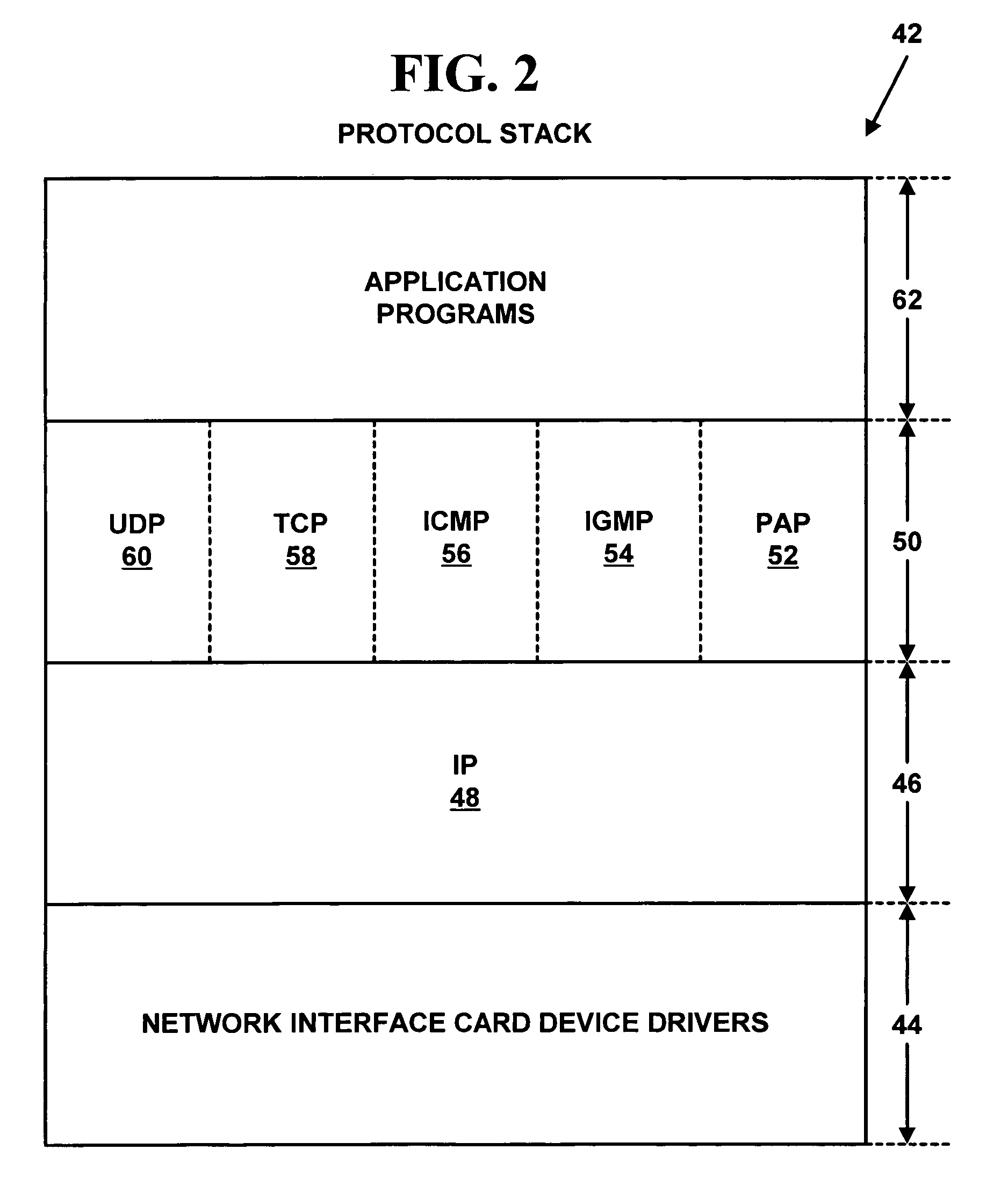
Patents
Literature
1827 results about "Network address translation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
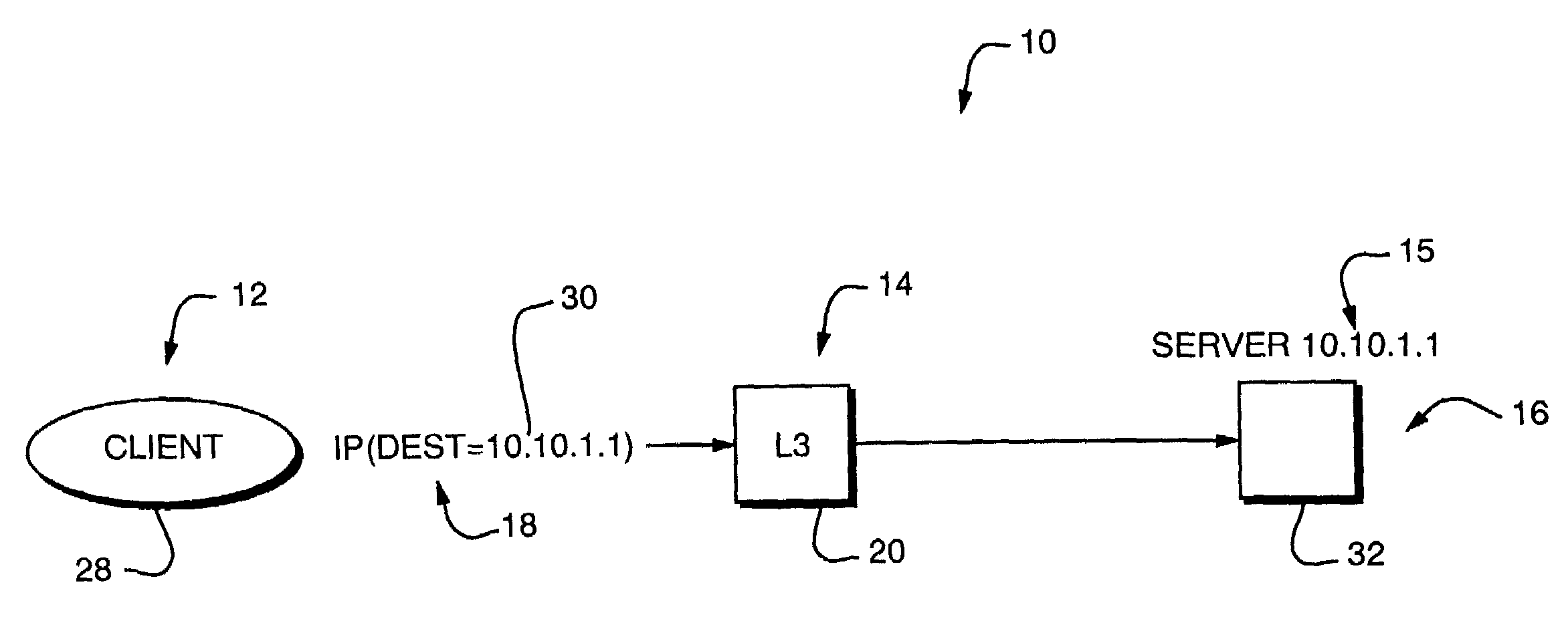
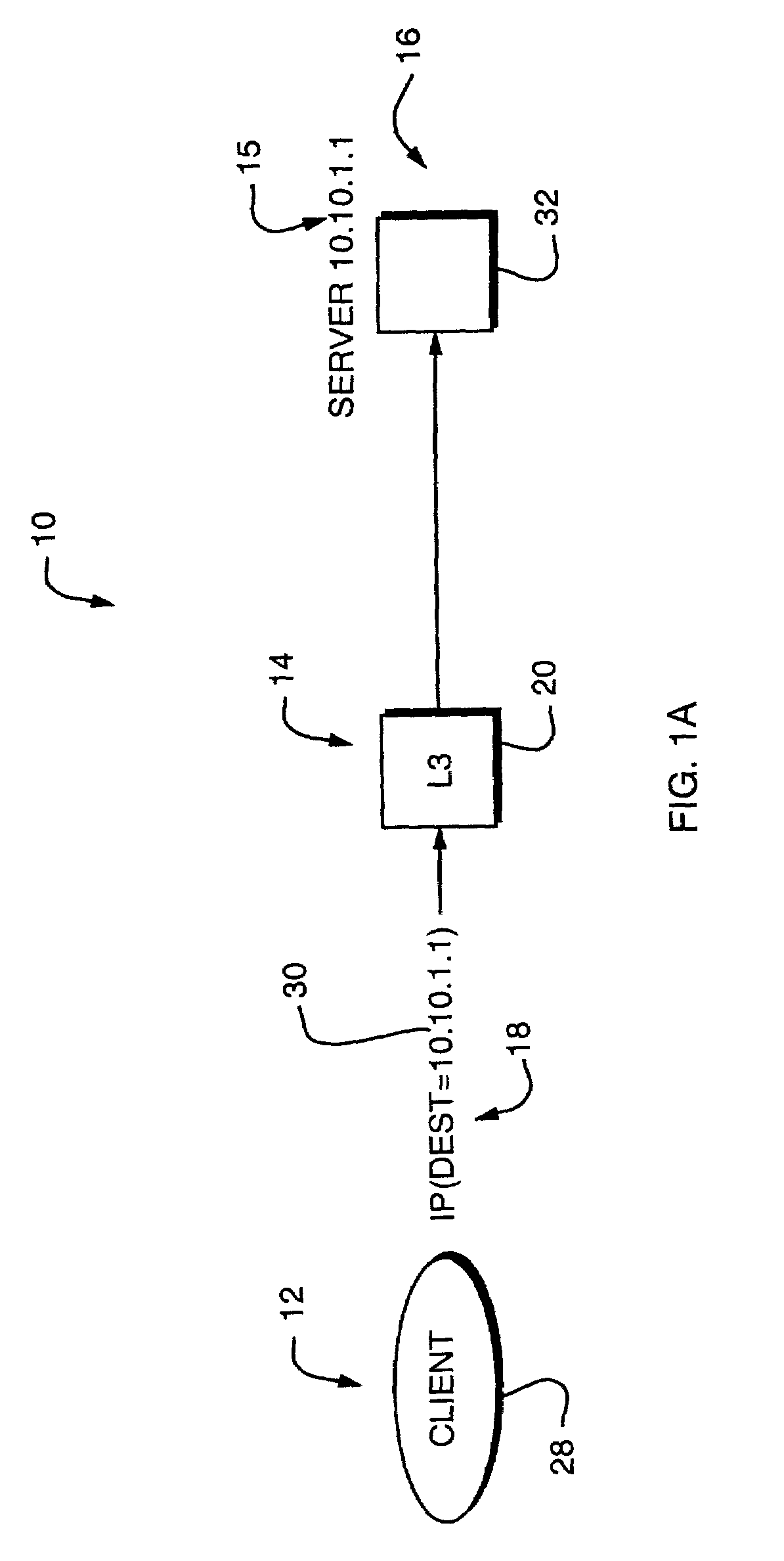
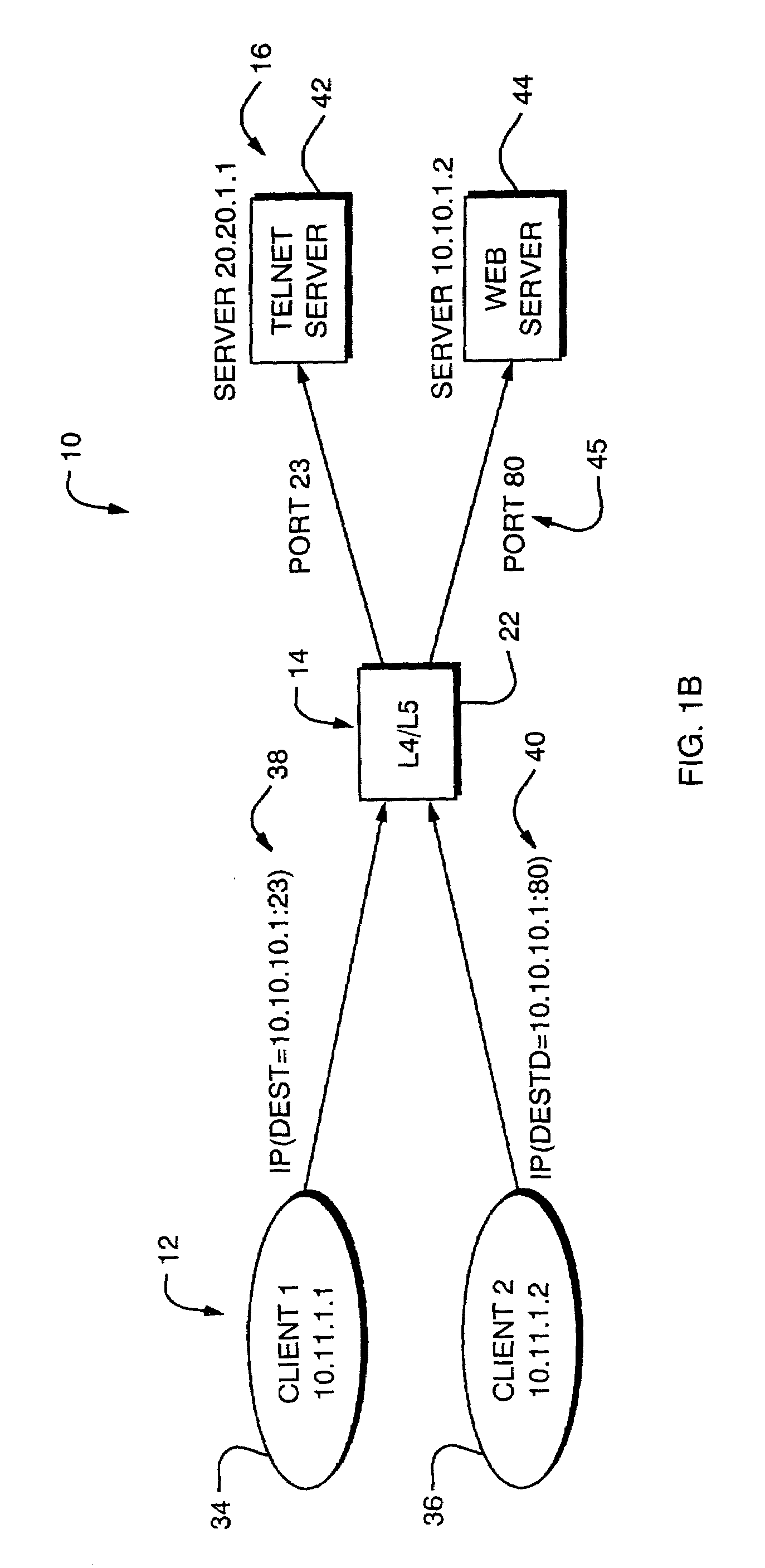
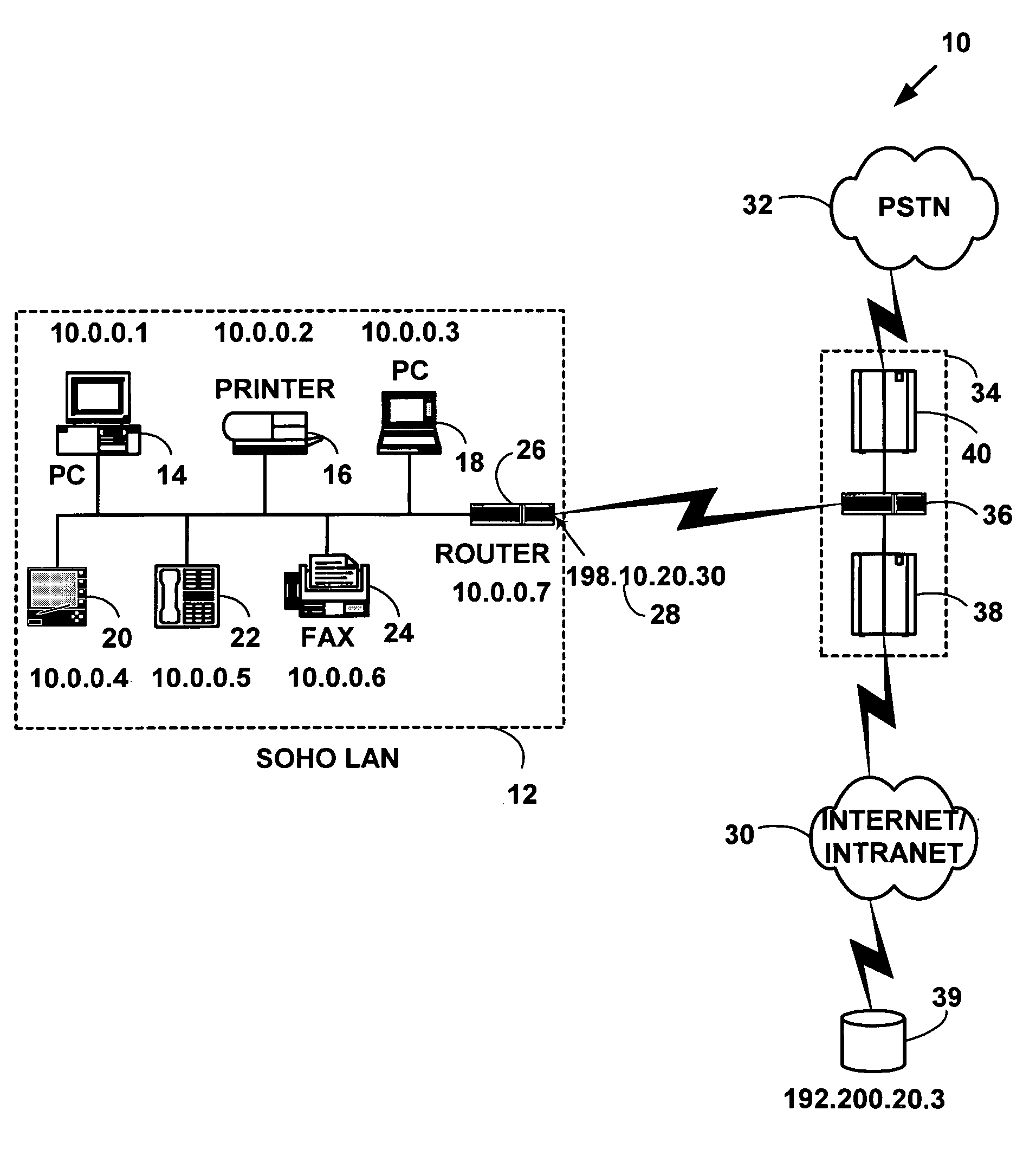
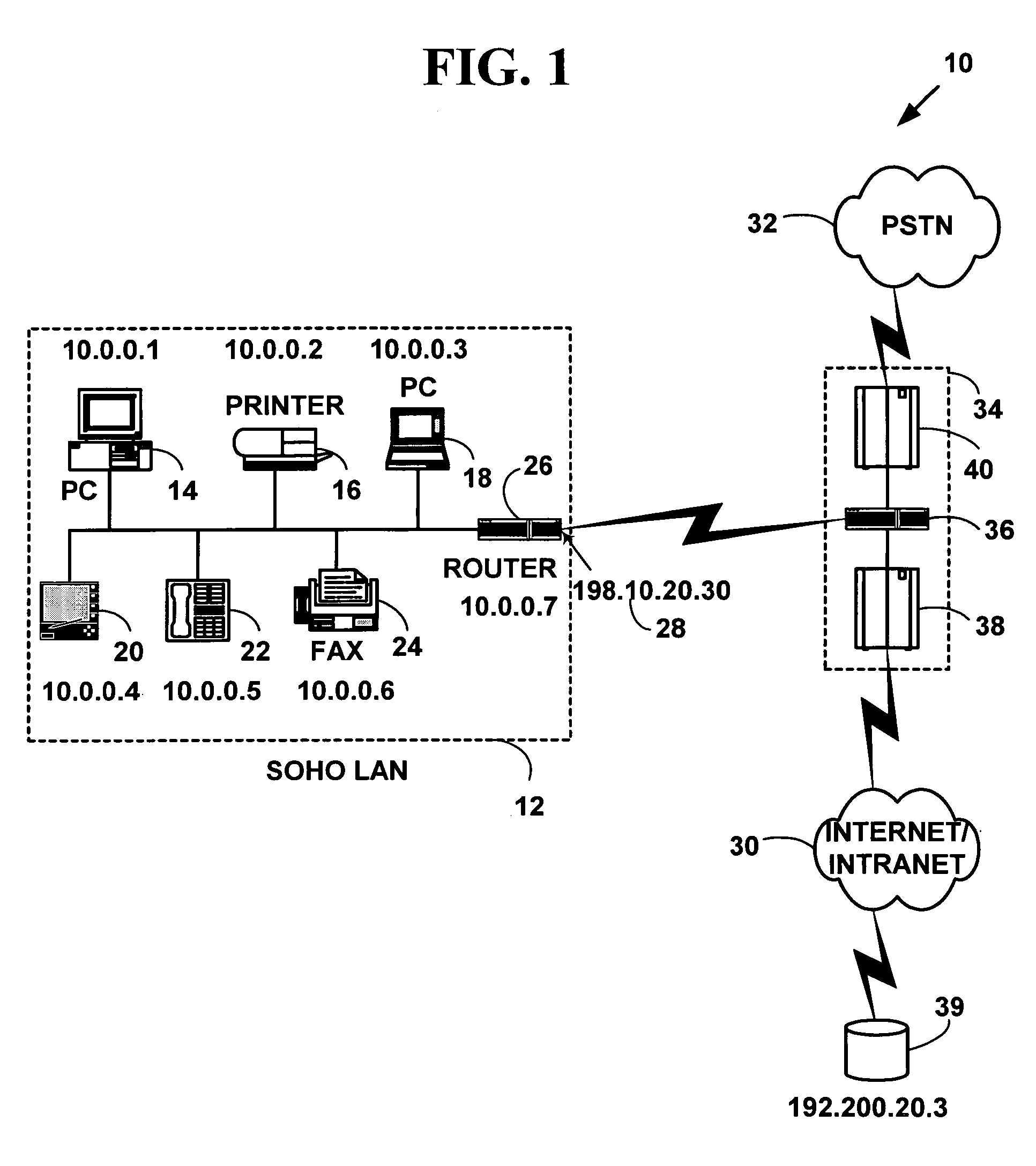
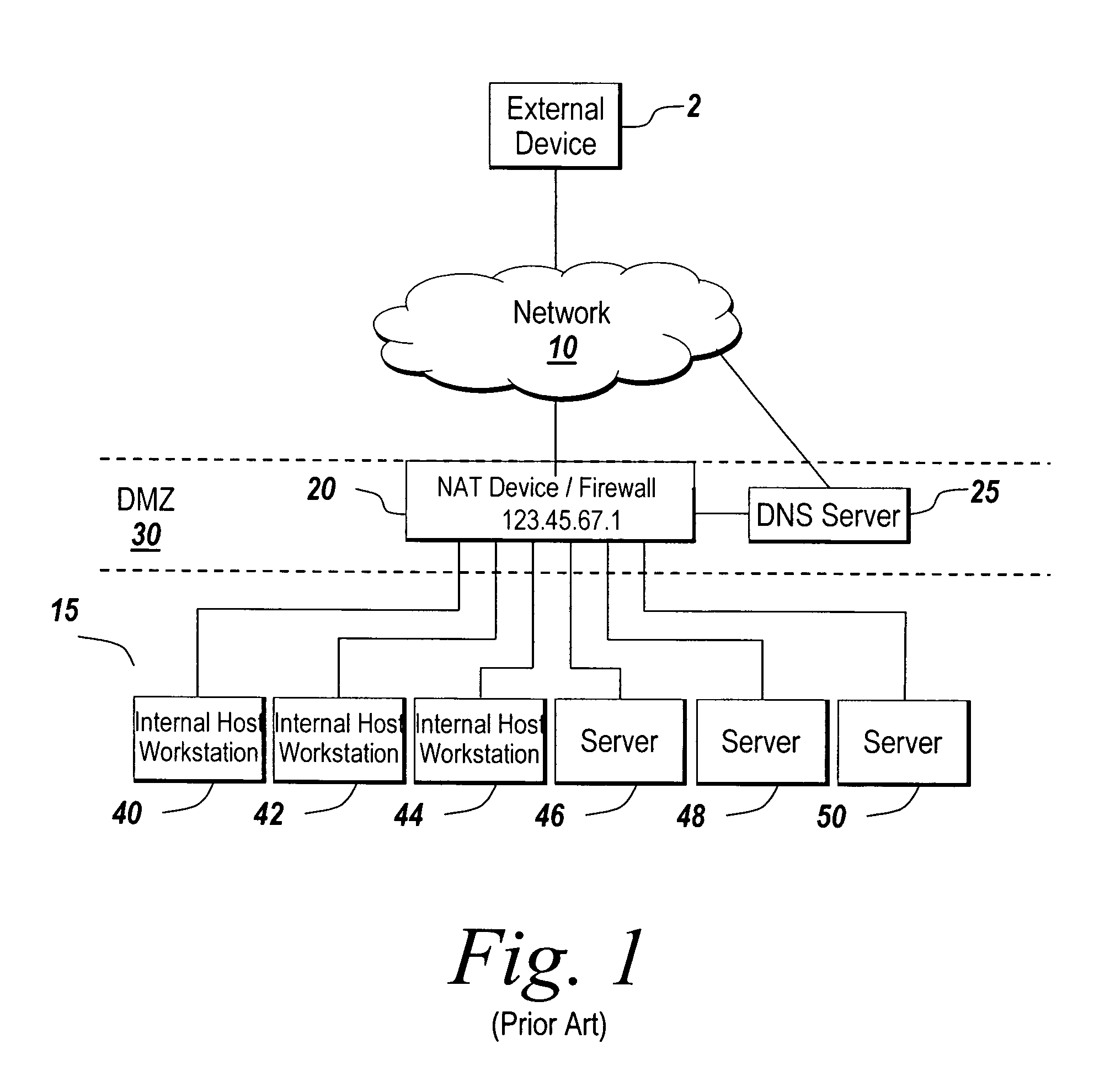
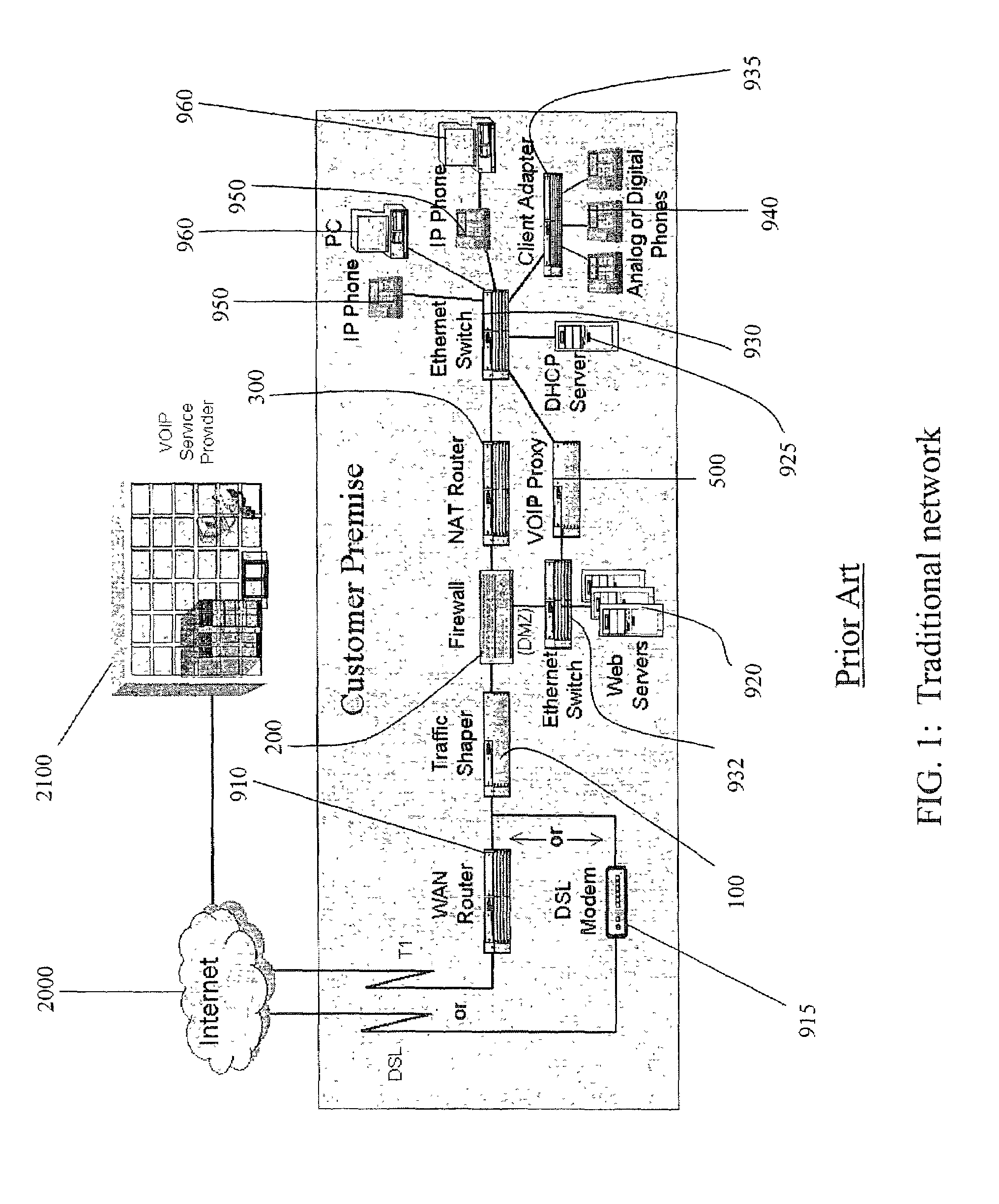
Network address translation (NAT) is a method of remapping one IP address space into another by modifying network address information in the IP header of packets while they are in transit across a traffic routing device. The technique was originally used as a shortcut to avoid the need to readdress every host when a network was moved. It has become a popular and essential tool in conserving global address space in the face of IPv4 address exhaustion. One Internet-routable IP address of a NAT gateway can be used for an entire private network.
