Patents
Literature
175 results about "Scalable system" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Scalable system is the system whose performance improves after adding hardware proportional to the capacity added is called scalable system. An algorithm, design, networking protocol, program or other system is sad to scale if it is suitably efficient and practical when applied to large situations.
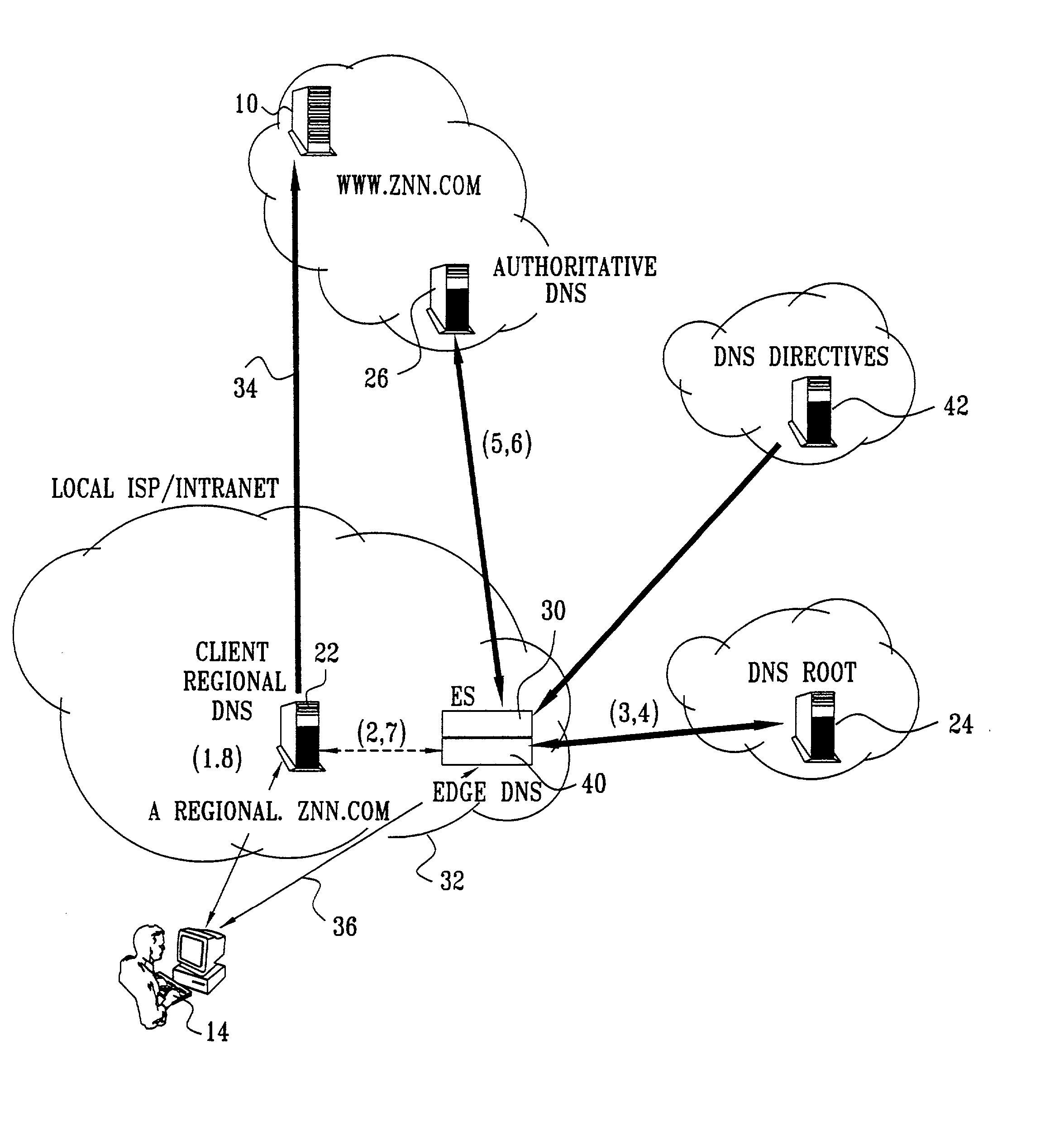
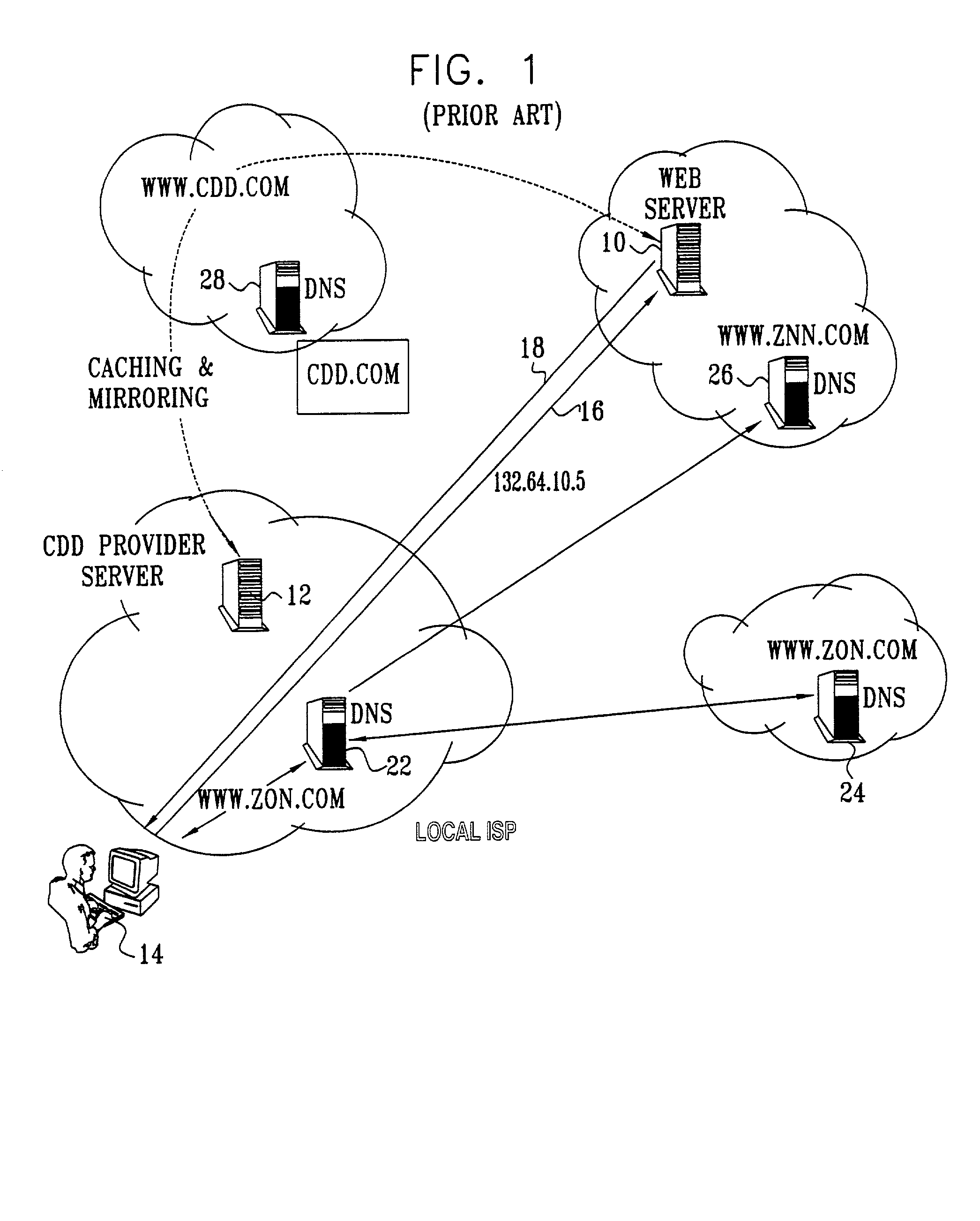
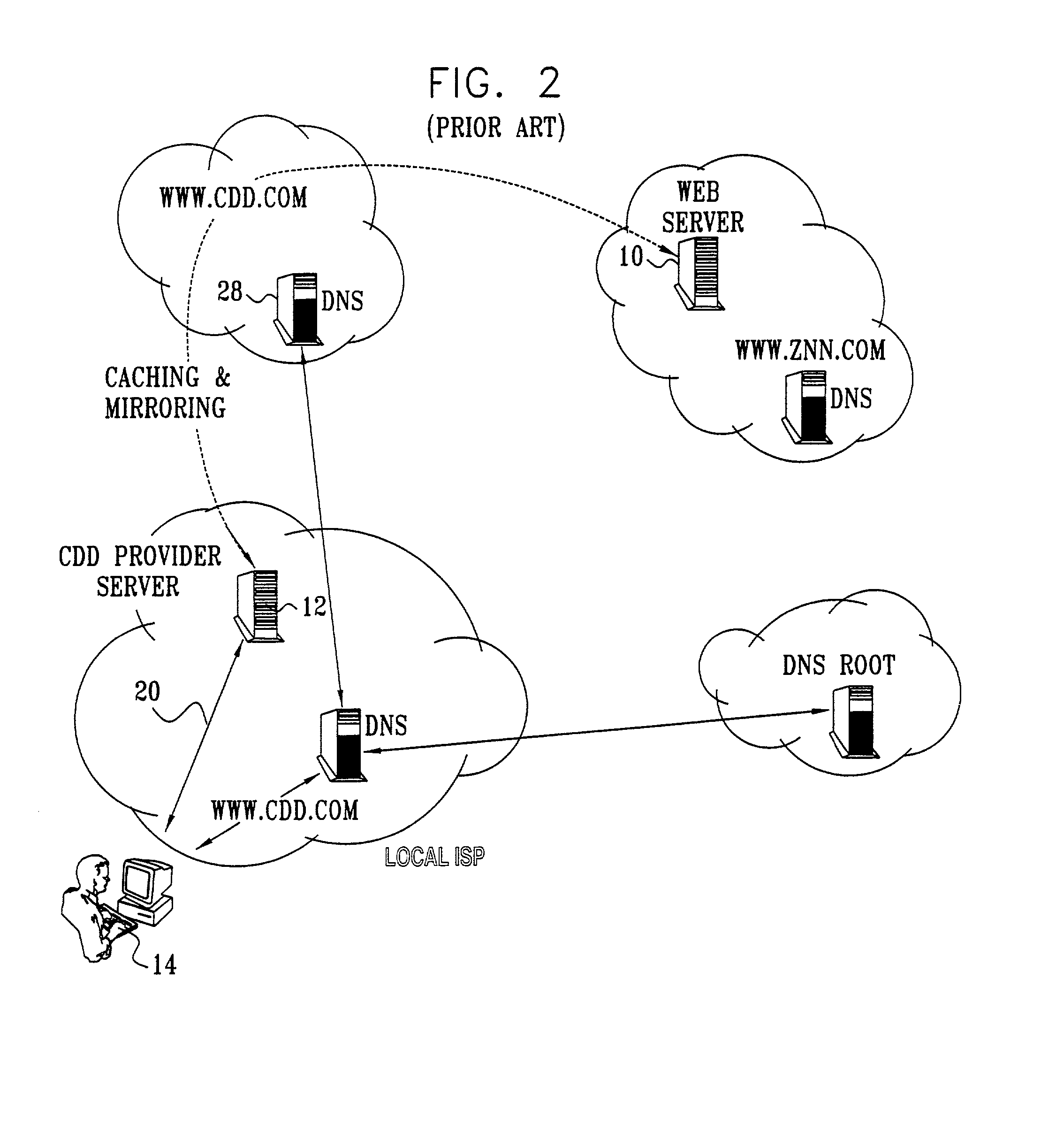
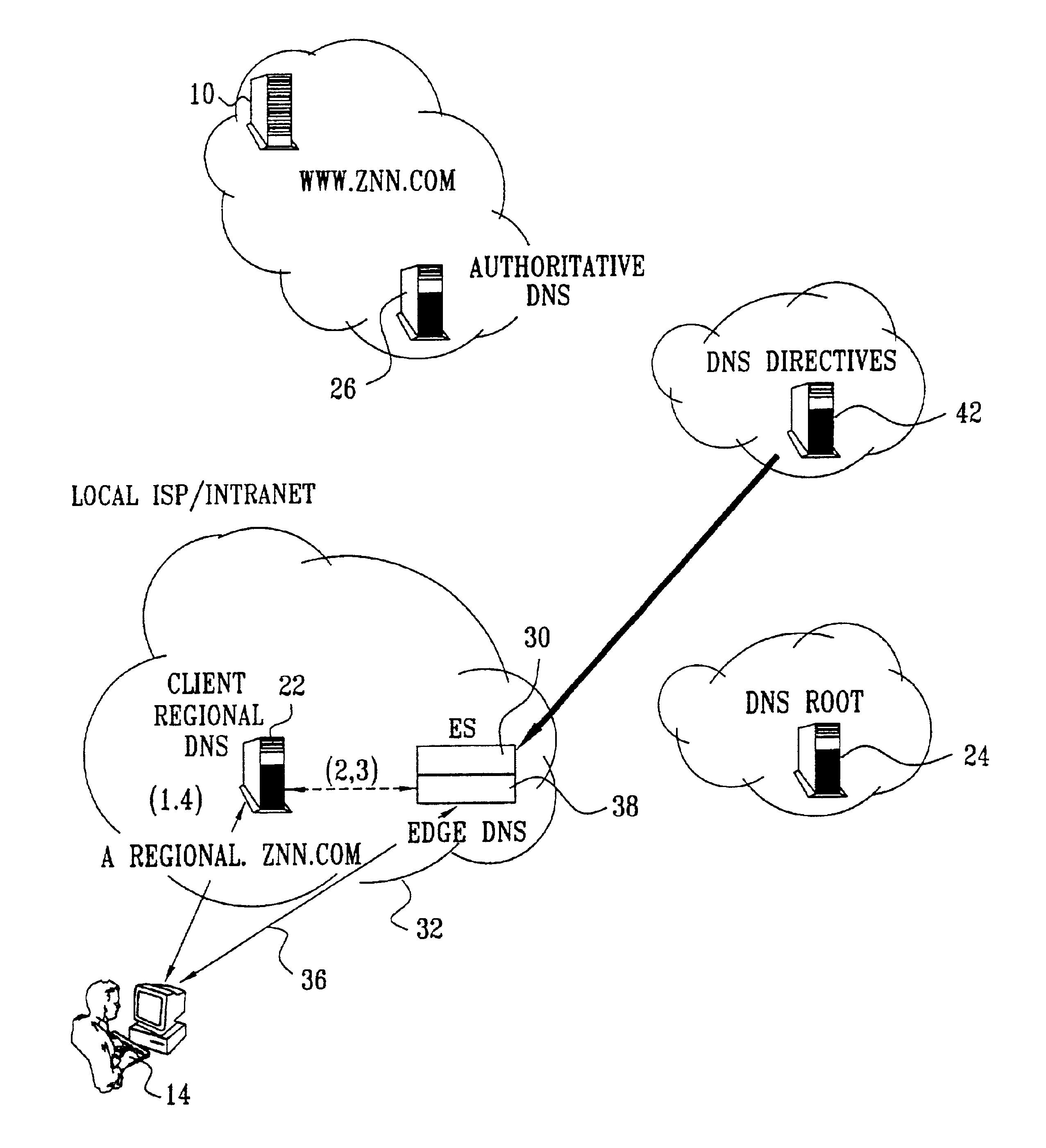
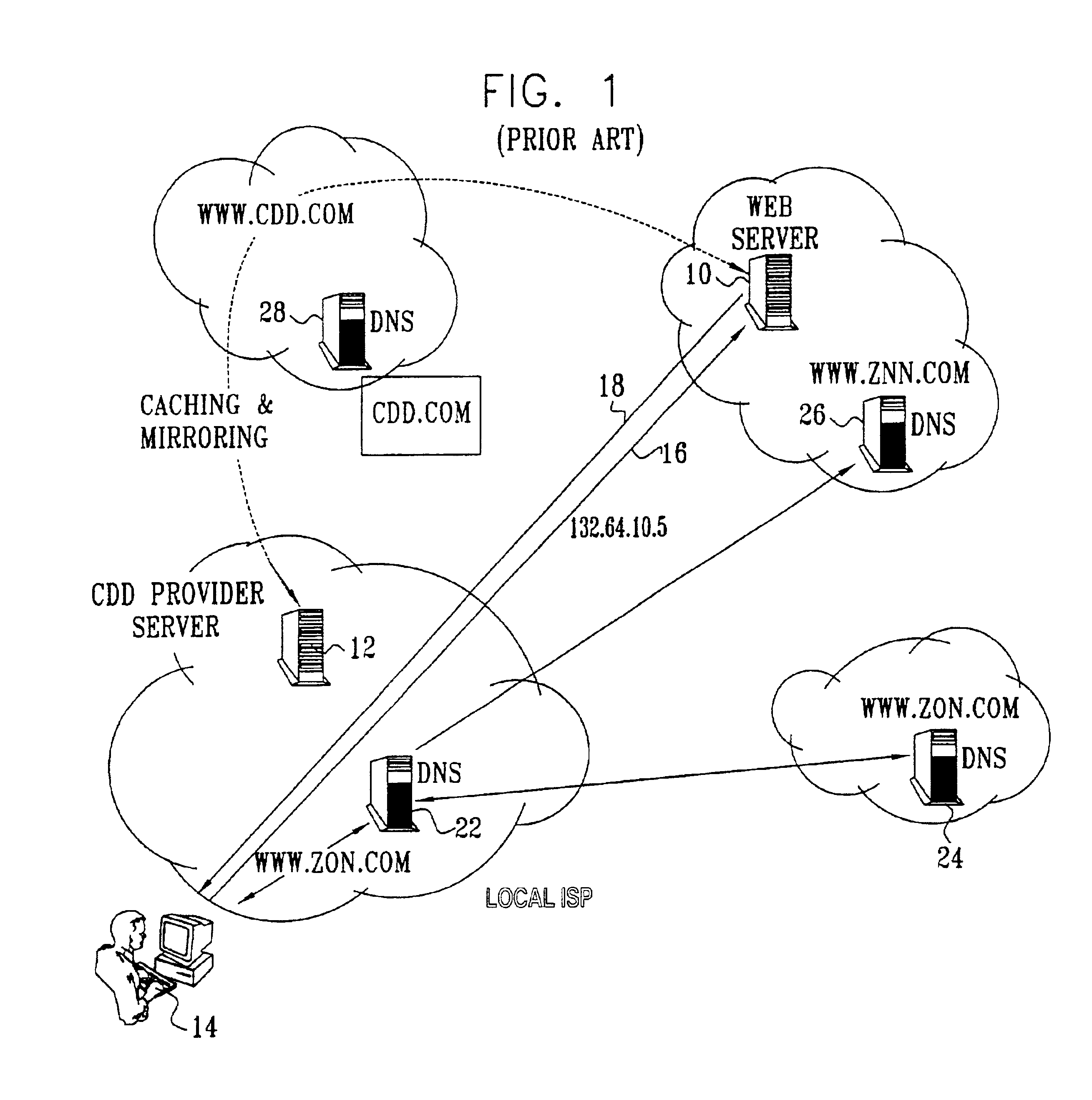
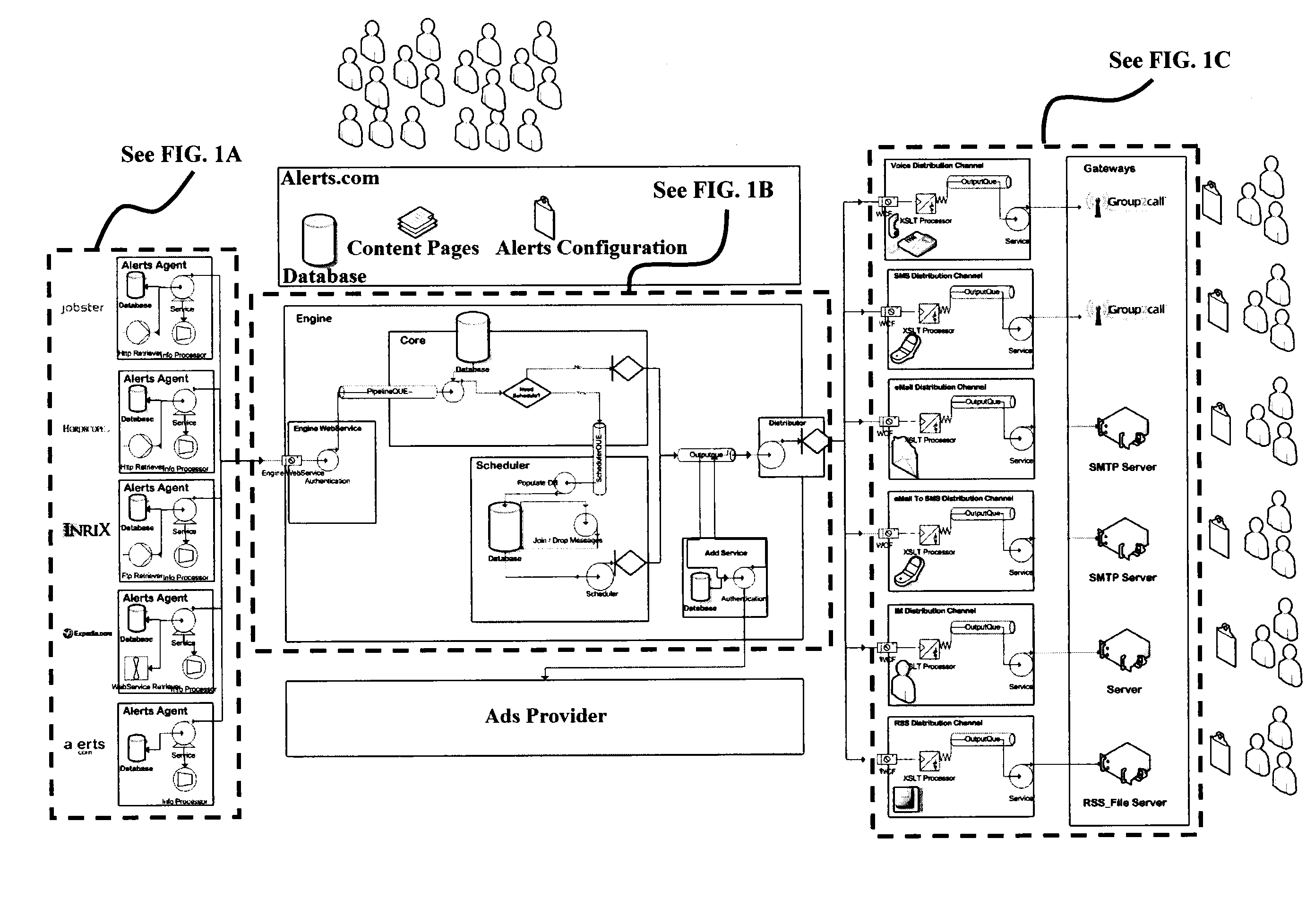
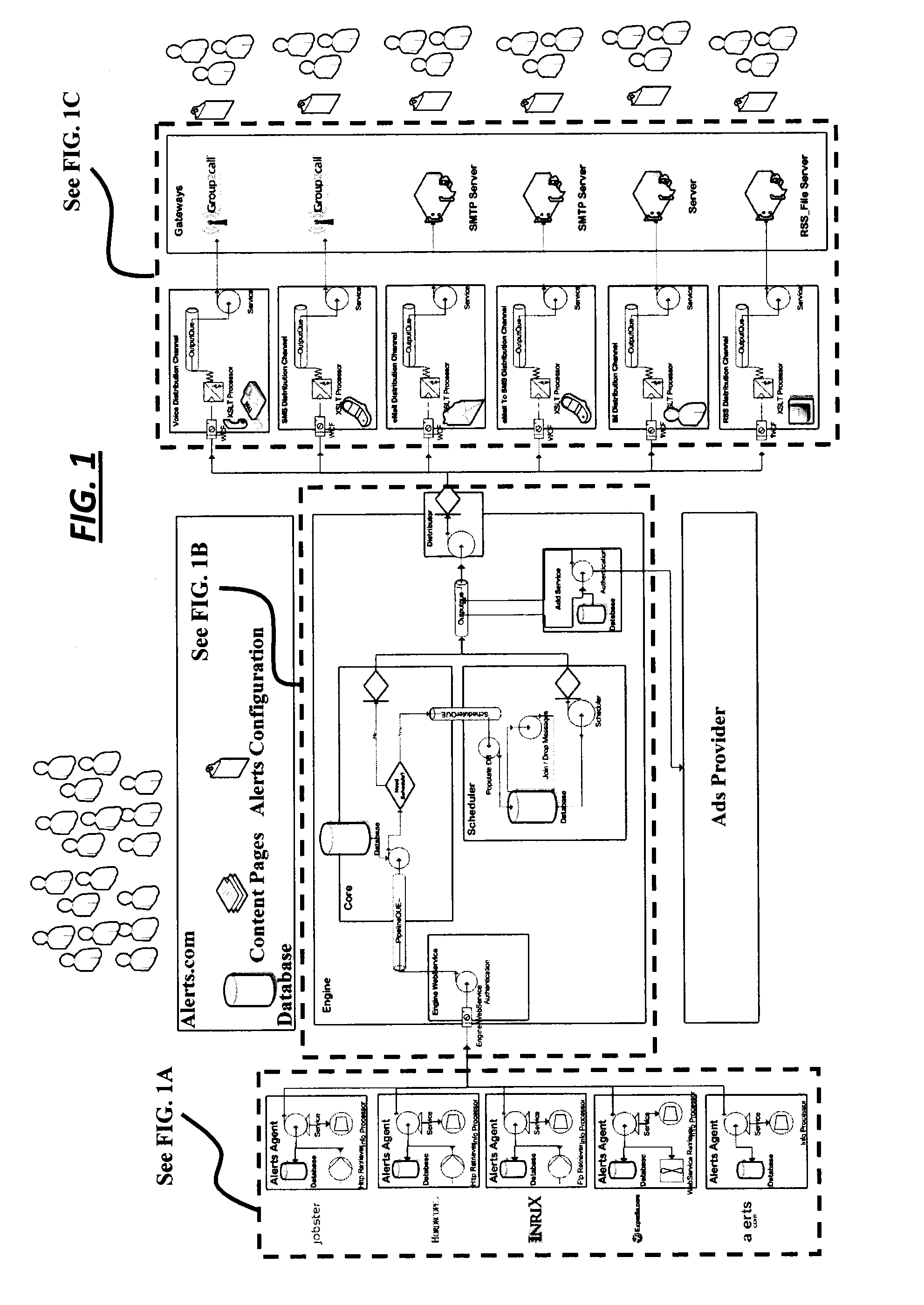
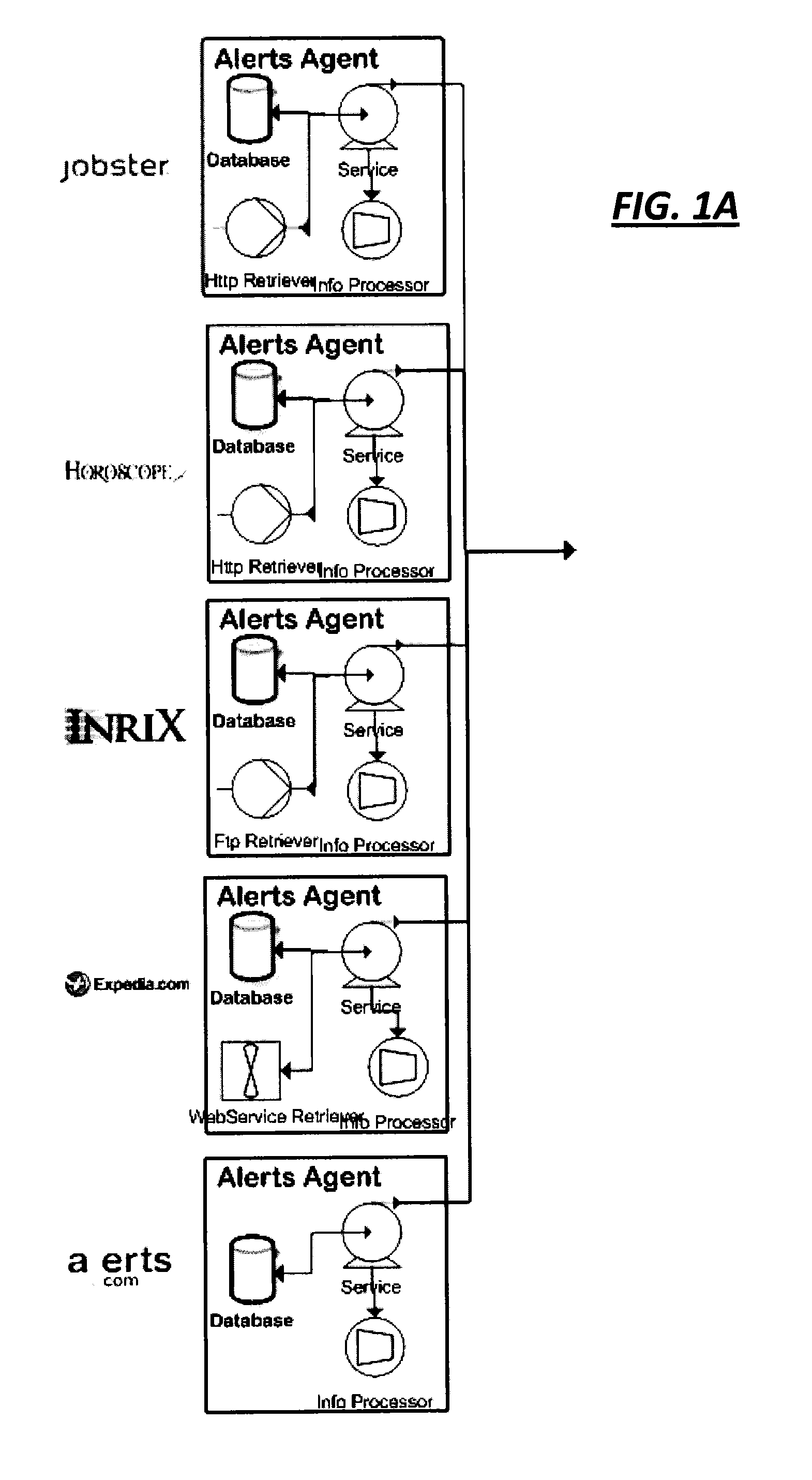
Differentiated content and application delivery via internet
InactiveUS20020010798A1Multiple digital computer combinationsWebsite content managementScalable systemEdge server
A technique for centralized and differentiated content and application delivery system allows content providers to directly control the delivery of content based on regional and temporal preferences, client identity and content priority. A scalable system is provided in an extensible framework for edge services, employing a combination of a flexible profile definition language and an open edge server architecture in order to add new and unforeseen services on demand. In one or more edge servers content providers are allocated dedicated resources, which are not affected by the demand or the delivery characteristics of other content providers. Each content provider can differentiate different local delivery resources within its global allocation. Since the per-site resources are guaranteed, intra-site differentiation can be guaranteed. Administrative resources are provided to dynamically adjust service policies of the edge servers.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Differentiated content and application delivery via internet
InactiveUS6976090B2Decentralized and differentiatedAdvanced technologyMultiple digital computer combinationsWebsite content managementScalable systemEdge server
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
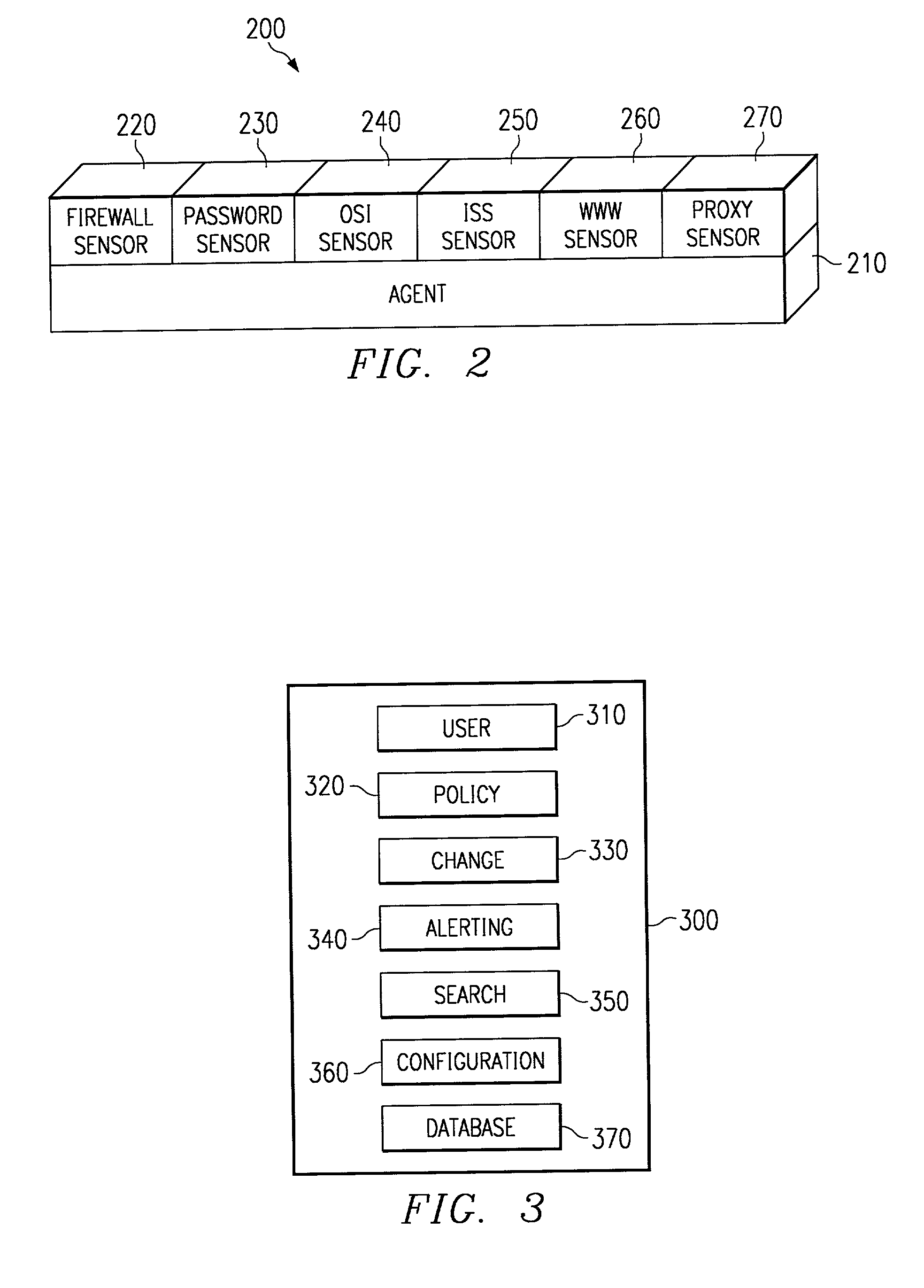
Scalable system for monitoring network system and components and methodology therefore
InactiveUS20020078382A1Memory loss protectionDigital computer detailsScalable systemSecurity software
The present invention is a security software methodology and system that takes an internal approach to mitigating security risks from authorized and unauthorized users. The security software system uses the methodology of monitoring, in great detail, any configuration changes made to information systems within a network. These systems and applications include web servers, firewalls, proxy servers, log servers, intrusion detection software systems, routers and any other device or application which can be considered a part of the enterprise information system infrastructure.
