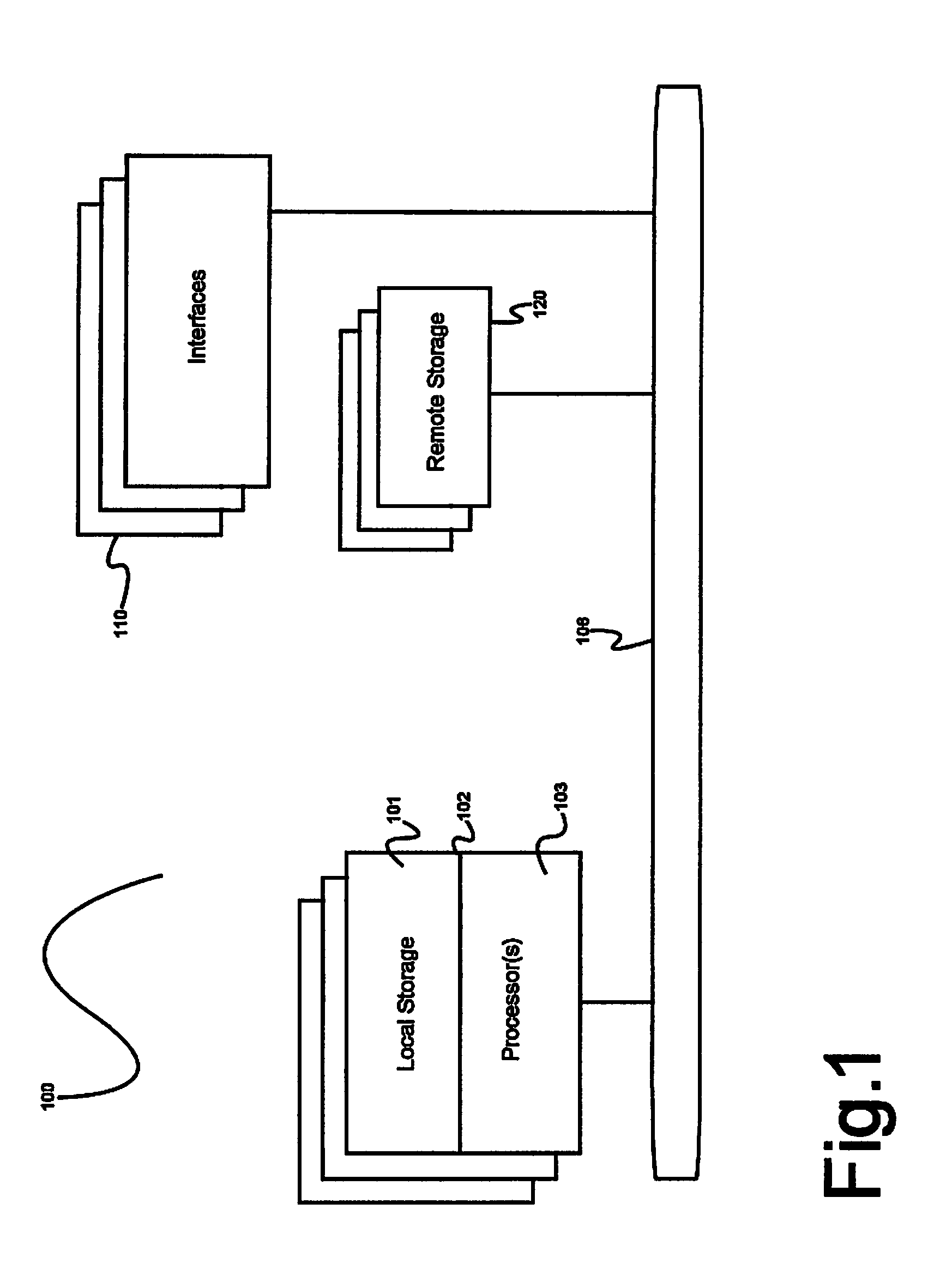
Patents
Literature
3978 results about "Media server" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
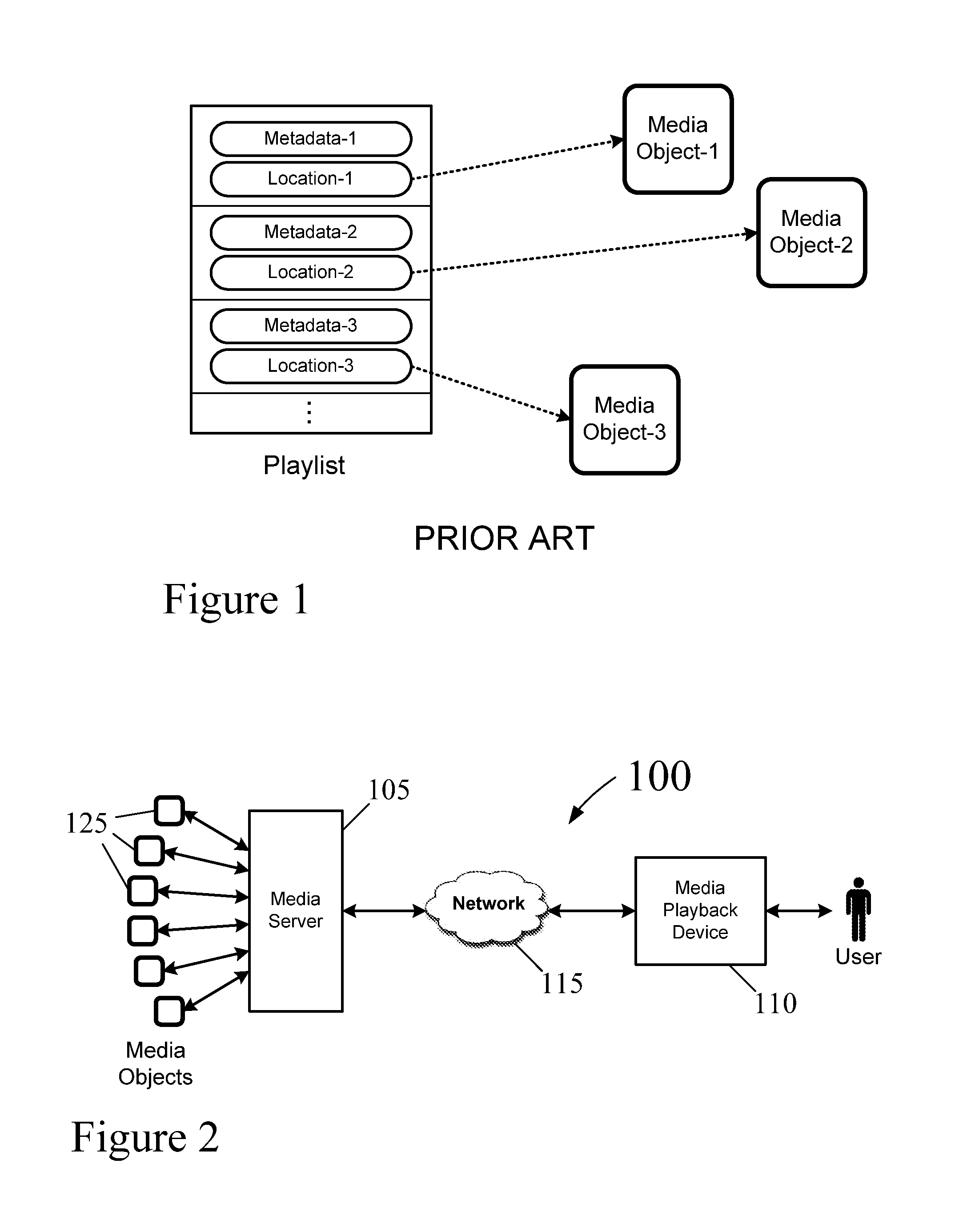
Delivering and processing multimedia bookmark
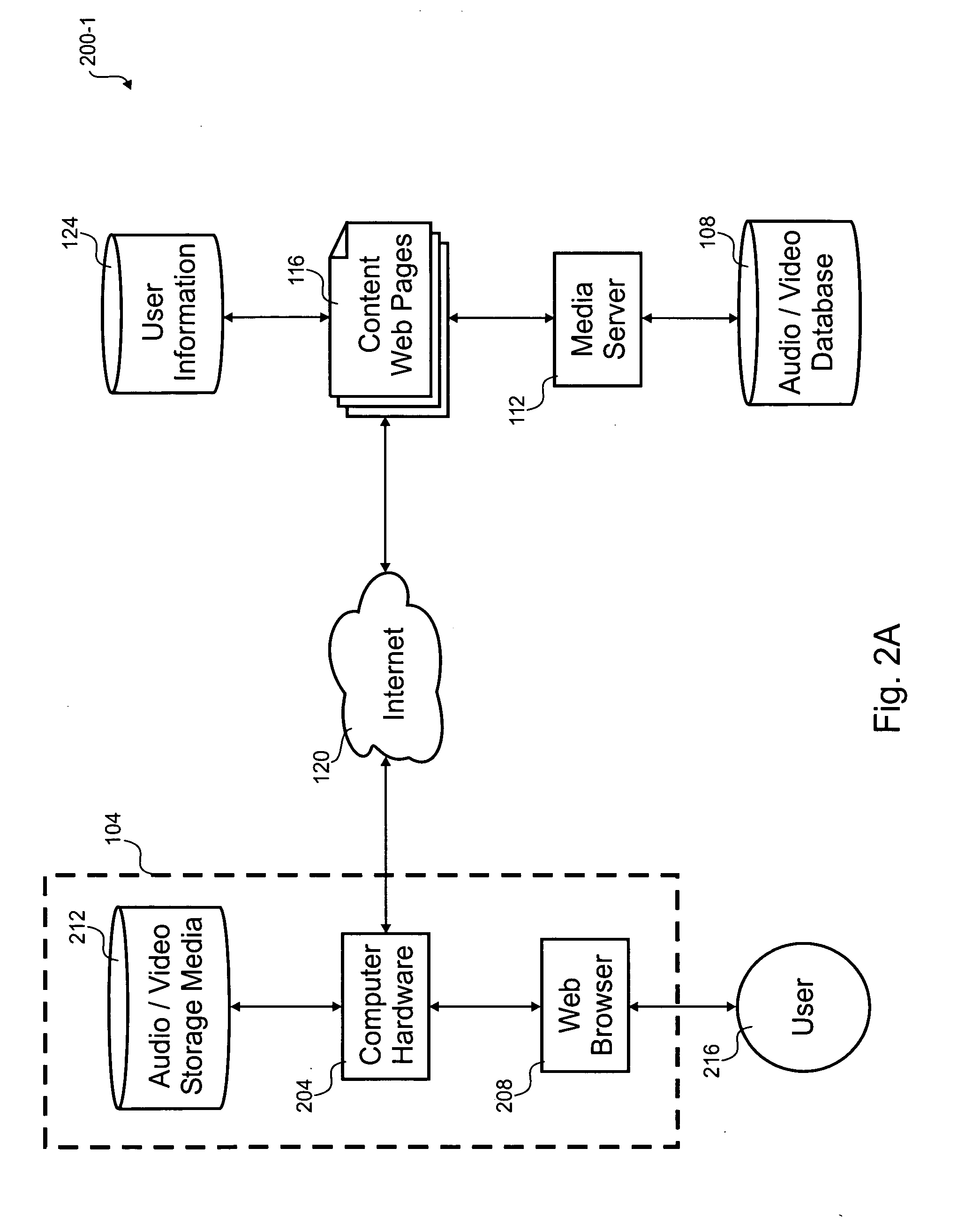
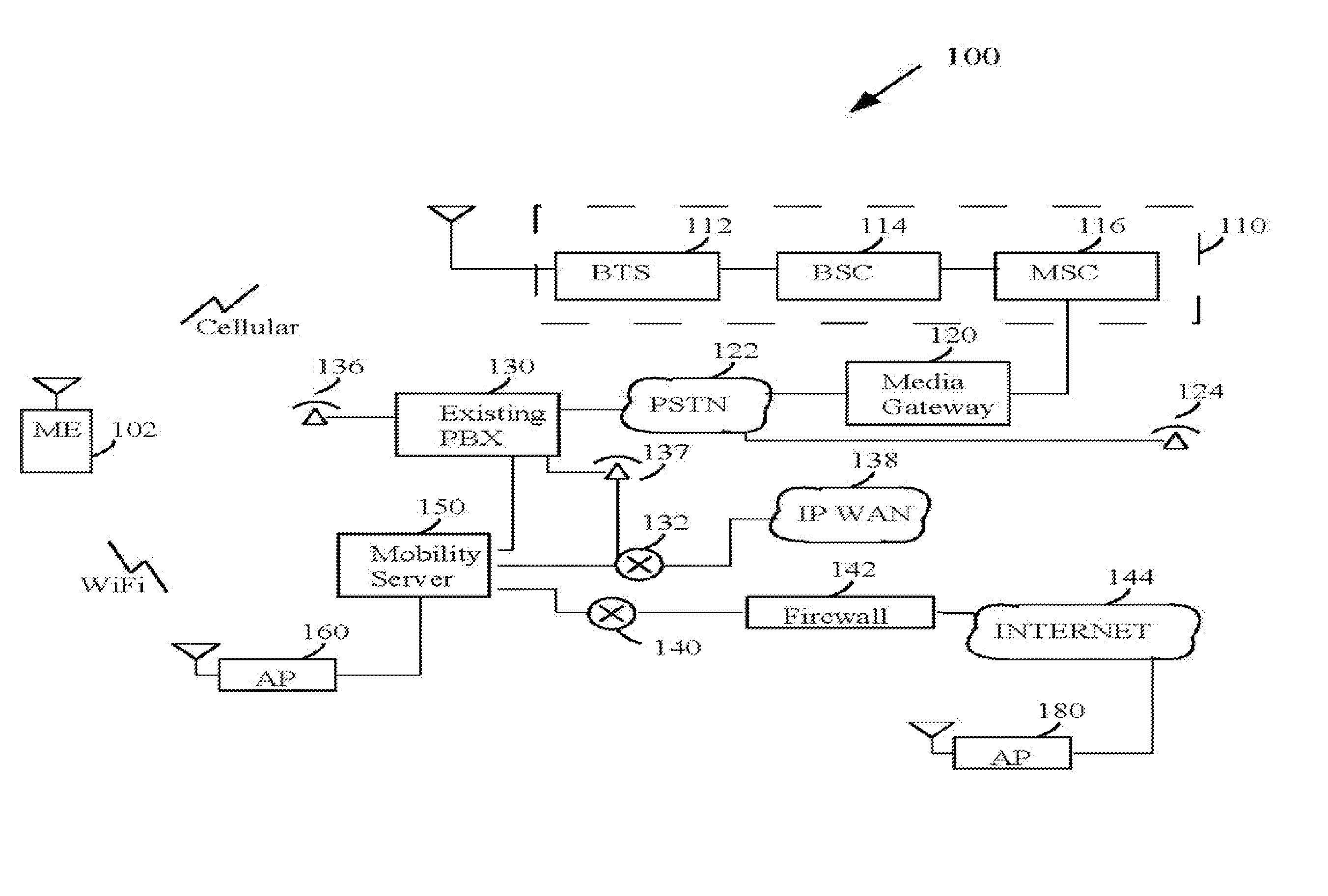
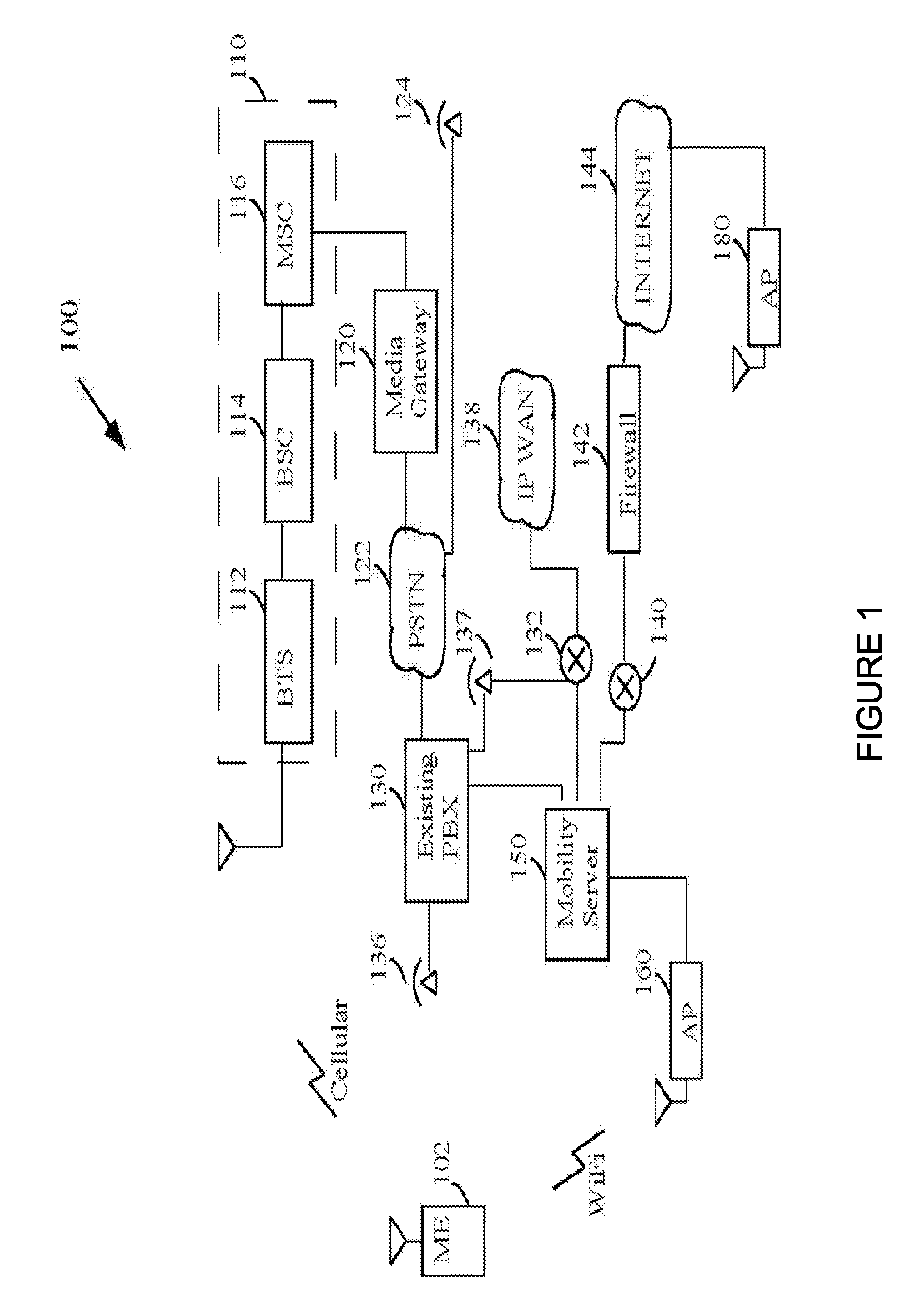
InactiveUS20050210145A1Easy to moveEasy detectionPulse modulation television signal transmissionDigital data information retrievalWeb browserMedia server
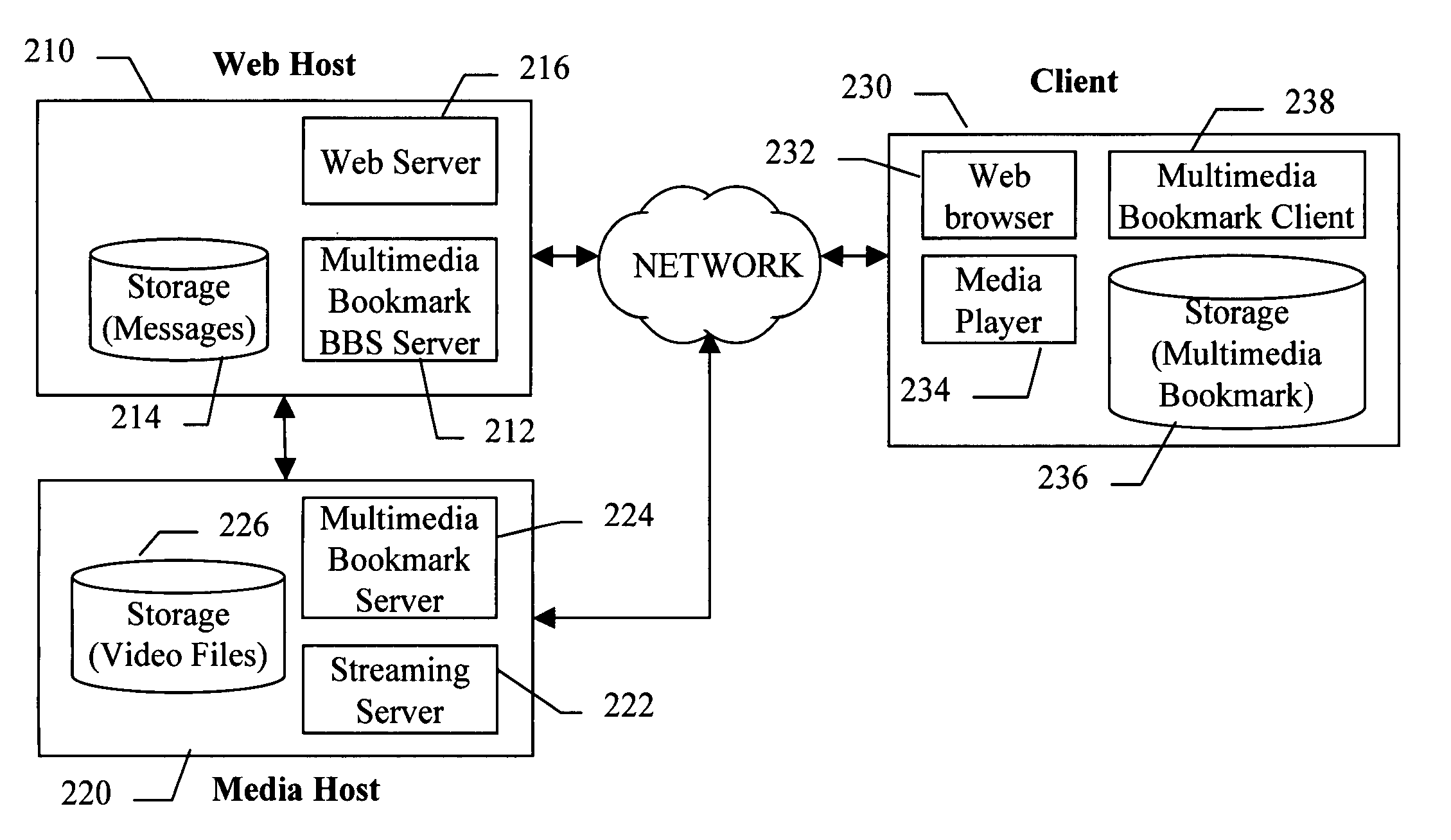
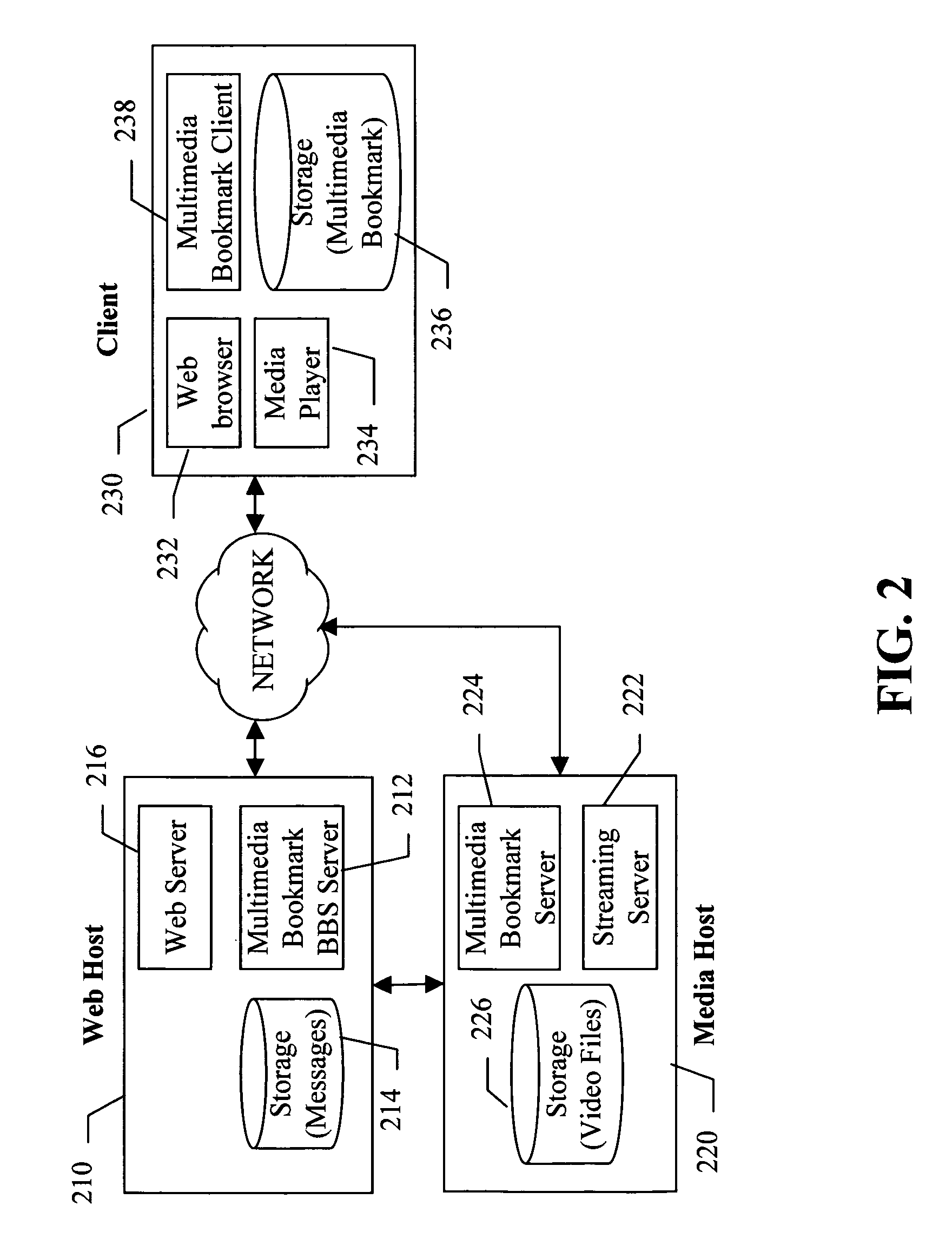
A multimedia bookmark (VMark) bulletin board service (BBS) system comprises: a web host comprising storage for messages, a web server, and a VMark BBS server; a media host comprising storage for audiovisual (AV) files, and a streaming server; a client comprising storage for VMark, a web browser, a media player and a VMark client; and a VMark server located at the media host or at the client; a communication network connecting the web host, the media host and the client. A method of performing a multimedia bookmark bulletin board service (BBS) comprises: creating a message including a multimedia bookmark for an AV file; and posting the message into the multimedia bookmark BBS. A method of sending multimedia bookmark (VMark) between clients comprises: at a first client, making a VMark indicative of a bookmarked position in an AV program; sending the VMark from the first client to a second client; and playing the program at the second client from the bookmarked position. A system for sharing multimedia content comprises: a multimedia bookmark bulletin board system (BBS); and means for posting a multimedia bookmark to the BBS.