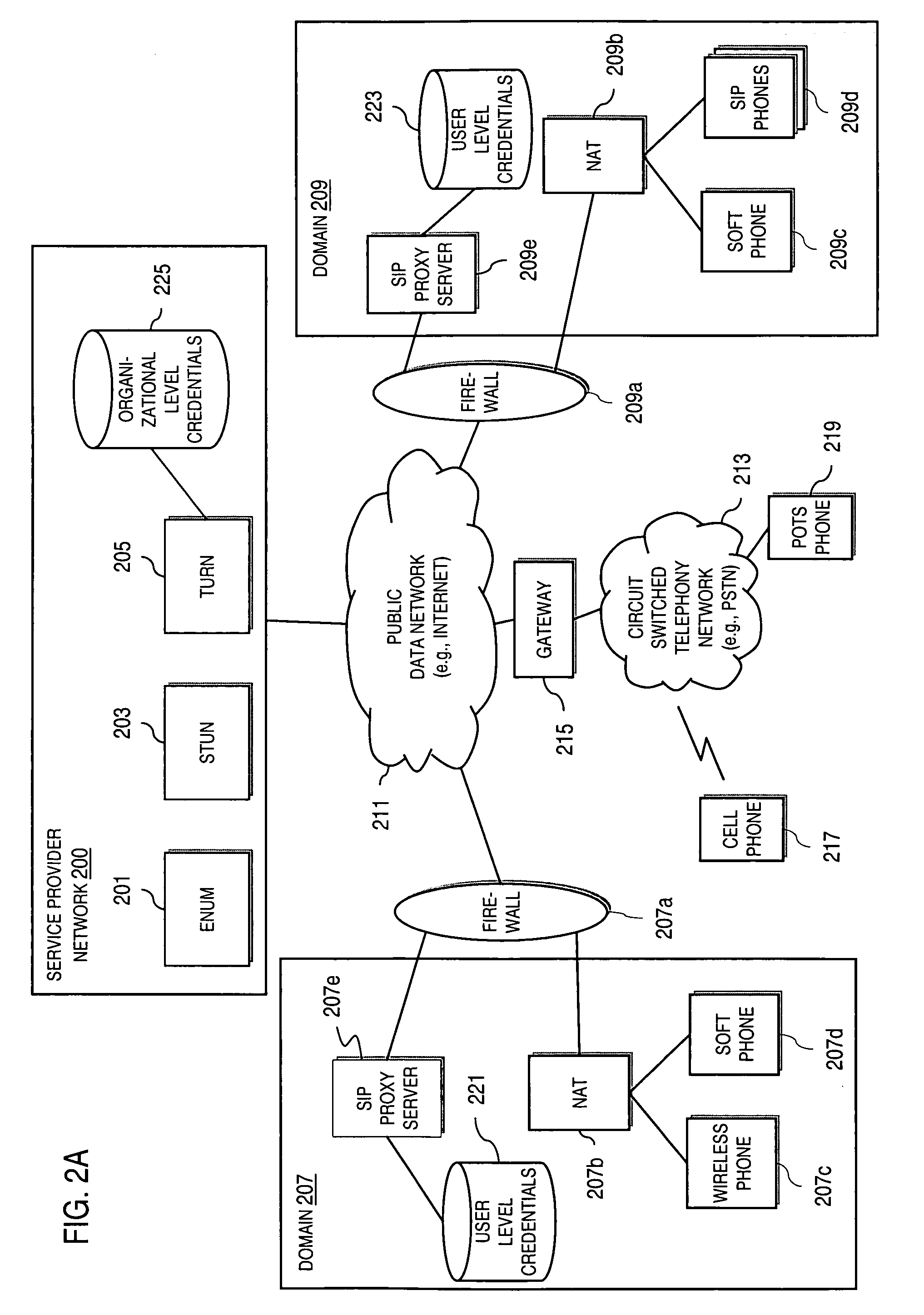
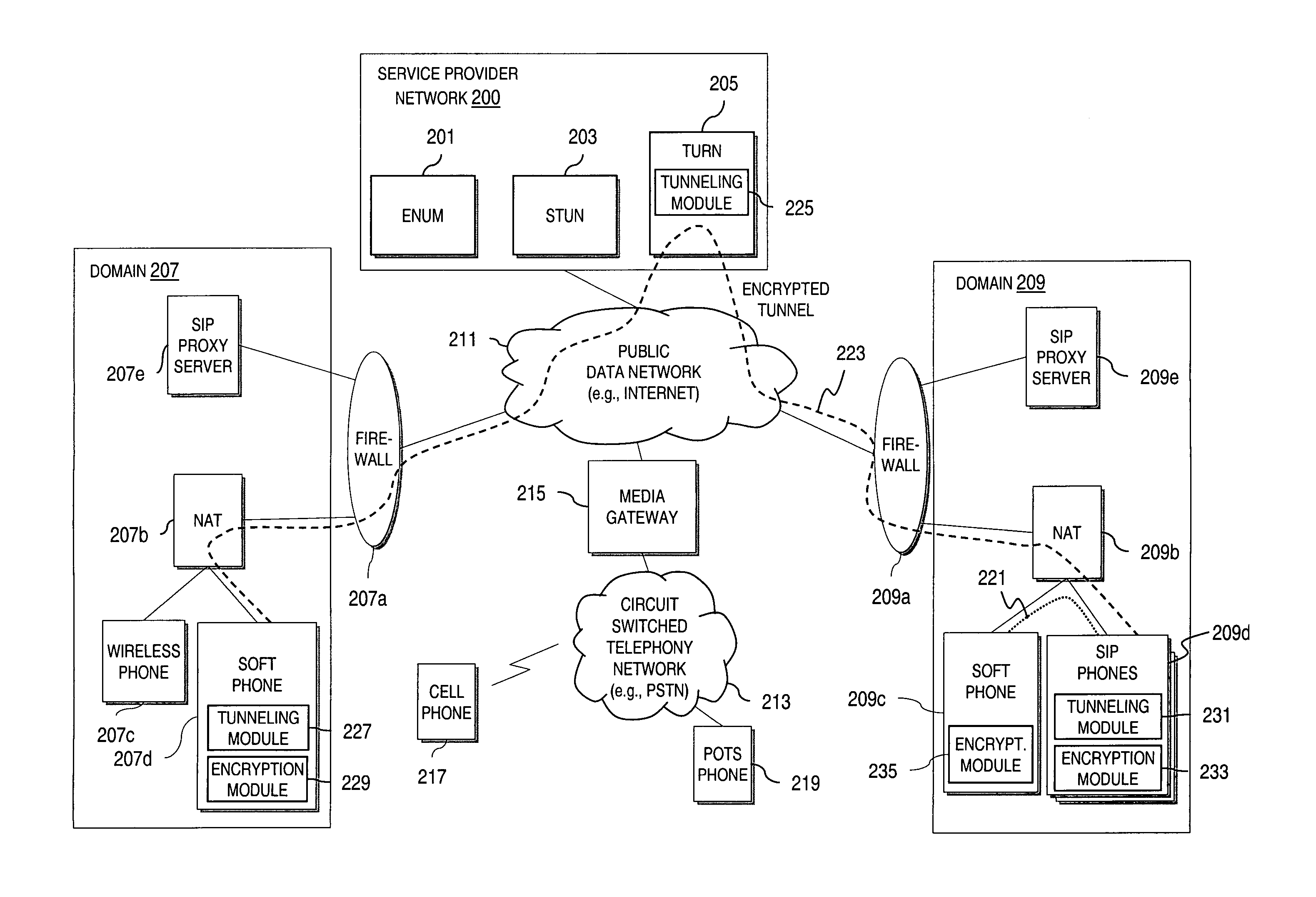
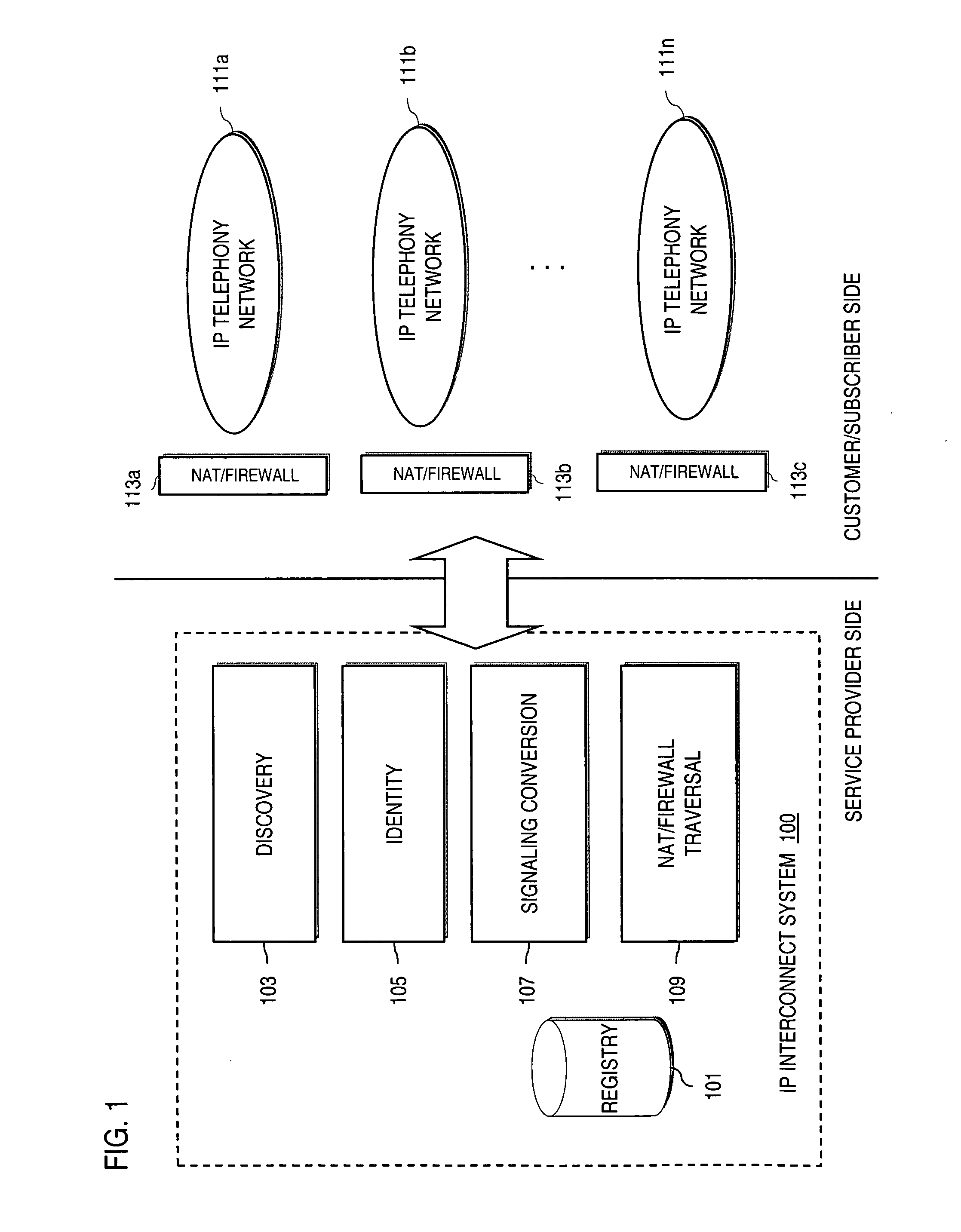
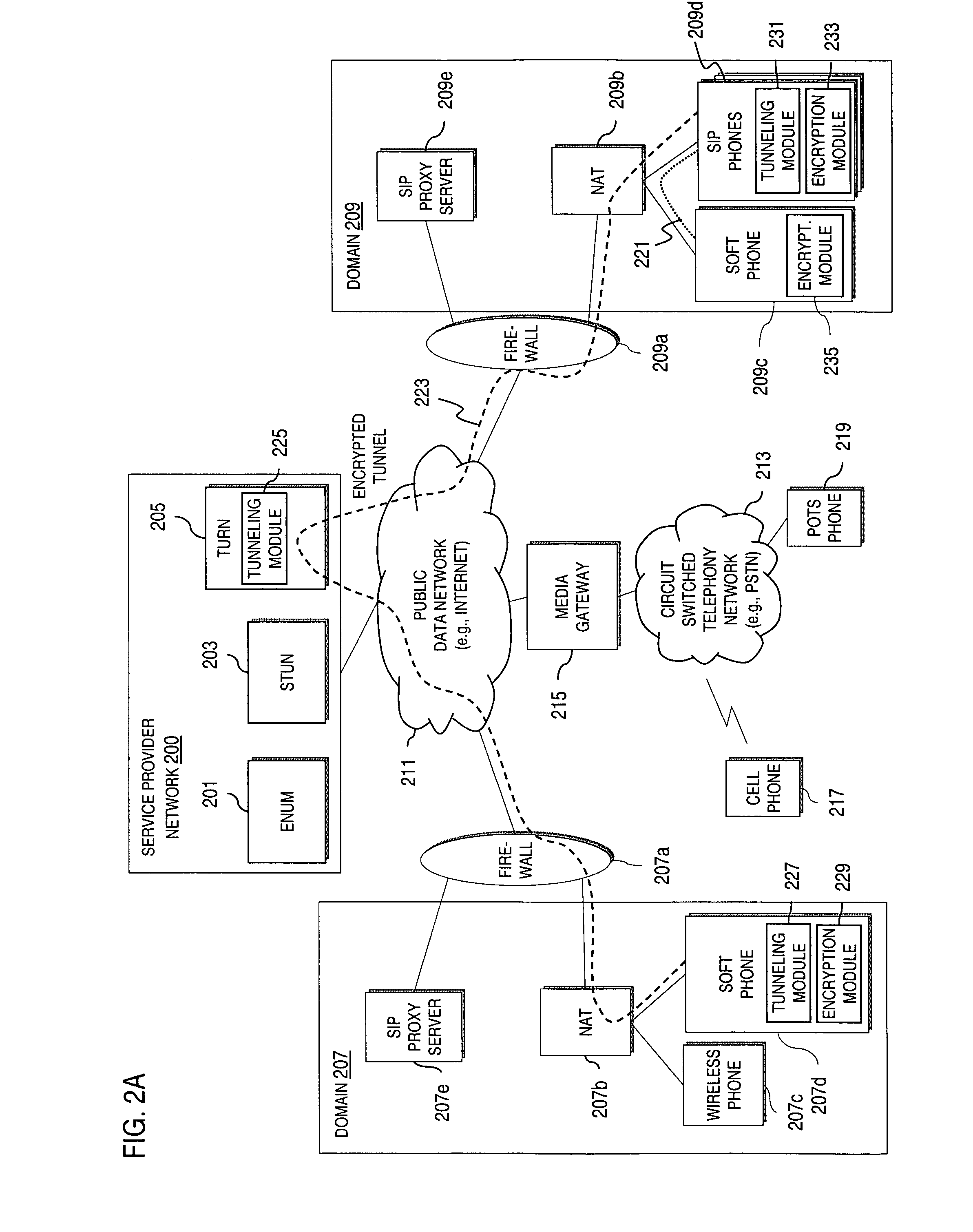
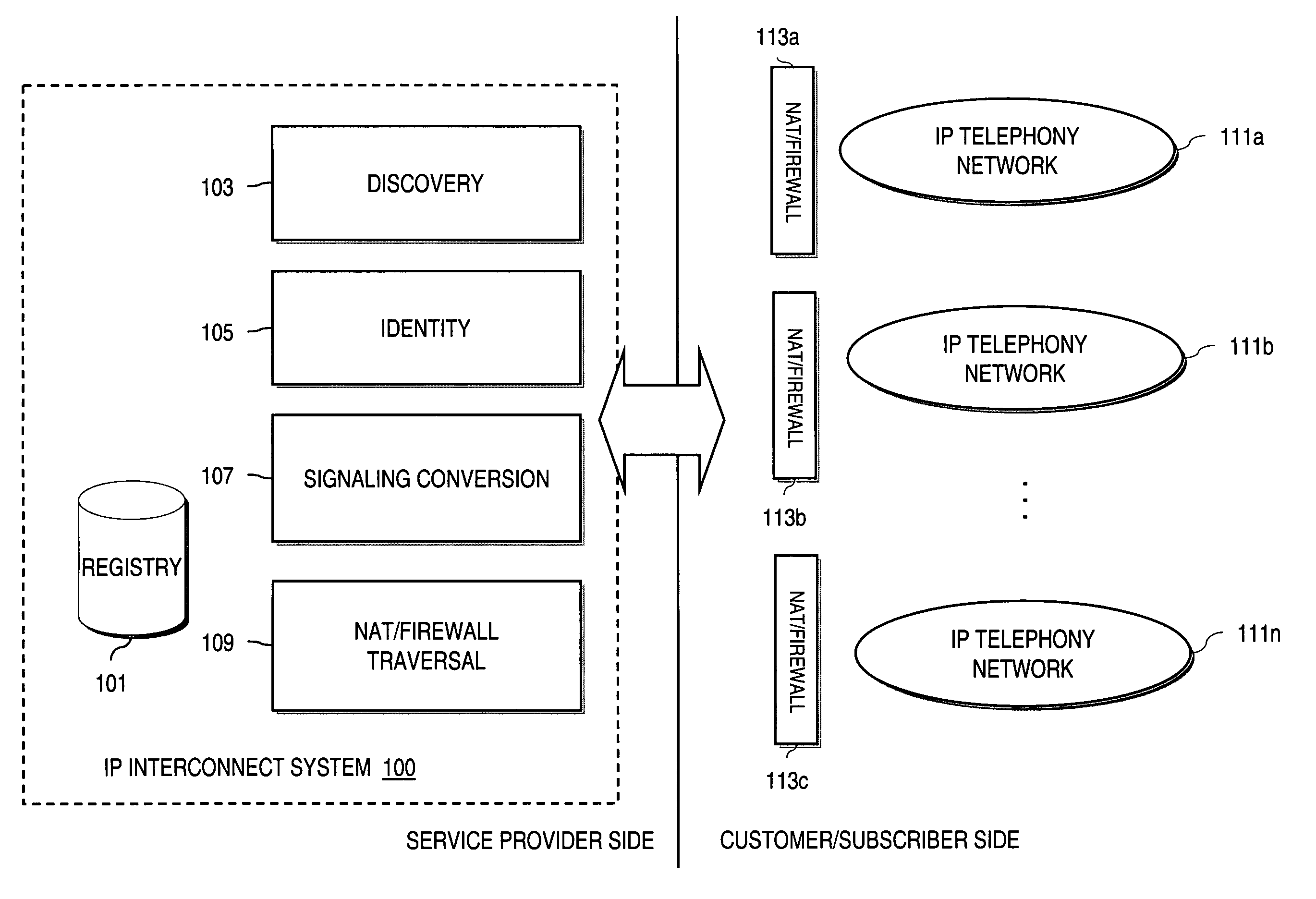
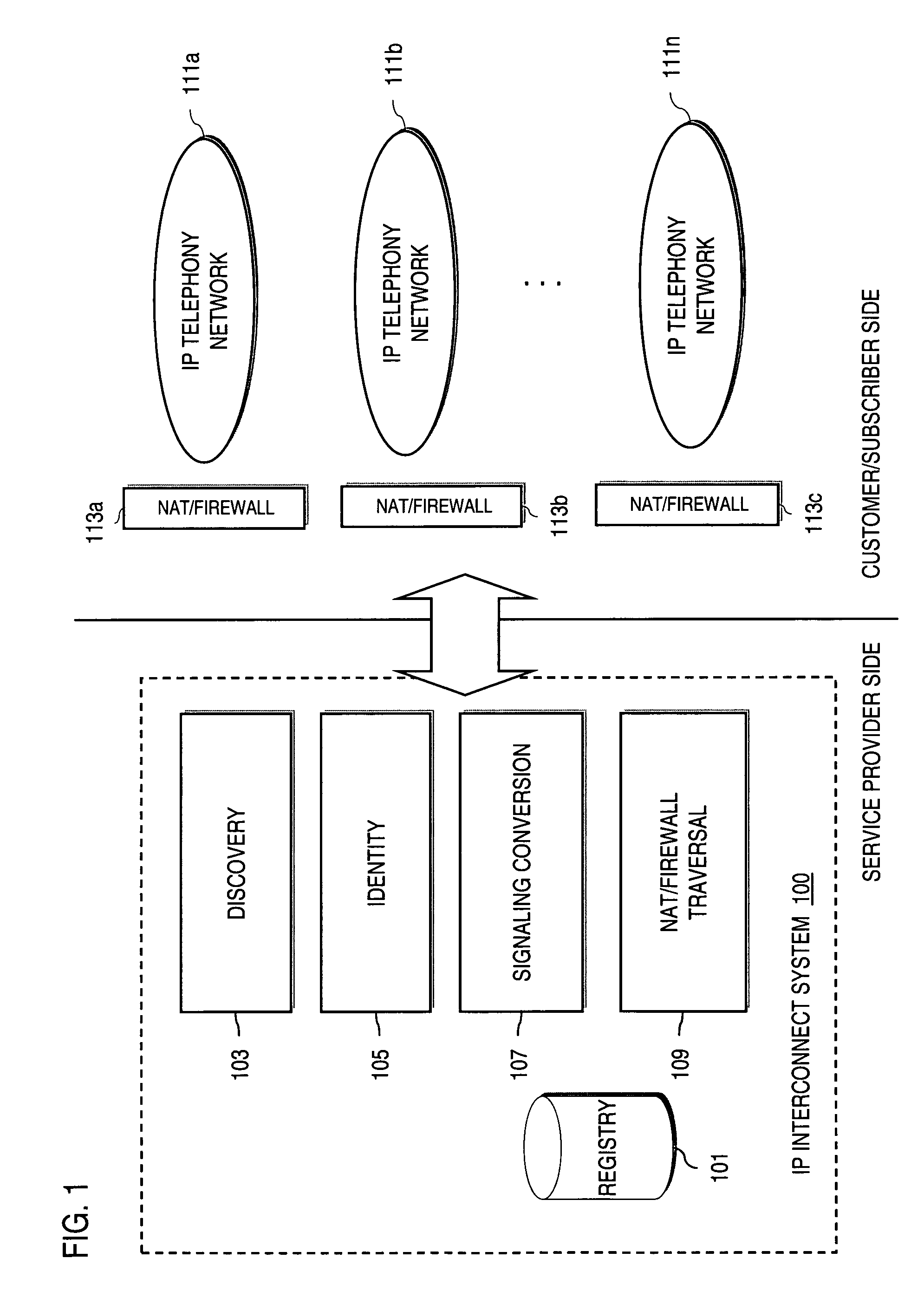
Method and system for providing secure credential storage to support interdomain traversal
An approach provides interdomain traversal to support packetized voice transmissions. A request is received from a first endpoint of a first domain for establishing a communication session with a second endpoint of a second domain. Encrypted user credential information is retrieved from a credentials database resident within the first domain, wherein the encrypted user credential includes a password associated with a user associated with the first endpoint. Further, the encrypted user credential information is transmitted to a tunneling server in response to the request, wherein the tunneling server is configured to selectively setup a tunnel to support the communication session based on the encrypted user credential information. The tunnel traverses a first firewall and a first network address translator of the first domain and a second firewall and a second network address translator of the second domain to reach the second endpoint.
Owner:VERIZON PATENT & LICENSING INC
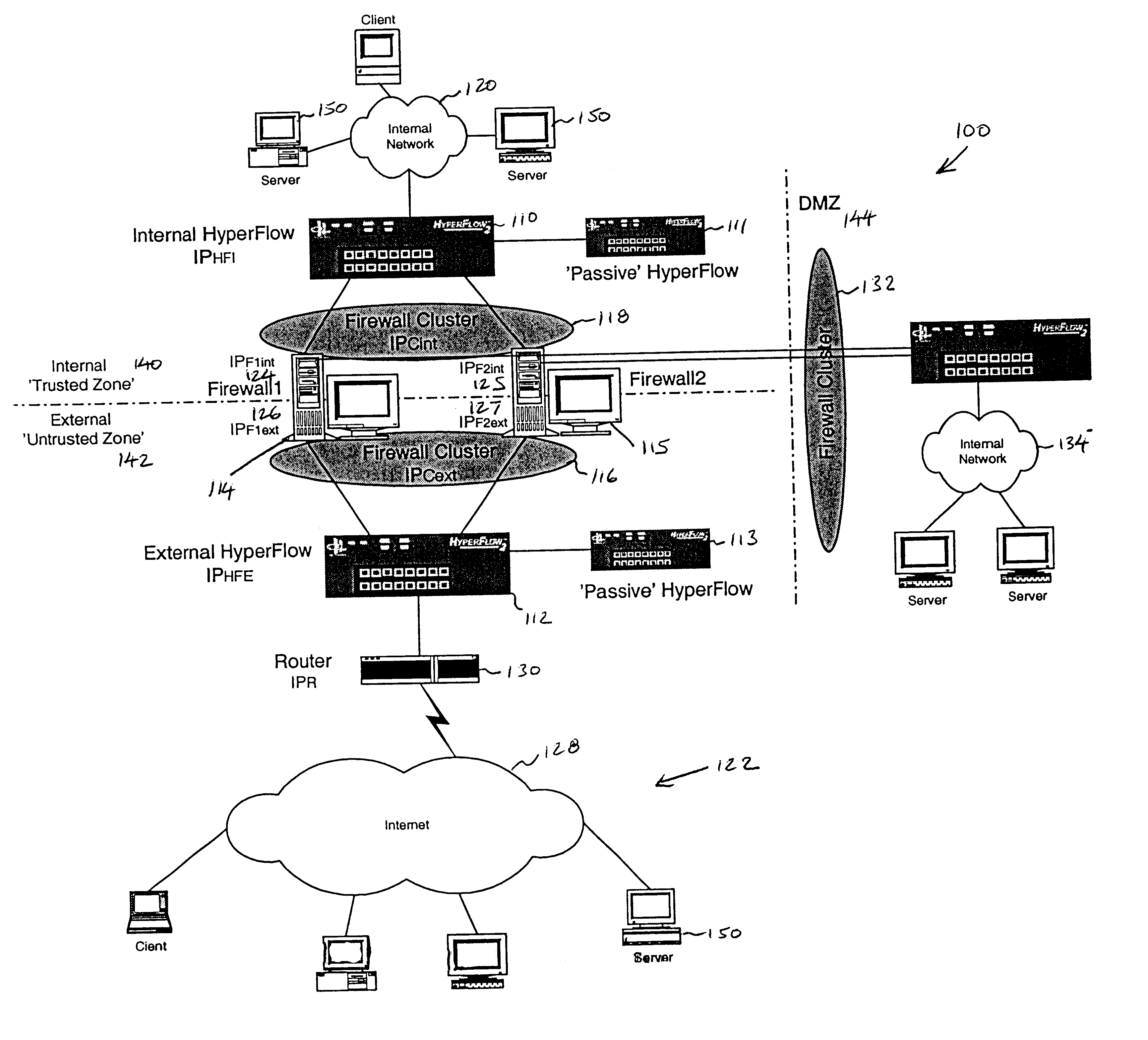
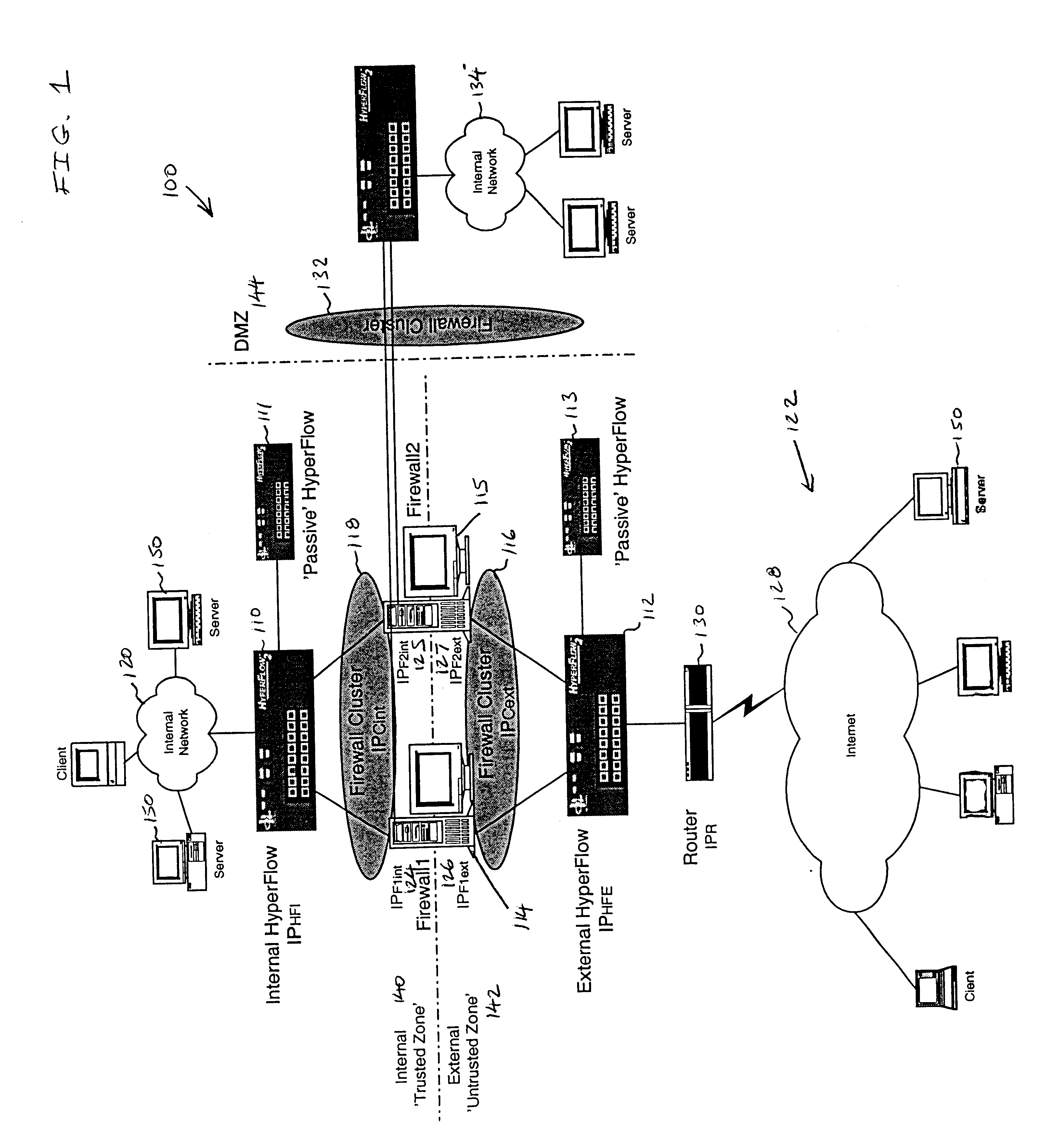
Firewall clustering for multiple network servers
InactiveUS6880089B1Increase capacityReduce calculationMultiple digital computer combinationsProgram controlTraffic capacityExtensibility
A firewall clustering system connects two or more firewalls between an internal network and an external network. The plurality of two or more firewalls are combined to supply high-availability and scaling of processing capacity. Firewalls maintain client-server state information. Flow controllers are connected to the firewalls and placed on both the internal “trusted” side and the external “untrusted” side of the firewalls. Flow controllers are placed on both sides of the firewalls to ensure that traffic for a given client-server session flows through the same firewall in both inbound and outbound directions. The firewalls perform filtering operations and / or network address translation (NAT) services. In both cases, the flow controllers supply high availability, scalability, and traffic distribution for the firewalls in the firewall cluster.
Owner:CITRIX SYST INC
A method and systems for securing remote access to private networks
ActiveUS20060037071A1Reduce the burden onImprove experienceMultiple digital computer combinationsProgram controlPrivate networkNetwork address translation
A method for securing remote access to private networks includes a receiver intercepting from a data link layer a packet in a first plurality of packets destined for a first system on a private network. A filter intercepts from the data link layer a packet in a second plurality of packets transmitted from a second system on the private network, destined for an system on a second network. A transmitter in communication with the receiver and the filter performing a network address translation on at least one intercepted packet and transmitting the at least one intercepted packet to a destination.
Owner:CITRIX SYST INC
Method for optimal path selection in traversal of packets through network address translators
InactiveUS20050259637A1Reduce administrative overheadFast convergenceMultiplex system selection arrangementsError preventionNetwork addressNetwork address translation
Reduction of administrative overhead in maintaining network information, rapid convergence on an optimal routing path through the data network, and utilization of only required network resources are realized by a novel method for establishing a call path between network users. The method is based upon deployment of a network information server that stores network topology information and that is addressable by each end user. In this method, the network information server receives a request to establish a call path. The request identifies at least the calling party. In response to the request, the network information server determines a network traversal between the calling party and a root network wherein the network traversal includes call path information about the sub-networks between the calling party and the root network. The request for establishing a call path can also identify the called party. Based on the calling and called party identification, the network information server also determines a second network traversal between the called party and the root network. The second network traversal is sent to either the calling party or the called party or to both the calling and called parties. The server can determine an intersection of the traversals and send the intersection information to the parties. The intersection information is known as a merge point and represents an optimal call path between the parties.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC
System and method for aggregating communications and for translating between overlapping internal network addresses and unique external network addresses
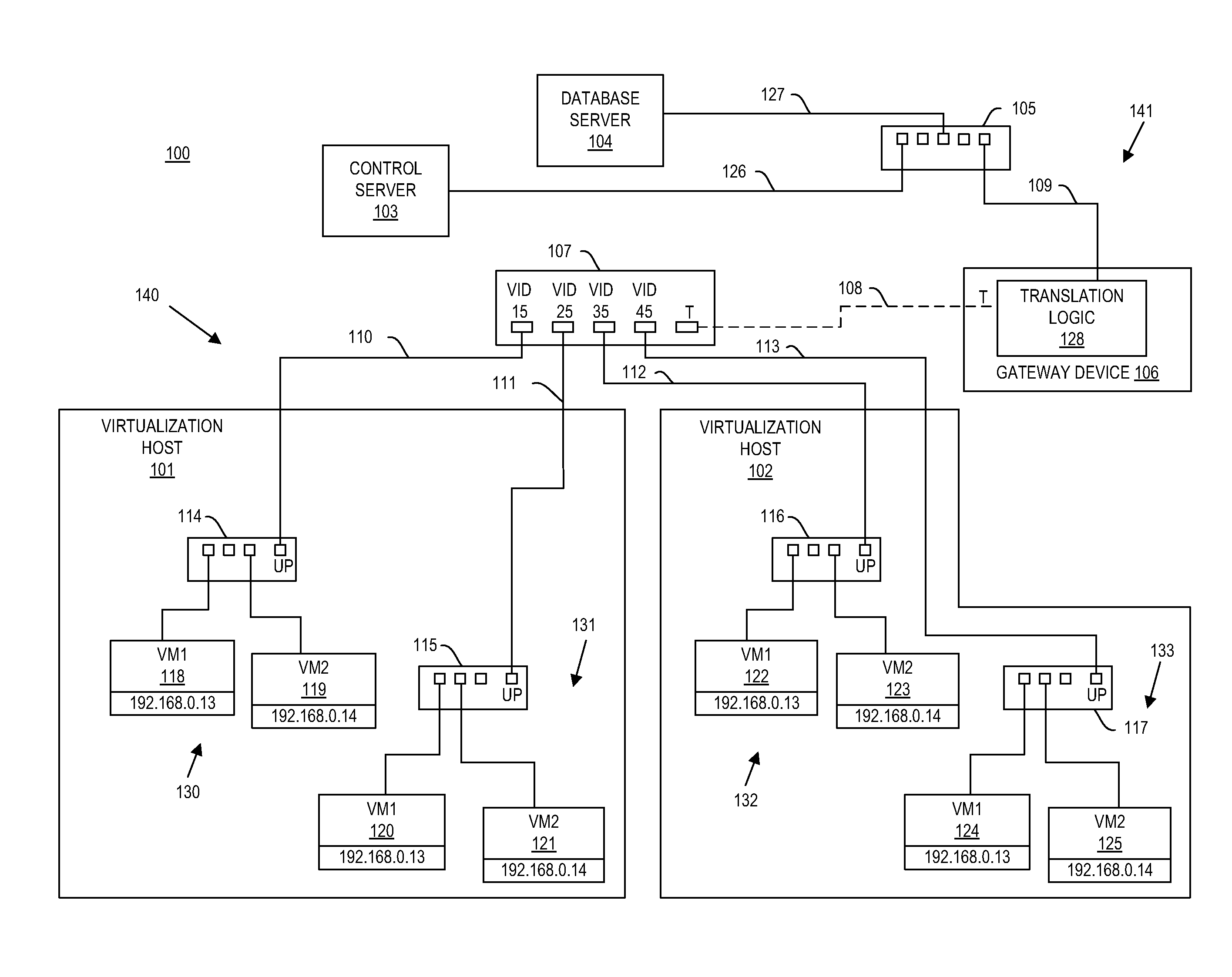
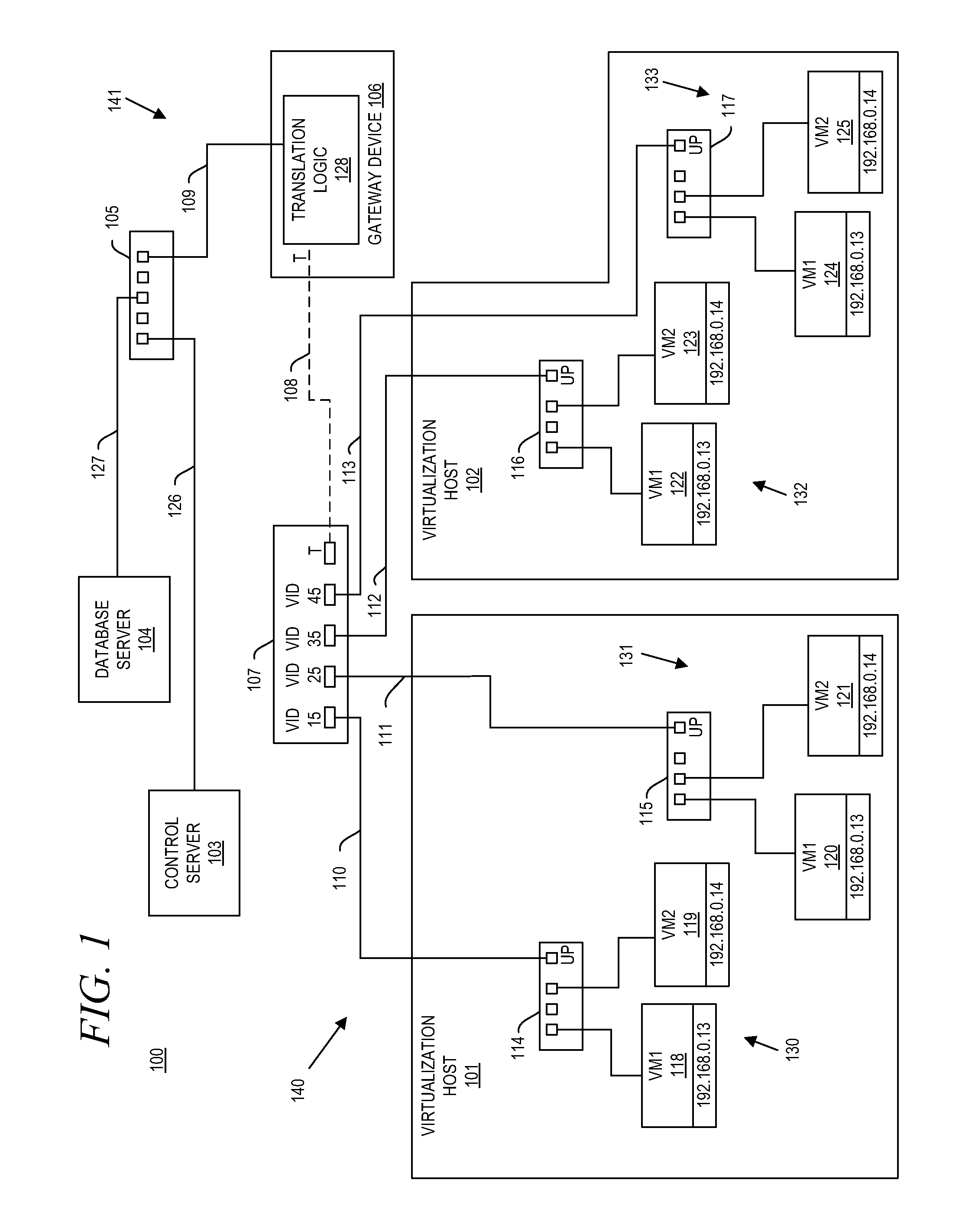
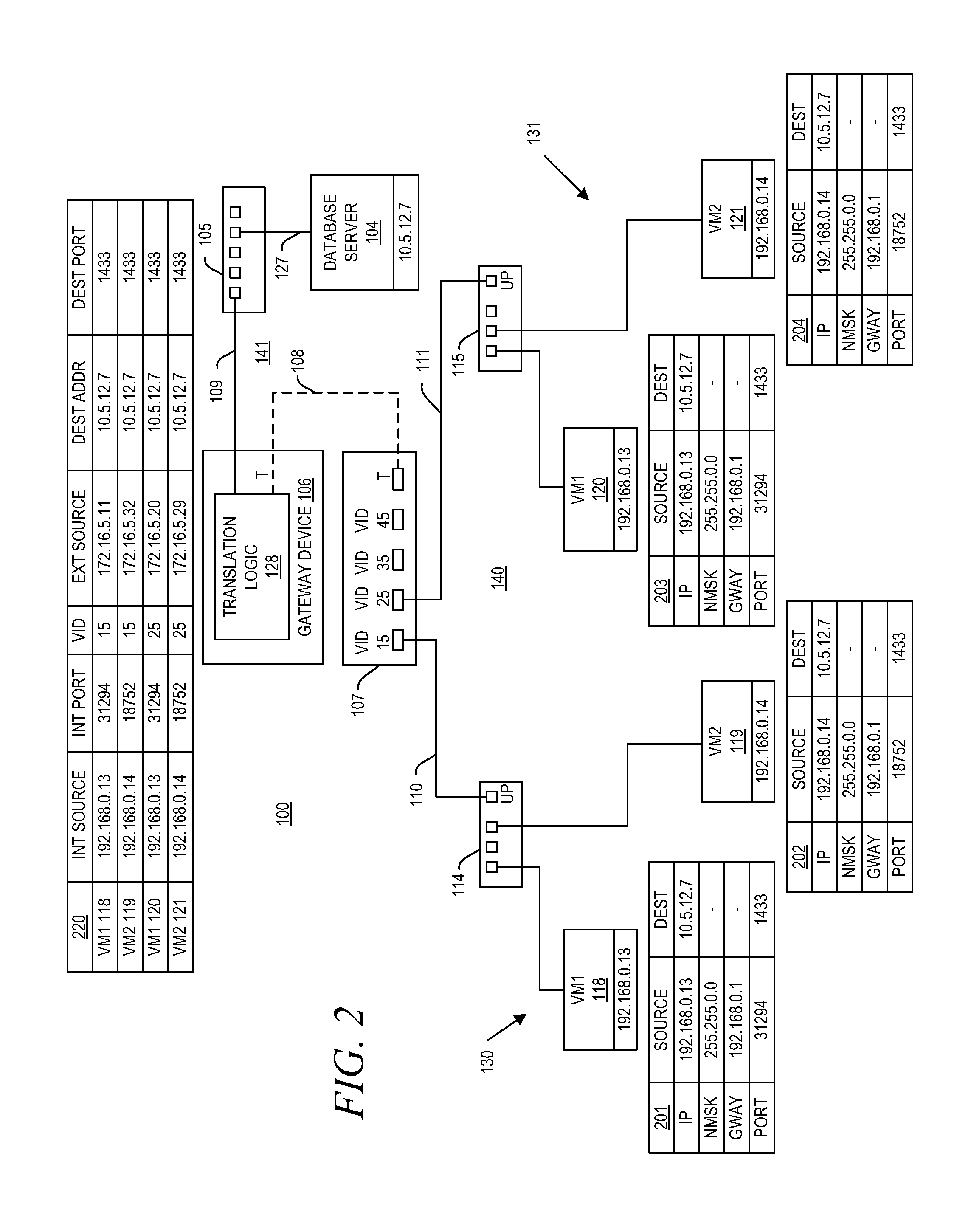
A gateway device including an access interface to an external network, a trunked interface, and translation logic. The access interface is associated with multiple external source addresses. The trunked interface is interfaced with multiple different virtual local area networks (VLANs), where each VLAN is associated with a corresponding VLAN tag and at least one of potentially overlapping internal source addresses. The translation logic translates between each external source address and each unique combination of internal source address and VLAN tag. A method of network address translation including assigning one of first network addresses to each first device of a first network, dividing the first network into a plurality of VLANs, separating the first devices with the same first network address into different VLANs, and assigning first devices with the same first address to different second network addresses.
