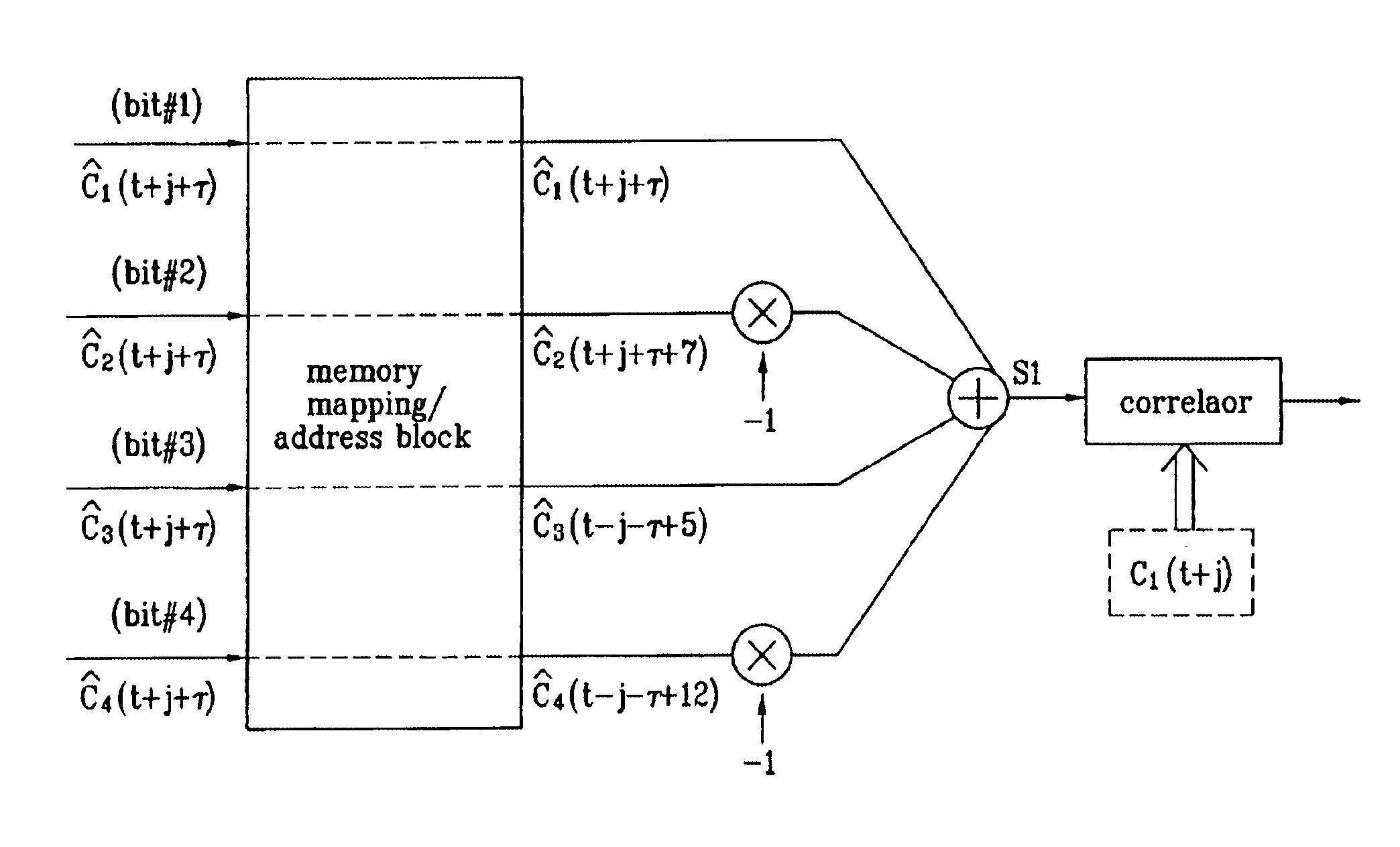
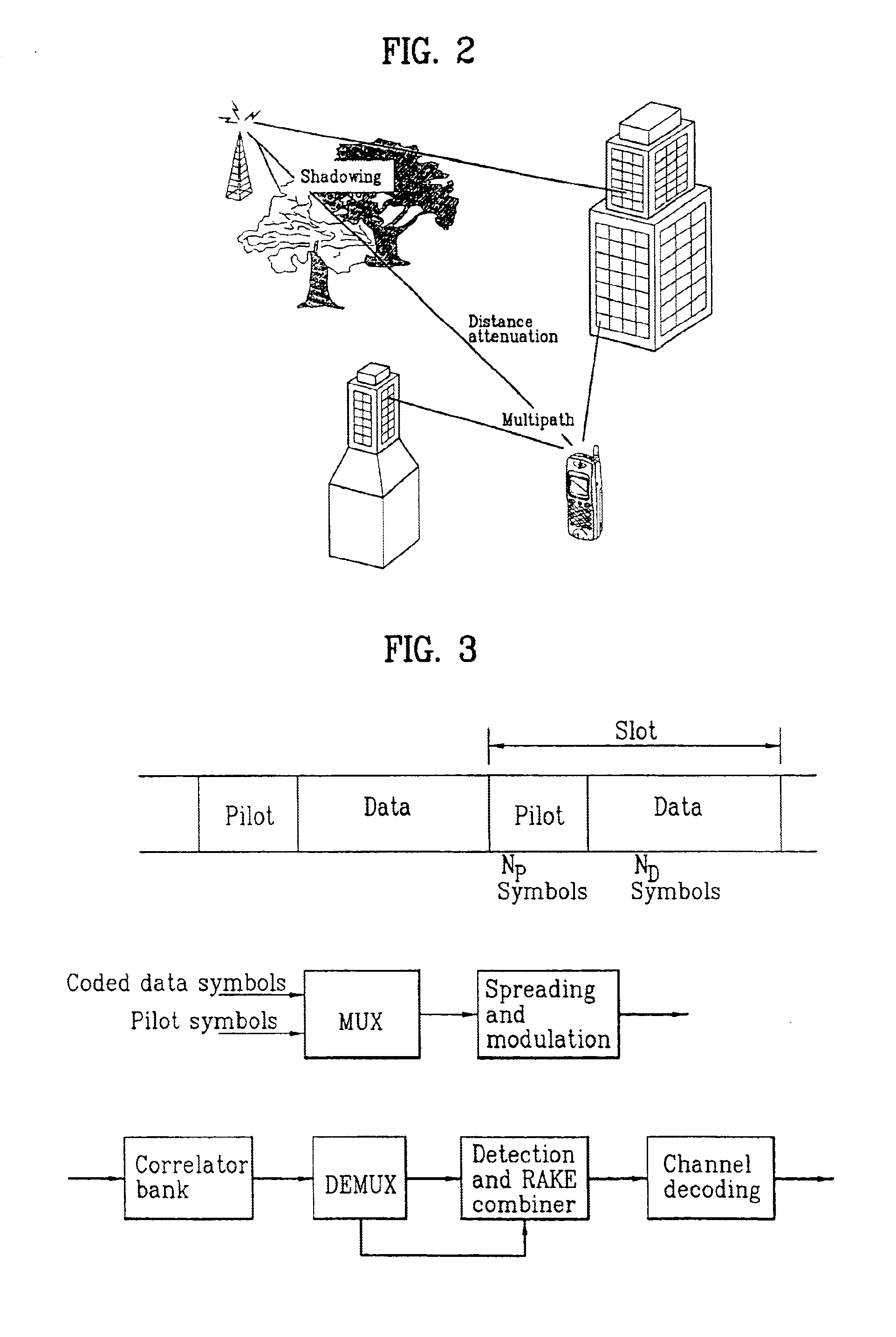
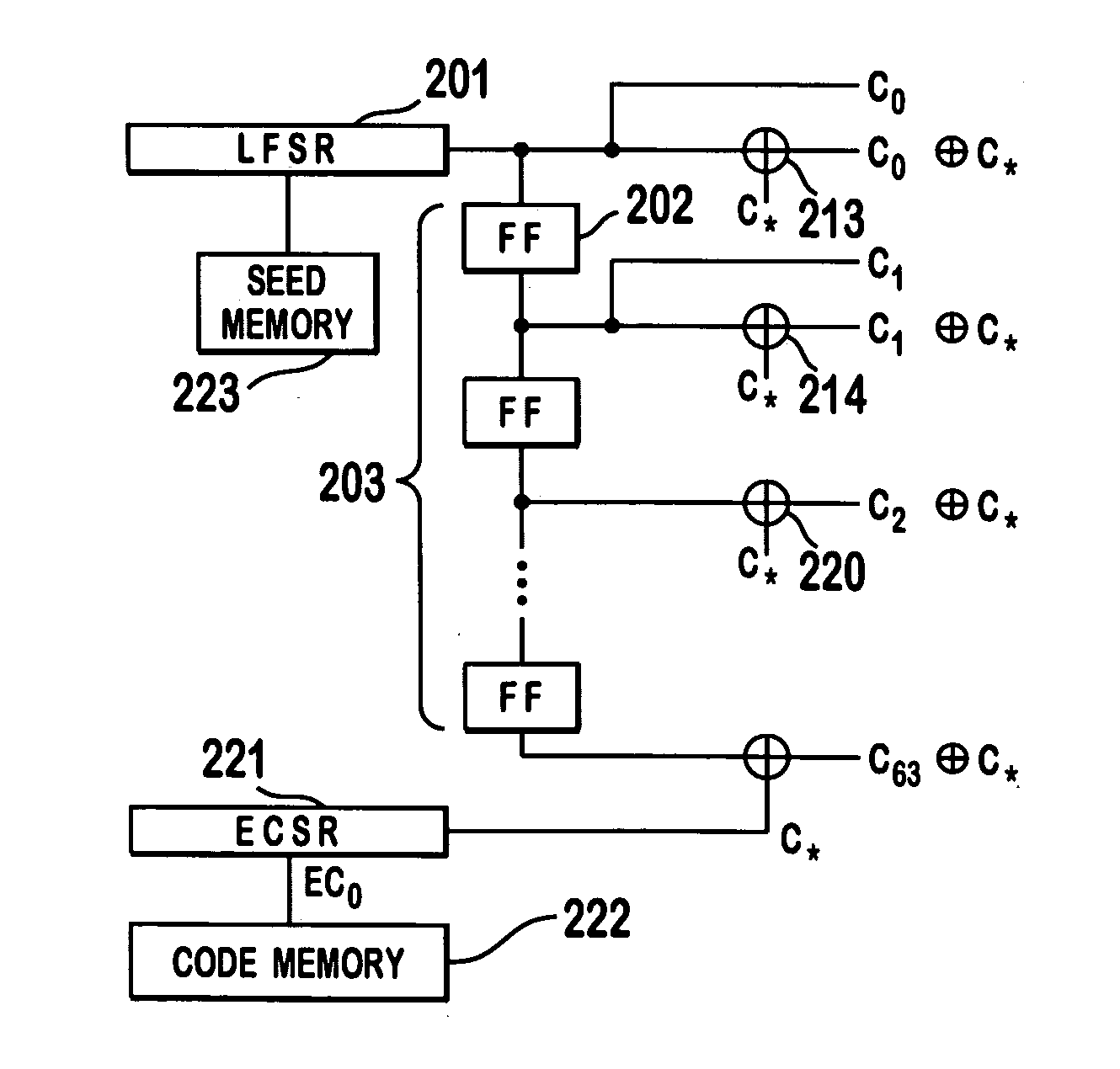
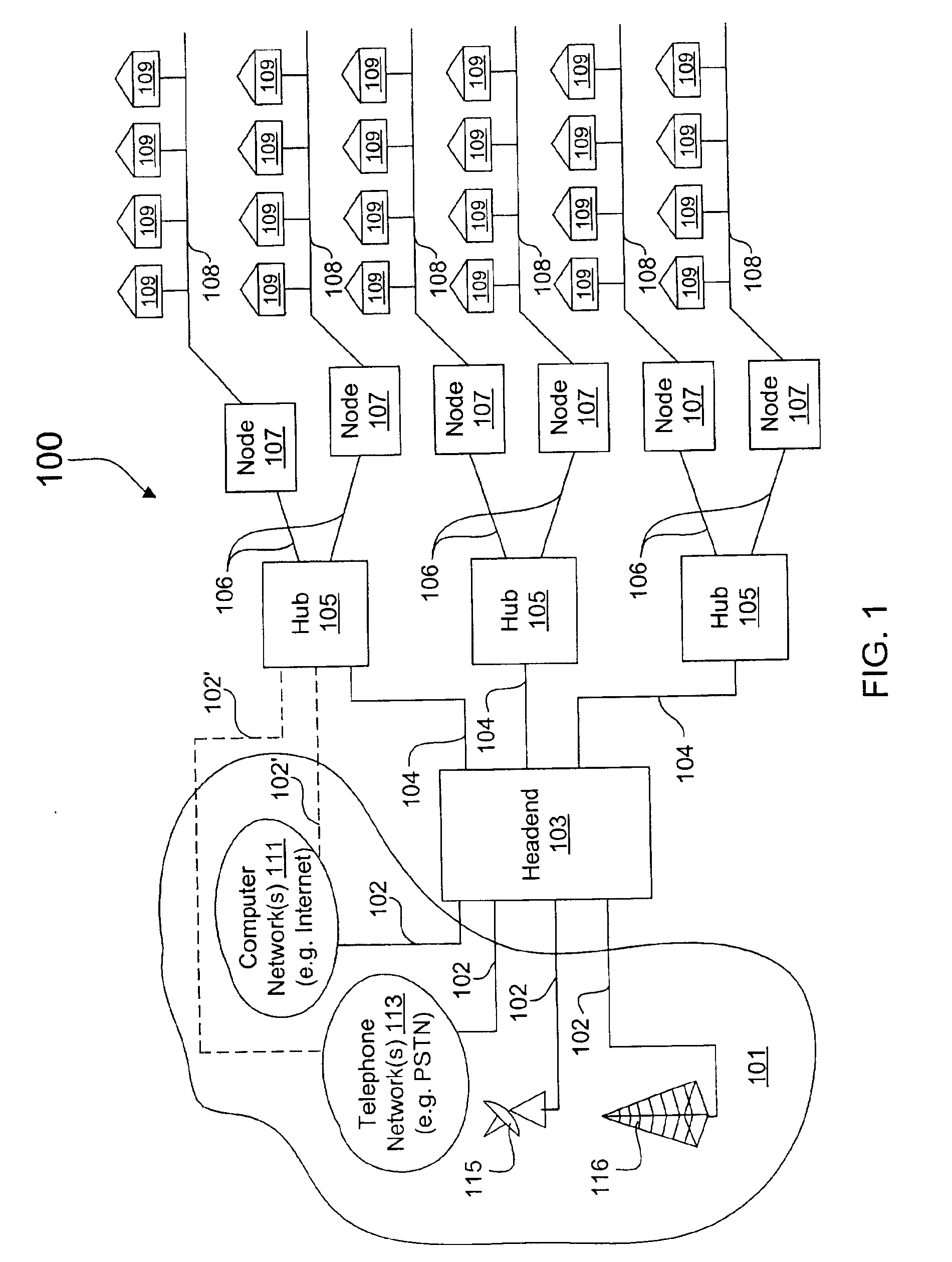
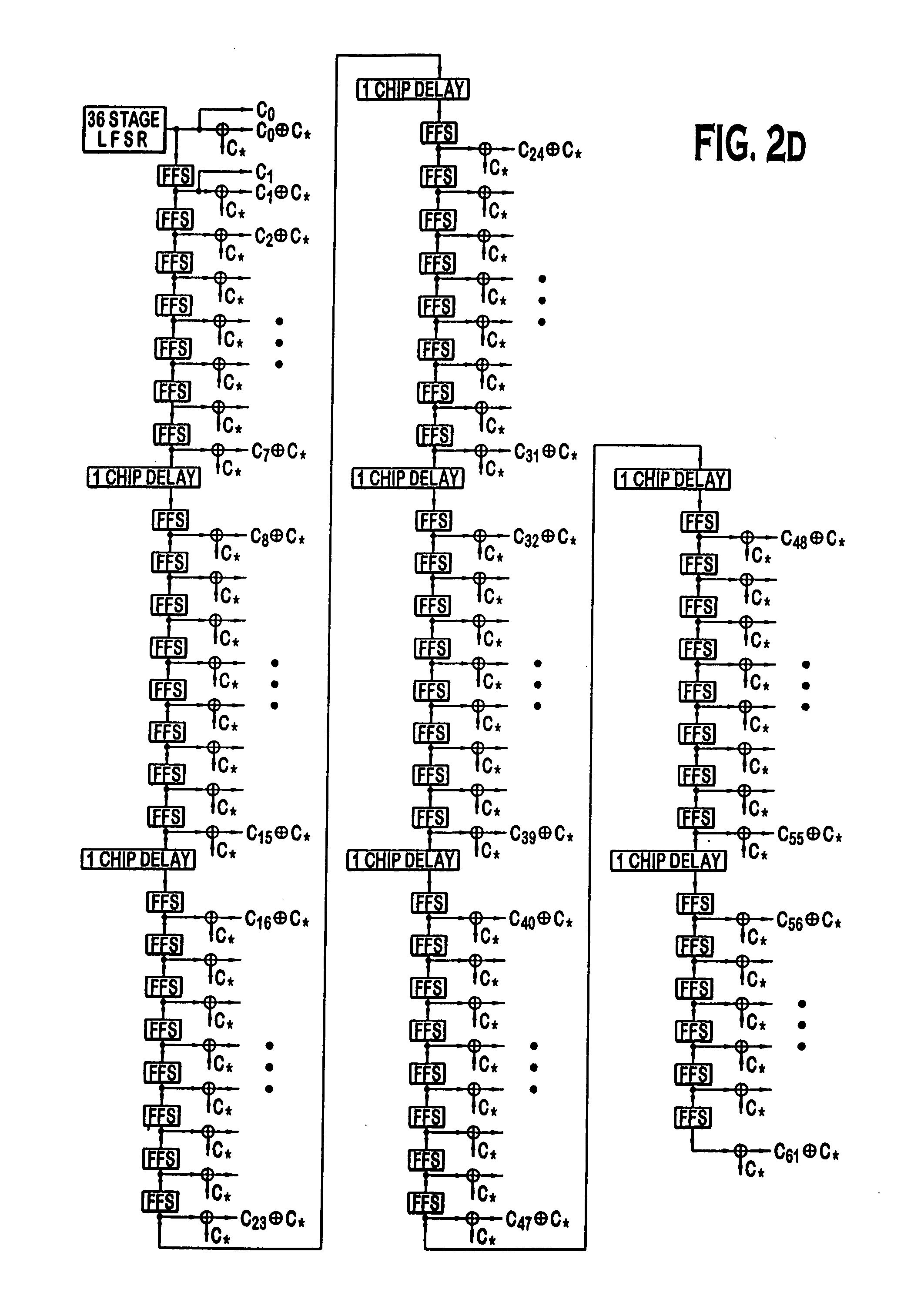
Patents
Literature
2521 results about "Code division multiple access" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Code-division multiple access (CDMA) is a channel access method used by various radio communication technologies. CDMA is an example of multiple access, where several transmitters can send information simultaneously over a single communication channel. This allows several users to share a band of frequencies (see bandwidth). To permit this without undue interference between the users, CDMA employs spread spectrum technology and a special coding scheme (where each transmitter is assigned a code).
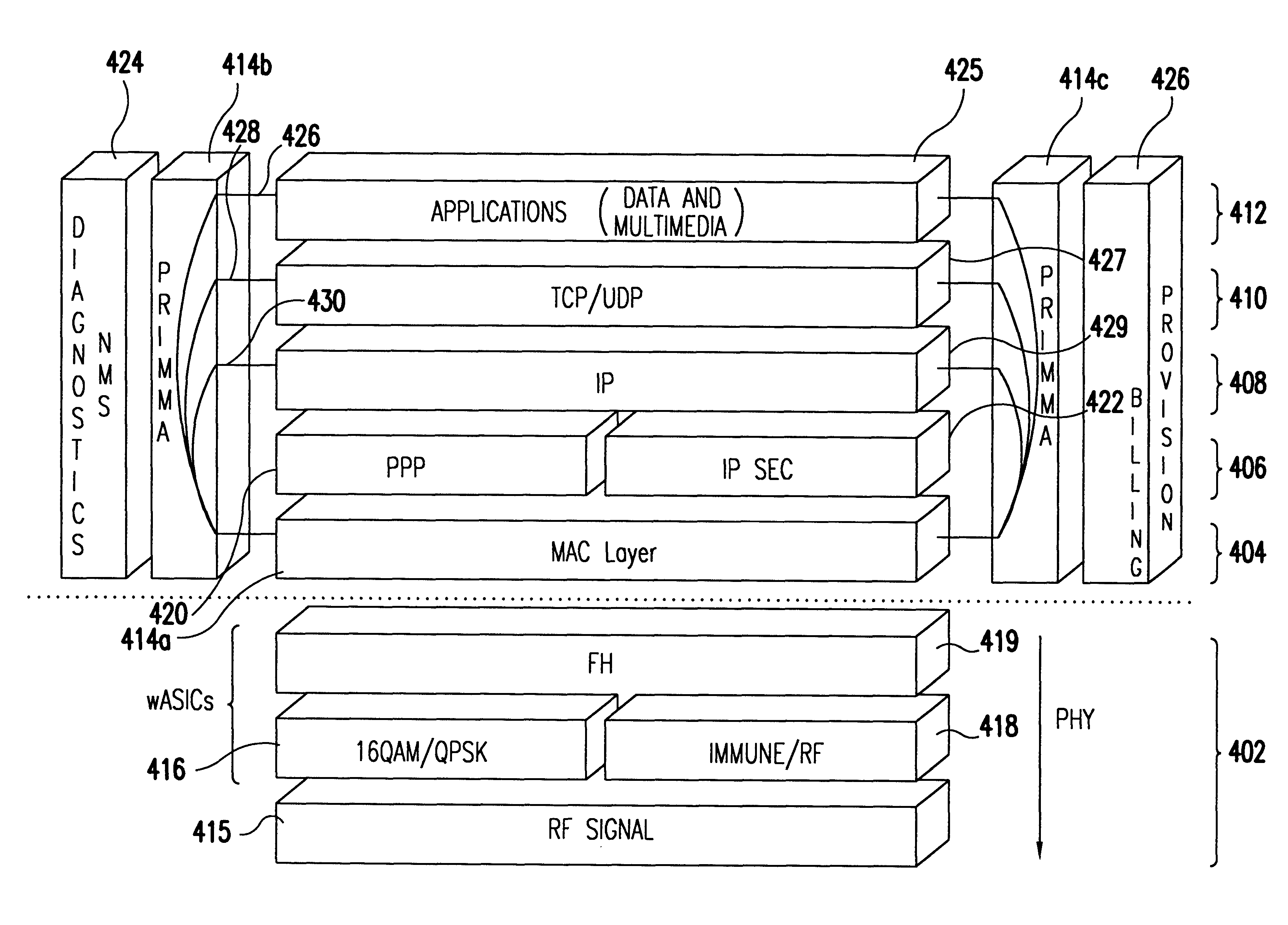
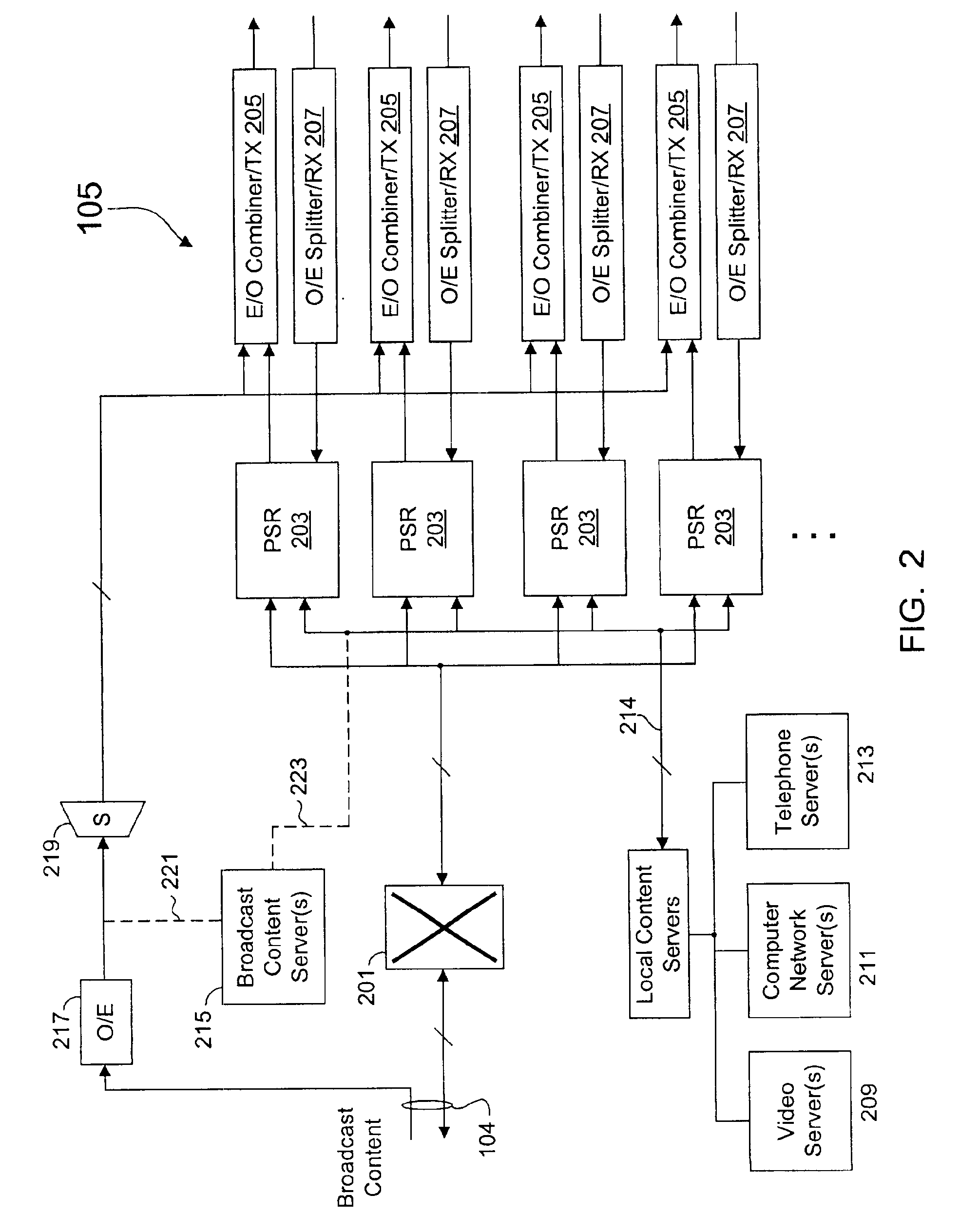
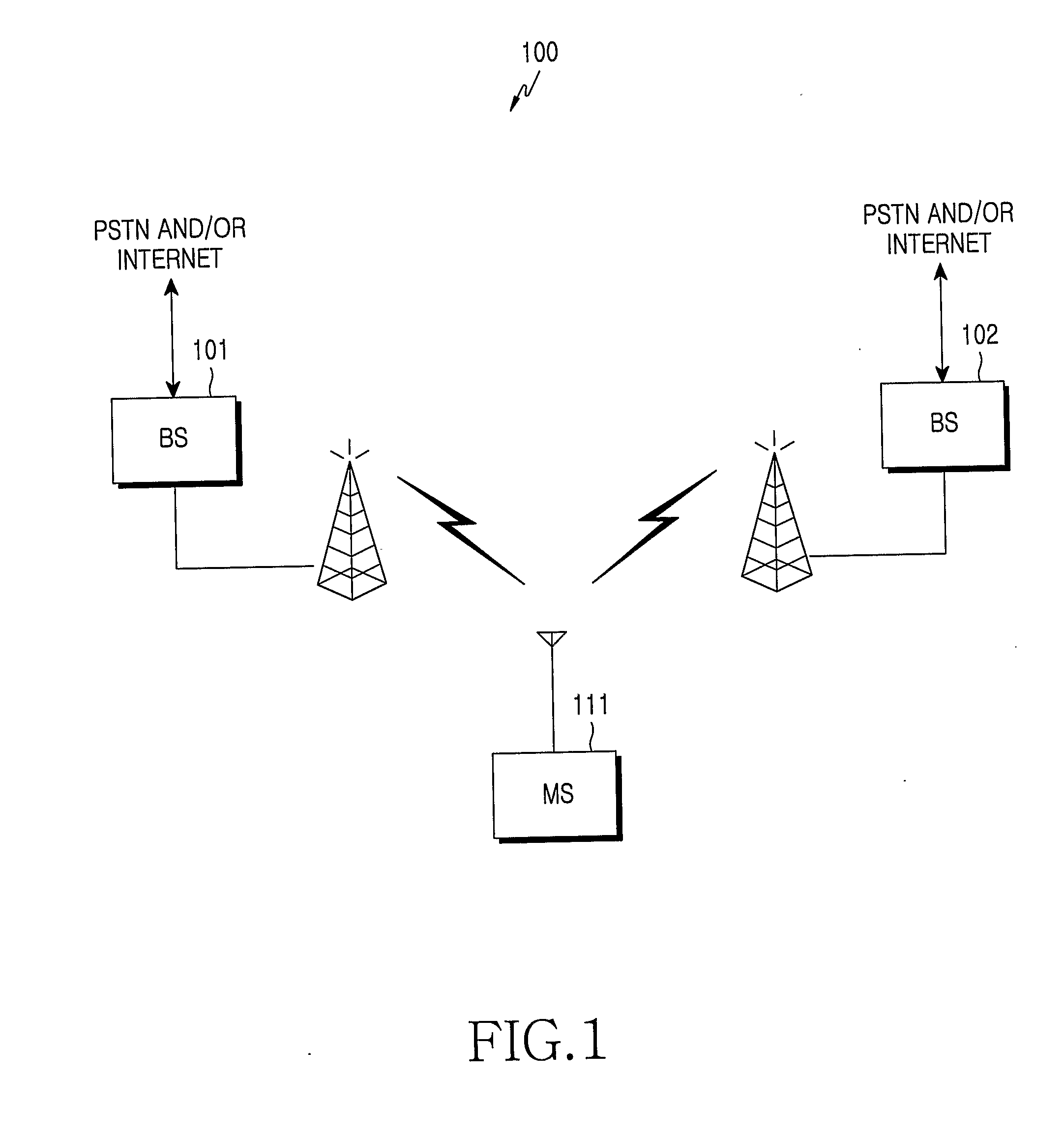
Transmission control protocol/internet protocol (TCP/IP) packet-centric wireless point to multi-point (PTMP) transmission system architecture
InactiveUS6862622B2Special service provision for substationError detection/prevention using signal quality detectorTransport systemWorkstation
A packet-centric wireless point to multi-point telecommunications system includes: a wireless base station communicating via a packet-centric protocol to a first data network; one or more host workstations communicating via the packet-centric protocol to the first data network; one or more subscriber customer premise equipment (CPE) stations coupled with the wireless base station over a shared bandwidth via the packet-centric protocol over a wireless medium; and one or more subscriber workstations coupled via the packet-centric protocol to each of the subscriber CPE stations over a second network. The packet-centric protocol can be transmission control protocol / internet protocol (TCP / IP). The packet-centric protocol can be a user datagram protocol / internet protocol (UDP / IP). The system can include a resource allocation means for allocating shared bandwidth among the subscriber CPE stations. The resource allocation is performed to optimize end-user quality of service (QoS). The wireless communication medium can include at least one of: a radio frequency (RF) communications medium; a cable communications medium; and a satellite communications medium. The wireless communication medium can further include a telecommunications access method including at least one of: a time division multiple access (TDMA) access method; a time division multiple access / time division duplex (TDMA / TDD) access method; a code division multiple access (CDMA) access method; and a frequency division multiple access (FDMA) access method.The first data network includes at least one of: a wireline network; a wireless network; a local area network (LAN); and a wide area network (WAN). The second network includes at least one of: a wireline network; a wireless network; a local area network (LAN); and a wide area network (WAN).
