewer as compared to embodiments which do not take into consideration individual user characteristics.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
CELP Post-processing for Music Signals
ActiveUS20100070270A1Improve perceived qualityElectrophonic musical instrumentsSpeech analysisCode-excited linear predictionHarmonic
In one embodiment, a method of receiving a decoded audio signal that has a transmitted pitch lag is disclosed. The method includes estimating pitch correlations of possible short pitch lags that are smaller than a minimum pitch limitation and have an approximated multiple relationship with the transmitted pitch lag, checking if one of the pitch correlations of the possible short pitch lags is large enough compared to a pitch correlation estimated with the transmitted pitch lag, and selecting a short pitch lag as a corrected pitch lag if a corresponding pitch correlation is large enough. The postprocessing is performed using the corrected pitch lag. In another embodiment, when the existence of irregular harmonics or wrong pitch lag is detected, a coded-excited linear prediction (CELP) postfilter is made more aggressive.
Owner:GH INNOVATION +1
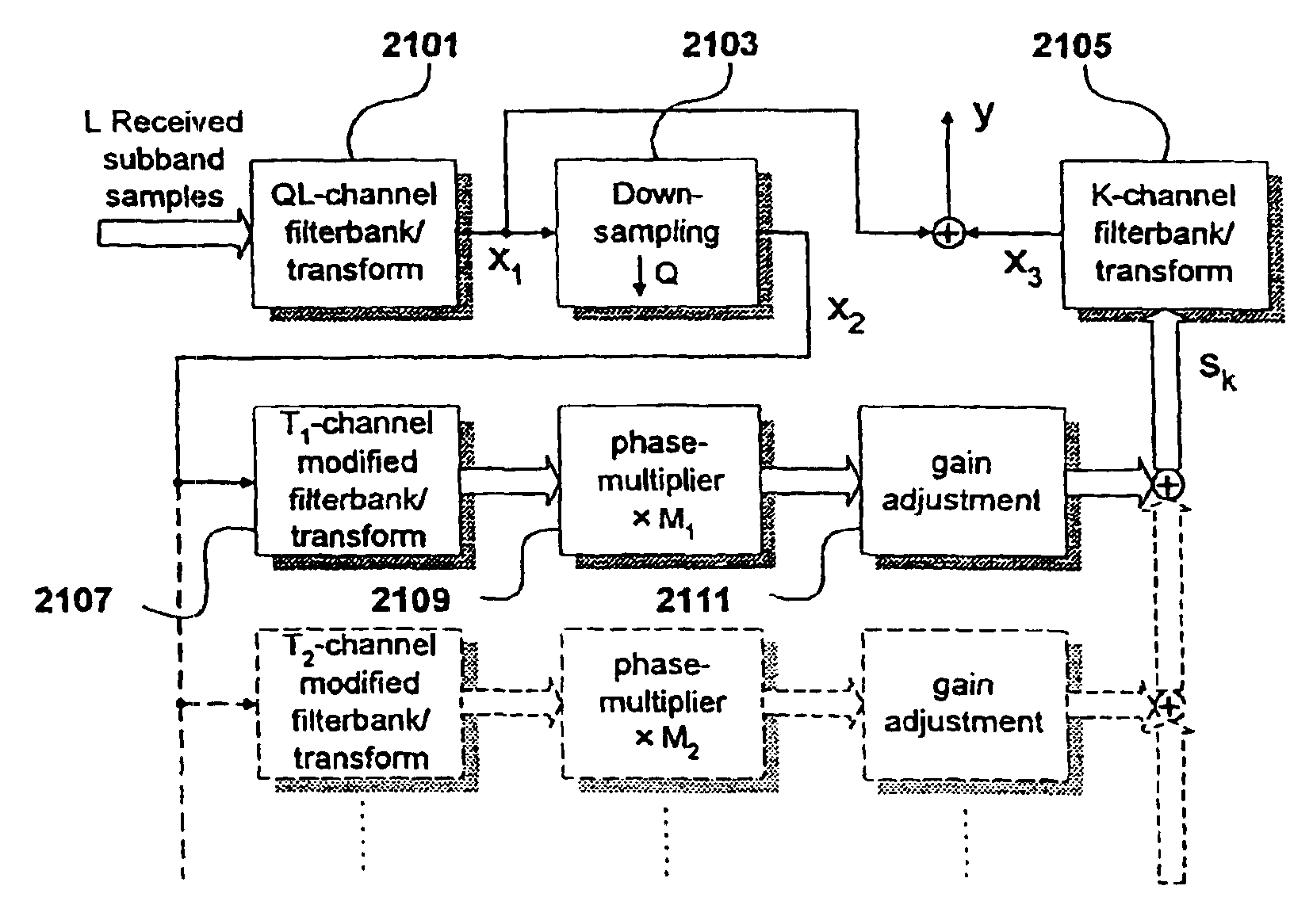
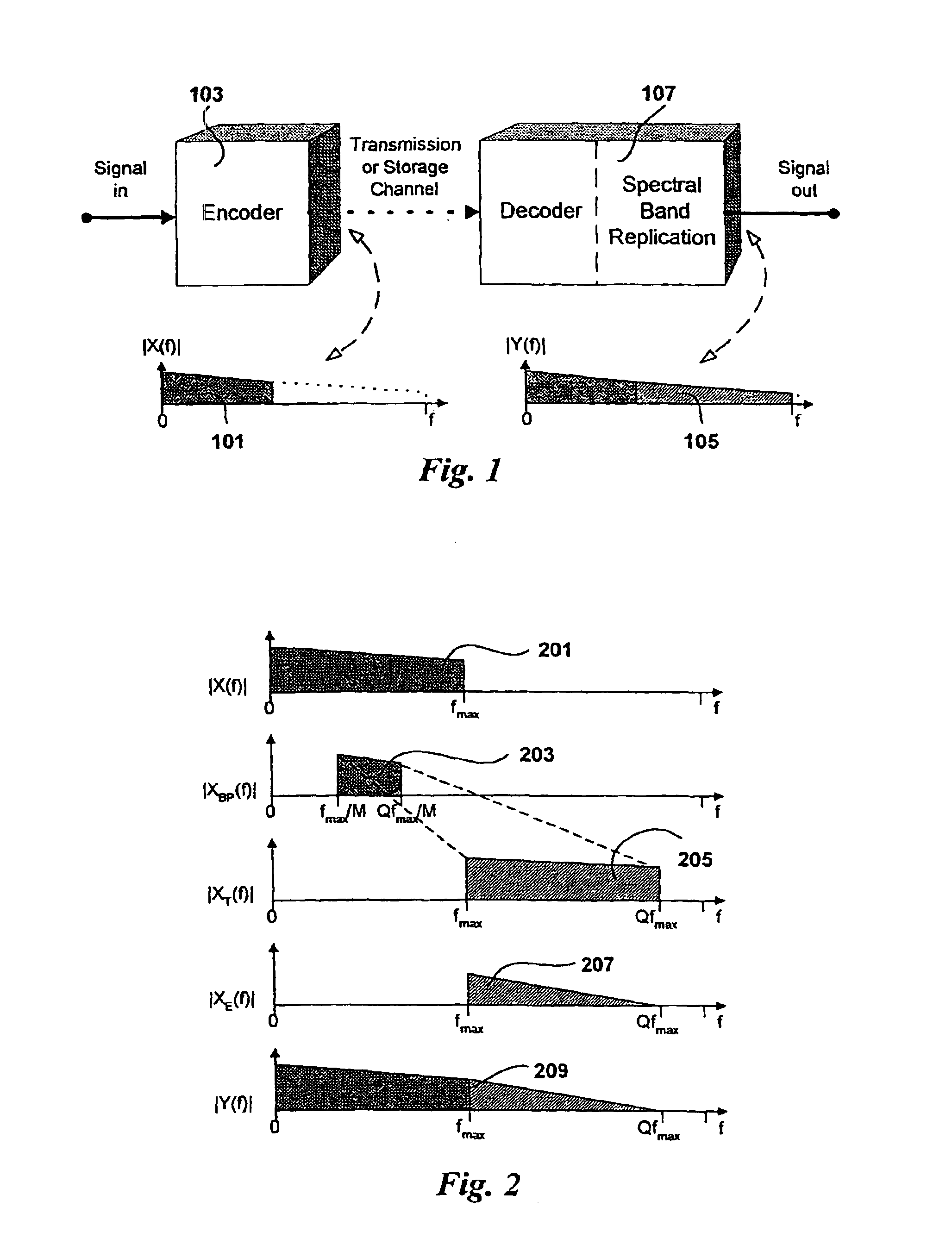
Source coding enhancement using spectral-band replication
InactiveUS7283955B2Improvements of audio codecsImprove perceived qualitySpeech analysisCode conversionFrequency spectrumComputer science
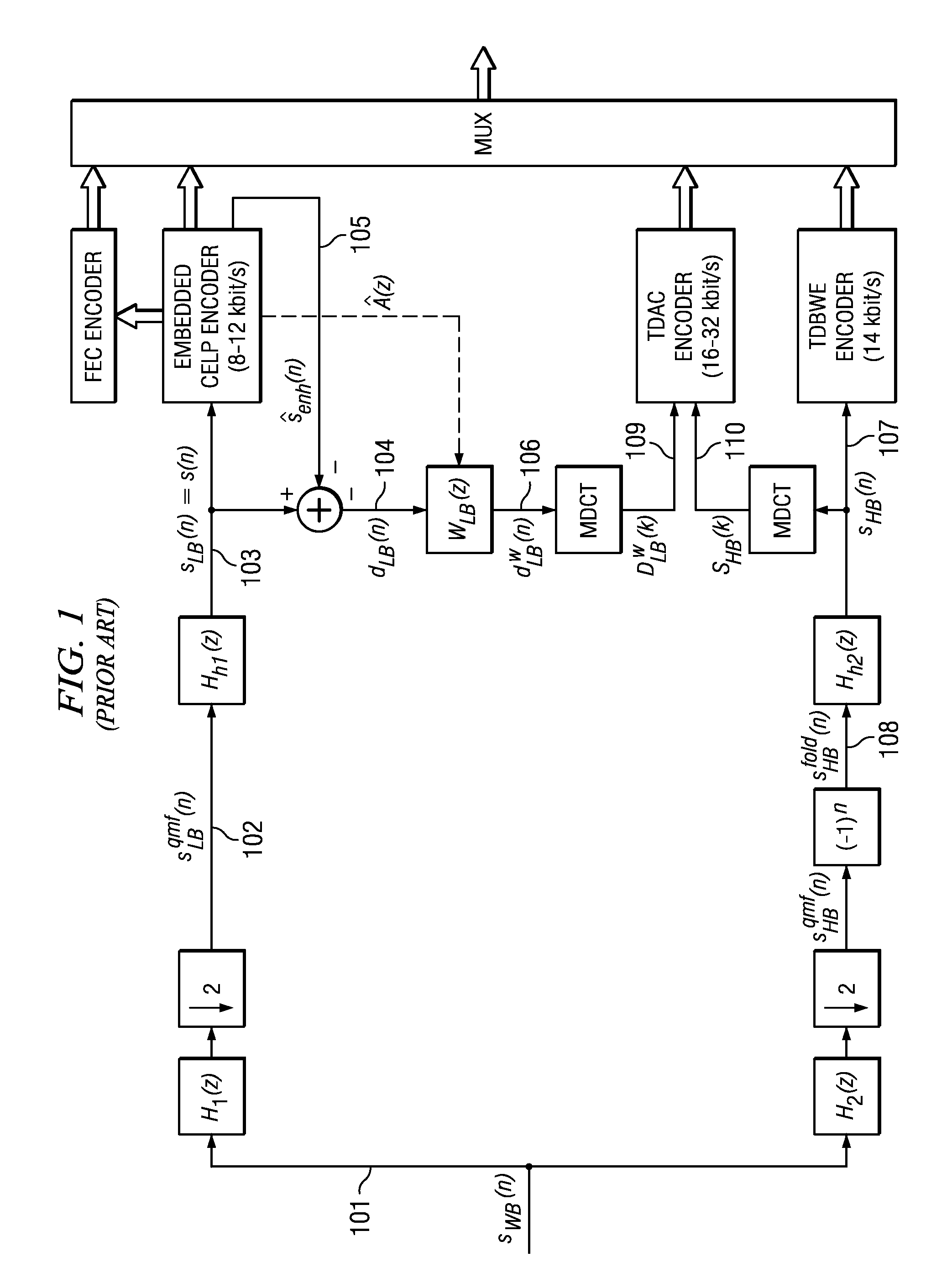
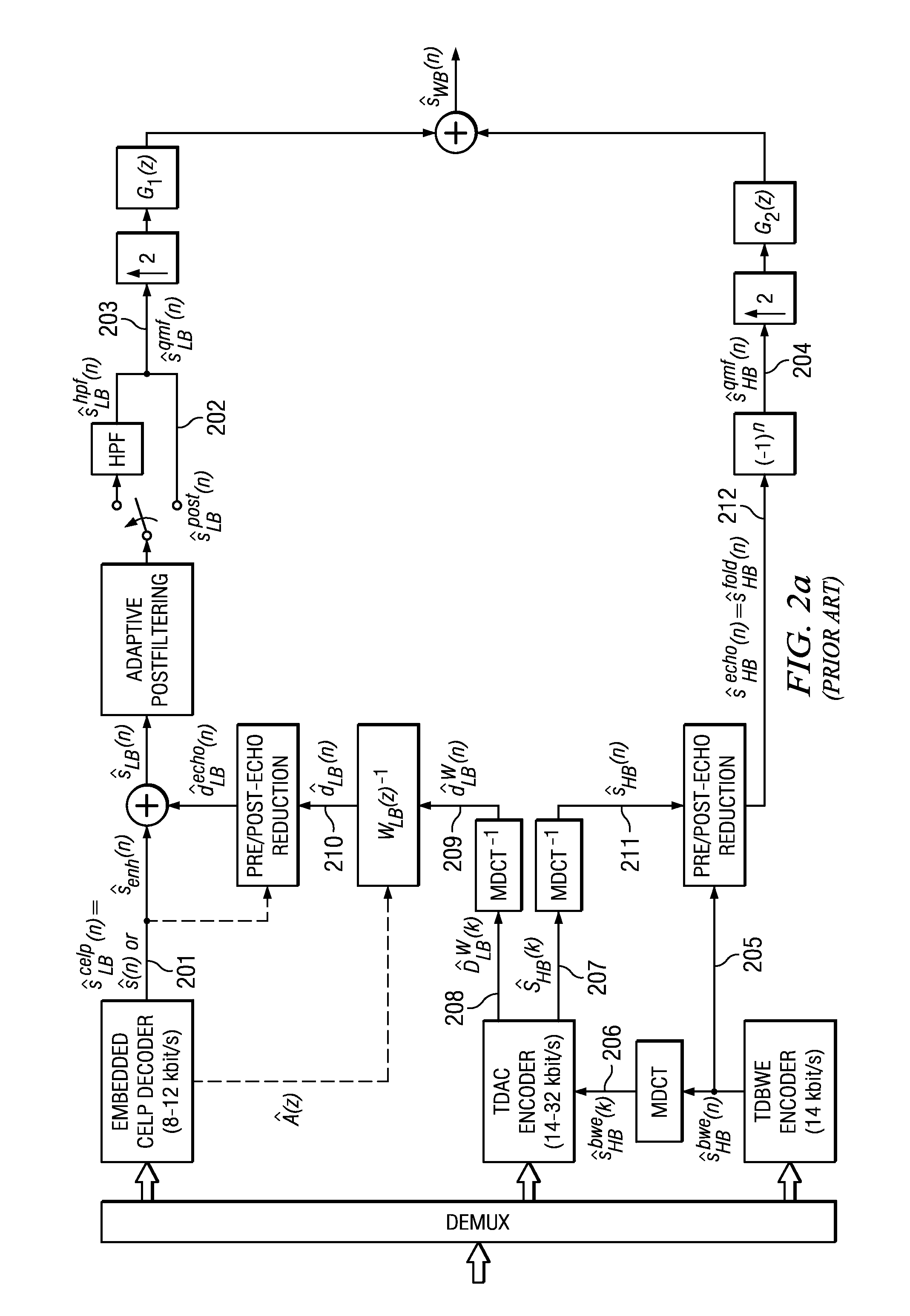
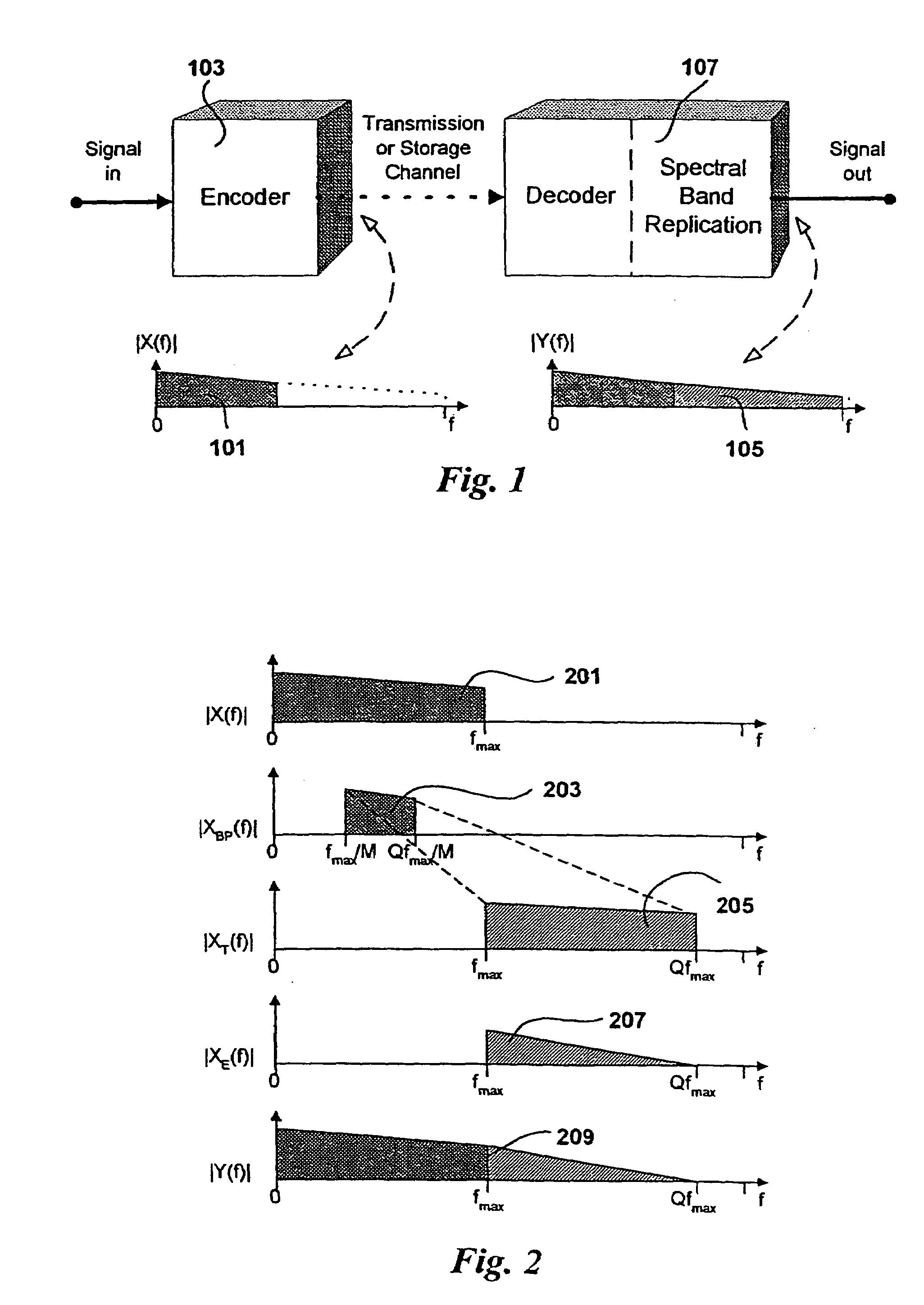
The present invention proposes a new method and apparatus for the enhancement of source coding systems. The invention employs bandwidth reduction (101) prior to or in the encoder (103), followed by spectral-band replication (105) at the decoder (107). This is accomplished by the use of new transposition methods, in combination with spectral envelope adjustments. Reduced bitrate at a given perceptual quality or an improved perceptual quality at a given bitrate is offered. The invention is preferably integrated in a hardware or software codec, but can also be implemented as a separate processor in combination with a codec. The invention offers substantial improvements practically independent f codec type and technological progress.
Owner:DOLBY INT AB
High resolution post processing method for a speech decoder
InactiveUS6138093AImprove perceived qualityReduce noiseCode conversionTransmissionTime domainFrequency spectrum
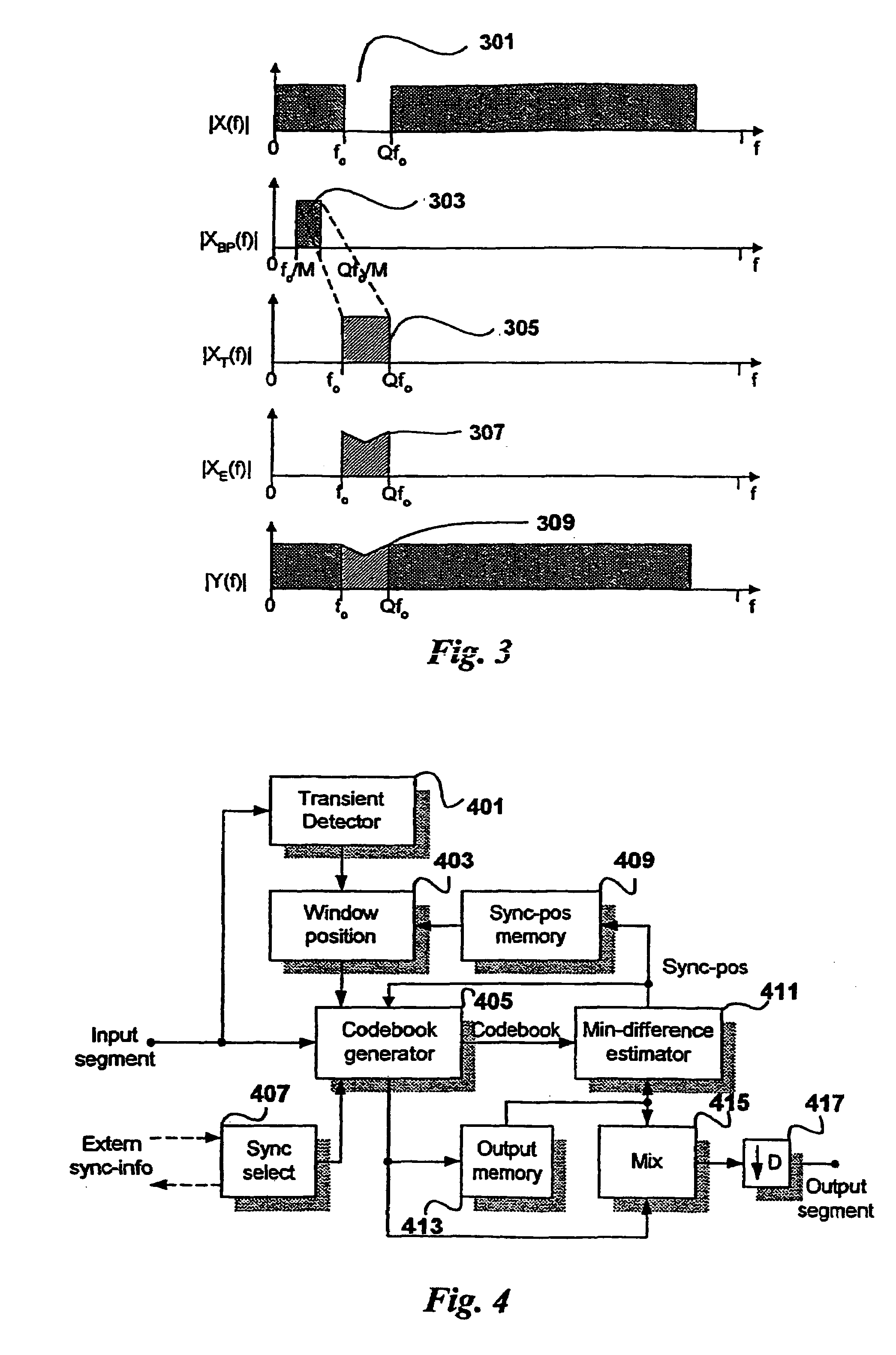
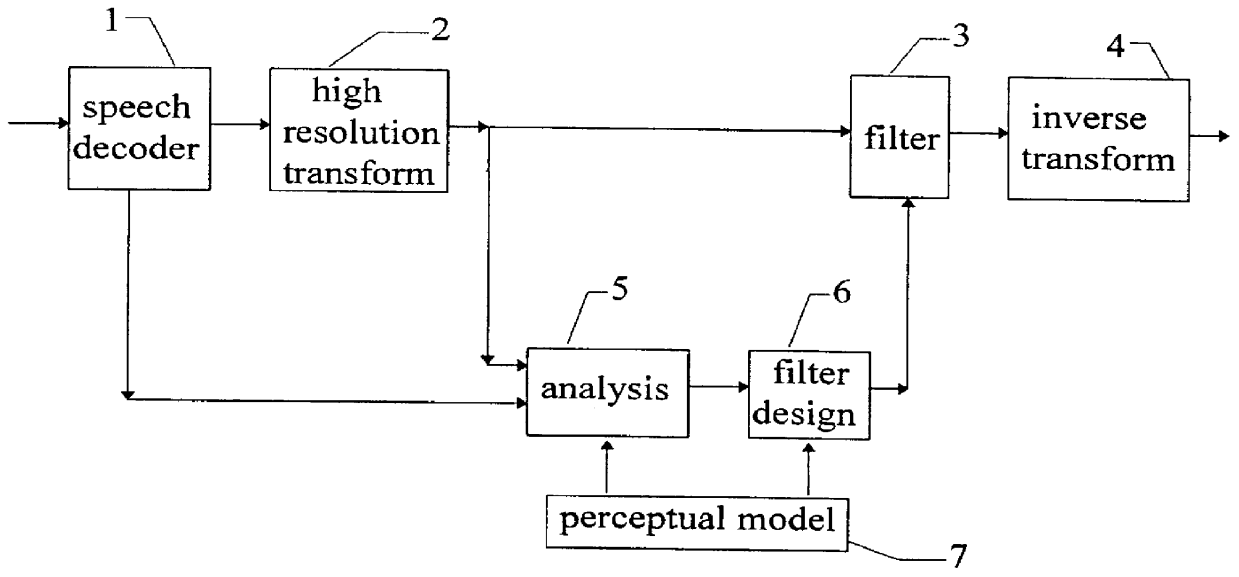
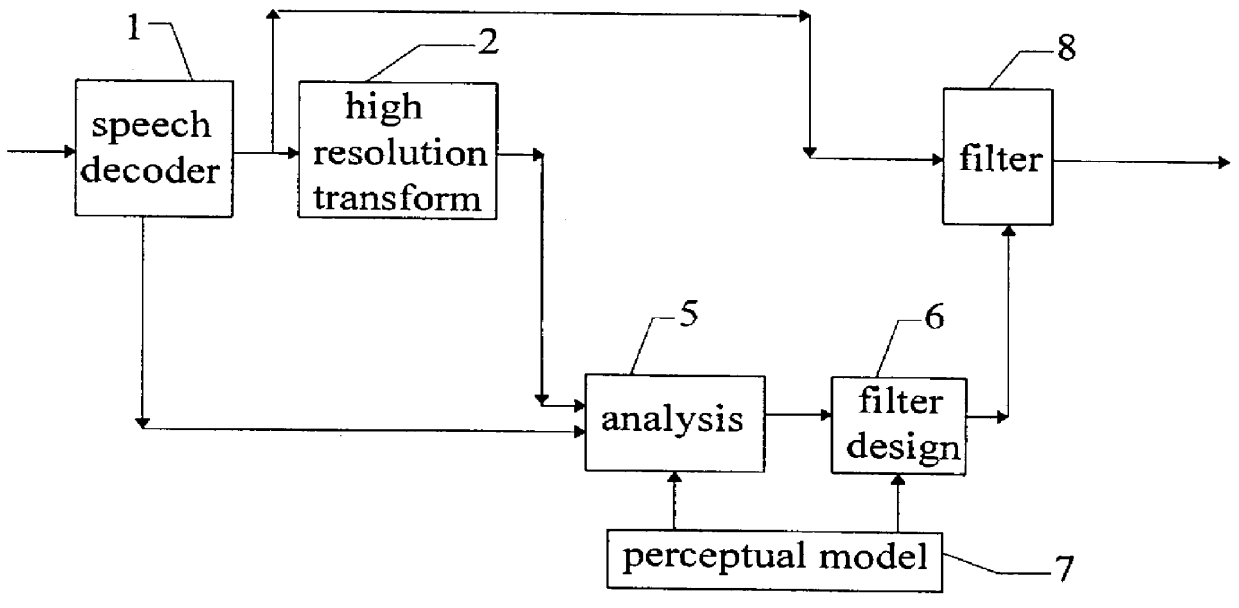
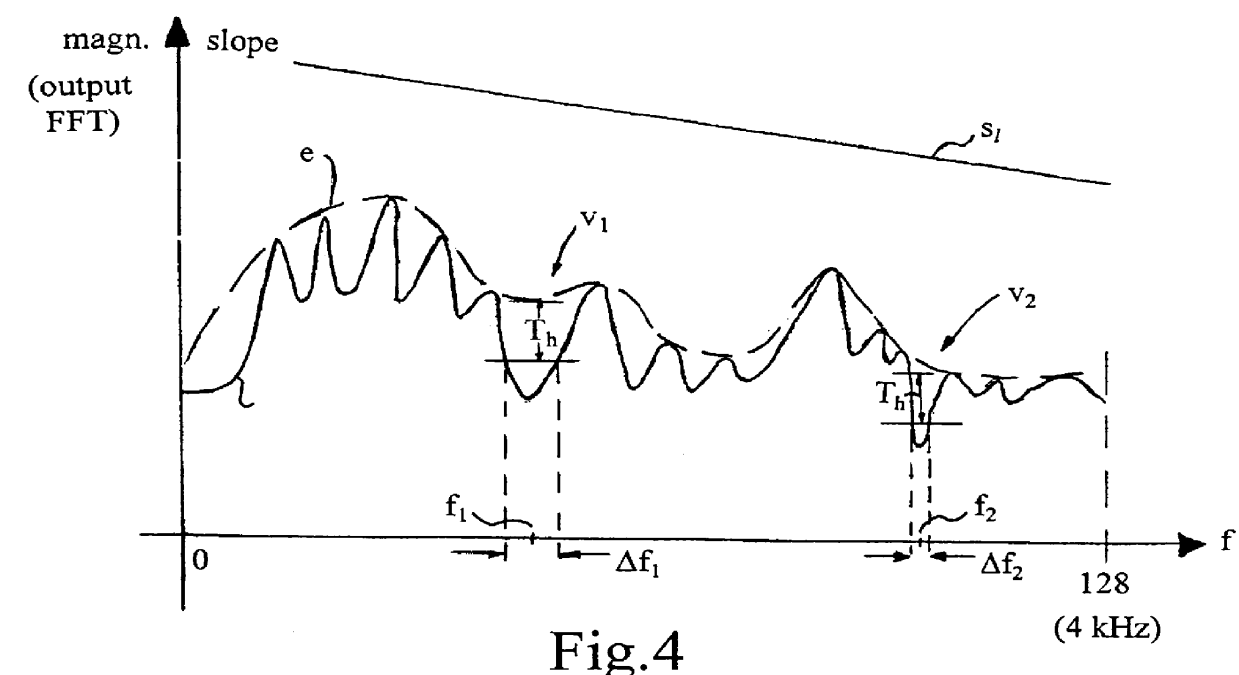
A post-processing method for a speech decoder which outputs a decoded speech signal in the time domain provides high frequency resolution based on a frequency spectrum having non-harmonic and noise deficiencies. This is obtained by transforming the decoded time domain signal to a frequency domain signal by using a high frequency resolution transform (FFT). Then an analysis of the energy distribution of the frequency domain signal is made throughout its frequency area (4 kHz) to find the disturbing frequency components and to prioritize such frequency components which are situated in the higher part of the frequency spectrum. Next, the suppression degree for the disturbing frequency components is found based on prioritizing. Finally the steps of controlling a post-filtering of the transform in dependence of the finding, and inverse transforming the post-filtered transform in order to obtain a post-filtered decoded speech signal in the time domain are performed.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Speech encoder adaptively applying pitch preprocessing with warping of target signal
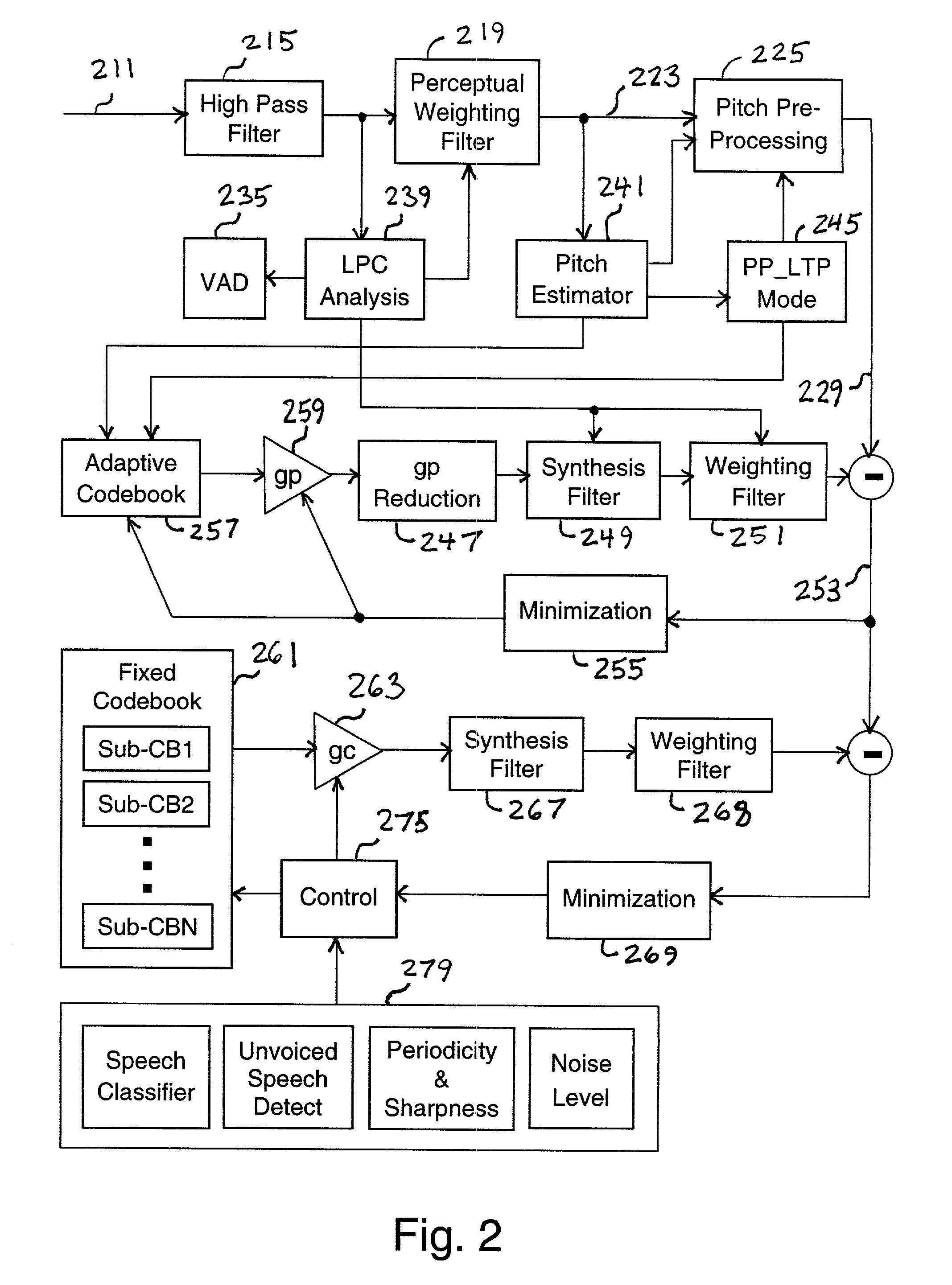
InactiveUS20010023395A1Efficient and effective of signalReduce bitrateSpeech analysisTarget signalClosed loop
A multi-rate speech codec supports a plurality of encoding bit rate modes by adaptively selecting encoding bit rate modes to match communication channel restrictions. In higher bit rate encoding modes, an accurate representation of speech through CELP (code excited linear prediction) and other associated modeling parameters are generated for higher quality decoding and reproduction. A speech encoder employing various encoding schemes based upon parameters including an available transmission bit rate. In addition, the speech encoder is operable to identify and apply an optimal encoding scheme for a given speech signal. The speech encoder may be applied code-excited linear prediction when the available bit rate is above a predetermined upper threshold. Pitch preprocessing, including continuous warping, may be applied when it is below a predetermined lower threshold. The encoder considers varying characteristics of the speech signal including the long term prediction mode of a previous frame, and a spectral difference between the line spectral frequencies of a current and a previous frame, a predicted pitch lag, an open loop pitch lag, a closed loop pitch lag, a pitch gain, and a pitch correlation.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Optimizing pitch and other speech stimuli allocation in a cochlear implant
ActiveUS7251530B1Easy to controlImprove sound qualityElectrotherapyAudiometeringOctaveCochlear implantation
Errors in pitch (frequency) allocation within a cochlear implant are corrected in order to provide a significant and profound improvement in the quality of sound perceived by the cochlear implant user. In one embodiment, the user is stimulated with a reference signal, e.g., the tone “A” (440 Hz) and then the user is stimulated with a probe signal, separated from the reference signal by an octave, e.g., high “A” (880 Hz). The user adjusts the location where the probe signal is applied, using current steering, until the pitch of the probe signal, as perceived by the user, matches the pitch of the reference signal, as perceived by the user. In this manner, the user maps frequencies to stimulation locations in order to tune his or her implant system to his or her unique cochlea.