Owner:QUEST SOFTWARE INC
Methods and apparatus for routing a content request
ActiveUS7315541B1Digital computer detailsData switching by path configurationNetwork address translationCommunication device
Mechanisms and techniques provide a method for routing a packet that includes a content request and an Internet Protocol address and port number that identify a source transmitting the packet. The method relates to selecting a routing policy to forward the packet, based upon at least a portion of content request. The method includes a data communications device receiving a packet having a content request and an Internet Protocol address and port number that identify a source transmitting the packet. The device performs a network address translation, based upon at least a portion of the content request, to translate the Internet Protocol address and port number of the packet to a respective communications device Internet Protocol address and communications device port number. The device then selects a routing policy based upon the communications device Internet Protocol address and routes the packet to a destination according to the routing policy.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Method and system for distributed network address translation with network security features
InactiveUS7032242B1Digital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationSecurity associationIp address
A method and system for distributed network address translation with security features. The method and system allow Internet Protocol security protocol (“IPsec”) to be used with distributed network address translation. The distributed network address translation is accomplished with IPsec by mapping a local Internet Protocol (“IP”) address of a given local network device and a IPsec Security Parameter Index (“SPI”) associated with an inbound IPsec Security Association (“SA”) that terminates at the local network device. A router allocates locally unique security values that are used as the IPsec SPIs. A router used for distributed network address translation is used as a local certificate authority that may vouch for identities of local network devices, allowing local network devices to bind a public key to a security name space that combines a global IP address for the router with a set of locally unique port numbers used for distributed network address translation. The router issues security certificates and may itself be authenticated by a higher certificate authority. Using a security certificate, a local network device may initiate and be a termination point of an IPsec security association to virtually any other network device on an IP network like the Internet or an intranet. The method and system may also allow distributed network address translation with security features to be used with Mobile IP or other protocols in the Internet Protocol suite.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
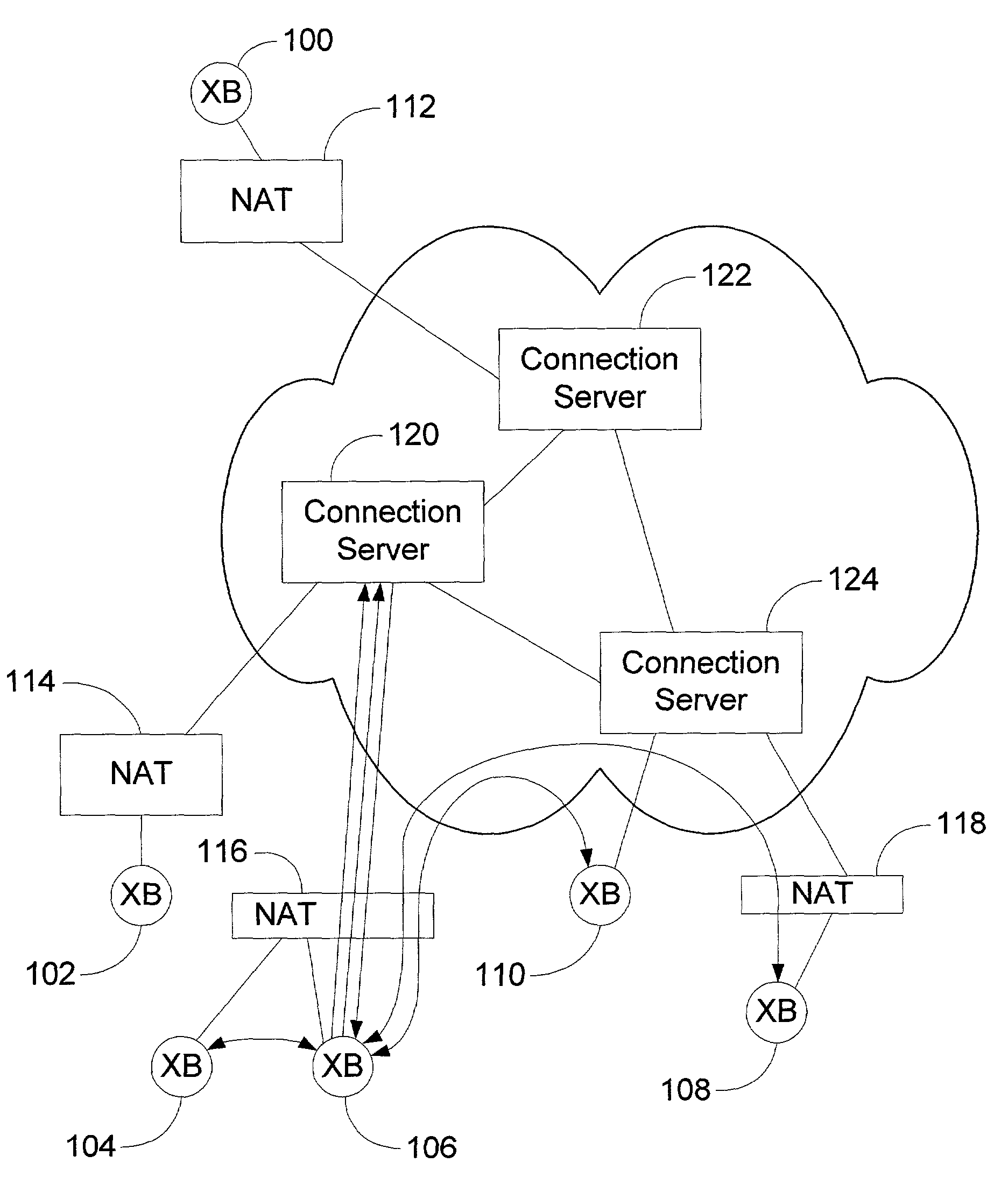
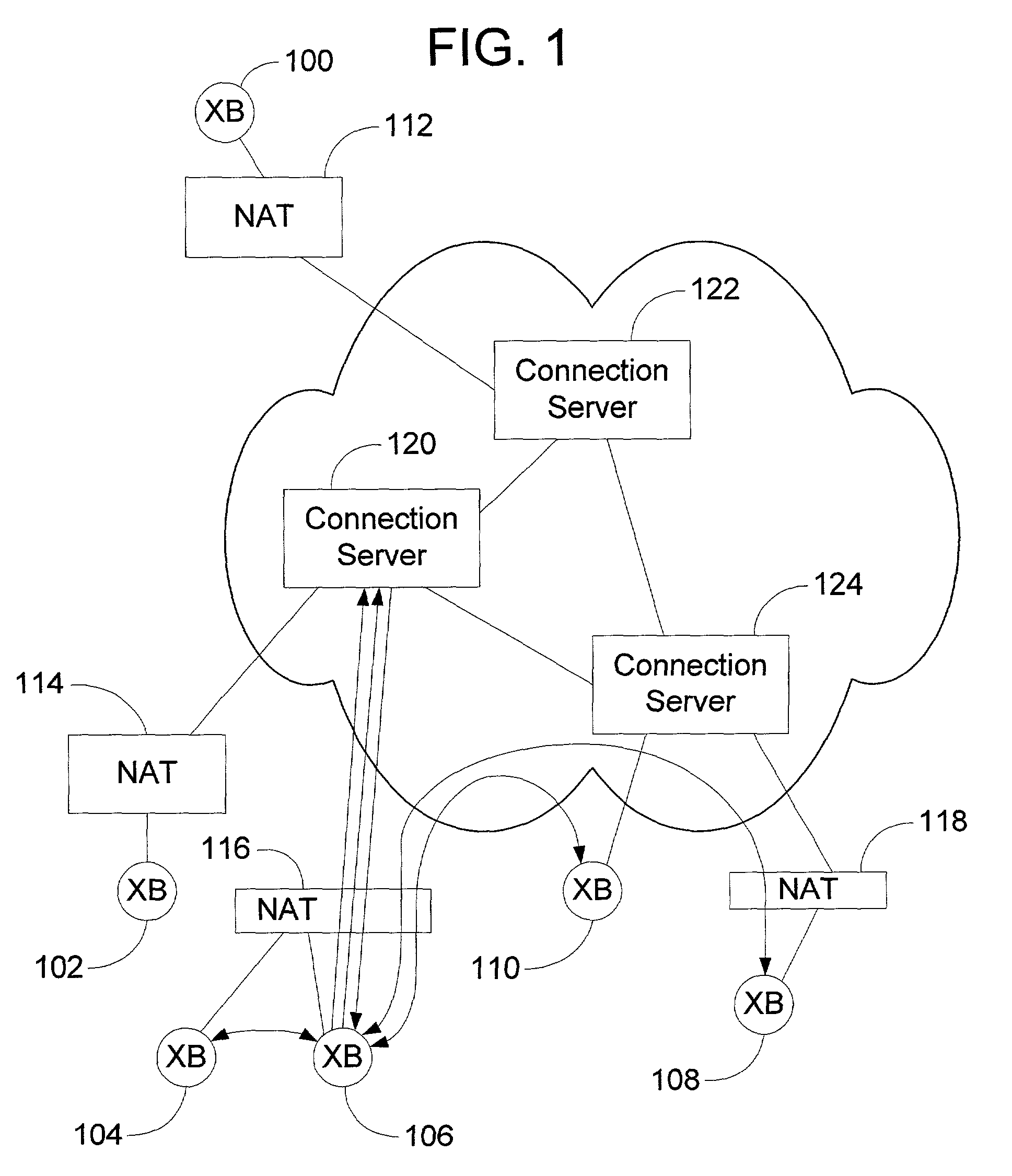
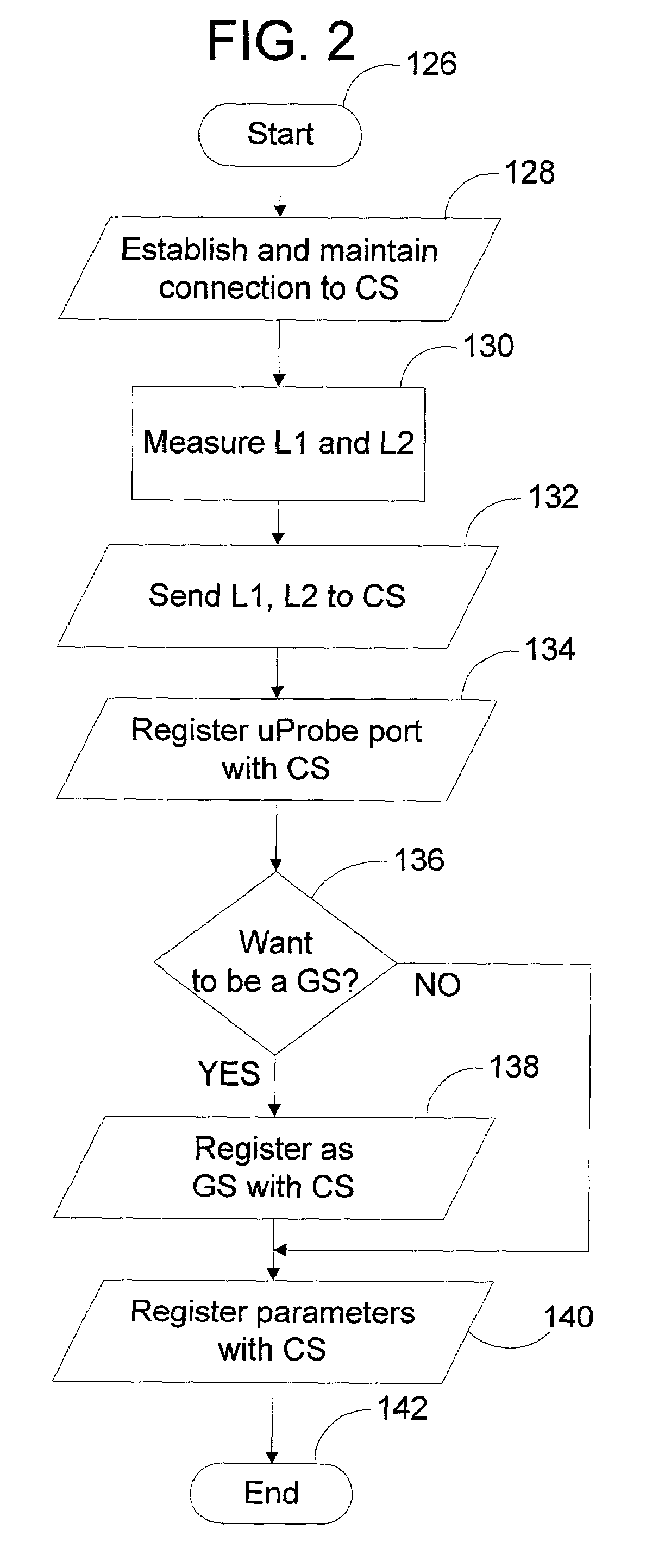
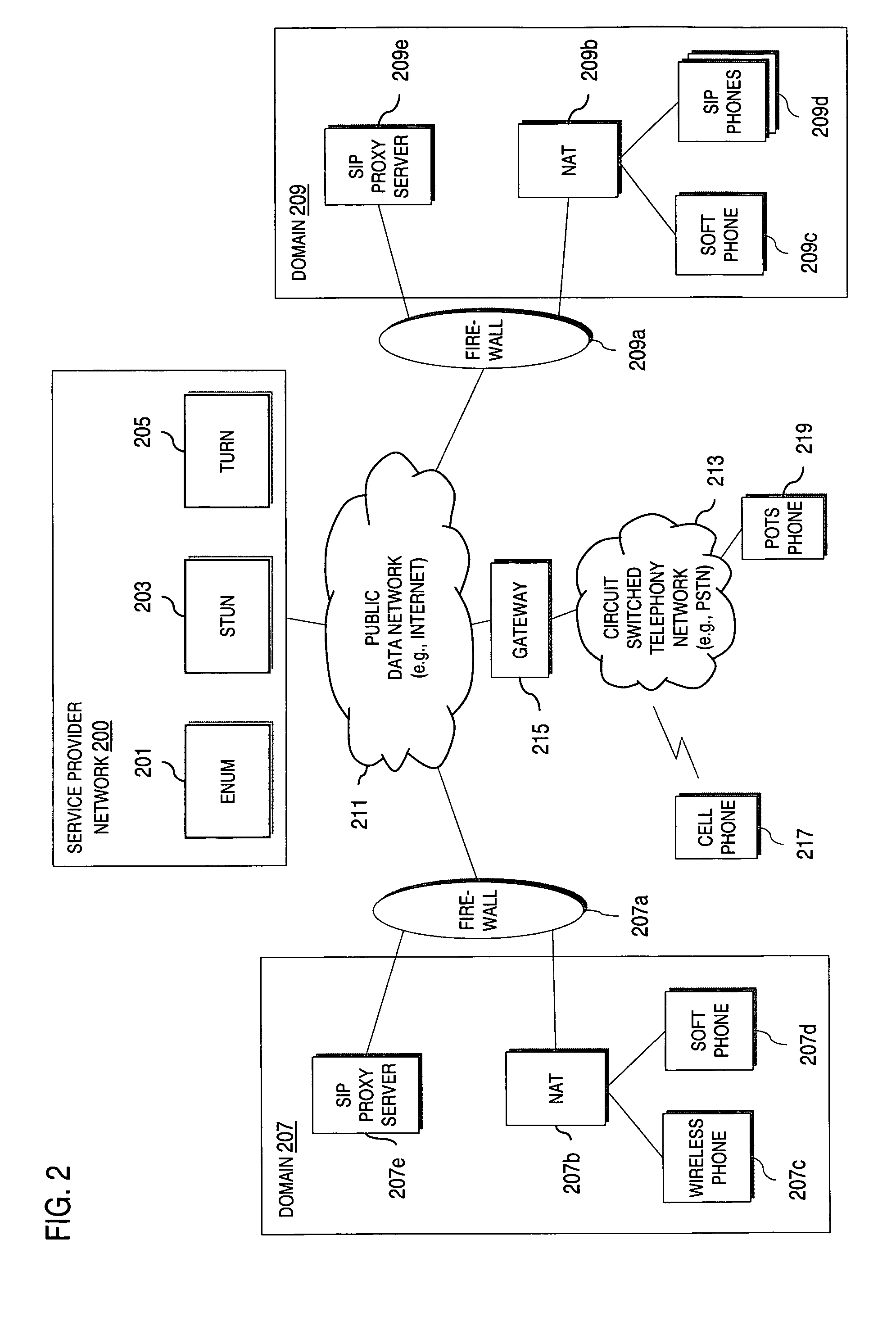
Peer-to-peer method of quality of service (QoS) probing and analysis and infrastructure employing same
InactiveUS7133368B2Improve gaming experienceImprove performanceError preventionTransmission systemsQuality of servicePacket loss
A peer-to-peer (P2P) probing / network quality of service (QoS) analysis system utilizes a UDP-based probing tool for determining latency, bandwidth, and packet loss ratio between peers in a network. The probing tool enables network QoS probing between peers that connect through a network address translator. The list of peers to probe is provided by a connection server based on prior probe results and an estimate of the network condition. The list includes those peers which are predicted to have the best QoS with the requesting peer. Once the list is obtained, the requesting peer probes the actual QoS to each peer on the list, and returns these results to the connection server. P2P probing in parallel using a modified packet-pair scheme is utilized. If anomalous results are obtained, a hop-by-hop probing scheme is utilized to determine the QoS of each link. In such a scheme, differential destination measurement is utilized.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
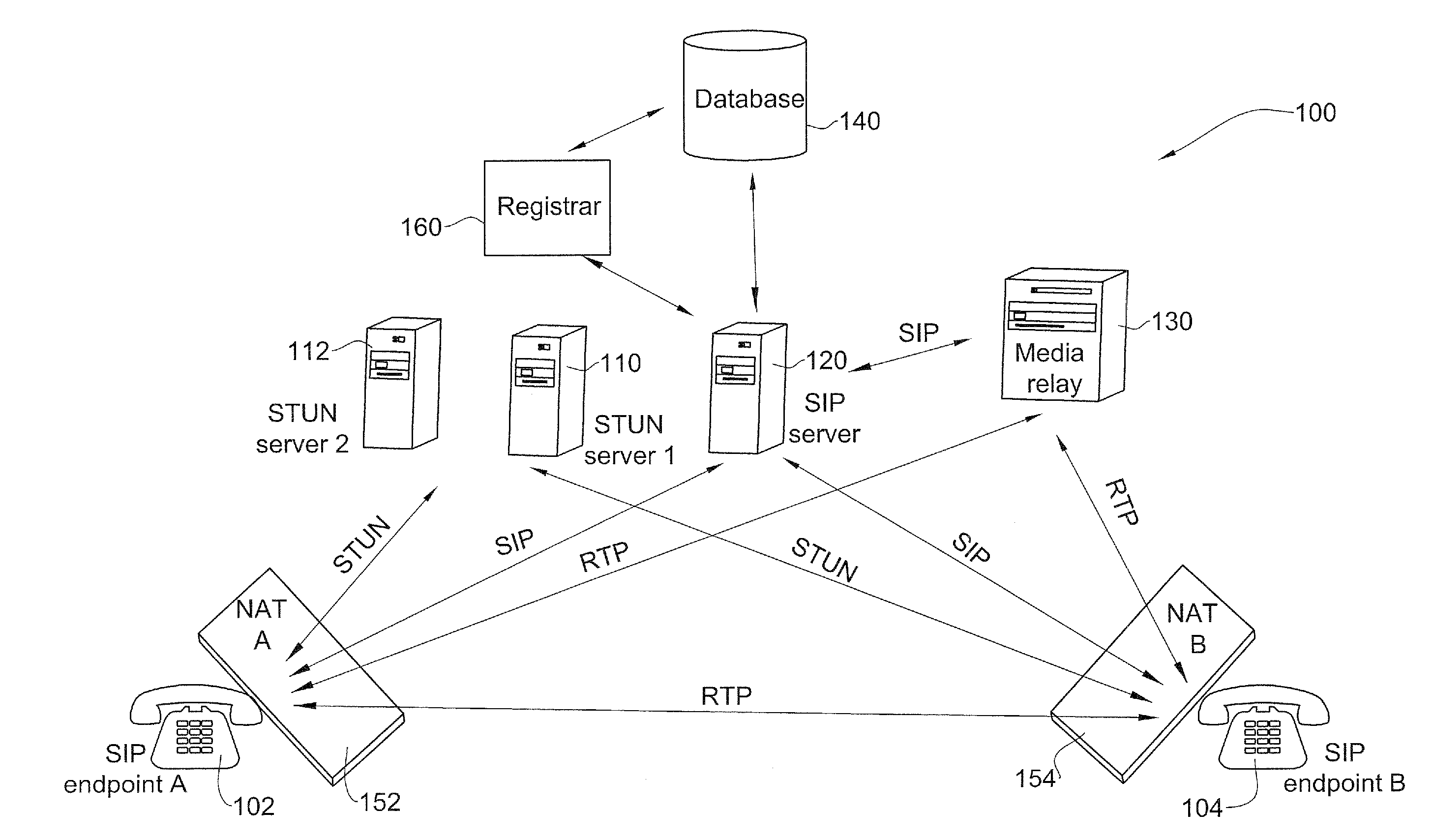
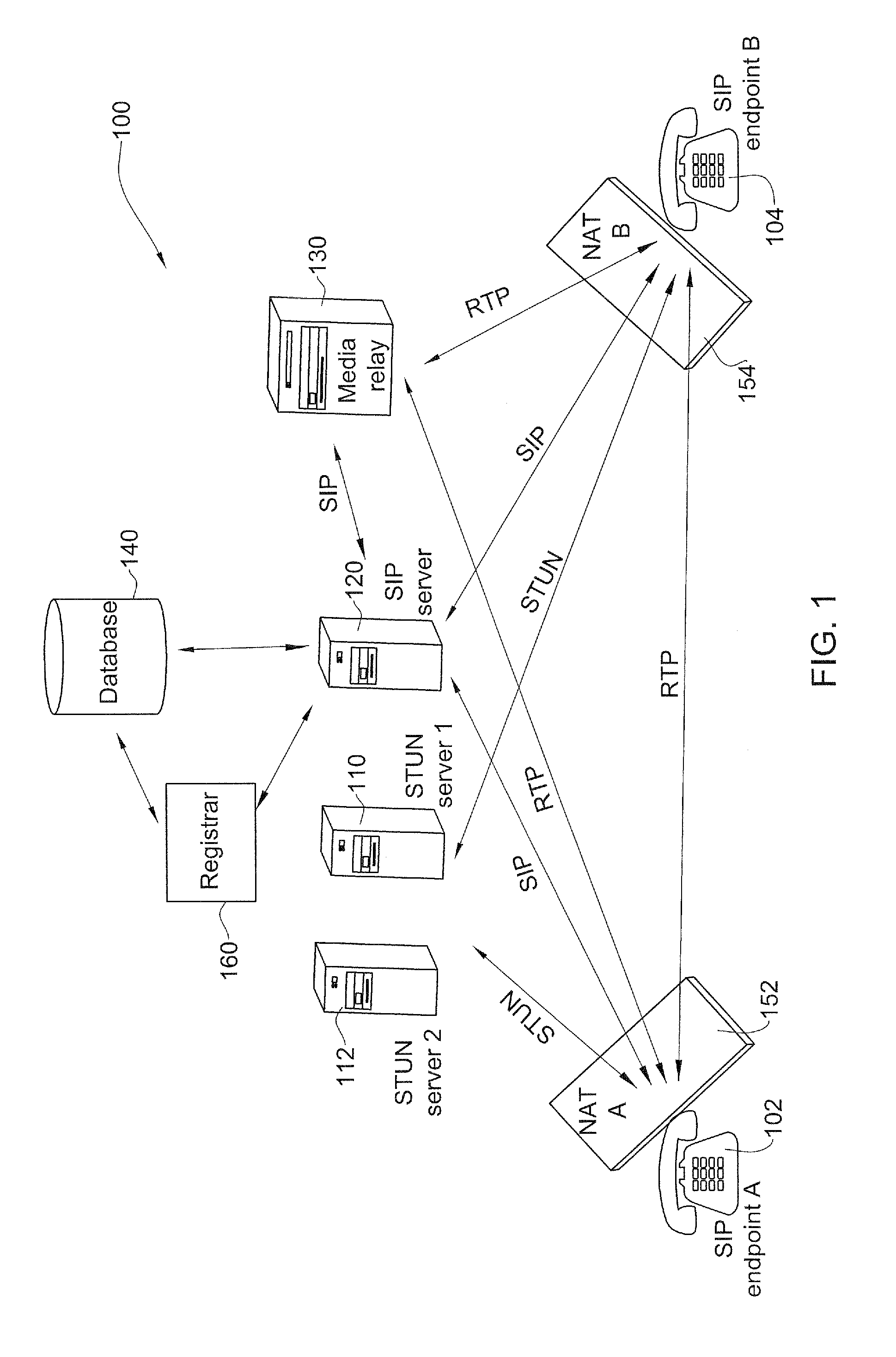
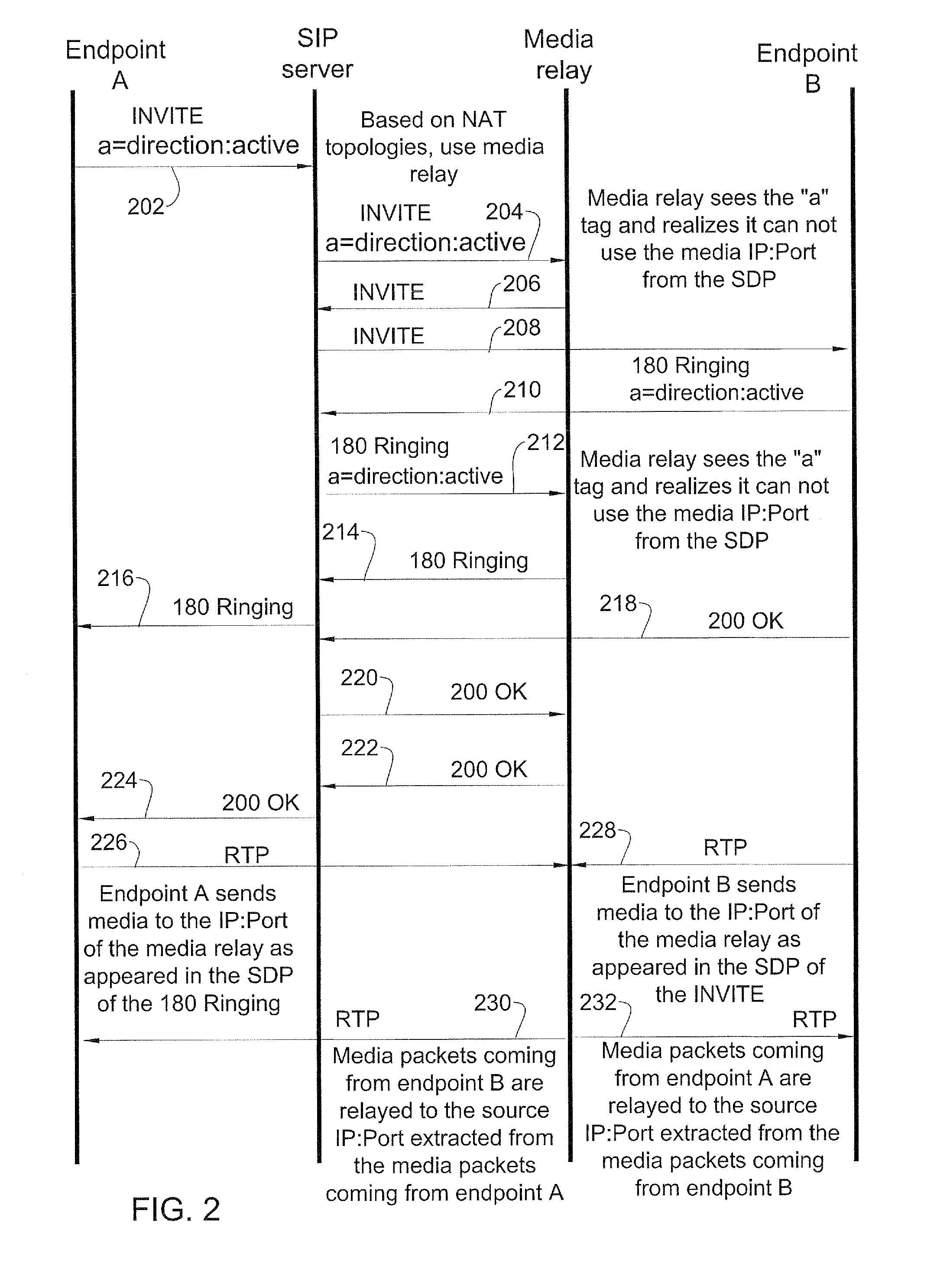
Routing path optimization between sip endpoints
InactiveUS20070253418A1Easy to routeData switching by path configurationNetwork address translationDirect path
Methods and systems for optimized routing of real time media session data between session initiation protocol SIP endpoints. In one embodiment of the invention, first and second SIP endpoints each provide notification of network address translation NAT topology thereof and based on the NAT topologies of the two endpoints an SIP server decides whether to route media between the two endpoints via a direct path or via a media relay.
Owner:DSP GROUP
Content service aggregation system
ActiveUS20030126233A1Easy to processMultiple digital computer combinationsElectric digital data processingPrivate networkStructure of Management Information
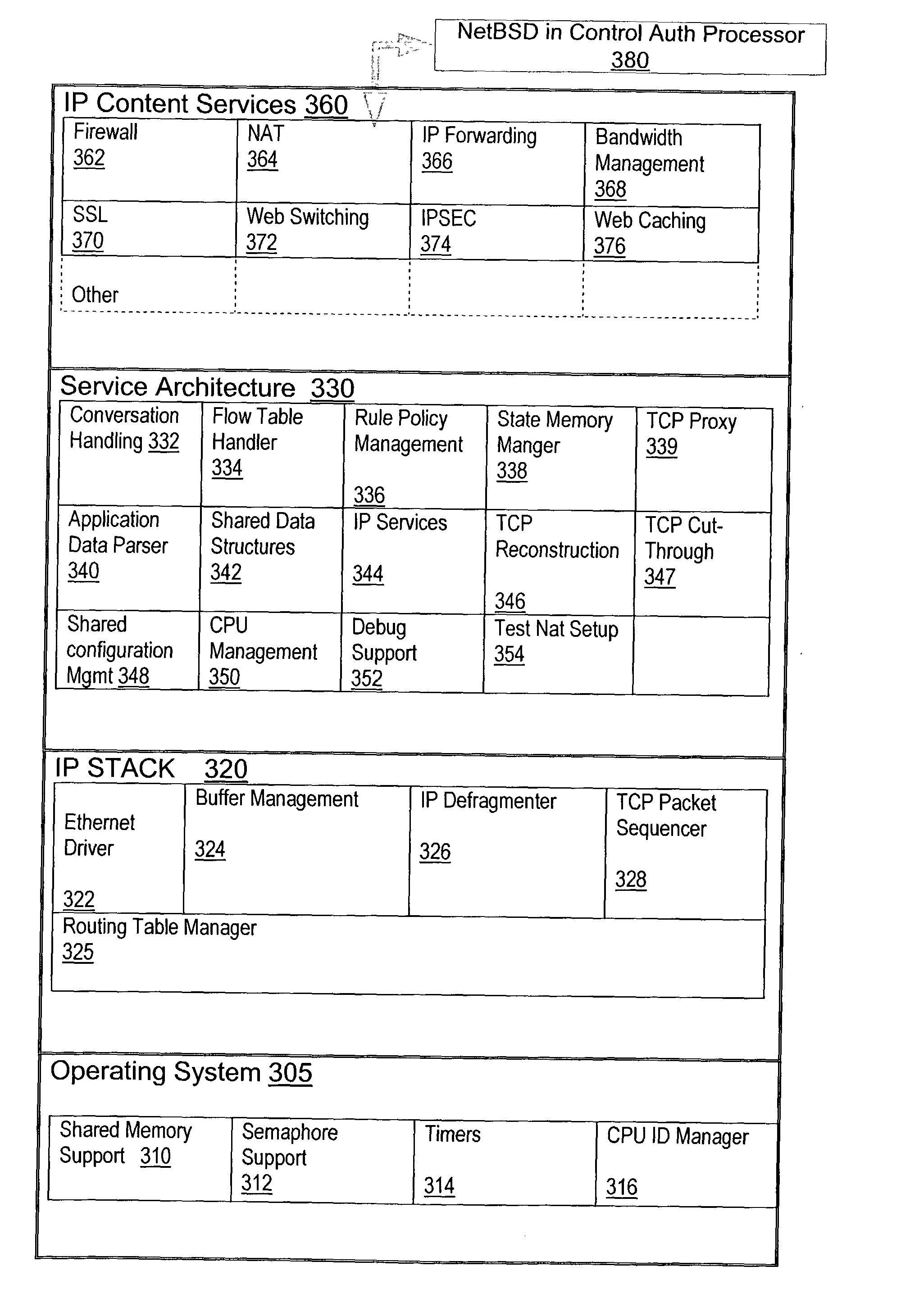
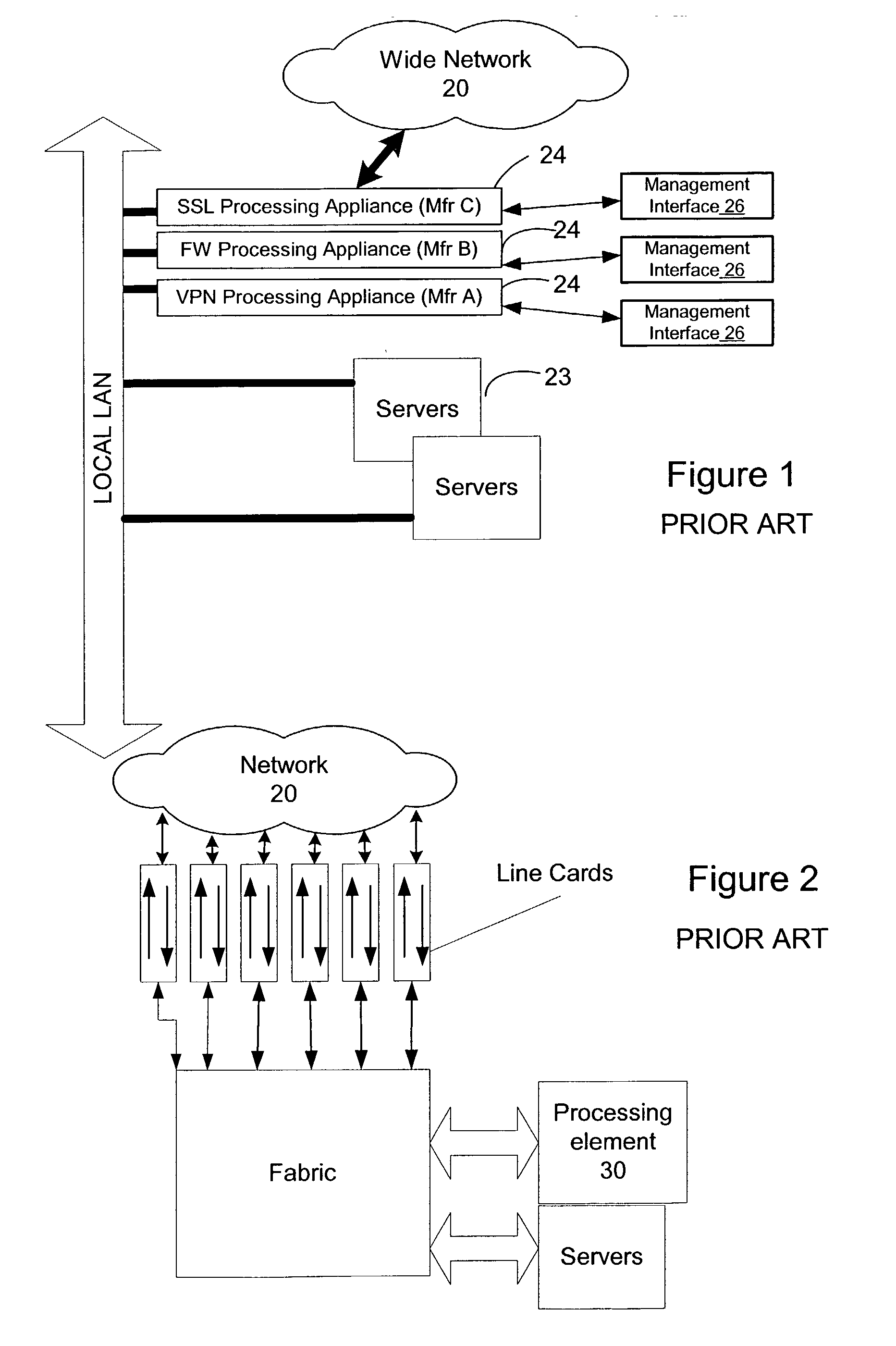
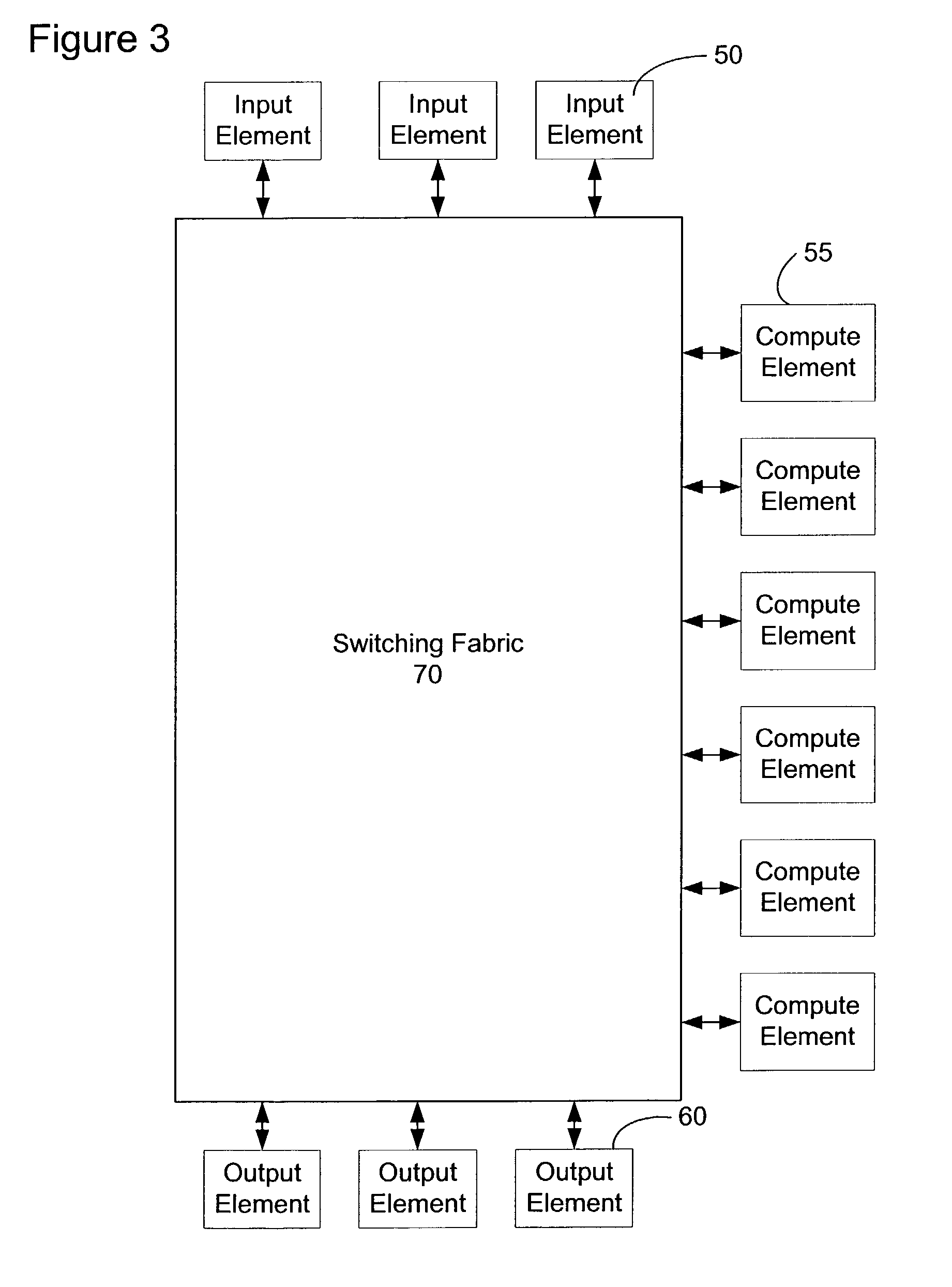
A network content service apparatus includes a set of compute elements adapted to perform a set of network services; and a switching fabric coupling compute elements in said set of compute elements. The set of network services includes firewall protection, Network Address Translation, Internet Protocol forwarding, bandwidth management, Secure Sockets Layer operations, Web caching, Web switching, and virtual private networking. Code operable on the compute elements enables the network services, and the compute elements are provided on blades which further include at least one input / output port.