Owner:VIVCOM INC
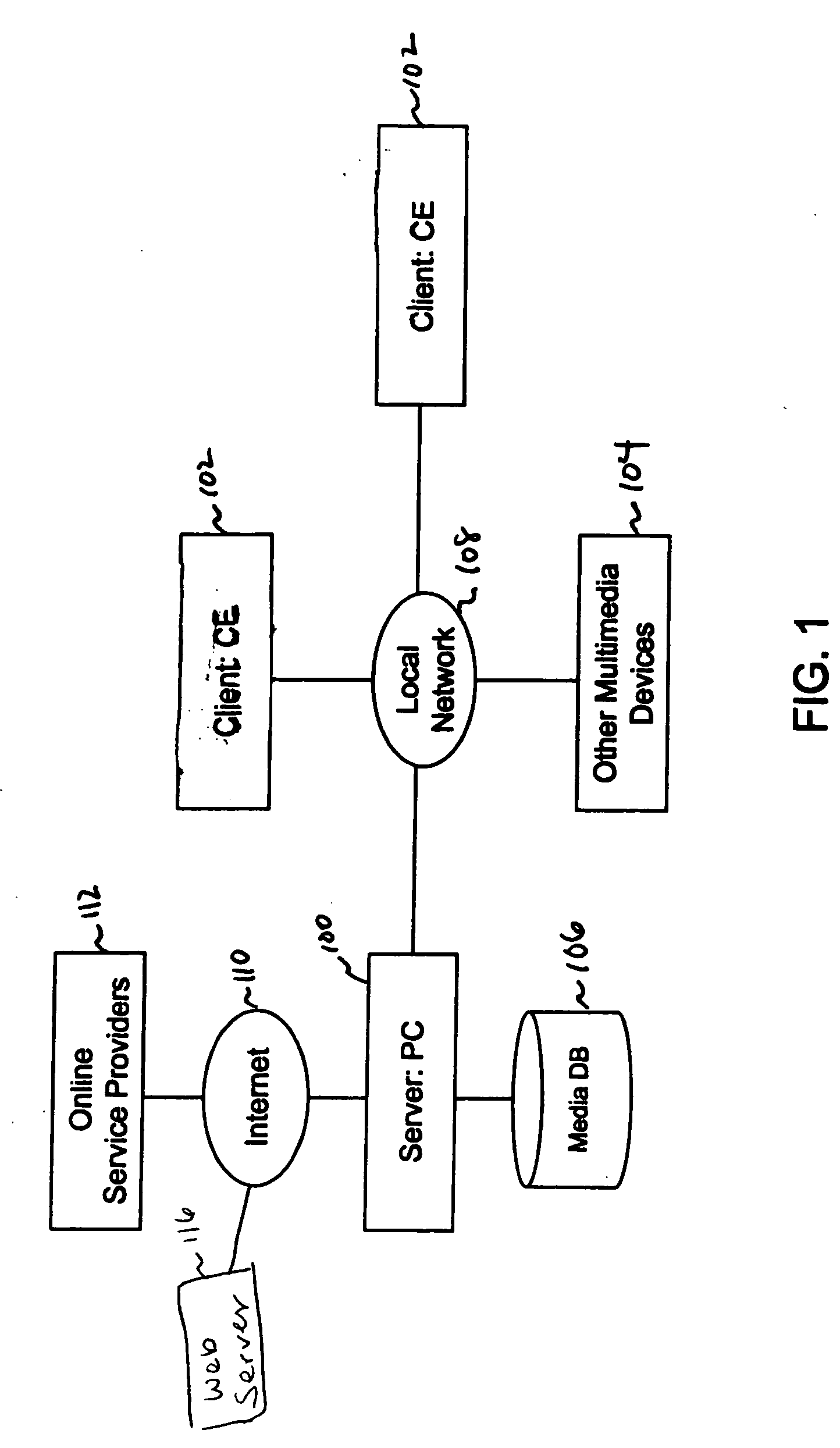
System and method for providing content, management, and interactivity for client devices
InactiveUS20050210101A1Digital data information retrievalSelective content distributionDigital dataFile synchronization
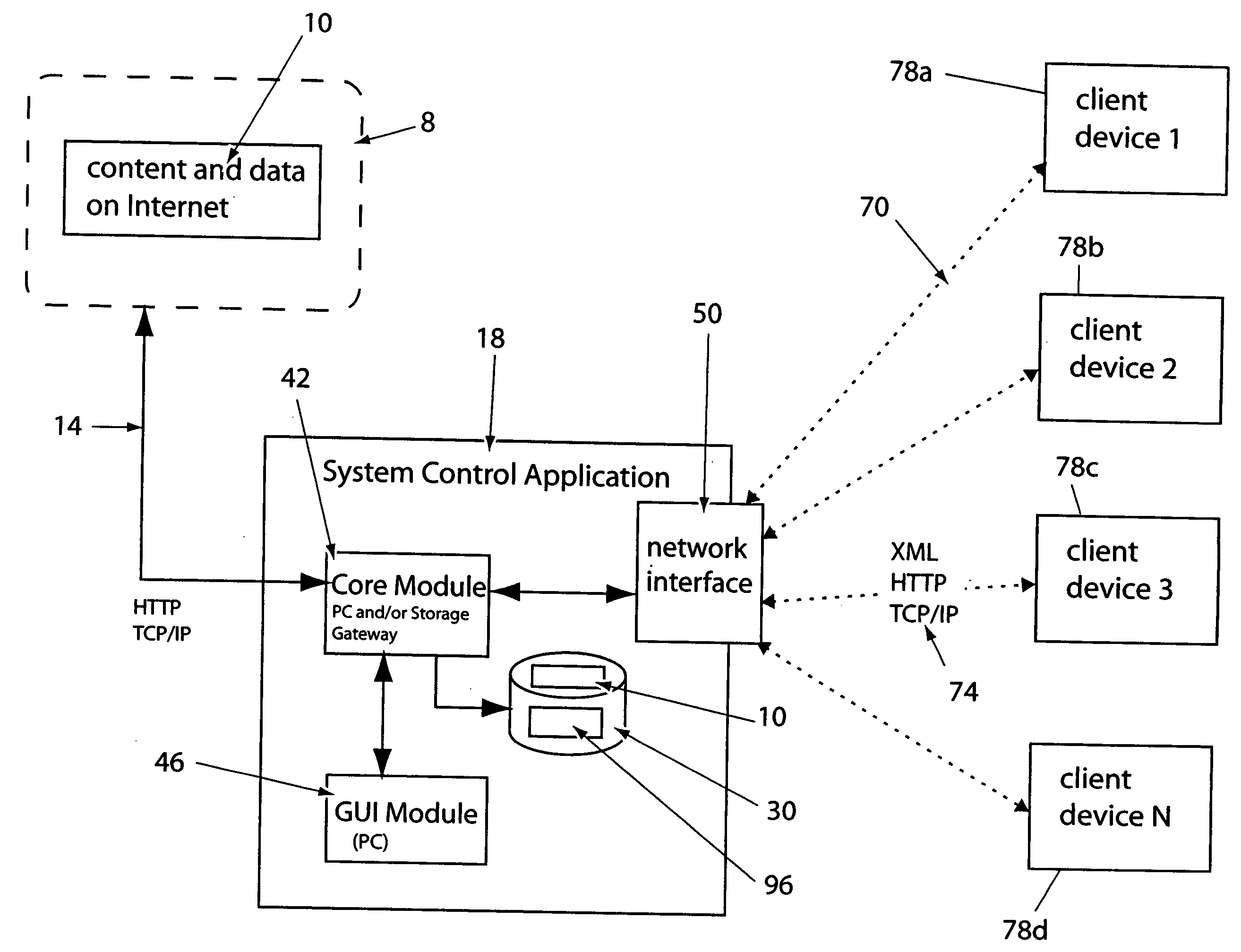
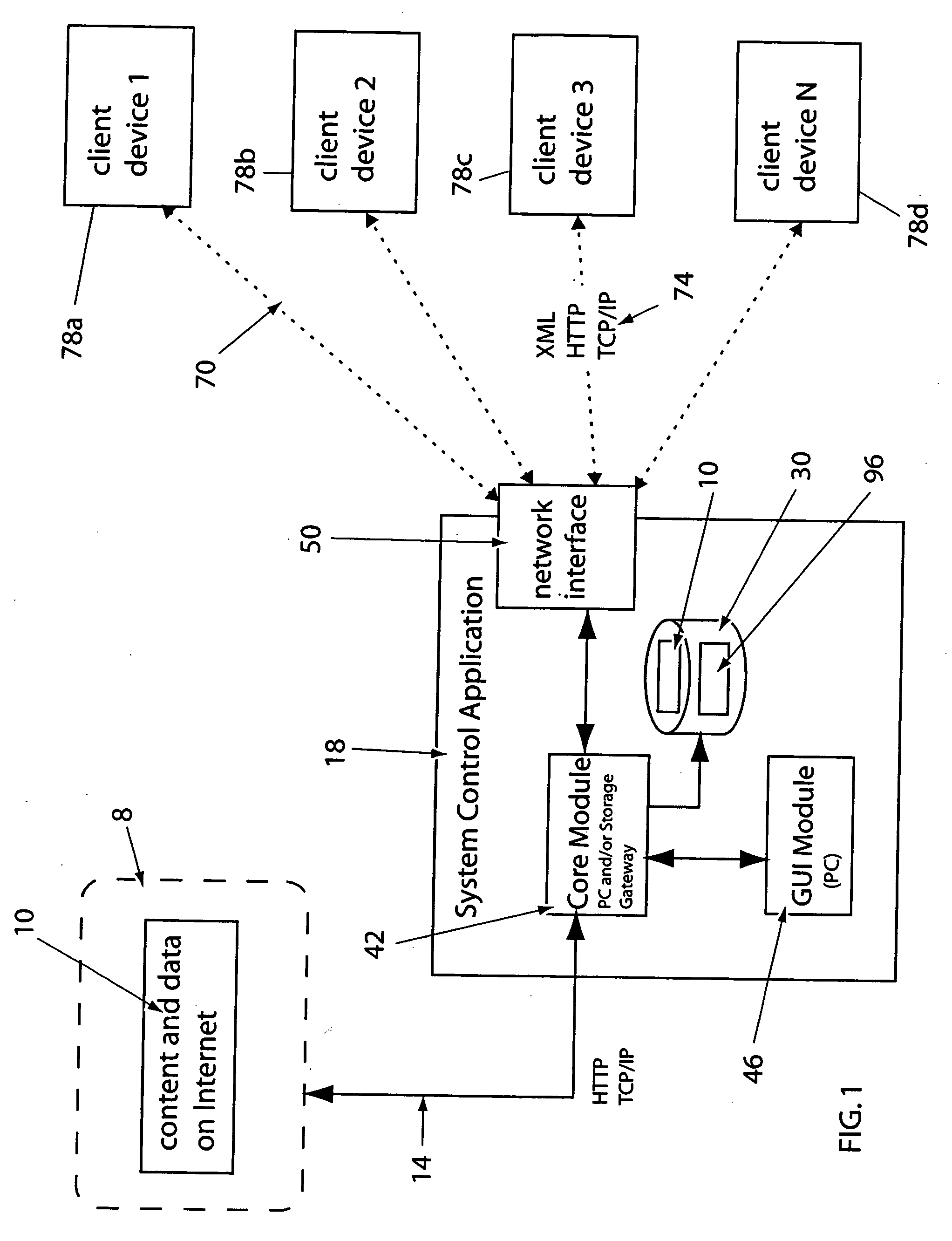
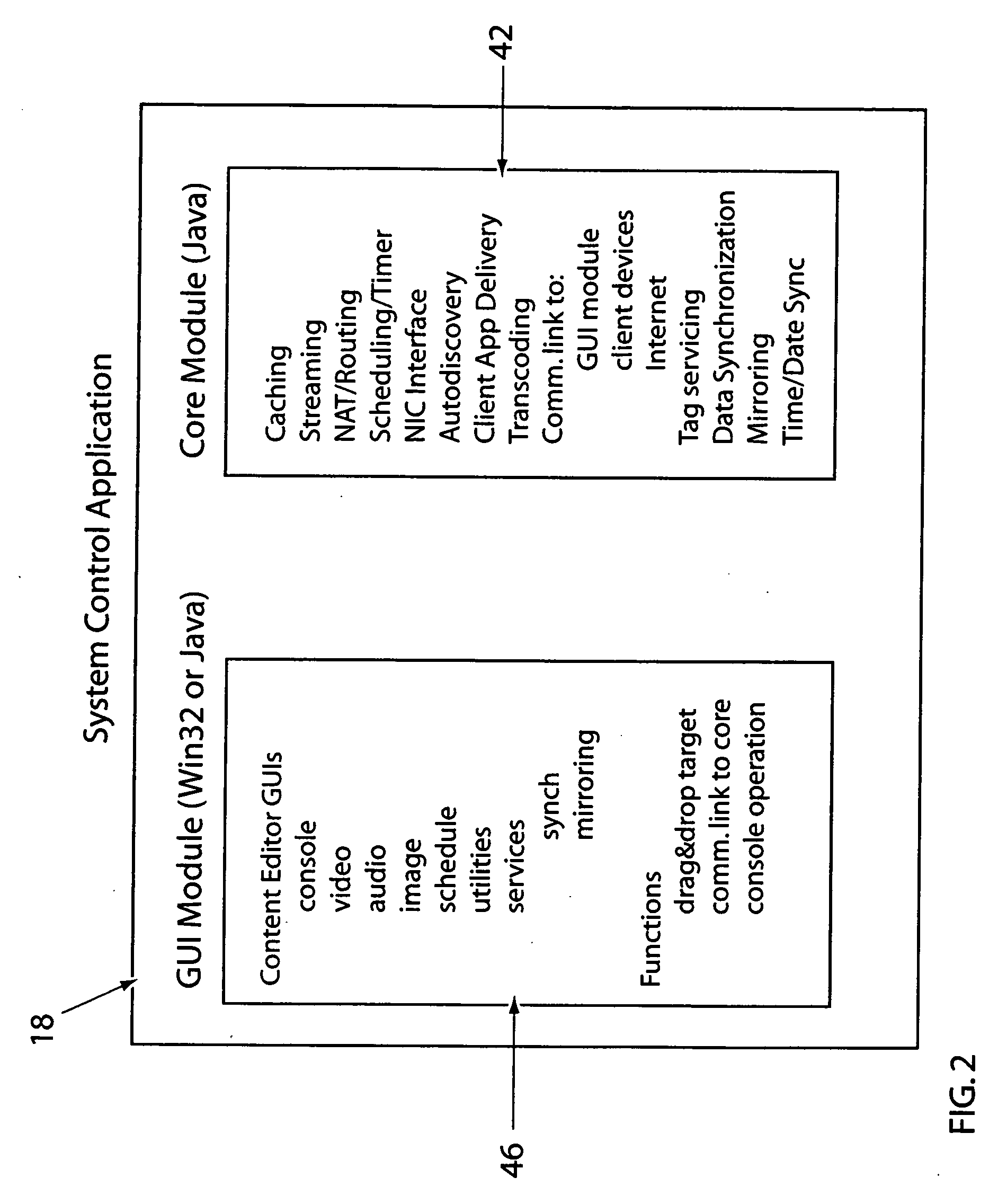
A system and a method for providing content, management and interactivity for client devices are provided. Digital data based on user specified preferences is automatically obtained and transferred from a wide area network to a media server computer. A system control application provides streaming media services to stream-playing client media player devices, and provides digital media file synchronization services to client storage devices, via a local area network. The digital data is then automatically sent from the computer to a client device using a wired or wireless data transceiver. In one embodiment, the client device is a television. In another embodiment the client device is a portable media playback device.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL VENTURES ASSETS 186 LLC +1
Online gaming spectator system
InactiveUS20060058103A1Improve experienceEasy to scaleData processing applicationsVideo gamesData streamMedia server
During an online event, a spectator process monitors a state of the event, updating a spectator model, so that spectator data streams can be generated and provided to spectators. The spectator data streams can be formatted and provided with content appropriate for use by different types of spectator devices used by the spectators. The spectator process can also automatically generate virtual commentary appropriate for the action occurring in the event for inclusion in the spectator data streams. A media server receives the rendered data streams and distributes them to the electronic devices being used by the spectators. The distribution can be delayed to avoid a spectator conveying information to a participant that would provide an unfair advantage. Executable code can be included in the spectator data stream to provide additional functionality and facilitate interaction between the spectators, and to enable a spectator to also “play” the game.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
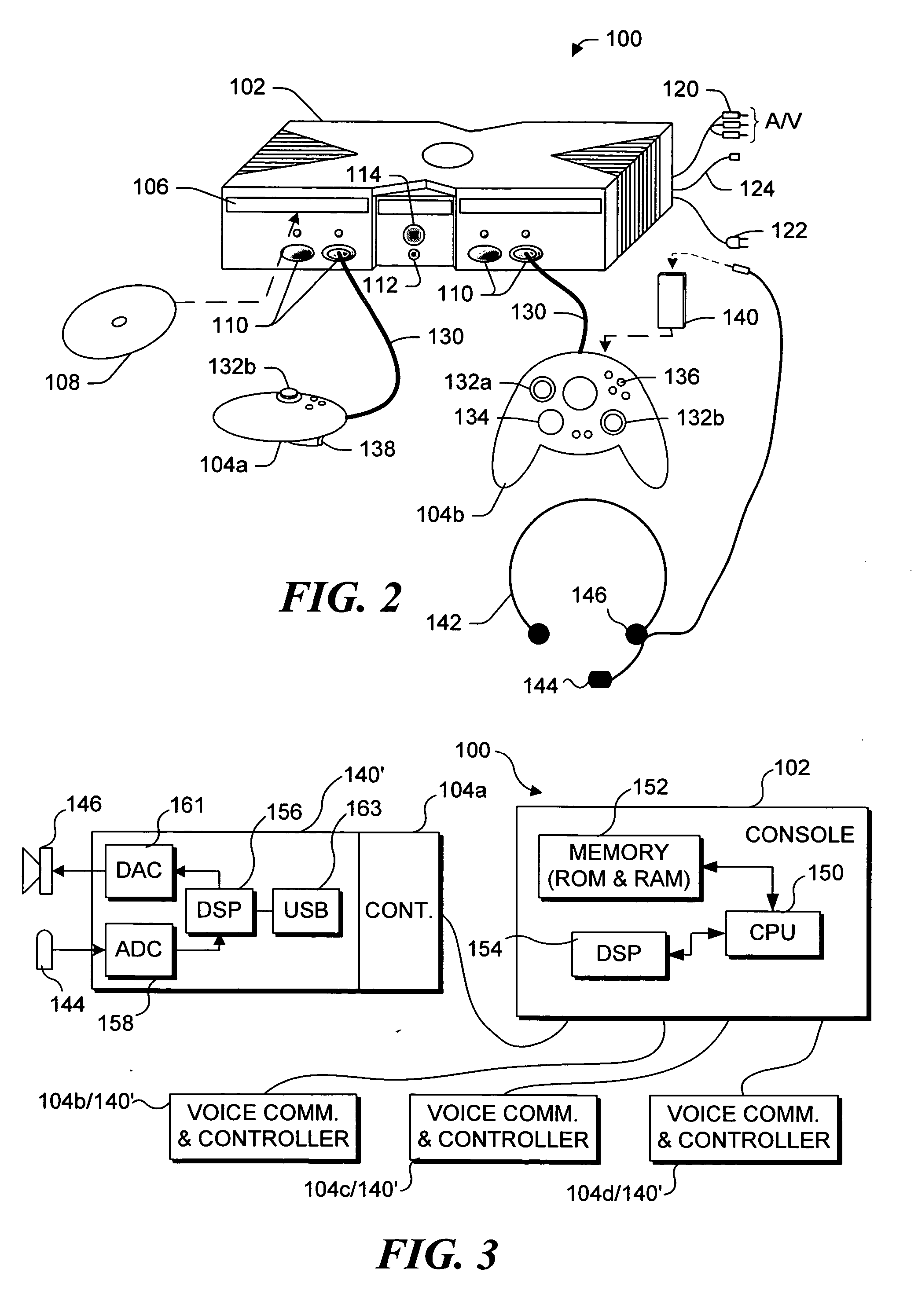
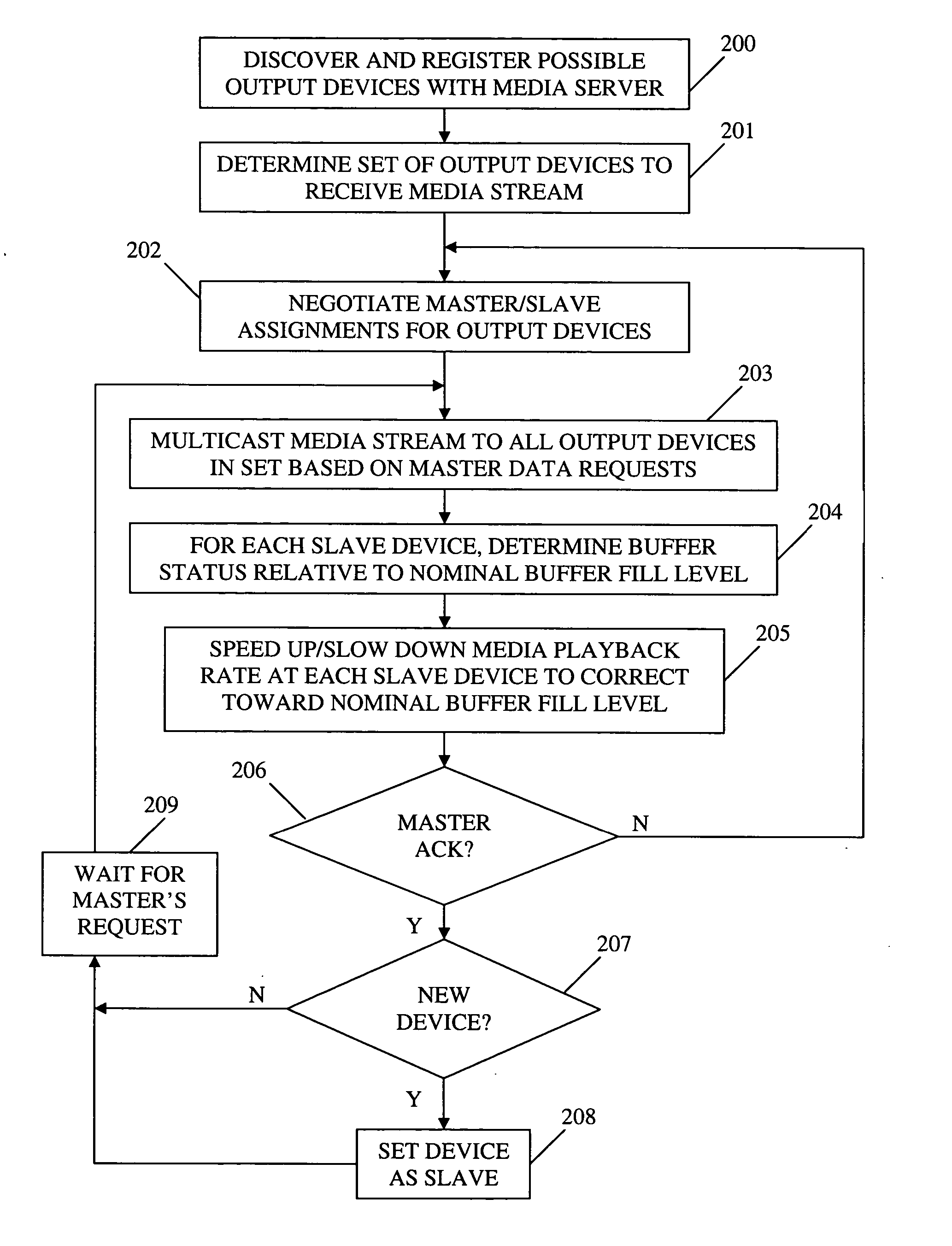
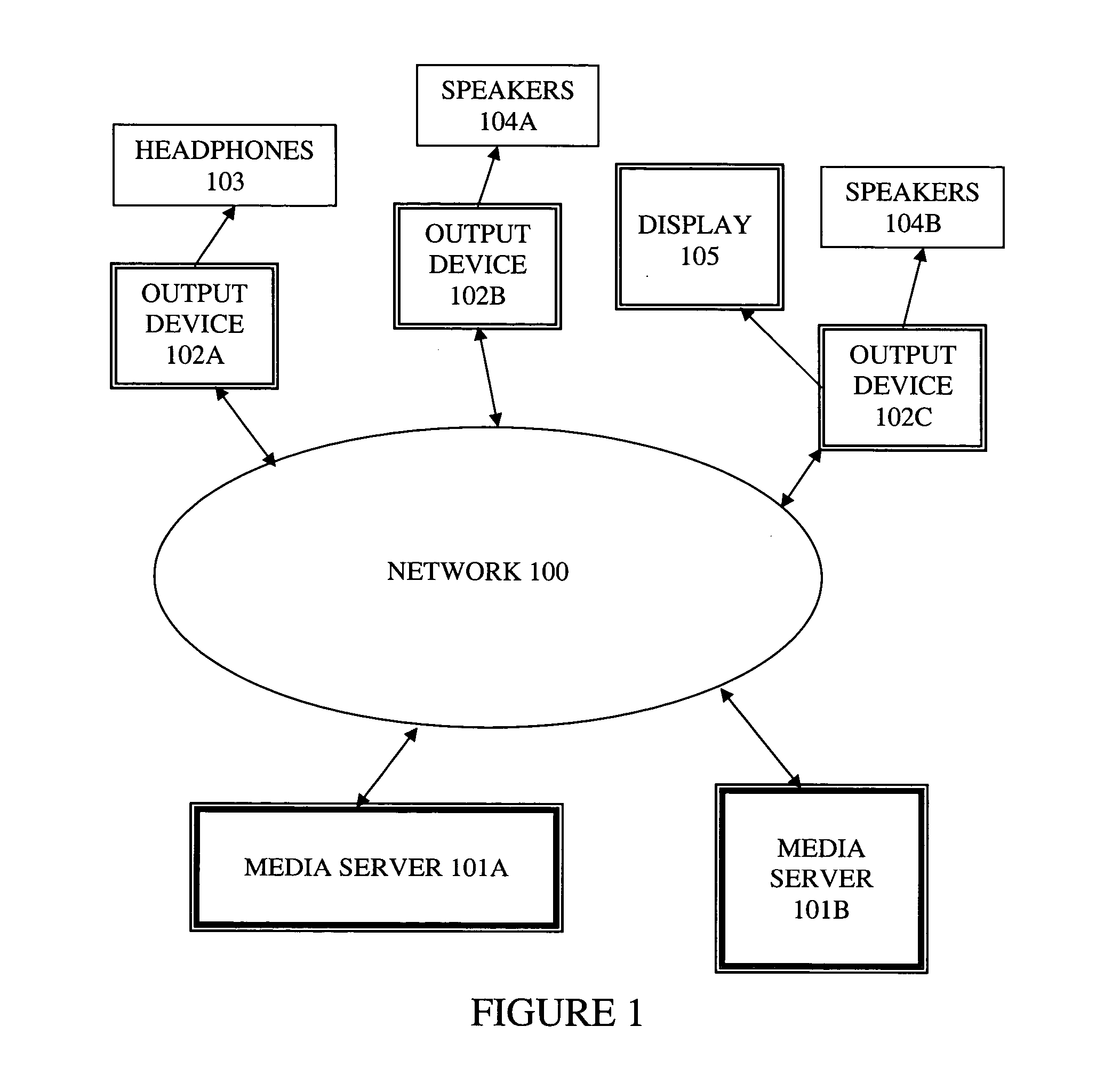
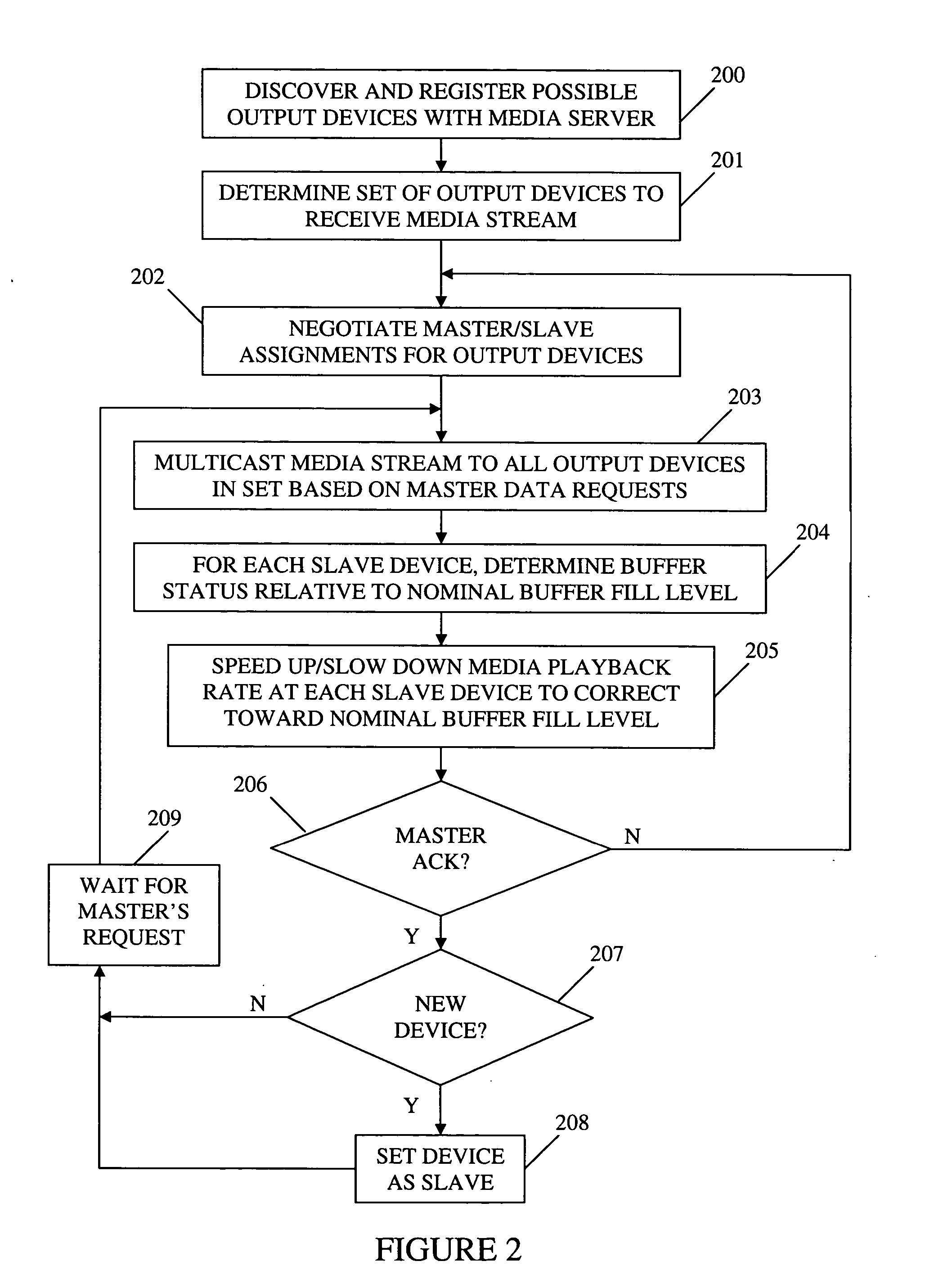
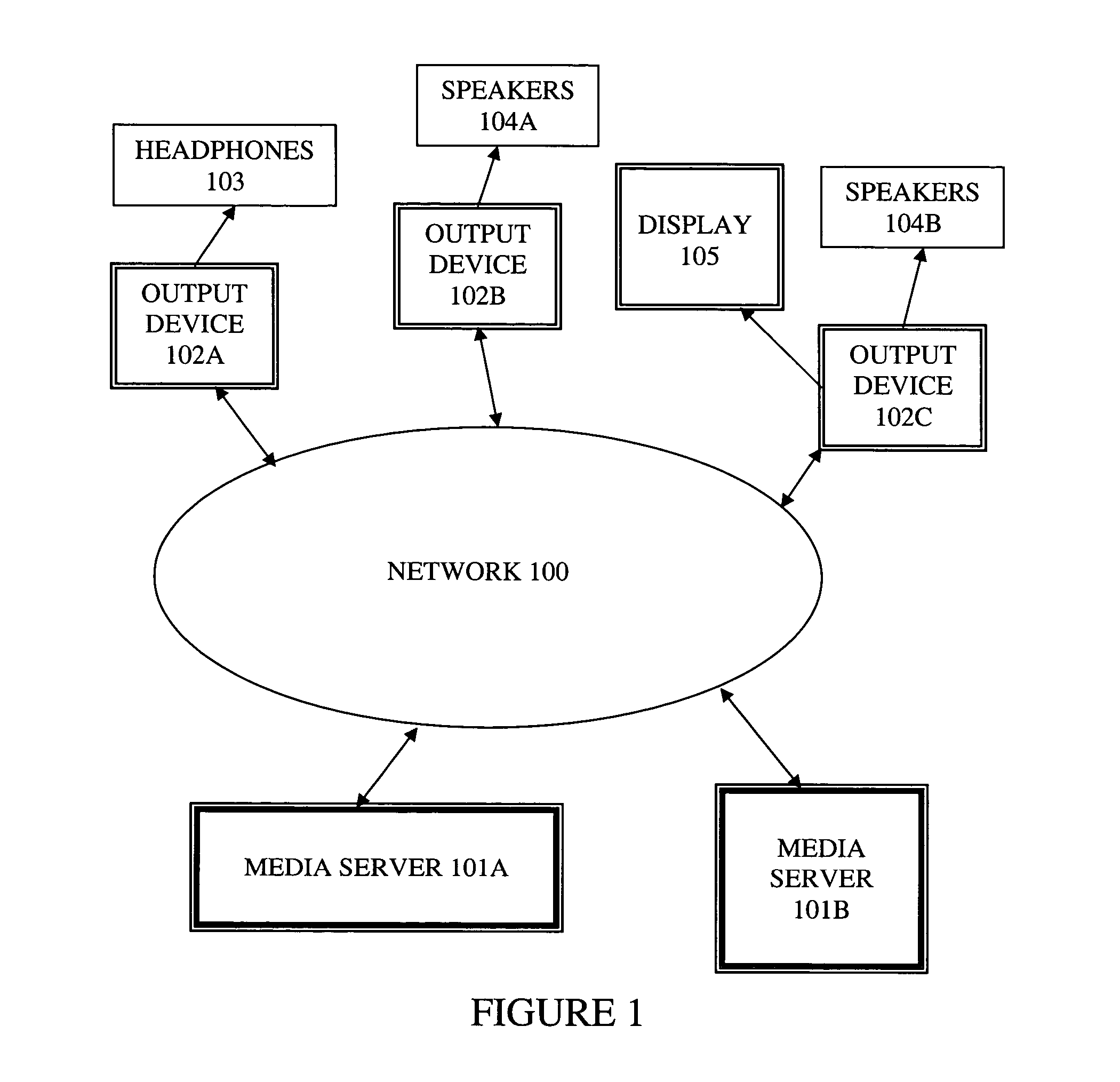
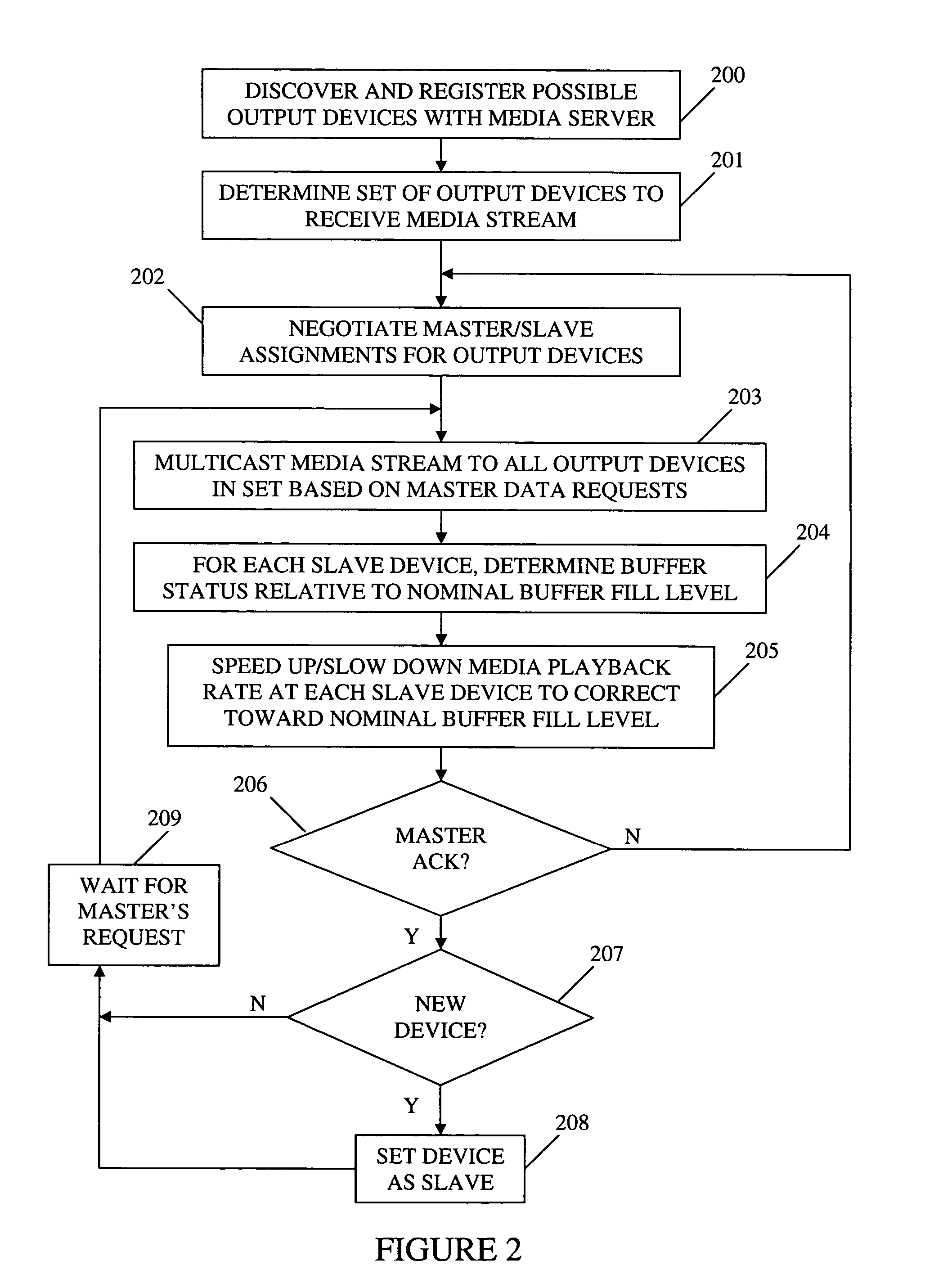
Method and apparatus for synchronizing playback of streaming media in multiple output devices
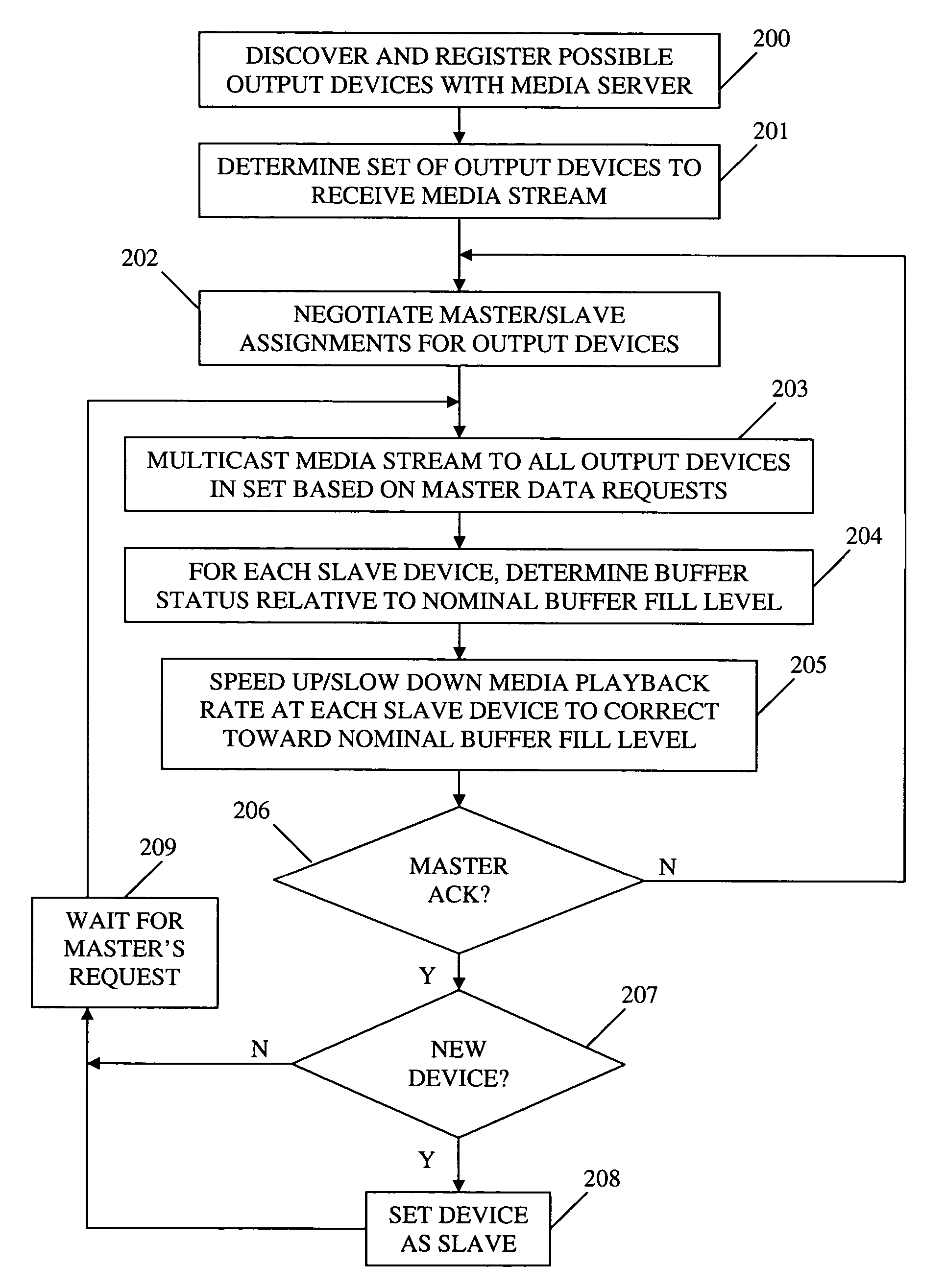
ActiveUS20060149850A1Maintaining average timing synchronizationError preventionTransmission systemsStreaming dataTimestamp
A method and apparatus for synchronizing streaming media with multiple output devices. One or more media servers serve media streams to one or more output devices (i.e., players). For playback synchronization, one output device is the “master”, whereas the remaining output devices are “slaves”. More data is requested from the media server by the “master” device to maintain a nominal buffer fill level over time. The “slave” devices receive streamed data from the media server at the rate determined by the master device's data requests, and the average rate of data flow over the streaming network is thus controlled by the frequency of the single “master” device's crystal. “Slave” devices make playback rate corrections to maintain respective buffer fill levels within upper and lower threshold levels. For slow networks, each media data packet timestamp is calculated from the time the master's buffer reaches nominal level.