Owner:ADVANCED BIONICS AG
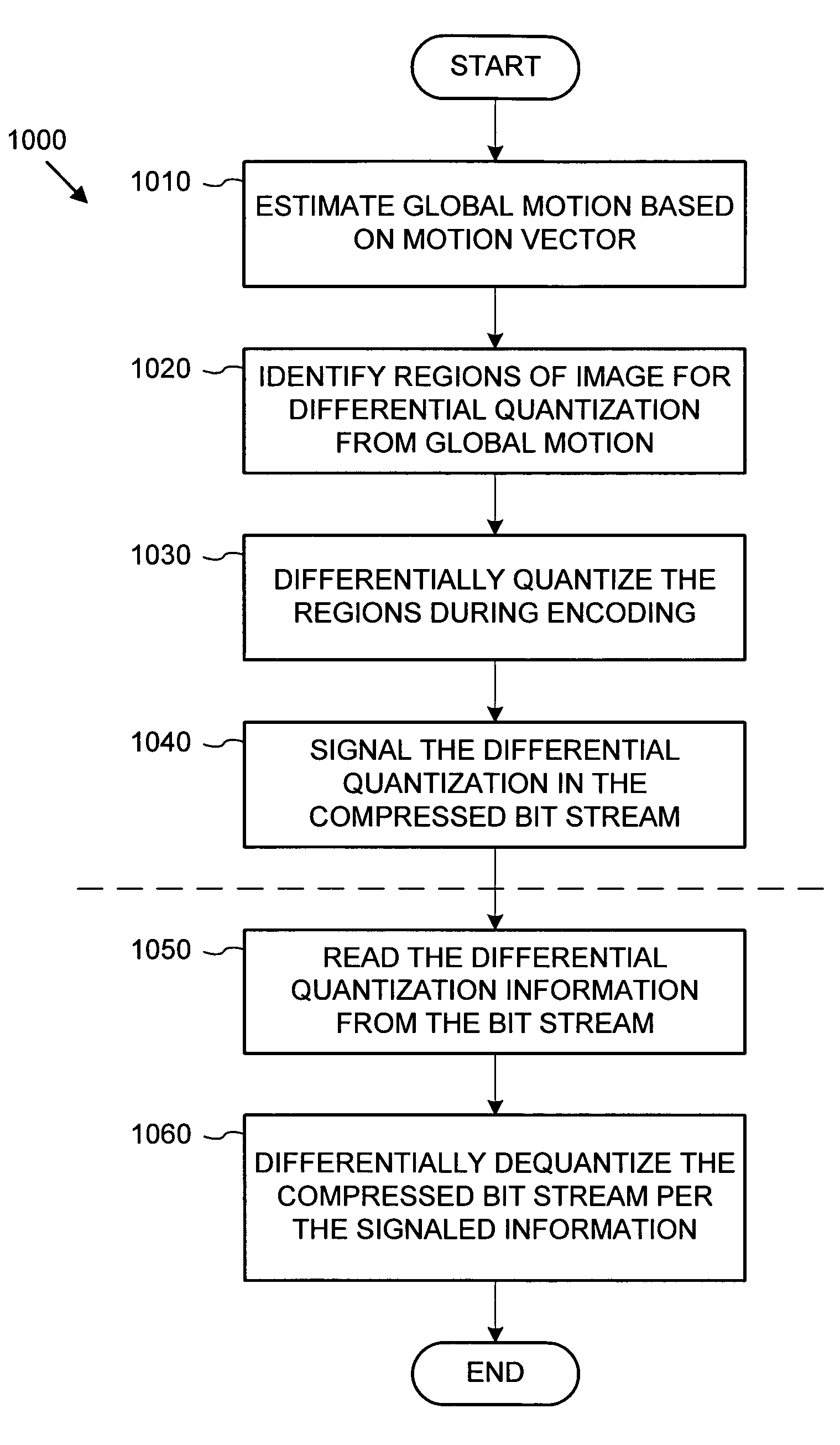
Intelligent differential quantization of video coding
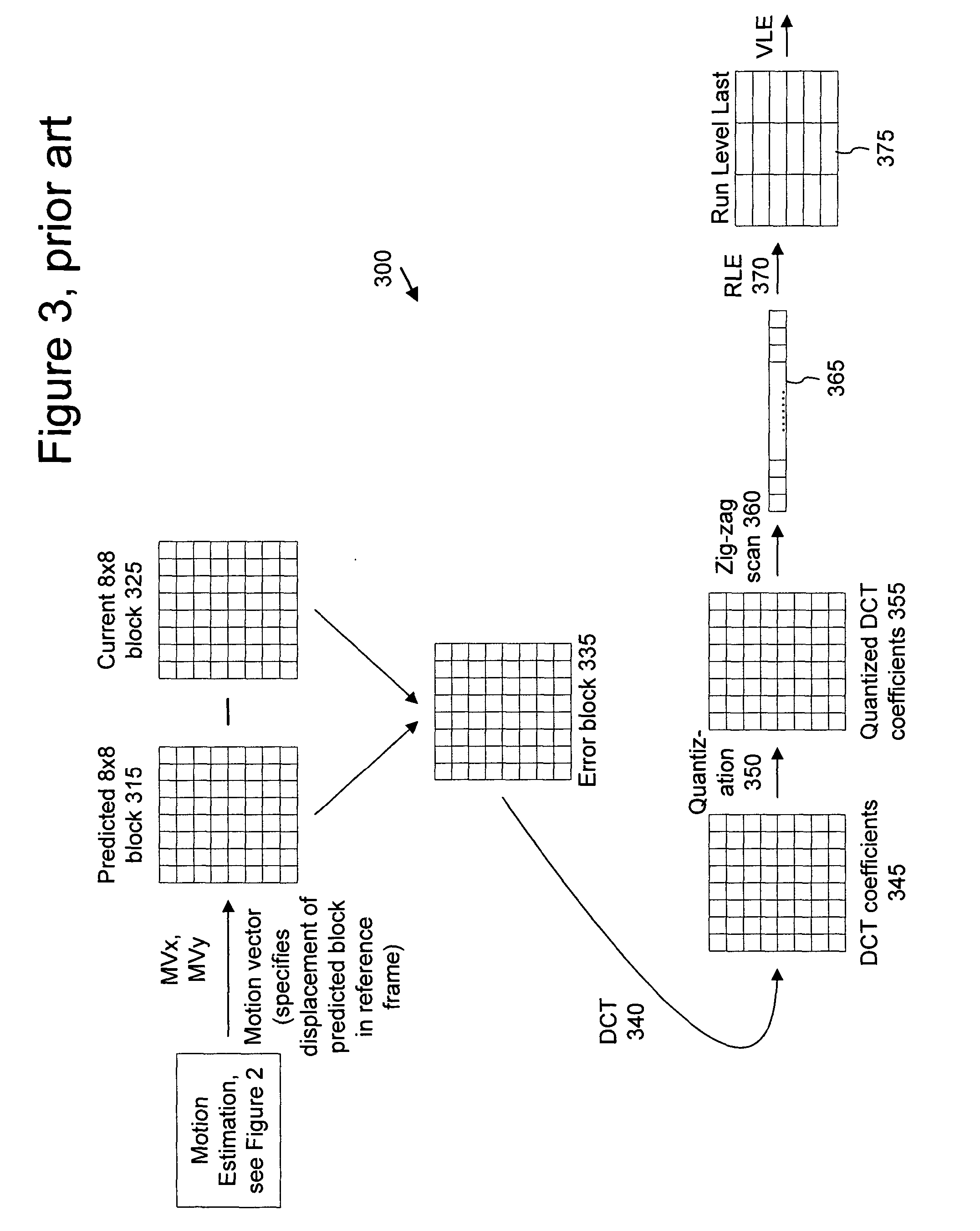
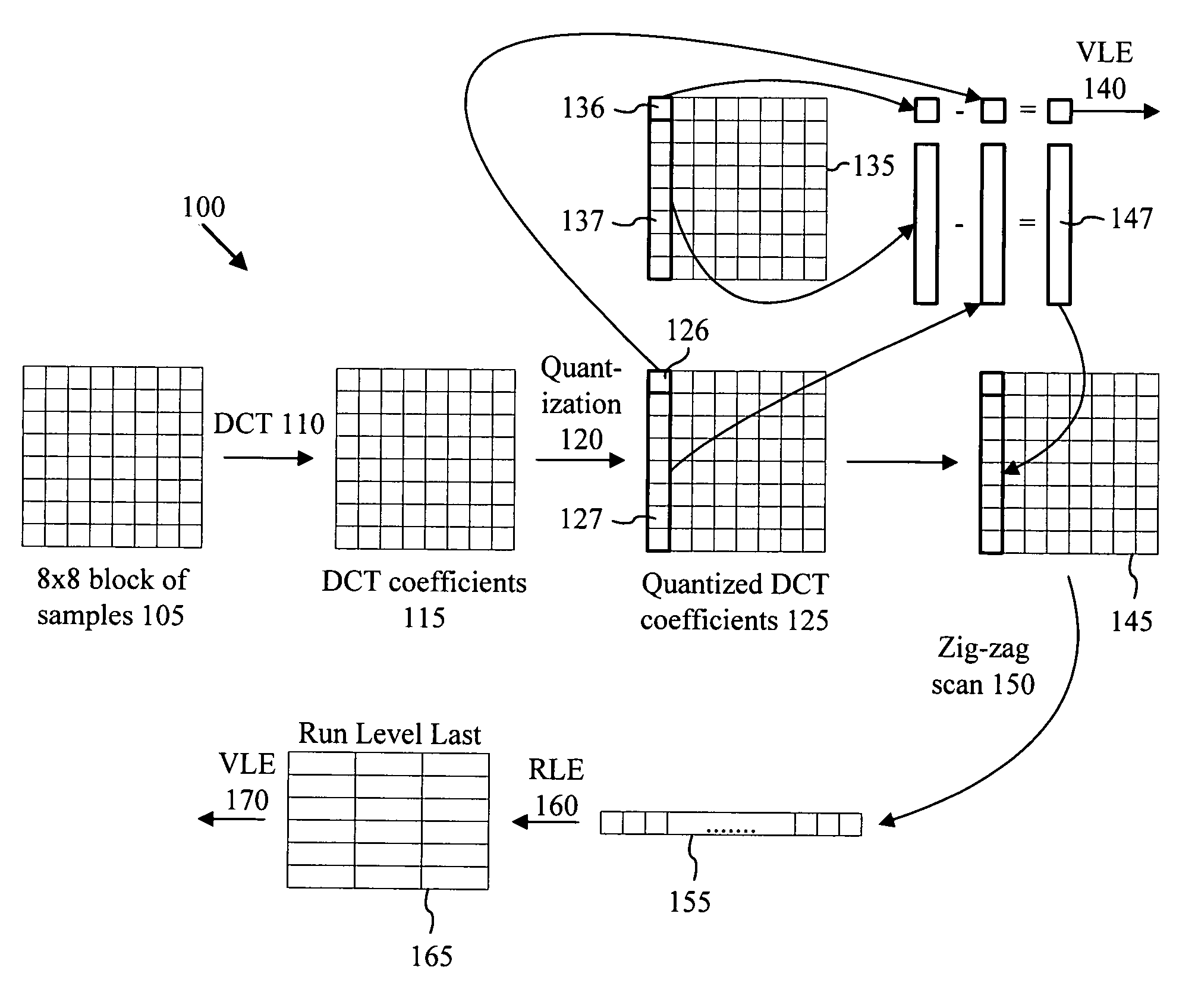
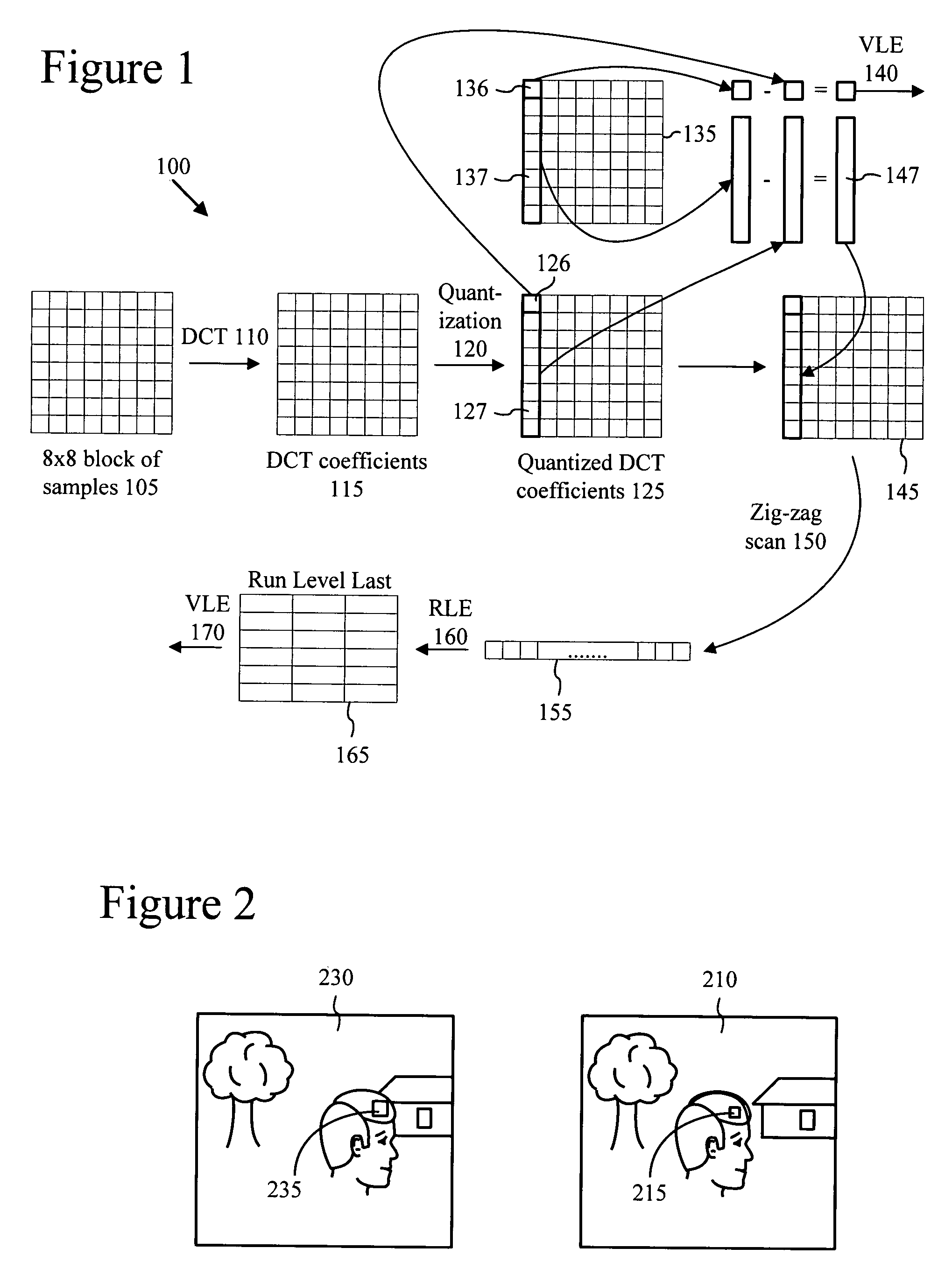
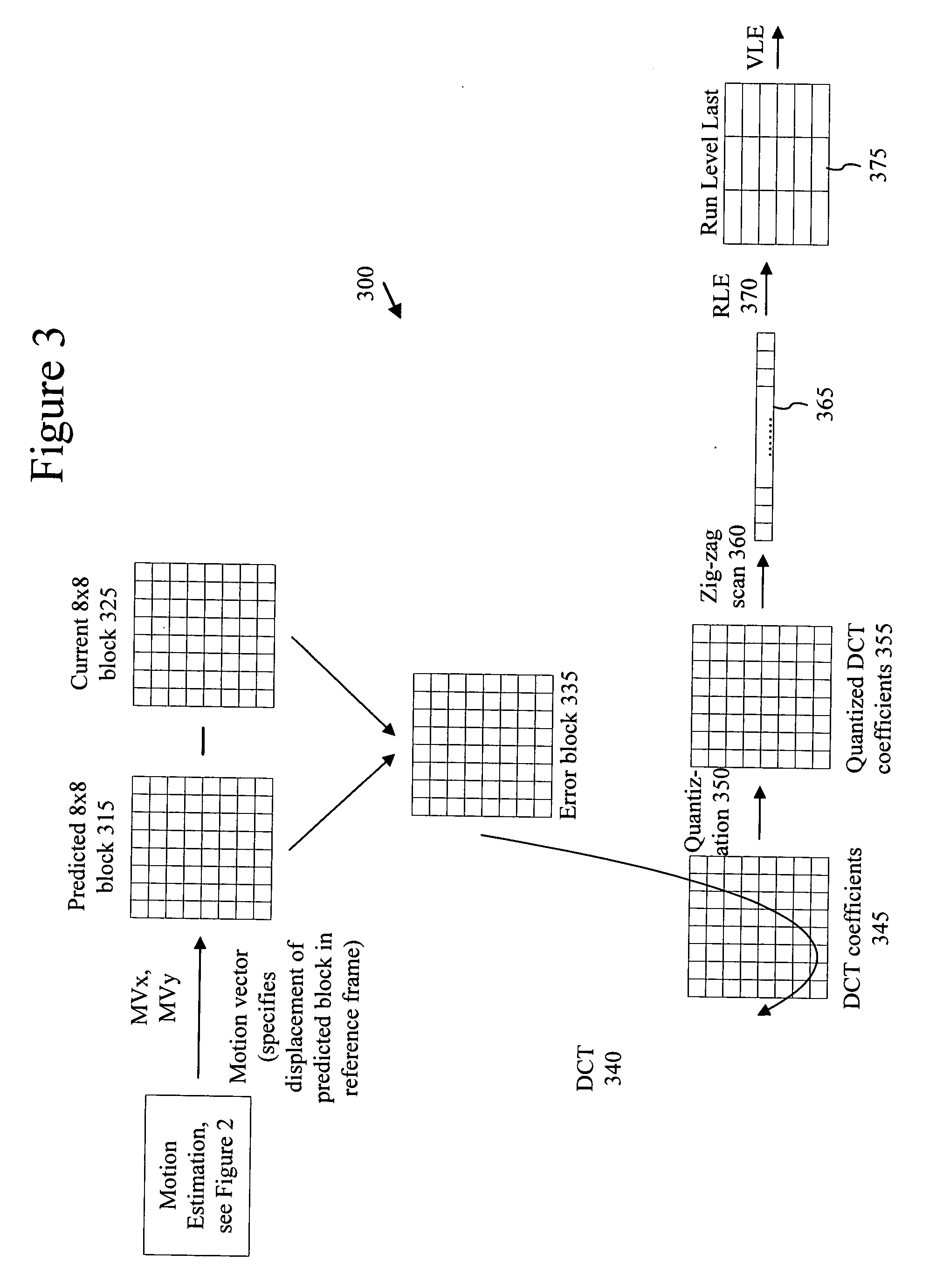
InactiveUS20050013500A1Readily handle compressed bitstreamImprove perceived qualityColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionPattern recognitionGranularity
With intelligent differential quantization, a video codec intelligently quantizes video at differing strength levels within a frame, such as on a macroblock (MB) or a group of MB basis. This allows the codec to control bit usage on a finer granularity than a frame to meet hardware constraints, as well as providing perceptual optimization by coarsely quantizing unimportant regions, while finely quantizing important regions within a frame. The intelligent differential quantization uses motion information gathered from encoding and analysis of the video to classify the importance of different regions of the image, and quantizes the regions accordingly. In addition, the intelligent differential quantization include efficient signaling of information as to the differential quantization strengths in the compressed bit stream.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Regions of interest for quality adjustments
InactiveUS20080240250A1Reduce bitrateEliminate redundancyColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionComputer scienceQuality adjustment
Quality settings established by an encoder are adjusted based on information associated with regions of interest (“ROIs”). For example, quantization step sizes can be reduced (to improve quality) or increased (to reduce bit rate). ROIs can be identified and quality settings can be adjusted based on input received from a user interface. An overlap setting can be determined for a portion of a picture that corresponds to an ROI overlap area. For example, an overlap setting is chosen from step sizes corresponding to a first overlapping ROI and a second overlapping ROI, or from relative reductions in step size corresponding to the first ROI and the second ROI. ROIs can be parameterized by information (e.g., using data structures) that indicates spatial dimensions of the ROIs and quality adjustment information (e.g., dead zone information, step size information, and quantization mode information).