Owner:NEXSI SYST +1
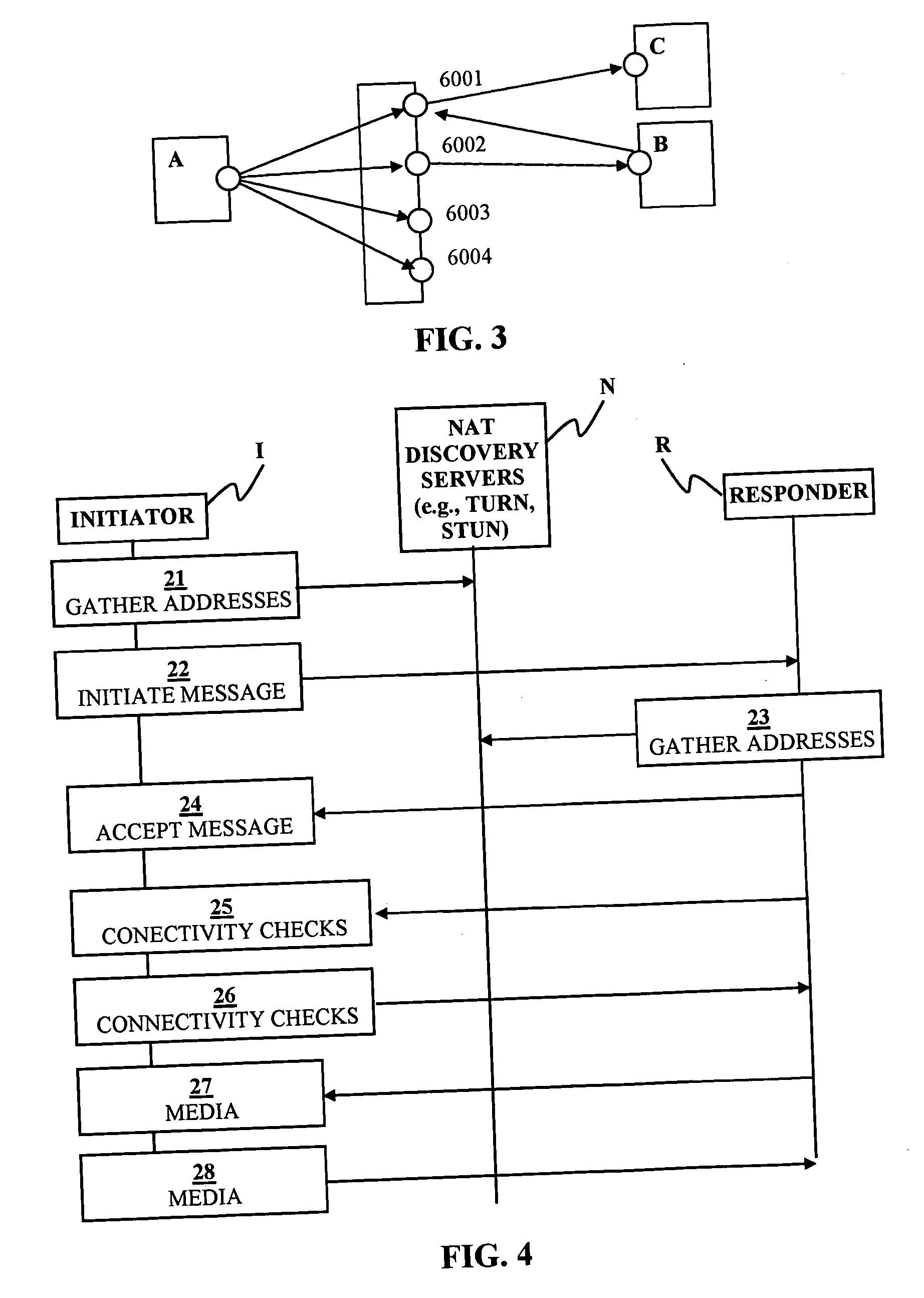
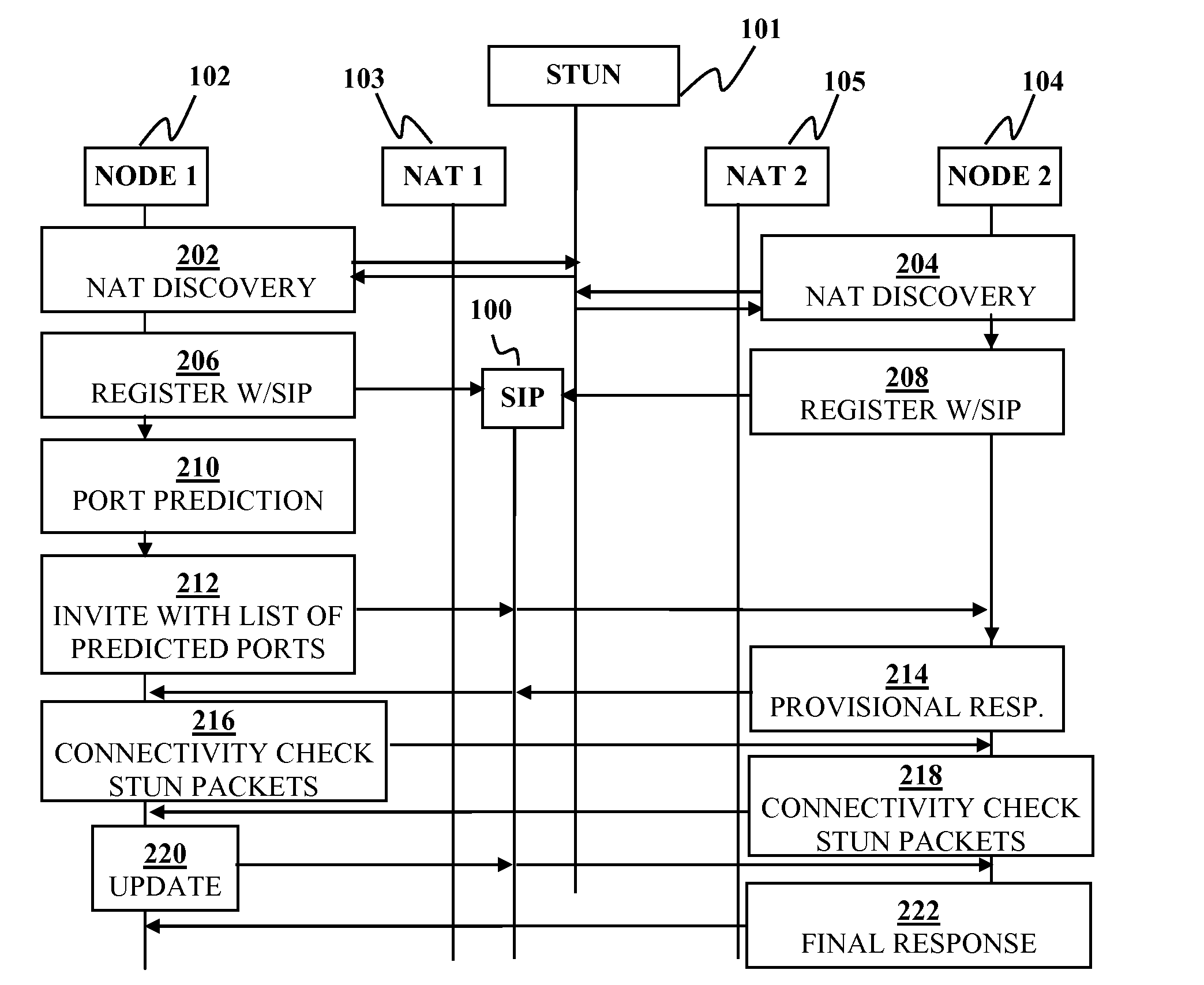
Peer-to-peer communication traversing symmetric network address translators
ActiveUS20070076729A1Data switching by path configurationMultiple digital computer combinationsNetwork addressingNetwork address
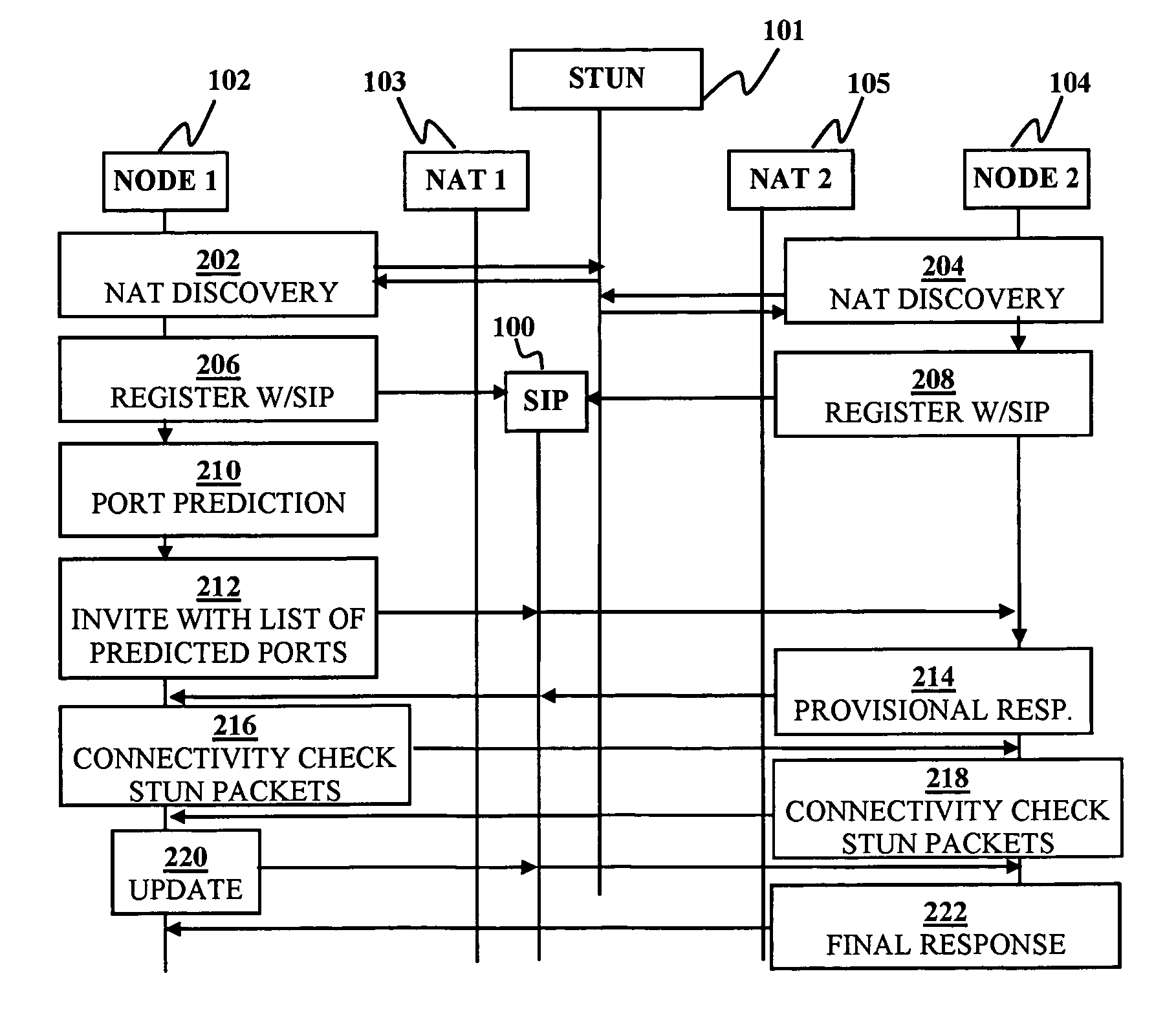
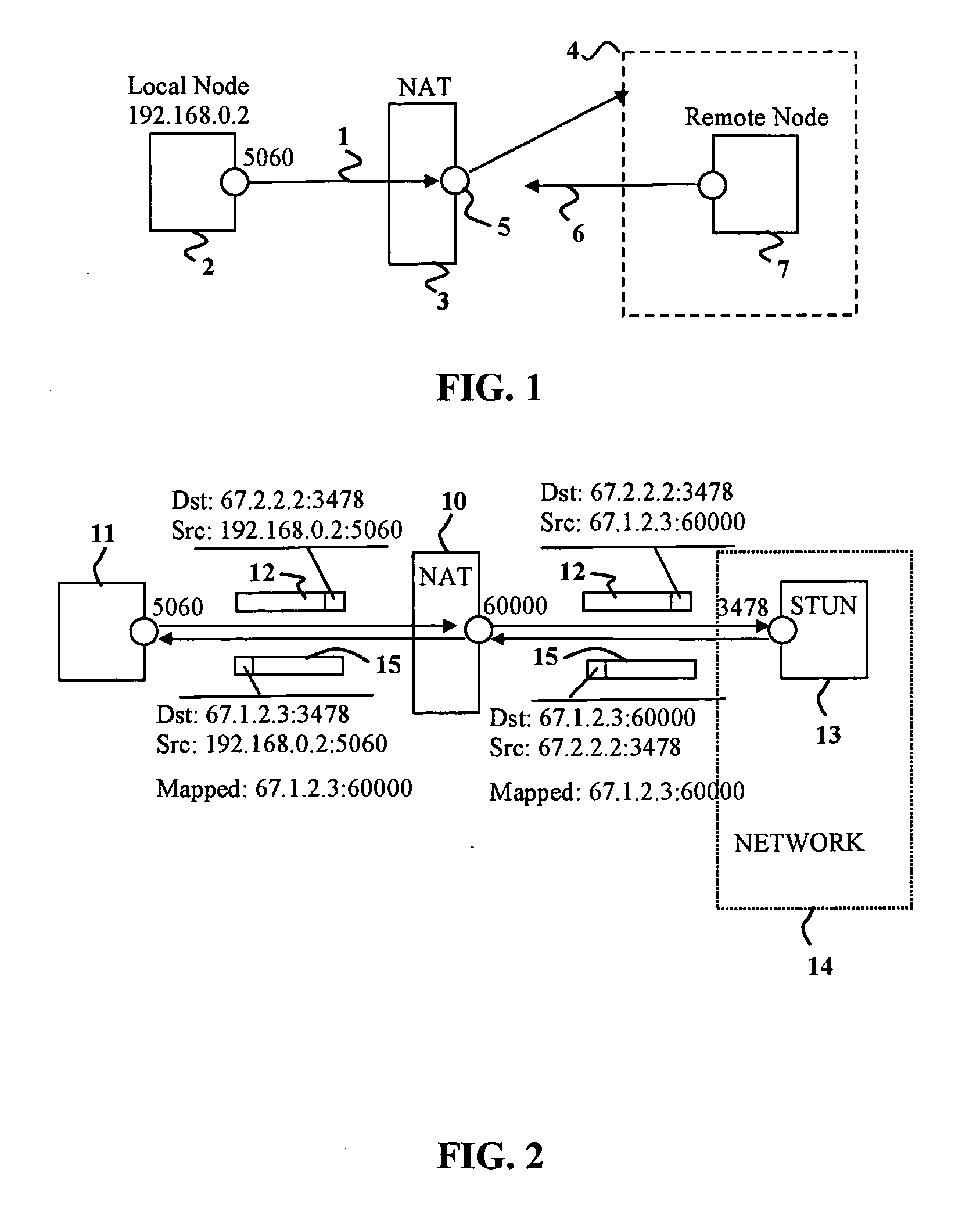
Disclosed are systems and methods for peer-to-peer communication over a network between a first node behind a first network address translator (NAT) and a second node behind a second NAT, despite the first NAT and the second NAT intervening between the first and second nodes. The first NAT is a Symmetric NAT. A port prediction is performed wherein the first node constructs a list of predicted transport addresses on the first NAT. A message containing the list of predicted transport addresses is sent from the first node to the second node. A connectivity check is performed with the second node using the predicted transport addresses.
Owner:SONY COMPUTER ENTERTAINMENT INC
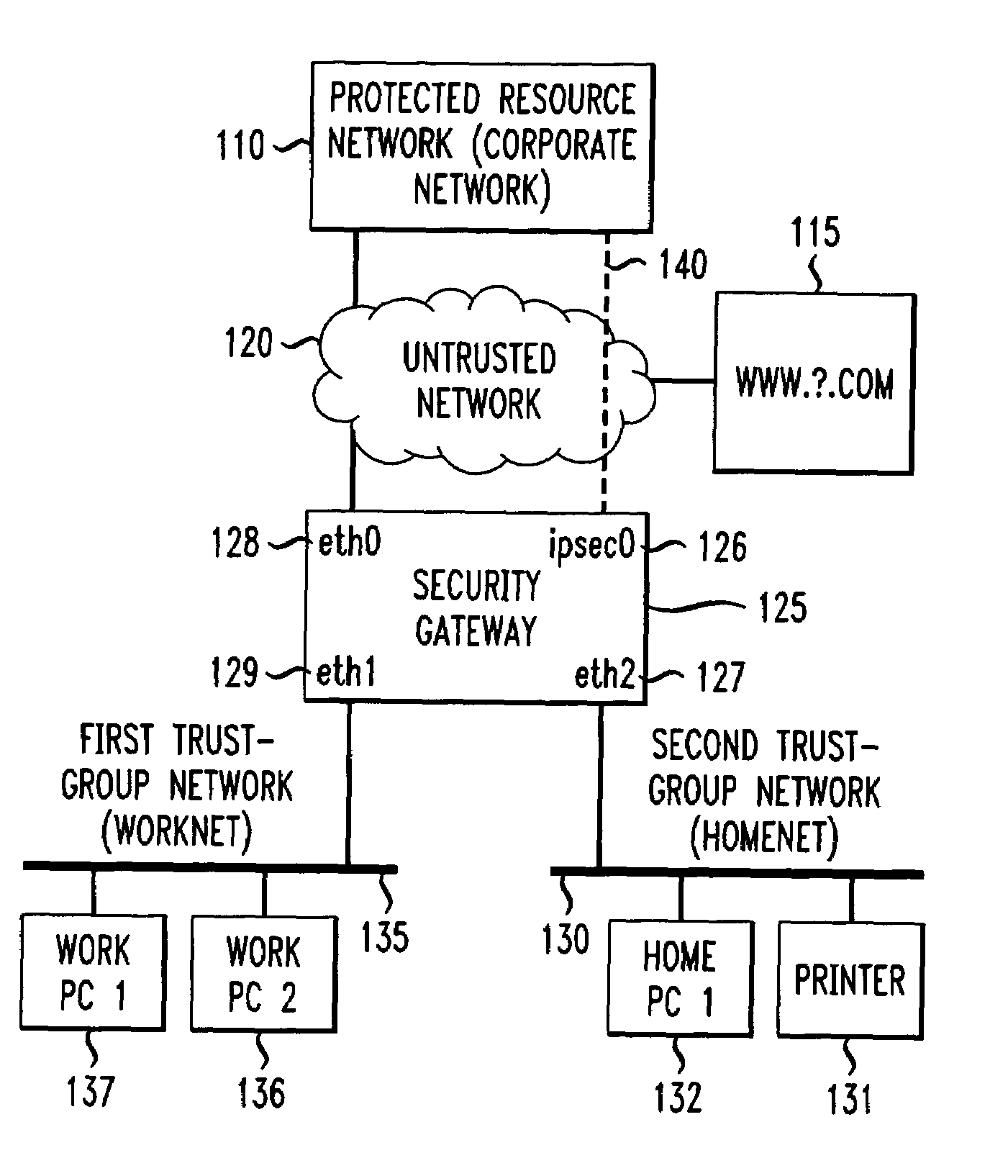
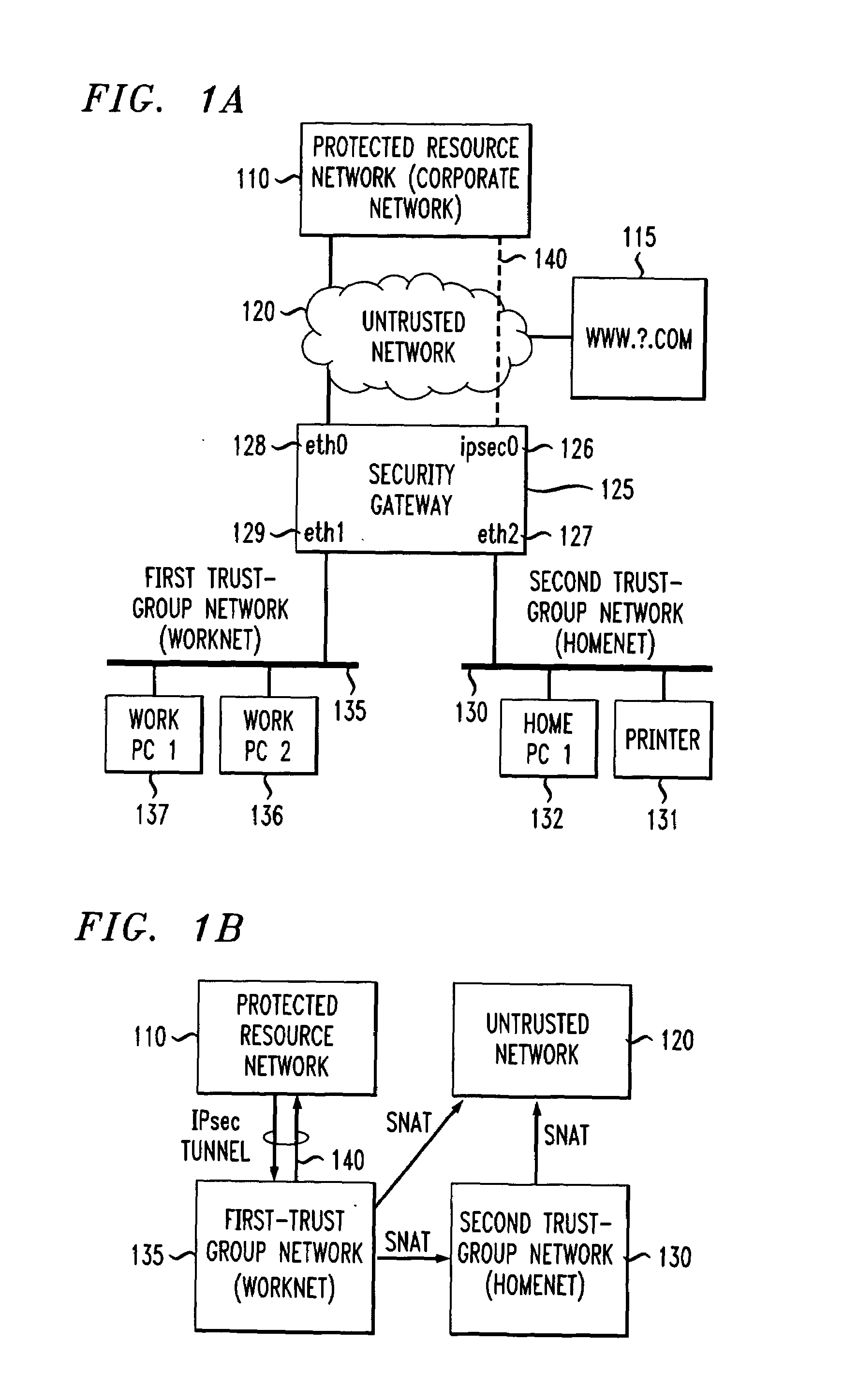
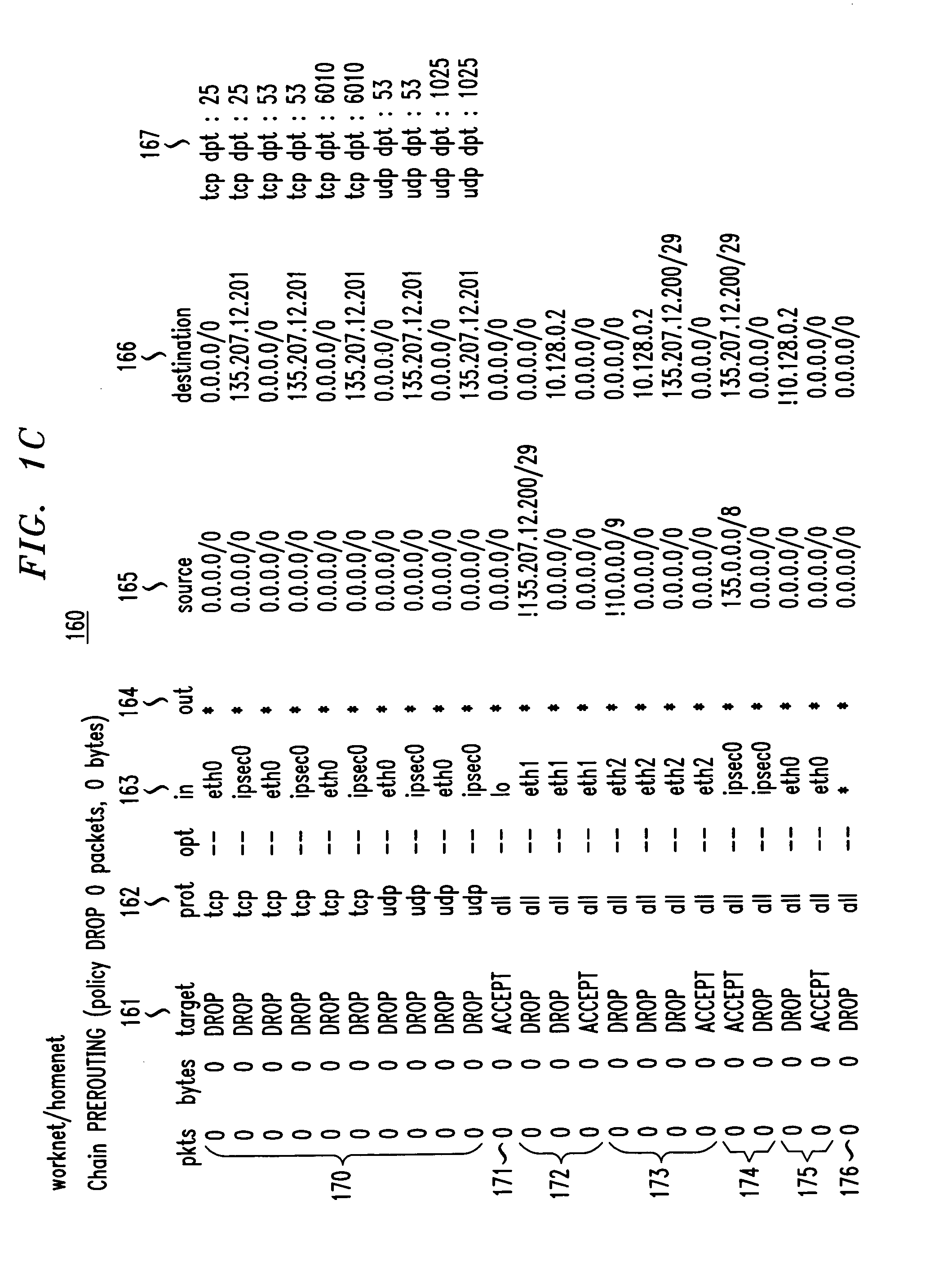
Method and apparatus for securely connecting a plurality of trust-group networks, a protected resource network and an untrusted network
InactiveUS7131141B1Improve securityMultiple digital computer combinationsProgram controlPrivate networkIp address
A security gateway provides a secure connection among one or more networks and a protected resource network. One of the local networks may be connected to the remote private network via a VPN IPsec tunnel. The networks may be local networks that share resources without compromising the security of the protected resource network. The local networks may have access to an untrusted network such as the Internet, sharing a single connection through the security gateway. Dynamic source network address translation is used to permit access from the network connected to the protected resource network to other, less trusted networks while concealing the actual IP addresses of hosts within that network.
Owner:AMERICAN TELEPHONE & TELEGRAPH CO
Method and apparatus for IP network interfacing
InactiveUS20080101357A1Facilitates multi-homingData switching by path configurationPrivate IPPrivate address
A method of operating a node of a telecommunications system, the node comprising a plurality of entities each arranged to send and receive IP packets to peer entities, via a Network Address Translation function, using a layer 4 control protocol which facilitates multi-homing by allowing an entity to include more than one IP address in a layer 4 packet chunk. The method comprises maintaining at each of said plurality of entities a table mapping one or more private addresses of the entity to one or more public addresses of the Network Address Translation function, and, for each association initiation message generated by an entity, including in said layer 4 packet chunk of the message the public IP address(es) of the Network Address Translation function obtained from said table for the corresponding private IP address(es).
