Patents
Literature
171 results about "Voice over packet" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
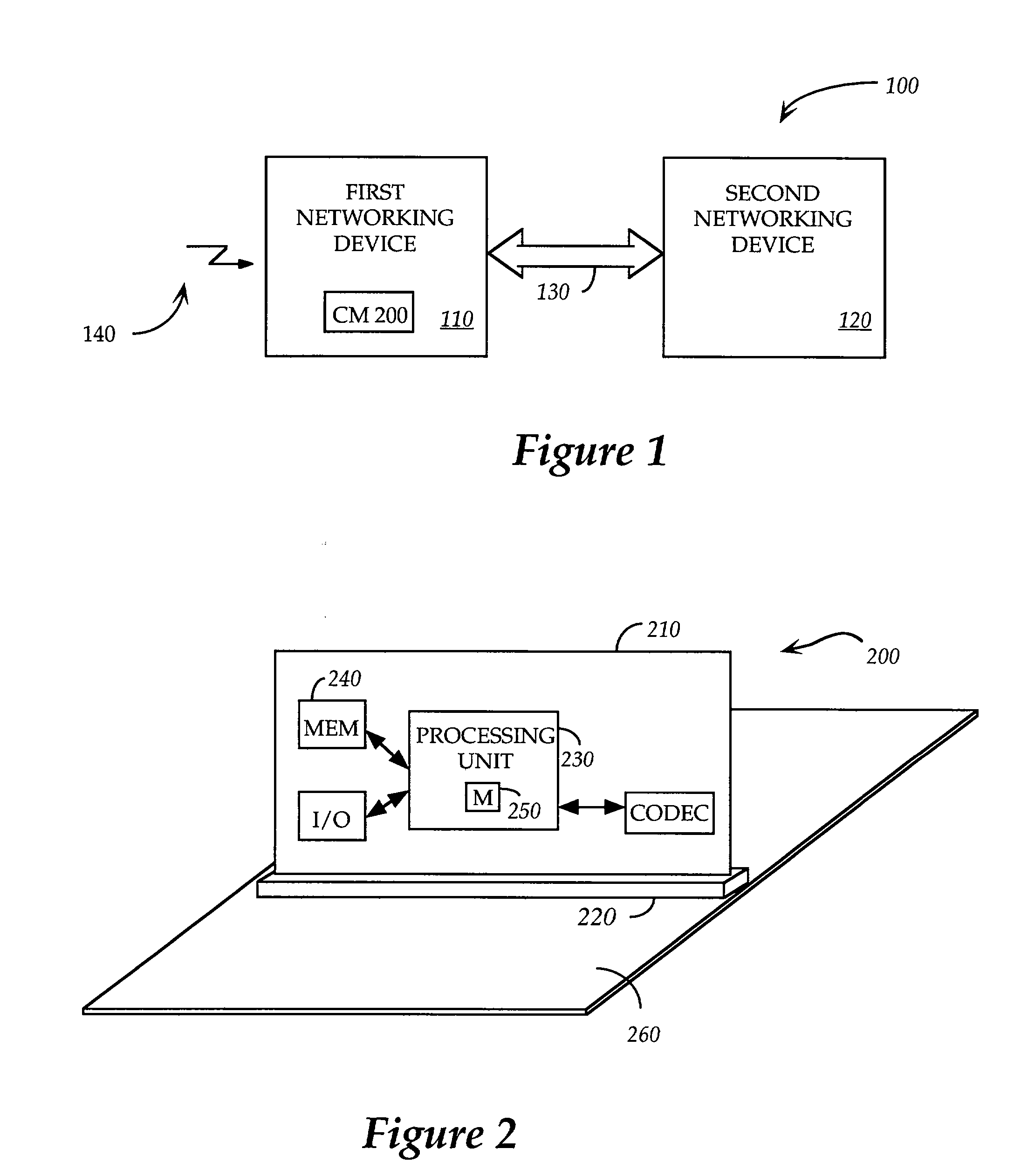
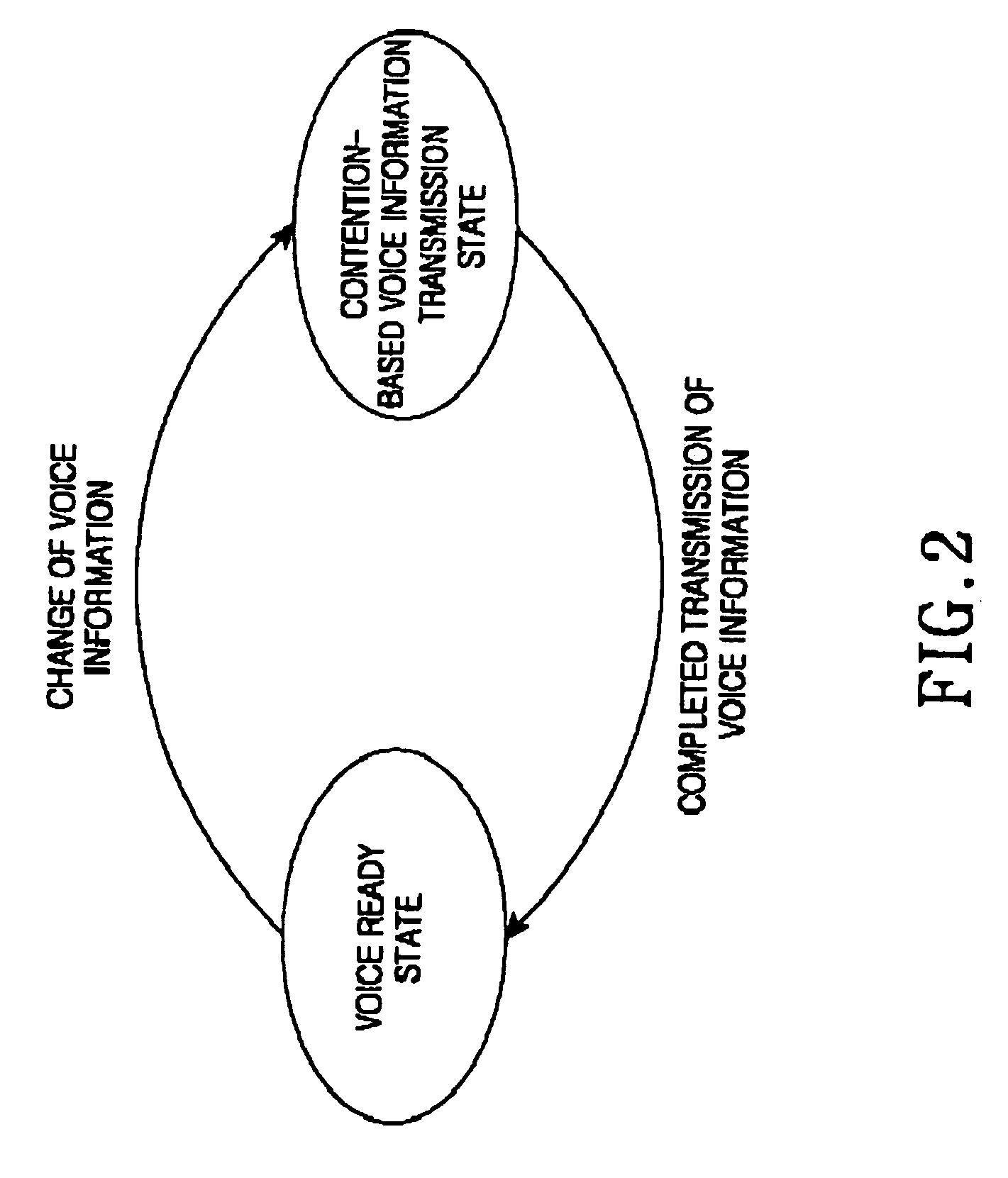
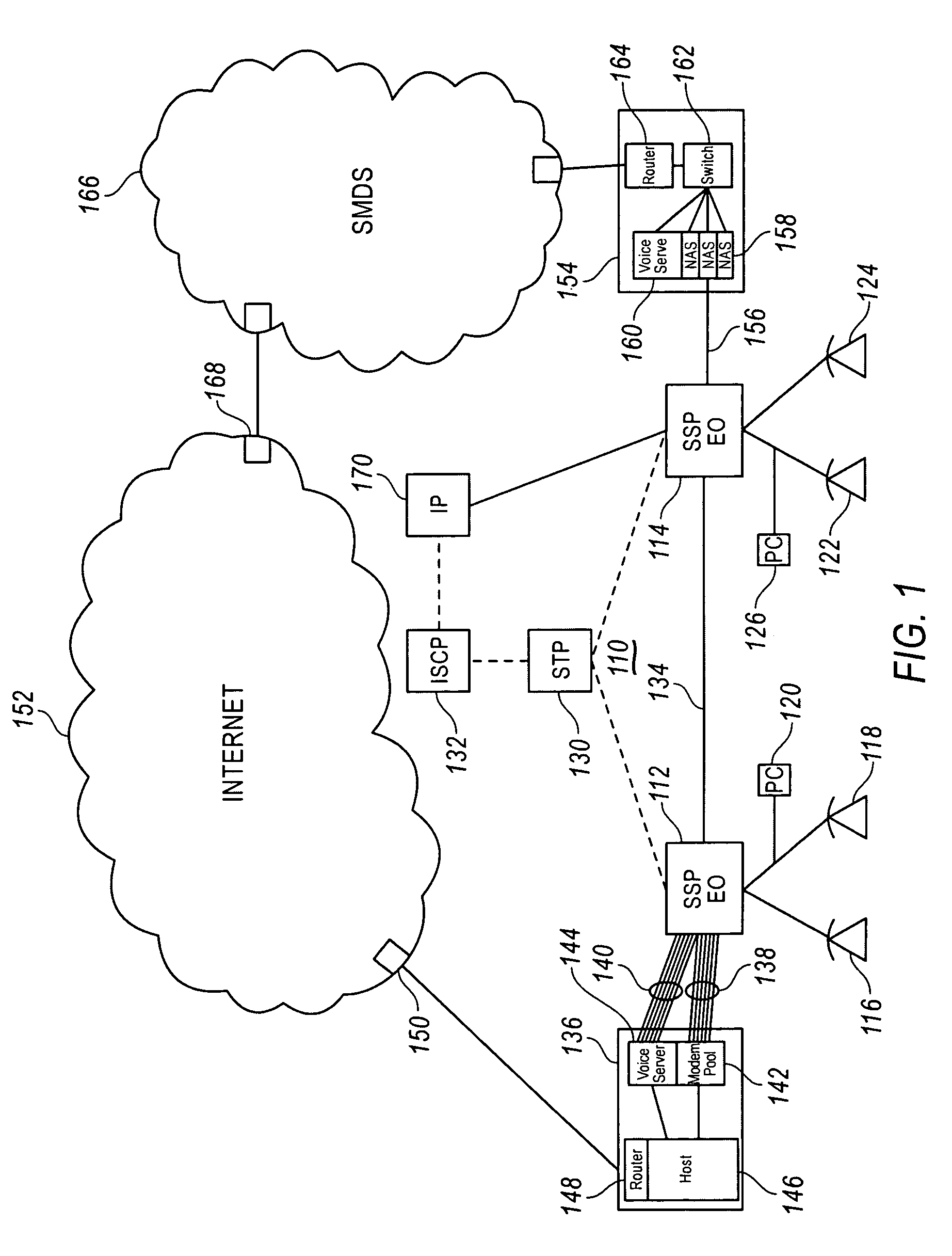
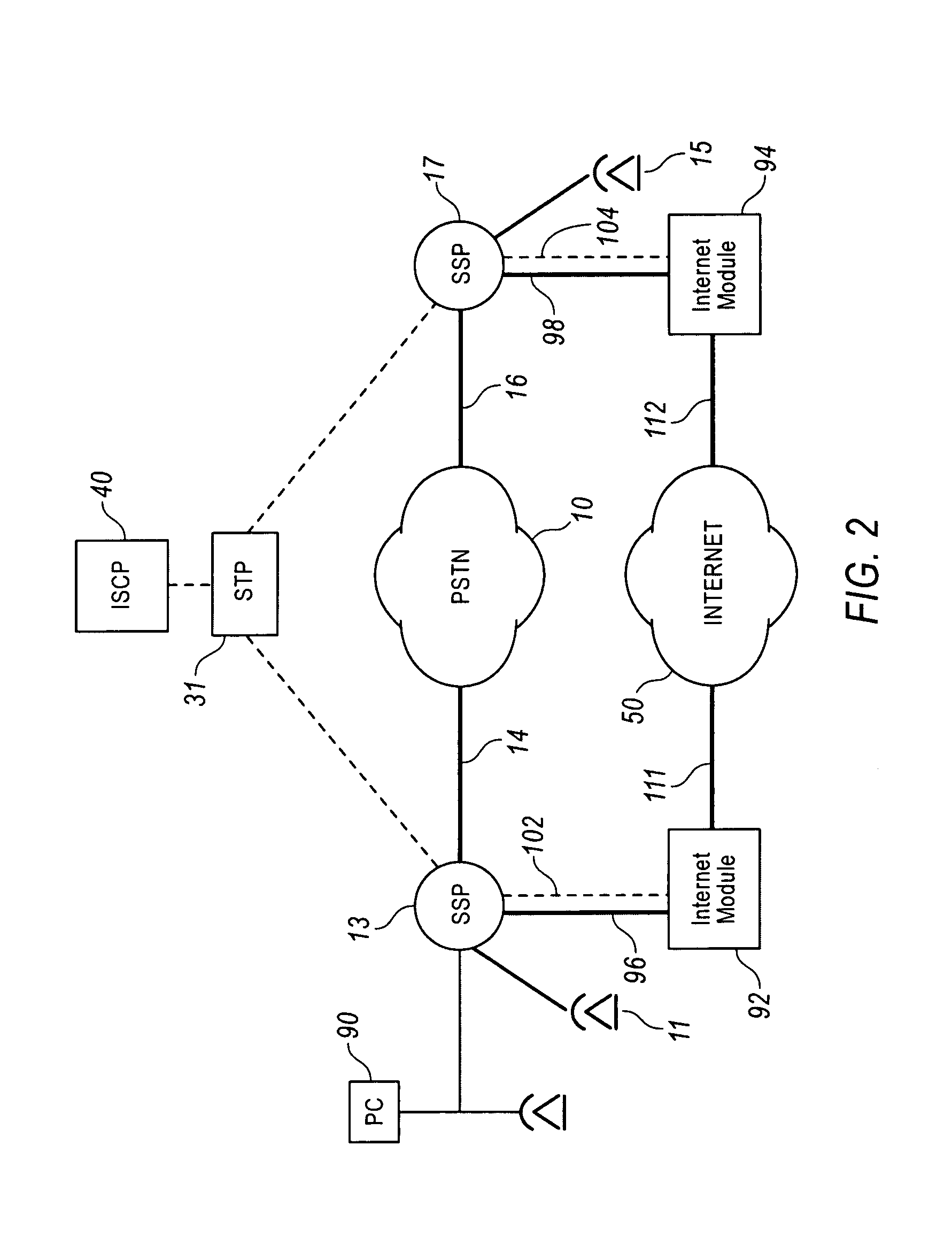
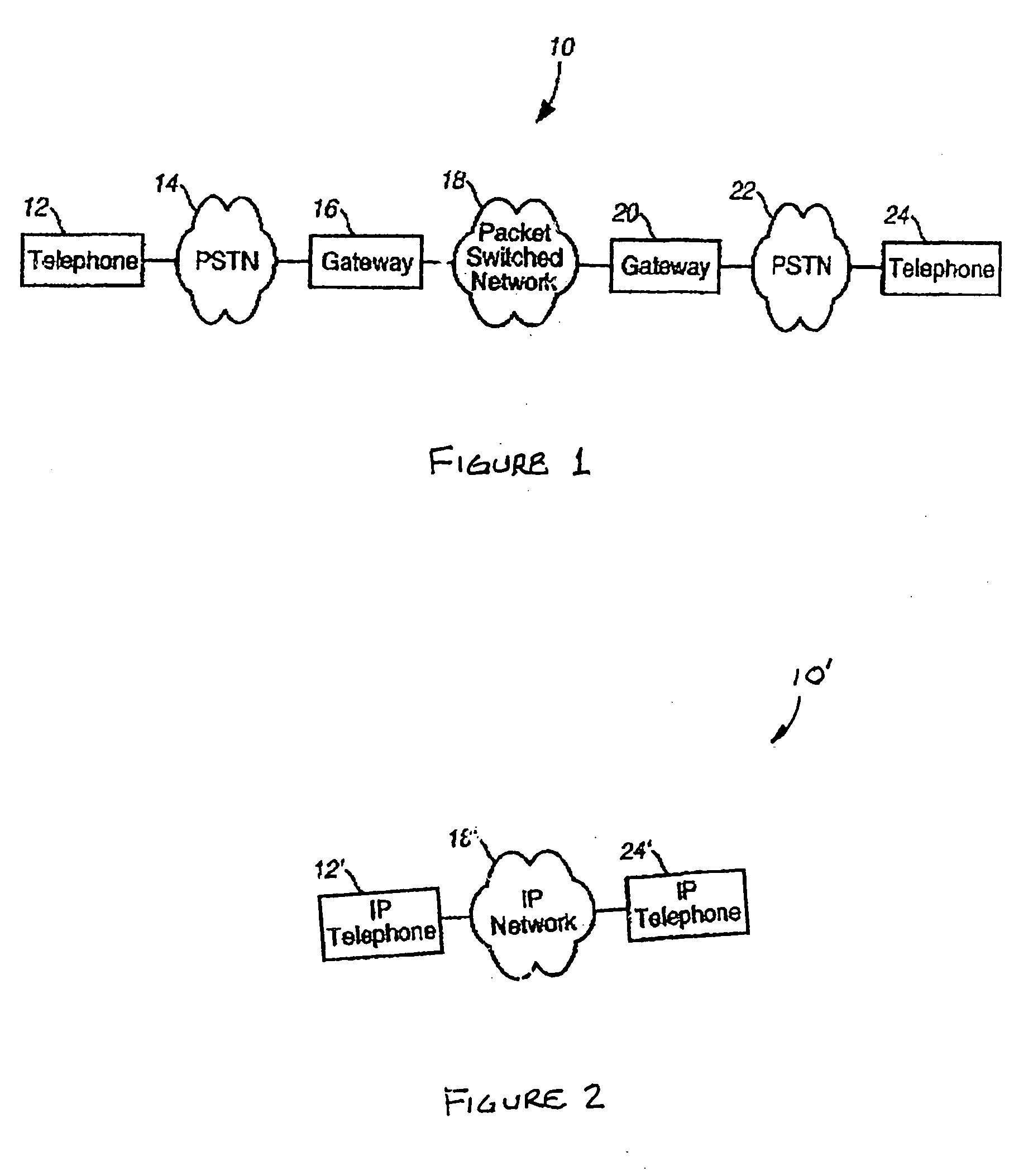
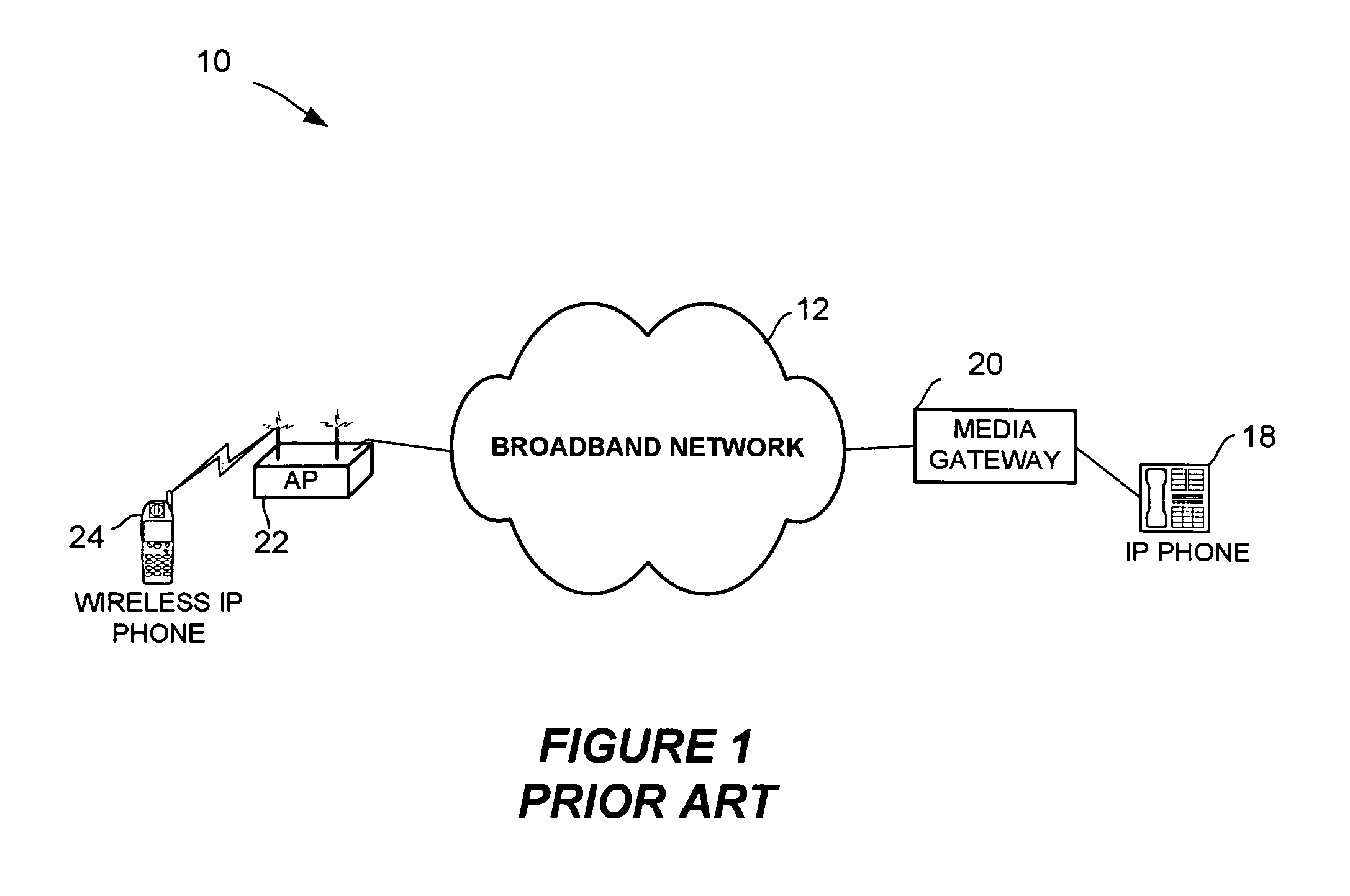
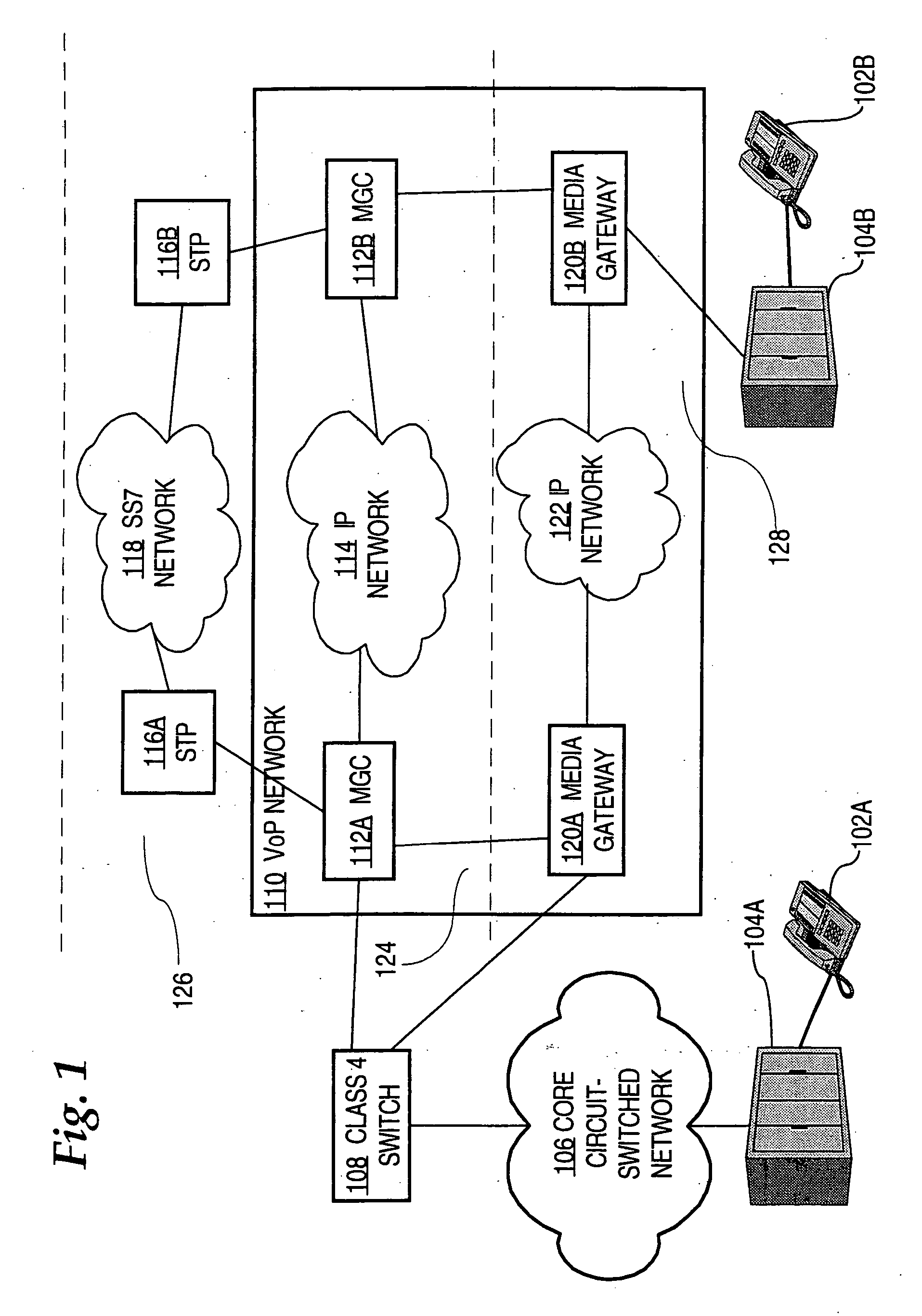
A Voice over Packet (VOP) application meets the challenges of combining legacy voice networks and packet networks by allowing both voice and signaling information to be transported over the packet network.
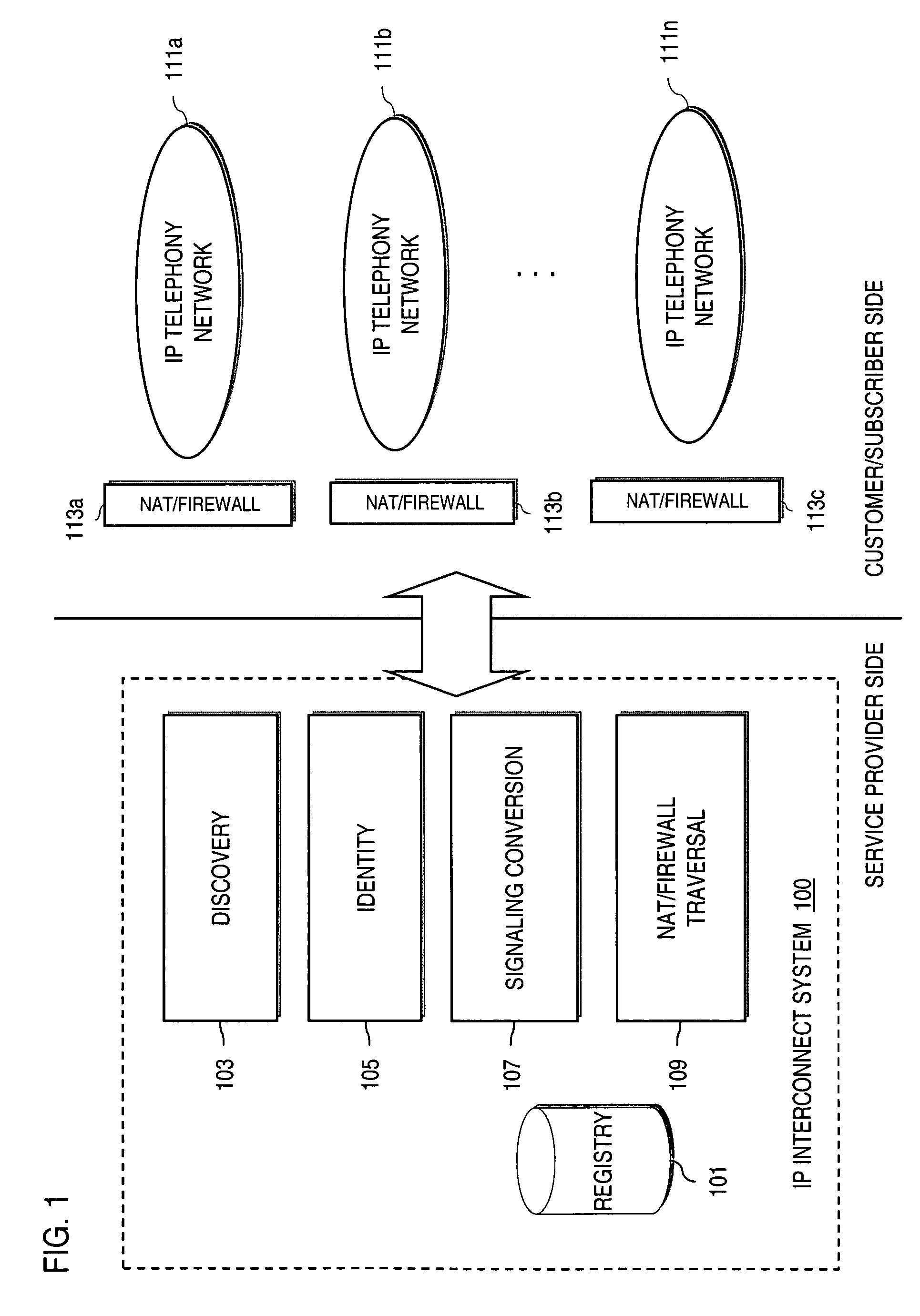
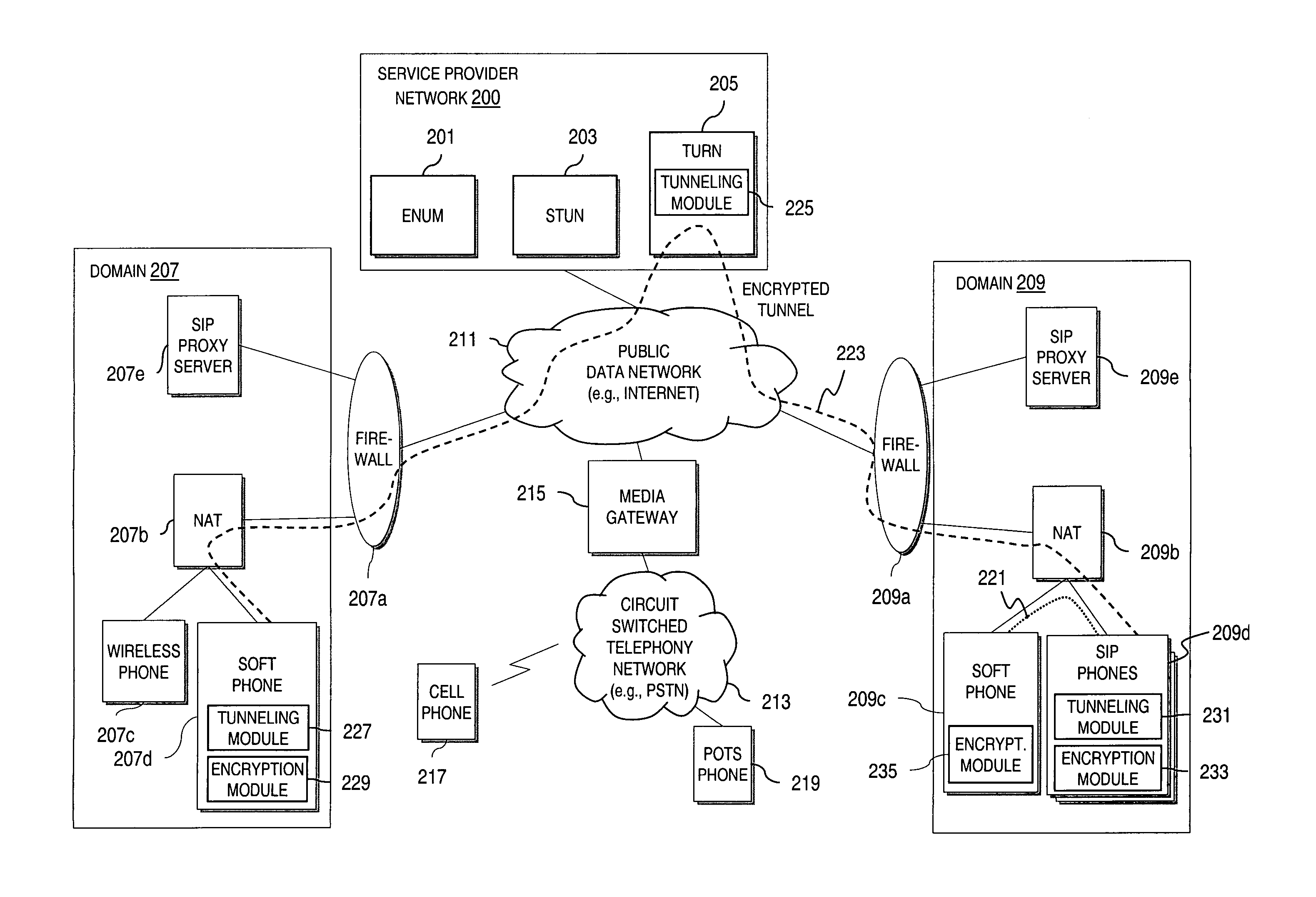
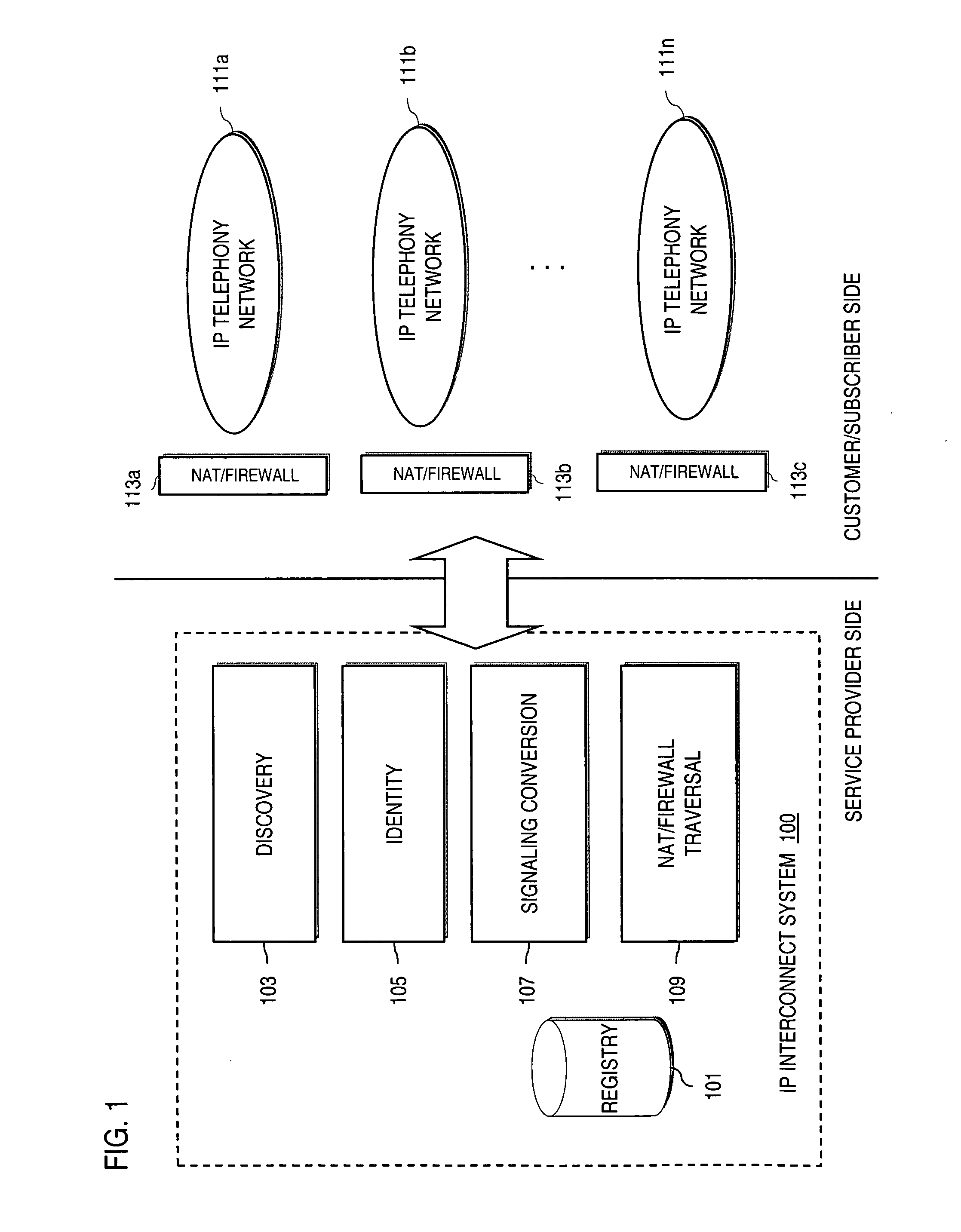
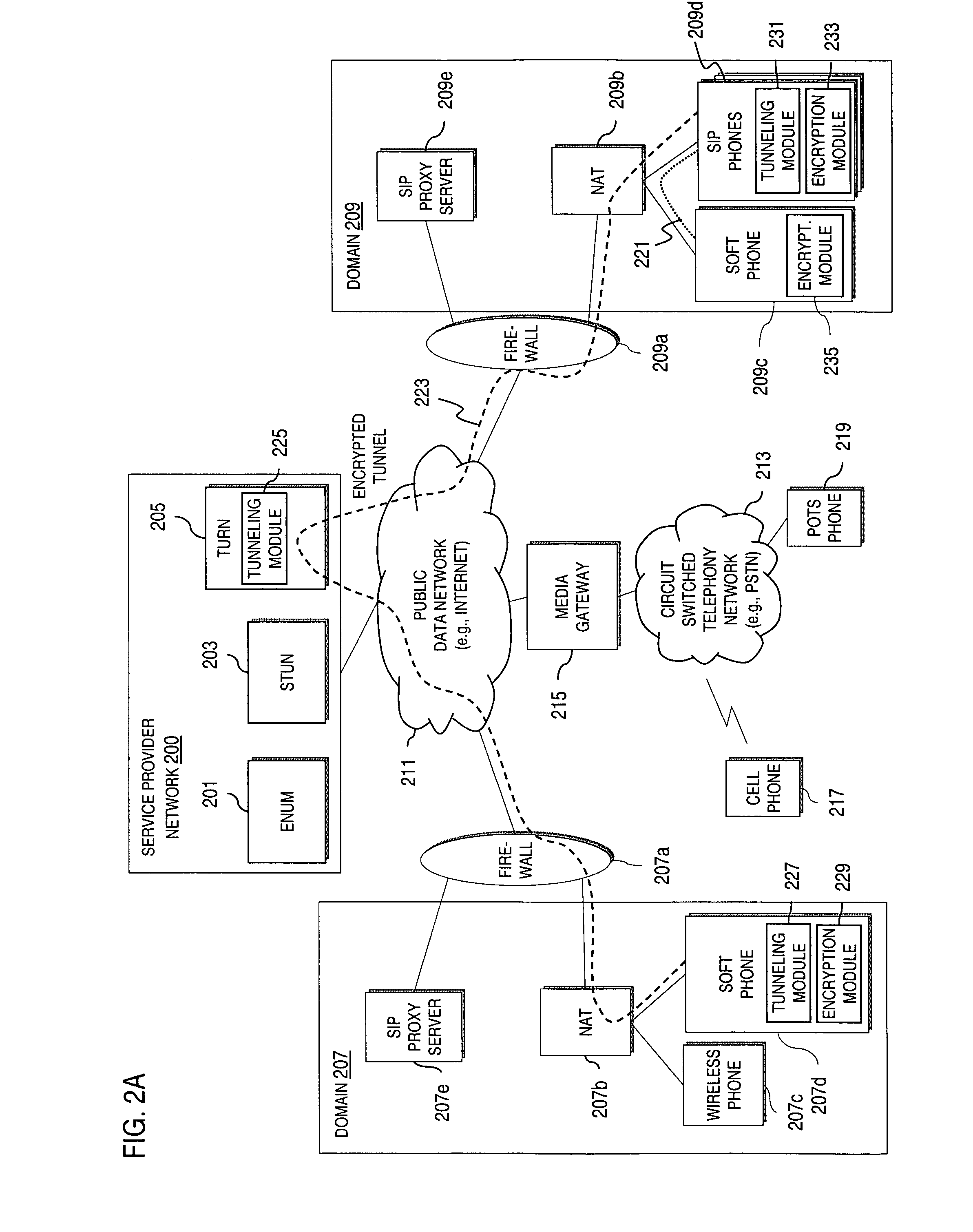
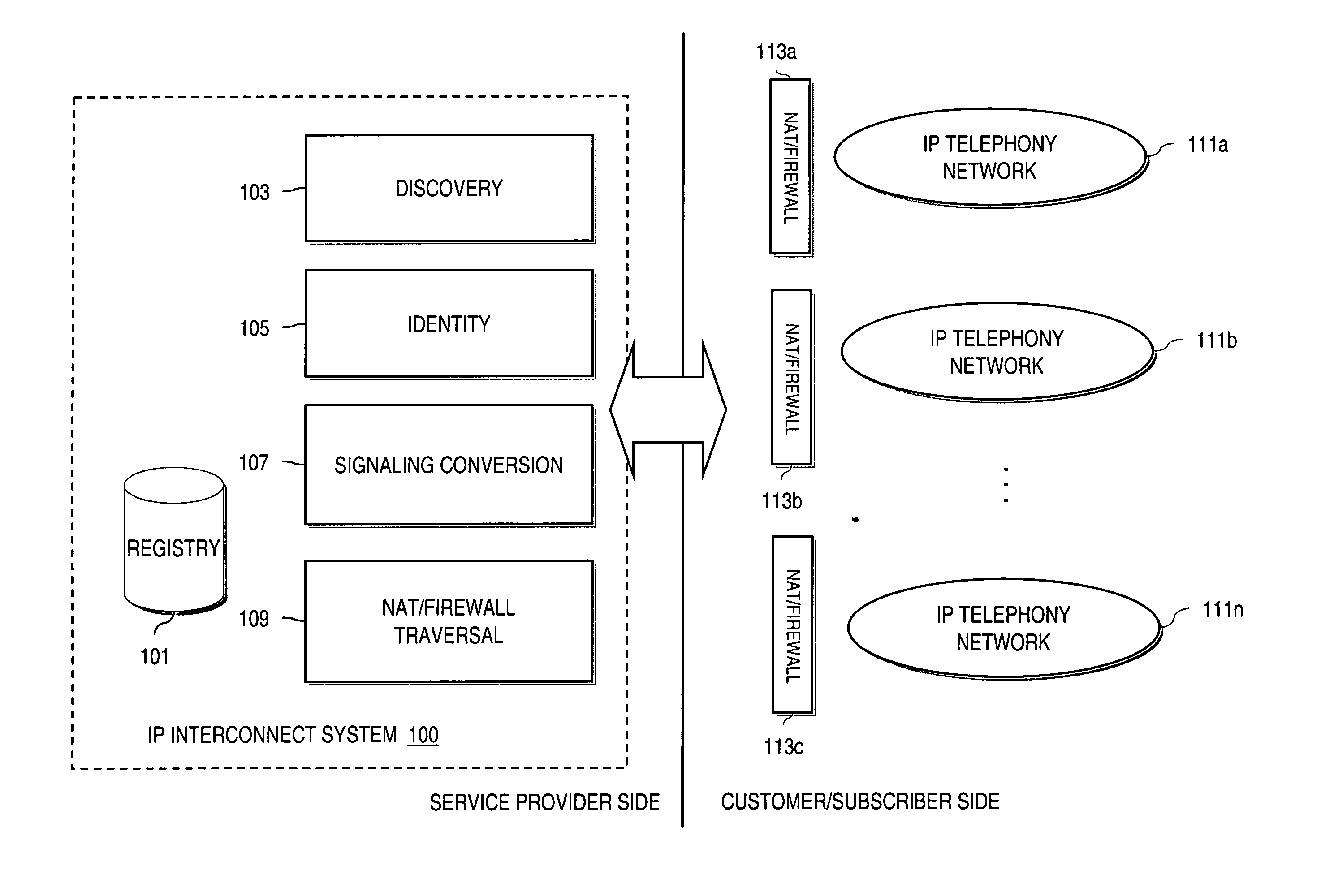
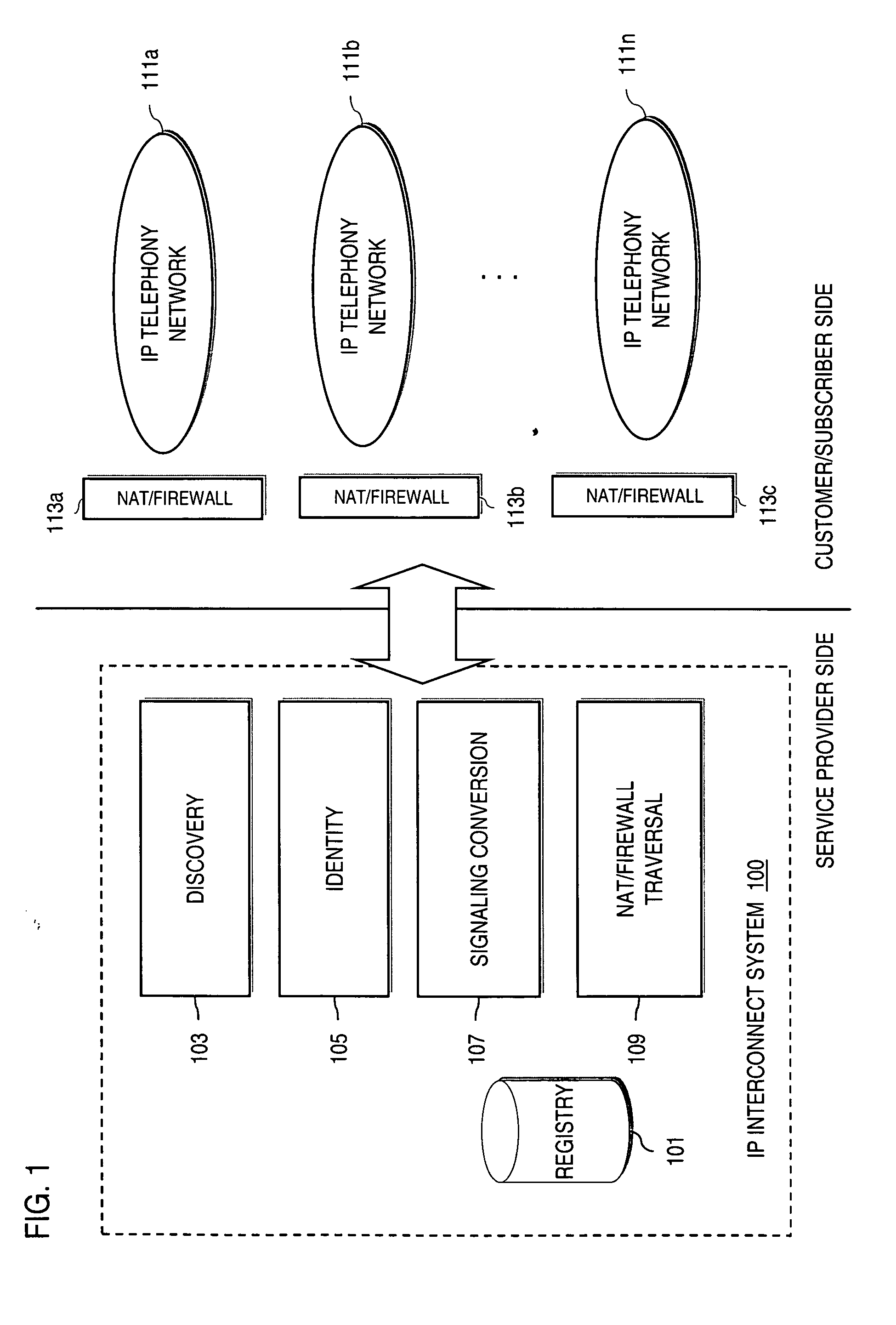
Method and system for providing secure credential storage to support interdomain traversal
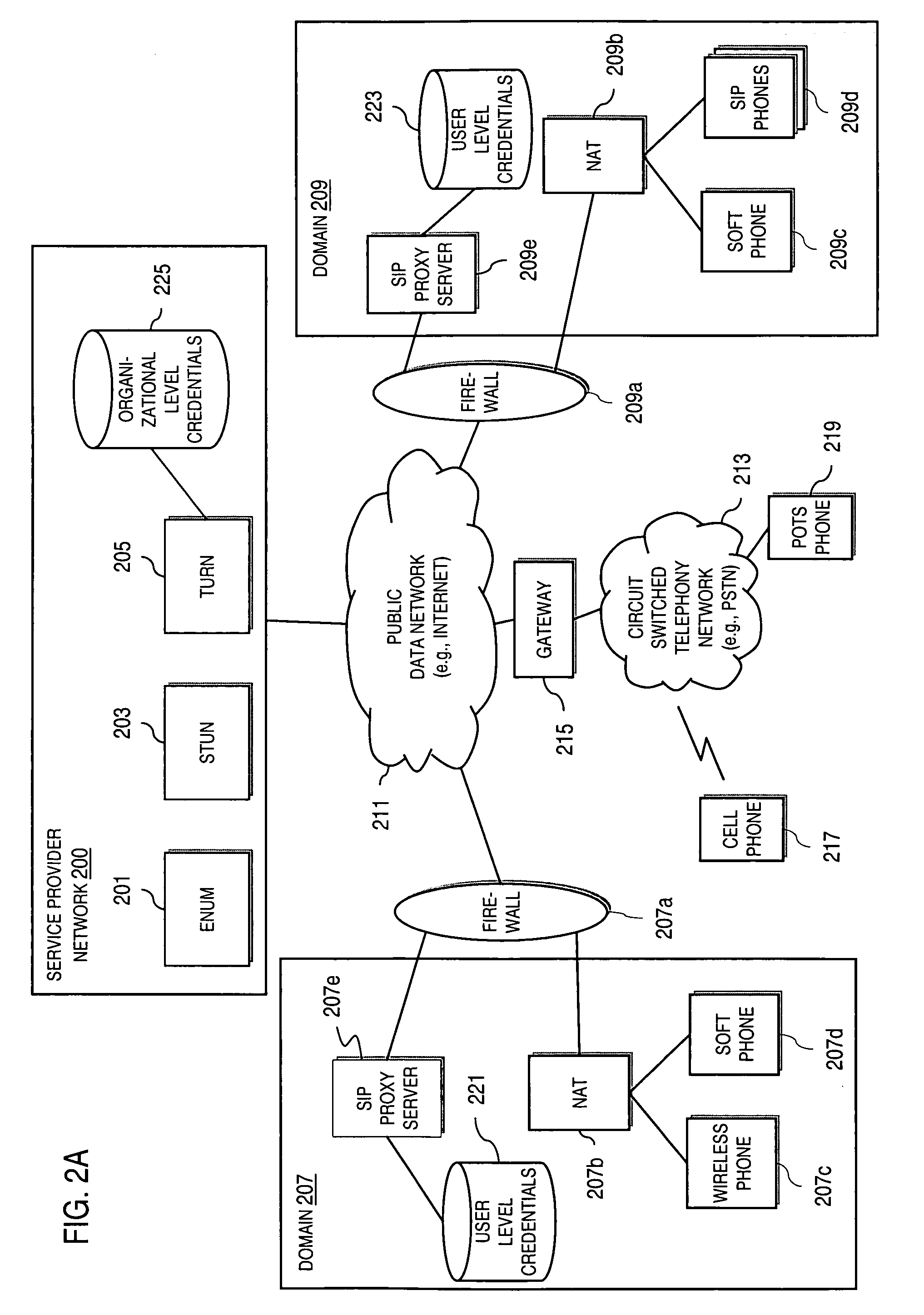
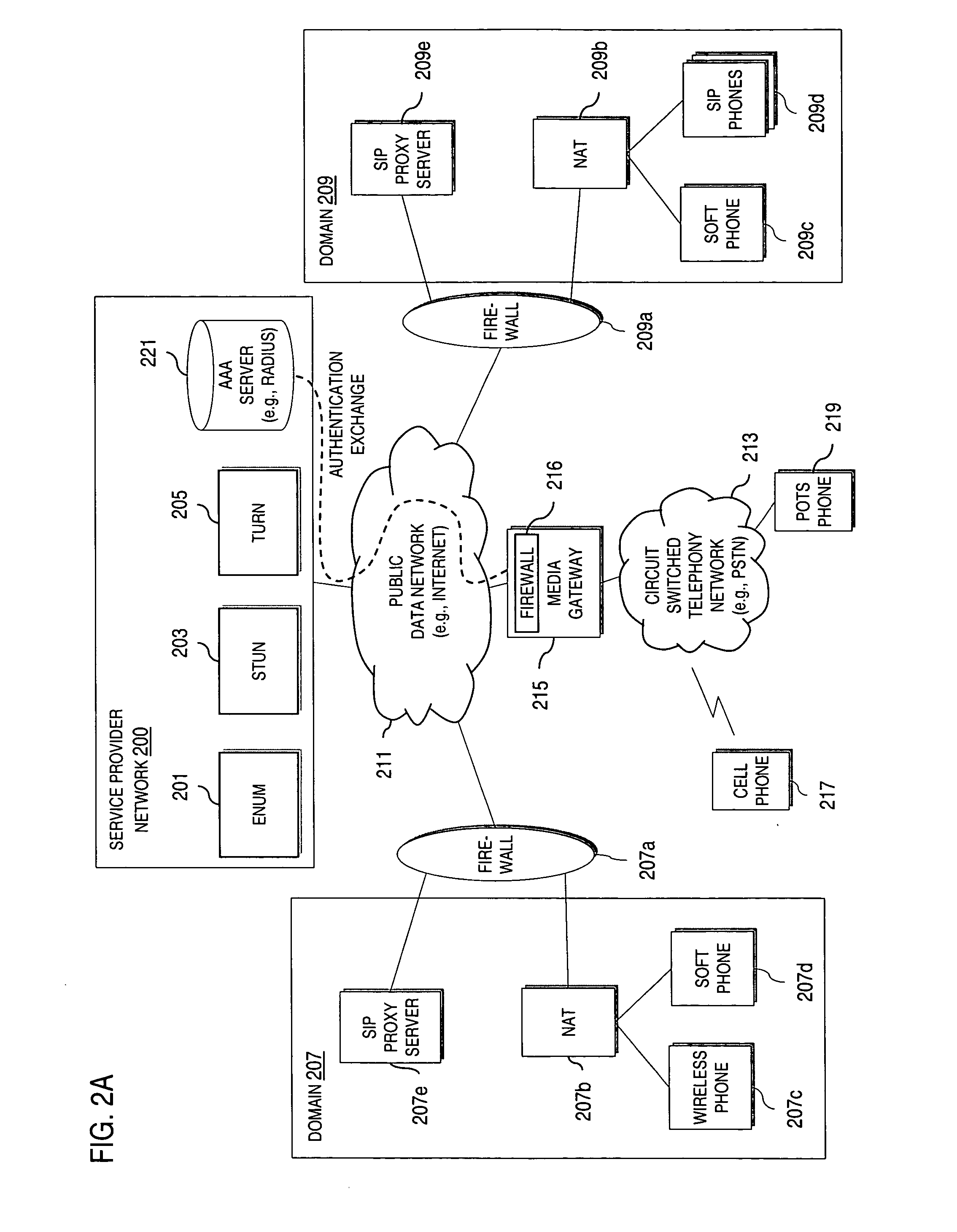
An approach provides interdomain traversal to support packetized voice transmissions. A request is received from a first endpoint of a first domain for establishing a communication session with a second endpoint of a second domain. Encrypted user credential information is retrieved from a credentials database resident within the first domain, wherein the encrypted user credential includes a password associated with a user associated with the first endpoint. Further, the encrypted user credential information is transmitted to a tunneling server in response to the request, wherein the tunneling server is configured to selectively setup a tunnel to support the communication session based on the encrypted user credential information. The tunnel traverses a first firewall and a first network address translator of the first domain and a second firewall and a second network address translator of the second domain to reach the second endpoint.