Owner:SECURITY & INTRUSION DETECTION RES LABS
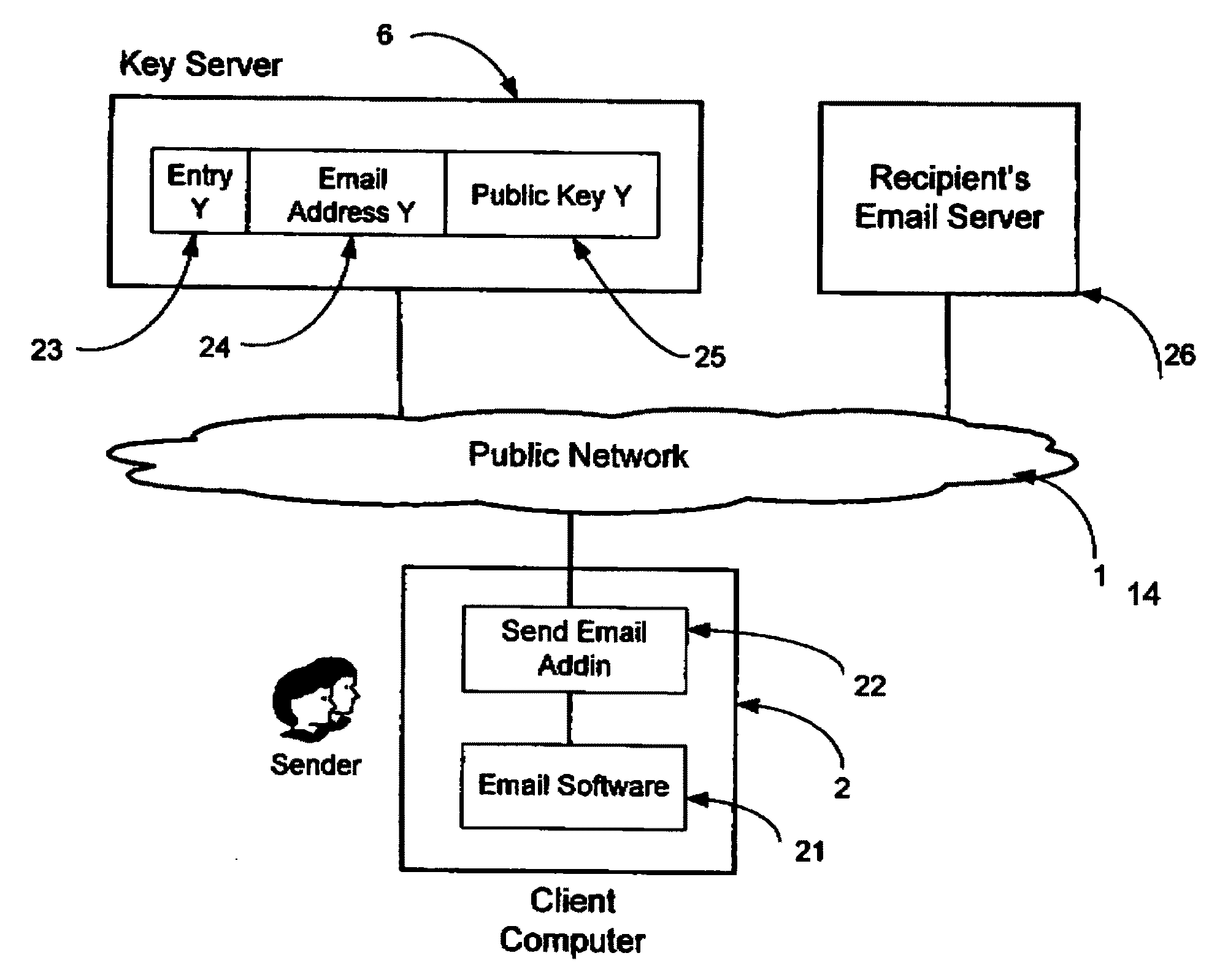
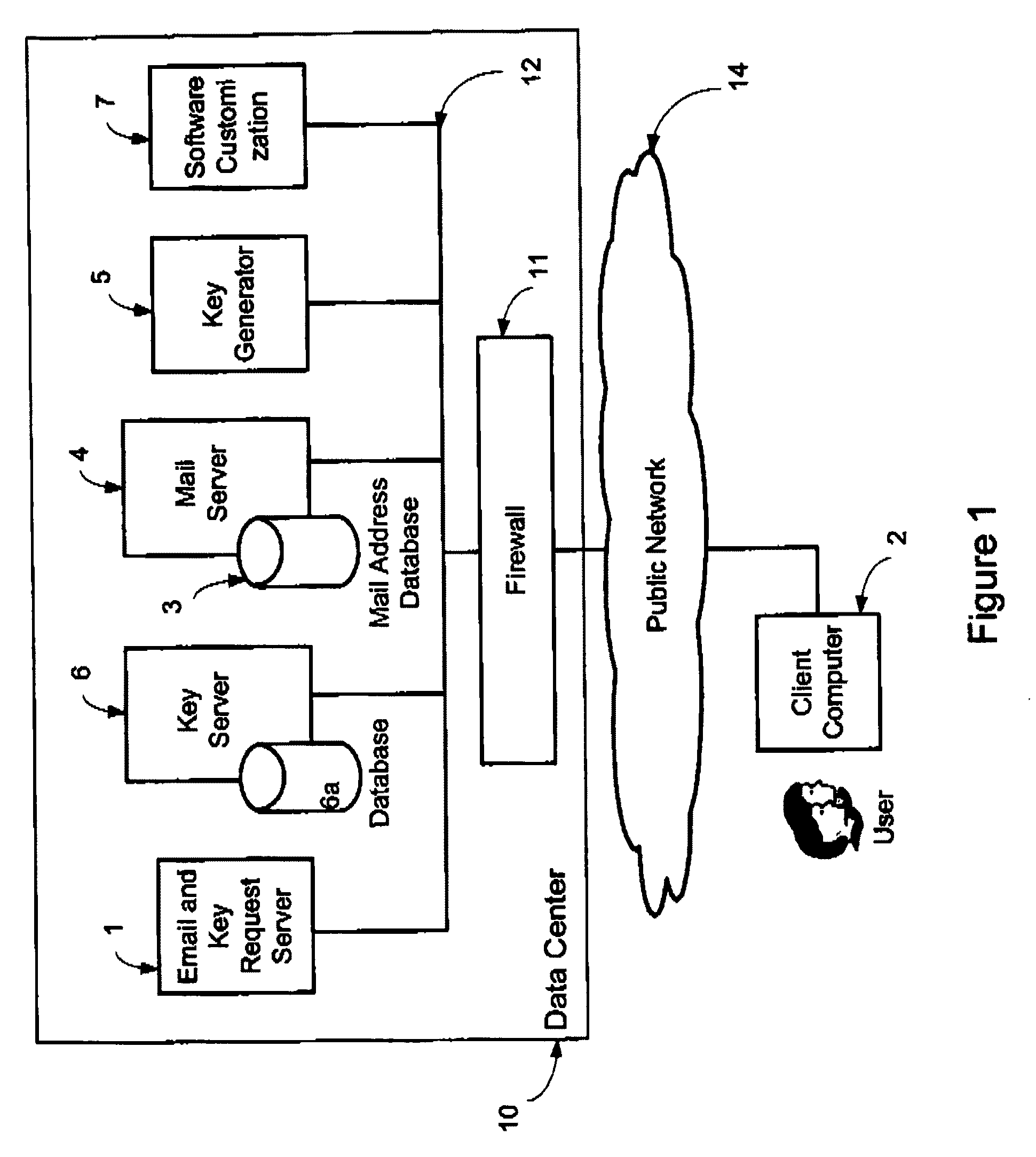
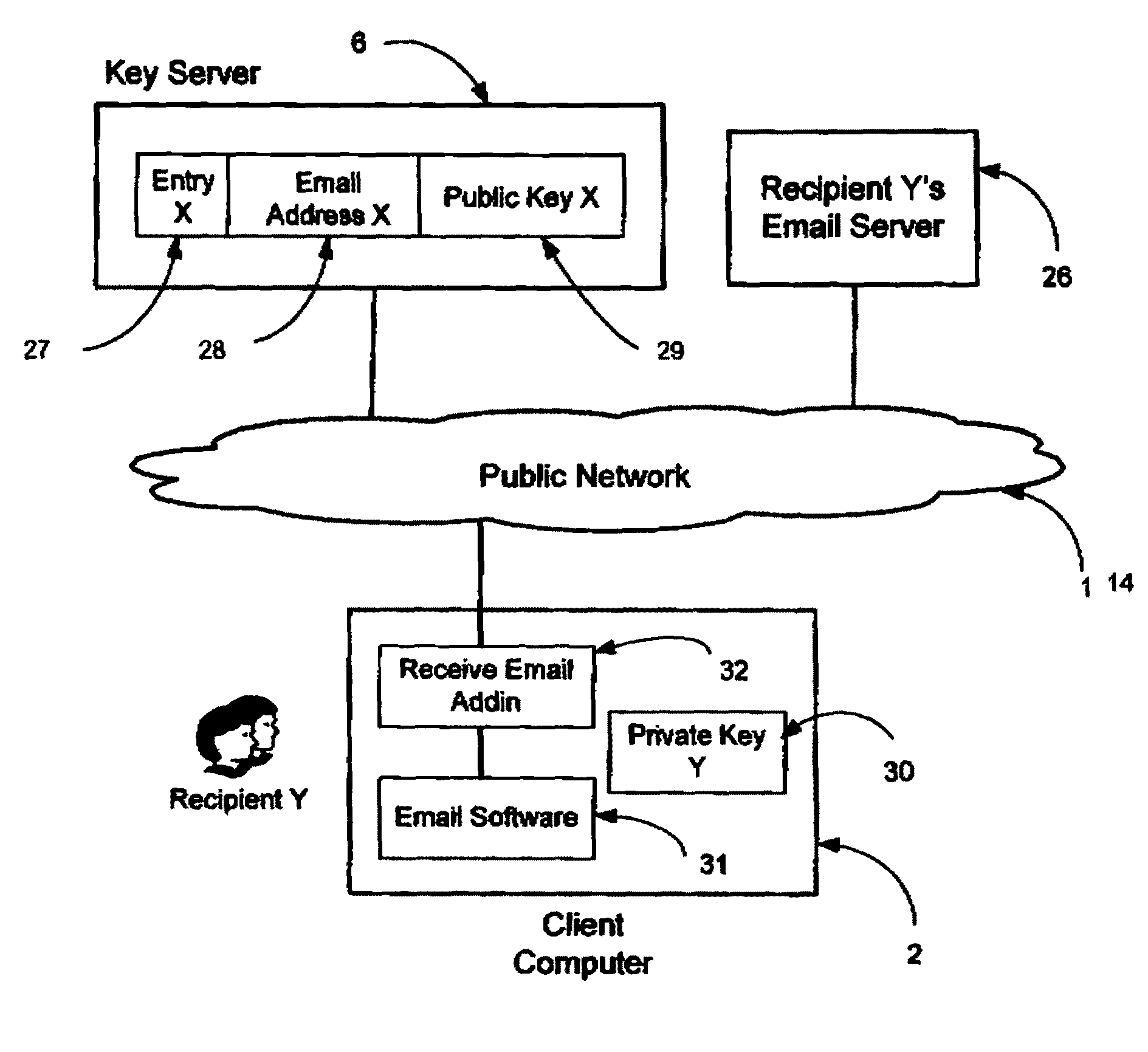
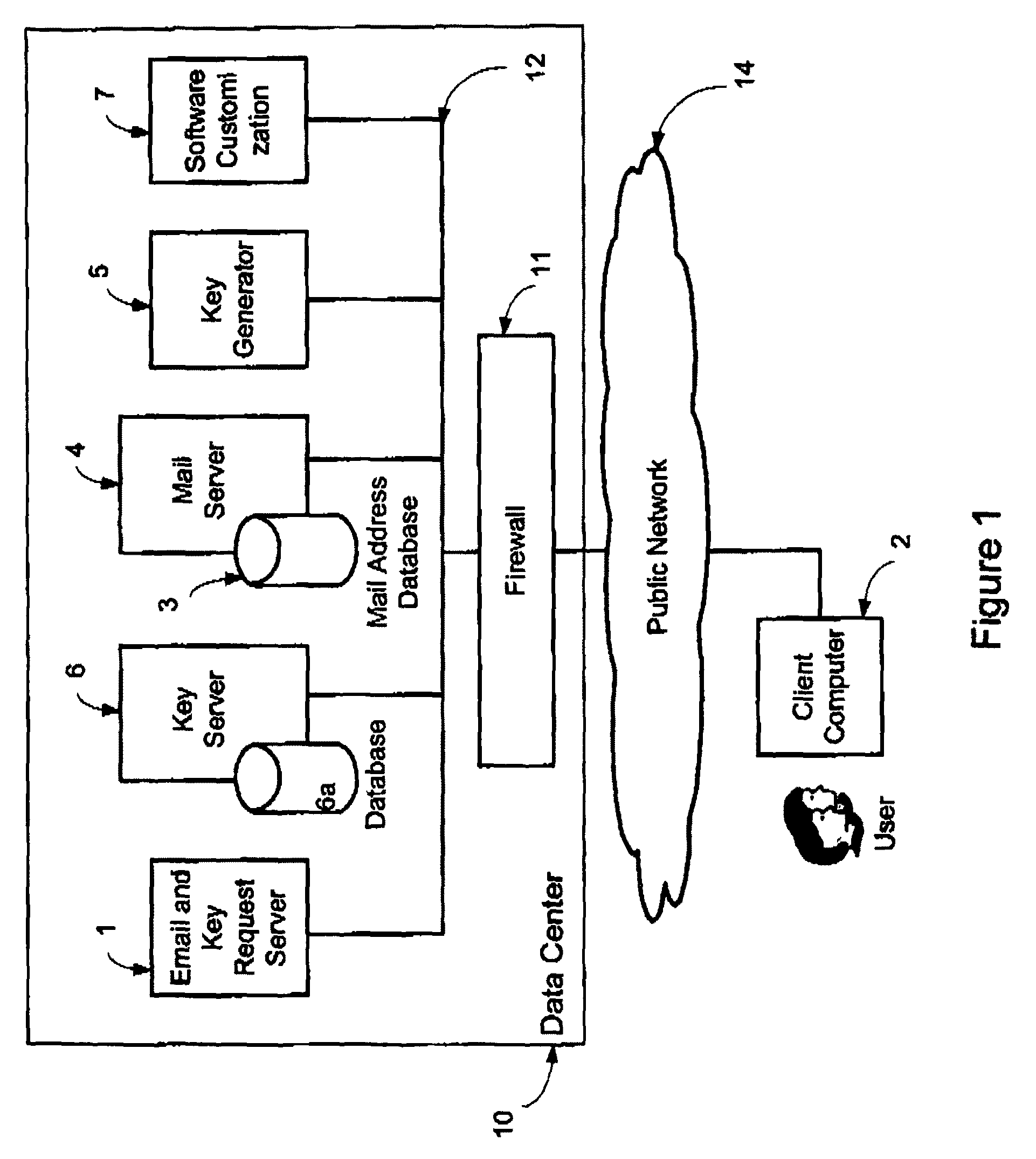
System and method for secure electronic communication services
InactiveUS20090198997A1Easy accessSecure transmissionKey distribution for secure communicationMultiple keys/algorithms usageScalable systemEmail address
A system, method and software module for secure electronic communication services, wherein a public key (25) of private-public-key pair (30,25) is associated with an email address (24), internet name or other registered unique identifier; the registered user of the unique identifier holds the private-key (30) securely, and the respective public-key (25) is made accessible on a key server (6) for look-up and retrieval by other users, for encryption of communications to be sent to the holder of the private-key, and optionally for message confidentiality, message integrity and authentication of sender and recipient, without requiring certificates. A distributed and scalable system is provided by a server network (600; 401, 501) for registration, key distribution and management preferably using a kDNS server hierarchy (601,602,603) or a key-DNS server hierarchy (701,702,) and associated protocols so that public-keys of recipients can be searched and retrieved over the internet based on the recipients email address or other unique identifier, thus facilitating secure communication between users in different network domains and organizations.
Owner:TOPOSIS CORP
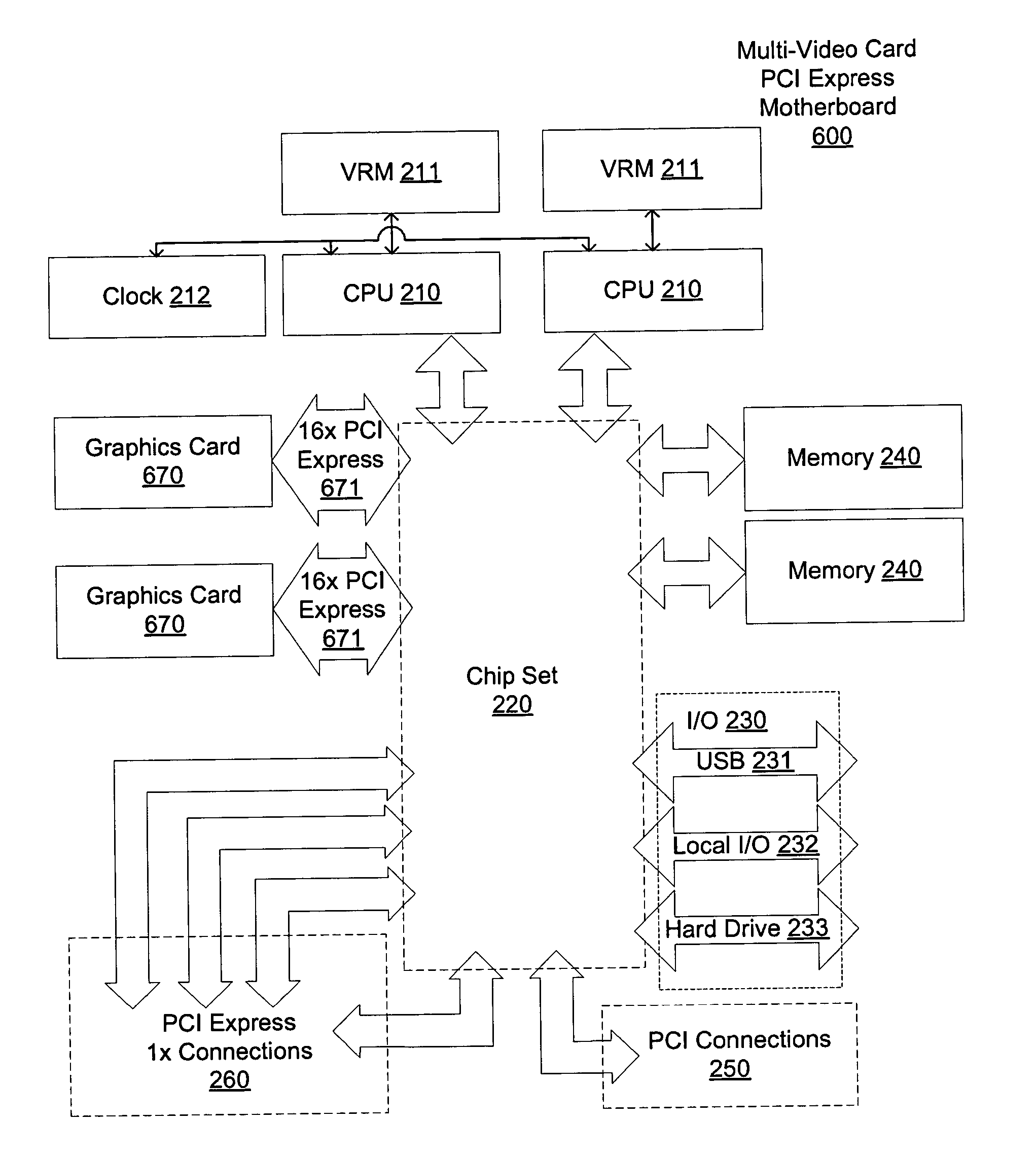
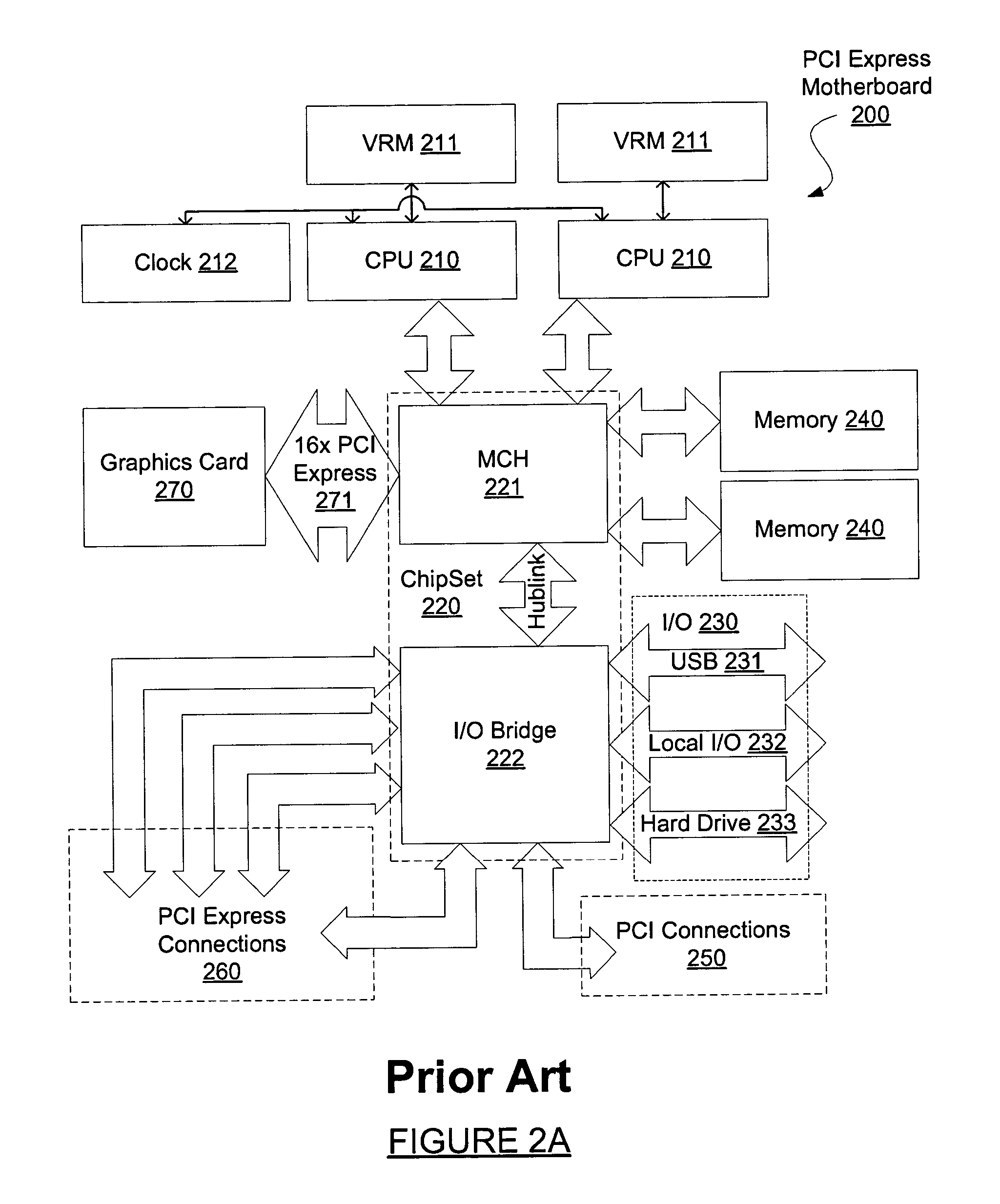
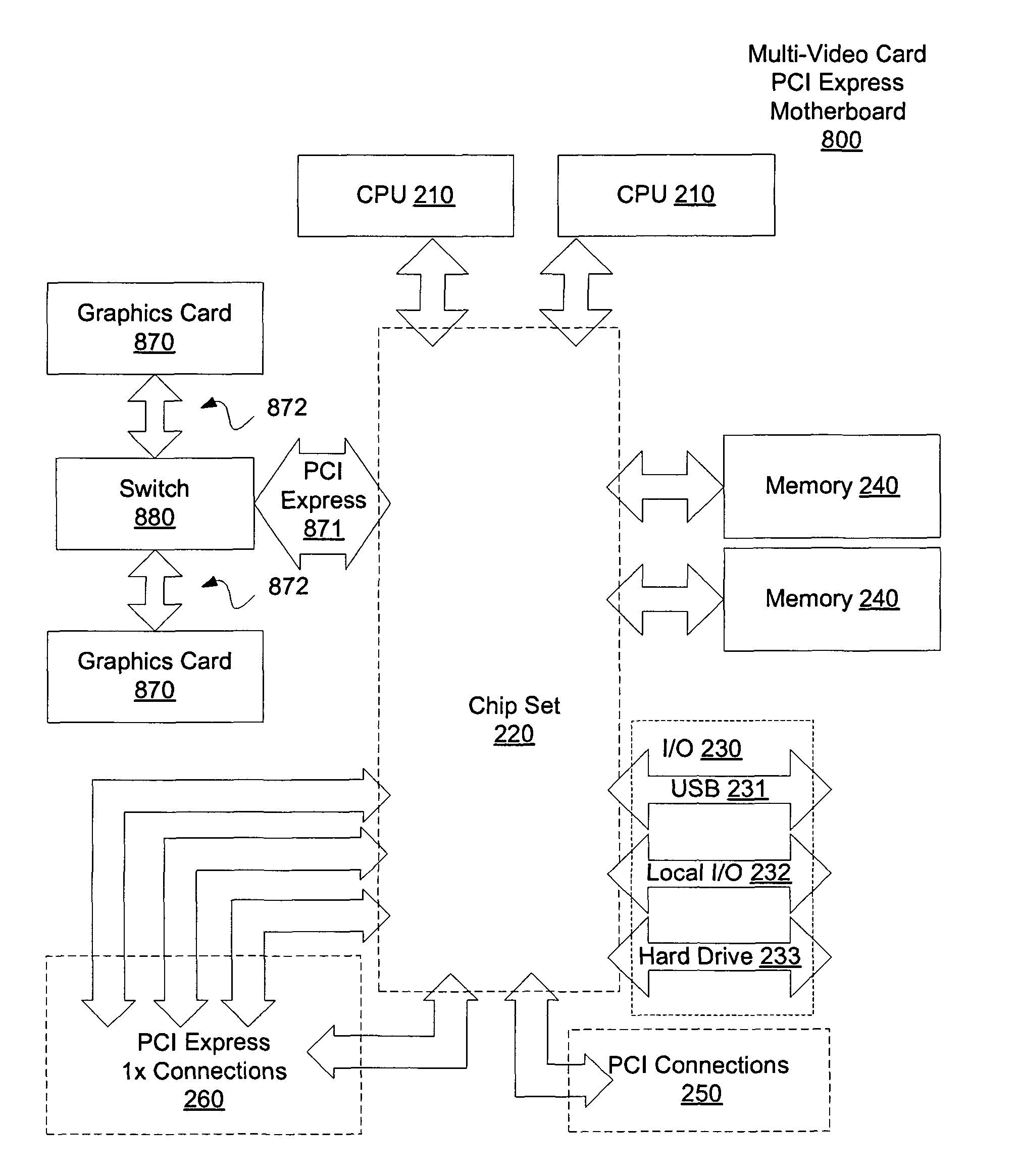
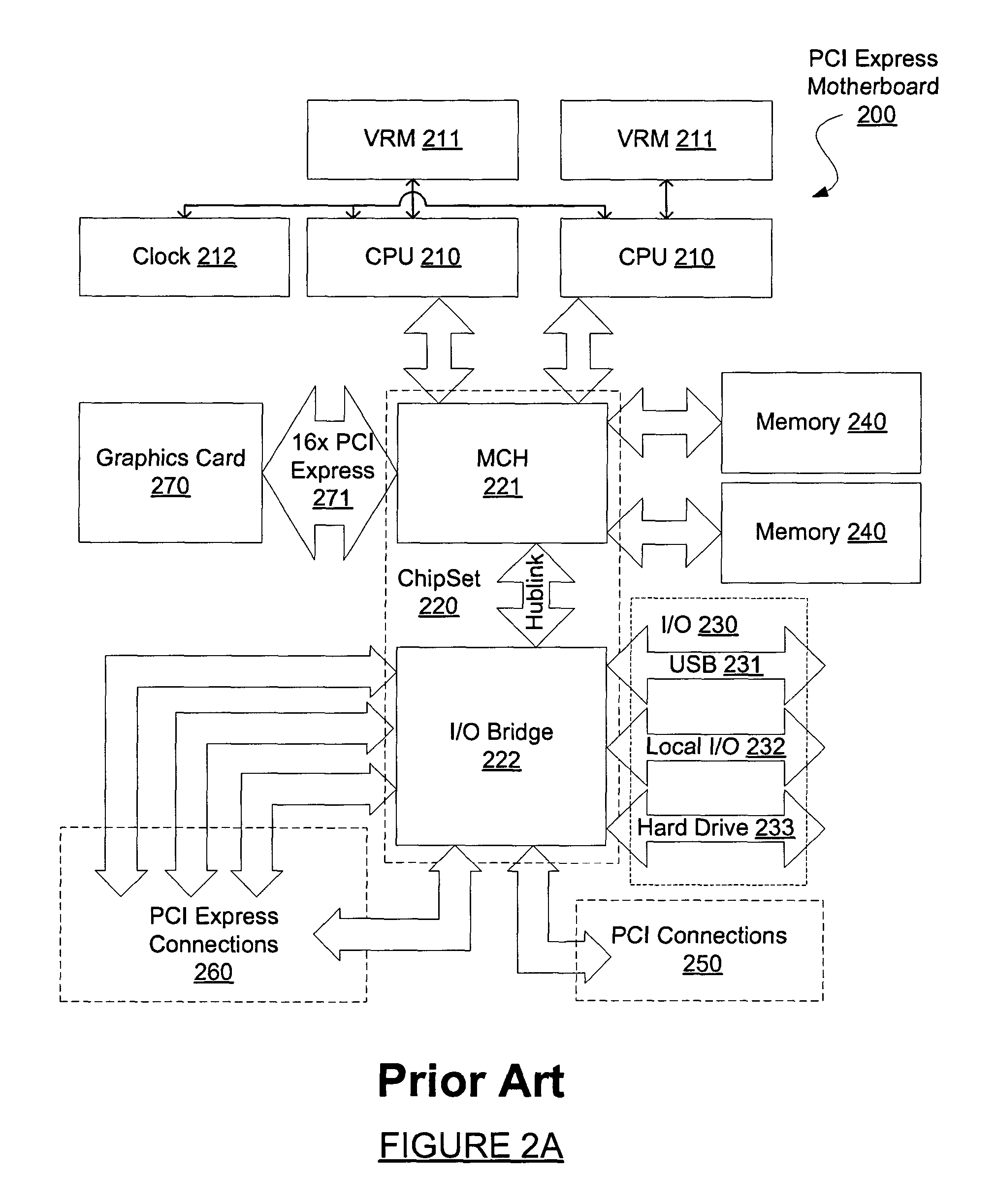
Motherboard for supporting multiple graphics cards
ActiveUS20050088445A1Cathode-ray tube indicatorsMultiple digital computer combinationsGraphicsScalable system
The present invention provides a motherboard that uses a high-speed, scalable system bus such as PCI Express® to support two or more high bandwidth graphics slots, each capable of supporting an off-the-shelf video controller. The lanes from the motherboard chipset may be directly routed to two or more graphics slots. For instance, the chipset may route (1) thirty-two lanes into two ×16 graphics slots; (2) twenty-four lanes into one ×16 graphics slot and one ×8 graphics slot (the ×8 slot using the same physical connector as a ×16 graphics slot but with only eight active lanes); or (3) sixteen lanes into two ×8 graphics slots (again, physically similar to a ×16 graphics slot but with only eight active lanes). Alternatively, a switch can convert sixteen lanes coming from the chipset root complex into two ×16 links that connect to two ×16 graphics slots. Each and every embodiment of the present invention is agnostic to a specific chipset.
Owner:DELL MARKETING
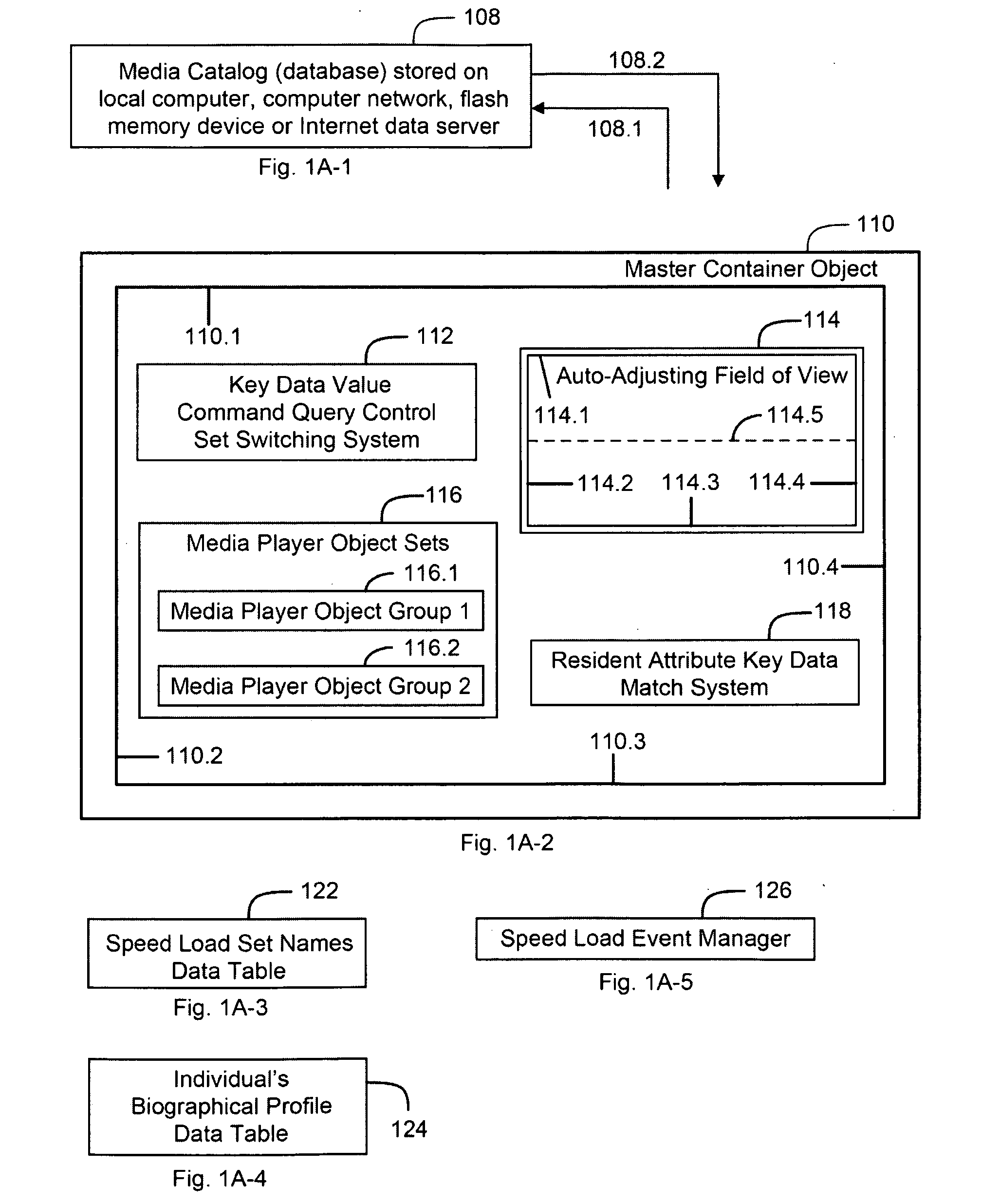
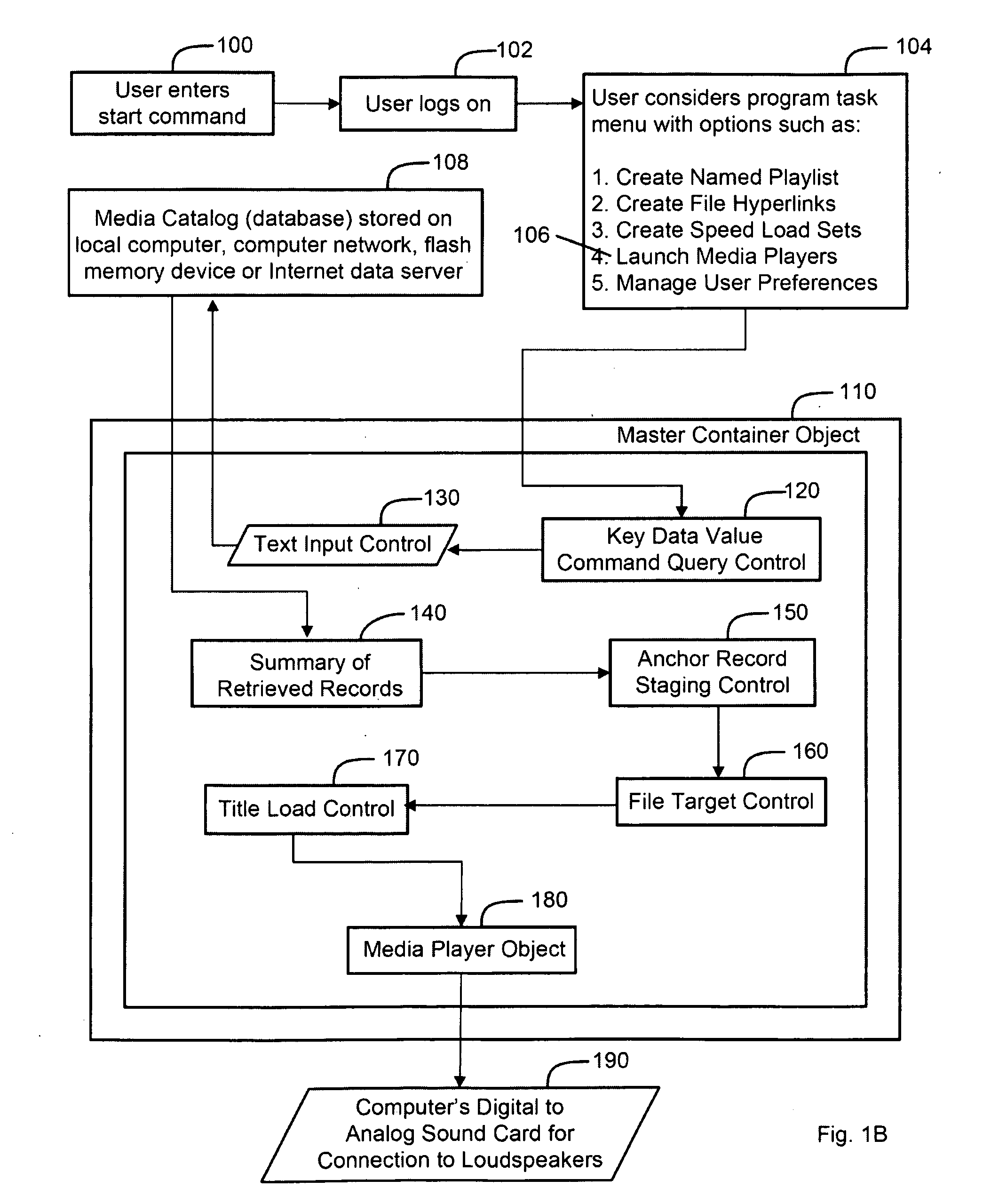
Scalable system and method for an integrated digital media catalog, management and reproduction system
InactiveUS20090177301A1Reduce stepsEfficient managementRecord information storageSpecial data processing applicationsScalable systemVisually guided
A system and method for creating an integrated digital media management and reproduction device comprised of a database with key data values for a plurality of records, and a module with search controls that include sets of compound parallel attribute queries that can execute instructions for a data category, and concurrently retrieve and display records across a plurality of related categories—thereby revealing the associations between discrete records. The invention also has a plurality of software instantiated media players which, through instructions managed by a “master container” design, function as if they were dynamically aware of user actions and the quantifiable states of each other player object—and respond according to logic rules, visually guiding event workflow. The system has a memory module for storing query information, a processor configured to retrieve data, a display unit for retrieved data and a digital-to-analog converter for providing capability for connection to loudspeakers.
