Patents
Literature
1868 results about "TTEthernet" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
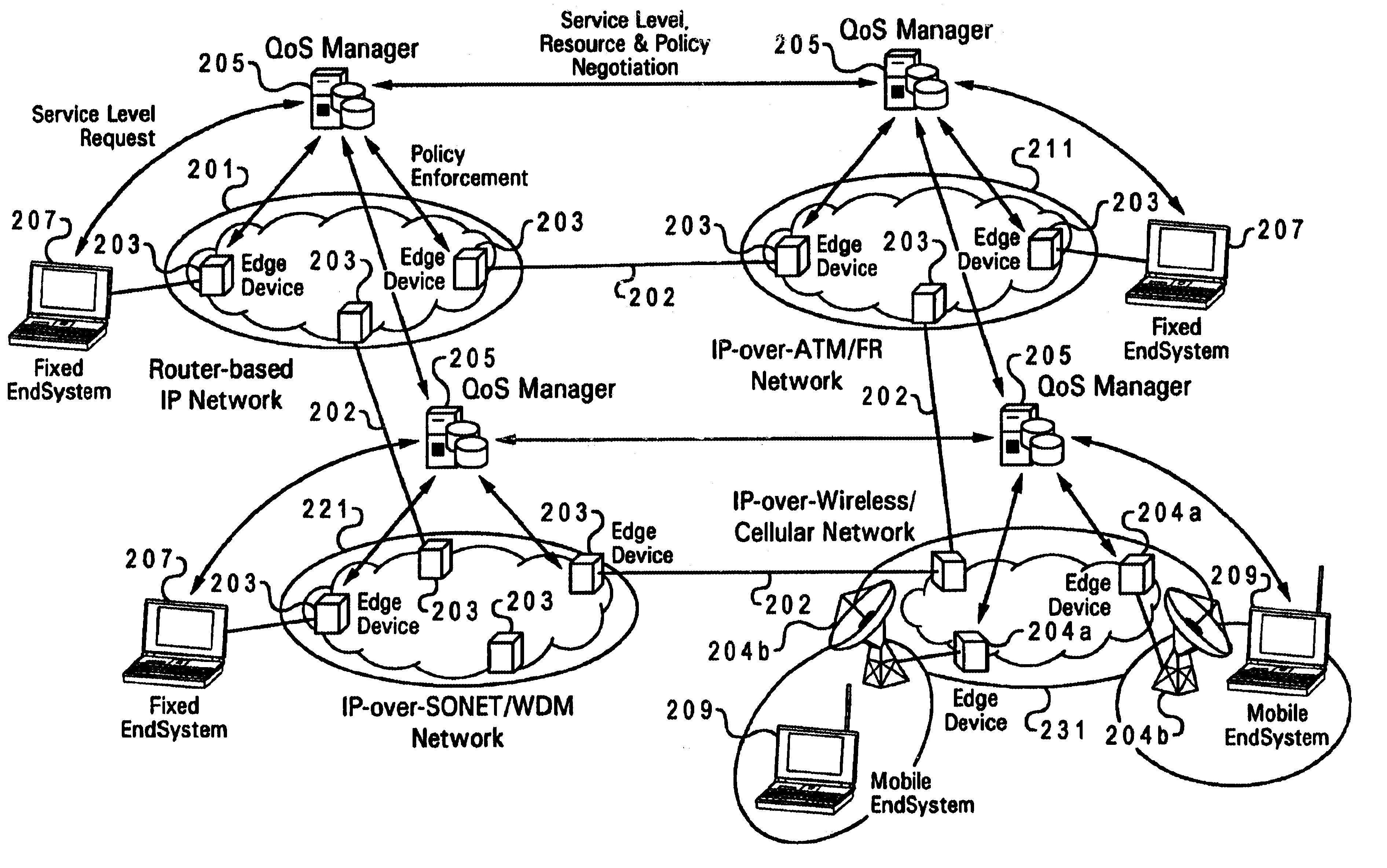
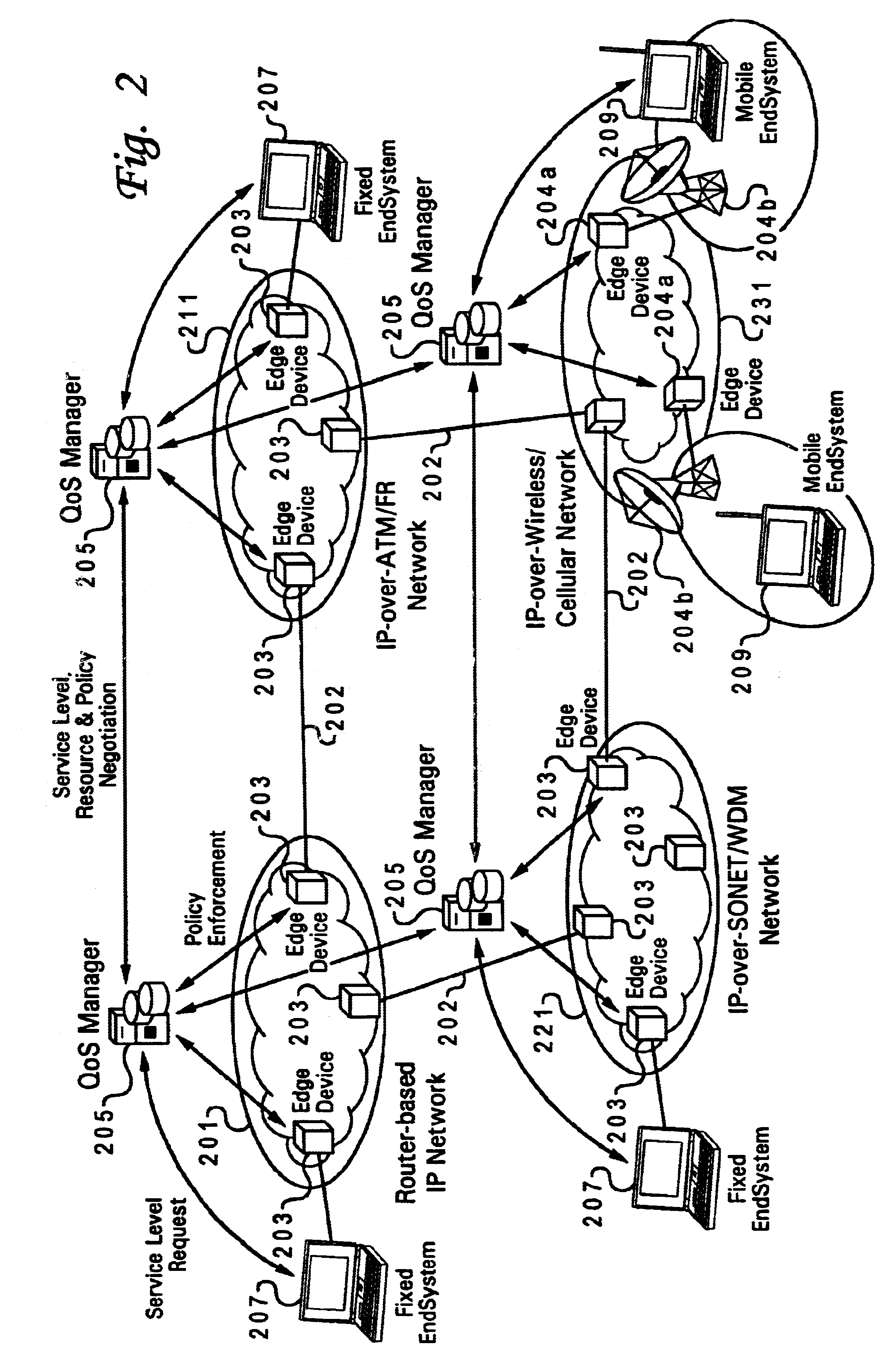
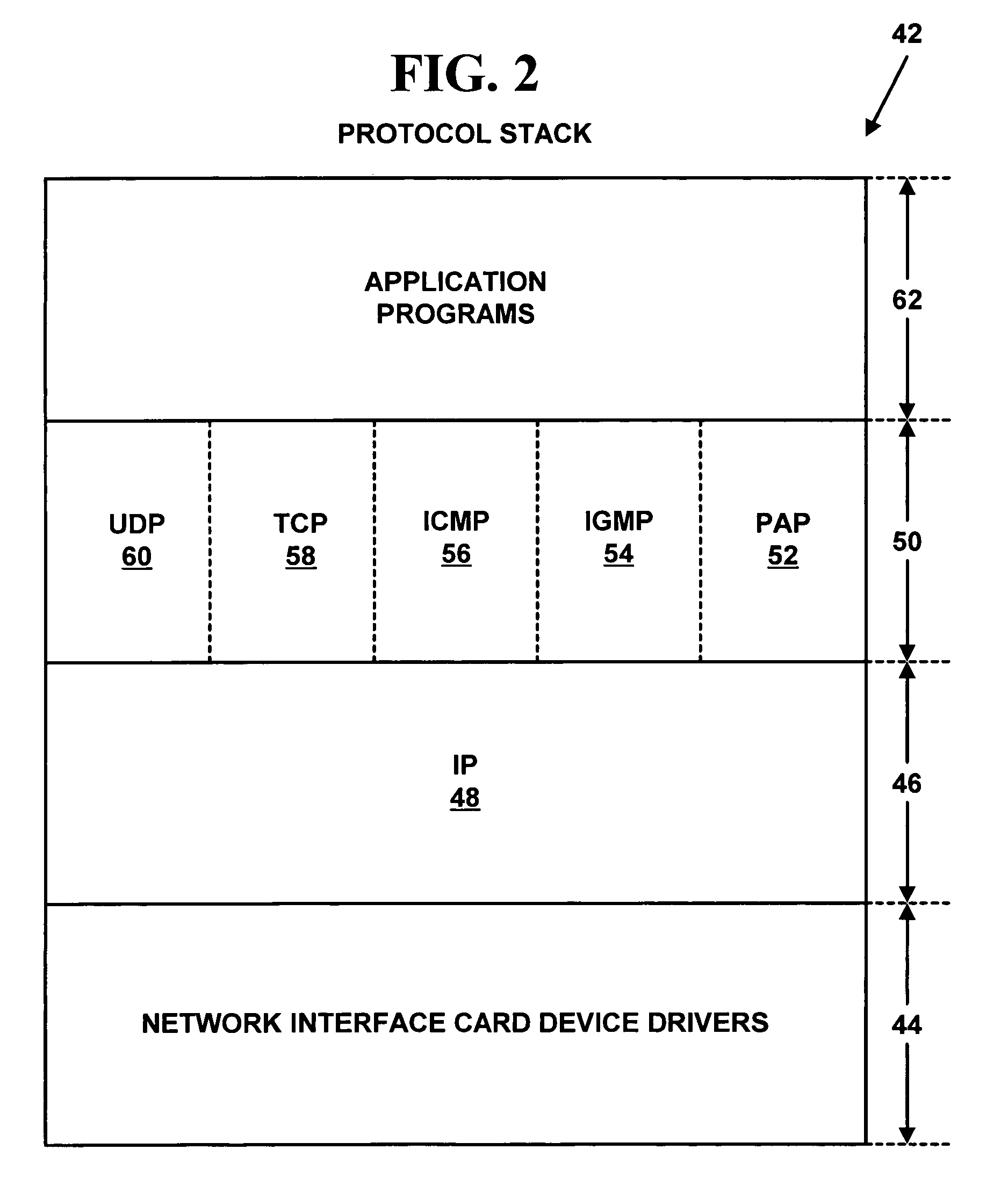
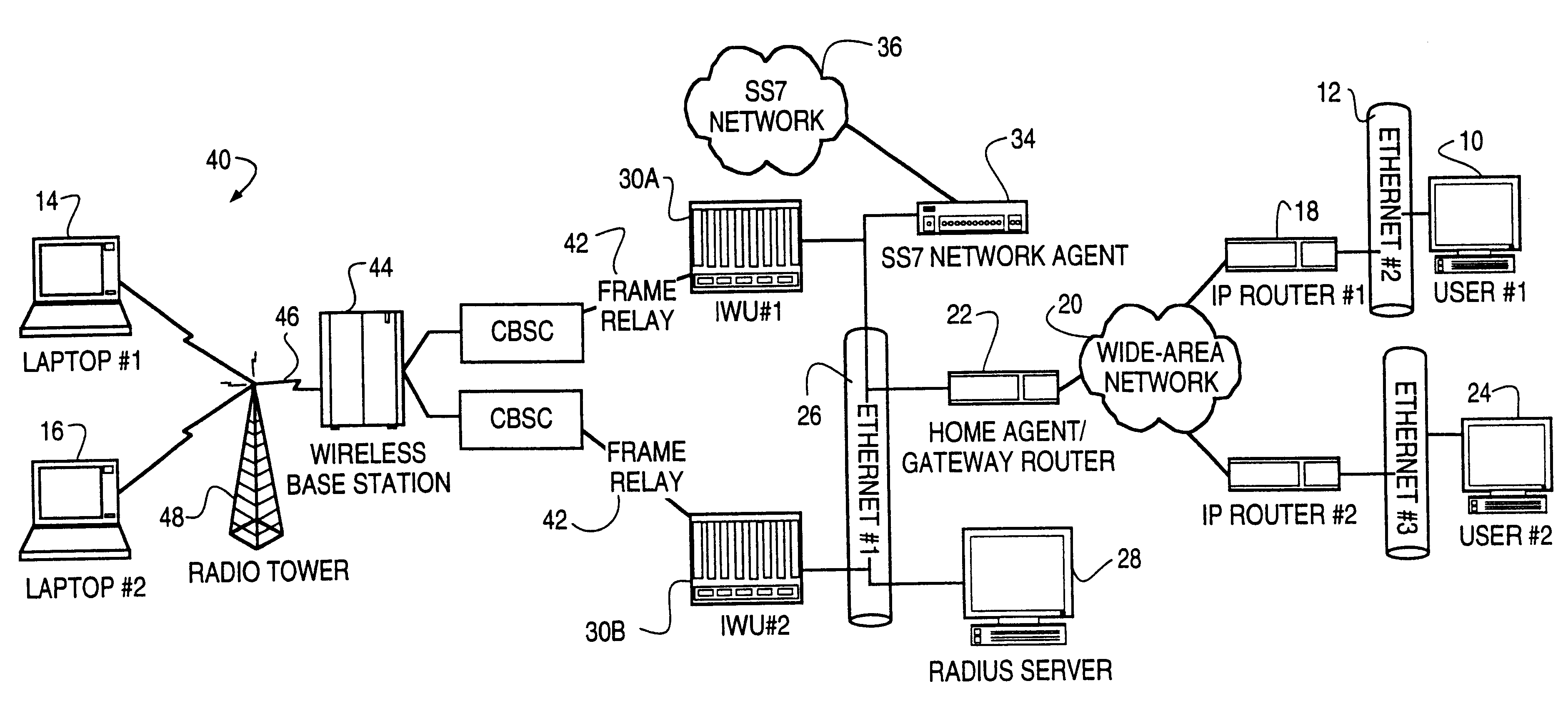
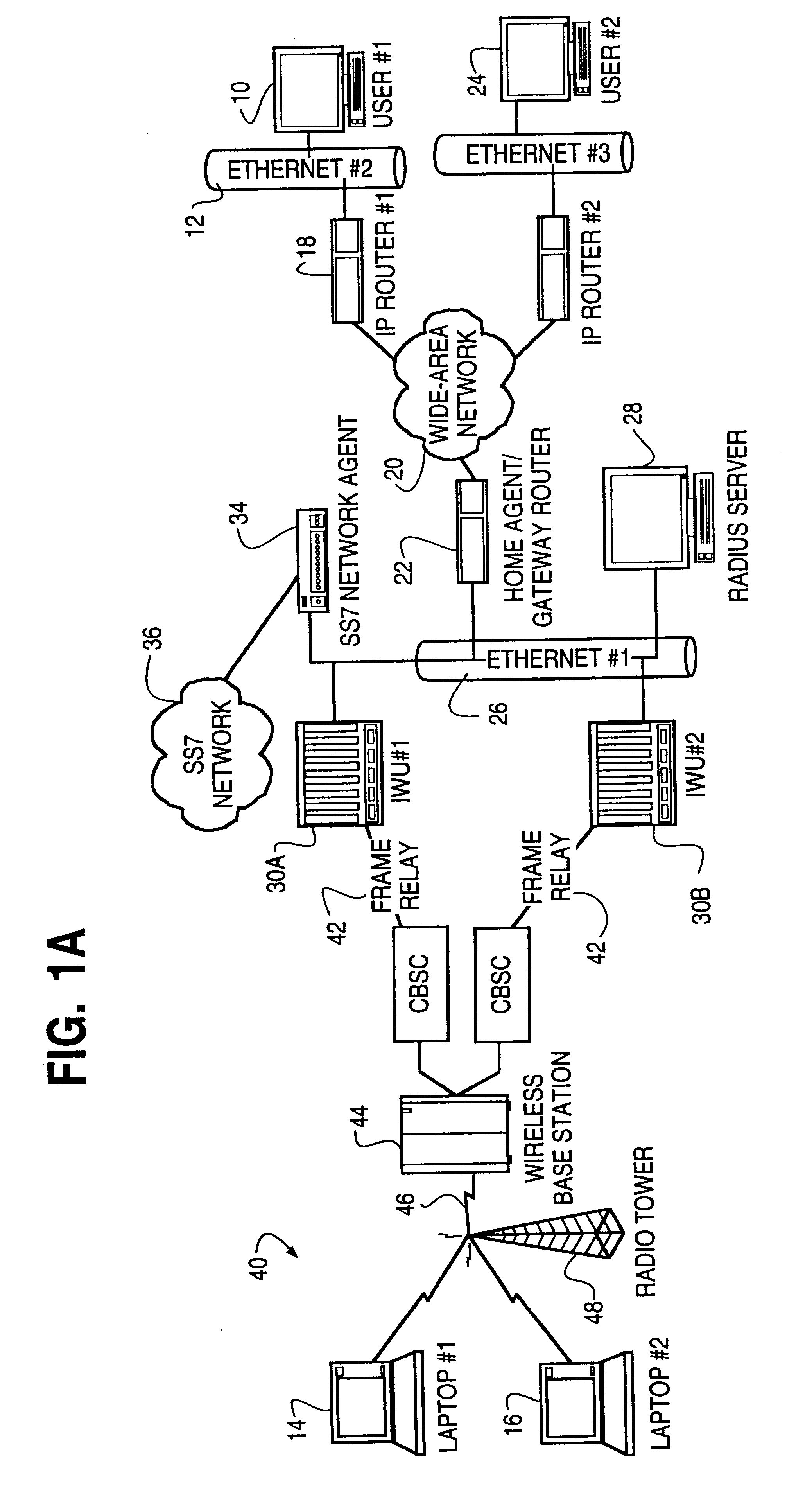
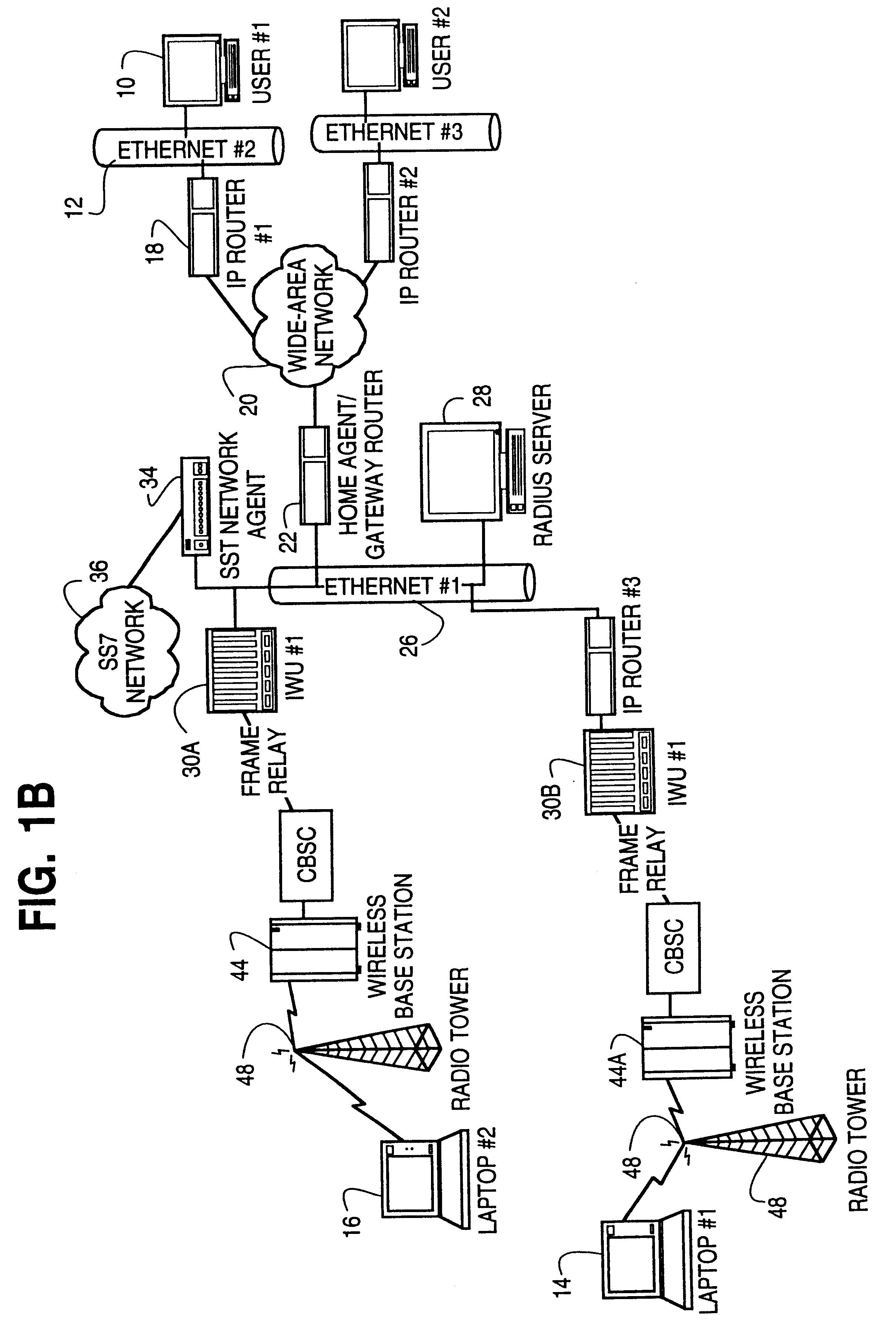
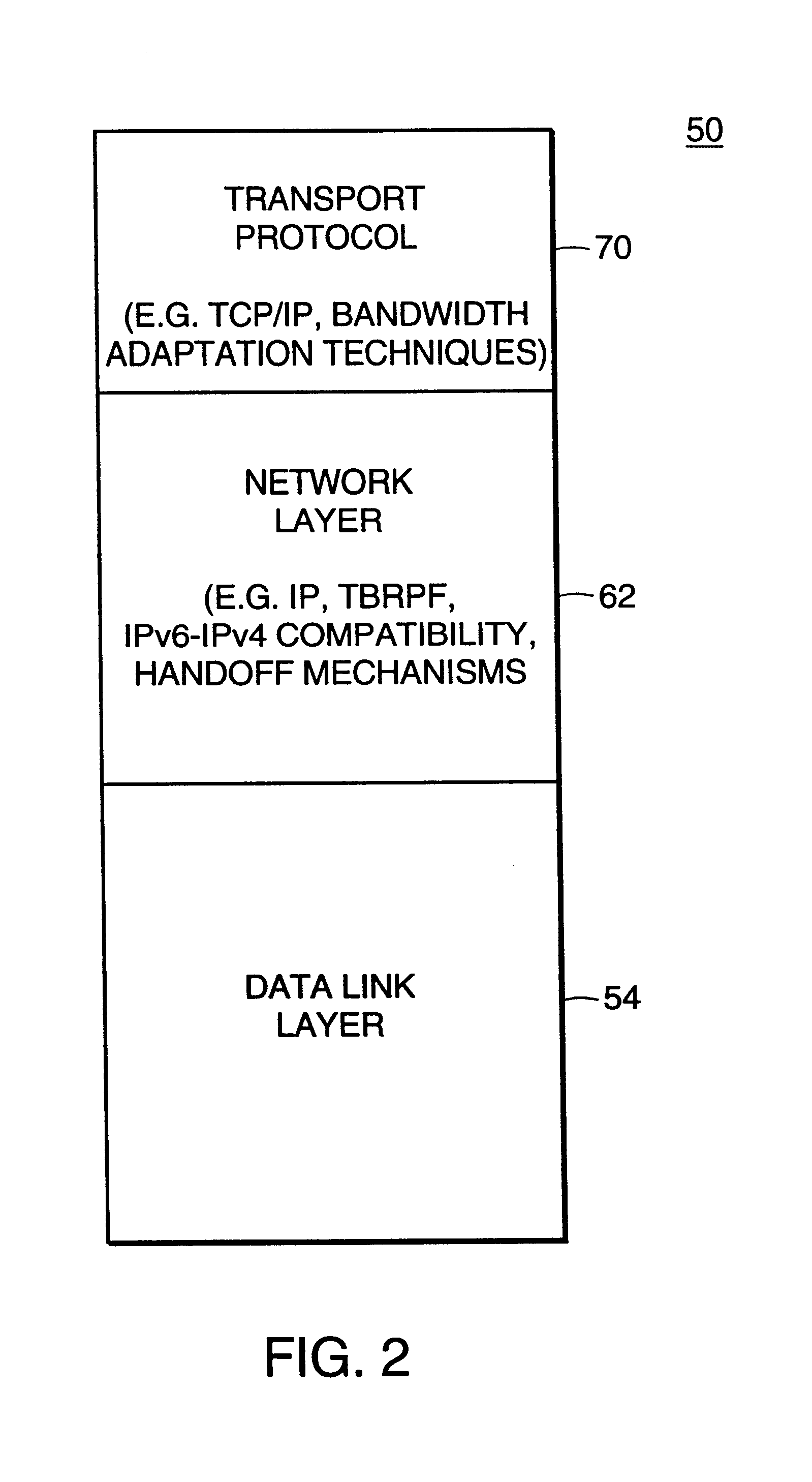
The Time-Triggered Ethernet (SAE AS6802) standard defines a fault-tolerant synchronization strategy for building and maintaining synchronized time in Ethernet networks, and outlines mechanisms required for synchronous time-triggered packet switching for critical integrated applications, IMA and integrated modular architectures. SAE International has released SAE AS6802 in November 2011.
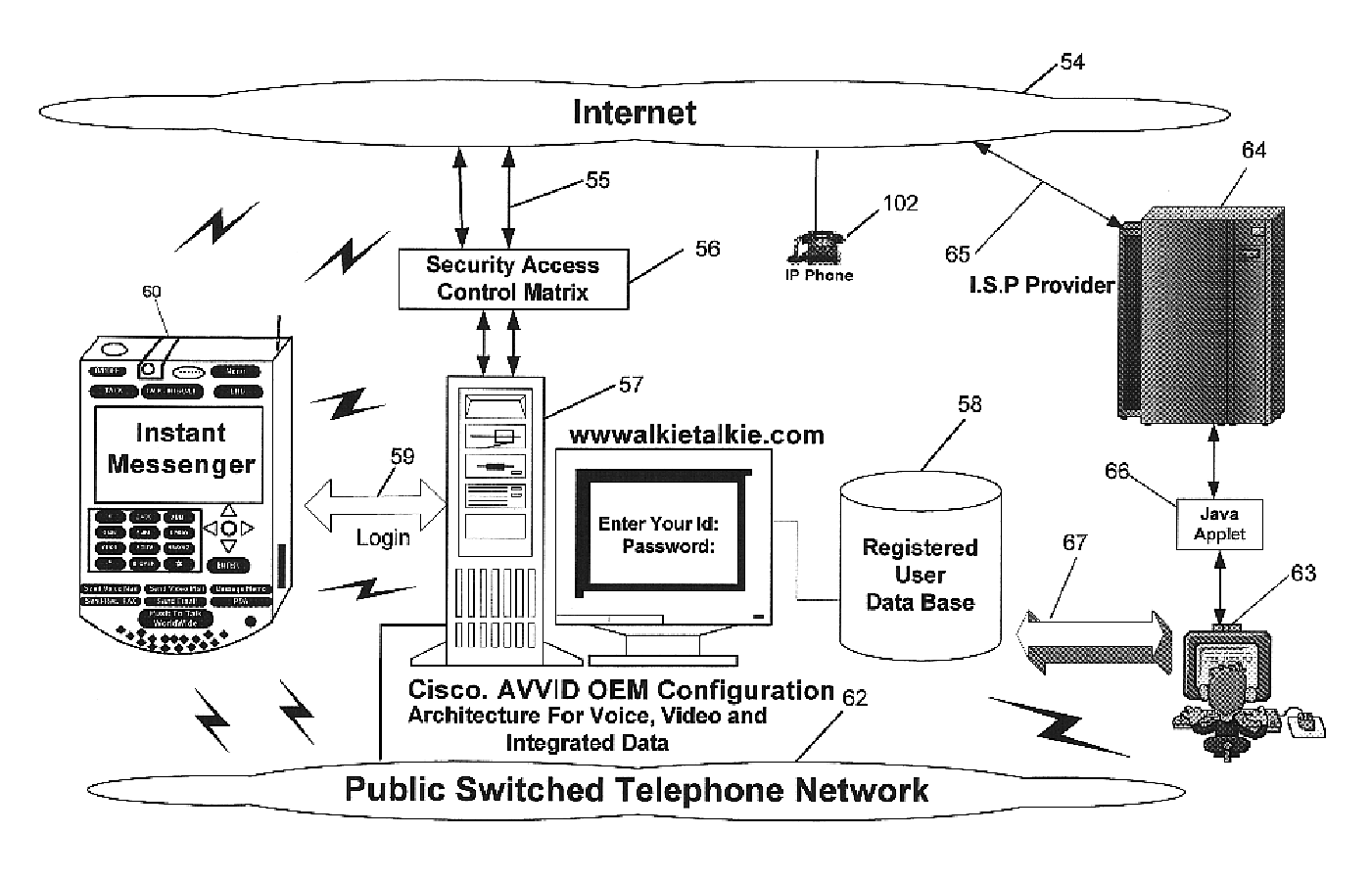
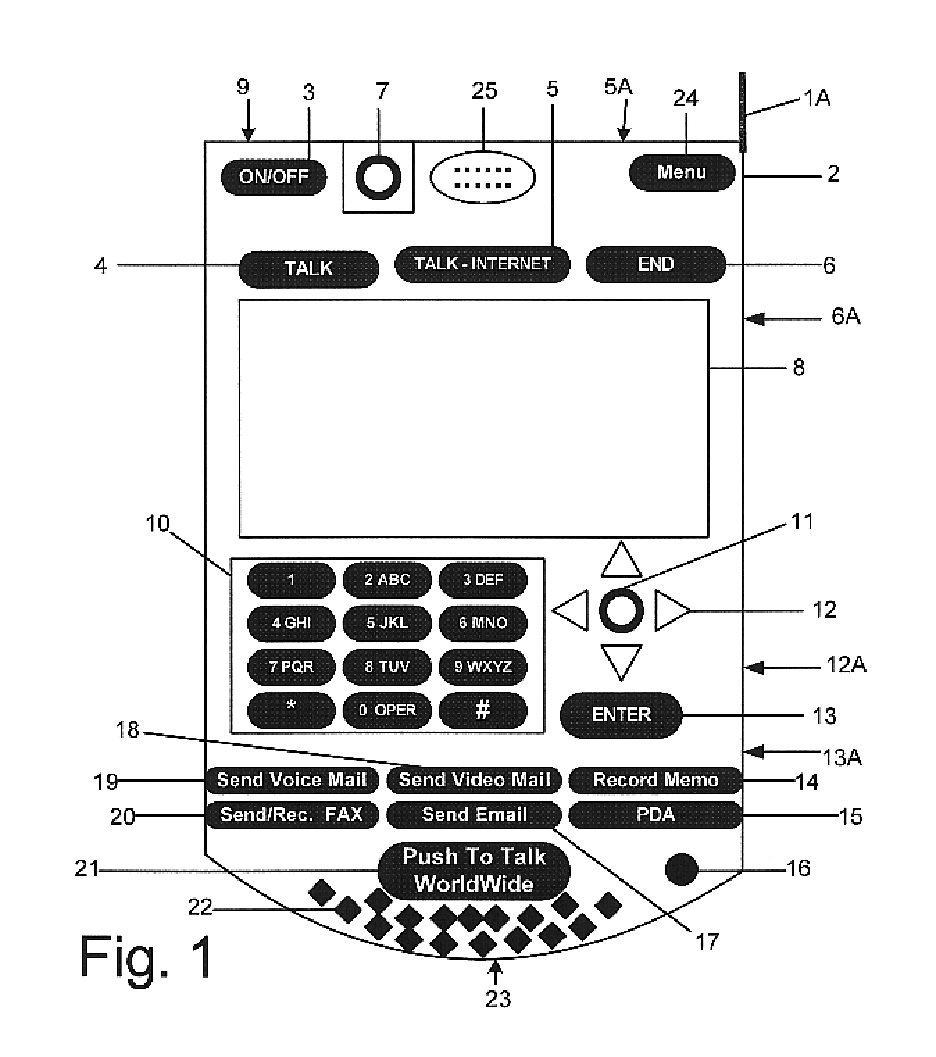
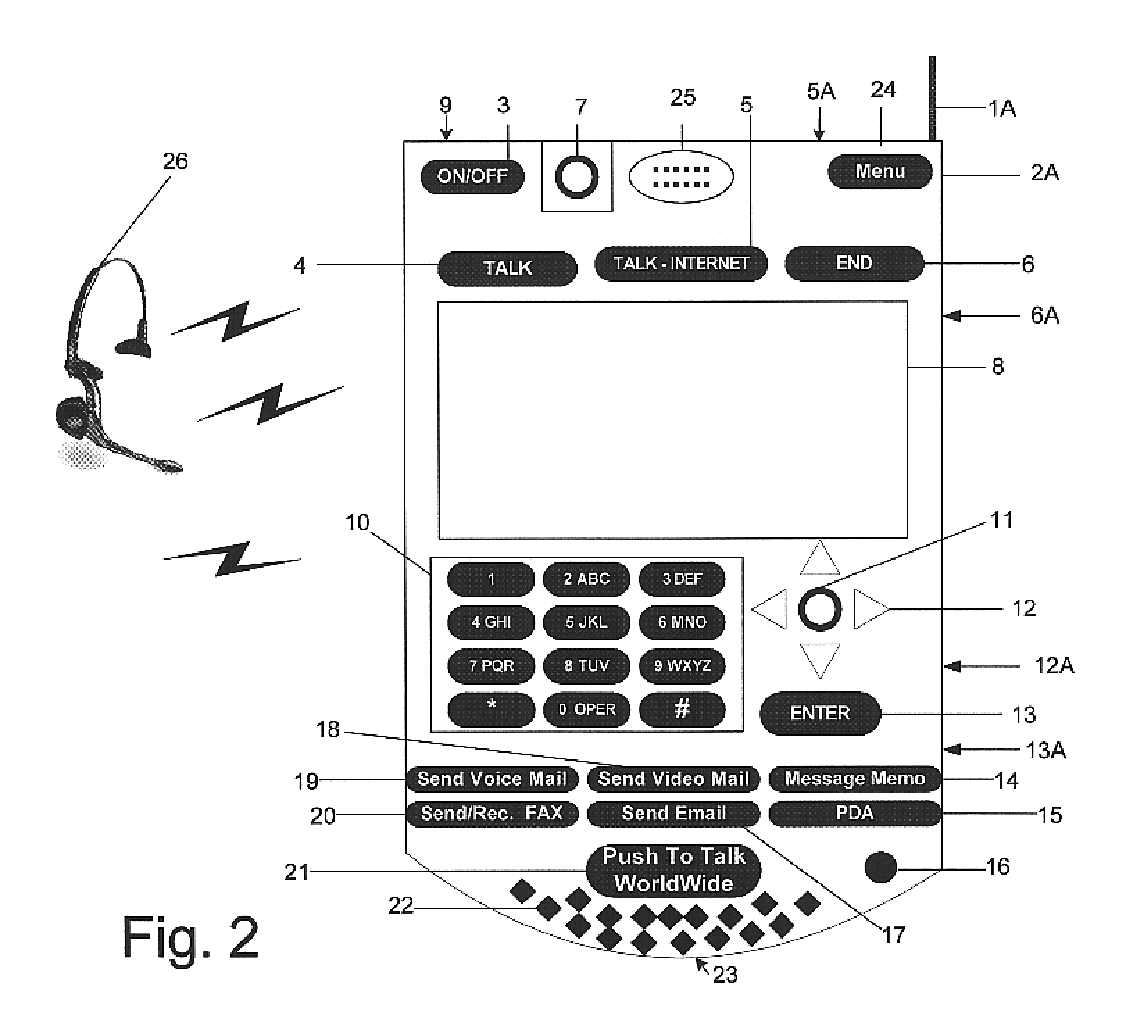
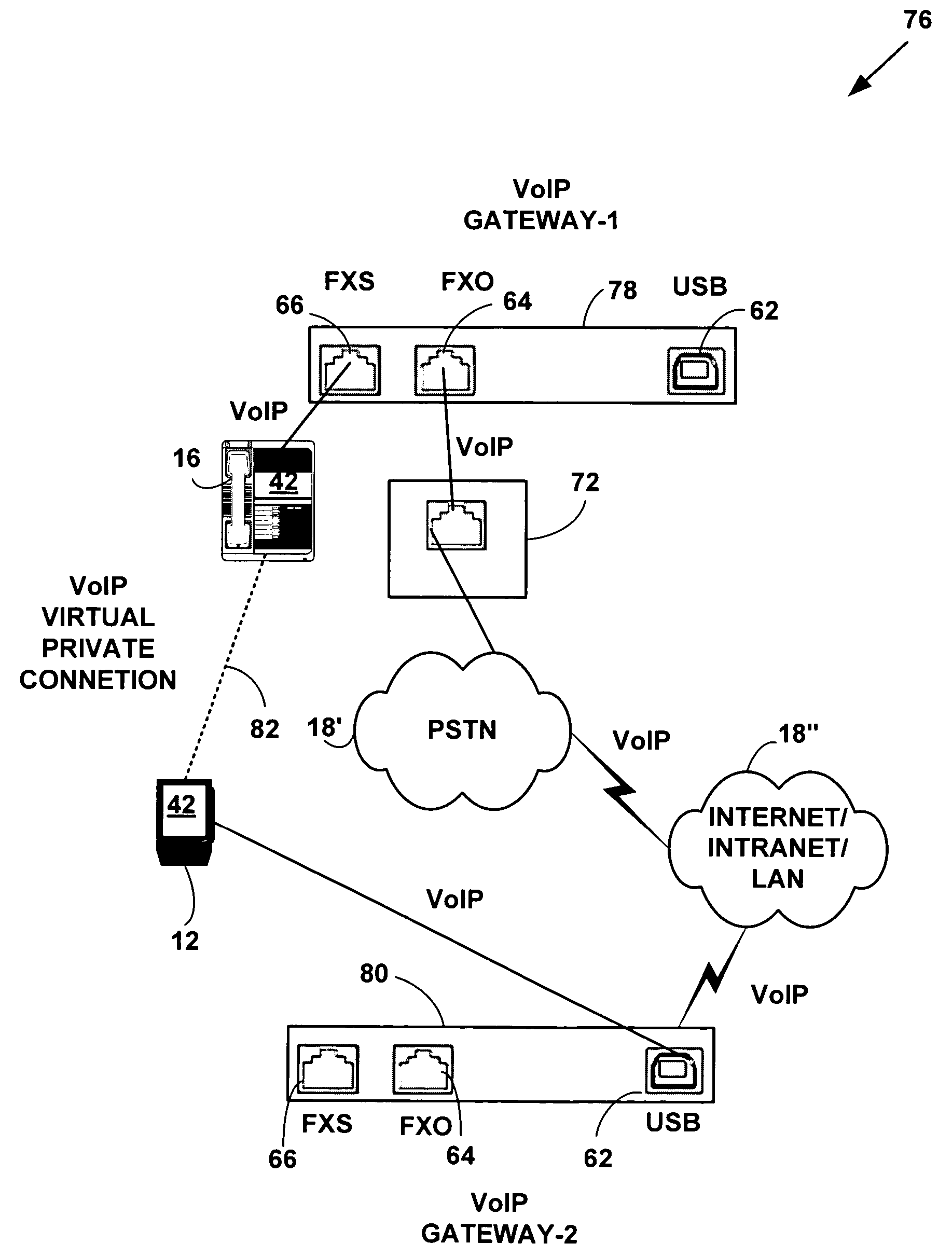
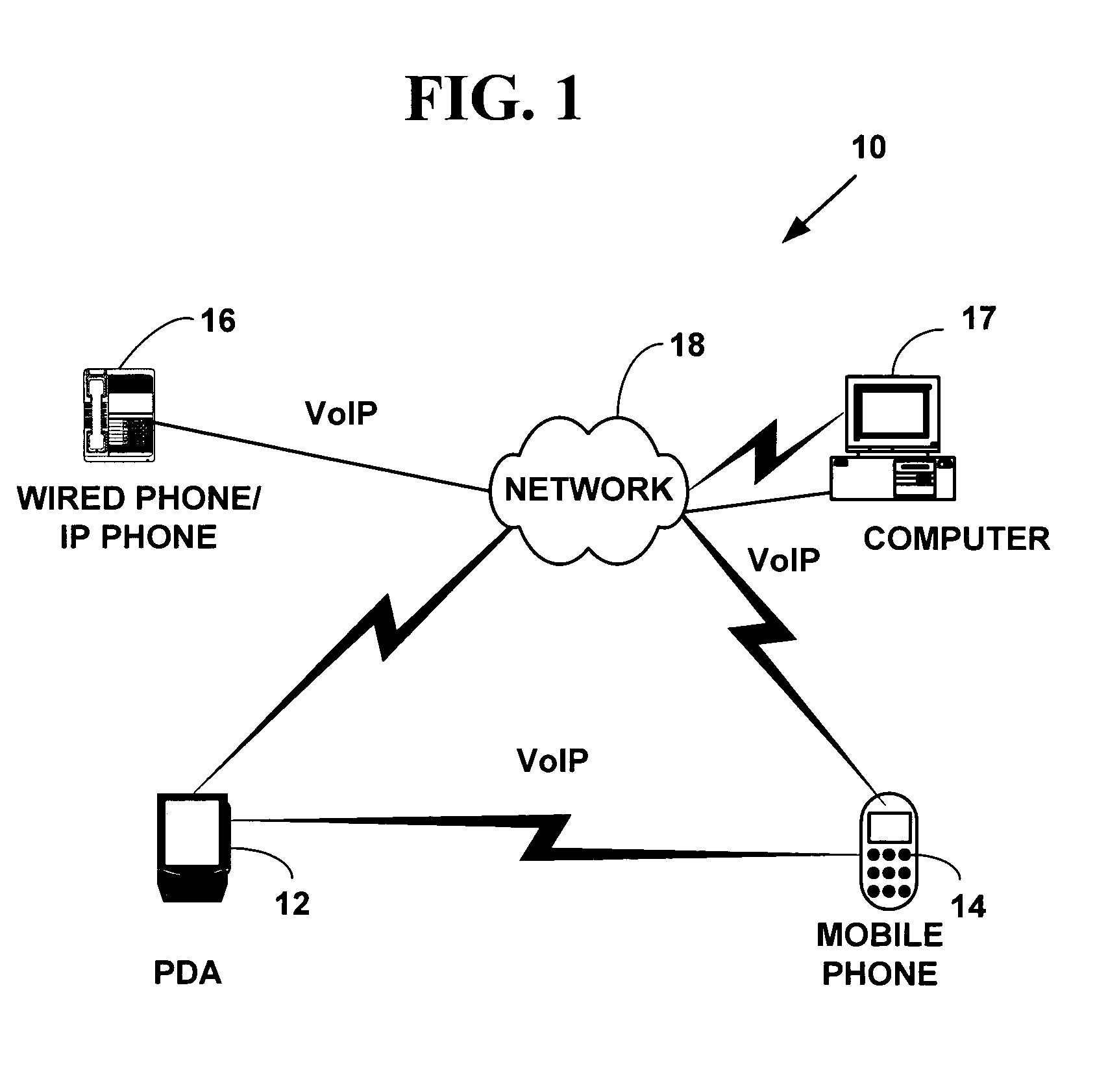
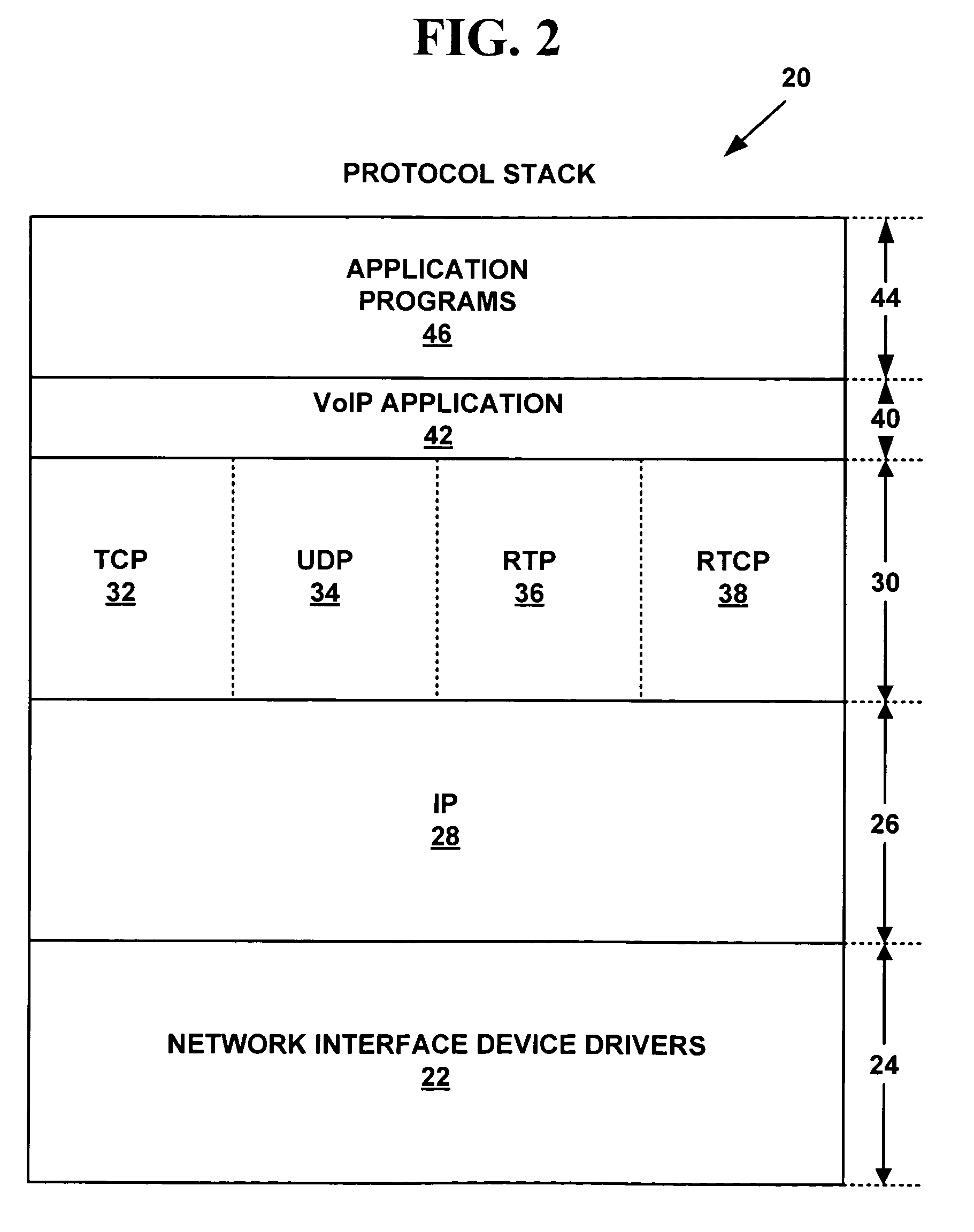
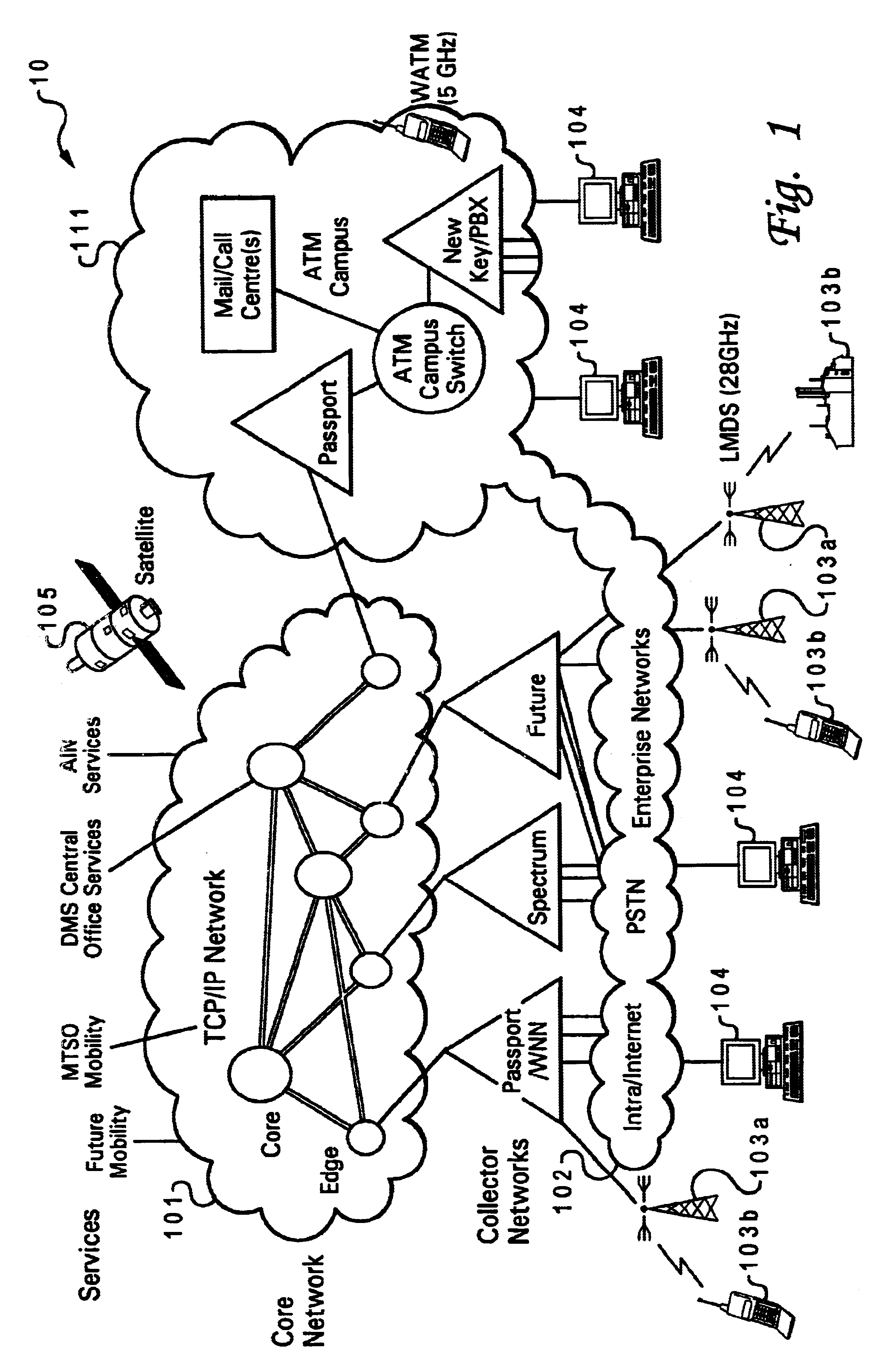
Multifunctional world wide walkie talkie, a tri-frequency cellular-satellite wireless instant messenger computer and network for establishing global wireless volp quality of service (QOS) communications, unified messaging, and video conferencing via the internet
InactiveUS6763226B1High quality voice and data communicationMinimal costCordless telephonesInterconnection arrangementsQuality of serviceMass storage
World-Wide-Walkie-Talkie, a high speed multifunction interstellar wireless computer / instant messenger communicator, Personal Digital Assistant (PDA), coupled with a resilient, robust, VoIP data network and internet server method, deploying multiple wireless networks and protocols such as Voice Over IP, GPRS, WAP, Bluetooth, PCS, I-Mode, comprising a high speed Intel Pentium 4 Mobile(TM) or compatible Processor, to formulate a internet gateway system (99) and network bridge (150) for establishing instant low cost, real time global communications to the Public Switched Telephone Network via the internet (54). A PUSH-TO-TALK-WORLDWIDE button (21) instantly initiates global bisynchronous communications, or videoconferencing sessions. Fax, VideoMail, and unified messaging services are immediately available. GPS and mass memory provides global navigational tracking and data storage. Internet users, telephones, and cellular / satellite phone users can intercommunicate with the invention via VoIP / IM services. The invention provides uniformed global wireless communications, eliminates traditional long distance costs, and operates anywhere on earth.
Owner:COMP SCI CENT
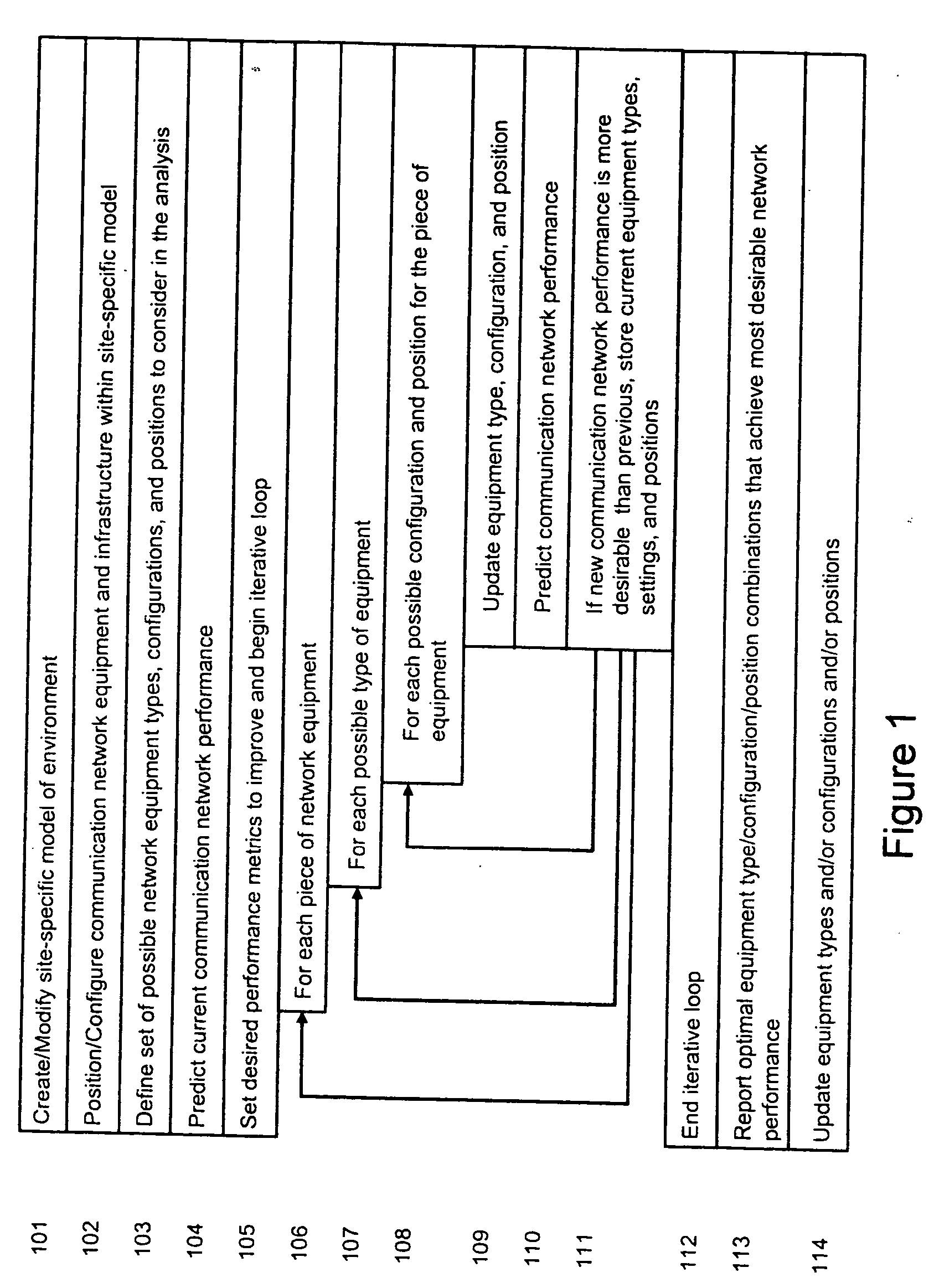
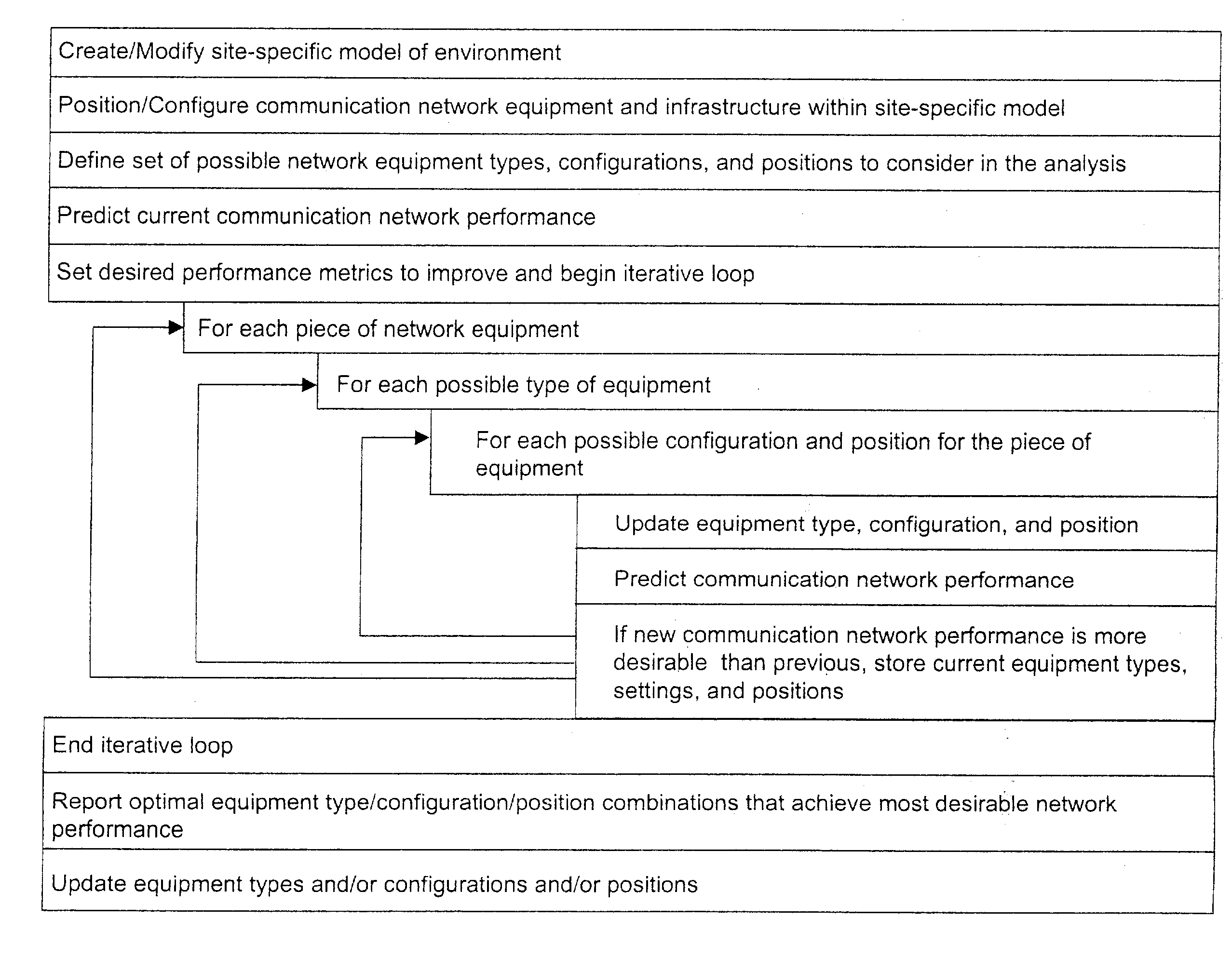
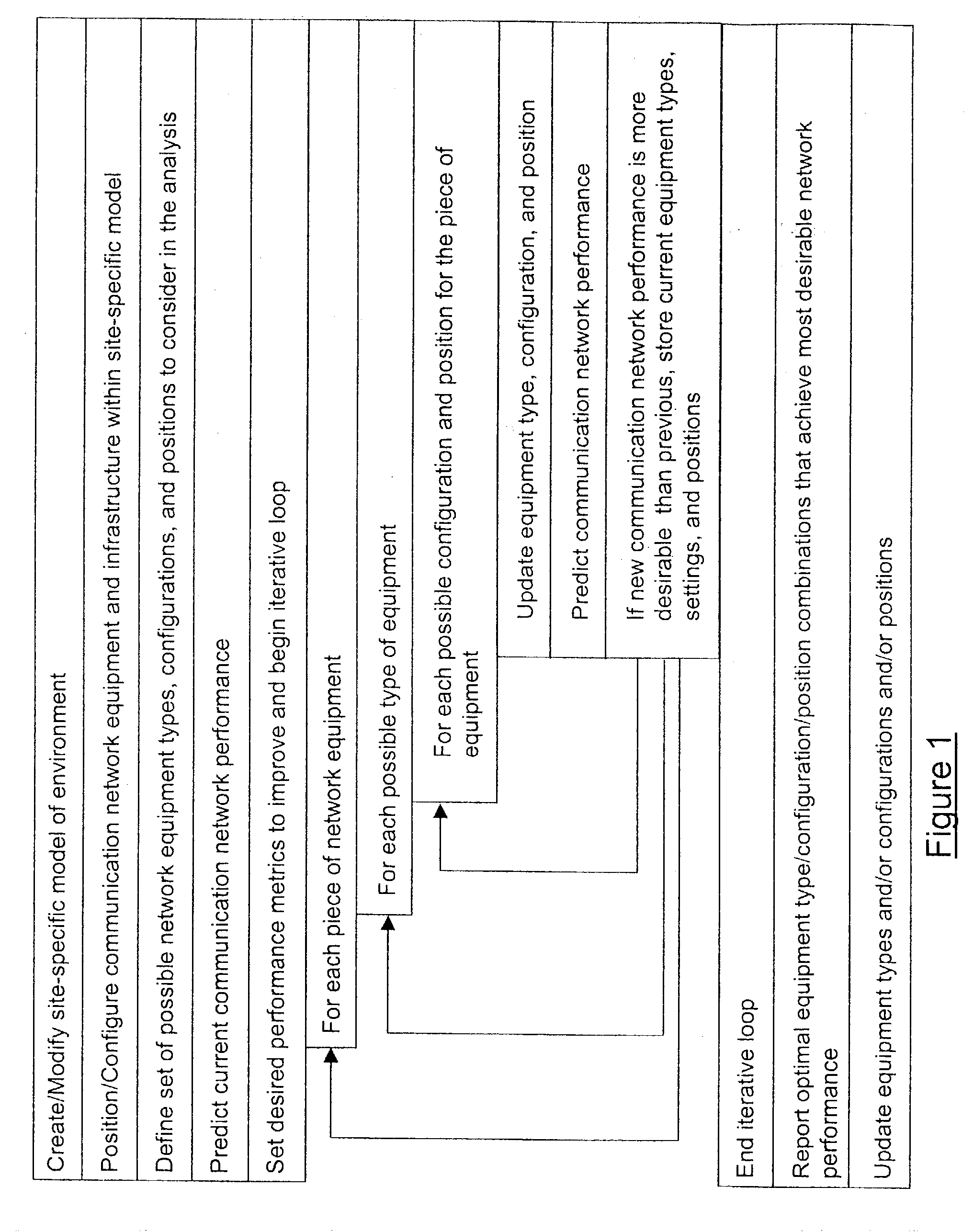
System and method for automated placement or configuration of equipment for obtaining desired network performance objectives and for security, RF tags, and bandwidth provisioning