Owner:VERIZON PATENT & LICENSING INC
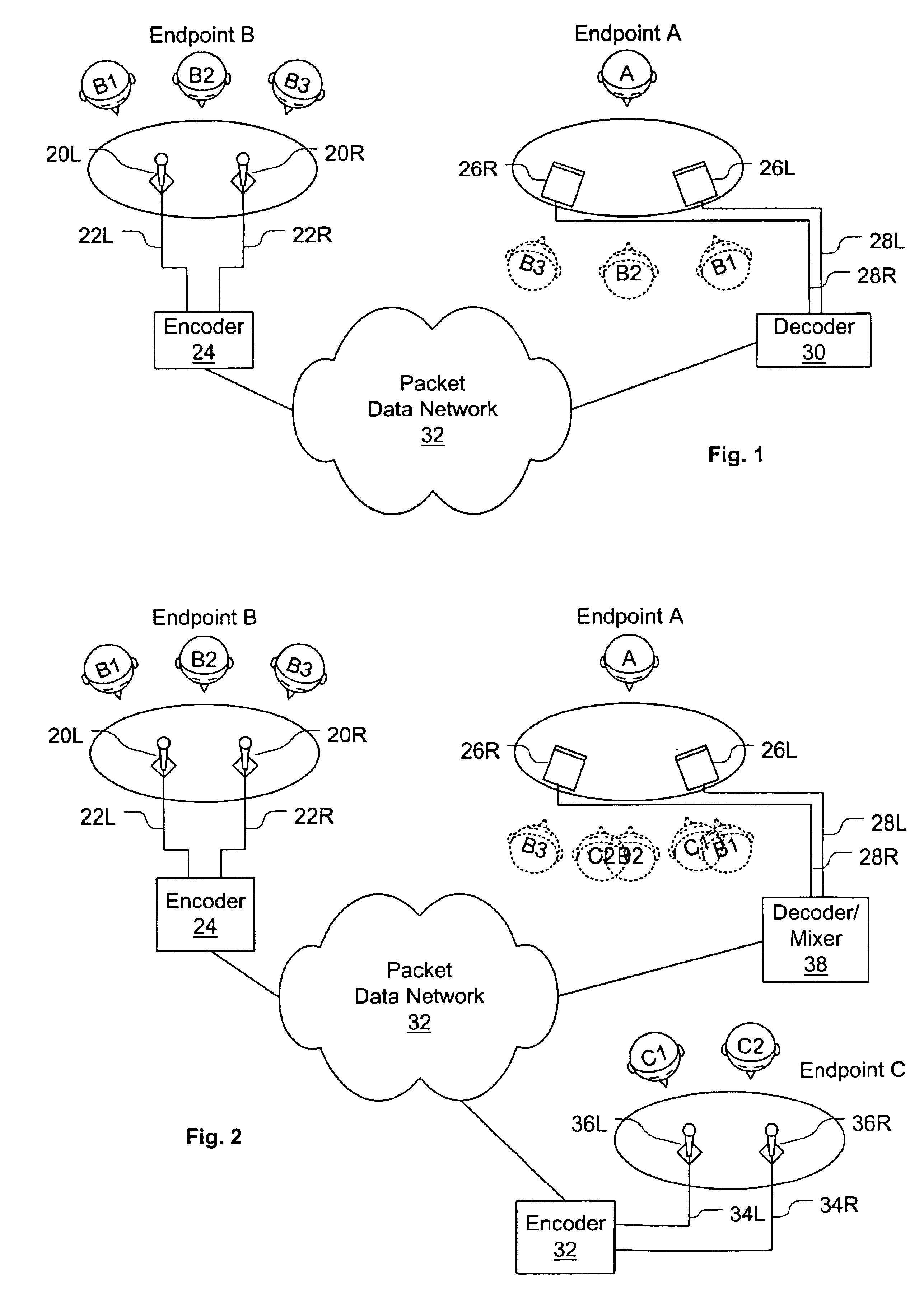
Virtual conference room for voice conferencing
InactiveUS6850496B1Increase voice comprehensionEasy to identifySpecial service provision for substationMultiplex system selection arrangementsConfusionVirtual conference
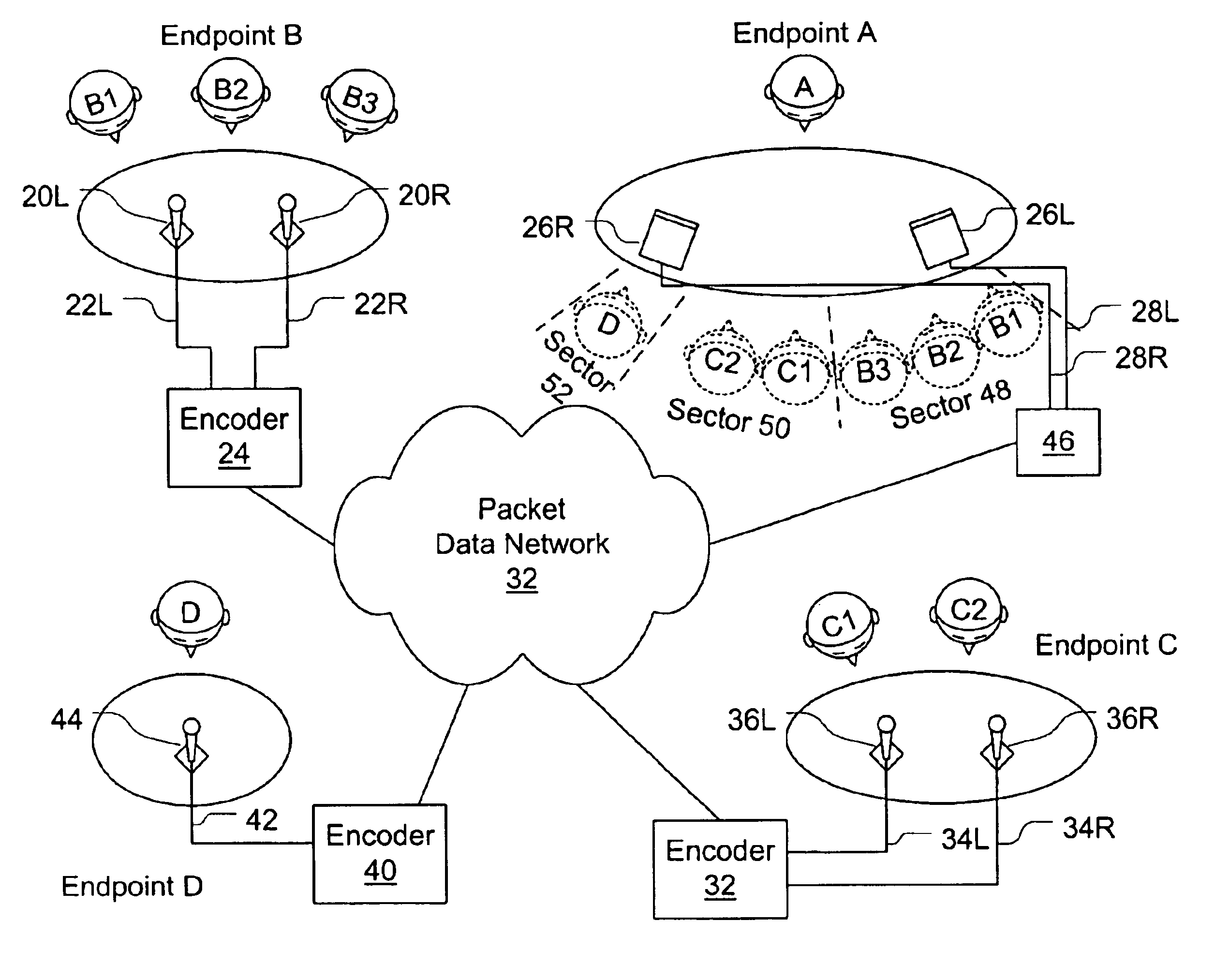
A system and method are disclosed for packet voice conferencing. The system and method divide a conferencing presentation sound field into sectors, and allocate one or more sectors to each conferencing endpoint. At some point between capture and playout, the voice data from each endpoint is mapped into its designated sector or sectors. Thereafter, when the voice data from a plurality of participants from multiple endpoints is combined, a listener can identify a unique apparent location within the presentation sound field for each participant. The system allows a conference participant to increase their comprehension when multiple participants speak simultaneously, as well as alleviate confusion as to who is speaking at any given time.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Packet voice gateway
InactiveUS20080002669A1Efficient constructionNew buildingNetwork connectionsQuality of serviceSpeech sound
The methods and apparatus of the present invention can be used to provide a high quality of service across a network that includes packet-based technology. Use of the present invention can yield networks that are more efficient, more resilient and more reliable than prior networks, thus allowing service providers to provide voice and other high quality services through the use of packet networks.