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Network traversal method and network communication system
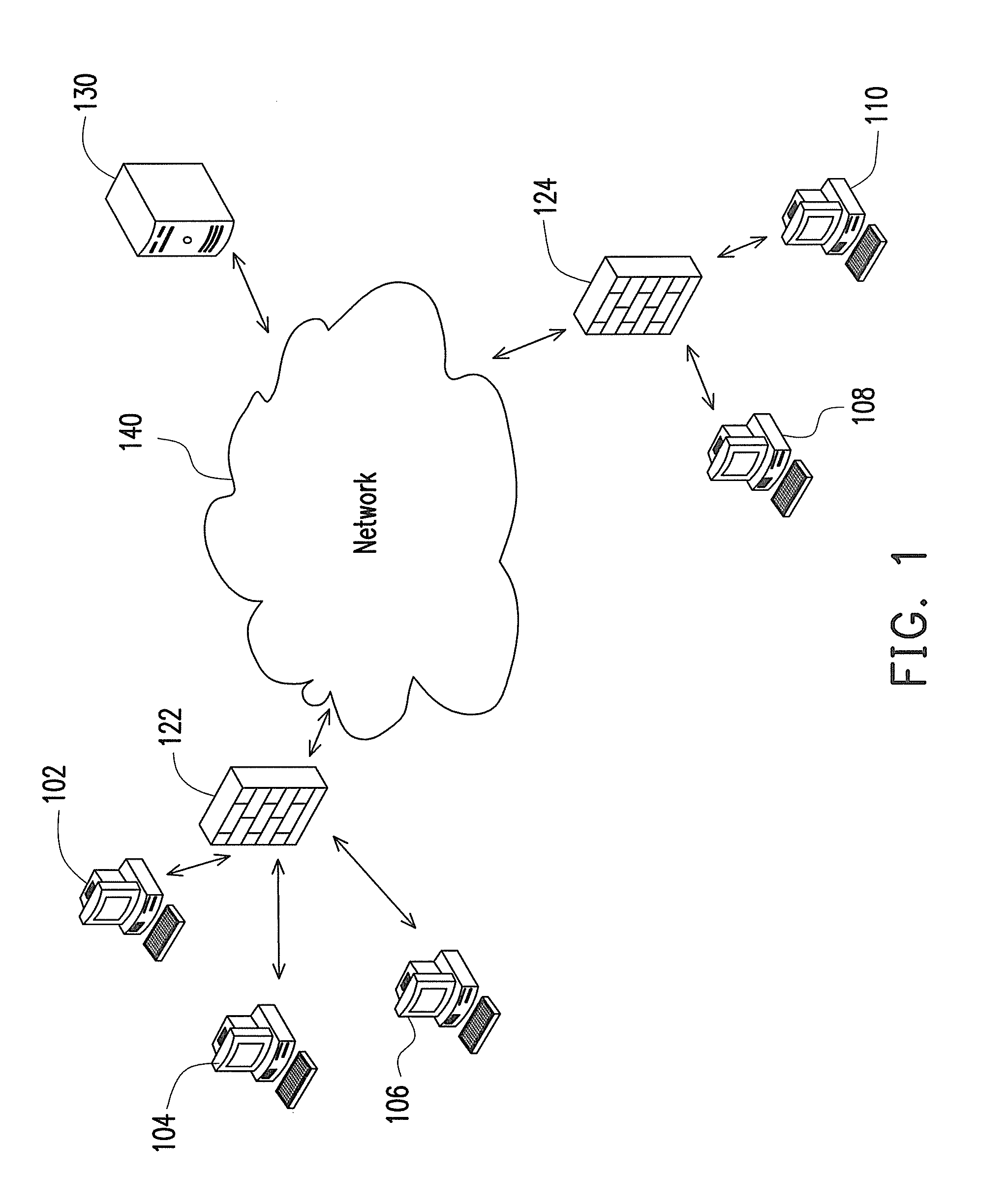
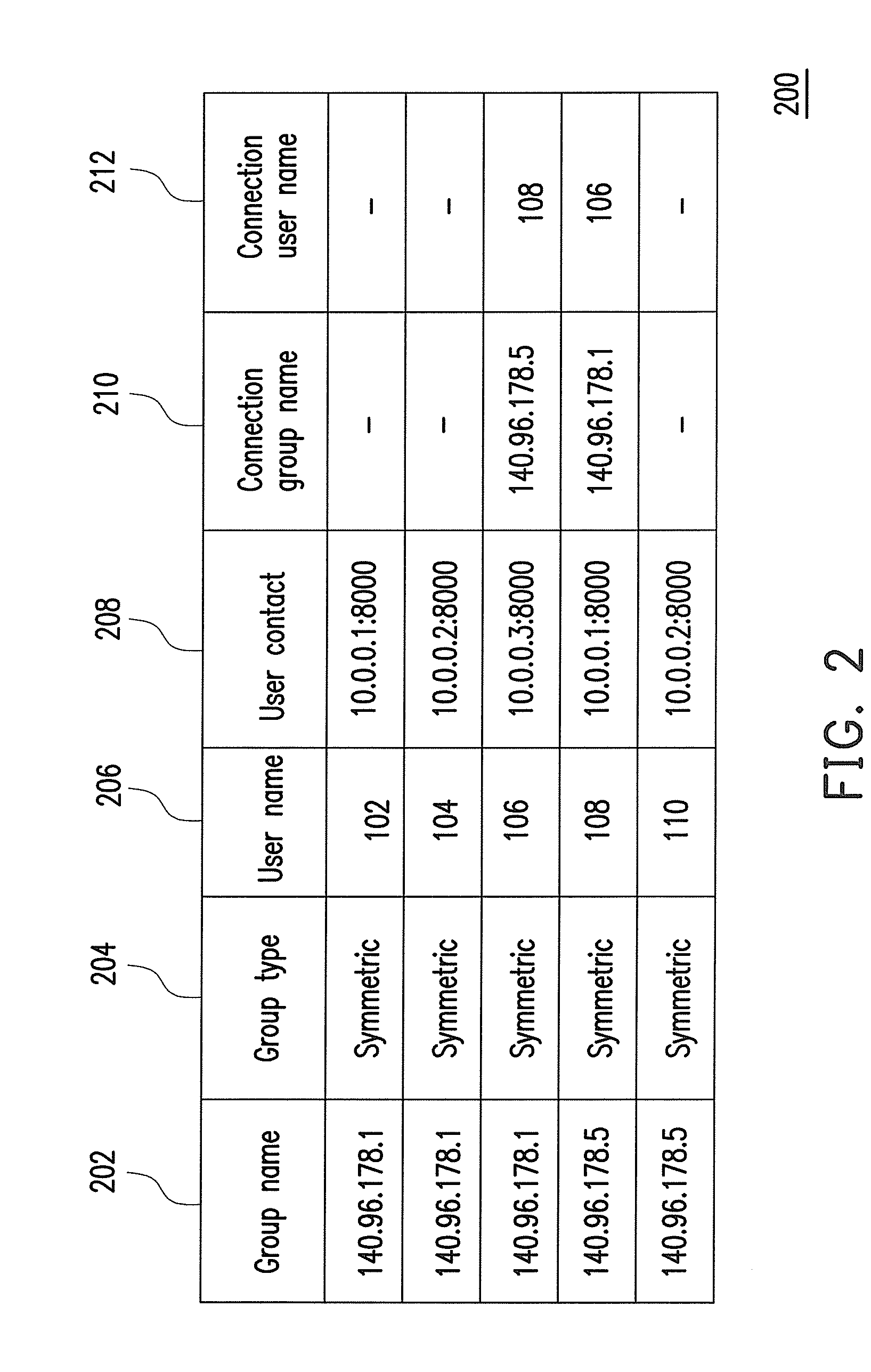
ActiveUS20110055392A1Reduce complexityLow costMultiplex system selection arrangementsSpecial service provision for substationNetwork addressingNetwork address translation
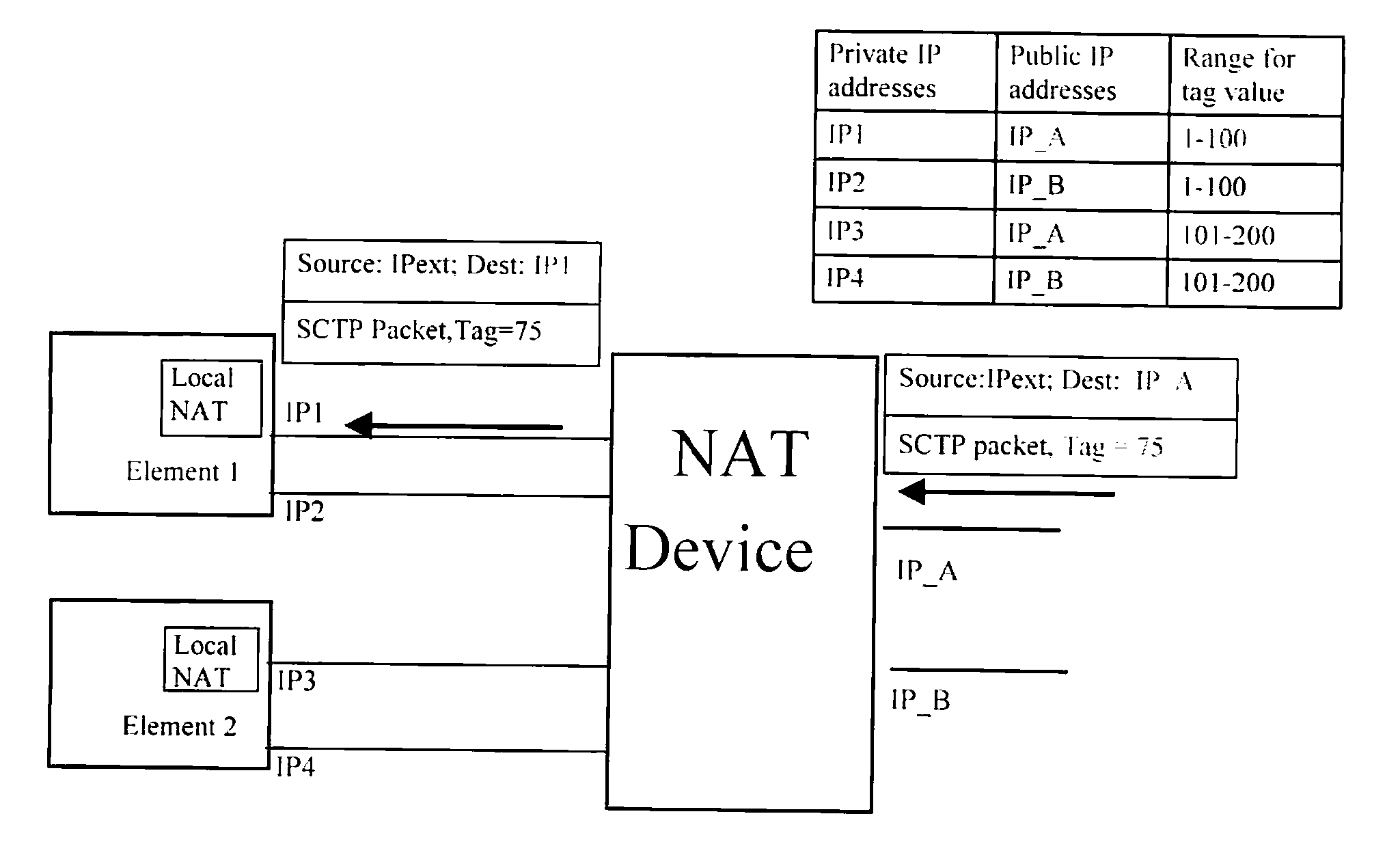
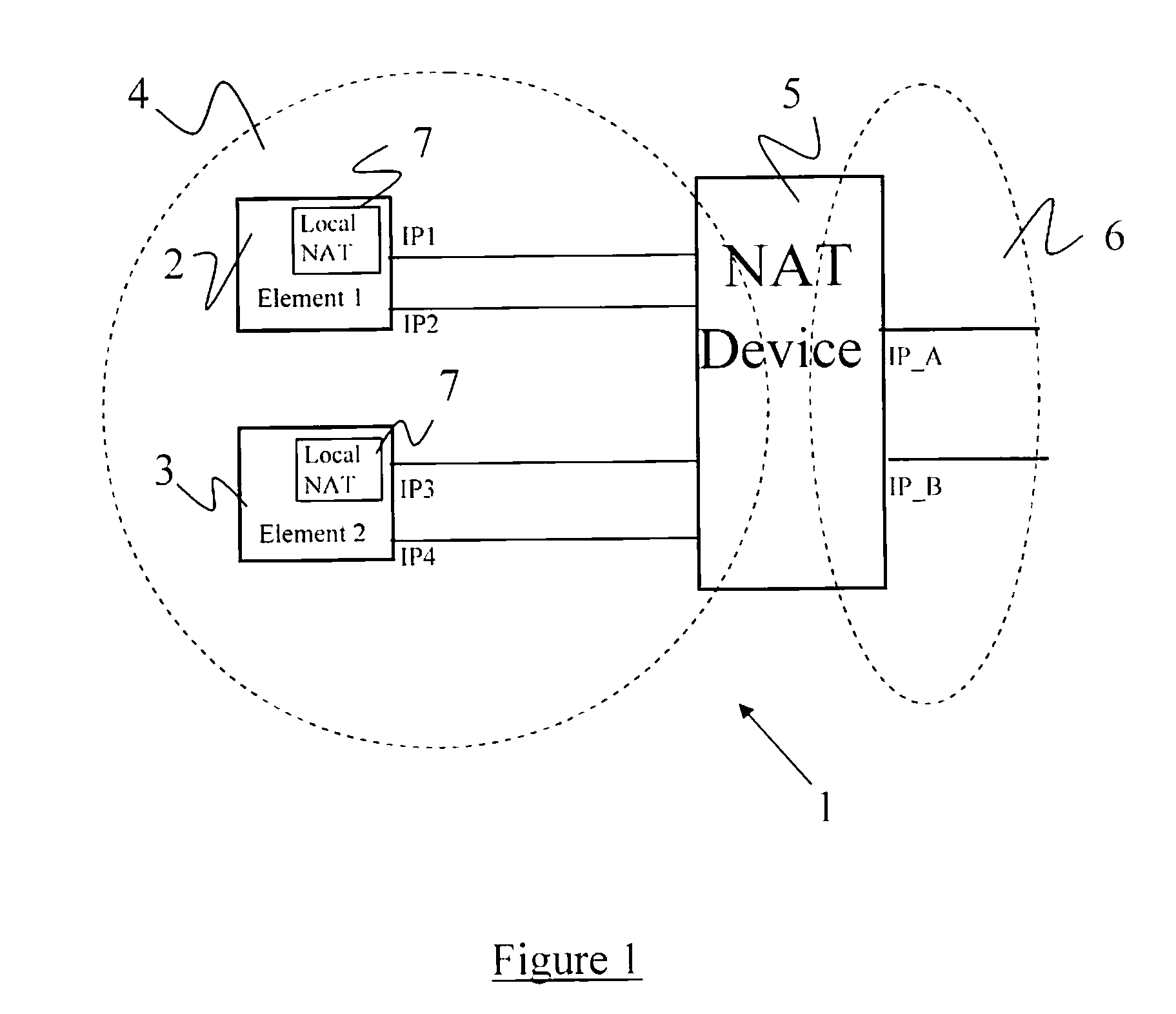
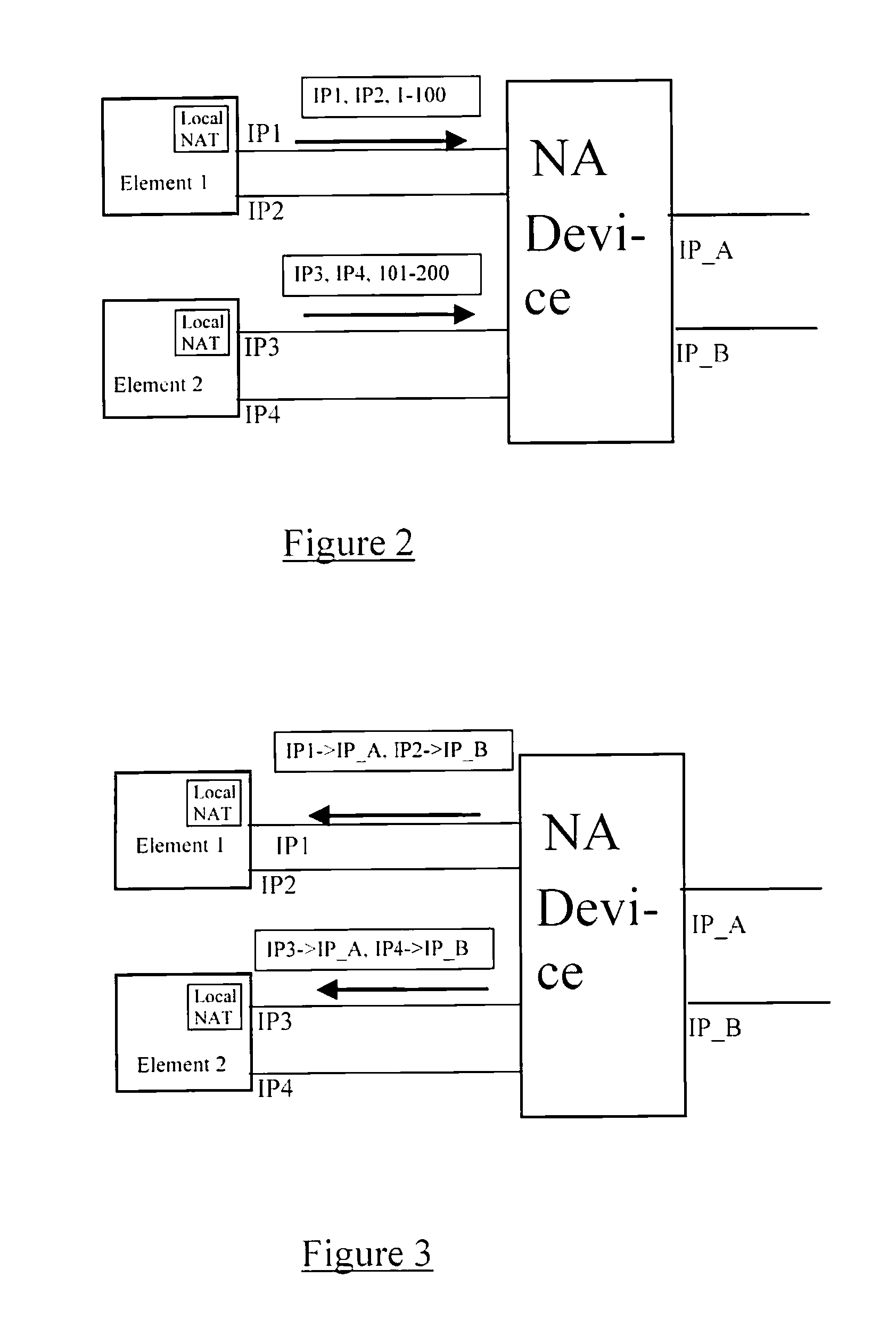
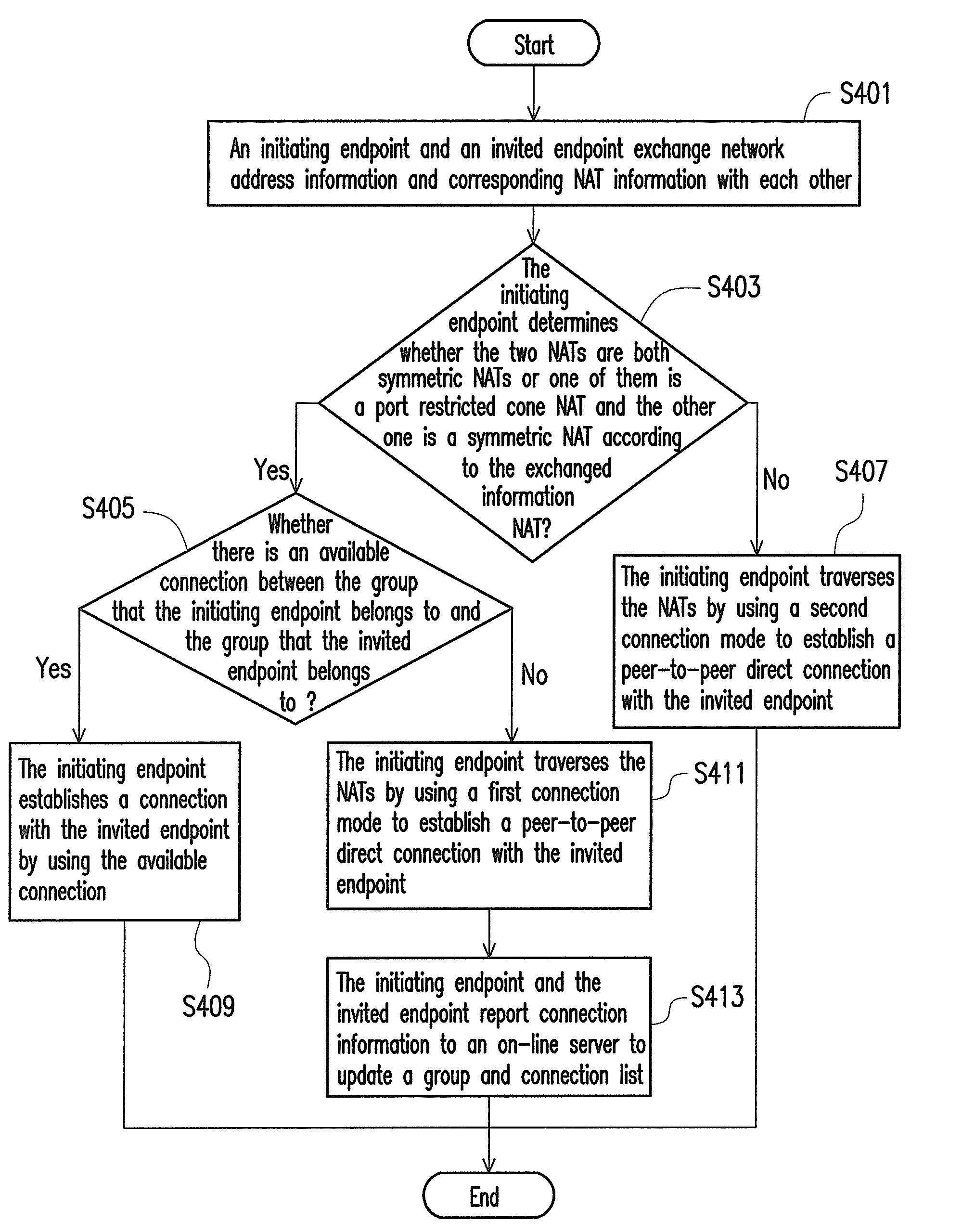
A network traversal method is provided. A plurality of endpoints in a plurality of network address translators (NATs) is grouped into a plurality of groups, and an on-line server is deployed for managing information related to the groups and information related to connections that have traversed the NATs, wherein the endpoints in the same NAT are grouped into the same group. In addition, when one of the endpoints is about to establish a connection with another one of the endpoints, whether there is a peer-to-peer direct connection between the groups corresponding to the two endpoints is determined. If there is the peer-to-peer direct connection between the groups corresponding to the two endpoints, the connection between the two endpoints is established by using the peer-to-peer direct connection. Thereby, the network traversal method can effectively reduce the time, cost, and complexity for traversing the NATs.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Peer-to-peer communication traversing symmetric network address translators
ActiveUS8224985B2Data switching by path configurationMultiple digital computer combinationsNetwork address translationNetwork address
Owner:SONY COMPUTER ENTERTAINMENT INC
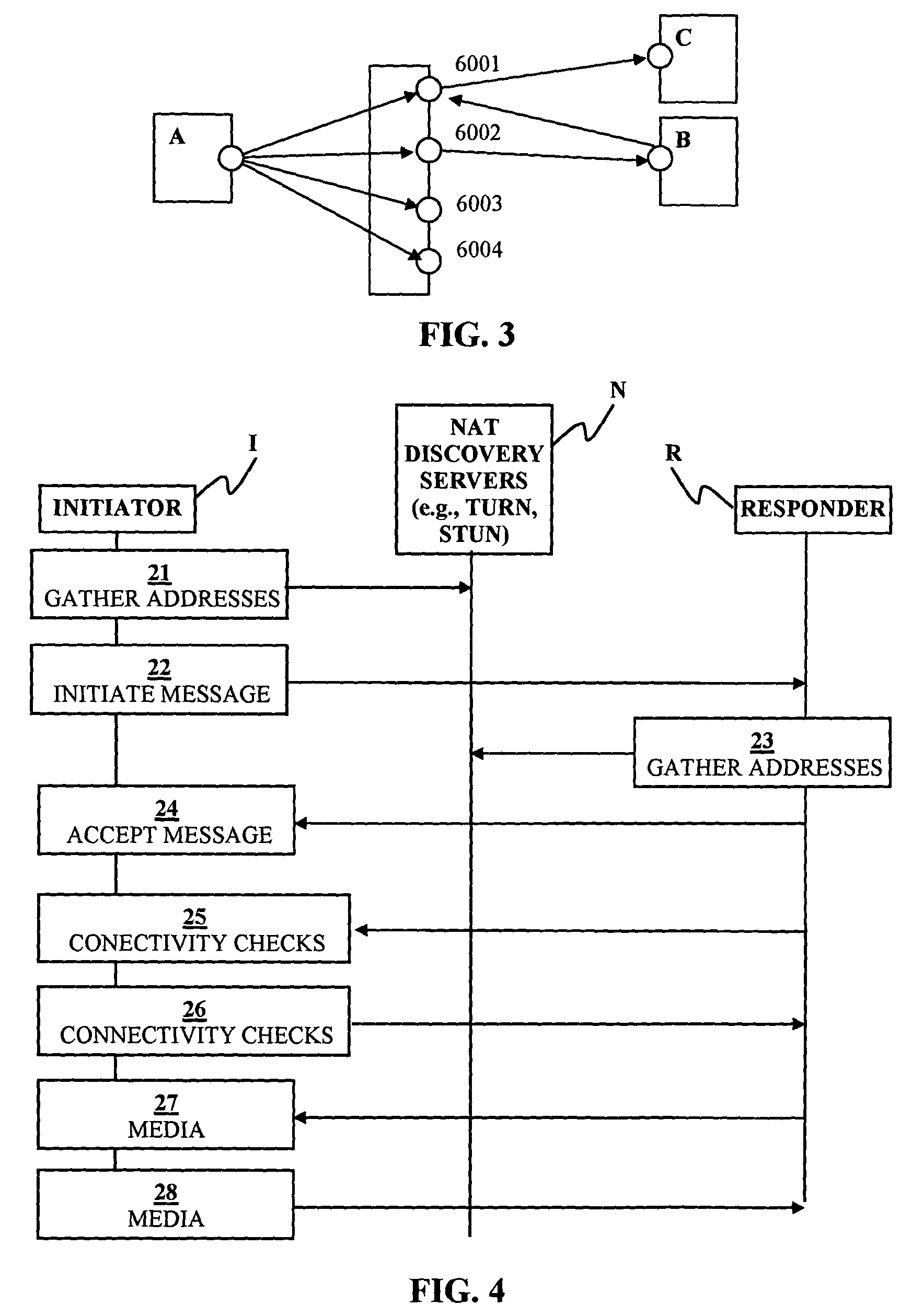
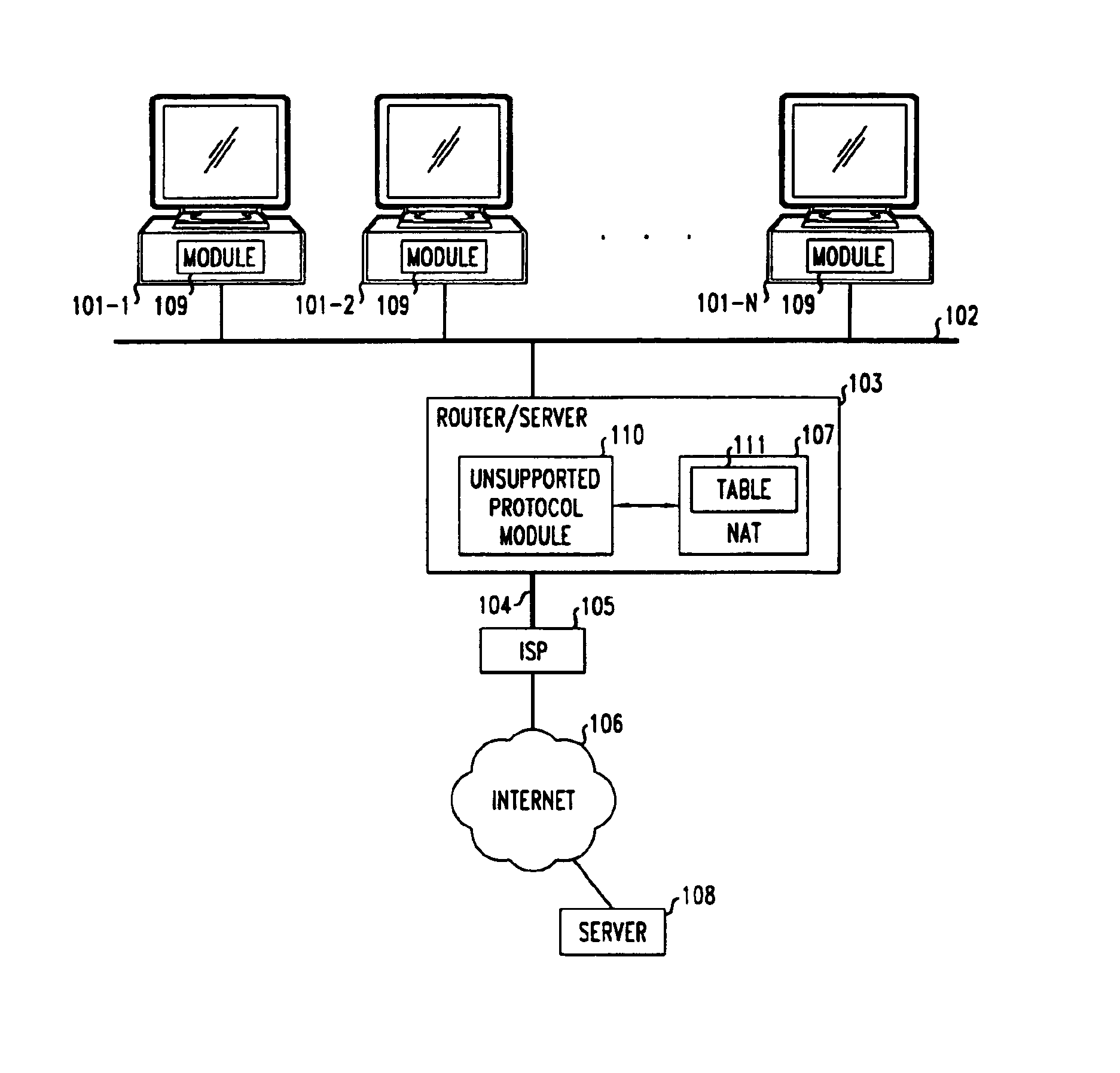
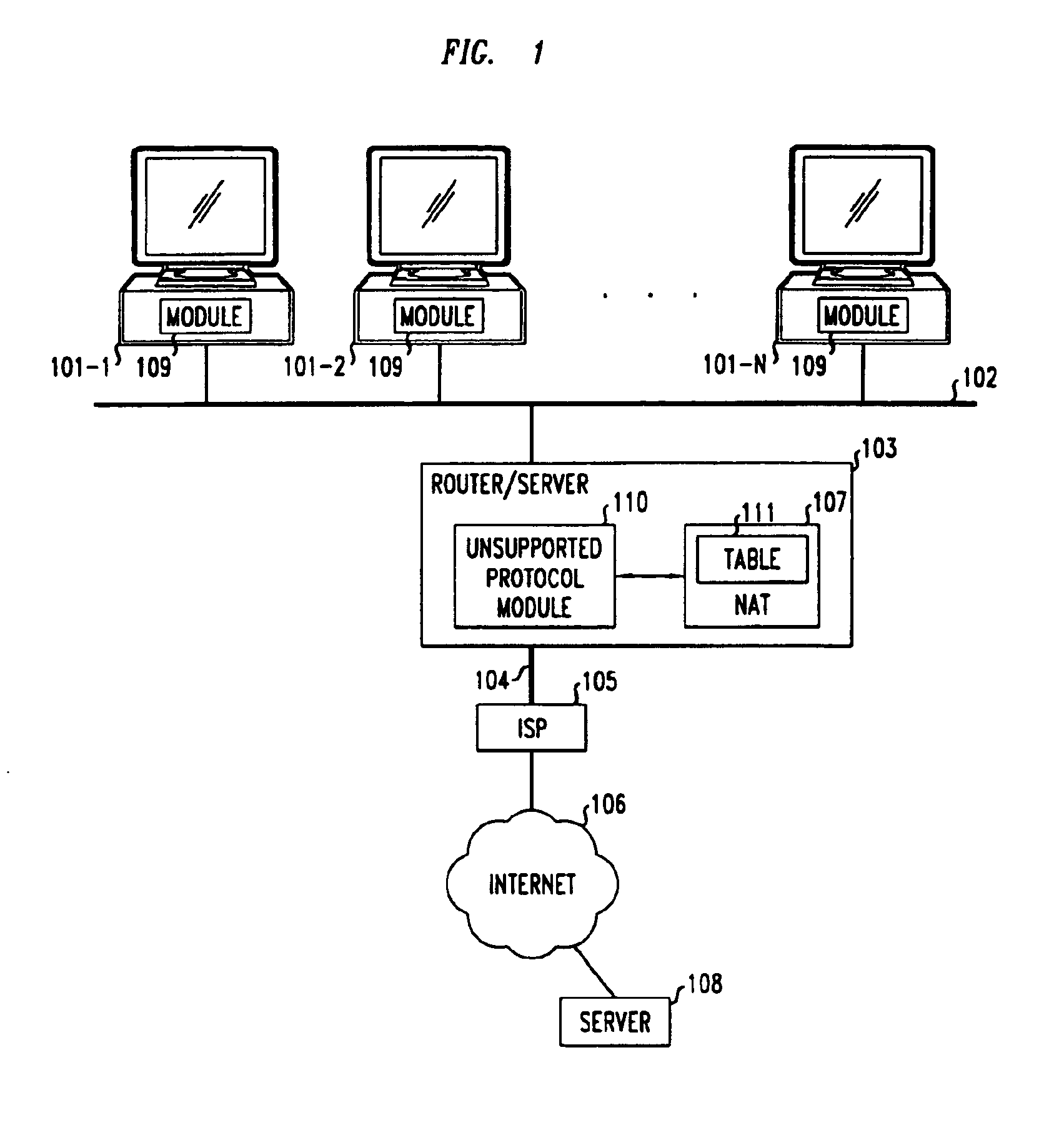
Method and apparatus for extending network address translation for unsupported protocols
InactiveUS6886103B1Ensure safetyMultiple digital computer combinationsProgram controlExpiration TimeIp address
Clients that are connected on a private network and which are assigned a private IP address that is not routable on the Internet can connect to the Internet through a router / server that includes a network address translator (NAT). For outgoing packets, the NAT translates the client's private source IP address and generalized port number (GPN) to the NAT's global IP address and GPN. For incoming packets sent to the NAT's global IP address and GPN, the NAT translates the global destination IP address and GPN to the client's private IP address and GPN. For protocols which cannot be directly supported by the NAT, such as those in the IPSec security protocol suite, the NAT is extended by creating in the NAT's translation table an entry that associates, for a specific unsupported protocol, a client's private IP address and GPN, the NAT's global IP address and GPN, and a foreign address on the Internet, that is valid until a specified or default expiration time. Outgoing packets from the client to that foreign address and incoming packets from that foreign address to the NAT's global IP address and GPN are translated according to the entry until the entry expires. In associations with these translations to outgoing and incoming packets, the client implements any Application Layer Gateway (ALG) that would otherwise be implemented at the NAT. Further, at the client, outgoing packets are modified before being transmitted so as to pre-compensate for the effects of the translations. Incoming packets at the client from the NAT are similarly modified so as to post-compensate for the effects of the translations. For the IPSec protocol, these modification include adjusting the checksum in the TCP or UDP header to account for IP address and TCP or UDP port number translations.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC
Method and system for securing real-time media streams in support of interdomain traversal
An approach provides interdomain traversal packetized voice transmissions. A request is received from a first endpoint of a first domain for establishing a communication session with a second endpoint of a second domain. A tunnel is established by a TURN (Traversal Using Relay NAT (Network Address Translation)) server to support the communication session. The TURN server is controlled by a service provider as part of a managed communication service. The tunnel traverses a first firewall and a first network address translator of the first domain and a second firewall and a second network address translator of the second domain to reach the second endpoint, wherein the communication session is encrypted and transported via the tunnel.
