Frequency planning and scrambling code planning method and device based on adjacent zone priority level
A frequency planning and priority technology, applied in the field of communications, can solve the problems of unreasonable adjacent cell planning, not taking too much into account the composite code interference factor, increasing the strong interference between adjacent cells, etc. Improve customer perception quality and minimize scrambling interference
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
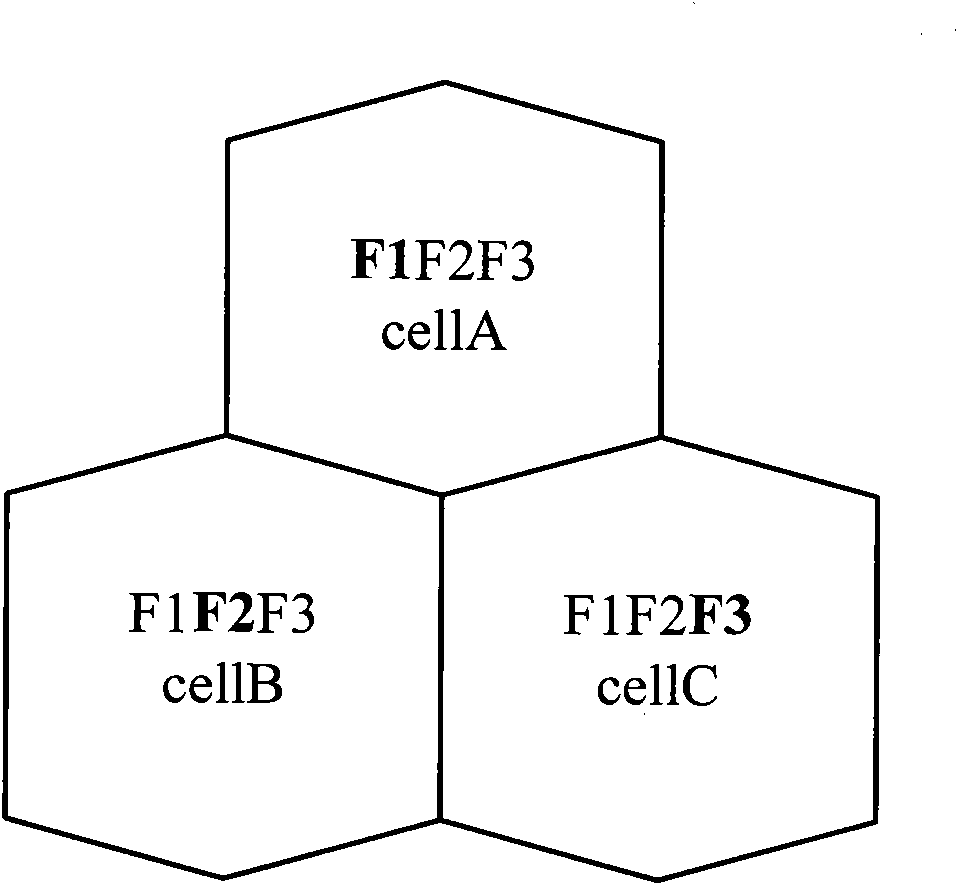