Owner:TELLABS OPERATIONS
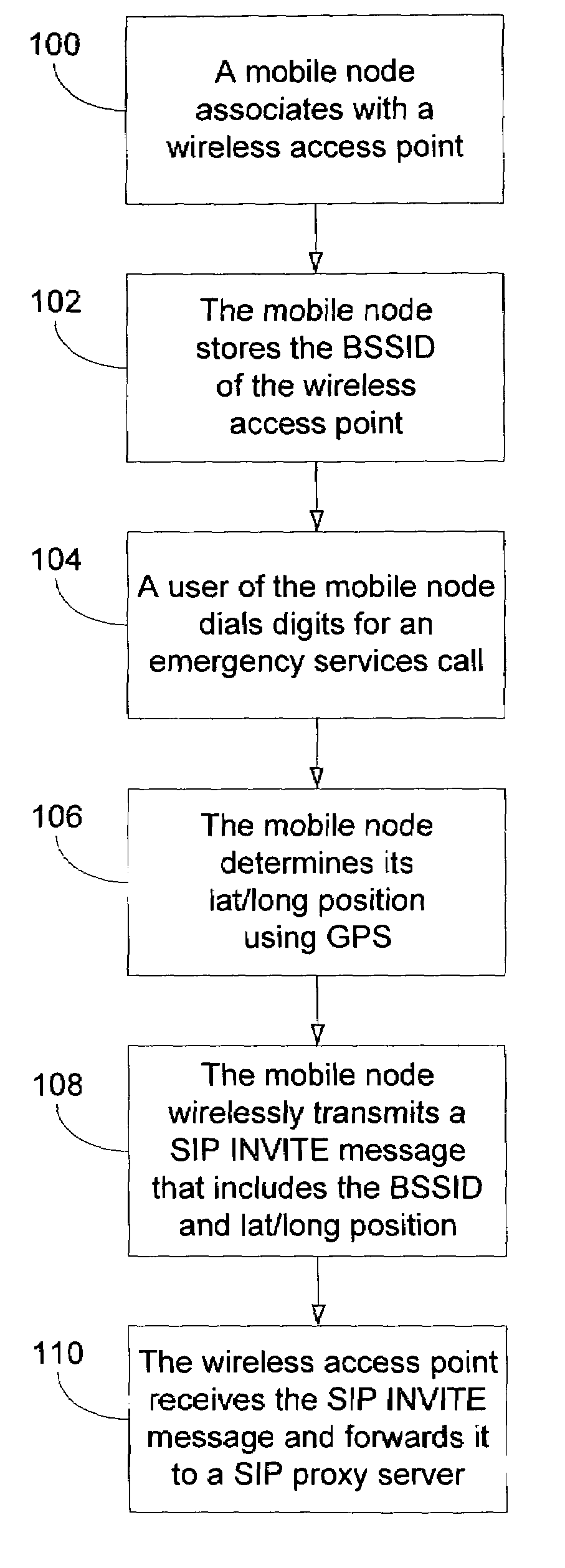
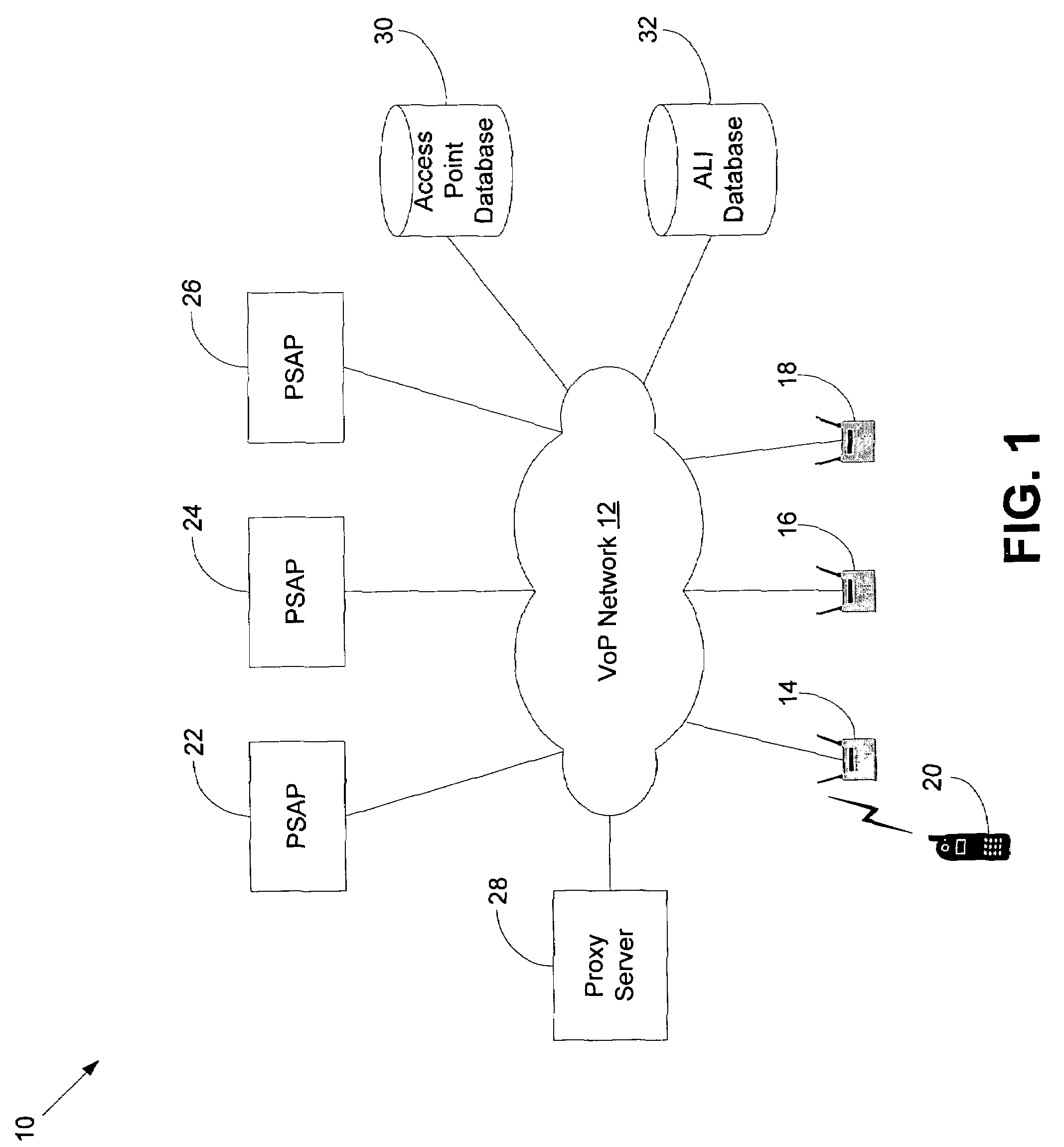
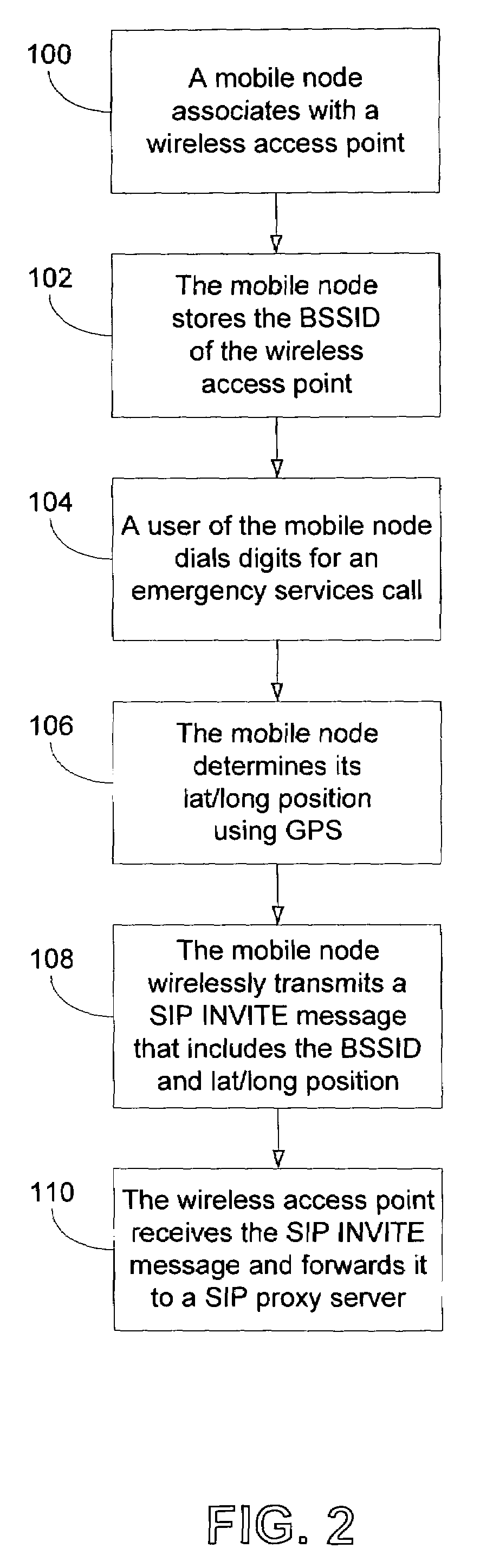
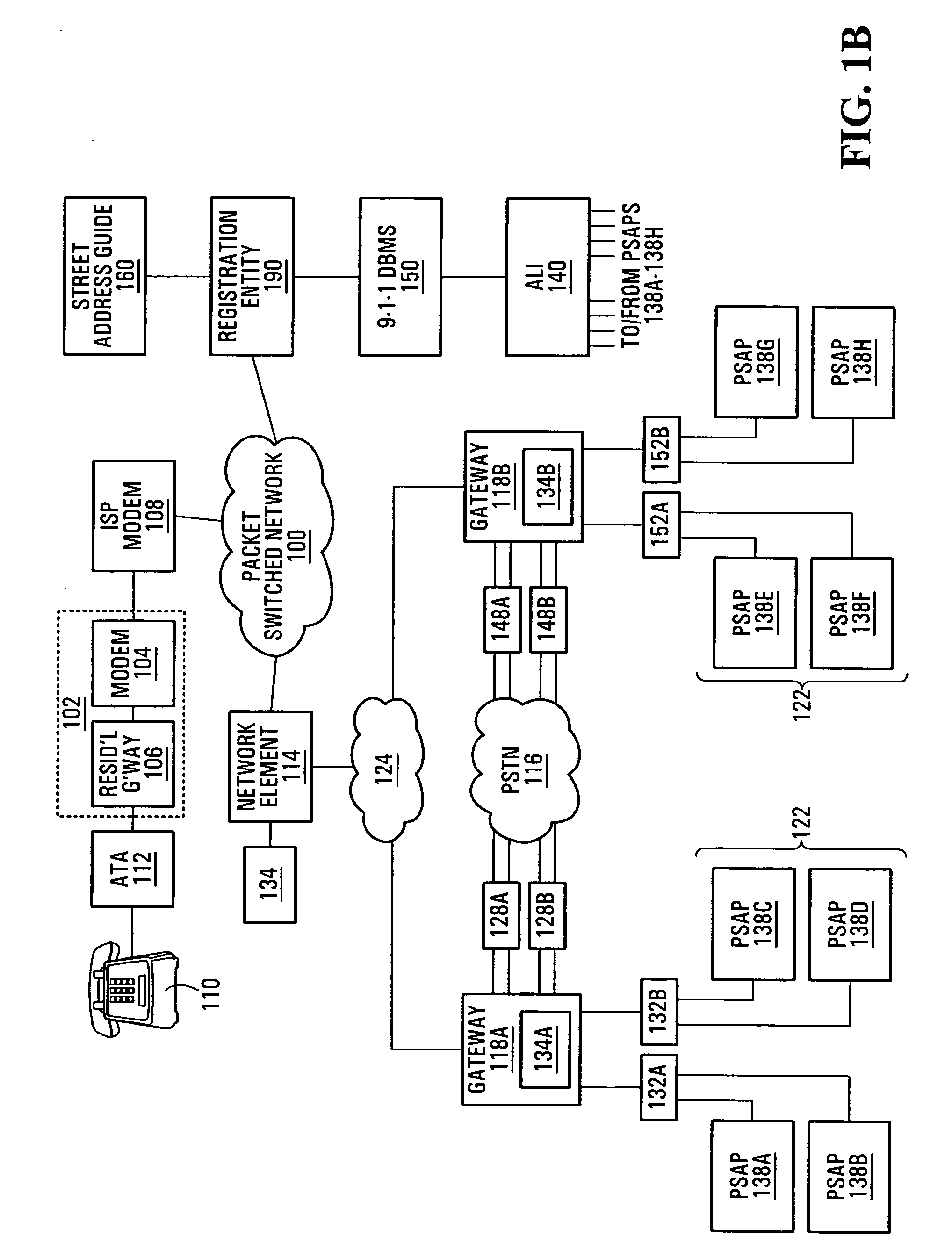
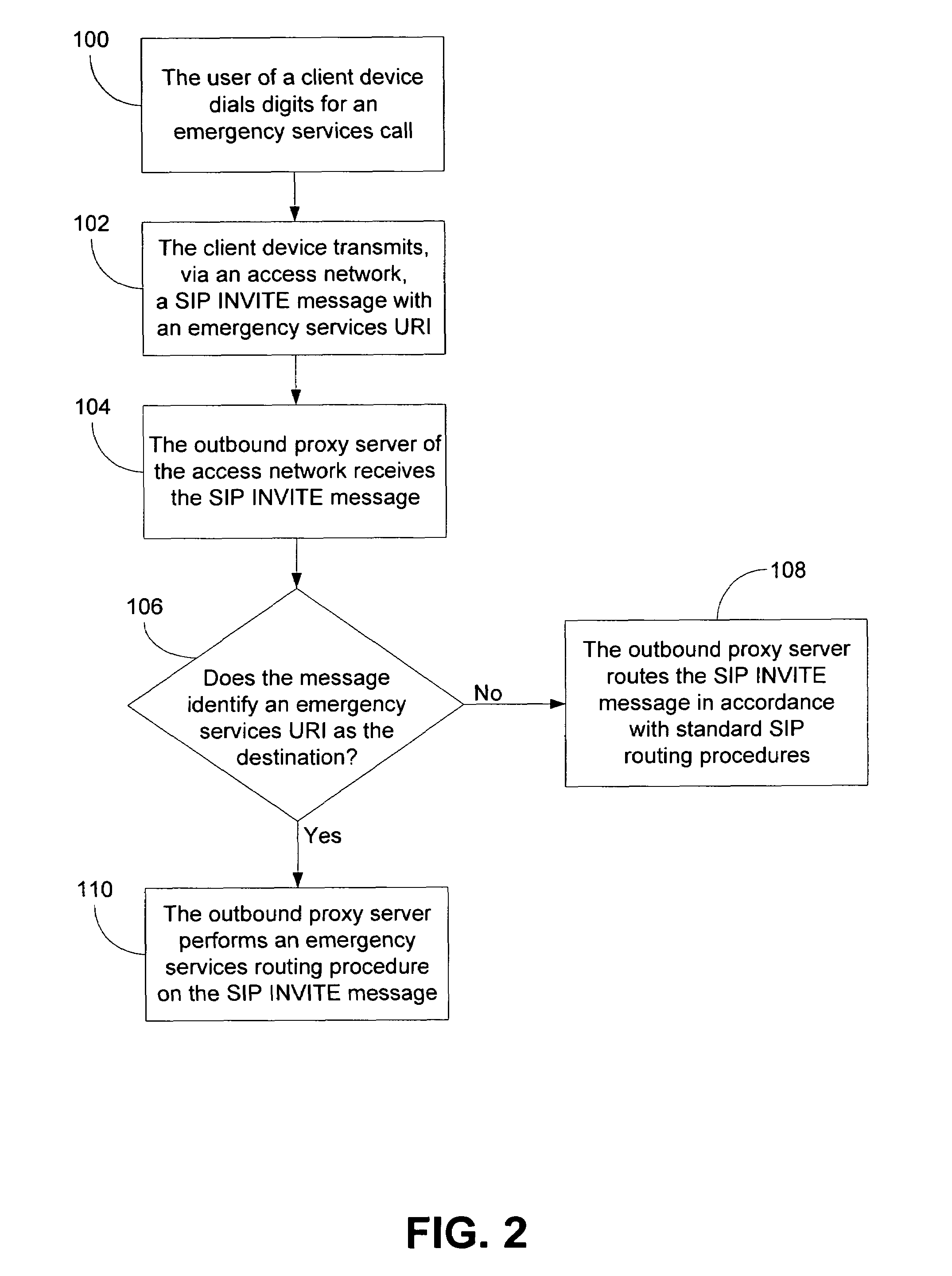
Method and system for using basic service set identifiers (BSSIDs) for emergency services routing
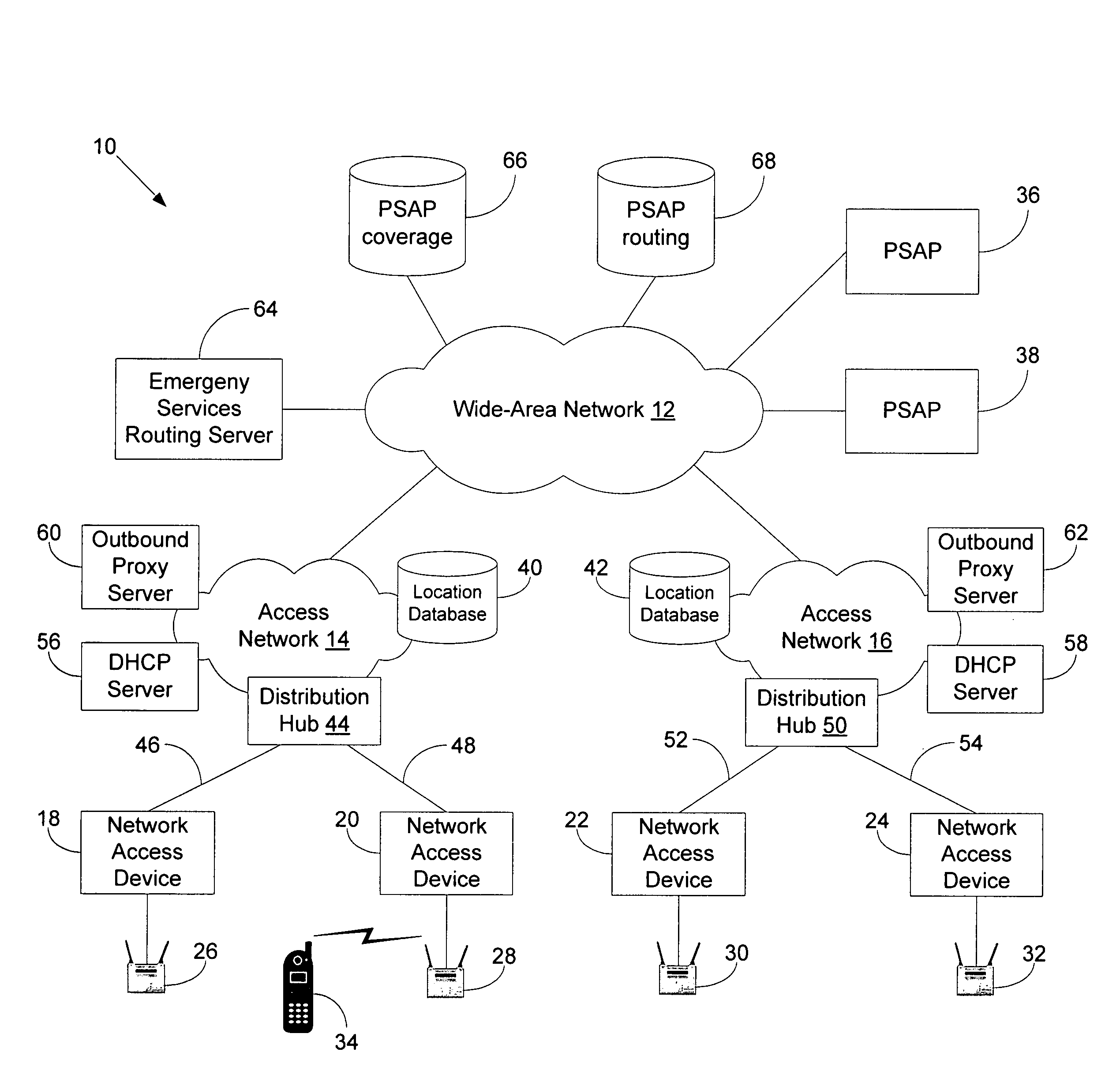
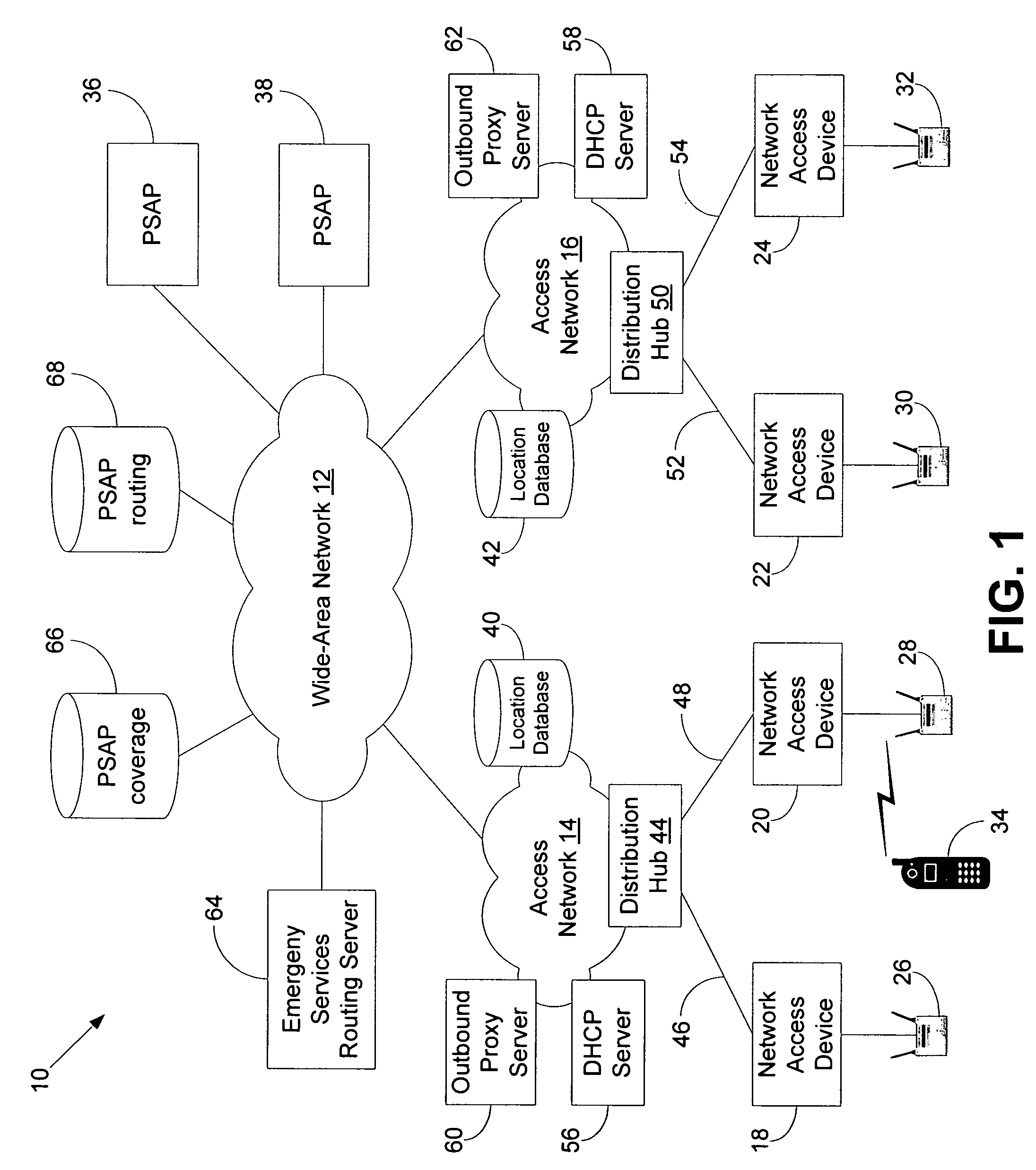
A plurality of public safety answering points (PSAPs) are accessible via a voice-over-packet (VoP) network. Each wireless access point of the VoP network is identified by a basic service set identifier (BSSID). A mobile node associates with a wireless access point and stores the wireless access point's BSSID as an indicator of the mobile node's location. A user of the mobile node dials digits for an emergency services call. In response, the mobile node transmits a SIP INVITE message that includes the BSSID and an additional indicator of the mobile node's location, e.g., determined using GPS or tower triangulation. A SIP proxy server receives the SIP INVITE message and attempts to determine the appropriate PSAP to answer the call based on the BSSID. If the attempt is unsuccessful, the SIP proxy server determines the appropriate PSAP based on the additional indicator.
Owner:SPRINT SPECTRUM LLC
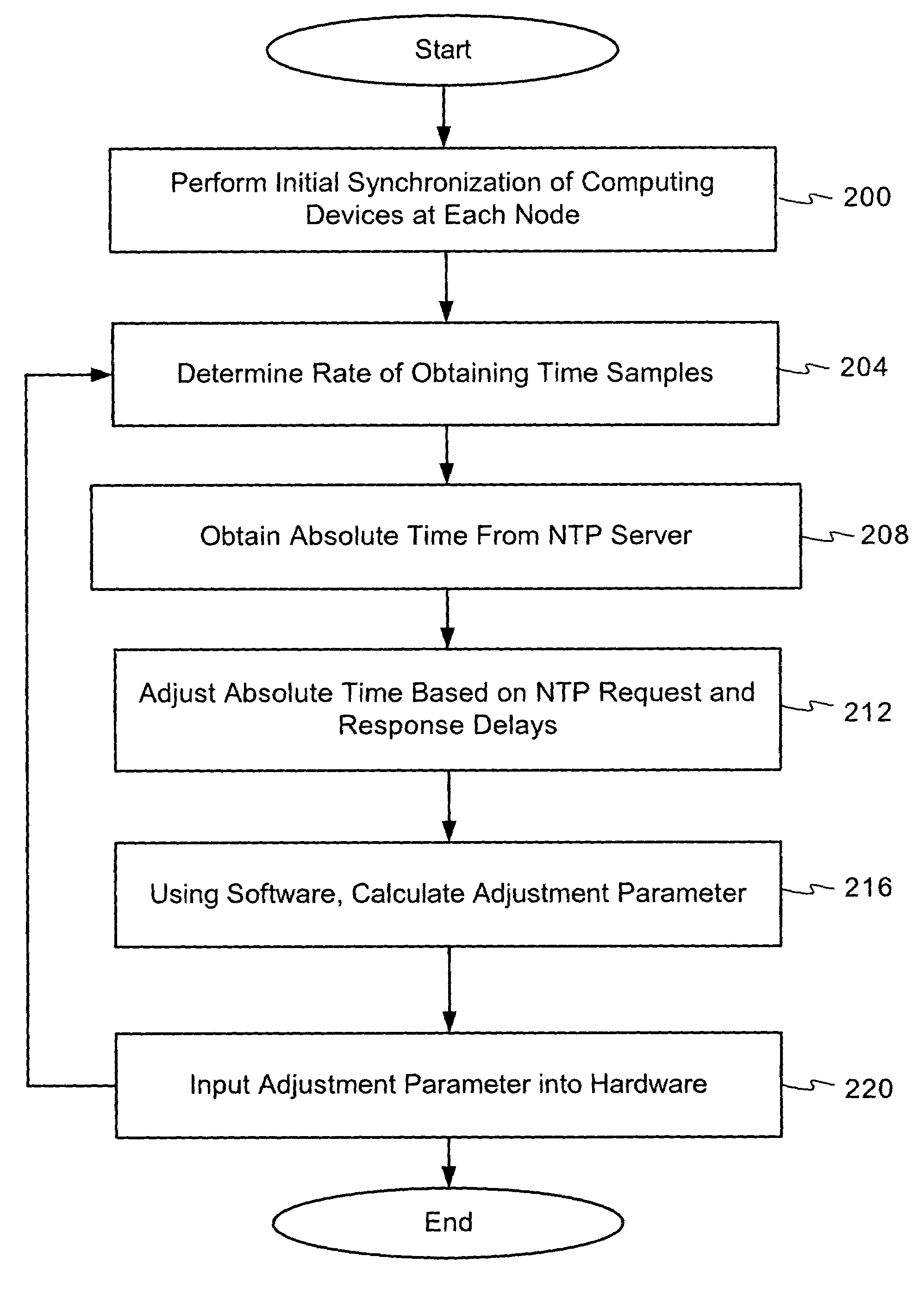
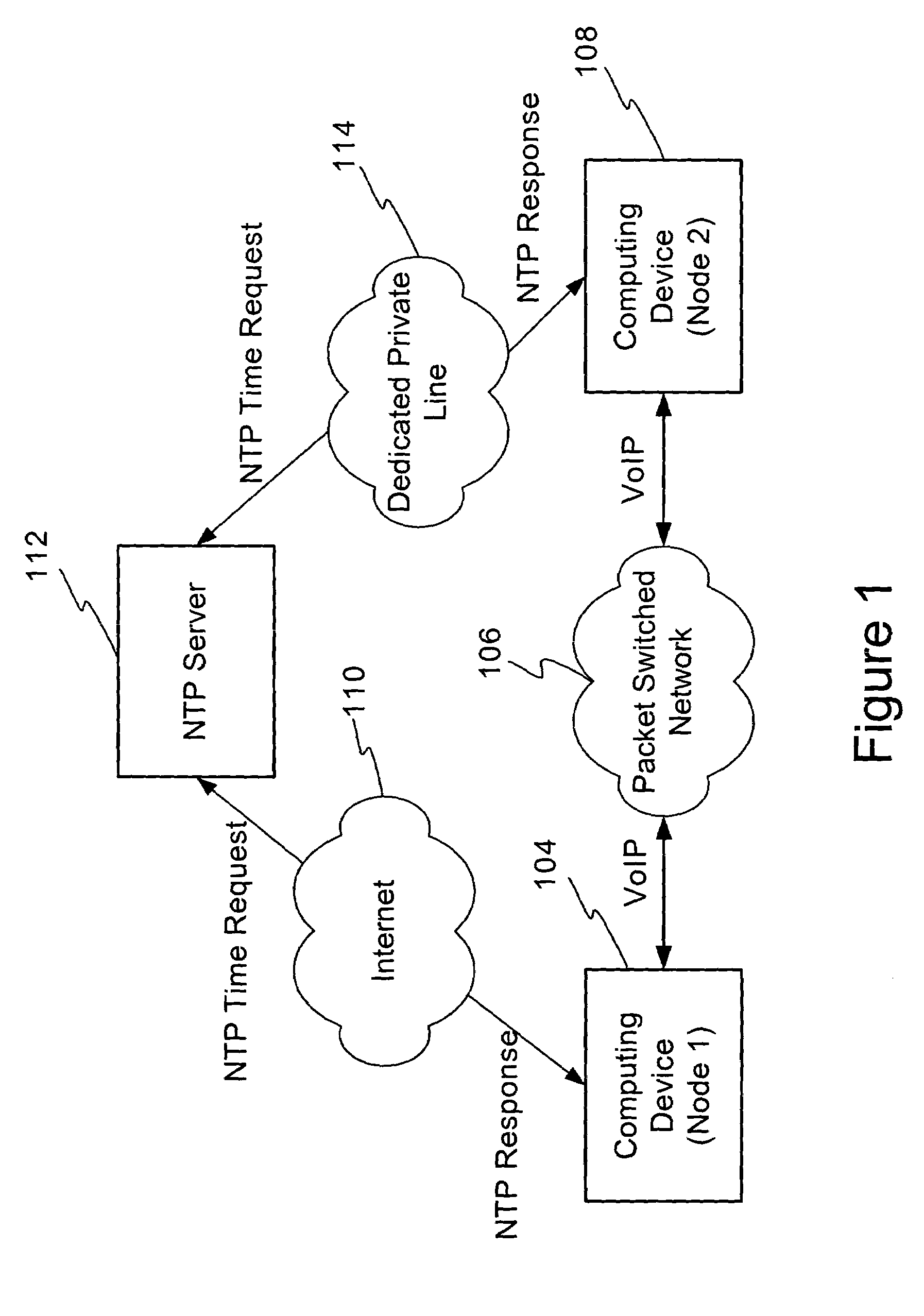
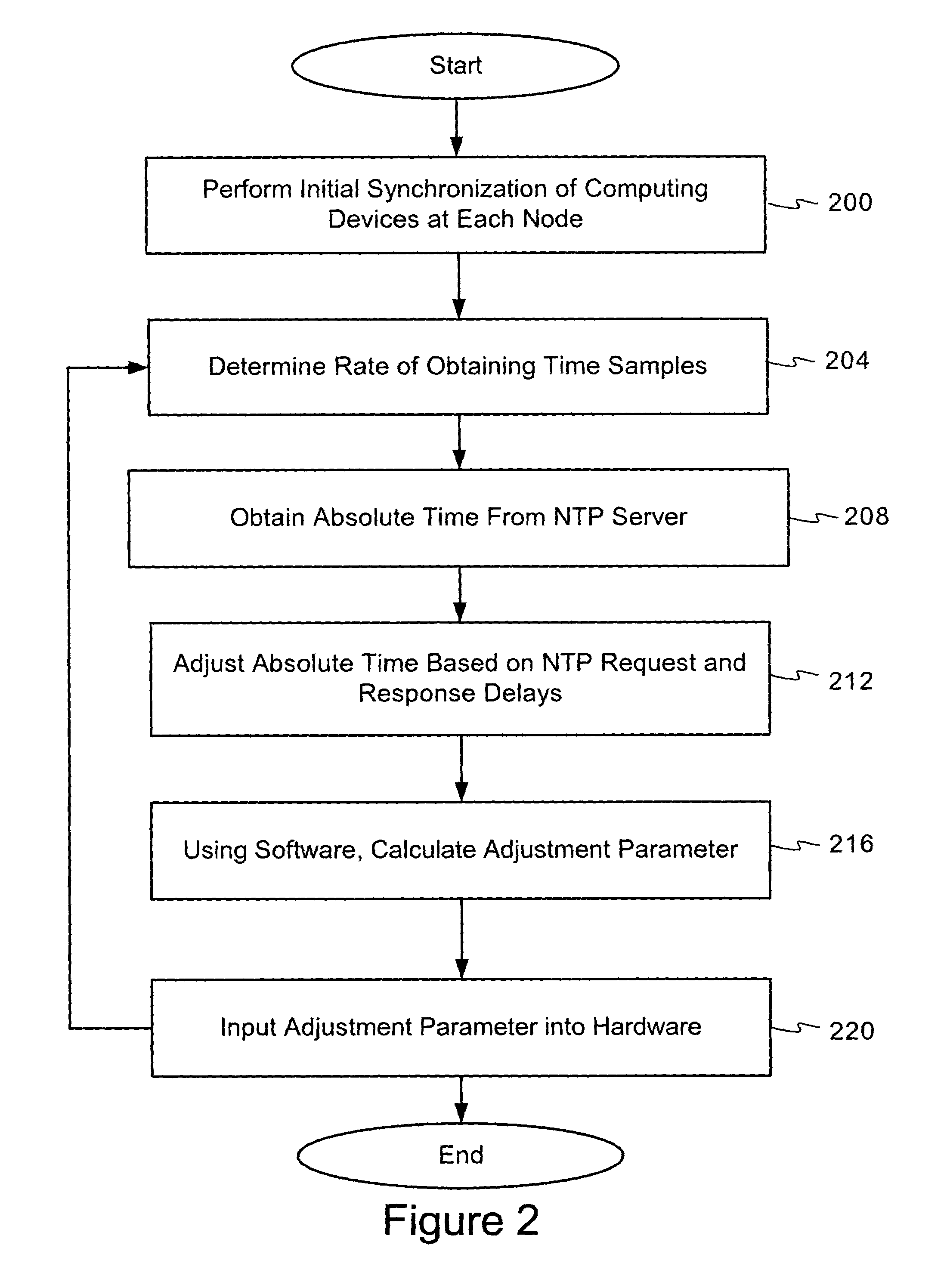
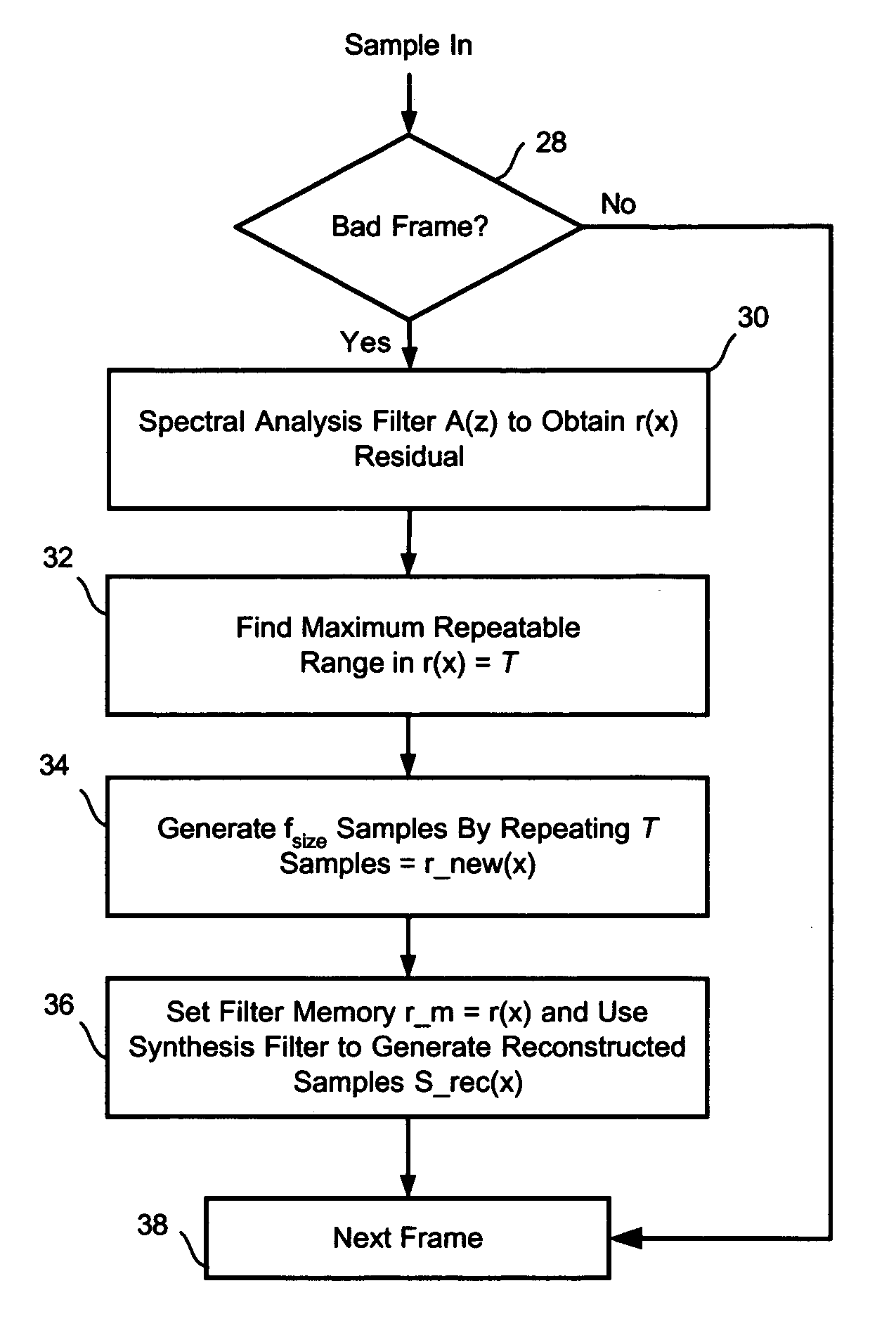
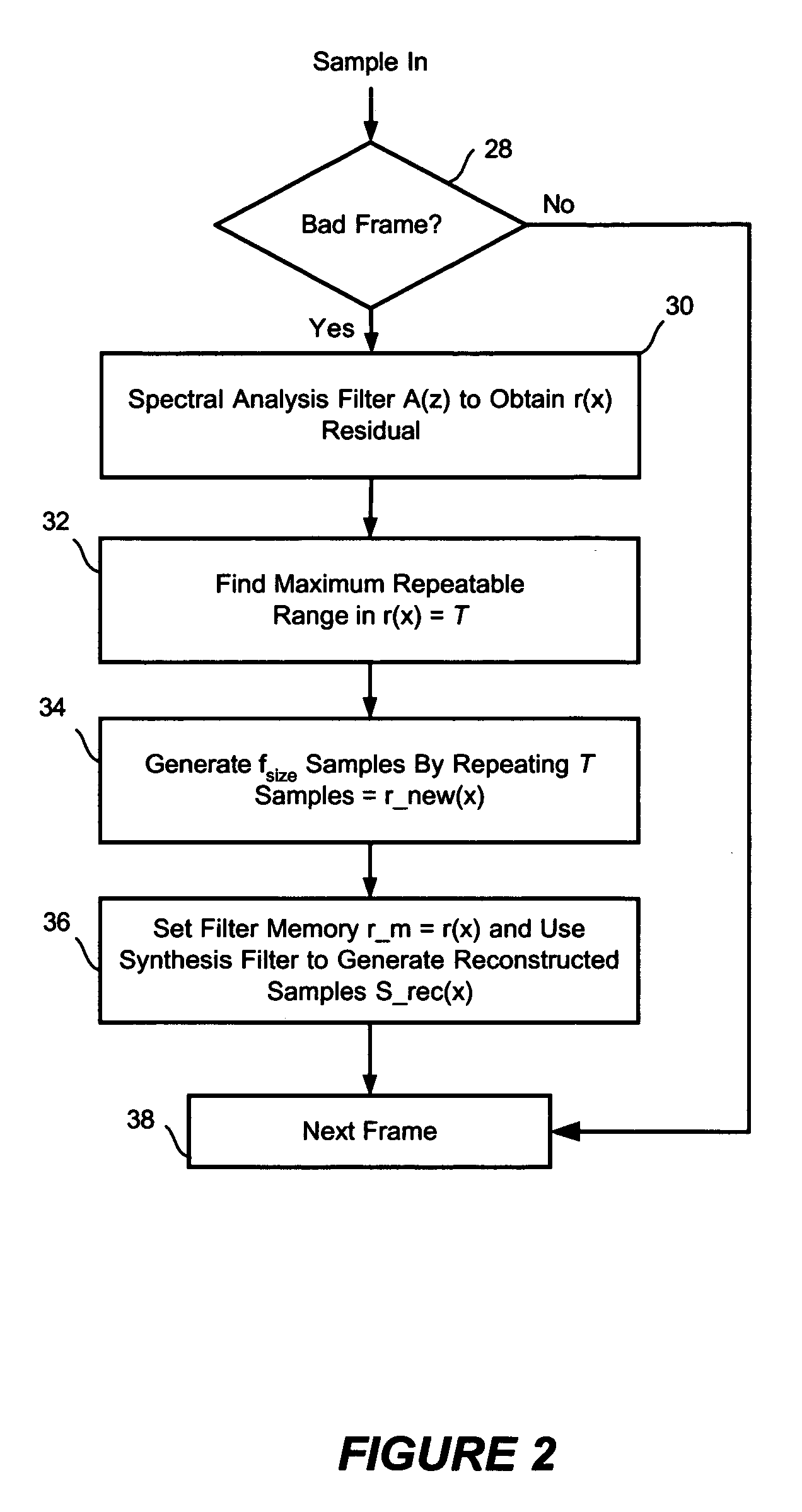
Using network time protocol in voice over packet transmission
ActiveUS7602815B2Guaranteed normal transmissionEffective maintenanceTime-division multiplexData switching by path configurationTTEthernetVoice over packet
One or more methods and systems of effectively transmitting voice and voice band data from one node to another are presented. In one embodiment, the system comprises an NTP time server generating absolute times to computing devices such as residential voice over internet protocol (VoIP) gateways. The NTP time server generates absolute times in response to NTP time requests made by one or more computing devices such as residential VoIP gateways. In one embodiment, the method comprises determining an adequate rate for requesting absolute times from an NTP server, making periodic requests to the NTP server, obtaining the absolute times from the NTP server, and generating an adjustment parameter for use by a computing device such as a residential VoIP gateway.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Method and system for securing real-time media streams in support of interdomain traversal
An approach provides interdomain traversal packetized voice transmissions. A request is received from a first endpoint of a first domain for establishing a communication session with a second endpoint of a second domain. A tunnel is established by a TURN (Traversal Using Relay NAT (Network Address Translation)) server to support the communication session. The TURN server is controlled by a service provider as part of a managed communication service. The tunnel traverses a first firewall and a first network address translator of the first domain and a second firewall and a second network address translator of the second domain to reach the second endpoint, wherein the communication session is encrypted and transported via the tunnel.
