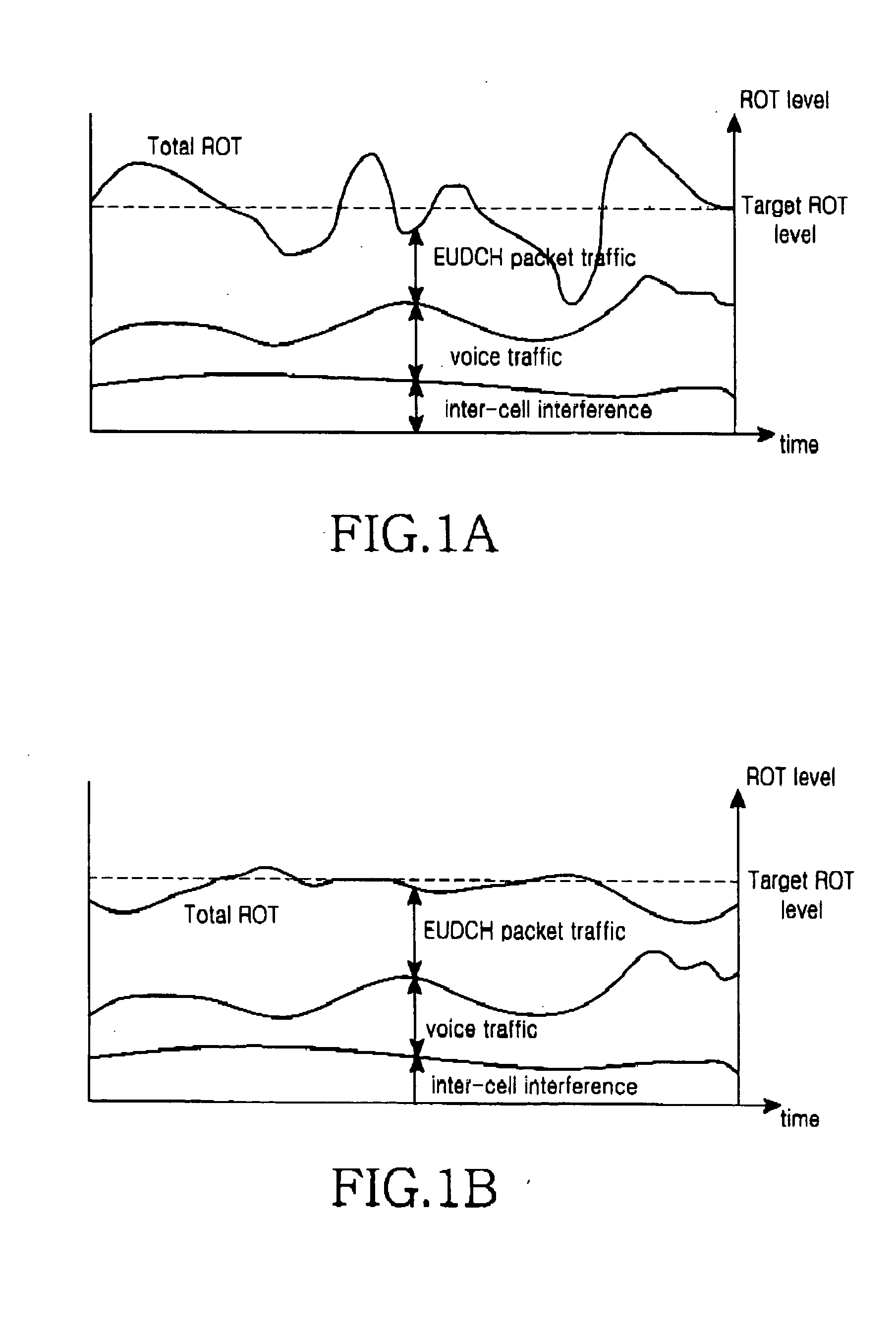
Patents
Literature
41464 results about "User equipment" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
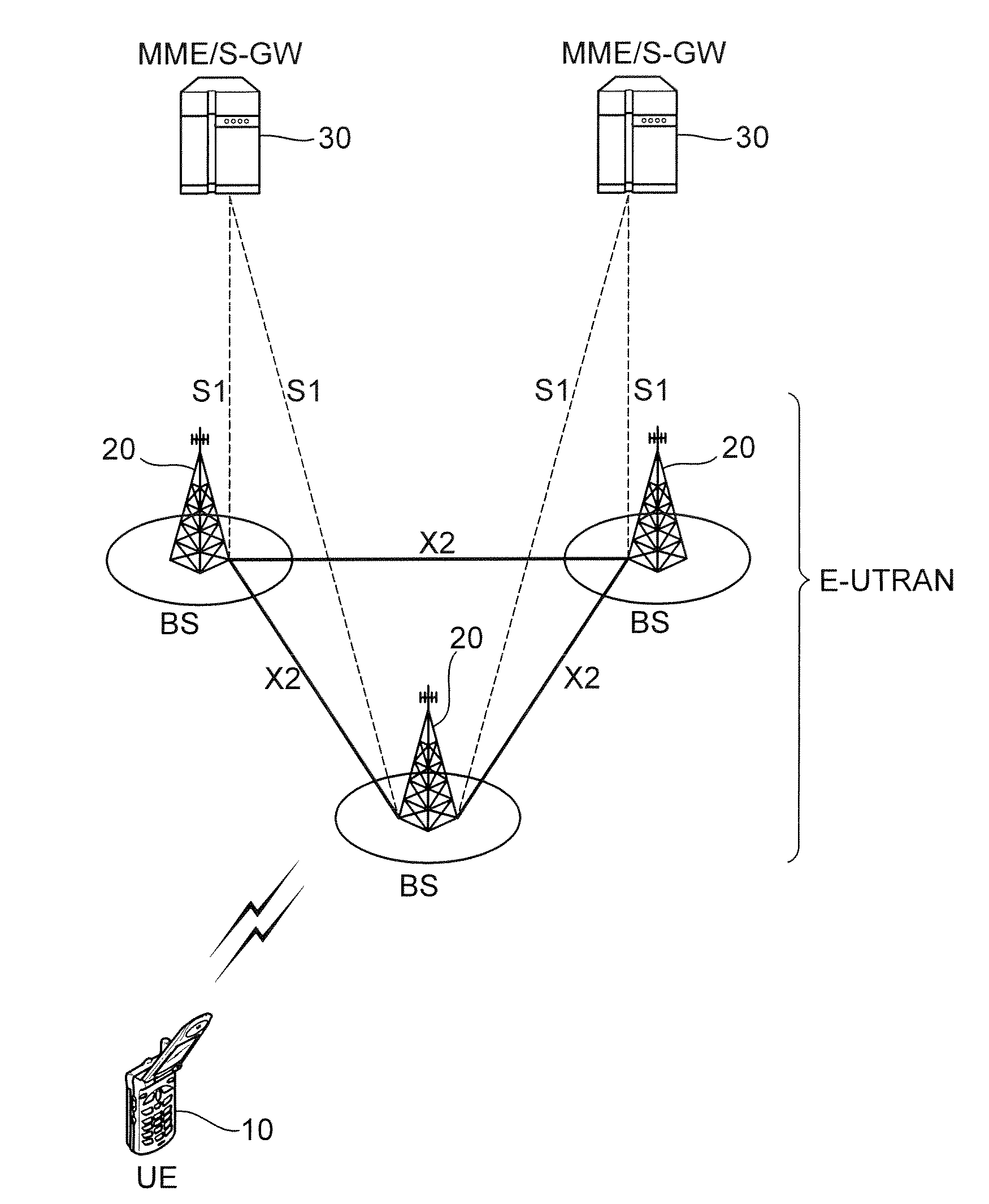
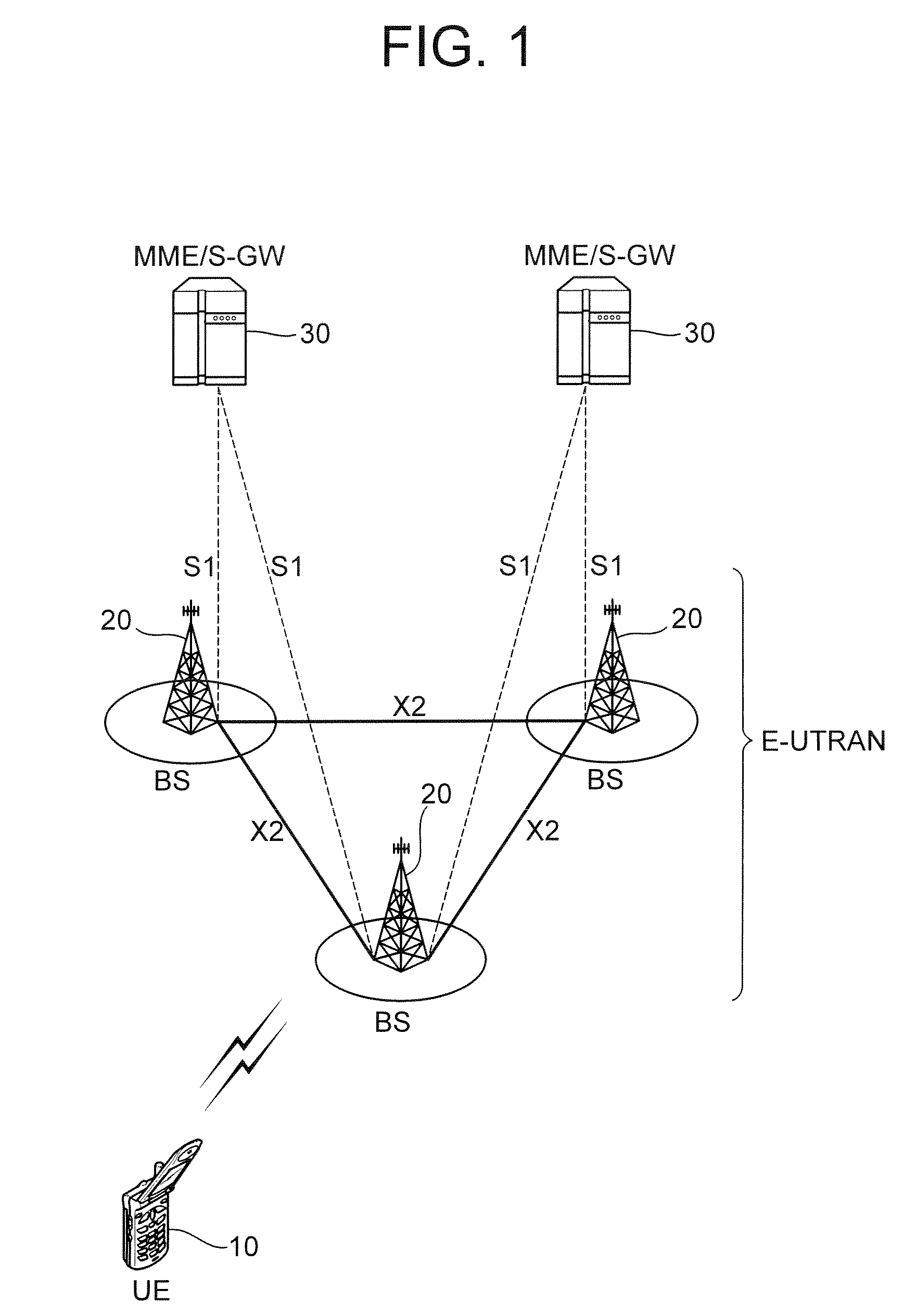
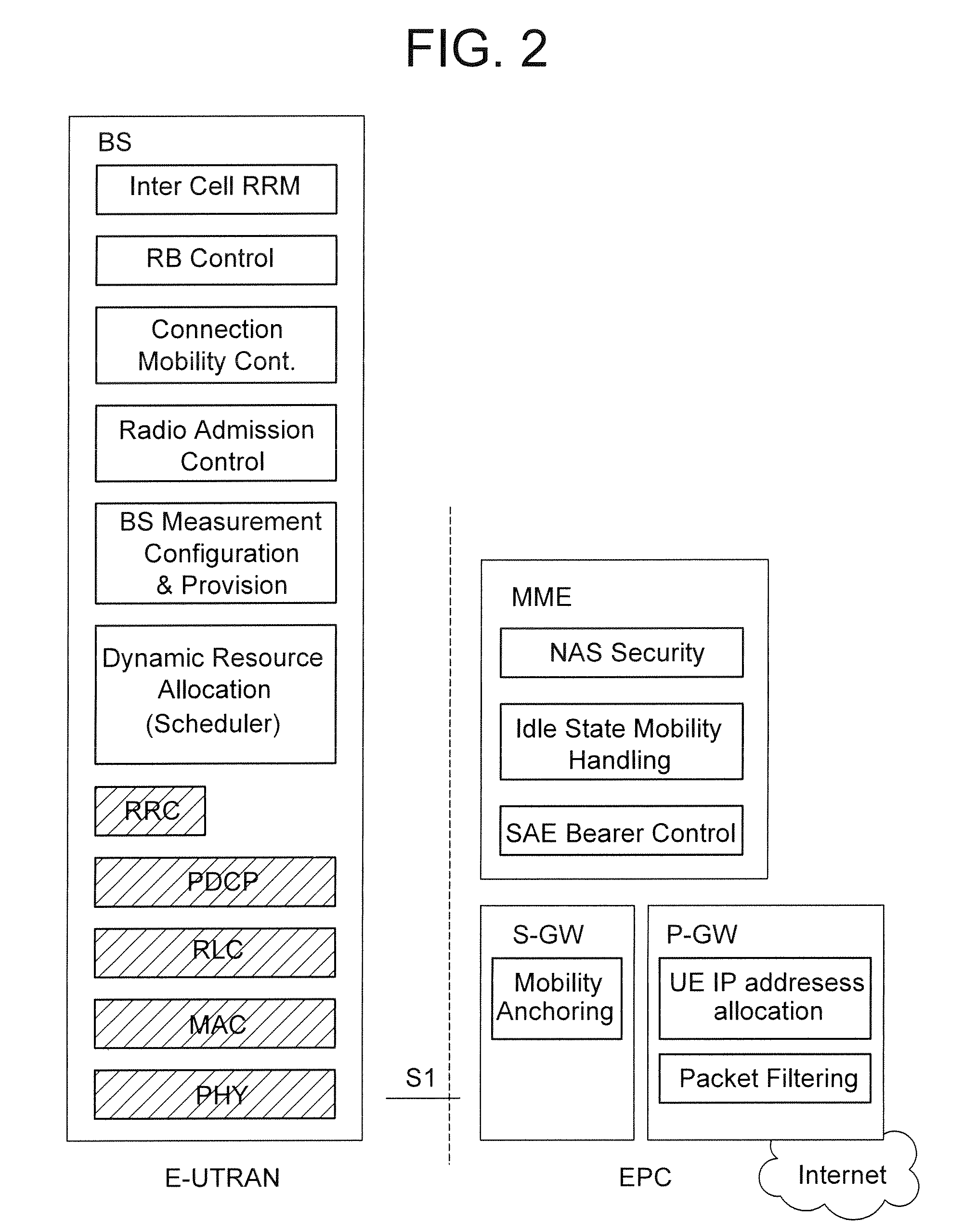
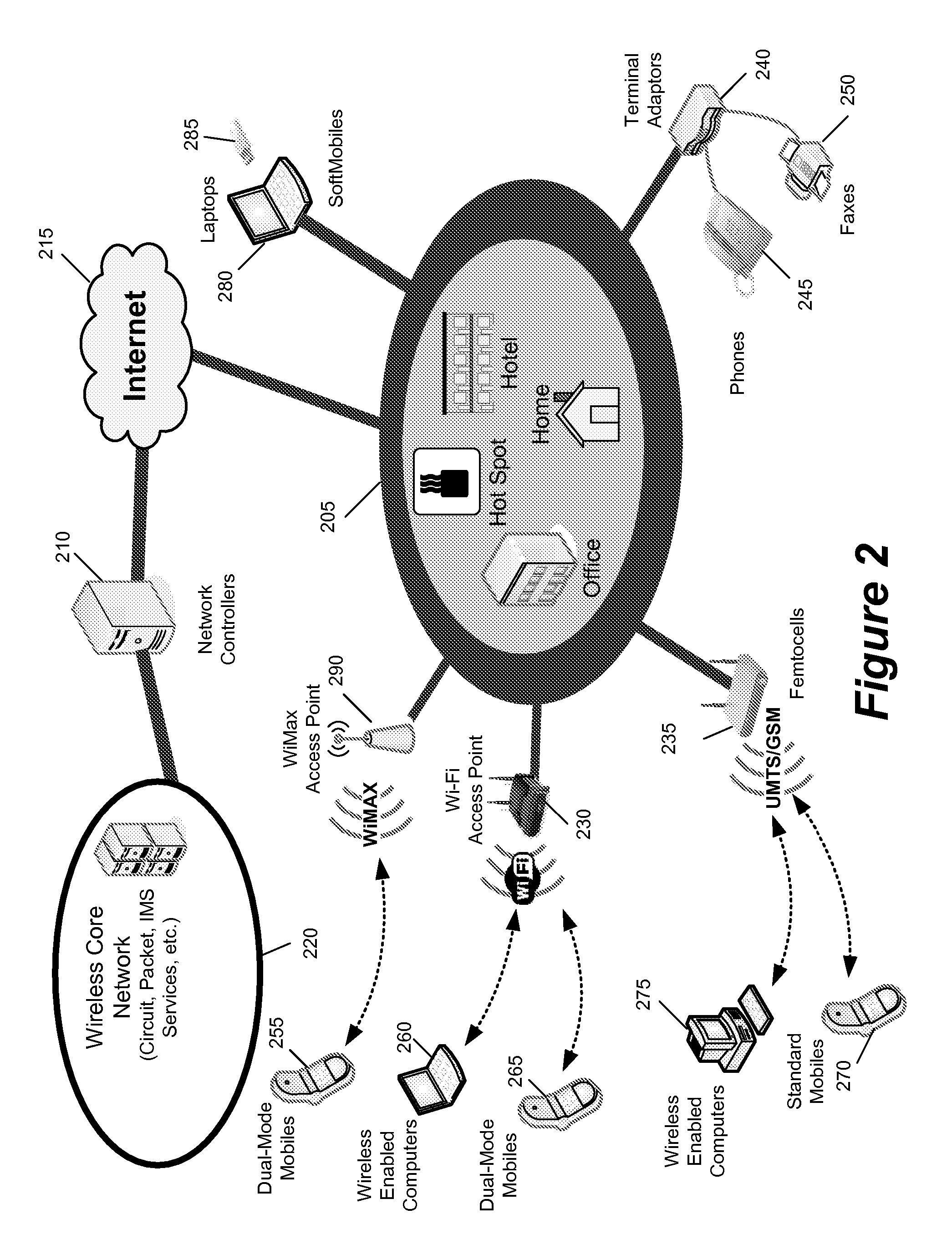
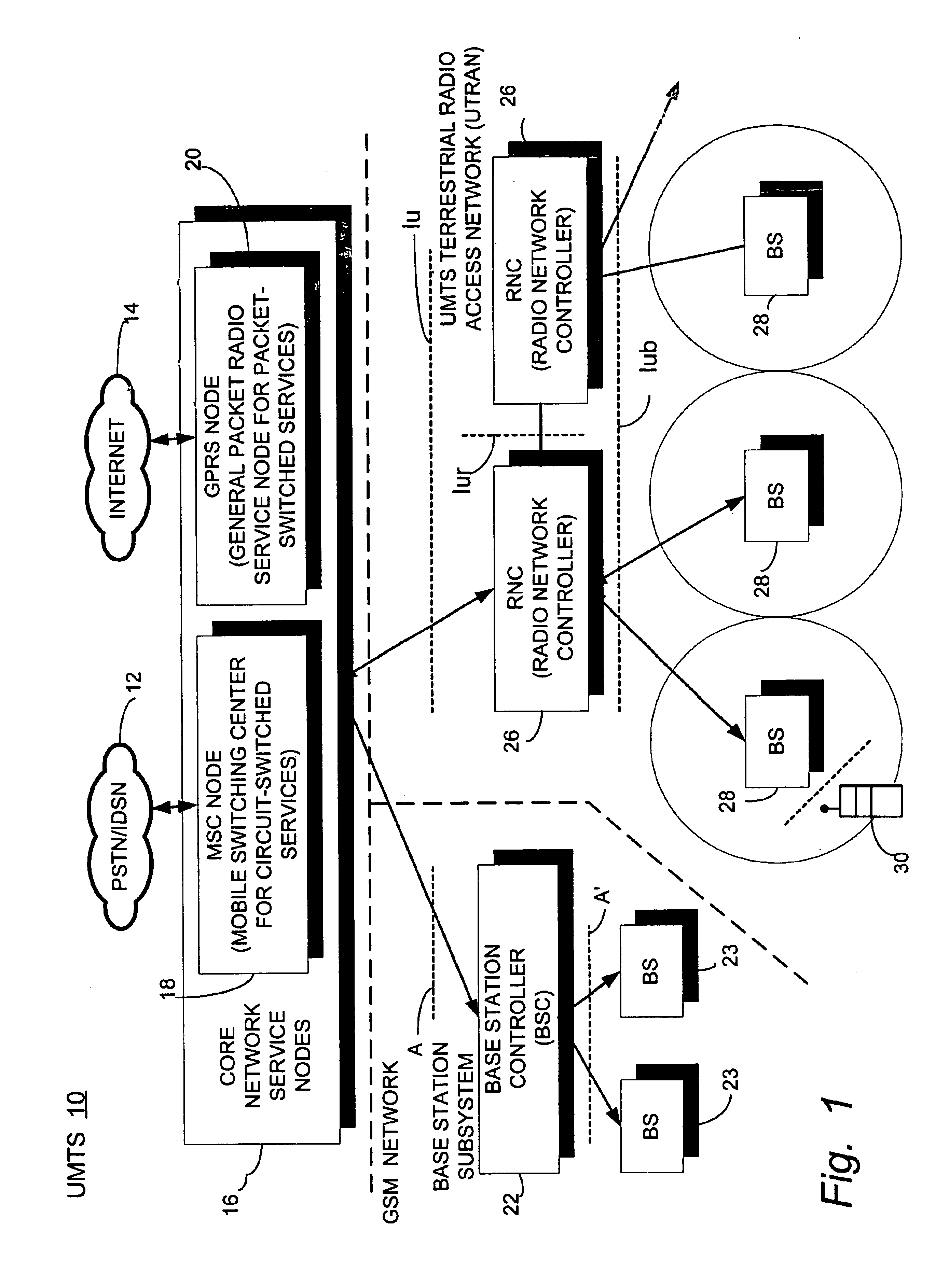
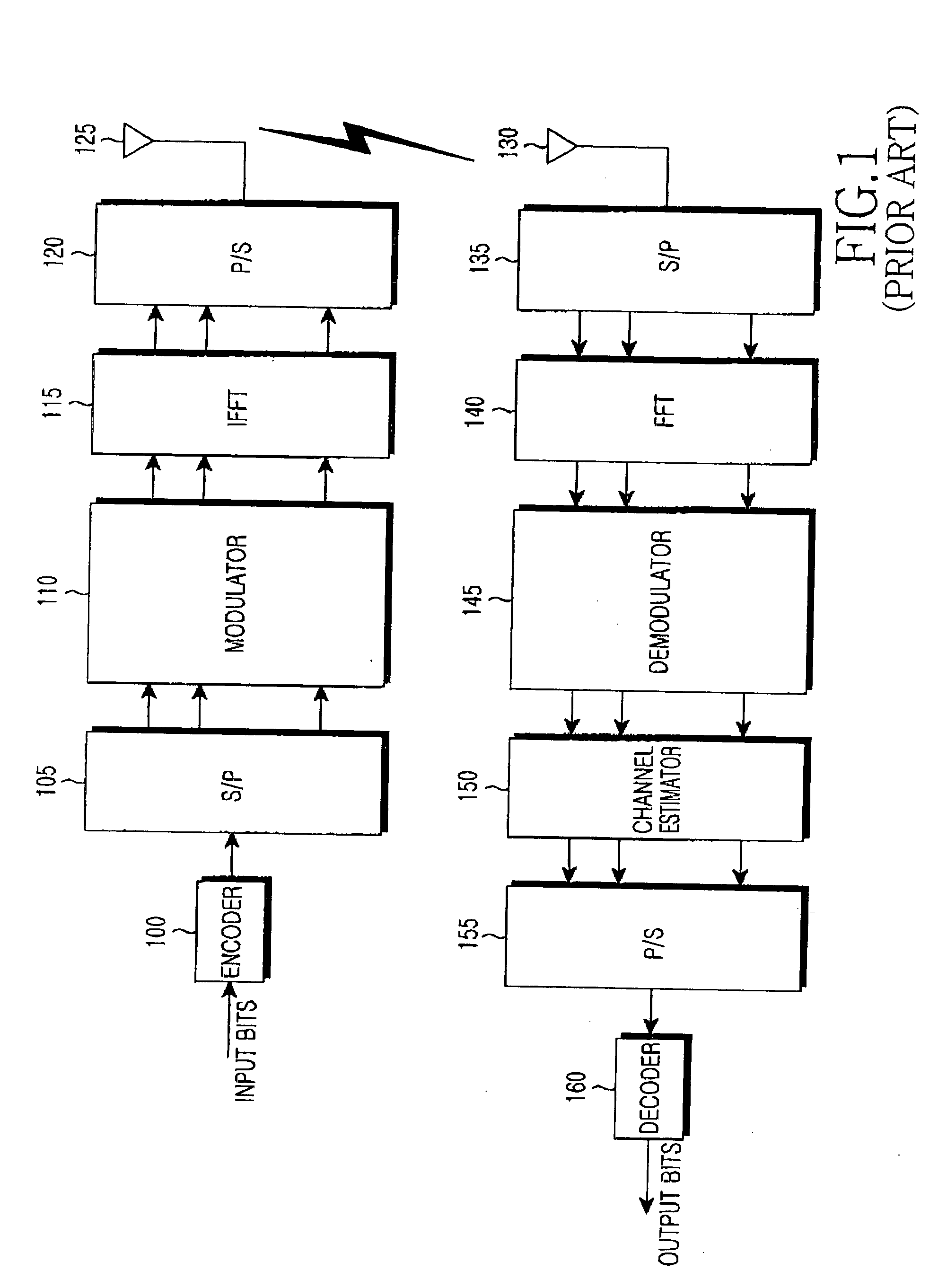
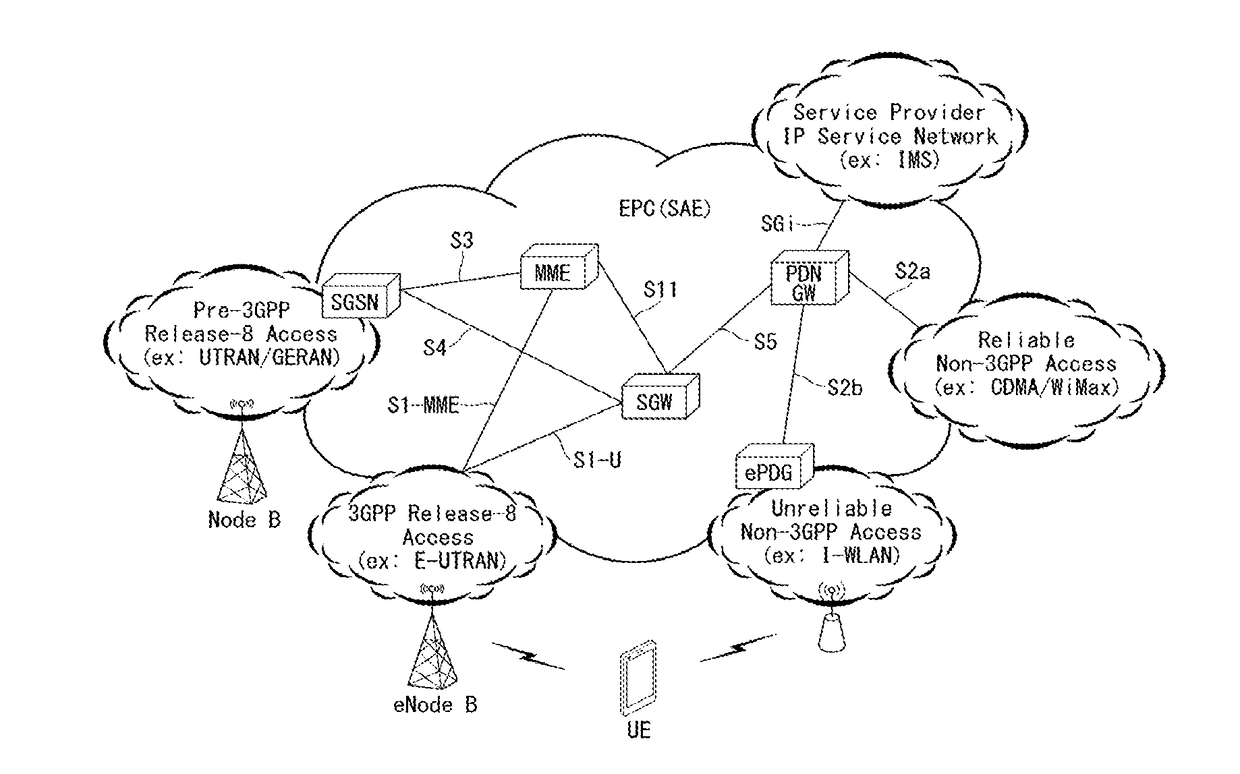
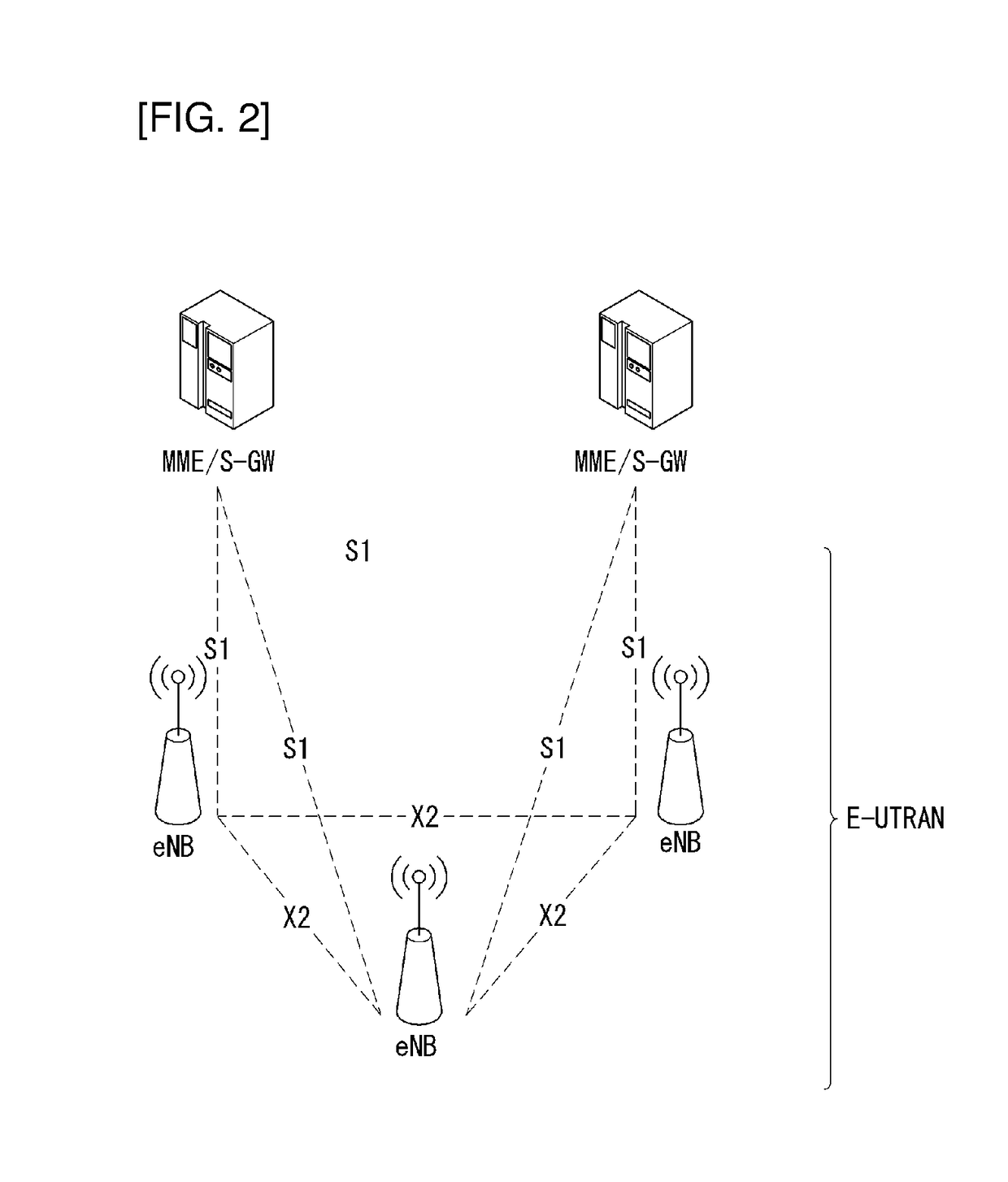
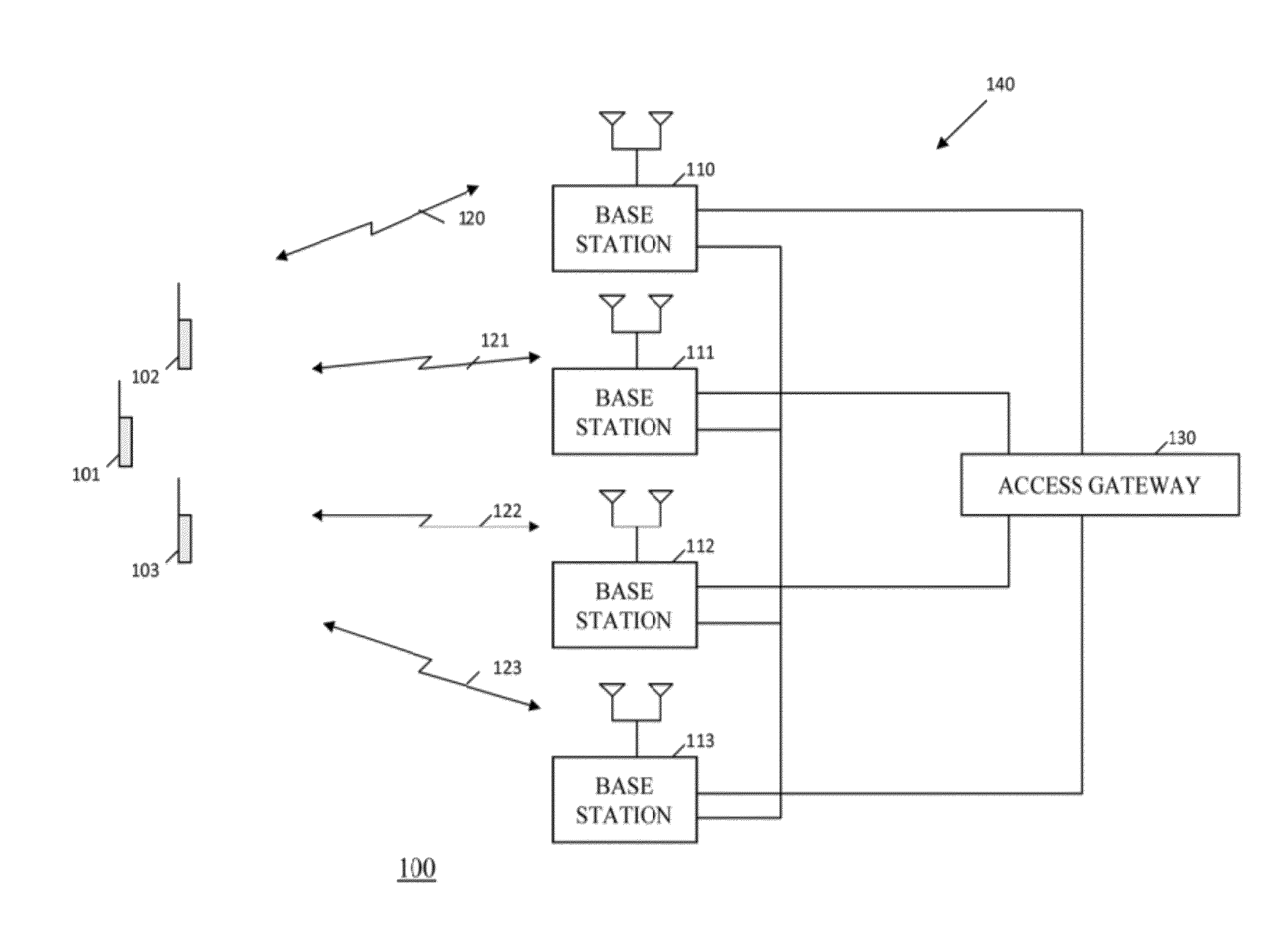
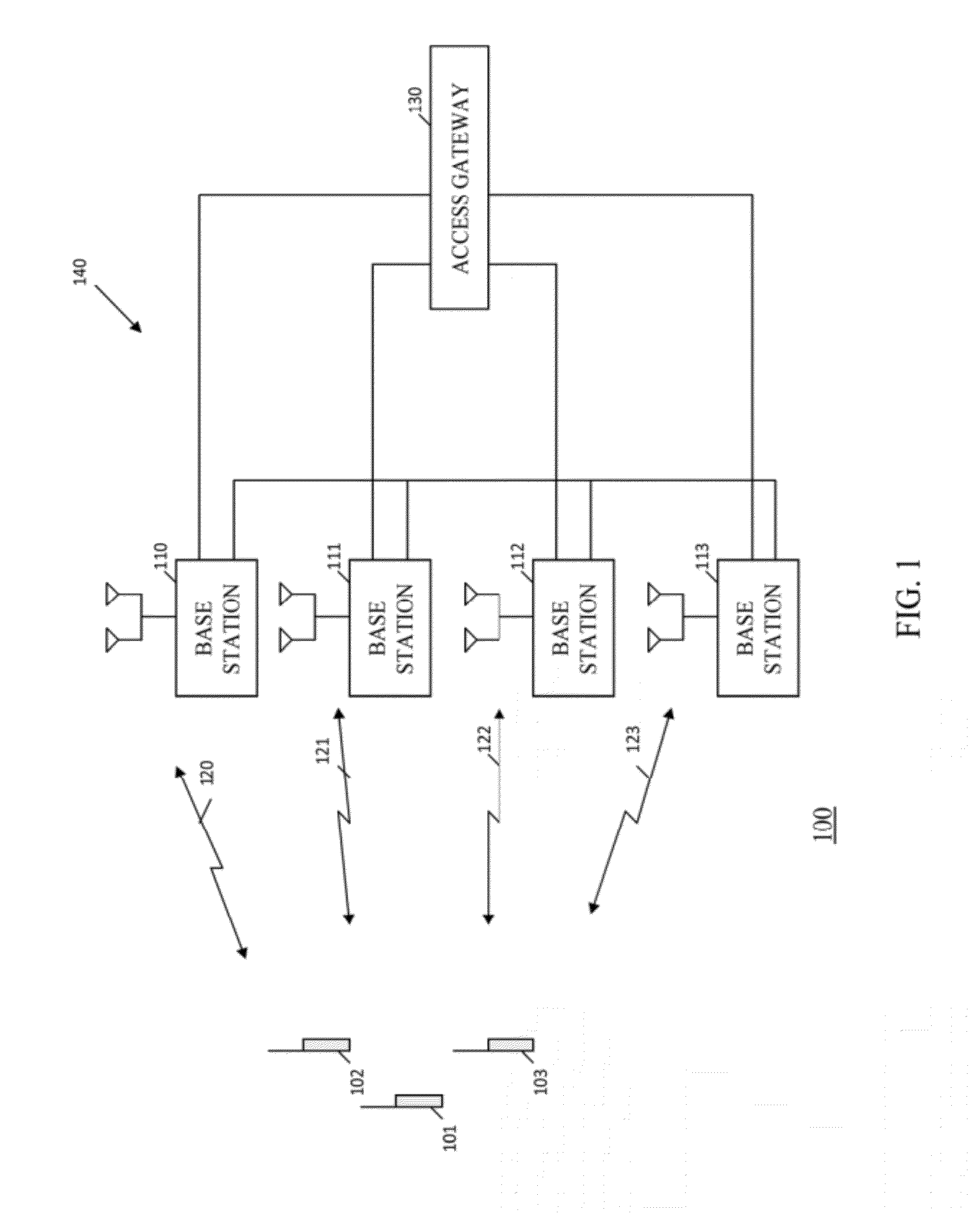
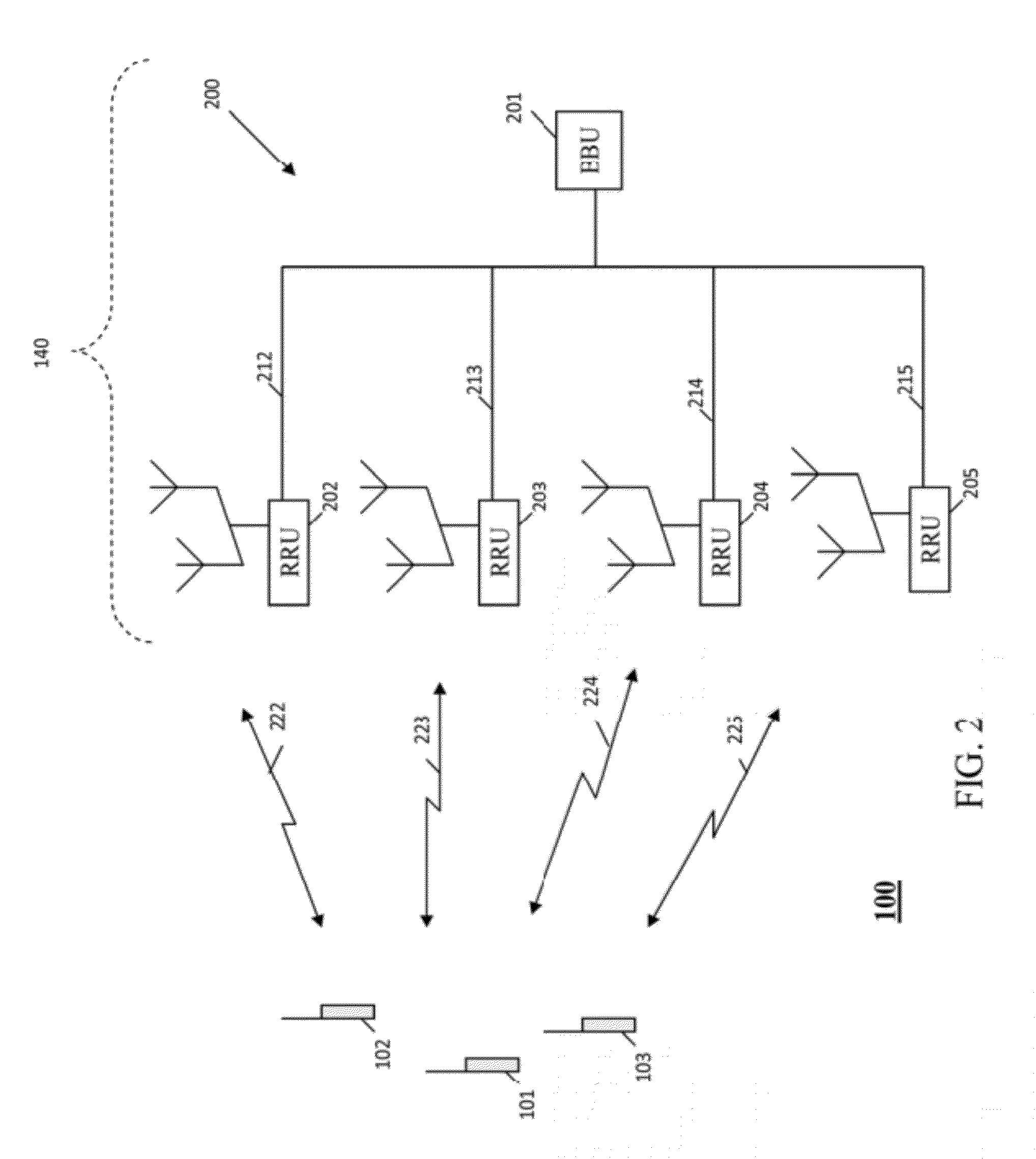
In the Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS) and 3GPP Long Term Evolution (LTE), user equipment (UE) is any device used directly by an end-user to communicate. It can be a hand-held telephone, a laptop computer equipped with a mobile broadband adapter, or any other device. It connects to the base station Node B/eNodeB as specified in the ETSI 125/136-series and 3GPP 25/36-series of specifications. It roughly corresponds to the mobile station (MS) in GSM systems.
Wireless communication system for monitoring physical downlink control channel
ActiveUS20090088148A1Reduce in quantityTransmission path divisionAssess restrictionCommunications systemTelecommunications