Owner:CODENTITY
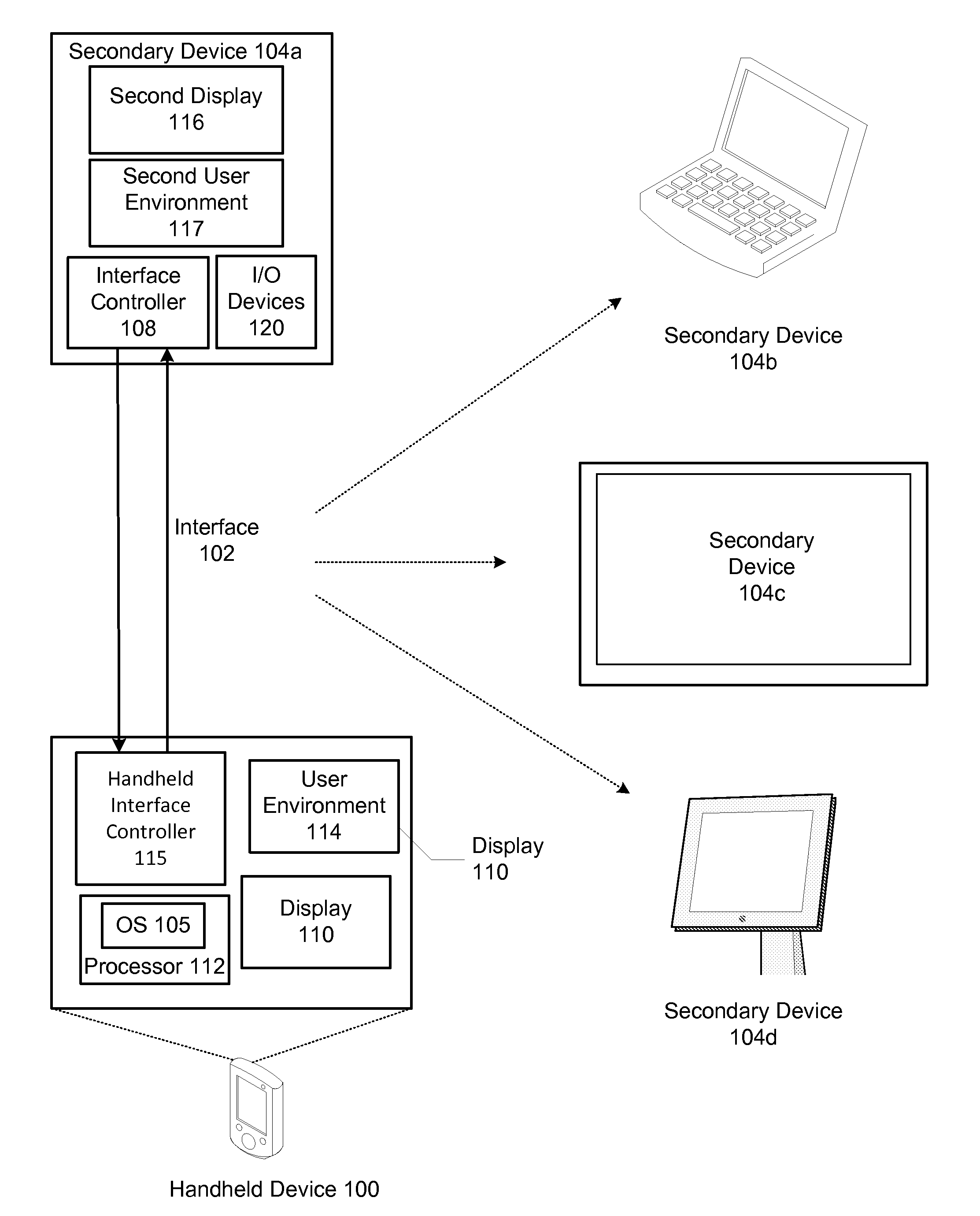
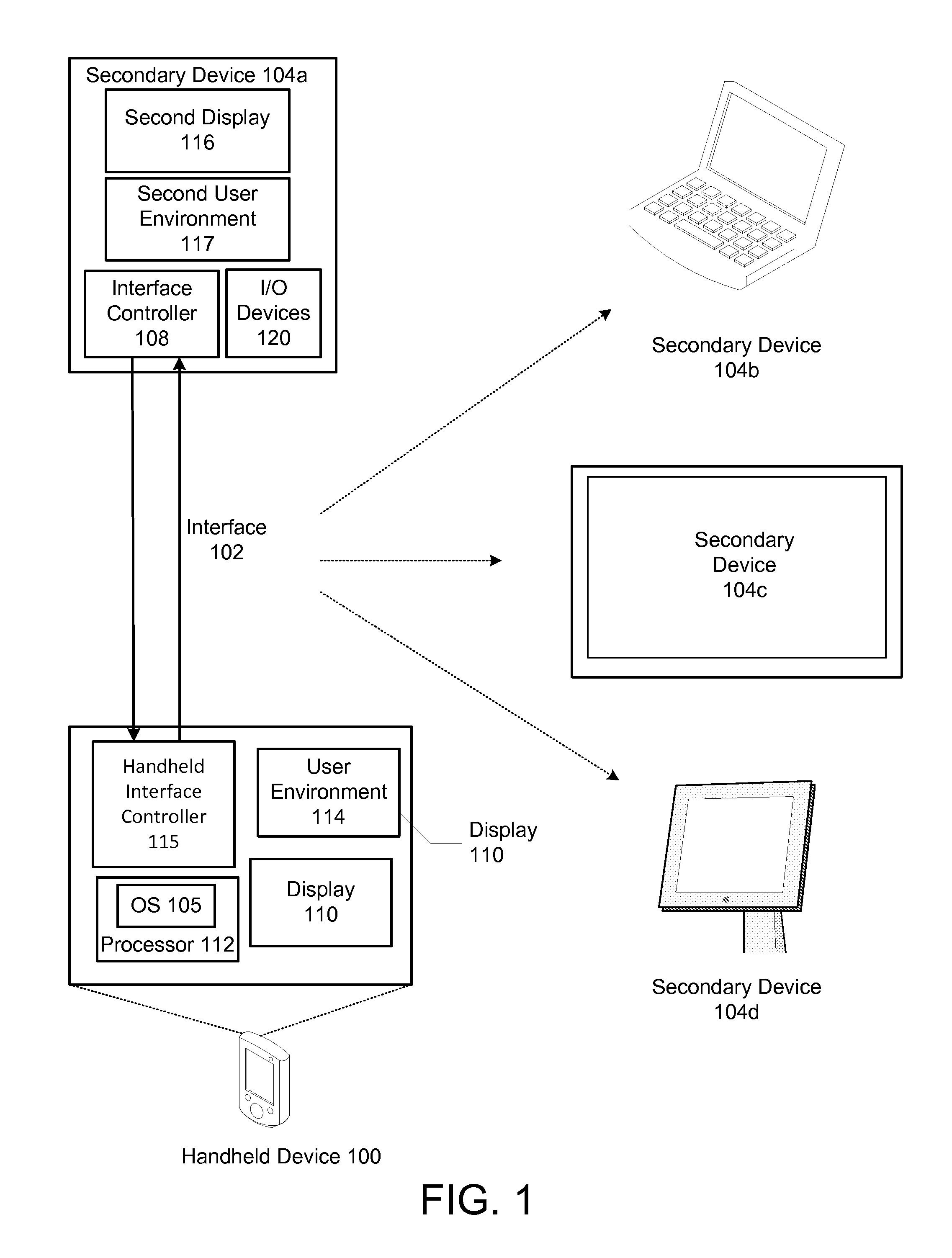
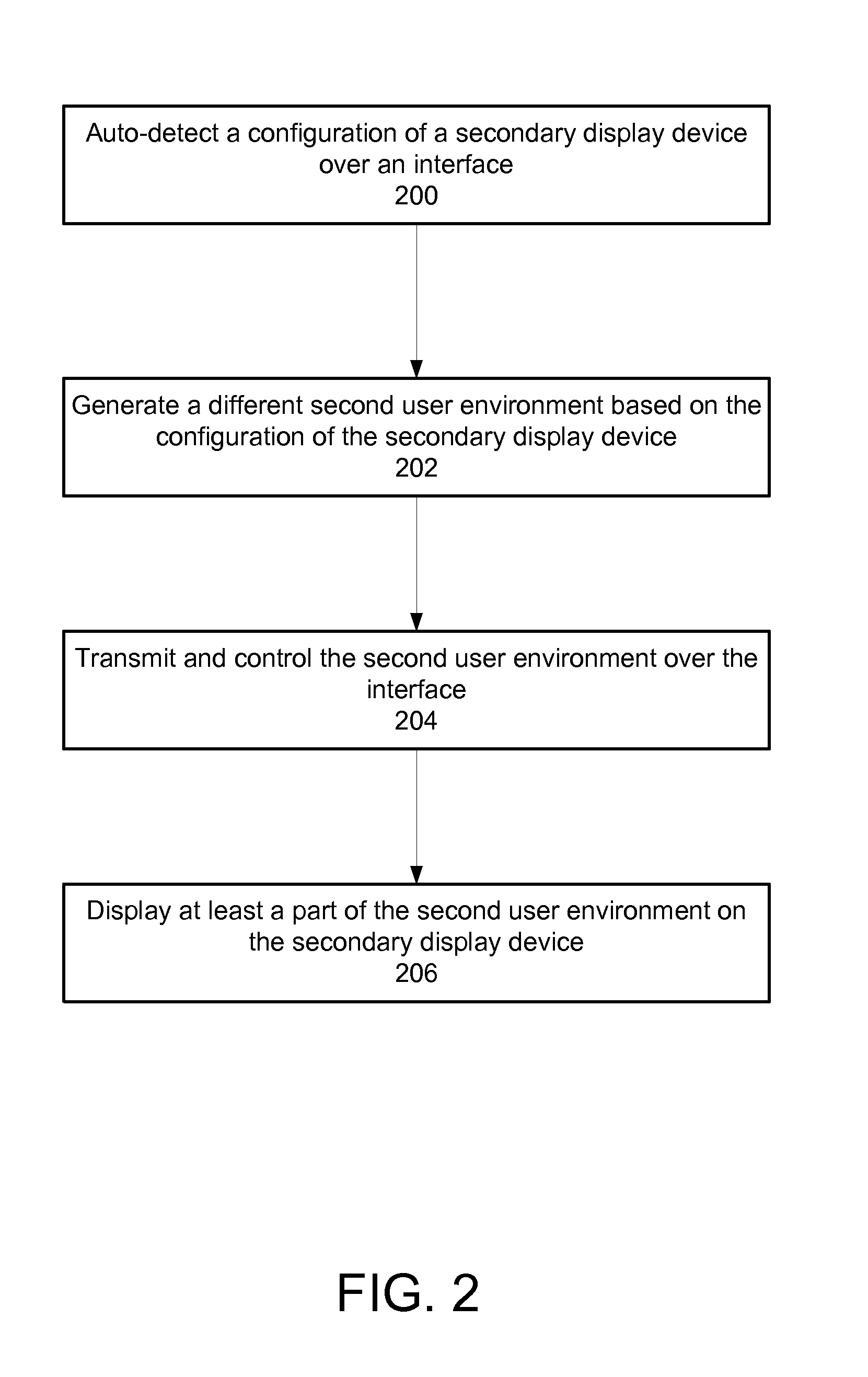
Expandable system architecture comprising a handheld computer device that dynamically generates different user environments with secondary devices with displays of various form factors
InactiveUS20100064228A1Input/output for user-computer interactionStatic indicating devicesScalable systemGraphics
An expandable system architecture comprising a self-configuring handheld device that dynamically generates different user environments with secondary devices with displays of various form factors is described. In one embodiment, the handheld device includes an operating system, a user environment, which includes a graphical user interface generated by the operating system, and a display that displays at least a portion of the user environment. The handheld device also has an interface that communicates with a secondary device with a second display, wherein the operating system enables a different second user environment, which in one embodiment includes a different second graphical user interface, that is transmitted across the interface for display at least partially on the second display based upon a configuration of the secondary device.
Owner:HANDHELD VENTURES
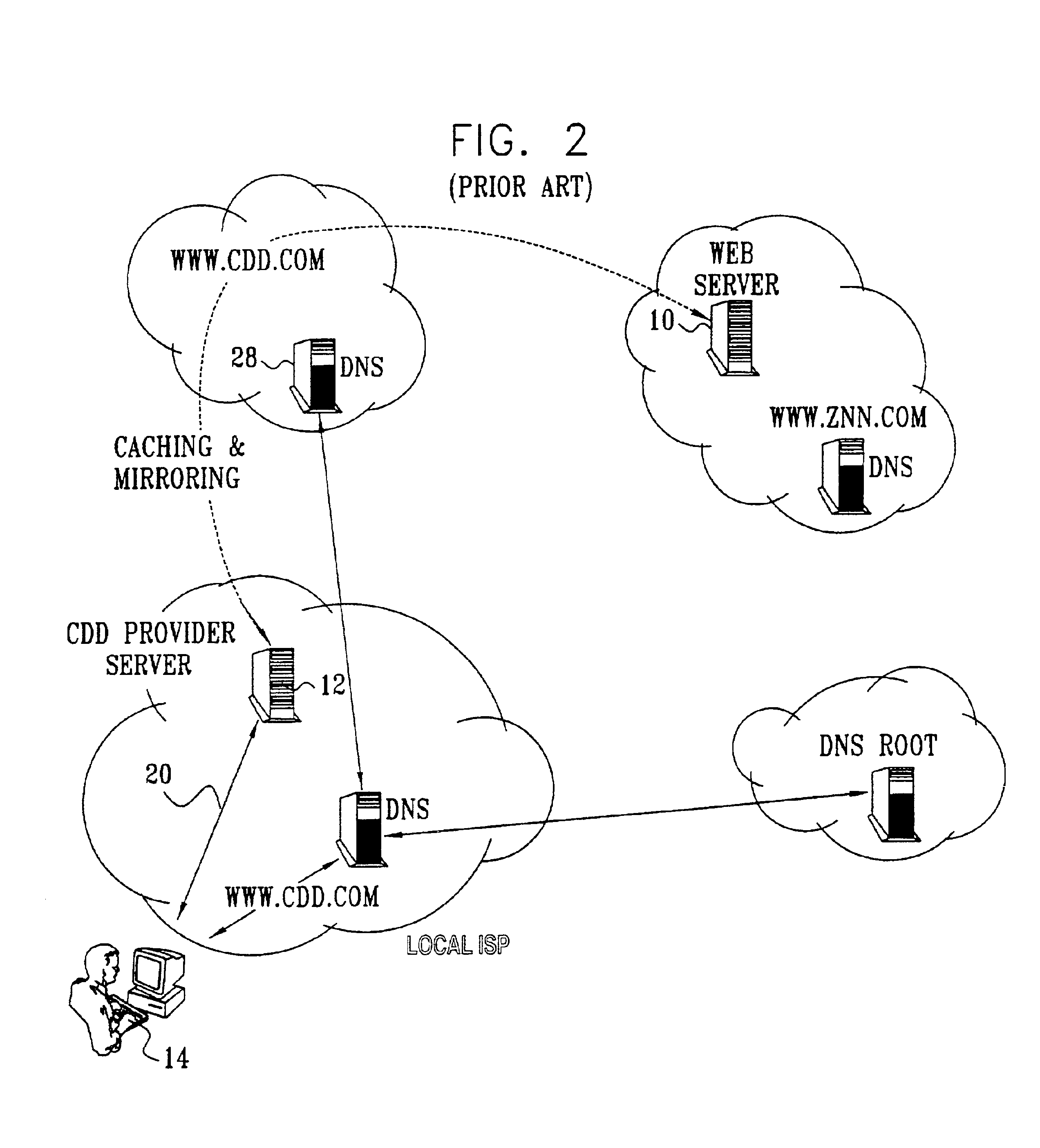
System and method for locating a closest server in response to a client domain name request
InactiveUS7020698B2Without overhead costSuitable for collectionMultiprogramming arrangementsMultiple digital computer combinationsScalable systemDomain name
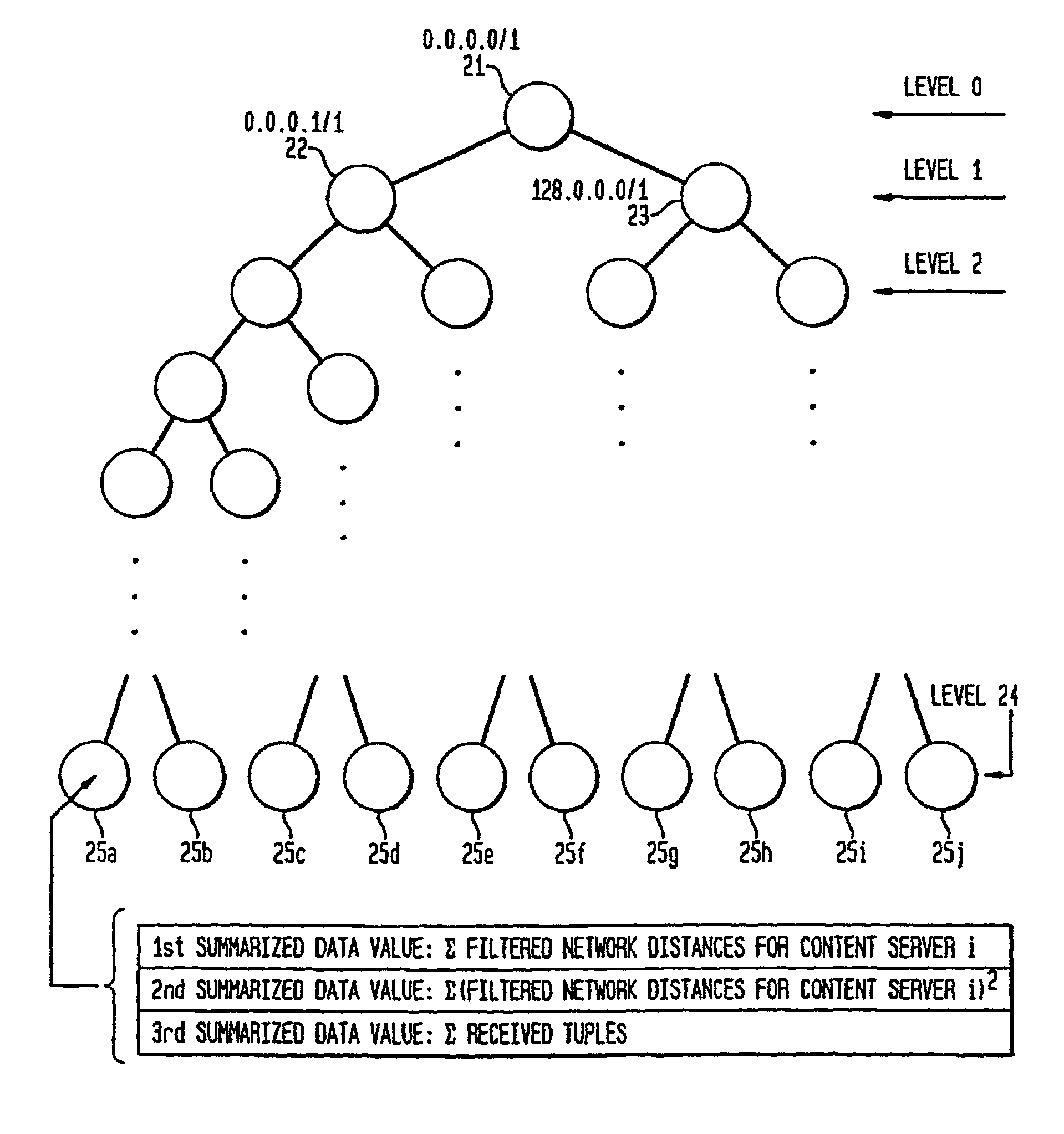
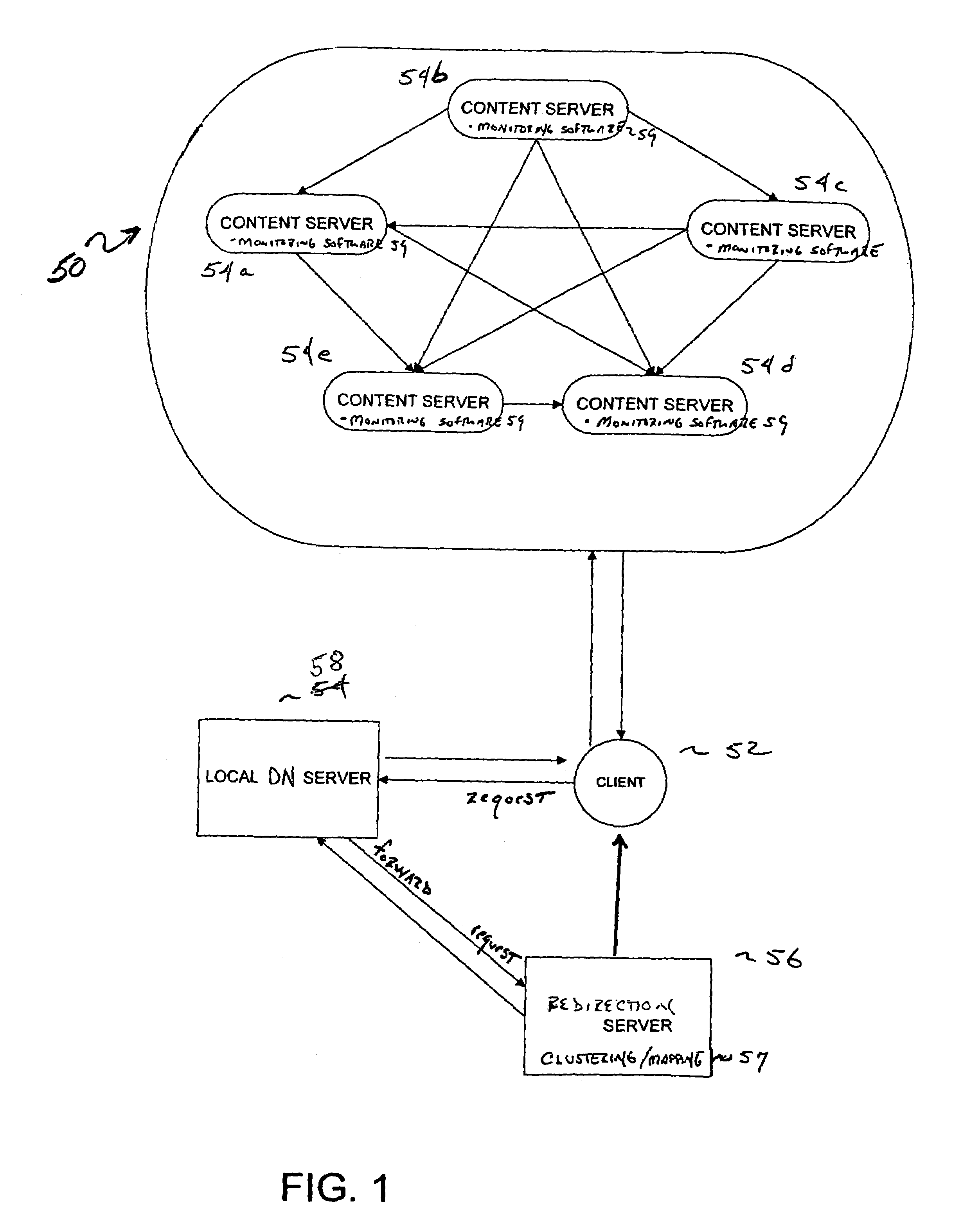
A scalable system and method for locating a closest server in response to a client request via an interactive distribution network, such as the Internet, are provided. A closest content server is defined as having the least round trip time for responding to a client request. The system including a plurality of content servers; and a local server in communication with a plurality of clients, the local server acting as a proxy for communicating client requests from clients to a redirection server. Client network distance and load information is periodically collected at each content server in the network from clients communicating with each of the respective content servers. The redirection server periodically aggregates the network distance and load information from each content server to create client clusters from both current and previously aggregated network distance and load information. Each client cluster represents a division or partition of the total IP address space. Each client cluster is then mapped (paired) to one or more content servers in the network. The mapping or pairing is then utilized to respond to client DN requests received from any client in the network. Another aspect of the invention involves considering the respective capacities of the content servers in the network. A selection probability is assigned to each content server / domain index pair to prevent the repeated selection of the content server having lowest round trip time thereby overloading that server's service capacity. The selection probabilities assigned to each content server effect a load balancing to prevent overloading. Another aspect of the invention involves collecting the distance and load information without incurring any overhead cost by passively collecting TCP information as it is transmitted from clients in communication with content servers in the course of normal communications.
Owner:RPX CORP +1
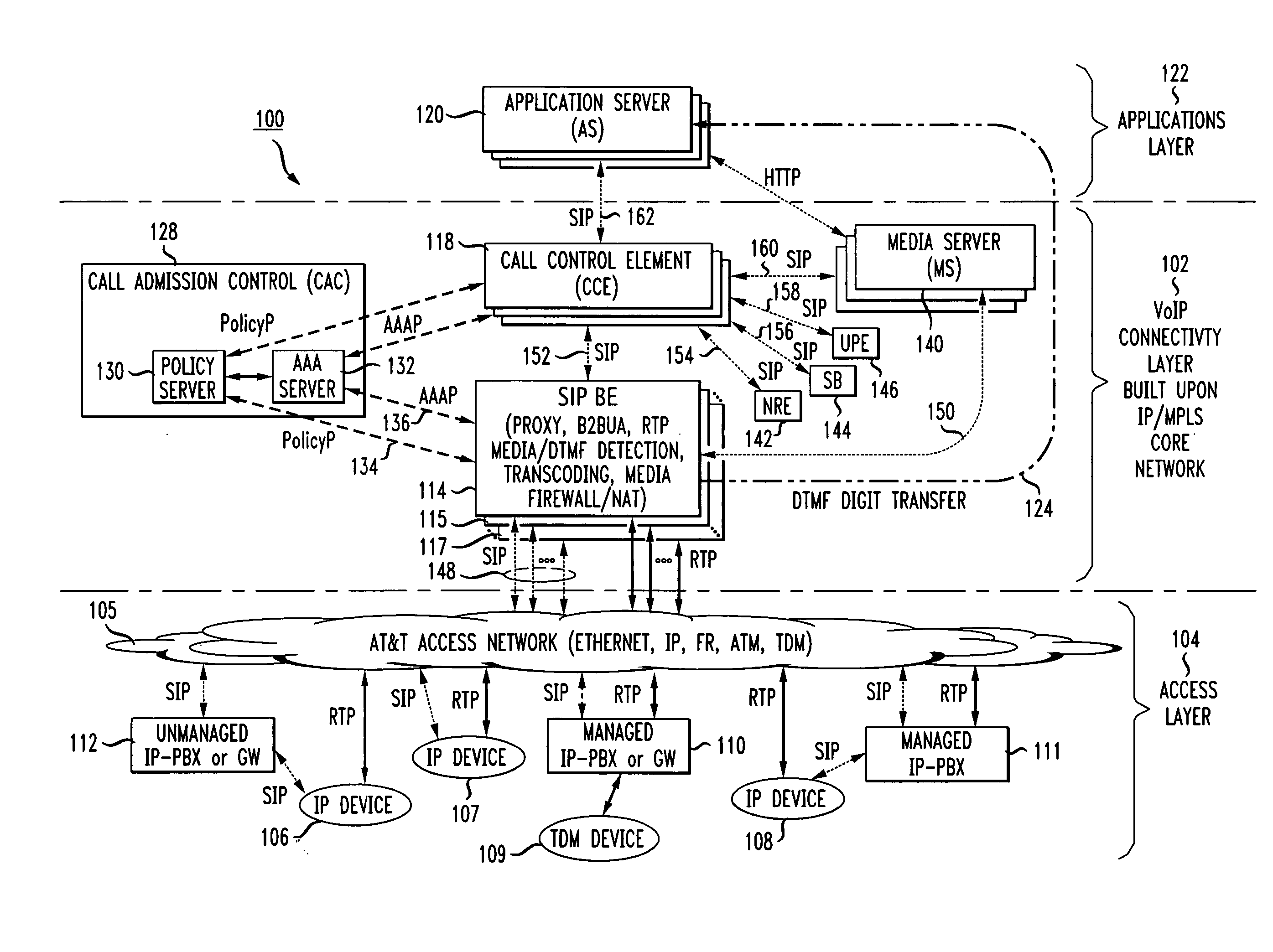
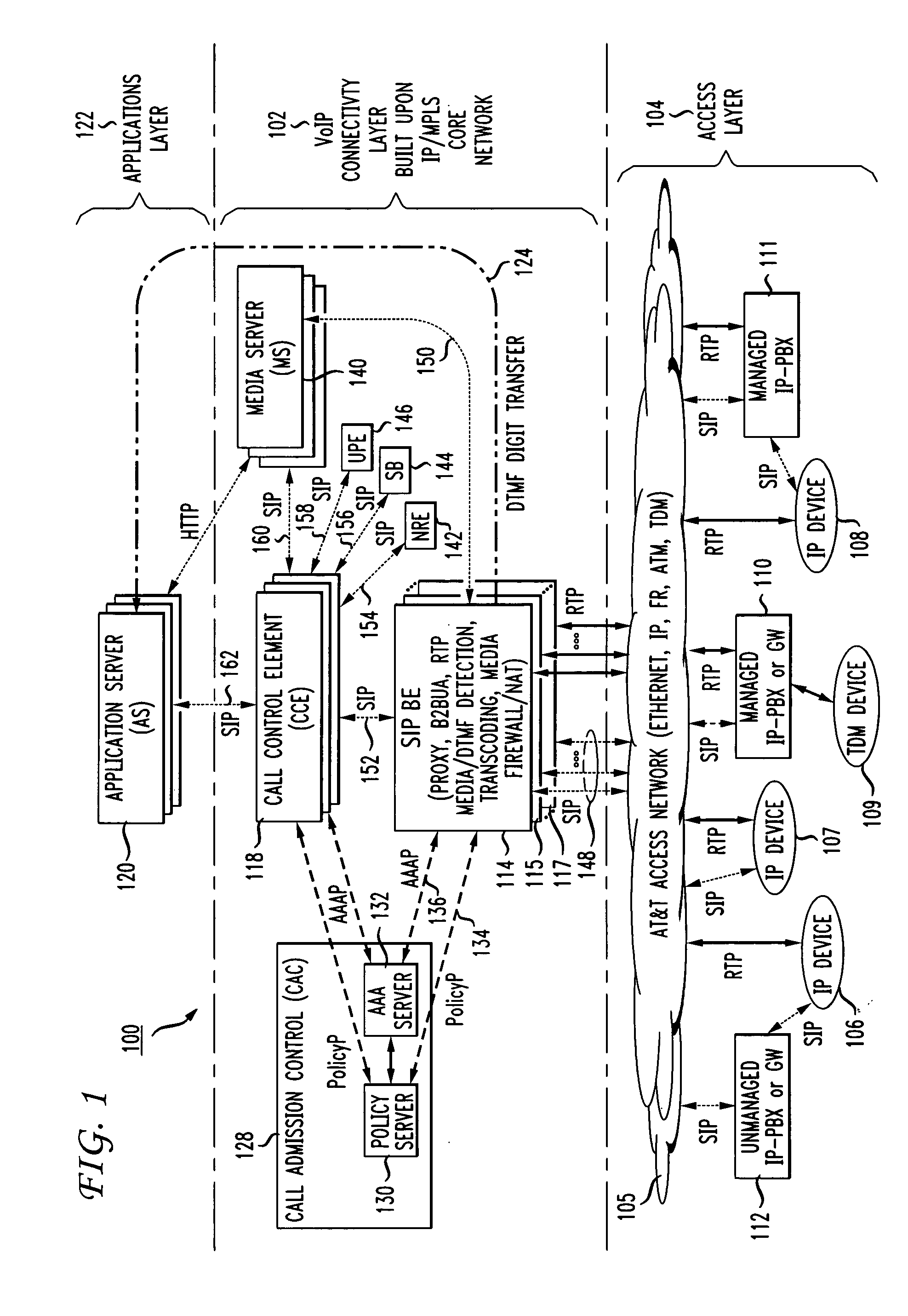
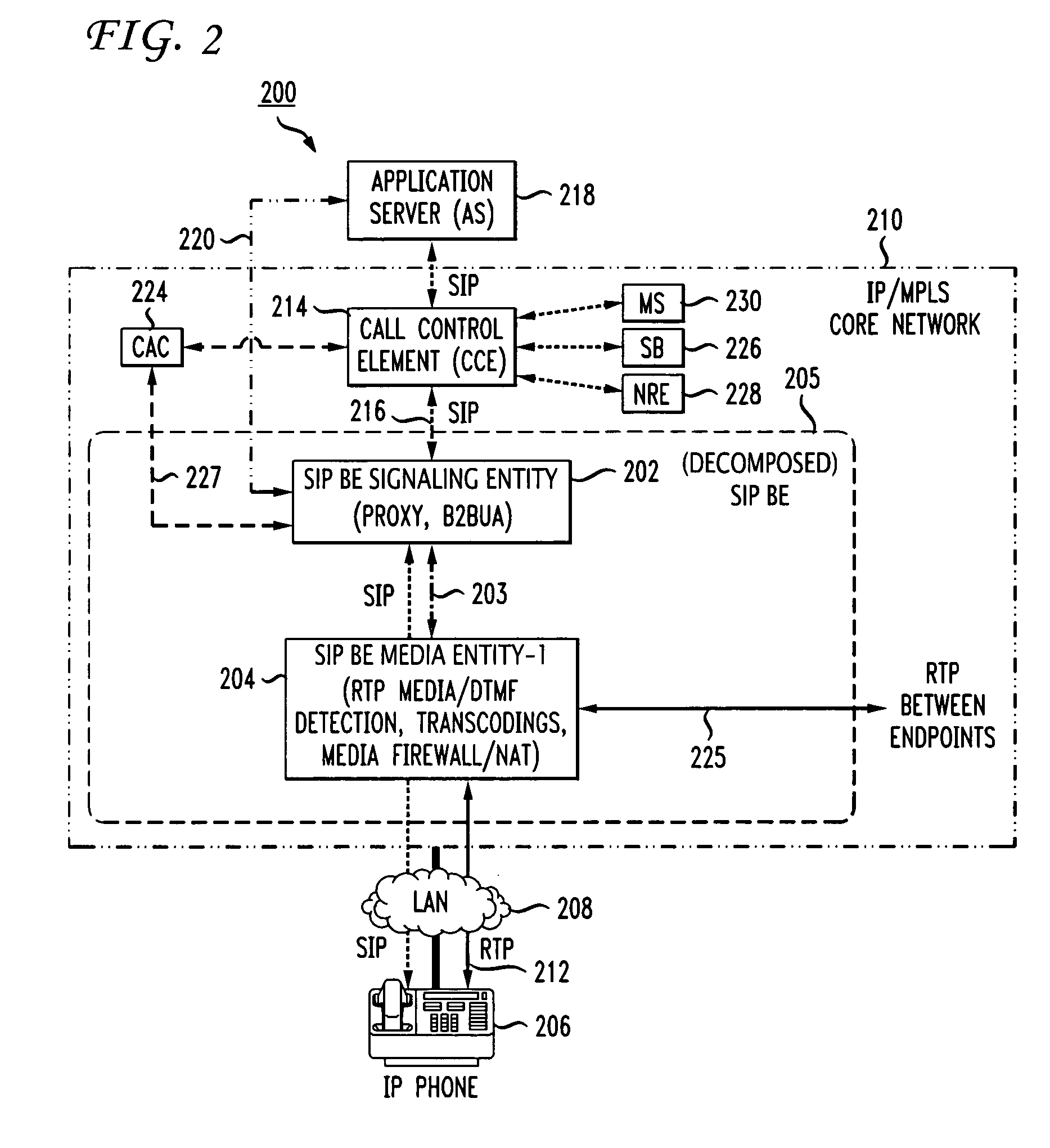
Method and apparatus for functional architecture of voice-over-IP SIP network border element
InactiveUS20050083912A1Improve system efficiencyImproves cost advantageMultiplex system selection arrangementsSpecial service provision for substationScalable systemDecomposition
In order to provide a single common cost-efficient architecture for real time communication services for audio, video, and data over internet protocol, a voice over internet protocol (VoIP) system and architecture is provided by placing border elements (BEs) at the interface boundaries between the access network the user devices use and the VoIP infrastructure. The BEs use SIP protocol as the access call control protocol over any access networking technologies, for example, IP, Ethernet, ATM, and FR, and provides all services transparently to the end users that use SIP-enabled devices. To enable a scalable system, the SIP BEs are decomposed into separate communicating entities that make the SIP BE scalable and provide new capabilities not previously available by a self-contained SIP BE. Further, multiple levels of decomposition of a SIP BE can be provided by the present invention supporting a flexible and scalable SIP BE design that further improves system efficiencies and cost advantages as compared to use of single integrated border or edge elements. Further, a scalable SIP BE, made up of a plurality of physical entities for optimization of a large scale design, acts as a single integrated functional entity to logically execute a set of functions at the border of a VoIP infrastructure.