Owner:VERIZON PATENT & LICENSING INC
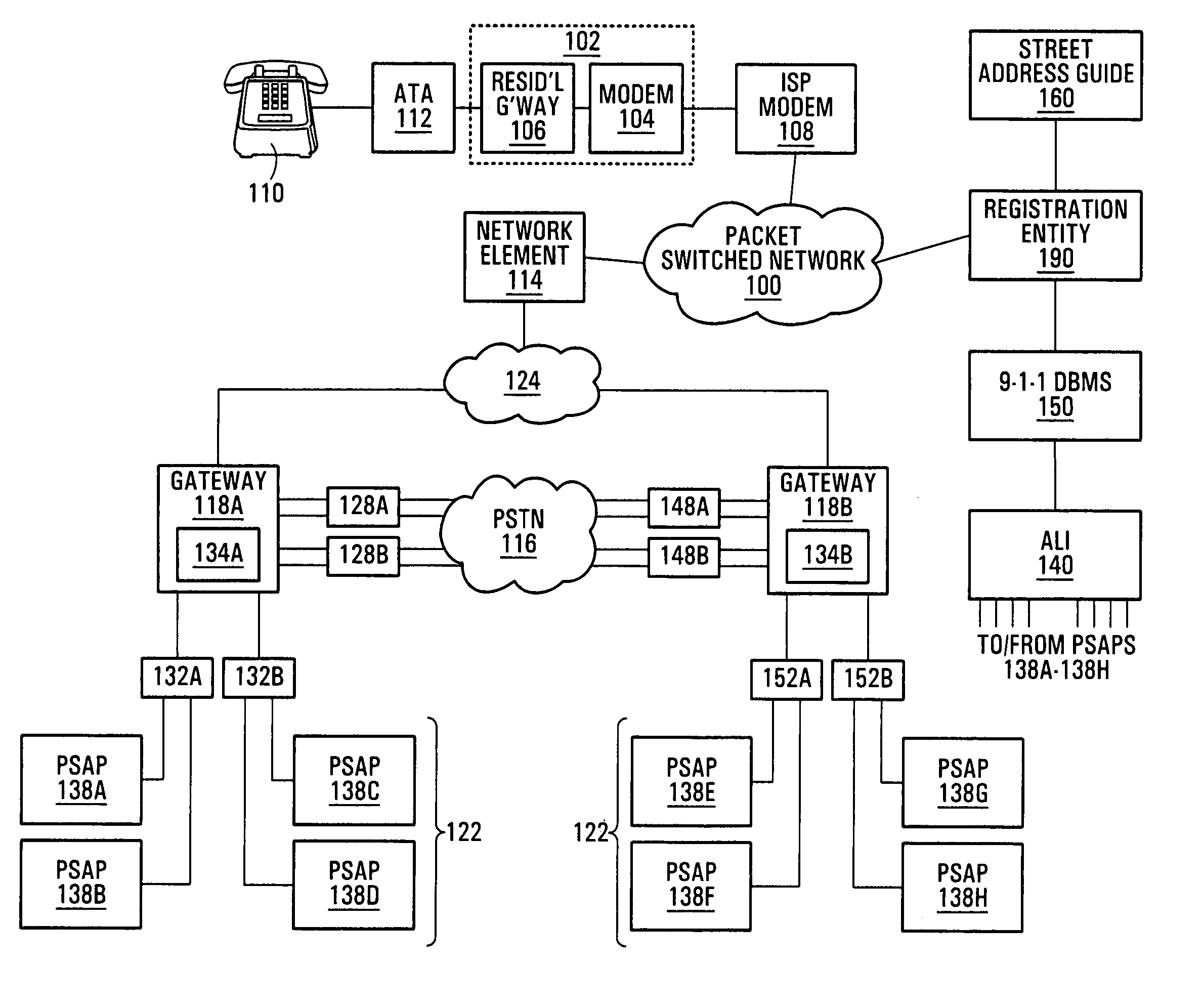
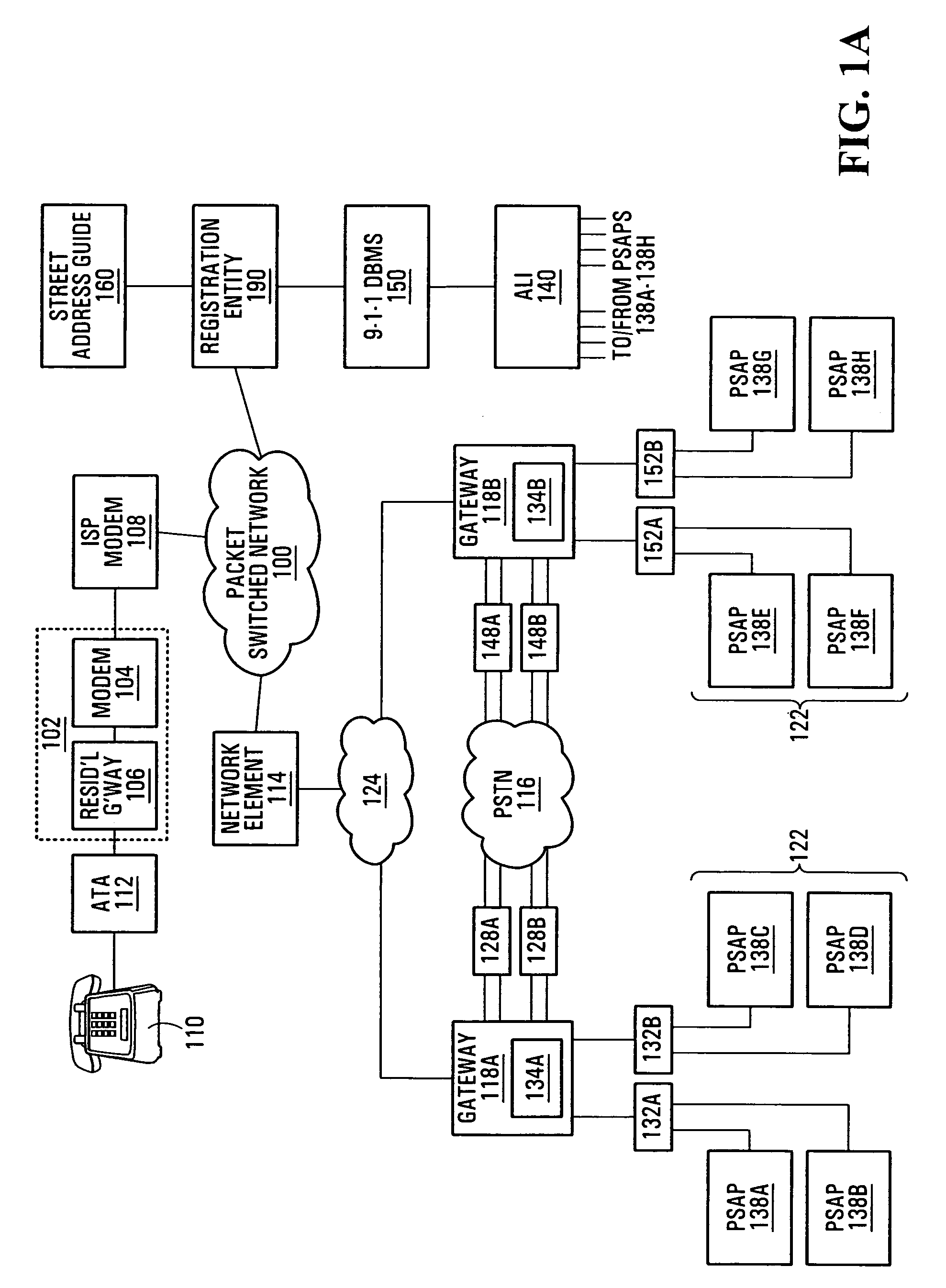
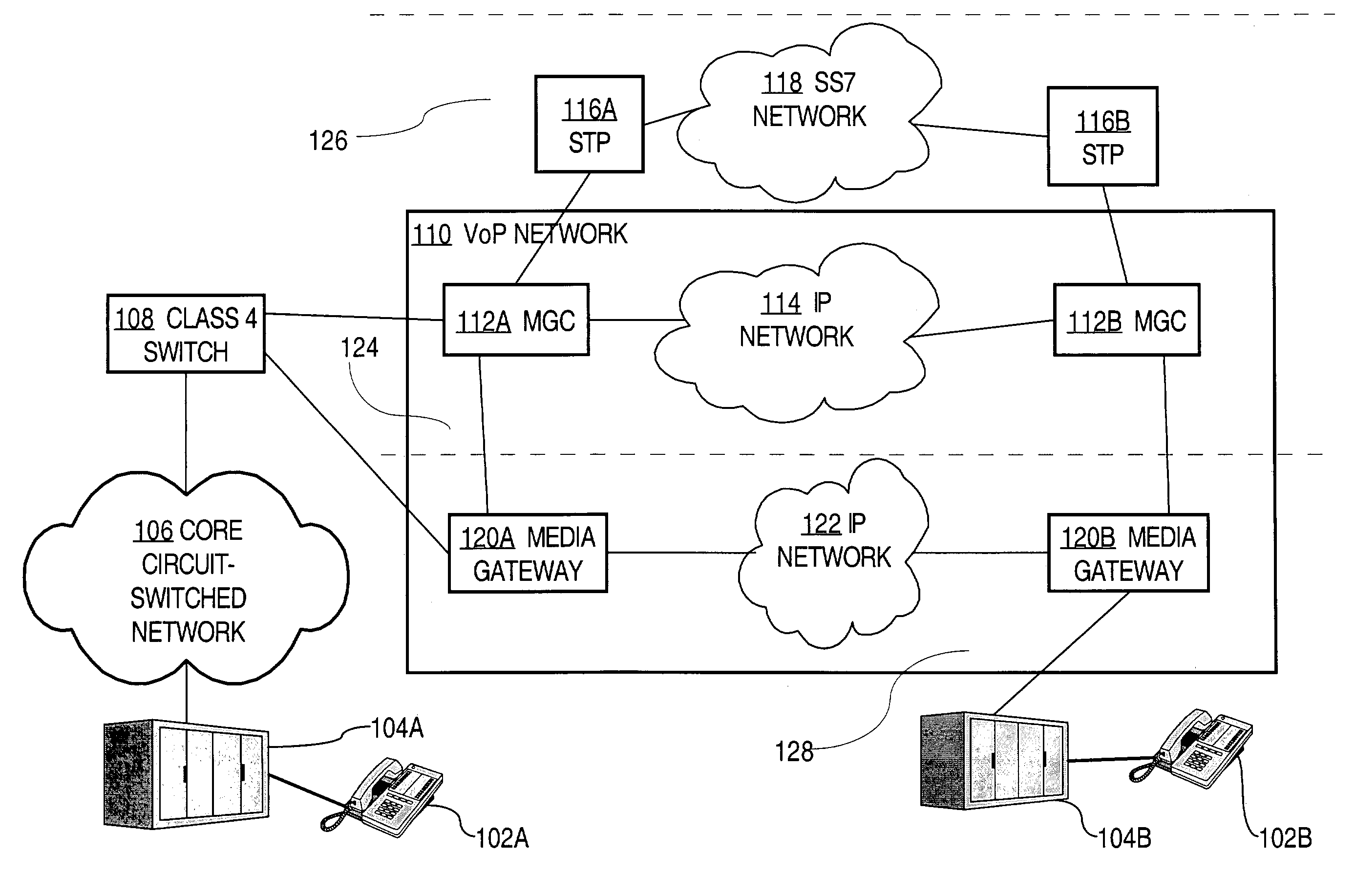
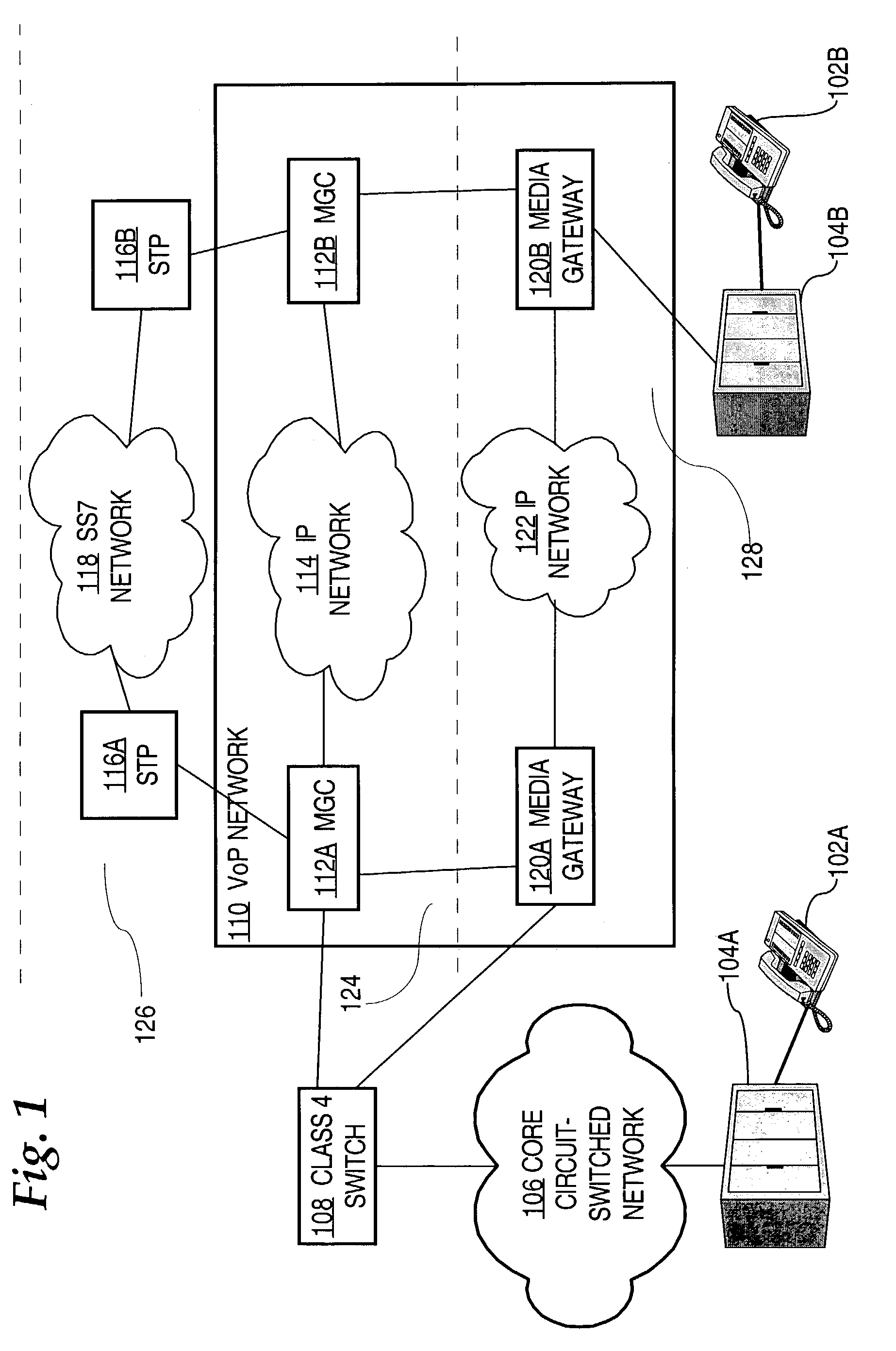
Emergency call handling in a voice-over-packet environment
A method of routing an emergency call received at a network element. The method comprises determining a directory number associated with a communication device having originated the emergency call, consulting a local database to obtain routing information associated with the directory number, and directing the call and the routing information over a path dedicated to emergency calls. Also, a network element which comprises the database as well as a control entity, the control entity being operative for receiving an incoming call originated by one of the communication devices, determining the directory number associated with the communication device having originated the call, determining whether the call is an emergency call and, responsive to the call being an emergency call, accessing the database to obtain the routing information related to the directory number and directing the call as well as the routing information over a trunk group dedicated to emergency calls.
Owner:BCE
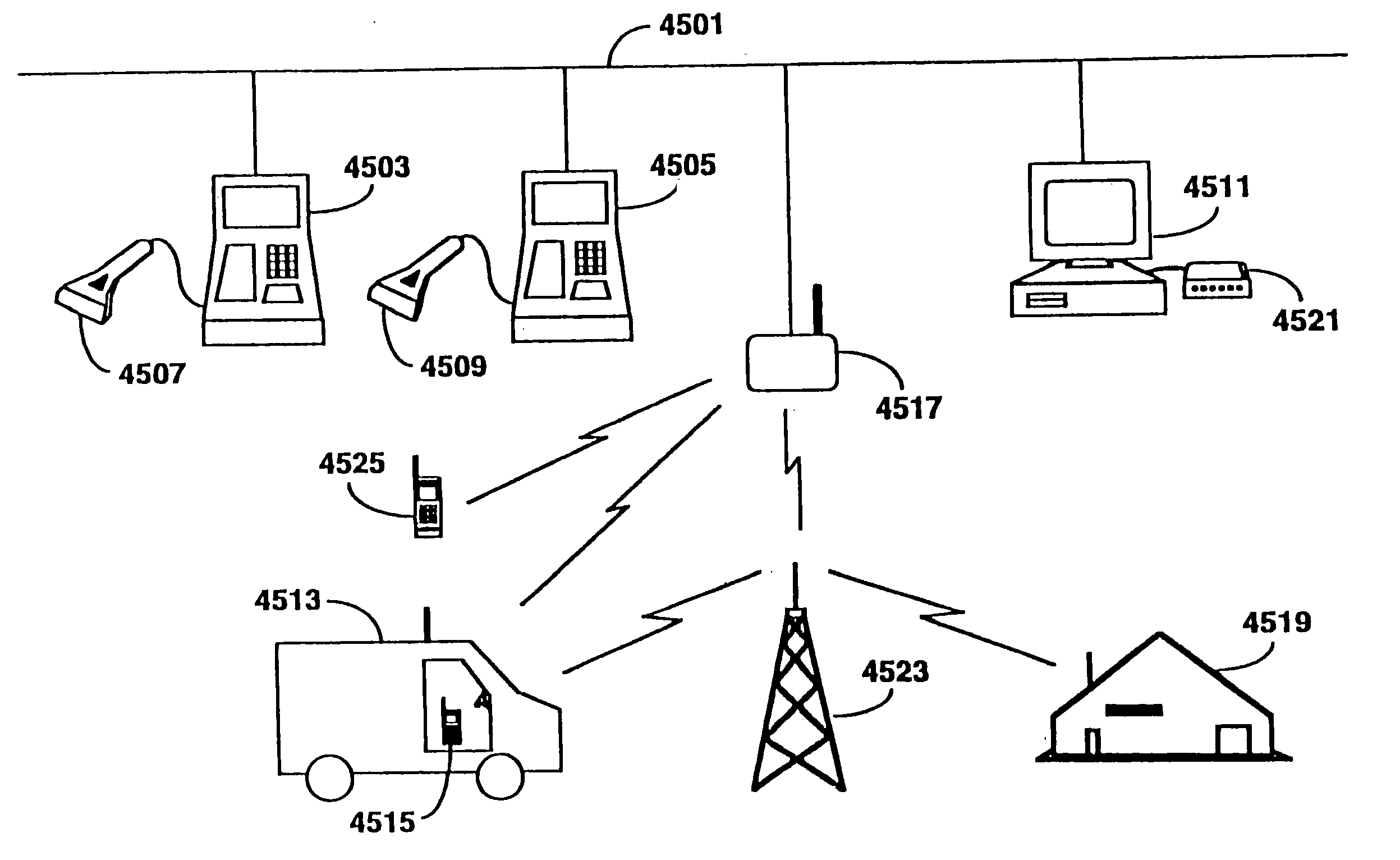
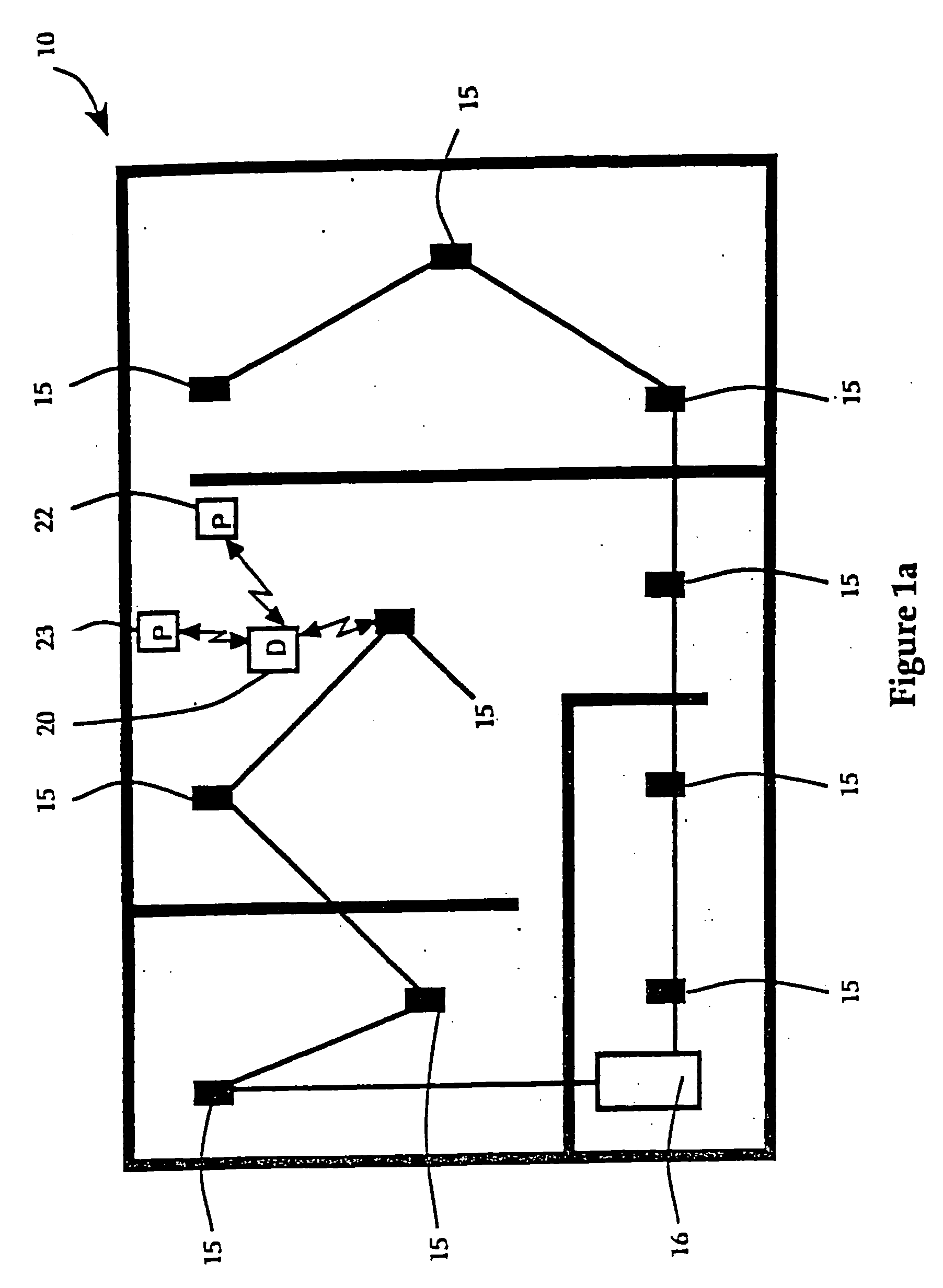
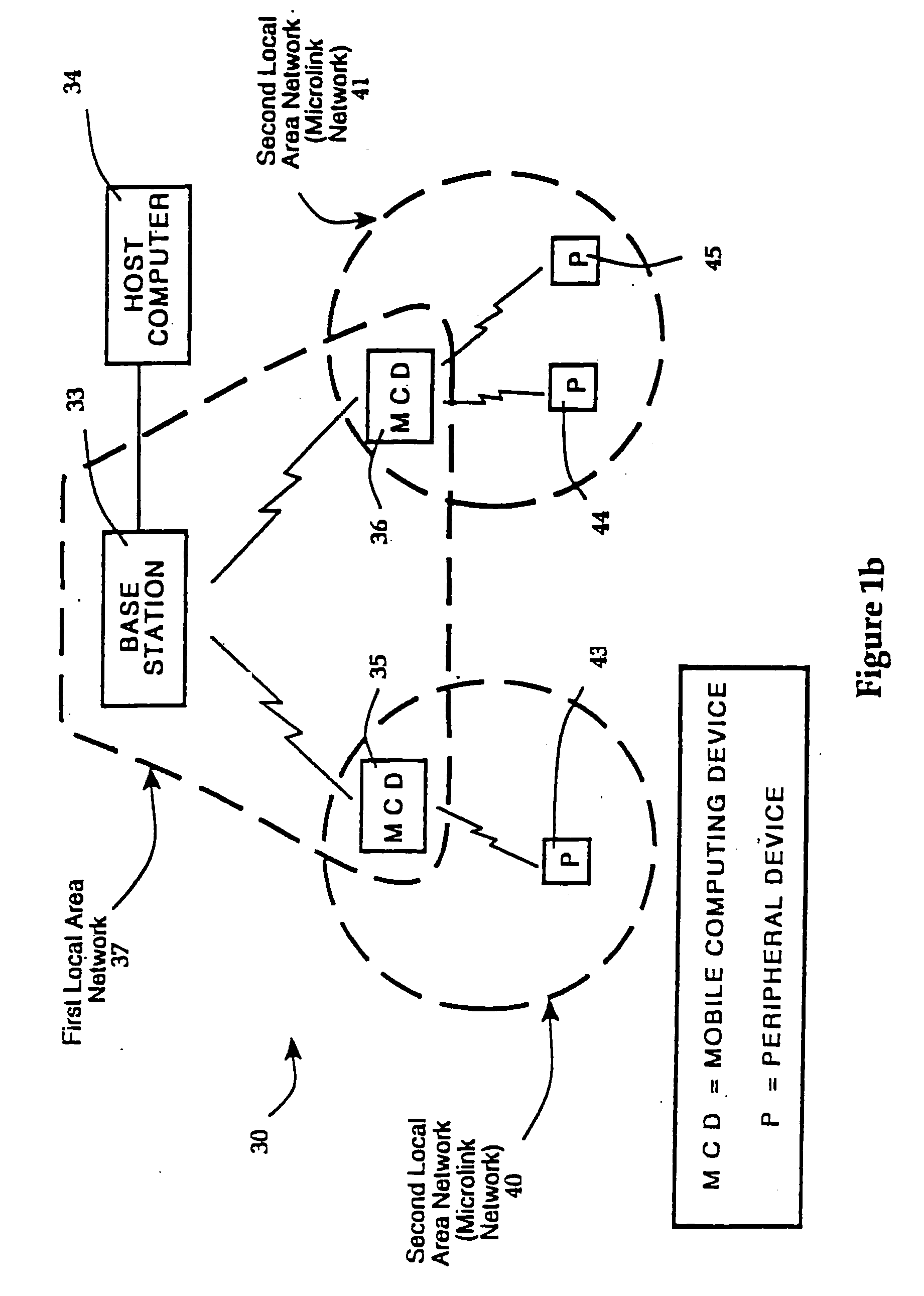
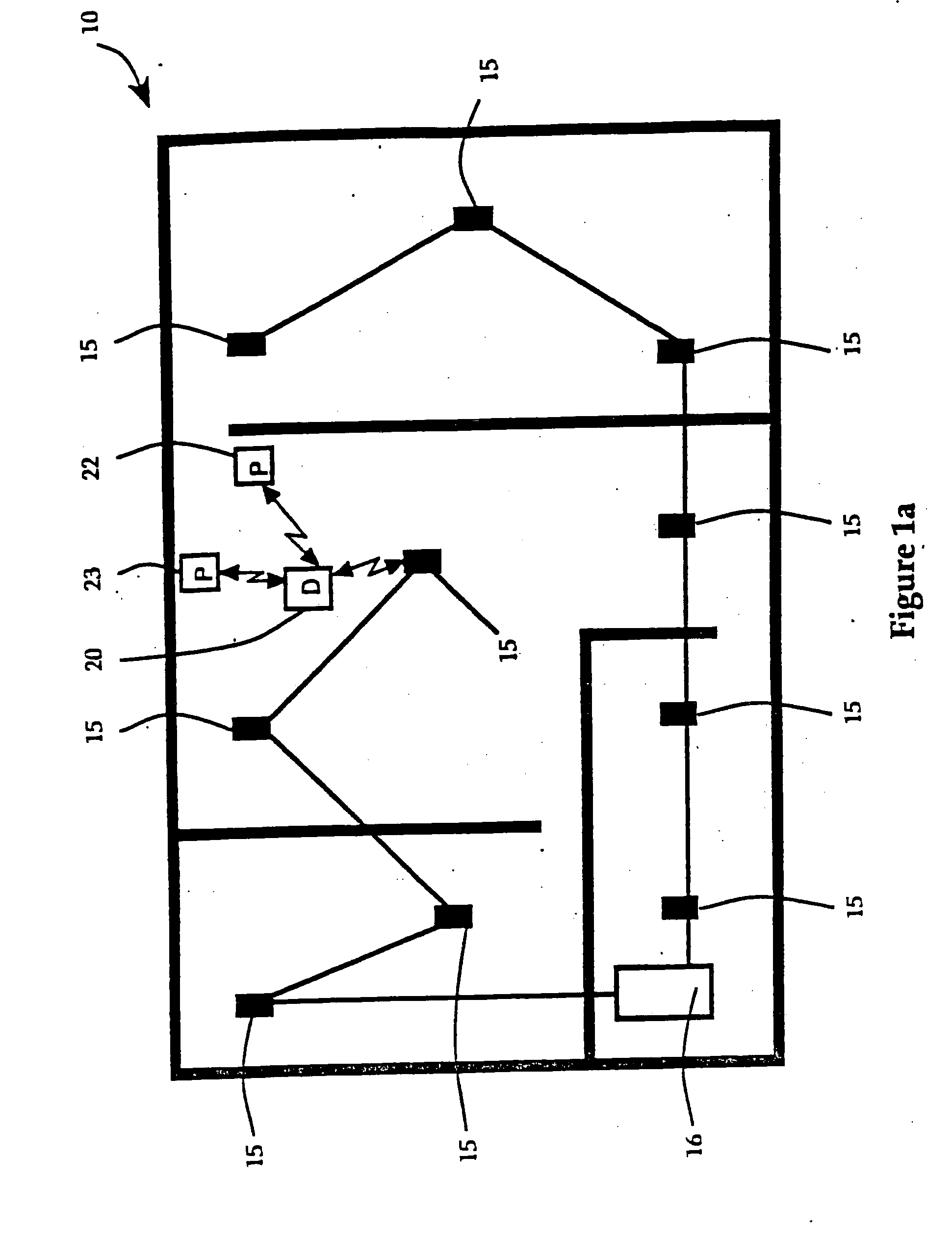
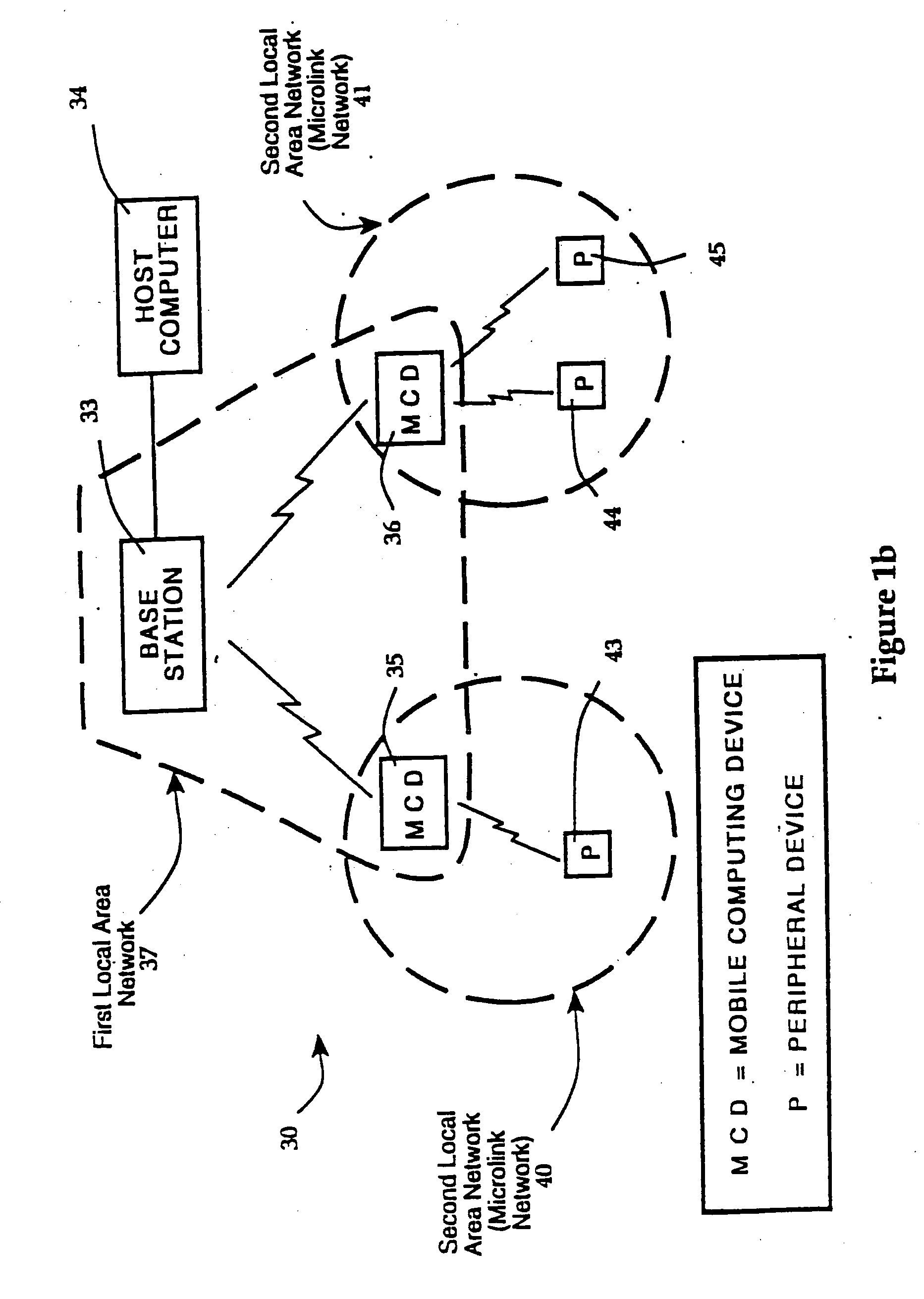
Hierarchical data collection network supporting packetized voice communications among wireless terminals and telephones
InactiveUS20040264442A1Efficient communication pathwayEfficient communicationDevices with card reading facilityError preventionVoice communicationThe Internet
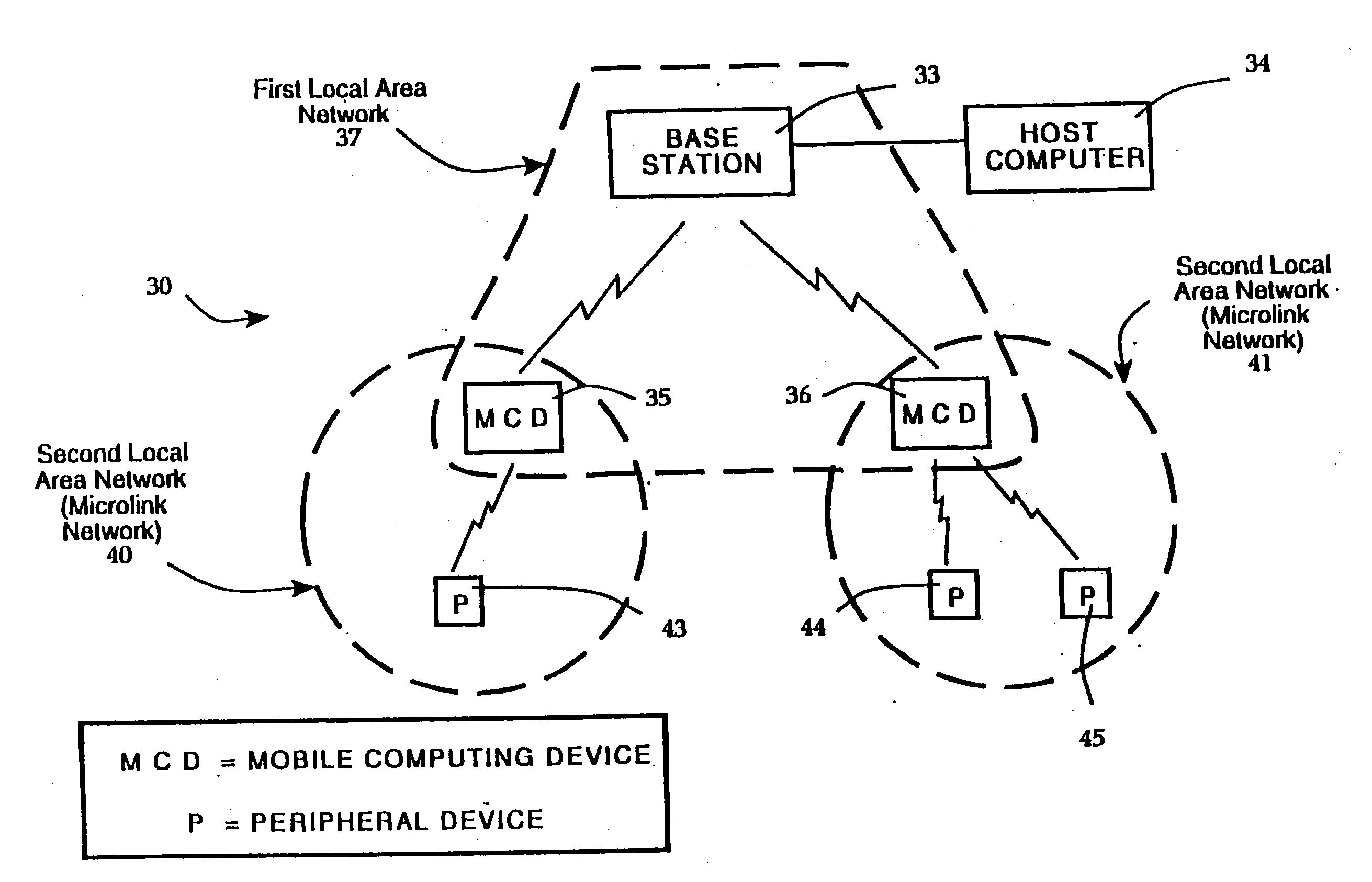
A packet-based, hierarchical communication system, arranged in a spanning tree configuration, is described in which wired and wireless communication networks exhibiting substantially different characteristics are employed in an overall scheme to link portable or mobile computing devices. The network accommodates real time voice transmission both through dedicated, scheduled bandwidth and through a packet-based routing within the confines and constraints of a data network. Conversion and call processing circuitry is also disclosed which enables access devices and personal computers to adapt voice information between analog voice stream and digital voice packet formats as proves necessary. Routing pathways include wireless spanning tree networks, wide area networks, telephone switching networks, internet, etc., in a manner virtually transparent to the user. A voice session and associate call setup simulates that of conventional telephone switching network, providing well-understood functionality common to any mobile, remote or stationary terminal, phone, computer, etc.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Method and system for providing secure media gateways to support interdomain traversal
ActiveUS20070019623A1Special service for subscribersData switching by path configurationNetwork addressNetwork address translation
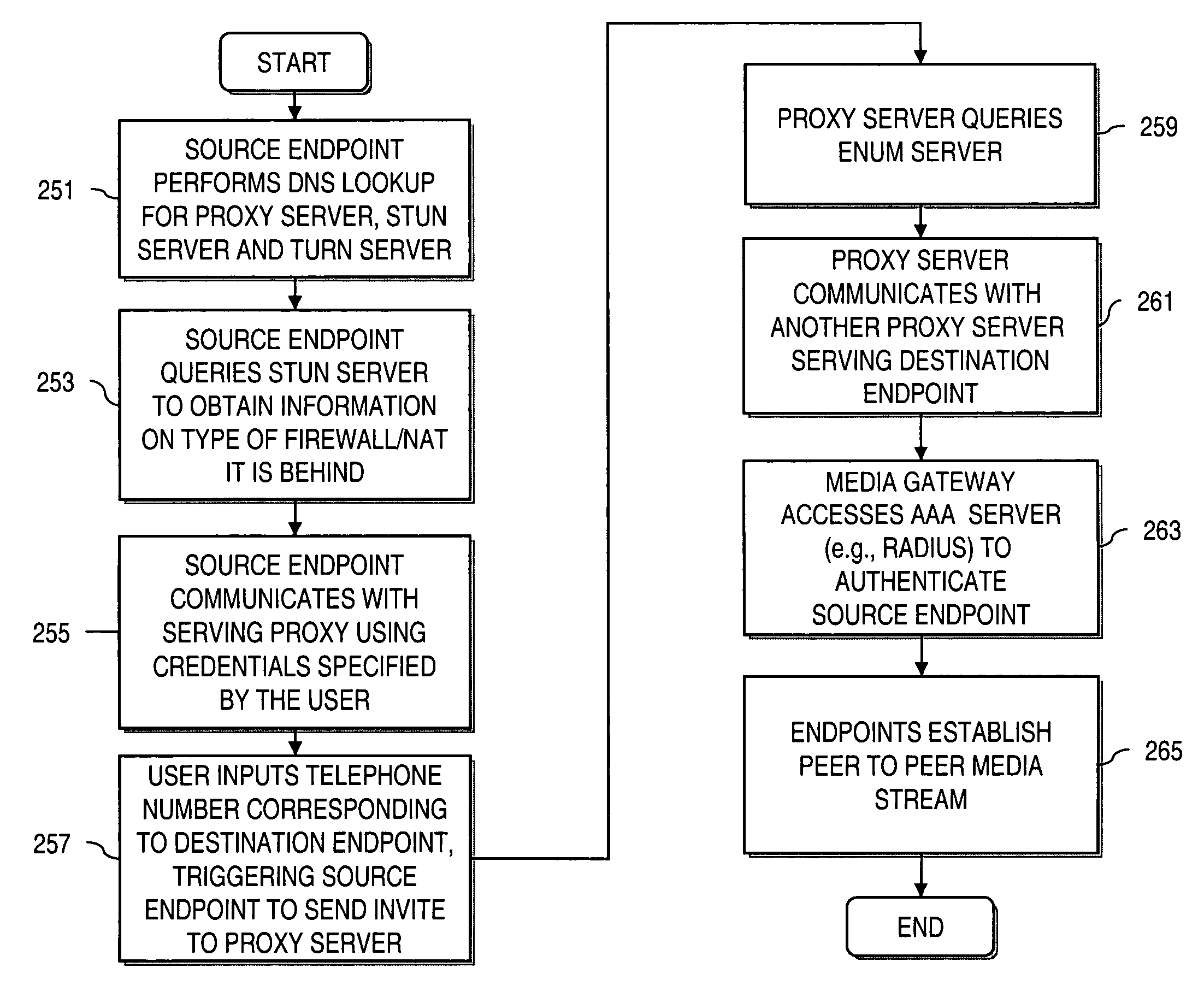
An approach provides interdomain traversal to support packetized voice transmissions. A signaling message is received for establishing a voice call from a first endpoint associated with a first domain to a second endpoint associated with a second domain. The first endpoint queries a STUN (Simple Traversal of UDP (User Datagram Protocol)) server to determine information relating to a firewall and network address translator that the first endpoint is behind, and to log into a TURN (Traversal Using Relay NAT (Network Address Translation)) server configured to establish a media path between the first endpoint and the second endpoint. A first proxy server serving the first endpoint communicates with an ENUM (Electronic Number) server to convert a directory number corresponding to the second endpoint to a network address. The first proxy server communicates with a second proxy server serving the second endpoint to establish the voice call. The STUN server, the TURN server and the ENUM server are maintained by service provider. The first endpoint is authenticated to permit exchange of a media stream over the media path. The media stream is relayed, if the first endpoint is successfully authenticated.
