Patents
Literature
849 results about "Security domain" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
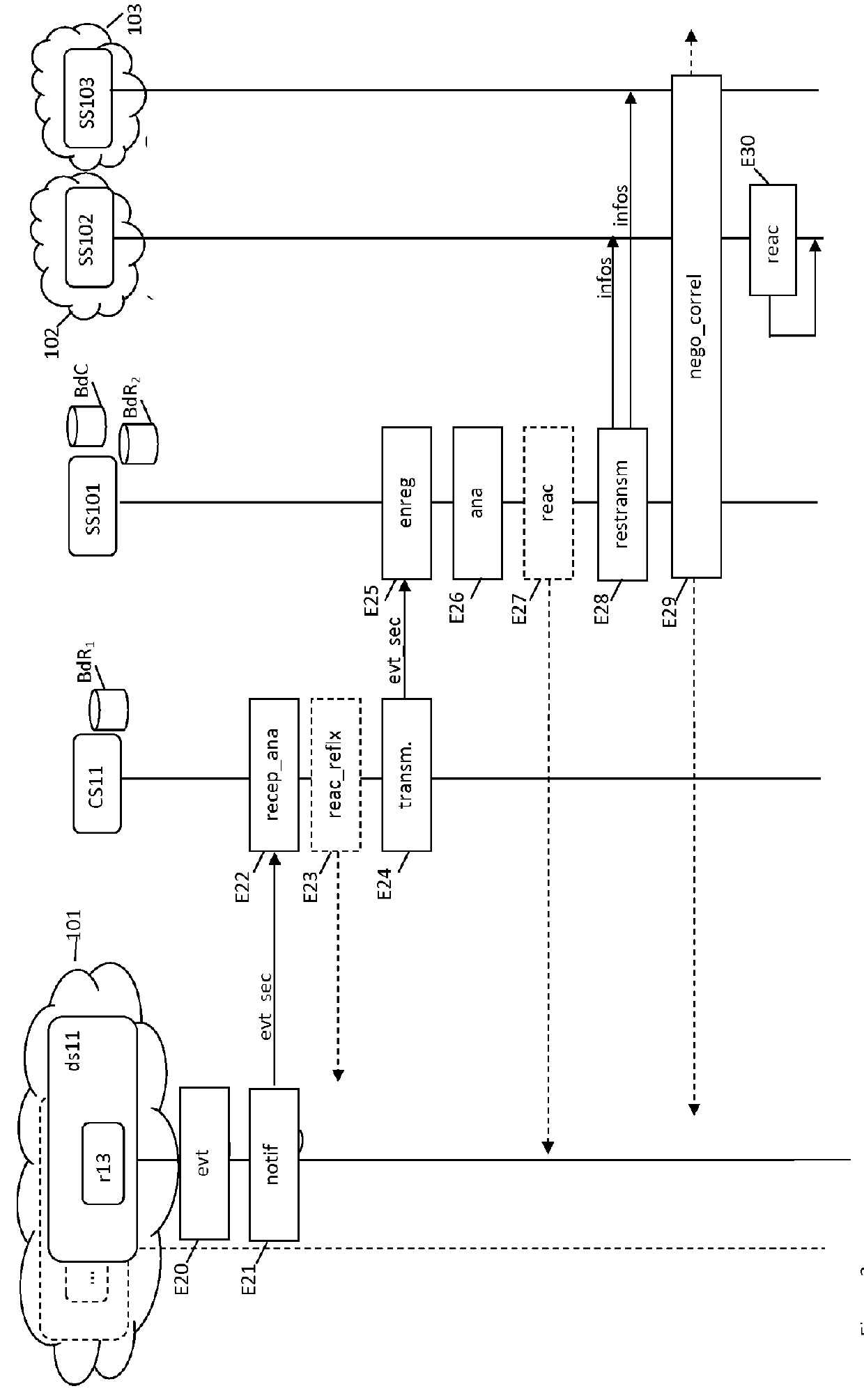
A security domain is the determining factor in the classification of an enclave of servers/computers. A network with a different security domain is kept separate from other networks. Examples: NIPRNet, SIPRNet. JWICS, NSANet are all kept separate.
Security Compliance Methodology and Tool
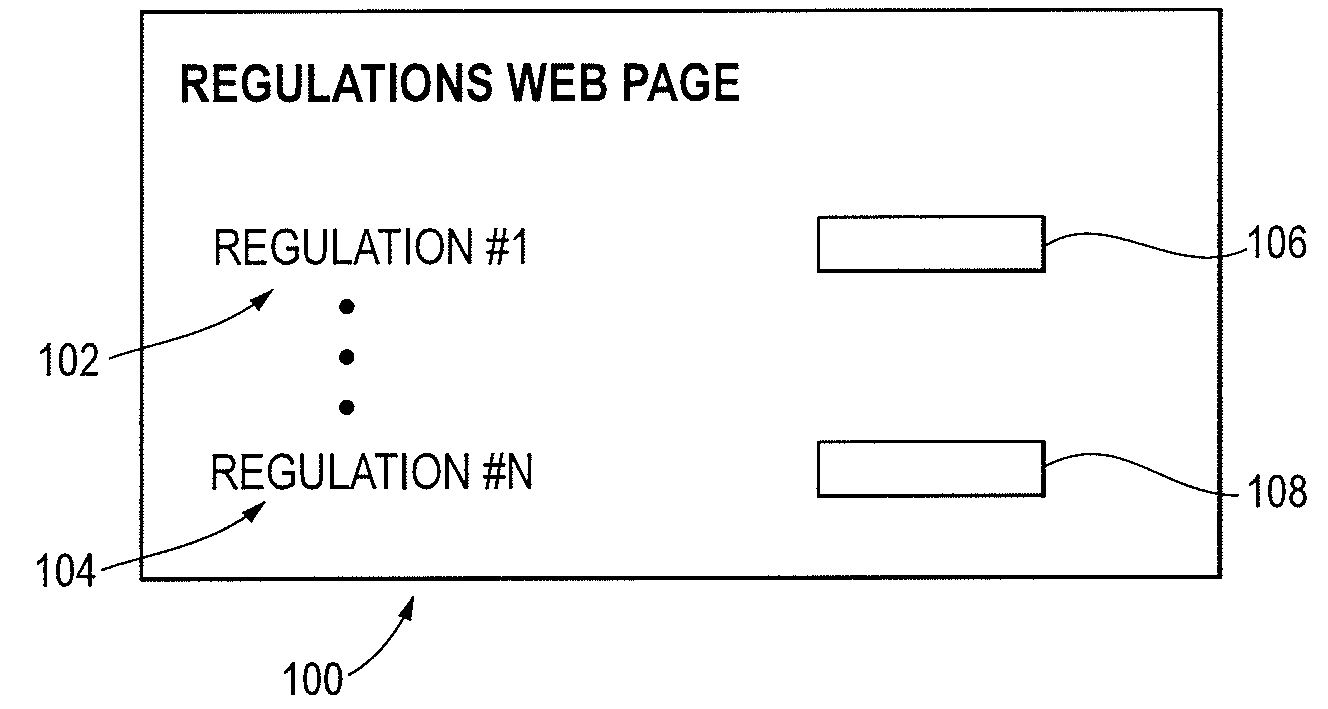
An apparatus is provided for evaluating risk to an organization. The apparatus includes a plurality of governmental rules directed to protecting shareholders, a plurality of security domains of the organization wherein each security domain is associated with a different asset of the organization and a request for an information risk assessment within at least one of the plurality of security domains of the organization formed under the plurality of governmental rules from a set of initializing inputs. The apparatus further includes a information risk assessment plan formed from the request for the information risk assessment, a set of information assessment templates and test cases formed from the information risk assessment plan, a set of information risk assessment tests conducted on the IT system using the assessment templates and test cases, a set of test results generated by the risk assessment tests, one or more security control gaps identified by the assessment responses and one or more gap remediation plans formed from the identified security gaps.
Owner:DENOVO ANDREW +1
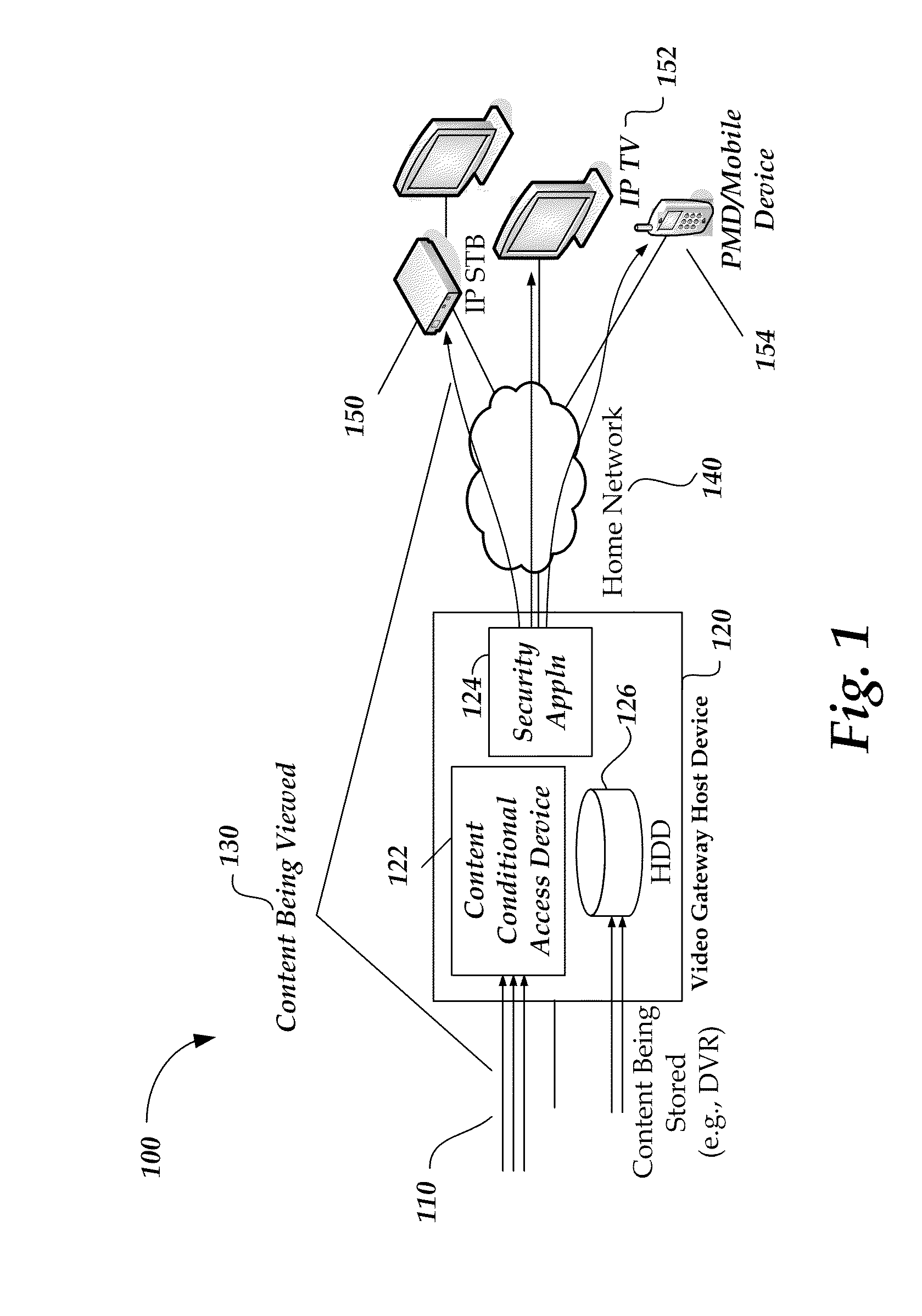
Content protection management system
ActiveUS20100287609A1Simple and consistent and reliableMultiple digital computer combinationsProgram controlSecurity domainContent security
A content protection management system that enables interoperability with other Content Protection and DRM technologies. A managed security domain provides a simple, consistent and reliable experience to whole-home network subscribers. The architectural concept for the whole-home network includes an underlying control plane with an overlaying content security control plane running a particular DRM technology.
Owner:COX COMMUNICATIONS
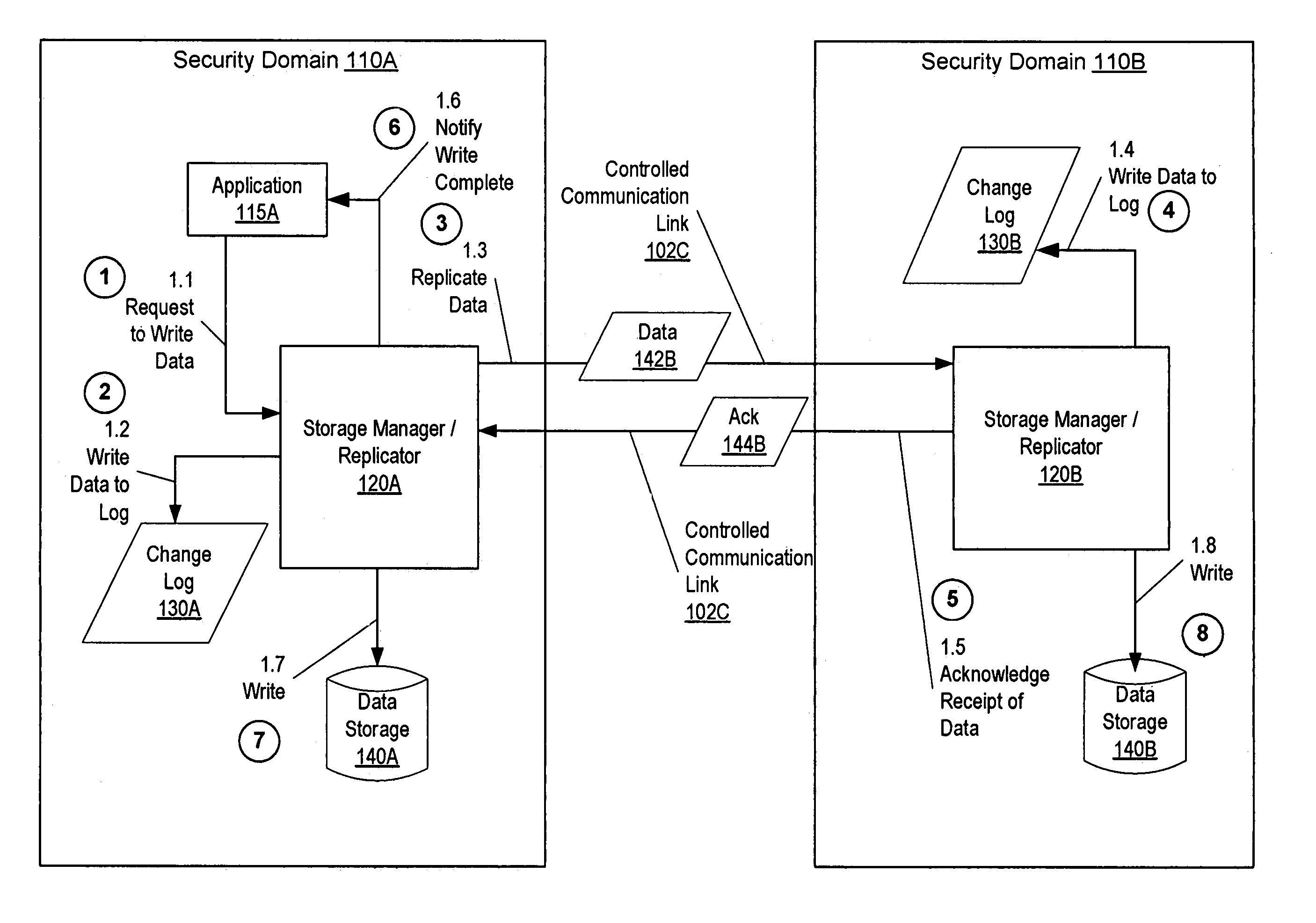
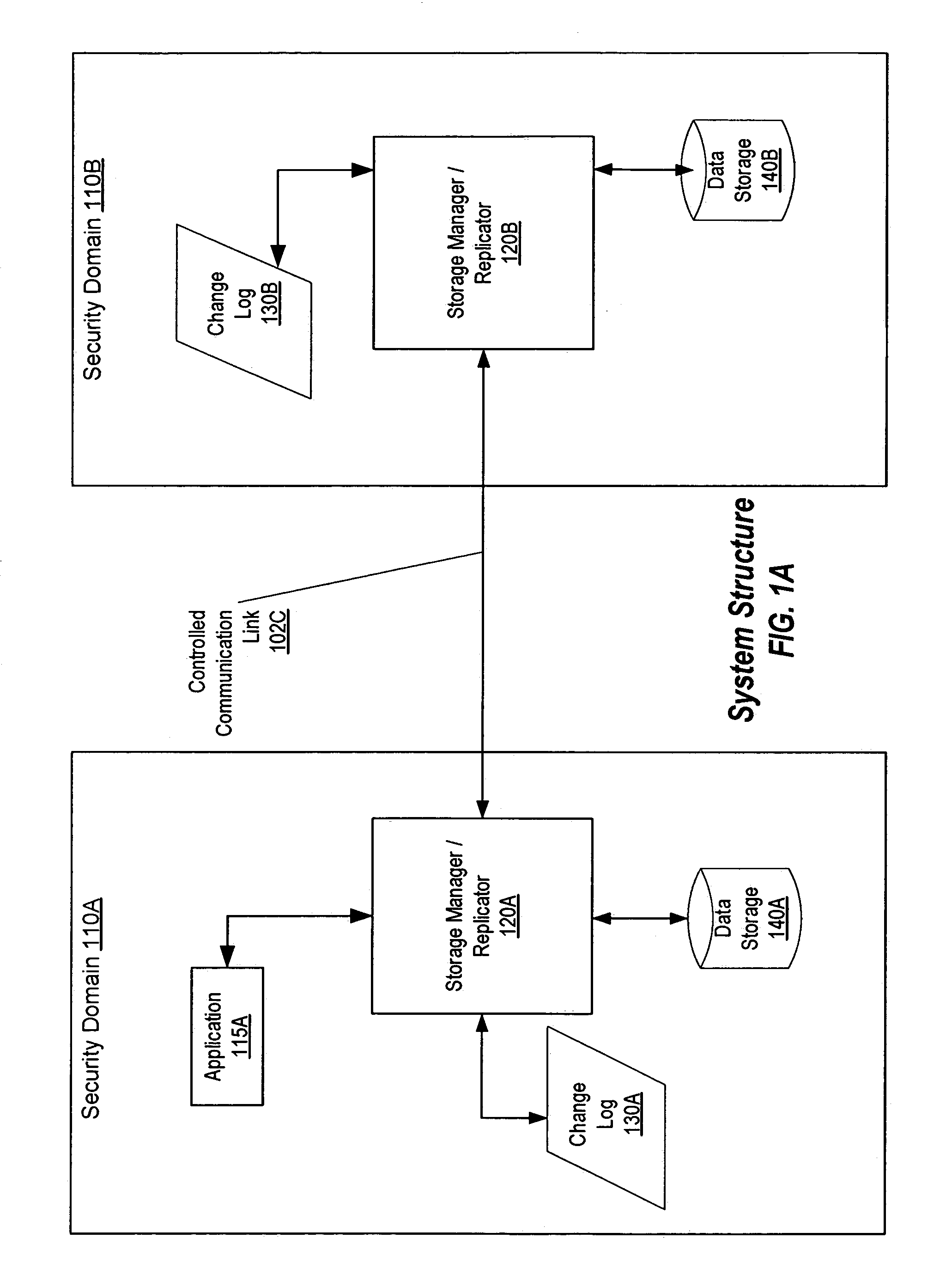
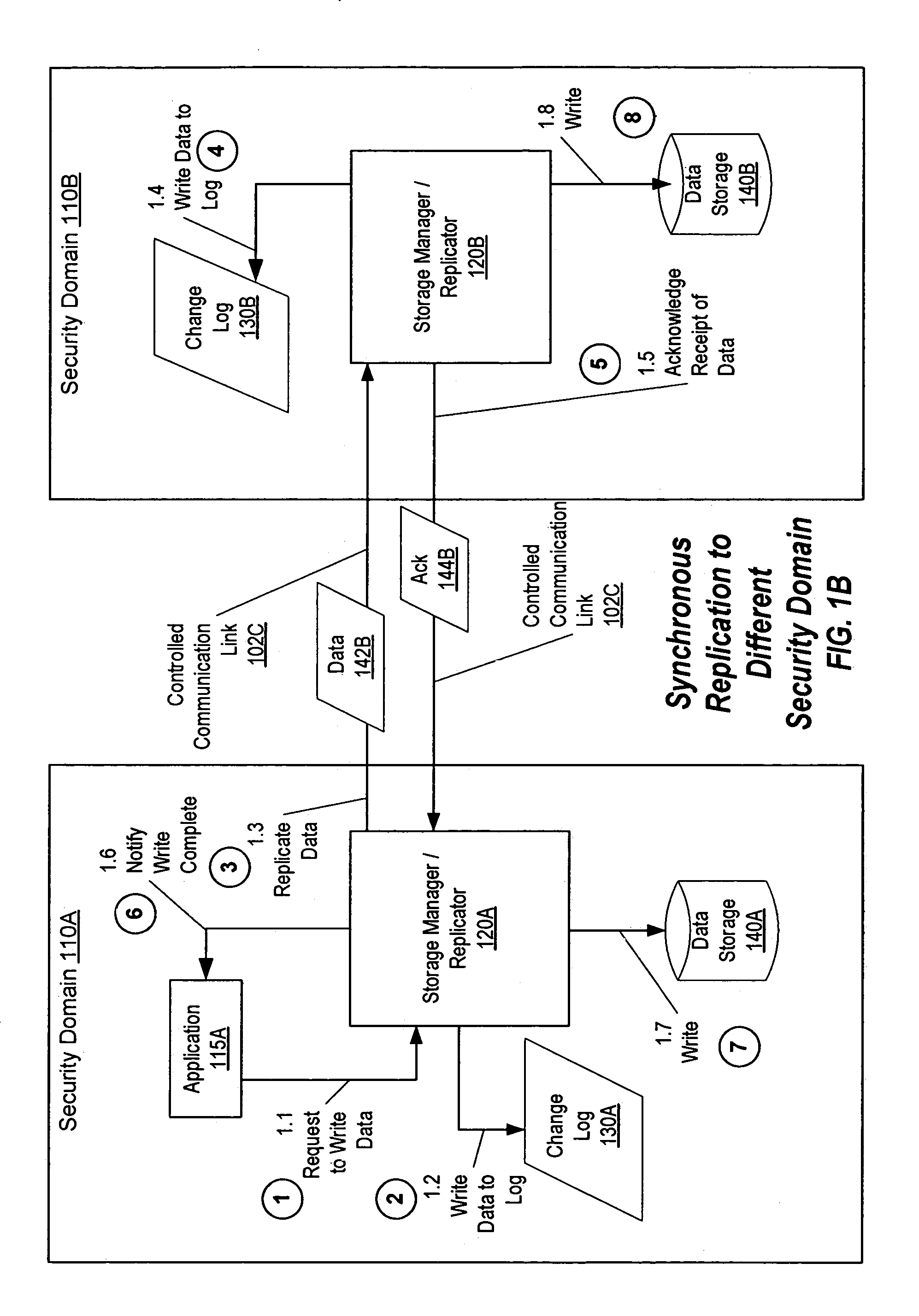
Synchronous replication for system and data security
ActiveUS7149858B1Ensure consistencyError detection/correctionUnauthorized memory use protectionSecurity domainData security
A method, system, and computer-readable medium for maintaining up-to-date, consistent backup copies of primary data that are immune to corruption even when security of the primary data is breached. Independent security domains are established for primary and secondary data, such that access to each security domain must be obtained independently of access to the other security domains. For example, a host computer system having access to data storage in the primary security domain does not have access to data storage in the secondary security domain, and vice versa. Changes to primary data are synchronously replicated over a tightly controlled replication link from primary data storage in the primary security domain to secondary data storage in the secondary security domain. A change to the data is completed in the primary security domain when an acknowledgement is received that the change to the data has been stored in secondary data storage.