ActiveUS20040236547A1Significant valueEasy to explainGeometric CADData taking preventionHard disc driveThe Internet
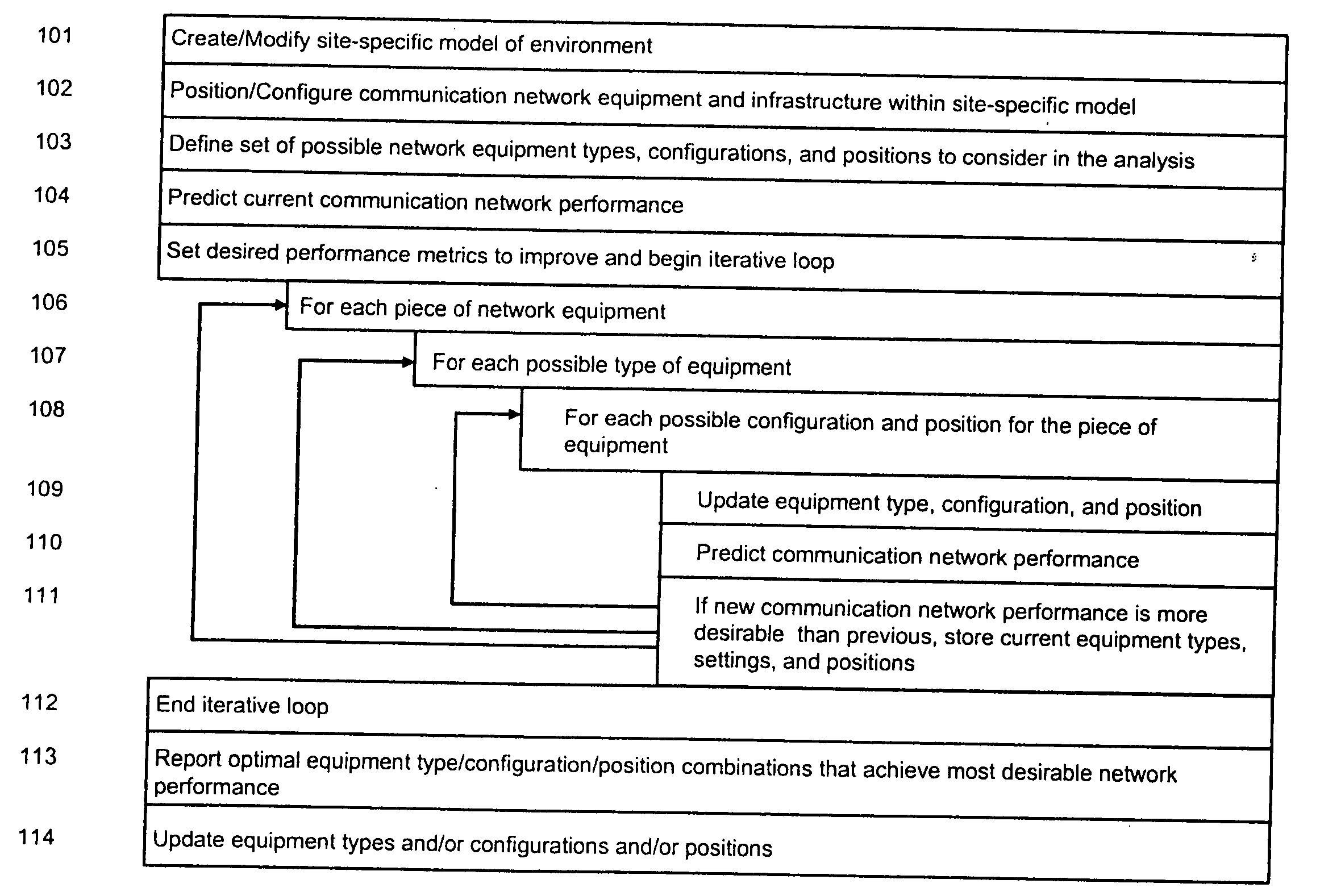
A method is presented for determining optimal or preferred configuration settings for wireless or wired network equipment in order to obtain a desirable level of network performance. A site-specific network model is used with adaptive processing to perform efficient design and on-going management of network performance. The invention iteratively determines overall network performance and cost, and further iterates equipment settings, locations and orientations. Real time control is between a site-specific Computer Aided Design (CAD) software application and the physical components of the network allows the invention to display, store, and iteratively adapt any network to constantly varying traffic and interference conditions. Alarms provide rapid adaptation of network parameters, and alerts and preprogrammed network shutdown actions may be taken autonomously. A wireless post-it note device and network allows massive data such as book contents or hard drive memory to be accessed within a room by a wide bandwidth reader device, and this can further be interconnected to the internet or Ethernet backbone in order to provide worldwide access and remote retrieval to wireless post-it devices.
Owner:EXTREME NETWORKS INC
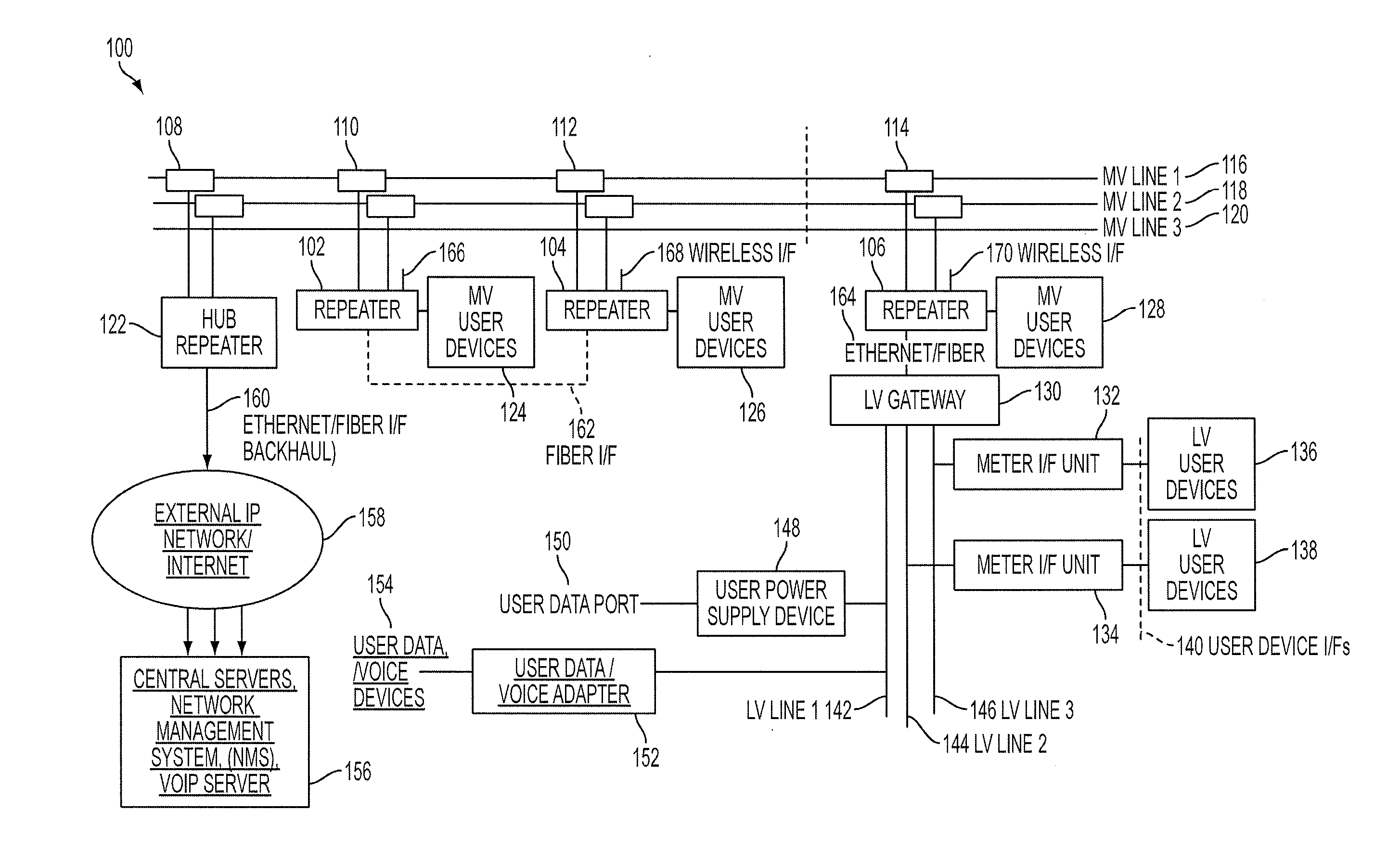
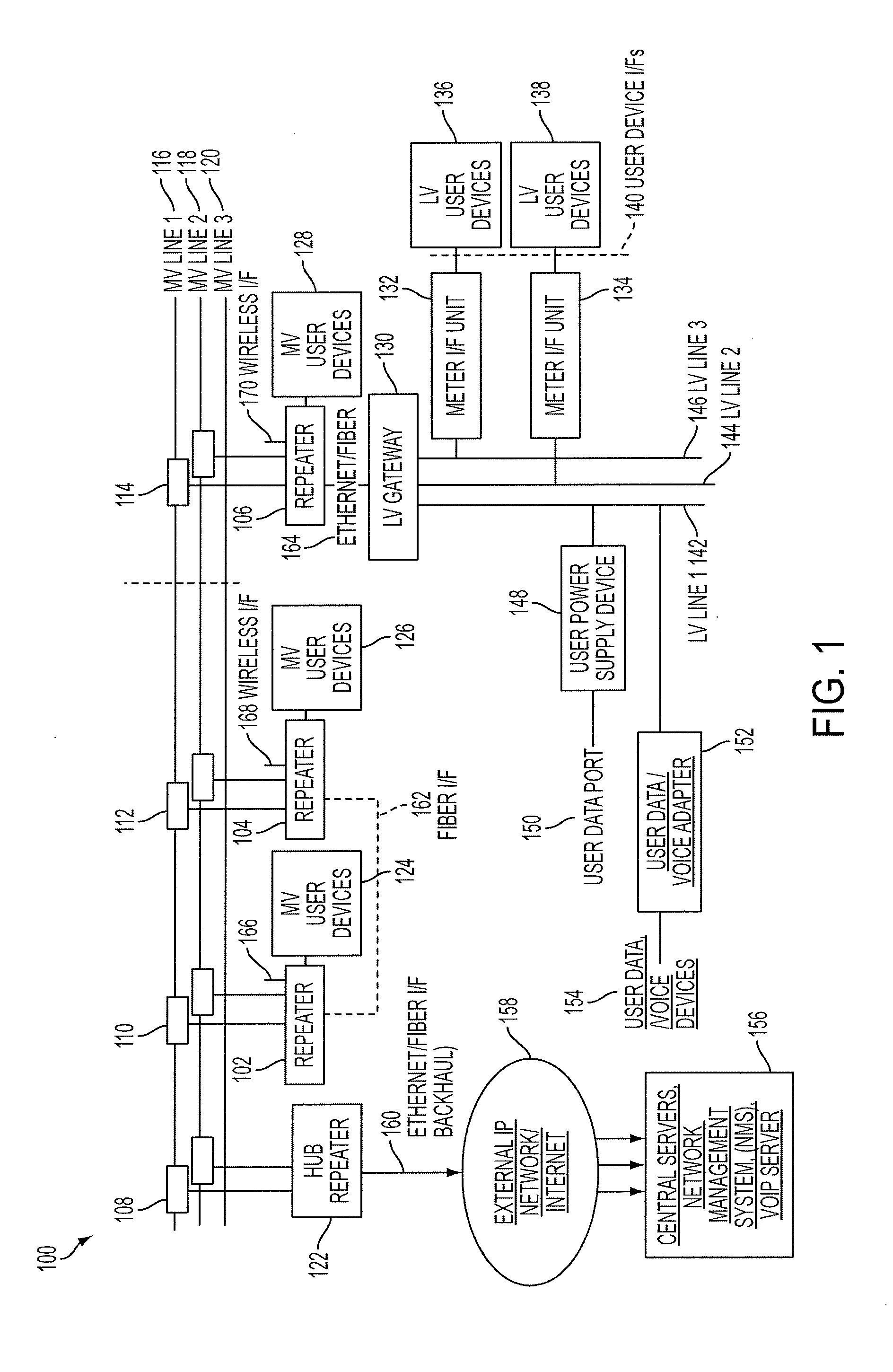
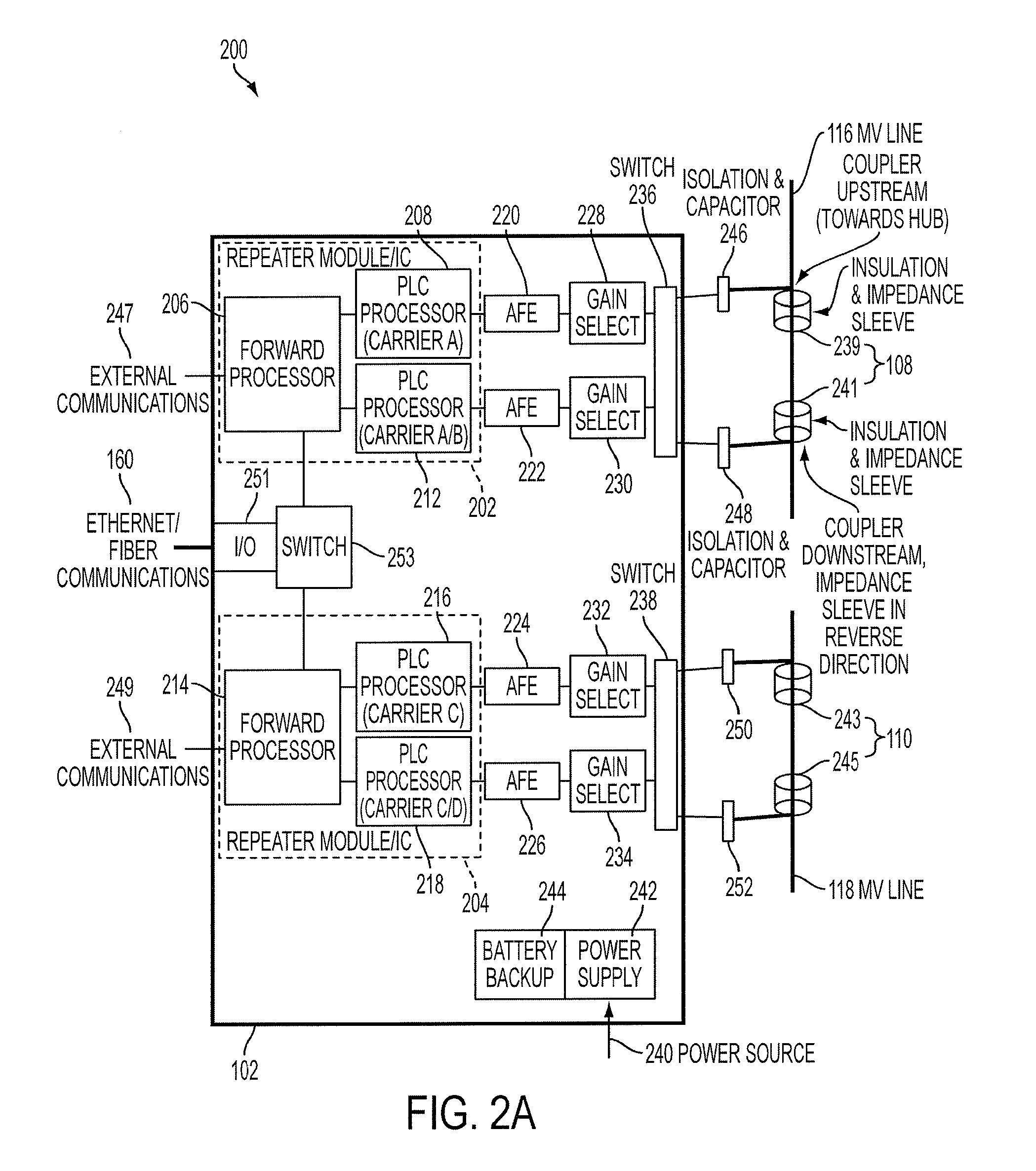
Reliable, long-haul data communications over power lines for meter reading and other communications services
InactiveUS20110140911A1Highly long-haulImprove reliabilityElectric signal transmission systemsPower distribution line transmissionPower qualitySignal quality
A system, method and computer program product provides for power line communications (PLC) over electric power lines includes a device mountable near an electrical distribution transformer (DT) to provide a high speed interface and communicates with one or multiple access devices, which provide low speed interfaces for analog signals or digital signals over RS 232, RS 485, optical, wireless and Ethernet. The device transmits data to / from these access devices over the electric lines to other repeaters over one or more wires of an electrical line or over multiple lines, and serves to strengthen and improve signal quality. Upon detecting a wire or line is having problems carrying data, the data is sent over other wires, and upon power line failures, wireless backup to mobile / GSM and WiMax networks is utilized. The device permits utilities and others to read electric meters, monitor the power quality of the distribution grid and detect power losses / failures / outages, and permits telecom service providers and others to provide a communications link to cell phone towers, WiFi Access Points and enable broadband Internet and telephony in rural, remote or sparely populated areas.