Owner:VERIZON PATENT & LICENSING INC
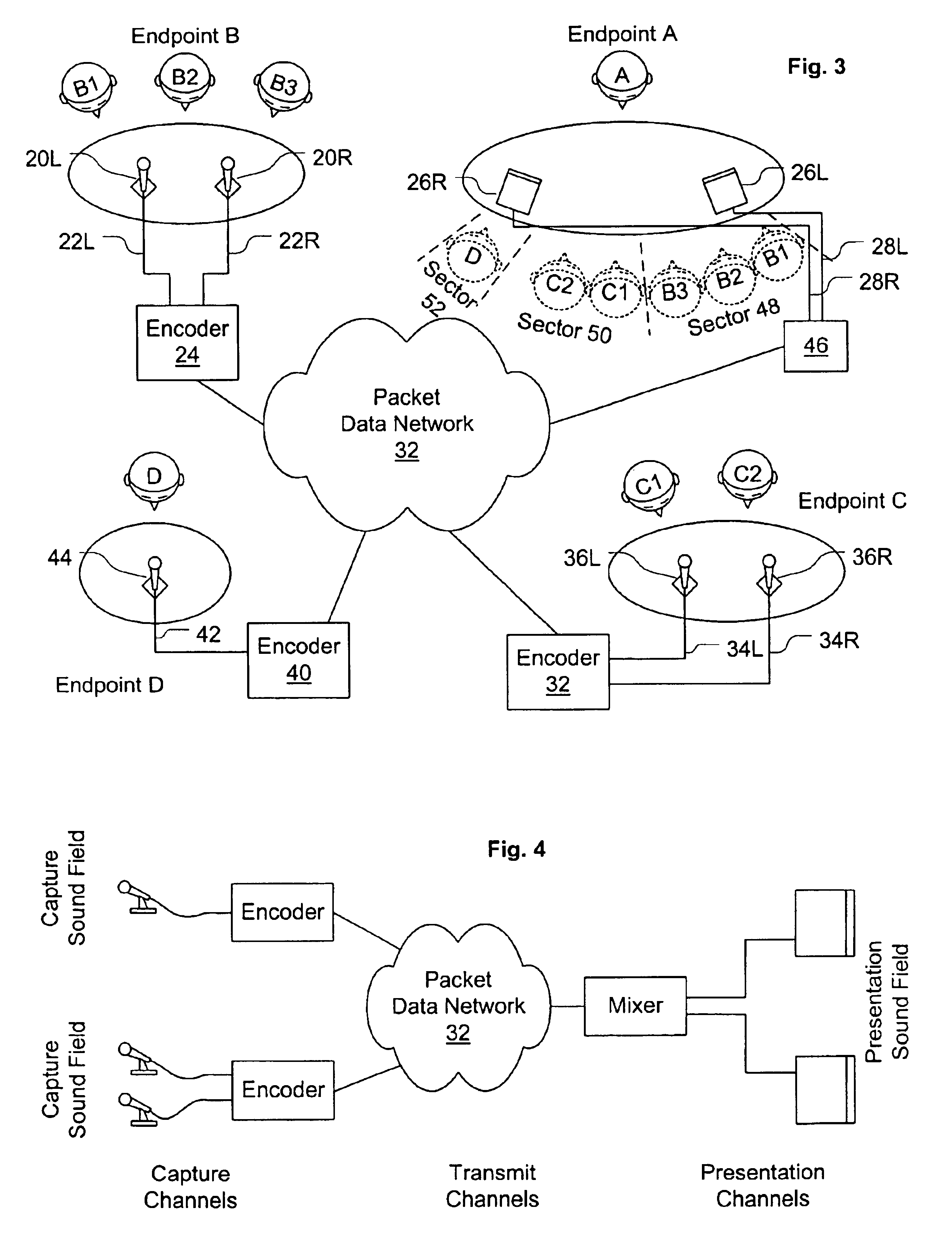
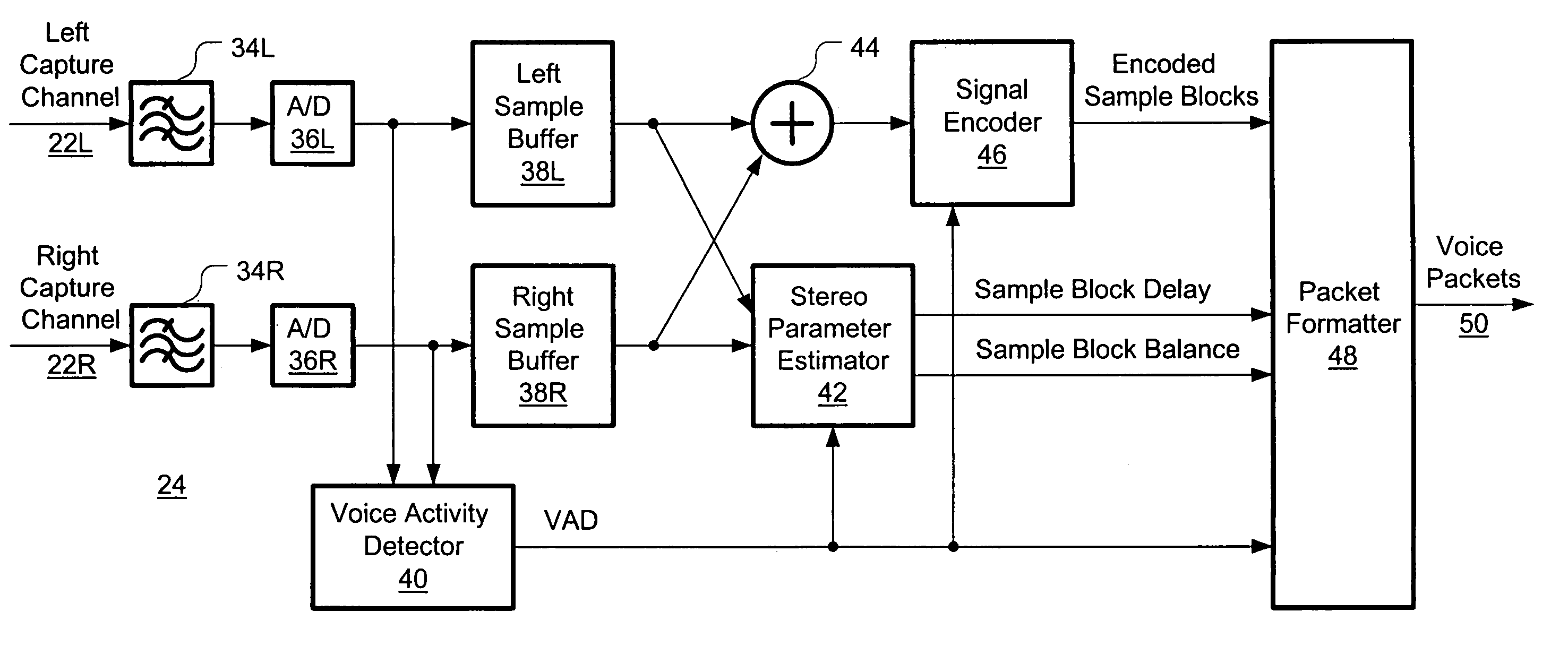
System and method for stereo conferencing over low-bandwidth links
InactiveUS6973184B1Satisfactory sound qualityTangible benefitTwo-way loud-speaking telephone systemsPublic address systemsVocal tractSpeech sound
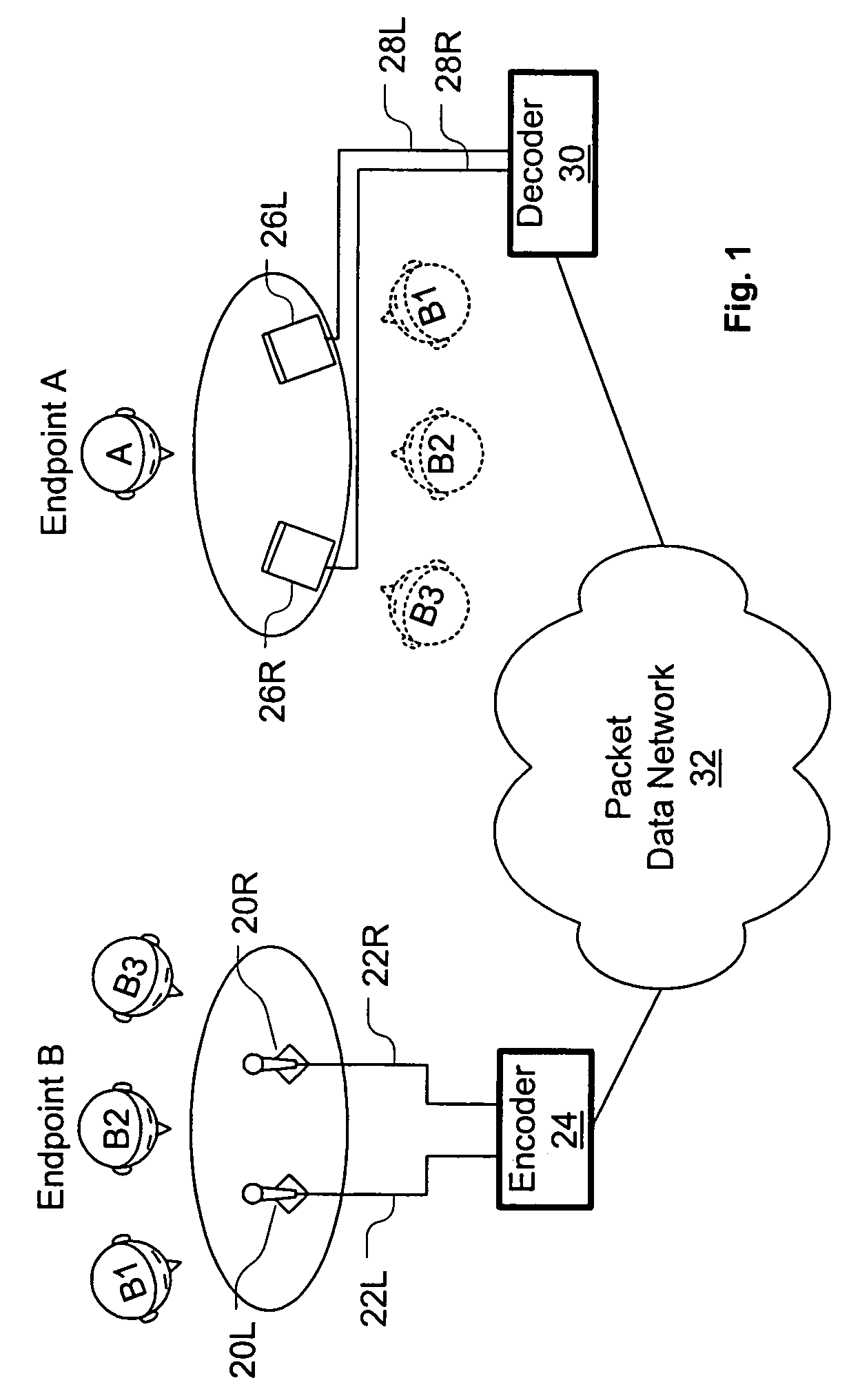
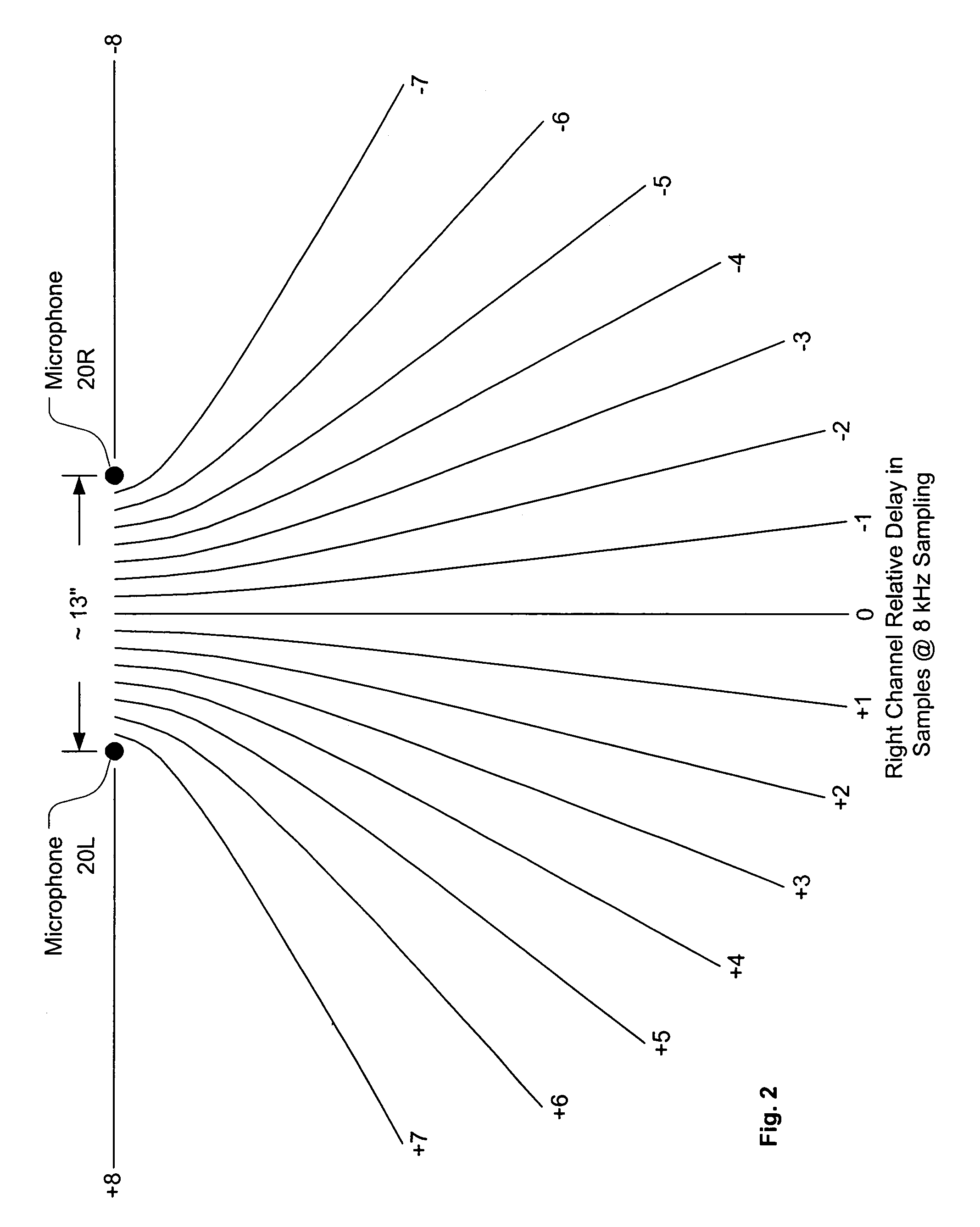
Systems and methods are disclosed for packet voice conferencing. An encoding system accepts two sound field signals, representing the same sound field sampled at two spatially-separated points. The relative delay between the two sound field signals is detected over a given time interval. The sound field signals are combined and then encoded as a single audio signal, e.g., by a method suitable for monophonic VoIP. The encoded audio payload and the relative delay are placed in one or more packets and sent to a decoding device via the packet network. The decoding device uses the relative delay to drive a playout splitter—once the encoded audio payload has been decoded, the playout splitter creates multiple presentation channels by inserting the transmitted relative delay in the decoded signal for one (or more) of the presentation channels. The listener thus perceives a speaker's voice as originating from a location related to the speaker's physical position at the other end of the conference. An advantage of these embodiments is that a pseudo-stereo conference can be conducted with virtually the same bandwidth as a monophonic conference.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Method and system for using a network-provided location for voice-over-packet emergency services calls
A client device transmits, via a voice-over-packet (VoP) access network, a message that requests an emergency services call. An outbound proxy server receives the message and obtains a network-provided location of the client device, e.g., by looking up the source address of the message in a location database maintained by the access network or by invoking an active network location function. The outbound proxy server inserts the network-provided location into the message, leaving any client-provided location in the message undisturbed, and forwards the message to an emergency services routing server. The emergency services routing server determines which public safety answering point (PSAP) should receive the call, based on at least one of the network-provided location and any client-provided location in the message.
Owner:SPRINT SPECTRUM LLC
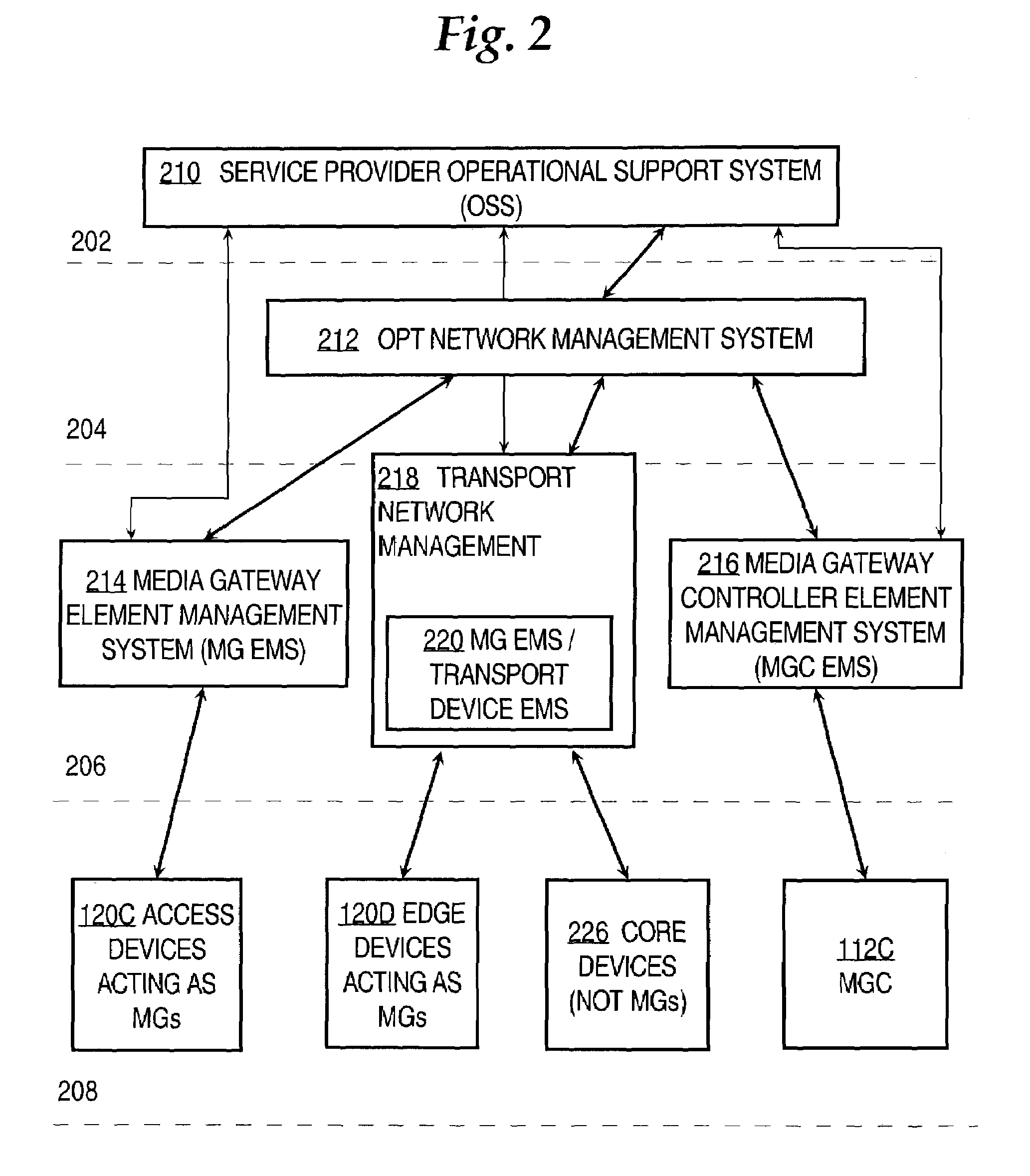
Automatically discovering management information about services in a communication network
An automatic service discovery approach allows a network management system to discover service managed objects from the network, eliminating the need for a user or other management application to provide such information. As a result, a network management system can automatically perform network-level or services level discovery of objects and services for which network components have no understanding. Embodiments are applicable, for example, in the context of management of packet voice (VoIP, VoATM) and metro Ethernet (TLS service) domains, as well as other domains.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
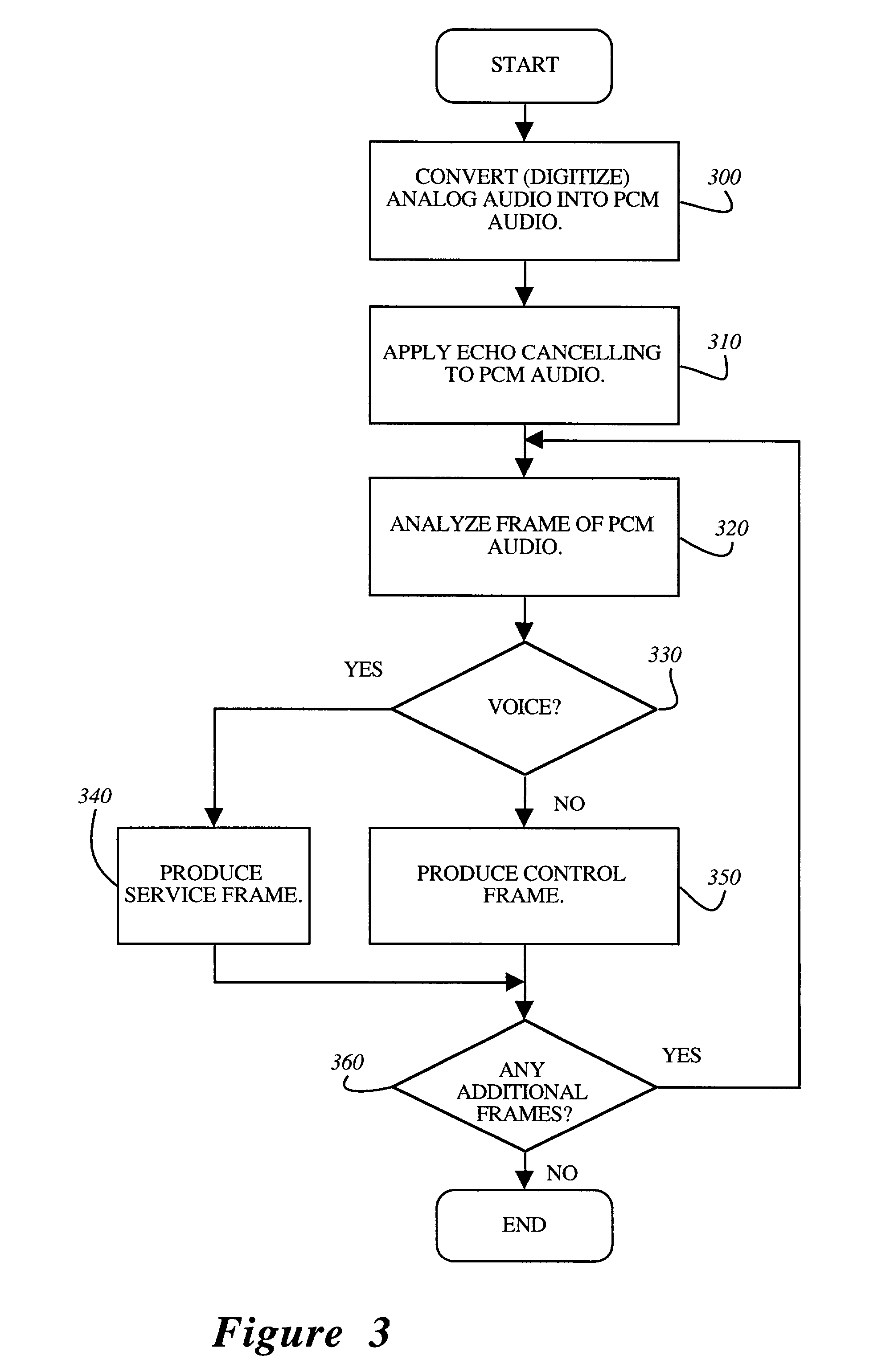
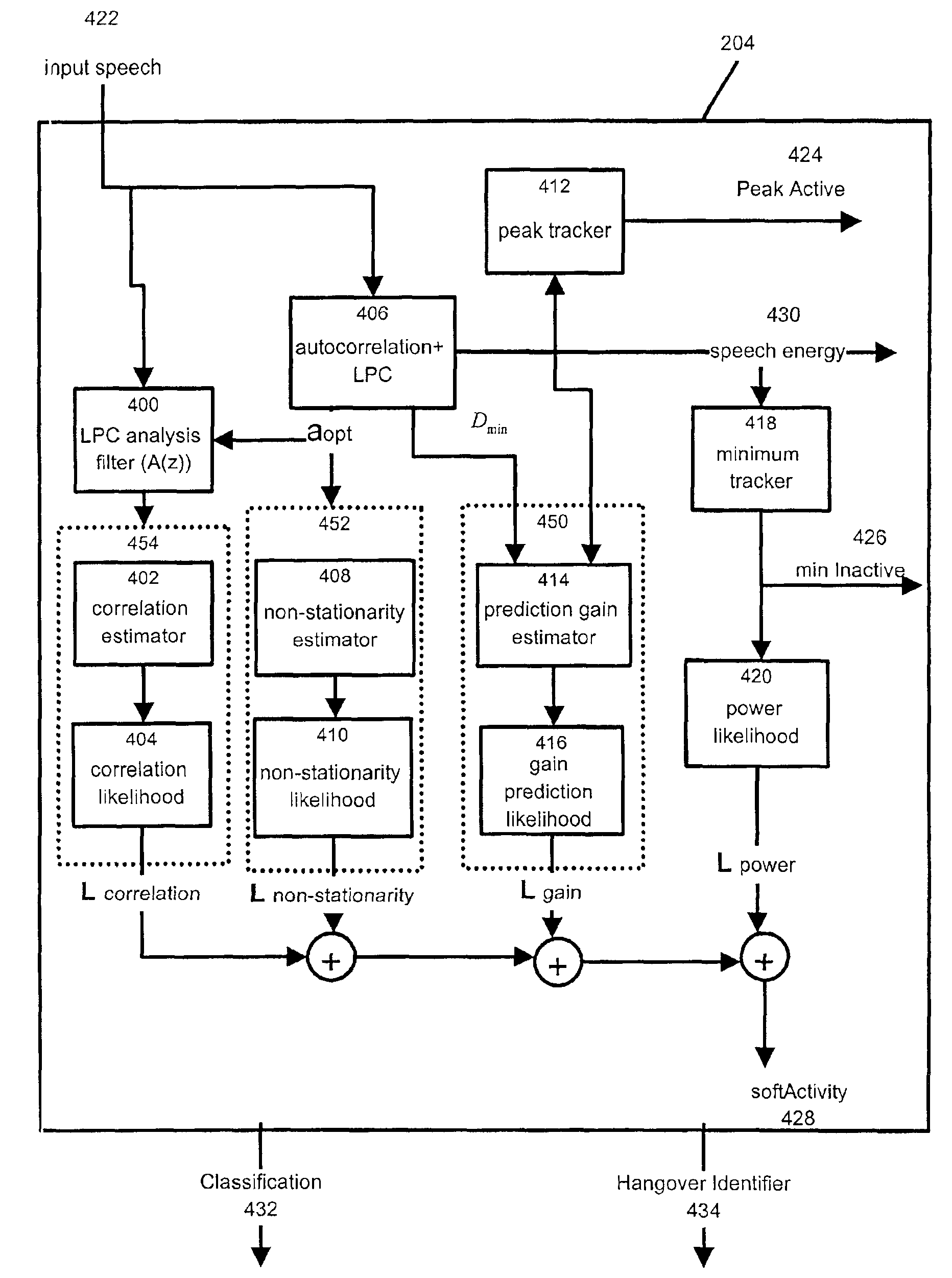
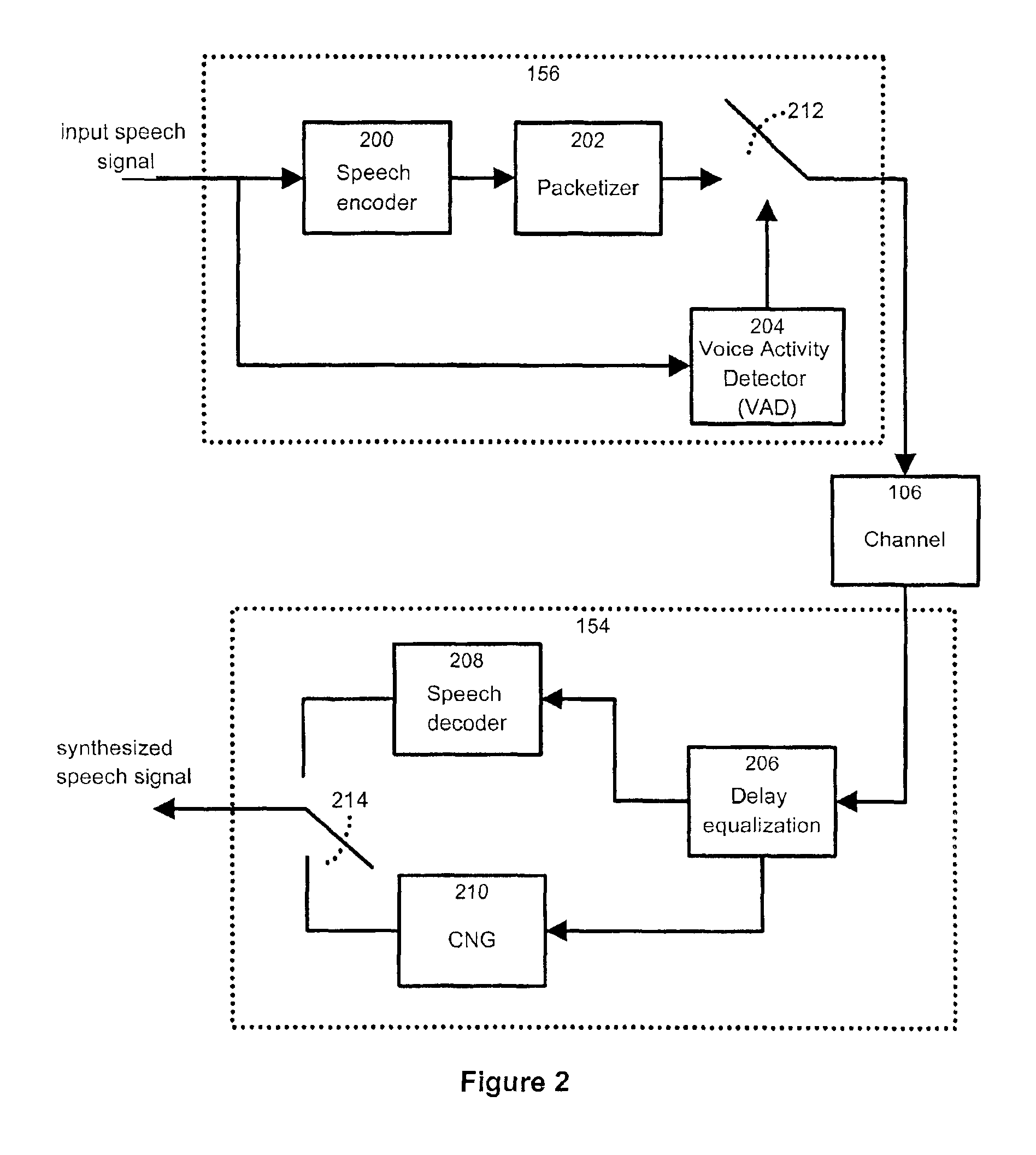
A voice activity detector for packet voice network
A voice activity detector to analyze a short-term averaged energy (STAE), a long-term averaged energy (LTAE), and a peak-to-mean likelihood ratio (PMLR) in order to determine whether a current audio frame being transmitted represents voice or silence. This is accomplished by determining whether a sum of the STAE and a factor is greater than the LTAE. If not, the current audio frame represents silence. If so, a second set of determinations is performed. Herein, a determination is made as to whether the difference between the LTAE and the STAE is less than a predetermined threshold. If so, the current audio frame represents voice. Otherwise, the PMLR is determined and compared to a selected threshold. If the PMLR is greater than the selected threshold, the current audio frame represents a voice signal. Otherwise, it represents silence.