Owner:INTELLECTUAL VENTURES I LLC
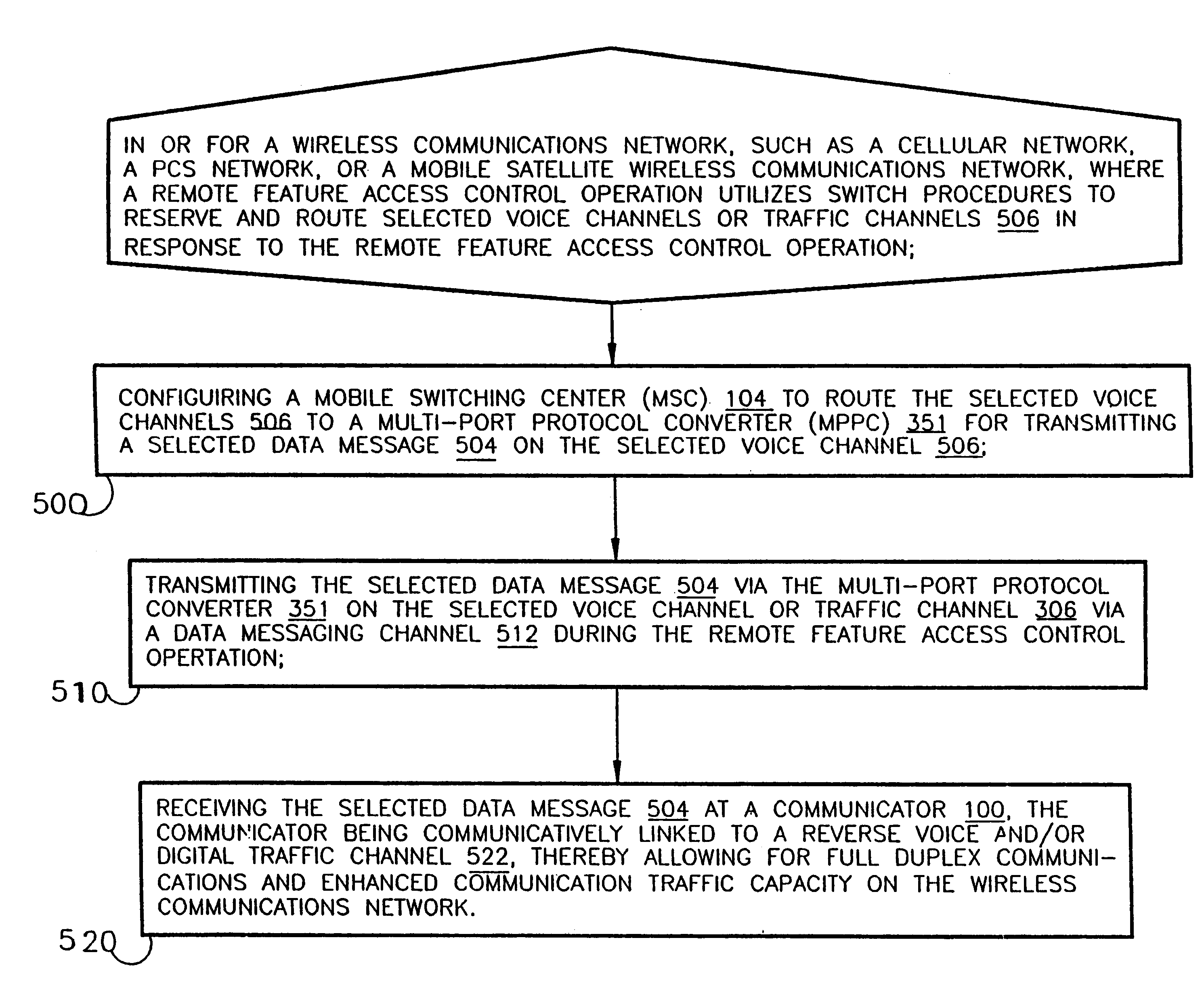
Time division multiple access downlink personal communications system voice and data debit billing method
InactiveUS6185198B1Increase capacityFunction increaseTime-division multiplexData switching by path configurationCode division multiple accessControl channel
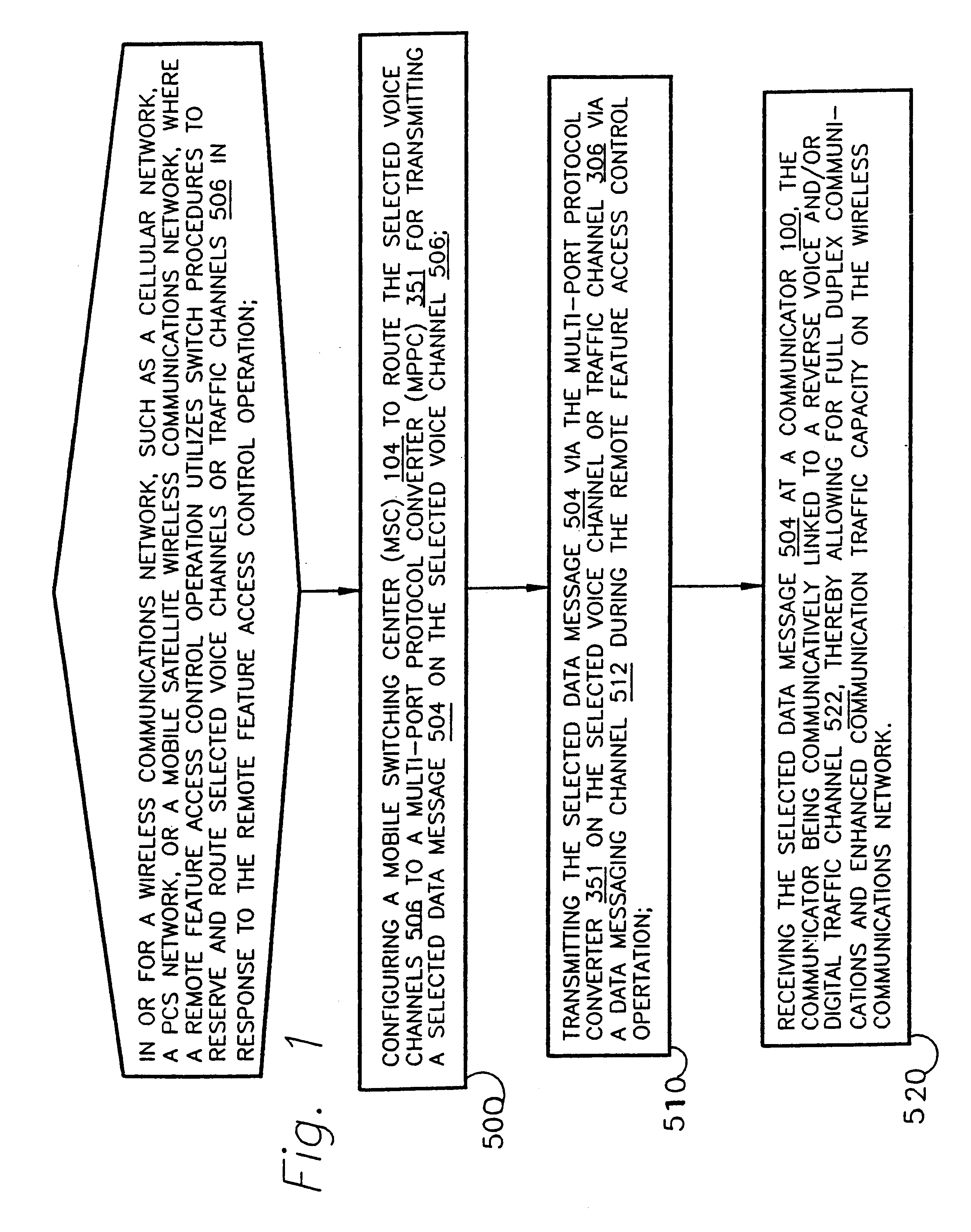
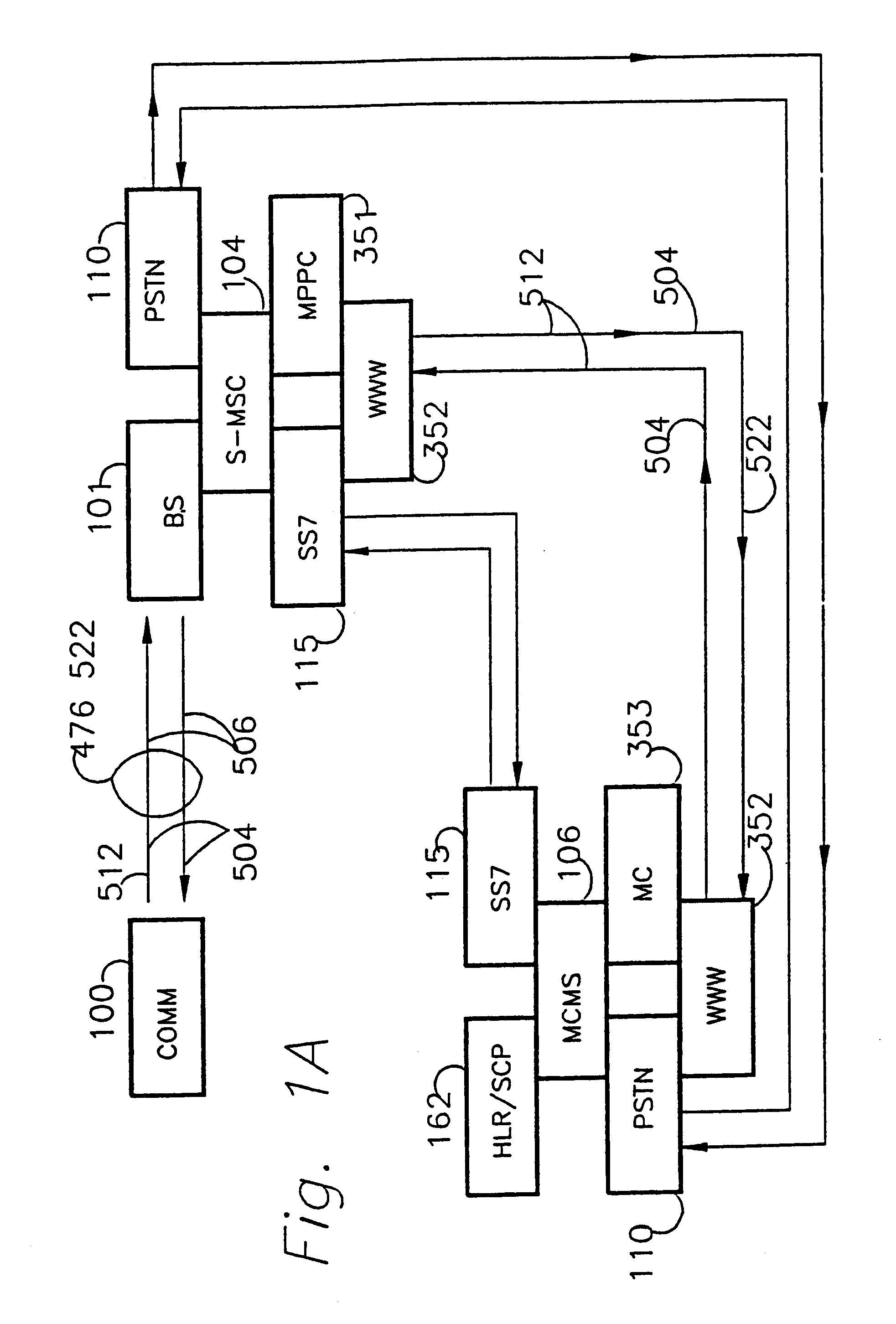
A method and apparatus for full-duplex data communication in or for a wireless communications network, such as a cellular network, PCS network, or mobile satellite network, where a remote feature access control operation utilizes a switch to reserve and route selected voice channels or traffic channels in response to the remote feature access control operation. The method comprising the steps of: configuring a mobile switching center (MSC) to route the selected voice channels to a multi-port protocol converter (MPPC) for transmitting a selected data message on the selected voice channel. Transmitting the selected data message via the multi-port protocol converter on the selected voice channel via a data messaging channel during the remote feature access control operation. Then the selected data message is received at a communicator, which is communicatively linked to a reverse voice and / or digital traffic channel of the wireless network, thereby providing for both forward and reverse messaging on the wireless communications network. An apparatus is disclosed for data communication in or for a wireless communications network for transmitting and receiving both forward and reverse voice, traffic, and control channel messages utilizing the disclosed methodology.
Owner:AERIS COMM
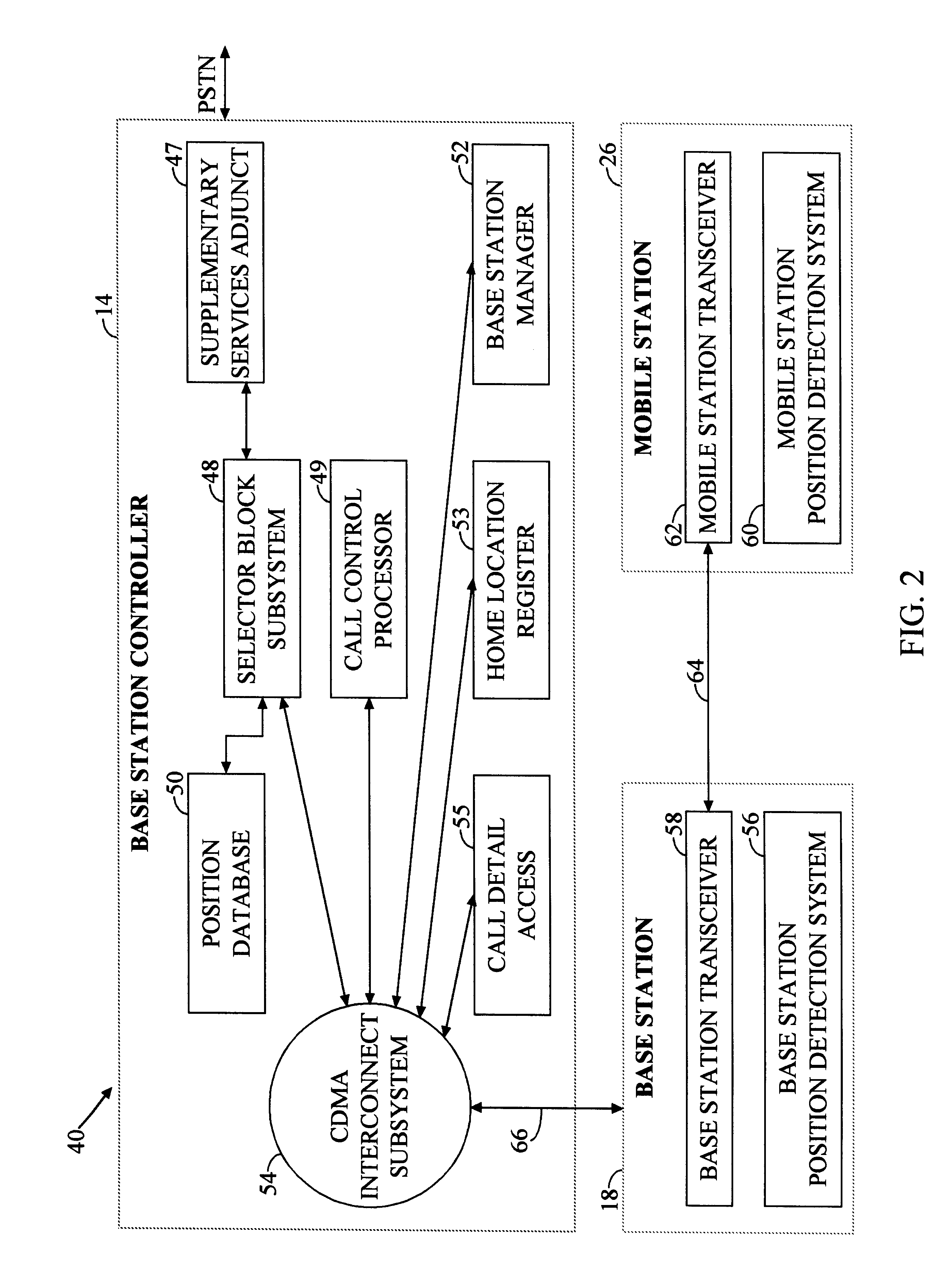
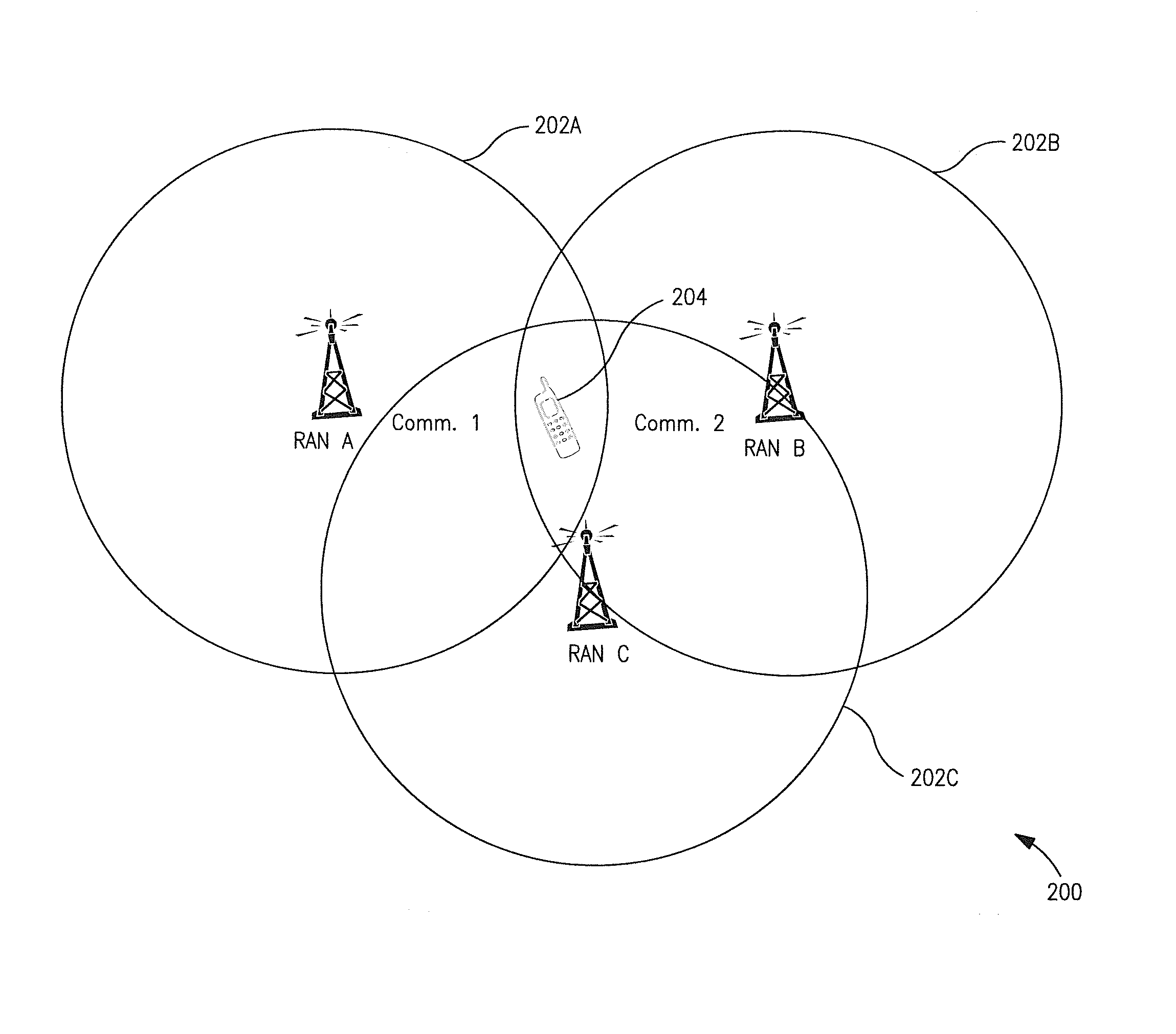
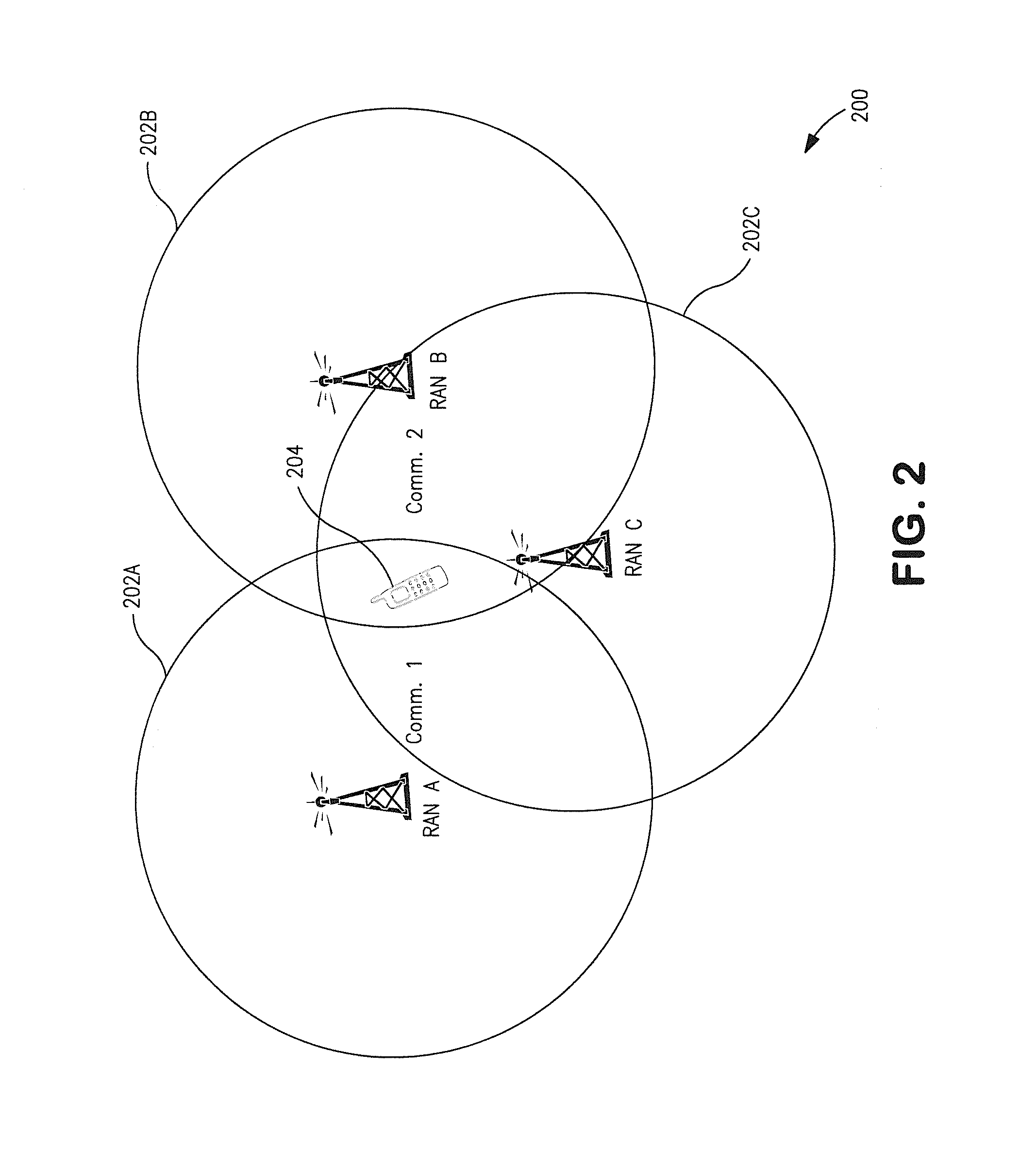
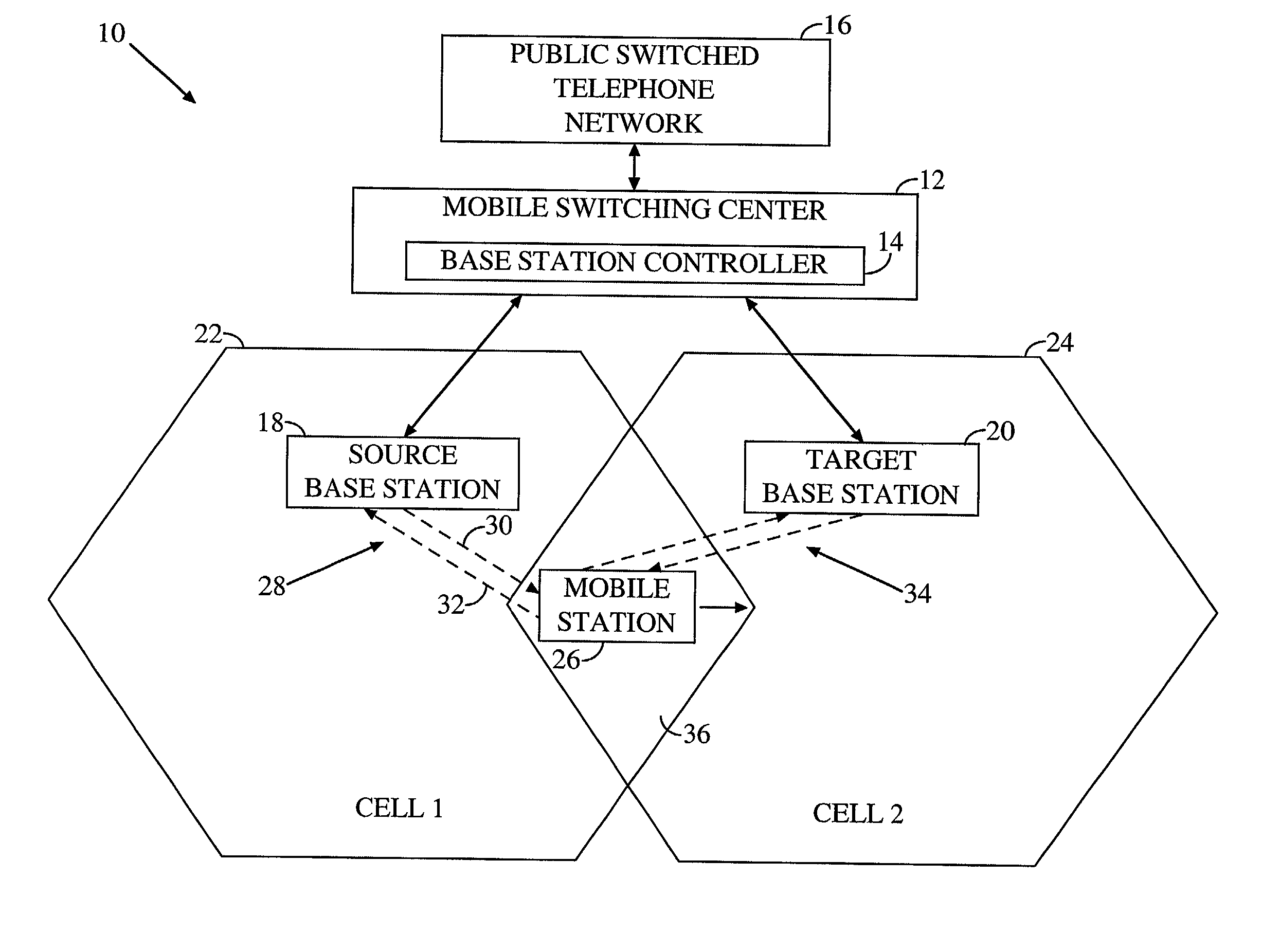
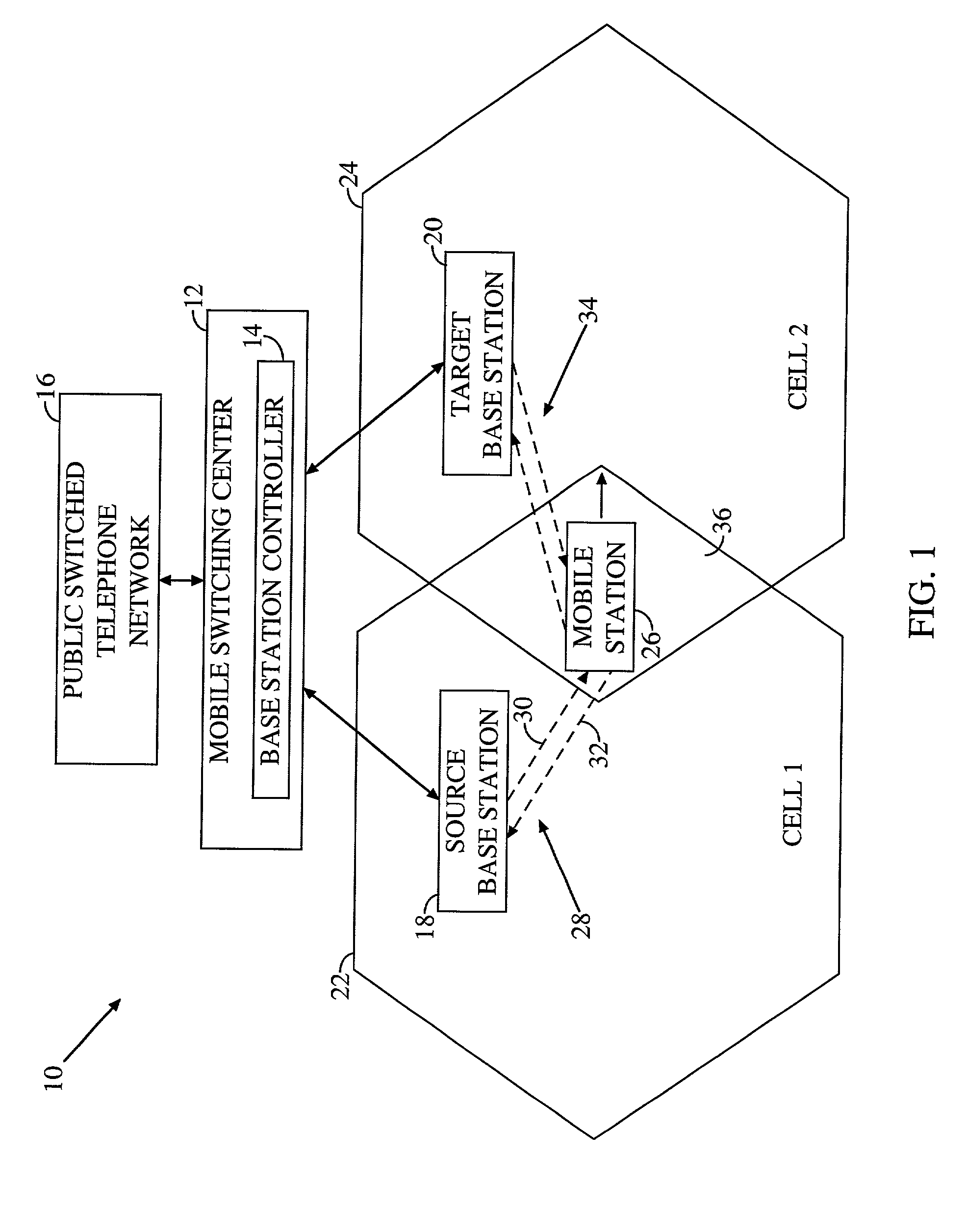
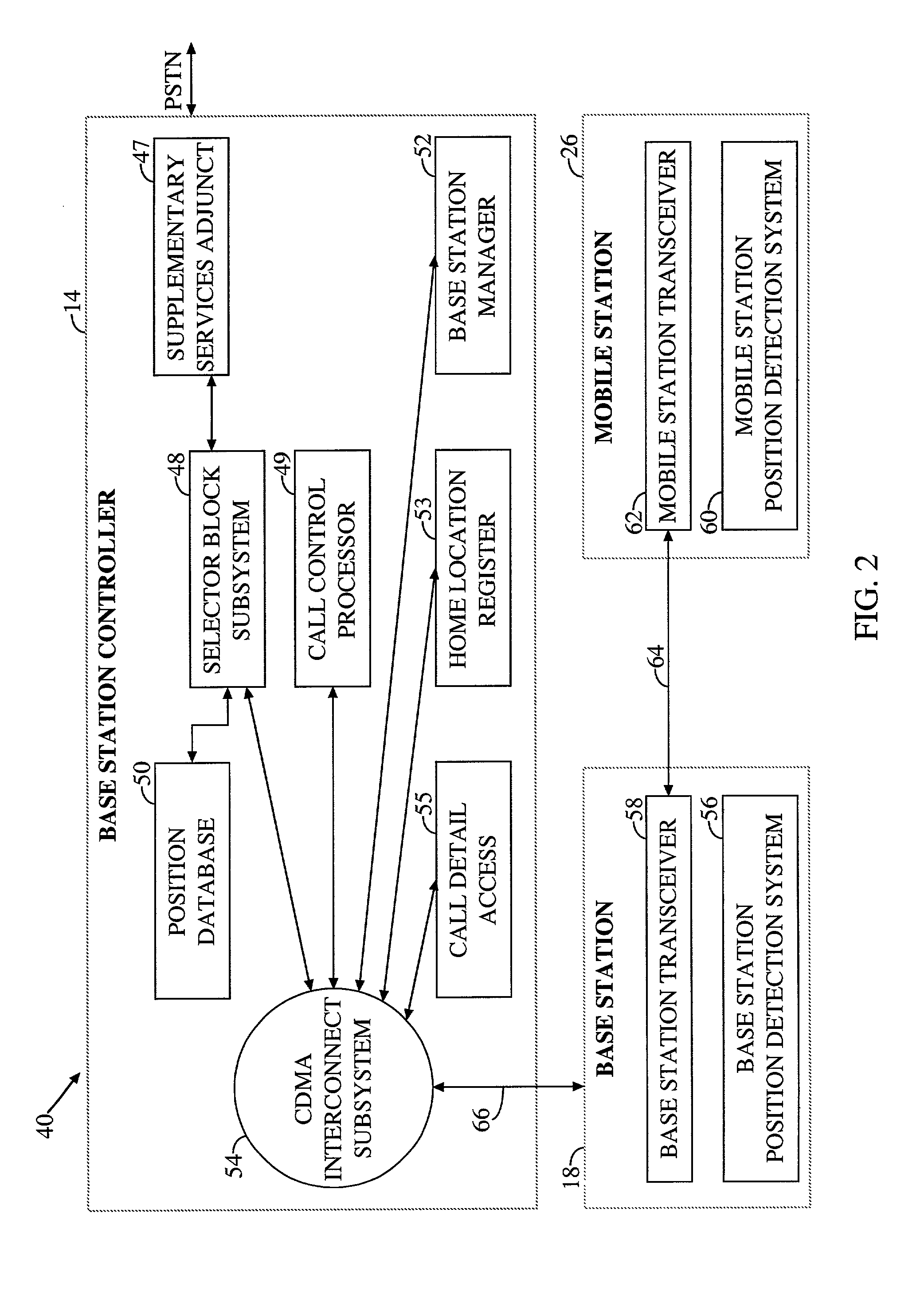
Mobile communication system with position detection to facilitate hard handoff
InactiveUS6321090B1Radio/inductive link selection arrangementsSatellite radio beaconingLocation detectionTransceiver
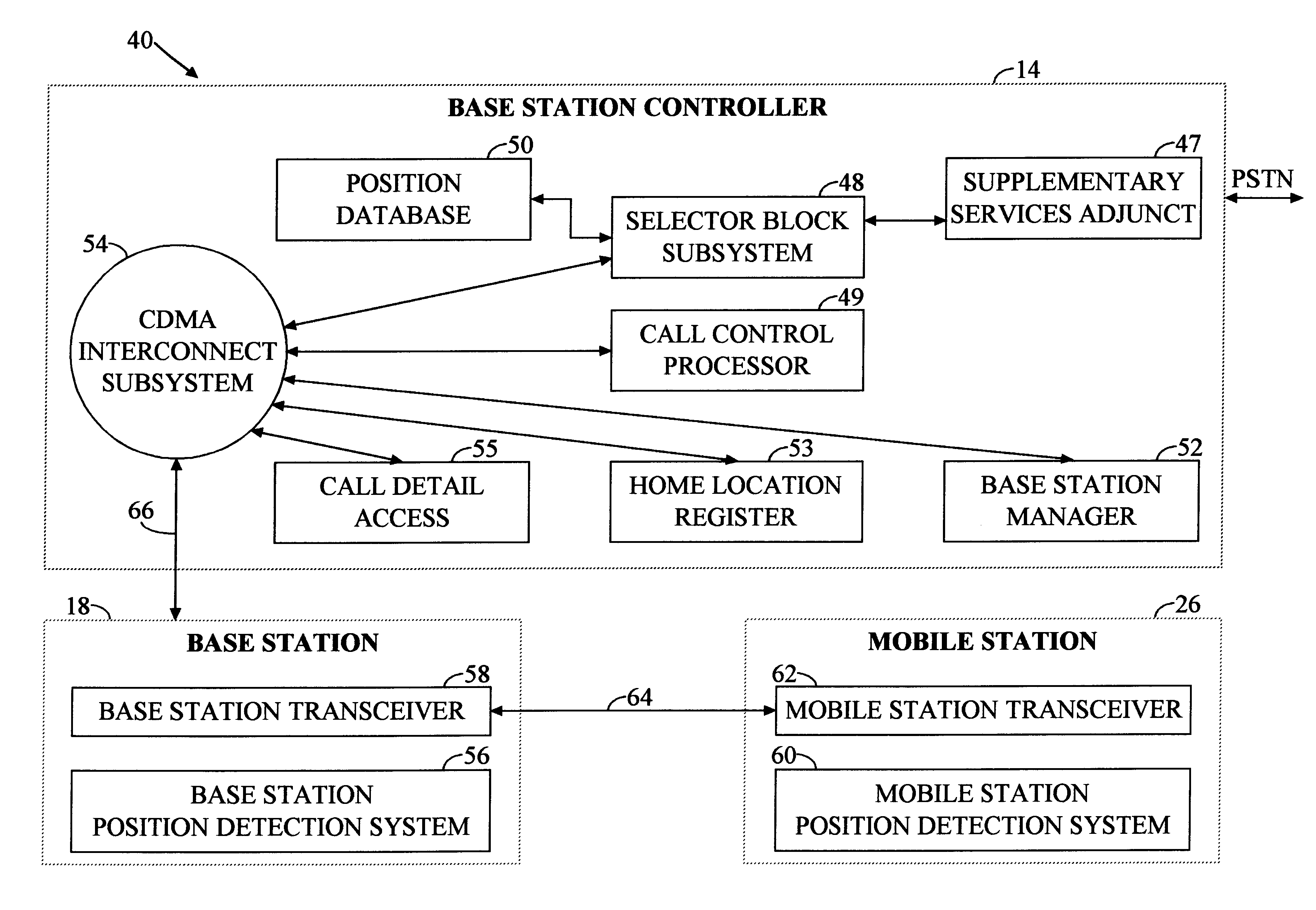
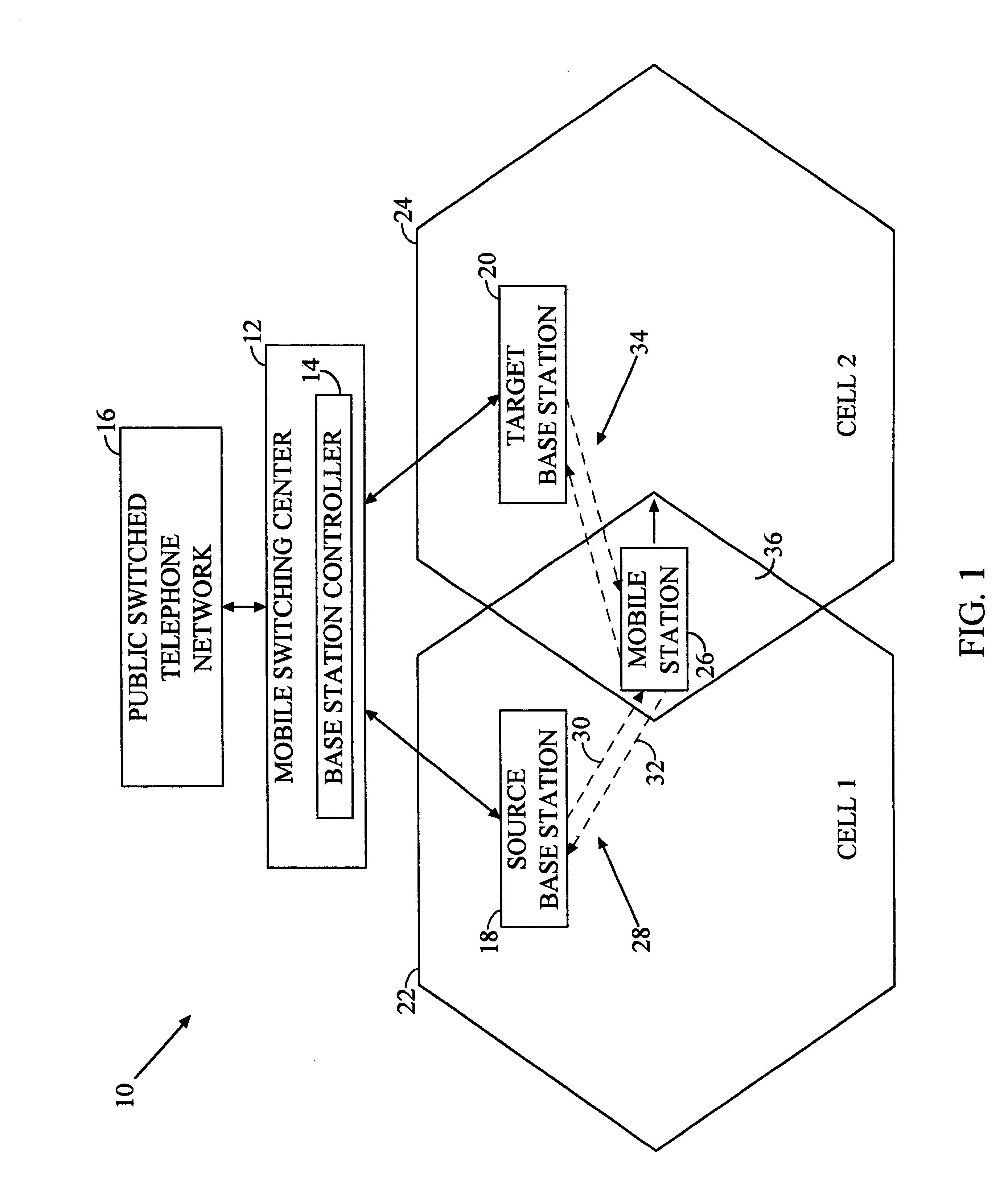
A system for facilitating handoff adapted for use with a telecommunications network. The system includes position equipment for determining the location of a mobile transceiver within a region containing a first cell and a second cell. A comparison circuit compares the location with a predetermined handoff area within the region and provides a control signal in response thereto. A handoff initiation circuit initiates handoff of the mobile transceiver between the first cell and the second cell in response to the control signal. In a specific embodiment, the handoff is a hard handoff. The position equipment includes Global Positioning System (GPS) equipment including a mobile unit GPS receiver and signal interface. The comparison circuit includes a positional database that stores latitudinal and