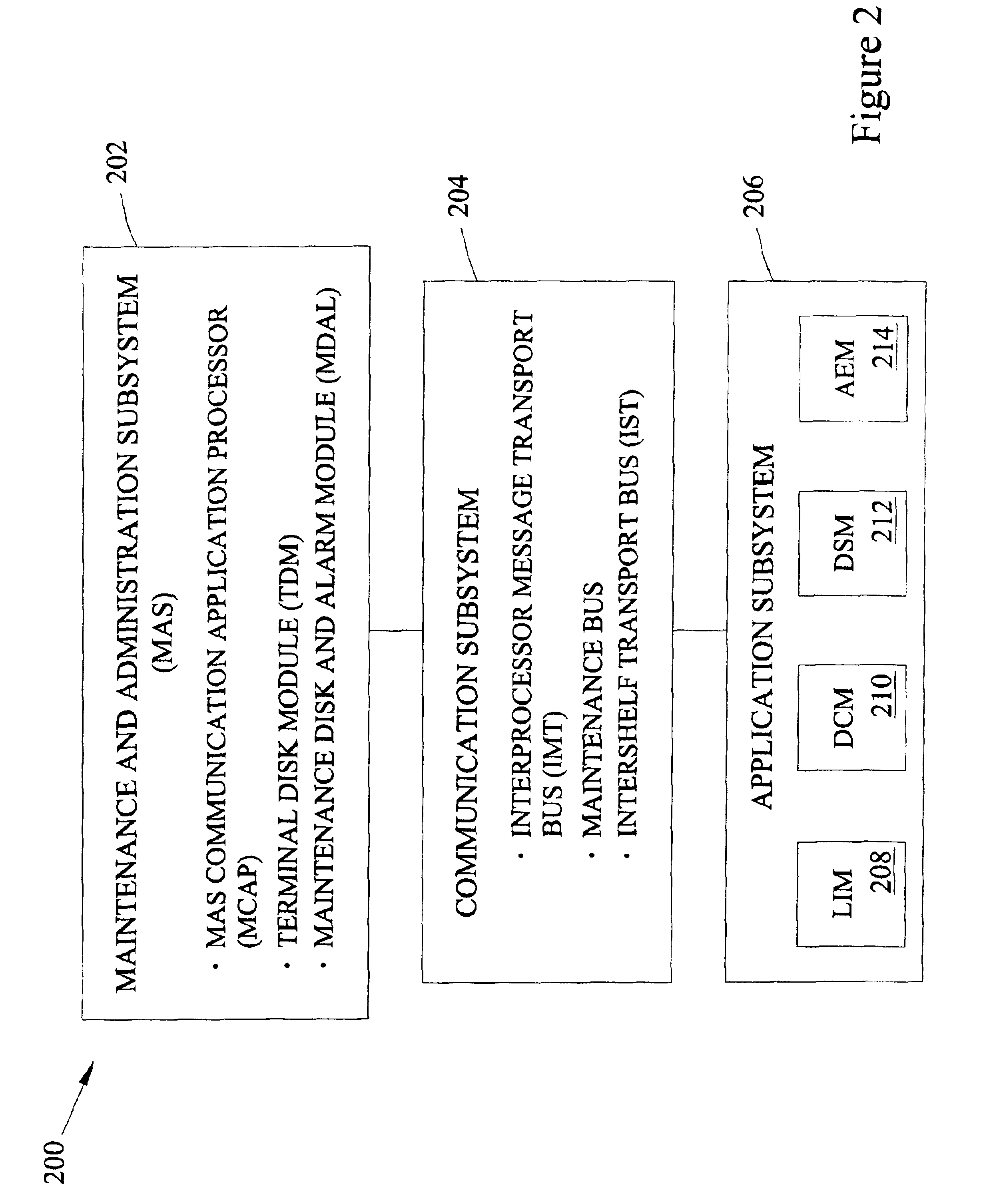
Patents
Literature
756 results about "Address resolution" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
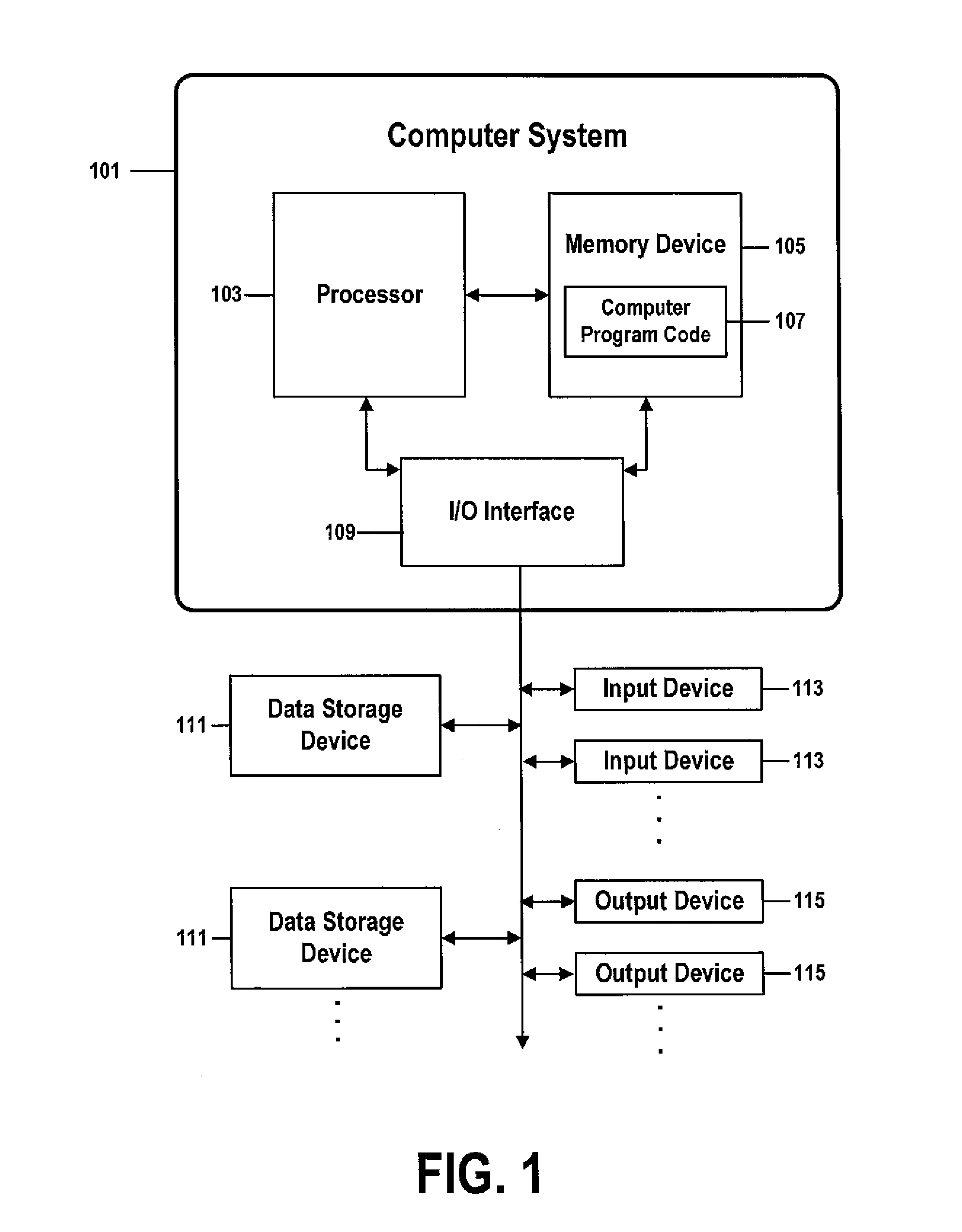
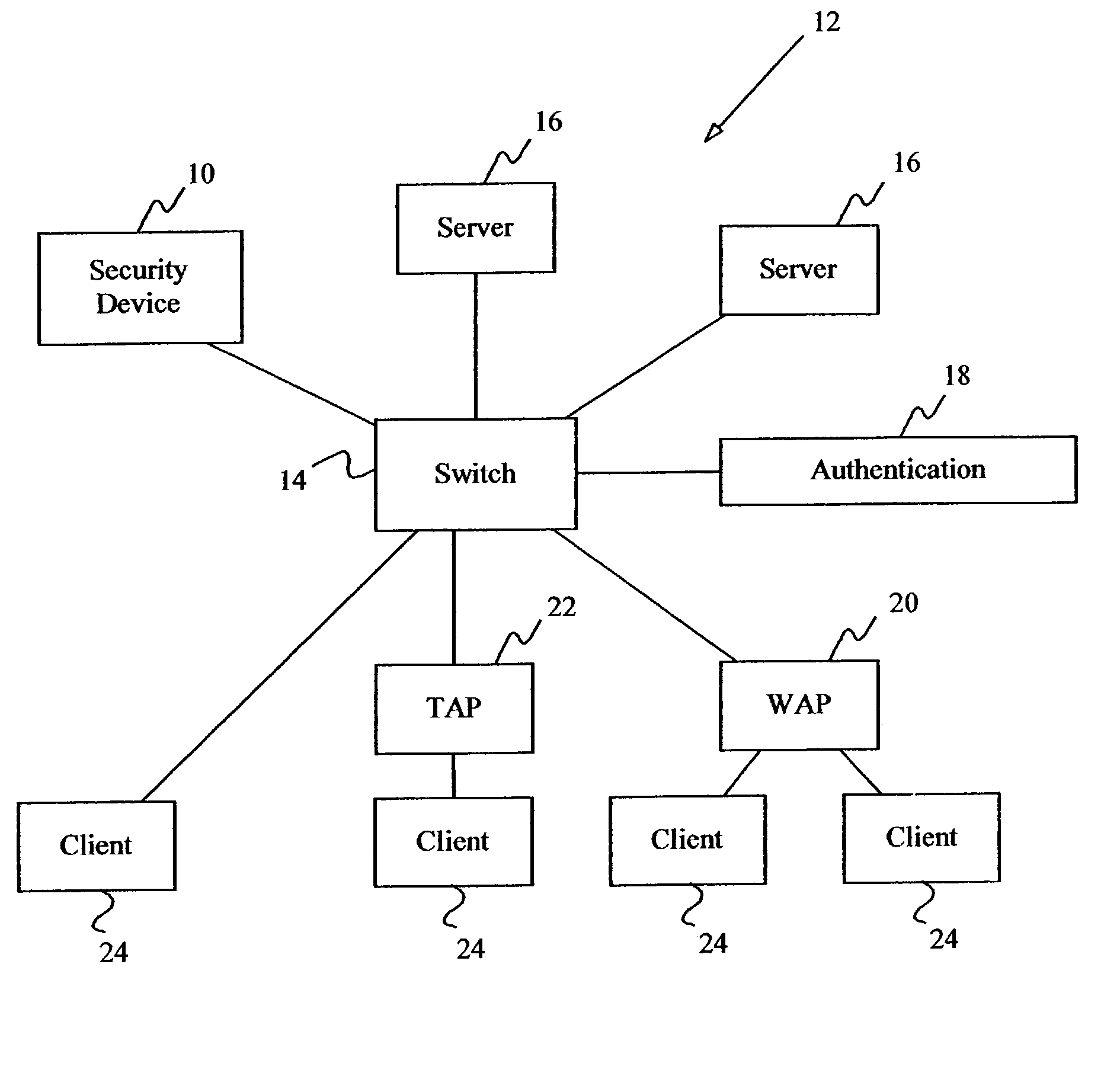
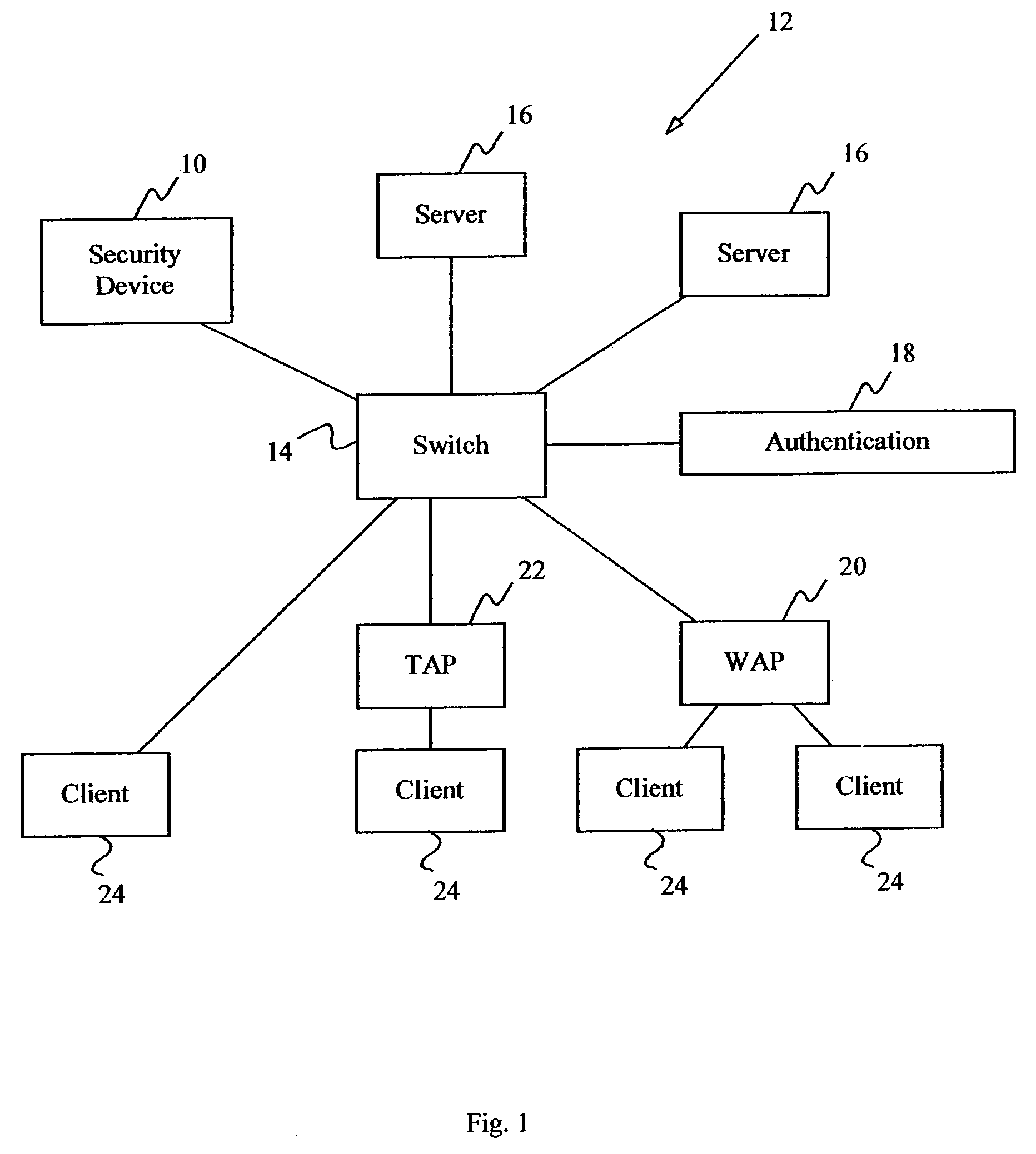
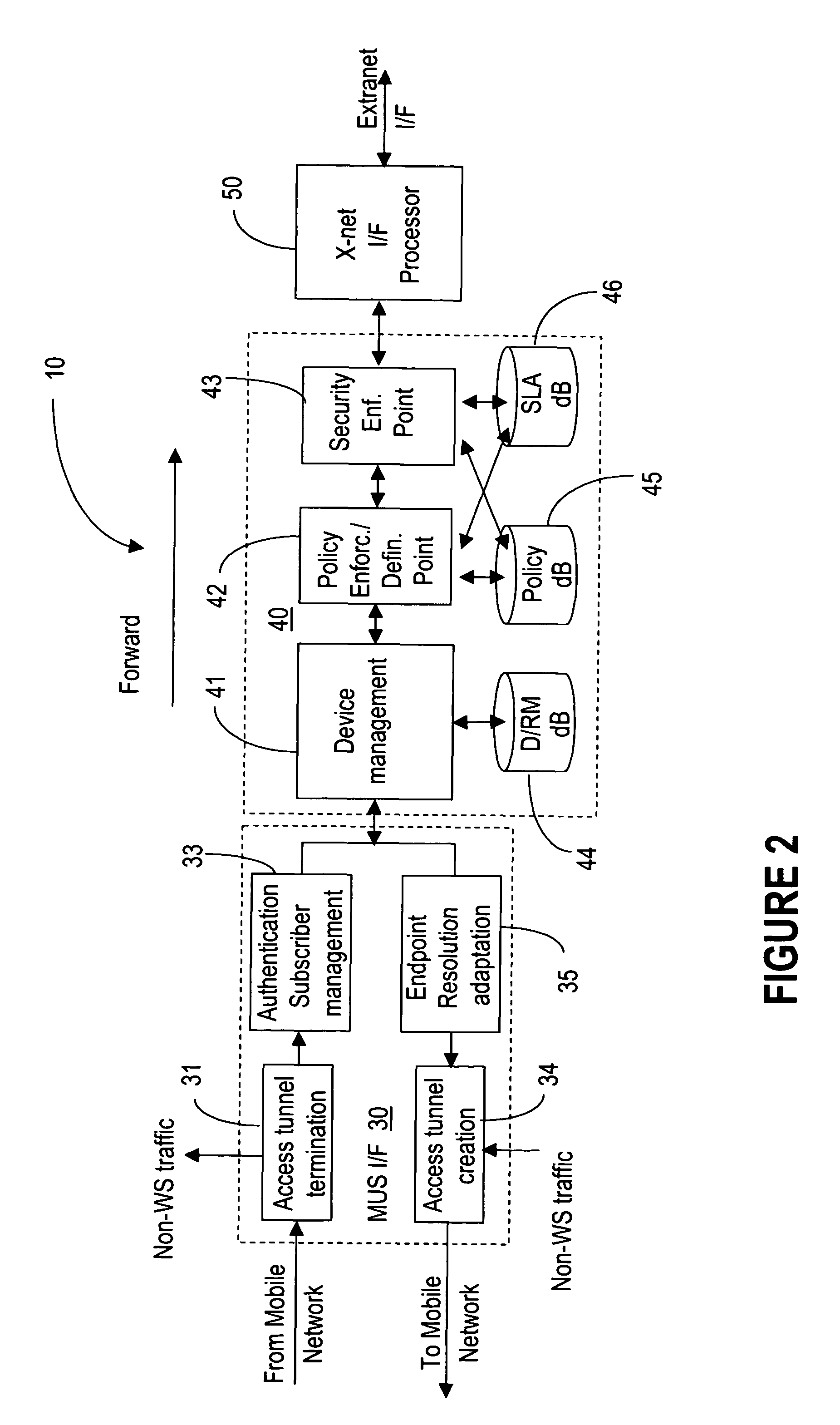
The term address resolution refers to the process of finding an address of a computer in a network. The address is "resolved" using a protocol in which a piece of information is sent by a client process executing on the local computer to a server process executing on a remote computer.
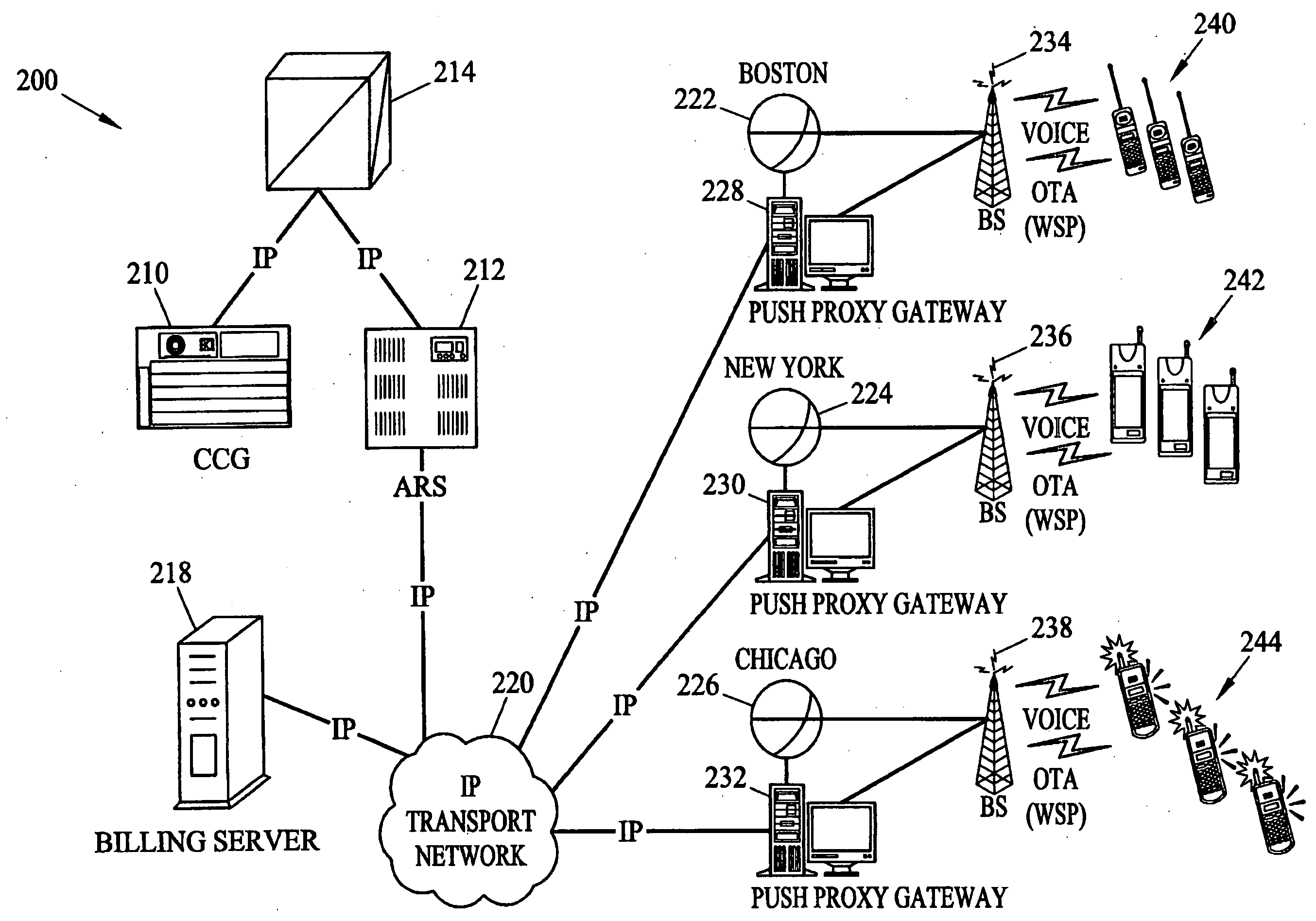
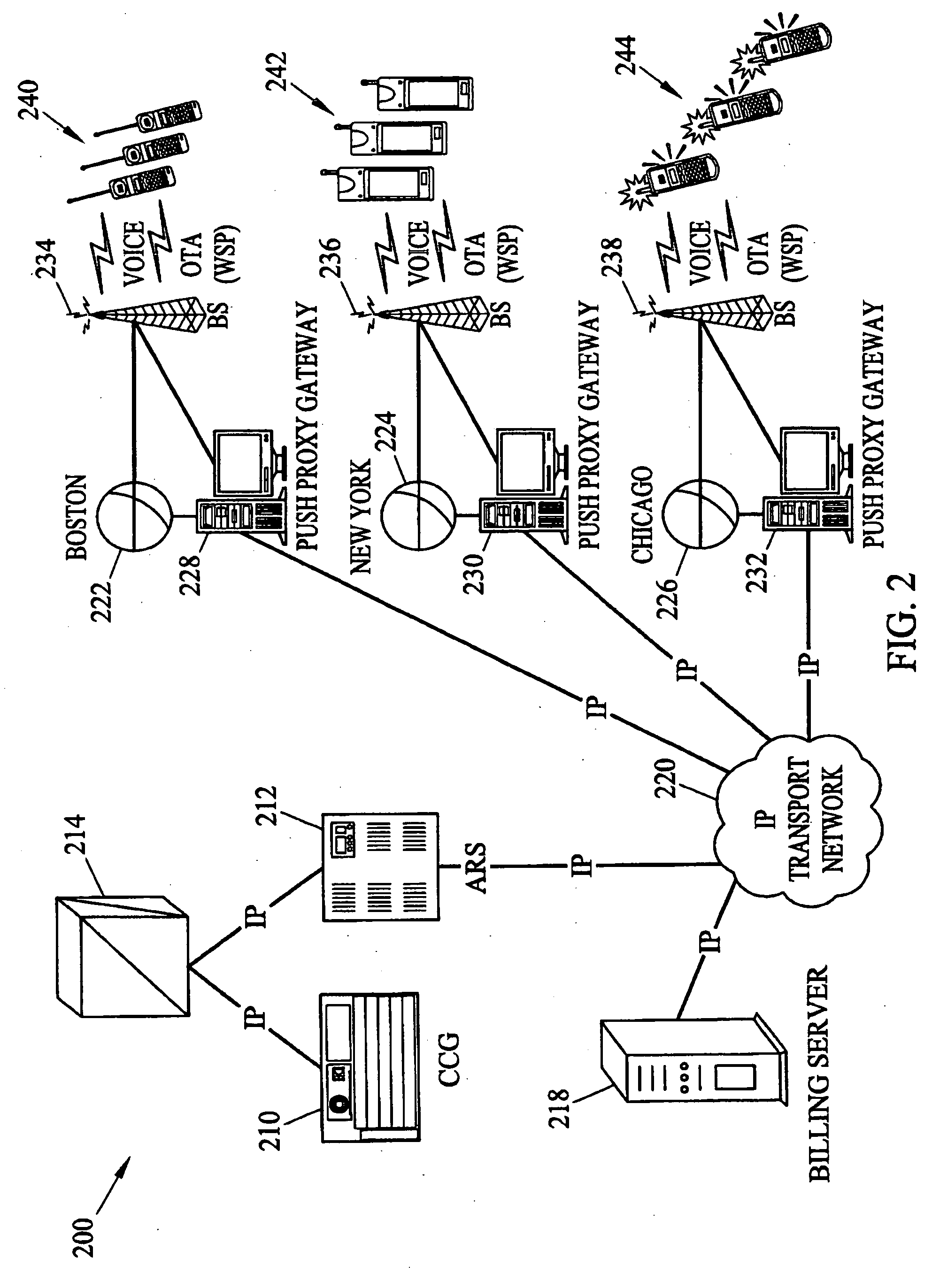
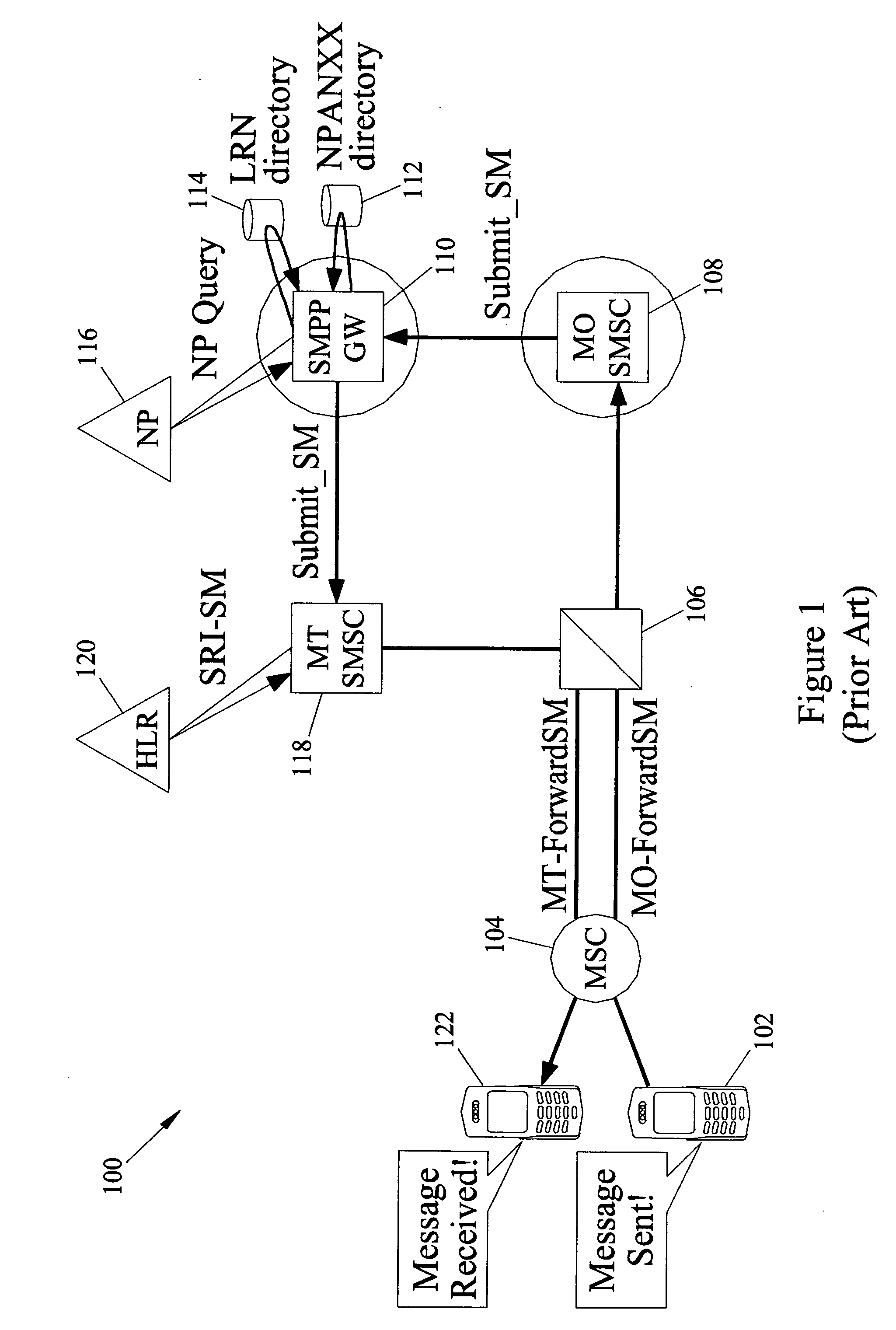
Methods and systems for generating, distributing, and screening commercial content
ActiveUS20040259553A1Broadcast systems characterised by addressed receiversBroadcast transmission systemsProcessor registerAddress resolution
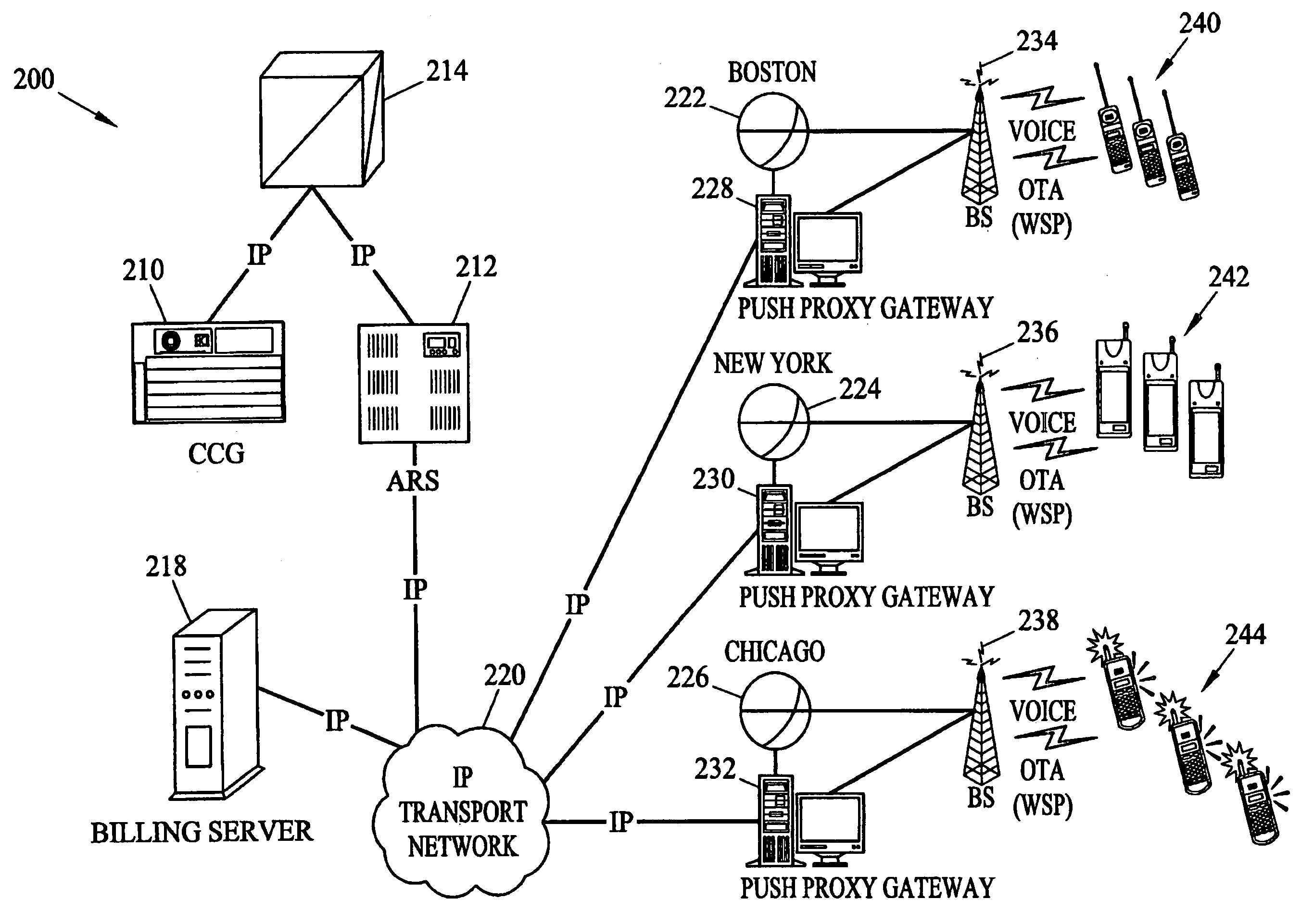
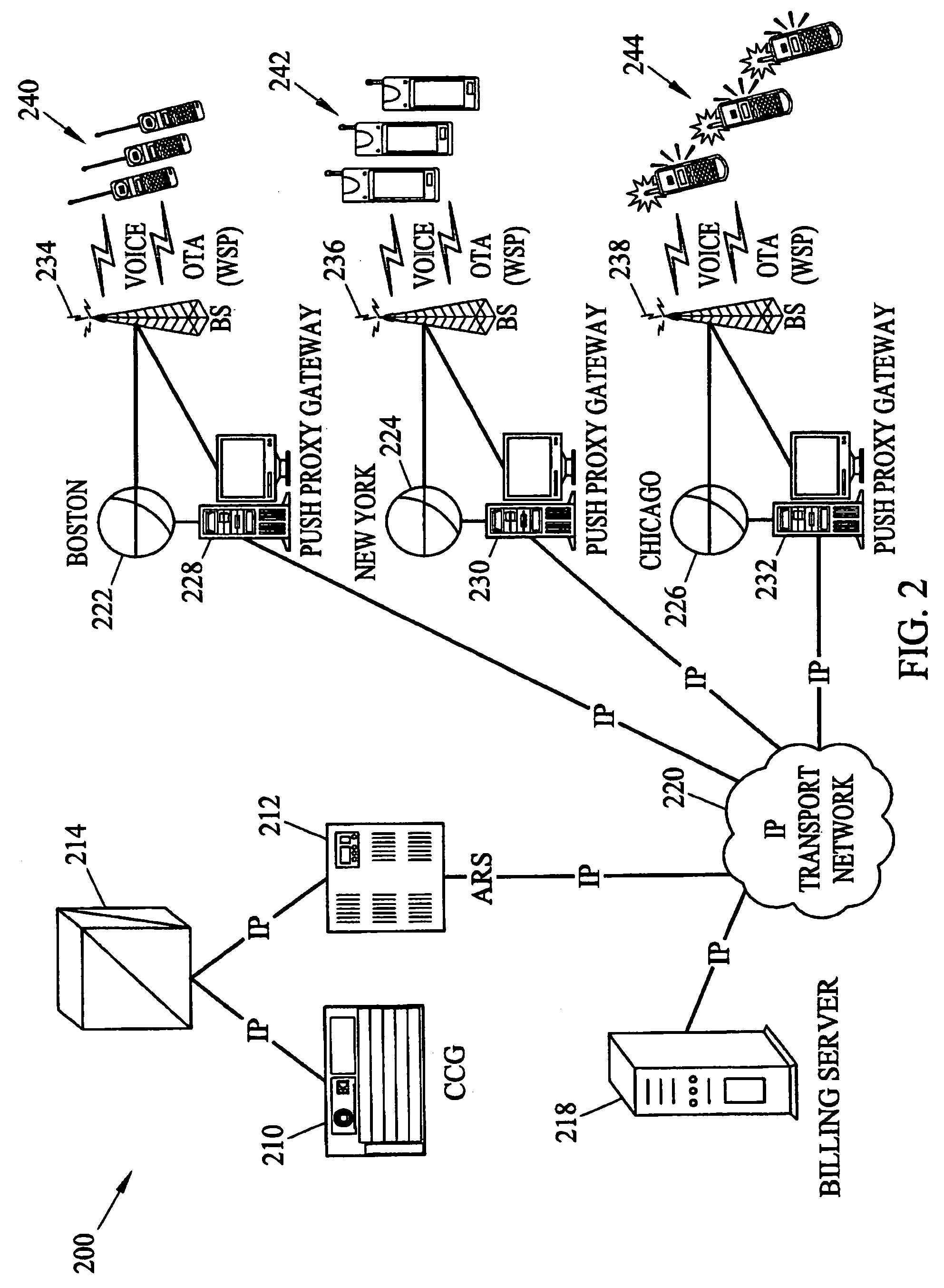
Methods and systems for generating, distributing, and screening commercial content are disclosed. A commercial content generator (CCG) generates commercial content message and obtains from a push proxy agent address resolution server the network routing address of each push proxy agent that is required for distribution of the message to the target mobile subscriber audience. A push proxy agent receives a message containing commercial content and resolves a mobile subscriber identifier for each mobile subscriber who is to receive the commercial content information using subscriber information obtained from a subscriber location register, such as a visitor location register (VLR). The push proxy agent may also negotiate media format characteristics for each member of the target mobile subscriber audience and facilitate delivery of the commercial content to each member of the target mobile subscriber audience.