Owner:NORTEL NETWORKS LTD
Hierarchical data collection network supporting packetized voice communications among wireless terminals and telephones
InactiveUS20050013266A1Modulated-carrier systemsDevices with card reading facilityVoice communicationThe Internet
A packet-based, hierarchical communication system, arranged in a spanning tree configuration, is described in which wired and wireless communication networks exhibiting substantially different characteristics are employed in an overall scheme to link portable or mobile computing devices. The network accommodates real time voice transmission both through dedicated, scheduled bandwidth and through a packet-based routing within the confines and constraints of a data network. Conversion and call processing circuitry is also disclosed which enables access devices and personal computers to adapt voice information between analog voice stream and digital voice packet formats as proves necessary. Routing pathways include wireless spanning tree networks, wide area networks, telephone switching networks, internet, etc., in a manner virtually transparent to the user. A voice session and associate call setup simulates that of conventional telephone switching network, providing well-understood functionality common to any mobile, remote or stationary terminal, phone, computer, etc.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
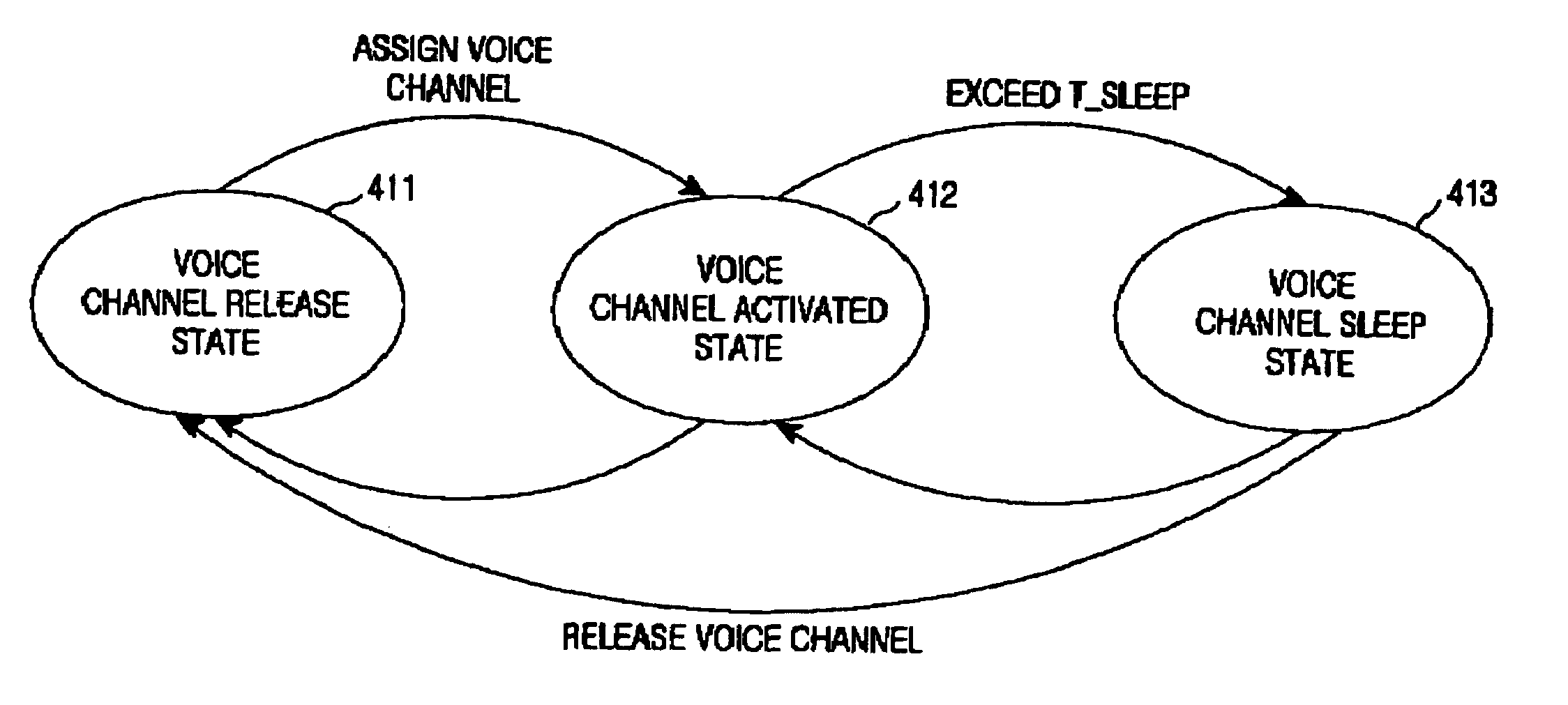
Device and method for communicating packet voice data in mobile communication system
InactiveUS6928289B1High-speed data serviceInterconnection arrangementsNetwork traffic/resource managementMobile communication systemsVoice over packet
A device and method for communicating voice data in packet form in a mobile communication system. In the packet voice data communication method, upon generation of voice data, a packet voice channel is assigned, and an active state is entered where packetized voice data is transmitted on the voice channel. If there is no voice data for a predetermined time period while in the active state, the assigned voice channel is released, and an inactive state is entered where no voice data is transmitted. If the next voice data is generated while in the inactive state, the voice channel active state is entered where a voice channel is assigned to transmit the next voice data, and the voice data is transmitted.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Telephony communication via varied redundant networks
InactiveUS7012898B1Increase heightReliable serviceIntelligent networksInterconnection arrangementsVoice communicationThe Internet
A switched telephone network is arranged in a manner to enable packet voice communication between telephone terminals via multiple redundant packet switched networks. The packet switched networks may utilize different protocols, be operated by different entities, and have primary functions other than voice communication. One example of such a network may be internetworked networks, such as the Internet. One example of an alternate packet switched network may be a network whose primary function is control of a circuit switched telephone network. The common channel interoffice switching system (CCIS) of a public switched telephone network (PSTN) is one such example.
Owner:VERIZON PATENT & LICENSING INC
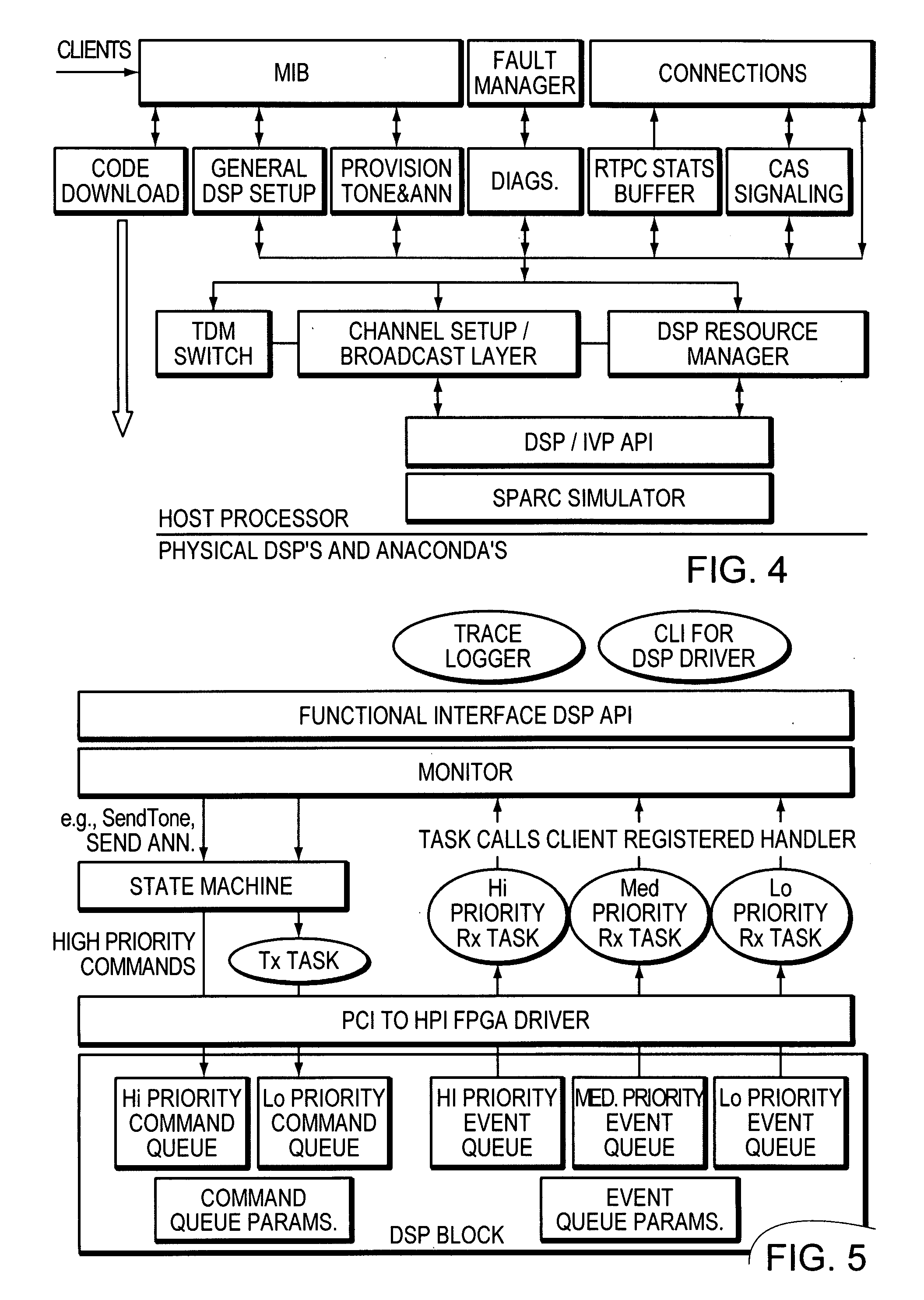
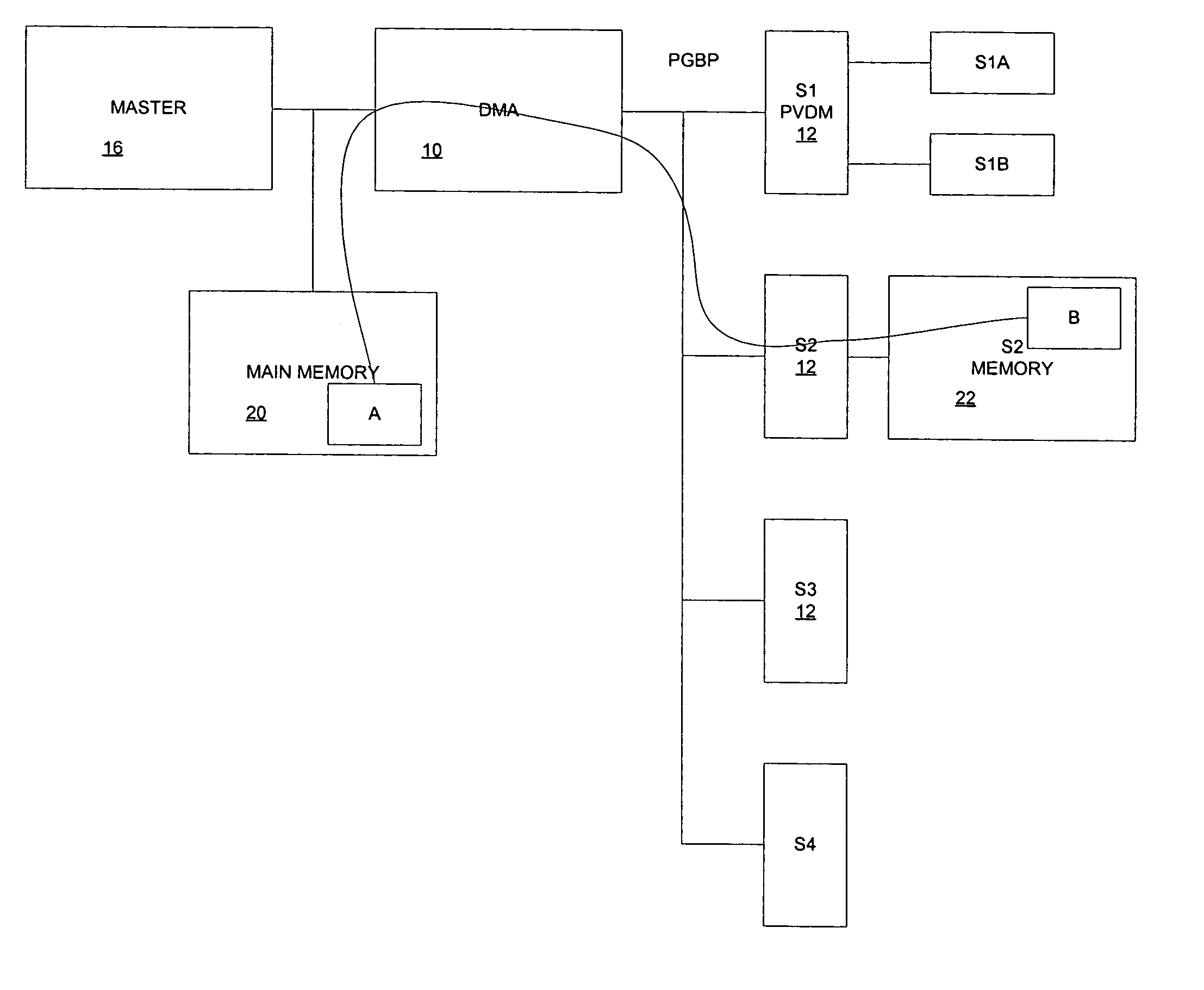
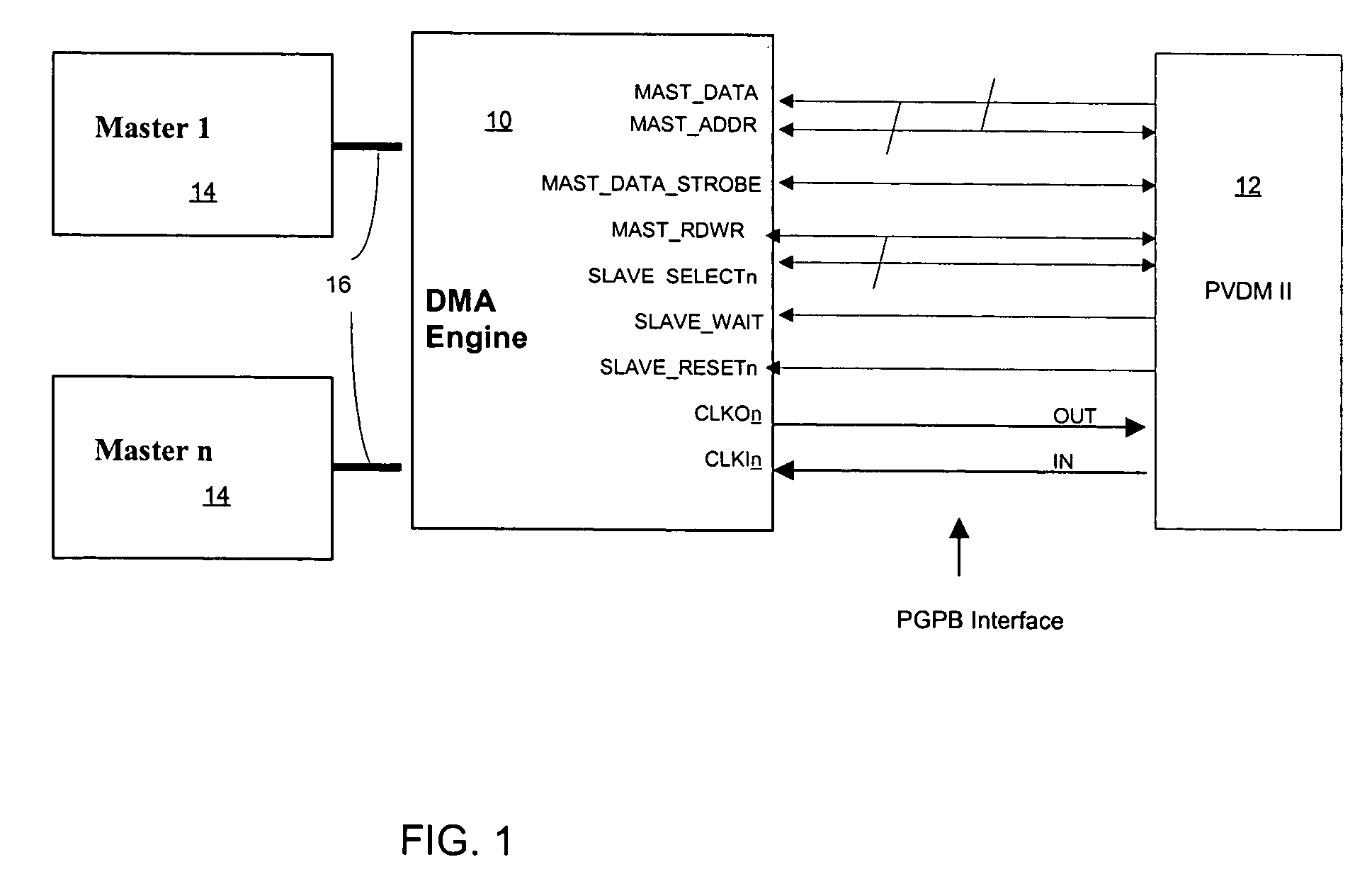
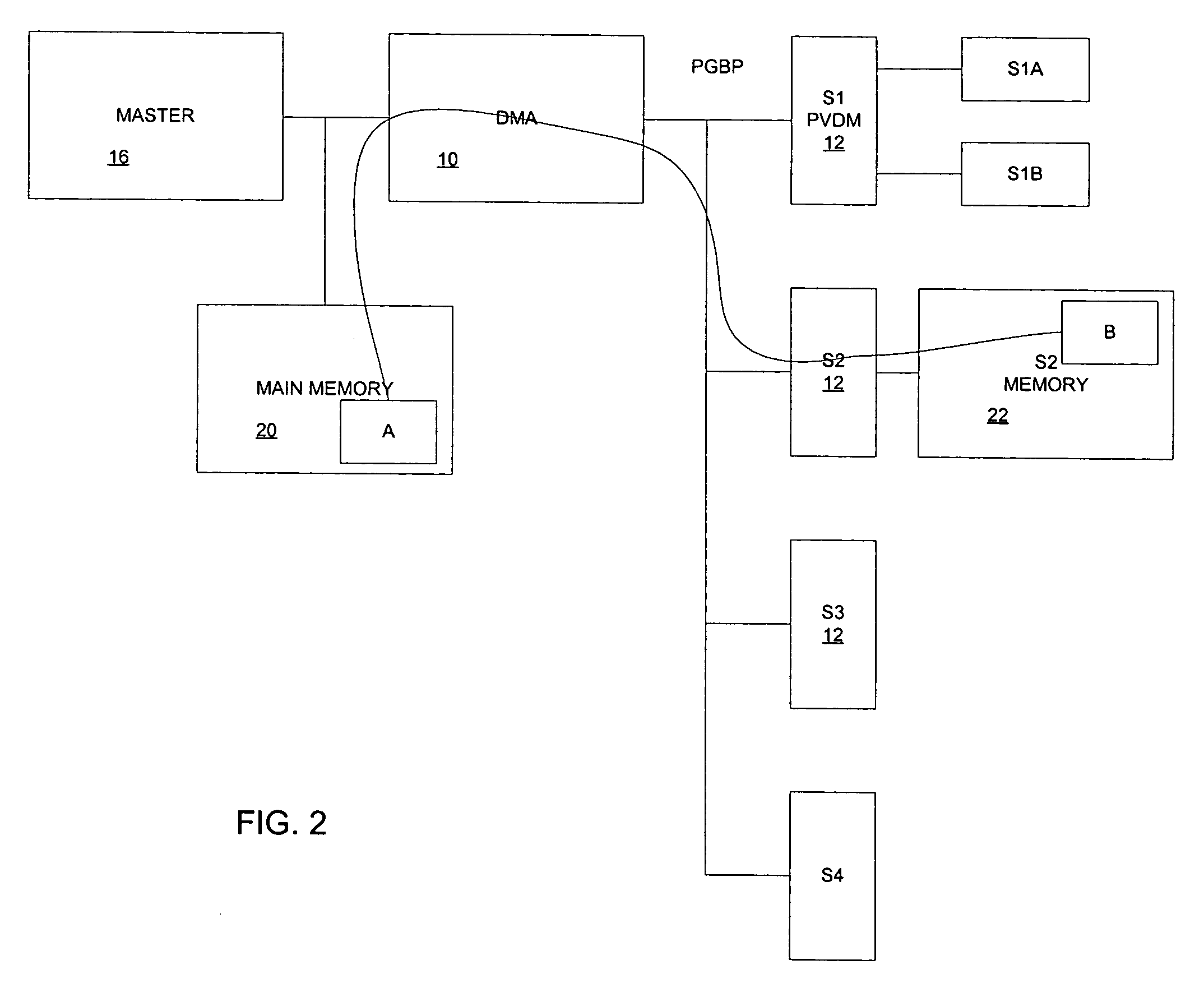
PVDM (packet voice data module) generic bus
A generic, parallel, n-bit wide data path communication bus allows a number of major slave devices (such as DSPs, Microprocessors, ASICs, FPGAs, etc) to be used with PVDMs and other devices. A higher level protocol allows a DMA engine to interface multiple Master devices directly with multiple slave modules through the DMA engine.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
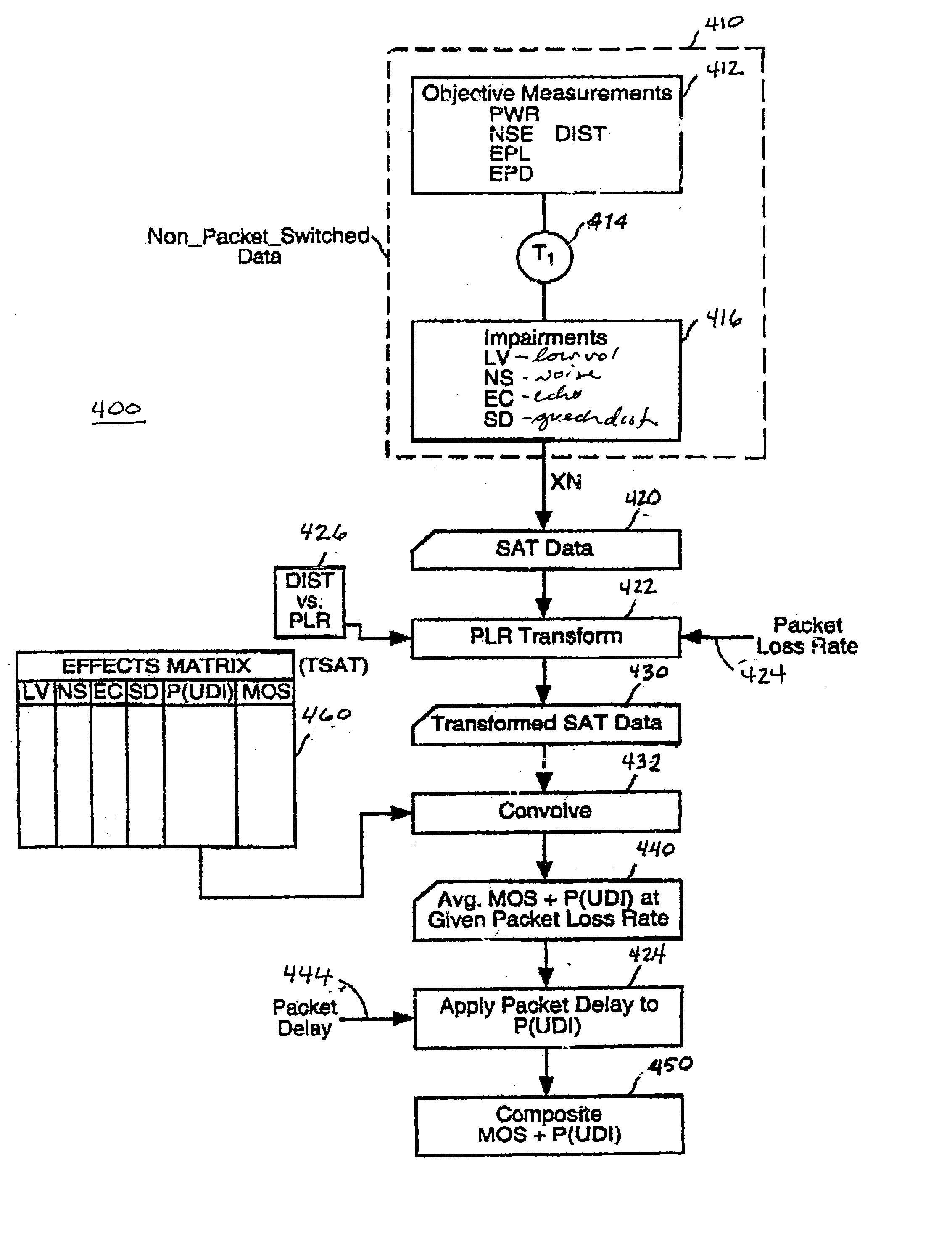
Real time monitoring of perceived quality of packet voice transmission
InactiveUS20050141493A1Distort measurementMonitoring voice qualityError preventionTransmission systemsVoice communicationObjective measurement
The present invention is directed to a system and method for monitoring perceived quality of a packet-switched voice service in a network. The method includes the step of receiving a packetized voice communication via the packet-switched voice service. At least one objective measurement is obtained from the received packetized voice communication. User perceived quality of voice data is derived from the at least one objective measurement. The user perceived quality of voice data is provided to a user. The steps of receiving, obtaining, deriving, and providing are performed in real-time.
Owner:FAR NORTH PATENTS LLC
Method and apparatus for improved voice activity detection in a packet voice network
InactiveUS6889187B2Reduce signalingImprove voice qualitySpeech recognitionVoice activityAudio frequency
A method and apparatus for detecting and transmitting voice signals in a packet voice network system. The method and apparatus make use of a voice activity detection (VAD) unit at a transmitter, for determining if an input signal contains active audio information or passive audio information, where the input signal includes a plurality of frames. For one or more frames of the input signal containing active audio information, the VAD computes a hangover time period. This computation includes determining whether the hangover time period has a fixed duration or a variable duration on the basis of characteristics of the active audio information contained in the one or more frames. When the VAD detects a frame containing passive audio information subsequent to the one or more frames containing active audio information, the input signal is suppressed after the expiry of the computed hangover time period from the detection of the passive audio information.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
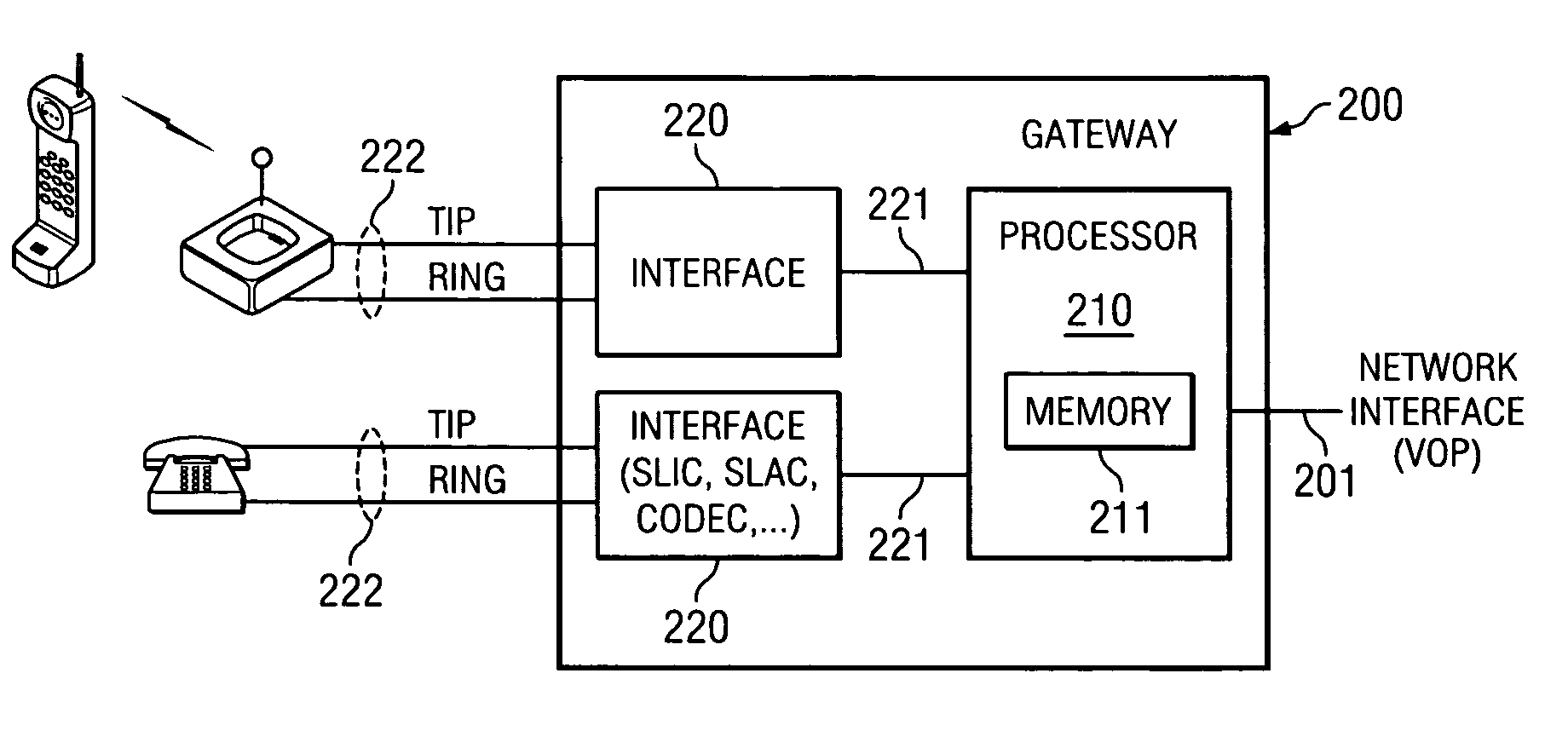
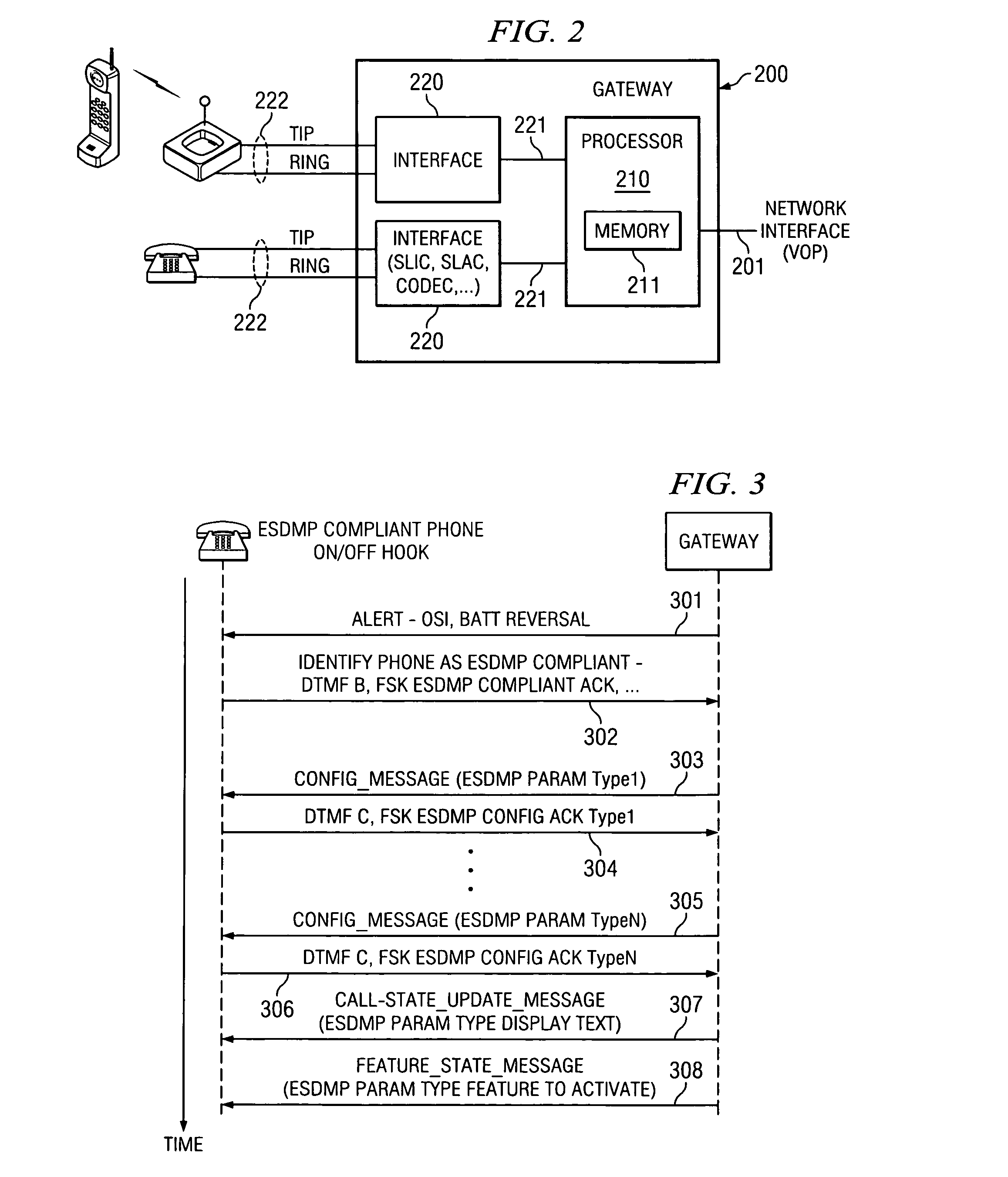
Method and apparatus for activating extended services in a user device using a voice over packet gateway
ActiveUS7403604B2Automatic call-answering/message-recording/conversation-recordingData switching by path configurationComputer hardwareFrequency-shift keying
An enhanced services display message protocol (ESDMP) facilitates display of messages in a compliant analog telephony device (ATD). An exemplary gateway device in a voice over packet (VOP) network can activate enhanced services in a compliant ATD using the ESDMP and includes a controller and first and second interfaces. One of the interfaces can transmit and receive communications over a VOP network. The other interface can transmit and receive voice band message data modulated according to a frequency shift keying (FSK) protocol. The ESDMP can be used to configure the gateway to activate features supported by the ATD, to update call state information and to display feature state information.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
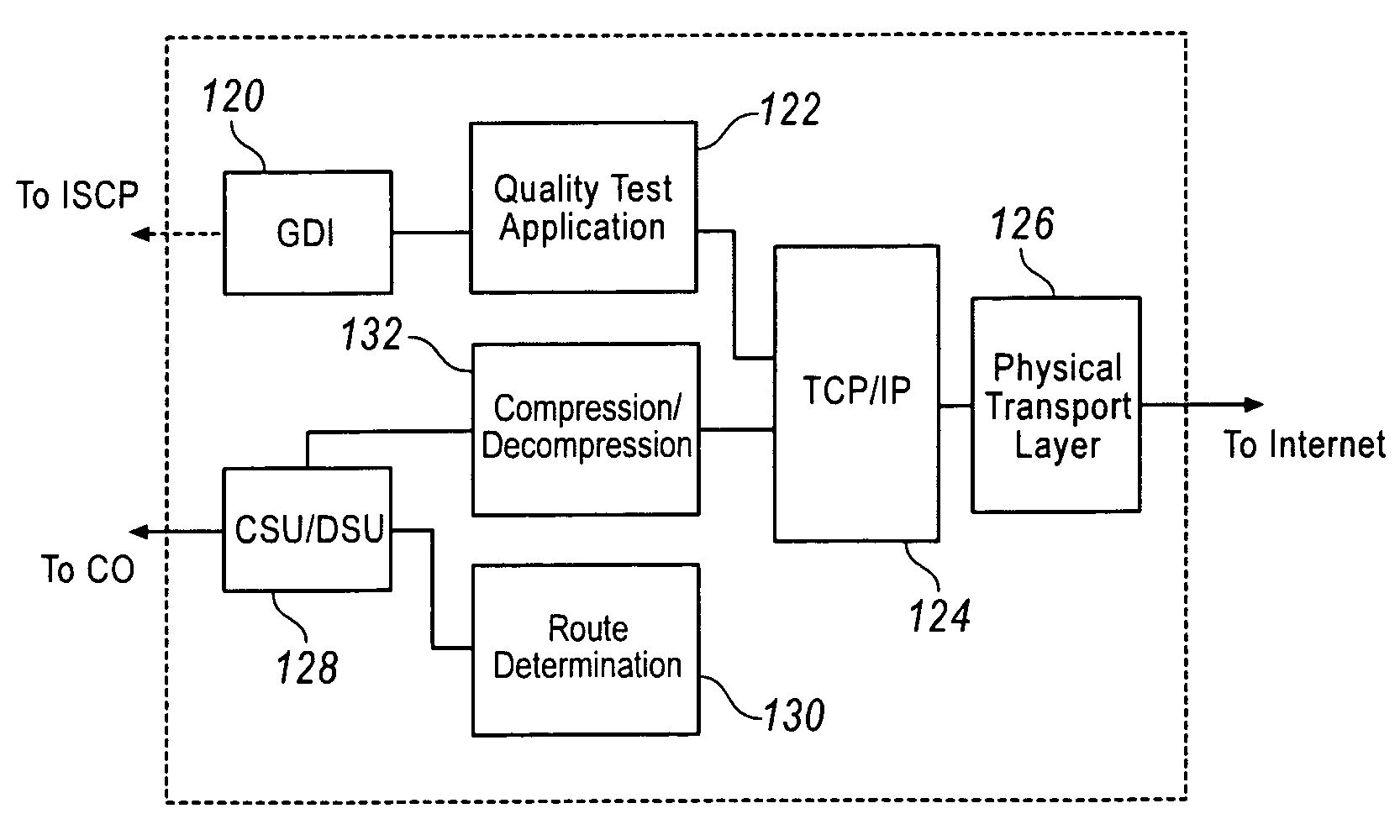
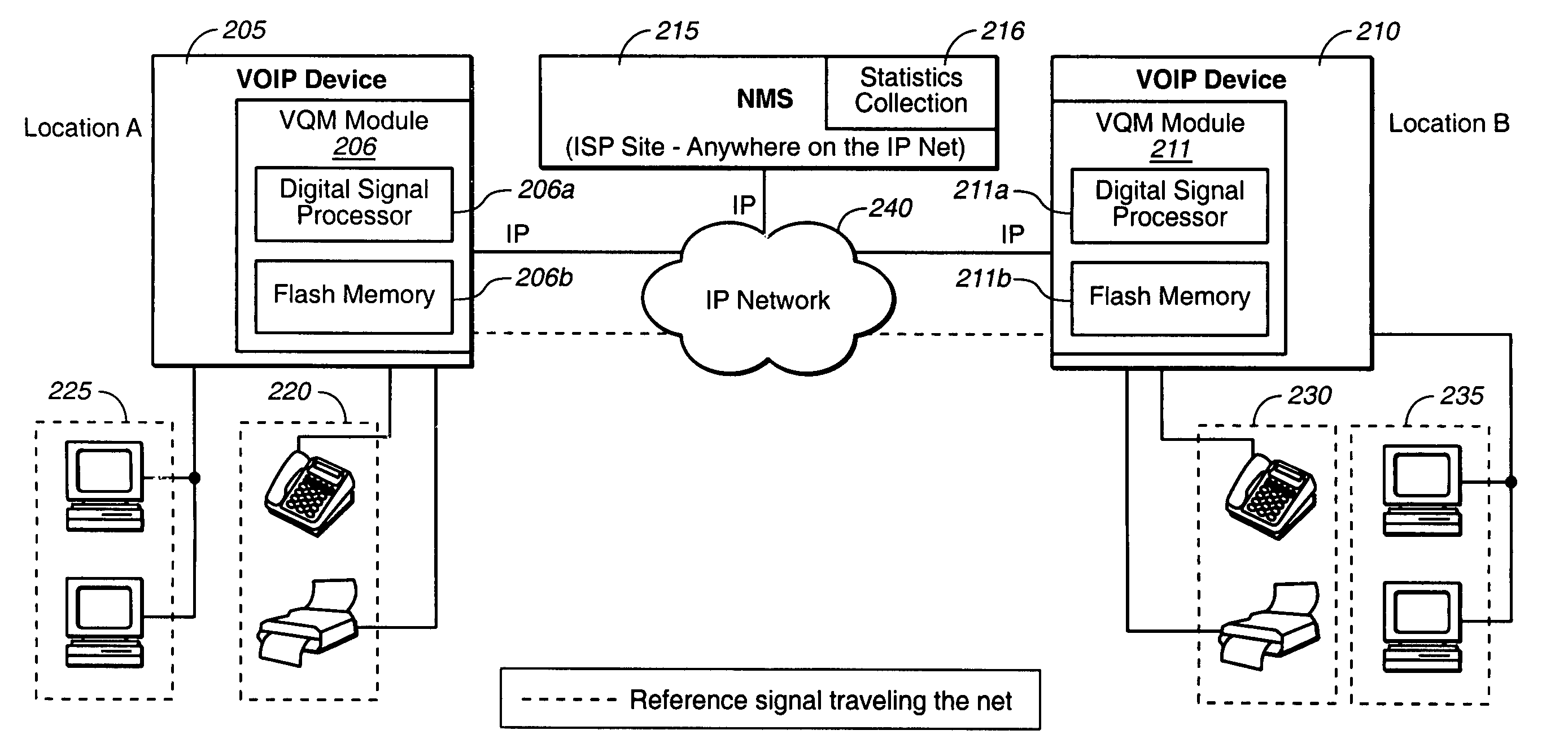
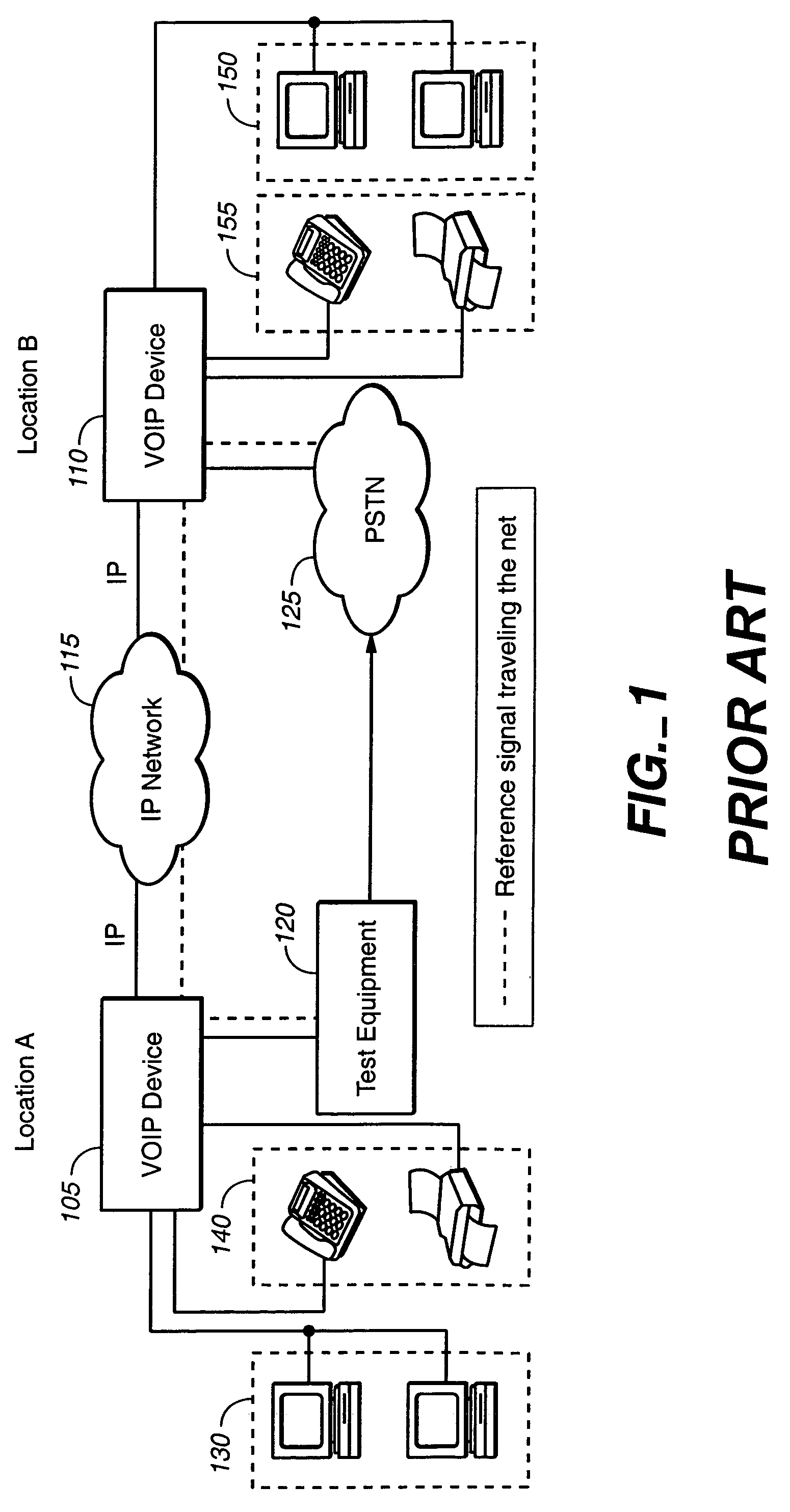
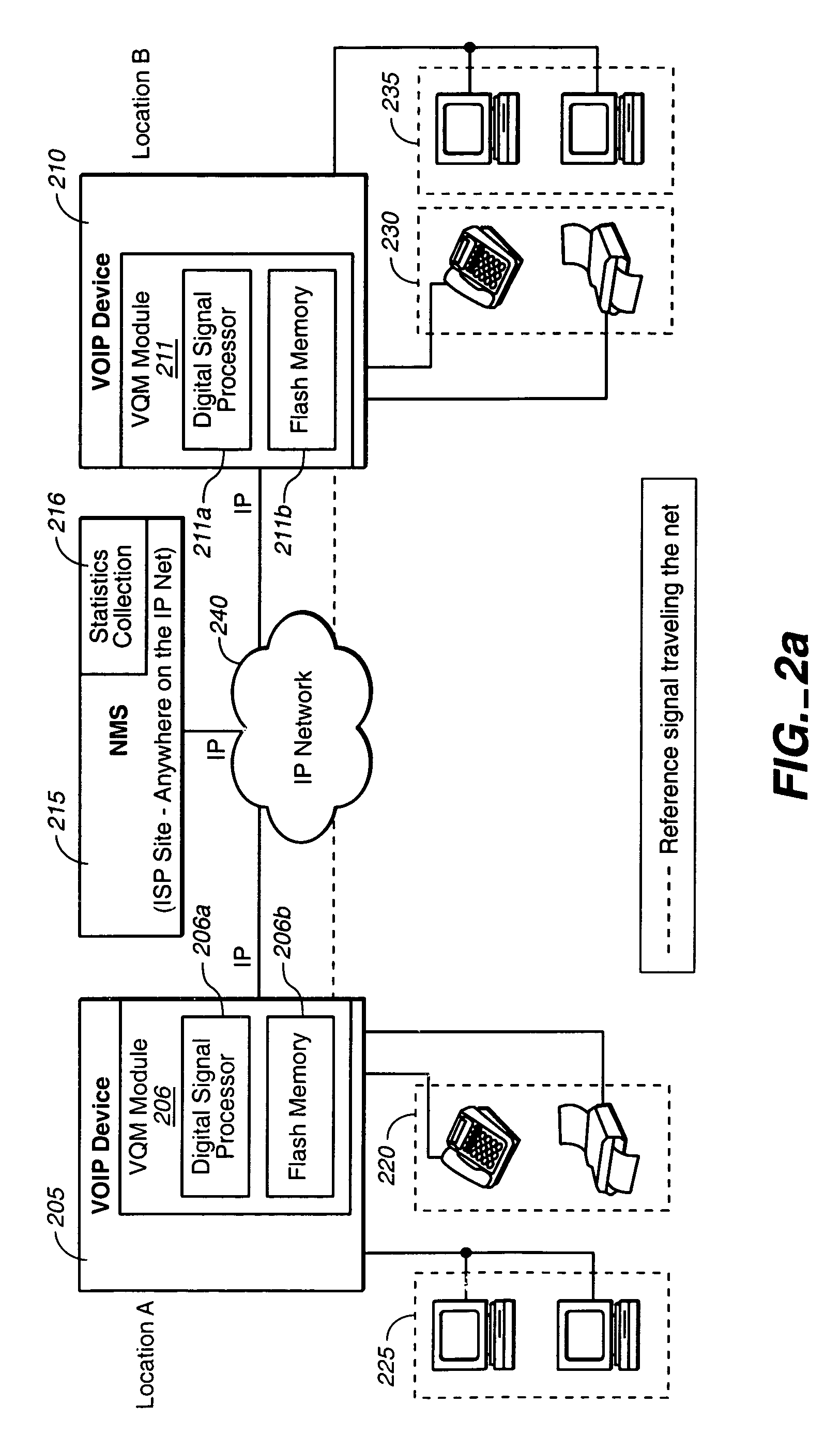
System for real time voice quality measurement in voice over packet network
InactiveUS7197010B1Measurement qualityEliminate needError preventionTransmission systemsStart timeObjective measurement
In assessing the capability of an IP based network to support toll telephony service, objective measurements of Speech Quality are taken. A module is used with Voice over Packet equipment that allows performance of voice quality measurements in real-time without using any external test equipment. A reference signal that includes a marker and a voice test signal is sent through the network from one Voice over Packet equipment containing or connected to the module to another. The received marker is compared to the reference marker to identify the onset time of the received voice test signal. The received and reference voice test signals are processed to measure the quality of the network. This may be implemented using the processing power and memory resources present in Voice over Packet equipment giving the network administrator an enhanced test capability at each node of the network. Voice quality measurements may be generated in a transparent way for the callers in real-time under severely degraded conditions of the network.