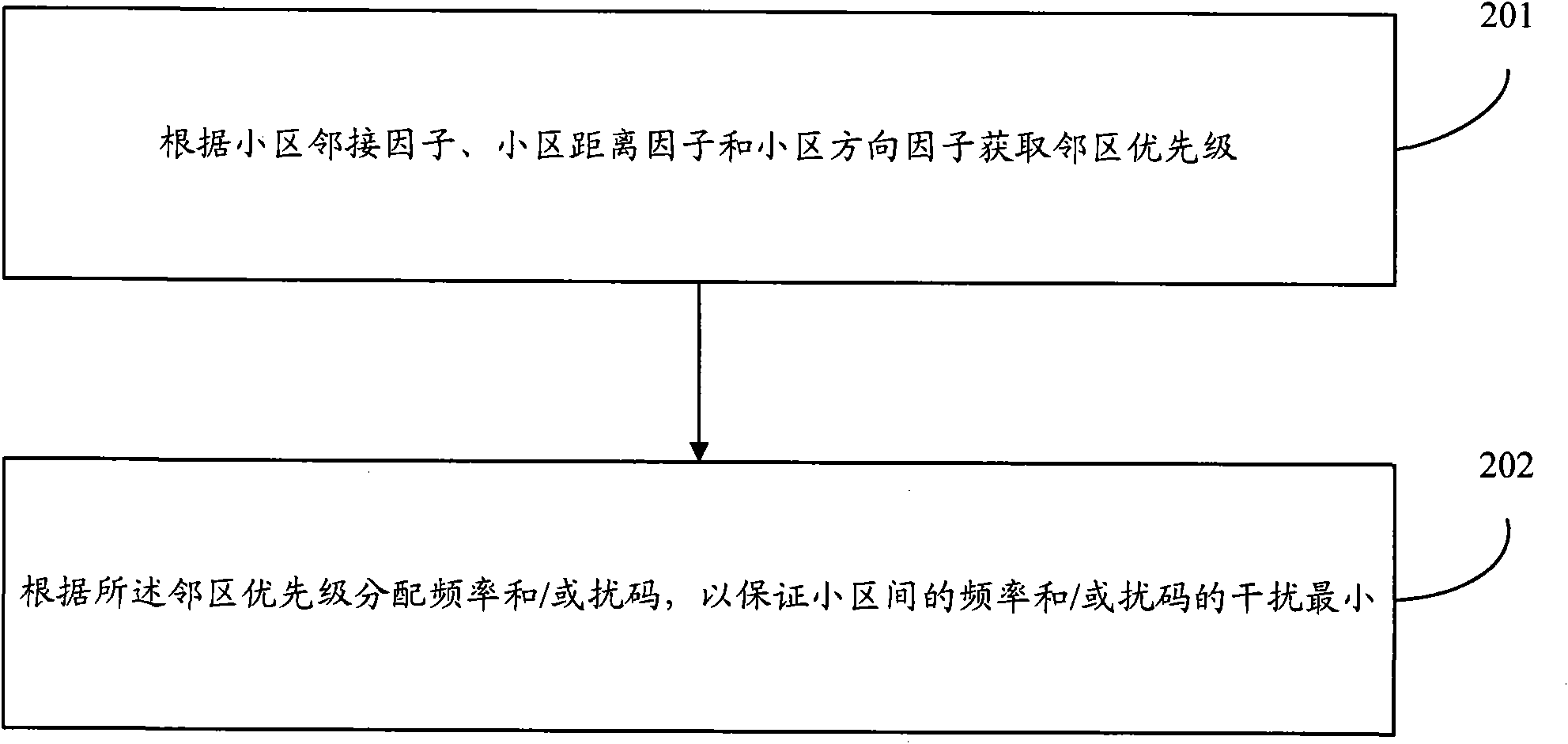
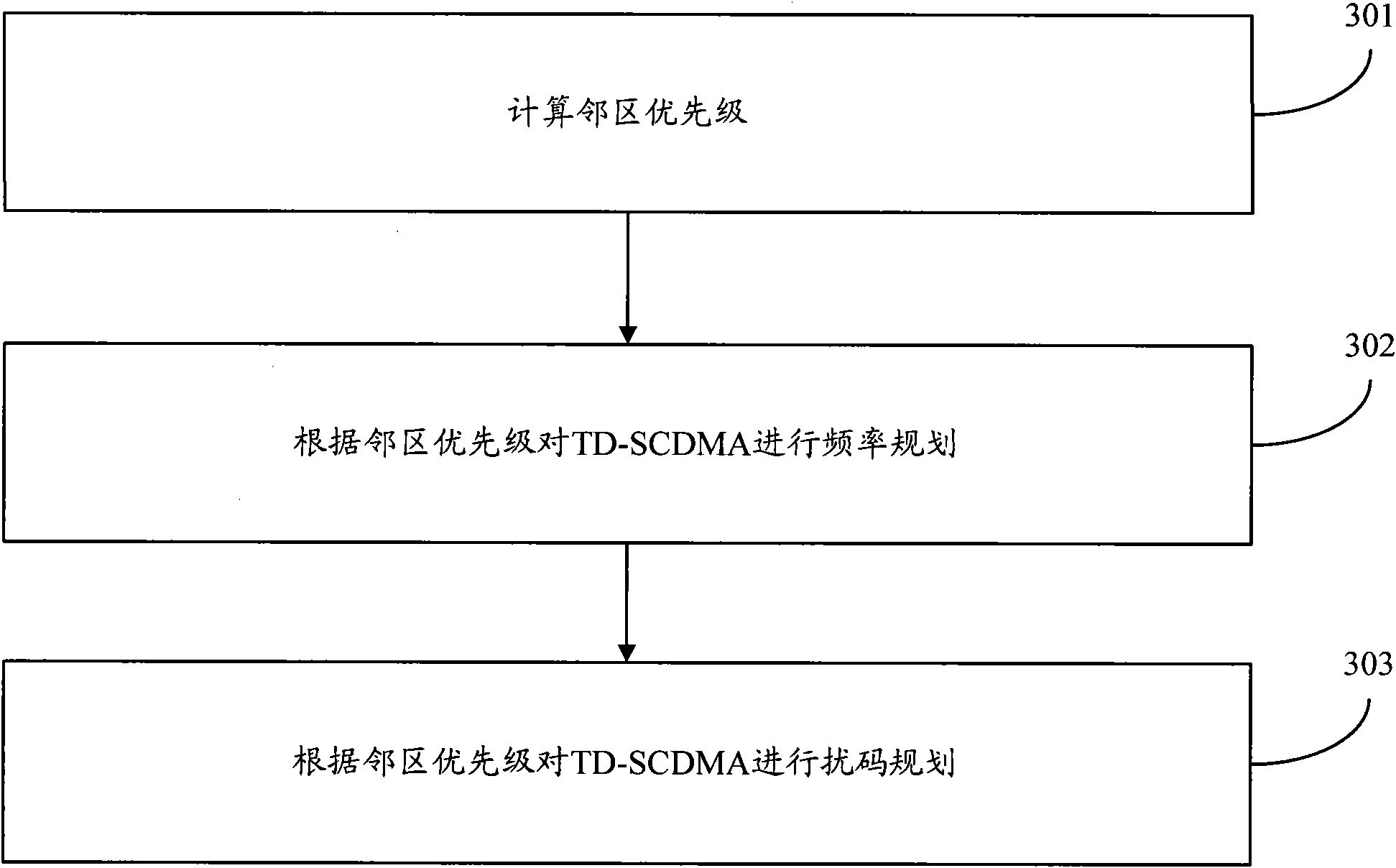
[0059] In the embodiment of the present invention, a method for quantitatively determining the priority of adjacent cells is provided, which realizes reasonable priority ranking of adjacent cells and improves the accuracy of adjacent cell planning in the wireless cellular network. Then, according to the priority order of neighboring cells, a reasonable main carrier reusable cell is selected, and the TD-SCDMA main carrier frequency (ie TD-SCDMA main carrier frequency) is automatically allocated to ensure the main carrier frequency on the basis of maximizing the application of frequency resources. Minimize the impact between the frequency and same-frequency reuse cells, that is, minimize the average interference between cells. Thirdly, according to the priority of adjacent cells and the allocation of main carrier frequency of the cell, the scrambling codes of the TD-SCDMA network are assigned to ensure the minimum interference between adjacent cells.
[0060] The technical solut...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com