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
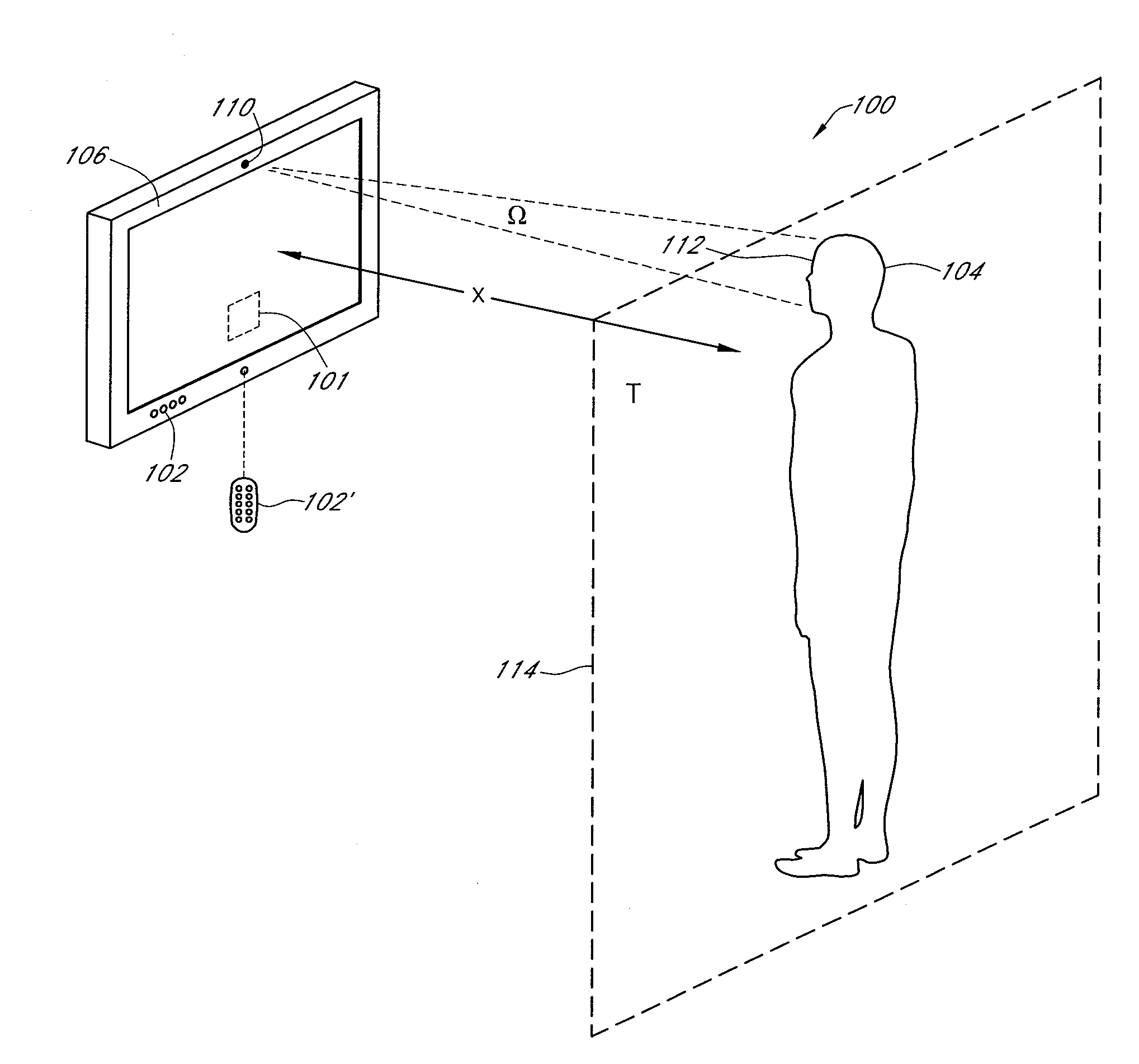
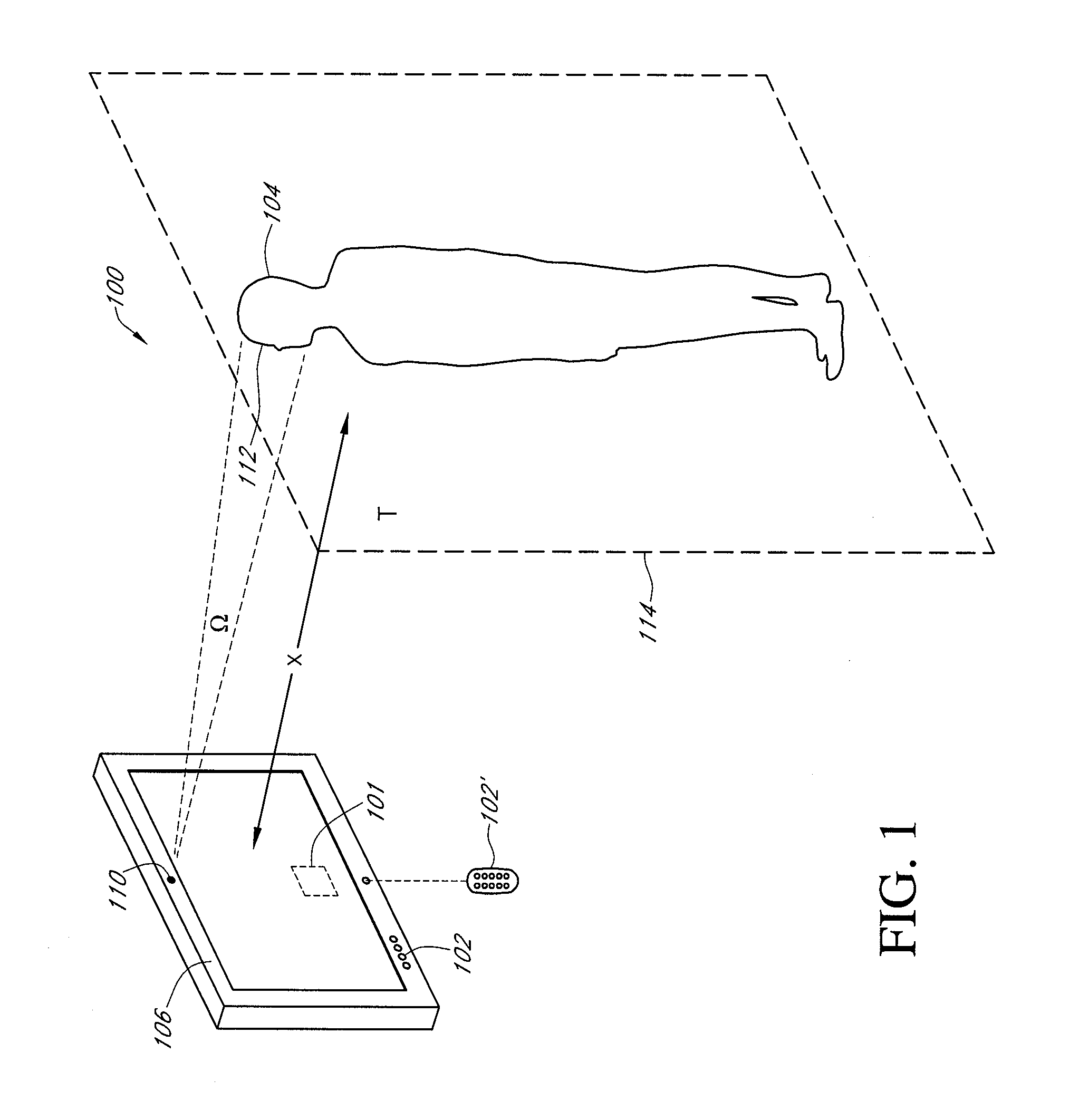
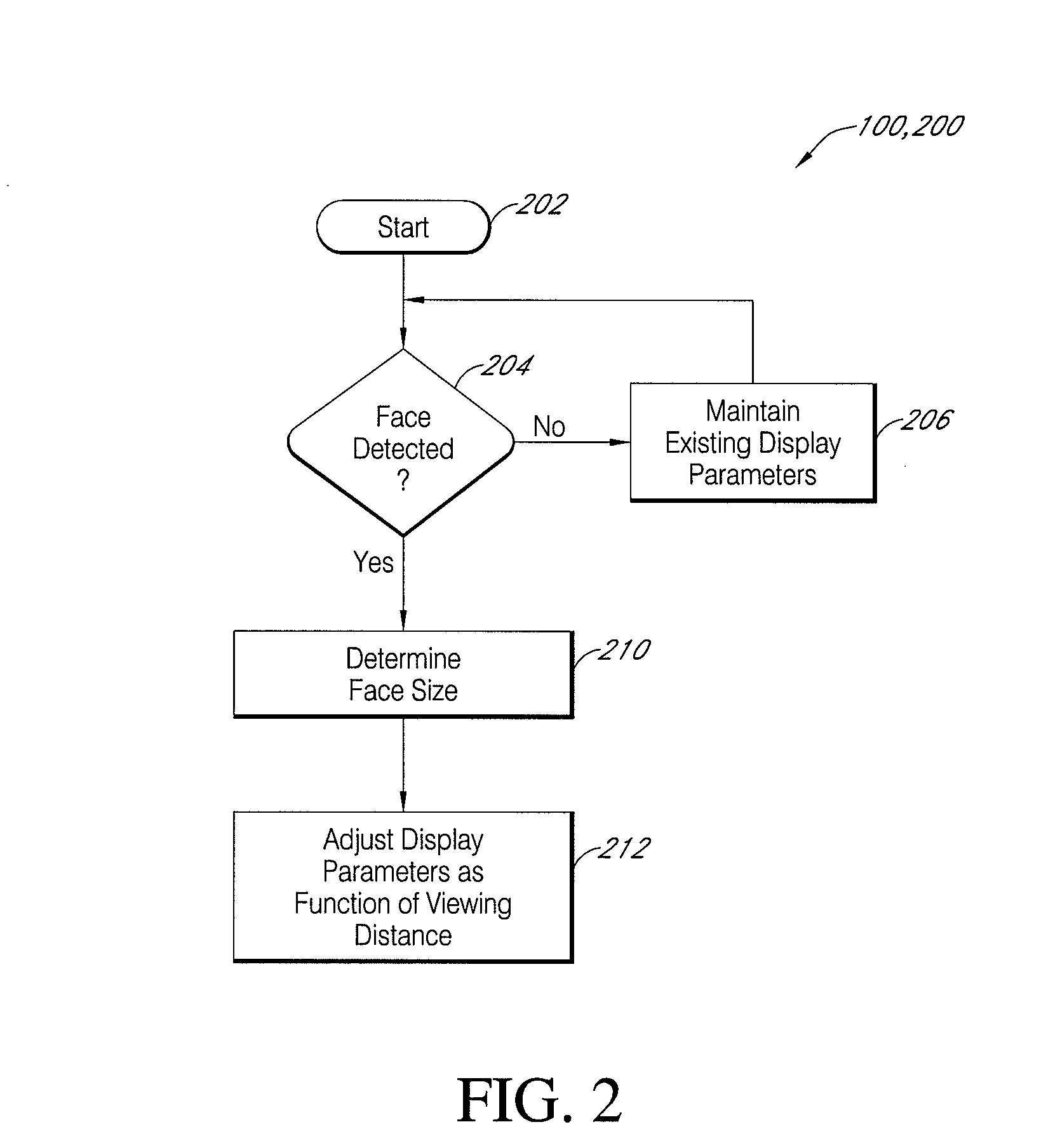
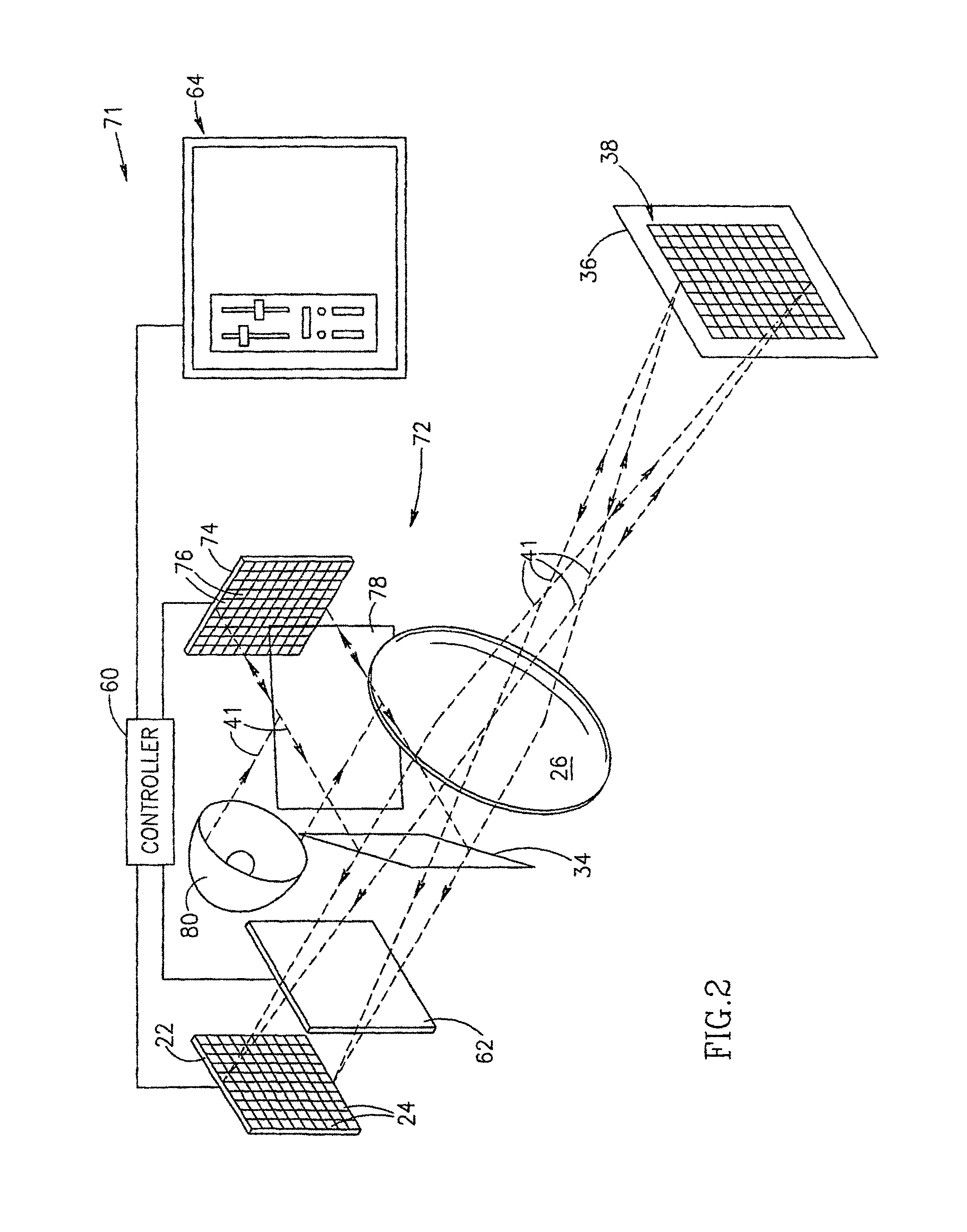
Video display enhancement based on viewer characteristics
InactiveUS20080316372A1Reduce the burden onImprove perceived qualityTelevision system detailsCathode-ray tube indicatorsComputer graphics (images)Imaging quality
A video display with a display screen adapted to display video images according to adjustable display parameters, for example brightness, contrast, and / or sharpness, and at least one viewer sensor configured to determine at least one variable viewing characteristic and wherein the display is adapted to adjust the display parameters to adjust the displayed video image quality at least partially as a function of the variable viewing characteristic. A method of adjusting displayed image quality of a video display system, including inducing the video display system to determine at least one characteristic of a current viewing situation and adjusting one or more variable display parameters at least partially as a function of the determined characteristics. The viewing characteristics can include viewing time, viewing distance, and other.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
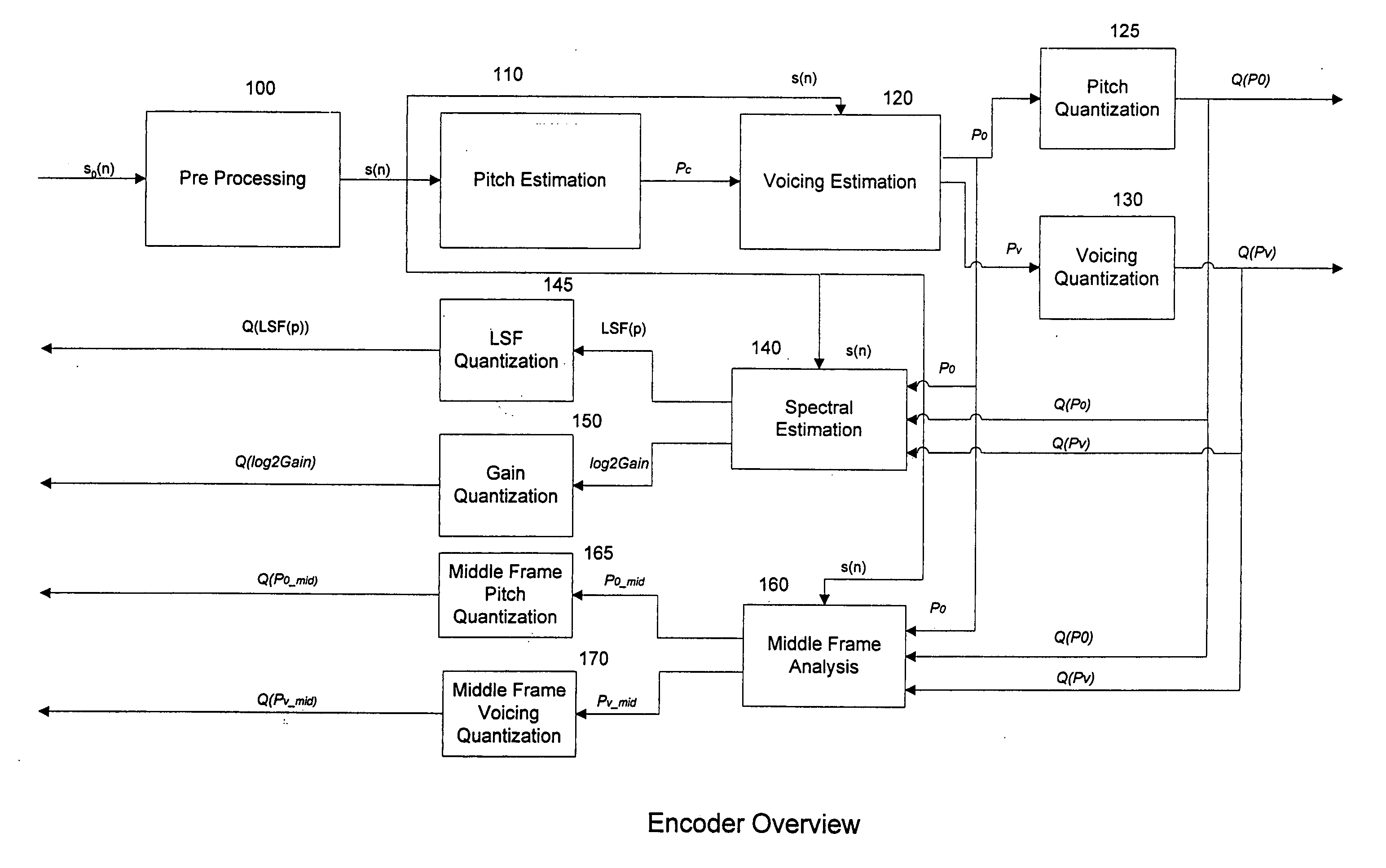
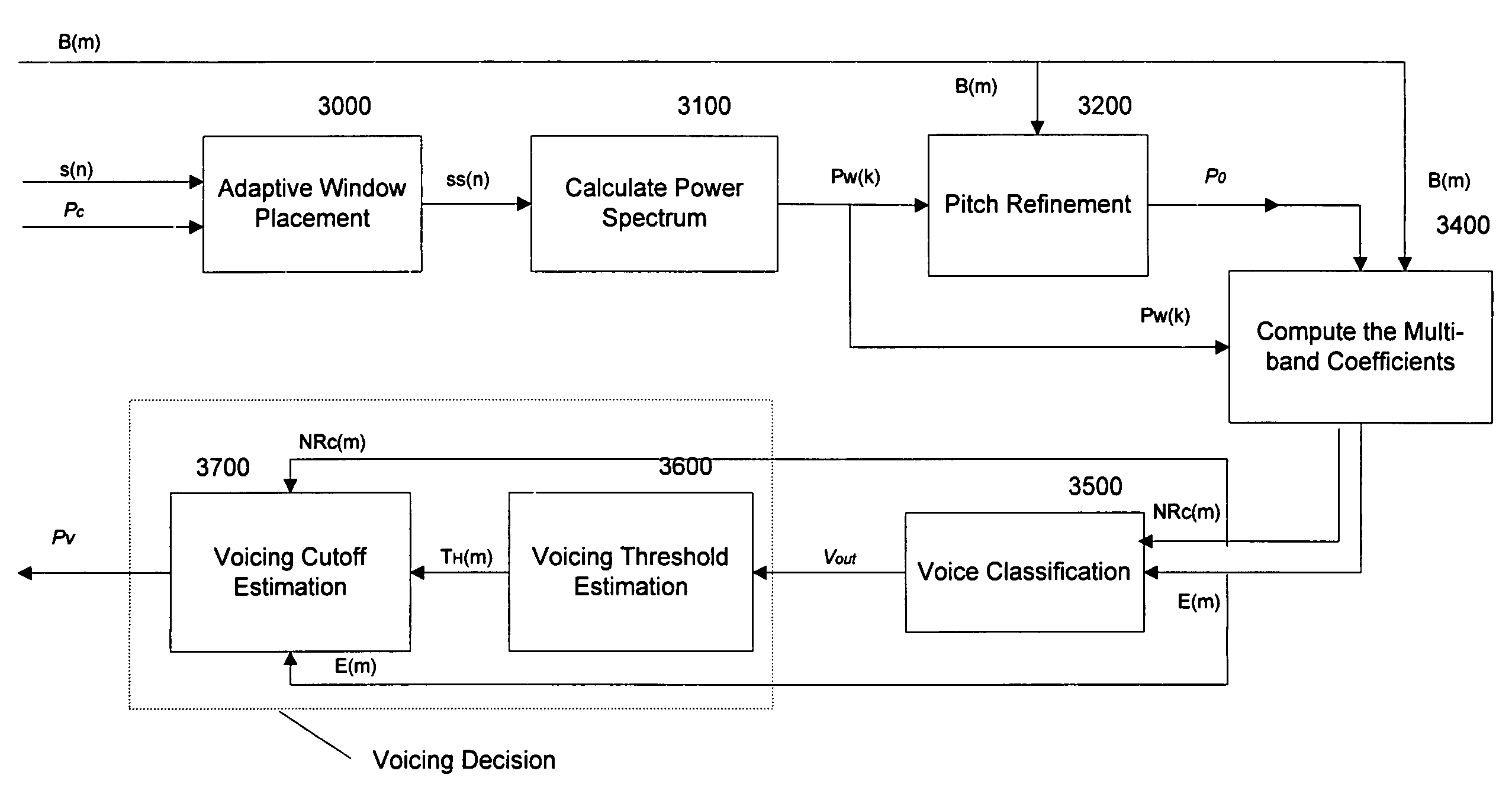
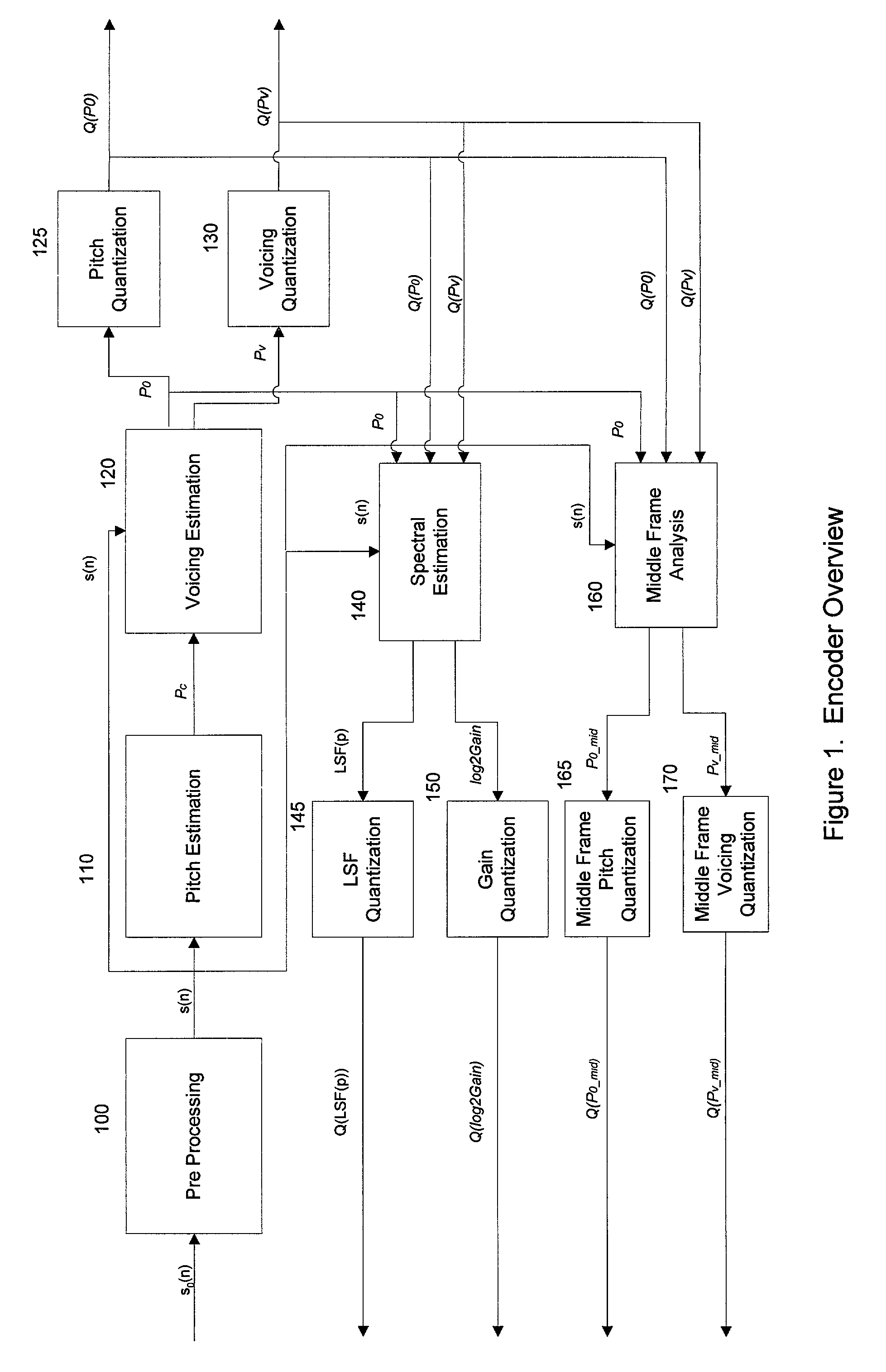
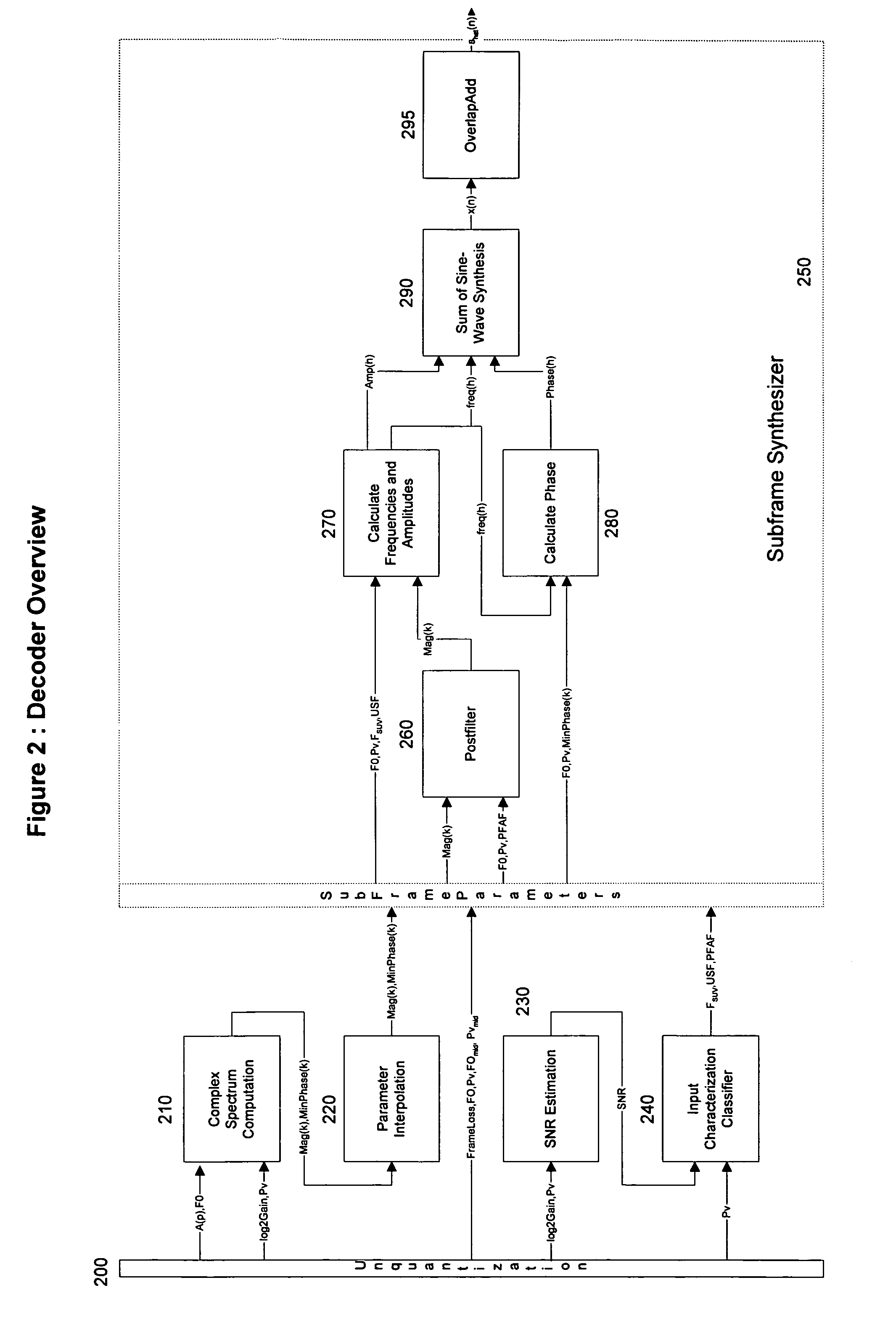
Parametric speech codec for representing synthetic speech in the presence of background noise
InactiveUS20060064301A1Accurate representationImprove perceived qualitySpeech recognitionSpeech synthesisFrequency spectrumBackground noise
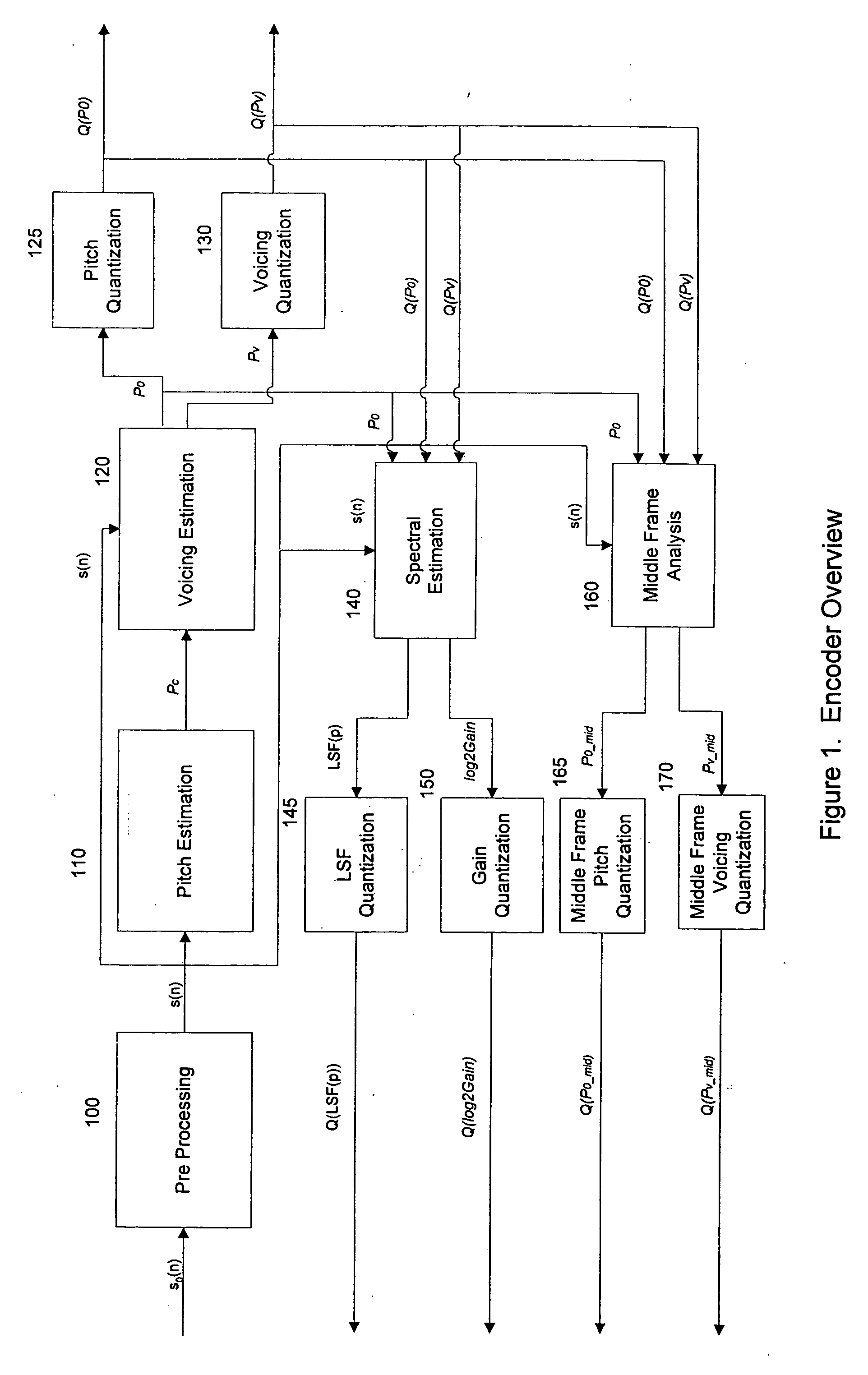
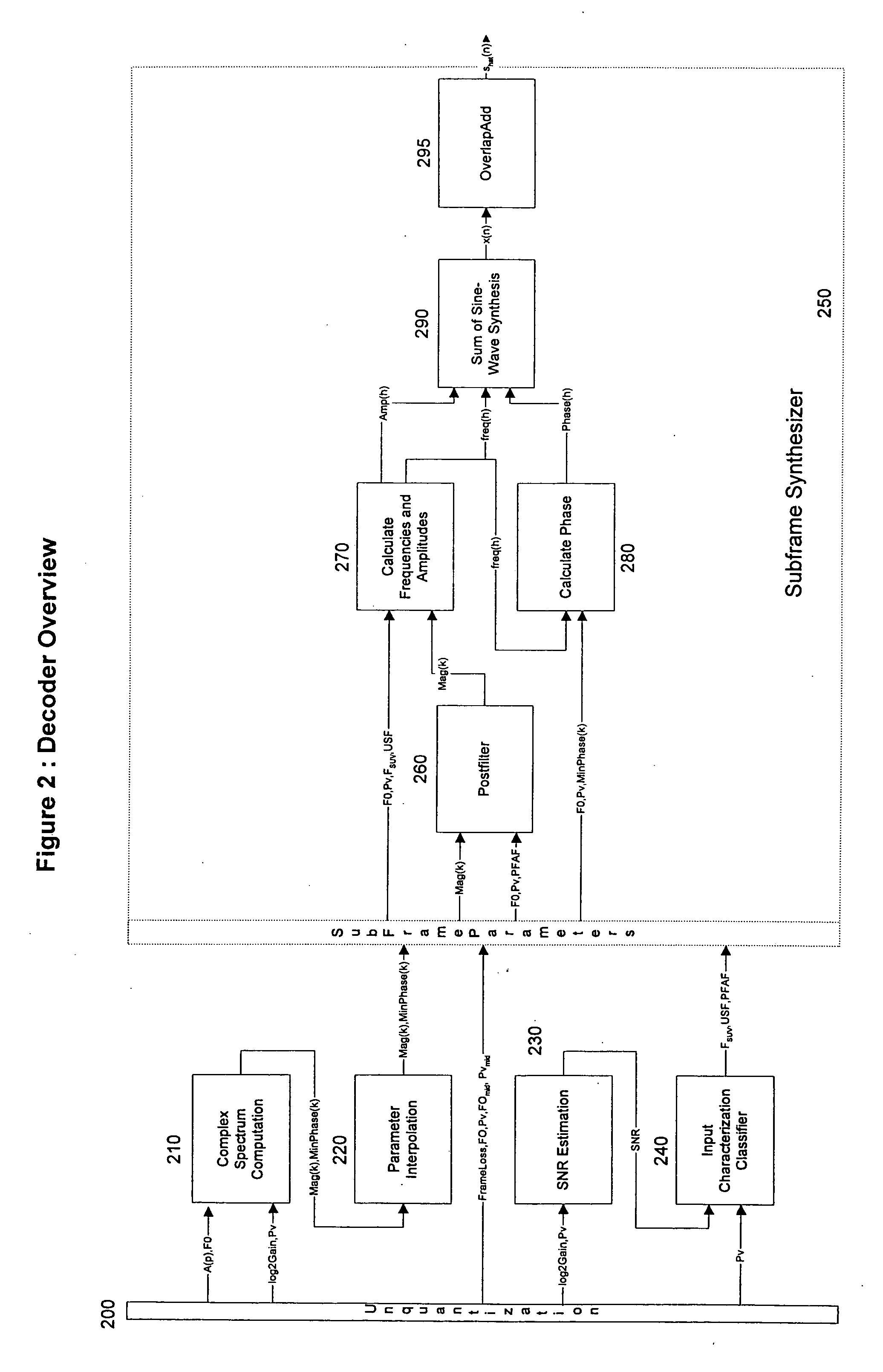
A system and method are provided for processing audio and speech signals using a pitch and voicing dependent spectral estimation algorithm (voicing algorithm) to accurately represent voiced speech, unvoiced speech, and mixed speech in the presence of background noise, and background noise with a single model. The present invention also modifies the synthesis model based on an estimate of the current input signal to improve the perceptual quality of the speech and background noise under a variety of input conditions. The present invention also improves the voicing dependent spectral estimation algorithm robustness by introducing the use of a Multi-Layer Neural Network in the estimation process. The voicing dependent spectral estimation algorithm provides an accurate and robust estimate of the voicing probability under a variety of background noise conditions. This is essential to providing high quality intelligible speech in the presence of background noise.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
Audio coding system using characteristics of a decoded signal to adapt synthesized spectral components
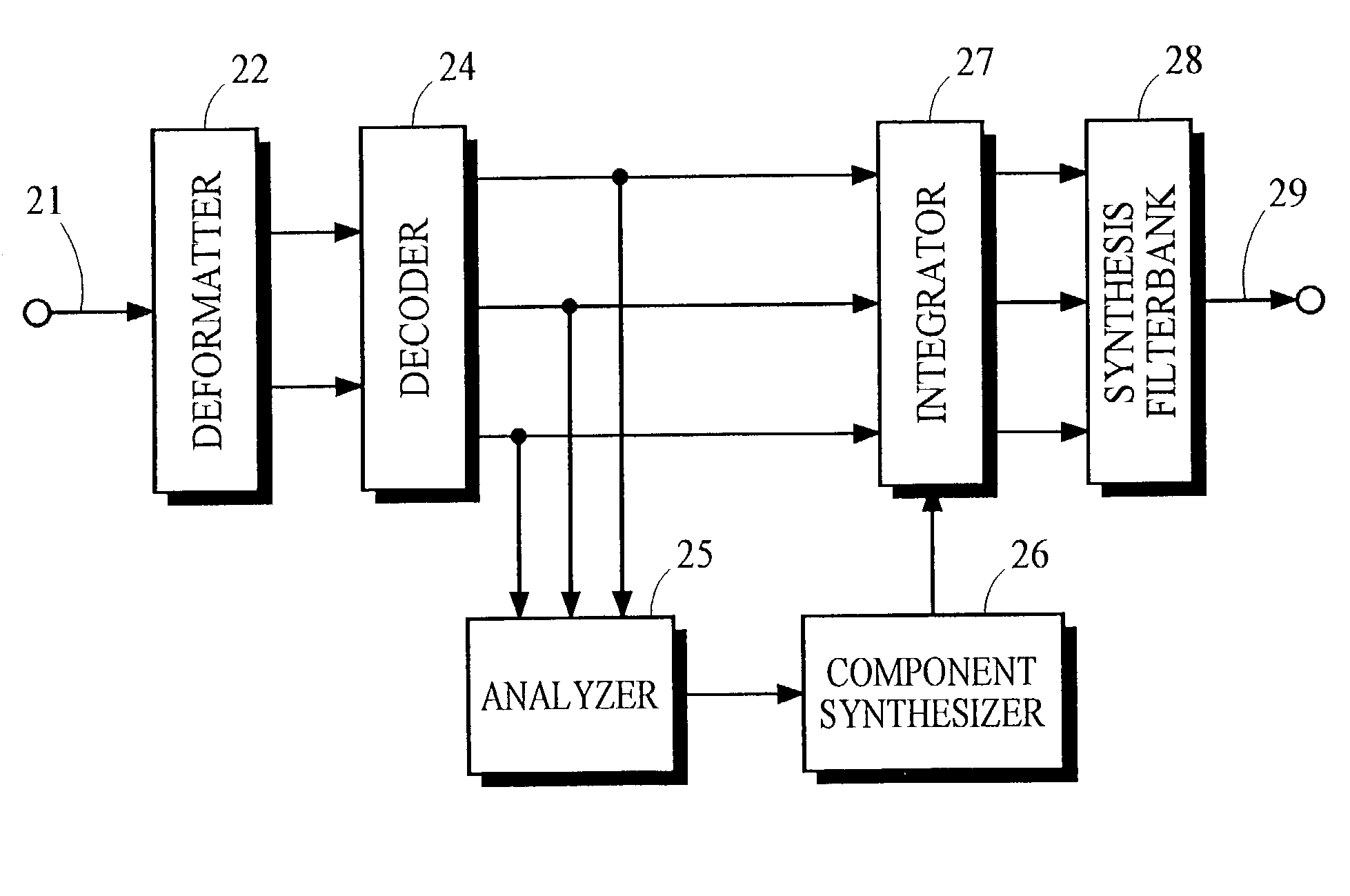
ActiveUS20030233236A1Improve perceived qualityCode conversionSpeech synthesisFrequency spectrumAudio frequency
A receiver in an audio coding system receives a signal conveying frequency subband signals representing an audio signal. The subband signals are examined to assess one or more characteristics of the audio signal. Spectral components are synthesized having the assessed characteristics. The synthesized spectral components are integrated with the subband signals and passed through a synthesis filterbank to generate an output signal. In one implementation, the assessed characteristic is temporal shape and noise-like spectral components are synthesized having the temporal shape of the audio signal.