Owner:TEKELEC
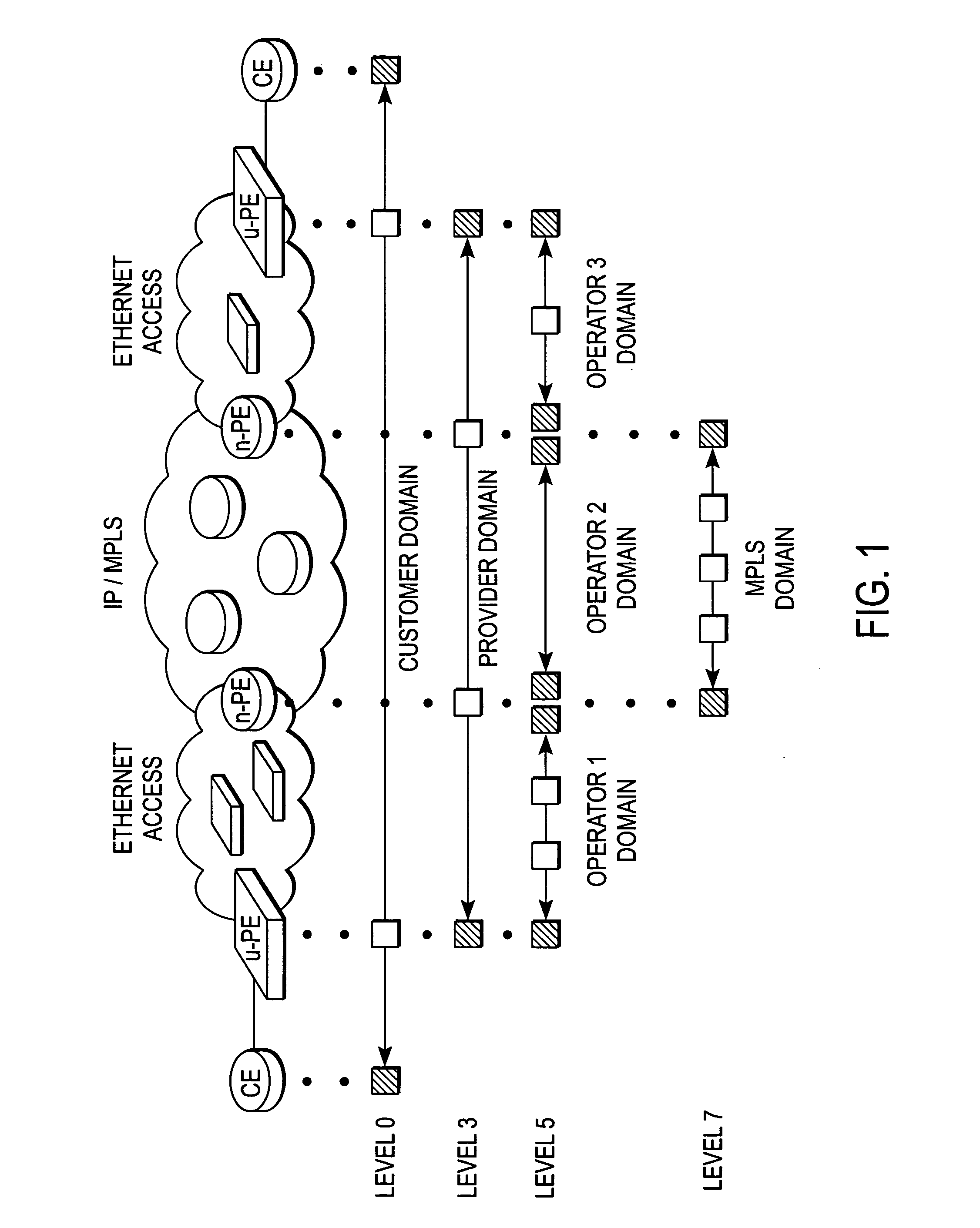
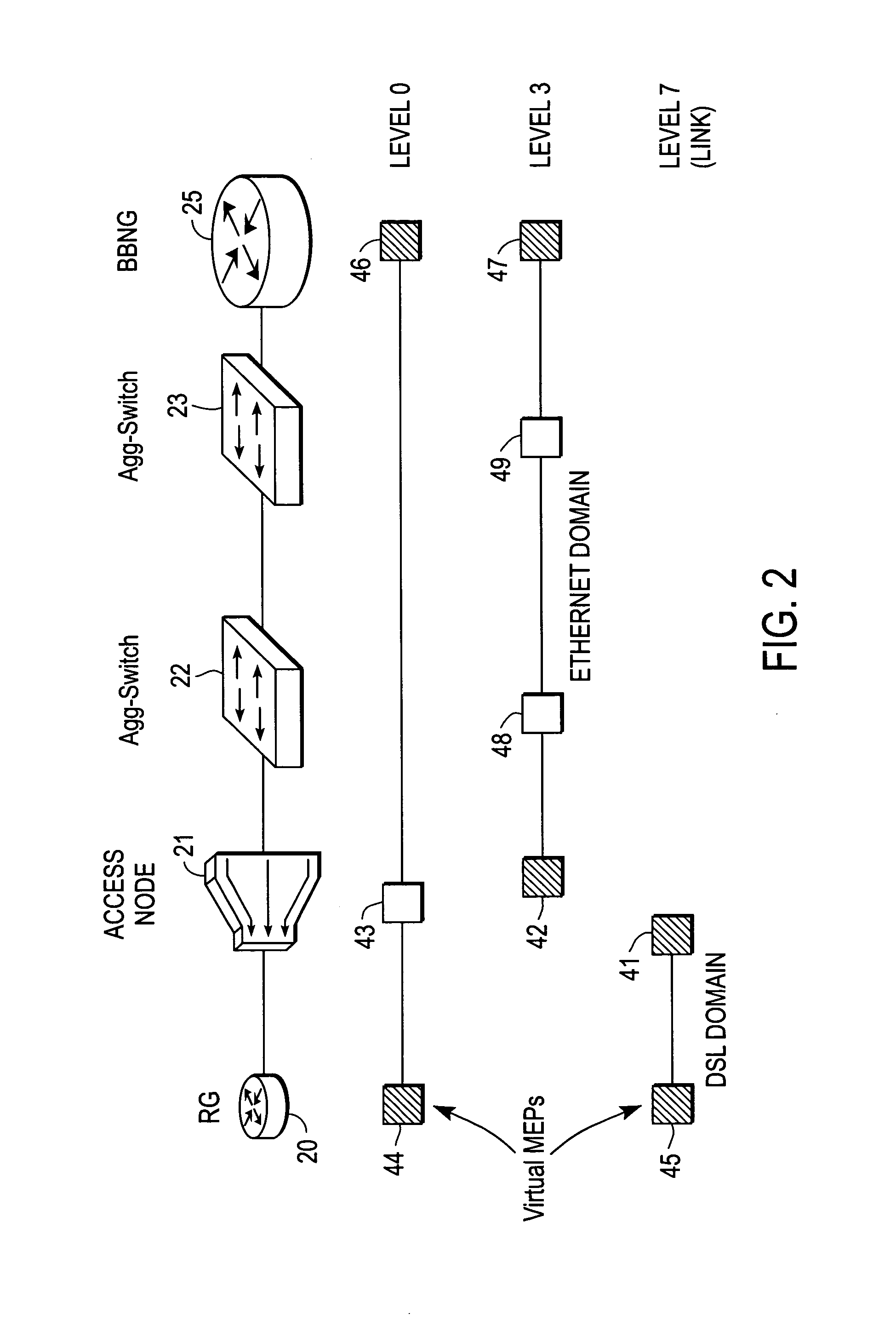
Address resolution mechanism for ethernet maintenance endpoints
A method of operation for a node of an Ethernet access network includes issuing a multicast message on the Ethernet access network by a maintenance end point (MEP) of the node. The multicast message contains a name of a target MEP. The node is further operable to receive a unicast reply message from the target MEP, the unicast message reply containing a MEP identifier (MEP-ID) and a MEP Media Access Control (MAC) address of the target MEP. It is emphasized that this abstract is provided to comply with the rules requiring an abstract that will allow a searcher or other reader to quickly ascertain the subject matter of the technical disclosure. It is submitted with the understanding that it will not be used to interpret or limit the scope or meaning of the claims.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
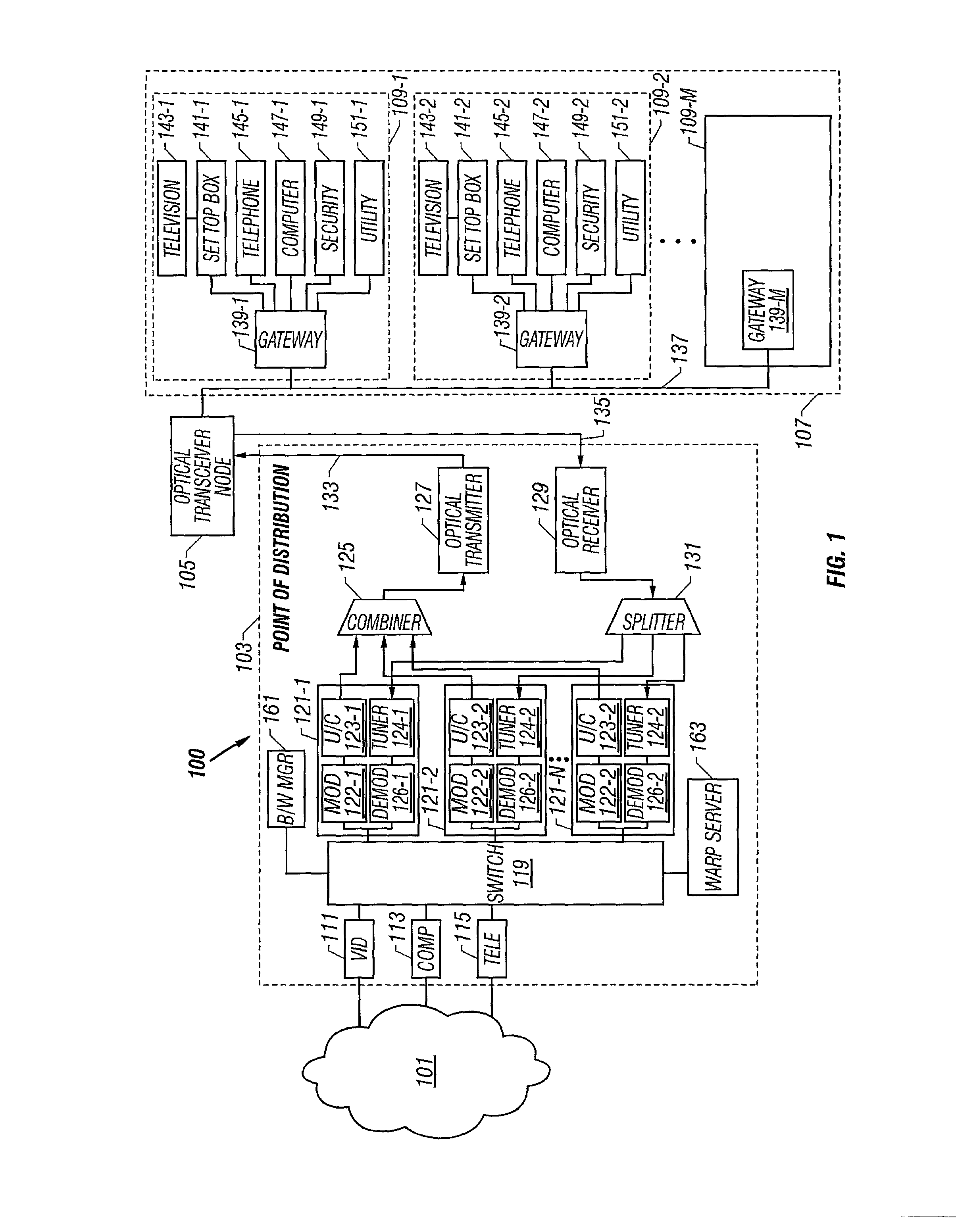
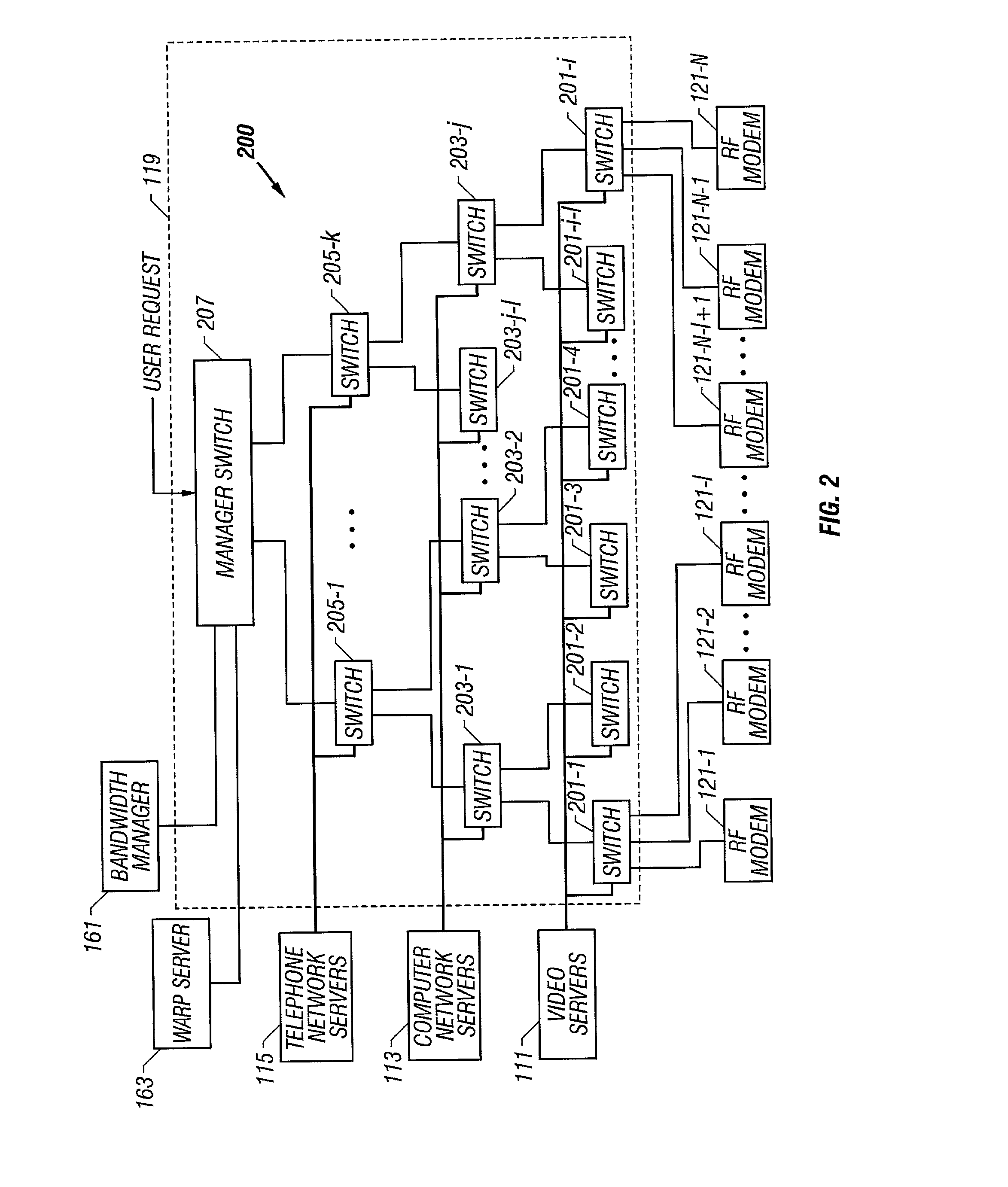
System and method for distributing information via a communication network
InactiveUS20010030785A1Wavelength-division multiplex systemsOptical transmission adaptationsFrequency spectrumModem device
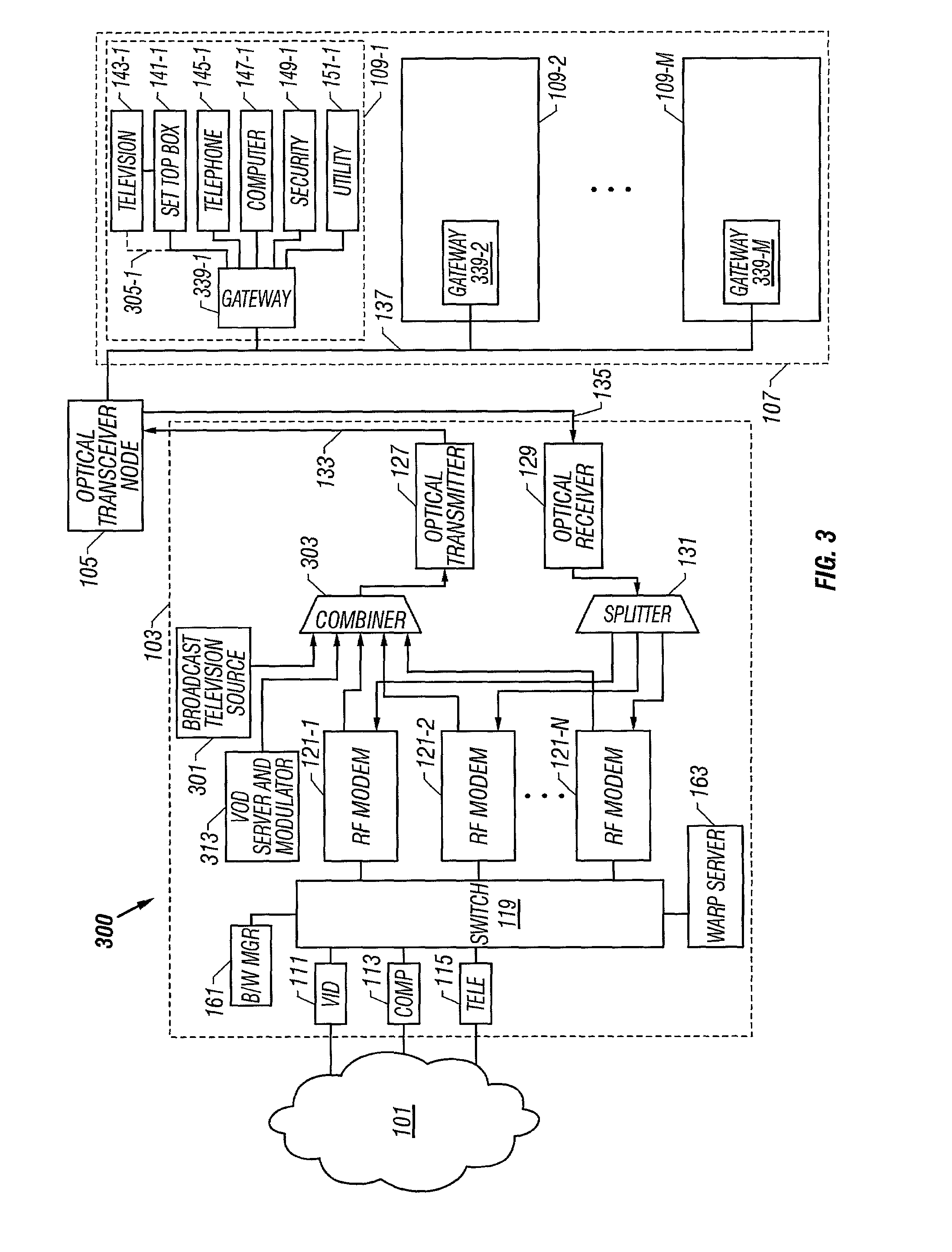
A communication system for distributing information via a network to one or more subscribers includes a multi-port switch, one or more radio frequency (RF) modems coupled to respective ports of the switch, a combiner and a transmitter. The switch forwards source information to the RF modems based on address information. Each RF modem modulates and up converts information from the switch to an RF signal within a respective subscriber channel of the television broadcast spectrum. Each channel is assigned to one or more subscribers, and each subscriber is allocated unshared bandwidth. Each channel may be further divided into unshared bandwidth increments, so that multiple subscribers may share a single channel. The combiner combines modulated information from each RF modem into a combined signal and the transmitter transmits the combined signal to the subscribers via the network. An HFC network including a distribution point and one or more optical nodes is contemplated, each optical node serving a particular geographic area via a corresponding coaxial cable. Each subscriber destination includes a gateway device or the like that is tuned to a corresponding channel to retrieve source information from that channel, and to deliver the information to one or more local subscriber devices. The gateway further includes converters, a modulator and an up converter to receive and transmit subscriber information upstream to the distribution point. The gateways and an address resolution server enforce point to point communications. A bandwidth manager allocates bandwidth and monitors bandwidth usage.
Owner:UBER TECH INC
Method and apparatus for managing hardware address resolution
InactiveUS20070248085A1Data switching by path configurationAddress Resolution ProtocolAddress resolution
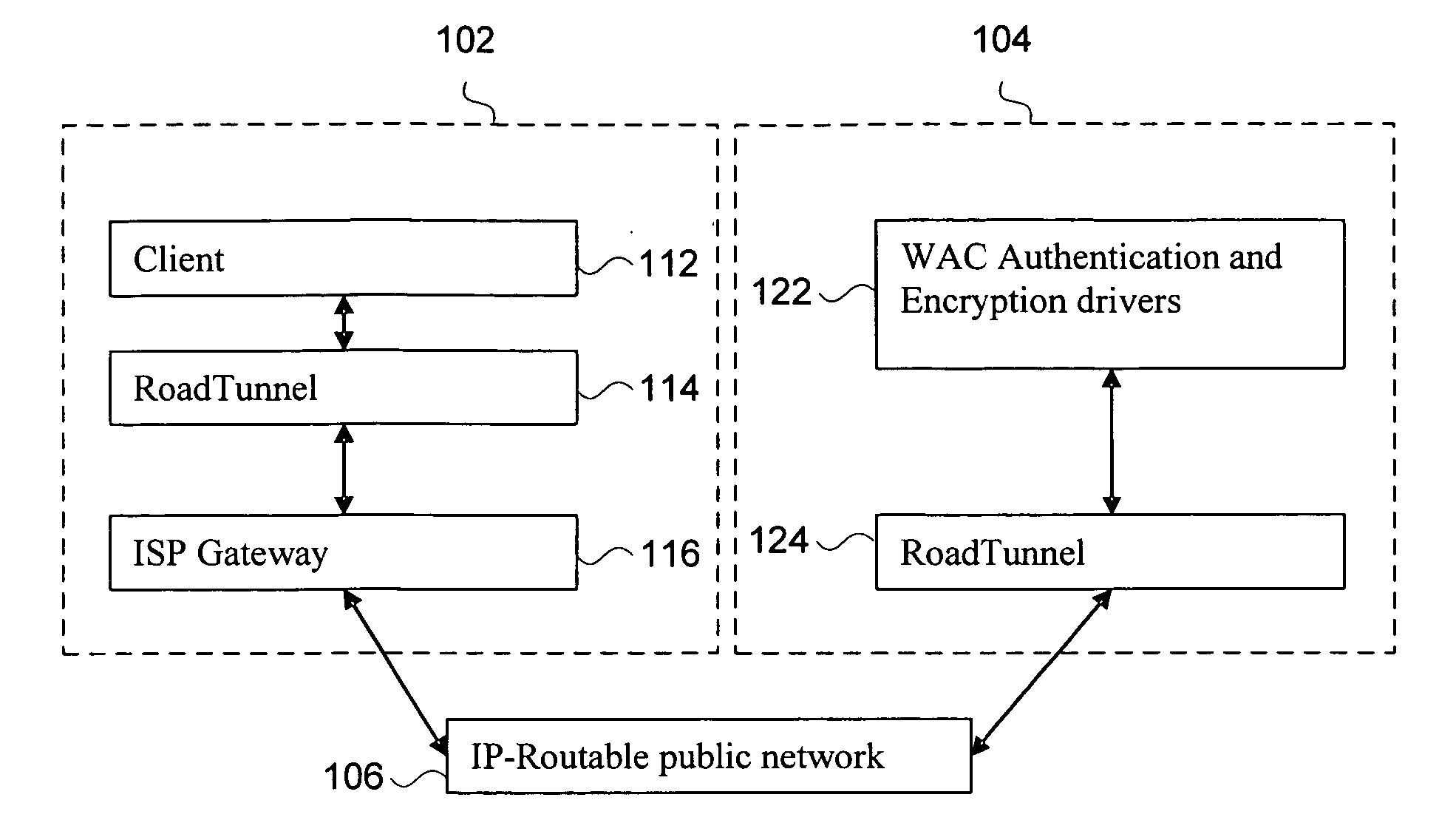
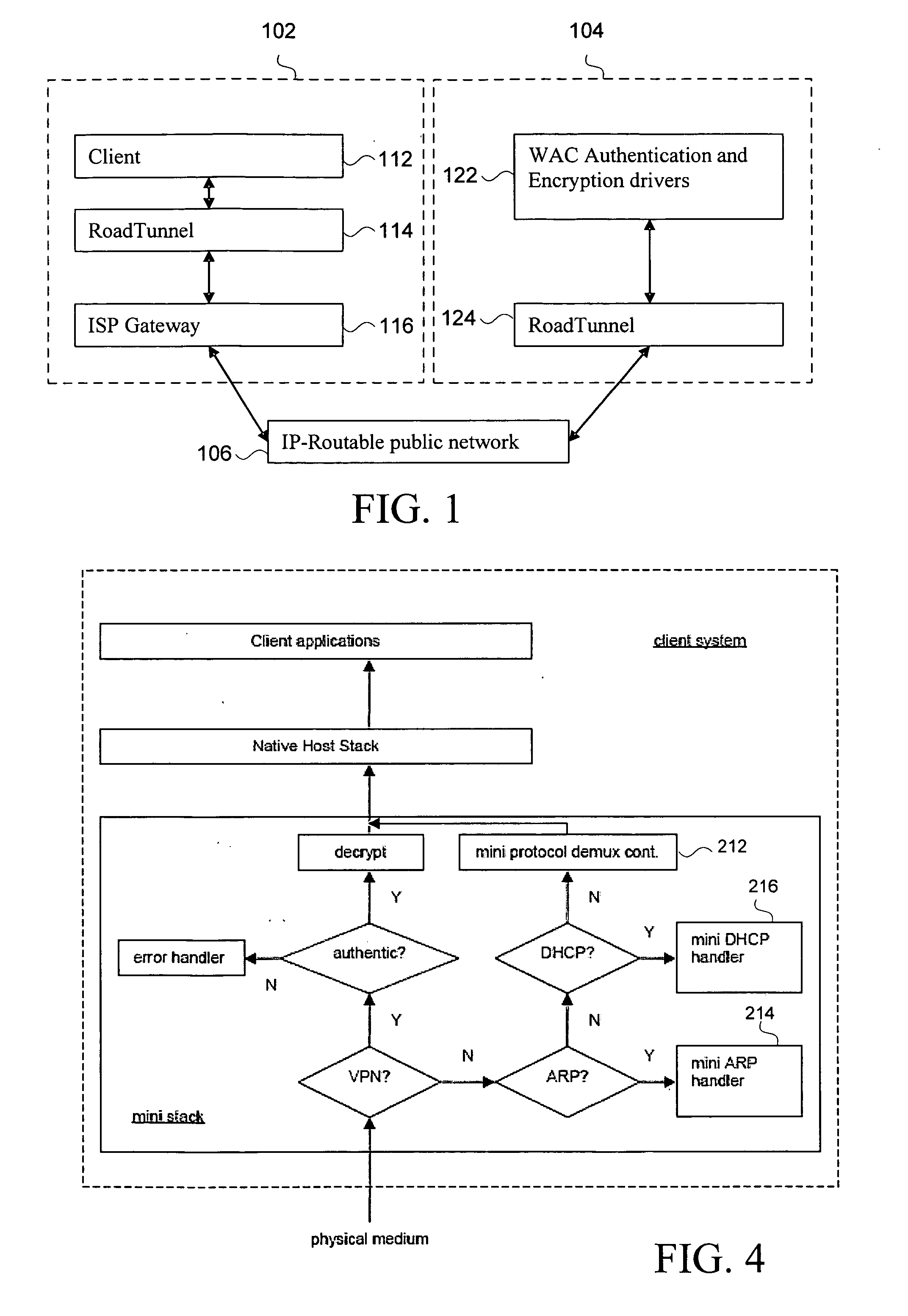
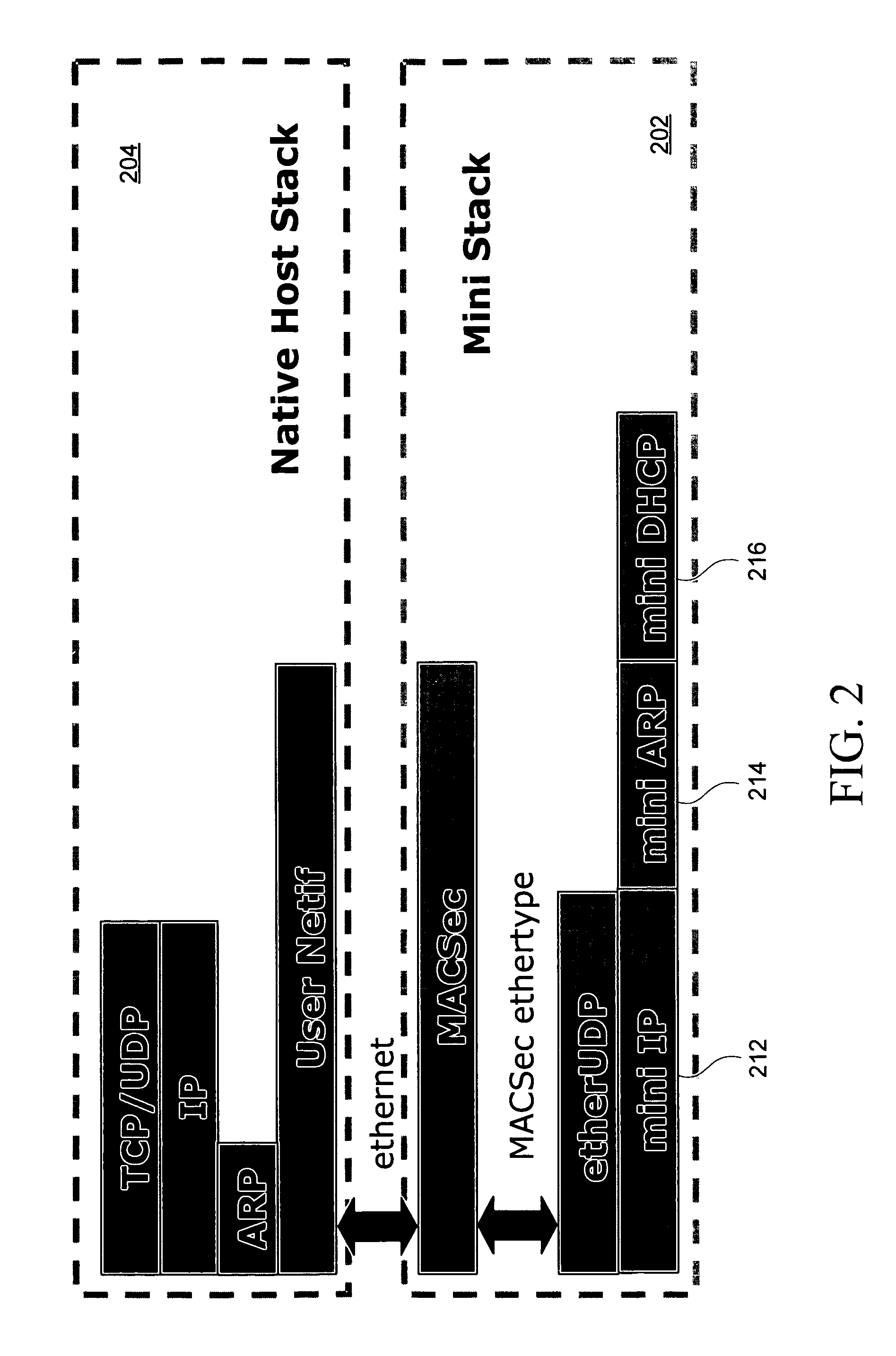
Disclosed herein is a network device, such as a host computer, that simultaneously has two IP identities: a local IP identity on a local network (e.g., a non-virtual private network) to which the host computer is connected; and a remote IP identity on a second network (e.g., virtual private network) that is remote to the host. Only the remote IP identity is visible to the host operating system's network stack. Each IP identity has its own ARP cache and Address Resolution Protocol (ARP). The local ARP cache is managed with respect to a connection of the host to a local subnet (e.g., an Internet Service Provider (ISP) subnet) and the remote ARP cache is managed with respect to a remote subnet reachable through a gateway on the local subnet.