Owner:POWERMAX GLOBAL
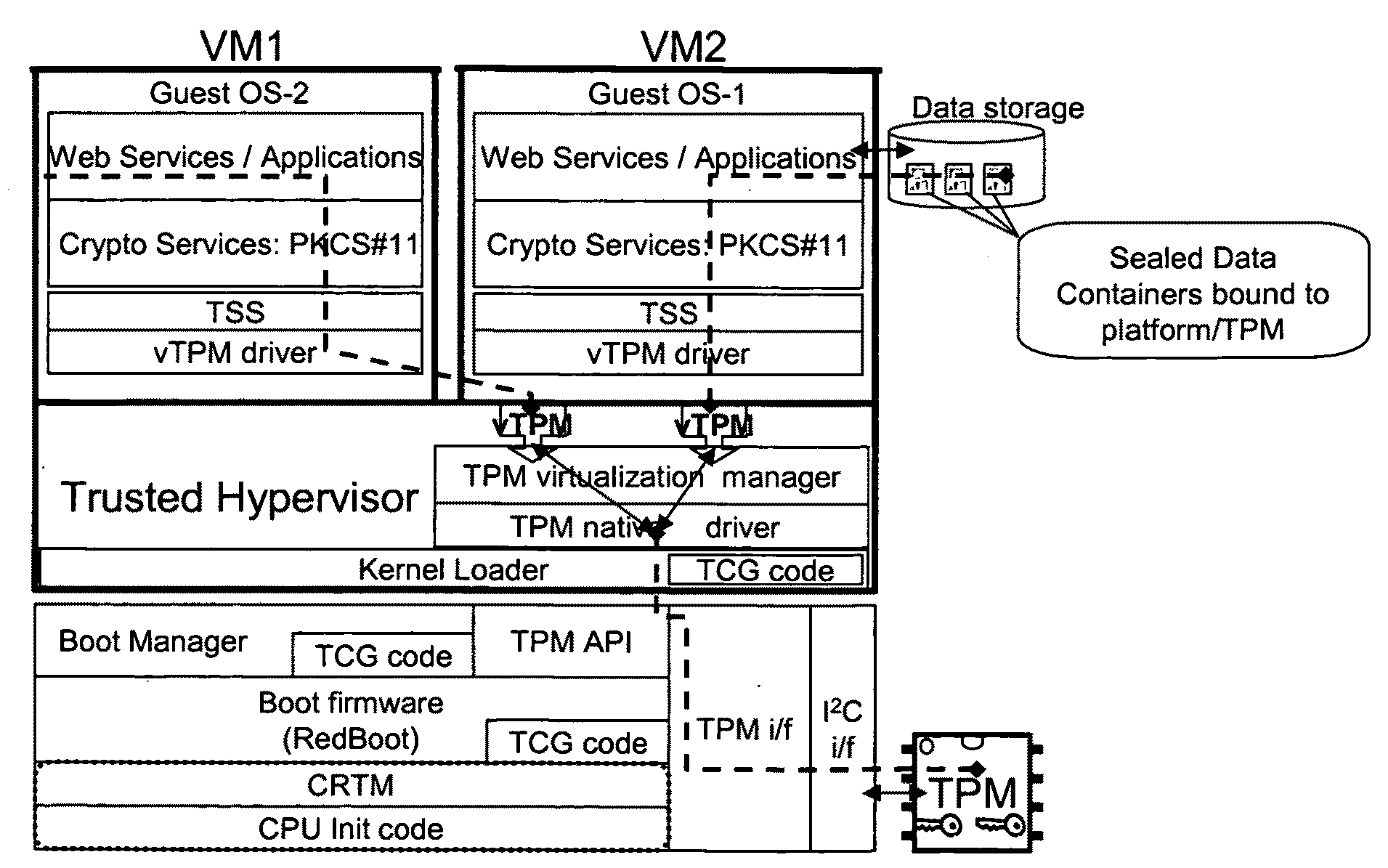
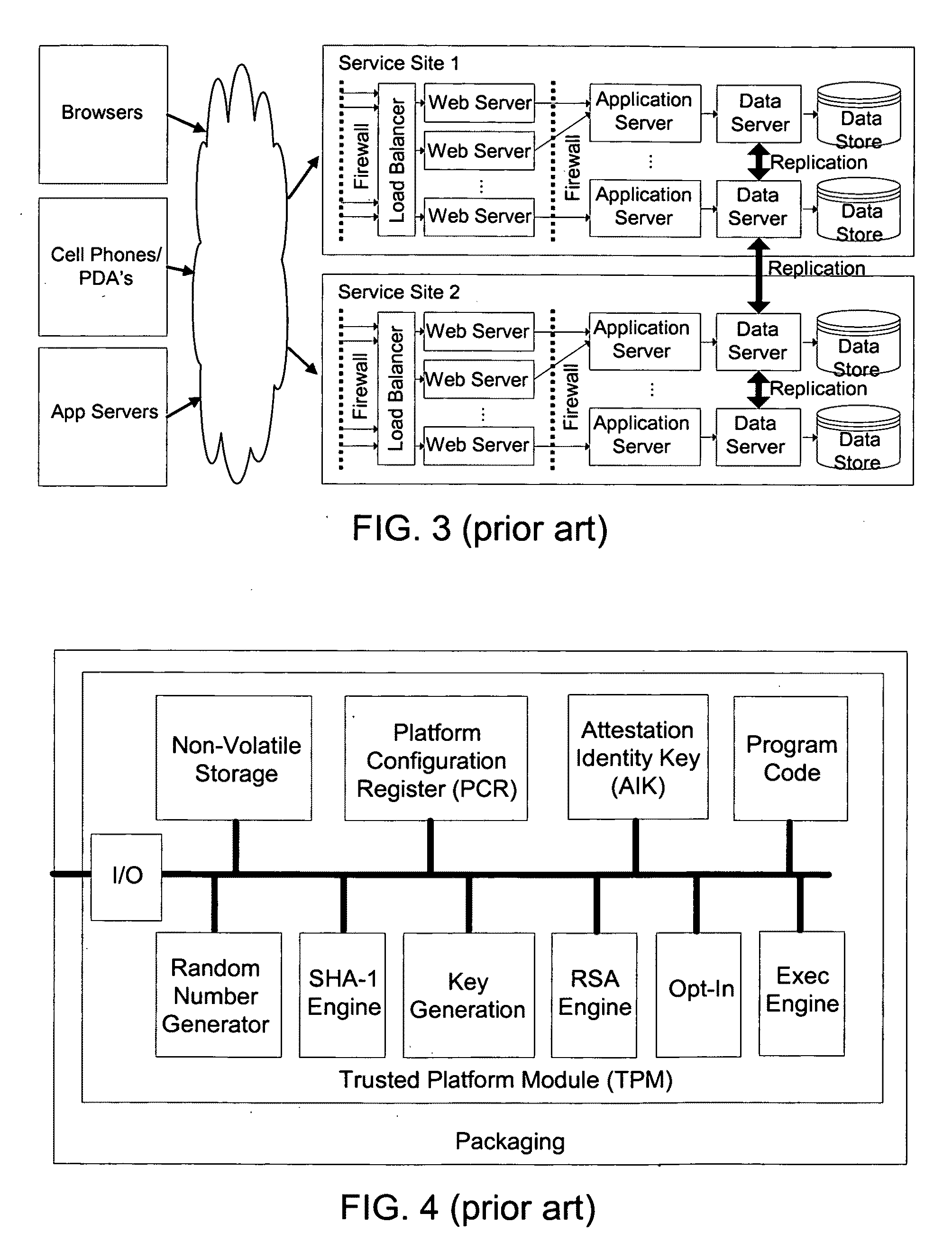
Distributed trusted virtualization platform
InactiveUS20090204964A1Key distribution for secure communicationMultiple digital computer combinationsVirtualizationEnd to end security
A platform architecture shifts the networked computing paradigm from PC+Network to a system using trusted mobile internet end-point (MIEP) devices and cooperative agents hosted on a trusted server. The MIEP device can participate in data flows, arbitrate authentication, and / or participate in implementing security mechanisms, all within the context of assured end-to-end security. The MIEP architecture improves platform-level capabilities by suitably (and even dynamically) partitioning what is done at the MIEP nodes, the network, and the server based infrastructure for delivering services.
Owner:MOTEGRITY +1
Method and system for providing private virtual secure Voice over Internet Protocol communications
InactiveUS20060187900A1Maintain privacyInterconnection arrangementsFrequency-division multiplex detailsVoice communicationPrivate network
A method and system for secure Voice over Internet Protocol (IP) (VoIP) communications. The method and system provide secure VoIP voice calls, video, Instant Messaging (IM), Short Message Services (SMS), or Peer-to-Peer (P2P) communications while maintaining privacy over the Internet and other communications networks such as the pubic switched telephone network (PSTN) to and from any network device through a virtual private network infrastructure interconnecting private VoIP network devices. The method and system allow a network device to function as an IP private branch exchange (PBX) or a private VoIP gateway and provide and control VoIP voice communications without using other public or private VoIP gateways or VoIP servers or devices on a communications network such as the PSTN or the Internet.
Owner:LESAVICH HIGH TECH LAW GRP SC
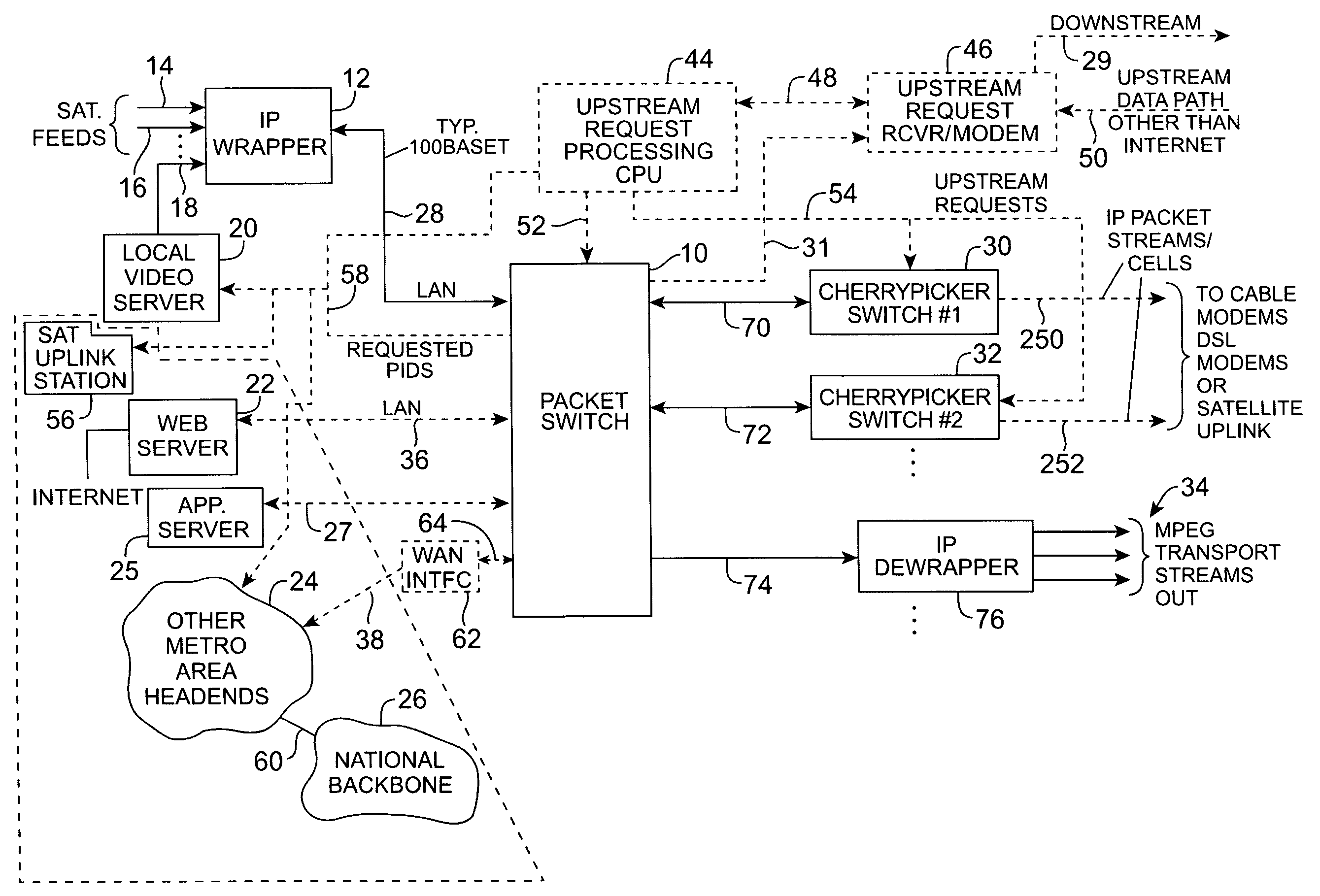
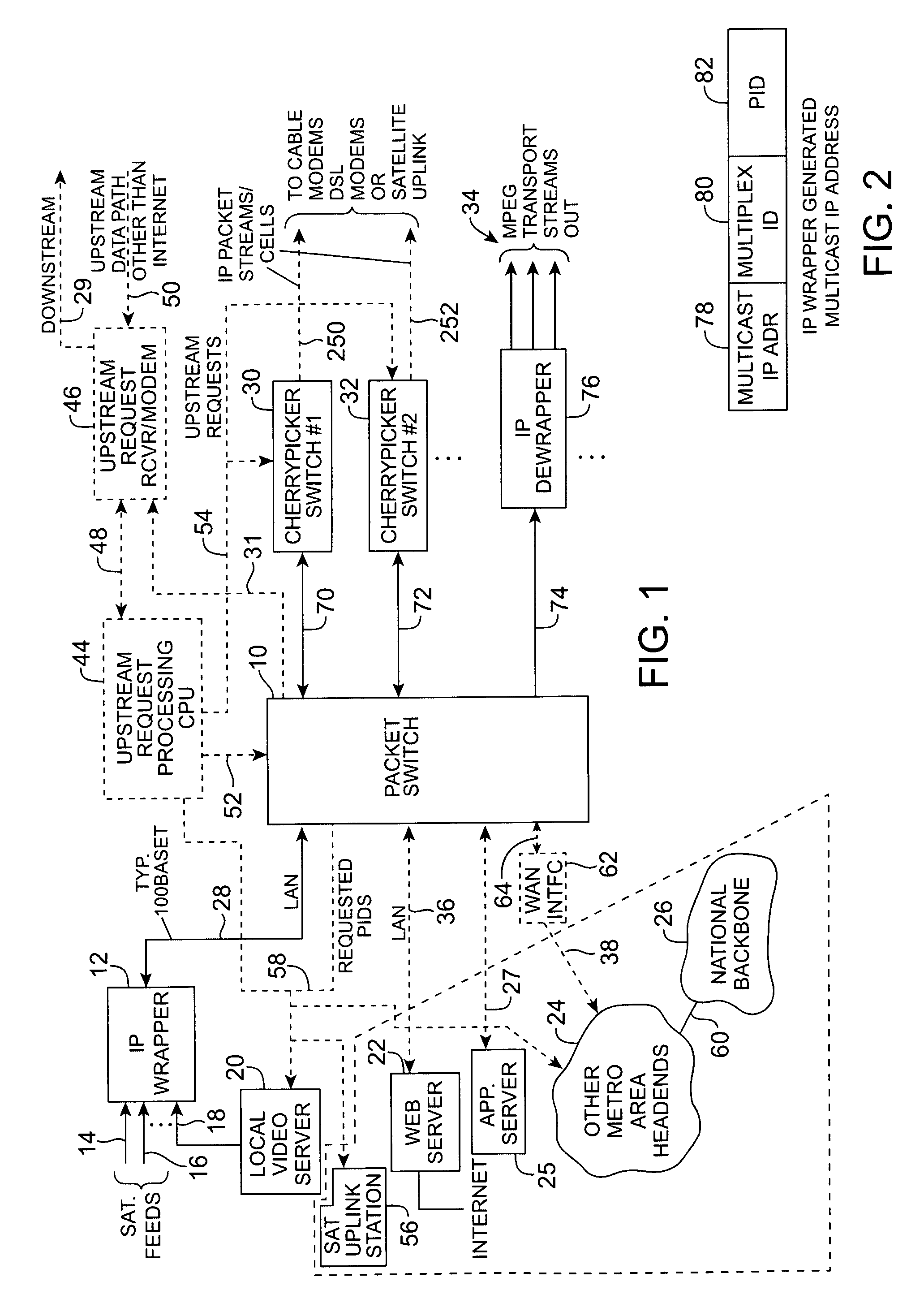
Headend cherrypicker multiplexer with switched front end
InactiveUS7039048B1Low costEasily scaledBroadband local area networksTime-division multiplexMPEG transport streamModem device
A headend or central office or satellite uplink facility for receiving upstream video-on-demand requests and MPEG transport streams containing video program data and packetizing said video data into TCP / IP or UDP / IP packets and LAN packets and routing them through a switch to one or more cherrypicker multiplexers. Each cherrypicker multiplexer receives LAN packets, depacketizes the MPEG data, partially or fully decompresses the data and recompresses the data to another smaller bandwidth, and repacketizes the data into MPEG packets or TCP / IP or UDP / IP packets. The repacketized TCP / IP or UDP / IP packets are transmitted directly to the customer as TCP / IP or UDP / IP packet data. MPEG packets generated by the cherrypicker multiplexer are, optionally, encapsulated in LAN packets addressed to an IP dewrapper circuit. There, they are depacketized back to MPEG packets and transmitted to the appropriate transmitter or modem for transmitting to a customer. Internet data and data from application servers, referred to as iData, can also be transmitted to customers through the cherrypicker multiplexers or a downstream modem, and upstream iData can be received through the modem.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
Internet appliance system and method
InactiveUS20060200253A1Minimize timeTelevision system detailsAdvertisementsPhysical securityThe Internet
An Internet appliance, comprising, within a single housing, packet data network interfaces, adapted for communicating with the Internet and a local area network, at least one data interface selected from the group consisting of a universal serial bus, an IEEE-1394 interface, a voice telephony interface, an audio program interface, a video program interface, an audiovisual program interface, a camera interface, a physical security system interface, a wireless networking interface; a device control interface, smart home interface, an environmental sensing interface, and an environmental control interface, and a processor, for controlling a data transfer between the local area network and the Internet, and defining a markup language interface communicated through a packet data network interface, to control a data transfer or control a remote device.
Owner:BLANDING HOVENWEEP
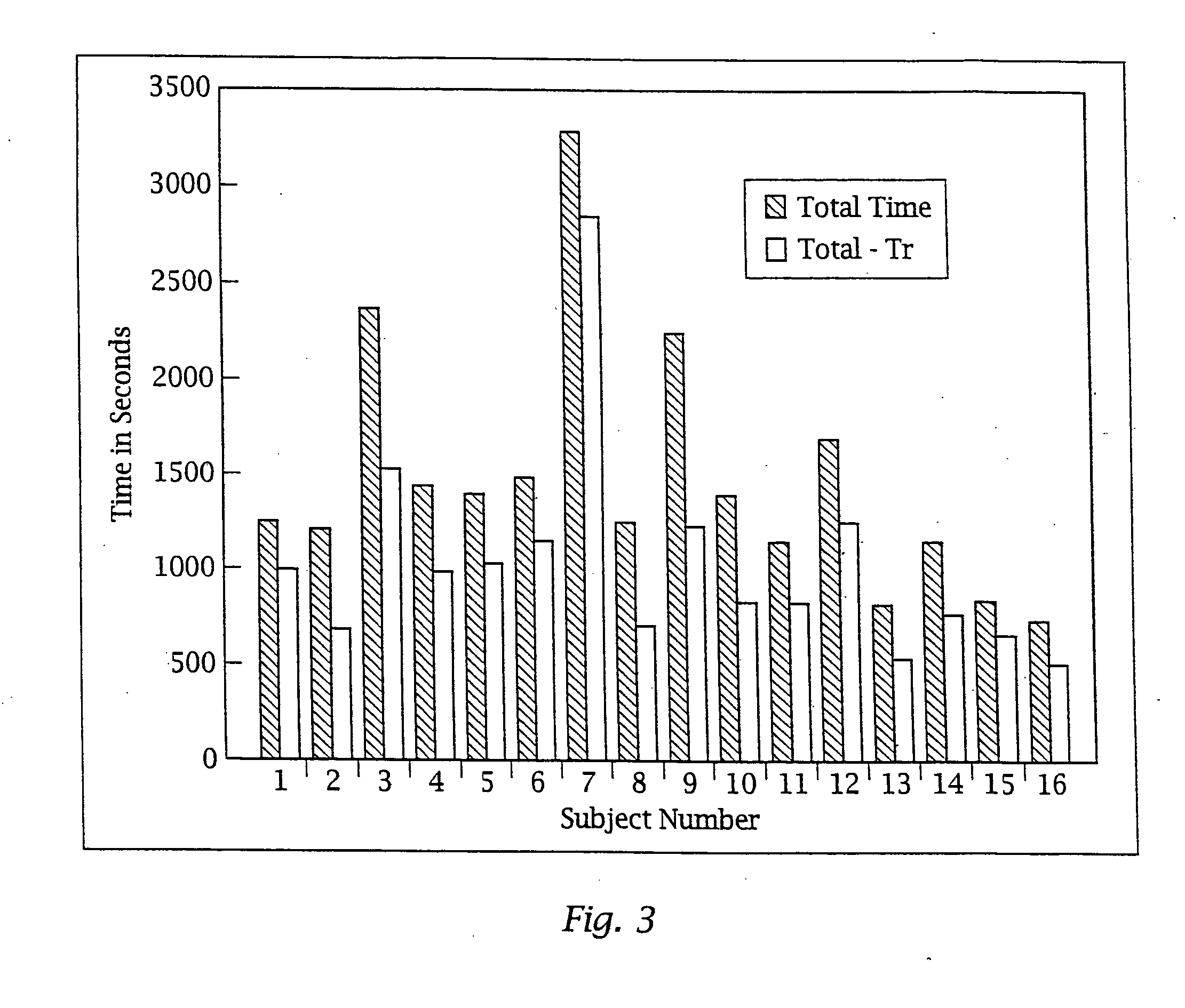
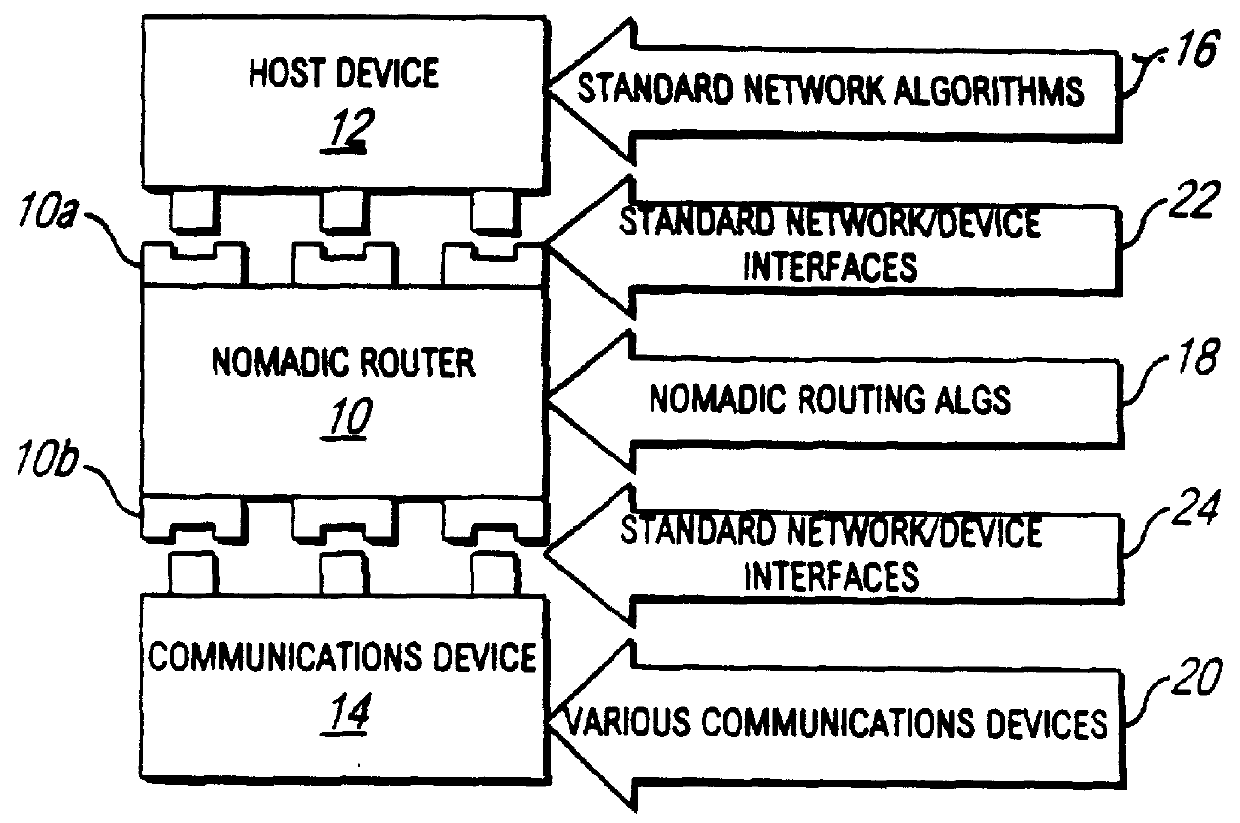
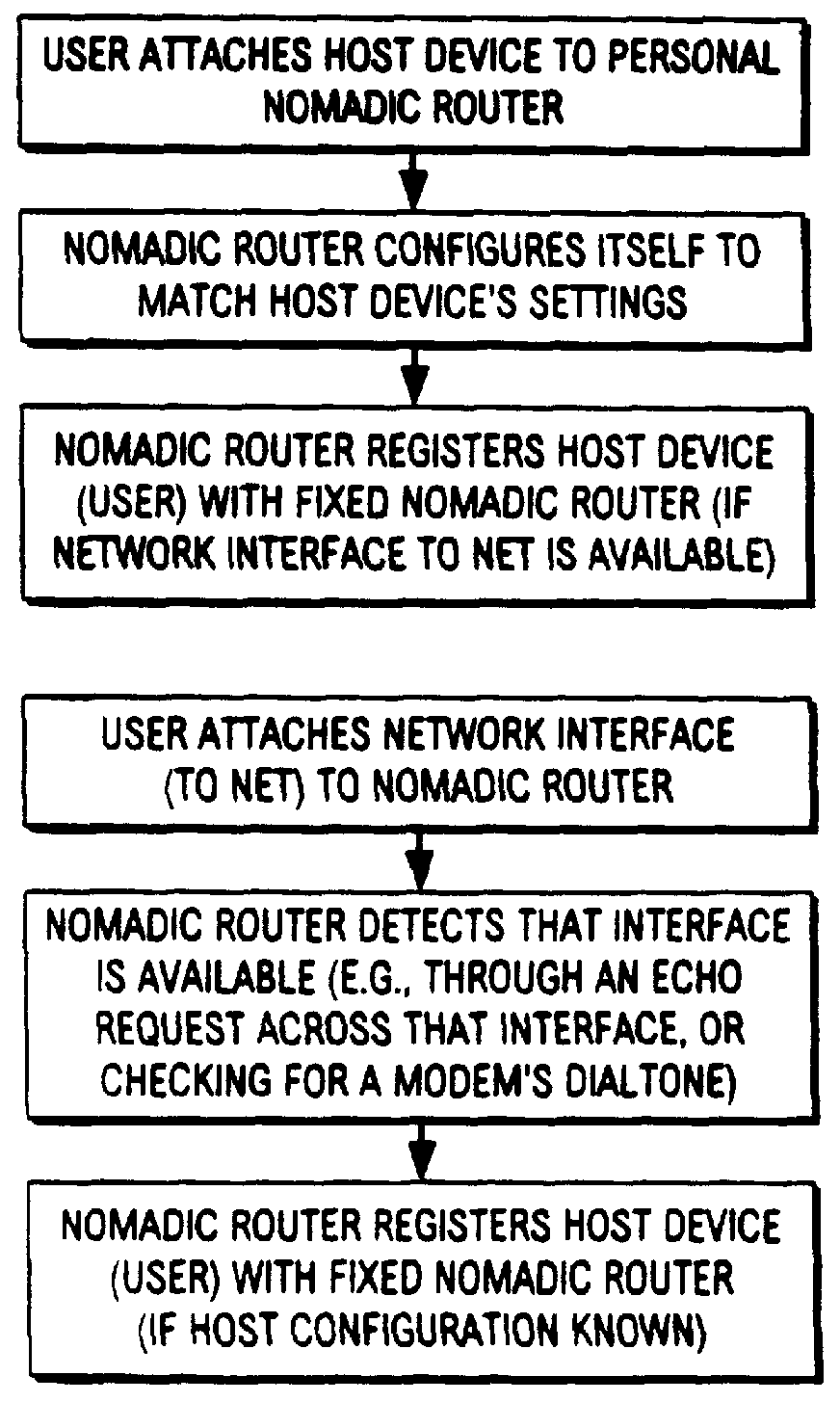
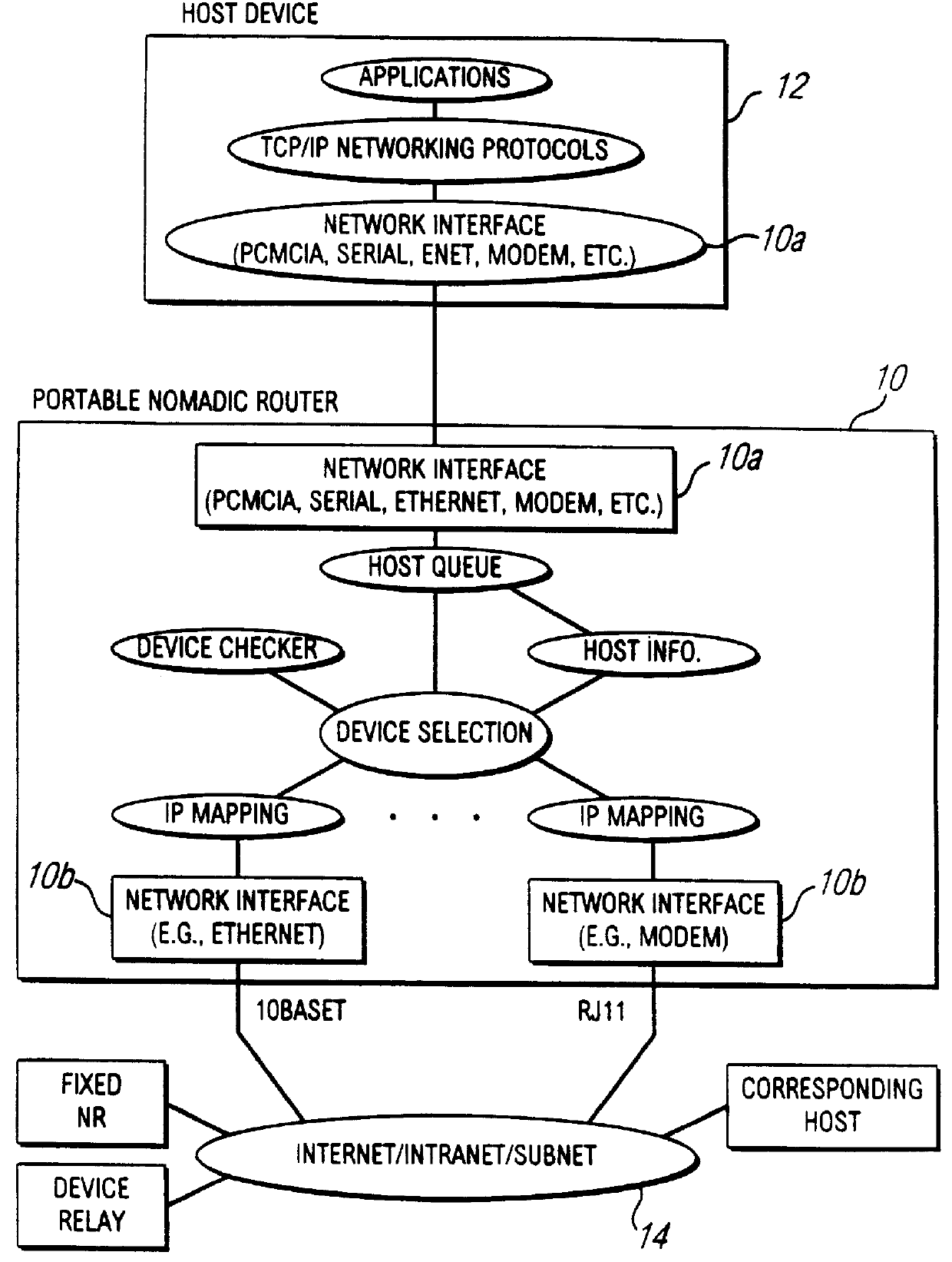
Nomadic translator or router
InactiveUS6130892ASupport mobilitySoft handoffNetwork topologiesTime-division multiplexDigital dataFile synchronization
A nomadic router or translator enables a laptop computer or other portable terminal which is configured to be connected to a home network to be connected to any location on the internet or other digital data communication system. The router automatically and transparently re-configures the terminal to its new location and processes outgoing and incoming data. The router includes a processor which appears as the home network to the terminal, and appears as the terminal to the communication system. The terminal has a permanent address, the router has a router or translator address, and the terminal transmits outgoing data to the system including the permanent address as a source address. The processor translates the outgoing data by replacing the permanent address with the router address as the source address. The terminal receives incoming data from the system including the router address as a destination address, and the processor translates the incoming data by replacing the router address with the permanent address as the destination address. Alternatively, the terminal can be directly connected to a point on a local network, and the router connected to another point on the network. The router can be employed to implement numerous applications including nomadic e-mail, network file synchronizer, database synchronizer, instant network, nomadic internet and trade show router and can also be utilized as a fixed nomadic router.