Owner:SYMANTEC OPERATING CORP
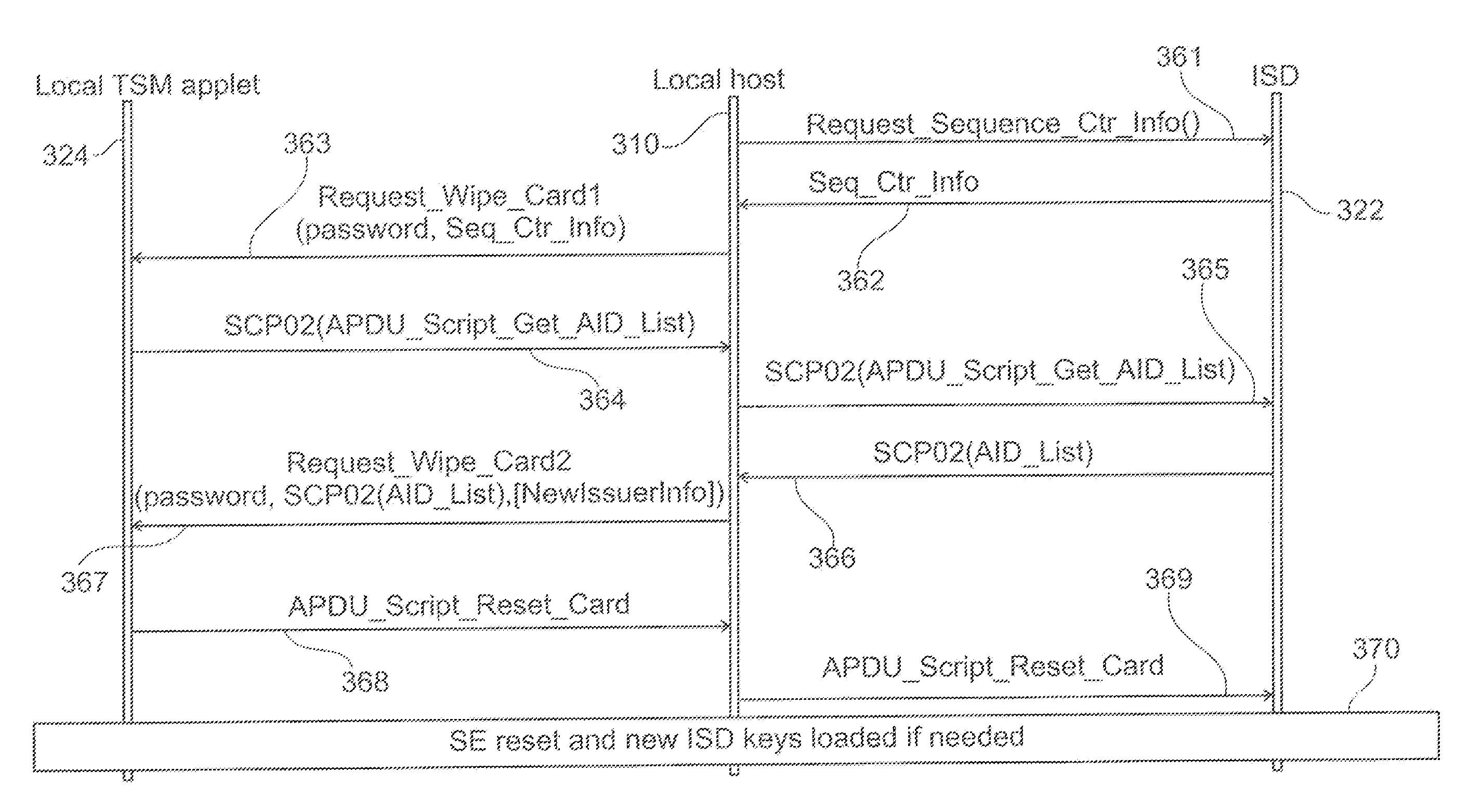
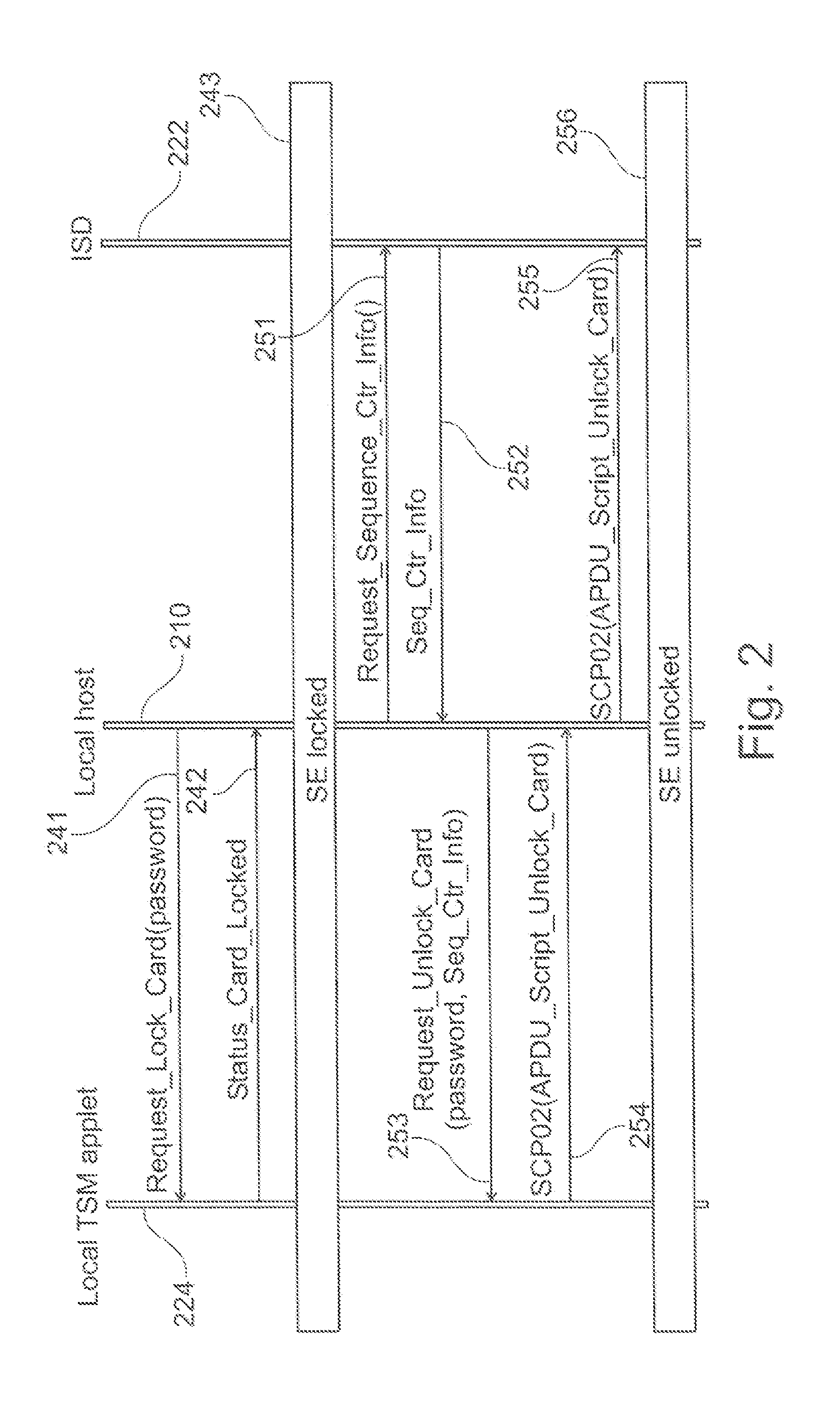
Local trusted service manager
ActiveUS20140047235A1Possible to provideDigital data authenticationProgram controlProgram unitTrusted service manager
Owner:NXP BV
Key distribution method and system
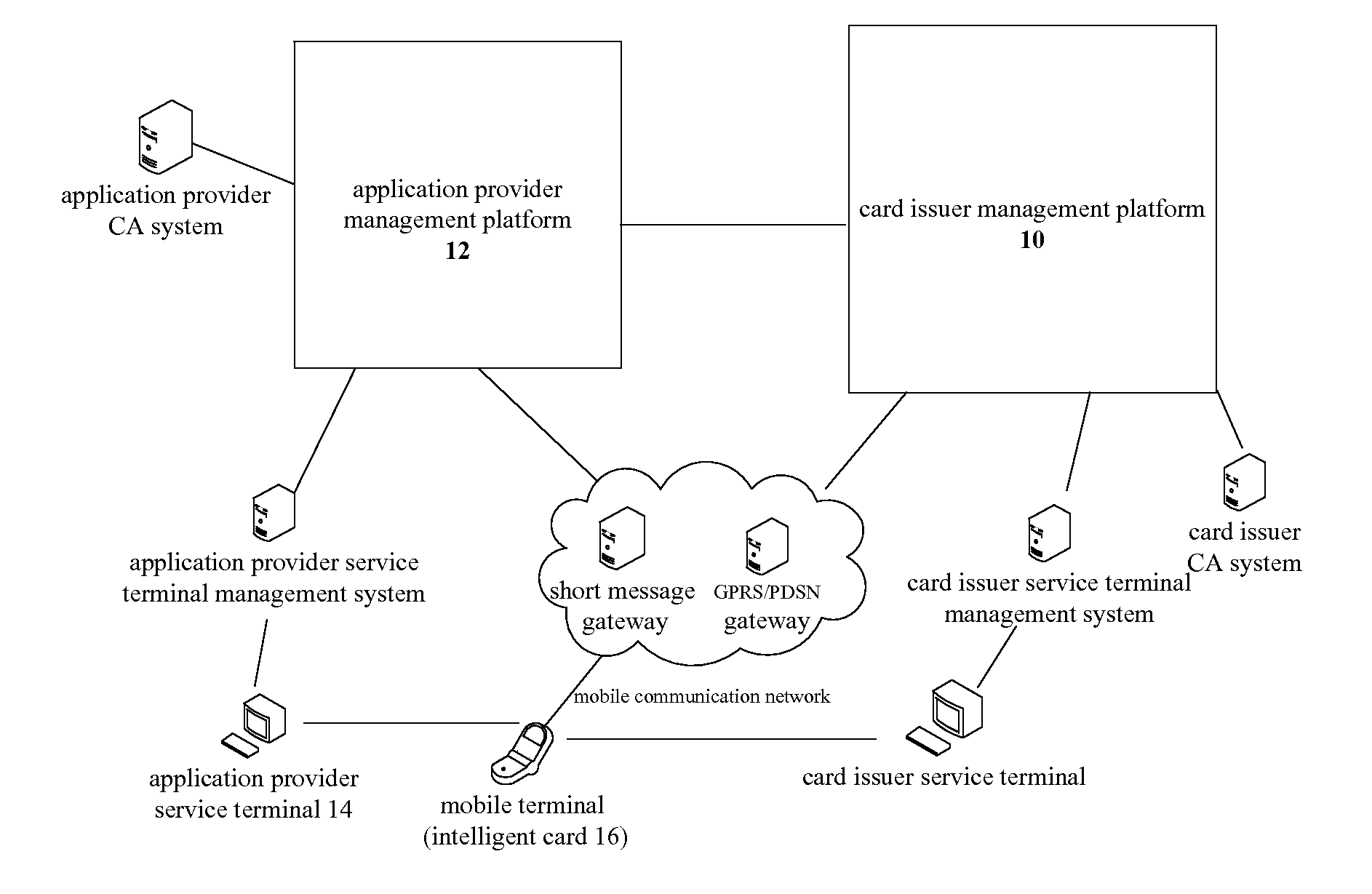
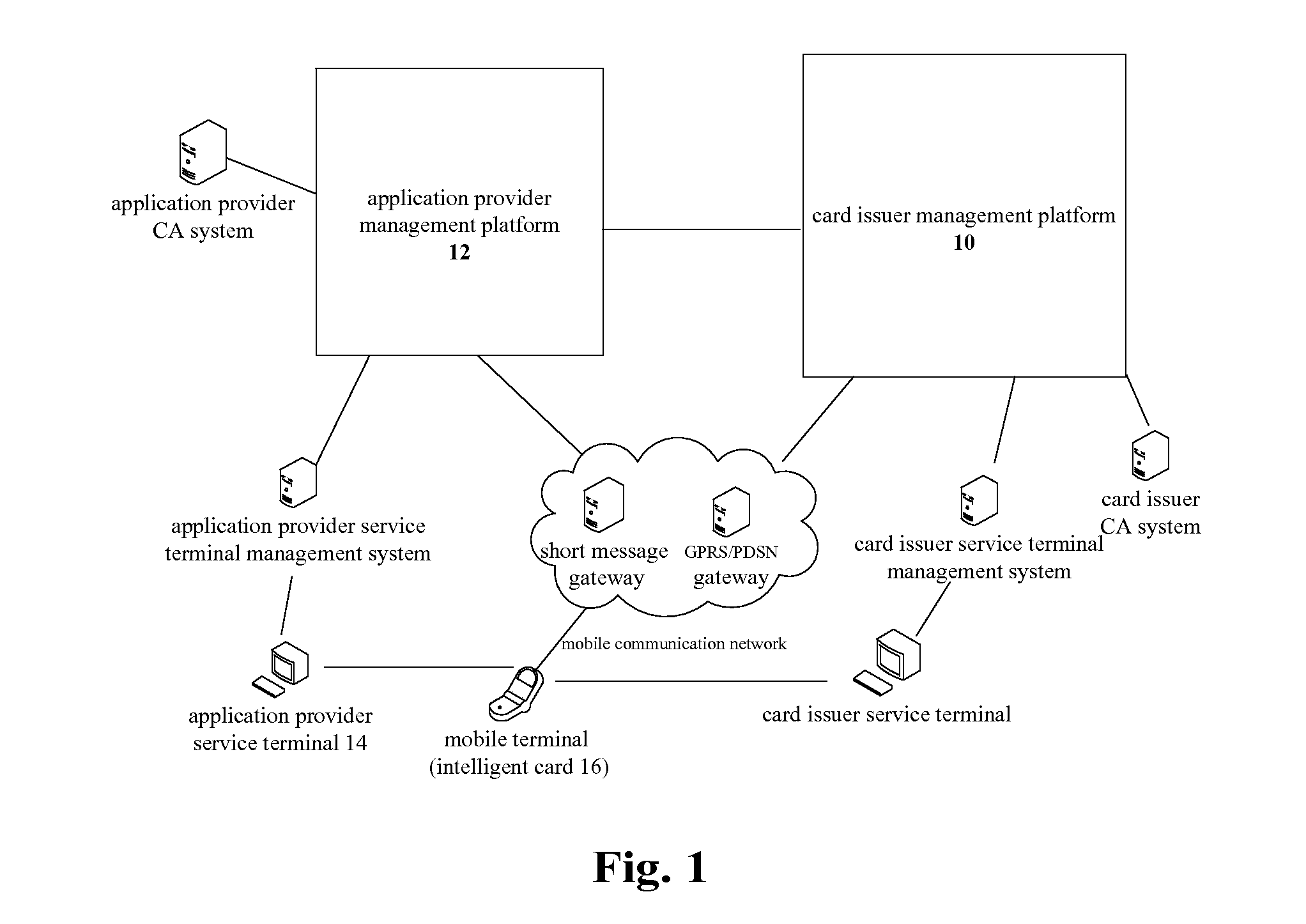
InactiveUS20110280406A1Improve securityKey distribution for secure communicationNear-field systems using receiversSecurity domainSmart card
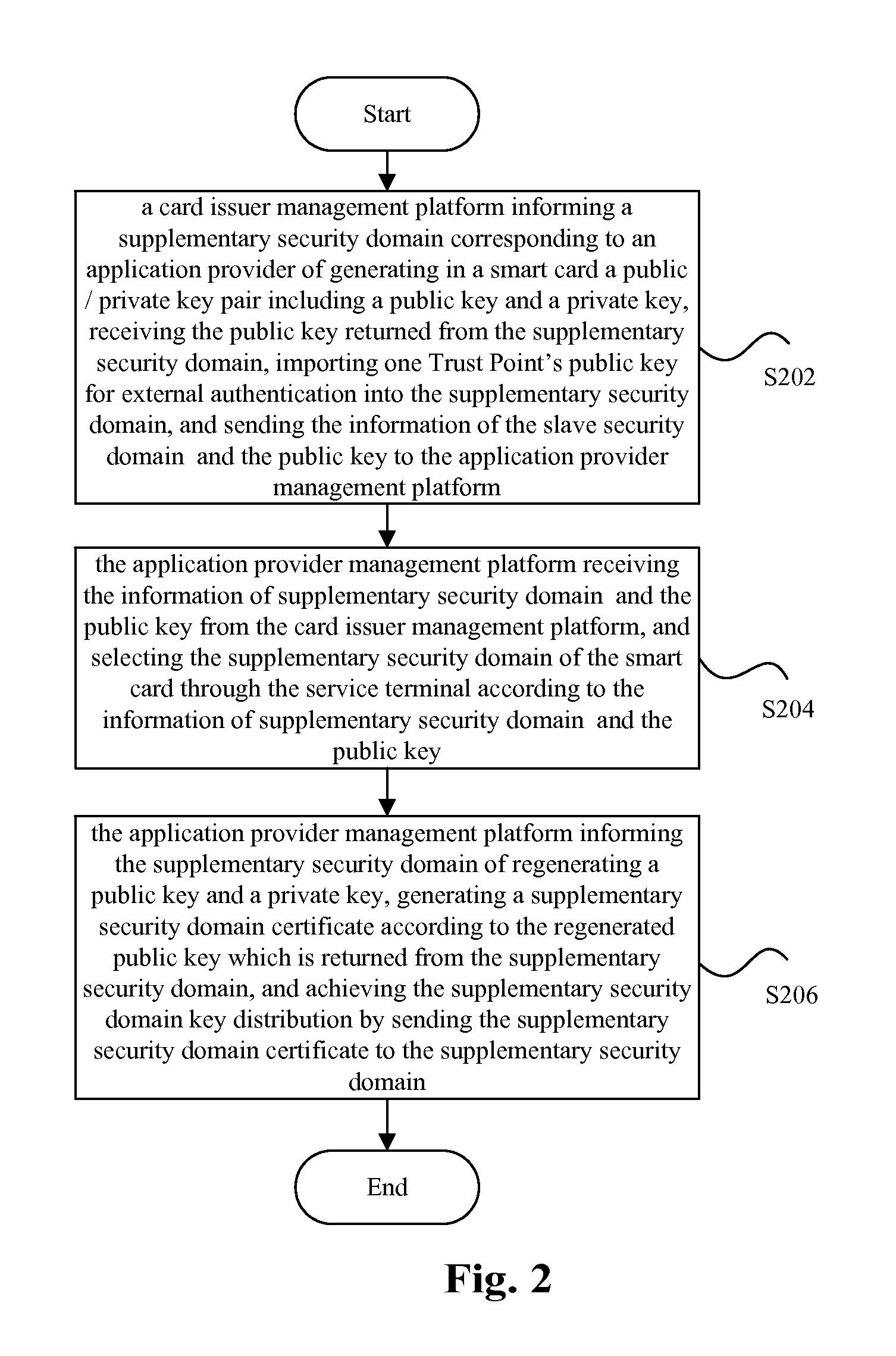
The present invention discloses a key distribution method and system, the method includes: a card issuer management platform informing a supplementary security domain corresponding to an application provider of generating in a smart card a public / private key pair including a public key and a private key, receiving the public key returned from the supplementary security domain, importing a public key for trust point for external authentication into the supplementary security domain, and transmitting the information of the supplementary security domain and the public key to the application provider management platform; the application provider management platform receiving the information of the supplementary security domain and the public key from the card issuer management platform, and selecting the supplementary security domain of the smart card by a service terminal according to the information of the supplementary security domain and the public key; the application provider management platform informing the supplementary security domain of regenerating a public key and a private key, generating a supplementary security domain certificate according to the regenerated public key which is returned from the supplementary security domain, and achieving the supplementary security domain key distribution by transmitting the supplementary security domain certificate to the supplementary security domain. The present invention can improve the security of the supplementary security domain key distribution.
Owner:ZTE CORP
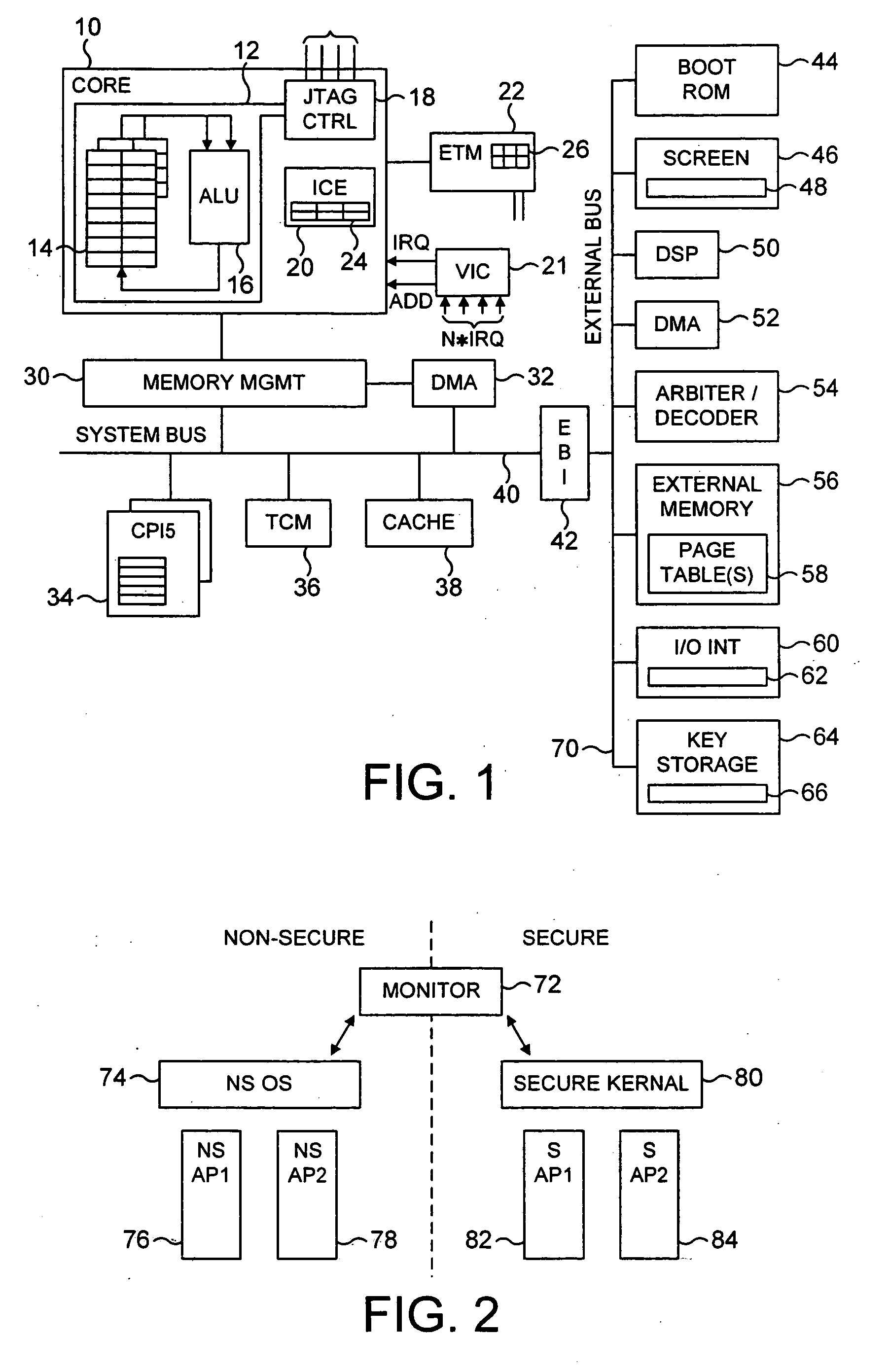
Control of access to a memory by a device
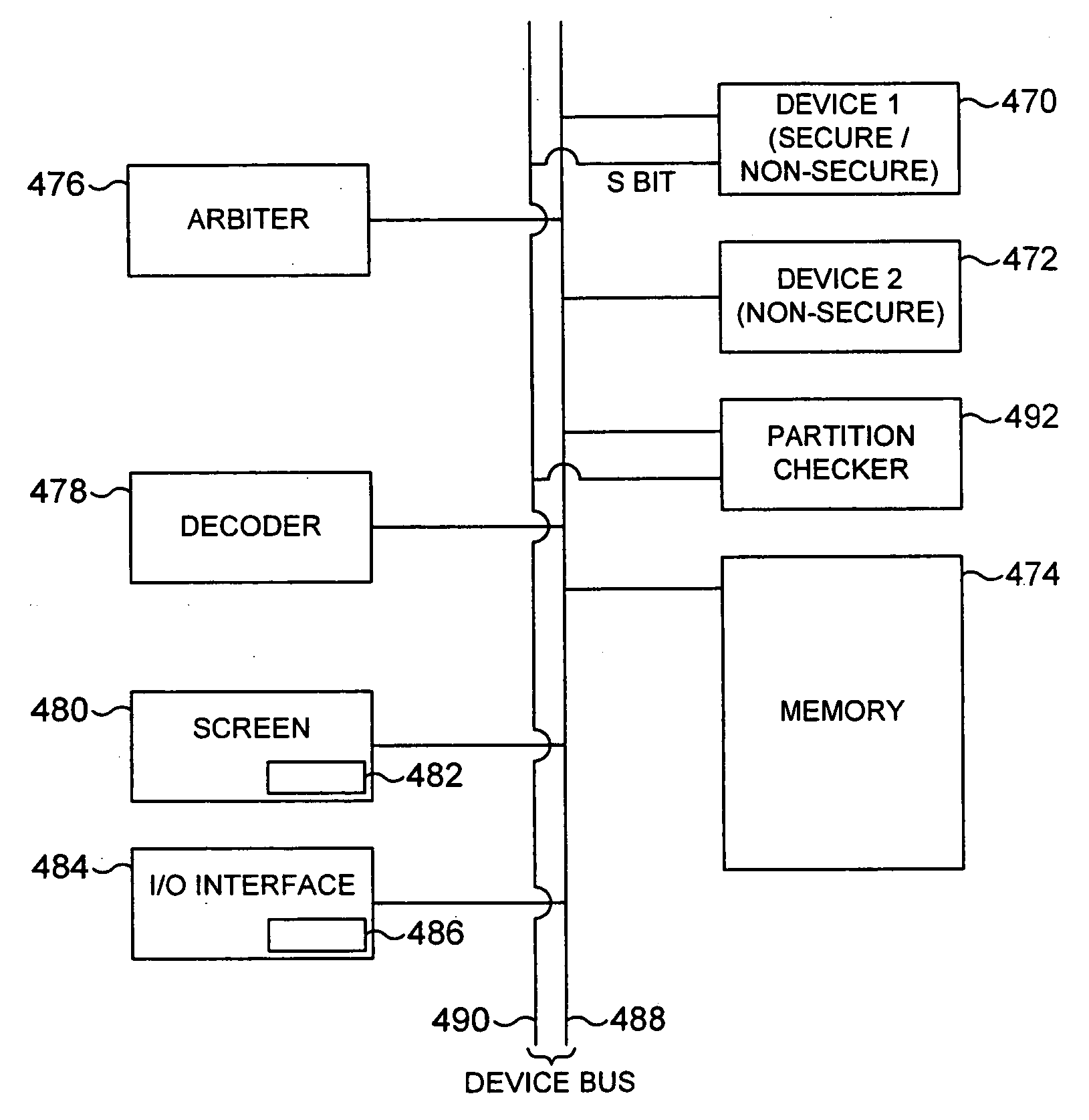
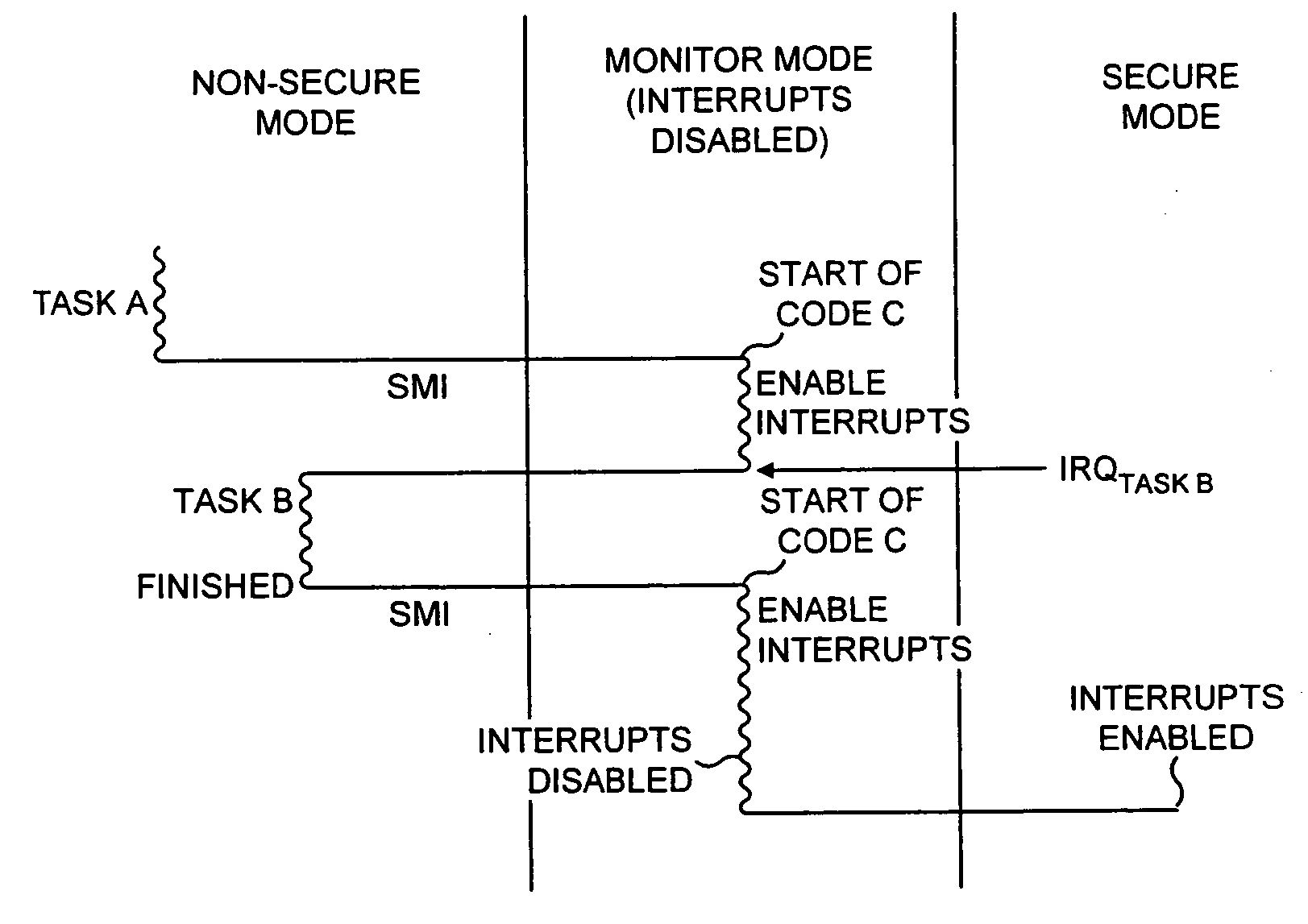
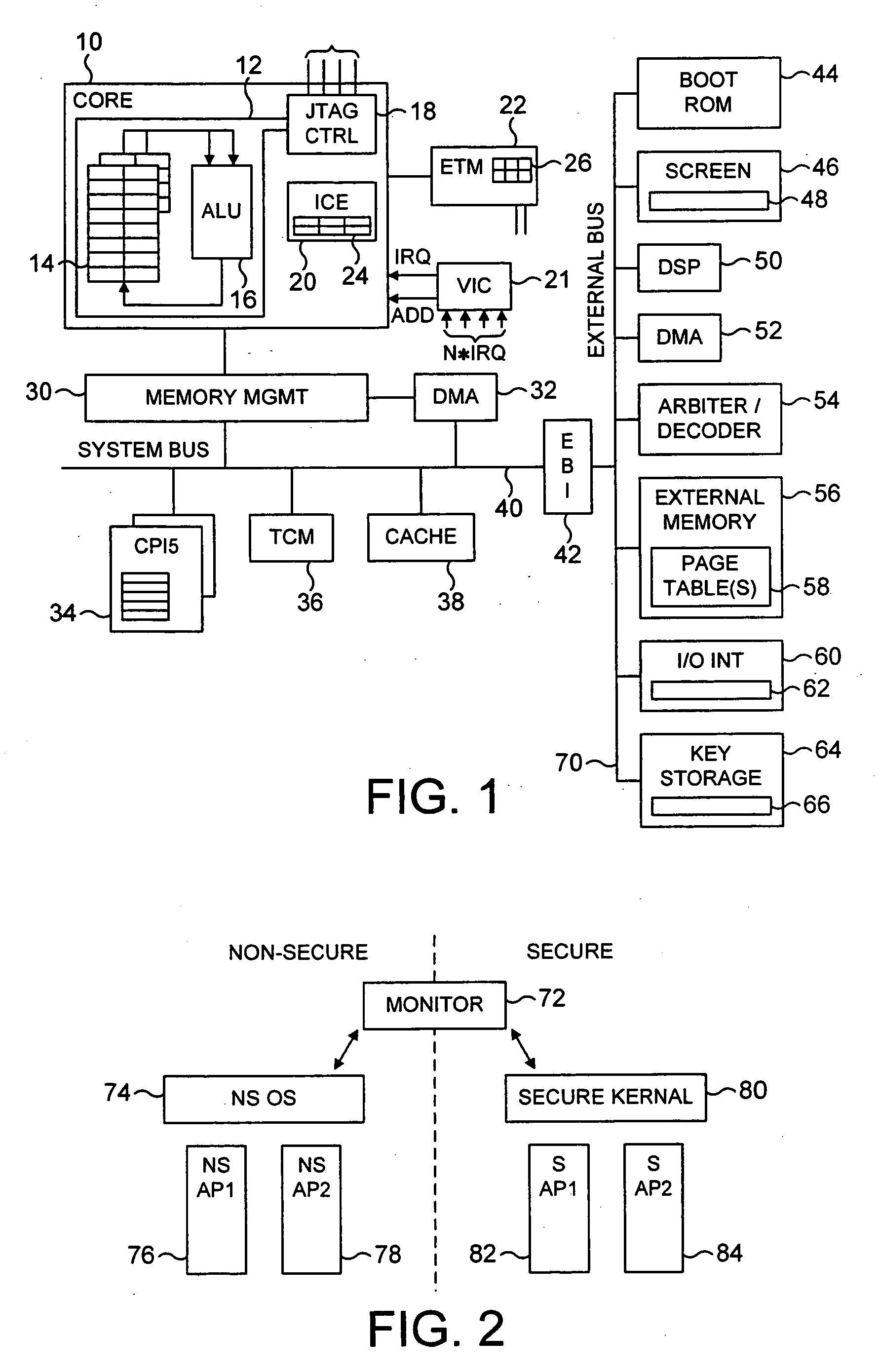
ActiveUS20040177261A1Prevent unauthorized accessAvoid it happening againMemory adressing/allocation/relocationDigital computer detailsComputer hardwareSecurity domain
The present invention provides a data processing apparatus and method for controlling access to a memory. The data processing apparatus has a secure domain and a non-secure domain, in the secure domain the data processing apparatus having access to secure data which is not accessible in the non-secure domain. The data processing apparatus comprises a device coupled to a memory via a device bus, and operable, when an item of data in the memory is required by the device, to issue onto the device bus a memory access request pertaining to either the secure domain or the non-secure domain. The memory is operable to store data required by the device, and contains secure memory for storing secure data and non-secure memory for storing non-secure data. In accordance with the present invention, the data processing apparatus further comprises partition checking logic coupled to the device bus and operable whenever the memory access request as issued by the device pertains to the non-secure domain, to detect if the memory access request is seeking to access the secure memory and upon such detection to prevent the access specified by that memory request. This approach significantly improves the security of data contained within a secure portion of memory.