Owner:E COLT SYST INC
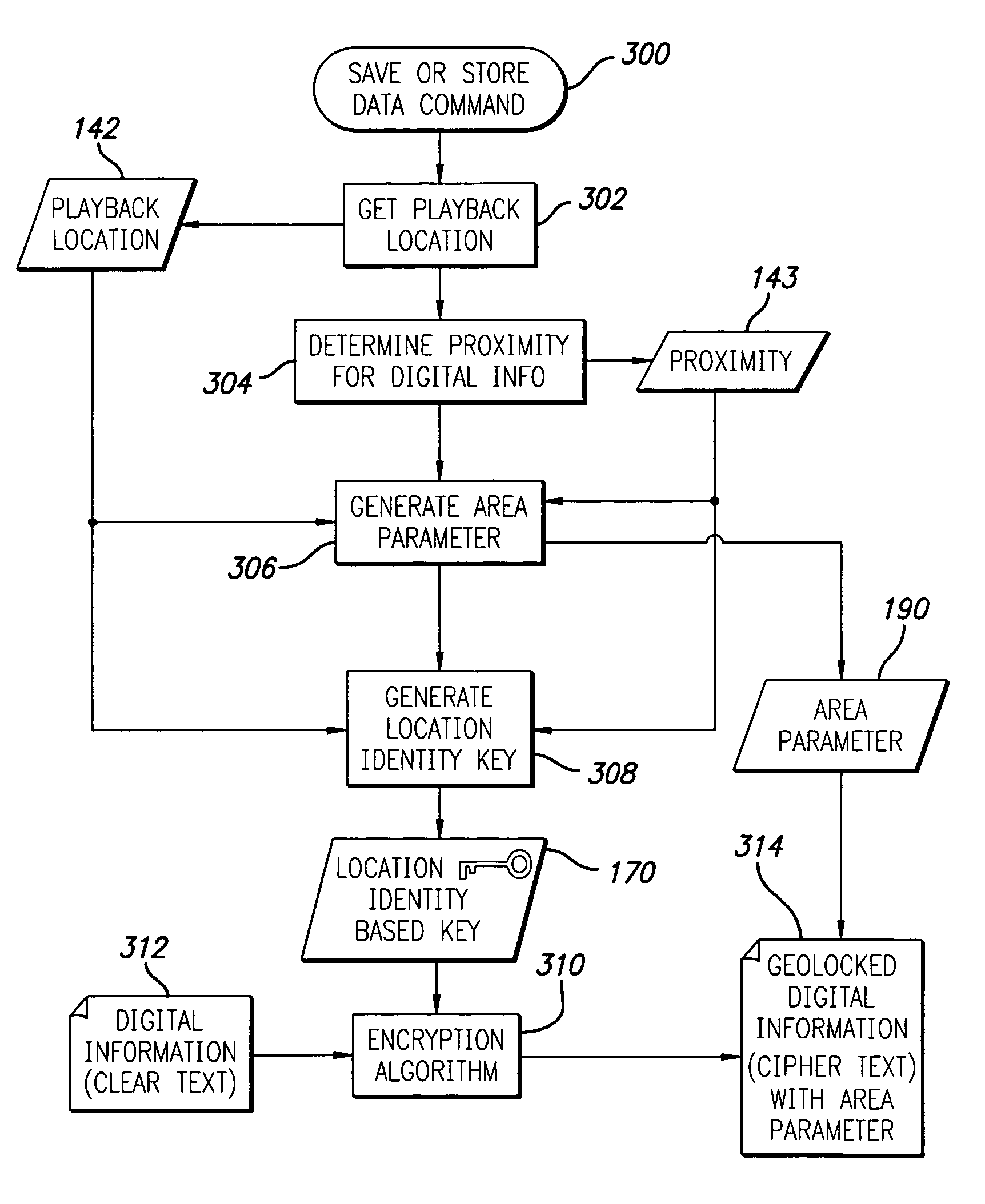
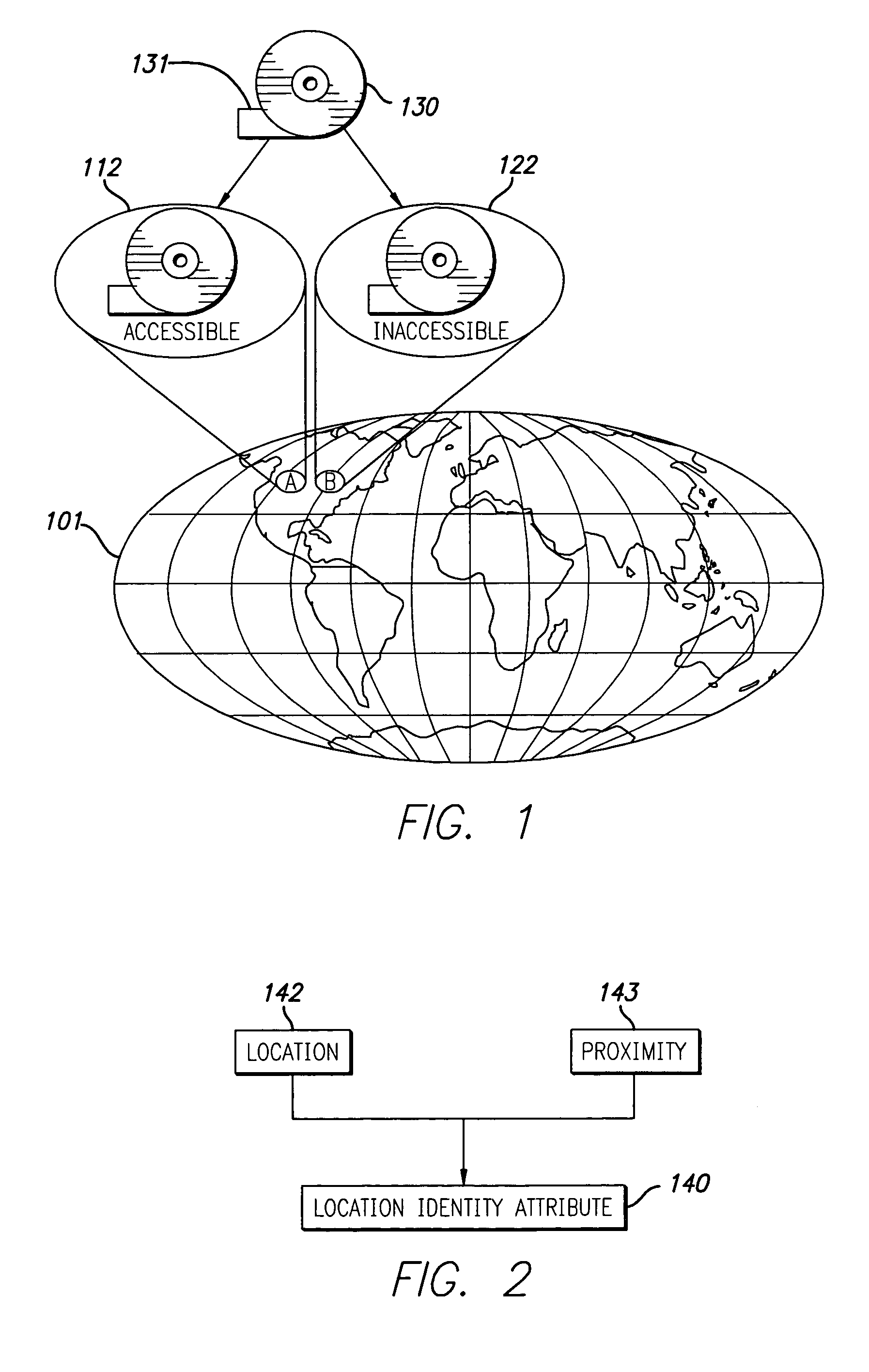
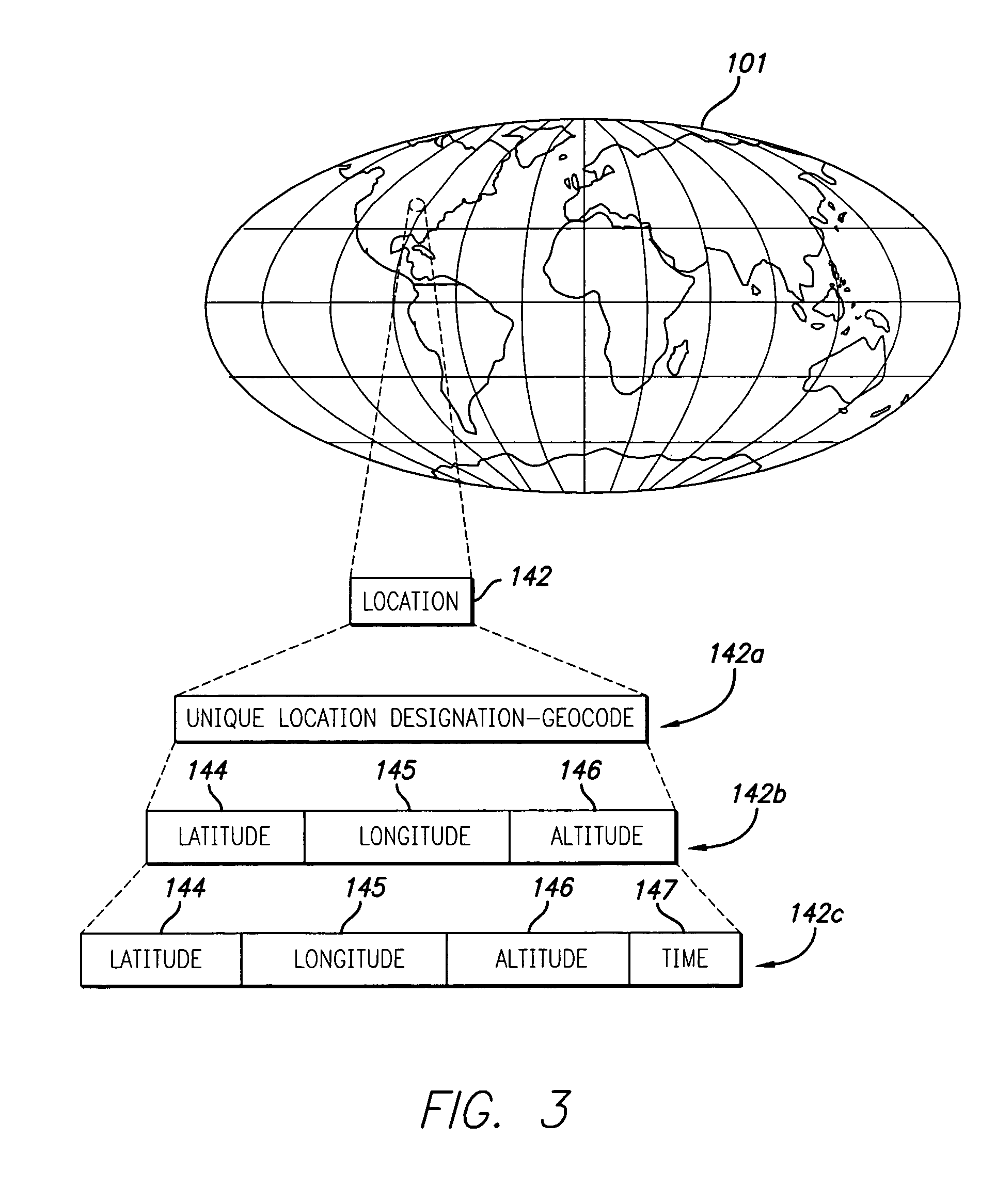
System and method for using location identity to control access to digital information
InactiveUS6985588B1Key distribution for secure communicationDigital data processing detailsAddress resolutionGeolocation
A method and apparatus for controlling access to digital information utilizes a location identity attribute that defines a specific geographic location. The location identity attribute is associated with the digital information such that the digital information can be accessed only at the specific geographic location. The location identity attribute further includes a location value and a proximity value. The location value corresponds to a location of an intended recipient appliance of the digital information, and may be further defined in terms of latitude, longitude and altitude dimensions. The location identity attribute is enforced by allowing access to the digital information only at the specific geographic location. As a first part of this enforcement process, the location of an appliance through which access to the digital information is sought is identified. The appliance location is then compared to the specific geographic location defined by the location identity attribute, and access to the digital information is allowed only if the appliance location falls within the specific geographic location. There are many ways to identify the location of the appliance, including: (1) resolving the appliance location from a street address for the appliance; (2) retrieving the appliance location from a file stored within the appliance; (3) recovering the appliance location from a GPS receiver embedded in the appliance; and (4) recovering the appliance location by triangulating RF signals received by the appliance.
Owner:LONGBEAM TECH LLC
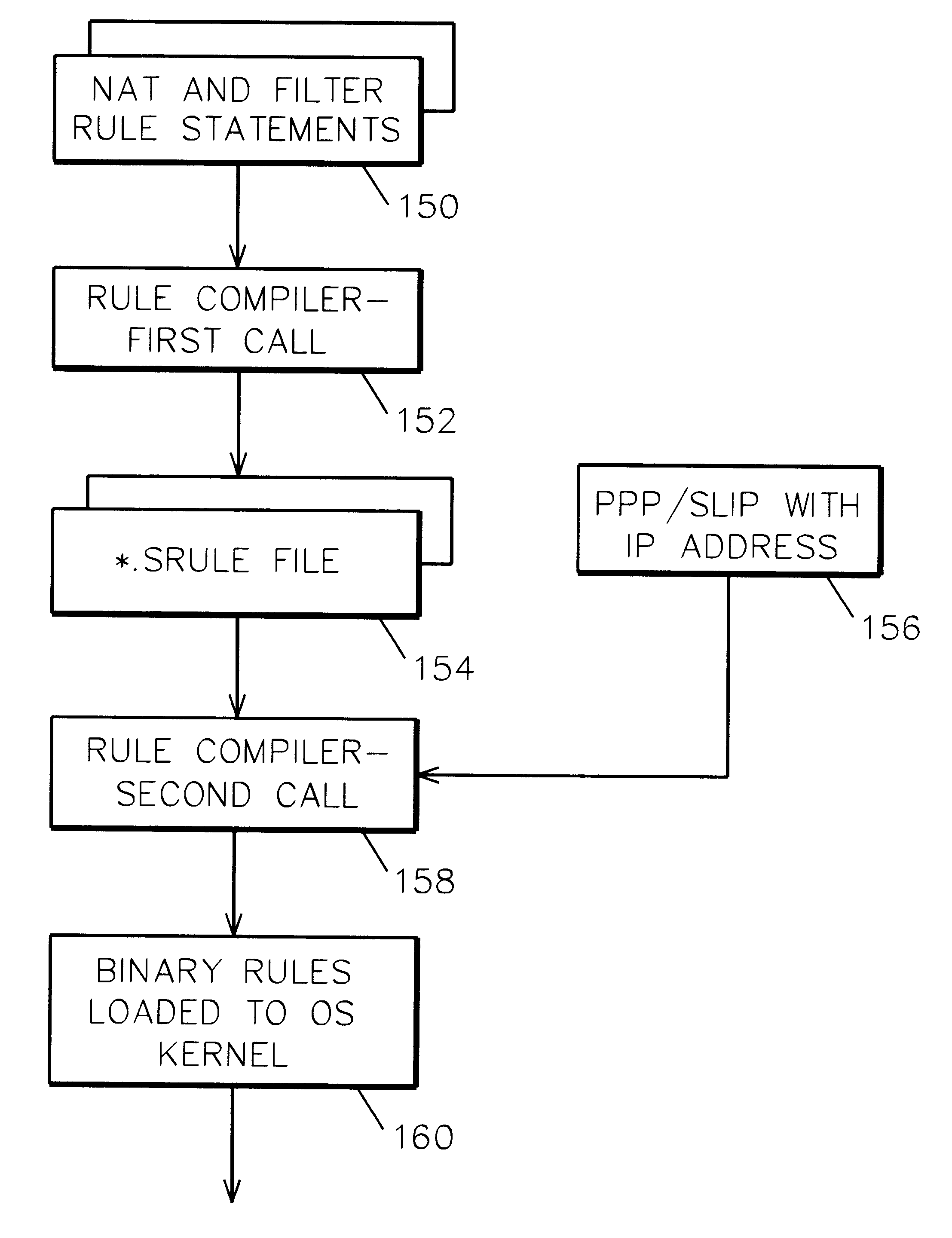
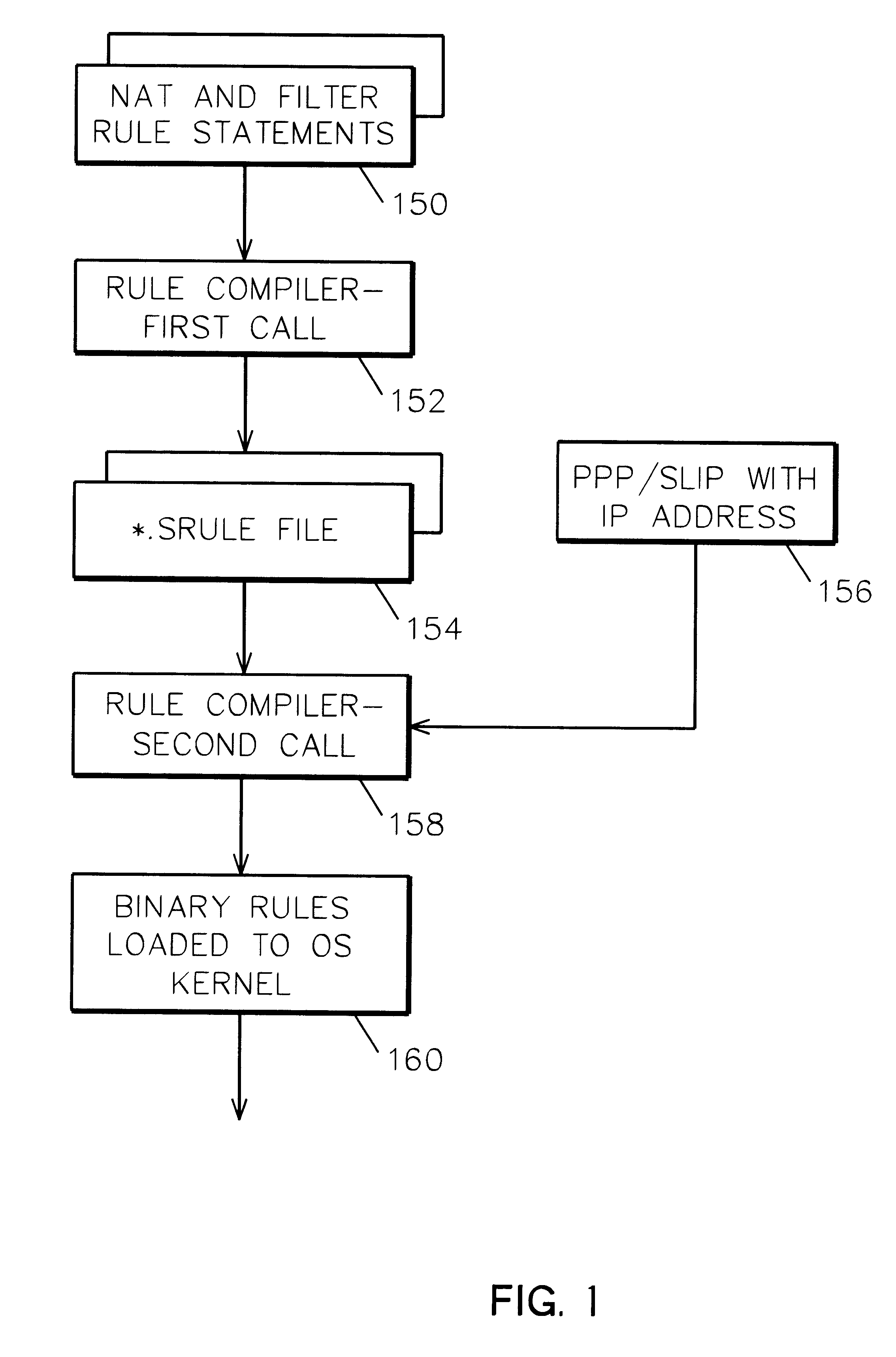
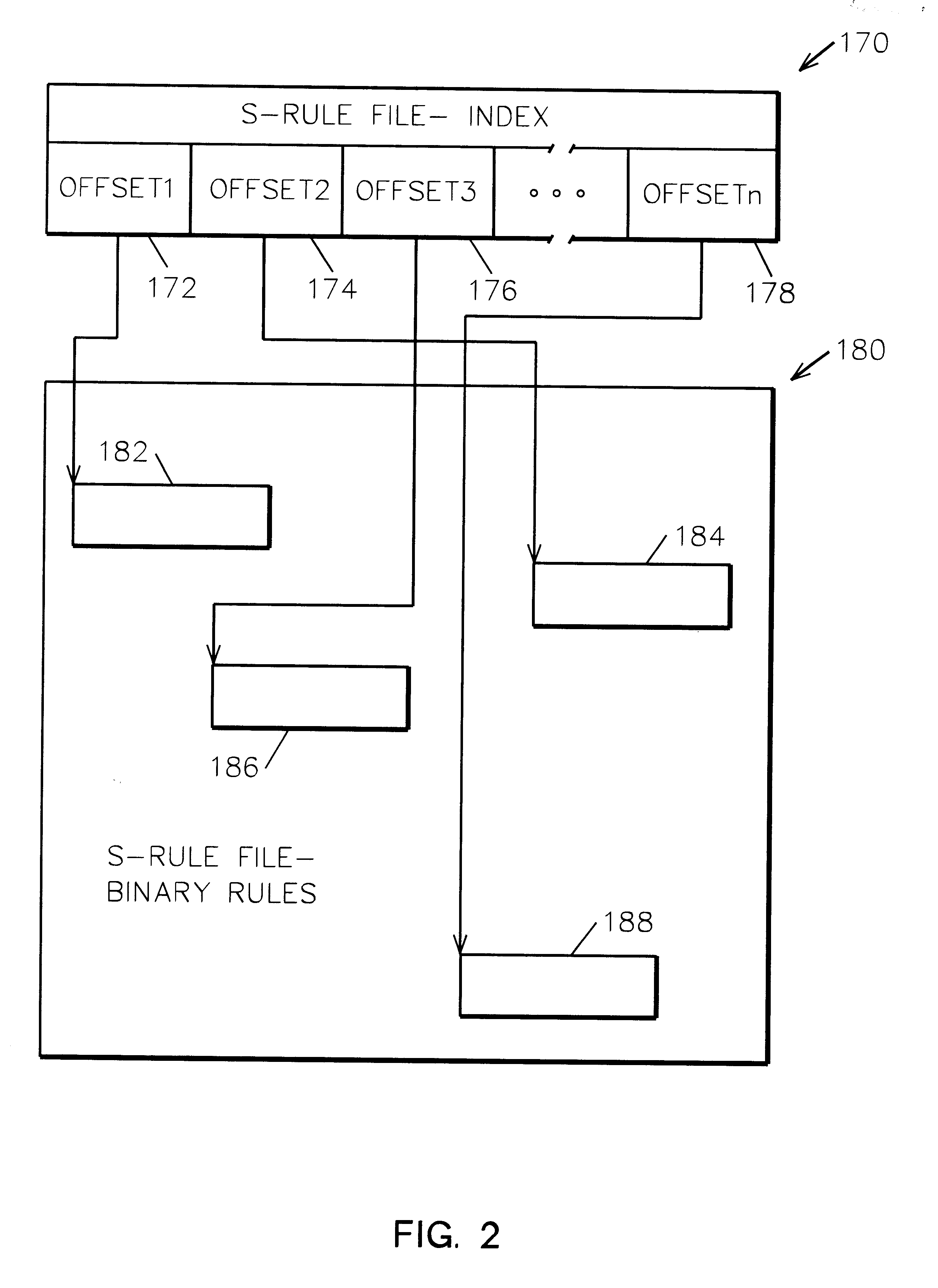
System and method for IP network address translation and IP filtering with dynamic address resolution
InactiveUS6266707B1Simple methodData switching by path configurationMultiple digital computer combinationsAddress resolutionIp address
IP network address translation (NAT) and IP filtering with dynamic address resolution in an Internet gateway system. Symbolic interface names are recognized in selected rule statements. An symbolic s-rule file is generated from these rule statements which includes symbolic interface names. During processing of a packet message, the s-rule file corresponding to the interface name in the packet message is processed, with symbolic addresses in the s-rule file resolved to the IP addresses obtained from the packet message.
Owner:IBM CORP
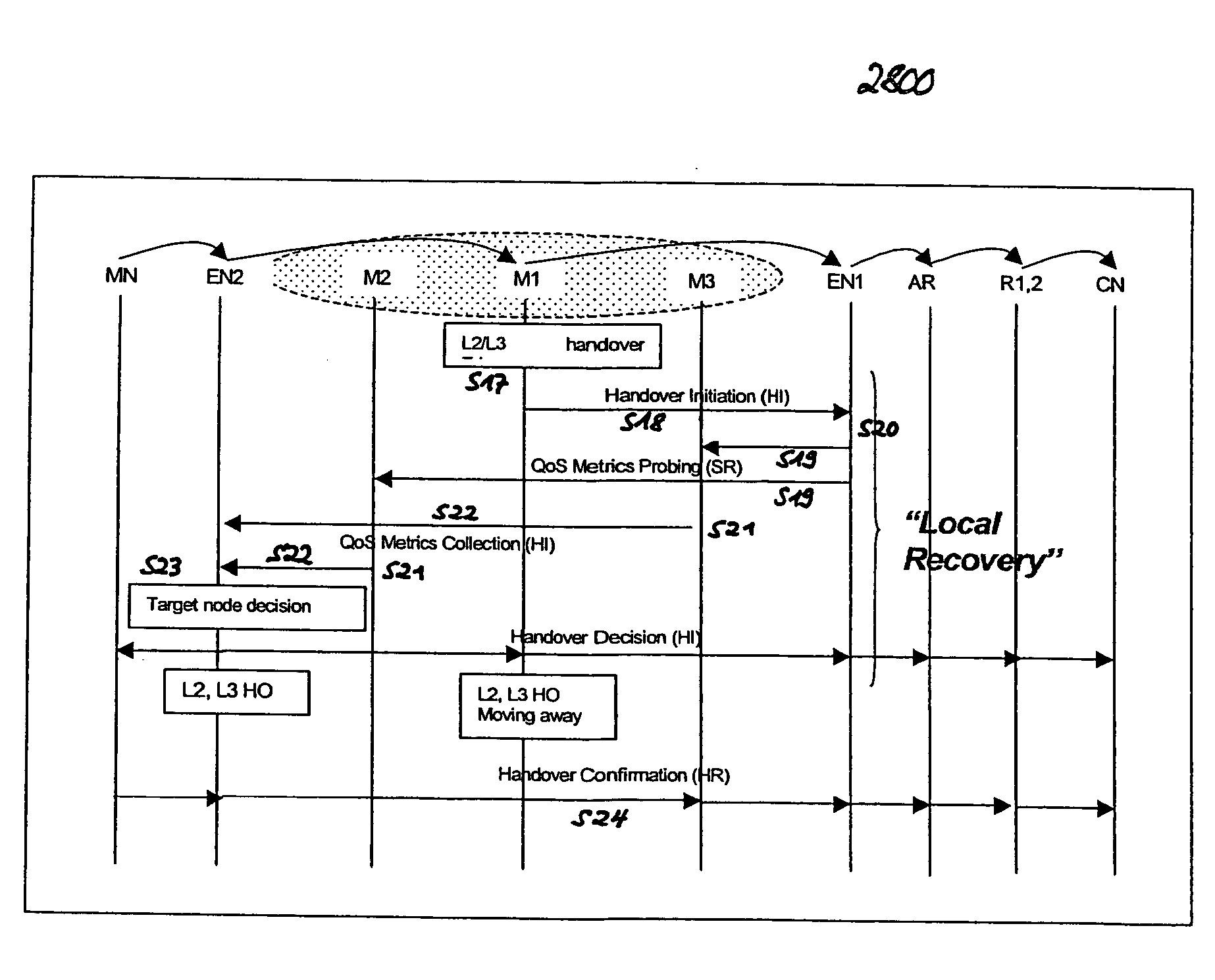
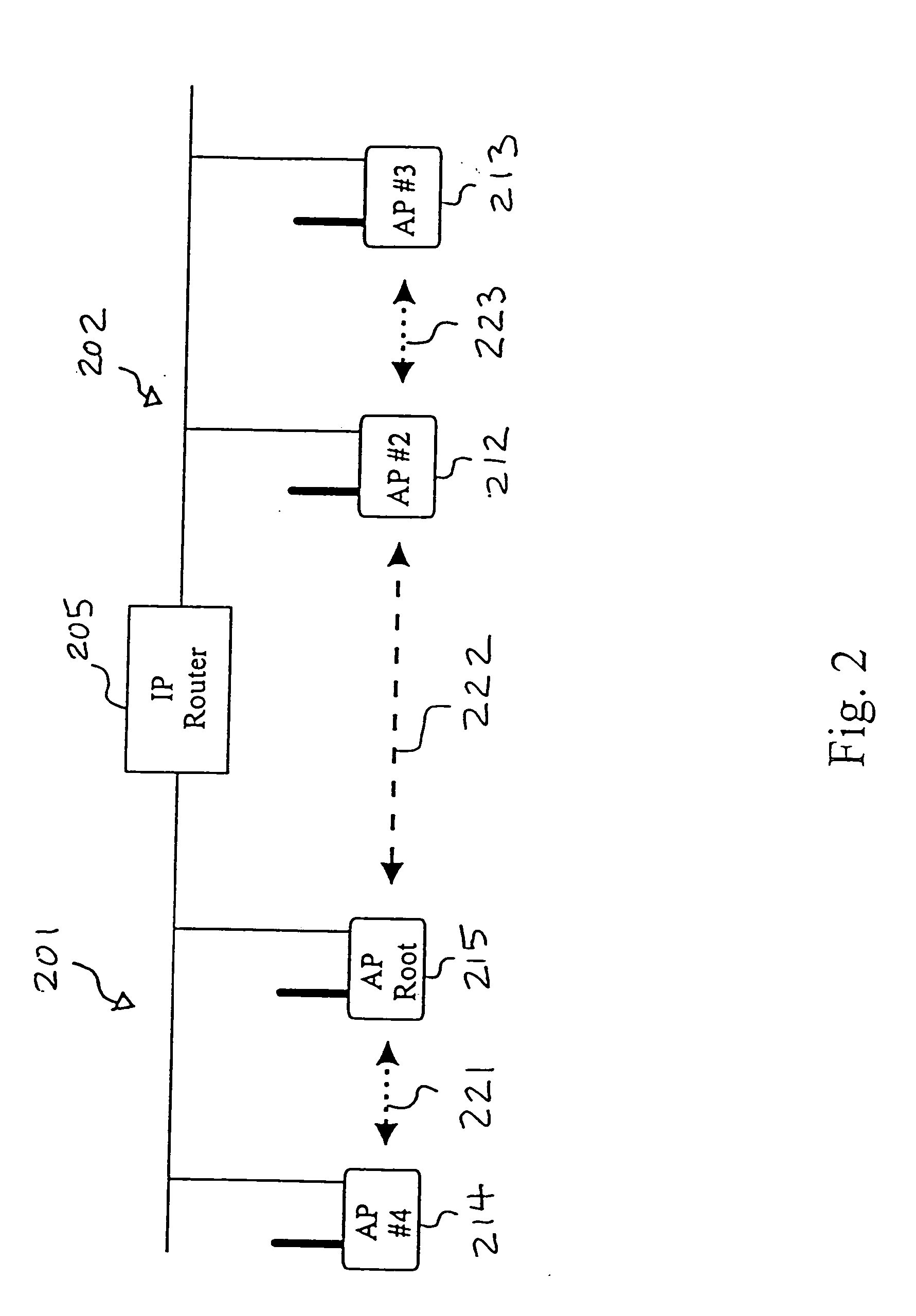
QoS-awar handover procedure for IP-based mobile ad-hoc network environments
InactiveUS20040228304A1Packet loss can be avoidedReduce the impactSpecial service provision for substationMultiplex system selection arrangementsTraffic capacityData stream
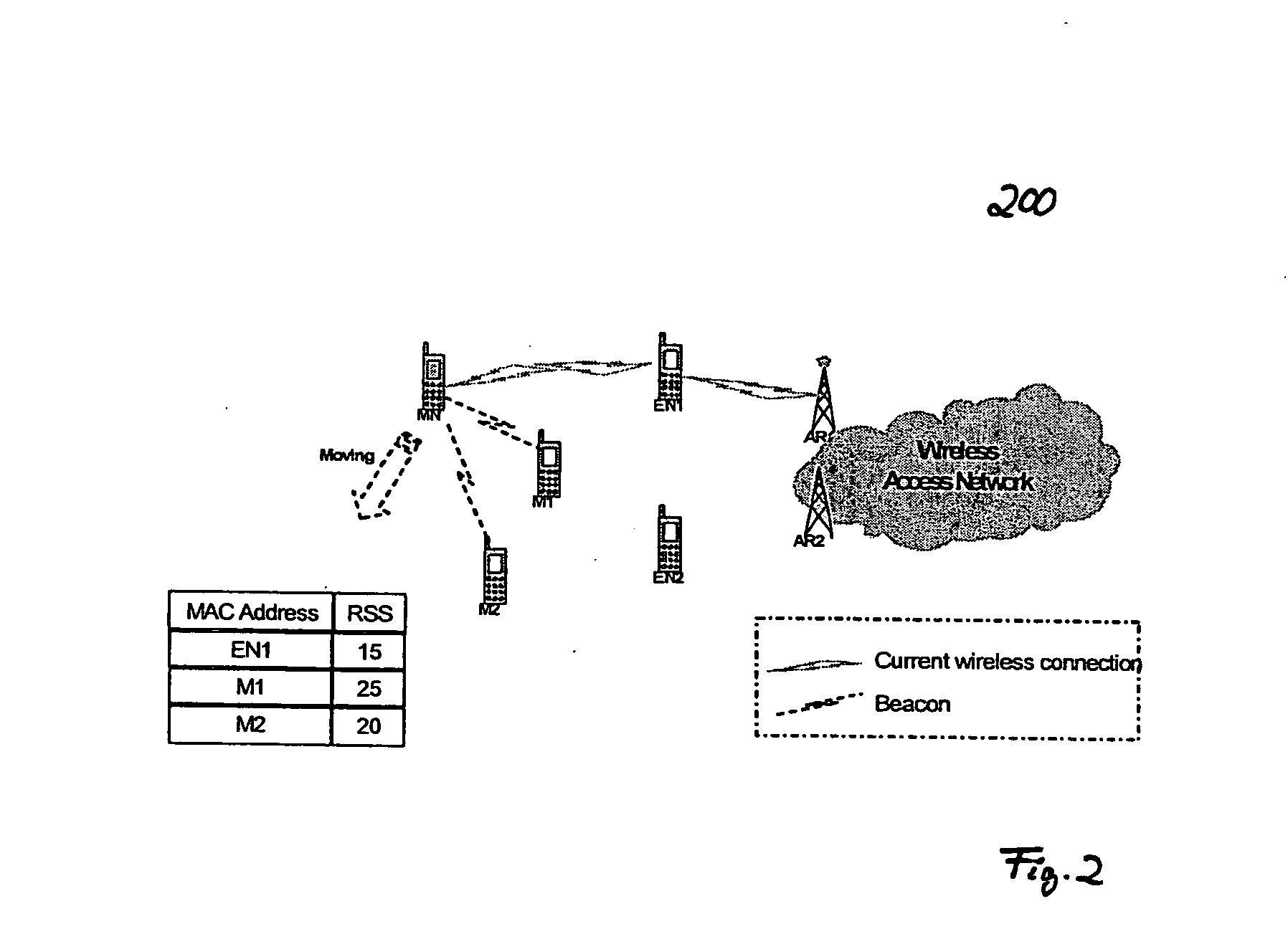
The invention targets at a QoS-aware handover procedure in a typical dynamic mobile ad-hoc scenario (cf. FIGS. 23 to 27) wherein the connectivity of fixed (AR1, AR2, CN) and / or mobile nodes (MN, M1, M2, M3, M4, EN1, EN2) is unpredictably time-varying and, due to the mobility of mobile nodes, handovers will inevitably frequently occur. Thereby, resources are pre-allocated along potential routing paths in advance, and the flow traffic is redirected to the path having the best available QoS capabilities. According to the new QoS situation of the selected path, adaptive real-time applications can have the opportunity to individually adjust traffic generation. With this concept, packet loss can be avoided and degradation effects on the running real-time application during the QoS-aware handover can be minimized. The QoS-aware handover procedure comprises the steps of handover candidates selection, handover initiation, QoS metrics probing and resource pre-allocation (soft reservation), QoS metrics collection, handover decision, handover confirmation (hard reservation), and reservation release. In particular, the proposed solution thereby pertains to a method for proactively probing the QoS situation of each potential routing path, pre-allocating resources along the best available QoS path before the handover of the QoS data flow to be transmitted to a new access point (AP) is initiated, providing efficient resource reservation management and maintenance within the underlying mobile ad-hoc networks and incorporating advanced QoS support features offered by adaptive real-time applications. The invention further proposes an "information dissemination" approach, which optimizes prior-art address resolution mechanisms.