Owner:NOMADIX INC
Method and system for wireless QOS agent for all-IP network
A wireless quality of service (QoS) agent for an all-Internet Protocol (IP) network. The QoS agent couples to an all-IP network. The coupling means includes communication means for transfer of information between the agent and a QoS manager of the all-IP network. The agent is also able to seamlessly extend QoS support for multimedia applications from wireline to wireless and control QoS of the multimedia applications sent over wireless connections on the all-IP network.
Owner:BLACKBERRY LTD
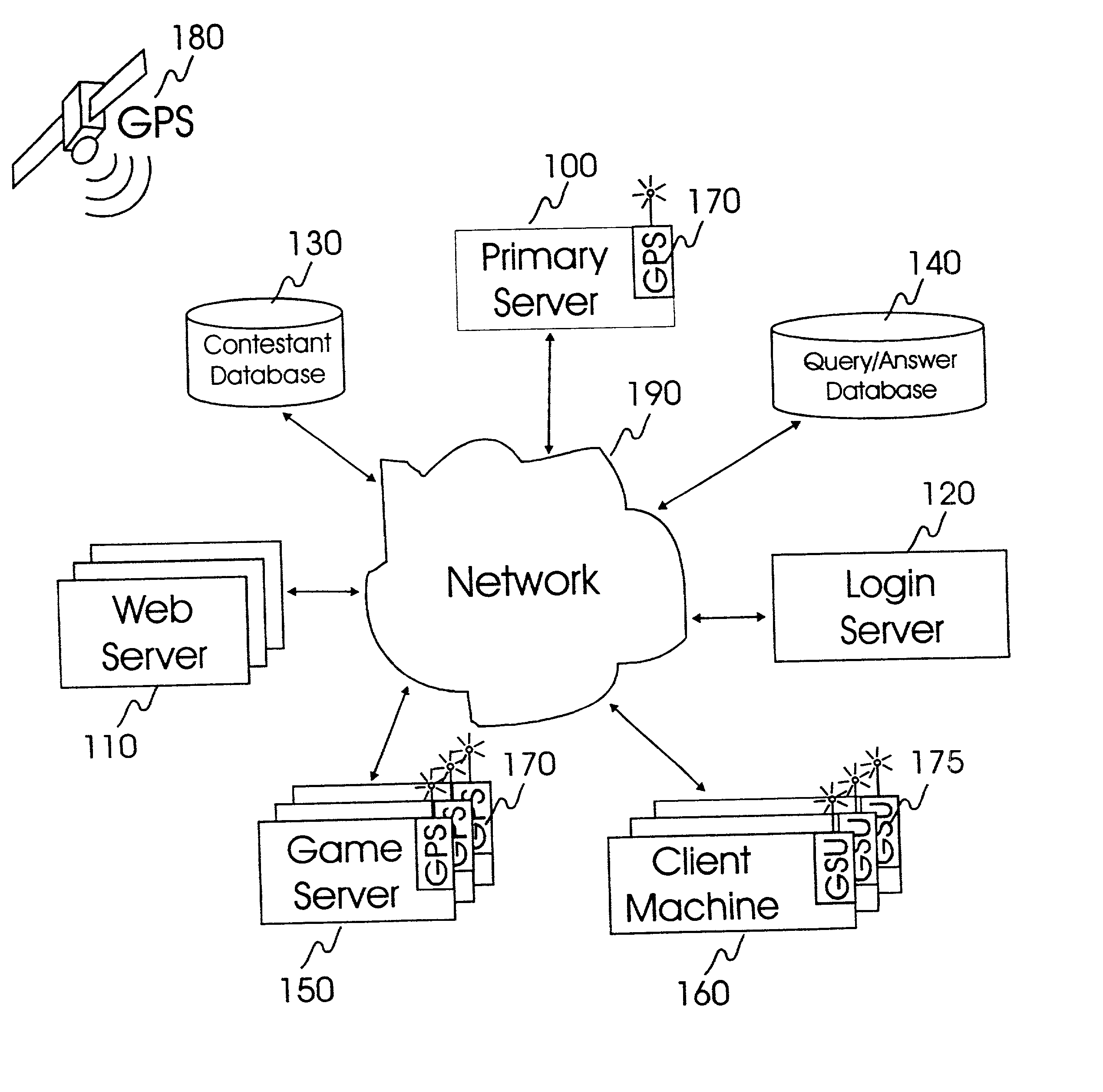
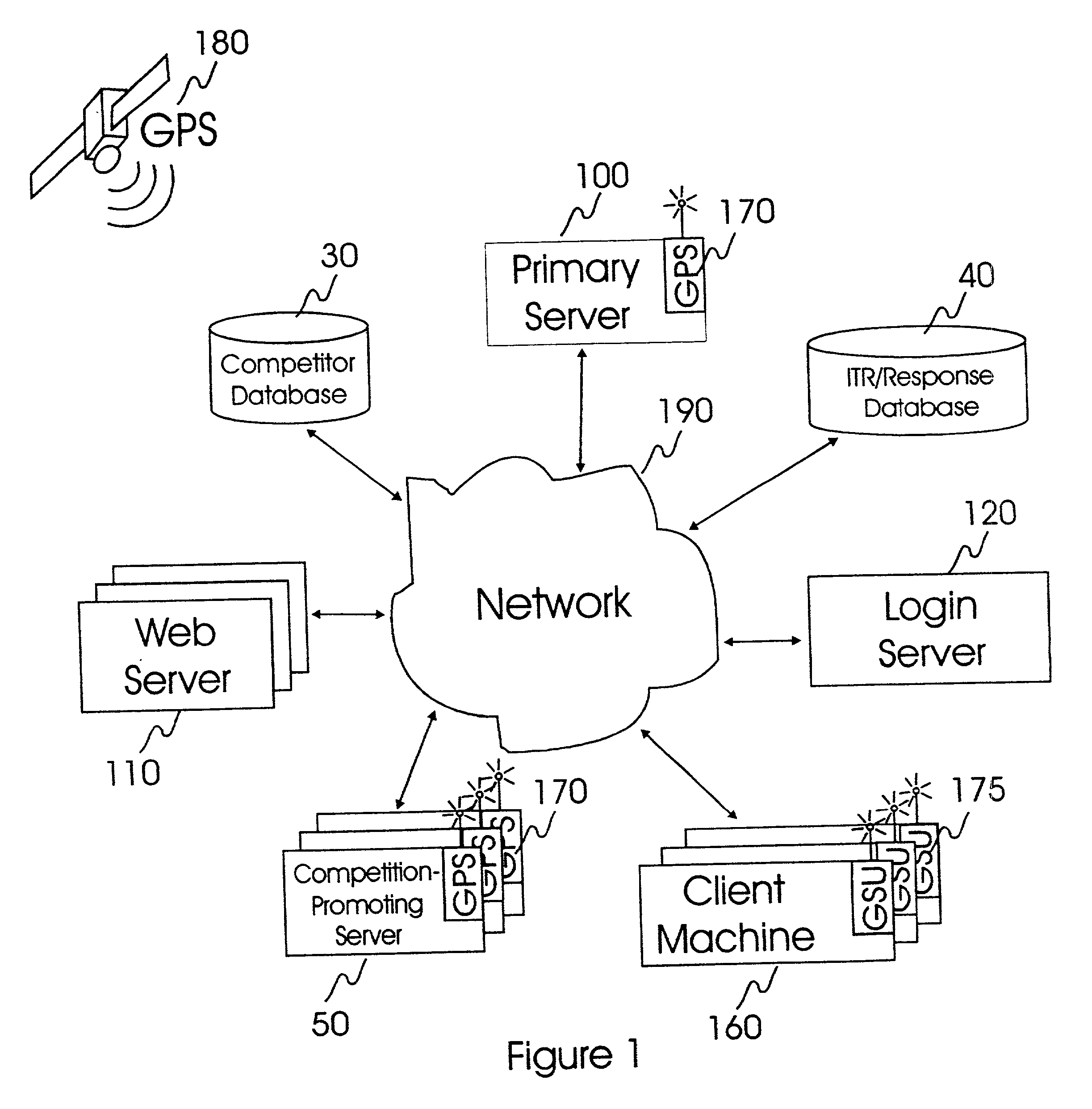
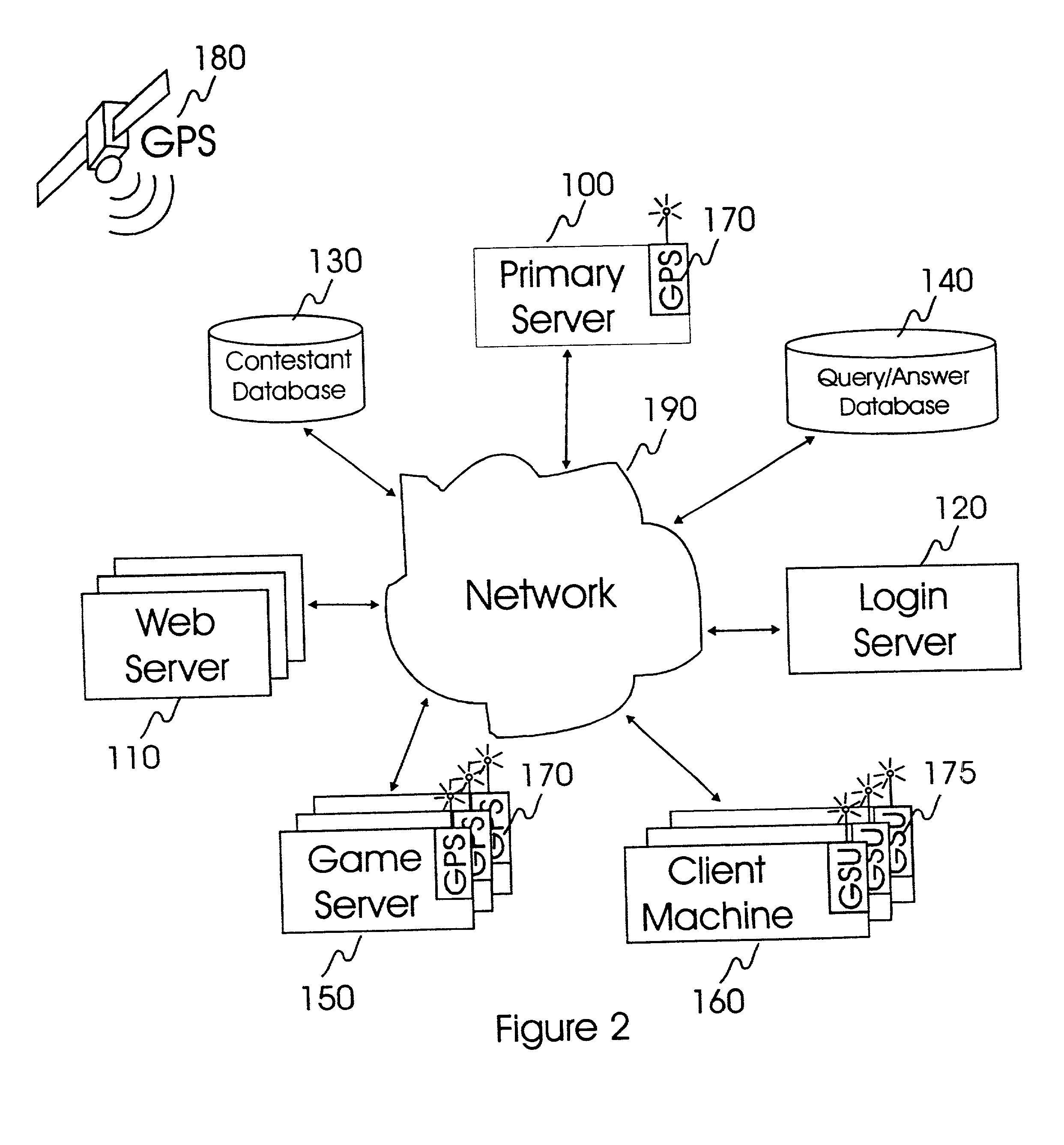
Internet-based system and method for fairly and securely enabling timed-constrained competition using globally time-sychronized client subsystems and information servers having microsecond client-event resolution
InactiveUS20020026321A1Avoiding shortcoming and drawbackBetterment of human societyBuying/selling/leasing transactionsVideo gamesTime responseTTEthernet
An improved system and method of fairly and securely enabling timed-constrained competitions over the Internet among millions of competitors while compensating for the variable network communication latencies experienced by client machines used by the competitors. The system employs globally time-synchronized Internet information servers and client machines in order to synchronize the initial display of each invitation to respond (e.g. stock price to buy or sell, query to answer, or problem to solve) on a client machine so each competitor can respond to the invitation at substantially the same time, regardless of his or her location on the planet, or the type of Internet-connection used by his or her client machine. Also, by using globally time-synchronized client machines, each competitor's response is securely time and space stamped at the client machine to ensure that competitor responses are resolved within microsecond accuracy.
Owner:REVEO
System and method for automated placement or configuration of equipment for obtaining desired network performance objectives
ActiveUS20040143428A1Significant valueEasy to explainGeometric CADProgram controlHard disc driveThe Internet
A method is presented for determining optimal or preferred configuration settings for wireless or wired network equipment in order to obtain a desirable level of network performance. A site-specific network model is used with adaptive processing to perform efficient design and on-going management of network performance. The invention iteratively determines overall network performance and cost, and further iterates equipment settings, locations and orientations. Real time control is between a site-specific Computer Aided Design (CAD) software application and the physical components of the network allows the invention to display, store, and iteratively adapt any network to constantly varying traffic and interference conditions. Alarms provide rapid adaptation of network parameters, and alerts and preprogrammed network shutdown actions may be taken autonomously. A wireless post-it note device and network allows massive data such as book contents or hard drive memory to be accessed within a room by a wide bandwidth reader device, and this can further be interconnected to the internet or Ethernet backbone in order to provide worldwide access and remote retrieval to wireless post-it devices.
Owner:EXTREME NETWORKS INC
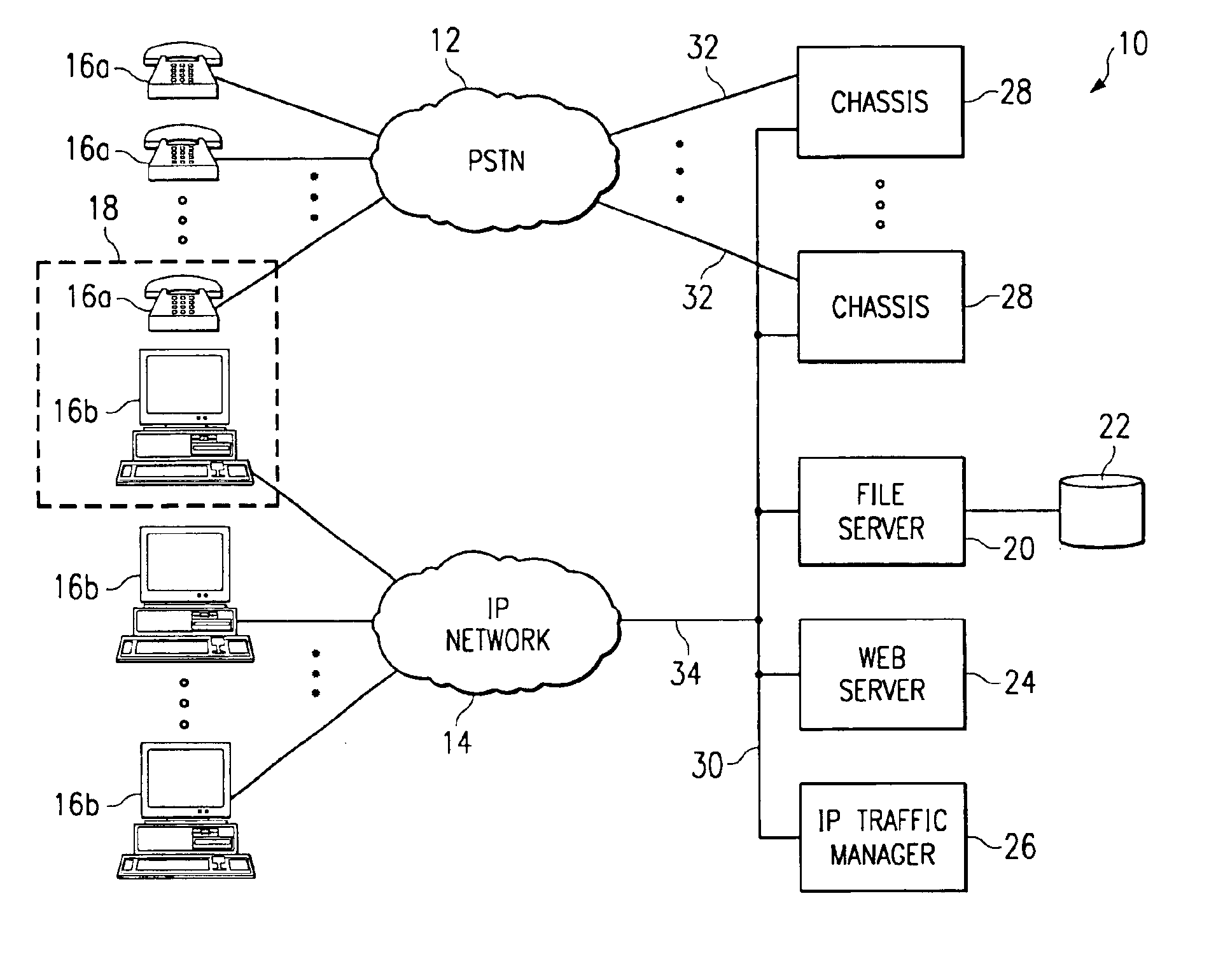
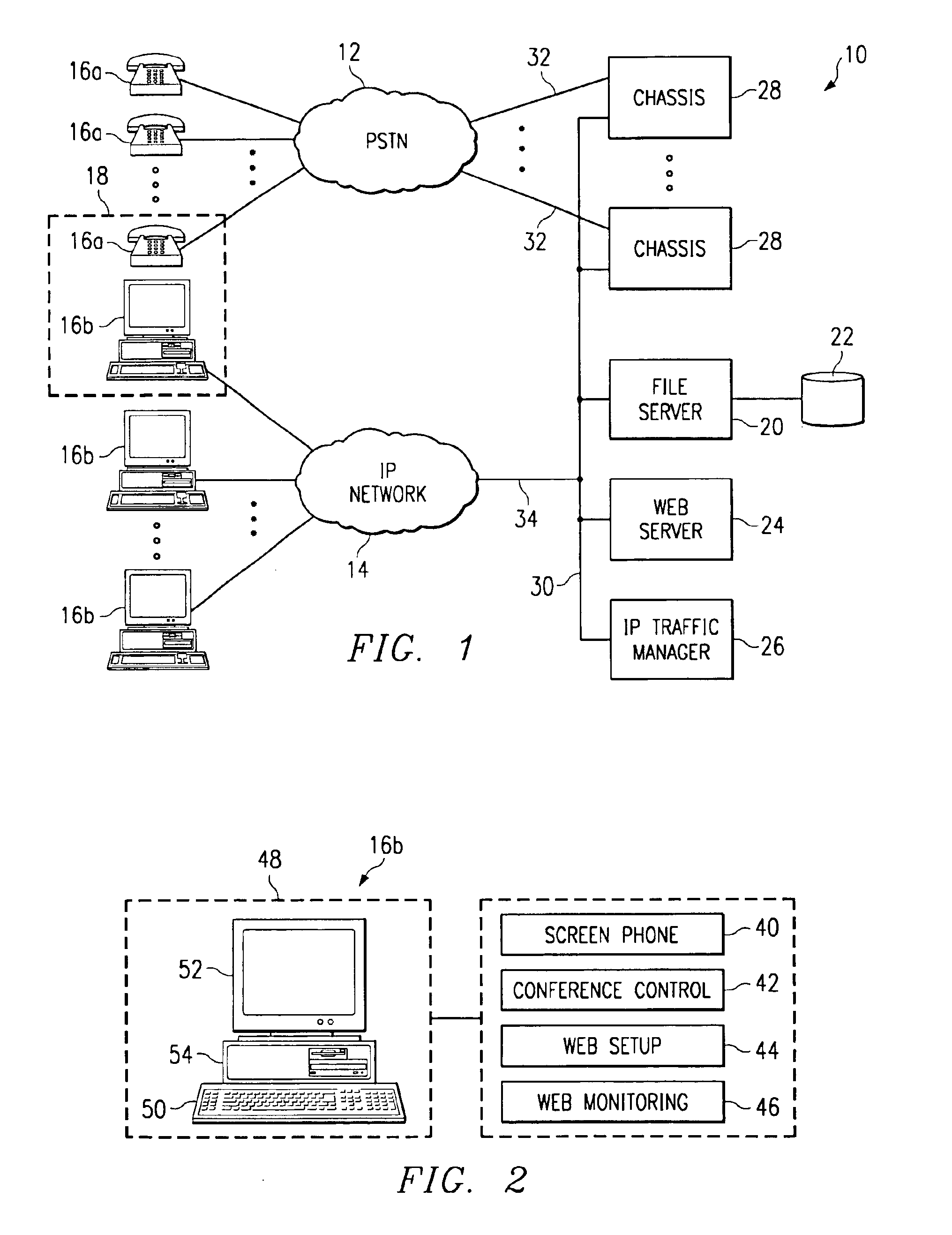
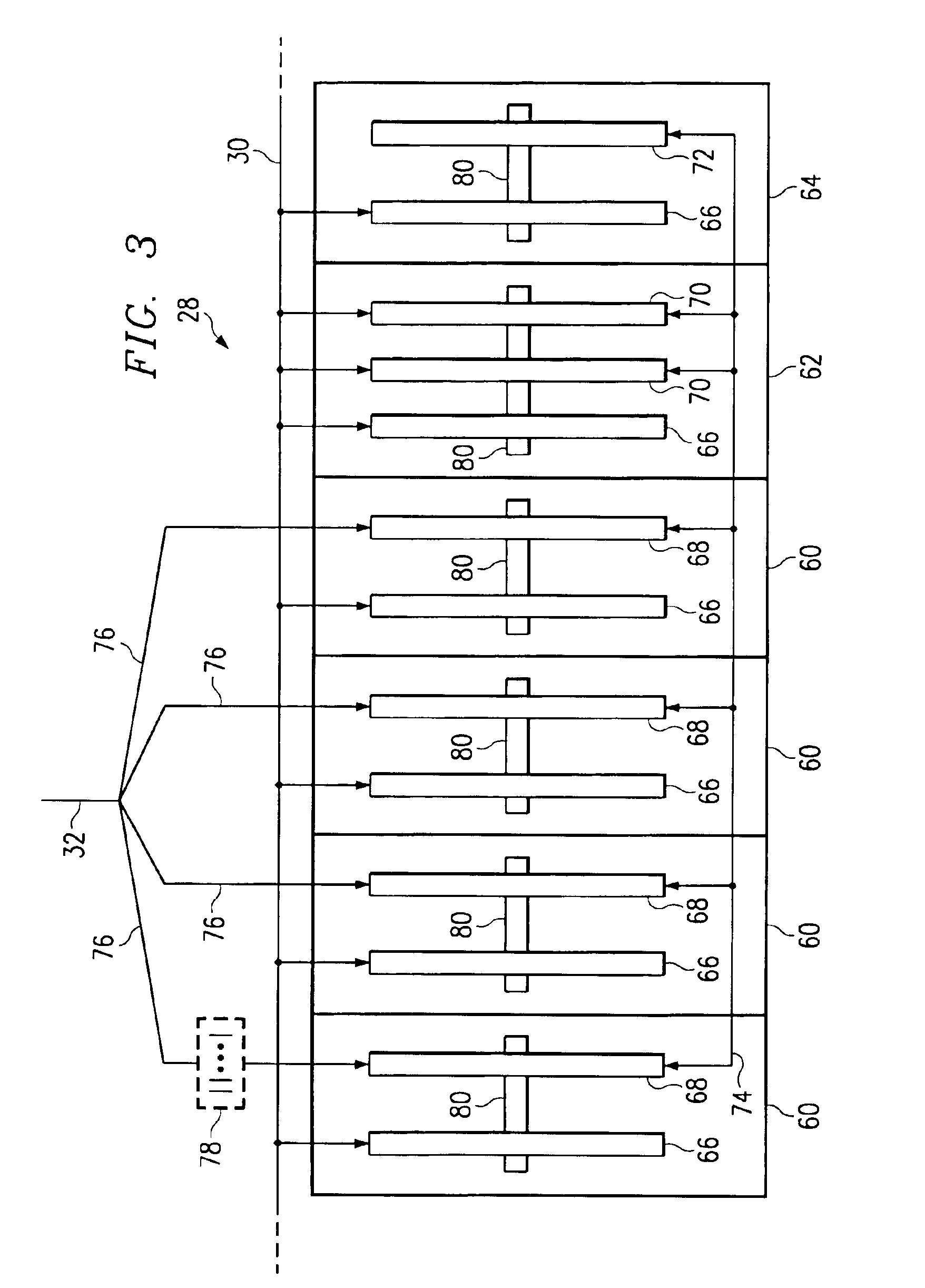
Internet-enabled conferencing system and method accommodating PSTN and IP traffic
InactiveUS6876734B1Special service provision for substationMultiplex system selection arrangementsStart timeTTEthernet
Owner:EMEETING NET
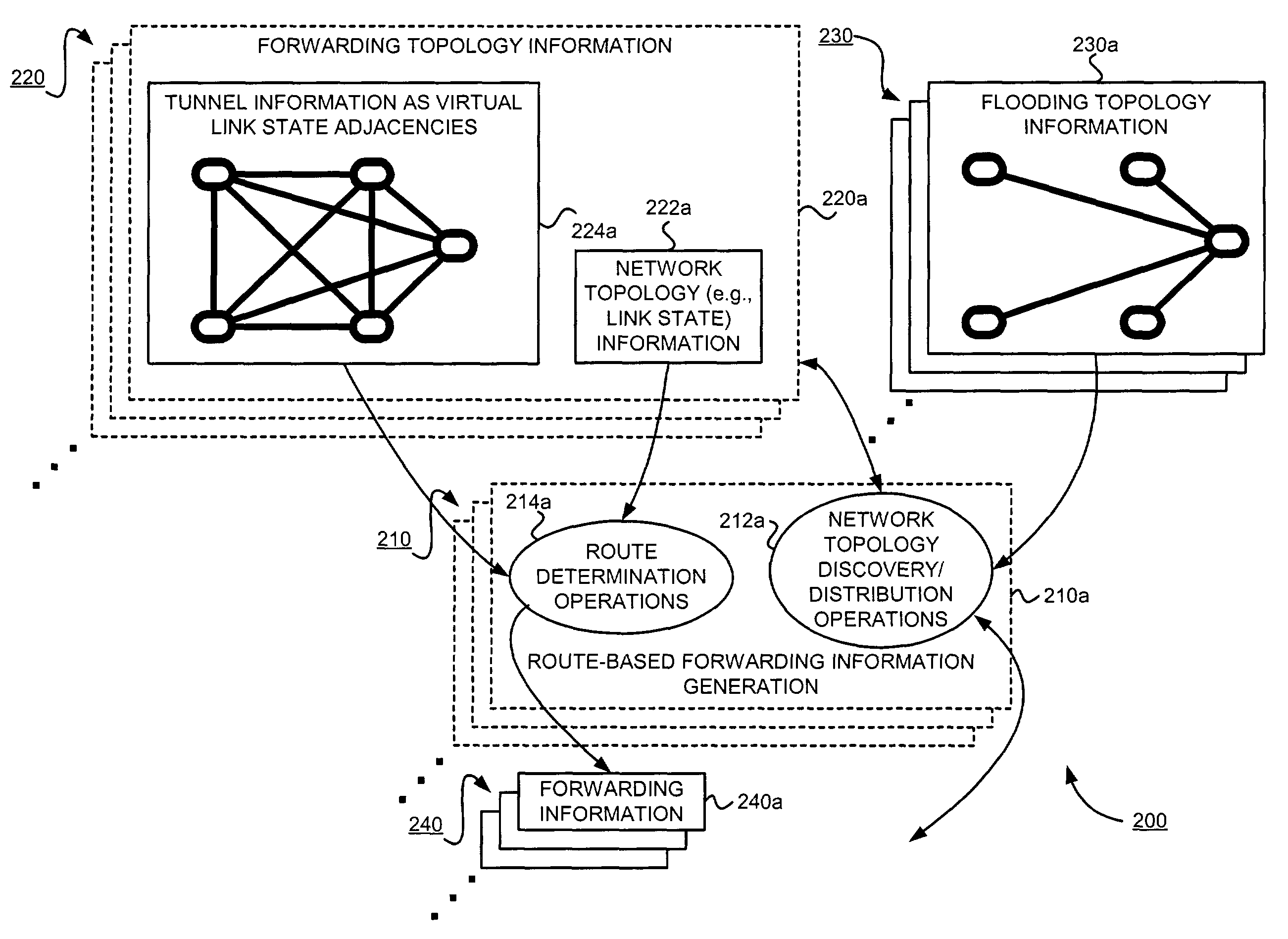
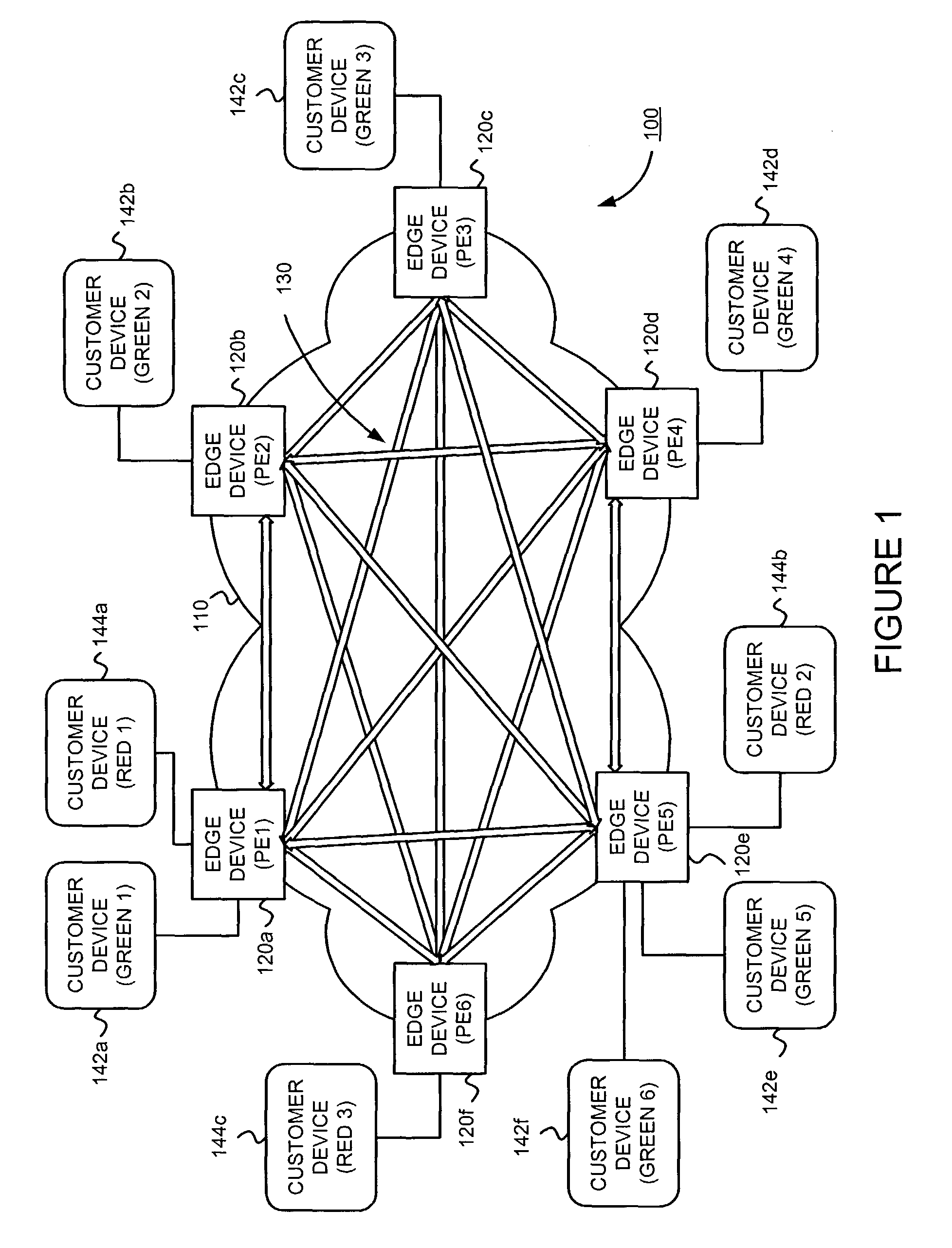
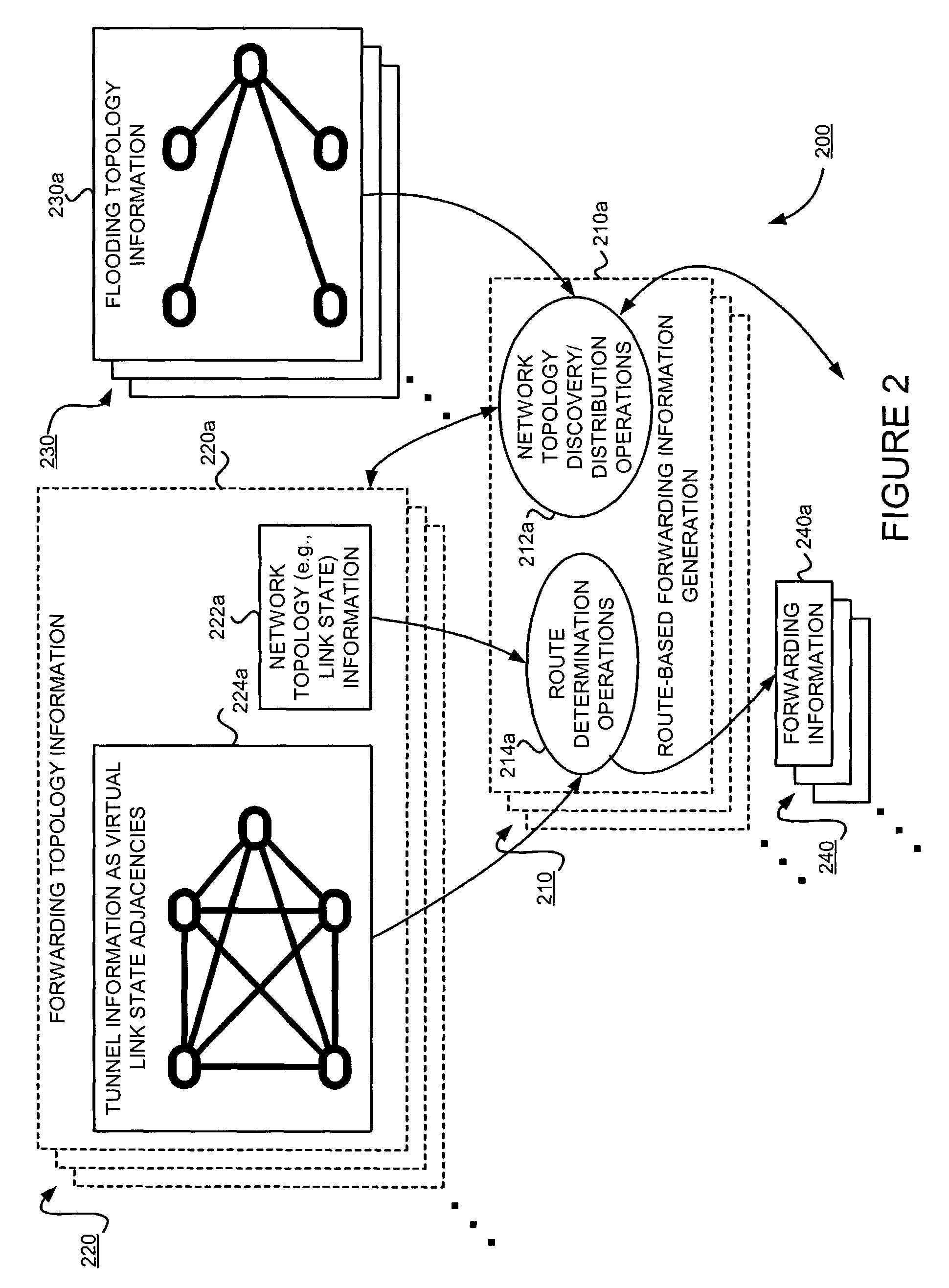
Supporting virtual private networks using a first network topology for forwarding and a subset of the first network topology or a smaller topology for signaling
InactiveUS7792987B1Avoid problemsError preventionTransmission systemsBorder Gateway ProtocolTTEthernet
Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) are supported in which customers may use popular internet gateway protocol (IGPs) without the need to convert such IGPs, running on customer devices to a single protocol, such as the border gateway protocol (BGP). Scaling problems, which might otherwise occur when multiple instances of an IGP flood link state information, are avoided by using a flooding topology which is smaller than a forwarding topology. The flooding topology may be a fully connected sub-set of the forwarding topology.