Owner:AMERICAN TELEPHONE & TELEGRAPH CO
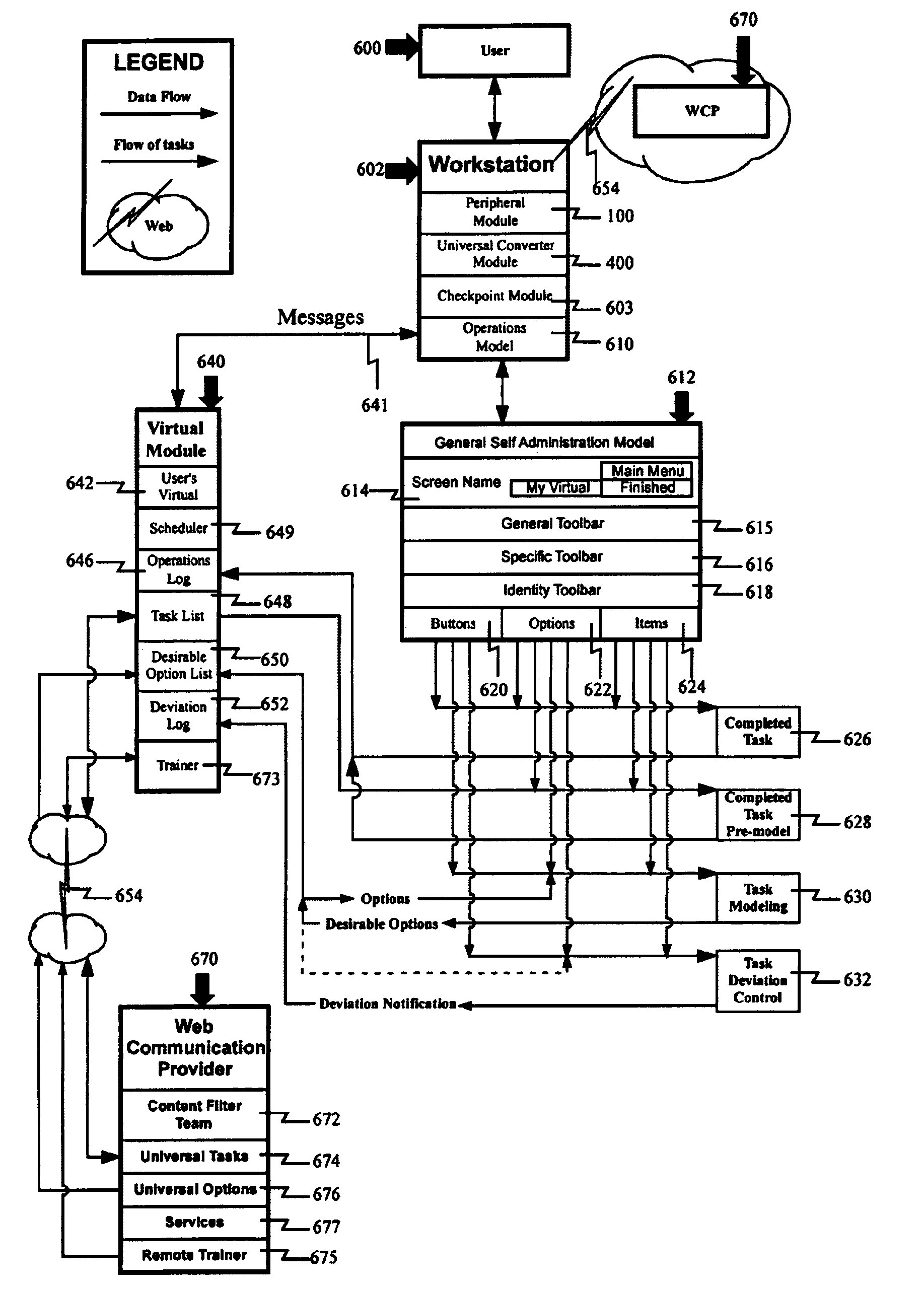
Information processing apparatus and method
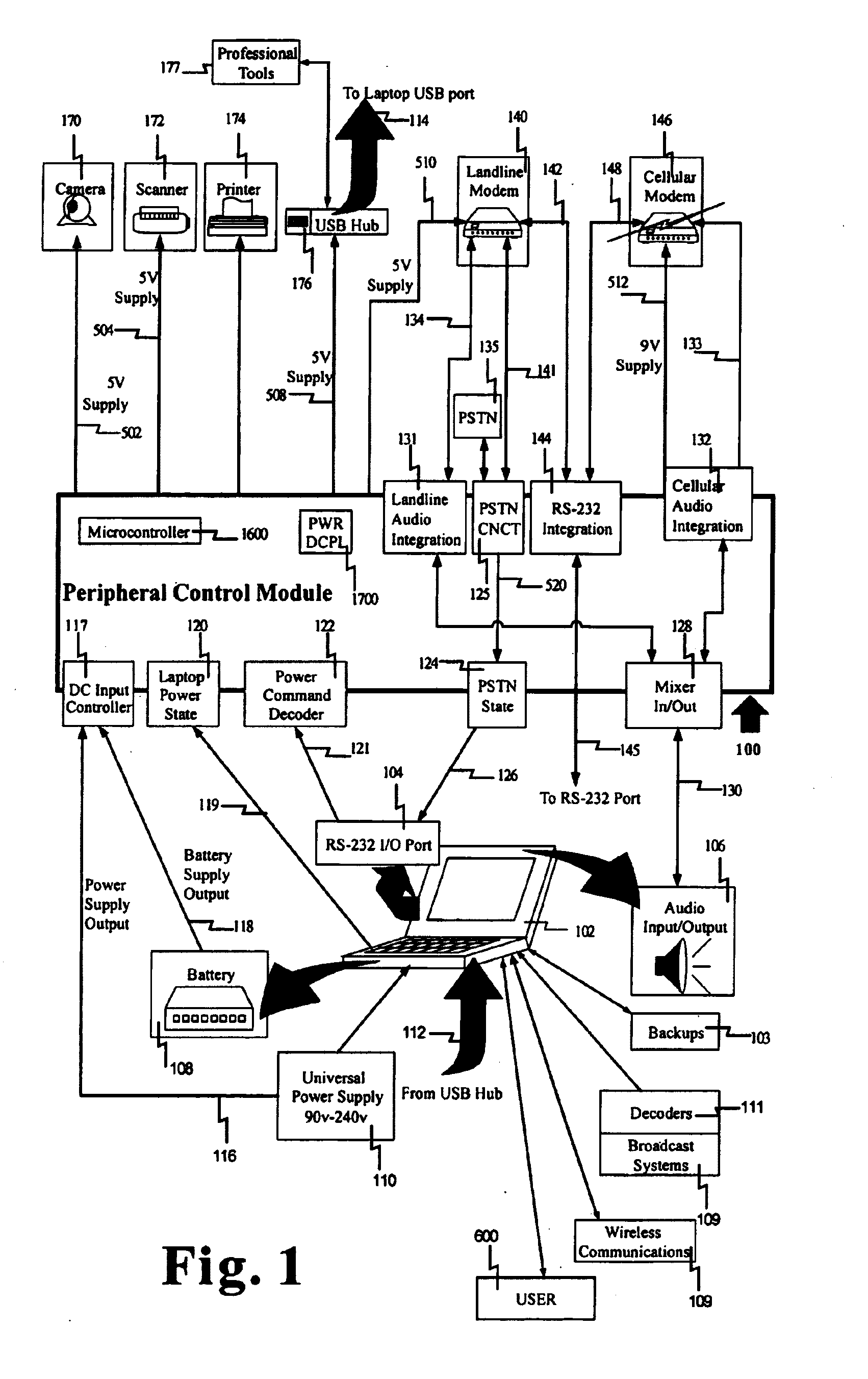
InactiveUS7032115B2Function increaseLow weight burdenVolume/mass flow measurementPower supply for data processingInformation processingScalable system
An information processing apparatus and method consisting of the modules 1) peripheral control including power management resulting in increased battery life where a plurality of peripherals use a single power source to eliminate external power supplies, 2) universal conversion, an extensible system for taking any information as input and converting to any desired feasible output, 3) virtual user production, which creates a digital representation of a user through constant recording and analysis of completed work, which is disintegrated and stored in lists comprising tasks and related options. A list captures and represents the user's preferences. Dynamic and evolving lists define a virtual user capable of repeating any previously recorded task. A corresponding Web based communication provider automatically feeds additional tasks and options to the invention, which can grow substantially unassisted by the user.
Owner:NEW AGE UTILITIES
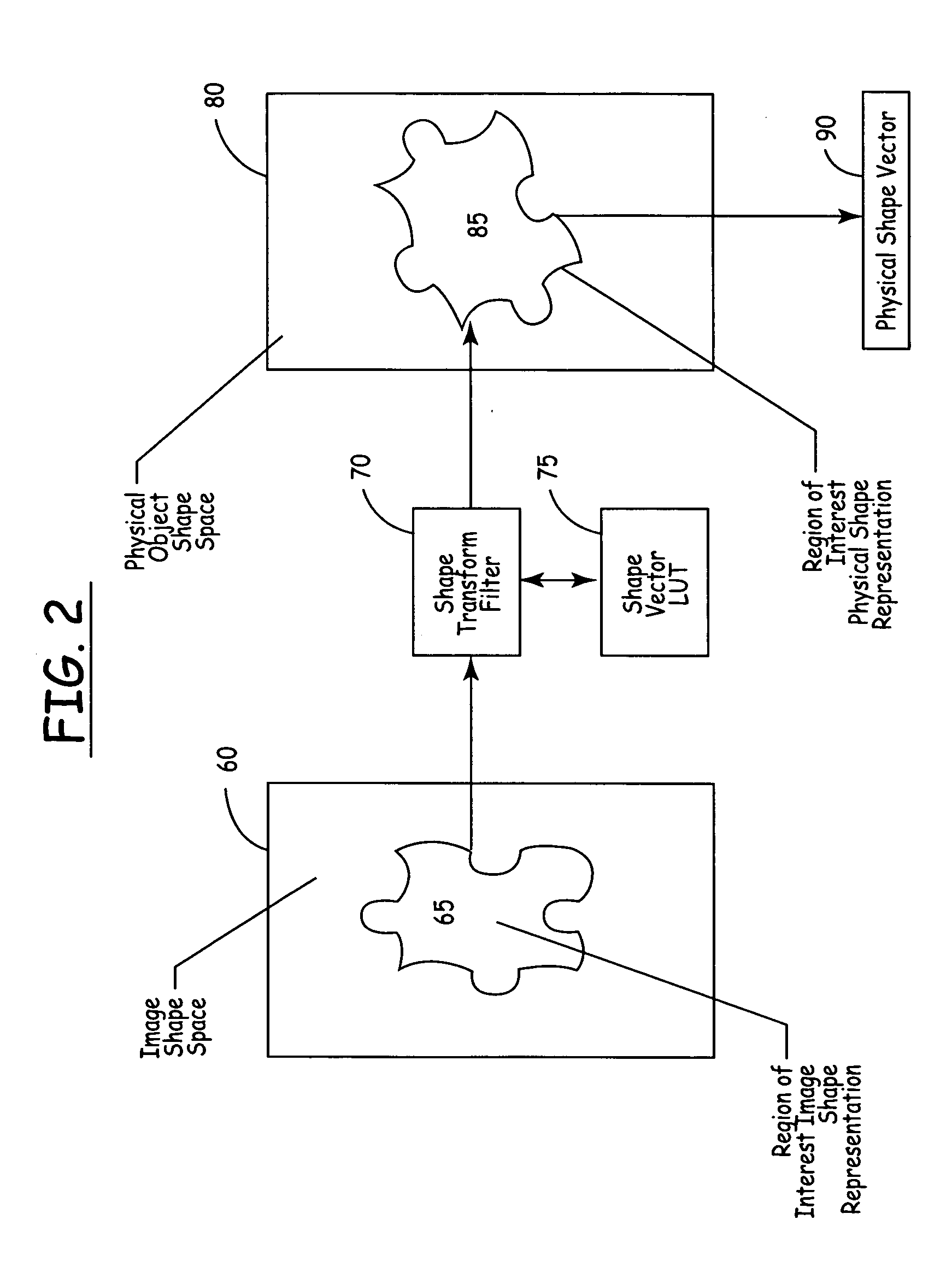
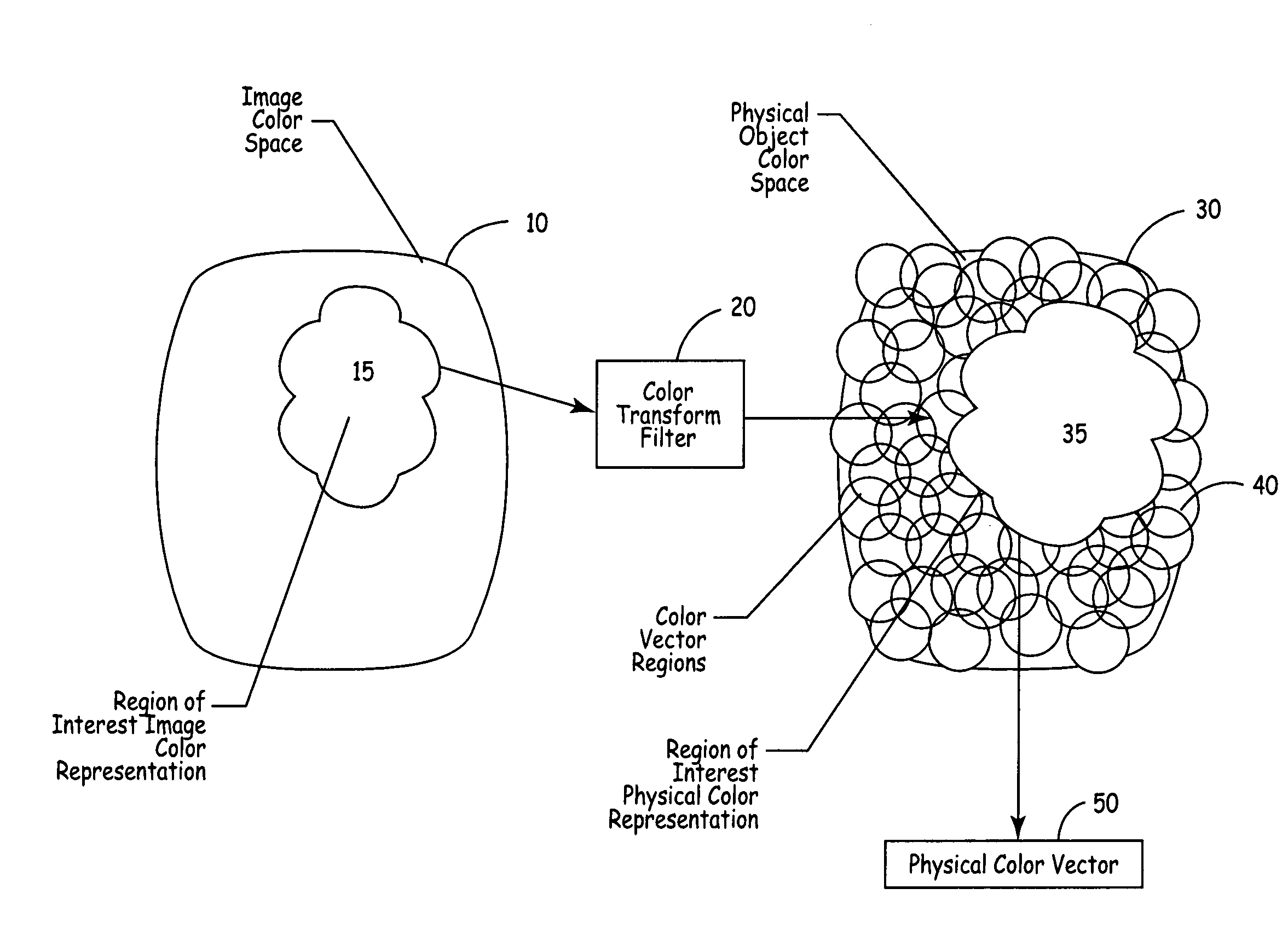
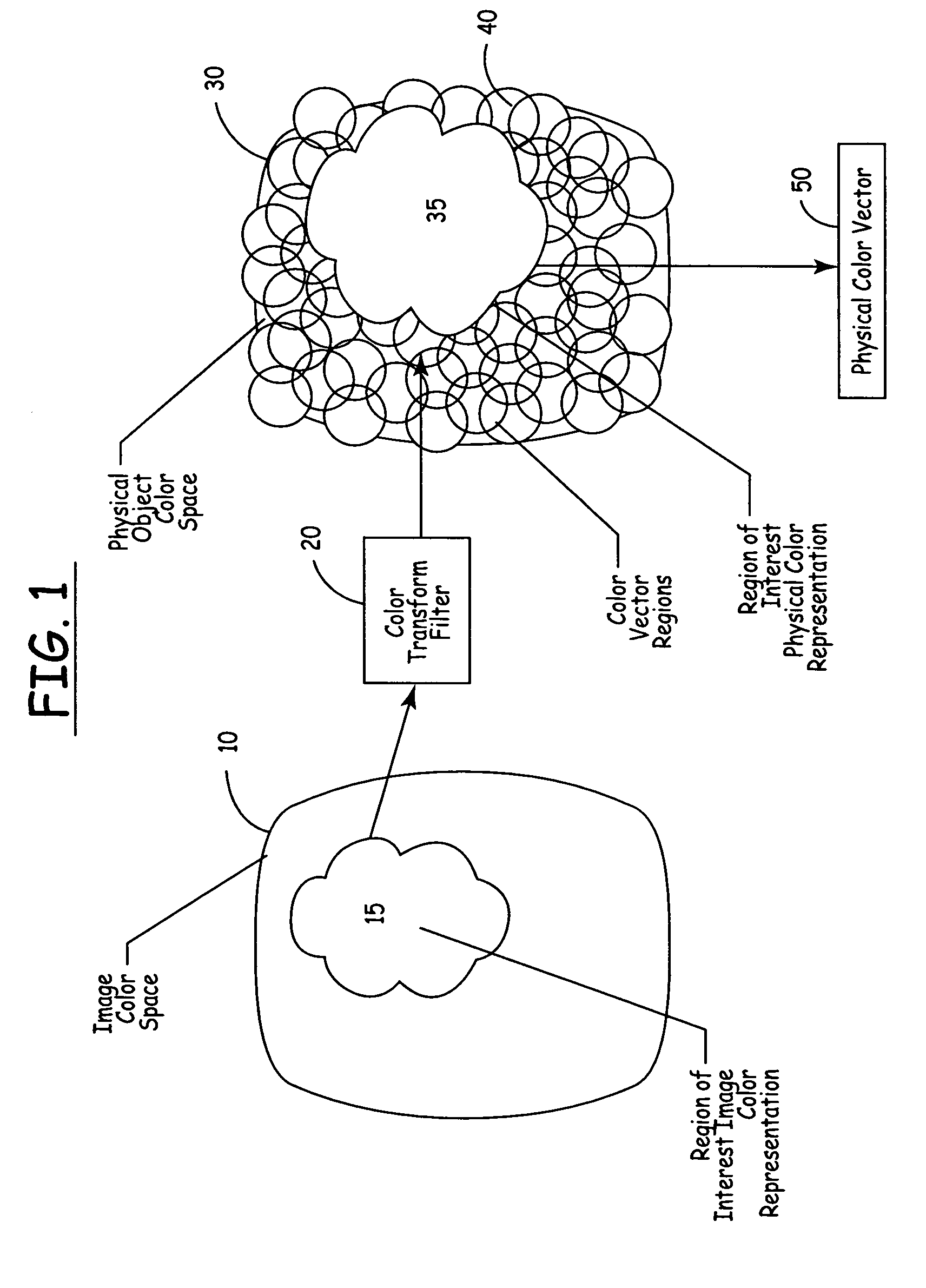
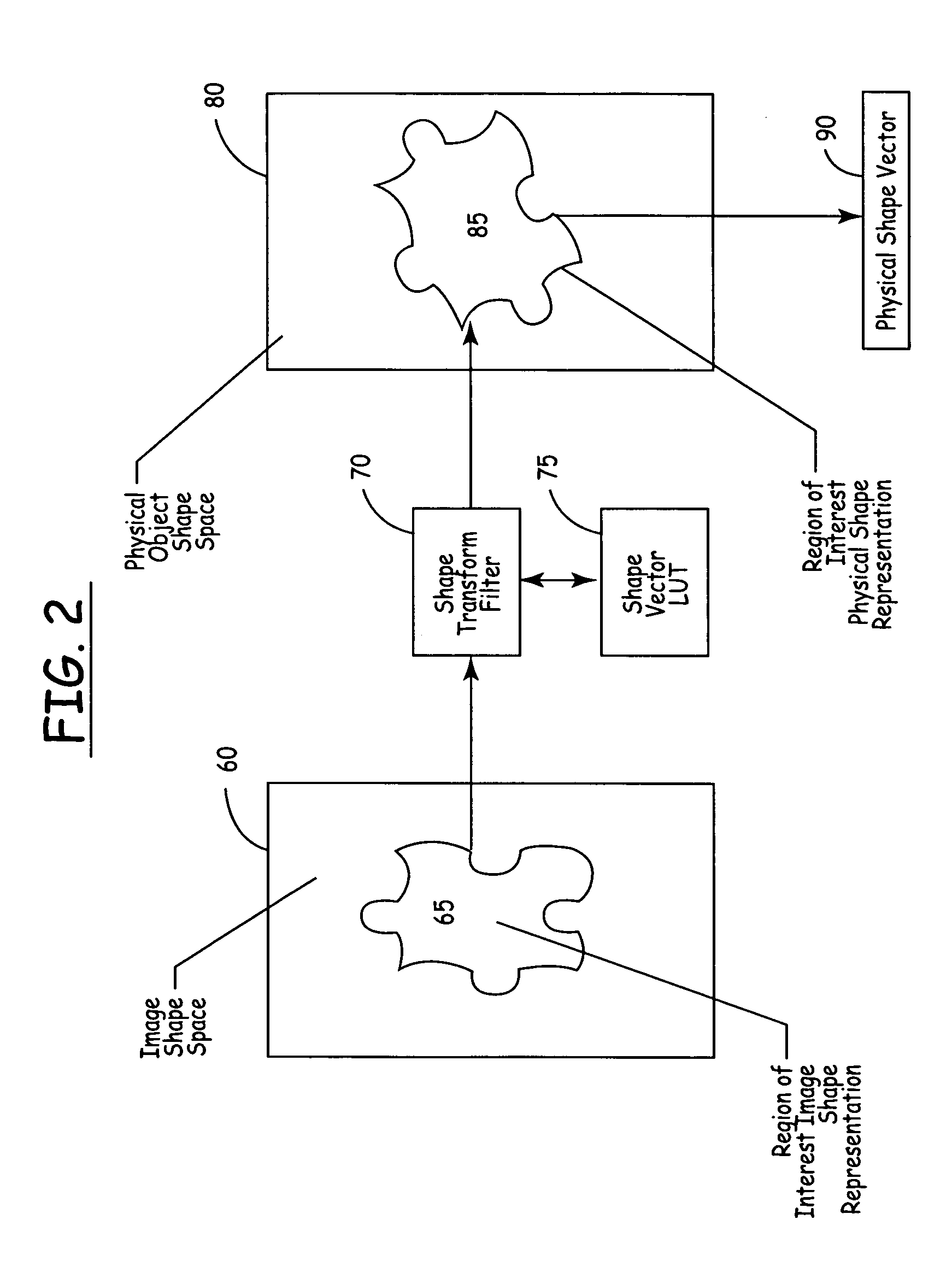
Methods and apparatus for automated true object-based image analysis and retrieval
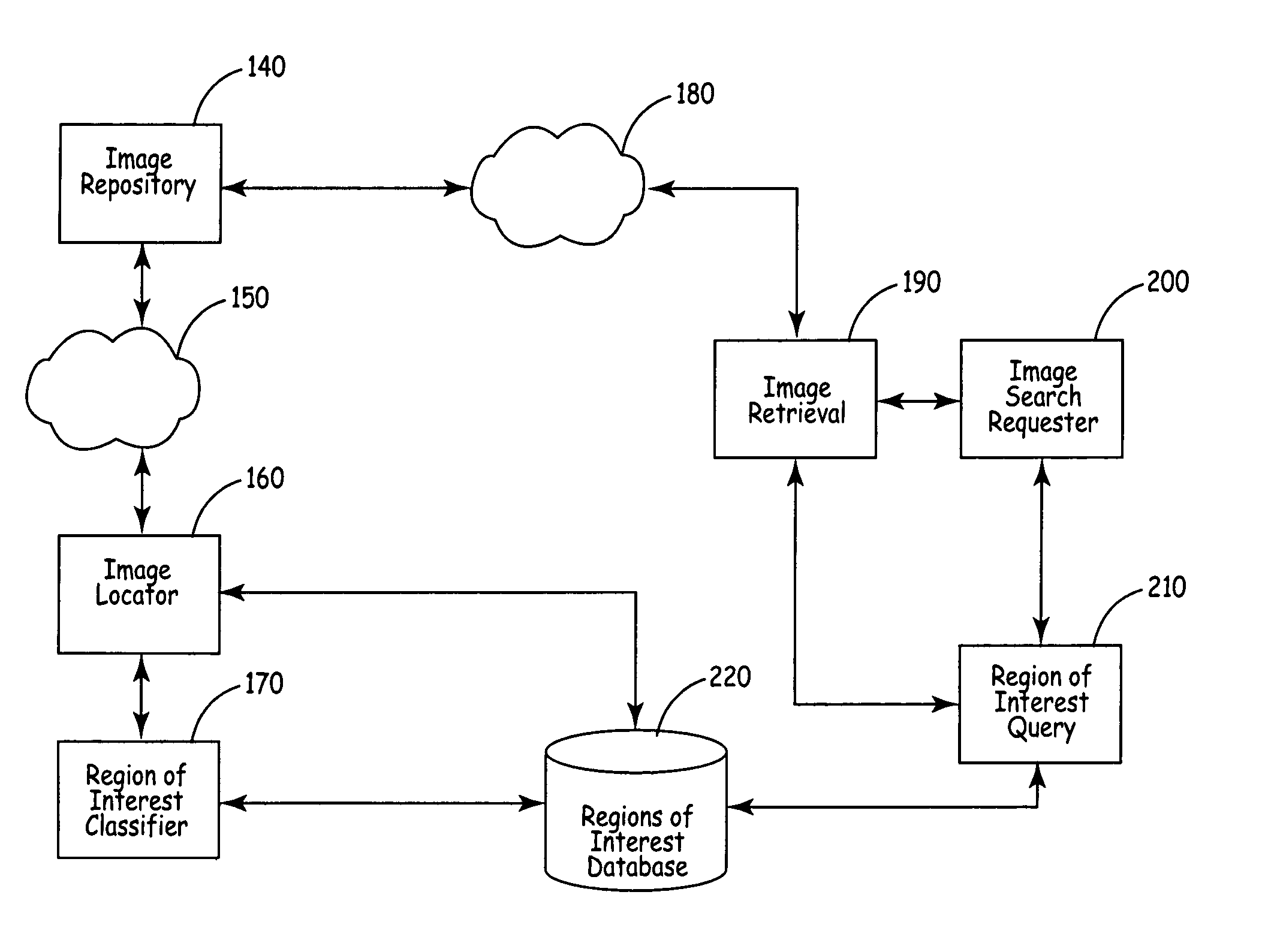
ActiveUS20050271304A1Data processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsAbstraction layerScalable system
The present invention is an automated and extensible system for the analysis and retrieval of images based on region-of-interest (ROI) analysis of one or more true objects depicted by an image. The system uses a Regions Of Interest (ROI) database that is a relational or analytical database containing searchable vectors that represent the images stored in a repository. Entries in the ROI database are created by an image locator and ROI classifier that work in tandem to locate images within the repository and extract the relevant information that will be stored in the ROI database. Unlike existing region-of-interest search systems, the ROI classifier analyzes objects in an image to arrive at the actual features of the true object, instead of merely describing the features of the image of that object. Graphical searches are performed by the collaborative workings of an image retrieval module, an image search requestor and an ROI query module. The image search requestor is an abstraction layer that translates user or agent search requests into the language understood by the ROI query.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
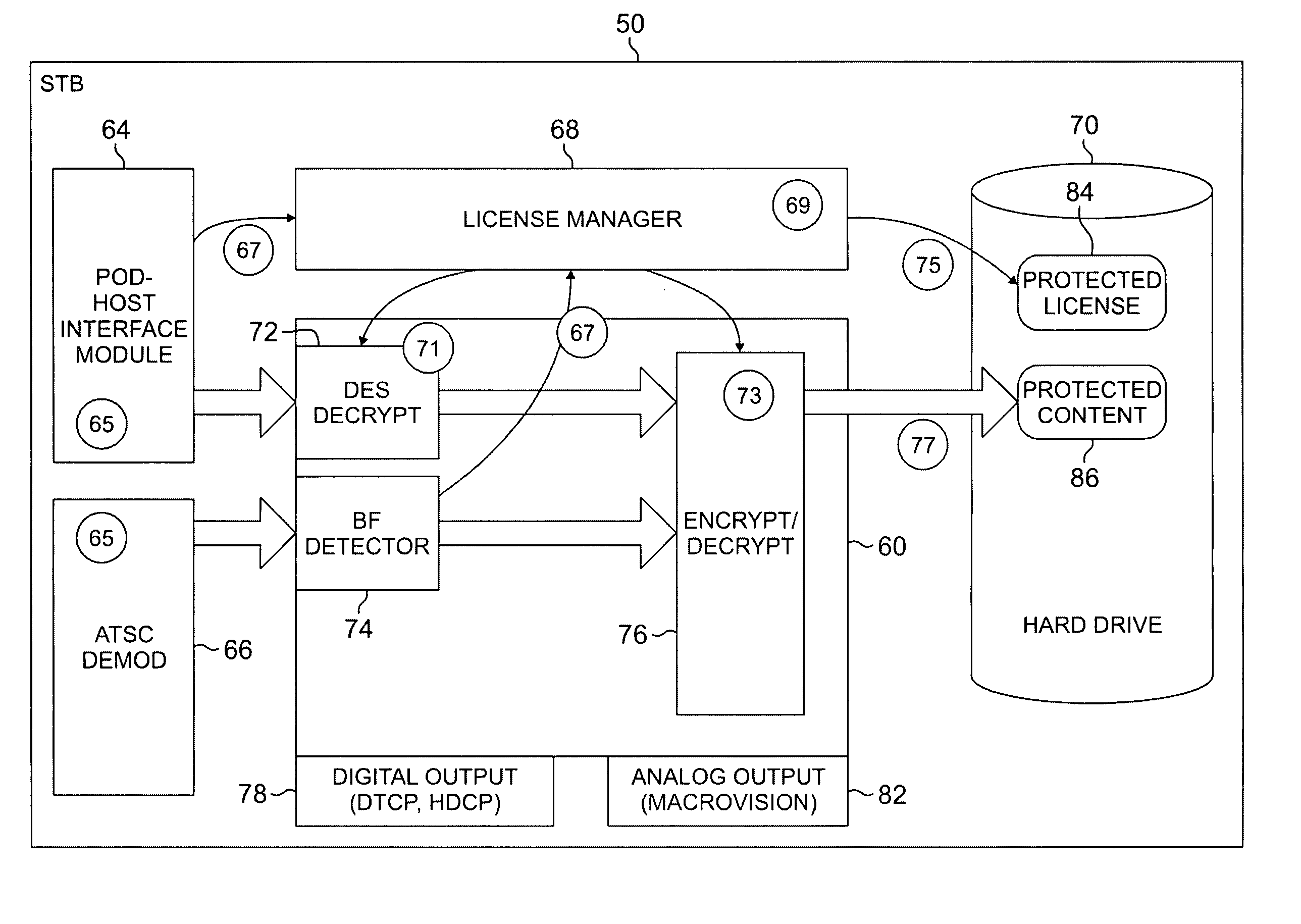
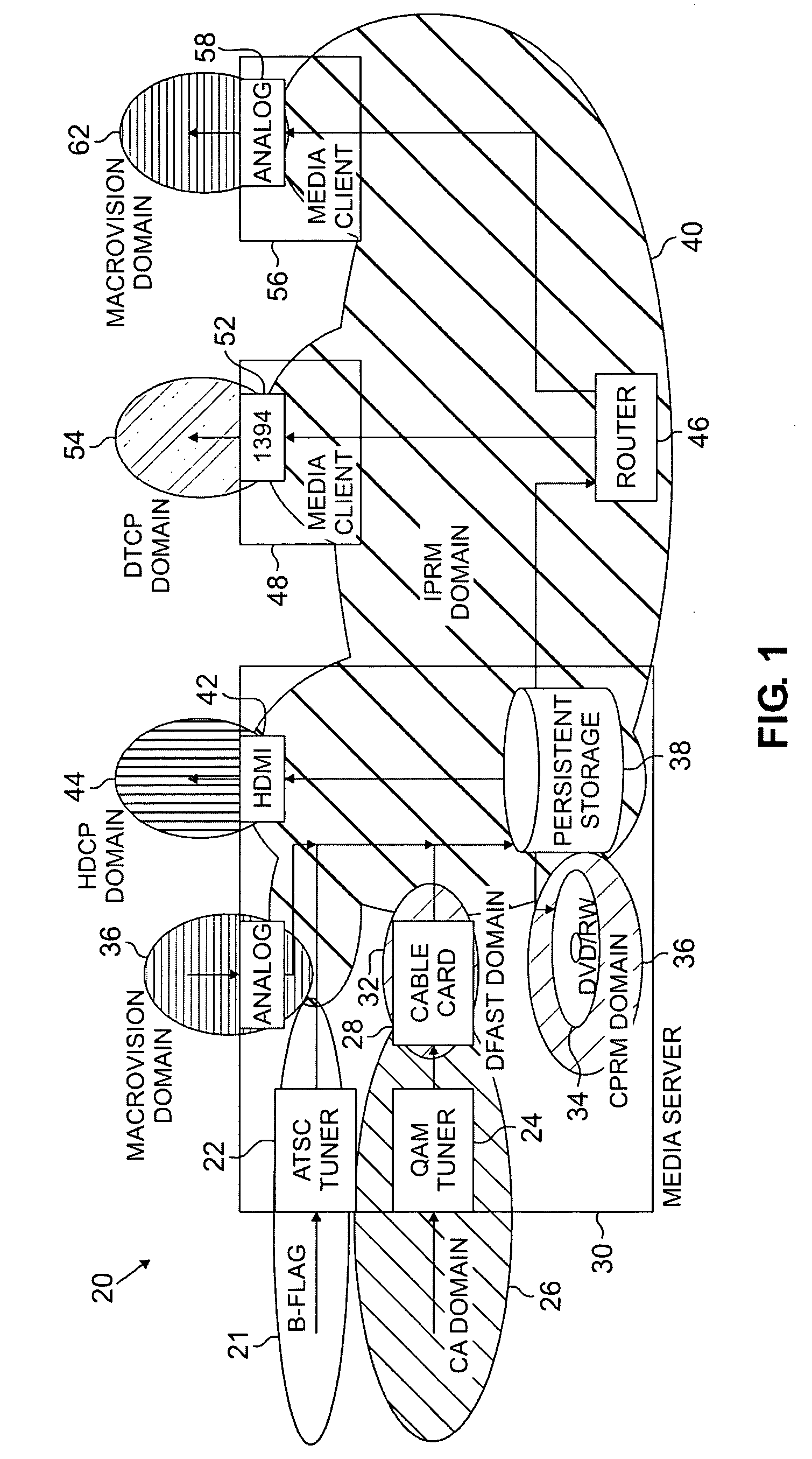
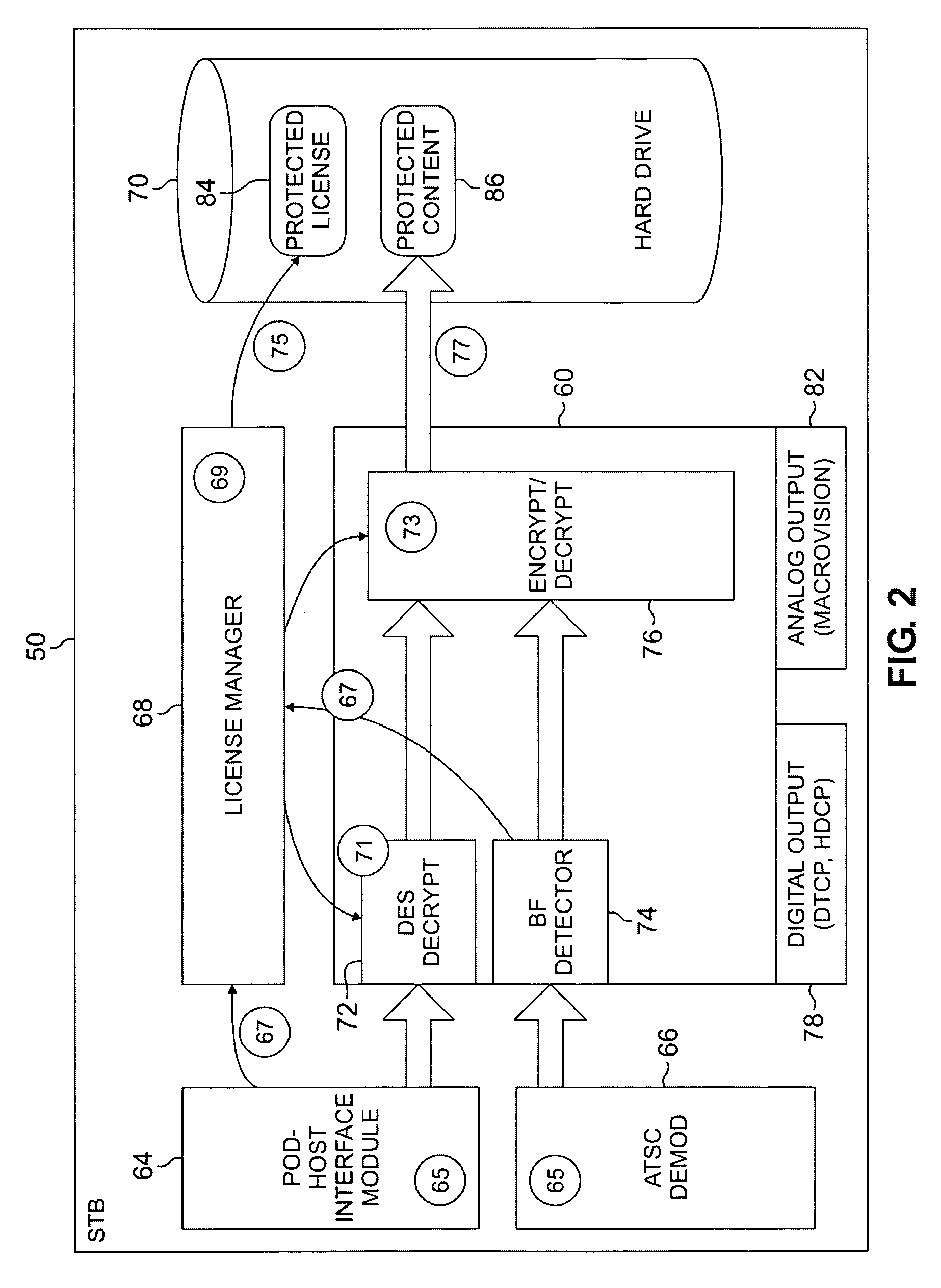
Digital rights management for local recording and home network distribution
The systems disclosed here provide a complete standards-based end-to-end scalable system for storage, delivery and in-home distribution of digital content over IP networks using standard protocols such as Real-time Transport Protocol (“RTP”) or IP-encapsulated MPEG-2 Transport Stream, or traditional MPEG-2 networks. Mechanisms are provided for receiving content from one security domain, re-encrypting that content uniquely for a receiving device, persistently storing that content, and playing back that content at a later time to and within another security domain. The systems also provide the ability to stream the persistently-stored content from the initial receiving device to another device that has been authenticated as part of a, e.g., home network. This allows a media server, e.g., a dual-tuner set-top box (“STB”) with hard drive, to deliver recorded content to any TV in the house by streaming to media clients such as STBs.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