Owner:SNAP ONE LLC
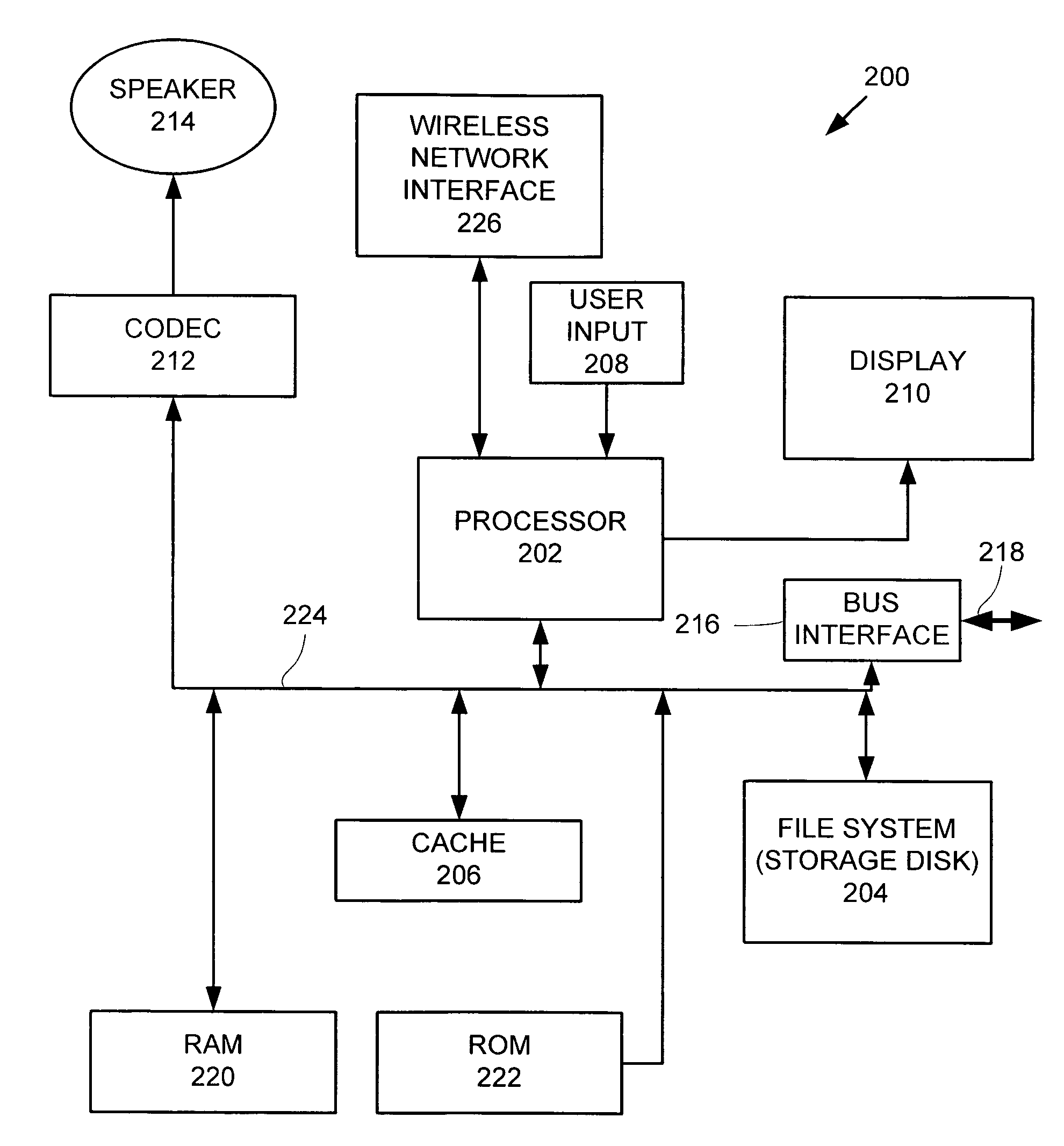
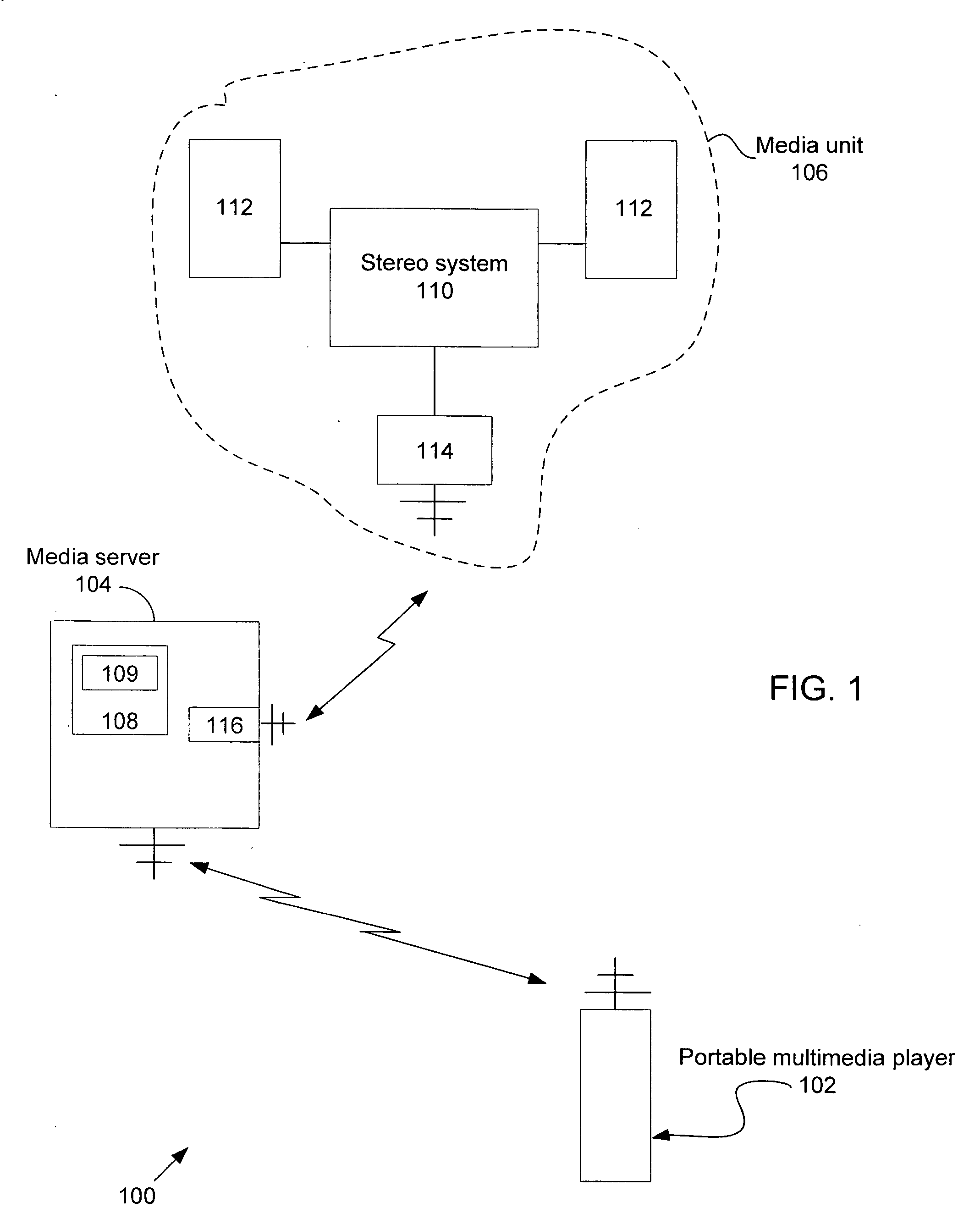
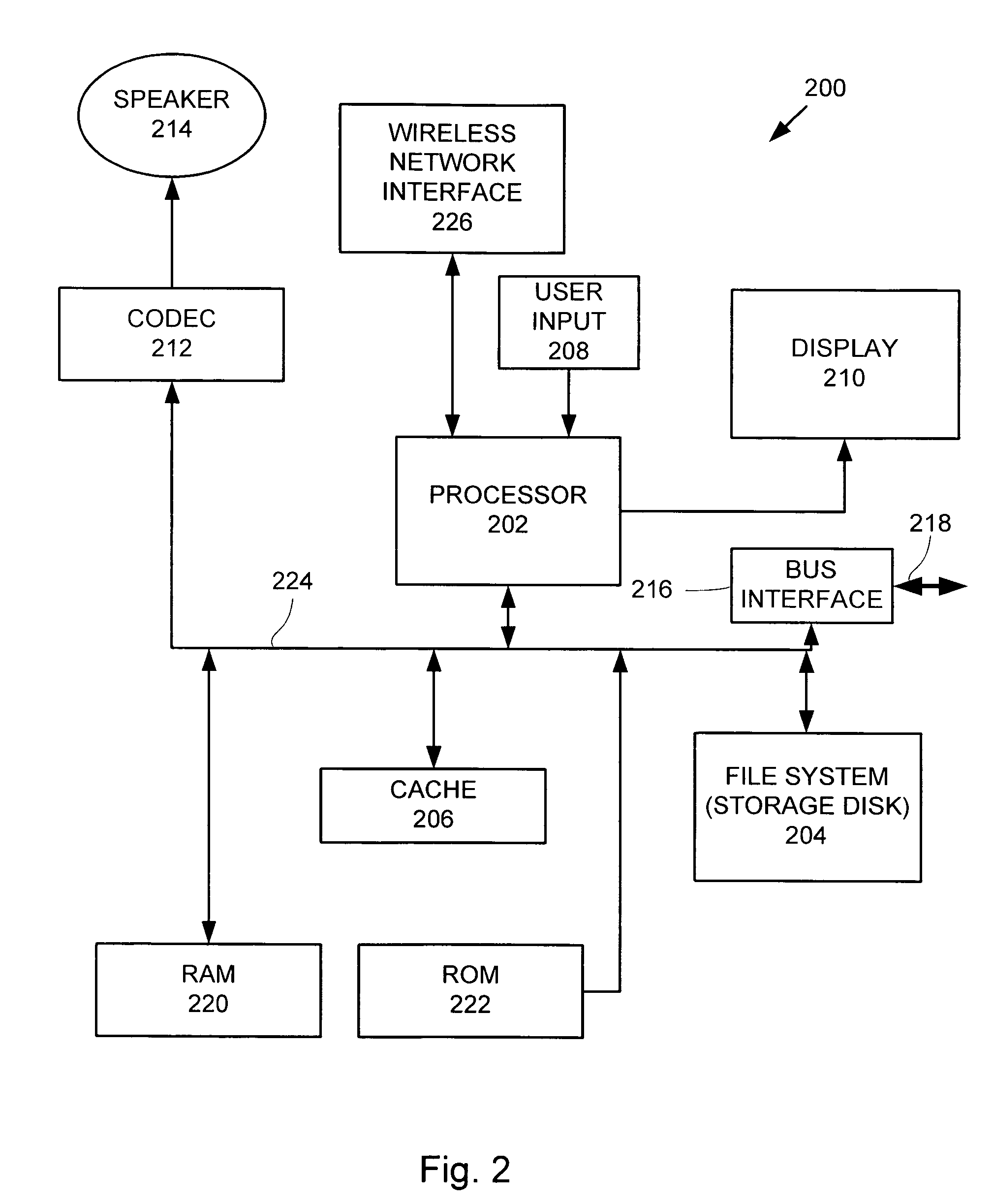
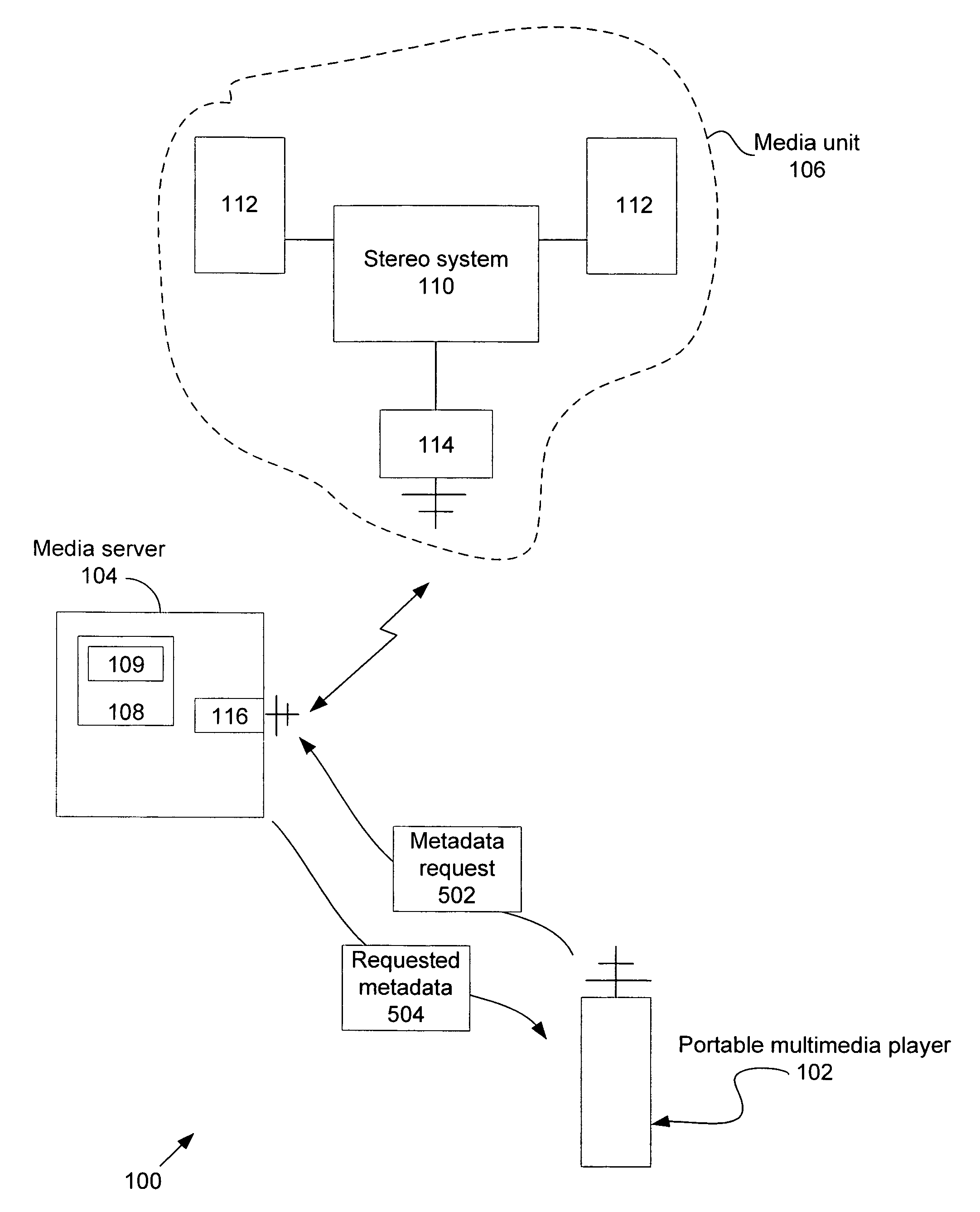
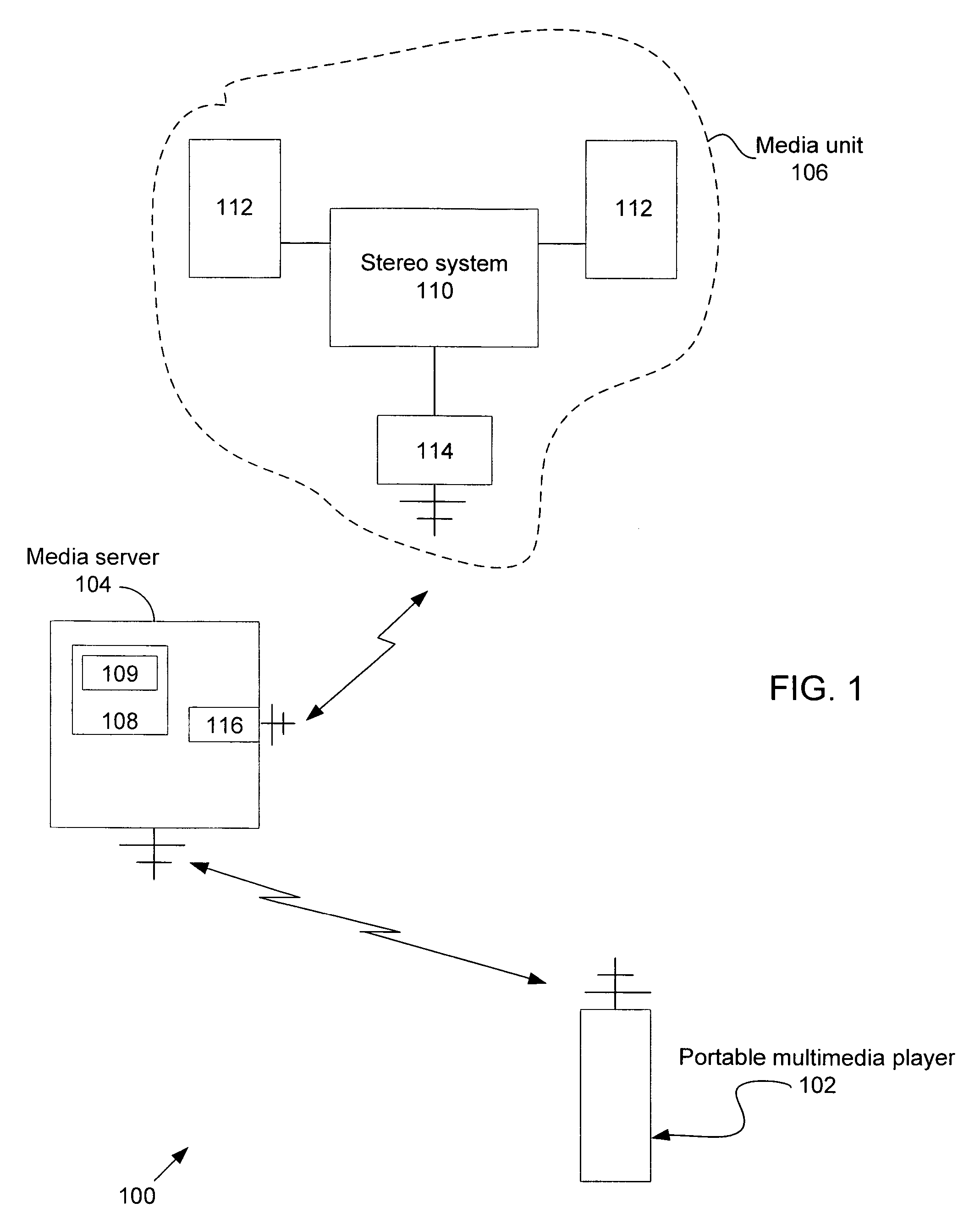
Portable media player as a low power remote control and method thereof
ActiveUS20070169115A1Multiple digital computer combinationsProgram loading/initiatingRemote controlMedia server
A portable multimedia player is used to wirelessly access and control a media server that is streaming digital media by way of a wireless interface to a media unit such as a stereo / speakers in the case of streaming digital audio. In one embodiment, the portable multimedia player is wirelessly synchronized to a selected one(s) of a number of digital media files stored on the media server in such a way that digital media file metadata (song title, author, etc.) associated with the selected digital media file(s) only is transferred from the media server to be stored in the portable media player.