Owner:JUMIPER NETWORKS INC
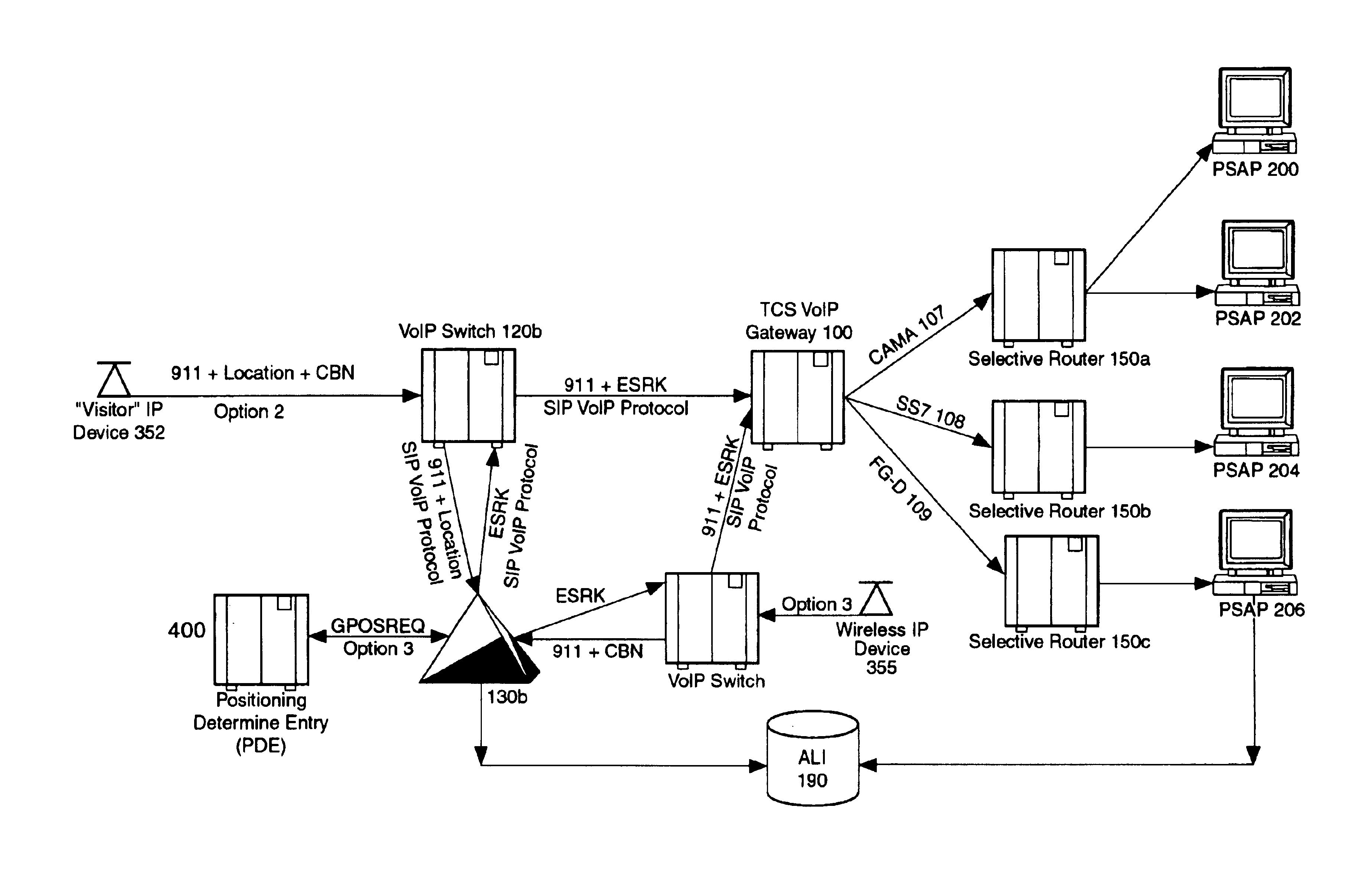
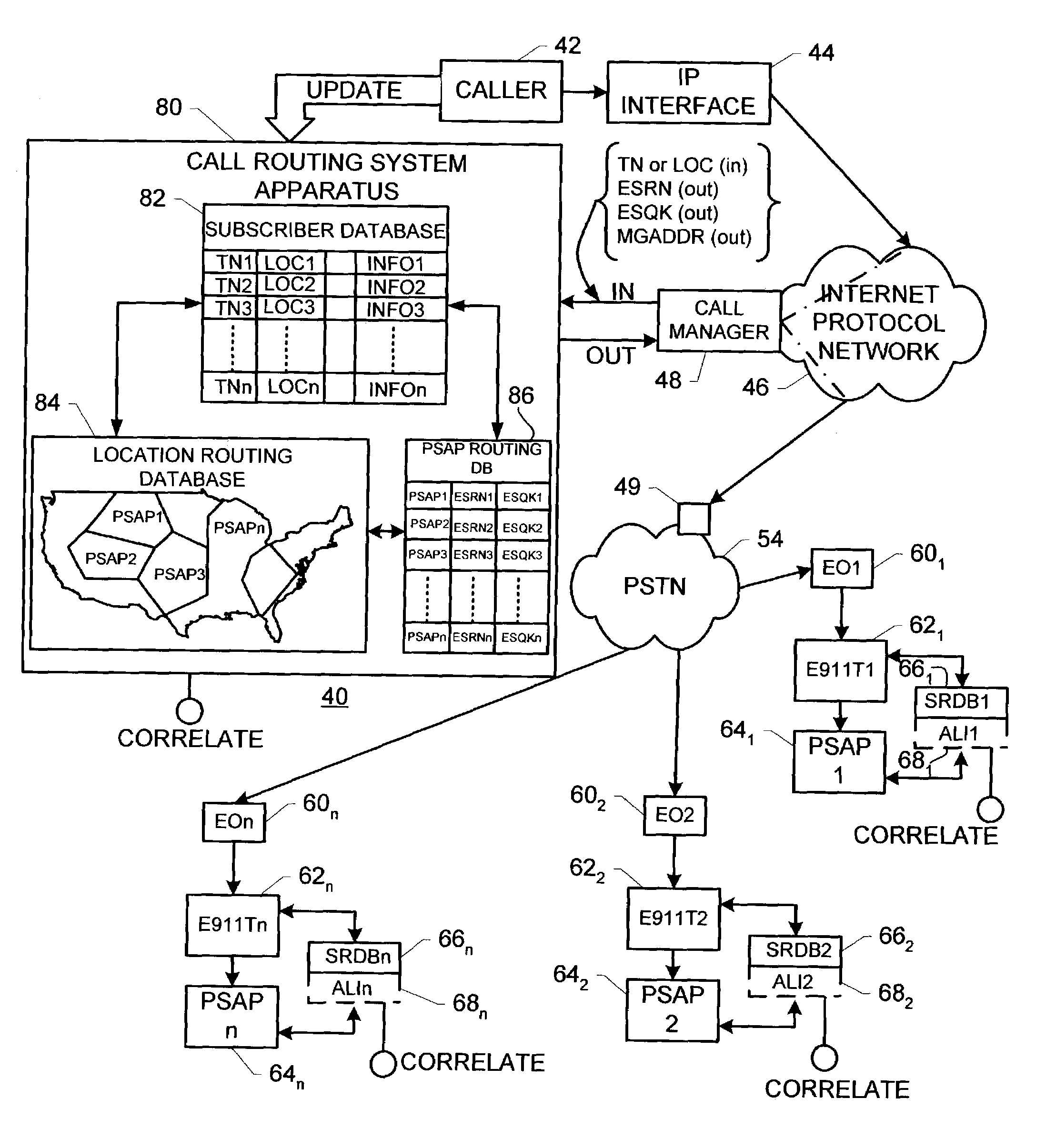
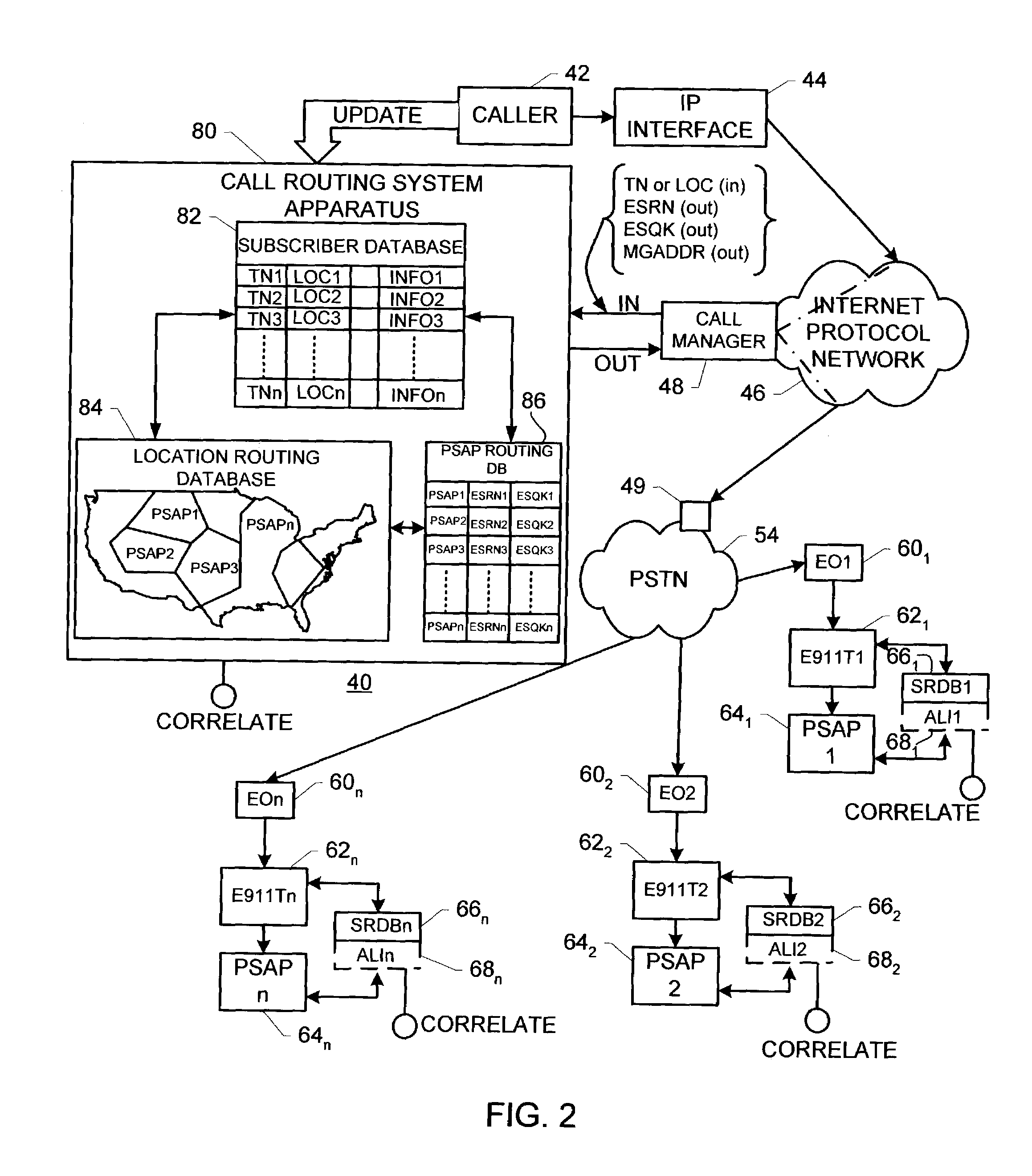
Enhanced E911 location information using voice over internet protocol (VoIP)
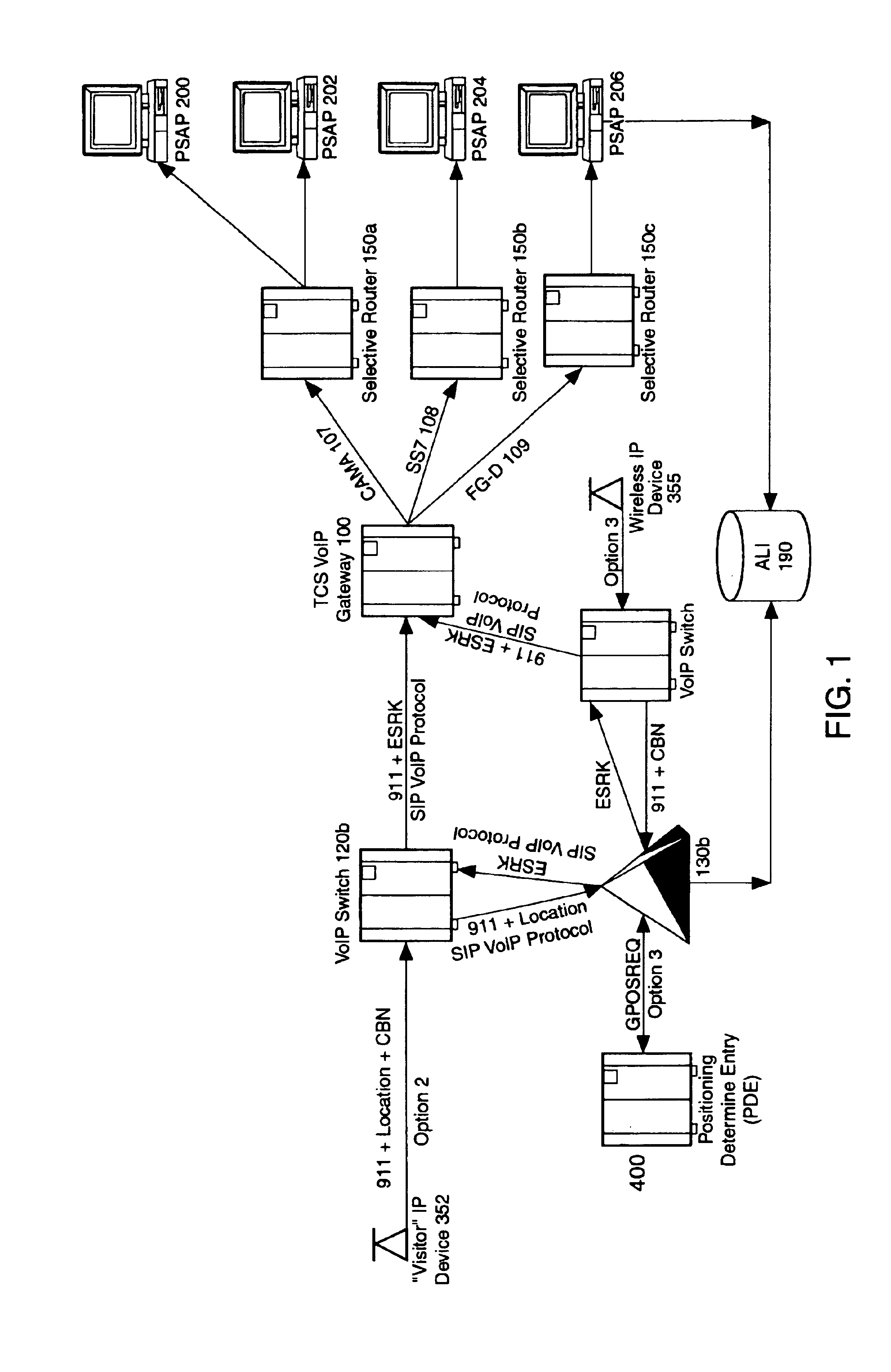
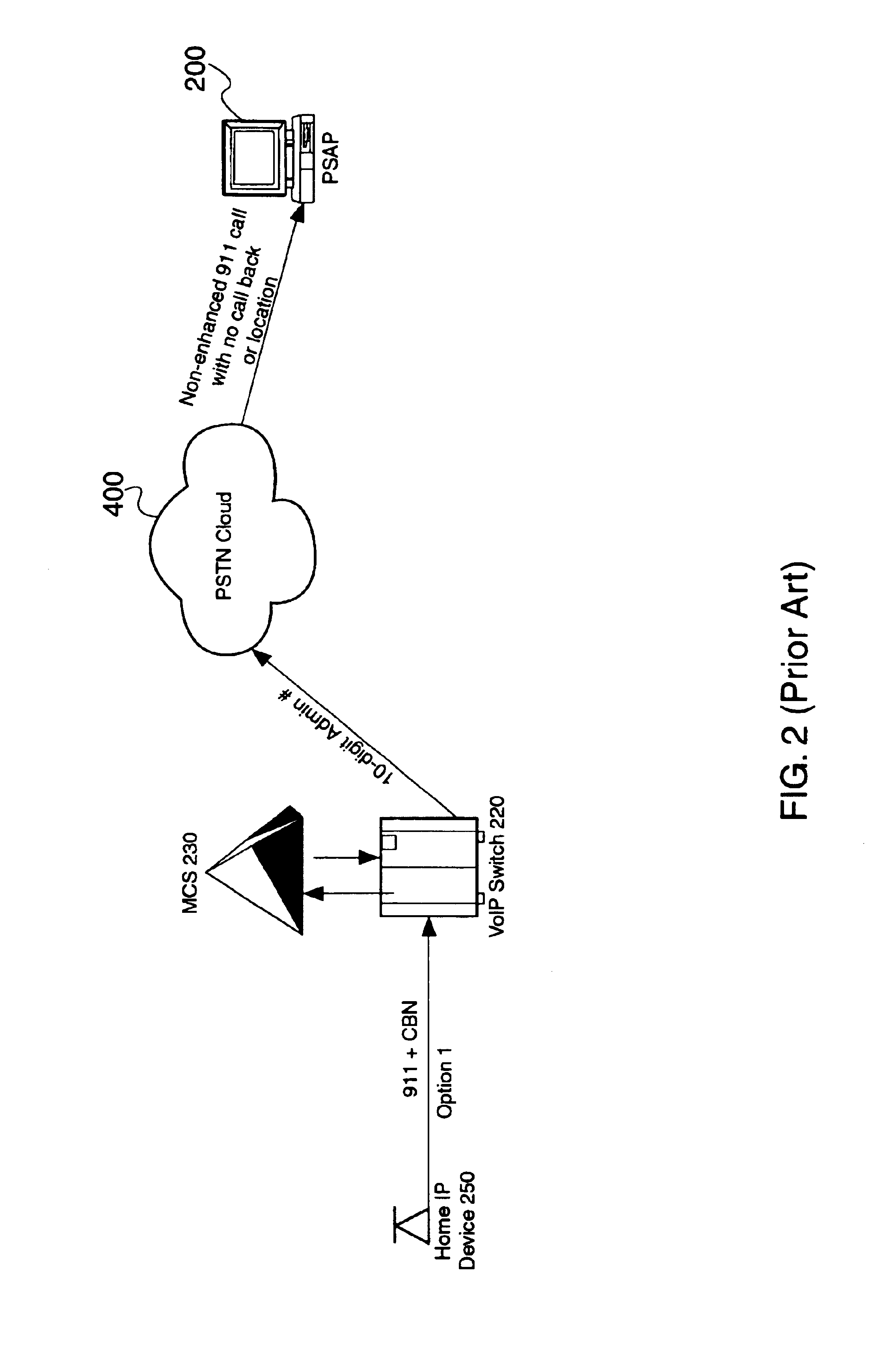
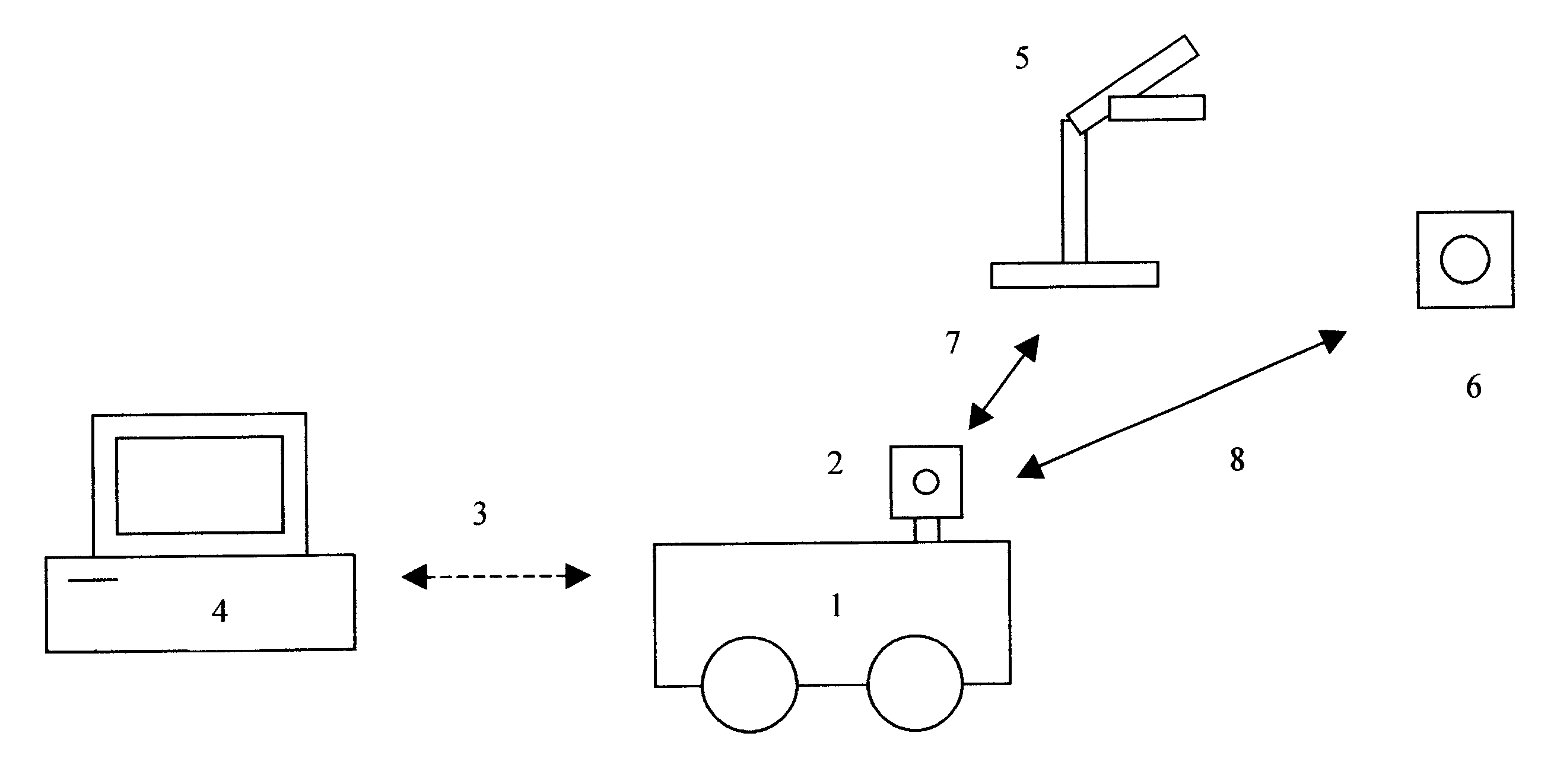
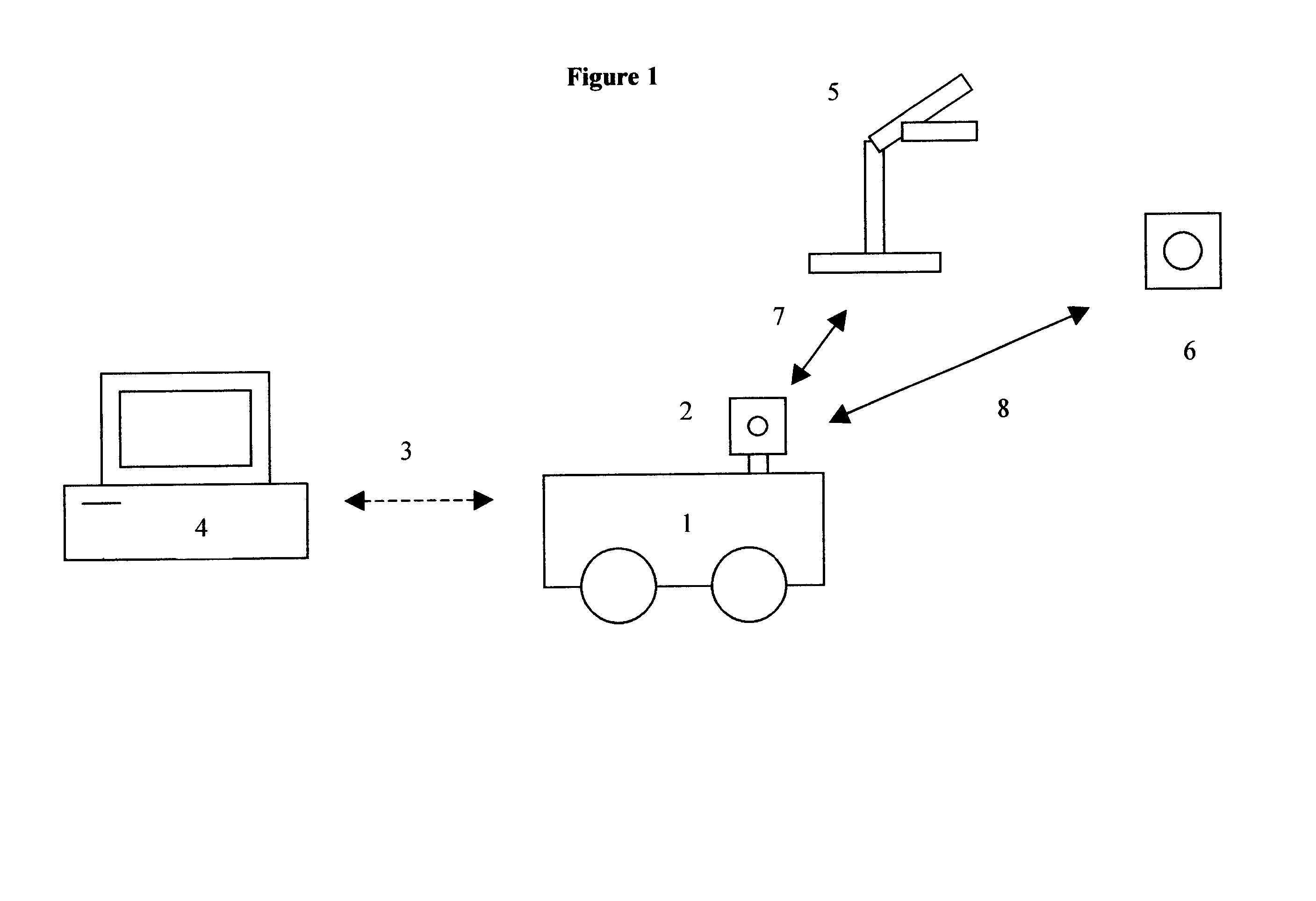
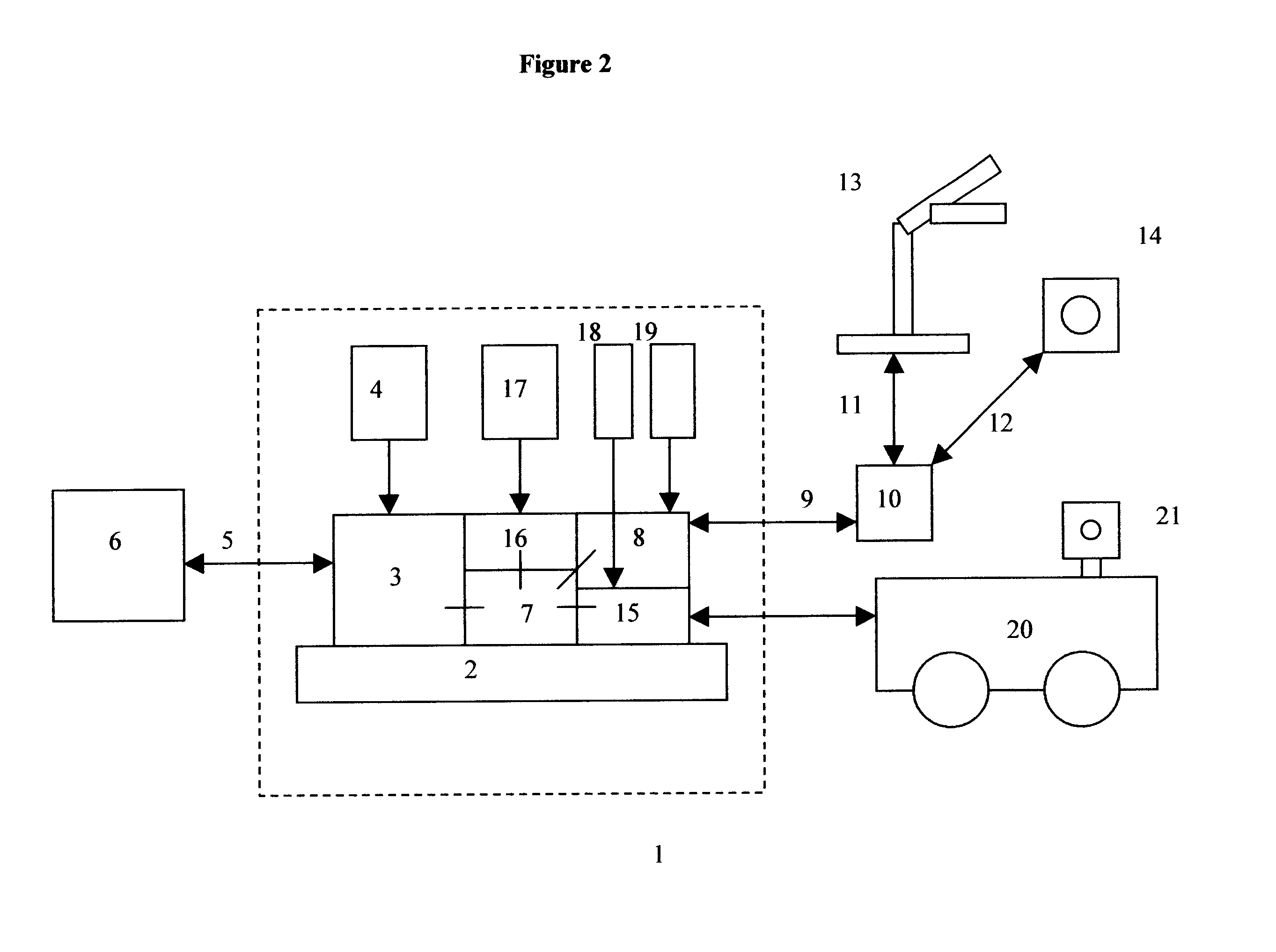
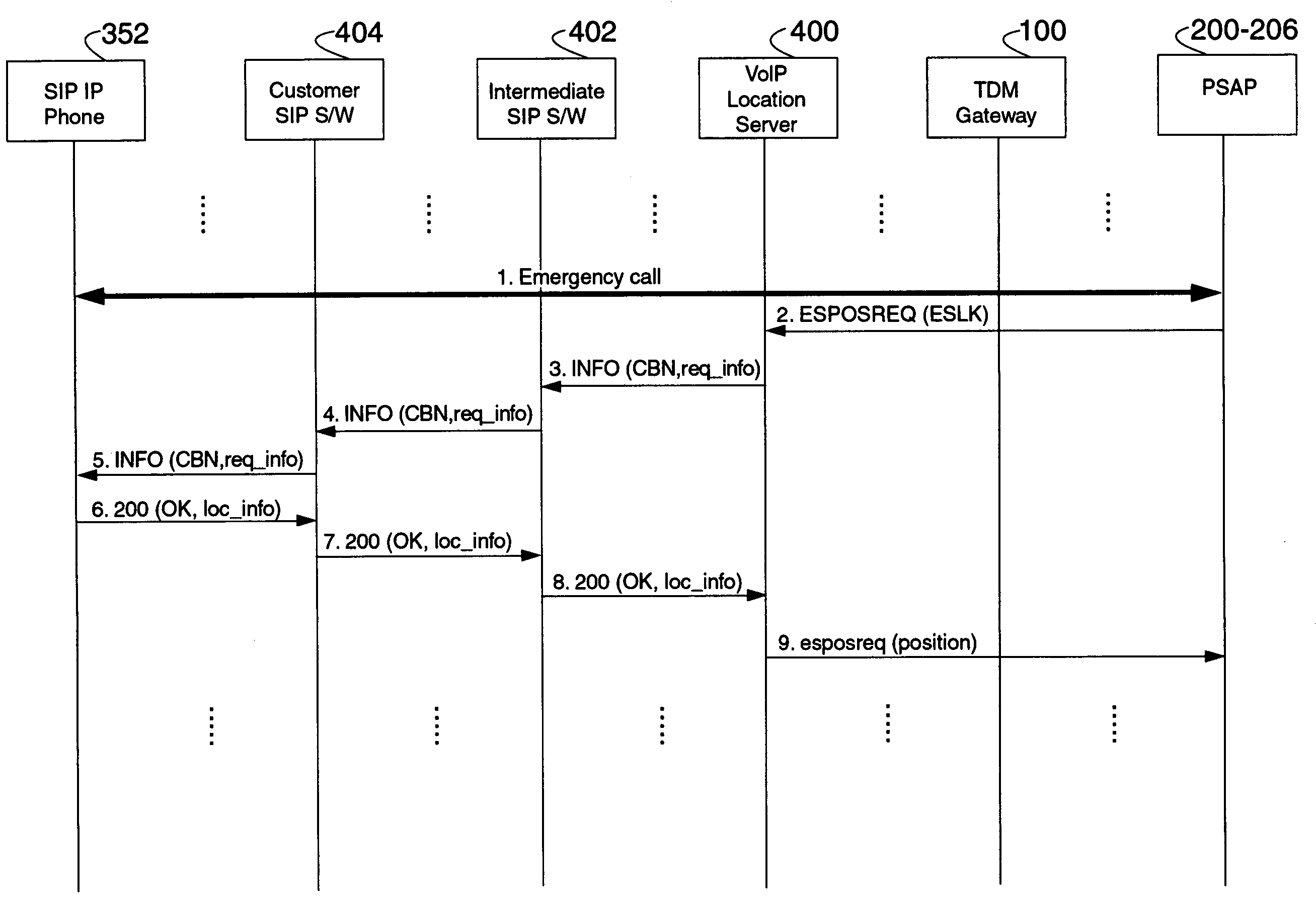
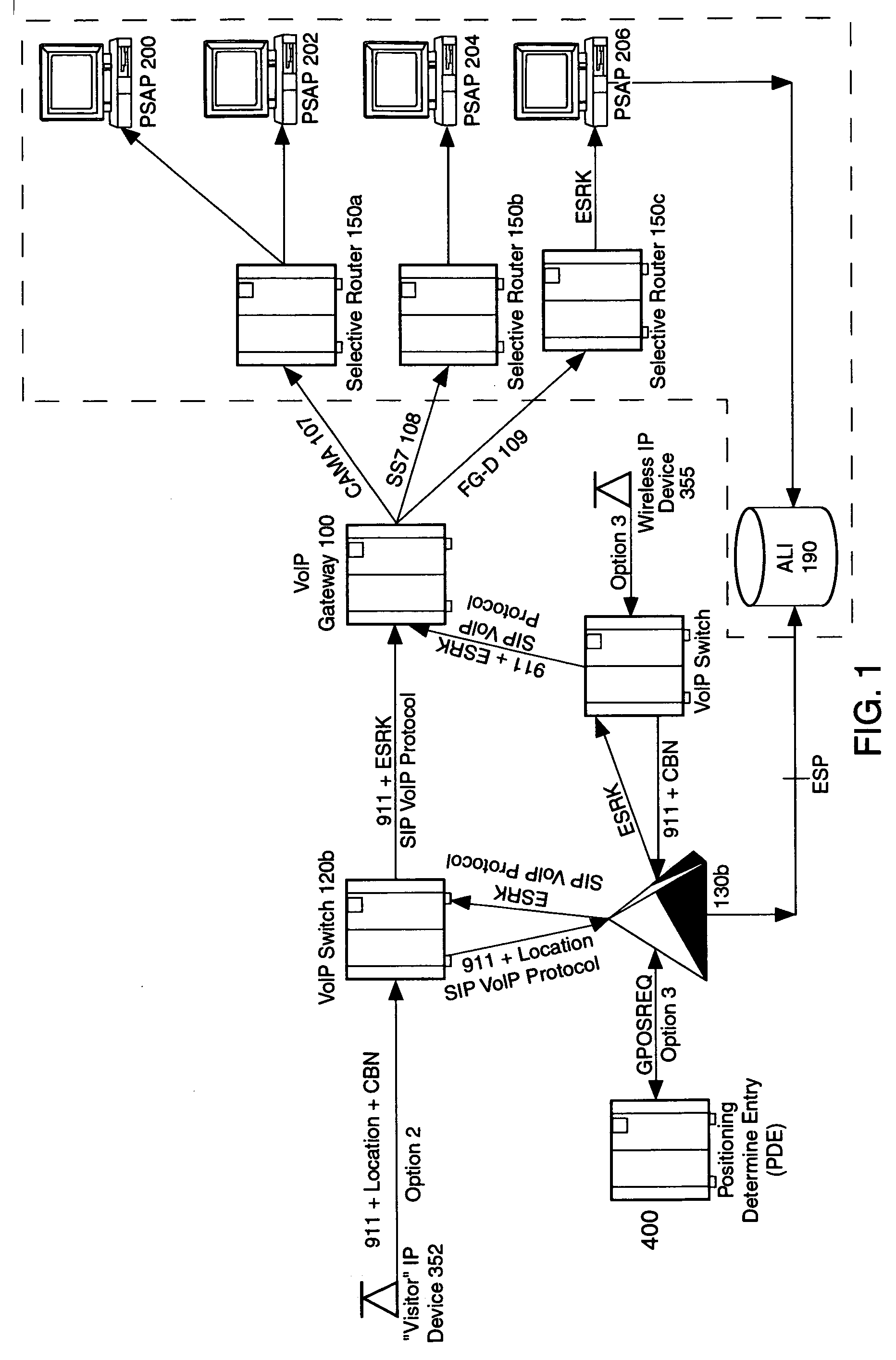
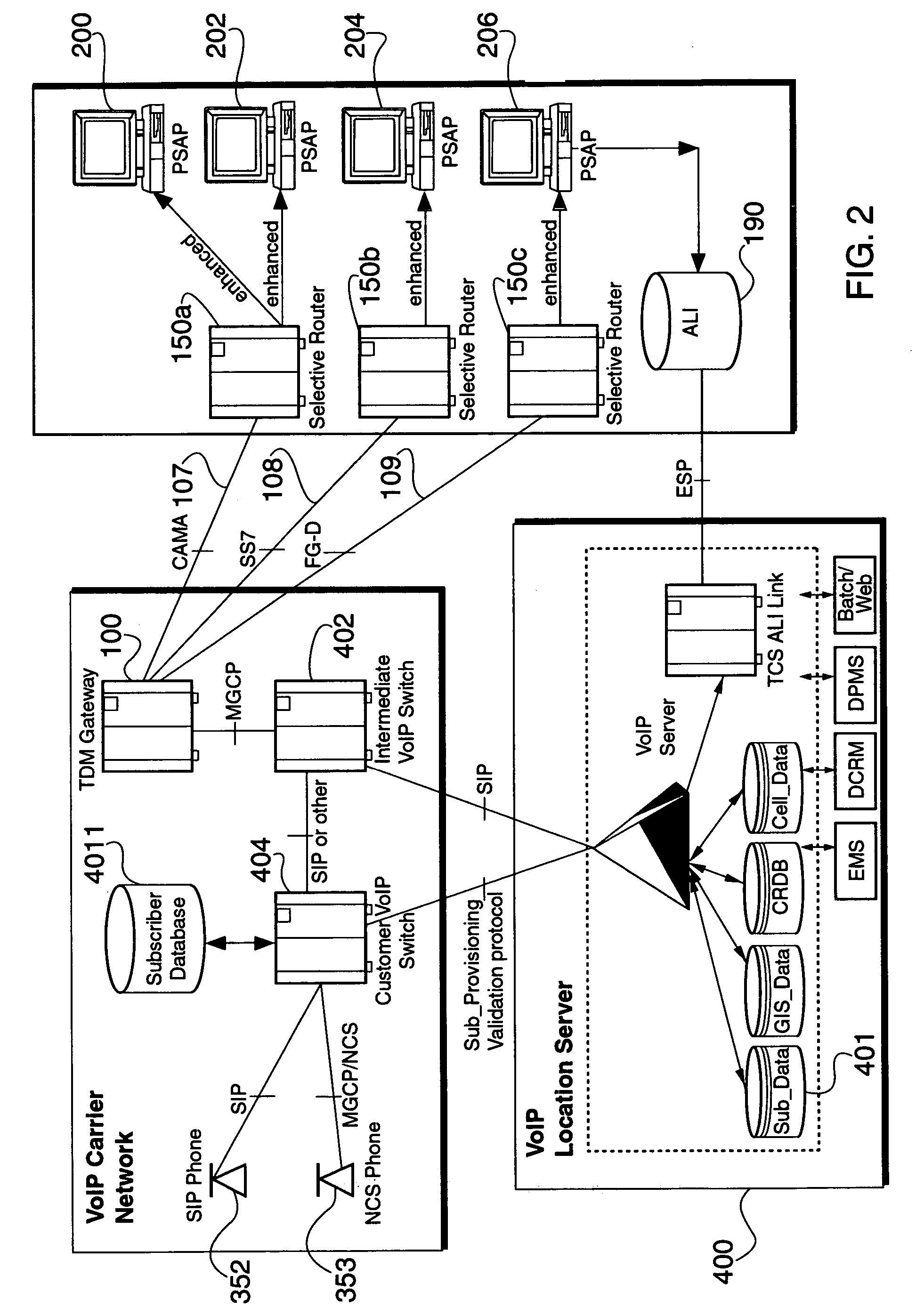
An E-9-1-1 voice-over-IP (VoIP) solution is provided wherein a 911 call from a wireless VoIP device is routed directly to the correct Public Safety Answer Point (PSAP) via dedicated trunks, together with correct location information and call-back number. VoIP gateways are implemented locally, at least one per LATA, and accept VoIP packetized data inbound, and convert it to standard wireline voice calls. Calls are routed to an IP address at the VoIP gateway, which then egresses the call to a voice port at a selective router. Dedicated voice trunks (CAMA, SS7, FG-D) are installed between each local VoIP gateway and appropriate selective routers. An Automatic Location Identification (ALI) database is provisioned with ESRKs dedicated for VoIP use. TCP / IP circuits may be established between some or all of the various local VoIP gateways.