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
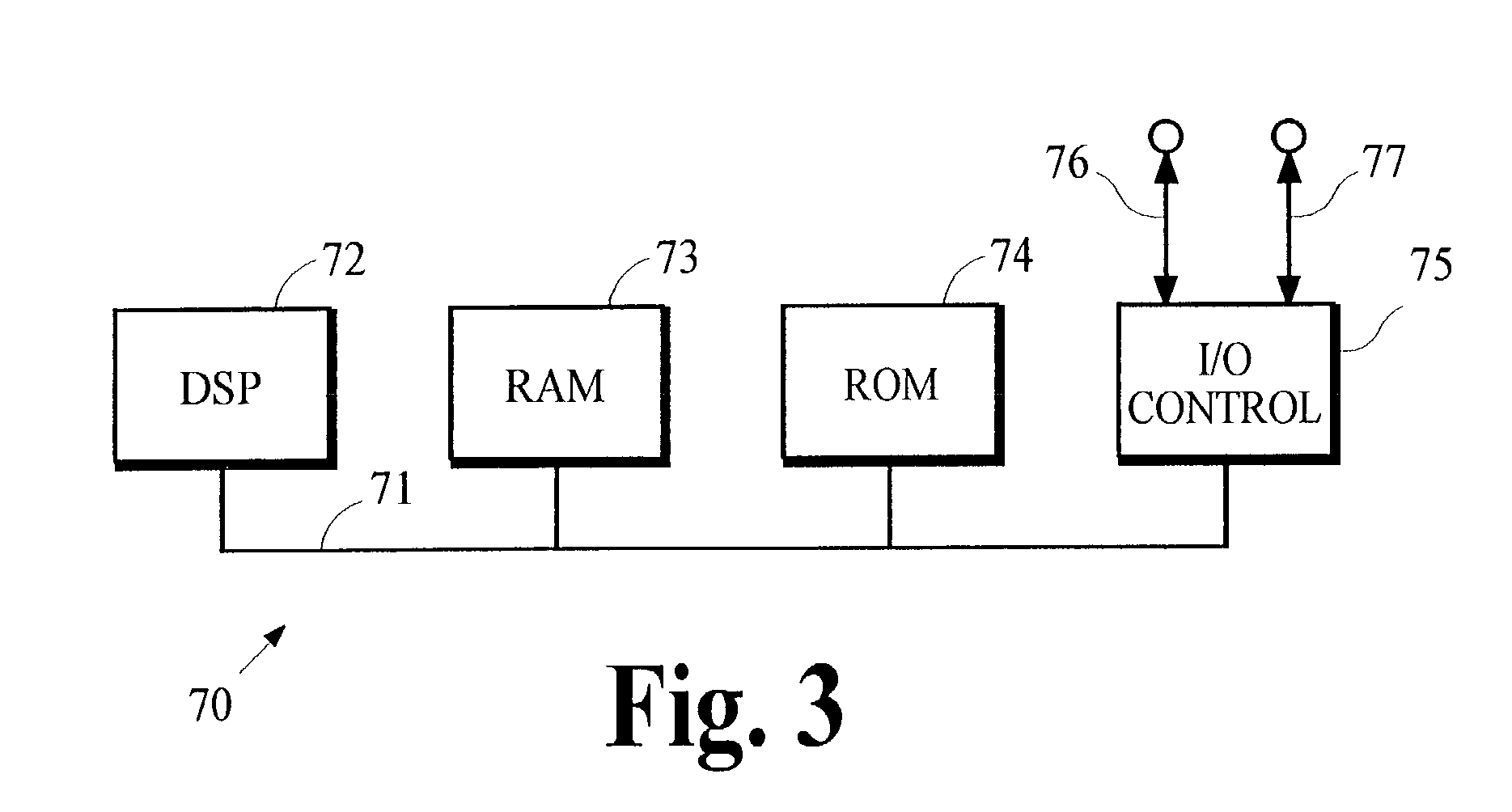
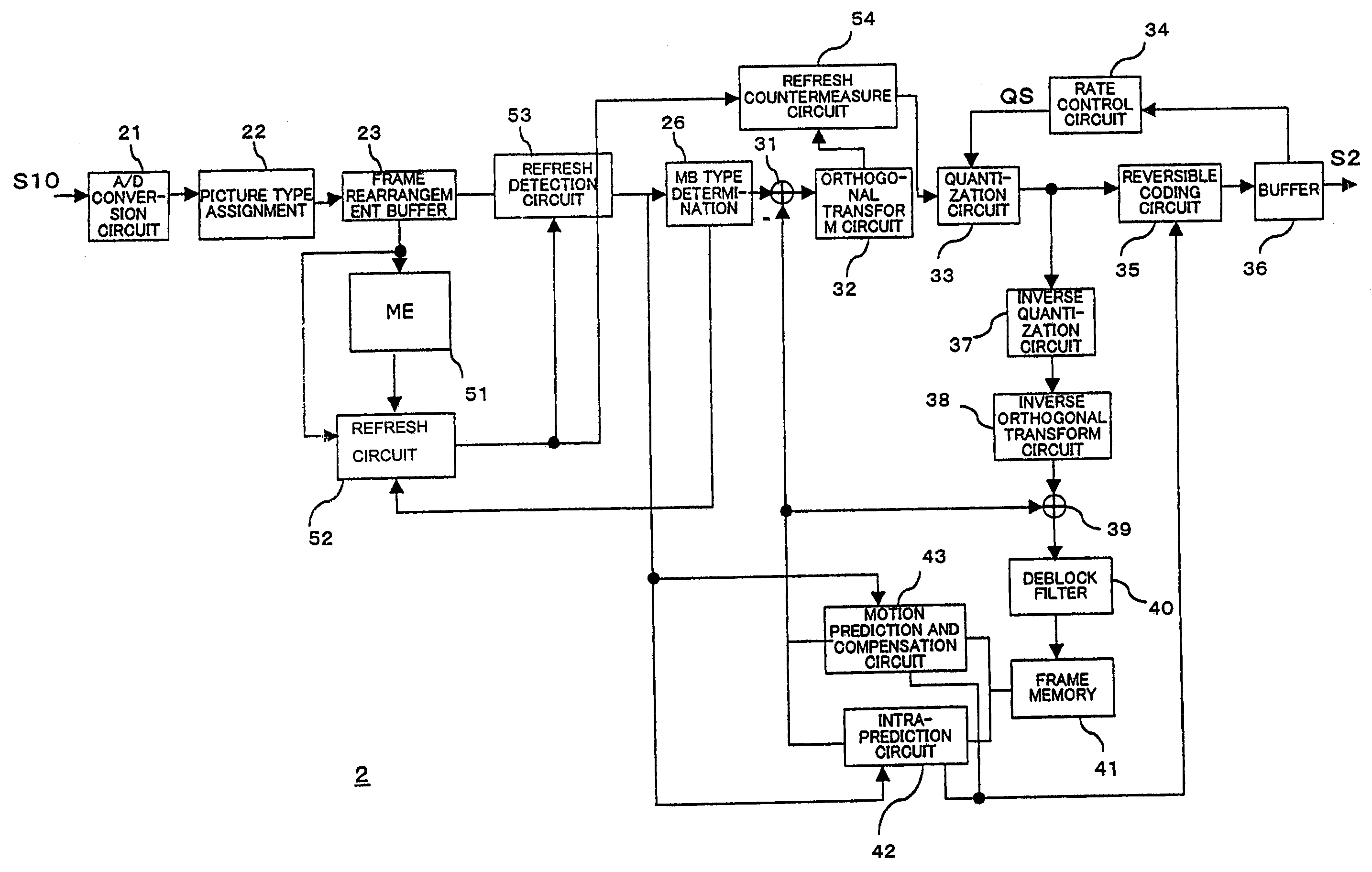
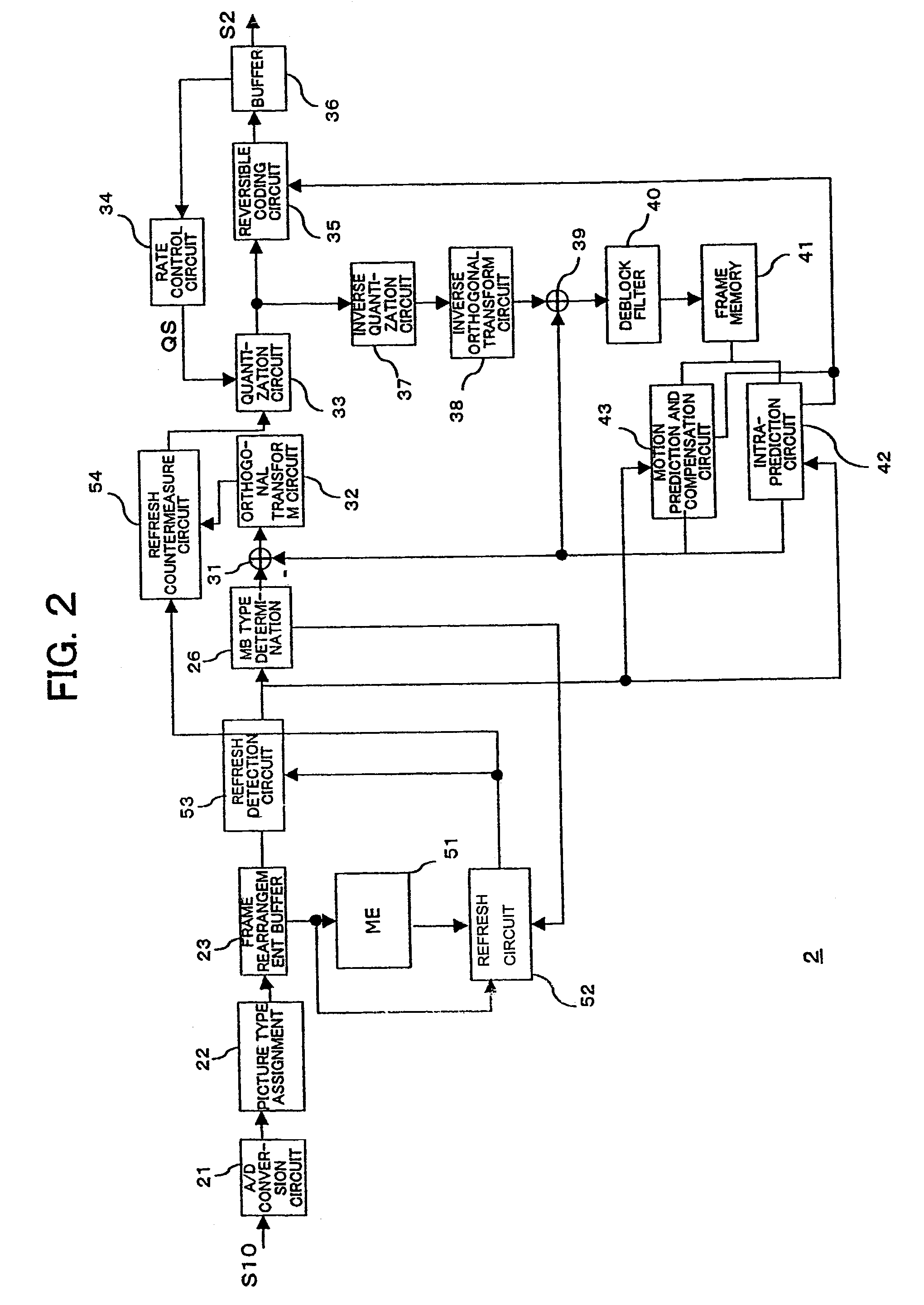
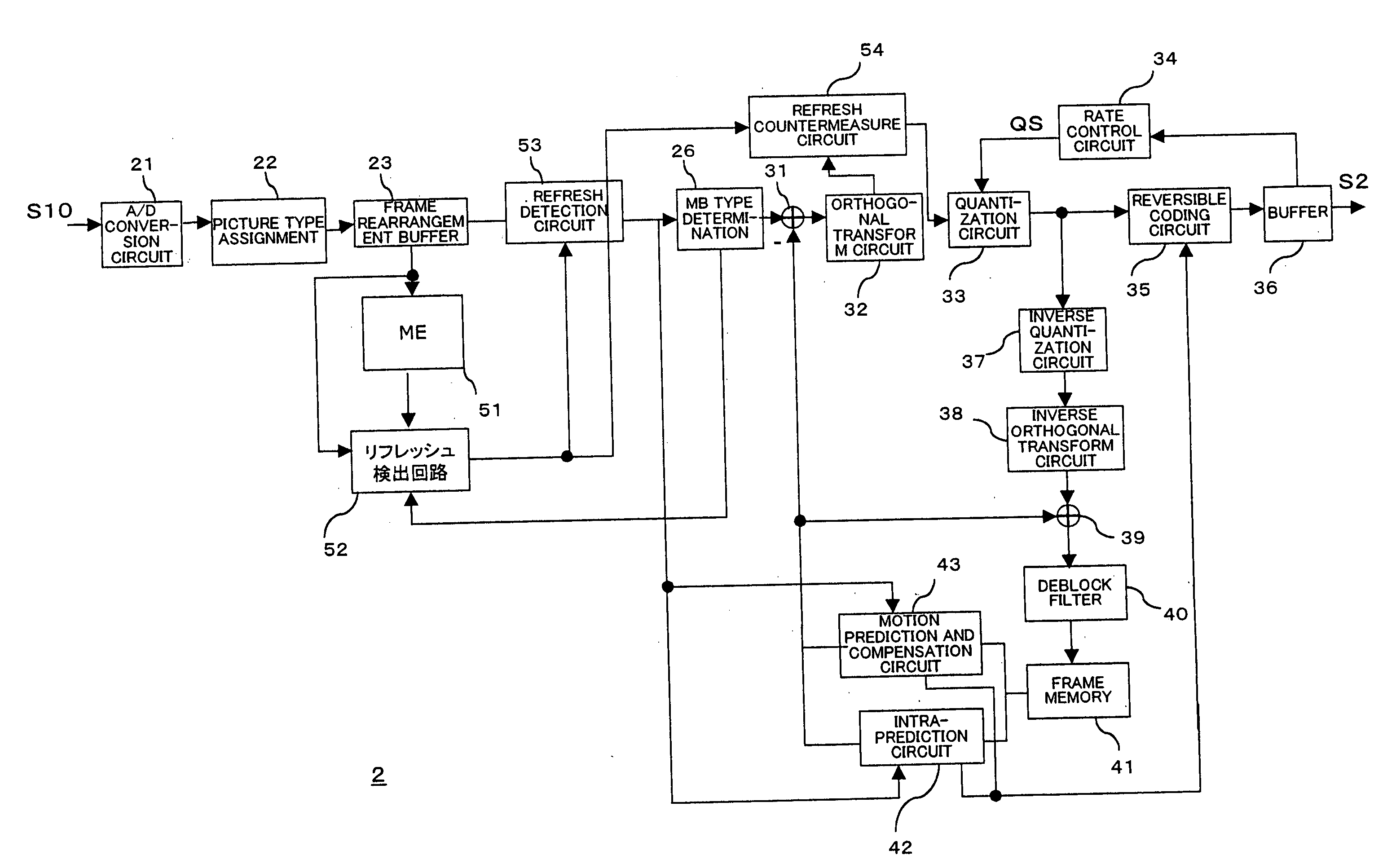
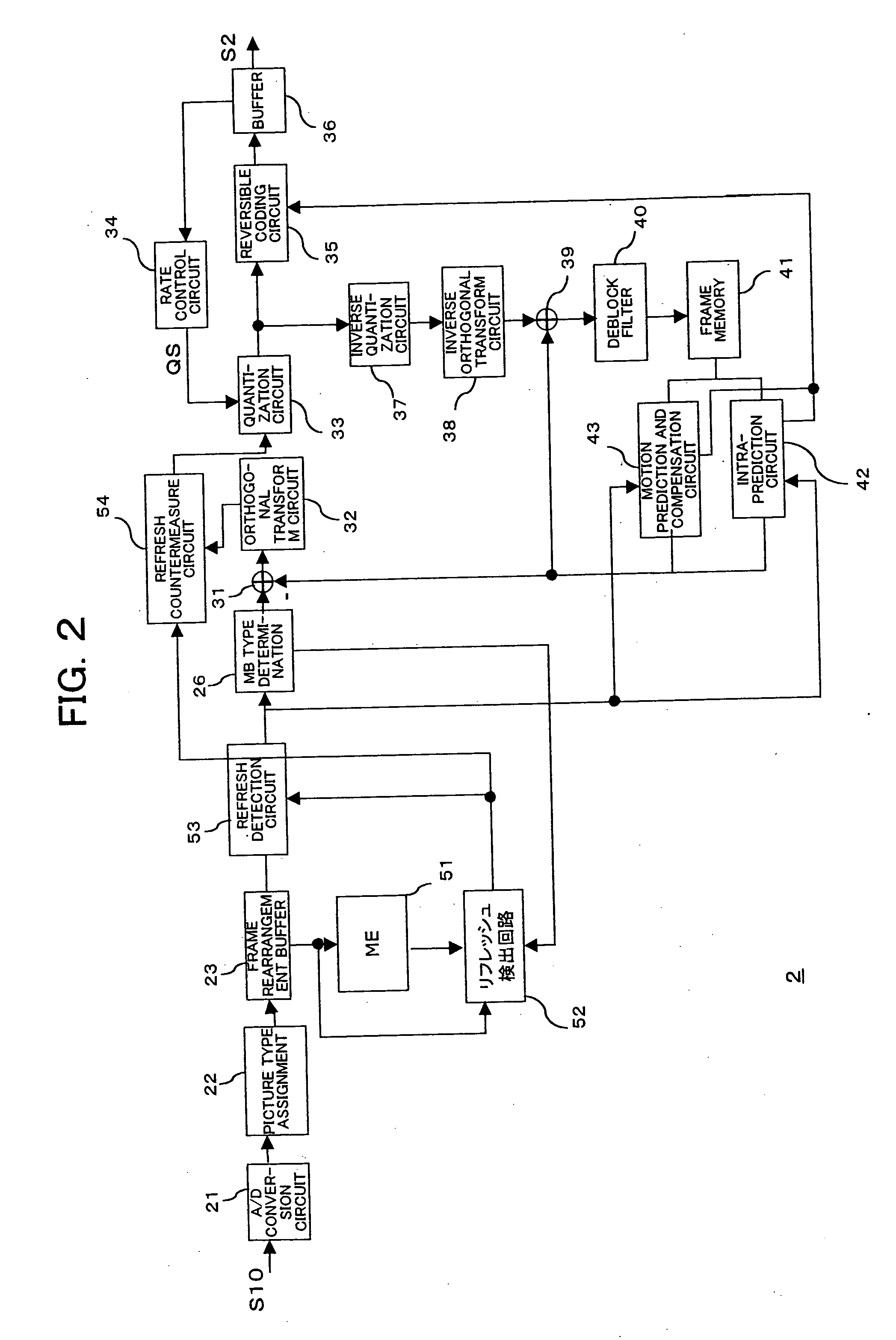
Coding device, coding method, decoding device, decoding method, and programs of same
InactiveUS7697783B2Improve perceived qualityImage enhancementTelevision system detailsComputer hardwareData encoding
A coding device having a specifying unit for specifying image region data to be processed for refreshing countermeasures in image data being coded based on that image data and a refreshing countermeasure unit for applying processing for refreshing countermeasures to image region data specified by the specifying unit when coding the image data.
Owner:SONY CORP +1
Coding device, coding method, decoding device, decoding method, and programs of same
InactiveUS20070025621A1Improve perceptual qualityImprove perceived qualityImage enhancementTelevision system detailsComputer hardwareData encoding
A coding device having a specifying unit for specifying image region data to be processed for refreshing countermeasures in image data being coded based on that image data and a refreshing countermeasure unit for applying processing for refreshing countermeasures to image region data specified by the specifying unit when coding the image data.
Owner:SONY CORP +1
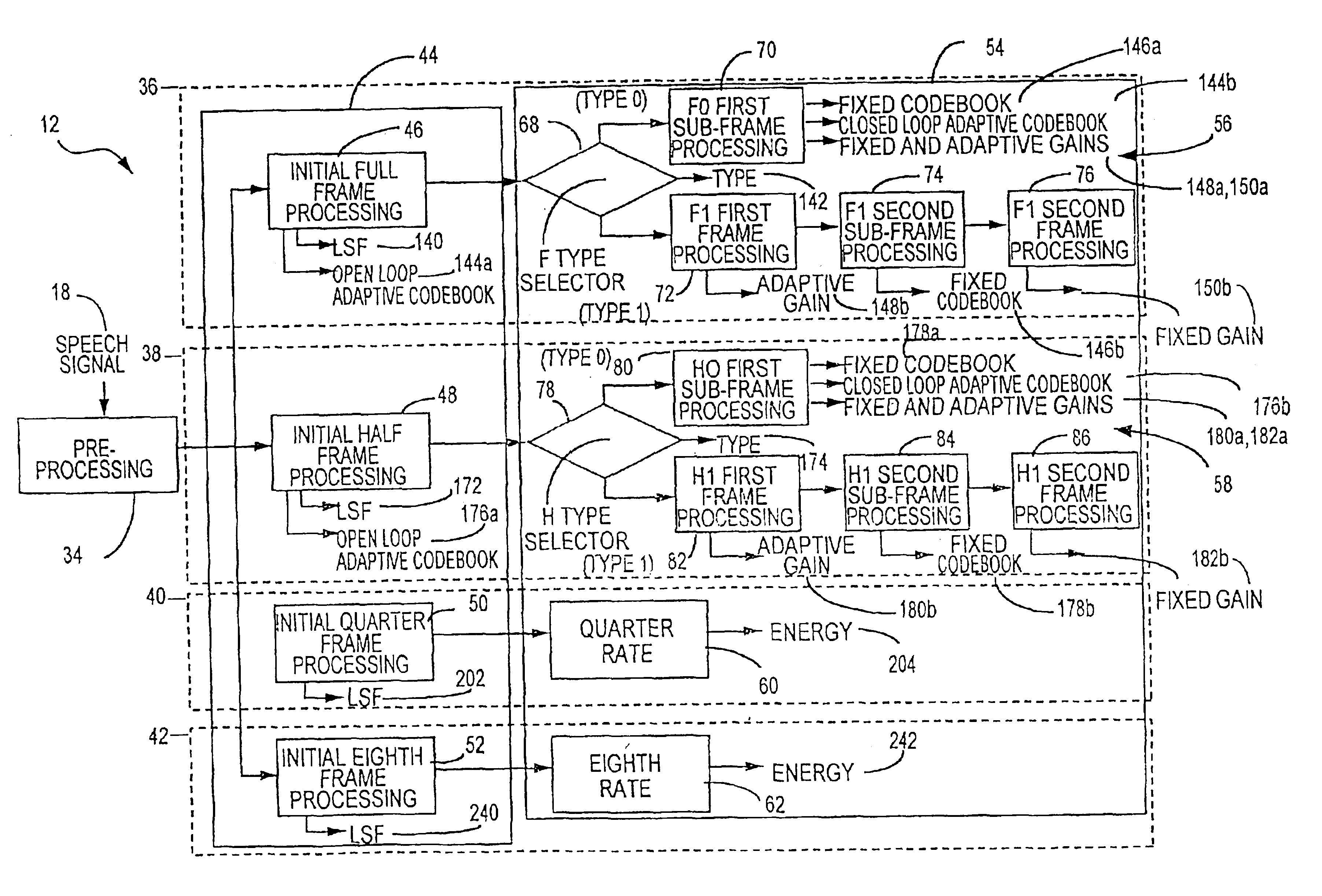
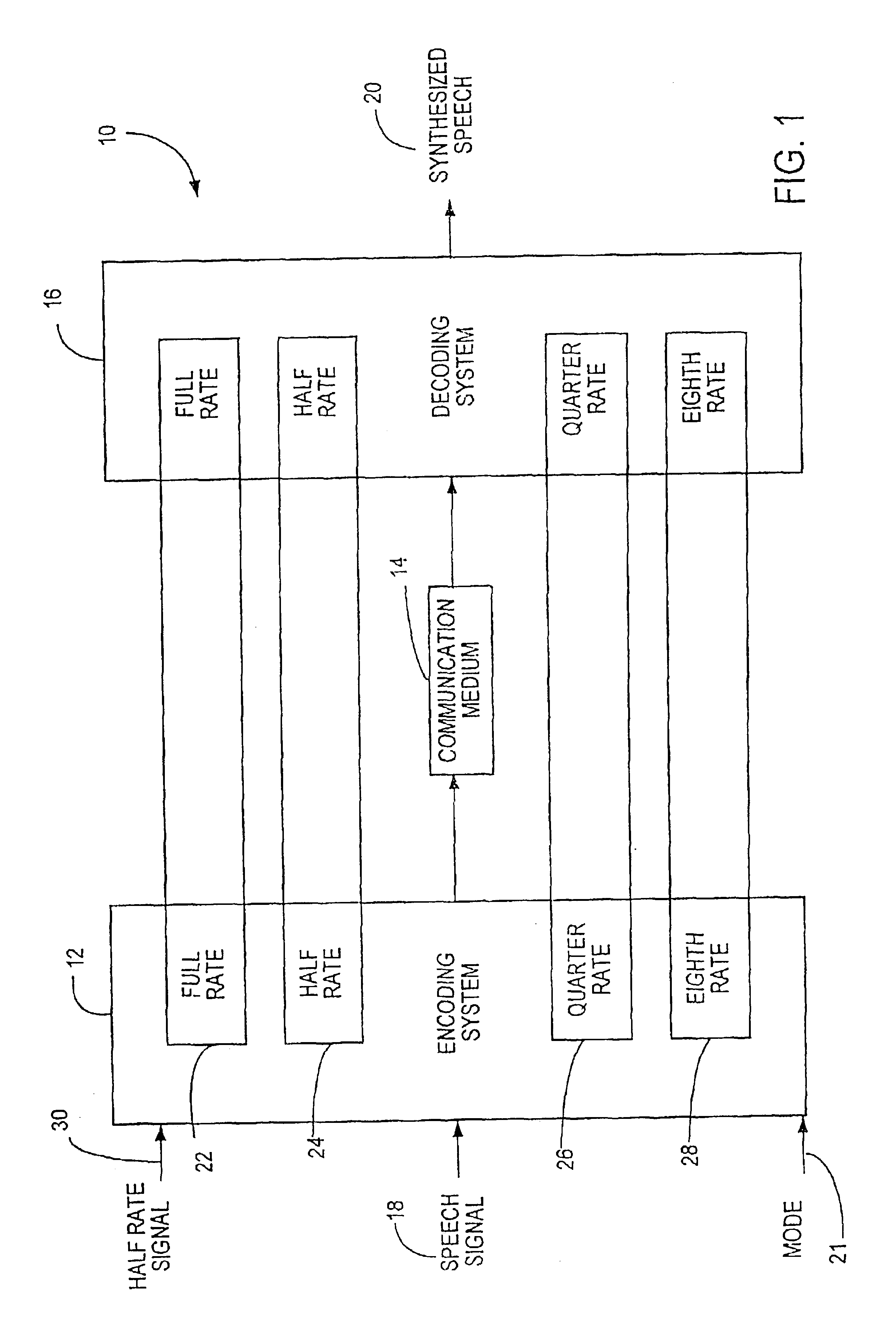
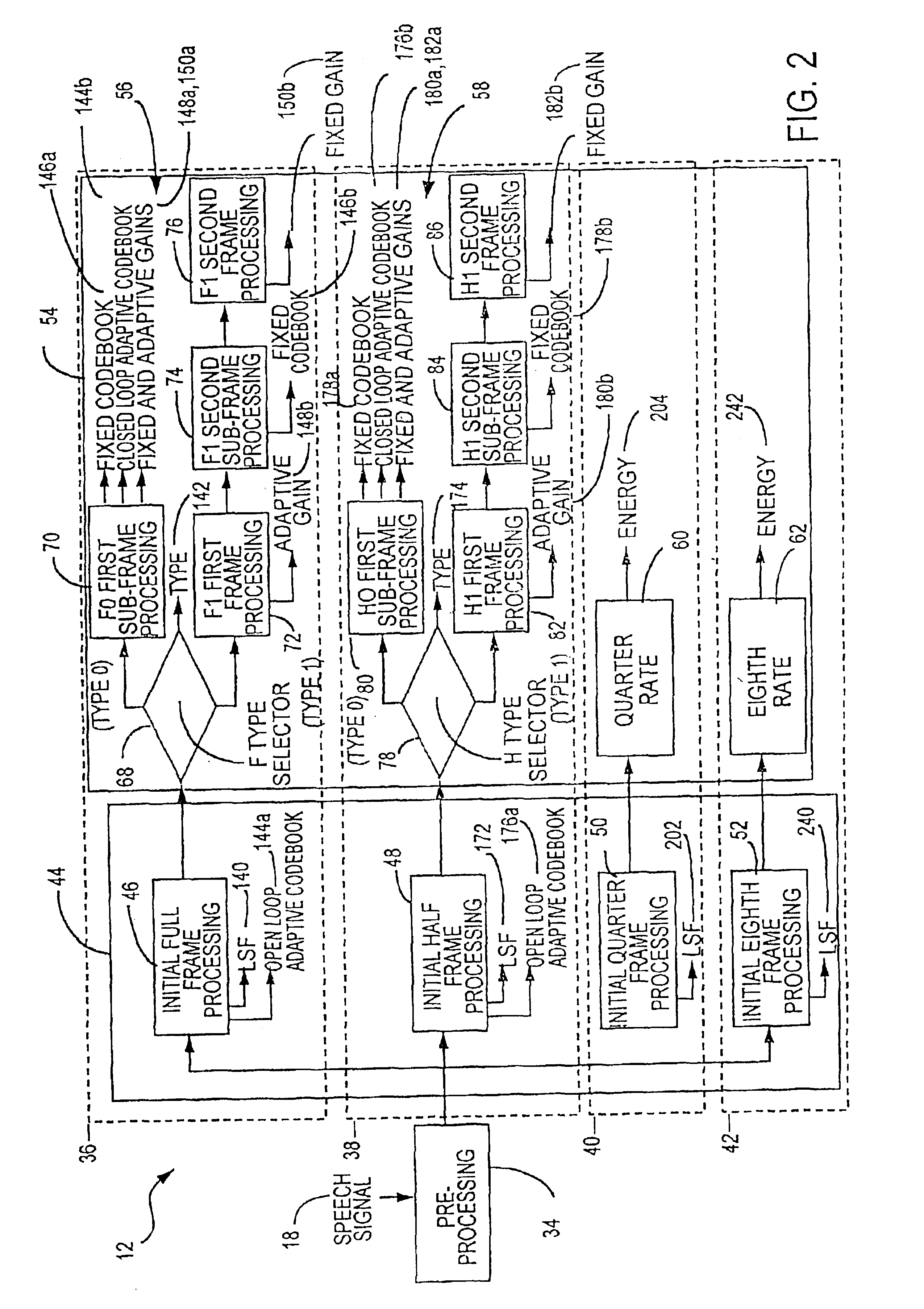
Multi-mode bitstream transmission protocol of encoded voice signals with embeded characteristics
InactiveUS6961698B1Optimize codeImprove perceived qualityModulated-carrier systemsGain controlTransmission protocolSpeech sound
A speech compression system capable of encoding a speech signal into a bitstream for subsequent decoding to generate synthesized speech is disclosed. The bitstream comprises a type component and a gain component. The type component is representative of a type classification of a frame of speech signal that is transmitted. The type component comprises a first type and second type. The gain component represents an adaptive codebook gain and a fixed codebook gain component comprises a fixed codebook gain component and an adaptive codebook gain component exclusively encoded as separate components of the bitstream as a function of the bit rate when the type classification is the second type.