Owner:APPLE INC
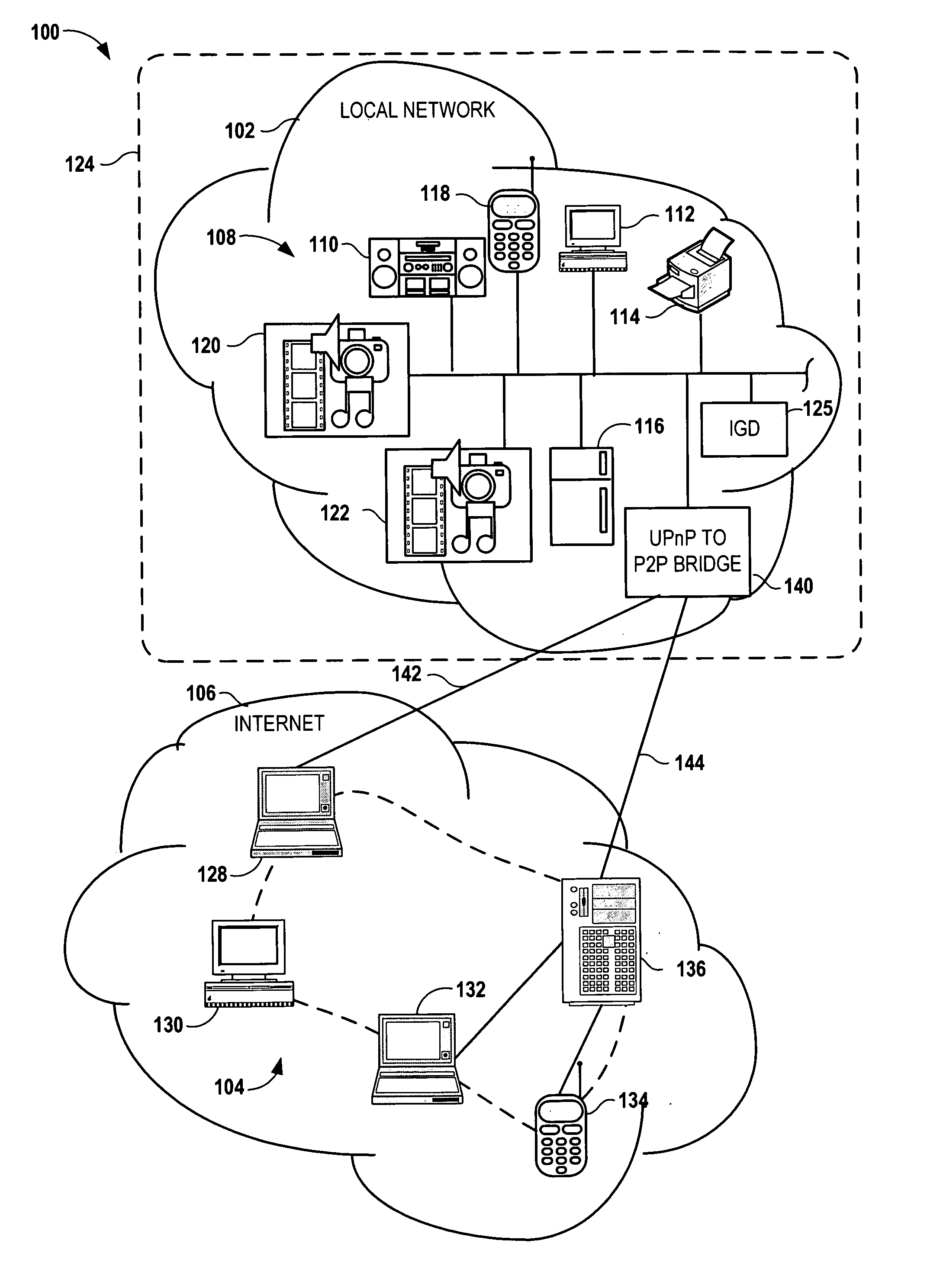
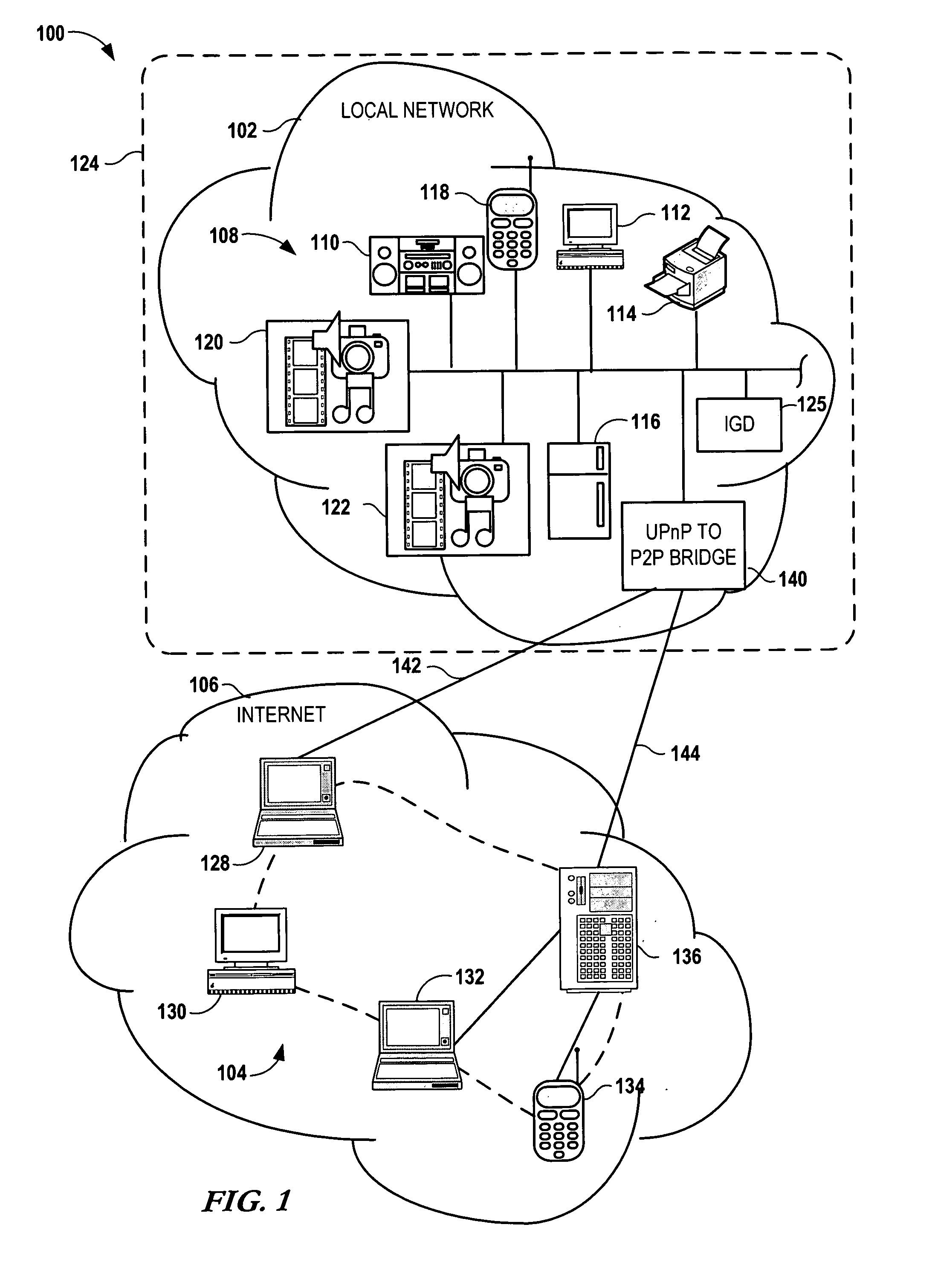
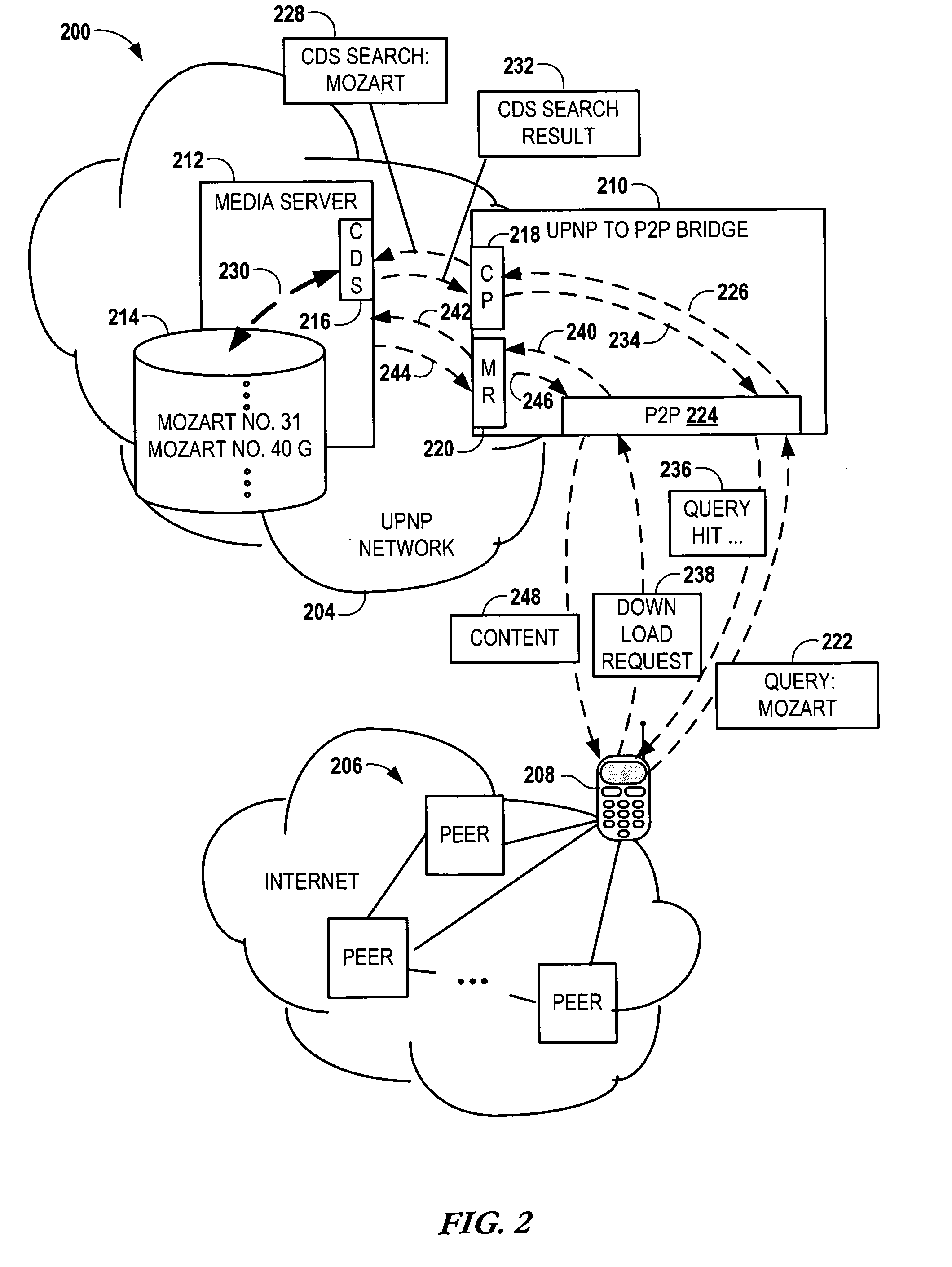
Bridging between AD HOC local networks and internet-based peer-to-peer networks
ActiveUS20070274327A1Easy to downloadFacilitate downloading the mediaData switching by path configurationMultiple digital computer combinationsNetworking protocolTTEthernet
Bridging between ad hoc local networks and Internet based peer-to-peer networks involves coupling a bridge device to a local network using an ad-hoc, peer-to-peer protocol used for exchanging data between consumer electronics devices. The bridge device is coupled to a public network using an Internet-based peer-to-peer networking protocol. In one arrangement, metadata related to media accessible from a media server of the local network is determined via the bridge device, and the metadata is transformed via the bridge device to enable peer-to-peer devices of the public network to discover the media via the bridge device using the Internet-based peer-to-peer networking protocol. In another arrangement, metadata related to media accessible from the public network is determined via the peer-to-peer networking protocol, and the metadata is transformed via the bridge device to enable a device of the local network to discover the media via the bridge device using the ad-hoc, peer-to-peer protocol.
Owner:CONVERSANT WIRELESS LICENSING LTD
Multiple object download
ActiveUS20050132083A1Digital data processing detailsMultiple digital computer combinationsThe InternetMedia server
According to the invention, a system for downloading a plurality of content objects from the Internet to a computer of a user is disclosed. The system includes first and second web pages, a database and a media server. The first web page allows selection of the number of content objects. The second web page includes a link to an application that includes embedded information that correlates the number of content objects to the application. The database stores the number of content objects. The media server composes an application that includes the embedded information. The number of content objects are selected by a user from the first web page. The media server allows download of the number of content objects after receiving the embedded information from a computer of a user.
Owner:LIMELIGHT NETWORKS
Method and apparatus for a multimedia value added service delivery system
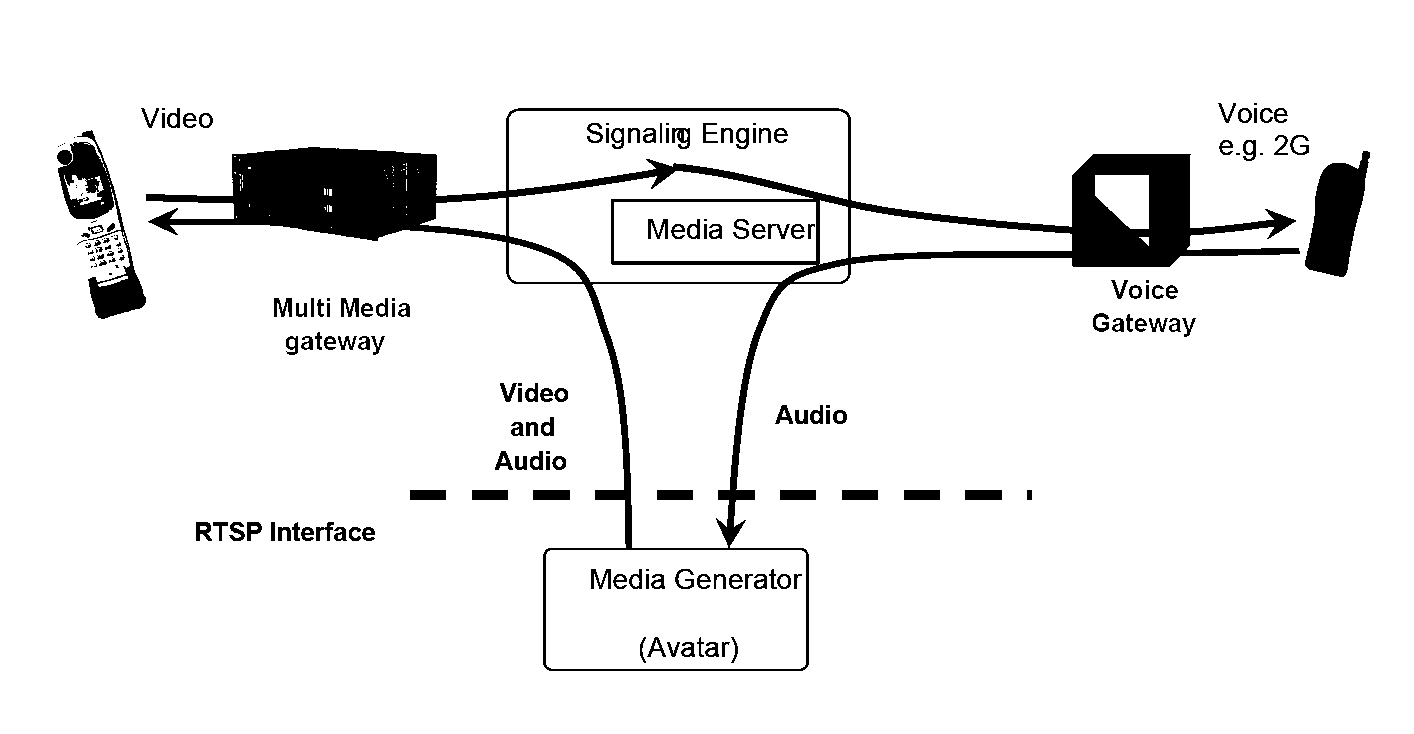
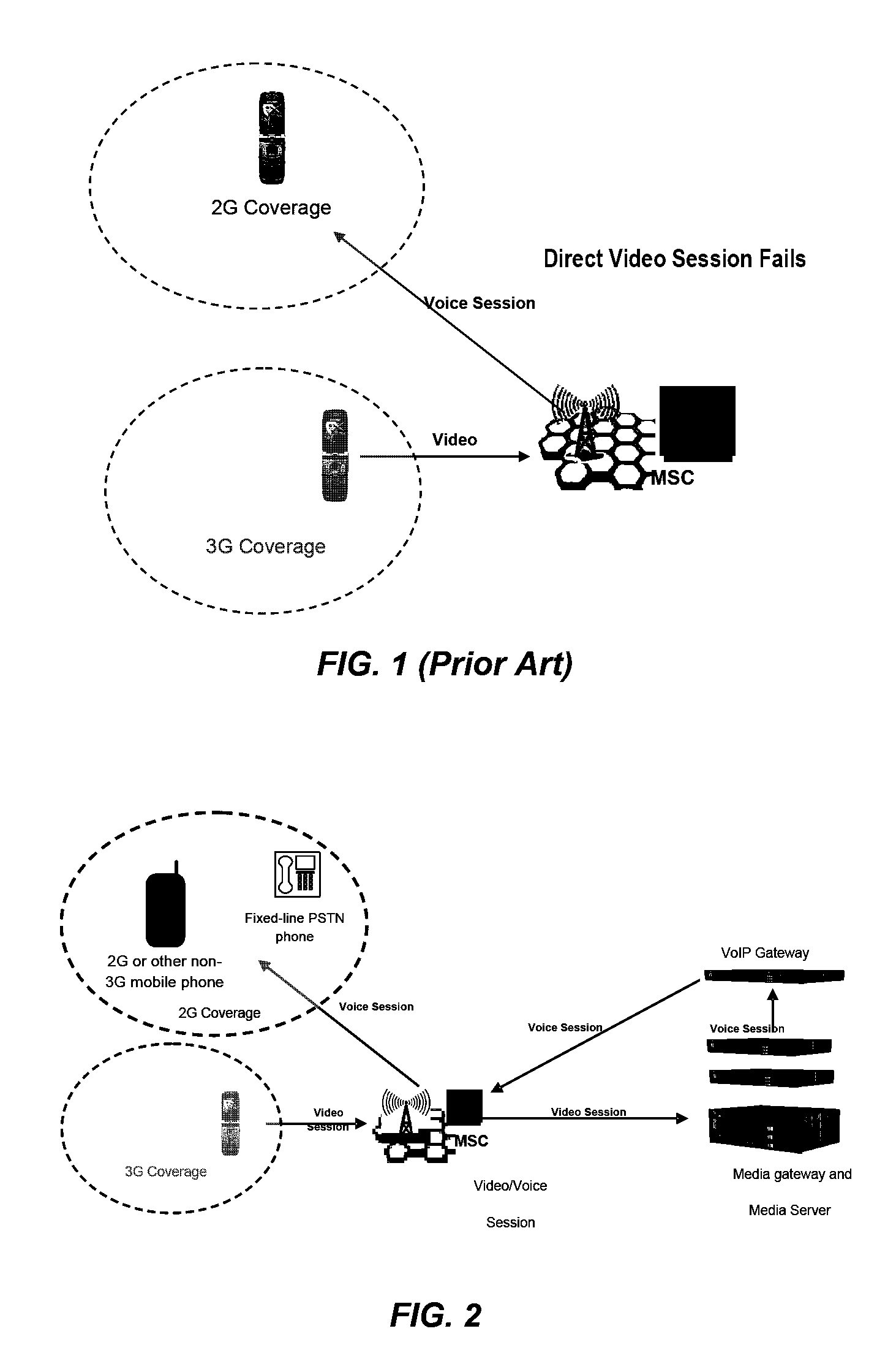
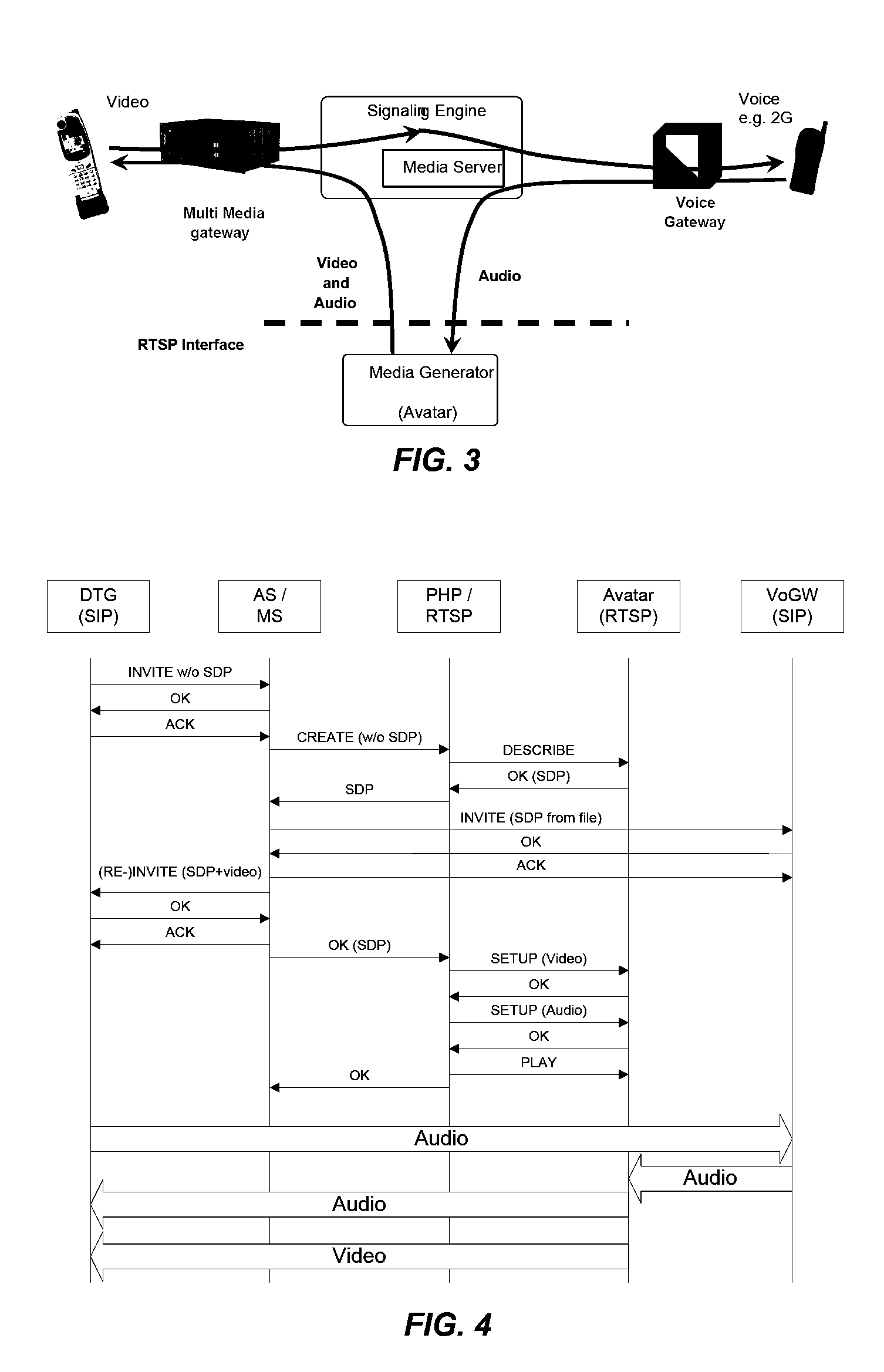
InactiveUS20080192736A1Easy to produceLess-costly to operateElectronic editing digitised analogue information signalsCarrier indicating arrangementsApplication serverTelecommunications network
A multimedia multi-service platform for providing one or more multimedia value added services in one or more telecommunications networks includes one or more application servers configured to operate in part according to a service program. The platform also includes one or more media servers configured to access, handle, process, and deliver media. The platform further includes one or more logic controllers and one or more management modules.