Owner:ARM LTD
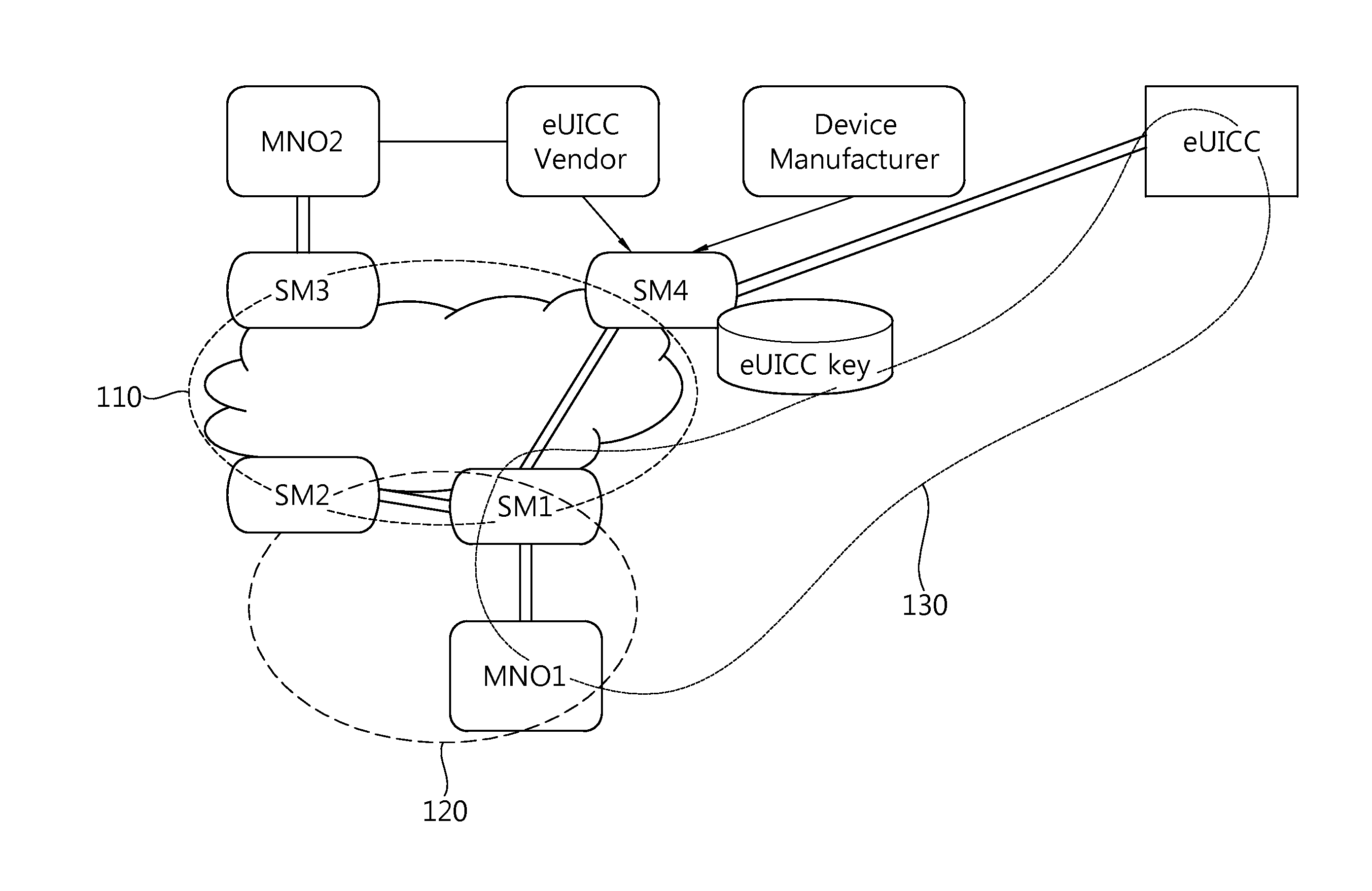
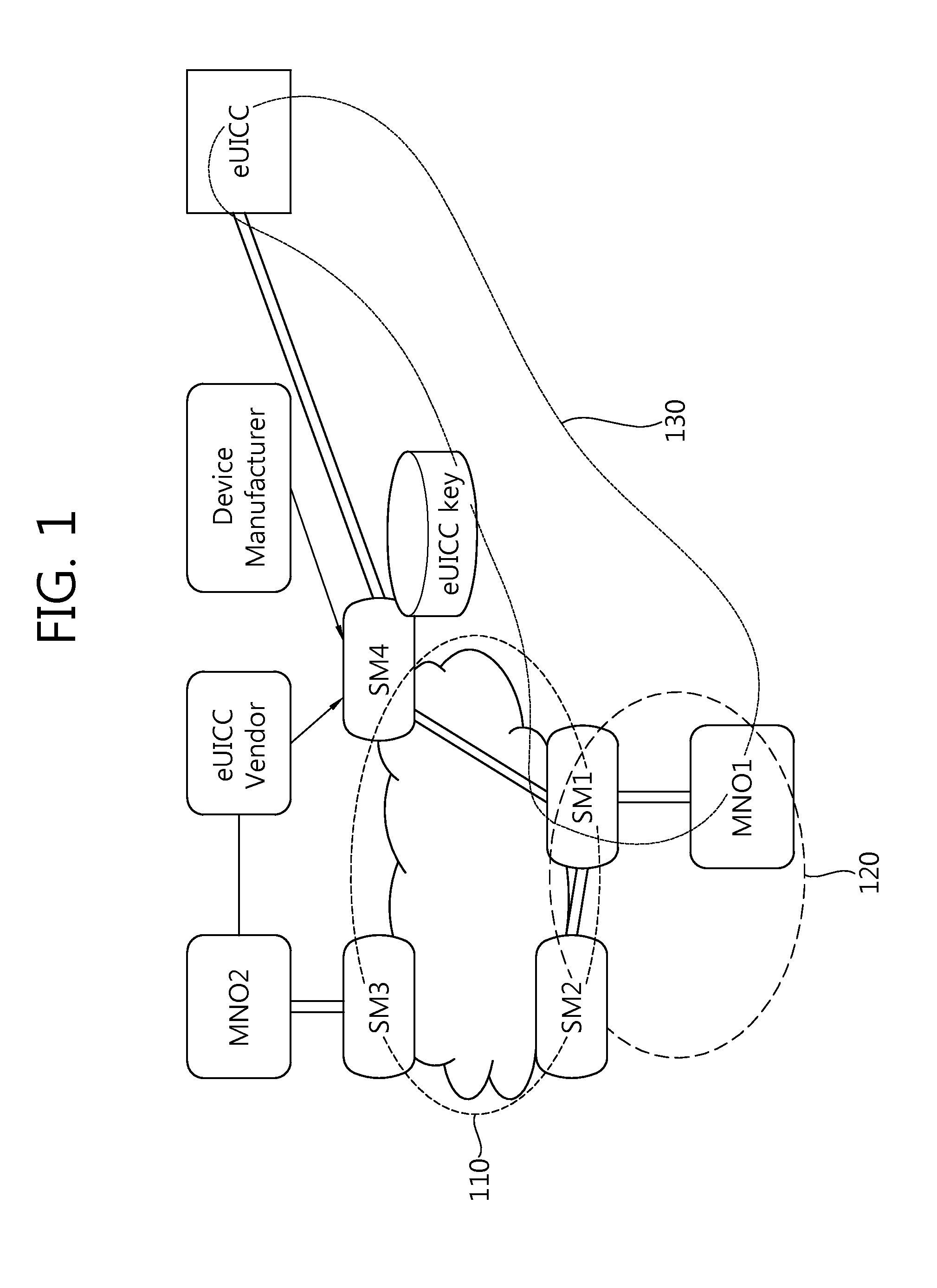
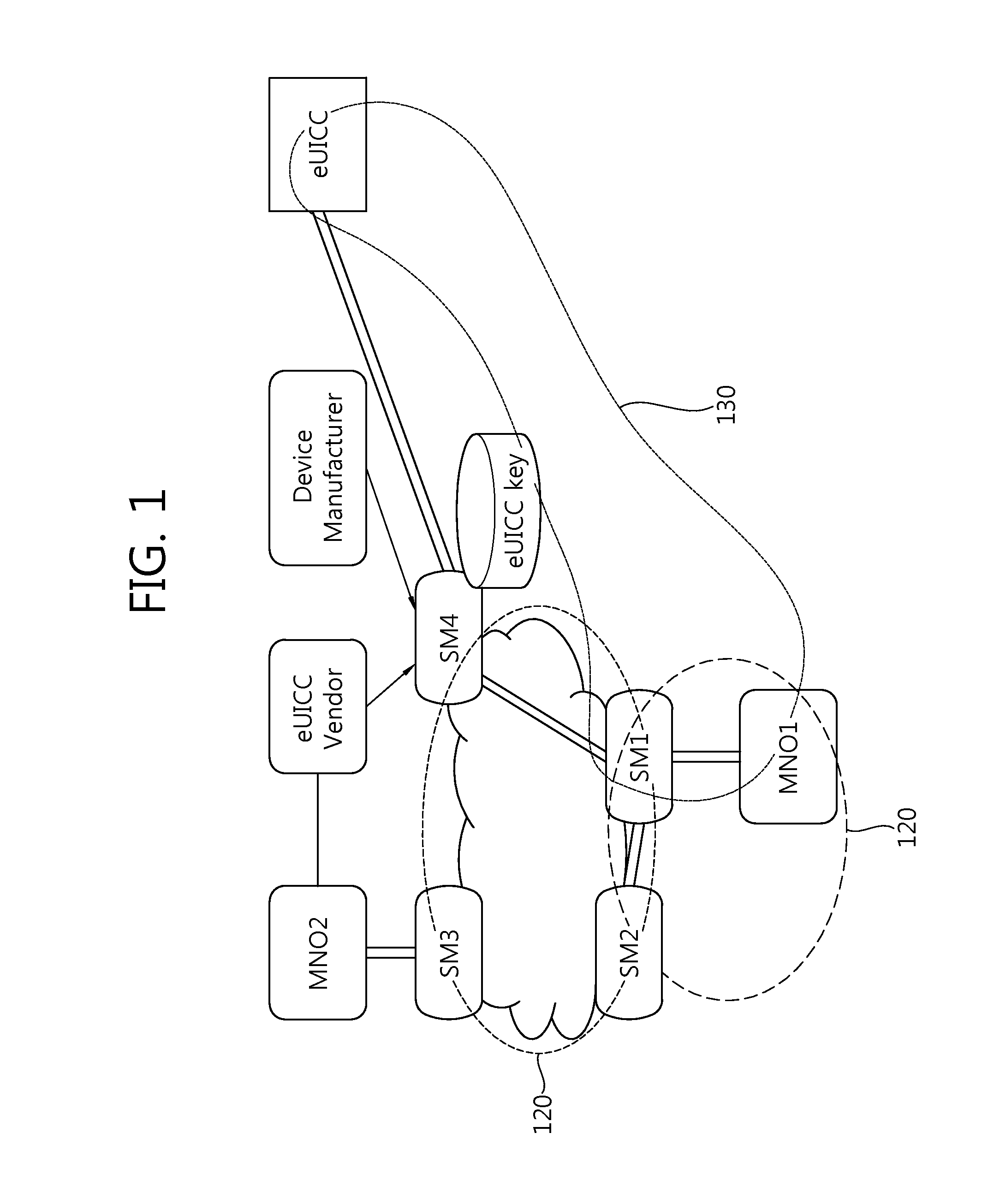
Method for changing mno in embedded sim on basis of dynamic key generation and embedded sim and recording medium therefor
The present invention Includes using an embedded SIM (eSIM) associated with a newly-opened mobile network operator (MNO) system and a receiving MNO system, the method performs the steps of: generating a security domain (SD) for a receiving MNO on the basis of a request from the newly-opened MNO system; injecting a prior SD key value; installing a secure applet for key generation and secure arithmetic operations, injecting a new SD key value on the basis of a request from the receiving MNO, and transmitting only a public key to the receiving MNO system after generating key pairs for the receiving MNO; and decoding a receiving MNO profile with a private key corresponding to the public key after receiving the receiving MNO profile from the receiving MNO system or the newly-opened MNO system.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Hidden link dynamic key manager for use in computer systems with database structure for storage of encrypted data and method for storage and retrieval of encrypted data
InactiveUS7362868B2Improve securityOpportunities decreaseMultiple keys/algorithms usageComputer security arrangementsCommon nameSecurity domain
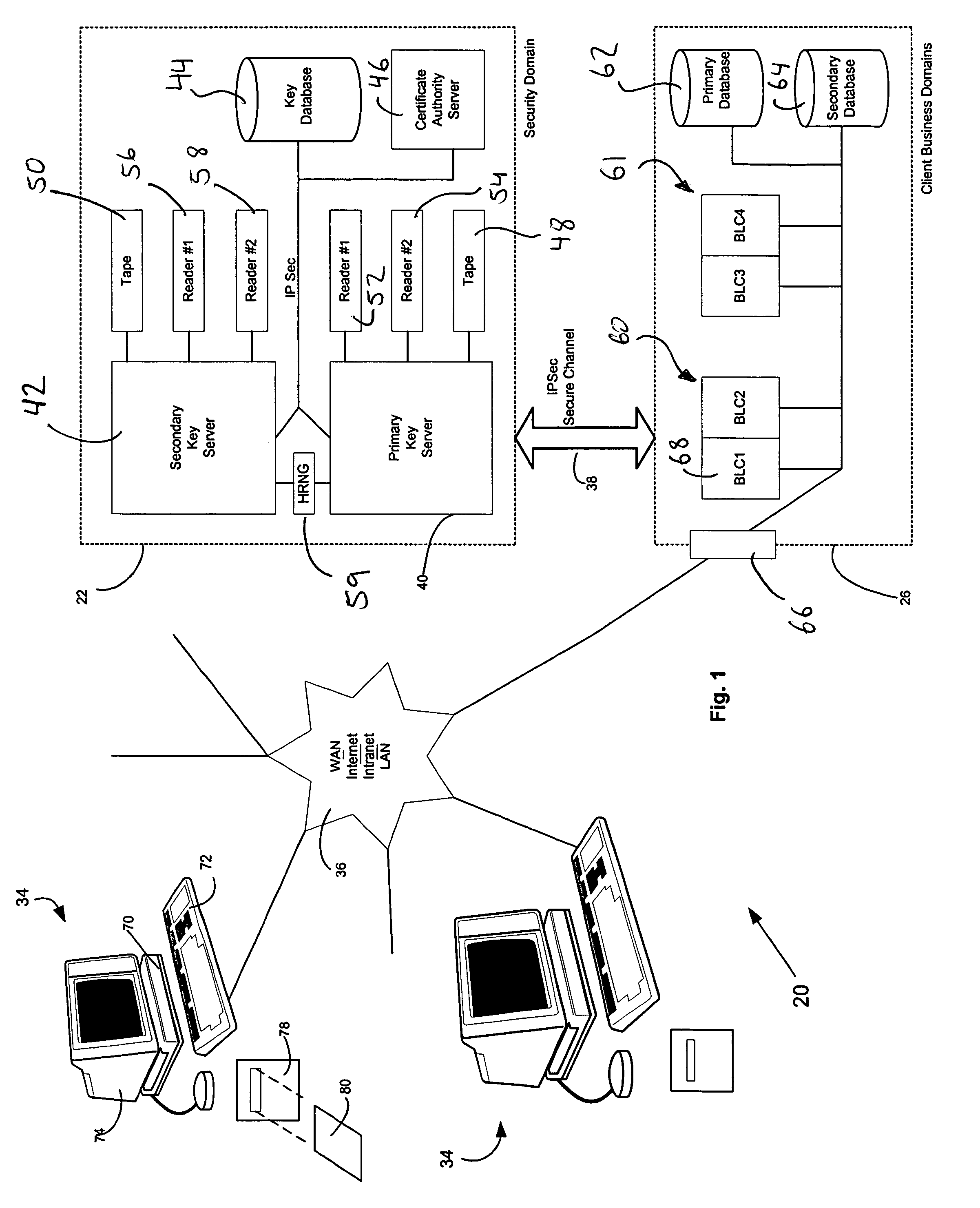
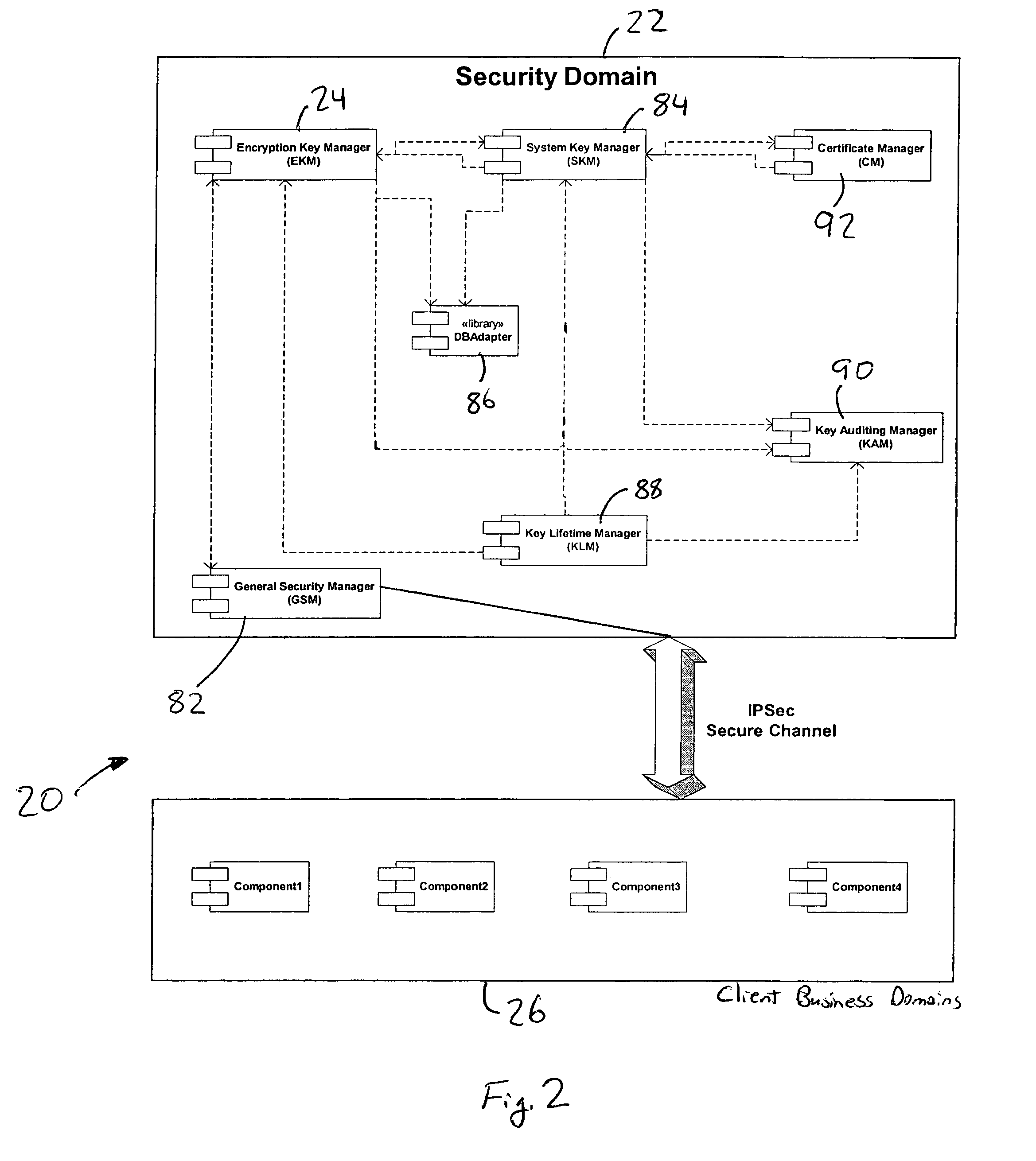
A computer system (20) having a security domain (22), at least one client business domain (26), and a plurality of client terminals (34) utilizes a hidden link dynamic key manager (24, 84) and a database structure that includes encrypted data entities (30C, 30D) and a security identification attribute (32) for storage of encrypted data. Methods for encrypting data and for storing, decrypting, and retrieving encrypted data operate on the computer system (20), which also includes an information database (62) and a key database (44). The key database (44) is isolated from the information database (62). The hidden link key manager is stored in the security domain (22) and includes a system key manager (84) operable to generate system keys with system key common names and an encryption key manager (24) operable to generate encryption keys having encryption key identifications. The key managers (24, 84) operate on a key server (40), which is mirrored by a secondary key server (42). A general security manager (82) also operates on the key server (40) to control access to the security domain (22). The security information attribute (32) is stored with a persistent data entity (30A) that is associated with the other encrypted data entities (30C, 30D) by a database schema. The encryption key identification (112) for the encryption key used to encrypt the data entities (30C, 30D) is encrypted by a system key and then stored as part of the security information attribute (32). The system key common name hash value (114) is also stored in the security information attribute (32). The information data entities (30) are stored on the information database (62), but the encryption key identification (153), encryption key (154), system key common name hash value (156, 157), and system key common name (158) are stored in the key database (44) inside the security domain (22). The system key itself is stored on a Smart Card reader (56) inside the security domain.
Owner:FARRUKH ABDALLAH DR +1
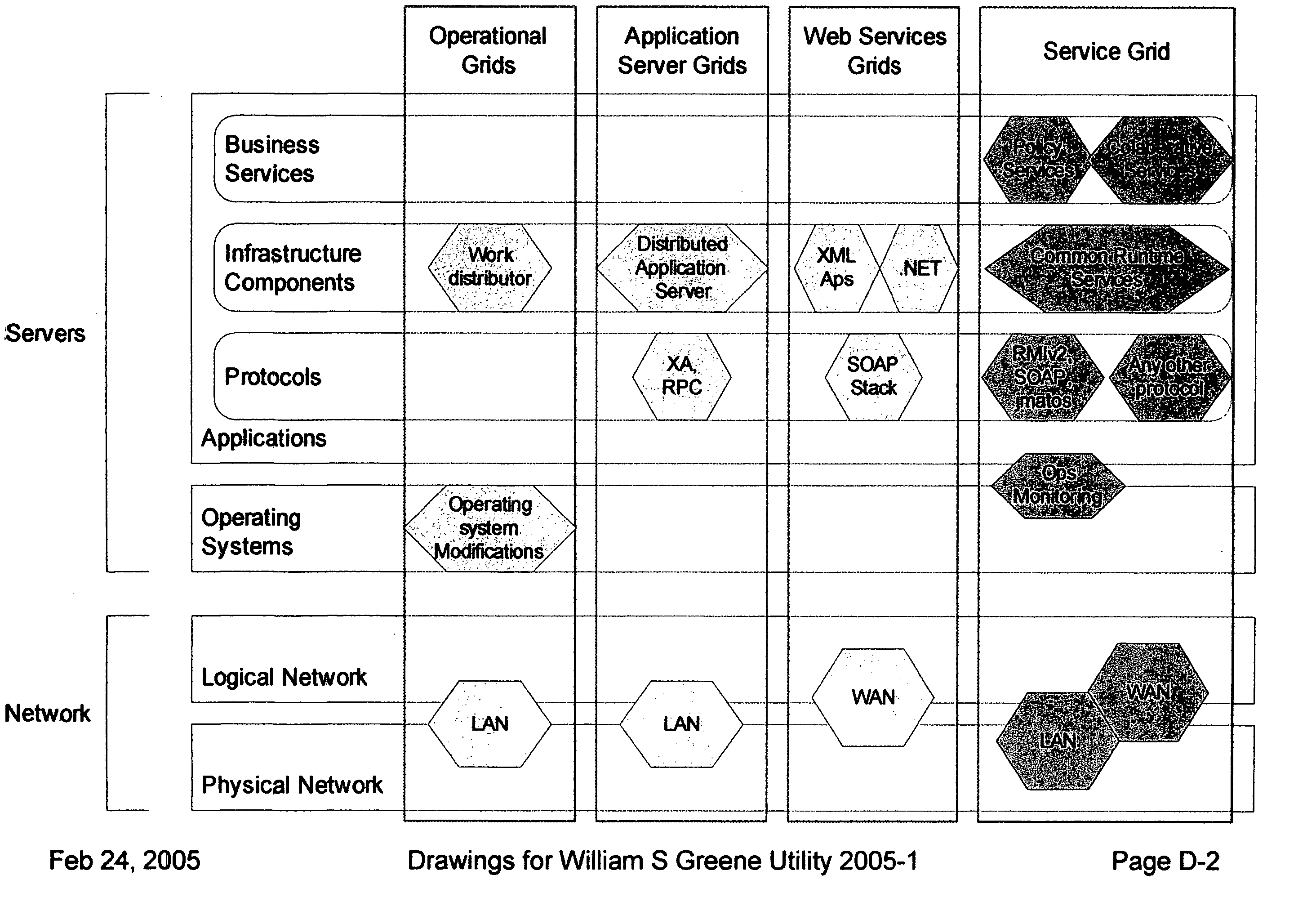
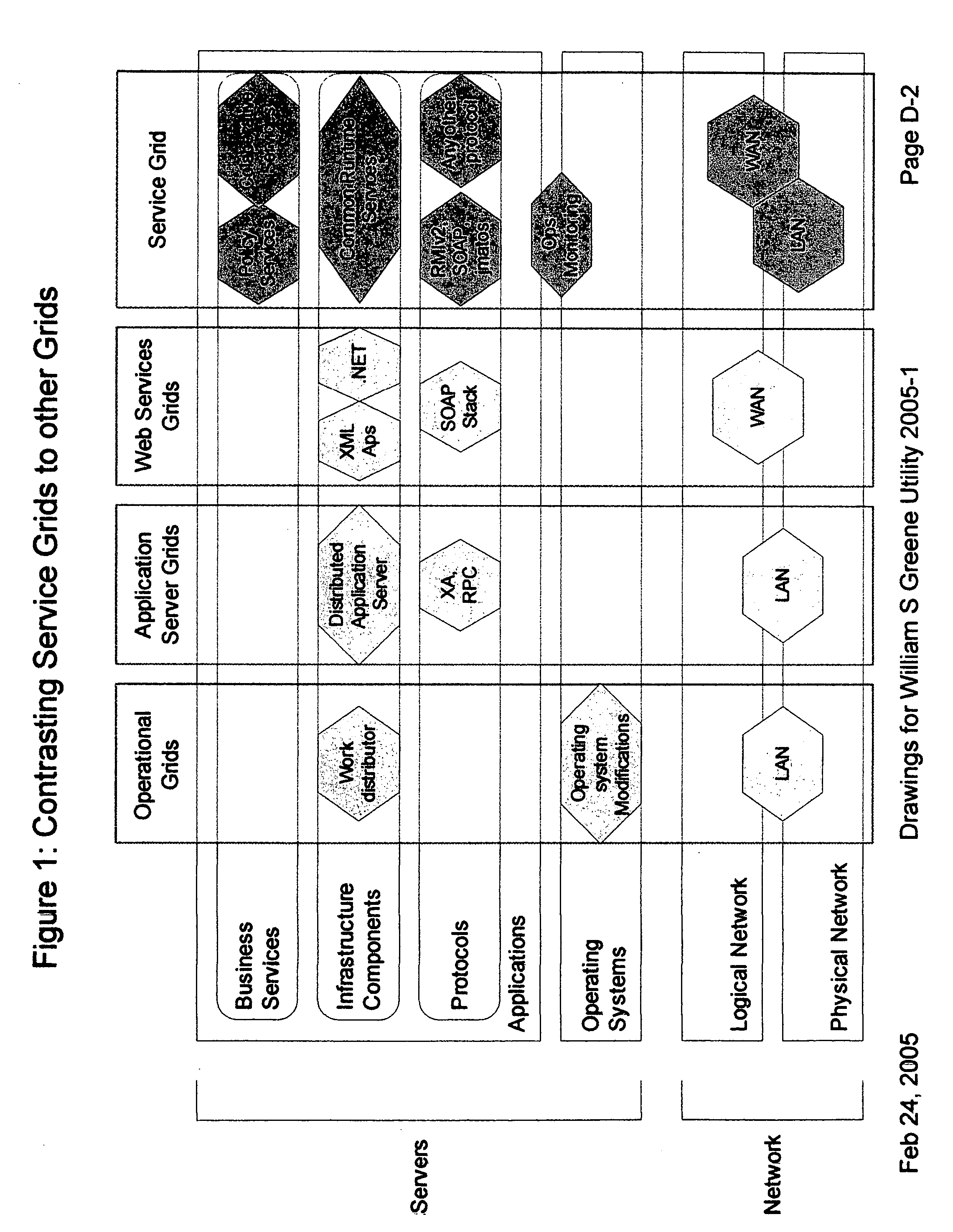
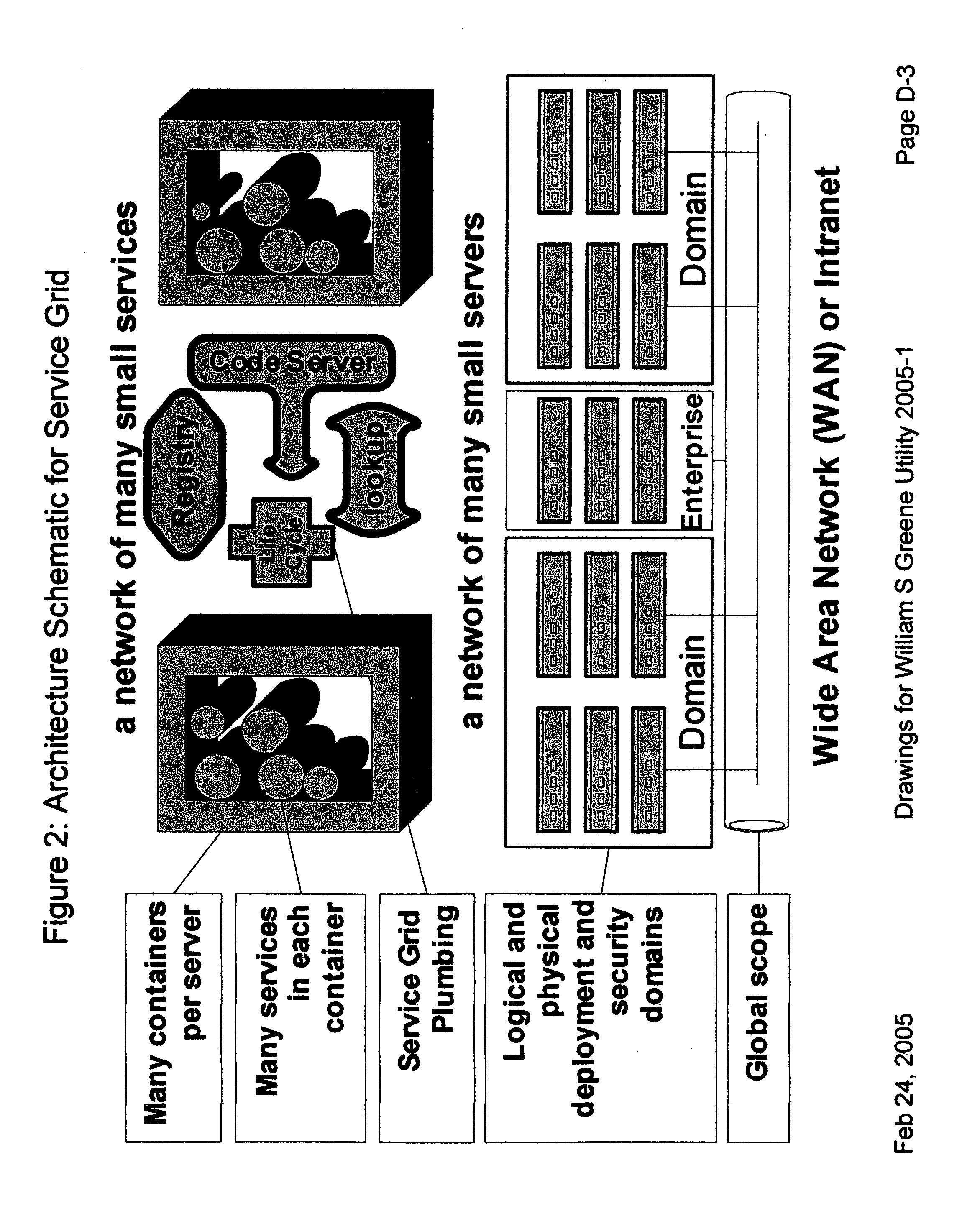
Providing secure data and policy exchange between domains in a multi-domain grid by use of a service ecosystem facilitating uses such as supply-chain integration with RIFD tagged items and barcodes
InactiveUS20050193222A1Simple methodImprove securityDigital data processing detailsMultiple digital computer combinationsSecurity domainRadio frequency
A system, method, and software implemented system of services provides enhanced security and management to multiple domain grids and allows intercommunications between the different grid domains providing for secure data exchange, policy exchange, and agent exchange between grids or grid domains. Via the exemplary example, utilizing the unique characteristics of the Service Grid and mobile agents, this is extended to provide enhanced security and management to supply chains: providing data exchange, policy exchange, and agent exchange between supply chain nodes and supply chain partners—facilitating enhanced methods of supply chain automation when using barcodes and Radio Frequency Identity (RFID) tags to identify and track goods through supply chains and consumer uses. Agents transport data and policy between supply-chain partners over an extranet, migrating across corporate boundaries and security domains, locating near where items are identified to provide local control, environmentally responsive policy, and ongoing permanent data capture & history.