Owner:MACOM TECH SOLUTIONS HLDG INC
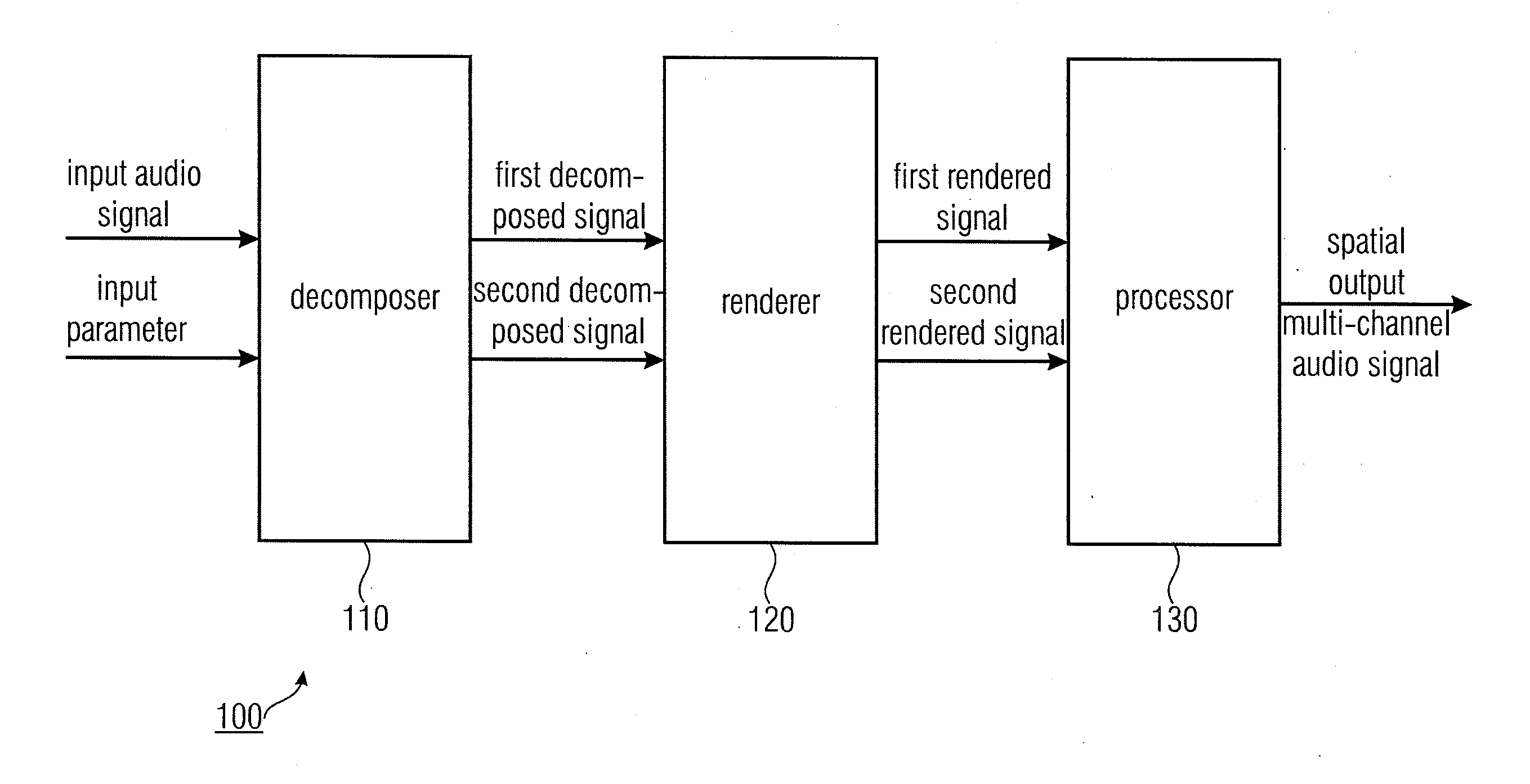
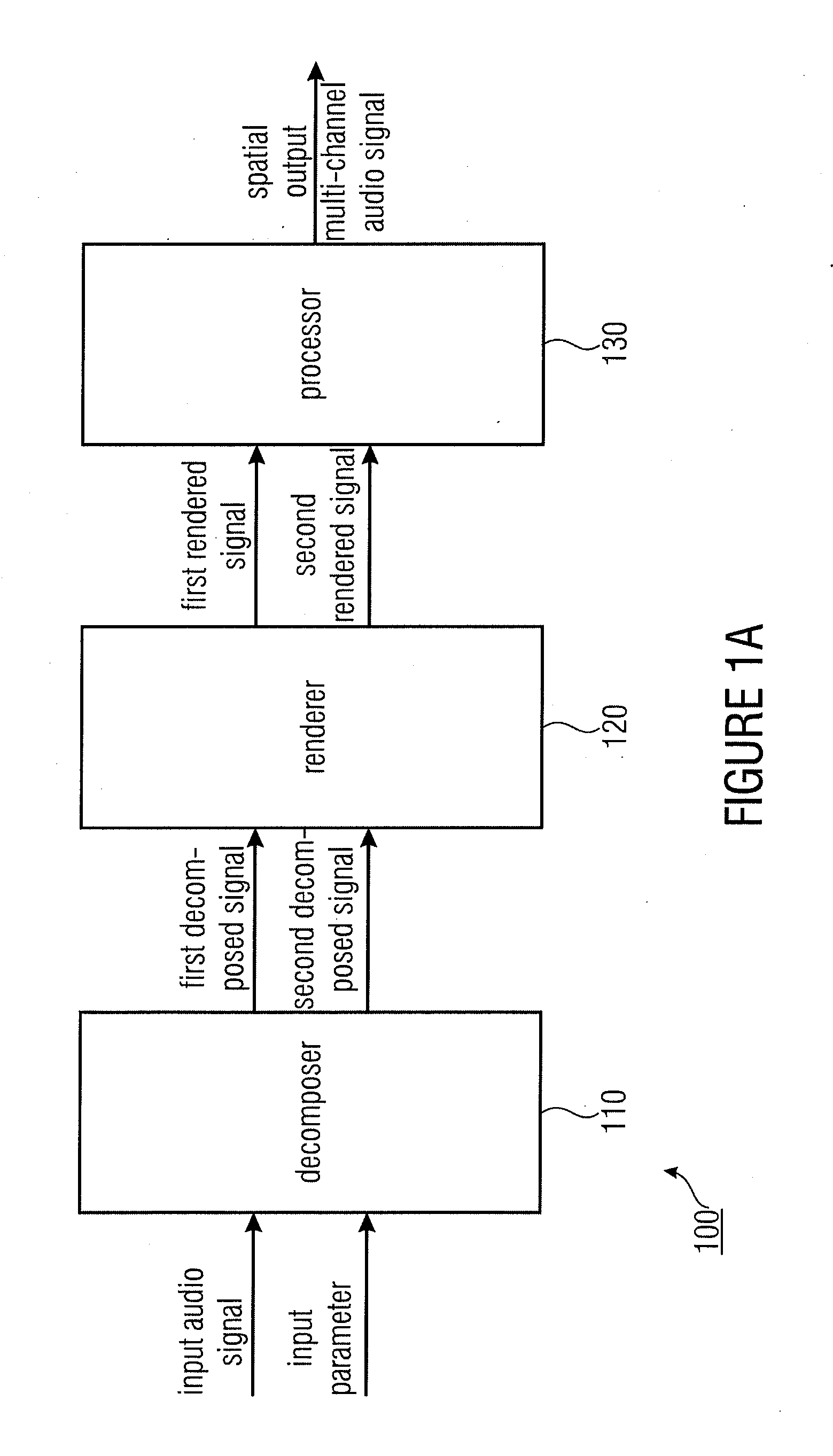
Apparatus for determining a spatial output multi-channel audio signal
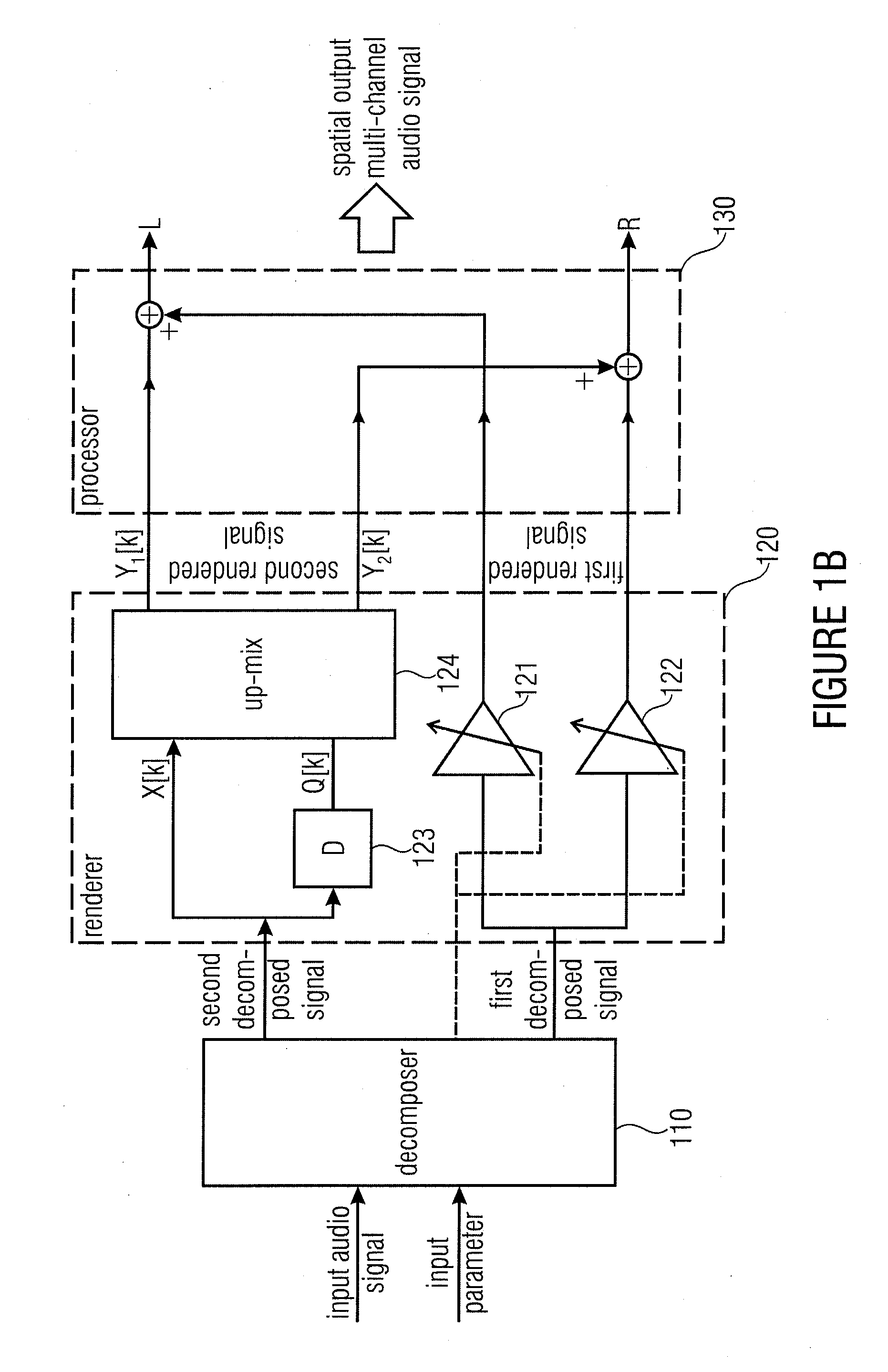
ActiveUS20110200196A1Better perceptual qualityReduce computing costStereophonic systemsStereophonic arrangmentsSemantic propertyVocal tract
An apparatus for determining a spatial output multi-channel audio signal based on an input audio signal and an input parameter. The apparatus includes a decomposer for decomposing the input audio signal based on the input parameter to obtain a first decomposed signal and a second decomposed signal different from each other. Furthermore, the apparatus includes a renderer for rendering the first decomposed signal to obtain a first rendered signal having a first semantic property and for rendering the second decomposed signal to obtain a second rendered signal having a second semantic property being different from the first semantic property. The apparatus comprises a processor for processing the first rendered signal and the second rendered signal to obtain the spatial output multi-channel audio signal.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
Conditioning system for nutritional substances
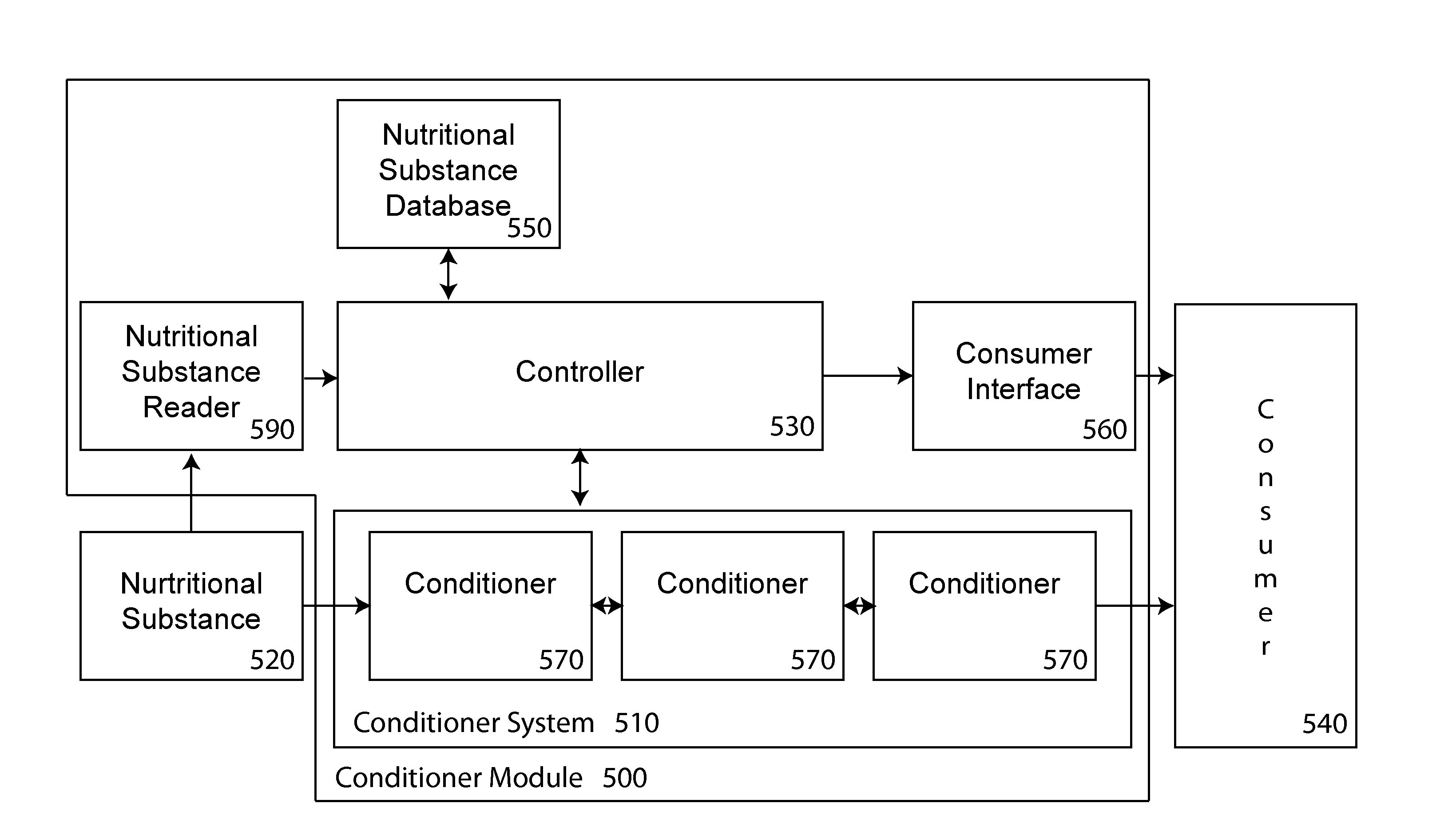
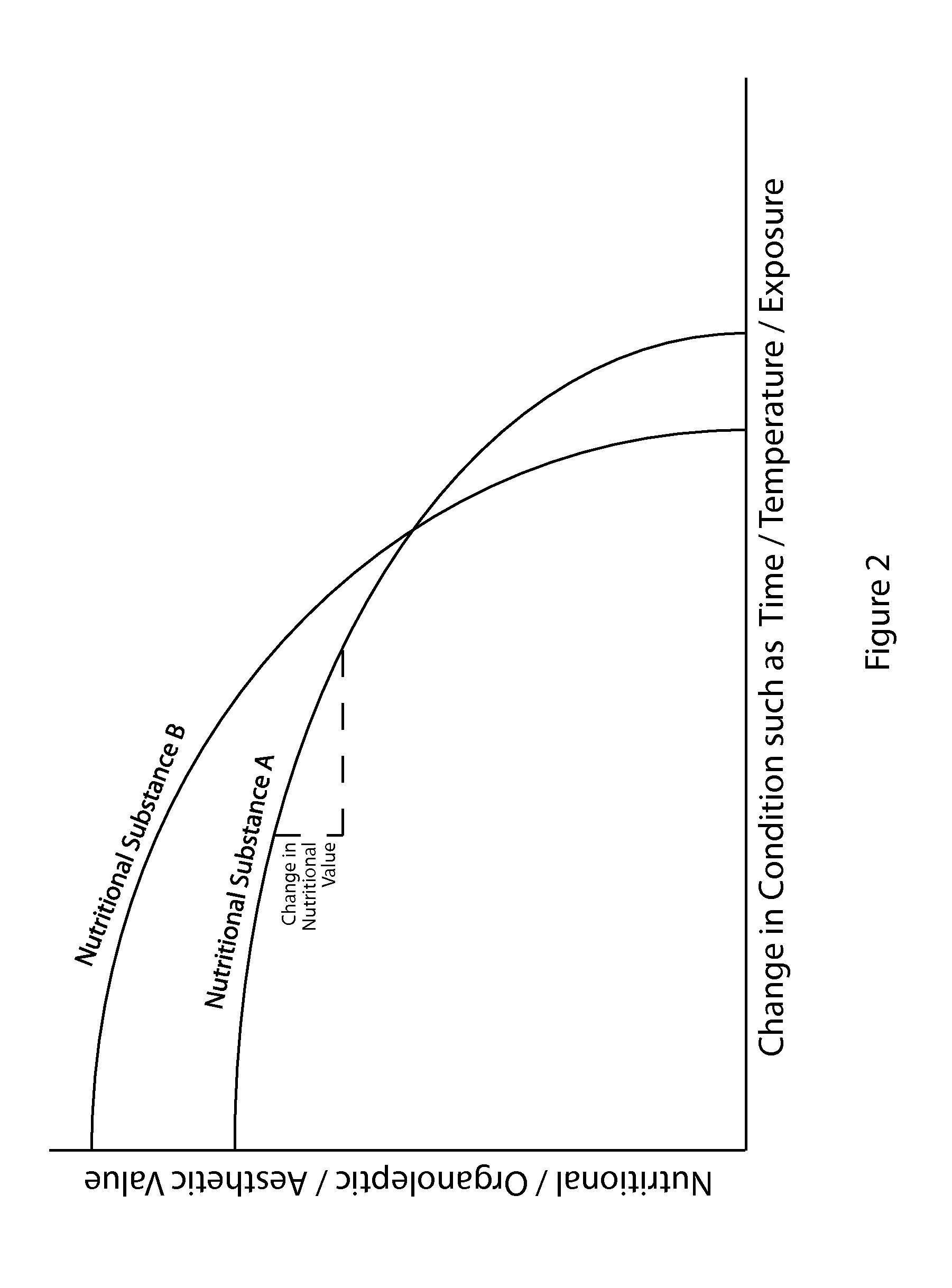
ActiveUS20130273217A1Minimize degradationHigh aesthetic valueDigital data processing detailsCocoaNutritional contentBiology
Disclosed herein is a conditioning system for nutritional substances. The conditioning system obtains information regarding the nutritional substance to be conditioned, the desired conditioning, and the desired properties, including nutritional content, of the conditioned nutritional substance, and dynamically controls the conditioning in response to this information optimize the organoleptic properties of the conditioned nutritional substance, while minimizing any detrimental changes to the nutritional content.
Owner:ICEBERG LUXEMBOURG S A R L
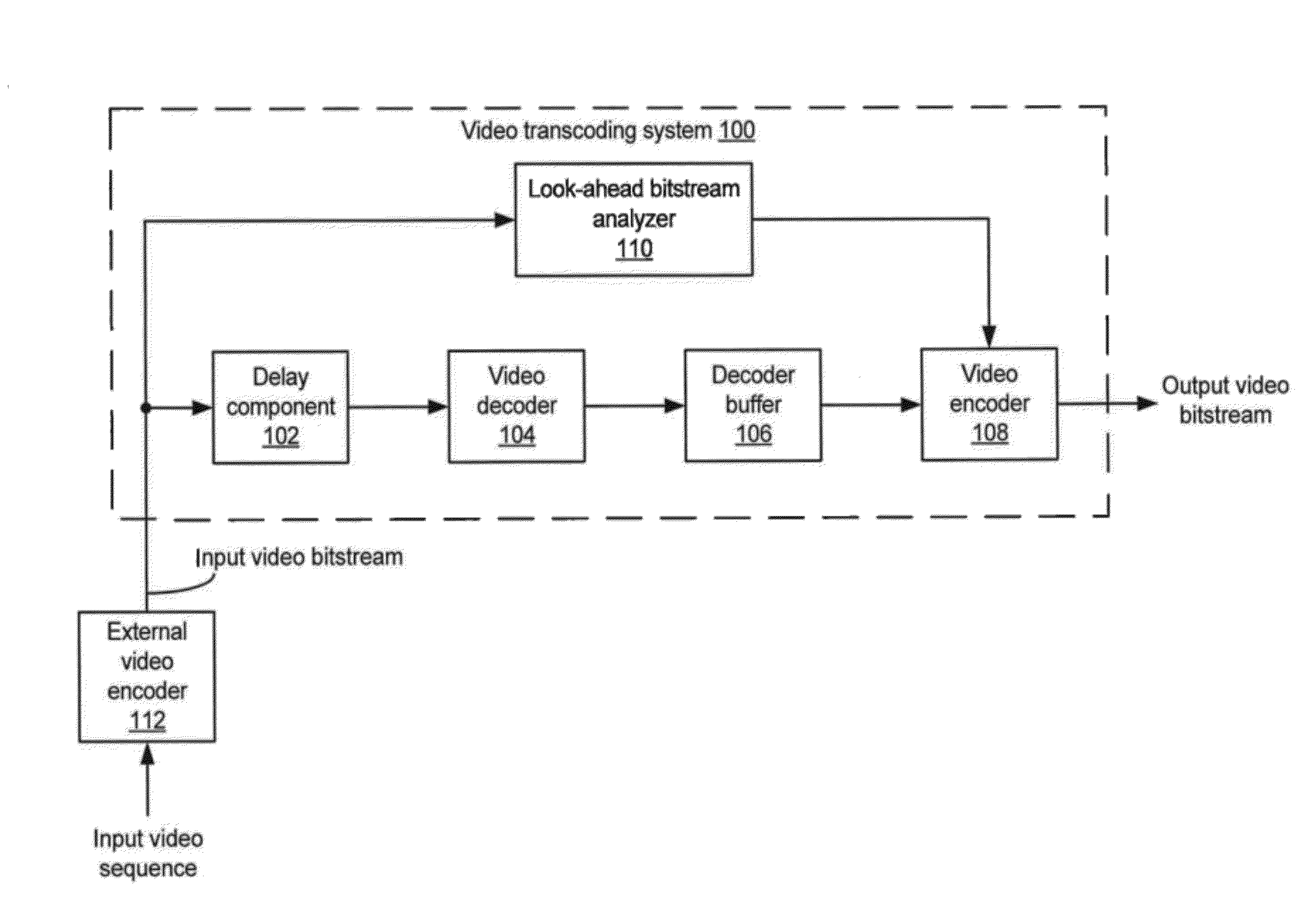
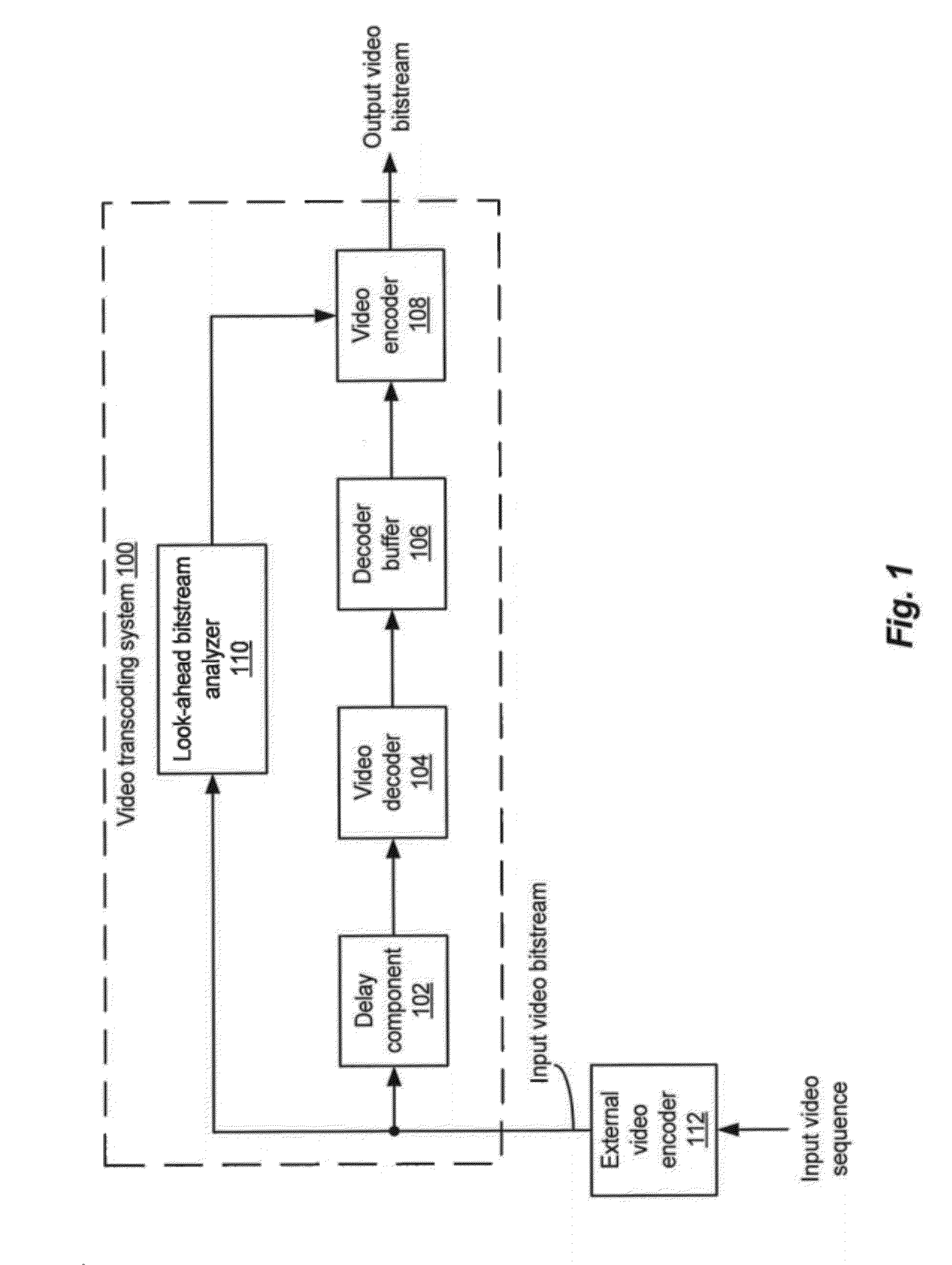
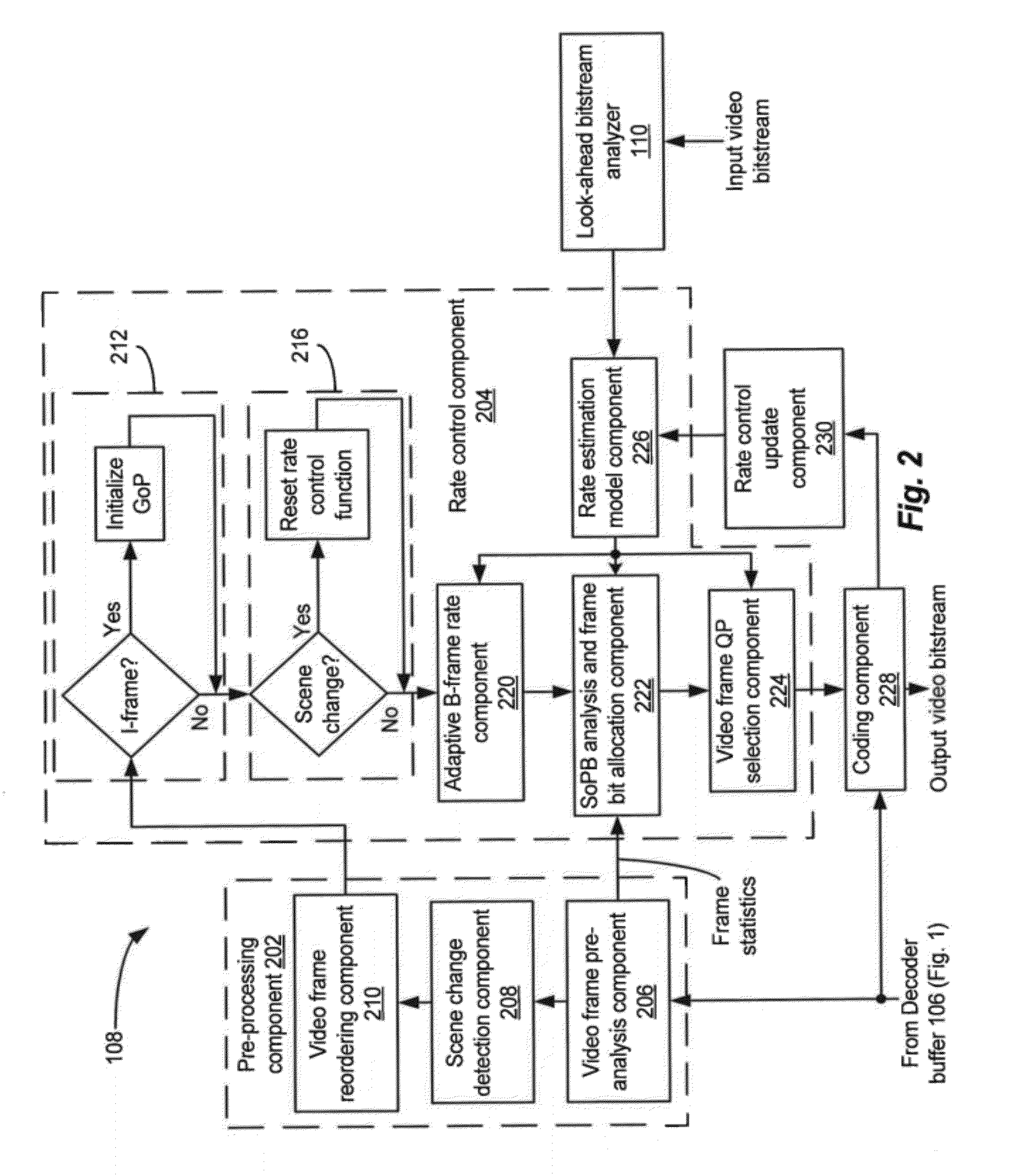
Rate control with look-ahead for video transcoding
ActiveUS20120269258A1Improve QoEImprove perceived qualityColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionVideo bitstreamComputer graphics (images)
Systems and methods of transcoding video bitstreams that employ look-ahead approaches to enhance the overall perceptual quality of transcoded video information, communications, and entertainment delivered to an end user. The disclosed systems and methods of transcoding video bitstreams take into account the scene characteristics and the local coding complexity of video frames in a video sequence before performing bit allocations for the video frames, thereby significantly improving the perceptual quality of transcoded video delivered to the end user.