Owner:SONY DEUT GMBH
Systems and methods for providing link management in a multi-core system
The present application is directed towards systems and methods for providing link management in a multi-core system. In some embodiments, the present application describes solutions for managing address resolution in IPv4 networks in a multi-core system. In other embodiments, the present application describes solutions for managing neighbor discovery in IPv6 networks in a multi-core system. In still other embodiments, the present application describes solutions for managing network bridging in a multi-core system. In yet other embodiments, the present application describes solutions for managing link aggregation in a multi-core system. And in still other embodiments, the present application describes solutions for managing virtual routers in a multi-core system.
Owner:CITRIX SYST INC
Gigabit switch supporting improved layer 3 switching
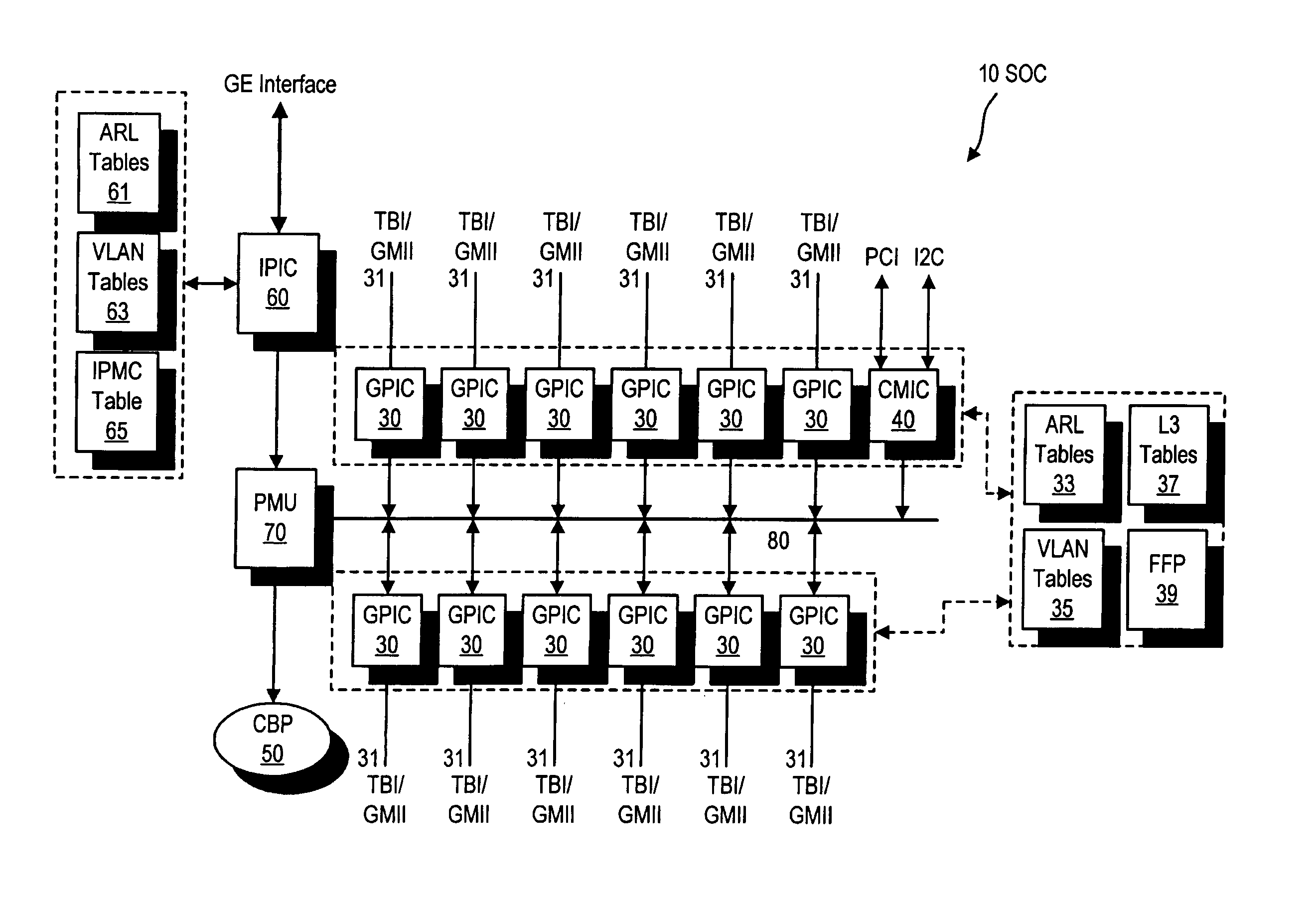
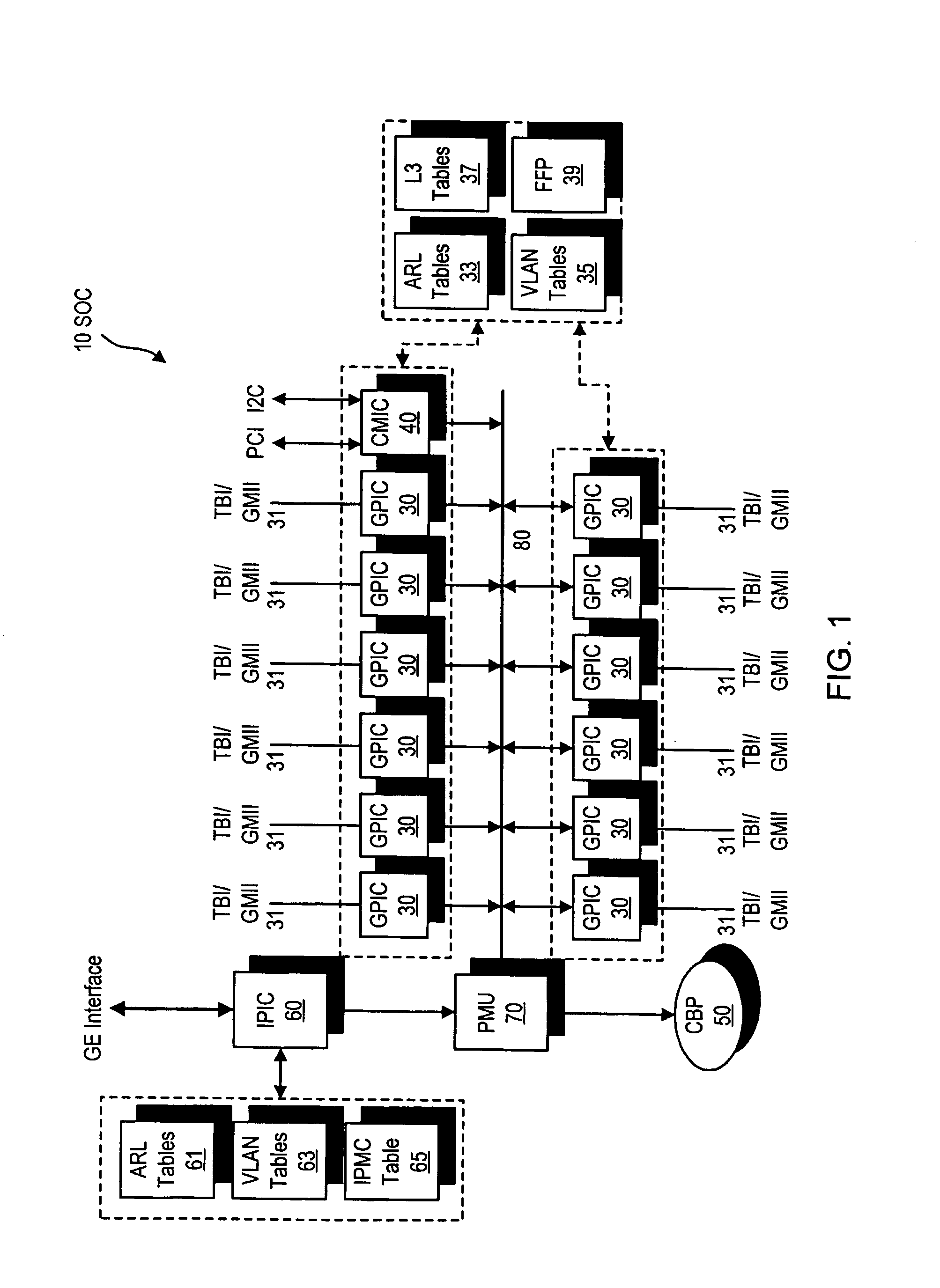
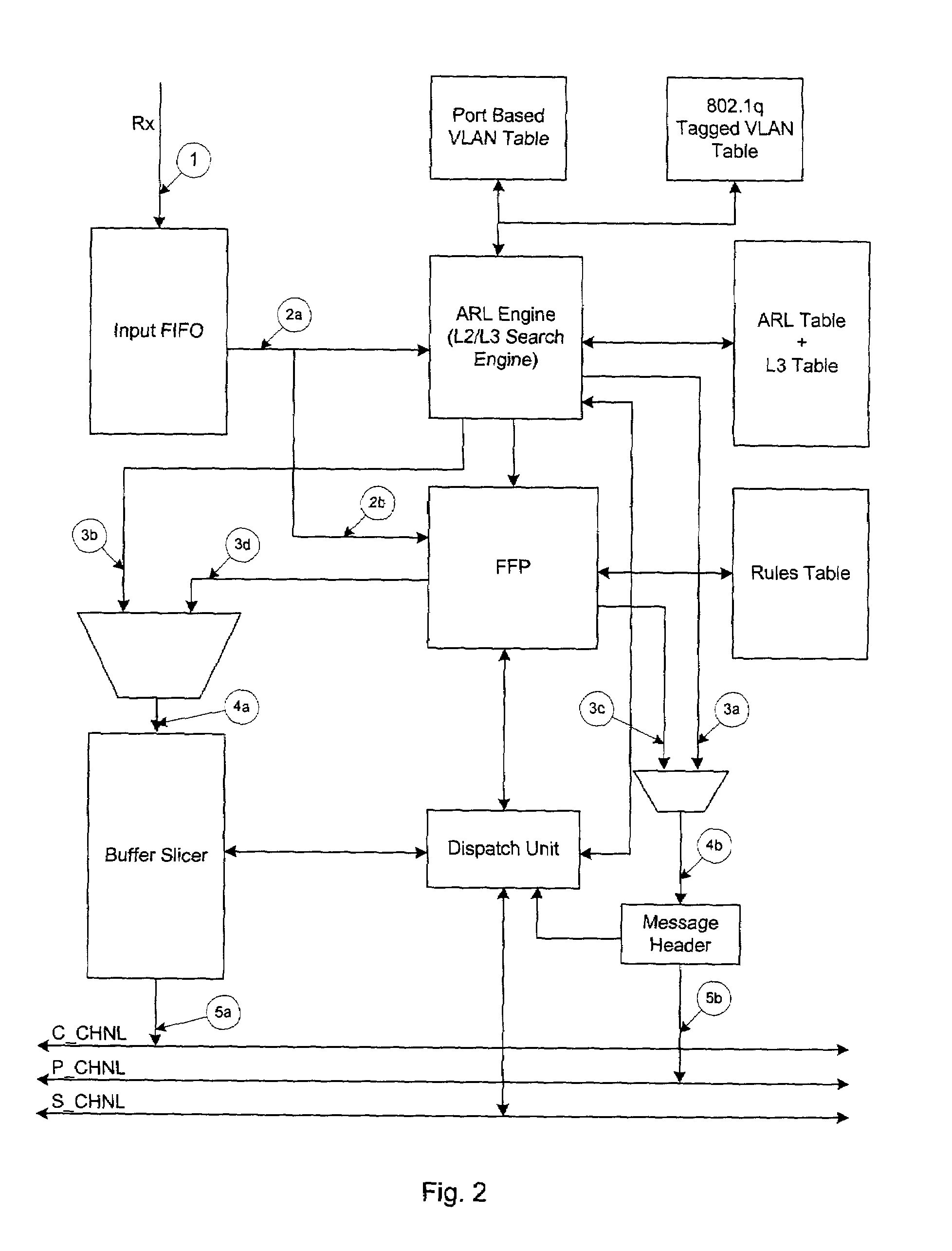
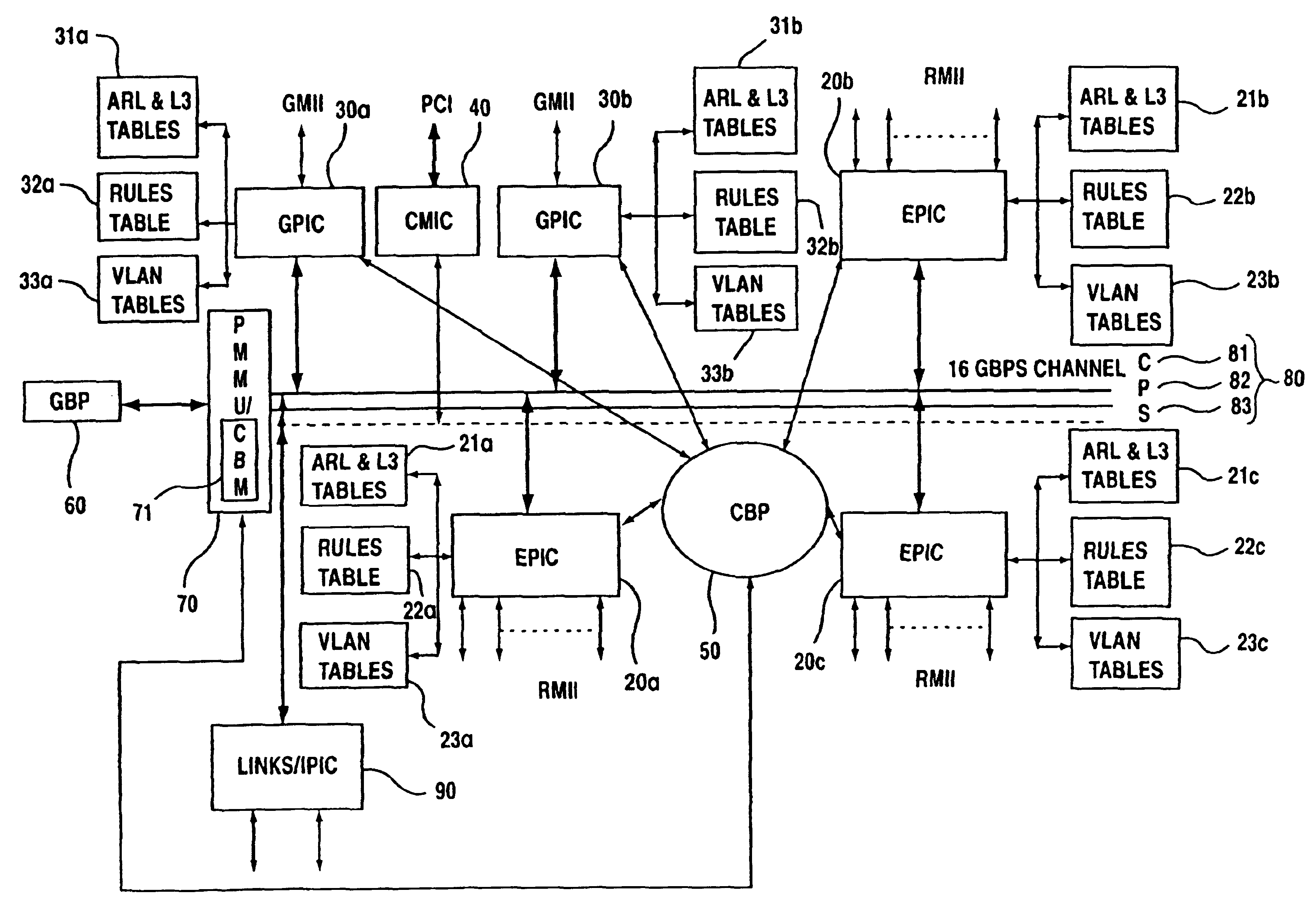
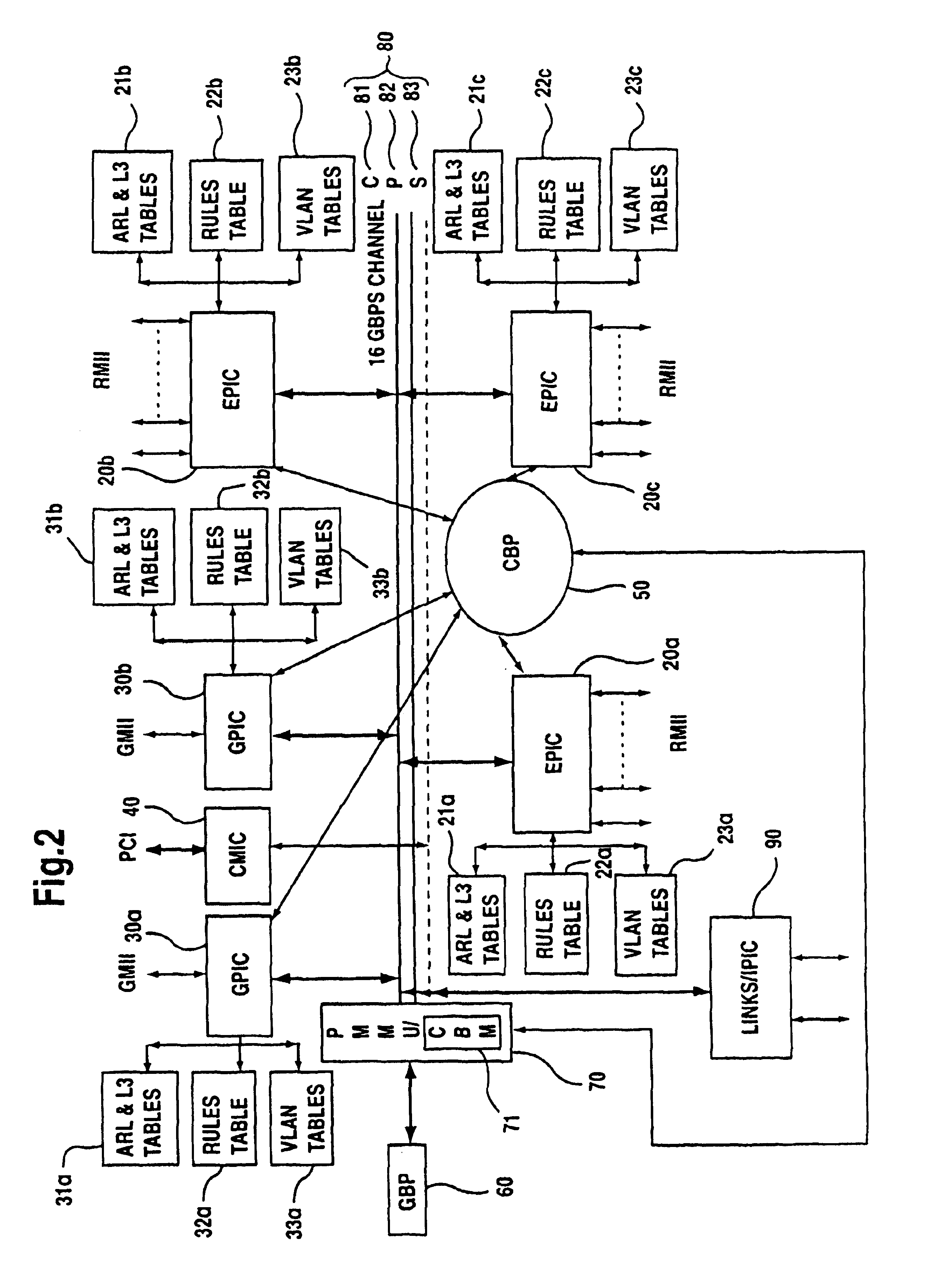
ActiveUS7009968B2Improved layer switchingEliminate needSpecial service provision for substationEnergy efficient ICTIP multicastNetwork communication
A network switch for network communications is disclosed. The switch includes a first data port interface, supporting at least one data port transmitting and receiving data at a first data rate and a second data port interface supporting a at least one data port transmitting and receiving data at a second data rate. The switch also has a CPU interface configured to communicate with a CPU and a memory management unit for communicating data from at least one of the first and second data port interfaces and a memory. It also has a communication channel for communicating data and messaging information between the first and second data port interfaces and the memory management unit and a plurality of semiconductor-implemented lookup tables including an address resolution lookup table, a layer three IP lookup table and VLAN tables. One of the first and second data port interfaces is configured to determine whether an incoming data packet is a unicast packet, a multicast packet or an IP multicast packet; and the address resolution lookup and layer three IP lookup tables are searched to find an egress port for the incoming data packet.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Isolation and security hardening among workloads in a multi-tenant networked environment
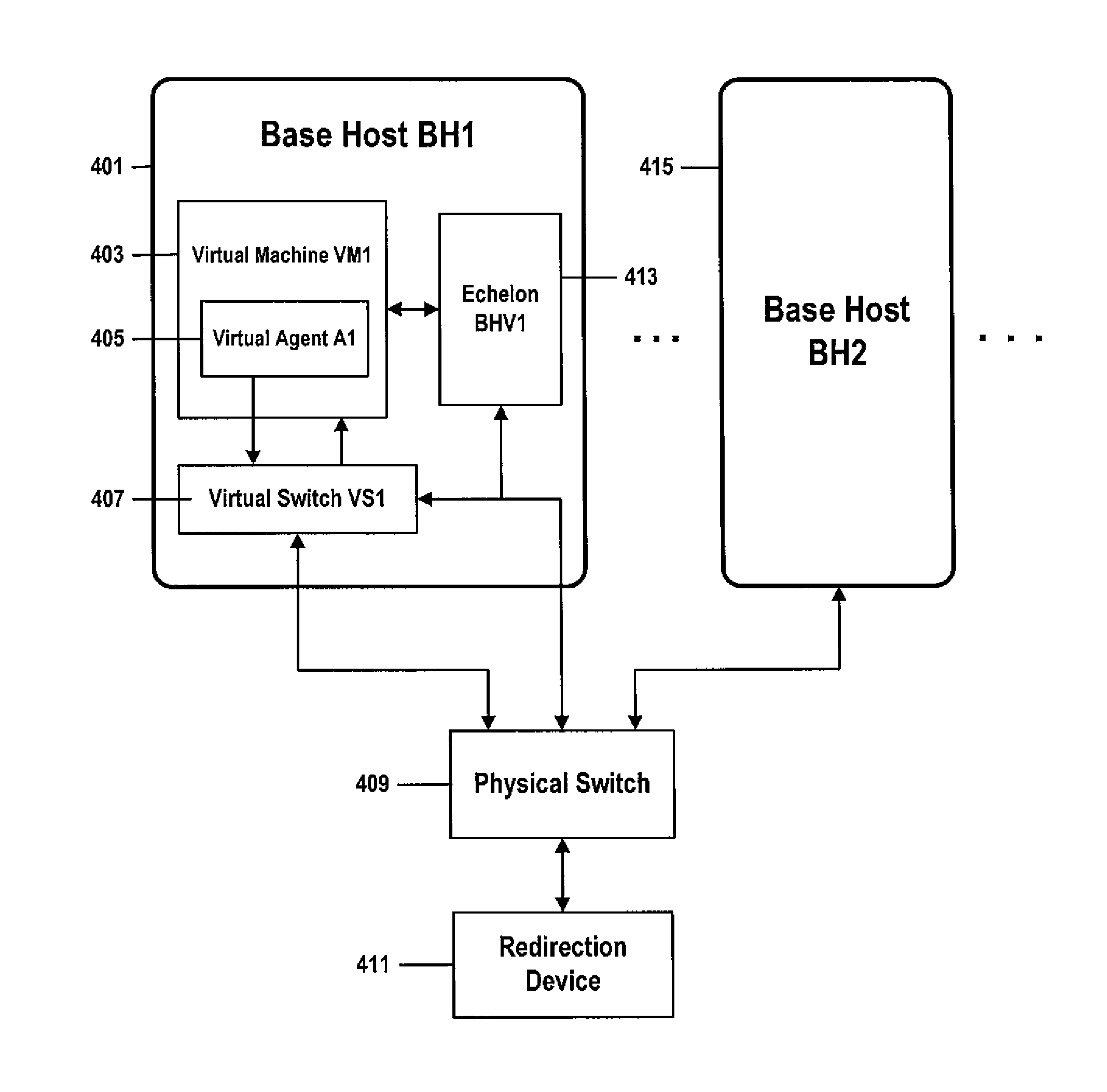
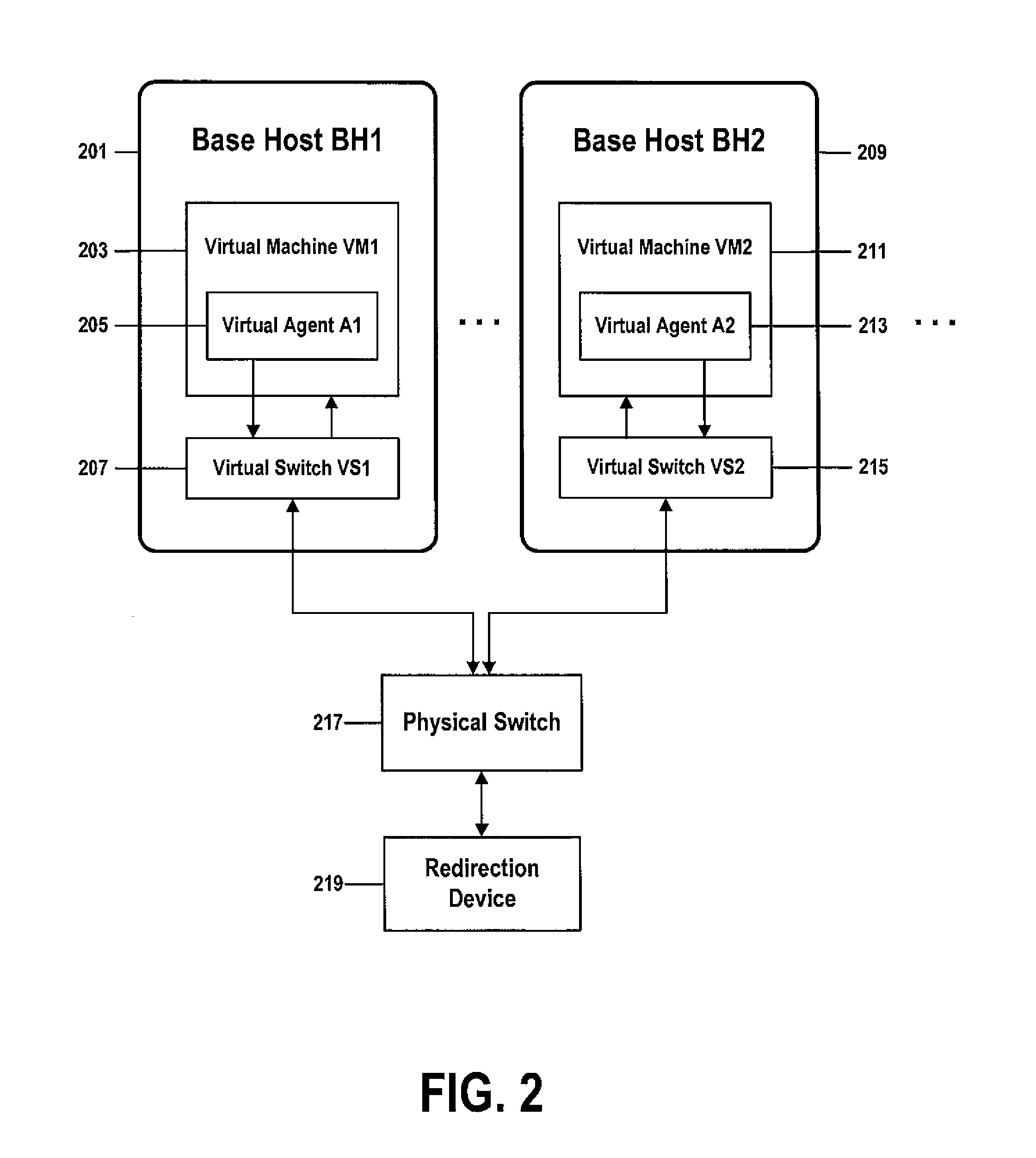
InactiveUS20130347095A1Improve isolationEnhanced security hardeningComputer security arrangementsMultiple digital computer combinationsAddress resolutionComputerized system
A method and associated systems for enhanced isolation and security hardening among multi-tenant workloads. An agent running on a processor of a networked computer system on which multicast and broadcast communications have been disabled captures an address-resolution query message from a querying tenant, converts the query message to a unicast message, and forwards the converted unicast query message to a switch. The switch forwards the converted unicast message to a redirection device and in response receives an address-resolution response message only after the redirection device verifies that the query and response messages comply with security policies. The switch forwards the address-resolution response to the querying tenant in conformance with security policies.