Owner:GREENE WILLIAM SPROTT
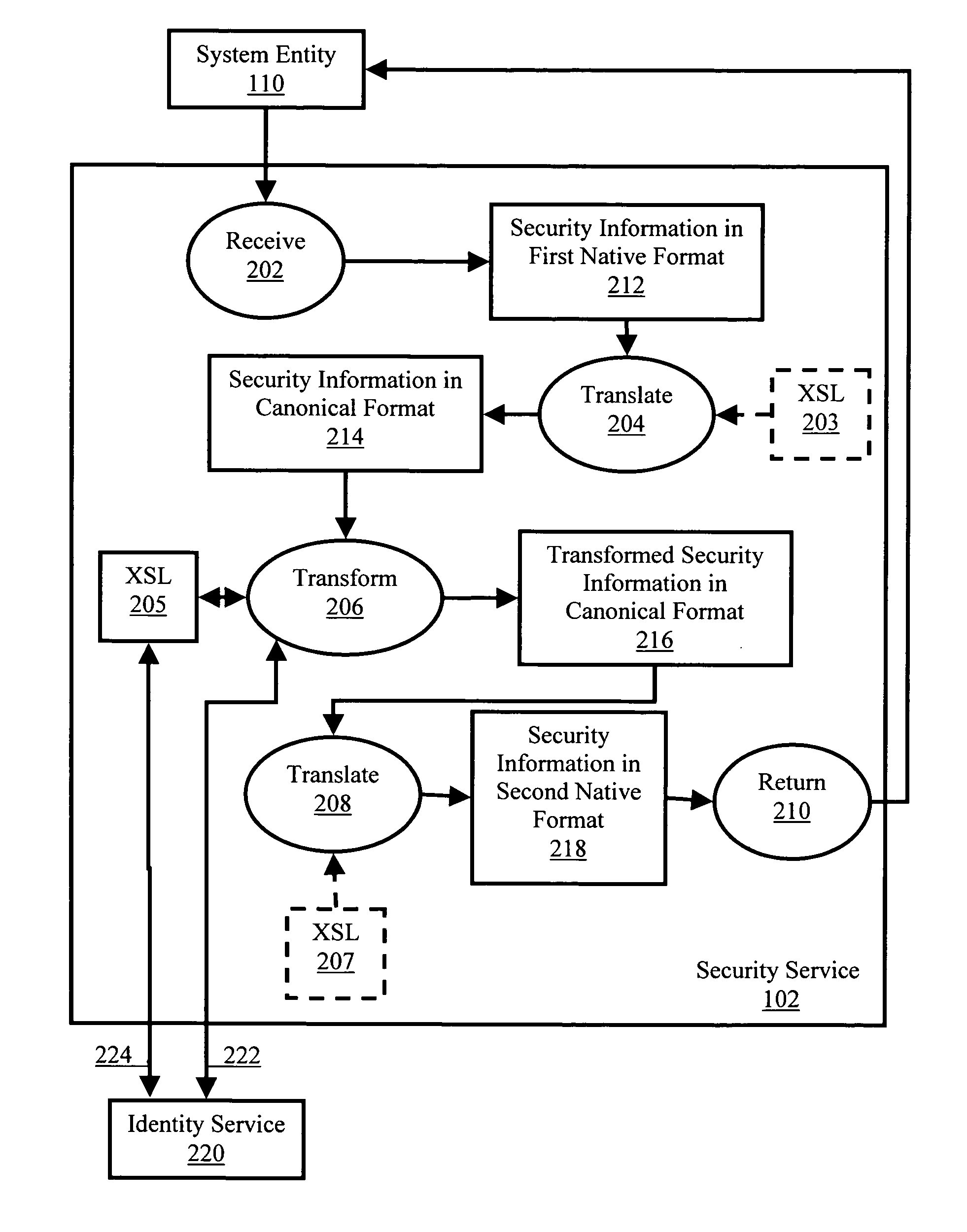
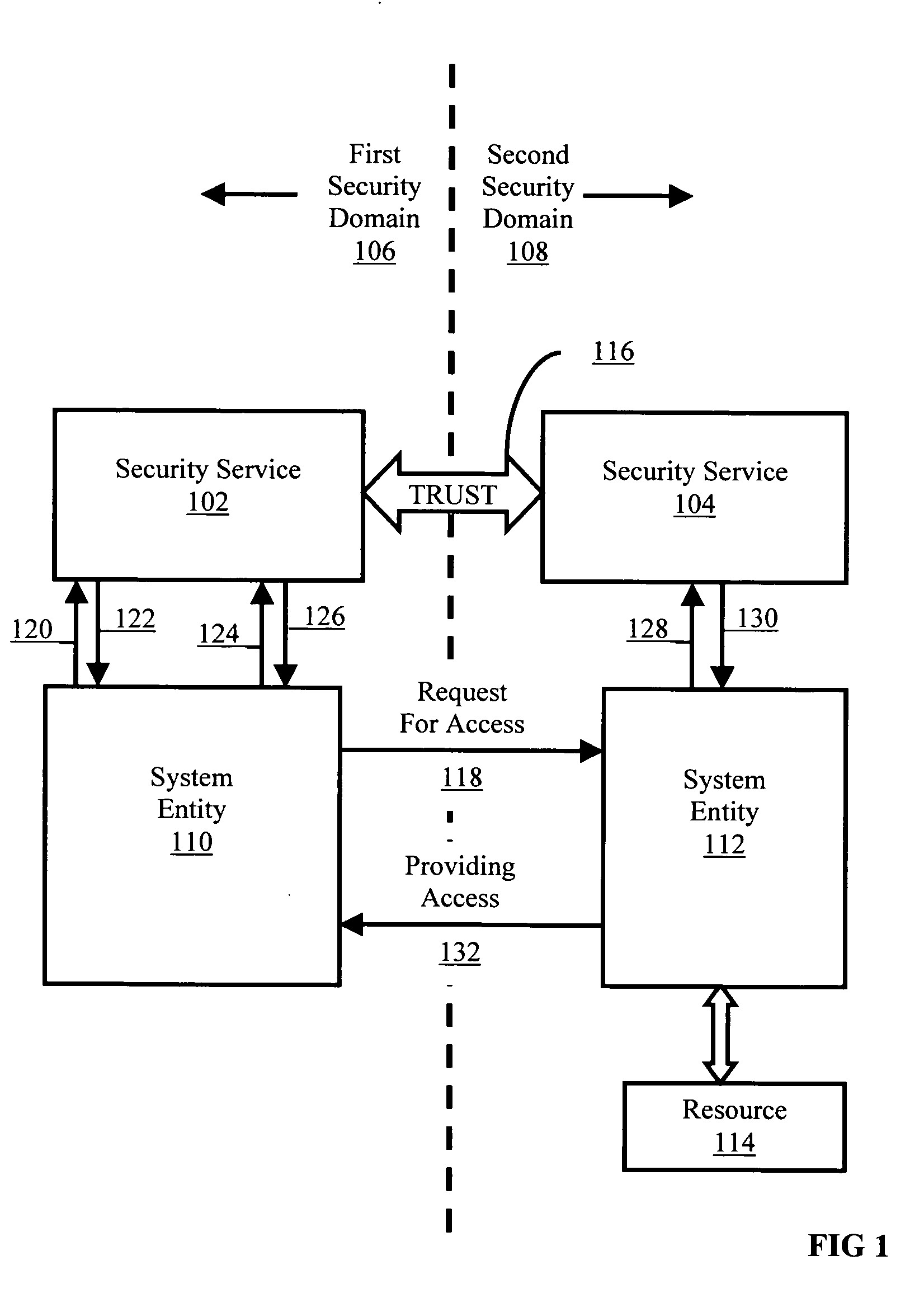
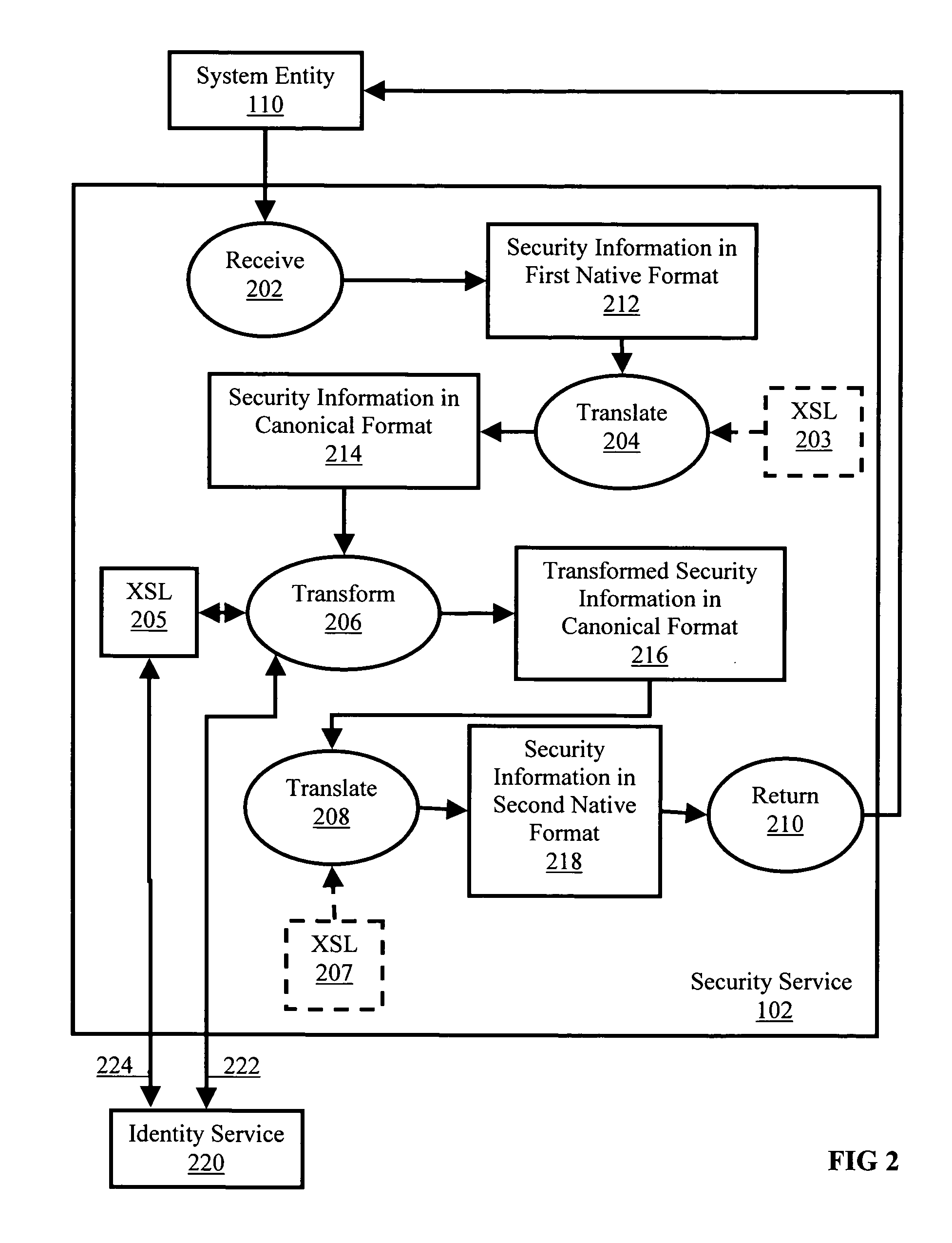
Cross domain security information conversion
ActiveUS20050223413A1Digital data processing detailsComputer security arrangementsSecurity domainSecurity information
Methods, systems, and computer program products are provided for cross domain security information conversion. Embodiments include receiving from a system entity, in a security service, security information in a native format of a first security domain regarding a system entity having an identity in at least one security domain; translating the security information to a canonical format for security information; transforming the security information in the canonical format using a predefined mapping from the first security domain to a second security domain; translating the transformed security information in the canonical format to a native format of the second security domain; and returning to the system entity the security information in the native format of the second security domain.
Owner:IBM CORP
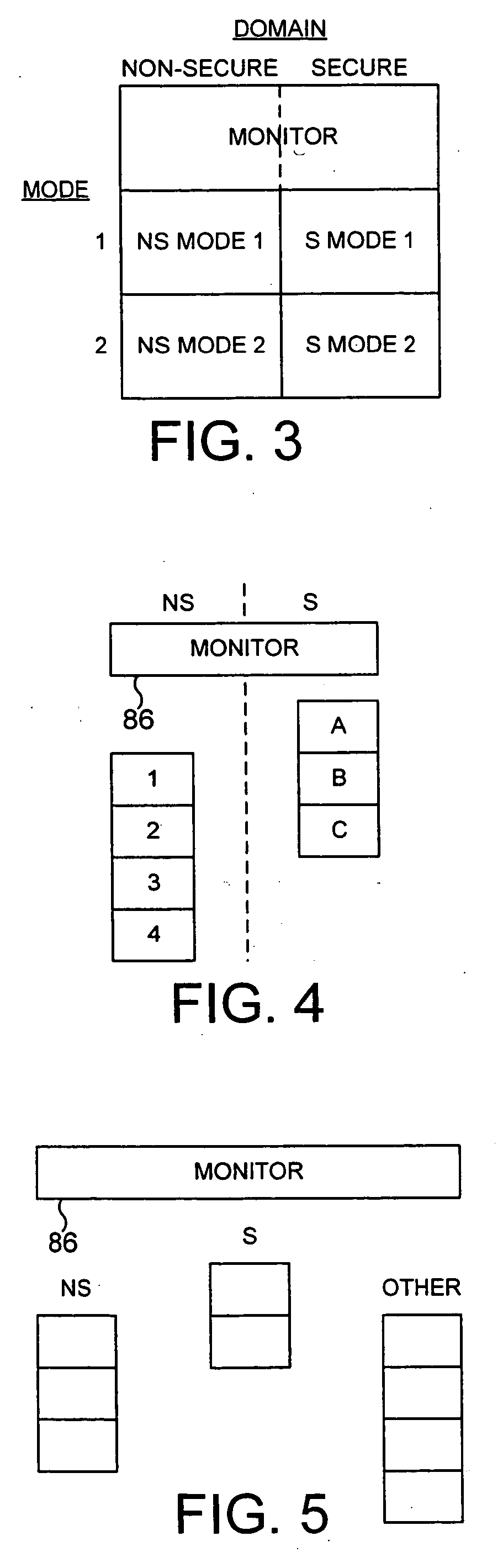
Apparatus and method for managing access to a memory
ActiveUS20040177269A1Performance is not affectedEasy to operateMemory architecture accessing/allocationDigital data processing detailsManagement unitMultiple modes
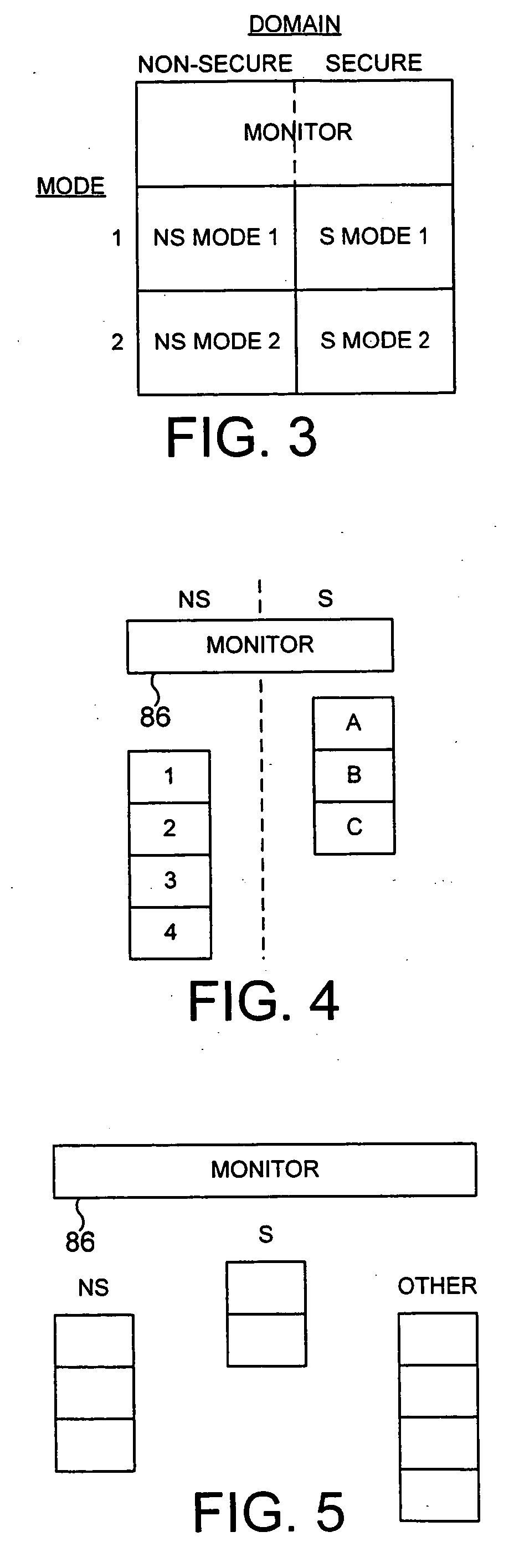
The present invention provides a data processing apparatus and method for managing access to a memory within the data processing apparatus. The data processing apparatus comprises a processor operable in a plurality of modes and a plurality of domains, said plurality of domains comprising a secure domain and a non-secure domain, said plurality of modes including at least one non-secure mode being a mode in the non-secure domain and at least one secure mode being a mode in the secure domain, said processor being operable such that when executing a program in a secure mode said program has access to secure data which is not accessible when said processor is operating in a non-secure mode. Further, a memory is provided for storing data required by the processor, and consists of secure memory for storing secure data and non-secure memory for storing non-secure data. The memory further contains a non-secure table and a secure table, the non-secure table being within the non-secure memory and arranged to contain for each of a number of first memory regions an associated descriptor, and the secure table being within the secure memory and arranged to contain for each of a number of second memory regions an associated descriptor. When access to an item of data in the memory is required by the processor, the processor issues a memory access request, and a memory management unit is provided to perform one or more predetermined access control functions to control issuance of the memory access request to the memory. The memory management unit comprises an internal storage unit operable to store descriptors retrieved by the memory management unit from either the non-secure table or the secure table, and in accordance with the present invention the internal storage unit comprises a flag associated with each descriptor stored within the internal storage unit to identify whether that descriptor is from the non-secure table or the secure table. By this approach, when the processor is operating in a non-secure mode, the memory management unit is operable to perform the predetermined access control functions for the memory access request with reference to access control information derived from the descriptors in the internal storage unit retrieved from the non-secure table. In contrast, when the processor is operating in a secure mode, the memory management unit is operable to perform the predetermined access control functions for the memory access request with reference to access control information derived from the descriptors in the internal storage unit retrieved from the secure table. This approach enables different descriptors to be used for the control of accesses to memory in either the secure domain or the non-secure domain, whilst enabling such different descriptors to co-exist within the memory management unit's internal storage unit, thereby avoiding the requirement to flush the contents of such an internal storage unit when the operation of the processor changes from the secure domain to the non-secure domain, or vice versa.
Owner:ARM LTD
Digital rights management for local recording and home network distribution
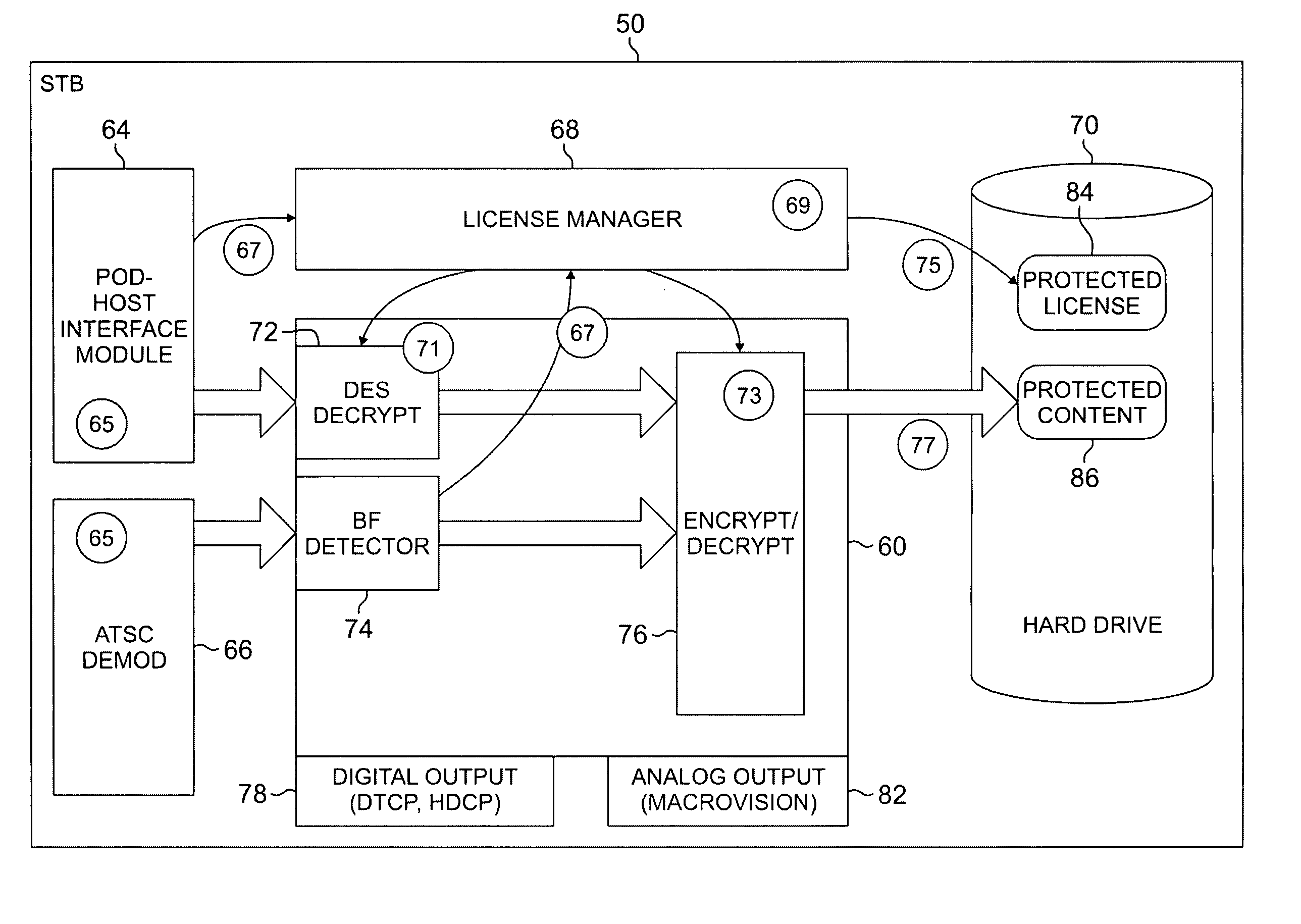
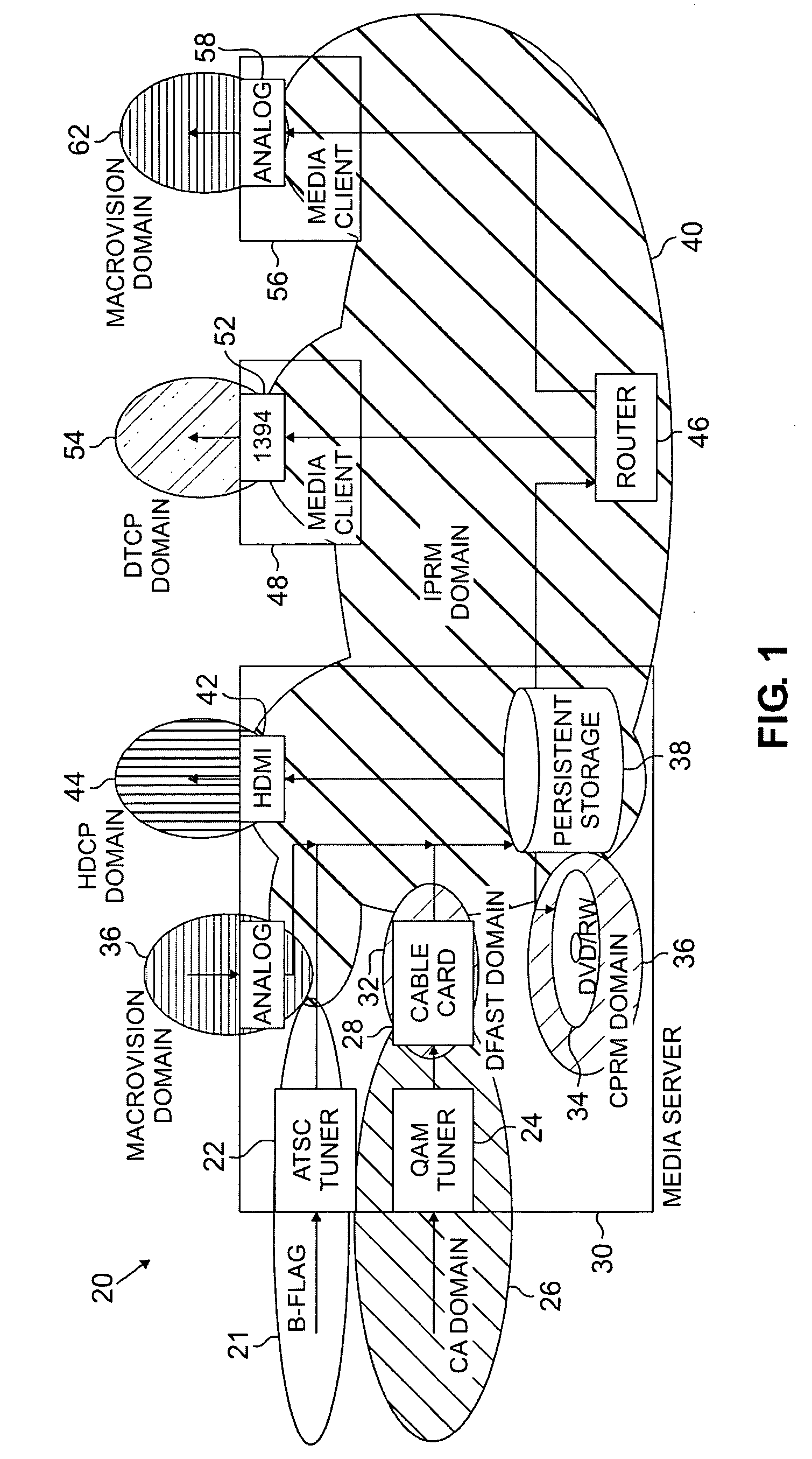
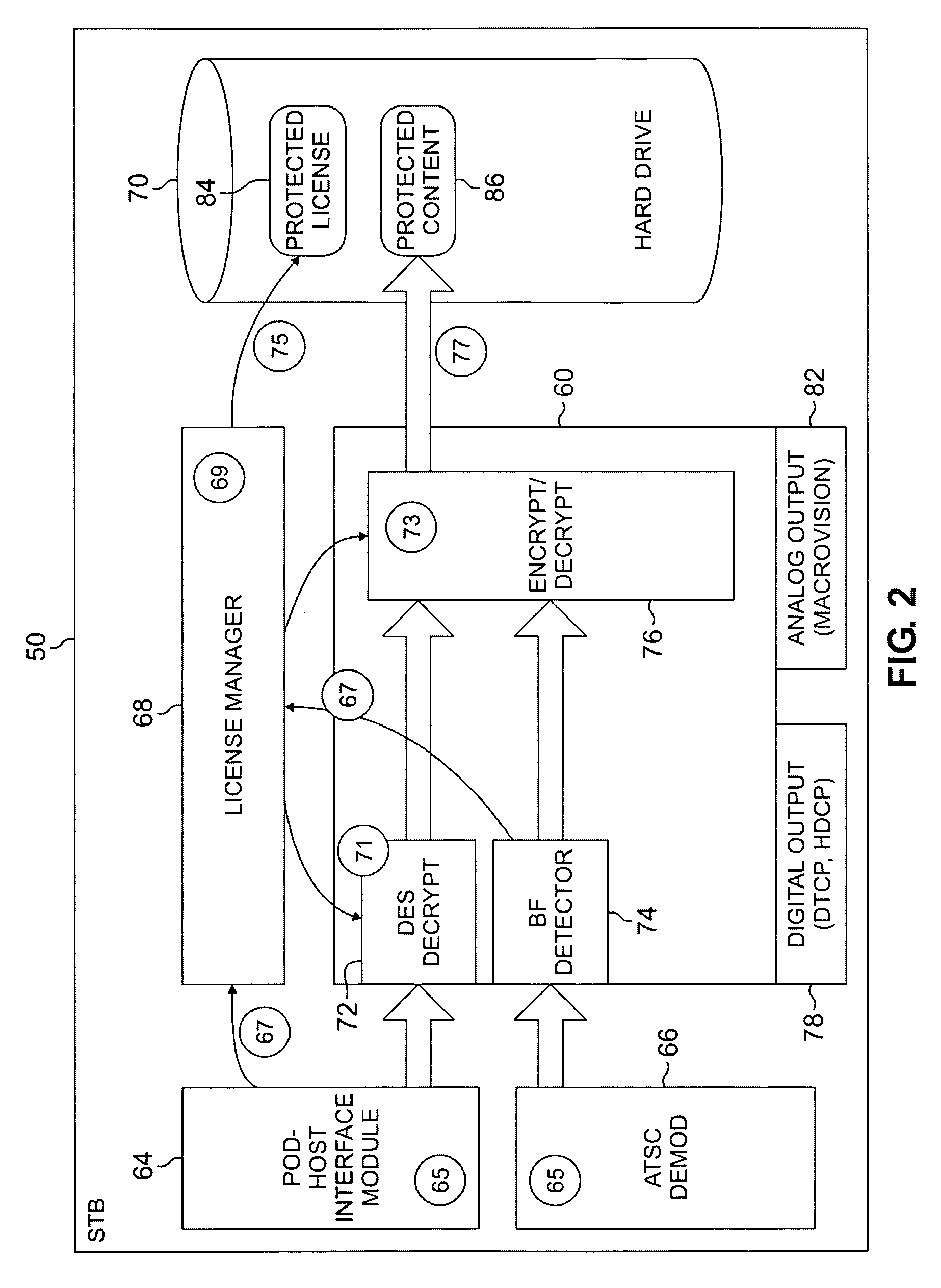
The systems disclosed here provide a complete standards-based end-to-end scalable system for storage, delivery and in-home distribution of digital content over IP networks using standard protocols such as Real-time Transport Protocol (“RTP”) or IP-encapsulated MPEG-2 Transport Stream, or traditional MPEG-2 networks. Mechanisms are provided for receiving content from one security domain, re-encrypting that content uniquely for a receiving device, persistently storing that content, and playing back that content at a later time to and within another security domain. The systems also provide the ability to stream the persistently-stored content from the initial receiving device to another device that has been authenticated as part of a, e.g., home network. This allows a media server, e.g., a dual-tuner set-top box (“STB”) with hard drive, to deliver recorded content to any TV in the house by streaming to media clients such as STBs.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
Computer security system
InactiveUS7013485B2Digital data processing detailsUnauthorized memory use protectionComputerized systemSecurity domain
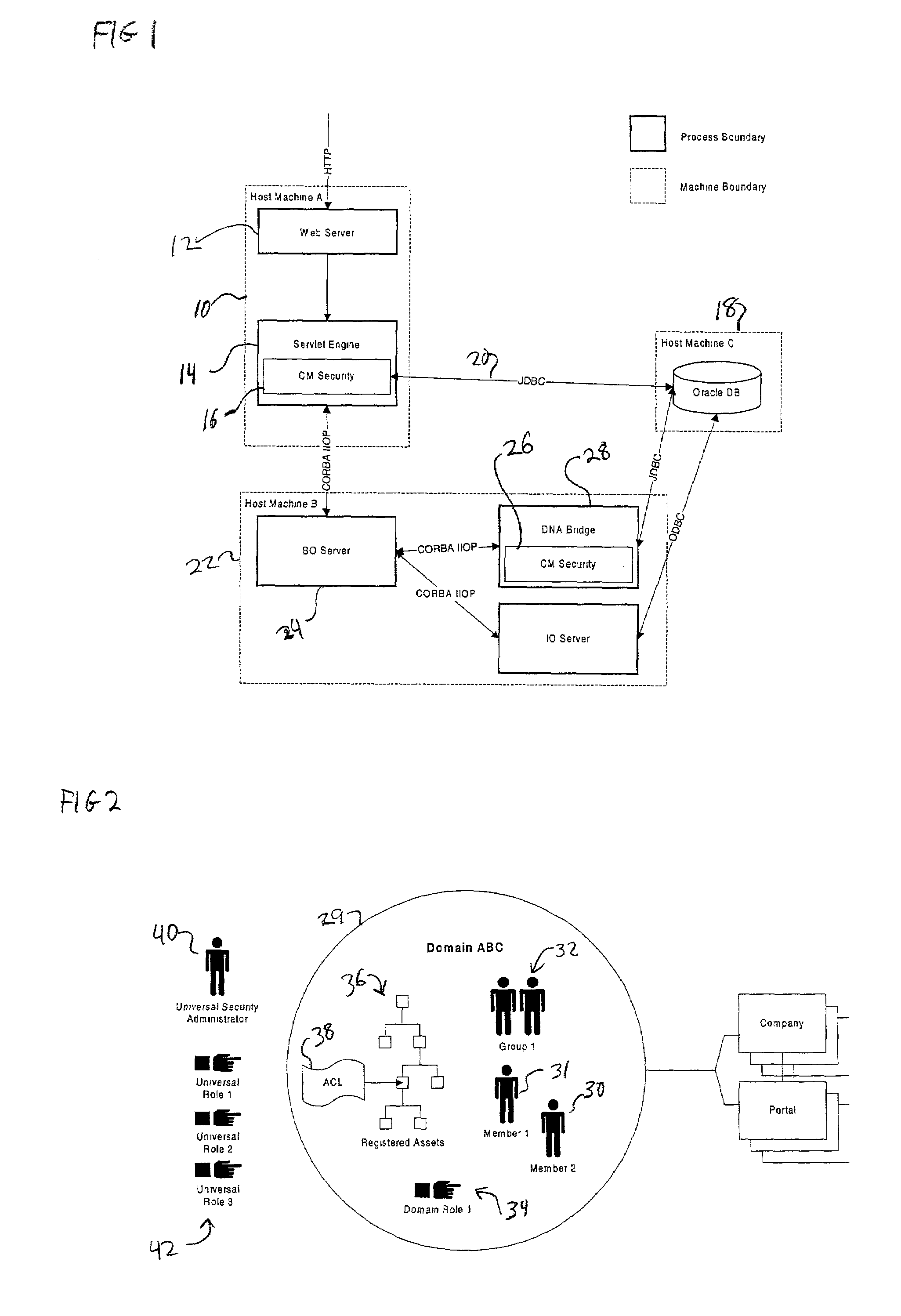
A security system for a computer system provides one or more security domains. Access to assets registered to the security system is controlled by rights and privileges. Rights are derived from roles, and each user is assigned one or more roles. Privileges are attached to assets, and an appropriate combination of rights and privileges is required before a user is granted the specified type of access to the asset.