Owner:DASAN ZHONE SOLUTIONS INC
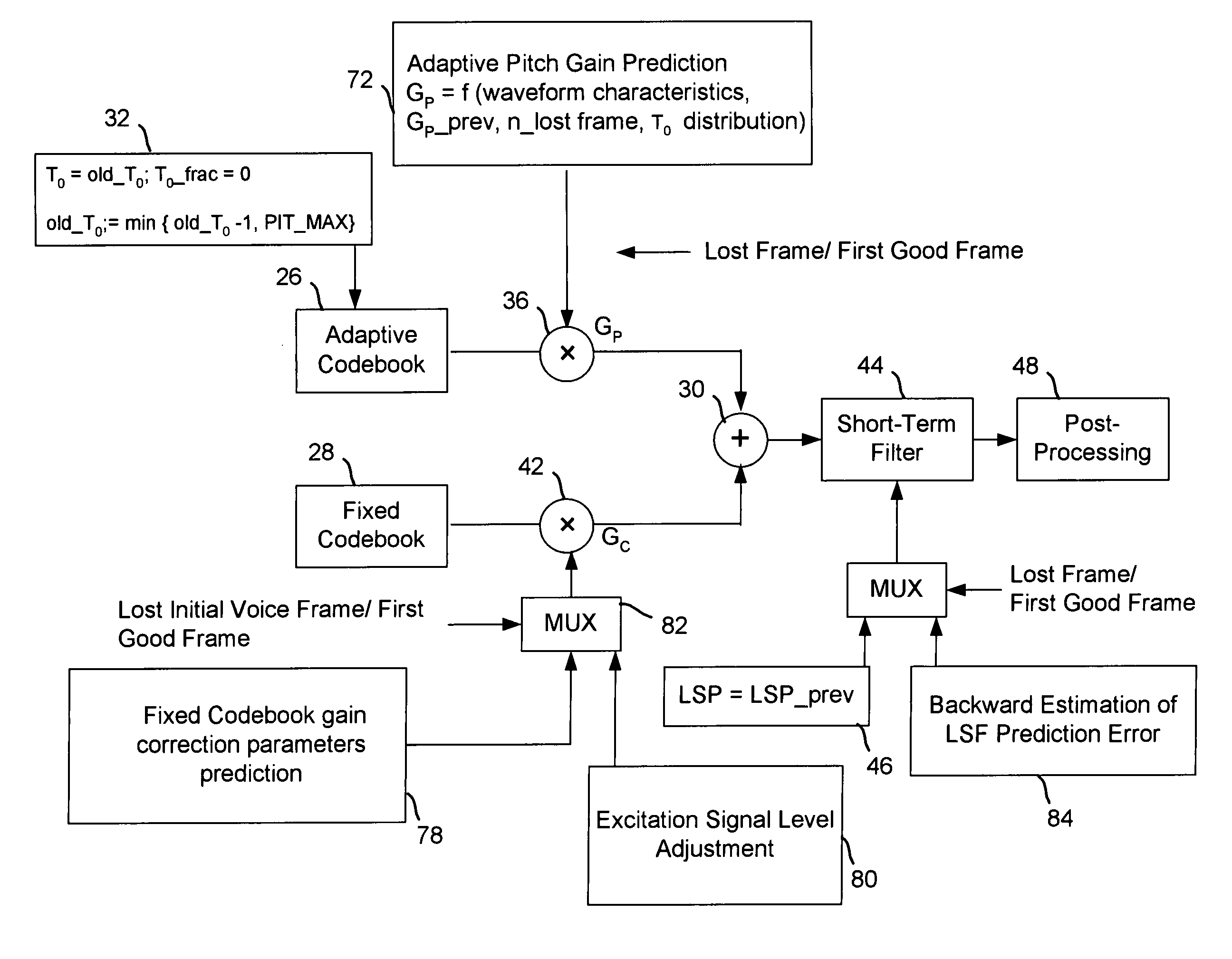
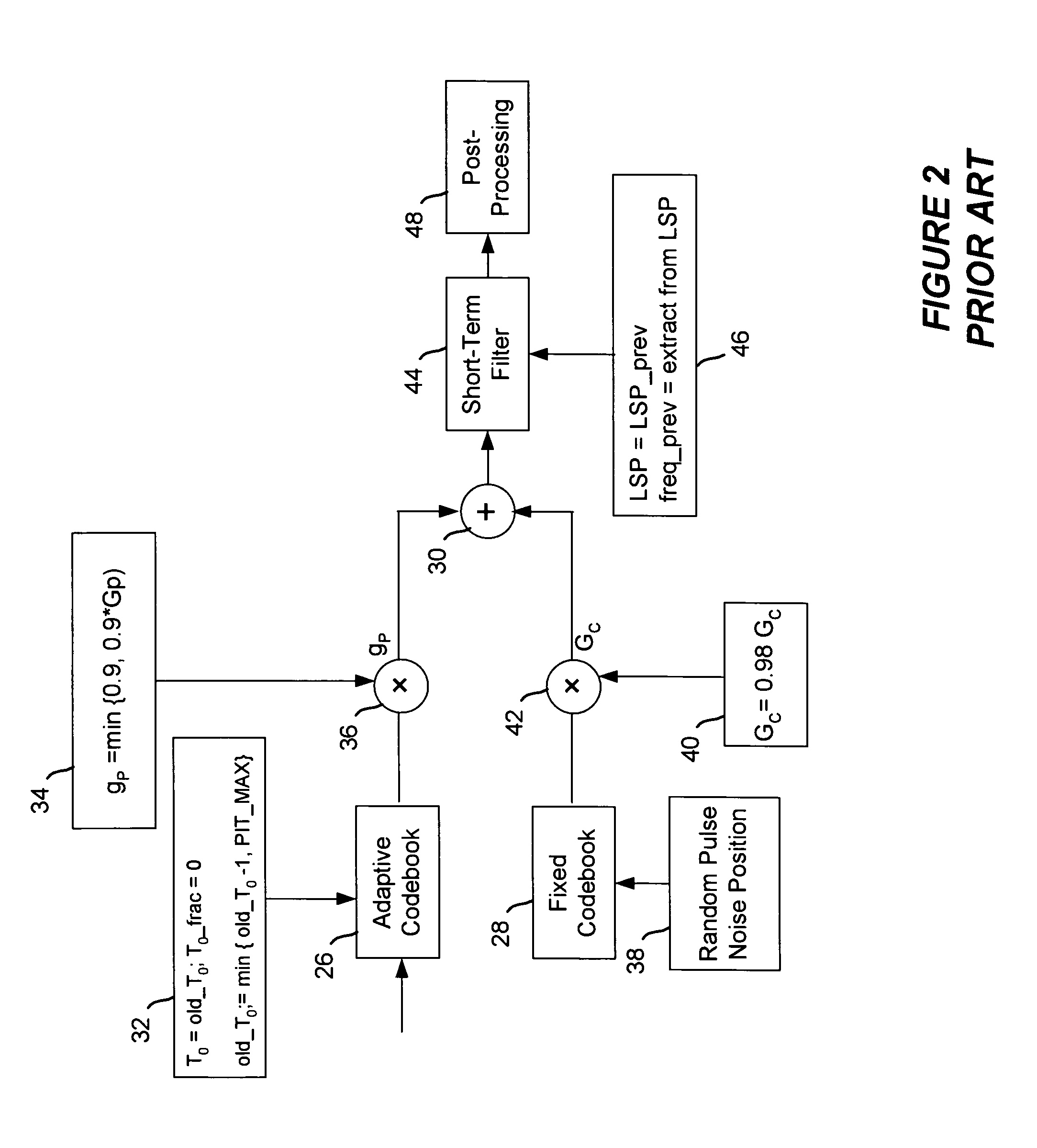
Packet loss concealment for a conjugate structure algebraic code excited linear prediction decoder
InactiveUS20070282601A1Speech analysisAlgebraic code-excited linear predictionClassification methods
A method to improve packet loss concealment for generation of a synthetic speech signal in a algebraic code excited linear prediction decoder for a voice over packet network. One method improves features for coding gains in the decoder and for post-filtering of the signals. An alternative method uses a classification method for the signal based on the bitstream in the decoder.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
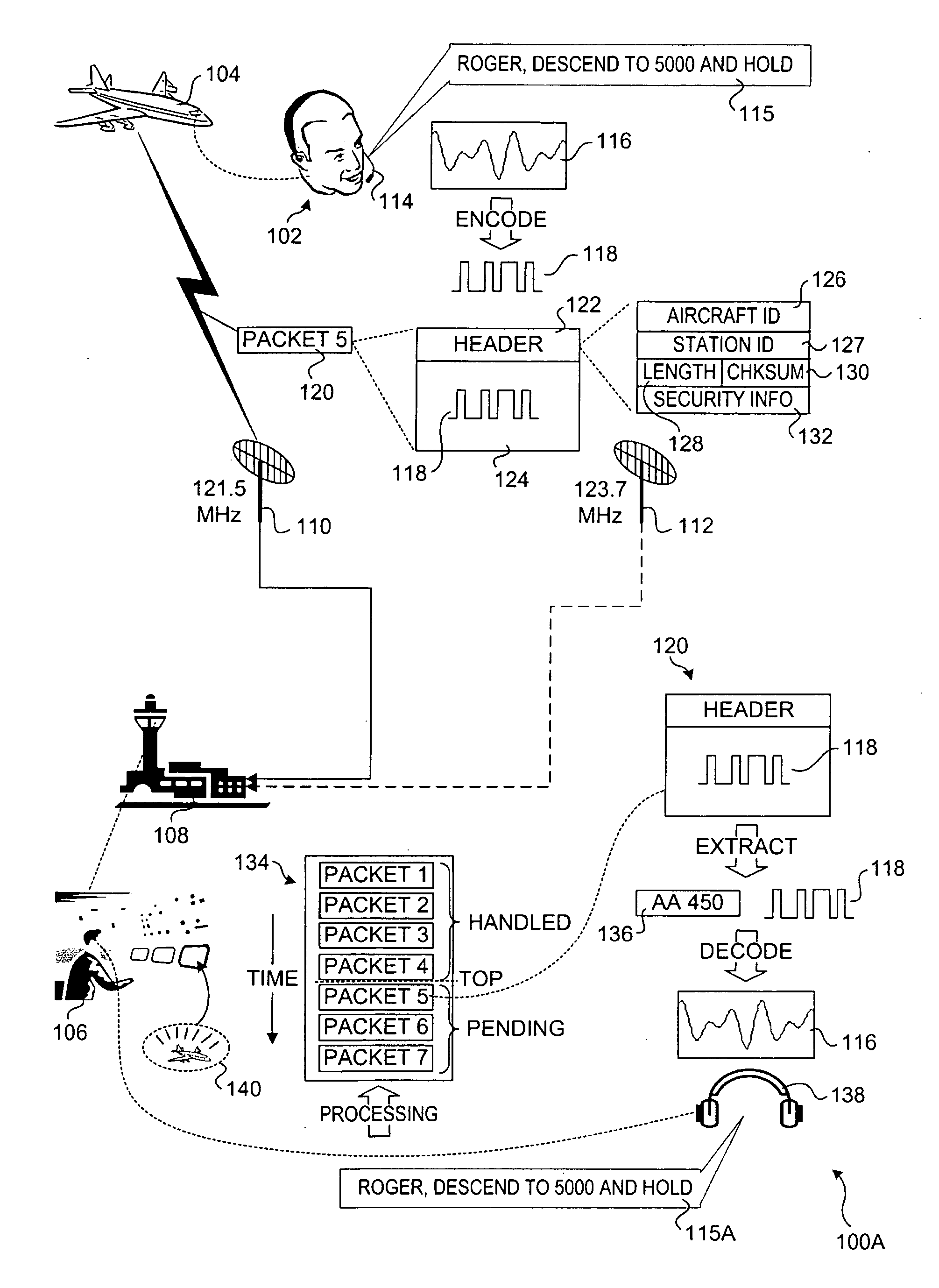
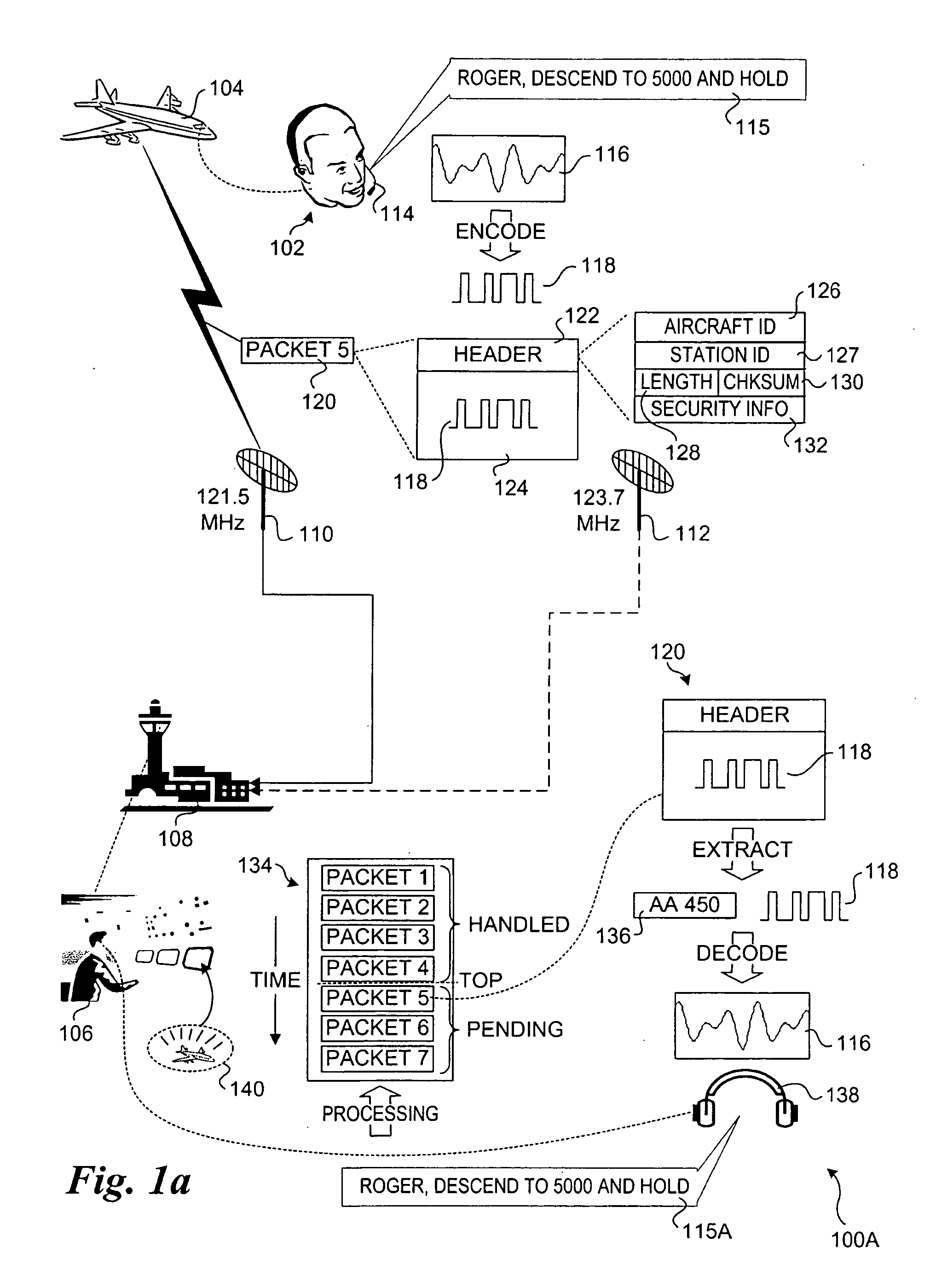
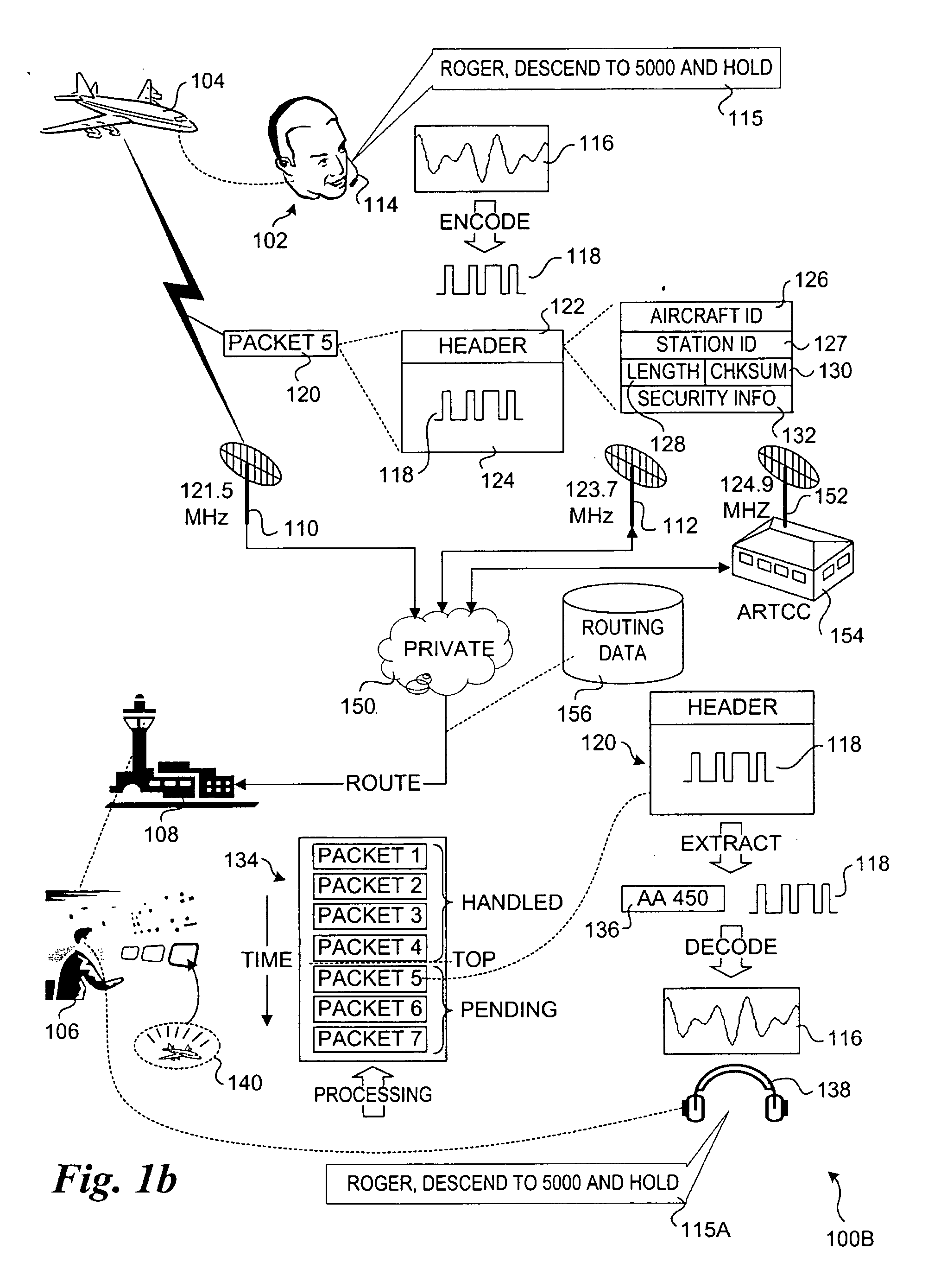
Packetized voice communication method and system
InactiveUS20060046715A1Easy to optimizeVerbal communicationAnalogue computers for vehiclesAnalogue computers for trafficVoice communicationGround station
A packetized voice communication method and system. Techniques are disclosed for supporting communication between aircraft and ground stations using packetized digitally-encoded messages. The encoded messages, which originate from verbalized messages, may be transmitted using conventional and future radio frequency (RF) radio communication technologies. Virtual channels are employed to enable a single ground station or controller to communicate with multiple aircraft by employing different physical radio transmission channels for the aircraft. Messages sent from aircraft to controllers are received by various ground antennas and routed to an appropriate ground station identified by each message's packet header. The messages for a given ground station are inserted into a queue that is manually or automatically advanced. Upon reaching the top of the queue, the message is decoded and played back at the controller's headset. Controller-to-aircraft messages are sent in a similar manner.