Owner:DIALOGIC INC
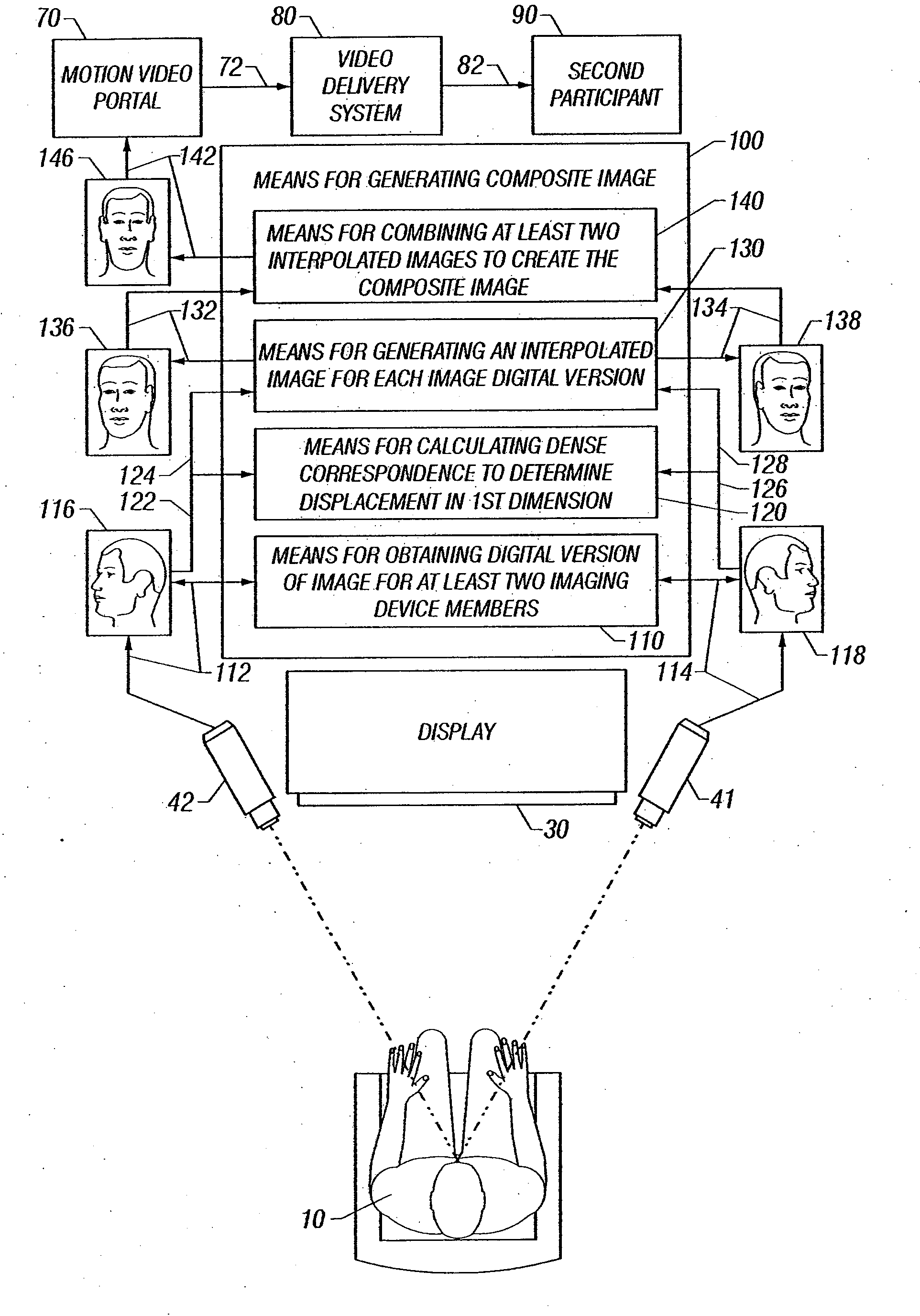
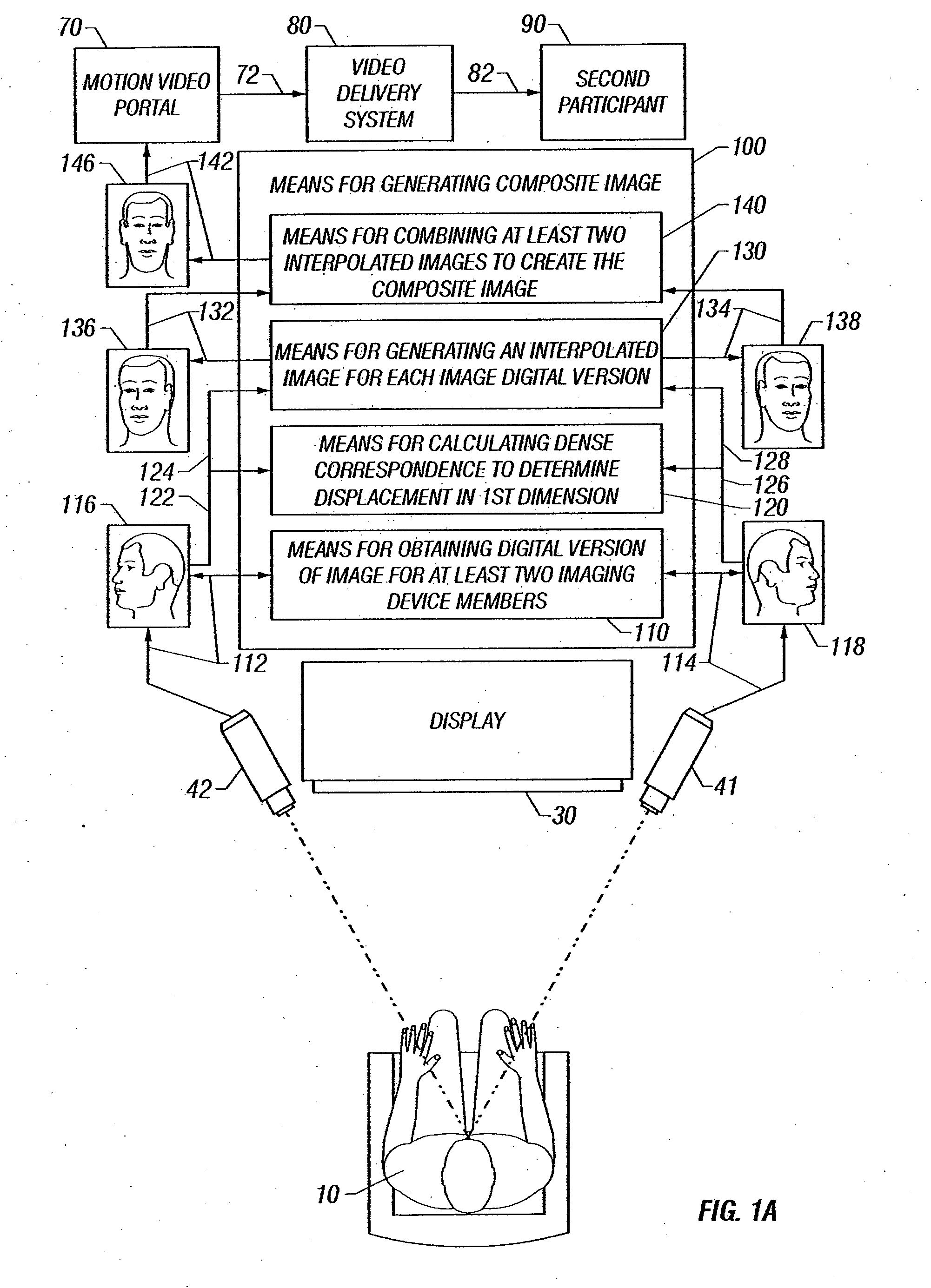
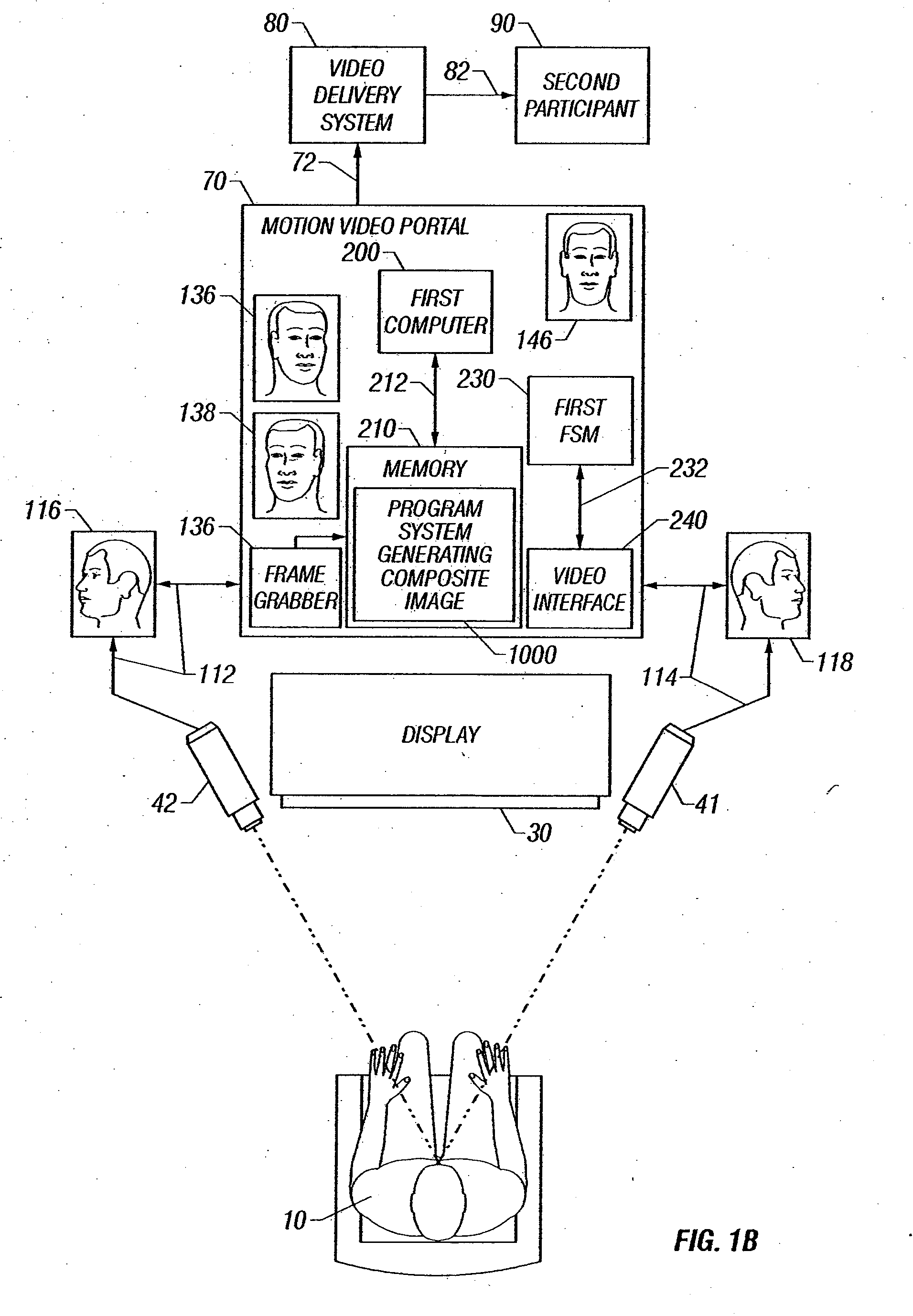
Method of Maintaining Eye Contact in Video Conferencing Using View Morphing
InactiveUS20070159523A1Improve overall senseImprove perceived qualityTelevision conference systemsTwo-way working systemsMorphingImage View
A view morphing algorithm is applied to synchronous collections of video images from at least two video imaging devices, and interpolating between the images, creates a composite image view of the local participant. This composite image approximates what might be seen from a point between the video imaging devices, presenting the image to other video session participants.
Owner:APPLIED INVENTION
Source coding enhancement using spectral-band replication
InactiveUS6925116B2Improvements of audio codecsImprove perceived qualitySpeech analysisCode conversionFrequency spectrumComputer science
The present invention proposes a new method and apparatus for the enhancement of source coding systems. The invention employs bandwidth reduction (101) prior to or in the encoder (103), followed by spectral-band replication (105) at the decoder (107). This is accomplished by the use of new transposition methods, in combination with spectral envelope adjustments. Reduced bitrate at a given perceptual quality or an improved perceptual quality at a given bitrate is offered. The invention is preferably integrated in a hardware or software codec, but can also be implemented as a separate processor in combination with a codec. The invention offers substantial improvements practically independent of codec type and technological progress.
Owner:DOLBY INT AB
Speech synthesiser
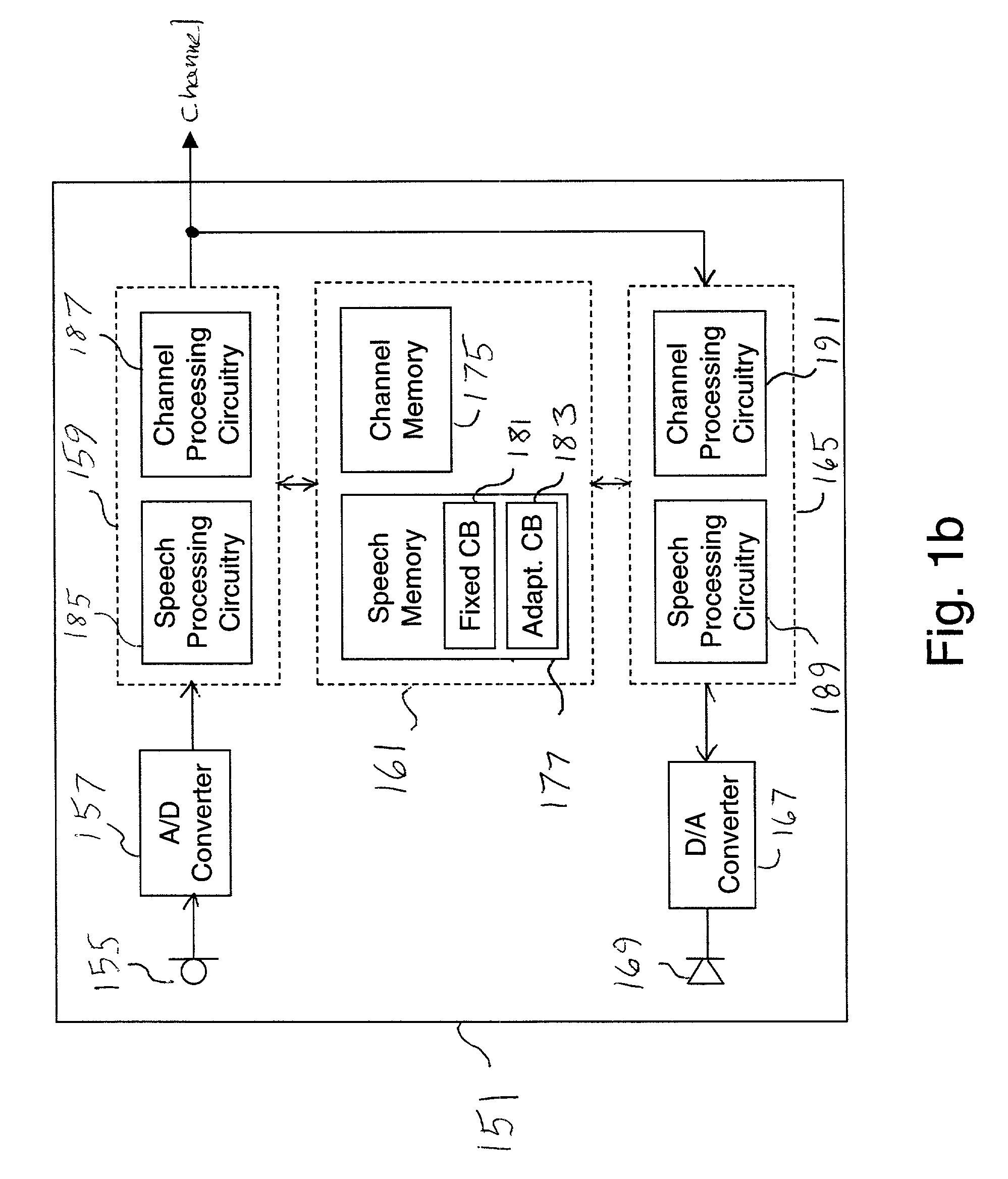
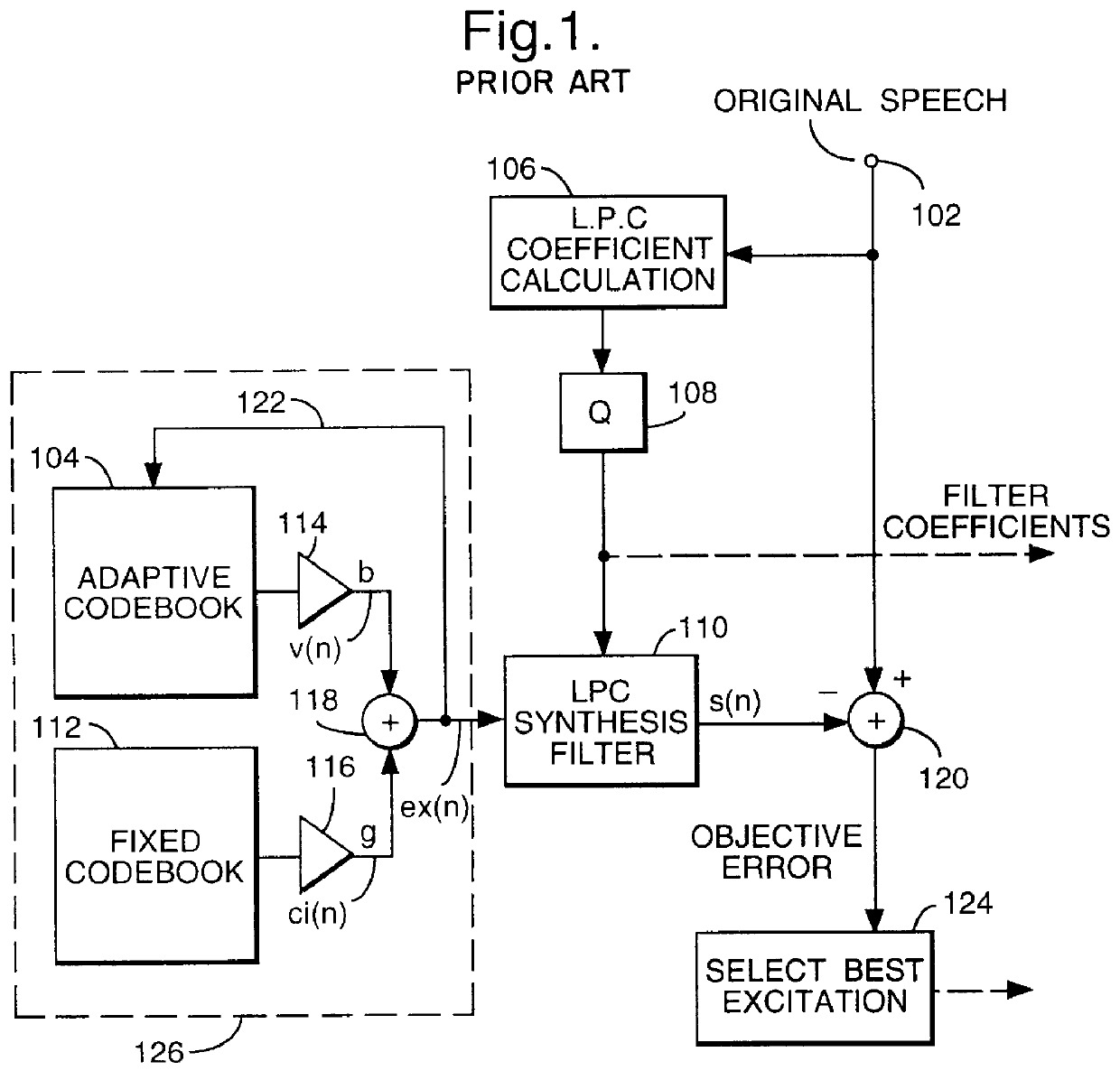
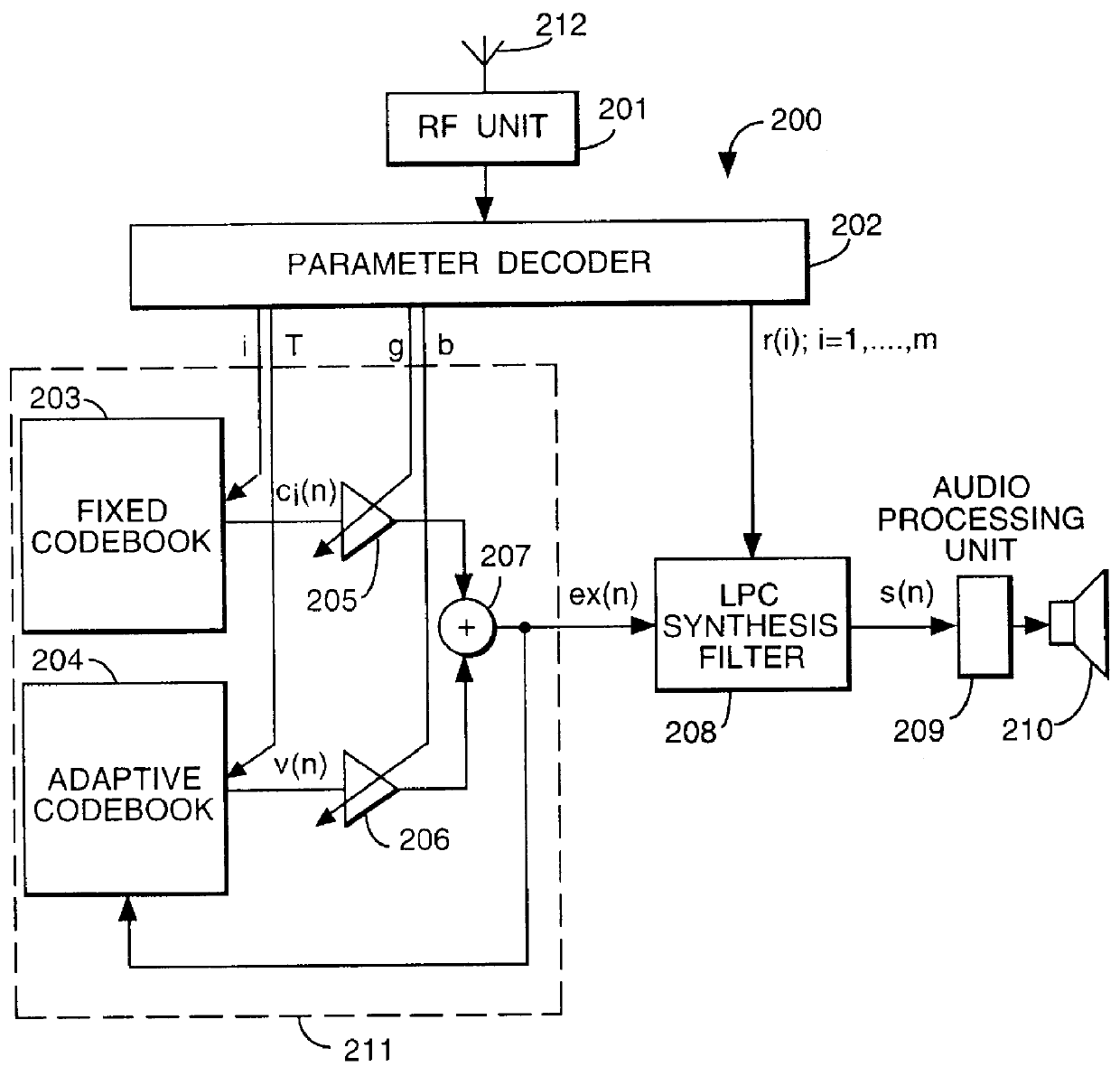
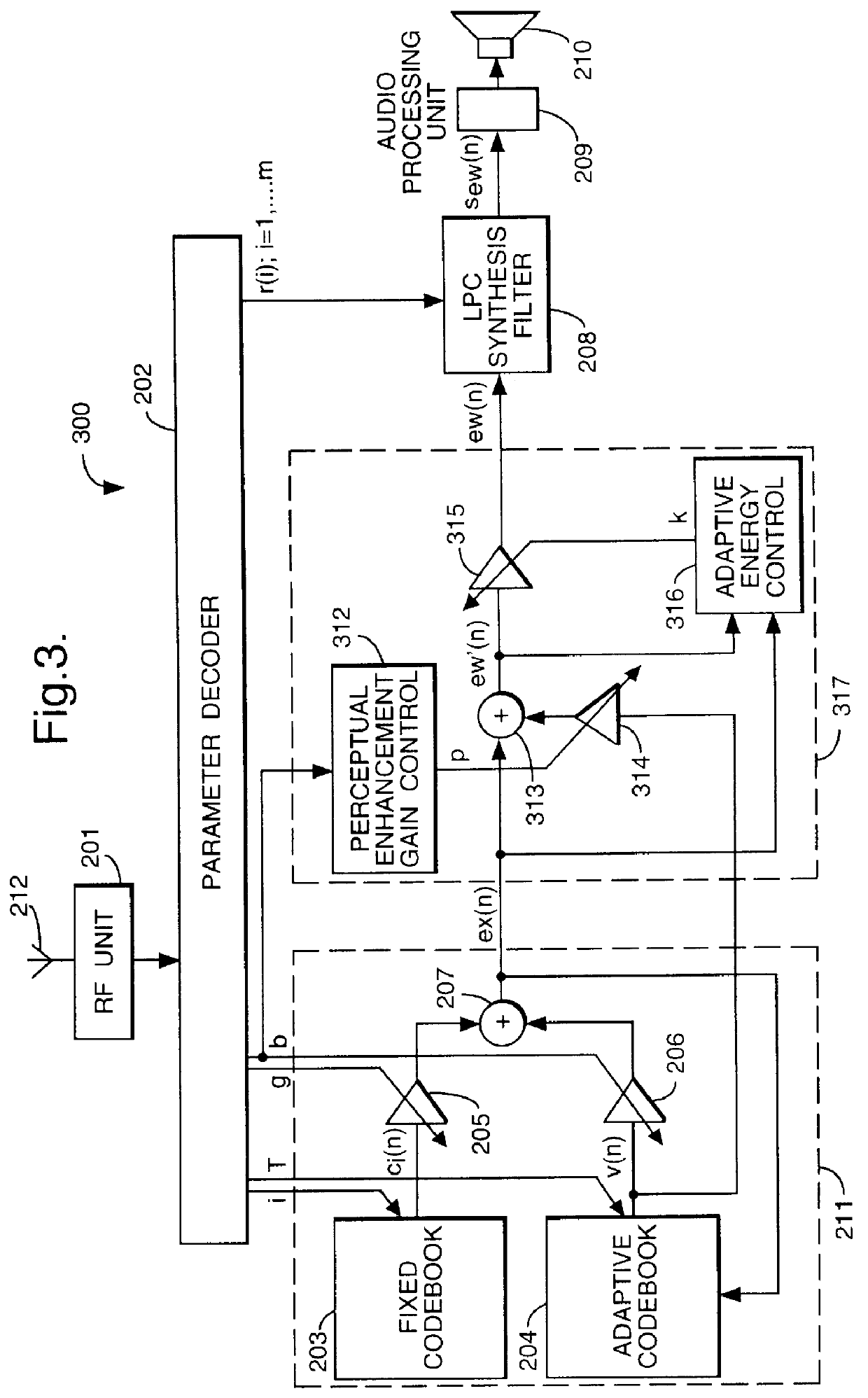
InactiveUS6029128AEnhance speechIntroduce distortionCode conversionSpeech synthesisCode bookProcessing element
A post-processor 317 and method substantially for enhancing synthesised speech is disclosed. The post-processor 317 operates on a signal ex(n) derived from an excitation generator 211 typically comprising a fixed code book 203 and an adaptive code book 204, the signal ex(n) being formed from the addition of scaled outputs from the fixed code book 203 and adaptive code book 204. The post-processor operates on ex(n) by adding to it a scaled signal pv(n) derived from the adaptive code book 204. A gain or scale factor p is determined by the speech coefficients input to the excitation generator 211. The combined signal ex(n)+pv(n) is normalised by unit 316 and input to an LPC or speech synthesis filter 208, prior to being input to an audio processing unit 209.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
System and method for embedded audio coding with implicit auditory masking
InactiveUS7110941B2Eliminate overheadImprove compression efficiencySpeech analysisMasking thresholdComputer science
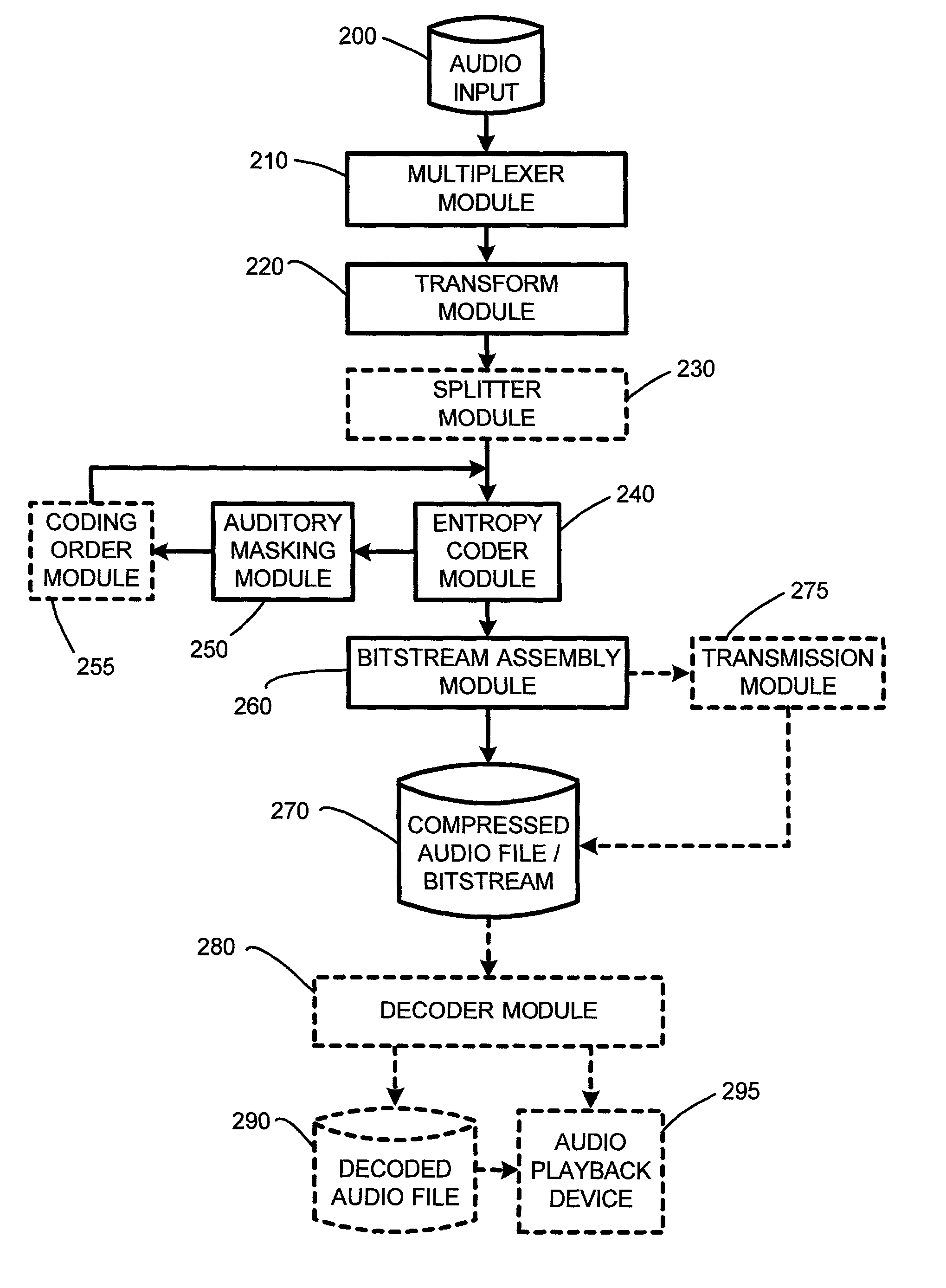
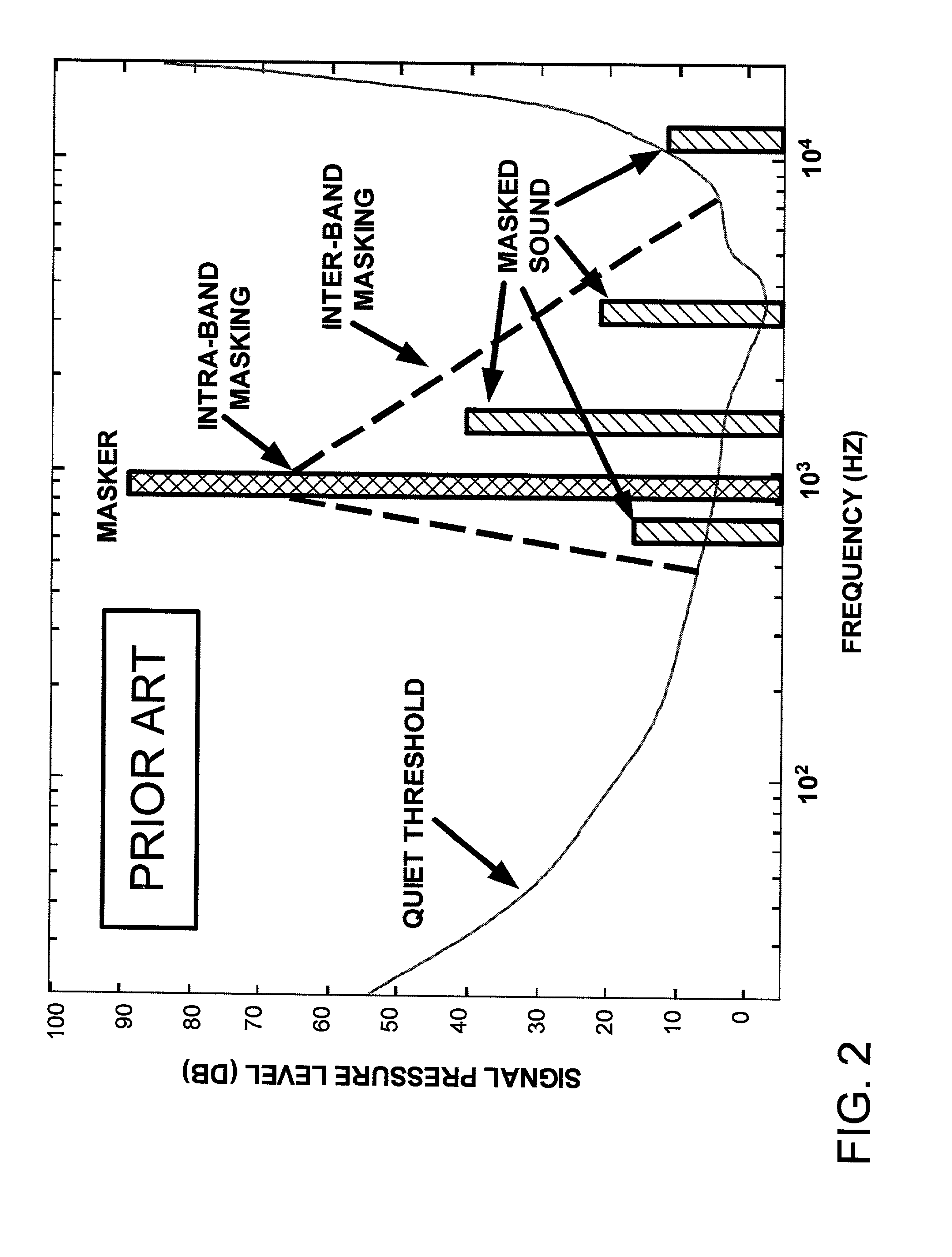