Owner:JDA SOFTWARE GROUP
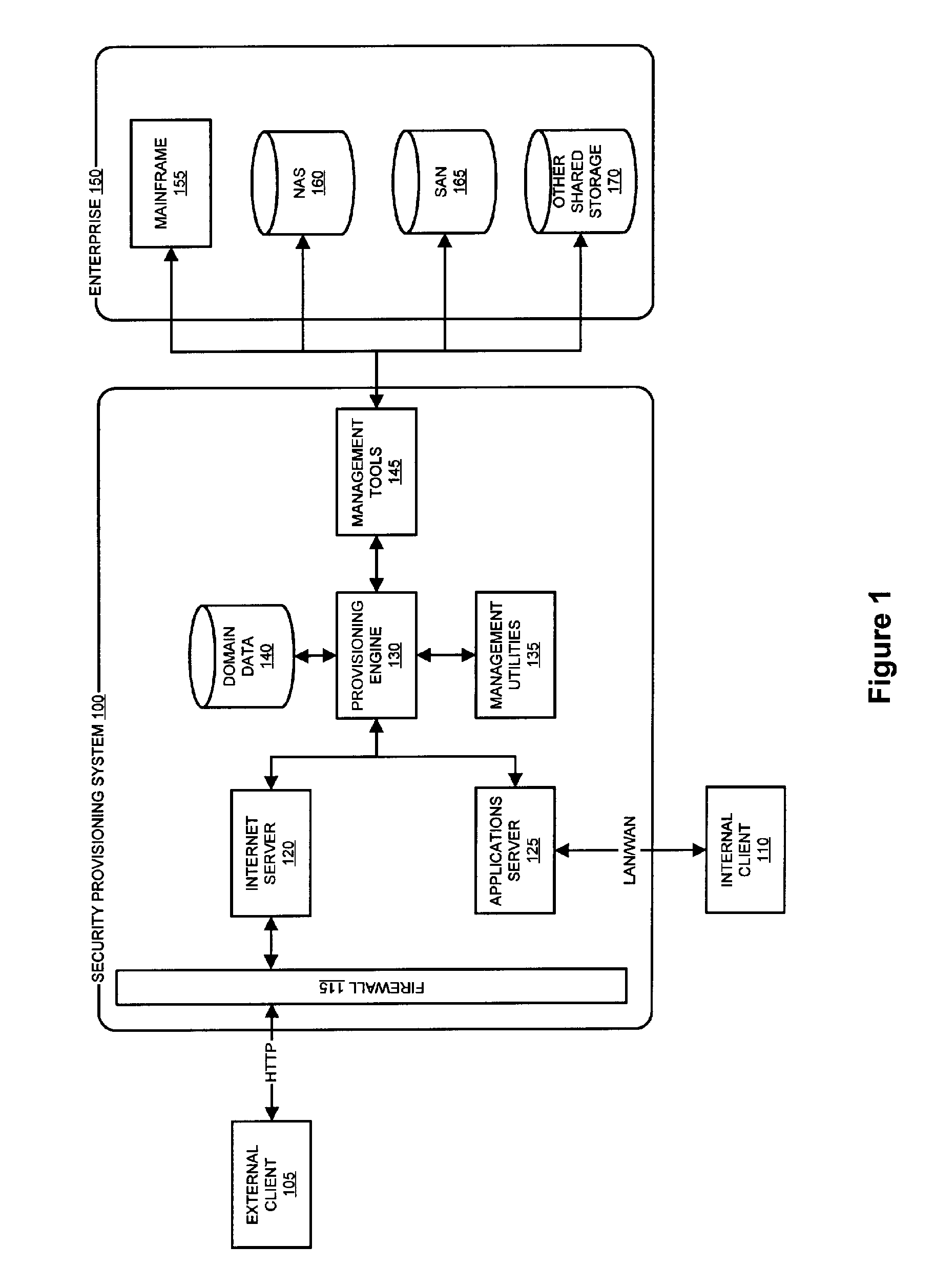
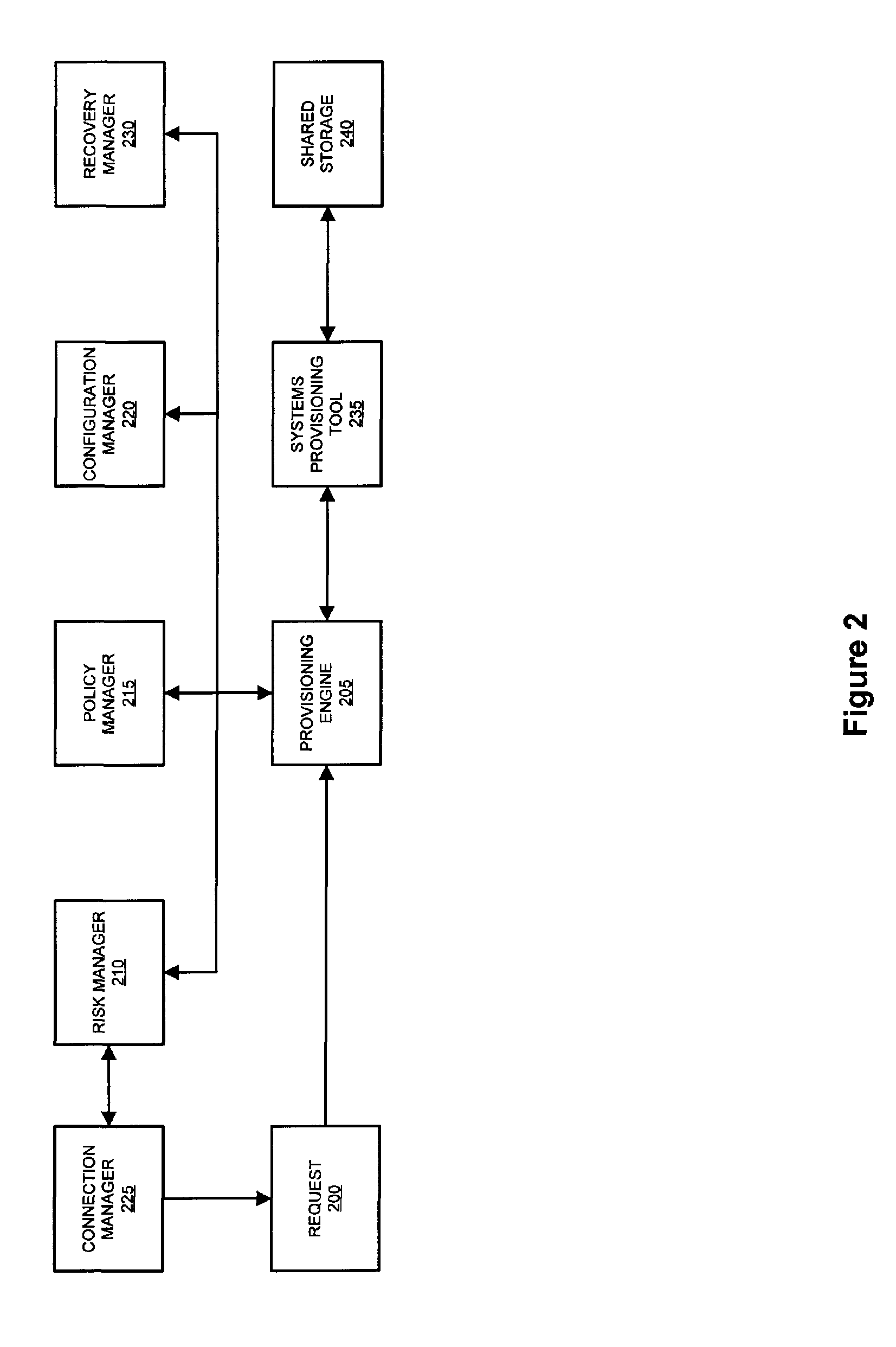
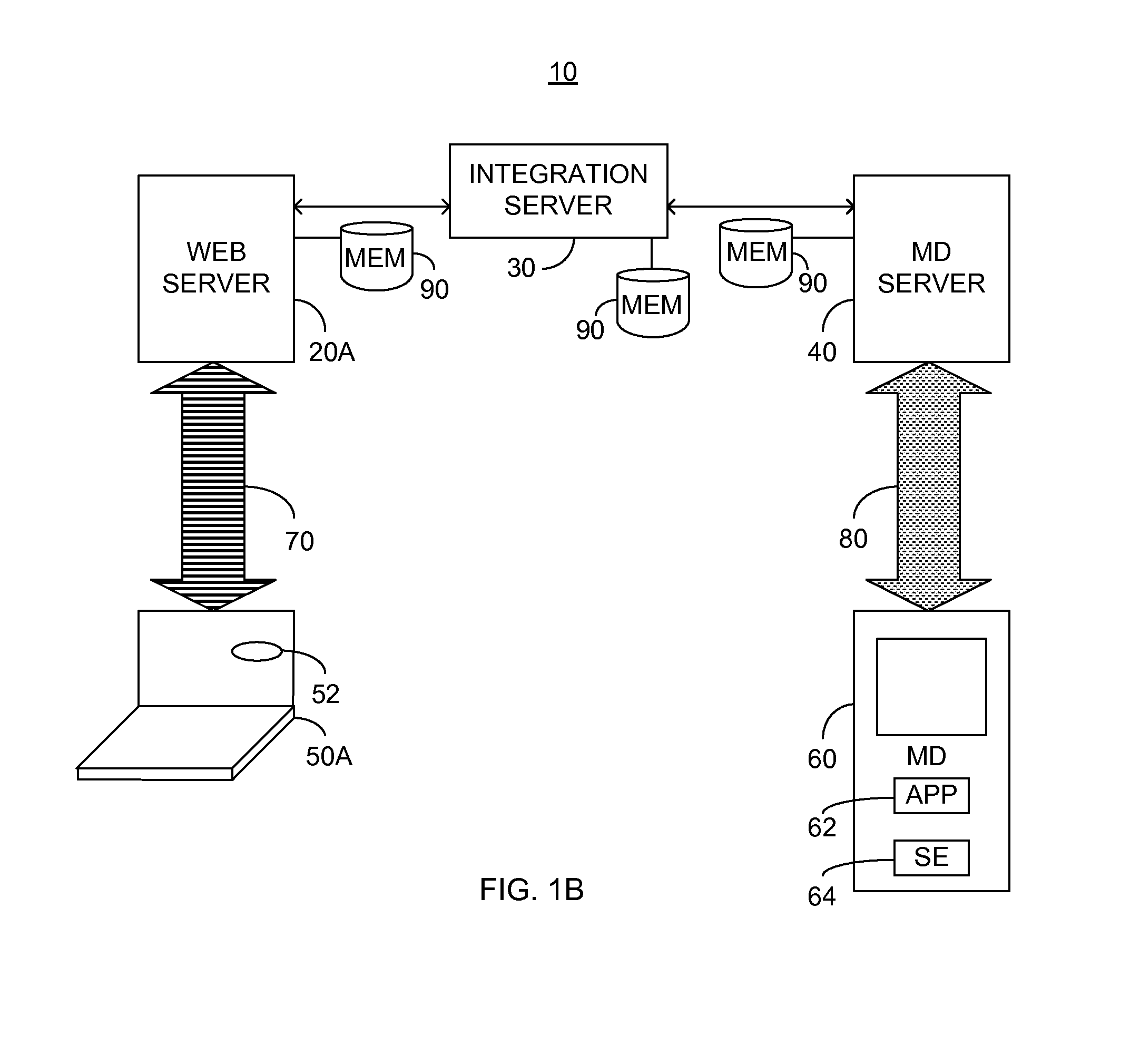
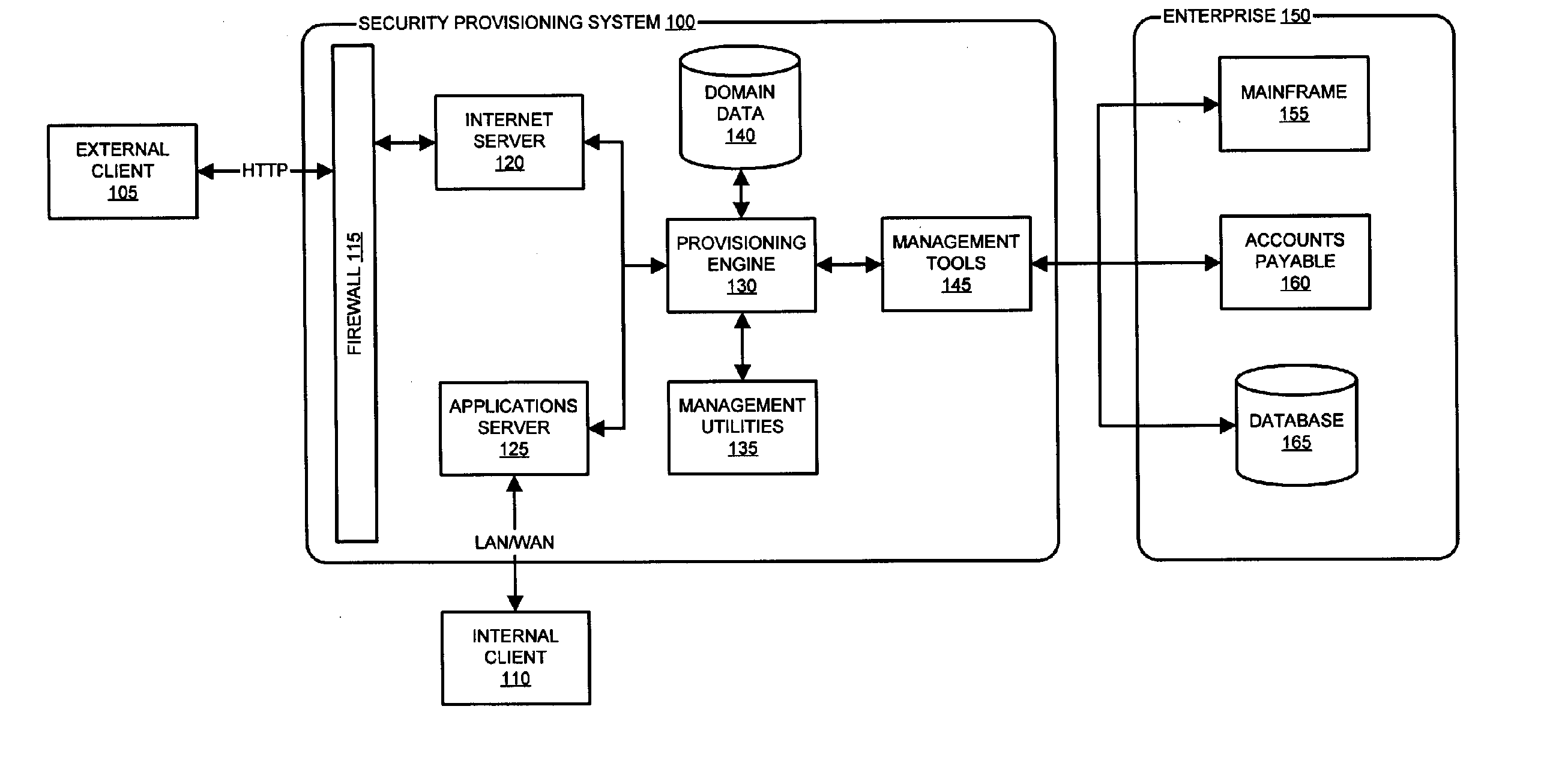
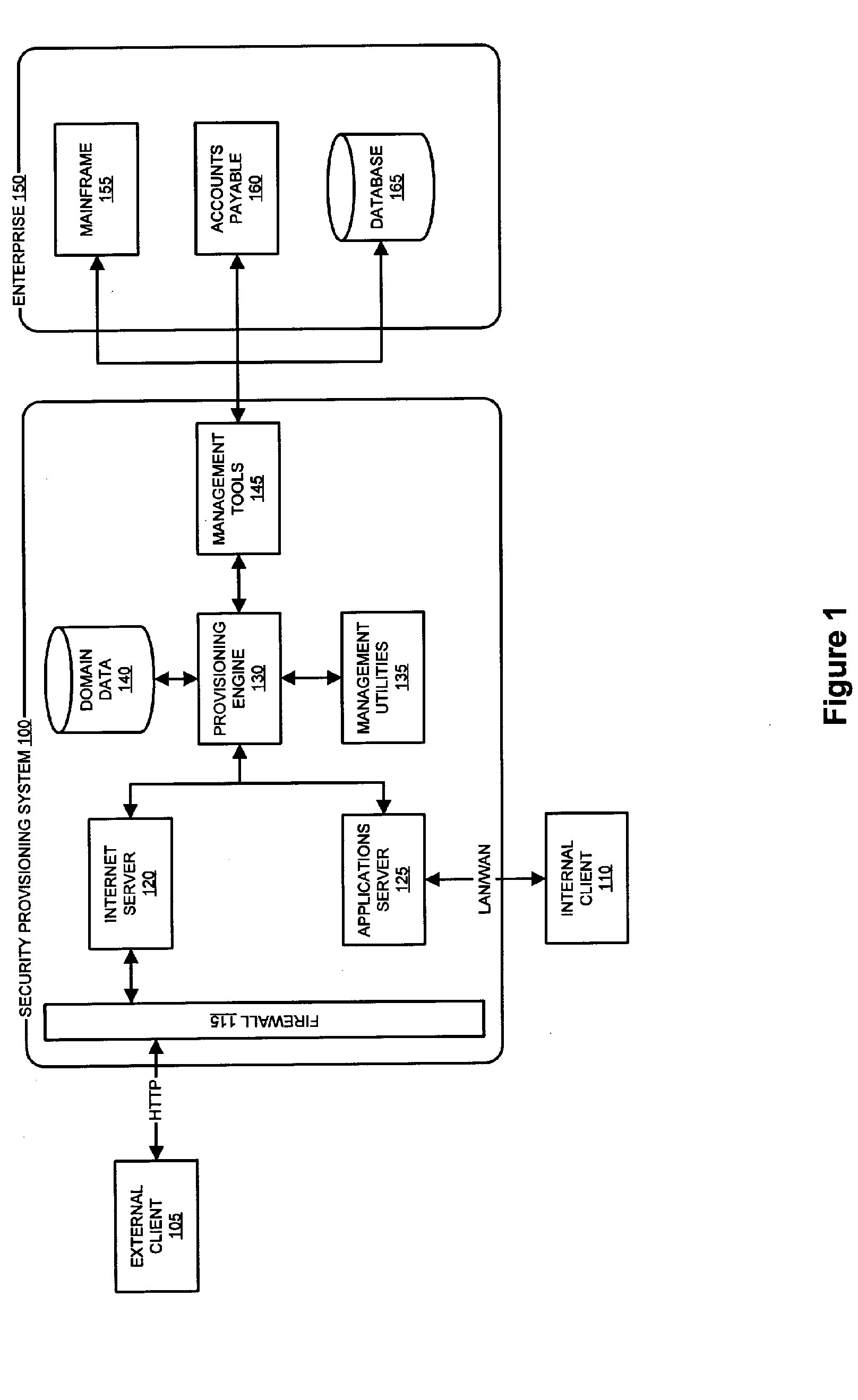
System and method for dynamic security provisioning of data resources
InactiveUS8266670B1Memory loss protectionUnauthorized memory use protectionComputer hardwareSecurity domain
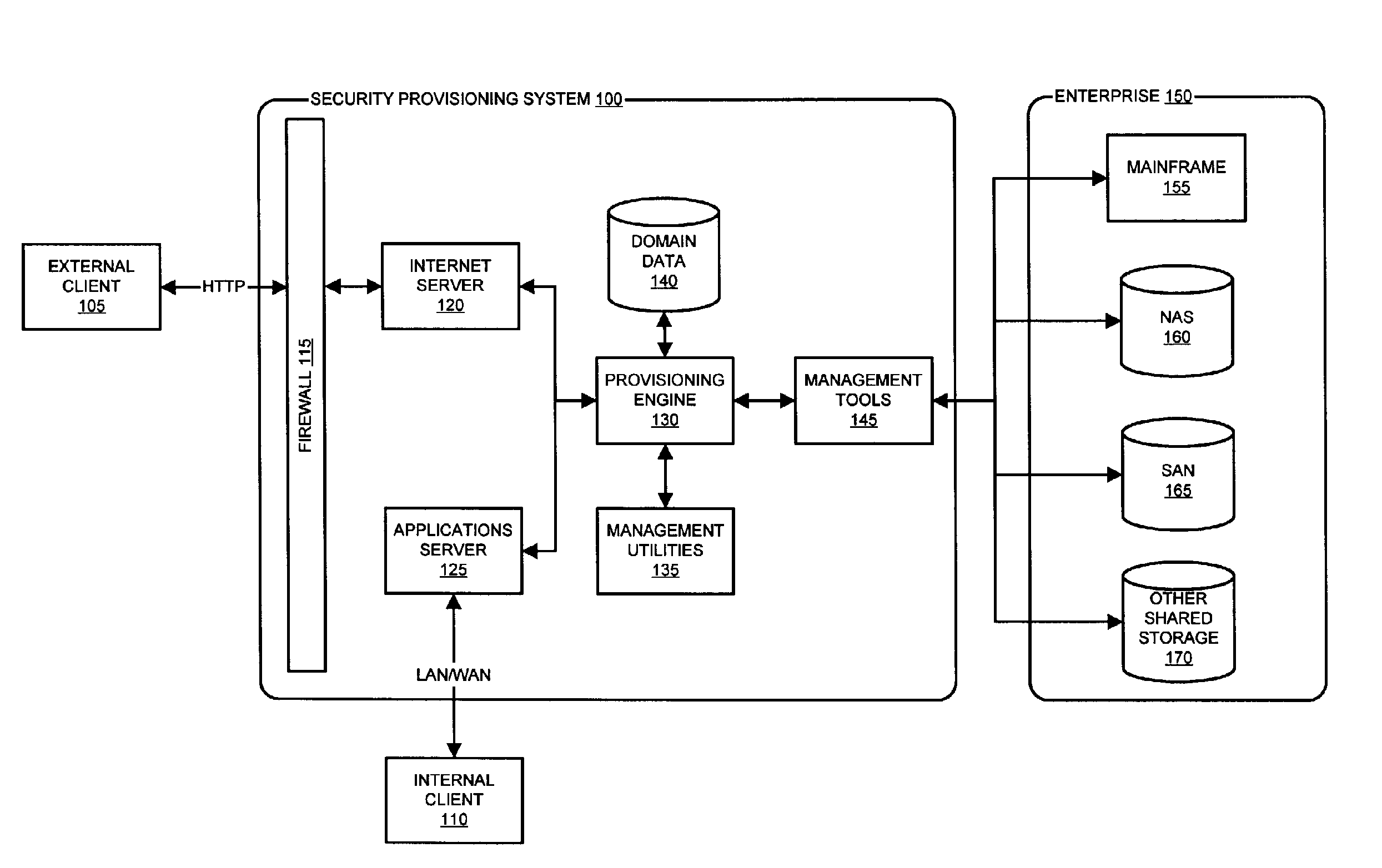
The present invention facilitates the dynamic provisioning of data assets in a shared storage environment. The invention provides a system and method for dynamically provisioning and de-provisioning shared storage resources based on multi-dimensional decision criteria. By employing specialized computing components configured to assess a data asset and requestor of a data asset, a provisioning engine is able to transform the input from the computing components into a specific configuration of shared storage resource provisioning and security controls. According to the rules and policies applying to a security domain, the provisioning engine may dynamically allocate shared storage resources in a manner that is both safe and efficient for the data asset.
Owner:LIBERTY PEAK VENTURES LLC
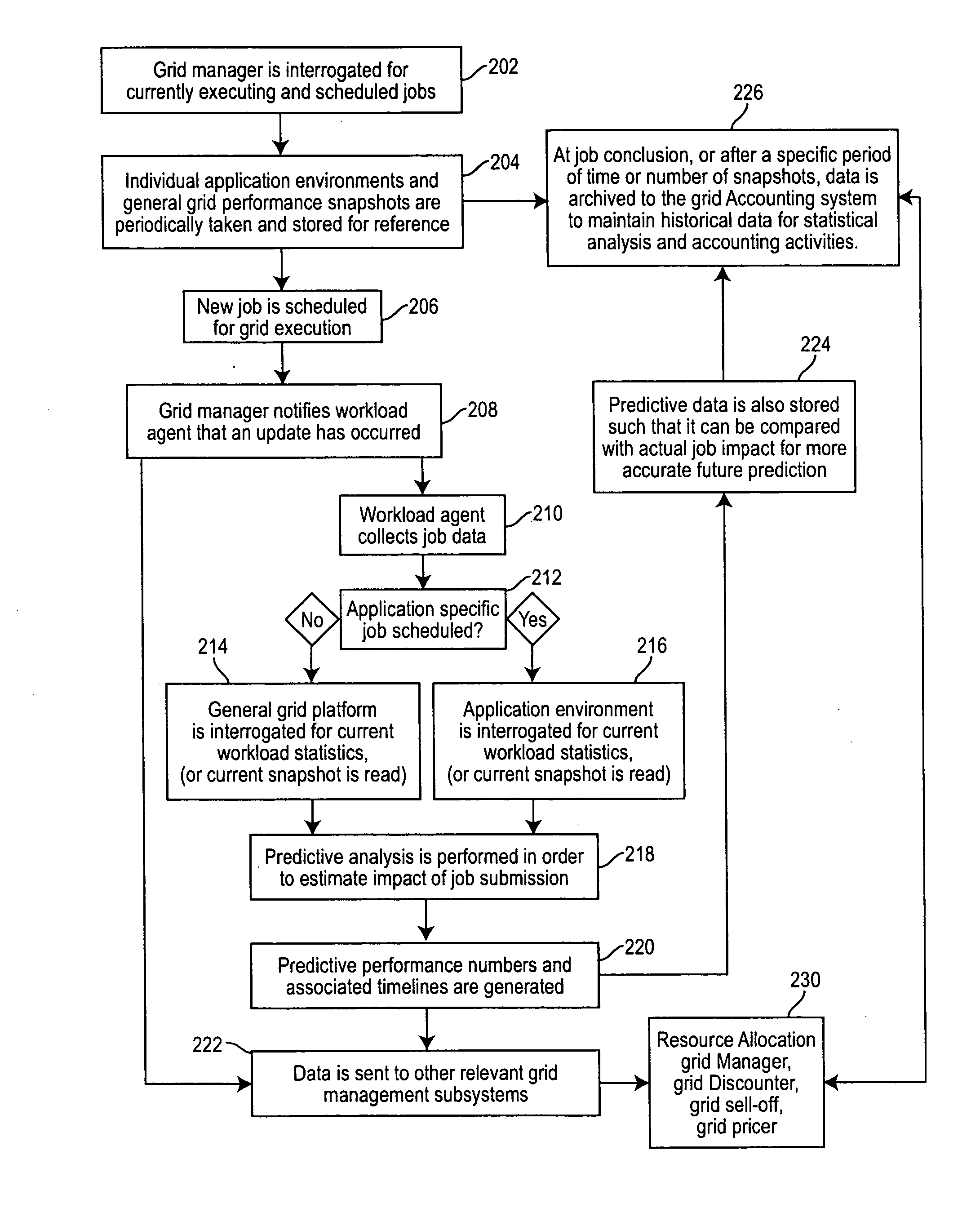
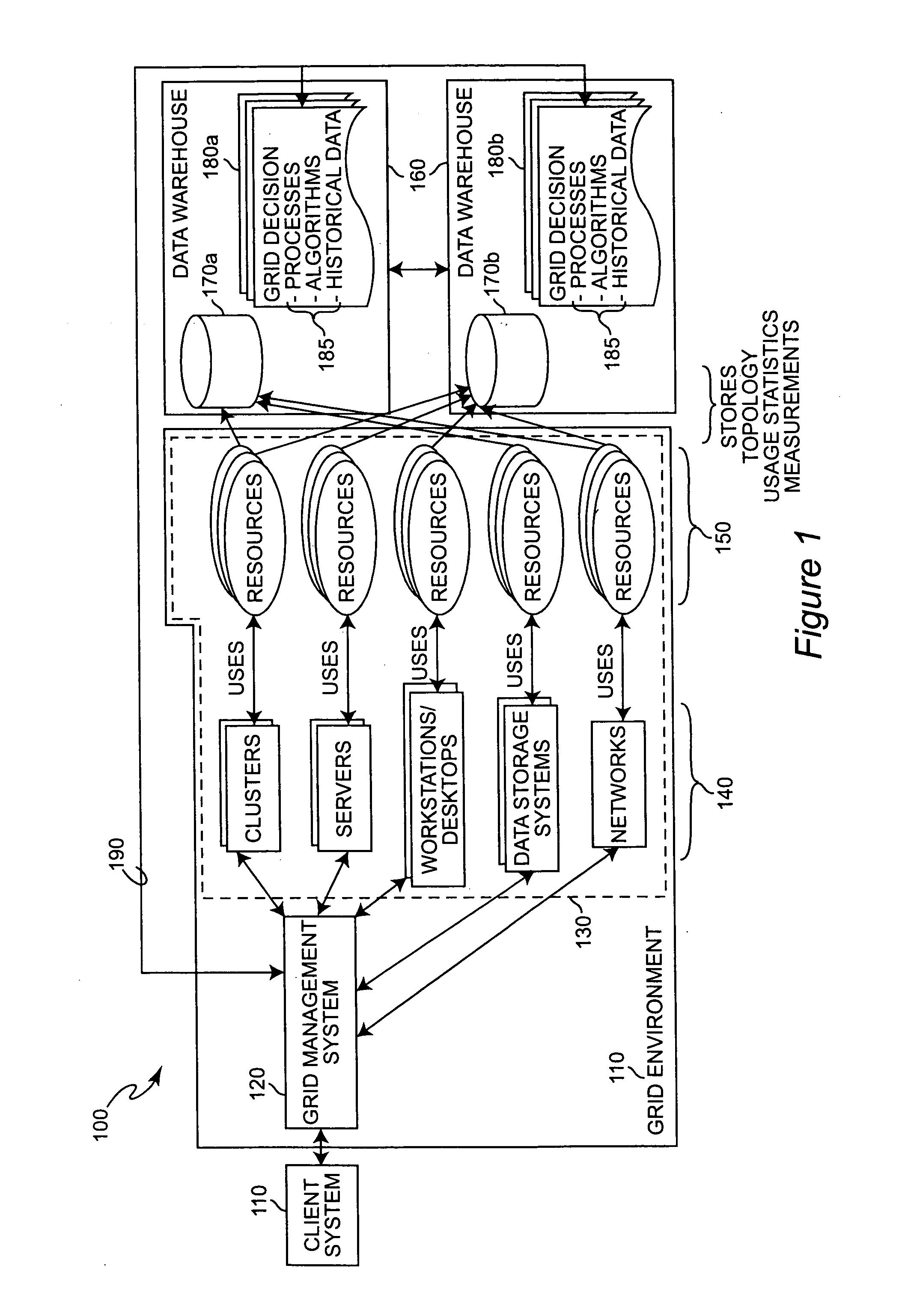
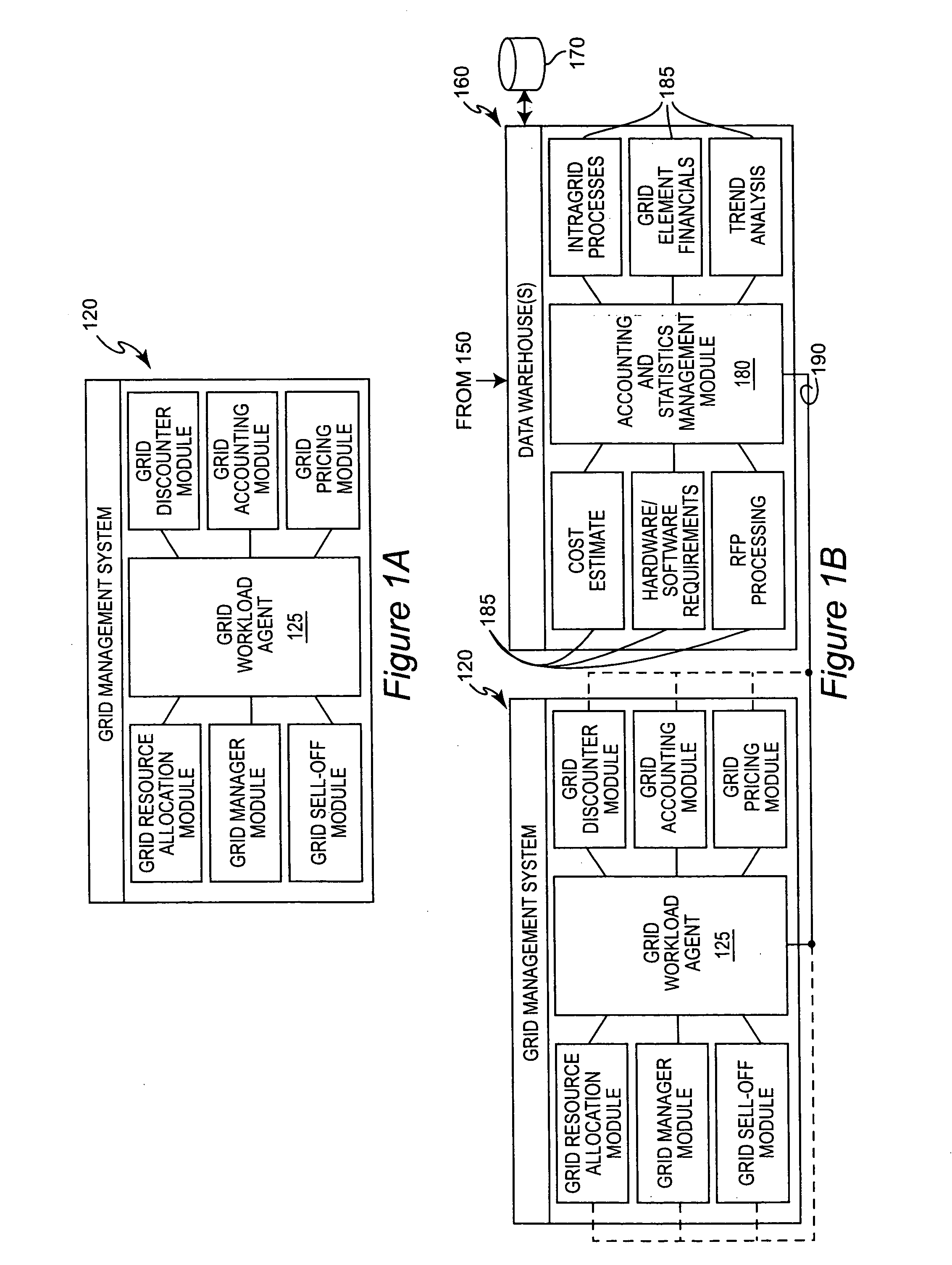
Grid computing accounting and statistics management system
InactiveUS20070078960A1Accurate and efficient managementError detection/correctionDigital computer detailsGrid managementGrid architecture
Performance data is captured periodically from resources and groups of resources in a grid computing environment and stored in a content-addressable data repository from which it can be accessed in response to an arbitrarily complex query in regard to specifics of particular jobs or job portions, particular resources utilized, grid architecture, application environment, concurrent jobs or job portions and the like. The data repository may be distributed or divided in regard to grid environment architecture, security domains or the like and each portion or division may be implemented in a modular fashion including an accounting and statistics management module and additional modules or computing engines for performing particular desired analyses or functions. Results of such analyses or functions may be communicated to a grid workload agent (and associated modules) to improve grid management on a fine-grained basis.