Owner:TELECOMM SYST INC
Method and system for distributed network address translation with network security features
InactiveUS7032242B1Digital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationSecurity associationIp address
A method and system for distributed network address translation with security features. The method and system allow Internet Protocol security protocol (“IPsec”) to be used with distributed network address translation. The distributed network address translation is accomplished with IPsec by mapping a local Internet Protocol (“IP”) address of a given local network device and a IPsec Security Parameter Index (“SPI”) associated with an inbound IPsec Security Association (“SA”) that terminates at the local network device. A router allocates locally unique security values that are used as the IPsec SPIs. A router used for distributed network address translation is used as a local certificate authority that may vouch for identities of local network devices, allowing local network devices to bind a public key to a security name space that combines a global IP address for the router with a set of locally unique port numbers used for distributed network address translation. The router issues security certificates and may itself be authenticated by a higher certificate authority. Using a security certificate, a local network device may initiate and be a termination point of an IPsec security association to virtually any other network device on an IP network like the Internet or an intranet. The method and system may also allow distributed network address translation with security features to be used with Mobile IP or other protocols in the Internet Protocol suite.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
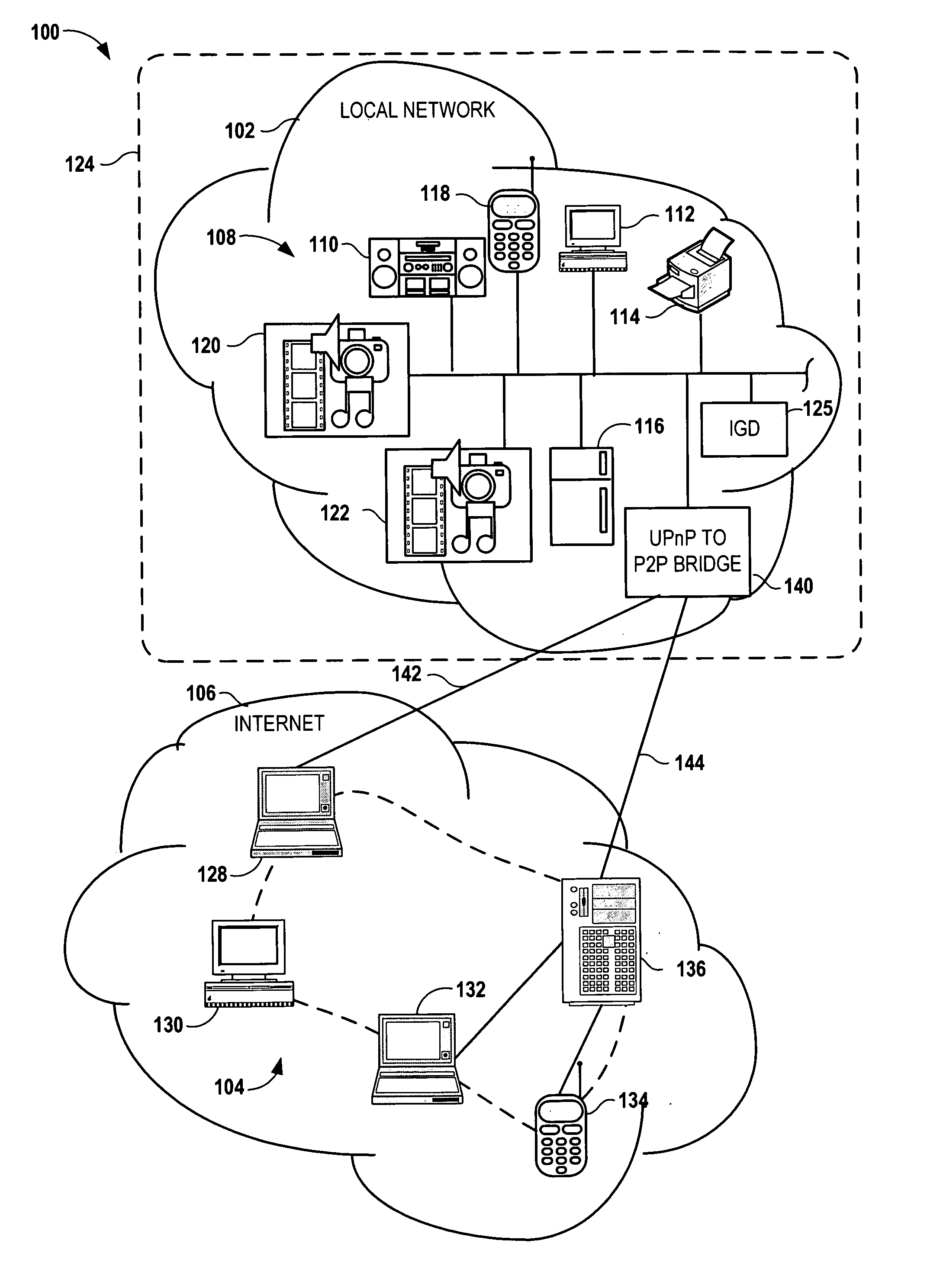
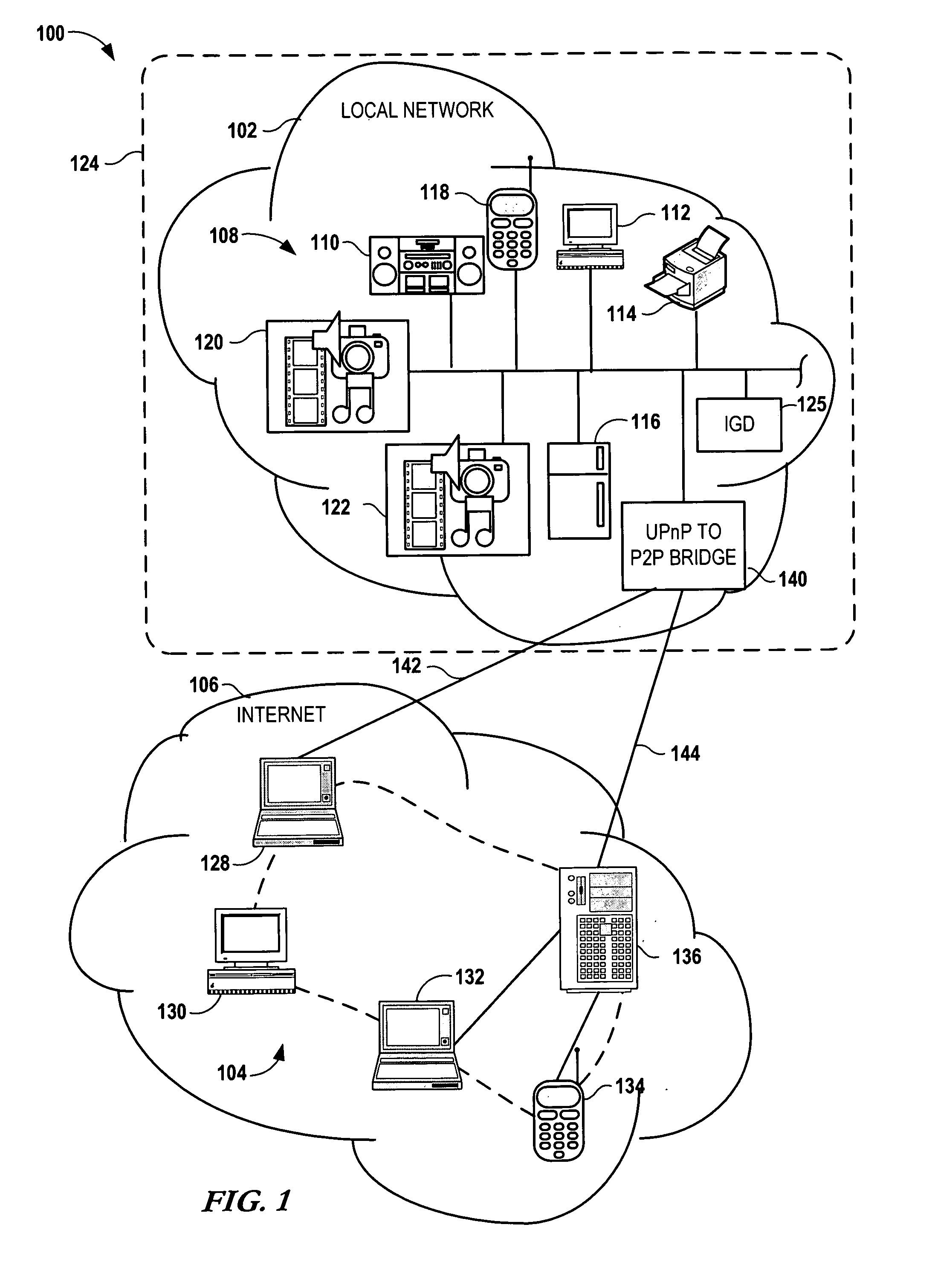
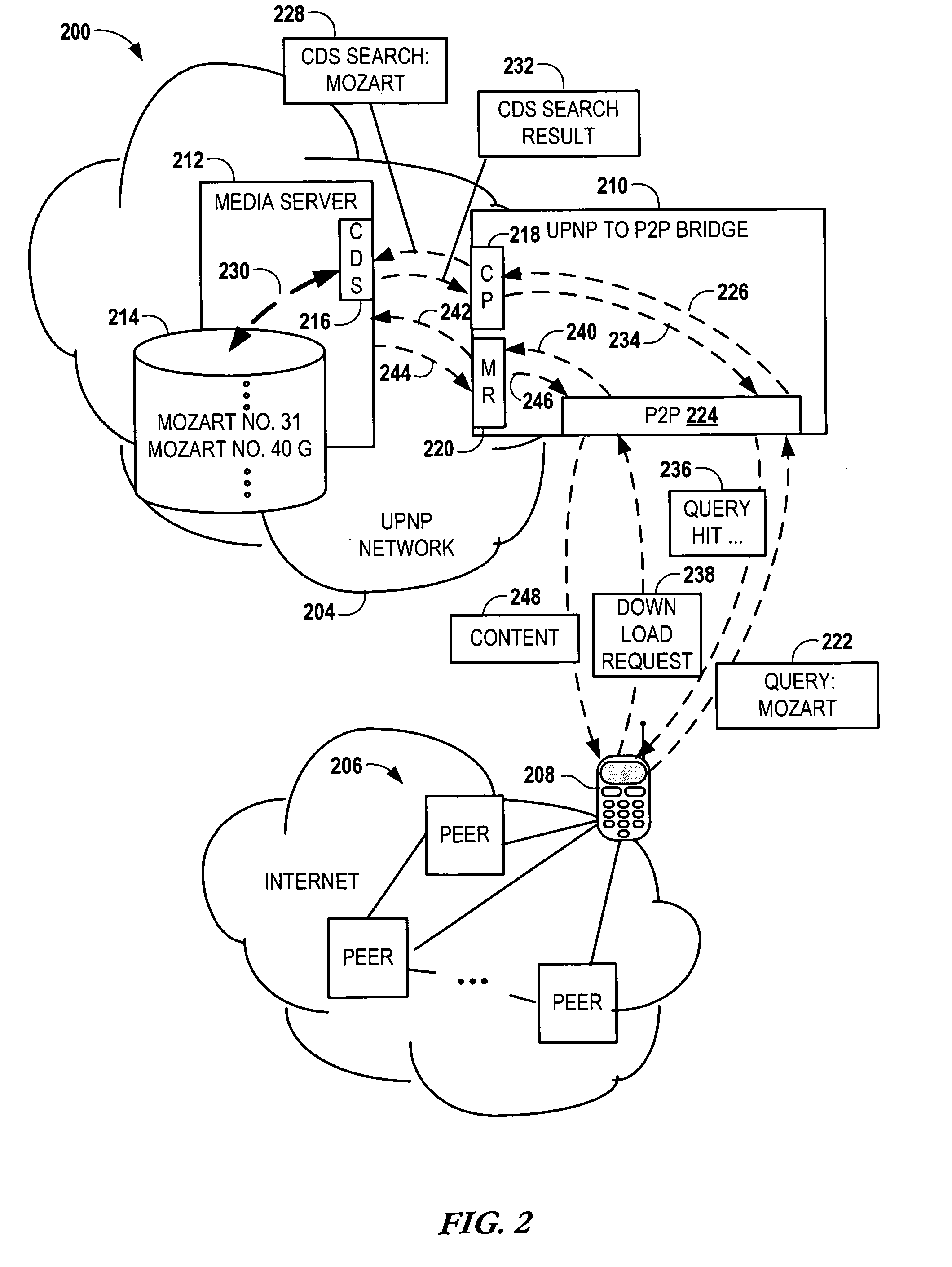
Bridging between AD HOC local networks and internet-based peer-to-peer networks
ActiveUS20070274327A1Easy to downloadFacilitate downloading the mediaData switching by path configurationMultiple digital computer combinationsNetworking protocolTTEthernet
Bridging between ad hoc local networks and Internet based peer-to-peer networks involves coupling a bridge device to a local network using an ad-hoc, peer-to-peer protocol used for exchanging data between consumer electronics devices. The bridge device is coupled to a public network using an Internet-based peer-to-peer networking protocol. In one arrangement, metadata related to media accessible from a media server of the local network is determined via the bridge device, and the metadata is transformed via the bridge device to enable peer-to-peer devices of the public network to discover the media via the bridge device using the Internet-based peer-to-peer networking protocol. In another arrangement, metadata related to media accessible from the public network is determined via the peer-to-peer networking protocol, and the metadata is transformed via the bridge device to enable a device of the local network to discover the media via the bridge device using the ad-hoc, peer-to-peer protocol.
Owner:CONVERSANT WIRELESS LICENSING LTD
Dynamic allocation of wireless mobile nodes over an internet protocol (IP) network
InactiveUS6272129B1Data switching by path configurationWireless network protocolsTTEthernetIp address
A method is described of automatically locating and connecting a mobile wireless communications device to a packet-switched network such as the Internet. An Internet Protocol (IP) packet from a terminal on the network, destined for receipt by the mobile device, is received at a home agent acting as a gateway or router linking the packet switched network to a second network, such as LAN, coupled to a wireless communications network. The home agent transmits an access-request message to an authentication server. The access-request message includes a destination IP address associated with the mobile device found in the IP packet. The authentication server responsively issues an access-accept message to the home agent if the mobile device is authorized to receive the IP packet. The access-accept message comprises (a) information uniquely identifying said device, such as the IMSI / ESN number for the device, and (b) information identifying a network to use to locate said device. The home agent issues a message containing the information uniquely identifying the device to a mobile node location server. The mobile node location server maintains a table mapping IP addresses for a plurality of mobile communication devices to information uniquely identifying the devices. In the event that the mobile node location server does not find an IP address for the device in the table, the device is paged via the wireless communications network. In response to the page, the mobile device dials into the wireless communications network and second network and initiates a connection to the packet switched network whereby the IP packet is transmitted to the device.
Owner:UTSTARCOM INC
Wide area network using internet with quality of service
InactiveUS7111163B1Reduces monthly costQuality improvementDigital data processing detailsMultiple digital computer combinationsQuality of serviceTTEthernet
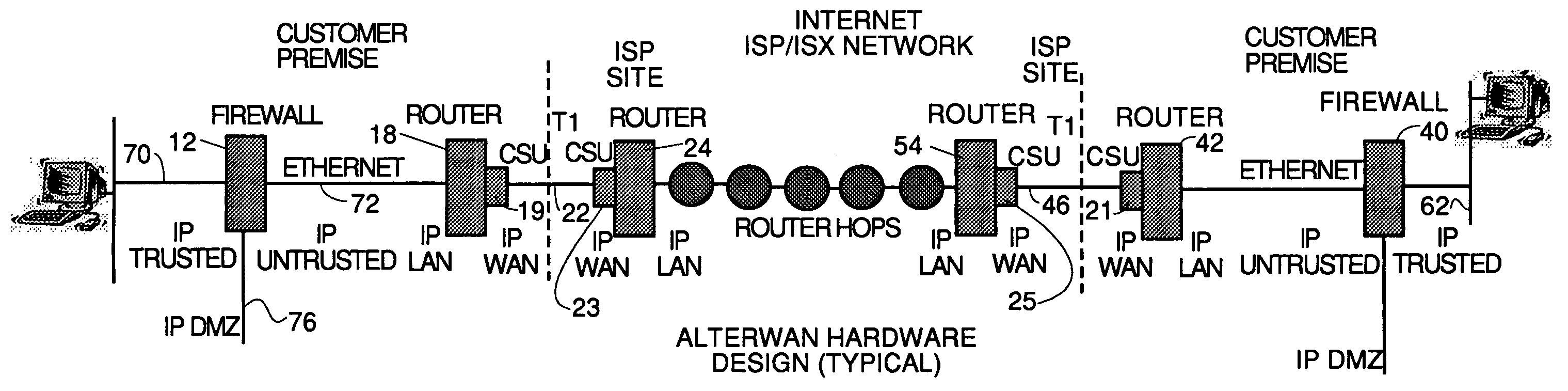
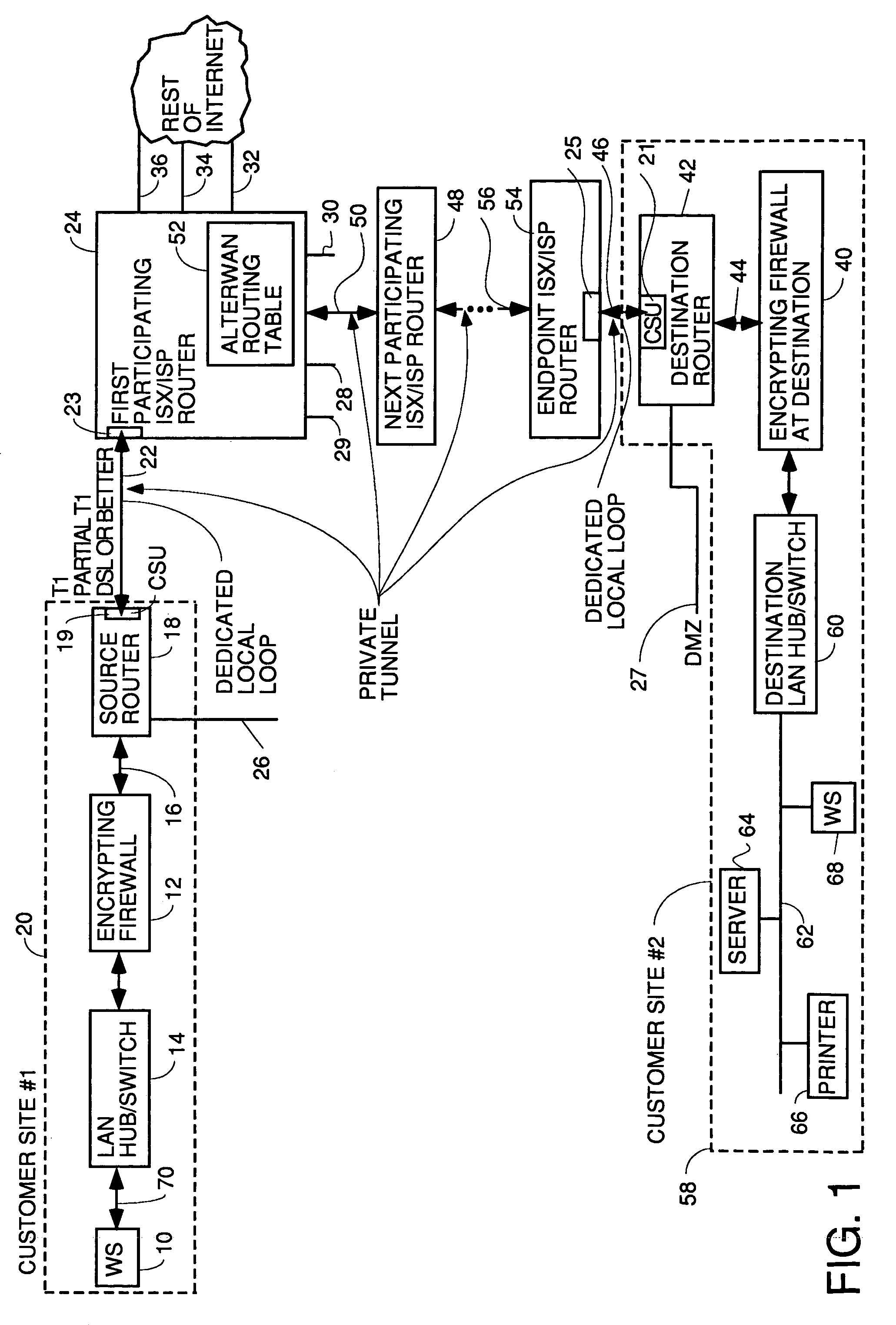
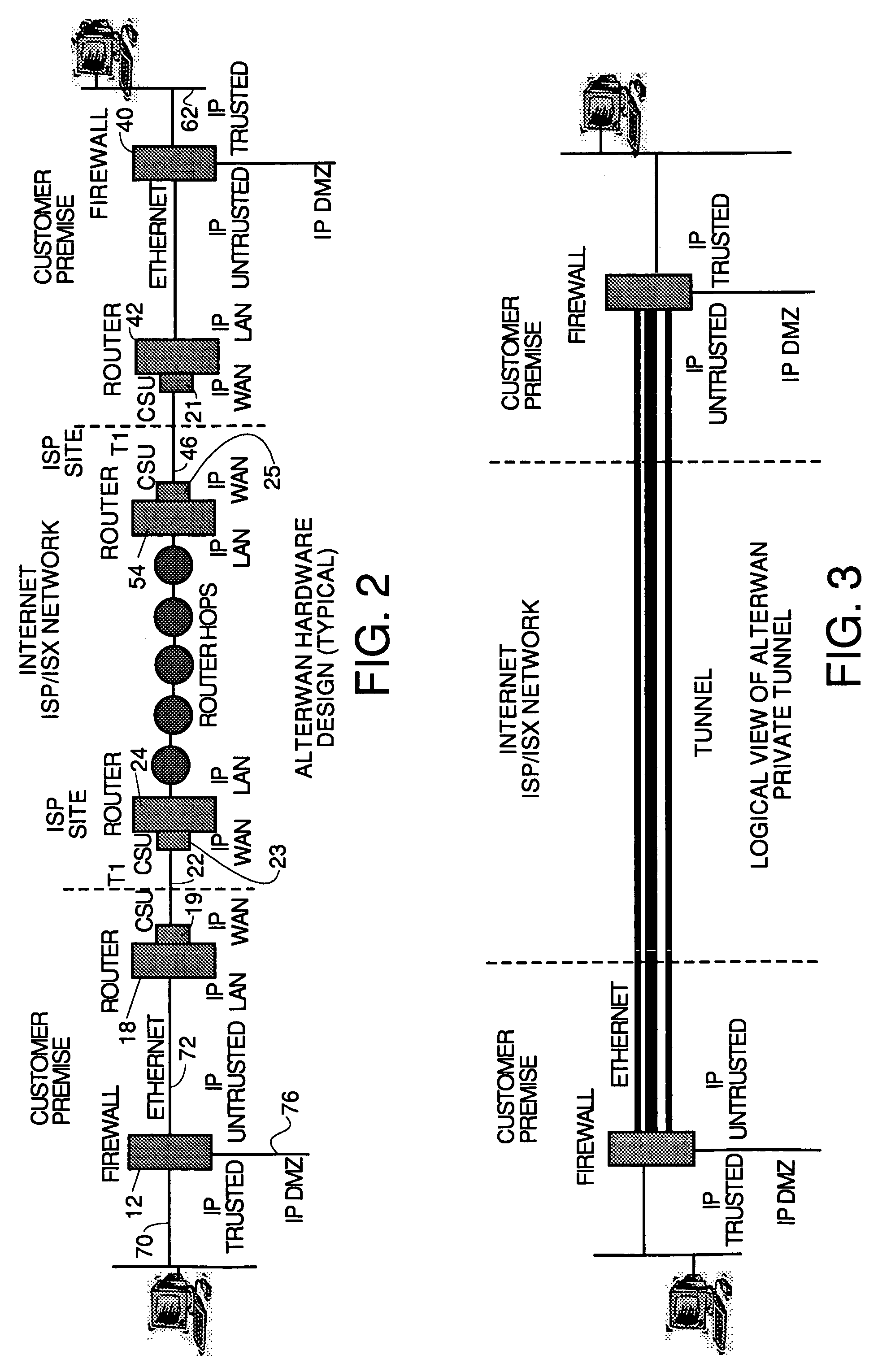
A wide area network using the internet as a backbone utilizing specially selected ISX / ISP providers whose routers route AlterWAN packets of said wide area network along private tunnels through the internet comprised of high bandwidth, low hop-count data paths. Firewalls are provided at each end of each private tunnel which recognize IP packets addressed to devices at the other end of the tunnel and encapsulate these packets in other IP packets which have a header which includes as the destination address, the IP address of the untrusted side of the firewall at the other end of the tunnel. The payload sections of these packets are the original IP packets and are encrypted and decrypted at both ends of the private tunnel using the same encryption algorithm using the same key or keys.