longitudinal information corresponding to the predetermined handoff area. The comparison circuit also includes a Code Division Multiple Access selector. The selector begins tracking the position of the mobile transceiver when it is within a predetermined range of the predetermined handoff area. In a specific embodiment, the handoff initiation circuit includes a base station controller. The position equipment includes a base station positional detection system and a mobile unit positional detection system for determining the location of the mobile transceiver. The position database has map information depicting the coverage area of the first and second cells and the predetermined handoff area. The selector runs software for comparing the location to the map information and providing the control signal when the location is within the predetermined handoff area. The base station includes and implements instructions for completing hard handoff in response to the control signal.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Channel assignment apparatus and method for a common packet channel in a WCDMA mobile communication system
InactiveUS6859445B1Improve reliabilityReduce complexityPower managementNetwork traffic/resource managementCommunications systemCollision detection
A common packet channel assignment method and device in a CDMA (Code Division Multiple Access) communication system is disclosed. The method comprises transmitting an access preamble signal having channel information which is used to access a base station, and then receiving an; access preamble acquisition indicator signal from the base station in response to the access preamble signal. A collision detection preamble for detecting a collision is transmitted in response to the received access preamble acquisition indicator signal. A first signal indicating acquisition of the collision detection preamble and a second signal indicating channel assignment are received, both of which the base station has transmitted in response to the collision acquisition signal. Upon receipt of the first signal, a common packet channel is assigned according to information designated by the second signal.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
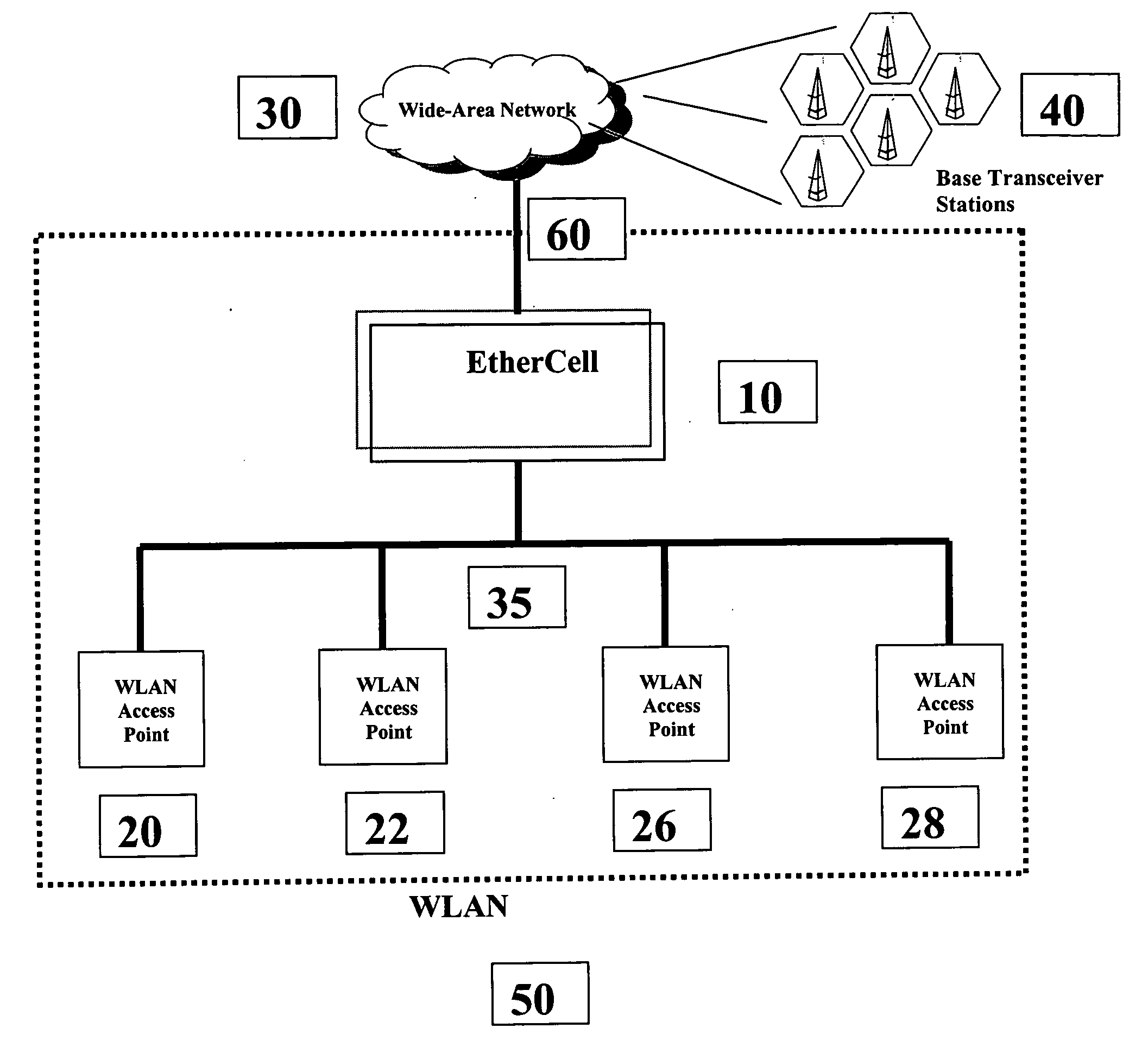
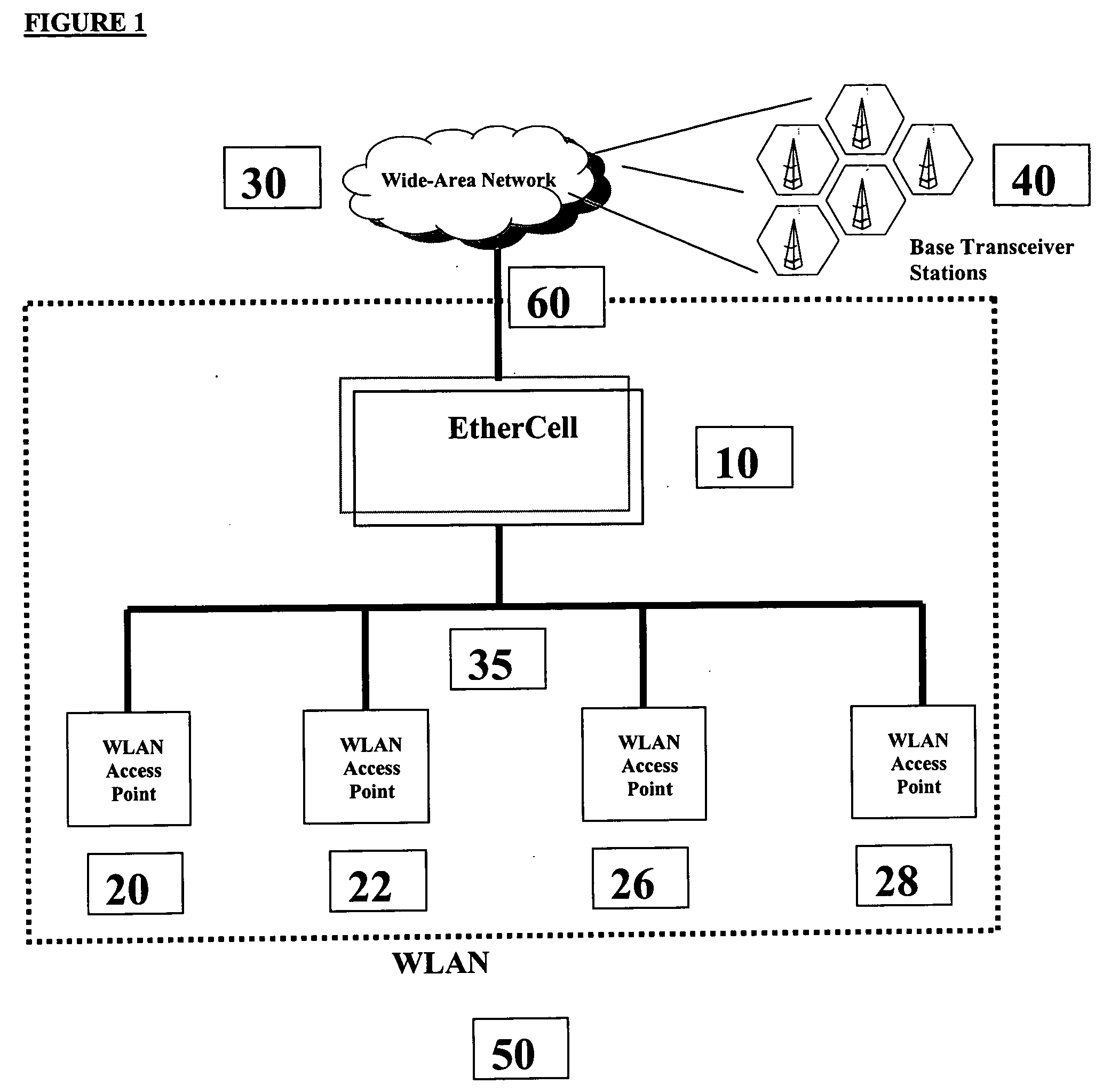
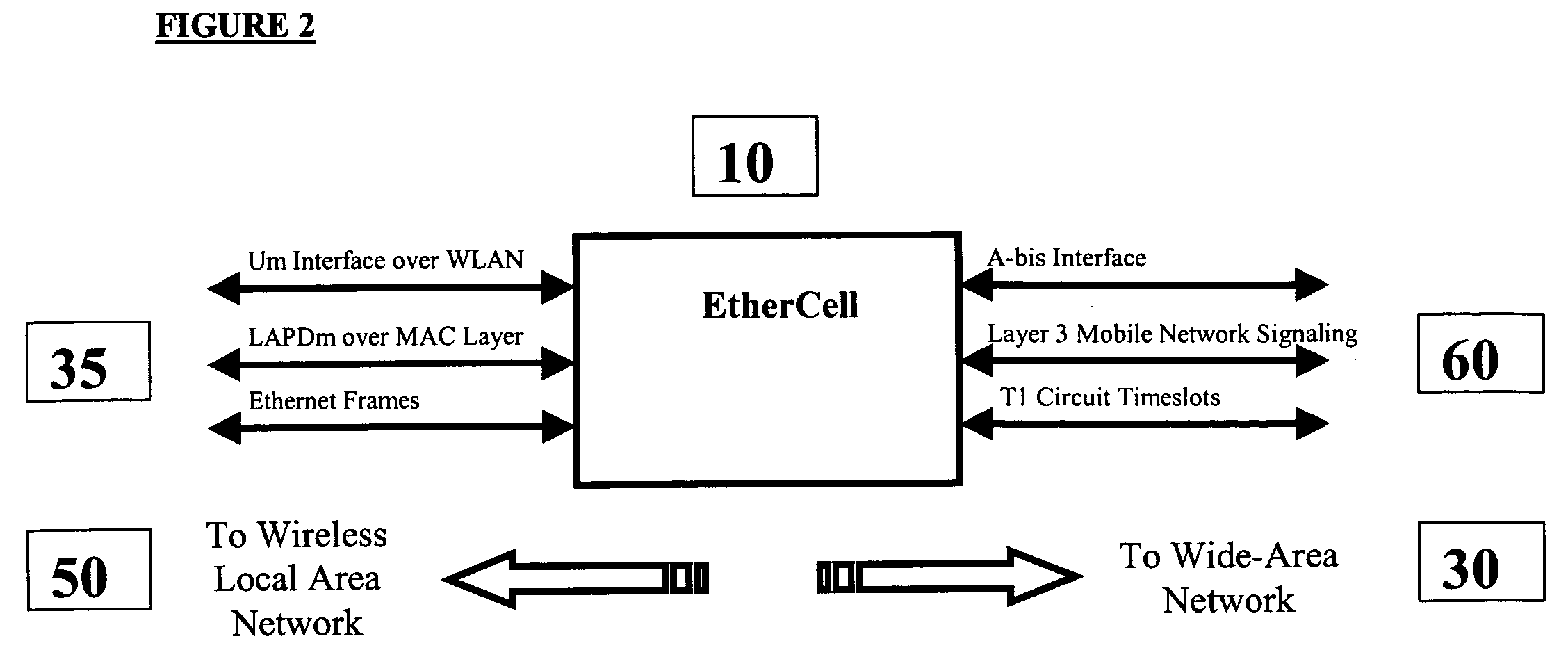
EtherCell
InactiveUS20040105434A1Frequency-division multiplex detailsNetwork topologiesBody area networkAir interface
Methods and apparatus for performing call-processing functions of wide-area mobile voice calls over a wireless local-area network (WLAN) are provided. Such methods allow the extension of wide-area call-processing protocols such as Global System for Mobile Communications (GSM) or Code Division Multiple Access (CDMA) into a WLAN which uses a completely different air-interface than GSM or CDMA. Such methods enable wide-area mobile voice communications to be available in a WLAN without the use of any Voice over IP (VOIP) related technologies such as SIP or H.323.