A method of monitoring a physical downlink control channel (PDCCH) in a wireless communication system is provided. A user equipment monitors a set of PDCCH candidates for a search space in a subframe. The search space includes a common search space monitored by all user equipments in a cell and a UE-specific search space monitored by at least one UE in the cell.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
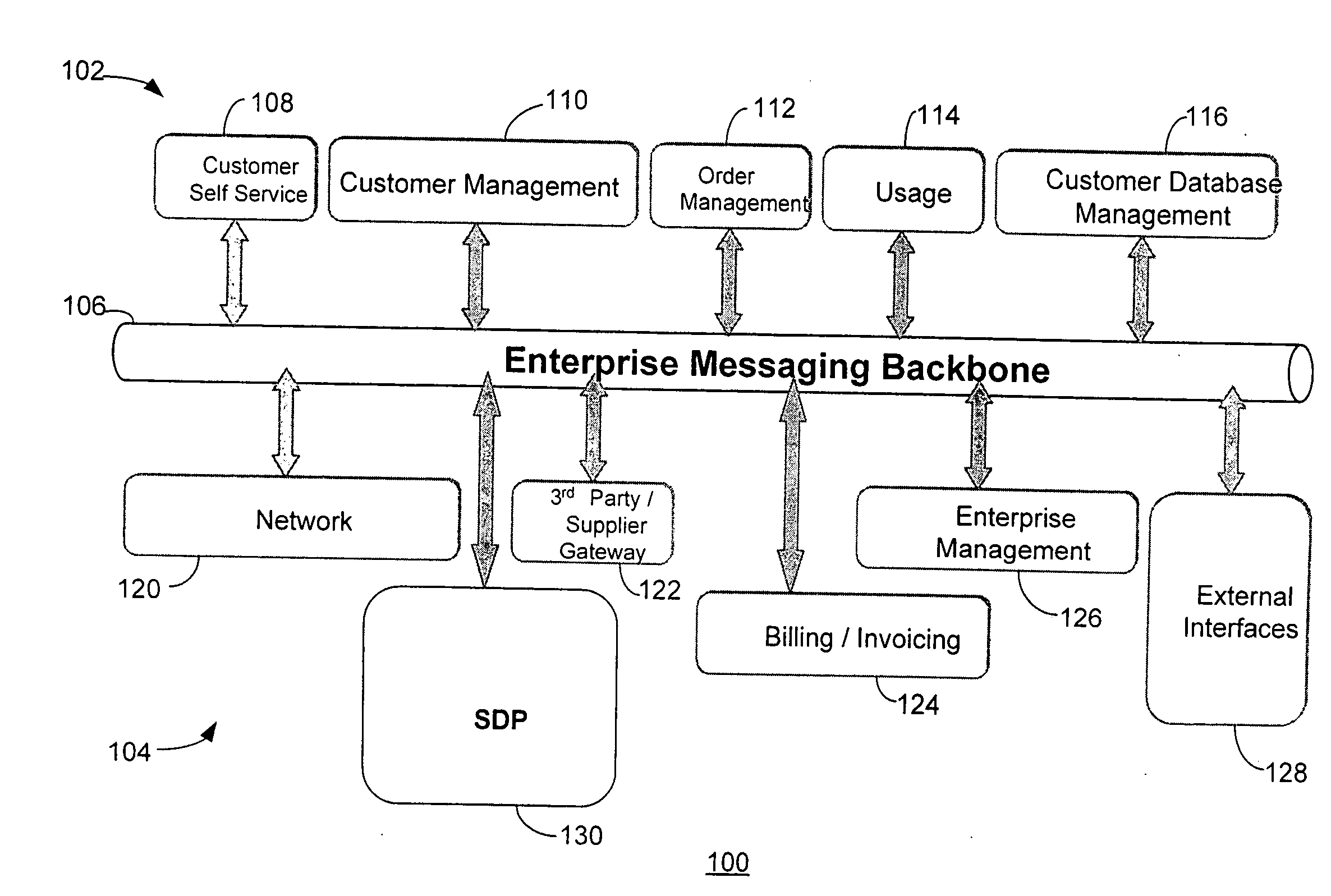
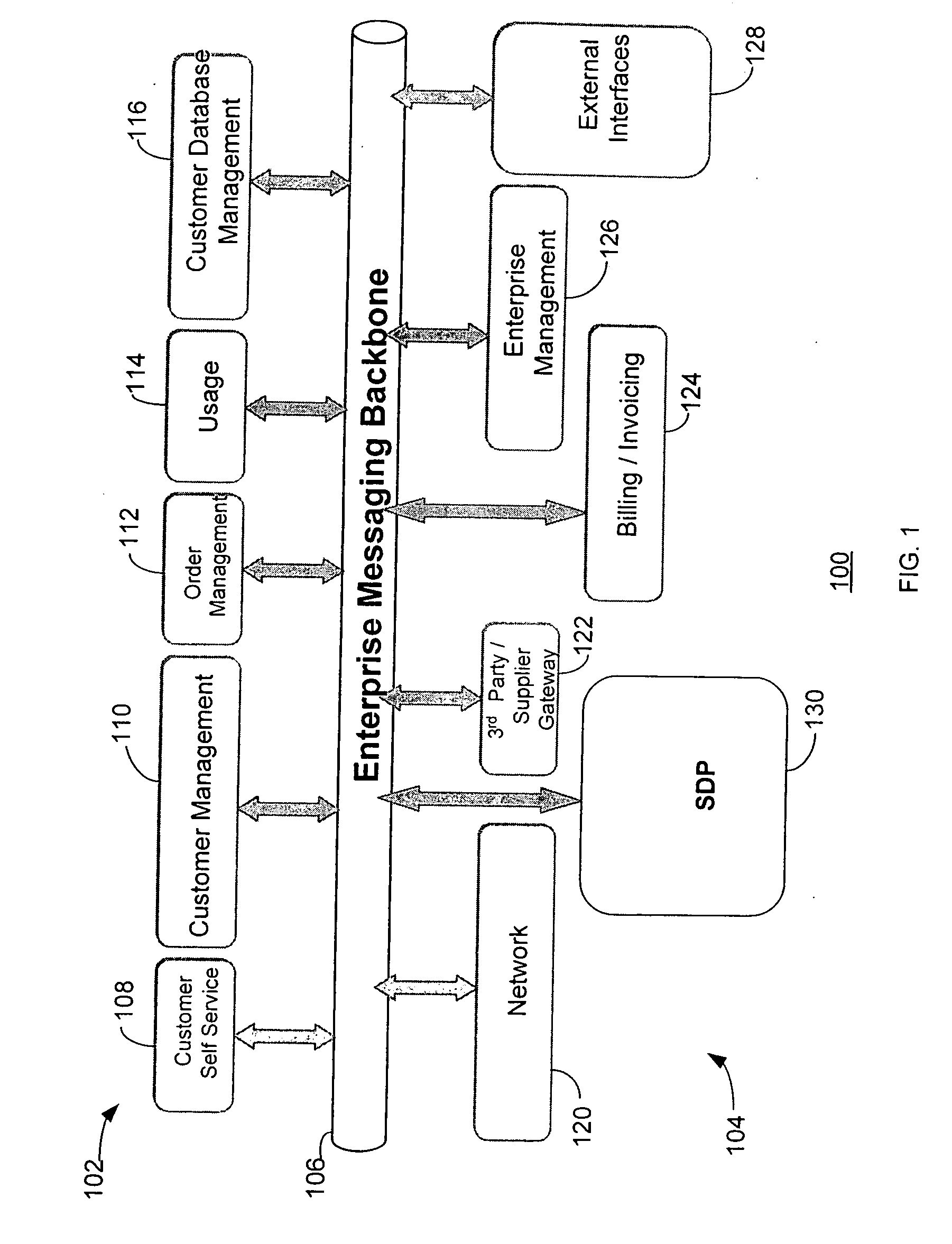
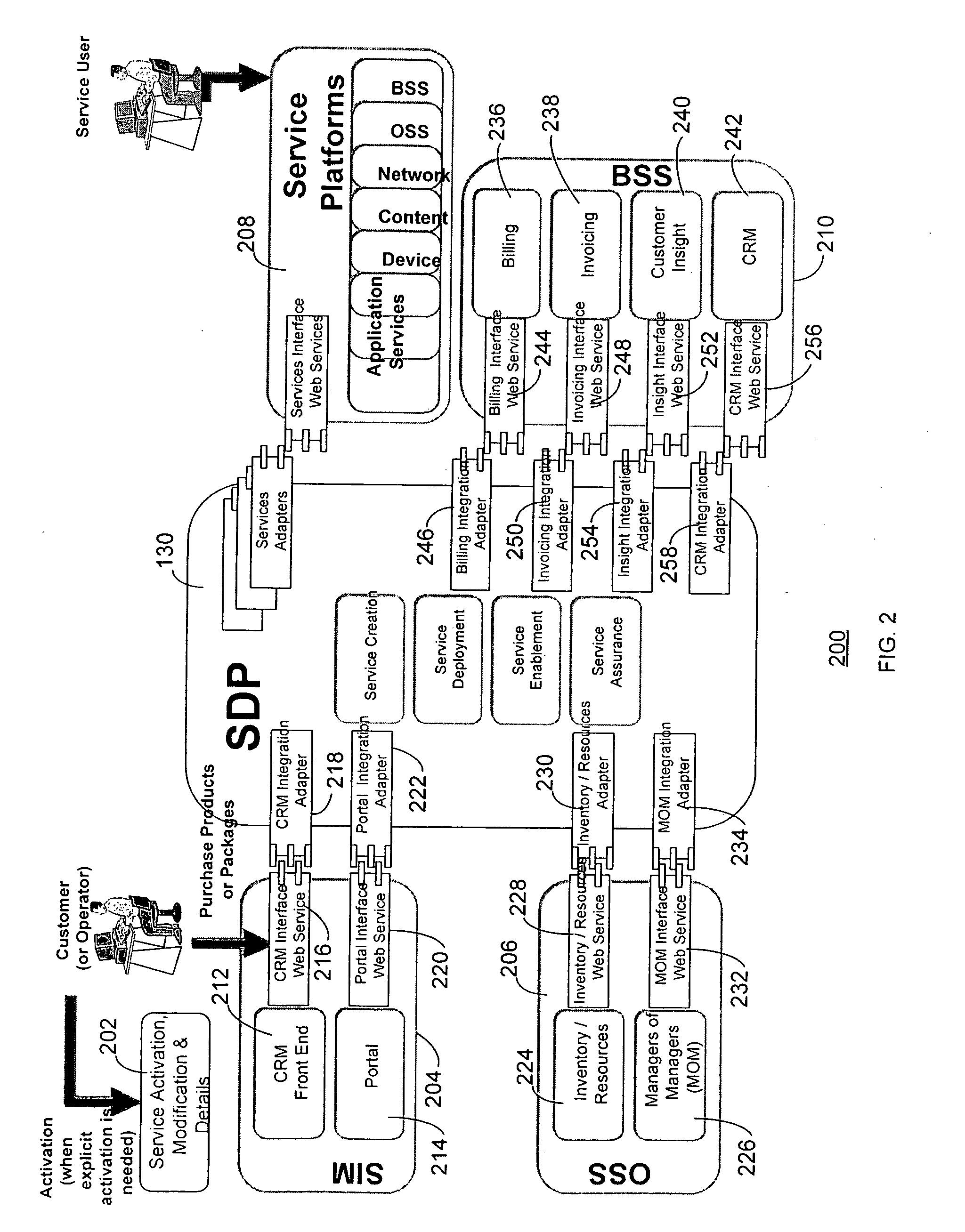
Service delivery platform
InactiveUS20070150480A1Easy to deployQuick serviceTechnology managementBilling/invoicingEngineeringUser equipment
A service delivery platform is disclosed, including method and apparatus for managing the delivery of a variety of services to customers or subscribers. Exemplary services that may be managed using the service delivery platform include telecommunication services such as cable, wire line and wireless services. The service delivery platform creates, hosts, and manages services over different channels and end user devices. The implementation of the service delivery platform will dramatically simplify service deployment and management, and allow an enterprise to develop new services more rapidly with the reduced development efforts.