Owner:ALTERWAN
High data rate wireless packet data communications system
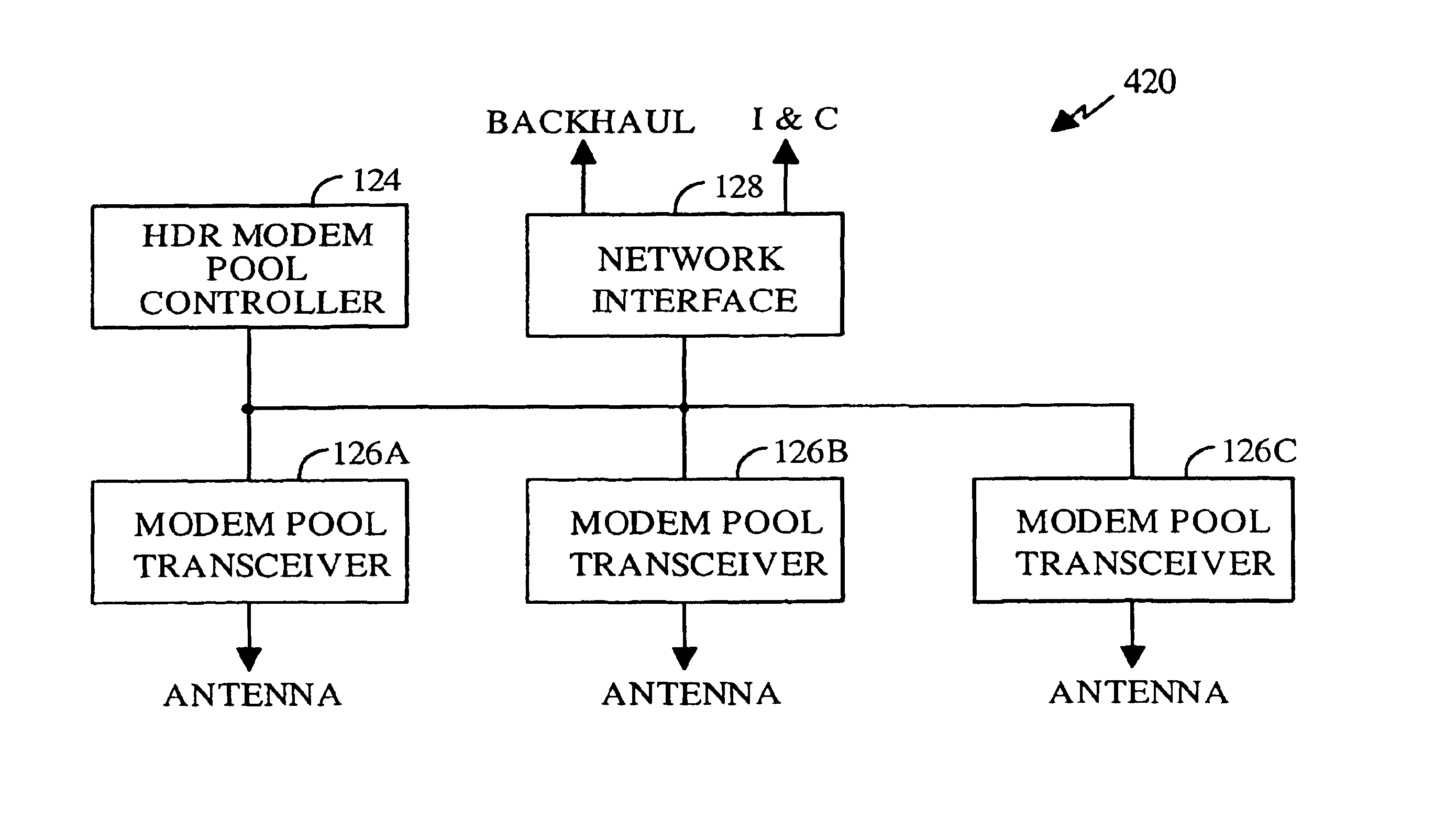
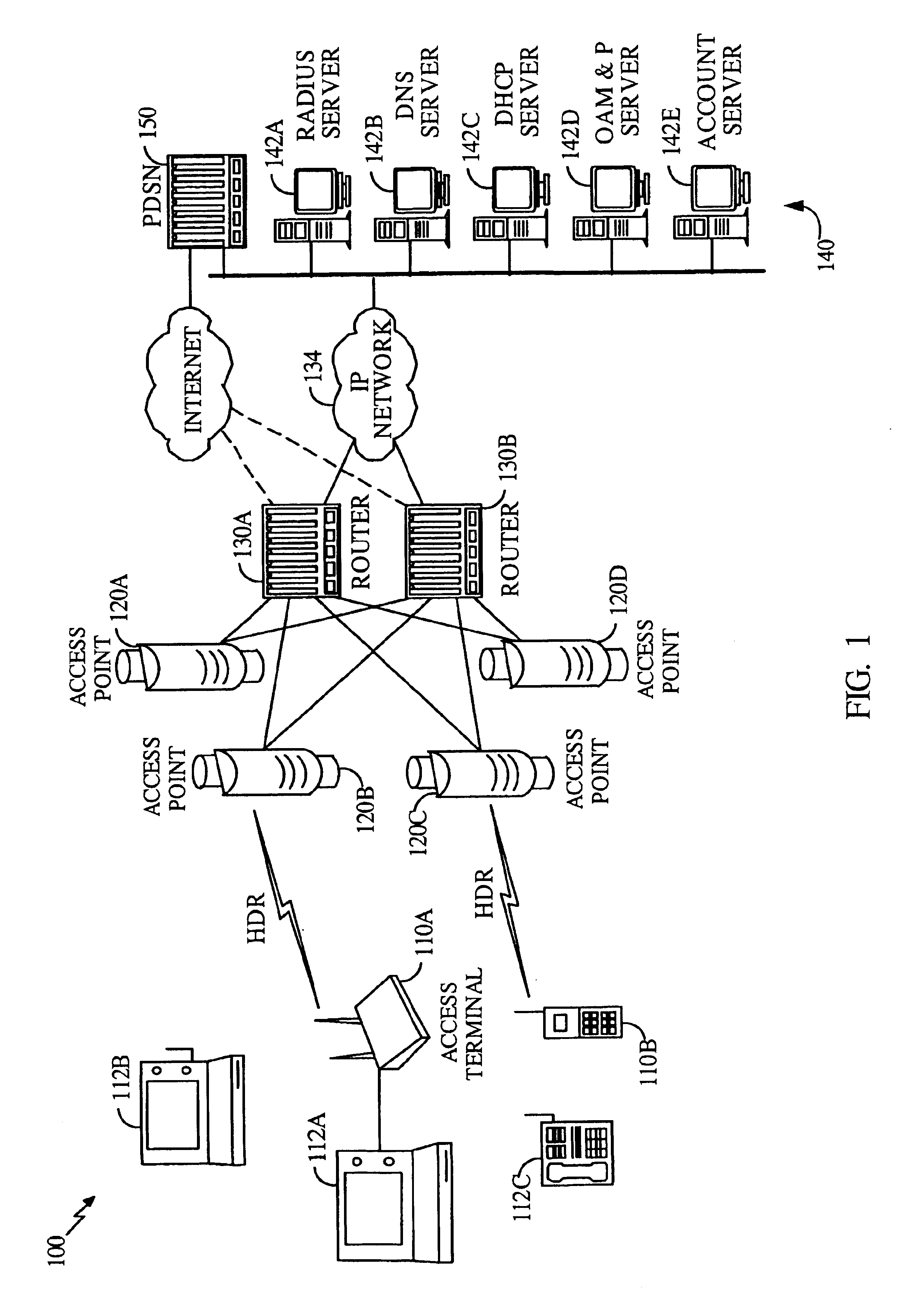
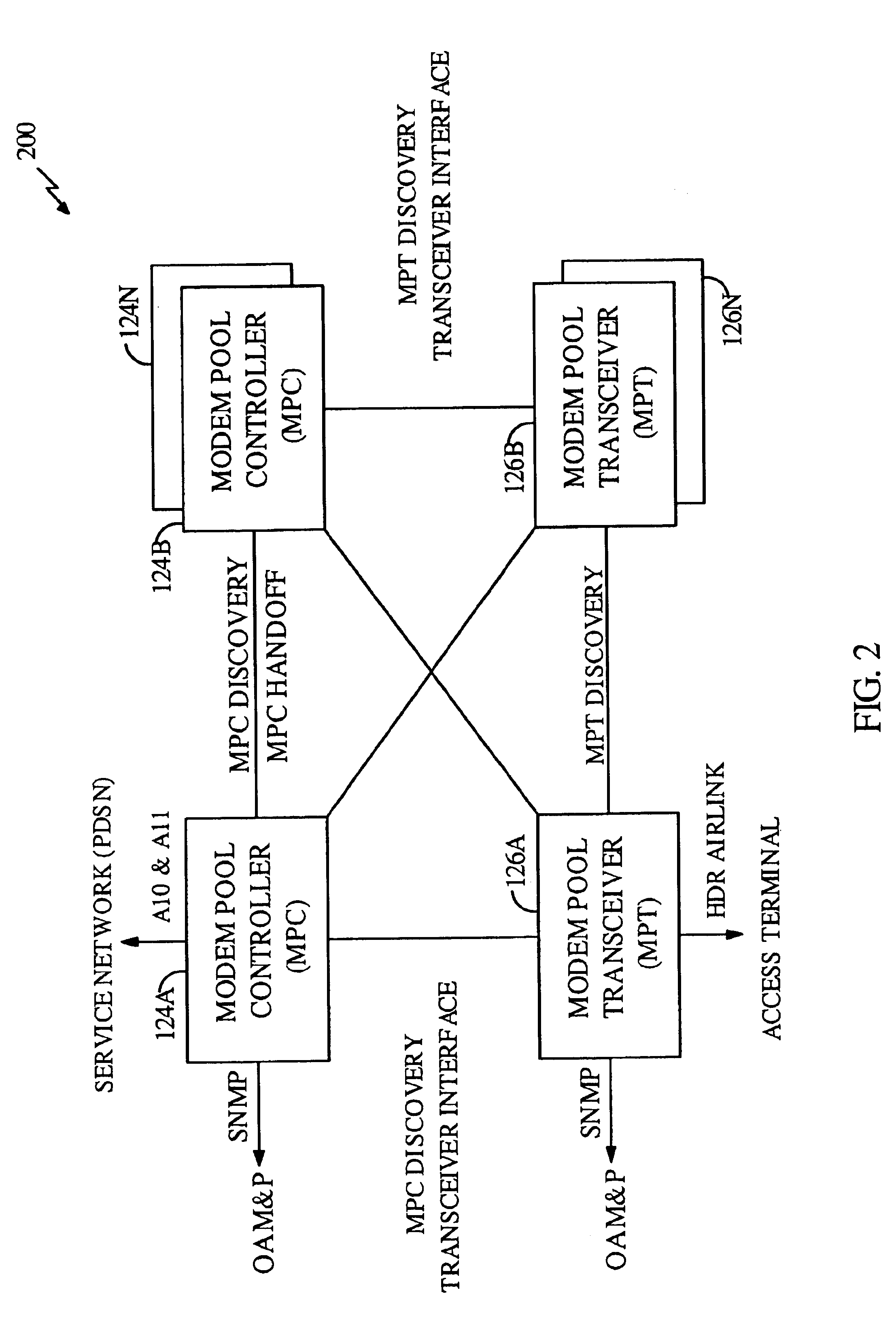
InactiveUS6894994B1Easy to deployEasy to upgradeError prevention/detection by using return channelNetwork topologiesTransceiverModem device
A wireless packet data communications system that includes a number of modem pool transceivers (MPTs), one or more modem pool controllers (MPCs), and one or more servers. Each MPT receives and processes data packets to generate a modulated signal (e.g., a CDMA spread spectrum signal) suitable for transmission over a terrestrial communications link. Each MPC provides call related processing for one or more MPTs. The servers couple to the MPTs and MPCs via an Internet Protocol (IP) back-bone and provide management of the communications system. The IP back-bone further interconnects the MPTs with one or more data networks and includes a number of routers that route data packets between the data networks and the MPTs. Each MPT can couple to two or more routers for redundancy. Each MPT is operated as an element in an IP network and is associated with an IP address that identifies the MPT. One to three MPTs can be deployed at each cell site to provide wireless data service coverage for up to three sectors at the cell site. The MPCs can either be centralized and coupled to the MPTs via the IP back-bone or distributed about the communications system.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
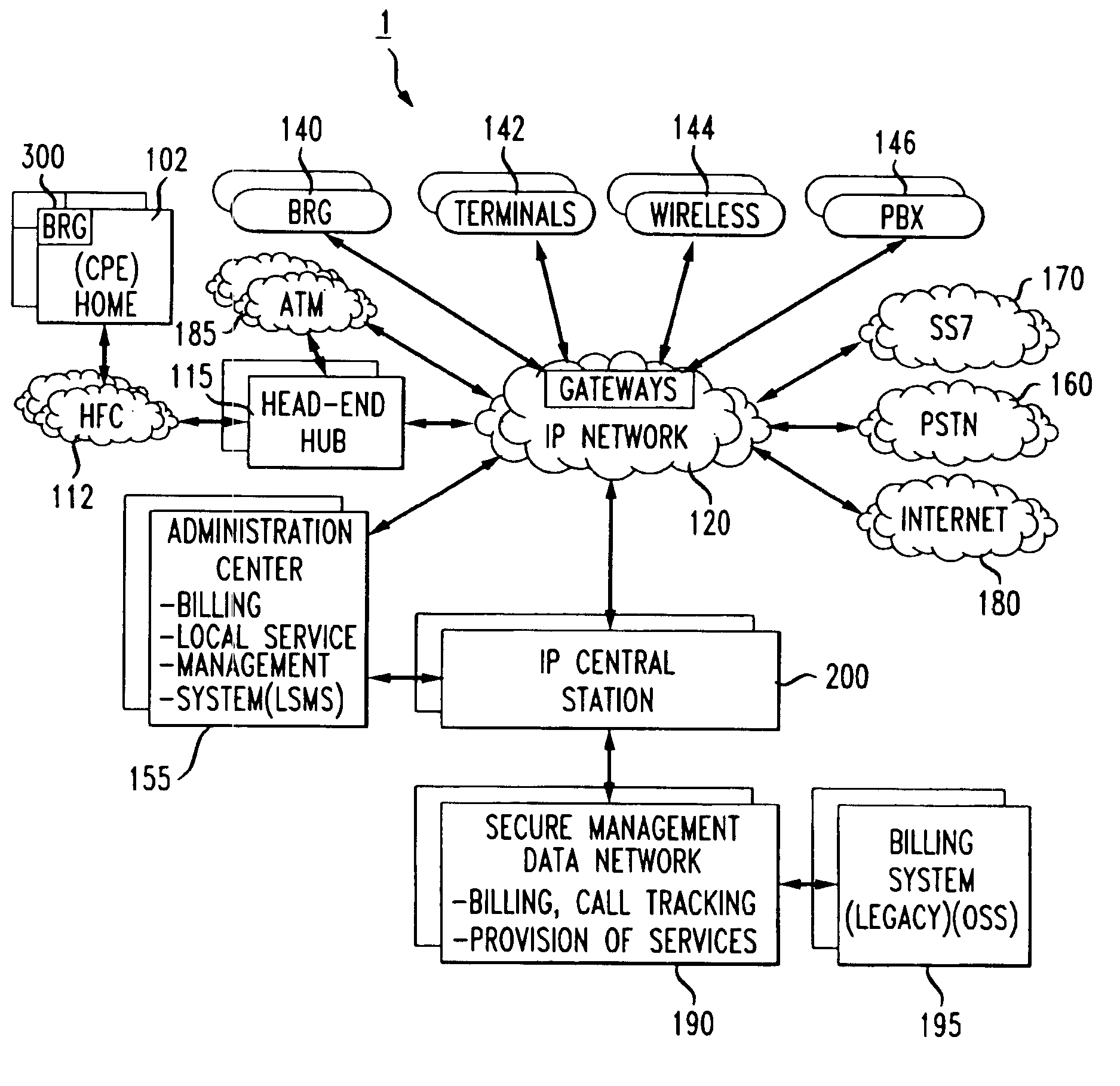
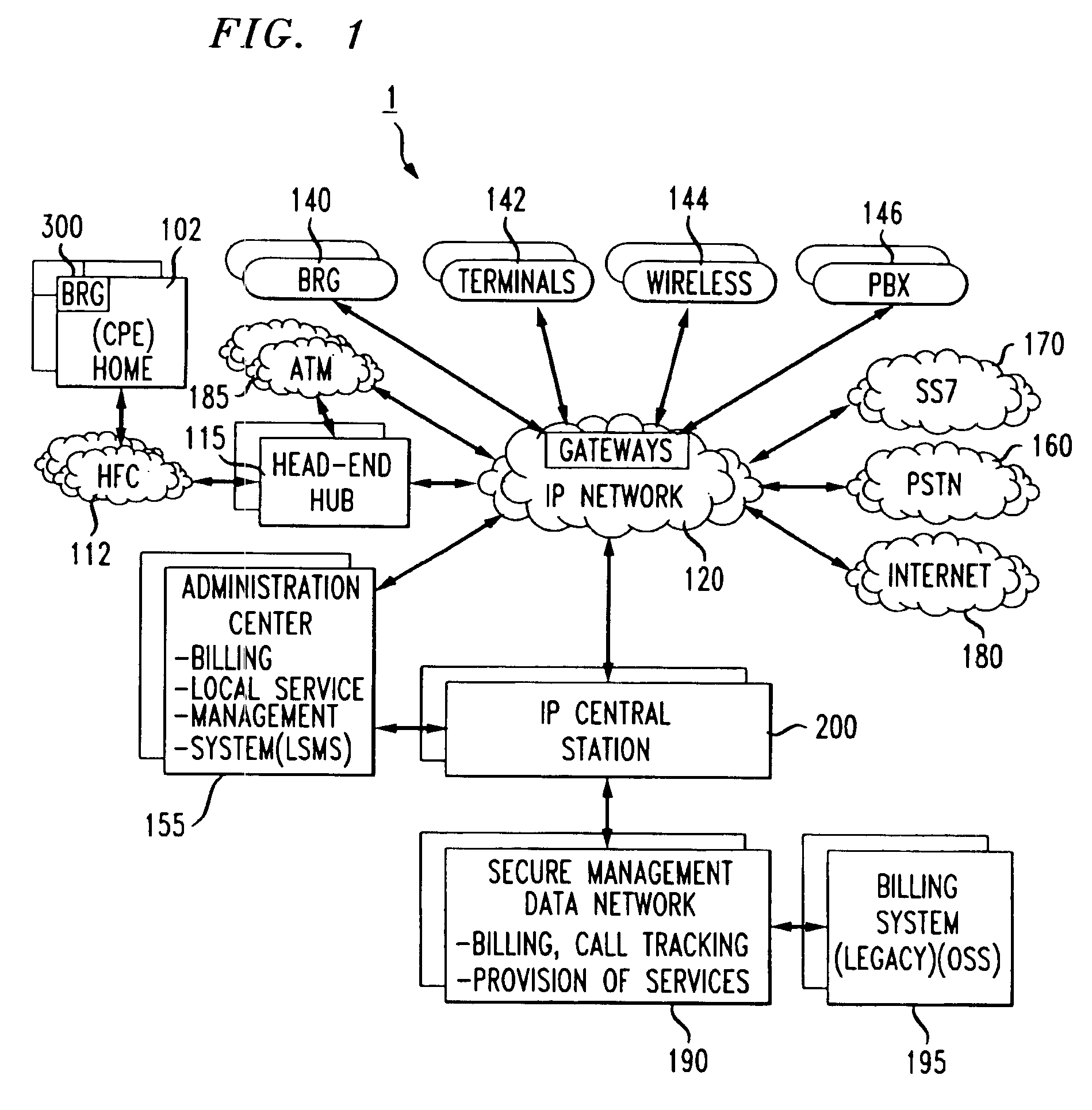
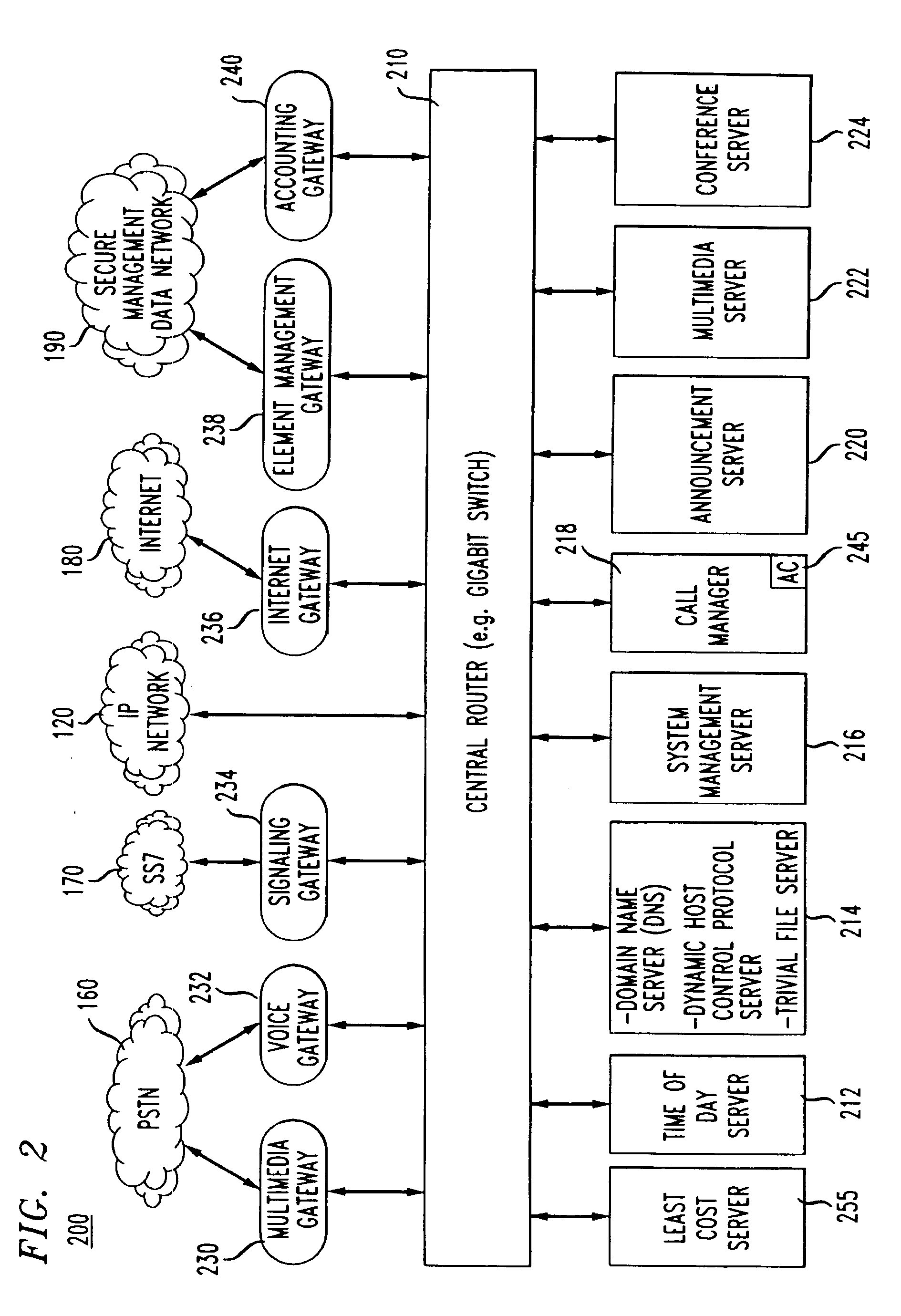
Broadband cable telephony network architecture IP ITN network architecture reference model
InactiveUS7120139B1Easy to deployMinimal costTelephone data network interconnectionsBroadband local area networksVoice communicationNetwork architecture
The present invention provides a system and method for a reliable, low-cost, secure Internet Protocol (IP) based network that provides broadband-based voice communications as well as video and data communications. The IP network is arranged to function with the infrastructure of the Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN), to control telephone calls in SS7 type networks and to provide the features, applications, and services of the typical SS7 networks in a voice over IP network. The present invention supports large effective call volumes, allows accommodation of a wide range of broadband-based service platforms, provides flexibility to support current and future calling feature services, and provides high quality voice transmission.
Owner:AMERICAN TELEPHONE & TELEGRAPH CO
Mobile robotic with web server and digital radio links
InactiveUS6658325B2Programme-controlled manipulatorDigital data processing detailsWeb serviceNetwork Communication Protocols
The invention is a computerized mobile robot with an onboard internet web server, and a capability of establishing a first connection to a remote web browser on the internet for robotic control purposes, and a capability of establishing a second short range bi-directional digital radio connection to one or more nearby computerized digital radio equipped devices external to the robot. The short-range bi-directional digital radio connection will typically have a maximum range of about 300 feet. In a preferred embodiment, this short-range wireless digital connection will use the 2.4 gHz band and digital protocols following the IEEE 802.11, 802.15, or other digital communications protocol. By employing the proper set of external short-range digital radio devices capable of interfacing with the robot (such as sensors, mechanical actuators, appliances, and the like), a remote user on the internet may direct the robot to move within range of the external devices, discover their functionality, and send and receive commands and data to the external devices through the CGI interface on the robot's onboard web server.
Owner:ZWEIG STEPHEN ELIOT
Solutions for voice over internet protocol (VoIP) 911 location services
ActiveUS7260186B2Emergency connection handlingSpecial service for subscribersInternet protocol suiteTTEthernet
An E-9-1-1 voice-over-IP (VoIP) solution is provided wherein a 911 call from a mobile VoIP device is routed directly to the correct Public Safety Answer Point (PSAP) via dedicated trunks, together with correct location information and call-back number. VoIP gateways are implemented locally, at least one per LATA, and accept VoIP packetized data inbound, and convert it to standard wireline voice calls. Calls are routed to an IP address at the VoIP gateway, which then egresses the call to a voice port at a selective router. Mid-call updating of location of a moving VoIP terminal is provided to a PSAP. The location of the VoIP is validated using HTTP based protocol by pushing location information to a VoIP location server, and comparing it against a geographic location database to confirm that a contained street address is valid.
Owner:TELECOMM SYST INC
Mobile ad hoc extensions for the internet
InactiveUS6845091B2Easy to addImprove robustnessError prevention/detection by using return channelNetwork traffic/resource managementTTEthernetNetwork measurement
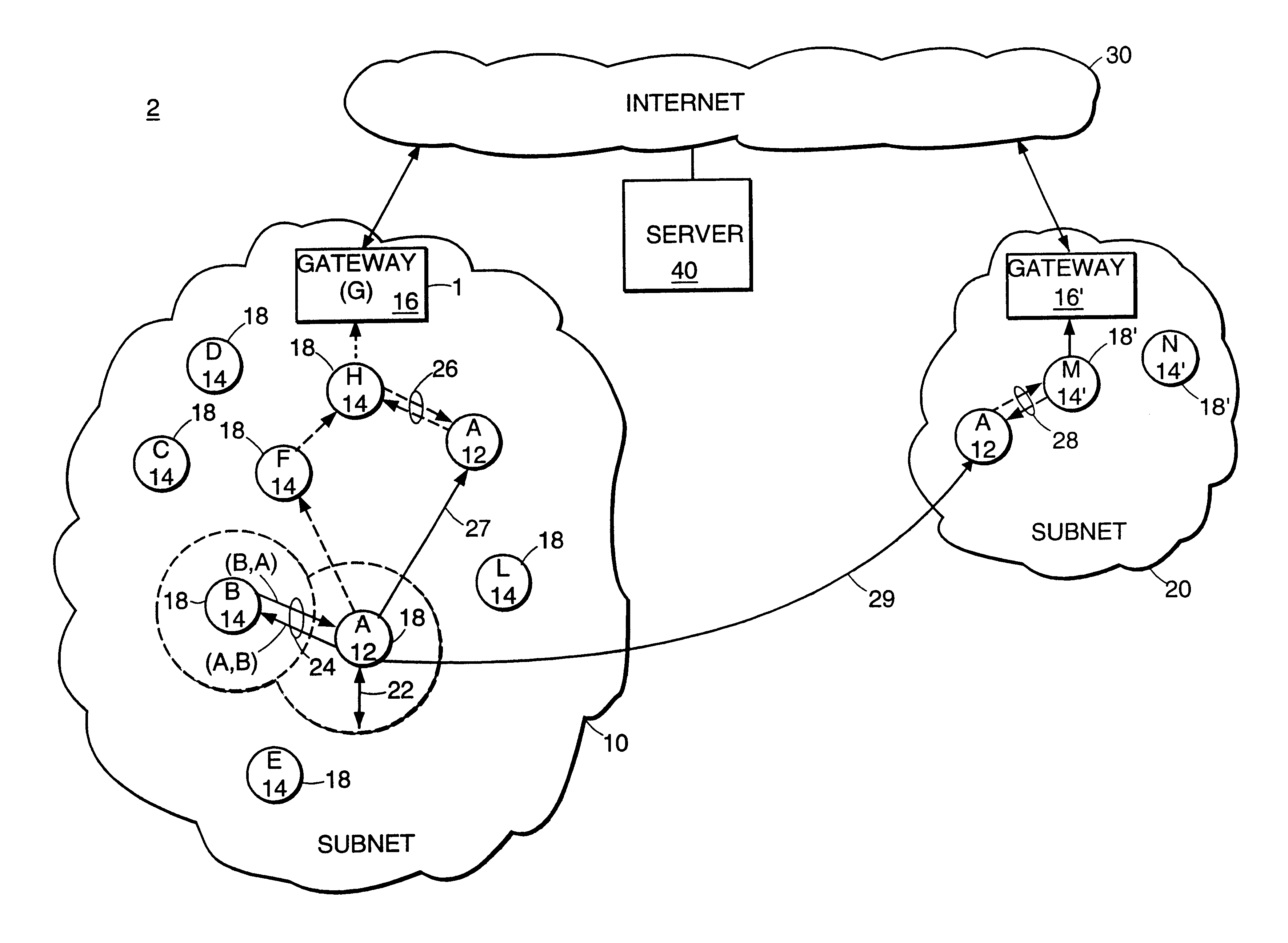
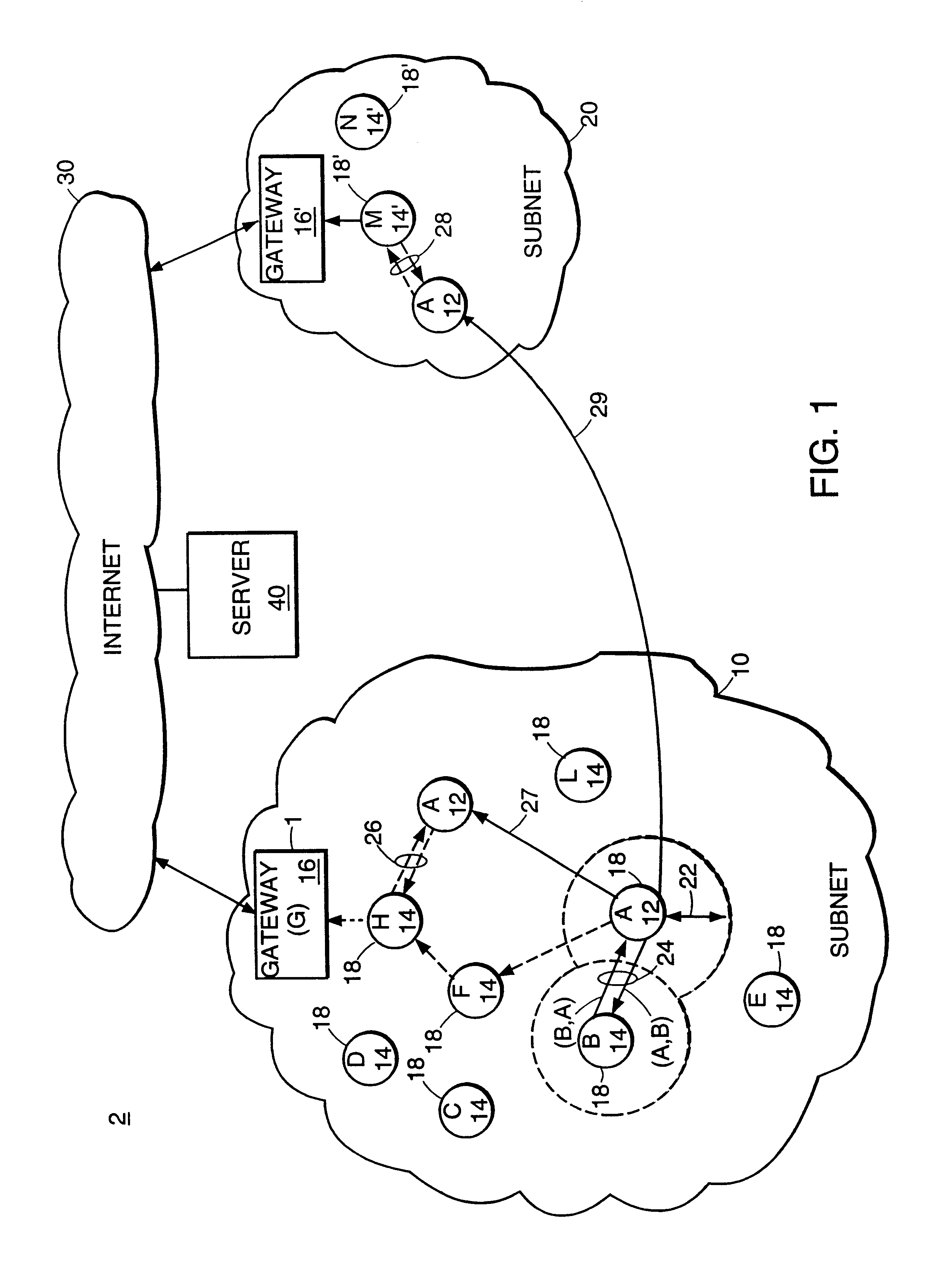
Described is an internetworking system having various mobile ad hoc extensions to the Internet that are particularly suited to the dynamic environment of mobile ad hoc networks. The internetworking system includes any combination of a link-state routing protocol for disseminating topology and link-state information over a multi-hop network comprised of nodes, a neighbor discovery protocol that can detect the appearance and disappearance of new neighbor nodes, an address format that facilitates deployment of IPv6 nodes in a predominantly IPv4 network infrastructure, a queuing mechanism that can update information upon resuming interrupted communications between nodes, and dynamic network measurement techniques for adaptively using wireless bandwidth when establishing and maintaining connections between nodes and a server.
Owner:SRI INTERNATIONAL
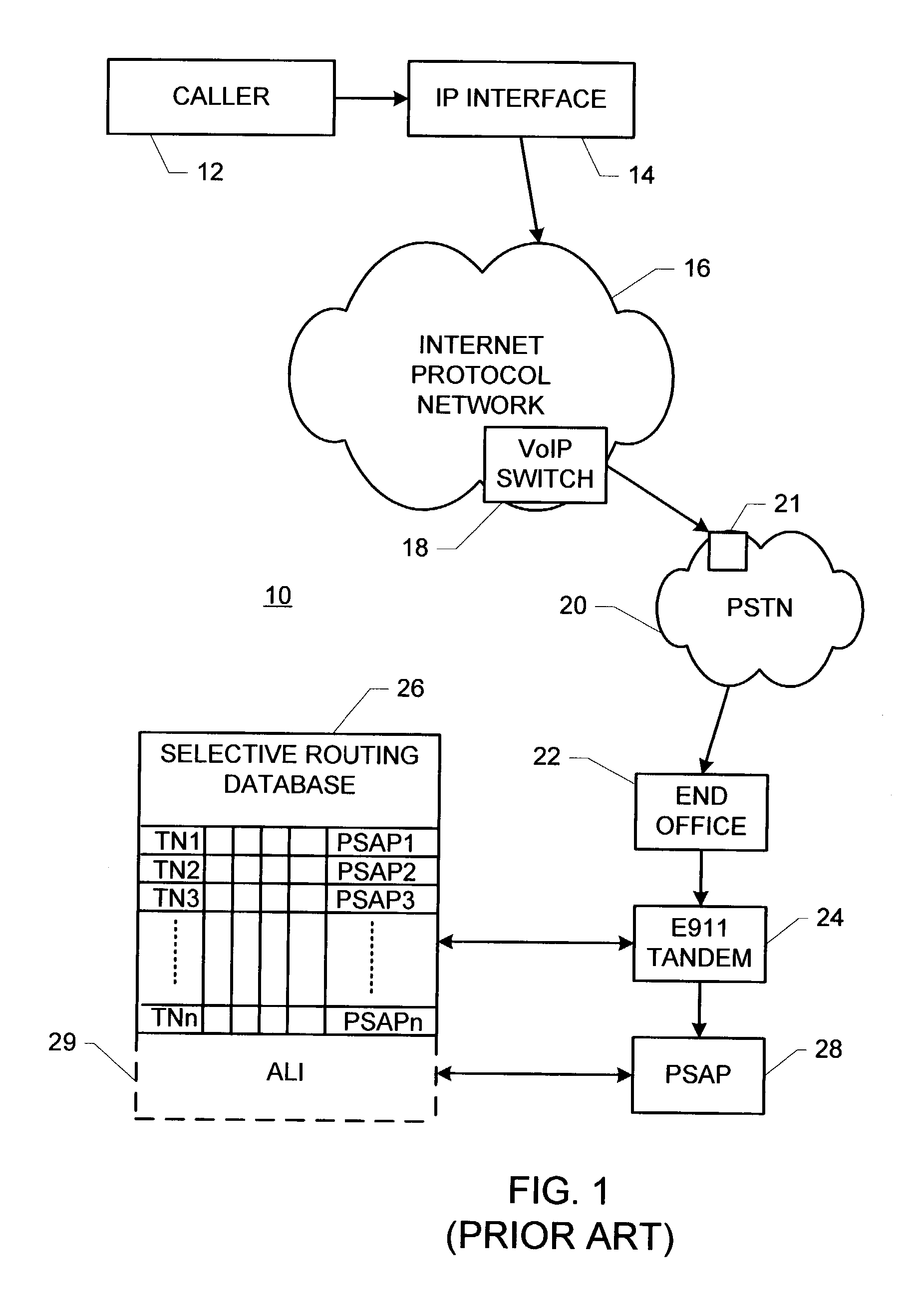
System and method for routing telephone calls involving internet protocol network
InactiveUS6963557B2Easy to routeMultiplex system selection arrangementsInterconnection arrangementsTTEthernetCoupling
A system for routing telephone calls from a calling party instrument to a called party instrument and involving at least one internet protocol network includes: (a) a first internet protocol interface apparatus effecting a first communicative coupling between the calling party instrument and the at least one internet protocol network; (b) a second internet protocol interface apparatus effecting routing telephone calls according to routing criteria to establish a second communicative coupling between the at least one internet protocol network and the called party instrument; and (c) a call routing system apparatus coupled with the second internet protocol interface apparatus and storing information relating to a geographical or geospatial relationship of calling party instruments and called party instruments. The second internet protocol interface apparatus and the call routing system apparatus cooperate to establish the routing criteria.
Owner:INTRADO LIFE & SAFETY INC
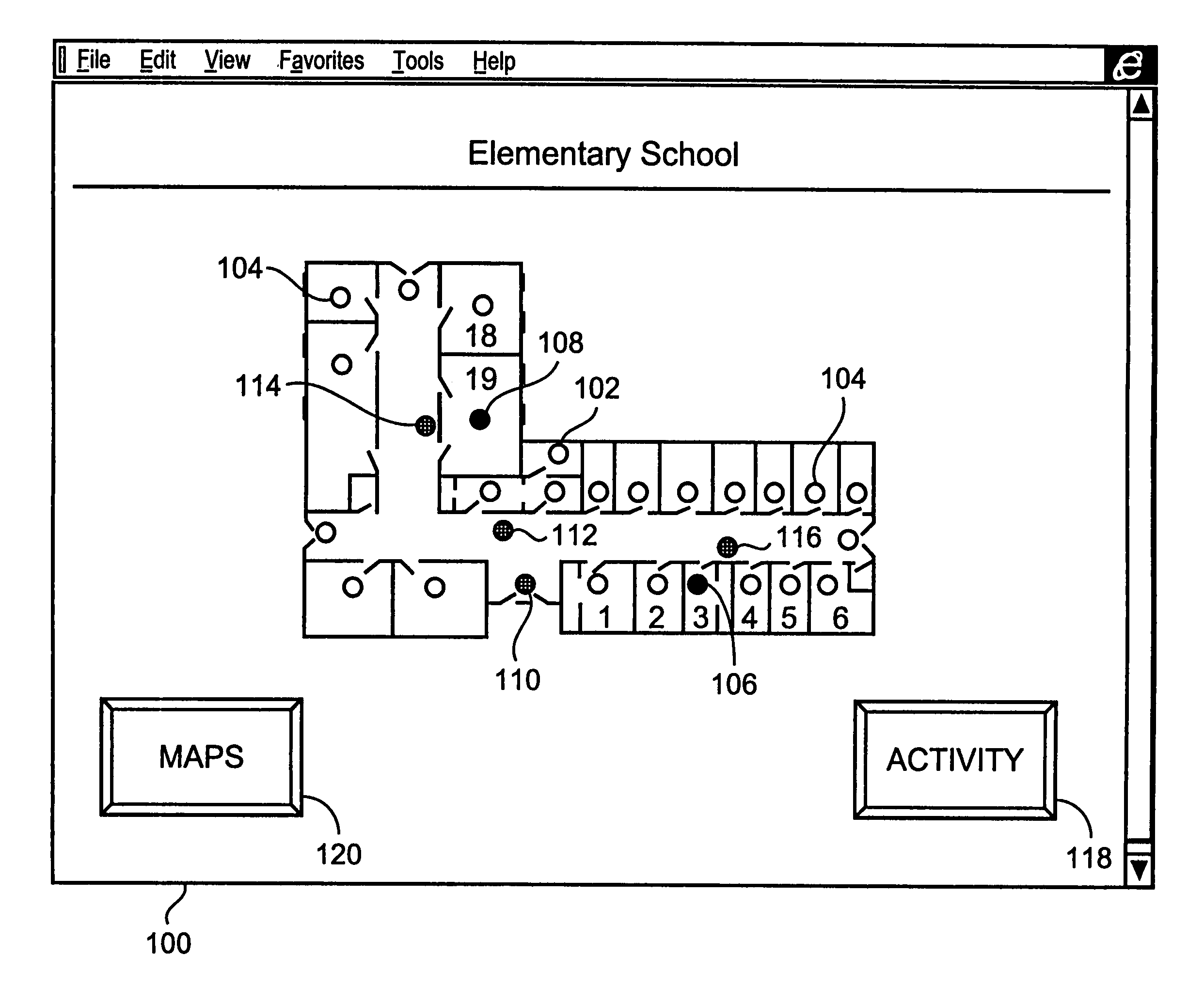
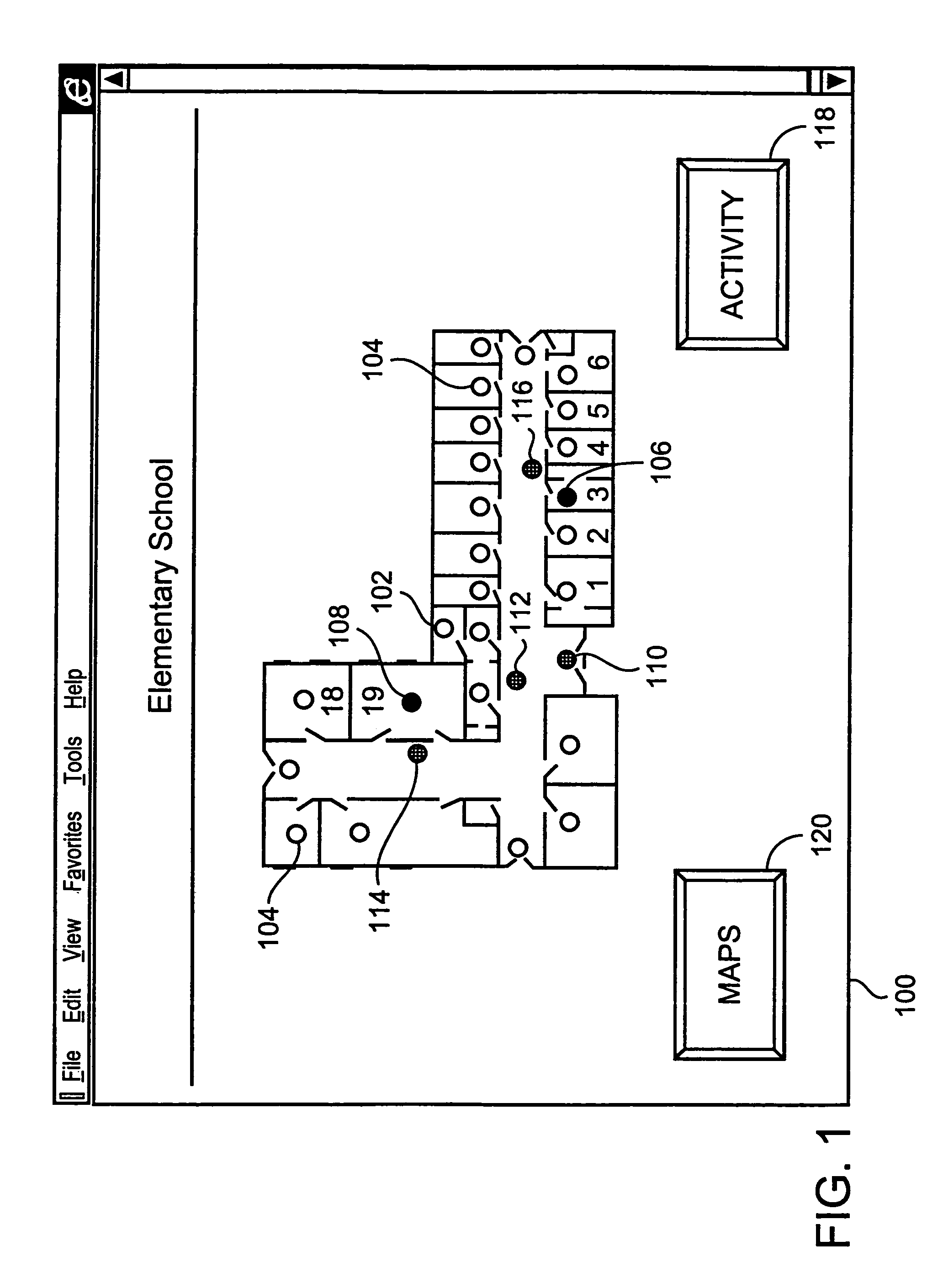
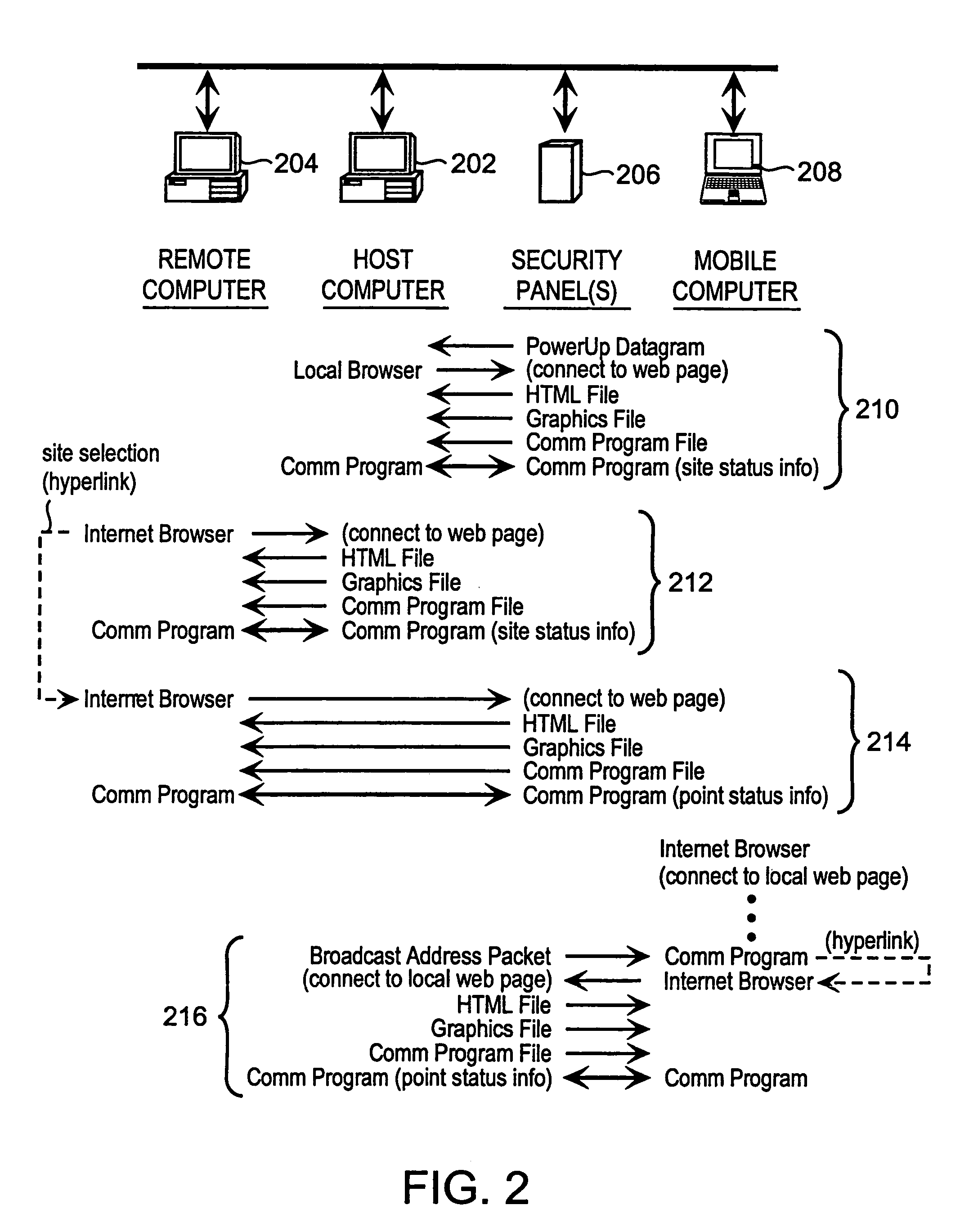
Method and apparatus for remotely monitoring a site
InactiveUS6972676B1Easy to distinguishAccurate locationElectric testing/monitoringElectric/electromagnetic visible signallingTime informationOperating energy
The present invention is directed to providing systems and methods for remotely monitoring sites to provide real time information which can readily permit false alarms to be distinguished, and which can identify and track the precise location of an alarm. In exemplary embodiments, monitoring capabilities such as intrusion / fire detection and tracking capabilities, can be implemented through the use of multistate indicators in a novel interface which permits information to be transmitted using standard network protocols from a remote site to a monitoring station in real-time over preexisting communication networks, such as the Internet. A wireless network can also be established using browser encapsulated communication programs (for example, active X control, Java applets, and so forth) to transmit data packets which comply with any standard wireless local area network protocol. Communications can thereby be established between a web server embedded in a centrally located host monitoring station and a separate security panel deployed in each of the buildings to be remotely monitored. In exemplary embodiments, communications can be handed off from the centrally located host monitoring station to a mobile monitoring station (for example, to a laptop computer in a responding vehicle, such as a police or fire vehicle). The handoff can be such that direct communications are established between a security panel site being monitored and the laptop, or over, for example, a cellular network or indirect communications can be established via the host monitoring station.