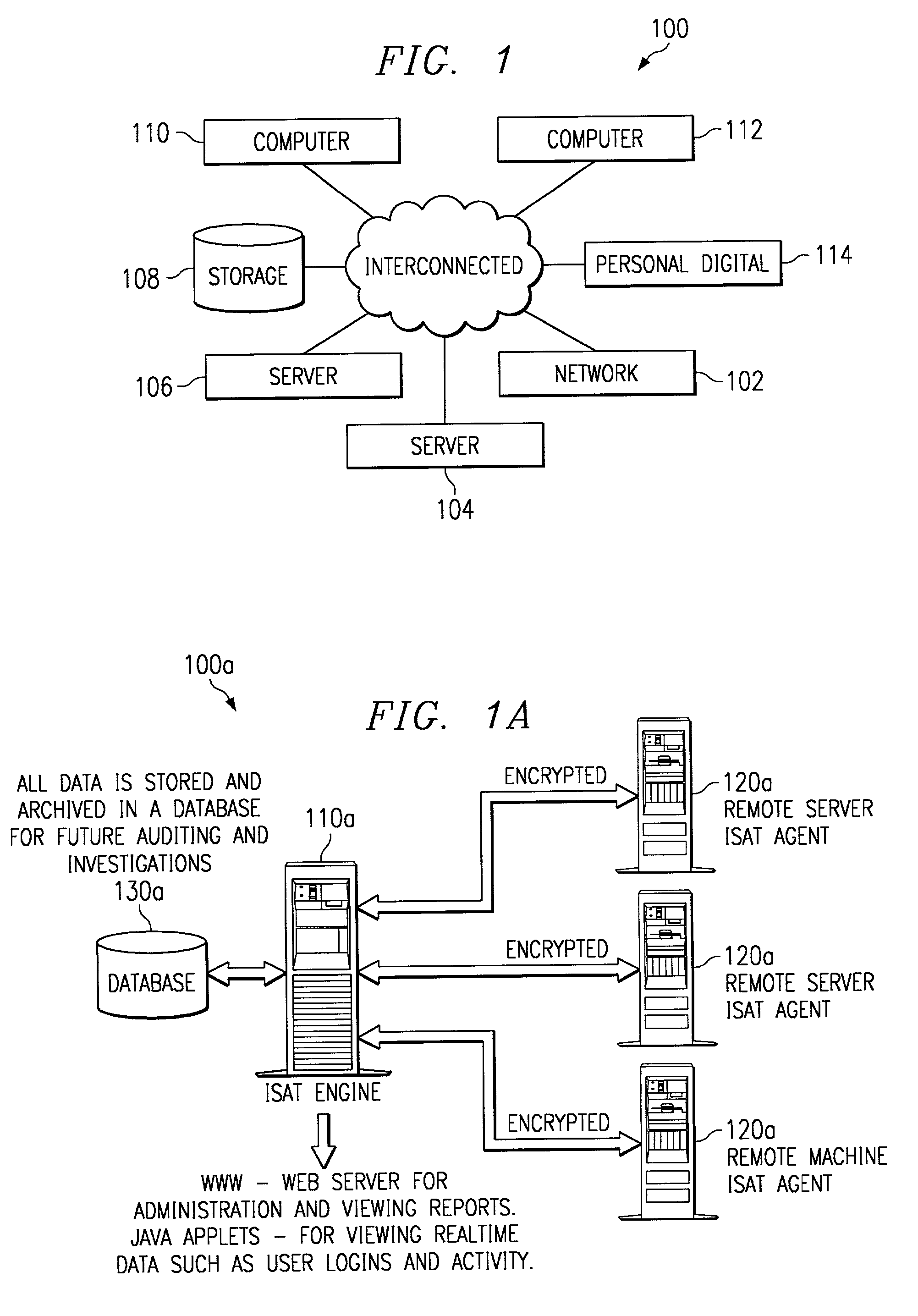
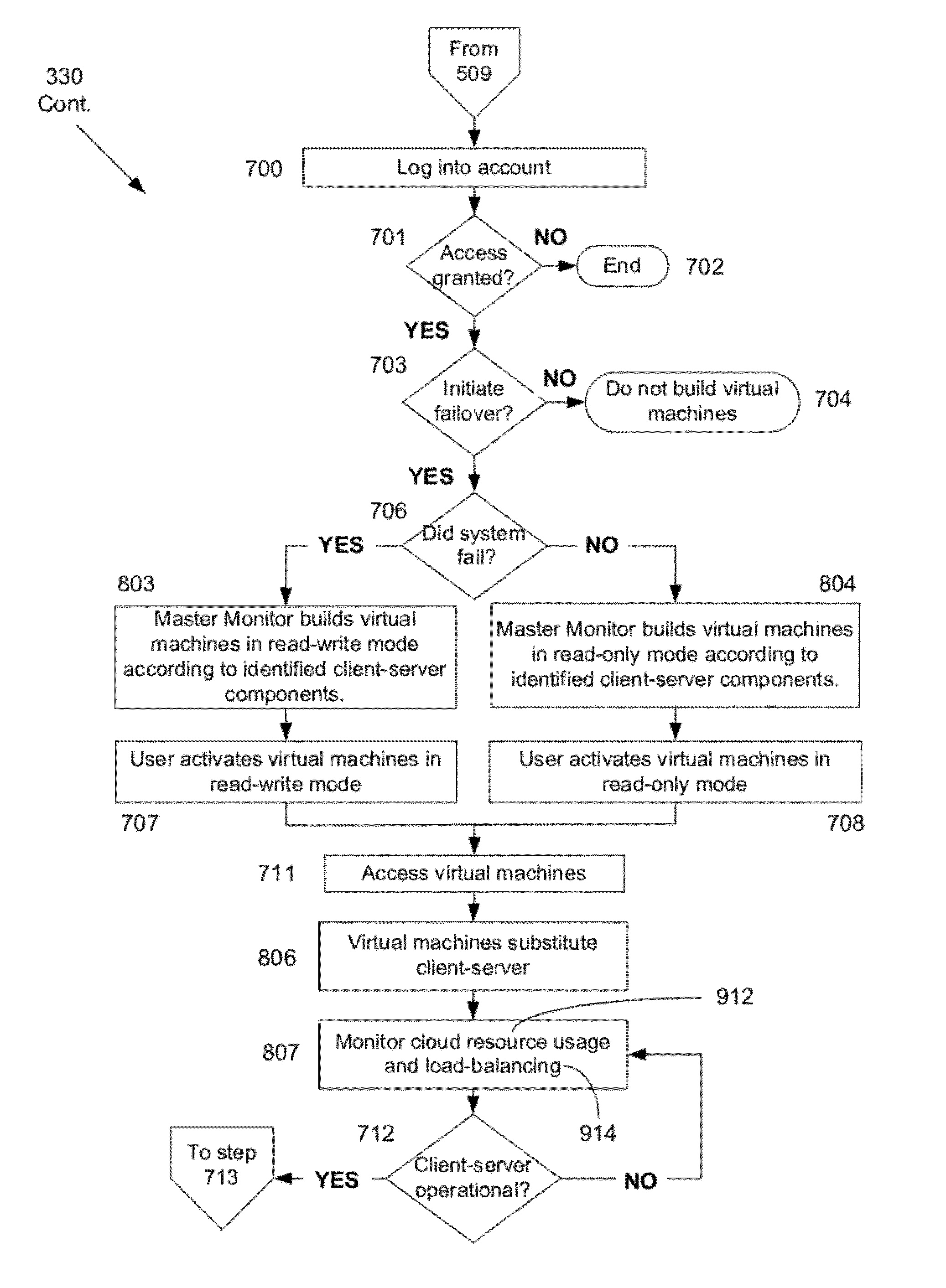
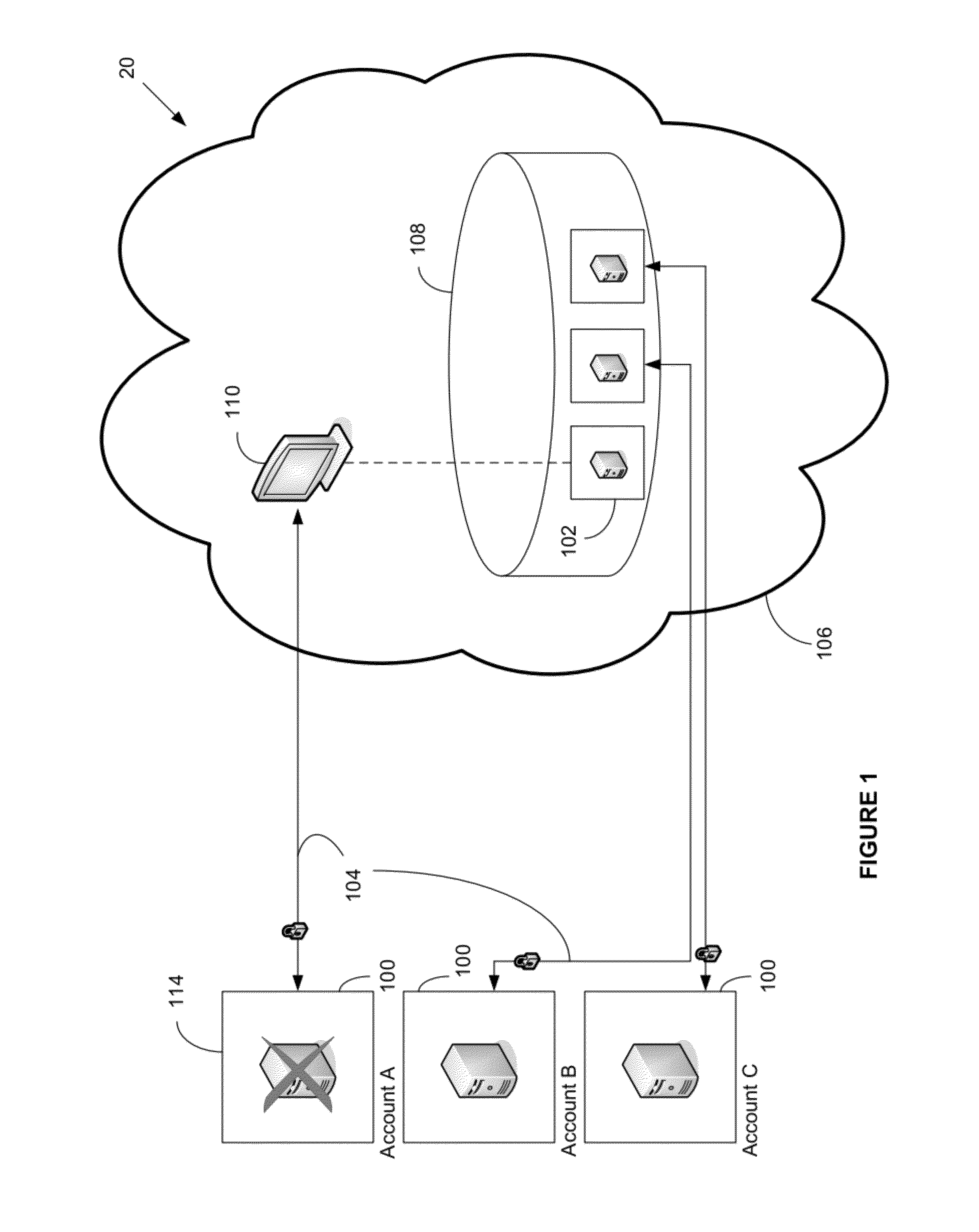
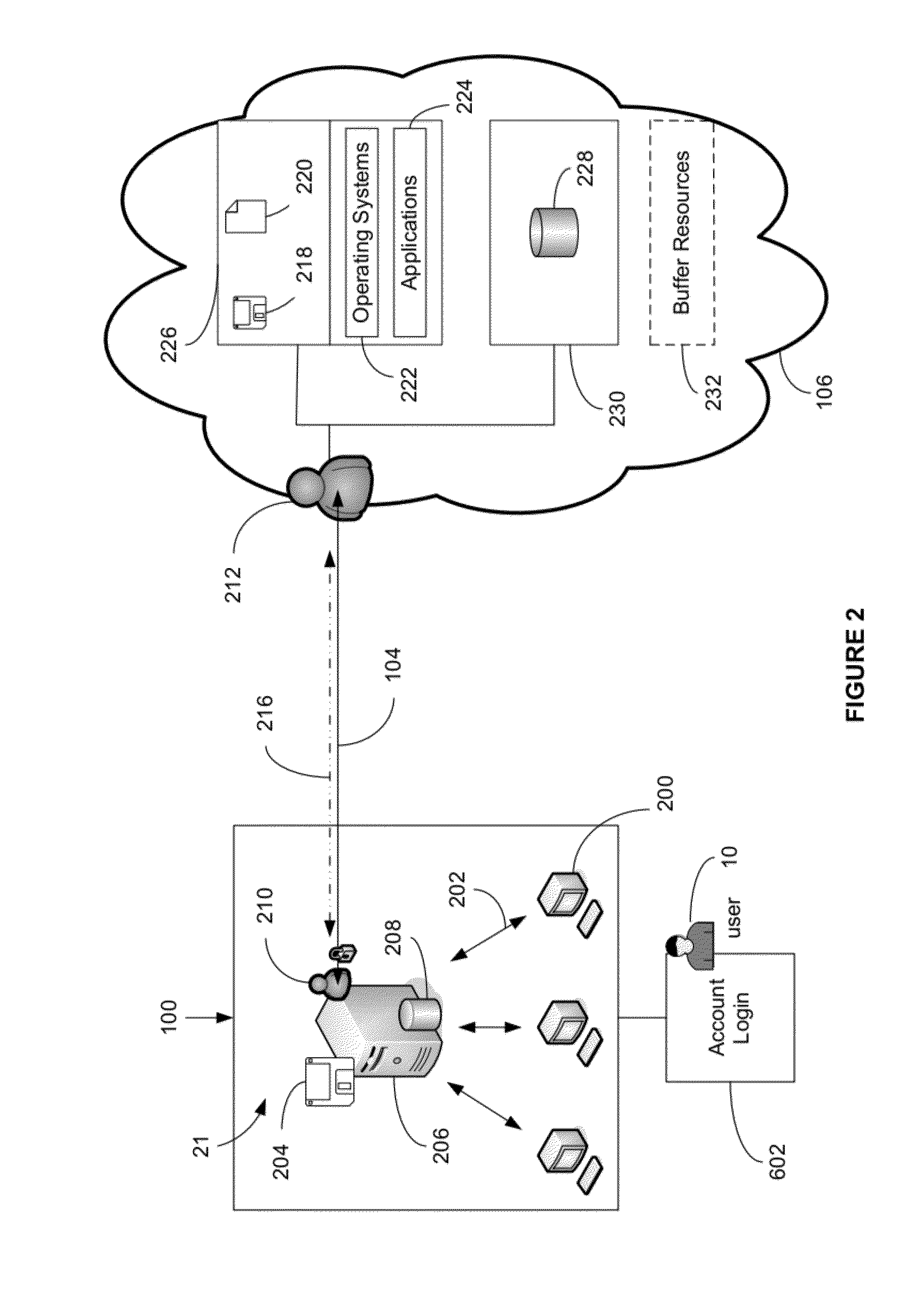
System and method for providing total real-time redundancy for a plurality of client-server systems
ActiveUS8103906B1Improve good performanceAvoid lostTransmissionSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationScalable systemNetwork connection
An automated and scalable system for total real-time redundancy of a plurality of client-server systems, wherein, data is replicated through a network connection and operationally located on a virtual machine that substitutes for a failed client-server system, wherein the virtual machine is activated and installed on the cloud computing environment. Monitoring applications are installed on both the client-server systems and the cloud computing environment. System components are identified, a network connection is initiated, a heartbeat is established, data replication is automated, system failure is detected, failover is initiated, and subsequent client-server restoration is automated.
Owner:MASS IP LLC
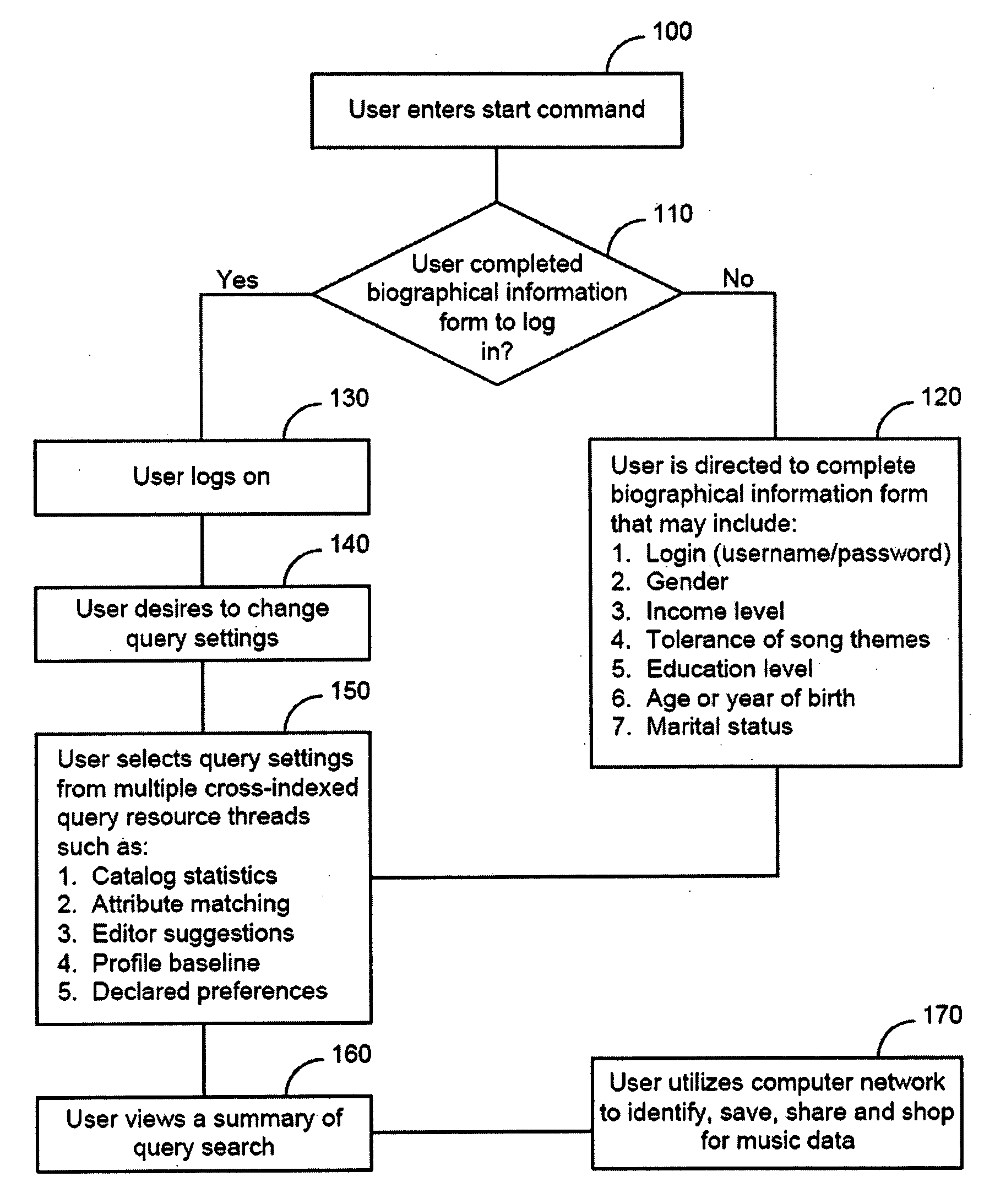
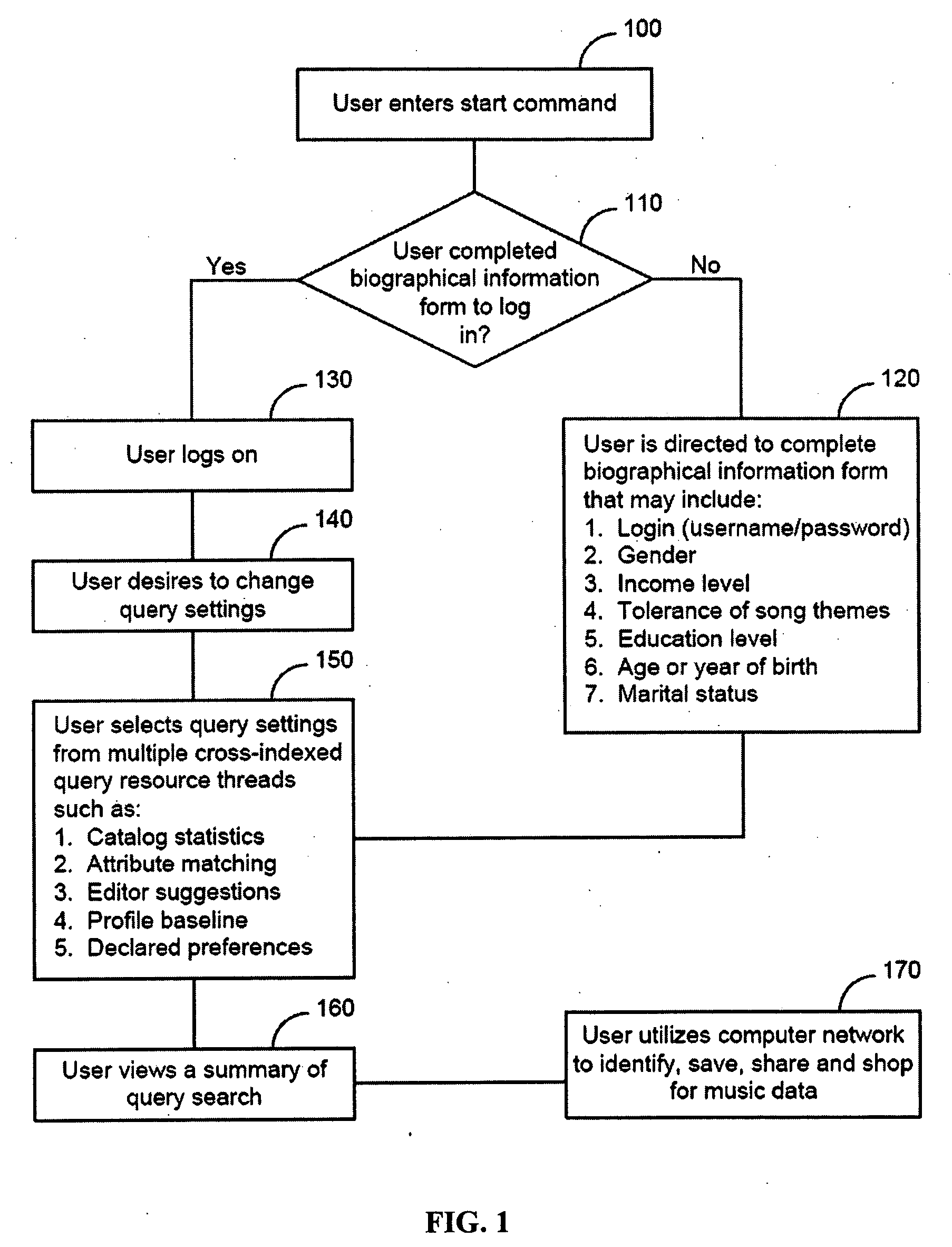
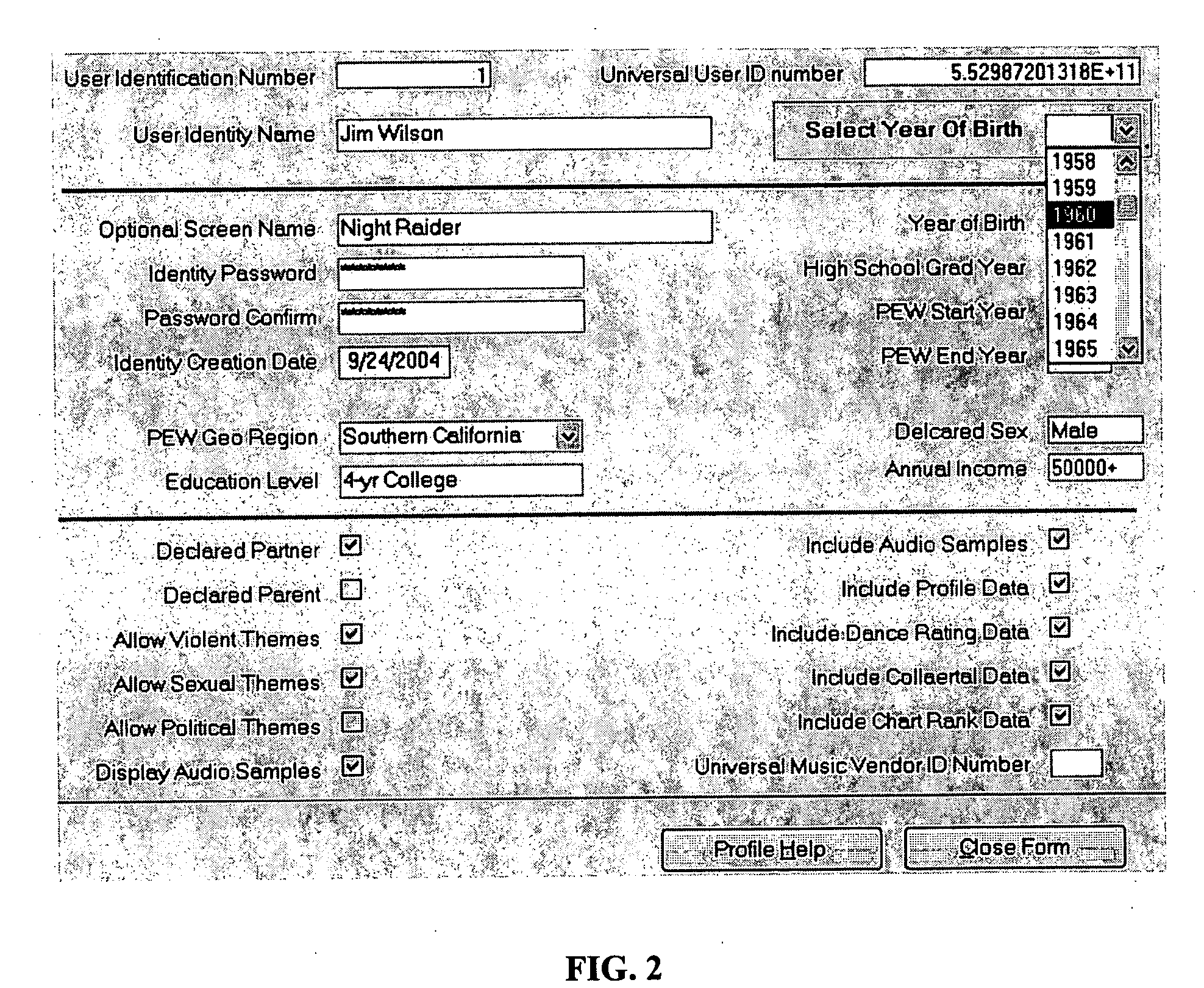
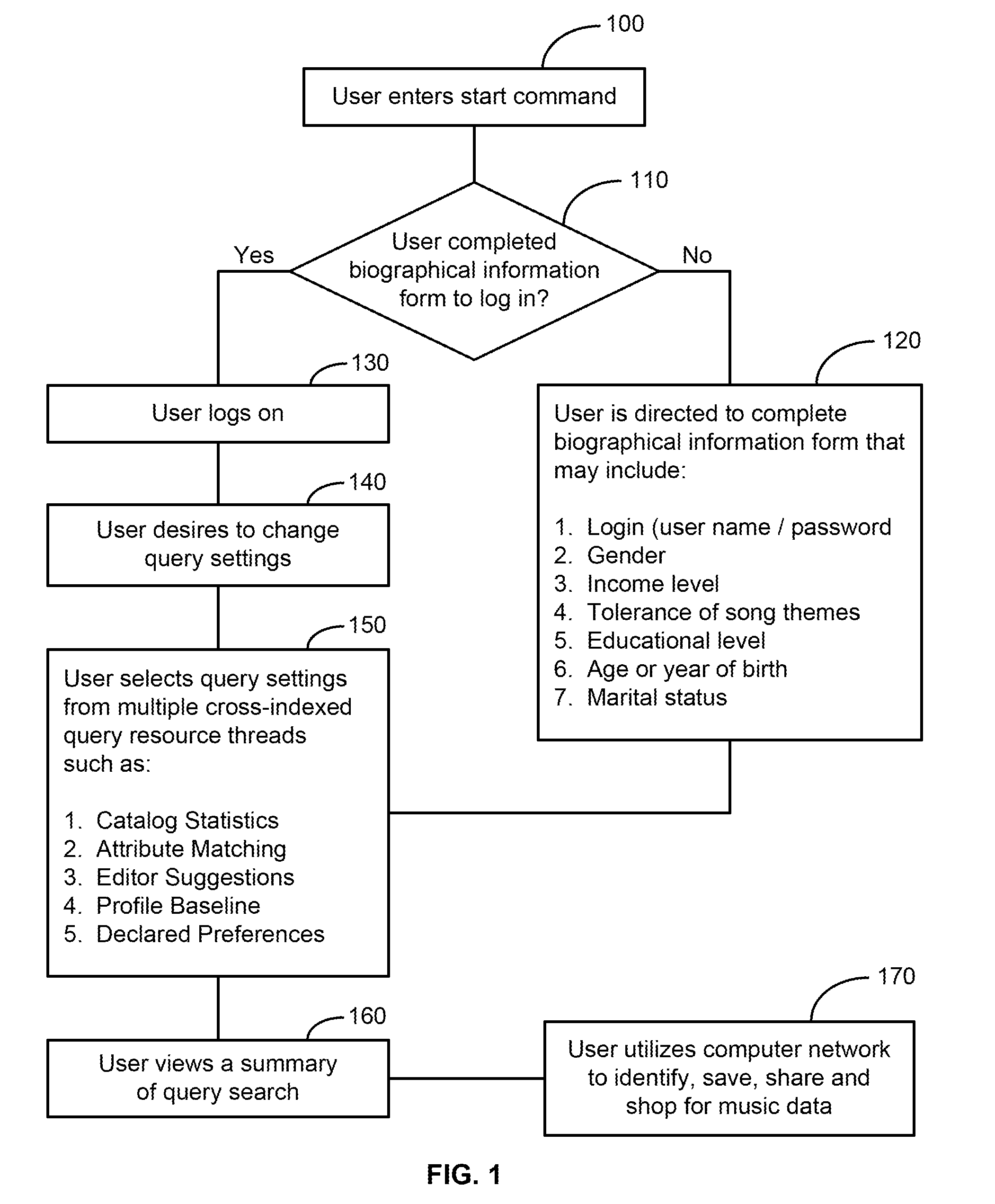
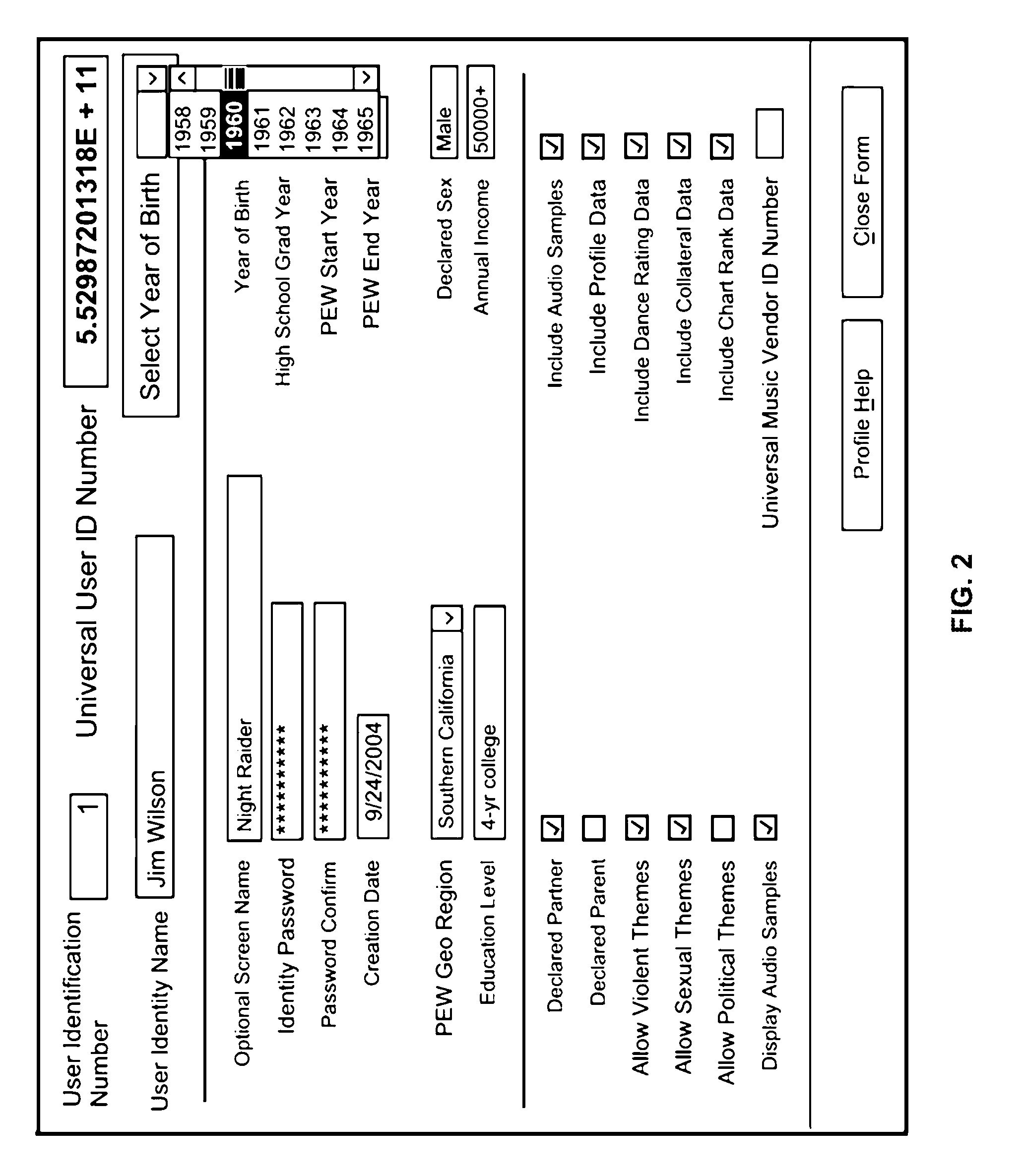
Scalable system and method for predicting hit music preferences for an individual
InactiveUS20060083119A1Electronic editing digitised analogue information signalsRecord information storageScalable systemComputer science
A system and method for creating and storing a user's hit-music preference list by receiving the user's biographical information, profiling the user based on the biographical information to determine music data that may be of interest to the user, receiving a rating from the user for a plurality of genres, wherein the music data is a member of one or more of the plurality of genres, and retrieving music data based on the user's rating for the plurality of genres. The system has a memory for storing the user's biographical information, a processor configured to profile the user based on the biographical information and to retreive music data that may be of interest to the user, and a display unit for displaying the music data retrieved.
Owner:HAYES THOMAS J
System and method for secure electronic communication services
InactiveUS8538028B2Easy accessSecure transmissionKey distribution for secure communicationPublic key for secure communicationSecure communicationScalable system
Owner:TOPOSIS CORP
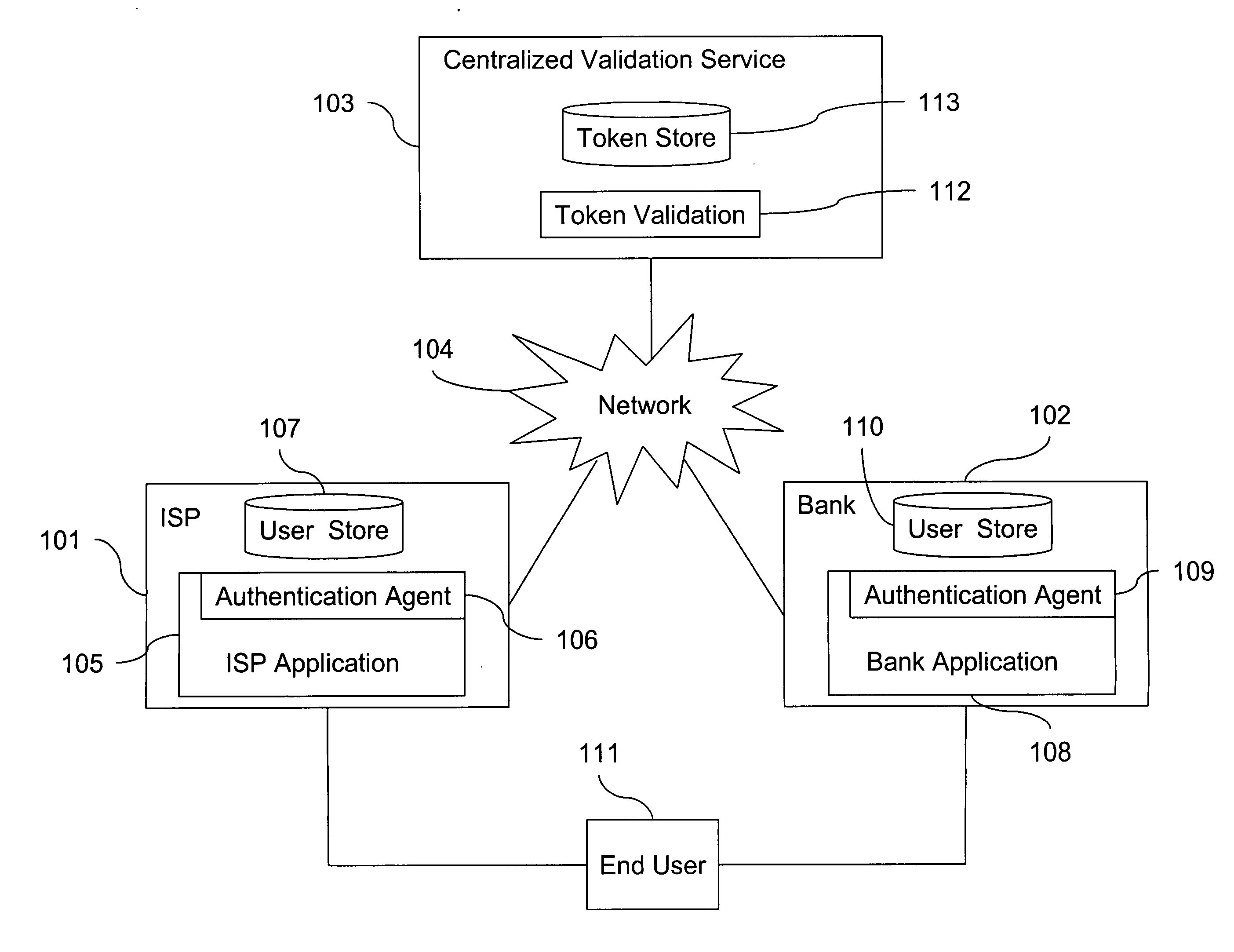
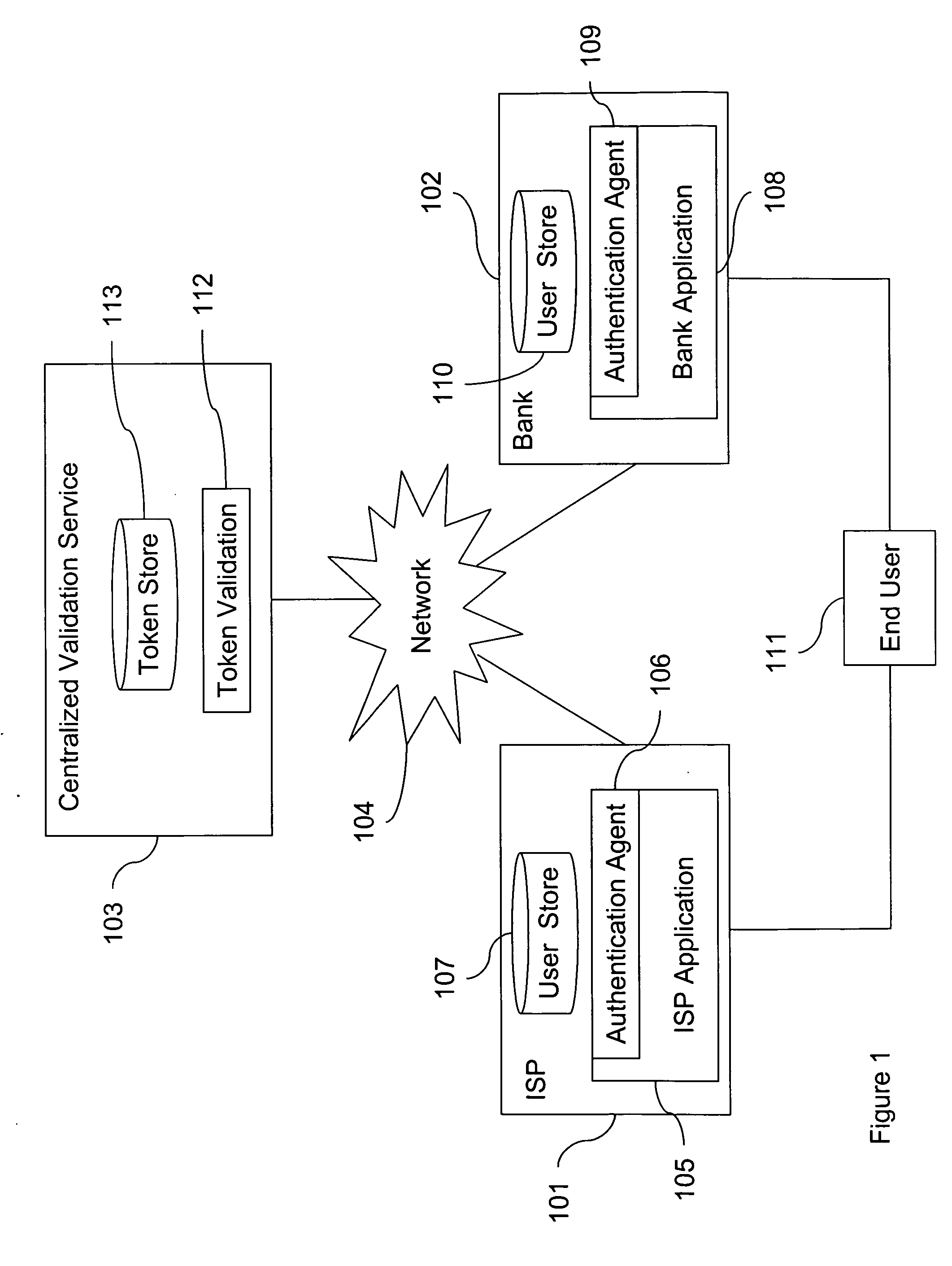
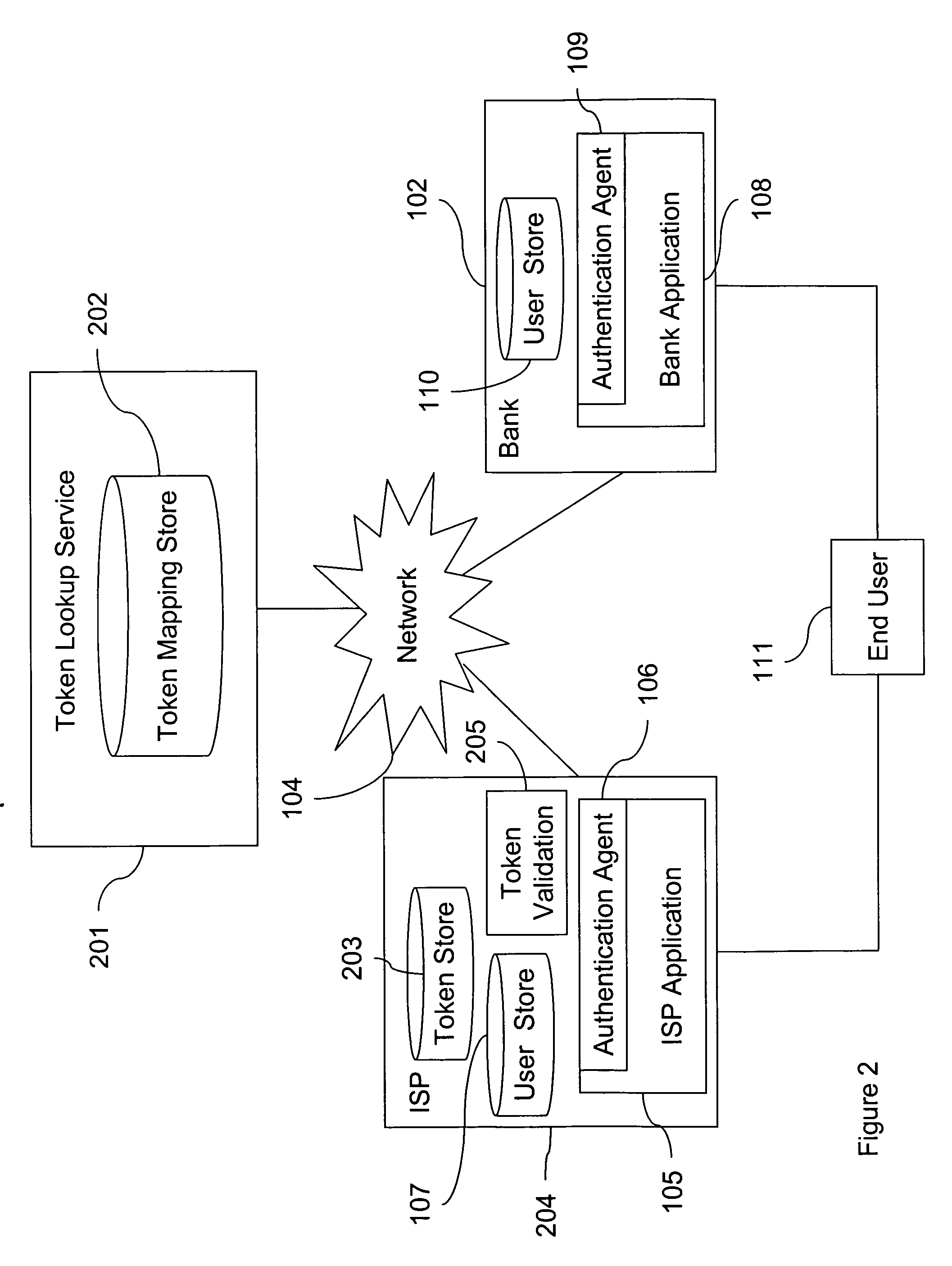
Token sharing system and method
A scalable system and method for authenticating entities such as consumers to entities with a diverse set of authentication requirements, such as merchants, banks, vendors, other consumers, and so on. An authentication credential such as a token can be shared among several resources as a way to authenticate the credential owner.