Owner:VERIZON PATENT & LICENSING INC
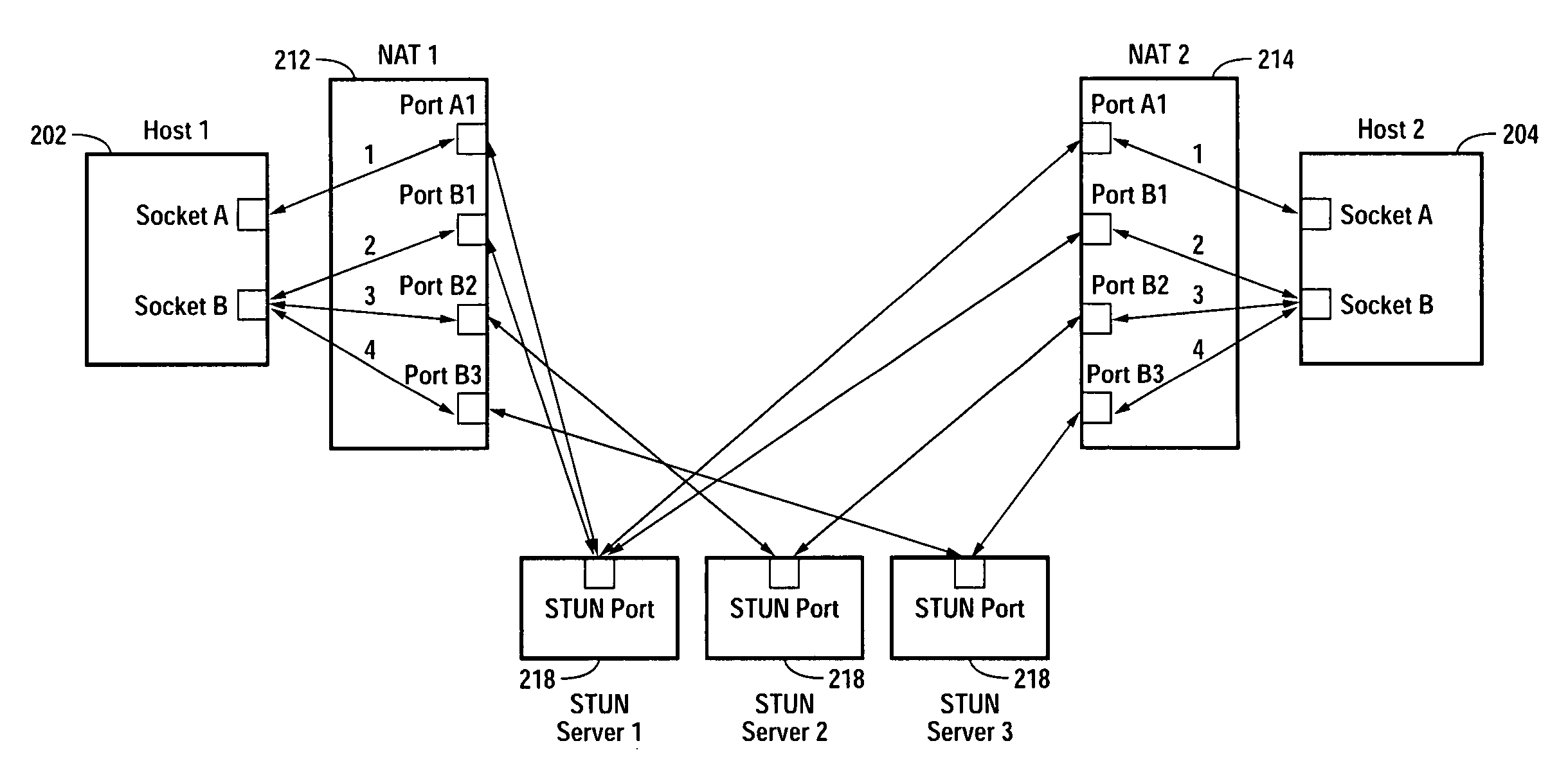
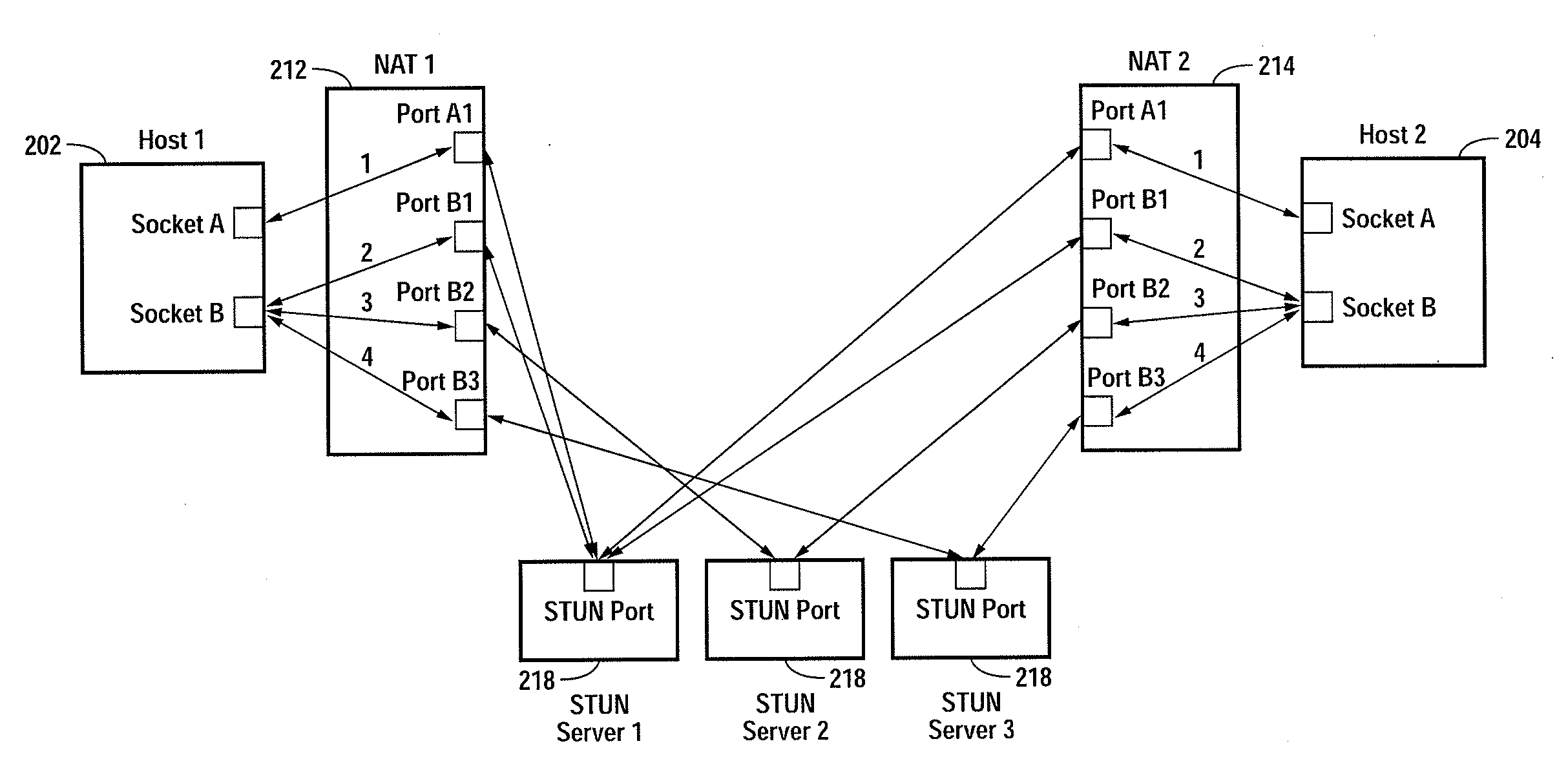
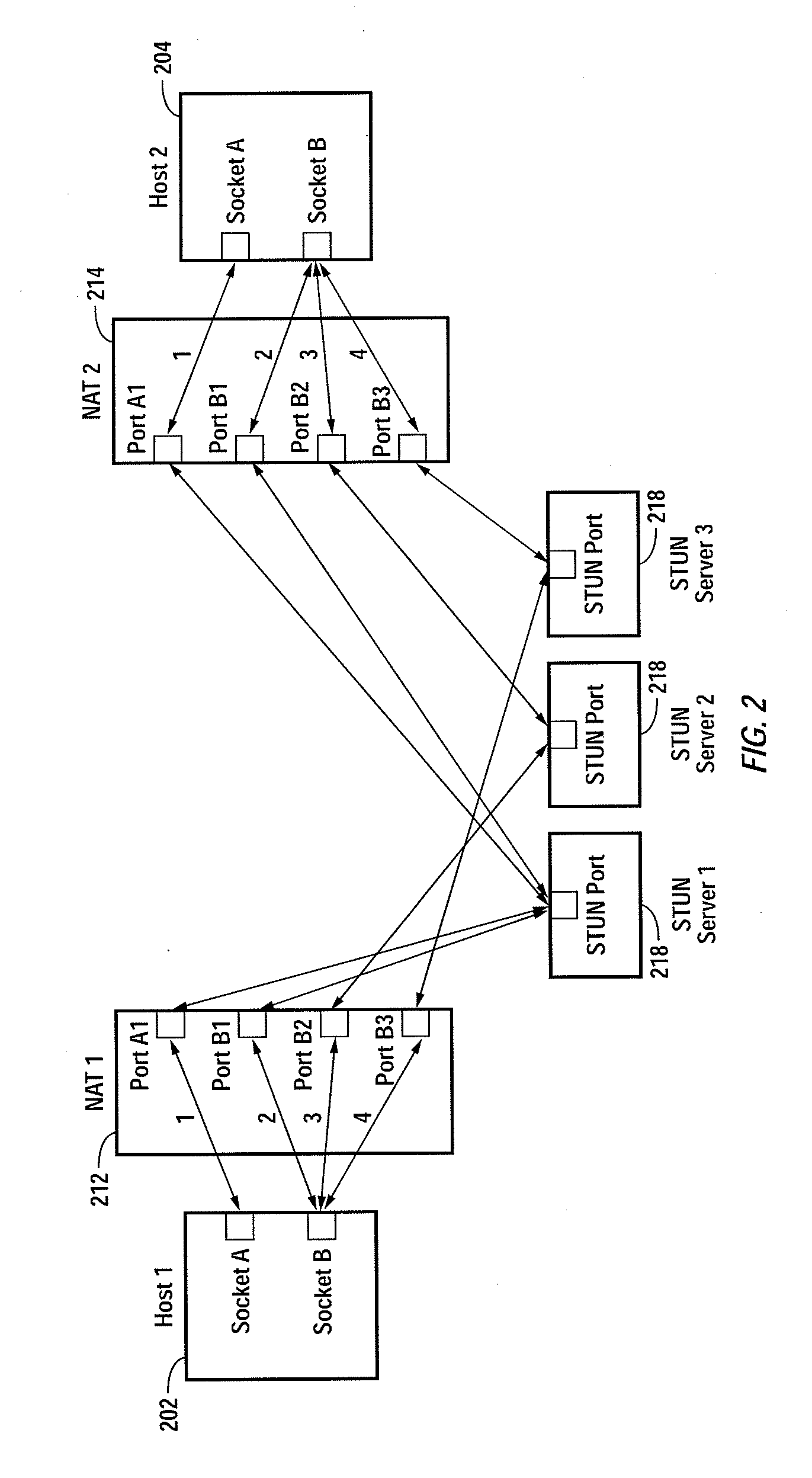
Multiplayer peer-to-peer connection across firewalls and network address translators using a single local port on the local host
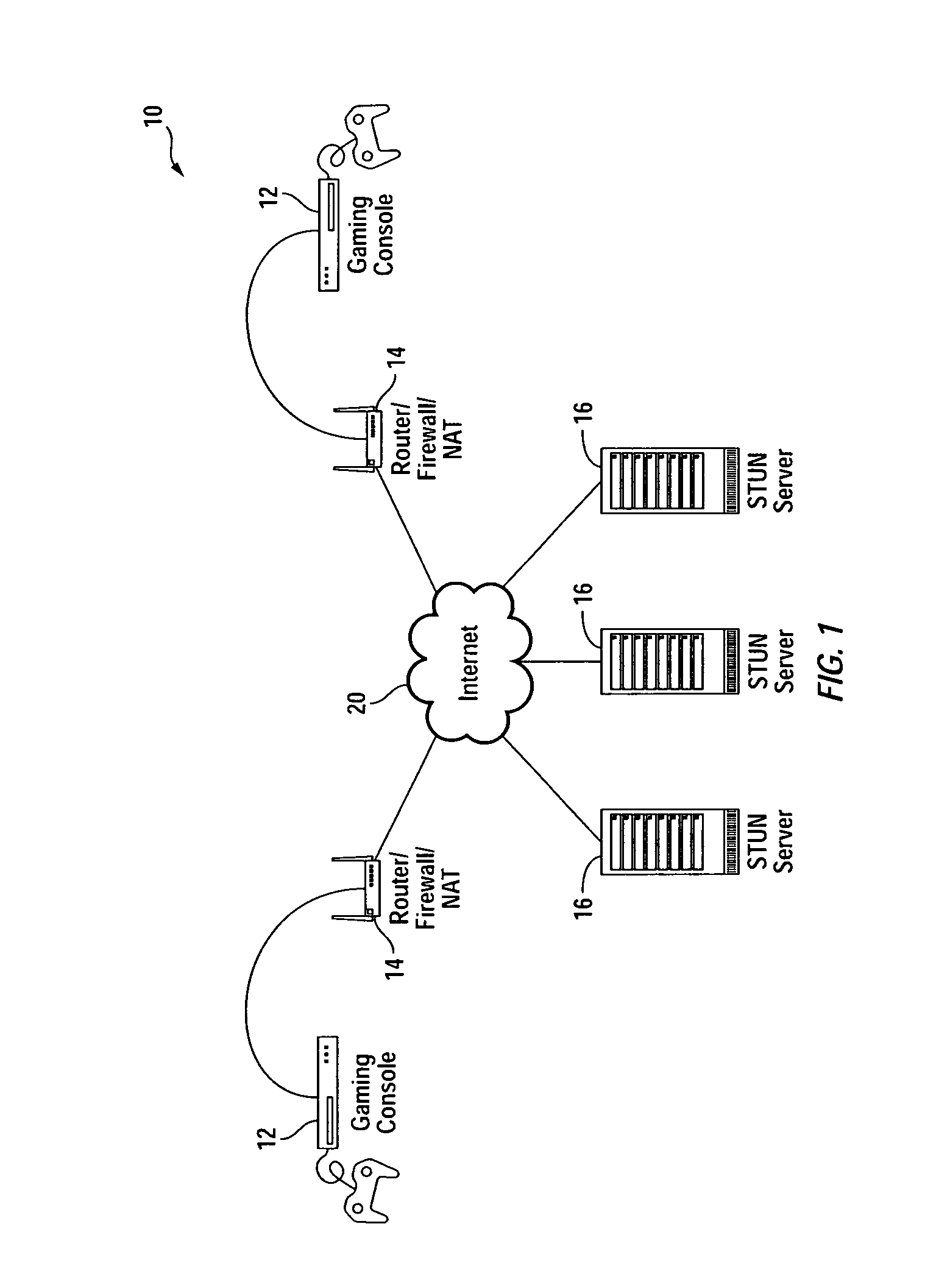
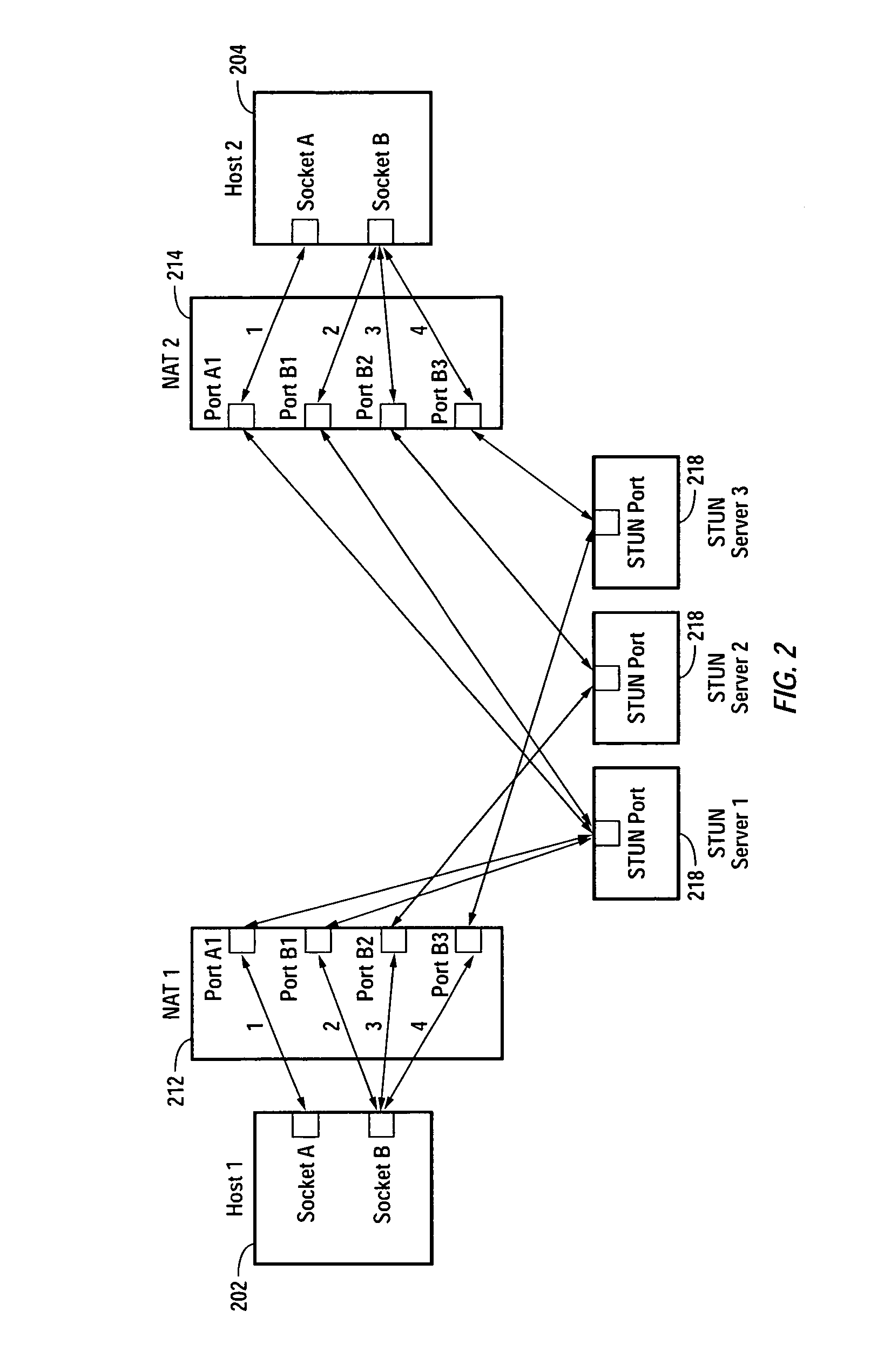
Embodiments of the invention achieve a very high success rate in multilayer peer-to-peer connection across firewalls and network address translators (NATs) using a single port on the local host. In one embodiment, a system of providing peer-to-peer connection comprises a plurality of host devices disposed behind corresponding NATs; and a plurality of STUN servers. Each host device includes a first socket bound to a first private port and a second socket bound to a second private port. Each host device sends a first STUN packet through the first socket to a first STUN server and a second group of STUN packets through the second socket to the STUN servers via public ports of the corresponding NAT. The STUN servers identify the public port numbers of the public ports. Each host device is configured to calculate a predicted public port number of the corresponding NAT for the second socket, based on the public port numbers of the public ports for the first socket and the second socket, the predicted public port number to be used for peer-to-peer connection between the second socket of the host device and other host devices.
Owner:LOGITECH EURO SA
System and method for providing access to a network with selective network address translation
ActiveUS7127524B1Avoid software conflictEasy to configureMultiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionComputer networkNetwork address translation
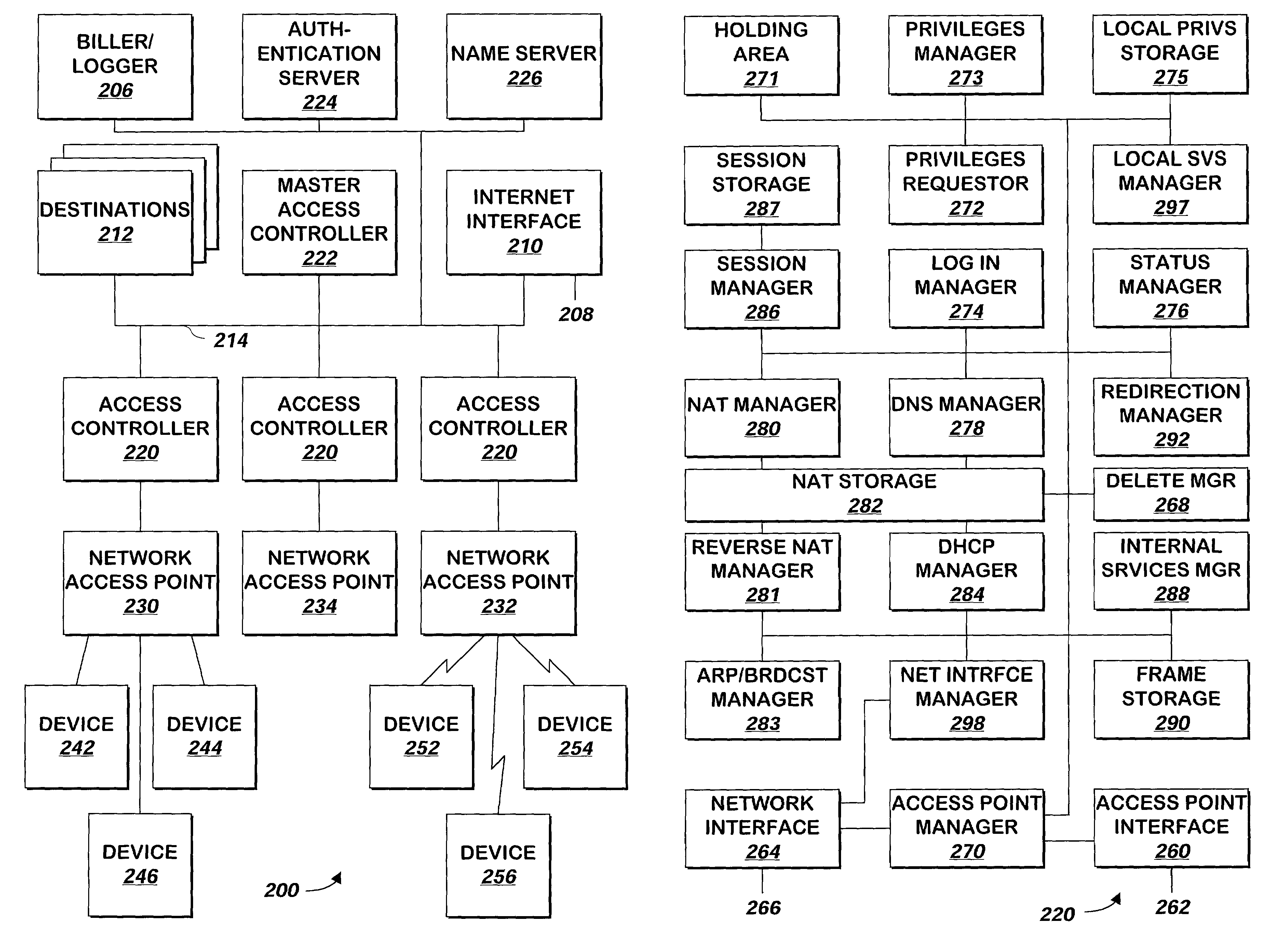
A system and method controls access to a network. The system and method intercepts communications received from, and responses and other communications to, devices on the network. Communications may be forwarded to their intended destination if the sending device has sufficient privileges to do so, or the communications may be handled by the system and method or forwarded to a different destination (e.g. a printer nearby the access point to which the user is communicating) using network address translation or redirection. Responses are received and stored by the system and method and may be forwarded to the device that sent the original communication, either directly or via a different device that requests the stored communications using a tunnel.
Owner:SILICON VALLEY BANK +1
Communication network and method of operation therefor
ActiveUS20100057929A1Improve performanceFacilitate and improve useMultiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionNetwork addressingNetwork address
A communication network comprising a Network Address Translator (NAT) arranged to translate between a public NAT address and a plurality of private NAT addresses. A network element has a plurality of network interfaces each of which corresponds to a private NAT address. A connection processor sets up a connection for data communication which is capable of supporting a plurality of network interfaces of the network element. An identifier processor initialises a network interface identifier for identifying individual network interfaces for the connection. The network interface identifier is distributed to the NAT and the network elements of the connection. Incoming data packets for the network elements are then adapted to include the network interface identifier and the NAT uses this to address the data packets in response to the first network interface identifier.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
Multiplayer Peer-to-Peer Connection Across Firewalls and Network Address Translators Using a Single Local Port on the Local Host
Owner:LOGITECH EURO SA
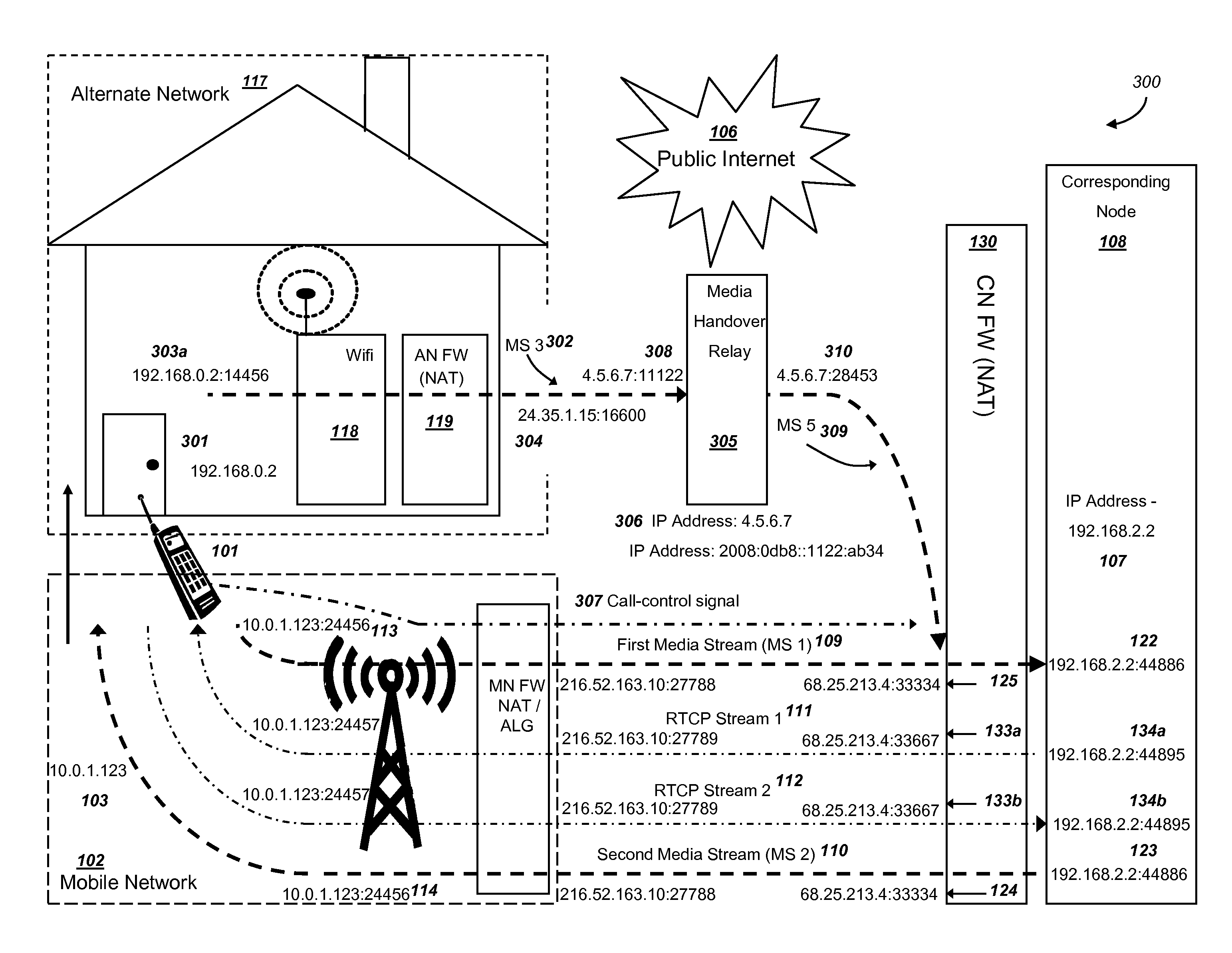
Efficient handover of media communications in heterogeneous IP networks using handover procedure rules and media handover relays
ActiveUS8228861B1Reduce complexityIncrease speedError detection/prevention using signal quality detectorChannel coding adaptationMedia controlsCable Internet access
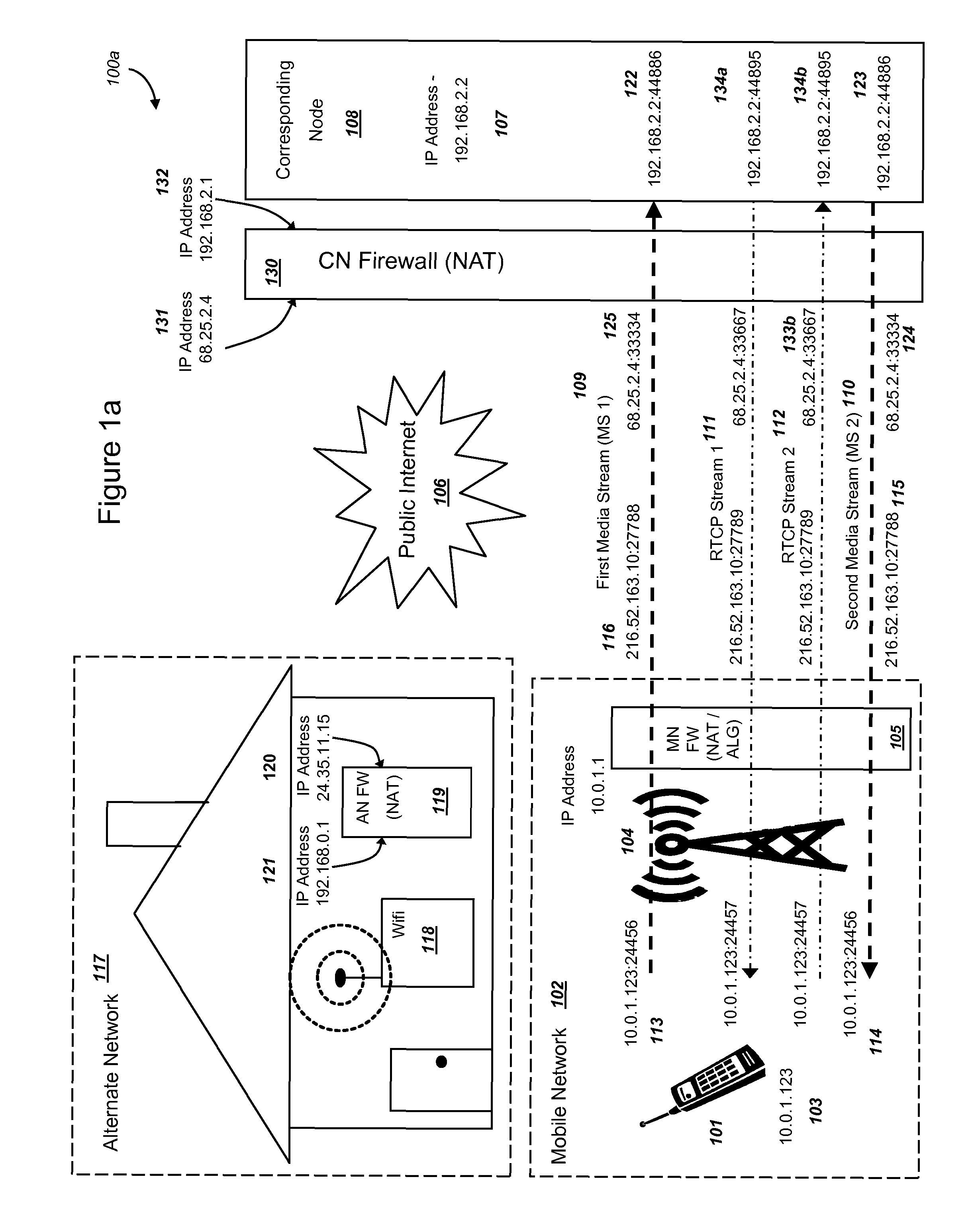
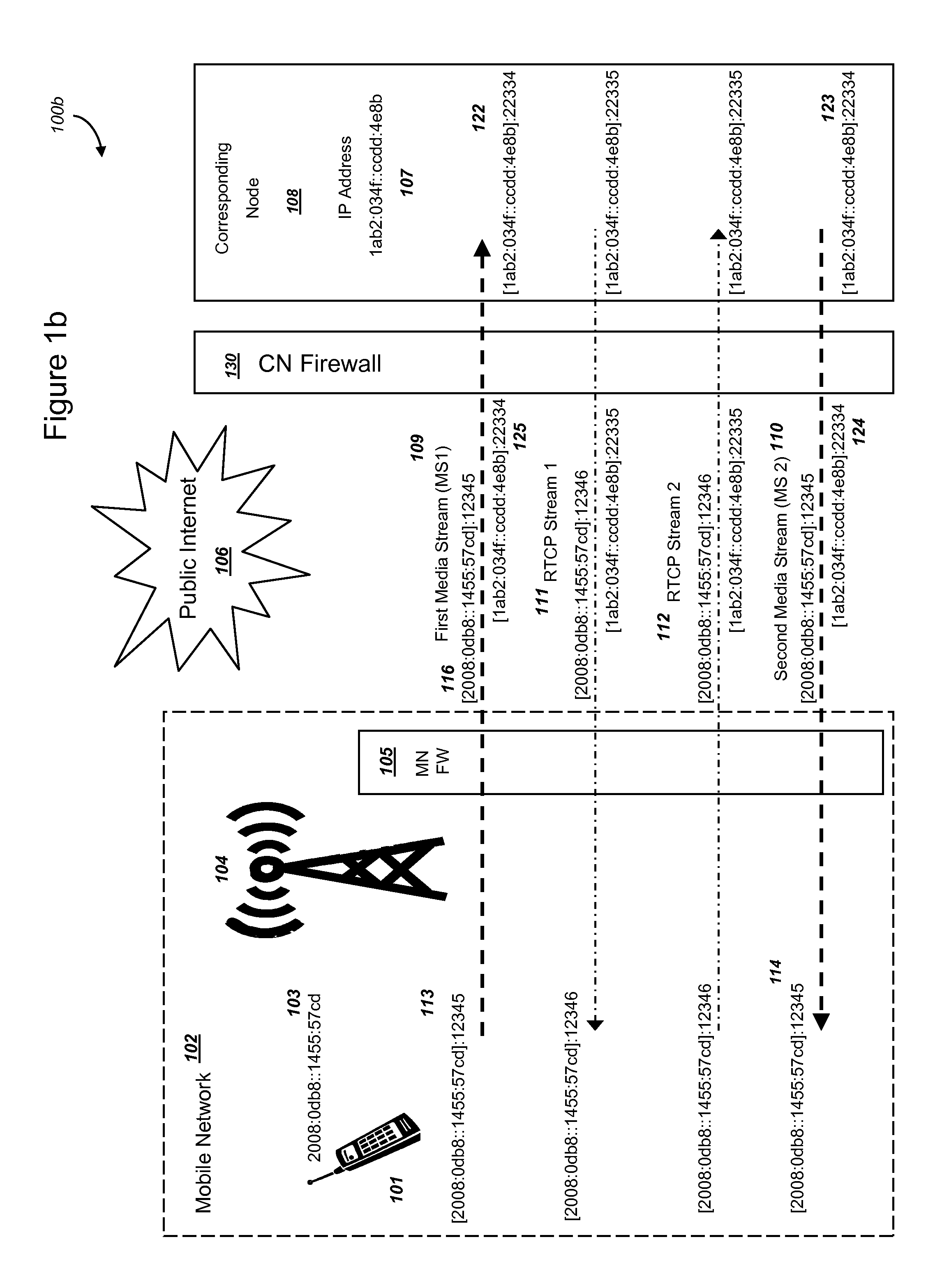
Methods and systems are provided for efficient handover of a media session between heterogeneous Internet Protocol (IP) networks. A mobile device with Internet access can operate a software program to communicate with a corresponding node. The corresponding node may access the Internet through a firewall which may include Network Address Translation (NAT)-routing functionality. The mobile device establishes a media session with a corresponding node via the transmission of a first media stream and receipt of a second media stream, and a media-control channel can optionally be implemented. The mobile device can acquire Internet access through a second IP address, and packets routed between the second IP address and the Internet may traverse a firewall. The mobile device can evaluate a set of network parameters at the second IP address from a stored Local Area Network (LAN) profile. A software routine can (i) evaluate that handover of the media session from the first IP address to the second IP address is preferred and (ii) select an efficient handover procedure according to handover procedure rules.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Establishing consistent, end-to-end protection for a user datagram
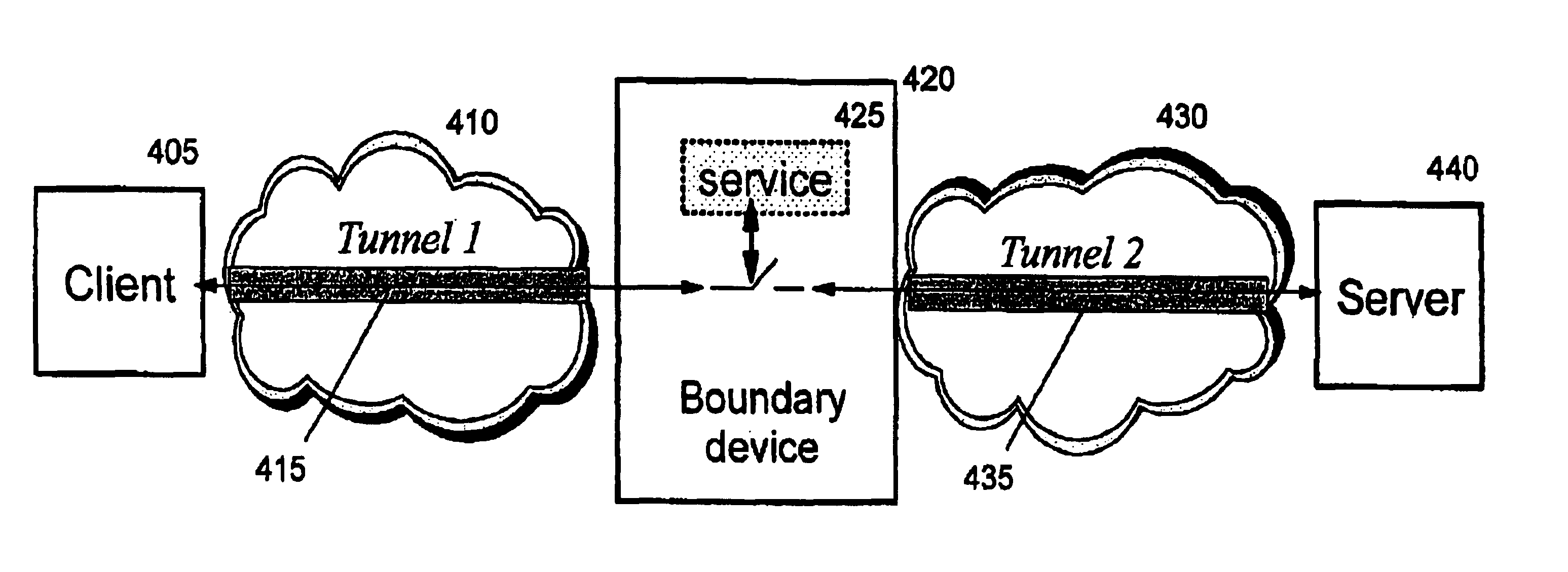
A method, system, and computer program product for providing consistent, end-to-end protection within a computer network for user datagrams (i.e. packets) traveling through the network. The network may comprise network segments that are conventionally assumed to be secure (such as those found in a corporate intranet) as well as network segments in non-secure networks (such as the public Internet or corporate extranets). Because security breaches may in fact happen in any network segment when datagrams are unprotected, the present invention discloses a technique for protecting datagrams throughout the entire network path by establishing cascaded tunnels. The datagrams may be exposed in cleartext at the endpoints of each tunnel, thereby enabling security gateways to perform services that require content inspection (such as network address translation, access control and authorization, and so forth). The preferred embodiment is used with the “IPSec” (Internet Protocol Security Protocol) and “IKE” (Internet Key Exchange) protocols, thus providing a standards-based solution.