Owner:ACCENTURE GLOBAL SERVICES LTD
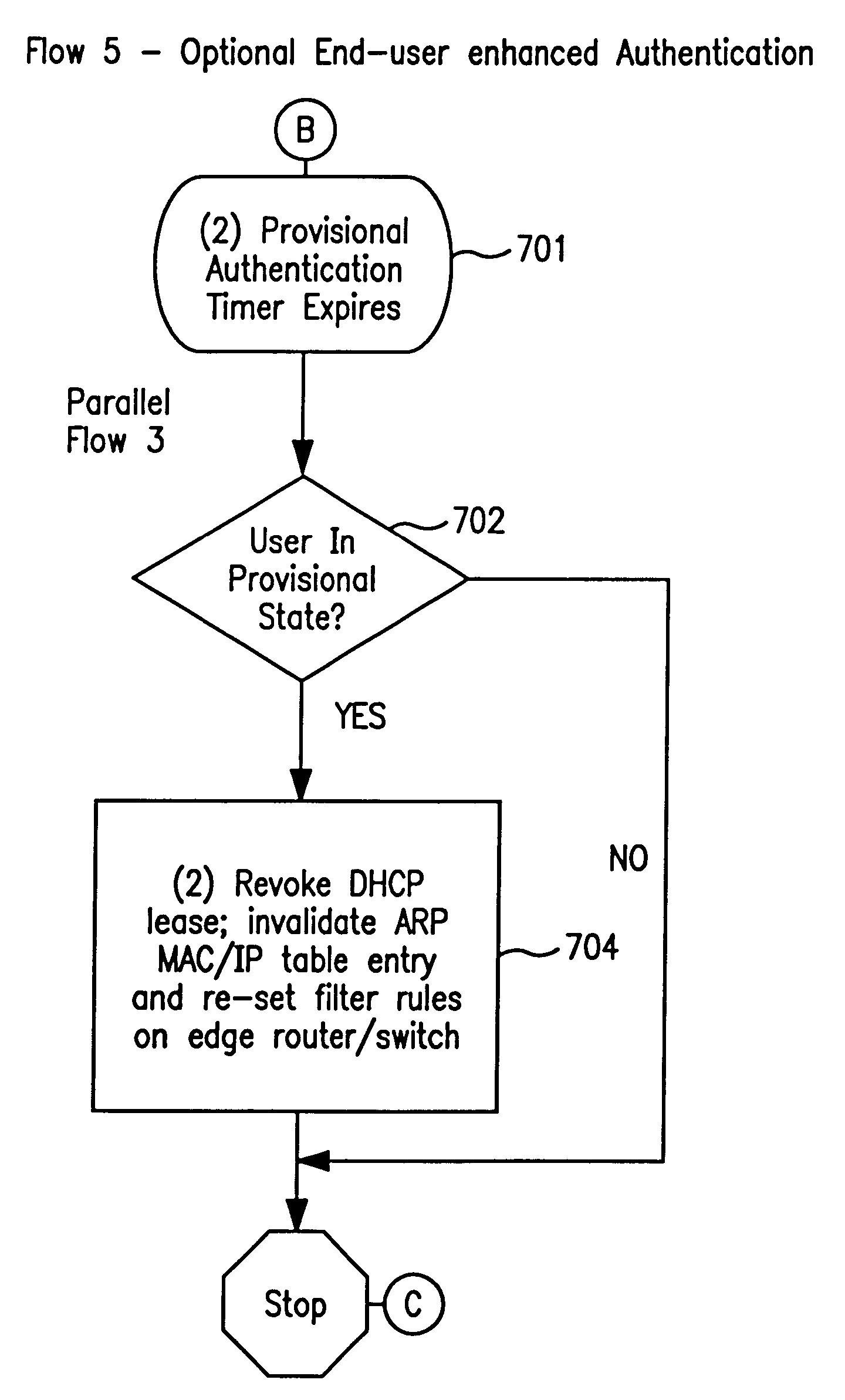
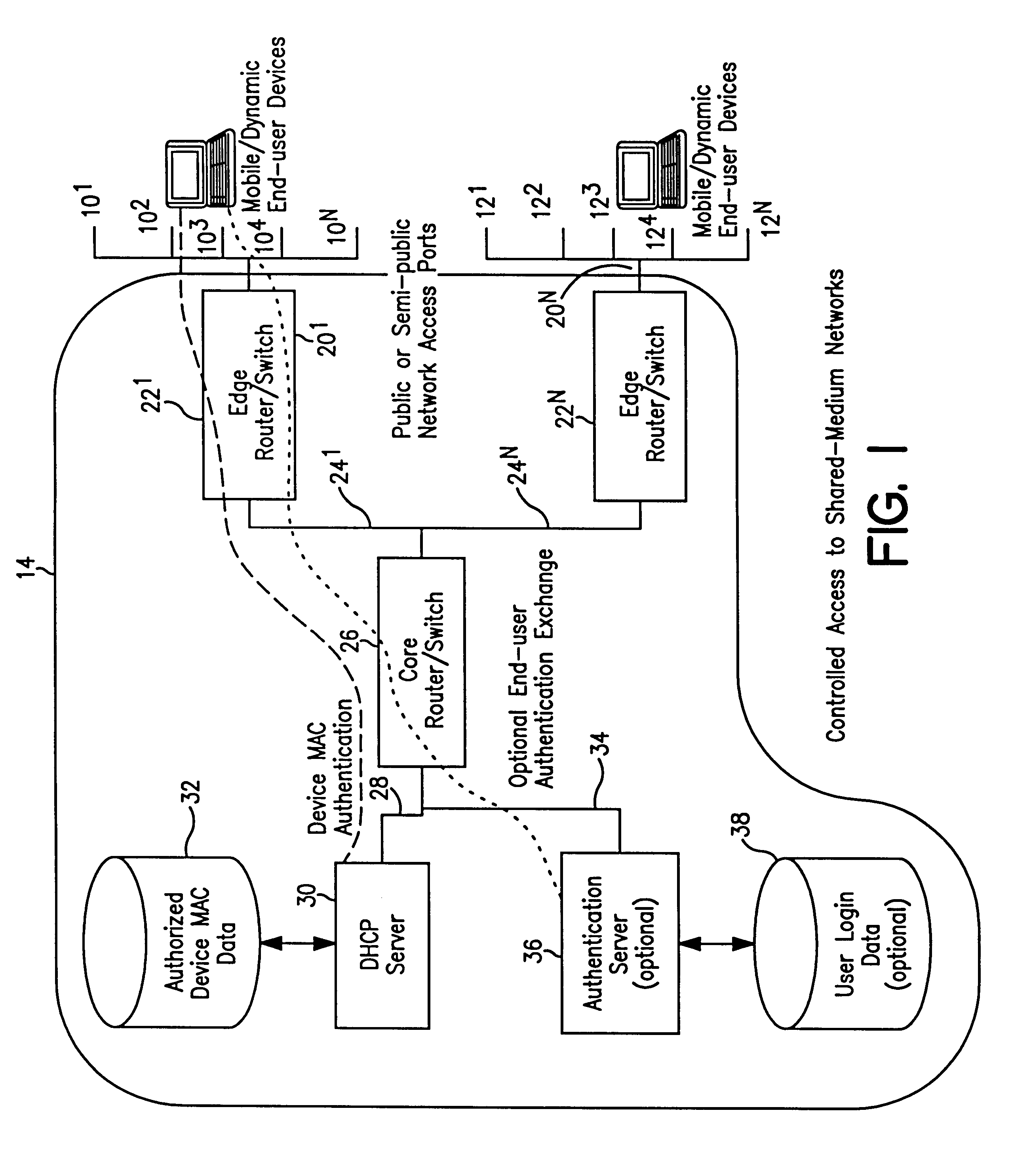
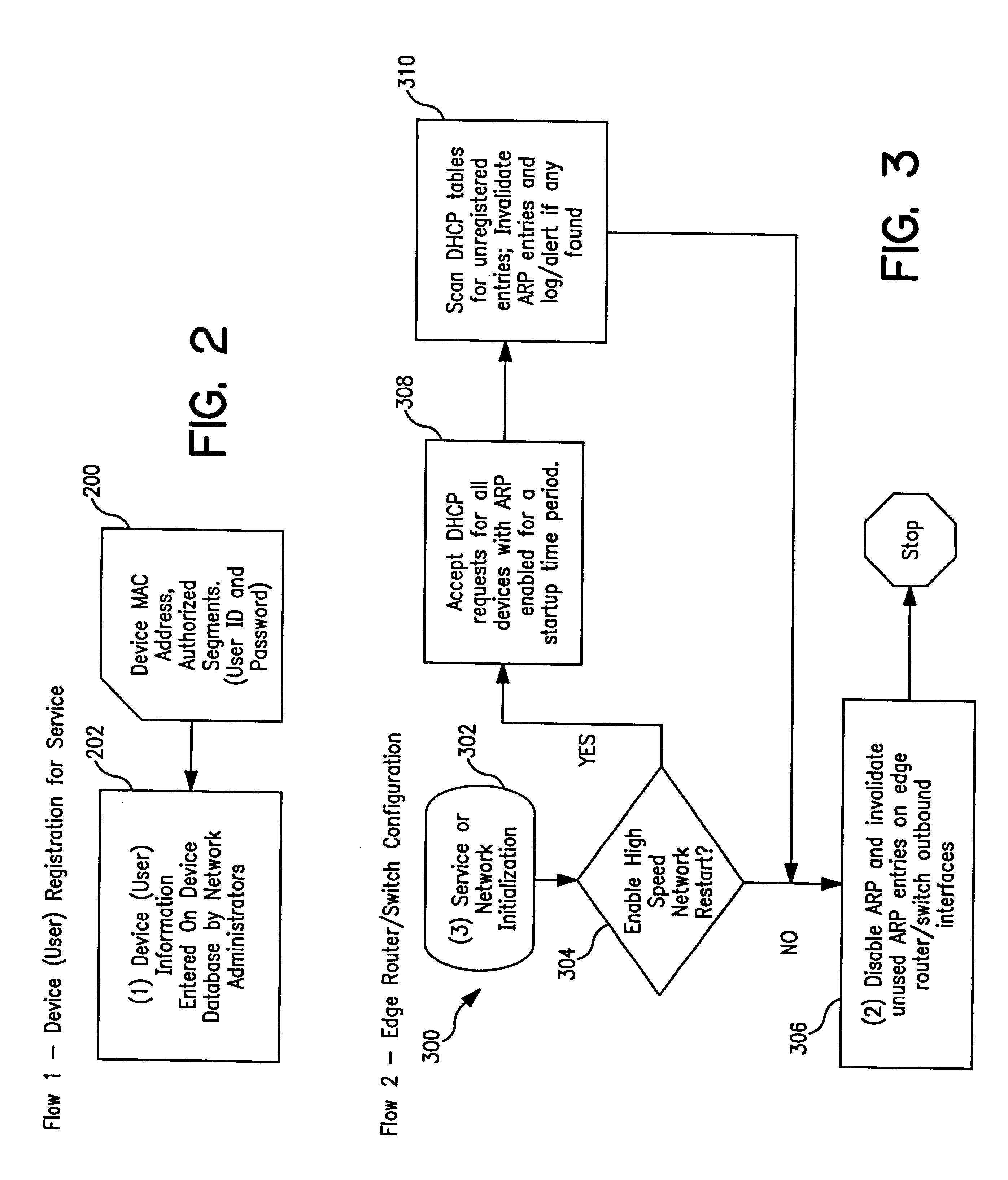
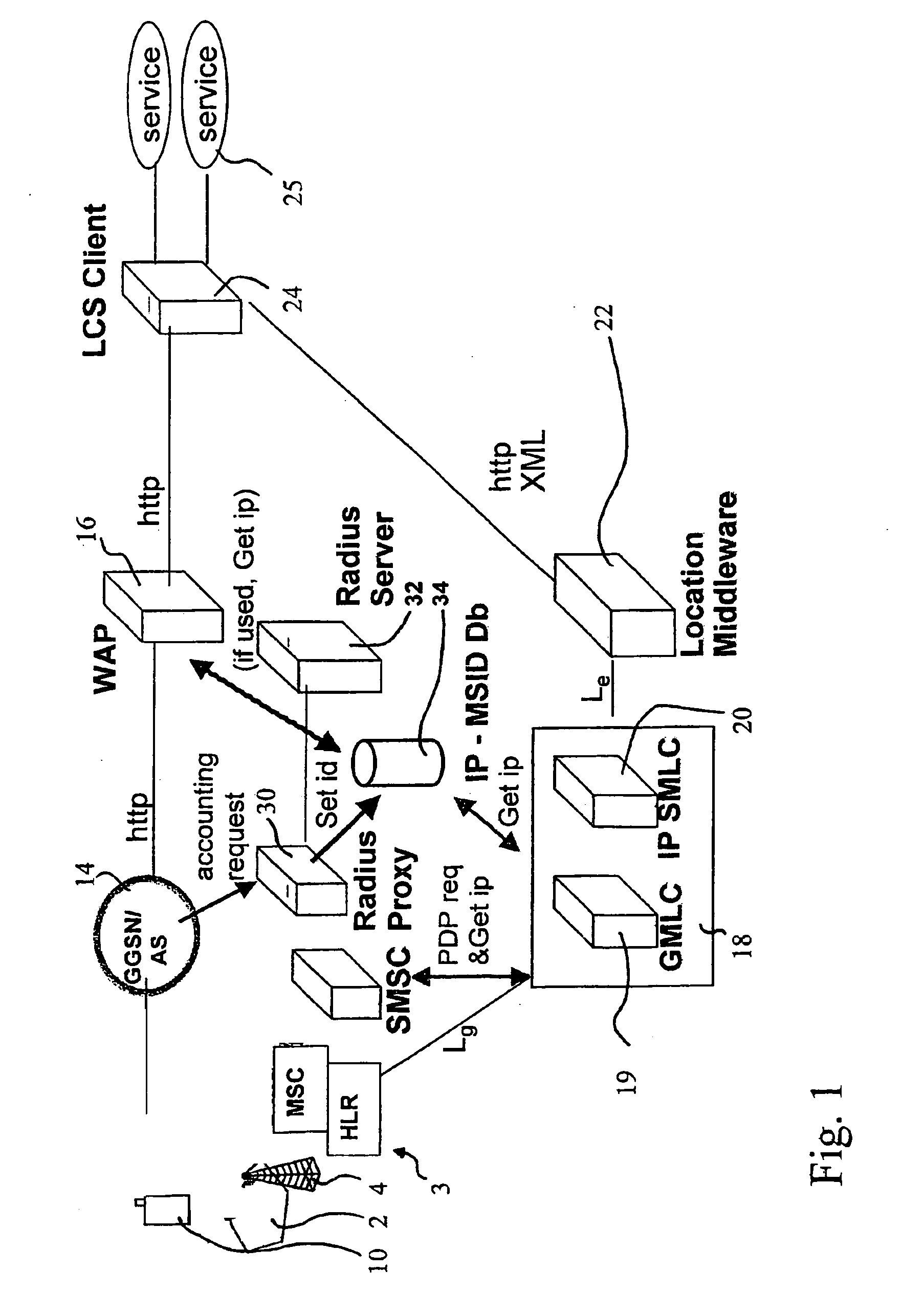
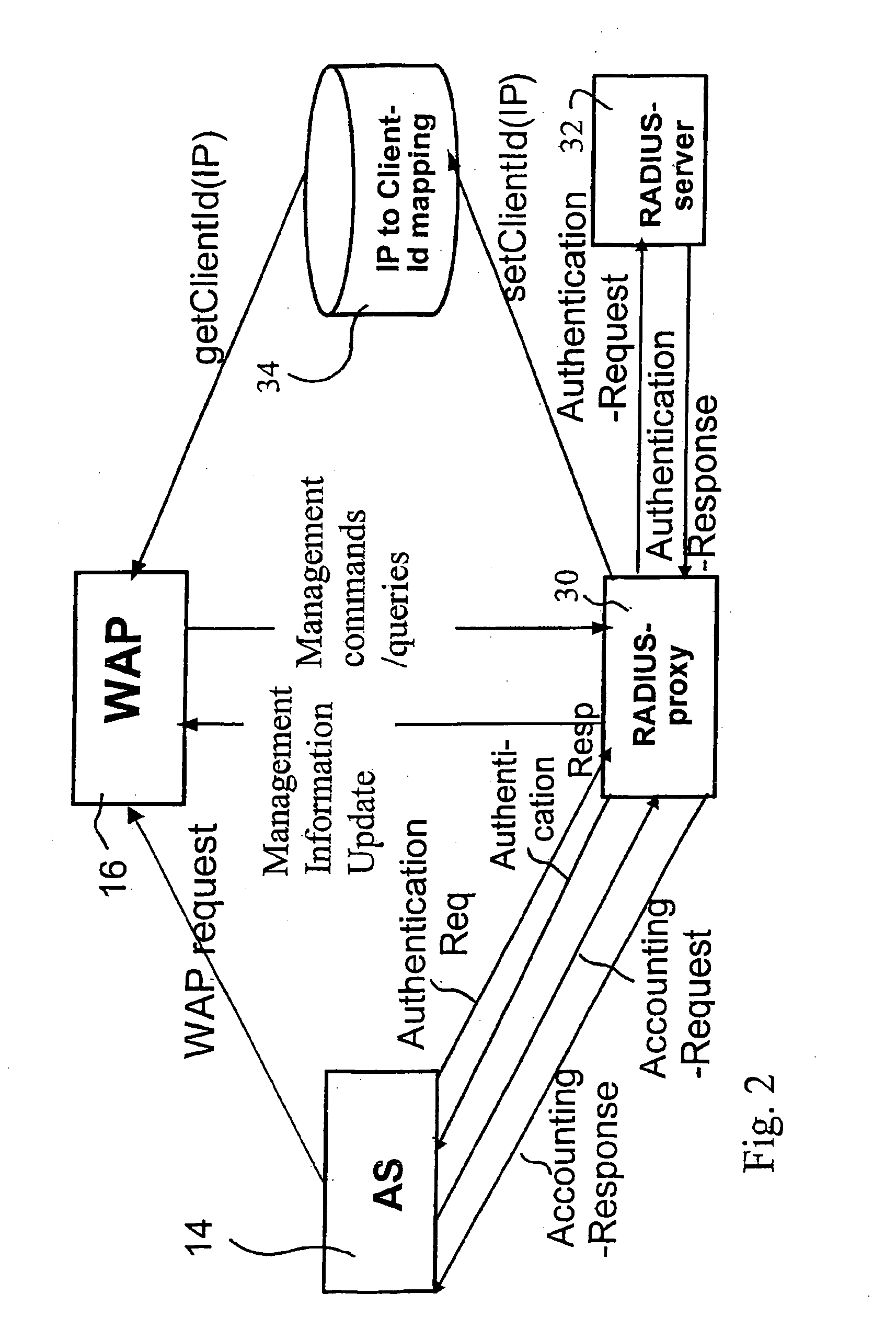
System and method for controlled access to shared-medium public and semi-public internet protocol (IP) networks
InactiveUS6393484B1Multiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionAddress Resolution ProtocolDevice register
A system and method prevent unauthorized users and devices, in a dynamic user / device environment, from obtaining access to shared-medium public and semi-public IP networks. A network includes a layered communication system and routers / switches for coupling users and devices to a Dynamic Host Control Protocol (DHCP) server and an authentication server. Databases support the servers. The network incorporates Address Resolution Protocol (ARP). Authorized users and devices register for service by providing the DHCP with user identification for log-in, passwords, MAC addresses, etc. When users connect to the network access point, a DHCP exchange is initiated to obtain a valid IP address and other associated parameters. The DHCP client initiates a MAC broadcast for IP addresses which contain in the request the end user's device MAC address. The associated router switch will pick up and forward to a DHCP server the end user's device request. The DHCP server will process the end user's request and extract the end user's device MAC address. With the end user's MAC address, the DHCP server accesses its device and / or user information in the database. If the MAC address is not registered, the DHCP server refuses to handle the request and logs the attempt, potentially alerting network operators of a security breach. If the MAC address is registered, a DHCP server selects an appropriate IP address and associated parameters to be returned to the requesting end user and connects via programming or command interface to the router switch that is forwarding the DHCP request on behalf of the end user device. The server adds an ARP IP to the MAC address table entry with the selected IP address and end user's MAC address. End user device authentication and IP lease are marked as provisional. A timer is started for a suggested duration. Optionally, the DHCP dynamically sets up filter rules in the router switch limiting access to a subset of IP addresses such as the address of a log-in server. Initial DHCP processing is completed and an IP address is assigned to the requesting end user's device by DHCP. When the timer expires, if the DHCP server finds the authenticating user state is provisional, it will revoke the IP lease, invalidate the corresponding ARP to MAC table entry in the associated router switch, and reset any IP-permissive filtering for that device. If the user is in the full authenticated state, it will simply remove the restrictive filtering.
Owner:IBM CORP
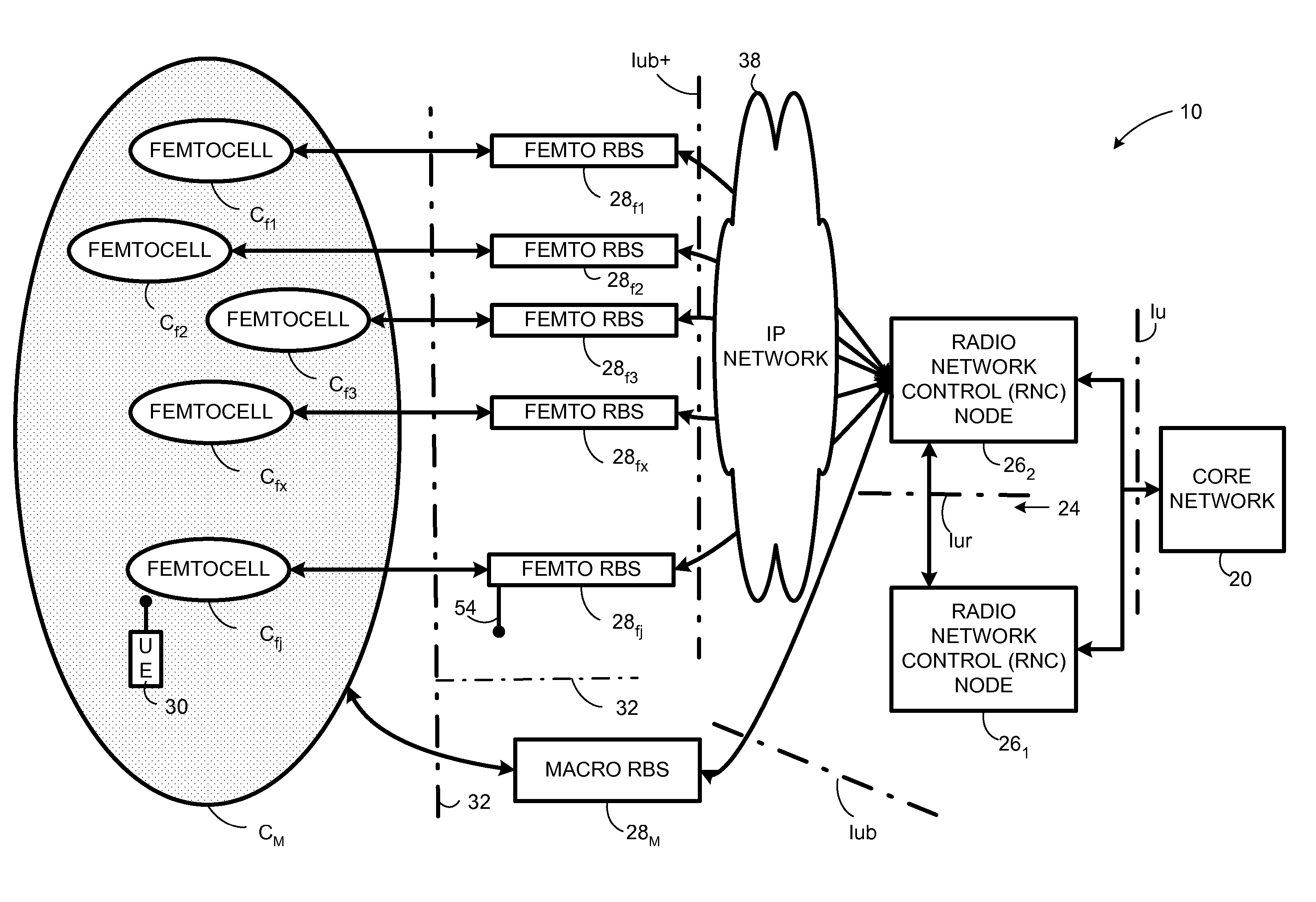
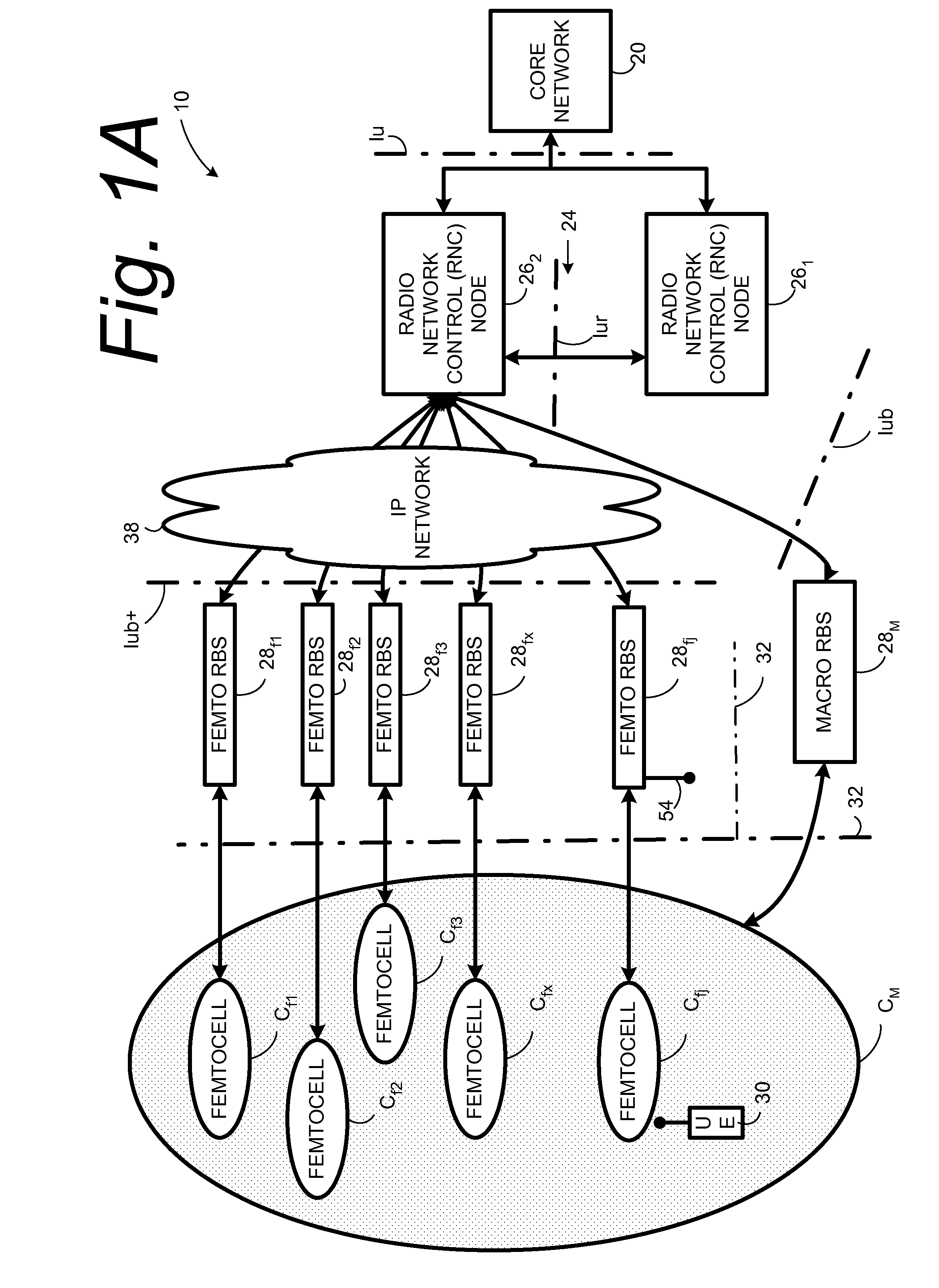
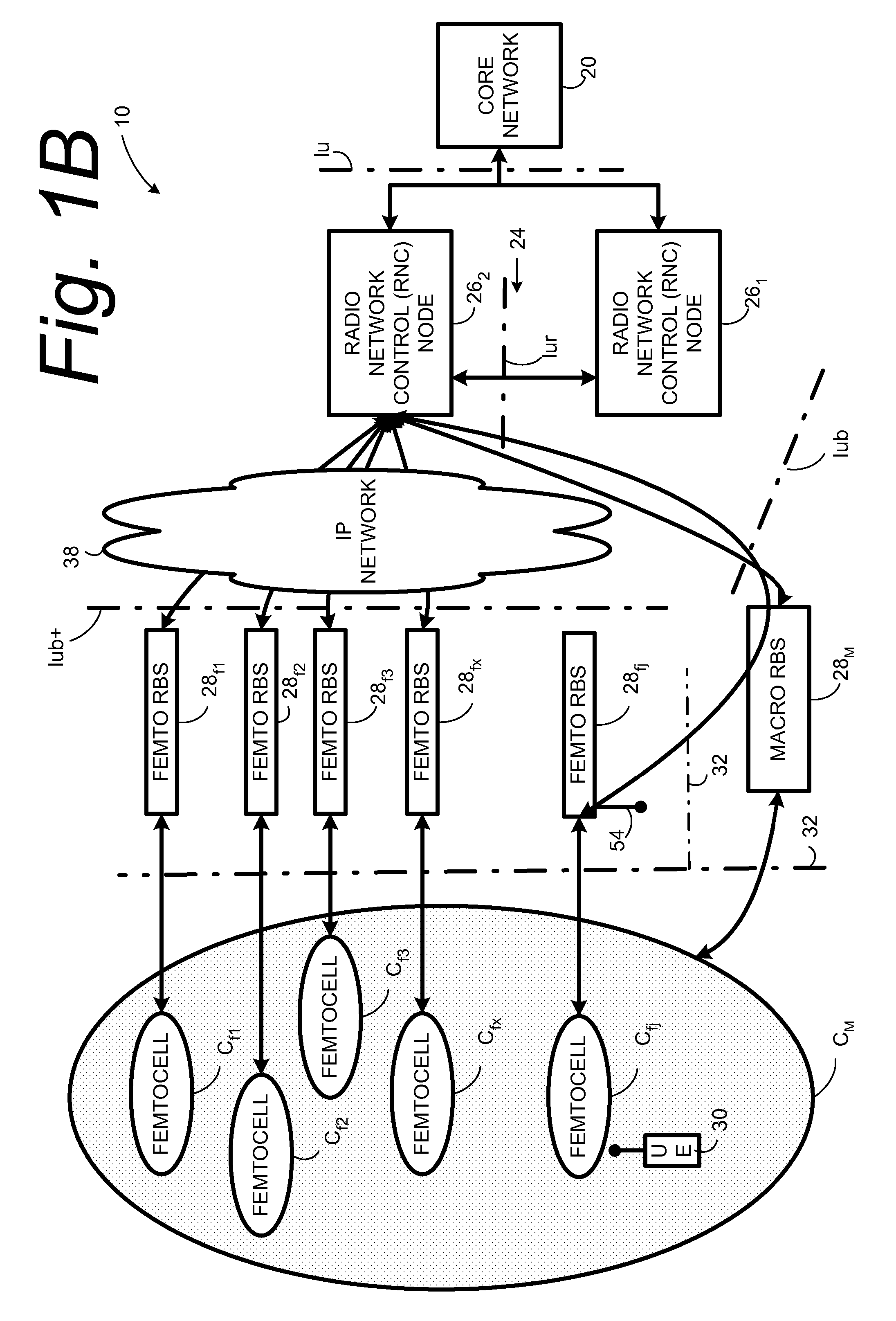
Automatic building of neighbor lists in mobile system
In a radio access network (24) a femto radio base station (28f) comprises a resident receiver (54) which acquires system information broadcast in a radio access network (24). At least part of the system information is used for building, at the femto radio base station (28f), a neighbor data structure (59) comprising information for neighboring cells. The neighbor data structure (59) is then used for building a neighbor list. The neighbor list is subsequently transmitted from the femto radio base station (28f) to a user equipment unit (30) served by the femto radio base station (28f). In some example embodiments and modes, the femto radio base station (28f) reports the neighbor data structure to a network node (26, 100) other than the femto radio base station. The other node (26, 100) uses the neighbor data structure for building the neighbor list at the other node. In some example embodiments and modes, acquisition of the system information comprises scanning a surrounding macro coverage area of the femto radio base station for obtaining cell identity information for detected cells. In other example embodiments and modes, the acquisition of the system information can additionally comprise camping on a macro cell and using / consulting at least one system information block in the camped-on macro cell is consulted / used for obtaining information about at least one neighboring cell.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