Owner:BURGEMEISTER ALVIN H
Method and System for Grouping Voice Messages
ActiveUS20080215323A1Eliminates and reduces of disadvantageEliminates and reduces of and problemAutomatic call-answering/message-recording/conversation-recordingAutomatic exchangesSpeech soundVoice over packet
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
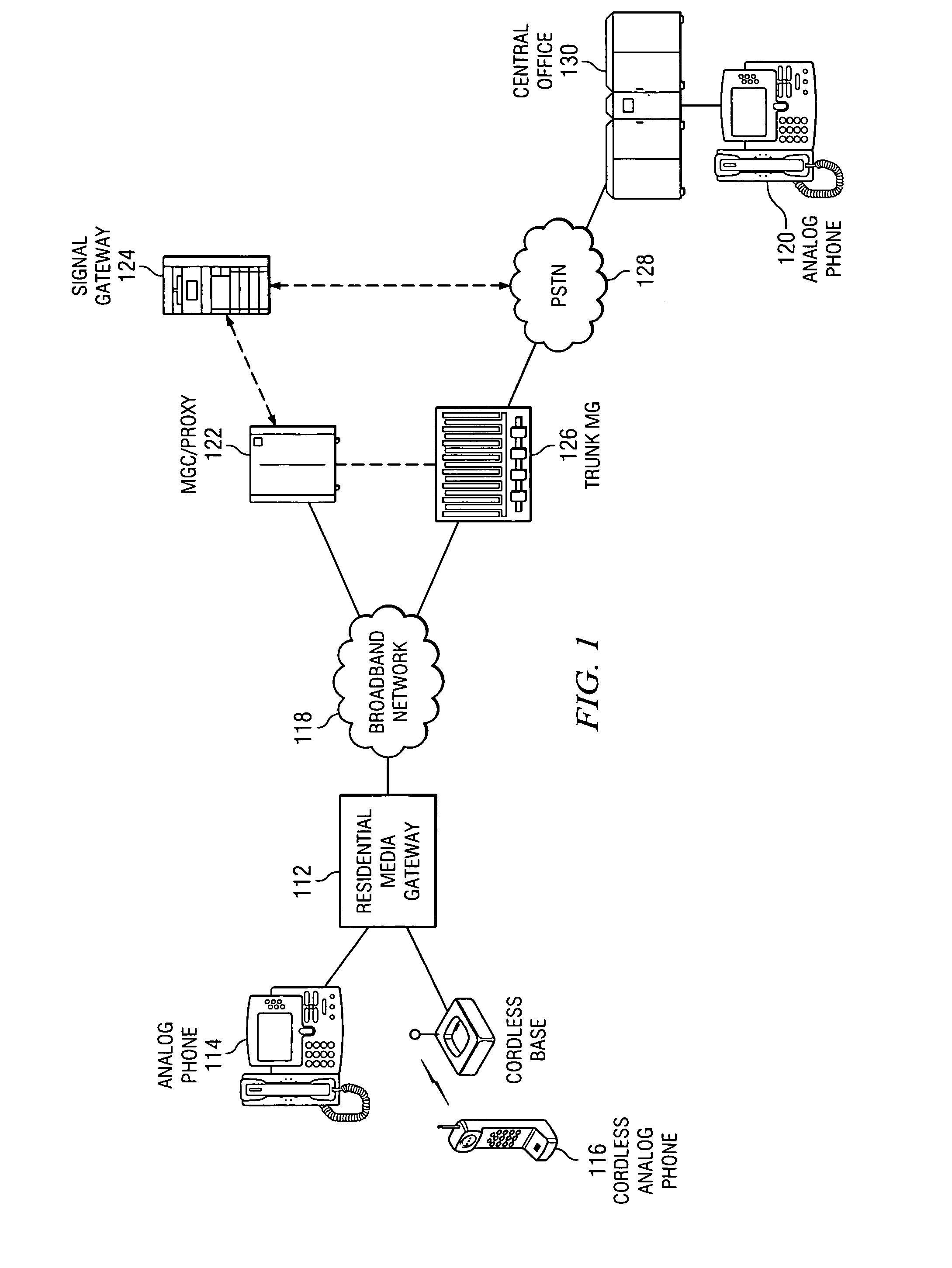
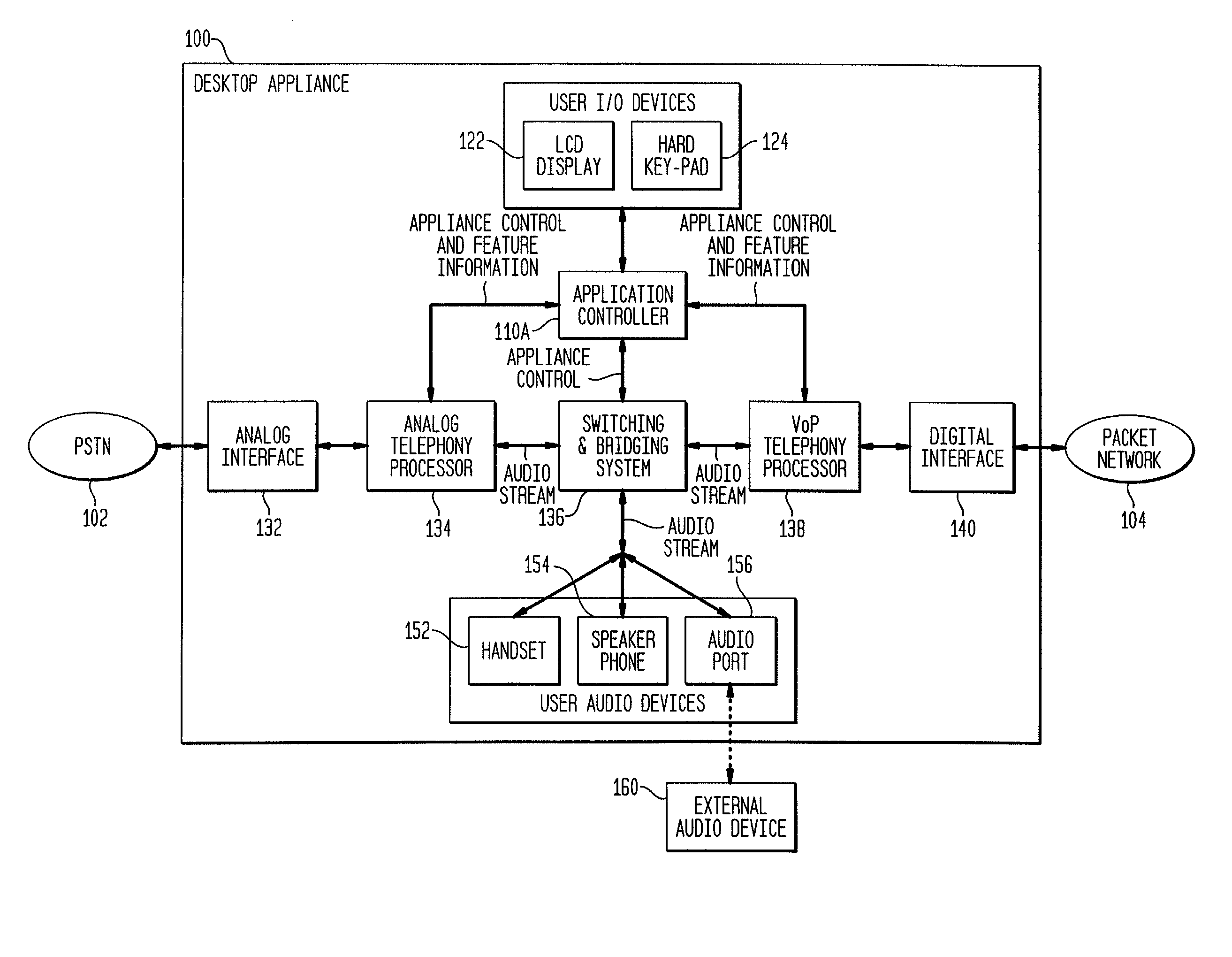
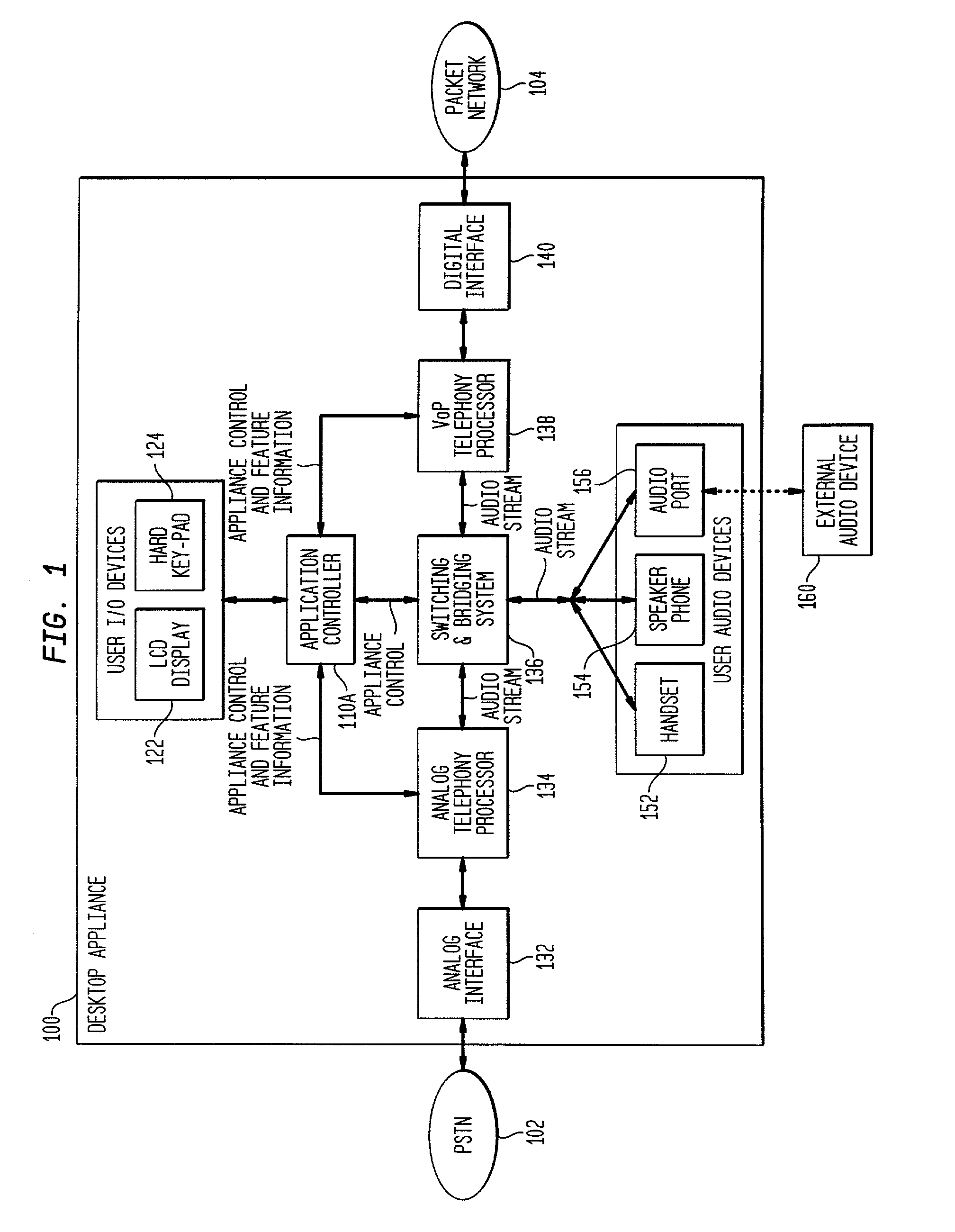
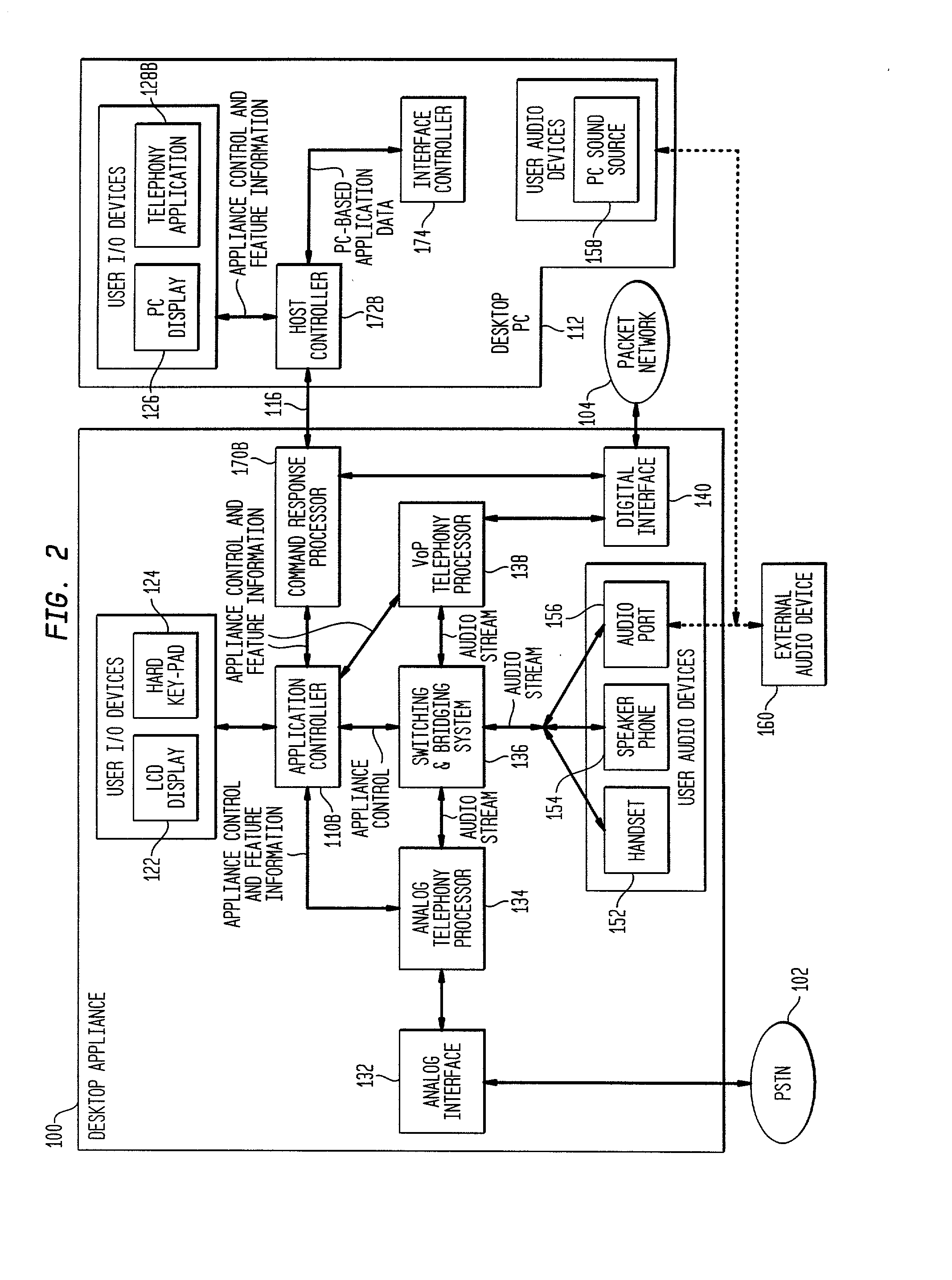
Interconnecting voice-over-packet and analog telephony at a desktop
InactiveUS20030026244A1Reduce amountSimplify the management processAutomatic call-answering/message-recording/conversation-recordingData switching by path configurationUser deviceDigital interface
PSTN and voice over packet telephony are integrated at a customer premises, thereby reducing the plurality of redundant user I / O devices on the desktop, simplifying management of multiple telephony interfaces, and interconnecting PSTN and VoP calls at the desktop. A desktop appliance interfaces to both the PSTN and a packet network and includes a single set of user I / O and user audio devices, analog telephony functionality, a digital interface, VoP telephony functionality, and a switching and bridging system for interconnecting / bridging the user devices, the PSTN, and the packet network. A desktop PC can also be incorporated with the appliance, the PC providing telephony applications and the appliance providing network connectivity for the PC. Similarly, the PC can provide network connectivity and telephony functionality, with the appliance integrating the PSTN and VoP calls.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL VENTURES II
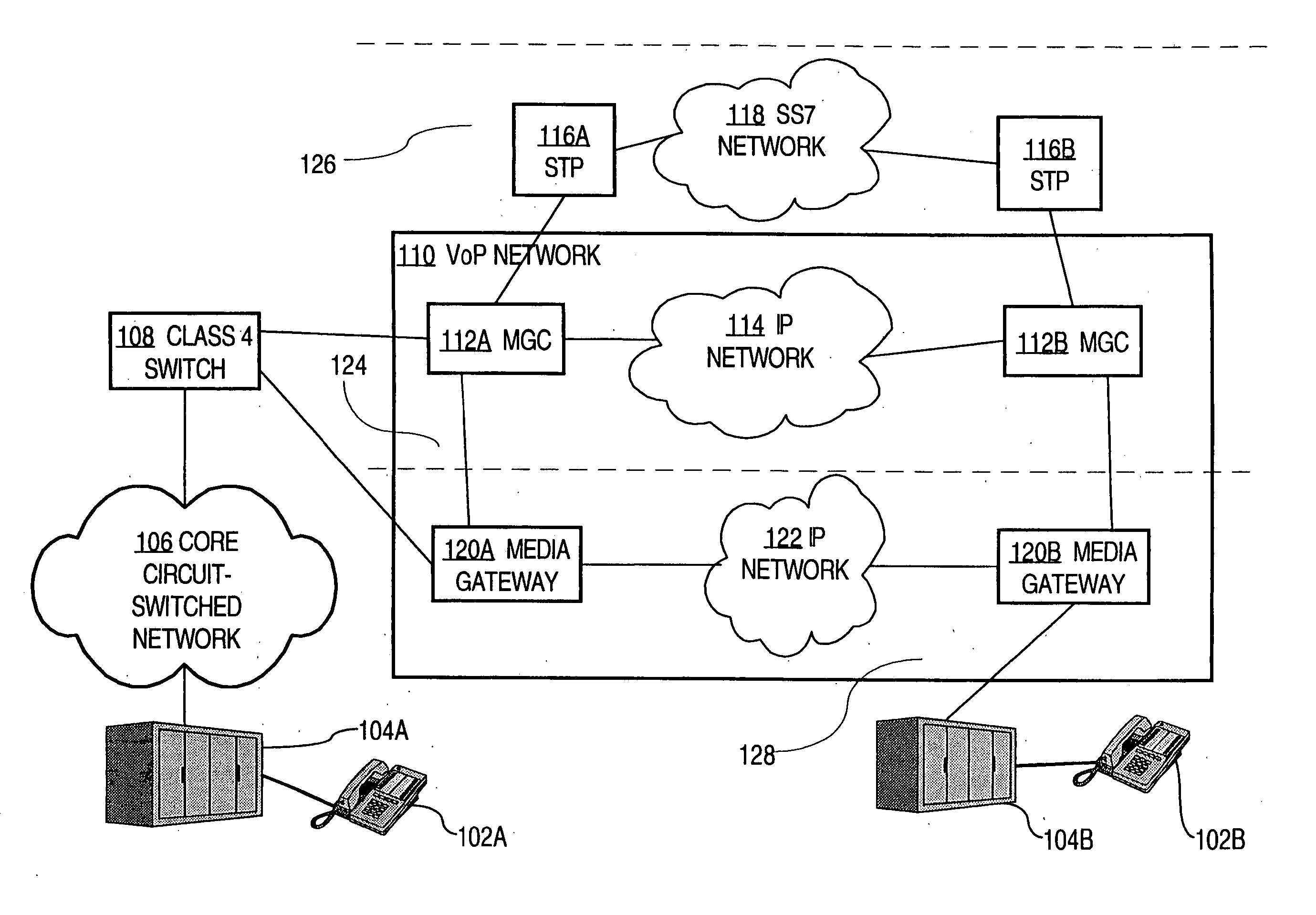
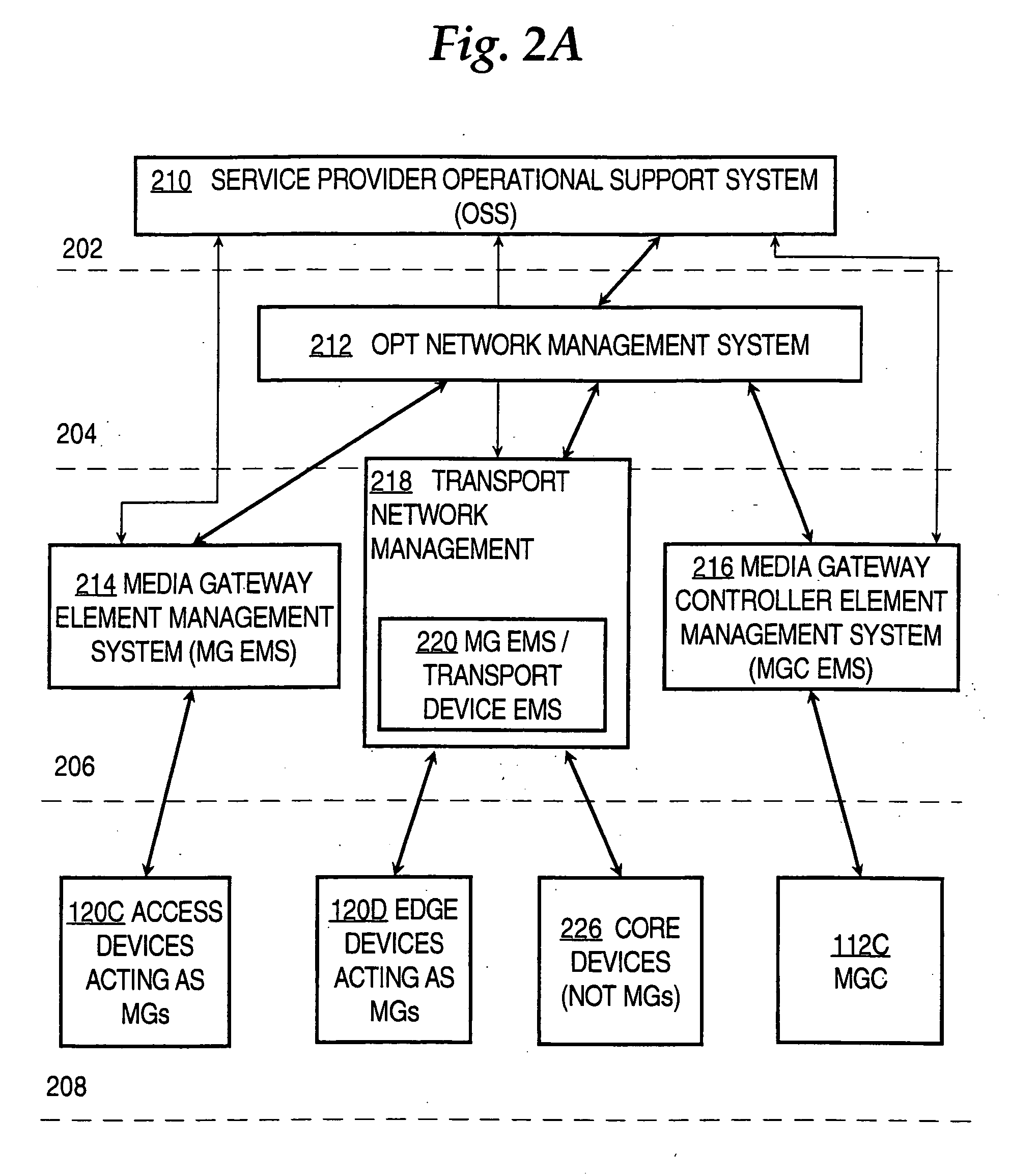
Managing packet voice networks using a virtual switch approach
InactiveUS20070008958A1Reduce in quantityTo offer comfortInterconnection arrangementsSupervisory/monitoring/testing arrangementsUser inputNetwork management application
A method for managing packet voice networks using a virtual switch approach and abstract information model approach is disclosed. A virtual switch object represents a virtual switch having a media gateway controller and one or more associated media gateways. User input specifies a configuration operation on the virtual switch and one or more parameter values. One or more configuration instructions are automatically issued to both the media gateway controller and the media gateway, resulting in configuring both the media gateway controller and the media gateway as specified in the user input. As a result, a user can configure or operate on a virtual switch as an atomic entity, for example, in a network management application, without involvement in complicated details of the actual network devices that provide a particular packet voice service.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
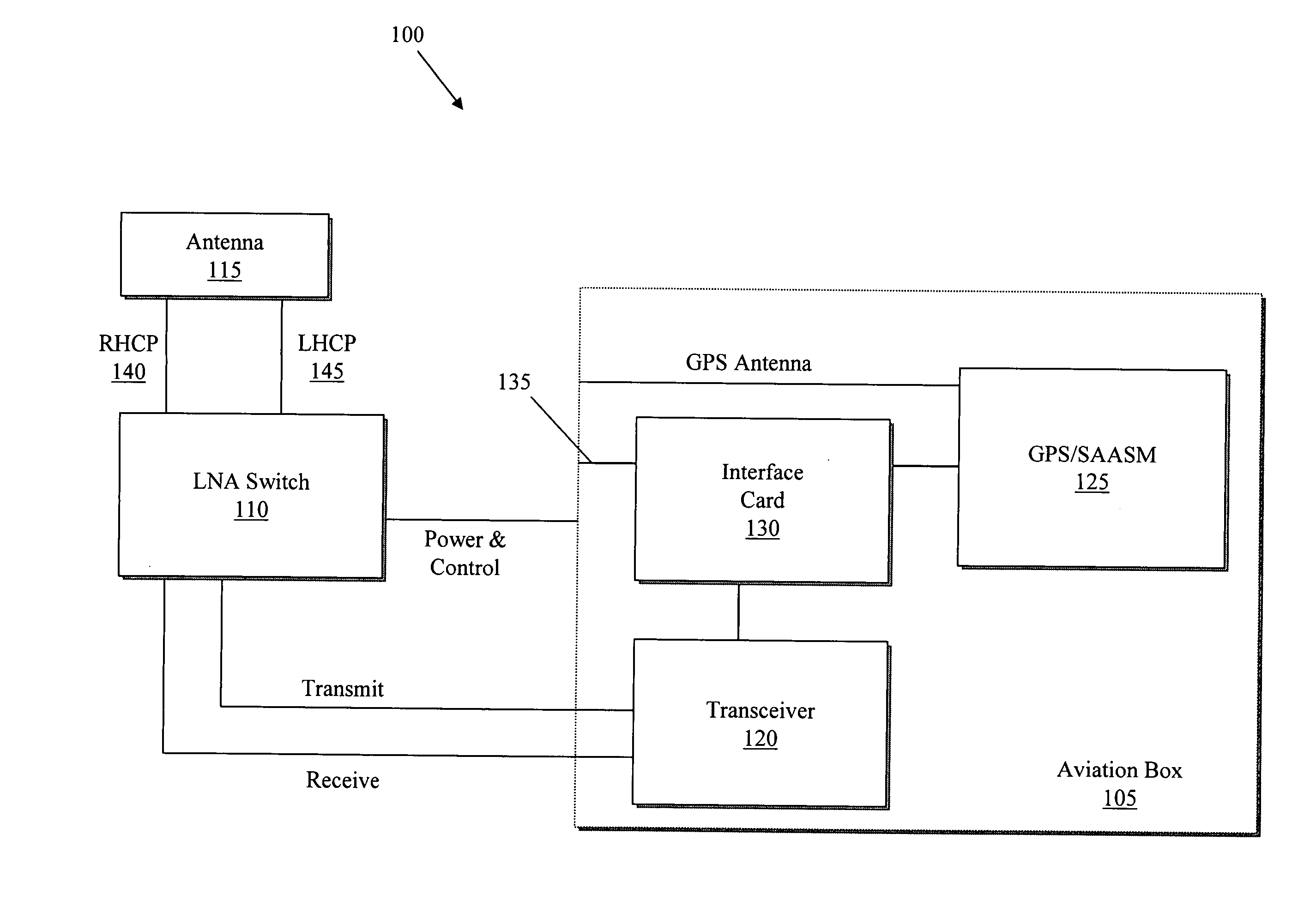
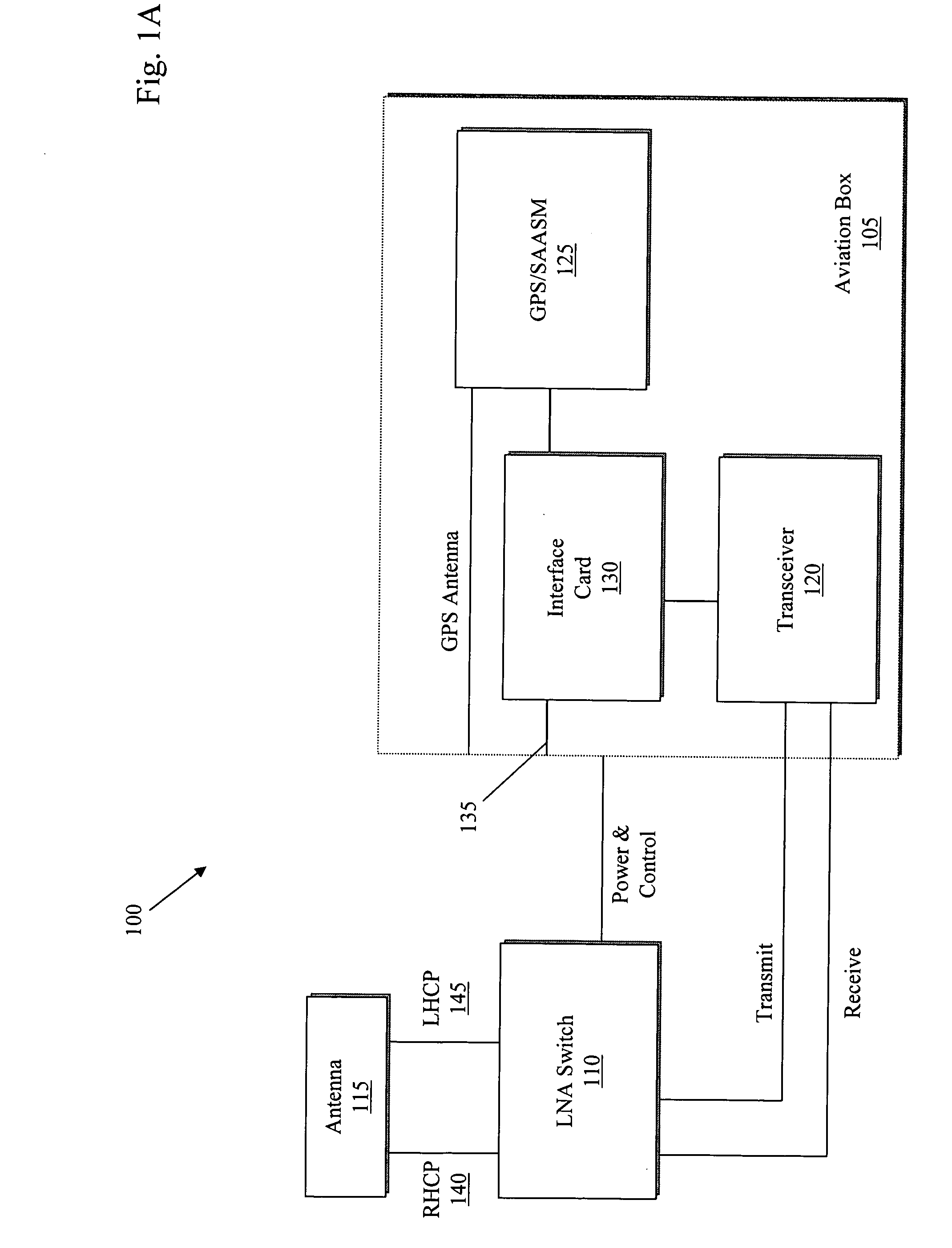
In-flight transceiver and locator system
ActiveUS20070298786A1Improve versatilityUnnecessary burdensome loadPosition fixationRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsAviationTransceiver
Military systems in particular face two specific problems: field casualties typically increase as unit visibility decreases and it is often difficult for ground stations and / or headquarters to maintain control and visibility of geographically dispersed assets. The system provides satellite communications such as two-way messaging, Voice over Packet, and global positioning information and reporting for fixed and rotary wing aircrafts where traditional methods of communications are not otherwise practical. The system provides communications between remote users and other remote users as well as between remote users and control stations. In some embodiments there is an in-flight transceiver system that includes an antenna, an aviation box, and a switch. The aviation box conforms to a one-half, ½ short Air Transport Rack (ATR) form factor and includes a transceiver, an interface card, and a global positioning system (GPS) unit. The switch is located between the aviation box and the antenna for controlling a data signal between the antenna and the transceiver of the aviation box.
Owner:COMTECH MOBILE DATACOM CORP
Packet loss concealment for voice over packet networks
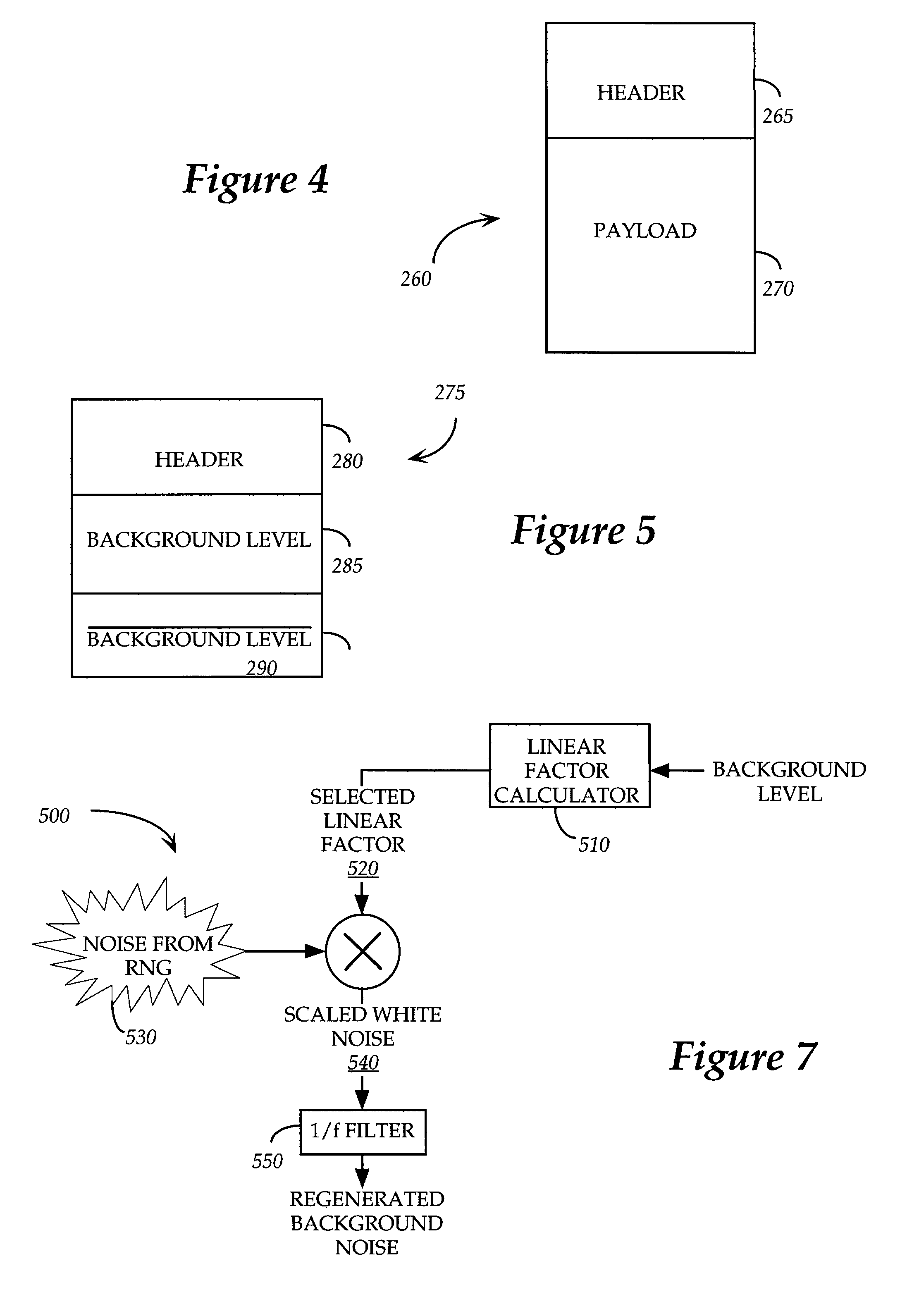
ActiveUS20060171373A1Few processing resourceLess resourcesSpeech analysisTime-division multiplexRepeating waveformsPulse-code modulation
A method to reduce memory requirements for a packet loss concealment algorithm in the event of packet loss in a receiver of pulse code modulated voice signals. Packet losses are concealed by using the spectral analysis filter memory to smooth a signal gap and by using a technique for determining a maximum repeatable waveform range instead of using the pitch period to reproduce lost packets. The invention uses fewer processing resources and results in improved performance compared to a packet loss concealment algorithm under G.711 Appendix I standards.
Owner:TELOGY NETWORKS
Simultaneous VoLTE and 2G/3G/LTE Data in Dual SIM Configuration
ActiveUS20160029222A1Connection managementCommmunication supplementary servicesRadio access technologyVoice communication
A user equipment (UE) device may perform uplink (UL) data communication using a first radio access technology (RAT) while performing an UL voice call communication using a second RAT. The UL data communication may be supported by a first subscriber identity module (SIM) and the UL packet switched voice call communication may be supported by a second SIM. The UL voice call communication may be a packet switched communication. The communications may be performed by a radio(s) of the UE. The radio(s) may include shared physical layer resources that are shared between the UL data and UL voice communications. The UE may also include a single transmitter that may be shared between the UL data and UL packet voice communications and the UL data communication may use a first portion of the single transmitter's TTI and the UL voice communication may use a second portion of the single transmitter's TTI.
Owner:APPLE INC
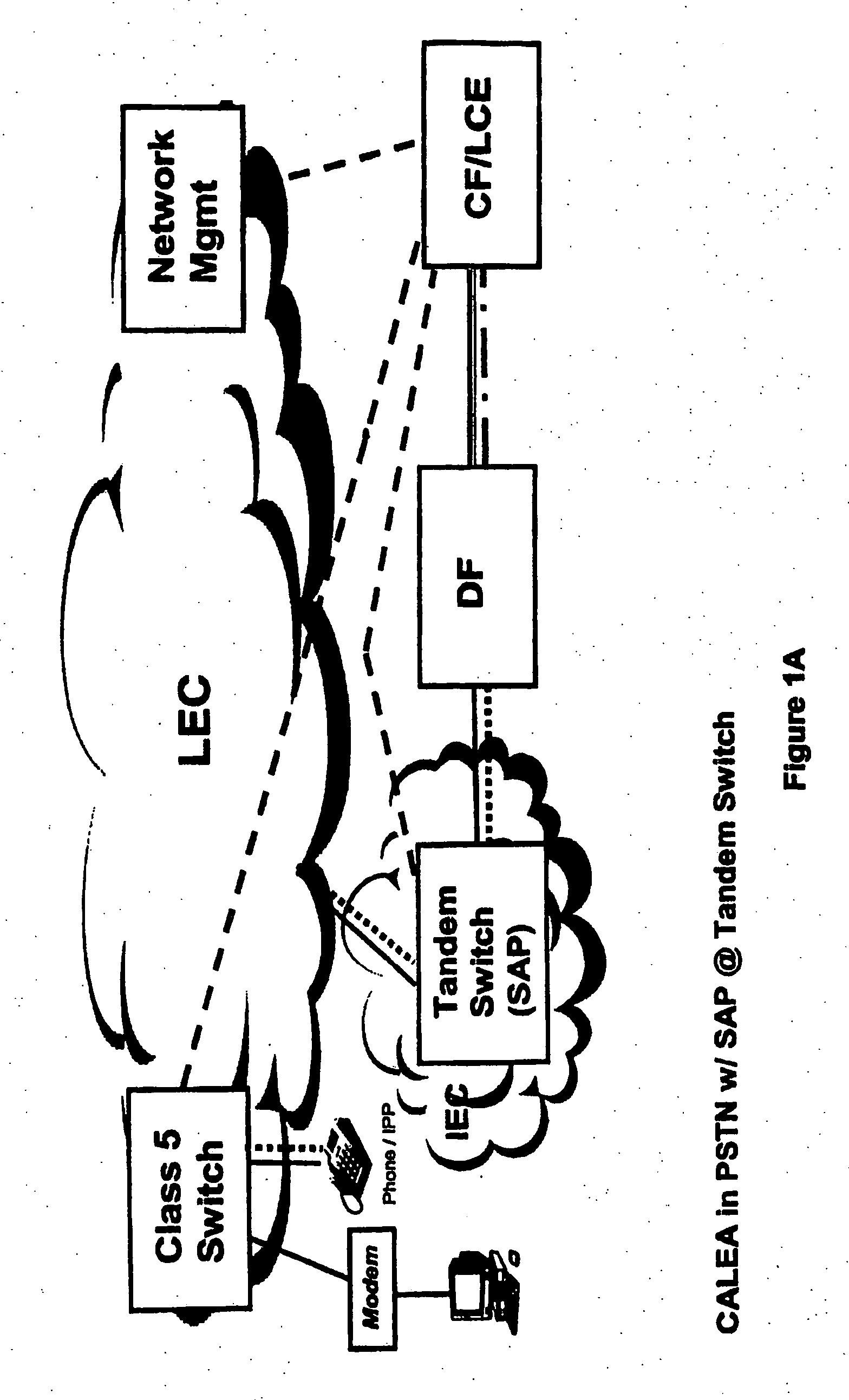
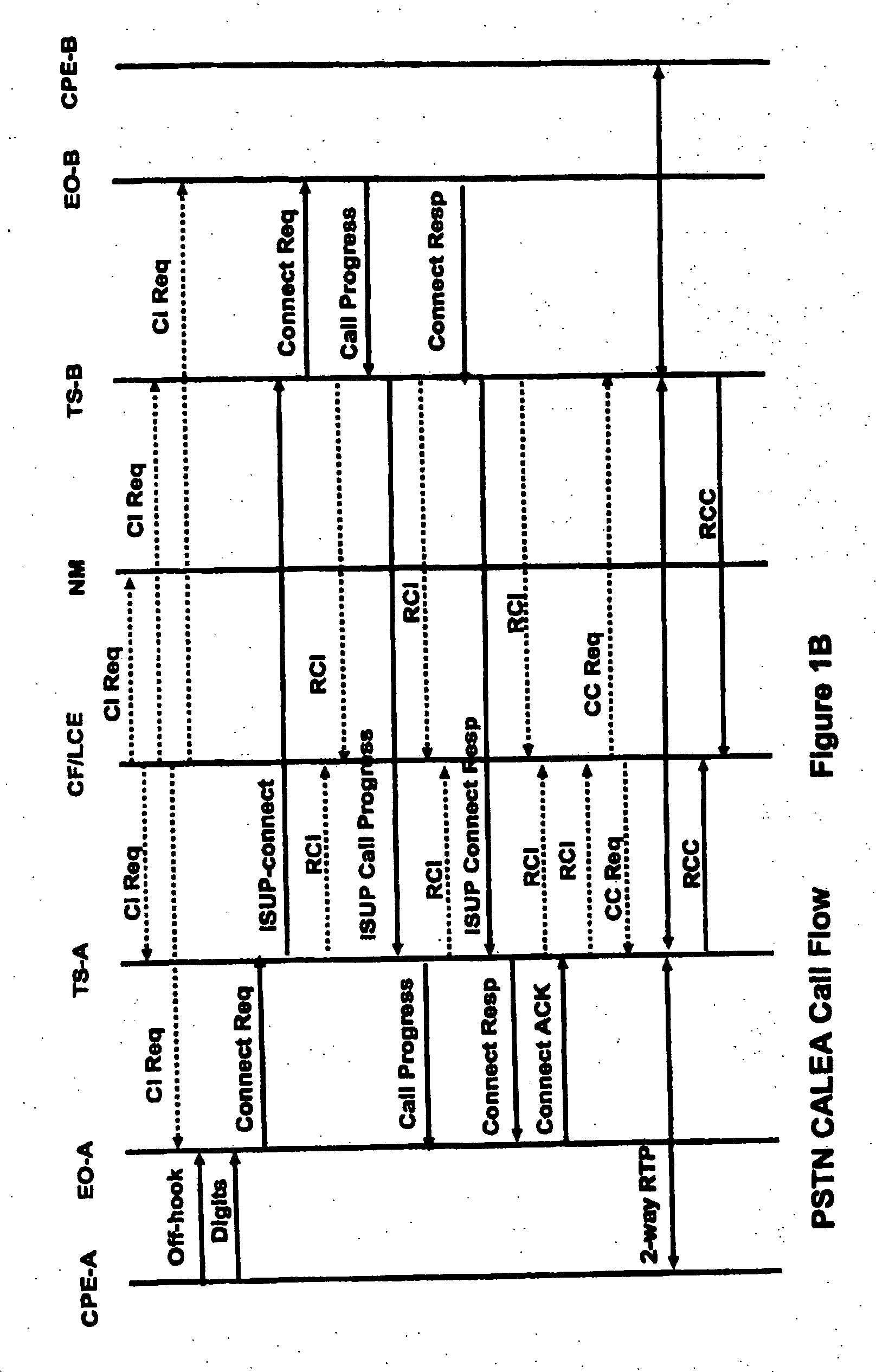
Surveillance implementation in a voice over packet network
InactiveUS20060212933A1Error preventionSupervisory/monitoring/testing arrangementsTransceiverIp address
A network infrastructure device in a voice over packet (VOP) network includes a transceiver and a processor. The transceiver can transmit and receive communications over a VOP network. The processor, responsive to receipt of a call setup information request (CIReq) specifying a particular target, can associate a public identifier with the particular target, and map the public identifier to an internet protocol (IP) address responsive to a communication. Also, the processor can identify communications to and / or from the particular target with the IP address. Further, responsive to receiving communications to and / or from the IP address, the processor can transmit the communications to a law enforcement agency (LEA) collection device.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com