The embedded audio coder (EAC) is a fully scalable psychoacoustic audio coder which uses a novel perceptual audio coding approach termed “implicit auditory masking” which is intermixed with a scalable entropy coding process. When encoding and decoding an audio file using the EAC, auditory masking thresholds are not sent to a decoder. Instead, the masking thresholds are automatically derived from already coded coefficients. Furthermore, in one embodiment, rather than quantizing the audio coefficients according to the auditory masking thresholds, the masking thresholds are used to control the order that the coefficients are encoded. In particular, in this embodiment, during the scalable coding, larger audio coefficients are encoded first, as the larger components are the coefficients that contribute most to the audio energy level and lead to a higher auditory masking threshold.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Method and apparatus in coding digital information
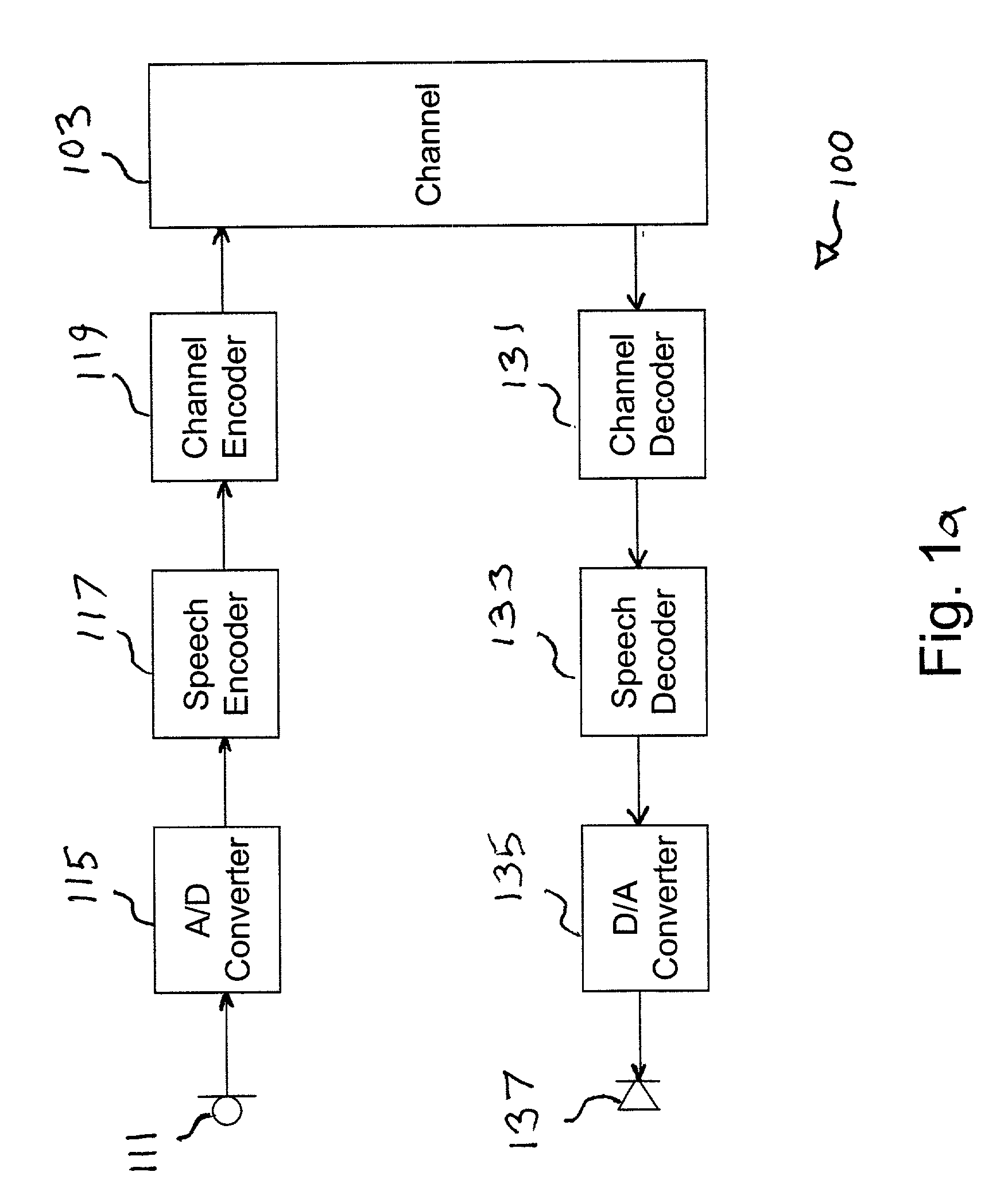
InactiveUS6012024AImprove perceived qualityTransmission control/equlisationCode conversionState variableSignal classification
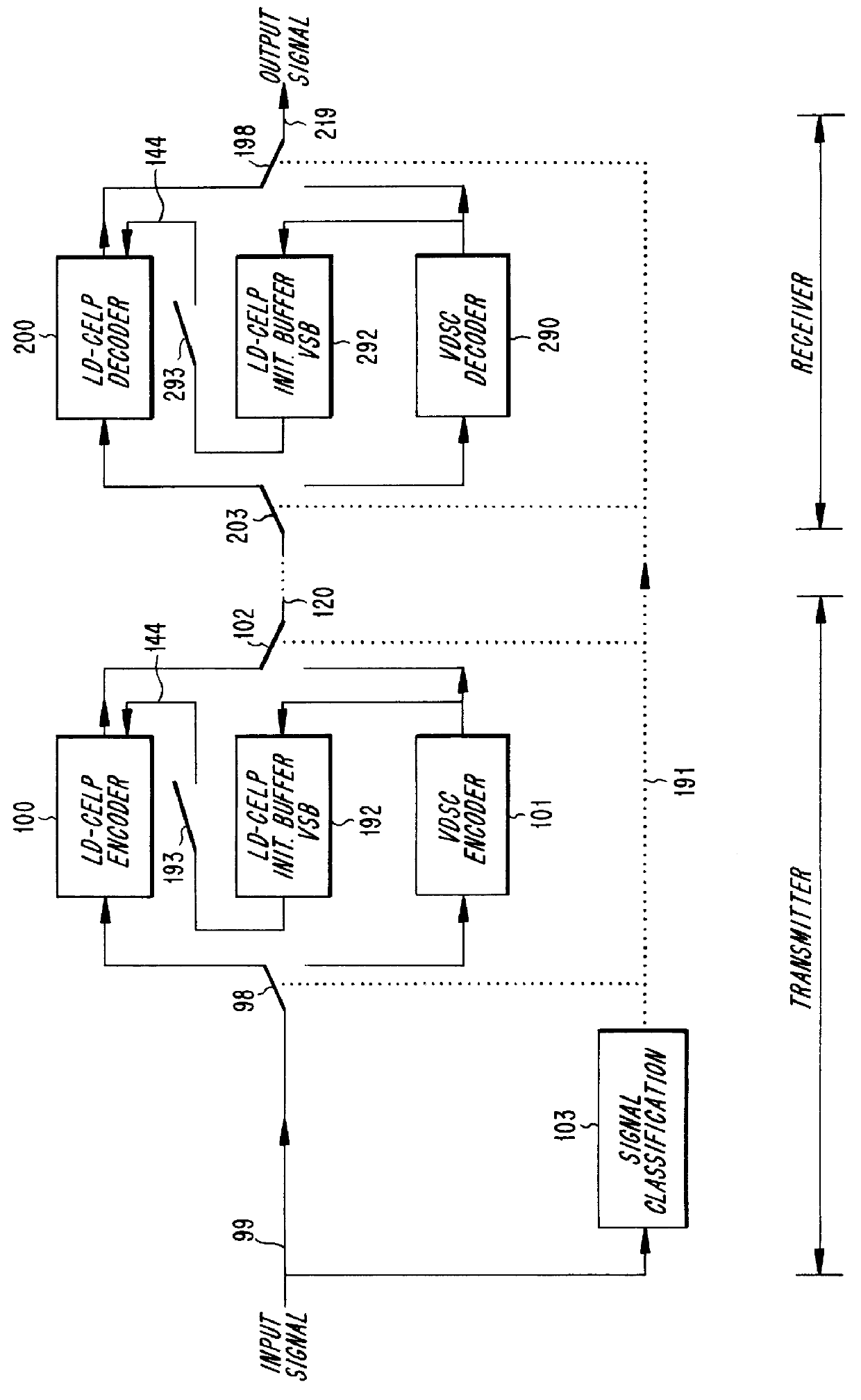
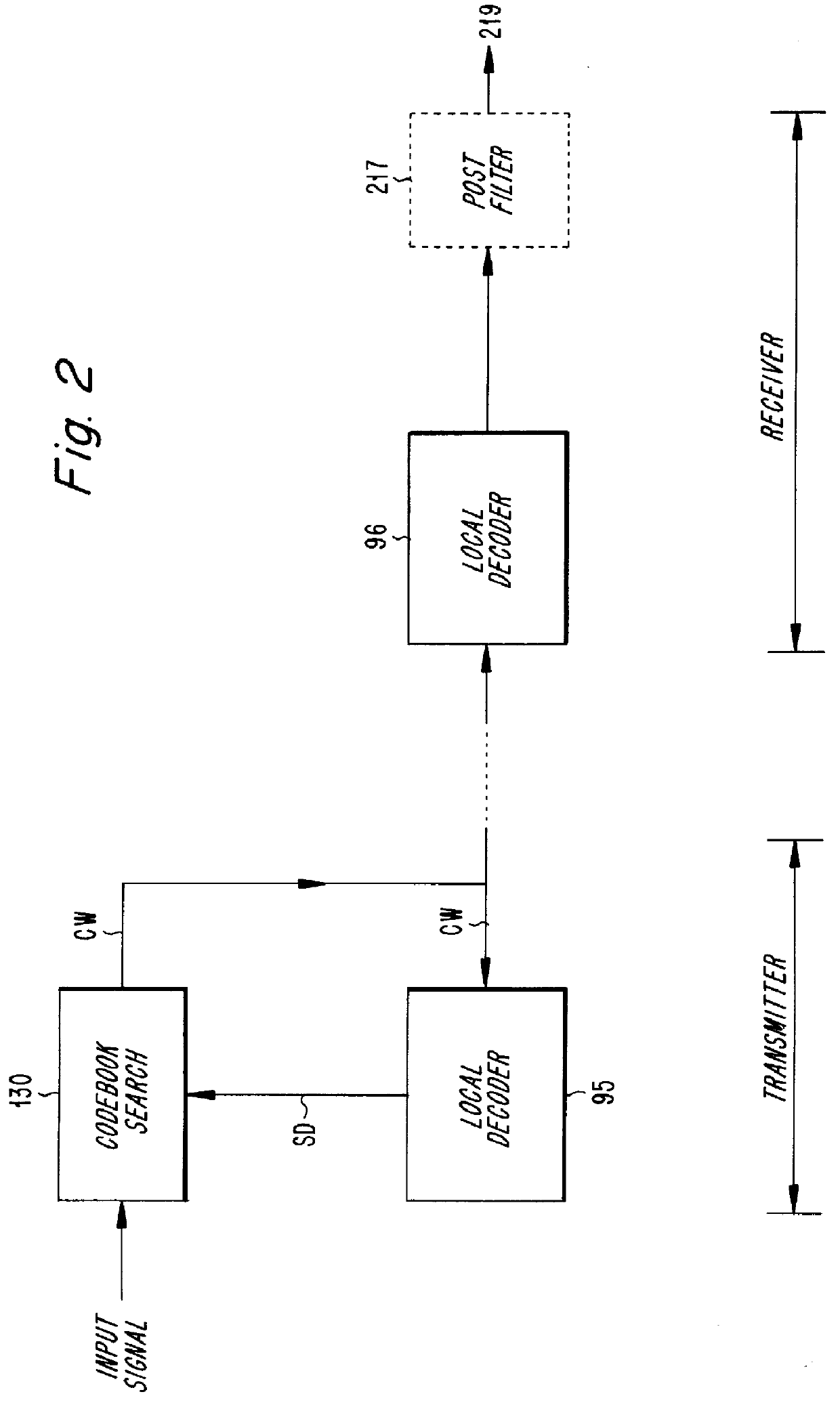
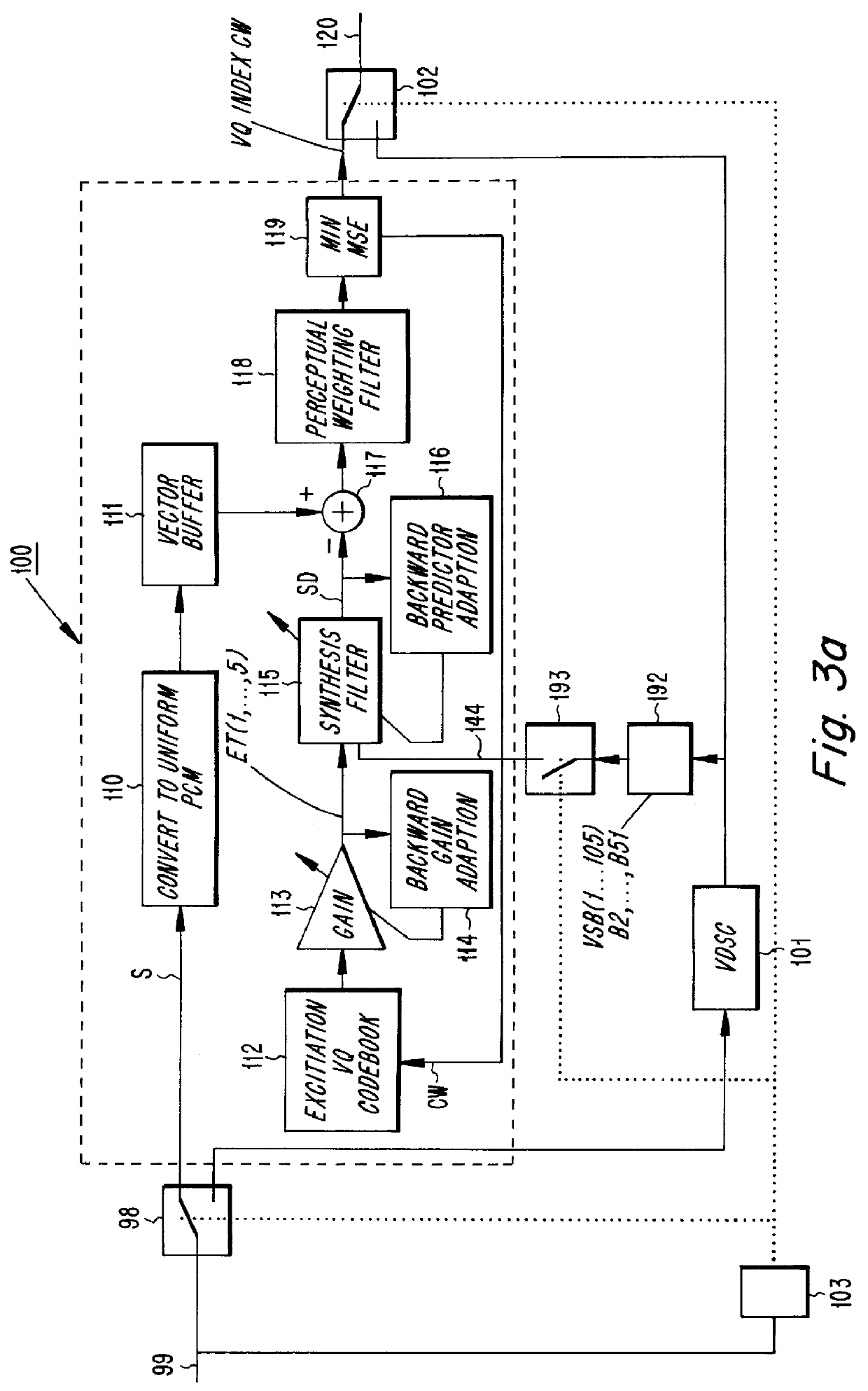
PCT No. PCT / SE96 / 00128 Sec. 371 Date Aug. 4, 1997 Sec. 102(e) Date Aug. 4, 1997 PCT Filed Feb. 2, 1996 PCT Pub. No. WO96 / 24926 PCT Pub. Date Aug. 15, 1996A speech encoder (100) receives speech signals (S) which are encoded and transmitted on a communication channel (120). Silence in the speech is utilized by a data encoder (101) to transmit data on the speech frequency band via the channel (120). A signal classifier (103) switches between the encoders (100, 101). The speech encoder has synthesis filter (115) with state variables in a delay line, predictor adaptor (116), gain predictor (113, 114) and excitation codebook (112). The data encoder (101) has delay line with state variables stored and updated in a buffer (192). On switching (103, 102, 193) from data to speech, the buffer state variables are fed into the synthesis filter delay line via an input (144) for smooth transition in the speech encoding. Coefficient values in the synthesis filter (115) and an excitation signal (ET(1 . . . 5)) are generated. Thereby a buffer in the gain predictor (113, 114) is preset and its predictor coefficients and gain are generated. The incoming speech signal (S) newly detected is encoded (CW) by the values generated in the speech encoder (100), which is successively adapted. The receiver side has corresponding speech and data decoders.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
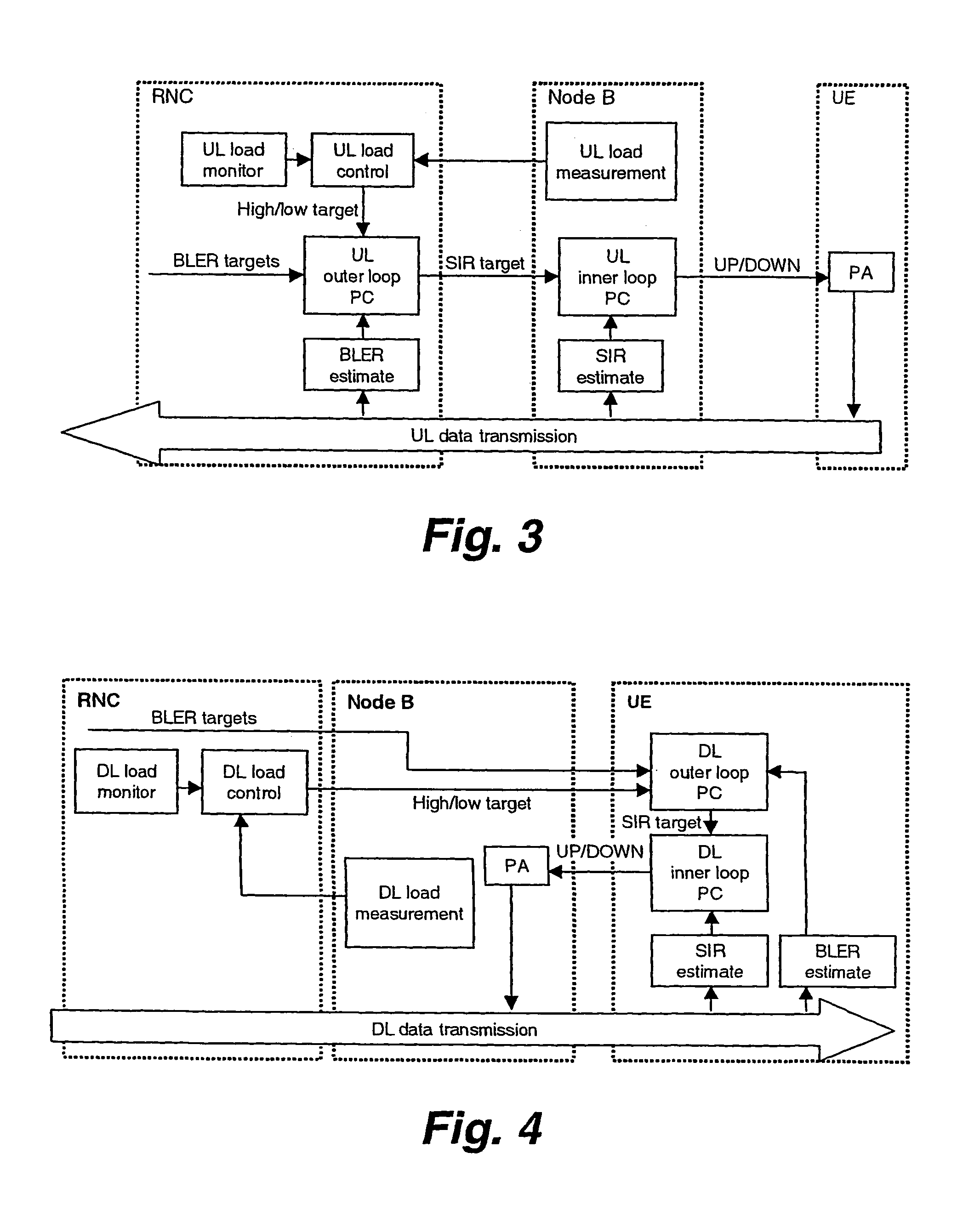
Method and system of link control
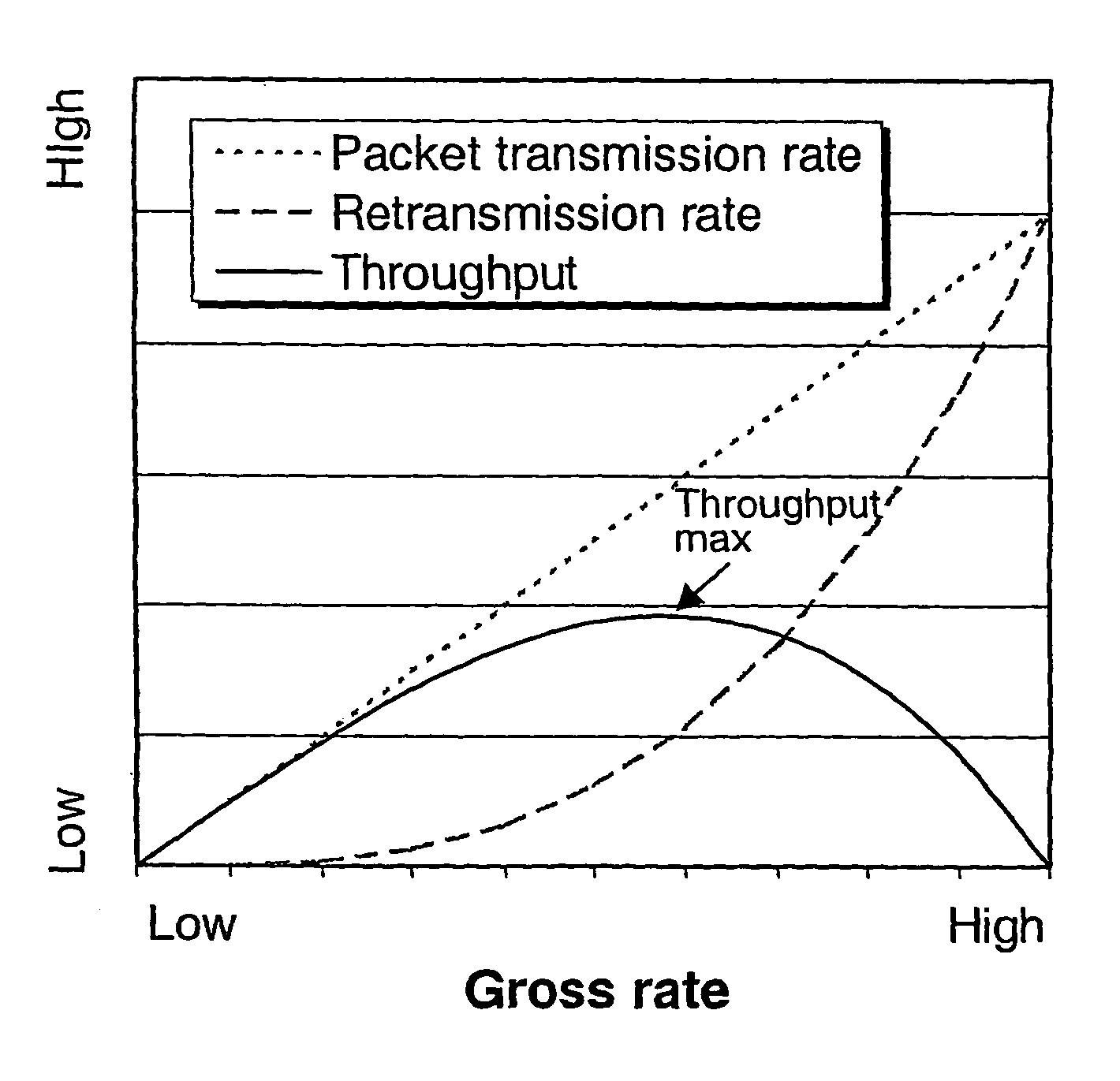
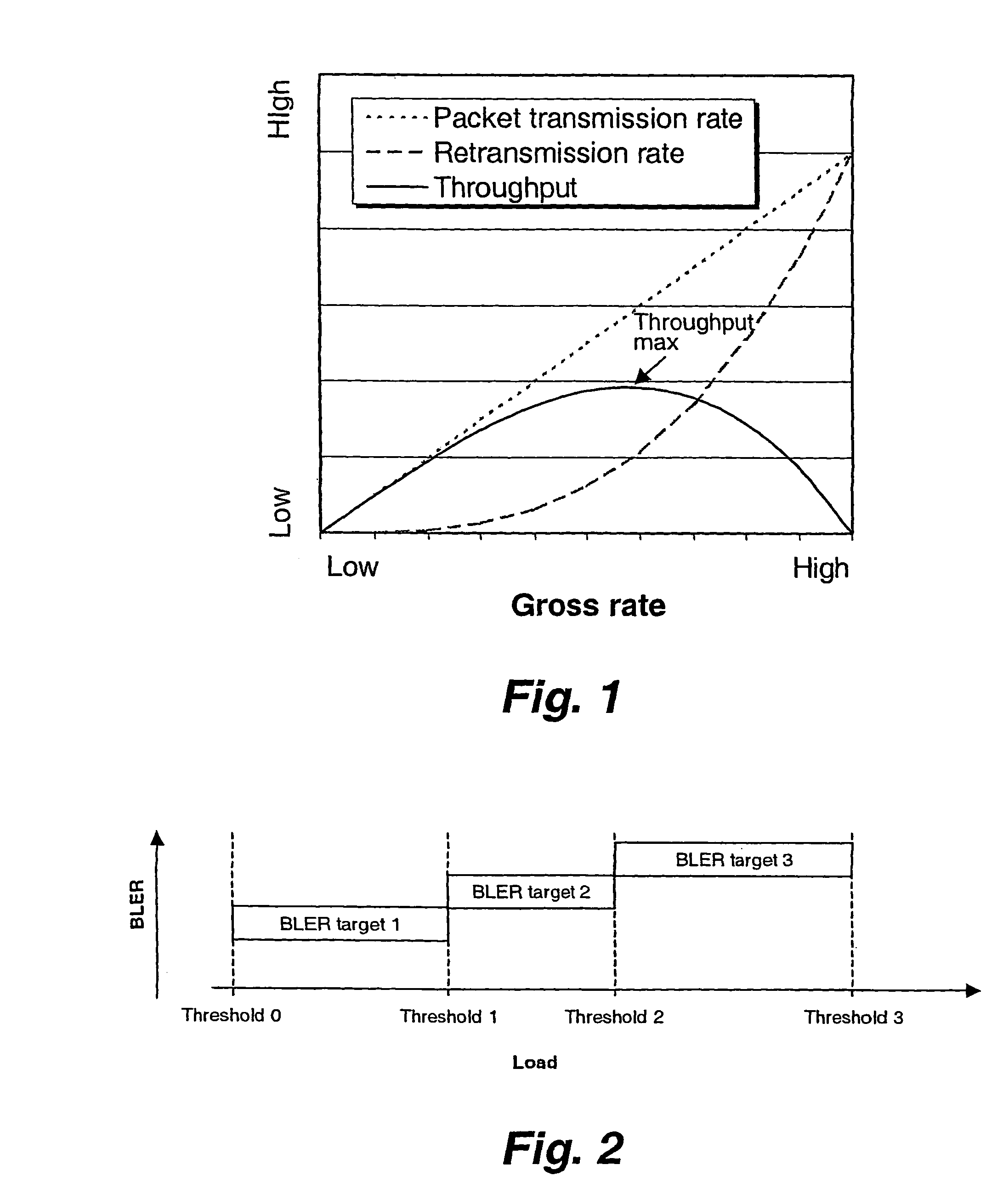
InactiveUS7120448B2Improve perceived qualityReduce delaysPower managementError prevention/detection by using return channelCommunications systemMobile radio
The present invention relates to retransmissions in a communications system and more especially it relates to link load control in a cellular mobile radio system particularly in a Universal Mobile Telecommunications System, UMTS. BLER targets are set depending on load.