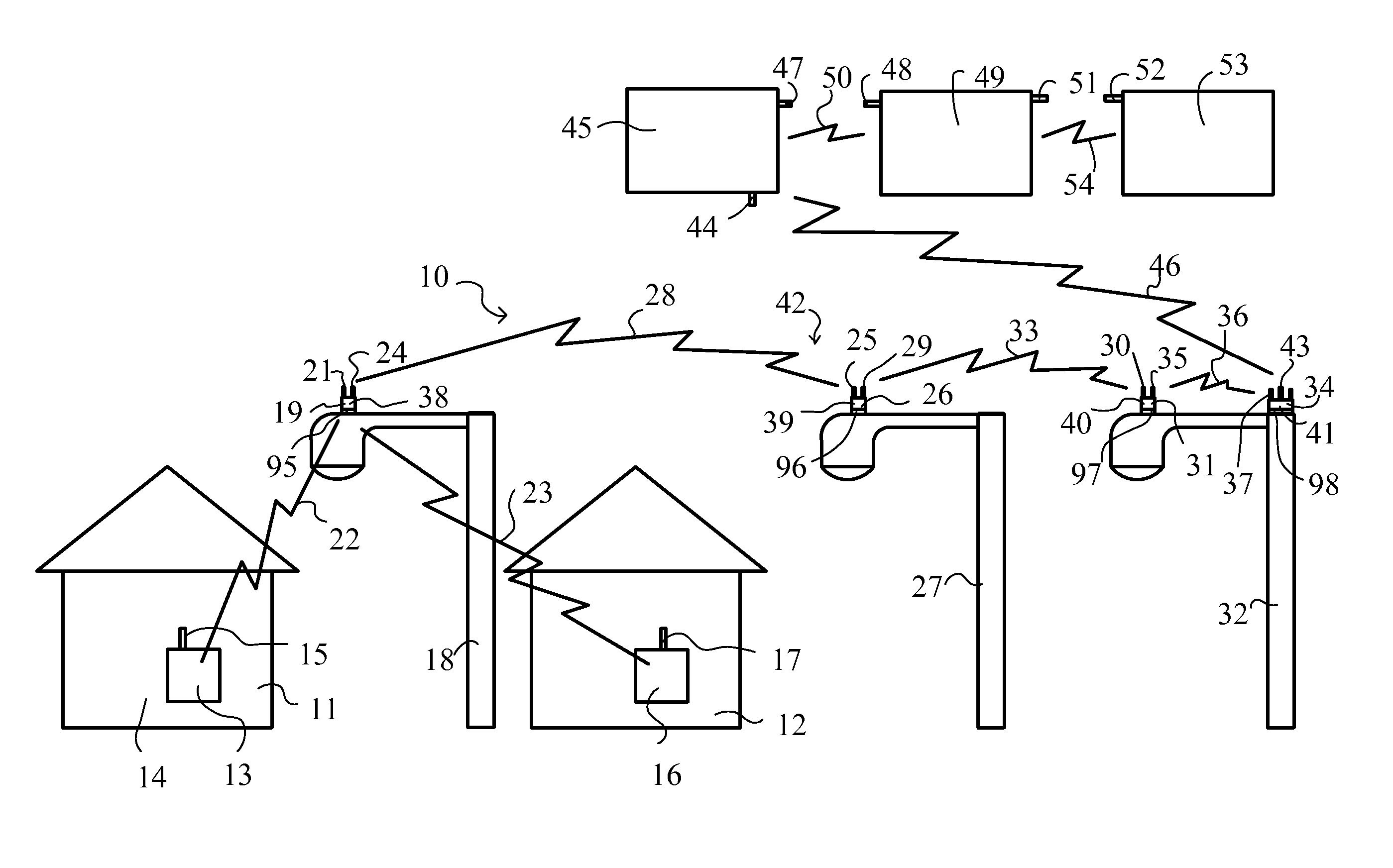
Remote monitoring and control system
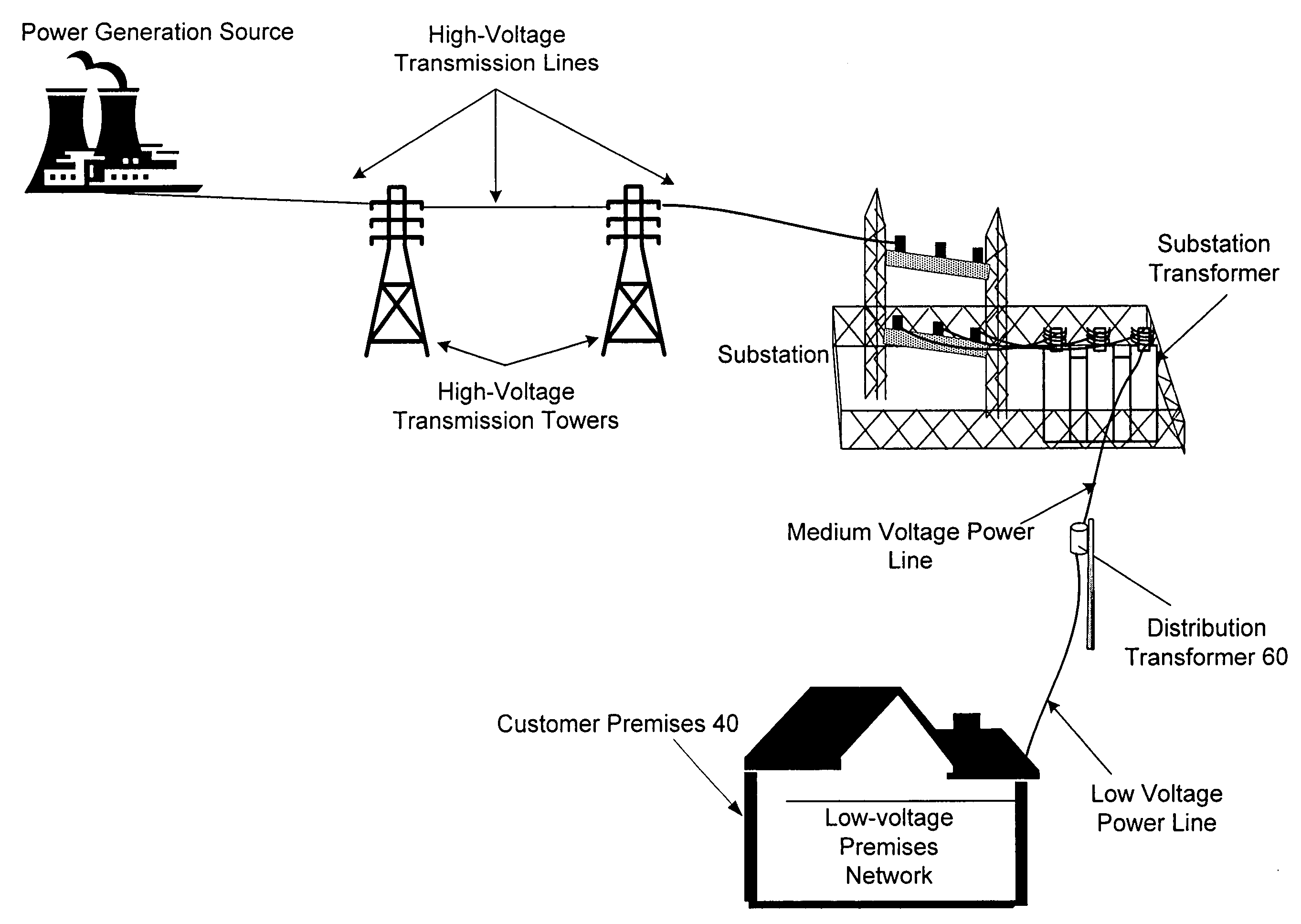
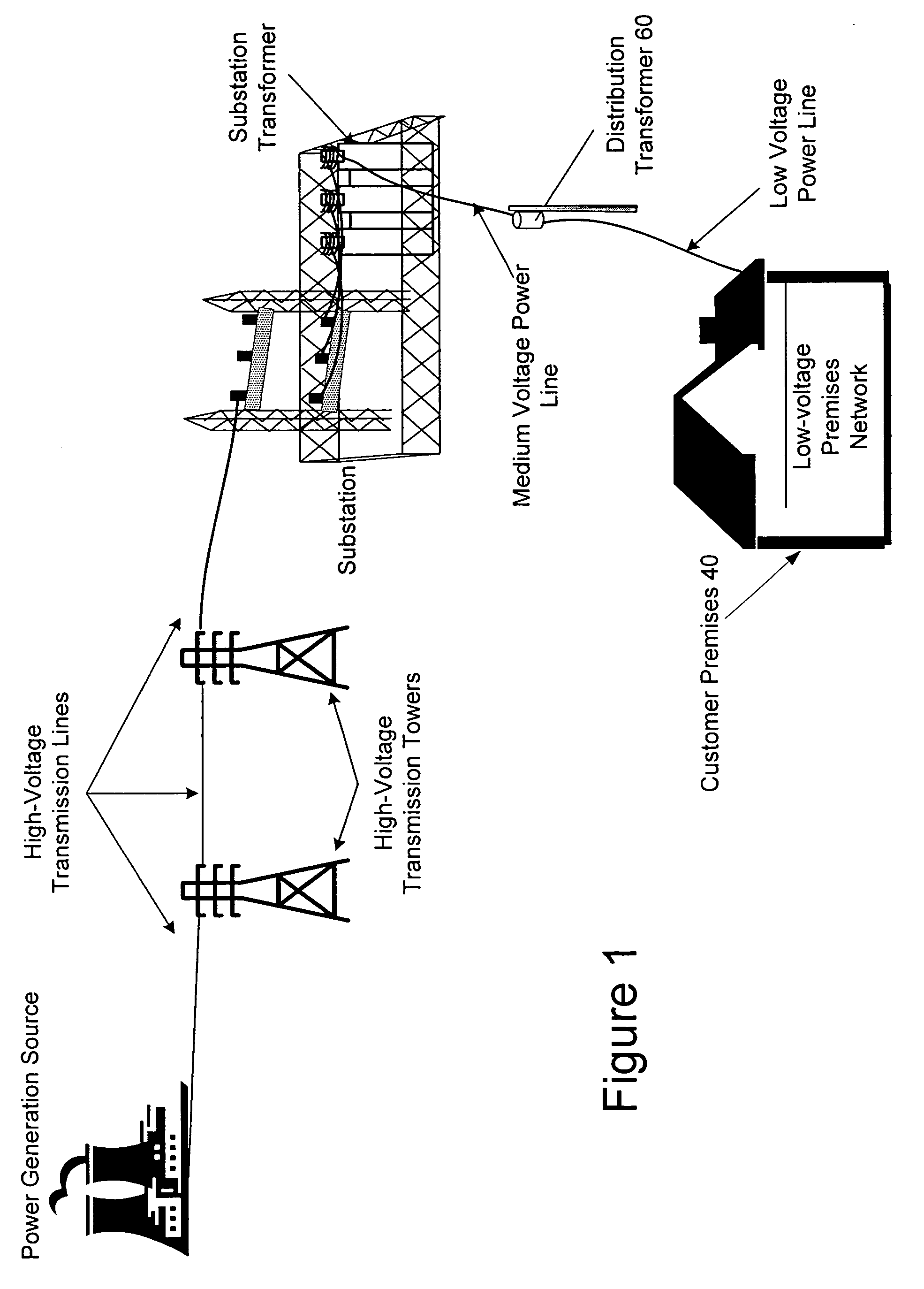
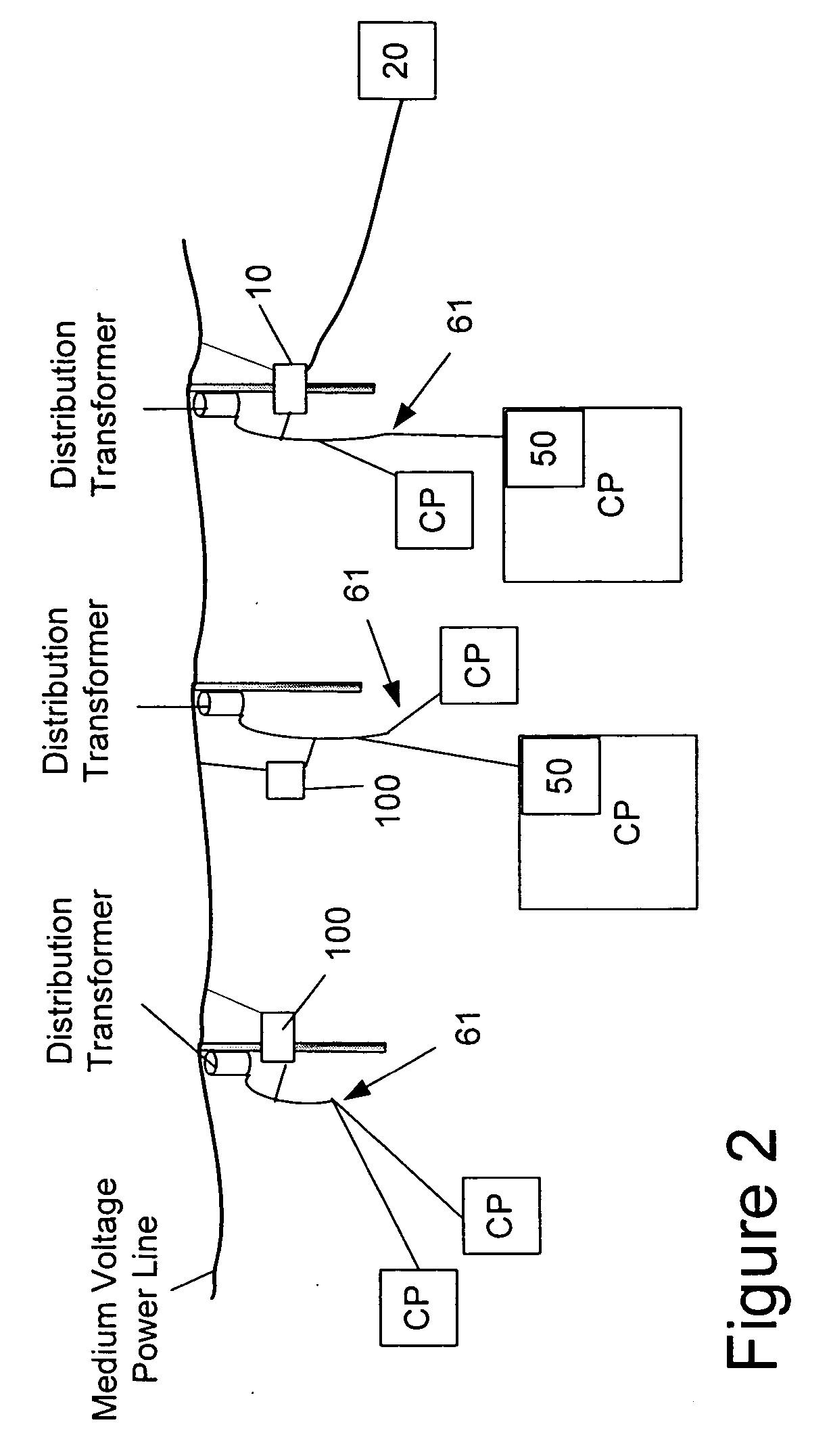
ActiveUS7825793B1Substation equipmentTransmissionCommunications systemNetwork Communication Protocols
A communication system that provides communication of information between an end user device and a remote end user. The system includes a communication node mounted on the upper part of a utility pole, and drawing its power from the utility pole through a standard NEMA Locking 3 Pole Receptacle, and adapted to communicate with a nearby user device using the low-power communication protocol, such as the ZigBee protocol (ANSI IEEE 802.15.4) or Radio Frequency Identification Device (RFID) technology, and also adapted to communicate with a neighborhood mesh network of nodes mounted on utility poles. The neighborhood mesh network is capable of communicating, through a regional computer network, with the remote end user.
Owner:SUNRISE TECH
Communicating information associated with provisioning of a service, over a user plane connection
InactiveUS20060063534A1Avoid problemsIncrease changeConnection managementWireless network protocolsCommunications systemService provision
A method of communicating information associated with provisioning of a service in a communication system and arrangement for the same is disclosed. In the method information about possible associations between an identifier of a mobile user equipment (10) and user plane addresses is stored in storage means (34). A service provisioning entity may receive a request for the service from a client (24) connected to the communication system. Said request includes an identifier of the mobile user equipment. It is verified if a user plane address can be found from the storage means based on the identifier. If such a user plane address is found from the storage means, data associated with provisioning of the requested service is communicated to the mobile user equipment over a user plane connection associated with said address found from the storage means. If no user plane address can be found from the storage means based on the identifier, a new user plane connection is established, and data associated with provisioning of the requested service is communicated to the mobile user equipment over said established user plane connection.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
Method and apparatus for resource management
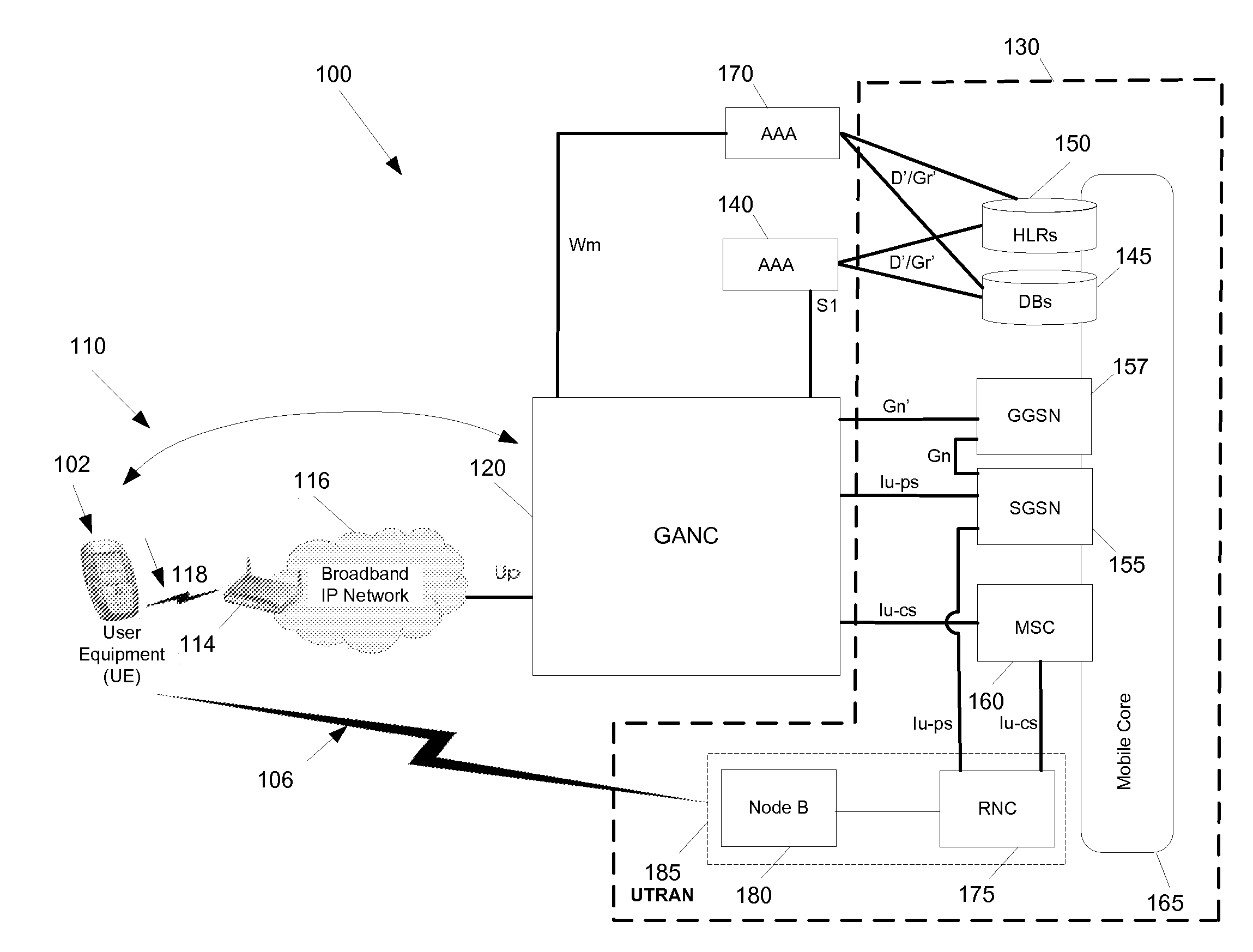
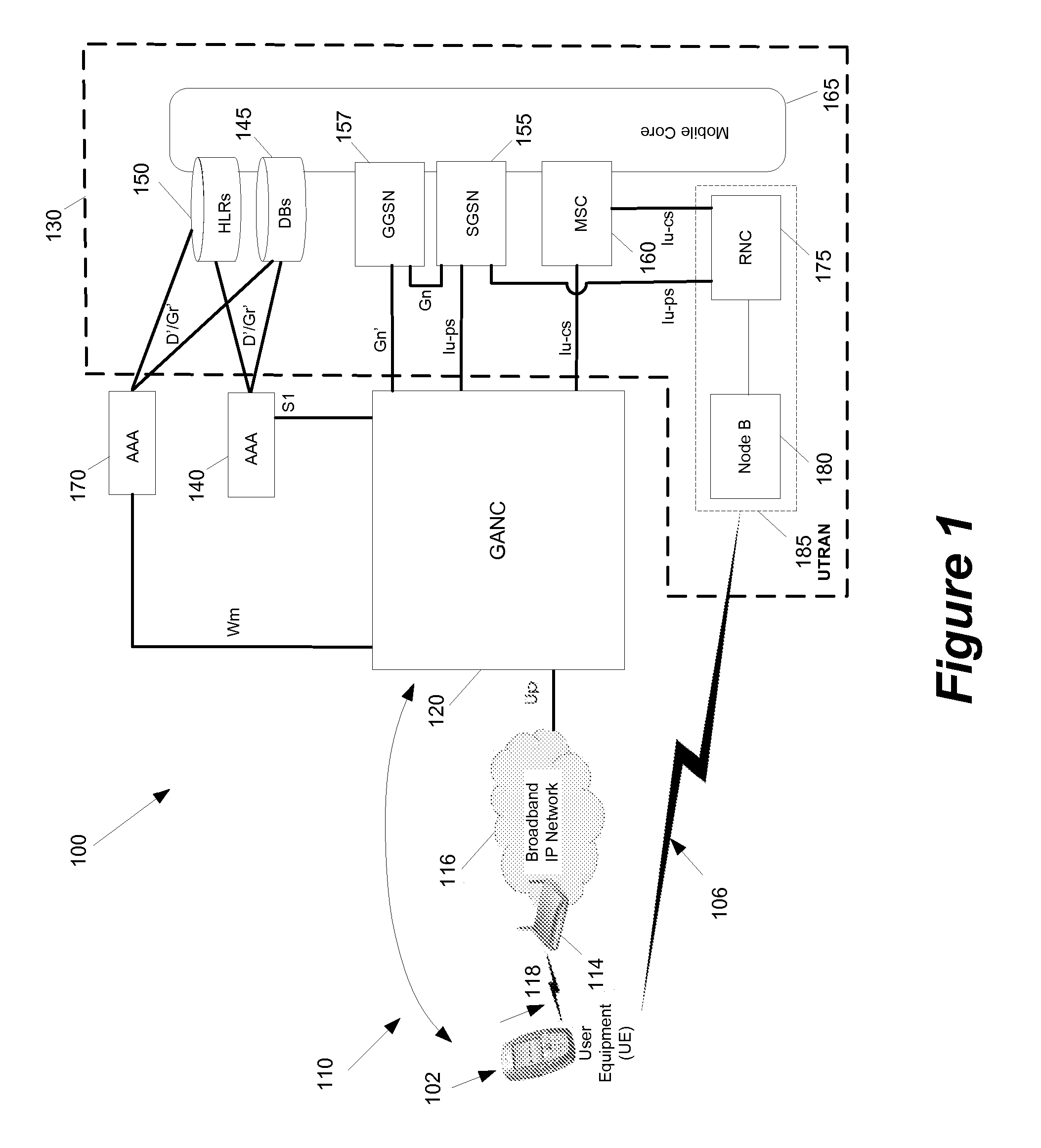
InactiveUS20080076425A1Prevent theftNetwork topologiesRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsCommunications systemNetwork control
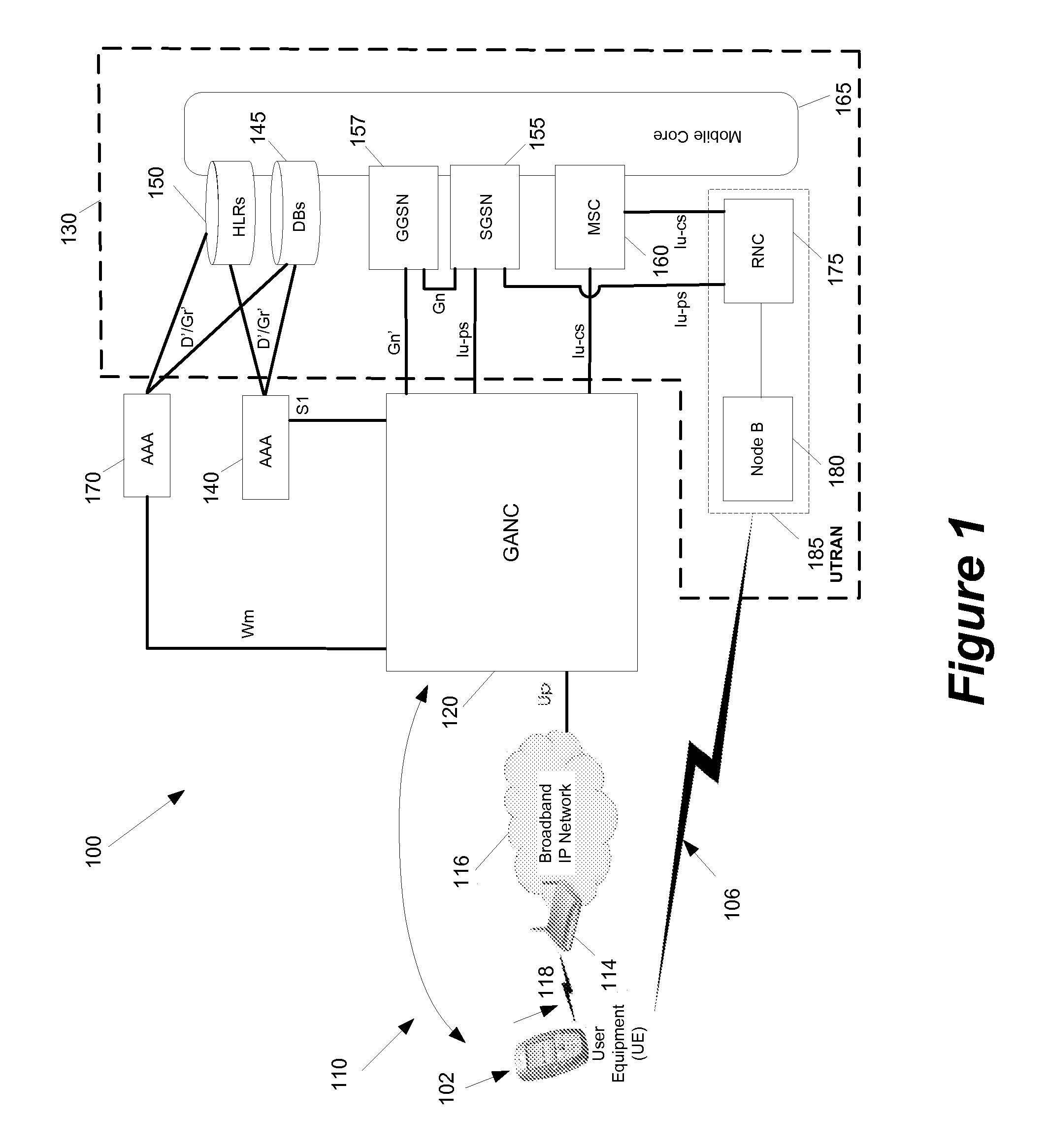
Some embodiments are implemented in a communication system that includes a first wireless communication system and a second wireless communication system that includes a Femtocell access point (FAP) and a network controller that can communicatively couple the FAP to the first wireless communication system. In some embodiments, the network controller can communicatively couple to the first wireless communication system through a UTRAN Iu interface. Some embodiments provide a resource management method that determines that a user equipment (UE) has roved in a region serviced by the FAP. The FAP includes a generic access resource control (GA-RC) protocol sub-layer. The method creates a separate GA-RC state dedicated to the UE in the GA-RC protocol sub-layer. The method also sets the GA-RC state dedicated to the UE to a deregistered state to indicate that the UE is not registered to use the services of the wireless communication system.
Owner:KINETO WIRELESS
Systems and methods for episode tracking in an interactive media environment
ActiveUS20070157249A1Amount of media available to usersValid choiceTelevision system detailsAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsUser equipmentInteractive media
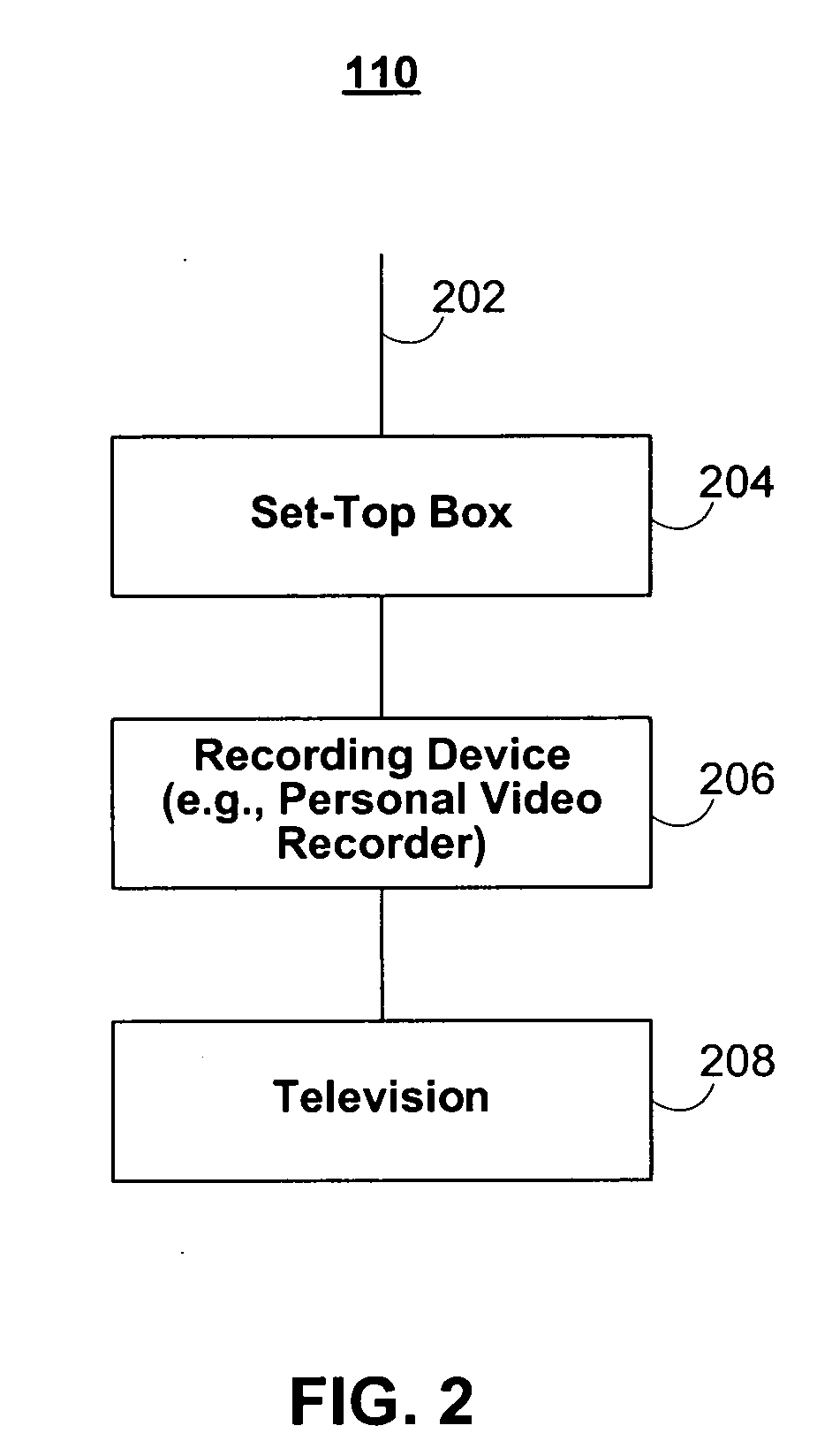
Systems and methods for monitoring a user's viewing progress of media in a series are provided. The user may setup a media profile containing a list of program series to be monitored. The interactive media monitoring application may track the user's viewing progress of programs in the program series on the user equipment and update the user's media profile. The user may request and watch programs in the series at the user's leisure while peripheral media content may be filtered to be consistent with the user's viewing progress in the series.