Owner:ONMOBILE GLOBAL LTD
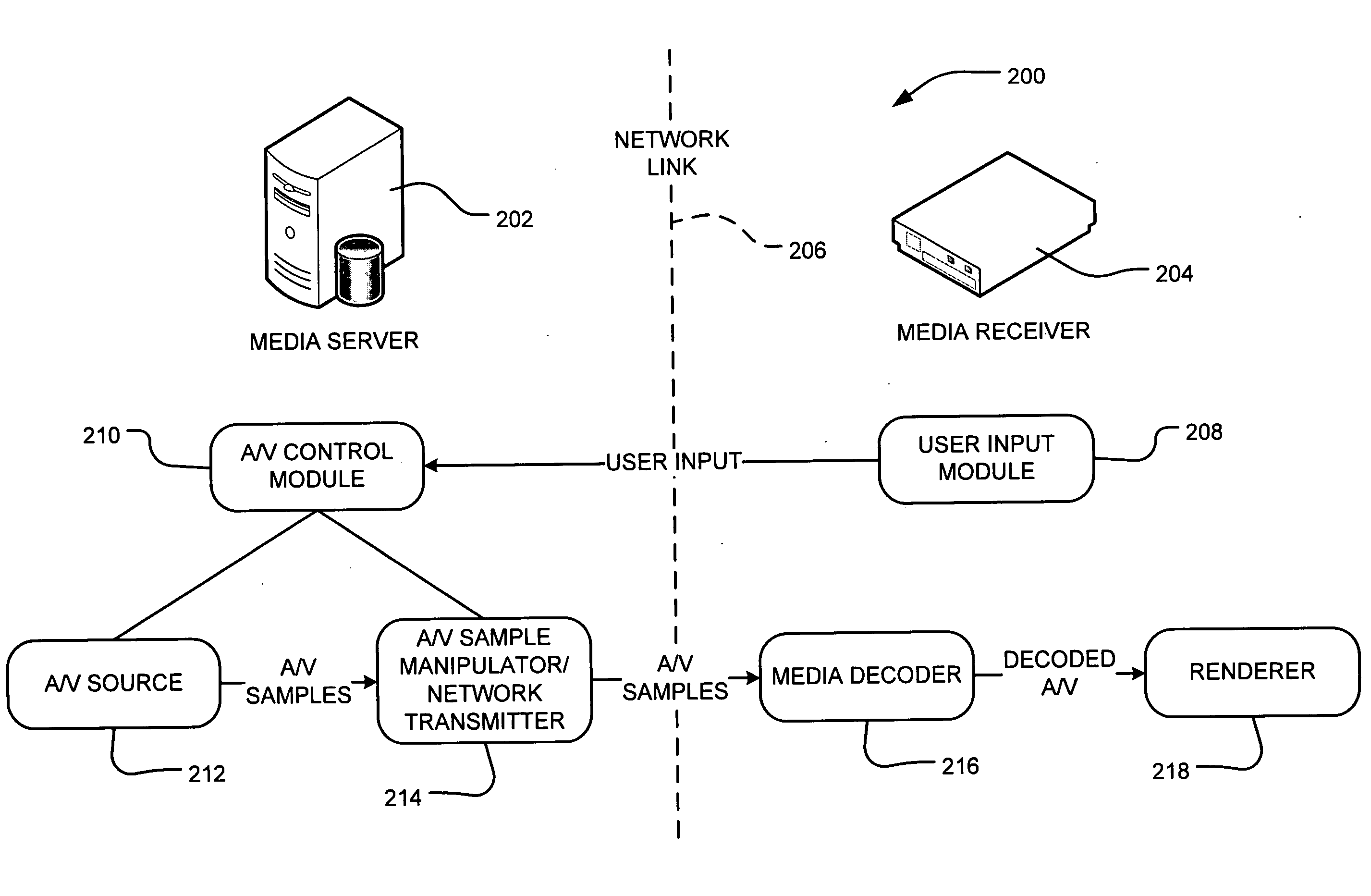
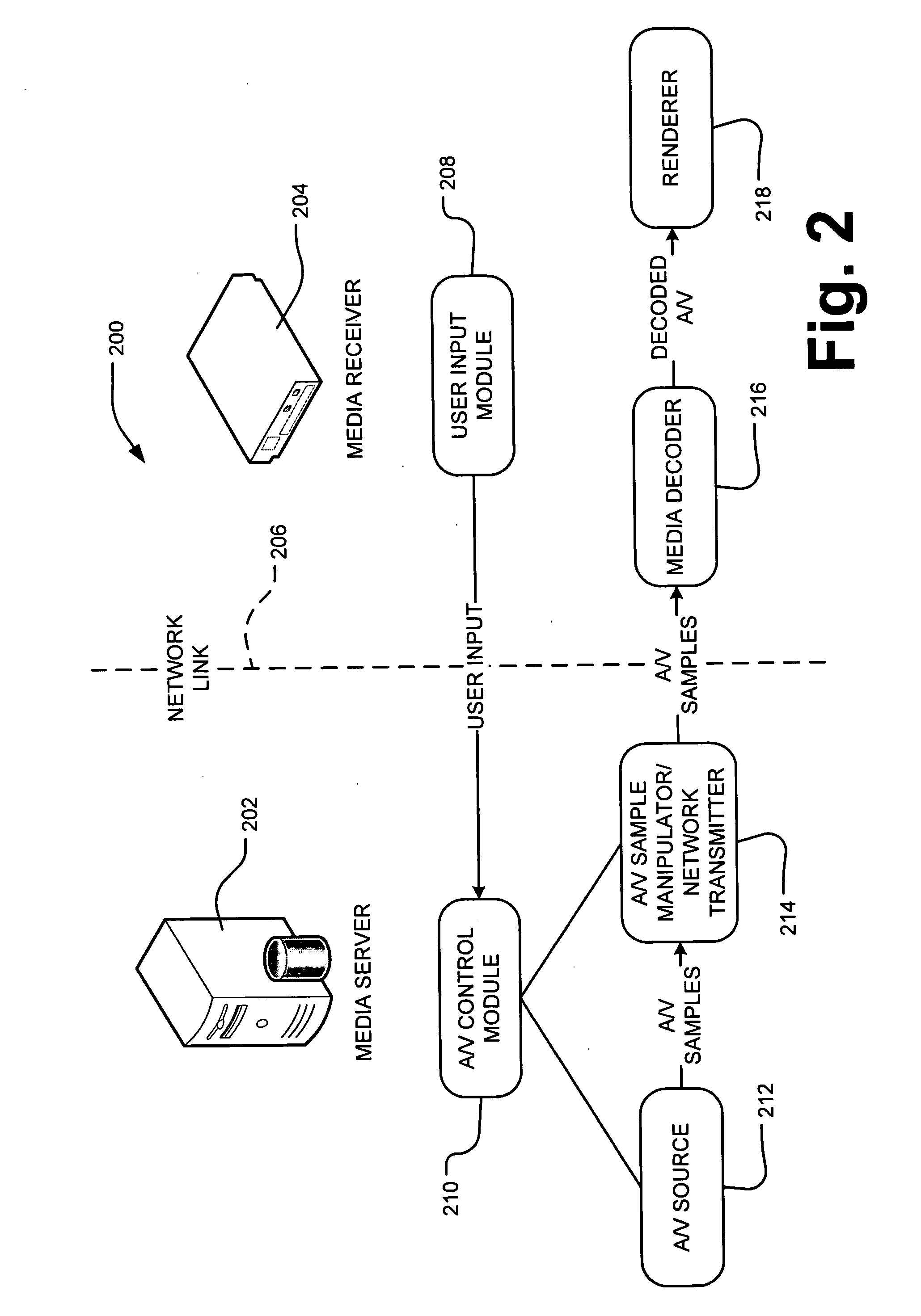
Server-side media stream manipulation for emulation of media playback functions
InactiveUS20070271388A1Avoid restrictionsLow costTelevision system detailsColor television detailsTimestampUser input
A media server in the home entertainment network allows a media rendering devices to act as a digital media receiver. The media server enables trick mode functions such as scan forward or reverse, slow motion, pause, and seek on rendering devices with capabilities limited to 1× playback. The media server receives commands from user input at the rendering device transmitted over the network to the media server. The media server manipulates the media stream before the transmission over the network by deleting or adding frames to the media stream as necessary to emulate the desired playback functions and replacing frame timestamps to create a media stream that appears to the media rendering device as a sequential 1× stream. The transmitted media stream may not contain all of the media content stored in the corresponding media file on the media server, thus avoiding limitations on the download bandwidth and local client storage.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
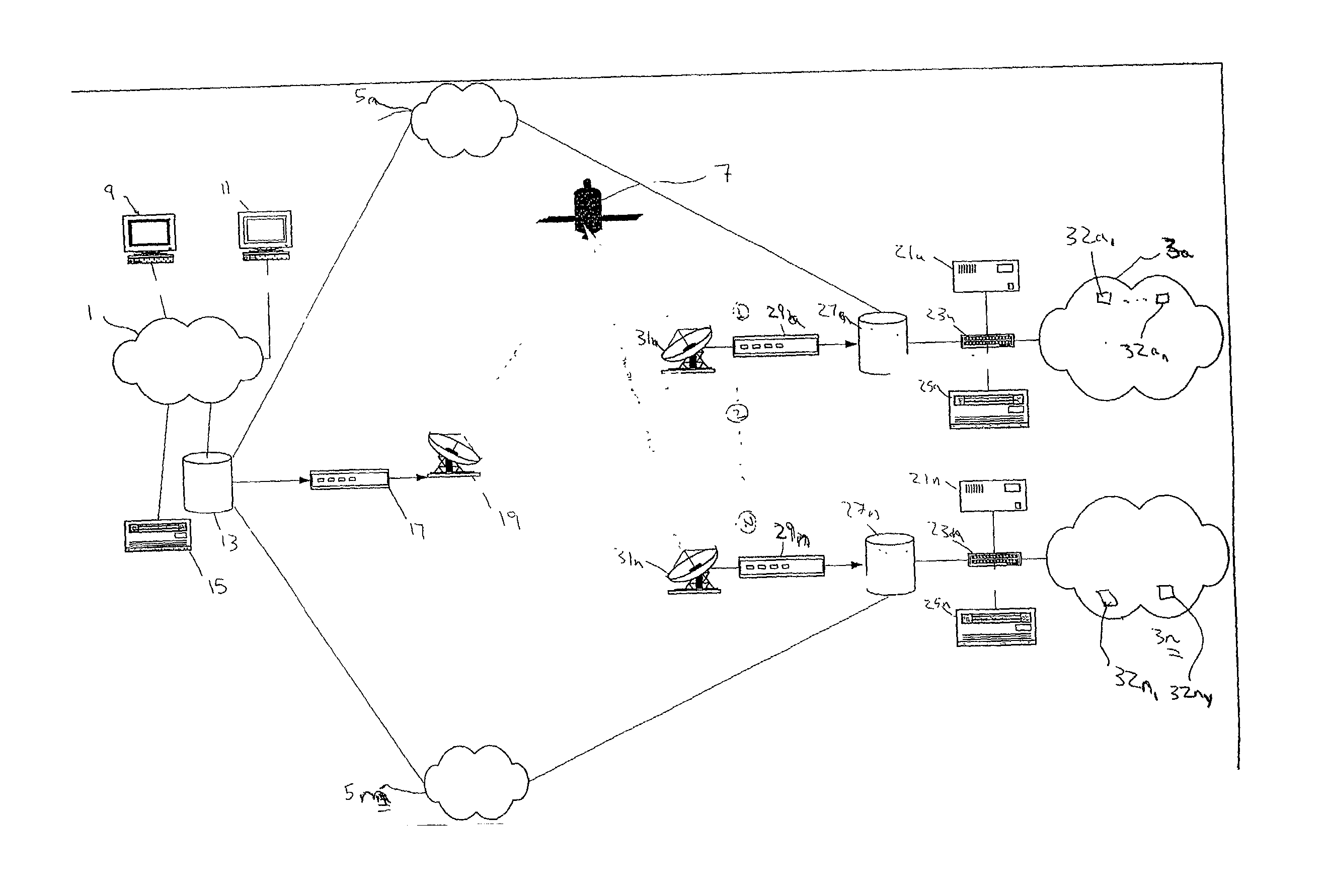
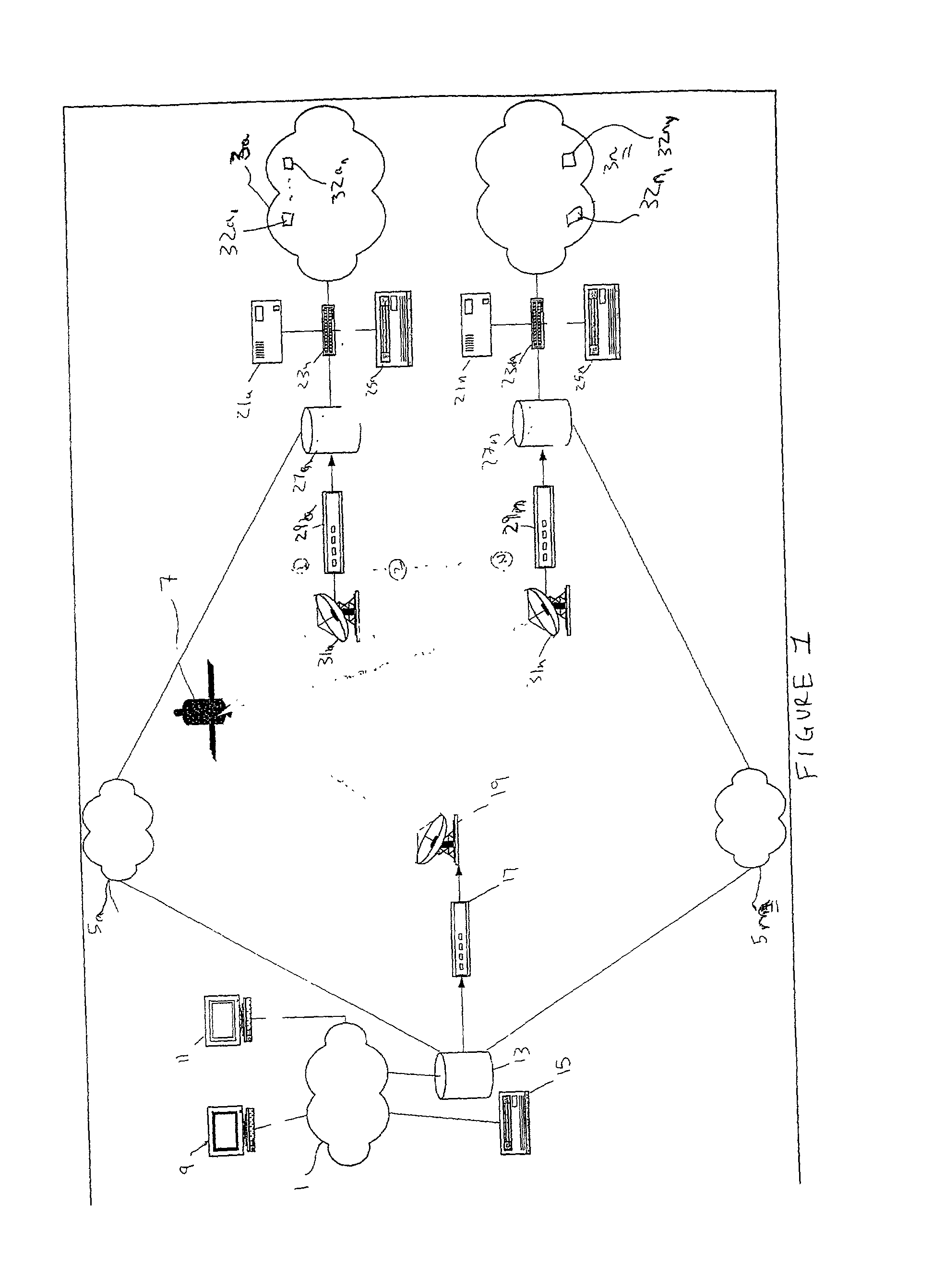
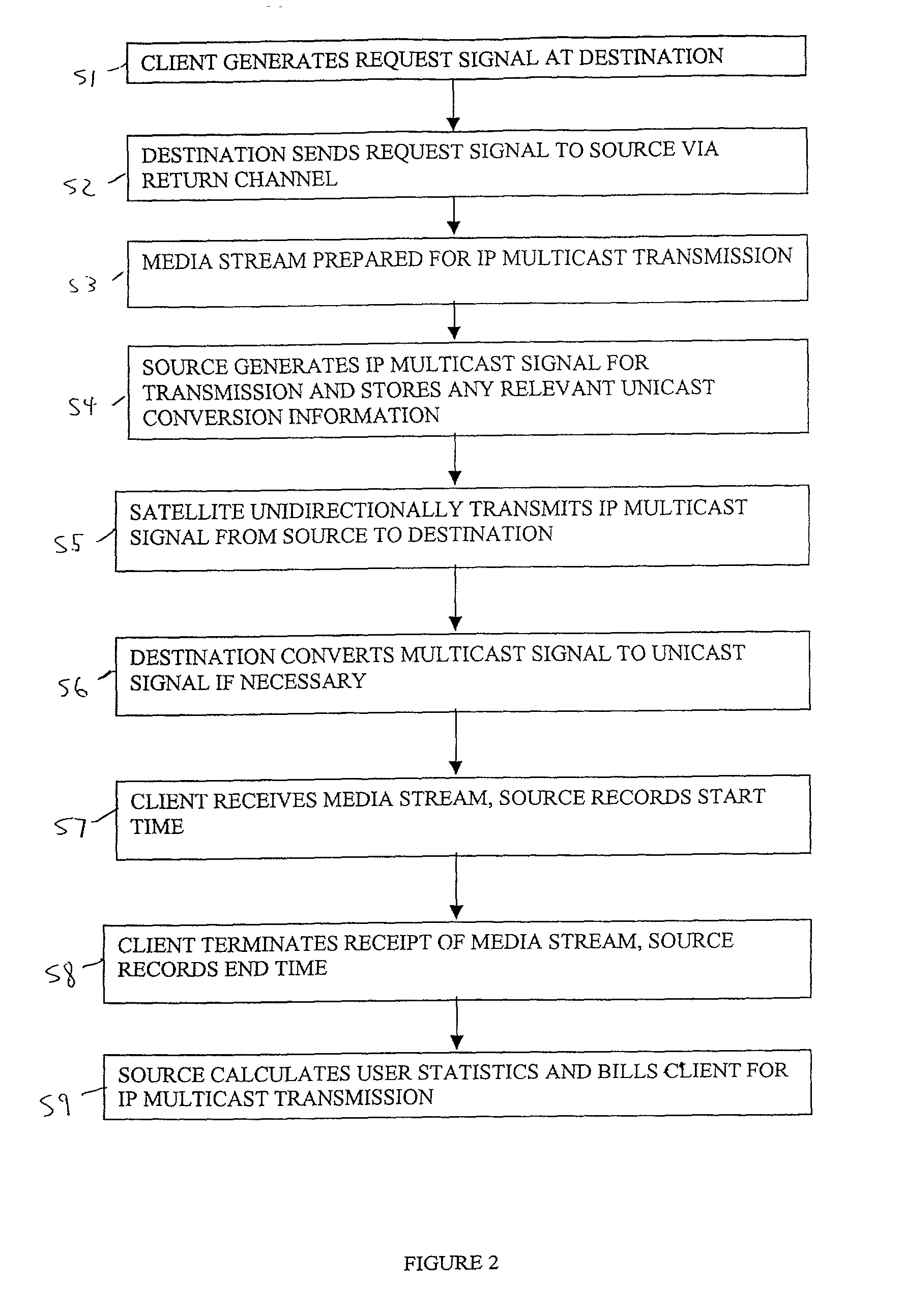
Satellite based content distribution system using IP multicast technology
InactiveUS7161934B2Multiplex system selection arrangementsSpecial service provision for substationContent distributionReal-time data
A method and system of performing IP multicast includes a client at one of many downstream networks that sends a request signal to an upstream network via a return channel (e.g., the Internet), and the upstream network sends the request to a media server. The media server, and for live data, a media encoder, processes a media stream to generate a real-time IP multicast communication that is output to a unidirectional satellite that transmits the IP multicast communication to the client without delay via the downstream network, and can convert the IP multicast to unicast. The bidirectional return channel allows the source to calculate billing information based on client usage statistics, and transmits confirmation acknowledgement based on a confirmation request from the upstream network. Because the routing configuration is transparent to the rest of the network, the invention applies to multi-hop networks on both sides of the satellite link.
Owner:INTELSAT SERVICES
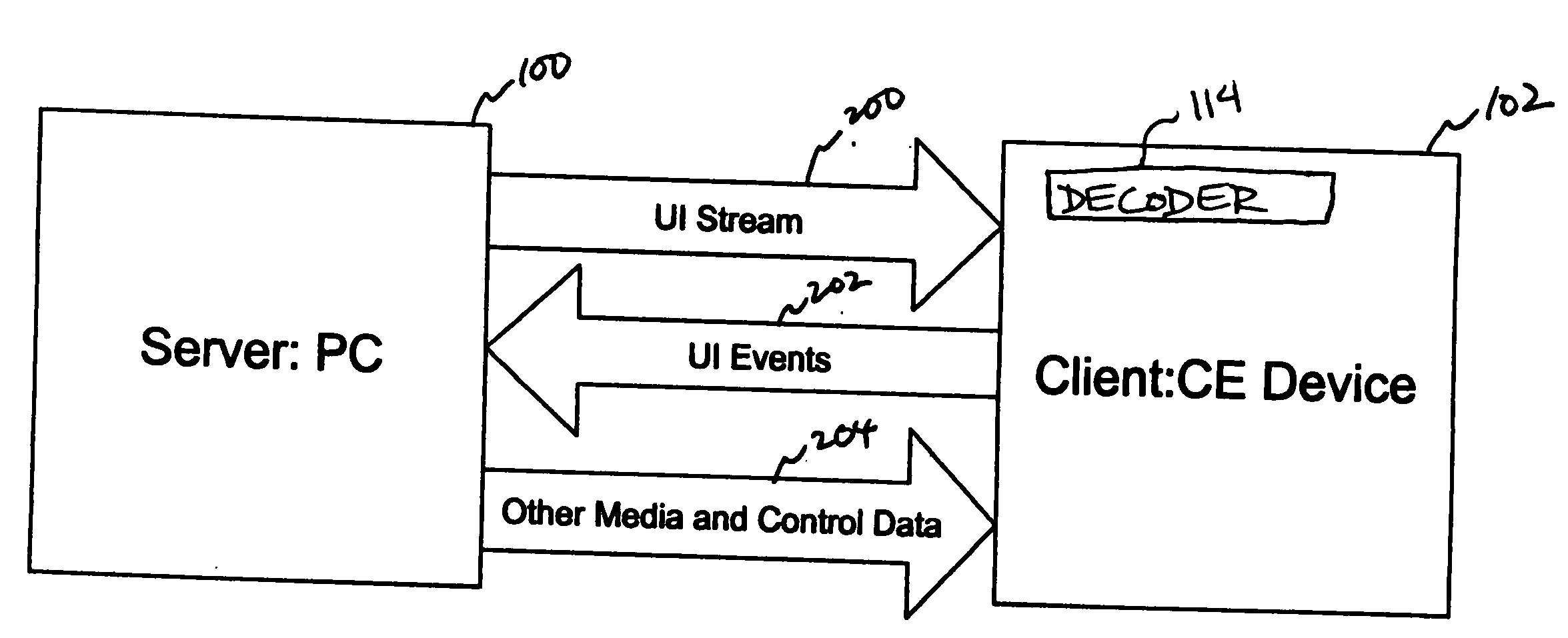
System and method for a remote user interface
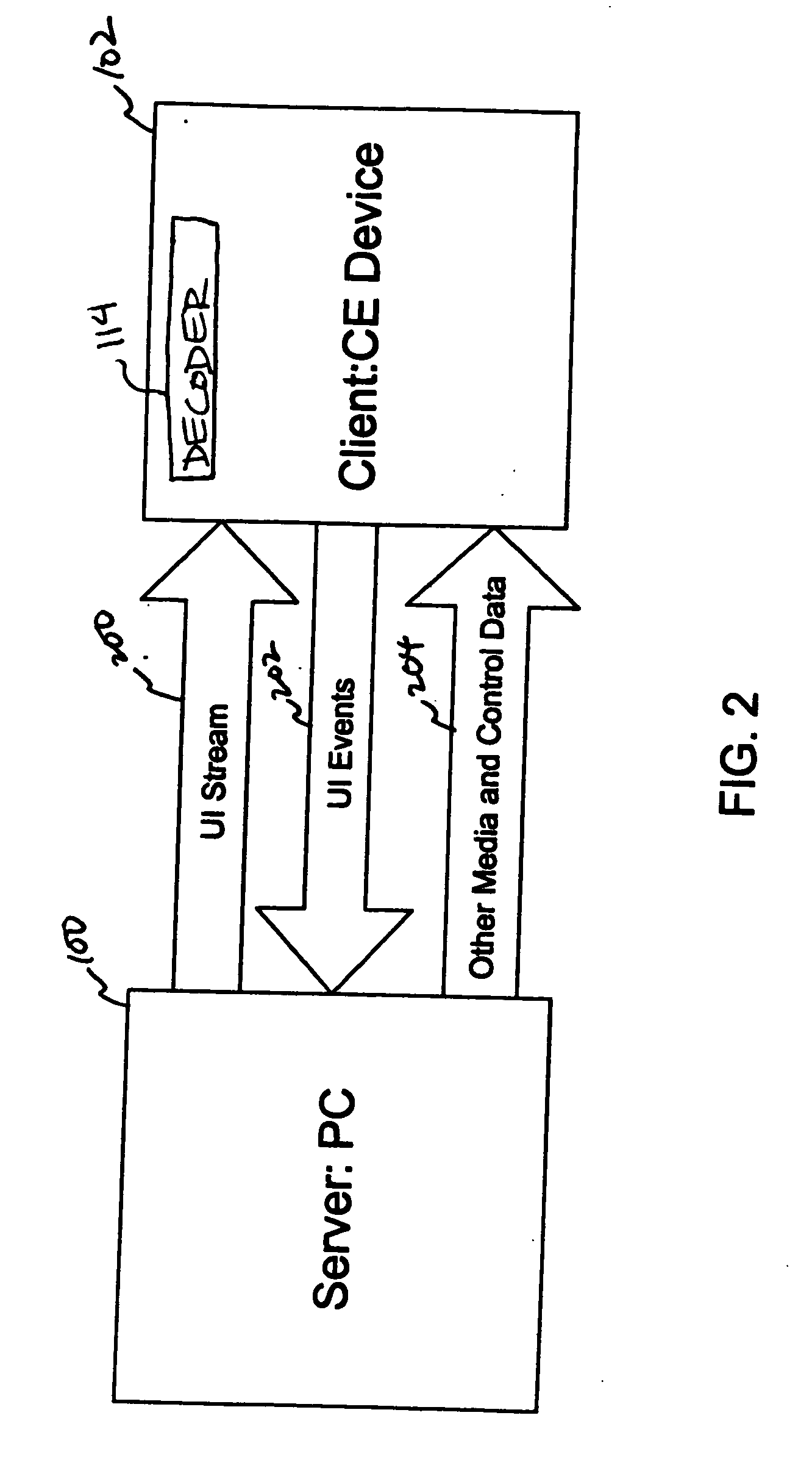
InactiveUS20060174026A1Cost efficientCE device may be kept relatively simpleMultiple digital computer combinationsTelevision systemsUser inputMedia server
A remote user interface provides a full motion, full-color, dynamic interface with complex visuals without imposing heavy hardware requirements on a consumer electronics device. Instead, the hardware requirements are placed on another computer device that is designated as a media server. The media server generates the complex UI, encodes the UI into one or more compressed video frames, and transmits the compressed video frames to the CE device. The CE device plays the UI video as it would any other video. User inputs for interacting with the UI are transmitted and interpreted by the media server. The media server updates the UI images based on the interaction.
Owner:DIVX INC
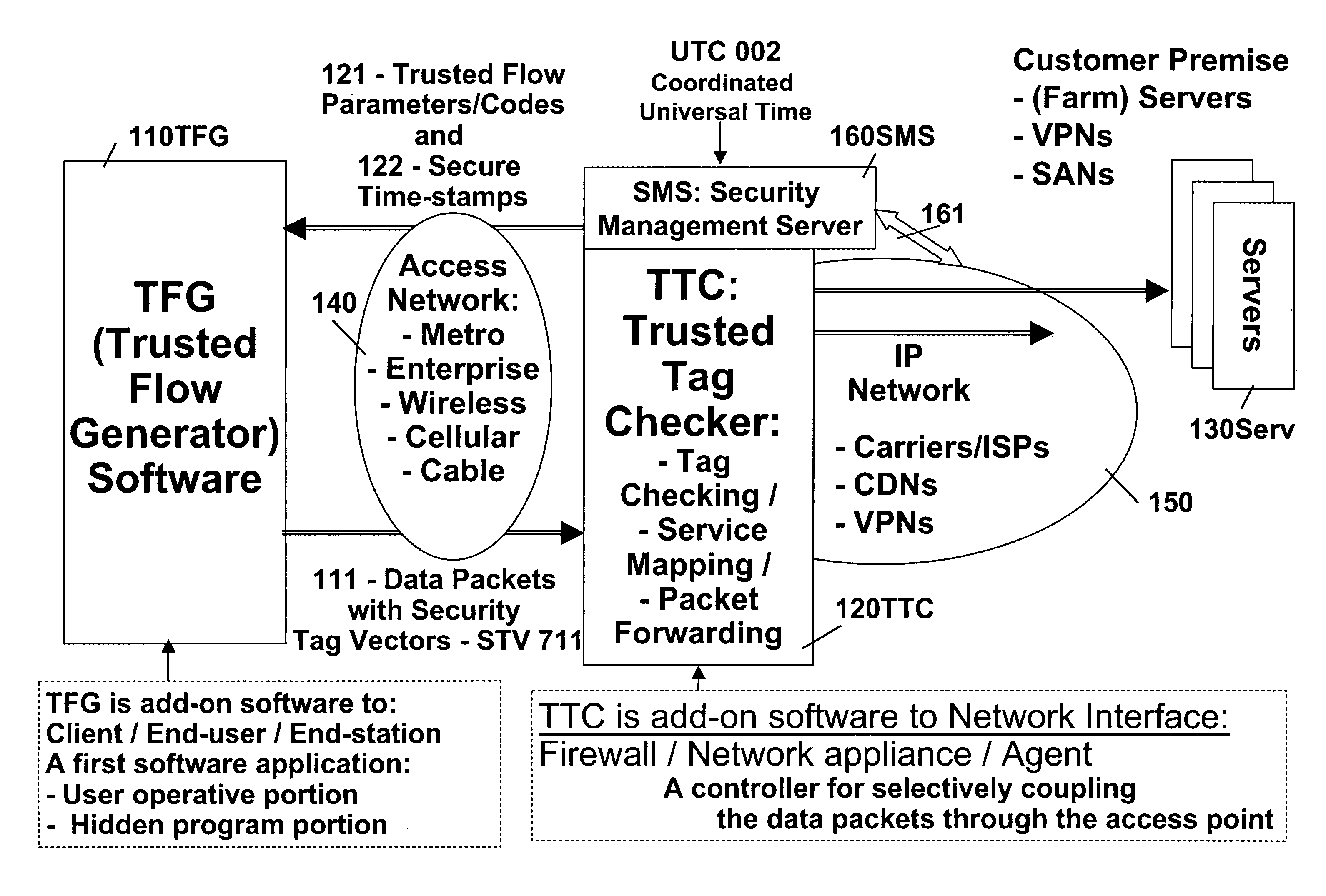
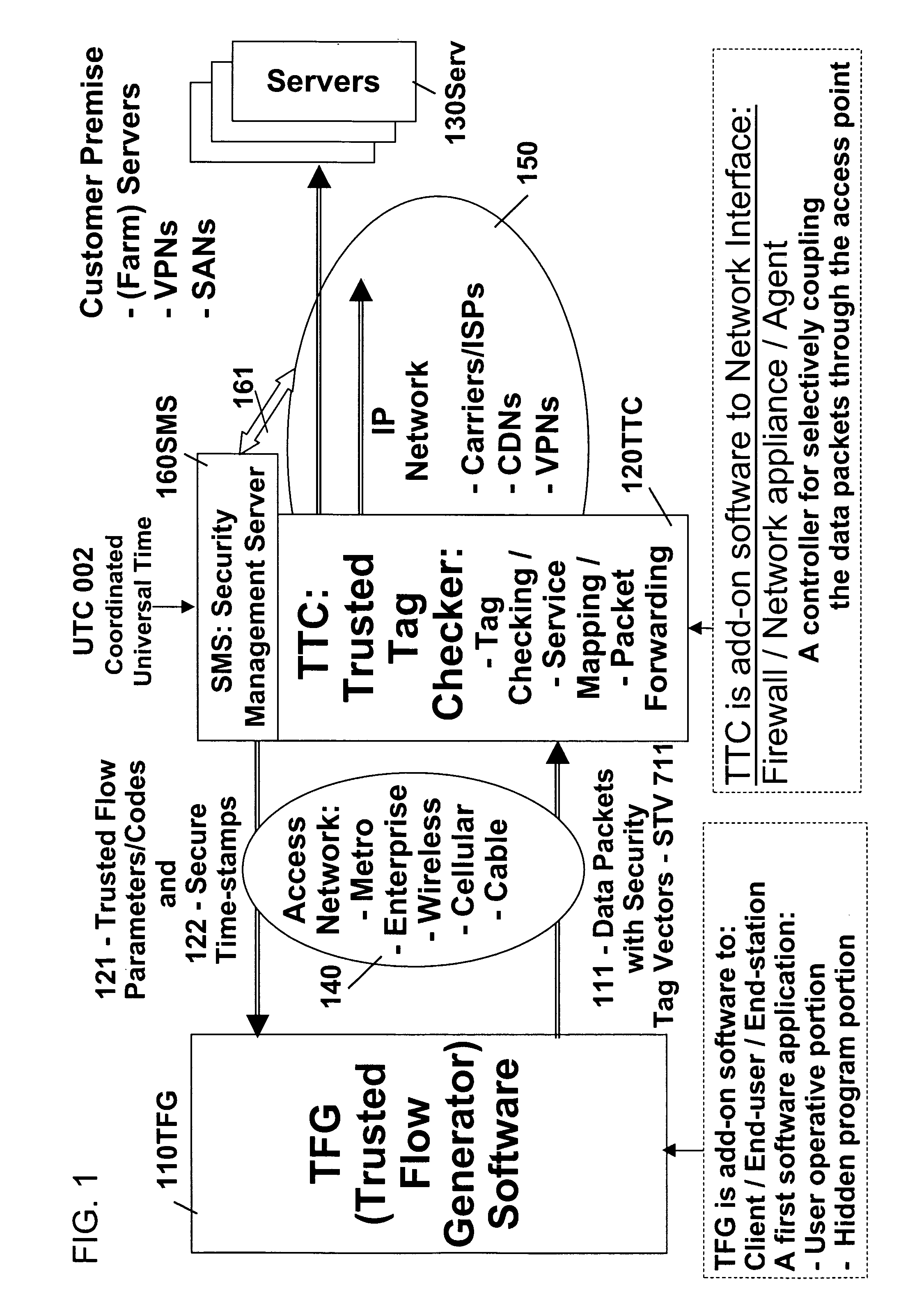
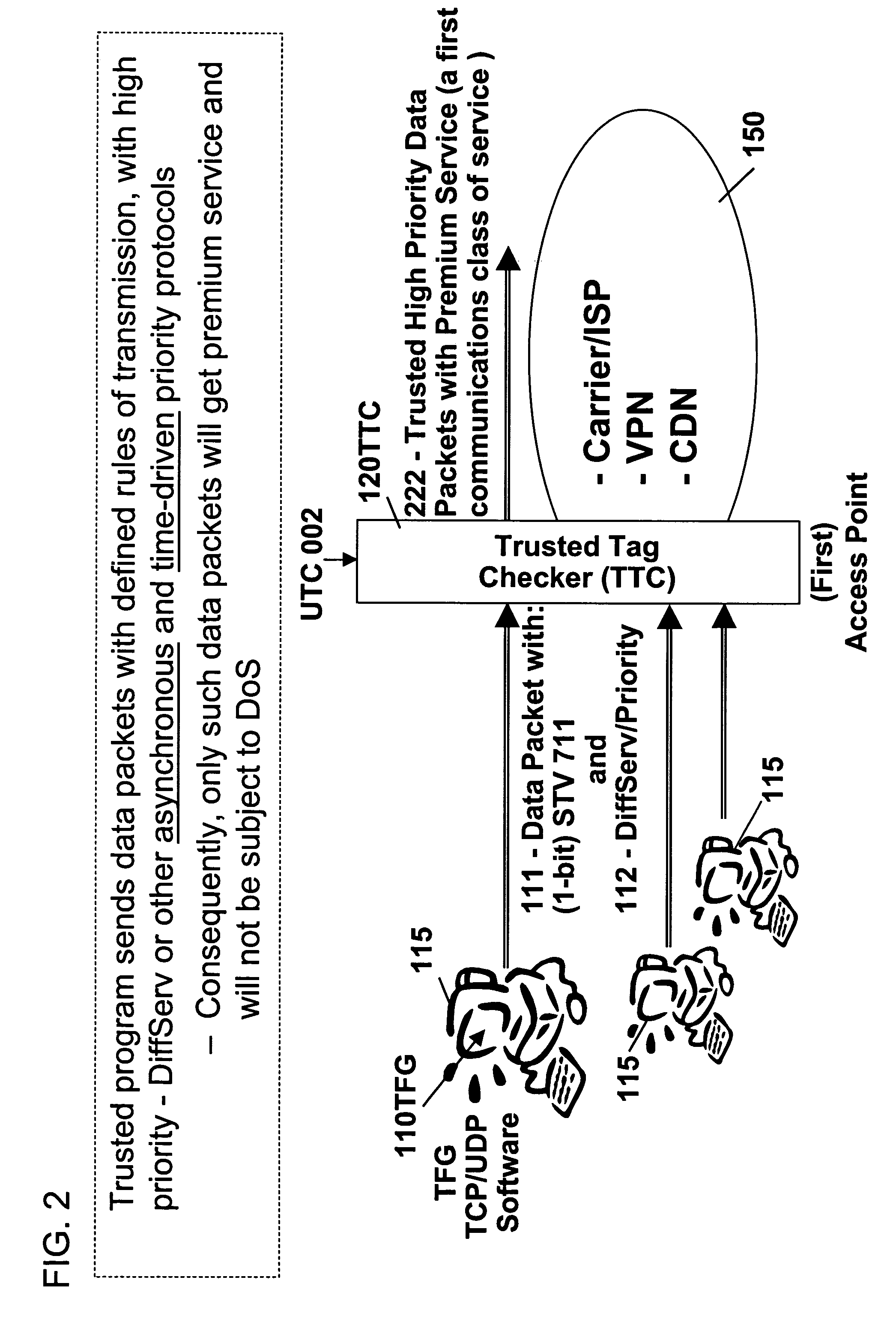
Remotely authenticated operation method
InactiveUS7509687B2Improvement effortsEfficient use ofDigital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationTrusted ComputingMedia server
The objective of this invention is to provide continuous remote authenticated operations for ensuring proper content processing and management in remote untrusted computing environment. The method is based on using a program that was hidden within the content protection program at the remote untrusted computing environment, e.g., an end station. The hidden program can be updated dynamically and it includes an inseparable and interlocked functionality for generating a pseudo random sequence of security signals. Only the media server that sends the content knows how the pseudo-random sequence of security signals were generated; therefore, the media server is able to check the validity of the security signals, and thereby, verify the authenticity of the programs used to process content at the remote untrusted computing environment. If the verification operation fails, the media server will stop the transmission of content to the remote untrusted computing environment.