Owner:IBM CORP
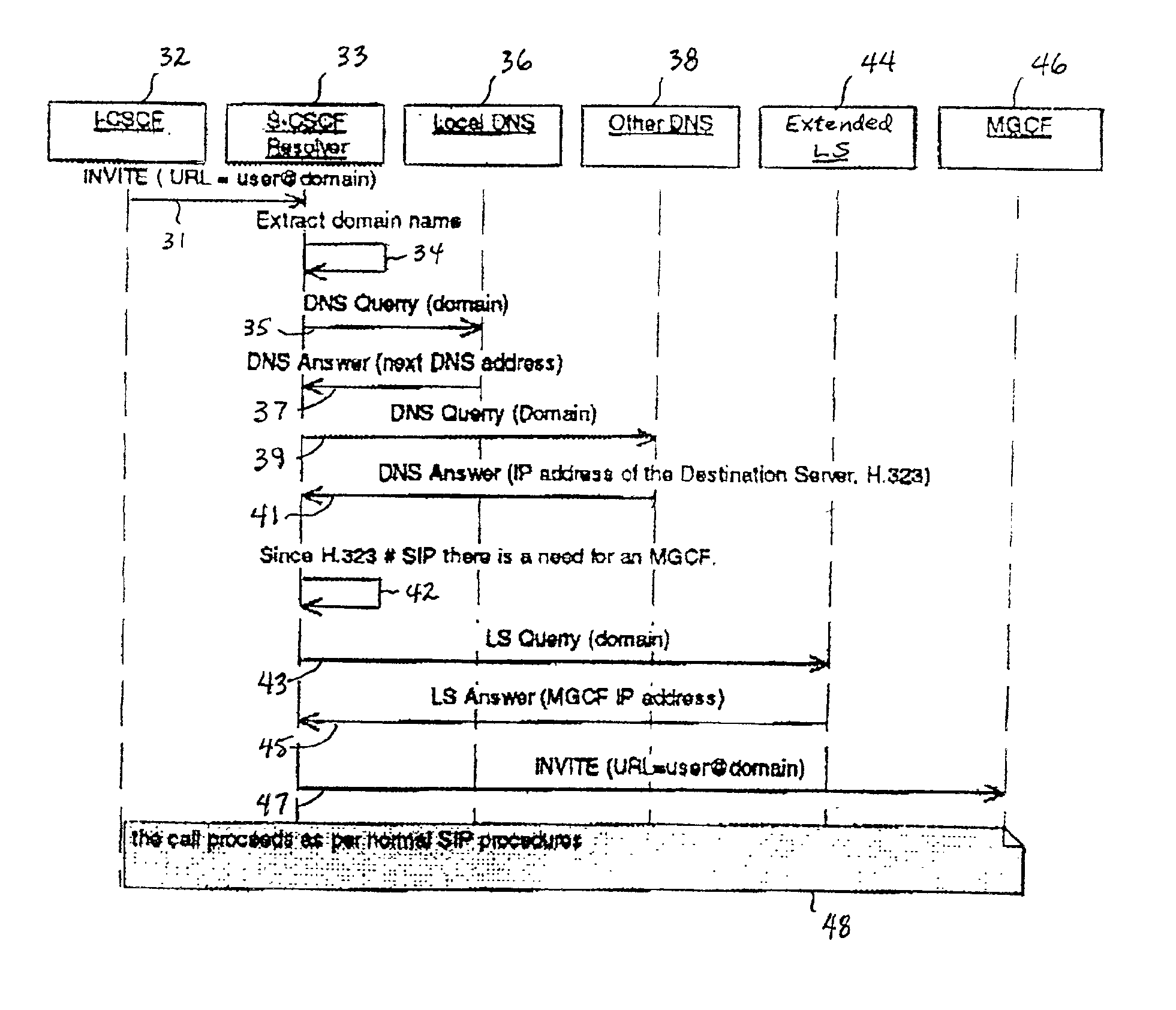
System and method for address resolution in internet protocol (IP) -based networks
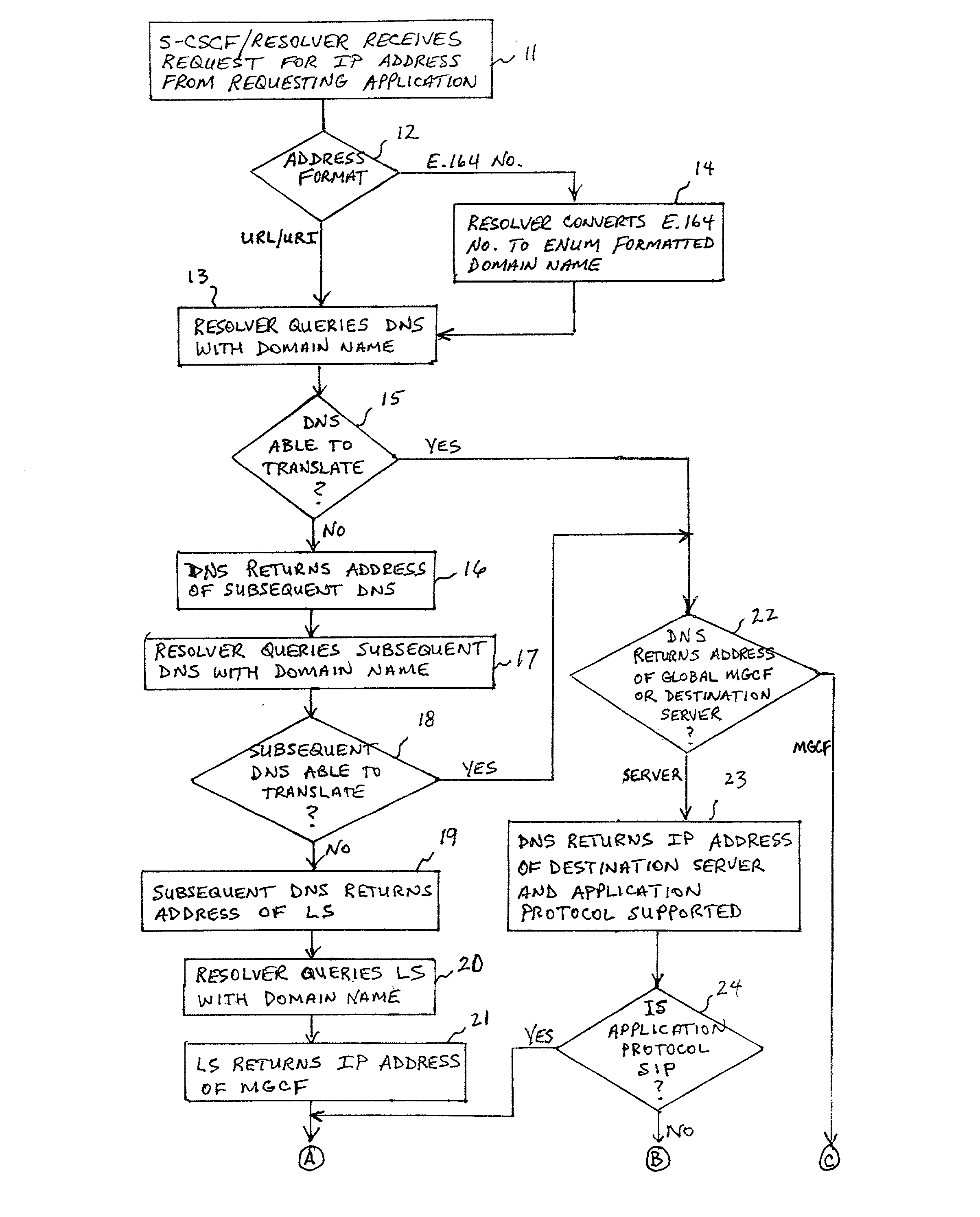
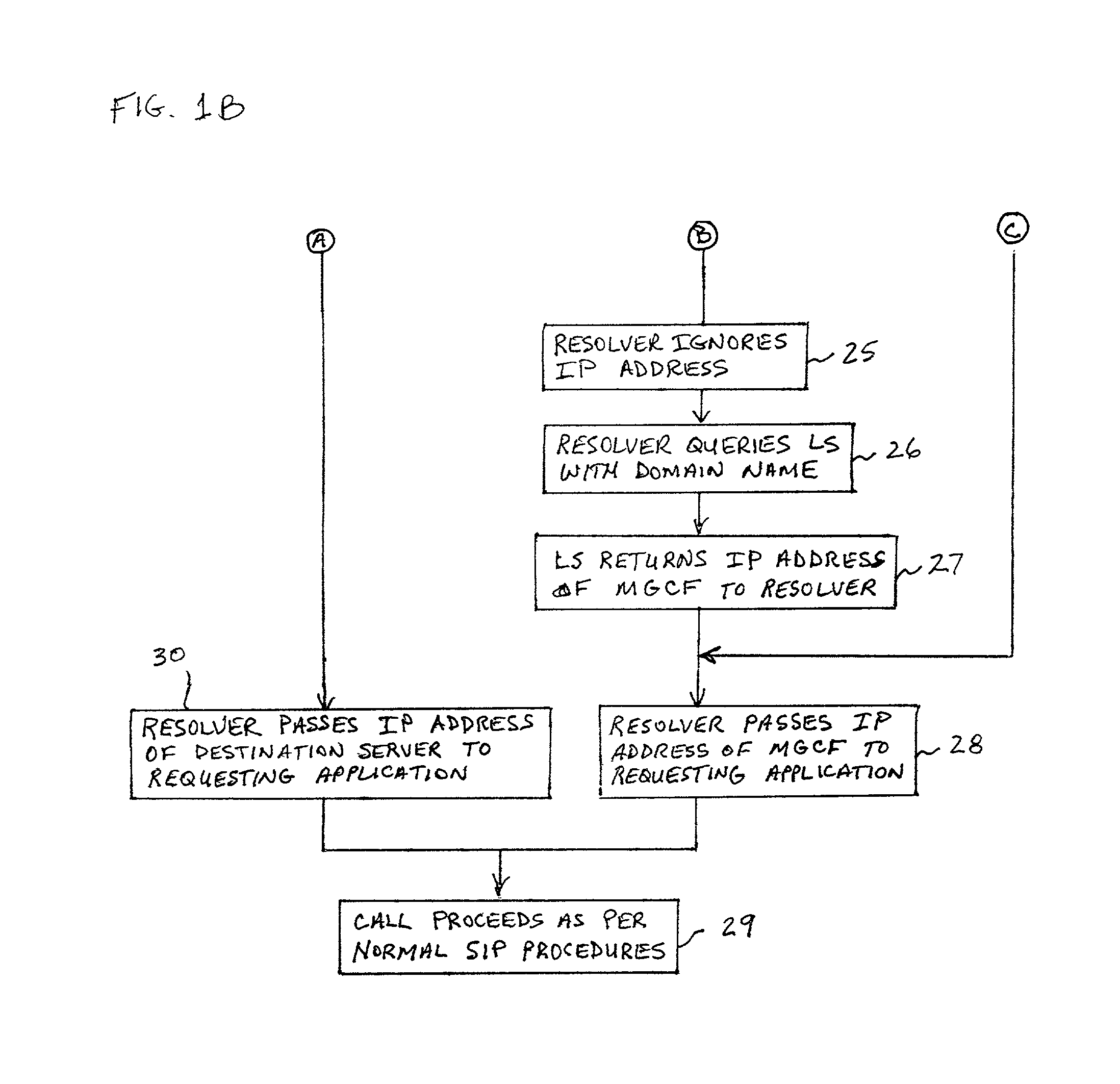
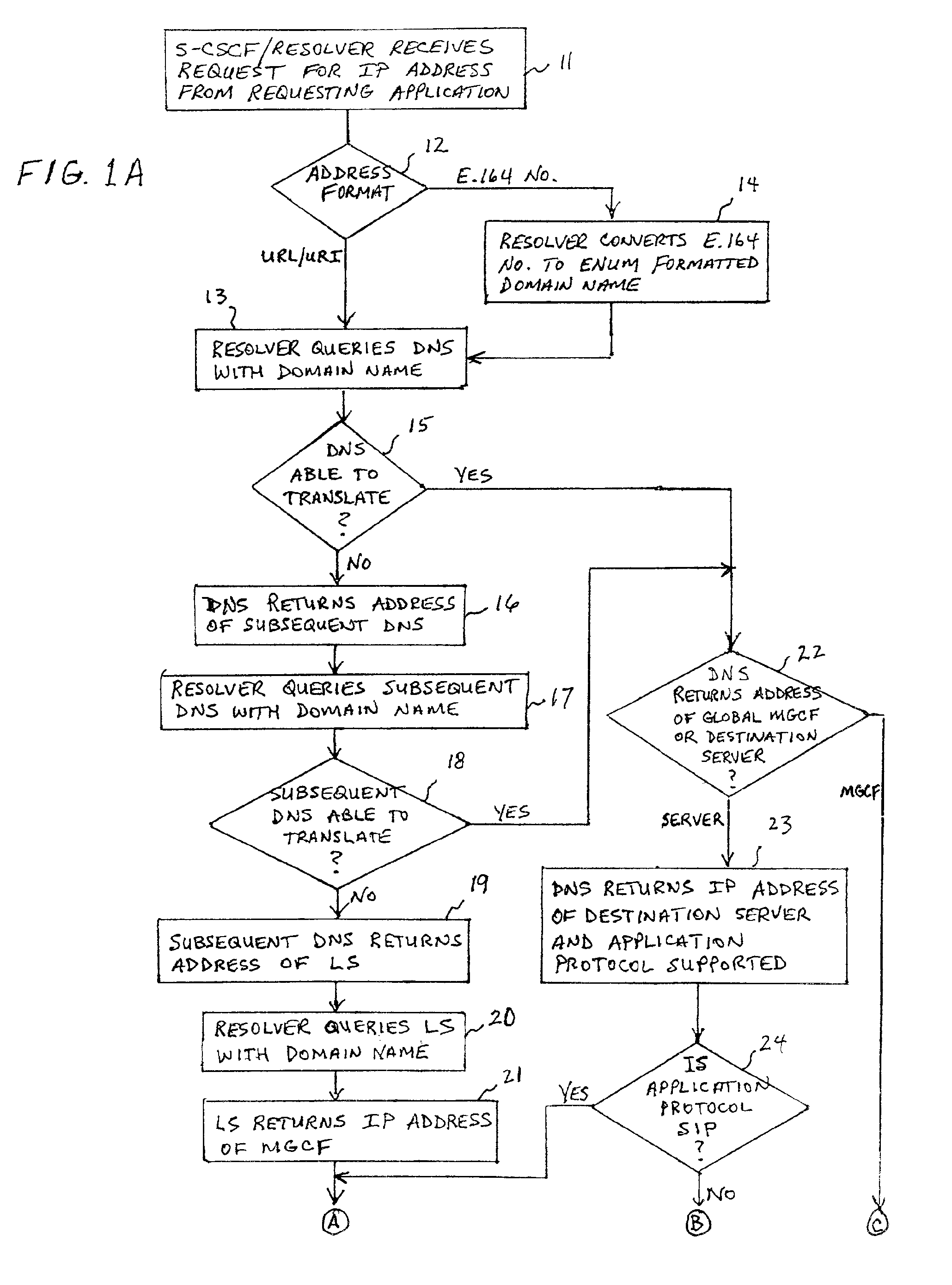
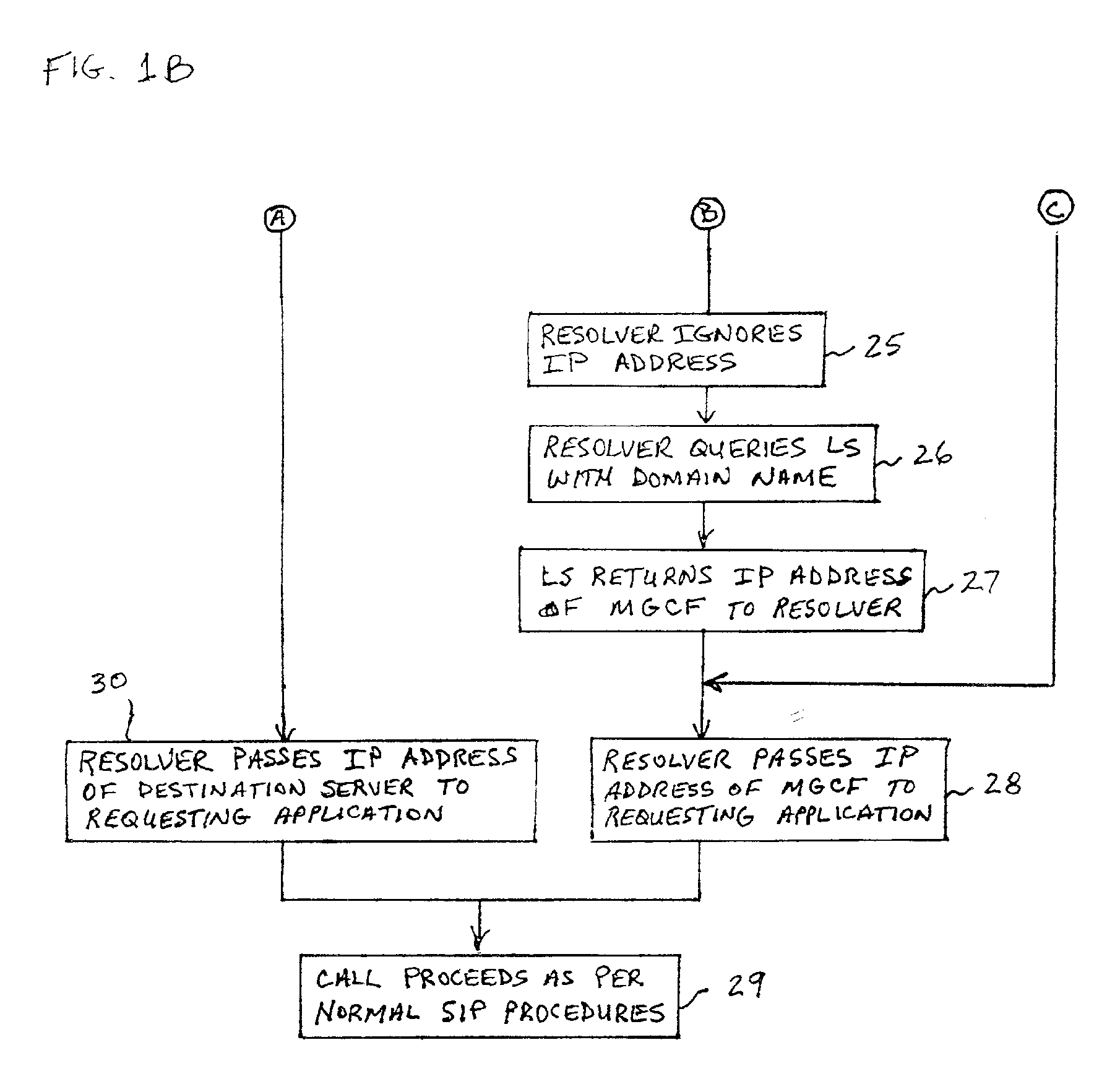
ActiveUS20020027915A1Data switching by path configurationNetwork connectionsInternet protocol suiteDomain name
A system and unified method of address resolution in an IP-based network. A Resolver determines whether an input address is a URL / URI, and if so, extracts a domain name. If the input address is an E.164 number, the Resolver converts the E.164 number into a domain name in ENUM format. The Resolver then sends a domain name query to a DNS which, if able, returns the IP address for either a Global MGCF or a destination server along with a supported Application protocol. If the DNS is unable to perform the translation, or the Application protocol returned is not supported by the requesting application, the Resolver sends a domain name query to an extended Location Server (LS) to obtain an IP address of a gateway function capable of interfacing with the destination server.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
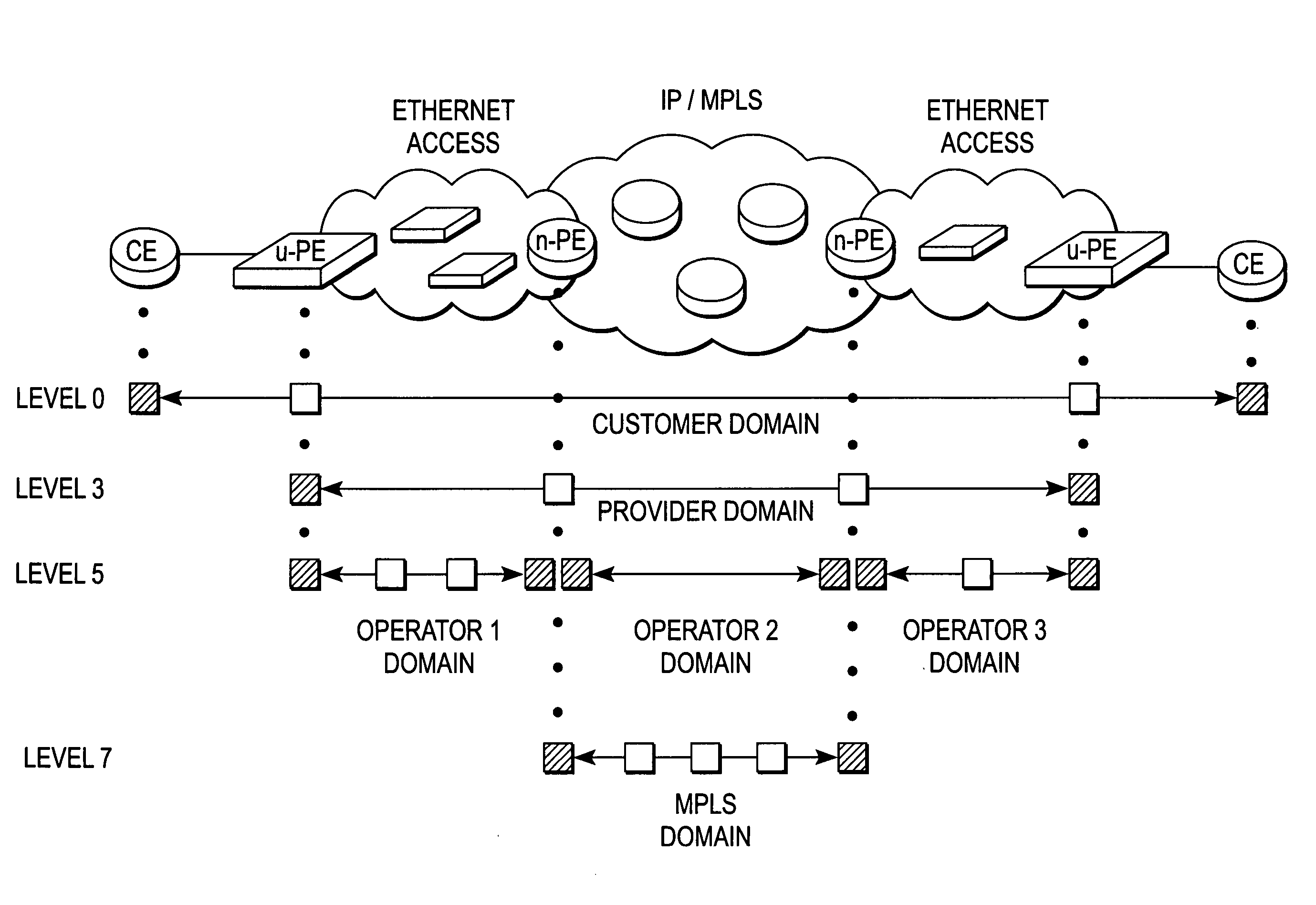
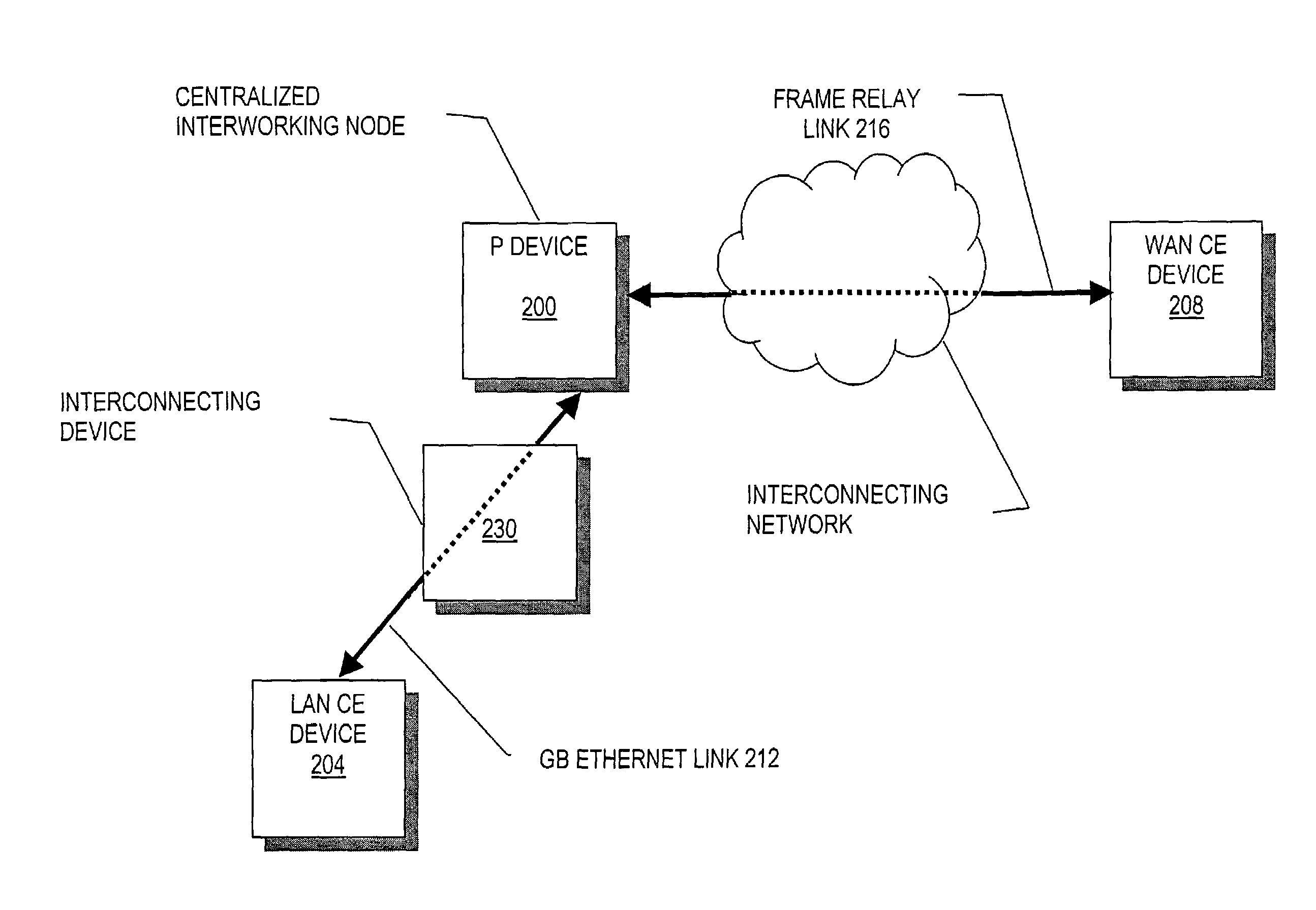
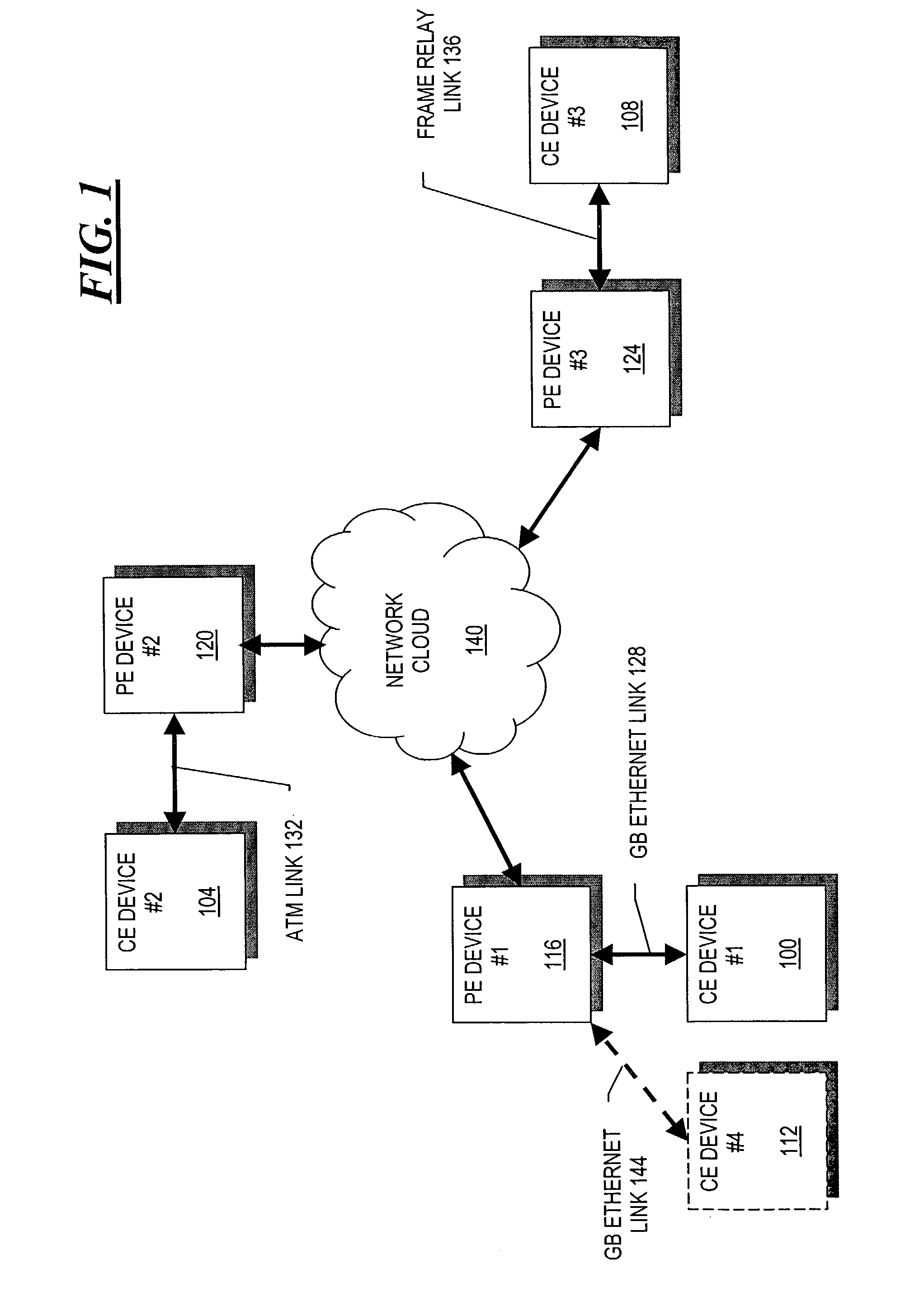
Methods and apparatus for automated edge device configuration in a heterogeneous network
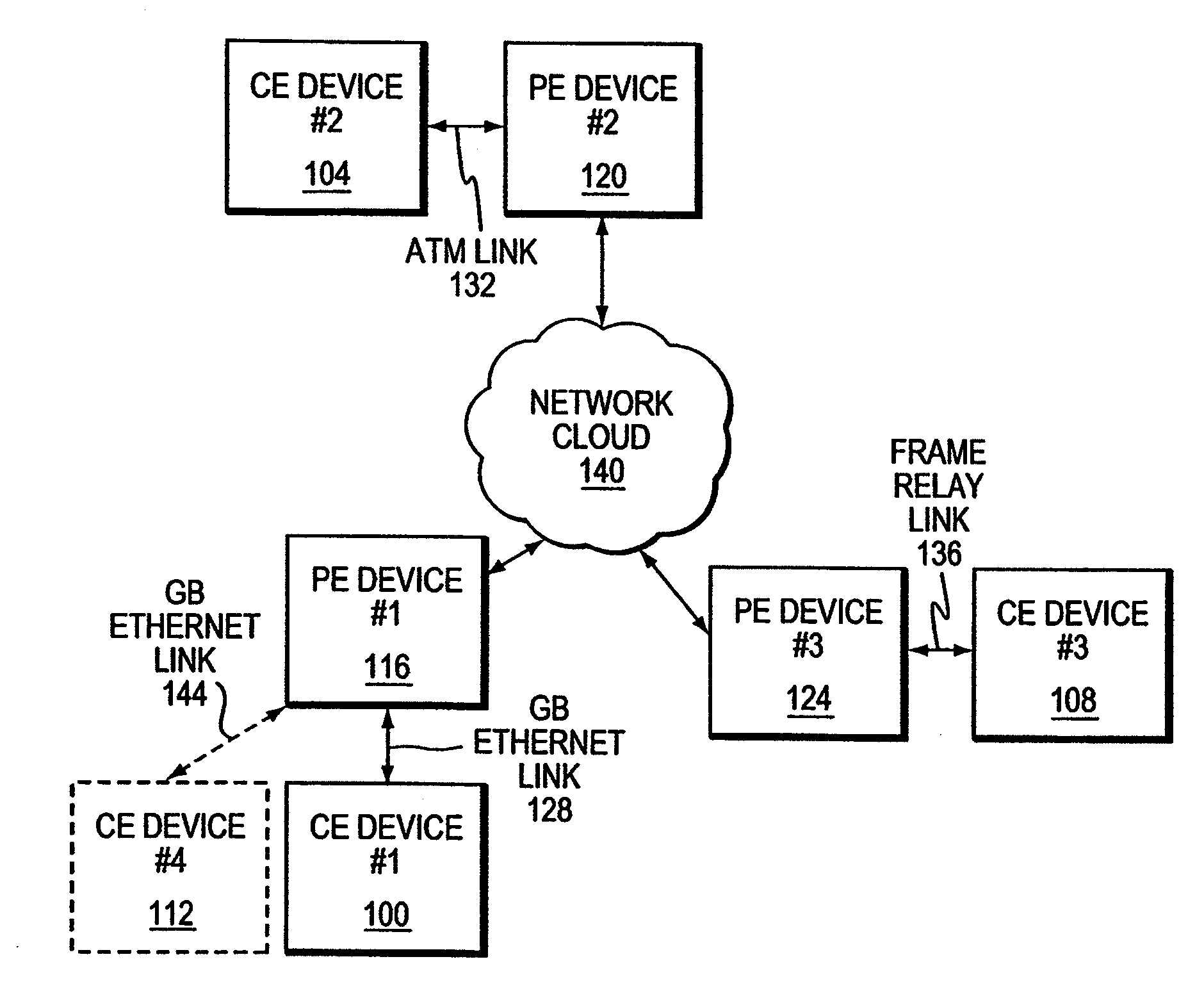
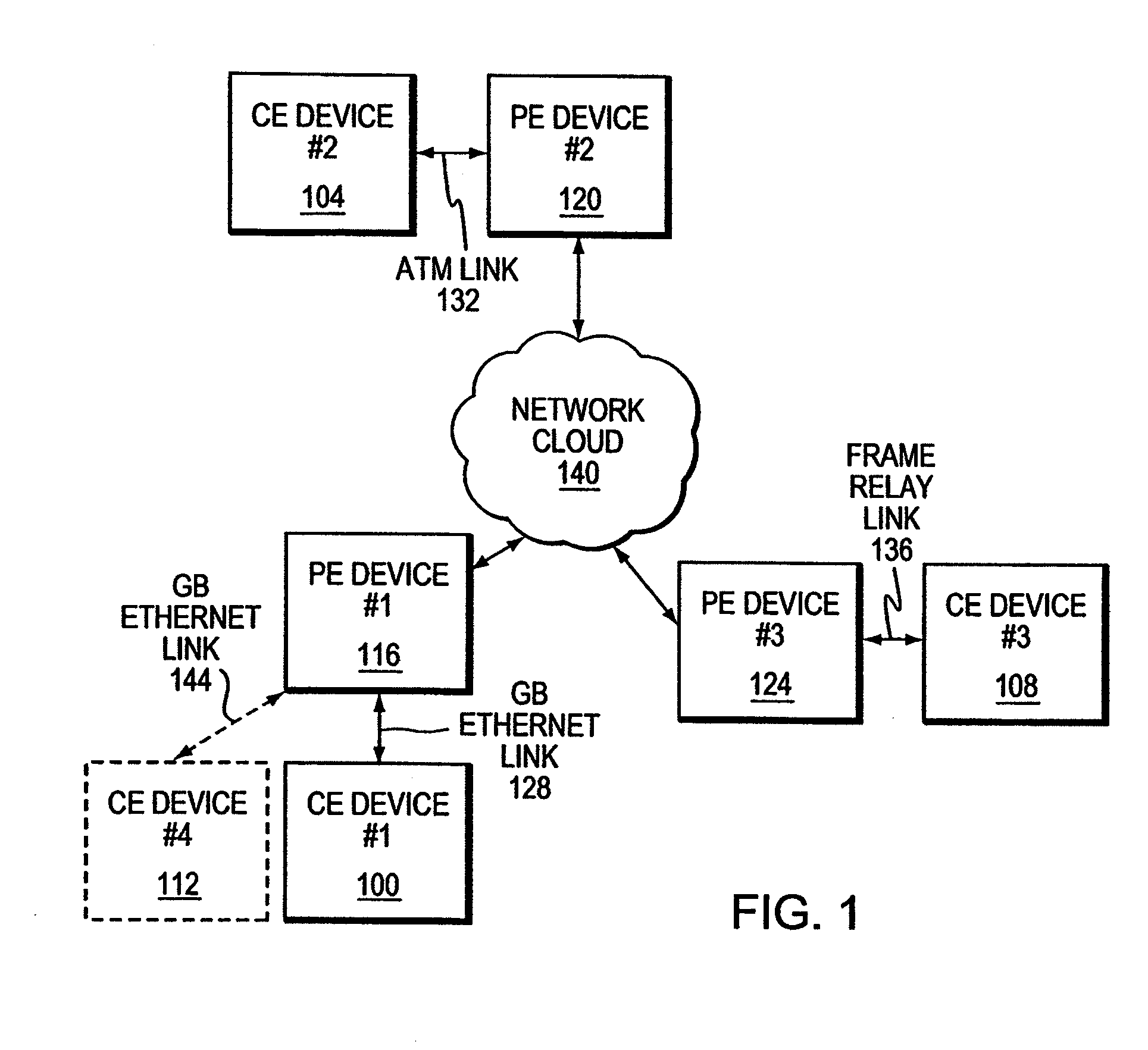
InactiveUS20080219276A1Facilitates automated configurationDigital computer detailsNetworks interconnectionComputer hardwareAuto-configuration
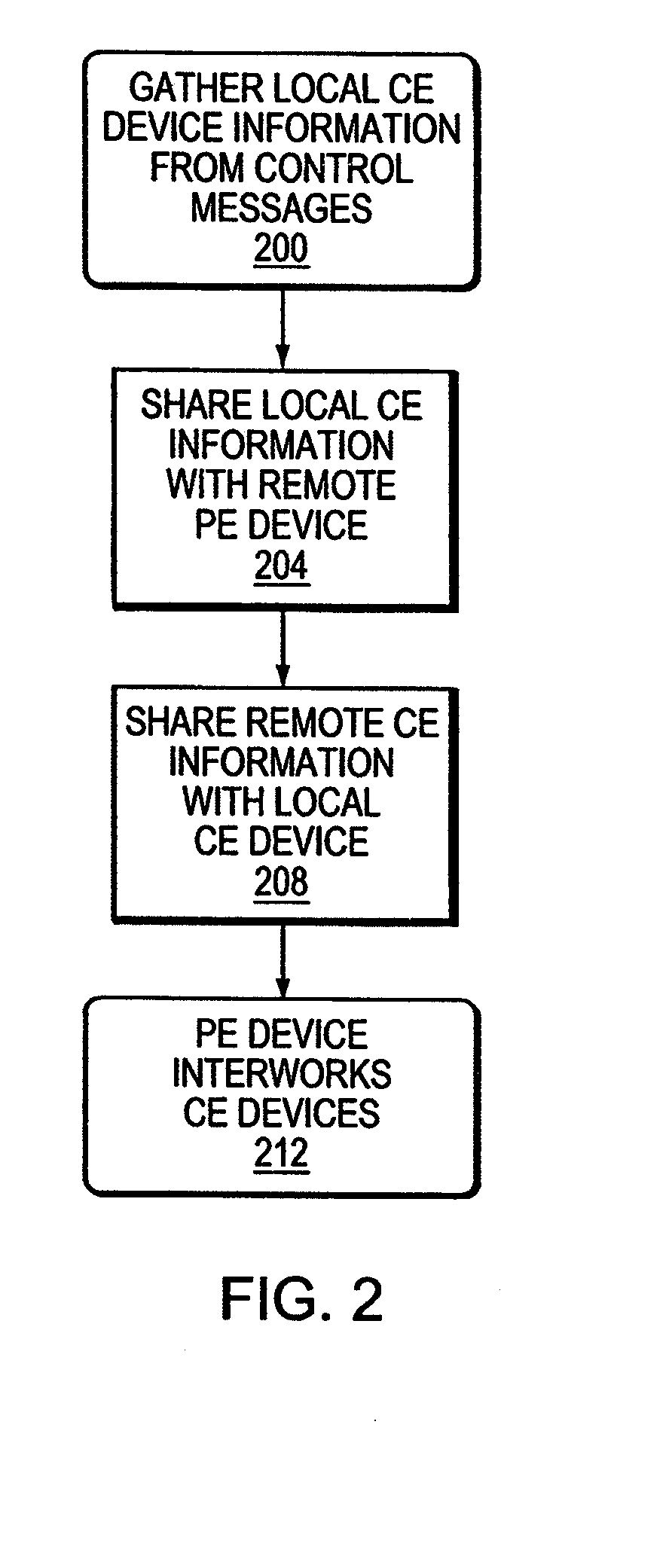
A PE device learns the address of a local CE device by monitoring the control messages, such as address resolution messages, originating from those local devices. In one embodiment, automated configuration of the PE devices participating in a Layer 2 VPN is facilitated by permitting a PE device to share the addresses for its locally-attached CE devices with the remote PE devices in the VPN. A PE device may share the addresses of the remote CE devices with the local CE devices by initiating its own control message or responding to an control message issued by one of its local CE devices. This latter mechanism in effect hides the distributed, heterogeneous nature of the network from a local CE device.