Owner:ROVI GUIDES INC
Inter-frequency measurement and handover for wireless communications
InactiveUS6845238B1Radio/inductive link selection arrangementsWireless commuication servicesHysteresisTelecommunications network
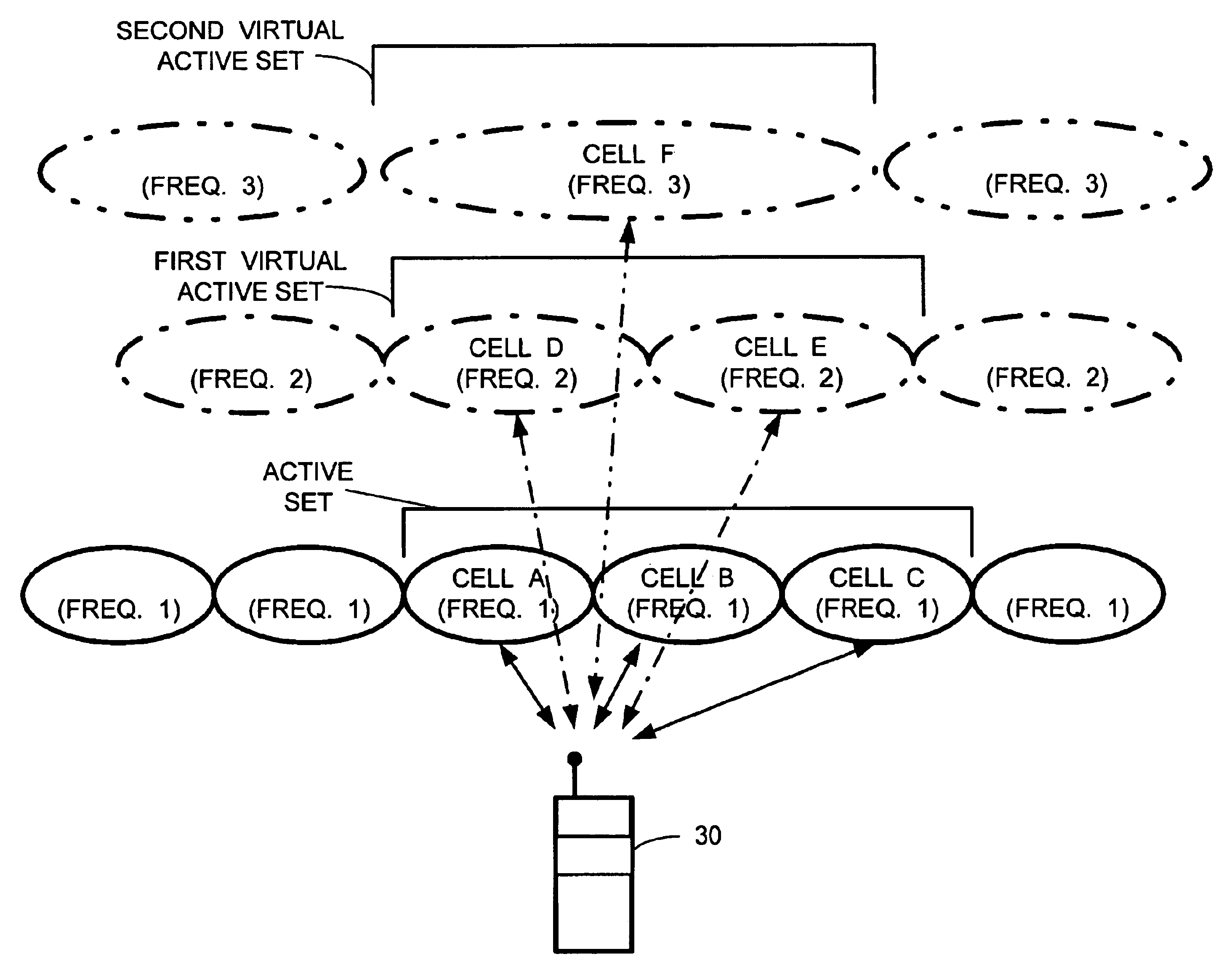
A telecommunications network performs an inter-frequency hard handover for a connection with a user equipment unit (UE) by switching either from a cell or a current active set of base stations on a first frequency to a virtual active set of base stations on another (new) frequency. The inter-frequency hard handover can be an inter-frequency handover within a same system, or an inter-system handover. The virtual active set of base stations is maintained at the user equipment unit (UE), and is updated in accordance with one of several updating implementations of the invention. In a first mode of the invention for implementing virtual active set updates, the network authorizes the user equipment unit (UE) to report to the network the occurrence of certain network-specified events which are acted upon by the network for communicating virtual active set update information to the user equipment unit (UE). In a second mode of the invention, the network authorizes the user equipment unit (UE) to perform an autonomous virtual active set update upon occurrence of certain network-specified events, with inter-frequency events being reported from the equipment unit (UE) to the network and the network issuing an inter-frequency handover command. Advantageously, events which trigger intra-frequency measurements can be reused for reporting inter-frequency measurements. In another of its aspects, the present invention provides the network with a quality estimate for a current active set as well as a quality estimate for the virtual active set. The quality estimate can be utilized in a context of a handover from one UTRAN frequency to another UTRAN frequency, or even in the context of an inter-system handover (e.g., a handover between a UTRAN system and a GSM system, for example). The quality estimate can be utilized to trigger a change or switch of frequencies / systems. Certain thresholds employed in the quality estimate-utilizing handovers provide hysteresis protection.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
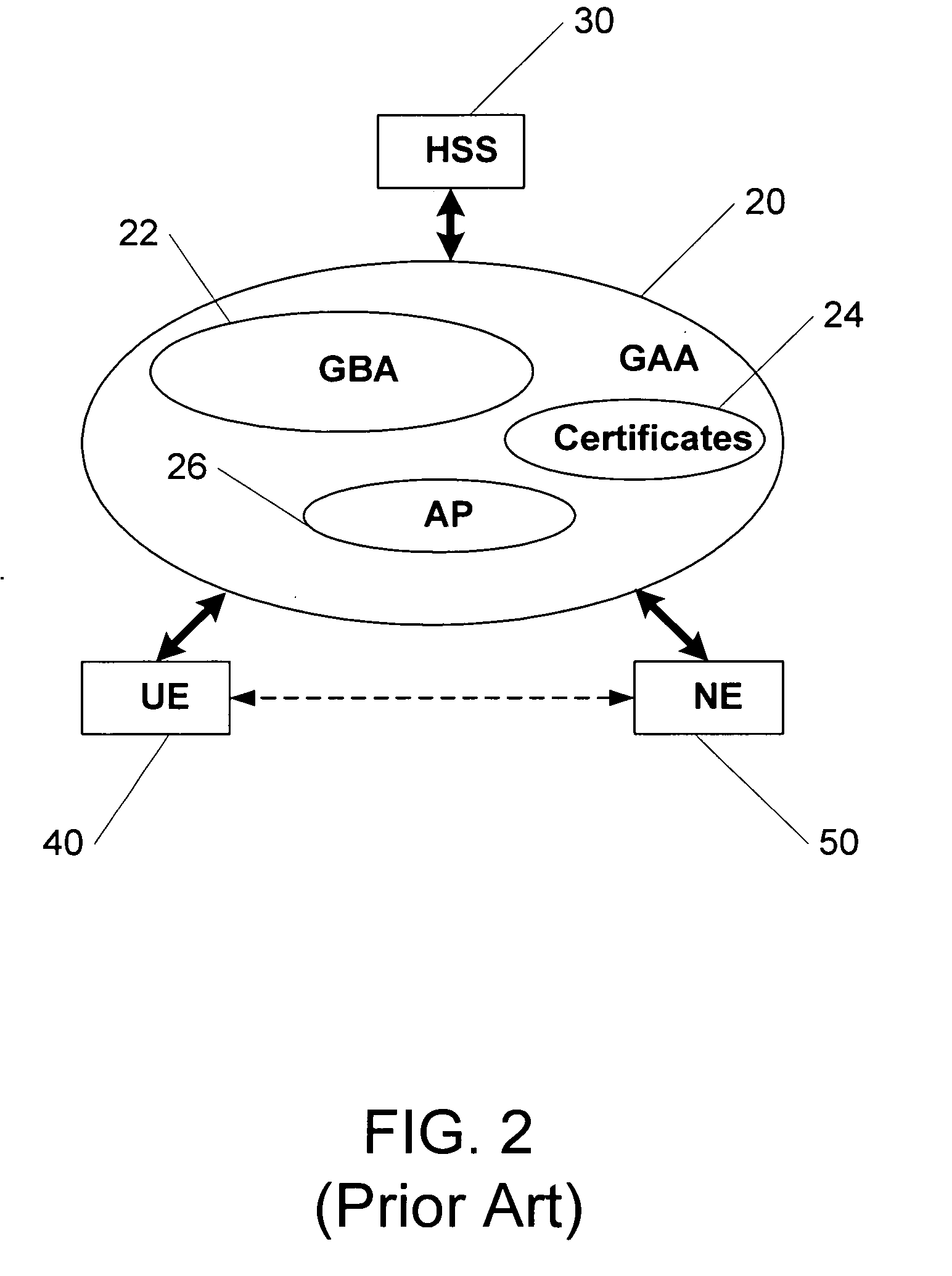
Methods, system and mobile device capable of enabling credit card personalization using a wireless network
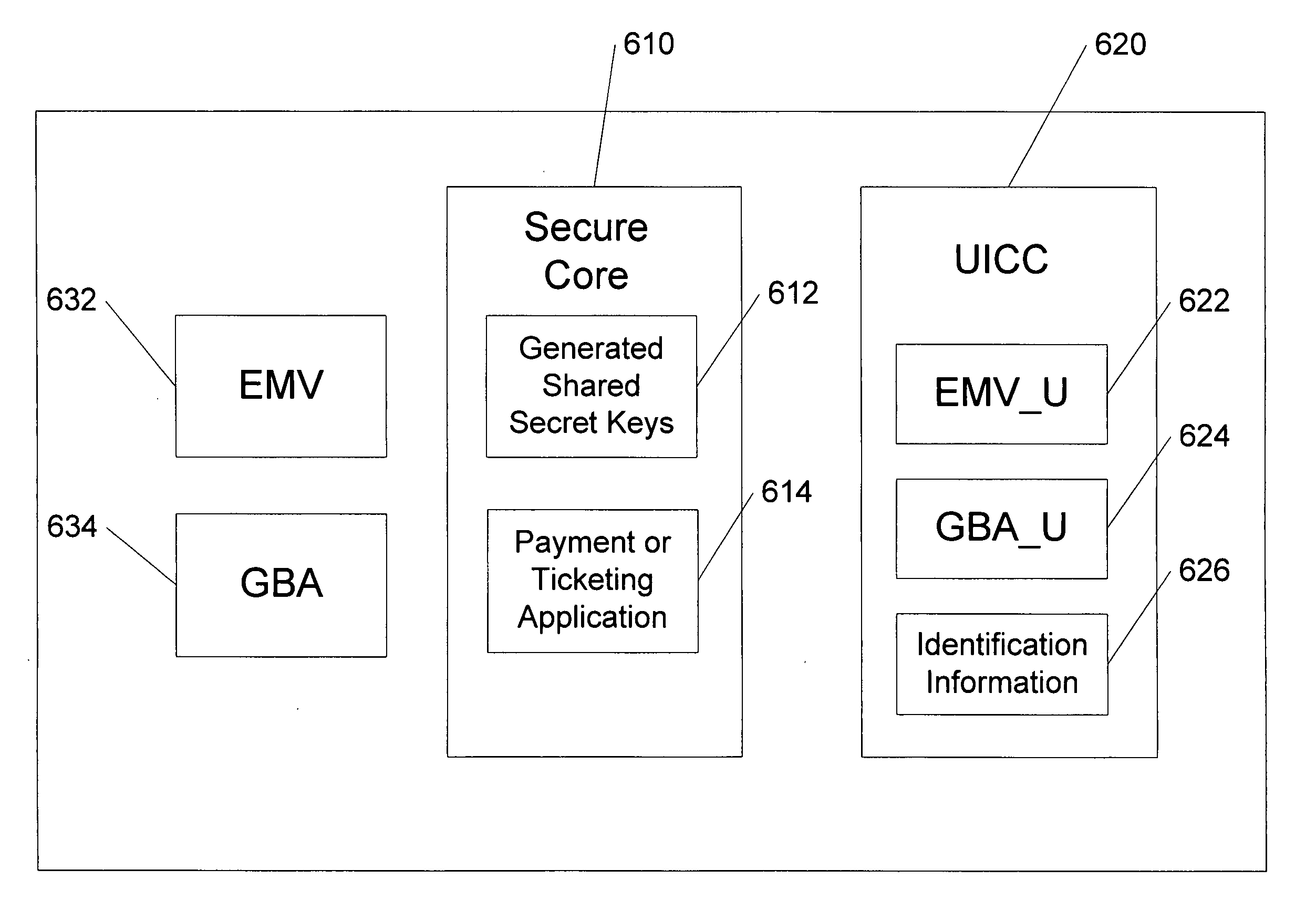
Methods of creating a secure channel over which credit card personalization data can be transmitted over the air (OTA) are provided. In particular, Generic Authentication Architecture (GAA) may be used to establish a secure communication channel between the user equipment (UE) and a personalization application server or bureau acting as a network application function (NAF) server. An user equipment, personalization application service (e.g., a NAF server), a system embodying a personalization application server and an user equipment, and a computer program product are also provided for creating a secure channel, such as via GAA, over which credit card personalization data can be transmitted OTA.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
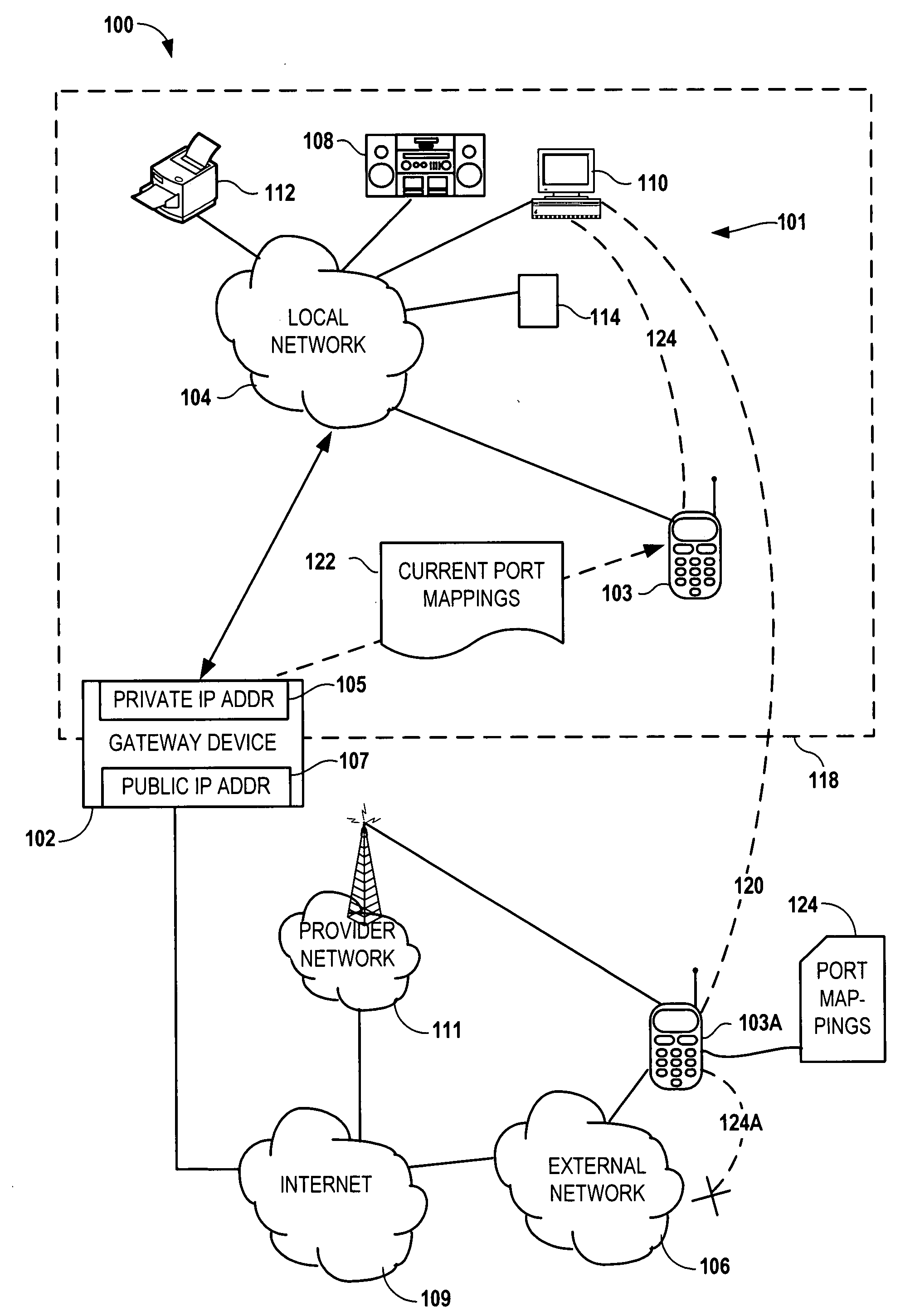
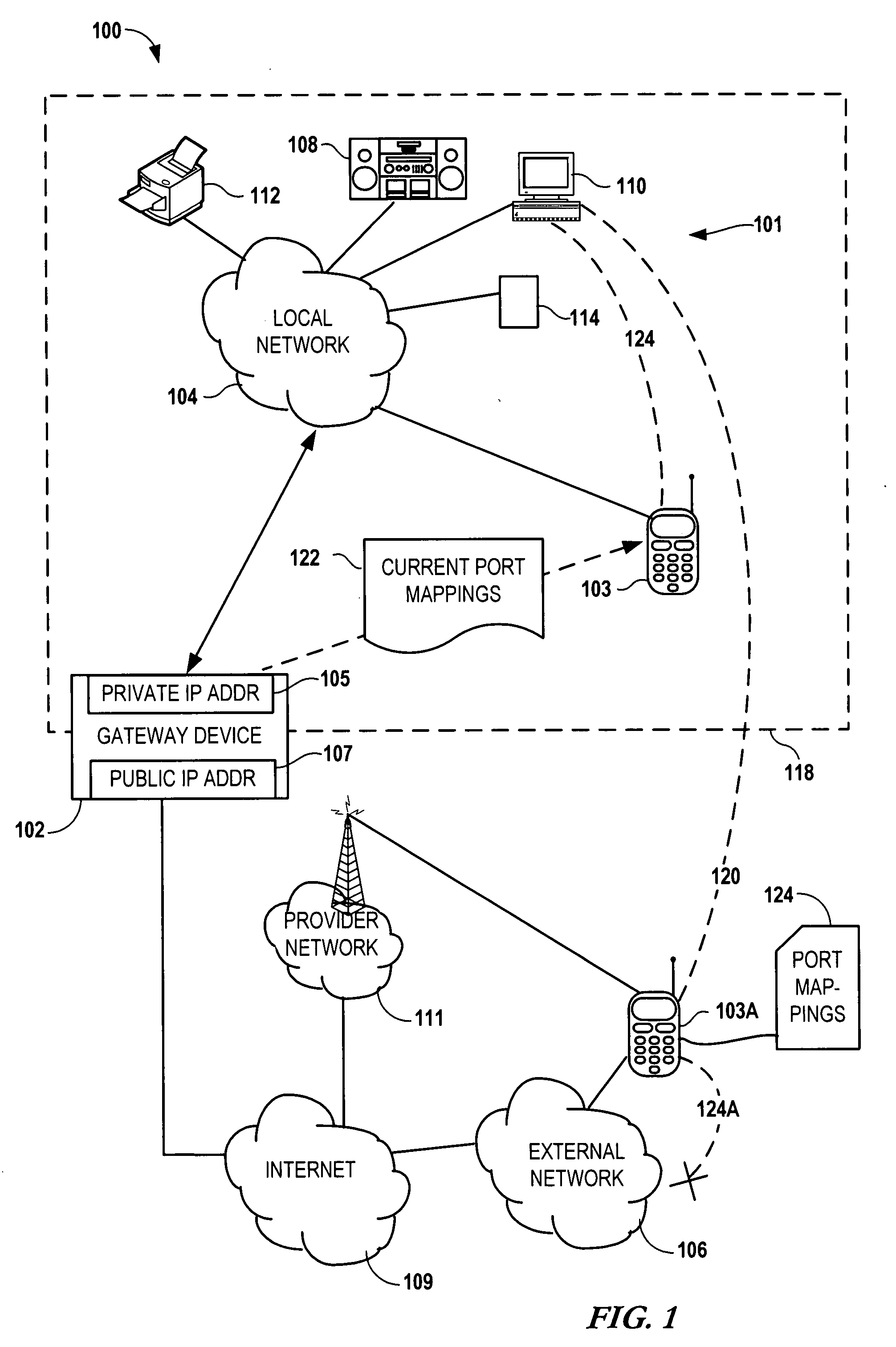
Configuring a user device to remotely access a private network
InactiveUS20090129301A1Network traffic/resource managementRadio transmissionPrivate networkPublic network
Configuring a mobile device to remotely access a private network involves determining, via the private network, first network parameters that enable the mobile device utilize to a computing service of the private network. The device also determines, via a gateway coupled to the private network, second network parameters that allow the mobile to utilize the computing service via a public network. The first and second network parameters are stored on the mobile device. A request is received from a user of the mobile device to access the computing service. It is determined that the mobile device is not on the private network. In response to determining that the mobile device is not on the private network, the second network parameters are utilized to access the computing service via the gateway in response to the request.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
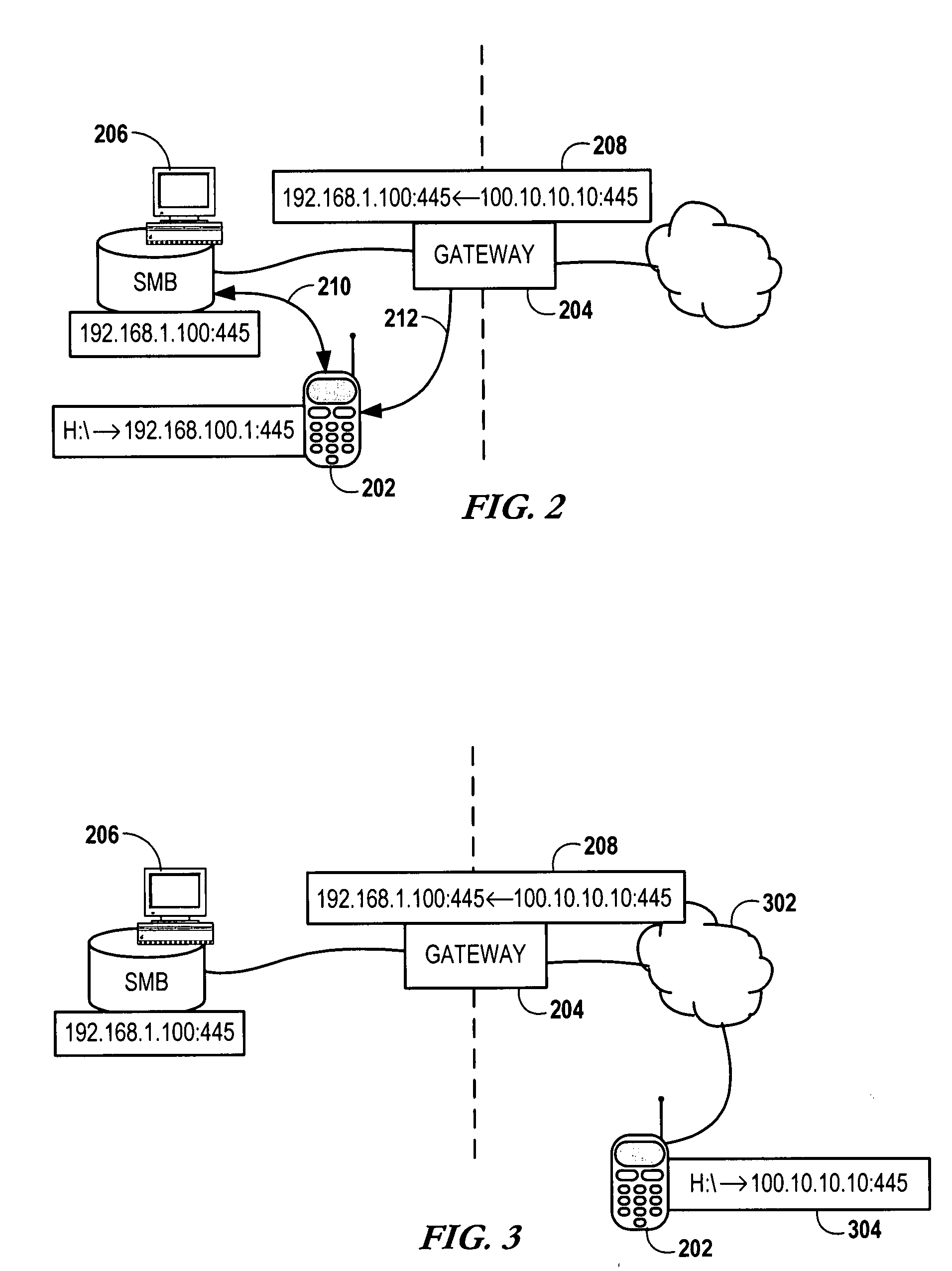
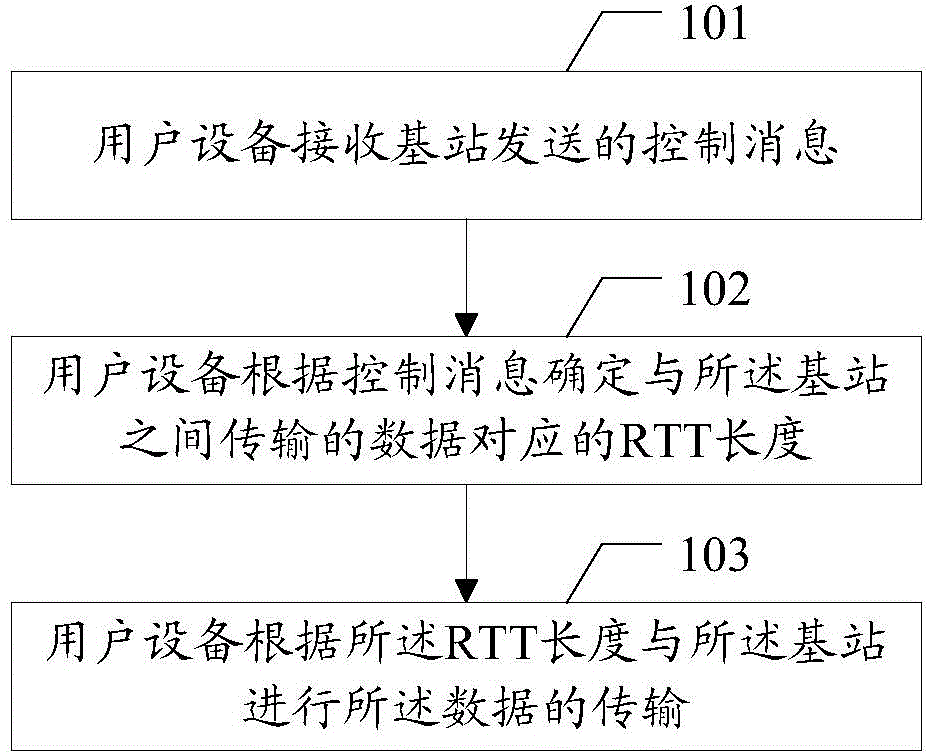
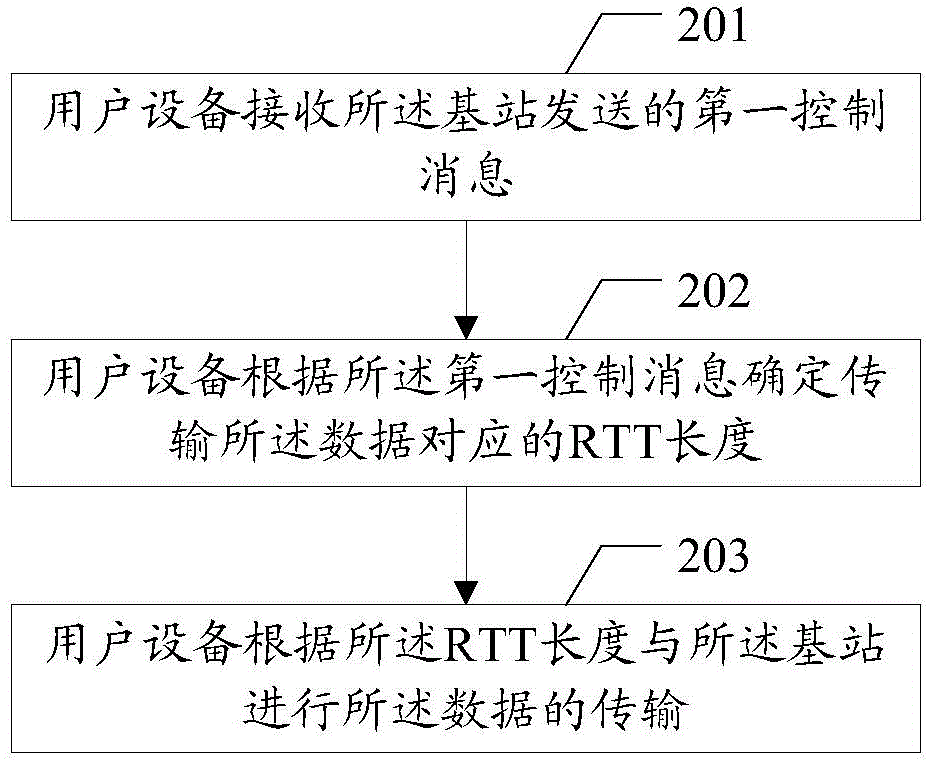
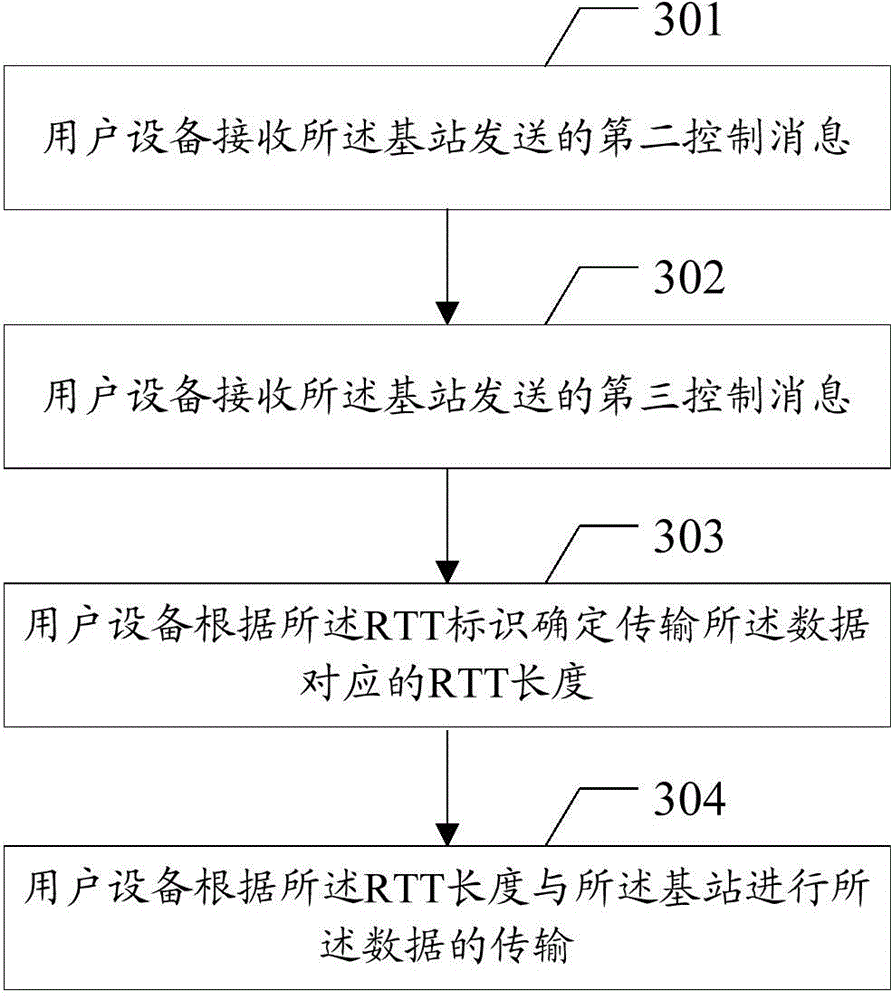
Data transmission method, user equipment and base station
InactiveCN104468030ASolve conflictsError preventionSignal allocationData transmission circuitUser equipment
The embodiment of the invention discloses a data transmission method, user equipment and a base station. The data transmission method, the user equipment and the base station are used for solving the problem about conflicts in the data transmission process under the condition of scene coexistence of different kinds of processing delay. The method includes the steps that the user equipment receives a control message sent by the base station, the control message is used for determining RTT length corresponding to data transmitted between the user equipment and the base station; the user equipment determines the RTT length corresponding to the data transmitted between the user equipment and the base station according to the control message; data transmission between the user equipment and the base station is achieved according to the RTT length.