Owner:UNWIRED PLANET
Audio coding system using characteristics of a decoded signal to adapt synthesized spectral components
ActiveUS7337118B2Improve perceived qualityCode conversionSpeech synthesisFrequency spectrumAudio frequency
A receiver in an audio coding system receives a signal conveying frequency subband signals representing an audio signal. The subband signals are examined to assess one or more characteristics of the audio signal. Spectral components are synthesized having the assessed characteristics. The synthesized spectral components are integrated with the subband signals and passed through a synthesis filterbank to generate an output signal. In one implementation, the assessed characteristic is temporal shape and noise-like spectral components are synthesized having the temporal shape of the audio signal.
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
Method for Weighted Overlap-Add
ActiveUS20080275580A1Effectively mitigatedFew artifactDigital data processing detailsSpeech analysisComputer scienceA-weighting
A method for generating an output sequence of samples in response to a first and a second subsequence of samples, the method comprising—applying a weighted overlap-add procedure to the first and second subsequences so as to generate the output sequence of samples, —optimizing a weighting function involved in the weighted overlap-add procedure in response to a measure of matching between the output sequence of samples and one or more target sequences of samples.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
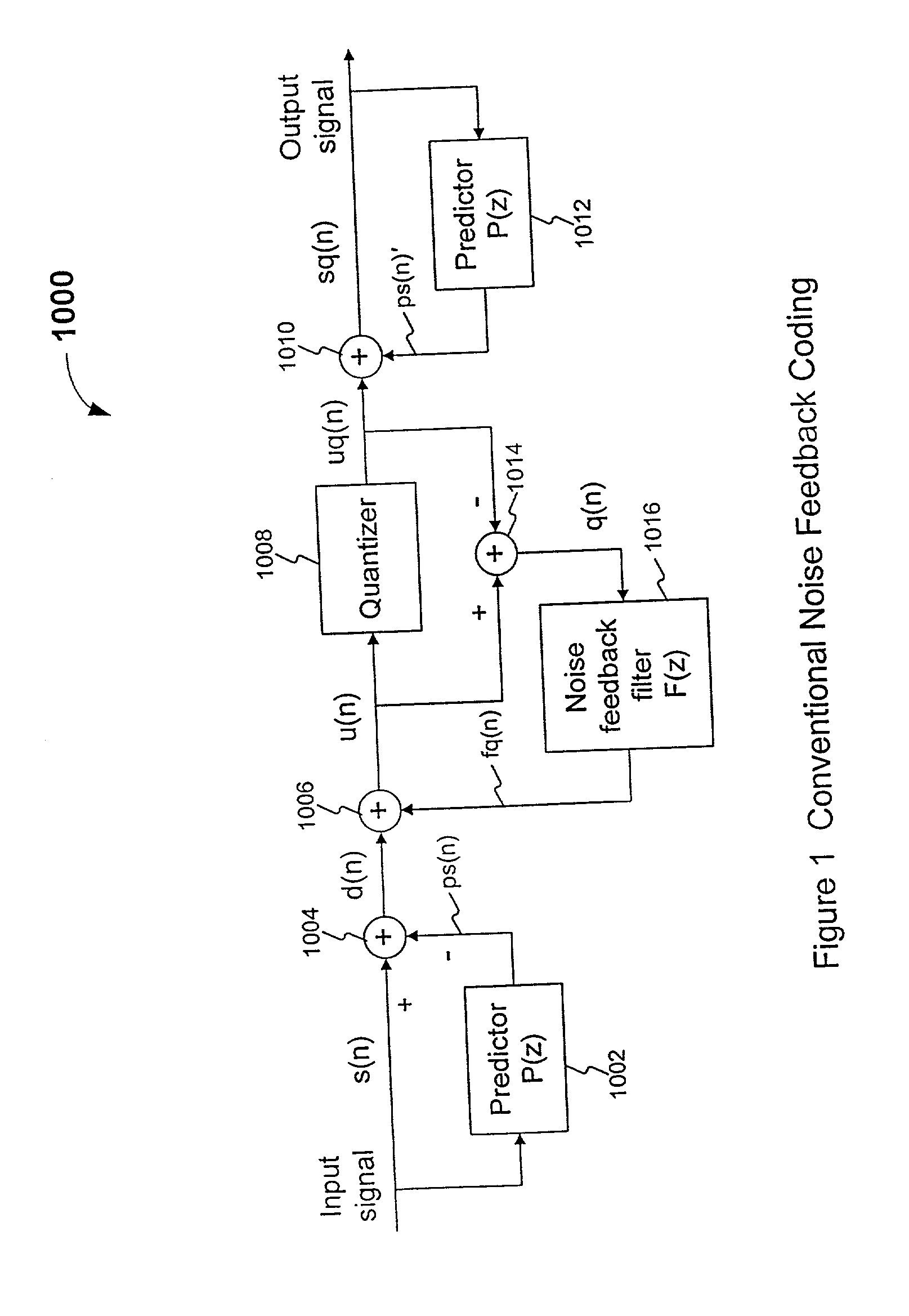
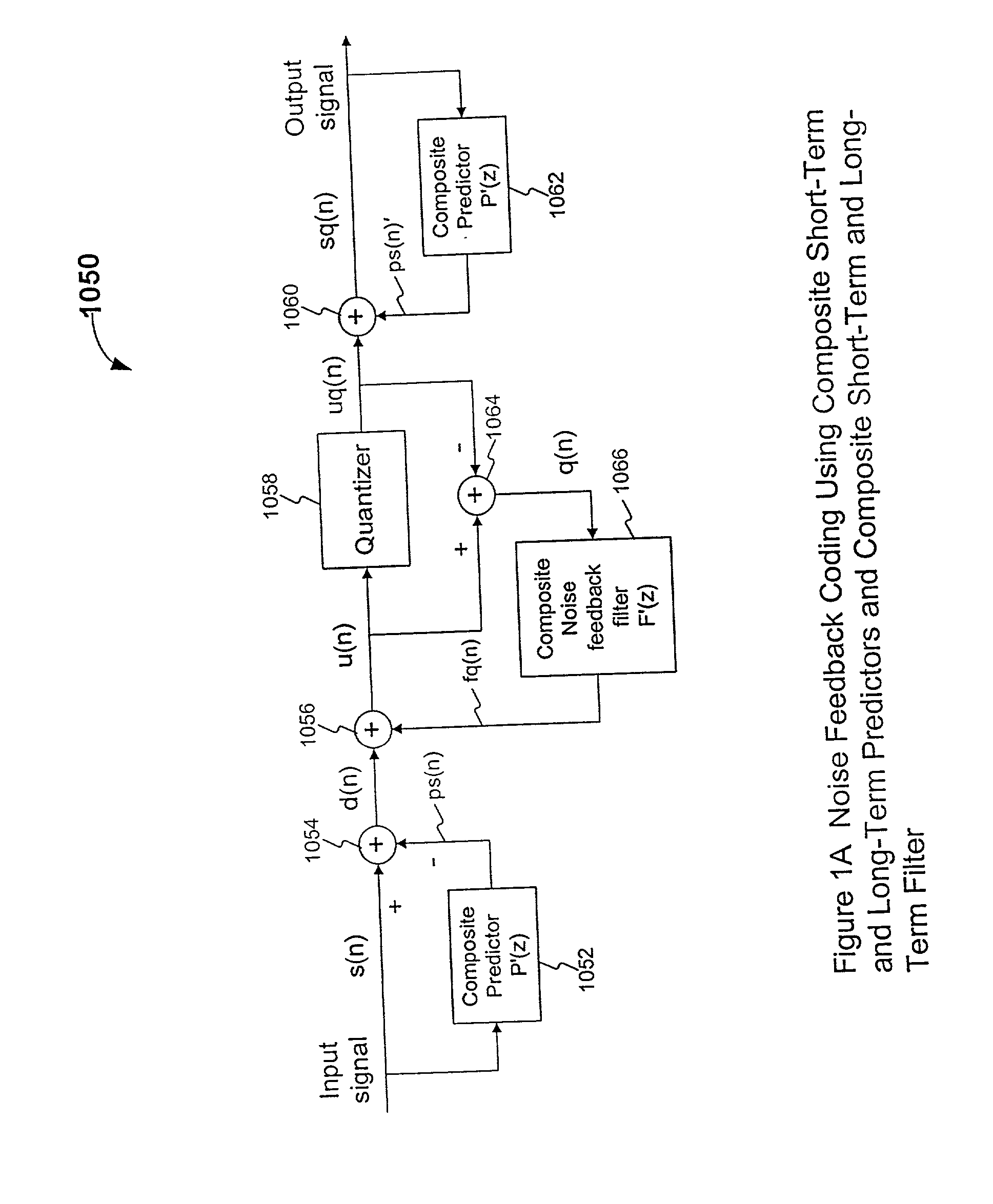
Noise feedback coding method and system for performing general searching of vector quantization codevectors used for coding a speech signal
InactiveUS20020069052A1Eliminate redundancyImprove perceived qualitySpeech analysisTwo-vectorAlgorithm
A method of searching a plurality of Vector Quantization (VQ) codevectors for a preferred one of the VQ codevectors to be used as an output of a vector quantizer for encoding a speech signal, includes determining a quantized prediction residual vector, and calculating a corresponding unquantized prediction residual vector and the energy of the difference between these two vectors (that is, a VQ error vector). After trying each of the plurality of VQ codevectors, the codevector that minimizes the energy of the VQ error vector is selected as the output of the vector quantizer
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
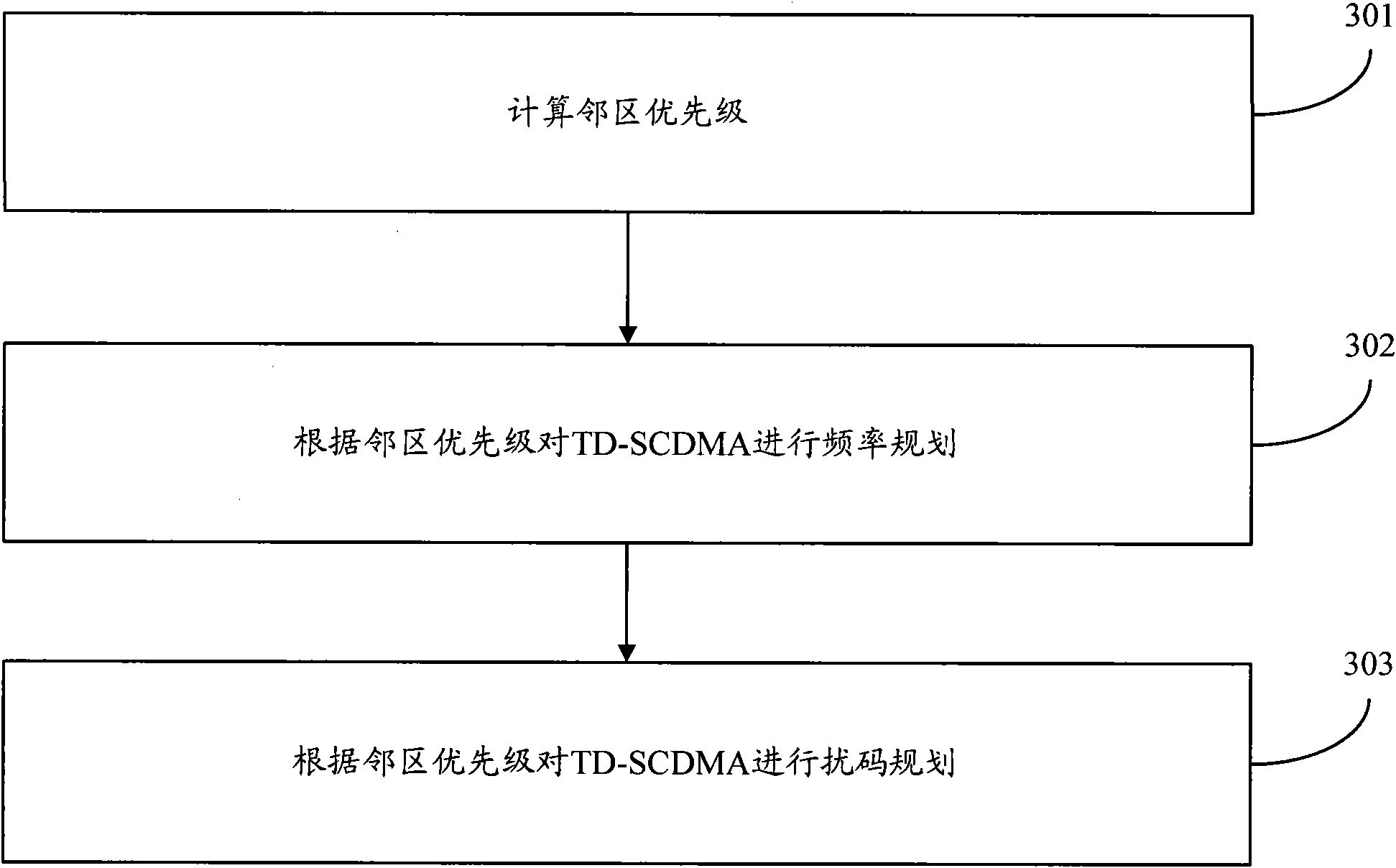
Frequency planning and scrambling code planning method and device based on adjacent zone priority level
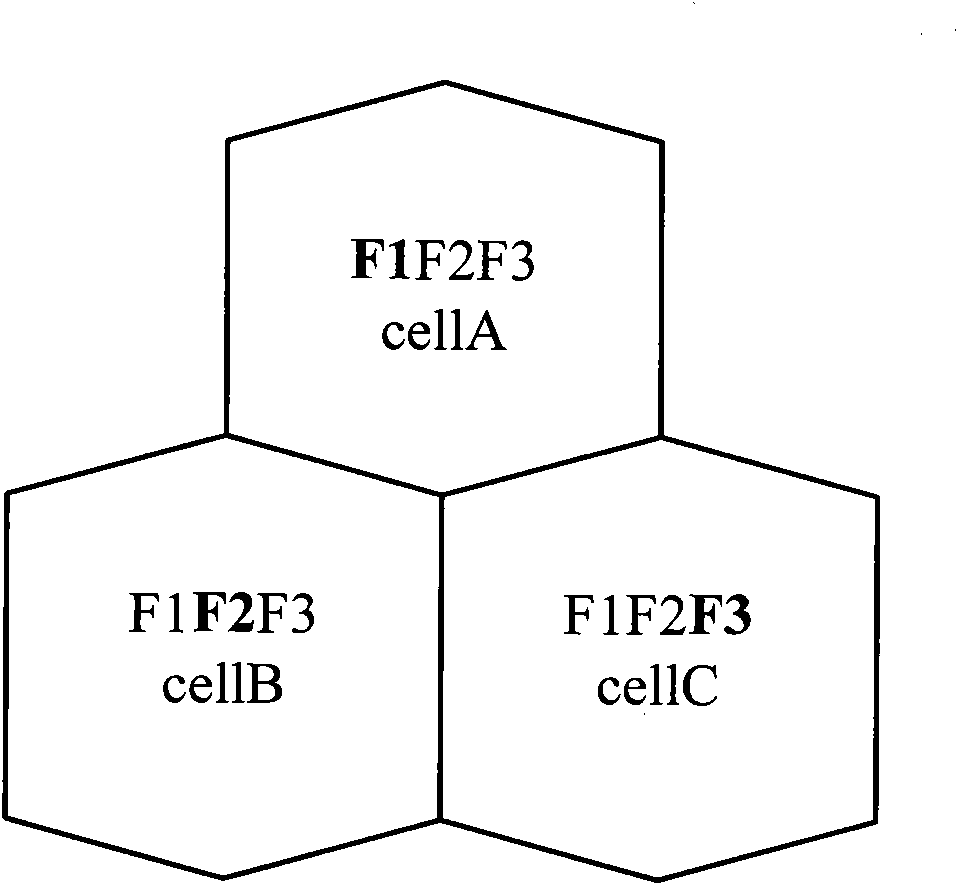
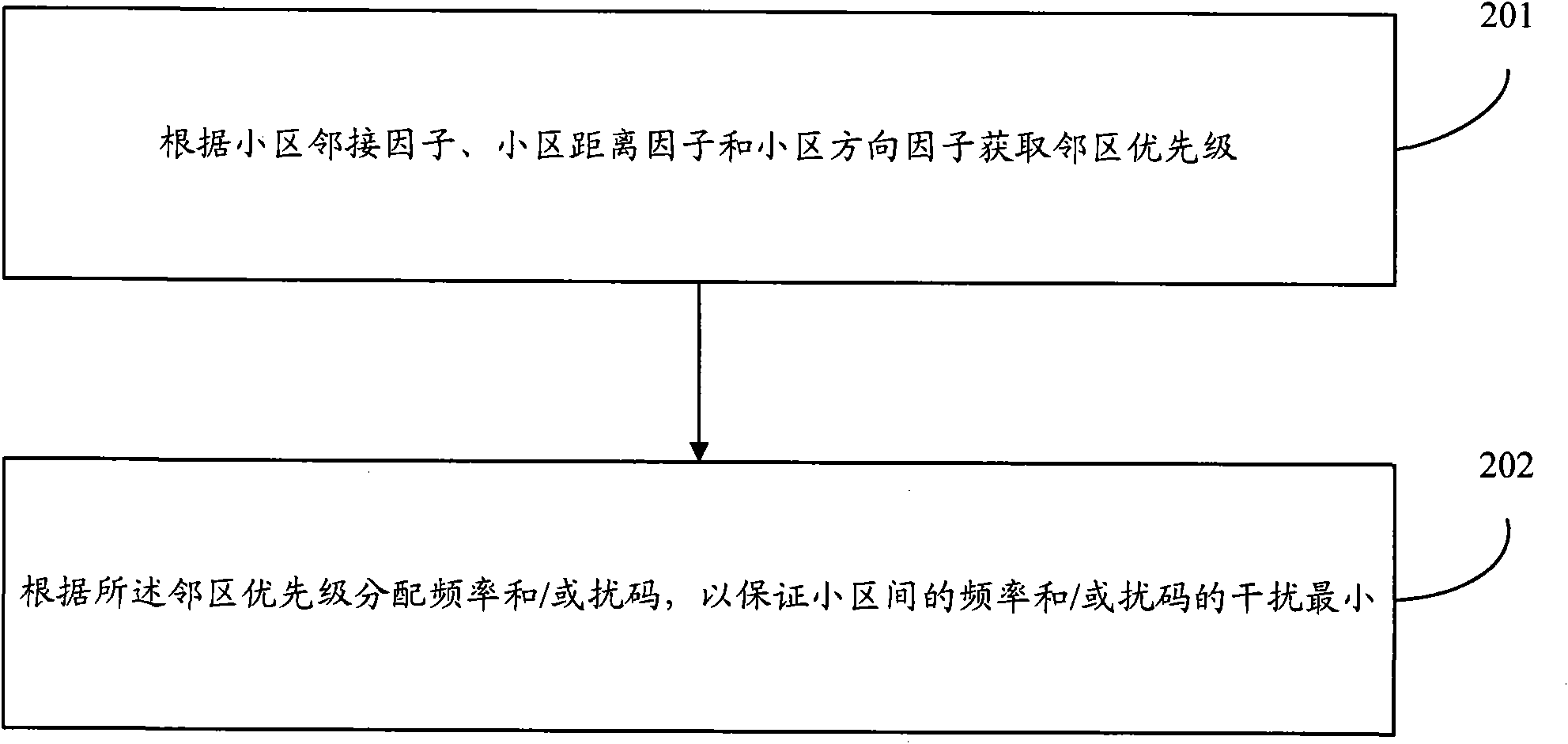
ActiveCN102083075AMaximize utilizationImprove perceived qualityNetwork planningFactor baseResource utilization
The embodiment of the invention discloses a TD (time division) frequency planning and scrambling code planning method based on an adjacent zone priority level, comprising: an adjacent cell priority level is generated through a zone adjacent factor, a zone factor and a zone direction factor based on the base station zone attribute according to the system technical scheme; and a TD main carrier frequency is distributed according to the generated adjacent zone priority level to ensure the minimality of the frequency interferences among zones; and then, a system assigns base scrambling code blocks and scrambling codes according to the adjacent zone priority level and the frequency so as to ensure the average minimization of the mutual interference of the frequency scrambling code among zones. According to the embodiment of the invention, the calculation method of the adjacent zone priority level is more reasonable, and the setting and switching process of the adjacent zone relationship is more reasonable. Furthermore, co-frequency encounter phenomena among the adjacent zones are avoided by adopting the scheme, so that the mutual correlation of the scrambling codes among the adjacent zones is minimal, and the maximal frequency resource and scrambling code resource utilization and the minimum frequency and scrambling code interferences among zones are ensured. And the network performance indexes such as call completing rate are improved, and the client perception quality is greatly improved.
Owner:CHINA MOBILE GROUP JIANGSU
Parametric speech codec for representing synthetic speech in the presence of background noise
InactiveUS7092881B1Accurate representationImprove perceived qualitySpeech recognitionFrequency spectrumAudio frequency
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
Audio signal system
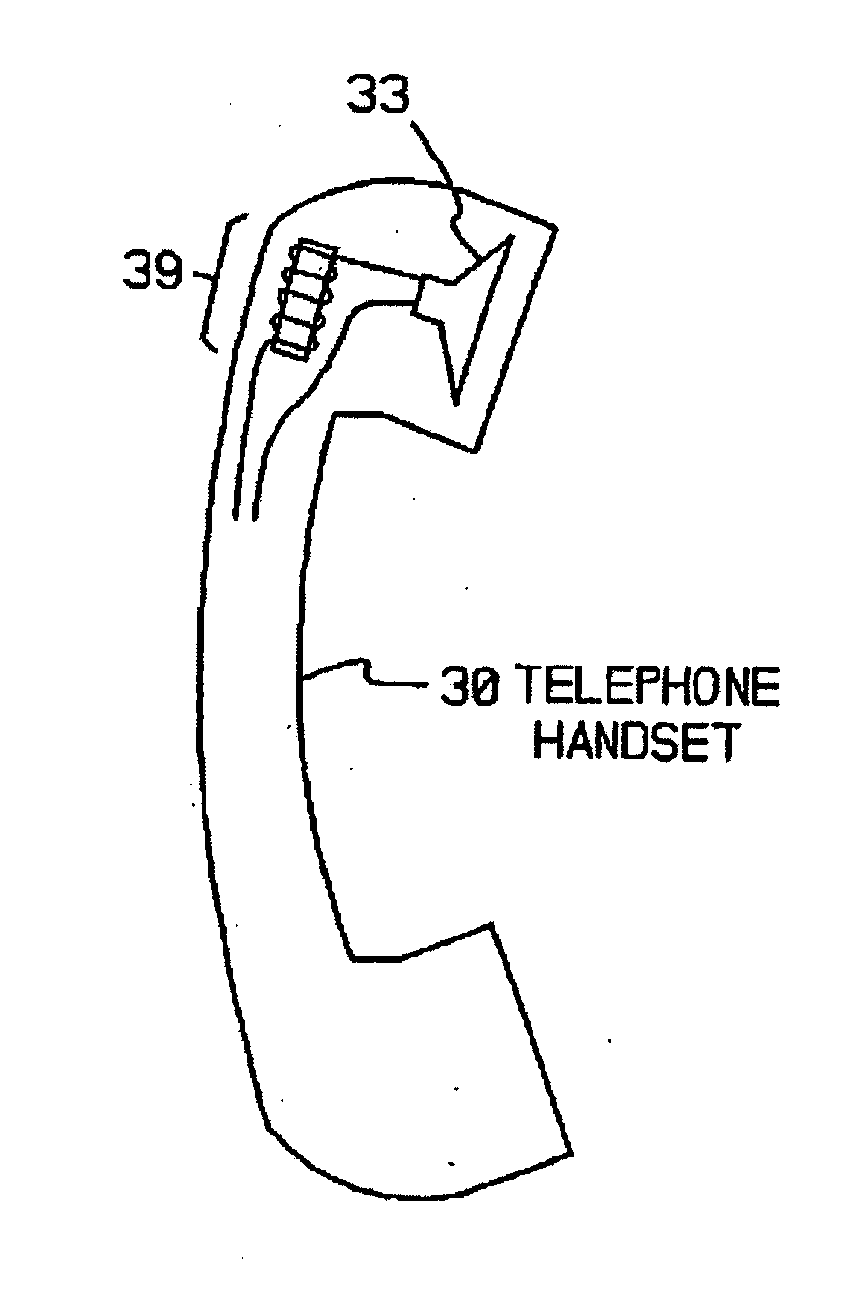
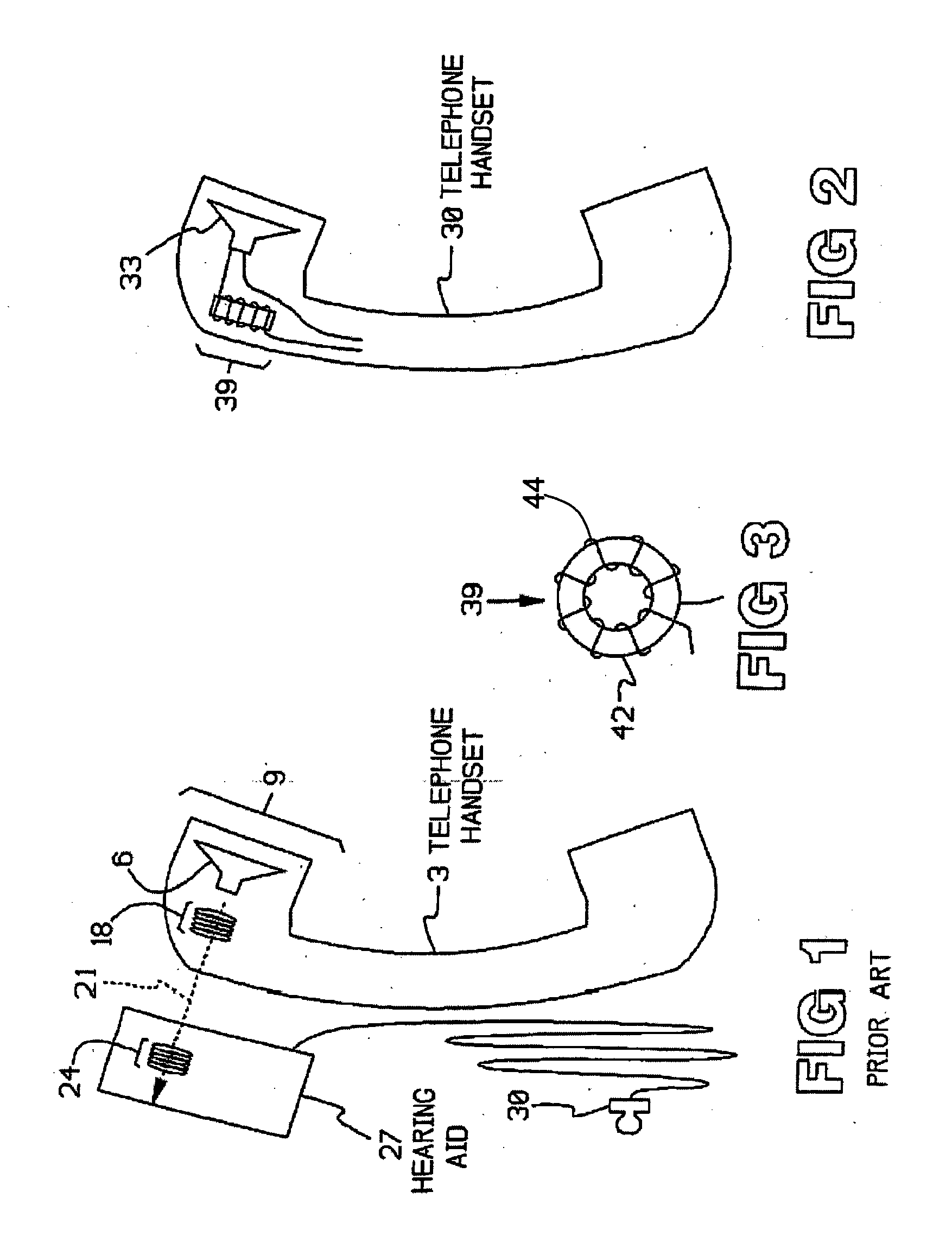
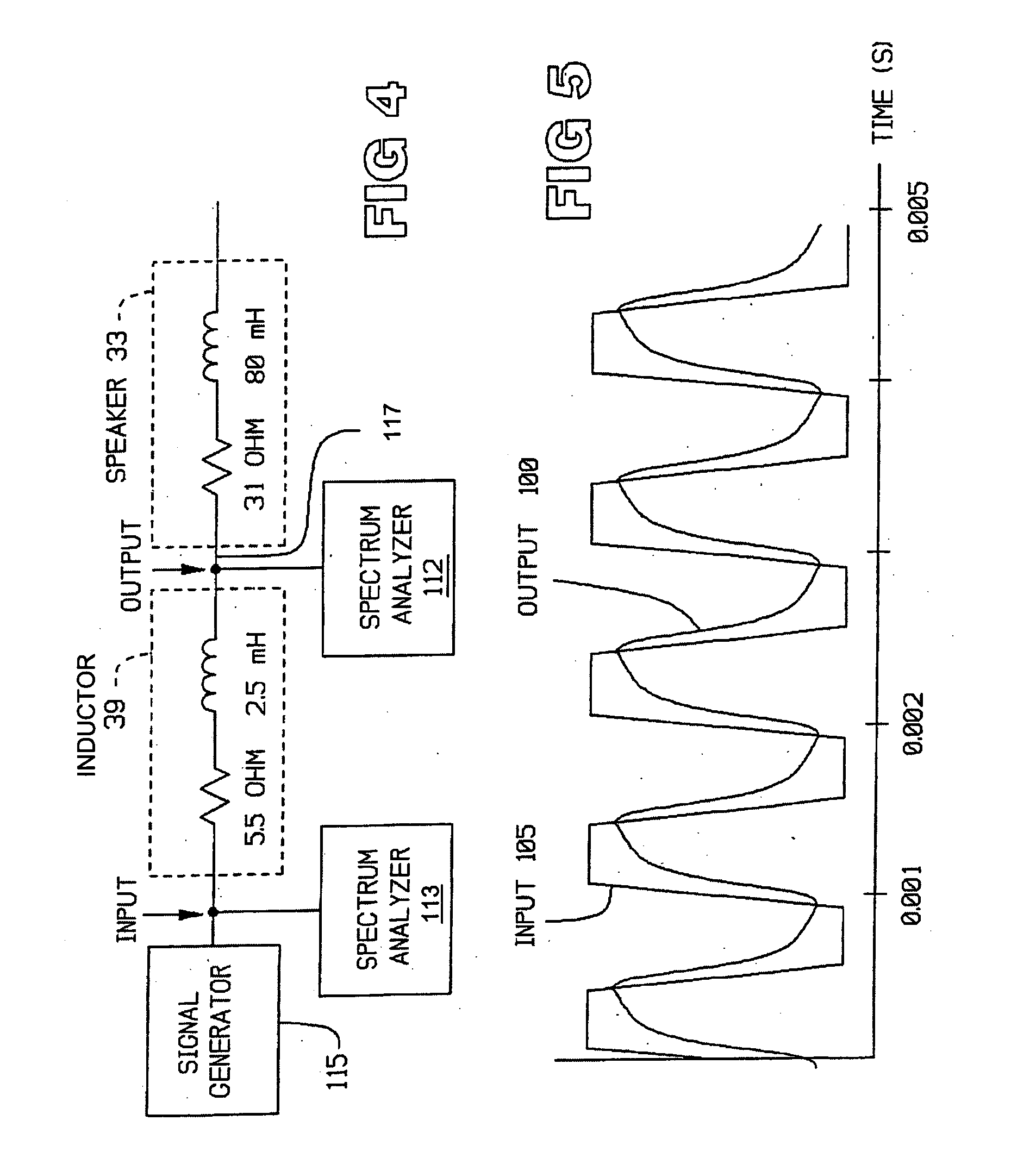
InactiveUS20060029248A1Improve audio signal qualityImprove perceived qualityTransducer detailsTelephone set constructionsDigital signal processingInductor
An audio signal system is provided having, in one embodiment, a magnetostrictive core of varying shapes, sizes, and permeability. The core is wound with a wire, thereby forming an inductor for producing a magnetic field when current is passed through the wire. A speaker, or other audio output device, is positioned in parallel or series with the inductor. In operation, an audio signal is received and transmitted to the speaker or other audio output device, wherein a replication of the received signal is produced. An output of the magnetostrictive inductor couples with the replicated audio signal to modify and enhance the quality of the projected signal. In yet another embodiment, digital signal processing may be used to modify the received signal as well.
Owner:ABLE PLANET
Camera having a through the lens pixel illuminator
InactiveUS7355648B1Improve perceived qualityReduce brightnessTelevision system detailsLighting and heating apparatusLighting systemField of view
A camera comprising: a photosurface comprising light sensitive pixels that generate signals responsive to light incident thereon and optics that focus an image of a scene onto the photosurface; and an illumination system for illuminating the scene, the illumination system comprising: an illuminator having a plurality of substantially contiguous, independently controllable light providing regions; optics that focuses an image or the illuminator on the scene so that light from the illuminator illuminates substantially all of and substantially only the field of view of the camera; and a controller that controls light provided by each light providing region.
Owner:MICROSOFT INT HLDG BV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com