Owner:BAW ALLAN
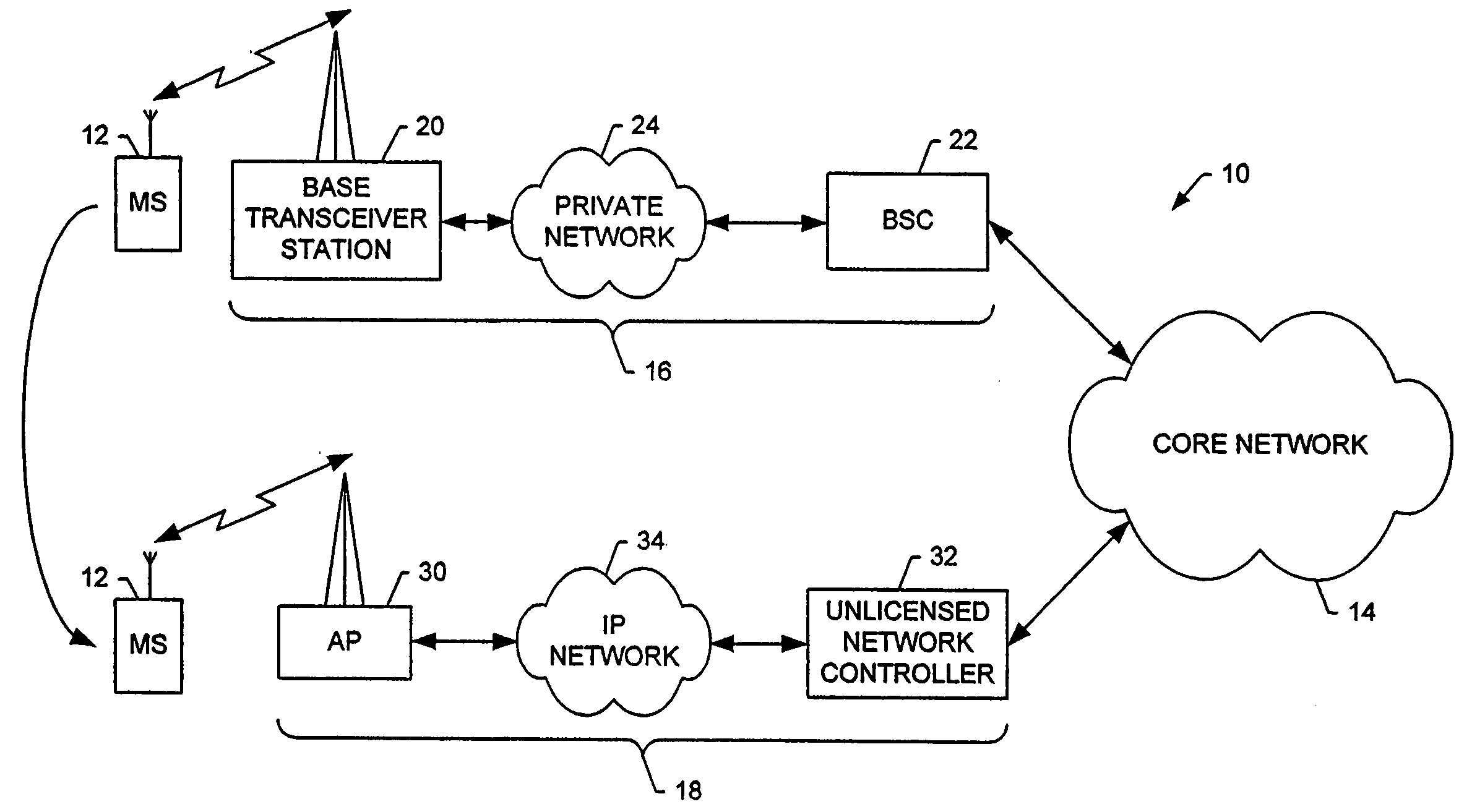
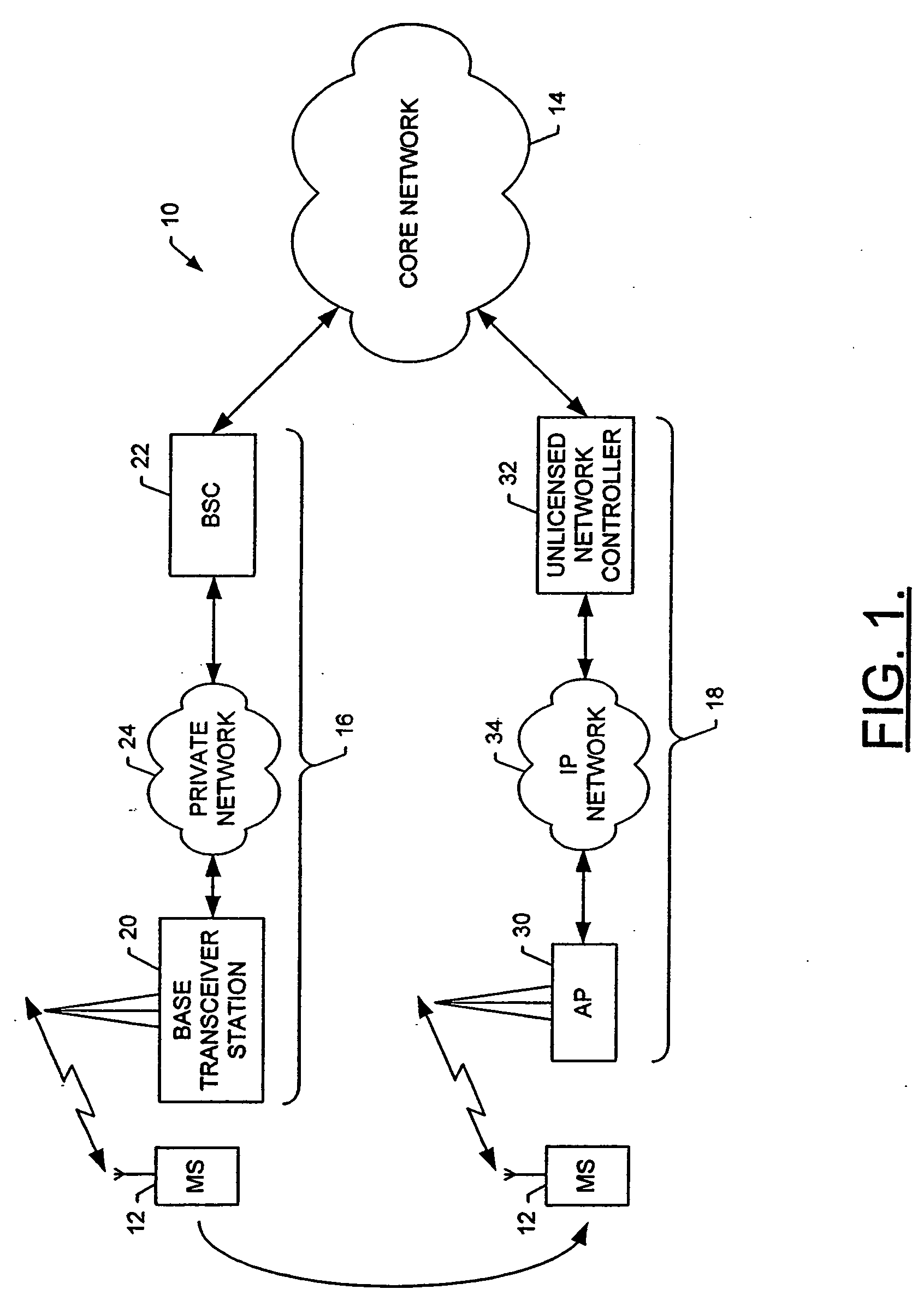
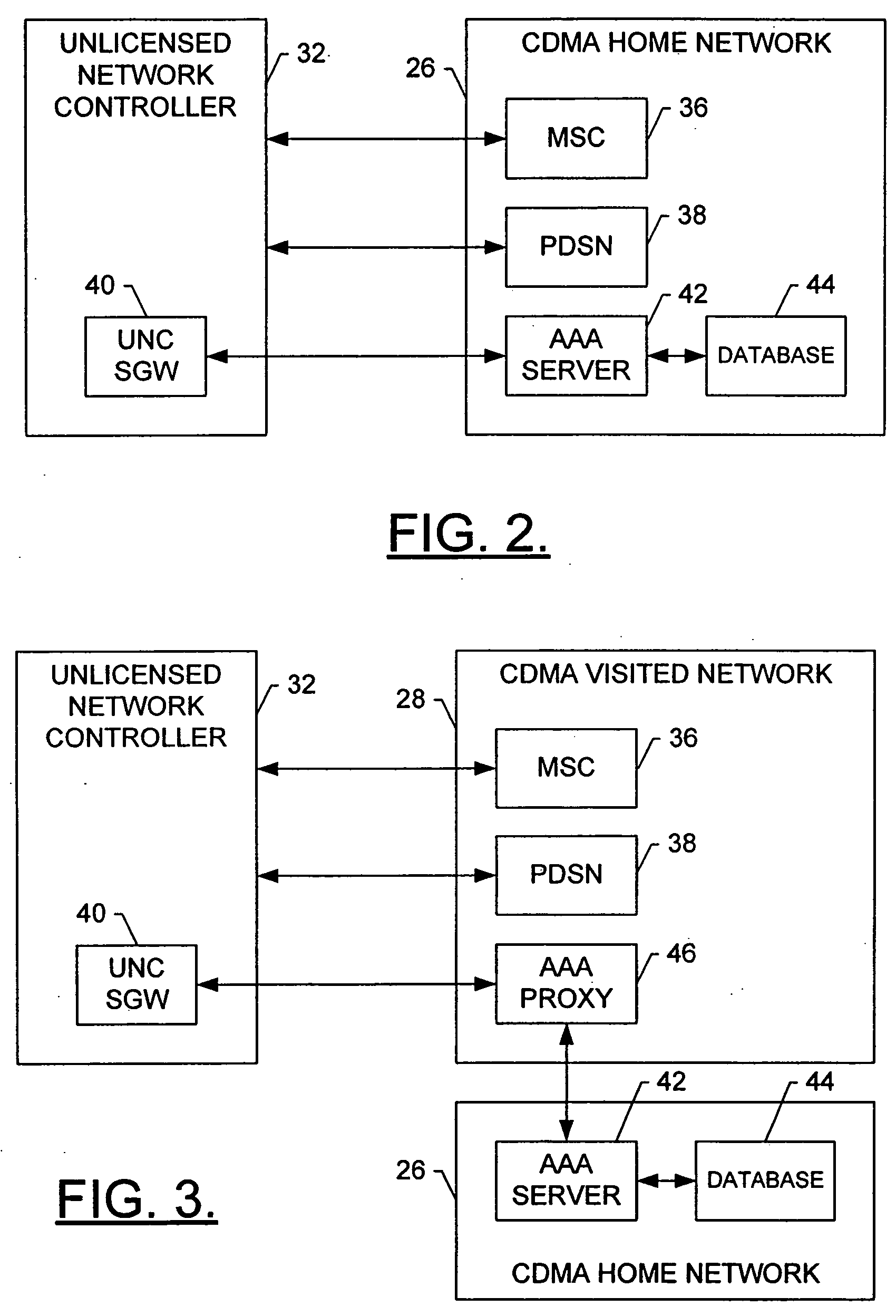
Method, system and mobile station for handing off communications from a cellular radio access network to an unlicensed mobile access network
InactiveUS20060094431A1Convenient handoverEasy transitionRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsWireless commuication servicesAccess networkCellular radio
A method, system and mobile station for handing off communications from a cellular radio access network, such as a code division multiple access (CDMA) radio access network, to an unlicensed mobile access network (UMAN) are provided. The handoff may be effected by a signaling sequence between the mobile station, an unlicensed network controller of the UMAN, a base station controller of the cellular radio access network and the core network. In this signaling sequence, the UMAN may be identified in various manners, such as by means of an otherwise unassigned pilot PN offset or by means of a band class and an invalid frequency.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
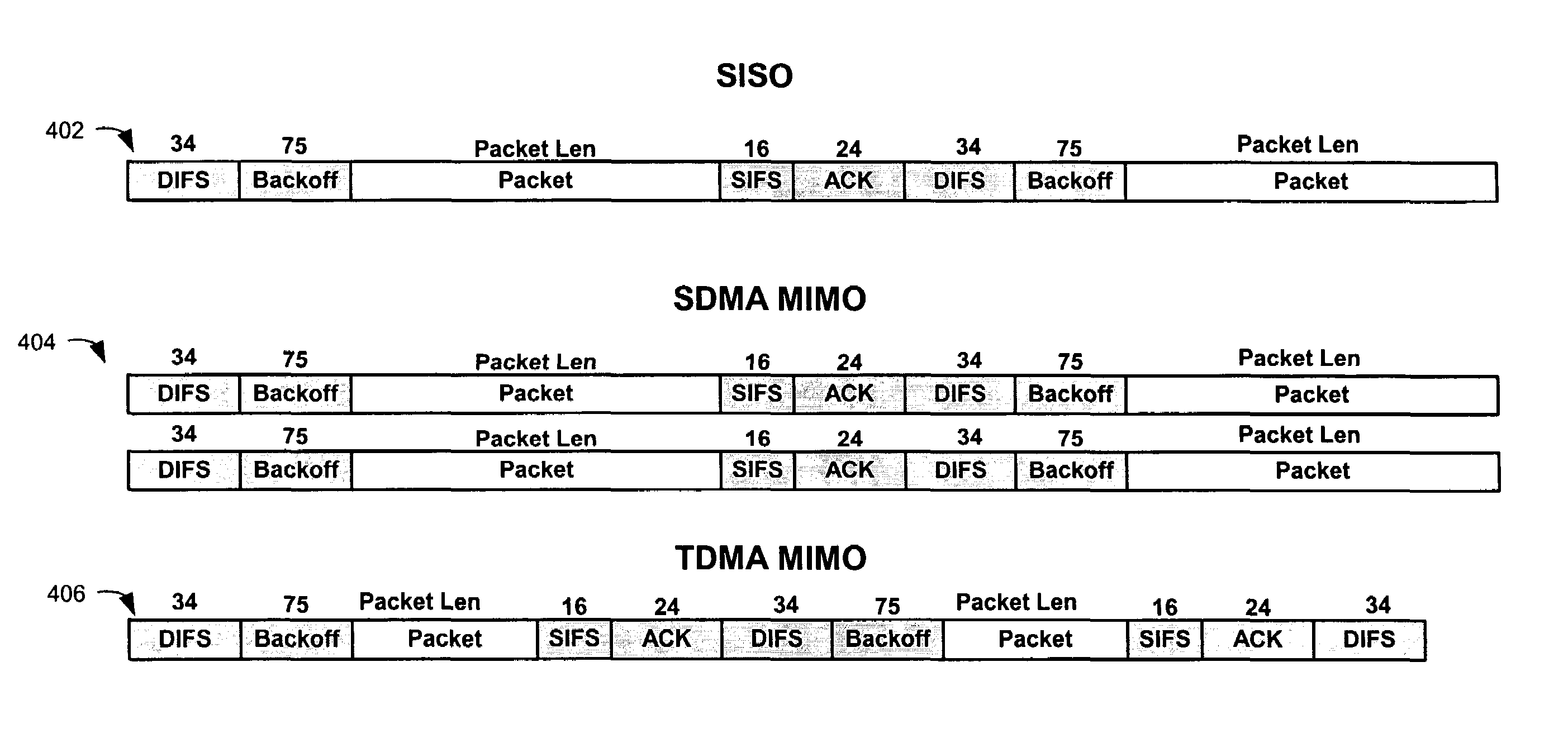
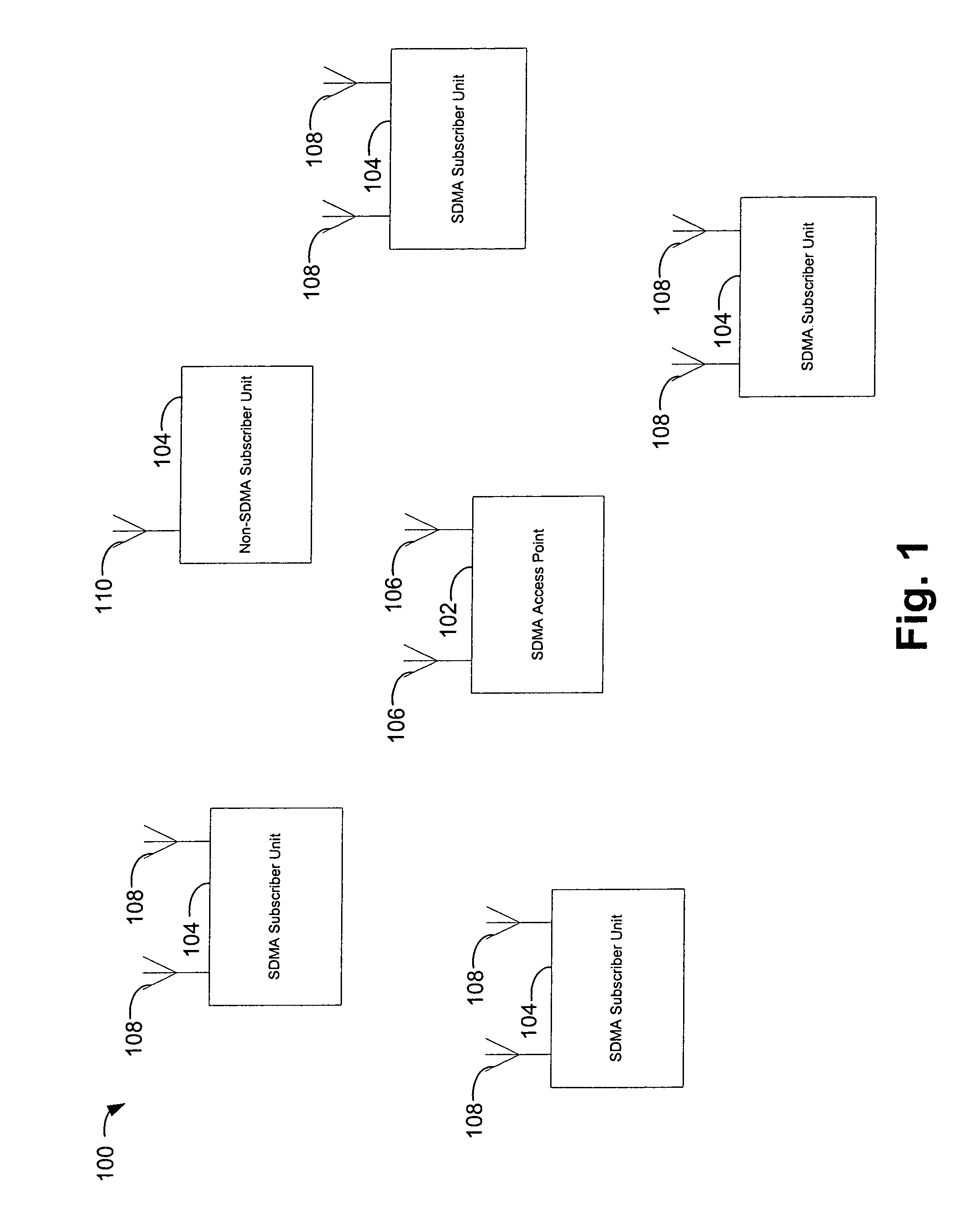
Spatial division multiple access for wireless networks
ActiveUS7352718B1Doubling and of network throughputIncrease system capacityPower managementPolarisation/directional diversityWireless mesh networkSystem capacity
Multiple Input Multiple Output (MIMO) technology in conjunction with the IEEE 802.11 standard enables simultaneous communication of data packets to or from multiple users in the same frequency. Spatial divisional multiple access (SDMA) is thus provided. In this way, system capacity can be increased to an extent that depends on available antenna resources and the multipath characteristics of the communication channel. Doubling or quadrupling of network throughput can be achieved.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
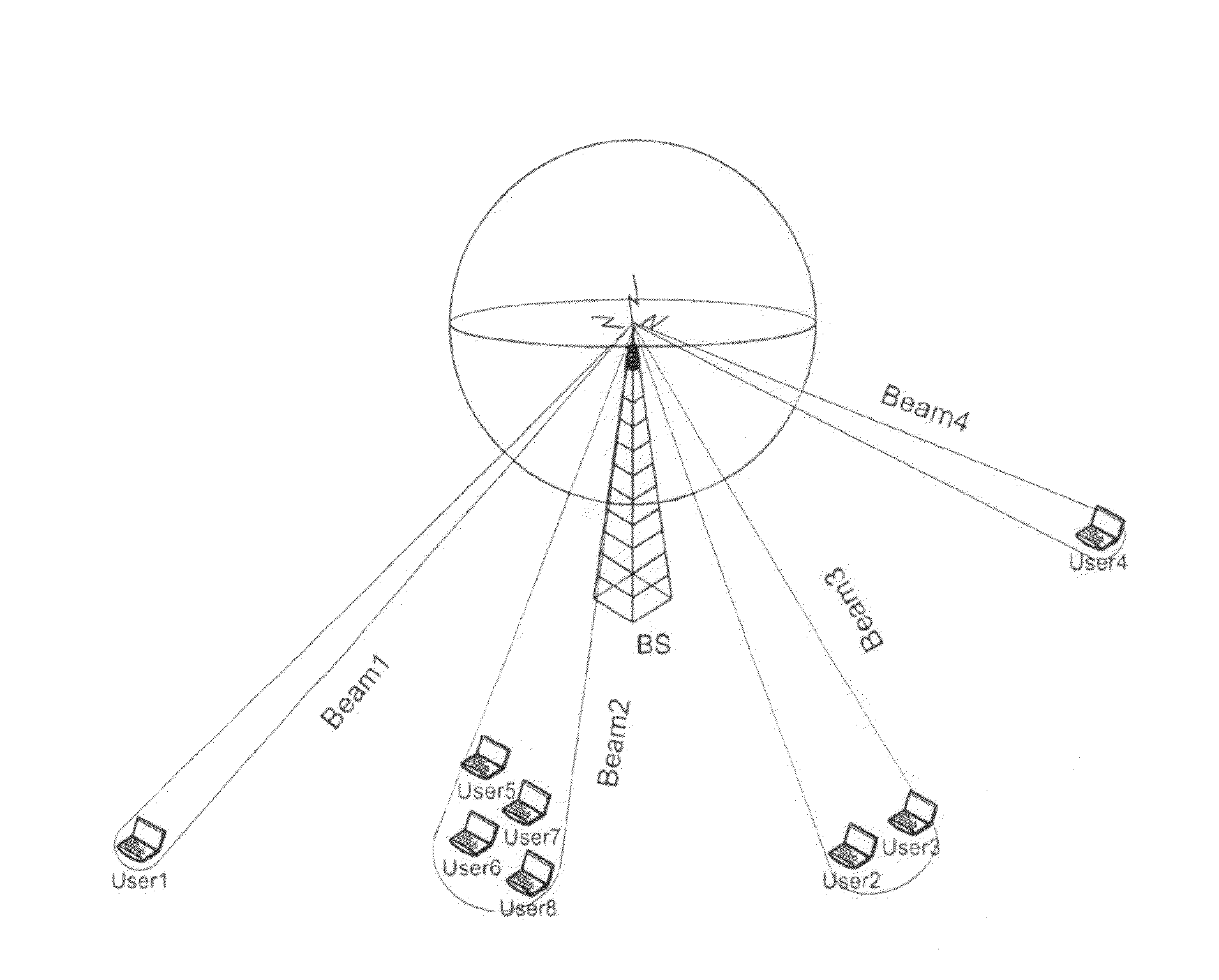
Providing space division multiple access in a wireless network
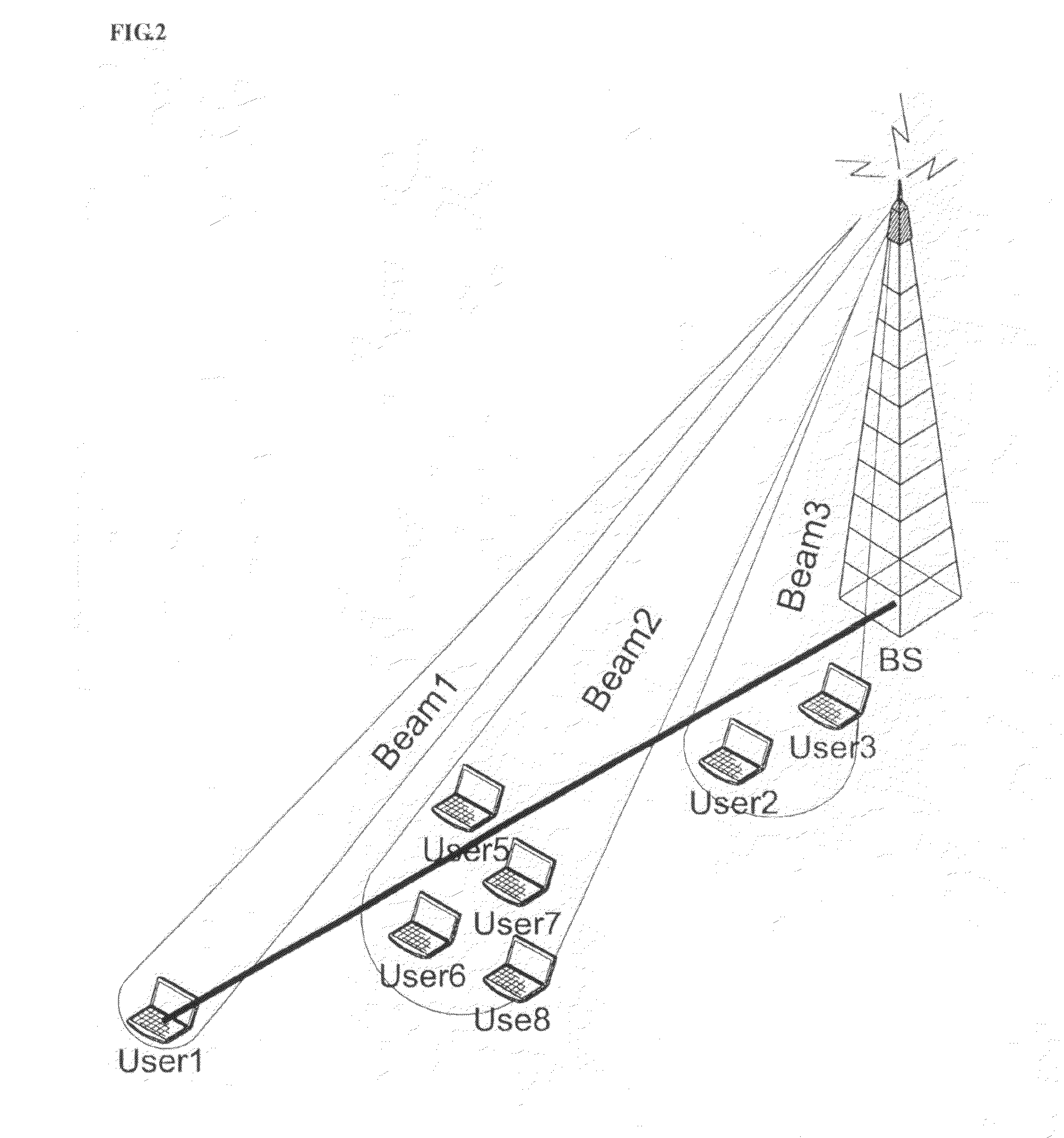
To provide space division multiple access in a wireless network, plural beams are transmitted within a cell segment. Different information sets are sent in the corresponding plural beams, where one or more of the information sets are detectable by a mobile station depending upon a location of the mobile station in the cell segment. An indication responsive to which of the different information sets is detected by the mobile station is received, and beam selection from among the plural beams is performed according to the received indication.
Owner:MALIKIE INNOVATIONS LTD
Methods and apparatus for access control client assisted roaming
InactiveUS20120108206A1Expand coverageUnauthorised/fraudulent call preventionAssess restrictionCost effectivenessCode division multiple access
Methods and apparatus that allow a device to migrate wireless service across multiple wireless networks. In one exemplary embodiment, the present invention enables storing and switching between multiple Electronic Subscriber Identity Modules (eSIM), where each eSIM is specific to a different carrier network. By loading the appropriate eSIM, the user device can authenticate itself with the selected carrier, rather than roaming. During roaming operation, the user equipment can load one or more of the previously stored eSIMs. Selection of the eSIM can be done manually by the user or can be driven by the user equipment based on desired context; for example, based on carrier signal strength, cost-effectiveness, etc. Support for multiple radio technologies also allows universal connectivity for wireless devices, even spanning previously incompatible technologies such as GSM (Global Standard for Mobile Communications), CDMA (Code Division Multiple Access), etc.