Owner:CA TECH INC
Scalable system for wide area surveillance
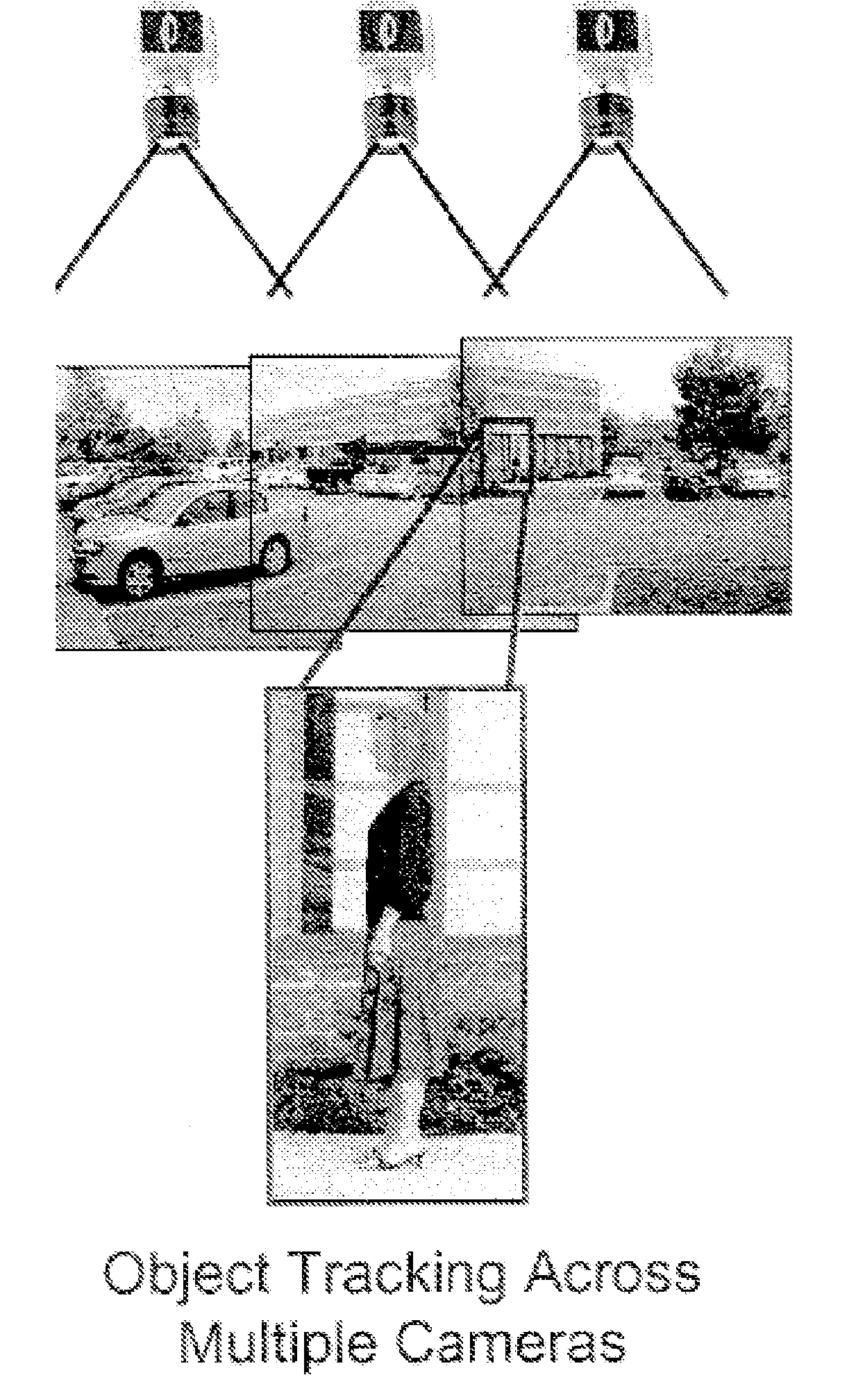
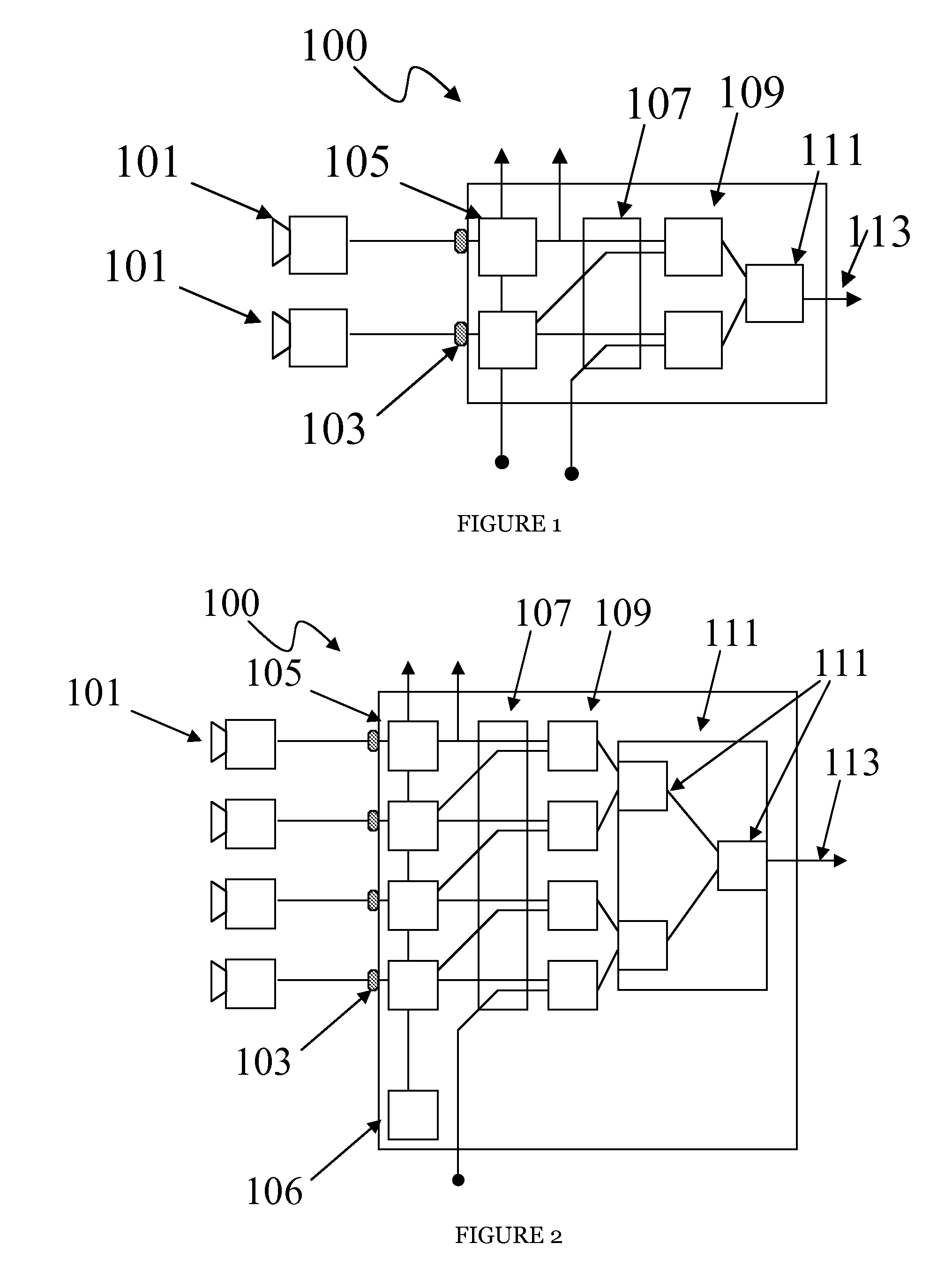
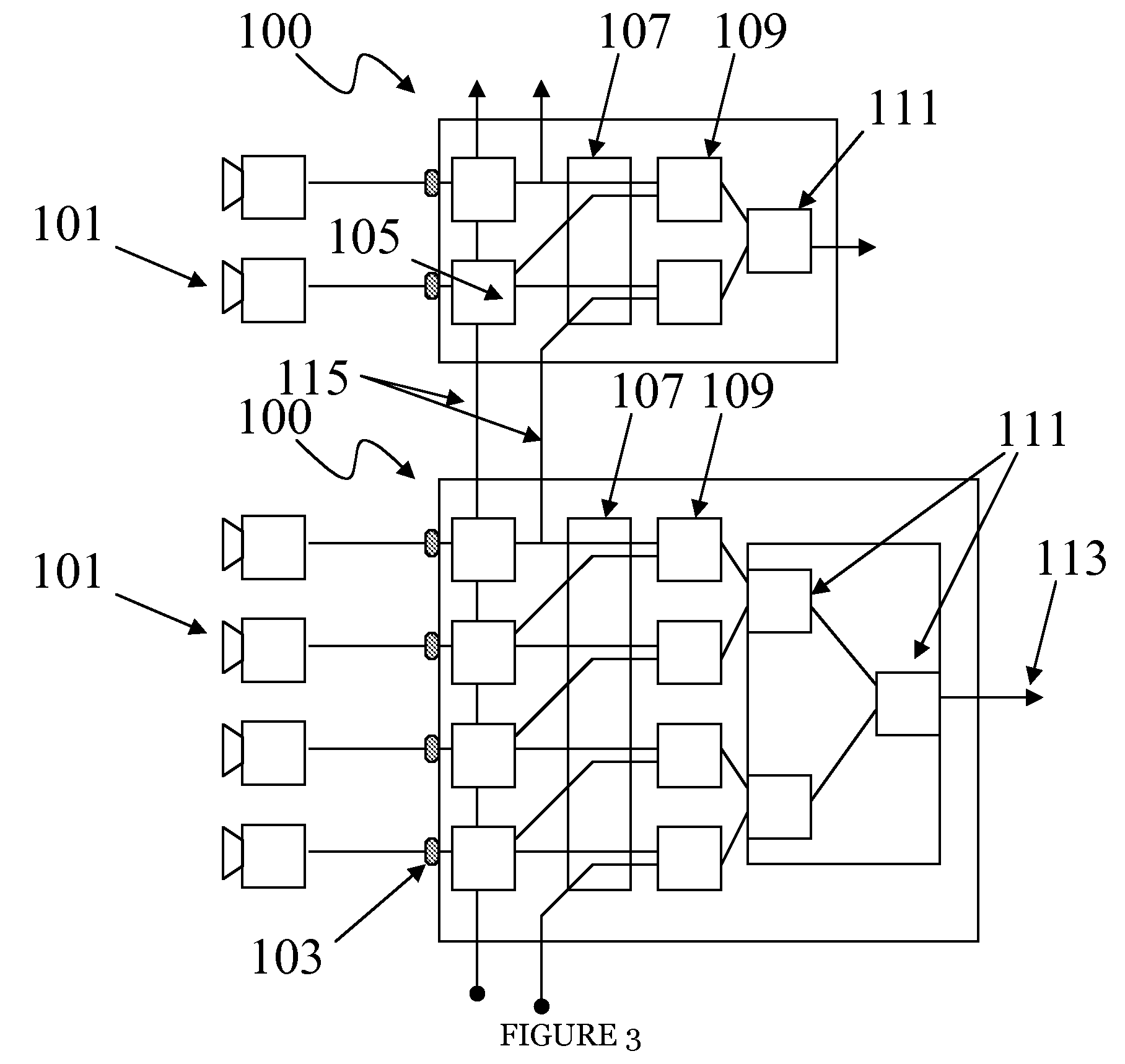
InactiveUS20080211915A1Character and pattern recognitionClosed circuit television systemsScalable systemWide area
According to one embodiment, a controller for a surveillance system includes ports for coupling a camera, synchronization logic blocks coupled to the ports, an information aggregation logic block coupled to the camera ports, and an output port coupled to the information aggregation logic block. According to another embodiment, a method of scaling a surveillance system includes synchronizing a plurality of cameras, capturing images from the synchronized cameras, aggregating at least two processed synchronized images, and processing the aggregated synchronized images.
Owner:PIXEL VELOCITY
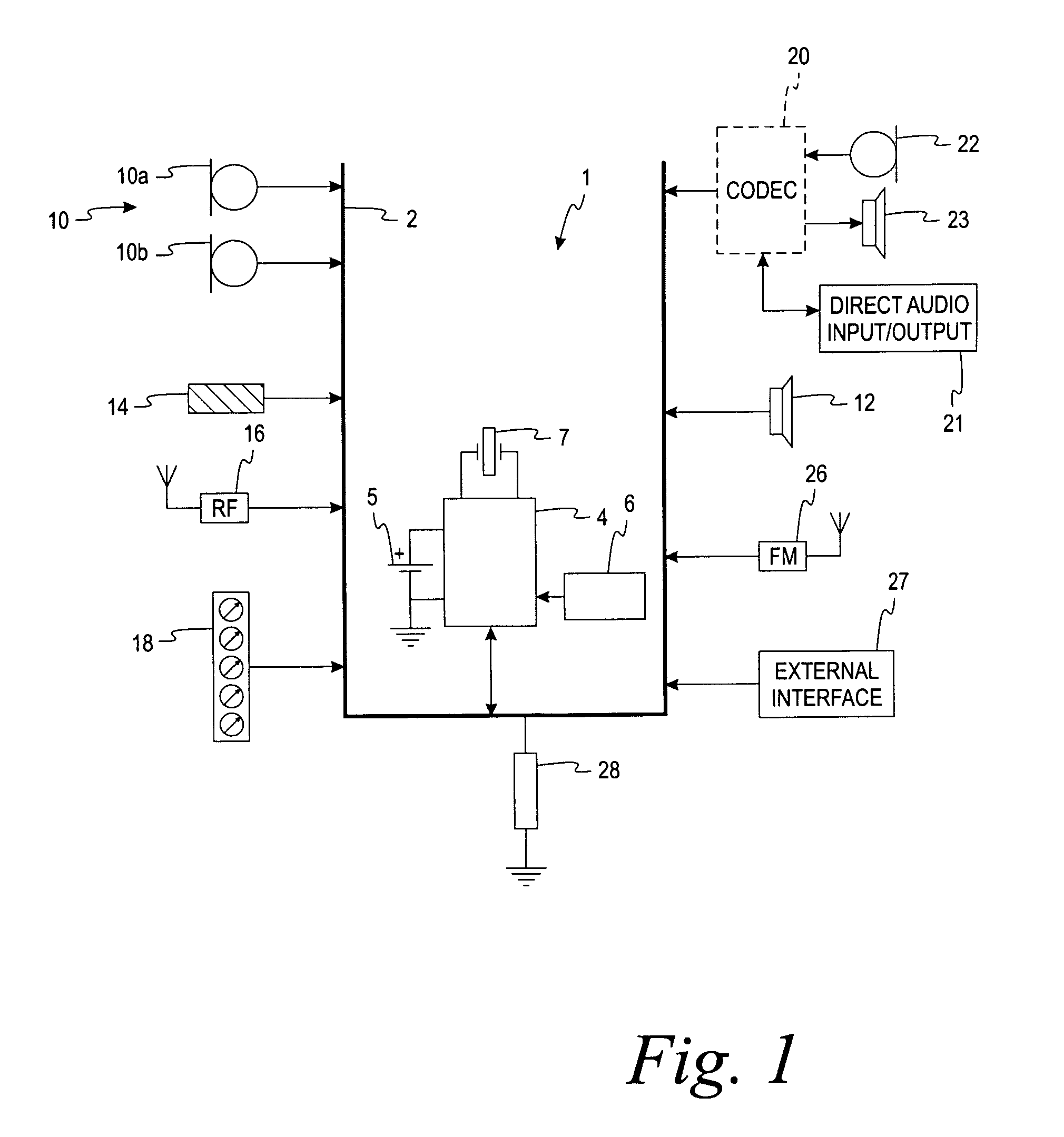
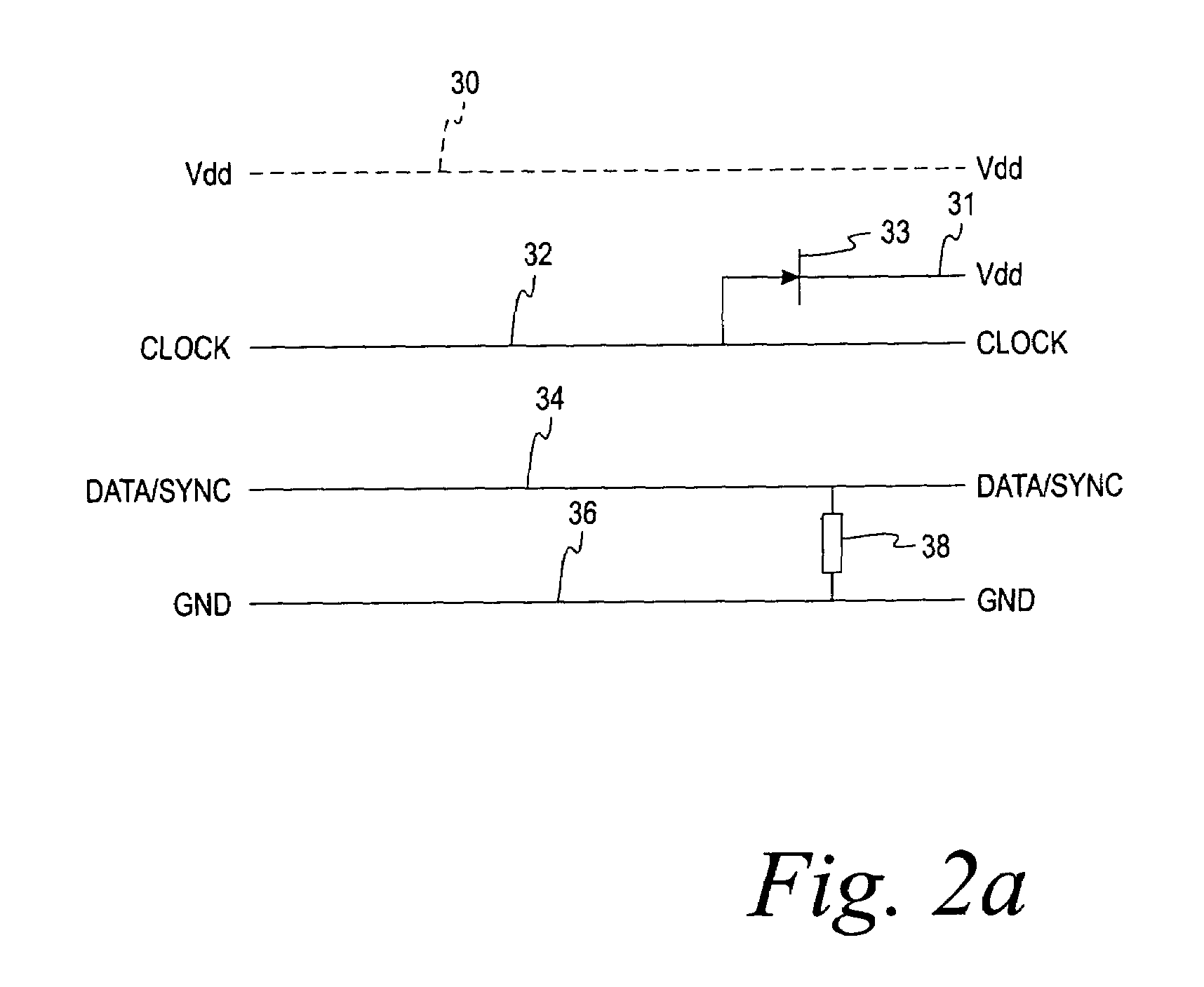
Digital system bus for use in low power instruments such as hearing aids and listening devices
InactiveUS7292876B2Avoids compromising bus speedReduce power consumptionEar supported setsSubstation equipmentScalable systemLow voltage
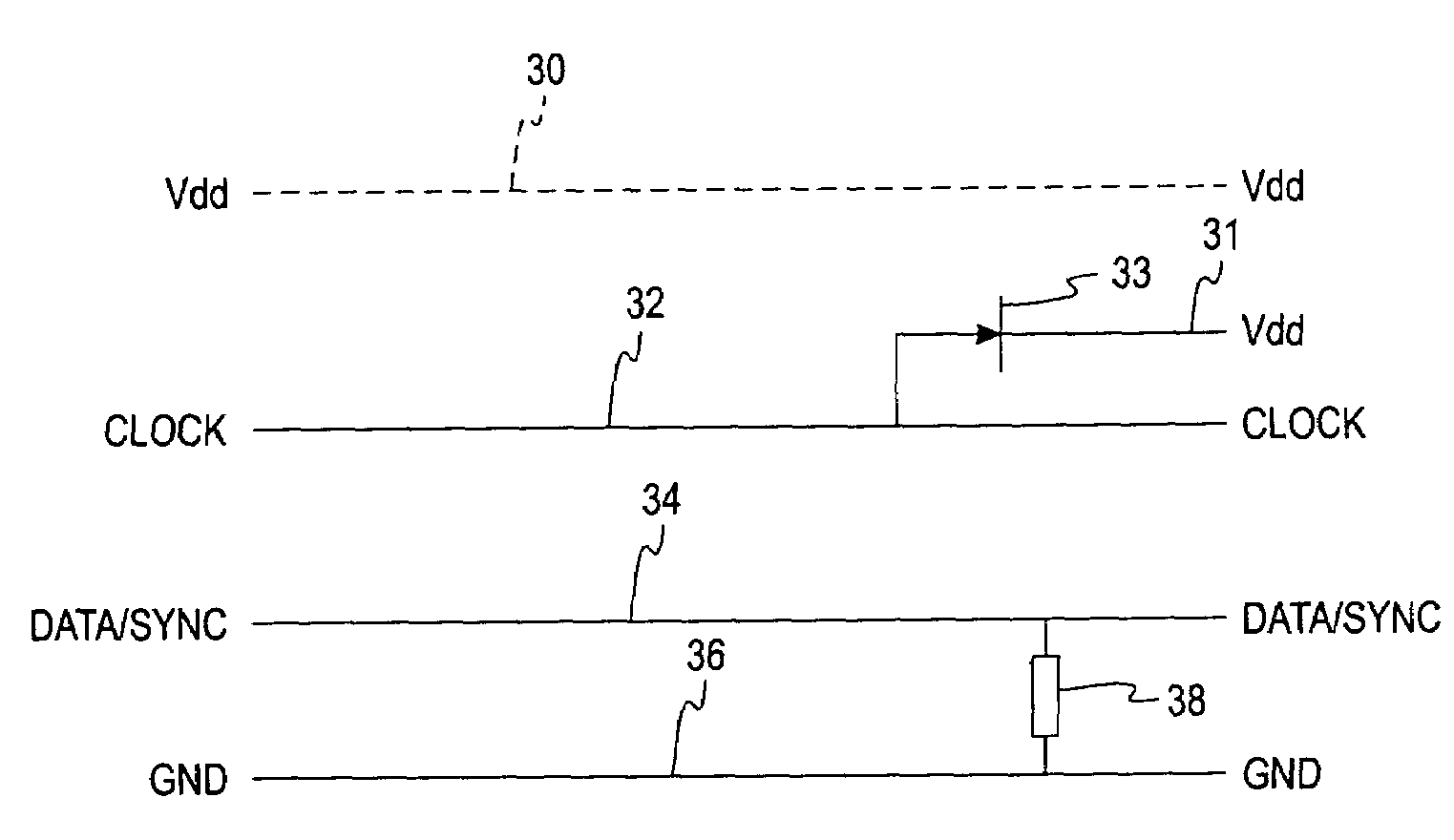
A low-voltage, low-power, synchronous, bidirectional, time-multiplexed, serial communication, scalable system bus carrying a number of signals over a fewer number of wires between a master device and peripheral devices or between peripheral devices. One of the wires carries a composite digital signal that includes a data signal and a synchronizing signal, though other combinations are contemplated. The system bus can support more peripheral devices than there are available time slots, and supports interrupt polling and servicing. In addition, peripheral devices that include an electro-mechanical or electro-acoustical component connected to the system bus can also communicate directly to each other without using the system bus. The system bus can be implemented in low voltage, low power devices, including listening devices such as hearing instruments and headsets, portable telephones, and personal digital assistants.
Owner:SONION NEDERLAND
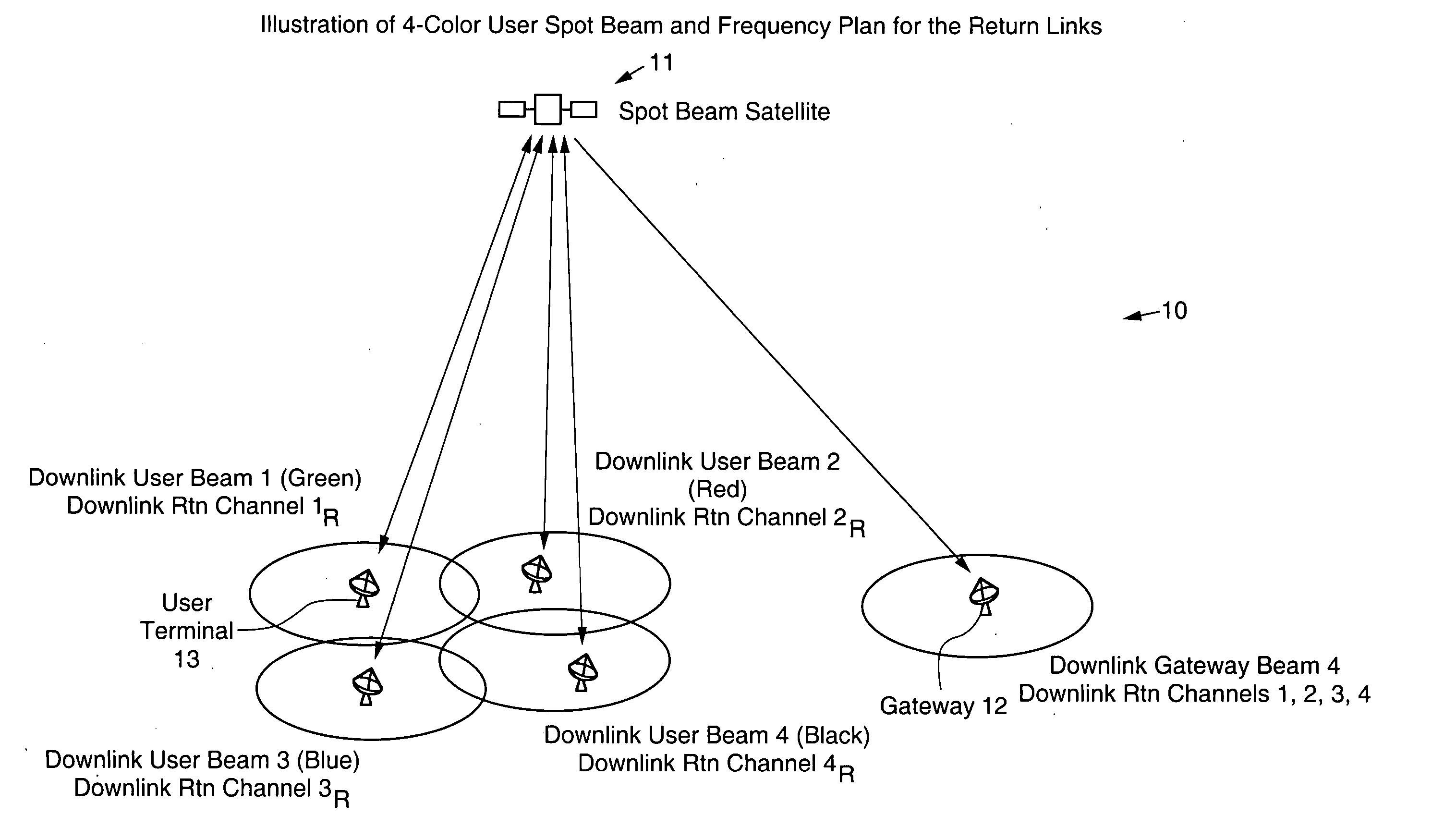
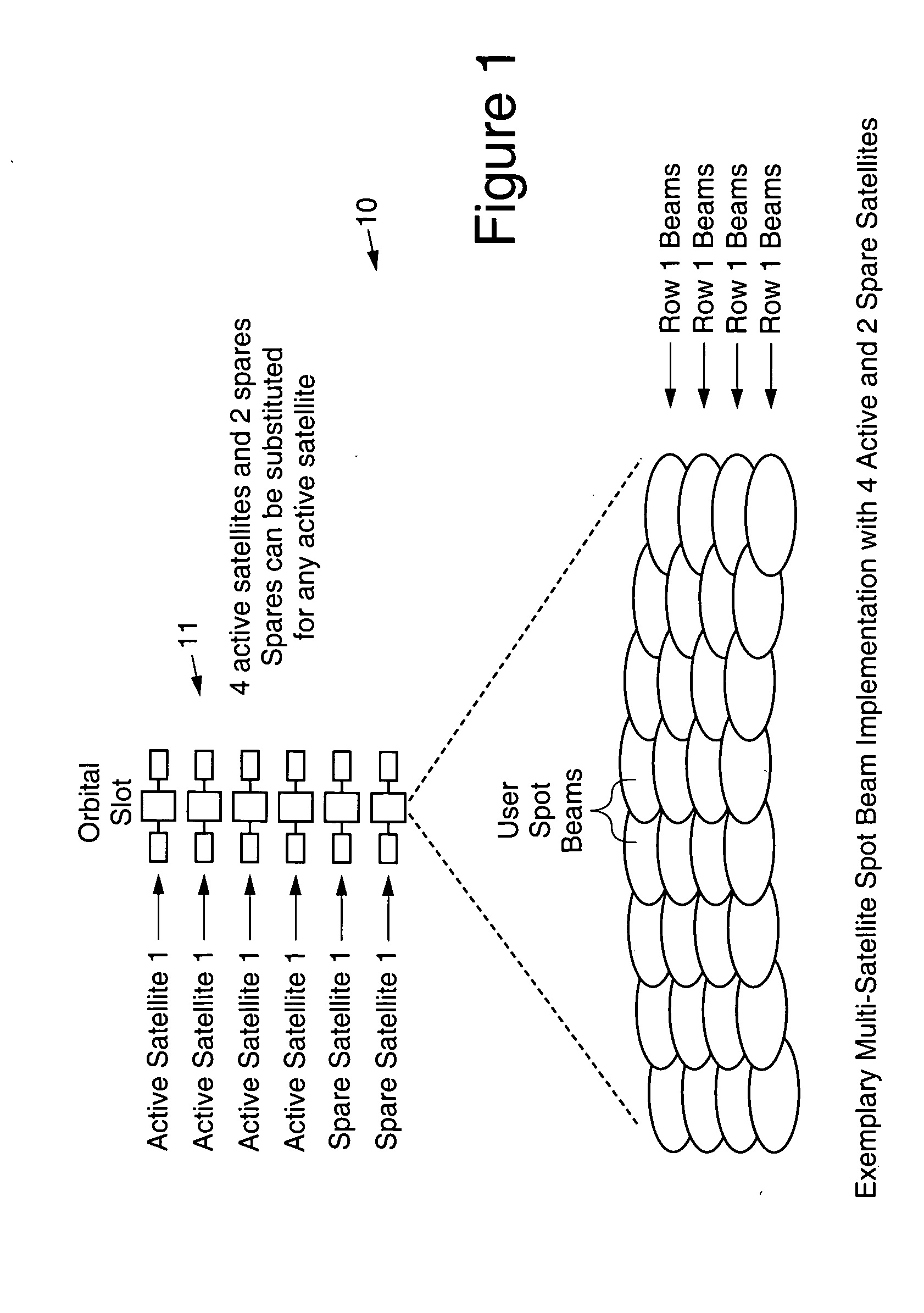
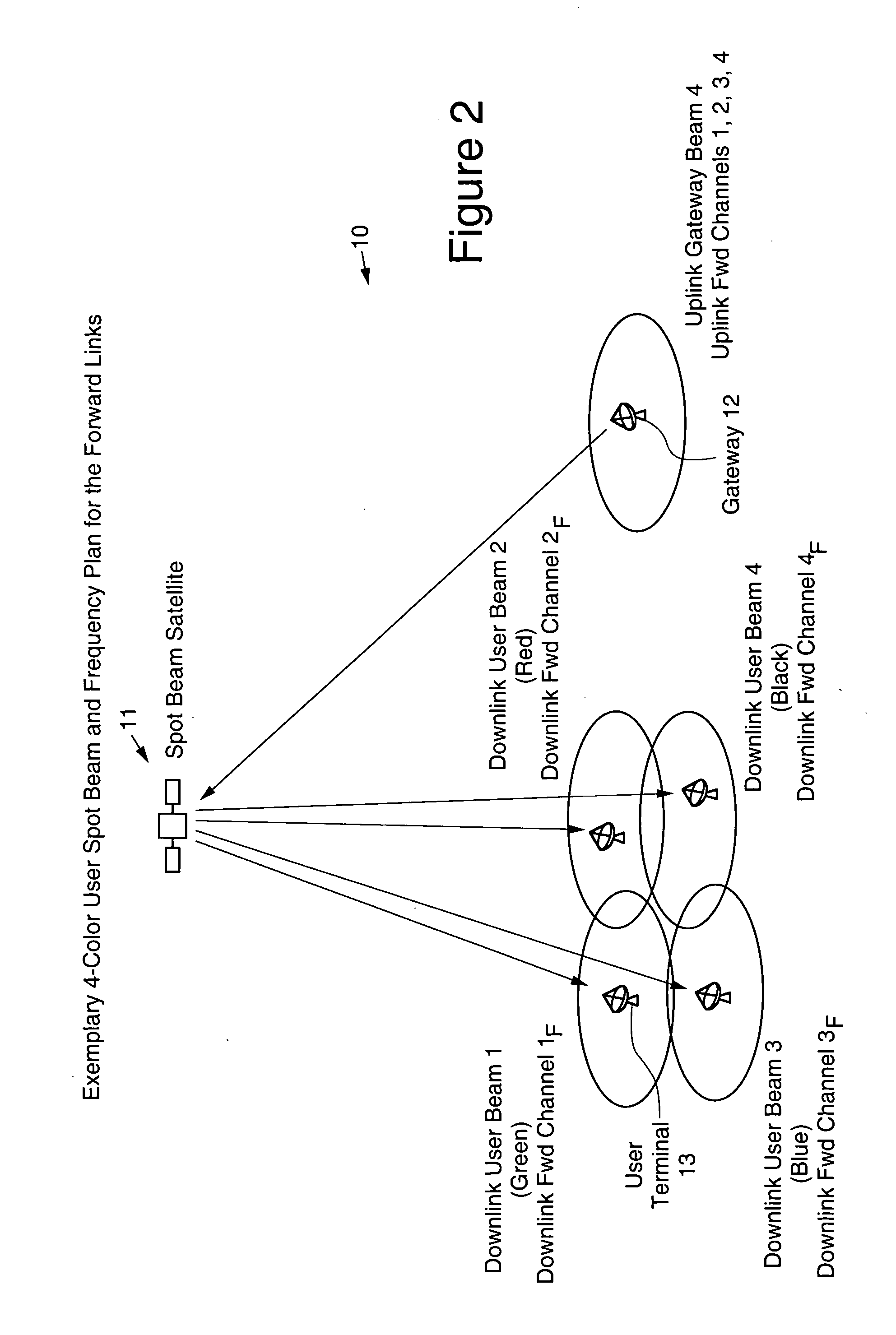
Scalable multi-satellite spot beam architecture
InactiveUS20050197060A1Active radio relay systemsHigh level techniquesScalable systemTelecommunications network
A scalable multi-satellite spot-beam network architecture that employs a plurality (N) of relatively small (low power) active spot beam satellites and a number (R) of spare satellites, all of which are substantially similar in design, has been described. The plurality of satellites is substantially collocated at a given orbital location to provide coverage of a desired geographic area. Each active satellite has 1 / N of the total capacity of a slot, and there is significant amount of interchangeability among the active and spare satellites, enabling the spare and active satellites to provide protection against partial or full failures of any satellite or even a few (up to R) satellites. The system is scalable since a fraction of the N active satellites is required to provide capacity to the full geographic area, and additional satellites can be launched and additional gateways can be deployed to augment the network capacity. Communication devices (users) located in any of the spot beams communicate with each other and the worldwide telecommunications network via satellites and gateways of the scalable system architecture.