Owner:ENTERASYS NETWORKS
System and method for secure electronic communication services
InactiveUS8538028B2Easy accessSecure transmissionKey distribution for secure communicationPublic key for secure communicationSecure communicationScalable system
Owner:TOPOSIS CORP
System and method for address resolution in internet protocol (IP)-based networks
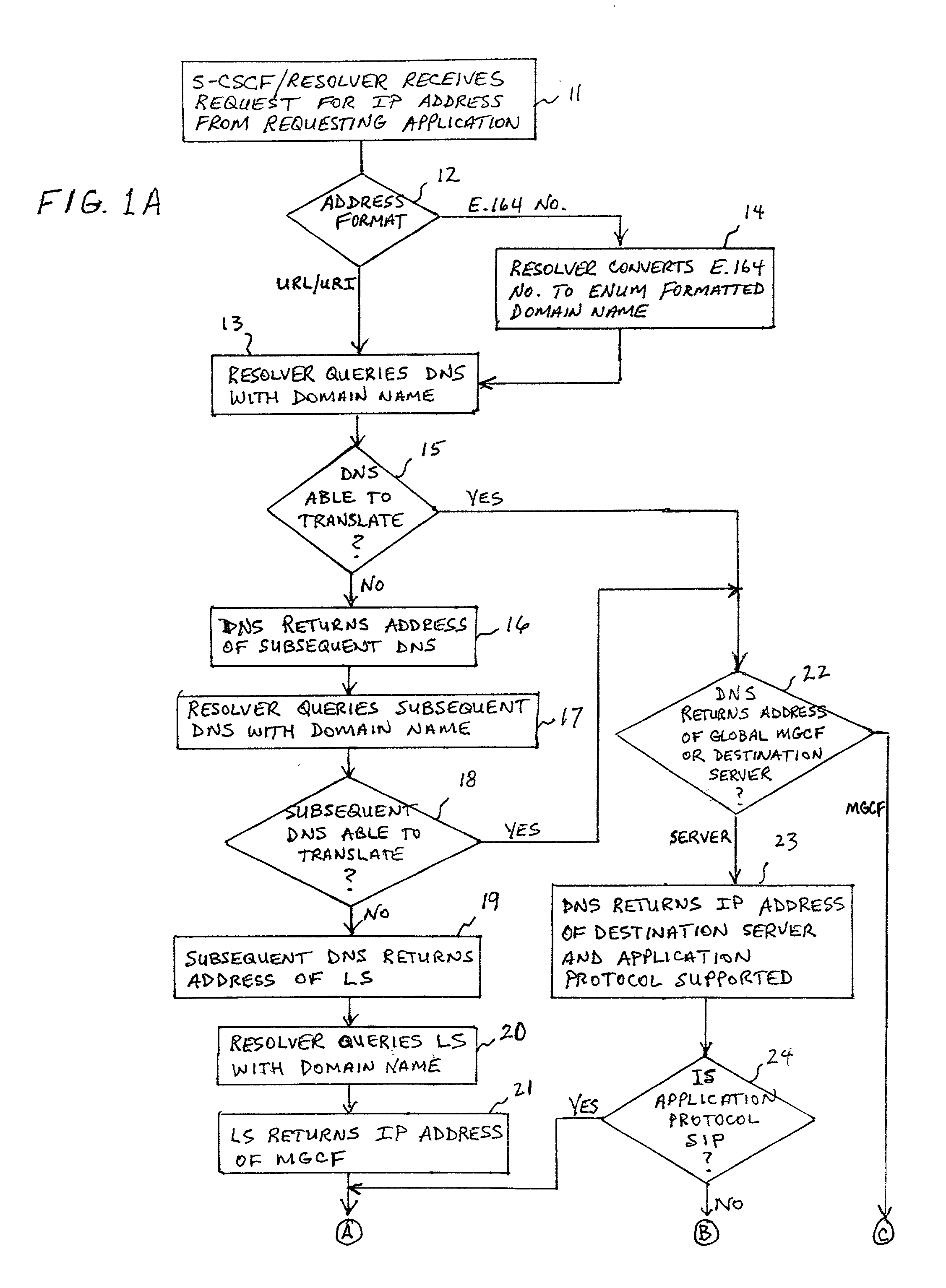
ActiveUS6917612B2Data switching by path configurationNetwork connectionsInternet protocol suiteDomain name
A system and unified method of address resolution in an IP-based network. A Resolver determines whether an input address is a URL / URI, and if so, extracts a domain name. If the input address is an E.164 number, the Resolver converts the E.164 number into a domain name in ENUM format. The Resolver then sends a domain name query to a DNS which, if able, returns the IP address for either a Global MGCF or a destination server along with a supported Application protocol. If the DNS is unable to perform the translation, or the Application protocol returned is not supported by the requesting application, the Resolver sends a domain name query to an extended Location Server (LS) to obtain an IP address of a gateway function capable of interfacing with the destination server.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Linked network switch configuration
A network device includes a first switch, a second switch, address resolution logic (ARL), and a CPU. The first and second switch having a groups of ports which are a subset of the plurality of ports and are numbered by a different numbering schemes. The CPU coupled to the first switch and the second switch and configured to control the first switch, the second switch, and the ARL. A first link port of the first group of ports is coupled to a second link port of the second group of ports. The ARL is configured to perform address resolution based on the first and second numbering schemes such that when the first network port a data packet received at the first network port destined for the second network port is directly routed from the first network port to the second network port.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
Tunneling scheme optimized for use in virtual private networks
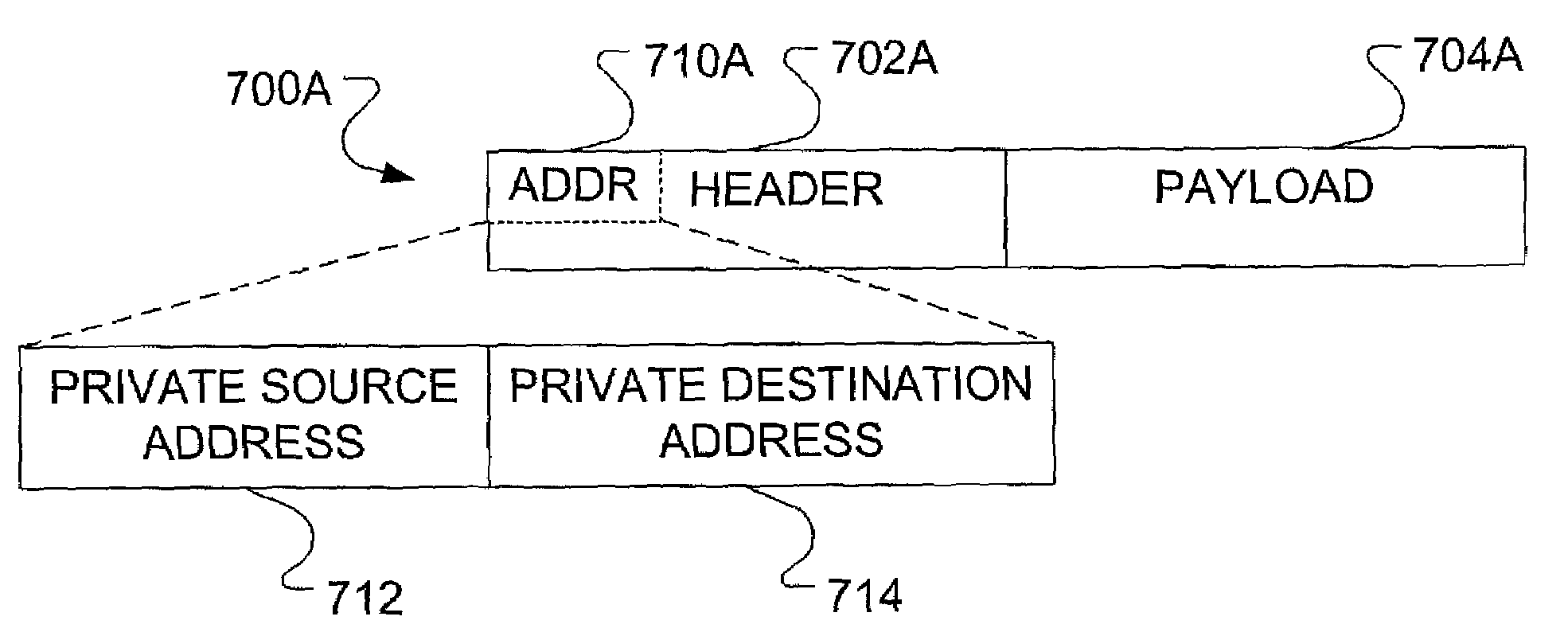
InactiveUS7379465B2Reduce Layer complexityTime-division multiplexNetworks interconnectionAddress Resolution ProtocolAddress resolution
A tunneling scheme includes the creation of tunnels having a source address and potentially multiple destination addresses. Each tunnel endpoint is divided into two sub-endpoints, where one sub-endpoint has a public network address and the other sub-endpoint has a private network address. Also included in the tunneling scheme is a static Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) table. The static ARP table contains information on virtual private network membership. More particularly, the static ARP table provides address resolution between public network addresses and private network addresses.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
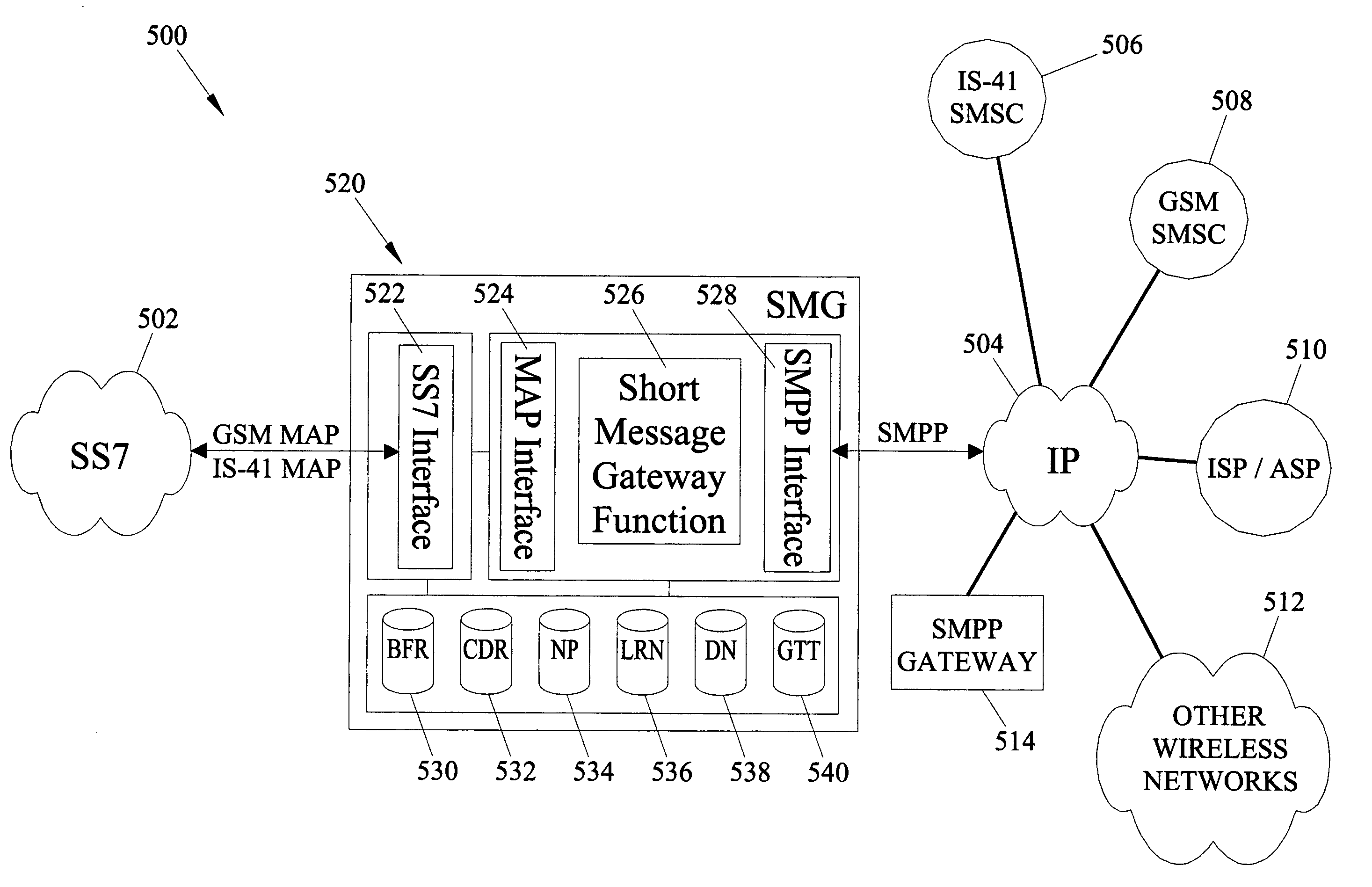
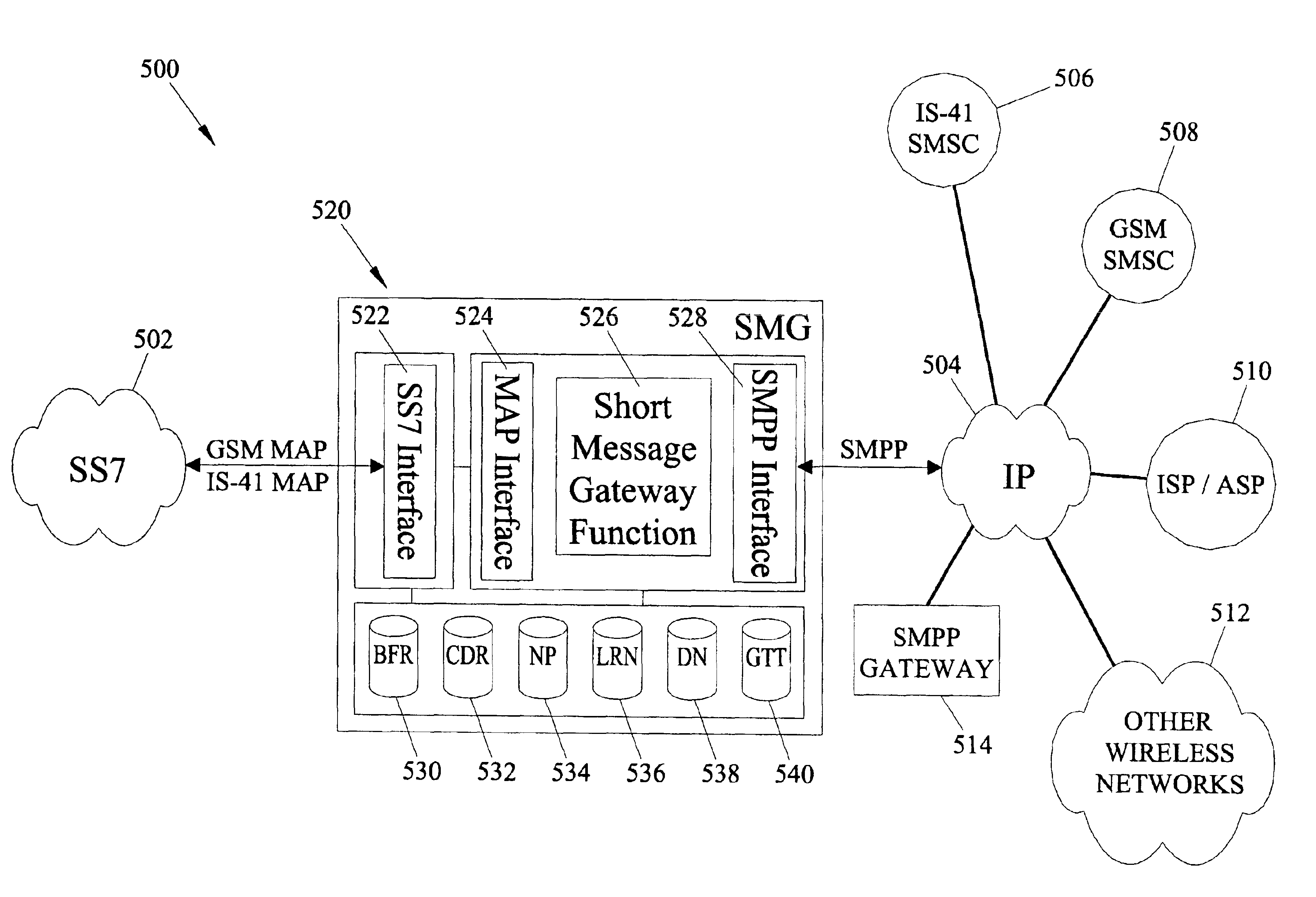
Methods and systems for providing short message gateway functionality in a telecommunications network
ActiveUS20050003838A1Interconnection arrangementsTime-division multiplexMessage deliveryAddress resolution
A short message gateway may include signal transfer point (STP) functionality, mobile originating short message service center (SMSC) functionality, and short message delivery point-to-point (SMPP) gateway functionality. The short message gateway may receive an SS7 message including a short message payload. The short message gateway may formulate an SMPP message including the short message payload and access one or more internal address resolution and / or number portability databases to determine the destination address for the SMPP message. The short message gateway may then forward the SMPP message to its destination.
Owner:TEKELEC GLOBAL INC
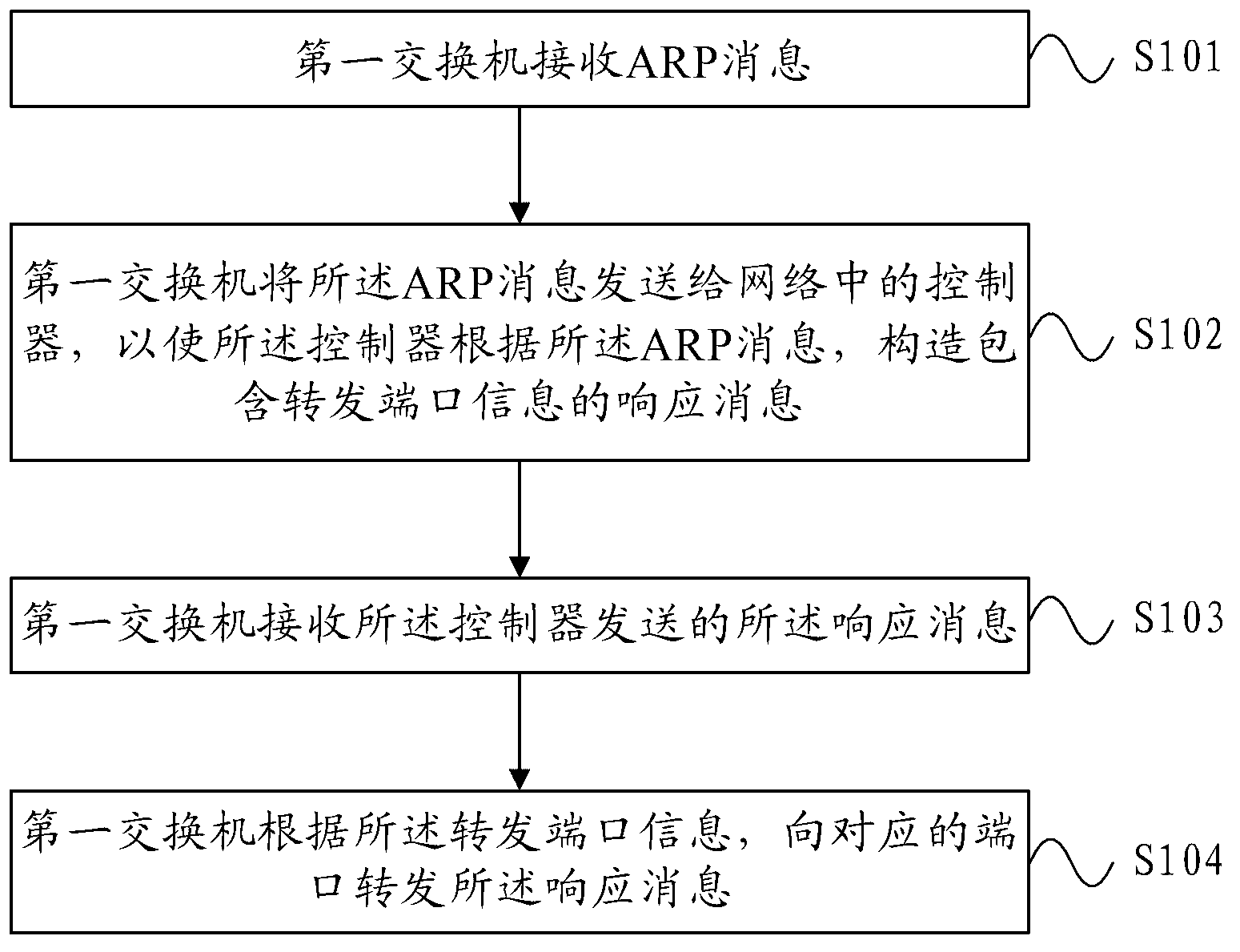
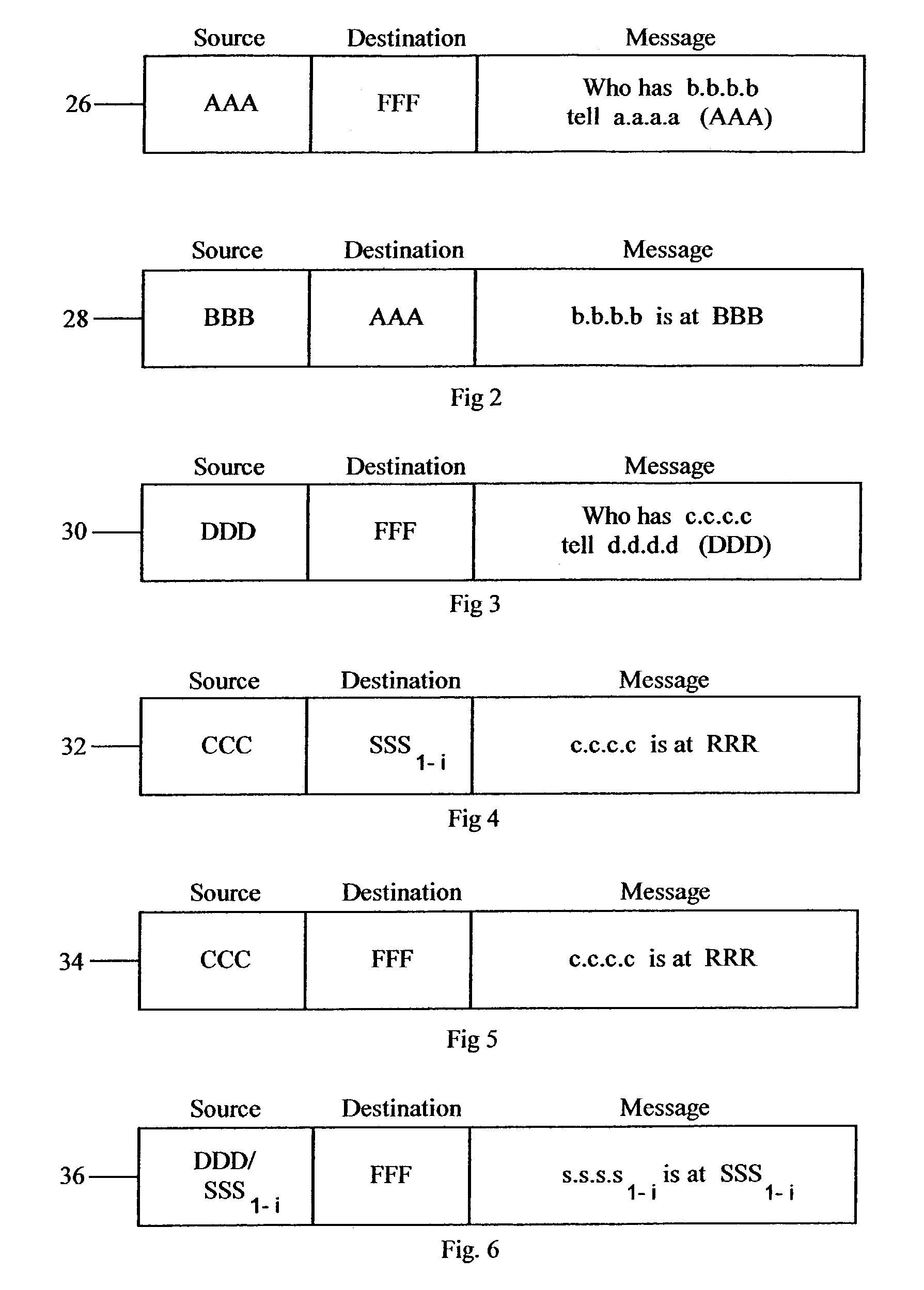
Address resolution protocol (ARP) message forwarding method, exchanger and controller
ActiveCN102938794ASave bandwidthImprove network efficiencyData switching networksAddress Resolution ProtocolAddress resolution
An embodiment of the invention provides an address resolution protocol (ARP) message forwarding method, an exchanger and a controller. The ARP message forwarding method includes: a first exchanger receives ARP messages; the first exchanger sends the ARP messages to the controller in the network to lead the controllers to construct response messages containing forwarding port messages according to the ARP messages; the first exchanger receives the response messages sent by the controller; and the first exchanger forwards the response messages to a corresponding port according to the forwarding port messages. The controller provides ARP service for a main machine of the network managed by the controller, and therefore network efficiency can be improved and network bandwidth can be saved.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Security apparatus and method for local area networks
ActiveUS7124197B2Digital data processing detailsMultiple digital computer combinationsAddress Resolution ProtocolAddress resolution
The present invention includes a method and apparatus for controlling data link layer access to protected servers on a computer network by a client device. Address resolution requests broadcast on the network by the client device seeking access to any network device are received and then processed to determine whether the client device is unknown. If the client device is unknown, restriction address resolution replies are transmitted to the protected devices to restrict access by the client device to the protected devices and allow access to an authentication server. The authentication server is monitored to determine if the client device is authorized or unauthorized by the authentication server. If the client device is authorized, access is allowed to the protected devices. If the client device is unauthorized, blocking address resolution replies are transmitted on the computer network to block access by the client device to all other network devices.
Owner:SYSXNET
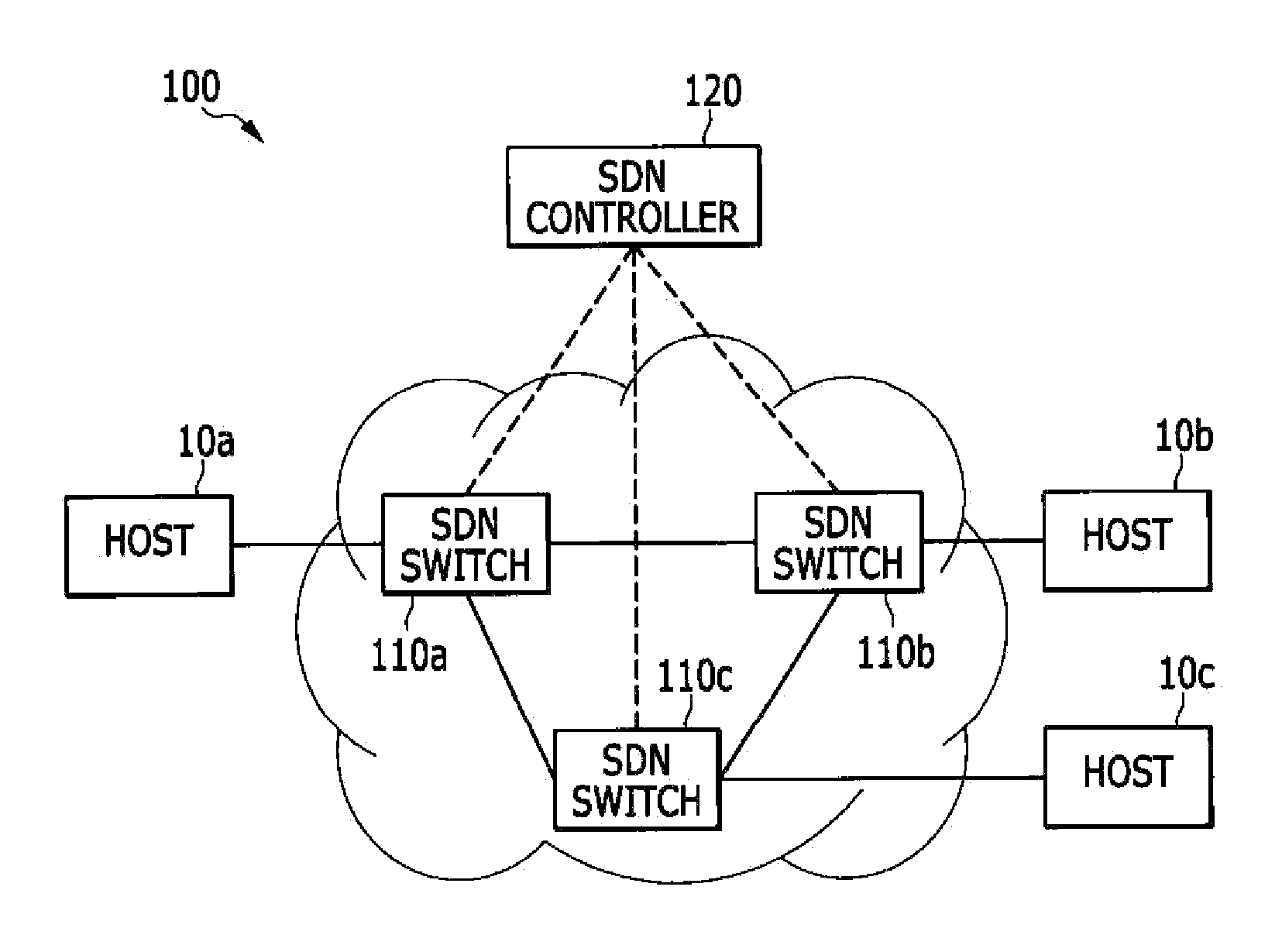
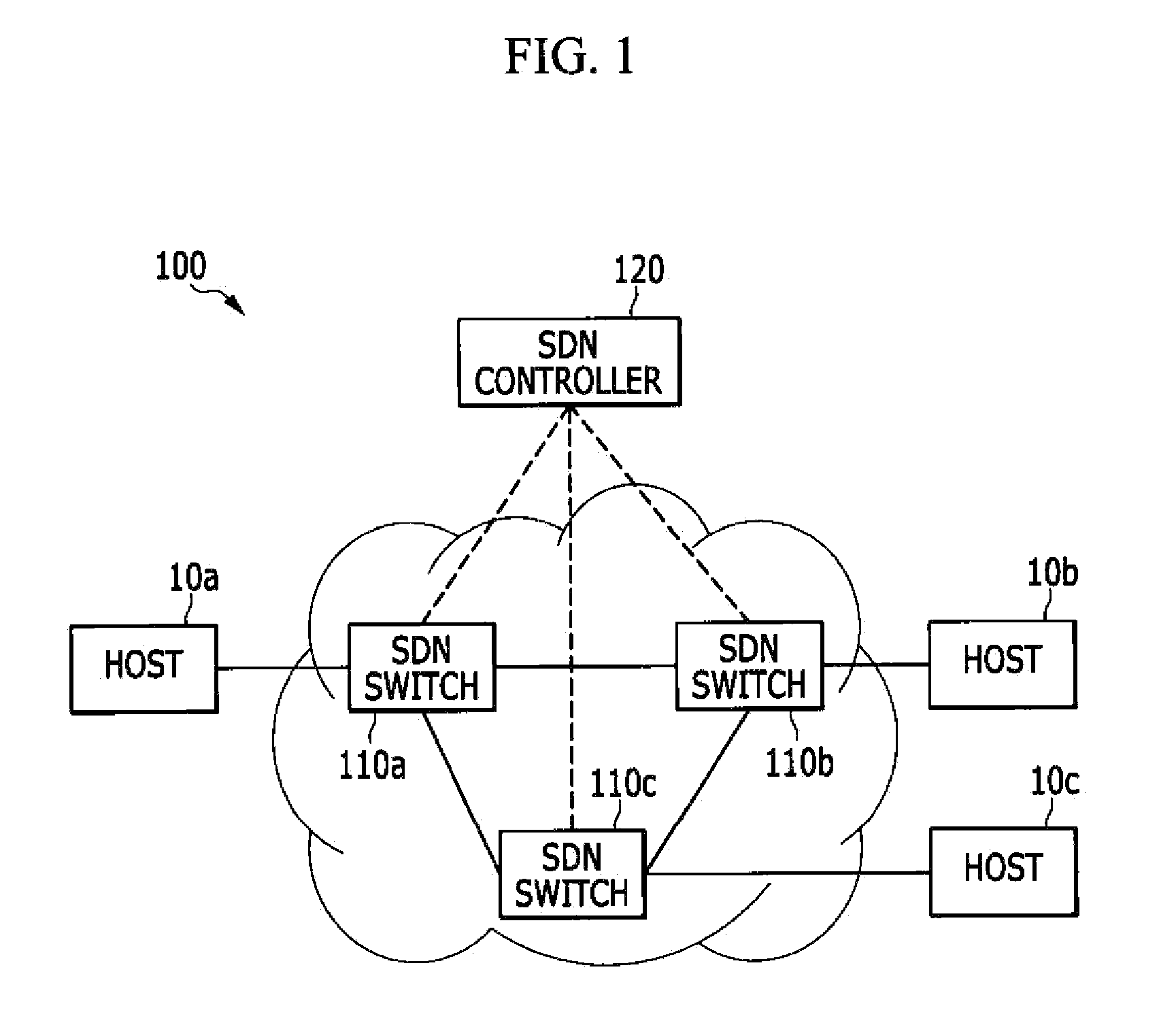
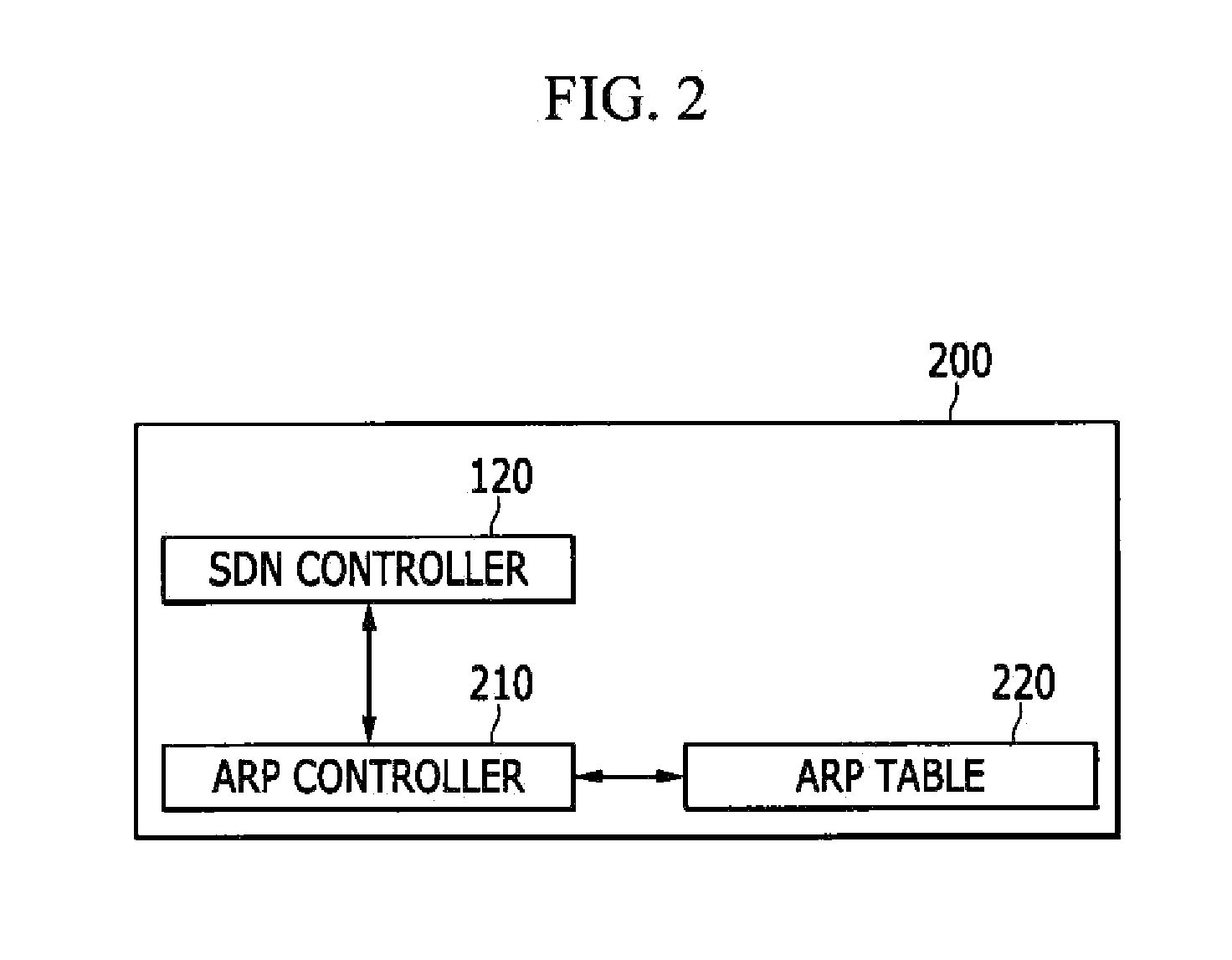
System and method for address resolution
InactiveUS20150071289A1Reduce in quantityData switching by path configurationAddress Resolution ProtocolIp address
In an address resolution system in a centralized network control environment including a plurality of software defined network (SDN) switches, an address resolution protocol (ARP) controller checks whether an ARP table has a MAC address corresponding to the destination IP address of an ARP request packet when the ARP request packet is received from a source host. An SDN controller determines whether to broadcast the ARP request packet according to the existence of the MAC address corresponding to the destination IP address in the ARP table.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Methods and systems for providing short message gateway functionality in a telecommunications network
ActiveUS6885872B2Interconnection arrangementsTime-division multiplexTelecommunications linkMessage delivery
A short message gateway may include signal transfer point (STP) functionality, mobile originating short message service center (SMSC) functionality, and short message delivery point-to-point (SMPP) gateway functionality. The short message gateway may receive an SS7 message including a short message payload. The short message gateway may formulate an SMPP message including the short message payload and access one or more internal address resolution and / or number portability databases to determine the destination address for the SMPP message. The short message gateway may then forward the SMPP message to its destination.