Owner:APPLE INC
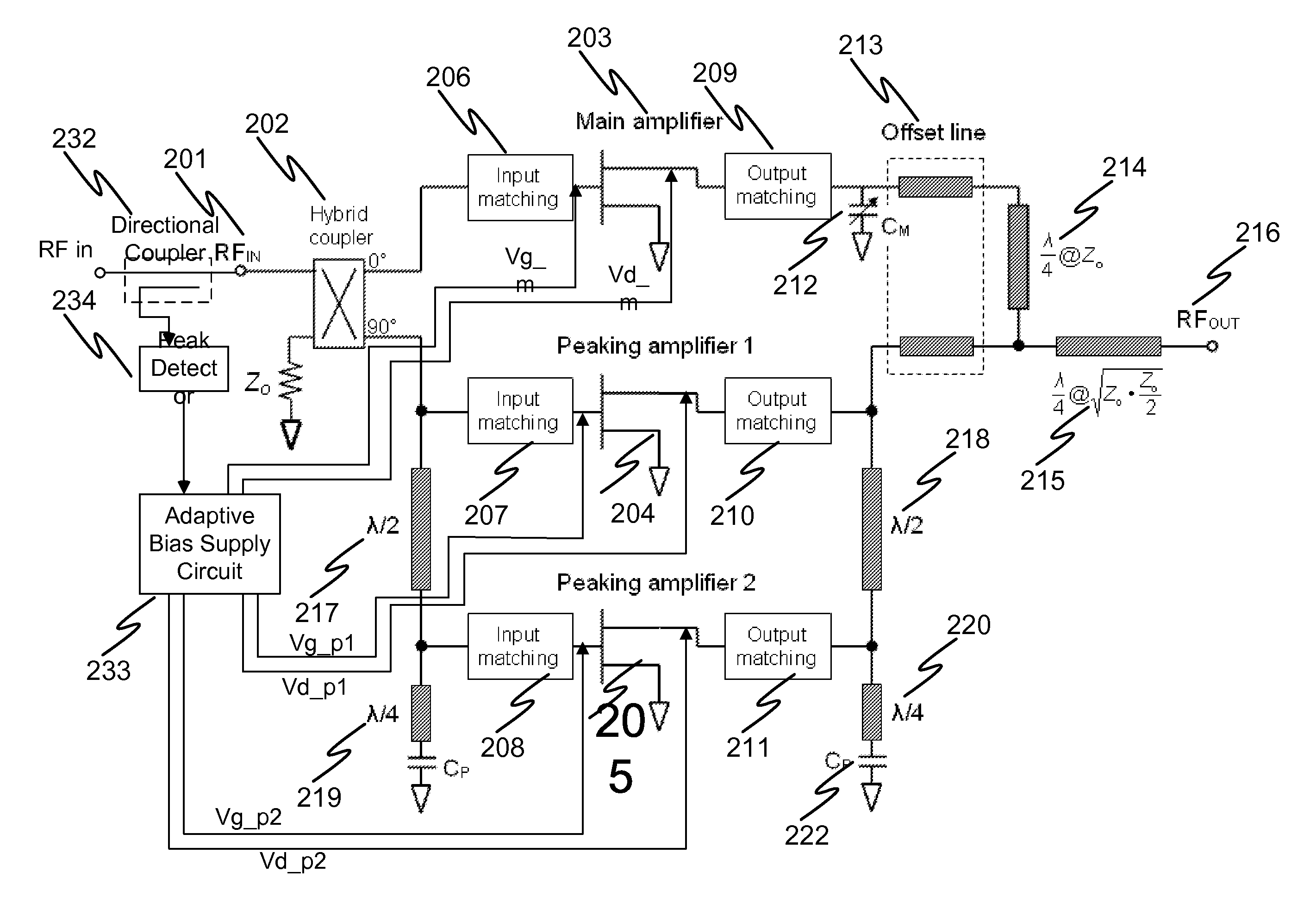
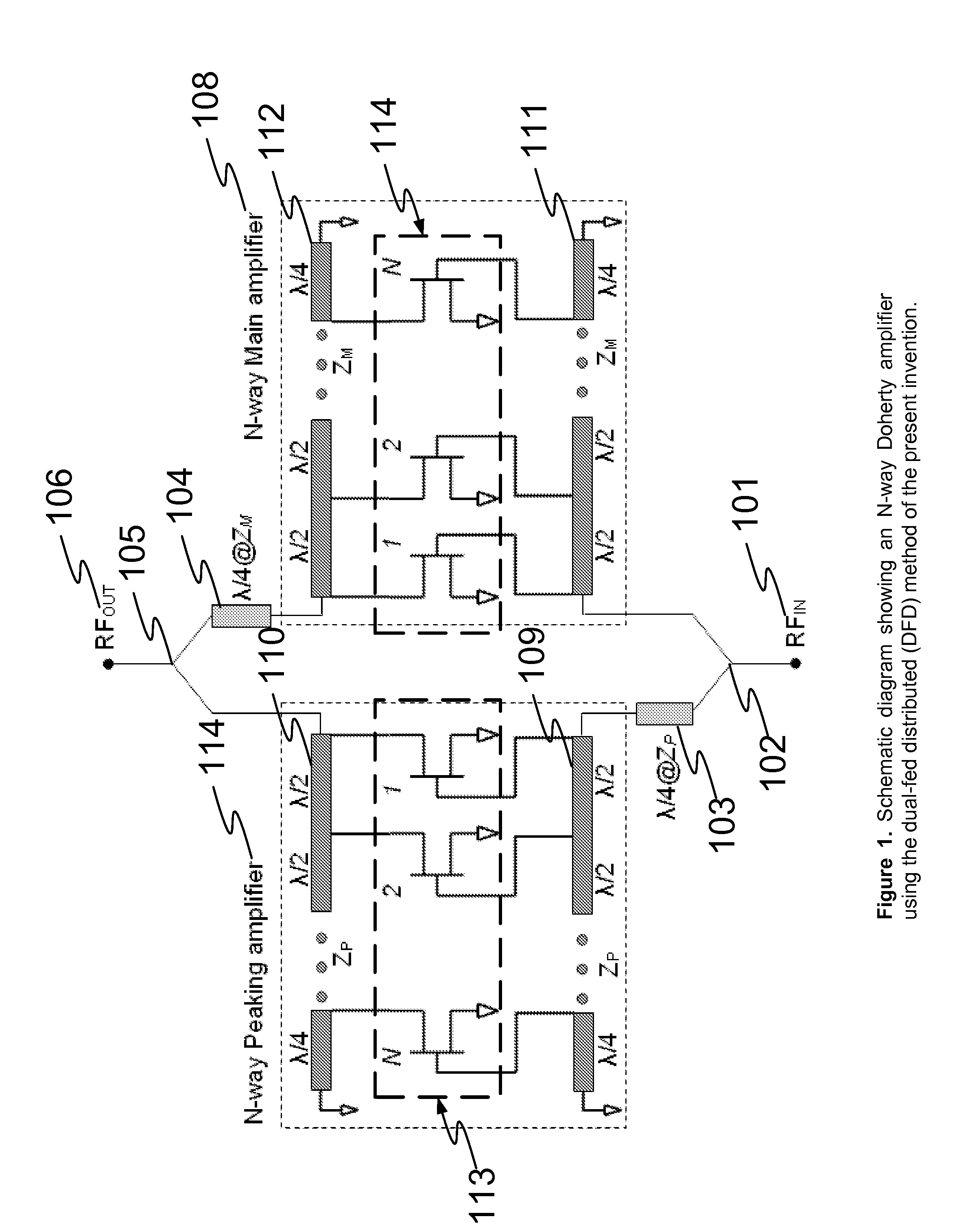
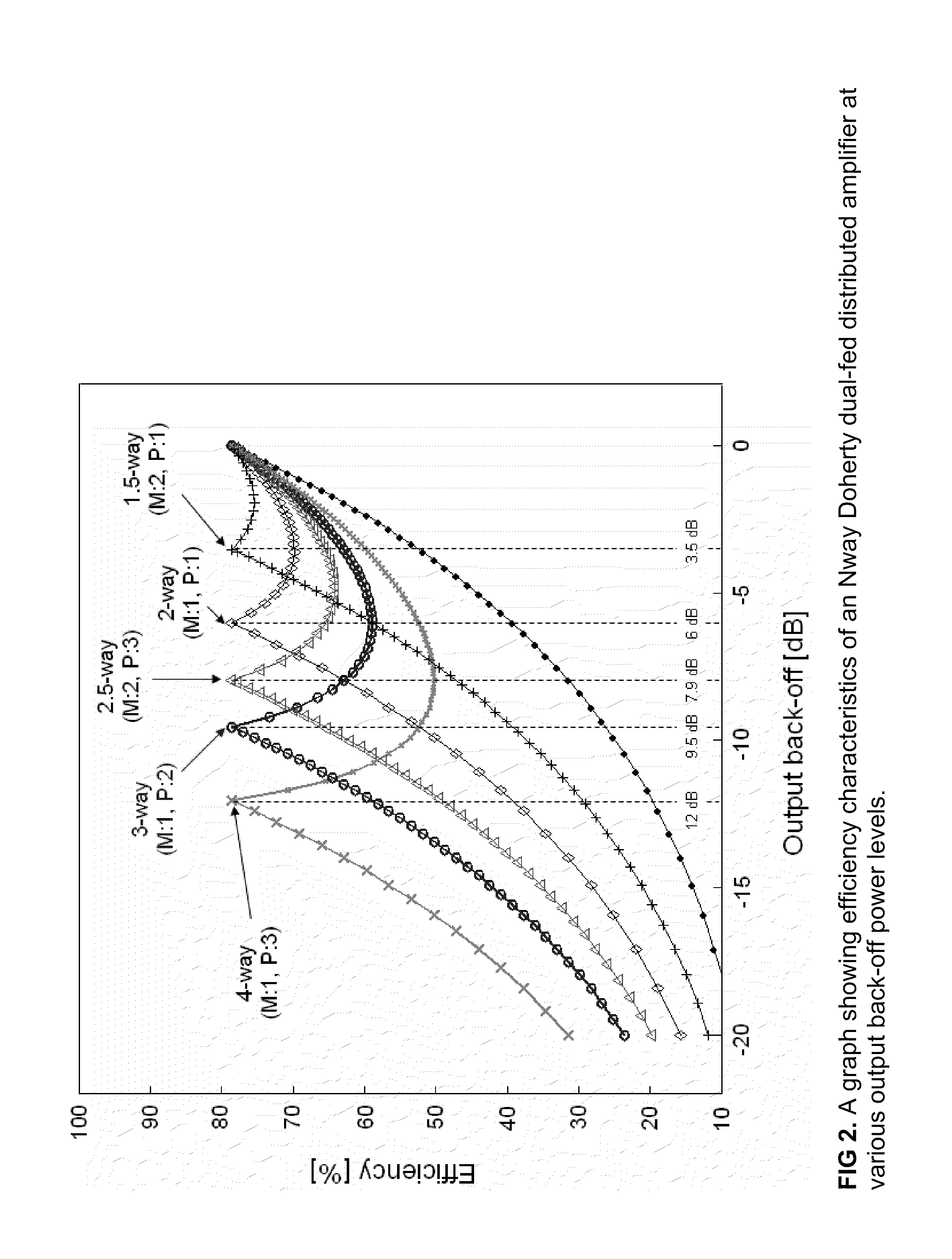
N-way Doherty distributed power amplifier with power tracking
ActiveUS8274332B2Improve performanceIncrease productionNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsAmplifier combinationsAdaptive biasMultiplexing
Owner:DALI SYST LTD
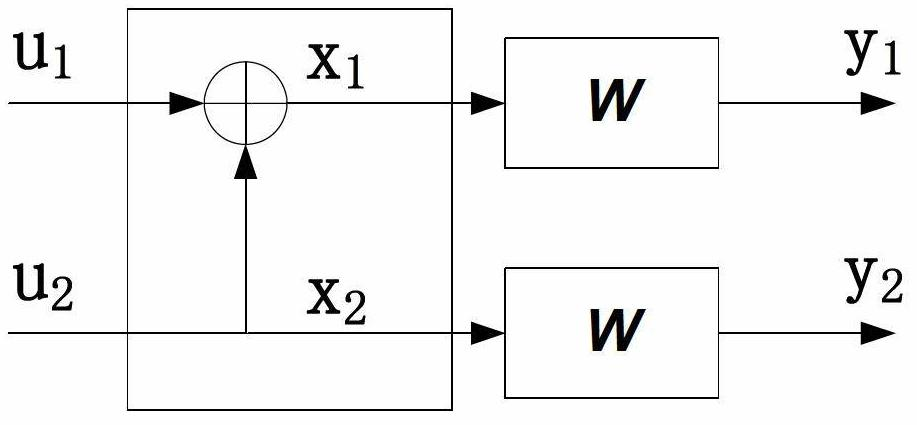
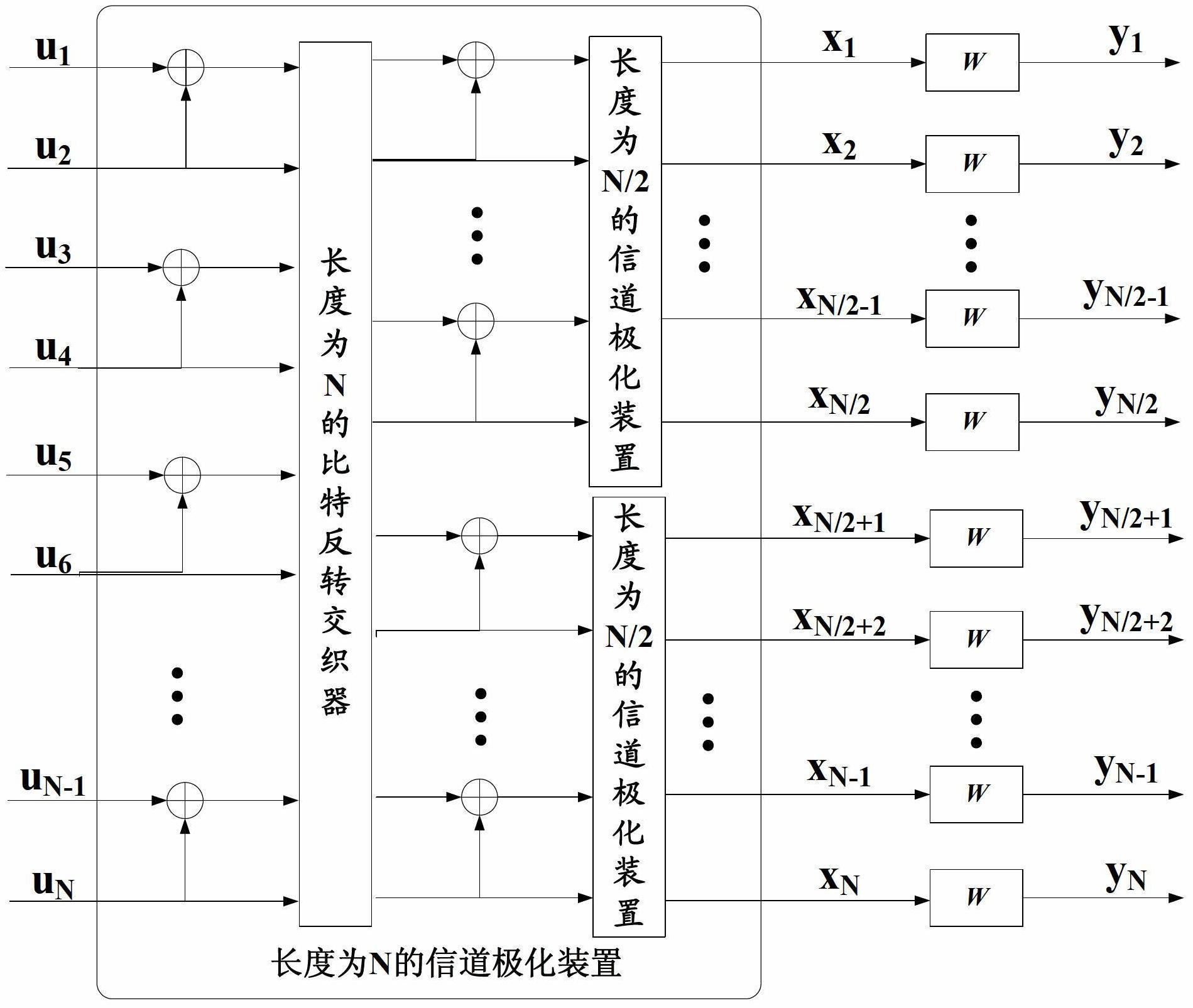
Polarization code decoding method for cyclic redundancy check assistance
InactiveCN102694625AStrong error correction abilityReduce operational complexityError preventionError correction/detection using linear codesCommunications systemCode division multiple access
The invention relates to a polarization code decoding method for cyclic redundancy check assistance. When a polarization code is decoded, in all the routes with cyclic redundancy check values of corresponding bit estimation sequences of being zero from a root node to leaf nodes on a code tree corresponding to the polarization code, one route with maximum reliability metric value is searched by taking a list or stack as assistance for route search, and the bit estimation sequence corresponding to the route is output as a decoding result. The method comprises the following operation steps of: determining parameters according to a search assistance method, constructing an auxiliary structure of the decoding method, searching a candidate bit estimation sequence and executing cyclic redundancy check. By adopting the method disclosed by the invention, error correcting capability of a communication system which adopts the polarization code as channel coding is greatly improved, operation steps are simpler, and operation complexity is equivalent to or even lower than that of a Turbo code coding and decoding method used in a WCDMA (wideband code division multiple access) system, thus the method disclosed by the invention has a good practical prospect.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Pilot signals for synchronization and/or channel estimation
InactiveUS6987746B1Optimal autocorrelation resultEliminate and prevent sidelobesSynchronisation arrangementTime-division multiplexCode division multiple accessCorrelation function
The frame words of the preferred embodiment are especially suitable for frame synchronization and / or channel estimation. By adding the autocorrelation and cross-correlation functions of frame words, double maximum values equal in magnitude and opposite polarity at zero and middle shifts are obtained. This property can be used to slot-by-slot, double-check frame synchronization timing, single frame synchronization and / or channel estimation and allows reduction of the synchronization search time. Further, the present invention allows a simpler construction of a correlator circuit for a receiver. A frame synchronization apparatus and method using an optimal pilot pattern is used in a wide band code division multiple Access (W-CDMA) next generation mobile communication system. This method includes the steps of storing column sequences demodulated and inputted by slots, in a frame unit, in detecting frame synchronization for upward and downward link channels; converting the stored column sequences according to a pattern characteristic related to each sequence by using the pattern characteristic obtained from the relation between the column sequences; adding the converted column sequences by slots; and performing a correlation process of the added result to a previously designated code column.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
System for using rapid acquisition spreading codes for spread-spectrum communications
InactiveUS20050265430A1Increase profitEnergy efficient ICTRadio transmission for post communicationCode division multiple accessCarrier signal
A system for rapidly acquiring a spreading code, used in a code division multiple access (CDMA) system, comprises a generator for generating a first long code and a second long code, with each long code having a length of N chips. The first long code is different from the second long code. A transmitter transmits the first long code and the second long code at a first phase angle and at a second phase angle, respectively, on a carrier signal over a communications channel using radio waves. The first long code and the second long code may be transmitted at an in-phase (I) angle and at a quadrature-phase (Q) angle, respectively, on the carrier signal. From the communications channel, an I acquisition circuit and a Q acquisition circuit may acquire, in parallel, the first long code and the second long code from the I angle and the Q angle, respectively, of the carrier signal by searching, in parallel, N / 2 chips of the first long code and the second long code.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL TECH CORP
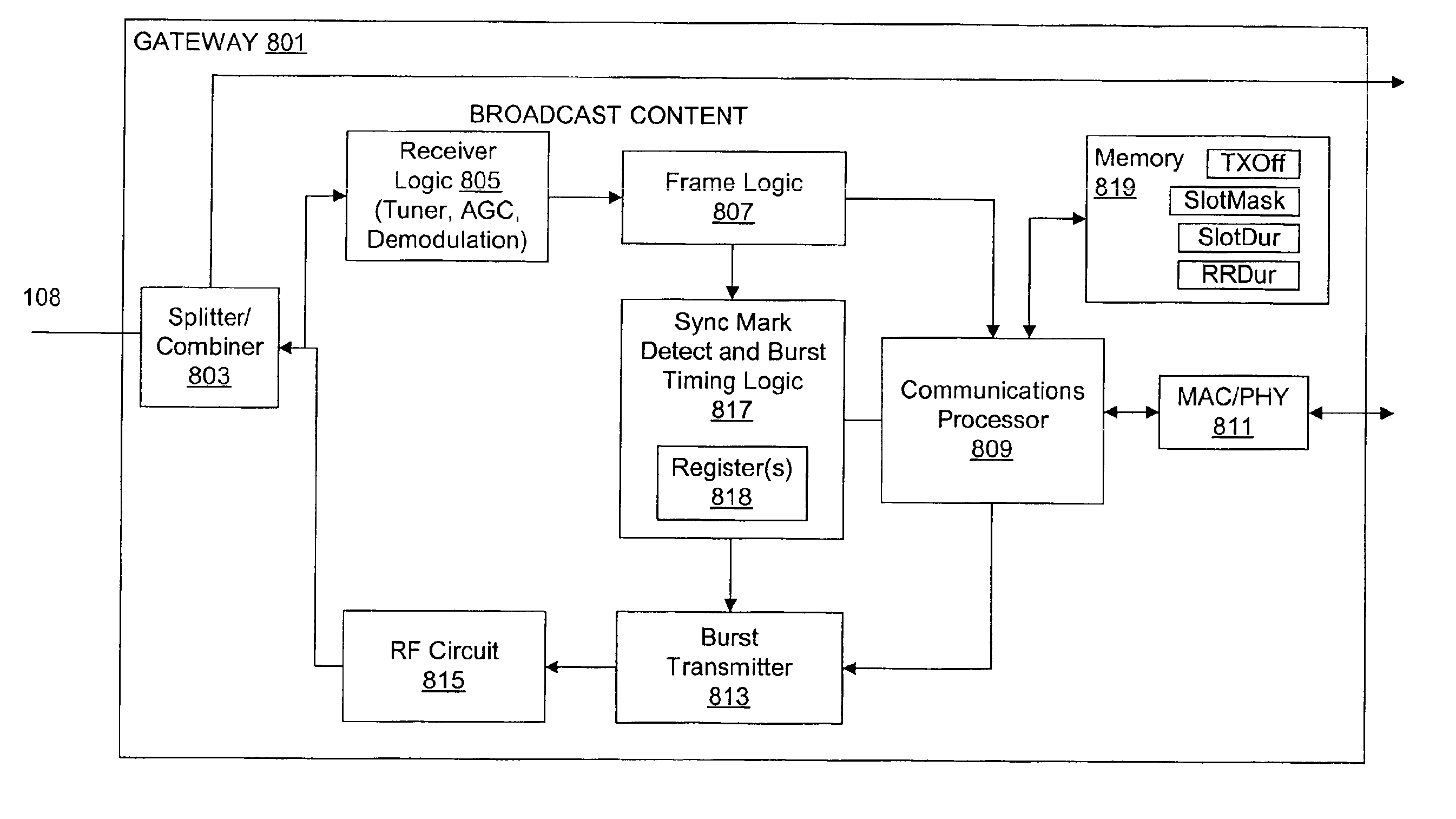
Time division multiple access over broadband modulation method and apparatus
InactiveUS6891841B2Accurate resolutionBroadband local area networksTime-division optical multiplex systemsTime division multiple accessBurst transmission
A communication system is disclosed for providing dedicated bandwidth to at least one subscriber location for transmitting to a common point of distribution via an HFC network. In an embodiment of the invention, the communication system includes a channel interface module and at least one gateway coupled across the HFC network. The channel interface module is located at the point of distribution and includes a transmitter that transmits a windowing signal via the HFC network. The gateway is located at a subscriber location and includes a processor that encapsulates subscriber data into data cells suitable for burst transmission, receive logic that receives the windowing signal, timing logic that indicates burst transmission times only at programmed time slots within each of repeating transmission windows based on the windowing signal and a predetermined transmission timing offset, and a burst transmitter that burst transmits subscriber data cells in a predetermined upstream frequency channel when indicated by the timing logic.
Owner:INCEPTIA +1
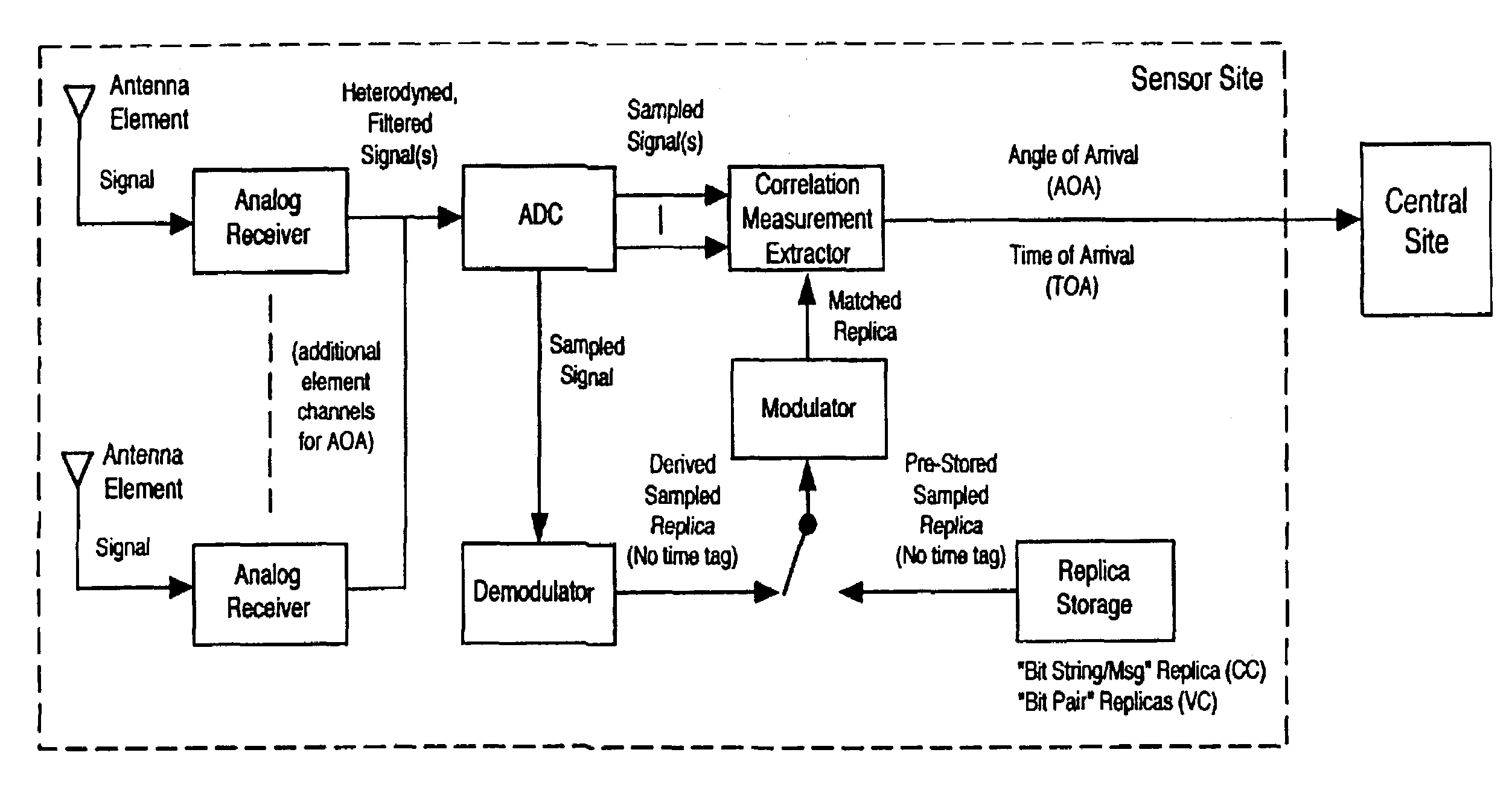
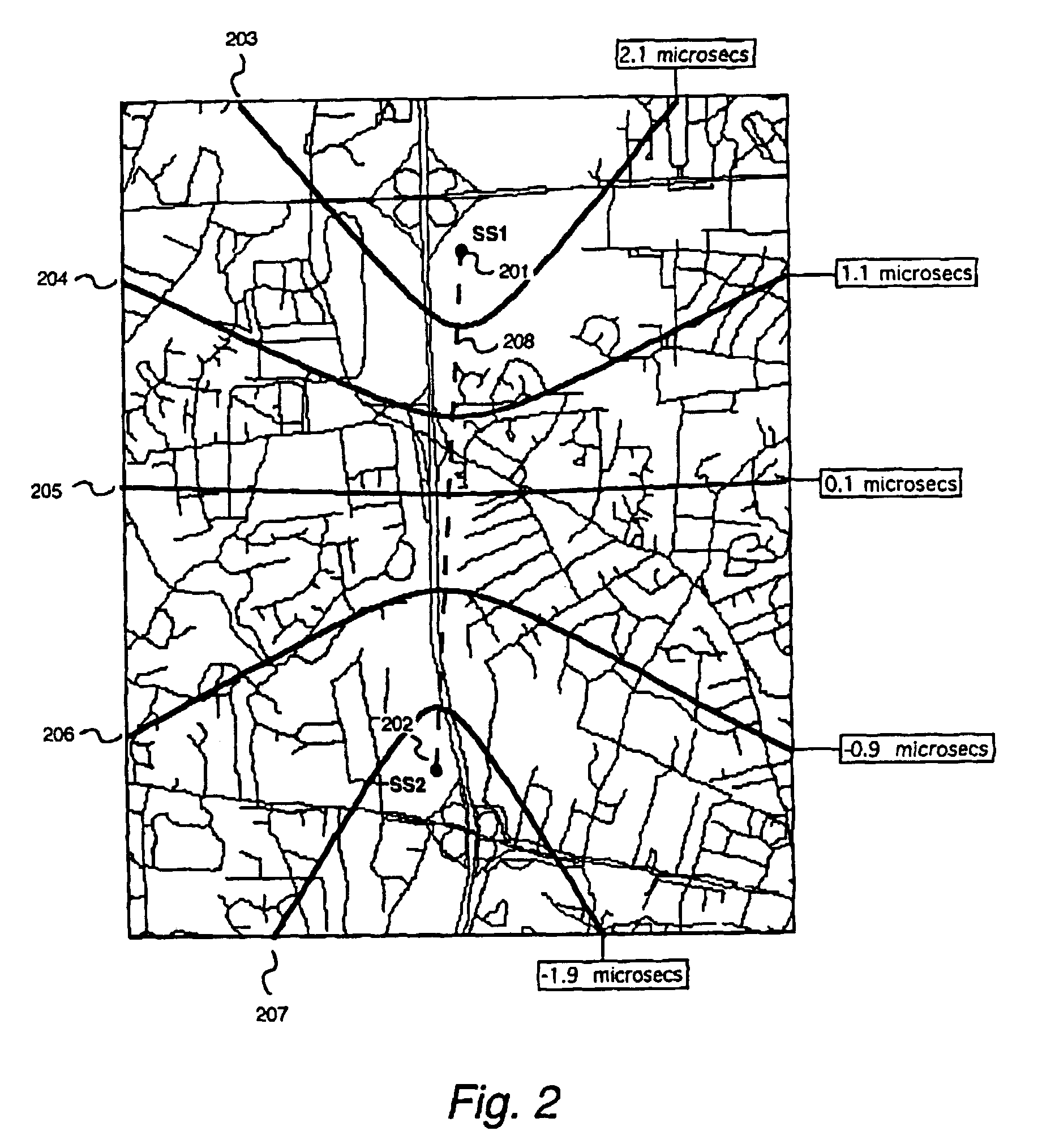
Robust, efficient, localization system
InactiveUS7340259B2Quick responseEasy to measure in real timeDirection finders using radio wavesPosition fixationLocalization systemCode division multiple access
Replica correlation processing, and associated representative signal-data reduction and reconstruction techniques, are used to detect signals of interest and obtain robust measures of received-signal parameters, such as time differences of signal arrival and directional angles of arrival, that can be used to estimate the location of a cellularized-communications signal source. The new use in the present invention of signal-correlation processing for locating communications transmitters. This enables accurate and efficient extraction of parameters for a particular signal even in a frequency band that contains multiple received transmissions, such as occurs with code-division-multiple-access (CDMA) communications. Correlation processing as disclosed herein further enables extended processing integration times to facilitate the effective detection of desired communications-signal effects and replication measurement of their location-related parameters, even for the communications signals modulated to convey voice conversations or those weakened through propagation effects. Using prior, constructed, signal replicas in the correlation processing enables elimination of the inter-site communications of the signal representations that support the correlation analyses. Reduced-data representations of the modulated signals for voiced conversation, or for the variable components of data communications, are used to significantly reduce the inter-site communications that support the correlation analyses.
Owner:TRUE POSITION INC
Access to communications systems
InactiveUS6850504B1Minimal costProvide flexibilityNetwork traffic/resource managementRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsCommunications systemCode division multiple access
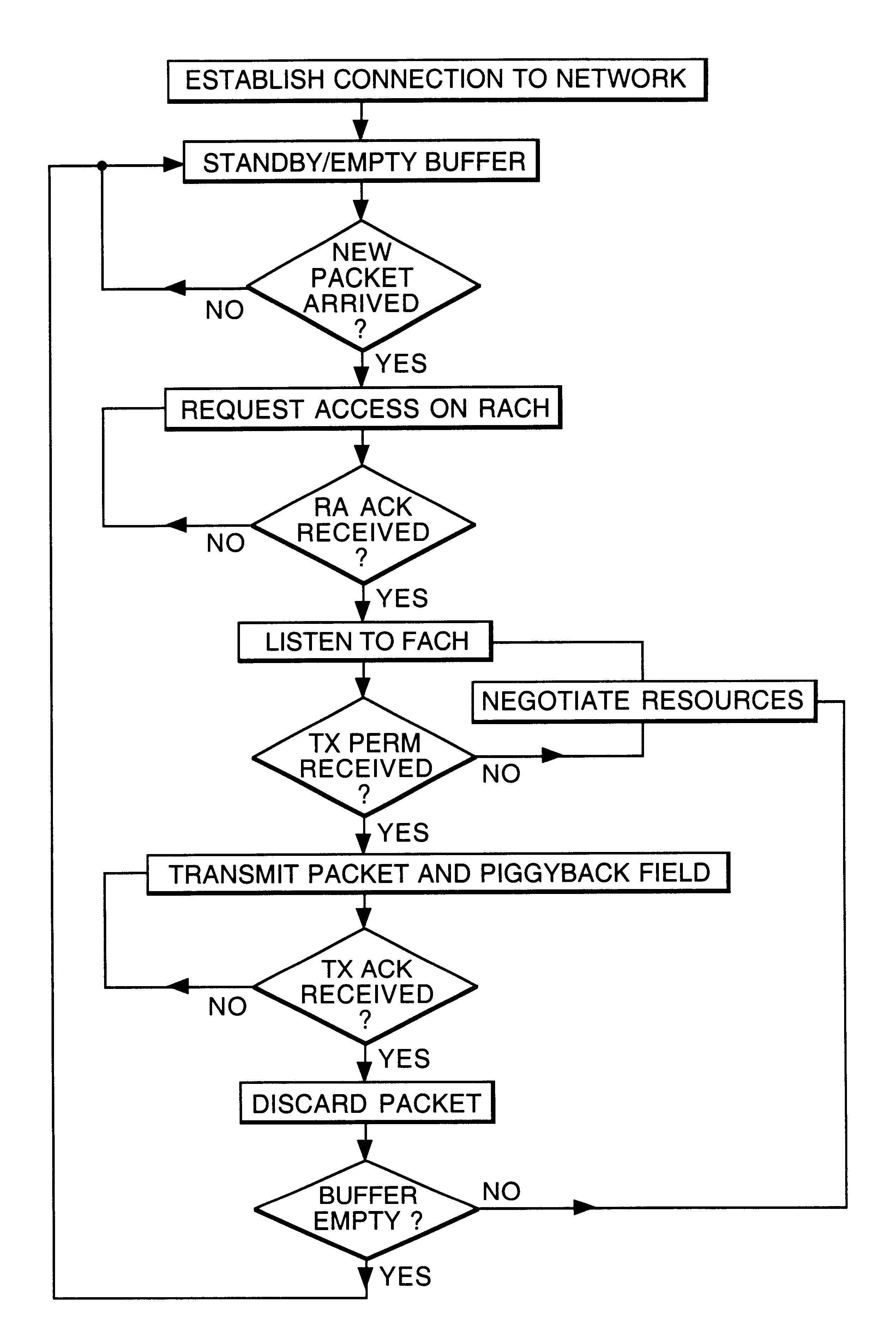
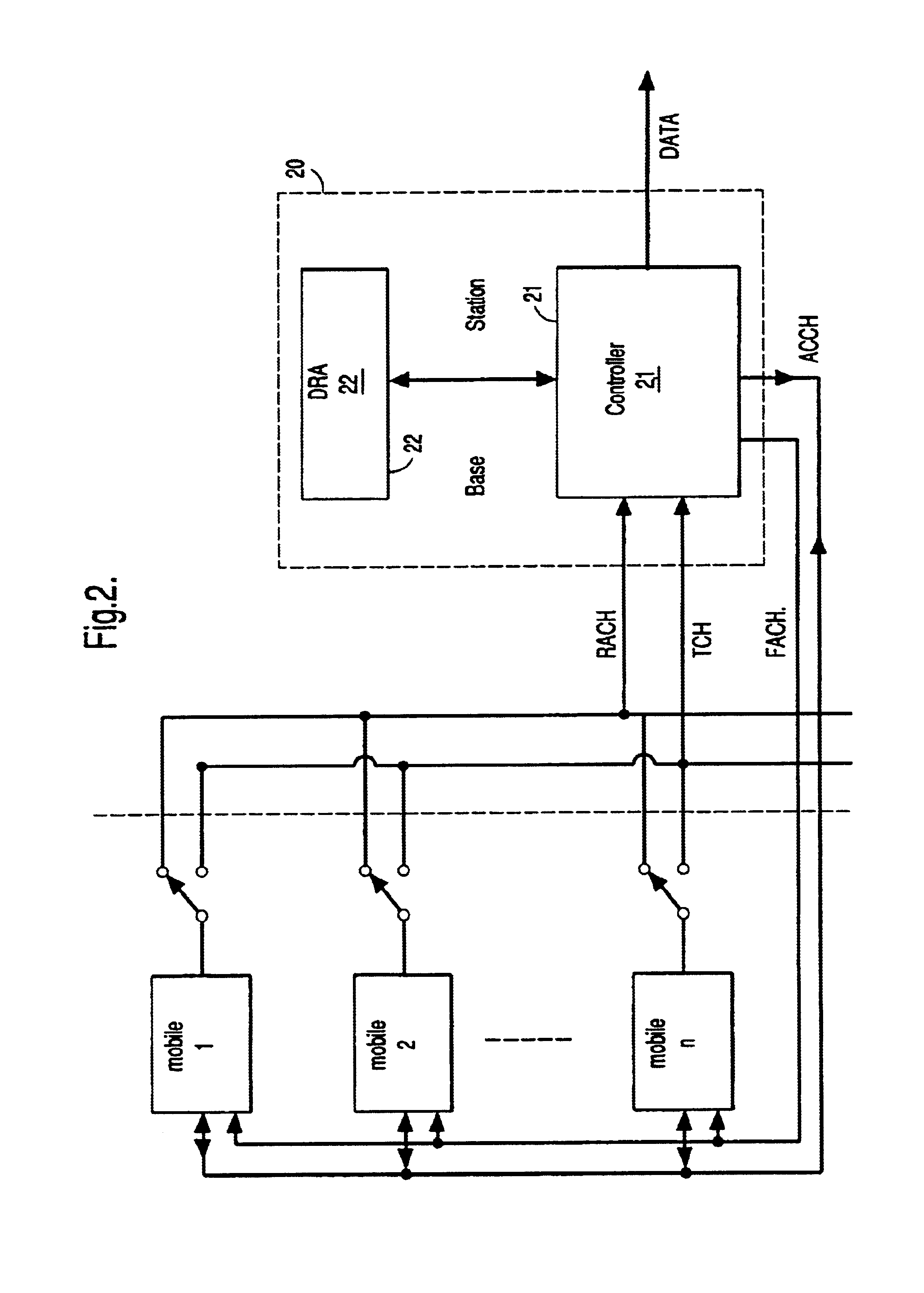
In a code division multiple access (CDMA) wireless system, a wireless terminal transmits information packets to a communications systems controller. Each information packet comprises a piggy back field which indicates to the communication systems controller resources requested by the wireless terminal for transmission of subsequent information packets.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
Multimode/Multiband Mobile Station and Method for Operating the Same
InactiveUS20070243832A1Reduce power consumptionLow sampling rateTransmissionCode division multiple accessMobile station
A multimode / multiband mobile station and a method for operating the same are provided. A transmission module transmits multimode / multiband signals through transmitters. A reception module receives radio signals for different services of the same frequency band among multimode / multiband signals through receivers for the same frequency band, and receives radio signals of different frequency bands among the multimode / multiband signals through receivers for the different frequency bands. As compared with the conventional mobile station, the multimode / multiband mobile station can reduce the number of receivers by making use of one receiver to receive radio signals for different services of the same frequency band. The multimode / multiband mobile station can use a duplexer of the conventional frequency division duplex (FDD) technique (e.g., wideband code division multiple access (WCDMA)) in a time division duplex (TDD) technique (e.g., Global System for Mobile Communication (GSM) 850 or Personal Communication Service (PCS) 1900).