Owner:NETTALON SECURITY SYST
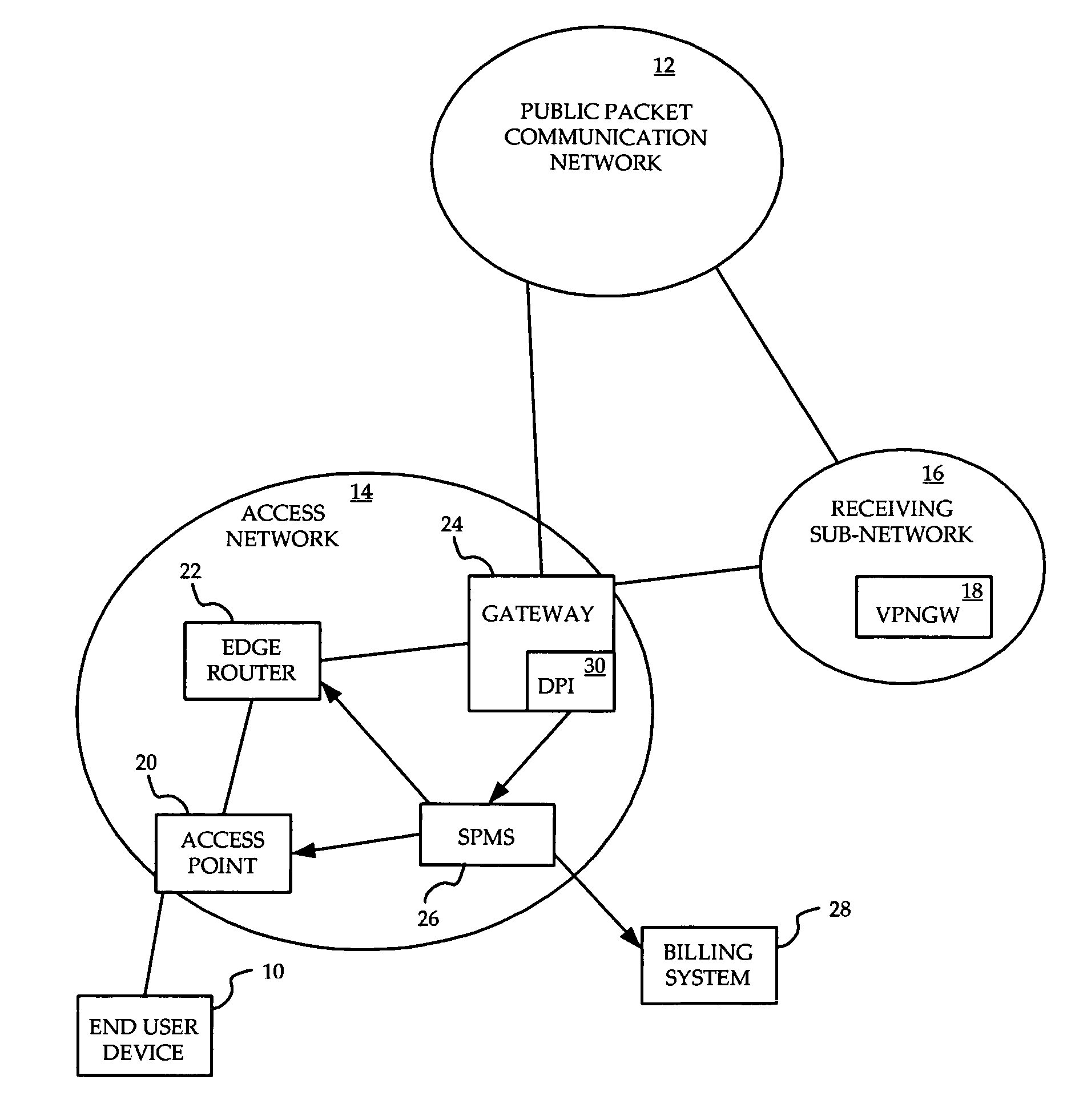
System and method for prioritization of traffic through internet access network
InactiveUS7881199B2Avoid allocation problemsRaise priorityError preventionTransmission systemsPacket communicationTraffic capacity
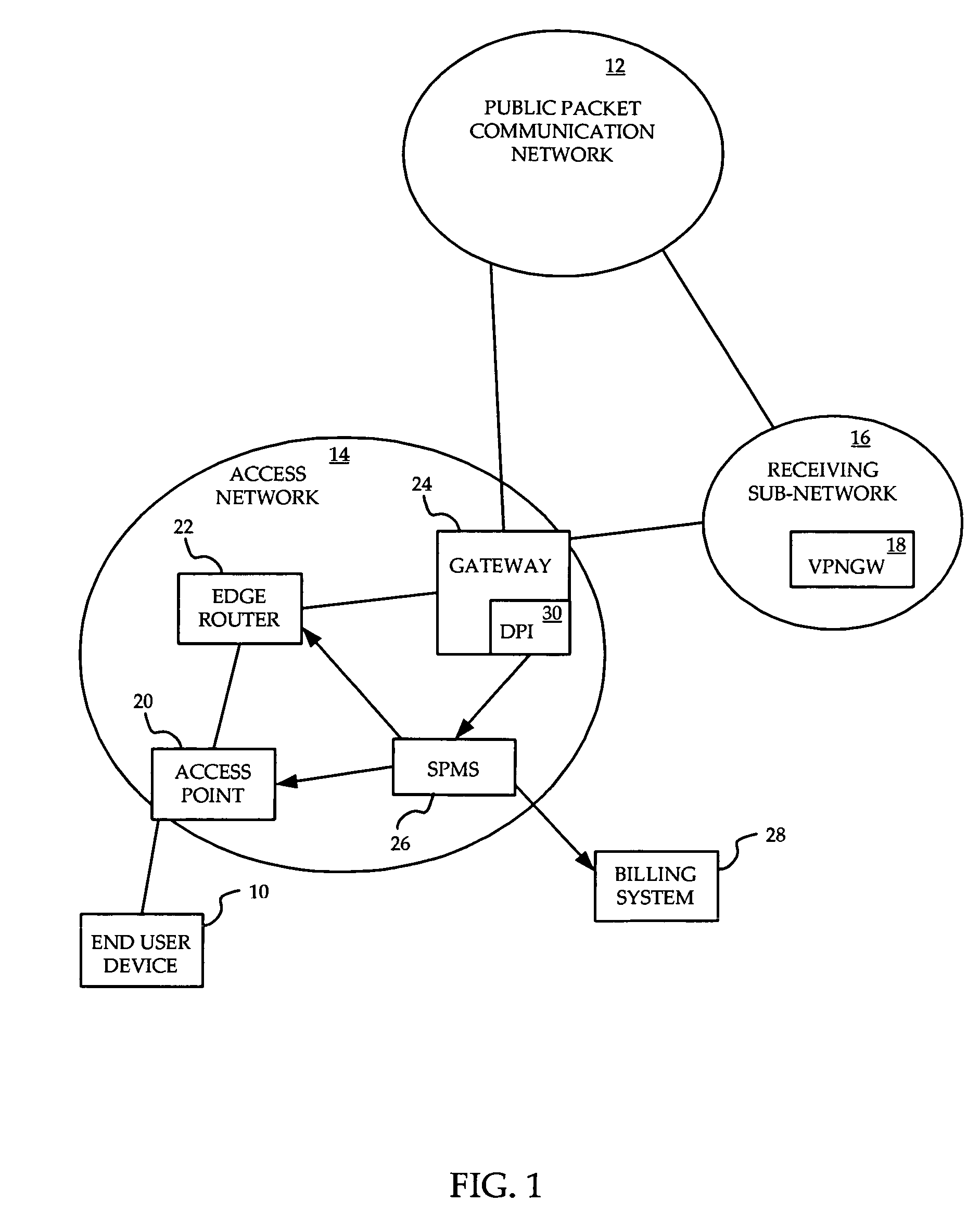
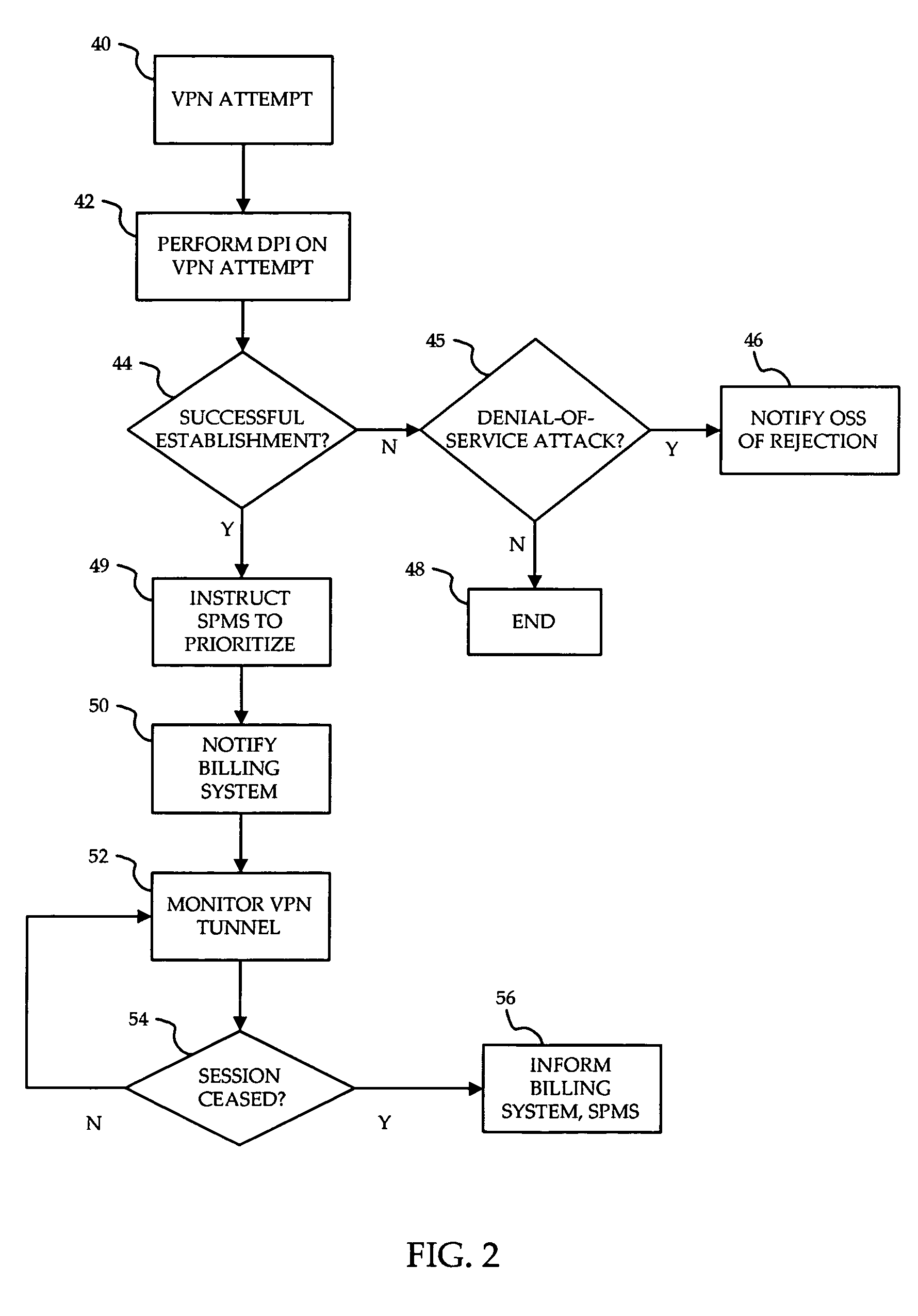
A method is provided for ensuring that specific traffic flows are adequately prioritized in a public packet communication network even when the network is heavily congested. Per-flow QoS capability is added to VPN tunnels. Connection requests are routed through a specific port in an access provider's network to designated VPN gateway. Deep packet inspection is performed on traffic through the port in an attempt to determine whether the connection request was accepted. If the connection request was accepted, the traffic flows associated with that session may be given a specific priority of QoS level when transiting a packet access network.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
Enabling incoming VoIP calls behind a network firewall
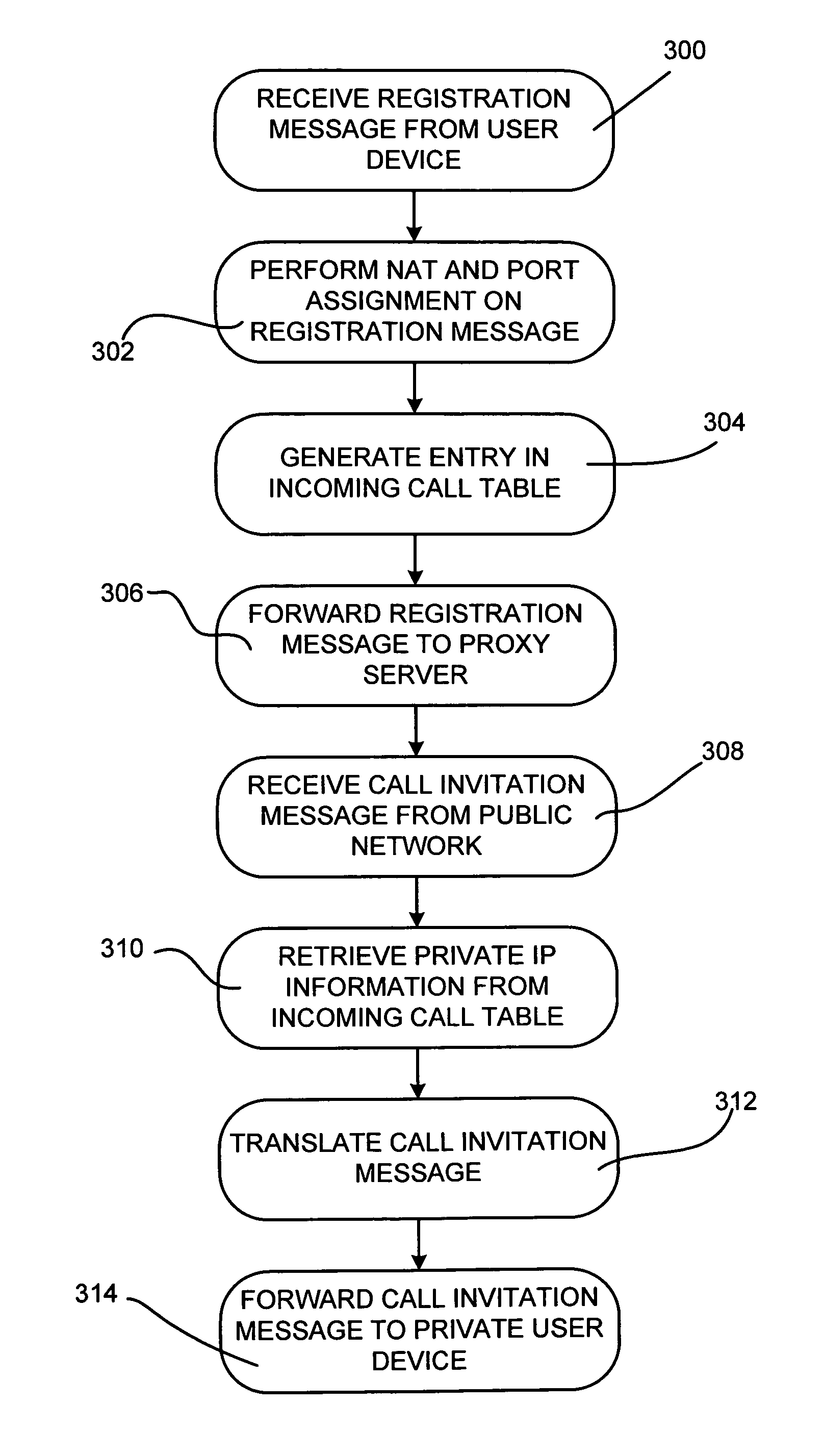
A network device is configured to receive a registration message from a private user device including a private internet protocol (IP) address associated with the private user device. A public IP address and discrete port number are assigned to the private user device and private IP address and stored in an incoming call table. The registration message is translated to include the public IP address and discrete port number. The registration message is forwarded to a proxy server for registration. An incoming call invitation message is received from a public user device, where the call invitation message is directed to the public IP address and discrete port number associated with the private user device. The call invitation message is translated to include the private IP address associated with the private user device based on the received public IP address and discrete port number and the incoming call table. The call invitation message is forwarded to the private user device.
Owner:JUMIPER NETWORKS INC
Internet-based telephone call manager
InactiveUS6212261B1Improve handlingImprove abilitiesInterconnection arrangementsSpecial service for subscribersData connectionData information
A method is provided that allows data access service provider subscribers to manage their telephone service through a data connection. The subscriber is enabled to obtain call data information and is provided real time control. During a data call, a visual incoming call indicator informs the subscriber, through a popup window, connected to the data access service provider that there is a call attempt. A visual message waiting indicator allows a subscriber, connected to the data access service provider to be notified of a pending message on the voice message system. A visual call disposition allows the subscriber, through the data connection, to dispose of calls. The call disposition options include forwarding a call to voice mail, playing an announcement to the calling party, forwarding the call to another line, sending a text message which could be converted to speech using text to speech technology, answering the call using voice over data call or terminating the data connection in order to accept the call.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
Wireless access of packet based networks
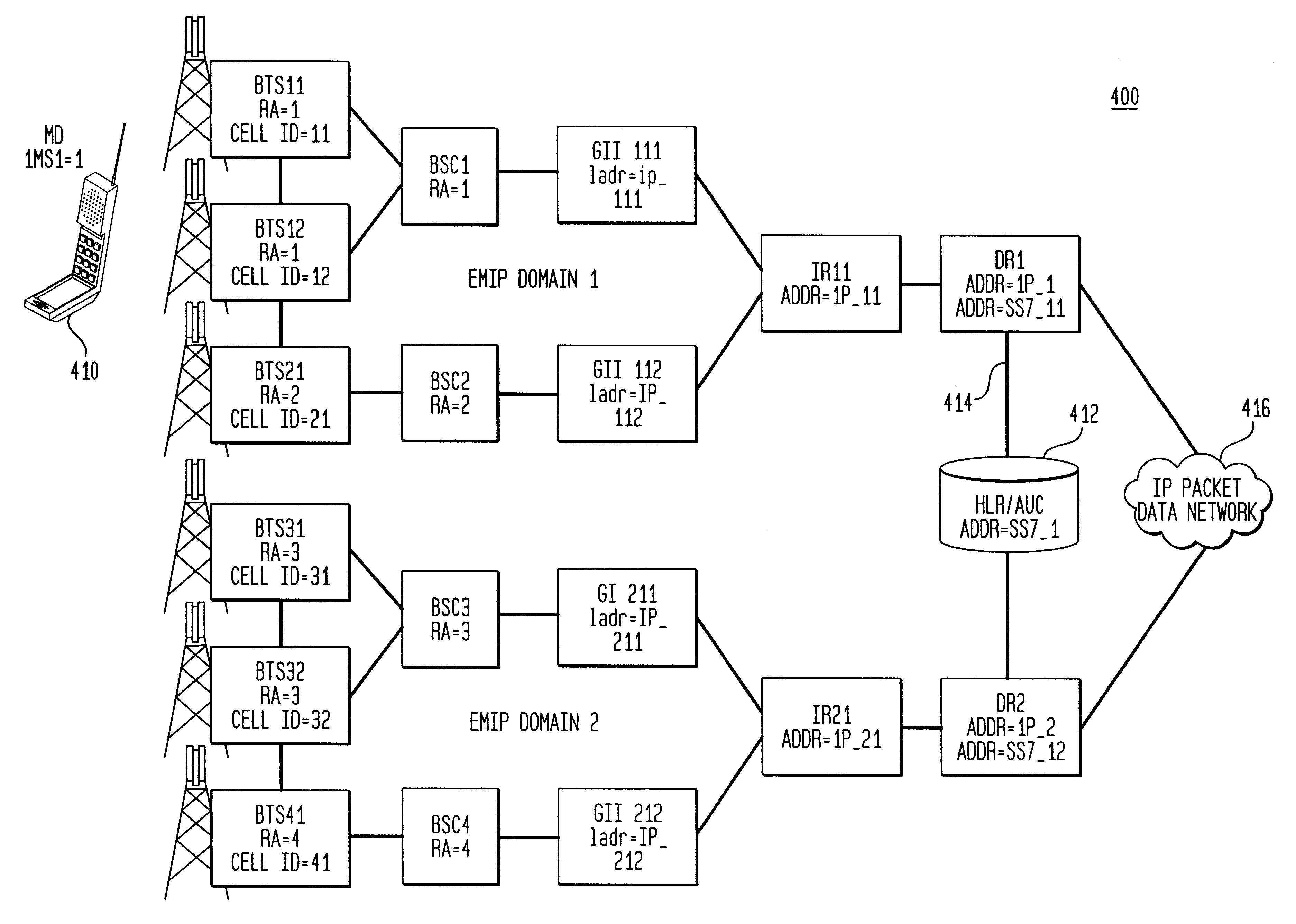
A General Packet Radio Service (GPRS) Accessed Extended Mobile Internet Protocol (EMIP) [G-EMIP] network is provided for wireless mobile device access to external packet data networks. Domains are defined to incorporate a subnet of standard GPRS and EMIP network entities accessed through a Domain Router. Packet access at the radio interface is provided using the base station portion of a GPRS network. Wireless link specific processing is relegated to this potion of the G-EMIP network. EMIP is utilized as a backbone network to provide mobility and service management and interconnection to external networks. A GPRS-IP Interworking entity (GII) interworks IP and GPRS protocols between GPRS and IP addressable network entities (i.e., translates messages of each protocol to corresponding messages of the other protocol). Mobility-related functionality is handled at the IP (network) layer. Mobile IP is used to support the macro-mobility and Handoff-Aware Wireless Access Internet Infrastructure (HAWAII) is used to support micro-mobility and paging. The Domain Router provides packet service management and interacts with a Home Location Register / Authentication Center, which provides GRPS registration, authentication and encryption.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC +1
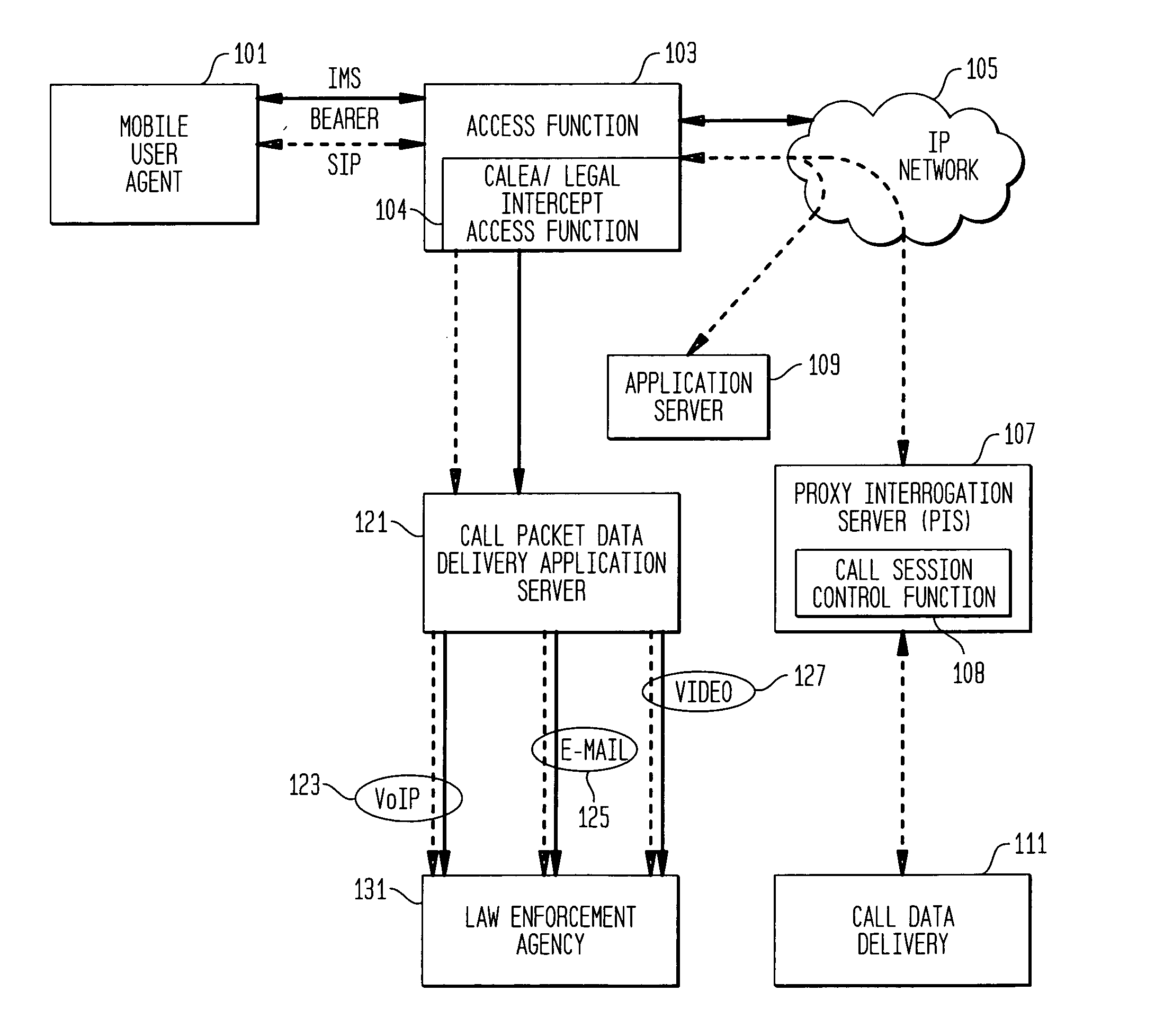
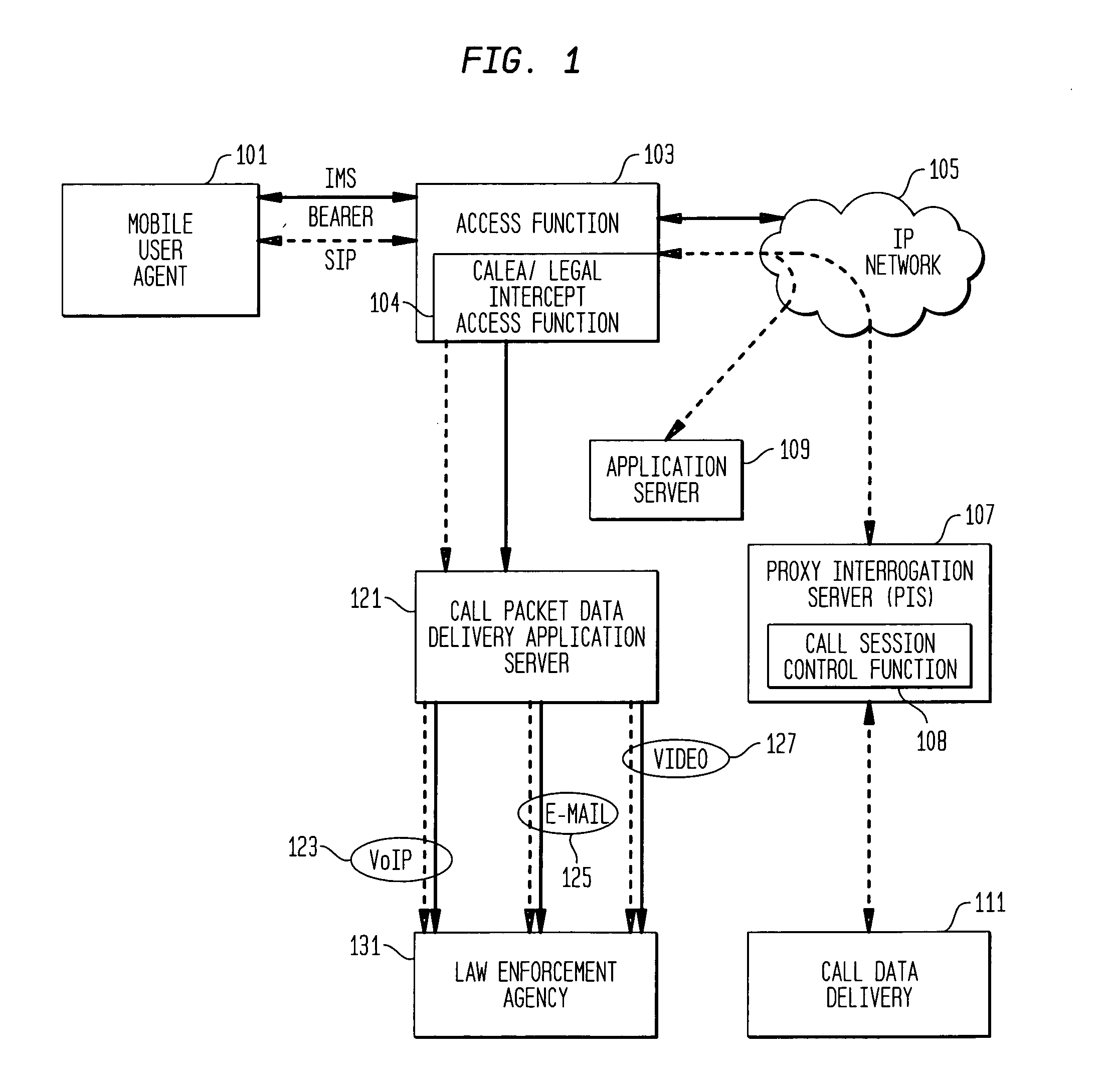
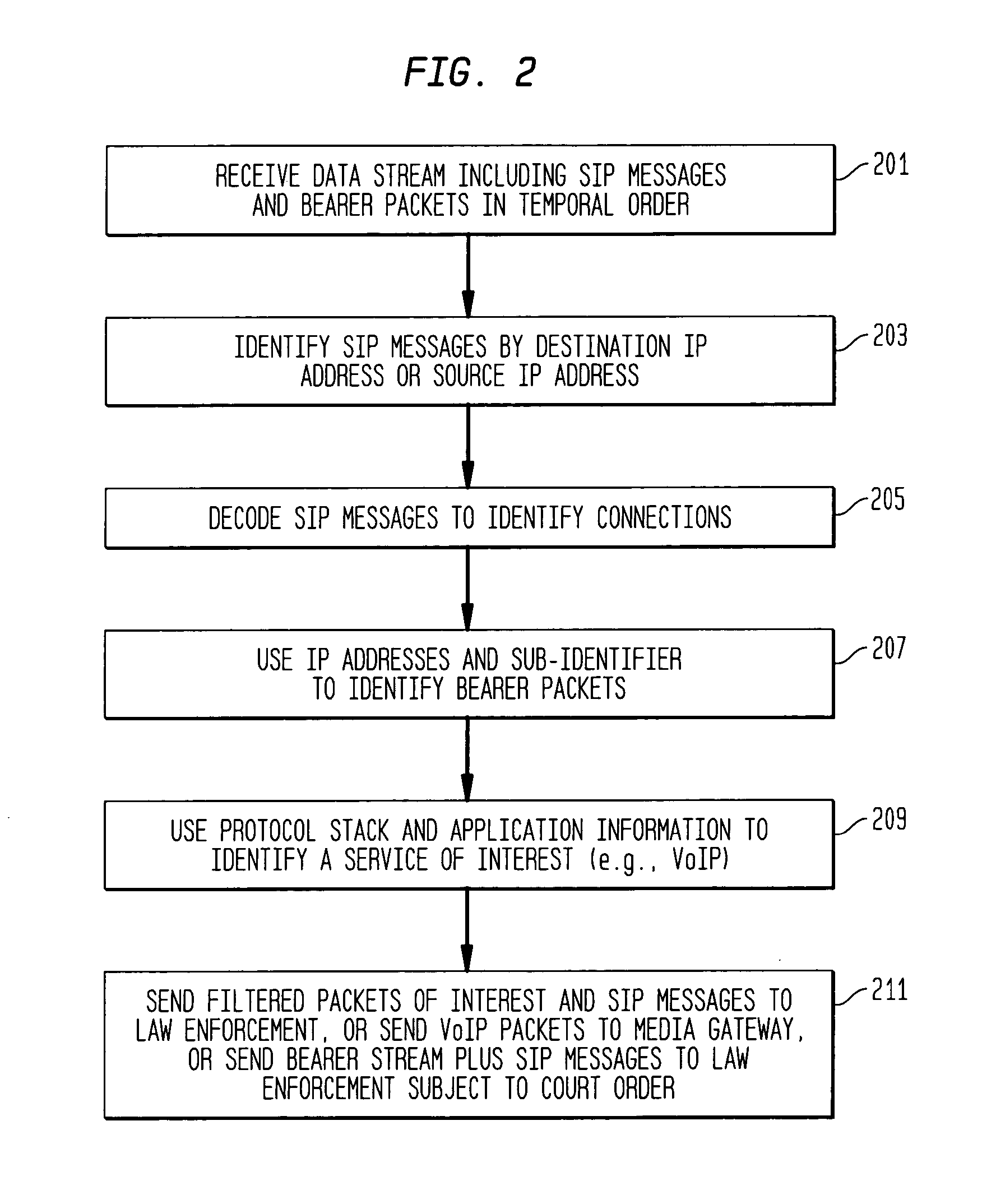
Providing CALEA/LegaI Intercept information to law enforcement agencies for internet protocol multimedia subsystems (IMS)
ActiveUS20060072550A1Supervisory/monitoring/testing arrangementsRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsData connectionApplication server
A method and apparatus for providing useful packet data to a CALEA / Legal Intercept collection function. At an access point to a network such as the Internet, sources and destinations of data connections are examined to determine whether any of the bearer messages should also be routed to a CALEA / Legal Intercept monitoring system. If this condition is recognized, the bearer messages and corresponding signaling control messages are correlated in a call packet delivery application server and then delivered to a CALEA / Legal Intercept monitoring system. Advantageously, the monitoring receives as a bundled message set the bearer message and the control messages used to route and otherwise process these bearer messages.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com