Owner:TEKELEC GLOBAL INC
Methods and systems for generating, distributing, and screening commercial content
ActiveUS7299050B2Reduce deliveryBroadcast systems characterised by addressed receiversTelephonic communicationProcessor registerAddress resolution
Methods and systems for generating, distributing, and screening commercial content are disclosed. A commercial content generator (CCG) generates commercial content message and obtains from a push proxy agent address resolution server the network routing address of each push proxy agent that is required for distribution of the message to the target mobile subscriber audience. A push proxy agent receives a message containing commercial content and resolves a mobile subscriber identifier for each mobile subscriber who is to receive the commercial content information using subscriber information obtained from a subscriber location register, such as a visitor location register (VLR). The push proxy agent may also negotiate media format characteristics for each member of the target mobile subscriber audience and facilitate delivery of the commercial content to each member of the target mobile subscriber audience.
Owner:TEKELEC
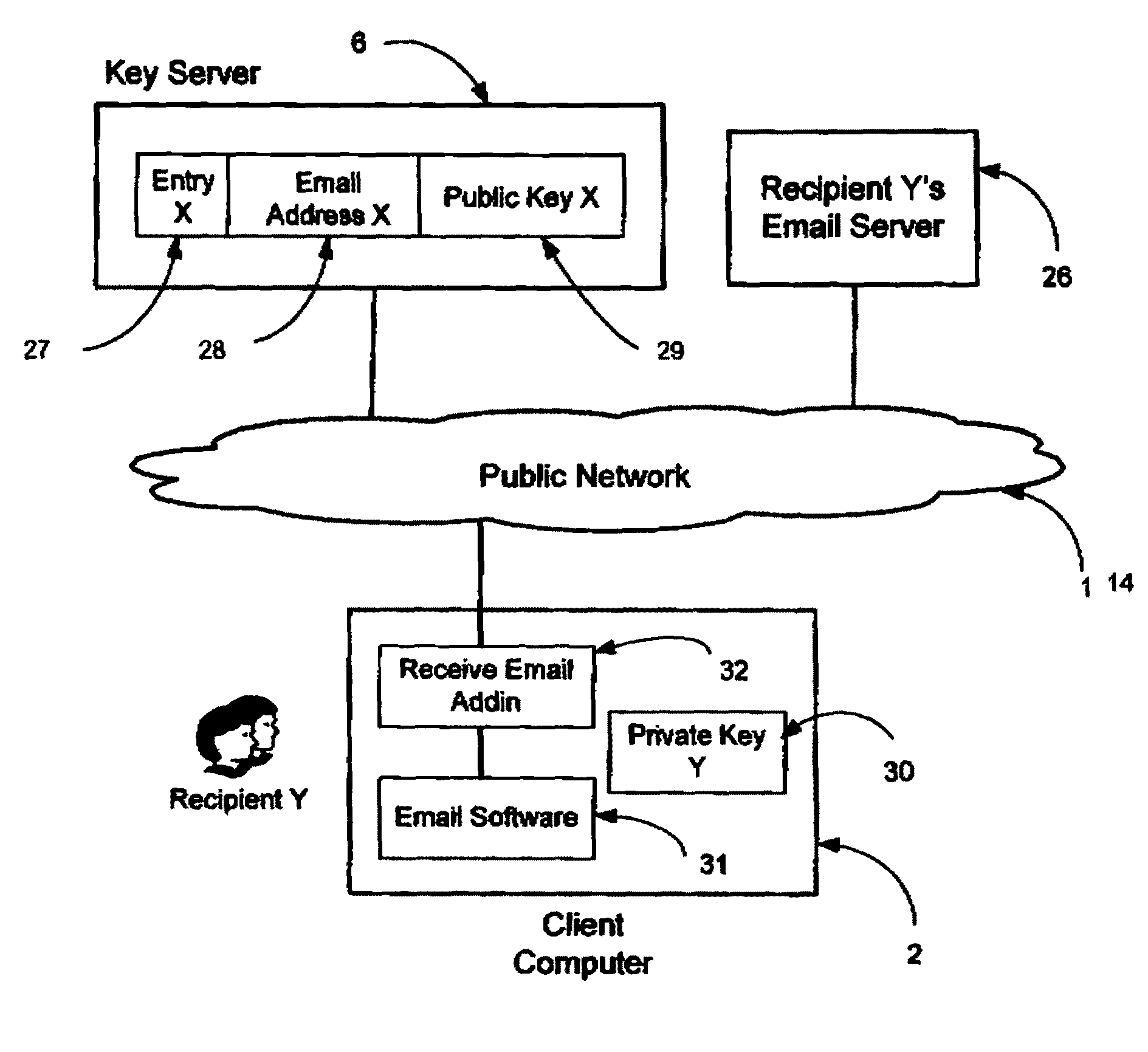
Method and apparatus for utilizing portable e-mail addresses
InactiveUS20070260693A1Improve efficiencyImprove securityMultiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionEmail addressAddress resolution
A signal bearing medium tangibly embodies a program of machine-readable instructions executable by a digital processing apparatus to perform operations comprising receiving an email message having an extended email address encoded virtual address, resolving said address to an actual email address, replacing the virtual address with the actual email address, and transmitting said email message.
Owner:IBM CORP
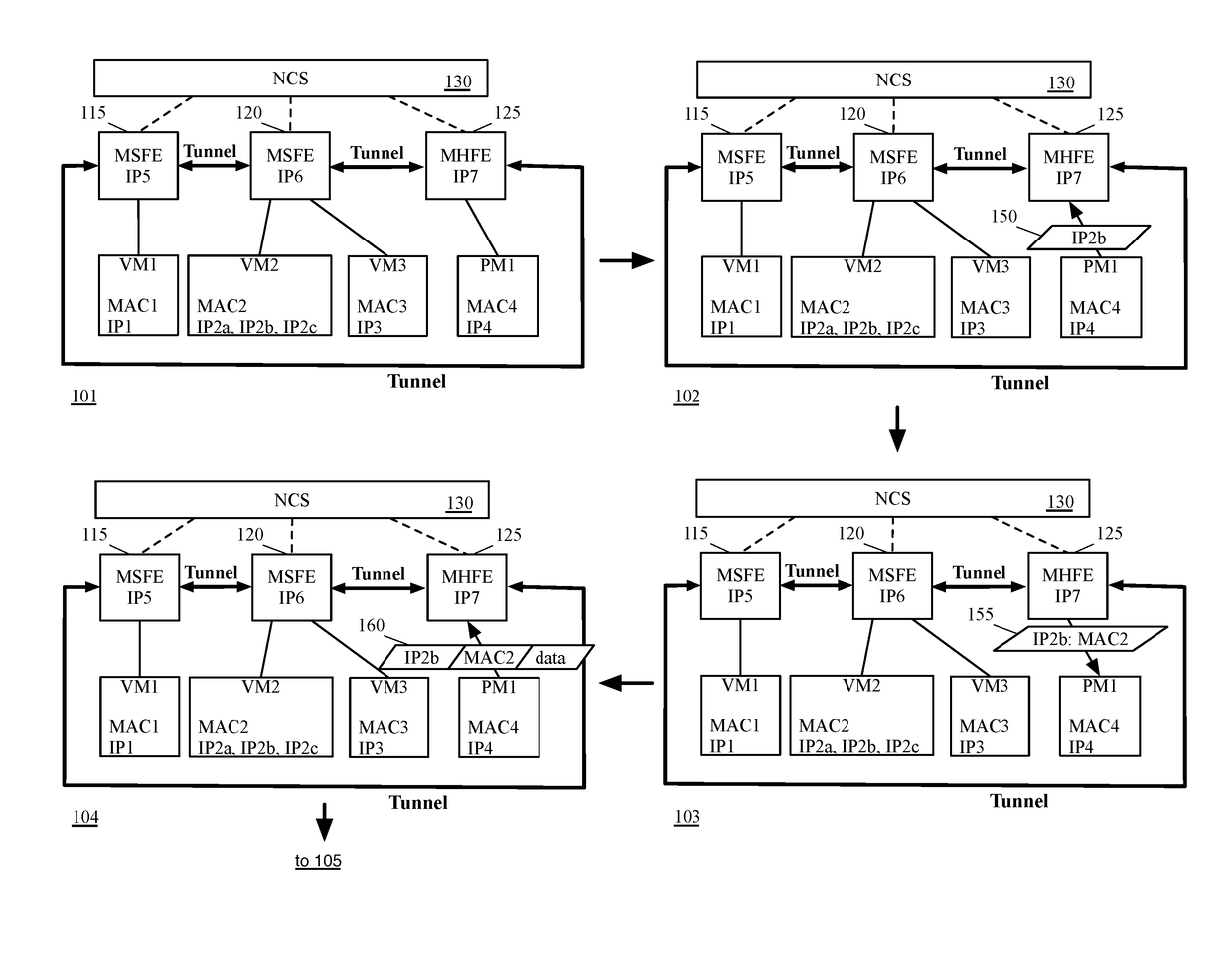
IP aliases in logical networks with hardware switches
ActiveUS20170093758A1Reduce decreaseMitigate issueData switching networksIP aliasingAddress Resolution Protocol
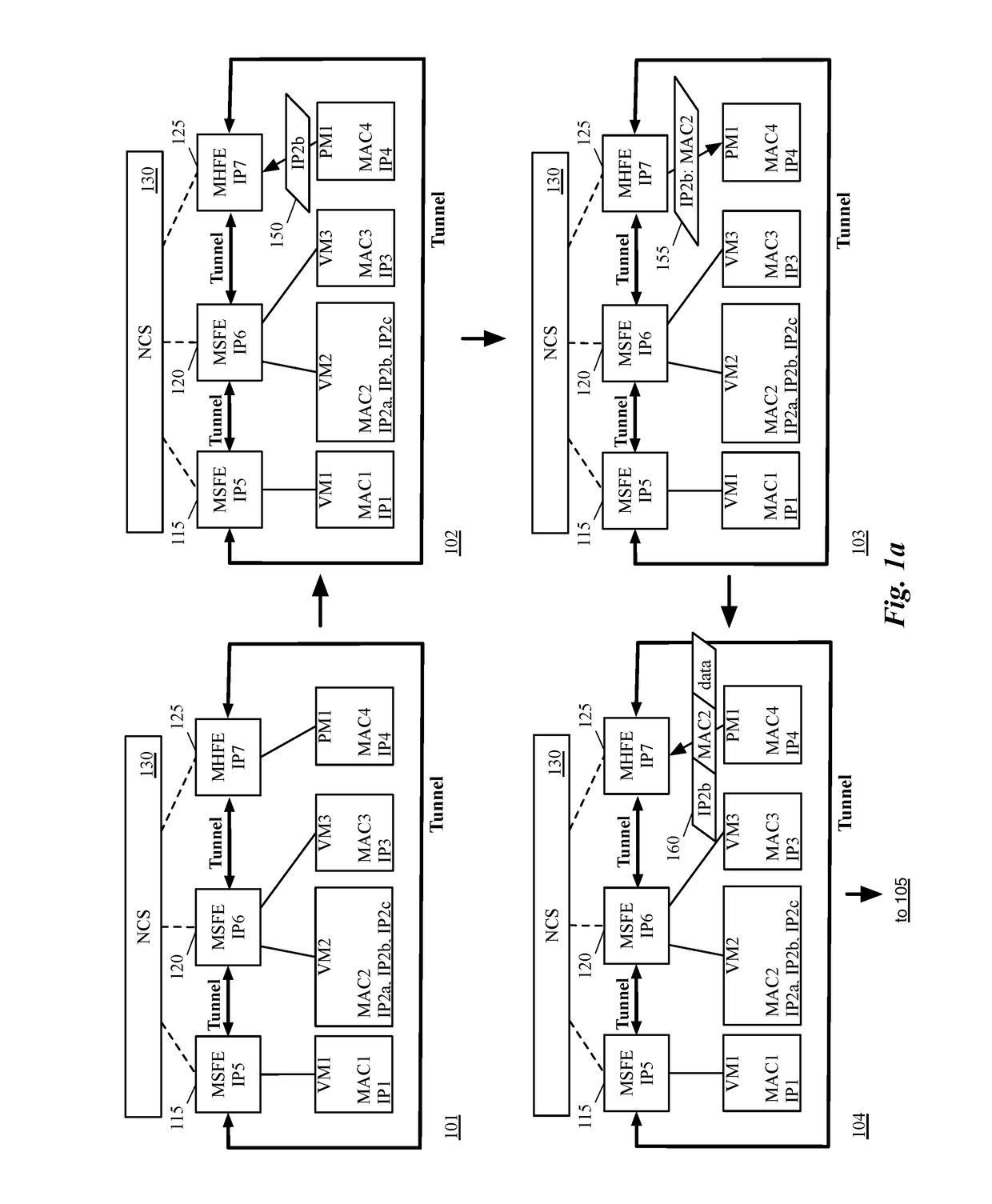
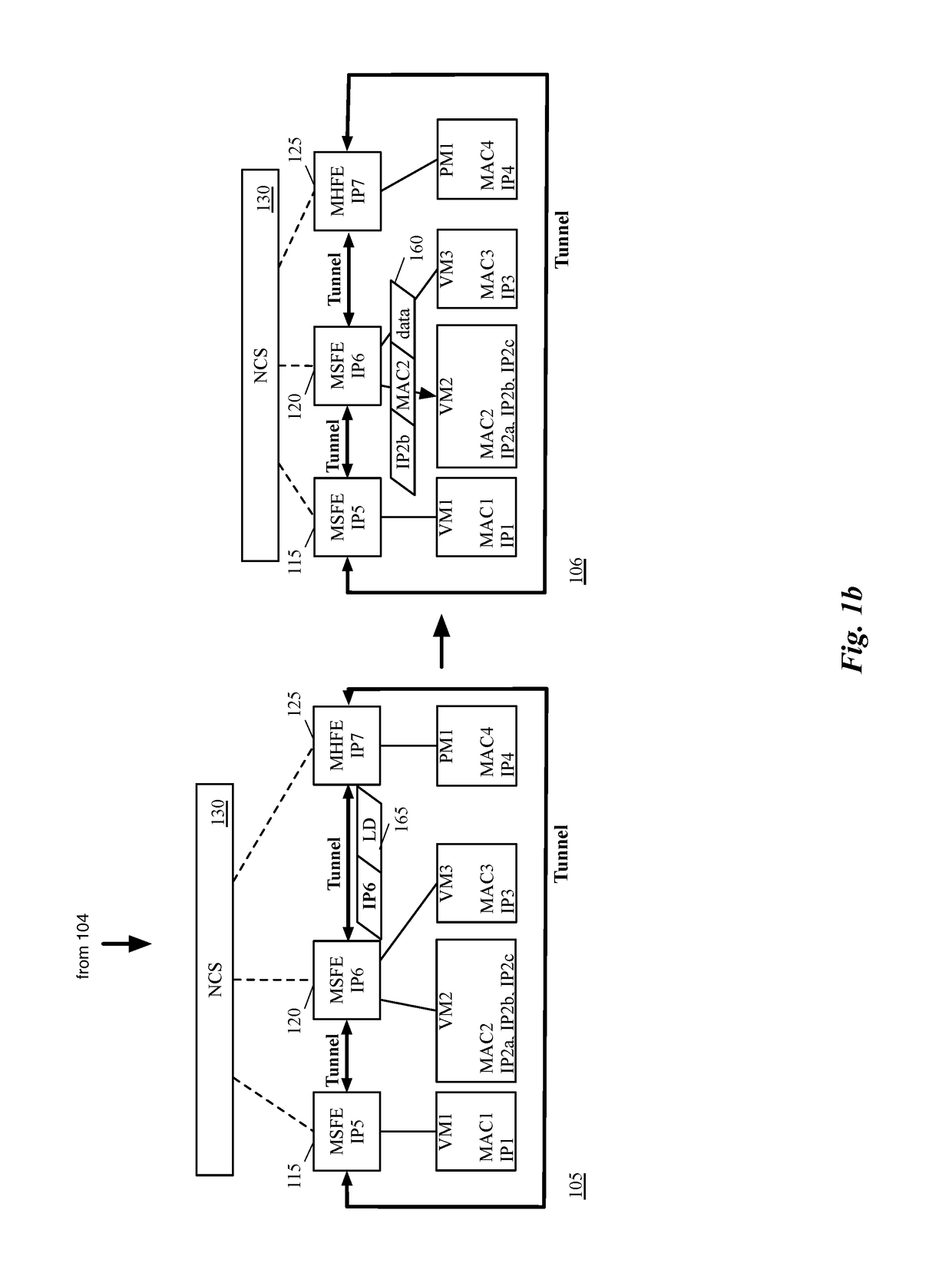
Some embodiments provide a novel method of configuring a managed hardware forwarding element (MHFE) that implements a logical forwarding element (LFE) of a logical network to handle address resolution requests (e.g., Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) requests) for multiple addresses (e.g., IP addresses) associated with a single network interface of the logical network. The method identifies a physical port of the MHFE with which the multiple addresses are to be associated. The physical port is coupled to an end machine (e.g., a virtual machine, server, container, etc.) of the logical network. The method then modifies associations stored at the MHFE to associate the physical port with the multiple addresses.
Owner:NICIRA
Mobile communication system
InactiveUS7123599B2Reducing packet lossReducing packet lossesAssess restrictionTime-division multiplexCommunications systemAddress resolution
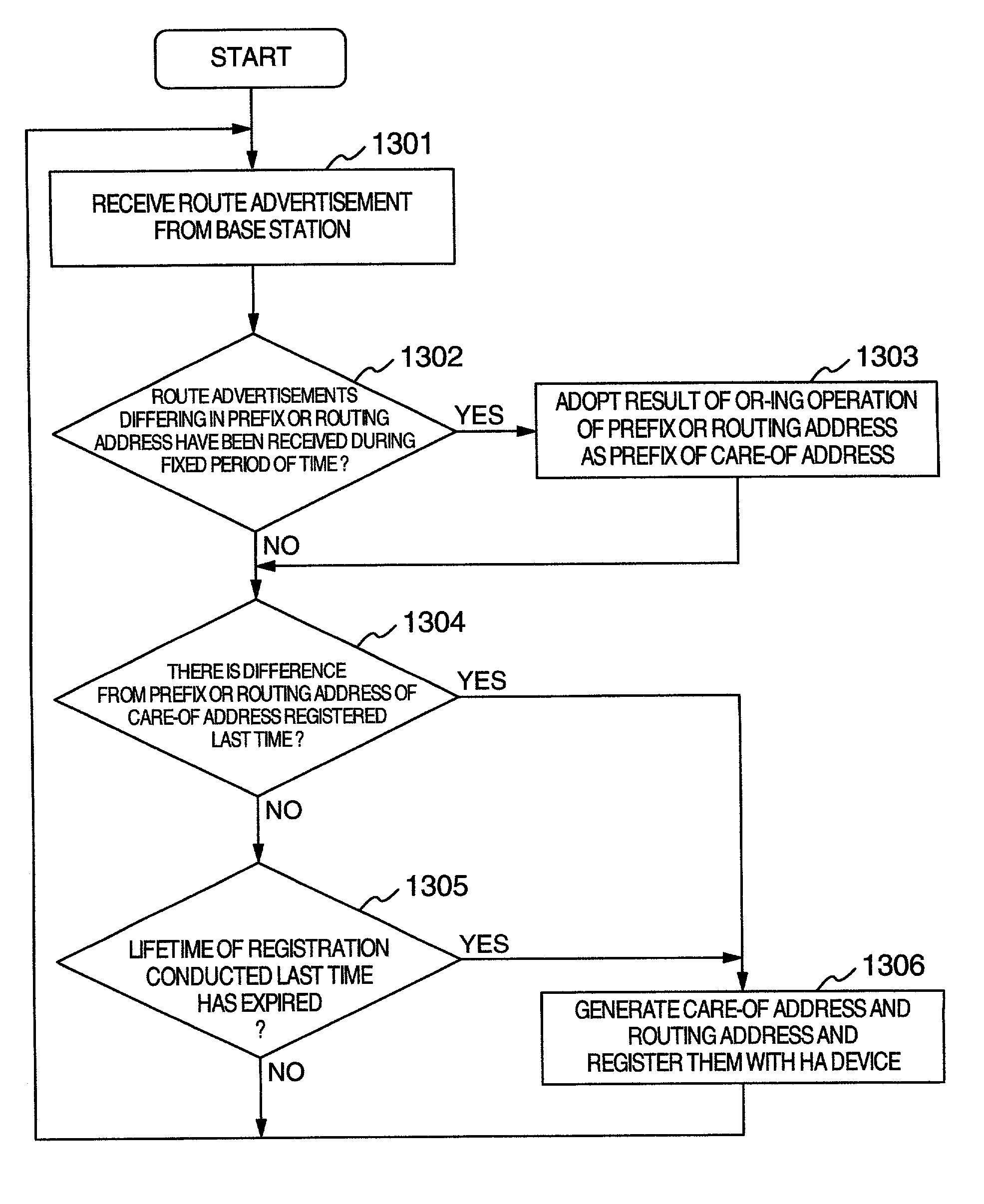
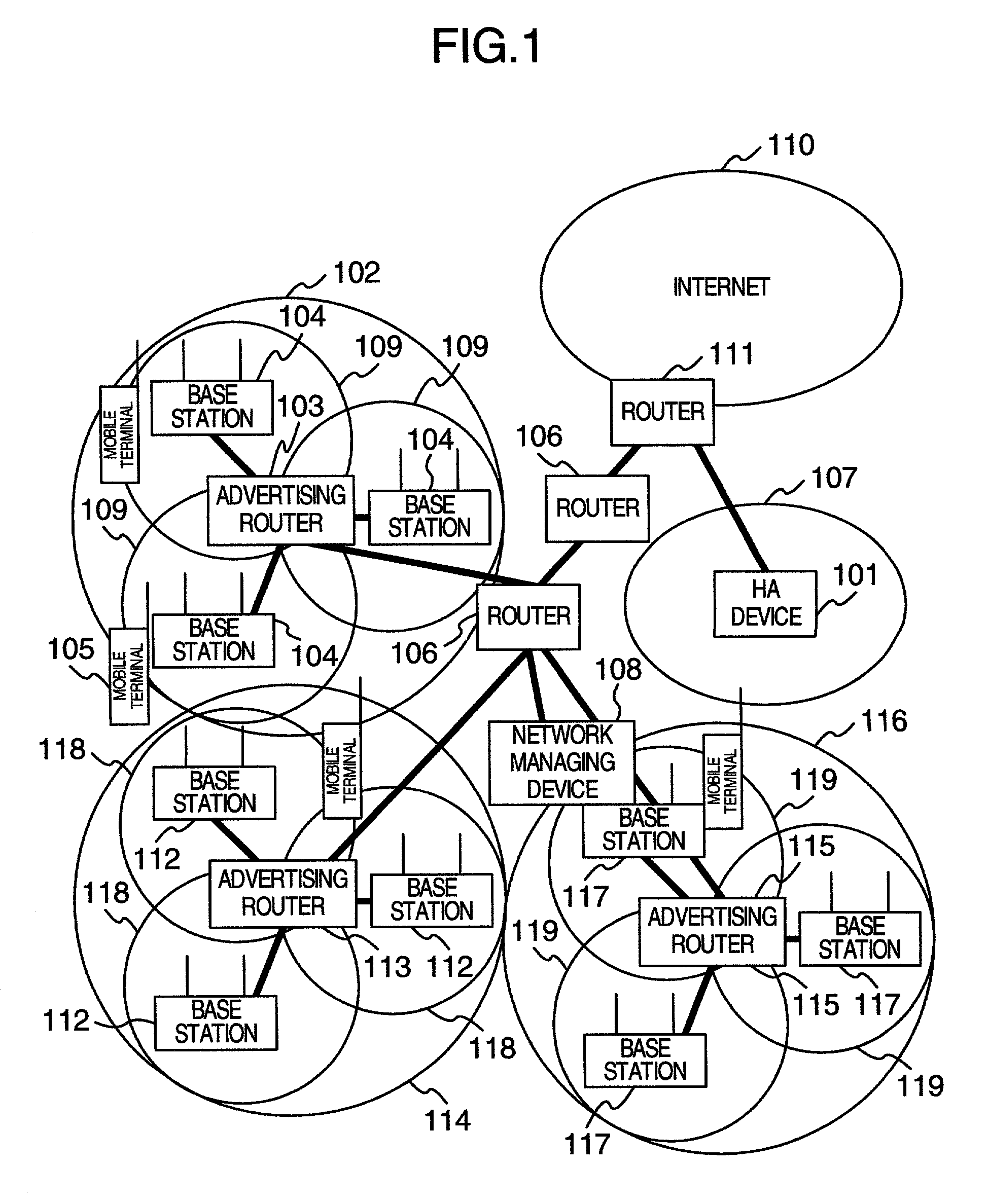
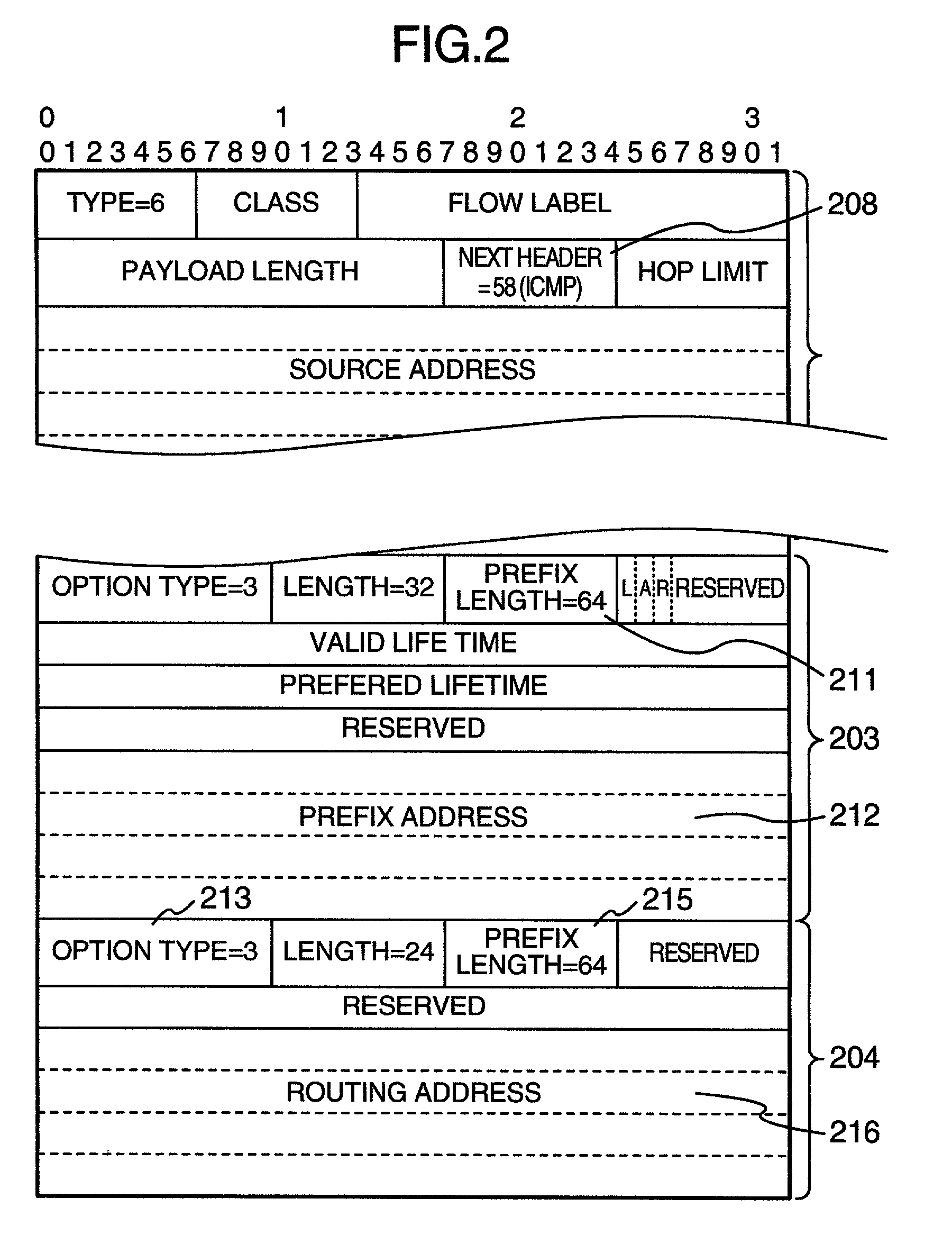
A mobile data communication system capable of shortening the interruption time of communication includes an HA device, advertising routers, base stations, routers, and mobile terminal devices. Each base station advertises an address having “1” set in a different bit of an interface ID of a routing address. When a mobile terminal has received radio waves from a plurality of base stations in the vicinity of a boundary between cells, the mobile terminal combines a plurality of received routing addresses by logical summation and registers a resultant routing address with the HA device. As for a packet delivered from the HA device to the routing address and having “1” in a plurality of bits of the host section, a router resolves the address of the host section into destination addresses each having “1” in one bit, generates packets each having one of resultant addresses, and transmits the generated packets.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Network address server
InactiveUS7280999B2Data processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsUnique local addressTransceiver
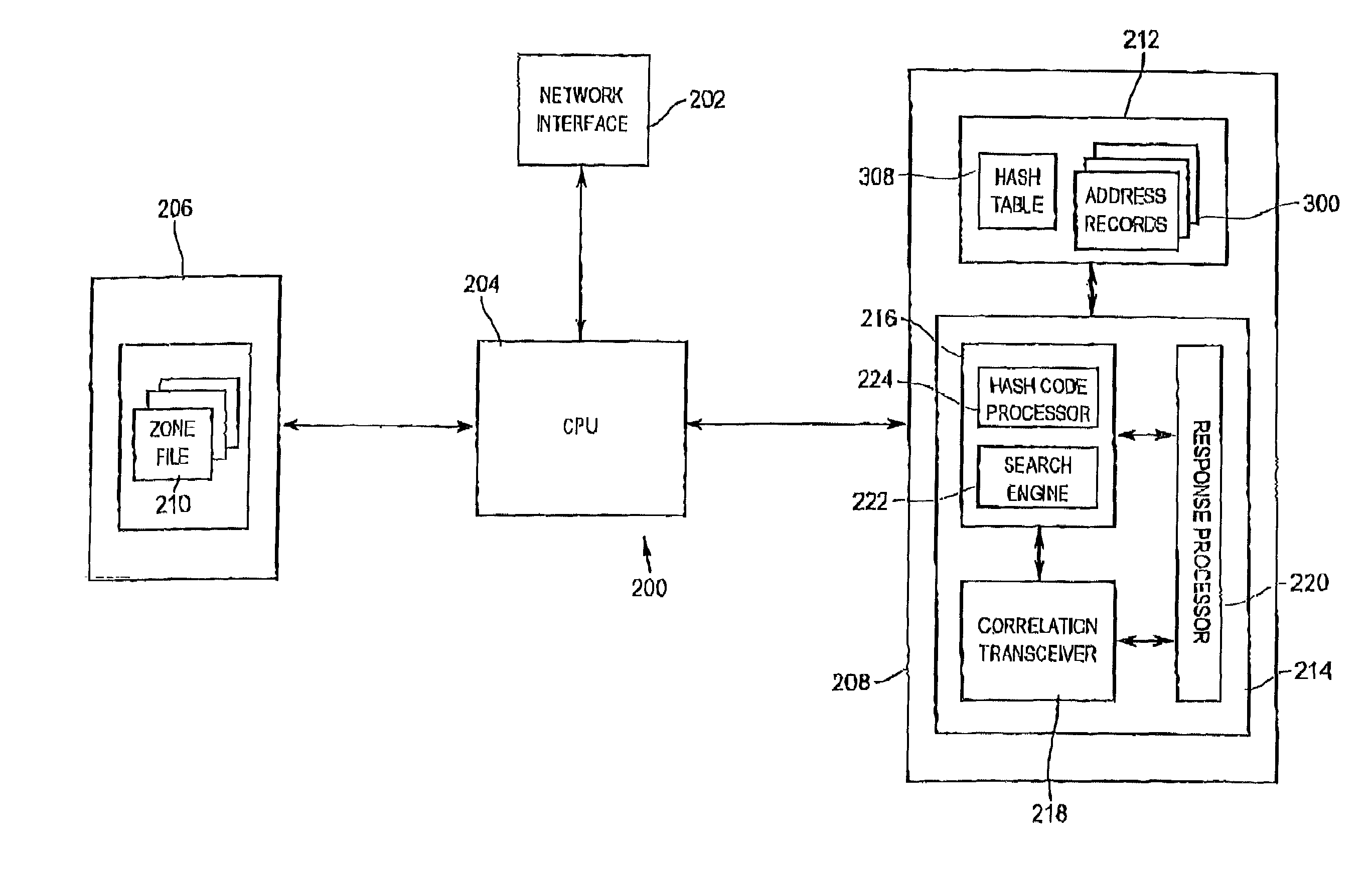
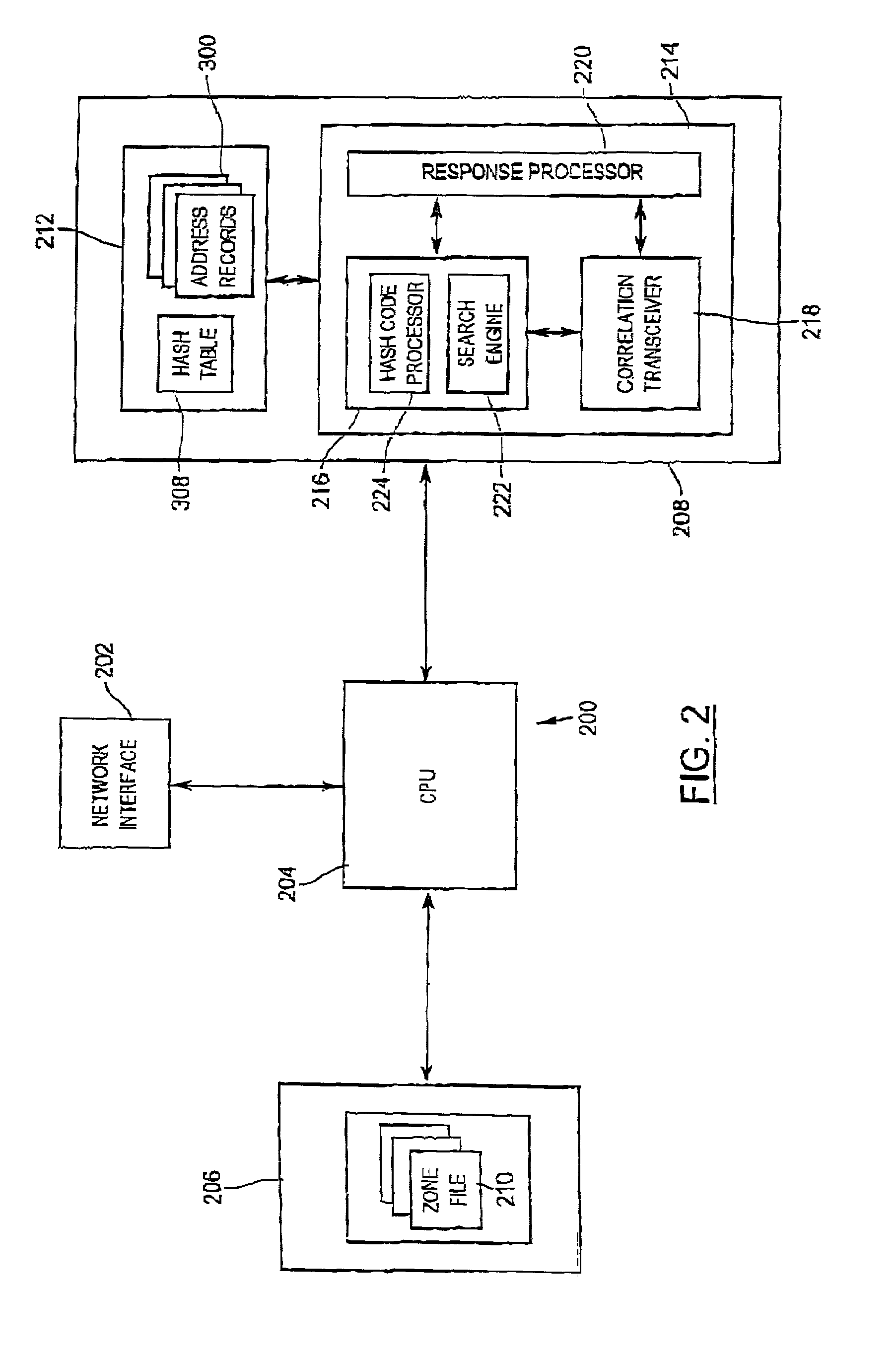
A network address server is configured to resolve a target network address name label with a network address, with the target address name label defining a branch of one level of a multi-level network address name space. The network address server is one of a plurality of network address servers each being uniquely associated with a respective region of the address name space level. The network server includes an address name database, and an address name processor in communication with the address name database for providing a response to a query for the network address corresponding to the target address name label. The address name database includes a number of database records, each identifying a unique address name label and a network address uniquely associated with the address name label. The address name processor includes a correlation processor, a correlation transceiver in communication with the correlation processor, and a response processor in communication with the correlation processor and the correlation transceiver. The correlation processor is configured to determine a correlation between the target address name label and the respective unique address name region. The correlation transceiver is configured to provide the other network address servers with a respective indication of the determined correlation and for receiving a corresponding correlation indication from at least one of the other network address servers. The response processor is configured to provide a response to the query in accordance with the correlation indications.