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
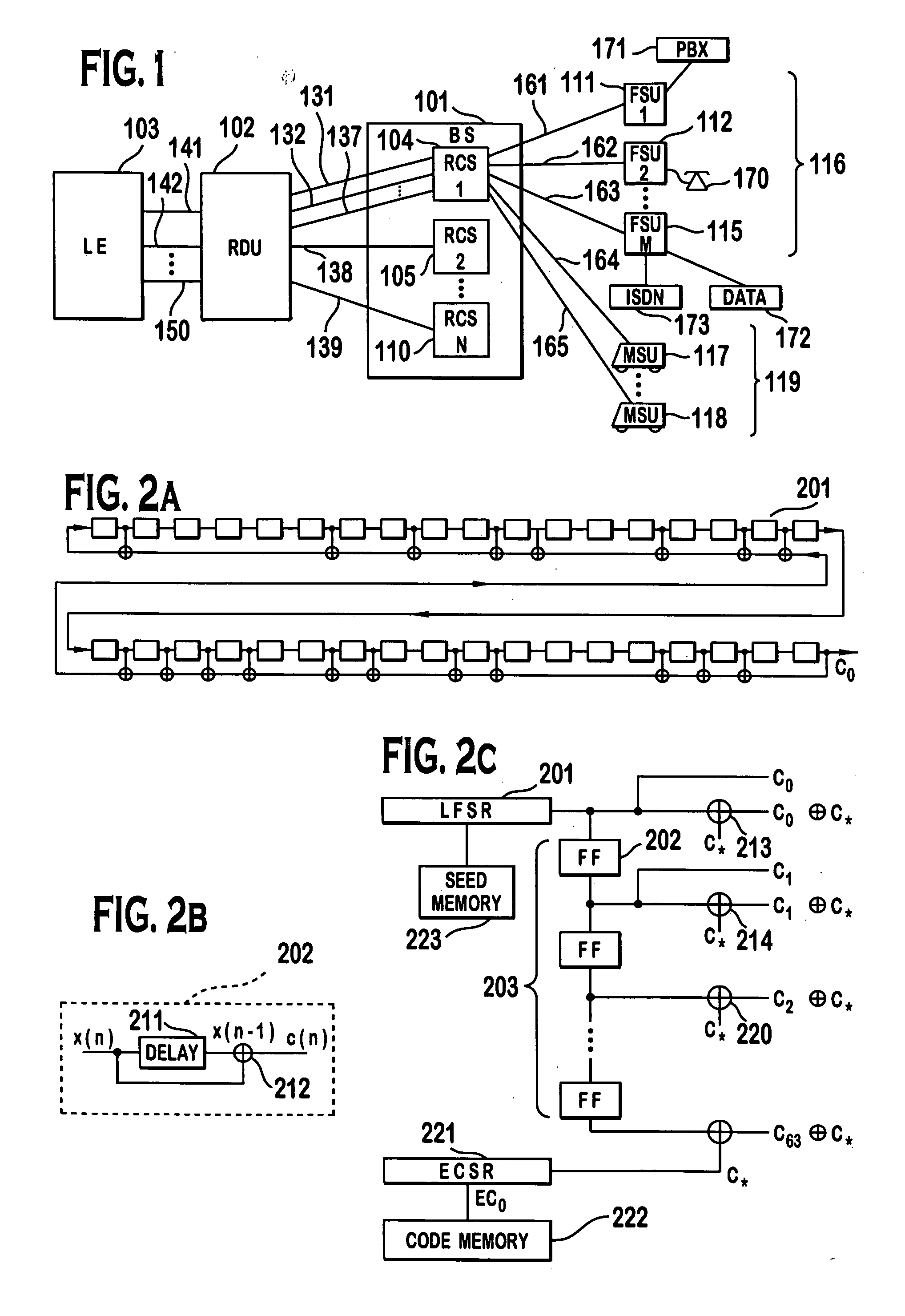
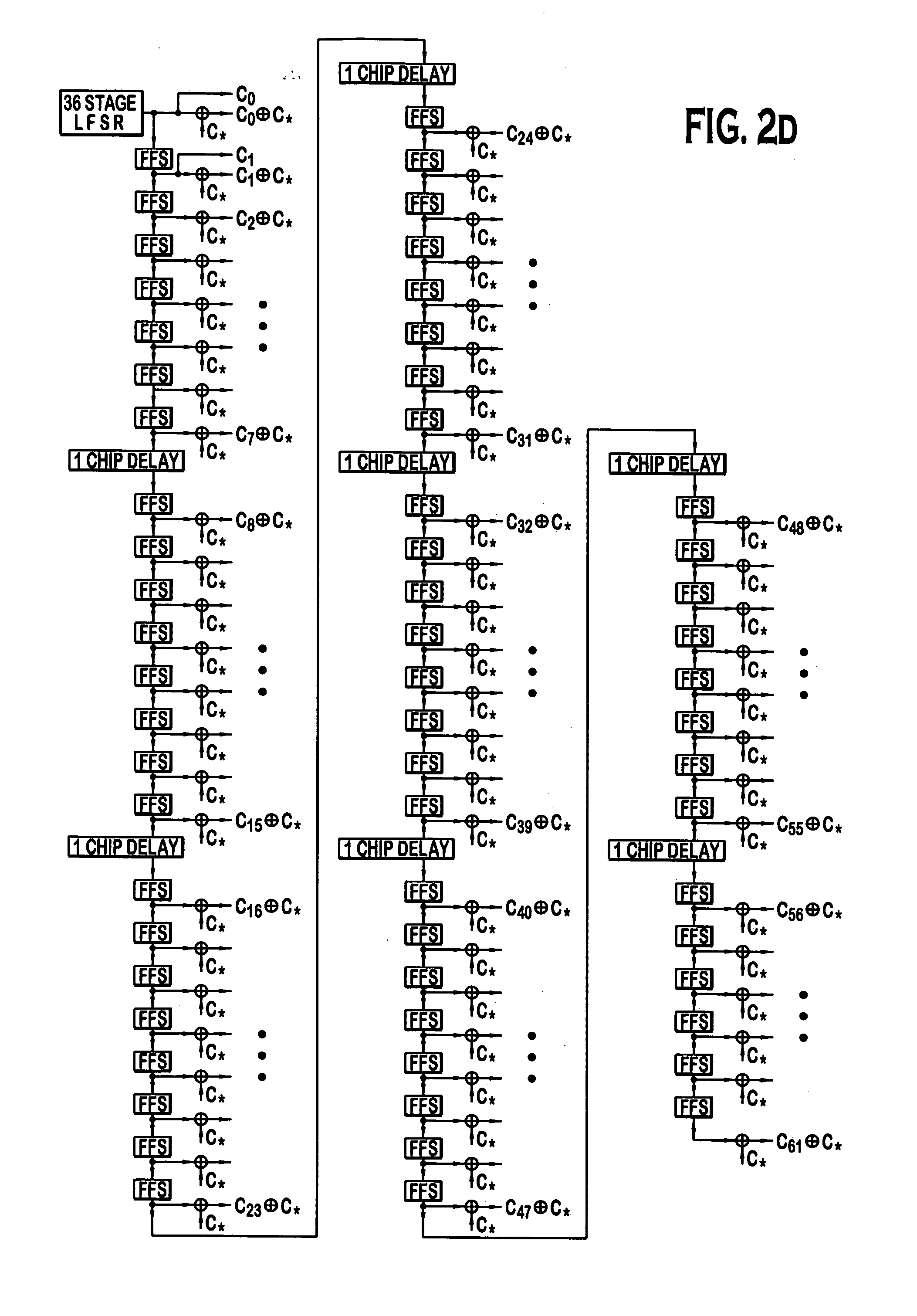
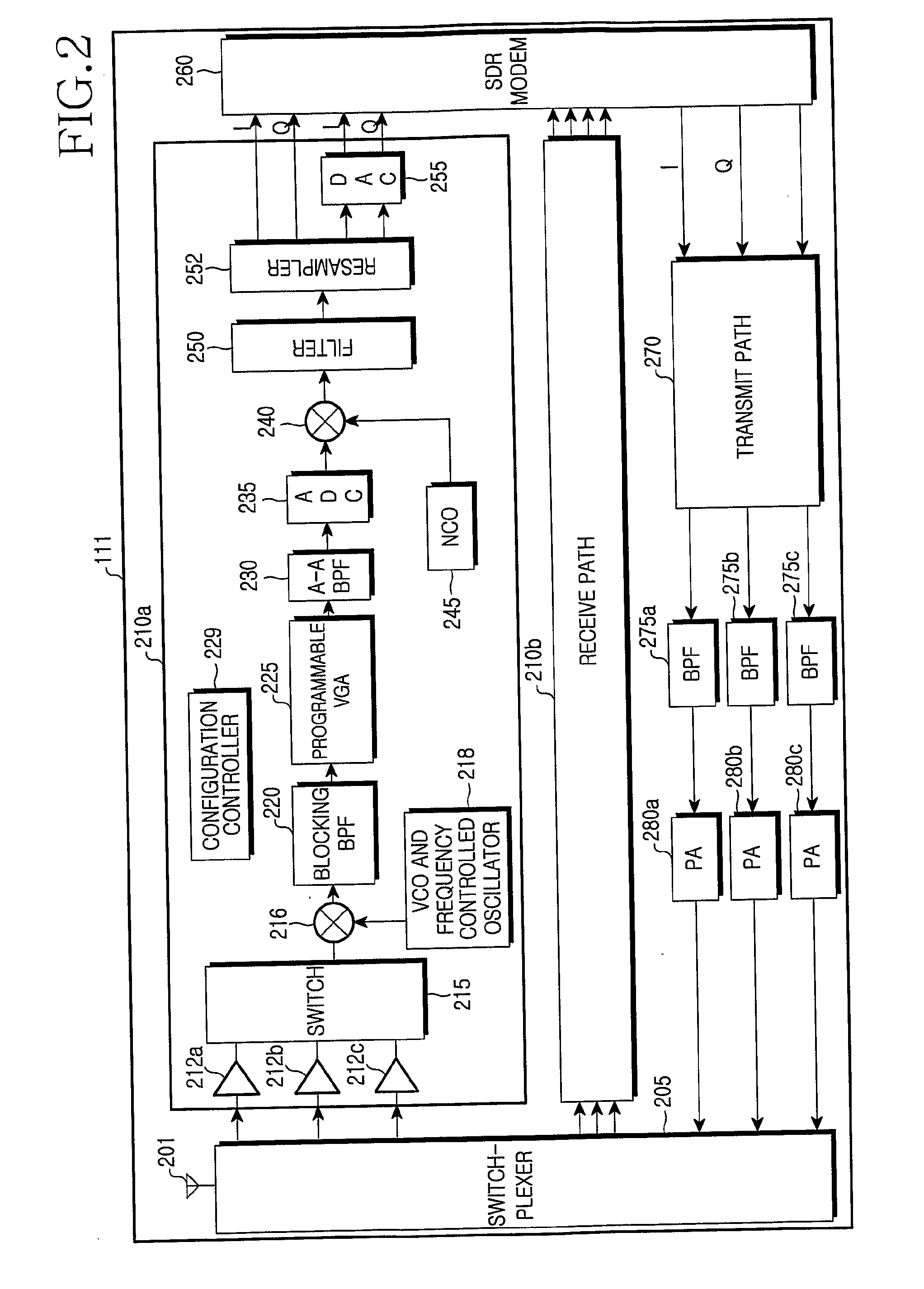
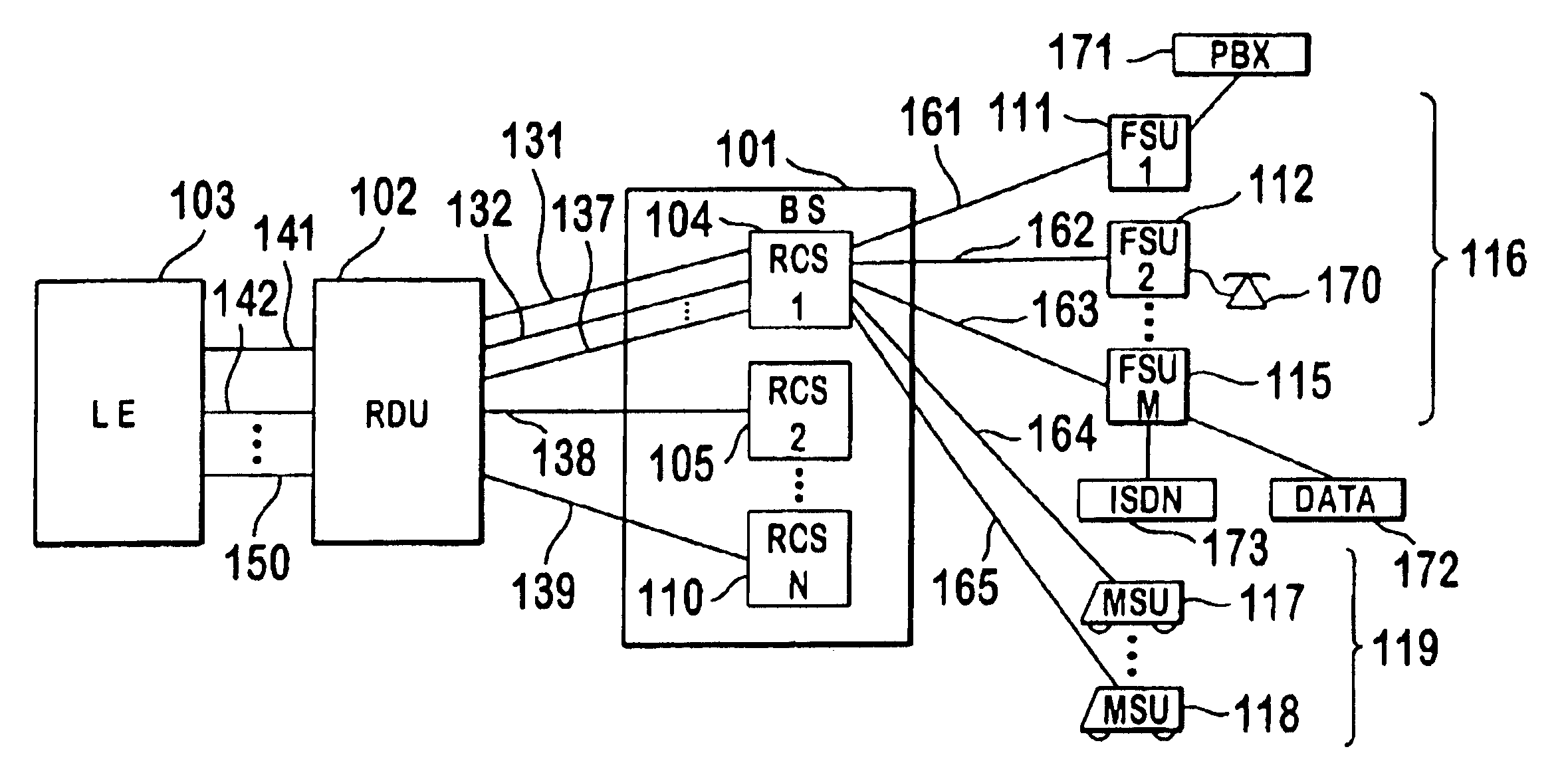
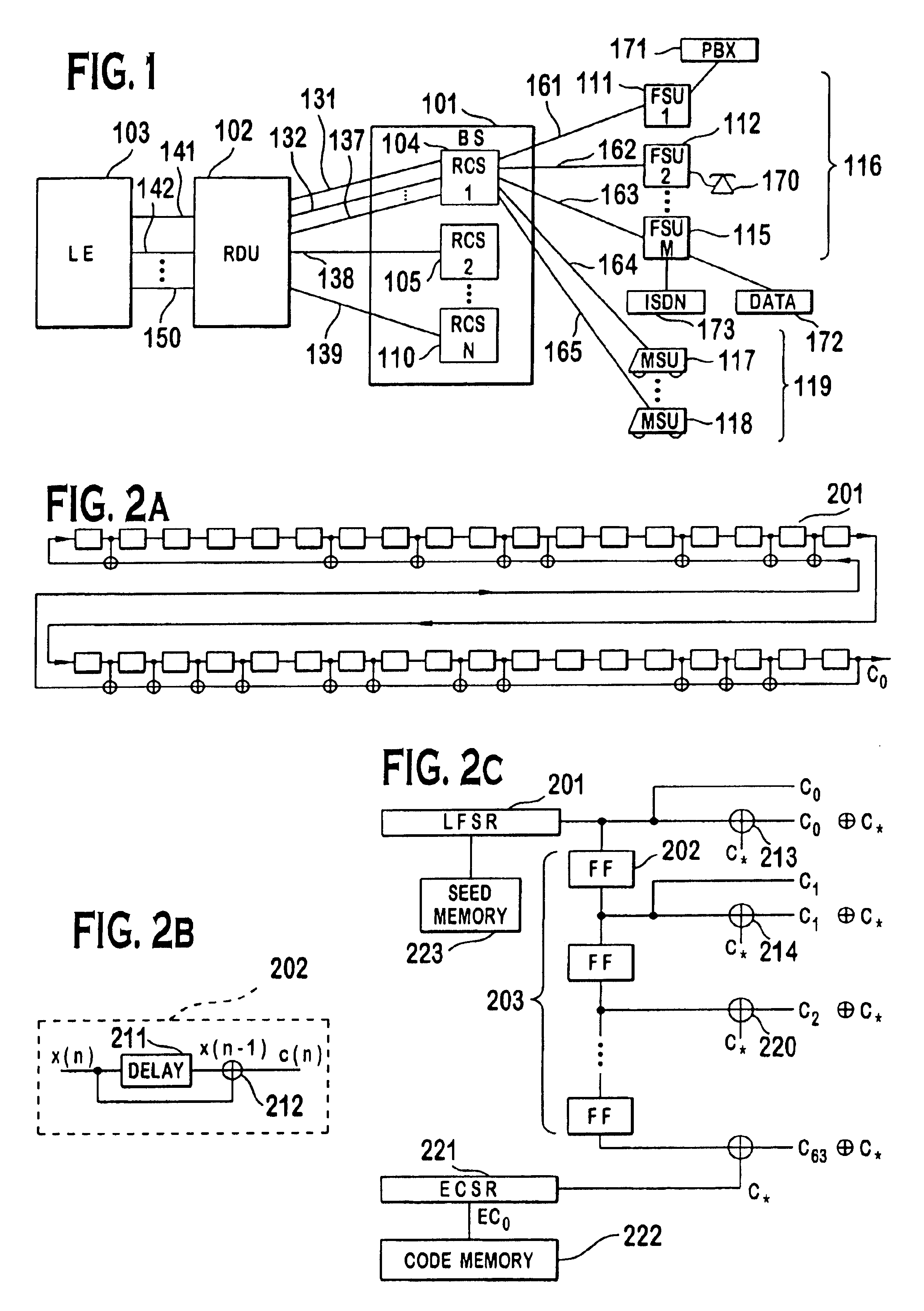
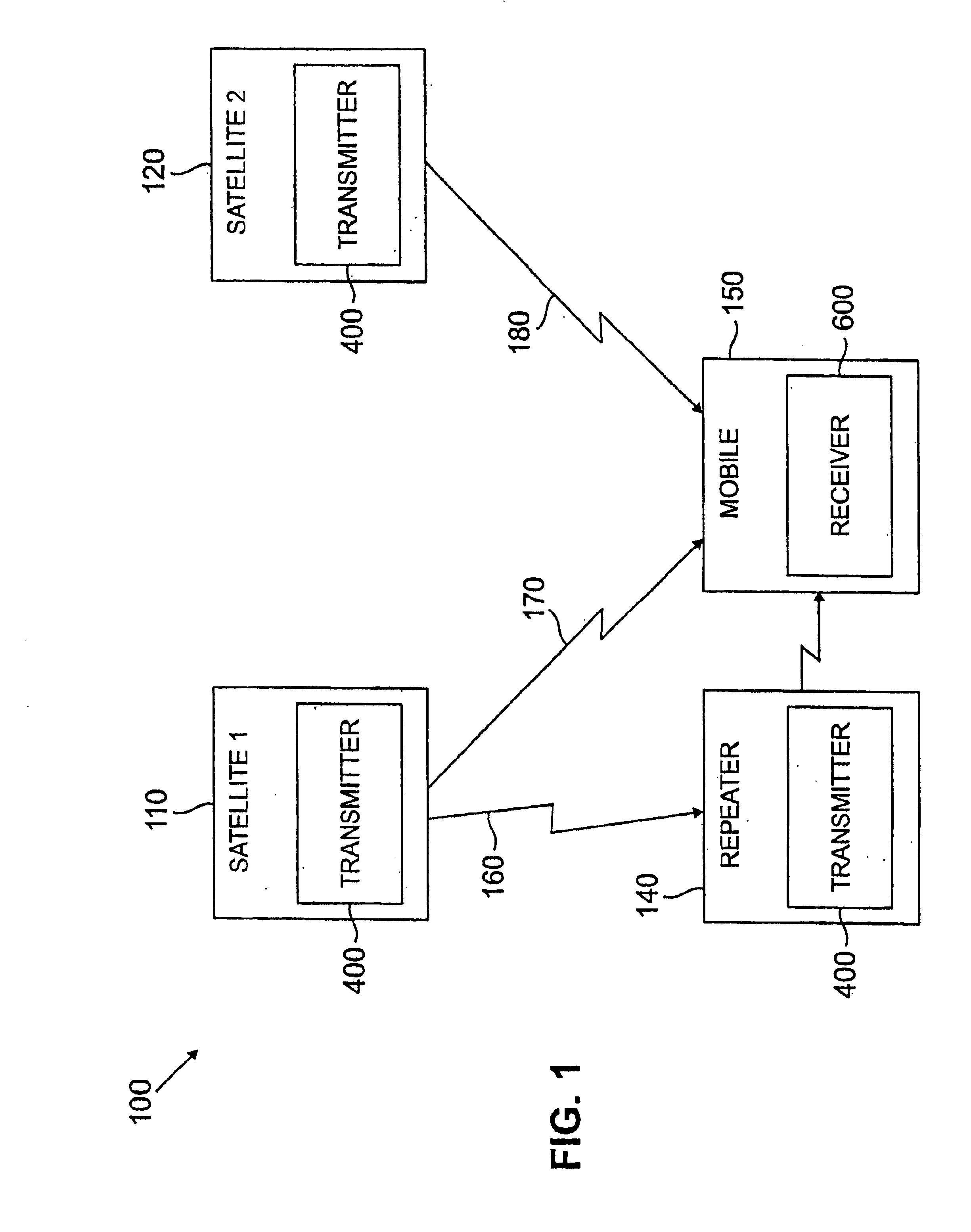
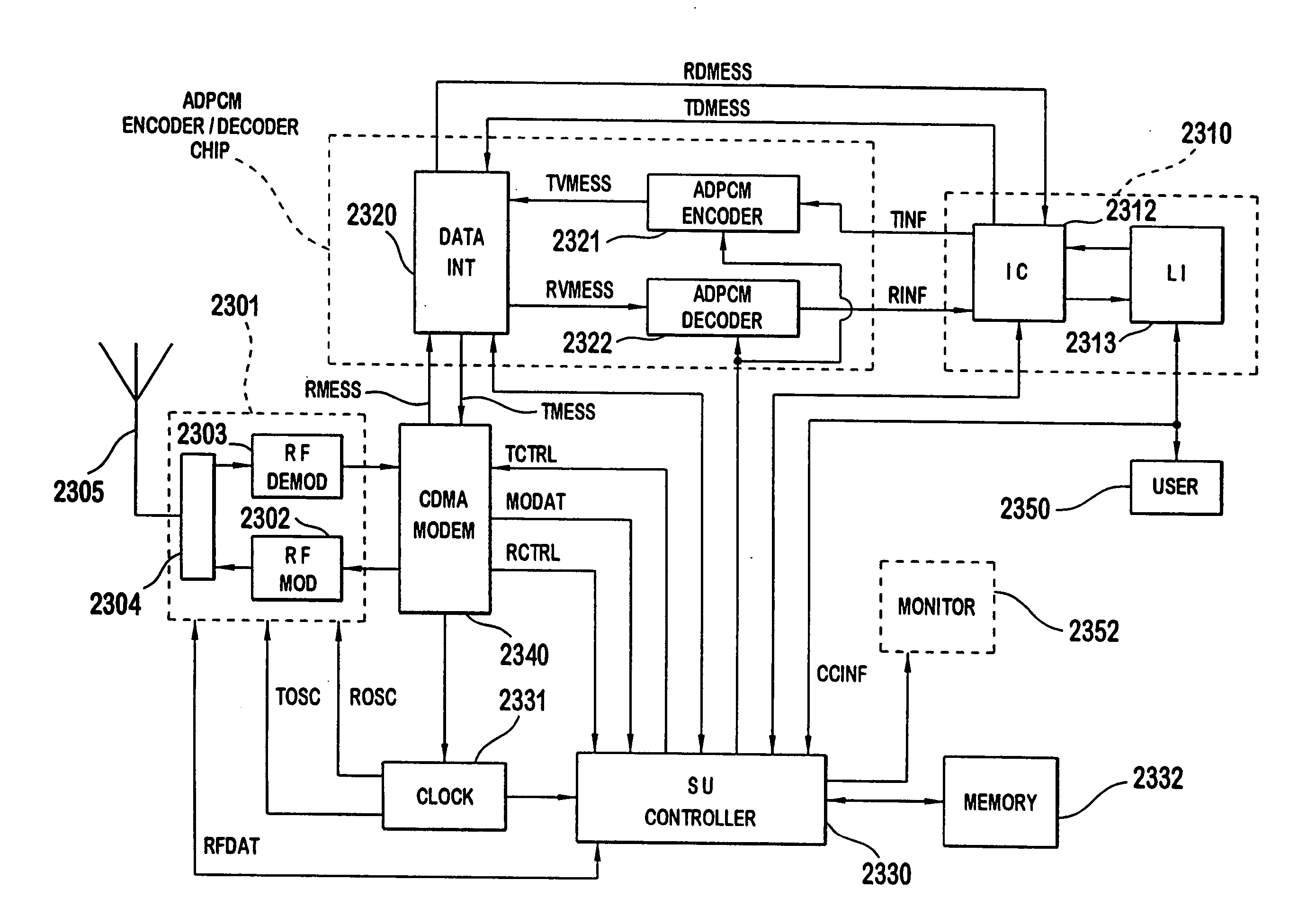
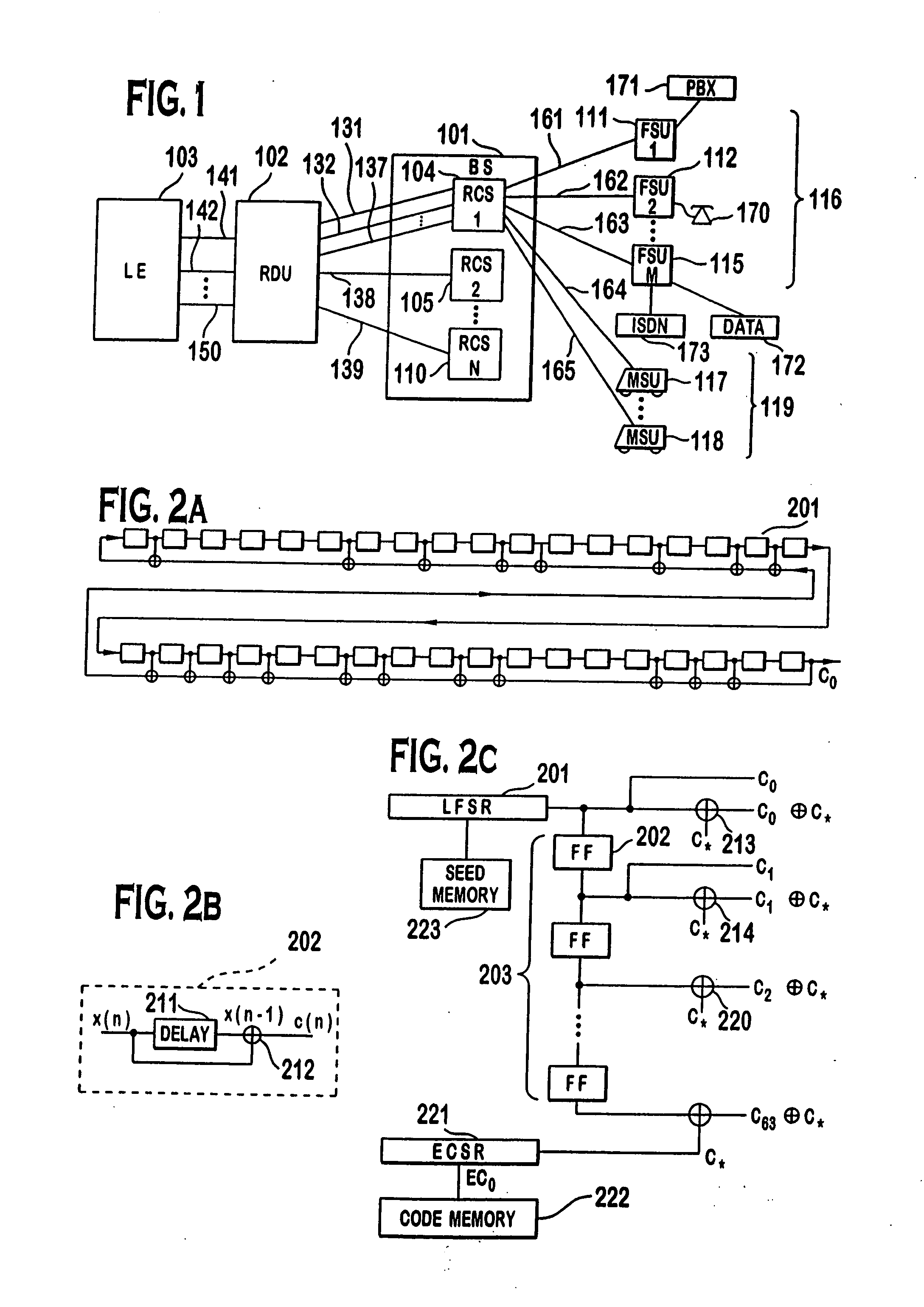
Code division multiple access (CDMA) communication system
InactiveUS6885652B1Increase profitPower managementBaseband system detailsModem deviceSystem capacity
A multiple access, spread-spectrum communication system processes a plurality of information signals received by a Radio Carrier Station (RCS) over telecommunication lines for simultaneous transmission over a radio frequency (RF) channel as a code-division-multiplexed (CDM) signal to a group of Subscriber Units (SUs). The RCS receives a call request signal that corresponds to a telecommunication line information signal, and a user identification signal that identifies a user to receive the call. The RCS includes a plurality of Code Division Multiple Access (CDMA) modems, one of which provides a global pilot code signal. The modems provide message code signals synchronized to the global pilot signal. Each modem combines an information signal with a message code signal to provide a CDM processed signal. The RCS includes a system channel controller is coupled to receive a remote call. An RF transmitter is connected to all of the modems to combine the CDM processed signals with the global pilot code signal to generate a CDM signal. The RF transmitter also modulates a carrier signal with the CDM signal and transmits the modulated carrier signal through an RF communication channel to the SUs. Each SU includes a CDMA modem which is also synchronized to the global pilot signal. The CDMA modem despreads the CDM signal and provides a despread information signal to the user. The system includes a closed loop power control system for maintaining a minimum system transmit power level for the RCS and the SUs, and system capacity management for maintaining a maximum number of active SUs for improved system performance.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL TECH CORP
Transmission control protocol/internet protocol (TCP/IP) packet-centric wireless point to multi-point (PtMP) transmission system architecture
InactiveUS20050232193A1Special service provision for substationError detection/prevention using signal quality detectorQuality of serviceCode division multiple access
Owner:INTELLECTUAL VENTURES I LLC
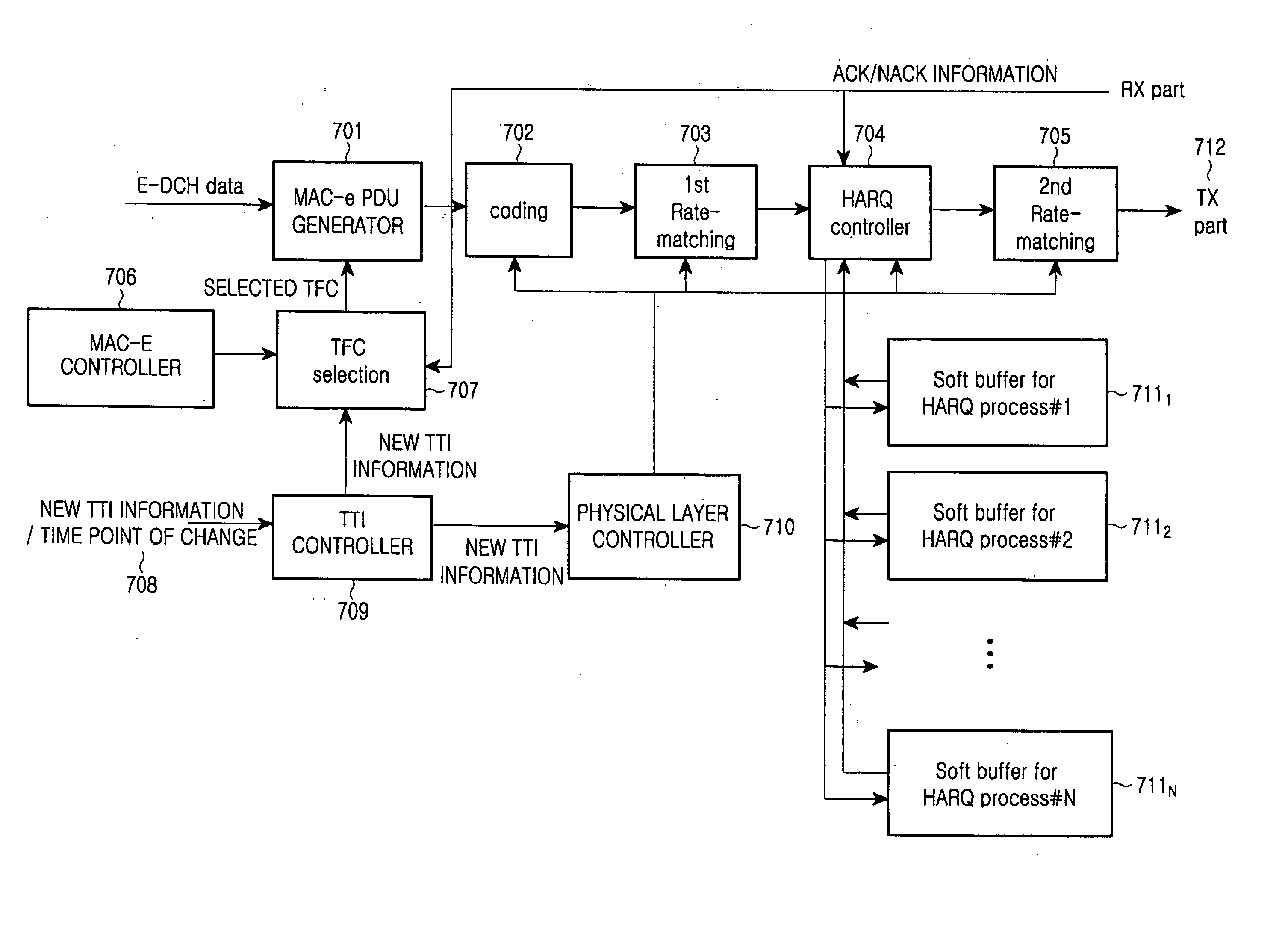
Method and apparatus for changing TTI based on a HARQ process in an enhanced uplink dedicated channel
ActiveUS20050249120A1Improve system performanceImprove uplink performanceError prevention/detection by using return channelTransmission systemsCommunications systemCode division multiple access
A method and apparatus for changing a Transmit Time Interval (TTI) based on a Hybrid Automatic Repeat Request (HARQ) process in a code division multiple access (CDMA) communication system that supports a packet data service through an Enhanced Uplink Dedicated transport Channel (E-DCH). According to the method and apparatus, a data transmission / reception is performed in a manner that a TTI change signal is received, the actual time point of TTI change is calculated based on the TTI change signal and the HARQ process of the previous TTI, and the TTI is changed at the calculated time point of TTI change.