Owner:ATTESTWAVE LLC
Hybrid central/distributed VOD system with tiered content structure
ActiveUS7690020B2Multiple digital computer combinationsTwo-way working systemsContent distributionFiber
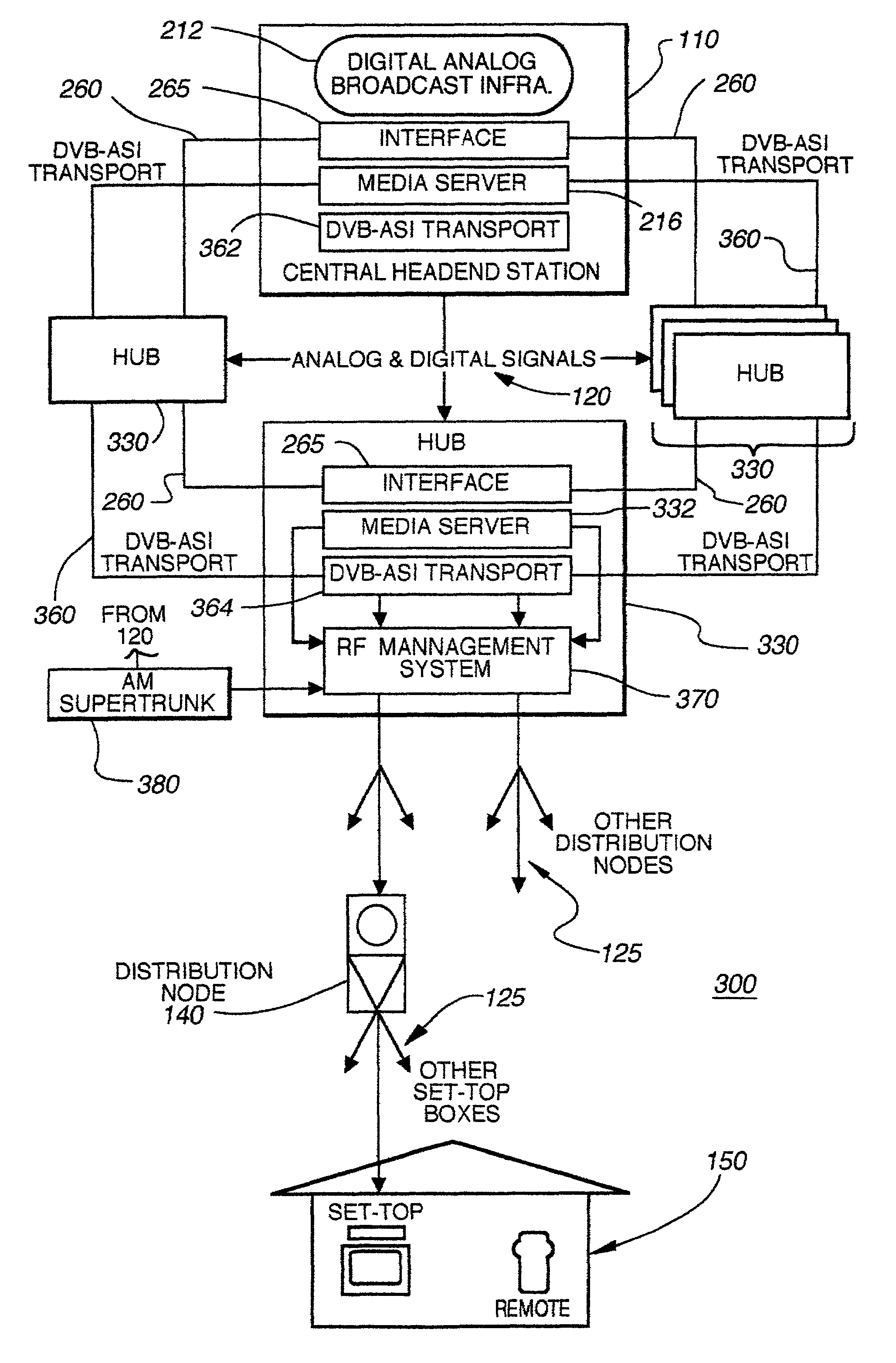
The present invention provides a hybrid central / distributed and tiered video on demand (VOD) service network with tiered content structure. In particular, the present invention uses media servers located in both the headend station and the hub stations. Set-top boxes generally would be supplied VOD services from the high-demand content media servers located in the hub station nearest to the user. The central media server located in the headend would be used as an installed backup to the hub media servers; as the primary source for lower demand VOD services and as the source of the real time, centrally encoded programs with PVR (personal video recorder) capabilities.By distributing the servers to the hub stations, the size of the fiber transport network associated with delivering VOD services from the central headend media server is reduced. The invention provides that each user has access to several server ports located on at least two servers. Multiple paths and channels are available for content distribution to each user, assuring high system reliability and enhanced asset availability. Substantial cost benefits are derived from the reduced need for a large content distribution network and the reduced storage capacity requirements for hub servers.
Owner:TIME WARNER CABLE ENTERPRISES LLC
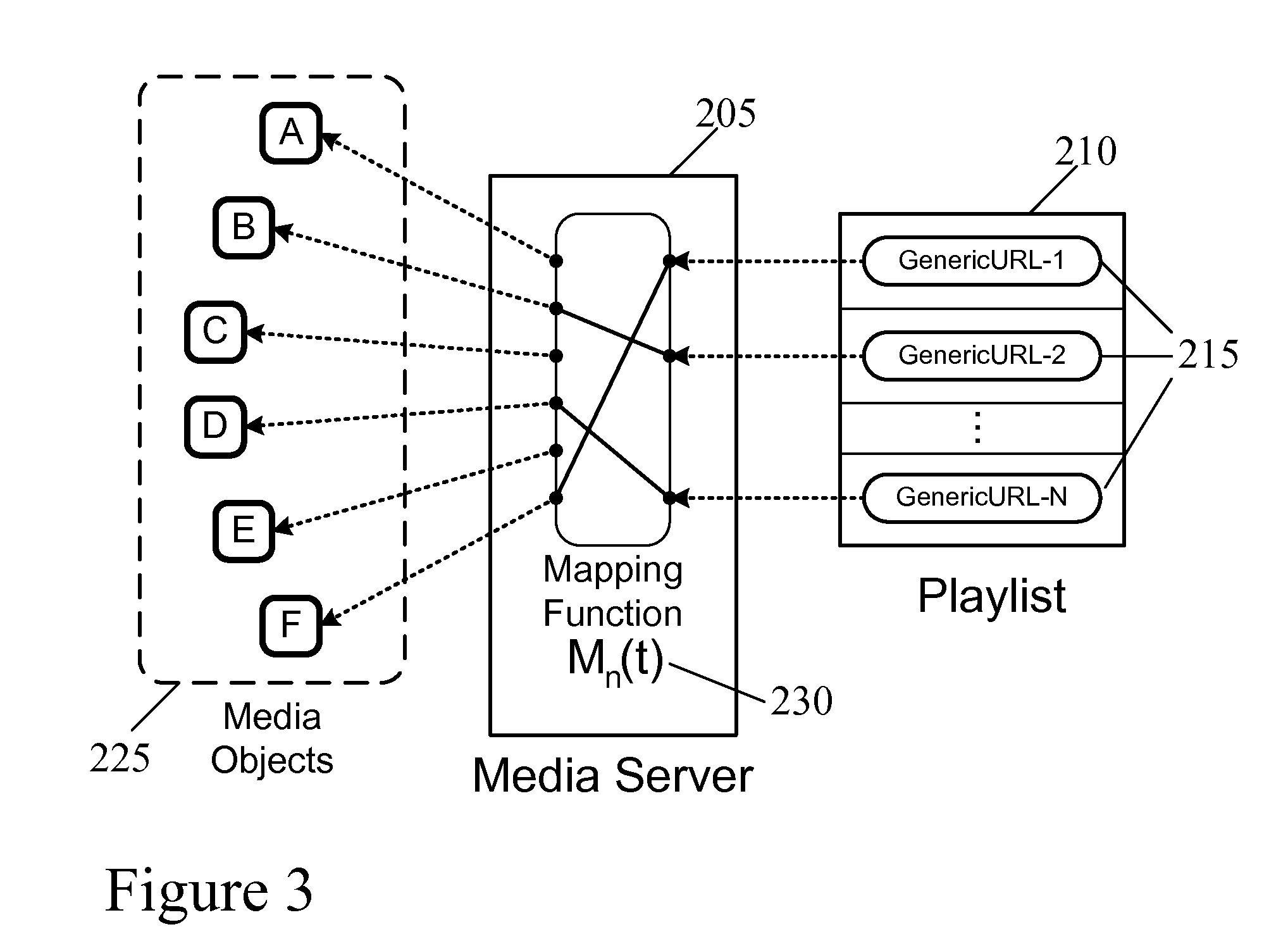
System and method for managing media content using a dynamic playlist
InactiveUS20140052770A1Provide methodMultiple digital computer combinationsSelective content distributionMedia serverMedia content
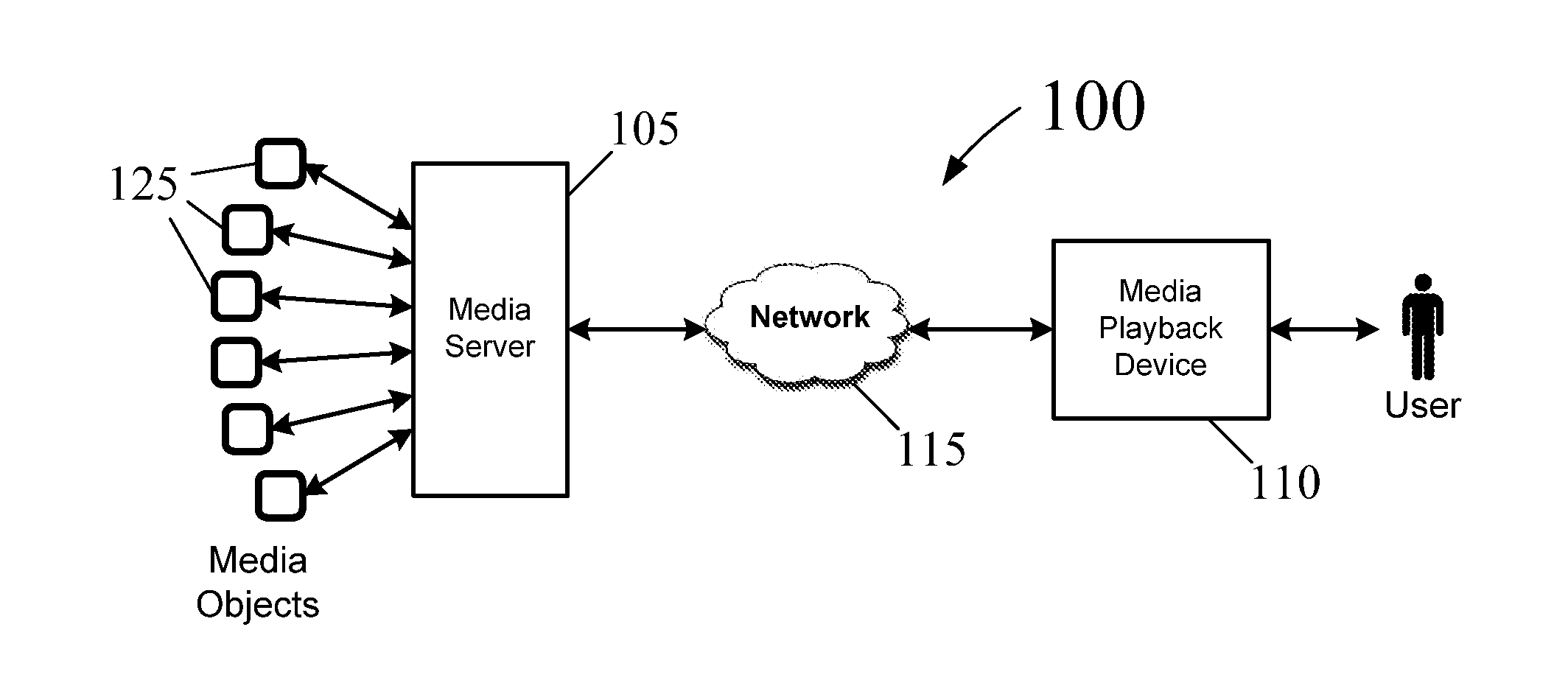
A system and a method for managing media content using a dynamic playlist are provided. The system has a media server which offers a dynamic queue of media objects to be played by a media playback device using a playlist of generic URLs. The content of the dynamic queue may be modified or adapted by the media server after the playlist is delivered to the media playback device or while the media playback device is simultaneously playing media objects from the queue using the playlist. The system and method provide that the media server may adapt the list of media objects referenced by a playlist after the playlist is delivered, despite the media server not having access to edit the delivered playlist. The media server may provide a dynamic media service to any media playback device which supports one or more standard, well-known playlist formats.
Owner:PACKETVIDEO
Portable media player as a low power remote control and method thereof
A portable multimedia player is used to wirelessly access and control a media server that is streaming digital media by way of a wireless interface to a media unit such as a stereo / speakers in the case of streaming digital audio. In one embodiment, the portable multimedia player is wirelessly synchronized to a selected one(s) of a number of digital media files stored on the media server in such a way that digital media file metadata (song title, author, etc.) associated with the selected digital media file(s) only is transferred from the media server to be stored in the portable media player.
Owner:APPLE INC
Method and apparatus for global call queue in a global call center
ActiveUS20060067506A1Loss of voice qualityLow costManual exchangesAutomatic exchangesCall forwardingContact center
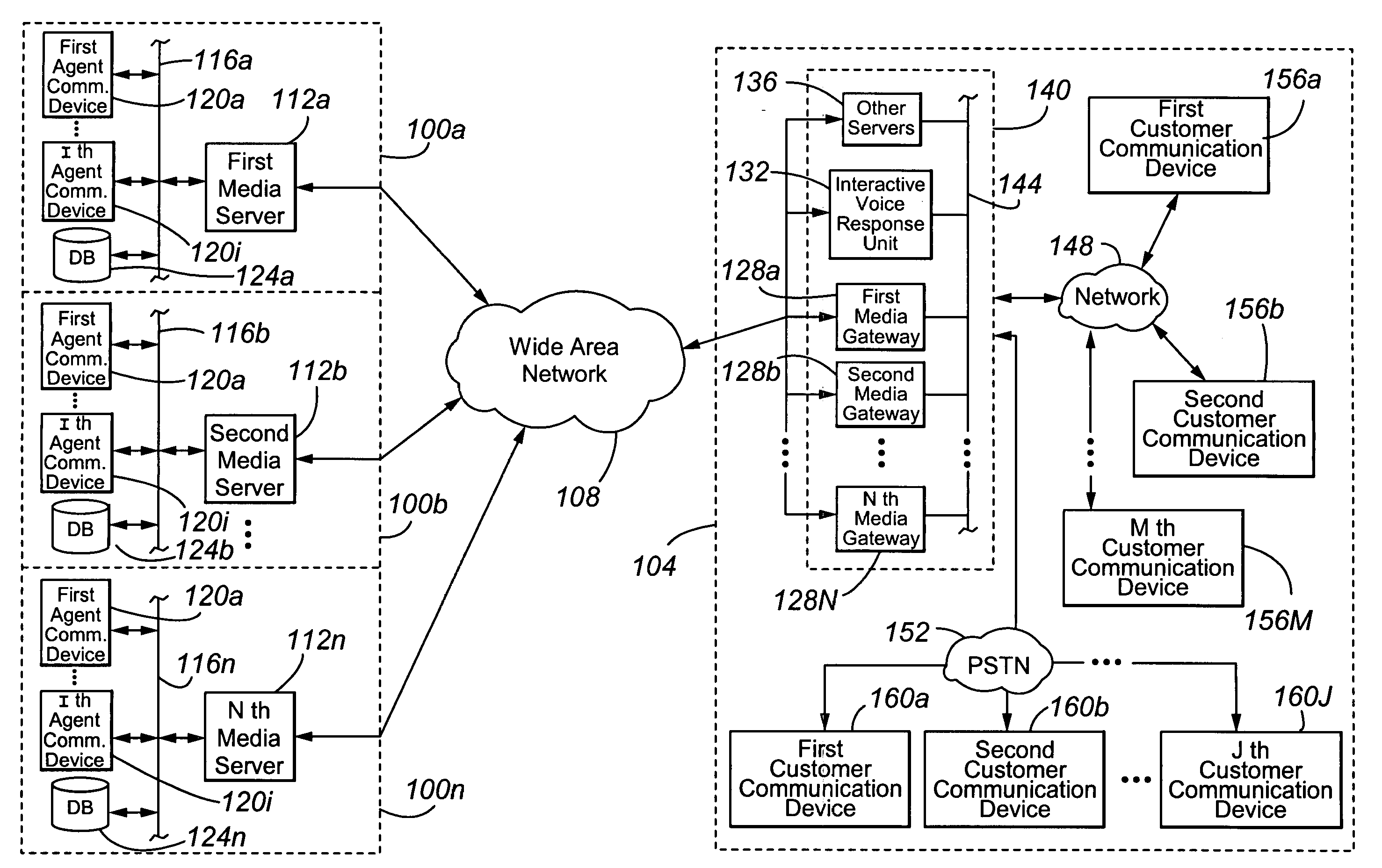
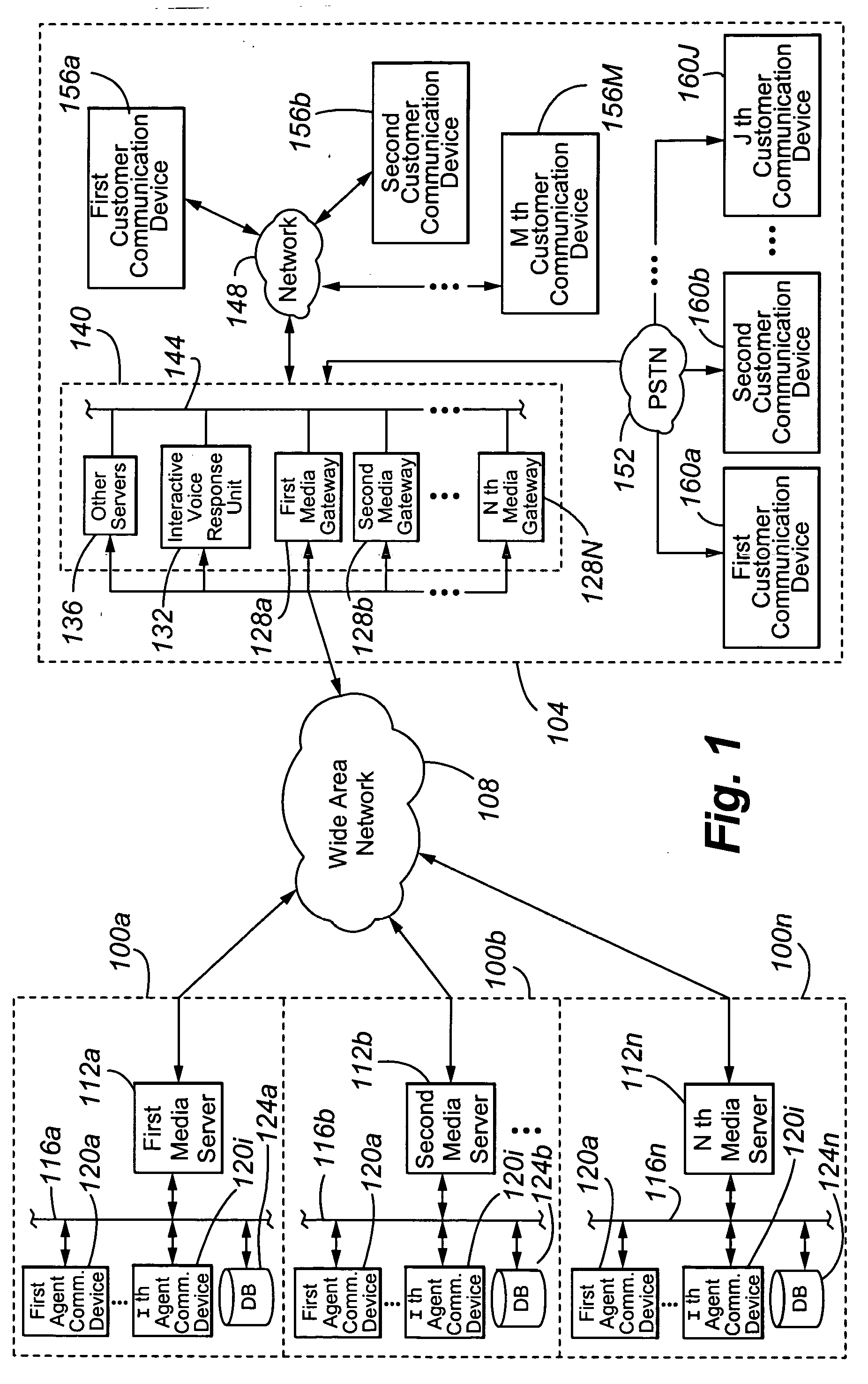
The present invention is directed to a contact center, comprising: (a) a plurality of media servers 112a-n, each of the media servers being associated with a plurality of corresponding agent communication devices 120a-i positioned in a respective agent domain 100a-n; (b) a plurality of gateways 128a-n, each of which is currently controlled by a corresponding one of the plurality of media servers 112a-n and positioned in a contactor domain 104; and (c) a packet-switched Wide Area Network (WAN) 108 connecting the plurality of media servers 128a-n and the plurality of gateways 112a-n. A first gateway 128a is operable to physically park an incoming customer contact in the customer domain 104 until the occurrence of a call transfer event and, upon the occurrence of a call transfer event, to transfer the parked customer contact from the first gateway 128a to at least one of (i) a second media gateway 128b for processing by the second media gateway's corresponding second controlling media server 112b and (ii) a first media server 112a controlling the first gateway 128a.
Owner:AVAYA INC
Secured media communication across enterprise gateway
InactiveUS20070091907A1Facilitate communicationCommmunication supplementary servicesData switching by path configurationNAT traversalClient-side
A method for implementing communication between at least two client devices is provided. The first client device of the at least two client devices is disposed externally with respect to a firewall of an internal network. The method includes performing NAT (Network Address Translation) traversal between the first client device and a media server that is disposed internally with respect to the firewall of the internal network. The NAT traversal is configured to ascertain a NAT scheme employed for exchanging packets with the first client device. The method also includes establishing a communication path at least between the media server and the first client device, wherein logic for implementing the NAT traversal and logic for implementing the establishing the communication path are both implemented in the media server. The method further includes employing the media server to facilitate the communication.
Owner:DIVITAS NETWORKS INC
Method of setting up a call-back
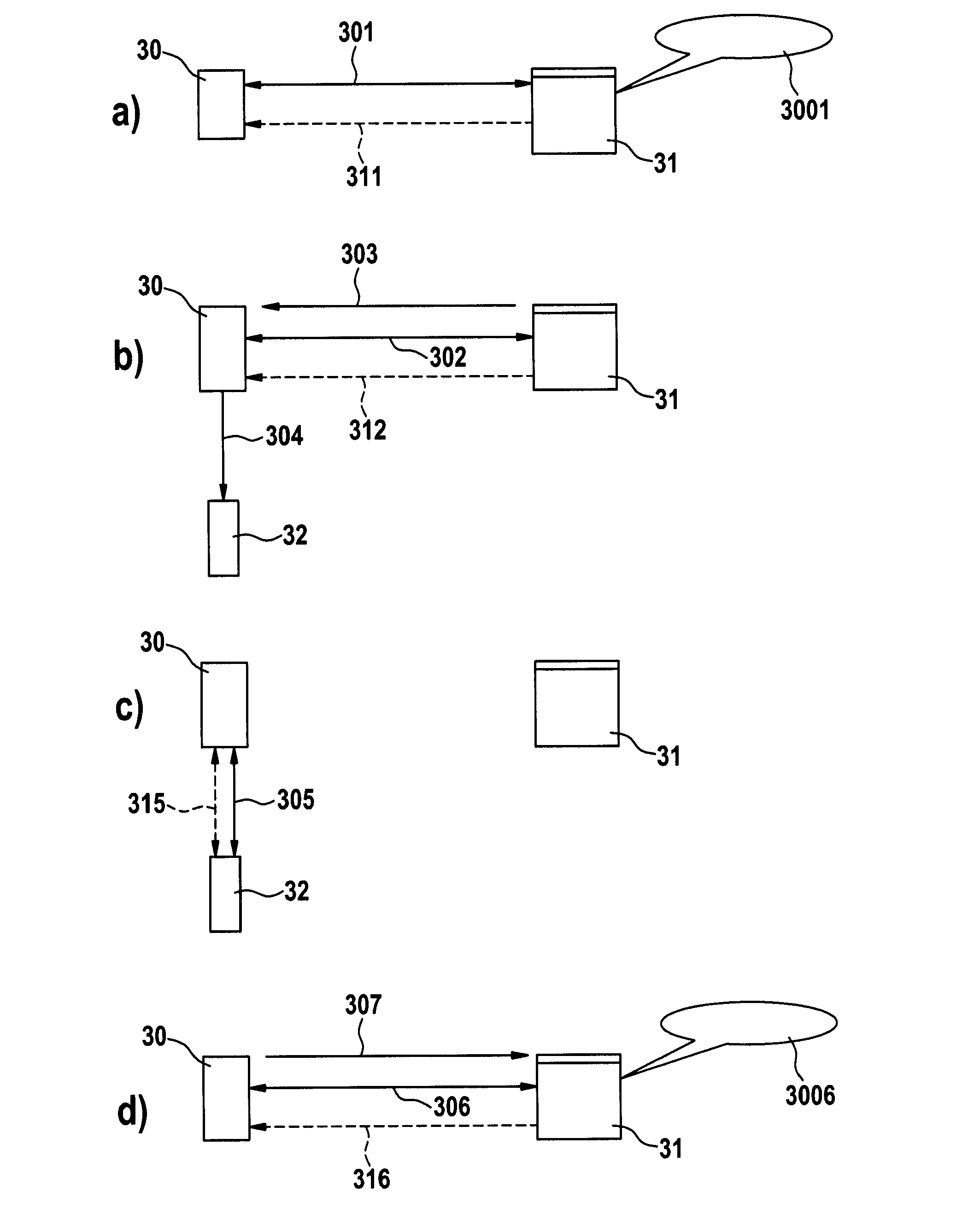
InactiveUS20080317233A1Special service for subscribersNetwork connectionsTelecommunications networkMedia server
The invention concerns a method of setting up a call-back (305, 315) to a caller (32) in a packet-based telecommunications network, and a terminal and a media server (31) to execute this method. The call-back (305, 315) is initiated by a user (30) receiving a media stream (311, 312, 316). The user (30) sets up a packet-based connection to a media server (31) and receives the media stream (311, 312, 316) from the media server (31). After choosing by the user (30) to call back the caller (32), the media server (31) generates a cookie with data defining a state of the media stream (311, 312, 316) and sends the cookie to the user (30). The user (30) initiates the call-back (305, 315) to the caller (32) independently of the media server (31). After termination of the call-back (305, 315), the data defining the state of the media stream (311, 312, 316) are sent to the media server (31) or an associated media server and are used to resume the transmission of the media stream (311, 312, 316) to the user (30) from a state following the state defined by the data.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
System and method for providing a callback cloud
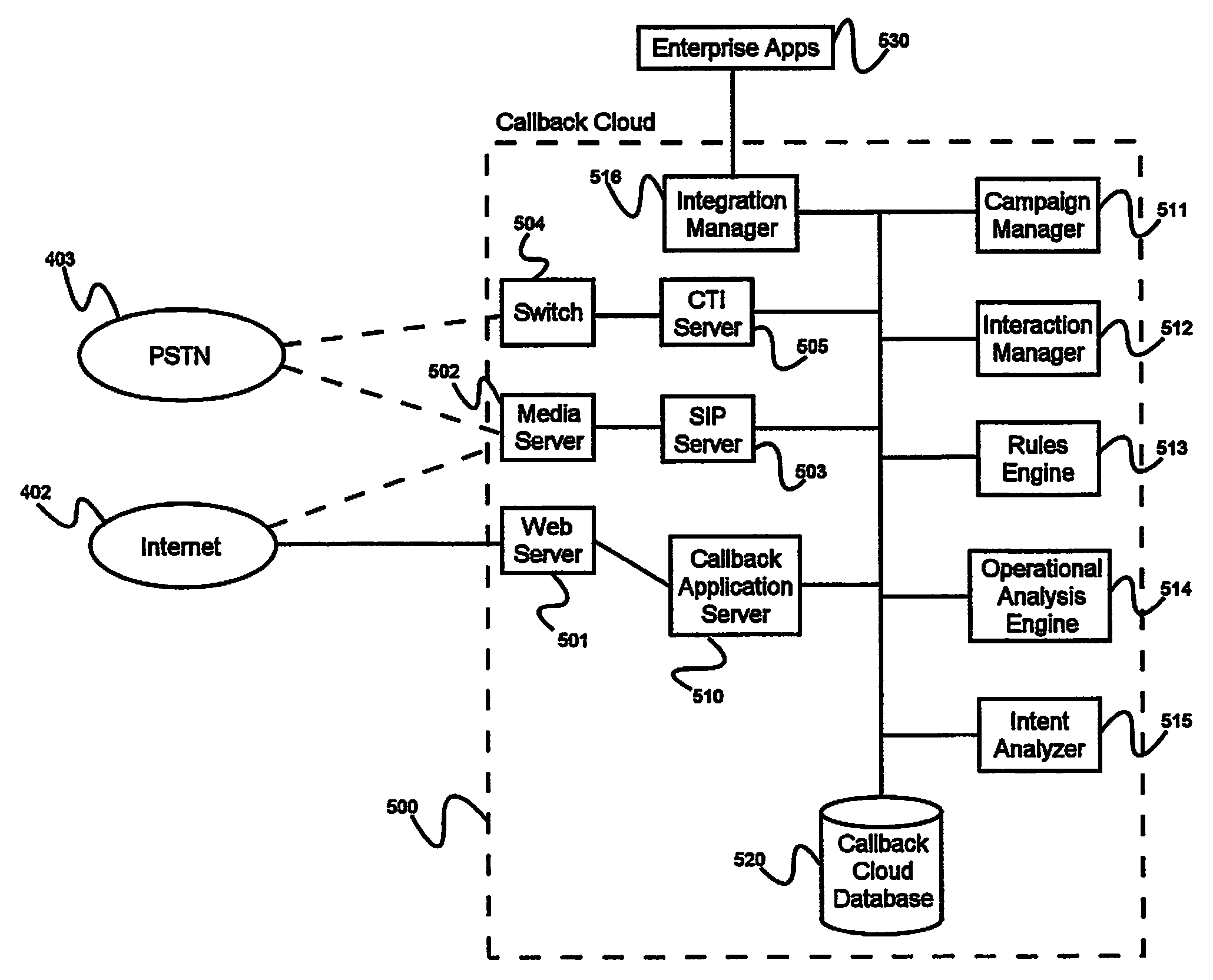
ActiveUS20130054684A1Avoid the needIncrease contactDigital data information retrievalReservationsSession managementMedia type
A system for providing a callback cloud, comprising an application server operated by a callback cloud service provider, a media server, a session management server, an interaction manager, and an intent analysis engine. The application server receives registrations from callback providers unaffiliated with the callback service provider. The application server is adapted to receive callback requests from users, comprising a specific callback provider from whom a callback is requested, when a requested callback should be made, and allowable media types. The application server directs the callback request to the interaction manager, and the interaction manager sends data elements pertaining to the request to the intent analysis engine and receives therefrom data elements pertaining to the callback request determined based on an analysis of the requester's intent. The interaction manager directs the session management server to initiate a callback, and the session management server provides signaling to the media server to conduct the callback.