Owner:AFILIAS LTD
Enhanced mobility and address resolution in a wireless premises based network
InactiveUS20050025129A1Increase overheadData switching by path configurationWireless network protocolsNetworking protocolAddress resolution
A premises based wireless network having a multi-segment wired network and a plurality of wireless access points connected to the wired network. The wired network operates according to a wired network protocol which may be the Internet Protocol. Wireless terminals communicate with the wireless access points according to a wireless network protocol, inconsistent with the wired network protocol. Each of the wireless terminals has a wired network address corresponding to one of the wireless access points. Each wireless terminal also has an address according to the wired network protocol. As the wireless terminals roam throughout the premises, protocol tunnels route communications between wireless terminals, thereby preserving communications while roaming by allowing the wireless terminals to retain their wired network addresses during the ongoing communications. The wireless terminals are connected to wireless access points. These wireless access points are in turn linked by data link tunnels to a root access point for a subnet. The data link tunnels enable the root access point for a subnet to forward data to the wireless access points. The forwarded data is not bridged onto the particular subnet that connects the wireless access point and the root access point for that subnet.
Owner:MEIER ROBERT C
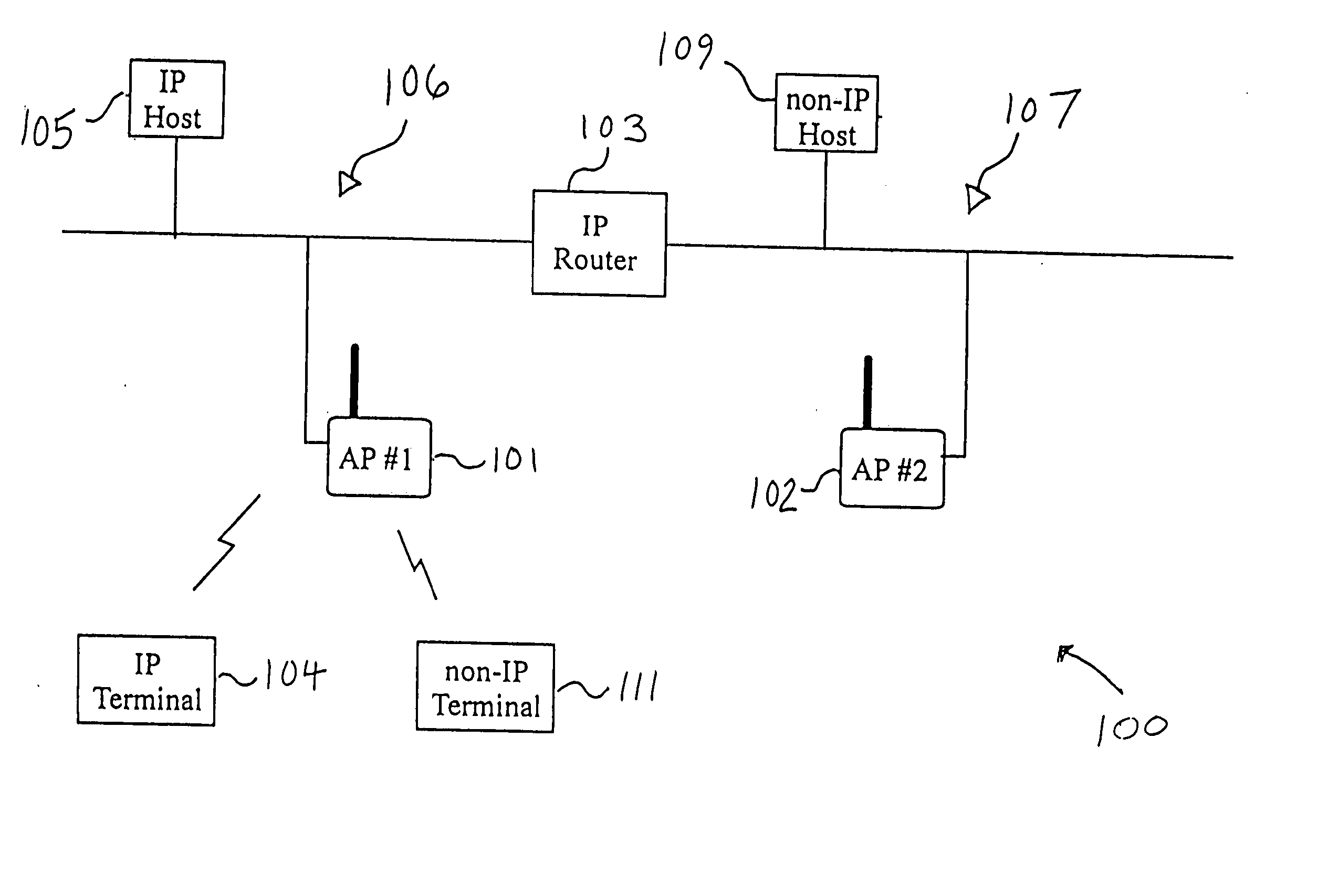
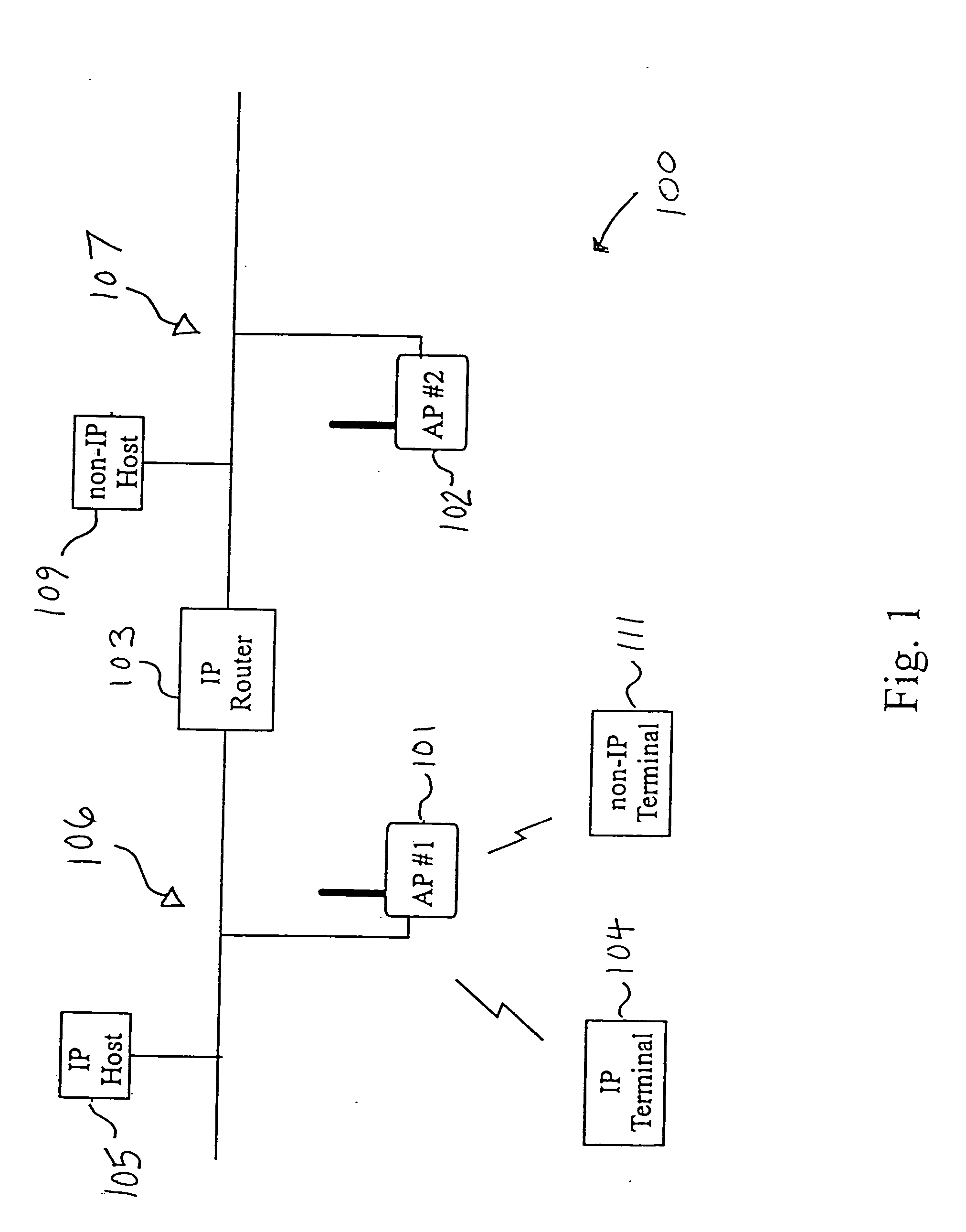
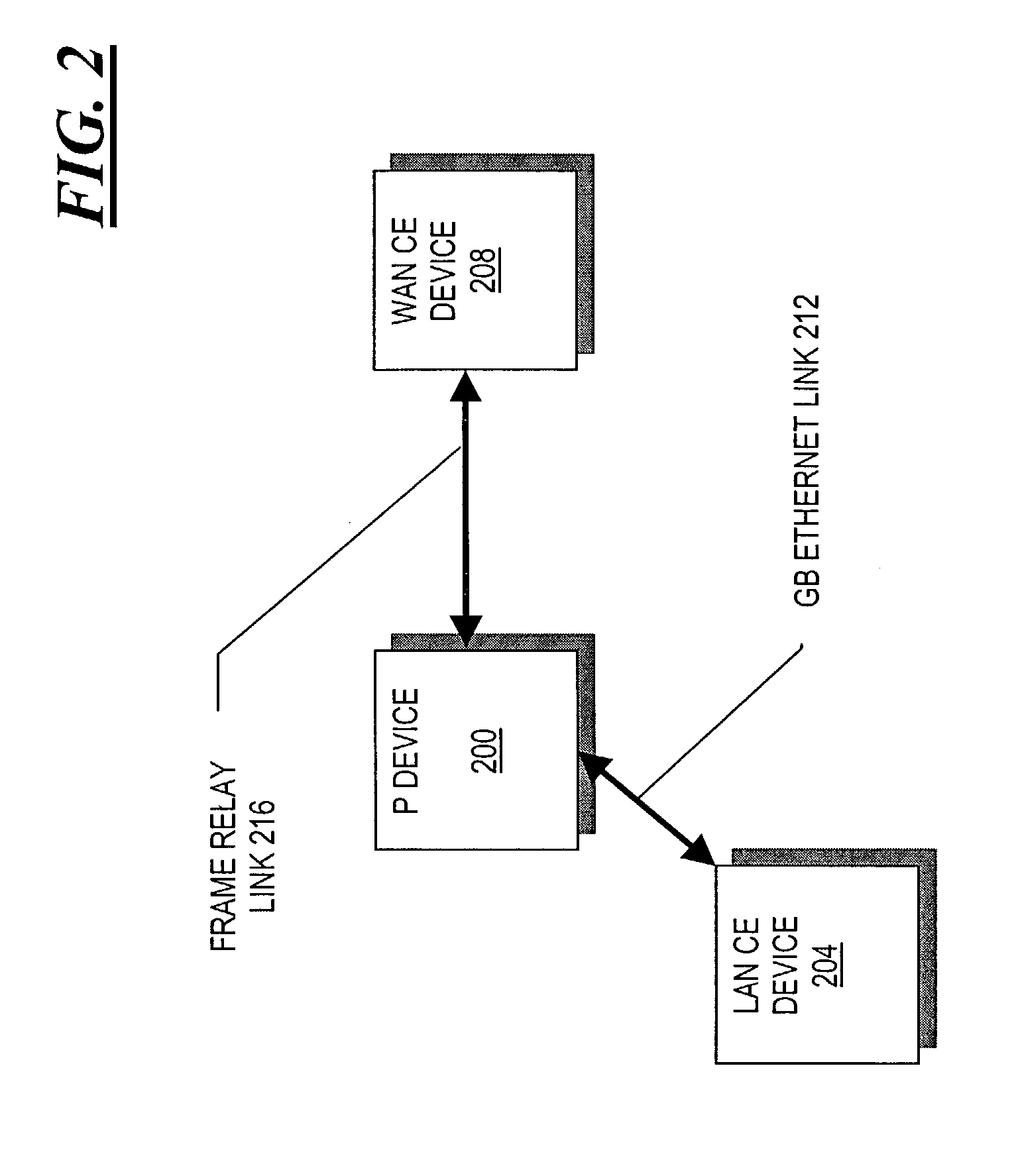
Methods and apparatus for broadcast domain interworking
ActiveUS7009983B2Time-division multiplexData switching by path configurationBroadcast domainAddress resolution
A P device interworks CE devices connected to the P device using different types of data links. The P device learns the address of a local CE device by monitoring the control messages, such as address resolution messages, originating from the local device. The P device may share the address of a local CE device with another local CE device by initiating a control message or responding to a control message issued by one of the local CE devices. This latter mechanism in effect hides the heterogeneous nature of the network.
Owner:EXTREME NETWORKS INC
Mobile gateway device
InactiveUS7769877B2Easy accessConnection managementMultiple digital computer combinationsWeb serviceMobile end
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
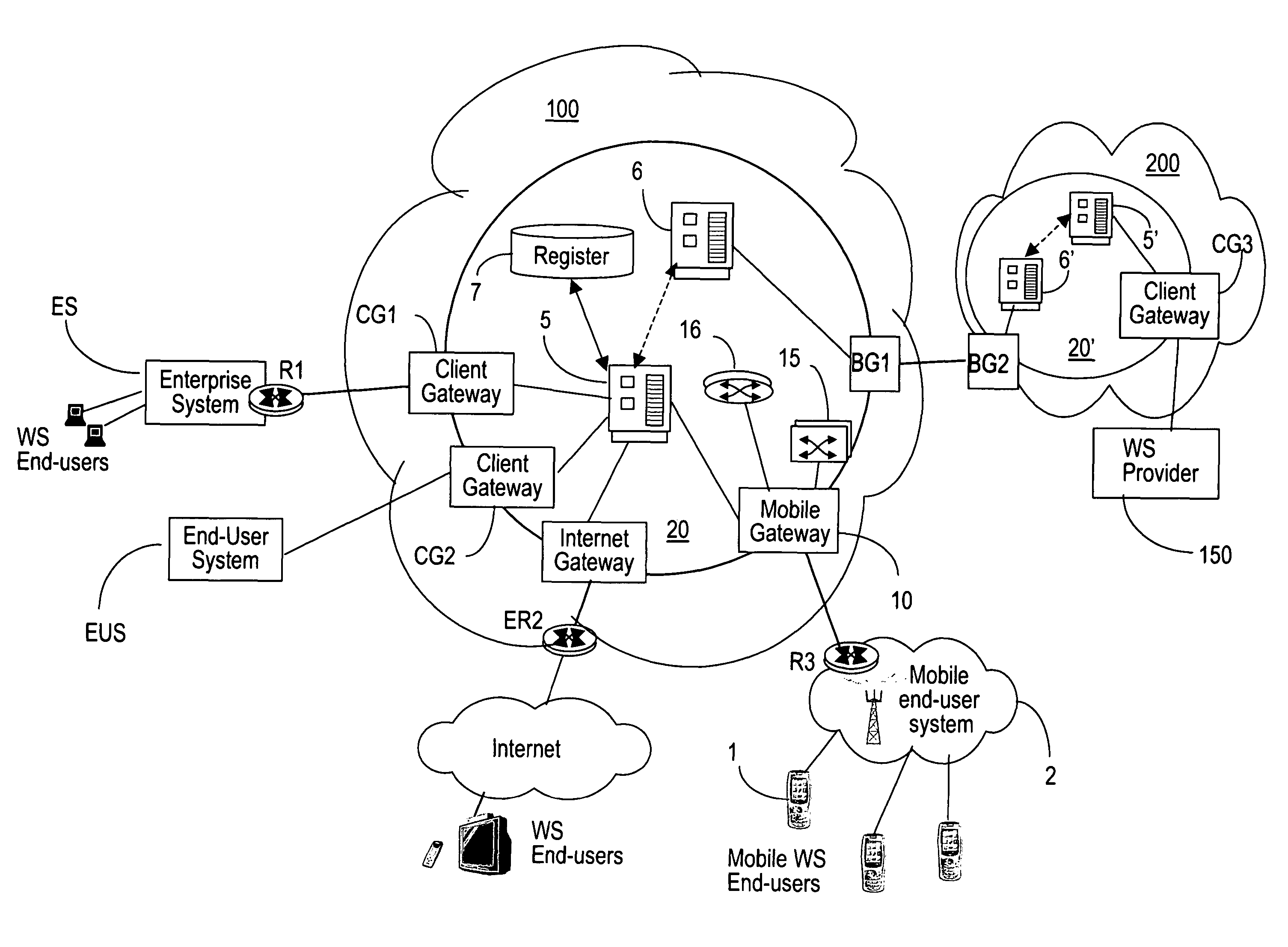
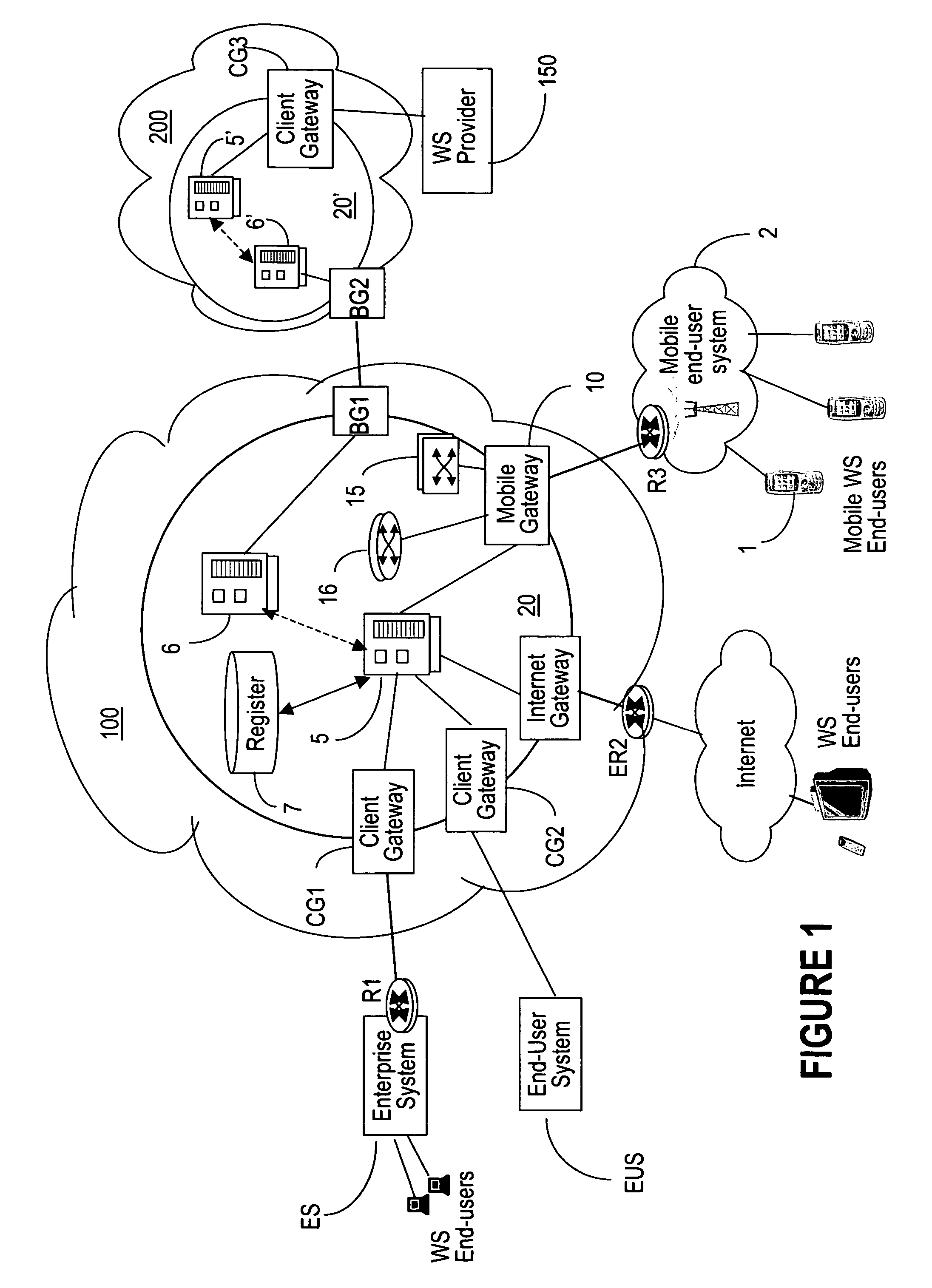
System, method, and computer program product for resolving addressing in a network including a network address translator
InactiveUS7797433B2Efficient managementData switching by path configurationMultiple digital computer combinationsSession Initiation ProtocolApplication server
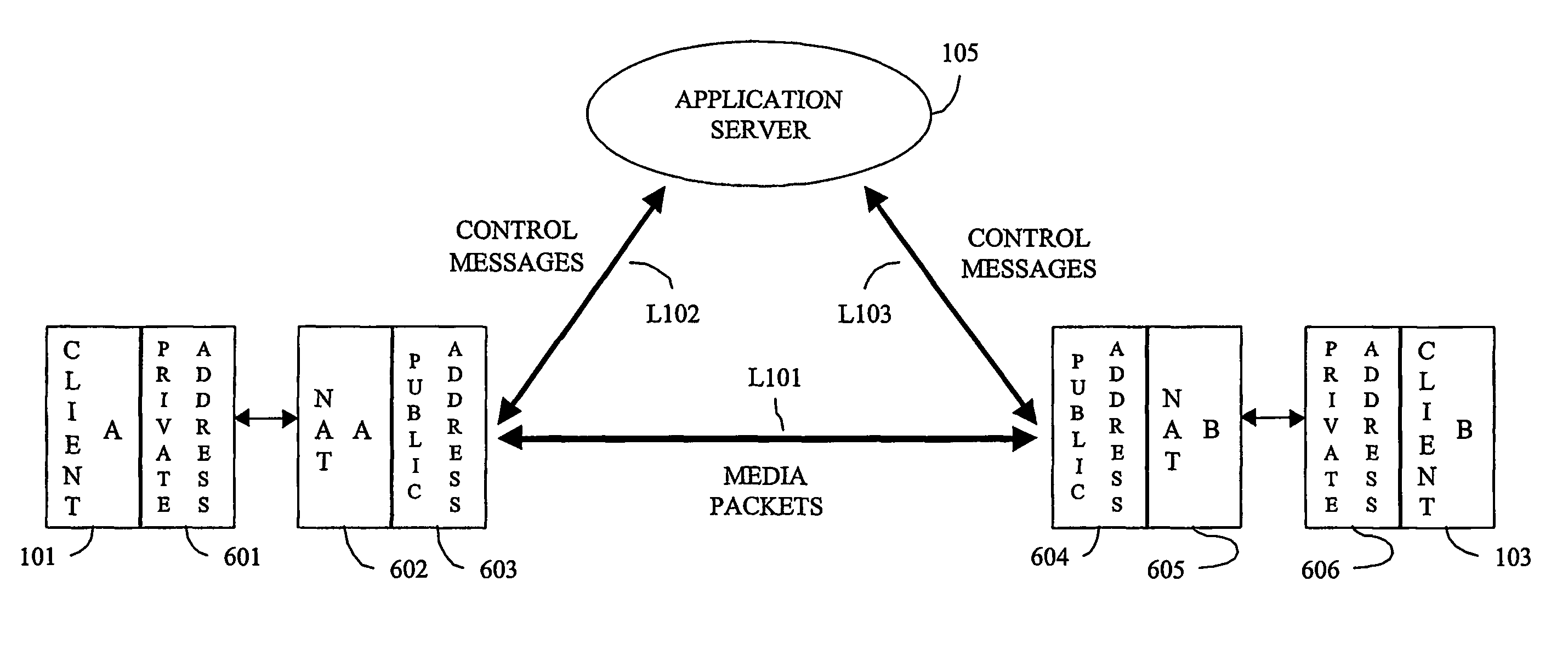
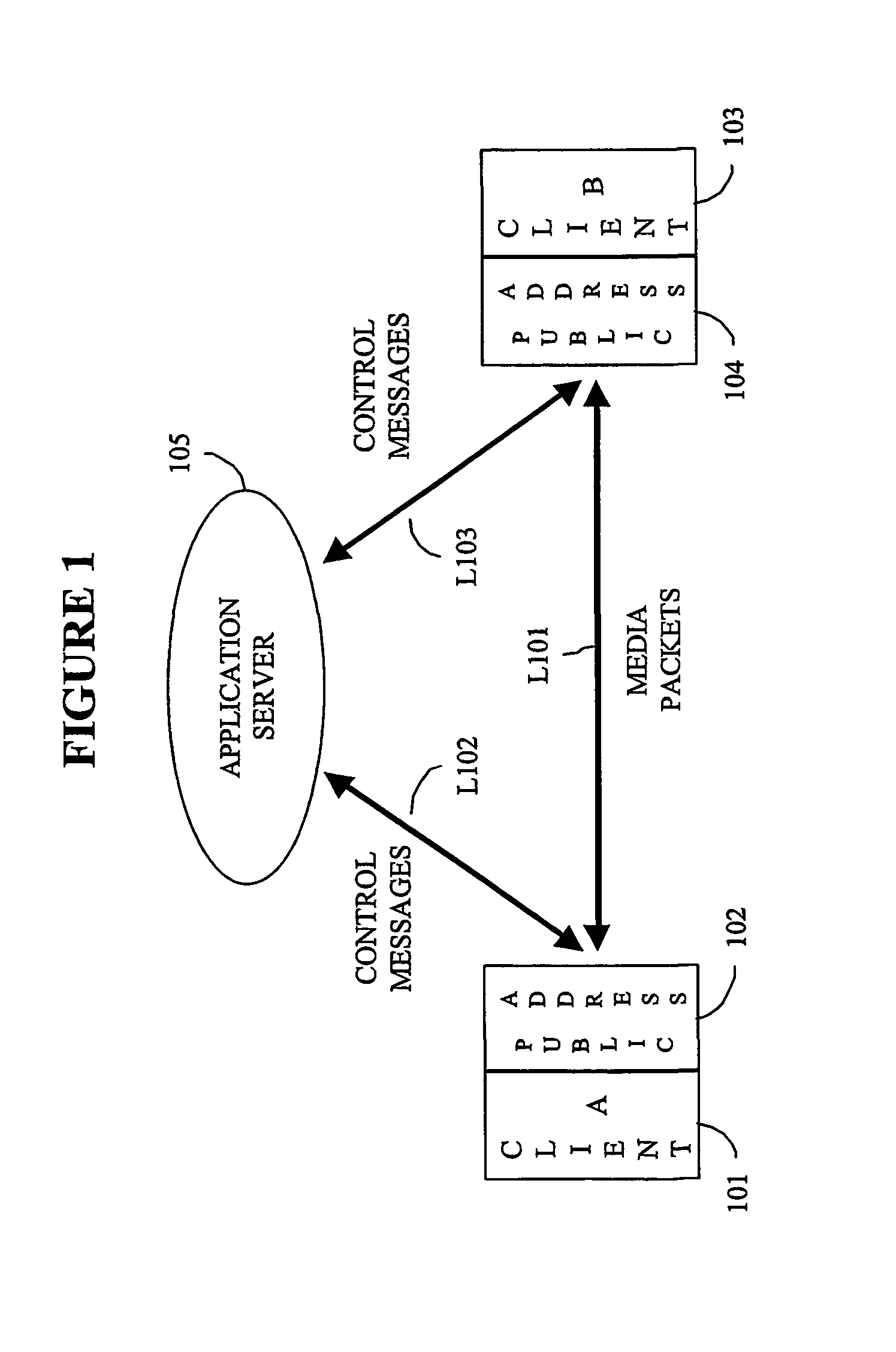
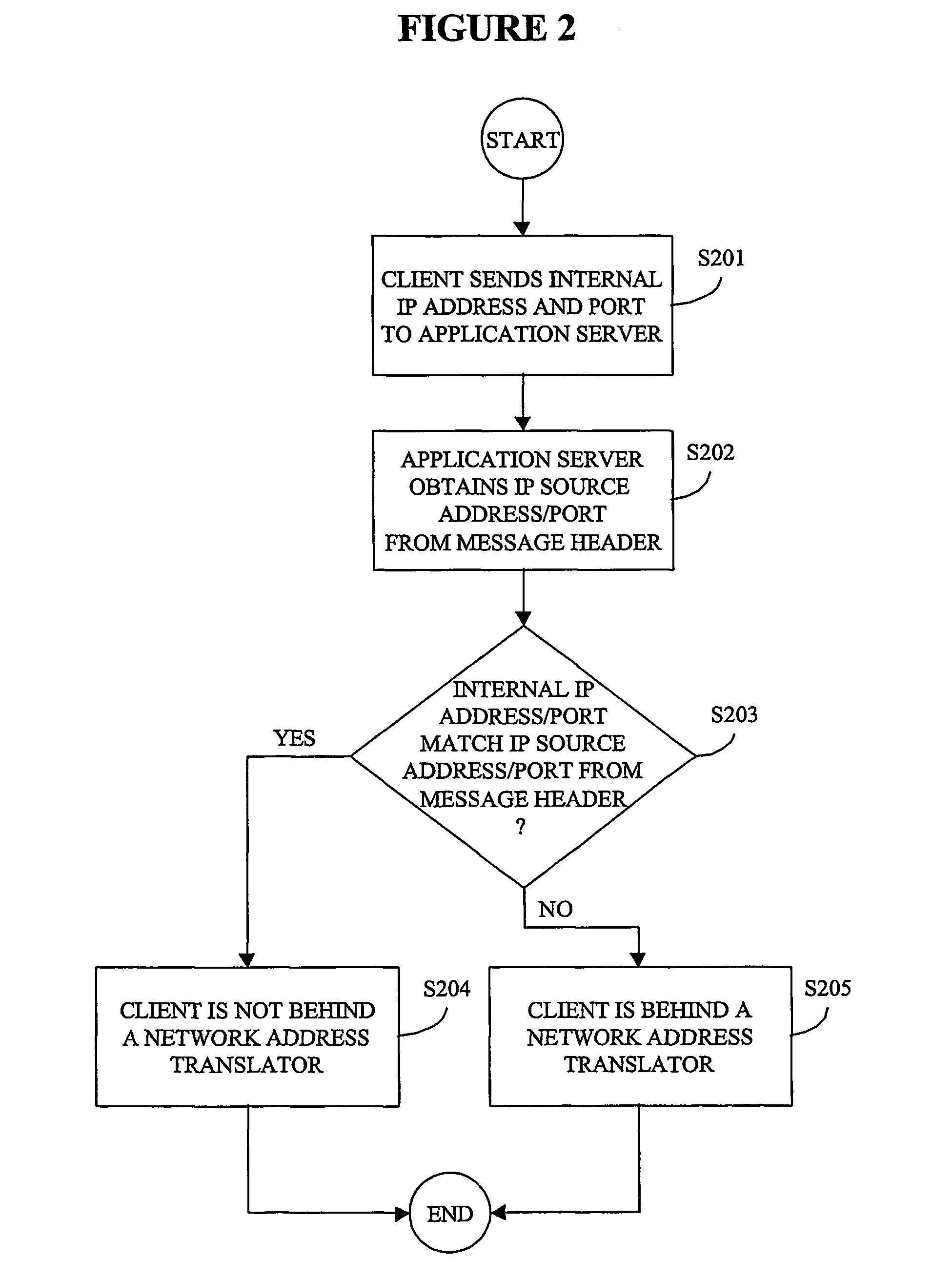
A system, method, and computer program product through which address resolution is performed for nodes (101, 103) of a network that are behind a network address translator (NAT). A determination is made upon the initiation of a communication session as to whether one or more of the nodes (101, 103) included in the session are behind a NAT. Based on the determination, information is exchanged (L102, L103) from an independent application server (105) to the nodes (101, 103) included in the session so as to resolve the addressing problems introduced by the NAT. The invention is applicable in applications including, but not limited to, IP telephony, and applications complying with the session initiation protocol (SIP).
Owner:NET2PHONE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com