Owner:IBM CORP
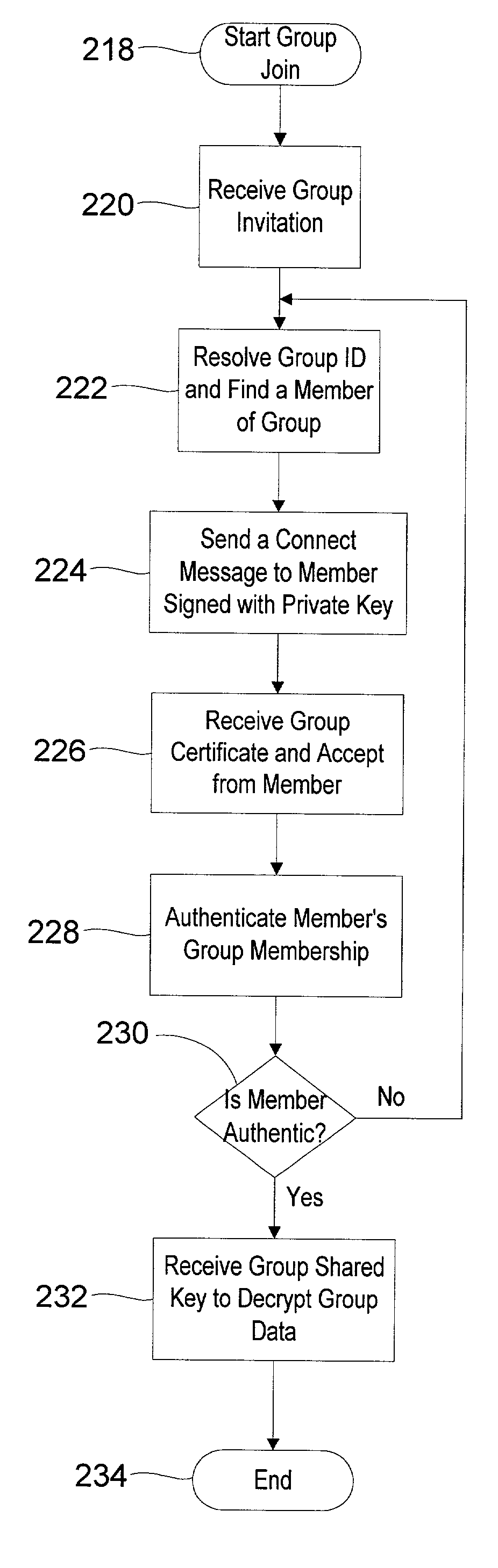
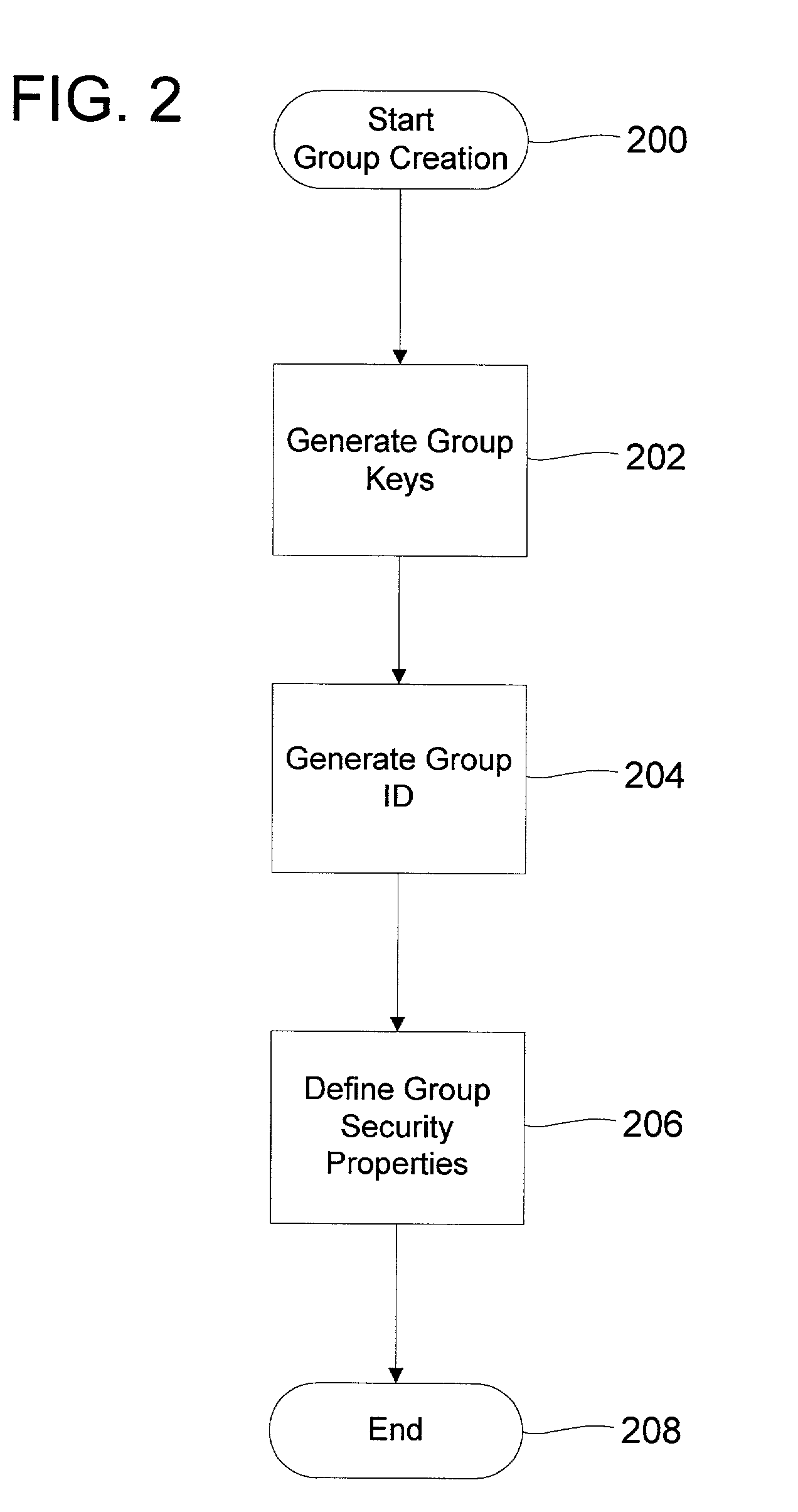
Peer-to-peer name resolution protocol (PNRP) group security infrastructure and method
InactiveUS7068789B2Improve securityIncrease flexibilityUser identity/authority verificationMultiple digital computer combinationsAddress Resolution ProtocolSecurity domain
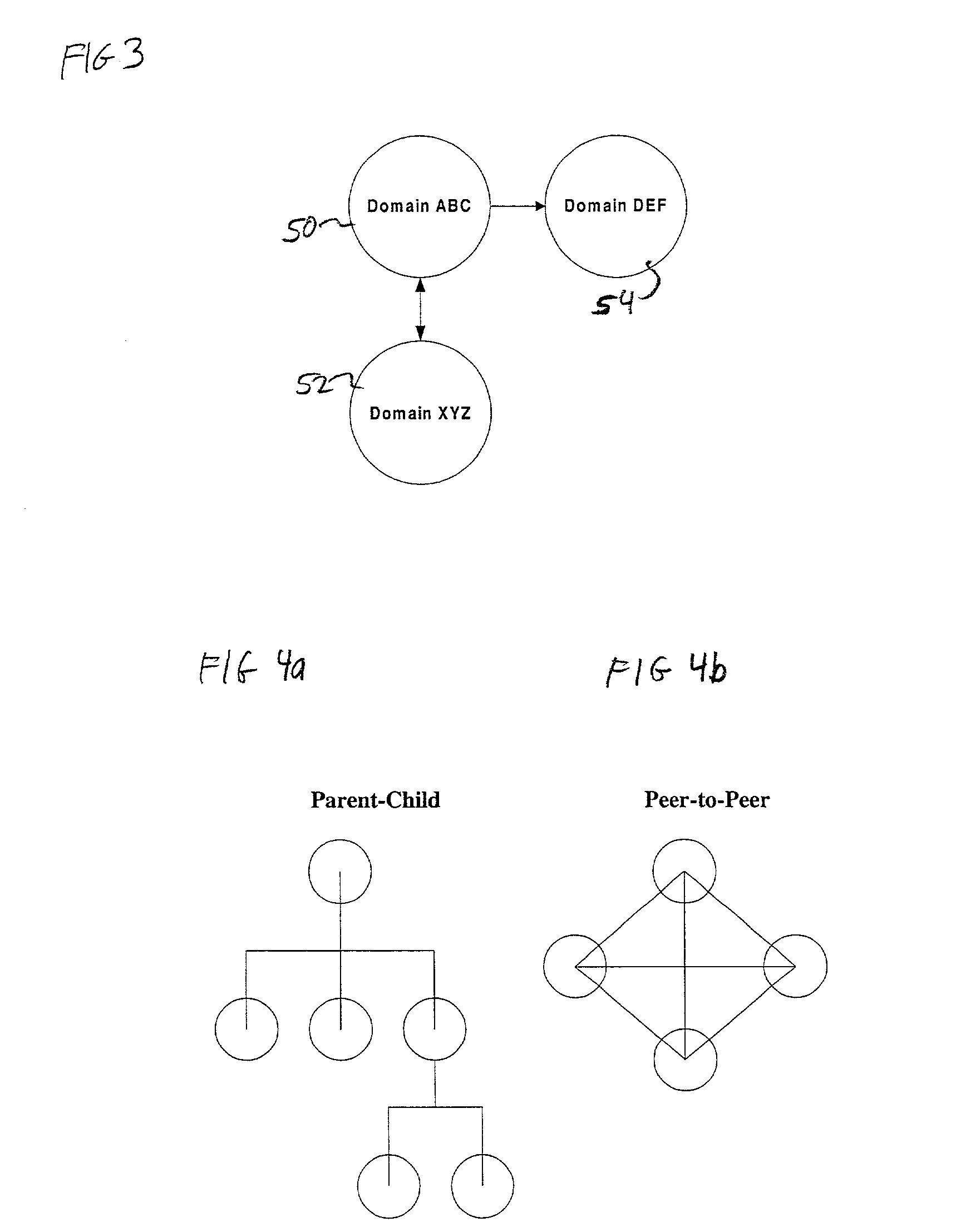
A method for ensuring valid and secure peer-to-peer communications in a group structure. Specifically, the system of the present invention presents a method of ensuring secure peer-to-peer group formation, group member addition, group member eviction, group information distribution, etc. Such functionality may be distributed to the individual peers in the group to further enhance the overall security of the group while enhancing flexibility. The P2P group security allows every peer who is a valid member of the group to invite new members. The recipients of these invitations are then able to contact any member of the group to join the group, not only the inviter. Further, groups may function when the group creator is not online. Likewise, the method allows the creation of secure groups with users from different security domains, relying on their security credentials in those domains for initial authentication.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
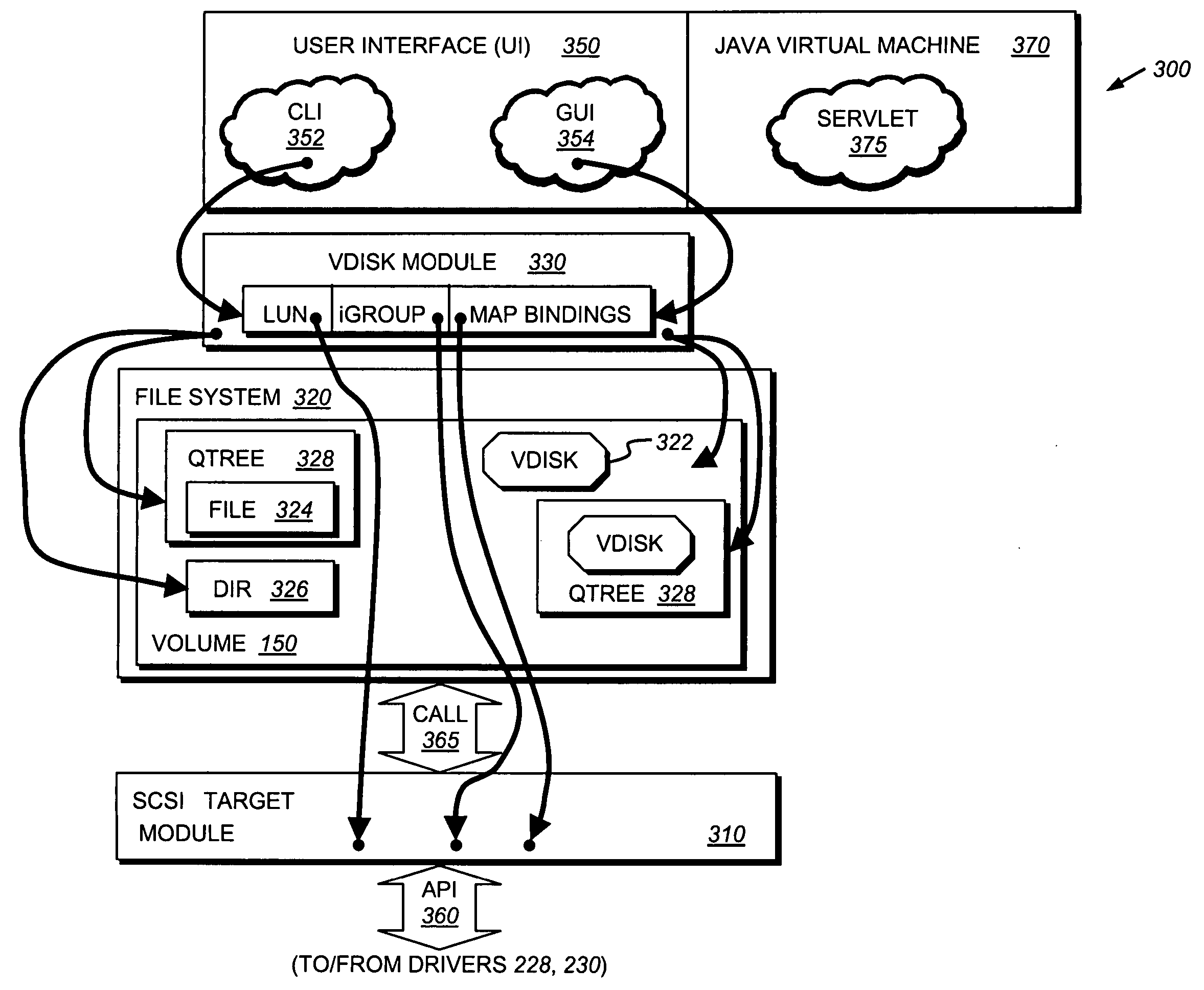
System and method for supporting block-based protocols on a virtual storage appliance executing within a physical storage appliance
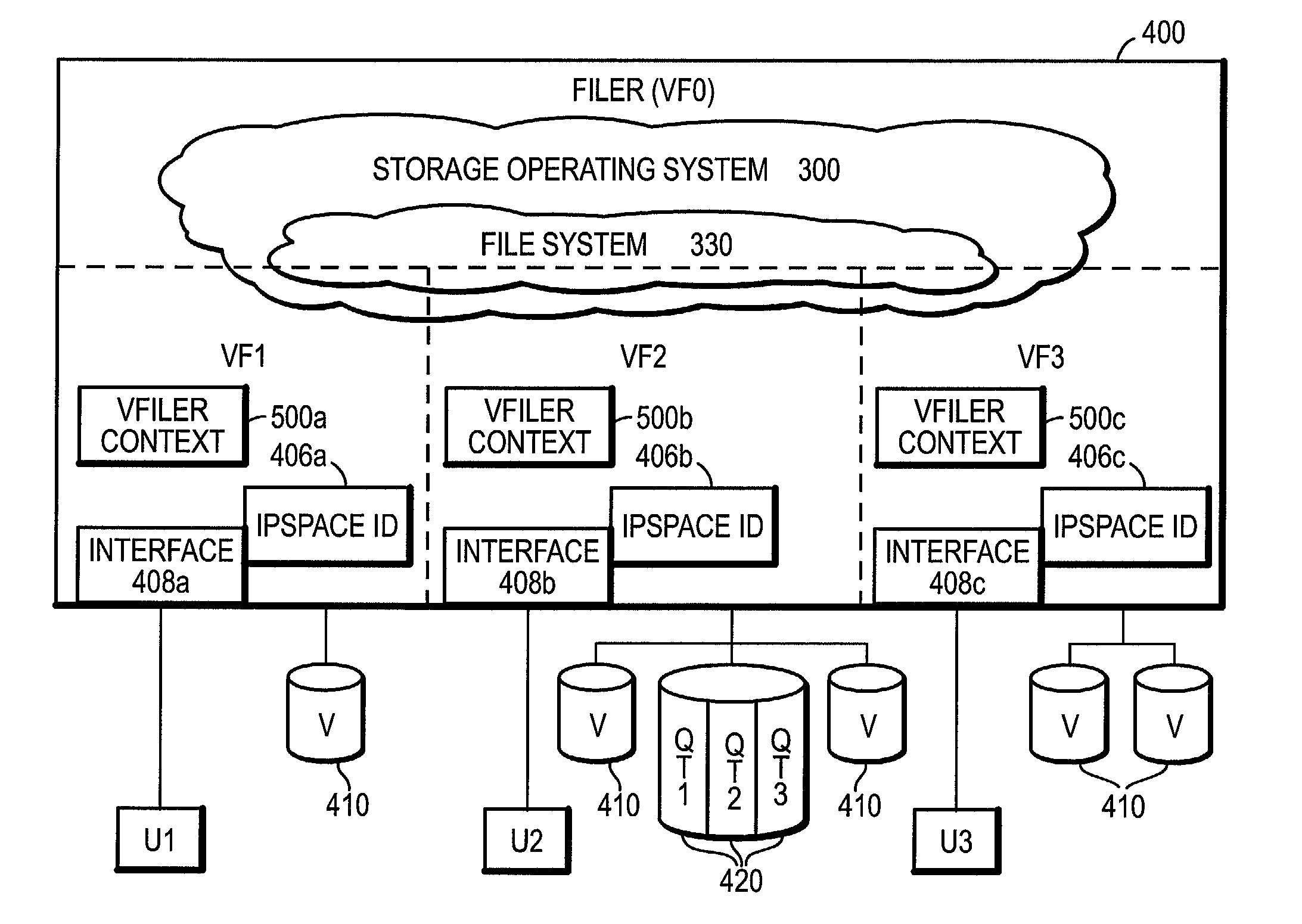
InactiveUS20050228835A1Input/output to record carriersComputer security arrangementsOperational systemSecurity domain
An architecture provides the ability to create and maintain multiple instances of virtual servers, such as virtual filers (vfilers), within a server, such as a storage appliance. A vfiler is a logical partitioning of network and storage resources of the storage appliance platform to establish an instance of a multi-protocol server. Each vfiler is allocated a subset of dedicated units of storage resources, such as volumes or logical sub-volumes (qtrees), and one or more network address resources. Each vfiler is also allowed shared access to a file system resource of a storage operating system. To ensure controlled access to the allocated and shared resources, each vfiler is further assigned its own security domain for each access protocol. A vfiler boundary check is performed by the file system to verify that a current vfiler is allowed to access certain storage resources for a requested file stored on the filer platform.
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
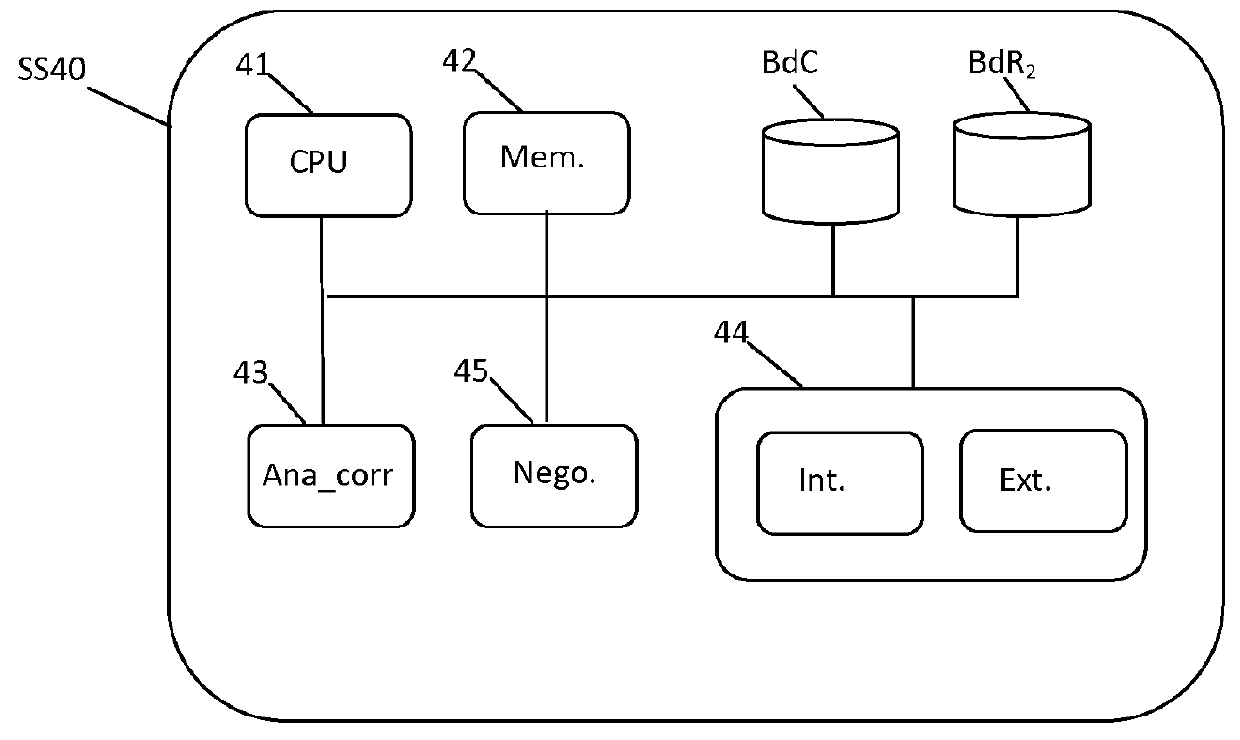
System for supervising the security of an architecture
ActiveUS9380075B2Special data processing applicationsSecuring communicationSecurity domainSecurity management
A method is provided for supervising security of an architecture having a plurality of interconnected clouds. A cloud includes a plurality of resources and a security supervisor. The plurality of resources forms in the cloud a plurality of groups of resources associated respectively with a security domain. A security controller supervises the resources of the domain, and a plurality of physical machines contains the resources of the plurality of clouds. The method includes: receiving a security event by a security controller of a first cloud, originating from a first resource associated with a first security domain; dispatching said security event to the security supervisor of the first cloud; and dispatching by the security supervisor of the first cloud a security order in reaction to the security event to at least one second security controller of the first cloud and dispatching the security order by the second security controller to a second resource supervised by the second controller.
Owner:ORANGE SA (FR)
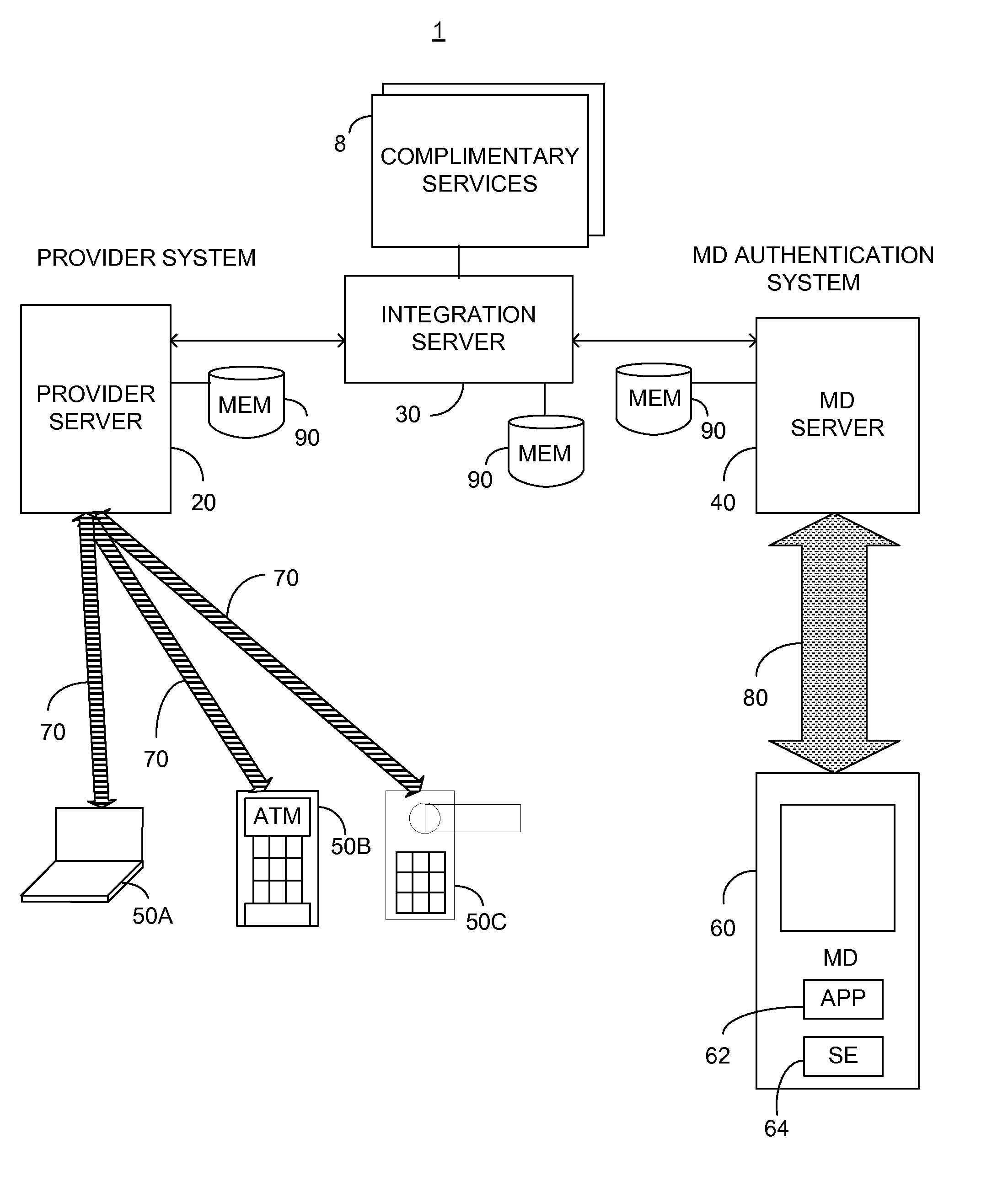
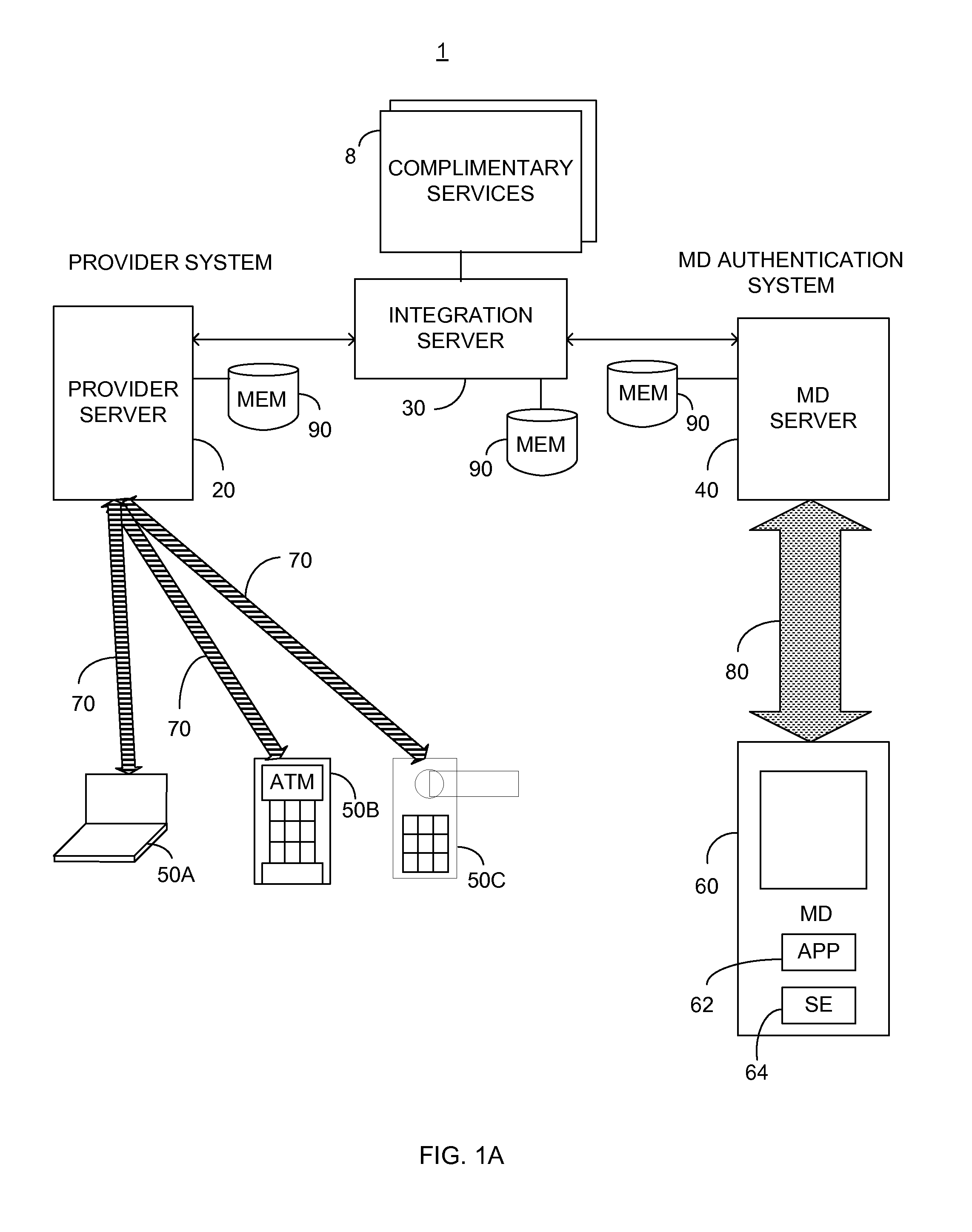
System and method for secure transaction process via mobile device
ActiveUS20140214688A1Overcome disadvantagesAcutation objectsPayment protocolsSecurity domainKey storage
A secure element with a user security domain thereon, the user security domain constituted of: a security domain control circuitry; an encoder / decoder functionality responsive to the security domain control circuitry; and a secured keys storage in communication with the security domain control circuitry, the encoder / decoder functionality arranged to: encode data responsive to at least one first key stored on the secured keys storage, and output an encoded data; and decode received data responsive to at least one second key stored on the secured keys storage, and output a decoded data.
Owner:PING IDENTITY
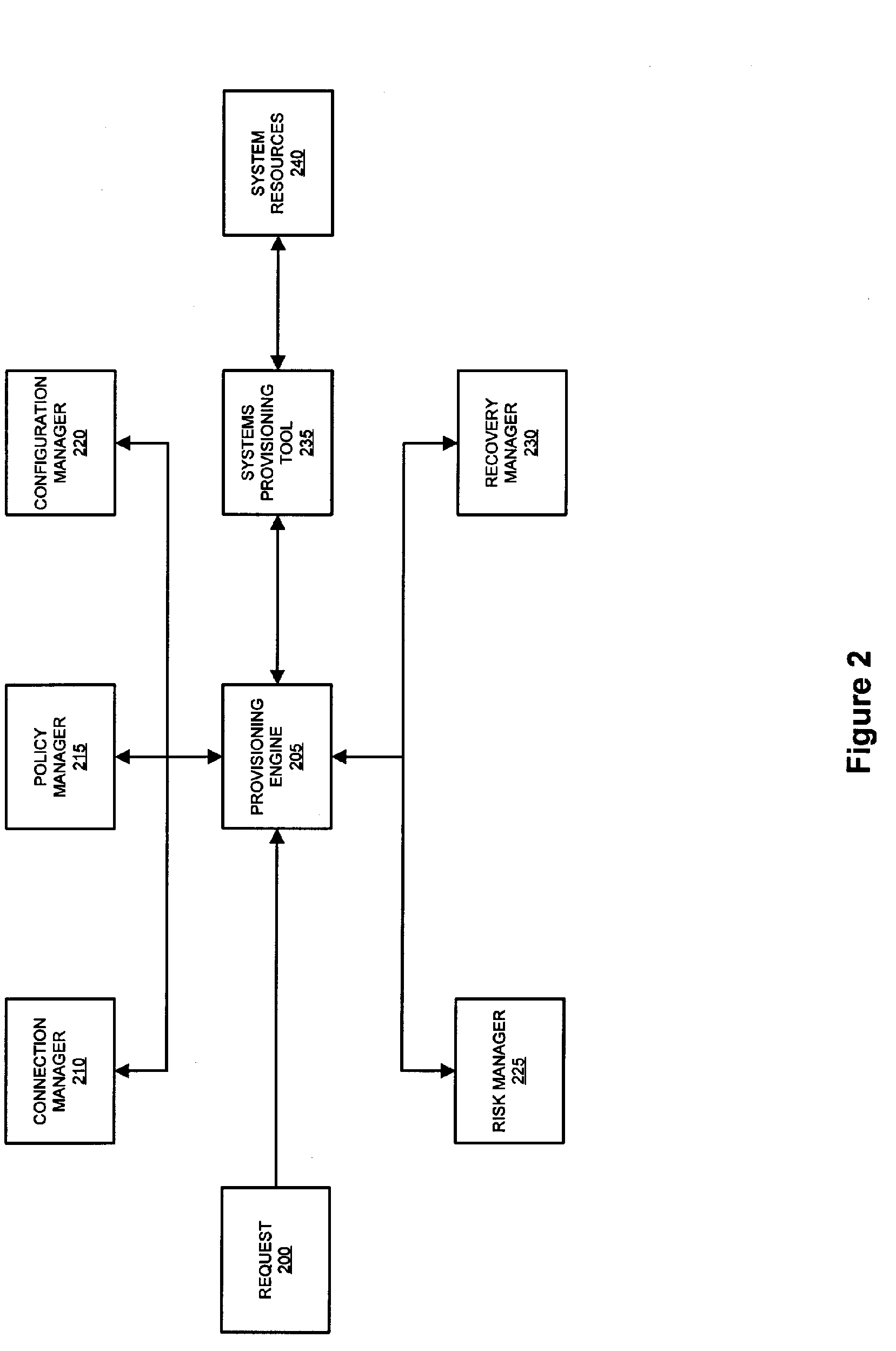
System and method for dynamic security provisioning of computing resources
InactiveUS20050251573A1Digital data processing detailsAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsSecurity domainResource based
The present invention facilitates the dynamic provisioning of computing and data assets in a commodity computing environment. The invention provides a system and method for dynamically provisioning and deprovisioning computing resources based on multi-dimensional decision criteria. By employing specialized computing components configured to assess an asset and requestor of an asset, a provisioning engine is able to transform the input from the computing components into a specific configuration of computing resource provisioning and security controls. According to the rules and policies applying to a security domain, the provisioning engine may dynamically allocate computing resources in a manner that is both safe and efficient for the asset.