Owner:SHANGHAI HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
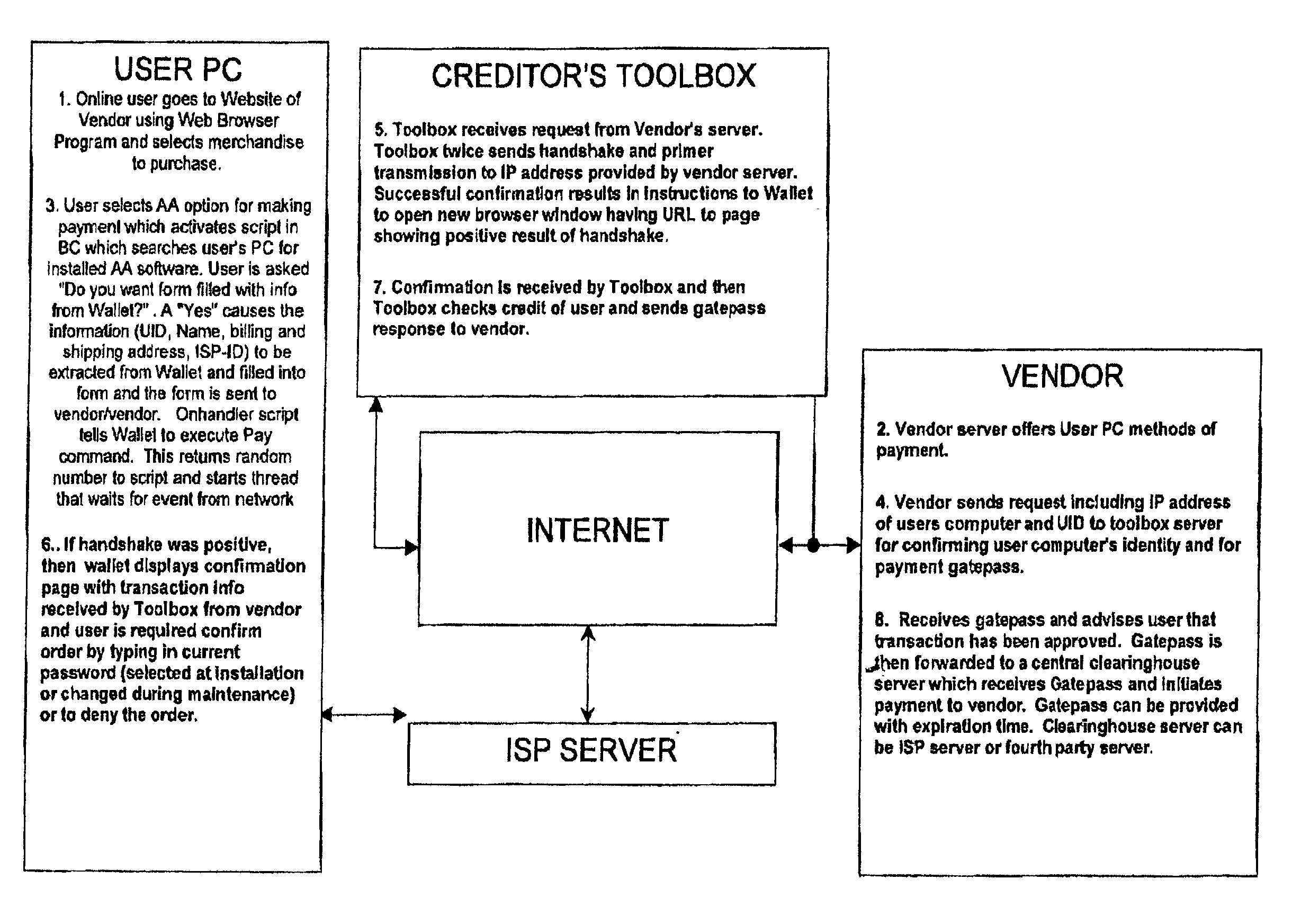
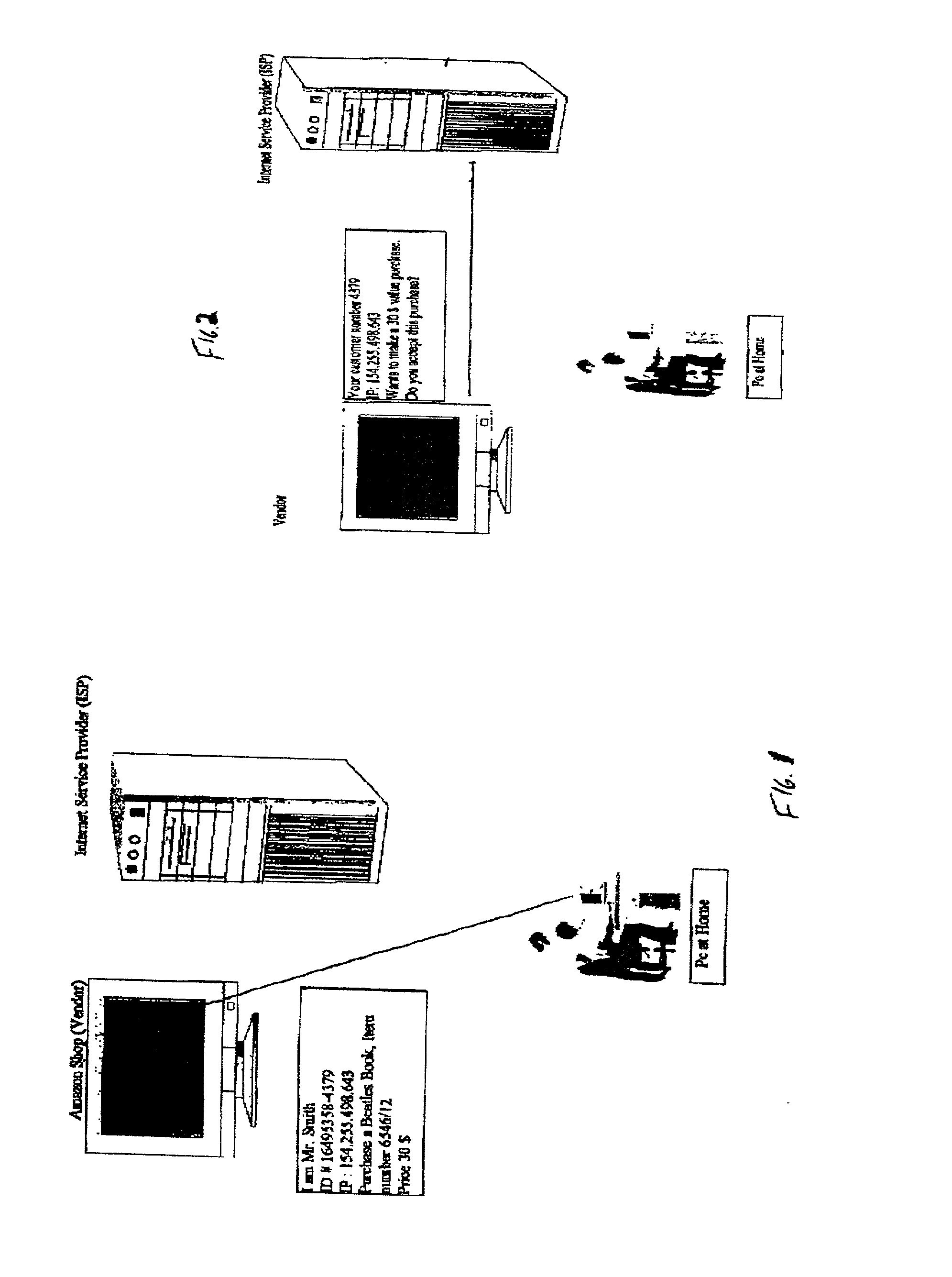
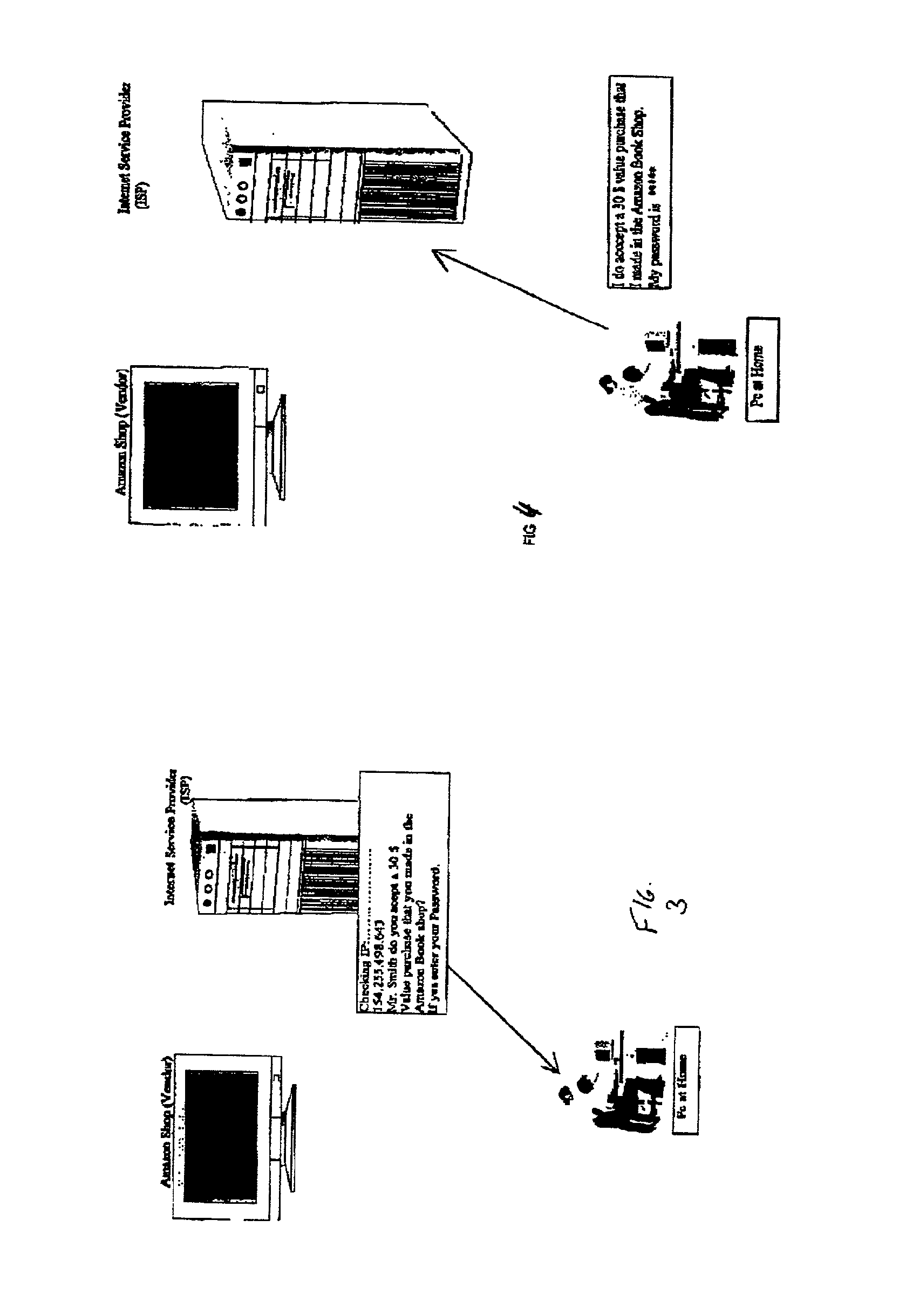
System and method for secure network purchasing
InactiveUS20020073046A1Improve securityCharacter and pattern recognitionDigital data authenticationSecure Electronic TransactionInternet privacy
A system for permitting a secure electronic transaction on a network is disclosed. The network has a user device having a fingerprint, a provider's server and a means for providing verification of user's identity. In response to a request by the provider's server the means for providing verification positively identifies the fingerprint of the user device. It thereupon requests a confirmation from the user device of the transaction and upon receiving the confirmation completes the transaction.
Owner:CHANNEL IP BV
Method and apparatus for scheduling assignment of uplink packet transmission in mobile telecommunication system
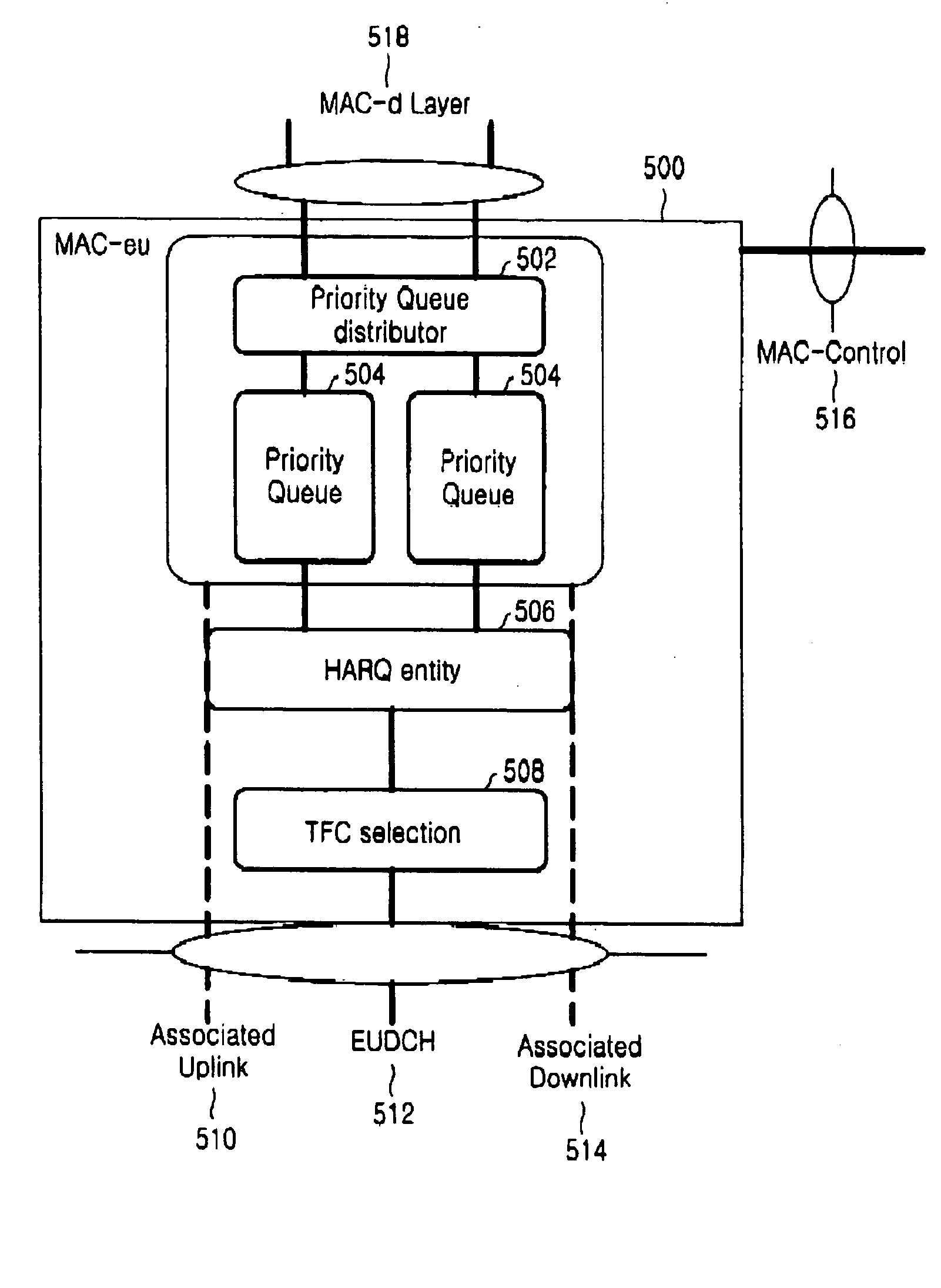
ActiveUS20050047416A1Easy to useNetwork traffic/resource managementNetwork topologiesMobile communication systemsData storing
A method and an apparatus for reporting a buffer status of a buffer storing packet data to be transmitted by a user equipment for a scheduling assignment of an uplink packet data service in a mobile communication system supporting the uplink packet data service are disclosed. A user equipment stores packet data having a priority corresponding to a plurality of priority queues having inherent priorities and relating to at least one service, and transmits buffer status information containing queue identifiers of the priority queues and buffer payload information representing an amount of the packet data stored in the priority queues. Herein, the user equipment inserts the buffer status information into a header part of a protocol data unit for the uplink packet data service, inserts the packet data into a payload part of the protocol data unit, and then transmits the protocol data unit.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
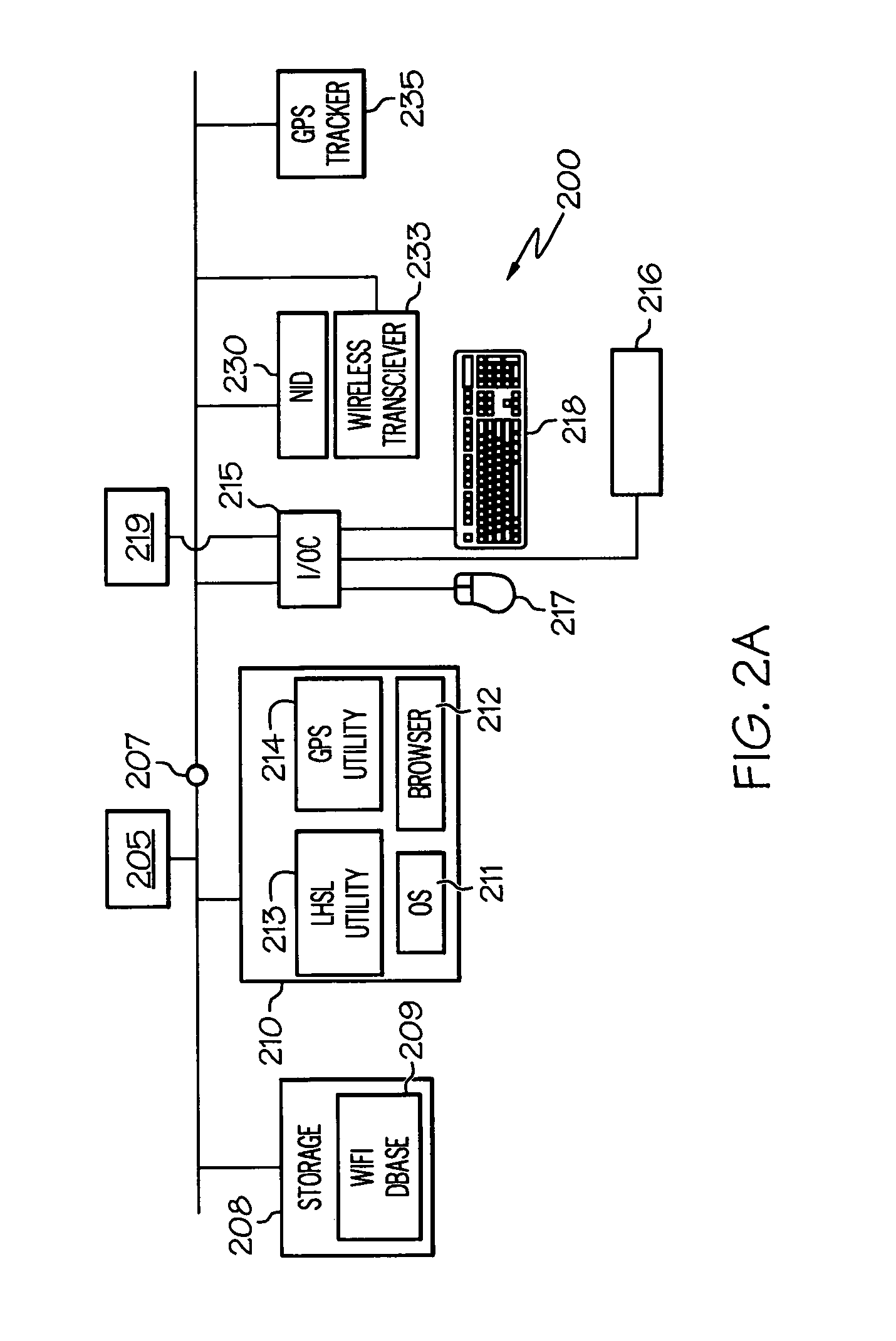
On-device mapping of WIFI hotspots via direct connection of WIFI-enabled and GPS-enabled mobile devices
InactiveUS20070167174A1Generate efficientlyRoad vehicles traffic controlError detection/correctionUser inputGeolocation
A WIFI-enabled and GPS-enabled user device executes a hotspot location utility, which enables the device to detect WIFI hotspots and update a locally-stored hotspot location database (LHLD) containing geographically-mapped hotspots. When a hotspot is detected, the device accesses the hotspot, retrieves identification information and usage terms from the hotspot, and measures performance metrics of the hotspot. The utility stores the identified hotspot with the current GPS coordinate as an entry within the LHLD. When a user later desires to locate hotspots within a particular geographic location, the user enters the physical address of the location, and hotspots with matching (or proximate) GPS coordinates of the entered address are presented to the user. The user may specify certain preferences for usage terms, performance metrics, and location criteria, and the utility filters all geographic hits and returns only hotspots in the geographic location that also satisfy these preferences.
Owner:IBM CORP
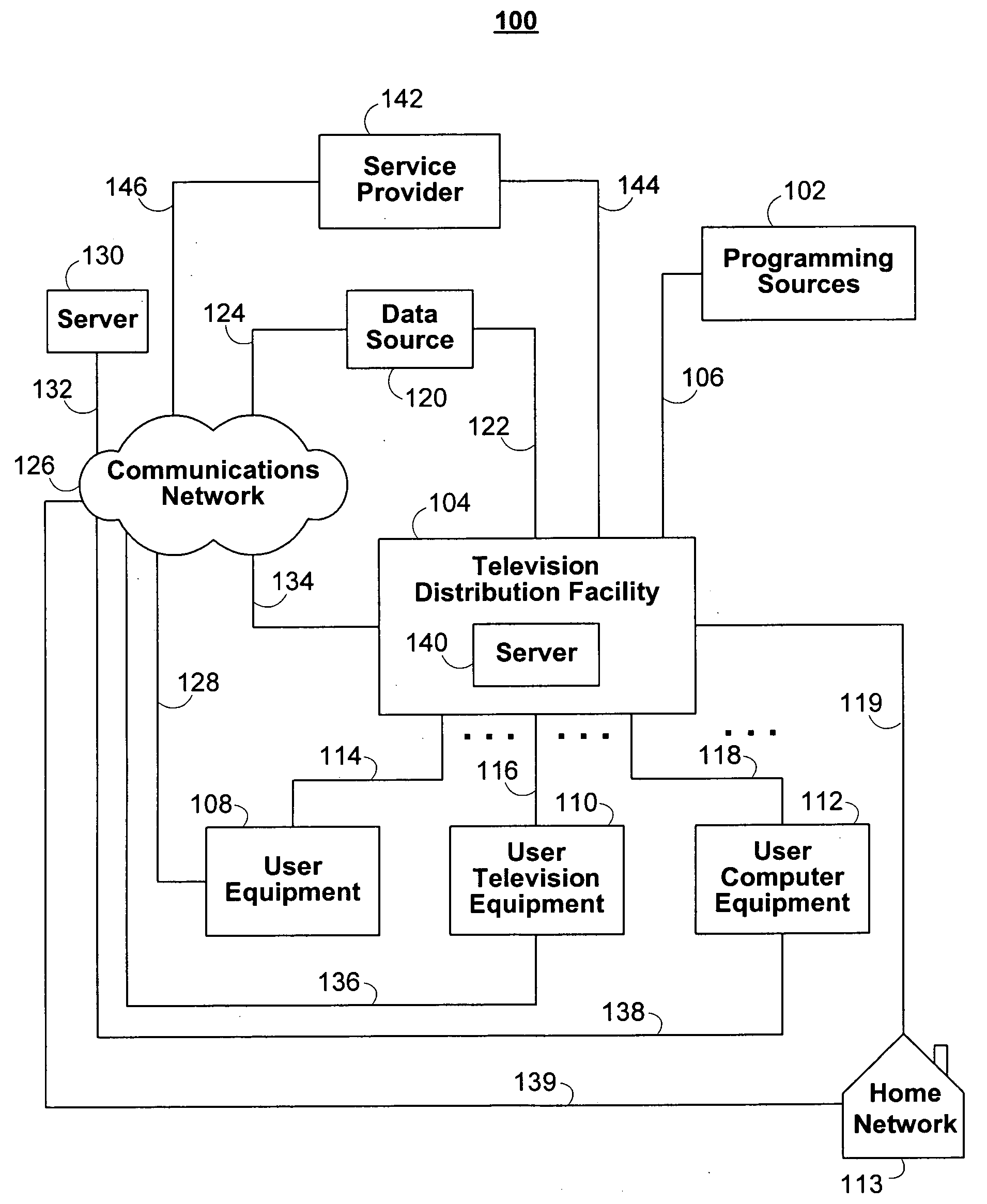
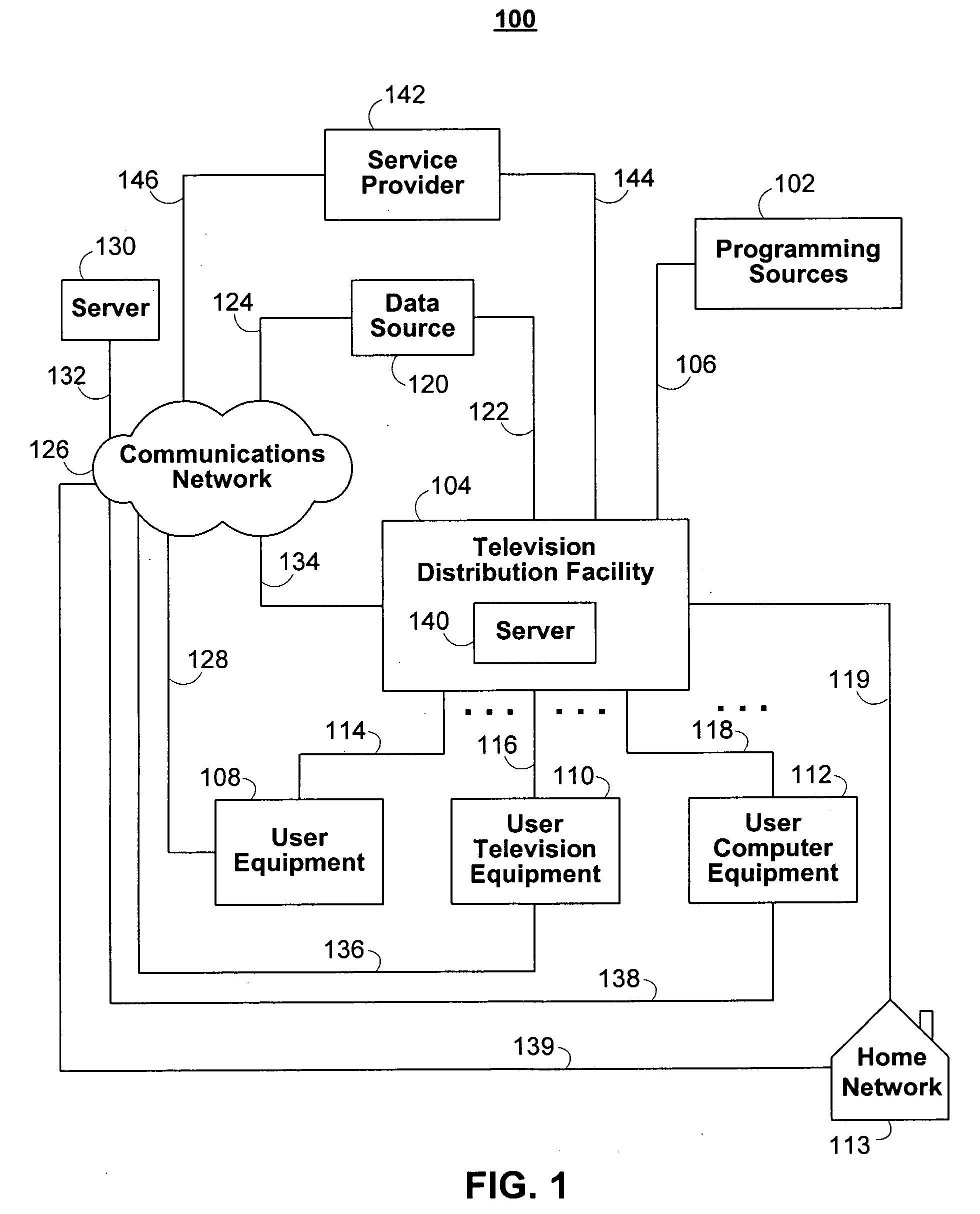
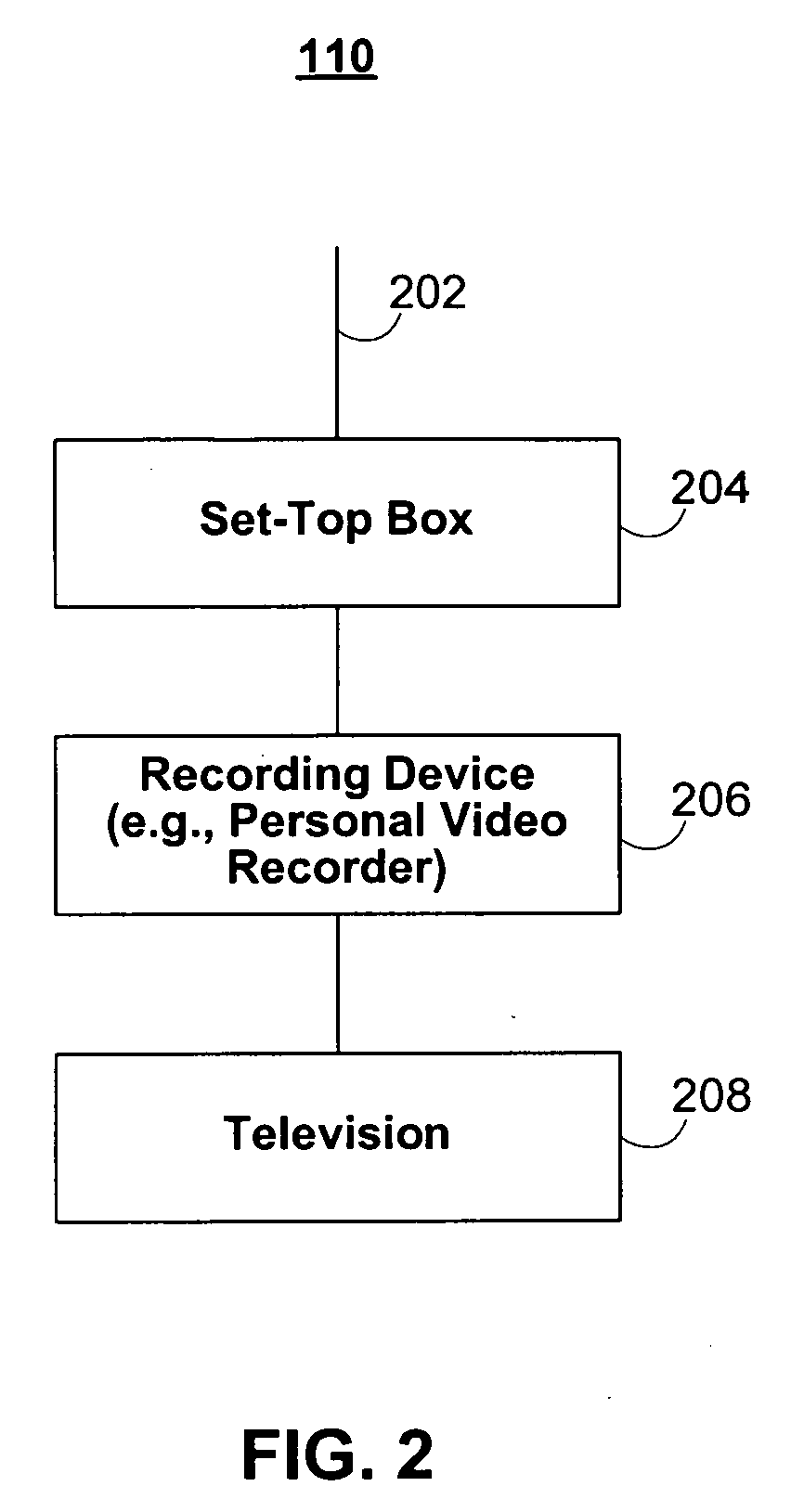
Interactive media guidance system having multiple devices
ActiveUS20080141303A1Limitation of display capacityTelevision system detailsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesGuidance systemComputer network
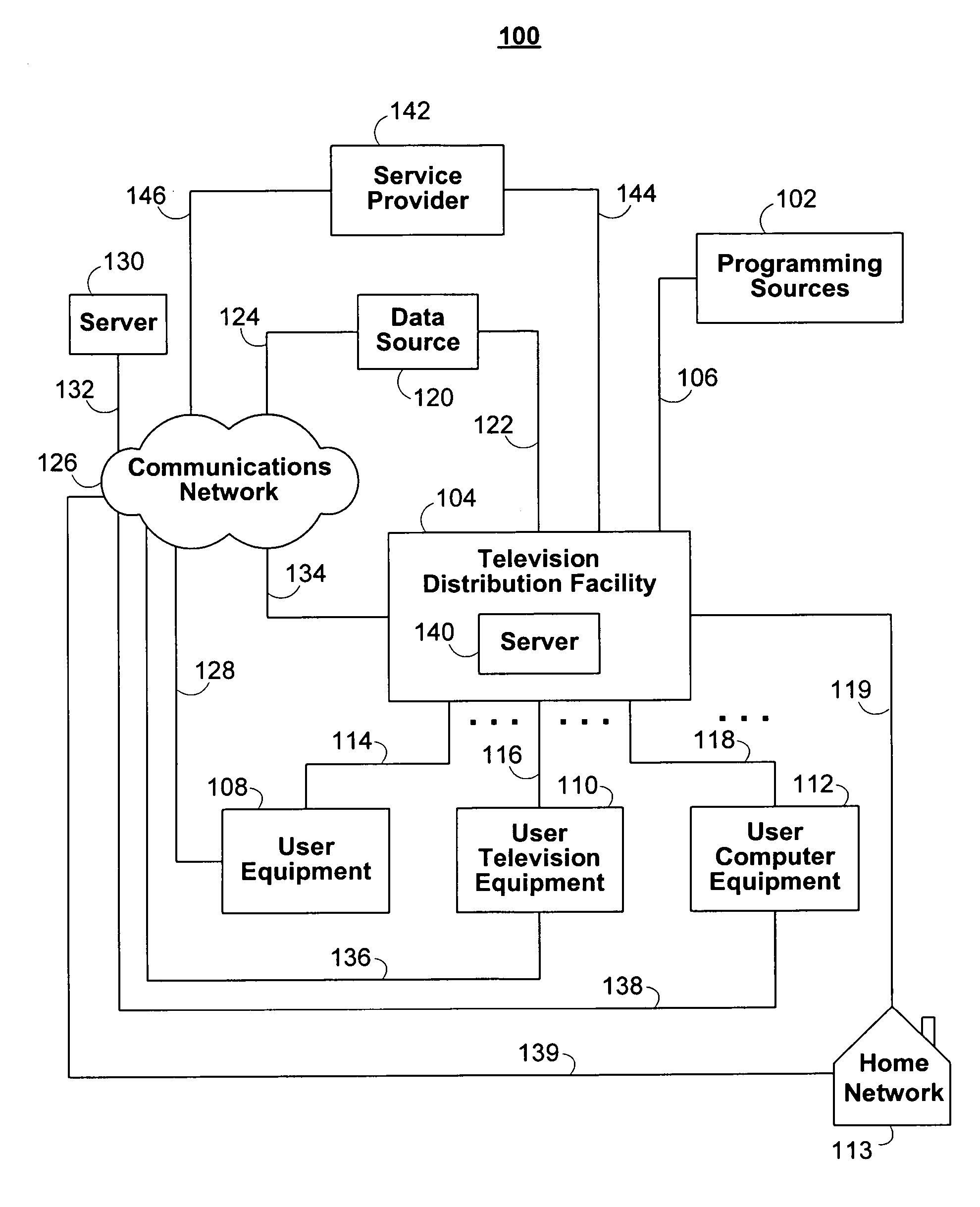
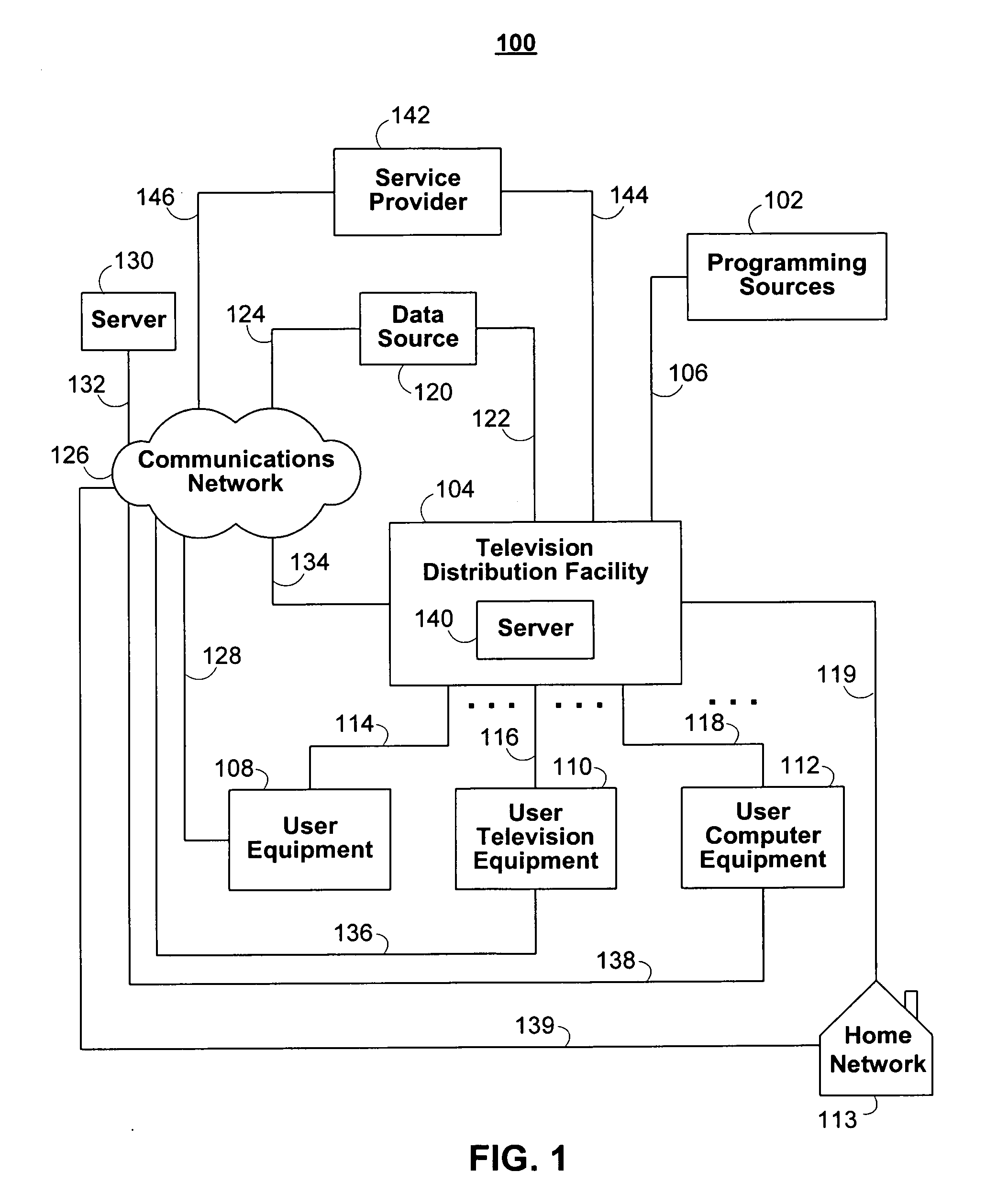
When selecting a television program for recording, a user may configure the delivery of the selected television program and associated data and interactive applications to different user equipment devices in a home network, which may have different capabilities. Because the user equipment devices in the home network may have different capabilities, the user may wish to deliver different types and amount of content, different amounts of data, and different versions of interactive applications to the user equipment devices in the home network.