Owner:VIRTUAL HOLD TECH
Cell phone audio/video in-flight entertainment system
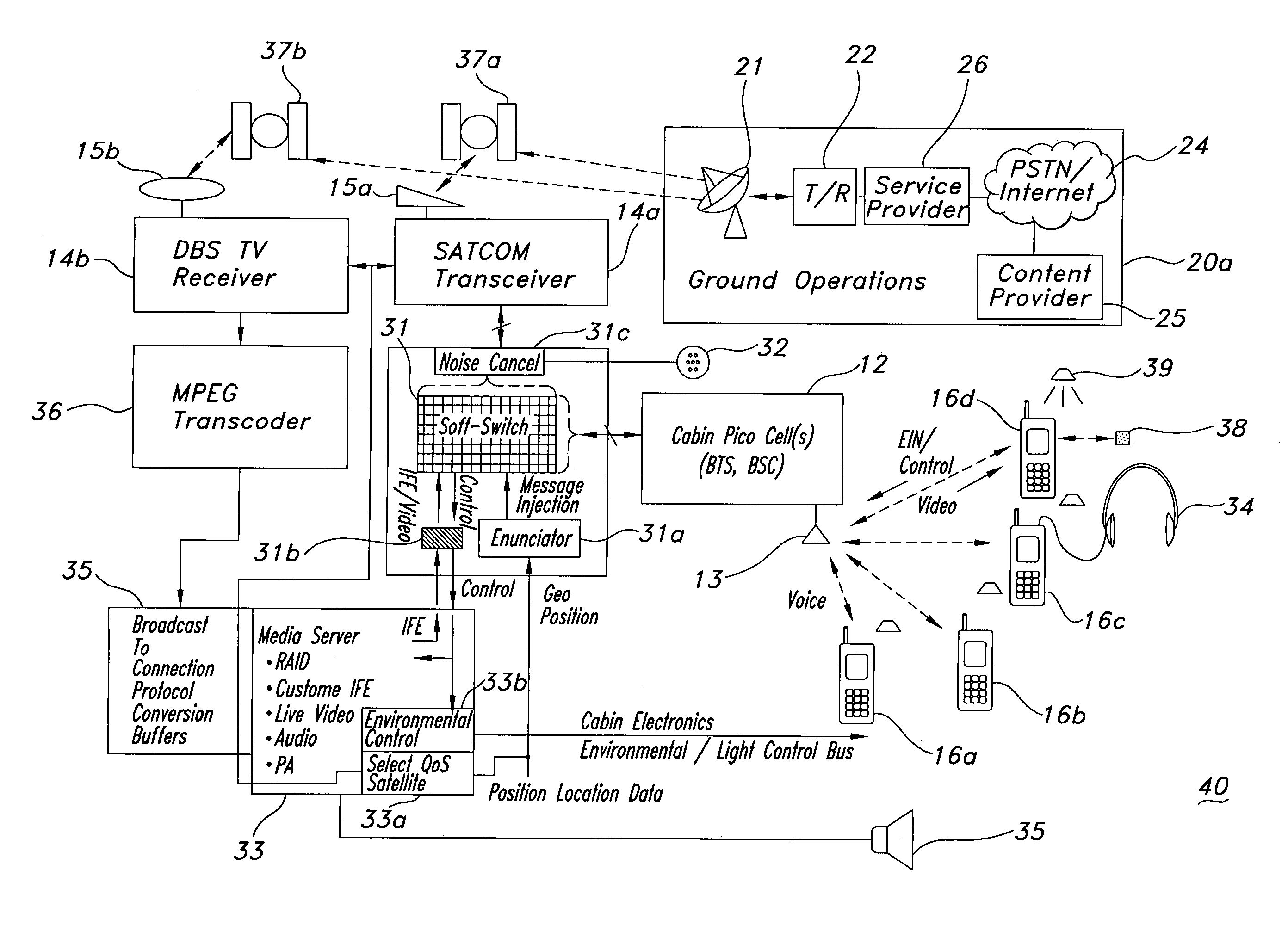
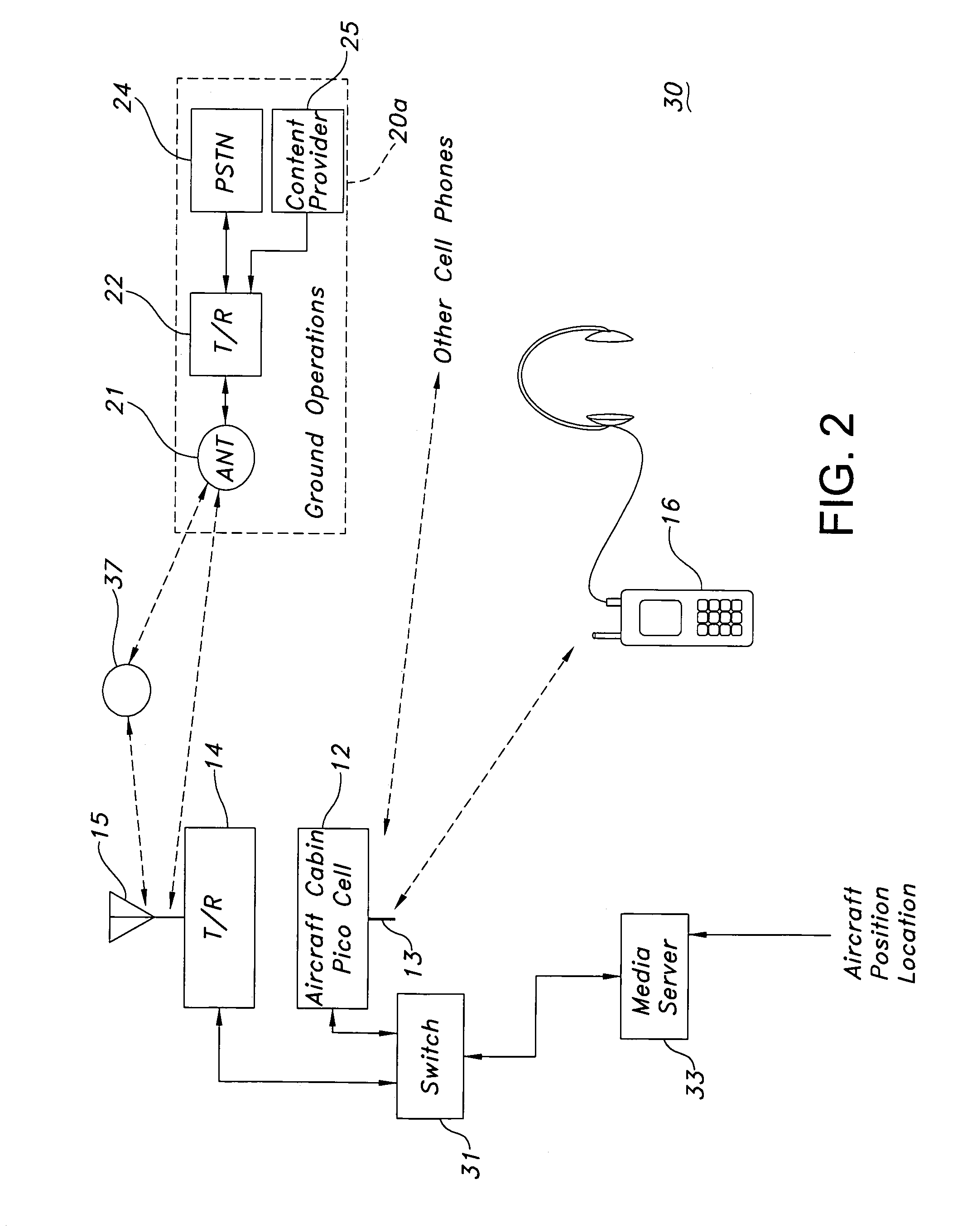
ActiveUS7343157B1Easy to installSatellite broadcast receivingBroadcast specific applicationsTransceiverMedia server
An airborne cell phone in-flight entertainment (IFE) system uses a cell phone for calls and IFE requests by dialing appropriate numbers. A pico cell receives the calls and the IFE requests. A soft switch switches the calls and IFE requests according to the telephone number. A transceiver receives the calls from the soft switch and sends them to a ground station that directs them to a telephone system. A media server receives IFE requests and provides IFE to the cell phone. A direct broadcast satellite (DBS) receiver on the aircraft receives DBS signals. A transcoder converts the received DBS signals from one compressed video format to another. A broad-to-connection protocol conversion process receives converted format DBS signals and converts them to video content blocks, stores the video content blocks to a continuously updated buffer and presents them to the media server and then to the cell phone.
Owner:BURRANA IP & ASSETS LLC
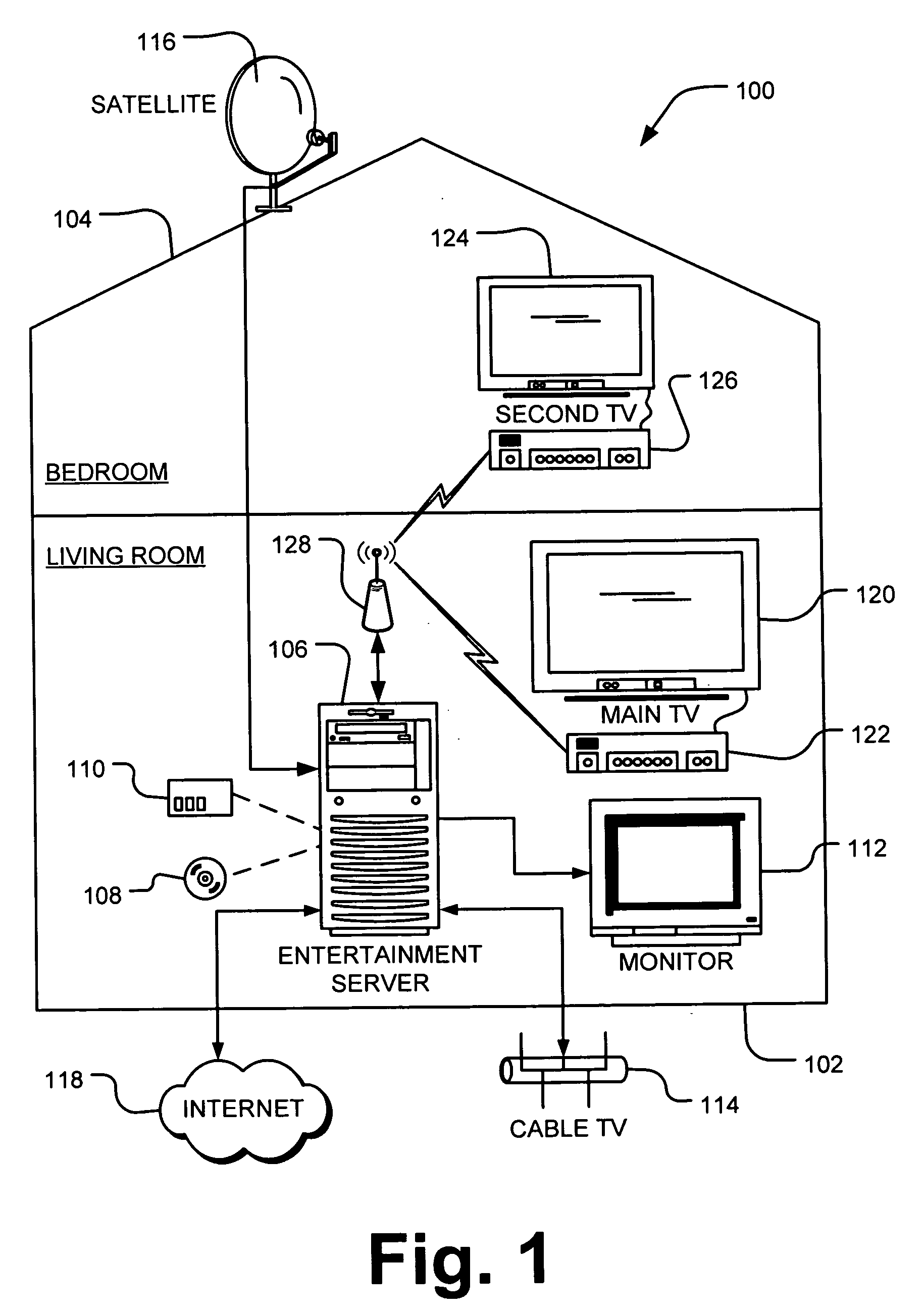
Systems and methods for a universal media server with integrated networking and telephony
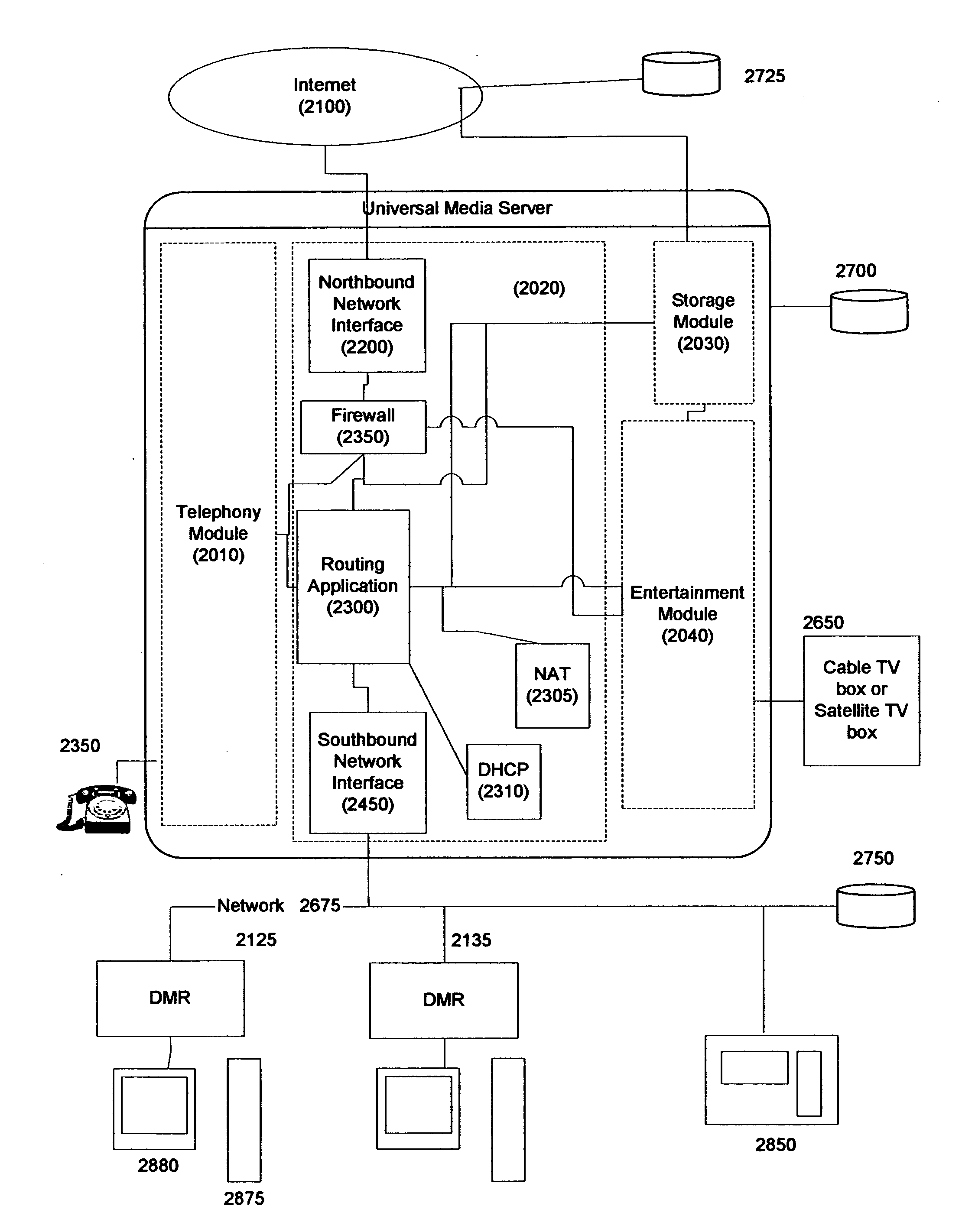
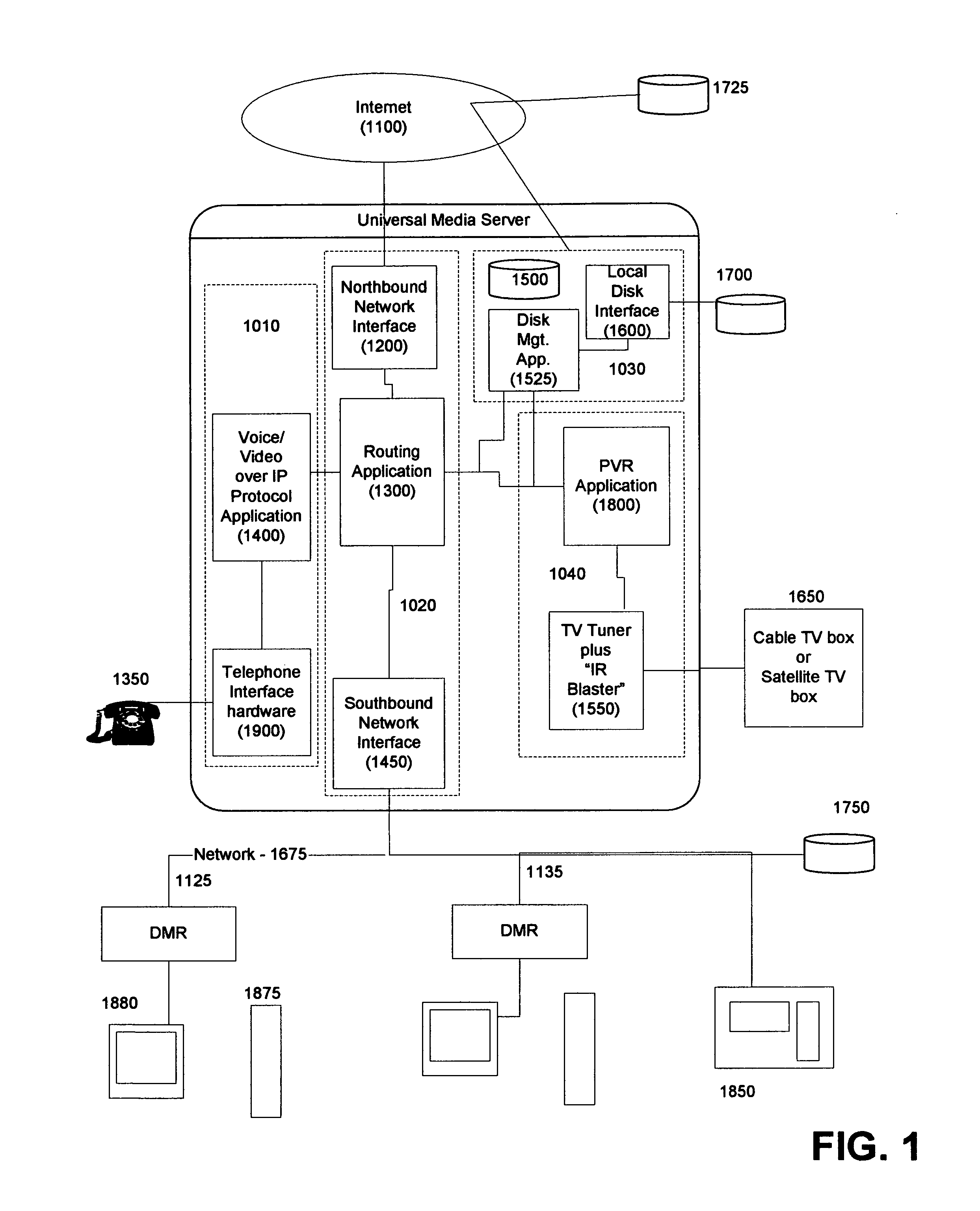
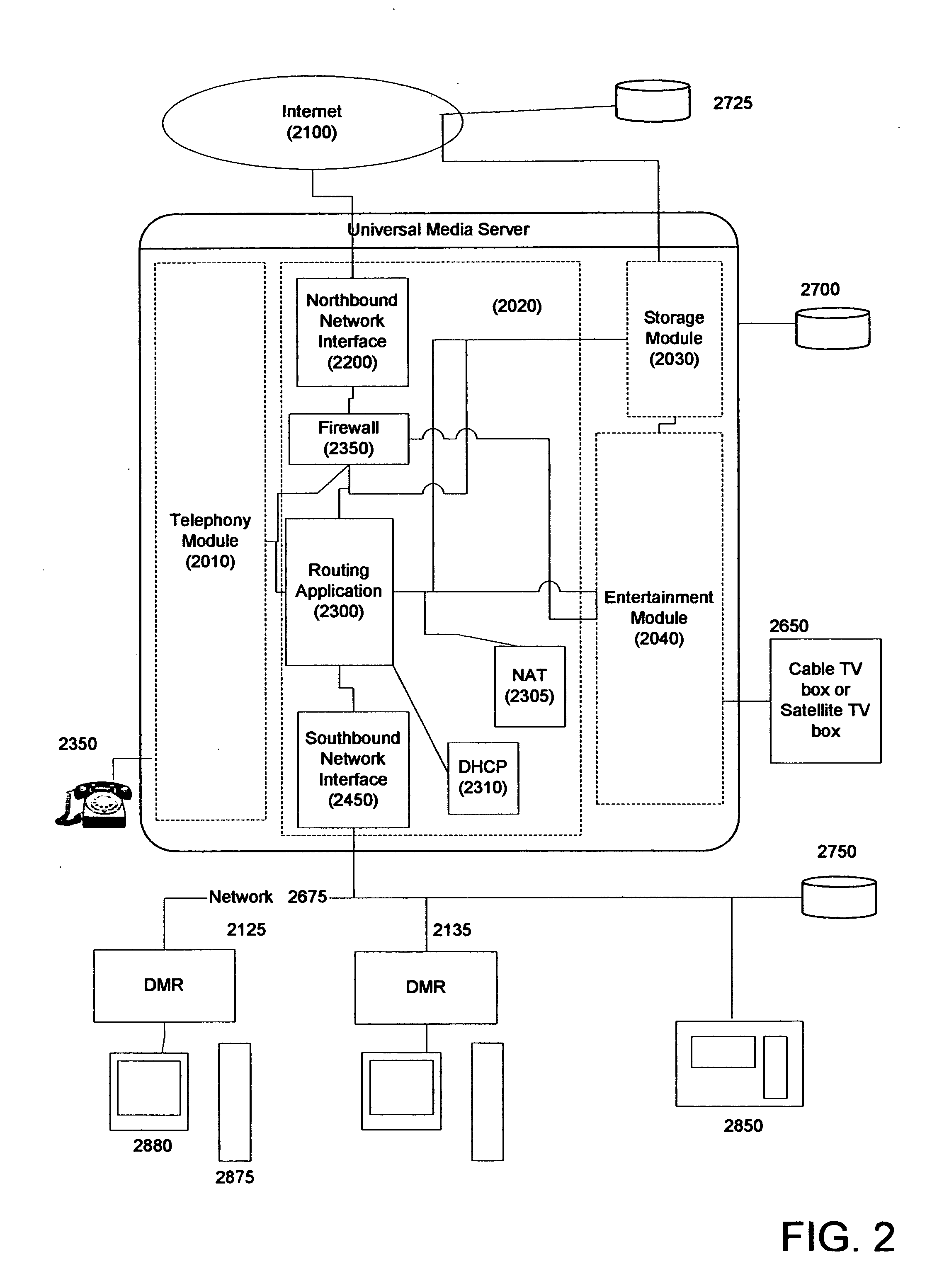
InactiveUS20050216949A1Reliable retentionLow costTelevision system detailsPulse modulation television signal transmissionMedia serverSecurity monitoring
Systems and methods for creating a Universal Media Server (UMS) and associated Digital Media Renders (DMRs) are disclosed. This system provides functions such as in-home wired or wireless network for media distribution with PVR functions from a distributed archive while at the same time including functions such as an answering machine, voice recorder, voice over IP gateway, firewall, NAT, DHCP, and security monitoring. A variety of advanced features and functions are also disclosed.
Owner:CANDELORA RAY +2
Method and apparatus for synchronizing playback of streaming media in multiple output devices
ActiveUS8015306B2Maintaining average timing synchronizationError preventionTransmission systemsTimestampNetwork packet
A method and apparatus for synchronizing streaming media with multiple output devices. One or more media servers serve media streams to one or more output devices (i.e., players). For playback synchronization, one output device is the “master”, whereas the remaining output devices are “slaves”. More data is requested from the media server by the “master” device to maintain a nominal buffer fill level over time. The “slave” devices receive streamed data from the media server at the rate determined by the master device's data requests, and the average rate of data flow over the streaming network is thus controlled by the frequency of the single “master” device's crystal. “Slave” devices make playback rate corrections to maintain respective buffer fill levels within upper and lower threshold levels. For slow networks, each media data packet timestamp is calculated from the time the master's buffer reaches nominal level.
Owner:SNAP ONE LLC
Systems and methods for multi-tuner recording
InactiveUS20050229213A1Television system detailsSpecific information broadcast systemsInteractive televisionMedia server
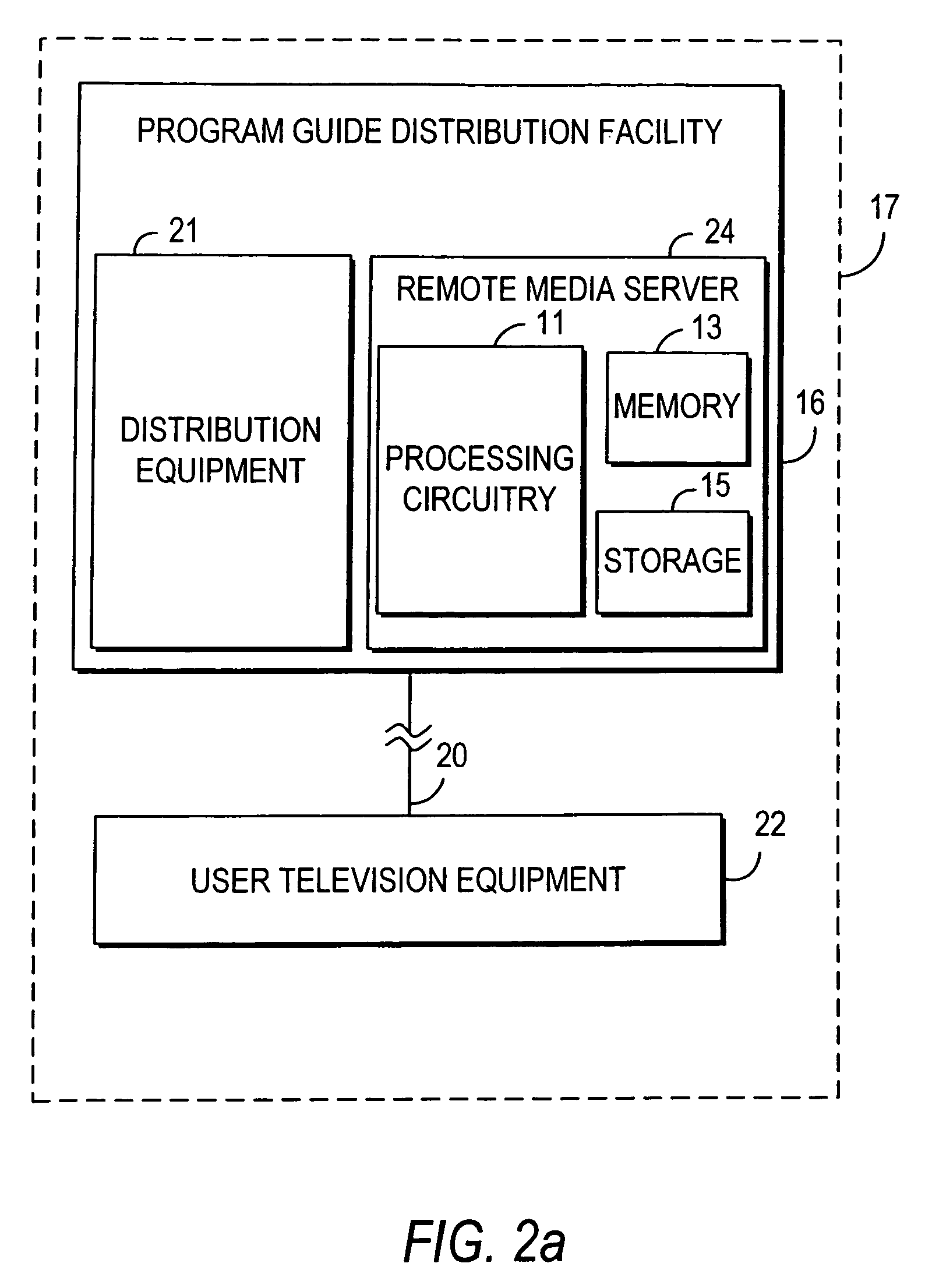
An interactive television program guide system is provided. An interactive television program guide provides users with an opportunity to select programs for recording on a remote media server. Programs may also be recorded on a local media server. The program guide provides users with VCR-like control over programs that are played back from the media servers and over real-time cached copies of the programs. The program guide also provides users with an opportunity to designate gift recipients for whom programs may be recorded.
Owner:ROVI GUIDES INC
System and method for rewriting a media resource request and/or response between origin server and client
InactiveUS7013322B2Efficient content deliveryImprove content delivery capabilityDigital data information retrievalMultiple digital computer combinationsWeb serviceNative client
A distributed network which is capable of dynamically changing media resource request metafiles, as well as the responses to those media resource requests by media servers in the network, to provide more efficient content delivery in the network. The network employs a system and method for intercepting a media resource request metafile client request, or a response to the media resource request by a media server in the network, and intelligently rewriting the response before sending it back to the requesting client. The file or protocol response can be rewritten according to localized information such as resource availability and client request information which the centralized web server may not have or even be able to obtain, such as the client's ISP, browser type, ISP's surfing trends and so on. The system and method thus enables the network to send the local client to either a local server or a remote server to receive the requested content.