Owner:LORAL SKYNET CORP
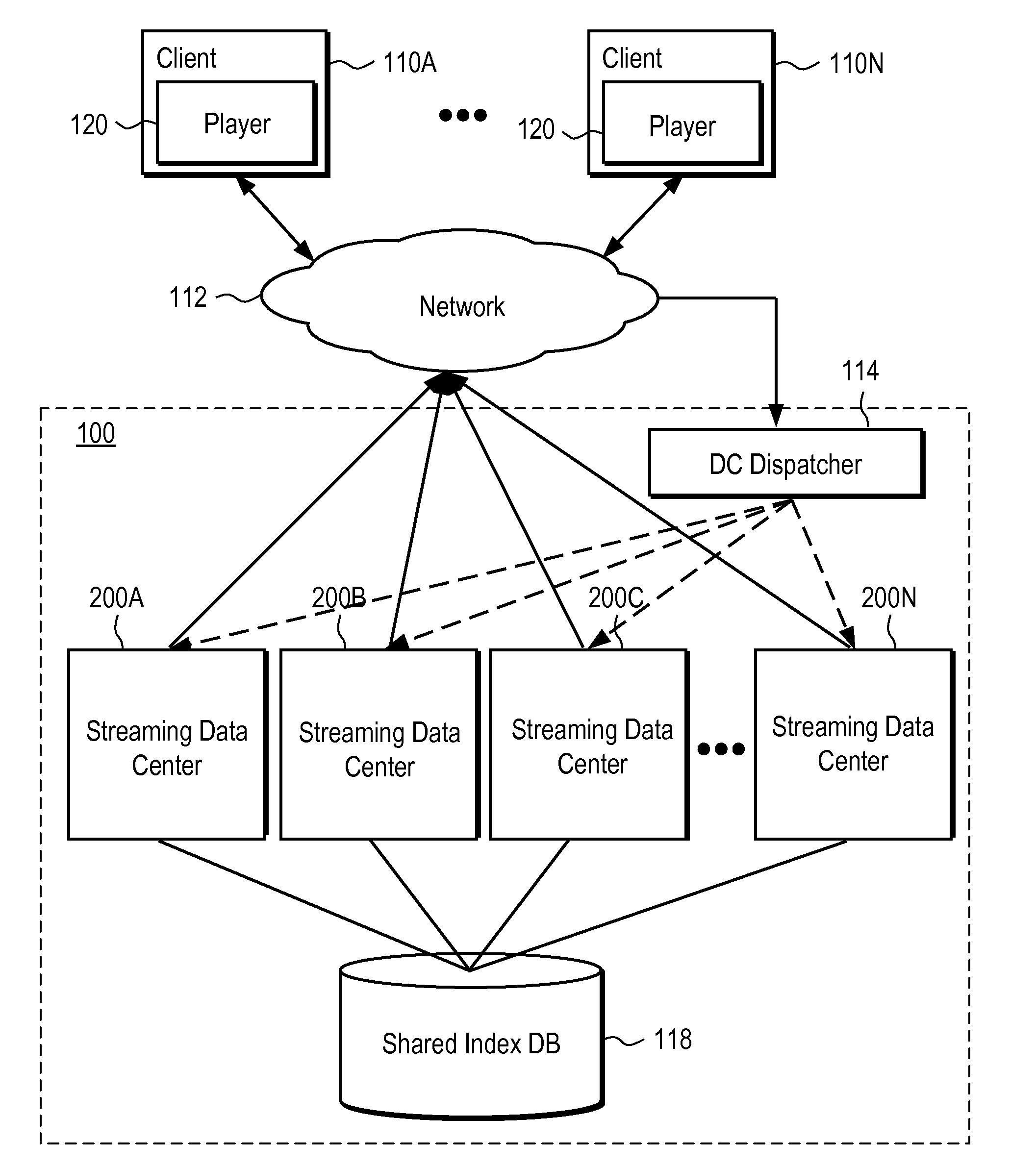
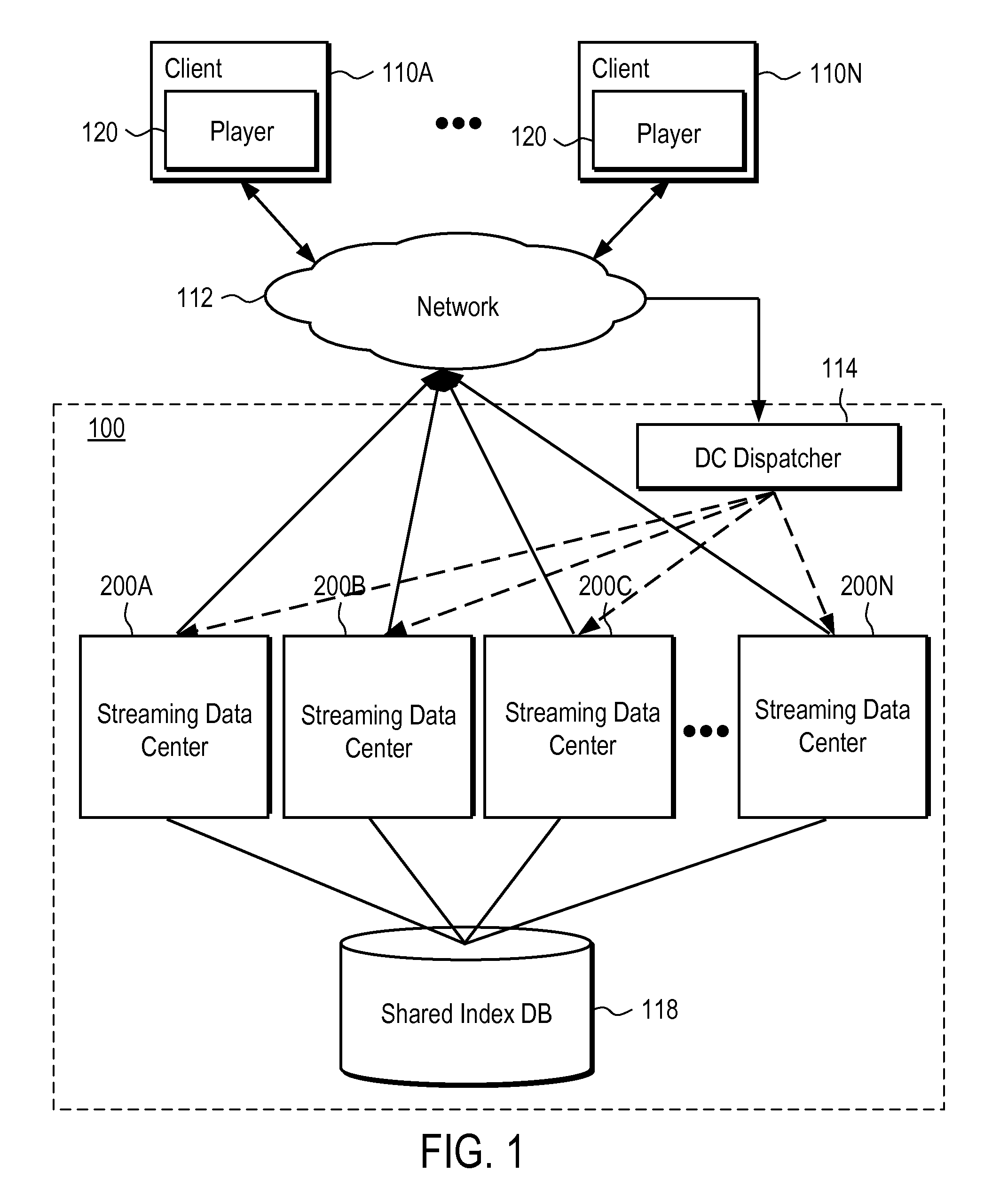
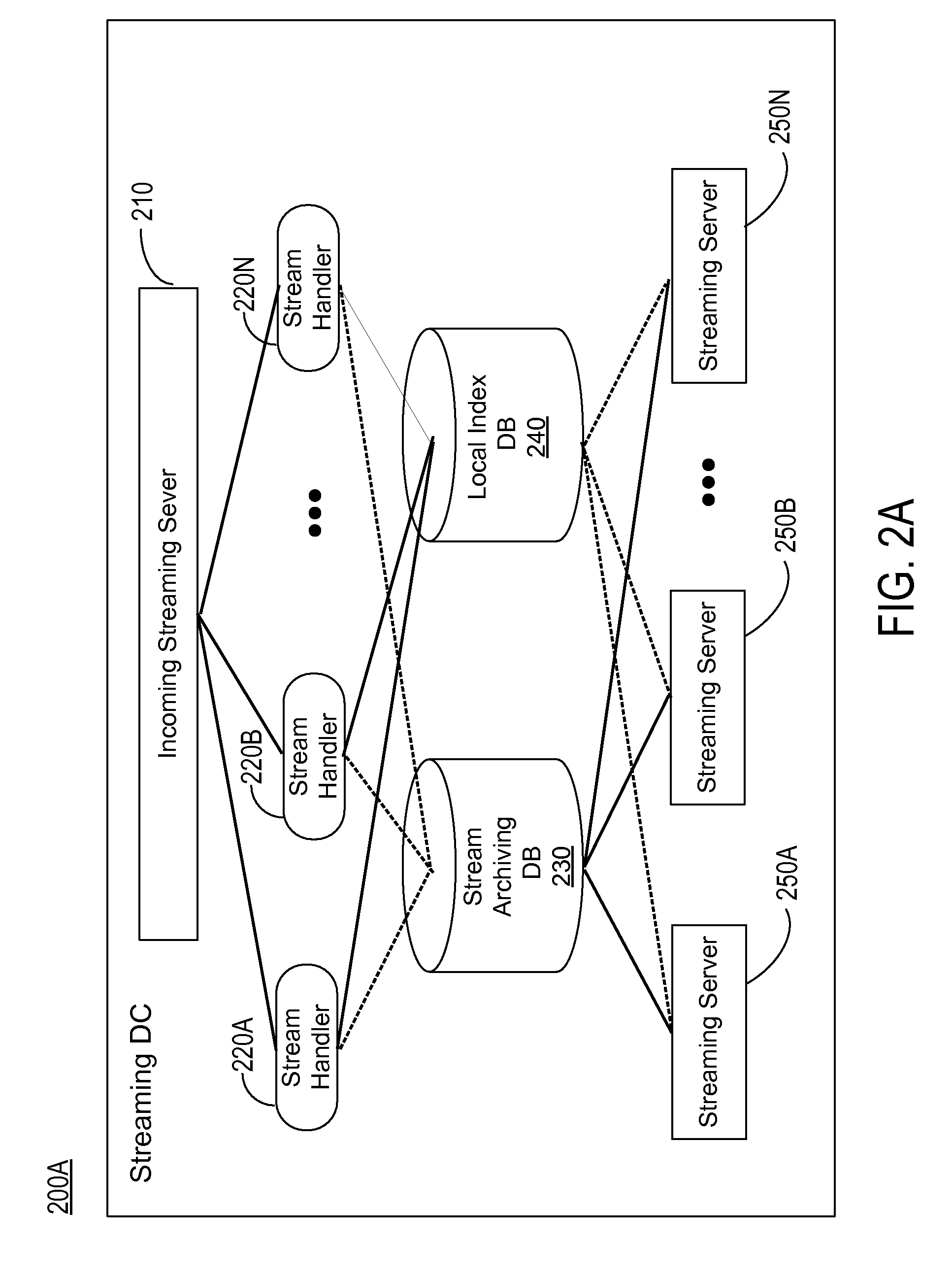
Server-side support for seamless rewind and playback of video streaming
A system and method provide server side support for seamless, scalable rewind and playback of a video stream. A video stream is stored and indexed in a network storage place. A video stream can be indexed at frame level where each intra frame of the video stream has an index indicating the file offset and the time stamp of the intra frame in the video stream. A user request for rewinding of a video stream while the video stream is being broadcast is processed by extracting the rewinding time requirement from the user request. The extracted rewinding time value is used to calculate the requested file offset. The video stream starting at the requested time is retrieved and played back according to the user request. The system also provides server side support for seamless rewinding of a video stream and scalable system performance across multiple streaming data centers.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
System and methods for facilitating user- requested content services and related technologies
InactiveUS20100042592A1Facilitating the set-up of AlertsDigital data processing detailsOffice automationScalable systemRSS
Aspects of the invention include a system and a method of providing a scalable system architecture and methods facilitating user-requested content alerts. Additionally, aspects of the invention are directed to a system and method of providing customized alerts to a user link atoms corresponding to discrete subjects of information requested by the user to form molecules which can be received by an interactive media device to display the information corresponding to each atom. Other aspects of the invention include a system and a method of facilitating user-requested content utilizing Real Simple Syndication (RSS). The present invention is further directed at providing a system and method for expanding user-requested content, and systems and methods of facilitating monetization of user-requested content via electronic mail.
Owner:STOLZ PASCAL +4
System and method for real-time tracking of objects
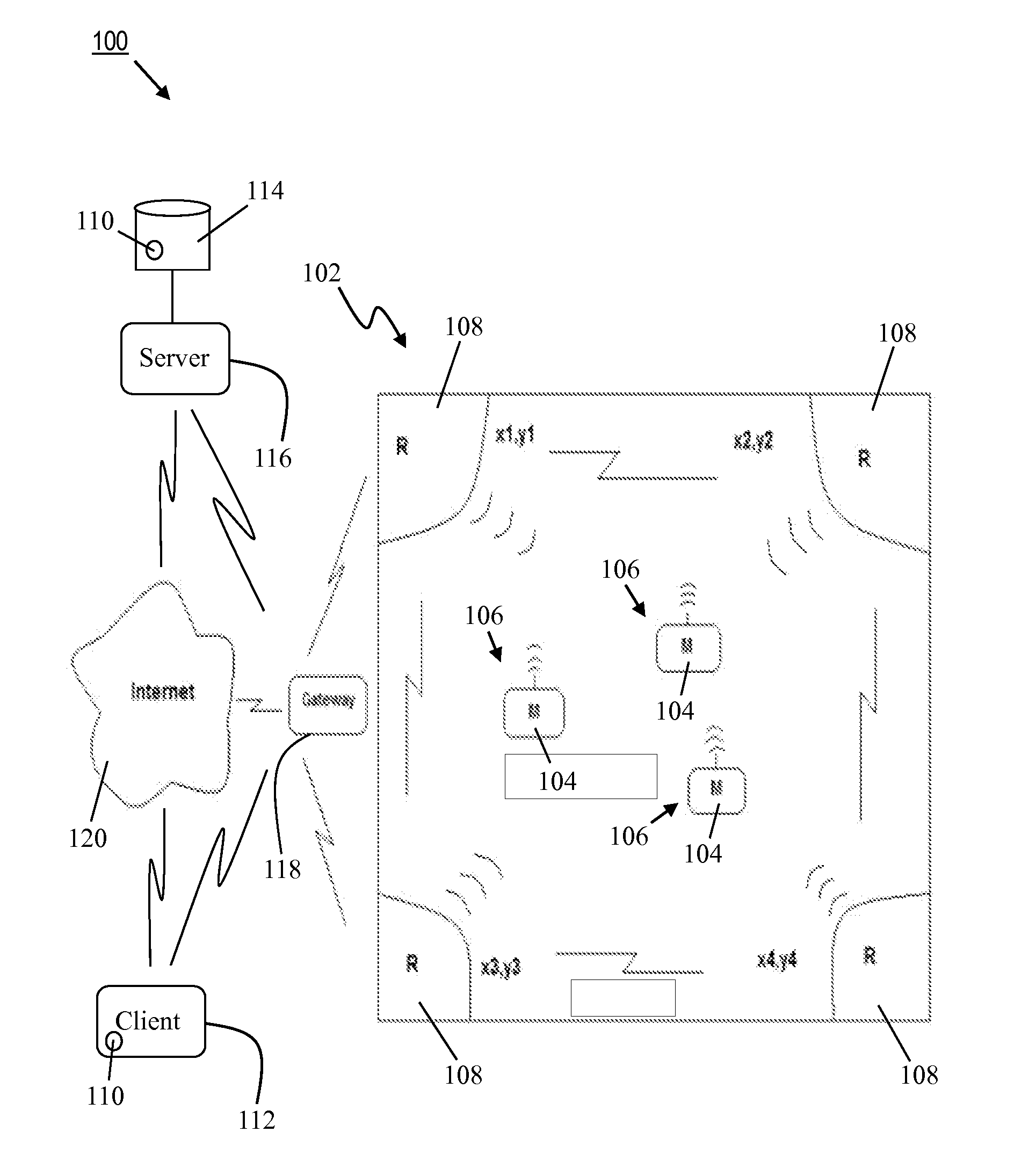
ActiveUS20110030875A1Small, low-power, and low-costLamination ancillary operationsControlling laminationScalable systemWireless mesh network
Real-time location systems and methods use small, battery operated sensors and radios. The radios conform to the IEEE 802.15.4 standard. The radios are attached to objects to form mobile nodes. Fixed nodes are positioned to define a wired or wireless mesh network representing an area in which the objects can be monitored and tracked. The real-time location systems / methods provide robust, flexible and highly scalable systems / methods for remotely, accurately, efficiently, and / or readily tracking and securing objects (e.g., equipment, inventory, people) at a relatively low cost.
Owner:VORTEX TECH GRP LLC
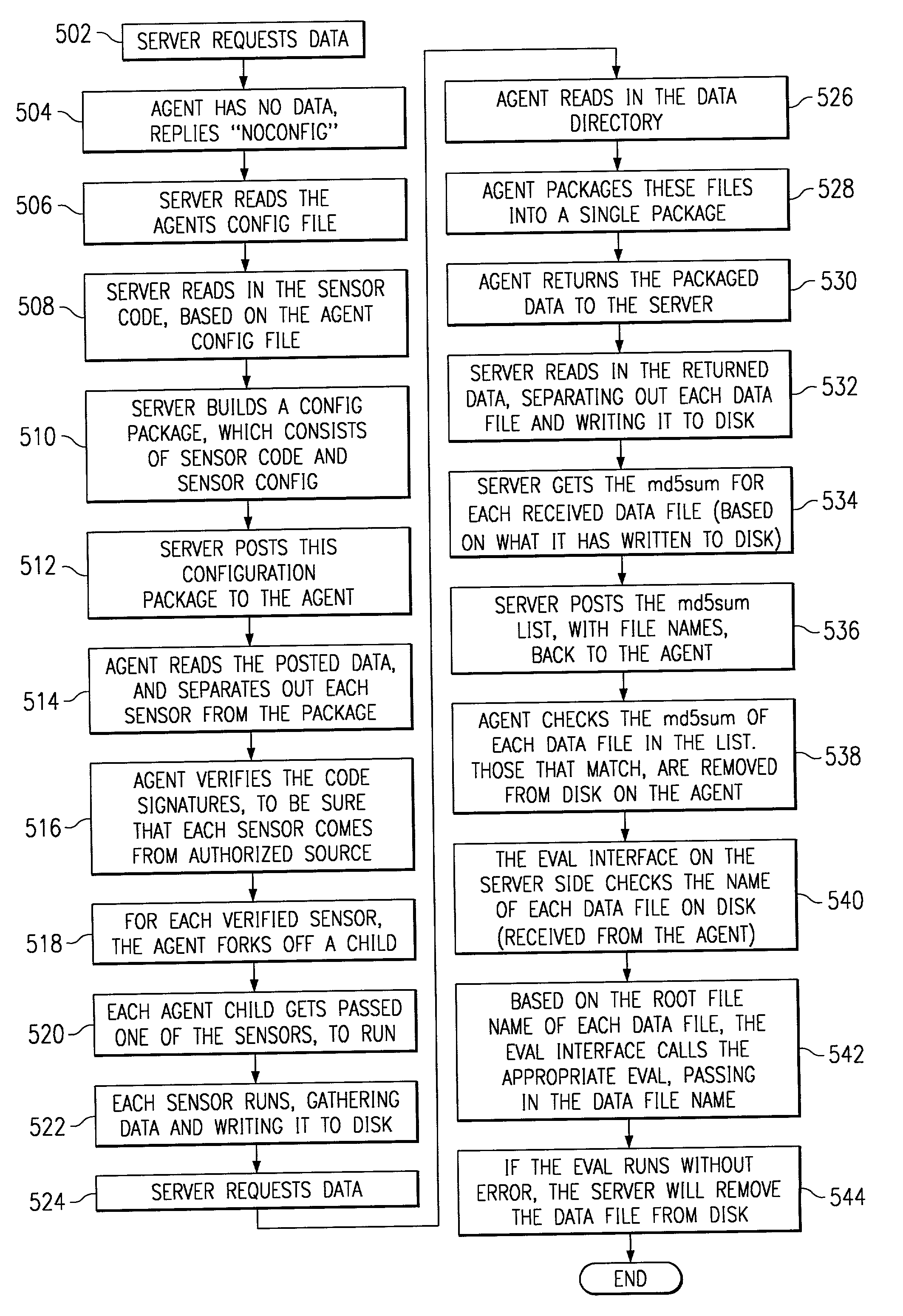
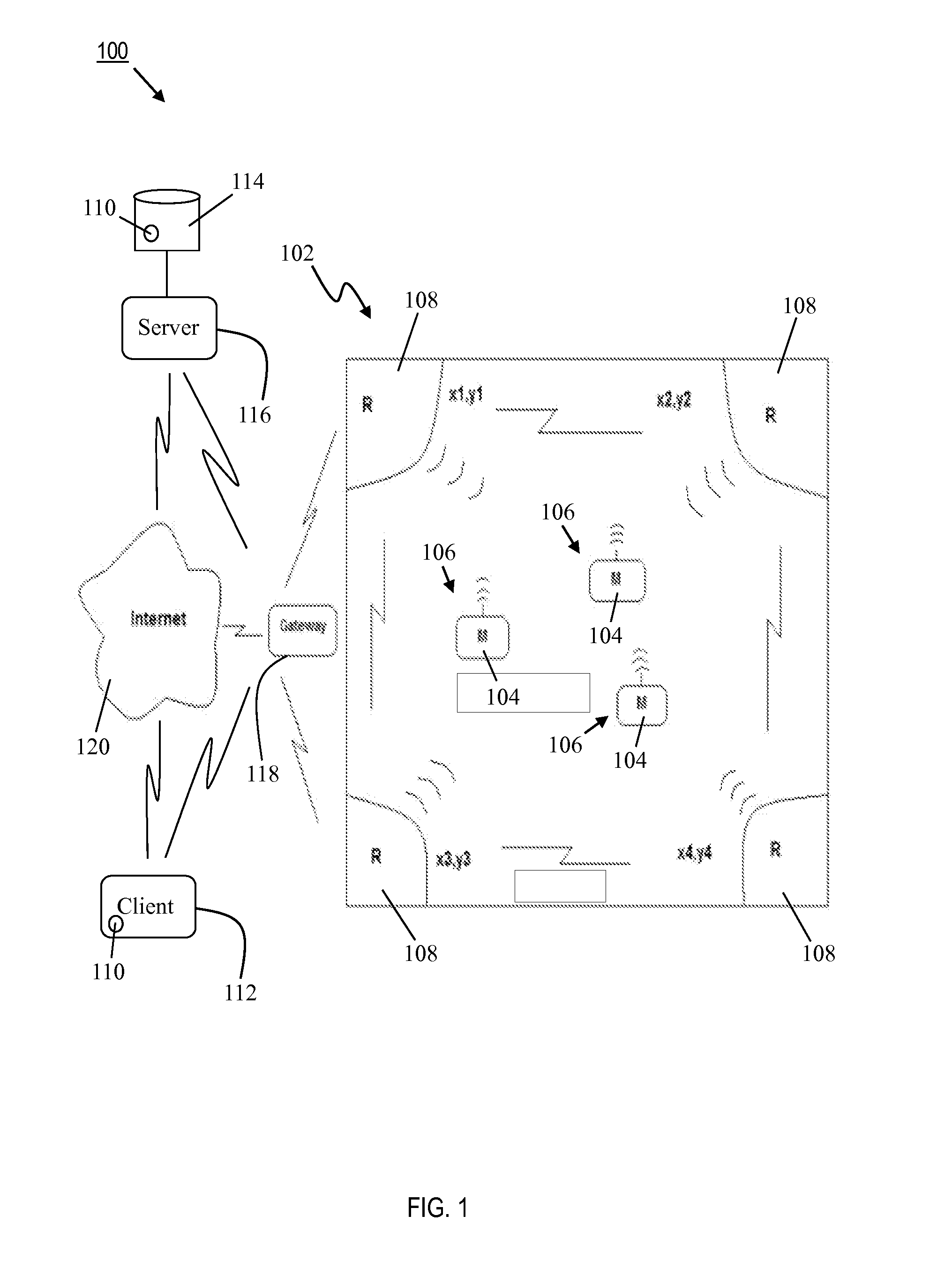
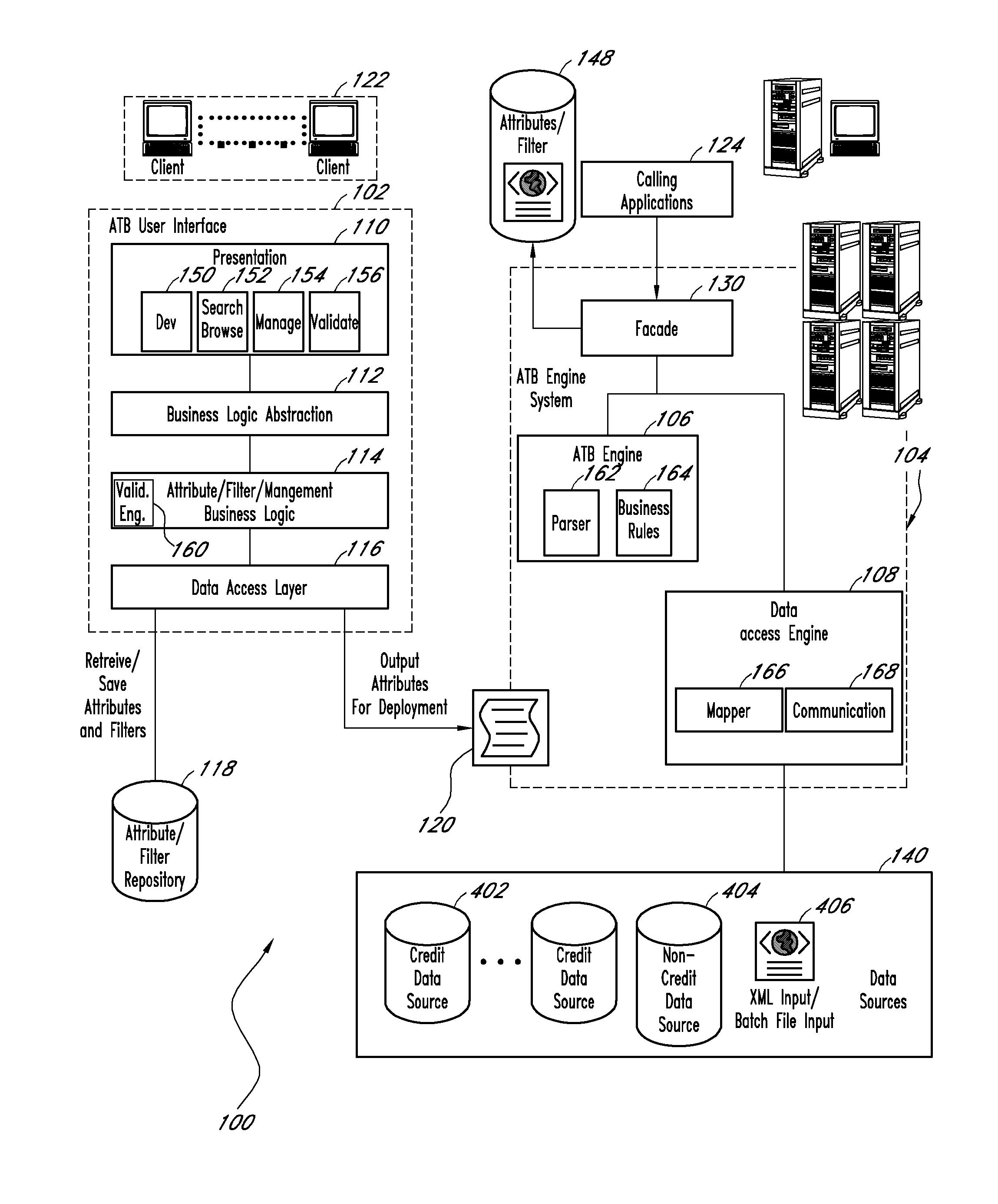
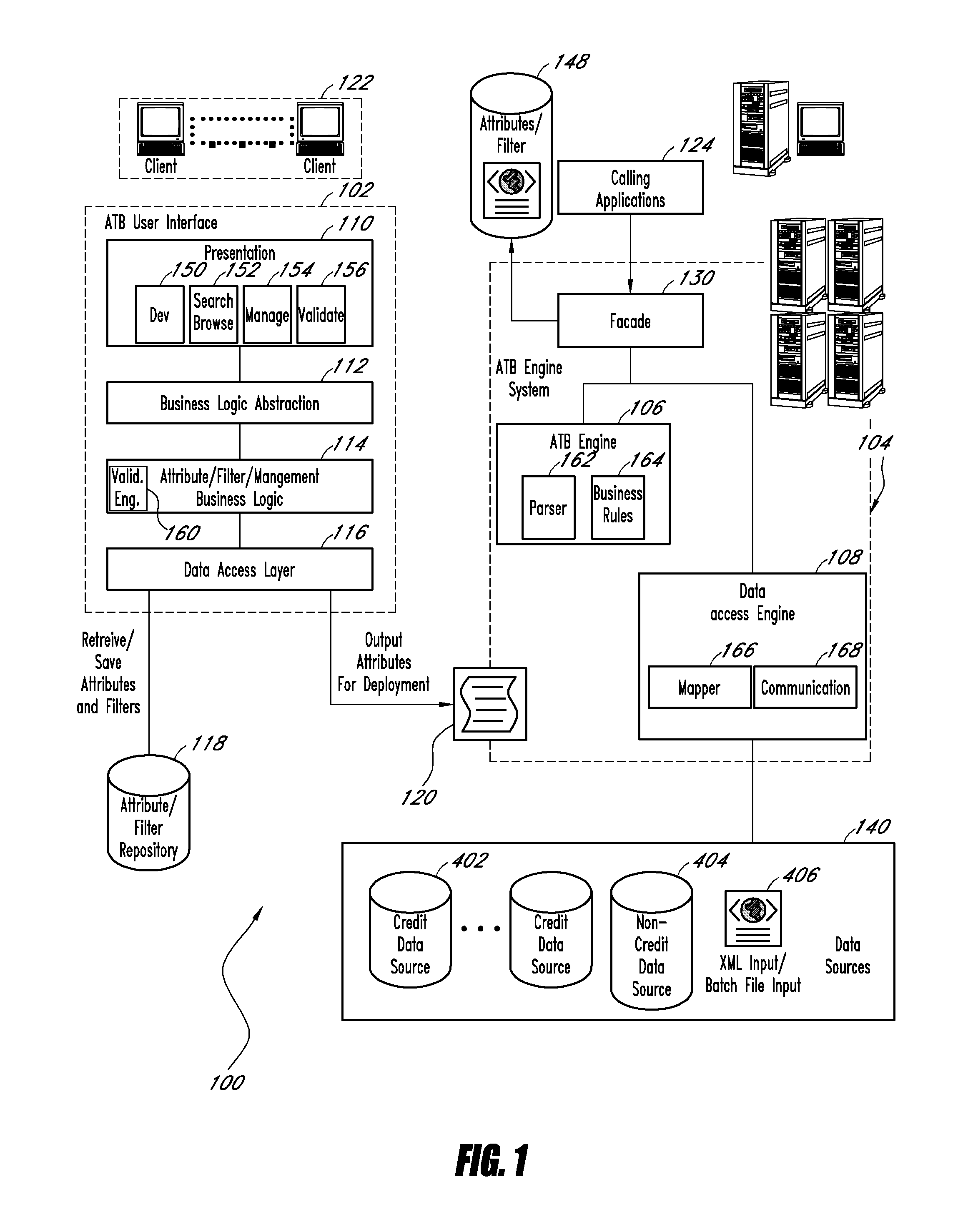
System and method for providing an aggregation tool
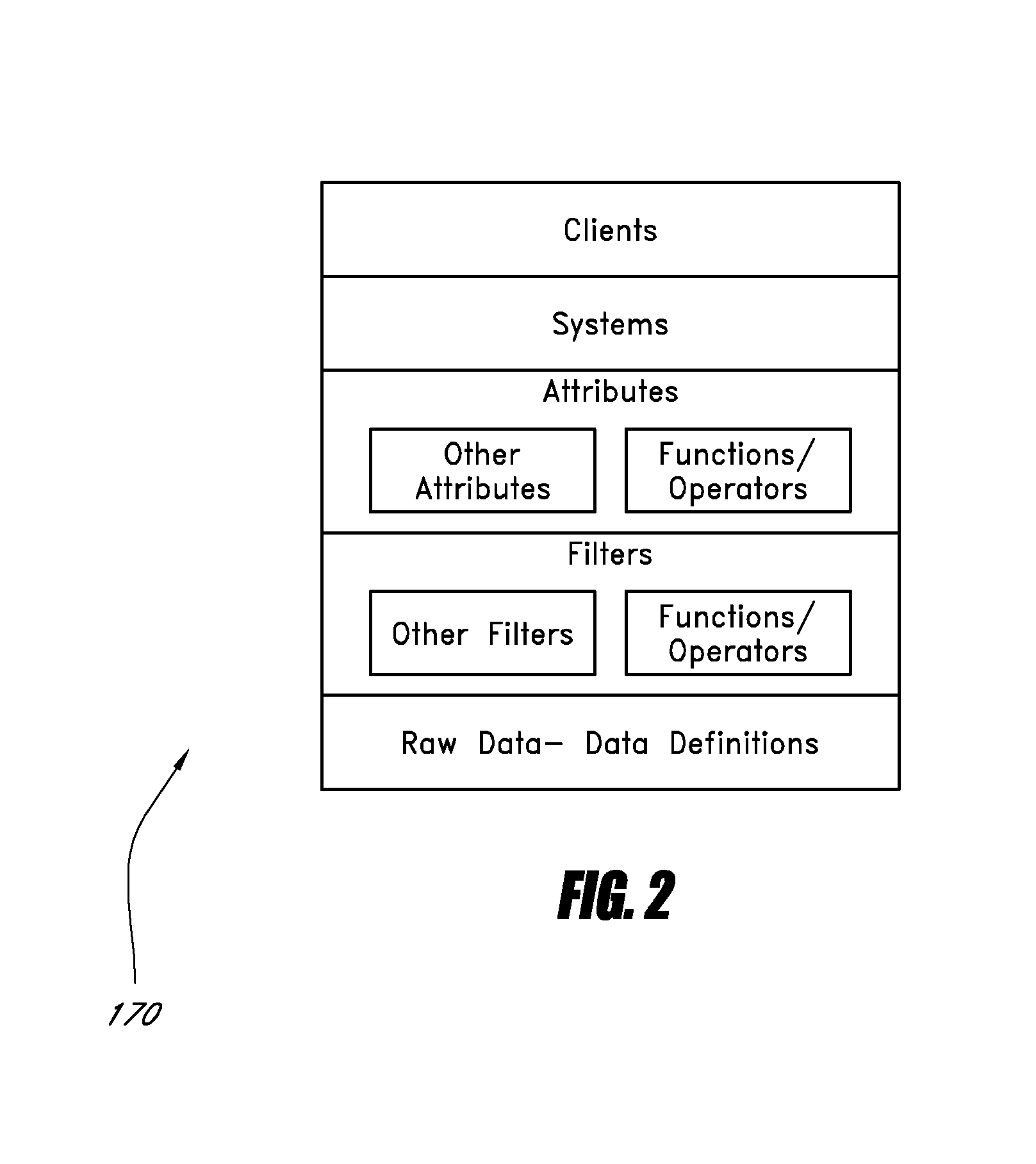
Embodiments of the present invention assist in the development, management, and deployment of aggregated data attributes for multiple data sources. One embodiment provides a development interface that allows for elements of attributes, including filters, to be moved into a coding area in which an attribute or an attribute element is being edited. In another embodiment, the user interface presents data fields to assist in the development of filters for multiple data sources with divergent formats. The application further provides a validation interface through which users can validate attributes and trace the results returned by various elements referenced by the attributes under validation. Another embodiment provides a system for managing attributes and deploying them to various systems by creating a deployment file that is used by an attribute calculation system. In one embodiment, the attribute calculation system is a scalable system that dynamically calculates attributes for multiple data sources.