Owner:ROVI GUIDES INC
Automated, remotely-verified alarm system with intrusion and video surveillance and digital video recording
ActiveUS20070262857A1High incidenceTelevision system detailsImage analysisDigital videoVideo monitoring
An automated self-monitored alarm verification solution including at least a premises portion, a server portion, and an end user device portion. Alarm verification includes capturing by an image capture device at least one image in response to a detection event, and transmitting a first data signal including the image to a local signal processing device. The signal processing device transmits a second signal including at least a portion of the image to a remote hosted server according to at least a first set of predetermined parameters. After receiving the second signal, the server transmits a third signal including at least a portion of the image from the hosted server to a user device. Using the user device, a user views the image and indicates a validity status of the alarm based at least in part on the content of the image. Based at least upon either the validation status indicated by the user, or upon a failure to receive a message including a validation status from the user within a predetermined duration of time, the server portion may send an alarm signal to an emergency response service.
Owner:CHECKVIDEO
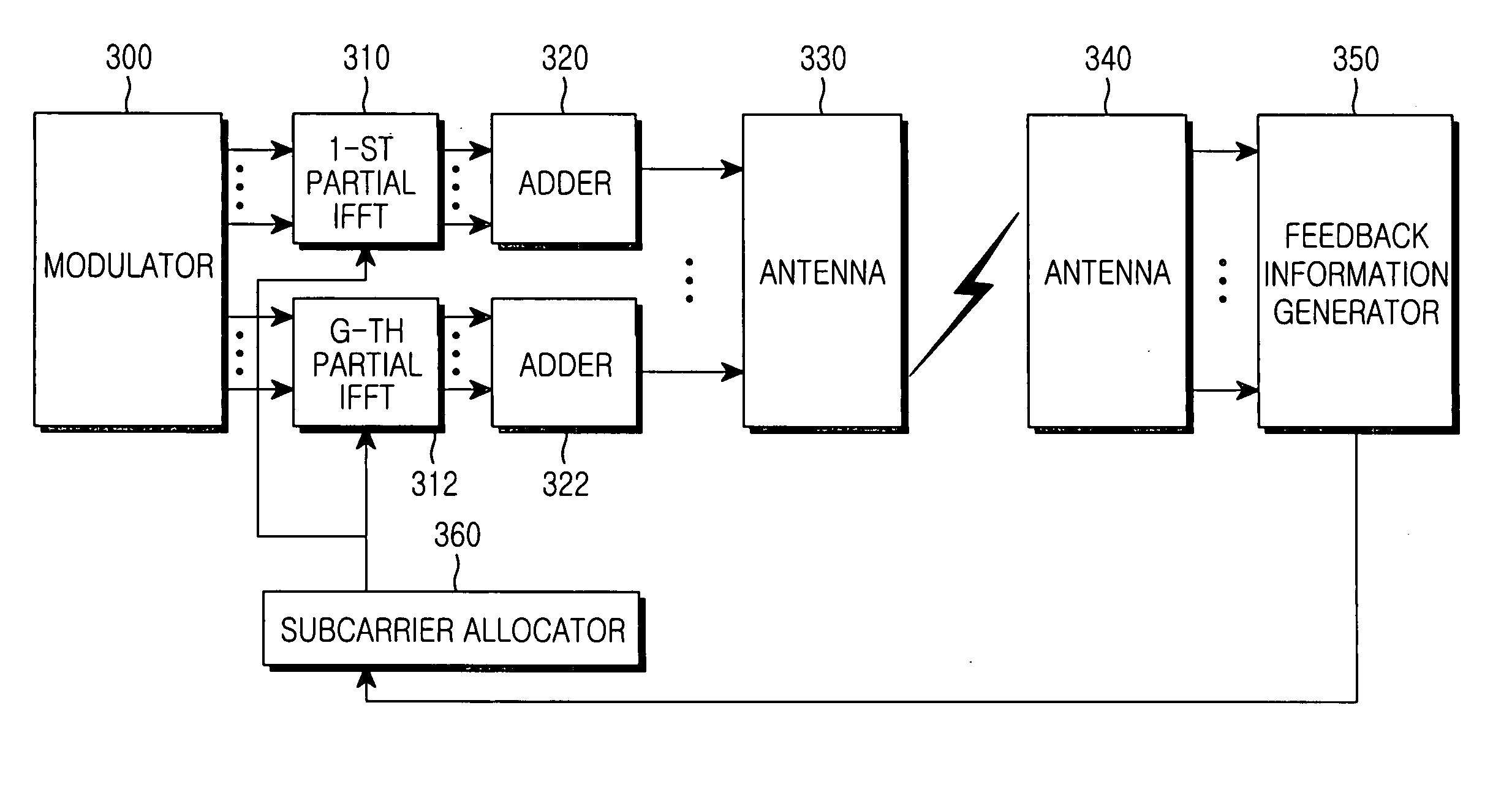
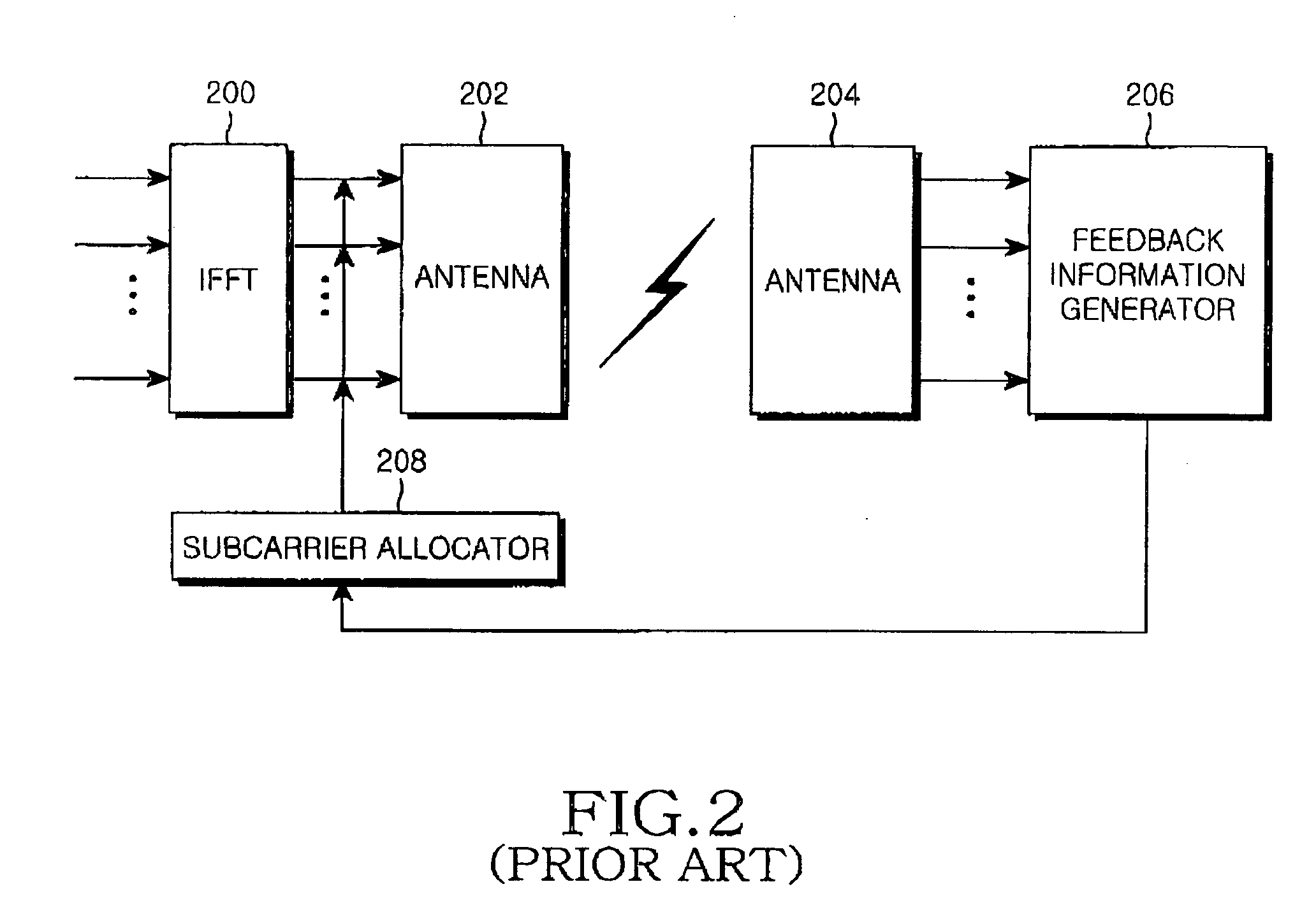
Apparatus and method for transmitting/receiving channel quality information of subcarriers in an orthogonal frequency division multiplexing system
InactiveUS20050128993A1Reducing uplink feedback informationError prevention/detection by using return channelSpatial transmit diversityTelecommunicationsCarrier signal
A method of transmitting / receiving channel quality information (CQI) of subcarriers in an OFDM system where data is transmitted on the subcarriers via one or more transmit antennas. The subcarriers are grouped into subcarrier groups each having at least one subcarrier and further grouped into subgroups each having one or more subgroups. A user equipment generates CQIs for one or more allocated subcarrier groups and the transmit antennas or CQIs for the allocated subcarrier groups, the subgroups of the subcarrier groups, and the transmit antennas. The group CQIs and the subgroup CQIs are transmitted to a Node B in one or more physical channel frames.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method and apparatus for user equipment registration
ActiveUS20080076420A1Prevent theftError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsCommunications systemUser equipment
Some embodiments are implemented in a communication system that includes a first wireless communication system and a second wireless communication system that includes a Femtocell access point (FAP) and a network controller that can communicatively couple the FAP to the first wireless communication system. In some embodiments, the network controller can communicatively couple to the first wireless communication system through a UTRAN Iu interface. In some embodiments, the FAP can communicatively couple to a user equipment using a short-range licensed wireless frequency. Some embodiments provide a method of performing a user equipment (UE) registration. The method establishes a unique connection dedicated to the UE between the FAP and the network controller. The method receives a register request message at the network controller from the FAP through the dedicated connection.
Owner:RIBBON COMM OPERATING CO INC
System and Method for Uplink Grant-Free Transmission Scheme
ActiveUS20140254544A1Transmission path divisionReceiver specific arrangementsTime frequency domainUser equipment
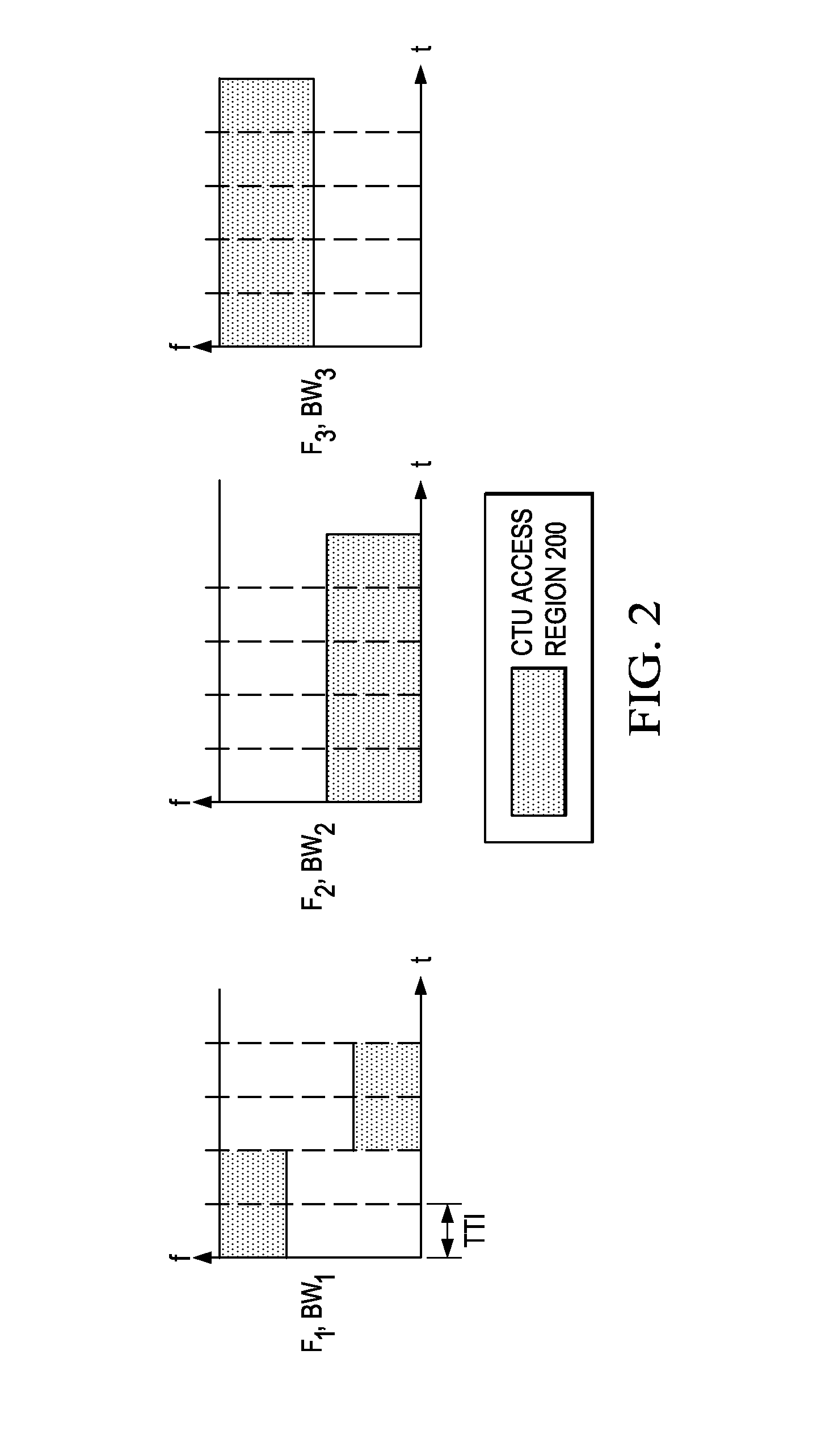
A method embodiment includes implementing, by a base station (BS), a grant-free uplink transmission scheme. The grant-free uplink transmission scheme defines a first contention transmission unit (CTU) access region in a time-frequency domain, defines a plurality of CTUs, defines a default CTU mapping scheme by mapping at least some of the plurality of CTUs to the first CTU access region, and defines a default user equipment (UE) mapping scheme by defining rules for mapping a plurality of UEs to the plurality of CTUs.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
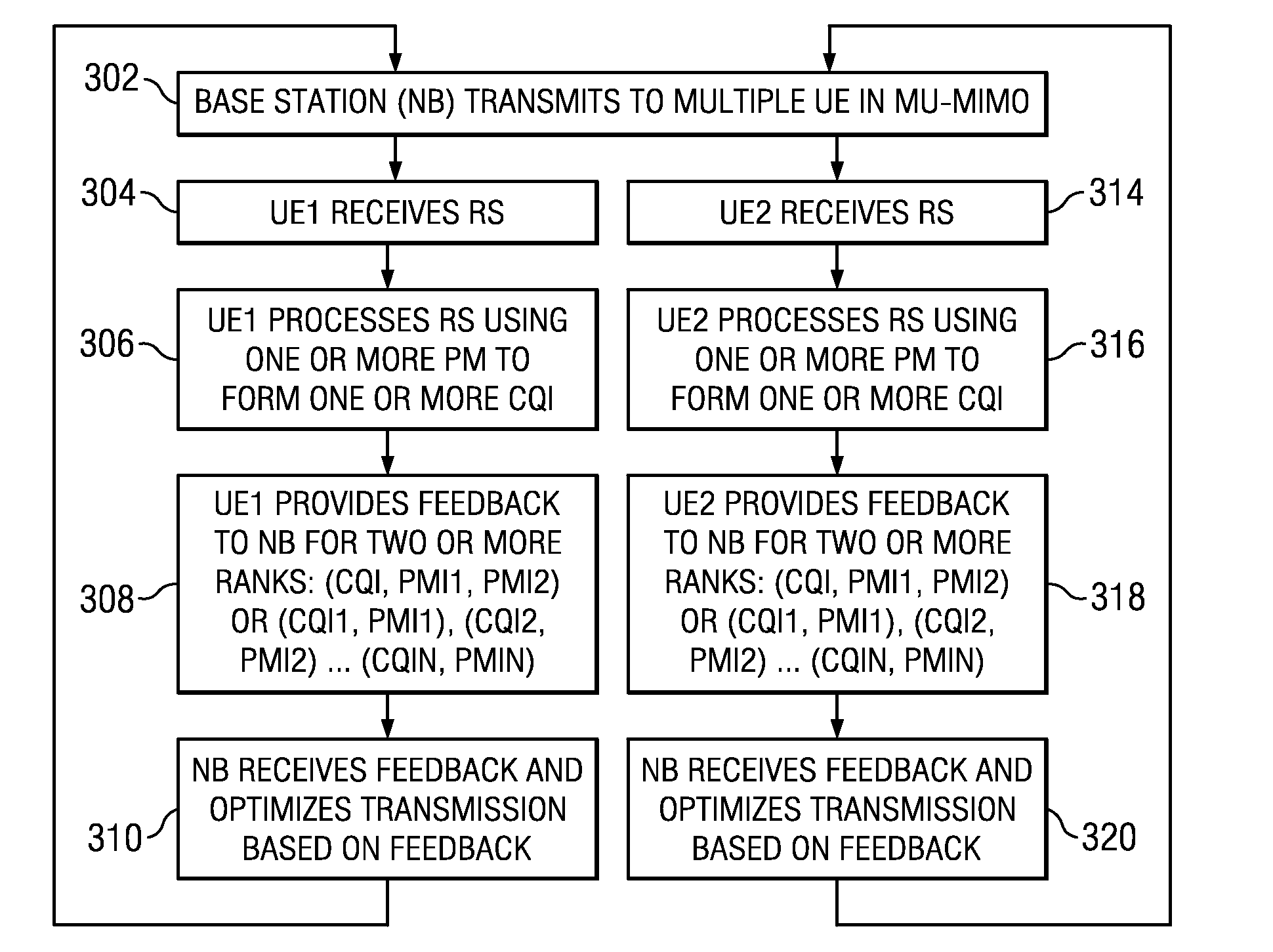
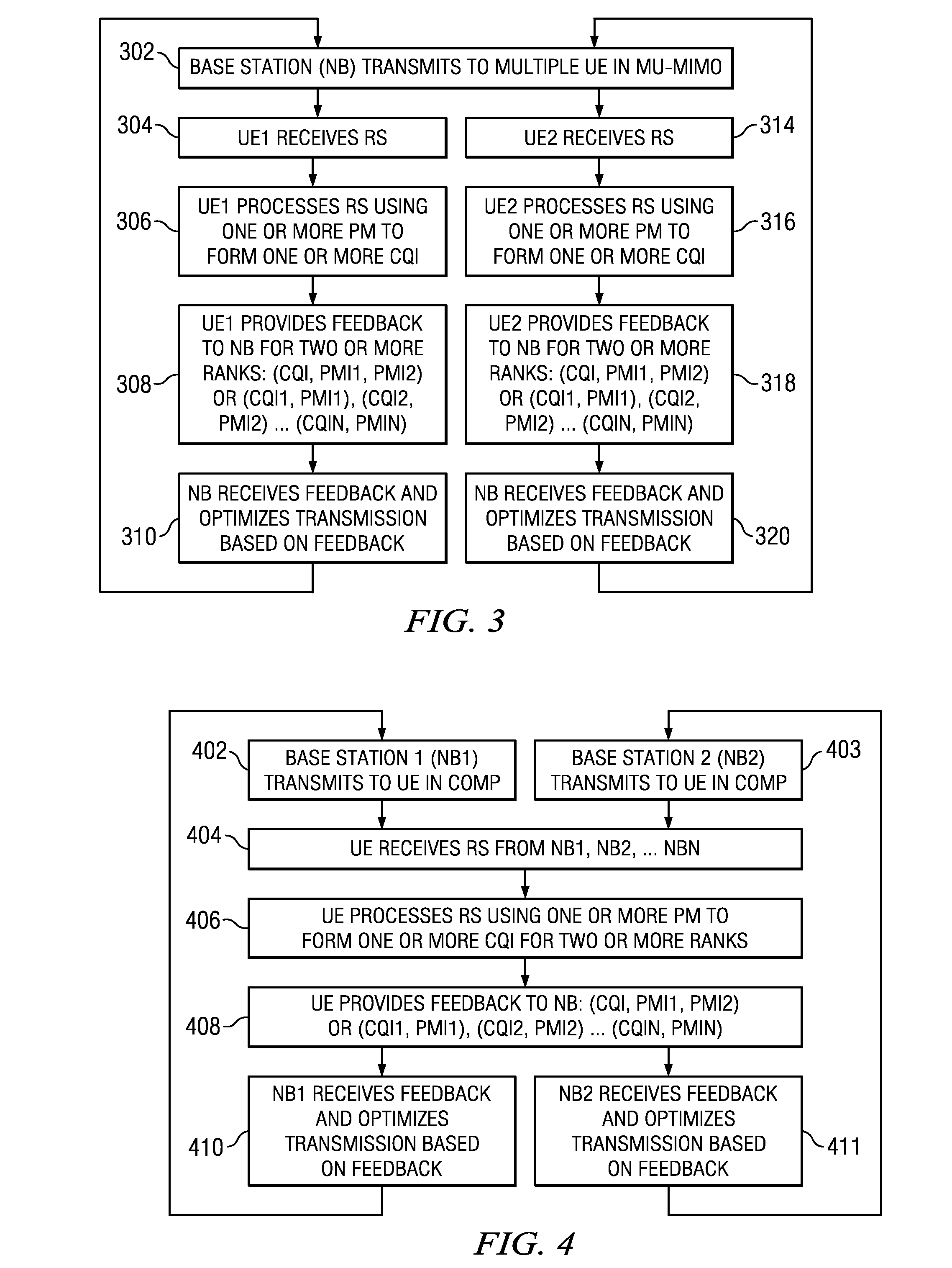
Multiple Rank CQI Feedback for Cellular Networks
Single user and multiuser MIMO transmission in a cellular network may be performed by a base station (eNB) transmitting either one, two, or more transmission layers. A user equipment (UE) receives a reference symbol from the base station. The UE processes the reference symbol with one or more of a plurality of precoding matrices to form a plurality of channel quality indices (CQI). The UE provides feedback to the eNB comprising one or more feedback CQI selected from the plurality of CQI and one or more precoding matrix indicators (PMI) identifying the one or more precoding matrices used to form each of the one or more feedback CQIs for two or more ranks.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Digital interactive delivery system for TV/multimedia/internet
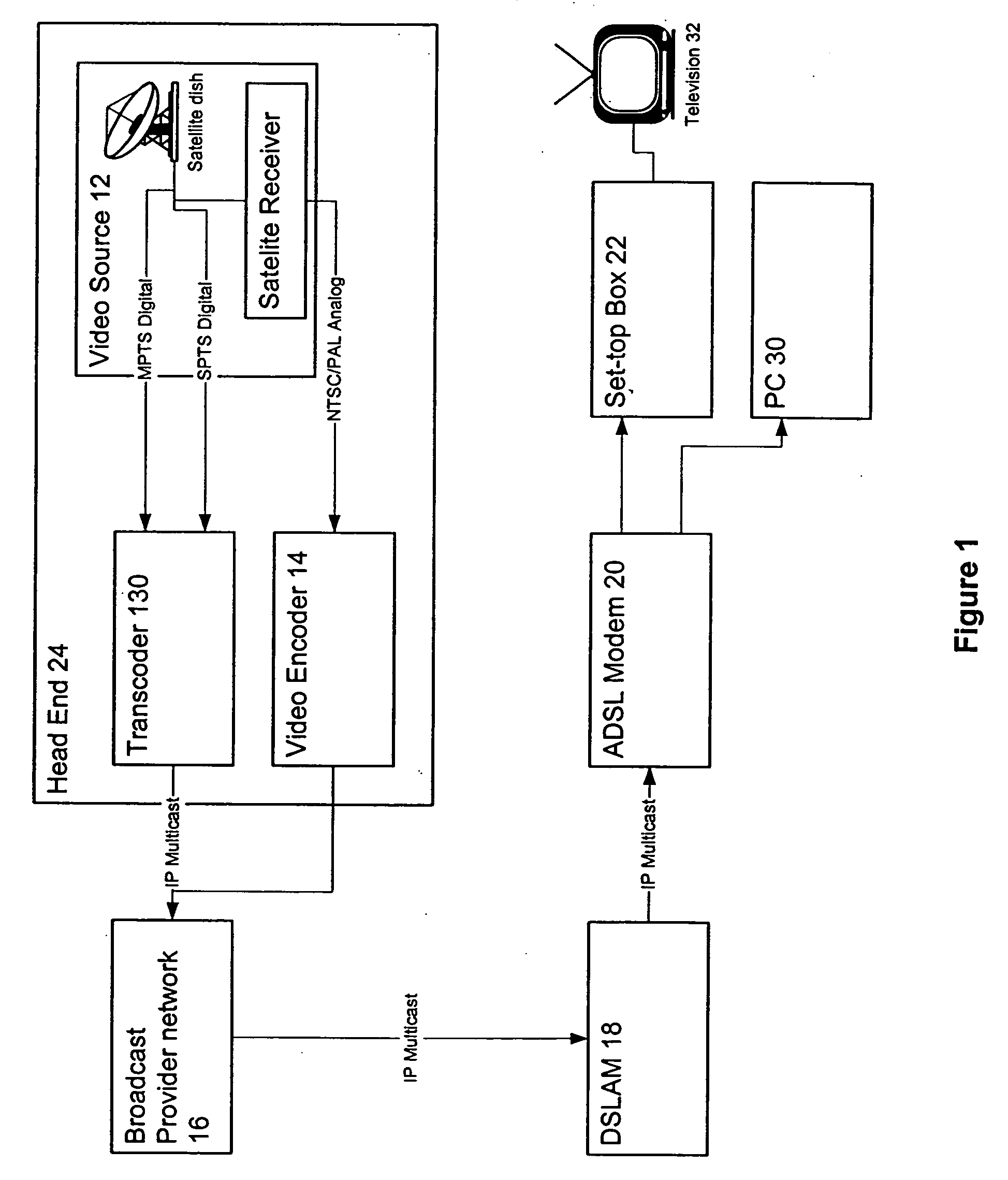
InactiveUS20050028206A1Television system detailsAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsSignal onIP multicast
Owner:IMAGICTV
Systems and methods for mobile application security classification and enforcement
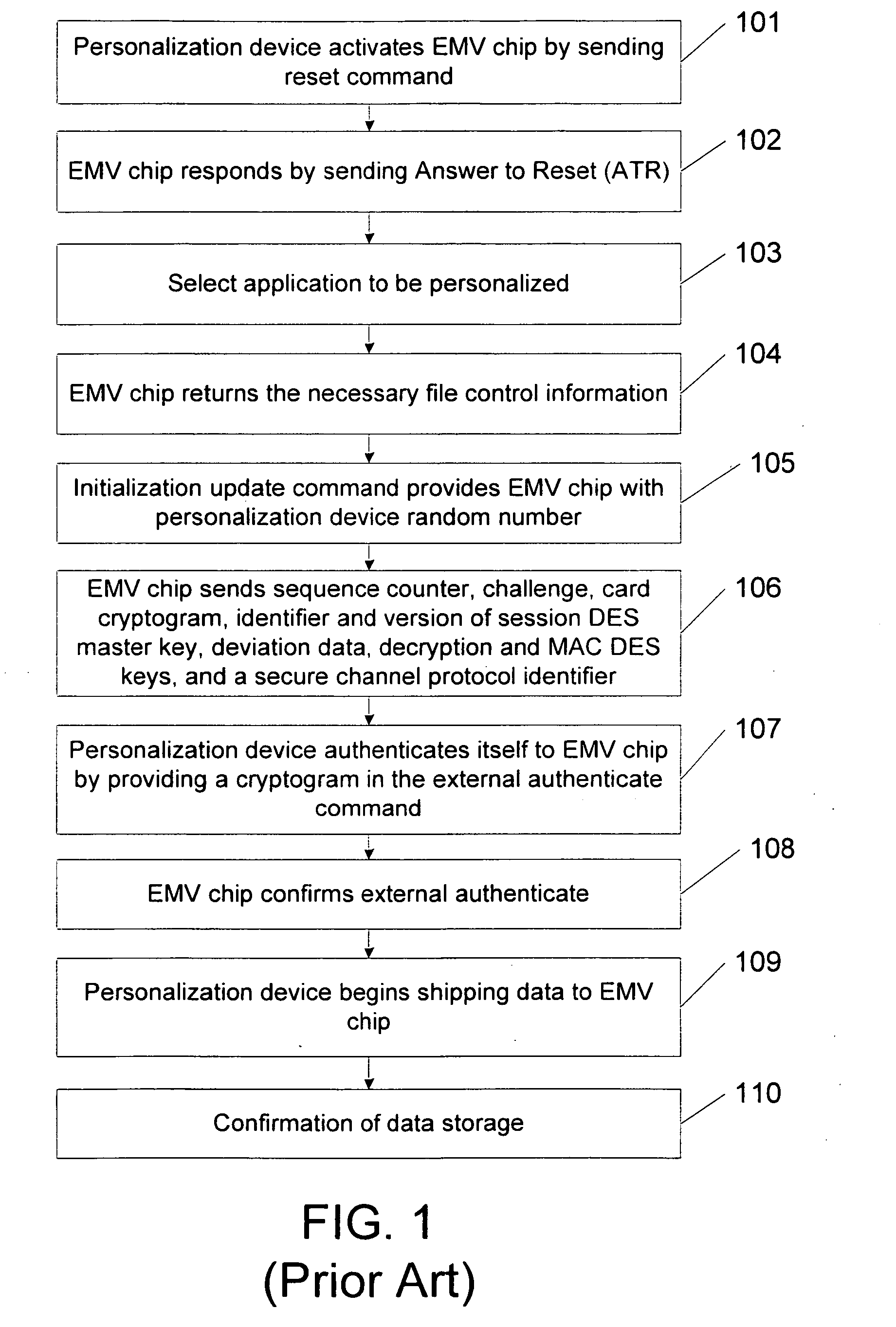
The present disclosure provides systems and methods for mobile application security classification and enforcement. In particular, the present invention includes a method, a mobile device, and a distributed security system (e.g., a “cloud”) that is utilized to enforce security on mobile devices communicatively coupled to external networks (i.e., the Internet). Advantageously, the present invention is platform independent allowing it to operate with any current or emerging mobile device. Specifically, preventing malicious applications from running on an end user's mobile device is challenging with potentially millions of applications and billions of user devices; the only effective way to enforce application security is through the network that applications use to communicate.