Owner:CREDIT SUISSE FIRST BOSTON ACTING THROUGH ITS CAYMAN ISLANDS BRANCH AS SECOND LIEN ADMINISTATIVE AGENT +1
Media file distribution system and method
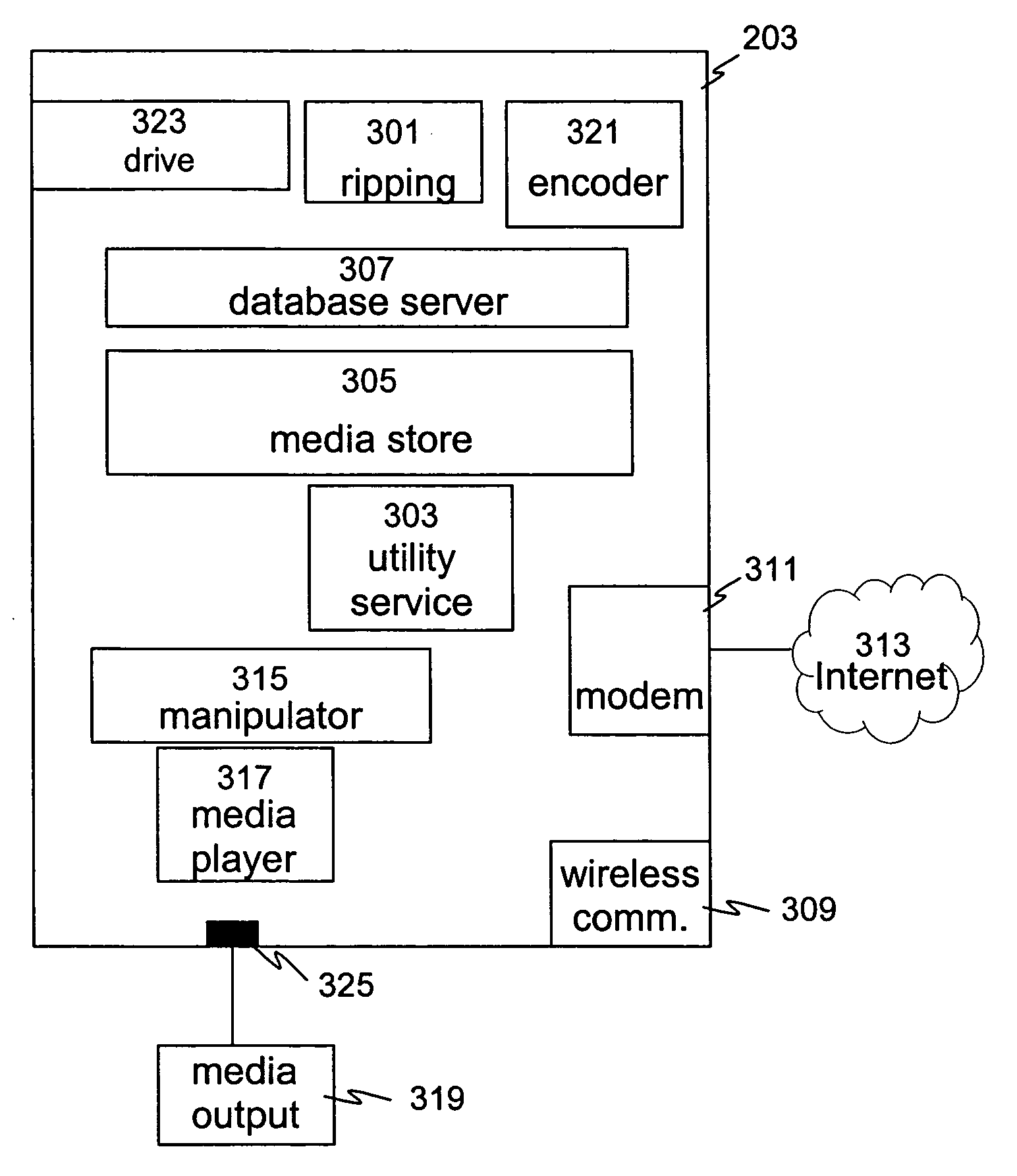
InactiveUS20040225746A1Quality improvementDigital data processing detailsData switching by path configurationDistribution systemOutput device
A media file distribution system comprising a media server and one or more satellite units, wherein the media server comprises a media file store for storing one or more media files and a first wireless communicator. The one or more satellite units comprise a second wireless communication means and a first output device for playing the one or more media files stored on the media server.
Owner:DIGIFI
Distributed Video Content Management and Sharing System
ActiveUS20080189617A1Efficient deliveryDigital computer detailsWebsite content managementWeb siteWeb service
The present invention relates to a system which enables cooperative rich media content management, sharing, and publishing across a distributed set of Web sites, Web servers, and media servers based on control information in an online database. Media files are housed on any number of heterogeneous media repositories. The system of the present invention is used for managing, sharing, and publishing rich media content including video, images, animations, audio, etc. Authorized viewers access media files through dynamically generated content and media links embedded on Web sites. Content administrators publish media entries to any number of such distributed Web sites, and can set viewer permissions for individual video entries when published on specific Web sites. Content administrators can also dynamically establish media sharing and access relationships.
Owner:SYMPHONY VIDEO INC
Networked digital video recording system with copy protection and random access playback
ActiveUS7231516B1Effective positioningHigh rateTelevision system detailsData resettingDigital videoDigital recording
In a multimedia recording and playback network for receiving from a content server a service package of multimedia content, the network including a media server in communication with the content server, a method of securely transmitting a master encryption key from the content server to the media server, including the steps downloading a service package certificate from the content server to the media server, authenticating, in the media server, the received service package certificate, the content server providing to the media server a key server certificate, a public key of the content server, and a client certificate request, the media server authenticating the key server certificate, providing to the content server, upon authentication of the key server certificate by the media server, a client certificate including a challenge signature, and a public key of the media server, the content server authenticating the client certificate including the challenge signature received from the media server, the media server requesting the master encryption key from the content server, and the content server responding by transmitting the master encryption key to media server.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
System and methods for use of voice mail and email in a mixed media environment
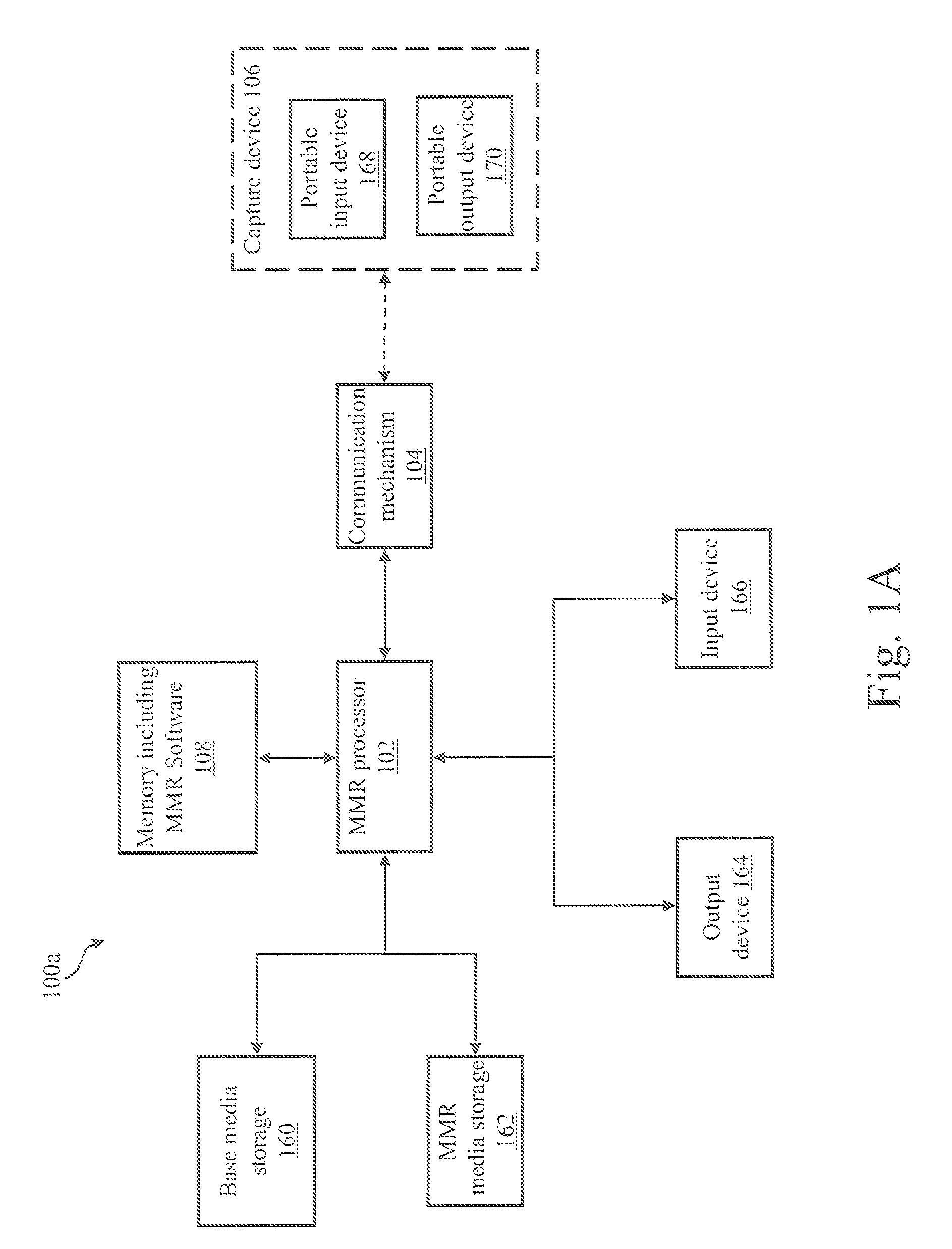
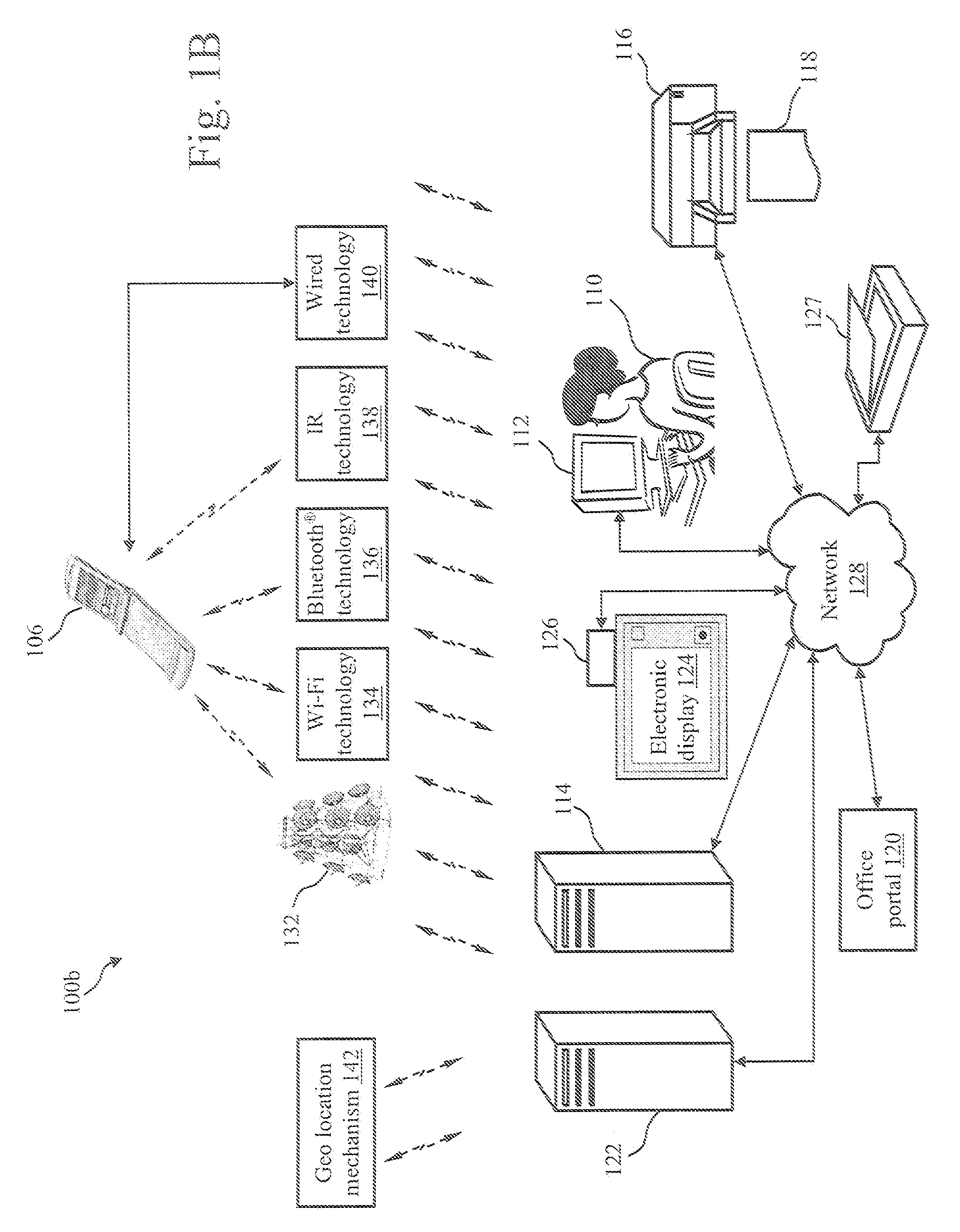
ActiveUS7812986B2Facilitate methodDigital data processing detailsAutomatic call-answering/message-recording/conversation-recordingGeotargetingMedia server
A mixed media reality (MMR) system includes an MMR user, a MMR computer, a user printer that produces a printed document, a networked media server, an office portal, a service provider server, an electronic display that is electrically connected to a set-top box, a document scanner, a network, a capture device, a cellular infrastructure, wireless fidelity (Wi-Fi) technology, Bluetooth® technology, infrared (IR) technology, wired technology, and a geo location mechanism. The MMR system provides mechanisms for forming a mixed media document that includes media of at least two types, such as printed paper as a first medium and a digital photograph, digital movie, digital audio file, or web link as a second medium. Furthermore, the MMR system facilitates business methods that take advantage of the combination of a portable electronic device, voice mail or email, and a paper document.
Owner:RICOH KK
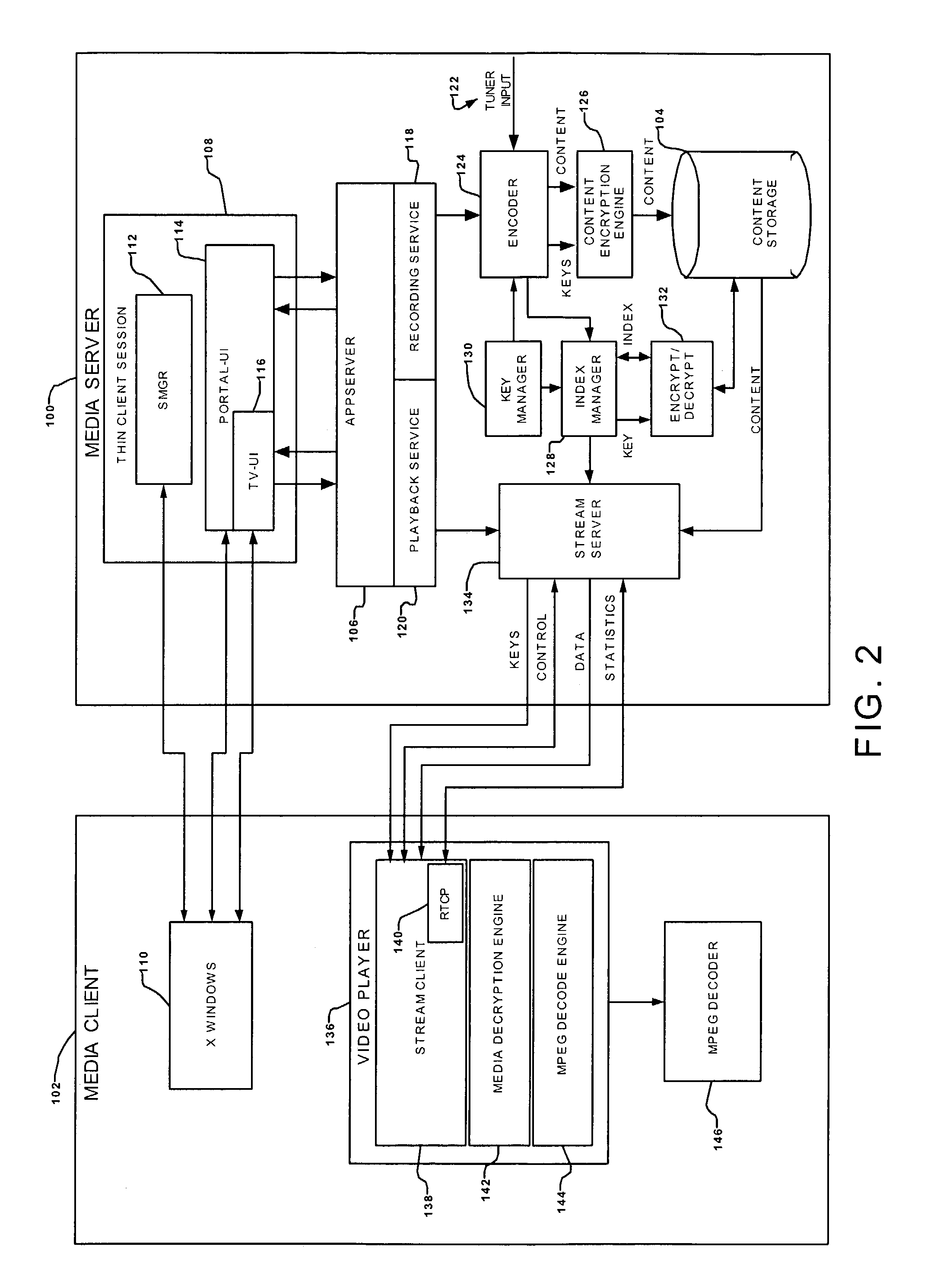
Systems and methods for securely streaming media content
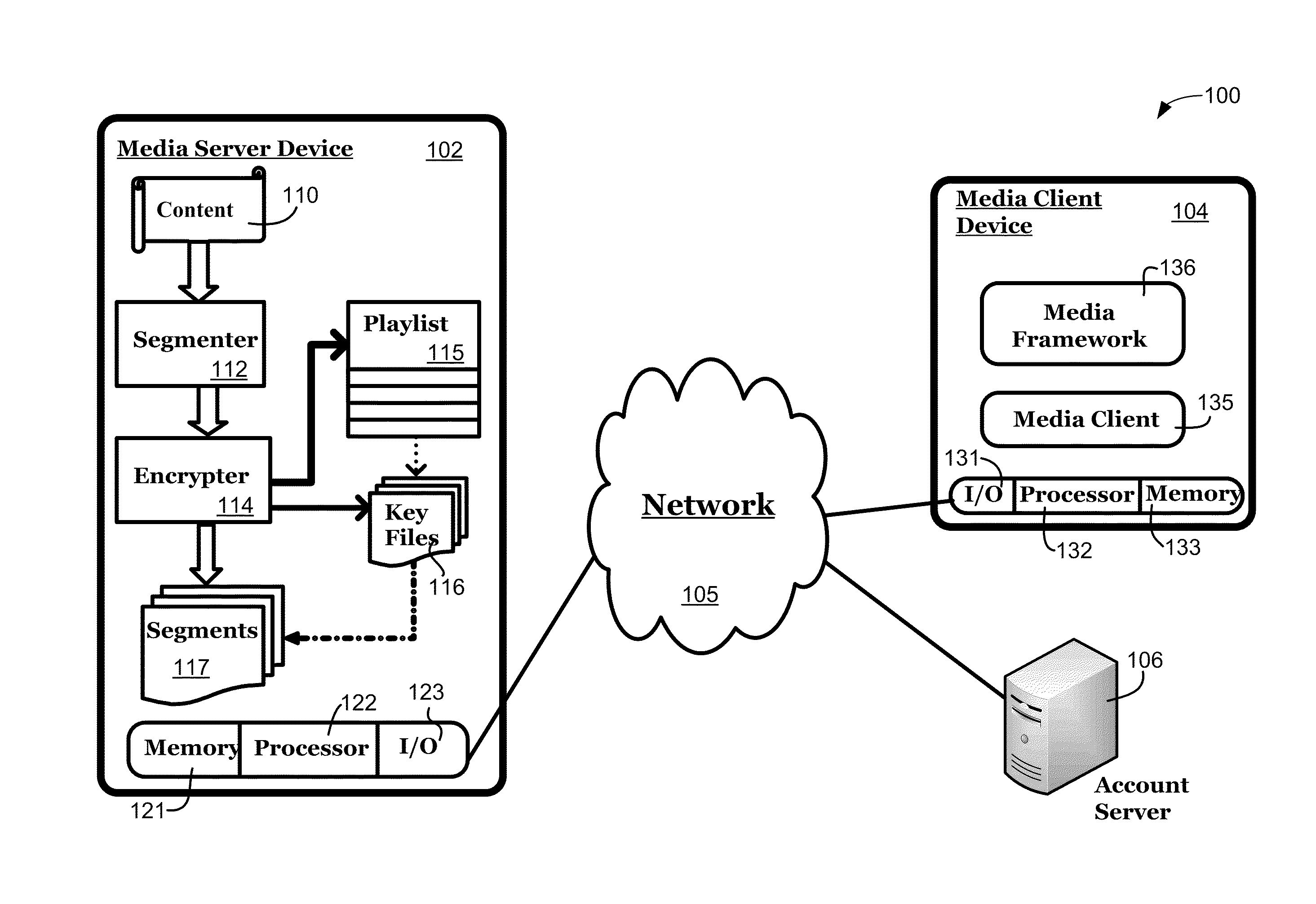
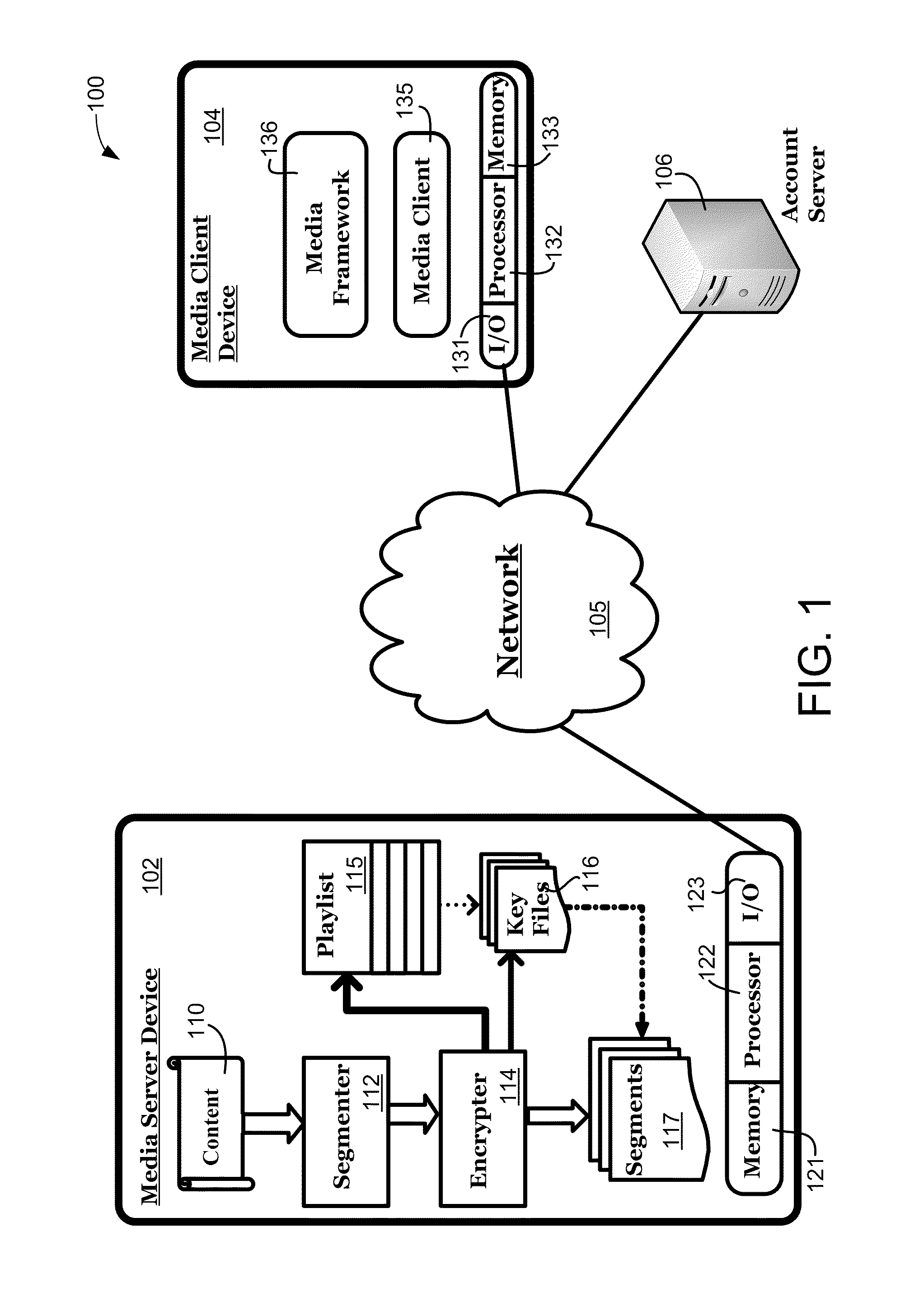
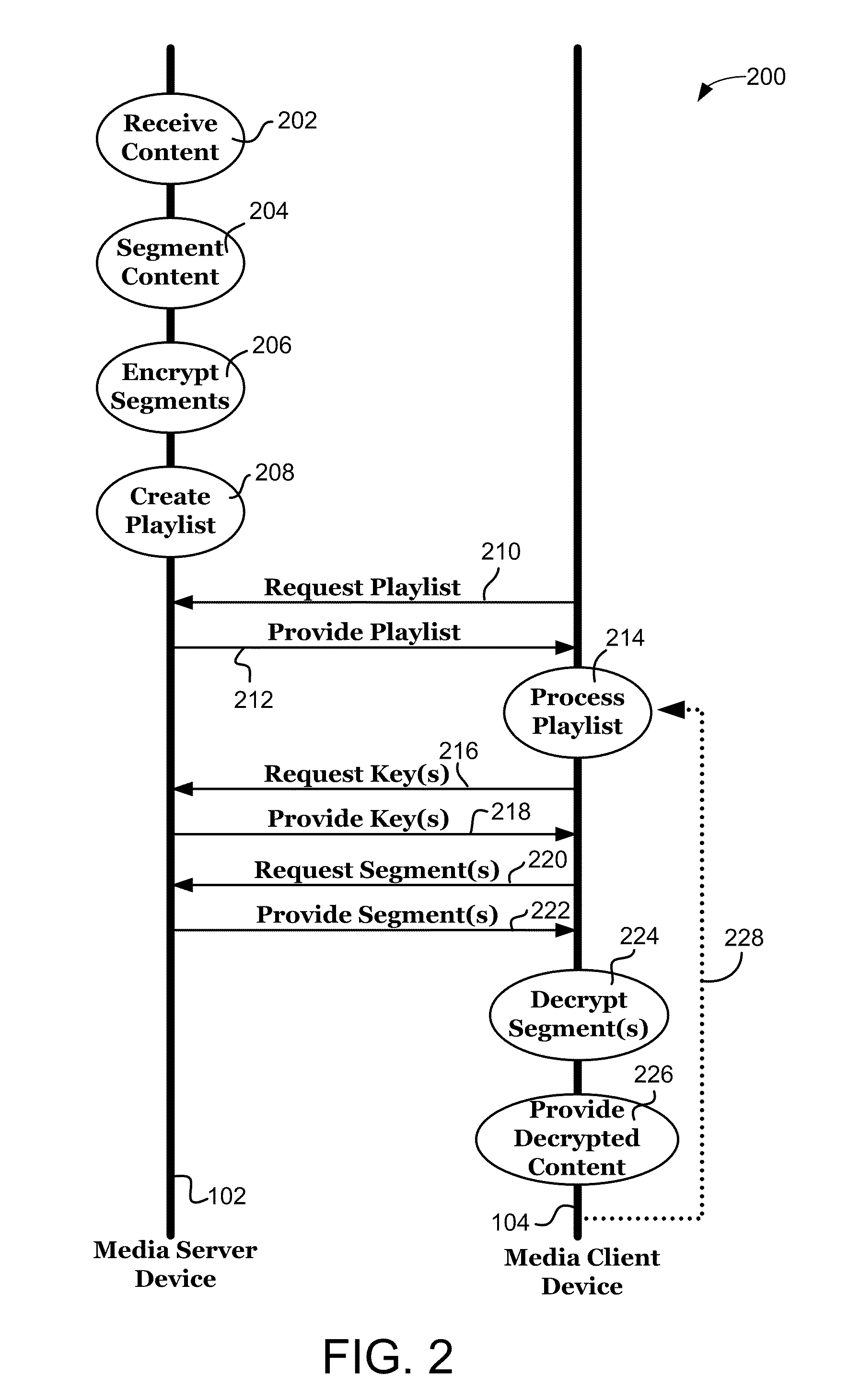
ActiveUS20110231660A1User identity/authority verificationMultiple digital computer combinationsMedia serverMultiple media
Systems and methods securely provide media content from a media server to a media client via a network. The media content is segmented to create multiple media segments that are each identified in a playlist, and at least one of the media segments is encrypted using a cryptographic key. The cryptographic key is also identified in the playlist, and the playlist is provided from the media server to the media client via the network. The various media segments and cryptographic keys may then be requested from and provided by the media server using hypertext transport protocol (HTTP) or similar constructs to allow the media client to receive and decrypt the various segments of the media content.
Owner:ECHOSTAR TECH LLC
System and method for providing a callback cloud
A system for providing a callback cloud, comprising an application server operated by a callback cloud service provider, a media server, a session management server, an interaction manager, and an intent analysis engine. The application server receives registrations from callback providers unaffiliated with the callback service provider. The application server is adapted to receive callback requests from users, comprising a specific callback provider from whom a callback is requested, when a requested callback should be made, and allowable media types. The application server directs the callback request to the interaction manager, and the interaction manager sends data elements pertaining to the request to the intent analysis engine and receives therefrom data elements pertaining to the callback request determined based on an analysis of the requester's intent. The interaction manager directs the session management server to initiate a callback, and the session management server provides signaling to the media server to conduct the callback.
Owner:VIRTUAL HOLD TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com