Owner:NOKIA SOLUTIONS & NETWORKS OY
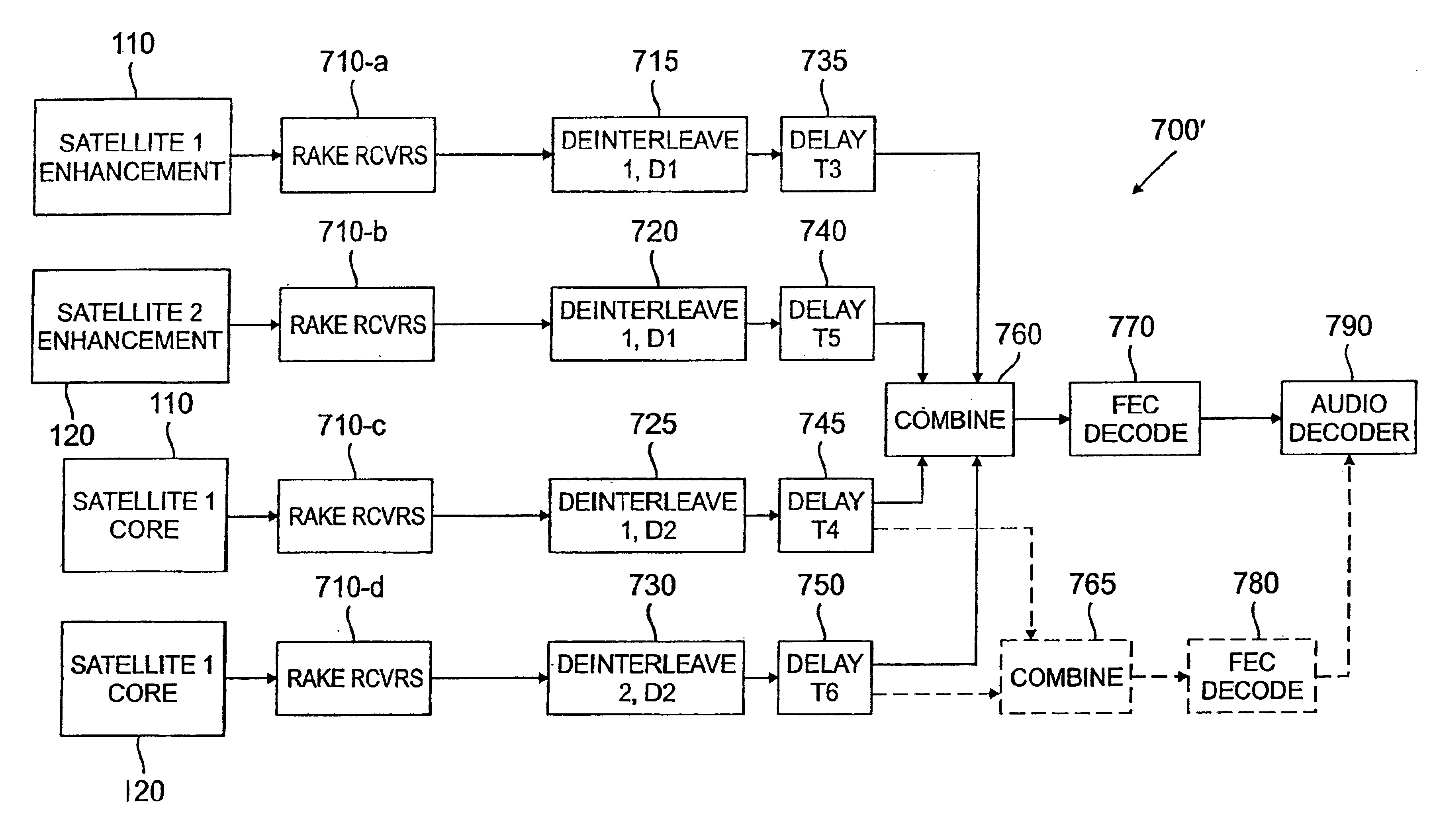
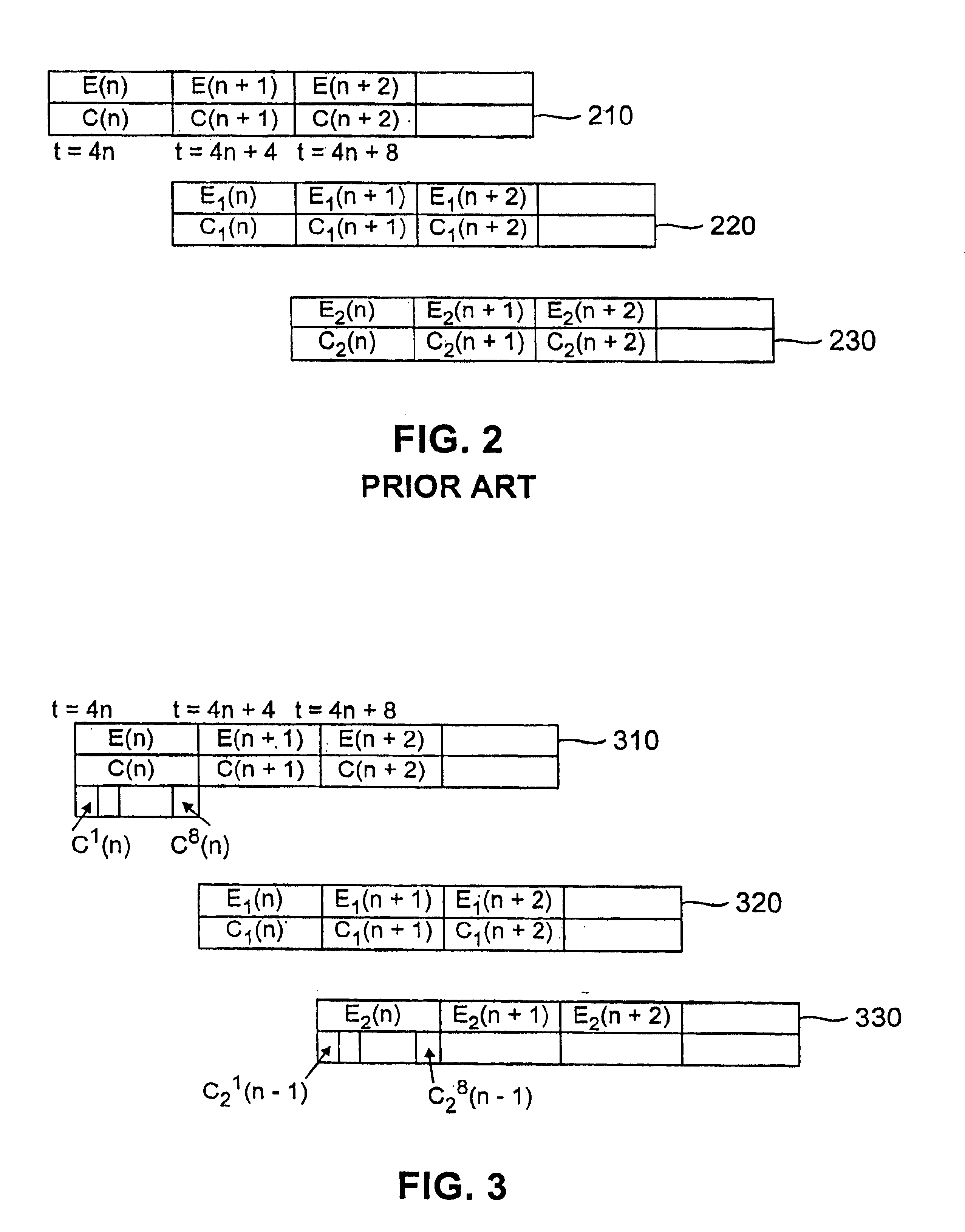
Tuning scheme for code division multiplex broadcasting system
InactiveUS6876623B1Reduce delaysSimple technologyGHz frequency transmissionBroadcast transmission systemsTransport systemCode division multiple access
A CDM satellite transmission system is disclosed that broadcasts programming content, such as audio and video information, using one or more geo-synchronous satellites based on Code Division Multiple Access technology. Forward error correction coding and interleaving are used prior to broadcasting the signals over the CDM channel to account for signal loss due to short-term fading. The CDM satellite transmission system provides a tuning channel corresponding to each program channel that reduces the delay when a mobile receiver is first tuned to a selected program channel. The tuning channel utilizes a shorter interleaver length, if any, than the corresponding primary program channel. The CDM satellite transmission system transmits a delayed version of a program signal with the on-time version of the audio output to accommodate uninterrupted reception in the event of such a blockage. In one implementation of the invention, the core layer, C(n), of the delayed version of the audio output of a scalable audio coding scheme is utilized as the tuning channel. The core layer, C1(n), and enhancement layers, E1(n), of the on-time signal and the enhancement layers, E2(n), of the delayed-time signal employ a representative block interleaver having a duration of four seconds. The tuning channel (C2(n), of the delayed-time signal) employs a representative block interleaver having a duration of 500 milliseconds.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Code division multiple access (CDMA) communication system
InactiveUS20040252668A1Easy to liftMaximize signal to noisePower managementBaseband system detailsSystem capacityCode division multiple access
A subscriber unit for use in a multiple access spread-spectrum communication system includes a spread spectrum radio interface, responsive to a rate function signal from a base station, and first and second despreaders. The base station assigns the rate function spread-spectrum message channels and the first despreader recovers and modifies an information signal one of the spread spectrum message channels. The information channel mode is then modified for processing by the second despreader, with the second despreader supporting a different information signal rate. The subscriber unit has a capability of communicating with a dynamically changing a transmission rate of an information signal which includes multiple spread spectrum message channels. The system includes a closed loop power control system for maintaining a minimum system transmit power level for a radio carrier station and the subscriber units, and system capacity management for maintaining a maximum number of active subscriber units for improved system performance.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL TECH CORP
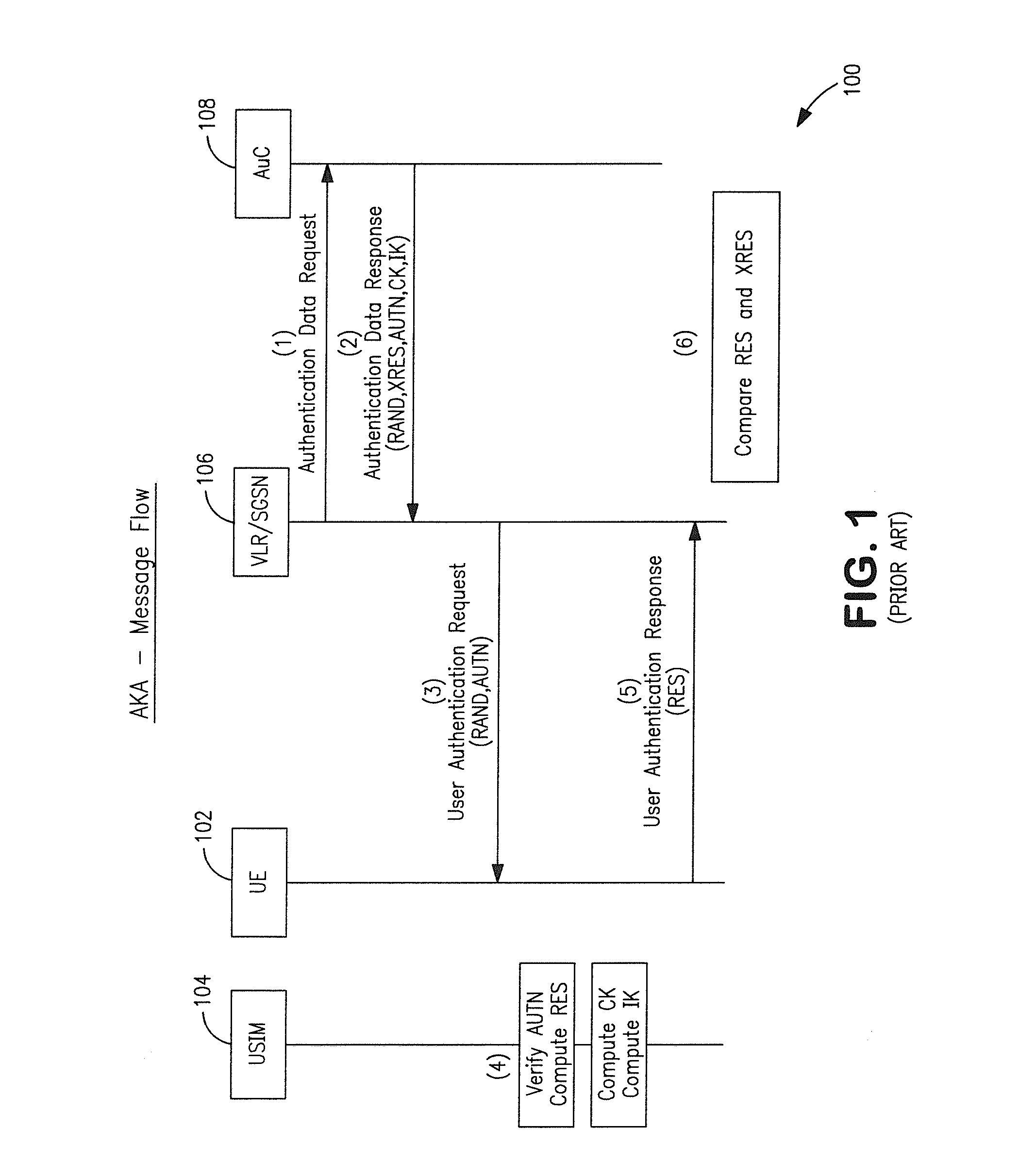
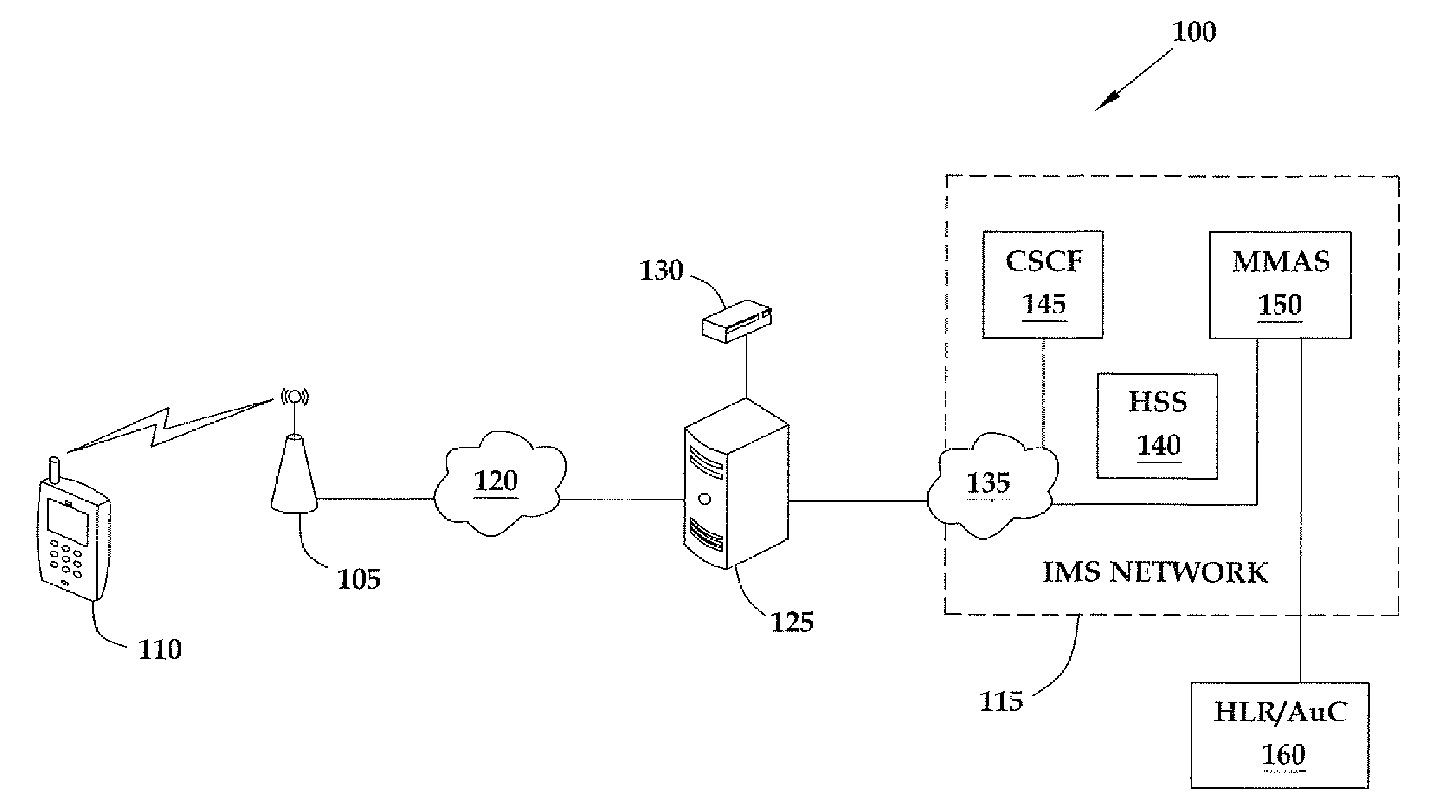
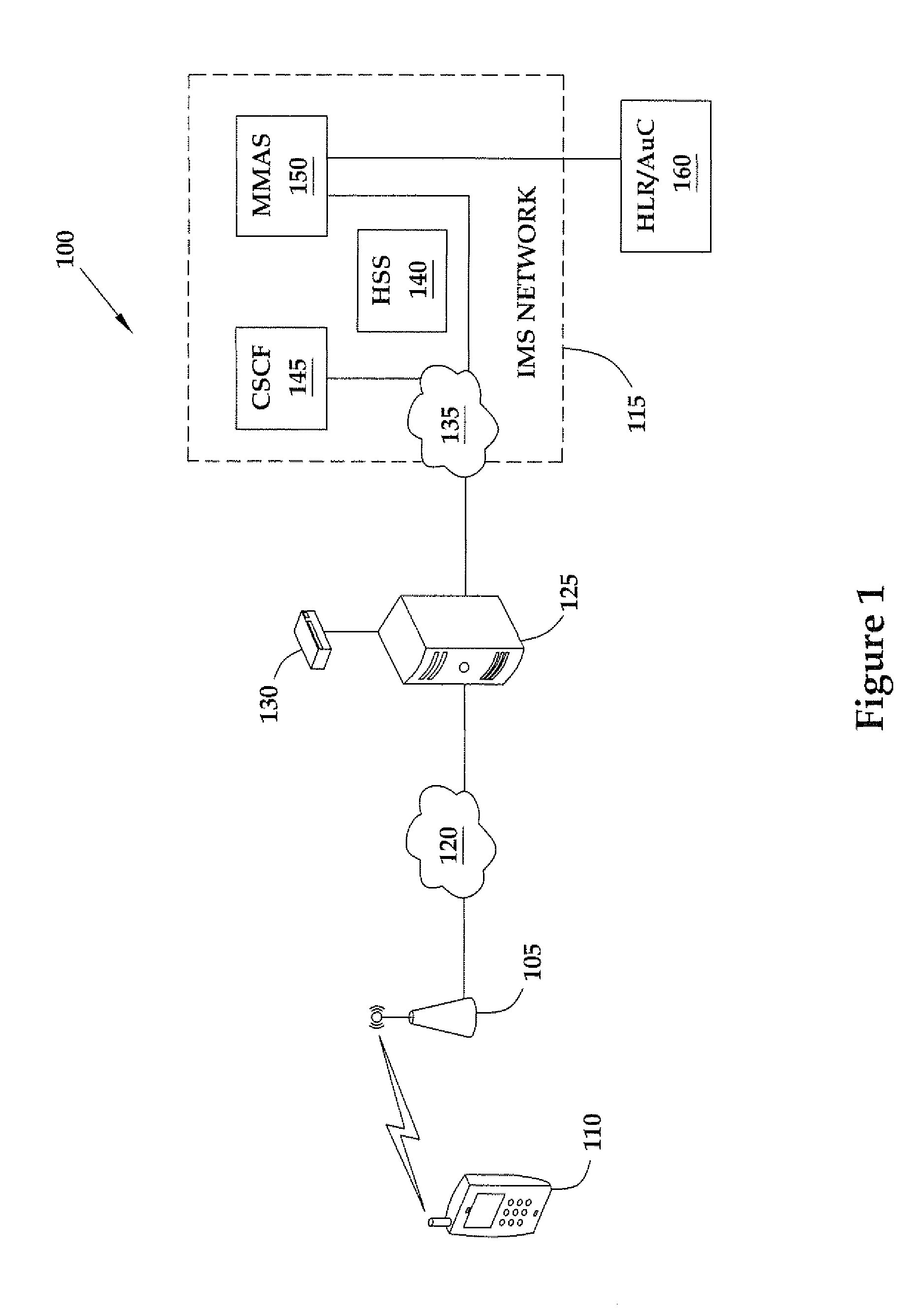
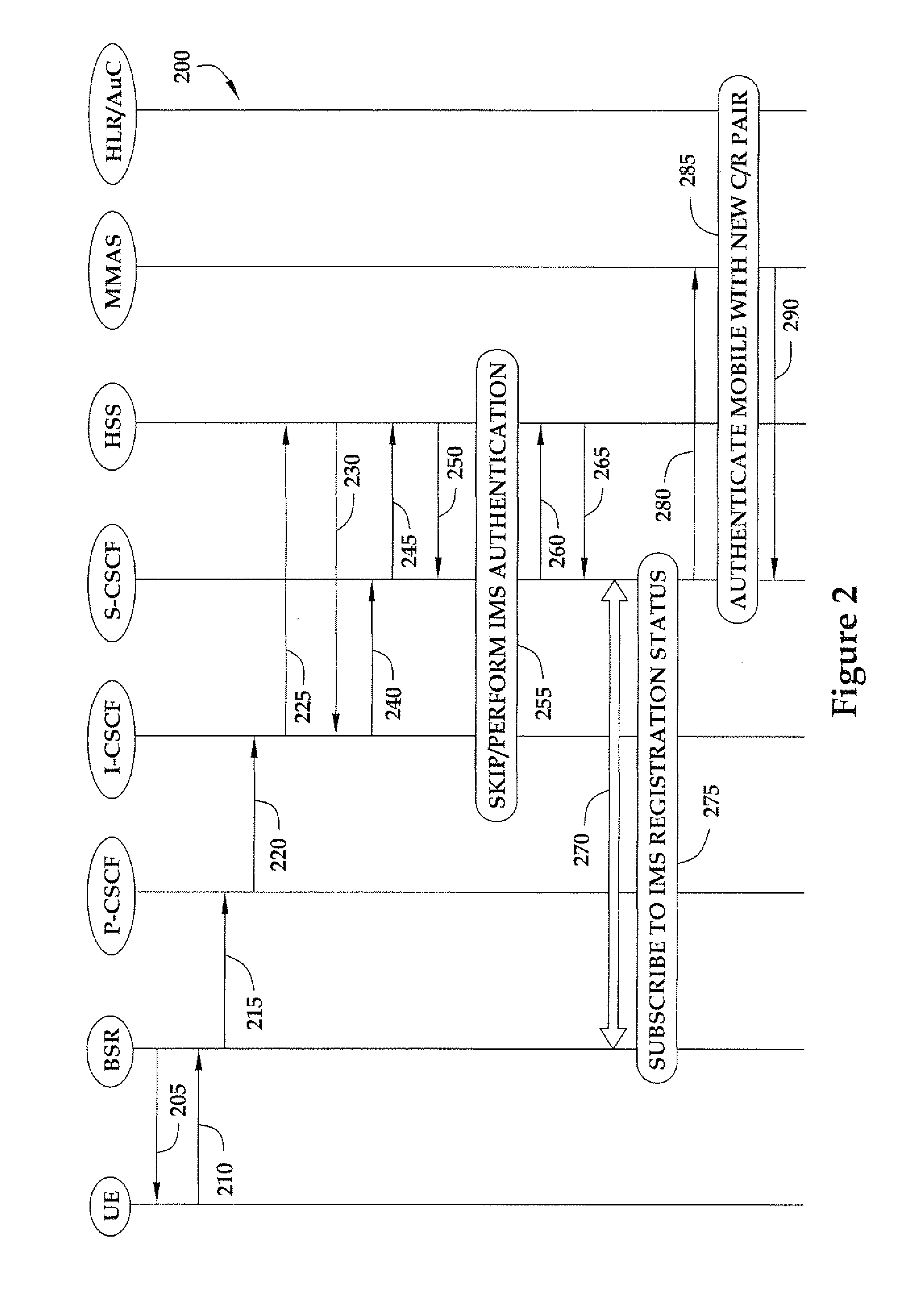
Method for authenticating a mobile unit attached to a femtocell that operates according to code division multiple access
ActiveUS20090191844A1Unauthorised/fraudulent call preventionDigital data processing detailsCode division multiple accessAuthentication server
The present invention provides a method involving a femtocell in communication with an Internet Protocol Multimedia Subsystem (IMS) network. In one embodiment, the femtocell operates according to code division multiple access (CDMA) standards. The method includes receiving, from the femtocell and at a first secure entity in the IMS network, first authentication information generated by the mobile unit using a first random number broadcast by the femtocell in a global challenge. The method also includes receiving, from a second secure entity in the secure network, at least one security key formed based on the global challenge and second authentication information for uniquely challenging the mobile unit. In one embodiment, the second secure entity is a CDMA-based authentication server. The method further includes providing the security key(s) to the femtocell in response to authenticating the mobile unit based upon the second authentication information.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
Method and apparatus for multicasting real time traffic in wireless ad-hoc networks
InactiveUS6721290B1Speed up decision making processSpecial service provision for substationNetwork traffic/resource managementQuality of servicePacket loss
A real-time multicast scheduler method and apparatus is presented, to facilitate multicasting of real-time constant bit rate data in wireless ad-hoc networks. Constant bit rate traffic cannot tolerate delay jitter. However, a small amount of packet losses may be tolerable. In order to ensure the provisioning of a desired level of quality of service, bandwidth is reserved on the multicast structure. A goal of the real-time multicast scheduler is to avoid packet collisions and to facilitate color re-use, where "color" is defined as a channel selected as a combination of time-division multiple access, frequency-division multiple access, and code-division multiple access schemes. The real-time multicast scheduler provides a self-healing network which corrects for disconnections caused by node movement and nodes moving out of range of each other, while accounting for colors already assigned for data transmission in order to prevent packet collisions.