Owner:IBM CORP
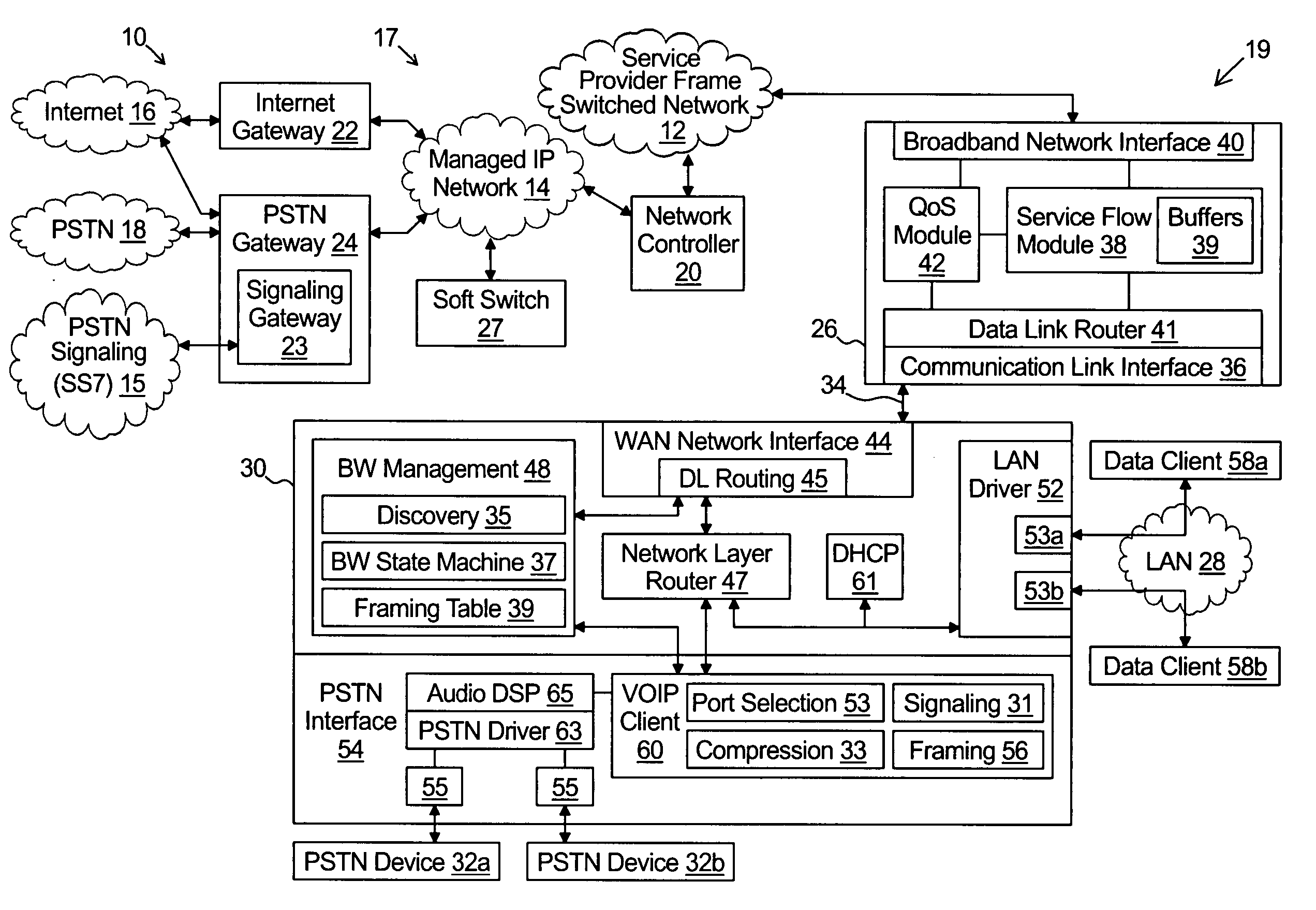
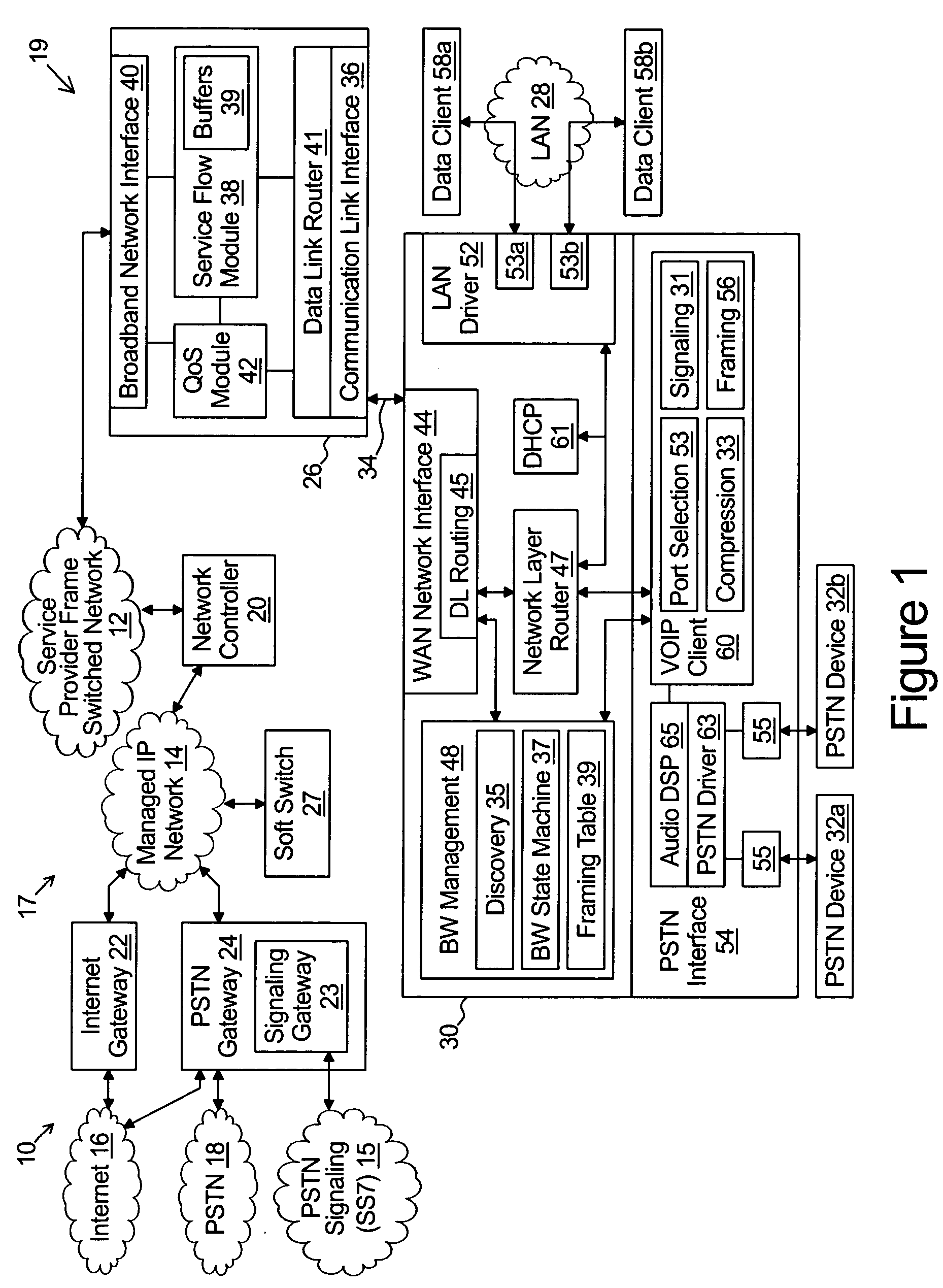
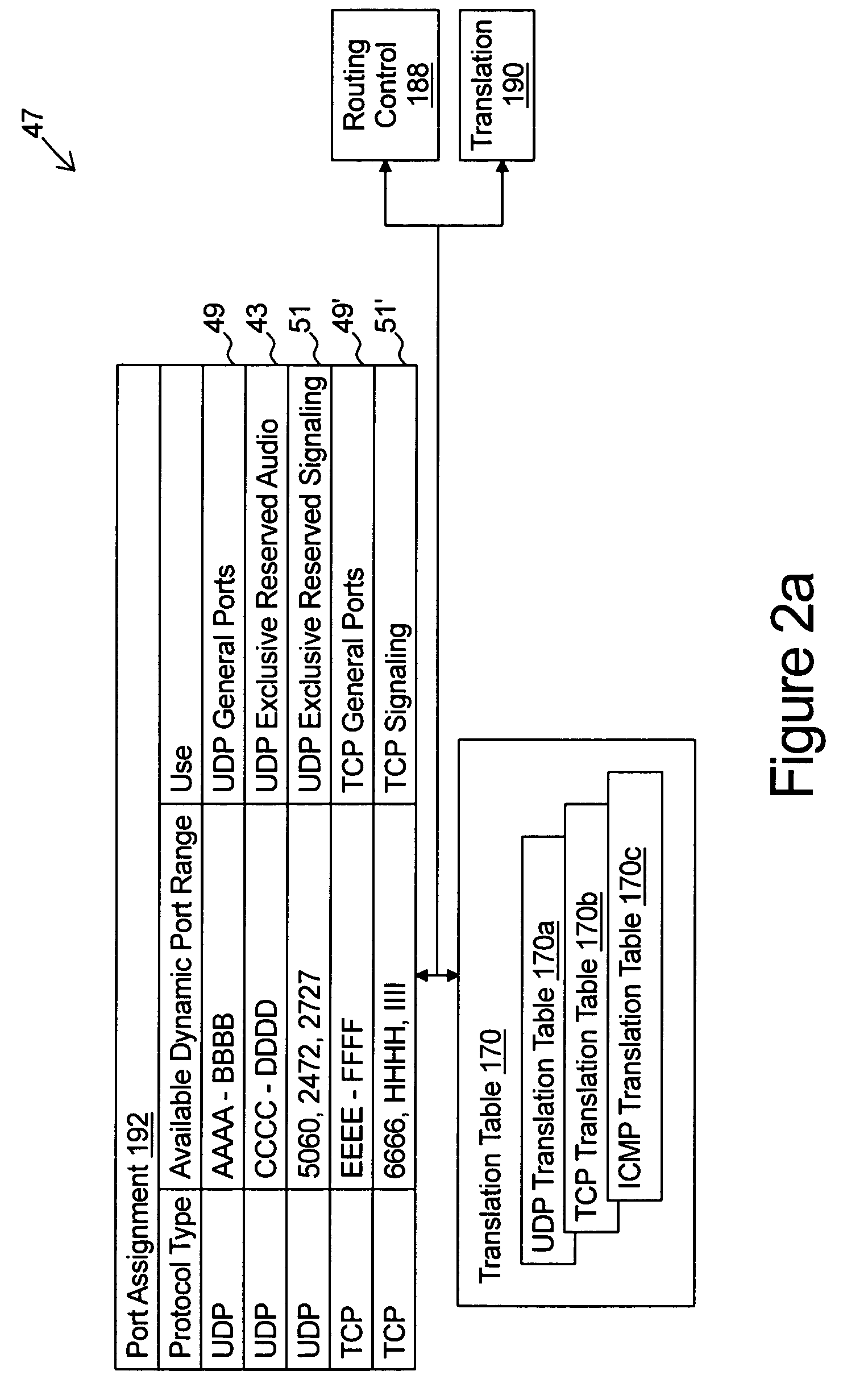
Stand alone multi-media terminal adapter with network address translation and port partitioning
ActiveUS20050018651A1Interconnection arrangementsFrequency-division multiplex detailsTelecommunications linkIp address
A multi-media terminal adapter couples to a network access module over a communication link. The network access module communicates IP frames over a frame switched network. The multi-media terminal adapter comprises a wide area network interface coupled to the communication link for exchanging IP frames with the access module and a local area network interface for receiving outbound data client IP frames from each of a plurality of data clients. Each outbound data client IP frame comprises a socket information that includes a local area network IP address and a data client port number. A VoIP module generates outbound VoIP frames. Each outbound VoIP frame comprises socket information that includes a VoIP port number selected from a first group of port numbers exclusively reserved for use by the VoIP module. A router module is coupled between the wide area network interface and each of the VoIP module and the local area network interface. The router receives the outbound data client IP frames and the outbound VoIP frames and performs port translation on only the outbound data client IP frames.
Owner:INNOMEDIA PTE
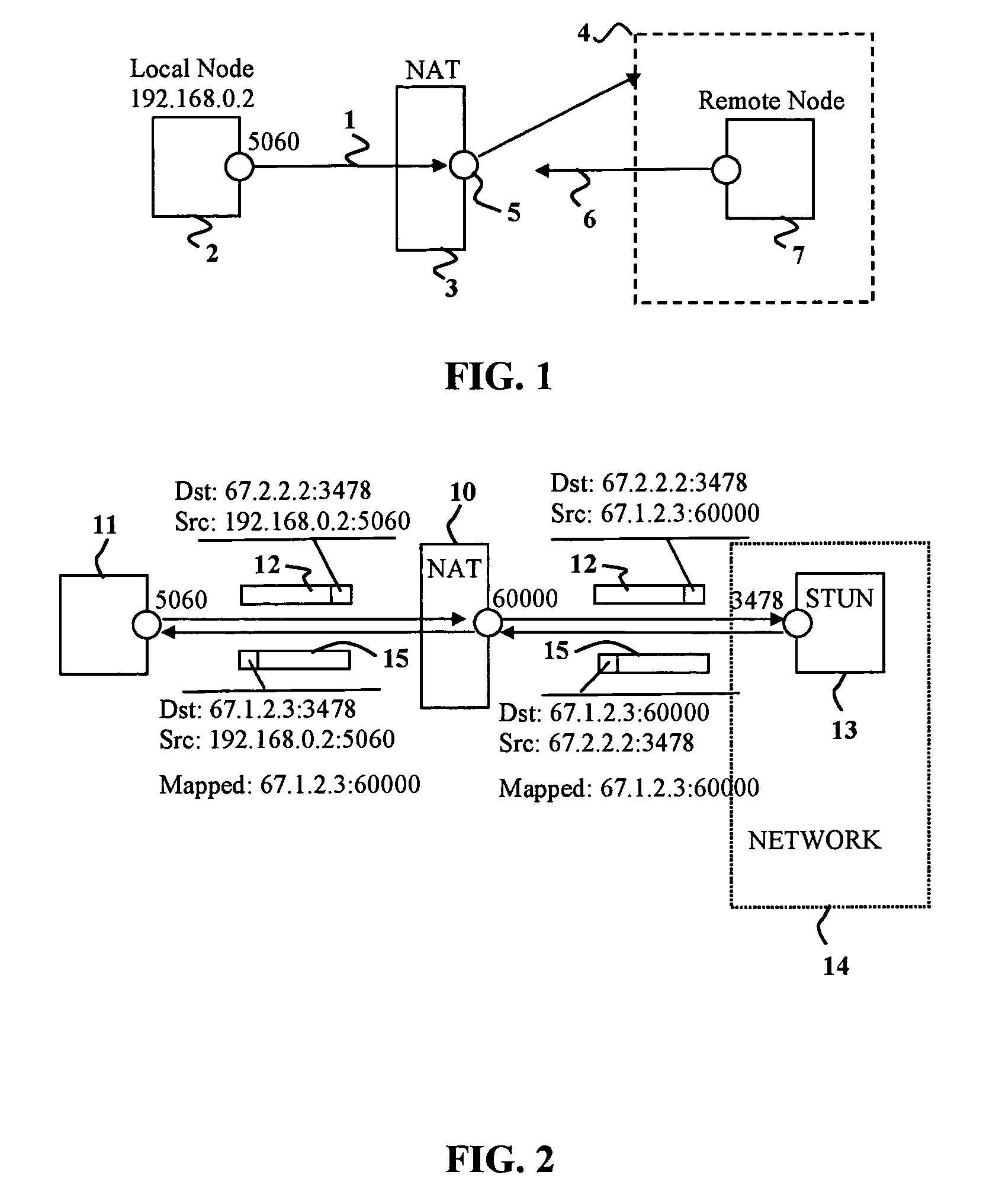
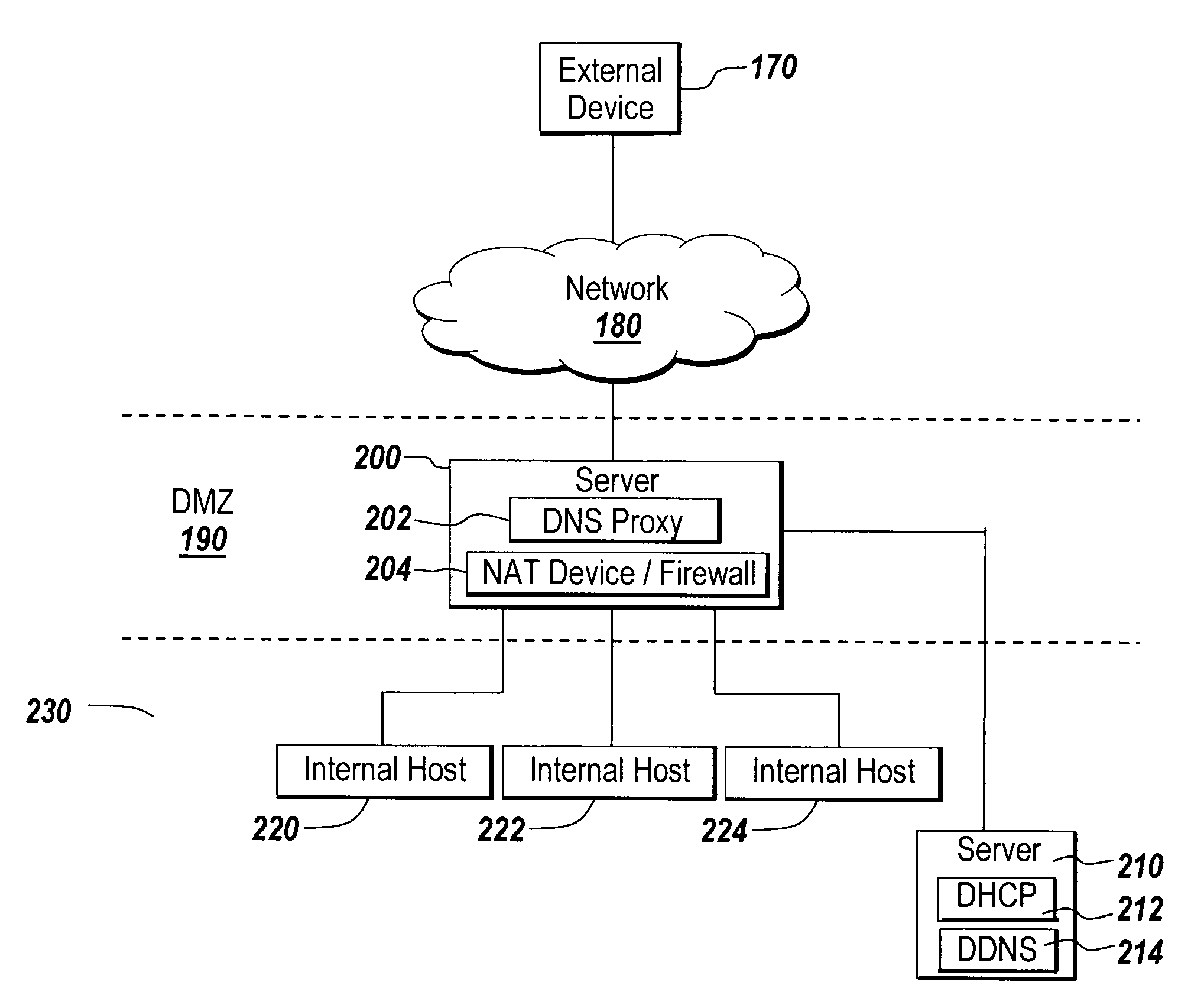
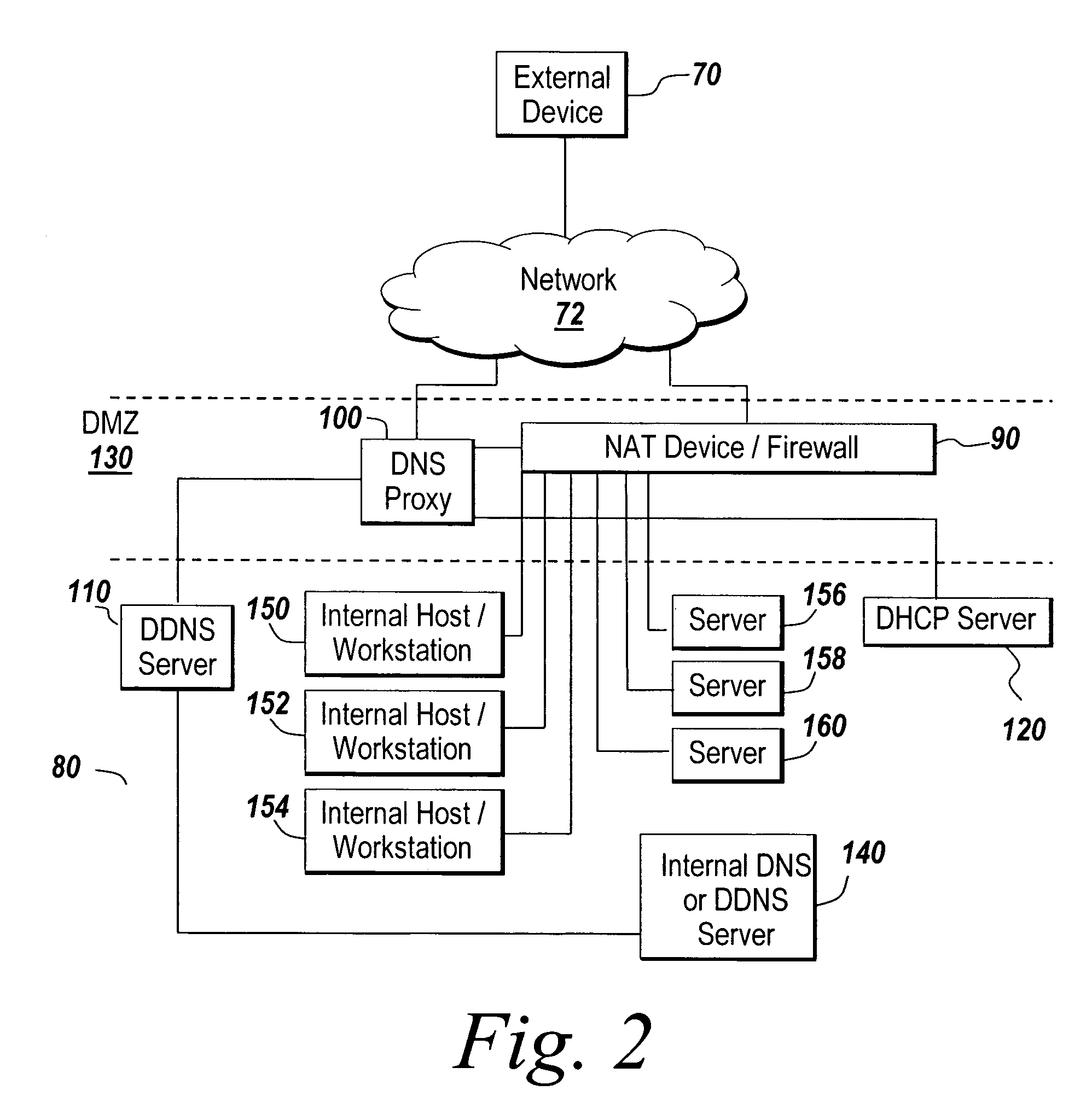
System and method for increasing host visibility in network address translation environments
ActiveUS7684394B1Data switching by path configurationMultiple digital computer combinationsVisibilityDomain name
A mechanism for dynamically performing Network Address Translation that allows external devices to contact internal host systems that would otherwise be hidden behind a NAT device is discussed. The dynamic NAT mechanism of the present invention maps internal host system addresses to external network addresses and reconfigures the NAT configuration of the network firewall to account for the new mapping on demand. Domain Name Service (DNS) lookup requests for an authorized internal system serve as a trigger to create a new mapping between the internal host system and the external network address. The new mappings may have a lifecycle controlled by dynamic leases that are created for each new mapping.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
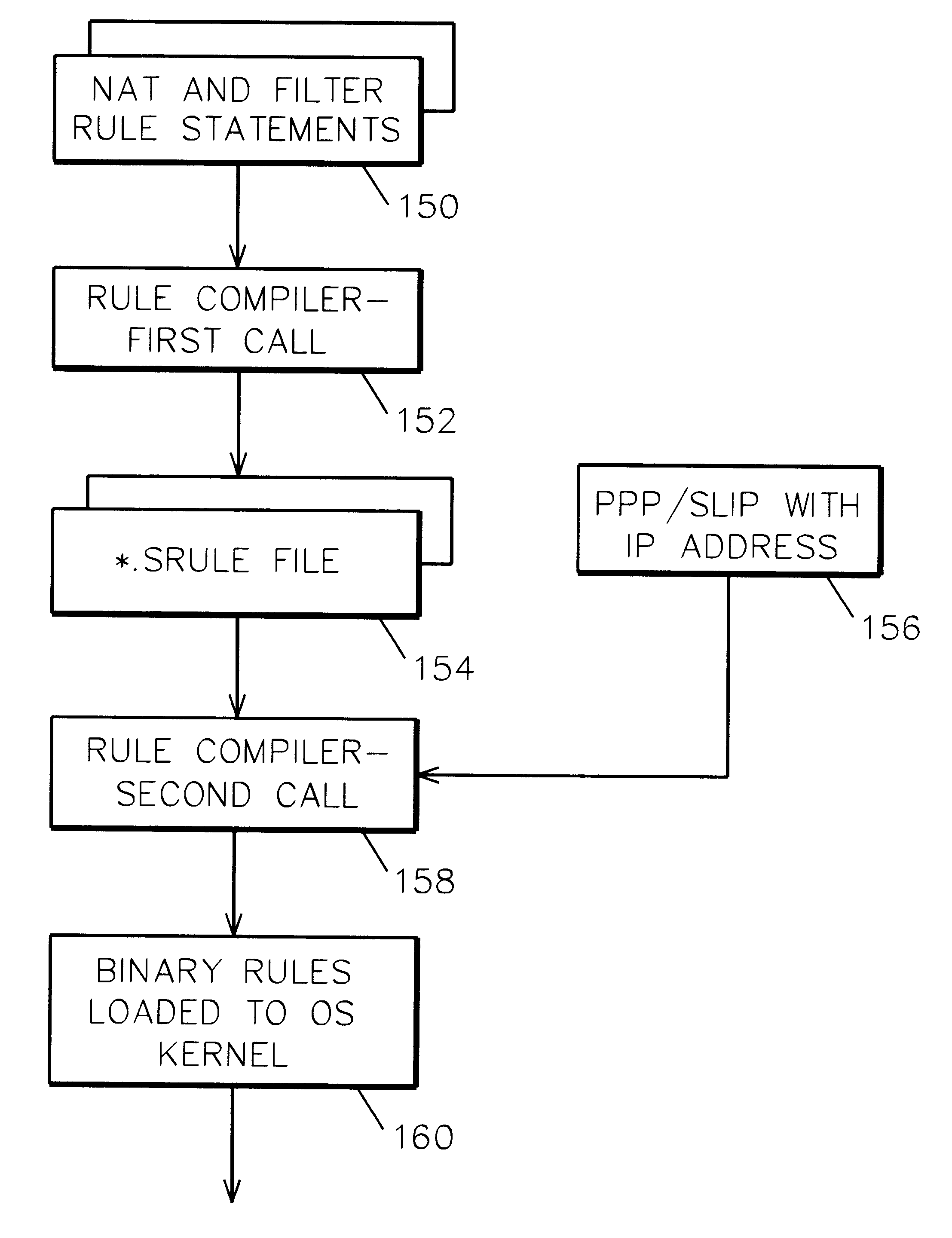
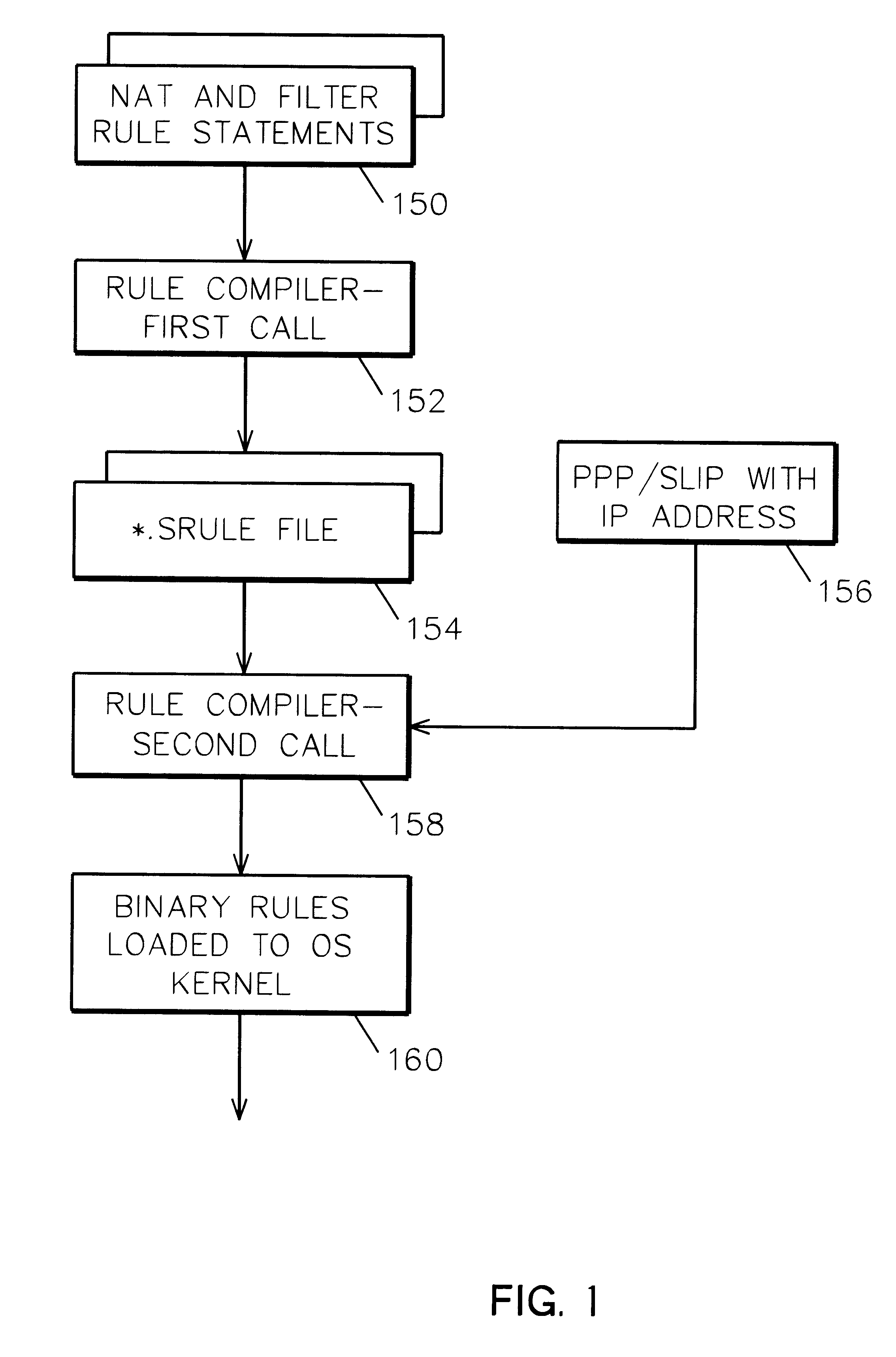
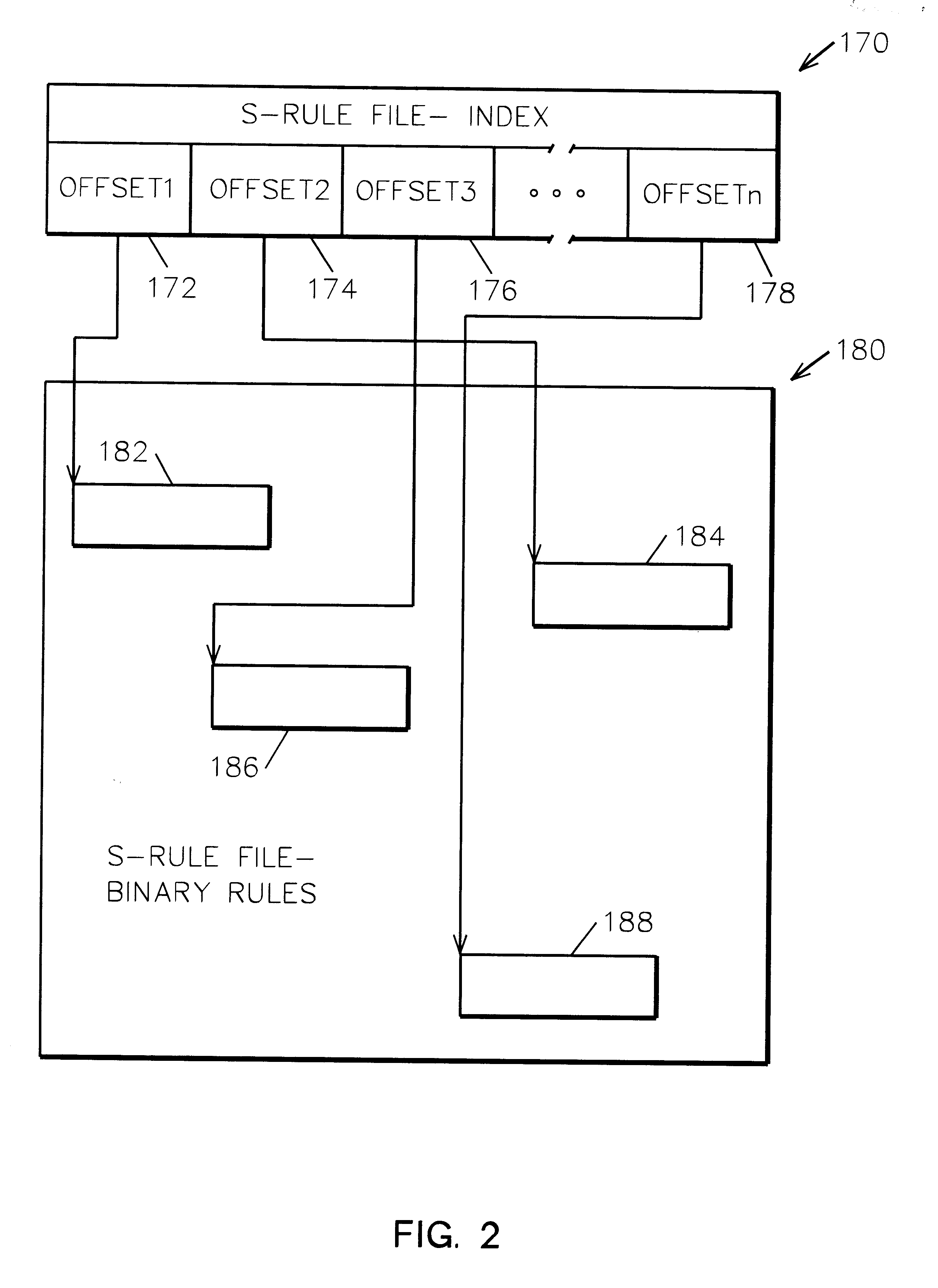
System and method for IP network address translation and IP filtering with dynamic address resolution
InactiveUS6266707B1Simple methodData switching by path configurationMultiple digital computer combinationsAddress resolutionIp address
IP network address translation (NAT) and IP filtering with dynamic address resolution in an Internet gateway system. Symbolic interface names are recognized in selected rule statements. An symbolic s-rule file is generated from these rule statements which includes symbolic interface names. During processing of a packet message, the s-rule file corresponding to the interface name in the packet message is processed, with symbolic addresses in the s-rule file resolved to the IP addresses obtained from the packet message.