Owner:LIBERTY PEAK VENTURES LLC
Method and apparatus for encrypting and decrypting data in a database table
ActiveUS7827403B2Improve performanceKey distribution for secure communicationDigital data processing detailsGranularitySecurity domain
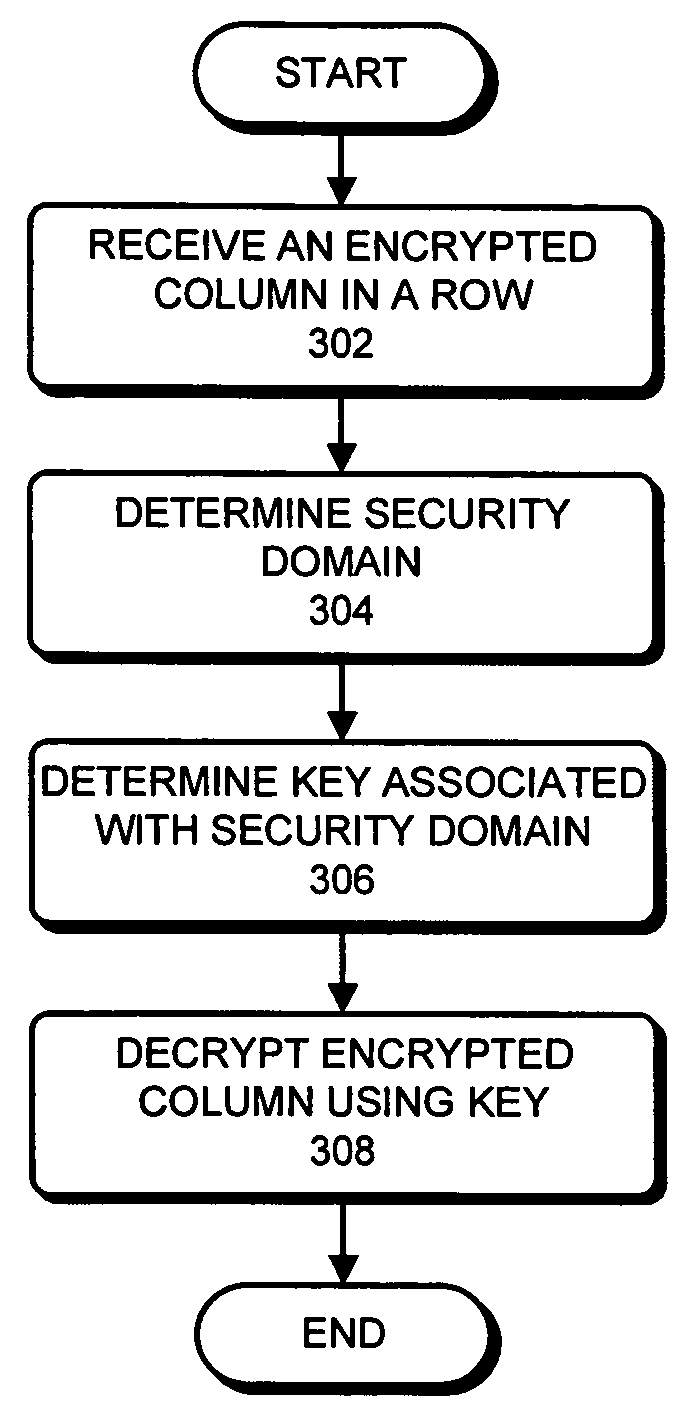
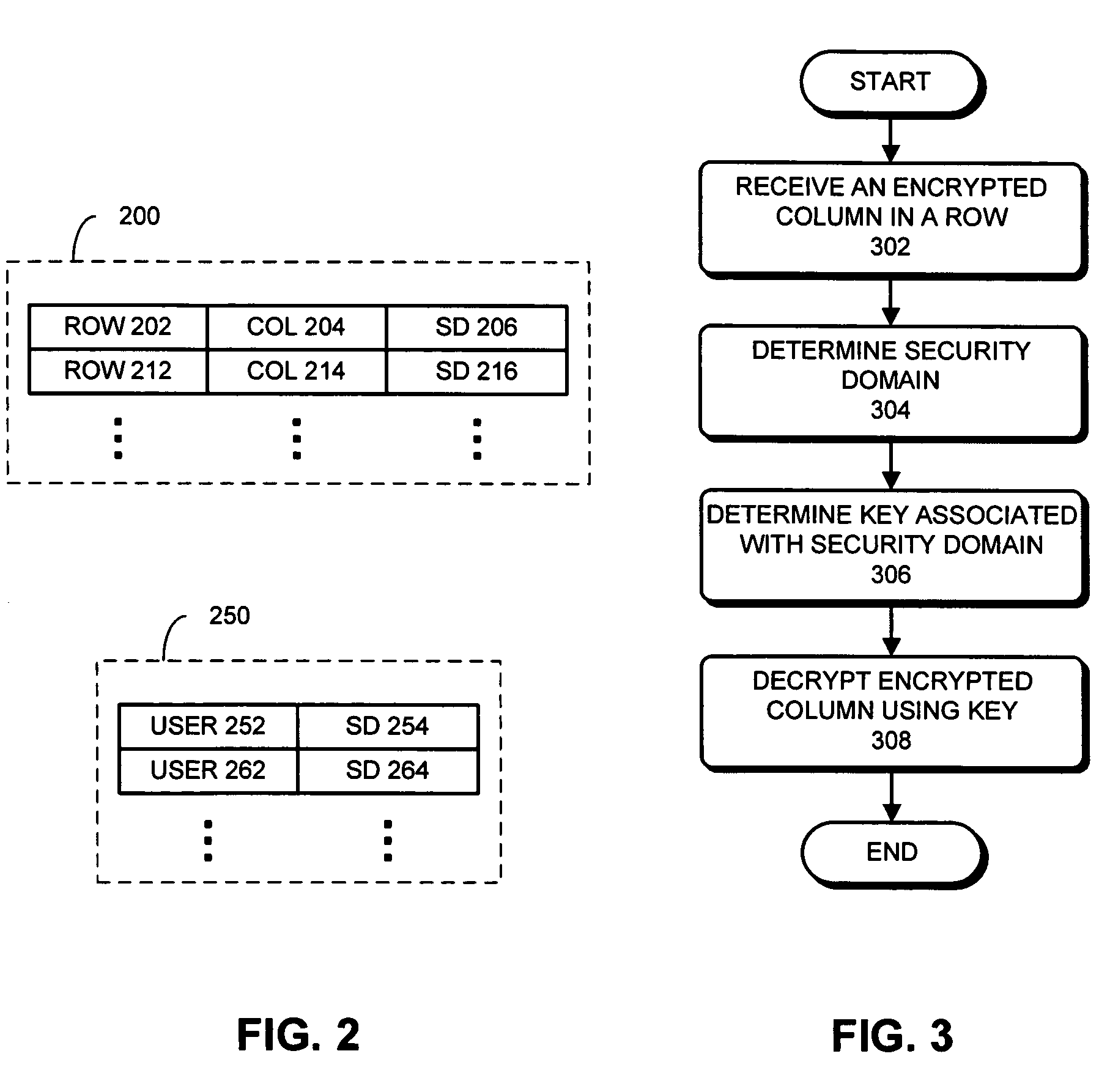
One embodiment of the present invention provides a system that decrypts an encrypted column in a row. During operation, the system receives the encrypted column in the row. The system then determines a security domain associated with the encrypted column in the row, wherein the security domain represents a set of columns in rows encrypted using the same key. Next, the system determines a key associated with the security domain. The system then decrypts the encrypted column in the row using the key. Note that using a security domain to represent a set of columns in rows enables the database to grant access to data within the database at arbitrary levels of granularity.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Method for changing mno in embedded sim on basis of special privilege, and embedded sim and recording medium therefor
ActiveUS20140134981A1Unauthorised/fraudulent call preventionAssess restrictionComputer hardwareSecure communication
The present invention provides a method and an apparatus for managing (mutual authorization with a SIM, secure communication, channel formation, application and data issuance, etc.) an embedded SIM (eSIM or eUICC) by generating and extraditing a security domain using GlobalPlatform technology in which authorized management privilege and delegated management privilege functions are implemented.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
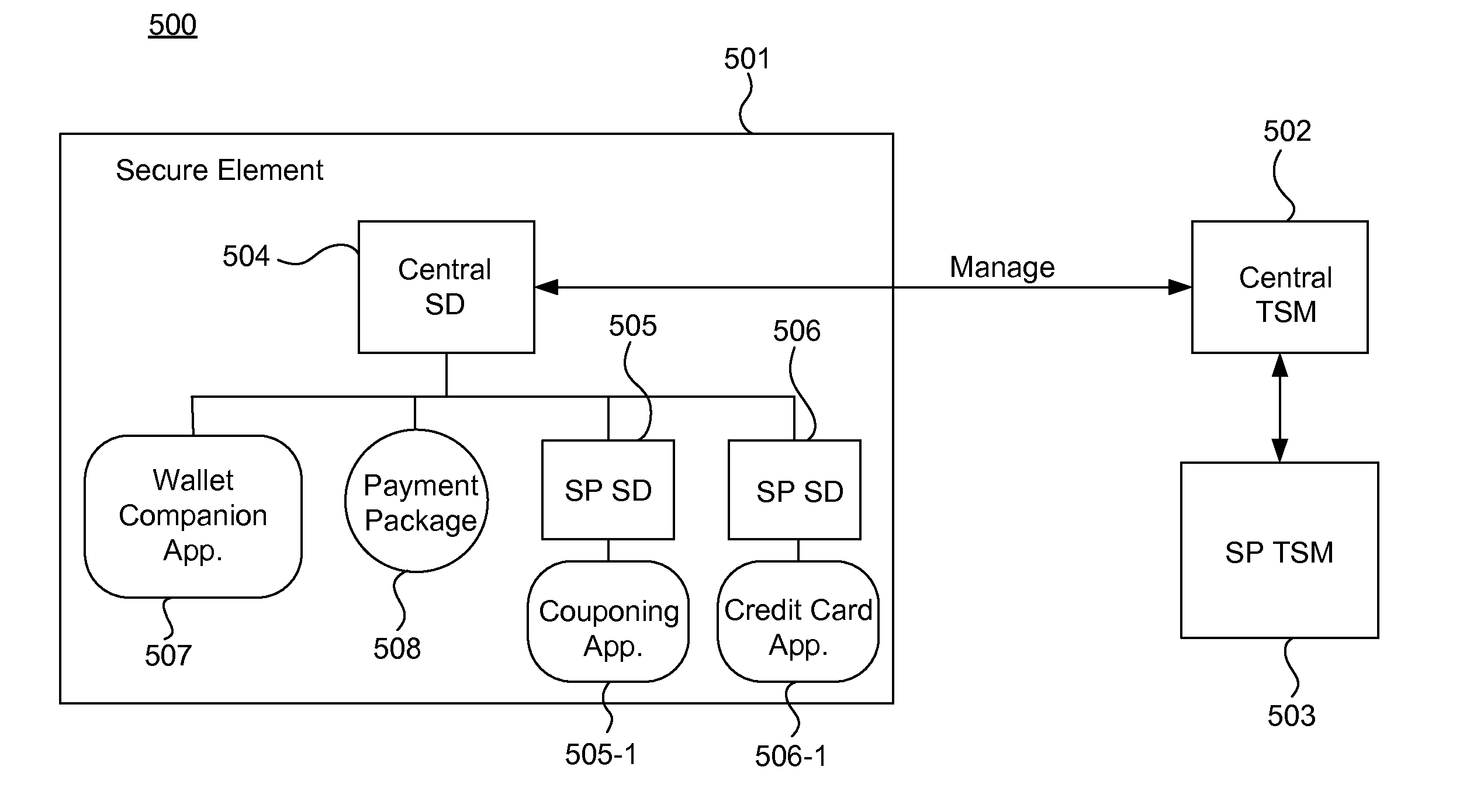
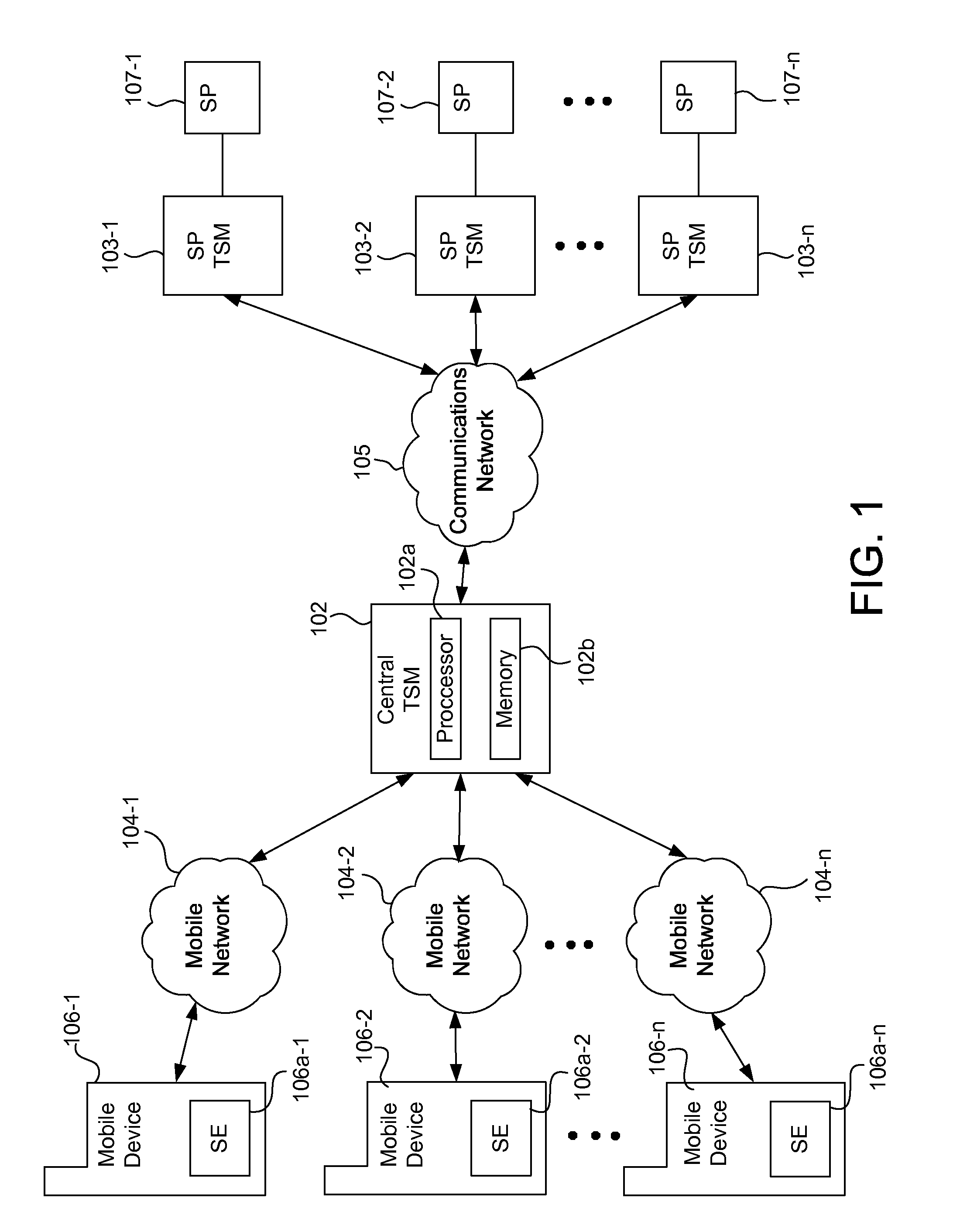
Systems, methods, and computer program products for managing secure elements
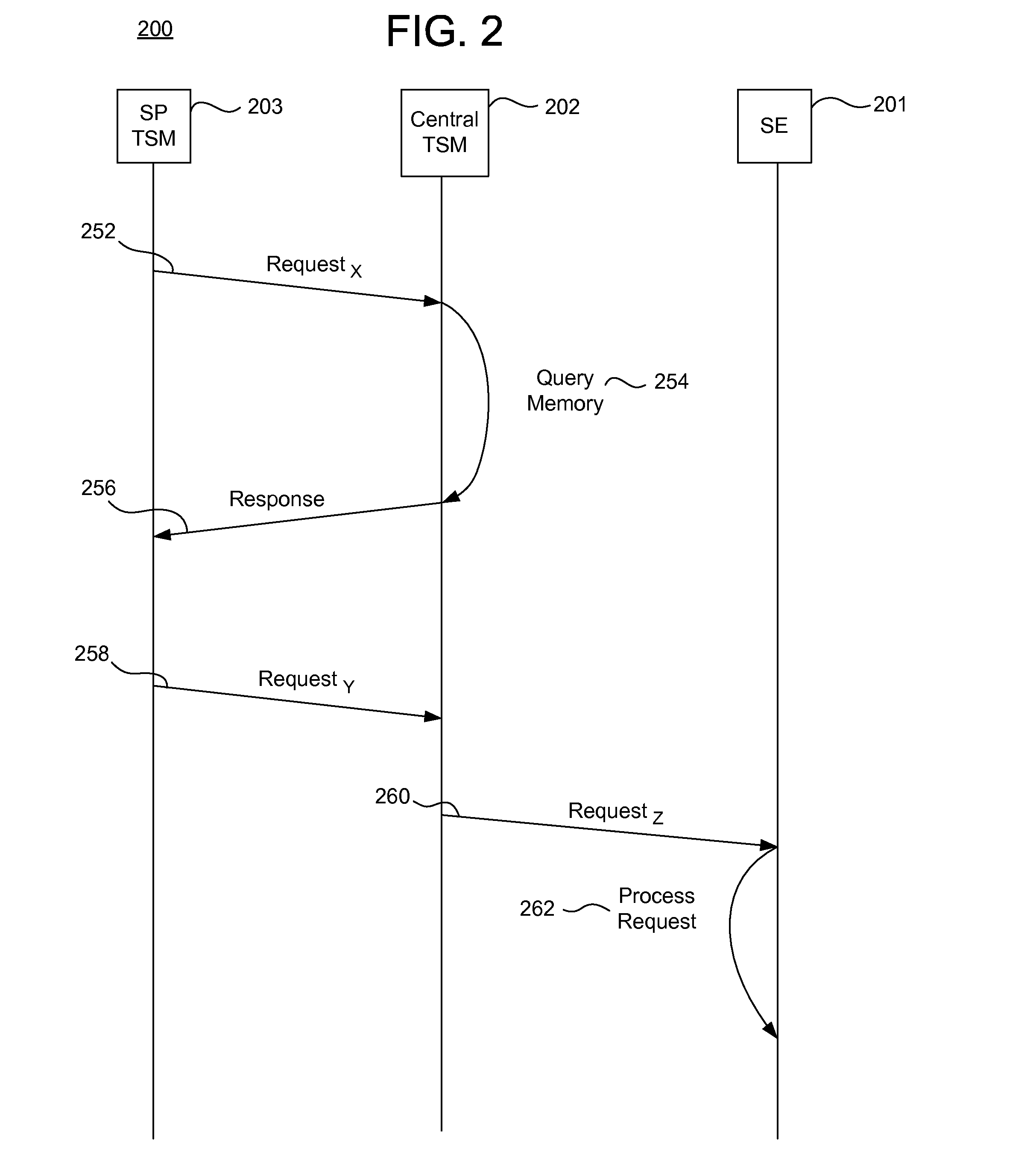
ActiveUS20130111546A1Easily and securely communicateKey distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationProcessing InstructionInternet privacy
Systems, methods, and computer program products are provided for performing content management operations. At least one memory stores data, and a central security domain manages instructions on behalf of one or more service provider security domains. The instructions are received, over a network, from a trusted service manager. The instructions are processed in at least one of the one or more determined service provider security domains, using the data stored in the at least one memory. The data includes one or more generic applications, each of which can be instantiated for one or more service providers.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
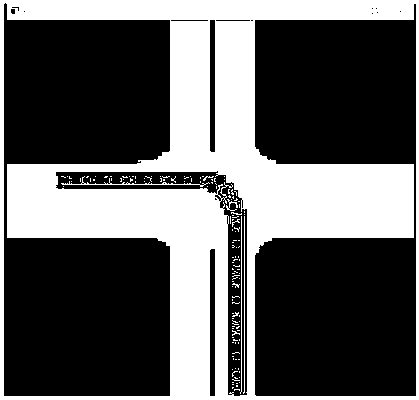
Unmanned local path planning method based on equal-step sampling A* algorithm
ActiveCN108444488ASatisfy steering constraintsReduce mechanical wear and tearInstruments for road network navigationNODALKinematics
The invention belongs to the field of unmanned path planning, and discloses an unmanned local path planning method based on equal-step sampling A* algorithm in order to meet the kinematic constraintsand actual traffic restrictions of automobiles. The method concretely comprises the following steps: 1, defining a search step size and a search security domain; 2, determining the starting point andthe target point of path search in a local grid map; 3, creating an Open list and a Closed list; 4, solving the cost functions of grid points in the Open list; 5, selecting the grid point with the lowest cost function value from the Open list; 6, respectively investing all security neighbor nodes of current nodes; 7, performing no sub-node processing on the current nodes in the search process; and8, repeating step 5 to step 7 until conditions are met, and returning to a feasible path or to search fail. The method is mainly applied to unmanned roads.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
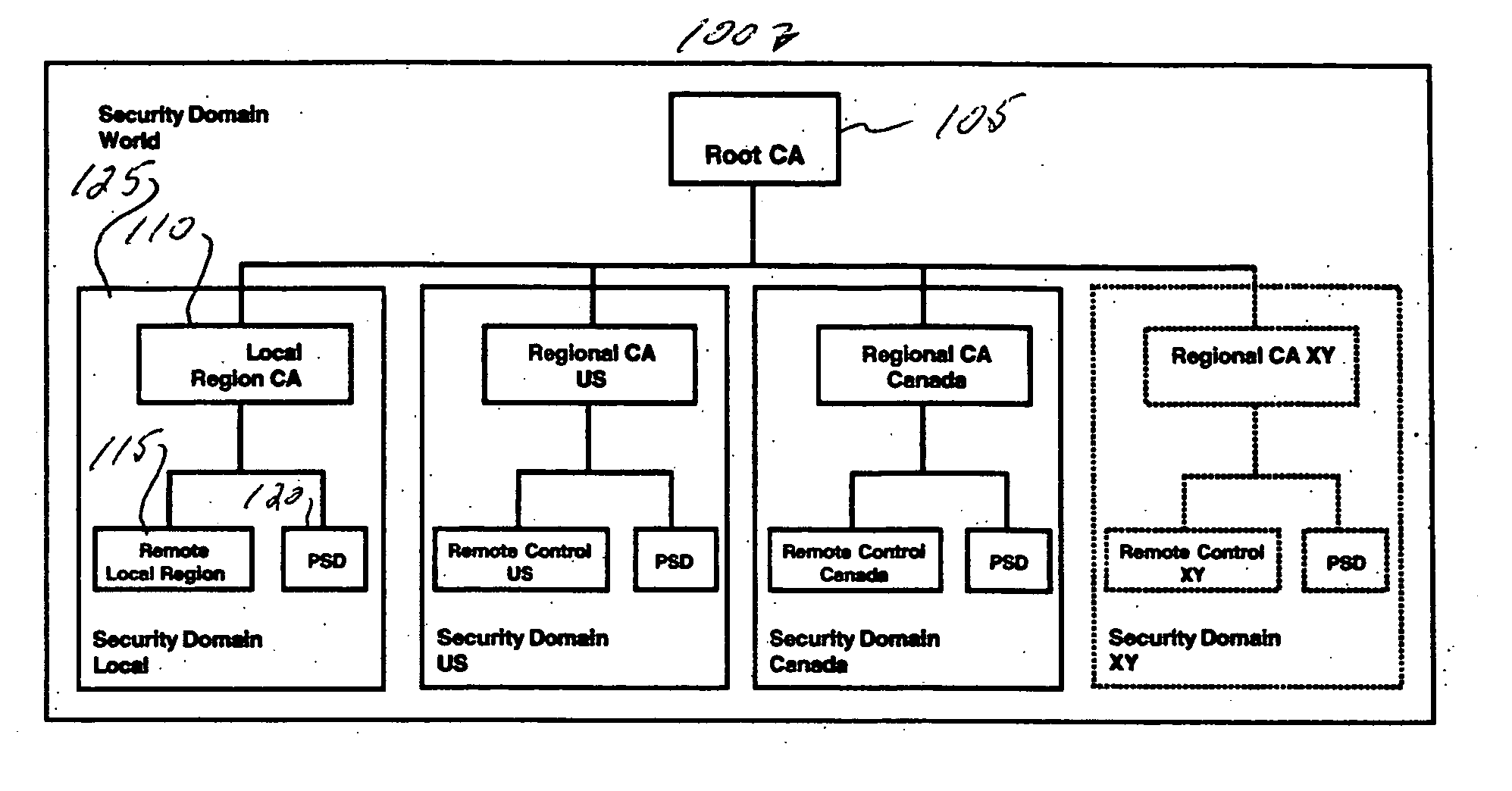
Multiple cryptographic key security device
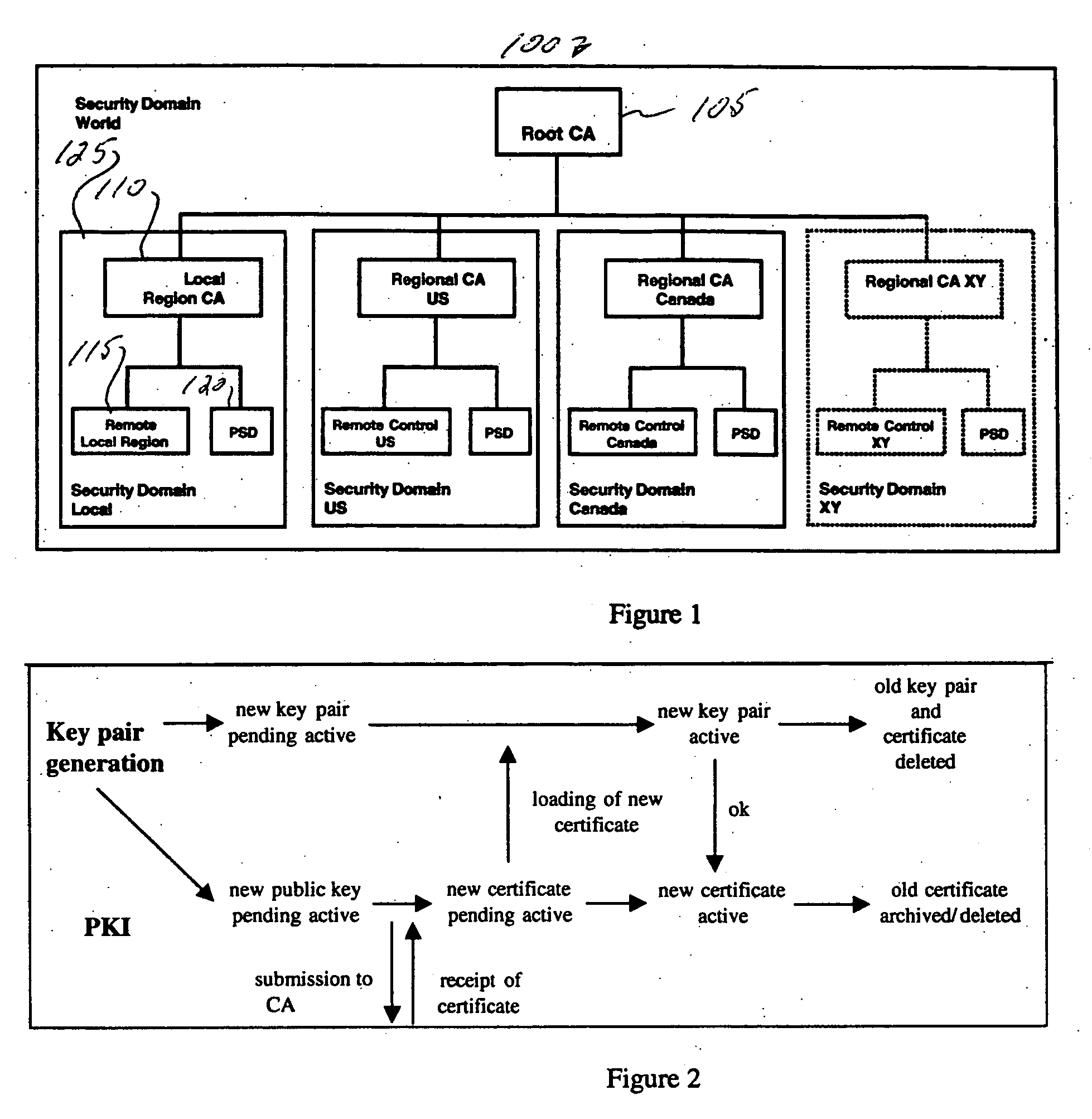
InactiveUS20060174125A1User identity/authority verificationPublic key infrastructure trust modelsRoot certificateDigital signature
A security domain for controlling PKI keys includes a root certificate authority, and one or more regional certificate authorities, each having a remote control and a postal security device. Different PKI keys are utilized to sign and to validate the authenticity of a digital signature for each certificate authority.