Owner:HRL LAB
Intelligent network burglar-proof door
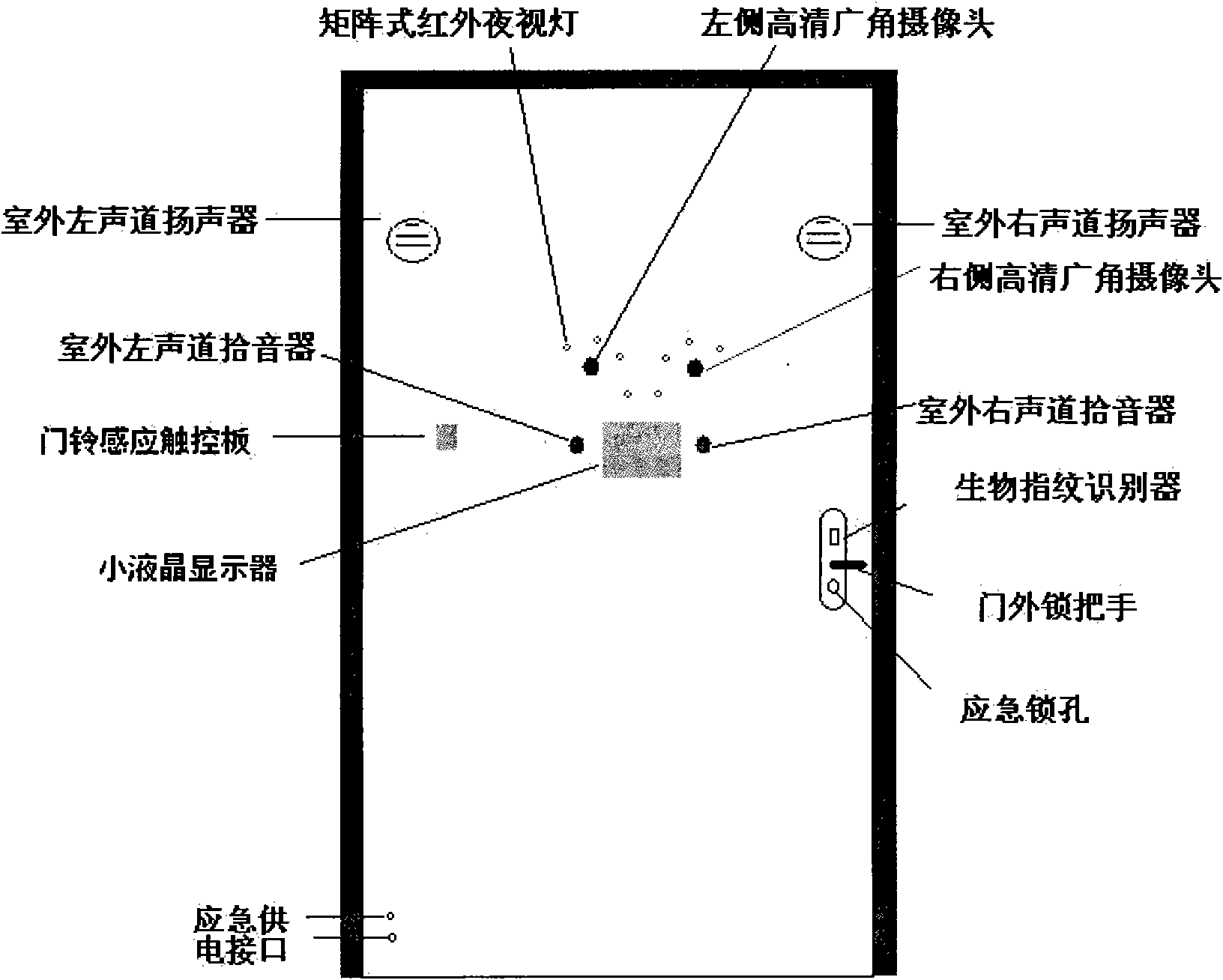
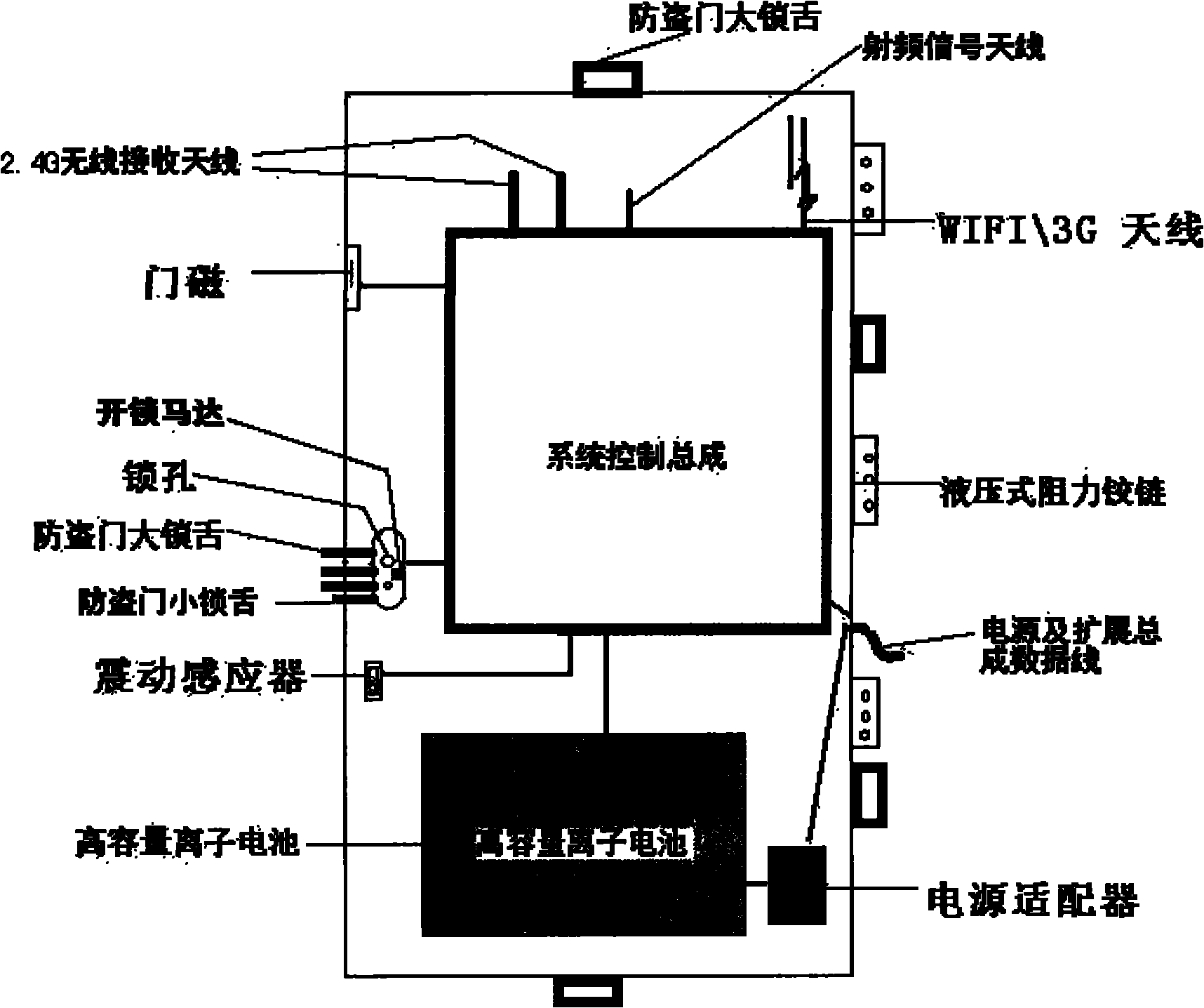
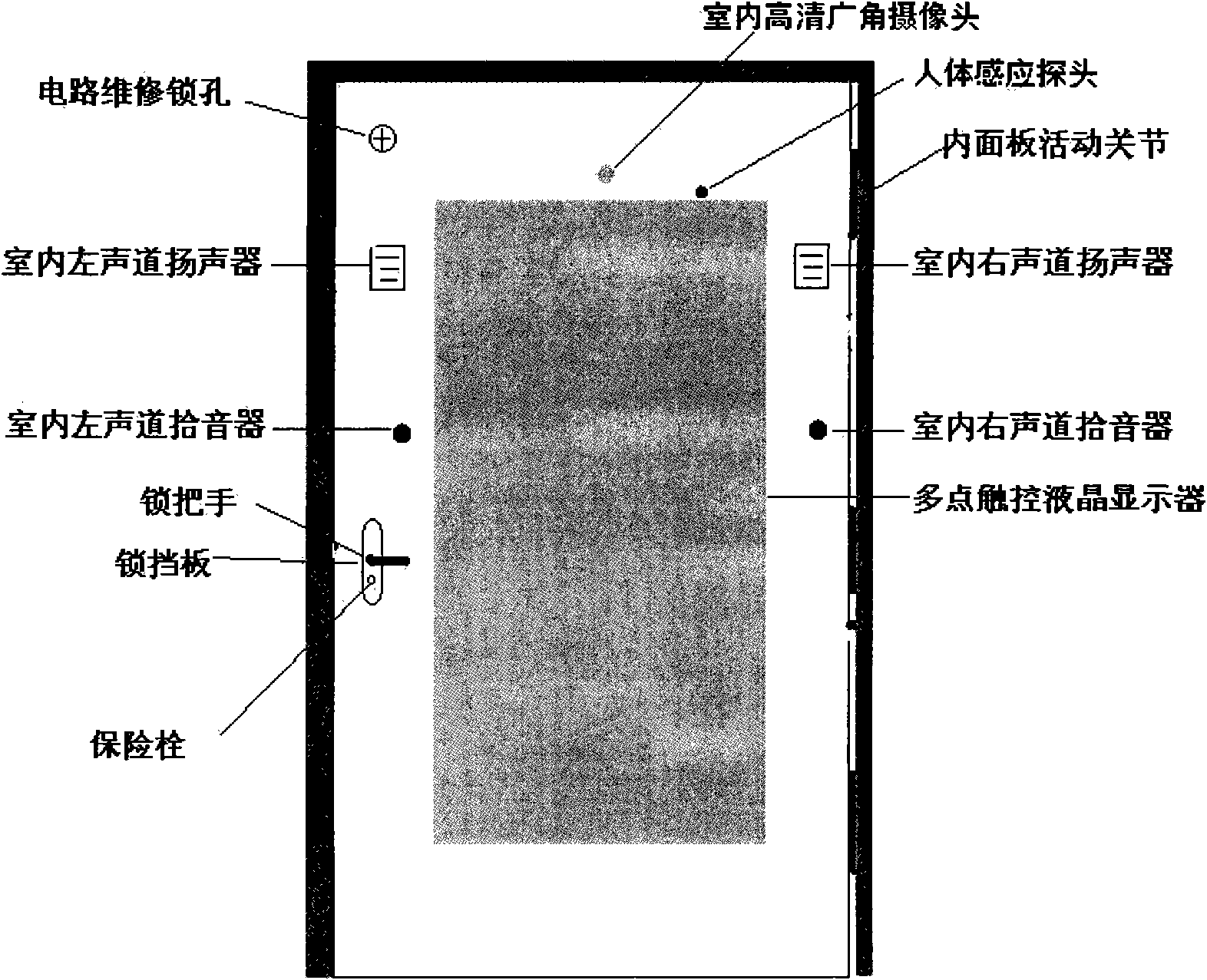
ActiveCN102074056ARealize multiple anti-theftAchieve activityElectric permutation locksIndividual entry/exit registersInternet communicationIntelligent Network
The invention discloses an intelligent network burglar-proof door composed of a hardware system and a software system. The intelligent network burglar-proof door is mainly characterized in that a software control part comprises an underlying operation system, an application software system, a human face recognition system, a fingerprint recognition system, a touch screen control system, a local / different-place storage system, an uninterruptible power supply management system, an extended interface system for controlling home appliances, a monitoring and alarming system for positioning and fortifying a multi-region zone PTZ (pan / tilt / zoom) electronic map, an access control system for controlling an unlocking motor, an intercom system capable of automatically responding, an H.264 video coding and decoding system, a 2.4G wireless video commutation system, a radio frequency communication system, a communication system for supporting TD / WCDMA (time division-wideband code division multiple access) and an Internet communication system. The intelligent network burglar-proof door checks information in real time or remotely backs up, improves data protection safety and intelligent and convenient maneuverability. The intelligent network burglar-proof door can widely serve as various burglar-proof doors, military guard burglar-proof doors, safety box doors and vehicle central door locks.
Owner:卫芯科技(浙江)有限公司
Method and System for Baseband Predistortion Linearization in Multi-Channel Wideband Communication Systems
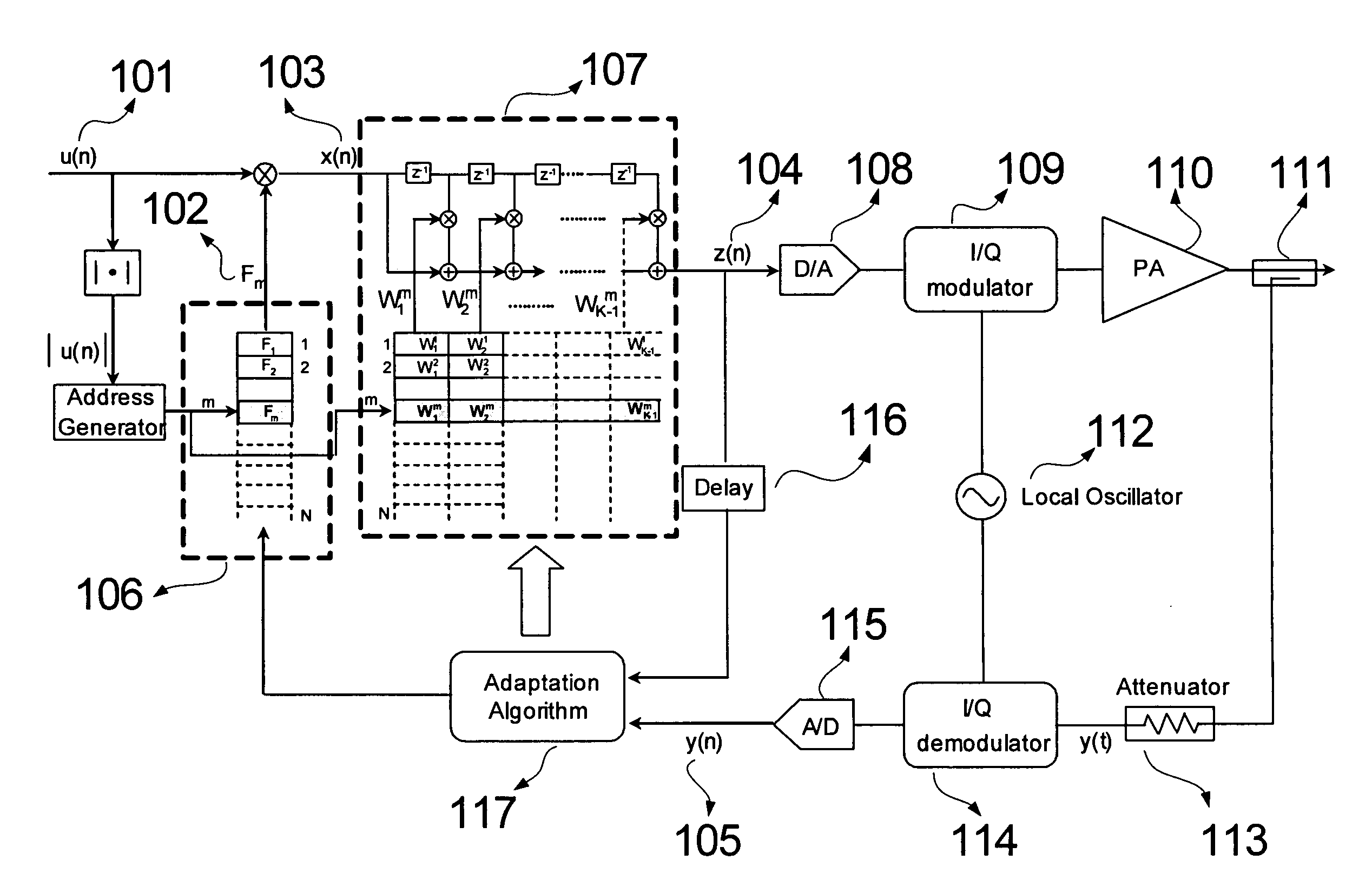
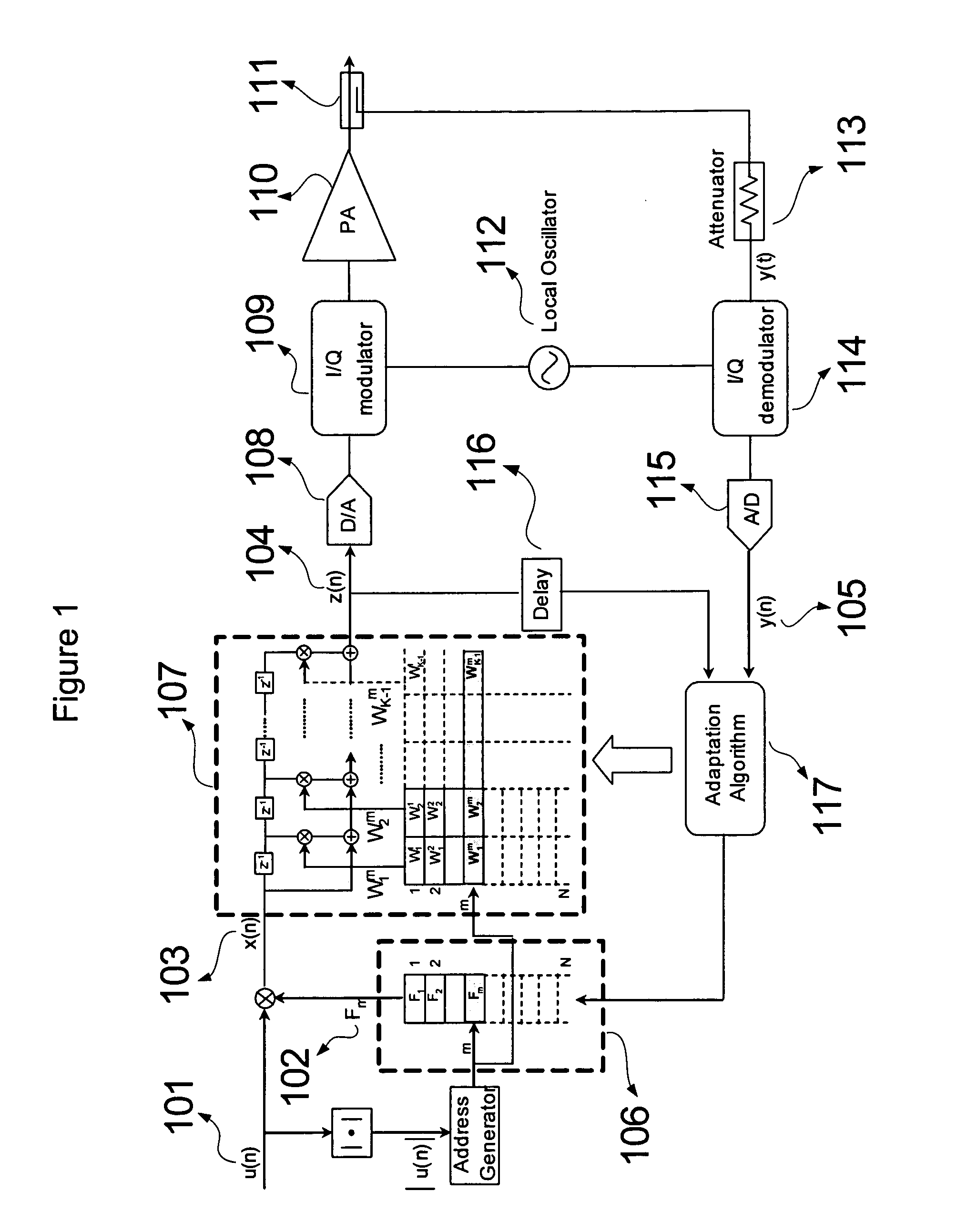
ActiveUS20080152037A1Reducing computational complexity and numerical instabilityMultiple-port networksElectric signal transmission systemsAdjacent channel power ratioFrequency spectrum
An efficient baseband predistortion linearization method for reducing the spectral regrowth and compensating memory effects in wideband communication systems using effective multiplexing modulation technique such as wideband code division multiple access and orthogonal frequency division multiplexing is disclosed. The present invention is based on the method of piecewise pre-equalized lookup table based predistortion, which is a cascade of a lookup table predistortion and piecewise pre-equalizers, to reduce the computational complexity and numerical instability for desired linearity performance with memory effects compensation for wideband transmitter systems. Therefore, the present invention could reduce the computational load, which saves hardware resources in an implementation and improve performance, in terms of adjacent channel power ratio.
Owner:DALI WIRELESS
Method and Apparatus for Using Multicarrier Interferometry to Enhance optical Fiber Communications
InactiveUS20070025421A1Energy efficient ICTWavelength-division multiplex systemsTime domainTime division multiple access
Owner:LOT 41 ACQUISITION FOUND +1
Distributed magnetic field positioning system using code division multiple access
InactiveUS6549004B1Position fixationUsing electrical meansCode division multiple accessComputational physics
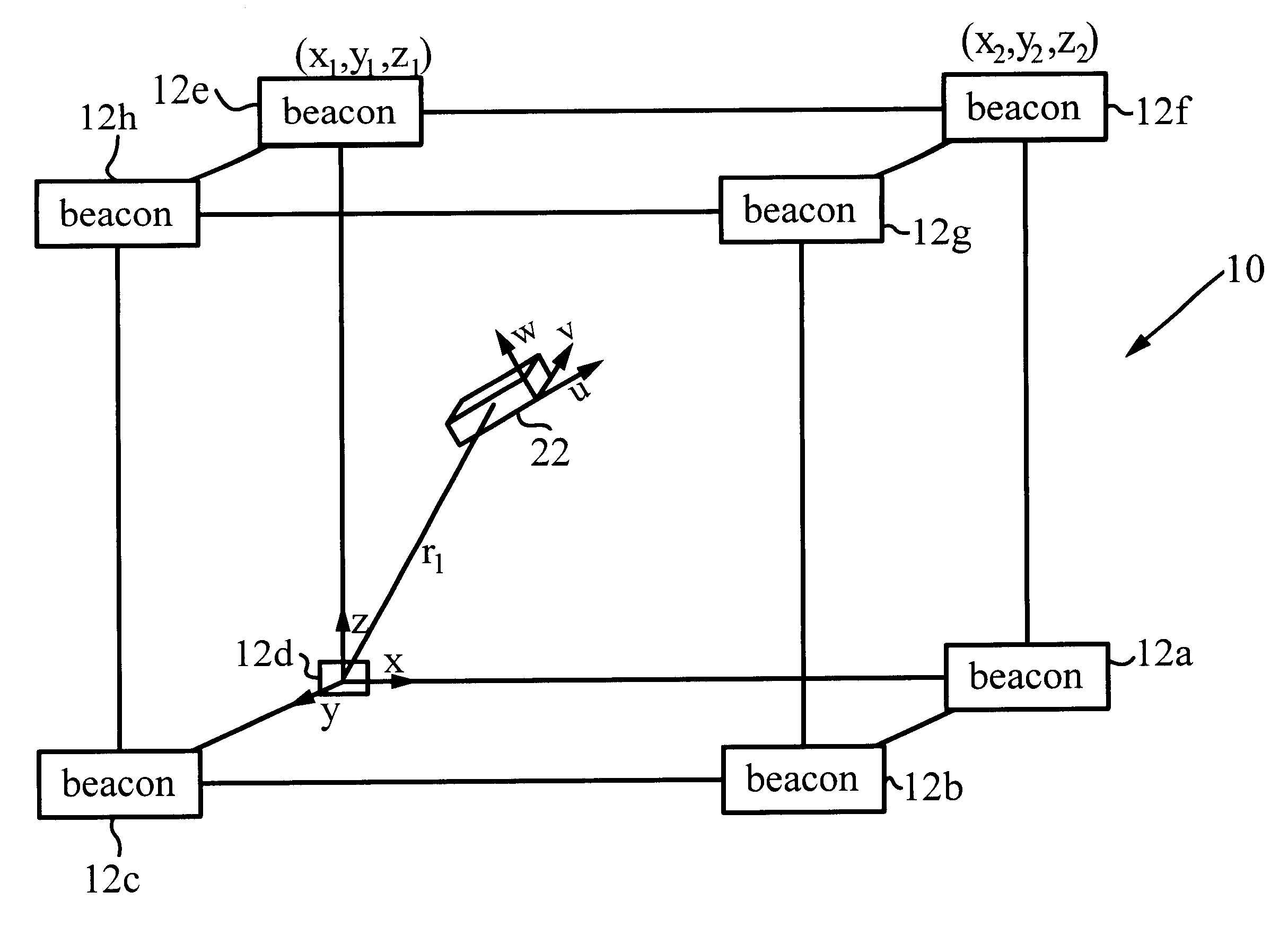
An apparatus and methods for a magnetic field positioning system use a fundamentally different, and advantageous, signal structure and multiple access method, known as Code Division Multiple Access (CDMA). This signal architecture, when combined with processing methods, leads to advantages over the existing technologies, especially when applied to a system with a large number of magnetic field generators (beacons). Beacons at known positions generate coded magnetic fields, and a magnetic sensor measures a sum field and decomposes it into component fields to determine the sensor position and orientation. The apparatus and methods can have a large "building-sized' coverage area. The system allows for numerous beacons to be distributed throughout an area at a number of different locations. A method to estimate position and attitude, with no prior knowledge, uses dipole fields produced by these beacons in different locations.
Owner:BOARD OF TURSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV THE
Mobile communication system with position detection to facilitate hard handoff
InactiveUS20020034947A1Radio/inductive link selection arrangementsSatellite radio beaconingLocation detectionTransceiver
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Beam division multiple access system and method for mobile communication system
InactiveUS20100165914A1Maximize the use of spaceEfficiently space resourceRadio transmissionWireless commuication servicesTime division multiple accessCode division multiple access
The present invention is related to a beam division multiple access system and a method thereof. The base station according to the present invention comprises a initial mobile station information receiver for receiving initial mobile station information that a mobile station omnidirectionally transmits in an initial communication step, a mobile station location and speed detector for detecting a location and a moving speed of the mobile station from the initial mobile station information, a downlink beam generator for generating a downlink beam based on the location and the moving speed of the mobile station transferred from the mobile station location and speed detector, and adjusting at least one of a width and a direction of each the downlink beam, and a downlink beam transmitter for transmitting the downlink beam generated by the downlink beam generator to the mobile station through a phase array antenna.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com