Owner:EXPERIAN INFORMATION SOLUTIONS
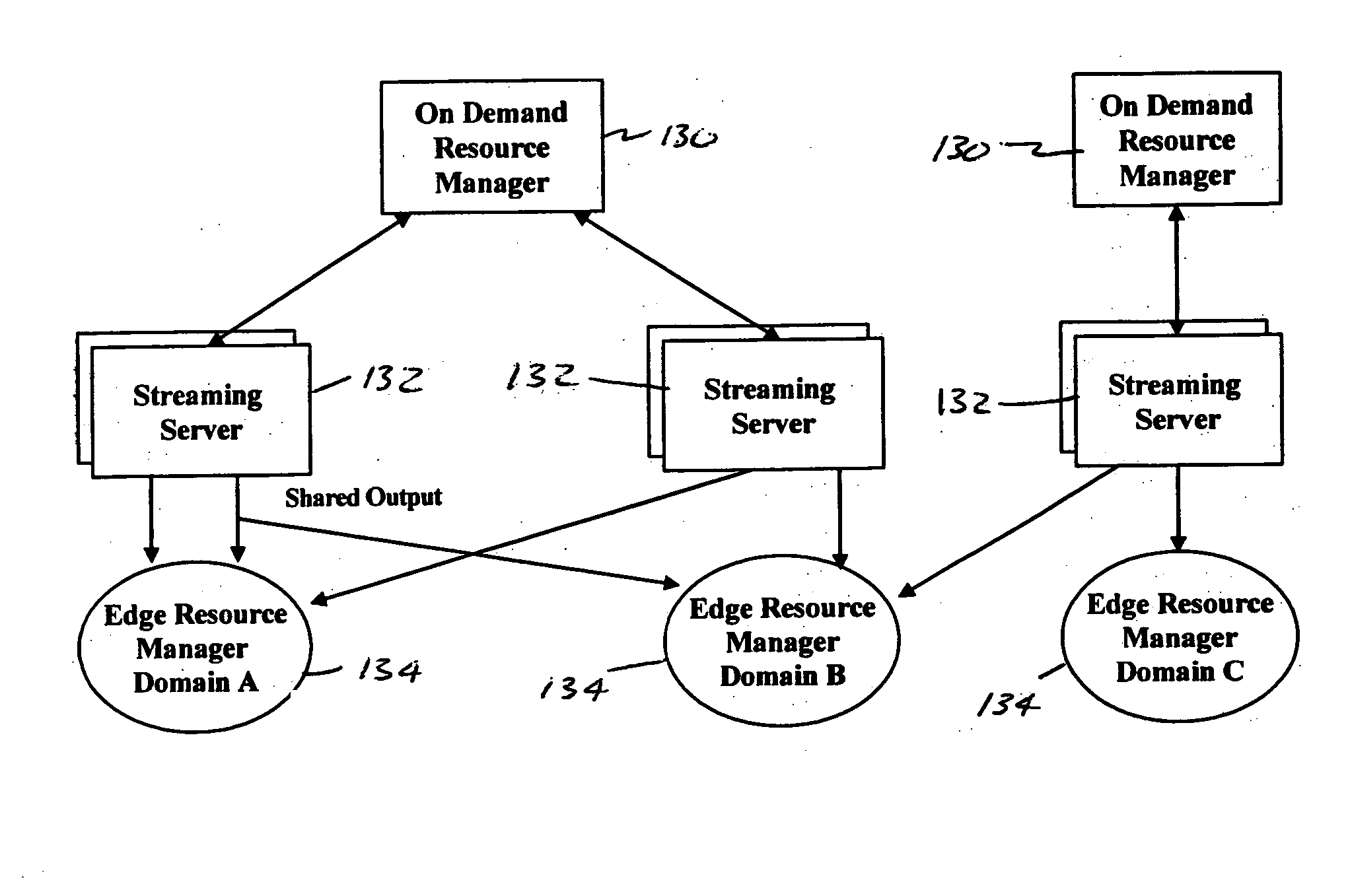
Signaling redirection for distributed session and resource management
A system for on demand session and resource management in an on demand platform for the delivery of on demand digital assets involve a session manager, a plurality of resource managers, and a resource manager redirector. These components cooperate to provide a distributed and scalable system for on demand session and resource management. Redirection of session and resource signaling messages among various session and resource managers by the resource manager redirector allows the unavailability of devices or resources to remain transparent to the session manager. The resource manager redirector redirects messages from the session manager as appropriate.
Owner:COMCAST CABLE COMM LLC
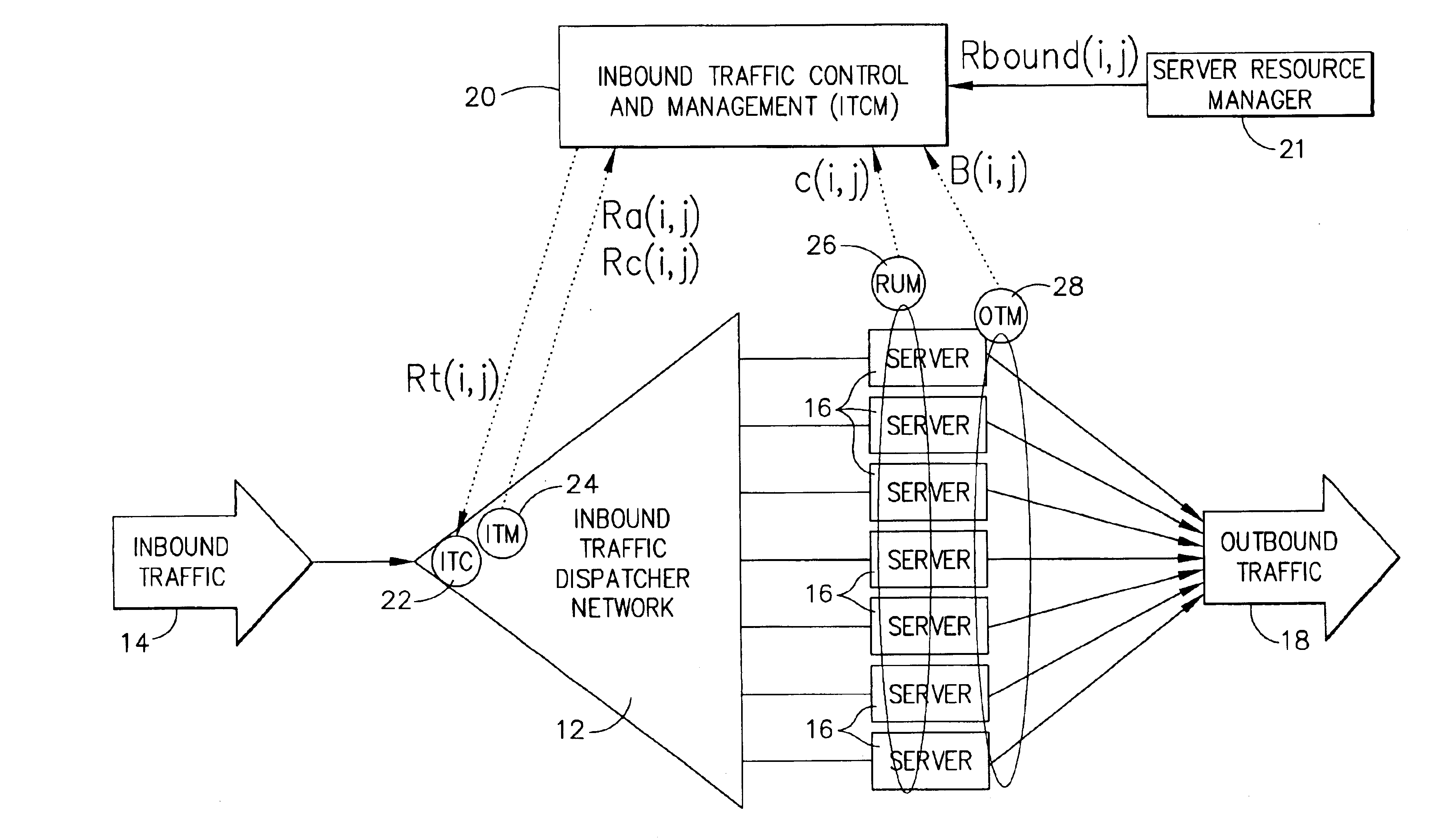
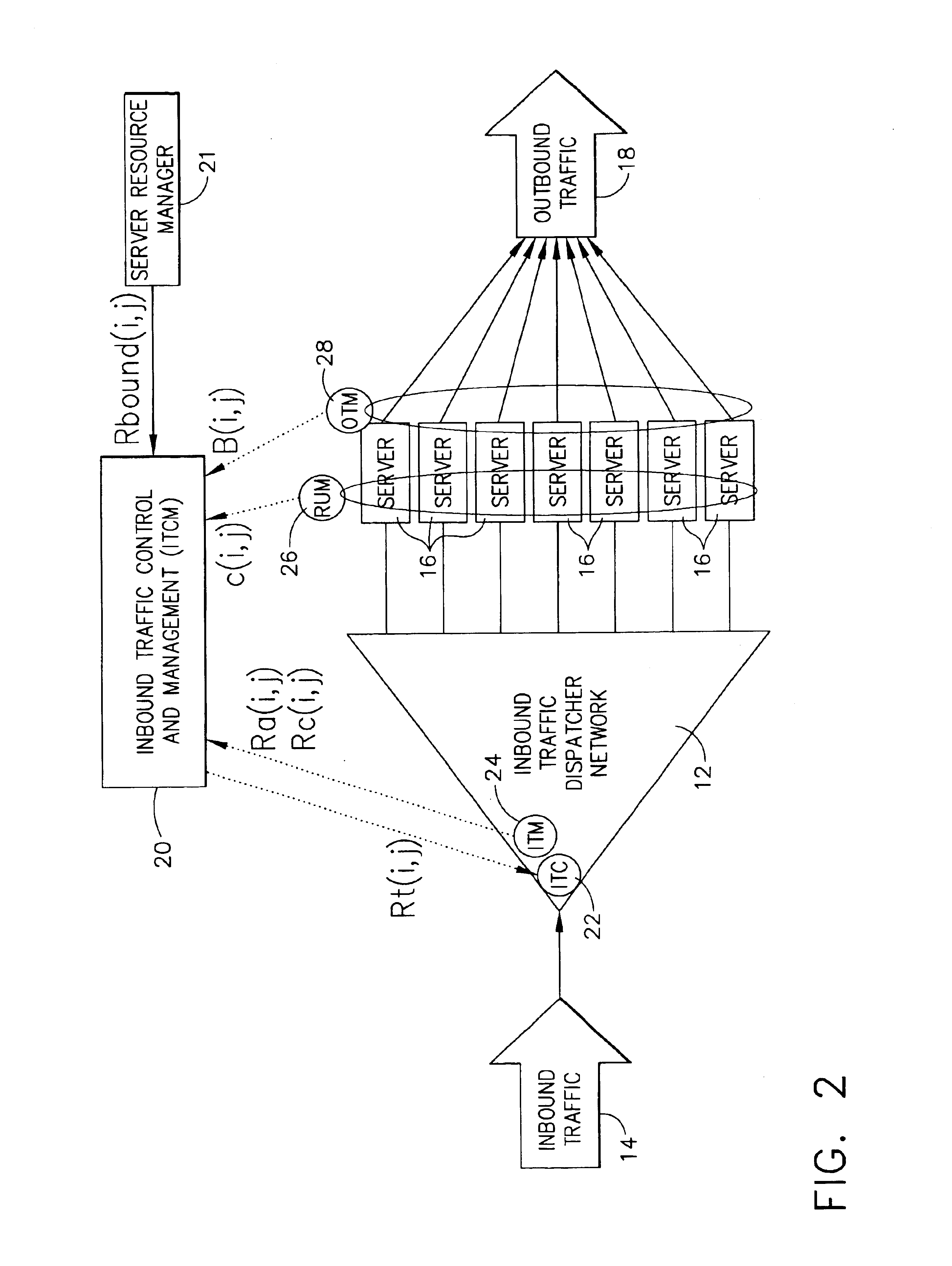
Highly scalable system and method of regulating internet traffic to server farm to support (min,max) bandwidth usage-based service level agreements
InactiveUS6857025B1Improve scalabilityInhibit outputMultiple digital computer combinationsData switching networksScalable systemService-level agreement
A highly scalable system and method for supporting (mim,max) based Service Level Agreements (SLA) on outbound bandwidth usage for a plurality of customers whose applications (e.g.,Web sites) are hosted by a server farm that consists of a very large number of servers. The system employs a feedback system that enforces the outbound link bandwidth SLAs by regulating the inbound traffic to a server or server farm. Inbound traffic is admitted to servers using a rate denoted as Rt(i,j), which is the amount of the ith customer's jth type of traffic that can be admitted within a service cycle time to servers which support the ith customer. A centralized device computes Rt(i,j) based on the history of admitted inbound traffic to servers, the history of generated outbound traffic from servers, and the SLAs of various customers. The Rt(i,j) value is then relayed to one or more inbound traffic limiters that regulate the inbound traffic using the rates Rt(i,j) in a given service cycle time. The process of computing and deploying Rt(i,j) values is repeated periodically. In this manner, the system provides a method by which differentiated services can be provided to various types of traffic, the generation of output from a server or a server farm is avoided if that output cannot be delivered to end users, and revenue can be maximized when allocating bandwidth beyond the minimums.
Owner:IBM CORP
Methods and apparatus for automated true object-based image analysis and retrieval
ActiveUS7590310B2Data processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsAbstraction layerScalable system
The present invention is an automated and extensible system for the analysis and retrieval of images based on region-of-interest (ROI) analysis of one or more true objects depicted by an image. The system uses a Regions Of Interest (ROI) database that is a relational or analytical database containing searchable vectors that represent the images stored in a repository. Entries in the ROI database are created by an image locator and ROI classifier that work in tandem to locate images within the repository and extract the relevant information that will be stored in the ROI database. Unlike existing region-of-interest search systems, the ROI classifier analyzes objects in an image to arrive at the actual features of the true object, instead of merely describing the features of the image of that object. Graphical searches are performed by the collaborative workings of an image retrieval module, an image search requestor and an ROI query module. The image search requestor is an abstraction layer that translates user or agent search requests into the language understood by the ROI query.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Motherboard for supporting multiple graphics cards
InactiveUS7782325B2Cathode-ray tube indicatorsMultiple digital computer combinationsScalable systemGraphics
The invention provides a motherboard that uses a high-speed, scalable system bus such as PCI Express® to support two or more high bandwidth graphics slots. The lanes from the motherboard chipset may be directly routed to two or more graphics slots. For instance, the chipset may route (1) thirty-two lanes into two ×16 graphics slots; (2) twenty-four lanes into one ×16 graphics slot and one ×8 graphics slot (the ×8 slot using the same physical connector as a ×16 graphics slot but with only eight active lanes); or (3) sixteen lanes into two ×8 graphics slots (again, physically similar to a ×16 graphics slot but with only eight active lanes). Alternatively, a switch can convert sixteen lanes coming from the chipset root complex into two ×16 links that connect to two ×16 graphics slots. The system according to the invention is agnostic to a specific chipset.
Owner:DELL MARKETING
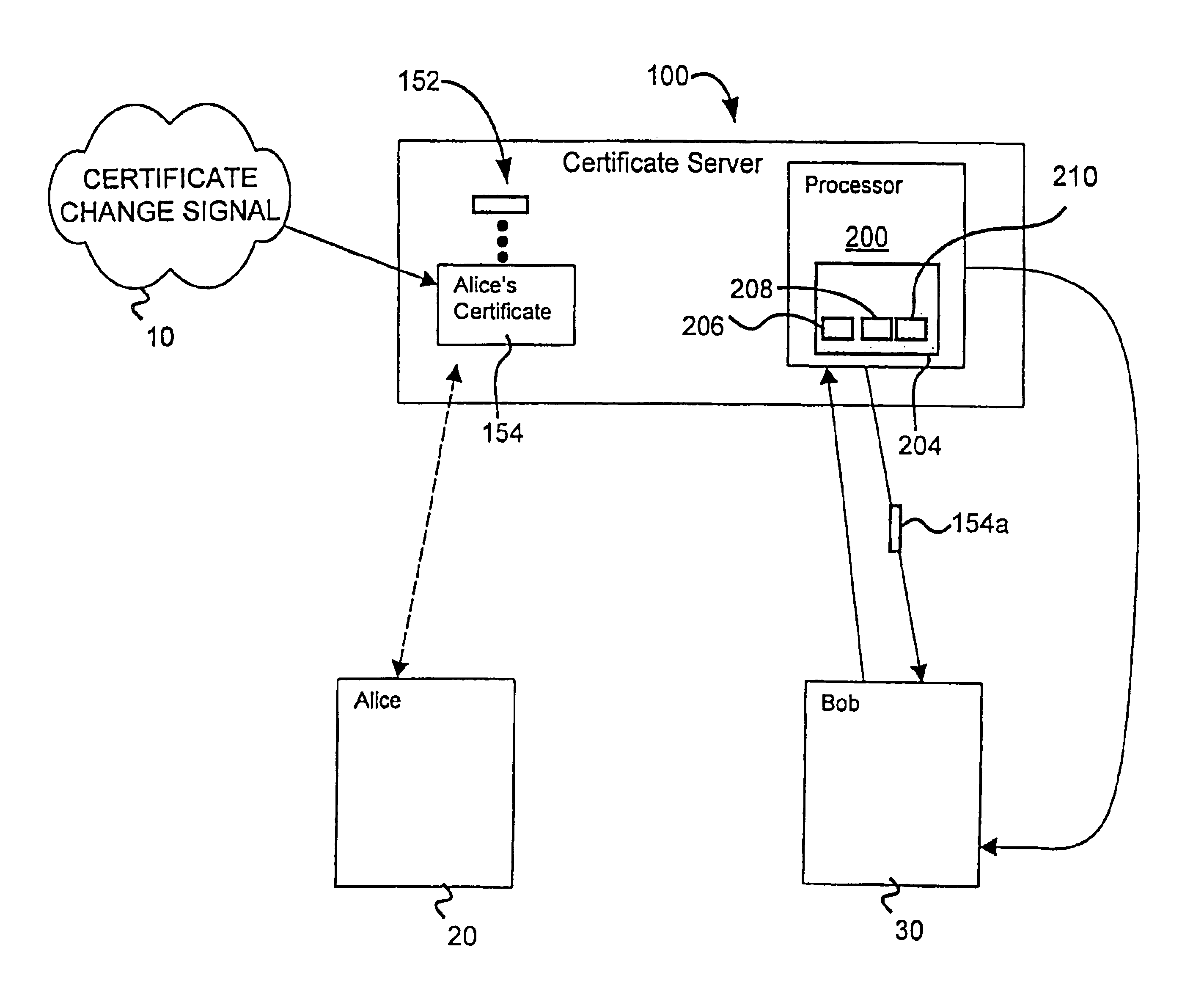
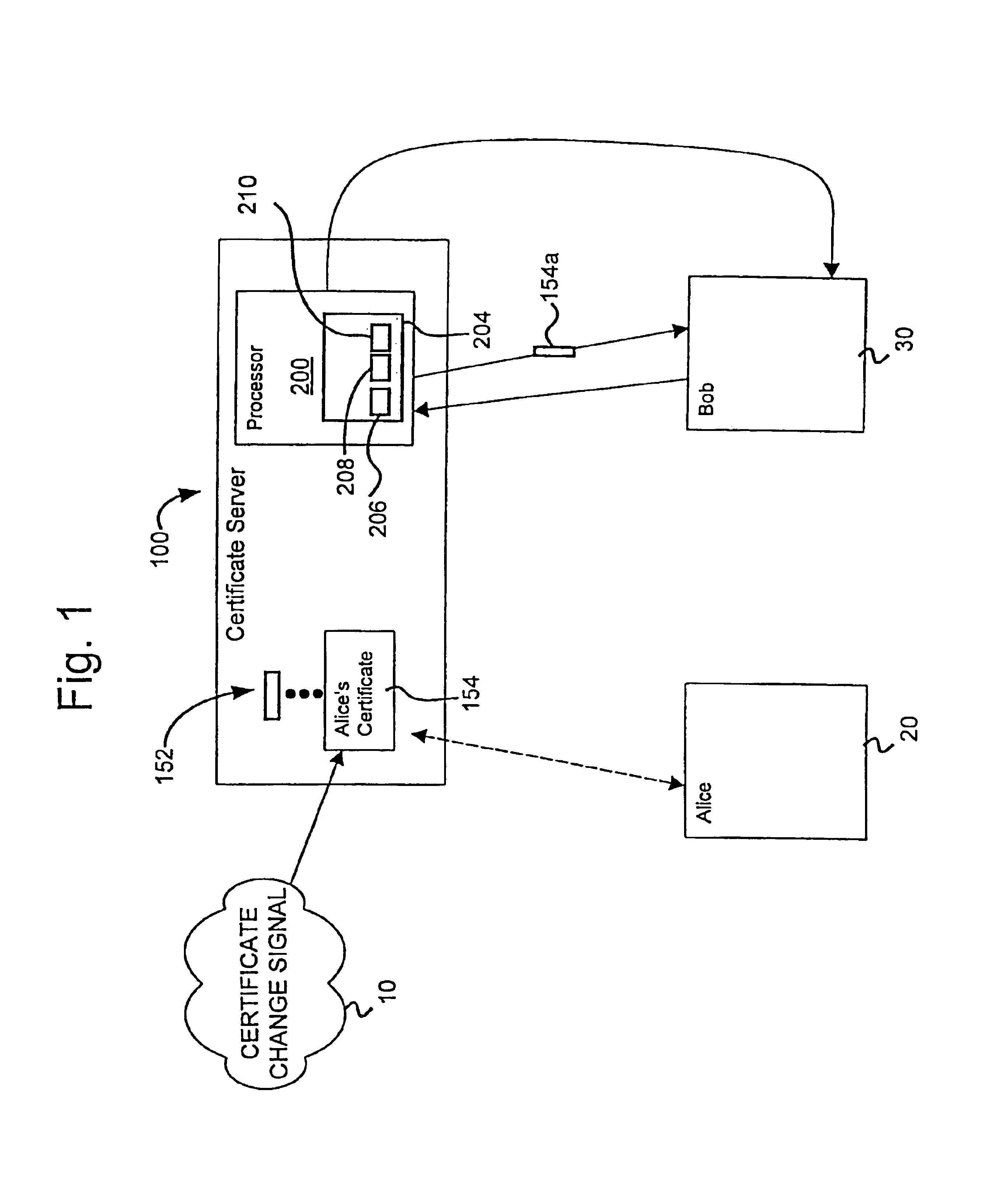
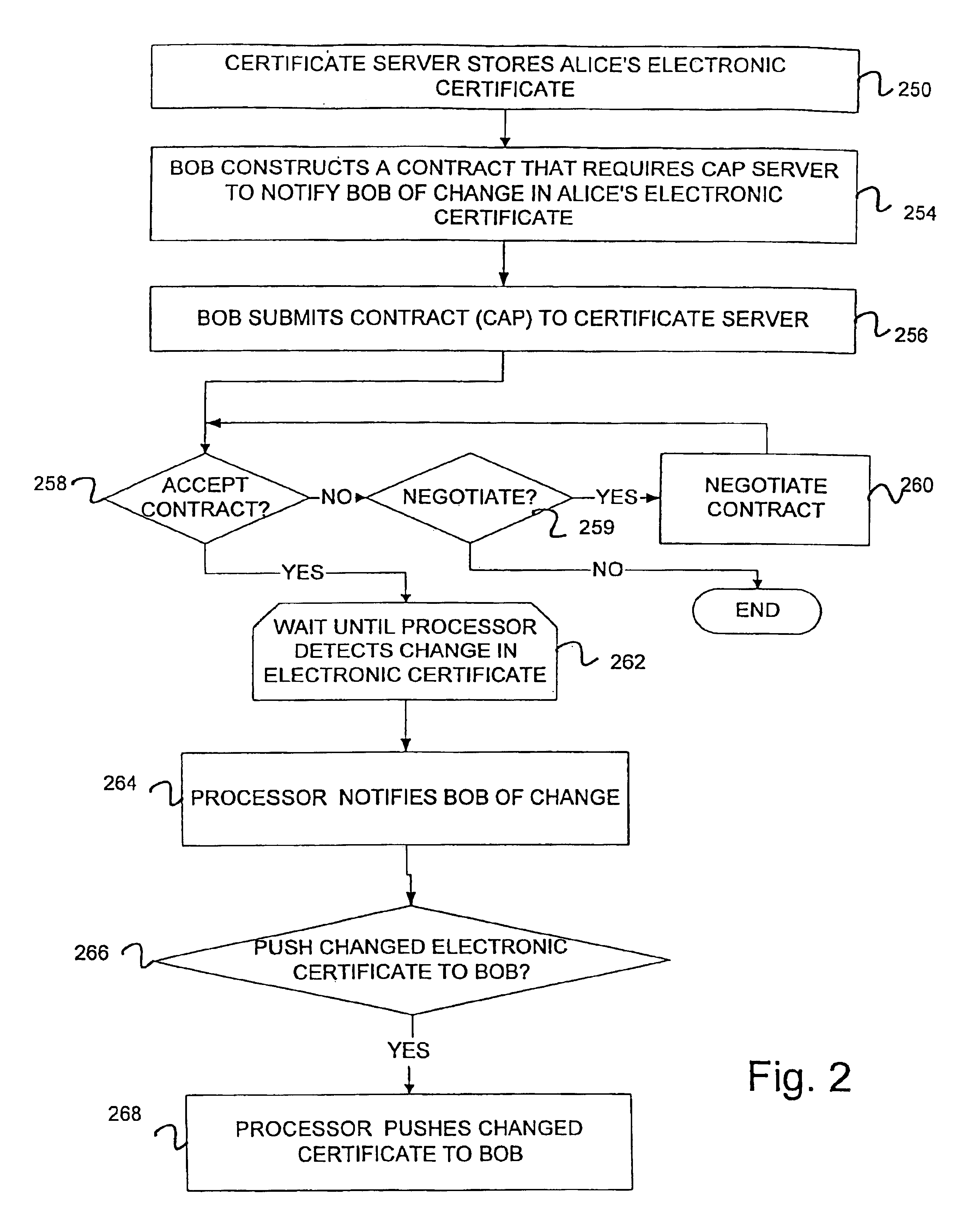
Scalable system and method for management and notification of electronic certificate changes
InactiveUS6922776B2System is scalableEffective monitoringMemory loss protectionError detection/correctionInformation typeScalable system
Owner:MCAFEE INC
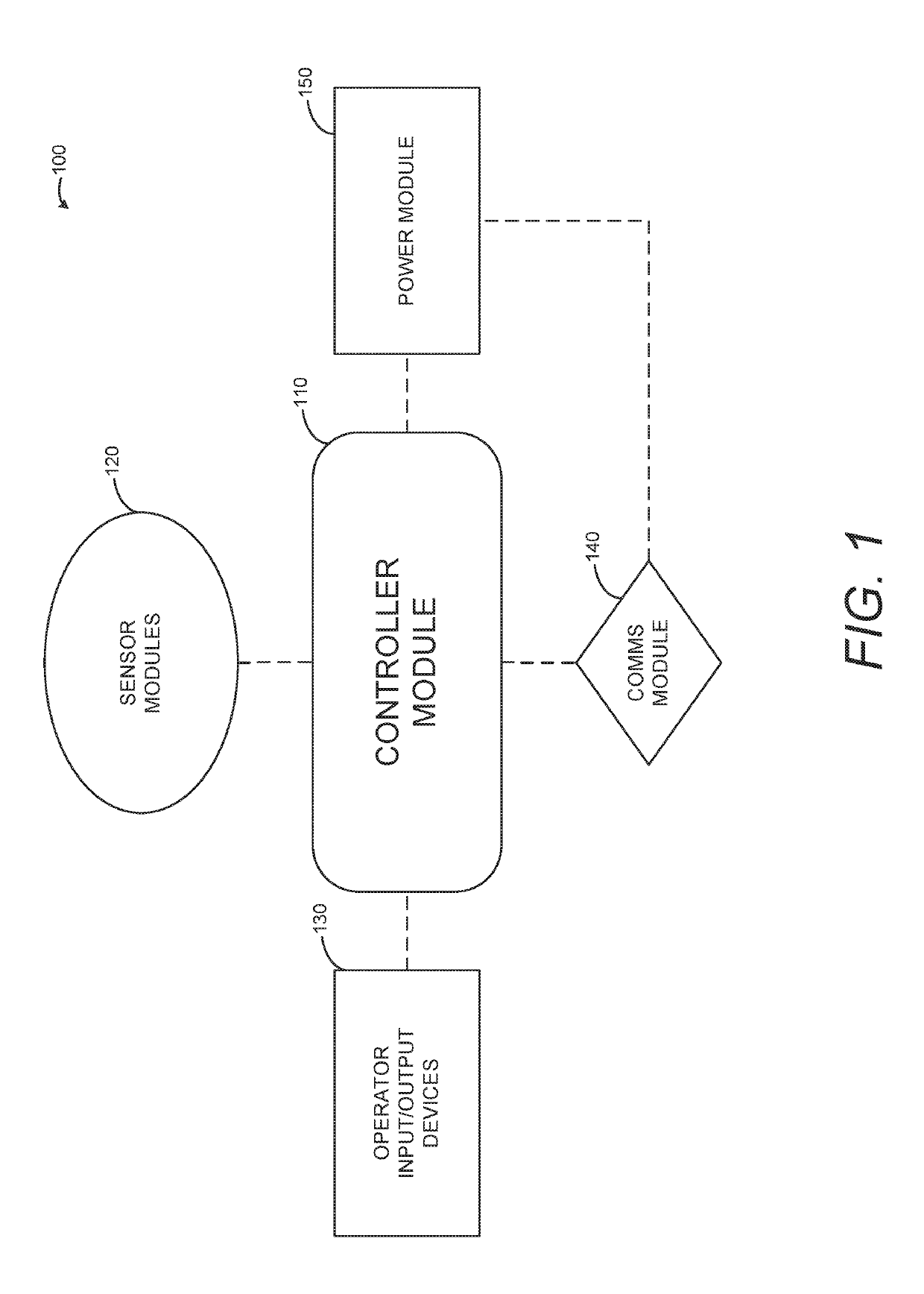
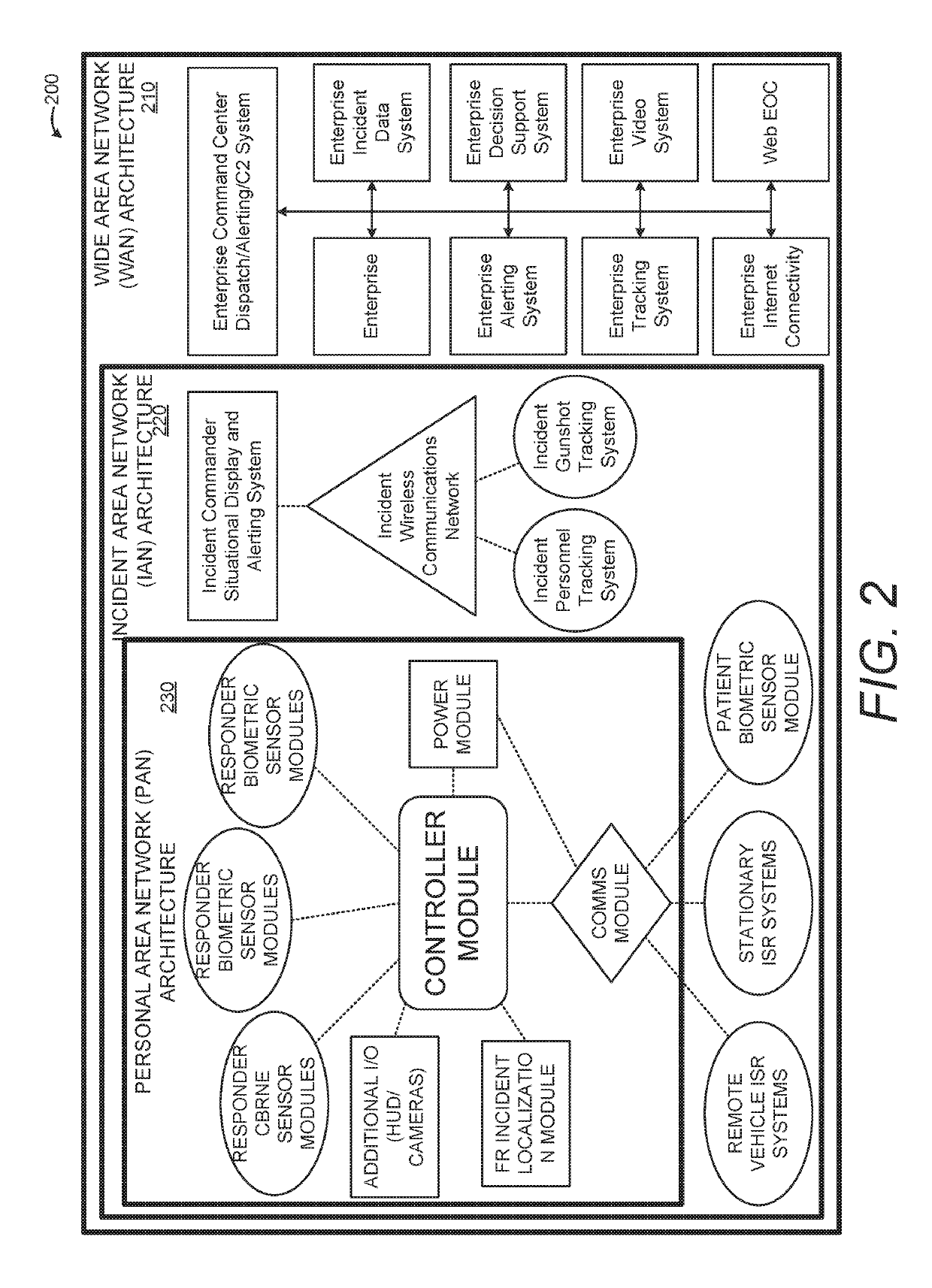
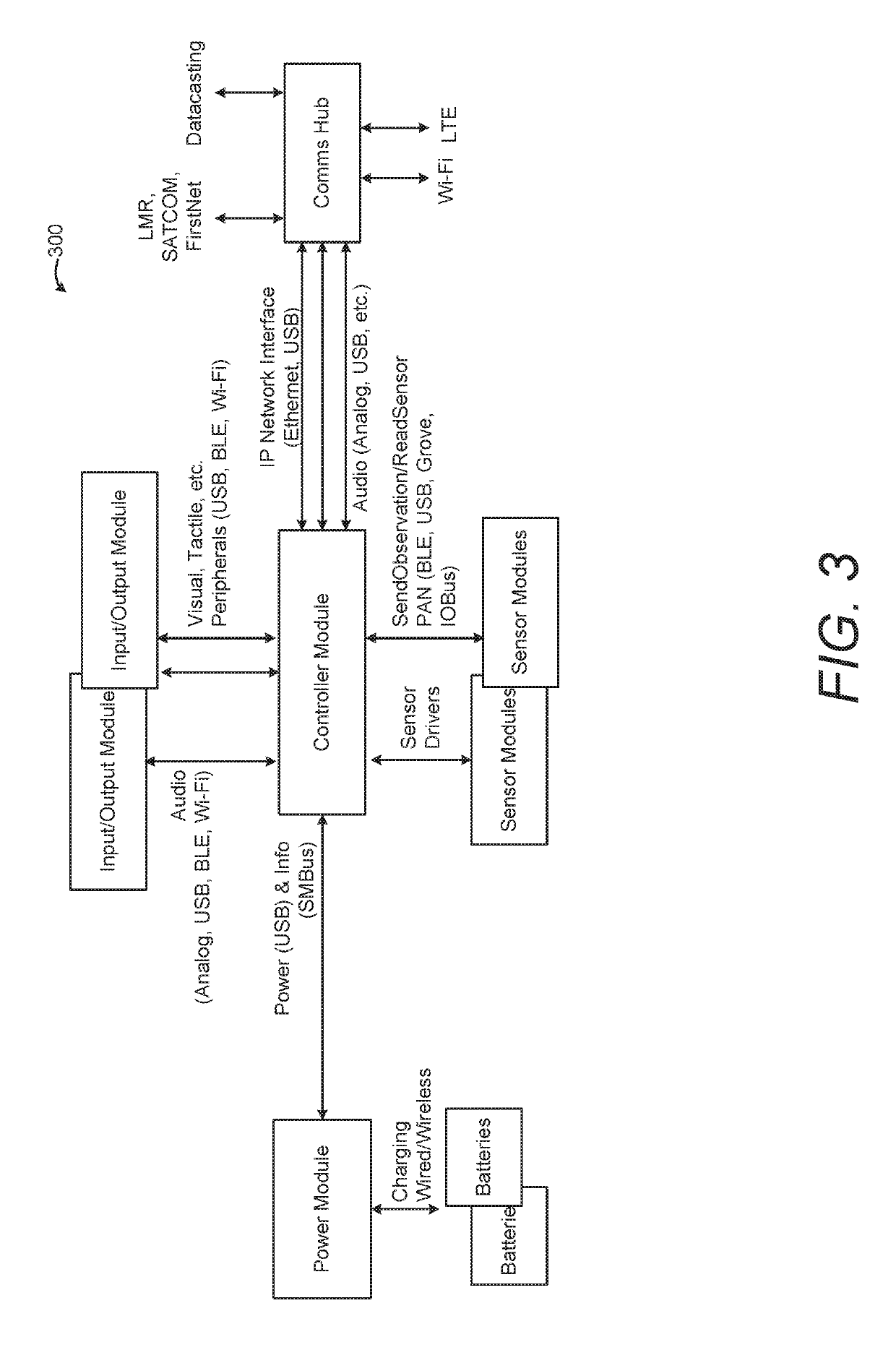
Systems and Methods for Integrating First Responder Technologies
ActiveUS20190174208A1Easy to integrateSub-station arrangementsVolume/mass flow measurementScalable systemHuman–computer interaction
Various embodiments of the present invention are directed towards a system and method relating to Next Generation First Responder (NGFR) modular and scalable systems capable of easily integrating various components via open standards and interfaces. For example, a wearable on-body first responder system includes at least one sensor configured to identify sensor information, a controller configured to provide a first responder mobile support architecture and that is configured to interface with the at least one sensor. The controller is configured to collect and distribute the sensor information, and an input / output (I / O) device is configured to interface with the controller and present the sensor information to a user of the on-body first responder system.
Owner:THE GOVERNMENT OF THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF HOMELAND SECURITY
Scalable system and method for predicting hit music preferences for an individual
InactiveUS20100063975A1Digital data processing detailsElectronic editing digitised analogue information signalsScalable systemComputer science
A system and method for creating and storing a user's hit-music preference list by receiving the user's biographical information, profiling the user based on the biographical information to determine music data that may be of interest to the user, receiving a rating from the user for a plurality of genres, wherein the music data is a member of one or more of the plurality of genres, and retrieving music data based on the user's rating for the plurality of genres. The system has a memory for storing the user's biographical information, a processor configured to profile the user based on the biographical information and to retrieve music data that may be of interest to the user, and a display unit for displaying the music data retrieved.
Owner:HAYES THOMAS J
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com