Owner:ZSCALER INC
Dynamic allocation of subframe scheduling for time divison duplex operation in a packet-based wireless communication system
ActiveUS20110211503A1Easy to useError preventionTransmission path divisionCommunications systemResource based
Systems and methods for enabling the dynamic allocation of certain sub frames as downlink or uplink resources in a time division duplexed over the air communications system. A base station or eNB may allocate certain subframes within a repeating radio frame of a TDD configuration as either DL or UL subframes for communicating to user equipment or UE devices to increase efficient use of system resources based on the data to be transmitted. Methods for determining the capabilities of a selected UE and based on the determining step, dynamically allocating certain subframes are disclosed. The methods and systems are compatible with user equipment that does not support the dynamic allocation of subframes.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
Interactive media guidance system having multiple devices
InactiveUS20070157260A1Limitation of display capacityTwo-way working systemsSelective content distributionGuidance systemComputer network
When selecting a television program for recording, a user may configure the delivery of the selected television program and associated data and interactive applications to different user equipment devices in a home network, which may have different capabilities. Because the user equipment devices in the home network may have different capabilities, the user may wish to deliver different types and amount of content, different amounts of data, and different versions of interactive applications to the user equipment devices in the home network.
Owner:UNITED VIDEO PROPERTIES
Network architecture and system for delivering bi-directional xDSL based services
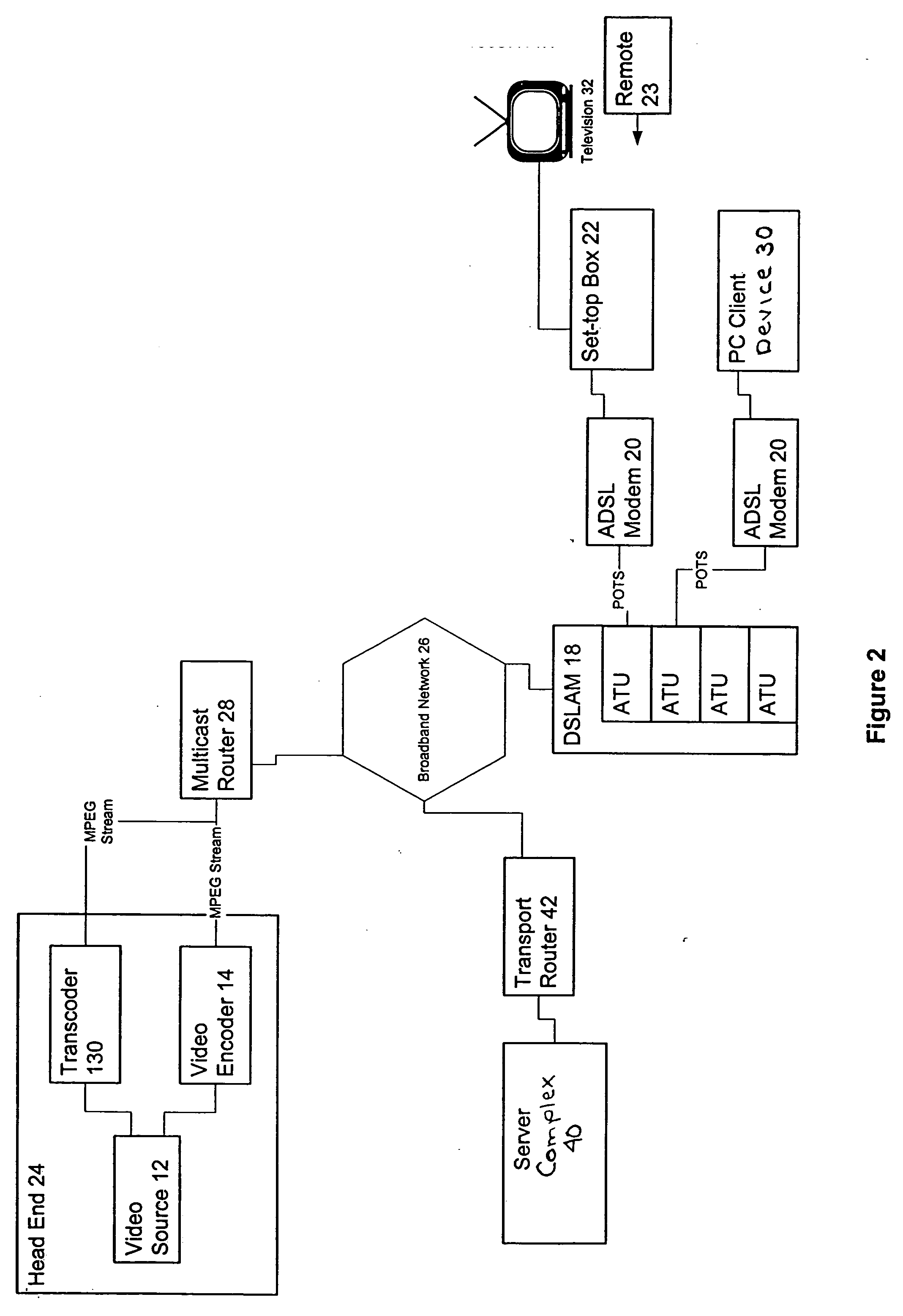
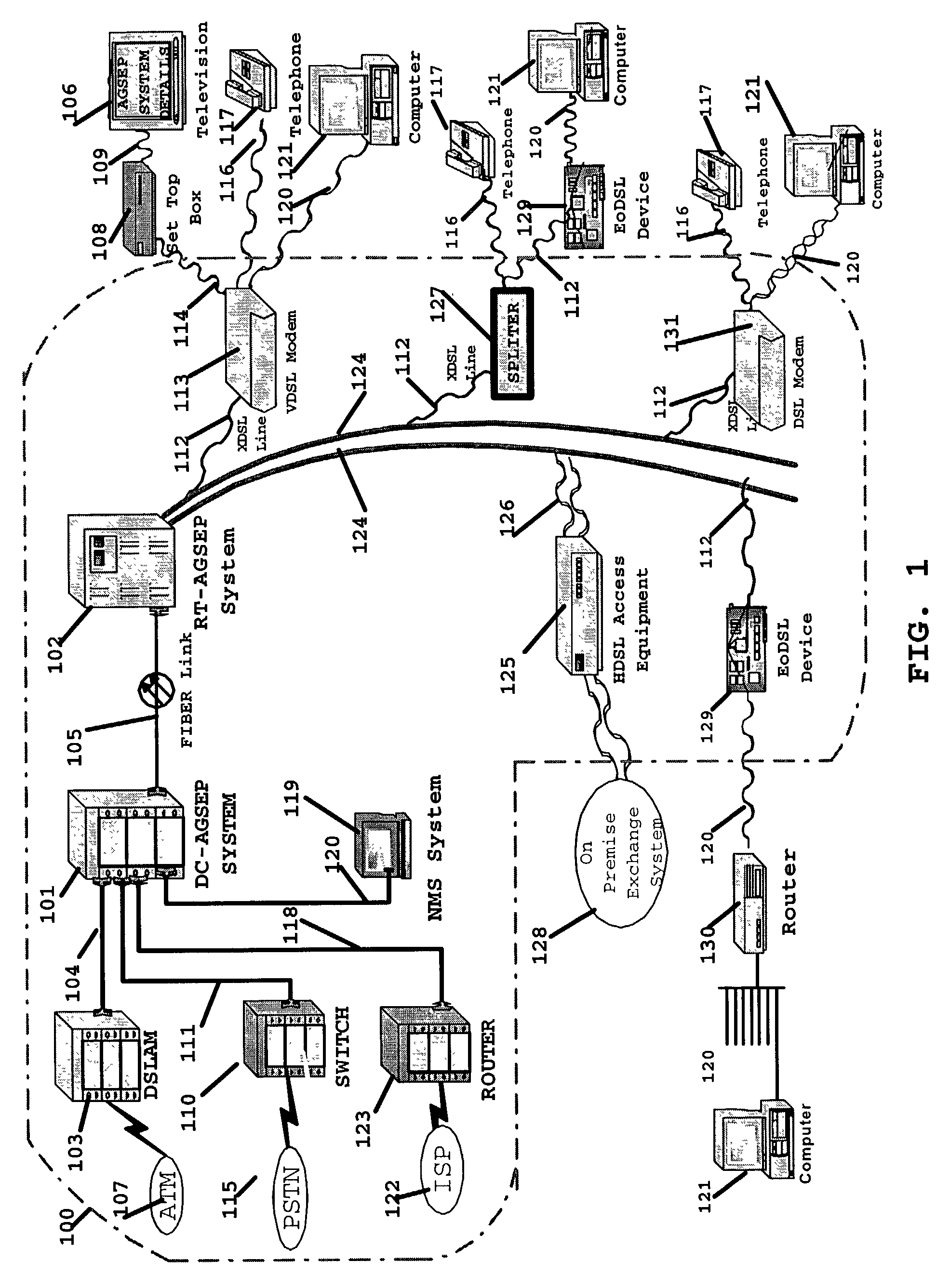
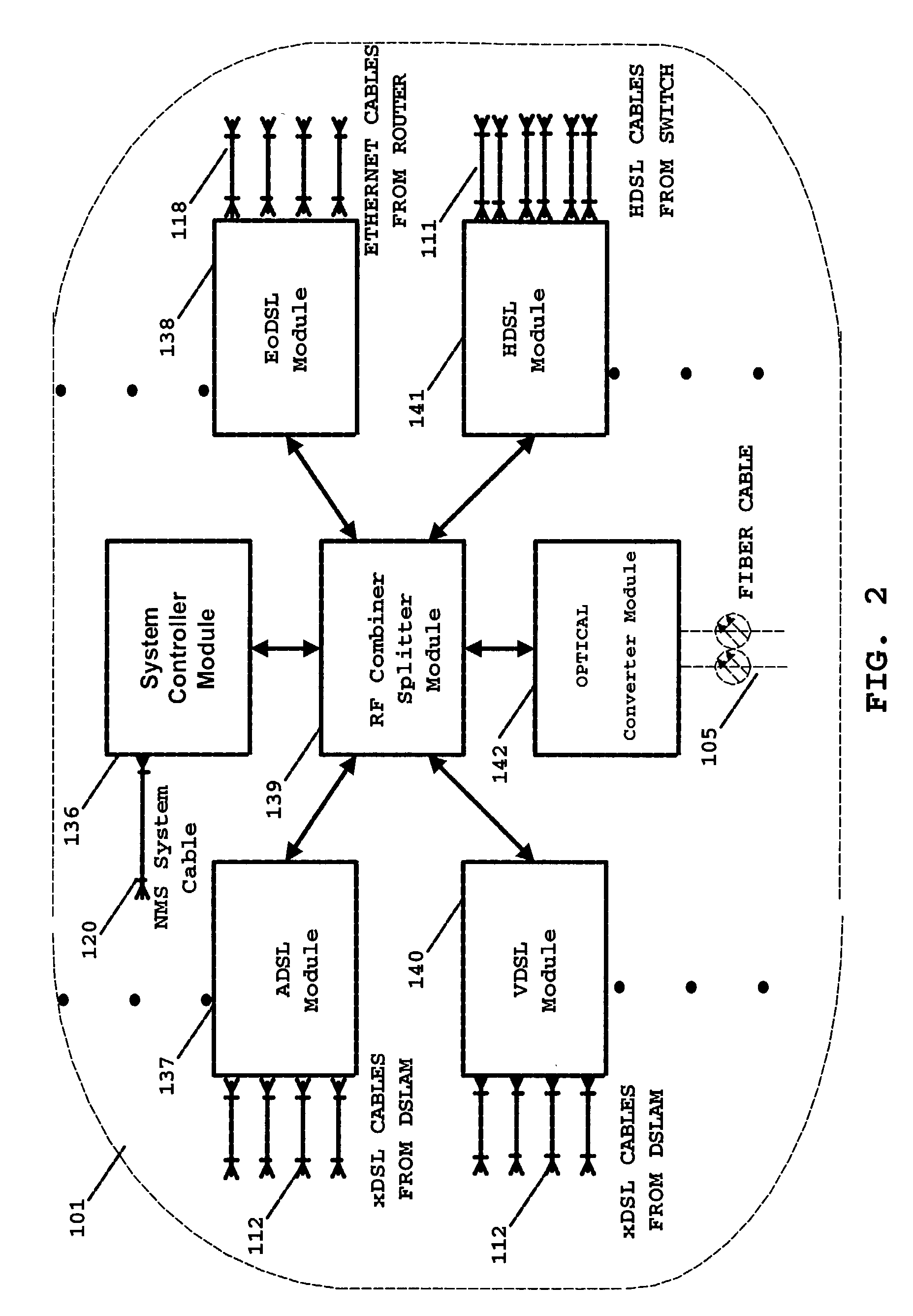
InactiveUS7136397B2Good serviceEnergy efficient ICTFrequency-division multiplex detailsTelecommunicationsNetwork architecture
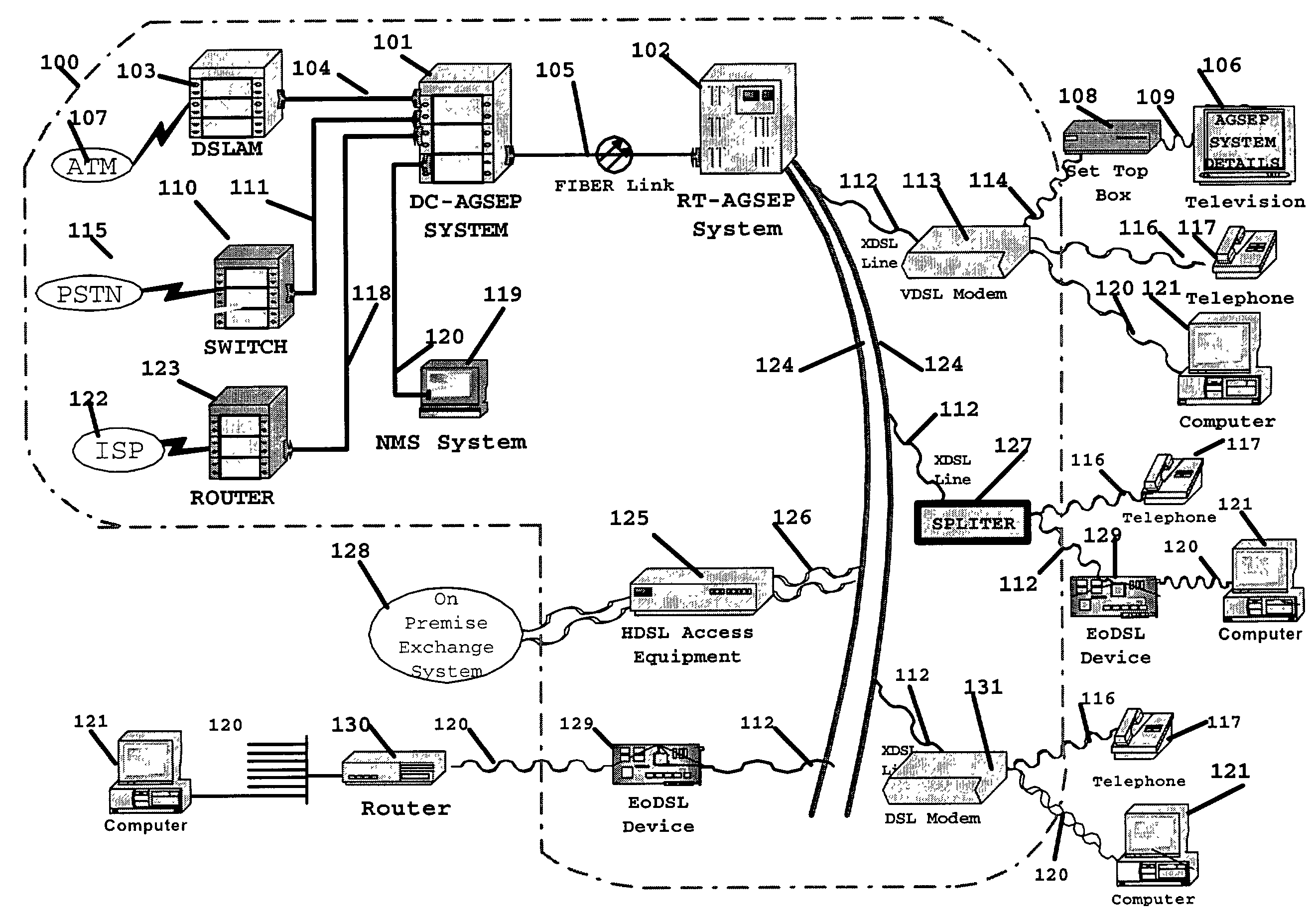
A simple network comprises of: xDSL service equipment located at a distribution center coupled to an Aggregator Separator (AGSEP) System located at a DC; AGSEP system at the DC is coupled, using a high-speed link, to another AGSEP system located at a remote site, which is coupled to subscriber equipment using drop cables. The AGSEP systems aggregate the xDSL signals originating at either DC xDSL equipment or subscriber equipment, are carried over the high-speed link. The AGSEP systems and separate the aggregated signals at either end to distribute the separated signal to the respective equipment.
Owner:RPX CORP
Method and apparatus for determining pdu session identity in wireless communication system
Disclosed are a method and apparatus for determining a PDU session identity in a wireless communication system. A method for determining, by a session management function (SMF) node, a packet data network (PDU) session identity during handover of user equipment (UE) in a wireless communication system, may include receiving a request message for requesting the establishment of a PDU session for the UE from an access and mobility management function (AMF) node, wherein a handover for the UE from a first wireless communication system to a second wireless communication system has been determined, determining a PDU session identity for the PDU session established for the UE when the request message is received, and sending a response message including the determined PDU session identity to the AMF node in response to the request message.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Power line communication rate limiting system and method
InactiveUS20070002771A1Rate limiting quality of service (QoS) controlError preventionTransmission systemsQuality of serviceRate limiting
A power line communications device that may provide rate limiting and quality of service control is provided. The device may include a first modem in communication with one or more user devices via a low voltage power line subnet and a second modem communicatively coupled to a second communications medium. The device also may include a controller in communication with the first and second modems and a computer readable medium encoded with instructions to control the operation of the controller. The controller may rate limit data to and / or from a destination and / or source based one or more parameters such as the destination address, the source address, the type of data, temporal parameters, and other criteria. In addition, the controller may implement QoS for data and transmit QoS parameters to power line modems to allow the power line modems to perform QoS.
Owner:CURRENT TECH
Method and apparatus for reference signal processing in an orthogonal frequency division multiplexing communication system
InactiveUS20120213261A1Electric signal transmission systemsError preventionChannel state informationCommunications system
A wireless communication includes a base station that configures a set of non-zero power reference signals corresponding to multiple potential transmission points to one or more users equipment UEs and configures at least one zero-power reference signal, with zero transmission power from one or more of the multiple transmission points. The base station transmits configuration information to at least one UE of the one more UEs, wherein the configuration information corresponds to a set of resource elements that are associated with a set of channel state information reference signals and wherein the set of channel state information reference signals include the set of nonzero-power reference signals and the at least one zero-power reference signal. The UE then performs a channel measurement based on one or more non-zero-power reference signals of the set of non-zero-power reference signals and performs an interference measurement based on the at least one zero-power reference signal.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
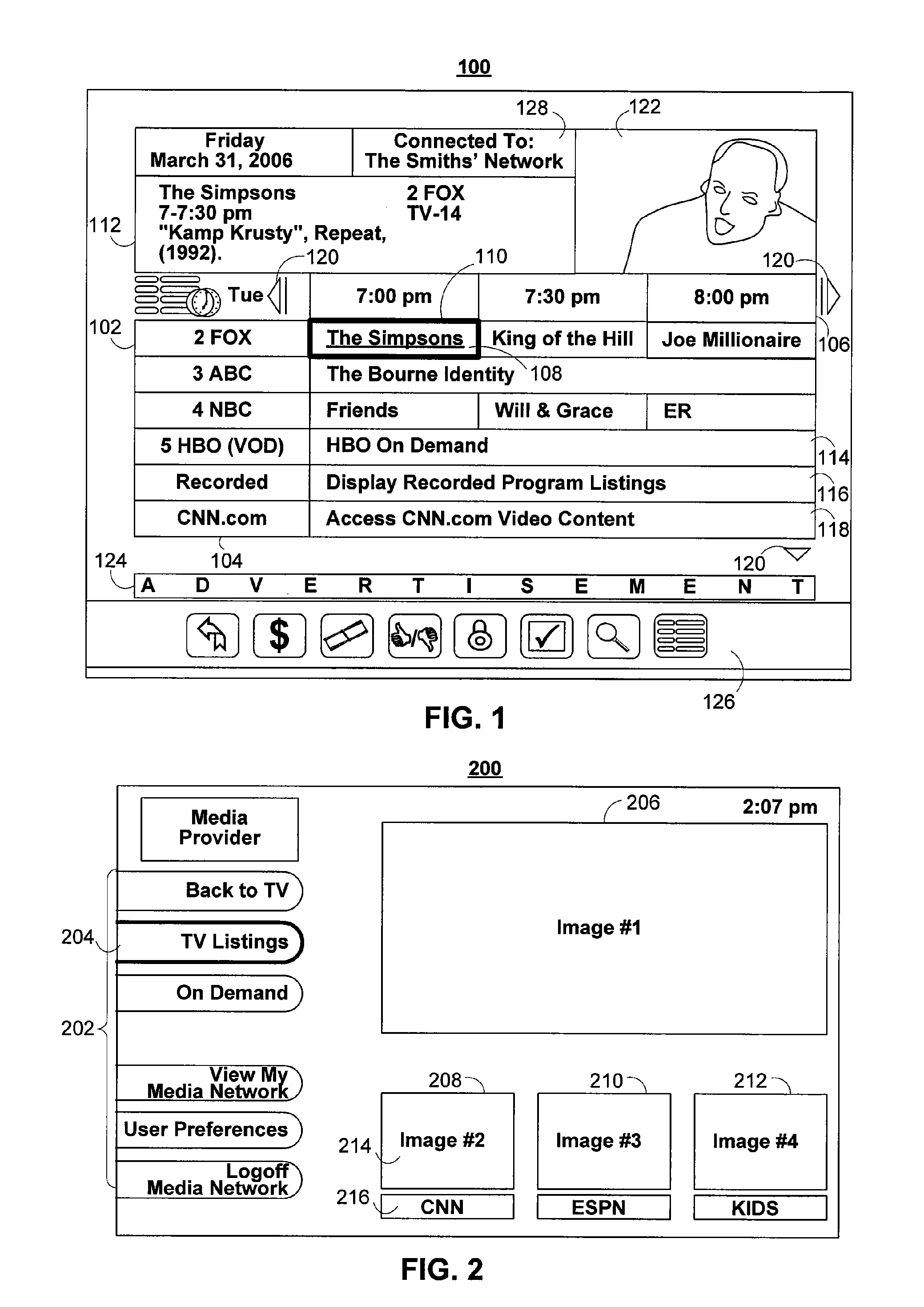
Management of profiles for interactive media guidance applications
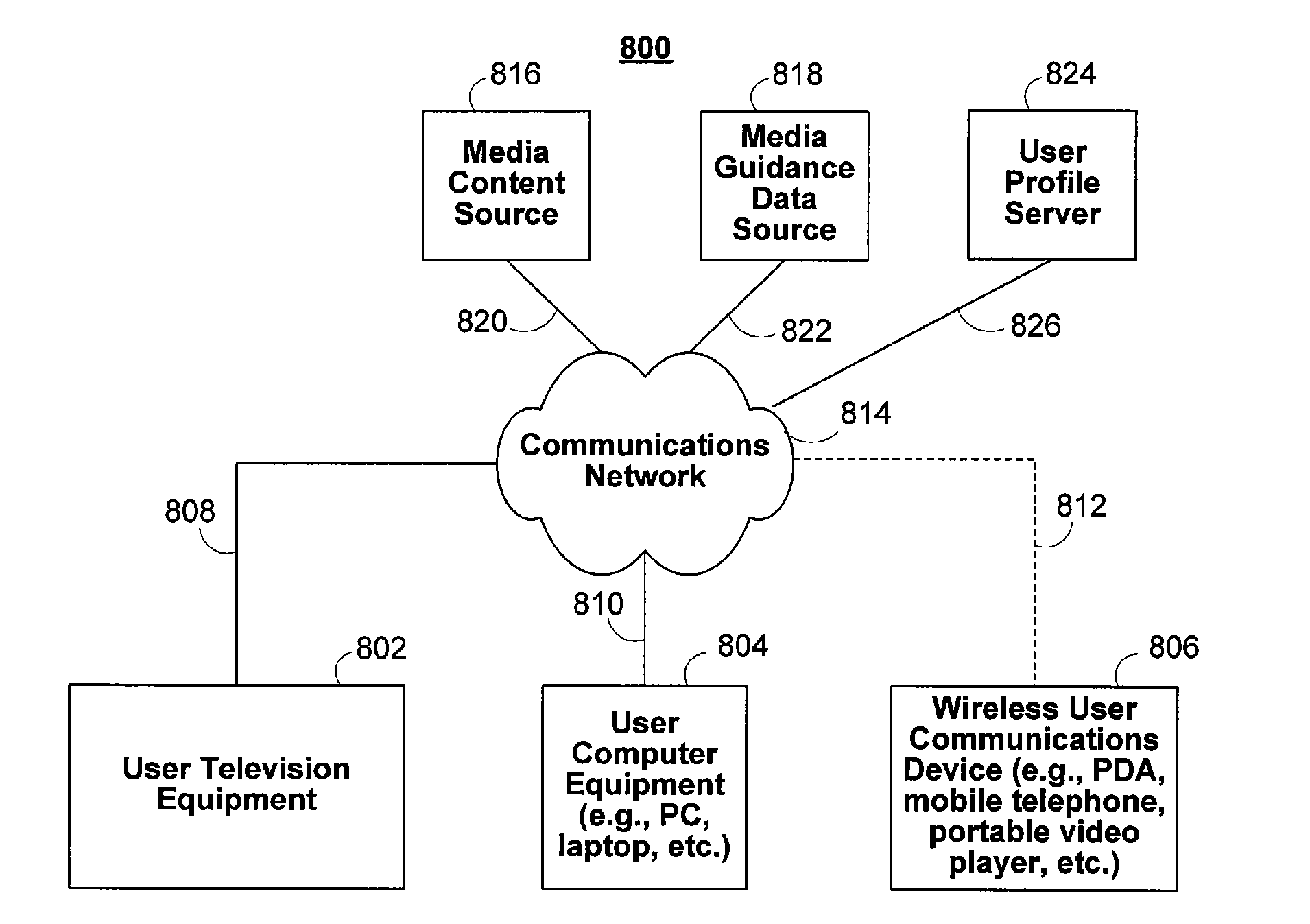
InactiveUS20100211636A1Multiple digital computer combinationsTelevision systemsUser profileUser equipment
Users of interactive media guidance applications may access media content and seek media guidance on a plurality of user equipment devices. A user profile server may be used for the management of a user's profile information. The user profile server may store a user's profile information including information about the user's media network and about user equipment devices associated with the user's media network. The user's profile information may be used to provide functionality to record media content on the most suitable user equipment device of a user's media network. The user's profile information may also be used to provide recommendations of media content based on a user's monitored interactions with a plurality of user equipment devices. The user's profile information may also be provided to user equipment devices of the media network not having the user profile information.
Owner:ROVI GUIDES INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com