Owner:IBM CORP
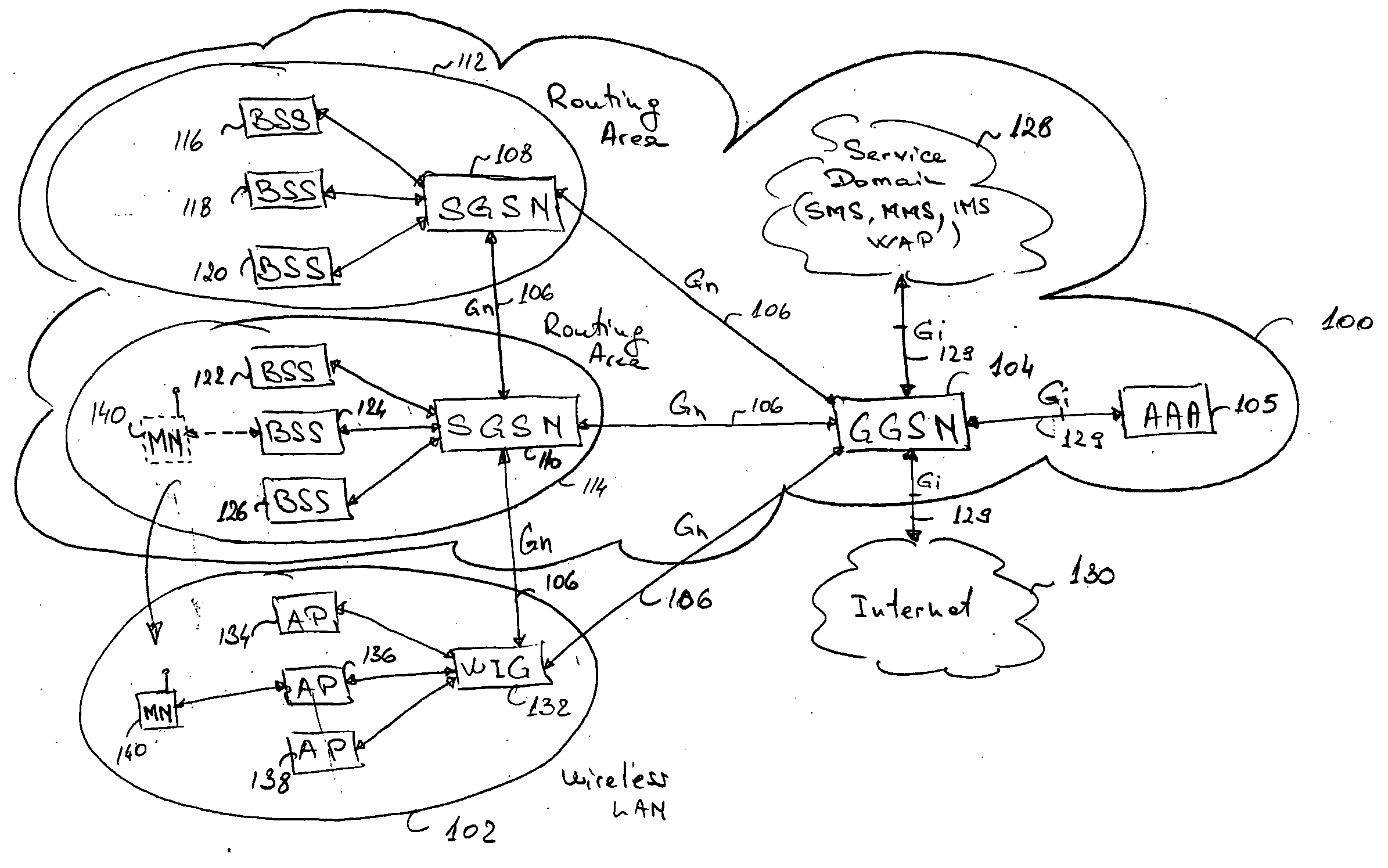
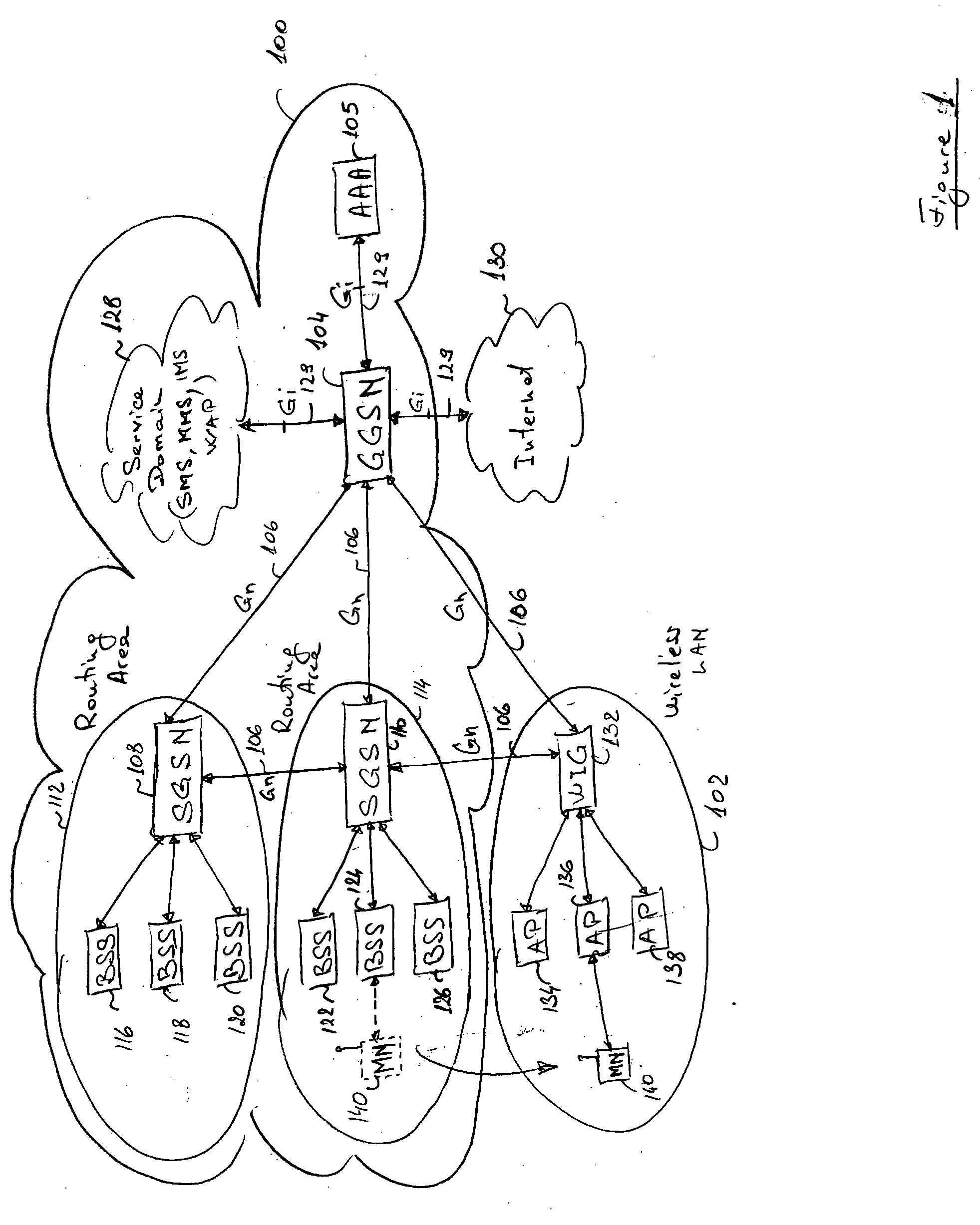
Seamless hand-off of mobile node to a wireless local area network (WLAN)
InactiveUS20050025164A1Data switching by path configurationWireless communicationTraffic capacityIp address
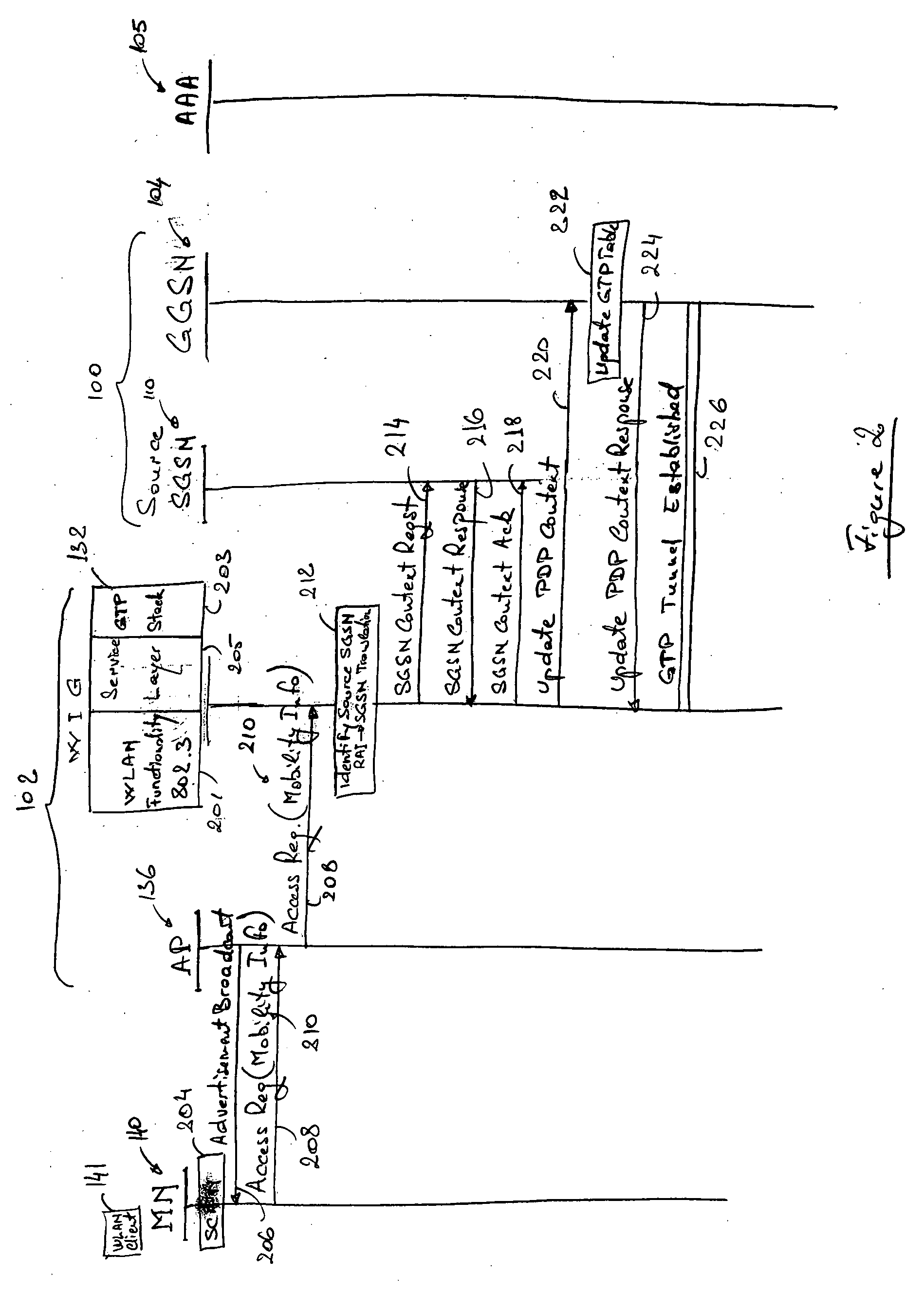
A method and system for seamlessly handing off a Mobile Node (MN) equipped with a Wireless Local Area Network (WLAN) adaptor from a cellular network such as a GRPS / UMTS network to a WLAN network without interrupting the ongoing IP connection / session. When entering a WLAN coverage area, the roaming MN sends mobility information to a WLAN Integration Gateway (WIG) node allowing the WIG node to identify the source Service GPRS Support Node (SGSN). The WIG node contacts the source SGSN to obtain PDP Context information relative to the roaming MN, and establishes a new GTP tunnel with the servicing GGSN in order to complete the handoff. The WIG node may route data traffic for the MN by assigning a new IP address to the MN and by either performing IP-in-IP encapsulation or Network Address Translation (NAT).
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Method and system for implementing and managing a multimedia access network device
ActiveUS7274684B2Telephonic communicationMultiple digital computer combinationsNetwork address translationAuthentication
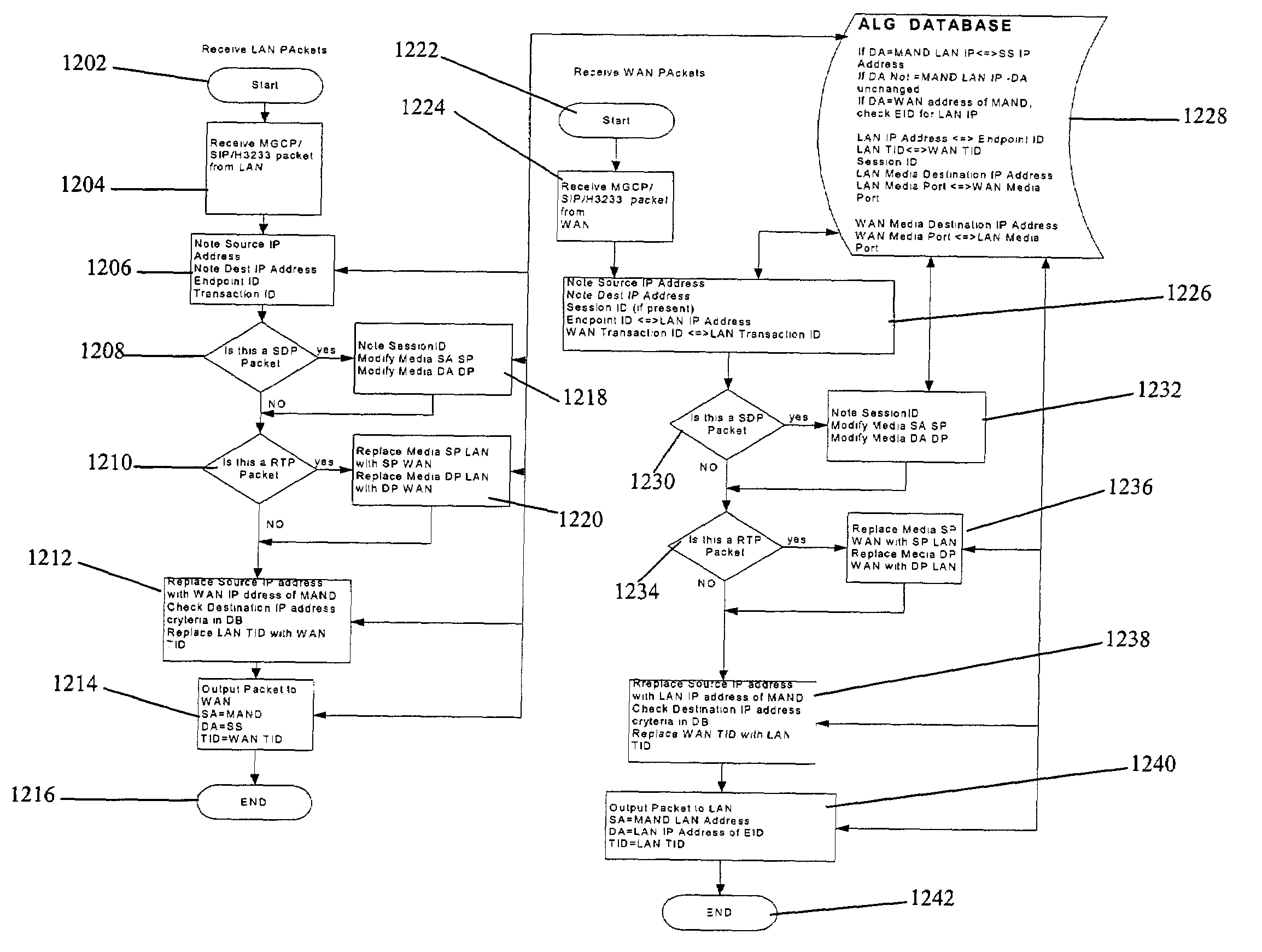
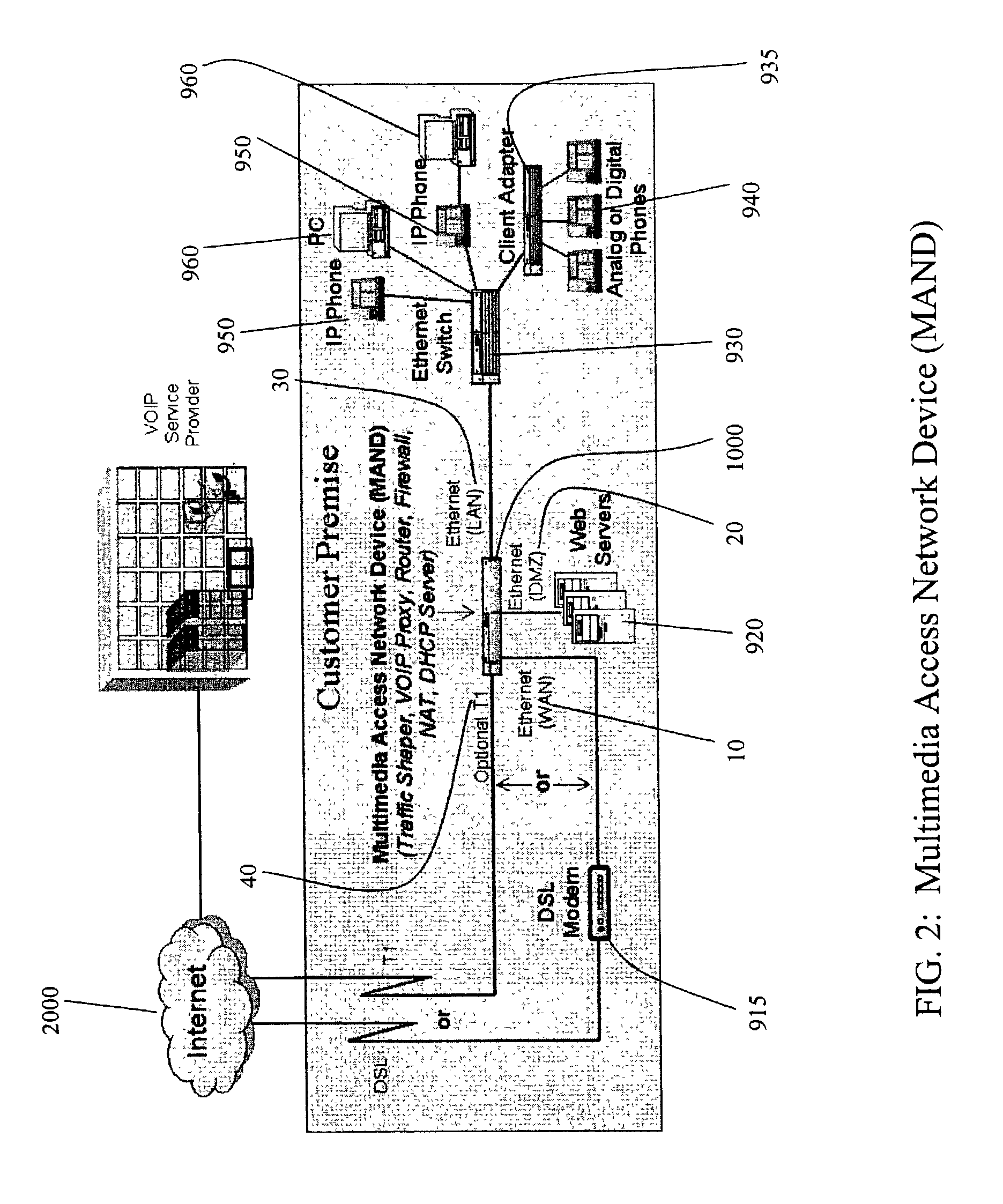
In a complete network-in-a-box system acting as an enterprise network demarcation point, packets such as voice, video and data packets, are routed over common network connections, such as LAN and WAN. The packets are mapped from a public address field (such as an IP address) and port number to a private address field and port number, the mapping process typically being handled by a NAT (Network Address Translation). The packets are also prioritized, by marking the packets for priority queuing and routing, and configuring the bandwidths of the WAN traffic and the voice traffic to predetermined quantities and configuring the address fields of the voice devices. Simultaneous transmission of the various packets can be limited to predetermined quantities, typically by utilizing a CAC (Client Access Control). Secure firewalls are also included as well as a performance test client application that provides a defined workload generated across the WAN interface for capacity planning measurements and allows remote monitoring of the QoS (Quality of Service) data, such as latency, jitter, lost packets and MOS scores. Optionally, a simple, common remote management interface is included, allowing service providers to configure, upgrade and manage the system. Additionally, address fields can be provided to voice, video or data devices attached to a LAN port. VPN authentication and encrypted sessions can be tunneled through the firewall for access to an internal network by using a VPN terminator. For power outages and other emergency purposes, additional ports that connect to PSTN (Public Switched Telephone Network) analog telephone lines as well as other analog telephones or devices, can be provided. Another advantageous element is that most of the above components or features may be enabled or disabled.
Owner:EDGEWATER NETWORKS
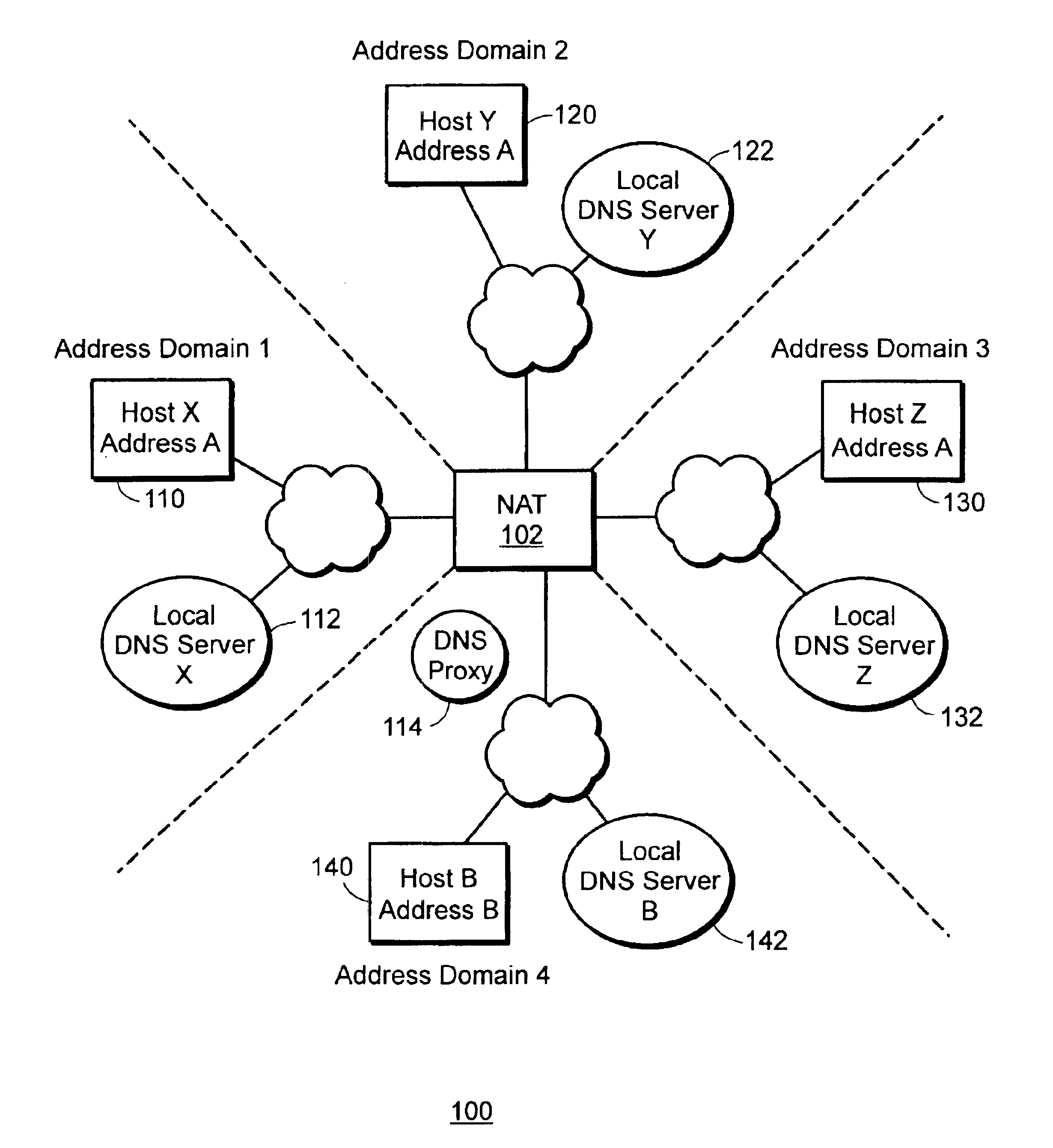
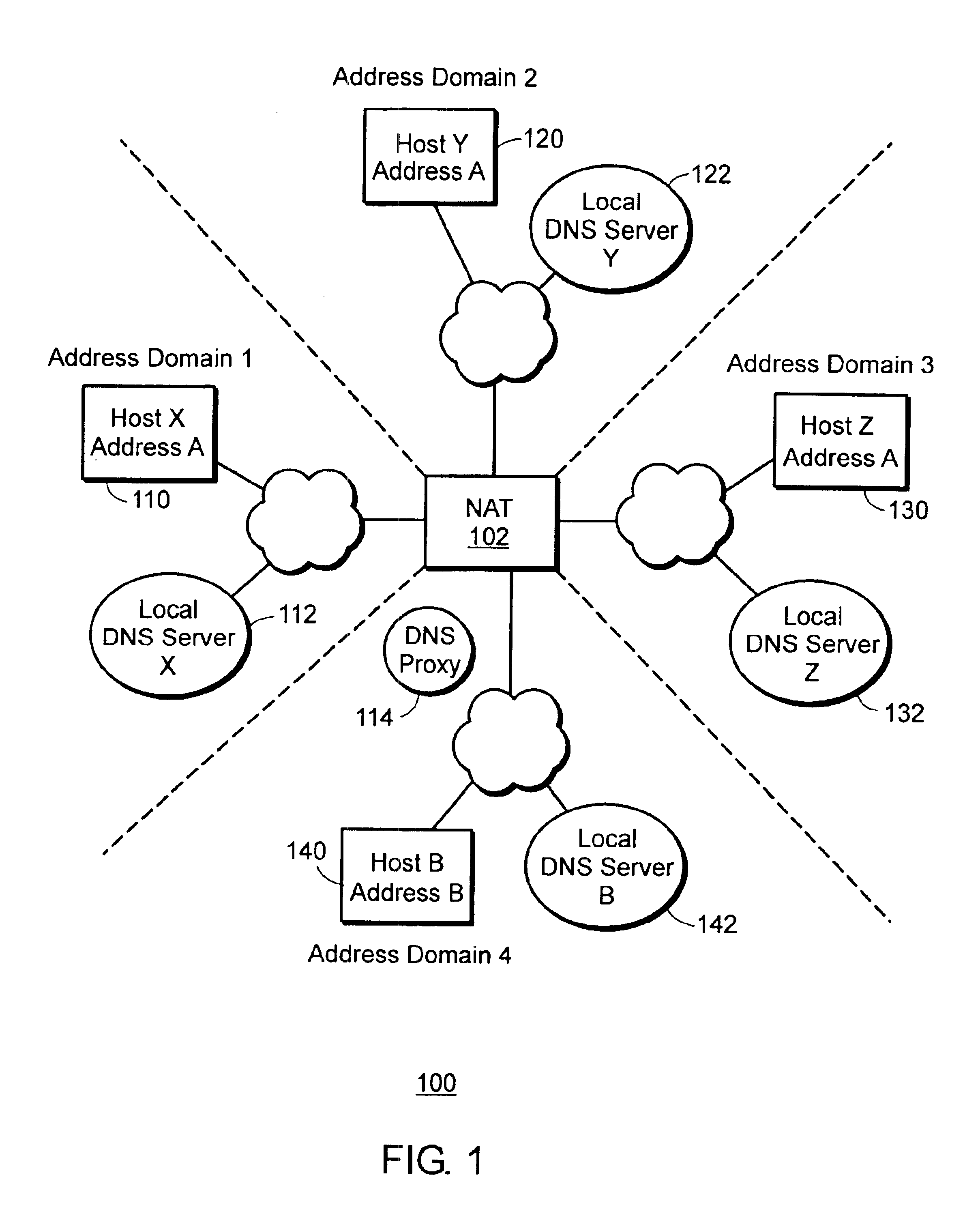
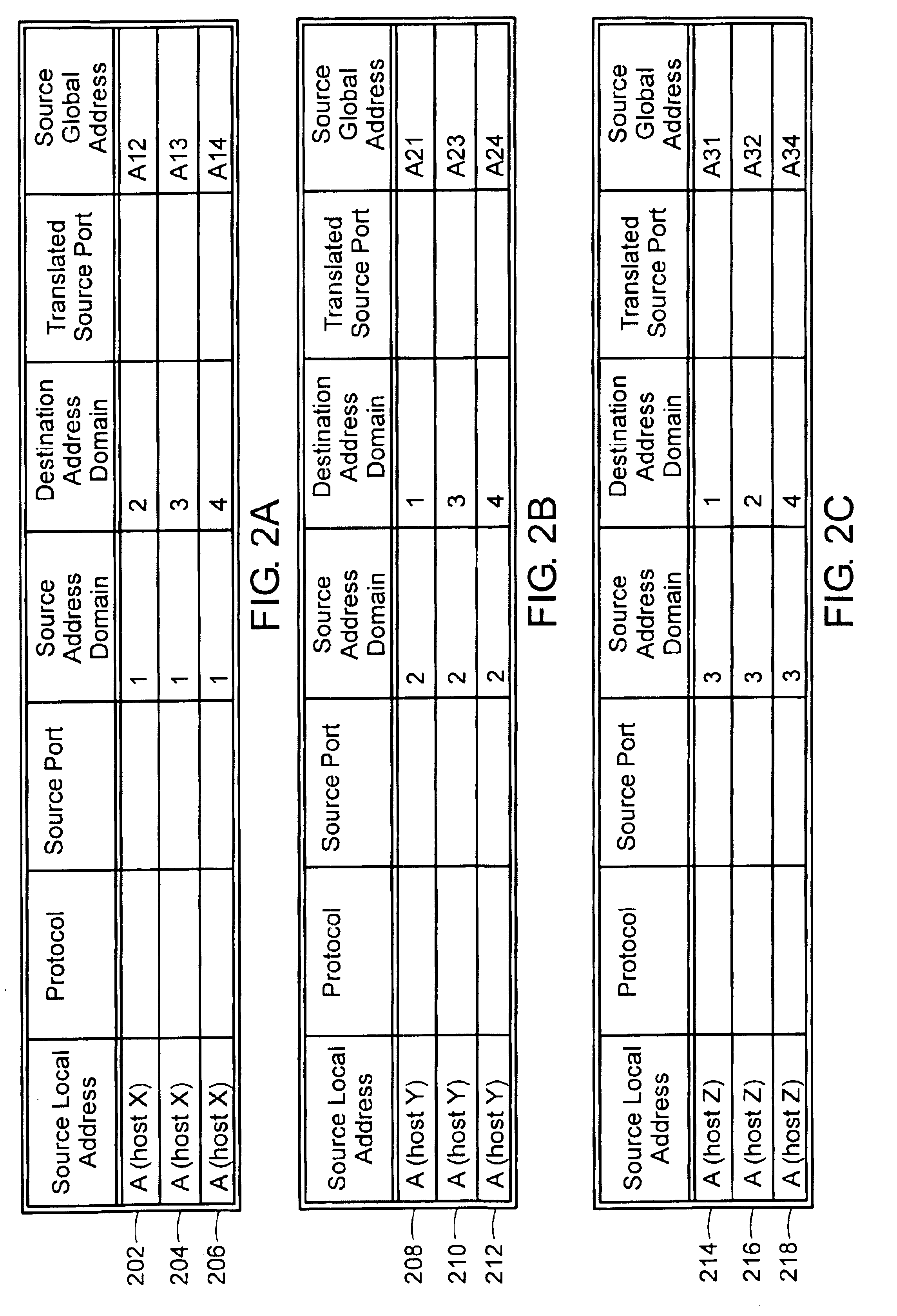
Management information base for a multi-domain network address translator
InactiveUS6892245B1Interconnection arrangementsMultiple digital computer combinationsManagement information baseInformation repository
A management information base (MIB) for a multi-domain network address translator provides management objects for configuring and controlling the multi-domain network address translator. The MIB includes management objects for defining a domain-specific source address filter range, which is a range of addresses used to detect domain-specific packets that require domain-specific network address translation forwarding. The domain-specific source address filter management objects include a beginning address, a prefix length, a domain indicator, and a domain-specific translation pool indicator. The MIB also includes management objects for defining a domain-specific translation pool, which is a range of addresses from which domain-specific translation addresses are selected for domain-specific network address translation forwarding. The domain-specific translation pool management objects include a beginning address, a prefix length, and a domain indicator.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
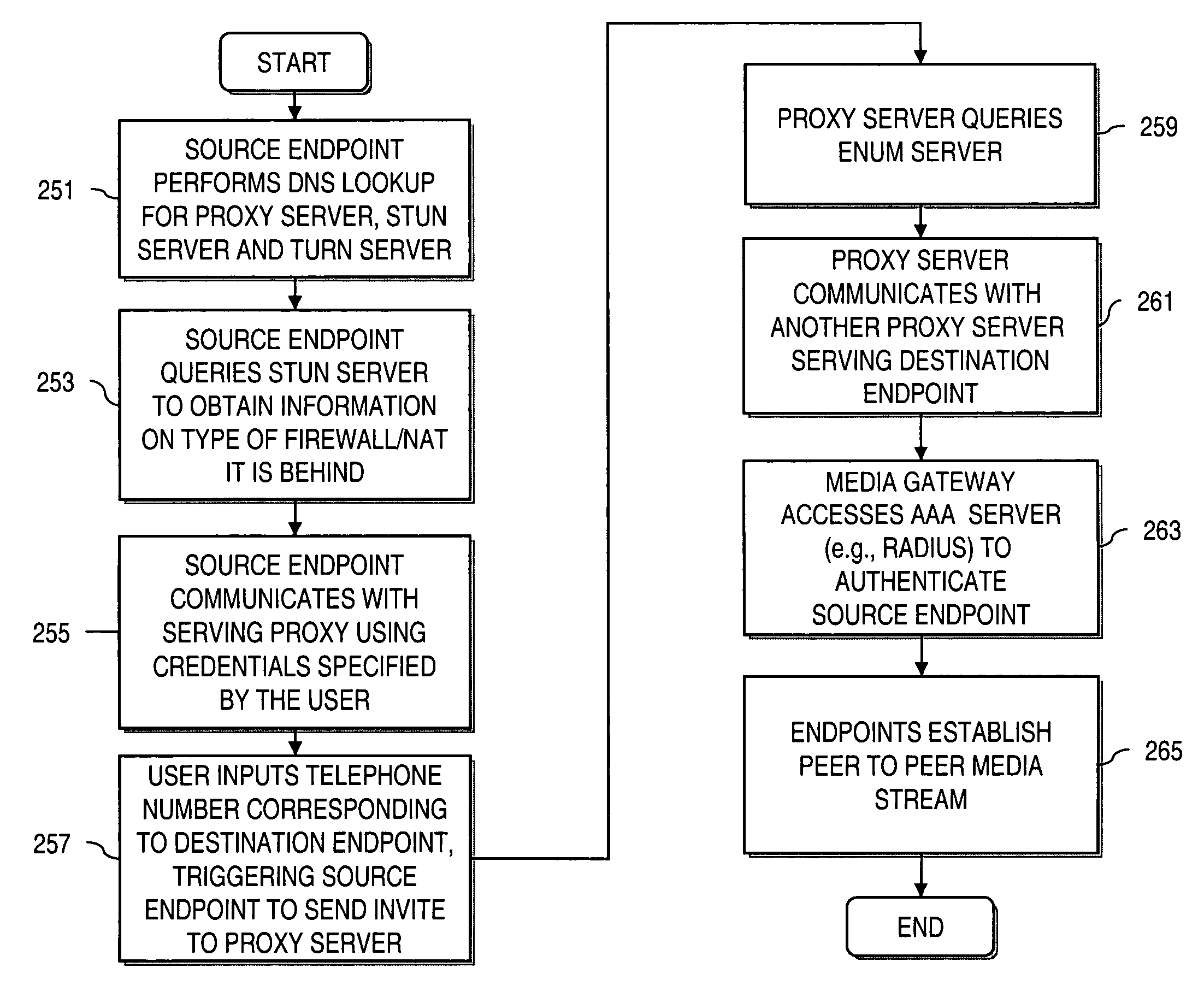
Method and system for providing interdomain traversal in support of packetized voice transmissions
ActiveUS20060209794A1Interconnection arrangementsTime-division multiplexNetwork addressingNetwork address translation
An approach provides interdomain traversal to support packetized voice transmissions. A request for establishing a voice call is received from a source endpoint behind a first network address translator of a first domain, wherein the request specifies a directory number of a destination endpoint within a second domain. A network address is determined for communicating with the destination endpoint based on the directory number. Additionally, existence of a second network address translator within the second domain is determined. If the network address can be determined, a media path is established between the source endpoint and the destination endpoint based on the network address to support the voice call.
Owner:VERIZON PATENT & LICENSING INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com