Owner:NEOPOST TECH SA
Architecture for creating and maintaining virtual filers on a filer
InactiveUS7360034B1Maximum flexibilityFine granularityDigital computer detailsUnauthorized memory use protectionOperational systemFile system
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
System and method for server security and entitlement processing
InactiveUS7392546B2Digital data processing detailsUnauthorized memory use protectionSecurity domainBusiness policies
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
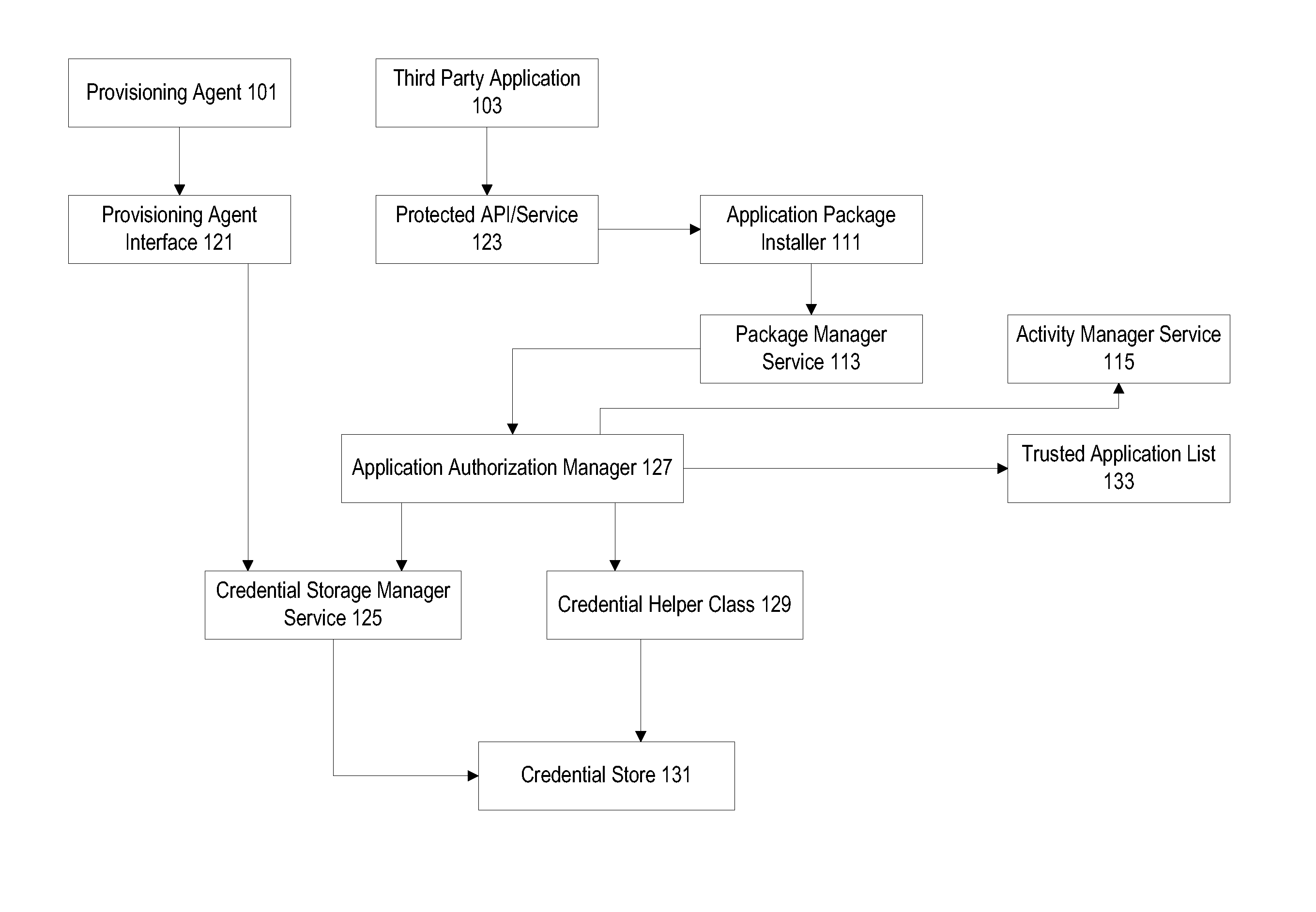
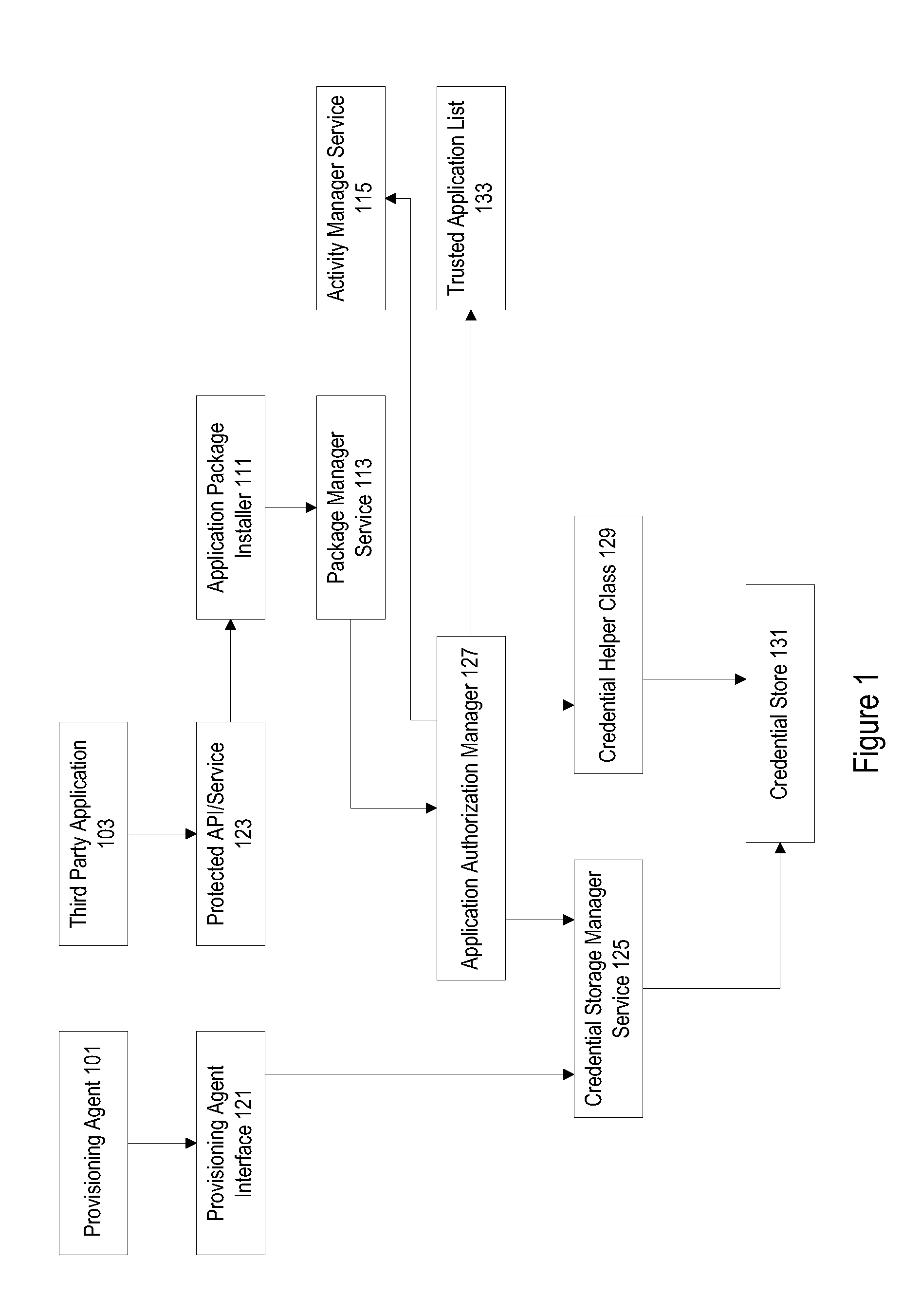
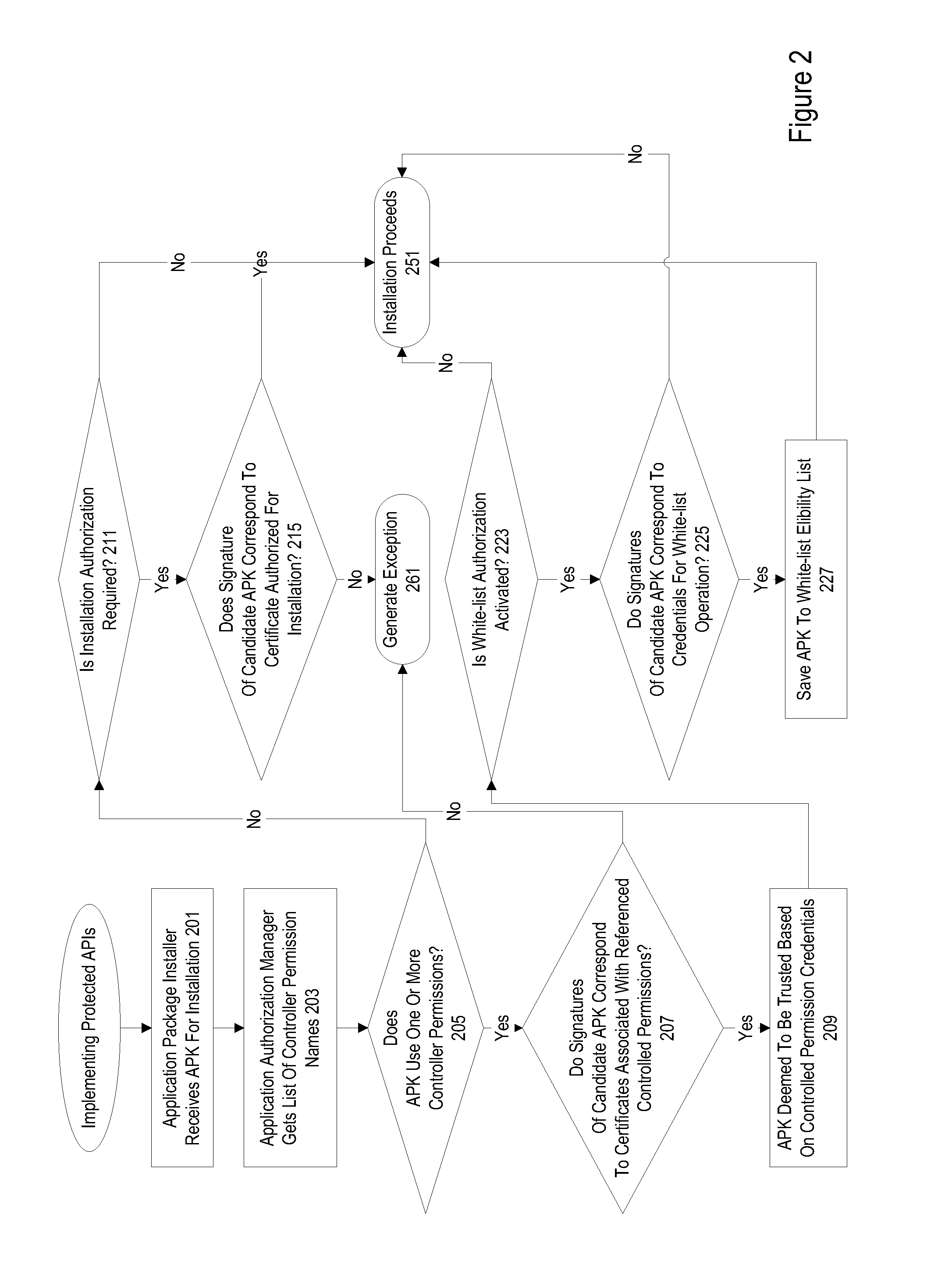
Protected application programming interfaces
ActiveUS20130160147A1Digital data processing detailsAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsApplication programming interfaceSecurity domain
Mechanisms are provided to allow particular parties and applications access to protected application programming interfaces (APIs) without the use of security domains. Trusted parties and applications may have access to protected APIs while unfrosted parties and applications may be restricted to a more limited set of APIs. Public keys associated with individual applications that are used to enforce licensing policies can be repurposed for use in a verification process to prevent unauthorized access to APIs. A credential storage manager can be used to maintain permission and certificate information. An application authorization manager may access credential storage and maintain trusted application information.
Owner:DELL PROD LP
Secure element for mobile network services
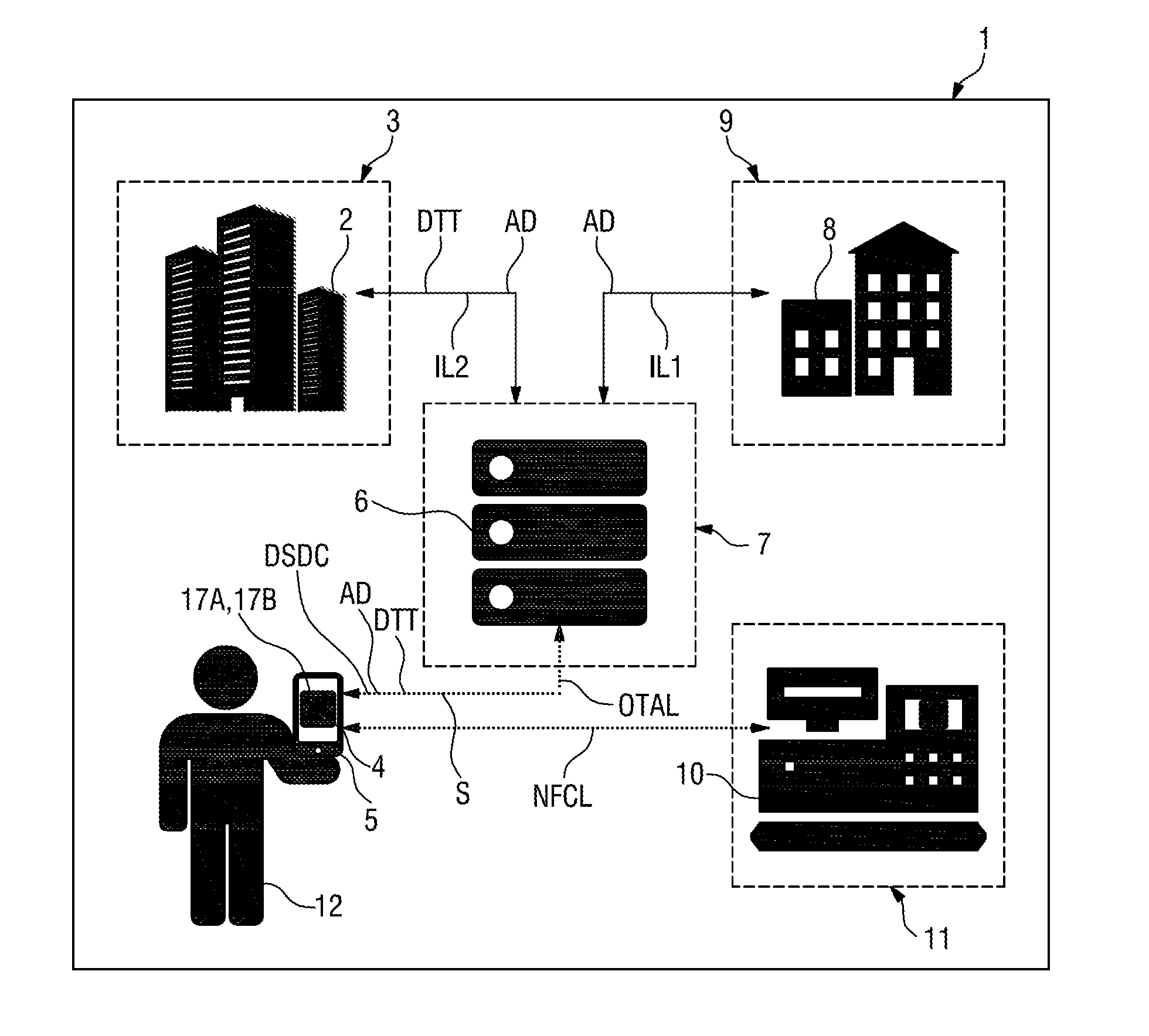
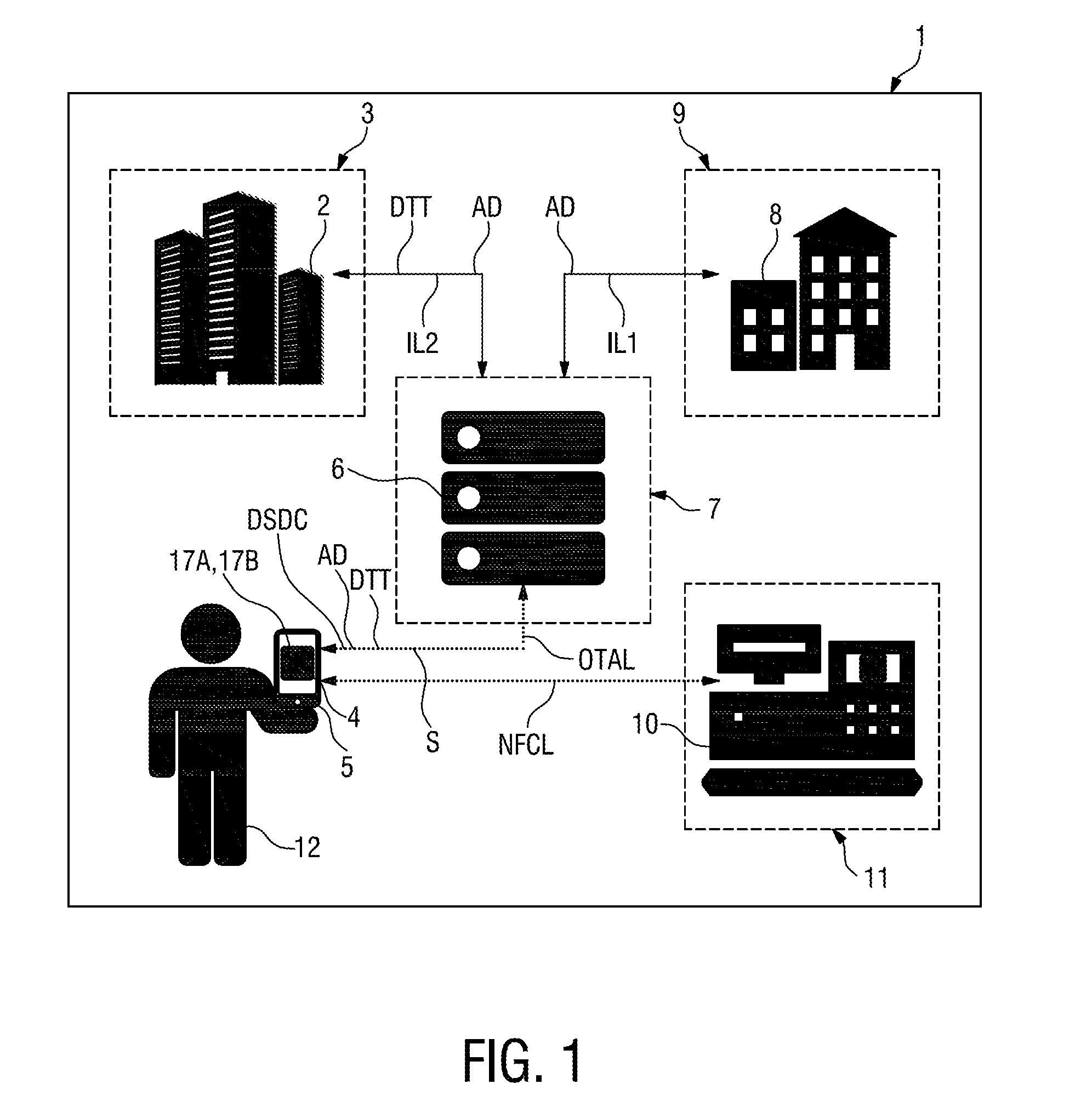
InactiveUS20130273889A1Generating revenue streamWide deploymentUnauthorised/fraudulent call preventionEavesdropping prevention circuitsMobile network codeSecurity domain
In a secure element (4) that comprises an application (17B) and / or a security domain (17A) a mode is proved, in which mode a transfer of data (AD) to said application (17B) and / or security domain (17A) requires pre-authorization.
Owner:KWALLET
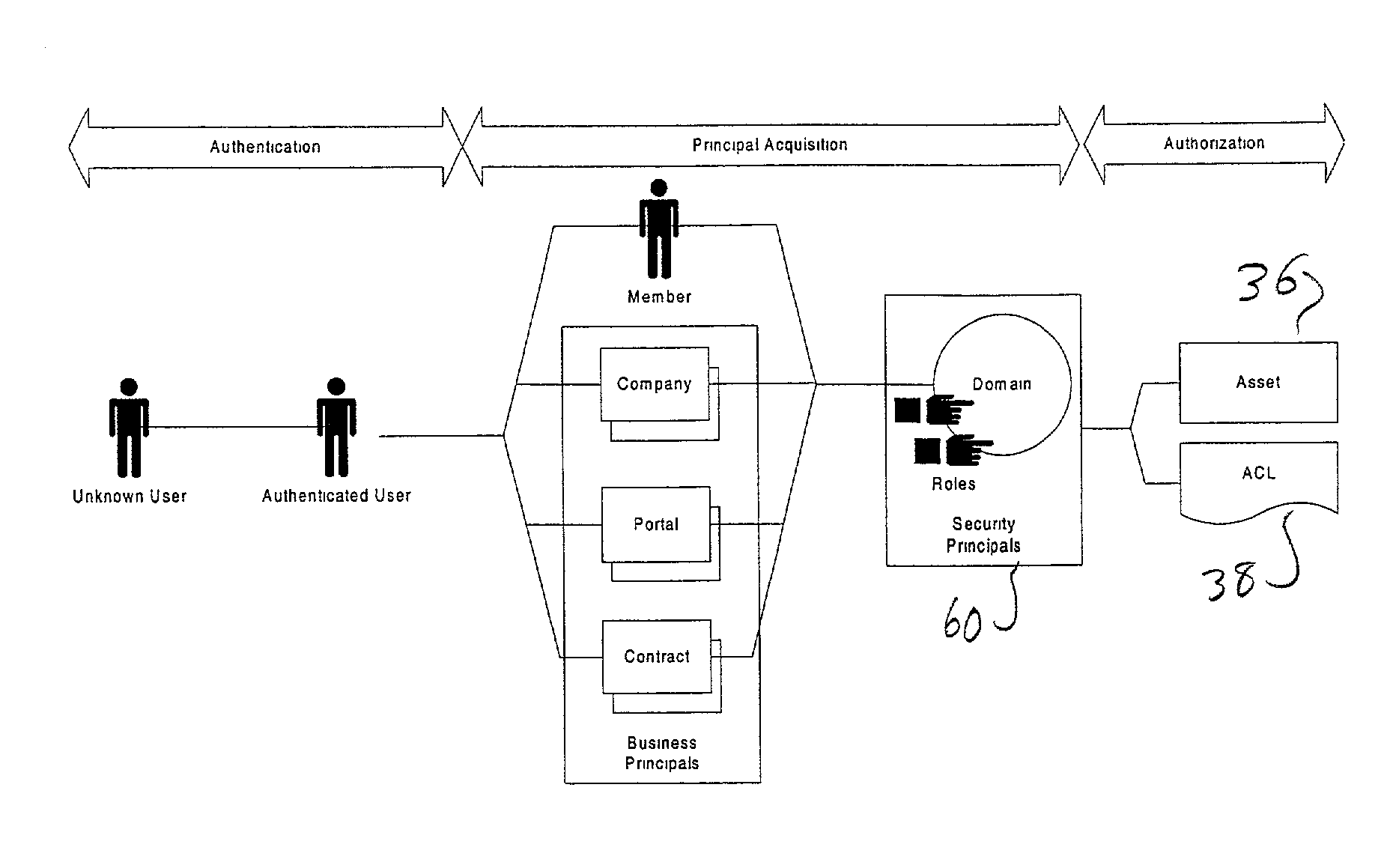
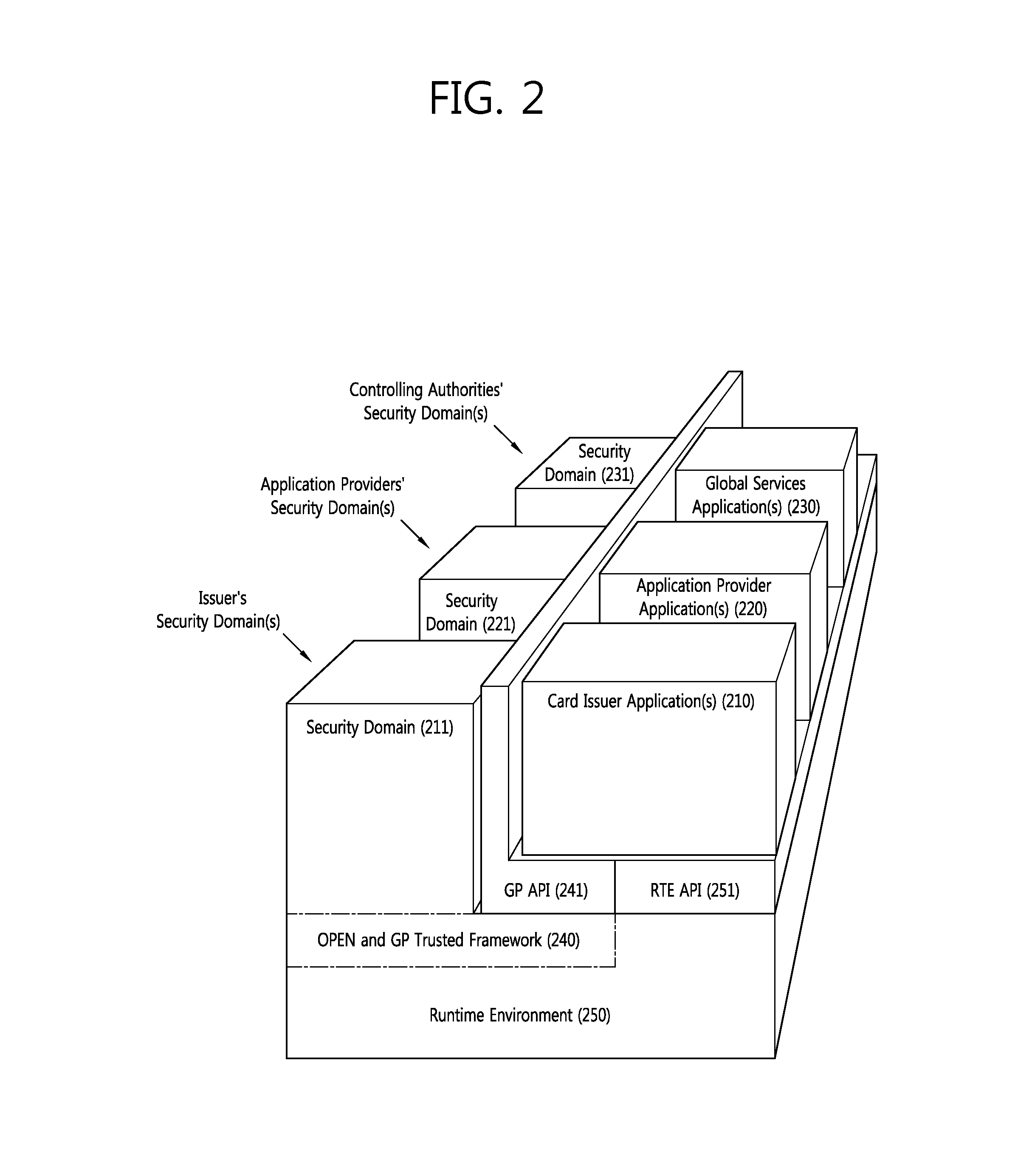
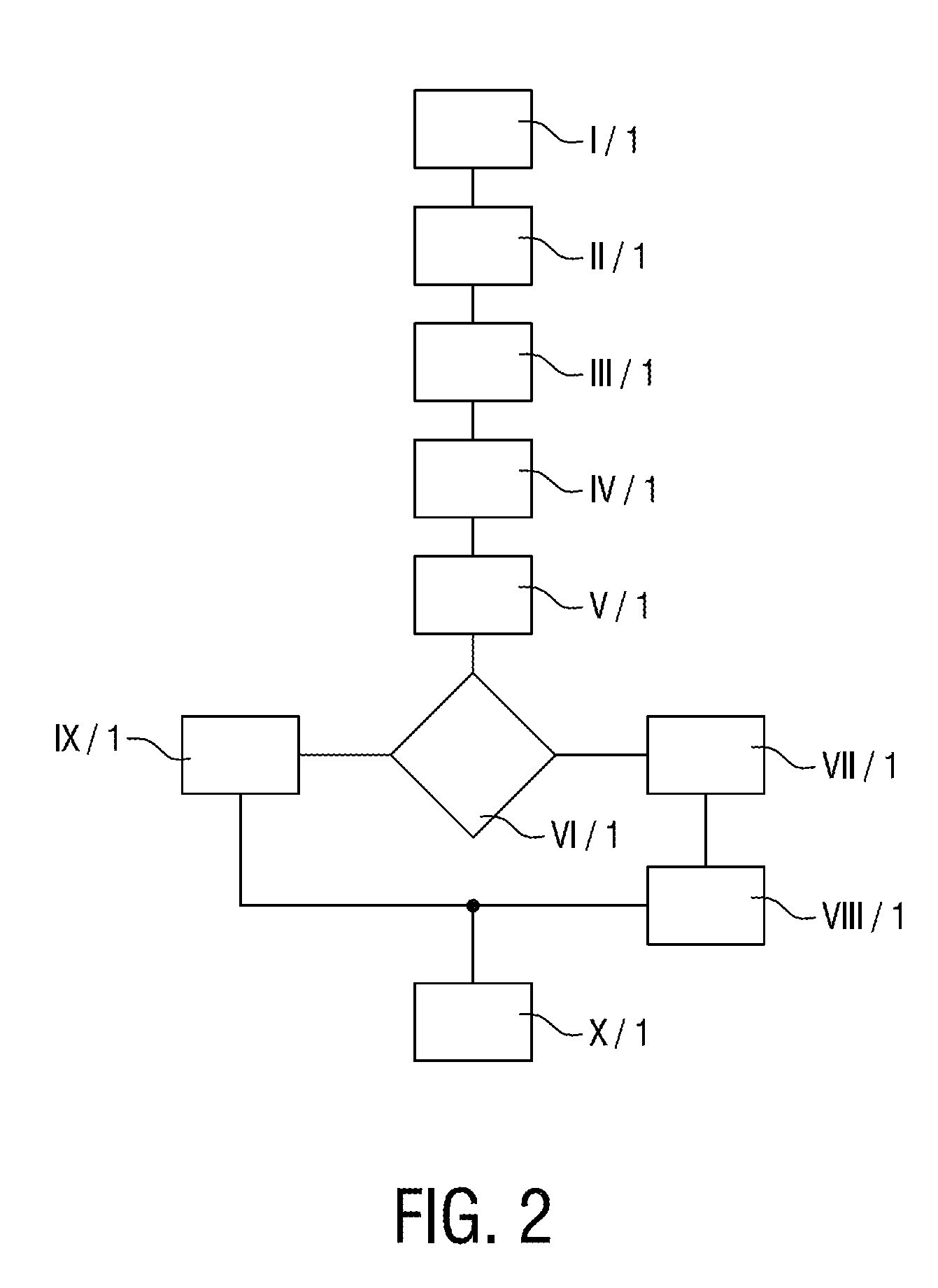
Hierarchical security domain model
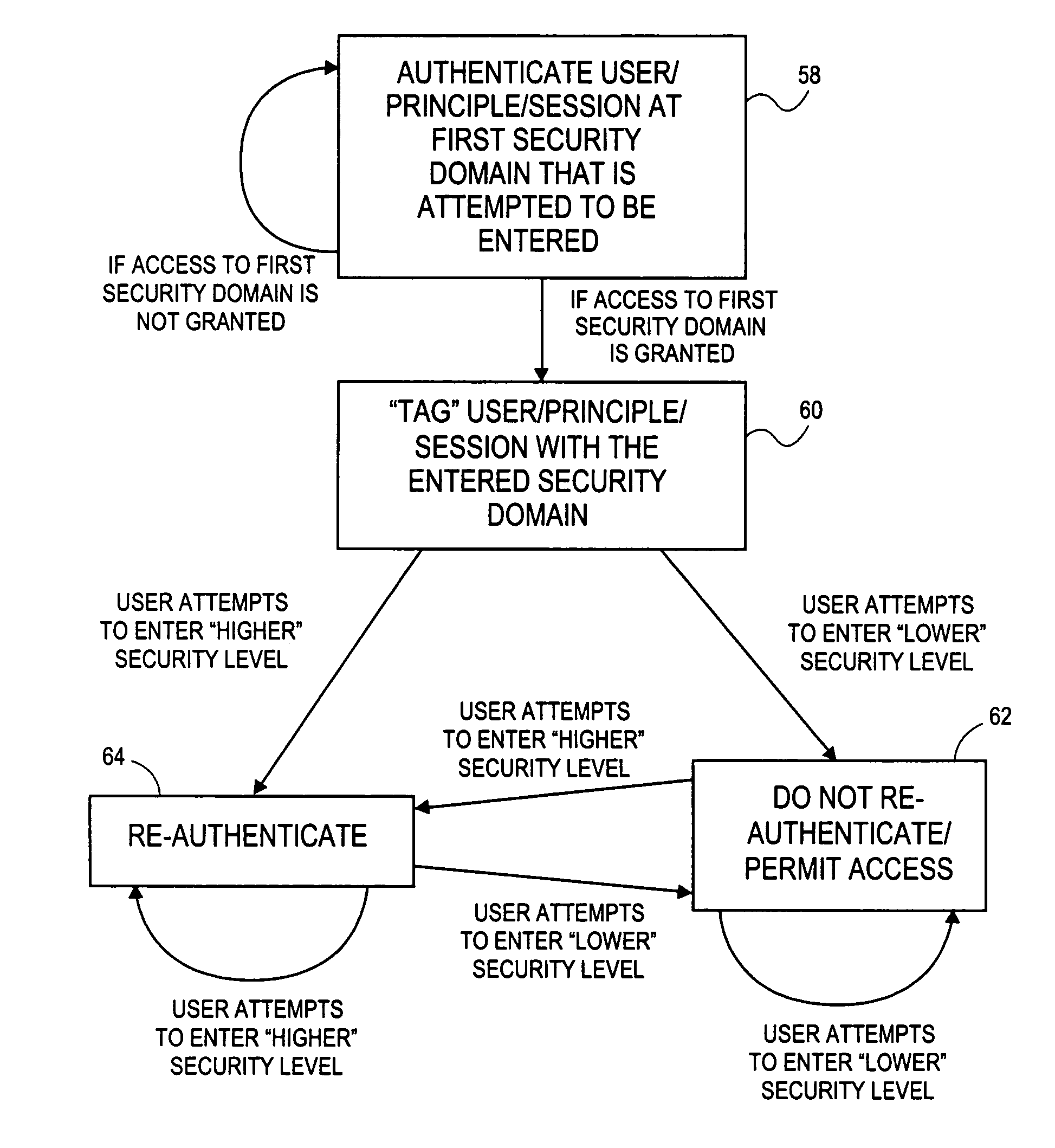
According to one aspect of the invention, a hierarchy of security domains and a method for granting a user access to the security domains are provided. The hierarchy of security domains includes multiple security levels and relationships between particular security domains. When a user is authenticated and / or authorized for access to a first security domain, the user is tagged as having been granted access to that security domain. If the user attempts to access a related security domain with a lower security level, the user is granted access without having to be re-authenticated and / or re-authorized. If the user attempts to access a related security domain with a higher security level, the user must be re-authenticated and / or re-authorized be access is granted to the security domain with the higher security level.
Owner:SAP AG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com